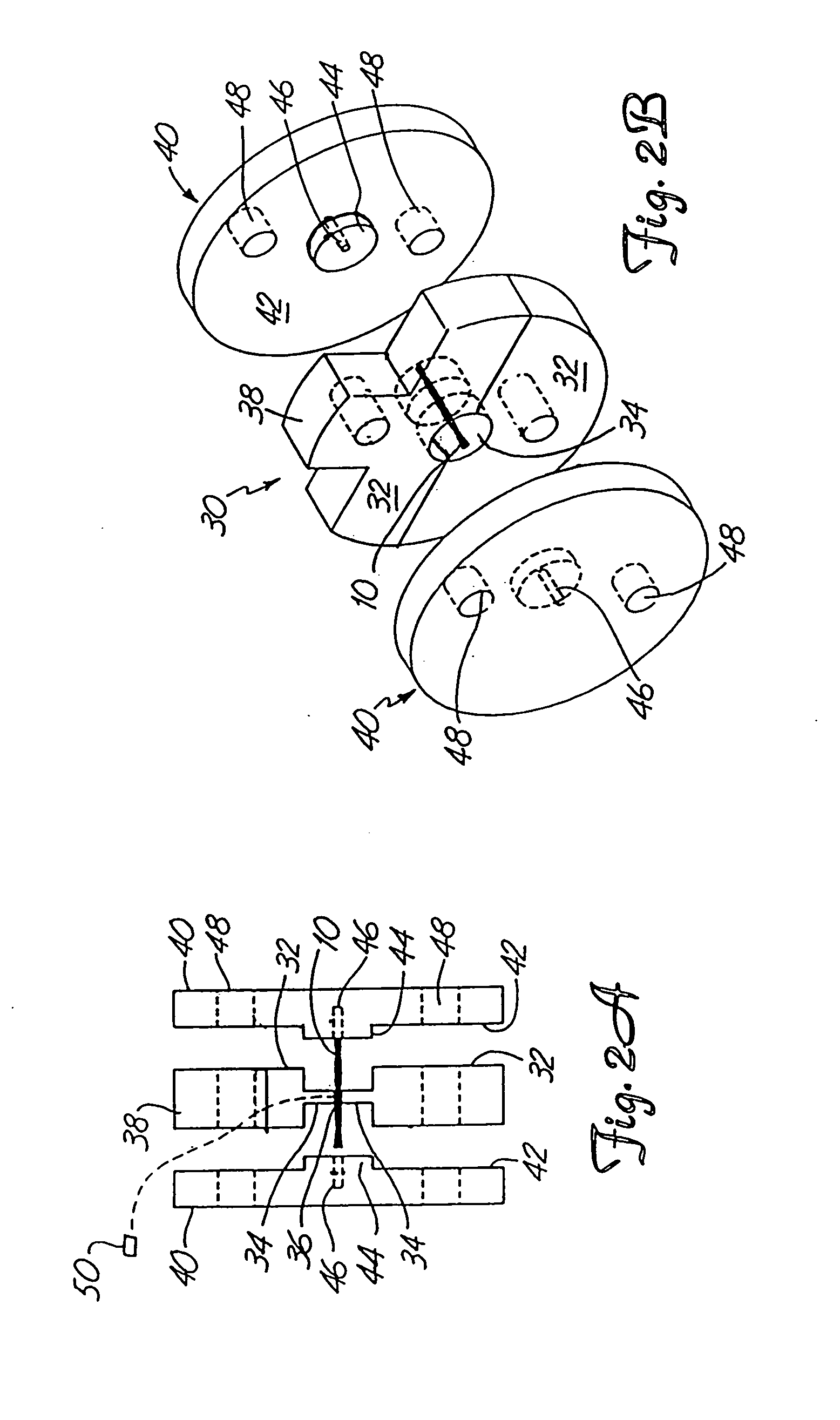
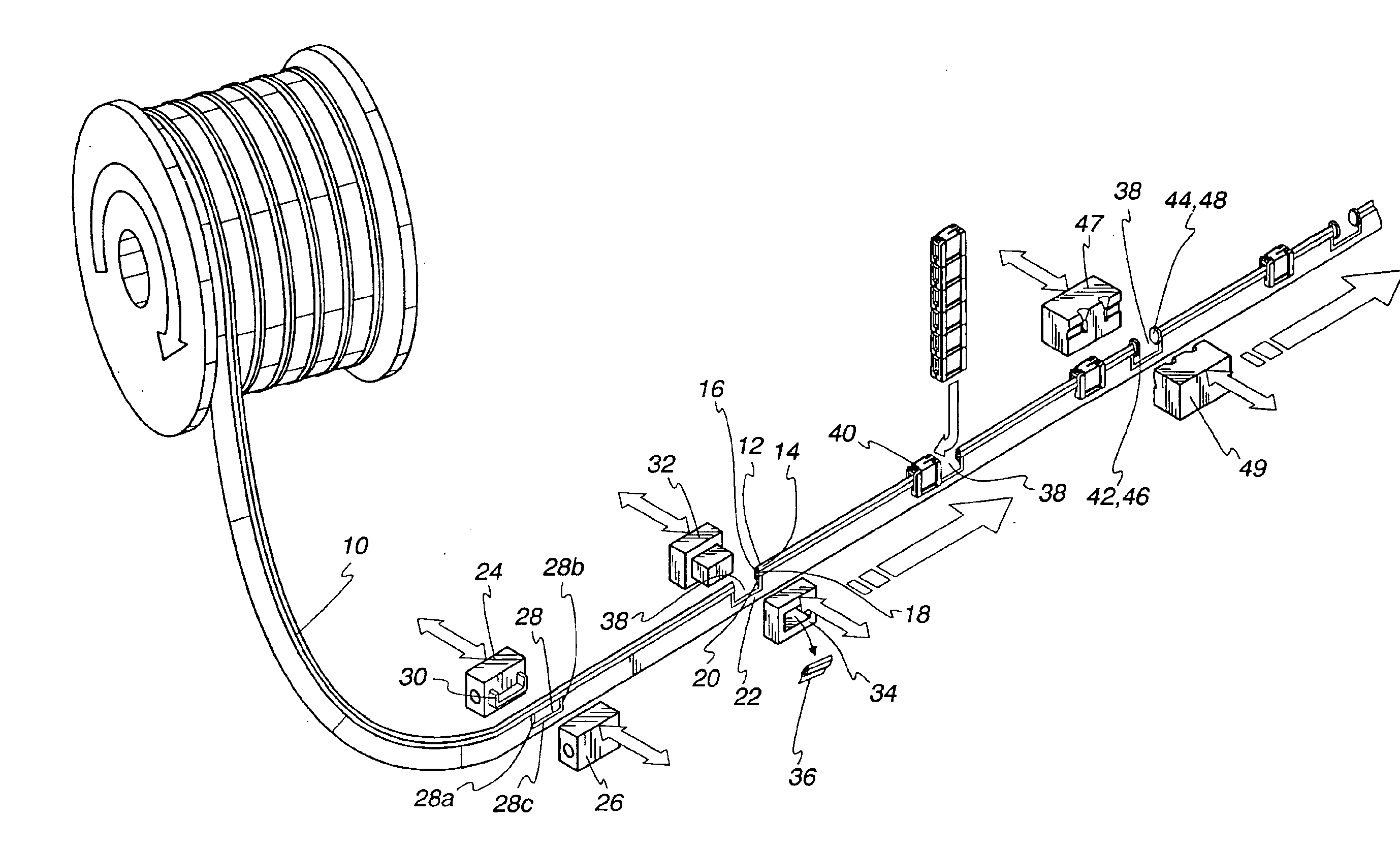
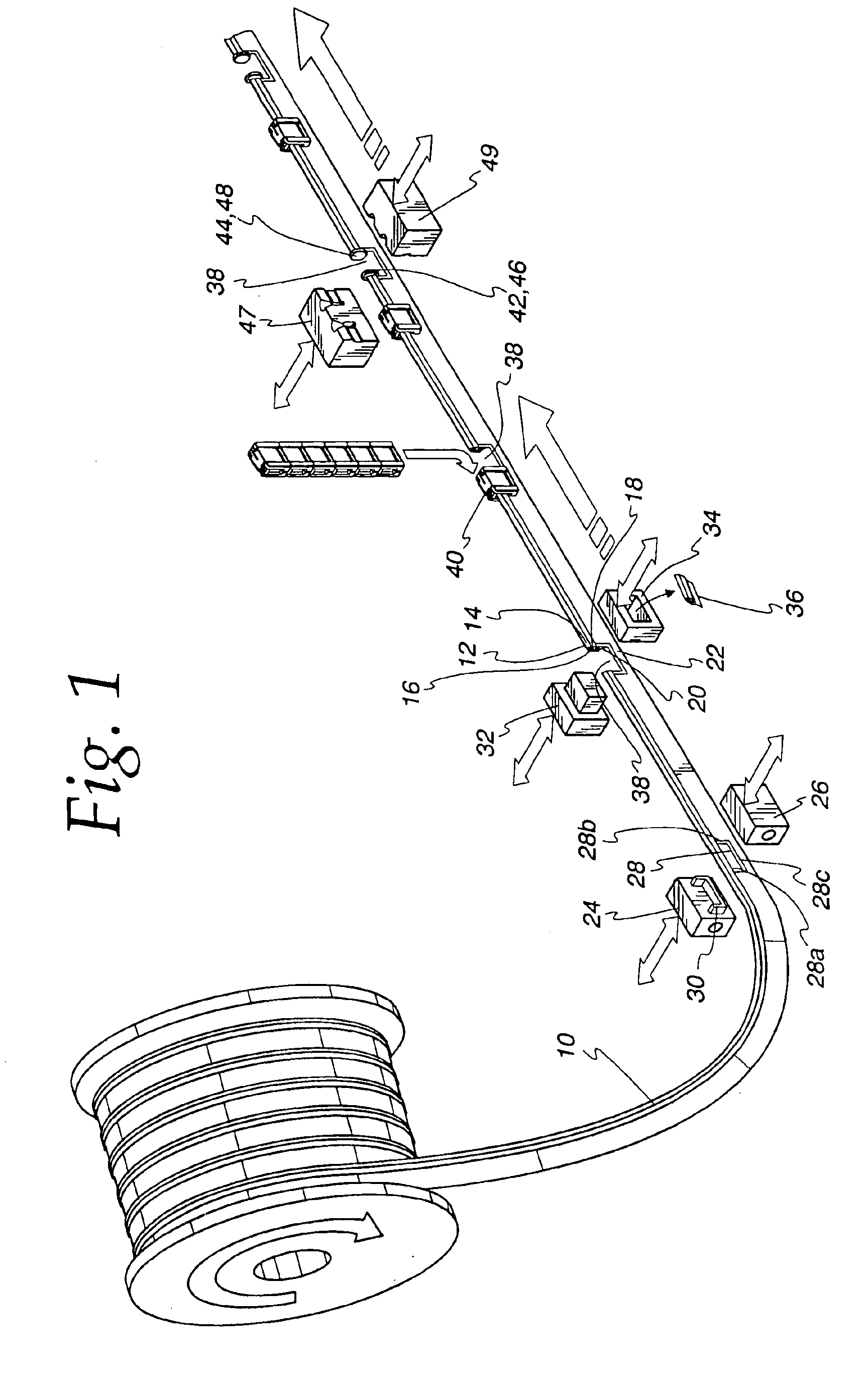
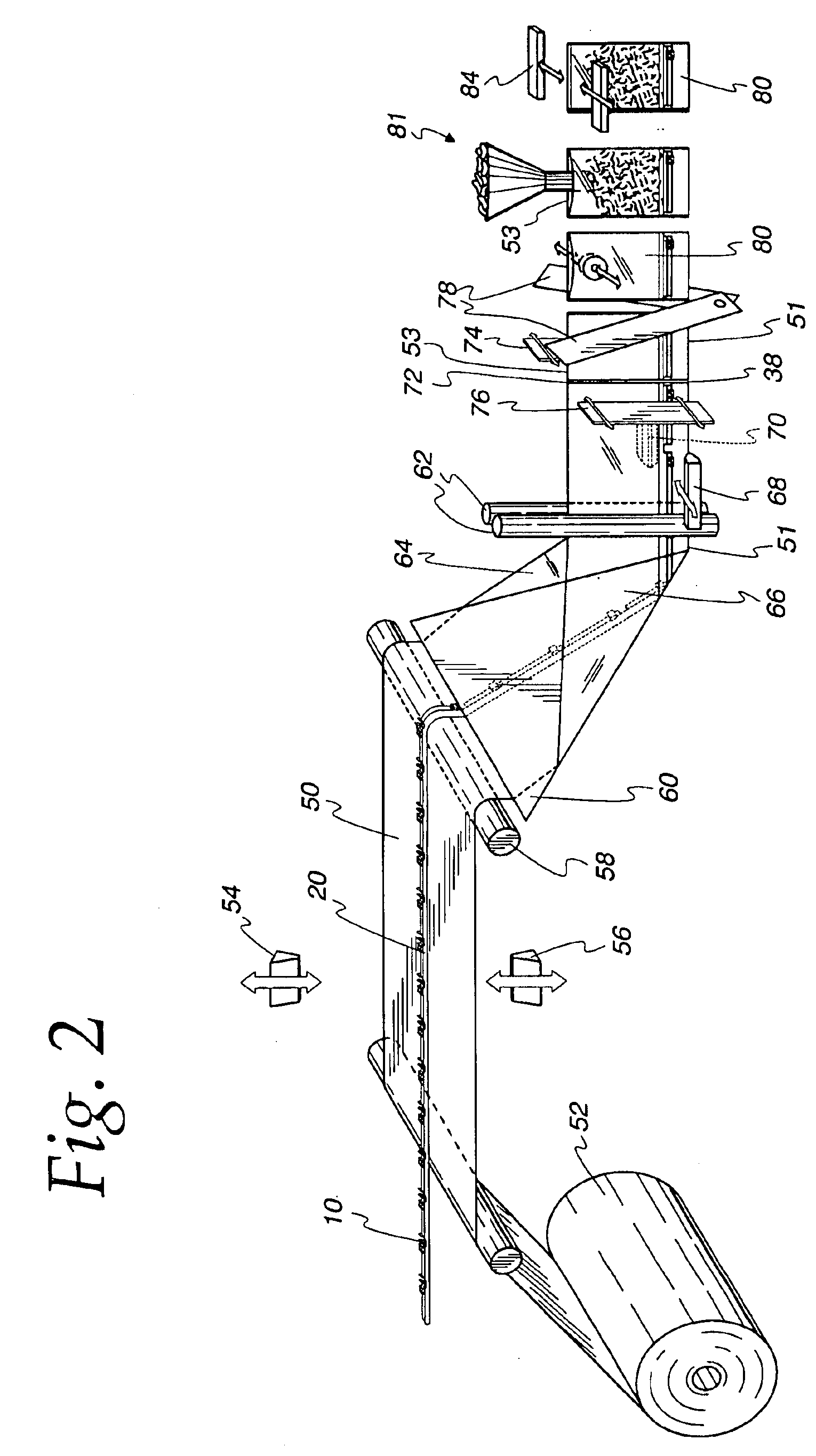
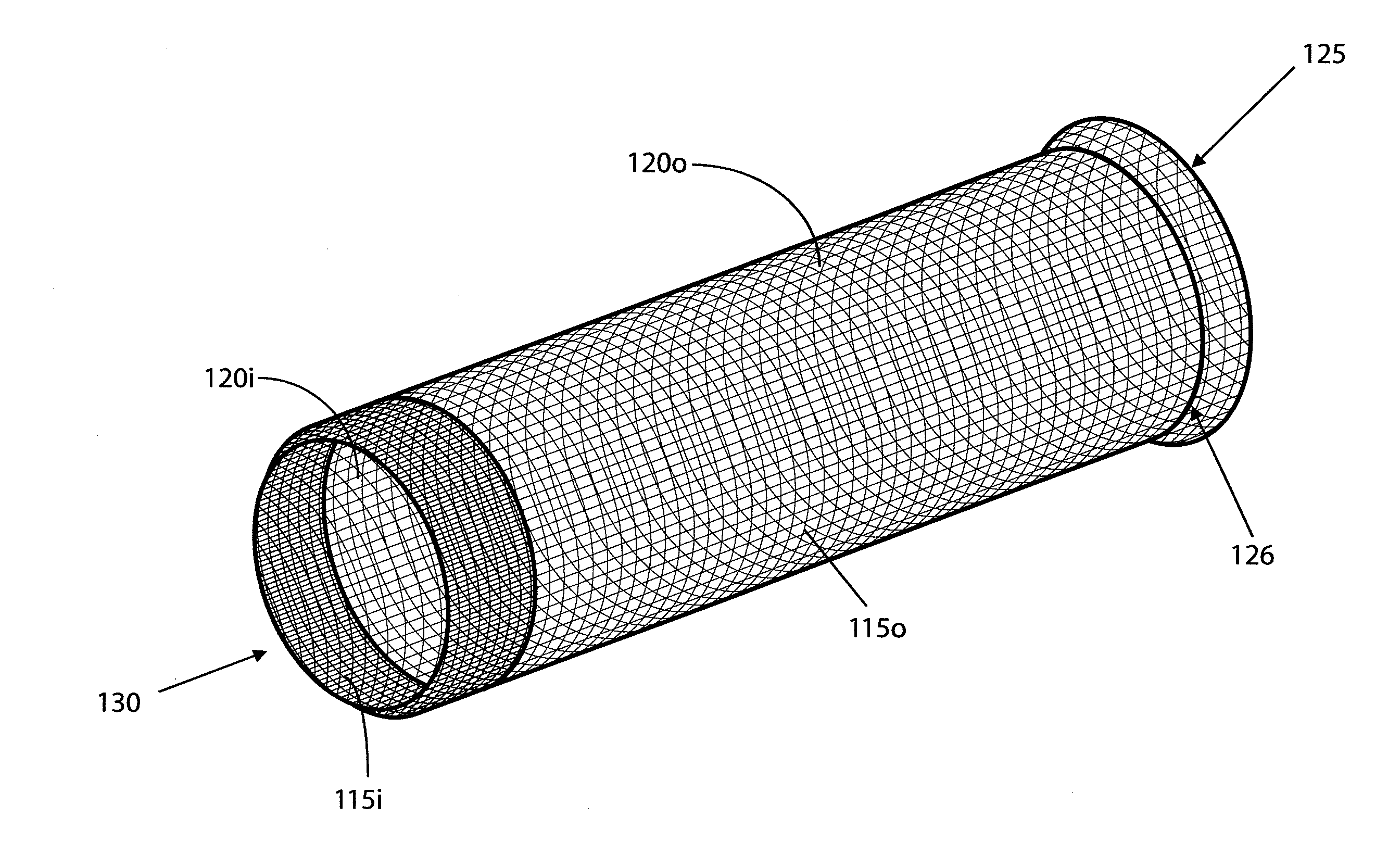
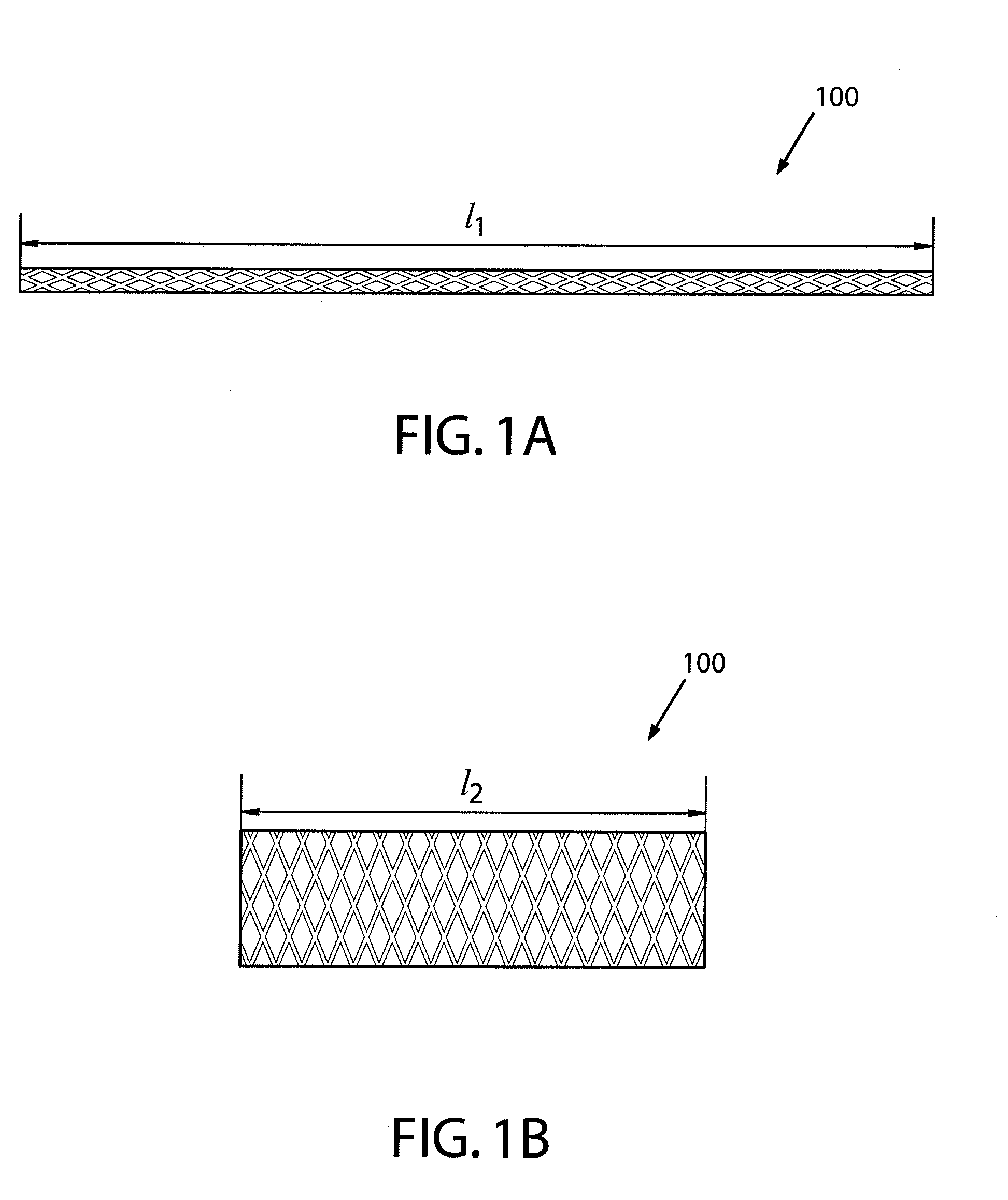
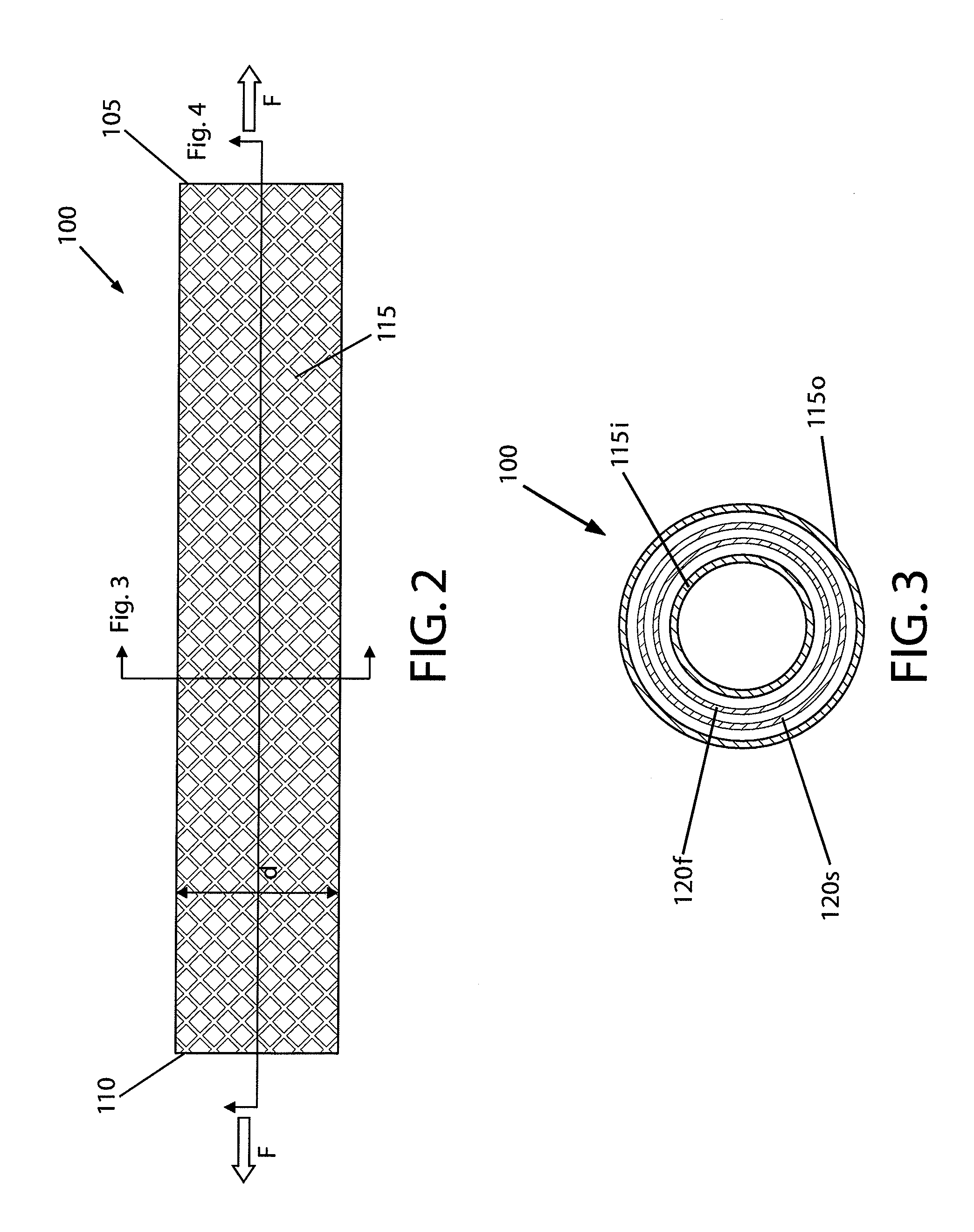
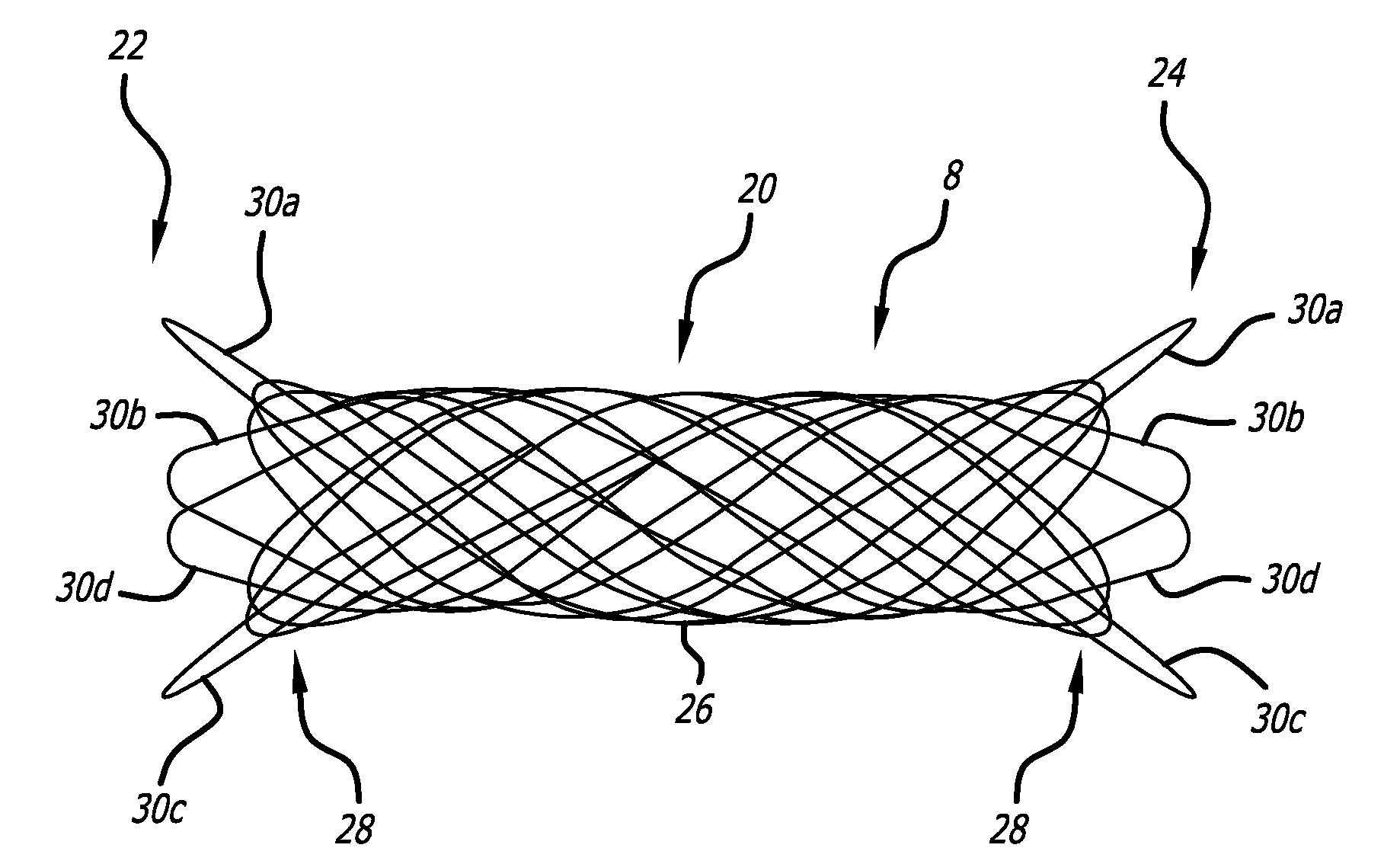
Patents
Literature
1204results about "Wire articles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
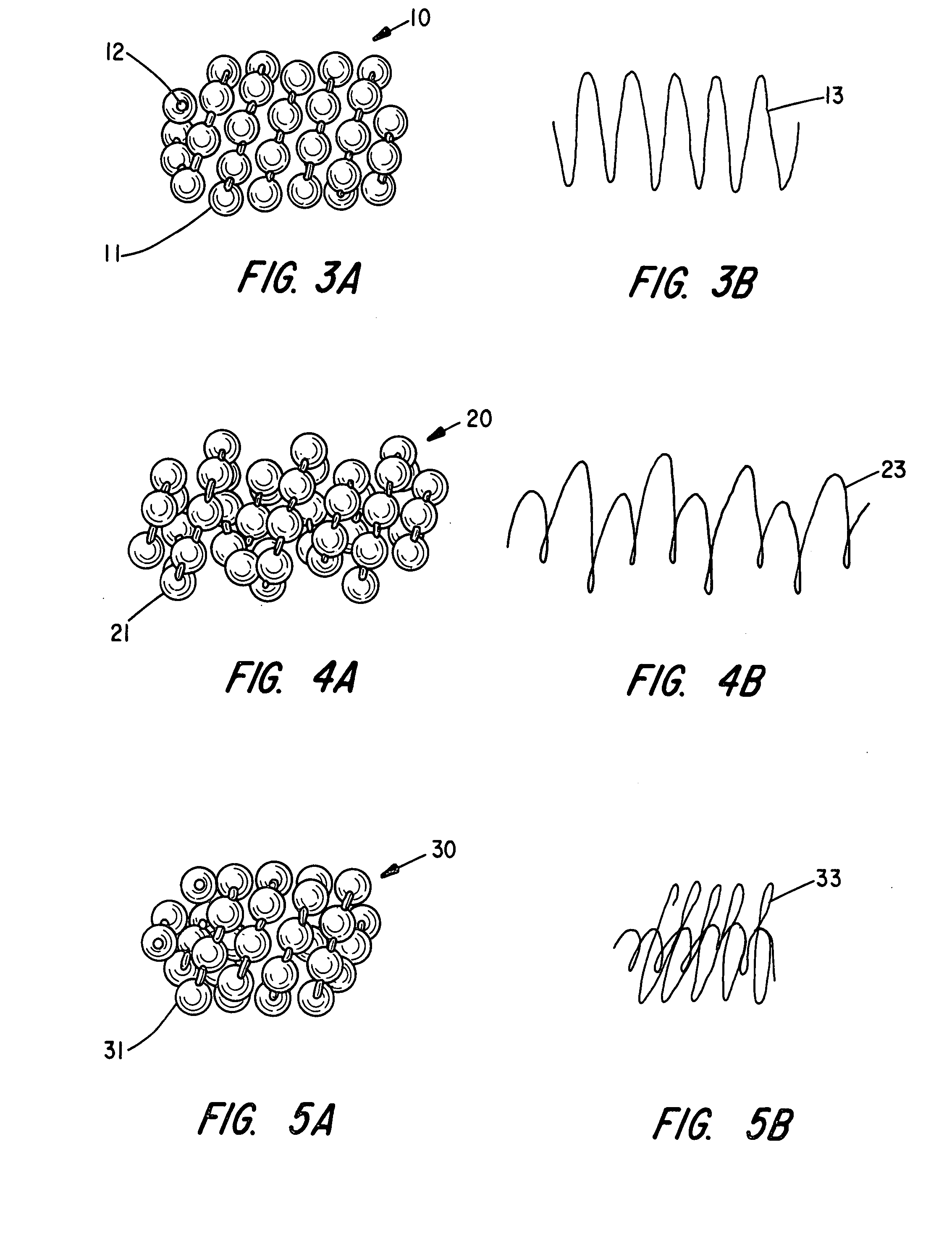
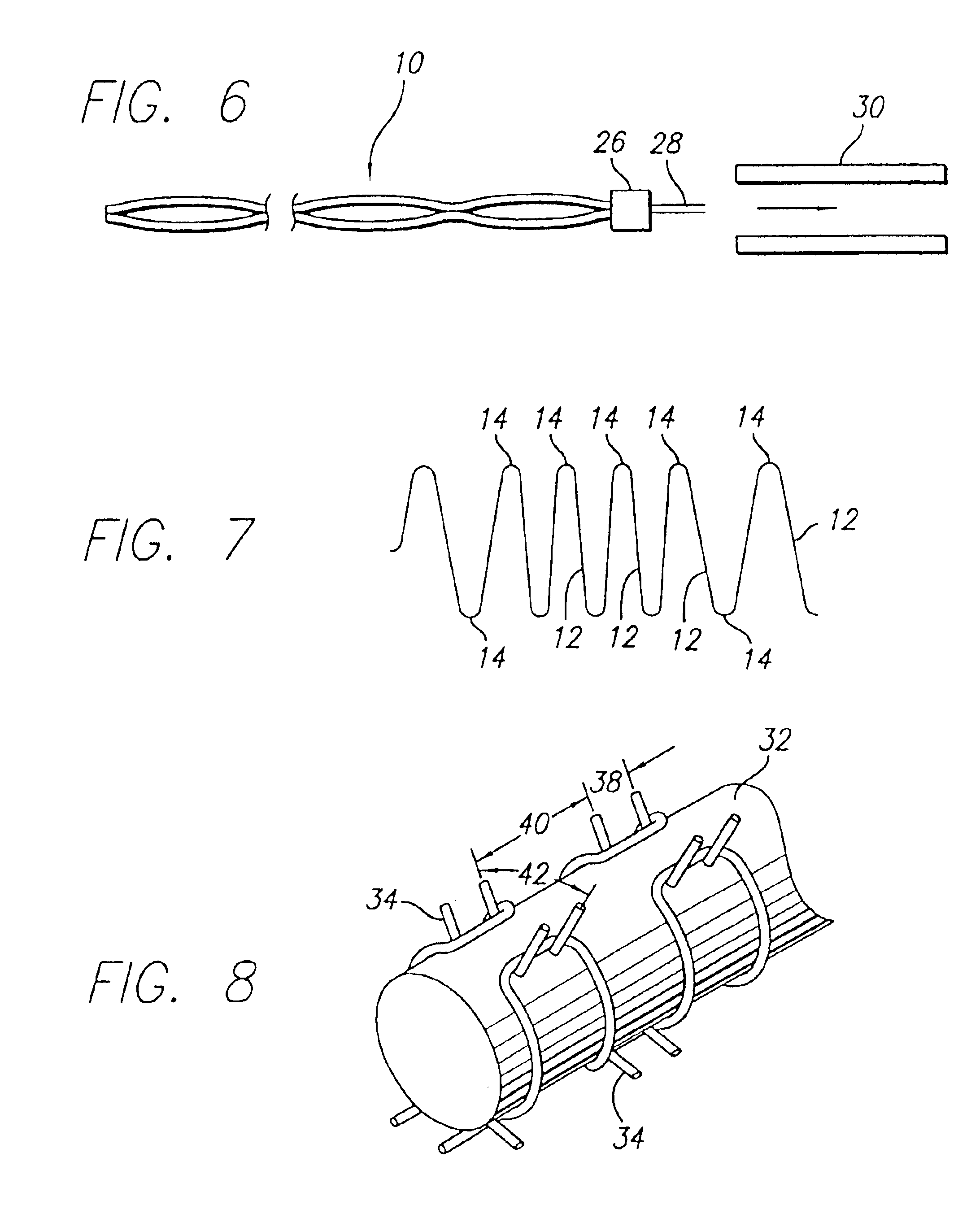
Method of forming a wire package
A method for making a wire package for use as staples or brads is recited as forming a plurality of round wires, forming a plurality of flattened bonding sides on each wire to prepare even bonding surfaces on each wire and bonding each wire to an adjacent wire by adhering the surfaces of each wire. Each staple includes two or more flat surfaces to improve the bonding strength of each staple. A package of diverging staples or brads are formed using the flat bonding surfaces
Owner:LIAO CHASE
Biocompatible crosslinked coating and crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating
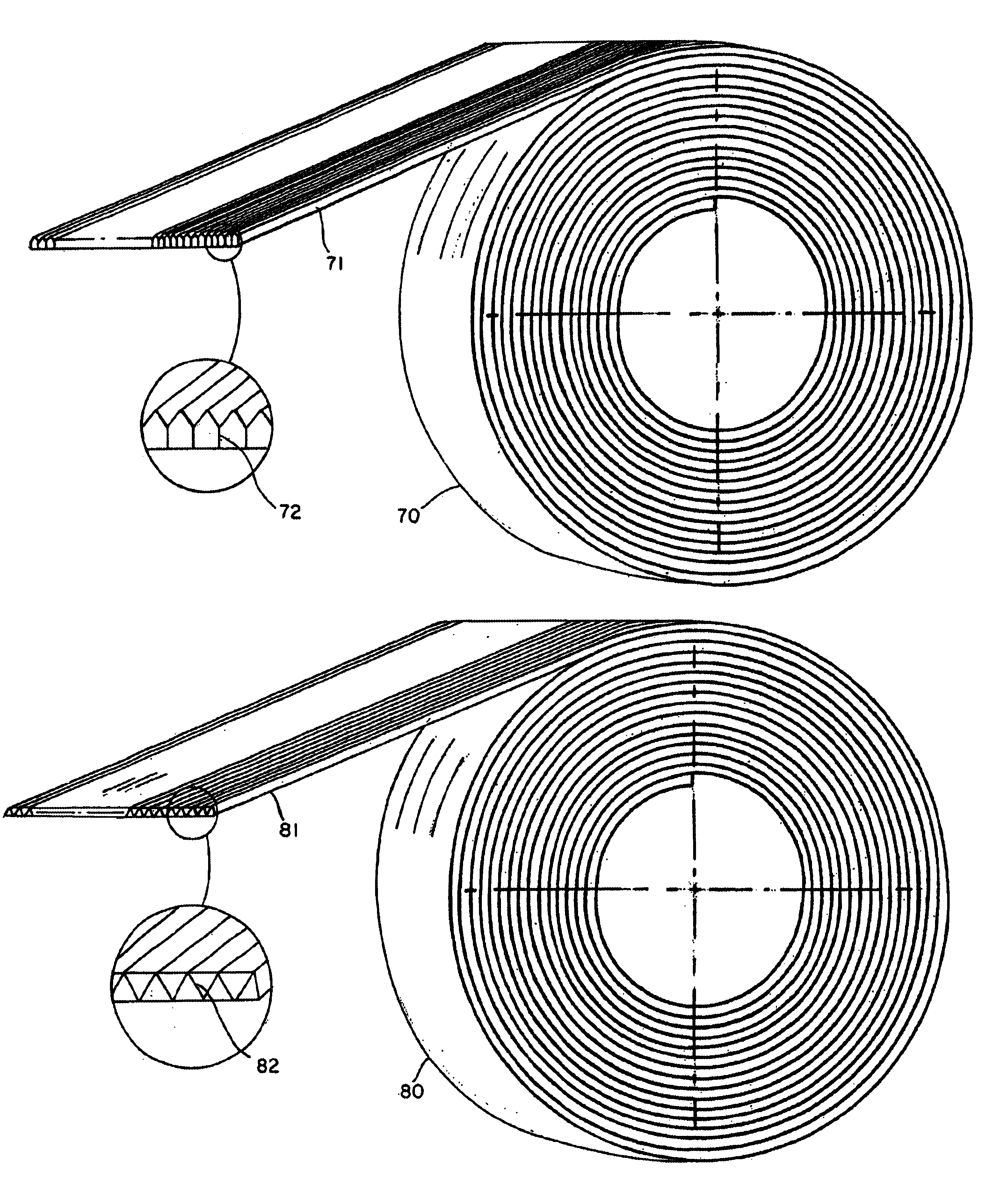
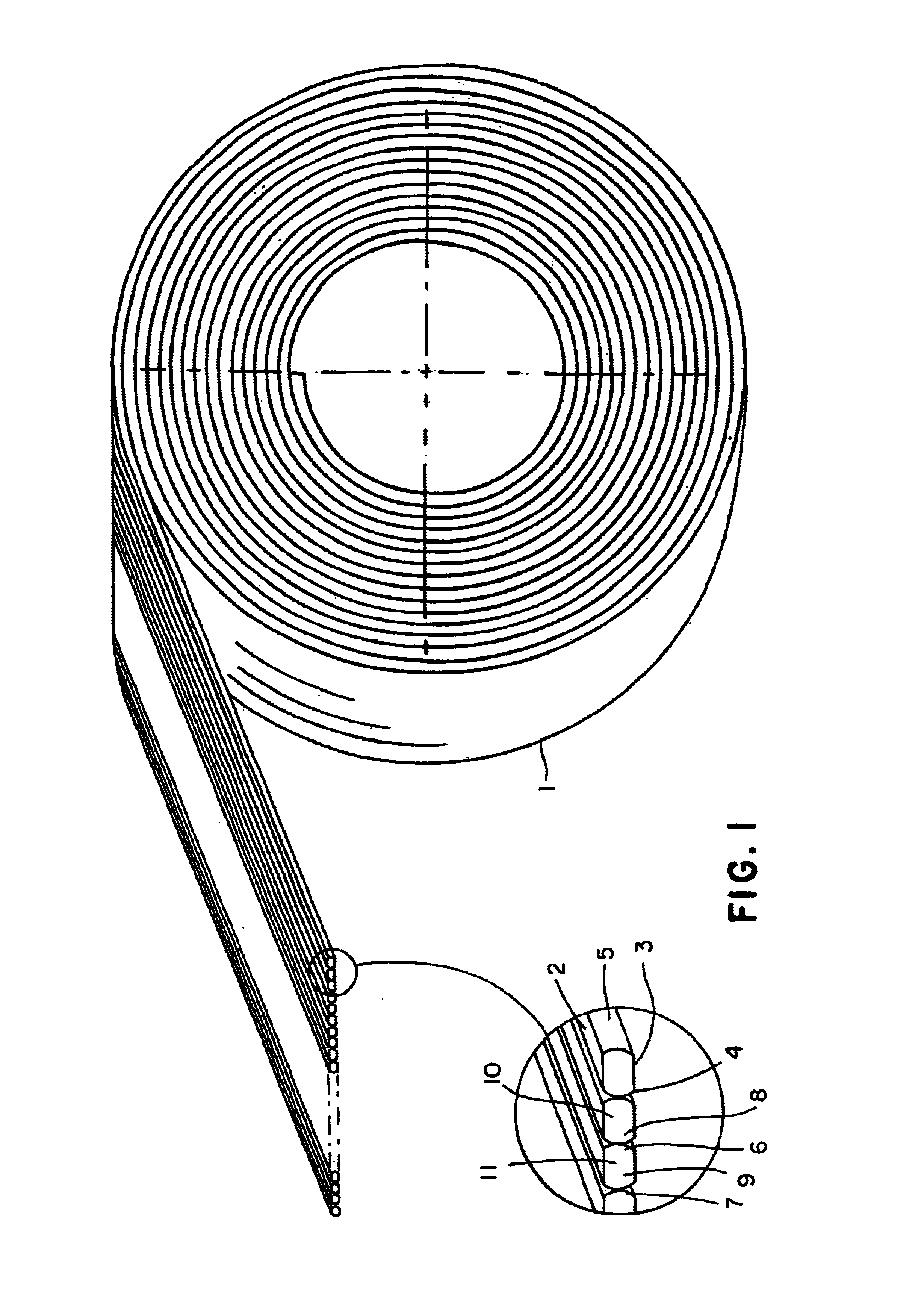
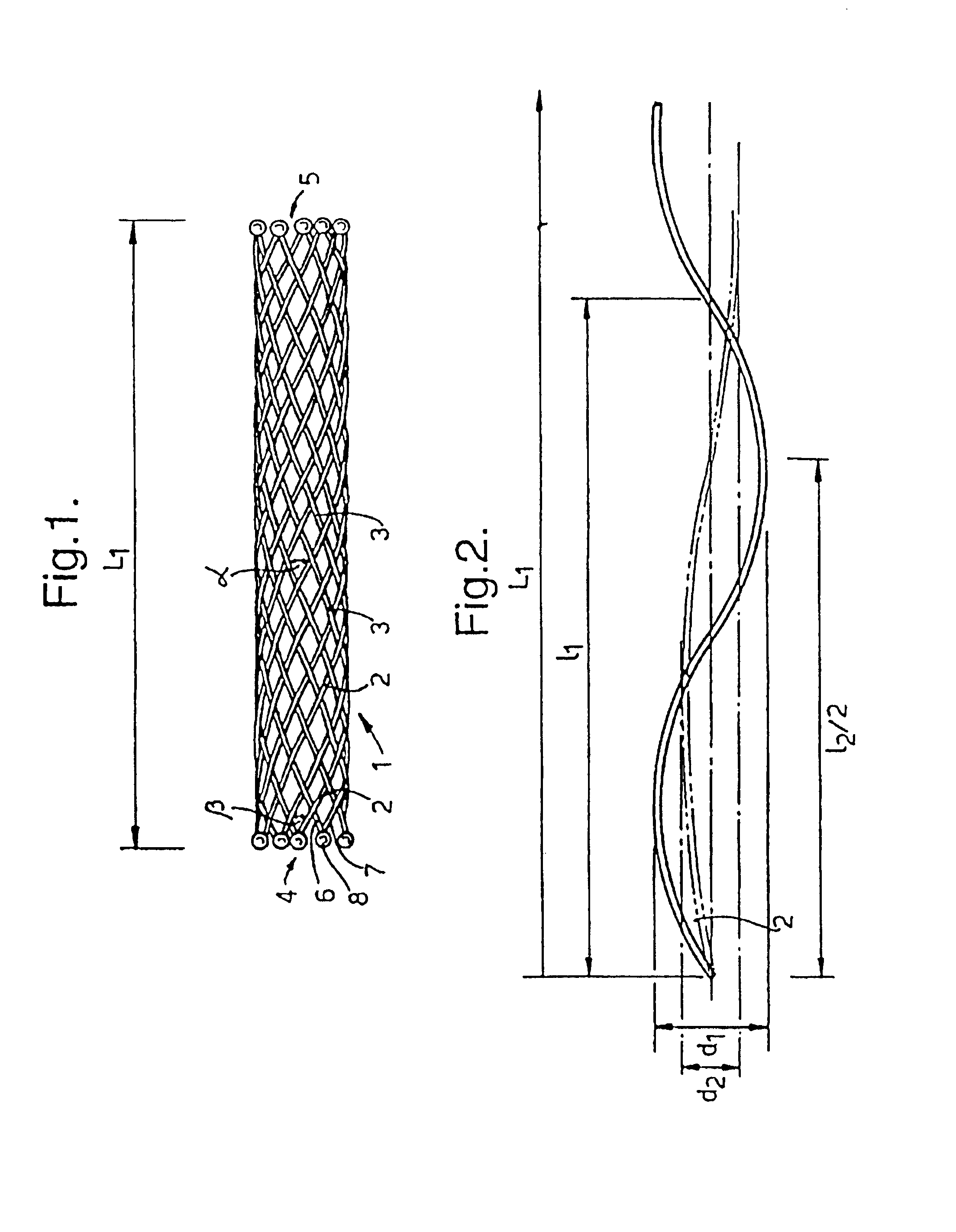
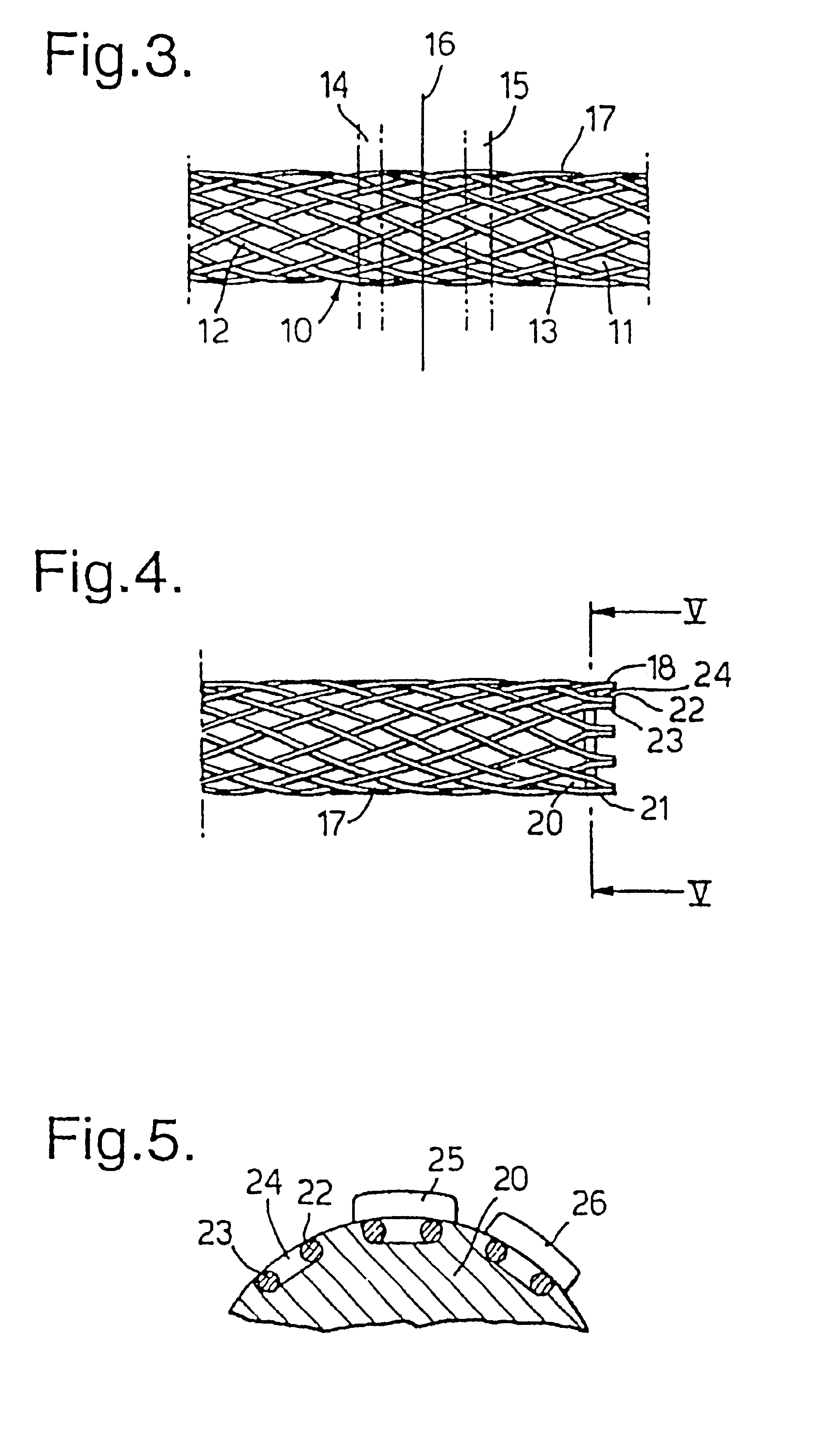
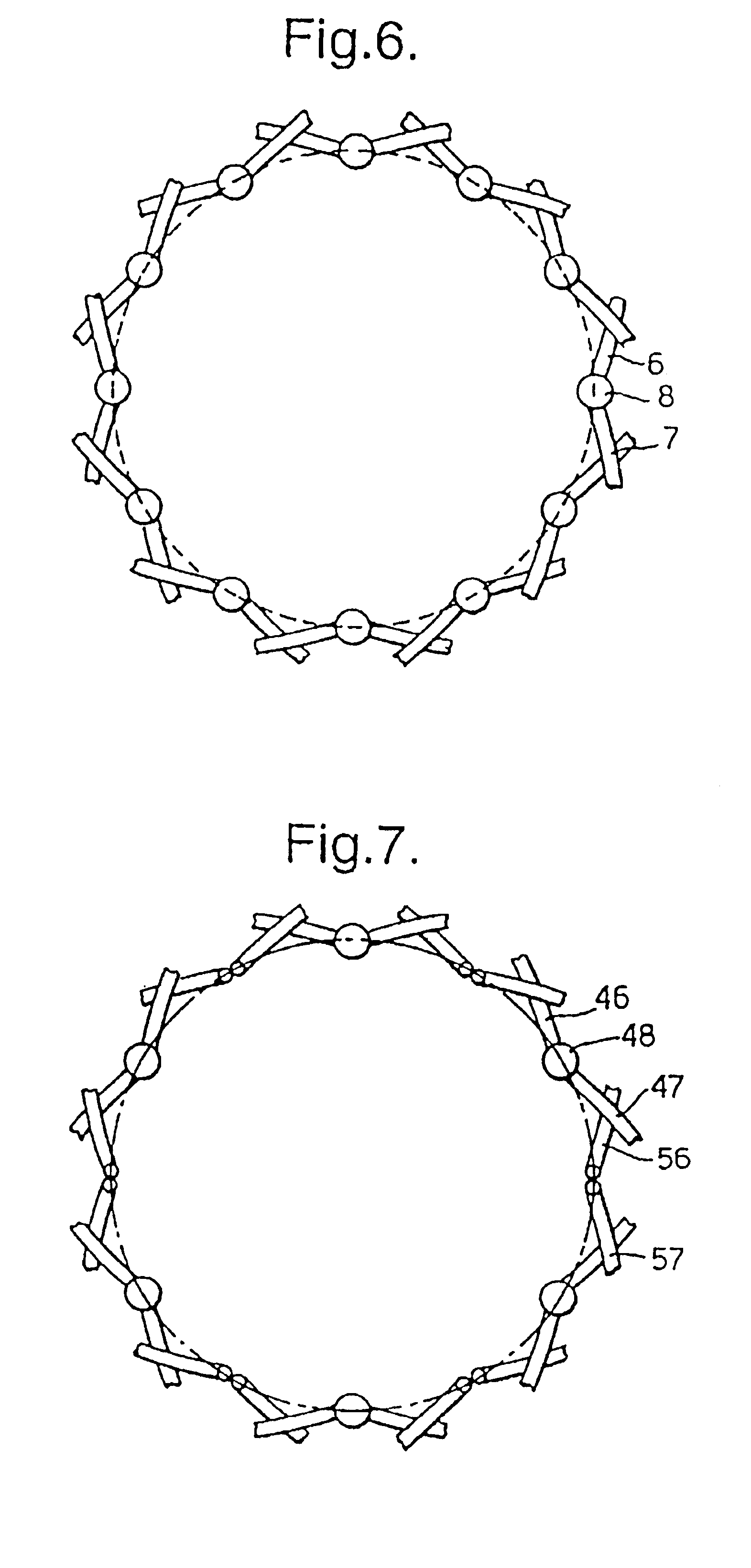
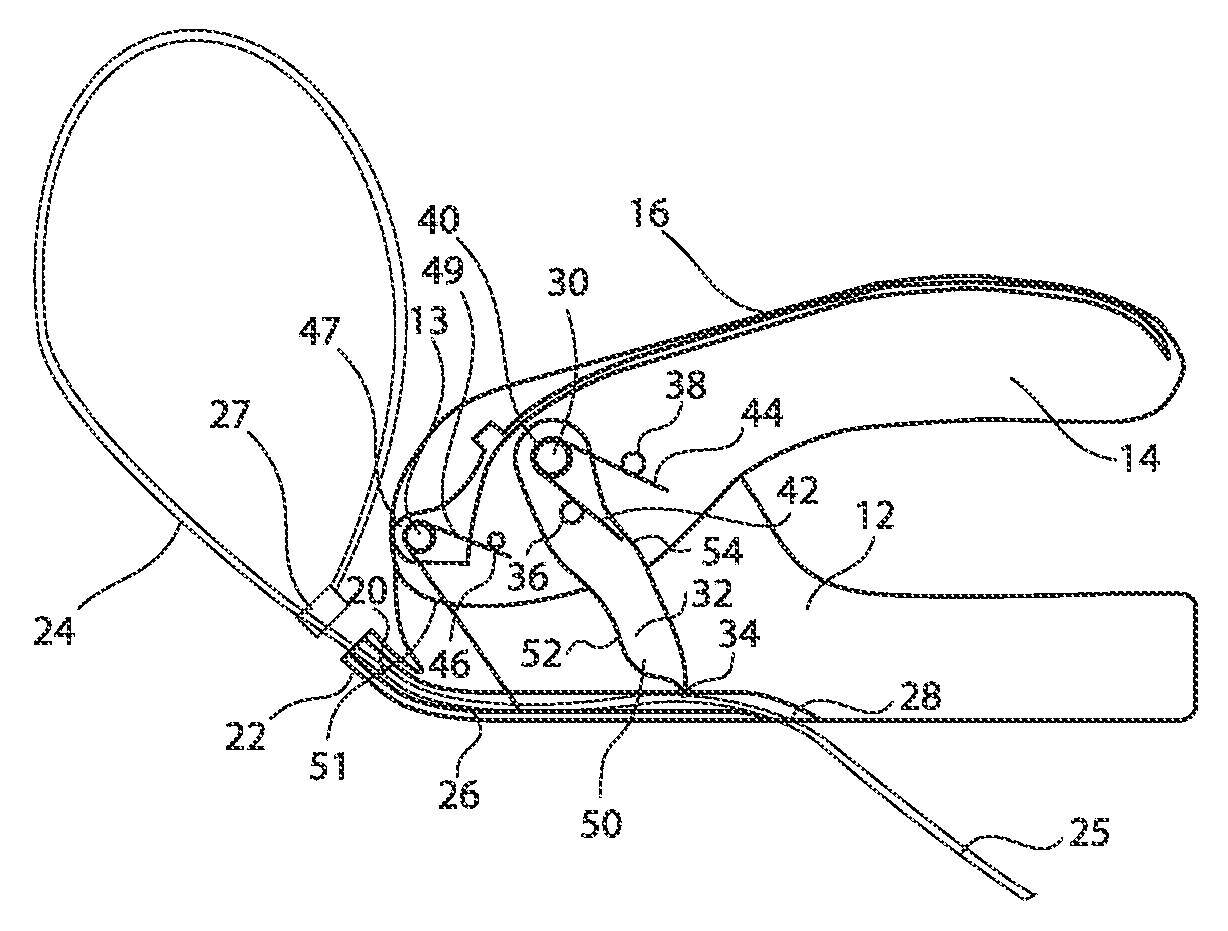
A braided stent (1) for transluminal implantation in body lumens is self-expanding and has a radial expanded configuration in which the angle α between filaments is acute. Some or all of filaments (6,7) are welded together in pairs at each end (4,5) of the stent to provide beads (8), thereby strengthening the stent and assisting its deployment from a delivery device. The stent is preferably completely coated using a biocompatible polymeric coating, said polymer preferably having pendant phosphoryl choline groups. A method of making the stent by braiding and welding is described as well as a delivery device for deploying the device.The present invention provides a biocompatible crosslinked coating and a crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating. The biocompatible crosslinked coating may be formed by curing a polymer of 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate. The crosslinkable coating polymer may include 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate.<?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
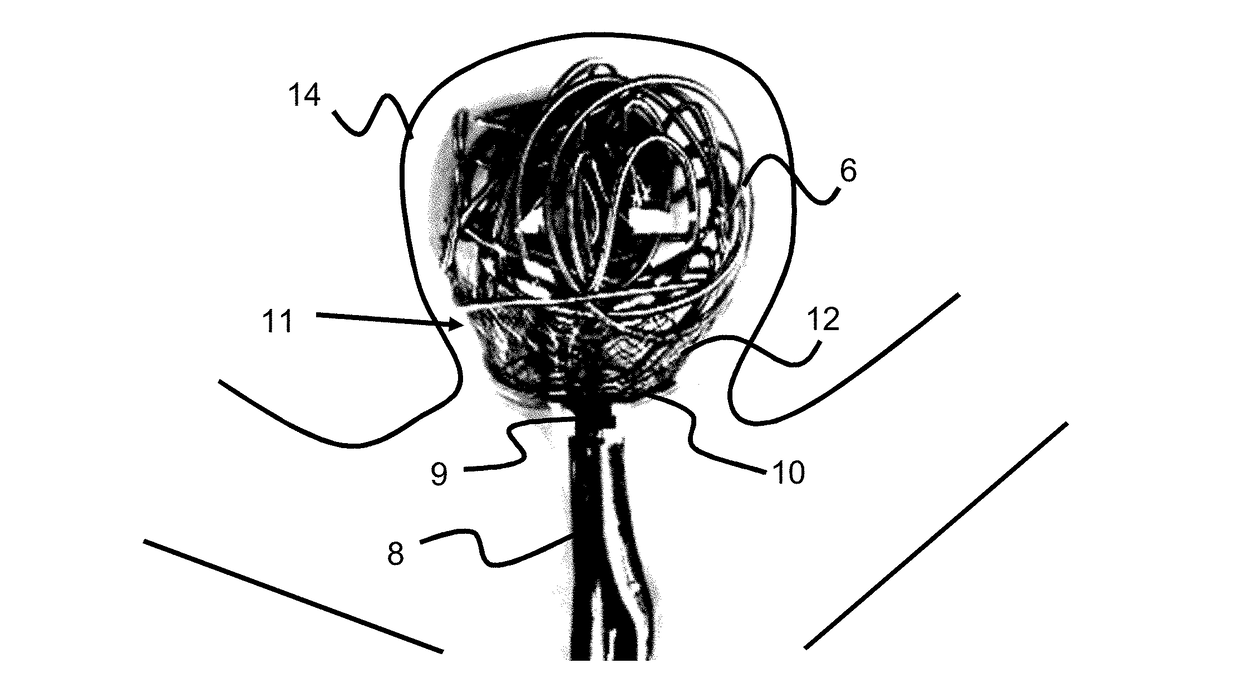
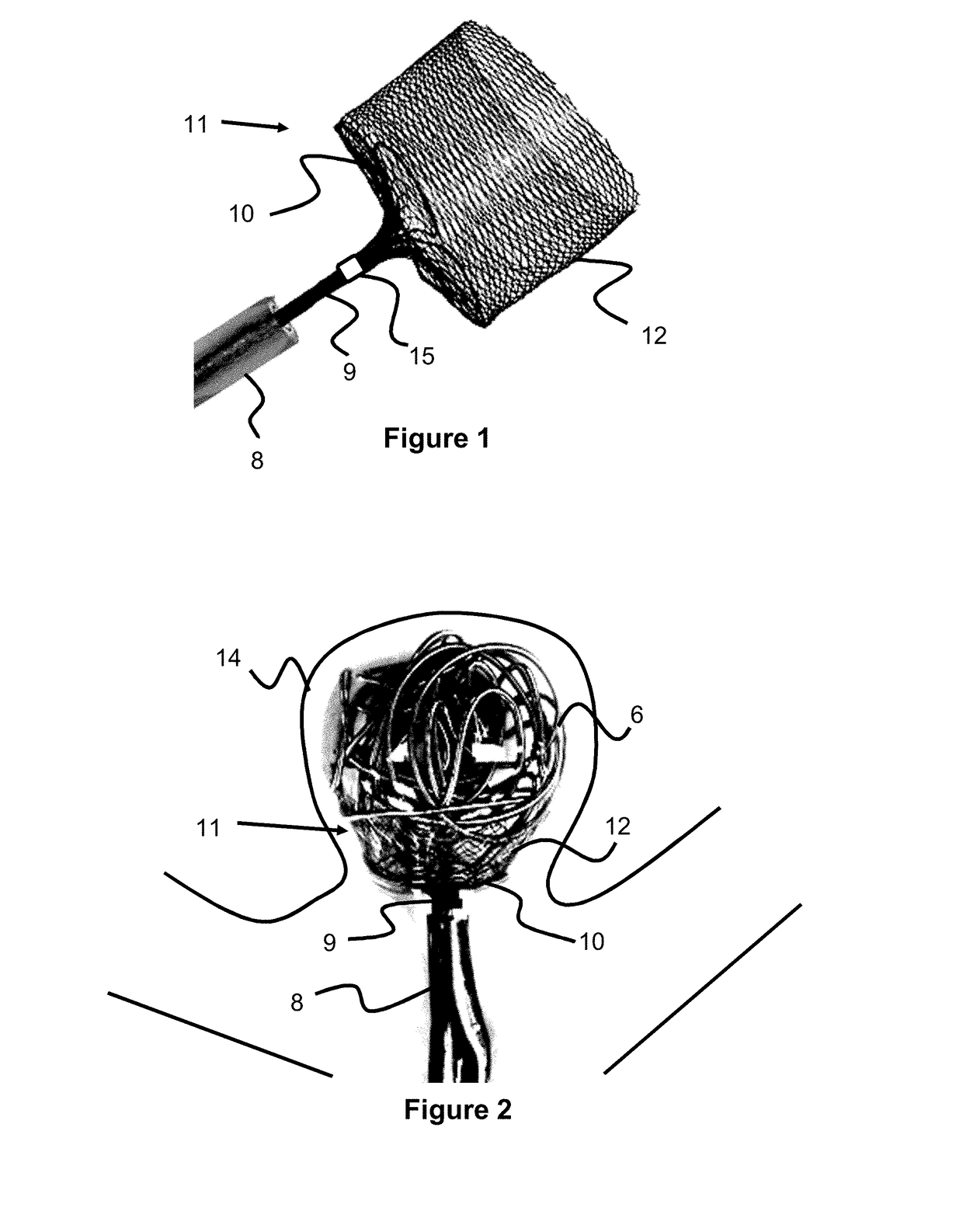
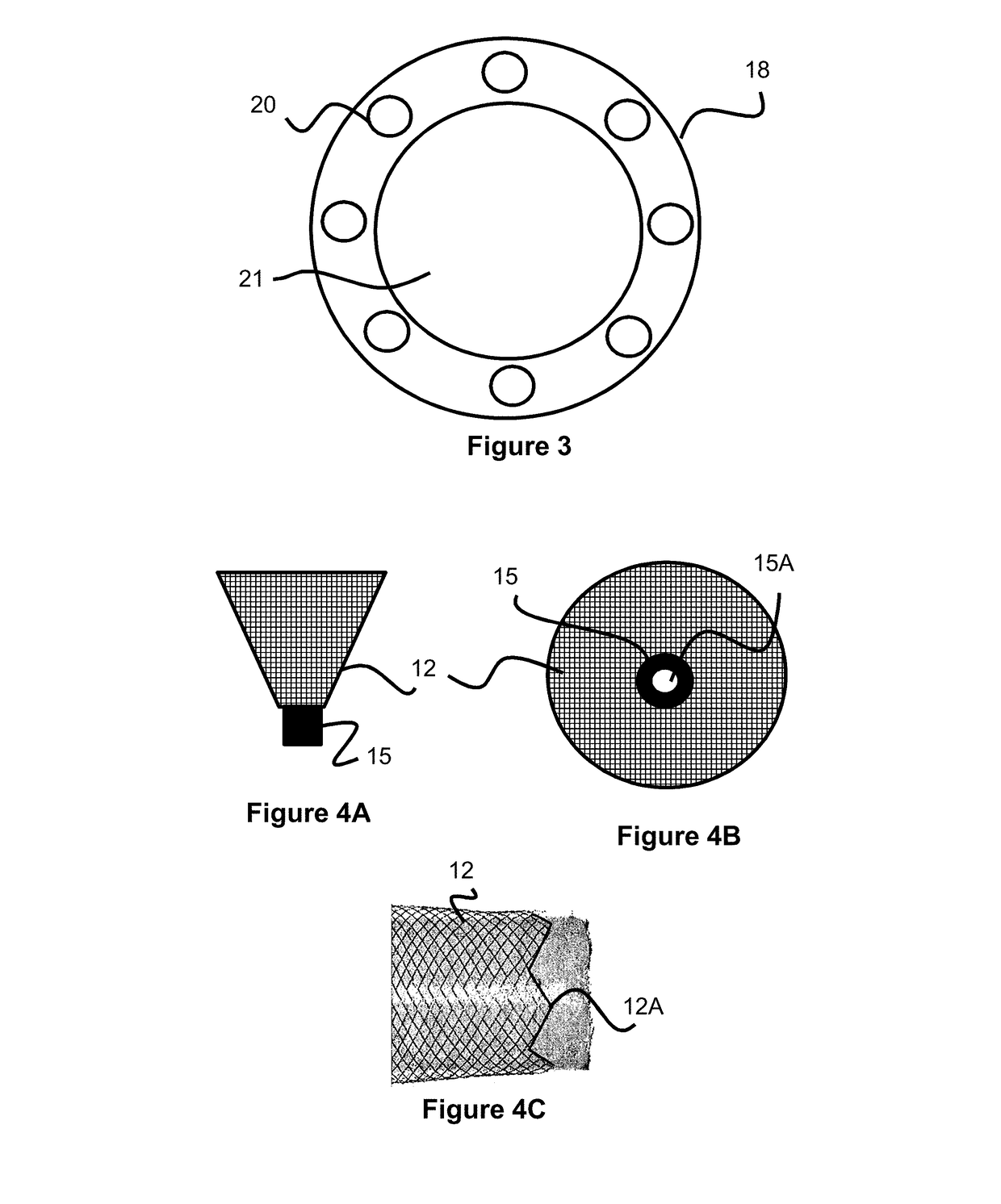
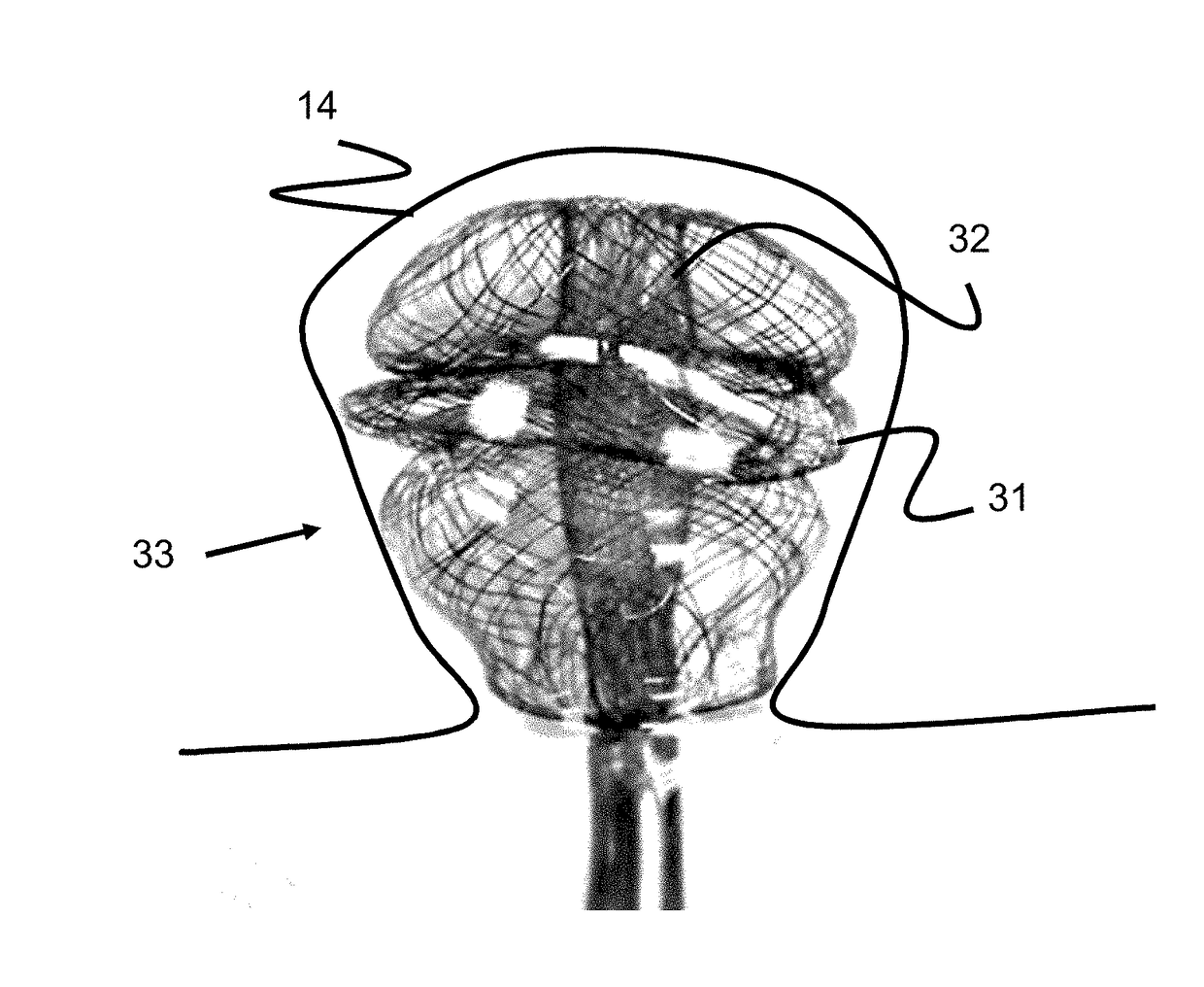
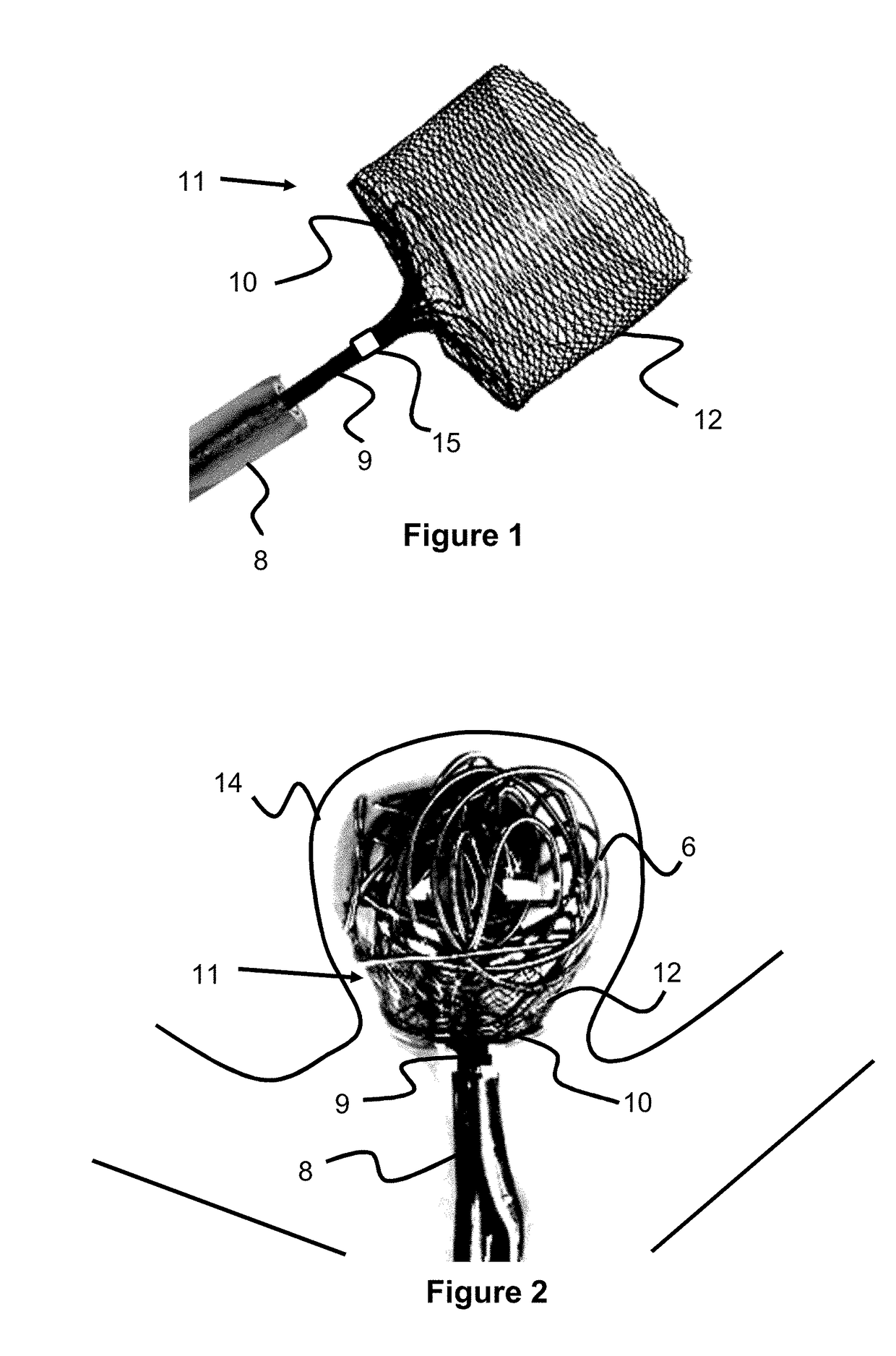
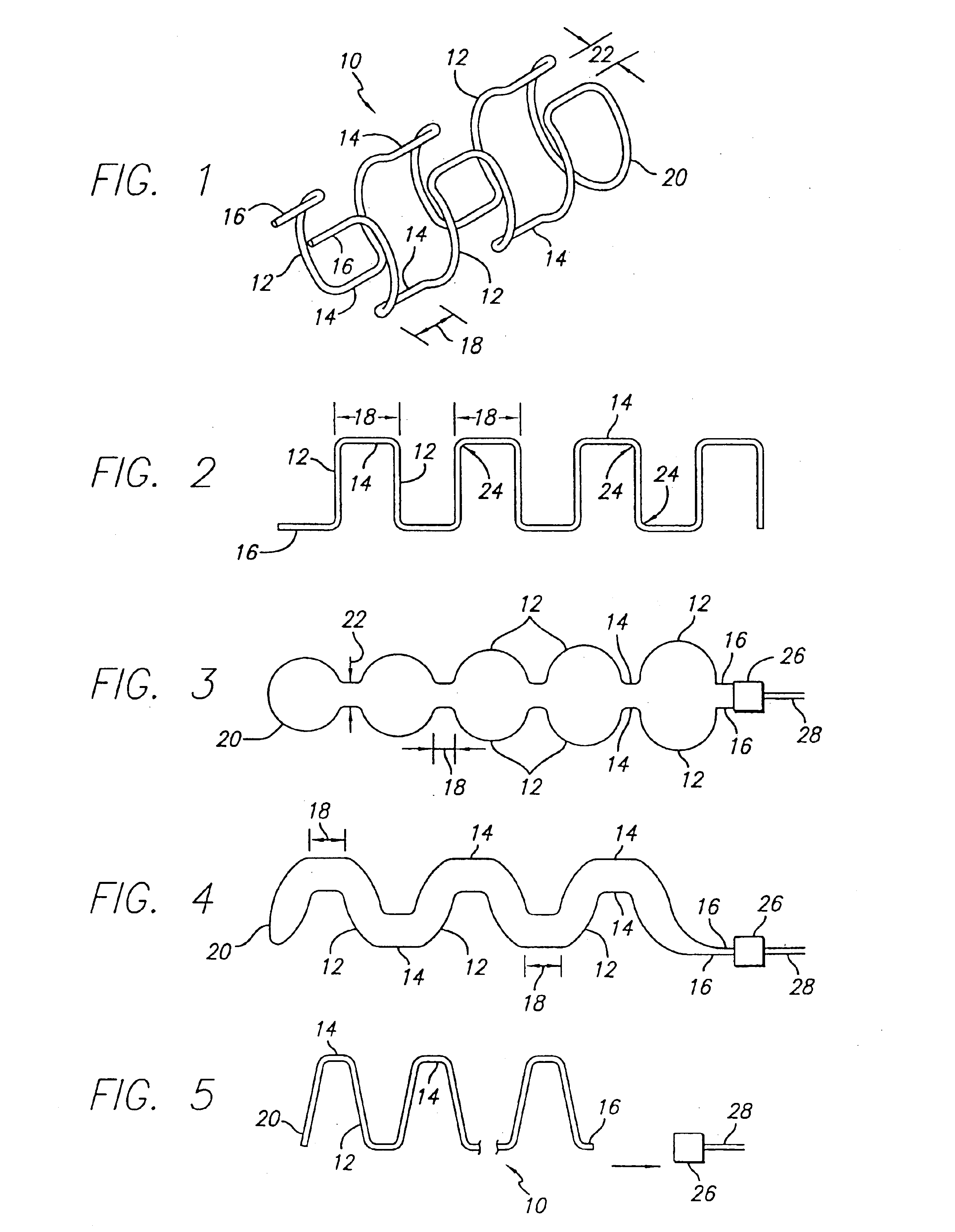
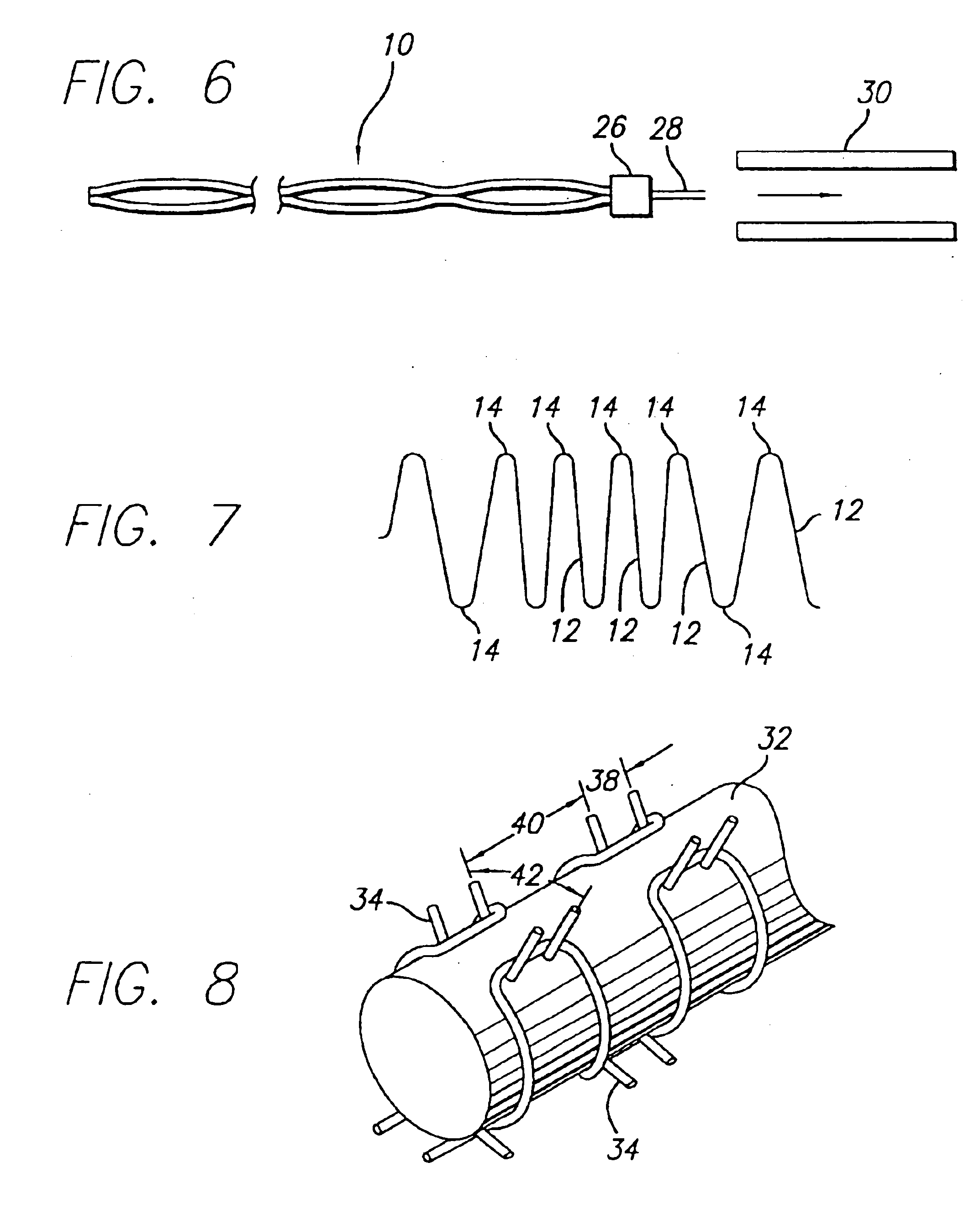
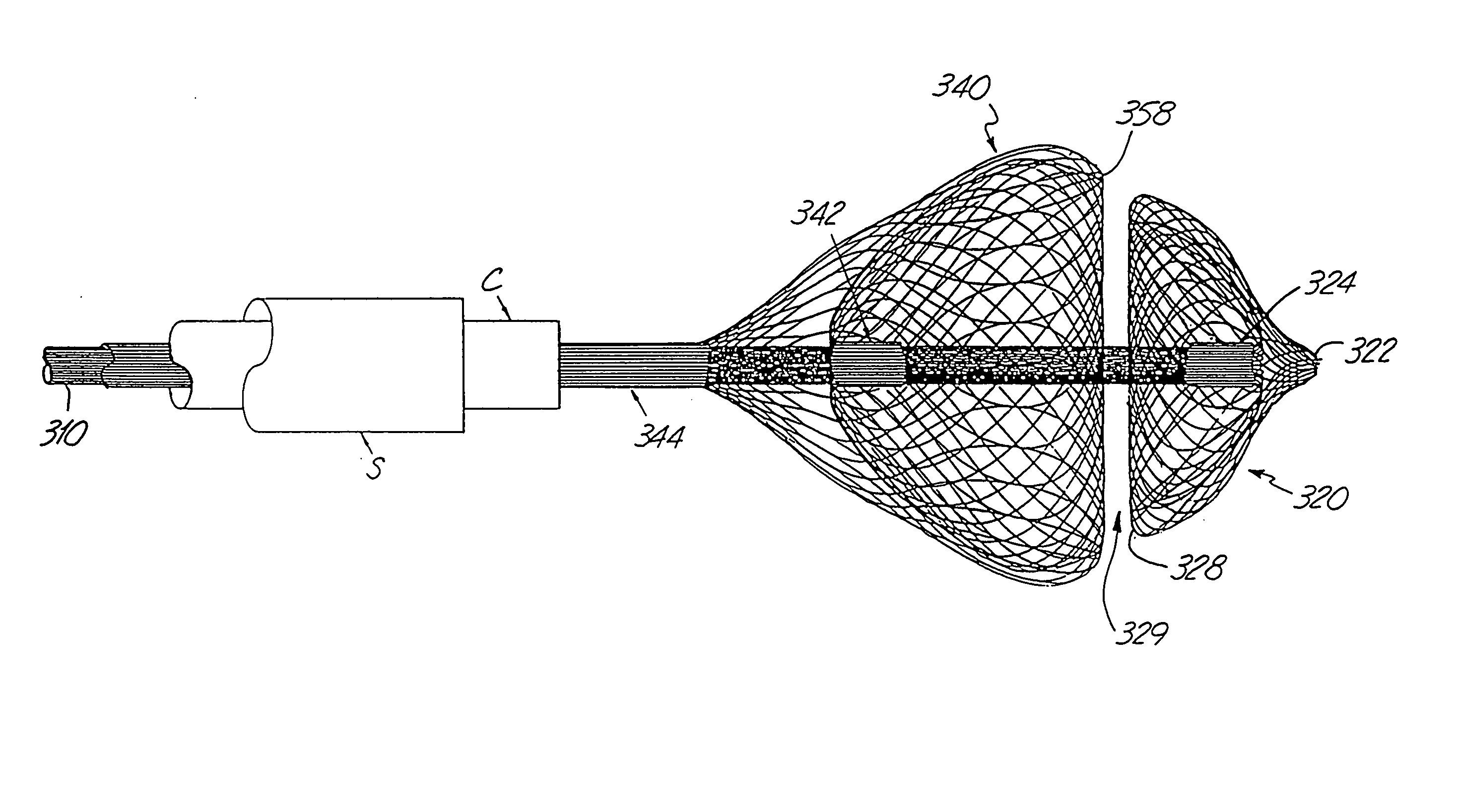
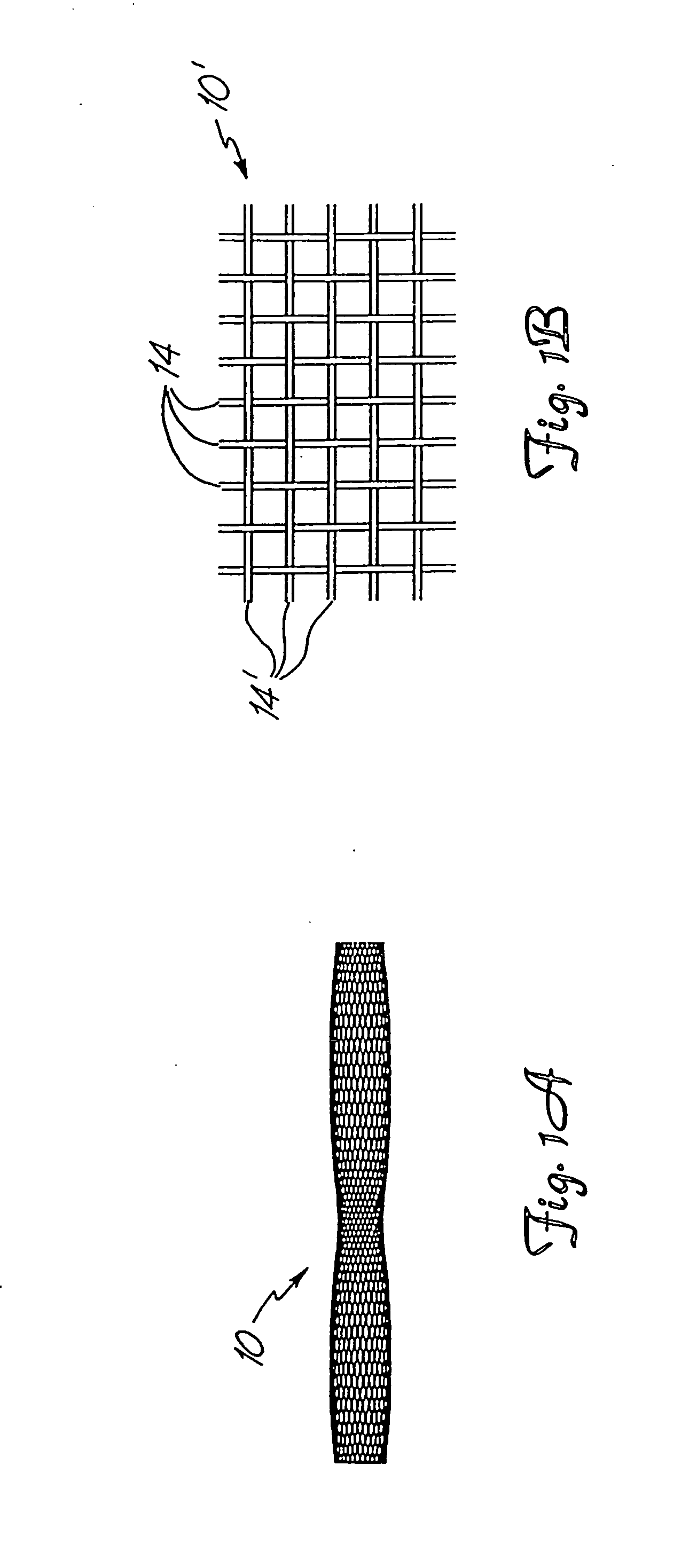
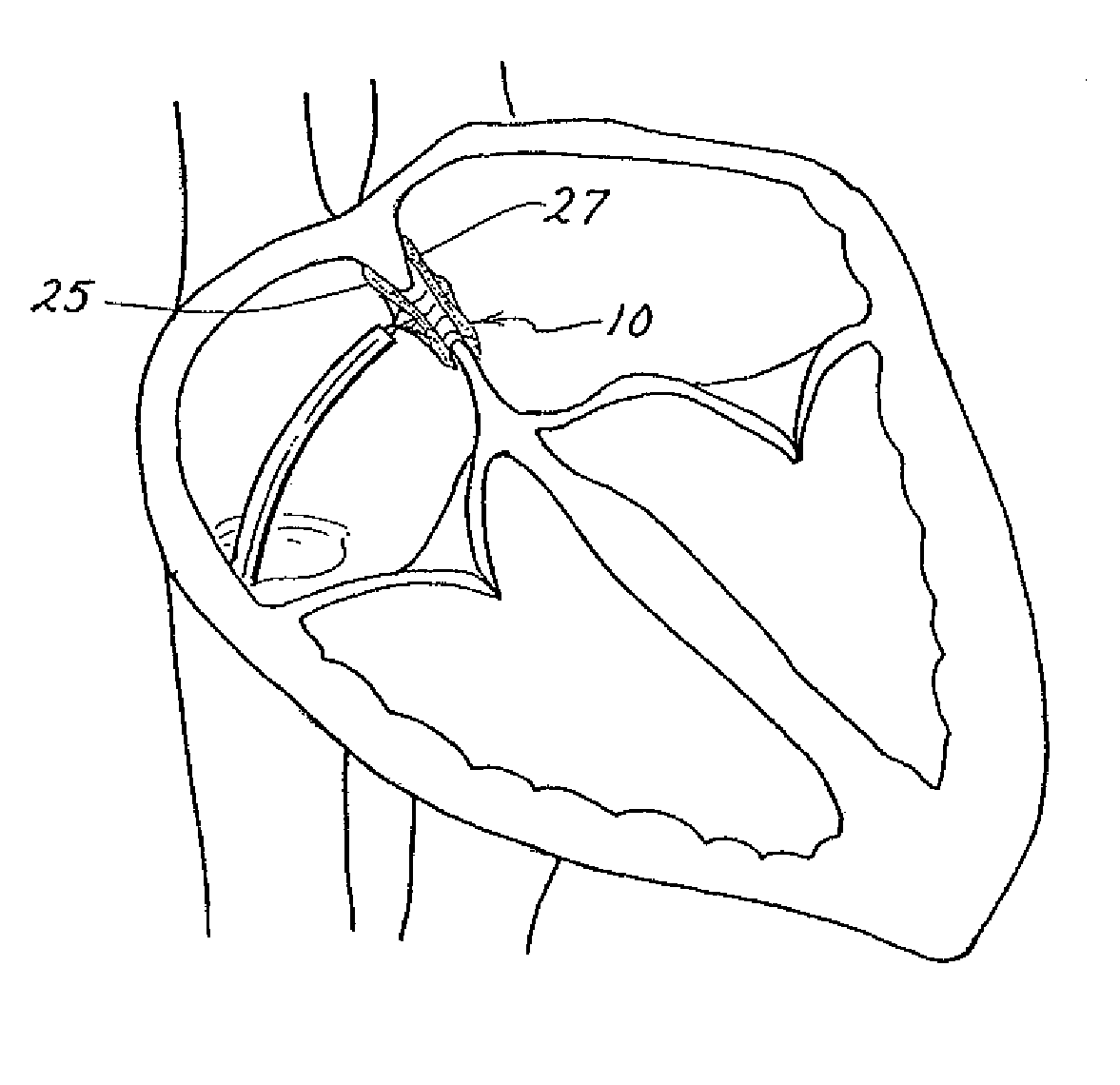
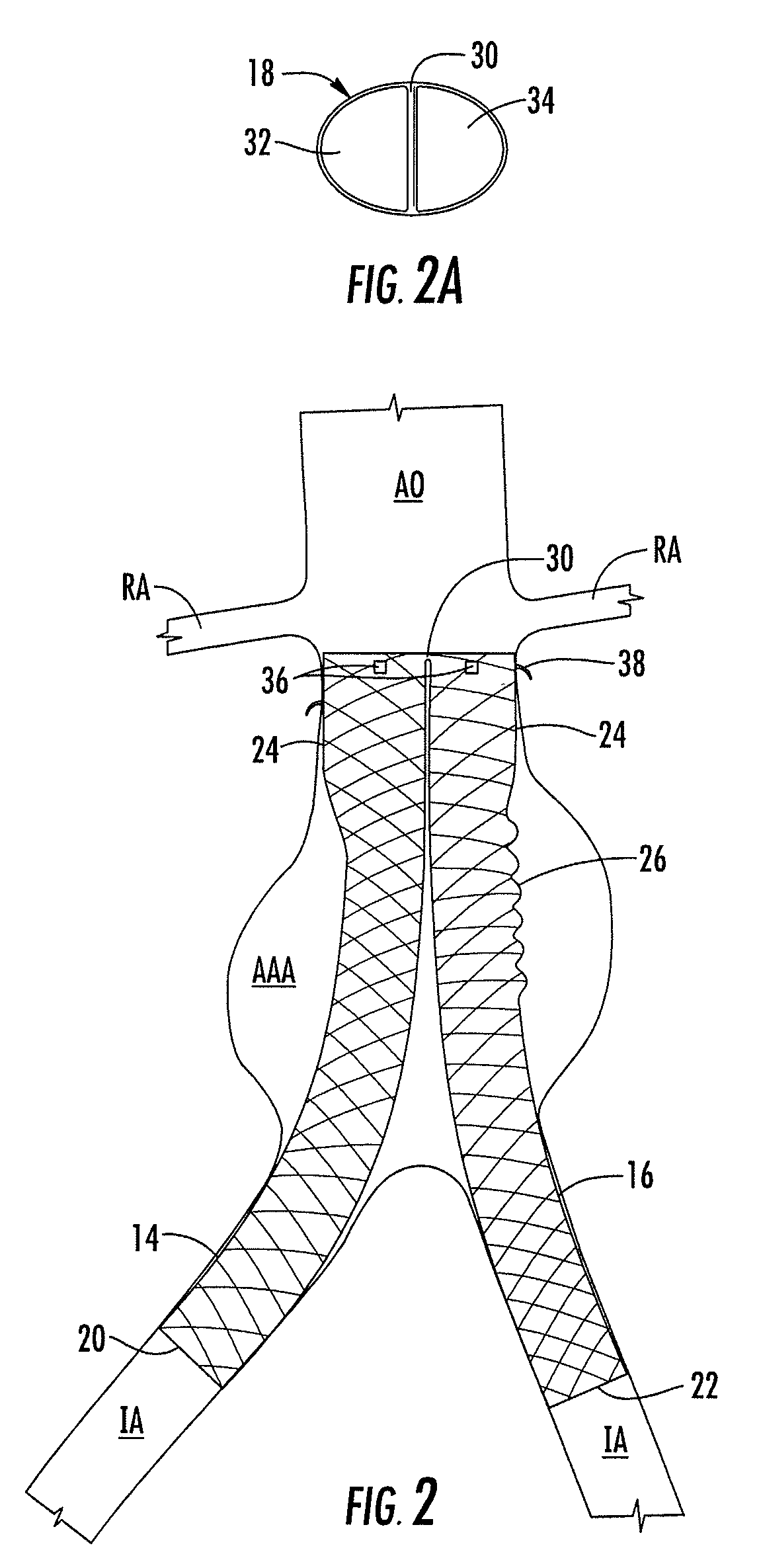
Braided occlusion device having repeating expanded volume segments separated by articulation segments
InactiveUS20090025820A1Occlude a vessel, channel, lumen, or cavity quicklyMeet high volumeWire articlesDilatorsBody organsVolume filling
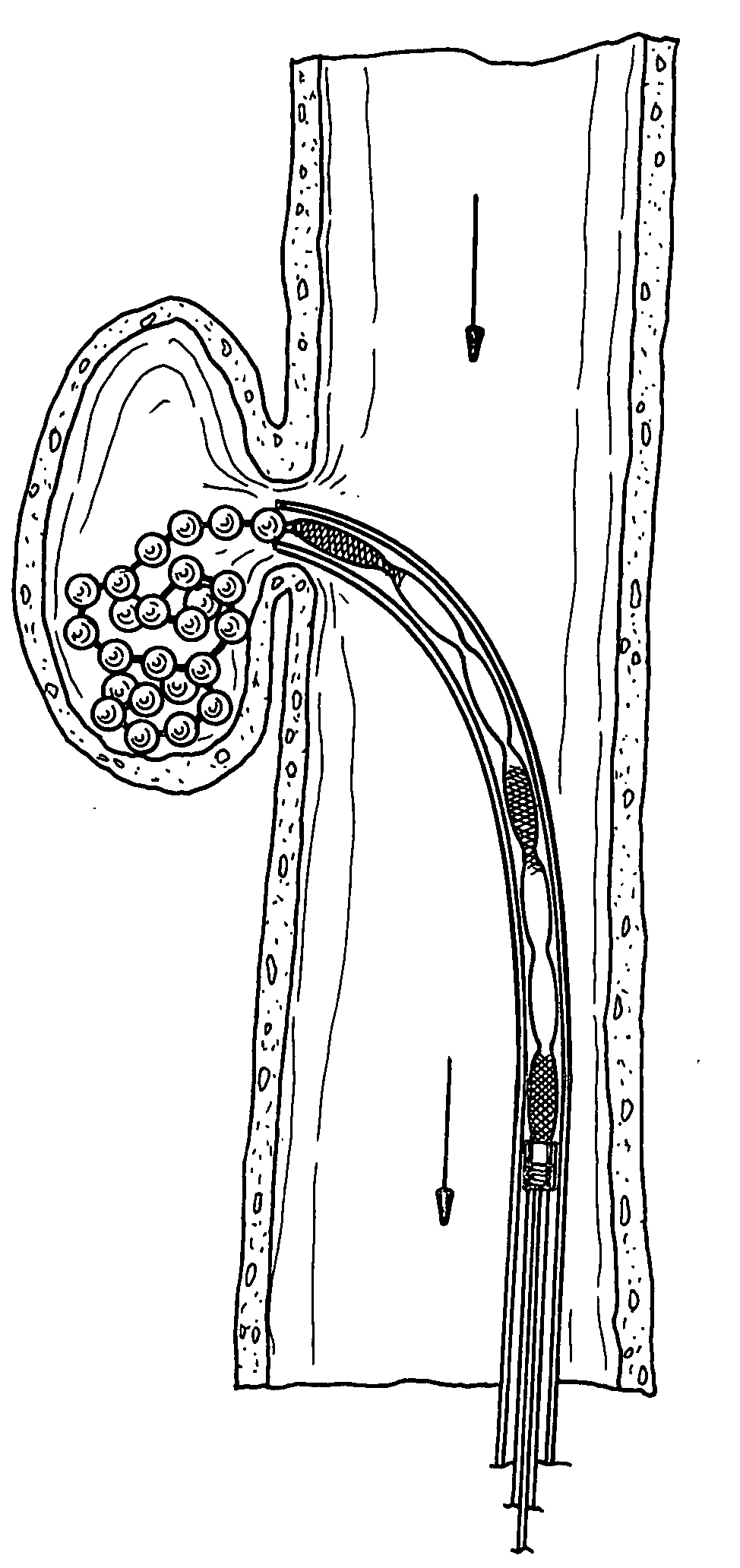
The present invention provides a flexible, low profile vascular occlusion device having large volume filling capability and high metal content for fast occlusion, of the type fabricated from braided tubular metal fabric having an expanded preset configuration and an elongated collapsed reduced diameter configuration for delivery through a catheter to a treatment site and shaped to create an occlusion of an abnormal opening in a body organ or vessel, the woven metal fabric having a memory property whereby the medical device tends to return to said expanded preset configuration when unconstrained. The device further includes a first shape formed from the braided tubular fabric consisting of a repeating pattern of expanded volume segments separated by small diameter articulation segments and a second overall device shape comprised of the first shape formed about itself in various shapes to occlude a vessel. In one embodiment a shaping wire contained coaxially within the tubular braid, provides or assists in the formation of the second overall device shape.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Devices for Vascular Occlusion
An occlusive device, occlusive device delivery system, method of using, and method of delivering an occlusive device, and method of making an occlusive device to treat various intravascular conditions is described.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Devices for Vascular Occlusion
An occlusive device, occlusive device delivery system, method of using, and method of delivering an occlusive device, and method of making an occlusive device to treat various intravascular conditions is described.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Thoracic Closure Device and Methods
A thoracic closure device. The device has a handle member, a base member, and a feed path, and is designed to accept and, with a ratcheting mechanism, tension a toothed closure tie. A guide member is also provided, and assists in the placement of a closure tie prior to tensioning. Methods of closing a median sternotomy using toothed closure ties are also disclosed.
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
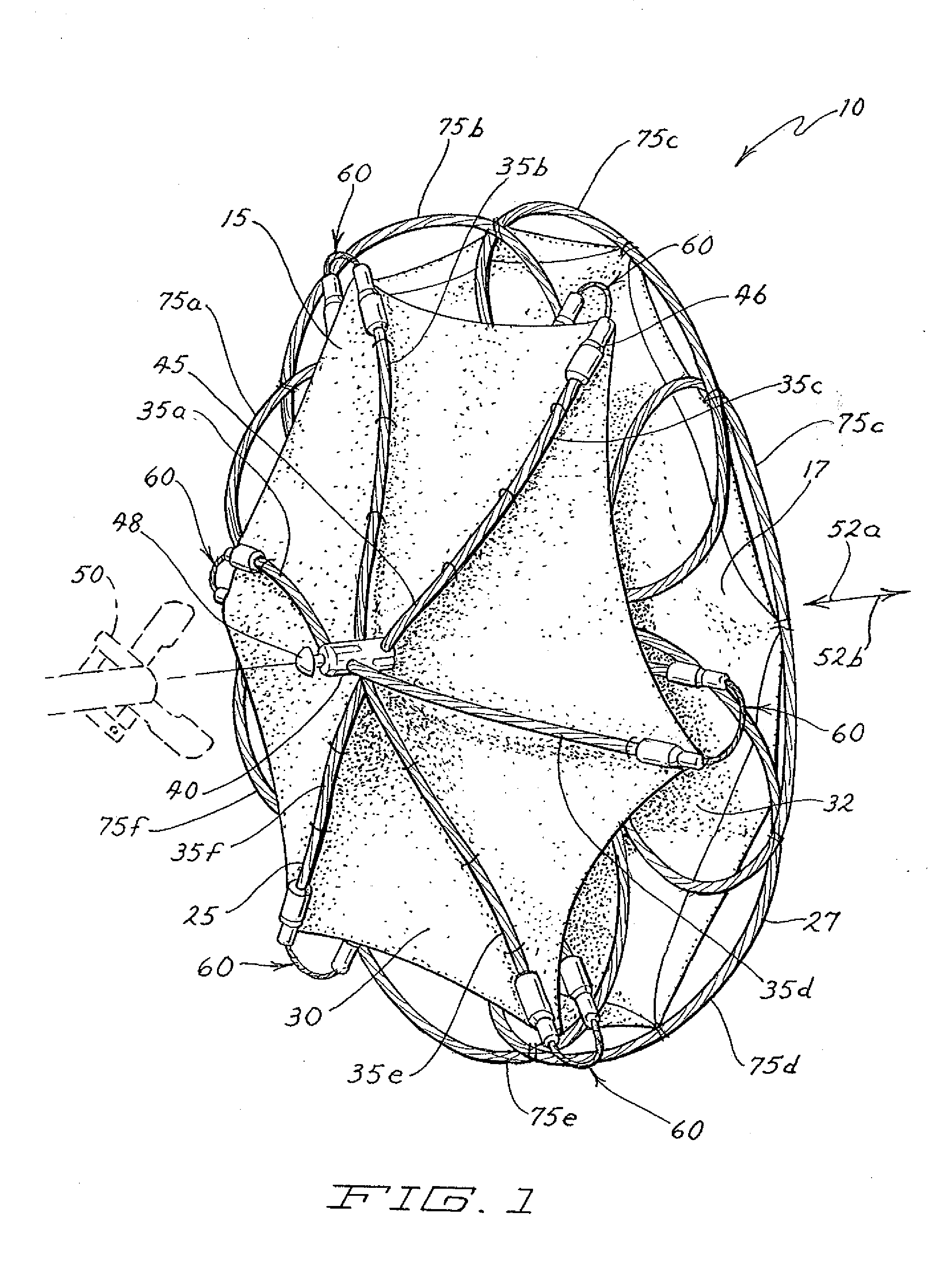
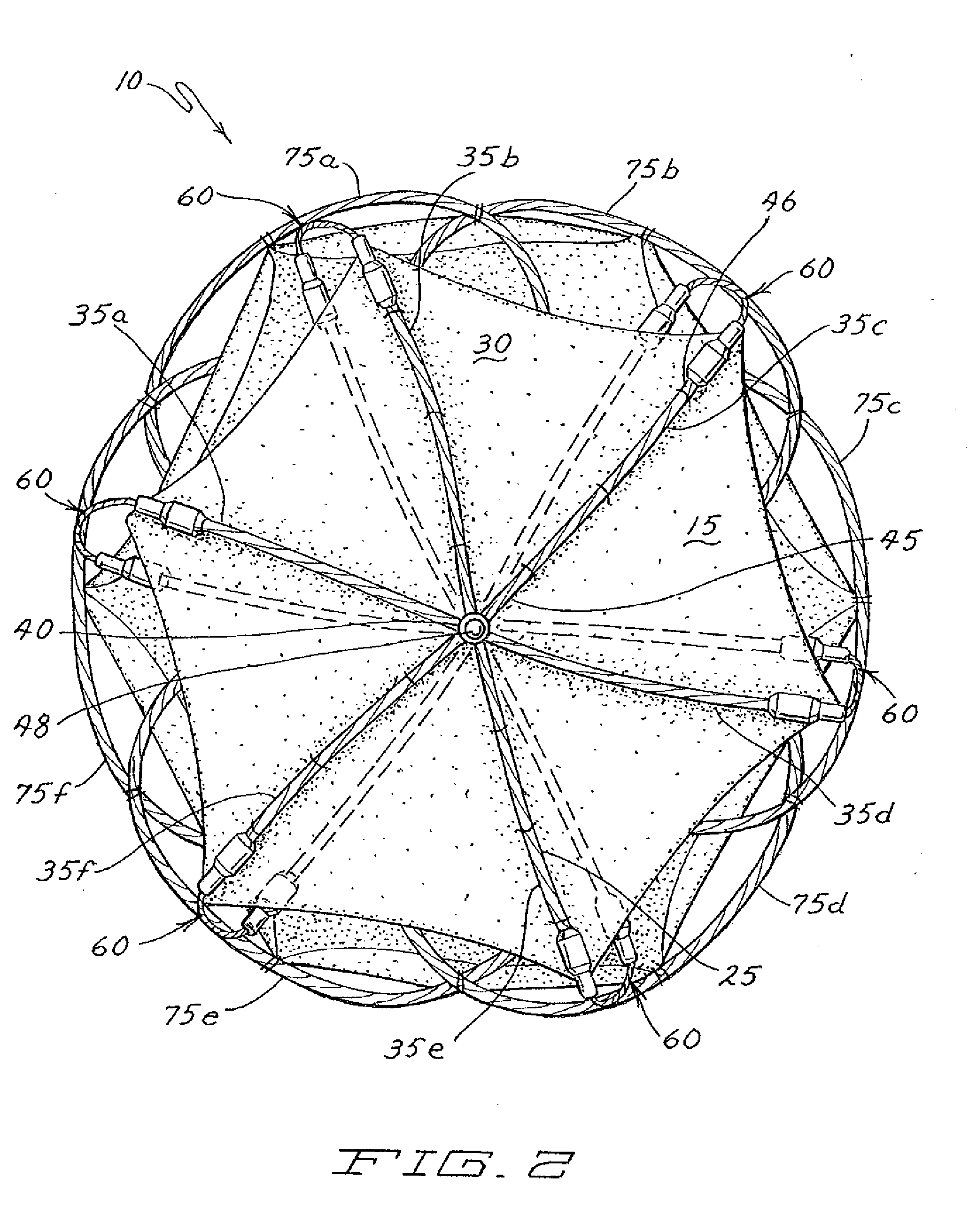
Intravascular flow modifier and reinforcement device
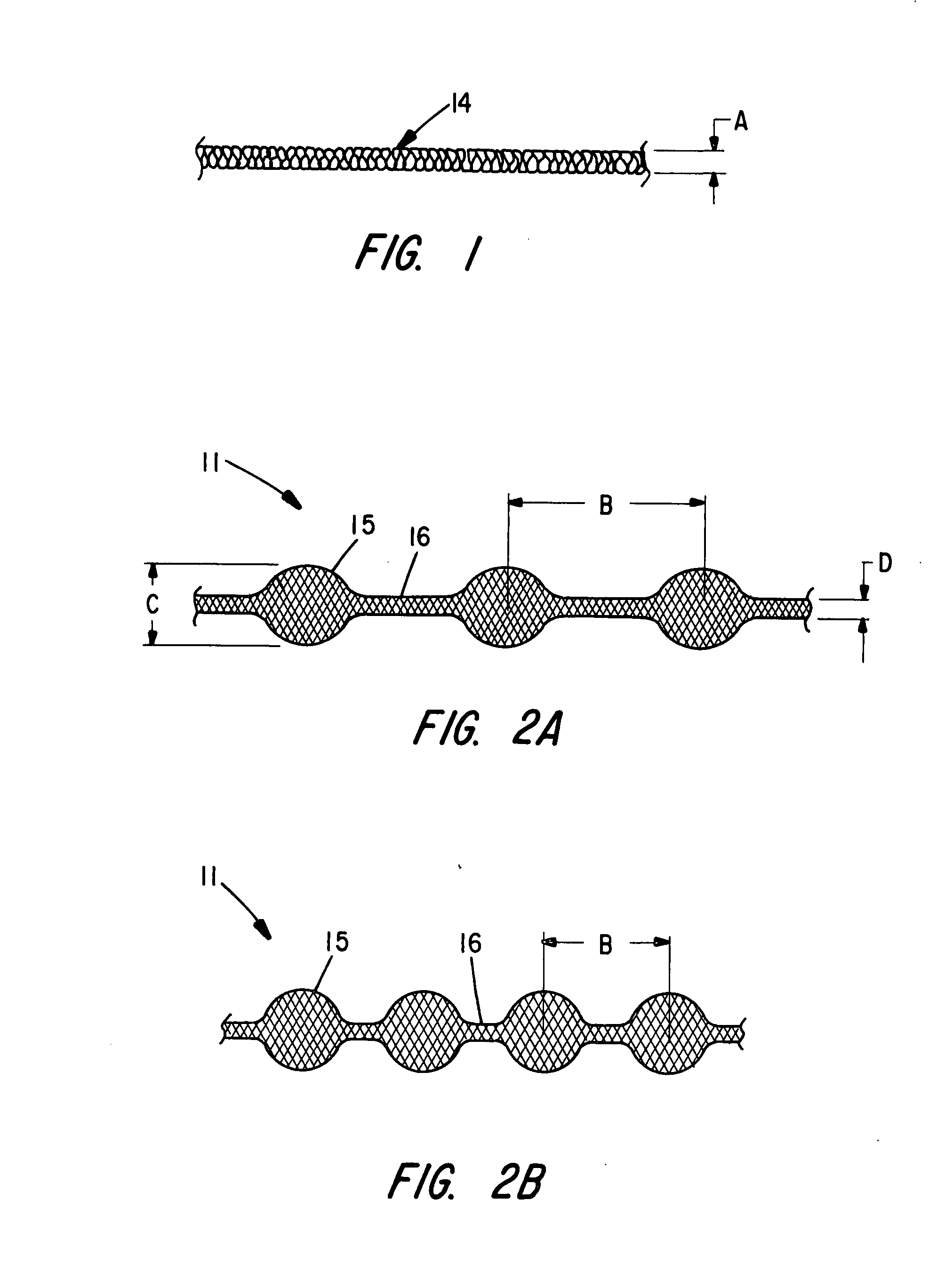
An intravascular flow modifier and vascular reinforcement for treatment of aneurysms is formed of one or more loops of wire of resilient material formed into a series of transverse loops and longitudinal connecting sections to configure an essentially cylindrical reinforcement device that still allows, if desired, access to the neck of an aneurysm for insertion of embolic coils and the like. The proximal and distal regions of the sinusoidal loops may be more tightly coiled than the intermediate regions of the loops, or may have a larger diameter than the intermediate regions. The intravascular flow modifier and vascular reinforcement device can be provided with an outer covering that can be formed as a fiber, and can be woven, or can be formed as a ribbon wound about the intravascular flow modifier and vascular reinforcement device. The wire of resilient material can also be coated with a hydrophilic material. One or more round or oval intermediate loops extending radially outward may also be provided. An apparatus for removing clots may also be formed from one or more loops of wire of resilient material in a hollow conical shape non-detachably joined to a deployment device, to trap and hold clots within a vessel.
Owner:MICRUS CORP
Endoscopic methods and devices for transnasal procedures
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Intravascular stent
InactiveUS6923828B1Small frontal areaLow profileStentsWire articlesIntravascular stentBalloon catheter
A medical device for use in the interior of a body lumen includes a balloon catheter and a radially expandable stent. The stent includes a plurality of zig-zags of a low memory metal formed into a hollow, open-ended cylindrical shape. The individual zig-zags have a curved portion forming a reversing bend which allows the zig-zags to expand and deform as the balloon radially expands the stent. The curved portions of the zig-zags are aligned along the length of the stent in a spaced-apart arrangement with some curved portions attached and others unattached to adjacent zig-zags. The resulting stent is longitudinally flexible throughout its length when unexpanded and is also capable of conforming to a bend in the body lumen when expanded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intravascular flow modifier and reinforcement device
Owner:MICRUS CORP
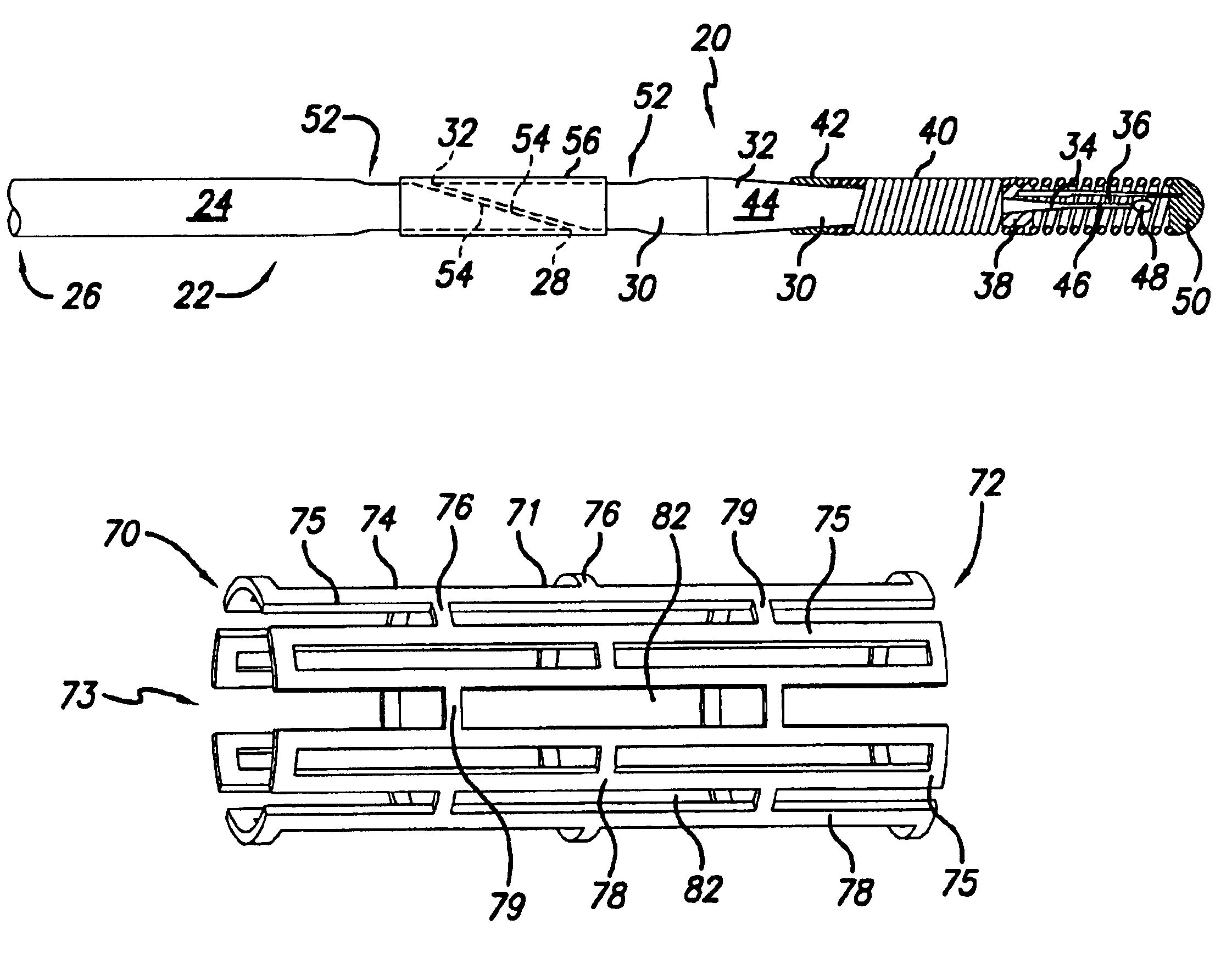
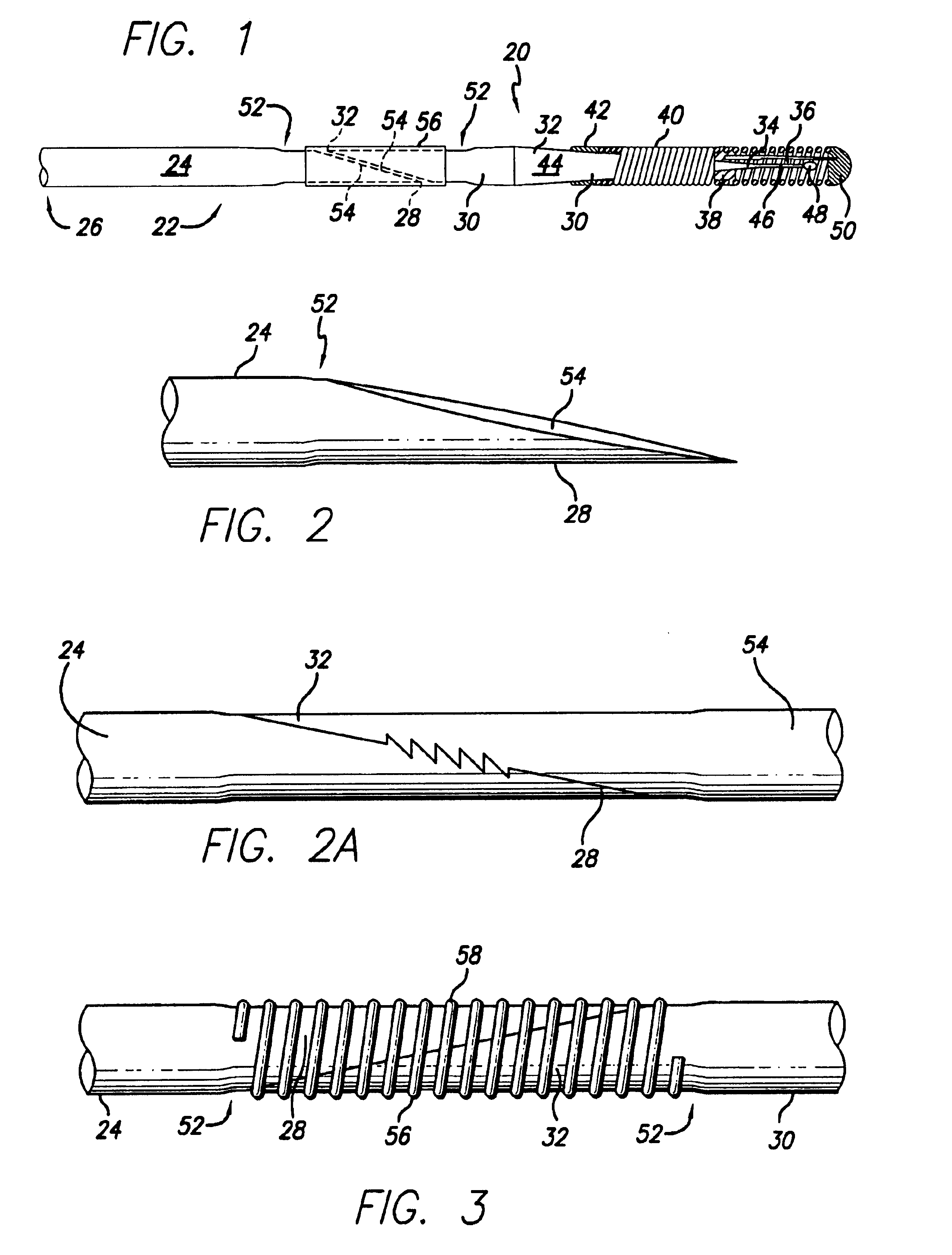
Enhanced method for joining two core wires
An intravascular guide wire having at least two core materials joined together. There is a wire core having a proximal core section with a proximal end and a distal end and a distal core section with a proximal end and a distal end. The distal end of the proximal core section and the proximal end of the distal core section are formed into complementary shapes, and then placed into a flexible sleeve in opposing directions. Inside the flexible sleeve, the complementary shaped ends are joined together through bonding, welding, brazing, cementing, or soldering. The flexible sleeve can be either a stretched coil or a polyimide sleeve, each with an outer diameter similar to the outer diameter of the core wire, therefore the guide wire does not require additional grinding to reduce the outer diameter of the joined section.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
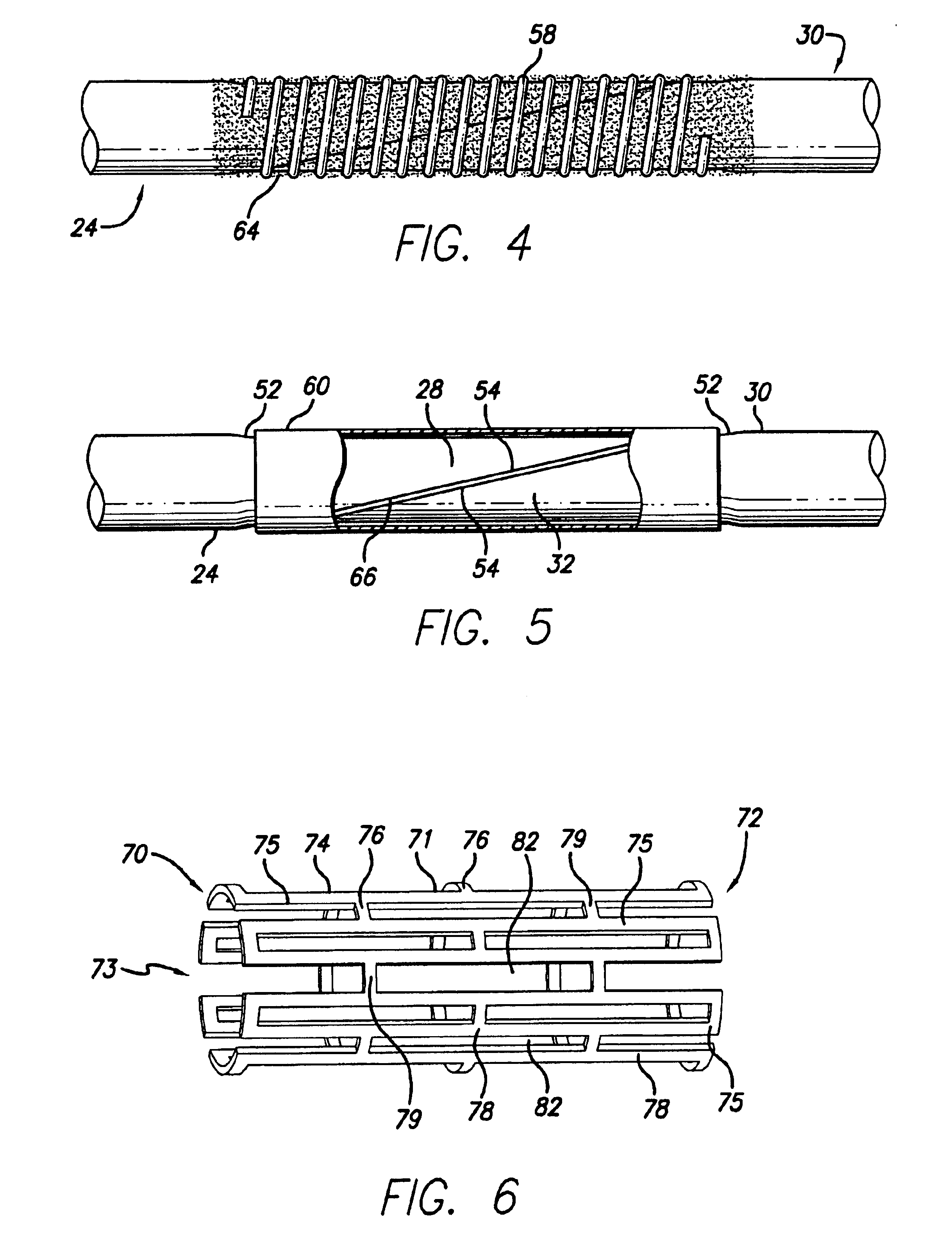
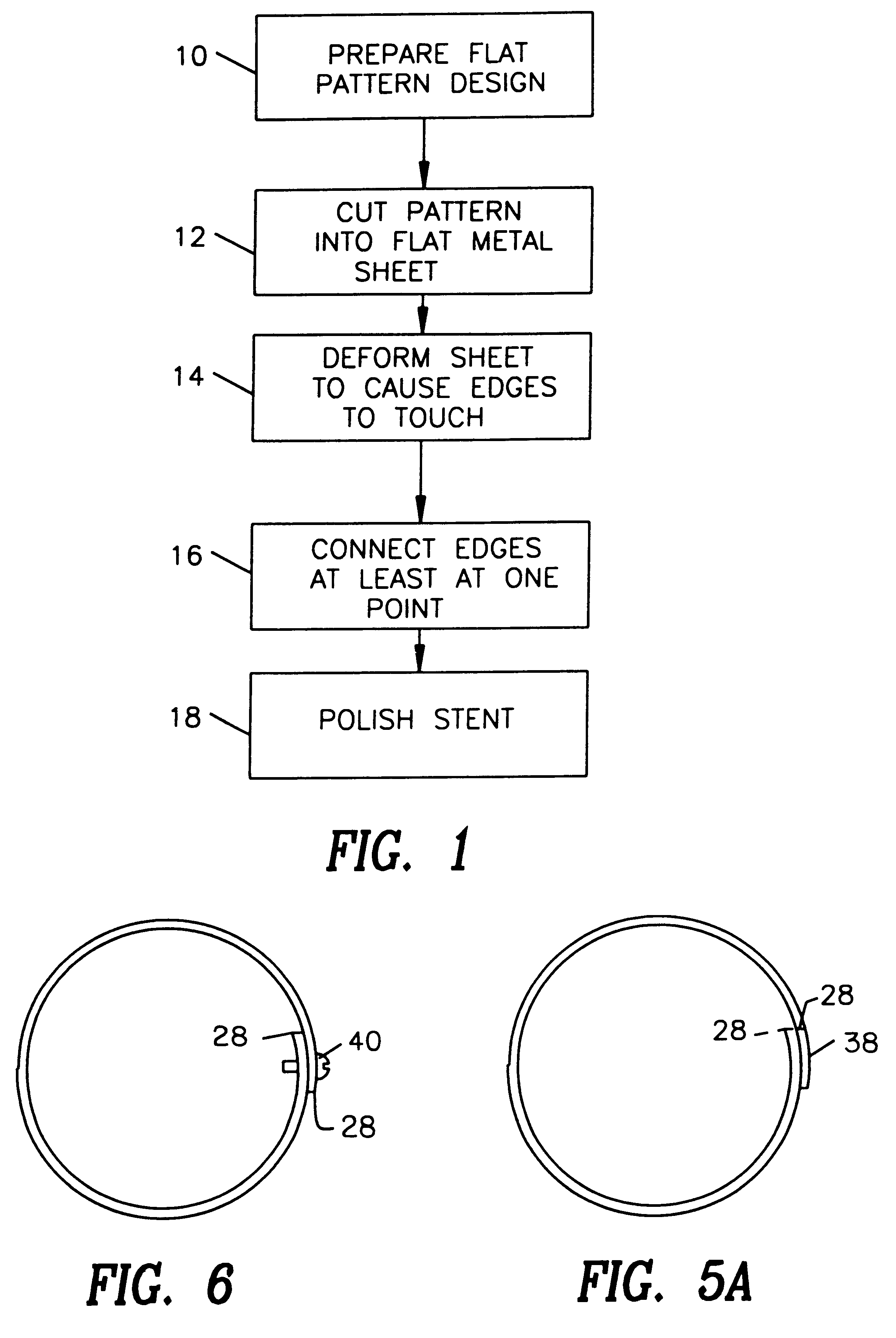
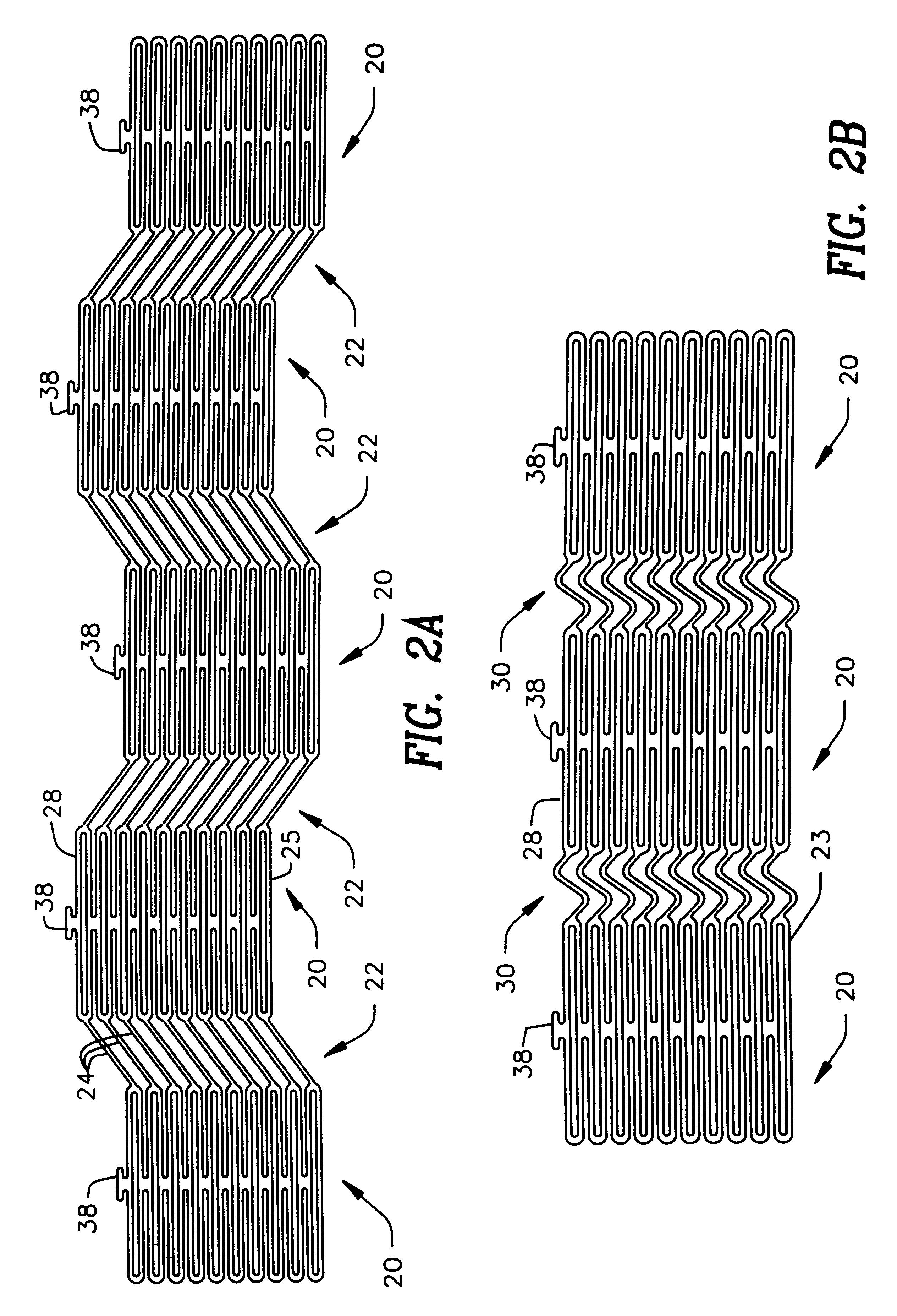
Stent
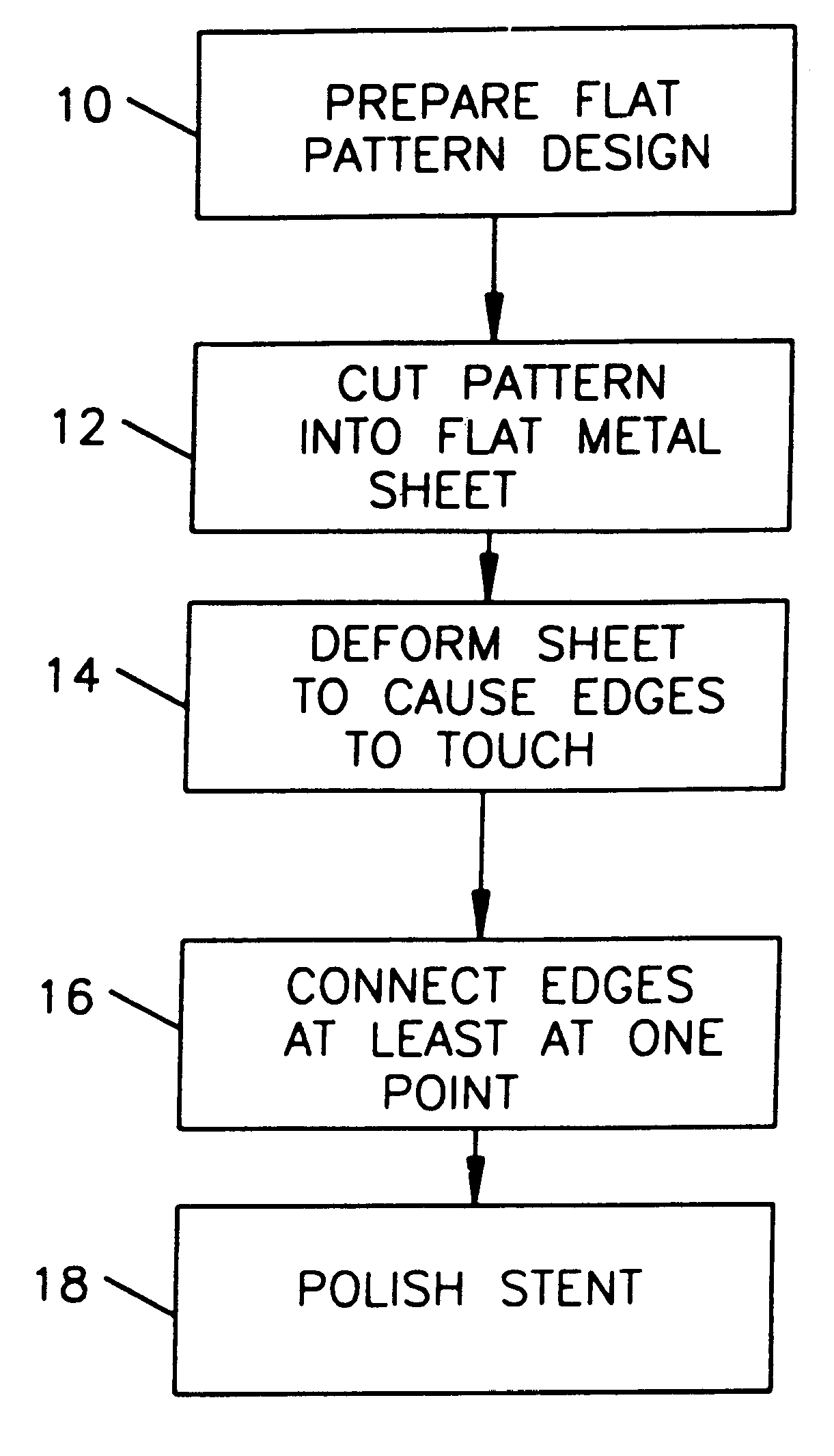
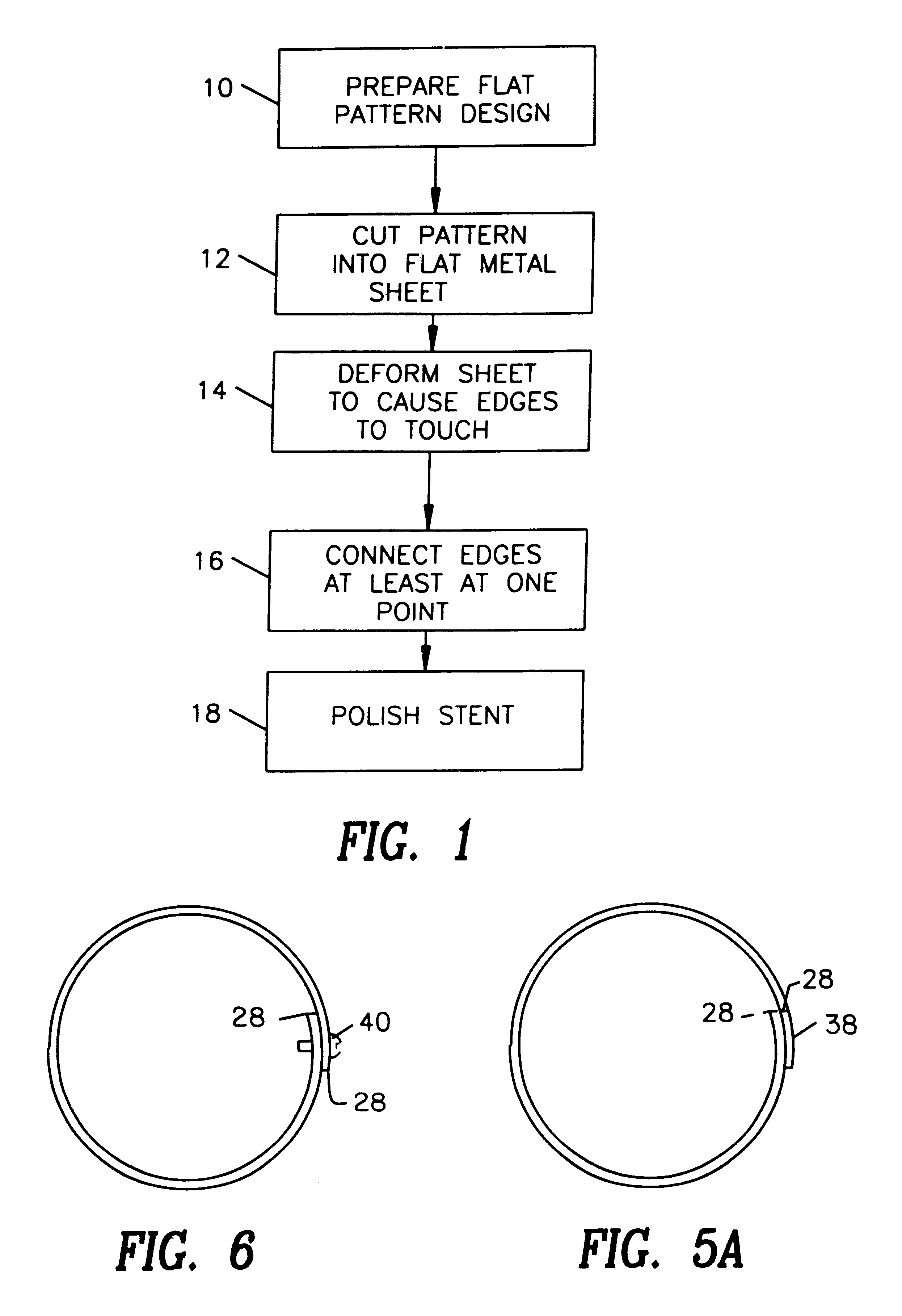
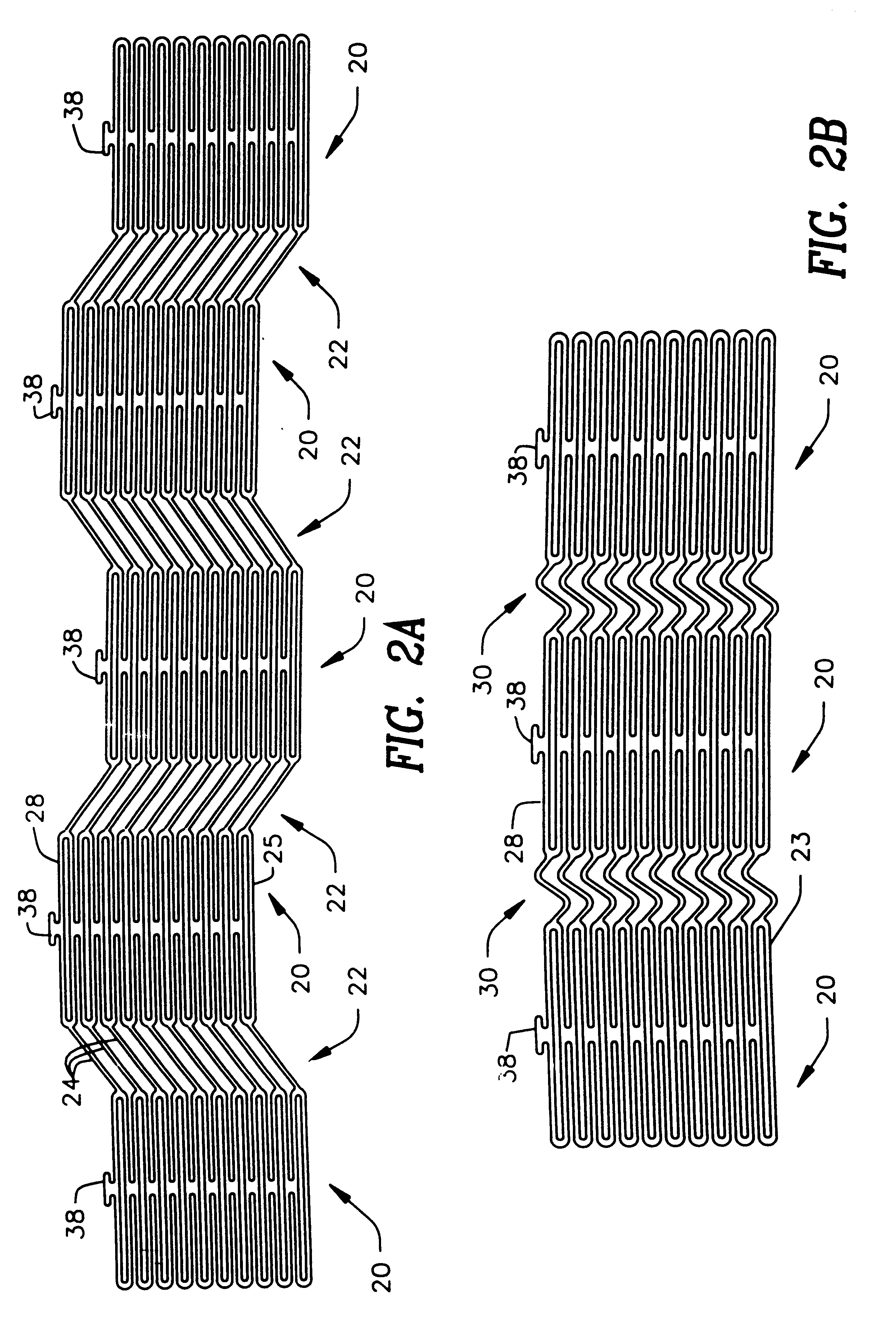
A stent and a method for fabricating the stent are disclosed. The stent has an originally flat pattern and connection points where the sides of the flat pattern are joined. The method includes the steps of a) cutting a stent pattern into a flat piece of metal thereby to produce a metal pattern, b) deforming the metal pattern so as to cause two opposing sides to meet, and c) joining the two opposing sides at least at one point. Substantially no portion of the stent projects into the lumen of the stent when the stent is expanded against the internal wall of a blood vessel.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing AC-generator's stator for vehicle
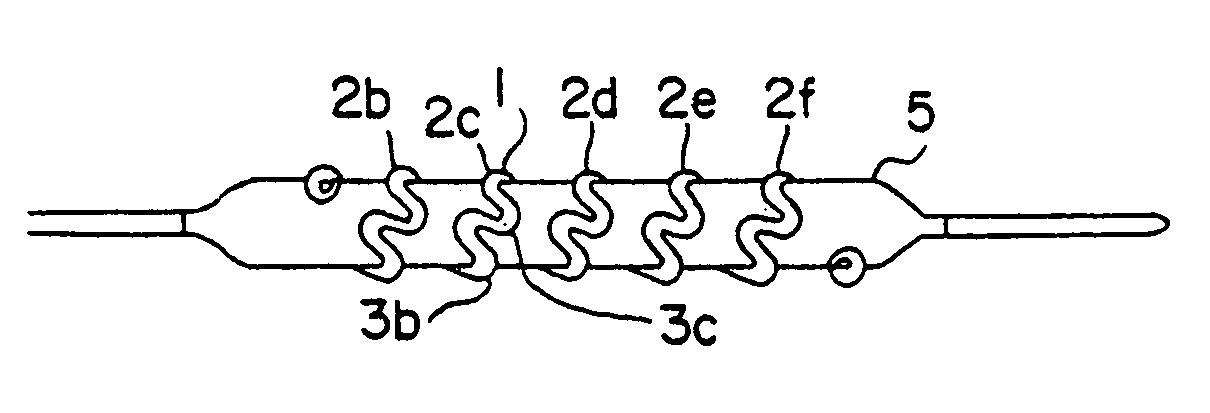
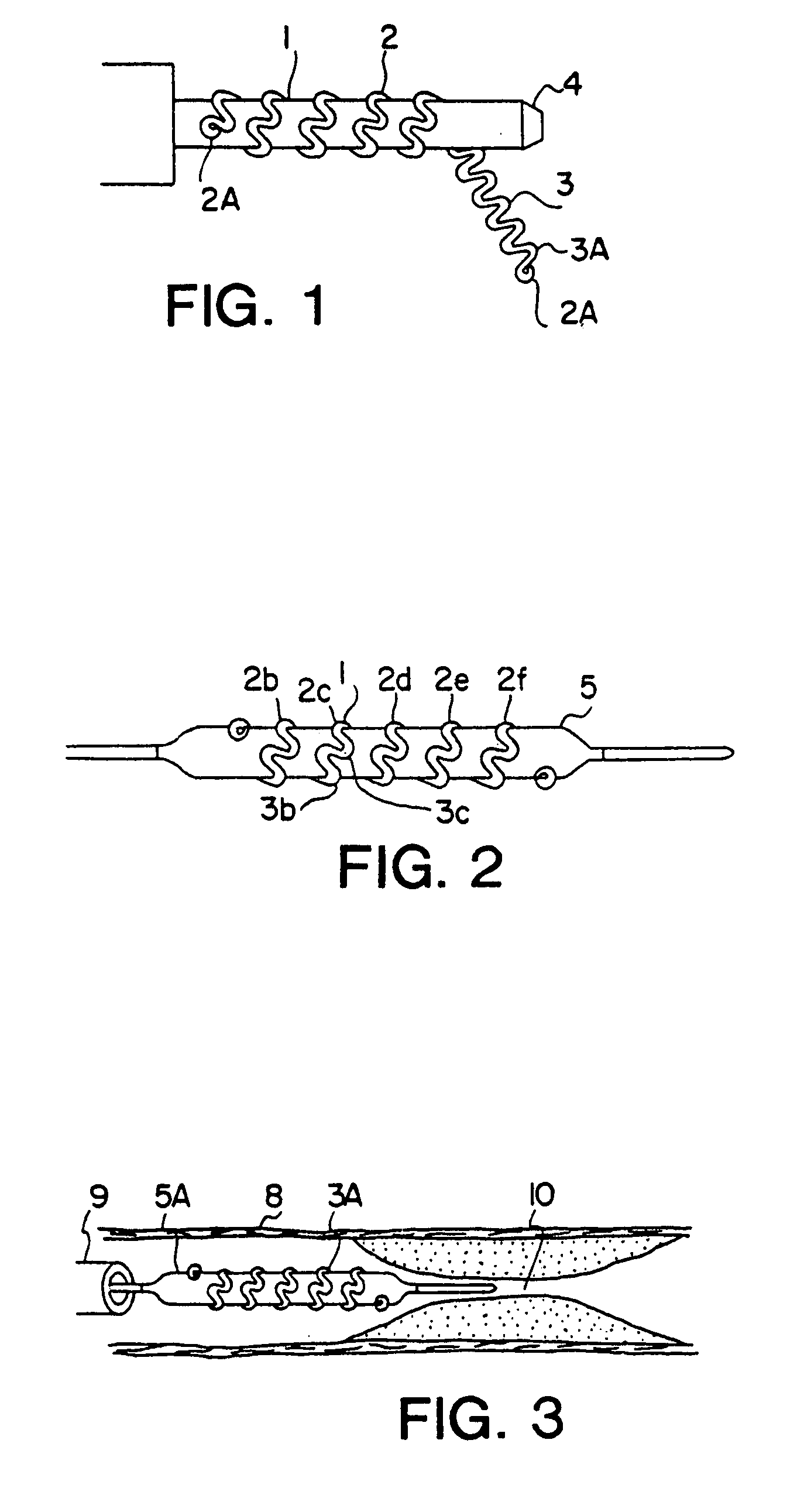
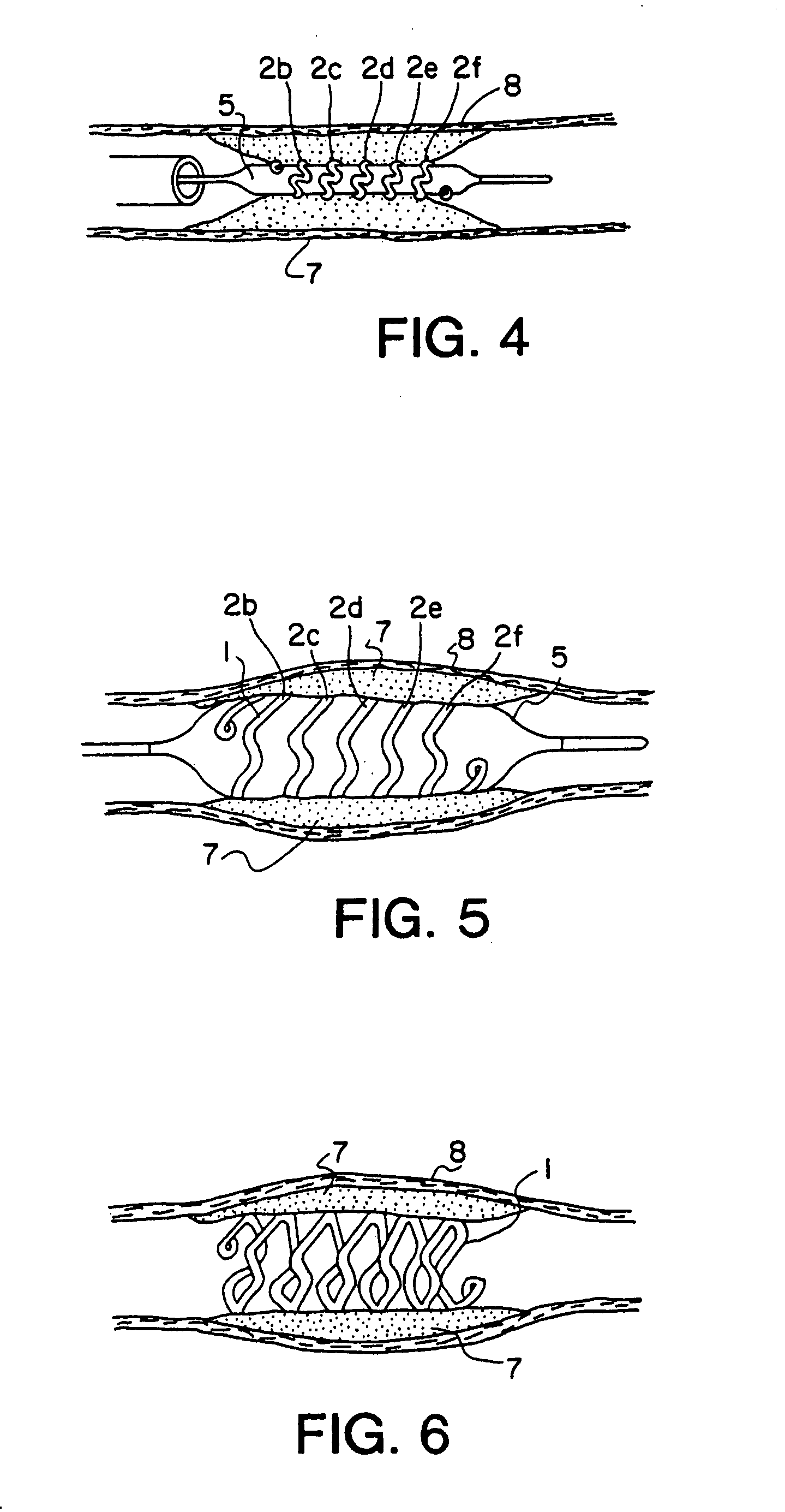
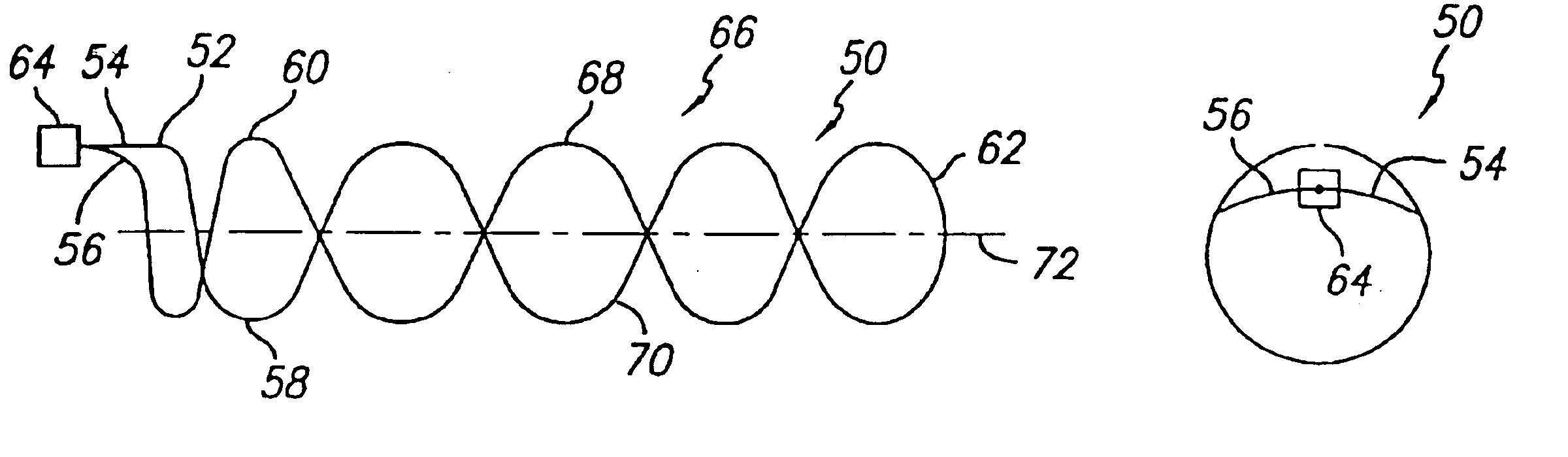
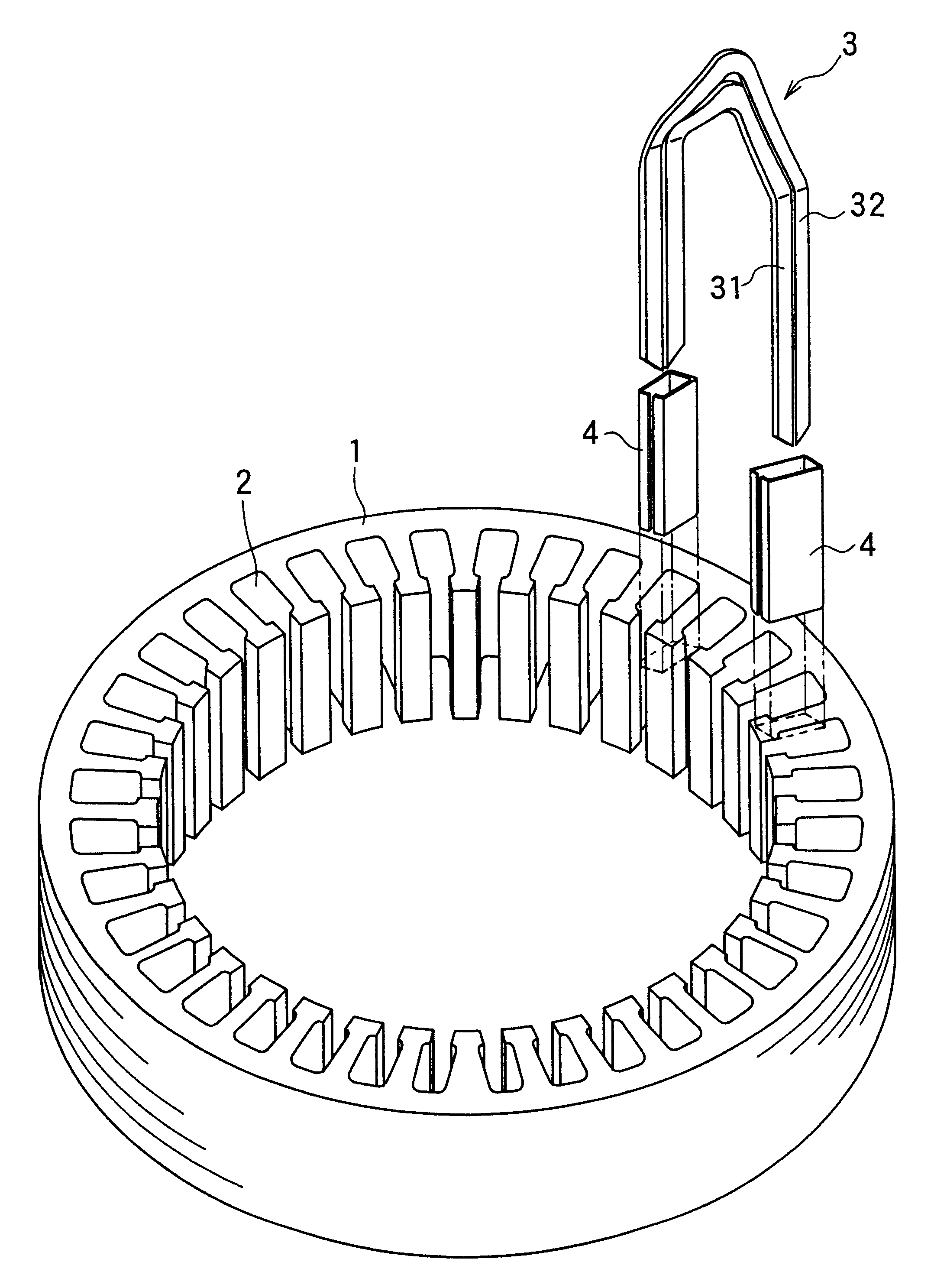
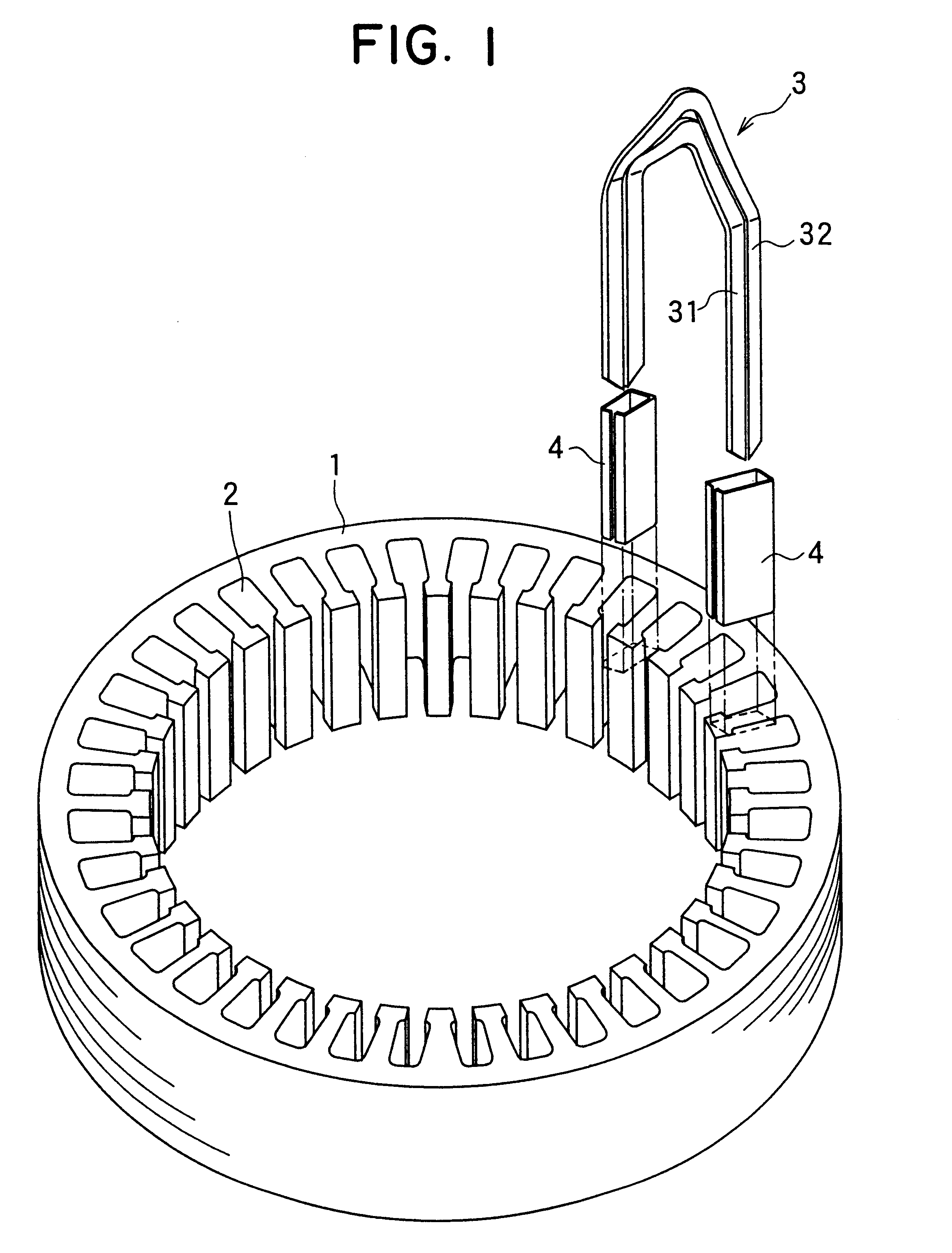
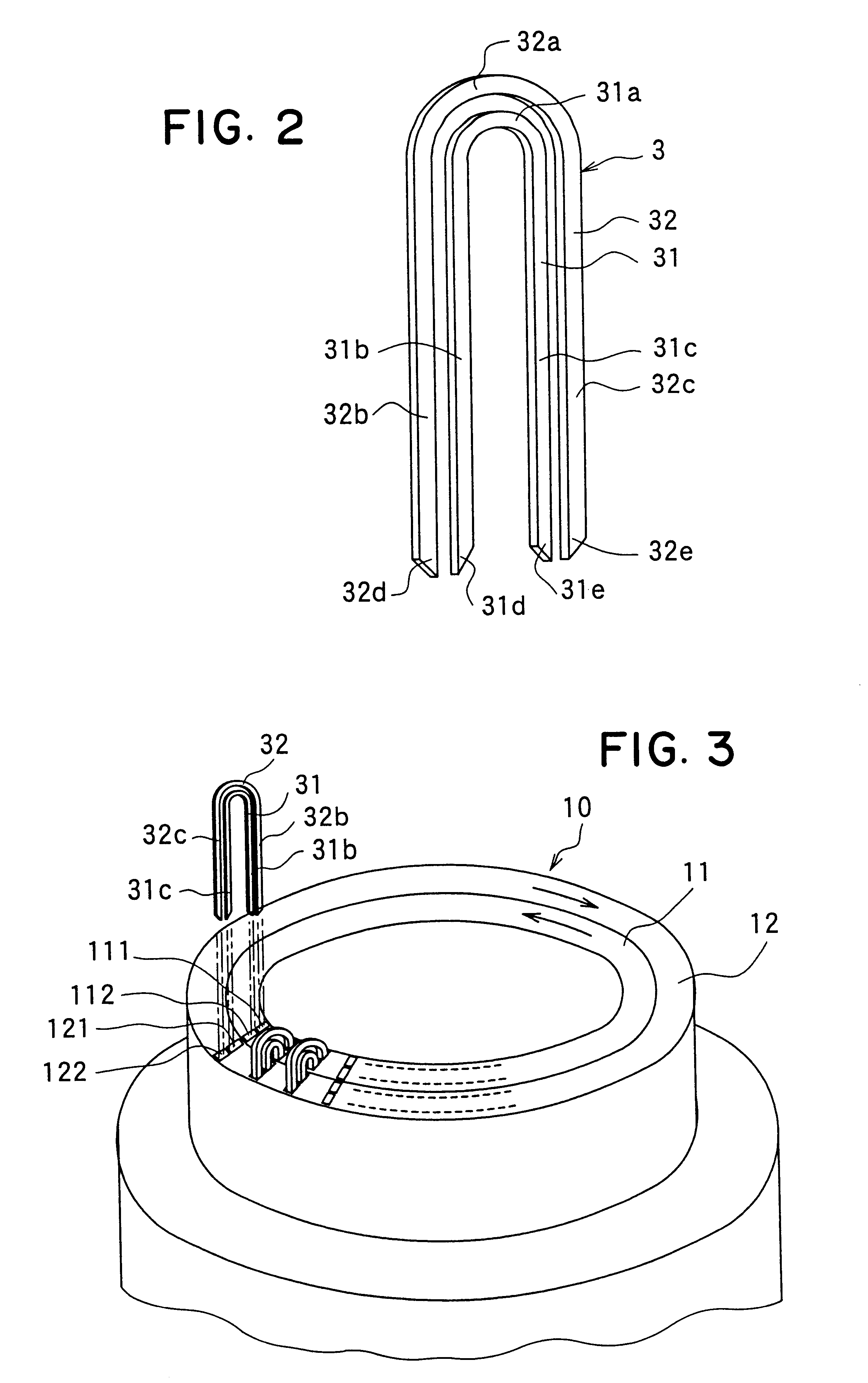
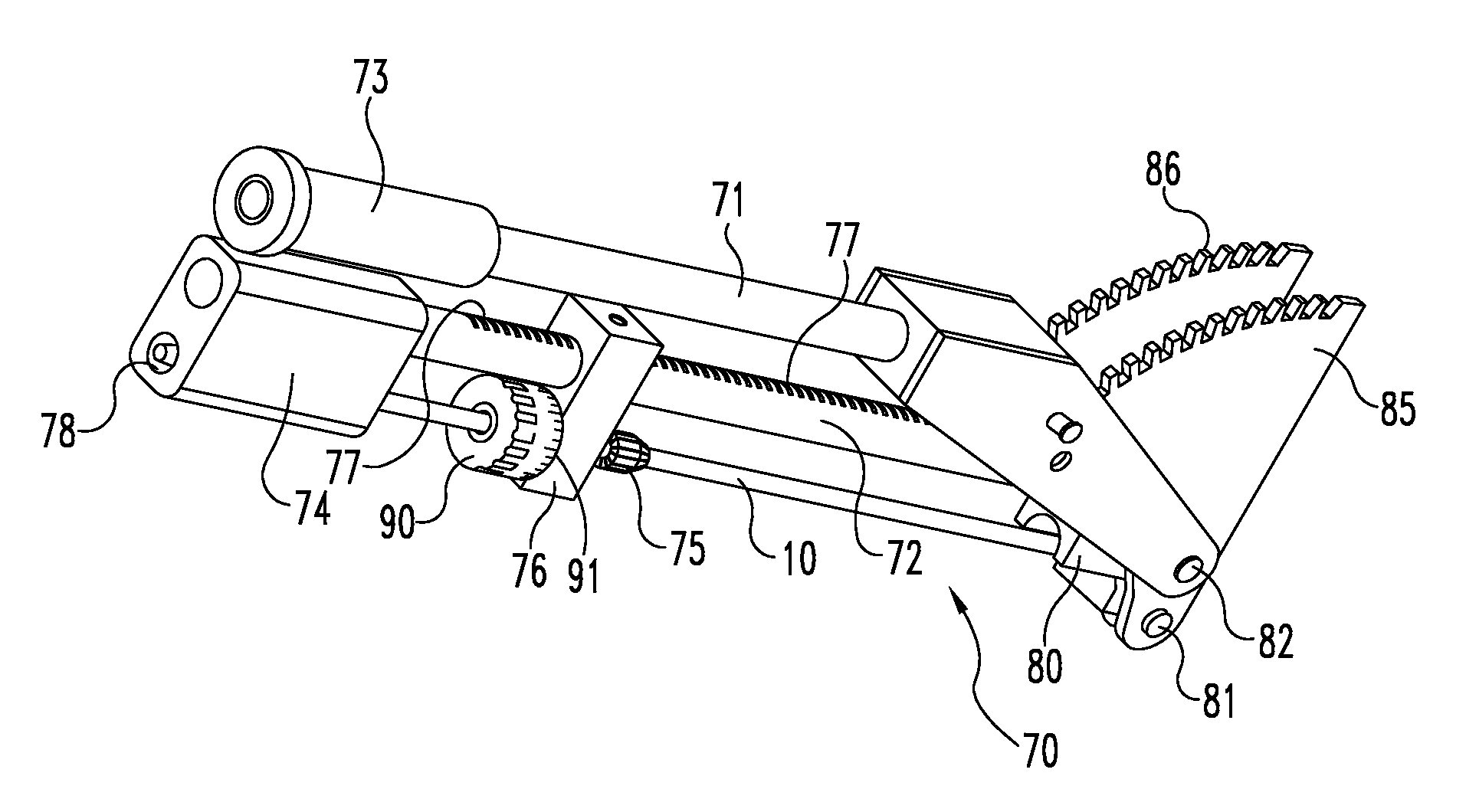
InactiveUS6249956B1Positioning-accuracy can be improvedAvoid damageWire articlesForging/hammering/pressing machinesElectrical conductorEngineering
The object of the present invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for manufacturing a stator to improve accuracy in inserting conductor segments (3, 31, 32) into slots (2). The apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductor holder (21, 22) holding the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) and an axial-moving-mechanisms (214) moving the conductor holder (21, 22) relative to a stator core (1) in an axial direction. The conductor holder (21, 22) holds straight portions (31b, 31c, 32b, 32c) of the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) to be inserted into the slots (2) from one end of the stator core (1).
Owner:DENSO CORP
System and device for designing and forming a surgical implant
A method is provided for determining the shape of a surgical linking device that is to be attached to a bony body structure such as the spinal column based on digitized locations of a plurality of attachment elements engaged to the bony structure. The method is implemented by a computer system through a GUI to generate an initial bend curve to mate with the plurality of attachment elements. The initial bend curve may be simplified based on user input to the GUI to reduce the number of bends necessary to produce a well-fitting linking device and may be altered to help obtain the goals of the surgery.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Method and device for filtering body fluid
Medical devices for filtering fluids flowing through a lumen and a method of forming medical devices. The devices can be used in vascular channels, urinary tracts, biliary ducts and the like, and filter emboli and other debris generated at a treatment site.
Owner:EV3
Method and apparatus for making reclosable plastic bags using a pre-applied slider-operated fastener
InactiveUS6871473B1Not adversely impactEasy to modifyEnvelopes/bags making machineryWire articlesThin membraneEngineering
A method and apparatus for making reclosable plastic bags is provided. In the method and apparatus, a fastener is attached to a moving flat web of plastic film, preferably in the direction of web movement and near the center of the web. A plurality of sliders are mounted to the fastener either before or after the fastener is attached to the flat web, but prior to conveying the web to a FFS machine. The flat web, with the slider-operated fastener already attached thereto, is then conveyed to a vertical or horizontal FFS machine where the flat web is formed into bags, and the bags are successively filled and sealed.
Owner:REYNOLDS PRESTO PRODS
Medical device for occluding a heart defect and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120150218A1Advantageously deformable constructionIncrease distanceWire articlesSurgical veterinaryMedical treatmentNatural state
An implantable device for occluding a septal defect has interleaved frame sections that allow flexibility to conform to a variety of defect geometries and provide reliable occlusion during endothelialization. Left and right frames connect to opposite ends of a floating connection post. The device is resiliently deformable and is biased into a natural state wherein, in situ in a variety of defect geometries, the device applies a sandwiching force to the tissue surrounding the defect that is relatively uniform across its diameter, improving stability and promoting occlusion.
Owner:CARDIA INC
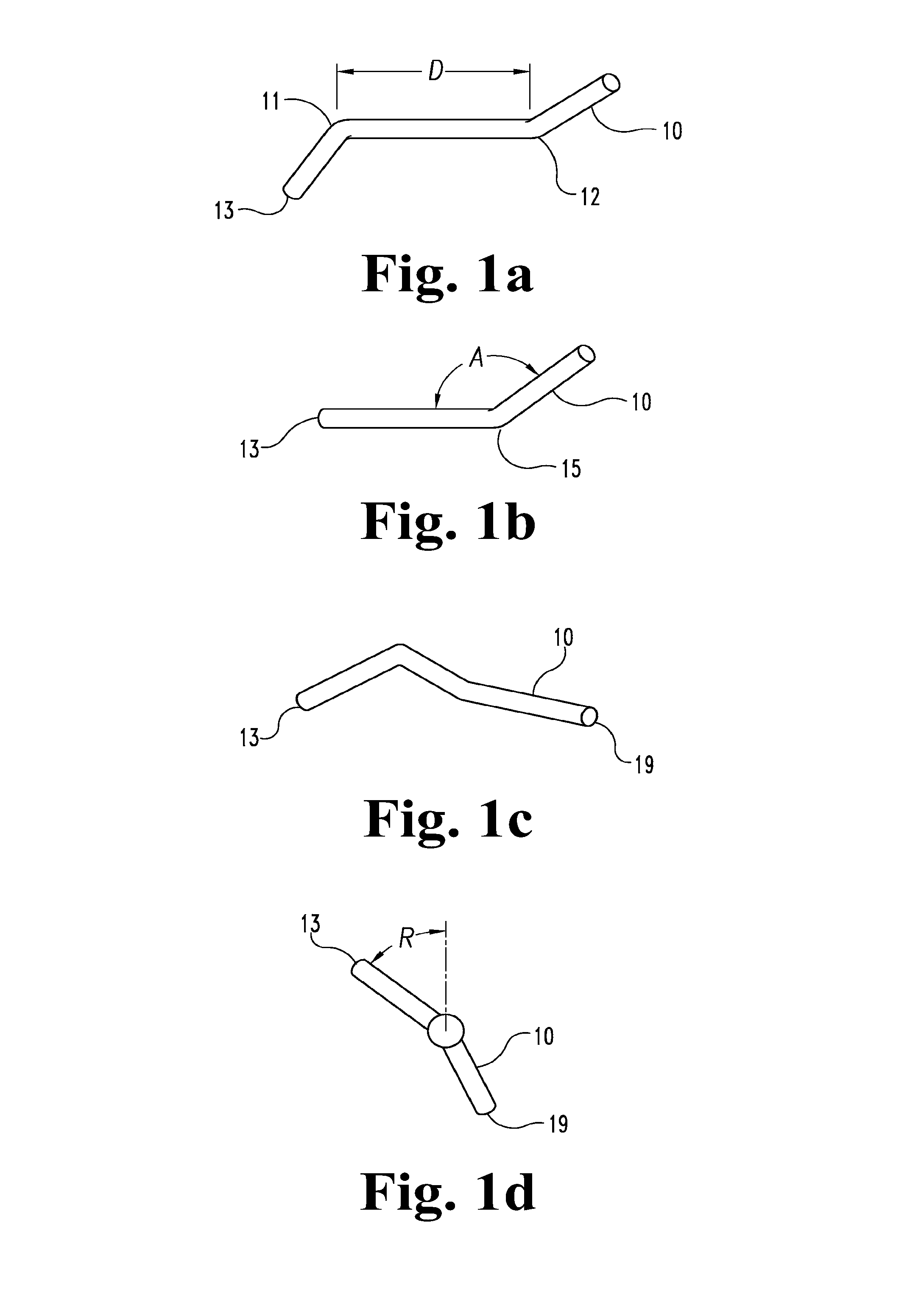
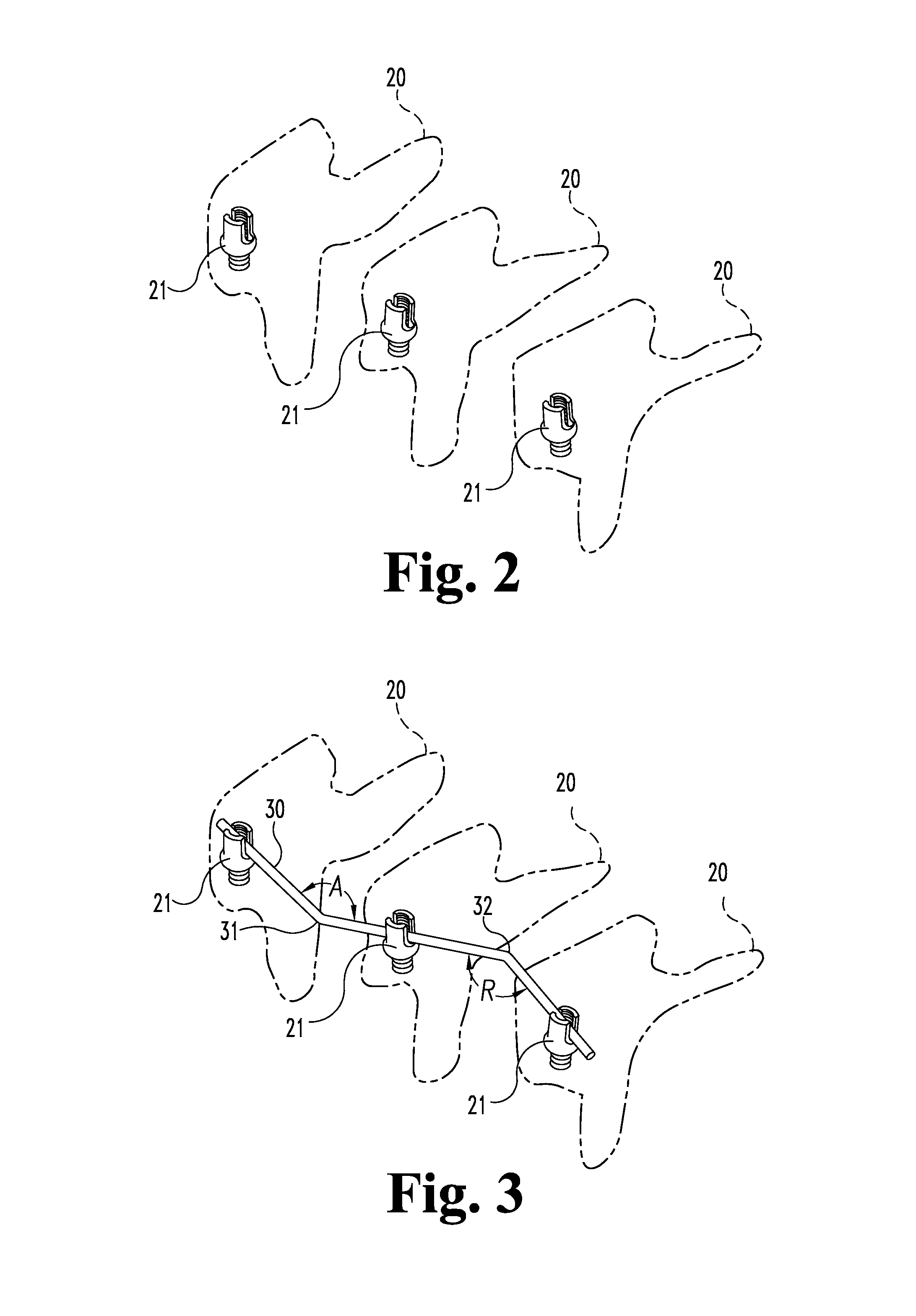
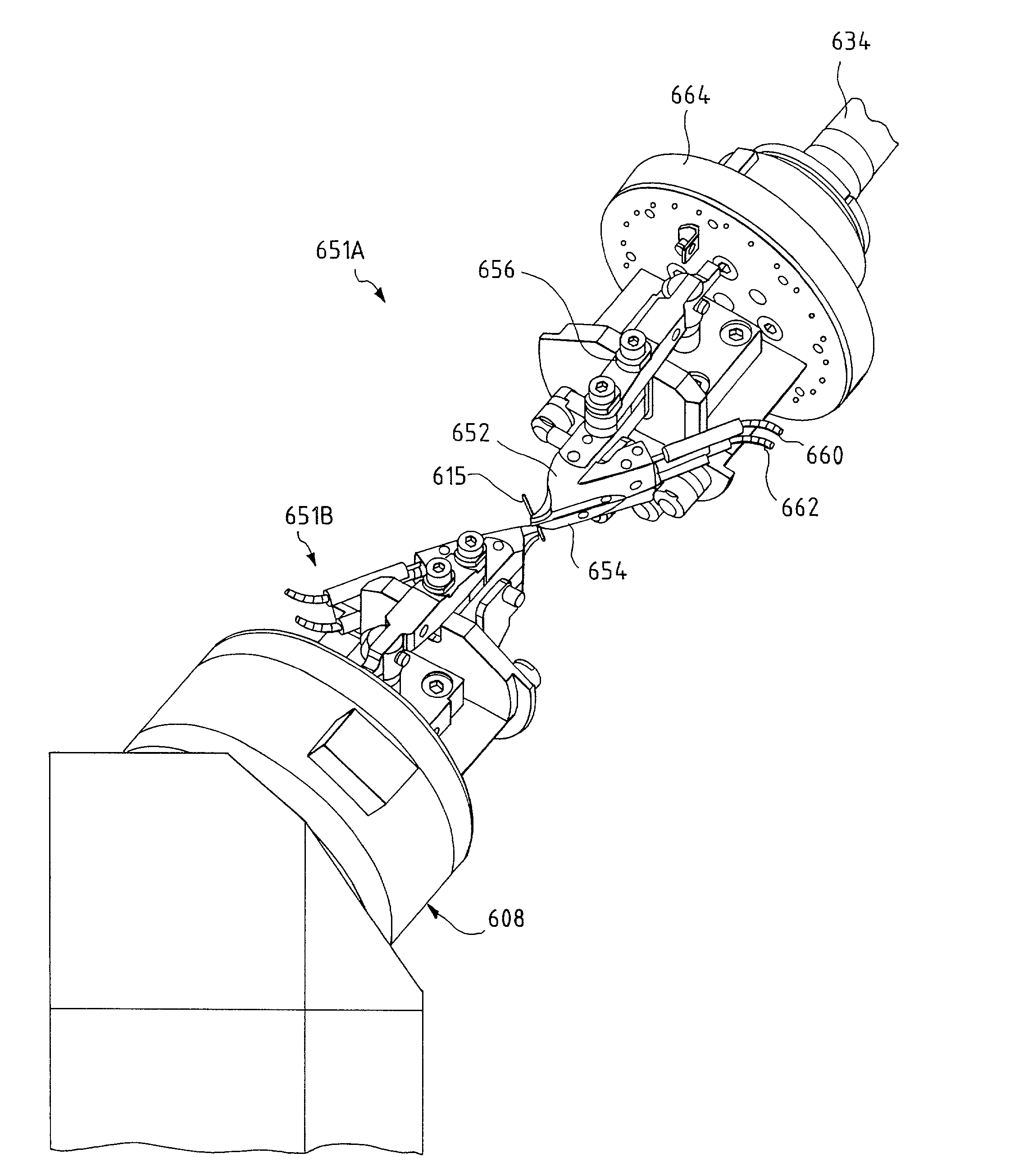
Robot and method for bending orthodontic archwires and other medical devices
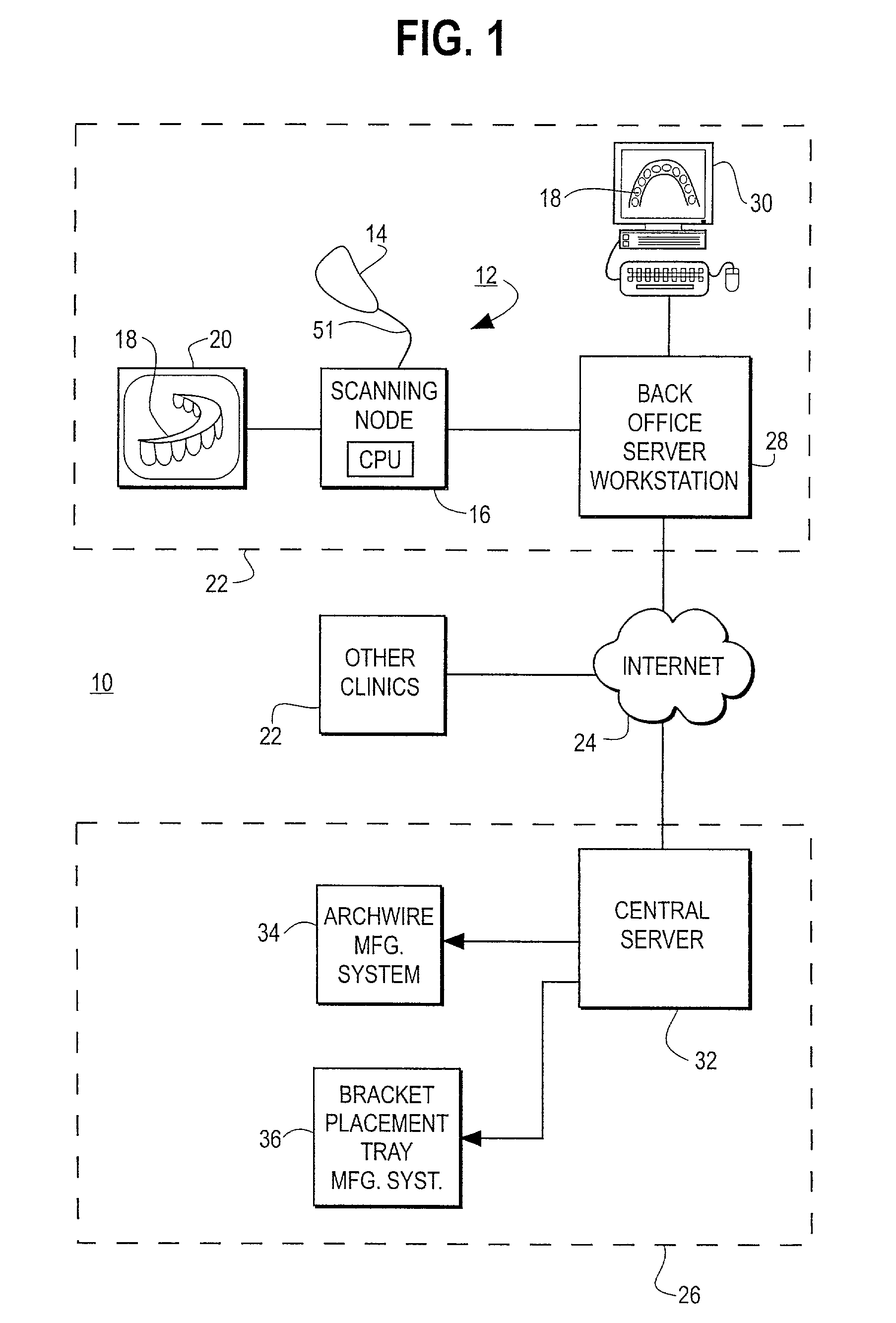
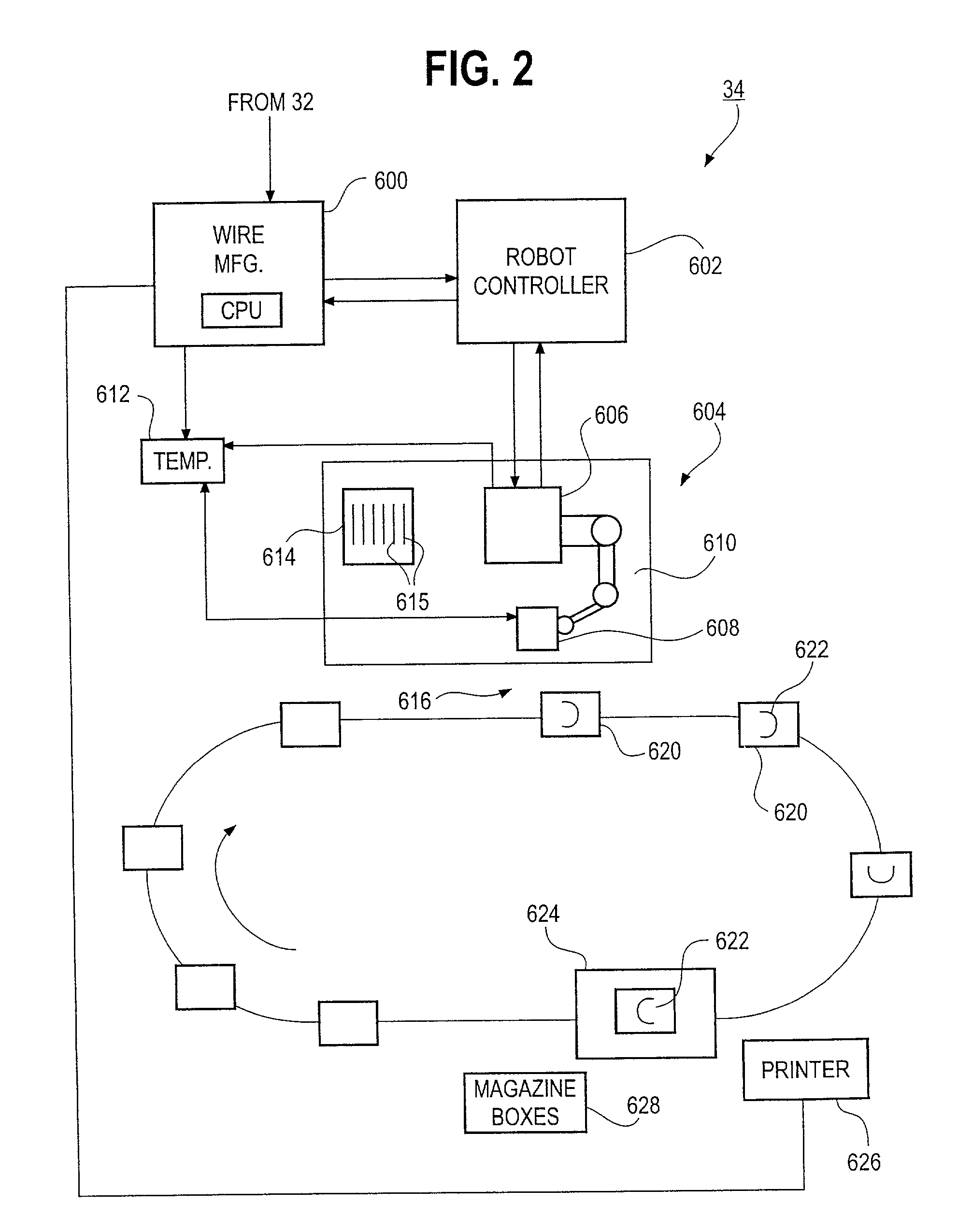
A robotic bending apparatus for bending archwires and other types of elongate, bendable medical devices into a desired configuration includes a first gripping tool and a moveable gripping tool. The first gripping tool can be either fixed with respect to a base or table for the robot or positioned at the end of robot am. The moveable gripping tool is mounted to the end of a moveable robot arm having a proximal portion also mounted to the base. The robot preferably comprises a six axis bending robot, in which the distal end of the moveable arm can move relative to the fixed gripping tool about three translational axes and three rotational axes. The gripping tools preferably incorporate force sensors which are used to determine overbends needed to get the desired final shape of the archwire. The robot may also include a resistive heating system in which current flows through the wire while the wire is held in a bent condition to heat the wire and thereby retain the bent shape of the wire. A magazine for holding a plurality of straight archwires needing to be bent and a conveyor system for receiving the wires after the bending process is complete are also described. The robot bending system is able to form archwires with any required second and third order bends quickly and with high precision. As such, it is highly suitable for use in a precision appliance-manufacturing center manufacturing a large number of archwires (or other medical devices or appliances) for a distributed base of clinics.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Bifurcated medical device for treating a target site and associated method
InactiveUS20100063578A1Reduced delivery profileImprove usabilityStentsWire articlesProximateStent grafting
Embodiments of the present invention provide medical devices and methods for treating a target site within the body. For example, one embodiment provides a stent graft for treating a target site proximate to a bifurcated lumen, wherein the stent graft includes a first tubular structure having proximal and distal ends and a side wall extending therebetween. The first tubular structure includes an opening defined within the side wall and is configured to define a first portion having first and second ends and a second portion having first and second ends. The opening corresponds to the first ends of the first and second portions and the second ends of the first and second portions respectively correspond to the proximal and distal ends of the first tubular structure, and at least a portion of the first and second portions are configured to be positioned within respective branches of a bifurcated lumen.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
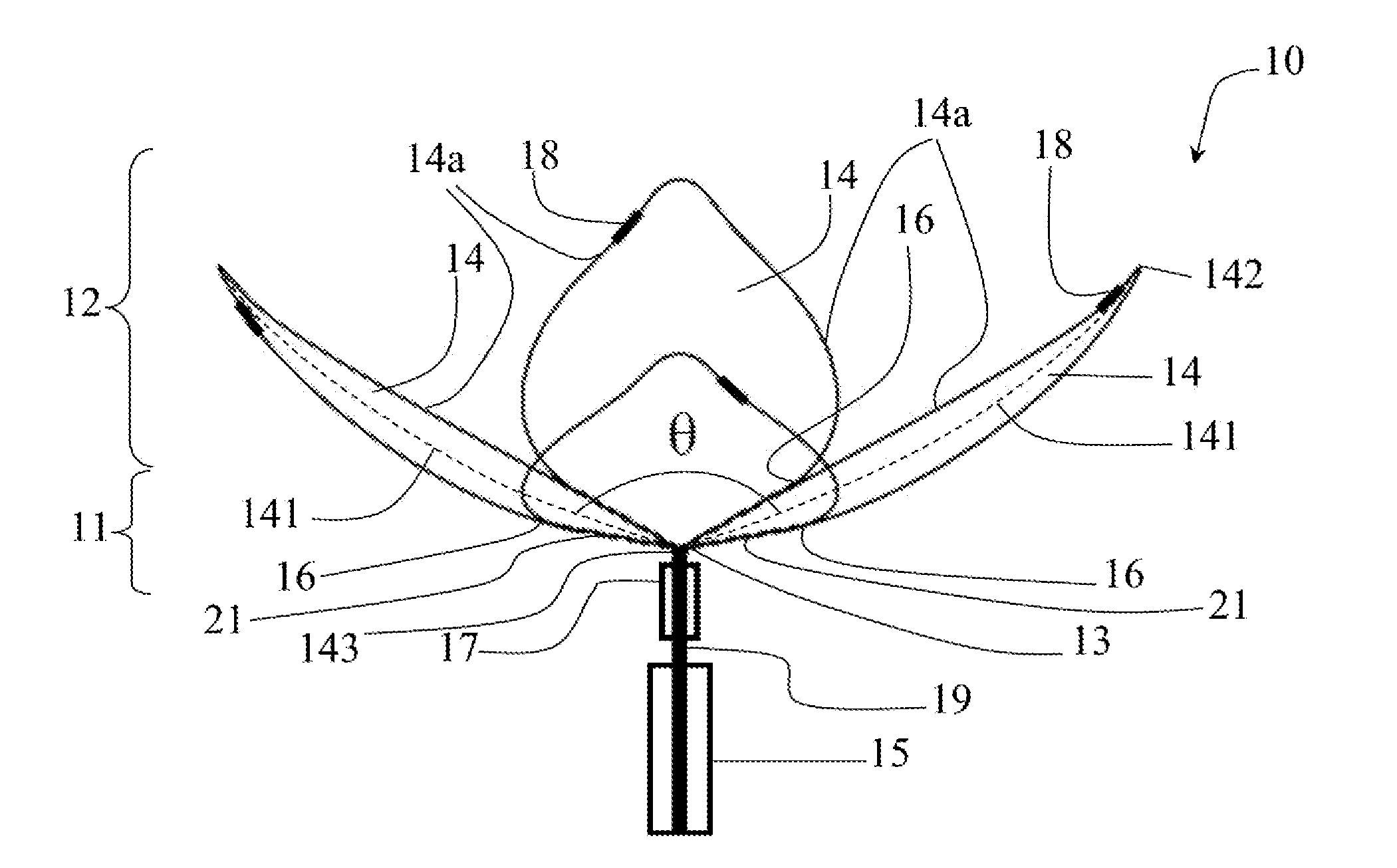
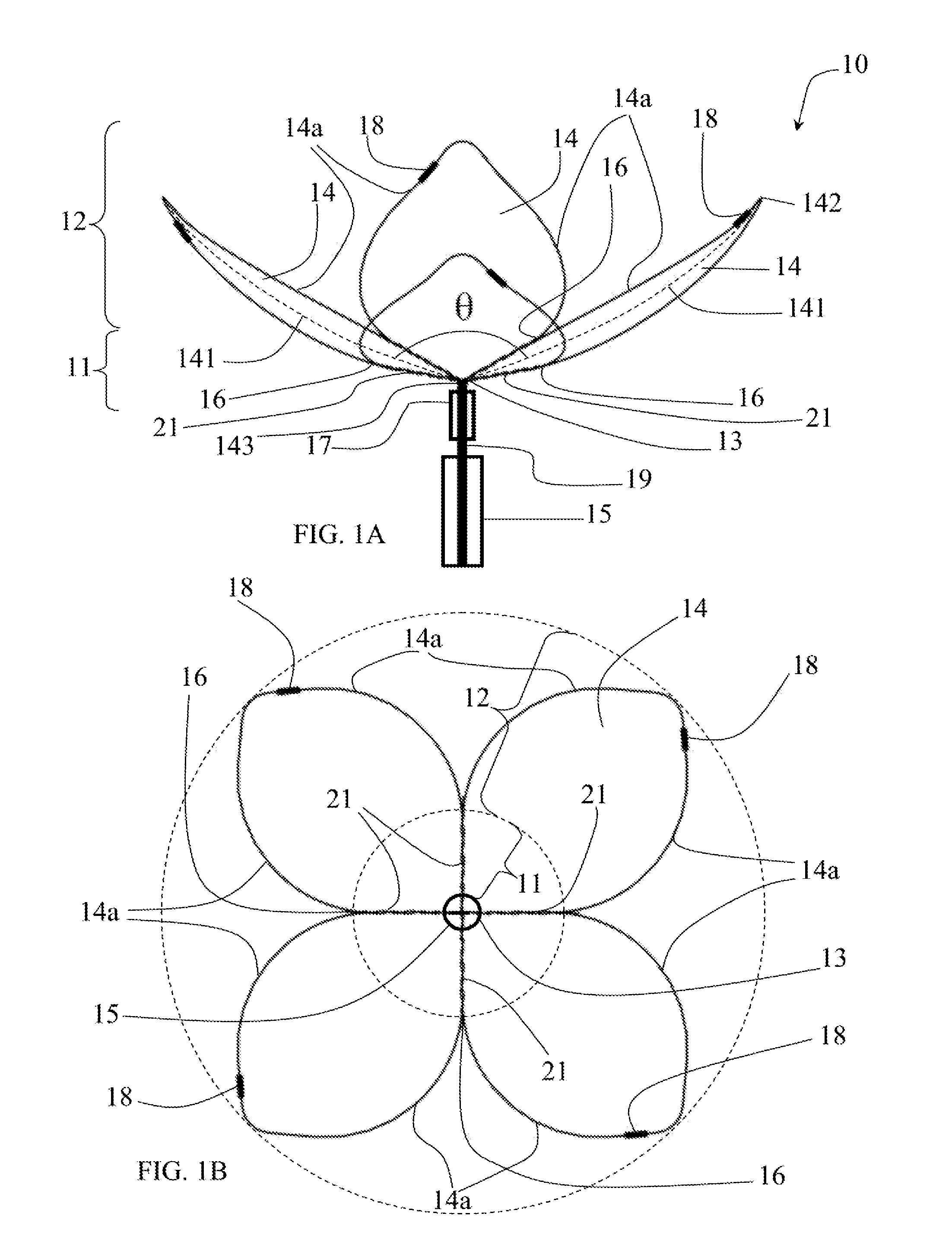
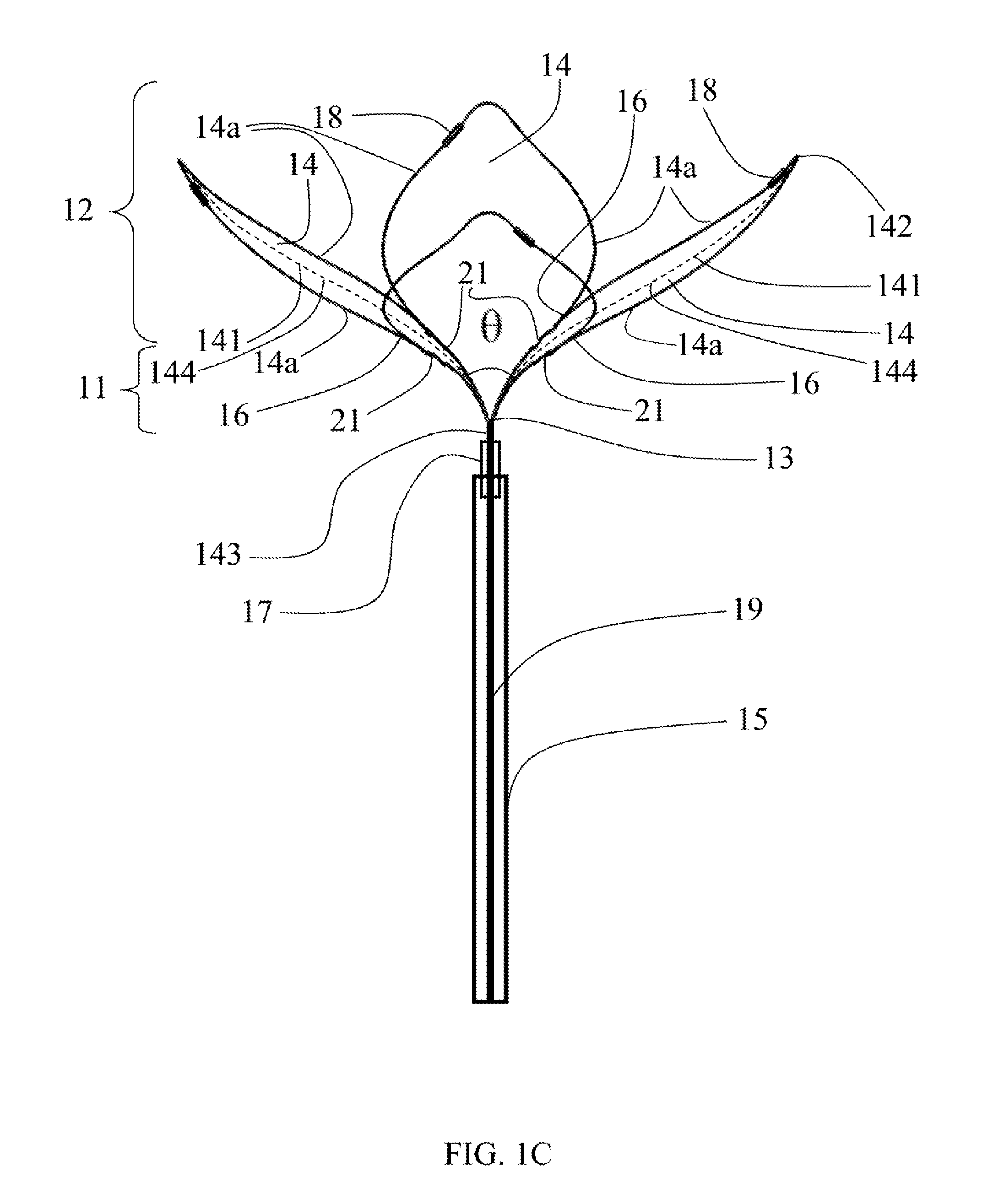
Retrieval snare for extracting foreign objects from body cavities and method for manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20080086149A1Provide structural rigidityProvide dilatation abilityWire articlesSurgeryDistal portionForeign object
A retrieval snare for entrapping and retaining a foreign object located in a body and a method for manufacturing of the snare are provided. The snare comprises a structure having a proximal portion and a distal portion and includes a plurality of filaments. The filaments extend from an end of the proximal portion towards the distal portion and return to the end of the proximal portion to form a plurality of loops. The loops are not interconnected at the distal portion, but each side of each loop are connected to a side of an adjacent loop in the proximal portion at more than one point, thereby providing structural rigidity and dilatation ability to the snare.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
Thoracic closure device and methods
A thoracic closure device. The device has a handle member, a base member, and a feed path, and is designed to accept and, with a ratcheting mechanism, tension a toothed closure tie. A guide member is also provided, and assists in the placement of a closure tie prior to tensioning. Methods of closing a median sternotomy using toothed closure ties are also disclosed.
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
Stent fabrication method and apparatus
A method is provided for electropolishing a stent. A stent is mounted on a rack having electropolishing mounts. Each of the mounts has a base and an electrically conductive first member having a first end and a second end. The first end is connected to the base and the second end contacts the external surface of the stent. Each of the mounts also has a non-electrically conductive second member having a first end and a second end. The first end of the second member is attached to the base and the second end is placed in the bore of the stent. The second ends of the first and second members bias towards each other to secure the stent between them. The stent is immersed in an electropolishing bath and an electrical current is applied to the first member.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Stationary band clamping apparatus
ActiveUS20090114308A1Easy accessEnhances operational repeatabilityWire articlesBinding material applicationPunchingEngineering
A tensioning device is provided that includes a separable punching and cutting mechanism. Provided is an impact head that holds a buckle while the band that resides within the buckle is tensioned. After a predetermined tension is achieved, a mechanism is used to lock the band with respect to the buckle then to cut the band. Various data related to tension and cutting performance may also be outputted by the invention.
Owner:BAND IT IDEX
Stent crimping method
An apparatus for crimping a stent by segmental radial compression, comprising a stationary base member; a rotatable drive hub which is moveable in relation to the stationary base member; and a crimping head aligned with respect to the stationary base member and to the rotatable drive hub. The crimping head includes at least ten segments. The segments each have a proximal end and an angled distal end with at least one angled side face terminating in an edge of a predetermined length, each segment having a centerline between the proximal and distal ends, each segment having a proximal point and a distal point, the distal point being disposed on the centerline and the proximal point being disposed off the centerline, and the proximal point being pivotally coupled by pins to the stationary base member and the distal point being pivotally coupled by pins to the rotatable hub member. The segments are arranged so that the segment distal ends are disposed adjacent to and a predetermined distance away from a central point and defining a central aperture with a cylindrical dimension. Also, the segment centerlines extend therefrom toward the segment distal ends and are oriented away from the central point. The segment distal ends move closer to the central point upon rotation of the rotatable hub member in a predetermined direction, whereby the stent is disposed around a base substrate, aligned in the central aperture and crimped round the base substrate upon rotation of the rotatable hub. A method of crimping a stent is also disclosed.
Owner:MACHINE SOLUTIONS
Device and method for treating vascular abnormalities
A vascular device is provided that includes a tubular structure and an occluding structure. The tubular structure has inner and outer layers, with the occluding structure located between the inner and outer layers. Each of the inner and outer layers may define a different pick count, and the tubular structure may include a leading edge at a transition between the pick counts. The leading edge may be disposed at the distal end of the vascular device when the device is deployed from a delivery device. Furthermore, the occluding structure may have first and second layers formed by the inversion or eversion of the occluding structure and the subsequent coupling of its free ends to form a continuous structure. Thus, any loose ends may be sealed to minimize unraveling and / or shifting of the occluding structure within the tubular structure. A method of making the vascular device is also provided.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Radiopaque super-elastic intravascular stent
The intravascular stent is formed from a composite wire includes an inner core of radiopaque metal, a polymer layer coaxially disposed about the inner core, and an outer metal layer coaxially disposed about the polymer layer. The intermediary polymer layer acts as a barrier material between the inner core and the outer sheath, so that the inner core and outer sheath may be made of dissimilar metallic layers, and the intermediary polymer layer will prevent a galvanic reaction between the inner core and the peripheral metal layer. The intravascular stent has ends flared radially outwardly to prevent radially and longitudinally inward deformation of the ends of the stent when the stent is disposed in a desired location in a patient's vasculature.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method of manufacturing a dental instrument
Method for manufacturing a dental instrument having a desired machined configuration, without twisting the instrument. A blank of superelastic material is brought to an annealed state comprising a phase structure including a rhombohedral phase alone or in combination with austenite and / or martensite, or a combination of martensite and austenite. In this annealed state, a portion of the annealed material is removed at low temperature, for example less than about 100° C., and advantageously at ambient temperature, to form a final machined configuration for the instrument. The instrument is then heat treated and rapidly quenched to a superelastic condition.
Owner:ORMCO CORP
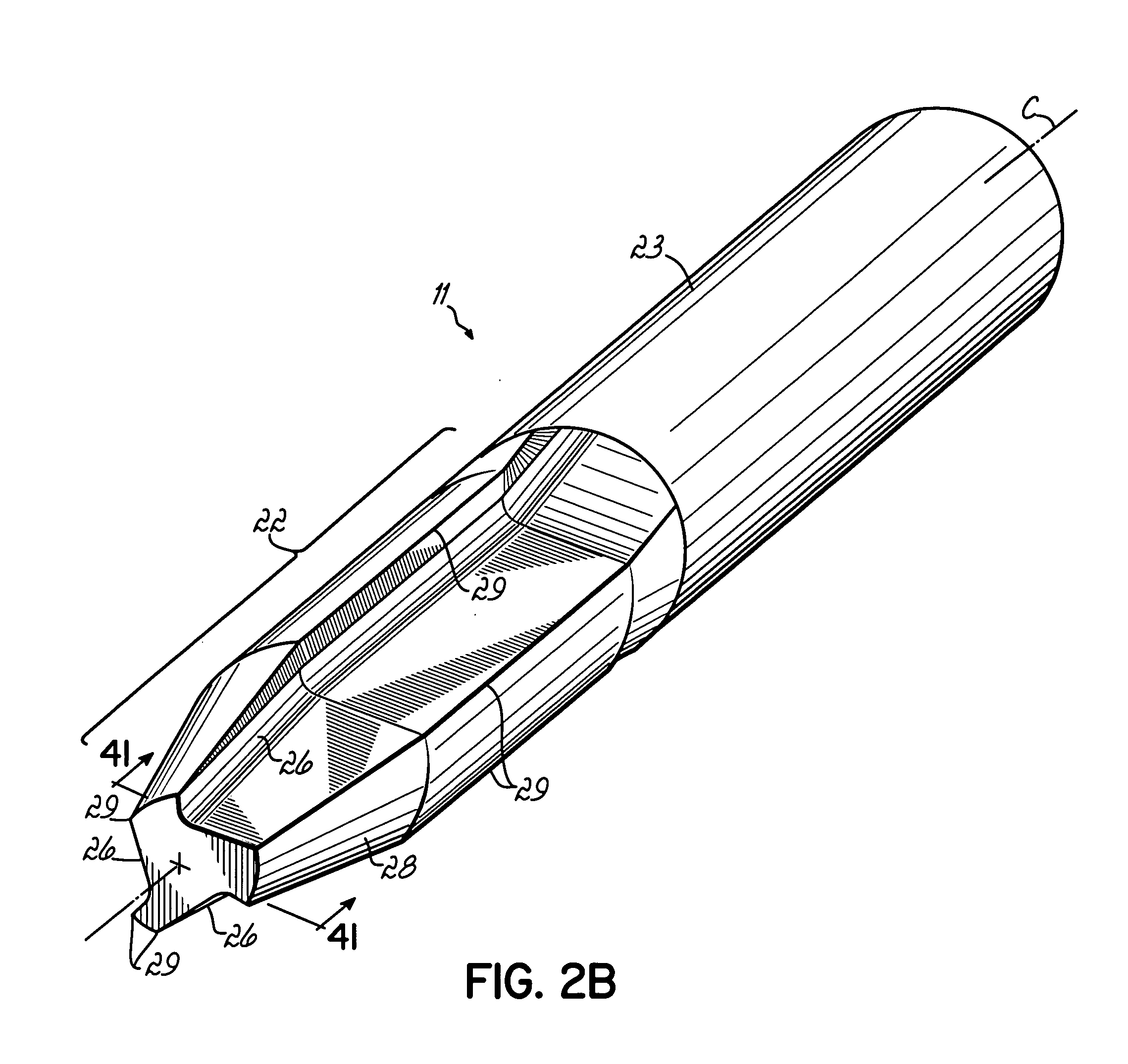
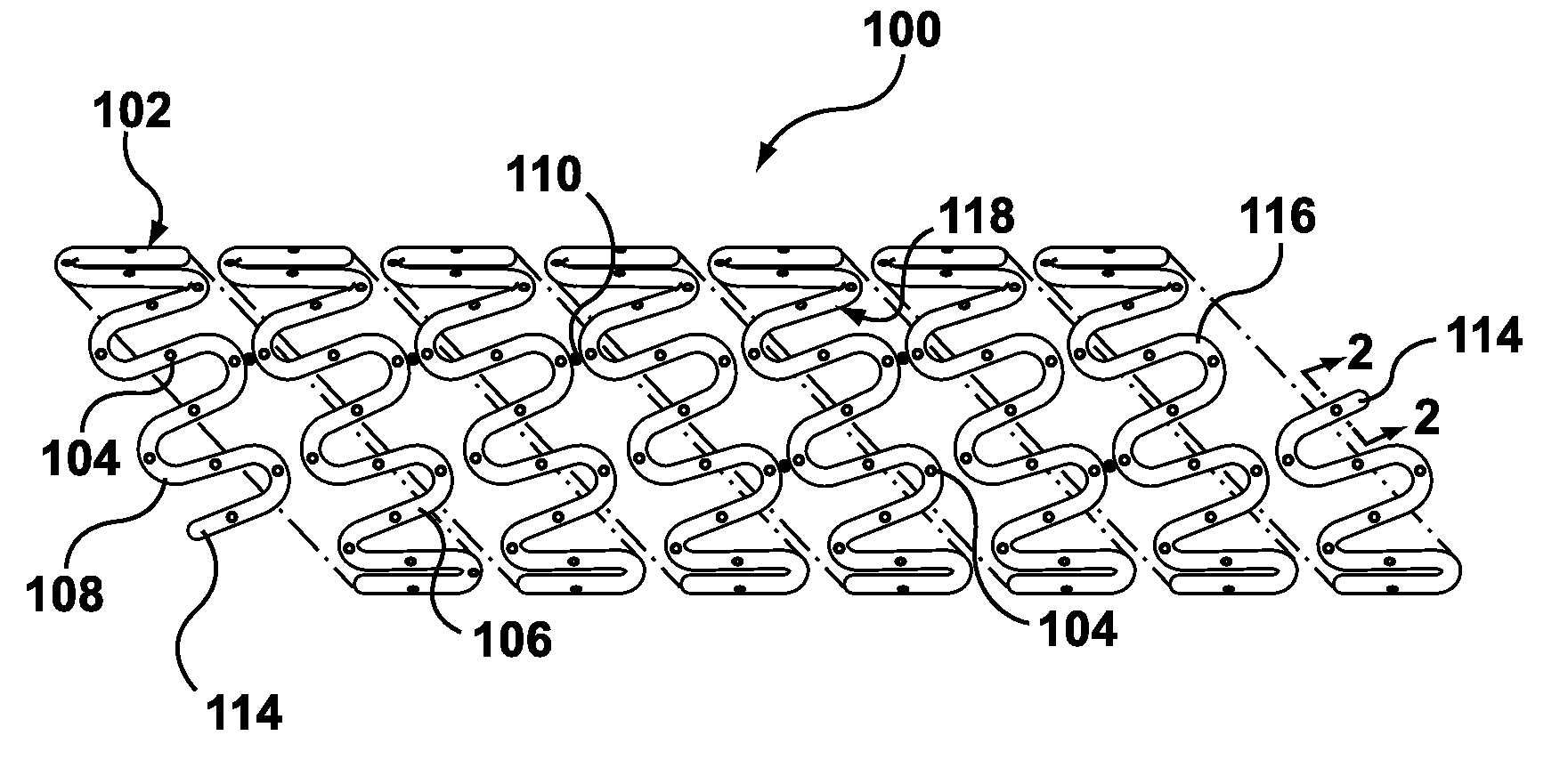
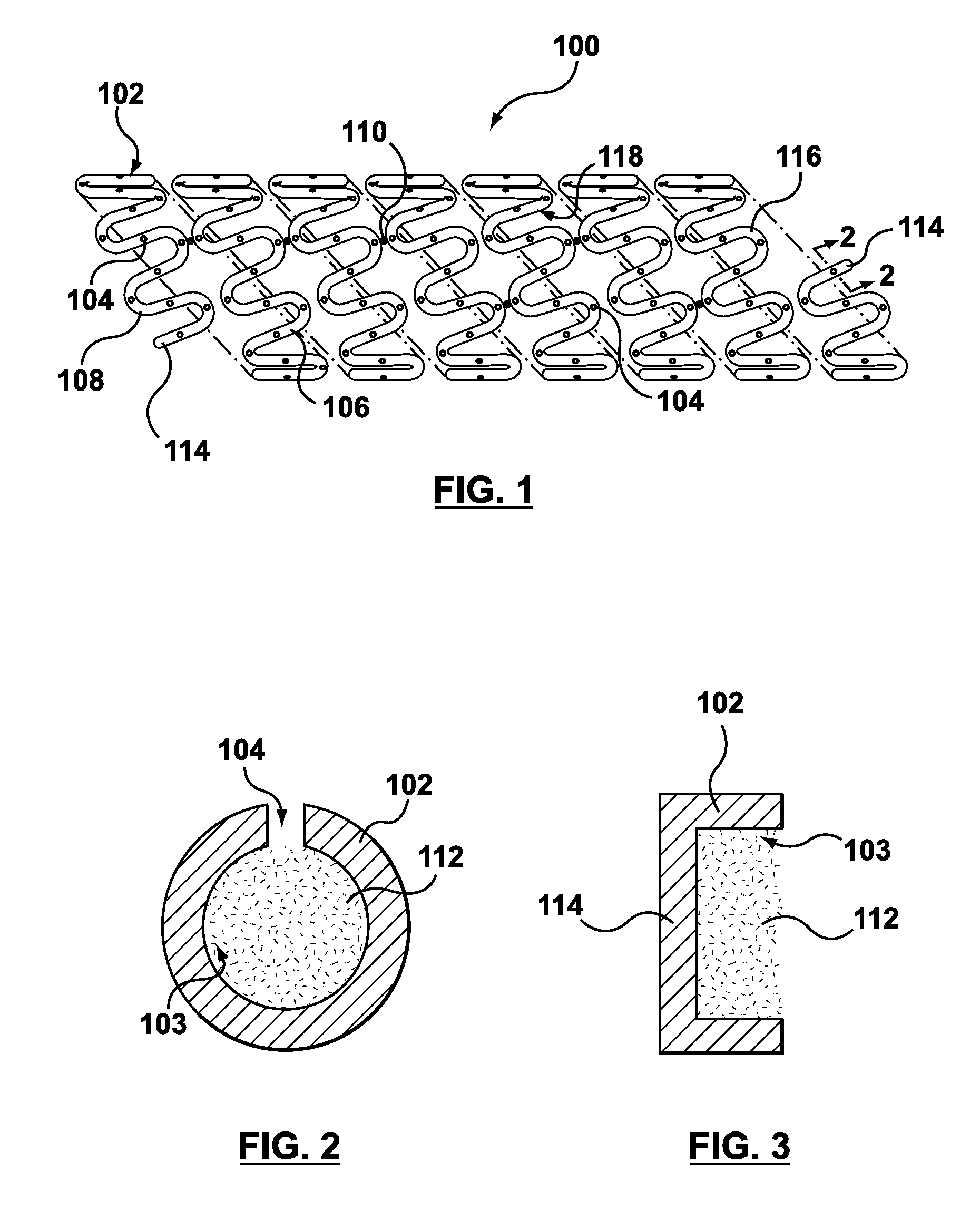
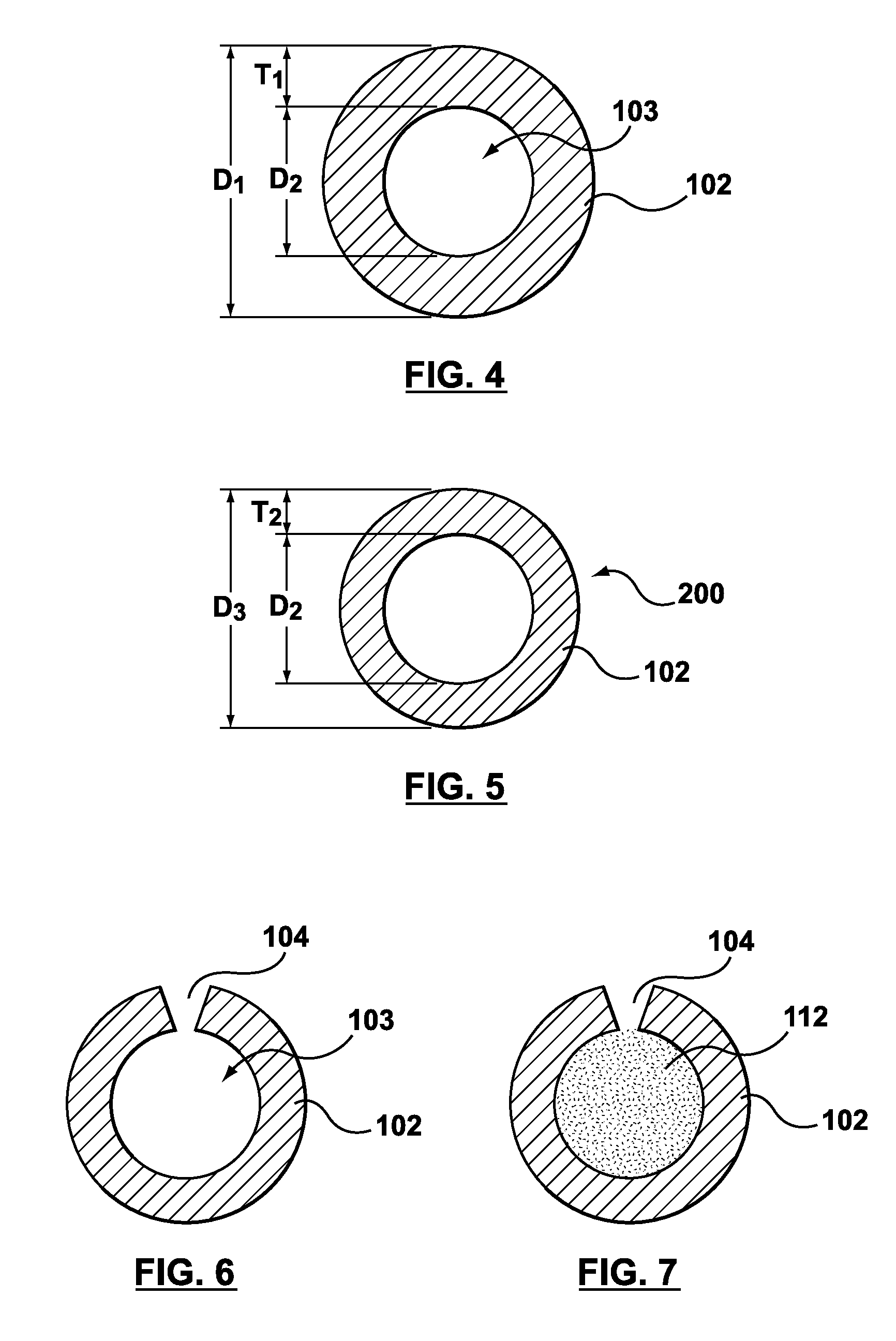
Apparatus and Method for Forming a Wave Form for a Stent From a Wire
An apparatus for forming a wave form for a stent from a wire includes a first forming member configured to move substantially parallel to a first axis and to move substantially parallel to a second axis that is orthogonal to the first axis, and a second forming member configured to move substantially parallel to the first axis and to move substantially parallel to the second axis. The second forming member is positioned opposite from the first forming member relative to the second axis along which the wire is configured to travel. The apparatus includes a controller configured to control movement of the first forming member relative to the wire and to control movement of the second forming member relative to the wire so that the first forming member and the second forming member deform the wire in opposite directions to form a portion of the wave form.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method of forming hollow tubular drug eluting medical devices
A method of a forming a hollow, drug-eluting medical device includes utilizing a hollow wire having an outer member and a lumen of the outer member, and filling the lumen with a fluid to form a supported hollow wire. The supported hollow wire is shaped into a stent pattern. Openings are formed through the outer member. The supported hollow wire is processed to remove the fluid from the lumen of the outer member without adversely affecting the outer member, leaving the hollow wire shaped into a stent pattern. The lumen is filled with a biologically or pharmacologically active substance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Interlaced wire for implants
InactiveUS20060041262A1Promotes tissue ingrowthFinger jointsWire articlesVolumetric Mass DensityMaterials science
The disclosure is directed to a material for in vivo implantation. The material includes a compressed interlaced wire shaped into a form having a porous structure suitable for tissue ingrowth, the interlaced wire compressed from an original starting density to a final density, the final density being greater than the original starting density.
Owner:INTELLIMED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com