Patents
Literature
3259results about "Braid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
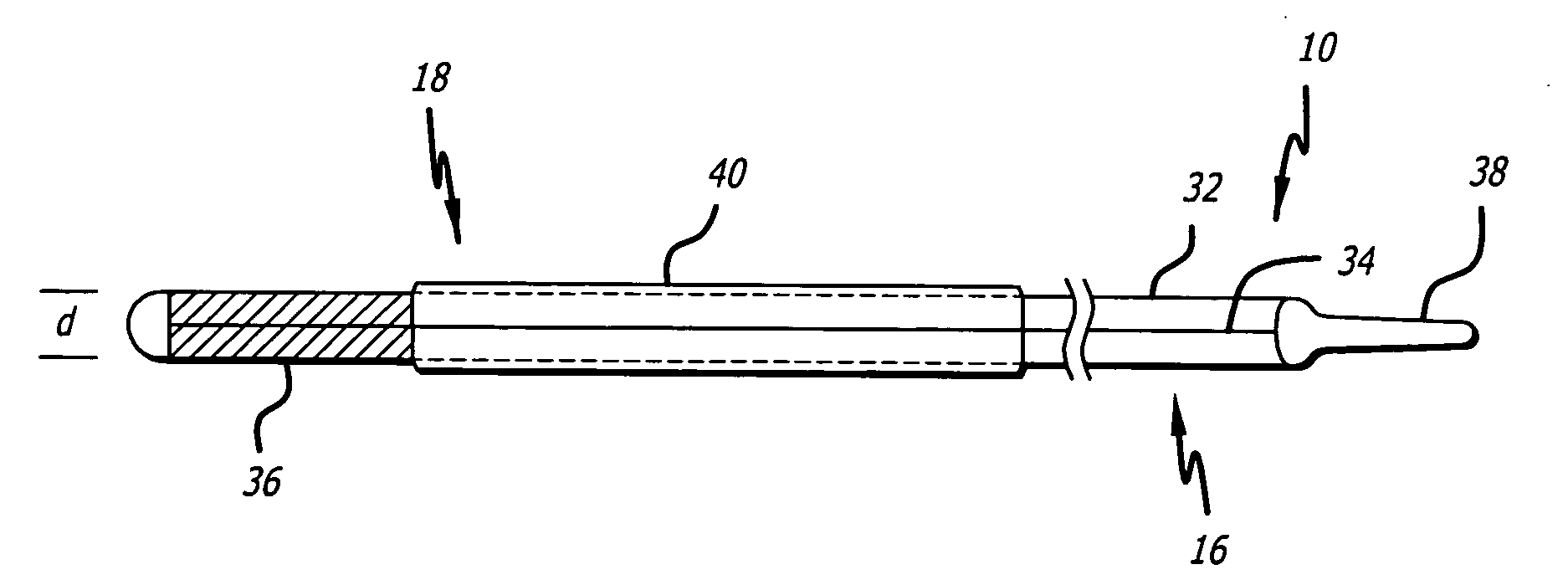
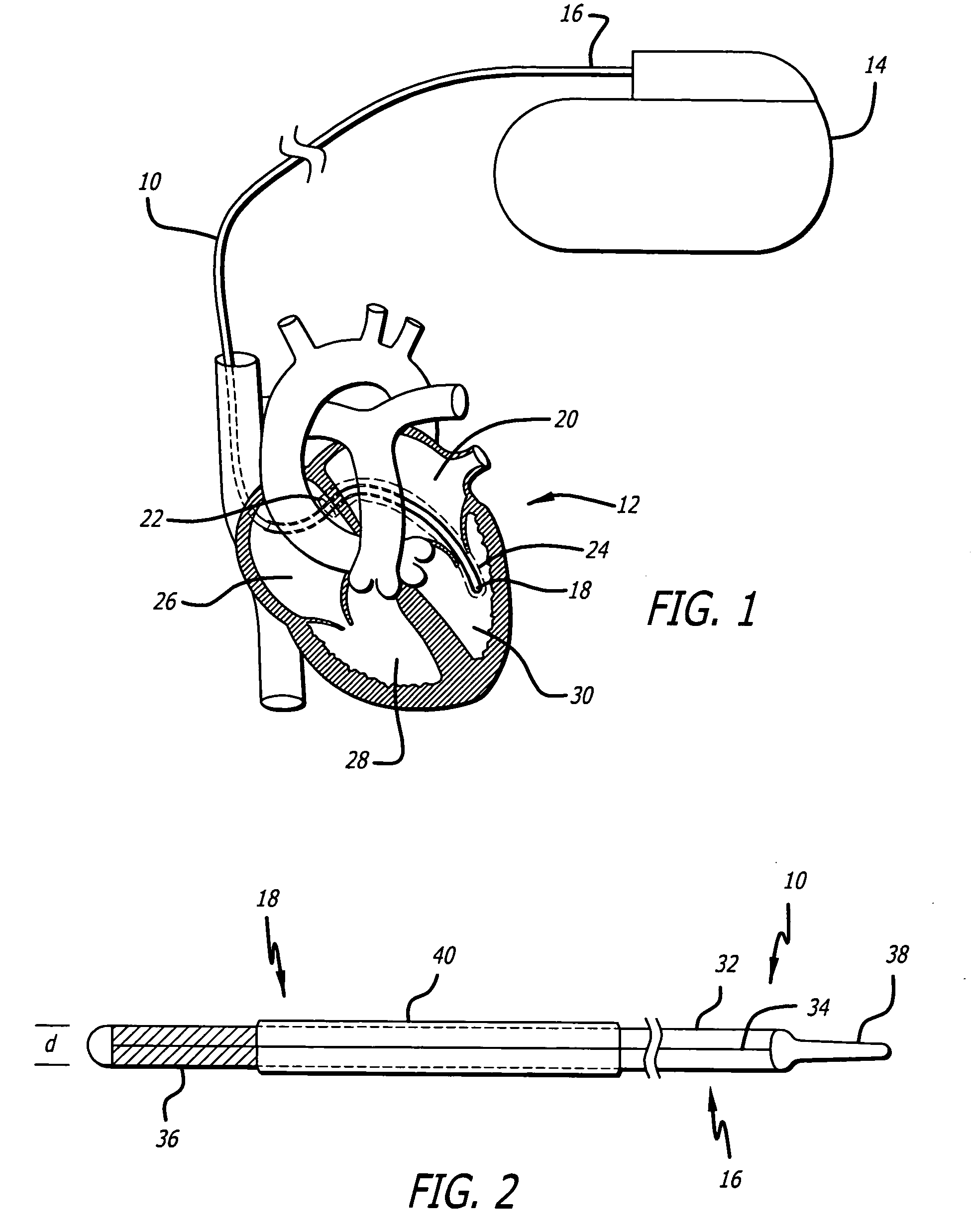
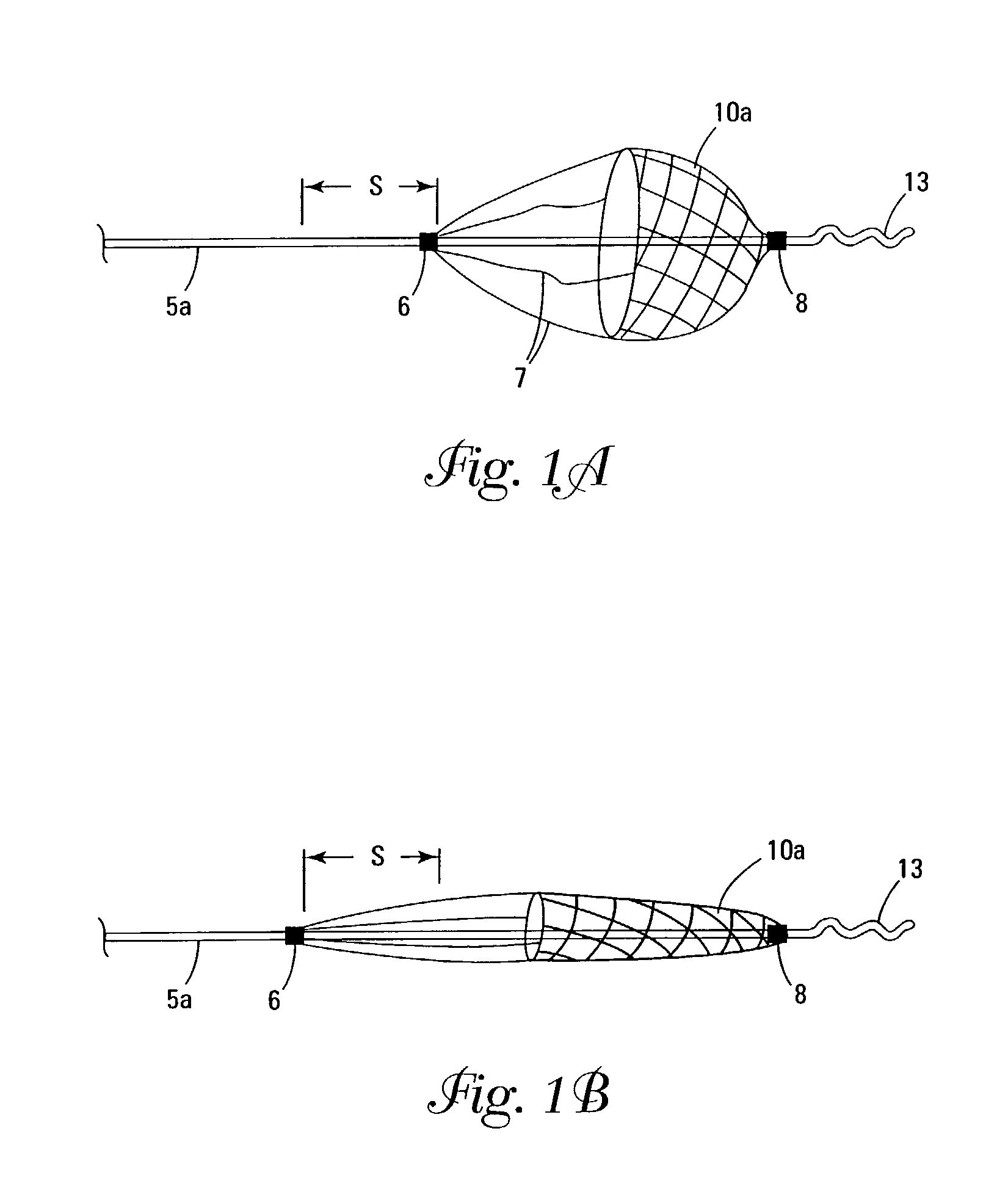
Delivery devices
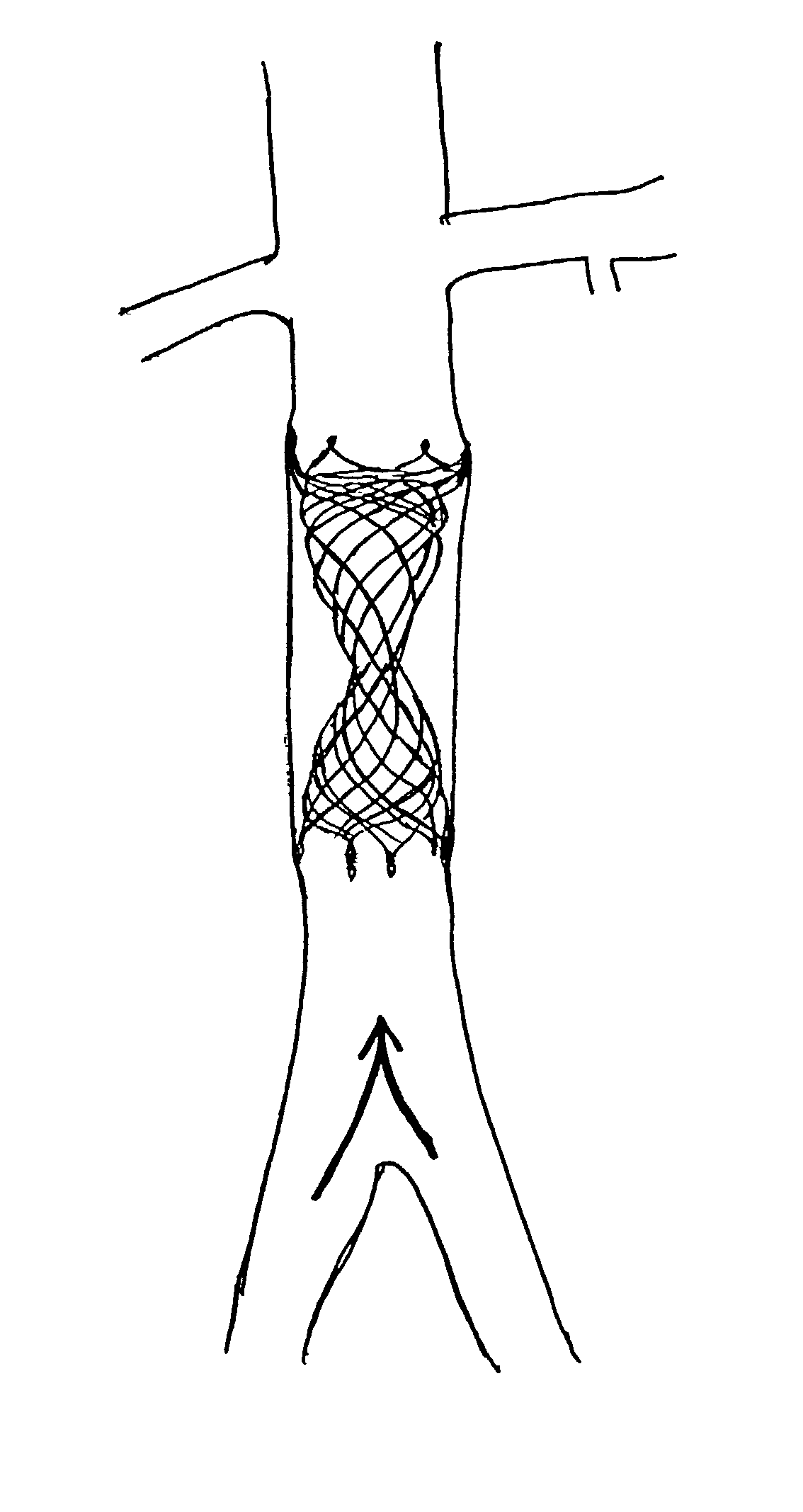
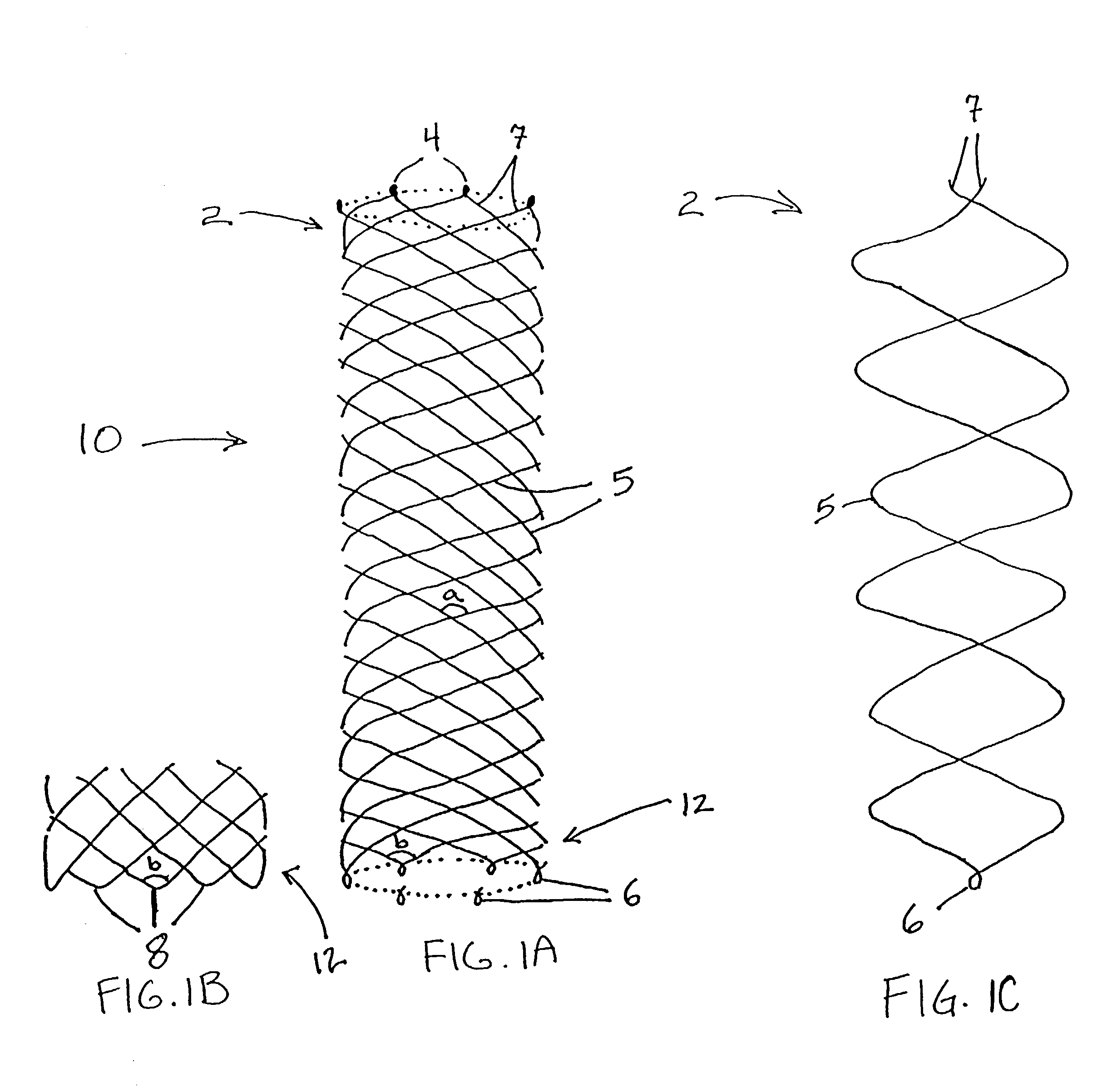
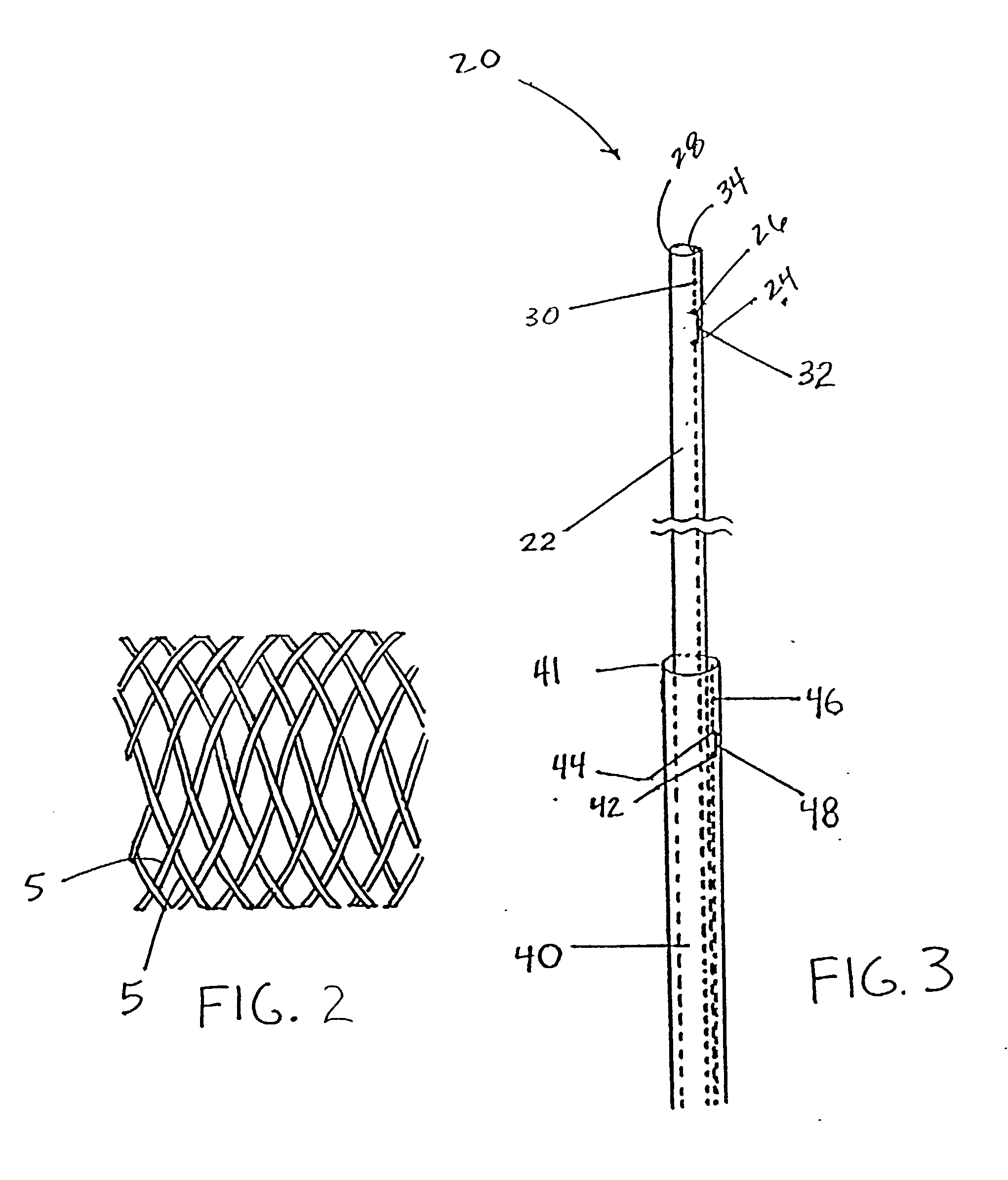
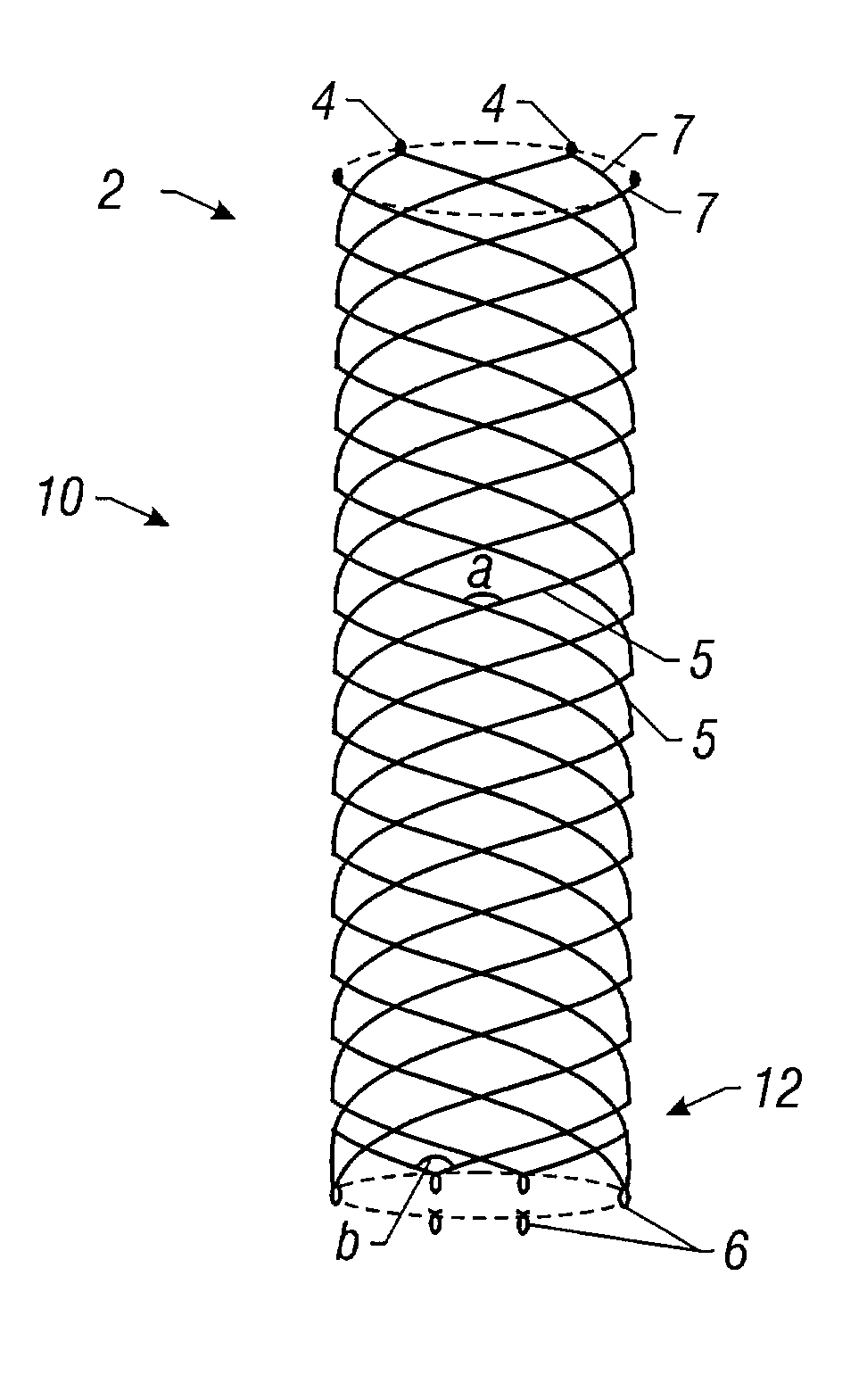
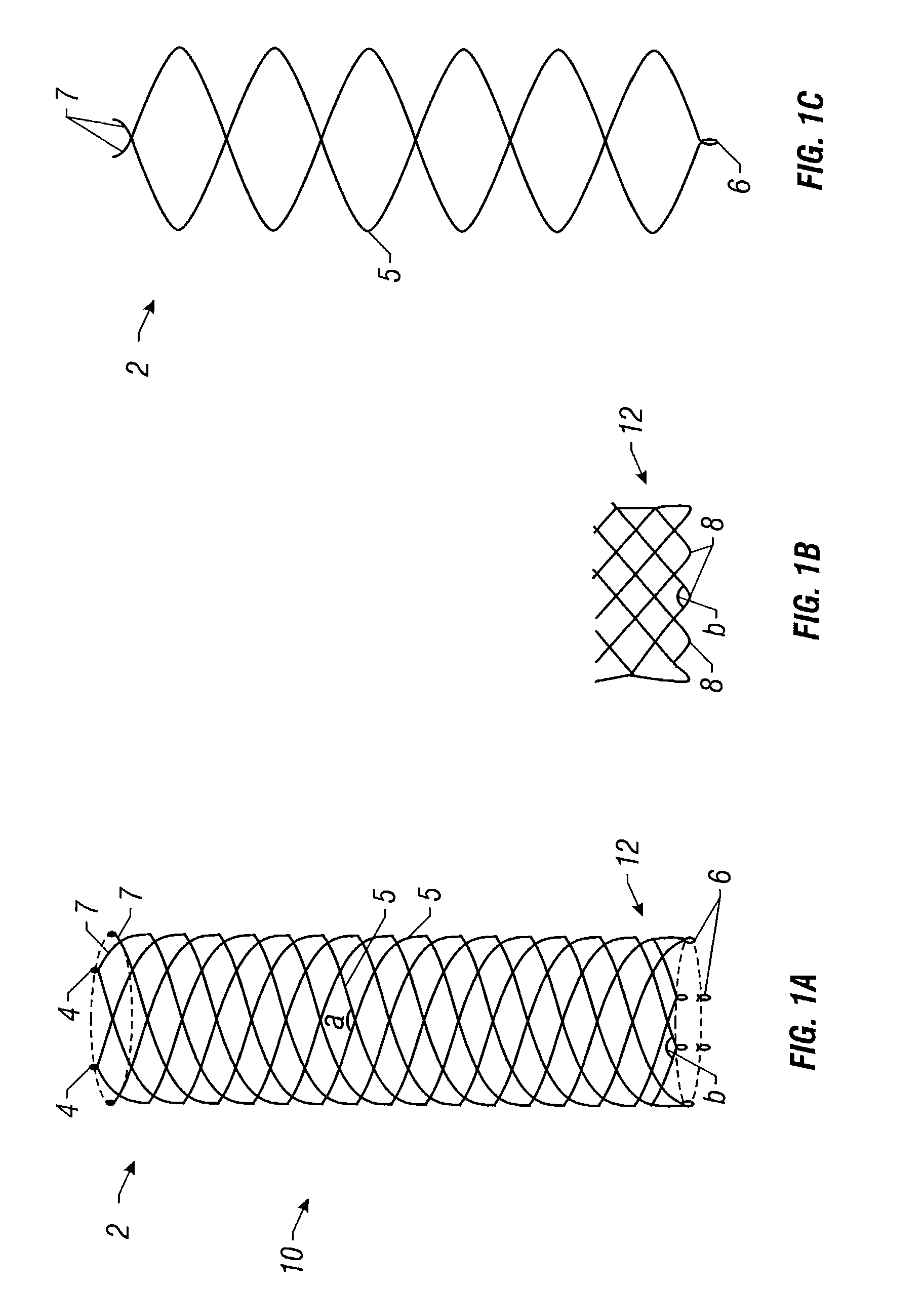
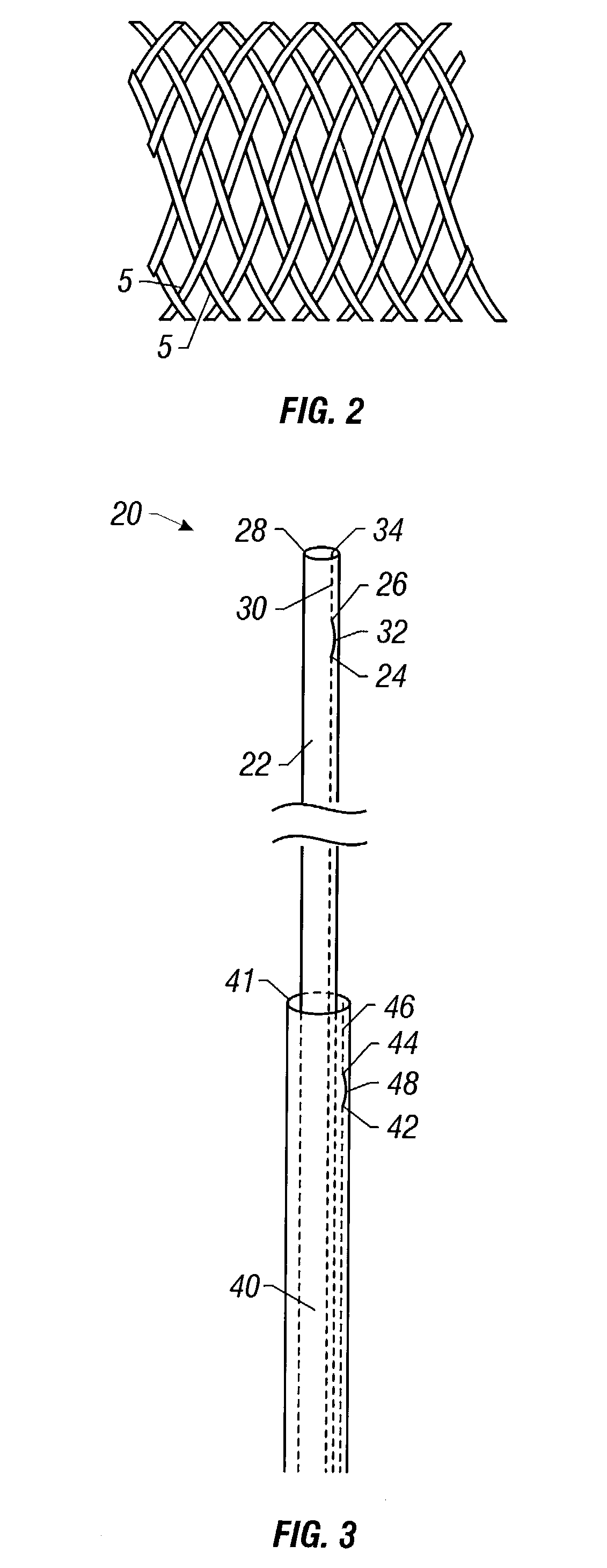
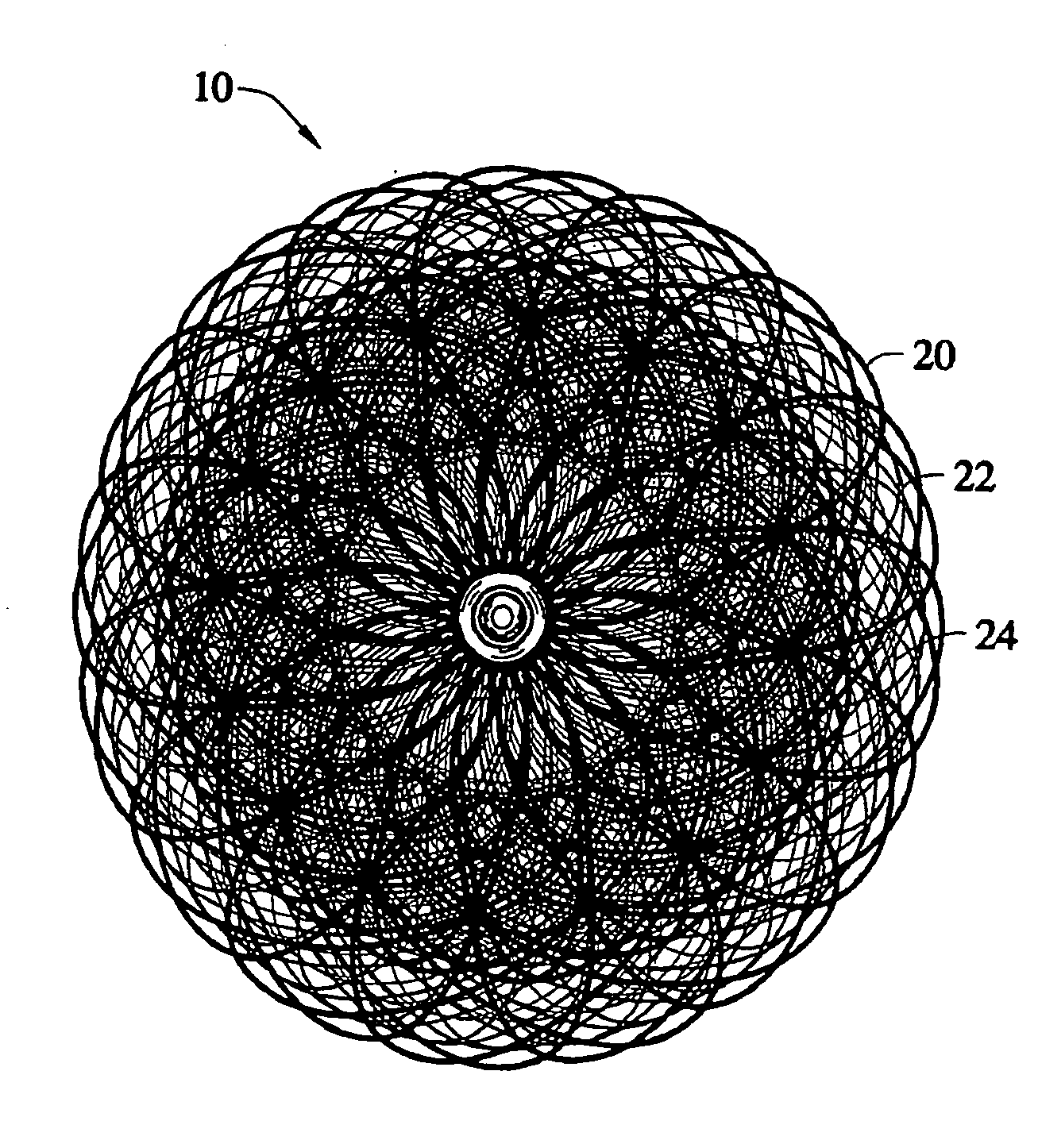
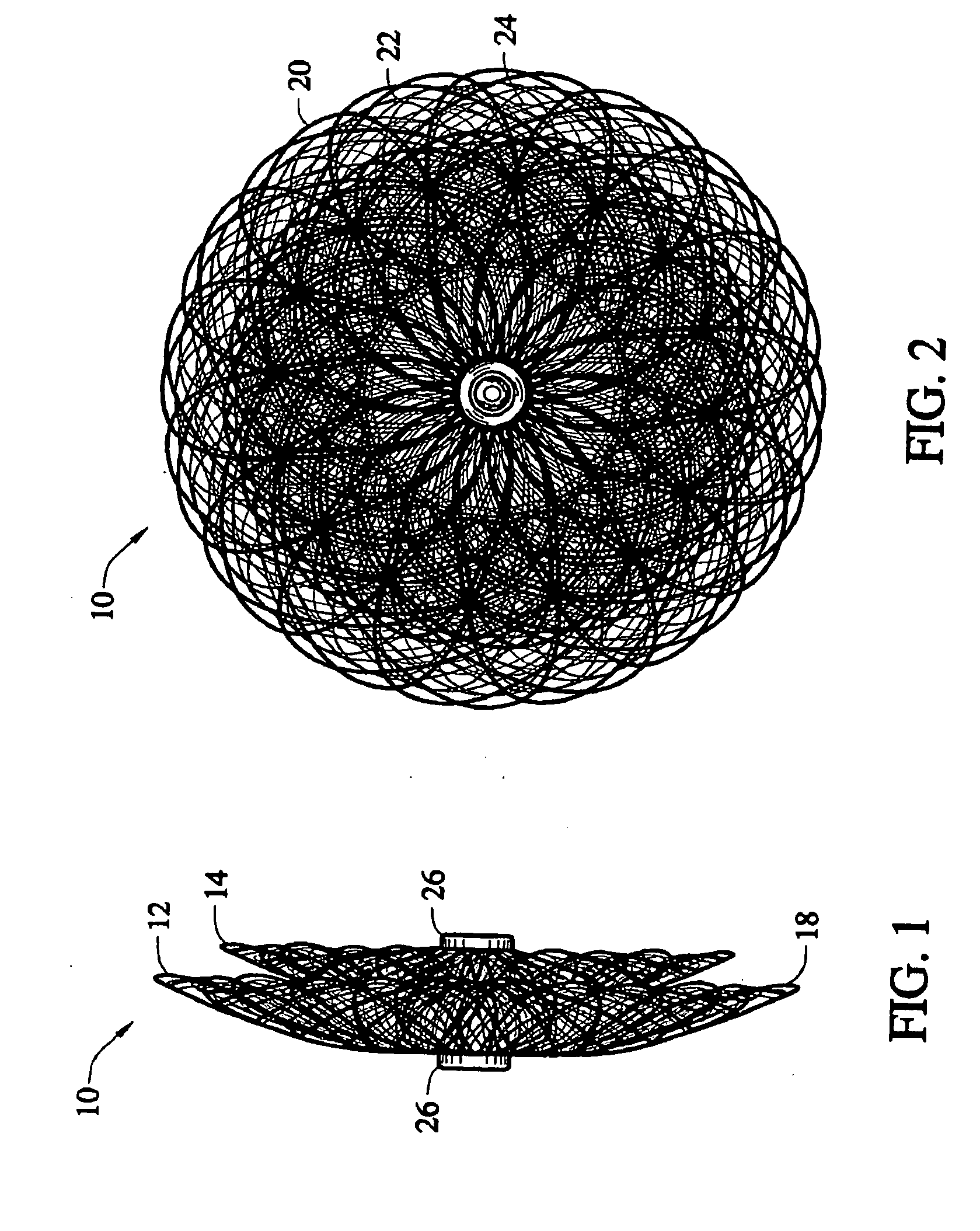
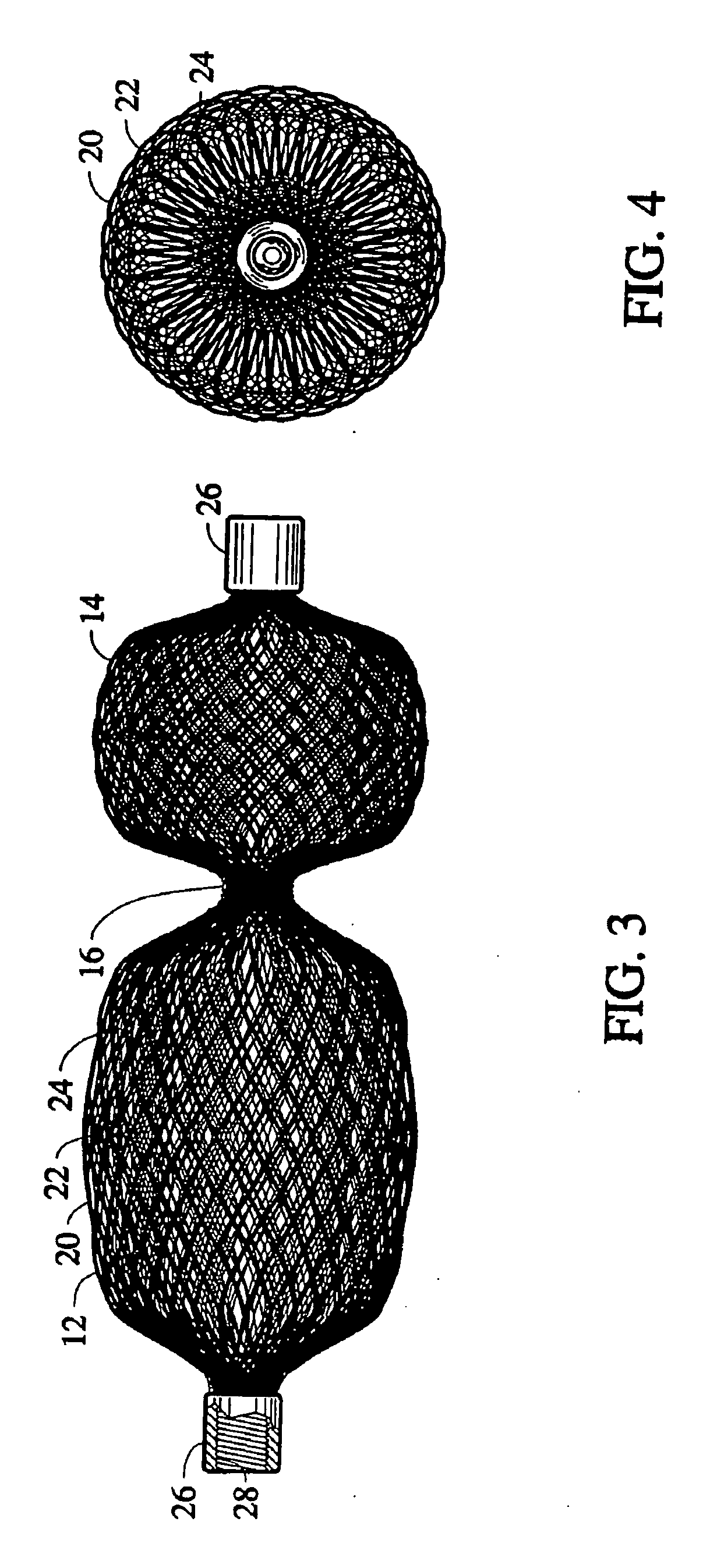
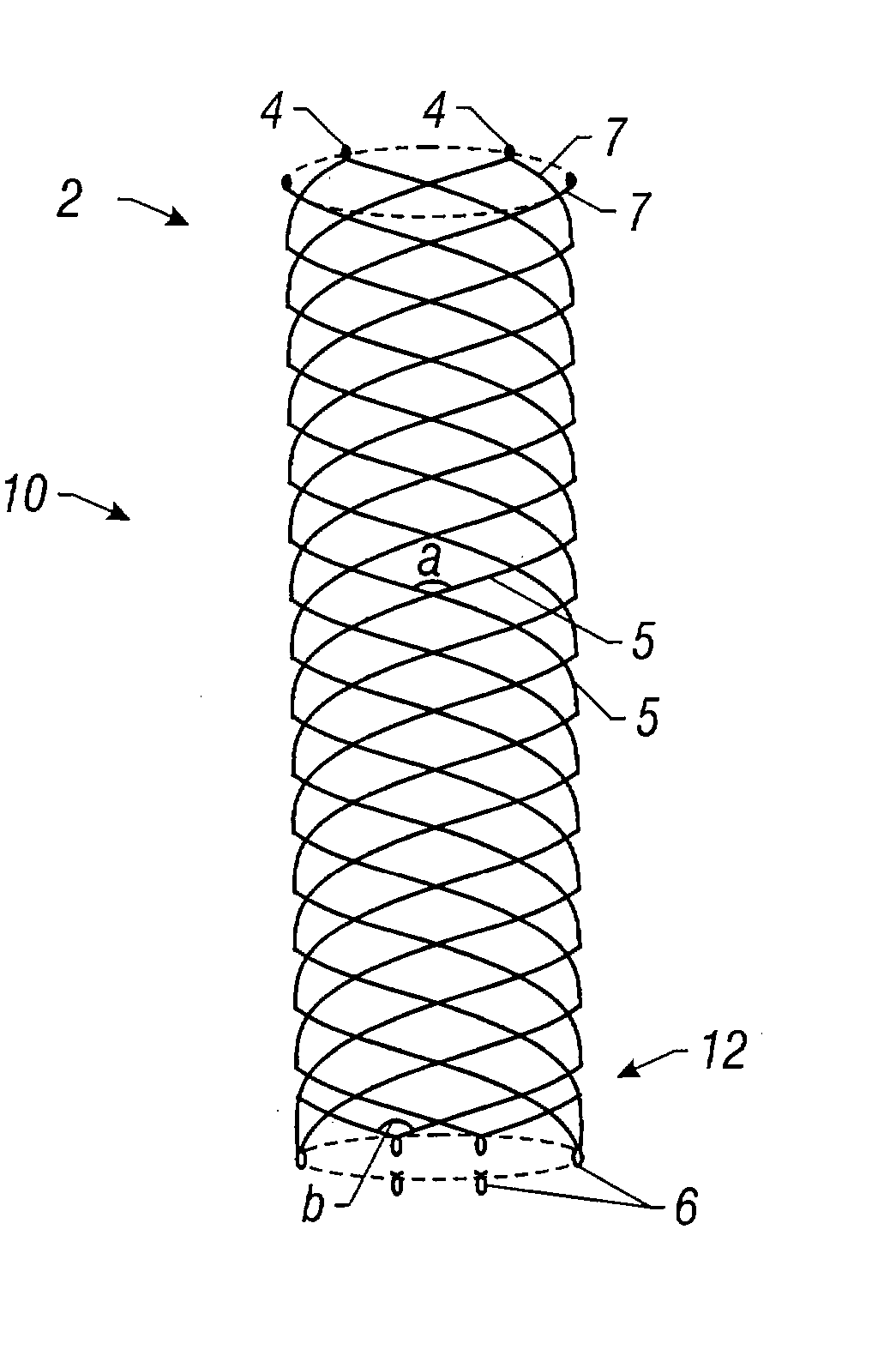
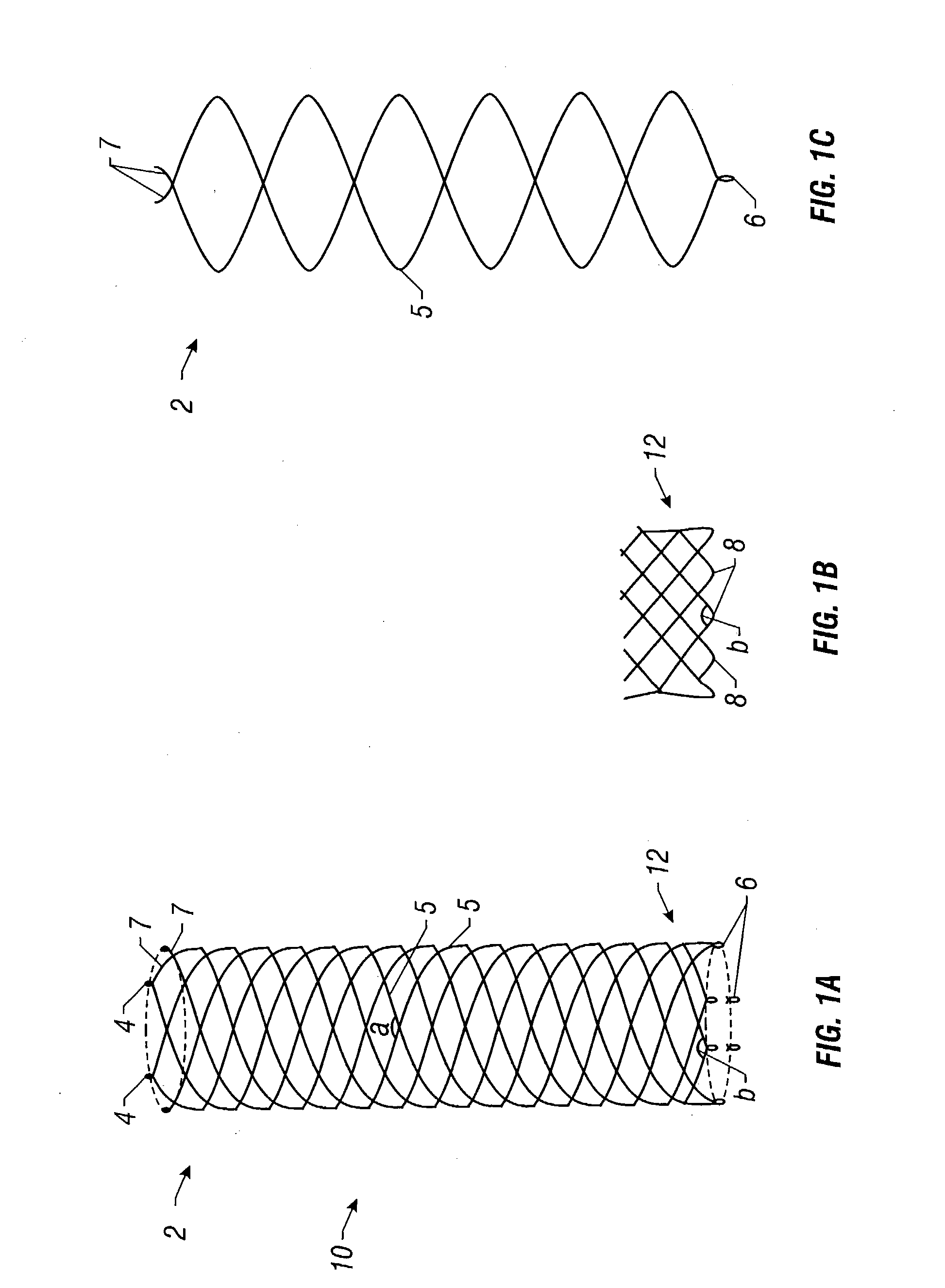
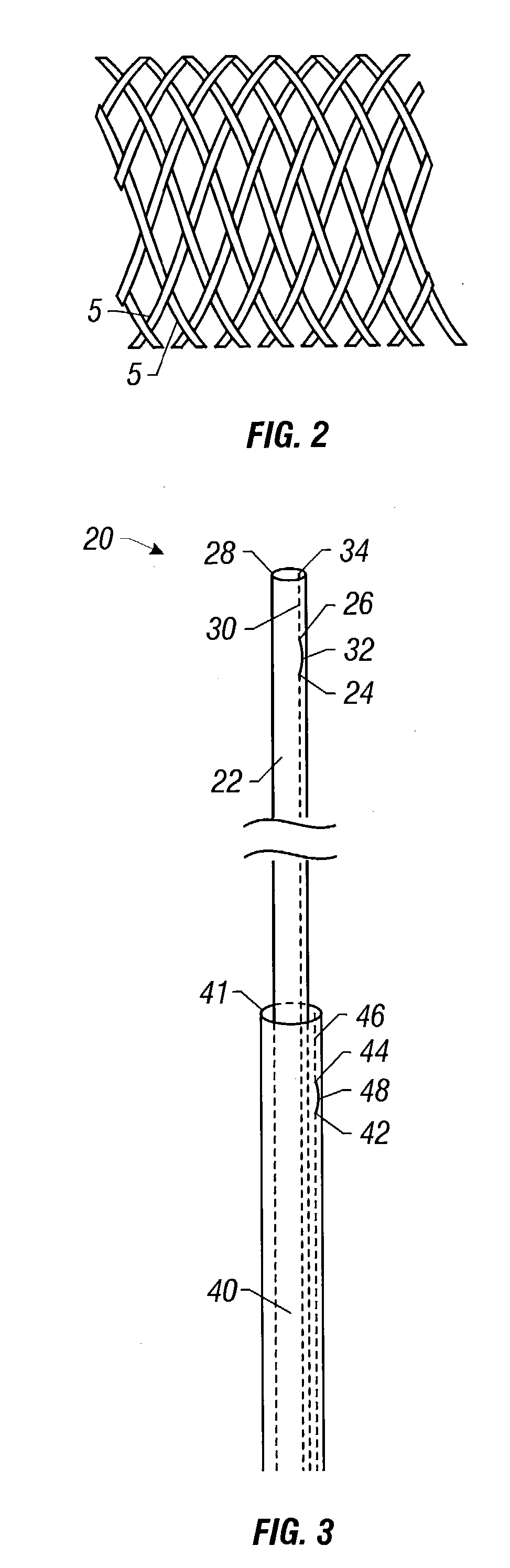
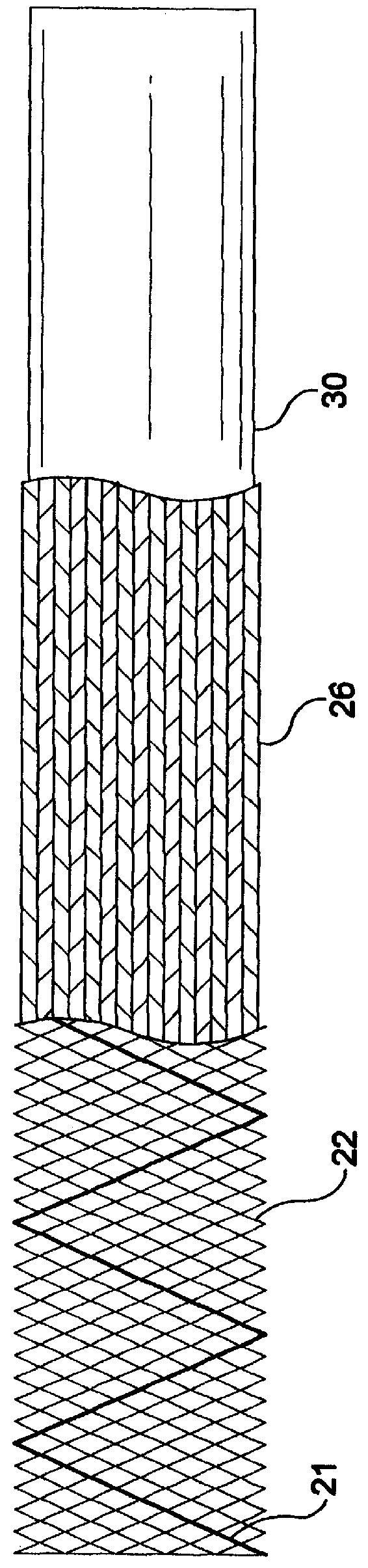
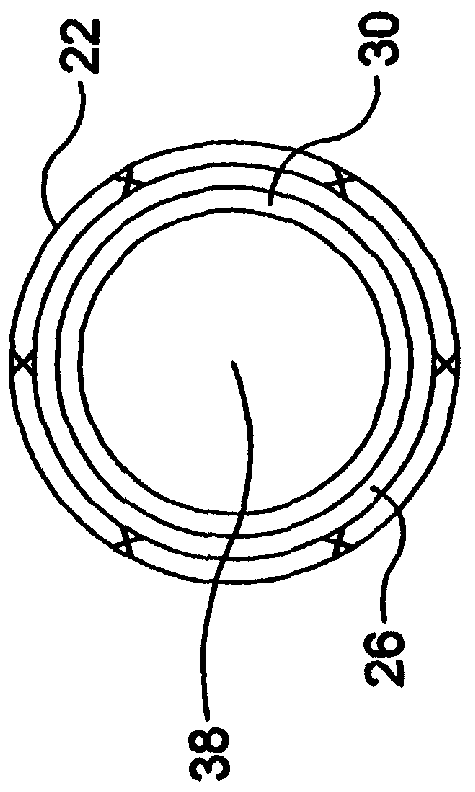
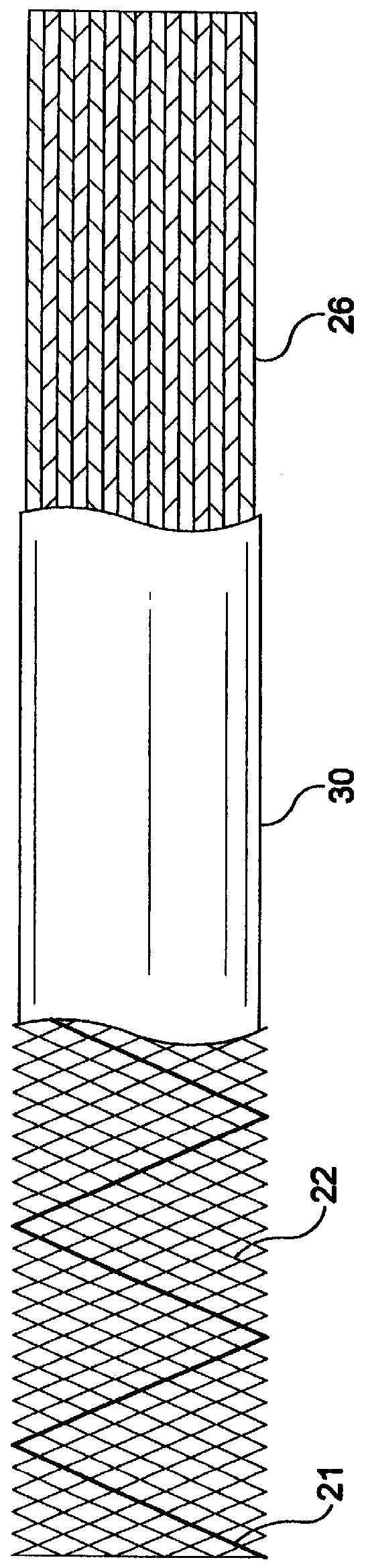
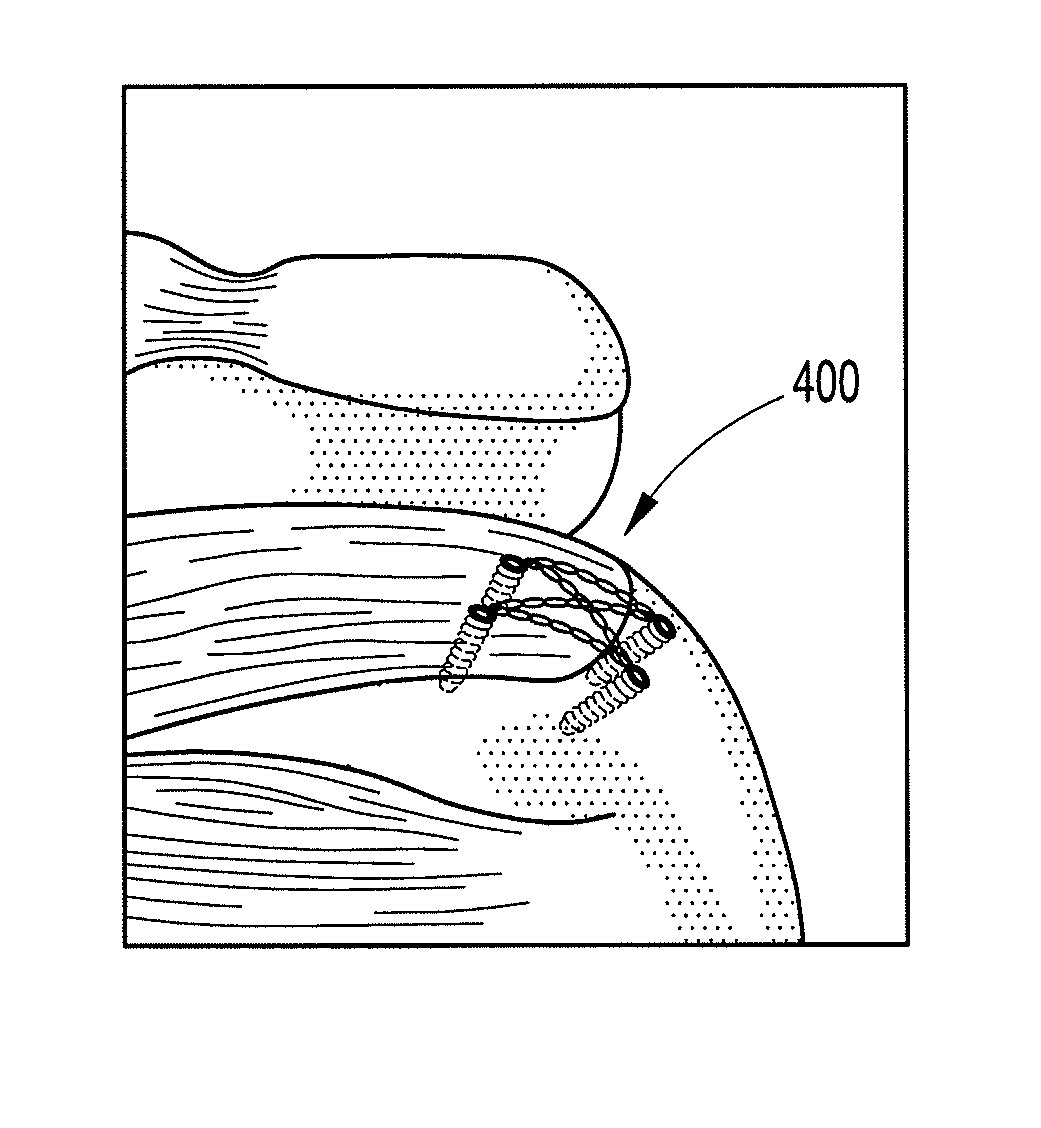
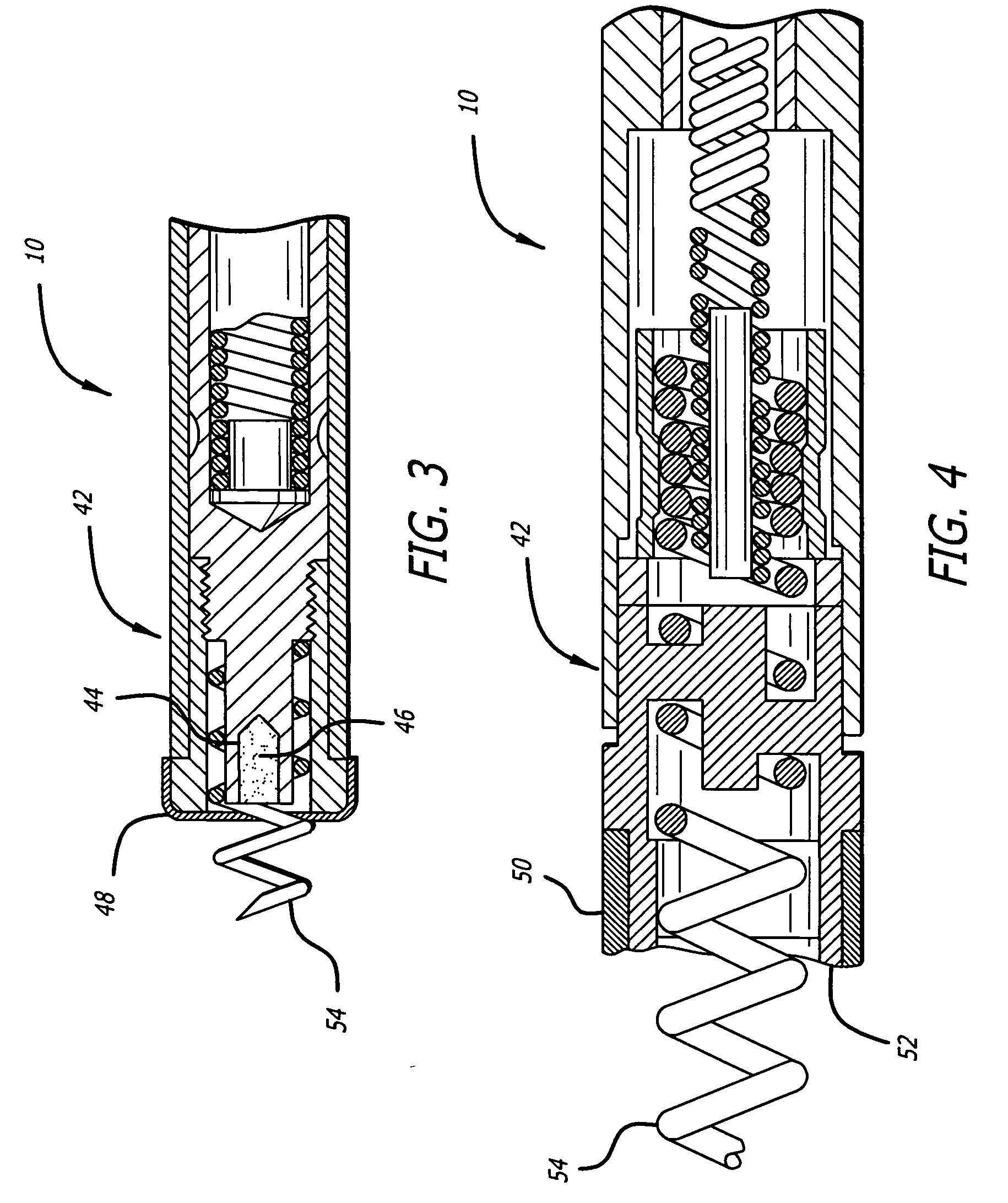
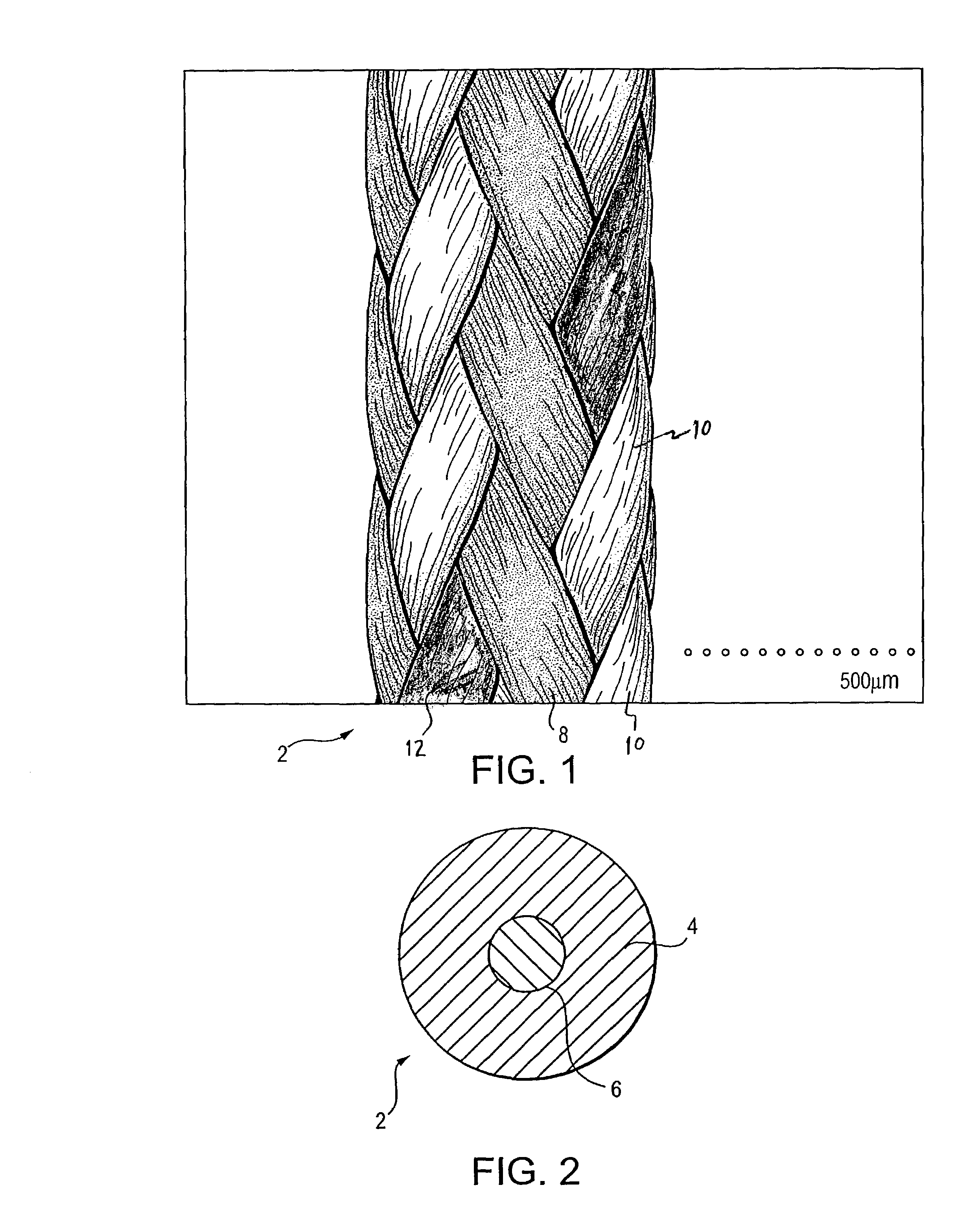
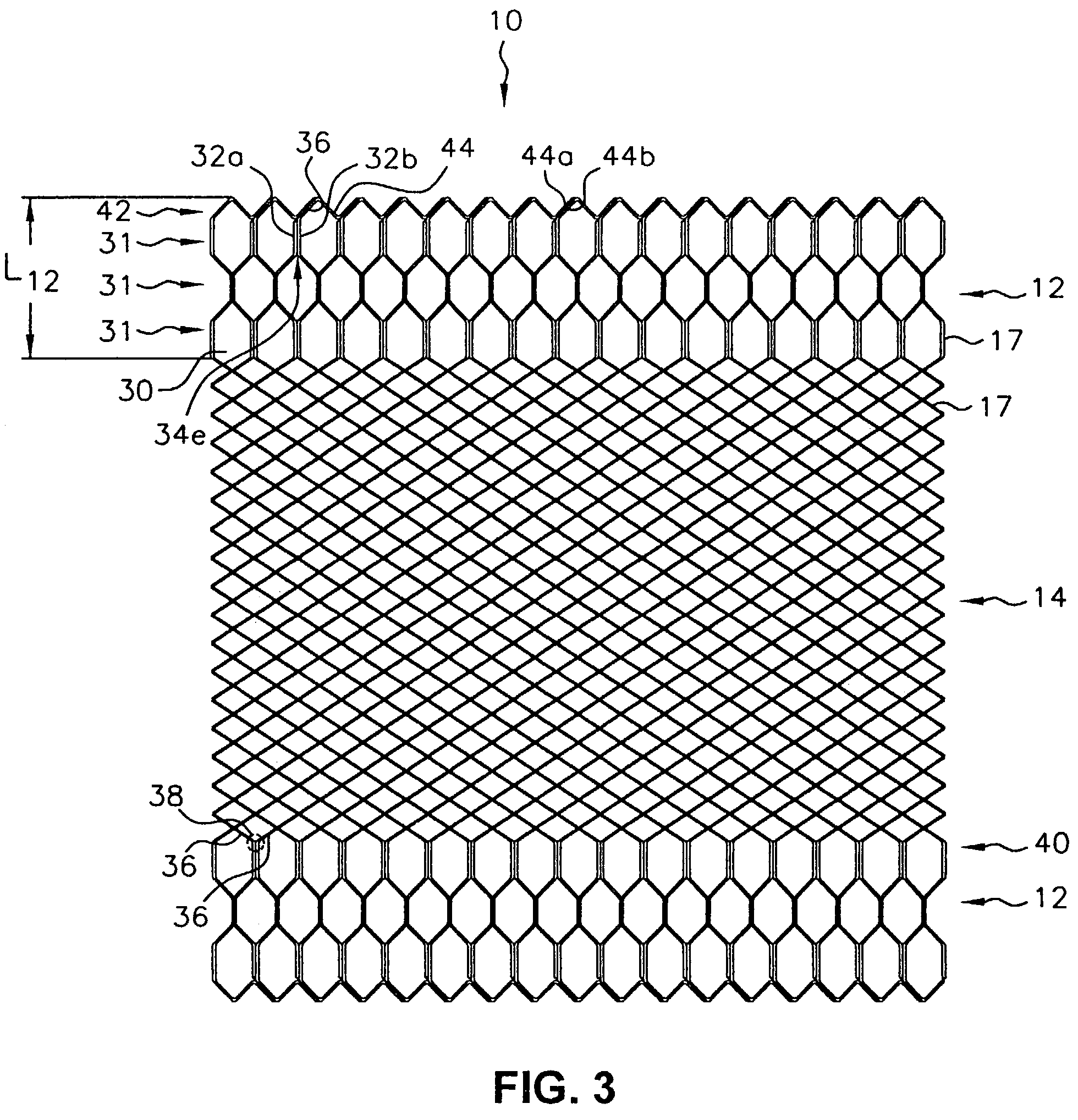
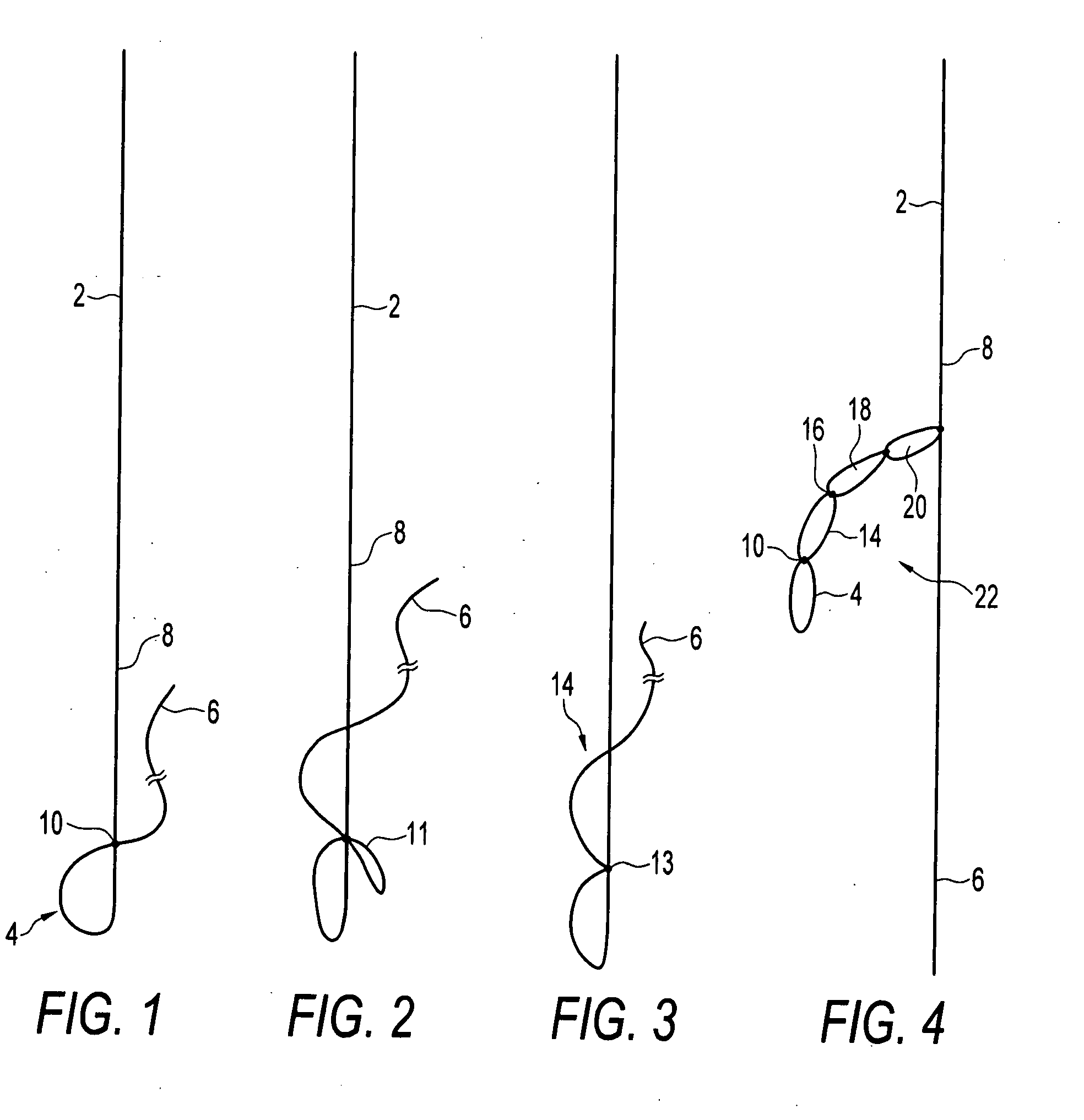
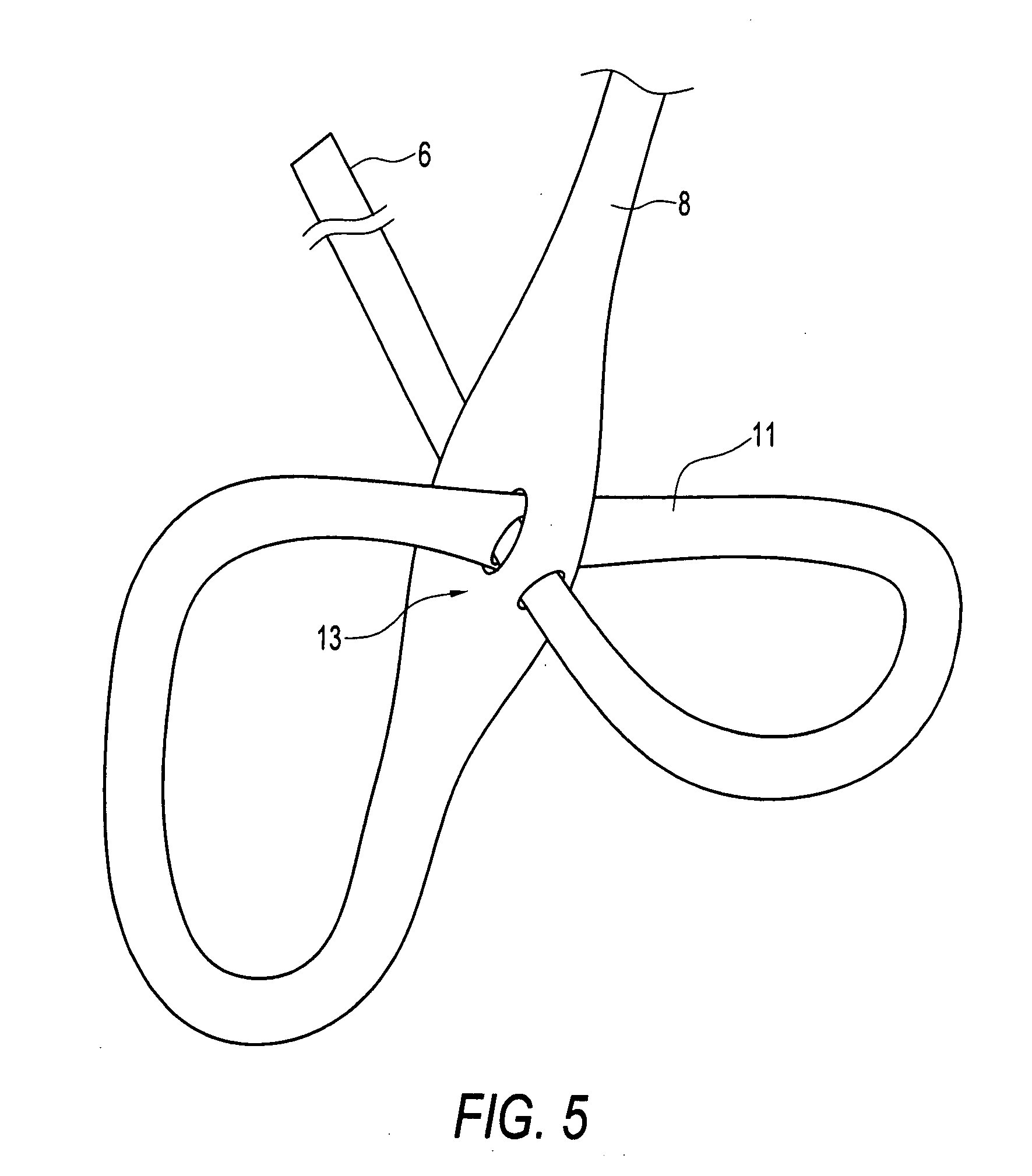
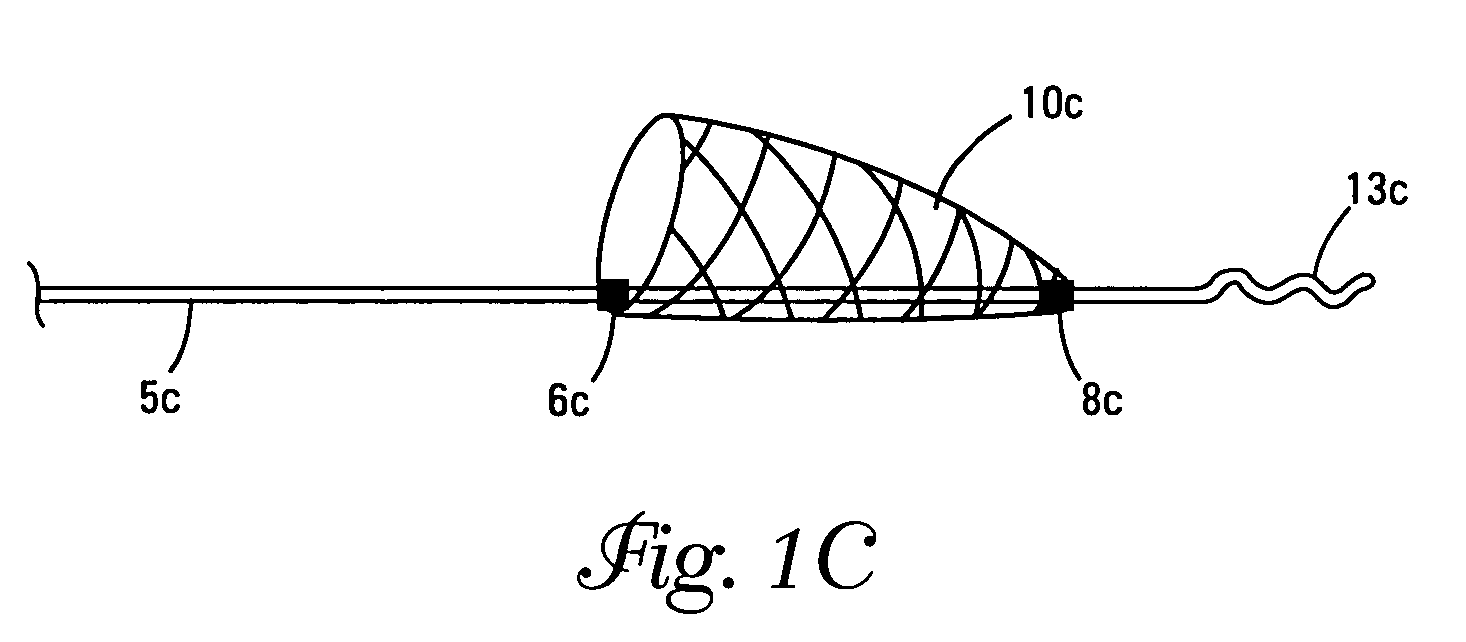
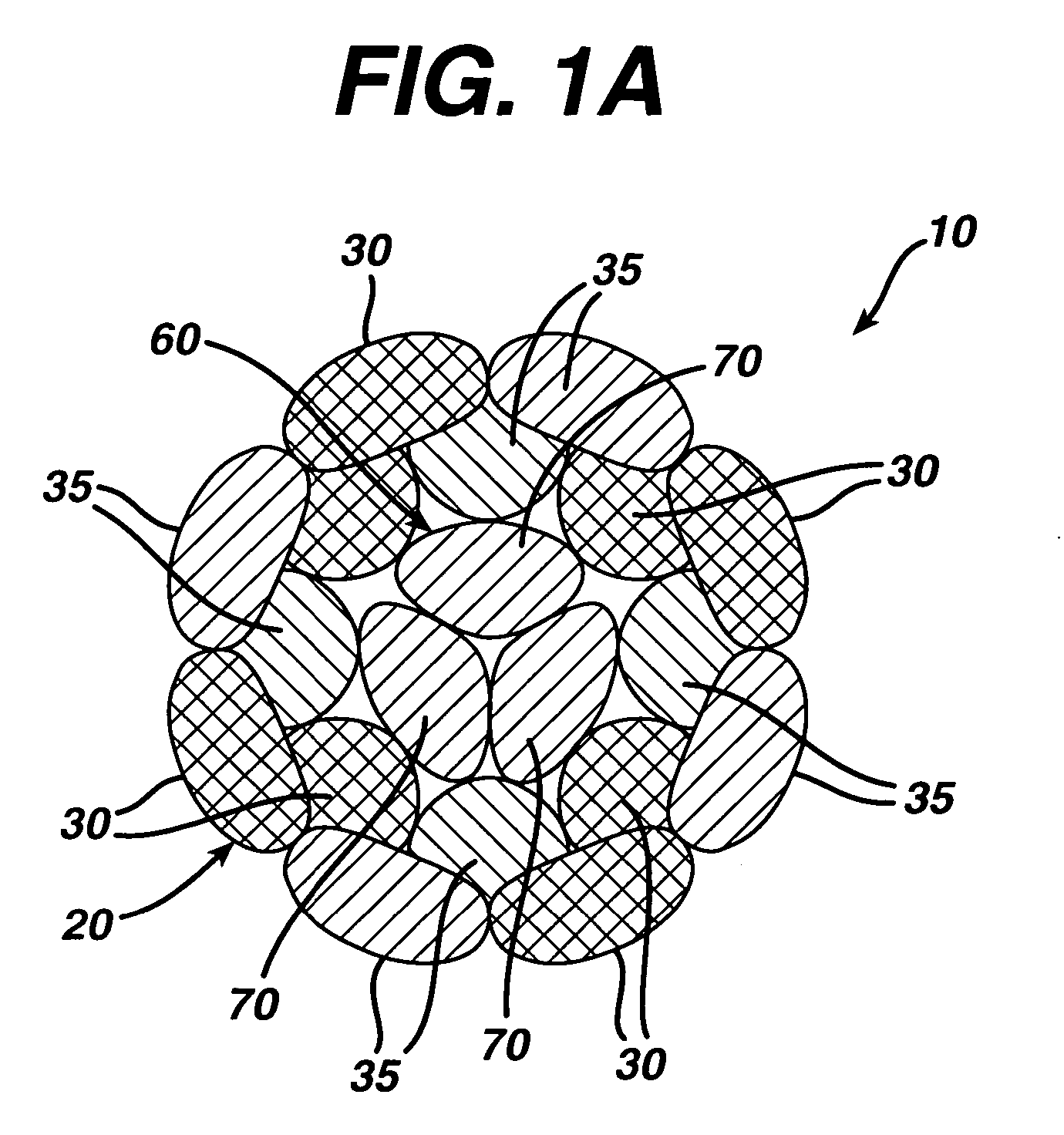
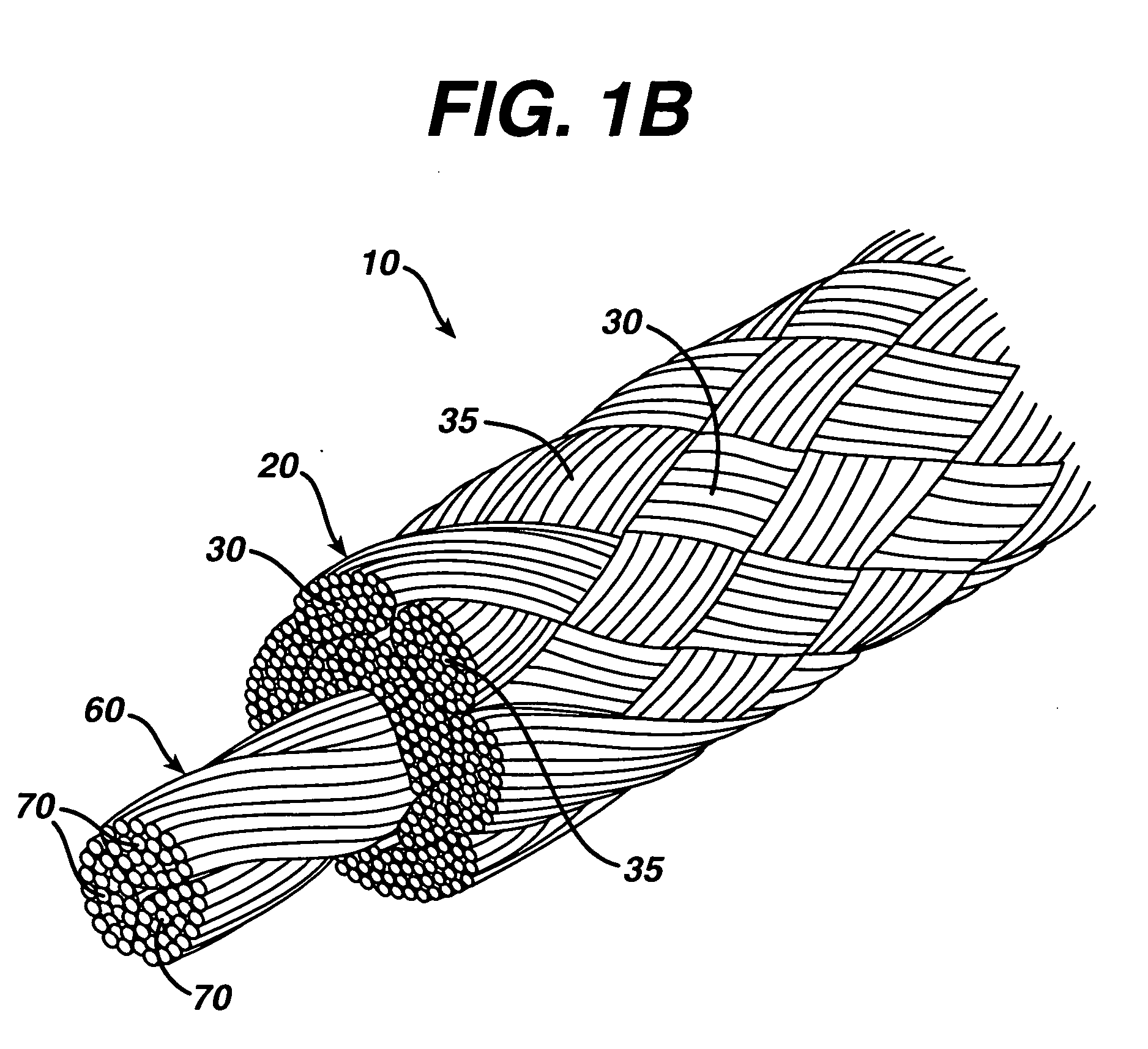
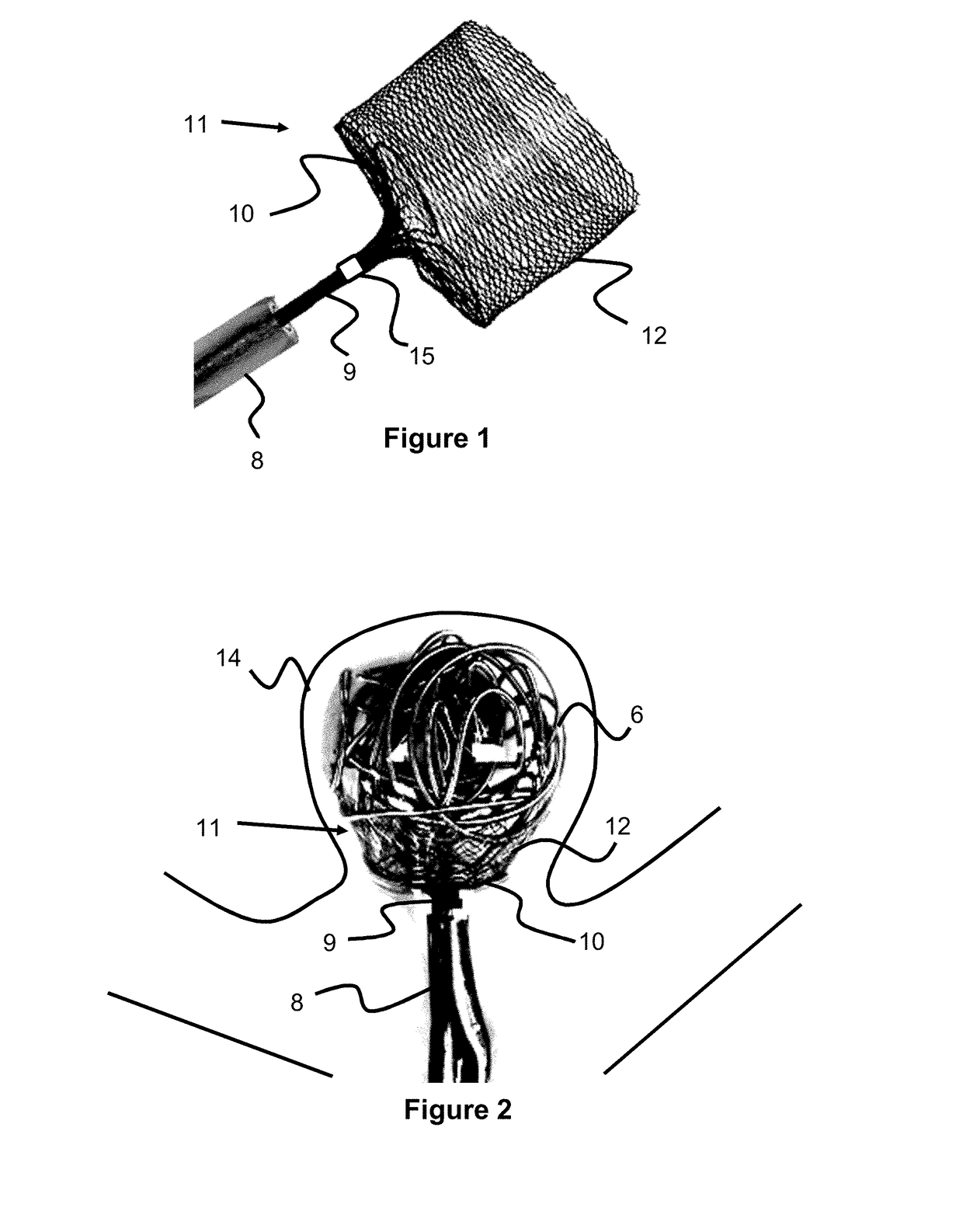
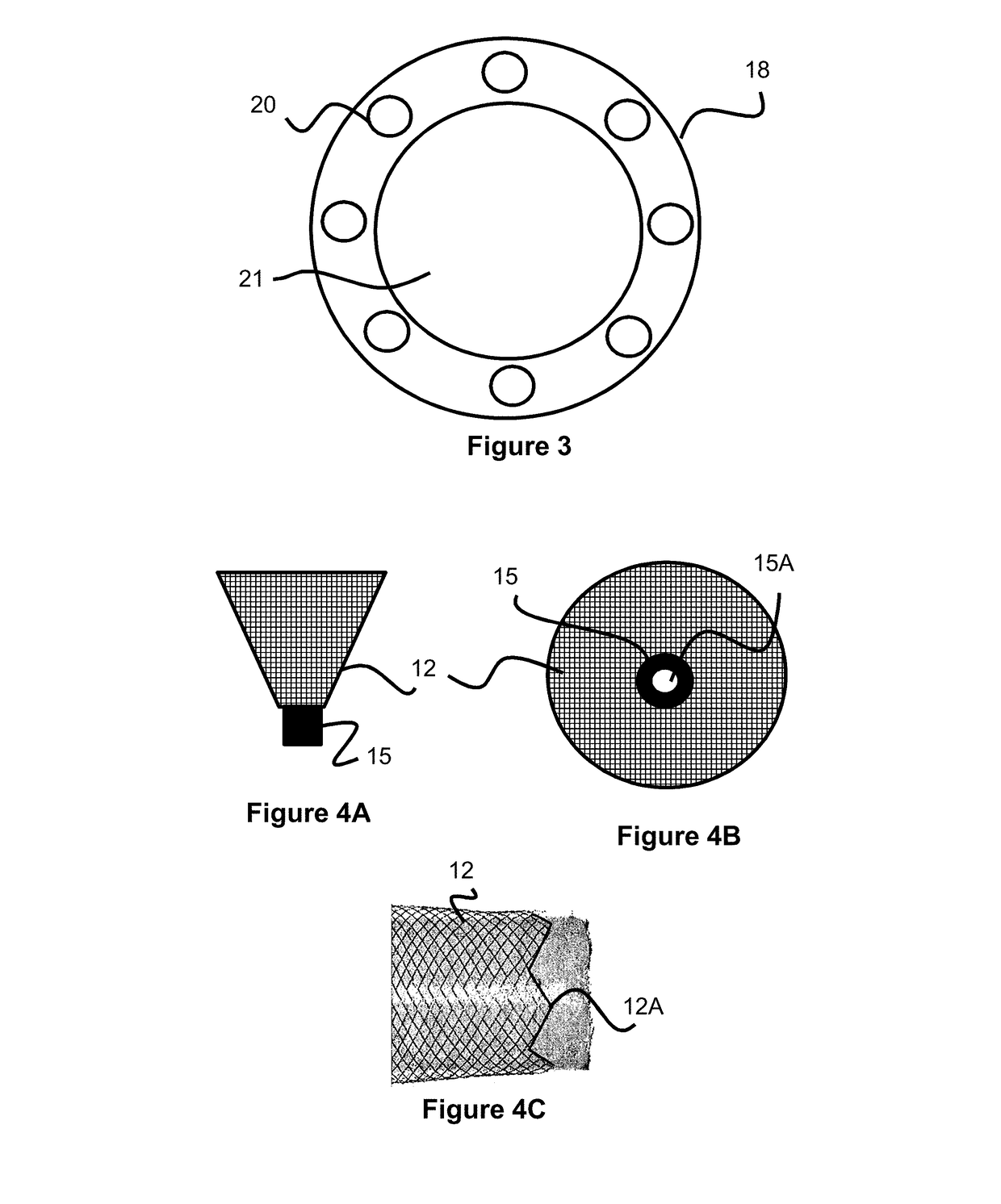
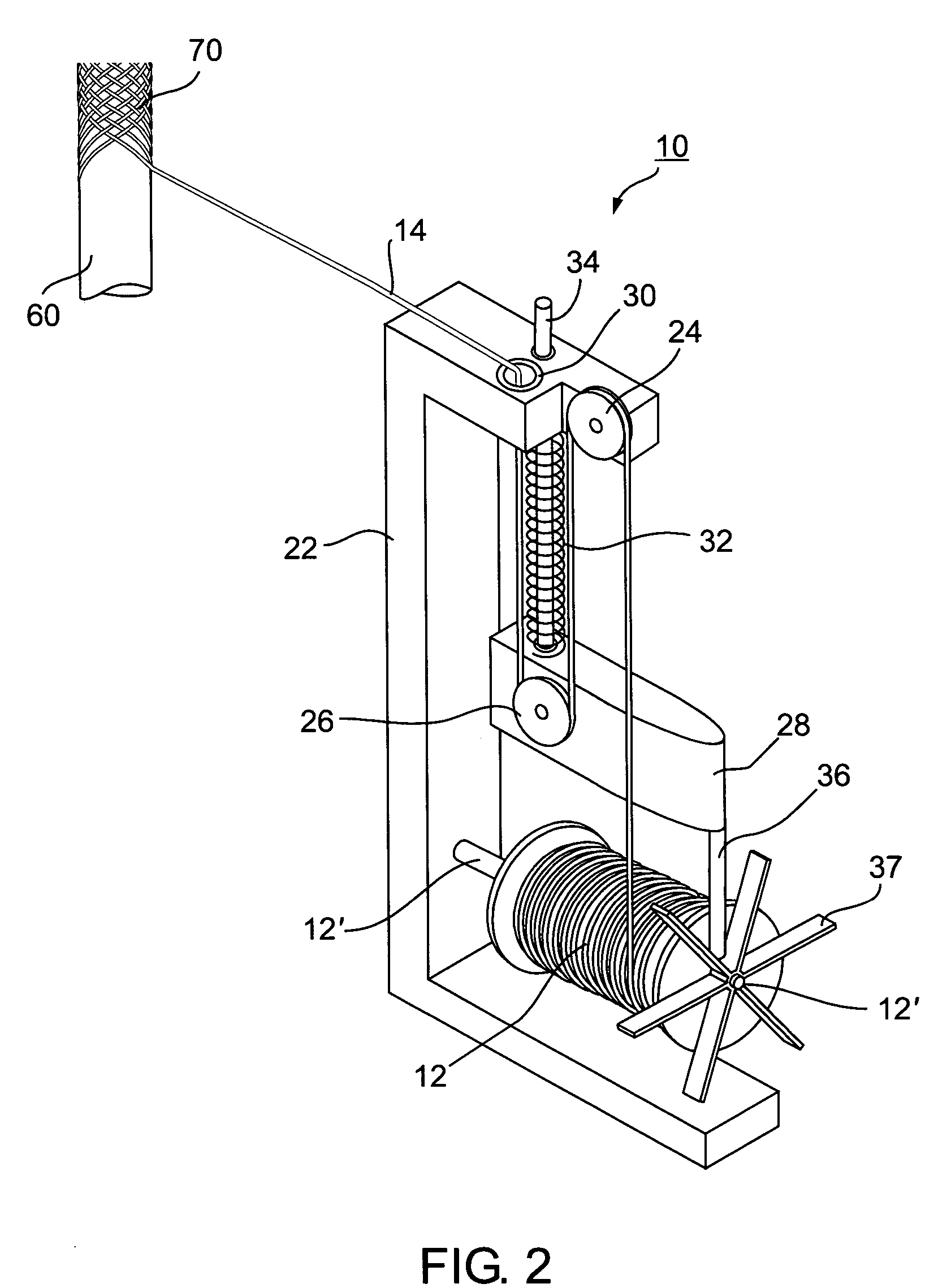
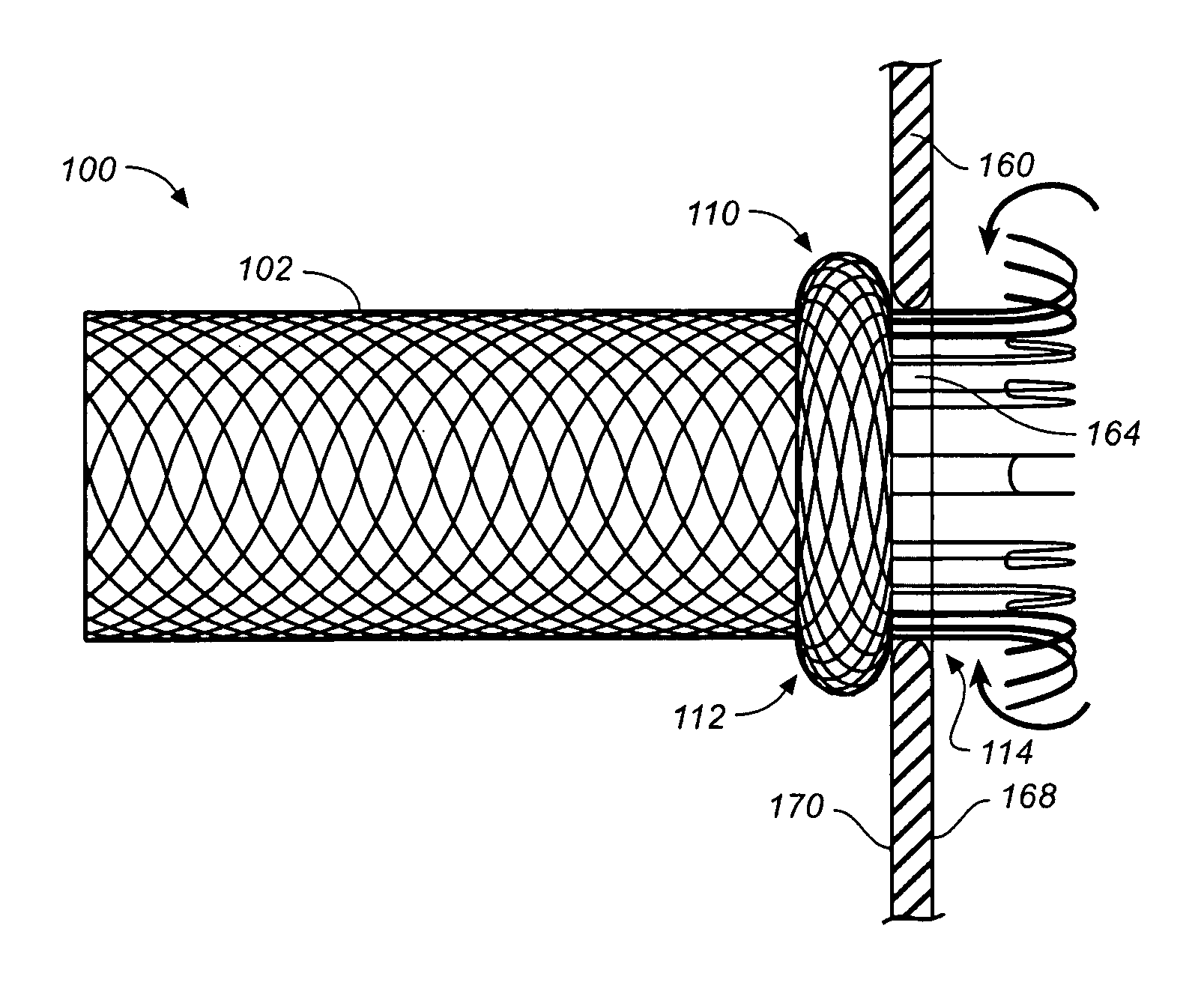
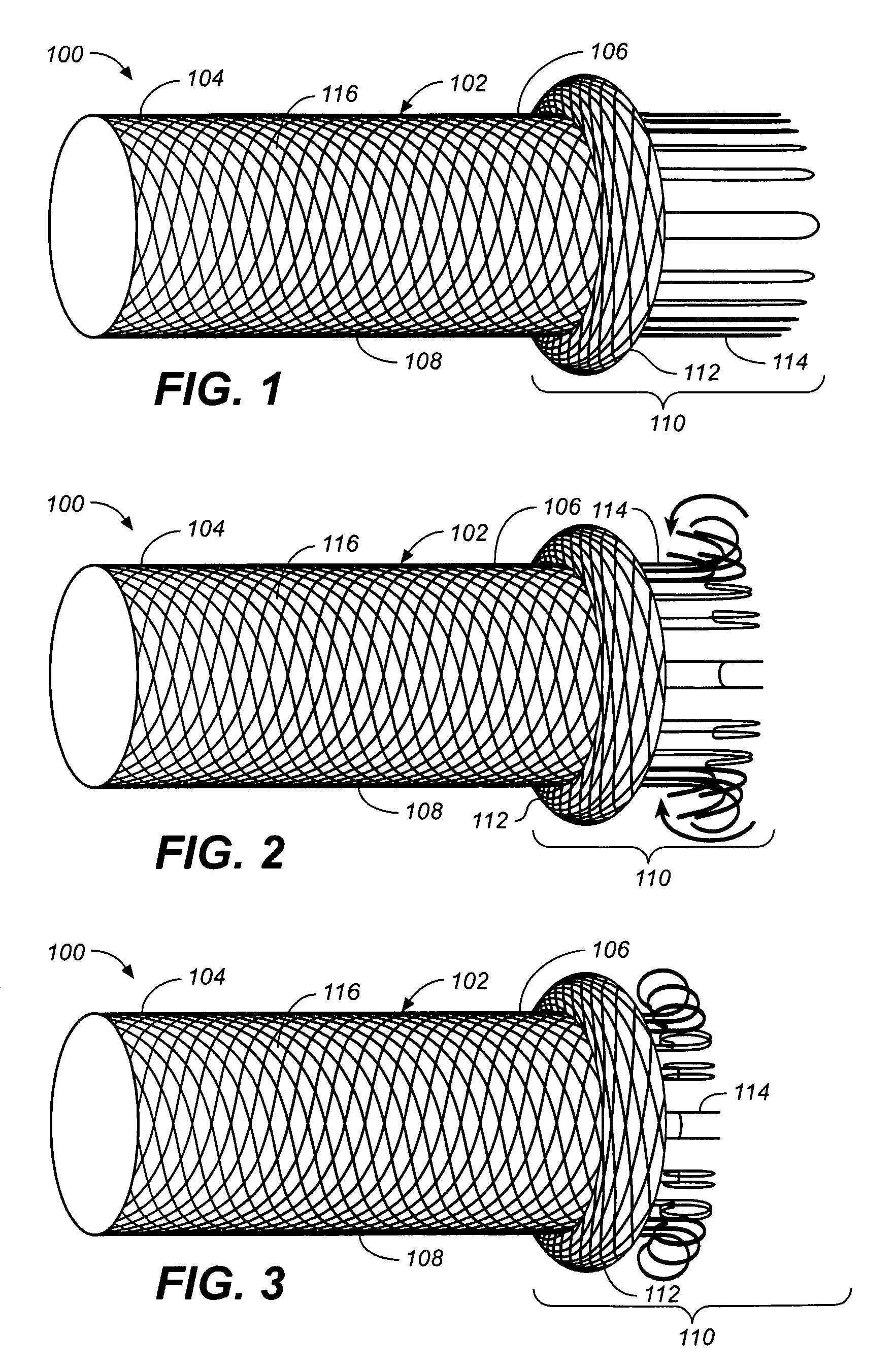
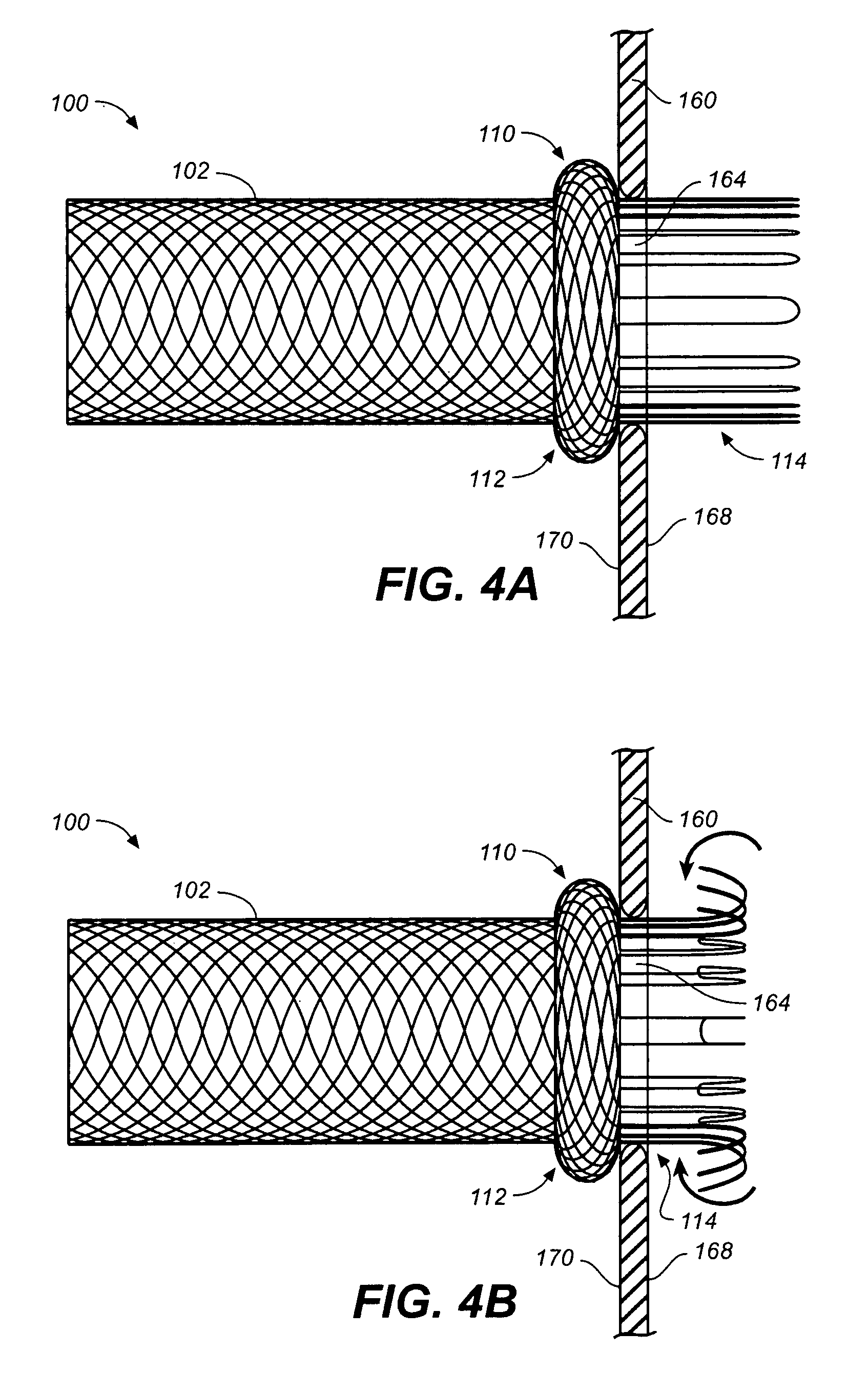
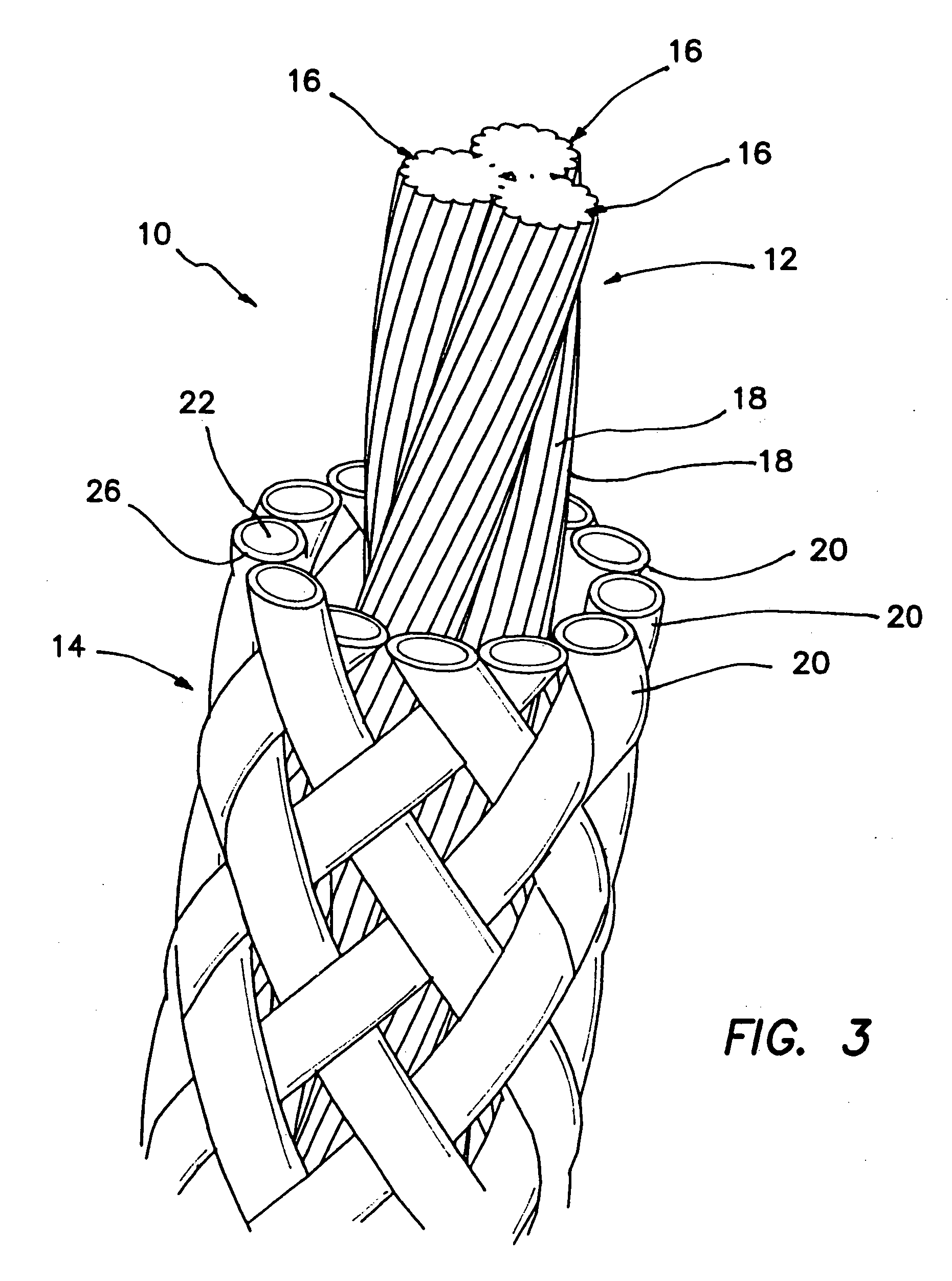
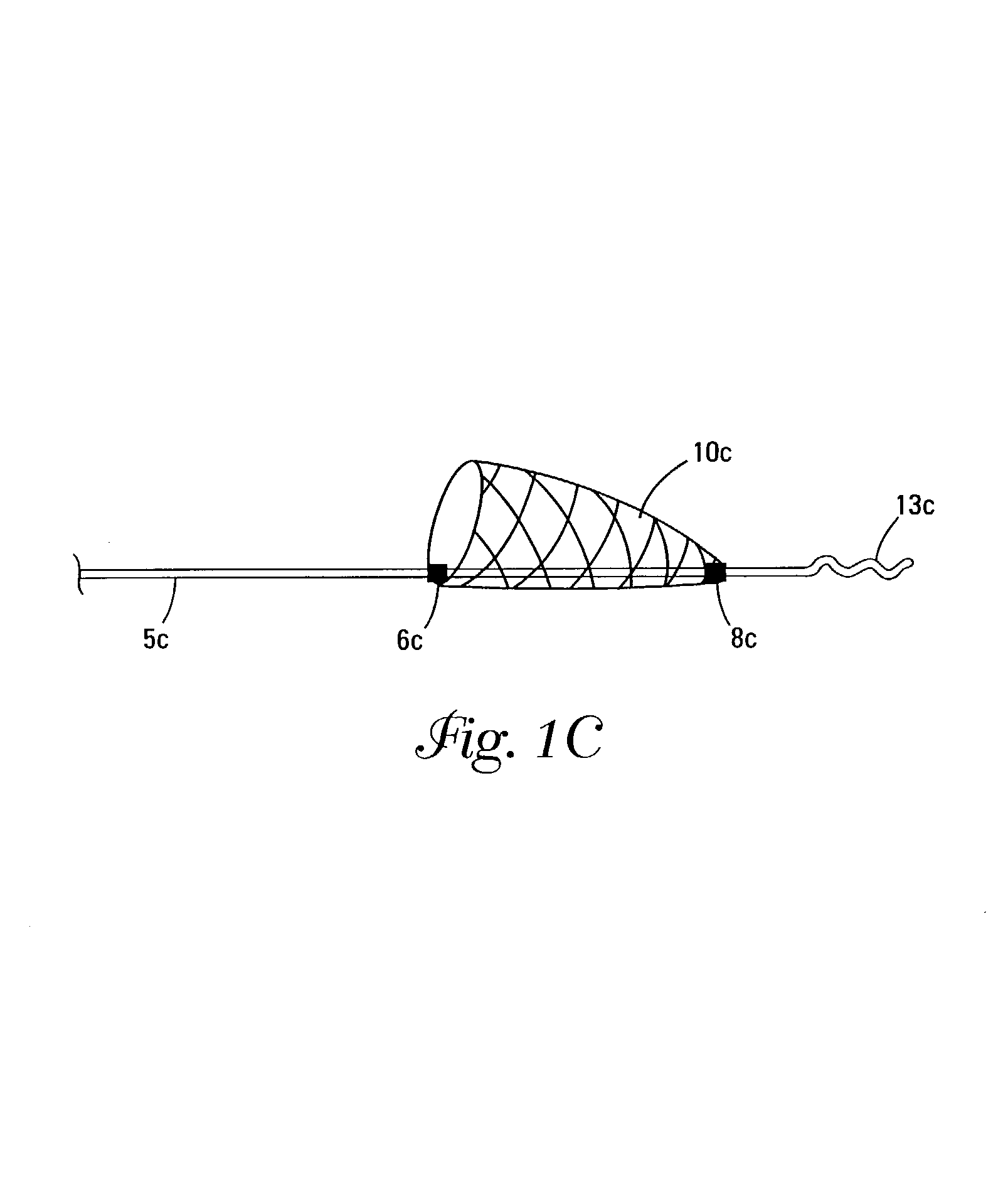
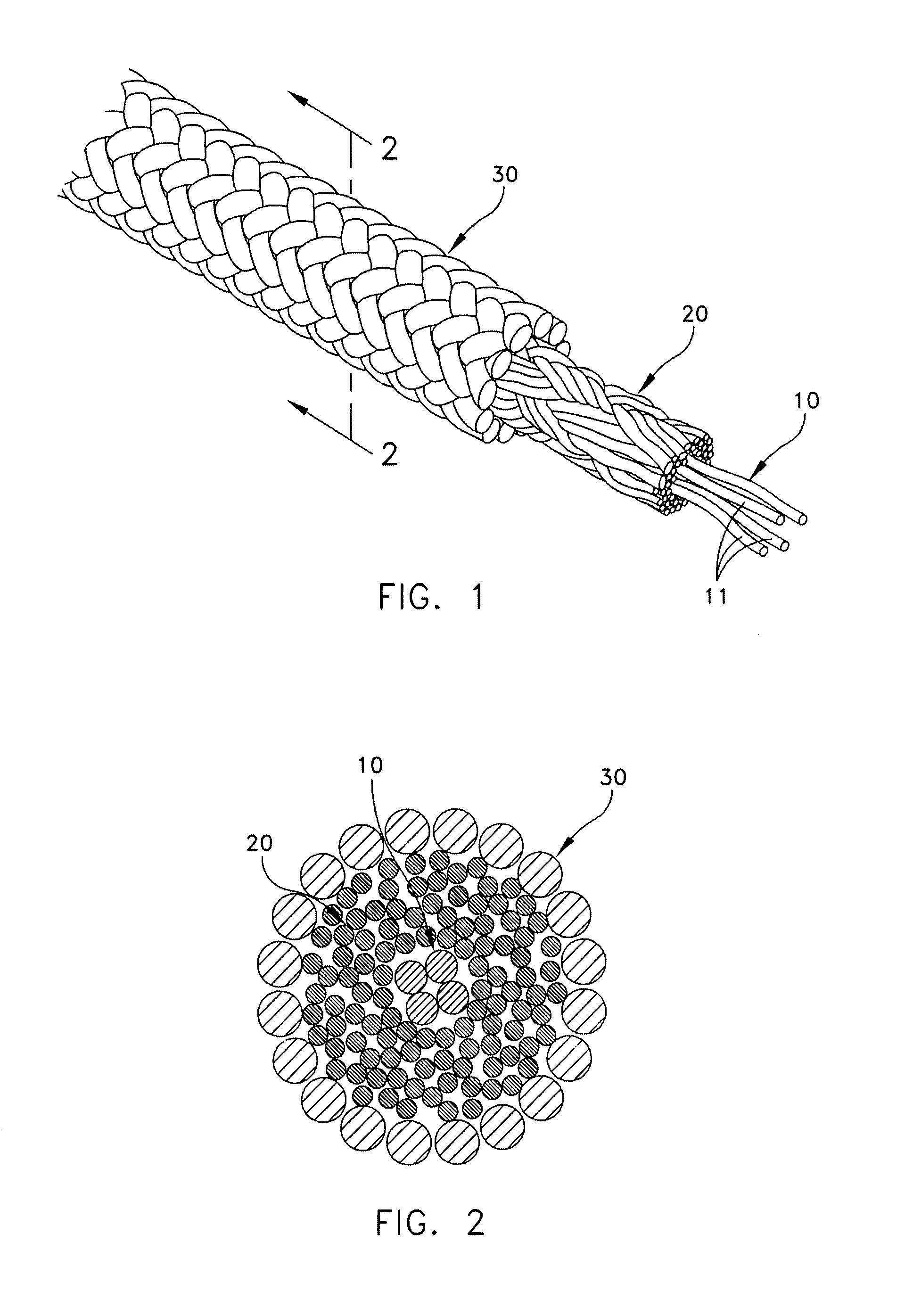
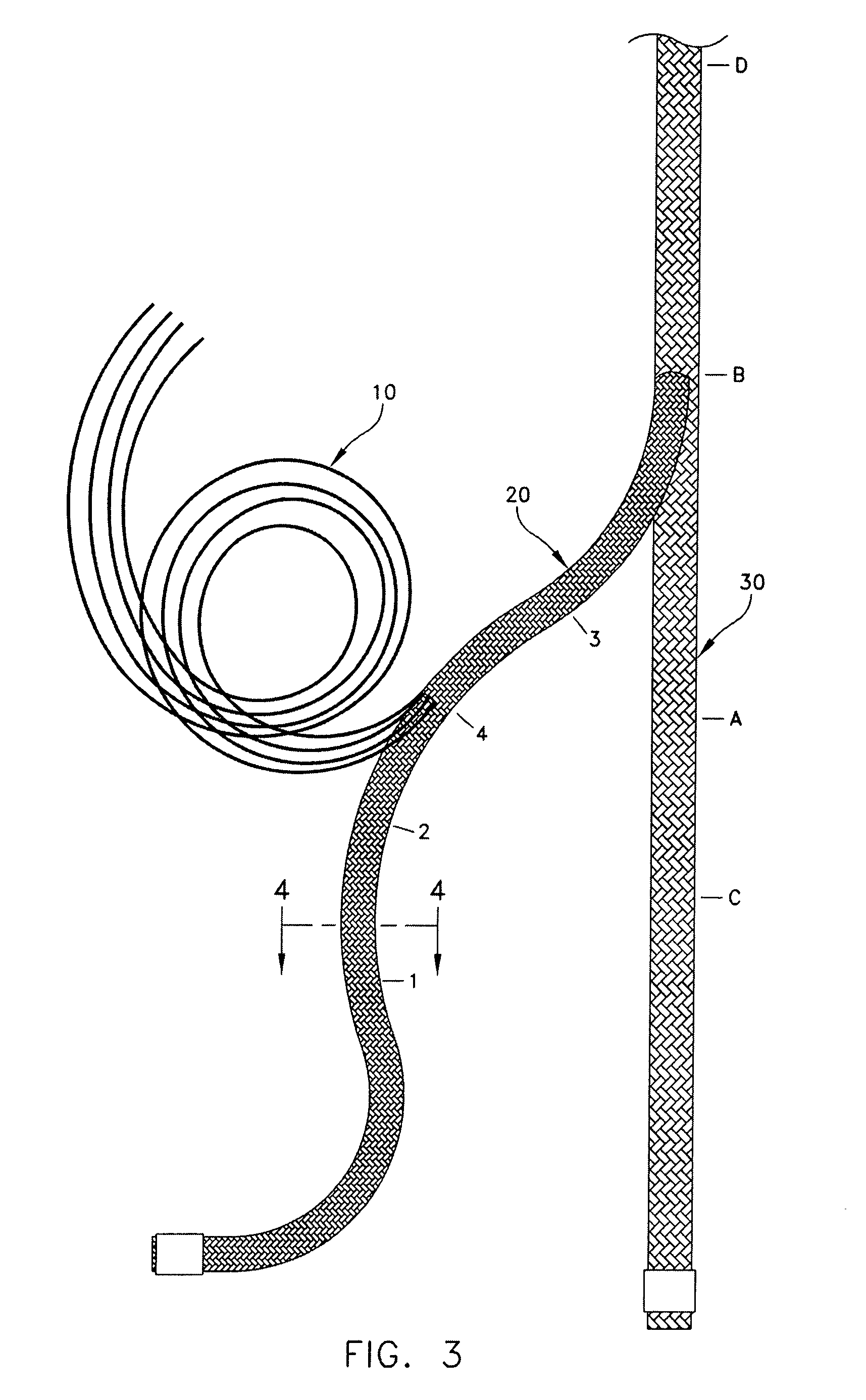
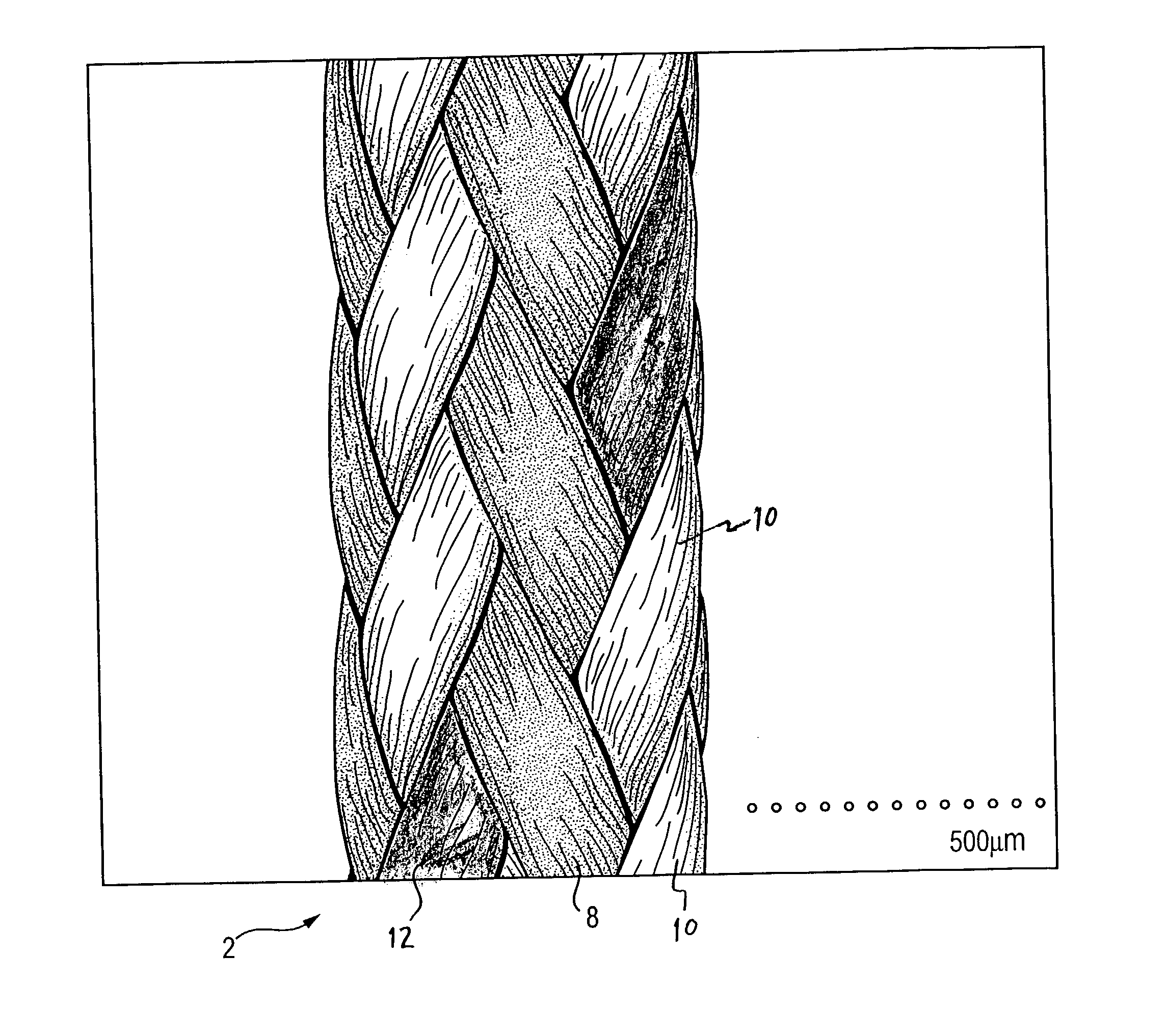
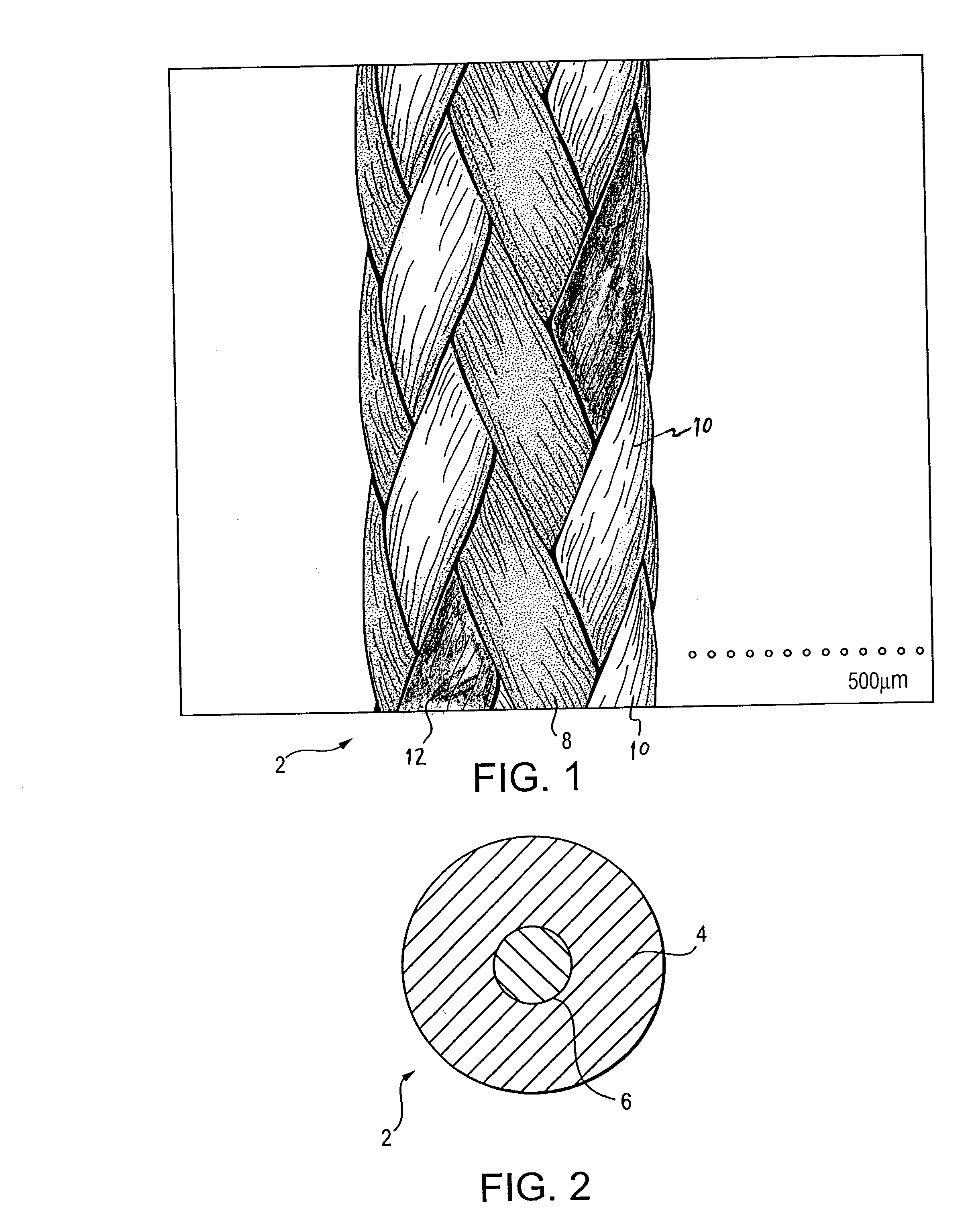
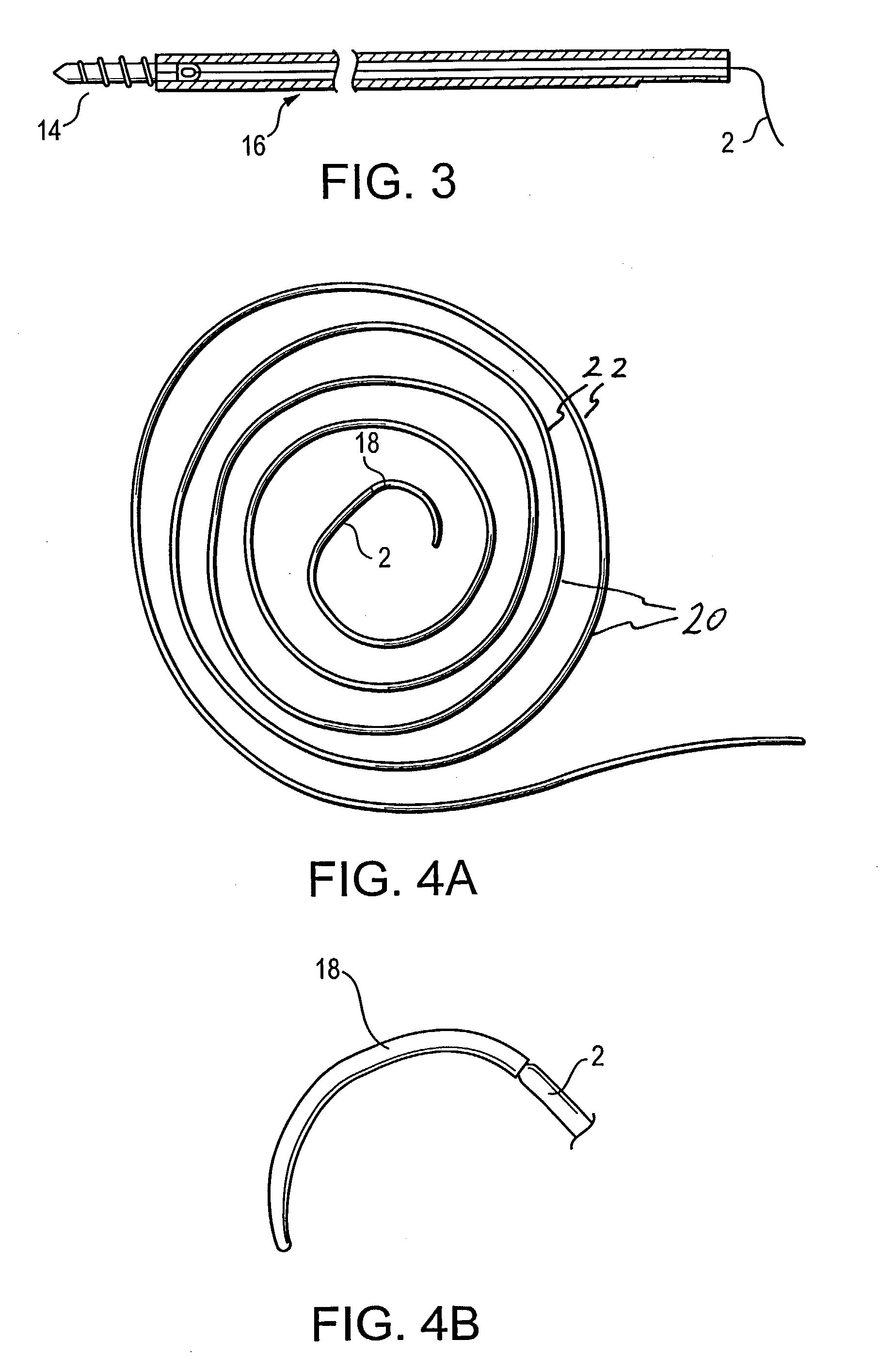
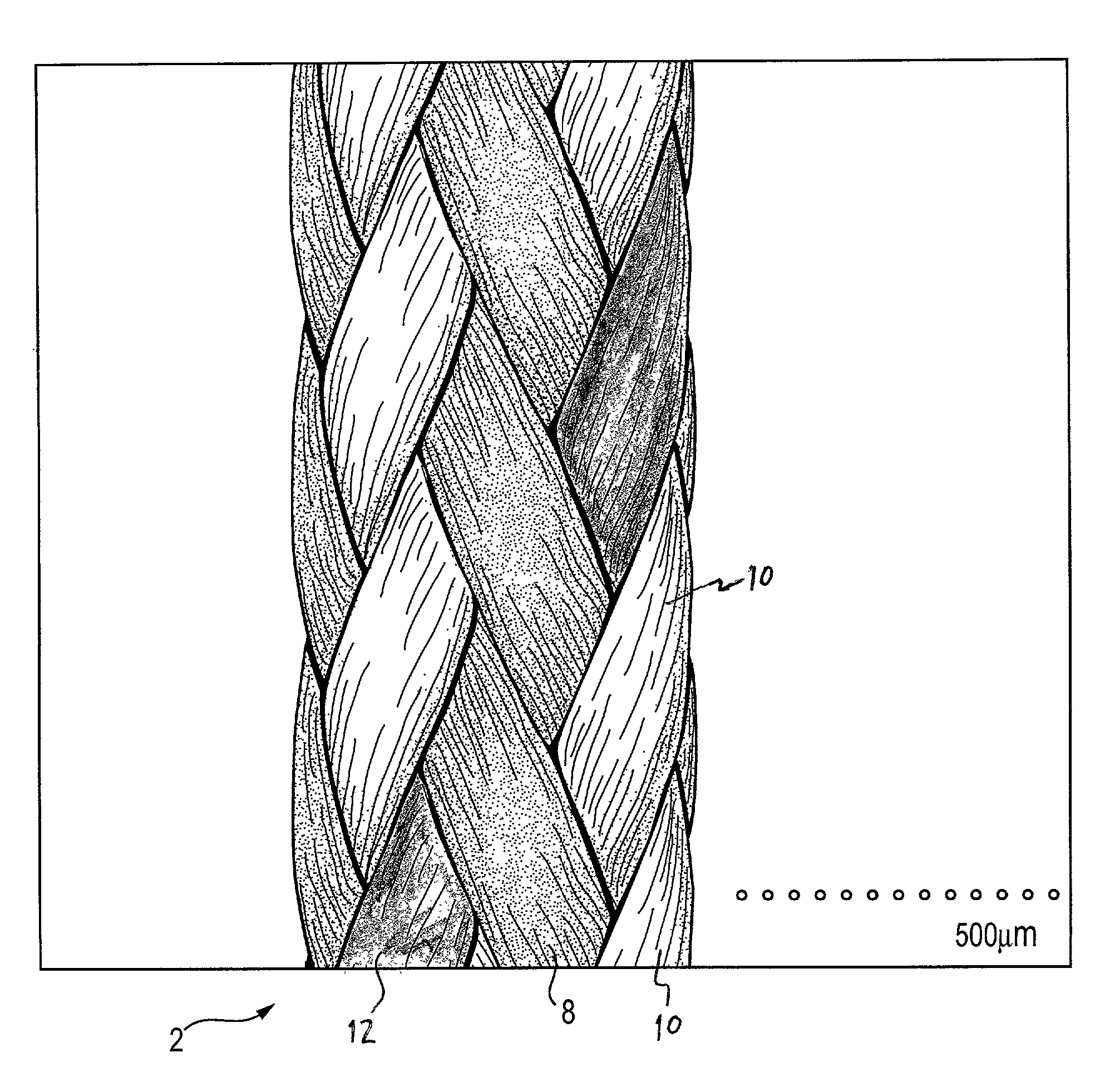
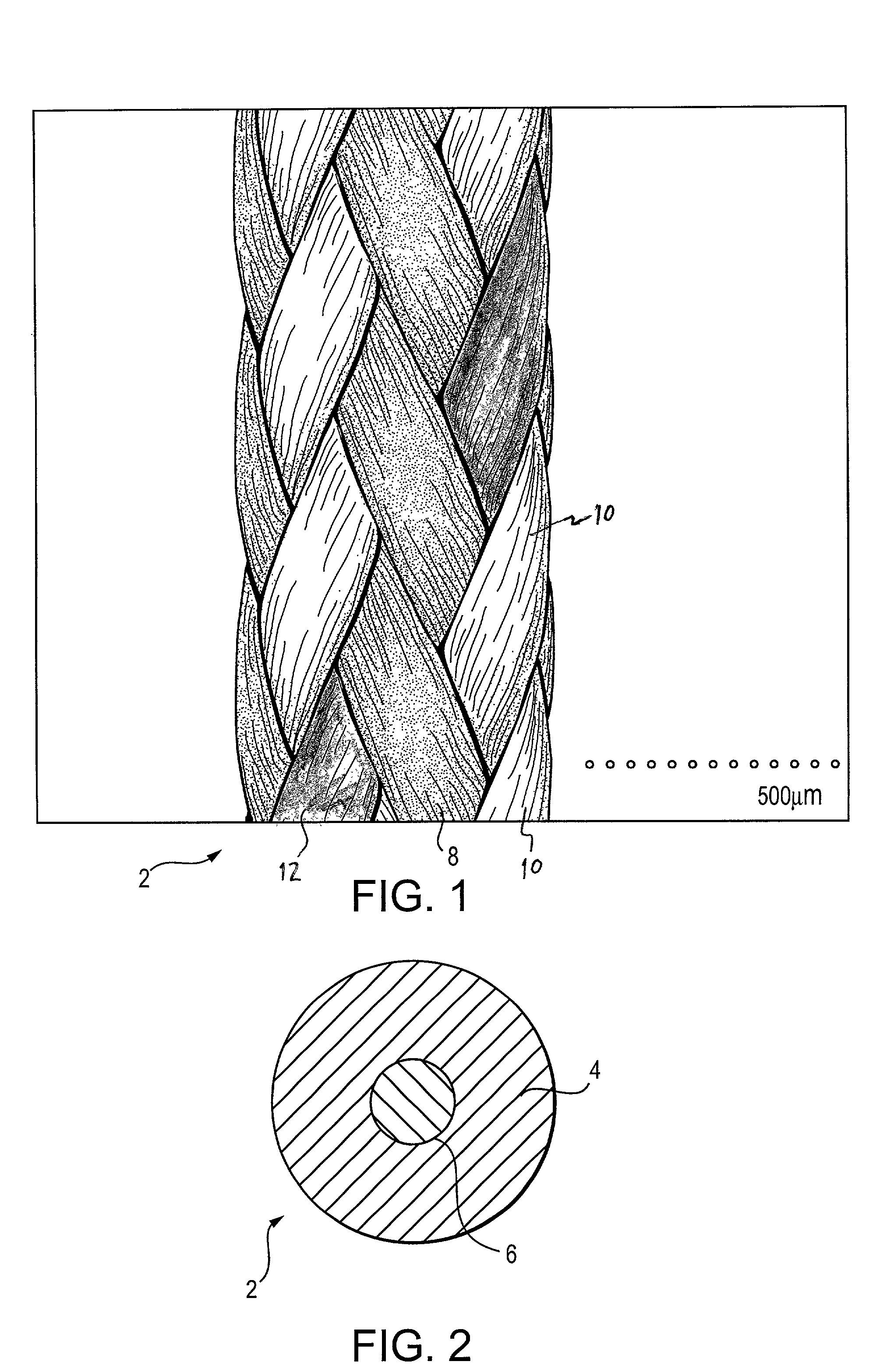
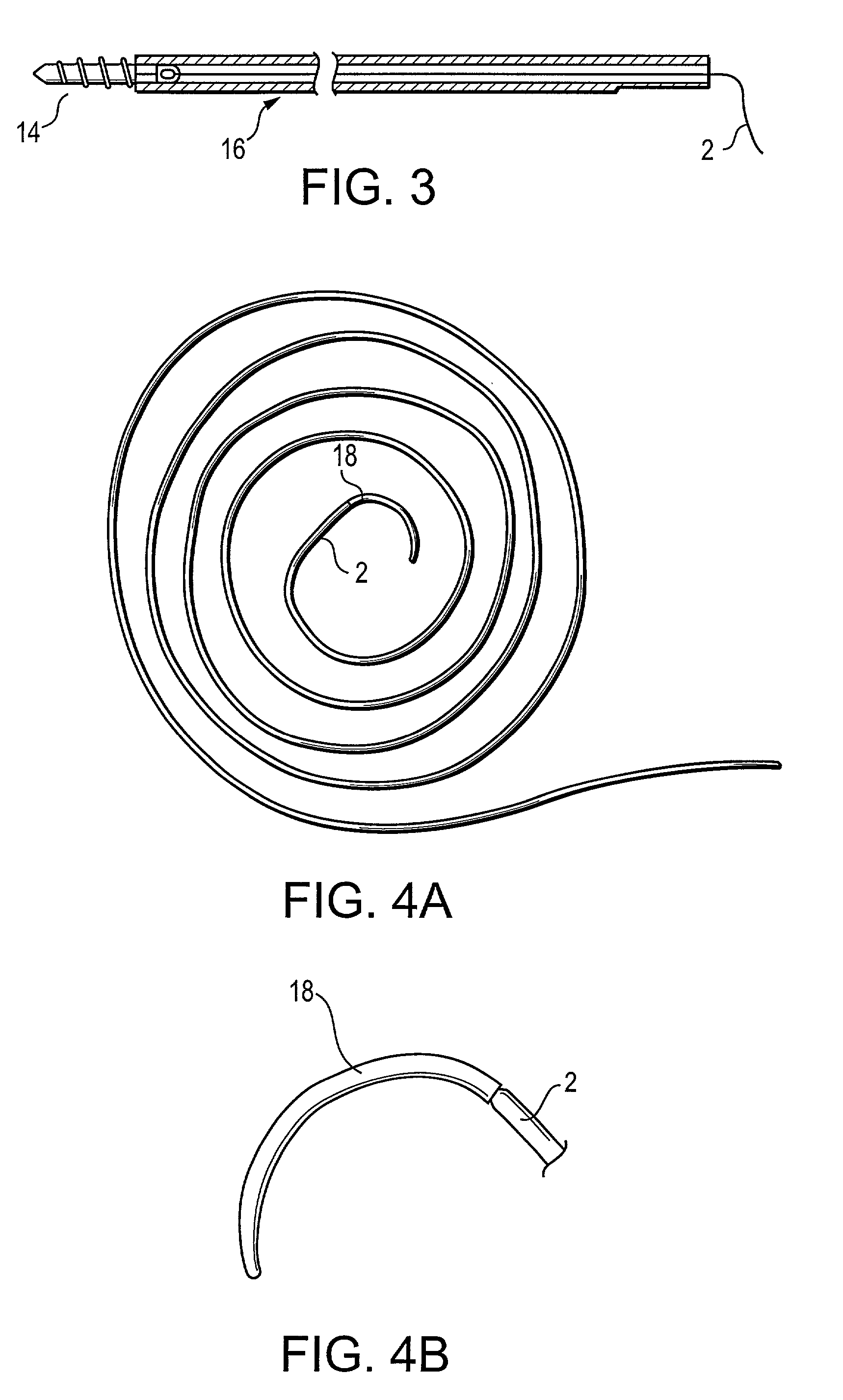
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:HYODOH HIDEKI +2
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
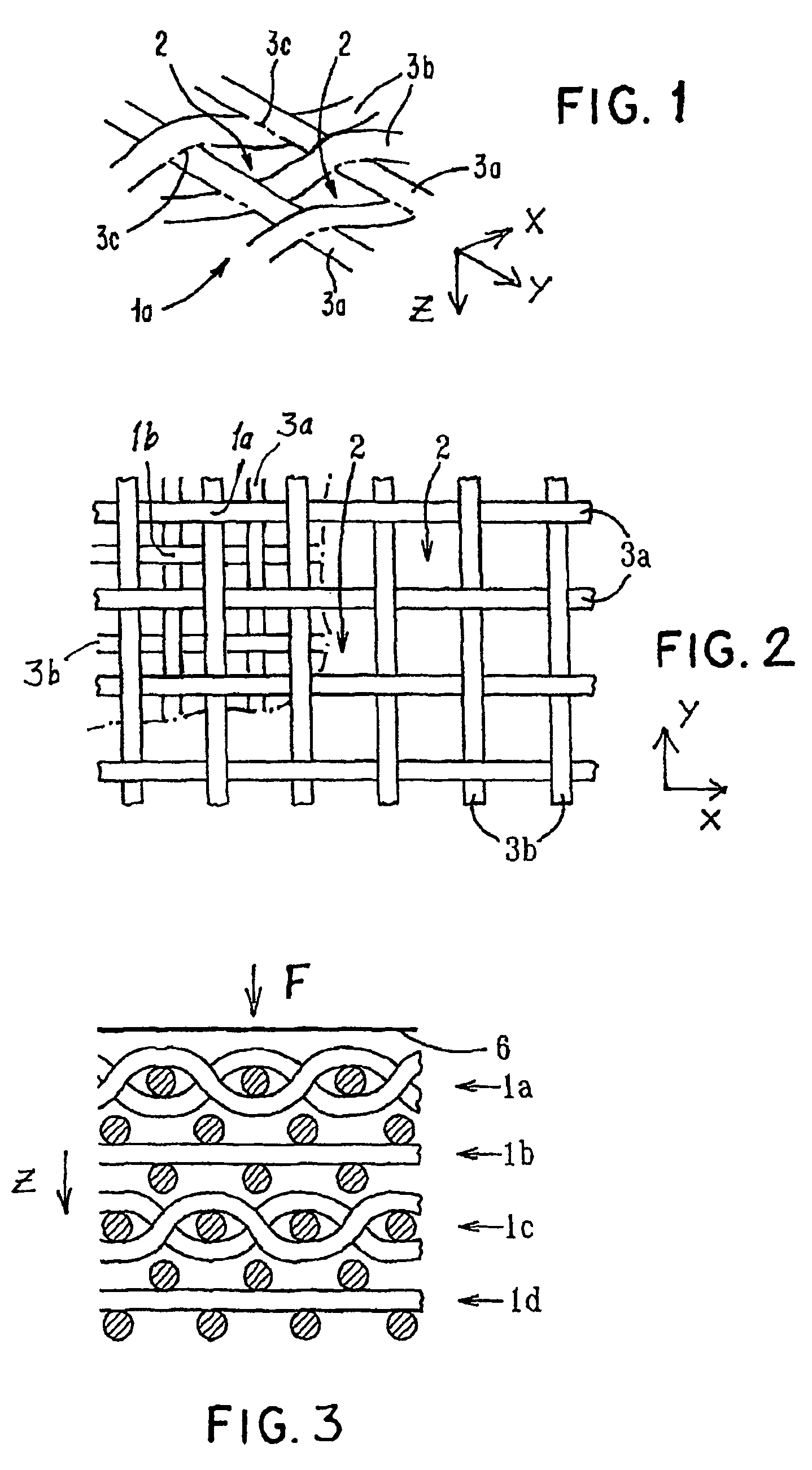
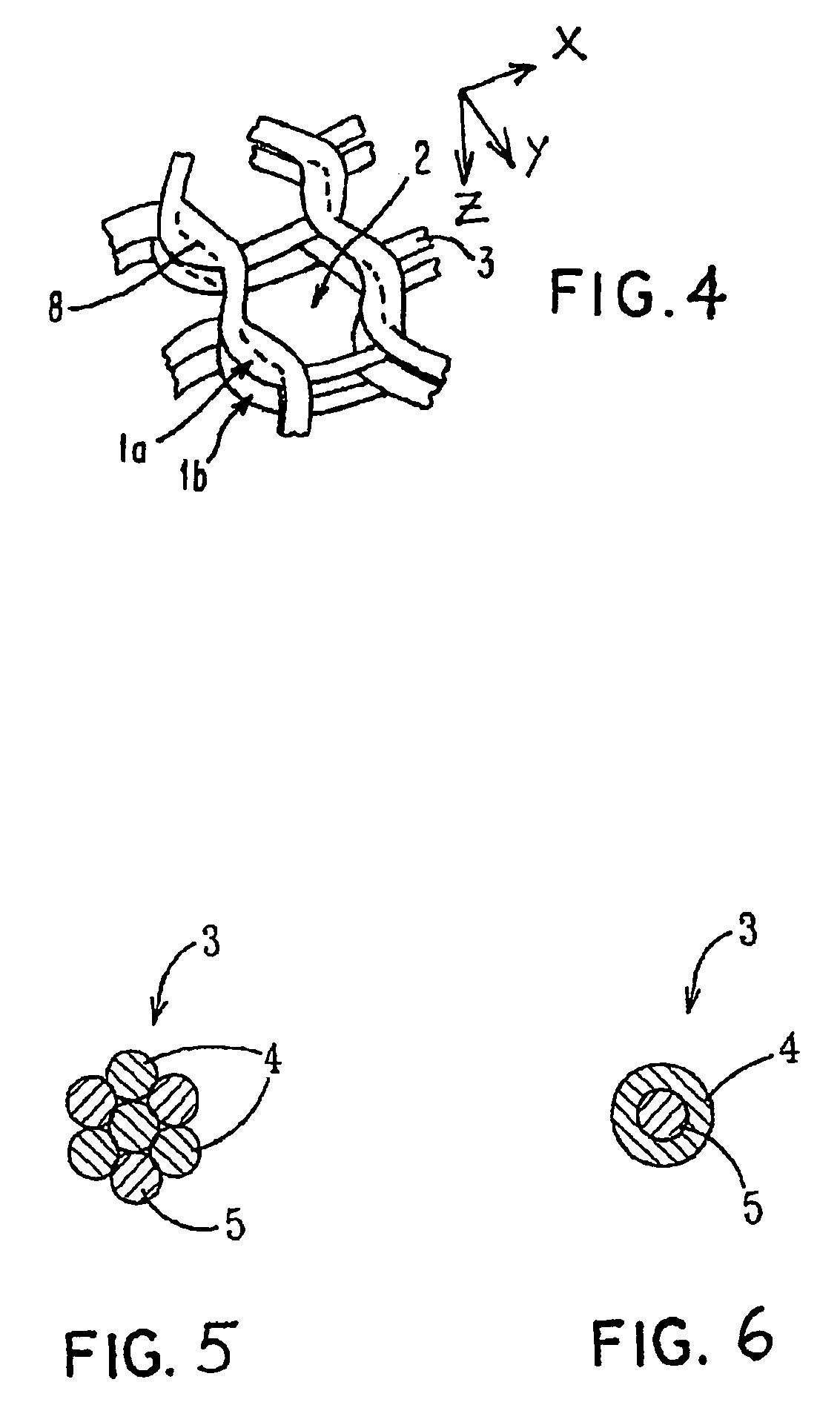
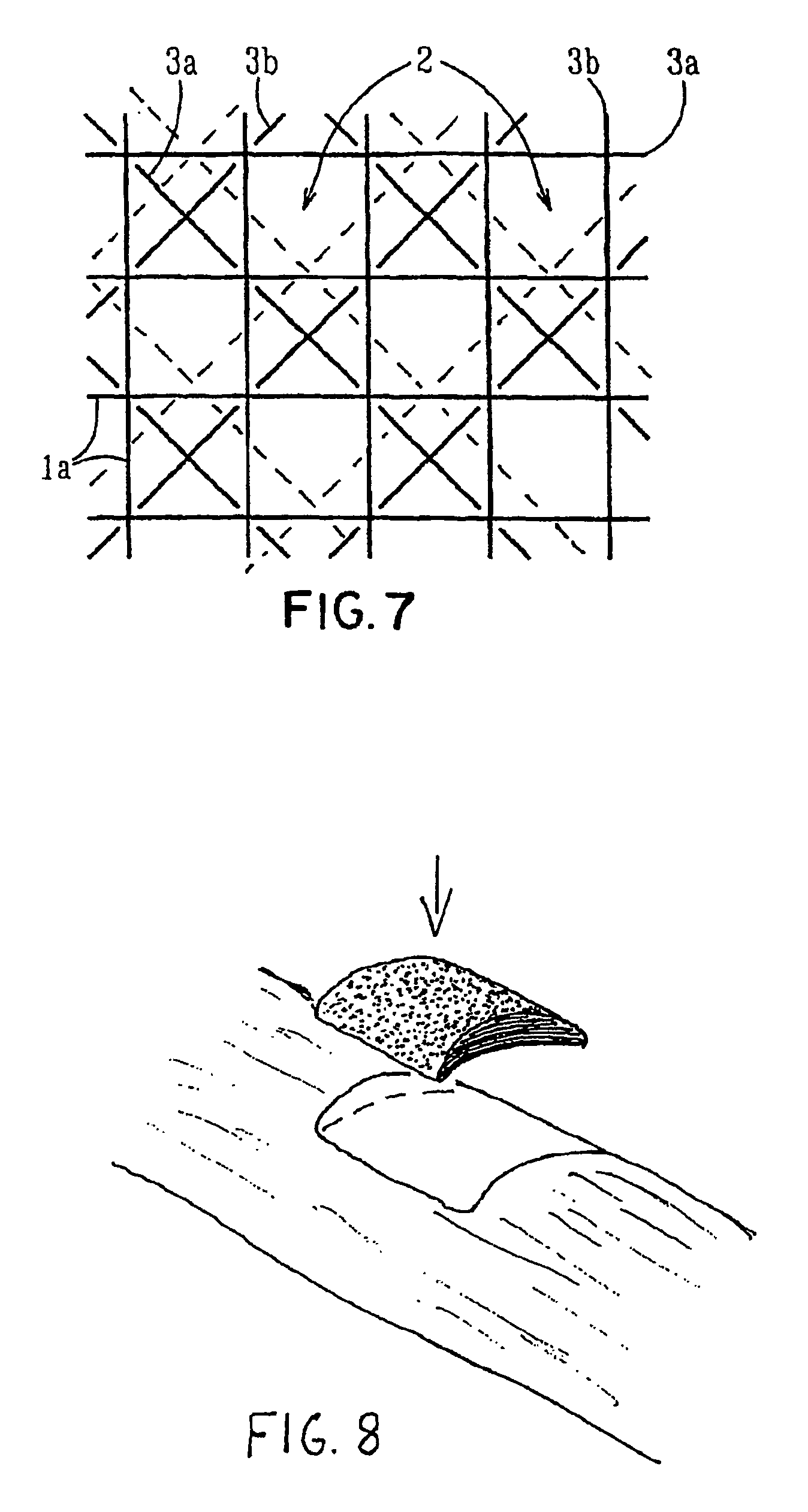
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Methods for creating woven devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Electronic smoking article with improved storage and transport of aerosol precursor compositions
The present disclosure relates to reservoirs for storing products in electronic smoking articles. The reservoir is manufactured from cellulose acetate fiber, thermoplastic fiber, non-thermoplastic fiber, or a combination thereof. The reservoir is substantially tubular in shape and is adapted to accommodate internal components of the smoking article thereby increasing reservoir capacity. The internal components particularly can comprise an atomizer, which may include a braided wick.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
Multi-layer braided structures for occluding vascular defects
A collapsible medical device and associated methods of occluding an abnormal opening in, for example, a body organ, wherein the medical device is shaped from plural layers of a heat-treatable metal fabric. Each of the fabric layers is formed from a plurality of metal strands and the assembly is heat-treated within a mold in order to substantially set a desired shape of the device. By incorporating plural layers in the thus-formed medical device, the ability of the device to rapidly occlude an abnormal opening in a body organ is significantly improved.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
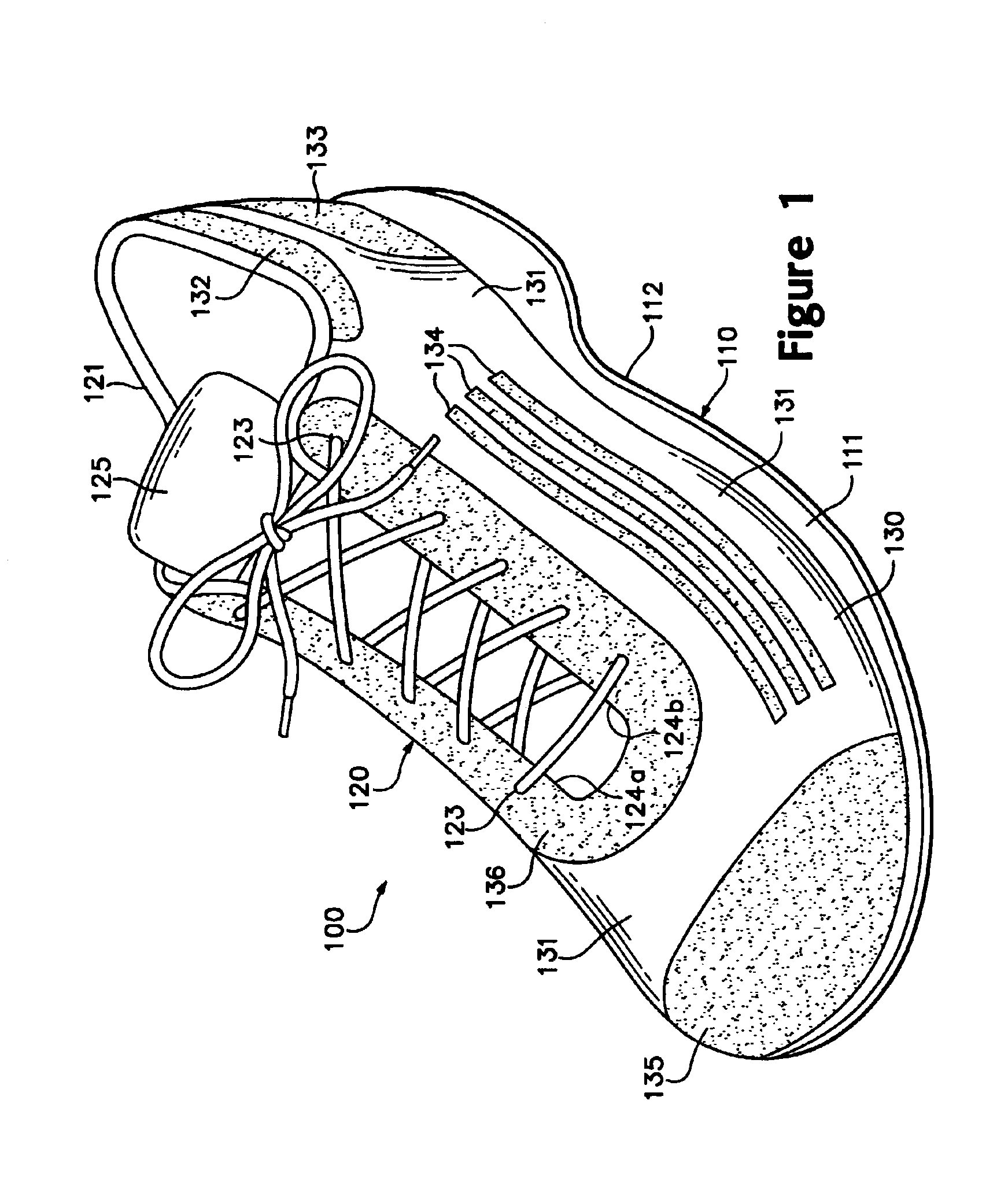
Footwear incorporating a textile with fusible filaments and fibers
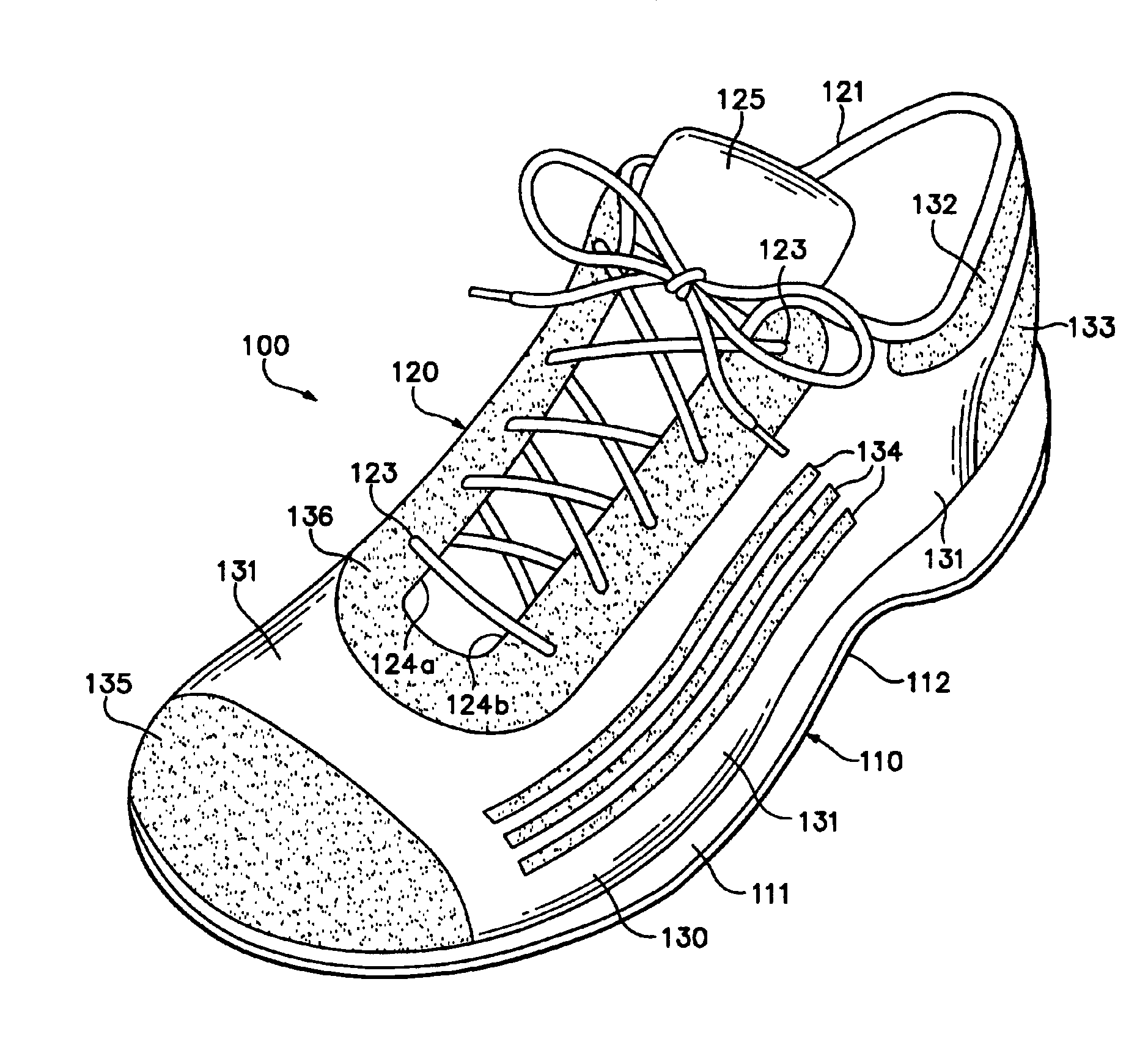
The invention is an upper for an article of footwear that includes a textile having fusible filaments or fibers. The textile is incorporated into the upper and specific areas of the upper are heated such that the fusible filaments or fibers fuse with other filaments or fibers to form fused areas. In comparison with unfused areas of the upper, the fused areas may impart properties that include greater stretch-resistance, stability, support, abrasion-resistance, durability, and stiffness, for example. In addition, the fused areas generally provide air-permeability without significantly increasing the weight of the footwear.
Owner:NIKE INC
Methods for creating woven devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Stent-graft-membrane and method of making the same
A braided self-expandable stent-graft-membrane made of elongated members forming a generally tubular body. A membrane layer and graft layer are disposed on a endoprosthesis such as a stent. The membrane layer is substantially impermeable to fluids. The outermost layer is biocompatible with the body tissue. The innermost layer is biocompatible with the fluid in the passage. An embodiment includes a graft layer disposed on the inside of a stent and a membrane layer disposed on the outside of the stent. The innermost layer is biocompatible with the fluid in the passage. The stent-graft-membrane is used at a treatment site in a body vessel or organ where it is desirous to exclude a first fluid located outside the endoprosthesis from reaching a second fluid located in the lumen. The membrane may be made of silicone or polycarbonate urethane. The graft may be braided, woven, spun or spray-cast PET, PCU, or PU fibers. The layers may include ePTFE or PTFE.
Owner:LIFEPORT SCI
Drug eluting implants to prevent cardiac apoptosis
Implantable devices are configured to be positioned in or near the heart and to carry and deliver an anti-apoptotic drug to a treatment site in or near the heart. The implantable devices include, but are not limited to, leads, stents, heart valves, atrial septal defect devices, cardiac patches and ventricular restraint devices. Depending on the composition of the device, the drug may be carried by the device through a coating applied to the device, or may be included in the device during the device manufacturing process. The drug may also be included in microparticles, such a microspheres, that are delivered locally through a conduit, such as a catheter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Biocompatible crosslinked coating and crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating
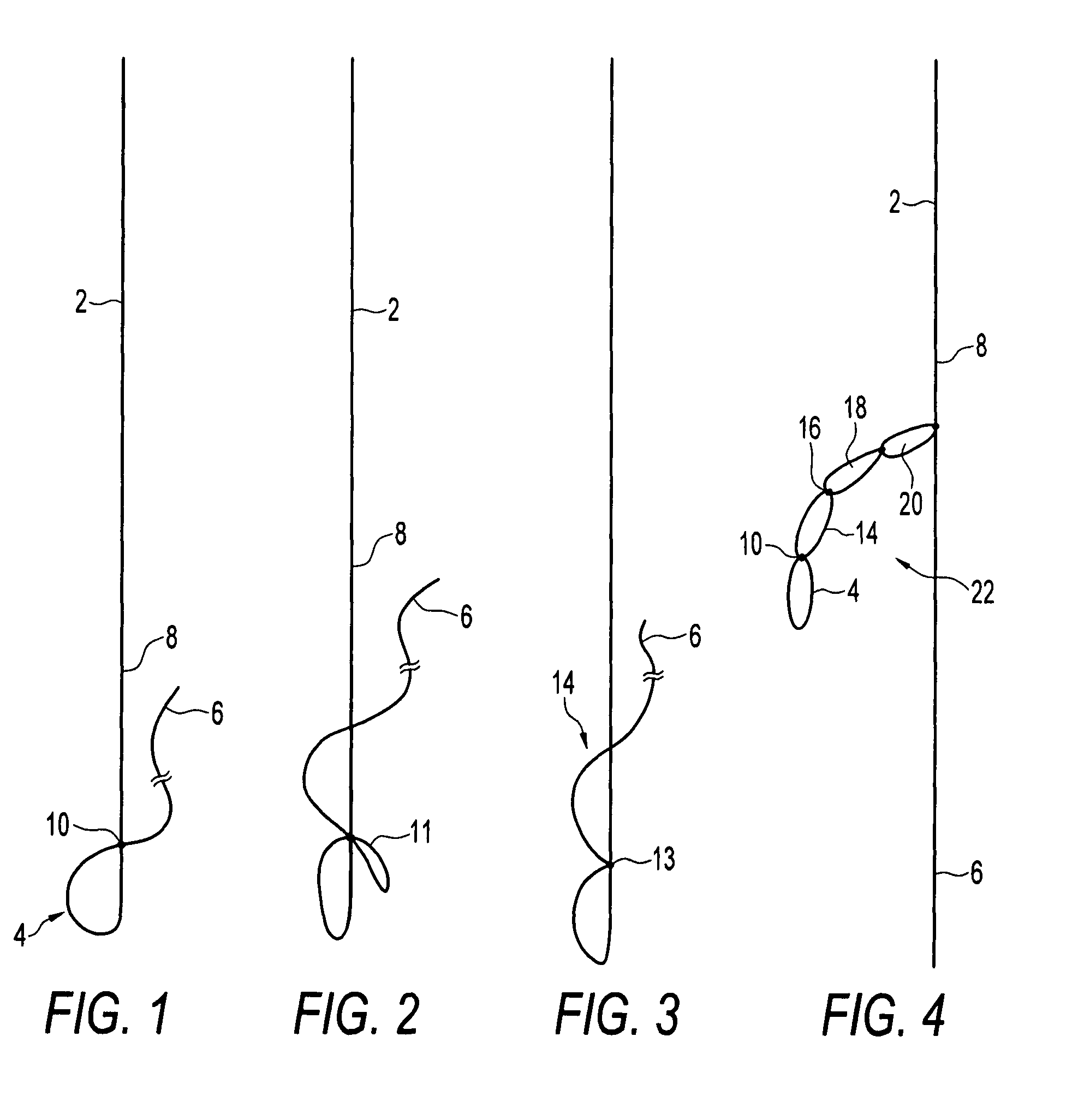
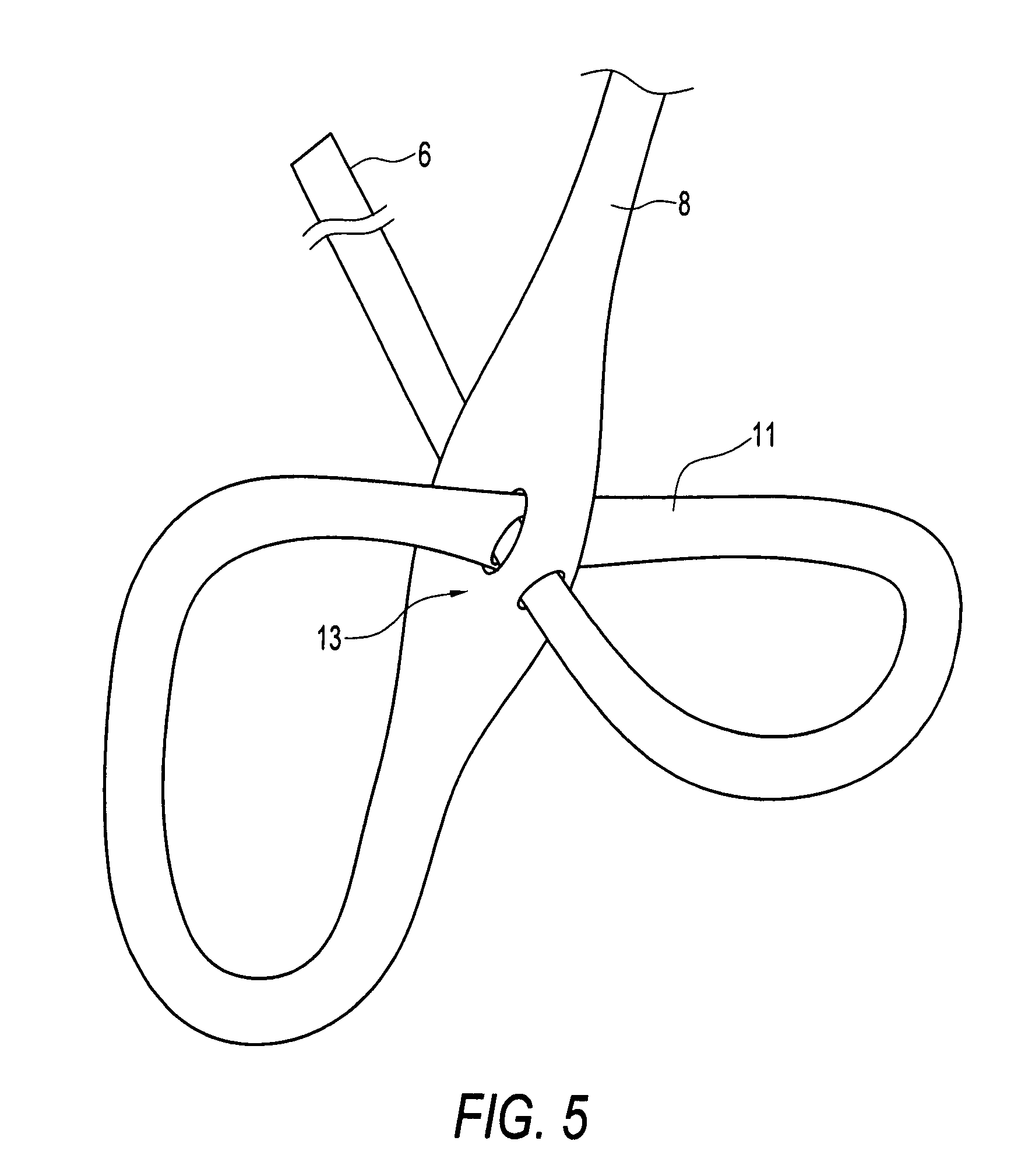
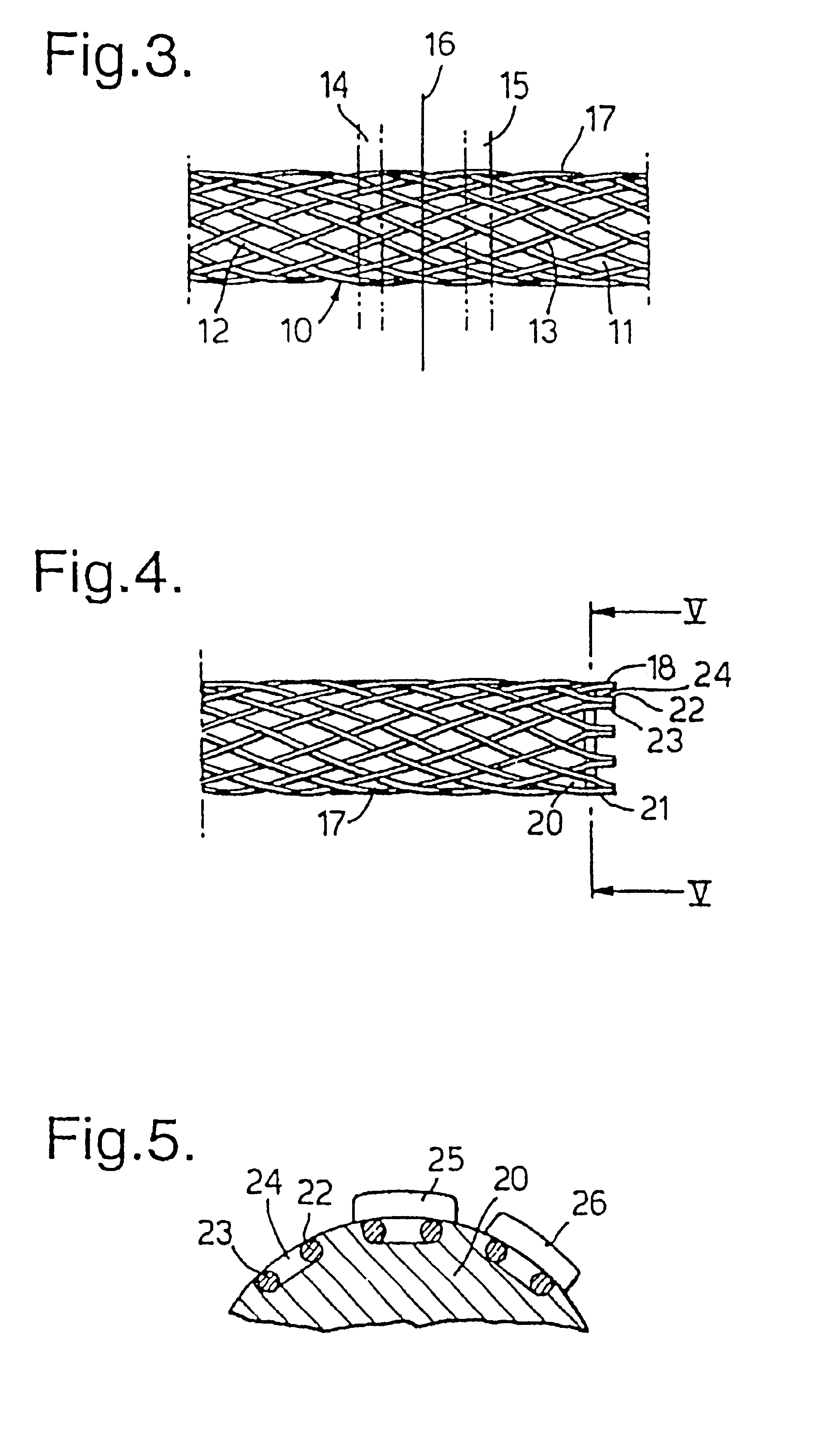
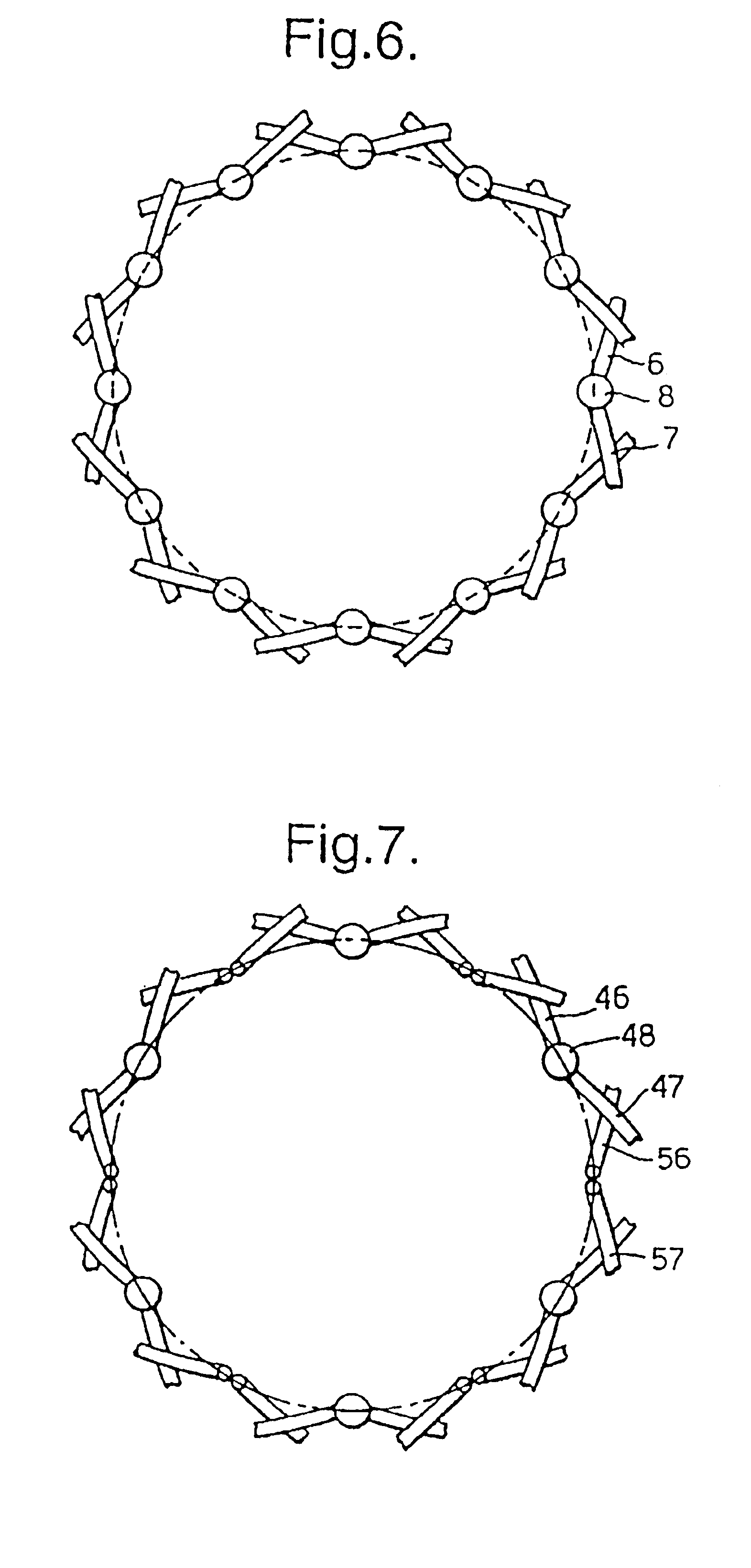
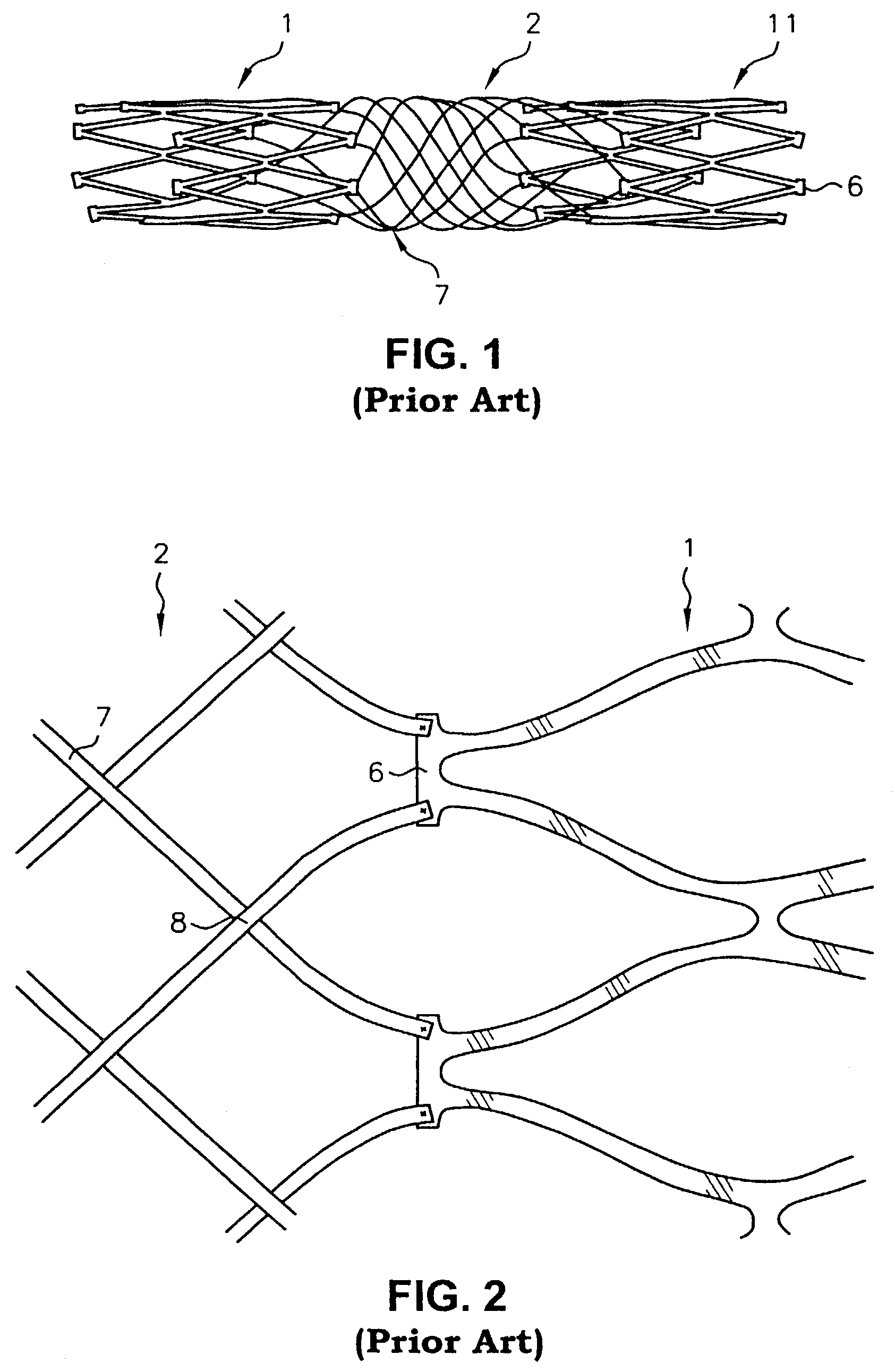
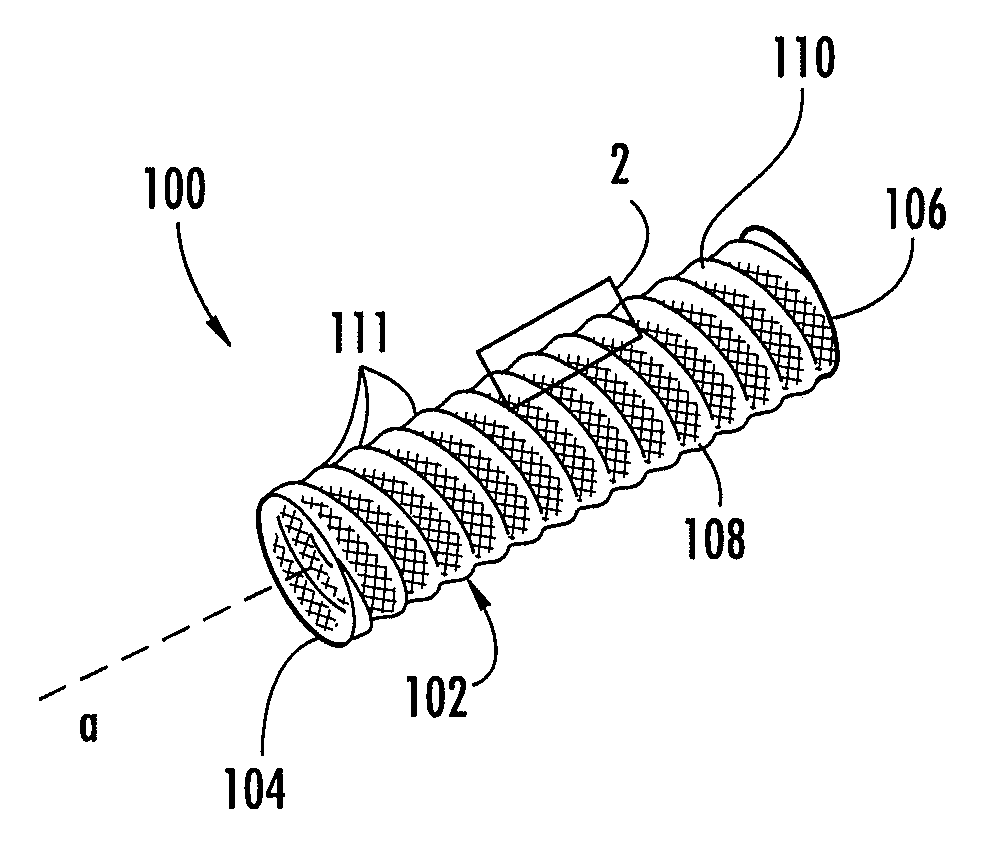
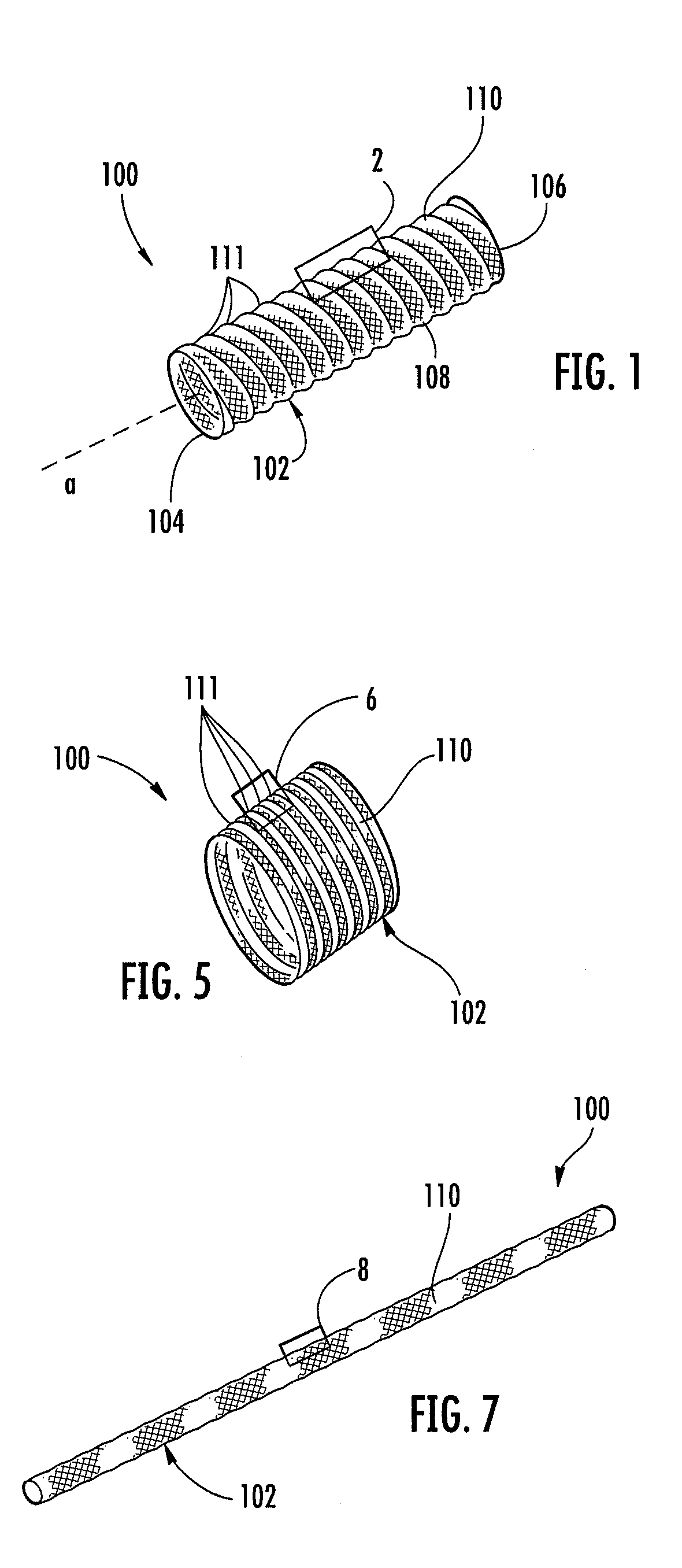
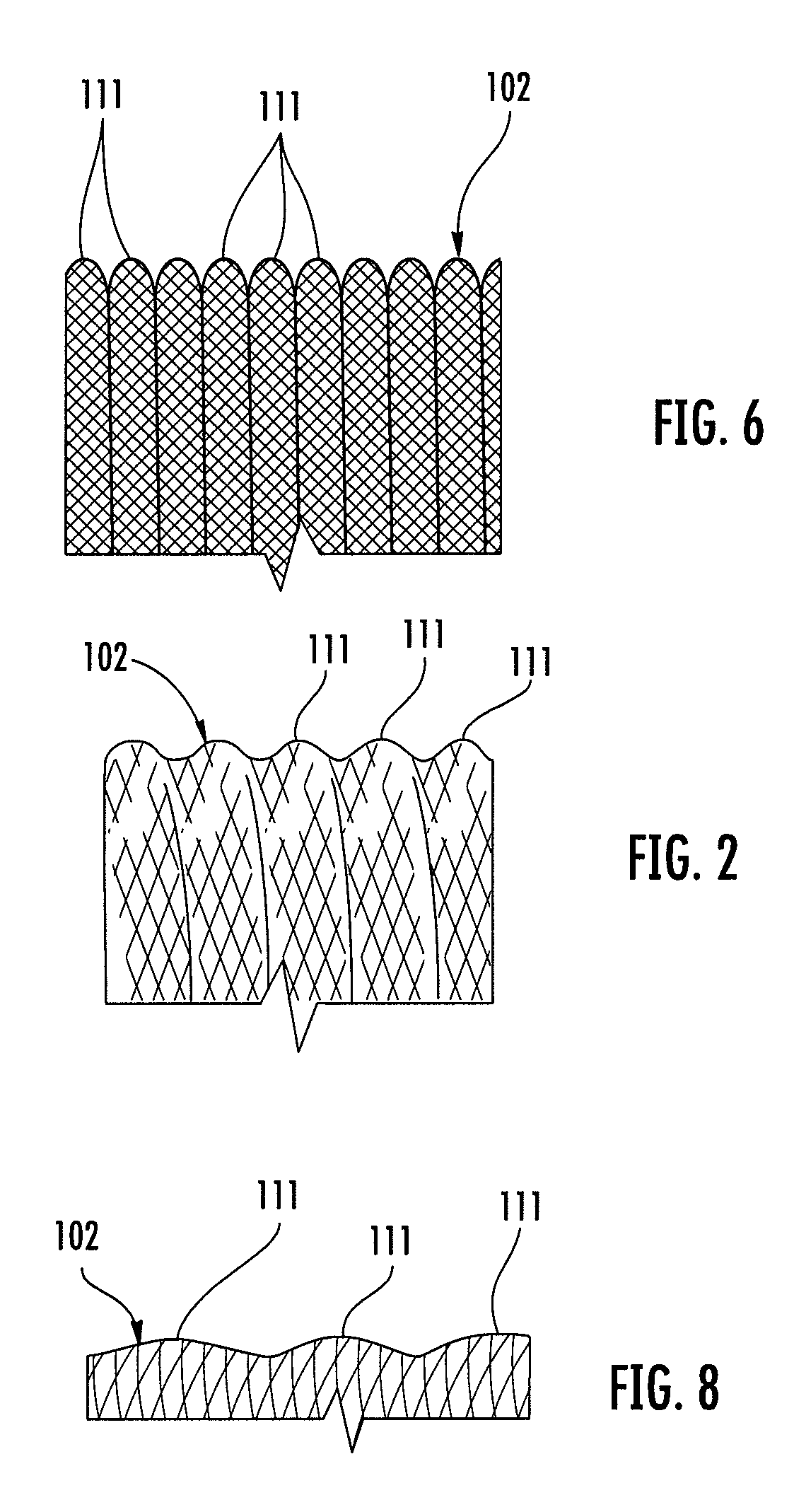
A braided stent (1) for transluminal implantation in body lumens is self-expanding and has a radial expanded configuration in which the angle α between filaments is acute. Some or all of filaments (6,7) are welded together in pairs at each end (4,5) of the stent to provide beads (8), thereby strengthening the stent and assisting its deployment from a delivery device. The stent is preferably completely coated using a biocompatible polymeric coating, said polymer preferably having pendant phosphoryl choline groups. A method of making the stent by braiding and welding is described as well as a delivery device for deploying the device.The present invention provides a biocompatible crosslinked coating and a crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating. The biocompatible crosslinked coating may be formed by curing a polymer of 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate. The crosslinkable coating polymer may include 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate.<?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
High strength suture with colored trace at one end
InactiveUS6994719B2High strengthImproved tie down characteristicSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsPolyesterEngineering
A high strength abrasion resistant surgical suture material with improved tie down characteristics is color coded for visualization and identification purposes. The suture features a multifilament cover formed of strands of ultra high molecular weight long chain polyethylene braided with polyester, nylon or a bioabsorbable material. Selected nylon fibers in the cover are provided in a color contrasting with the other cover fibers to provide an identifiable trace. The cover surrounds a core formed of twisted strands of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The suture, provided in a #2 size, has the strength of #5 Ethibond, is ideally suited for most orthopedic procedures, and can be attached to a suture anchor or a curved needle. The identifiable trace preferably is provided along one half of the length of the suture, so that when the suture is loaded onto a suture anchor, for example, the two legs of the length of suture on either side of the suture anchor can be readily identified.
Owner:ARTHREX INC
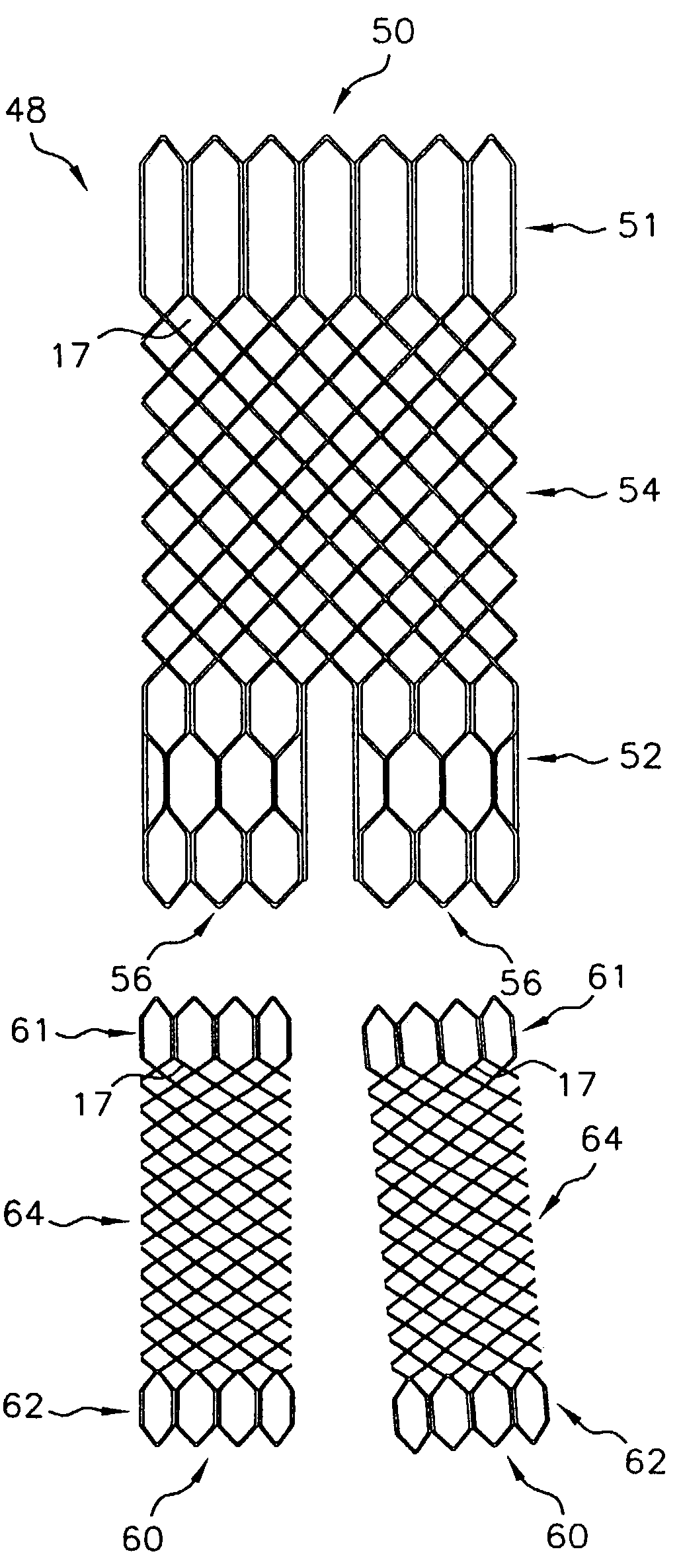
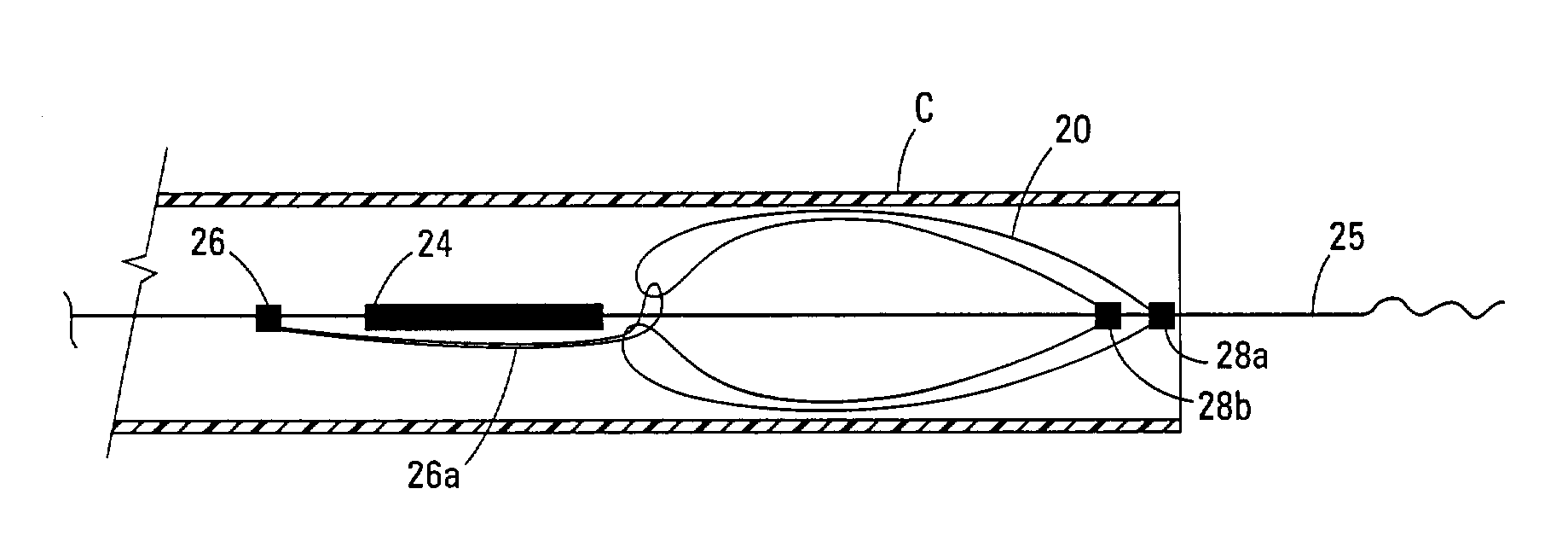
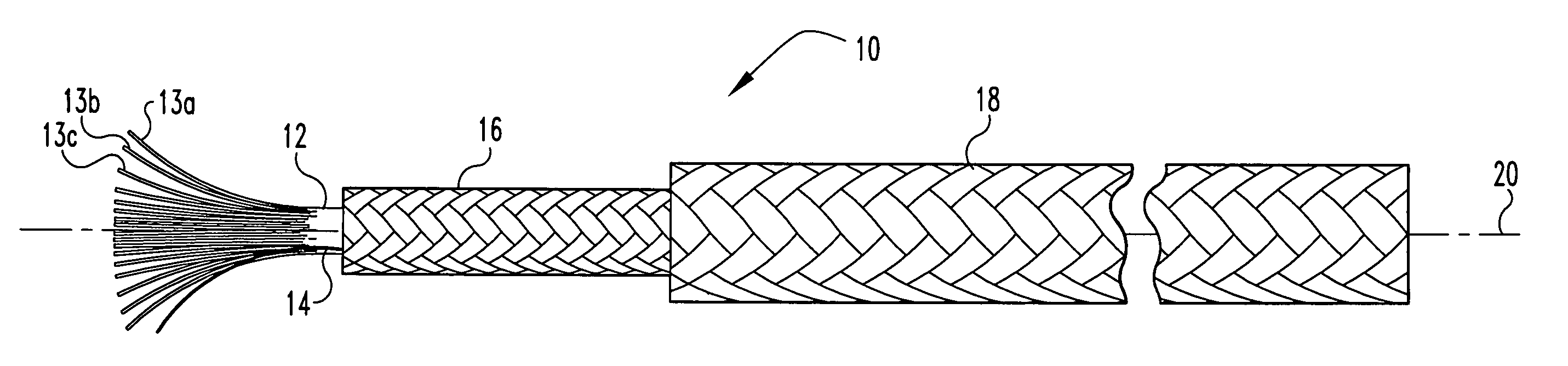
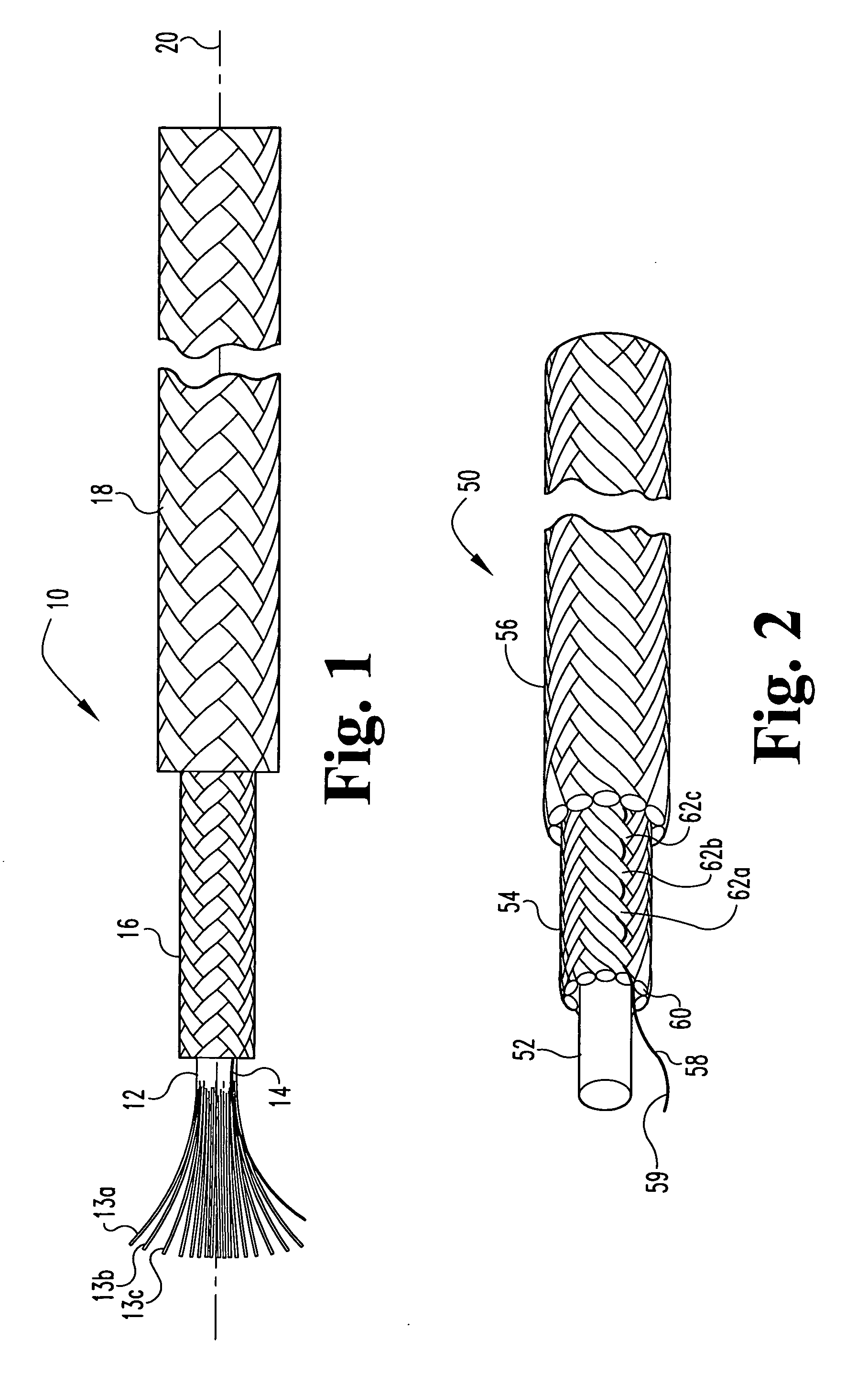
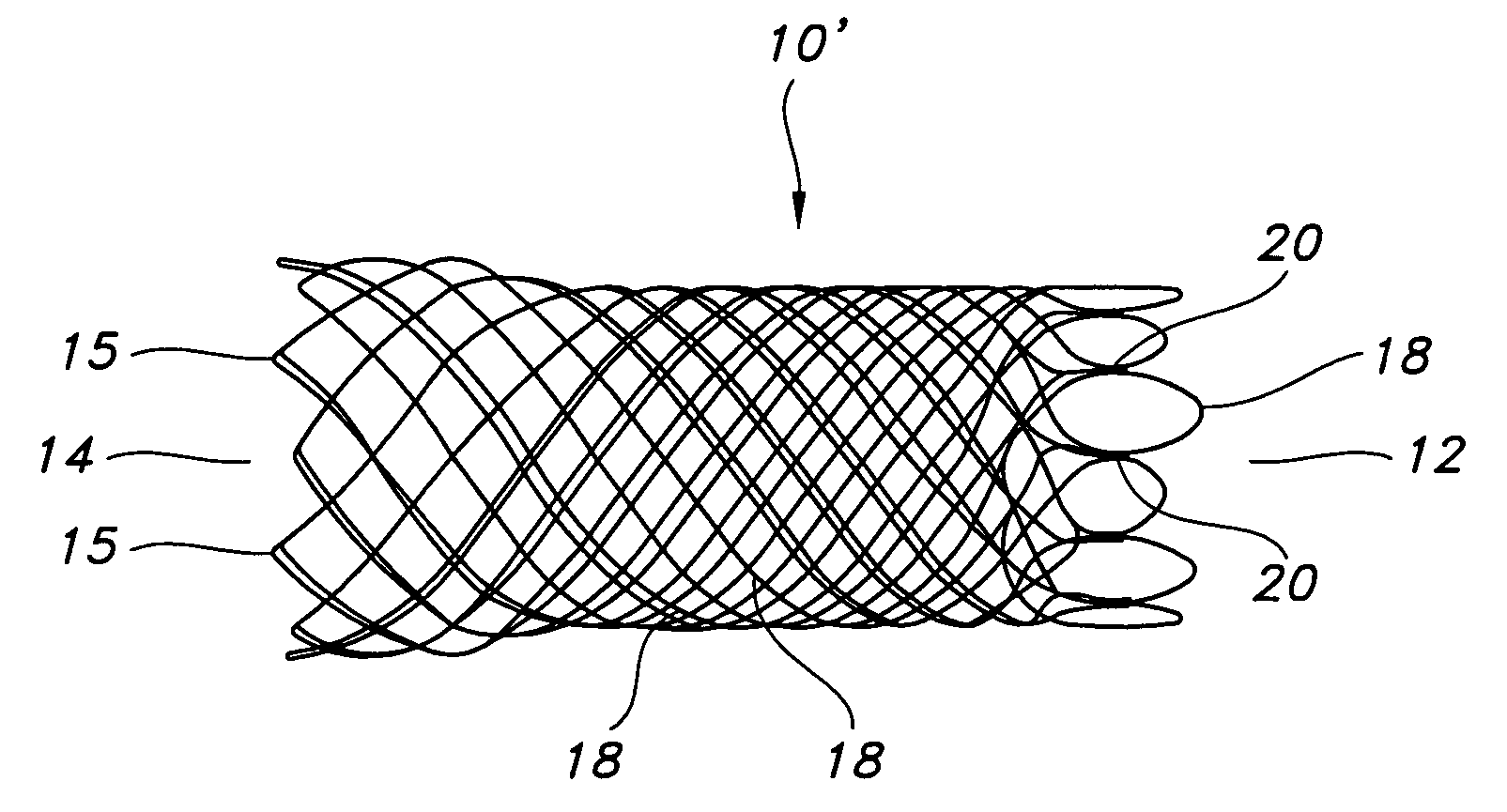
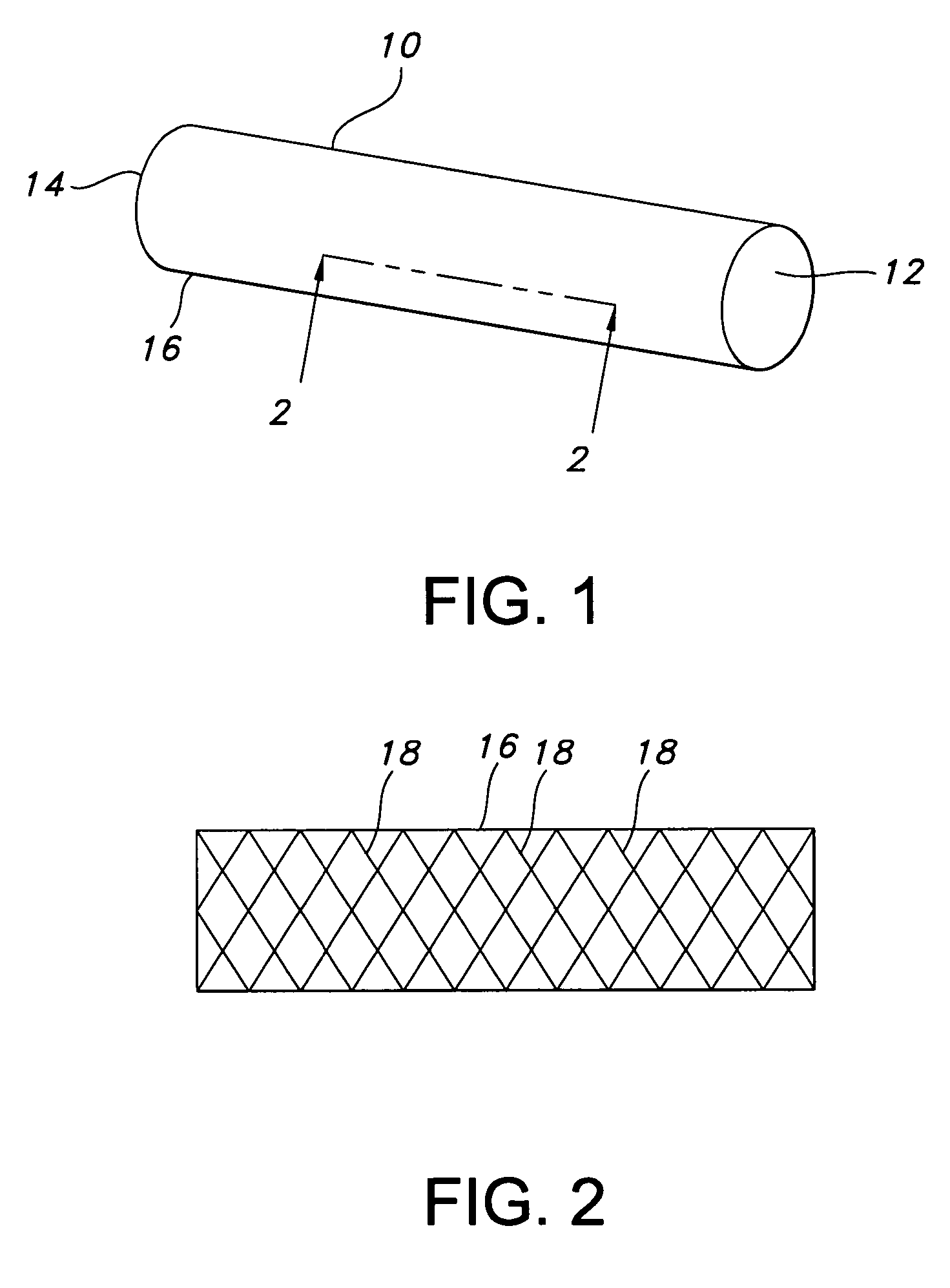
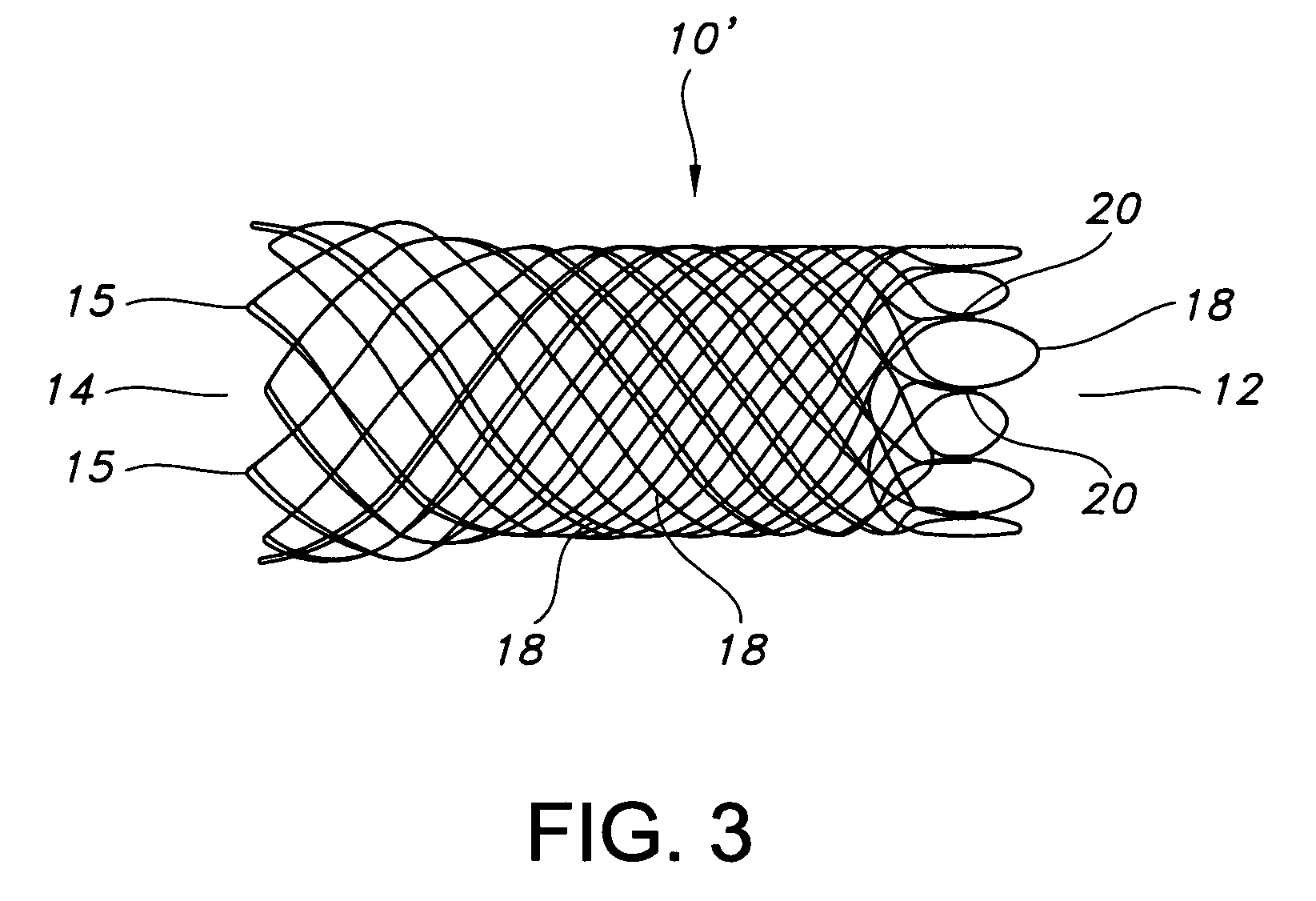
Multi-section filamentary endoluminal stent
A multi-section filamentary stent comprises a braided section, which is a cylindrical mesh of a first set of filaments, connected to at least one wound section comprising a second set of one or more filaments having a repeating configuration with a bent portion. The two sections are preferably connected by at least one continuous filament extending into both sections. The two sections may be connected by a weld, a suture, a common graft, an overlapping portion of the two sections, or one or more filaments of one section looping through portions of the other section. The stent may comprise a first section, having a braided first stent architecture with a first flexibility and a first radial force, and a second section, having a non-braided second stent architecture with a second flexibility less than the first flexibility and a second radial force greater than the first radial force, in which at least one continuous filament is integral to both the first and second sections. The stent may have a radially compressed configuration and a radially expanded configuration, in which the first section has a first shortening ratio, and the second section has a second shortening ratio less than the first shortening ratio. Such multi-section stents may comprise modular components of a modular stent, such as a bifurcated modular stent, adapted for joining together in situ. The multi-section stent may comprise a first section having a first percentage of open area and a second section having a second percentage of open area. The stent may also comprise a first section having a first stent architecture with an end effect wherein the radial strength at the end is less than elsewhere in the stent, and a second section having a second stent architecture to counteract the end effect. Methods for treating body lumen by implanting the stents as described herein are also disclosed, as is a method for counteracting a stent architecture end effect.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
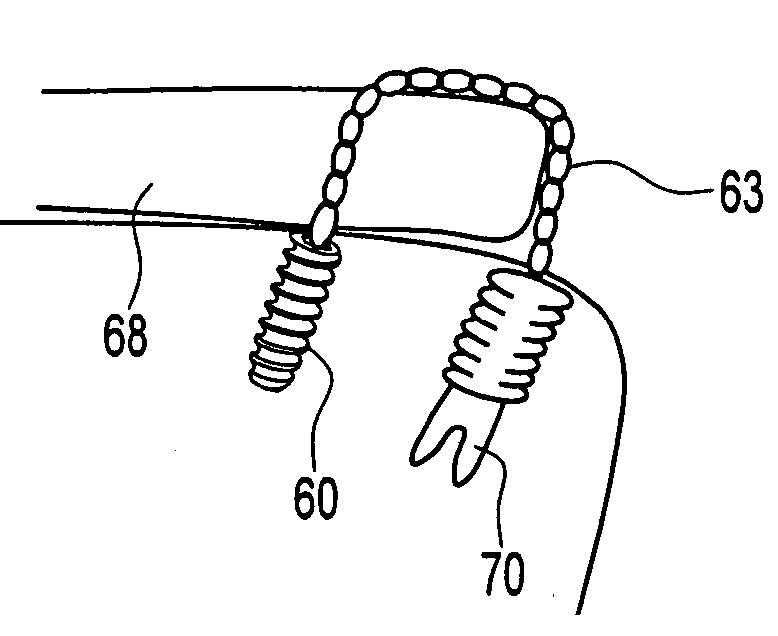
Knotless fixation of tissue to bone with suture chain
ActiveUS20070135843A1High strengthReduce tensionSuture equipmentsLigamentsHigh intensityRotator cuff
A chain of loops of braided high strength suture for soft tissue to bone fixation. The suture chain is advantageous for use in knotless fixation of soft tissue to bone, and can be used for knotless side-to-side suturing of U-shaped defects, such as rotator cuff tears. The soft tissue to bone fixation includes: (i) providing a first medial row constructed with a first plurality of fixation devices, at least one of the first plurality of fixation devices being an anchor; (ii) providing a second lateral row constructed with a second plurality of fixation devices, at least one of the second plurality of fixation devices being a knotless fixation device, (iii) providing a suture loop construct that includes at least two loops formed of and connected by suture; and (iv) fixating the suture loop construct so that it extends over the soft tissue and is secured in place by at least one of the fixation devices or anchors.
Owner:ARTHREX
Embolic filters with controlled pore size
The invention provides a device for filtering emboli from blood flowing through a lumen defined by the walls of a vessel in a patient's body comprising a filter element. The filter is expandable from a collapsed configuration when the filter element is restrained to an expanded configuration when the filter element is unrestrained, and the filter element comprises a self-expanding material having pores. When the filter element is in the expanded configuration, the average pore size is from 30 to 300 microns and the standard deviation of the pore size is less than 20 percent of the average pore size.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
High strength suture with absorbable core and suture anchor combination
ActiveUS20050149118A1Improved absorption profileReducing knot profile of knotSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesYarnMedicine
A novel high tensile strength semi-absorbable composite suture with minimized non-absorbable mass. The suture has a core made from a bioabsorbable polymer. The core is covered by a braided sheath. The braided sheath is made from an absorbable yarn and a bioabsorbable yarn. The bioabsorbable yarn is made from a least one filament of a bioabsorbable polymer. The nonabsorbable yarn is made from at least one filament of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
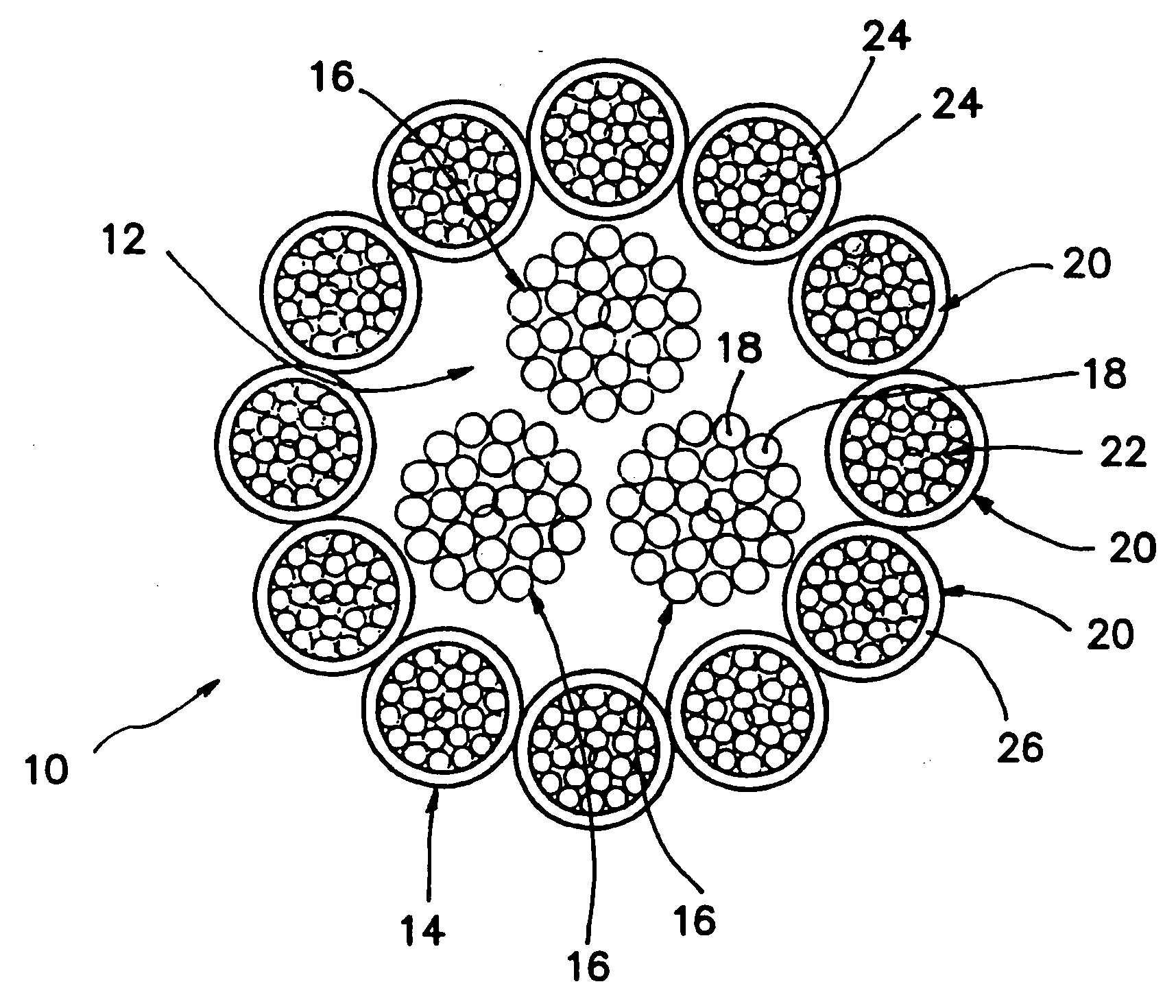
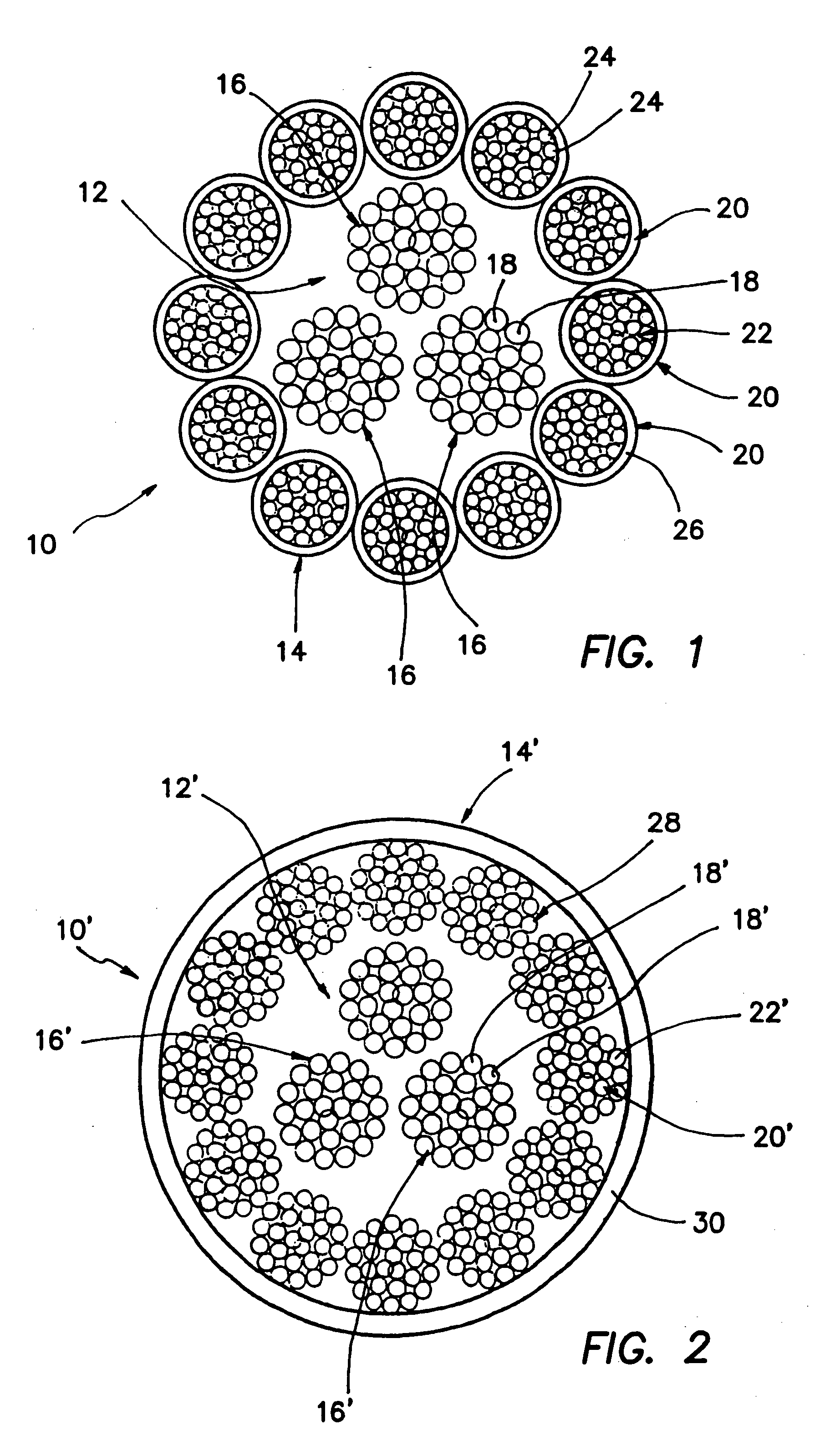
Woven and/or braided fiber implants and methods of making same
Owner:SHRINERS HOSPITALS FOR CRIPPLED CHILDREN
Devices for Vascular Occlusion
An occlusive device, occlusive device delivery system, method of using, and method of delivering an occlusive device, and method of making an occlusive device to treat various intravascular conditions is described.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
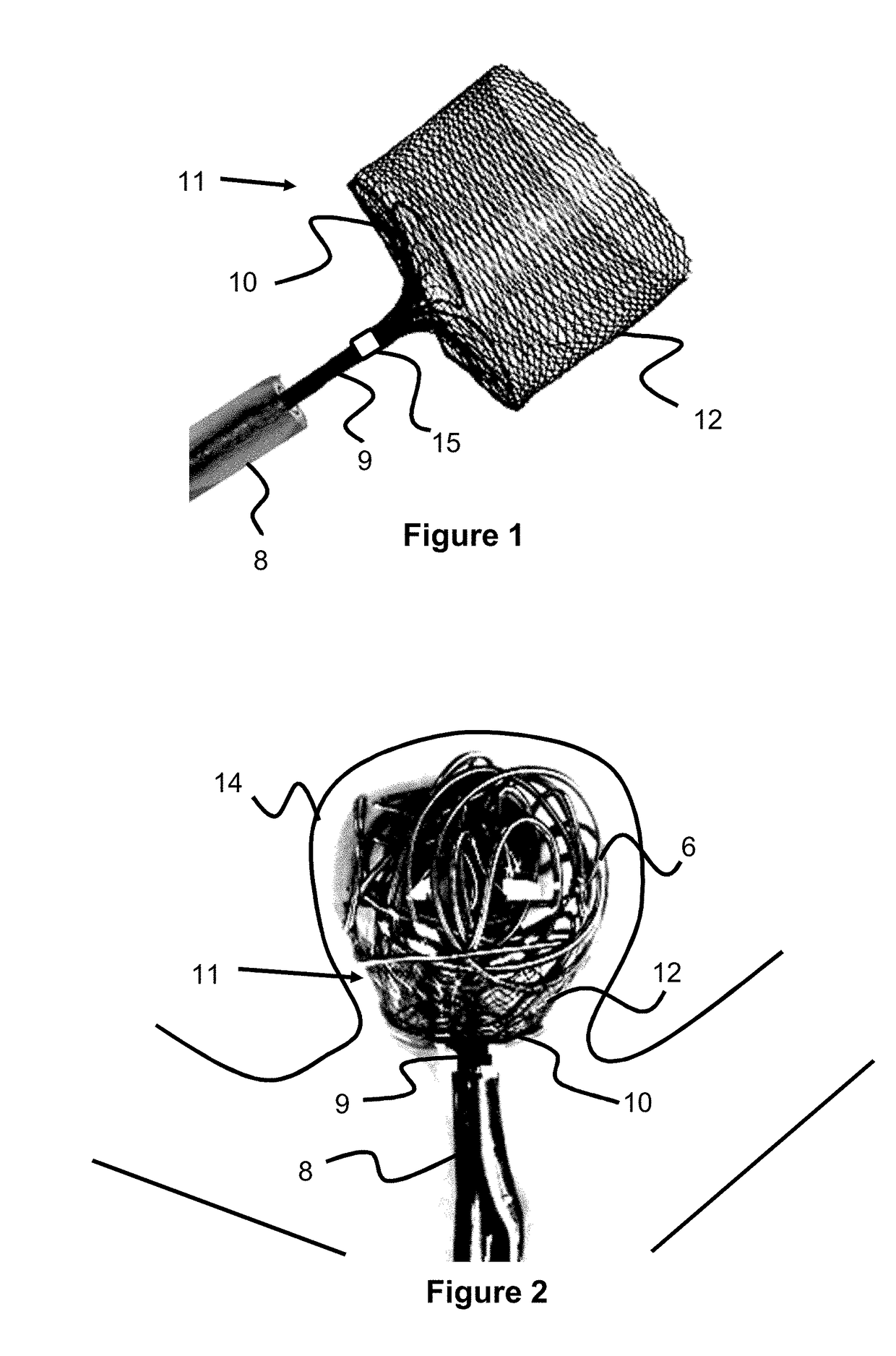
Method and apparatus for making intraluminal implants and construction particularly useful in such method and apparatus
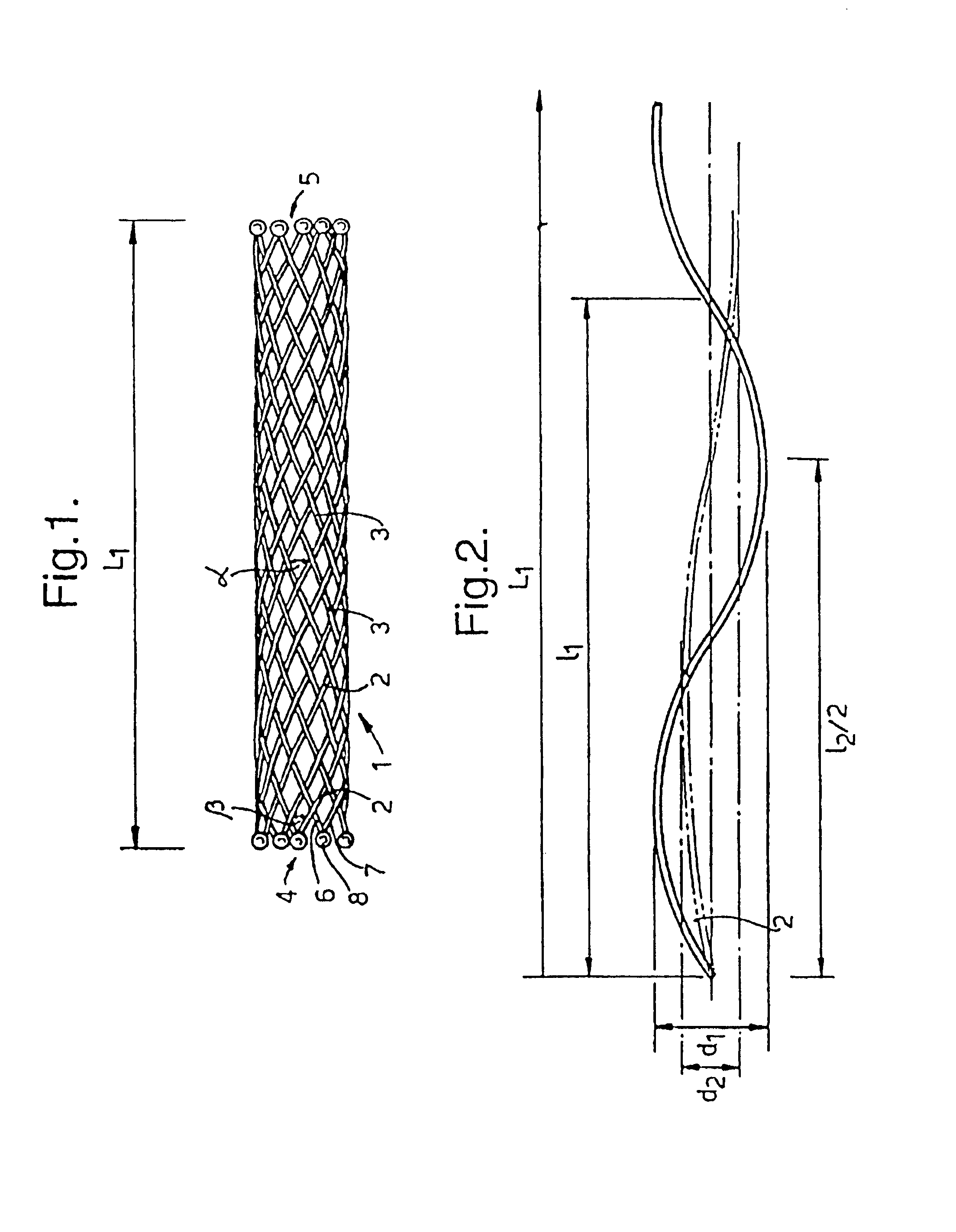
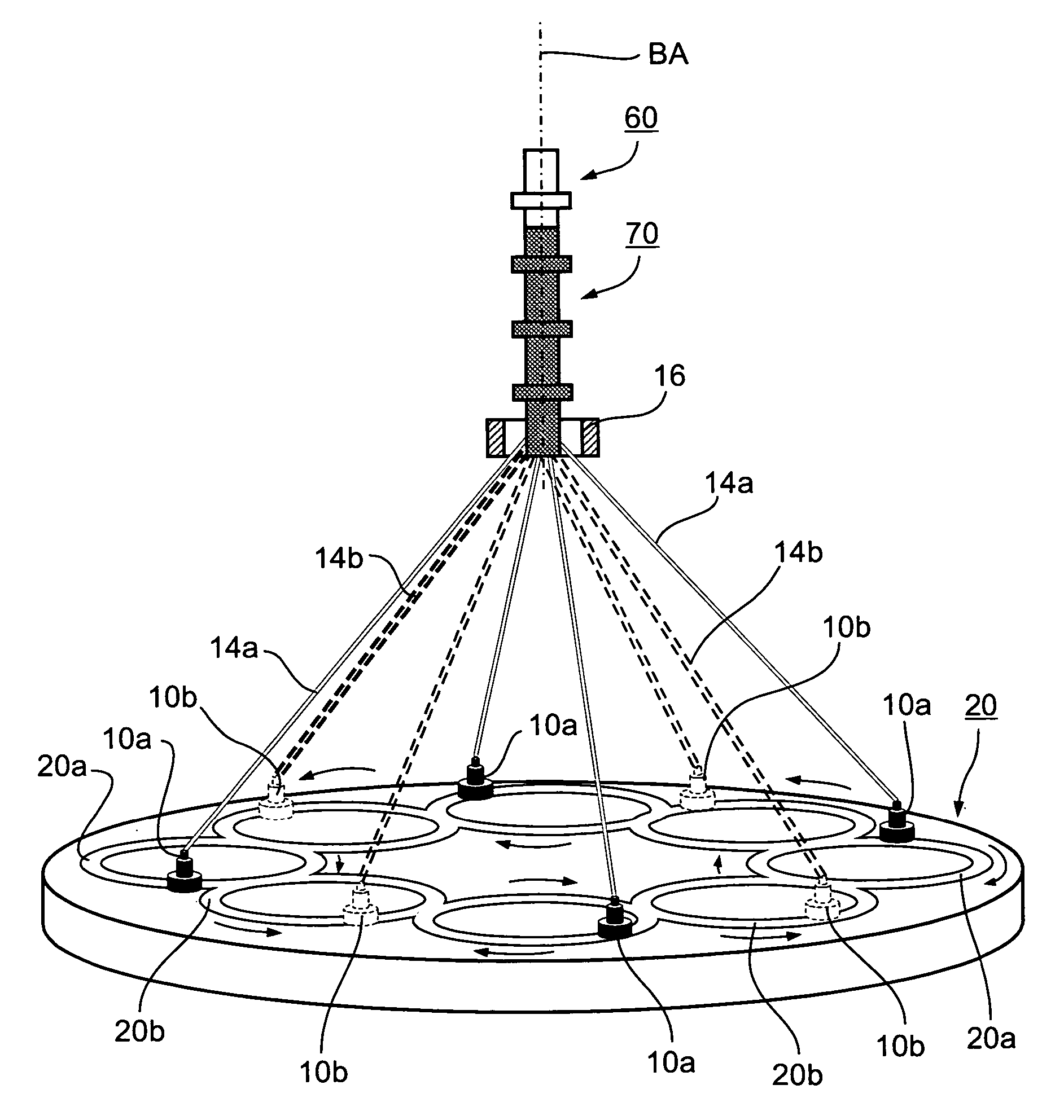
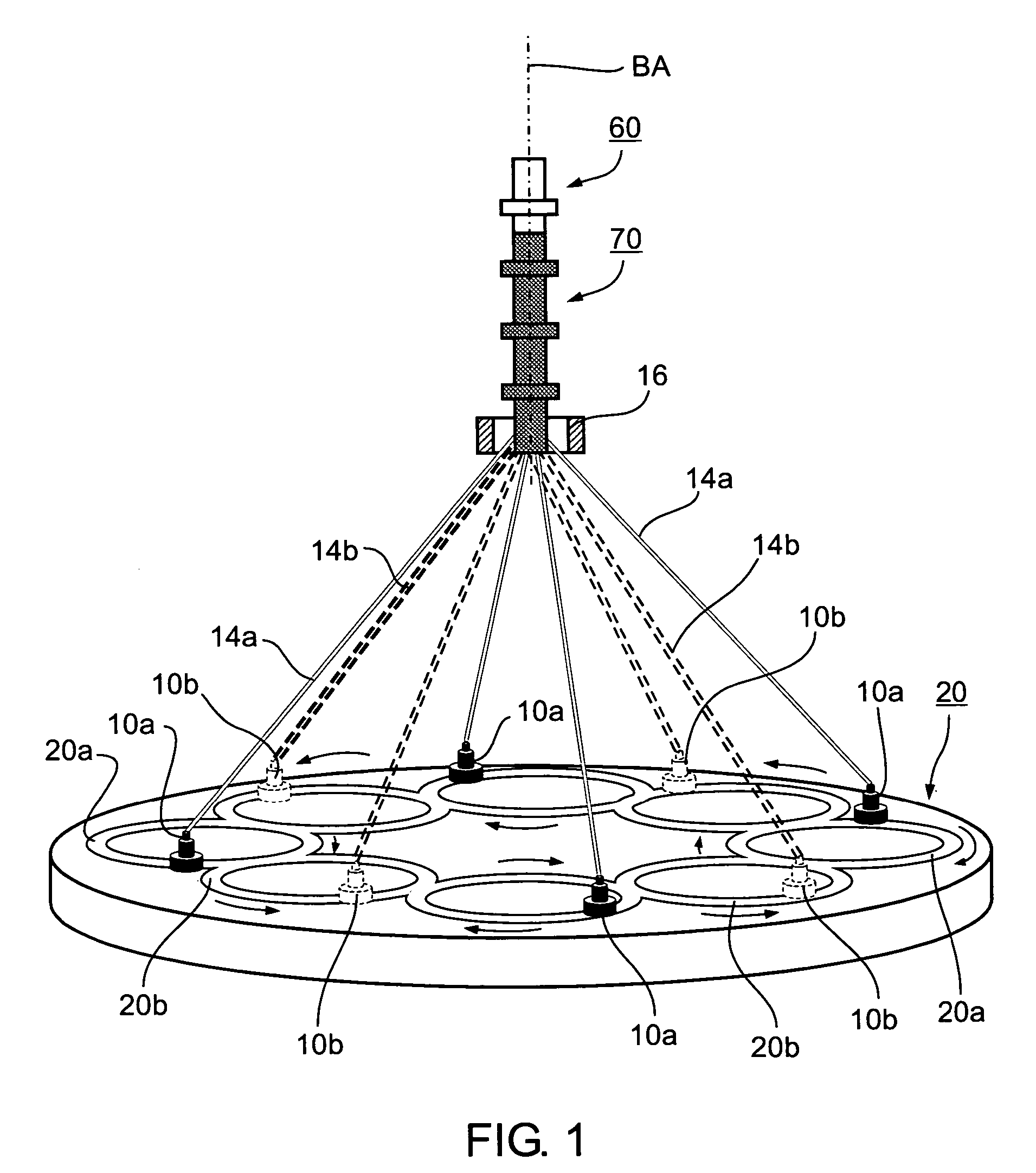
A method of and an apparatus for making a braided intraluminal implant, by providing a mandrel having at least one small-diameter section joined at least at one end to a large-diameter section; interweaving a plurality of filaments to form a tubular braid enclosing at least a part of the small-diameter section and at least a part of the large-diameter section; and cutting the tubular braid to produce a tubular braid segment having outwardly flared ends at its opposite ends. One flared end is produced by the large-diameter section of the mandrel, and the opposite outwardly flared end may be produced either by another large-diameter section of the mandrel, or by cutting the tubular braid at a portion formed by the small-diameter section of the mandrel but at a location wherein the release of stresses in the filaments inherently produces an outward flaring of the braid at that end.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Devices for Vascular Occlusion
An occlusive device, occlusive device delivery system, method of using, and method of delivering an occlusive device, and method of making an occlusive device to treat various intravascular conditions is described.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Branch vessel prosthesis with a roll-up sealing assembly
A branch prosthesis configured for placement in a branch vessel includes an expandable tubular body portion, an expandable annular flange attached to a proximal end of the body portion, and a sealing sleeve proximally extending from the annular flange. The sealing sleeve is adapted to deform to a generally straight cylindrical hollow shape during implantation. When deployed, the sealing sleeve rolls up to a tightly-wound coil that bears against the annular flange. When used in conjunction with a main prosthesis having a side opening and deployed within in a main vessel, the annular flange of the branch prosthesis engages an outer surface of the main prosthesis around a perimeter of the side opening and the sealing sleeve engages an inner surface of the main prosthesis around the perimeter of the side opening to form a fluid-tight seal between the main prosthesis and the branch prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
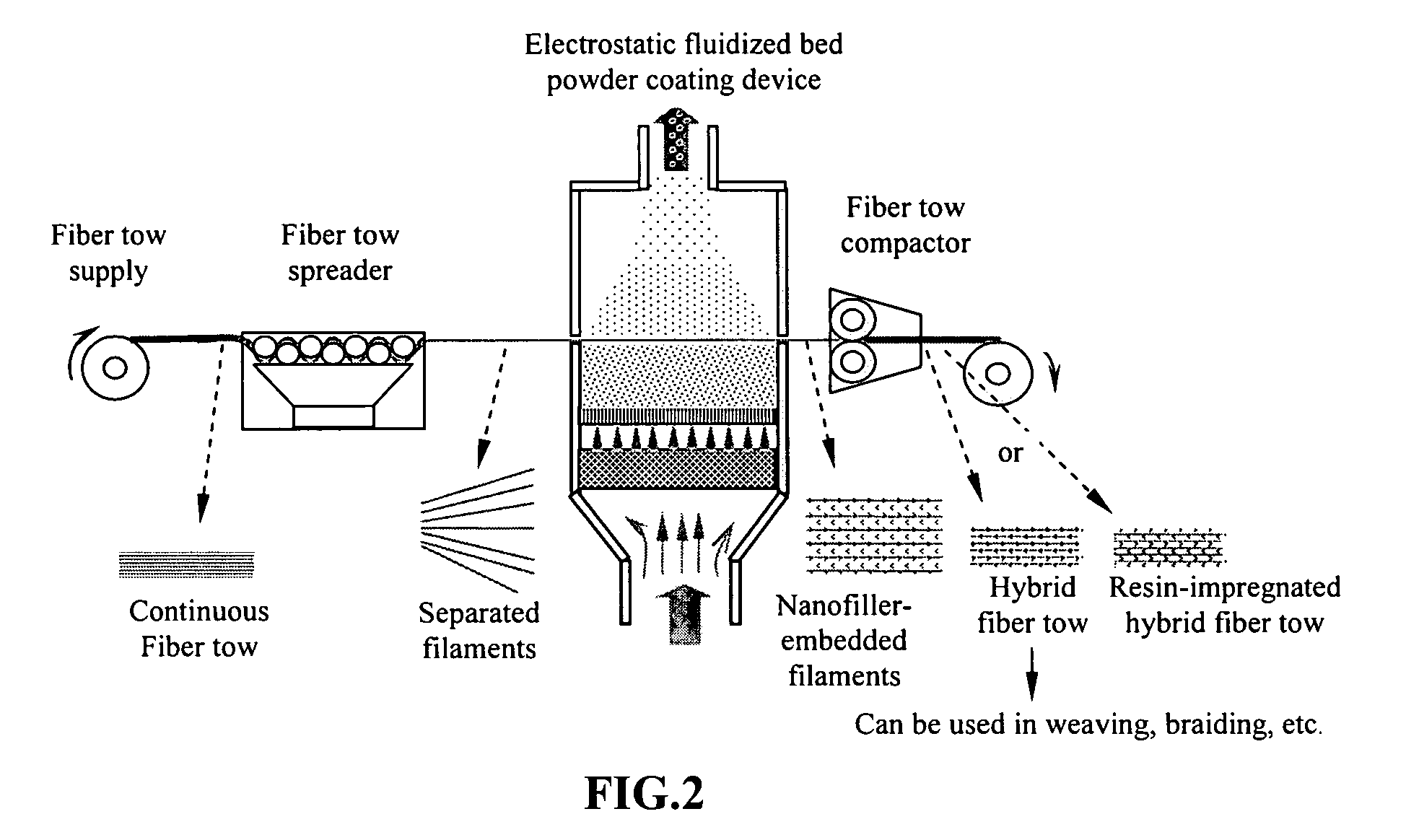
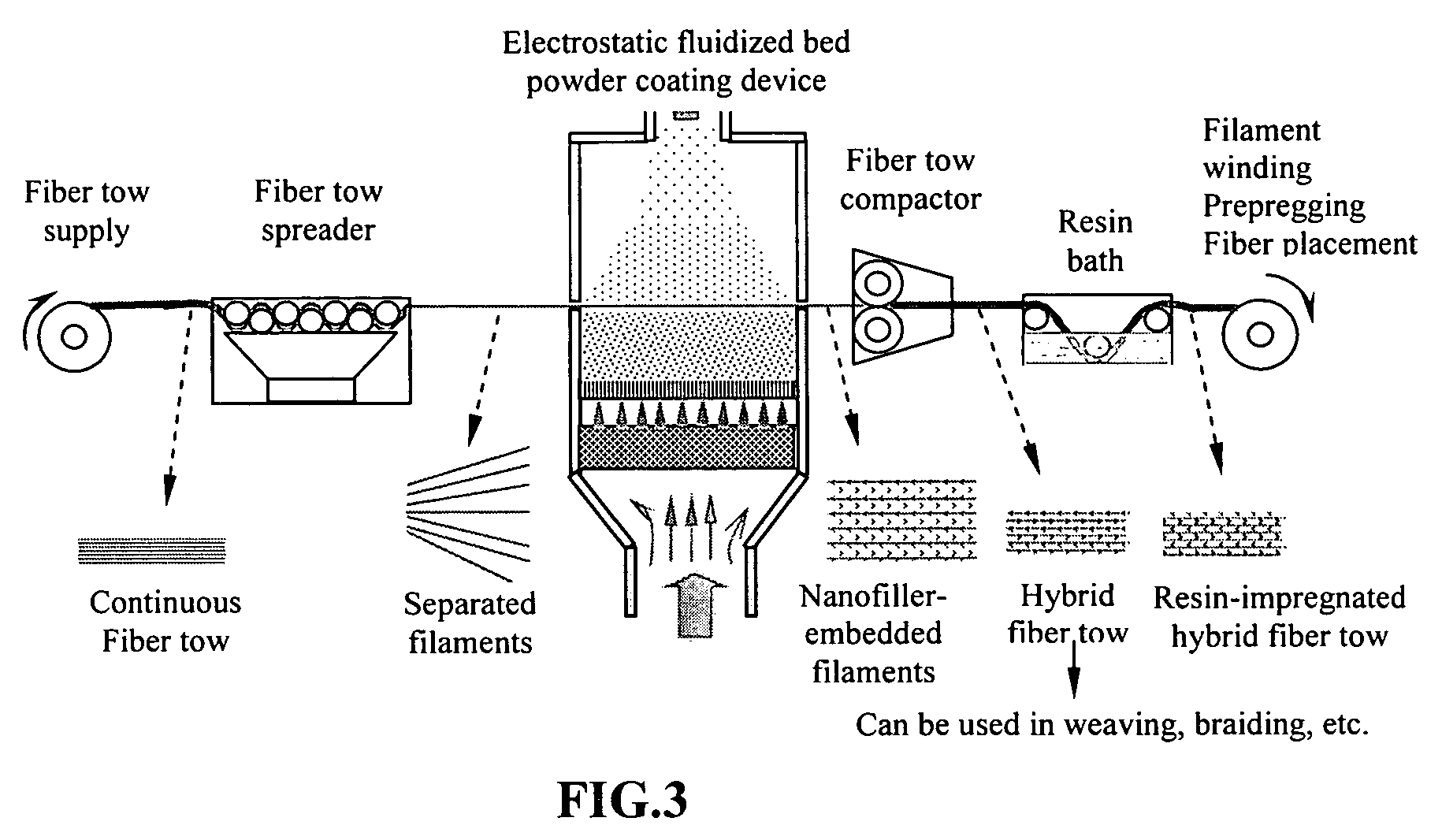
Hybrid fiber tows containning both nano-fillers and continuous fibers, hybrid composites, and their production processes
Disclosed is a hybrid fiber tow that comprises multiple continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers embedded in the interstitial spaces between continuous filaments. Nanoscale fillers may be selected from a nanoscale graphene plate, non-graphite platelet, carbon nano-tube, nano-rod, carbon nano-fiber, non-carbon nano-fiber, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed are a hybrid fiber tow impregnated with a matrix material and a composite structure fabricated from a hybrid fiber tow. The composite exhibits improved physical properties (e.g., thermal conductivity) in a direction transverse to the continuous fiber axis. A roll-to-roll process for producing a continuous fiber tow or matrix-impregnated fiber tow and an automated process for producing composite structures containing both continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers are also provided.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR
Optimized suture braid
A high strength abrasion resistant surgical suture material with industry standard knot tying characteristics and color marking characteristics includes a core formed of a plurality of twisted fibers of a first material, surrounded by a braided cover made from fibers of a second material different than the first material. The first material is preferably ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene and the second material is preferably a polymeric material having good knot-tying characteristics.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
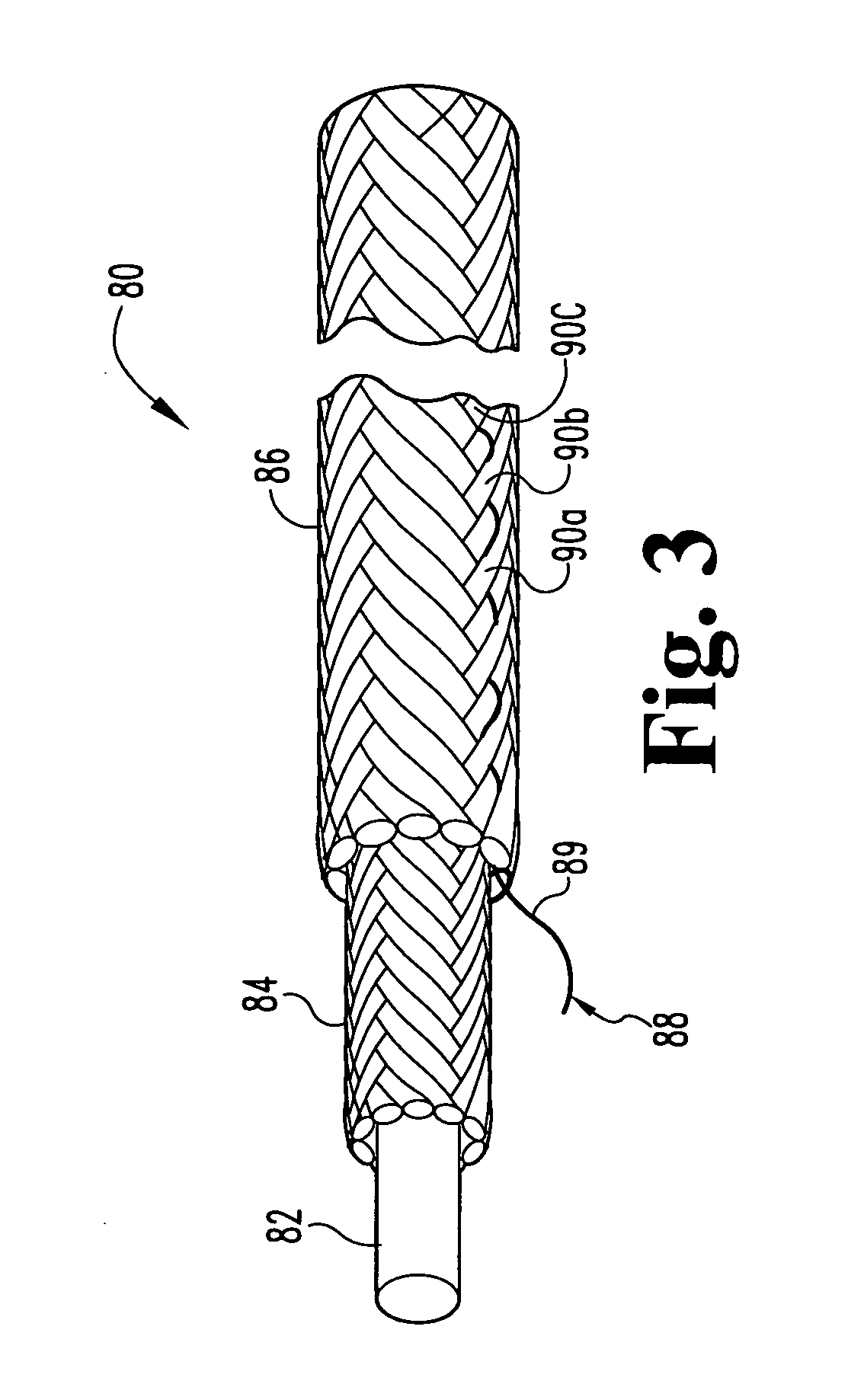
Medical device including corrugated braid and associated method
Embodiments of the present invention provide medical devices for treating a target site within the body and associated methods for fabricating and delivering medical devices. According to one embodiment, a medical device includes a tubular structure having proximal and distal ends and a side wall extending therebetween. At least a portion of the side wall can have a corrugated surface. The side wall further includes at least one layer of a metallic fabric configured to be compressed and heat set to define the corrugated surface. The tubular structure may comprise an expanded shape, and may be configured to be constrained to a smaller diameter than the expanded shape for delivery within a catheter to a target site and to assume the expanded shape upon release from the catheter.
Owner:AGA MEDICAL CORP MS US
Embolic filters having multiple layers and controlled pore size
The invention provides a device for filtering emboli from blood flowing through a lumen defined by the walls of a vessel in a patient's body comprising a filter element. The filter element is expandable from a collapsed configuration when the filter element is restrained to an expanded configuration when the filter element is unrestrained. When the filter element is in the expanded configuration, the average pore size is from 30 to 300 microns and the standard deviation of the pore size is less than 20 percent of the average pore size. The filter element has two or more filtering layers, each filtering layer having pores, each filtering layer being adjacent to at least one other filtering layer, and at least one of the filtering layers being made of a self-expanding material.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Climbing rope
InactiveUS7703372B1Ease in splicing without excessive dimensional irregularitySlow splicingMountaineeringBuilding rescueBiomedical engineering
A rope is disclosed that is firm for climbing purposes and in which the end of the rope can be spliced. The rope includes a core of a plurality of strands; a first braided tubular sheath disposed about the core; and a second braided tubular sheath disposed about the first braided tubular sheath. The plurality of strands fill at least a length of a center void formed in the first braided tubular sheath. The plurality of core strands are formed in an un-braided manner in at least one of twisted and non-twisted strands. At the splice the splice tucks fill the center void while the core strands fill only center void outside of the splice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND ROPES
Radiopaque, coaxial orthopedic tether design and method
InactiveUS20050192581A1Good imaging propertiesInternal osteosythesisLigamentsFiberBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to orthopedic tethers and their use to treat orthopedic defects. The tethers of the present invention include a central or inner load bearing fiber or cable surrounded by one or more protective sheaths. Additionally the tethers of the present invention provide enhanced imaging characteristics and can include one or more a radiopaque elements that can readily observed under common diagnostic imaging techniques.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Atraumatic stent with reduced deployment force, method for making the same and method and apparatus for deploying and positioning the stent
An implantable stent includes a plurality of elongate wires braided to form a hollow tubular structure having a tubular wall to define an interior surface and an exterior surface and having opposed open first and second ends, wherein the opposed open first and second ends are atraumatic ends The atraumatic ends of the stent are desirably free of any loose wire ends. The wires include composite wires to enhance visibility of the wires to provide improved external imaging of the wires in the body. The elongate composite wires of the stent may be metallic wires having an outer metallic portion including a first metal, such as nitinol, and an inner metallic core portion including a second metal, which is a radiopaque material, such as gold, barium sulfate, ferritic particles, platinum, platinum-tungsten, palladium, platinum-iridium, rhodium, tantalum or combinations thereof.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High strength suture with colored trace at one end
Owner:ARTHREX
High strength suture with coating and colored trace
A high strength abrasion resistant surgical suture material with improved tie down characteristics is color coded for visualization and identification purposes. The suture features a multifilament cover formed of strands of ultra high molecular weight long chain polyethylene braided with polyester, nylon or a bioabsorbable material. Selected nylon fibers in the cover are provided in a color contrasting with the other cover fibers to provide an identifiable trace. The cover surrounds a core formed of twisted strands of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The suture, provided in a #2 size, has the strength of #5 Ethibond, is ideally suited for most orthopedic procedures, and can be attached to a suture anchor or a curved needle.
Owner:ARTHREX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com