Hybrid fiber tows containning both nano-fillers and continuous fibers, hybrid composites, and their production processes
a technology of hybrid fibers and nano-fillers, applied in the field of hybrid fiber tows, can solve the problems of poor delamination resistance, poor thickness-direction and shear strength and moduli of continuous carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite laminates, and excellent in-plane properties of composite materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
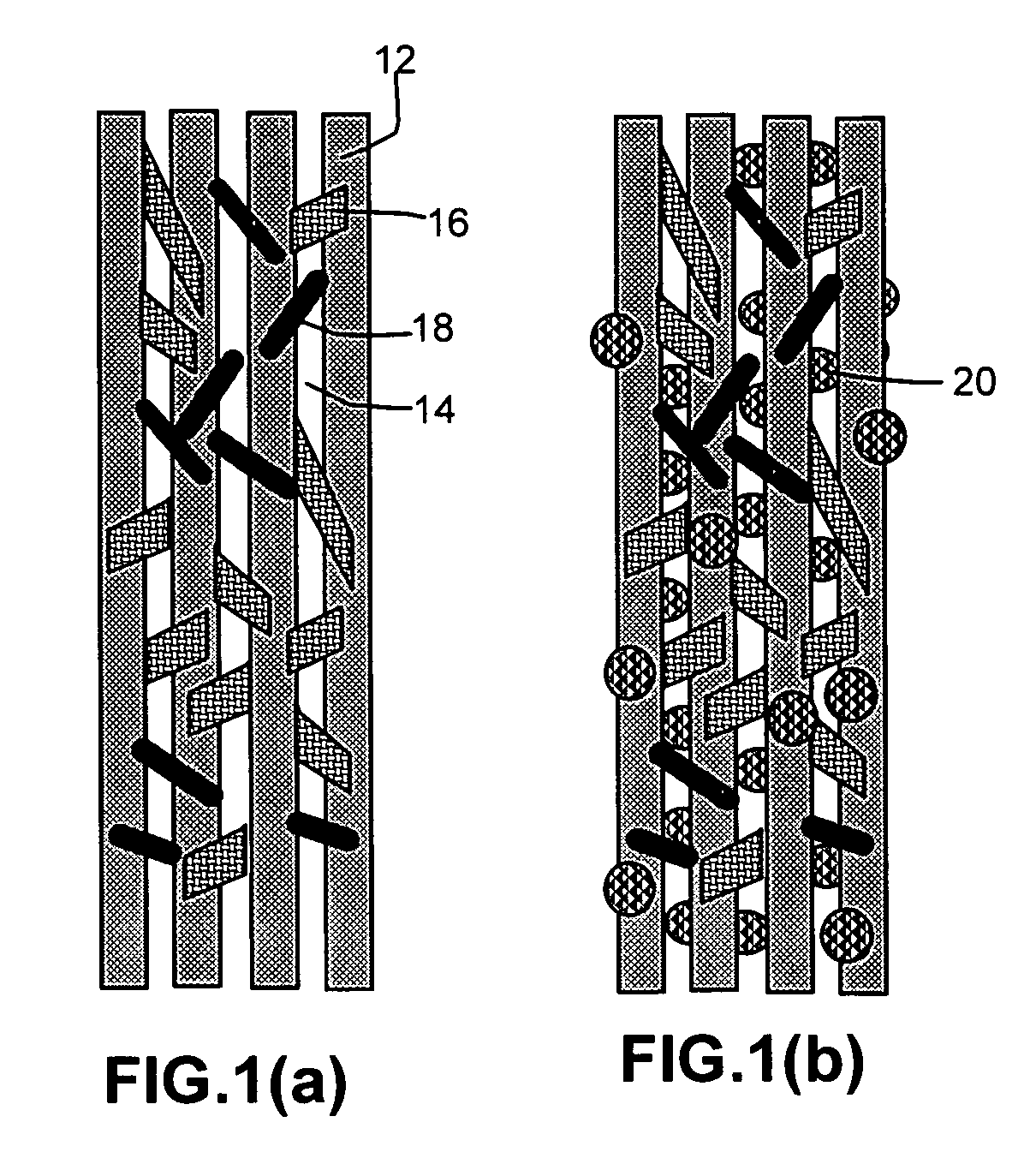
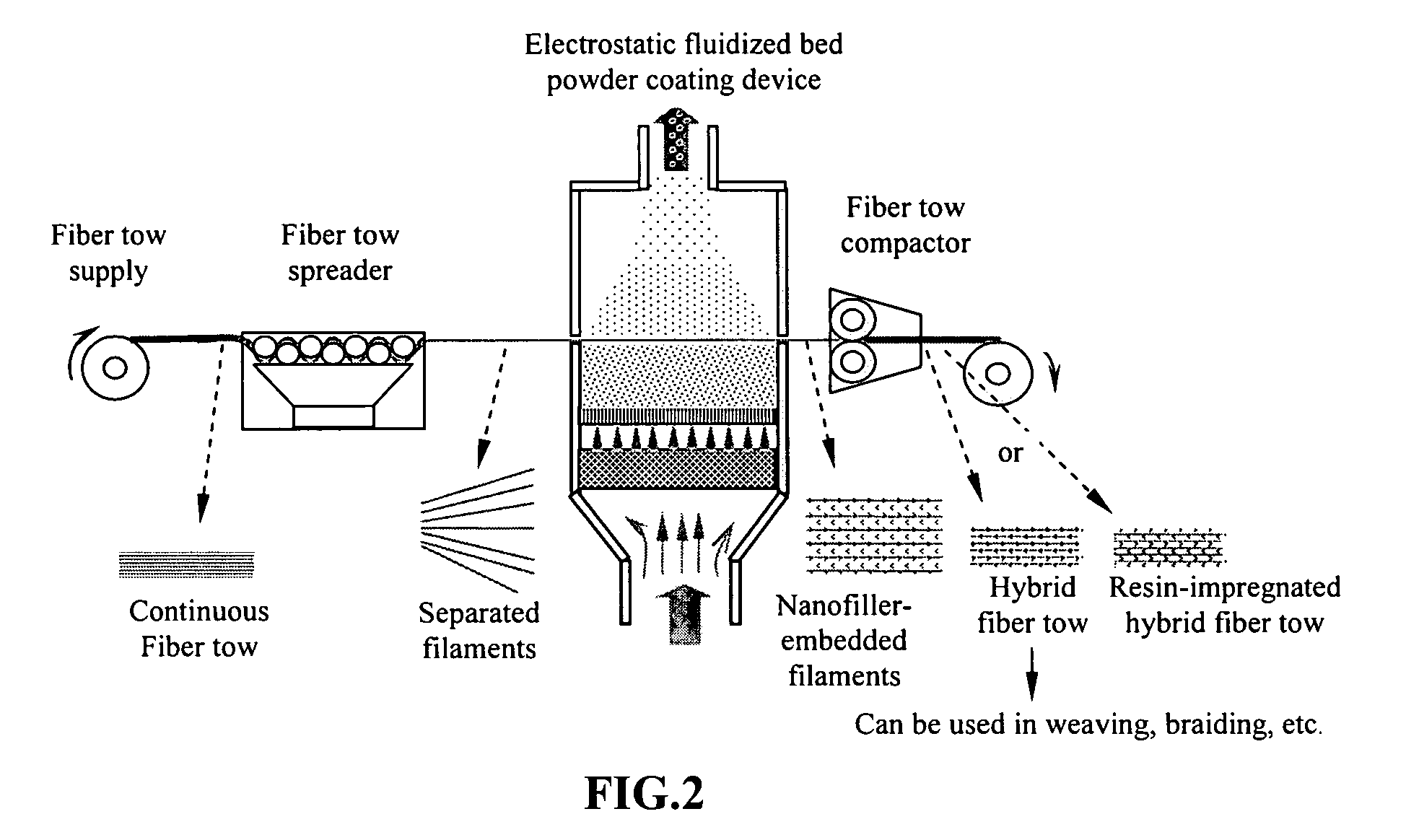
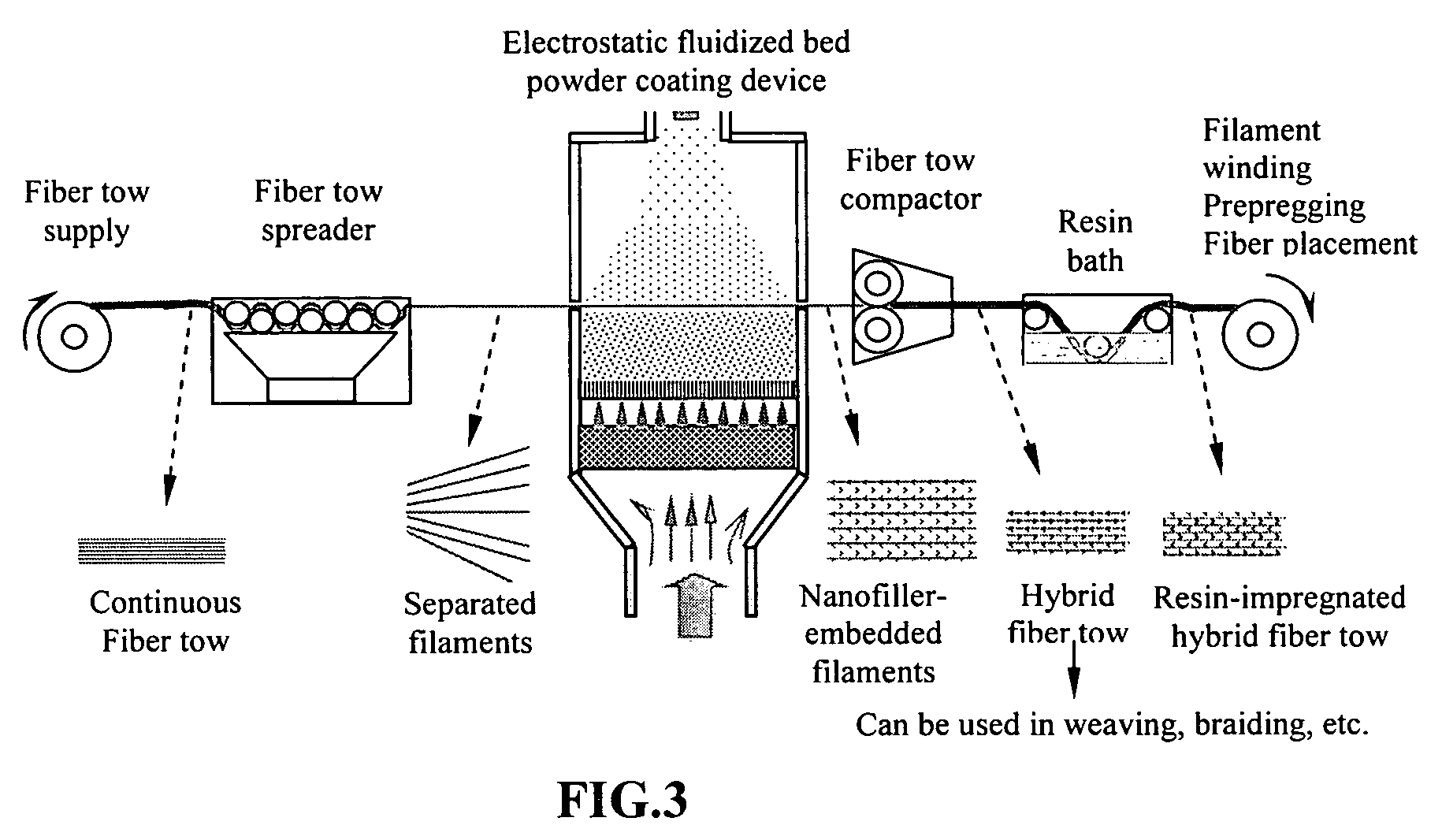
[0020]The conventional approach to fabricating composite materials containing both continuous fibers and fillers (such as nanoscale fillers, short fibers, etc.) typically involves mixing the fillers with a resin first, followed by impregnating the continuous fiber tows with the resin / filler mixture. It is now well-recognized that a small amount of nano-fillers like carbon nano-tubes (CNTs) and carbon nano-fibers (CNFs) could dramatically increase the viscosity of a matrix resin. The resulting nano-filler / resin mixture is typically so viscous that it becomes extremely difficult to disperse continuous fibers in this matrix. Hence, it is also commonly believed that only a small amount of nano-fillers can be incorporated in a hybrid composite.
[0021]Furthermore, the prior-art sequence of mixing nano-fillers with a resin and then impregnating continuous fibers with the nano-filler / resin mixture tends to produce a hybrid composite with fillers oriented along the continuous fiber axis. Such...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com