Patents
Literature
9314results about "Dilators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
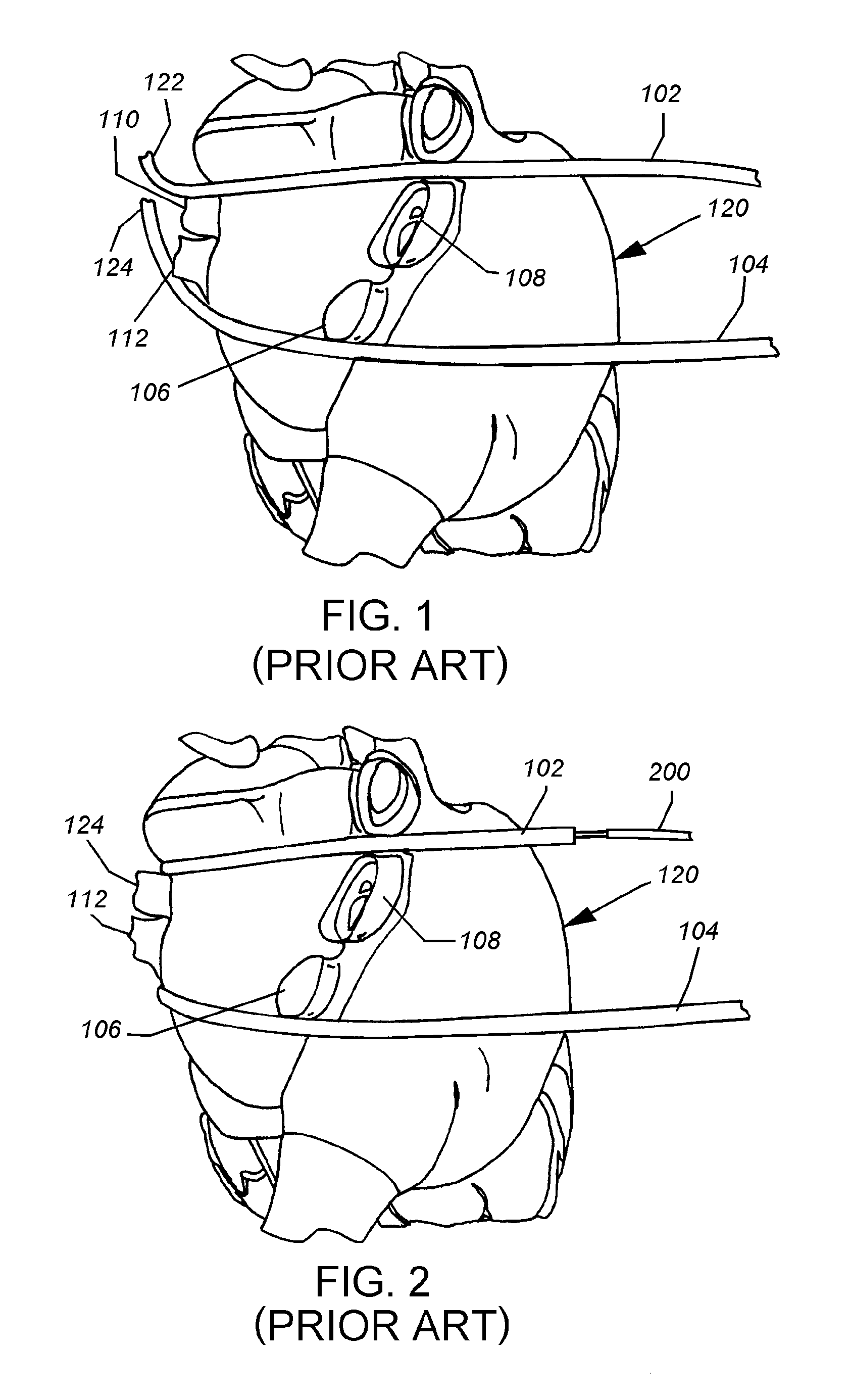
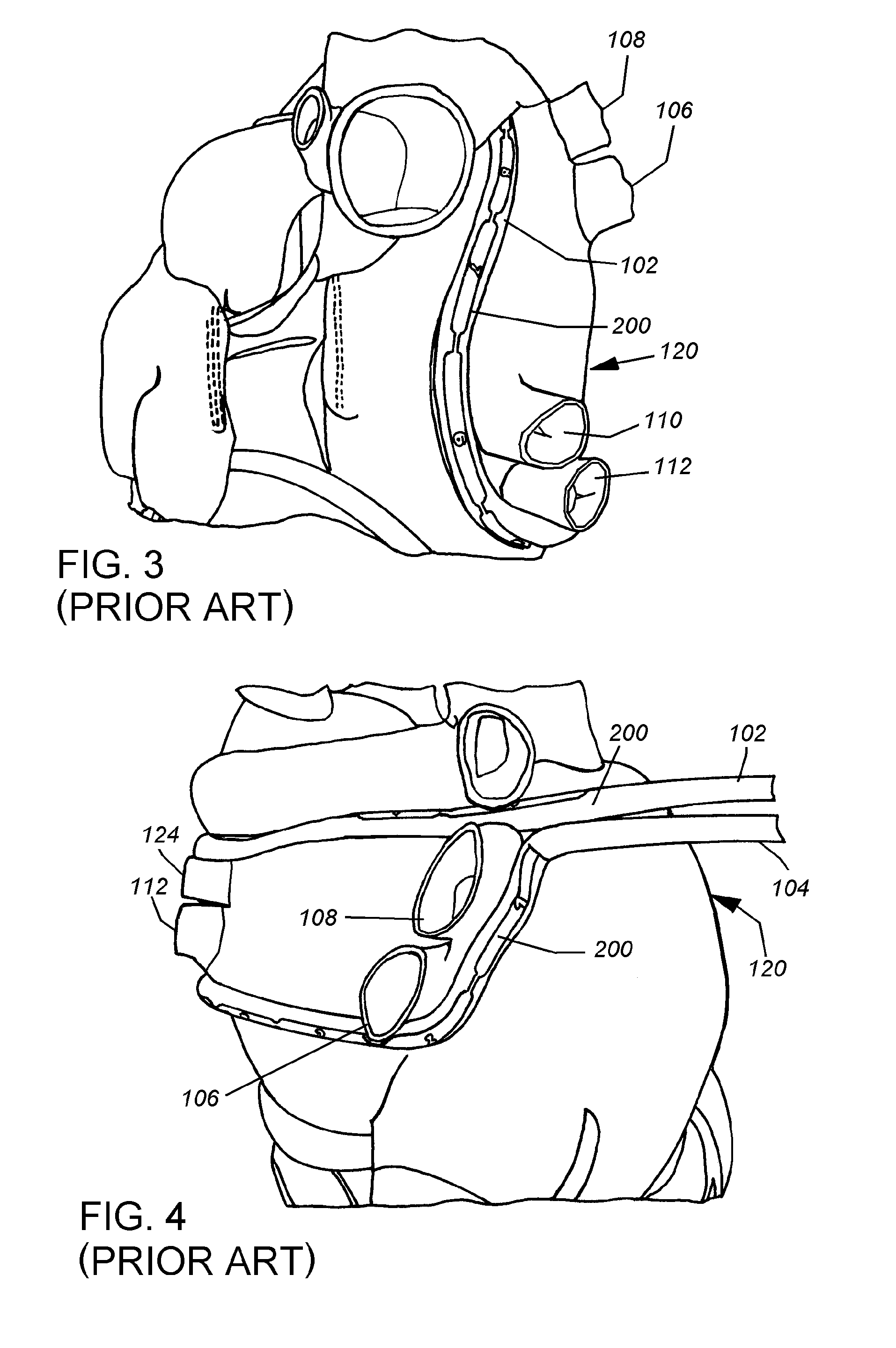
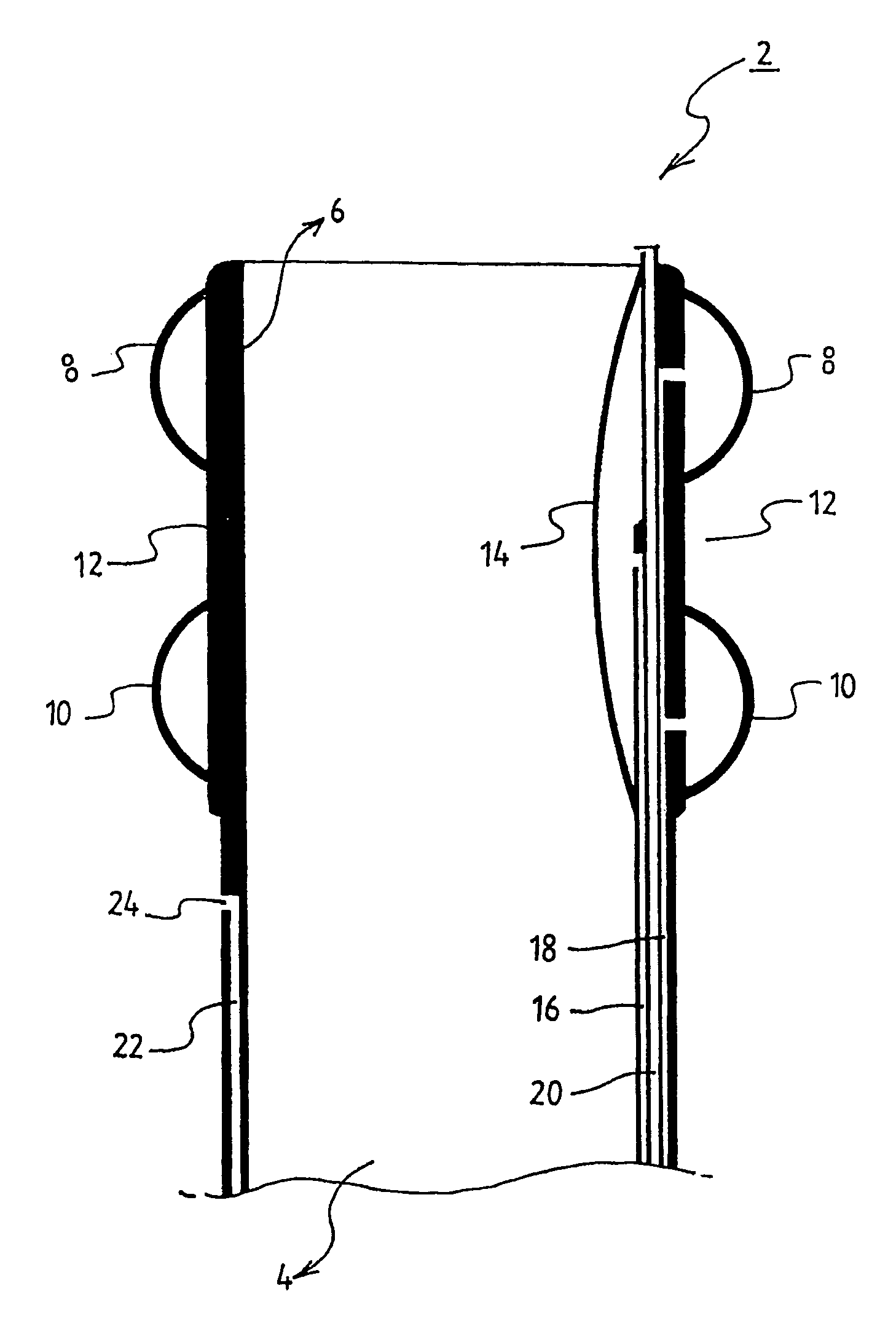
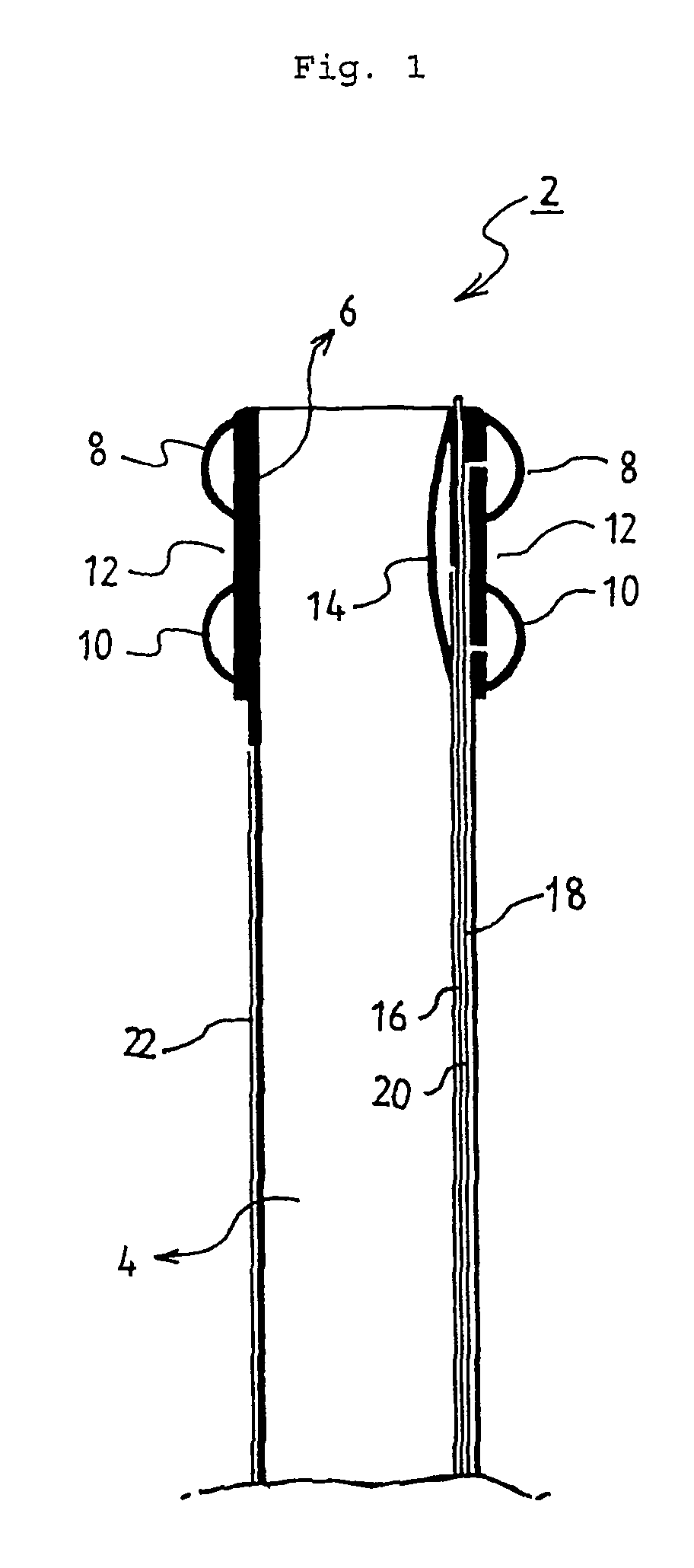
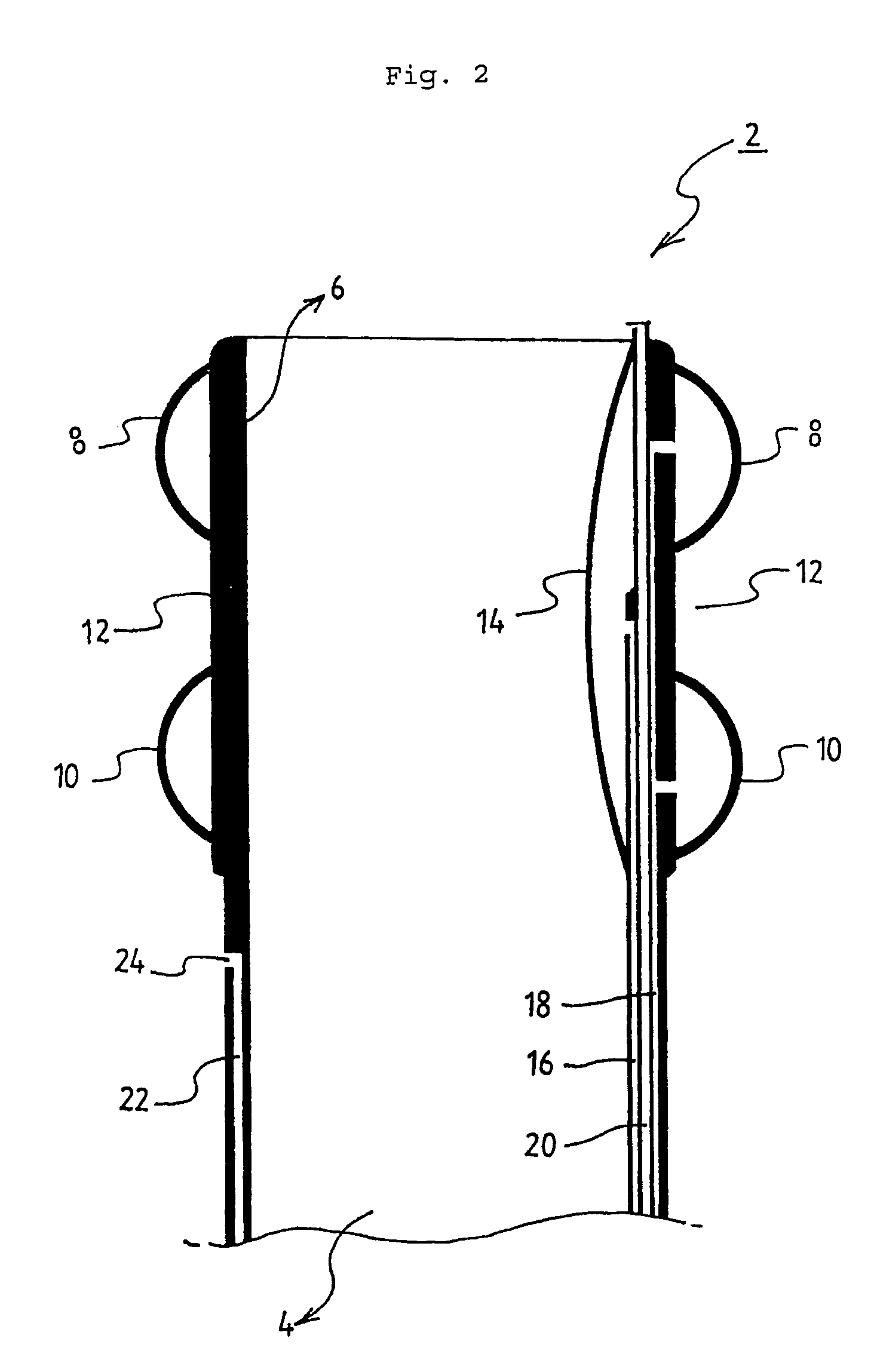
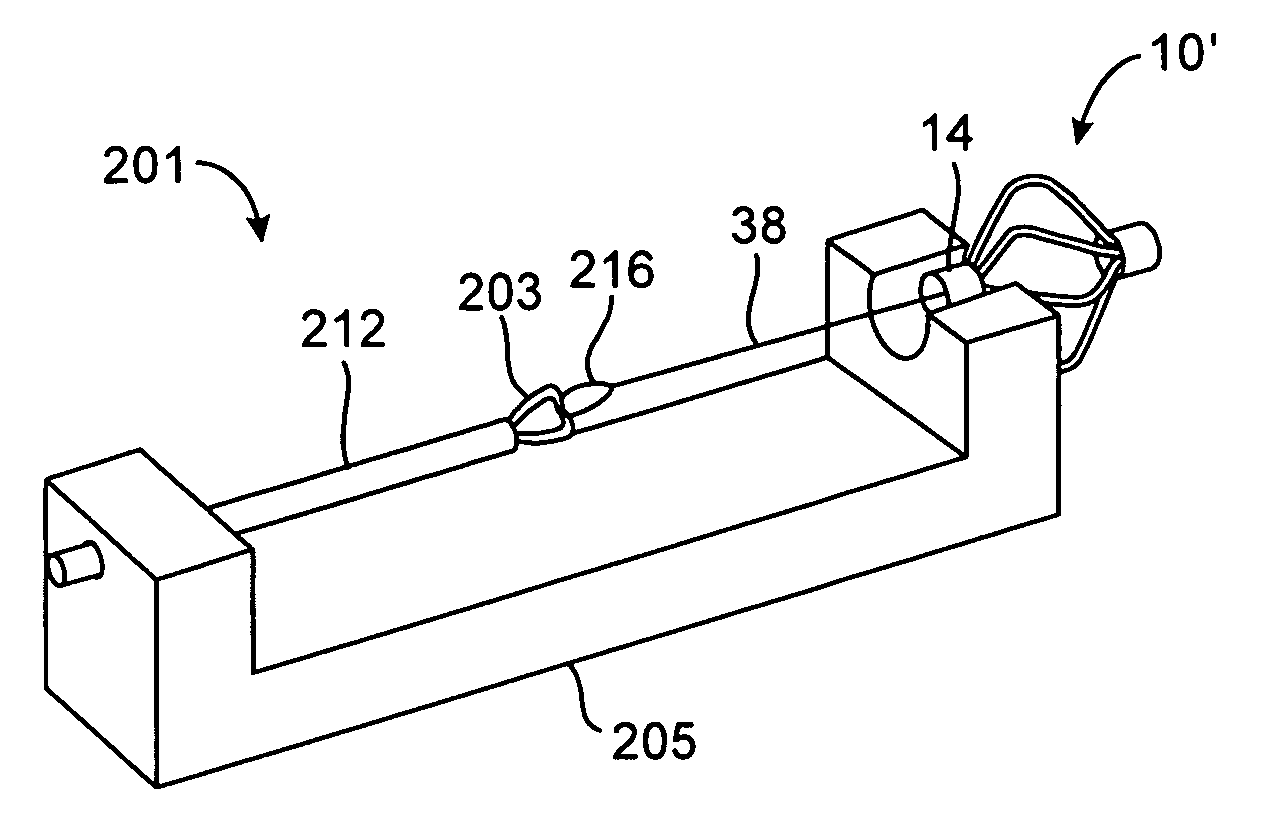
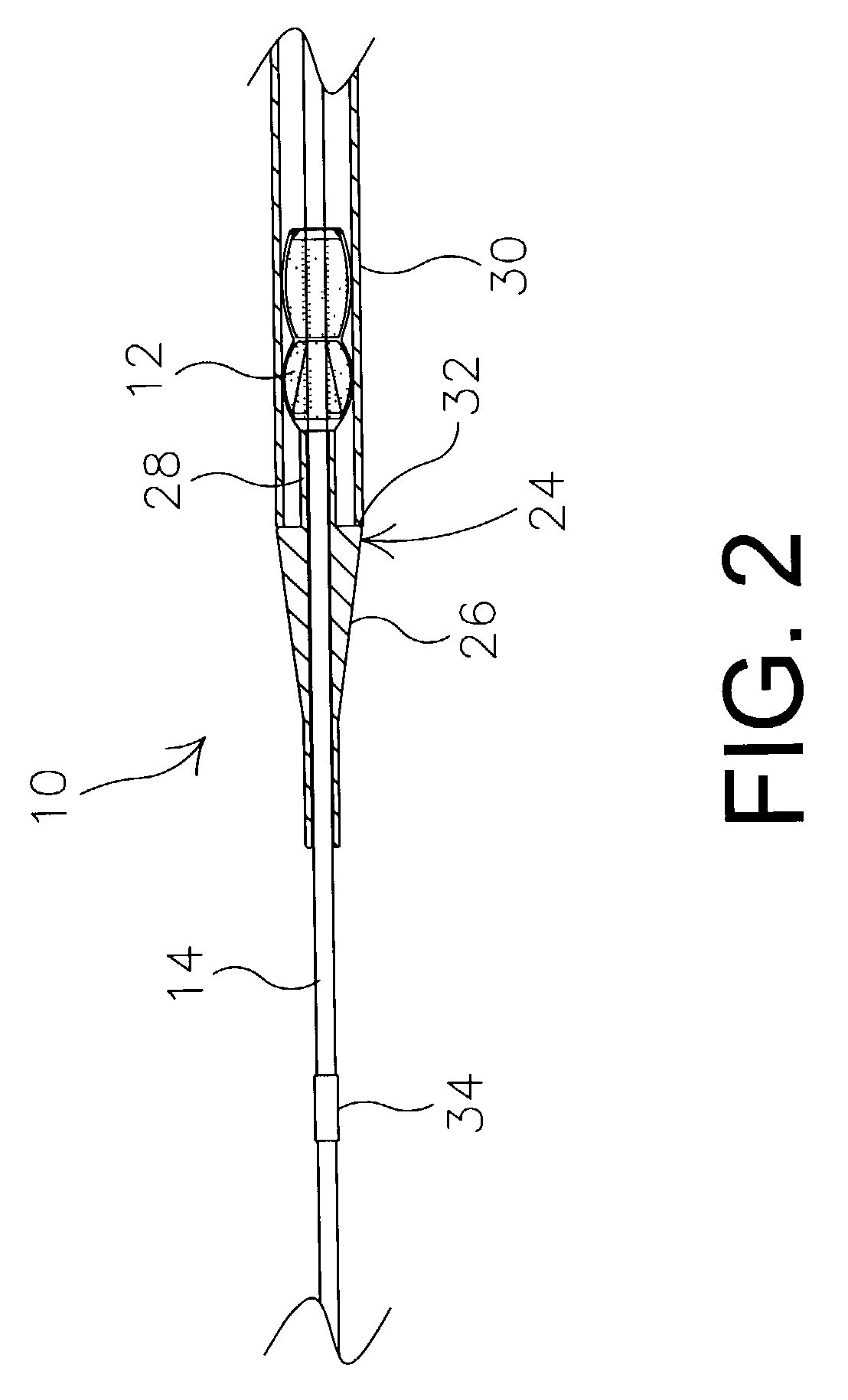
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS7018406B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchor may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand within the deficient native valve, and the anchor engages the lumen wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
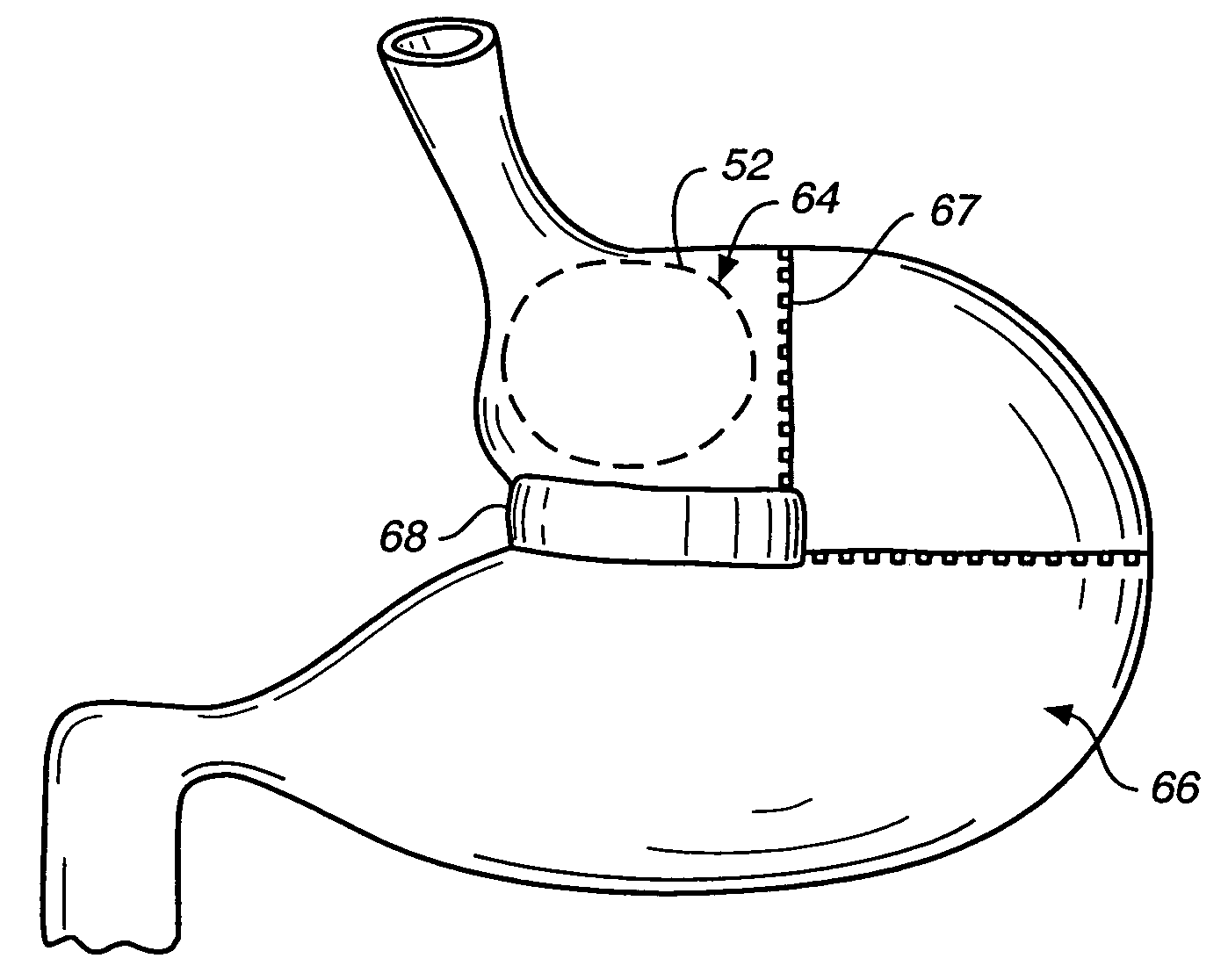
Methods and devices for maintaining a space occupying device in a relatively fixed location within a stomach
Methods and devices for maintaining a space-occupying device in a fixed relationship relative to a patient's stomach by manipulation of the stomach. In one variation, two or more regions of the stomach wall are brought into appromixation with one another and secured together in a manner that secures a space-occupying device within the stomach of the patient. In another variation, two or more regions of the stomach wall are wrapped around a space-occupying device to maintain the position of the space-occupying device relative to the stomach wall. In another variation, a system having a space-occupying member and a locking member capable holding the space-occupying member against the inner wall of the stomach are provided. In a further variation, a pouch is created within the stomach that receives and retains a space-occupying device.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Transgastric method for carrying out a partial fundoplication
The invention is a transgastric method for the endoscopic partial fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The method makes use of an articulated endoscope, which is introduced through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach of the patient. A cutting tool is introduced through the working channel of the endoscope to cut a hole in the wall of the stomach. The endoscope is pushed through the hole and a grabbing tool is introduced through the working channel and used to grab the tissue at a location on the outer surface of the stomach and move the grabbed tissue close to the esophagus. The grabbed tissue is then stapled to the esophagus using a stapling device that is an integral part of the endoscope. If desired, after stapling the endoscope can be rotated one or more times and the procedure repeated. After the selected portions of the stomach wall have been attached to the esophagus, the endoscope is withdrawn from the body of the patient and the hole in the stomach wall is closed, preferably by means of a dedicated endoscopic stapling device especially designed for the task of closing holes in tissue.
Owner:MEDIGUS LTD
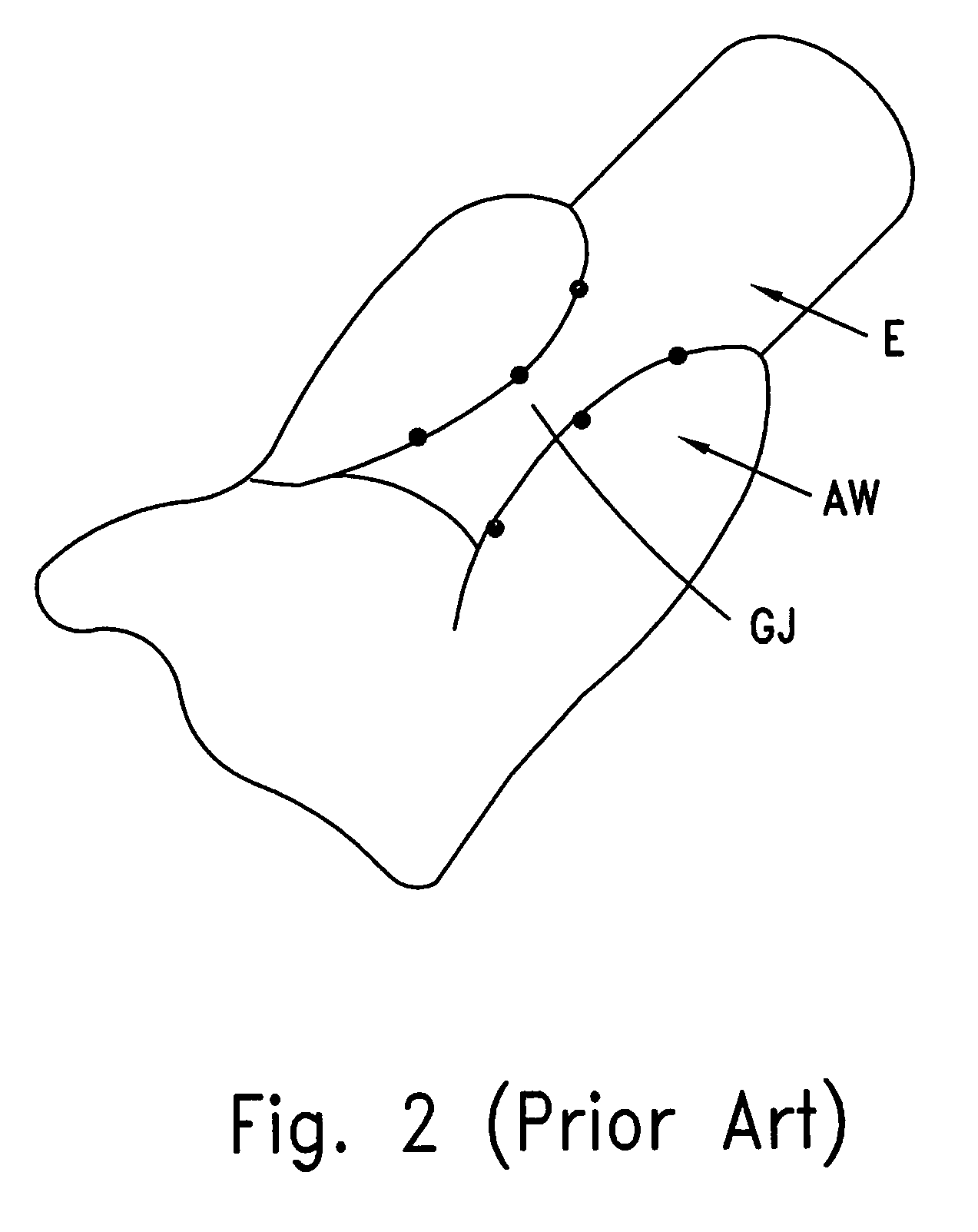
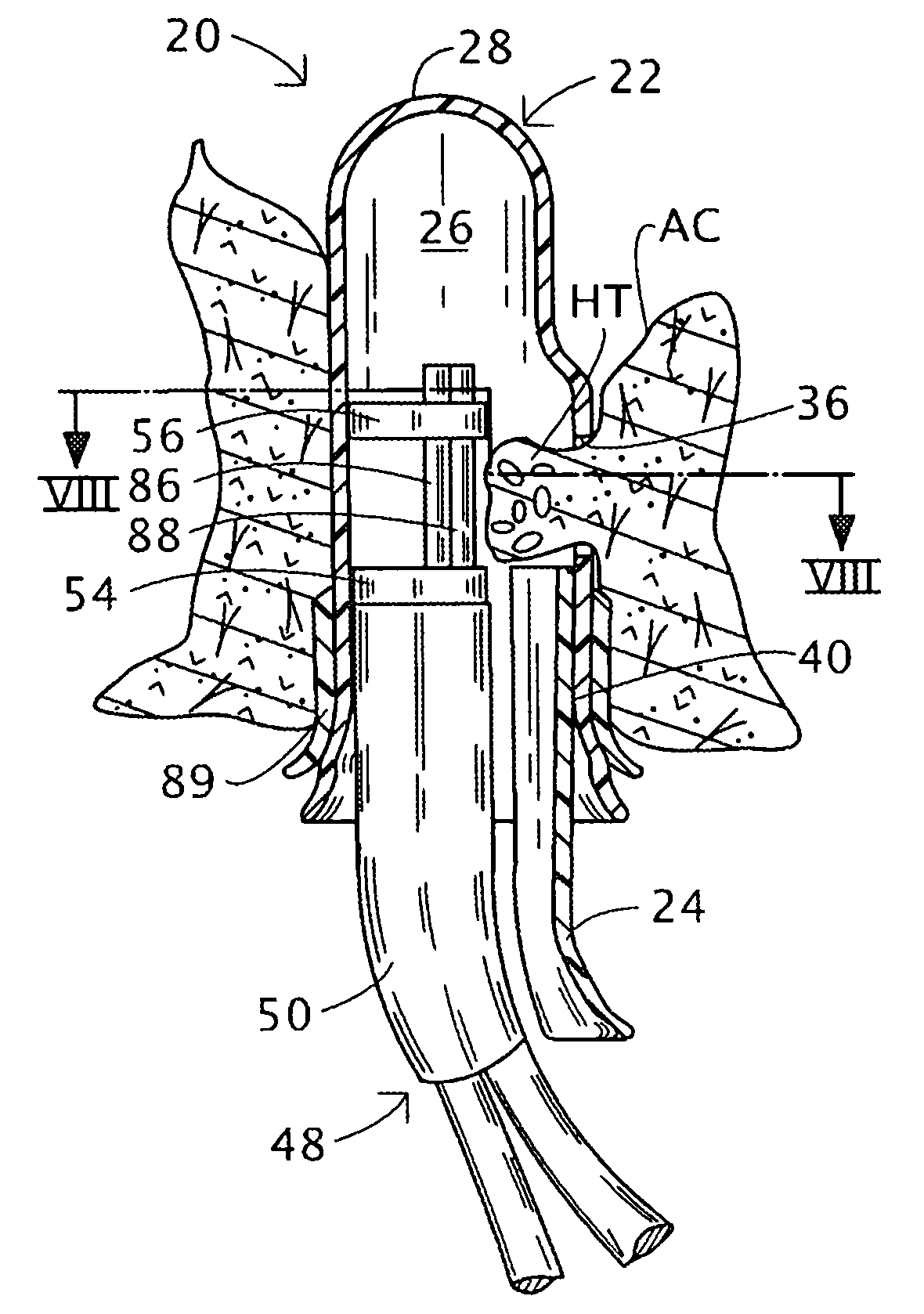
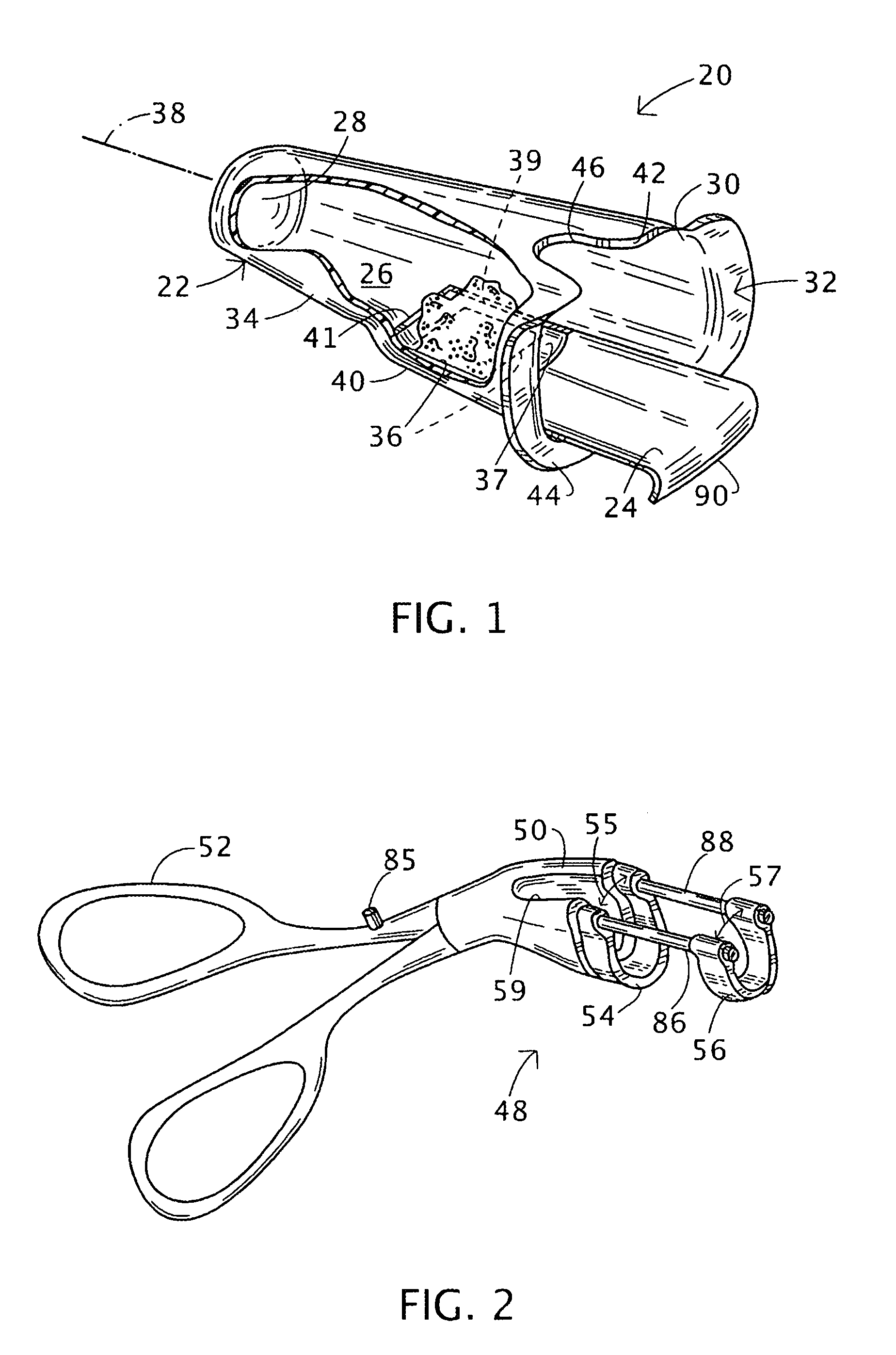
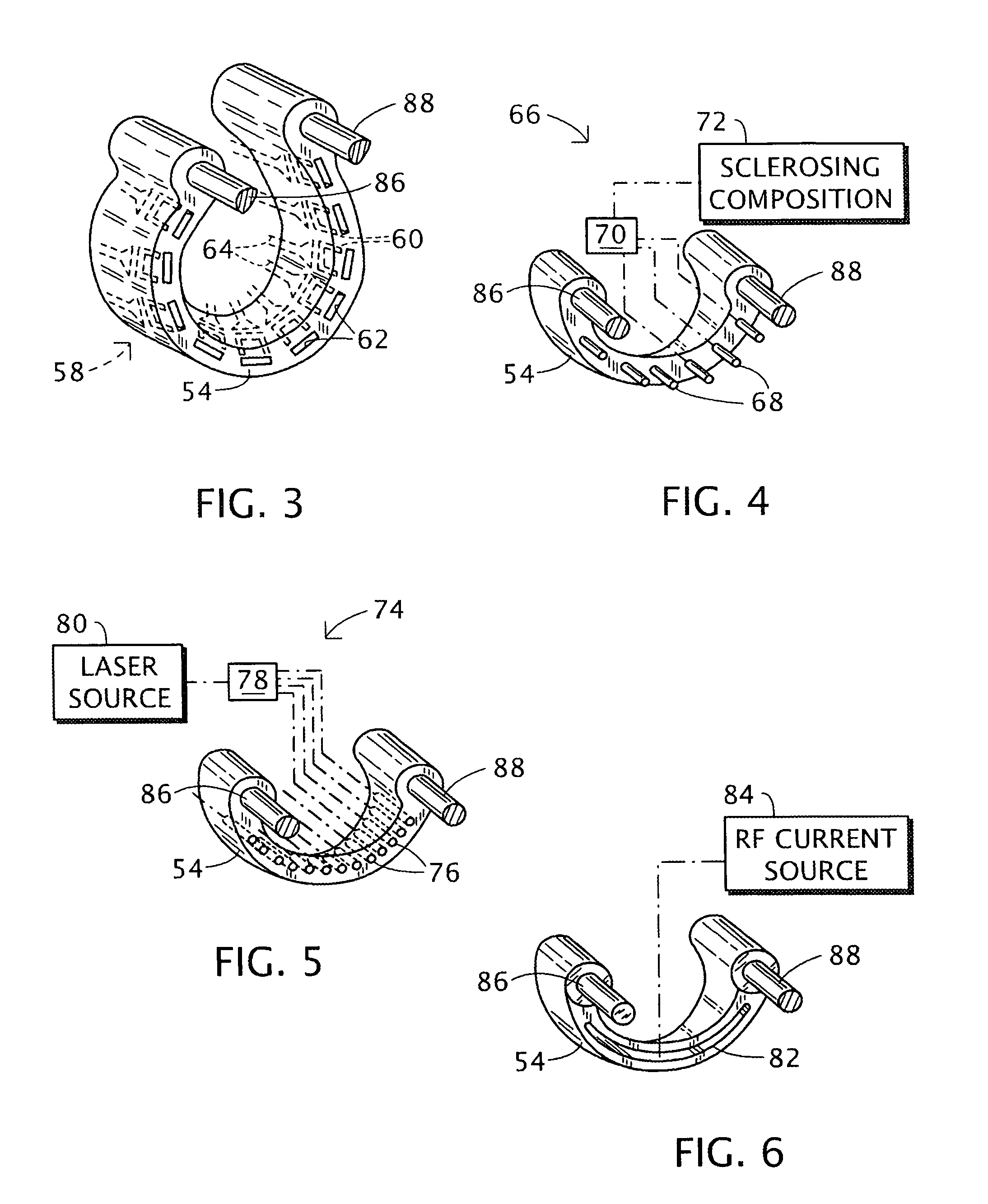
Hemorrhoids treatment method and associated instrument assembly including anoscope and cofunctioning tissue occlusion device
ActiveUS7118528B1Less traumaticMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsStapling toolsHemorrhoidsSurgical device
A surgical instrument assembly for the treatment of hemorrhoids includes an anoscope and a hemorrhoid occlusion device. The anoscope includes a hollow body closed at a distal end and at least partially open at a proximal end to define a longitudinal channel. The hollow body has a sidewall provided with a window spaced from the distal end and the proximal end. A shutter member is slidably attached to the hollow body for selectively covering the window during an insertion operation and for opening the window to allow hemorrhoidal tissues to protrude through the window into the anoscope. The hemorrhoid occlusion device includes an instrument shaft provided at a distal end with two jaws, at least one of the jaws including a C- or U-shaped clamping member movable alternately away and towards the other of the jaws for clamping and occluding hemorrhoidal tissues protruding through the window into the anoscope.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
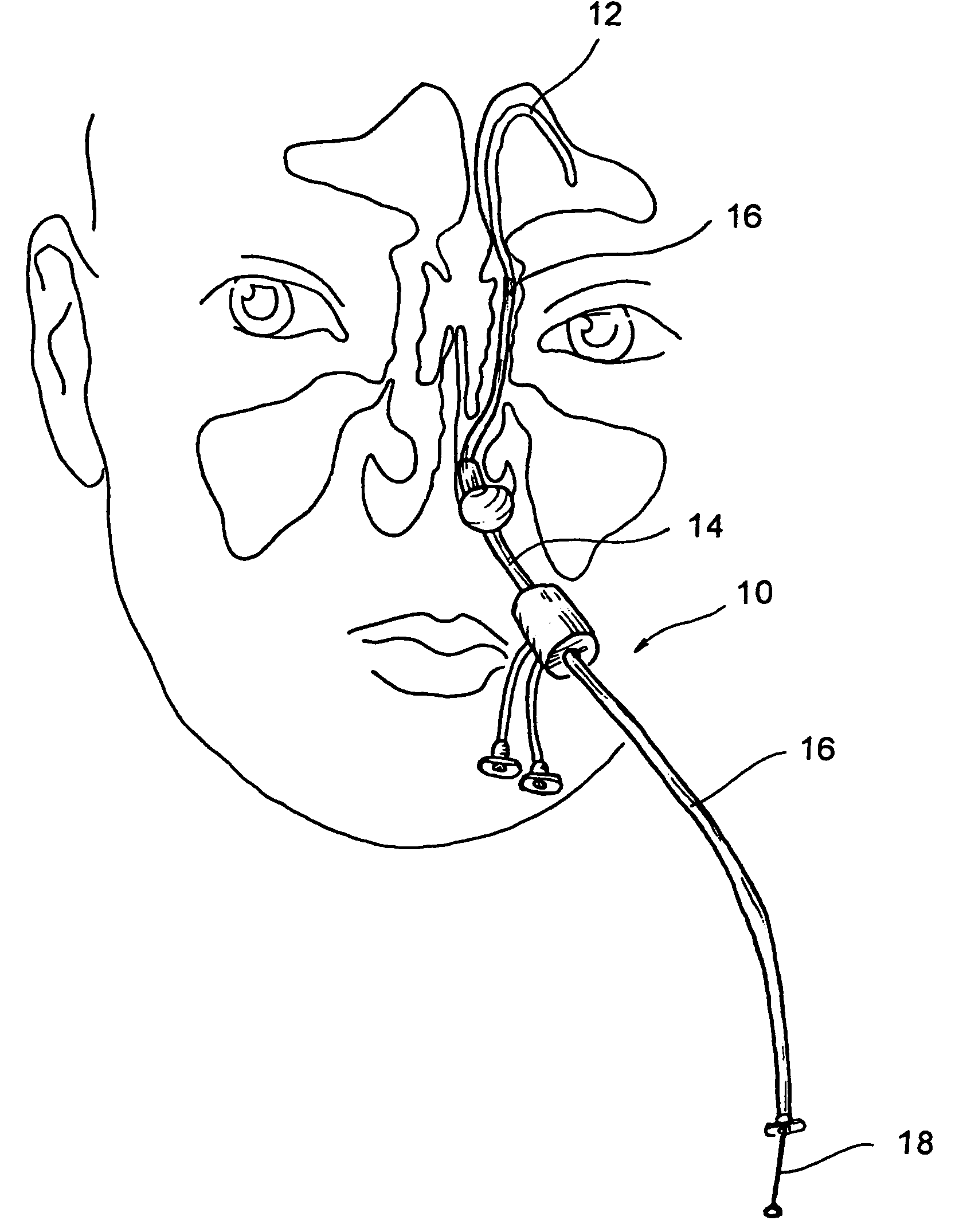
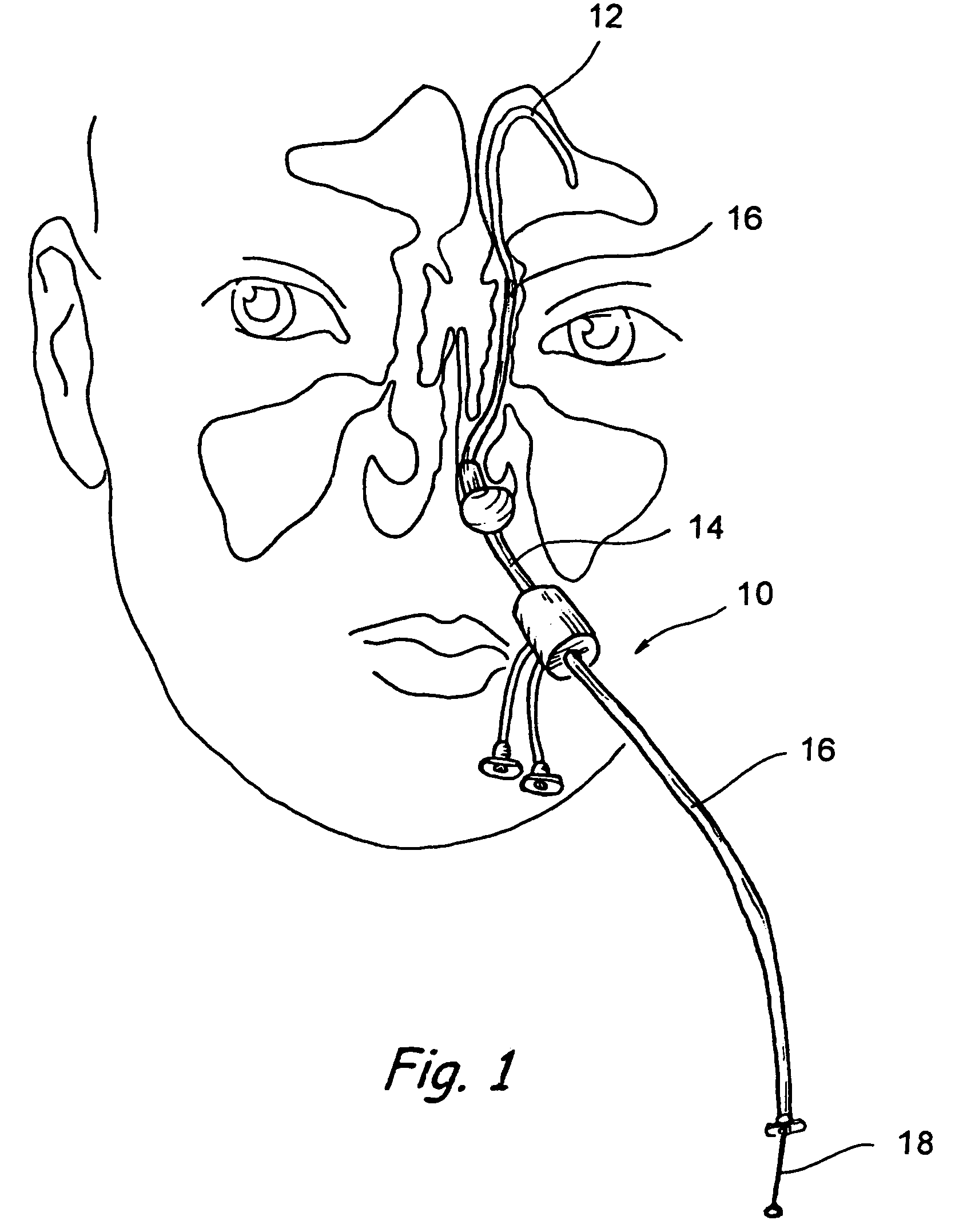
Implantable device and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to treat sinusitis and other disorders
Implantable devices and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to locations within the body of a human or animal subject to treat or diagnose sinusitis and a variety of other disorders. The invention includes implantable substance delivery devices that comprise reservoirs and barriers that control the rate at which substances pass out of the reservoirs. The delivery devices may be advanced into the body using guidewires, catheters, ports, introducers and other access apparatus. In some embodiments the delivery devices may be loaded with one or more desired substance before their introduction into the body. In other embodiments the delivery devices are loaded and / or reloaded with a desired substance after the delivery device has been introduced into the body.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
System and method for advancing, orienting, and immobilizing on internal body tissue a catheter or other therapeutic device
This invention provides a system and method that allows a therapeutic device, such as an atrial fibrillation microwave ablation catheter or ablation tip to be guided to a remote location within a body cavity and then accurately immobilized on the tissue, including that of a moving organ, such as the heart. In various embodiments, the system and method also enables accurate movement and steering along the tissue, while in engagement therewith. Such movement and engagement entails the use of vacuum or microneedle structures on at least two interconnected and articulated immobilizers that selectively engage to and release from the tissue to allow a crawling or traversing walking across the organ as the therapeutic catheter / tool tip applies treatment (AGE devices). In further embodiments that lack a movement capability (AID devices), the immobilizers allow a predetermined position for the introduced device to be maintained against the tissue while a treatment is applied to the location adjacent thereto. In the exemplary AID devices, variety of steering mechanisms and mechanisms for exposing and anchoring a catheter against the underlying tissue can be employed. In the exemplary AGE devices, a variety of articulation and steering mechanisms, including those based upon pneumatic / hydraulic bellows, lead screws and electromagnetic actuators can be employed.
Owner:ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY FRONTIERS SPA
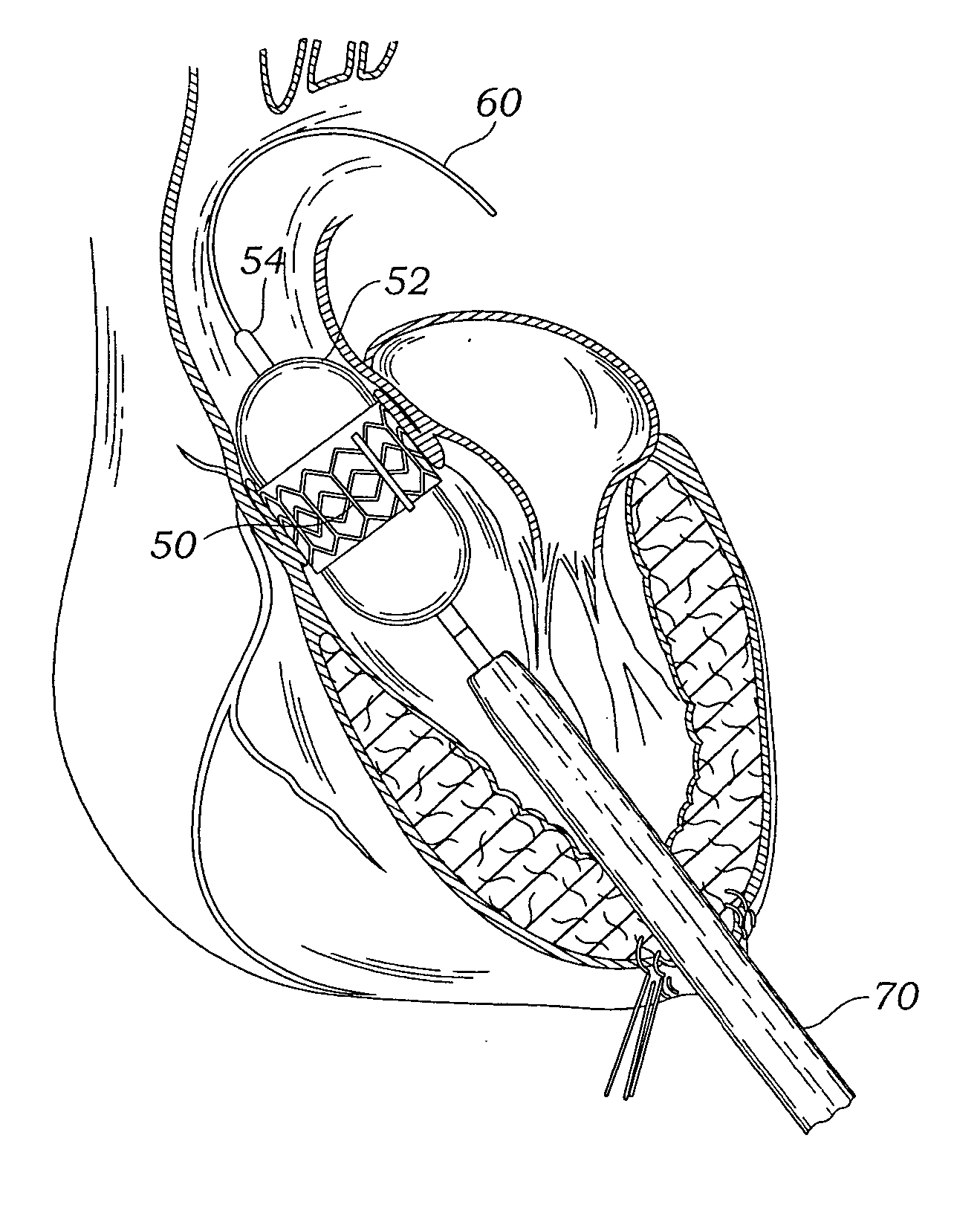
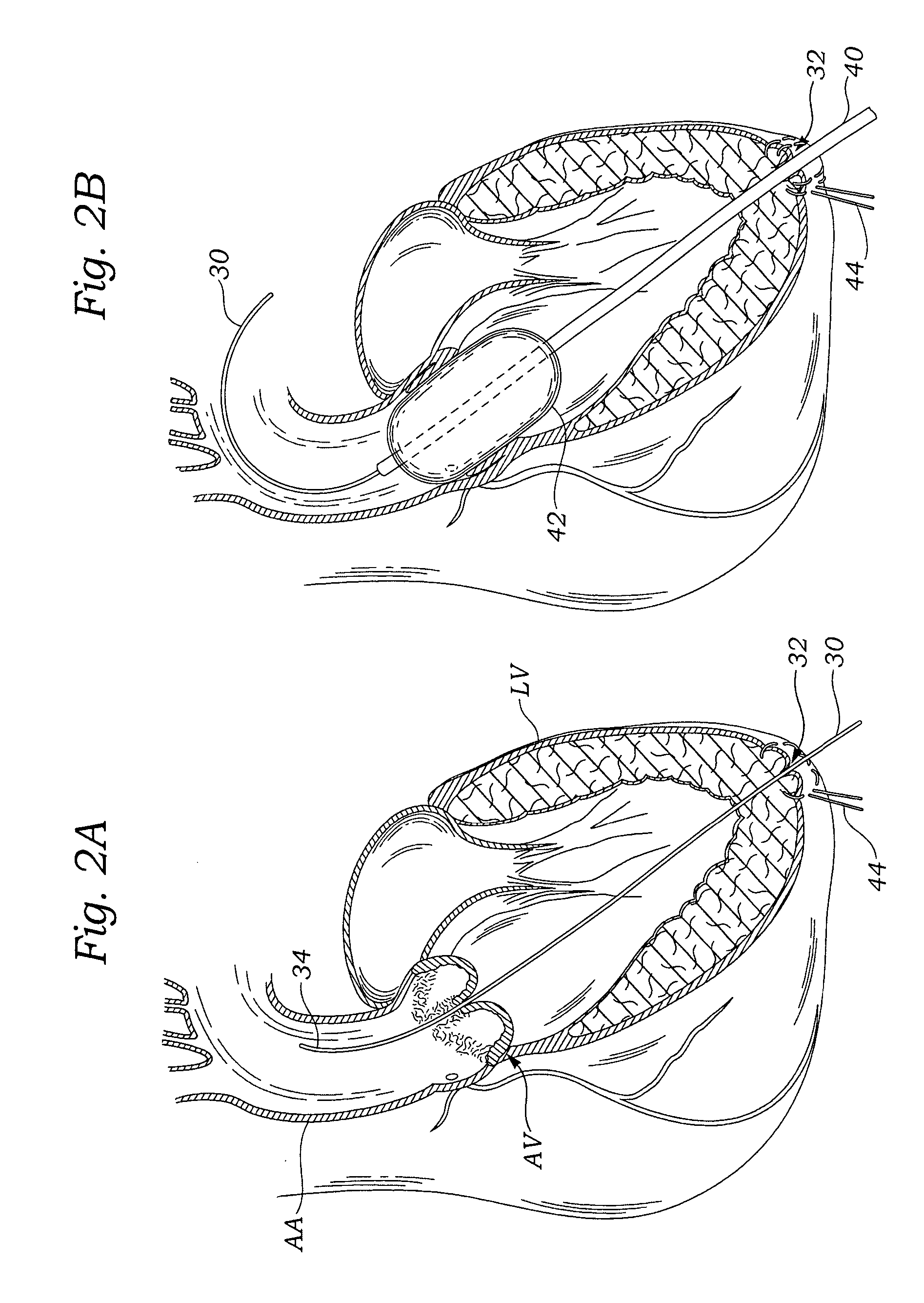
Transapical heart valve delivery system and method
ActiveUS20070112422A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic heartLeft ventricular apex
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a balloon catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve through an introducer in an antegrade fashion to the aortic annulus. The balloon catheter passes through an introducer that accesses the left ventricle through its apex and a small incision in the chest wall. The balloon catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to the distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A slider in a deflection handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment. The method includes using two concentric rings of purse-string sutures around the puncture in the left ventricular apex to maintain a good seal around instruments passed therethrough. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
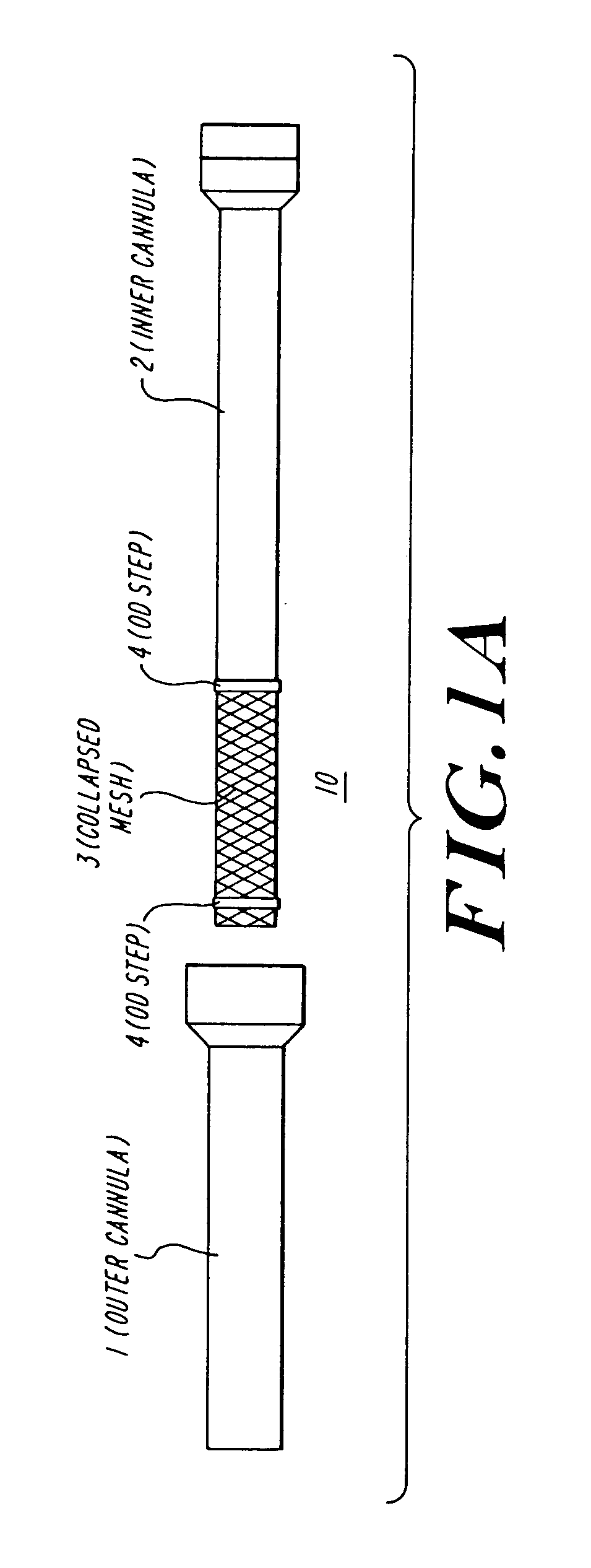
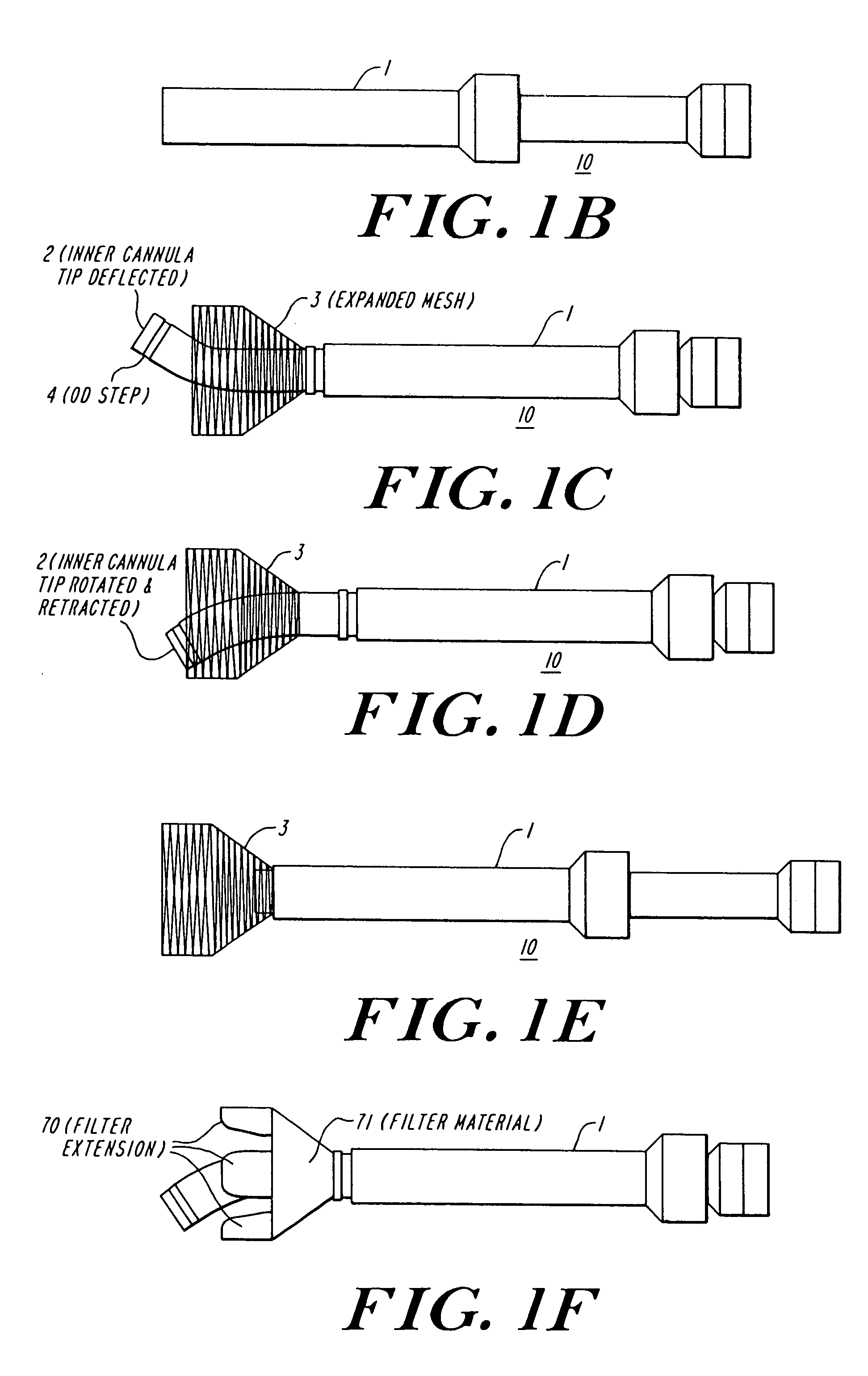
Dissecting cannula and methods of use thereof
Methods and devices described herein facilitate improved access of locations within the body by providing a variety of dissection modes on a single access device.
Owner:ATRICURE
Vessel and lumen expander attachment for use with an electromechanical driver device
A selectively coupleable and remotely actuateable surgical attachment for use with an electromechanical driver device for use in expanding occluded vessels and lumens. The attachment includes an axial rod which is coupleable to the electromechanical driver device, and which is selectively rotateable in accordance with the action of the electromechanical driver device. The rod is also threaded in opposing orientations at either end thereof. A pair of nuts are mounted to the rod, and specifically on the opposing threads. The rod and nuts are disposed within an axial track which permits the rod to turn, but constrains the rotational motion of the nuts, thereby permitting the nuts to move axially along the threadings of the rod when the rod turns. Attached to the nuts are a series of jointed spokes which are coupled to a flexible tubular shroud which surrounds the entire assembly. The jointed spokes are radially extended and retracted in accordance with the motion of the nuts in an umbrella-like fashion in accordance with the actuation of the electromechanical driver device. The radial expansion of the flexible tubular shroud provides the necessary force to expand an occluded vessel or lumen.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
Balloon-type actuator for surgical applications
An actuator for surgical applications includes an inflation fluid conduit extending from a proximal end which, when the actuator is in an operative configuration, remains outside a patient's body, to a distal end and an inflatable member coupled to the distal end of the inflation fluid conduit so that, when inflation fluid is supplied to the inflatable member via the inflation fluid conduit, the inflatable member is expanded from a collapsed configuration to an expanded configuration, wherein, when in the collapsed configuration, the inflatable member includes a fold extending substantially transverse to a longitudinal axis thereof so that, when inflation fluid is supplied thereto, the inflatable member expands substantially along the longitudinal axis.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Delivery devices
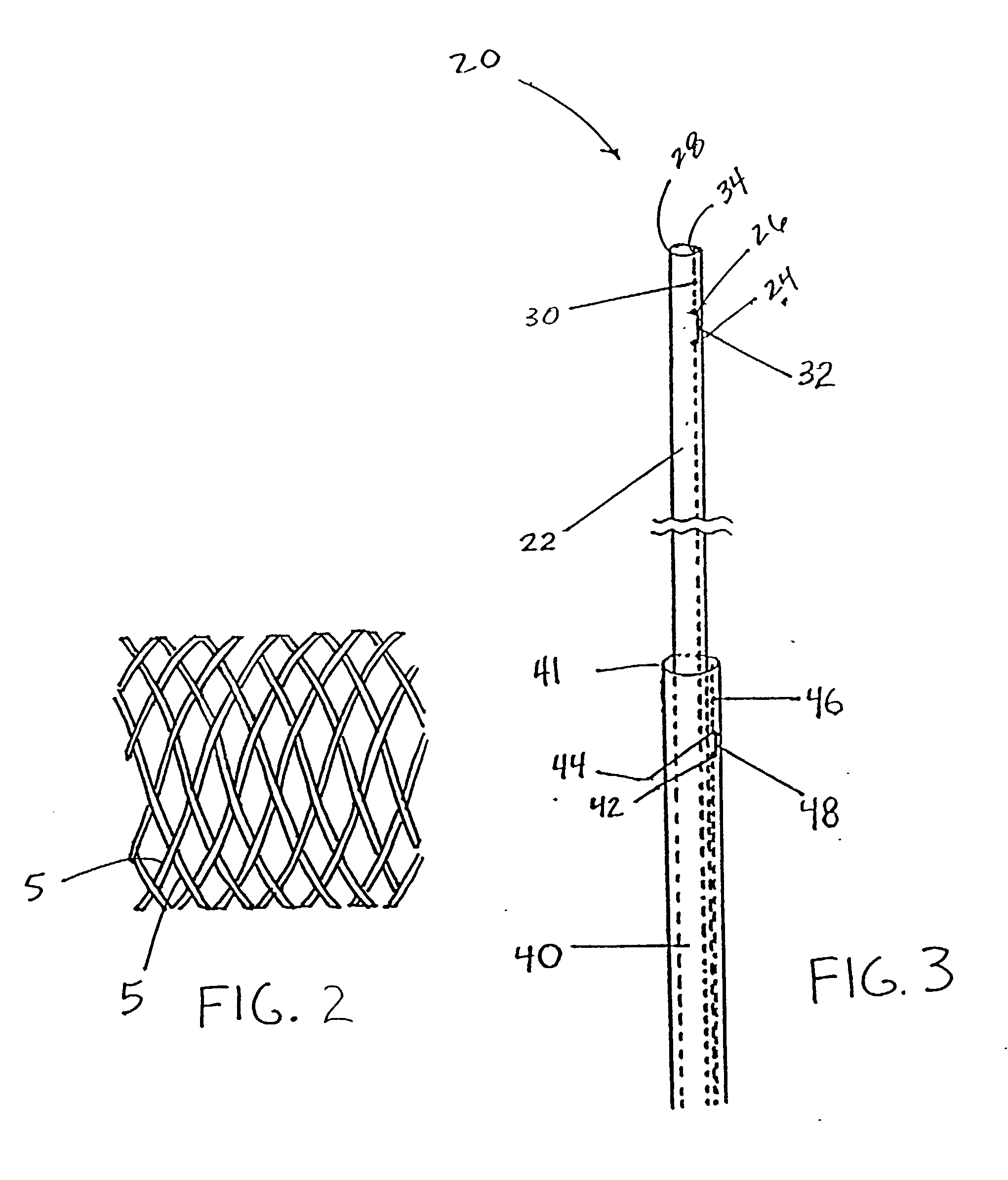
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:HYODOH HIDEKI +2
Endovascular fastener applicator
Endovascular fastener applicator for endoluminally fastening prosthetic grafts to vessels, are provided. The endovascular fastener applicator includes a delivery assembly configured for positioning within a vessel, and a control assembly mounted to a proximal end of the outer sheath for extracorporeal control of the delivery assembly. The delivery assembly includes an expandable portion disposed adjacent a distal end of an outer sheath and being expandable to support a prosthetic in contact with an inner surface of a vessel; a yoke assembly disposed within the expandable portion; an applicator head assembly pivotably mounted to the yoke assembly and movable between a loading position longitudinally aligned with the yoke assembly, and a firing position oriented substantially perpendicular to the yoke assembly; and a fastener assembly connectable to a distal end of the expandable portion, the fastener assembly retaining at least one fastener therein.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electroactive polymer actuated medical devices
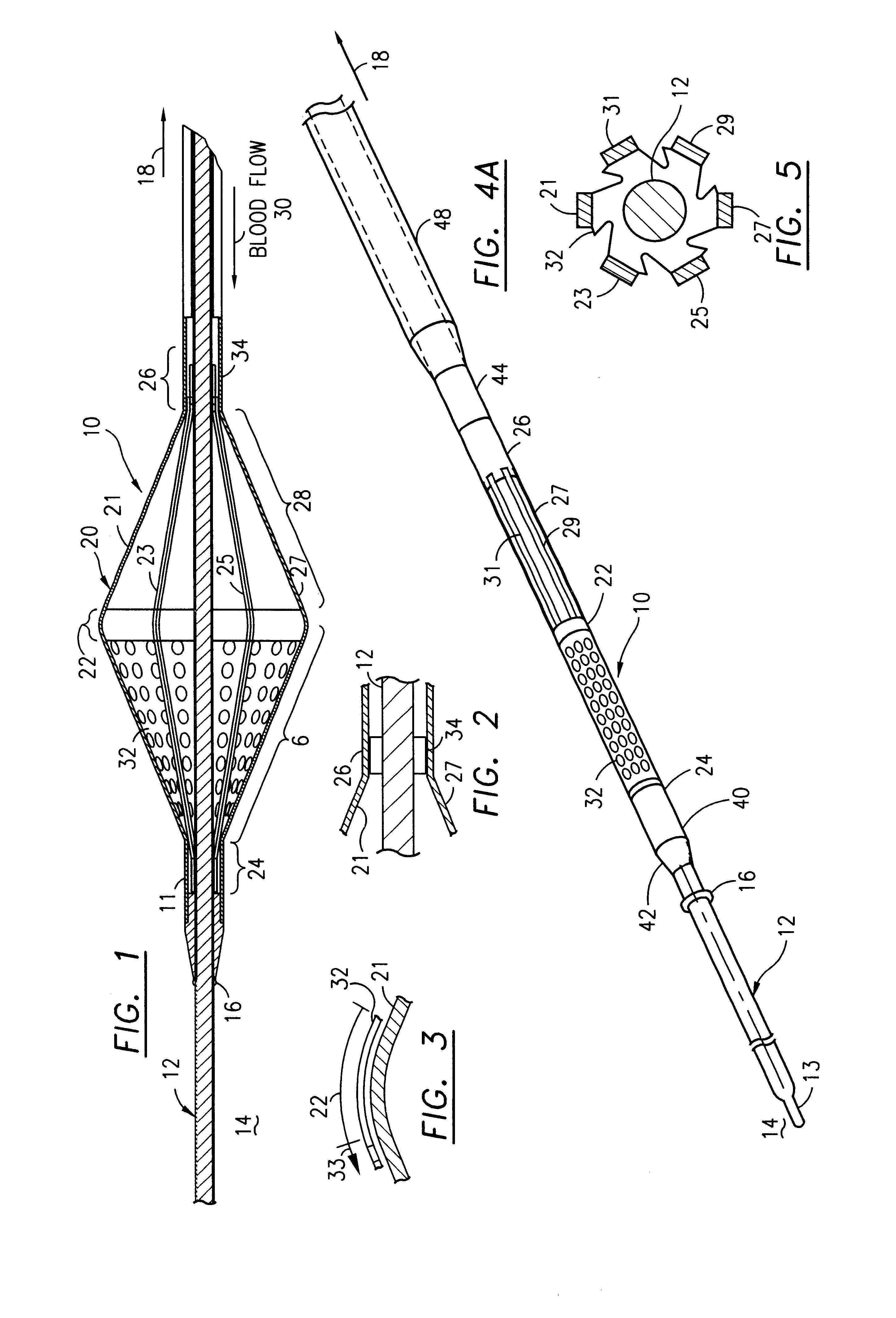
ActiveUS6969395B2High degreeLimited accessSuture equipmentsDilatorsBiomedical engineeringMedical procedure
The present invention is directed to novel apparatus for use in medical procedures relating to tubular body fluid conduits. According to a first aspect of the invention, a filter apparatus is provided for delivery over a guidewire within a tubular body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The filter apparatus comprises: (a) a filter element transformable between a collapsed state and a deployed state, wherein the filter element is adapted to filter particulate matter from fluid within the tubular body conduit while in the deployed state; and (b) a locking member comprising one or more electroactive polymer actuators which switch the locking member between (i) a locking state wherein the locking member securely engages the guidewire and (ii) a release state wherein the locking member is movable along the length of the guidewire. According to a second aspect of the invention, a connector apparatus is provided for use in making an anastomotic connection between first and second tubular fluid conduits in a patient. The connector apparatus comprises: (a) a locking member, which further comprises one or more electroactive polymer actuators that switch the locking member between a locking state and a release state; and (b) a connector body that is configured to permit flow of bodily fluid between the first and second tubular fluid conduits. The connector body has a first portion configured for insertion into an axial end of the first tubular fluid conduit and a second portion configured for insertion through a sidewall of the second tubular fluid conduit. The second portion of the connector body is further configured to securely engage the locking member when the locking member is in the locking state.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Apparatus for imparting physician-determined shapes to implantable tubular devices
A tubular sleeve is provided for enabling a physician to impart a preselected shape in an implantable tubular device, such as a cardiac lead, a catheter, or some other tubular structure. The sleeve may be deformed by the surgeon before or at the time of implantation to customize the shape of the tubular device to the particular anatomical structures to be encountered by the device. To retain the deformation imparted by the physician, the sleeve may be composed of a heat-sensitive shape-memory material or an elastomeric material provided with a plastically deformable rib.
Owner:INTERMEDICS
Heart valve delivery system
ActiveUS20070005131A1Easy to navigateIncrease thrustBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthetic heartBalloon catheter
A delivery system for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to a native valve site within the human vasculature. The prosthetic valve is disposed on a balloon at the end of a balloon catheter. The balloon catheter passes through a delivery sleeve assembly and handle. A pull wire travels from the handle to a distal end of the delivery sleeve assembly. Actuation of the handle pulls on the pull wire, which causes openings in a slotted tube of the delivery sleeve assembly to close, thus causing the delivery sleeve assembly to bend. A stretchable cover is placed over the slotted tube for biasing the steerable catheter toward a straight position. Once advanced to the native valve site, the prosthetic valve is deployed by inflating the balloon.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods for creating woven devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Indwelling fecal diverting device
ActiveUS8398669B2Improve securityEasy to installBalloon catheterAnti-incontinence devicesFecesSurgery
Disclosed is an indwelling fecal diverting device. The device comprises an elongate tube formed, at an upper end thereof, with a tubular body part; a pair of fixing balloons attached up and down to an outer surface of the tubular body part such that a clamping portion is defined between the fixing balloons; and a tube opening and closing balloon attached to an inner surface of the tubular body part. An injection passage is defined in the tube so that a remedial liquid can be injected through the injection passage to the outside of the tube to medically treat an anastomosed portion of an intestinal tract of a patient. The indwelling fecal diverting device is fitted into the intestinal tract of the patient, air is supplied into the fixing balloons to inflate them, and the intestinal tract is clamped around the clamping portion using a clamping band.
Owner:YUSHIN MEDICAL +1
System for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS7695493B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Systems for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Method and system for cardiac valve delivery
The invention provides methods and systems for introducing a delivery device in the heart at or near the apex of the heart, wherein the delivery device includes a prosthesis, advancing the prosthesis to the target site, and disengaging the prosthesis from the delivery device at the target site for implantation. Specifically, the present invention provides valve replacement systems for delivering a replacement heart valve to a target site in or near a heart. The valve replacement system comprises a trocar or other suitable device to penetrate the heart at or near the apex of the heart, a delivery member that is movably disposed within the trocar, and a replacement cardiac valve disposed on the delivery member. The delivery member may further comprise mechanical or inflatable expanding members to facilitate implantation of the prosthetic valve at the target site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
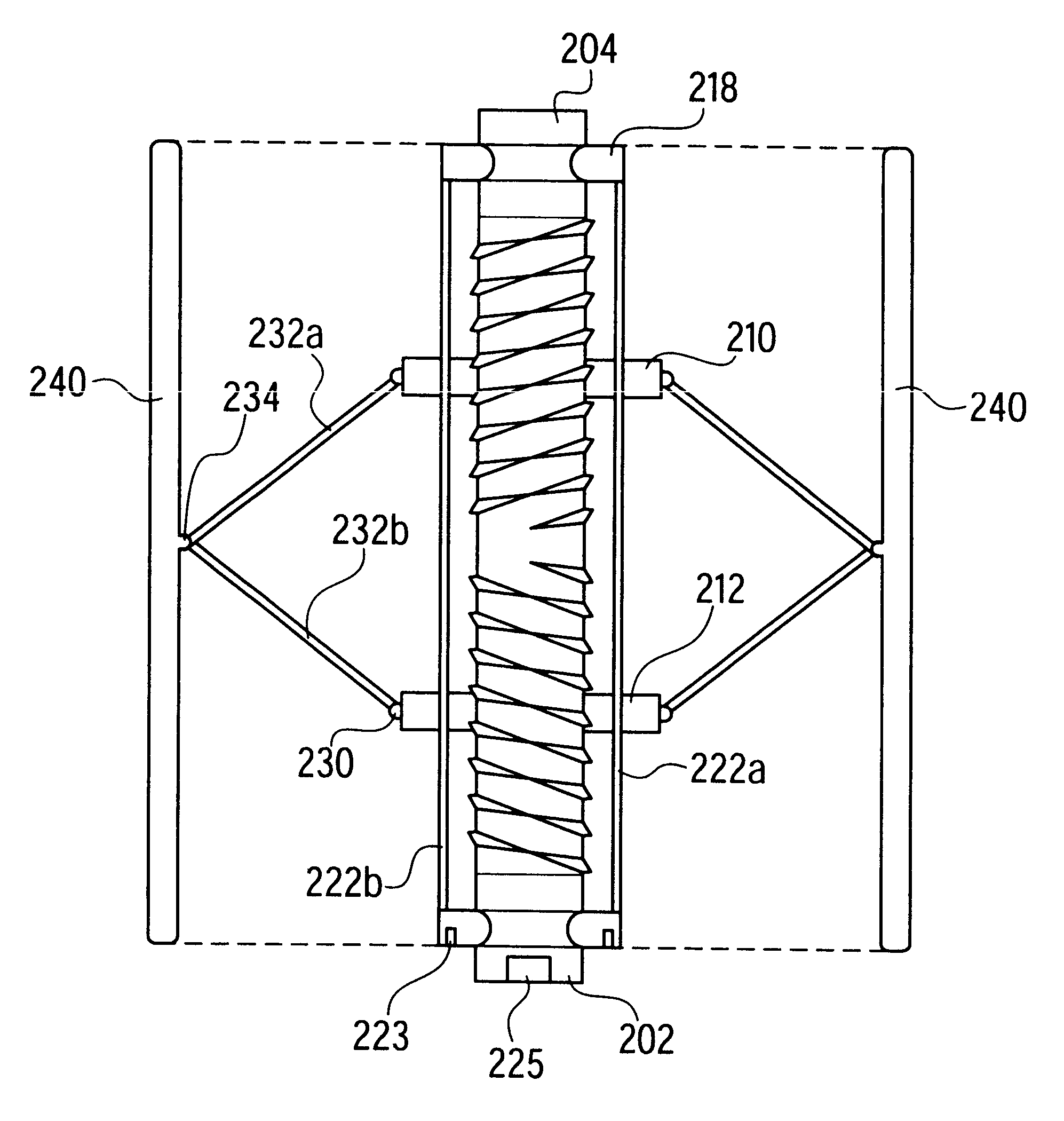
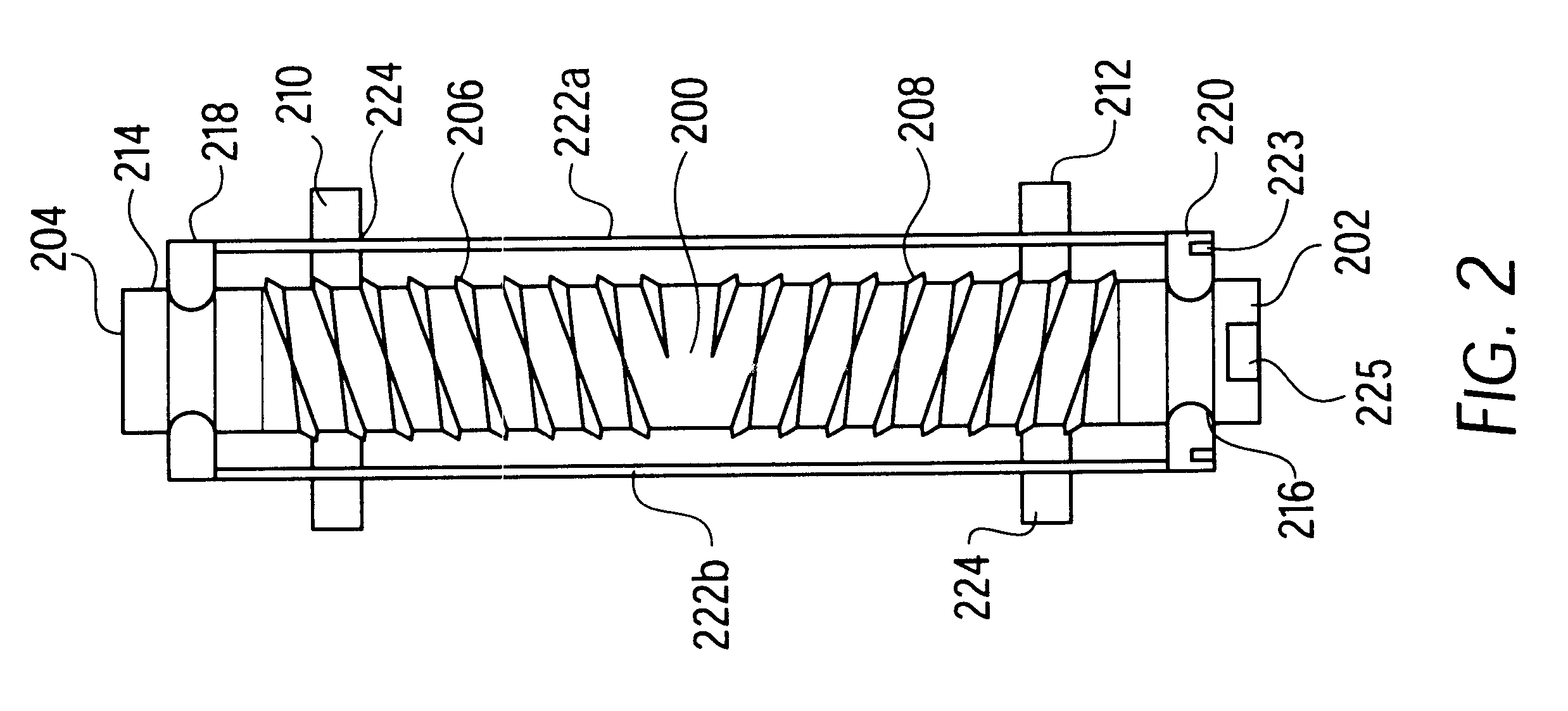
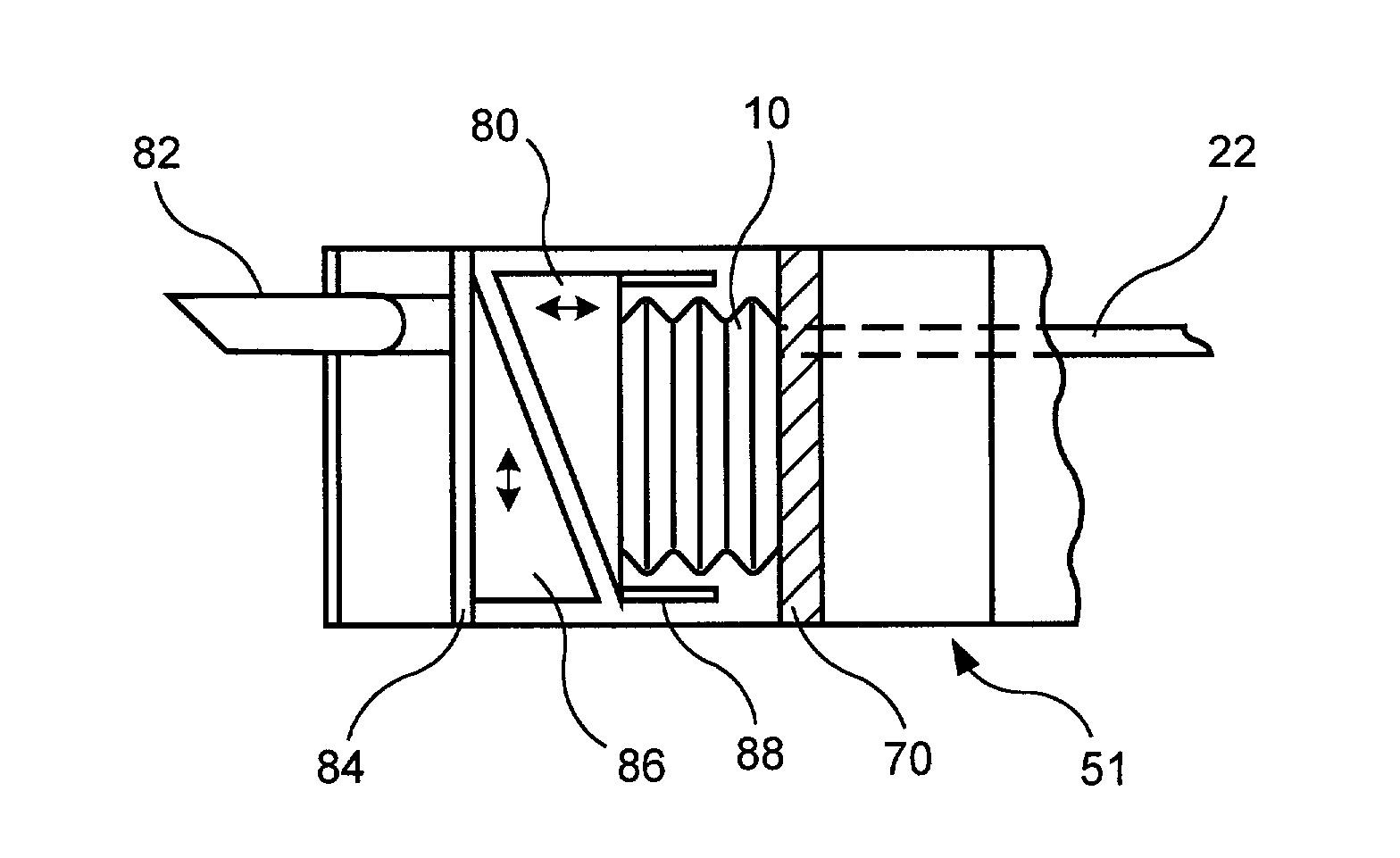
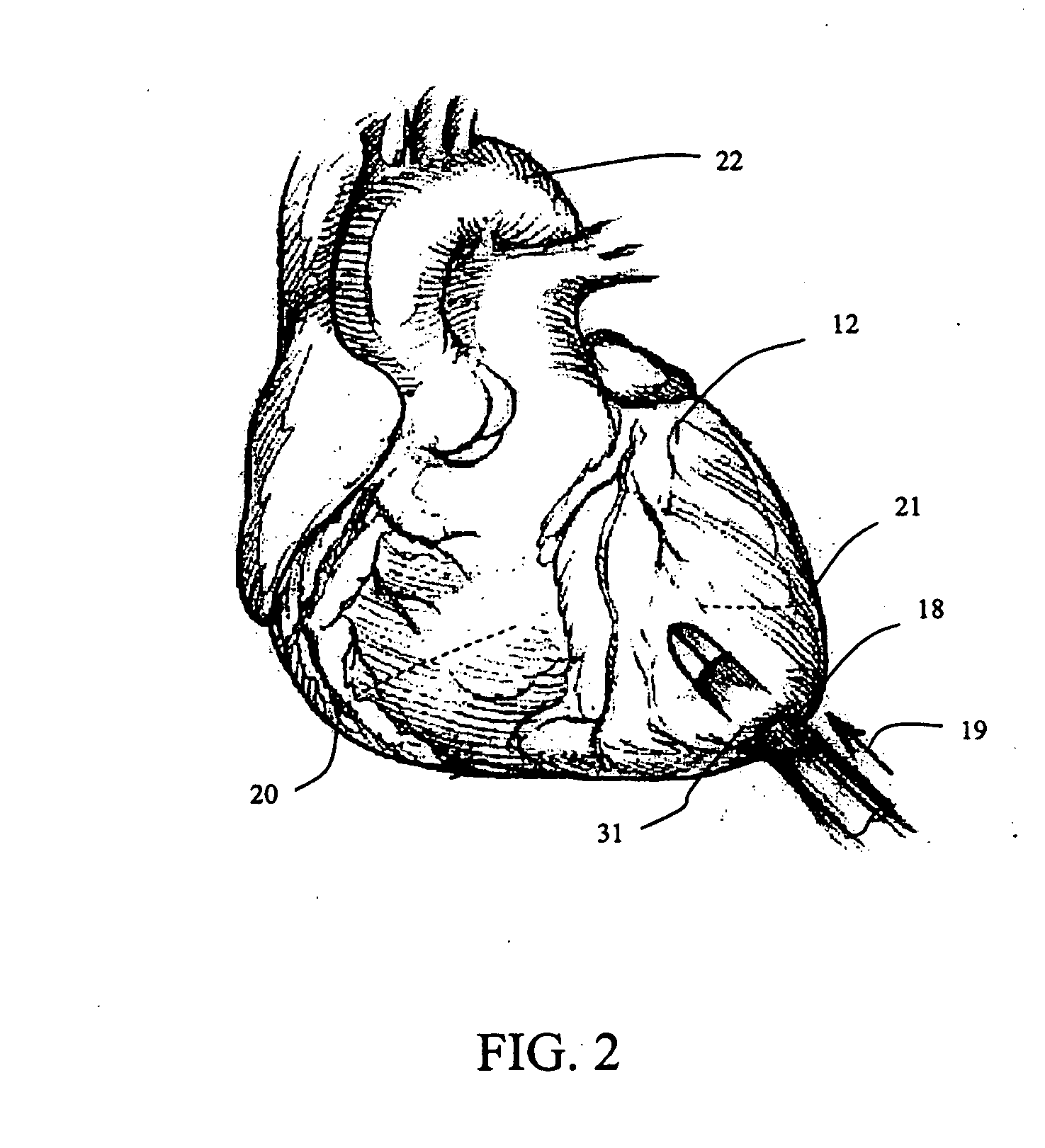
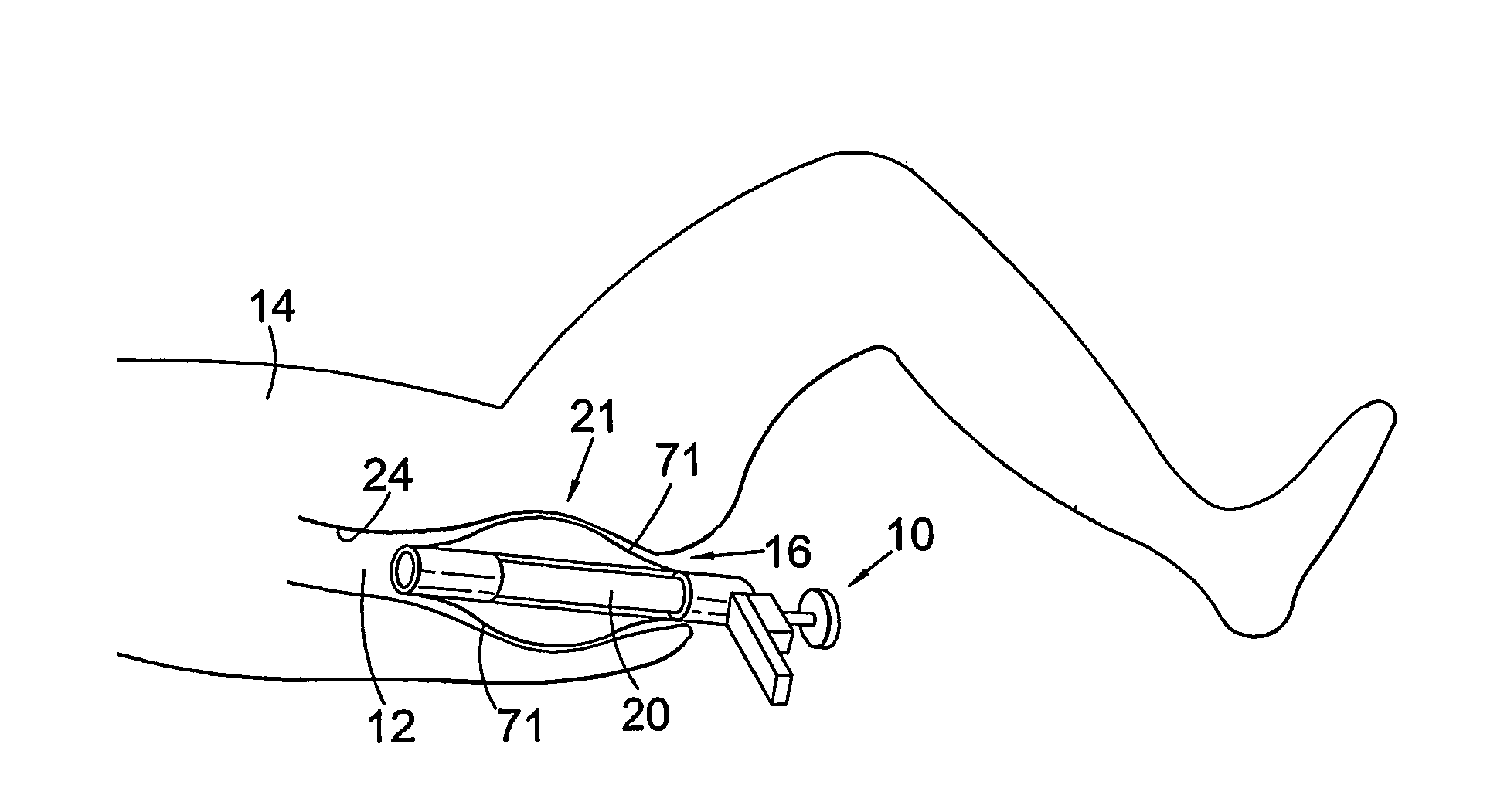
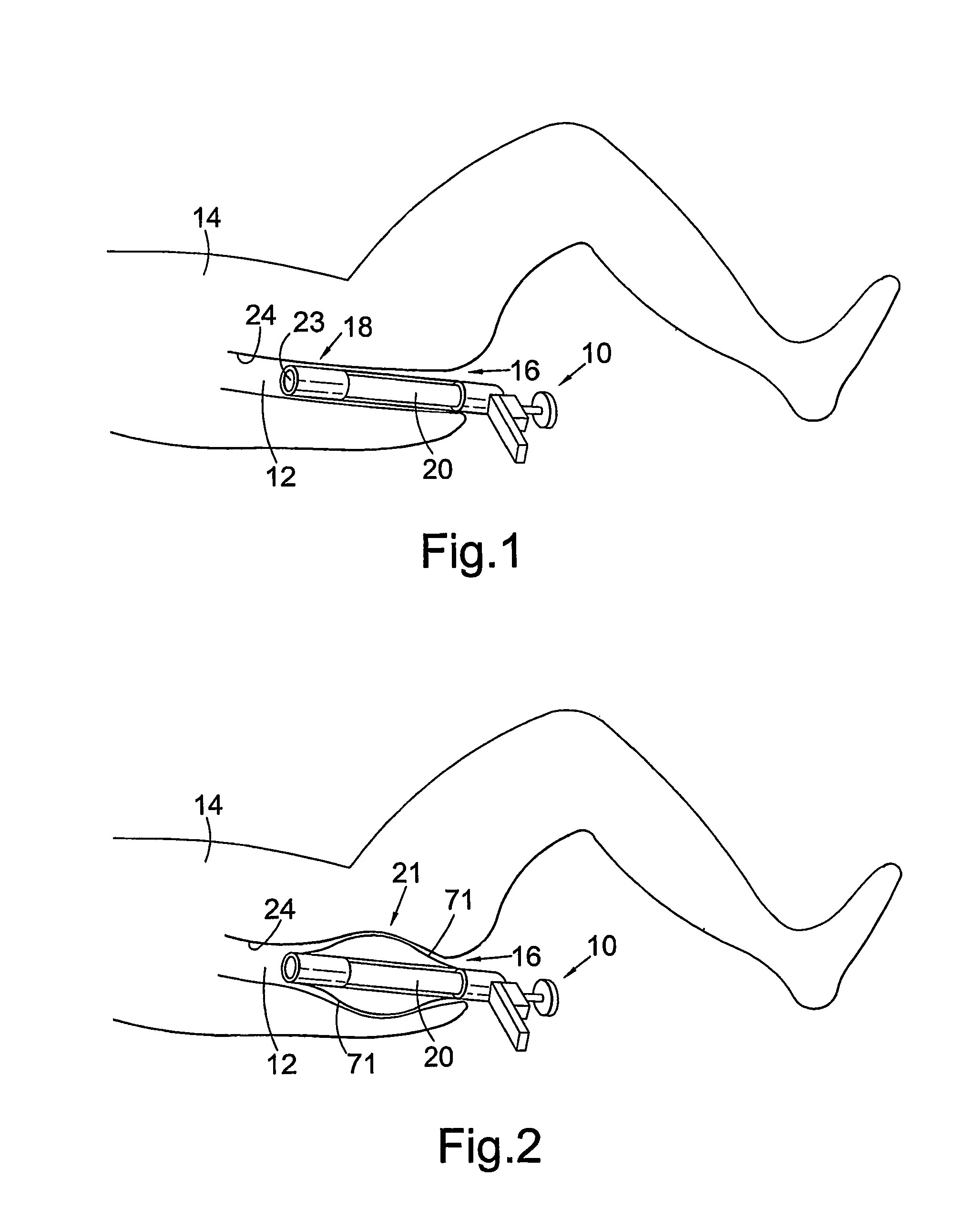
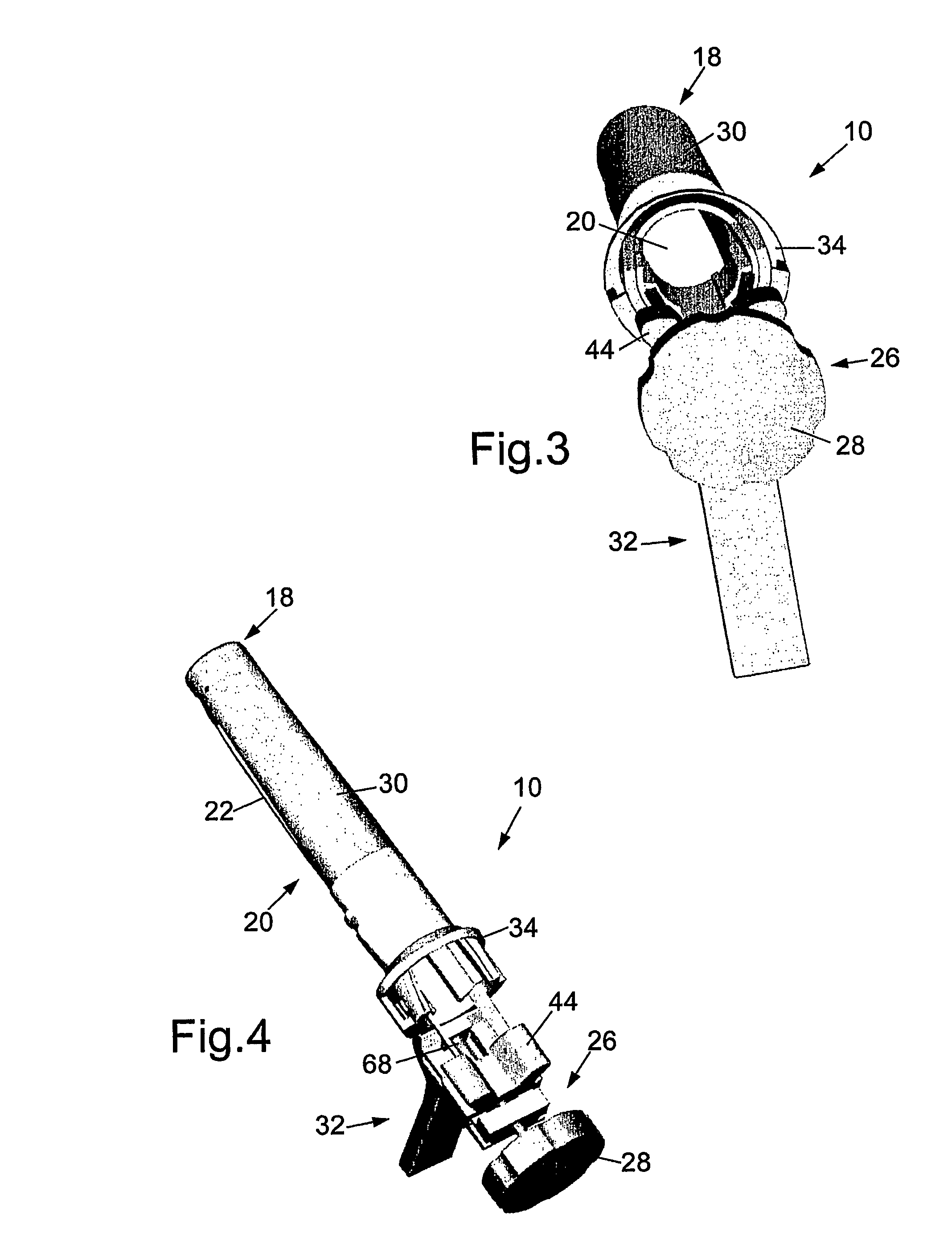
Rectal expander
There is disclosed medical apparatus of the type for use in surgery such as transanal endoscopic microsurgery, as well as methods of providing access to, inspecting and enabling surgery within a body passage. In one embodiment of the invention, medical apparatus in the form of a rectal expander (10) is disclosed, the expander (10) being adapted for location at least partly within a body passage such as the rectum (12) of a patient (14), the expander (10) having a leading end (18) and an access area in the form of an opening (20) for access from the expander (10) into the rectum (12), at least part of the opening (20) being spaced from the leading end (18), and the expander (10) being controllably movable between collapse and expansion positions, for expanding the rectum (12).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DUNDEE
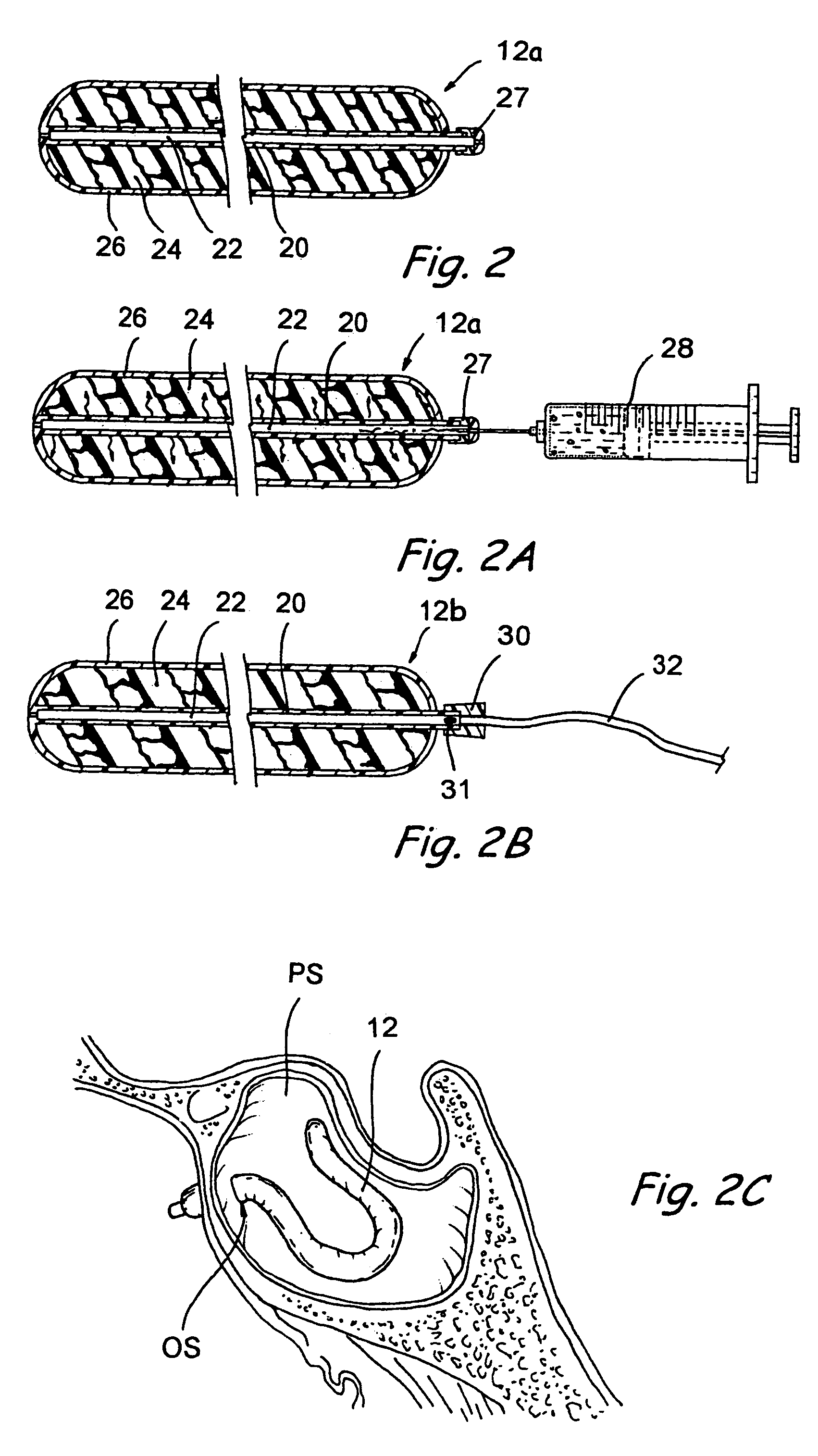
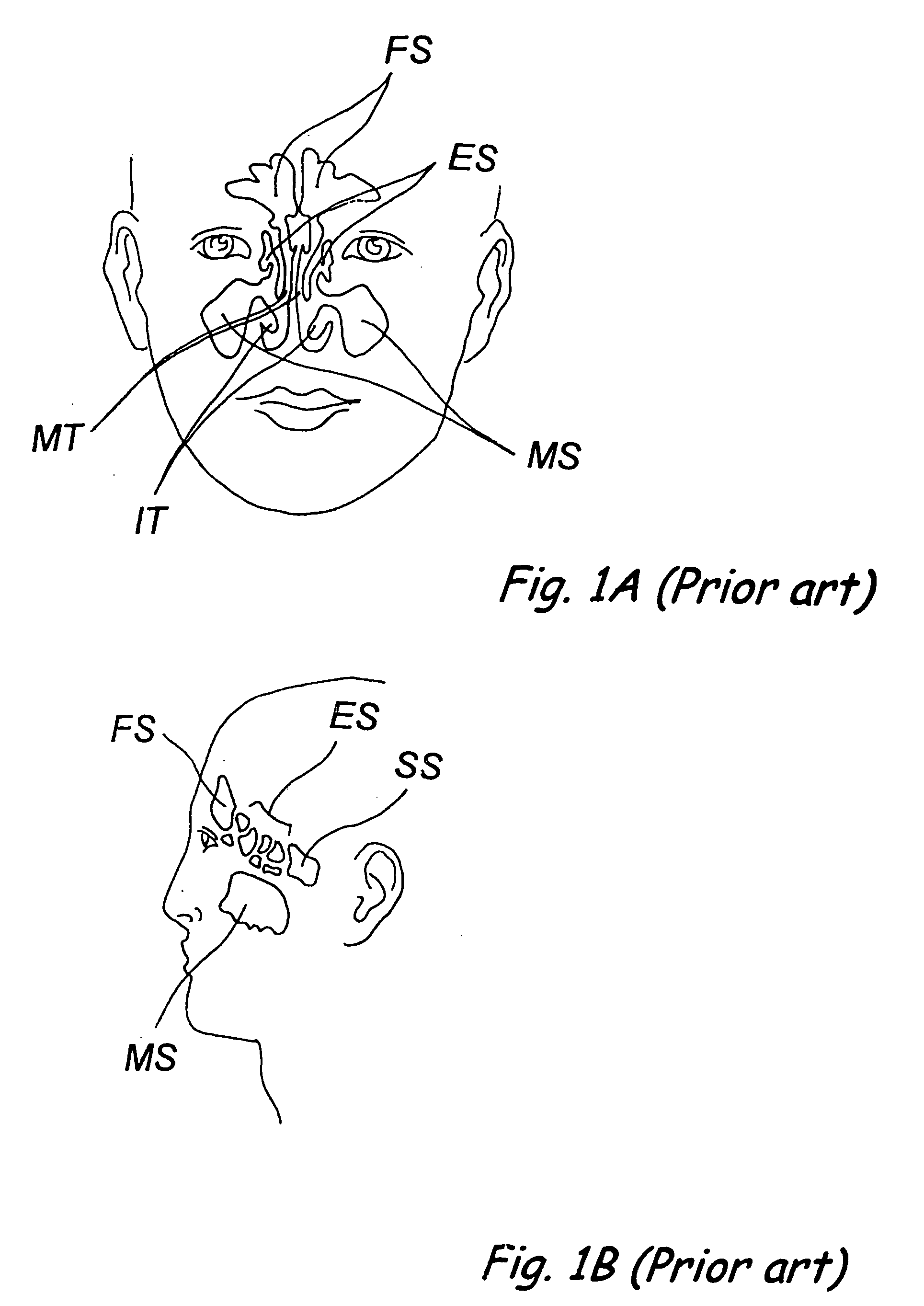
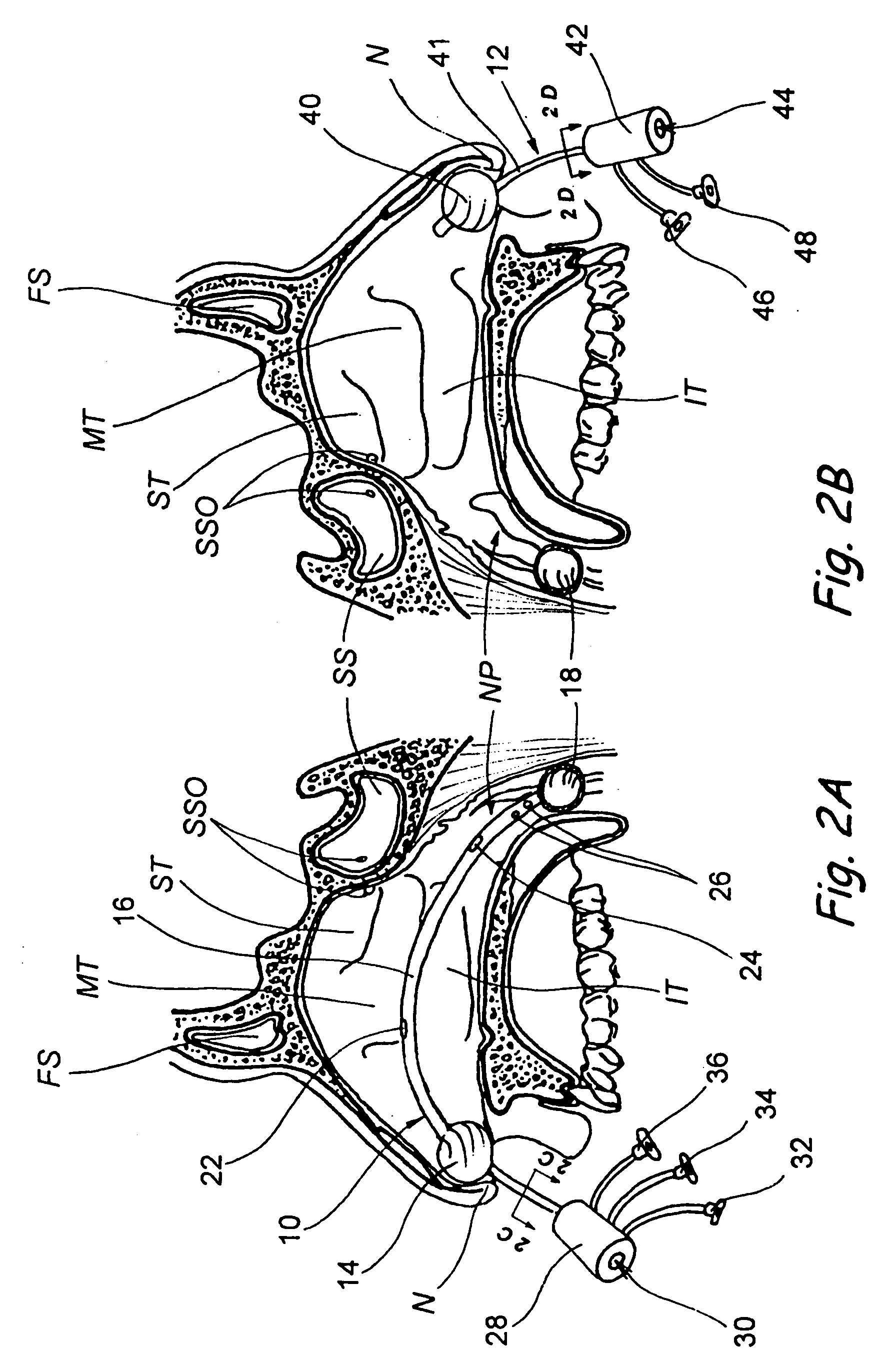
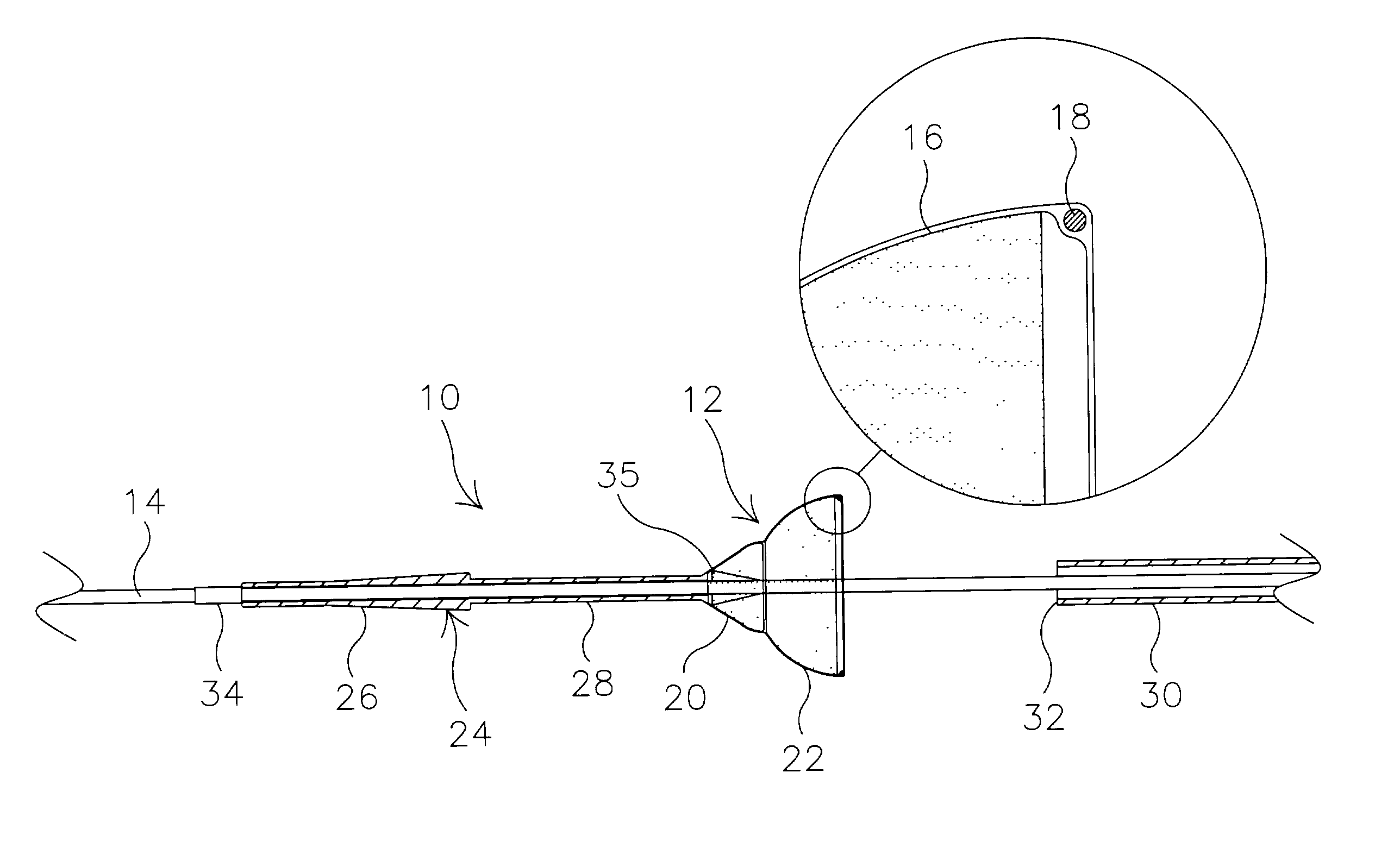
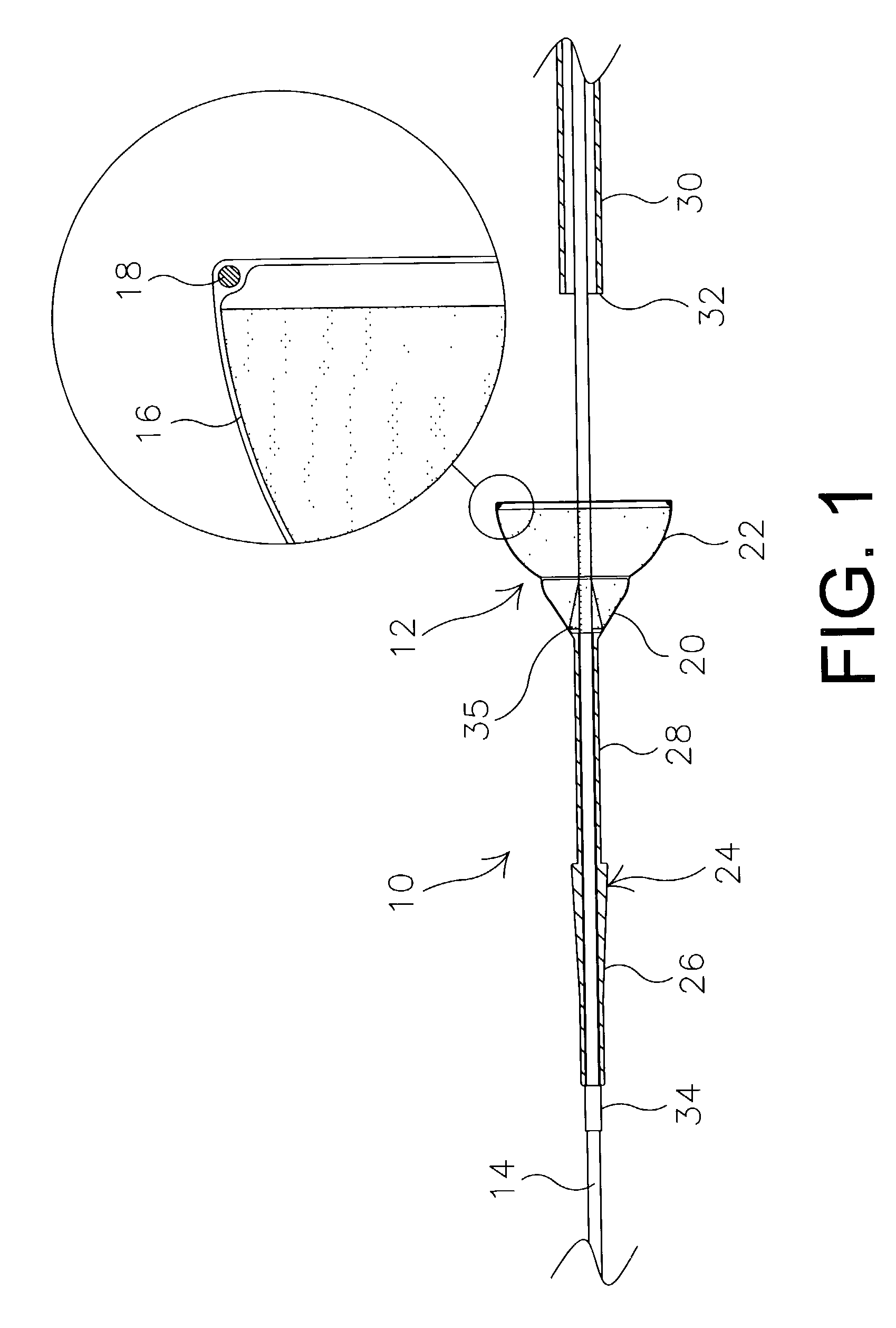
Apparatus and methods for dilating and modifying ostia of paranasal sinuses and other intranasal or paranasal structures
Sinusitis and other disorders of the ear, nose and throat are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches with flexible or rigid instruments. Various methods and devices are used for remodeling or changing the shape, size or configuration of a sinus ostium or duct or other anatomical structure in the ear, nose or throat; implanting a device, cells or tissues; removing matter from the ear, nose or throat; delivering diagnostic or therapeutic substances or performing other diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Introducing devices (e.g., guide catheters, tubes, guidewires, elongate probes, other elongate members) may be used to facilitate insertion of working devices (e.g. catheters e.g. balloon catheters, guidewires, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, devices for implanting elements like stents, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for delivering diagnostic or therapeutic agents, substance delivery implants, scopes etc.) into the paranasal sinuses or other structures in the ear, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Devices, systems and methods for diagnosing and treating sinusitus and other disorders of the ears, nose and/or throat
Sinusitis, enlarged nasal turbinates, tumors, infections, hearing disorders, allergic conditions, facial fractures and other disorders of the ear, nose and throat are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches and, in many cases, flexible catheters as opposed to instruments having rigid shafts. Various diagnostic procedures and devices are used to perform imaging studies, mucus flow studies, air / gas flow studies, anatomic dimension studies, endoscopic studies and transillumination studies. Access and occluder devices may be used to establish fluid tight seals in the anterior or posterior nasal cavities / nasopharynx and to facilitate insertion of working devices (e.g., scopes, guidewires, catheters, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for injecting diagnostic or therapeutic agents, devices for implanting devices such as stents, substance eluting devices, substance delivery implants, etc.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Method of making an embolic filter
Embolic protection filters and methods of making and using such devices are disclosed. An illustrative method of making a device for filtering embolic debris from a body may include the steps of molding a filter assembly that includes a distal tip and a filter portion, forming a plurality of apertures within the filter portion, and coupling a support member to the filter assembly that is adapted to shift the filter portion between a collapsed configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Paravalvular leak detection, sealing, and prevention
The present invention provides a series of new percutaneous concepts of paravalvular repairs including identifying the leak location, several repair techniques and finally built-in means for leak prevention, built on percutaneous valves. A catheter-delivered device locates cavities occurring between a prosthetic valve and the wall of the body vessel where the valve is implanted, the cavities producing paravalvular leaks during diastole, the device comprising at least one of a plurality of flexible wires, the wire having attached to it a balloon, wherein the balloon is pulled by the leak through the cavity and wherein the wire then serves to mark the cavity location.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
Tissue electroperforation for enhanced drug delivery
The present invention relates to a method and a device for transporting a molecule through a mammalian barrier membrane of at least one layer of cells comprising the steps of: ablating the membrane with an electric current from a treatment electrode; and utilizing a driving force to move the molecule through the perforated membrane.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Filter for embolic material mounted on expandable frame
The filter device captures embolic material in a blood vessel and is placed in the blood vessel via a guide wire. The guide wire has a proximal end, a distal end and a stop near its distal end. The filter device includes an expandable frame of frame struts having a closed, radially compact form and an open, radially expanded form. The frame, in the radially expanded form, has frame struts forming a pair of facing frustoconical frame structures. Filter material is attached to one of the pair of frustoconical frame structures. In one embodiment, the filter material is a perforated membrane. The guide wire extends through the expandable frame and the expandable frame is freely movable over the guide wire (likewise, the guide wire is freely movable within the frame), both rotatably and longitudinally, except distally beyond the stop near the distal end of the guide wire. This mobility of the guide wire with respect to the expandable frame enables to guide wire to be guided by the operator through the blood vessel.
Owner:SCION CARDIO VASCULAR
Expandable guide sheath and apparatus with distal protection and methods for use
Apparatus and methods provide distal protection while accessing blood vessels within a patient's vasculature. A flexible sheath and distal protection element, e.g., a balloon or filter, are carried by a stiffening member. The sheath is lubricious and has a relatively thin wall, thereby providing a collapsible / expandable guide for delivering fluids and / or instruments. The sheath is advanced into a blood vessel in a contracted condition, expanded to an enlarged condition to define a lumen, and the distal protection element is deployed within the vessel beyond the sheath. Fluids and / or instruments are introduced into the vessel via the sheath lumen, the distal protection element retaining the fluids and / or capturing emboli released by the instruments. Upon completing the procedure, the sheath, distal protection element, and stiffening member are removed from the vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
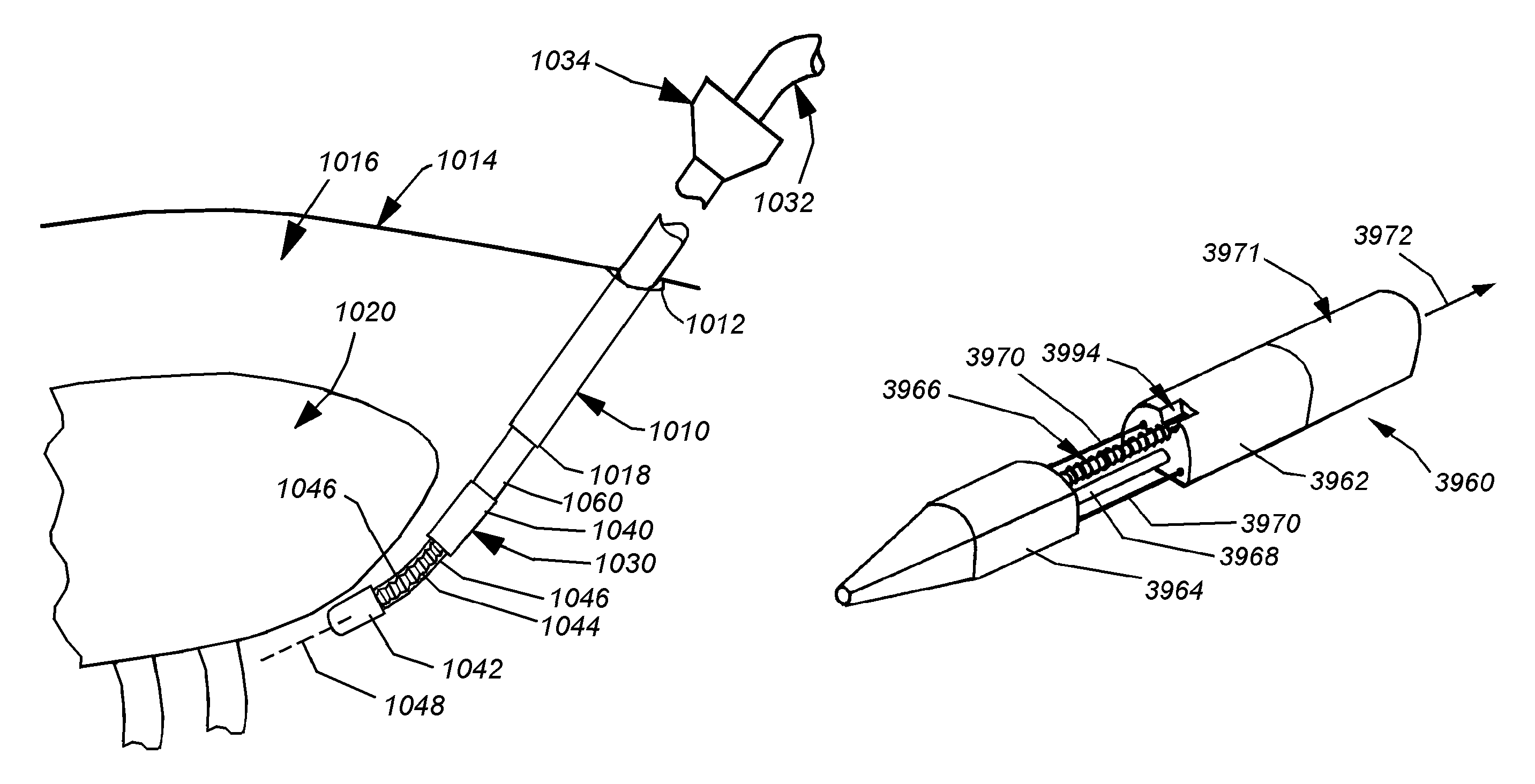
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose and throat
InactiveUS20060063973A1Improve visualizationEasy accessBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesAnatomical structuresDisease
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, including methods and apparatus for dilating ostia, passageways and other anatomical structures, endoscopic methods and apparatus for endoscopic visualization of structures within the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, navigation devices for use in conjunction with image guidance or navigation system and hand held devices having pistol type grips and other handpieces.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Mechanically-guided transoral bougie
The present invention is referred to a mechanically-guided transoral bougie, comprising an elongated body with an external end and a distal end; said external end includes a guiding mechanism mechanically connected to said distal end to allow the surgeon to move said distal end in any direction once the bougie is inserted into the stomach. Said guiding mechanism includes a manually operated guiding control.
Owner:JACOBS MOISES
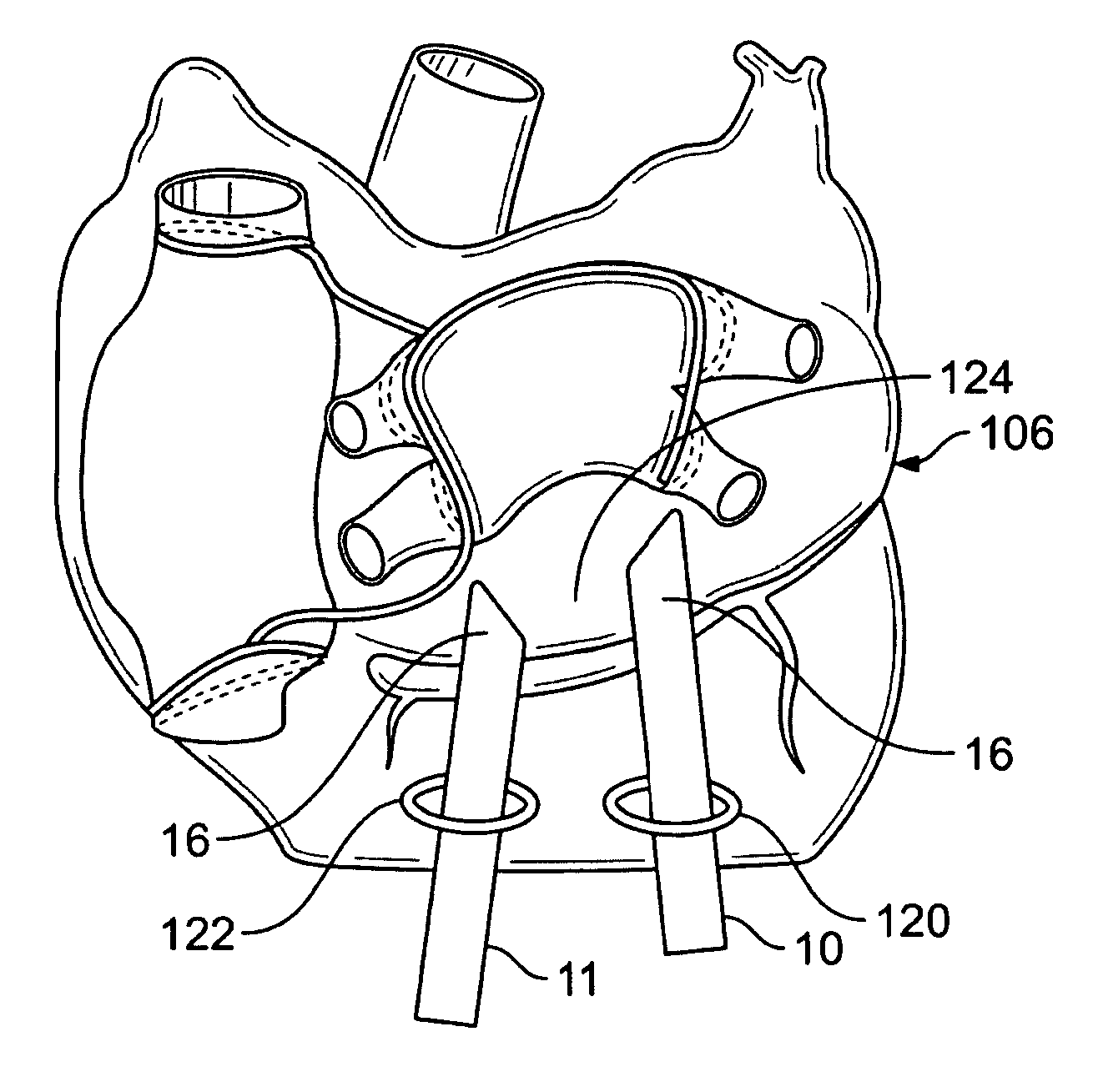
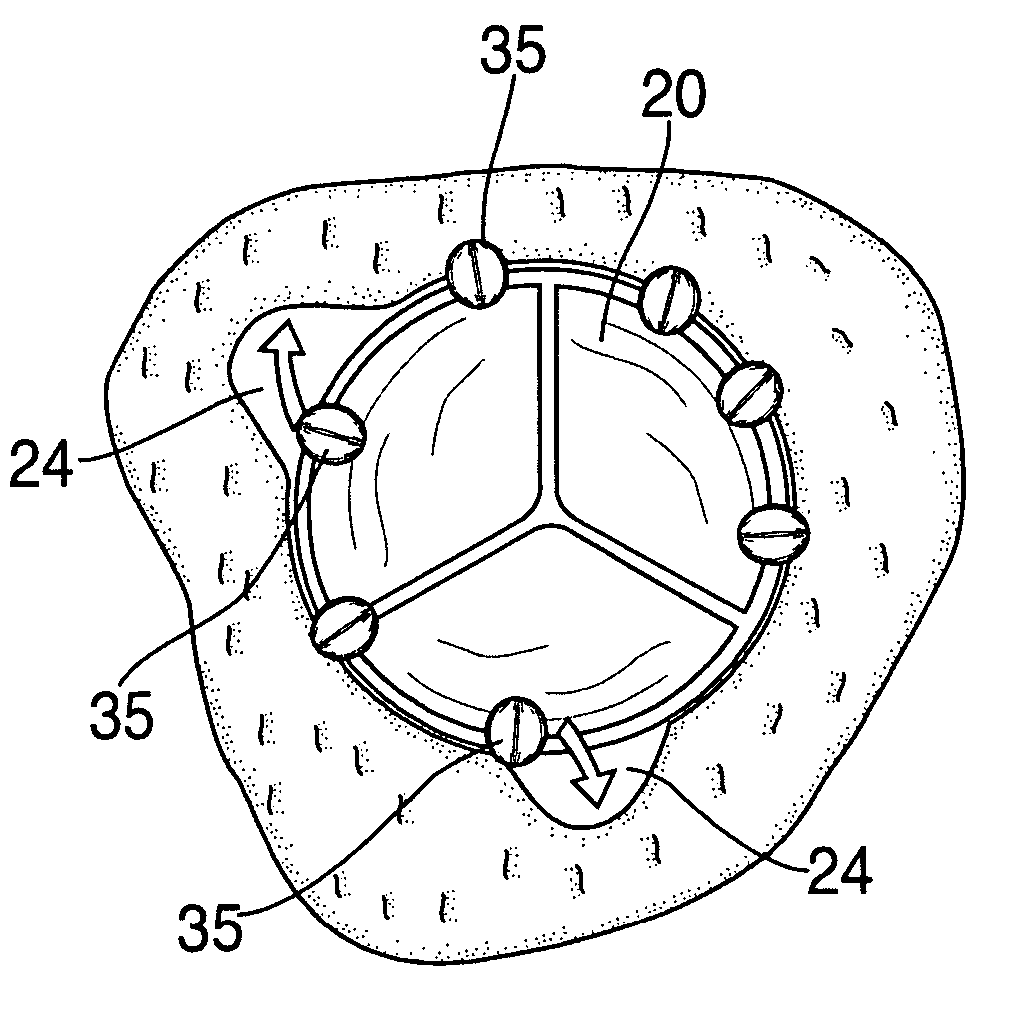
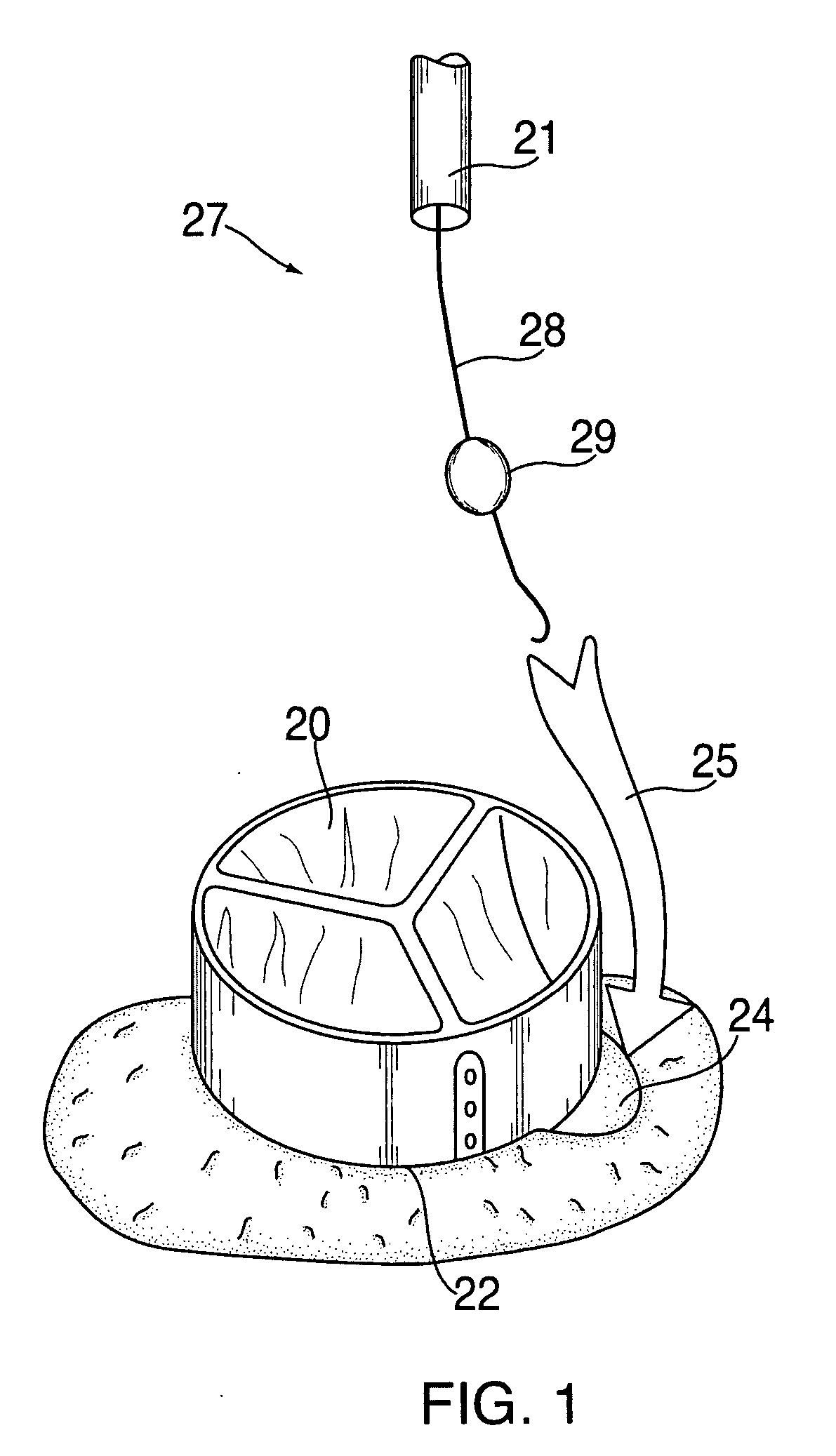
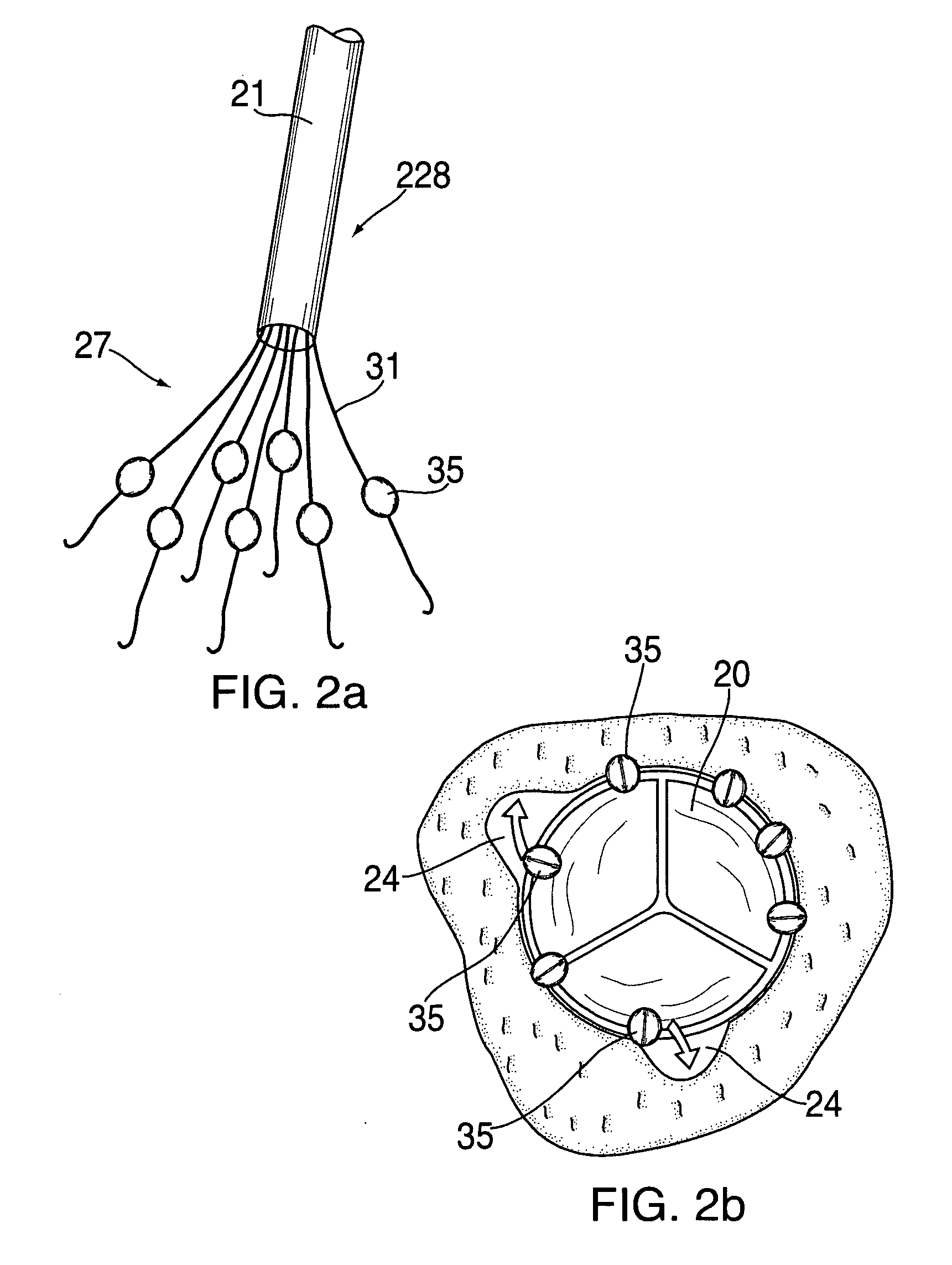
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves.The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta.The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow.The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com