Patents
Literature
205 results about "Femoral artery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
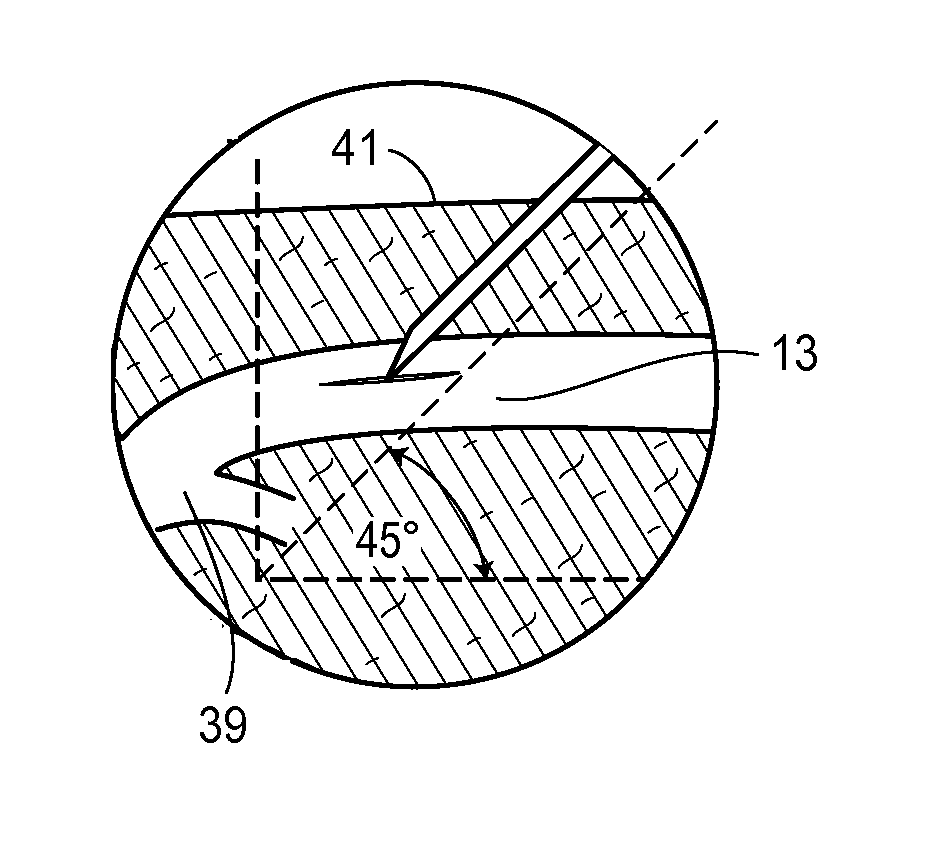
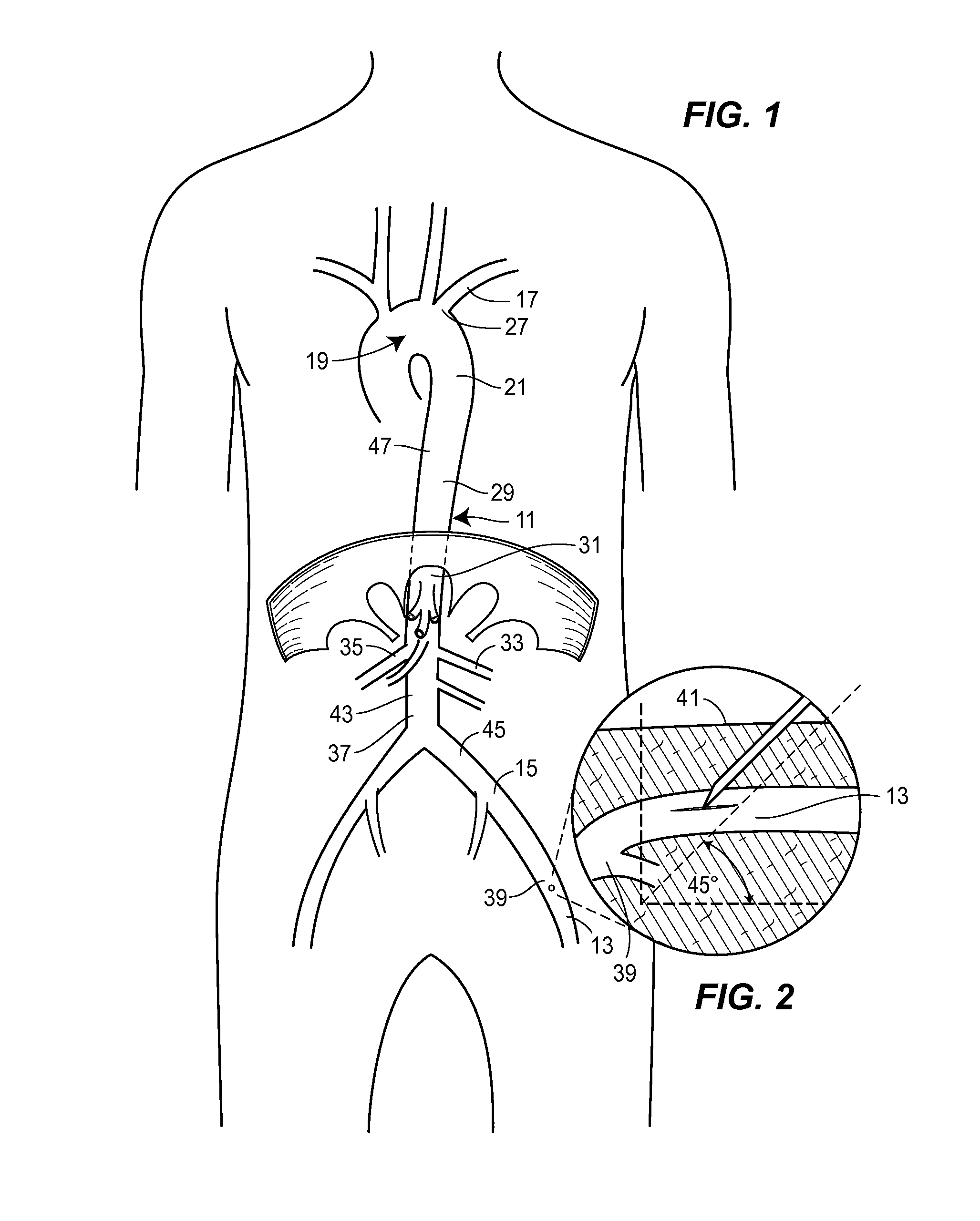
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. It enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery.
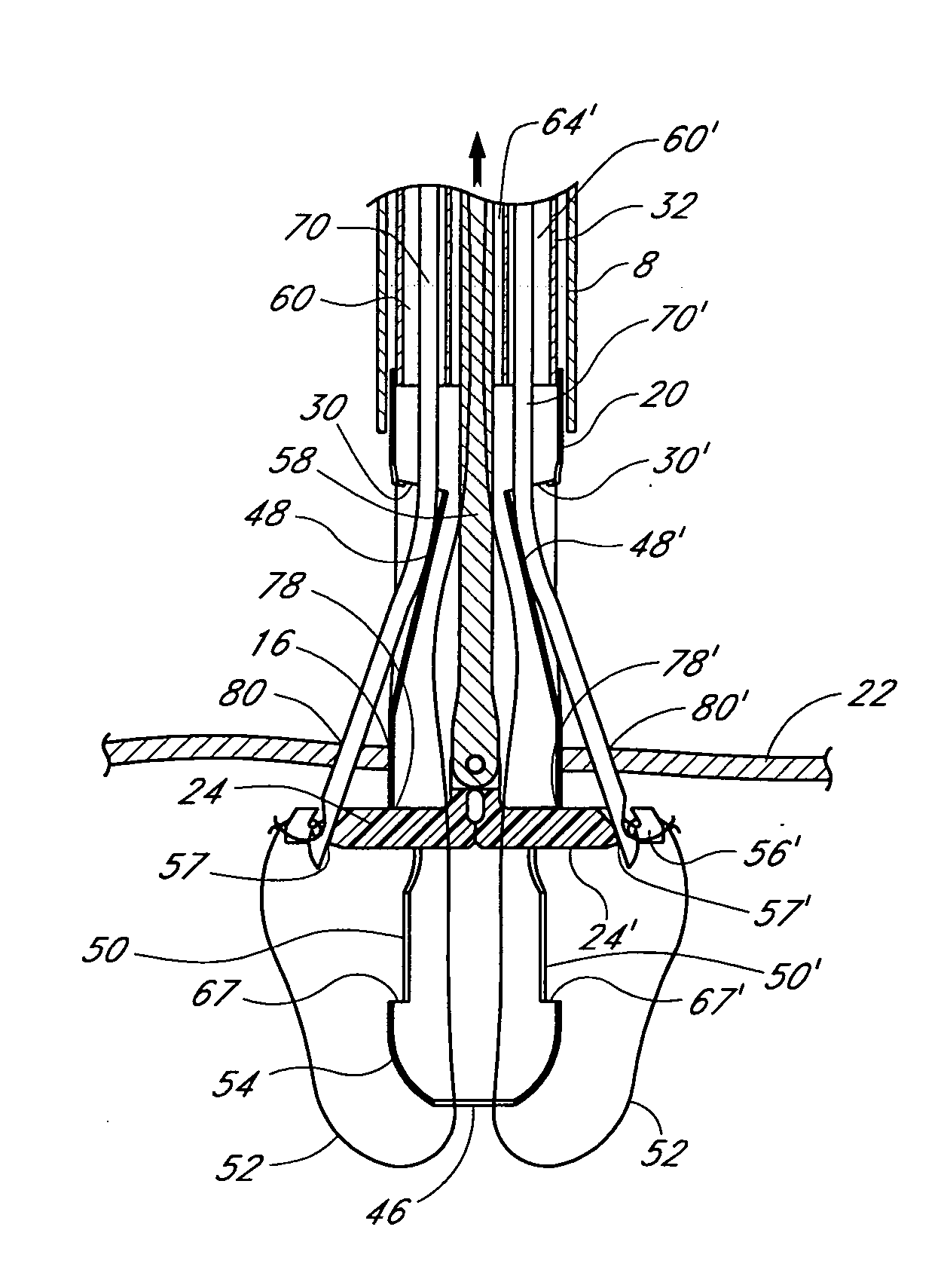
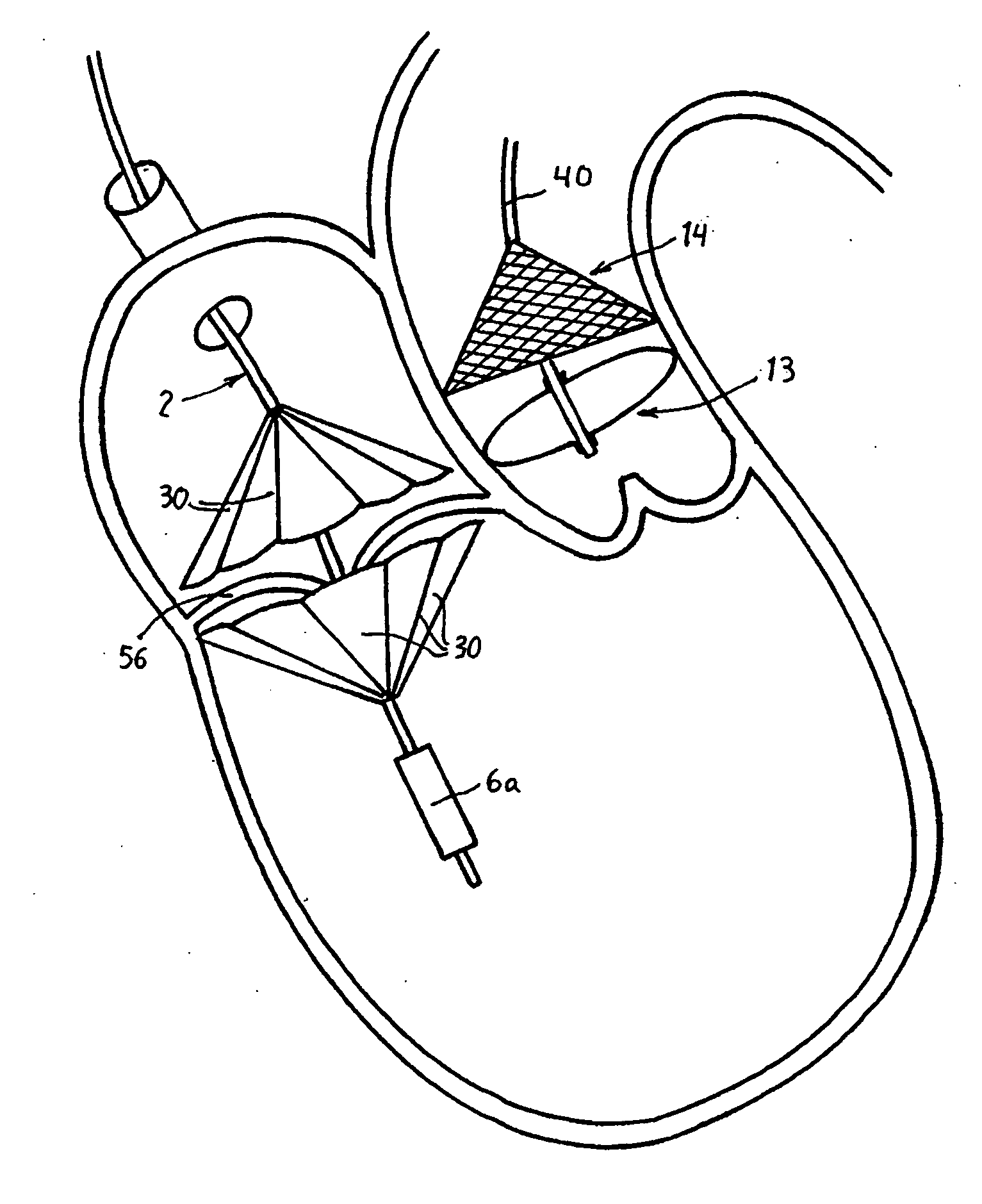
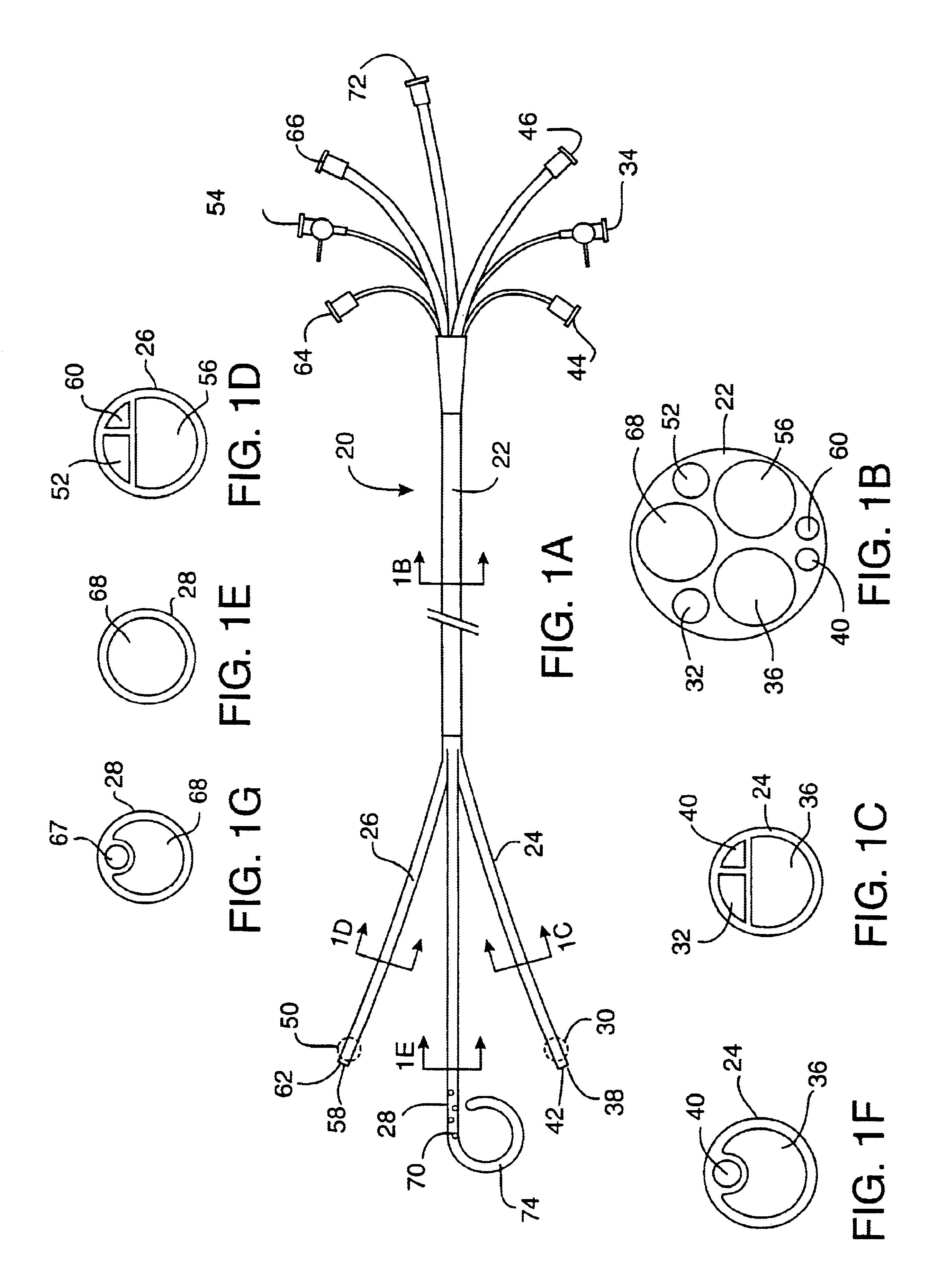
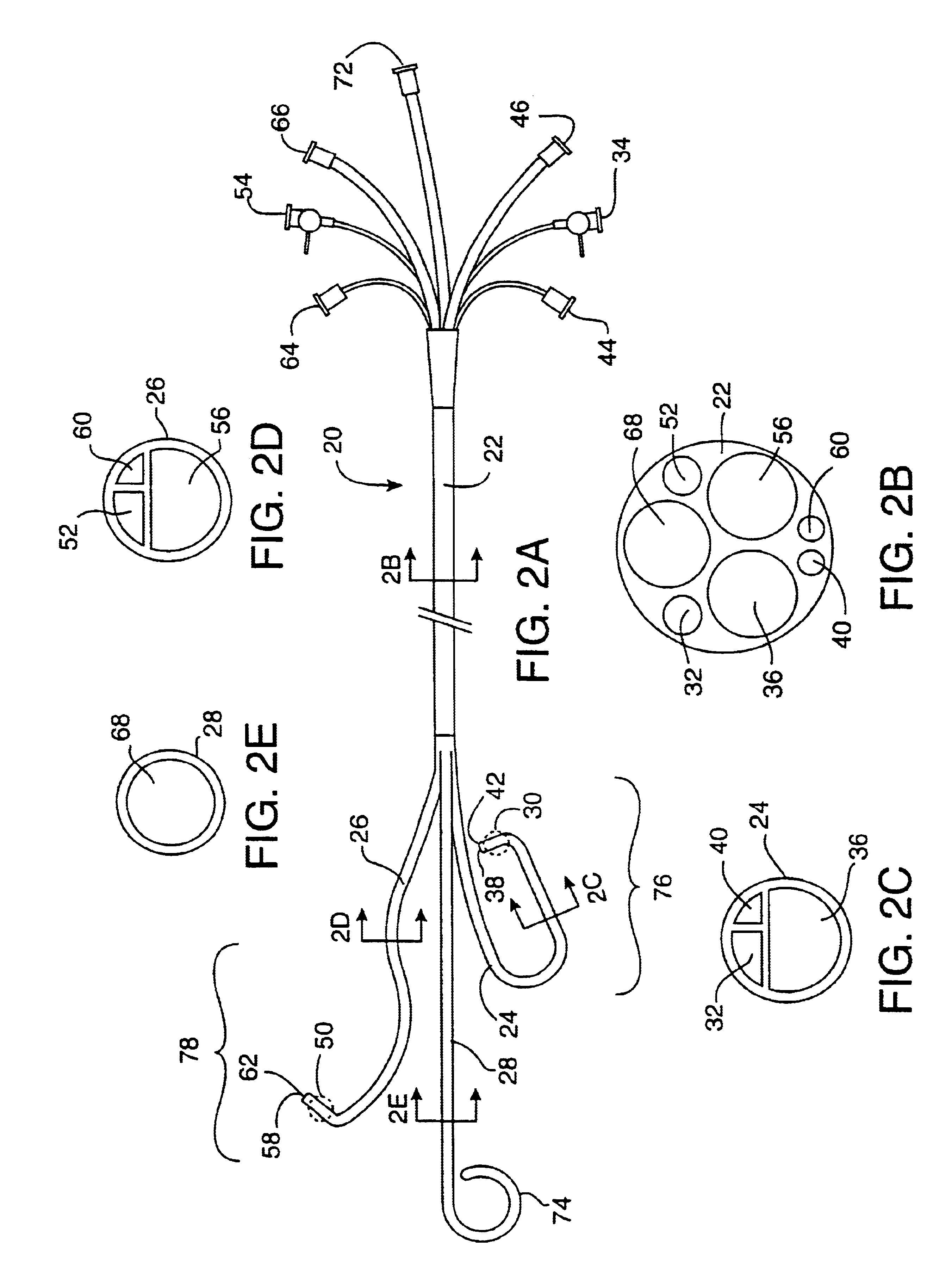
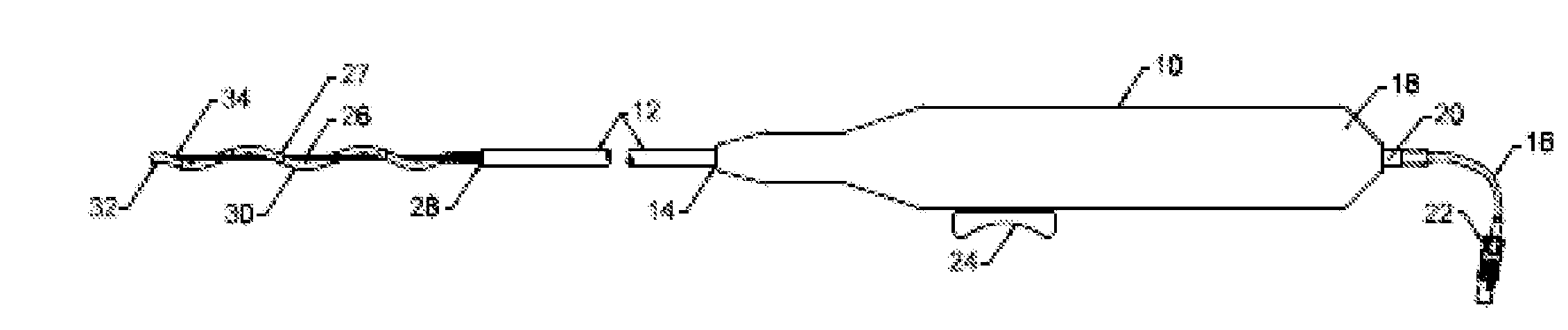
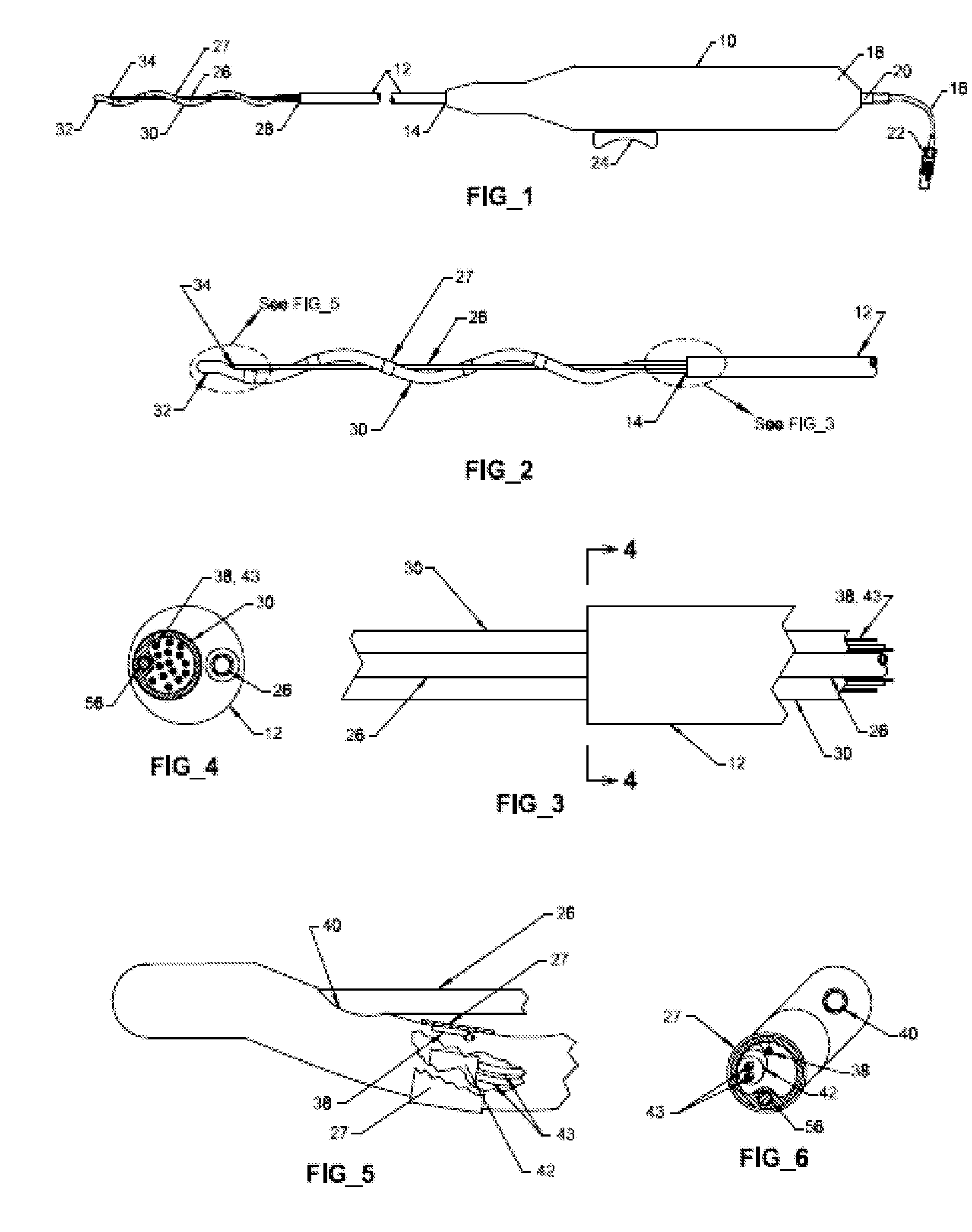
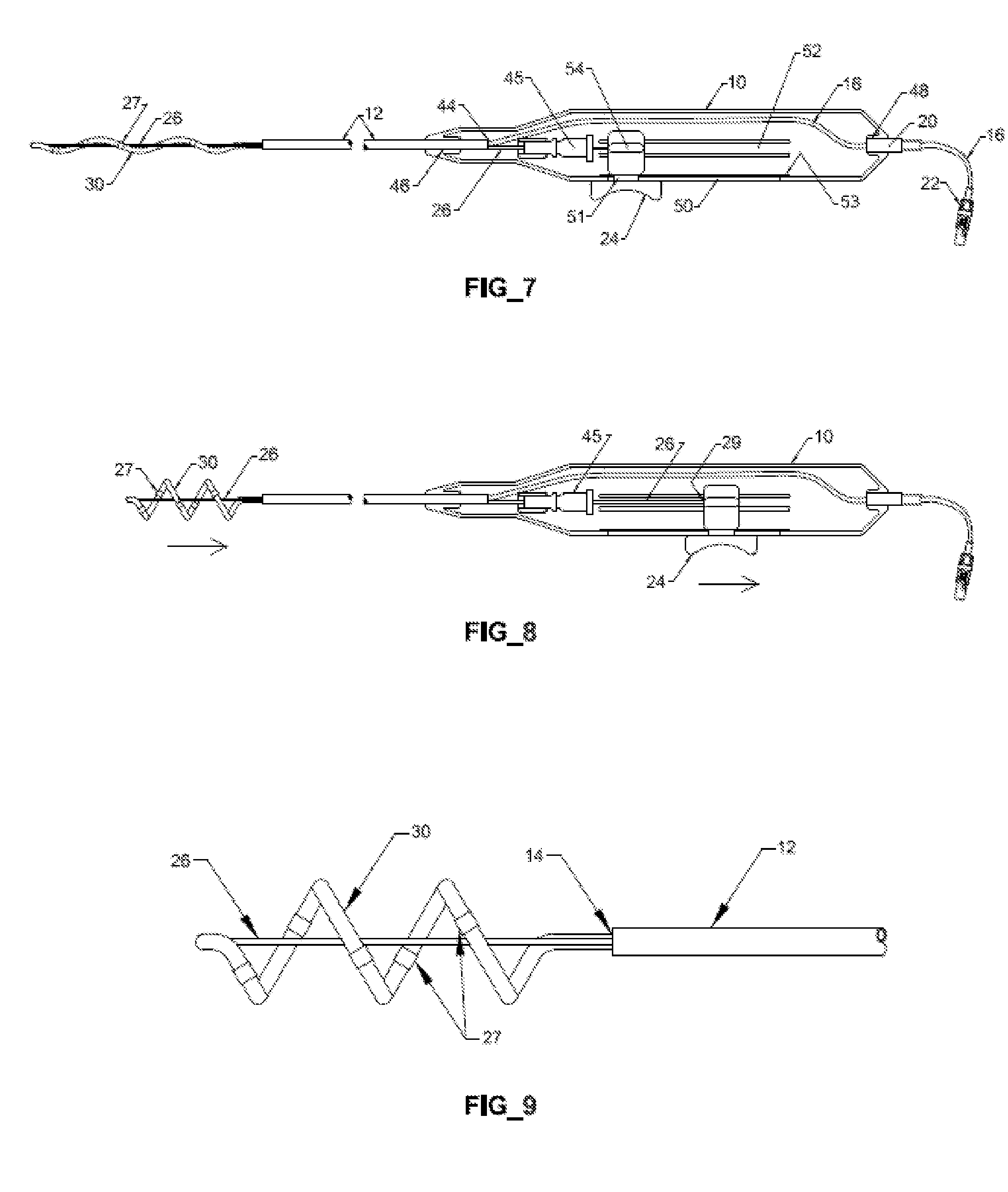
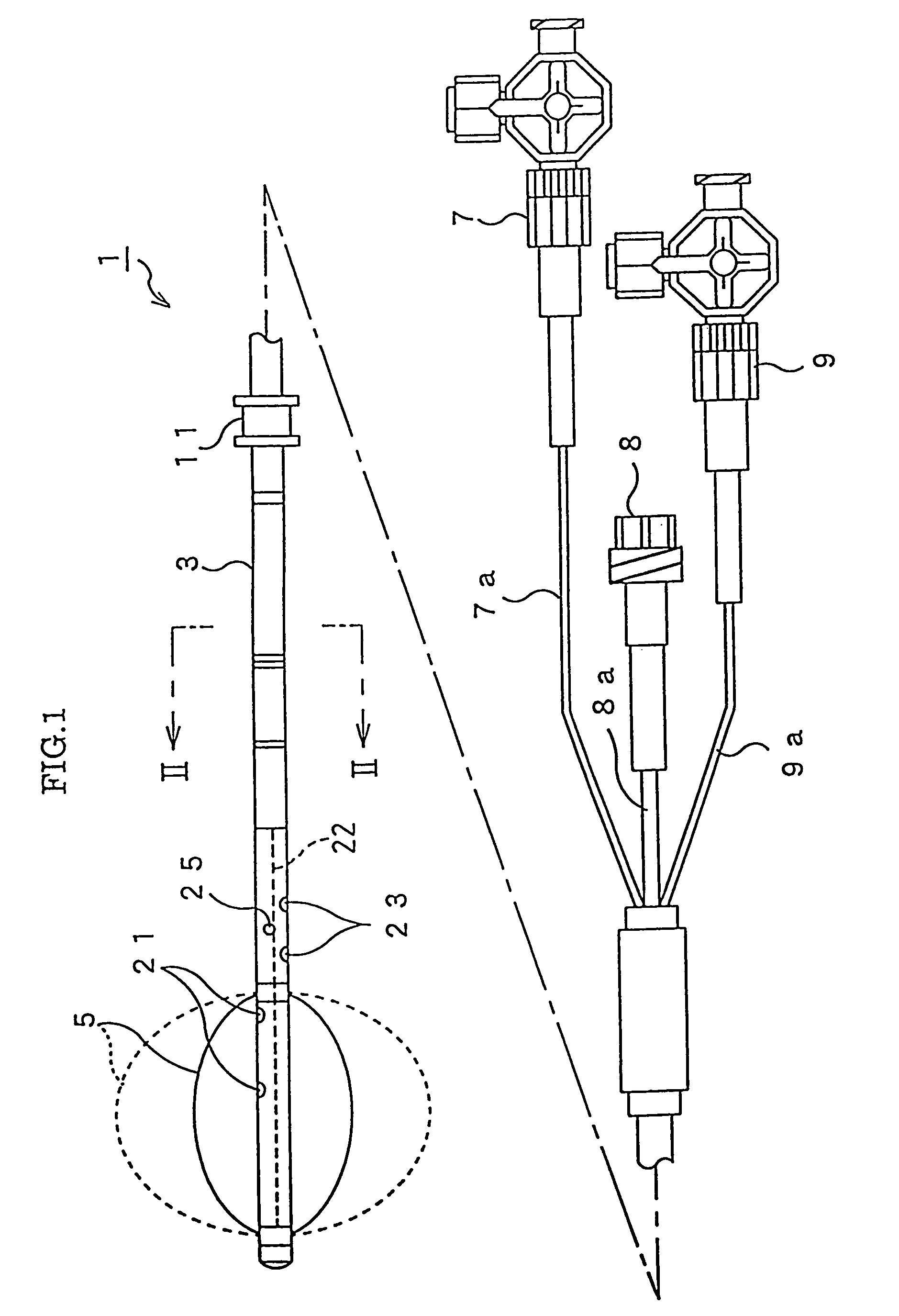
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS7018406B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchor may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand within the deficient native valve, and the anchor engages the lumen wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Non-cylindrical prosthetic valve system for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS20070043435A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesCoronary arteriesProsthesis
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable prosthesis frame. If desired, one or more expandable anchors may be used. The prosthesis frame, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the prosthesis frame may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. The prosthesis frame is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthesis frame expands to an expanded position such that the valve and prosthesis frame expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. The prosthesis frame has a non-cylindrical configuration with a preset maximum expansion diameter region about the valve opening to maintain the preferred valve geometry. The prosthesis frame may also have other regions having a preset maximum expansion diameter to avoid blockage of adjacent structures such as the coronary ostia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Prosthetic Valve for Transluminal Delivery
InactiveUS20100004740A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesVenous accessImplantation Site
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchors may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary ostia. A radial restraint, comprising a wire, thread or cuff, may be used to ensure expansion does not exceed the preset diameter. The valve support may optionally comprise a drug elution component. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. A blood pump may be inserted into the catheter to ensure continued blood flow across the implantation site during implantation procedure. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand at the implantation site and the anchor engages the lumen wall. Insertion of the catheter may optionally be performed over a transseptally delivered guidewire that has been externalized through the arterial vasculature. Such a guidewire provide dual venous and arterial access to the implantation site and allows additional manipulation of the implantation site after arterial implantation of the prosthetic valve. Additional expansion stents may be delivered by venous access to the valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS8016877B2Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
A method for deploying a prosthetic valve assembly is provided. The prosthetic valve assembly replaces a deficient native valve and comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. Portions of the valve support may expand to a preset diameter to maintain coaptivity of the replacement valve and to prevent occlusion of the coronary oslia. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
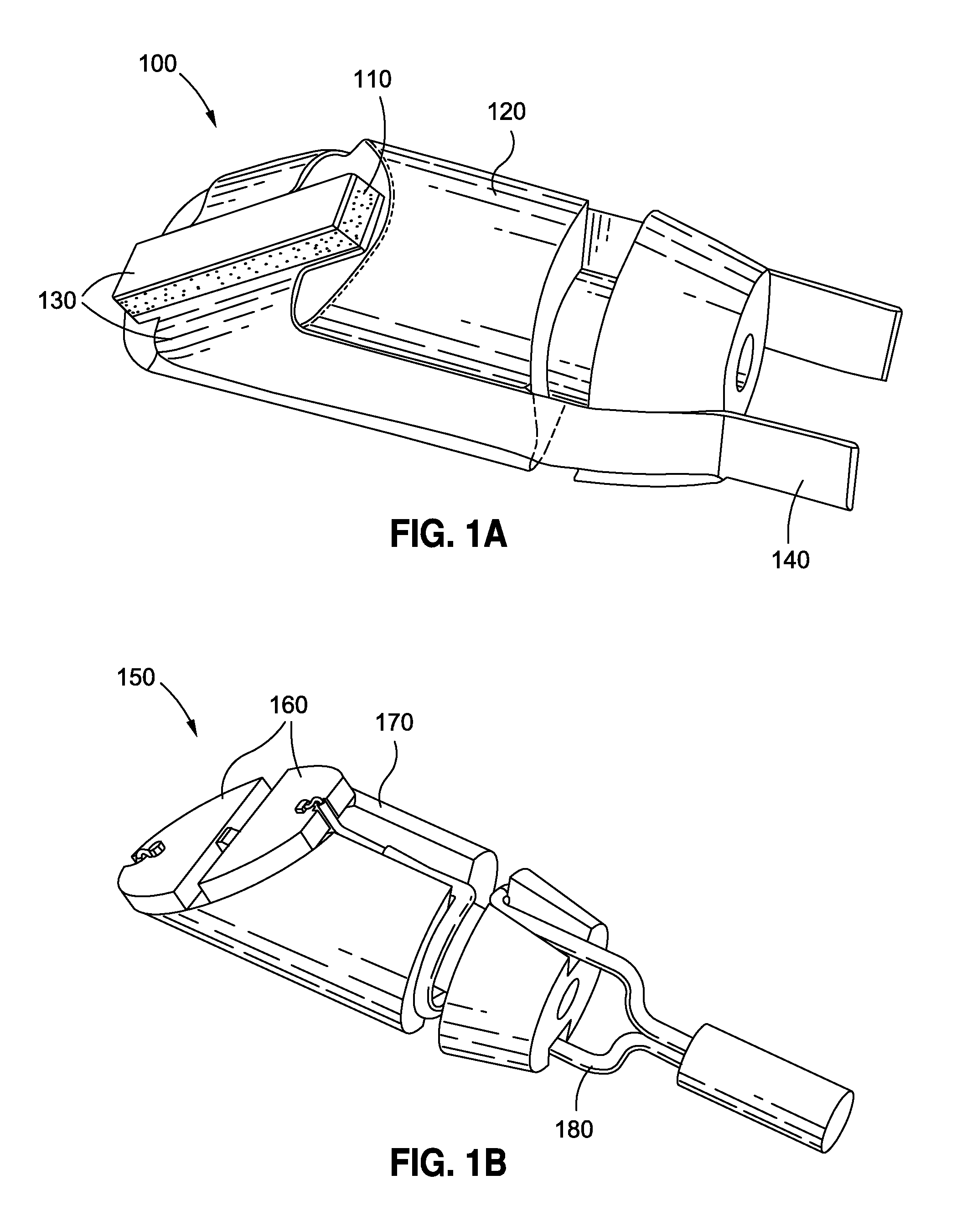
Handle for suturing apparatus
ActiveUS20060069397A1Easy to operatePossibility of errorSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesExisting catheterThrombus
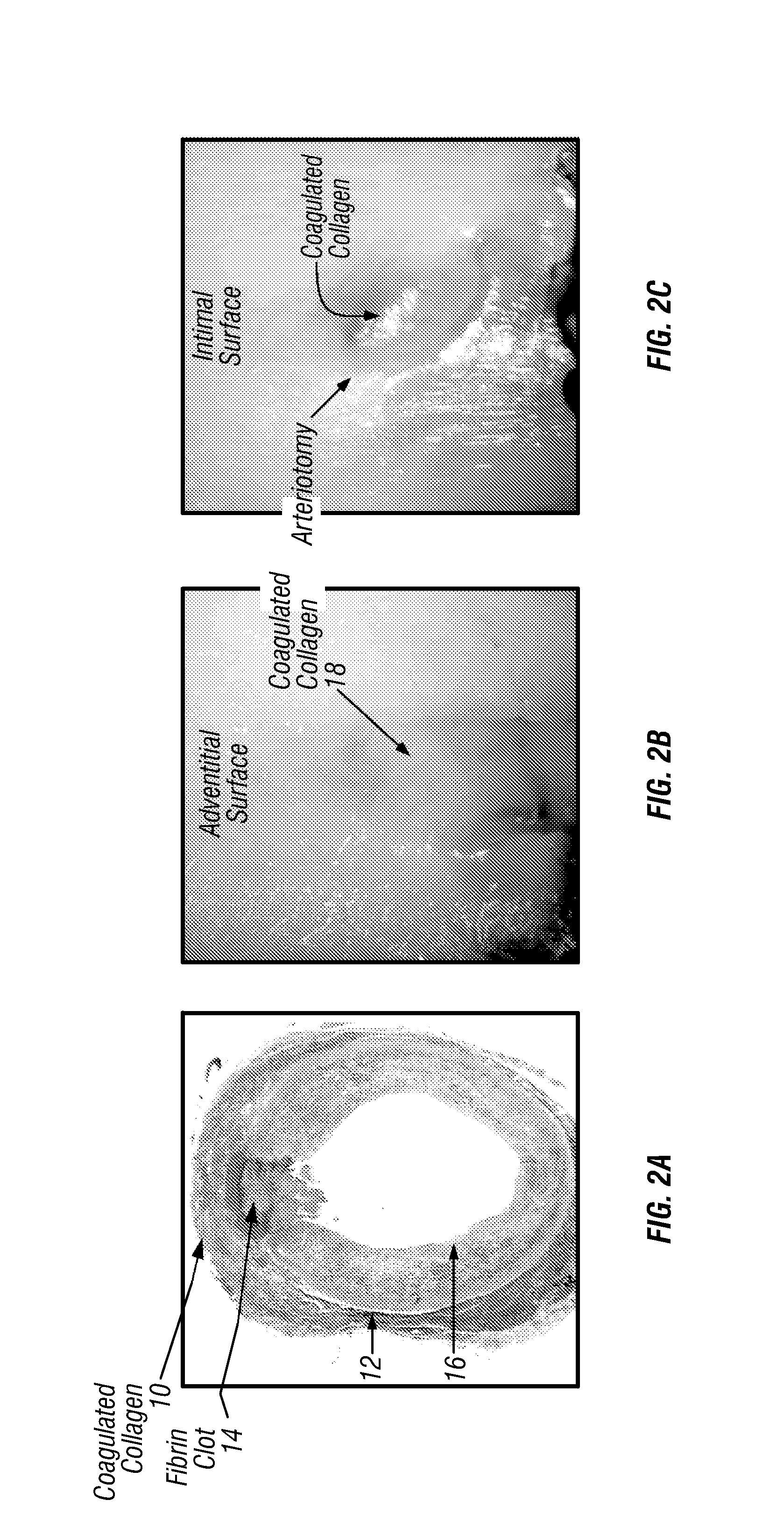
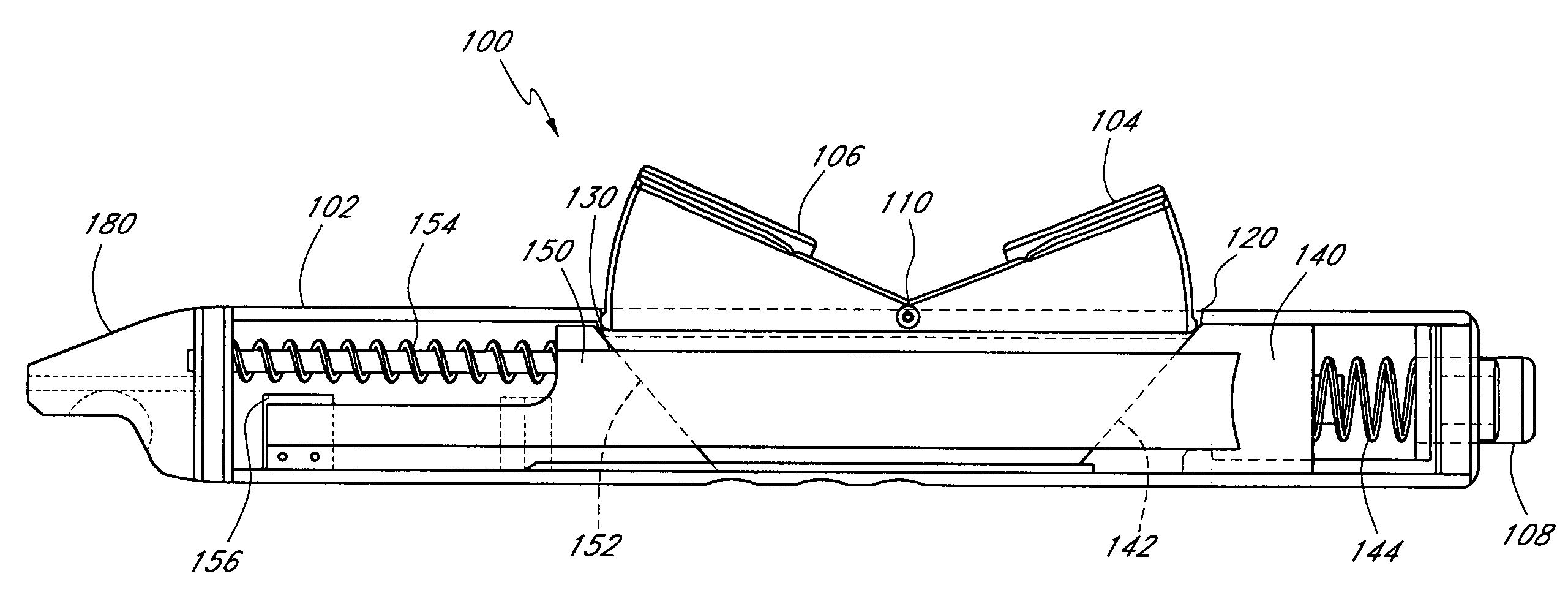
Methods and apparatus are provided for closing incisions within biological tissue. In one embodiment, a device and method are provided for suturing biological tissue, such as, for example, an organ or blood vessel. The suturing apparatus is particularly well suited for suturing an incision made in an artery, such as the femoral artery, following a catheterization procedure. The device eliminates the need to apply pressure to a patient's thigh for an extended period of time, and eliminates many of the complications and costs associated with the creation of a thrombus patch. In addition, the device comprises an improved handle portion which enables the physician to quickly and easily apply suture. The handle portion is very reliable and easy to manipulate. The suturing may be used in combination with existing catheter sheath introducers.
Owner:SCARAB TECH SERVICES LLC +6
Prosthetic valve for transluminal delivery
InactiveUS20060129235A1Preventing substantial migrationEliminate the problemBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisCommissure
A prosthetic valve assembly for use in replacing a deficient native valve comprises a replacement valve supported on an expandable valve support. If desired, one or more anchor may be used. The valve support, which entirely supports the valve annulus, valve leaflets, and valve commissure points, is configured to be collapsible for transluminal delivery and expandable to contact the anatomical annulus of the native valve when the assembly is properly positioned. The anchor engages the lumen wall when expanded and prevents substantial migration of the valve assembly when positioned in place. The prosthetic valve assembly is compressible about a catheter, and restrained from expanding by an outer sheath. The catheter may be inserted inside a lumen within the body, such as the femoral artery, and delivered to a desired location, such as the heart. When the outer sheath is retracted, the prosthetic valve assembly expands to an expanded position such that the valve and valve support expand within the deficient native valve, and the anchor engages the lumen wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
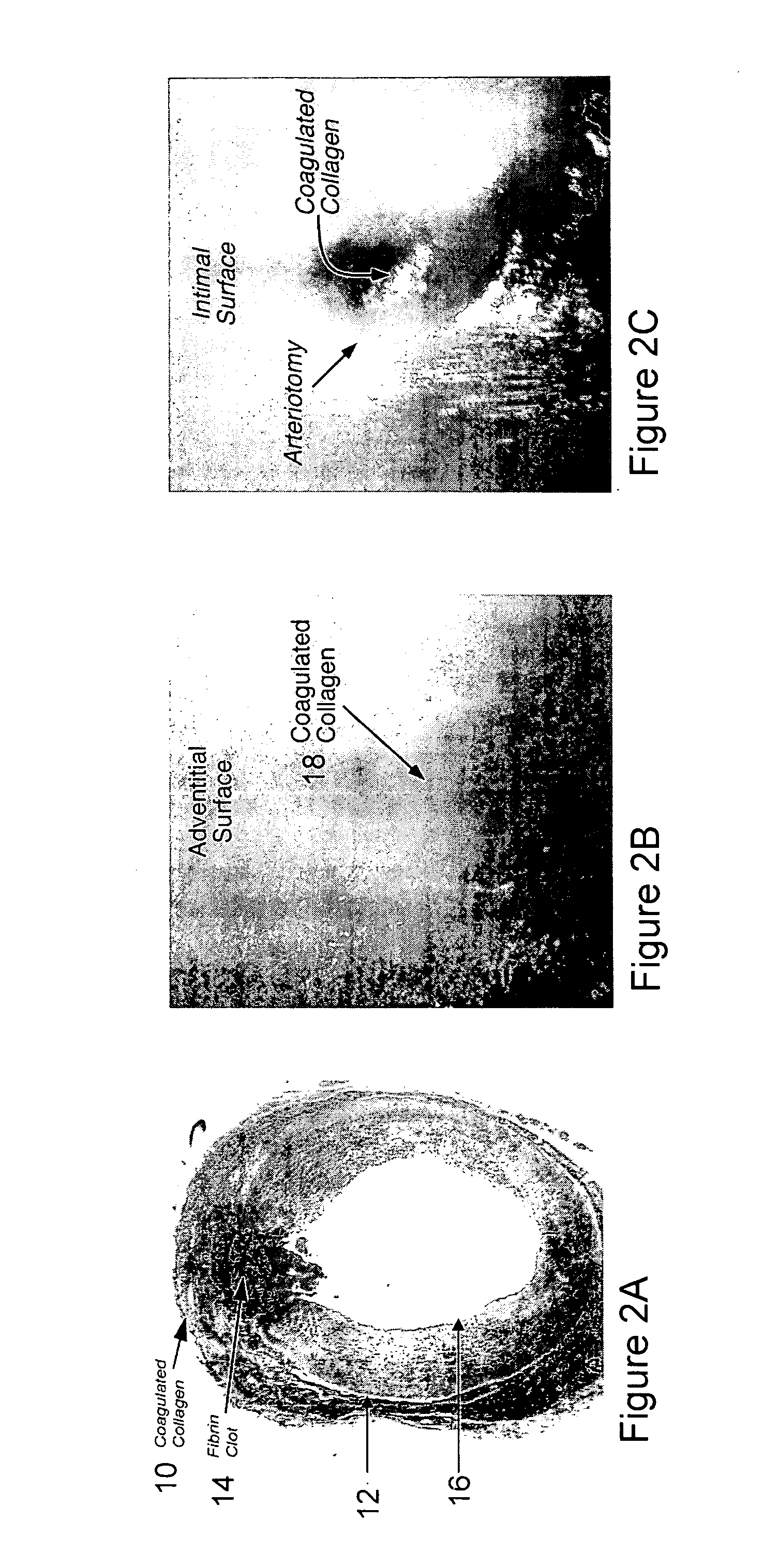
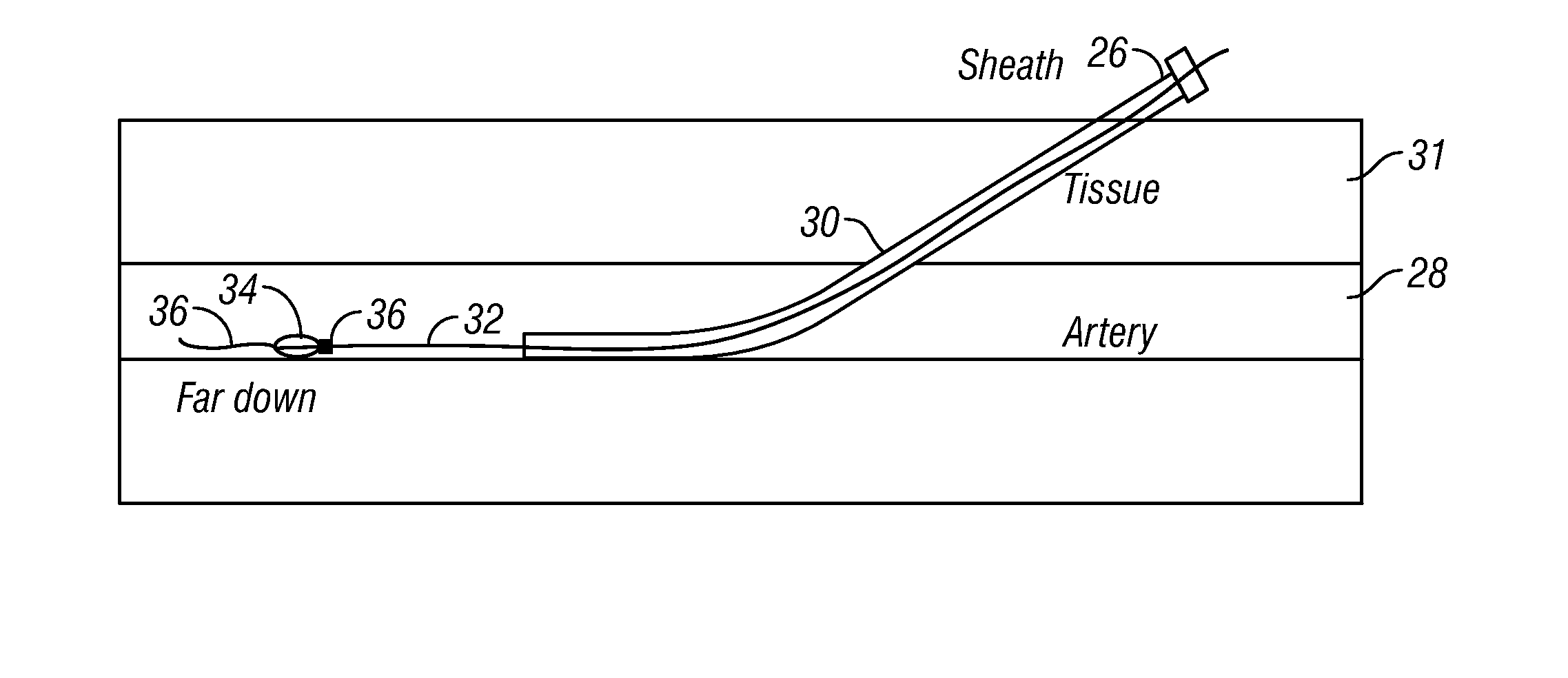
Systems and methods for arteriotomy localization
InactiveUS20070213616A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsCatheterization procedureFemoral artery
A targeting catheter is used to locate an arteriotomy, such as is formed during a femoral artery catheterization procedure. The targeting catheter includes one or more targeting aids, such as an inflatable balloon or sensor (e.g., Doppler or temperature sensor), to locate the arteriotomy. The targeting aid may be positioned at the arteriotomy. An ultrasonic beacon on the catheter may then be located relative to a therapeutic ultrasonic applicator (e.g., by using acoustic time-of-flight) so that the focus of ultrasonic energy from the applicator can be aligned with the arteriotomy.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
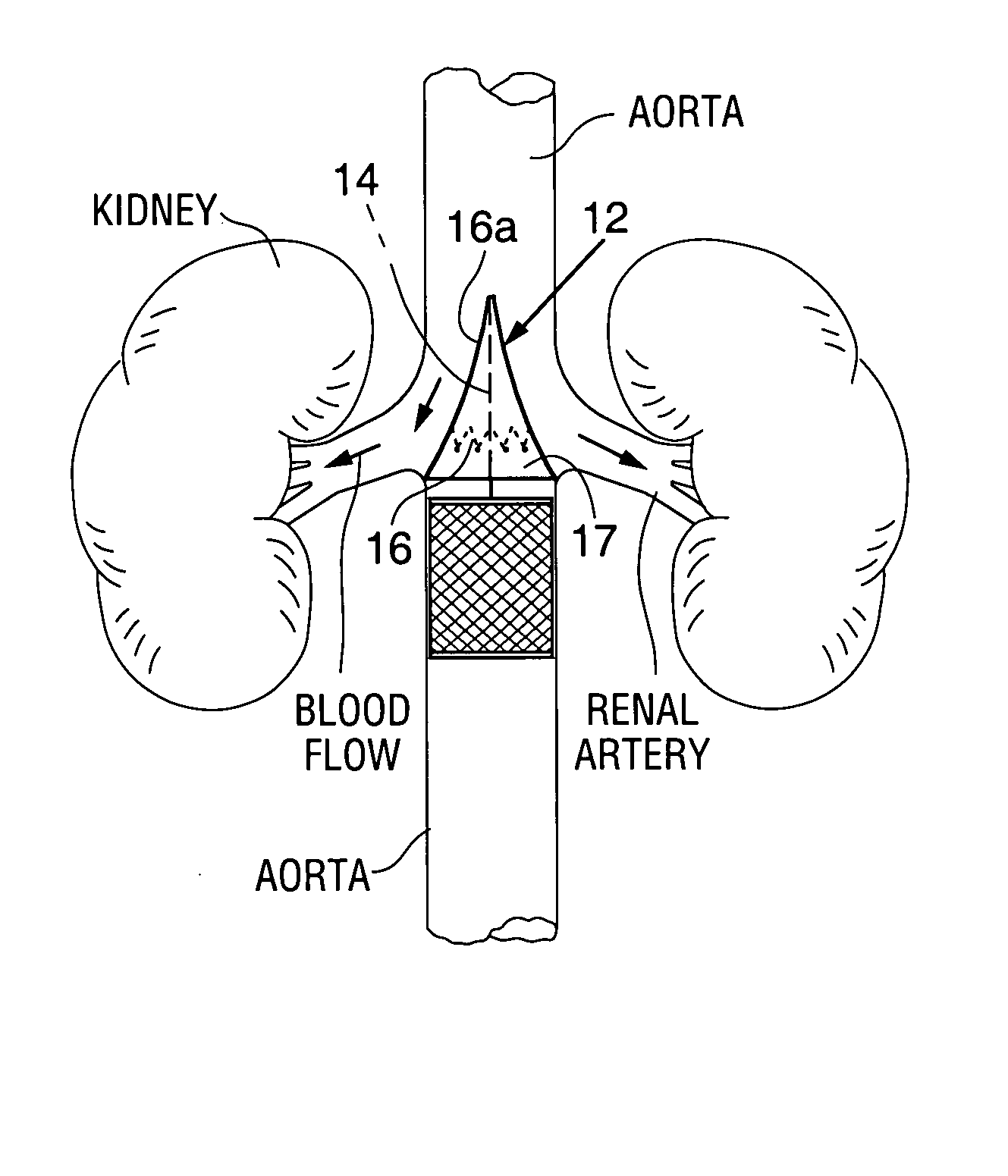
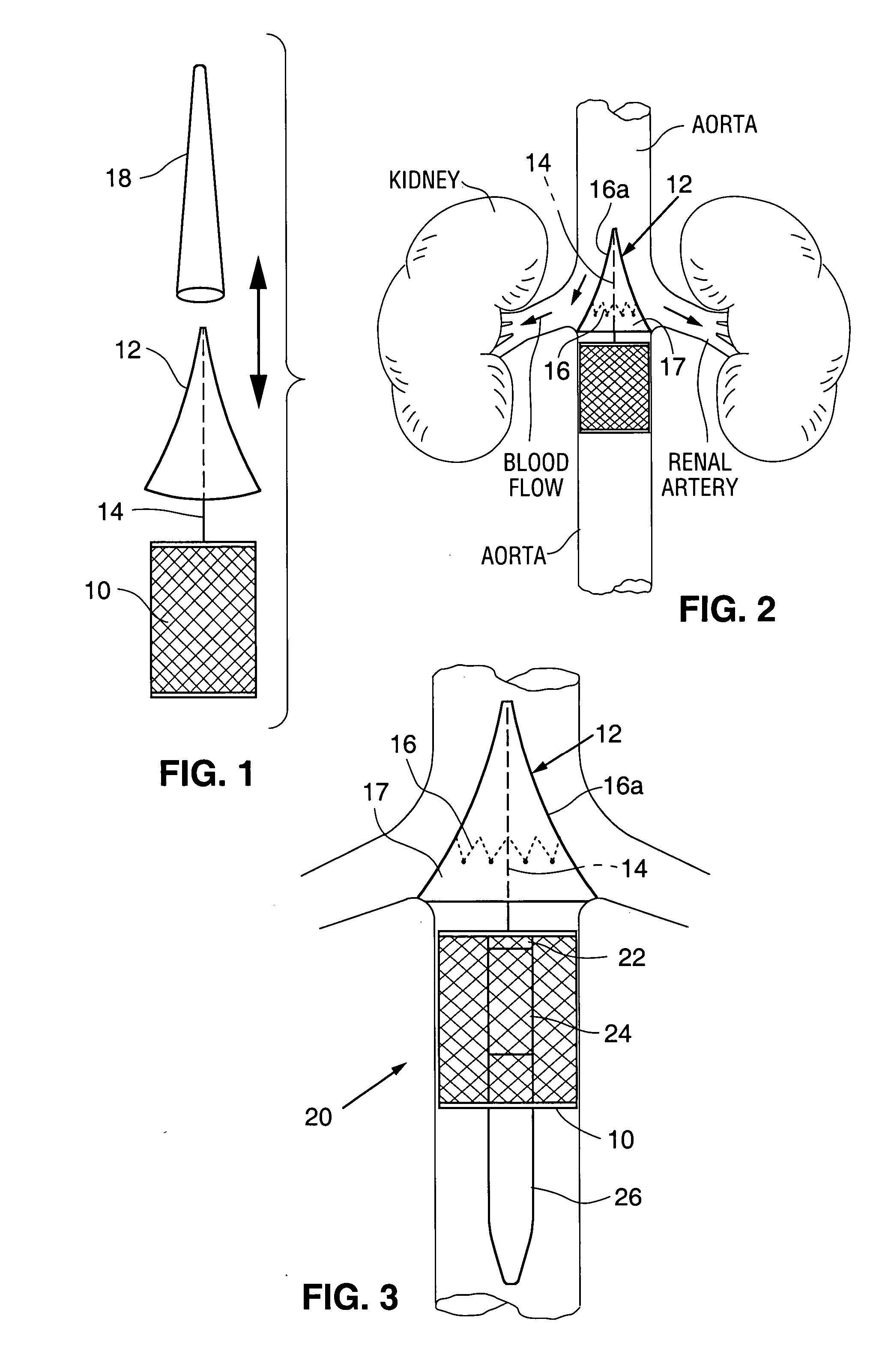
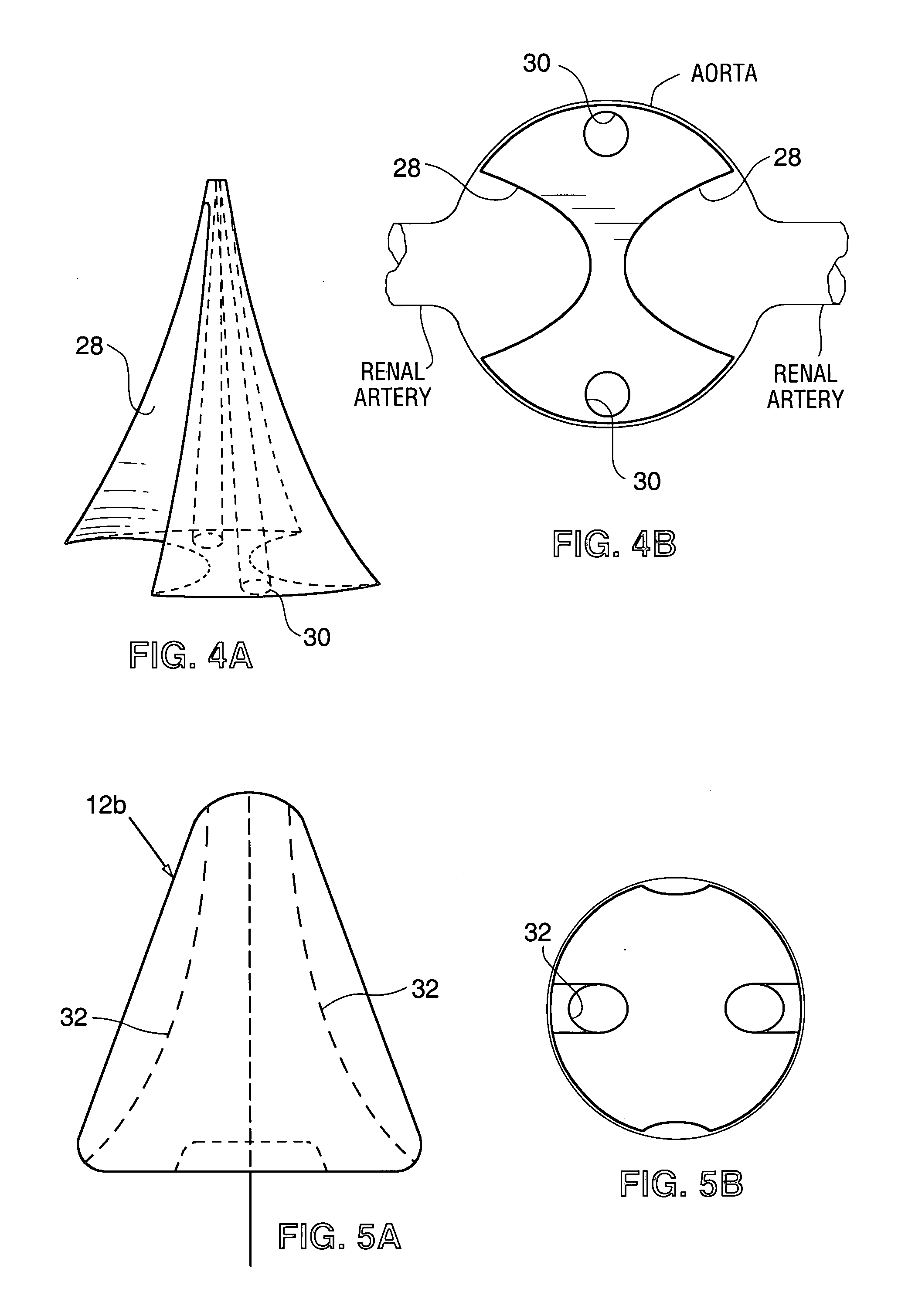
Renal blood flow augmentation for congestive heart failure treatment
Intravascular devices are delivered to the aorta percutaneously via the femoral artery. The devices are anchored within the vasculature in the region of the renal artery ostia. These embodiments function to increase the flow of blood from the aorta to the renal arteries, thus delivering a higher relative percentage of the blood flowing through the aorta to the kidneys. The elevation in blood low to the kidneys improves the natural removal of excess fluids from the body. In one embodiment, the device is a diverter element positionable upstream of the renal artery ostia. In another embodiment, the device is a flow restrictor positionable downstream of the ostia to cause an elevation is pressure upstream of the ostia.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
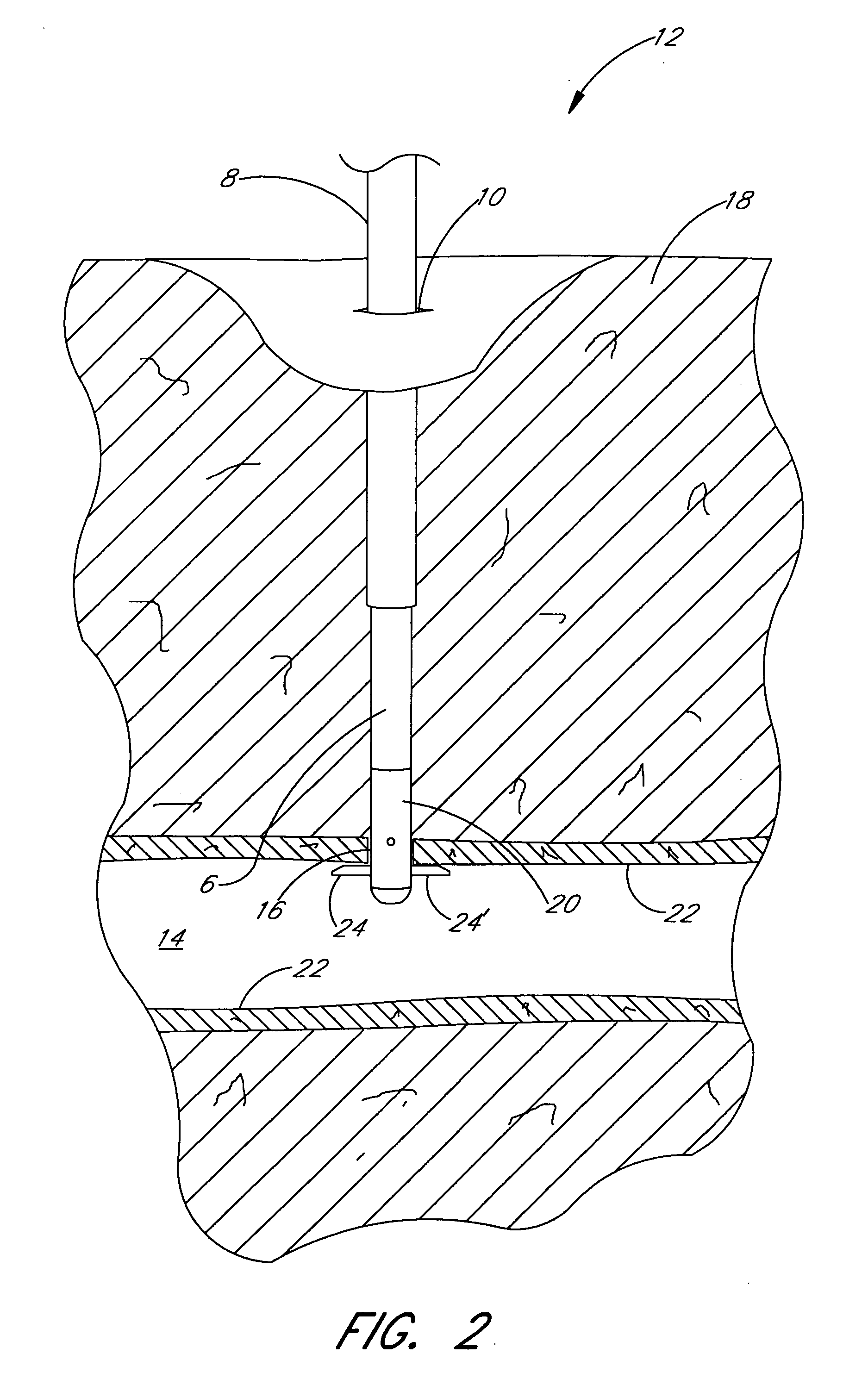
Vascular sealant delivery device and sheath introducer and method
A sheath introducer is inserted through the skin and into a body lumen, e.g., the femoral artery, for a medical procedure. Upon completion of the medical procedure, the sheath introducer is partially withdrawn from the body lumen so that at least one through-wall hole in a body region of the sheath introducer is positioned outside the body lumen, but under the skin. An opening in a distal end tip of the sheath introducer is sealed so that no blood is flowing into the sheath introducer the after sheath introducer is partially withdrawn. A surgical sealant is injected into the sheath introducer and flows out of the at least one through-wall hole and surrounds the access site. After injection of the surgical sealant, the sheath introducer is removed. The surgical sealant seals the puncture and minimizes any blood flow from the body lumen through the puncture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method for delivering a fluid to the coronary ostia
InactiveUS6913601B2Maintenance stopReduce in quantityGuide needlesStentsMinimally invasive cardiac surgeryCoronary artery ostium
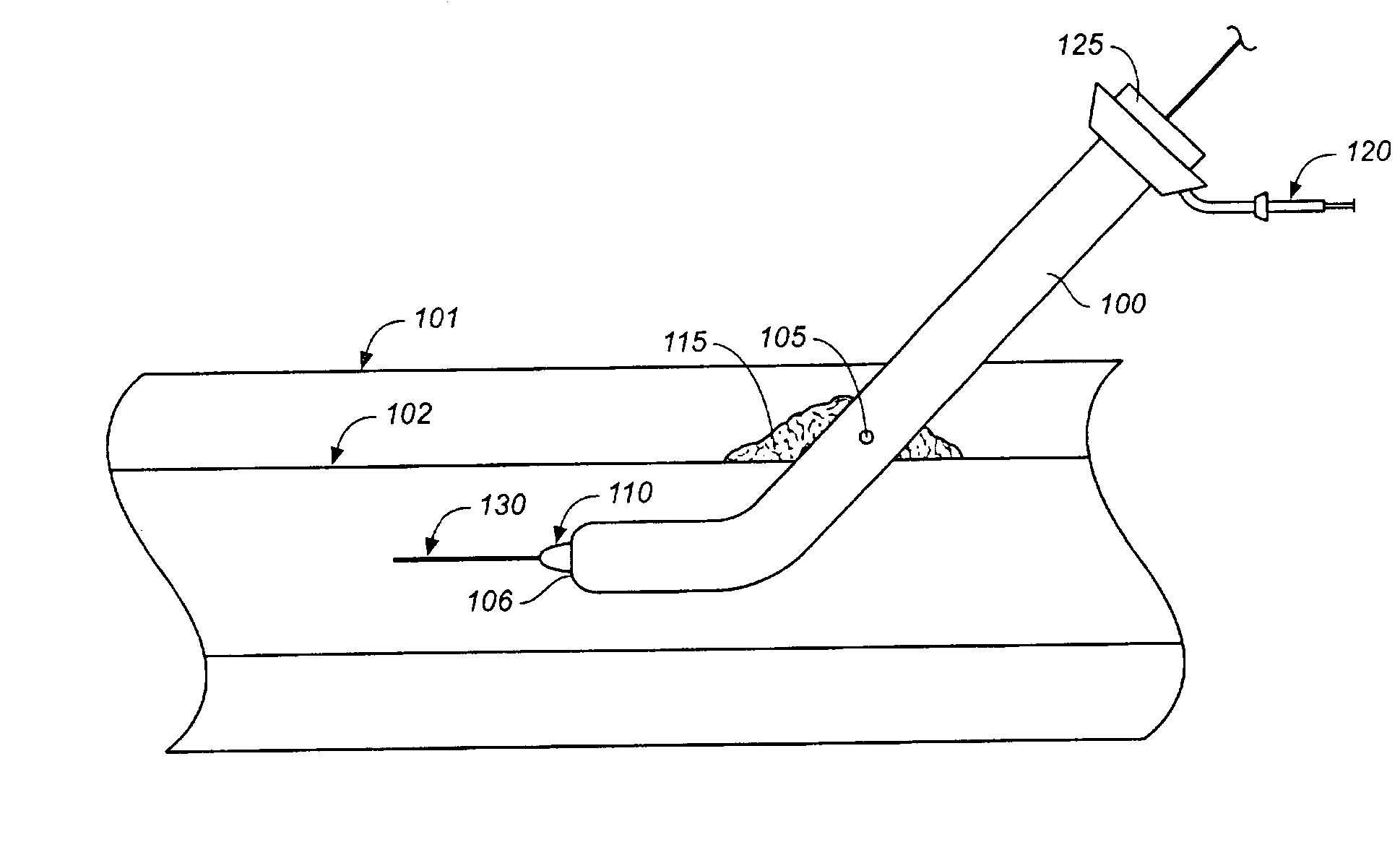
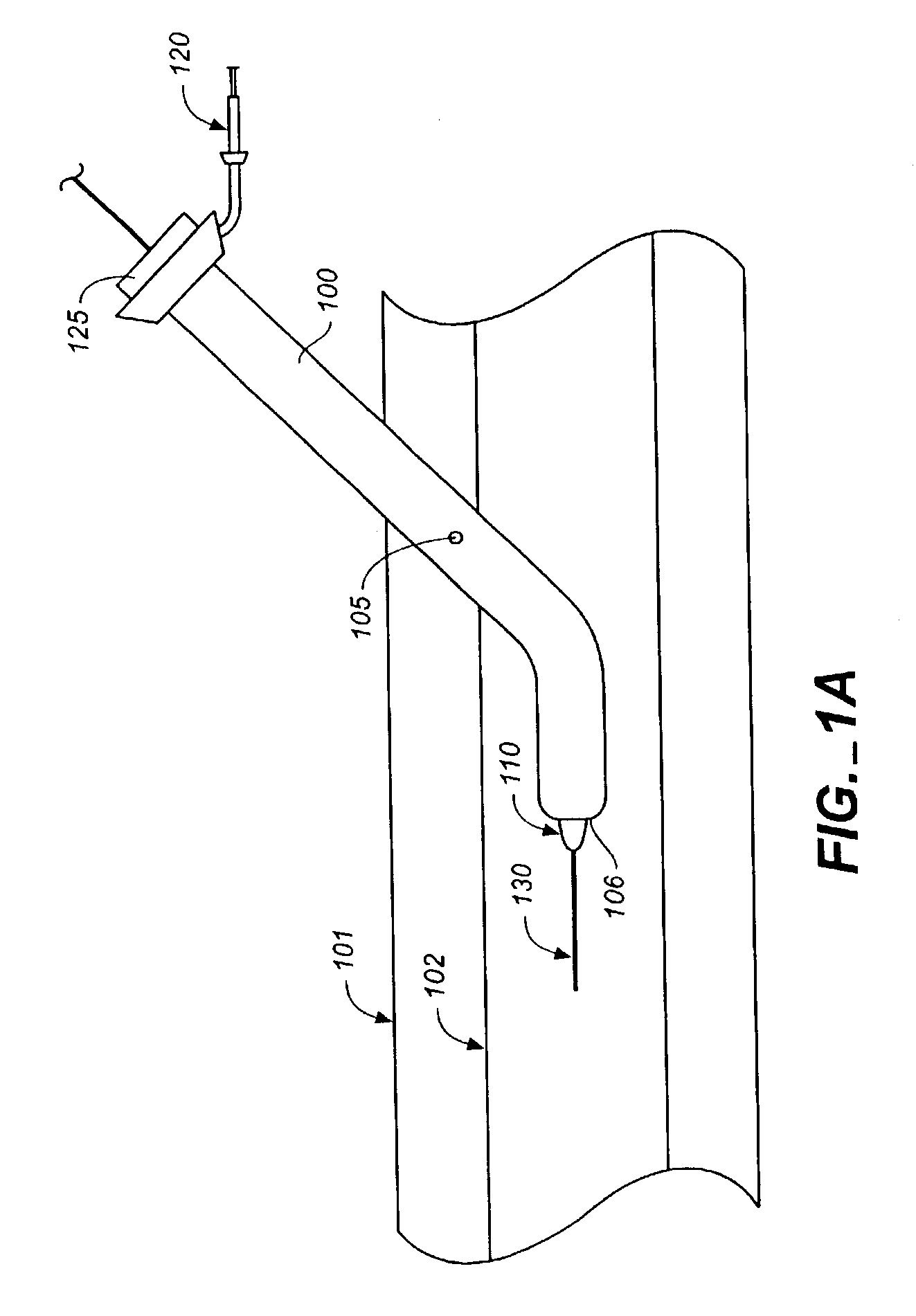
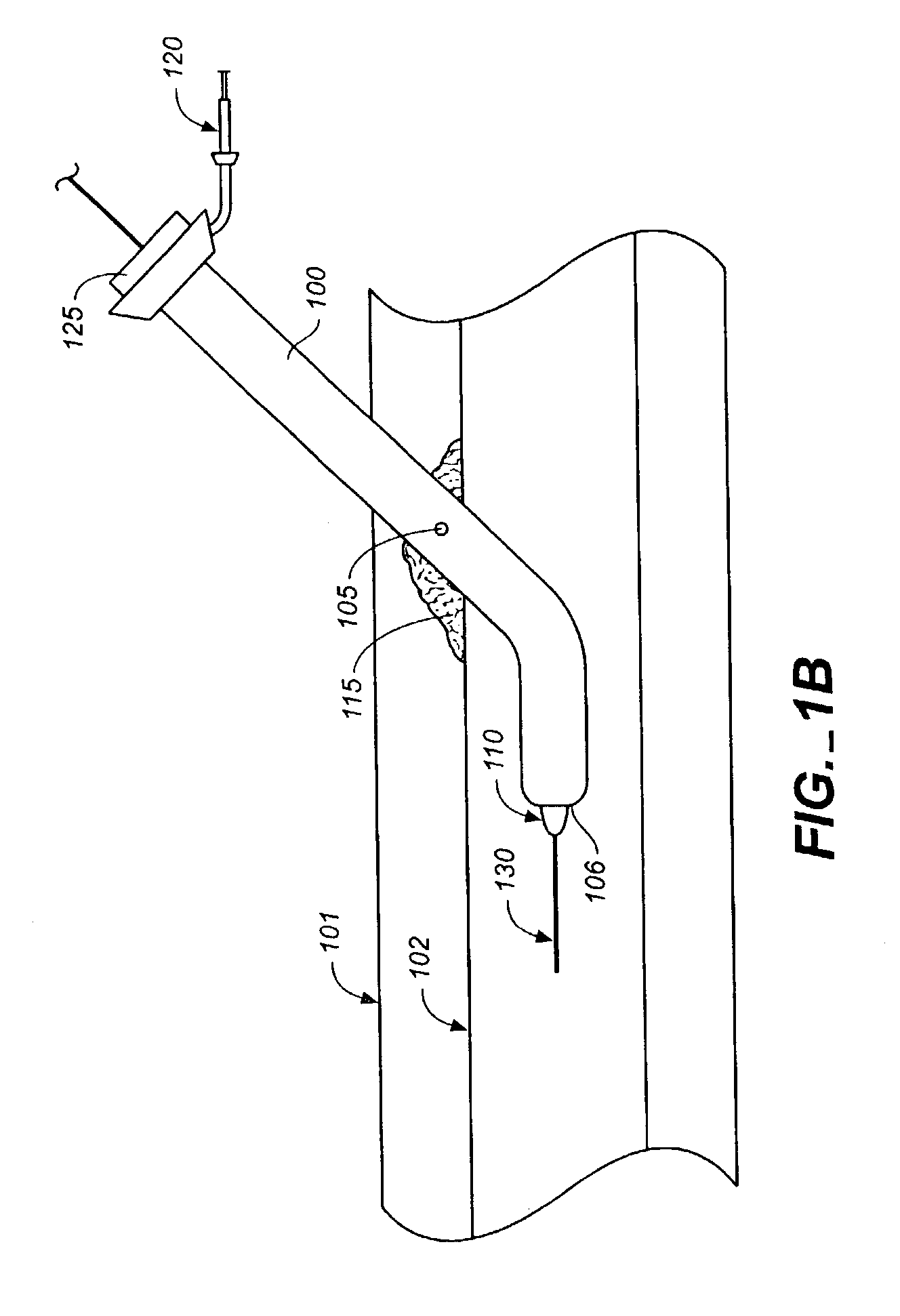
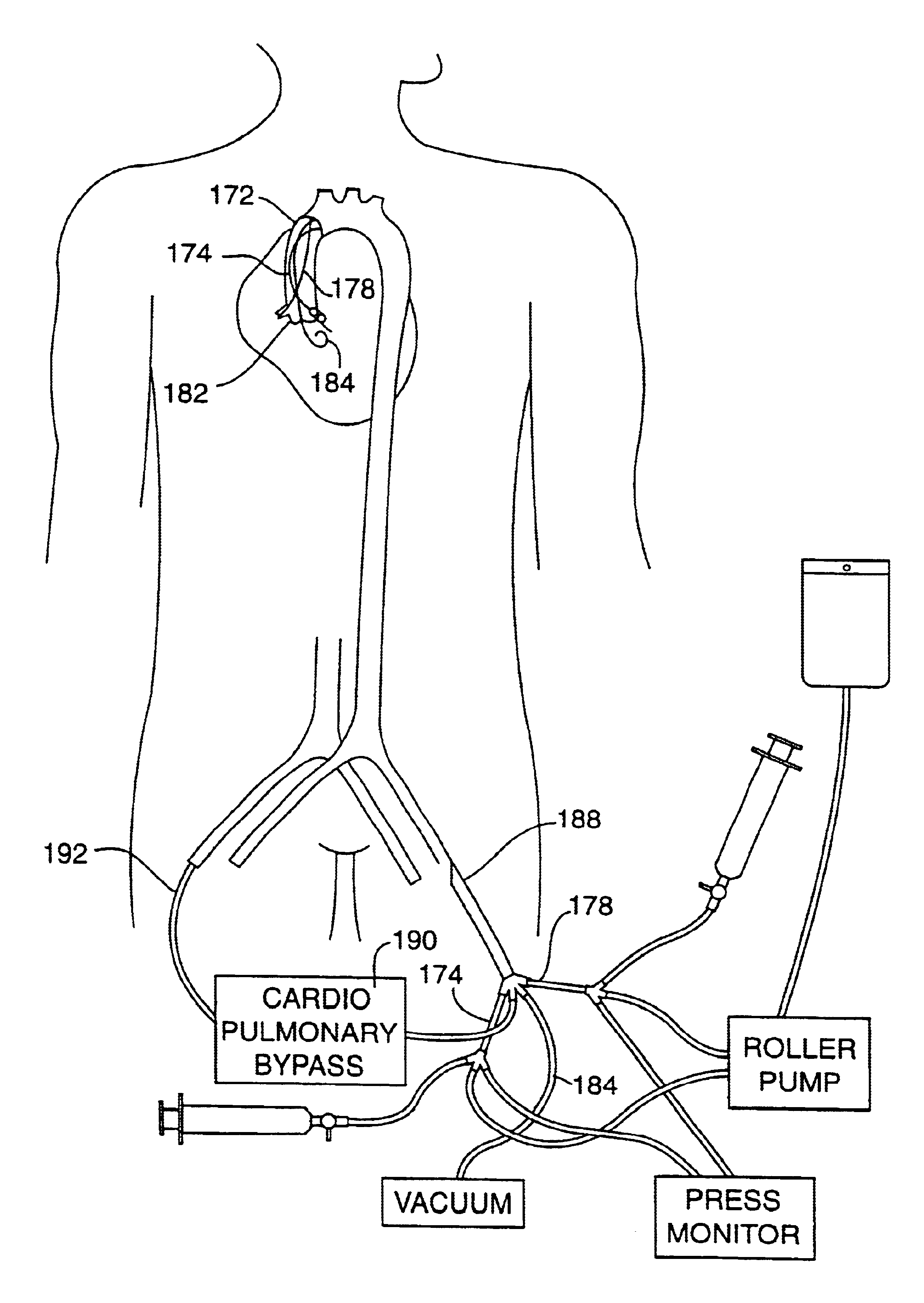
A catheter system is provided for accessing the coronary ostia transluminally from a peripheral arterial access site, such as the femoral artery, and for inducing cardioplegic arrest by direct infusion of cardioplegic solution into the coronary arteries. In a first embodiment, the catheter system is in the form of a single perfusion catheter with multiple distal branches for engaging the coronary ostia. In a second embodiment, multiple perfusion catheters are delivered to the coronary ostia through a single arterial cannula. In a third embodiment, multiple perfusion catheters are delivered to the coronary ostia through a single guiding catheter. In a fourth embodiment, multiple catheters are delivered to the coronary ostia through a single guiding catheter which has distal exit ports that are arranged to direct the perfusion catheters into the coronary ostia. In each embodiment, the catheters are equipped with an occlusion means at the distal end of the catheter for closing the coronary ostia and isolating the coronary arteries from the systemic blood flow. The occlusion means can take the form of an inflatable occlusion balloon cuff, a tapered occlusion device or an O-ring encircling the distal end of the catheter. An optional ventricular venting catheter can be included in the system for venting blood and fluids from the left ventricle of the heart. The catheter system is combined with a femoral-to-femoral cardiopulmonary bypass system to provide a system for cardioplegic arrest and total cardiopulmonary support during minimally invasive cardiac surgical procedures.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Systems and methods for sealing a vascular opening
InactiveUS20070233185A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES +1
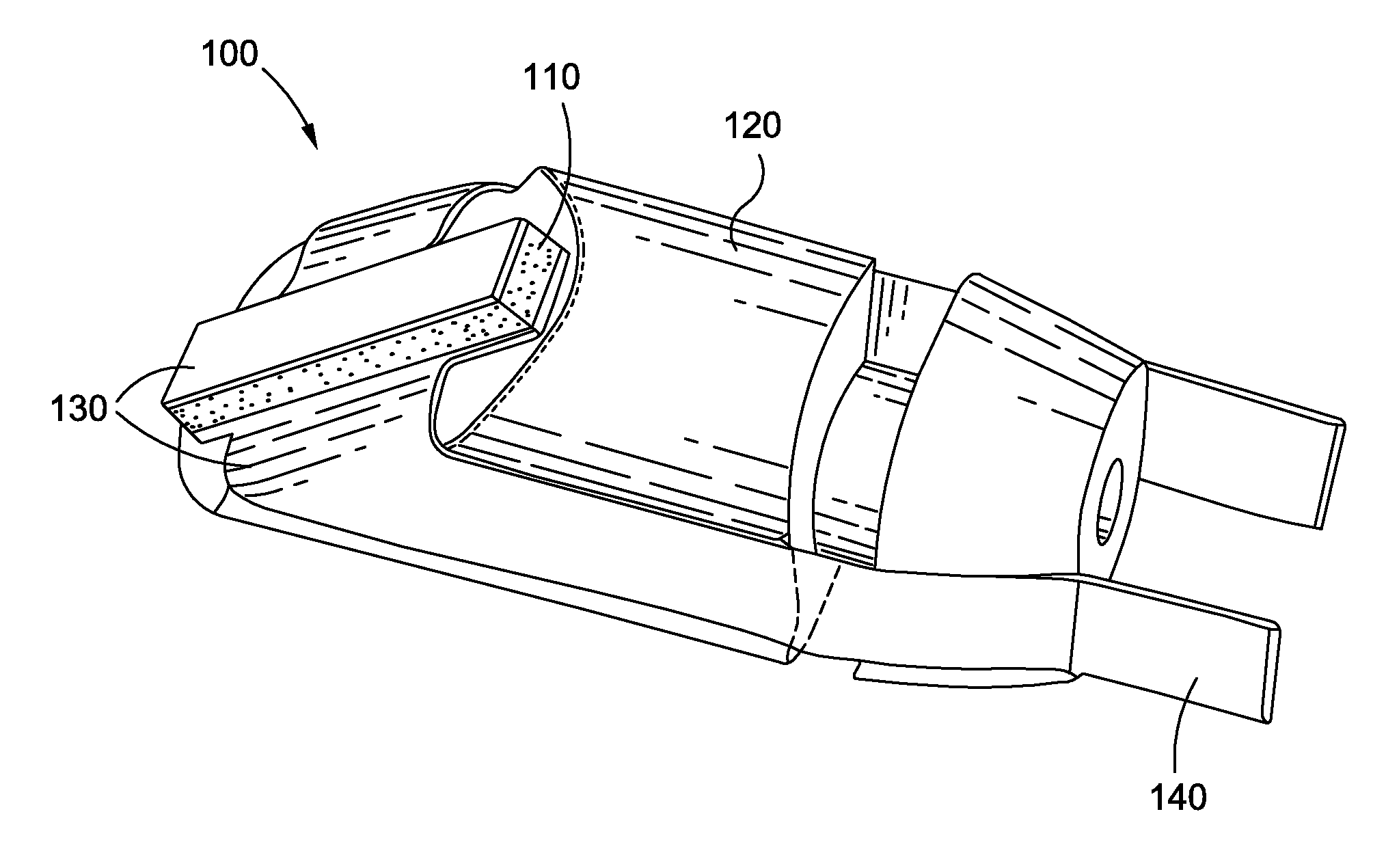
Handle for suturing apparatus
ActiveUS7803167B2Easy to operatePossibility of errorSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesThighExisting catheter
Methods and apparatus are provided for closing incisions within biological tissue. In one embodiment, a device and method are provided for suturing biological tissue, such as, for example, an organ or blood vessel. The suturing apparatus is particularly well suited for suturing an incision made in an artery, such as the femoral artery, following a catheterization procedure. The device eliminates the need to apply pressure to a patient's thigh for an extended period of time, and eliminates many of the complications and costs associated with the creation of a thrombus patch. In addition, the device comprises an improved handle portion which enables the physician to quickly and easily apply suture. The handle portion is very reliable and easy to manipulate. The suturing may be used in combination with existing catheter sheath introducers.
Owner:SCARAB TECH SERVICES LLC +6
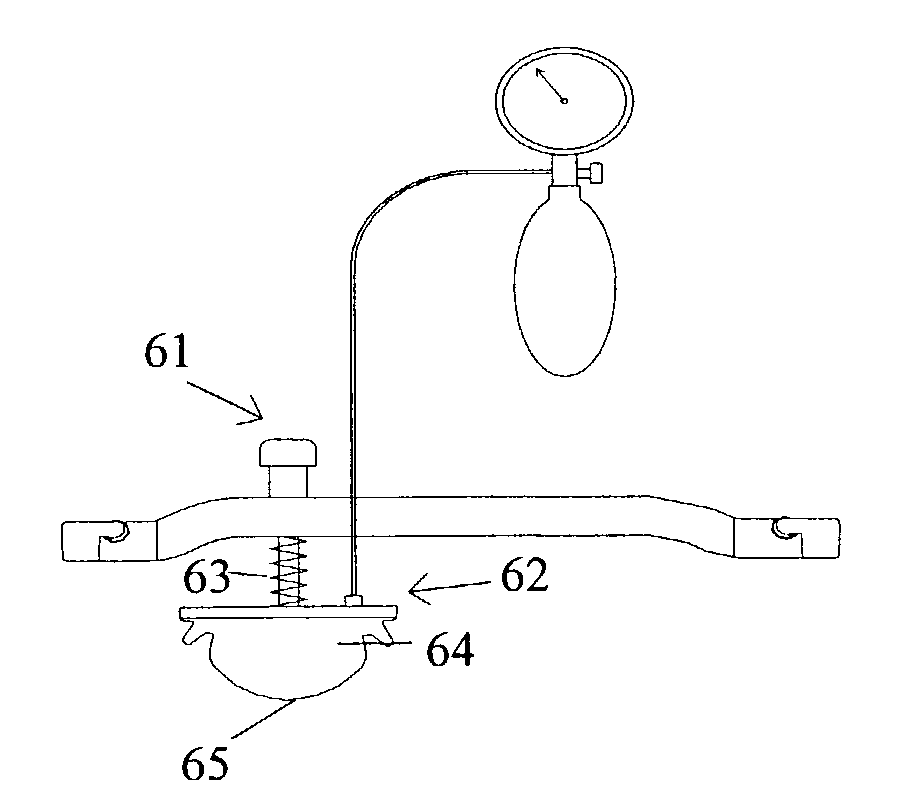
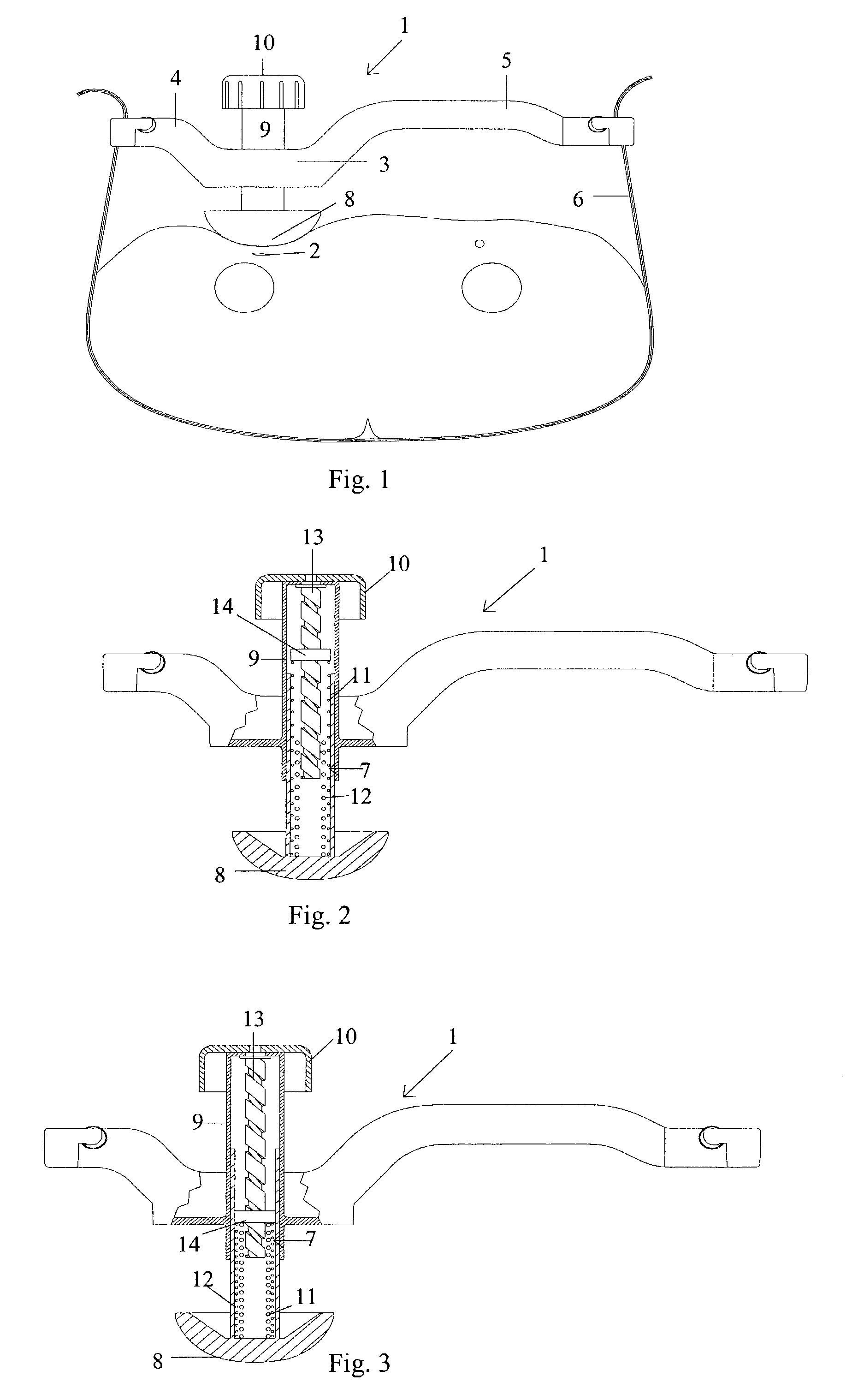
Femoral compression device with support
A femoral compression device includes a pressure applying device for compressive bearing at a puncture site at a femoral artery of a patient and for applying pressure on the puncture site, a belt adapted to be fixed around the patient's body, and a base plate provided with first and second extensions, with the end of the first extension being closer to the pressure applying device than the end of the second extension and being provided with a fastener in the ends thereof for fastening of an end of the belt. The compression device also includes a support plate, which is attached to the second extension and which is adapted to bear against the patient's body, thereby compensating for the imbalance, which originates from the different extents of the two extensions, that otherwise would be present.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
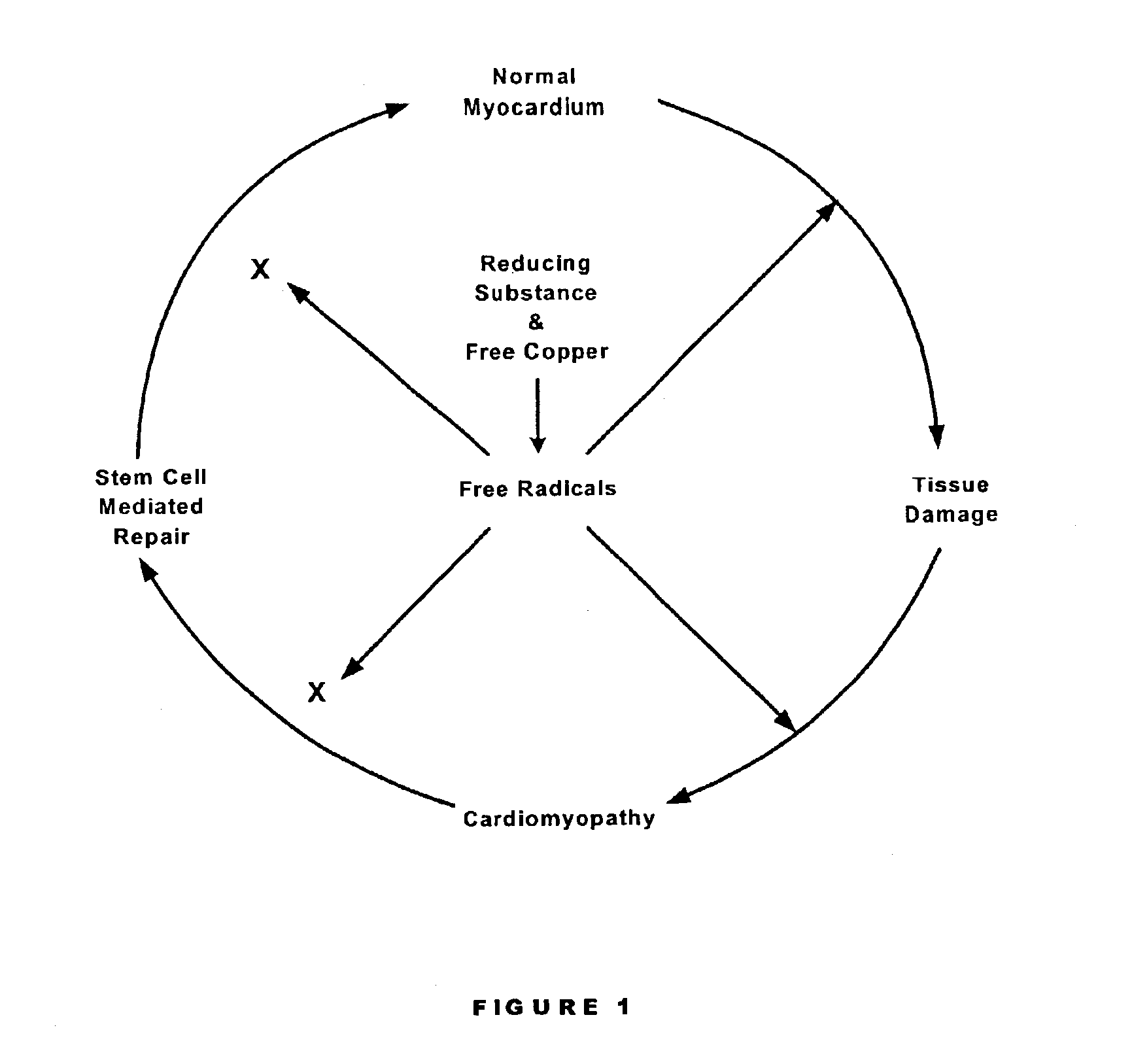
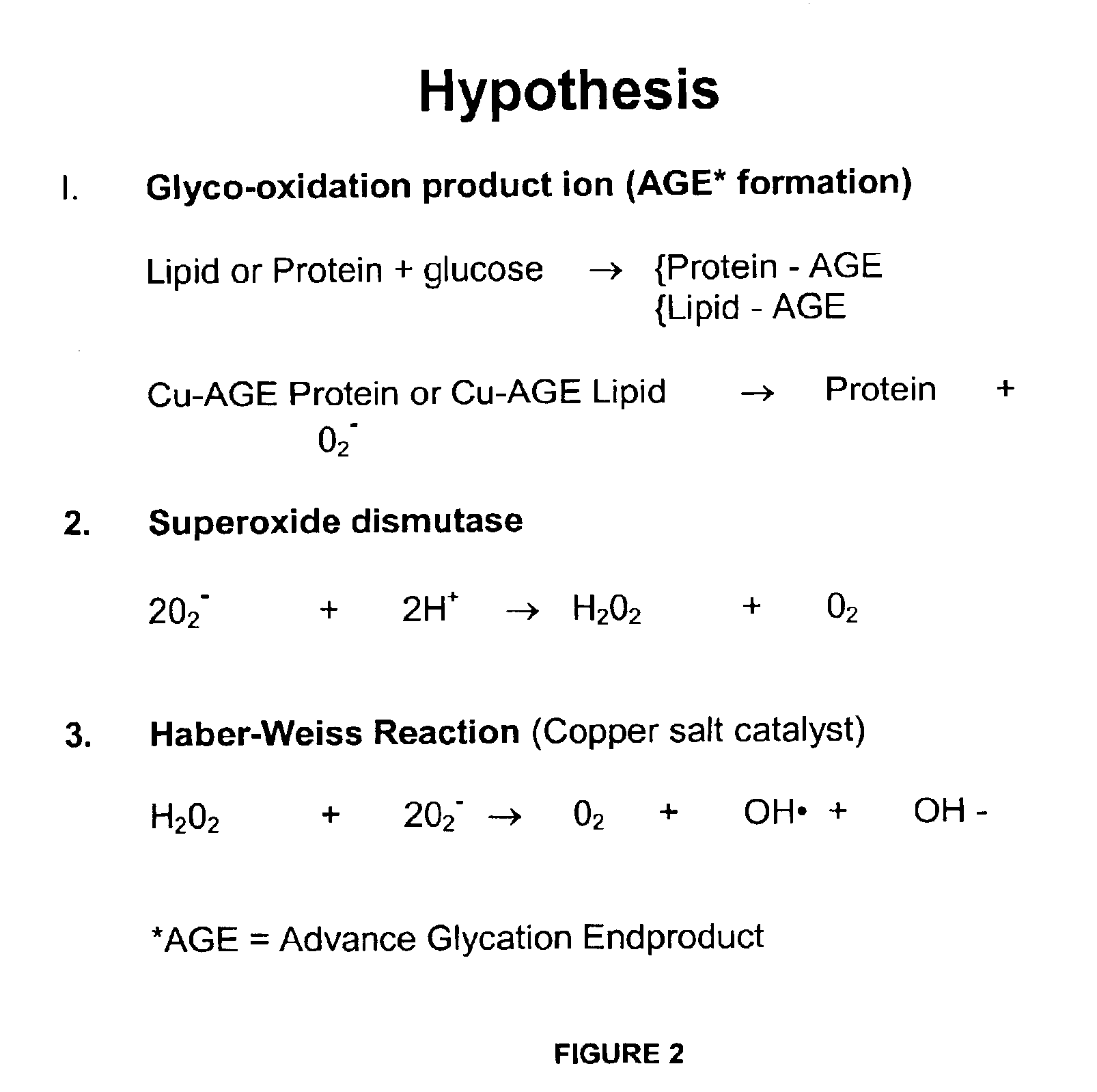
Preventing and/or treating cardiovascular disease and/or associated heart failure
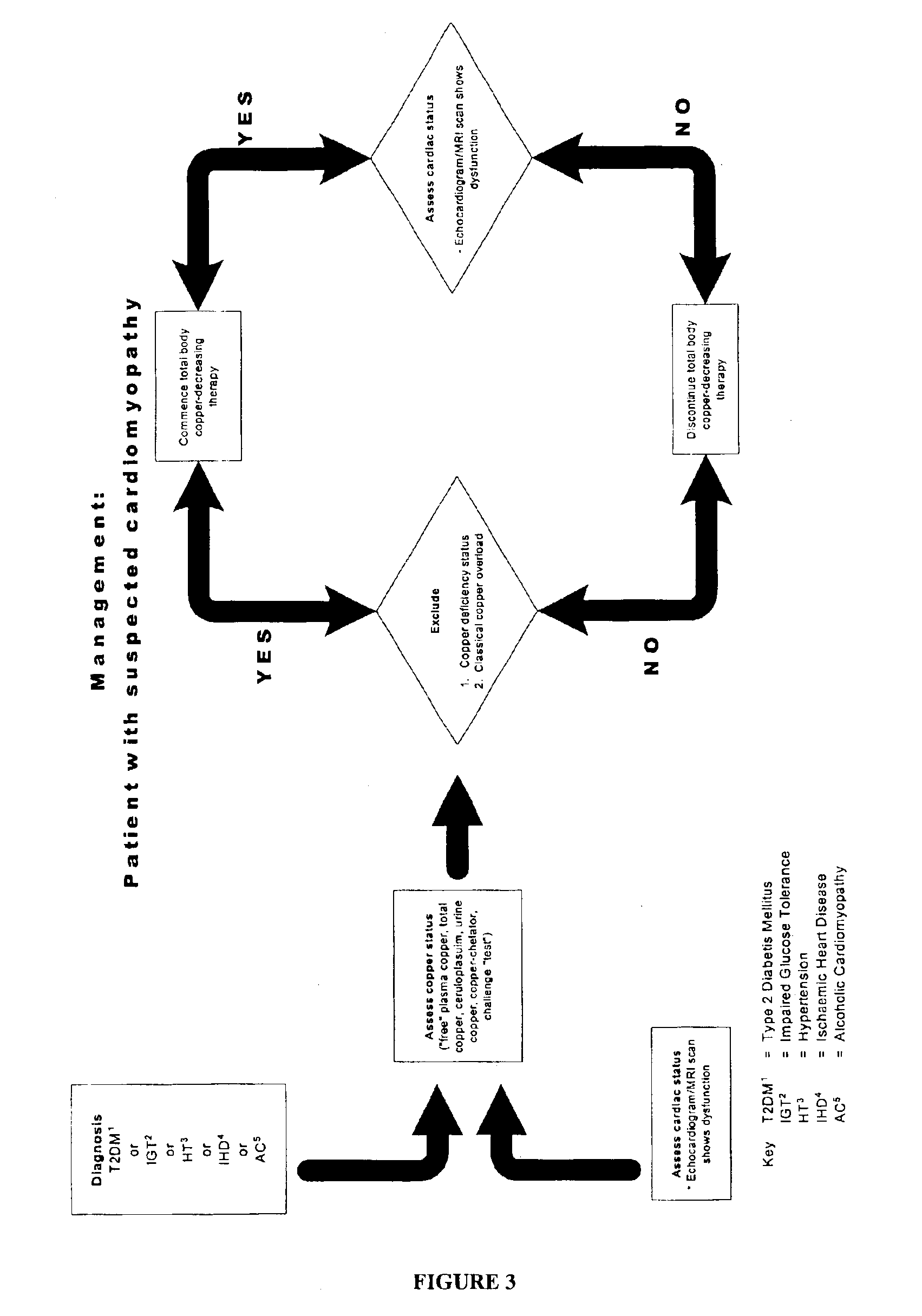
Methods are provided for reducing copper values for, by way of example, treating, preventing or ameliorating tissue damage such as, for example, tissue damage that may be caused by (i) disorders of the heart muscle (for example, cardiomyopathy or myocarditis) such as idiopathic cardiomyopathy, metabolic cardiomyopathy which includes diabetic cardiomyopathy, alcoholic cardiomyopathy, drug-induced cardiomyopathy, ischemic cardiomyopathy, and hypertensive cardiomyopathy, (ii) atheromatous disorders of the major blood vessels (macrovascular disease) such as the aorta, the coronary arteries, the carotid arteries, the cerebrovascular arteries, the renal arteries, the iliac arteries, the femoral arteries, and the popliteal arteries, (iii) toxic, drug-induced, and metabolic (including hypertensive and / or diabetic disorders of small blood vessels (microvascular disease) such as the retinal arterioles, the glomerular arterioles, the vasa nervorum, cardiac arterioles, and associated capillary beds of the eye, the kidney, the heart, and the central and peripheral nervous systems, (iv) plaque rupture of atheromatous lesions of major blood vessels such as the aorta, the coronary arteries, the carotid arteries, the cerebrovascular arteries, the renal arteries, the iliac arteries, the fermoral arteries and the popliteal arteries, (v) diabetes or the complications of diabetes.
Owner:PHILERA NEW ZEALAND +1
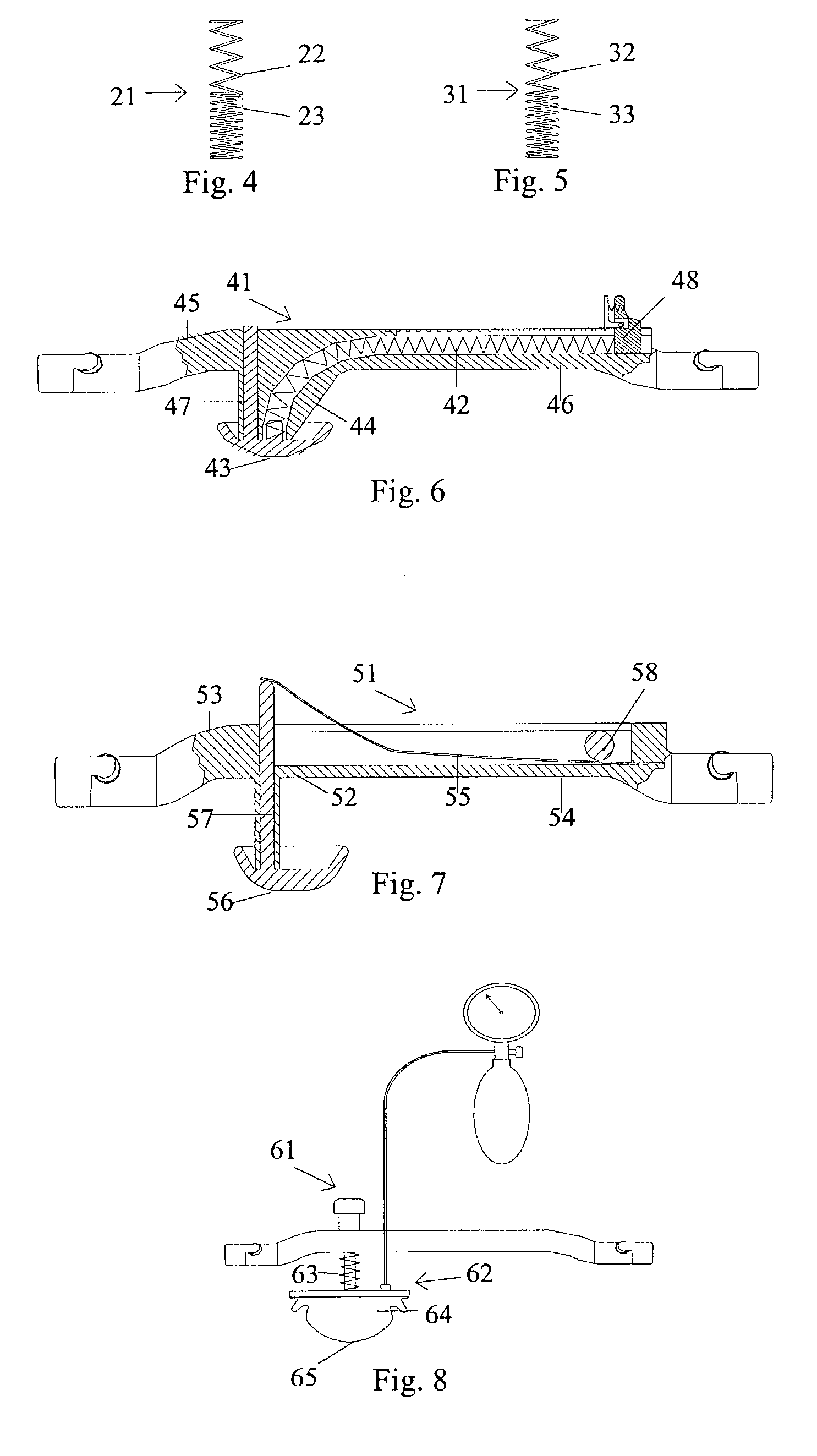
Femoral compression device
InactiveUS7329270B2Large internal resilienceInsensitive to movementTourniquetsCoil springCompression device
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
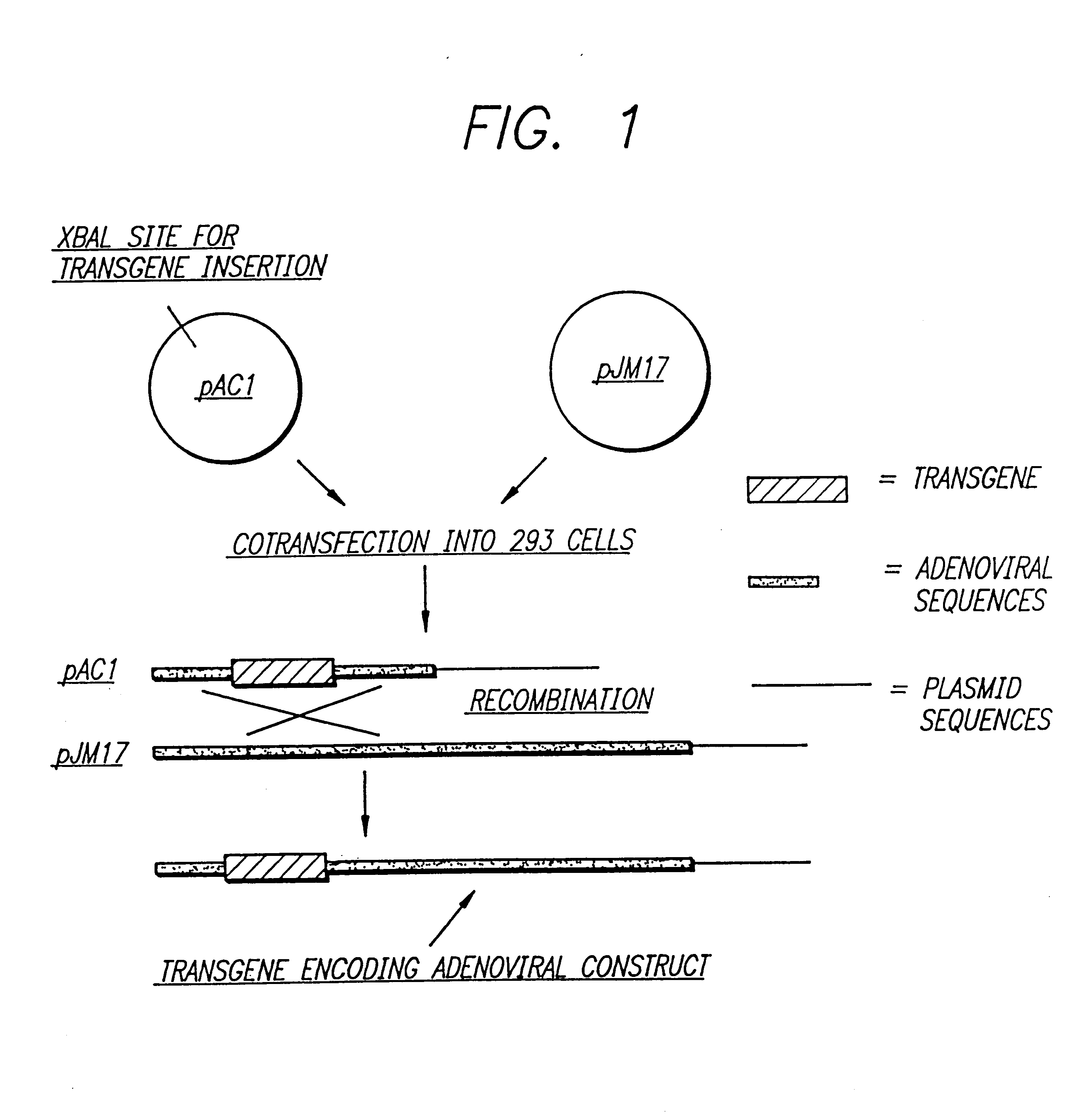
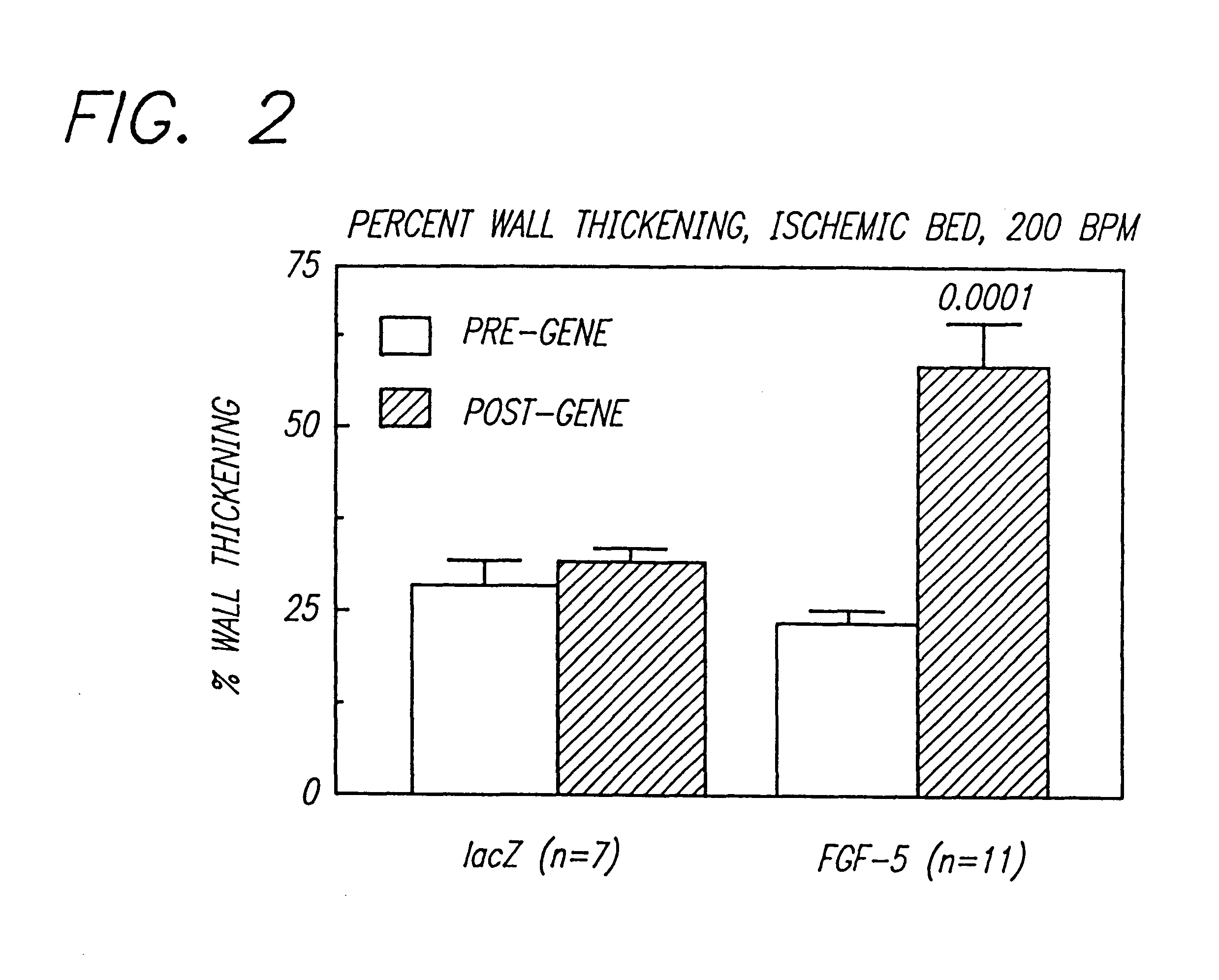
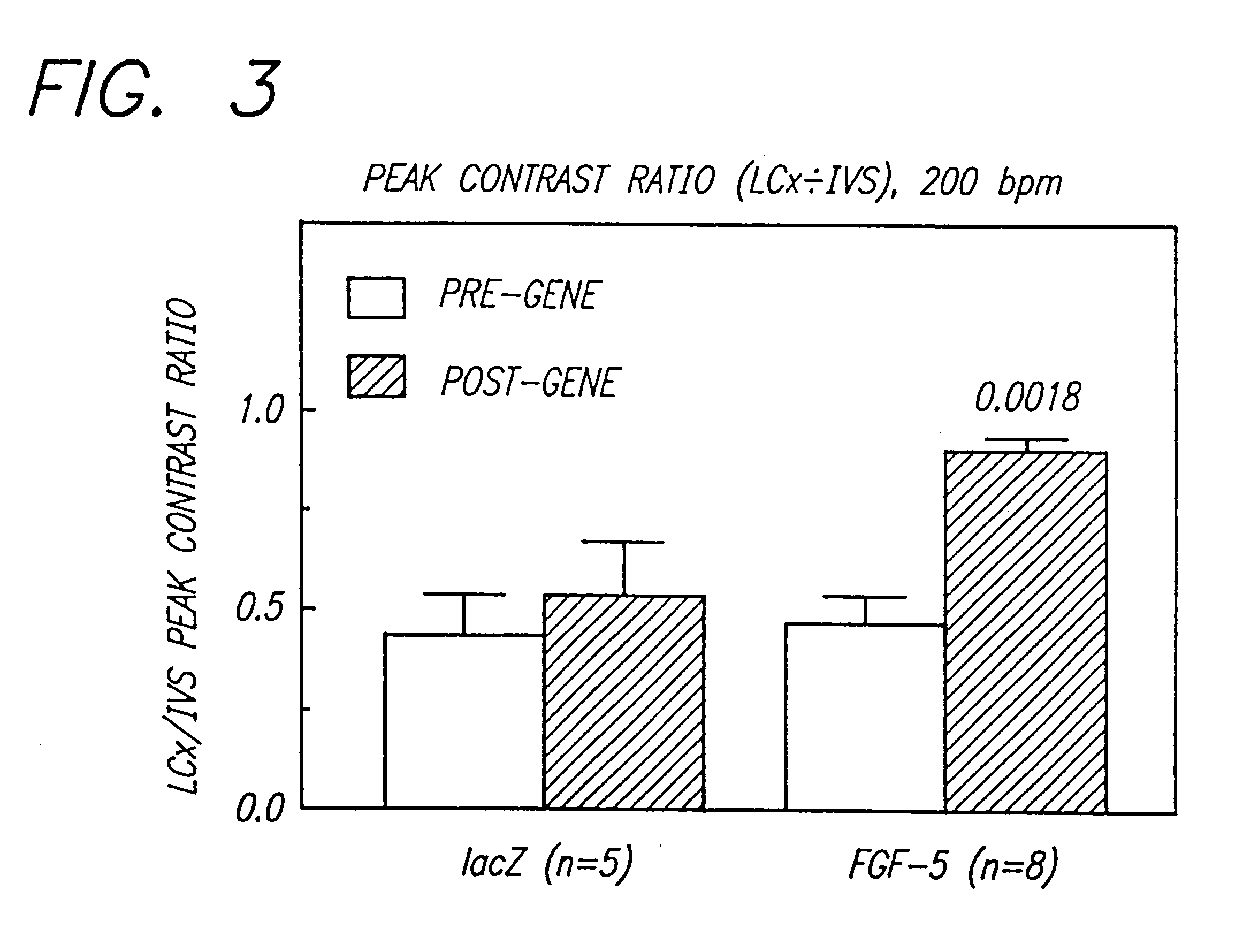
Gene therapies for enhancing cardiac function
The transgene-inserted replication-deficit adenovirus vector is effectively used in in vivo gene therapy for peripheral vascular disease and heart disease, including myocardial ischemia, by a single intra-femoral artery or intracoronary injection directly conducted deeply in the lumen of the one or both femoral or coronary arteries (or graft vessels) in an amount sufficient for transfecting cells in a desired region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Femoral compression device with progressive pressure device
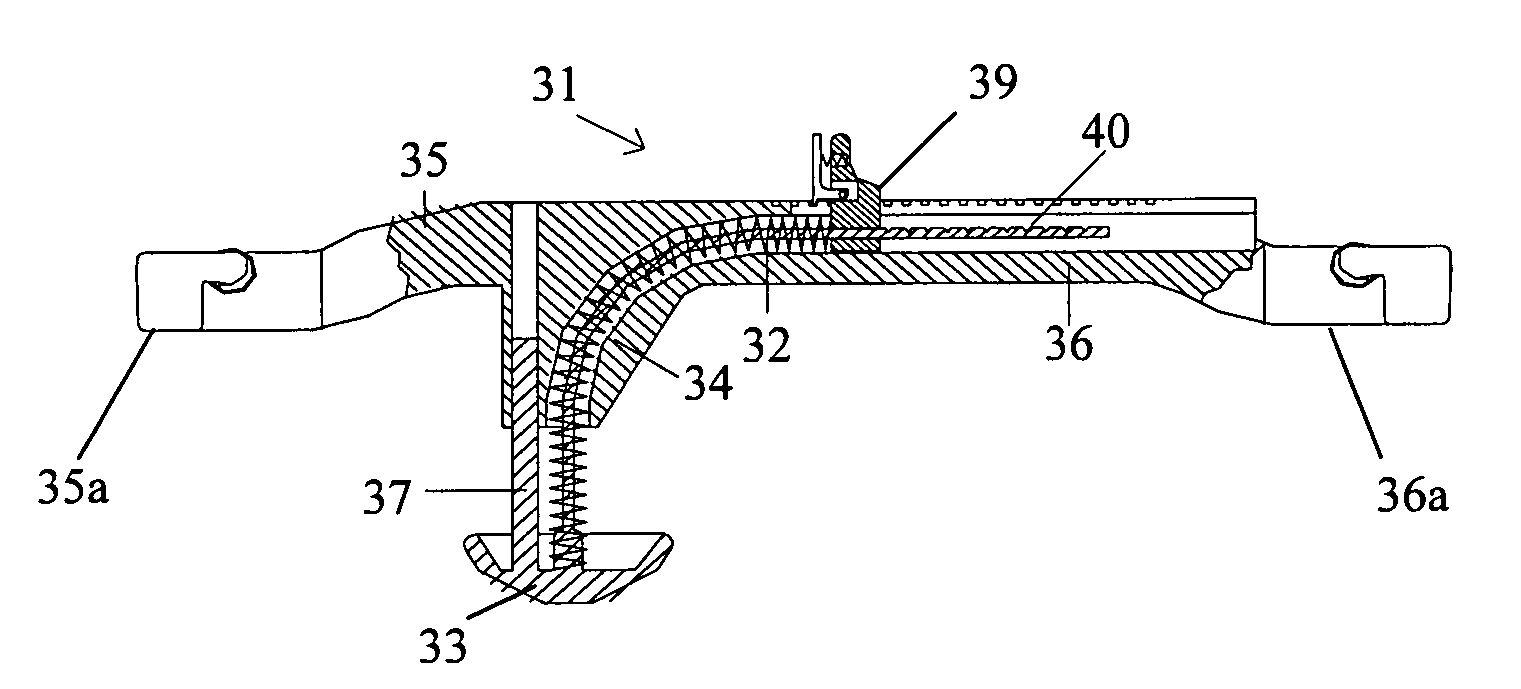
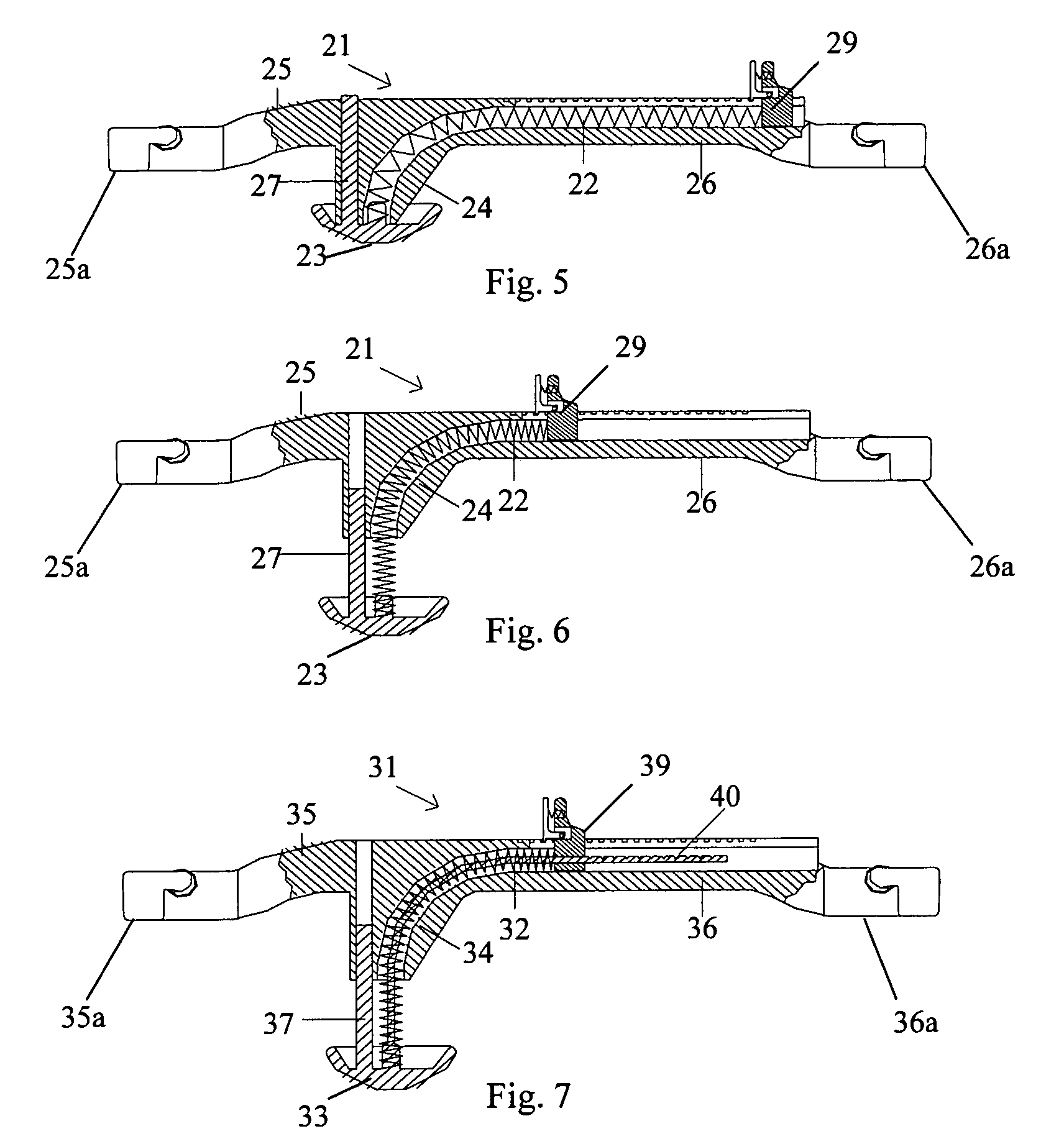
A femoral compression device (1; 41; 51; 61) for compressing a femoral artery of a patient is provided. The femoral compression device (1; 41; 51; 61) comprises a pressure device (7; 21; 31; 42; 55; 62), a compression member (8; 43; 56; 65) for compressive bearing against a puncture site, a base portion (3; 44; 52) provided with two opposing extensions (4, 5; 45, 46; 53, 54), to the ends of which a belt (6), which is adapted to be arranged around the patient's body, can be fixed. According to the invention, the pressure device (7; 21; 31; 42; 55; 62) is characterized by non-uniform overall action constants, such that when a low compression pressure is applied, the pressure device (7; 21; 31; 42; 55; 62) exhibits a small action constant, and when a high compression pressure is applied, the pressure device (7; 21; 31; 42; 55; 62) exhibits a large action constant.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Hemostasis valve device
The present invention relates to a hemostasis valve device which allows a wire or a catheter to be inserted into the left or right coronary artery via the femoral artery or an arm artery when a Cardiac Catheterization or Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty operation is performed, wherein two independent sealing members are opened and closed by press and release actions of push buttons coupled to a body and the rotation of a fastening tube, respectively, so that the leakage of blood or the inflow of outside air is simply and effectively blocked during the operation, and a drug influx tube for allowing a medicine such as a thrombolitic drug to flow into a patient during the operation pivots and is adjusted in a stepwise manner within a certain range of angles according to body conditions or movements of the patient.
Owner:HUBIOMED INC
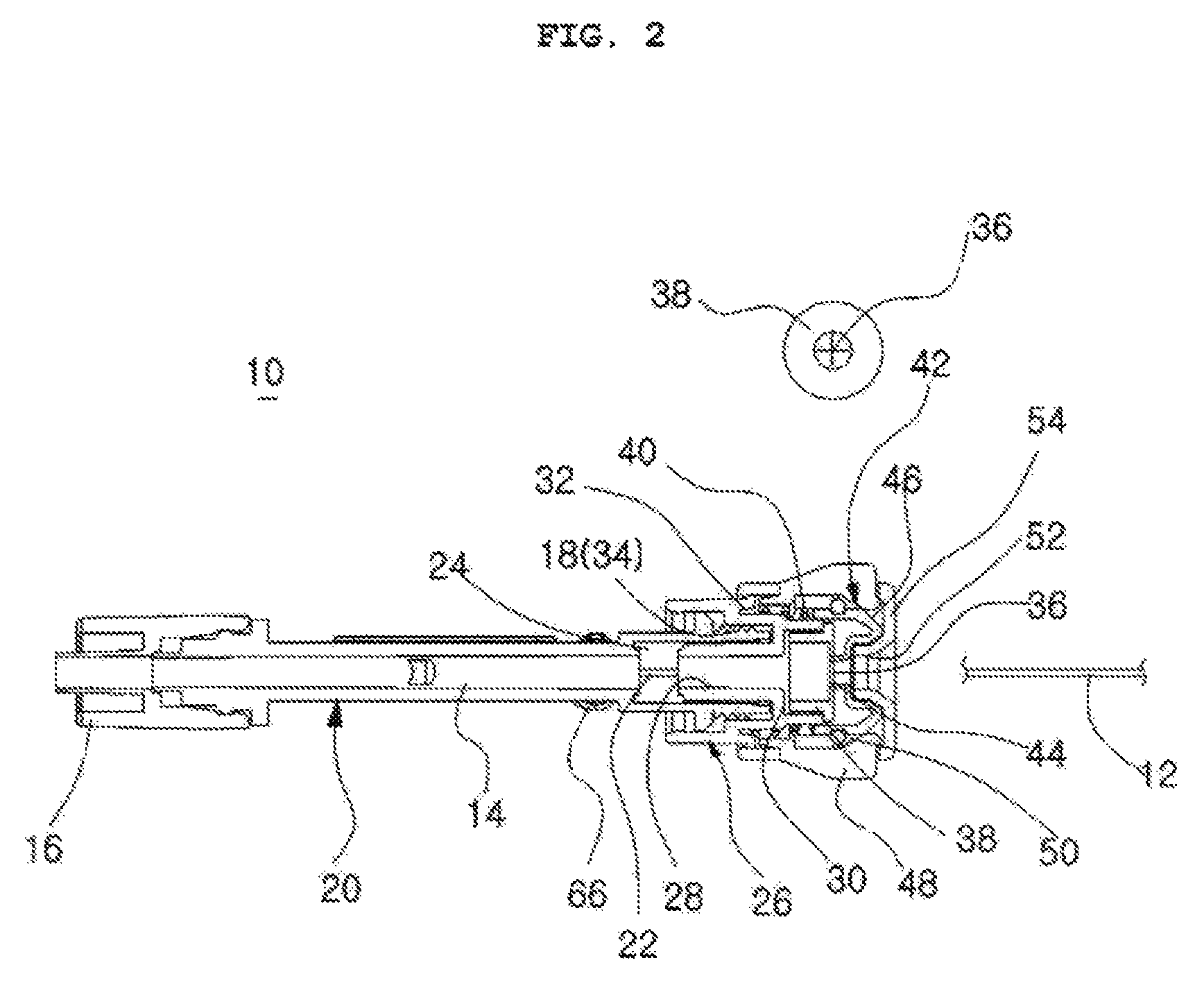
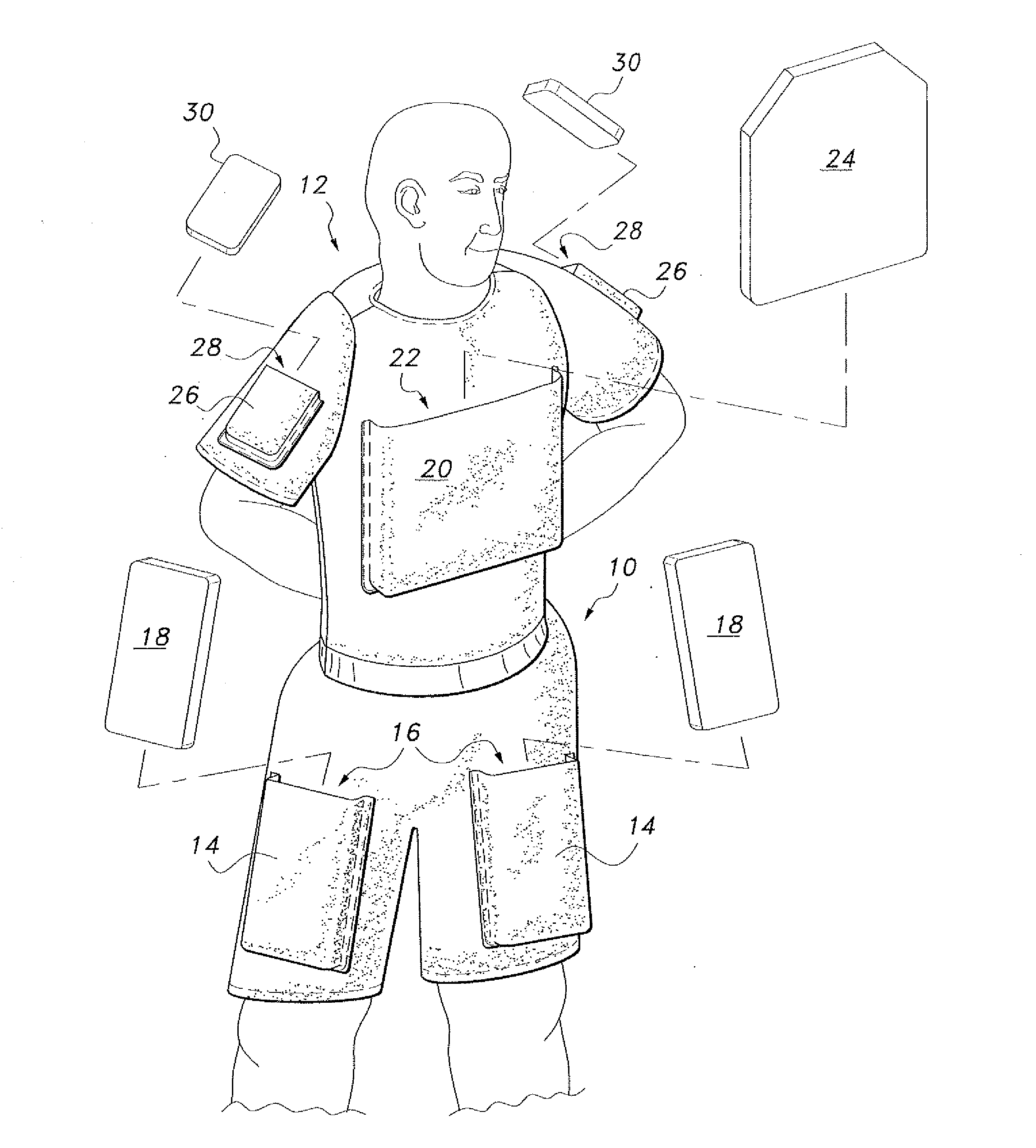
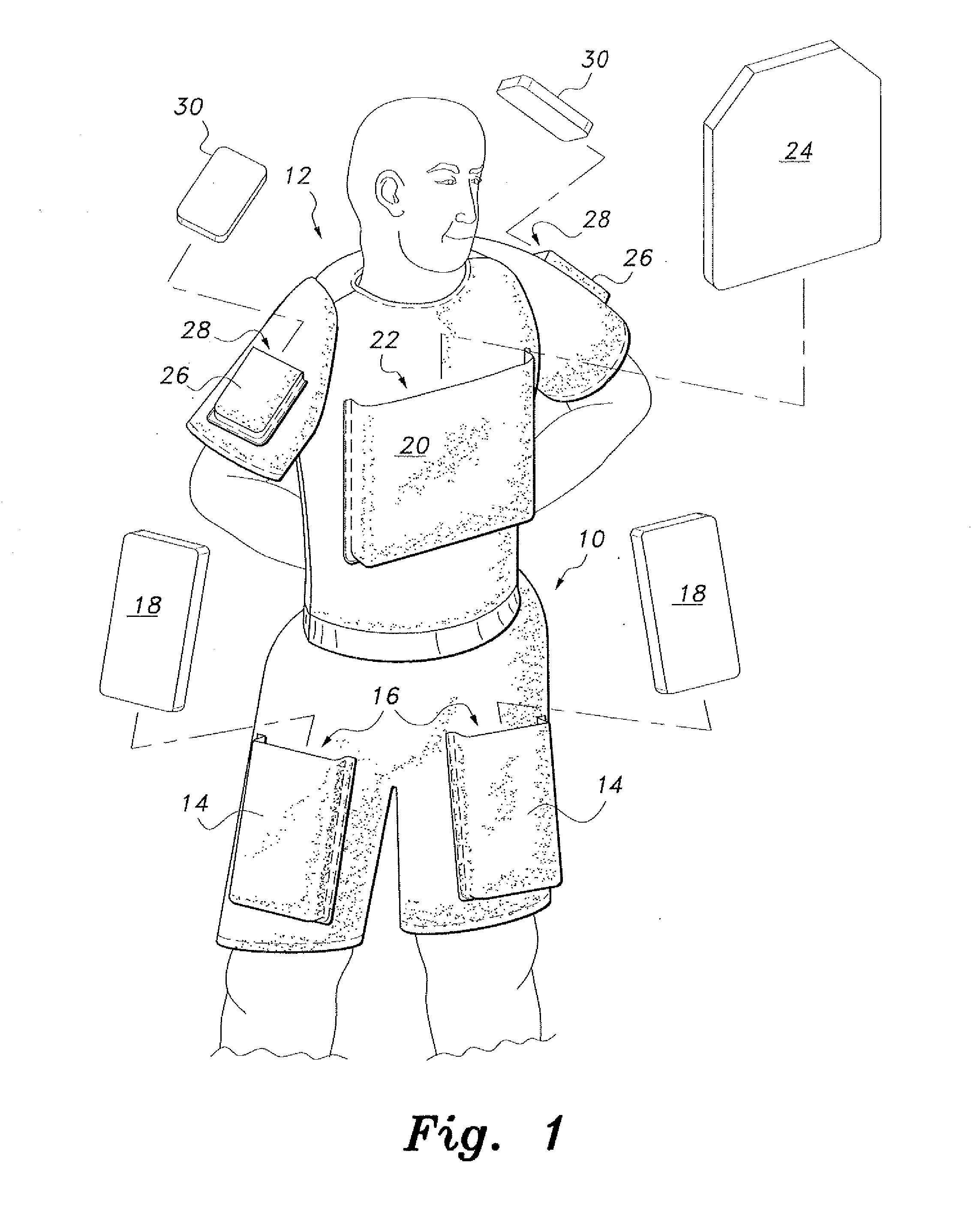
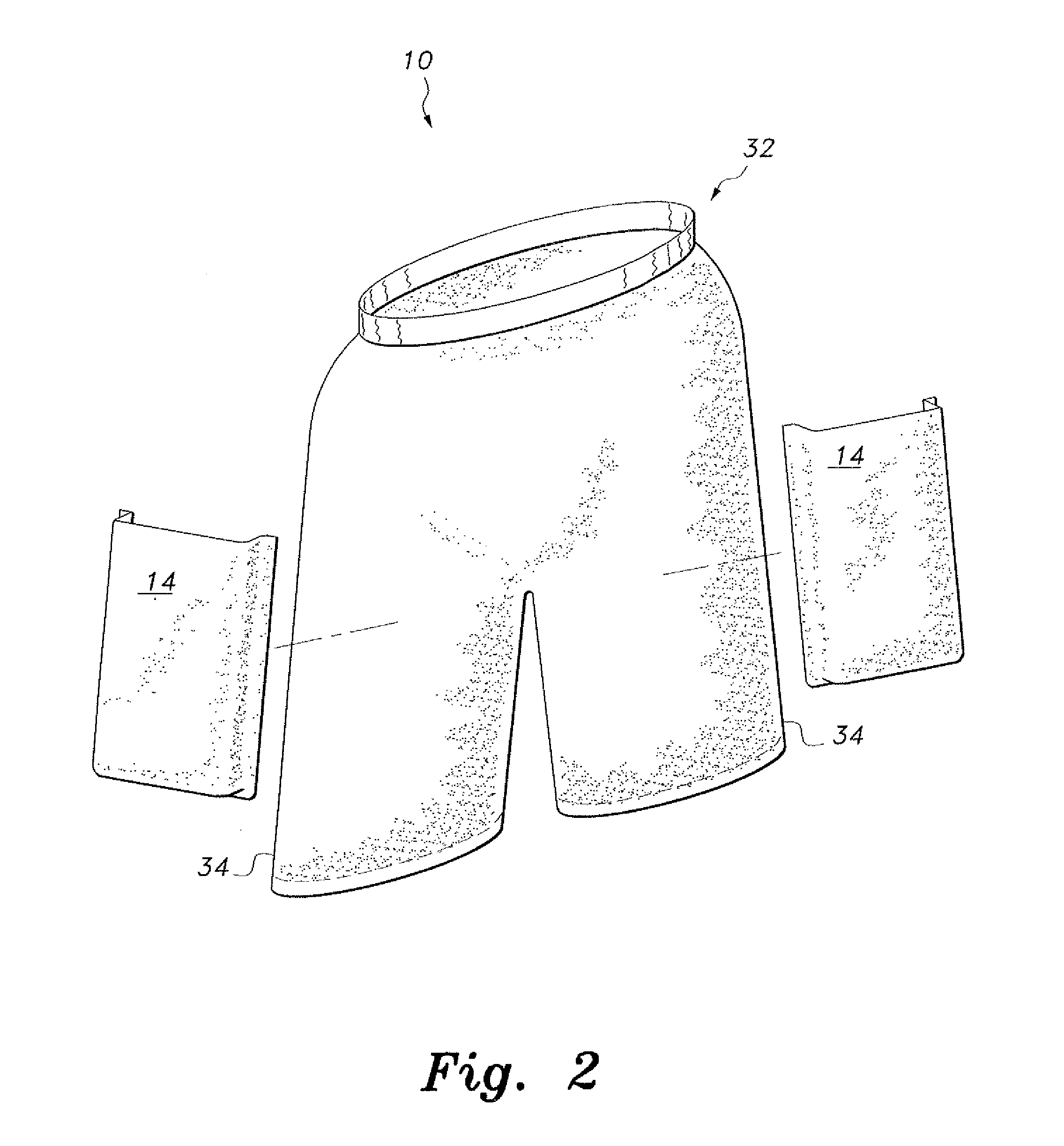
Ballistic shield support undergarments
InactiveUS20110131694A1Comfortable supportPersonal protection gearProtective garmentFemoral arteryMechanical engineering
The ballistic shield support undergarments are undergarments for use by soldiers, tactical personnel and the like, providing comfortable support for ballistic shielding, without limiting the wearer's dexterity or freedom of movement. The ballistic shield support undergarments include both underpants and an undershirt, preferably worn as a set. The pair of undershorts include a waist portion and a pair of leg portions, as is conventionally known. A pair of pockets are provided, with each pocket being secured to a respective one of the leg portions by stitching or the like. A pair of ballistic shields, such as small arms protective inserts (SAPIs) or the like, are further provided, with each ballistic shield being removably received within a respective one of the pockets. Each pocket is positioned on the respective leg portion so that the respective ballistic shield received therein covers the wearer's femoral artery.
Owner:FEARON WILLIAM G
Retrograde entry antegrade placement for femoral artery access
A Retrograde Entry Antegrade Placement (REAP) method and apparatus facilitate the antegrade (i.e., in the direction of blood flow) placement of endovascular devices for treatment of lower extremity arterial disease. Initially, a retrograde entry is made into the arterial system of a patient at an entry point with a curved needle, which then exits at an exit point proximal to the entry point, with a first wire then passed through the lumen of the curved needle. From the skin exit point, a Dual-Lumen Access Director (DAD) device is advanced in the antegrade direction down the first wire in a first lumen and enters the CFA 1 lumen. A second wire is passed down a second lumen in the DAD device and follows the SFA lumen in the antegrade direction. The DAD device is removed, and a standard dilator sheath is inserted over the second wire and the endovascular treatment begins.
Owner:POLR ANGIOSCI LLC
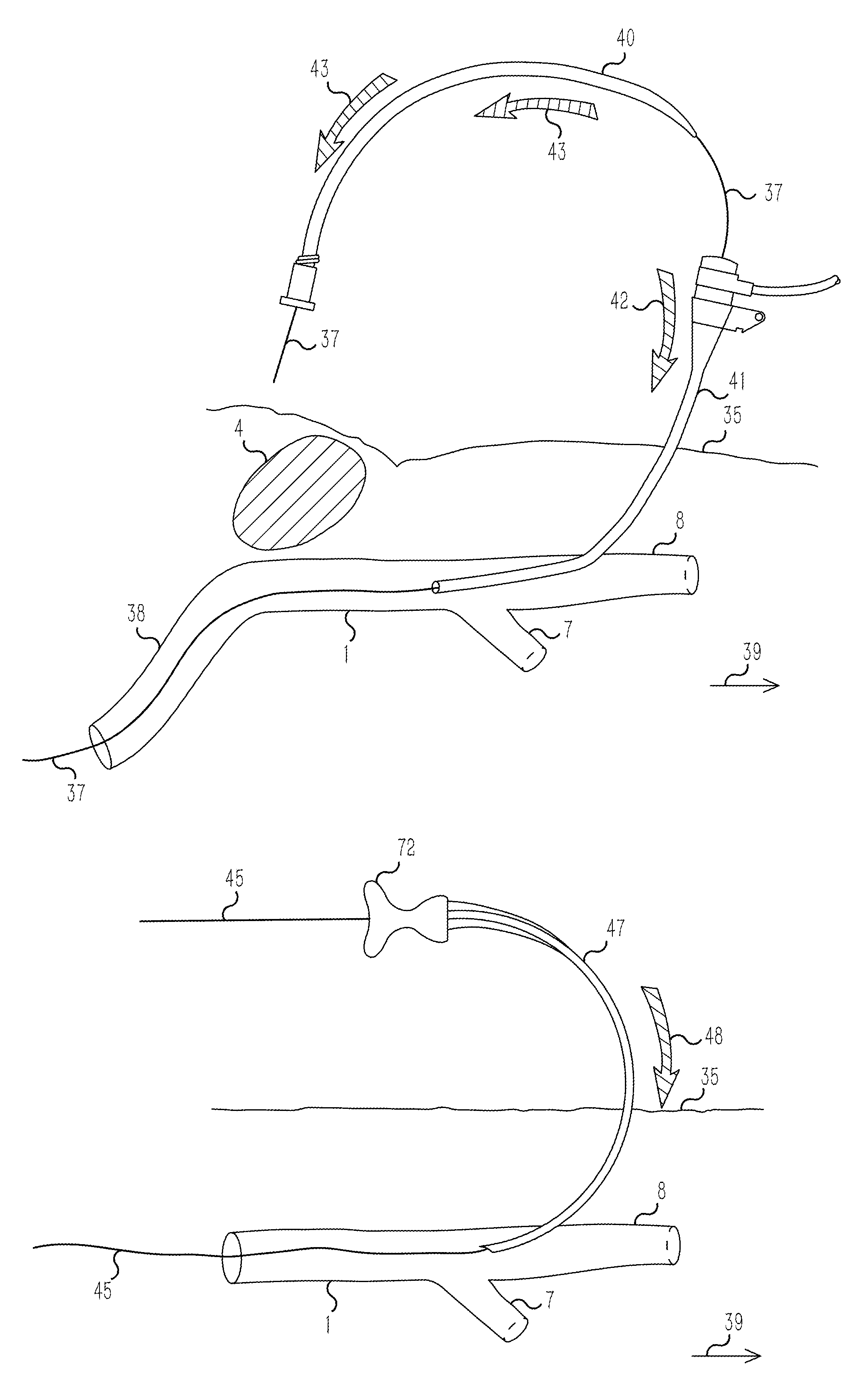
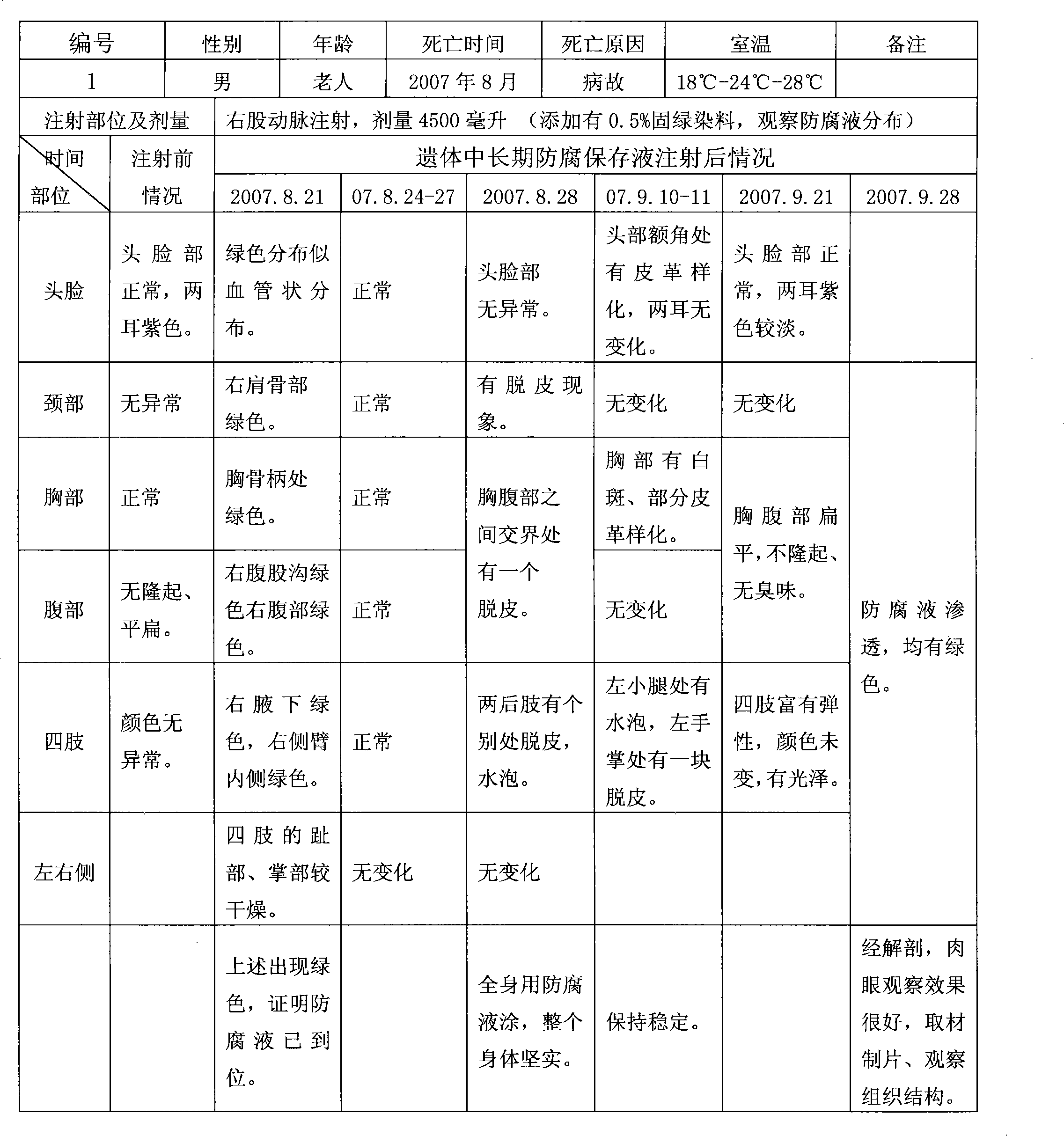
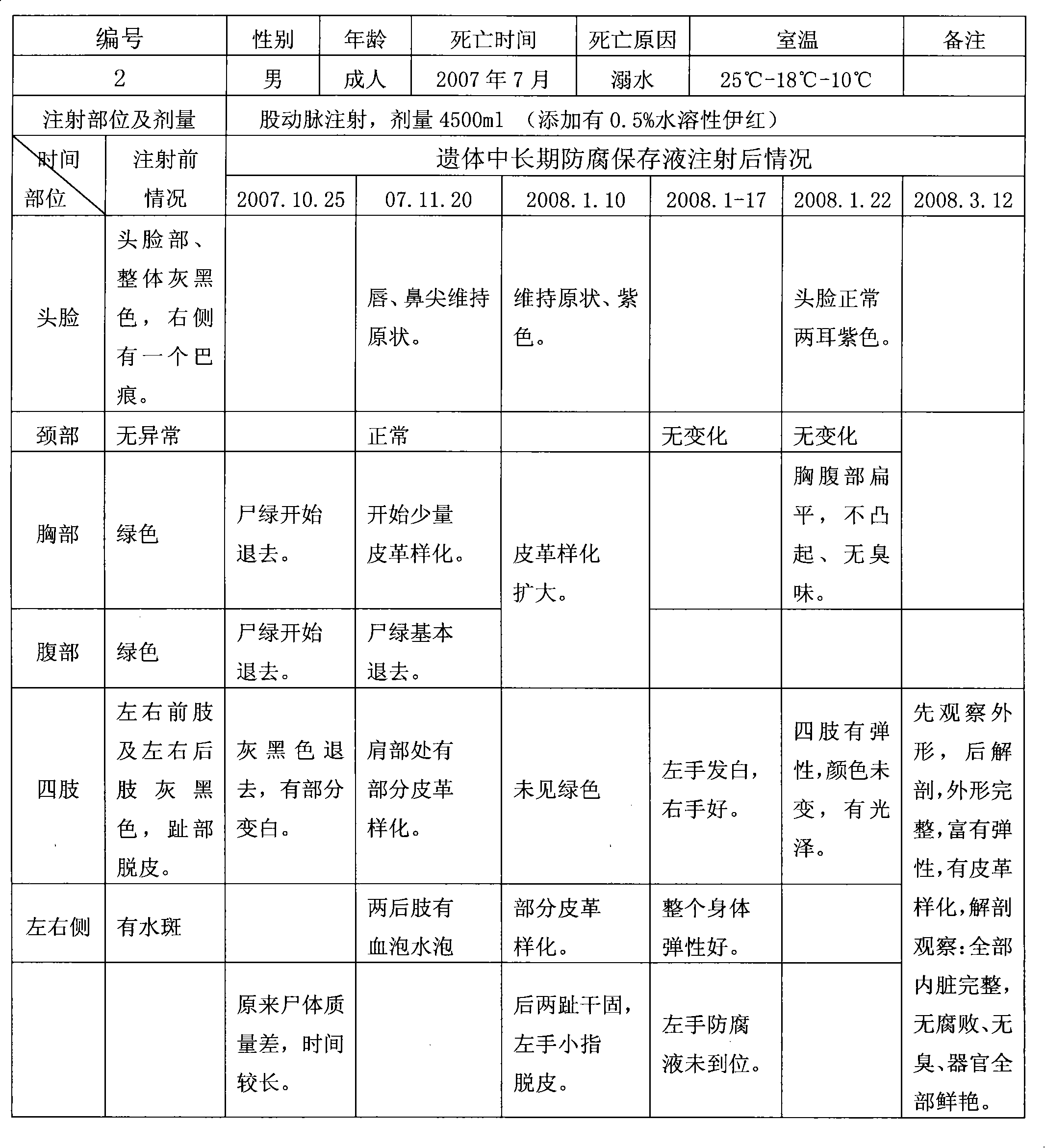
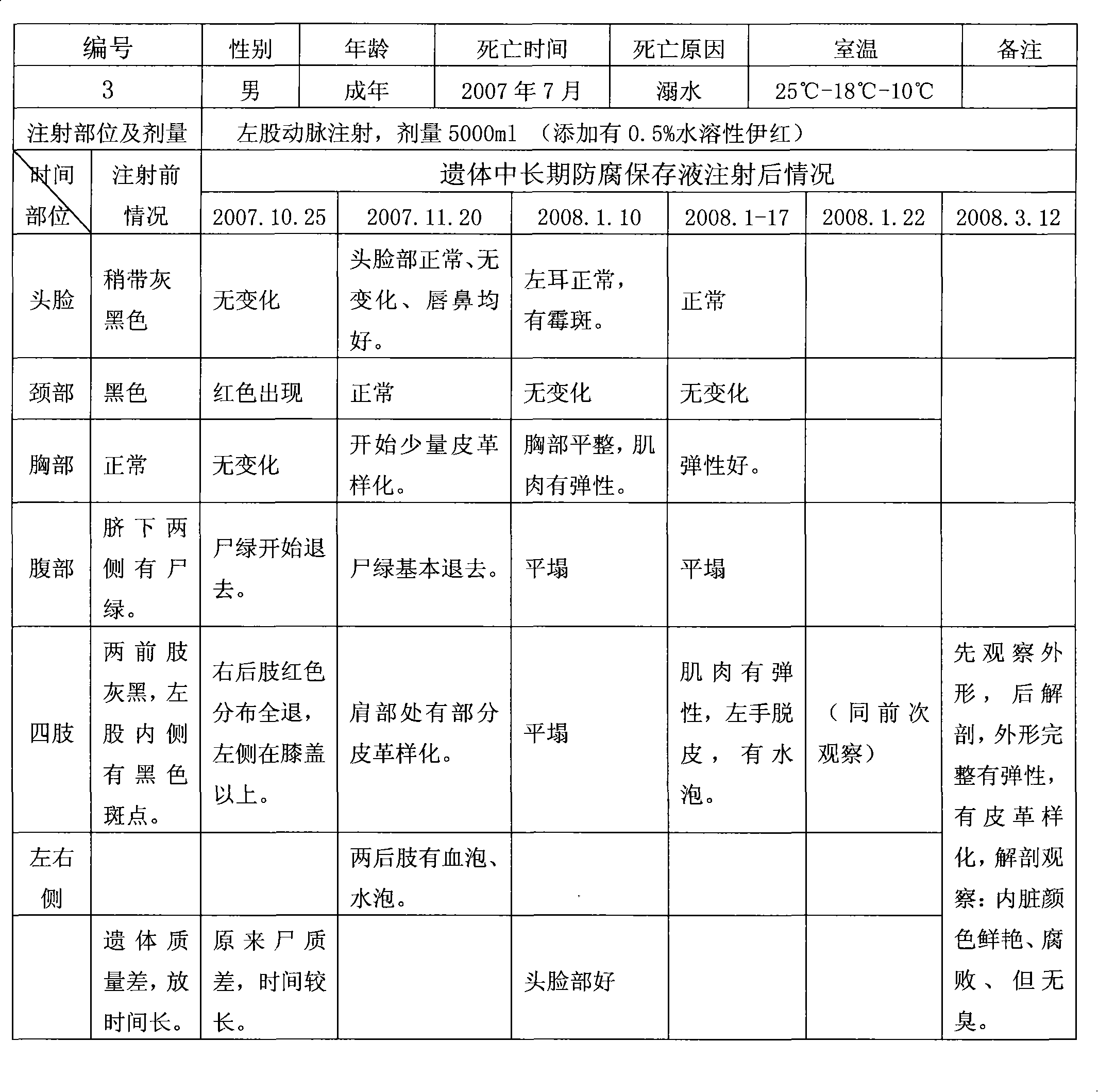
Long-term antiseptic preserving fluid of remains and application thereof
ActiveCN101601377AImprove disinfection effectReasonable formulaDead animal preservationPropanoic acidAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a long-term antiseptic preserving fluid of remains, which comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 15-40% of glycerine, 5-80% of alcohol, 1-20% of propionic acid, 0.5-25% of hexamine, 0.1-15% of 5chlorine-2-4methyl-4isothiazole-3ketone and the balance of water. The preserving fluid is applied to the remains of people and fish, amphibian and reptile and animal specimens gathered in the field and injected into the remains mainly through the axillary artery and / or the femoral artery of the remains, and the remains can be antiseptically preserved for 15-100 days under the conditions of a room temperature of 18-27 DEG C and a relative humidity of 45-60 percent. The invention has the advantages of reasonable formula, safe ingredient, accordance to environmental protection, no poison and harm to operators, no stimulation, no damages and blackening of tissues and organs by the antiseptic preservation of the remains, maintenance of a natural state of the remains, simple preparation method, convenient use and benefit to popularization.
Owner:上海市殡葬服务中心
Fluoroscopy-independent, endovascular aortic occlusion system
ActiveUS20130102926A1Quick measurementIncrease perfusionBalloon catheterOther printing matterArterial occlusionsLeft subclavian artery
A system for deploying and selectively inflating a thoracic aortic balloon at a desired location within the thoracic aorta for resuscitative aortic occlusion, inferior to the left subclavian artery, without the aid of fluoroscopy is described. Using CT imaging data, a distance between readily identifiable and consistently located external landmarks of torso extent is measured. Next, using the same data, a second distance from the femoral artery to a desired aortic occlusion location inferior to the left subclavian artery is determined. A correlation between the external measure of torso extent and the desired intra-arterial (i.e. endovascular) distance within the torso is made. Using a nomogram, a calibrated endovascular resuscitative thoracic aortic occlusion system can be positioned to this desired location on any injured individual with end-stage shock and impending cardiovascular collapse or death without the aid of fluoroscopy for delivery or balloon inflation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Magnetohydrodynamic cardiac assist device
InactiveUS6440059B1Less invasive procedureReduce morbidityControl devicesSurgeryLeft ventricular sizeElectrode polarity
A left ventricular assist device (LVAD) utilizing MHD principles, wherein an aortic electrode assembly is located within a main femoral artery in the aorta, in the vicinity of the heart of a patient, which electrode assembly is exposed to a high density magnetic field generated outside of the patient. The high density magnetic field urges electrified blood within the artery in the vicinity of the electrode along the length of the electrode in a uniform direction, thereby providing a fluid pumping force and pressure commensurate with the magnetic field strength and electrode current in accordance with MHD theory and practice. A cardio bypass system is also taught, wherein in addition to the aortic electrode assembly, as second electrode assembly is placed in the inferior vena cava having an opposite electrode polarity to the aortic electrode assembly, such that the second electrode assembly directs blood flow toward the heart. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the magnetic field is generated exterior of the patient via a superconducting magnet which is designed to bridge the torso of the patent, such that the electrodes are generally centrally disposed within the magnetic field, along a longitudinal axis aligned with the aorta (and inferior vena cava), and generally orthogonal to the magnetic field. Sensors monitoring the patient may utilize ECG, blood pressure, and other data to control the magnet, varying the magnetic field so as to emulate the pumping action and intensity of the patents heart in real time, or simulate same.
Owner:CIMEX BIOTECH L C
Inflatable blanket for use in cardiac surgery
A method of performing cardiac surgery on a patient's heart, including covering a patient with an inflatable blanket for a forced air convection system, the inflatable blanket having at least one separable seal line within the blanket. The separable seal line may be separated to form a slit. A patient's femoral artery is accessed through the slit, and an elongate medical instrument is passed through the slit, and through the femoral artery toward the patient's heart. Cardiac surgery is performed with the elongate medical instrument, and the elongate medical instrument is withdrawn from the femoral artery through the slit.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
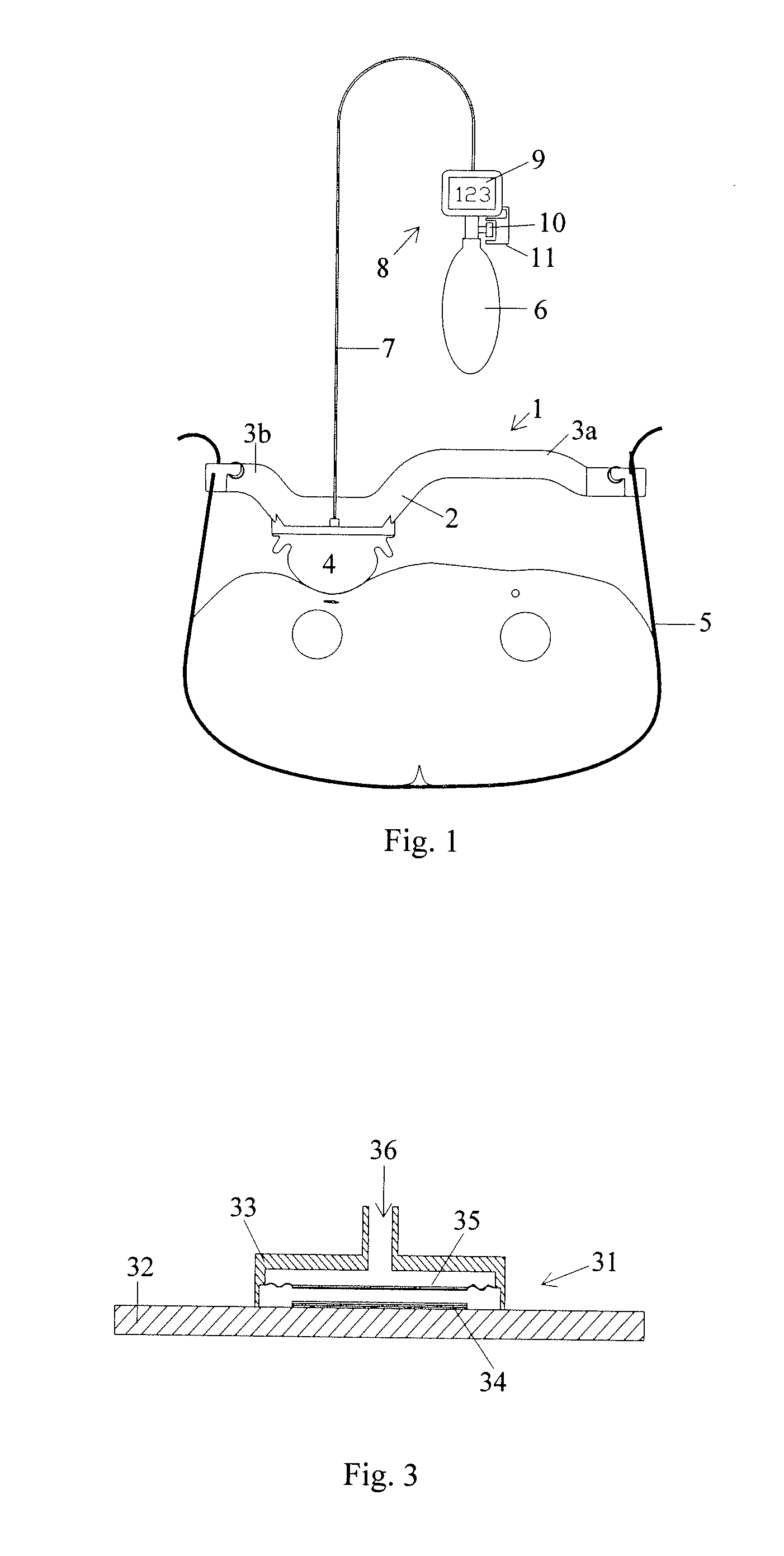
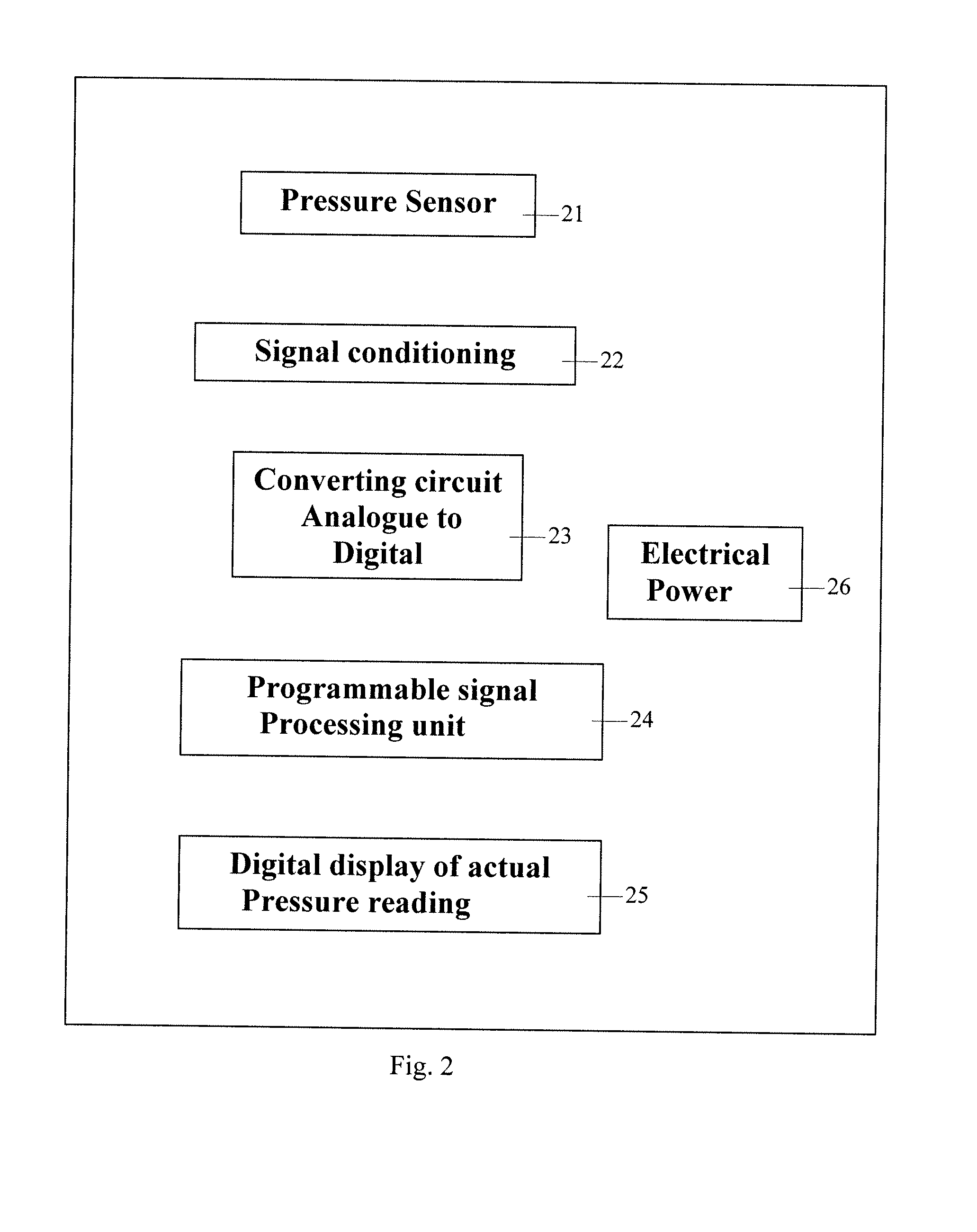
Femoral compression device
ActiveUS7938846B2Spares the patient from discomfortExtended treatment timeCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringFemoral boneCompression device
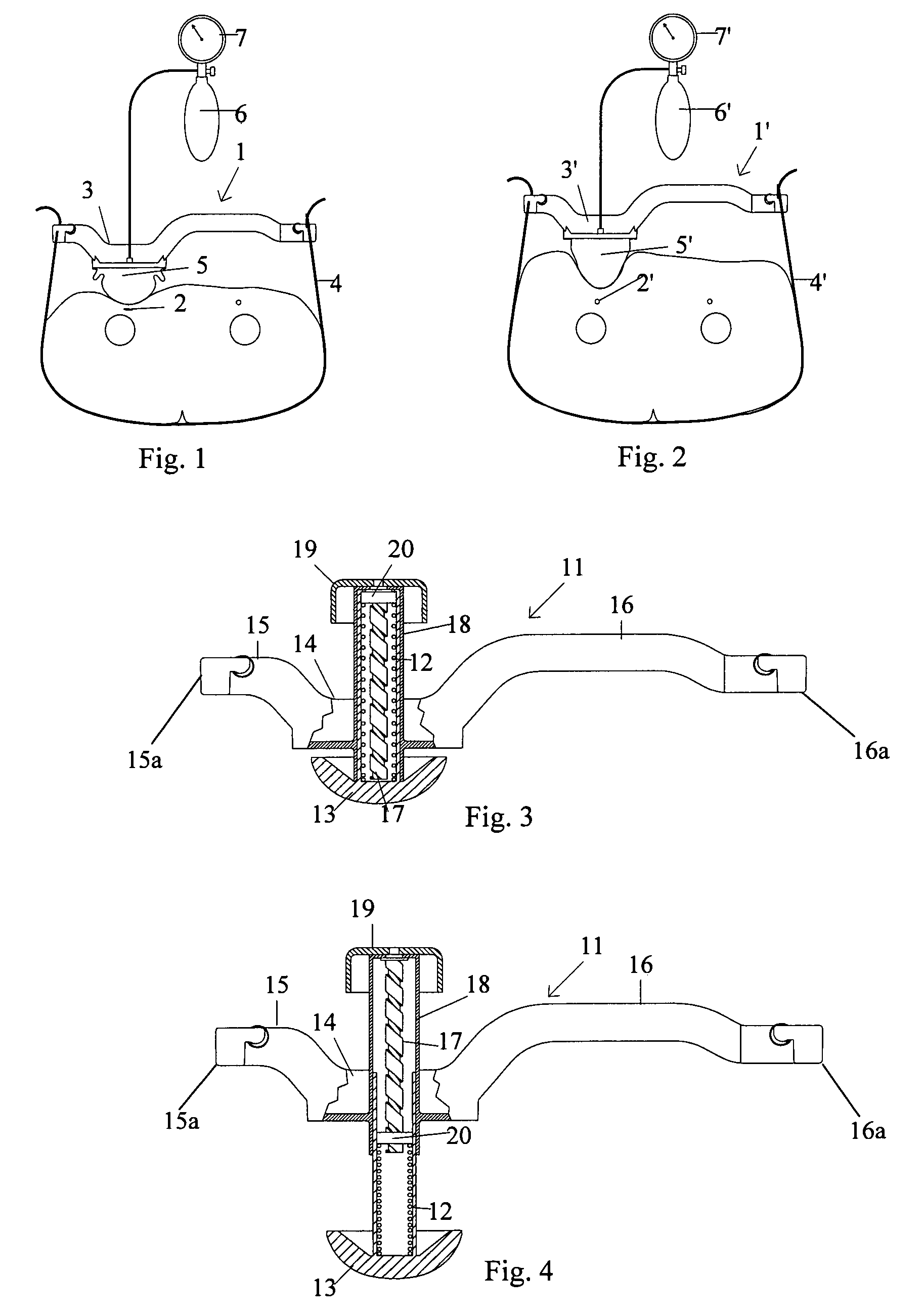
A femoral compression device (1) for compressive bearing against the femoral artery of a patient, comprising a base plate (2), an inflatable air cushion (4), and an electronic manometer (8) connected to the inflatable air cushion for measurement of the current pressure difference between the pressure prevailing inside the inflatable air cushion and the ambient air pressure. The femoral compression device can further comprise a mechanical device (11; 46) which prevents an air opening leading to the inflatable air cushion from being closed before the manometer is zeroed. In another embodiment, an electronic manometer is provided such that a current characteristic of an electric signal representing the current pressure difference can be compared with a corresponding characteristic which was obtained at zero pressure difference and which was stored in the electronic manometer, wherein the manometer cannot be zeroed as long as the current characteristic deviates more than a predetermined amount from the stored characteristic.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
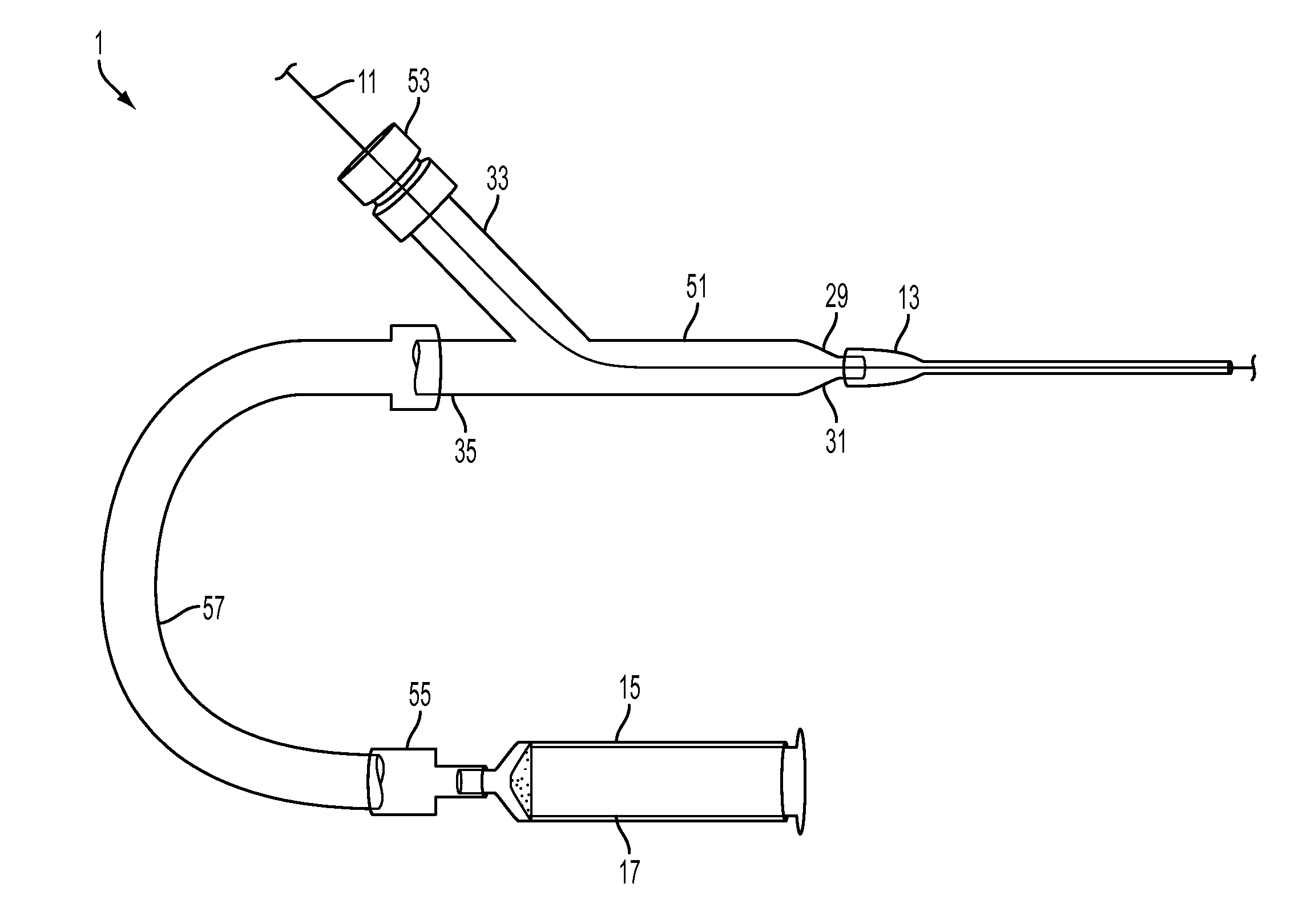
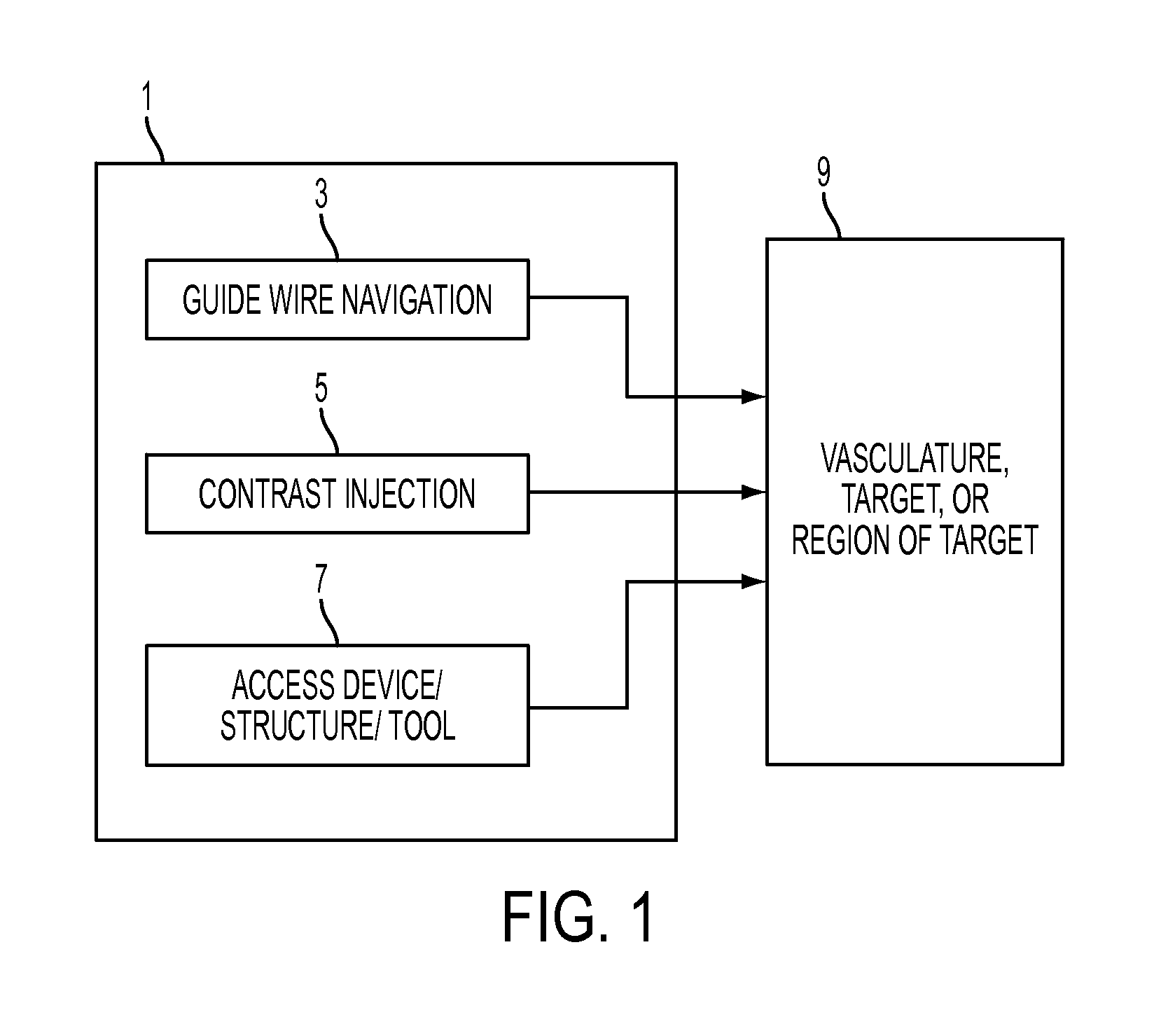
Access system for femoral vasculature catheterization and related method
InactiveUS20130096428A1Prevent backflowSafely and reliably punctureMedical devicesCatheterVeinCatheter
An access system and method for obtaining access to the interior vascular structures or other regions or collections of fluid or fluid-filled cavities inside the body. The system and method provides for injection of contrast agents (to confirm ideal position or condition), the passage of guide wires, and the eventual catheterization of the heart and other parts of the body via the pathway established through the puncture of a femoral artery. The system and method provides the ability to inject a contrast material and pass a guide wire through the same introducer device simultaneously (without necessarily moving it or removing any parts), with the device designed to prevent the backflow of the contrast material through the guide wire port during the contrast injection process The ideal location of access in the vein or artery can be seen by injecting contrast from a needle inside the structure and then using fluoroscopy.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
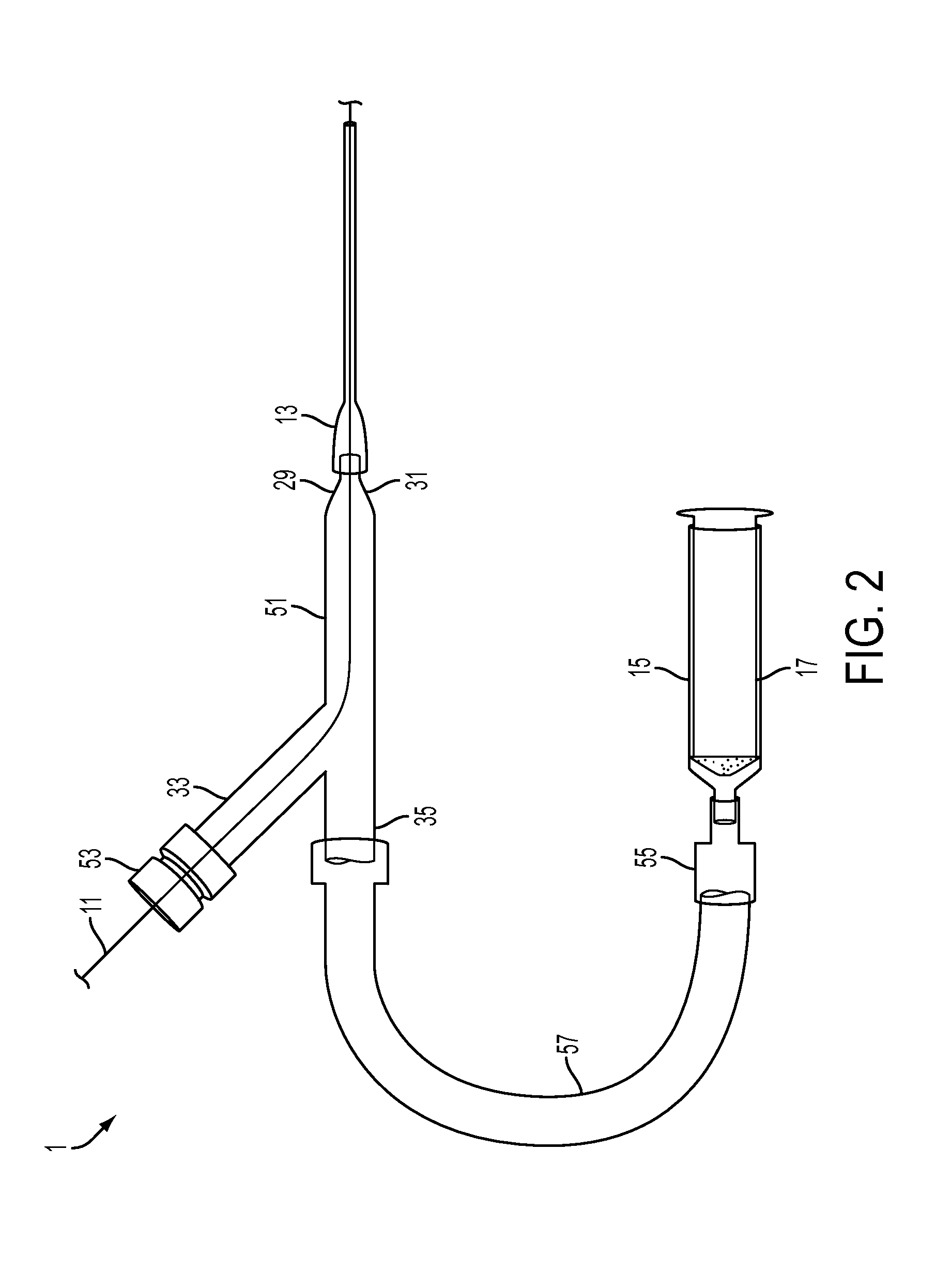
System and method for image segmentation, bone model generation and modification, and surgical planning
A computer-implemented method of preoperatively planning a surgical procedure on a knee of a patient including determining femoral condyle vectors and tibial plateau vectors based on image data of the knee, the femoral condyle vectors and the tibial plateau vectors corresponding to motion vectors of the femoral condyles and the tibial plateau as they move relative to each other. The method may also include modifying a bone model representative of at least one of the femur and the tibia into a modified bone model based on the femoral condyle vectors and the tibial plateau vectors. And the method may further include determining coordinate locations for a resection of the modified bone model.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Helical DeNervation Ablation Catheter Apparatus
A catheter apparatus carrying RF ablation electrodes on a helically configured portion of a flexible tube that can be inserted into the femoral artery of a patient, advanced into a renal artery, and then be manipulated to properly position electrodes carried by the helical tube to contact the endoluminal surface of the artery. While instrumentally monitoring the endoluminal surface's temperature and impedance (measured with electrodes that are in an intimate contact with the surface), a low level of RF energy can be applied to selected sites on the interior (endoluminal) surface of the artery in order to ablate the renal sympathetic nerves without affecting the abdominal, pelvic, or lower-extremity nerves.
Owner:MOGUL ENTERPRISES
Occlusion catheter for the ascending aorta
An occlusion catheter for the ascending aorta capable of obstructing the blood flow within the ascending aorta without inserting through the femoral artery. The occlusion catheter is provided with a drug release aperture formed in the region, which is closer to the proximal end of the catheter tube than a balloon on the outer circumference of the distal end and which is to be located in the vicinity of the coronary ostium when the balloon is placed within the ascending aorta. The present occlusion catheter, when inserted directly into the ascending aorta in the vicinity of the heart to obstruct the blood flow therewithin, enables delivery of a cardiac muscle protective drug to the vicinity of the coronary ostium without inserting the occlusion catheter through the femoral artery in the conventional manner.
Owner:VAYU
Method and Apparatus for Hemodynamic Monitoring Using Combined Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Measurement
ActiveUS20110137173A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionMeasurement deviceBlood flow
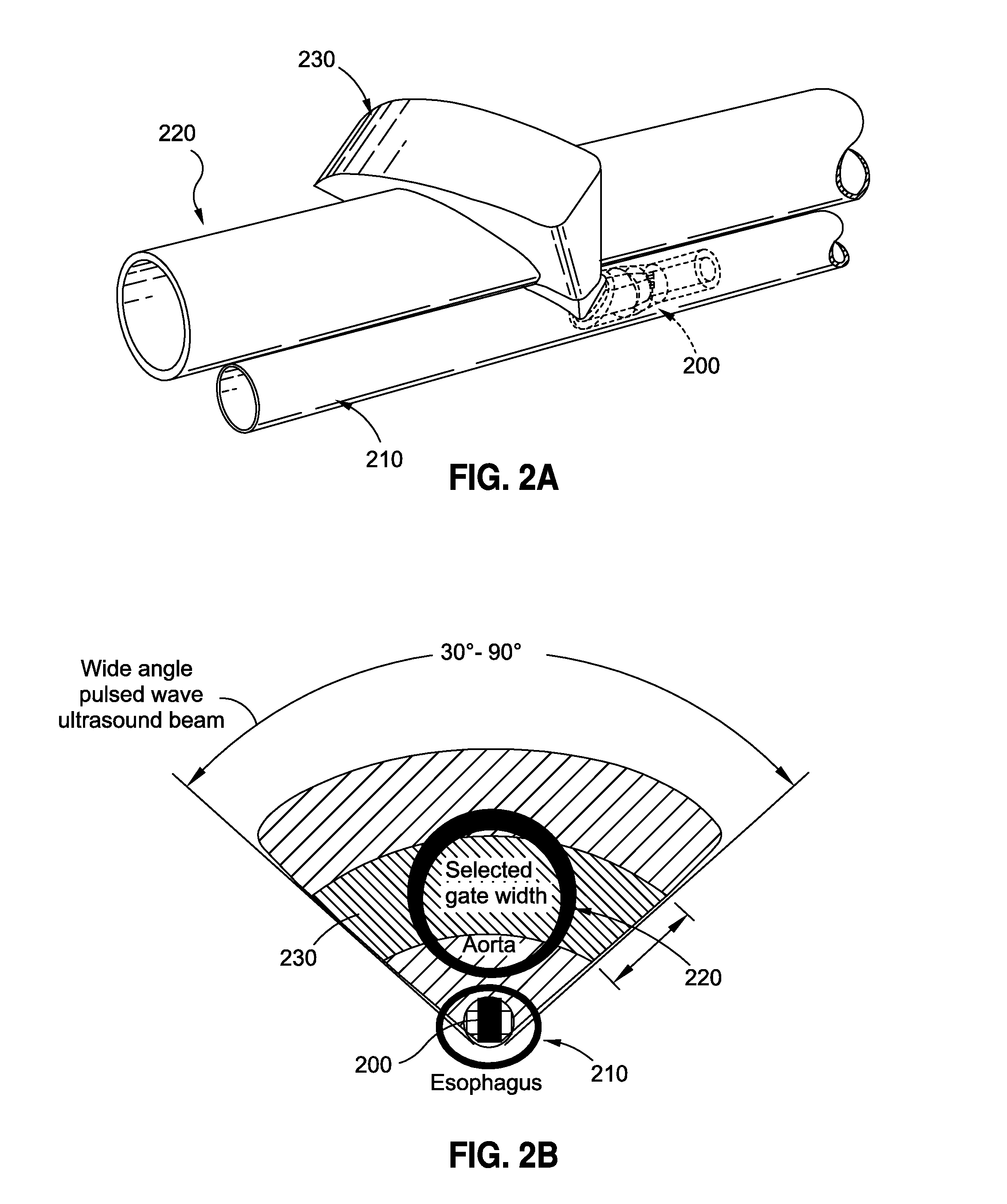
Combined blood flow and blood pressure measurements are used for the calculation of central vascular blood flow parameters. Blood flow measurements may be made simultaneously with arterial pressure measured either centrally or peripherally and central venous pressure for the monitoring of human subjects. A combined blood flow and blood pressure measurement device for hemodynamic monitoring may include a Doppler ultrasound probe utilizing a continuous wave or pulse wave ultrasound beam for the measurement of blood flow in the aorta, combined with arterial pressure measurement, or signal input from a suitable pressure transducer system from one of either the radial, brachial, dorsalis pedis or femoral artery. The ultrasound probe may comprise either an esophageal or suprasternal ultrasound probe, while the blood pressure measurement may be either an electronic transducer blood pressure sphygmomanometer on the arm, or a finger cot infrared light optical pulse detector.
Owner:DELTEX MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com