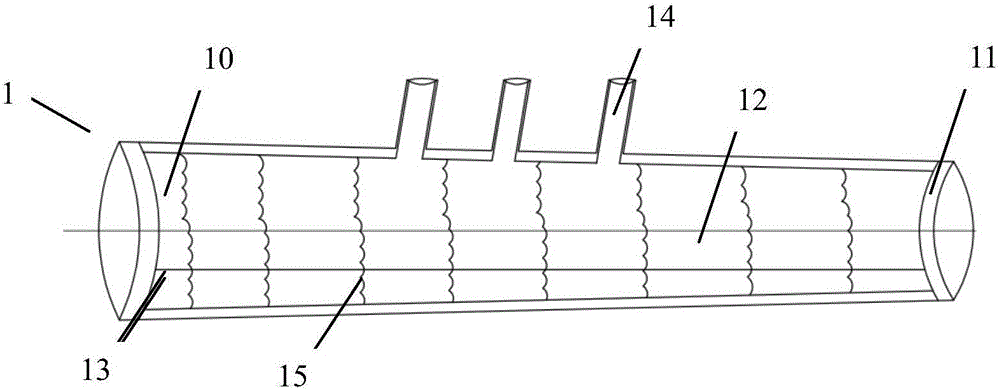
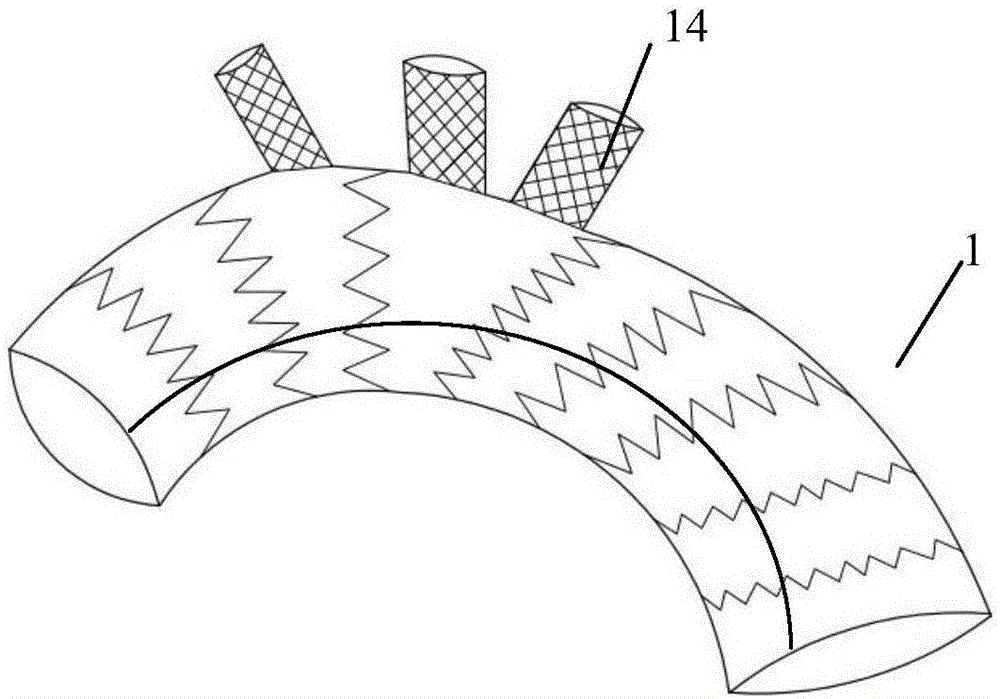
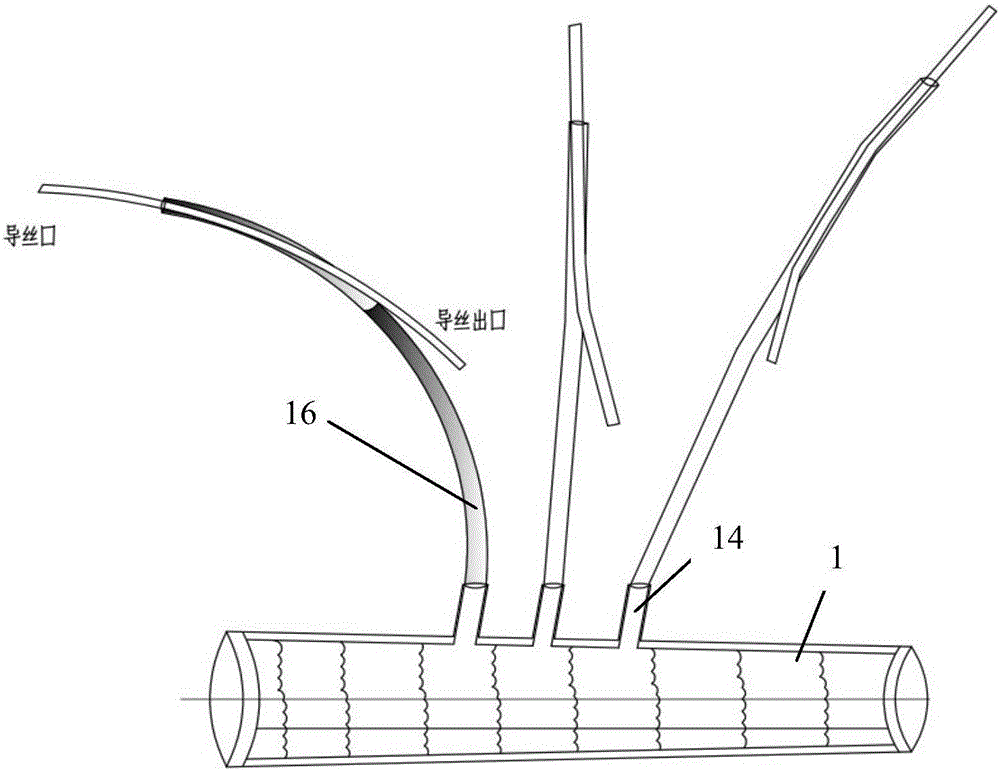
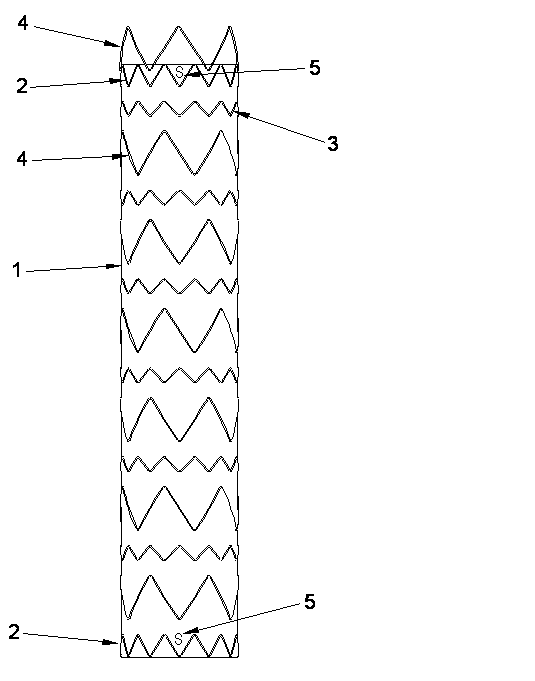
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Thoracic aorta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The descending thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the descending aorta and contained in the posterior mediastinal cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra where it is continuous with the aortic arch, and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta.
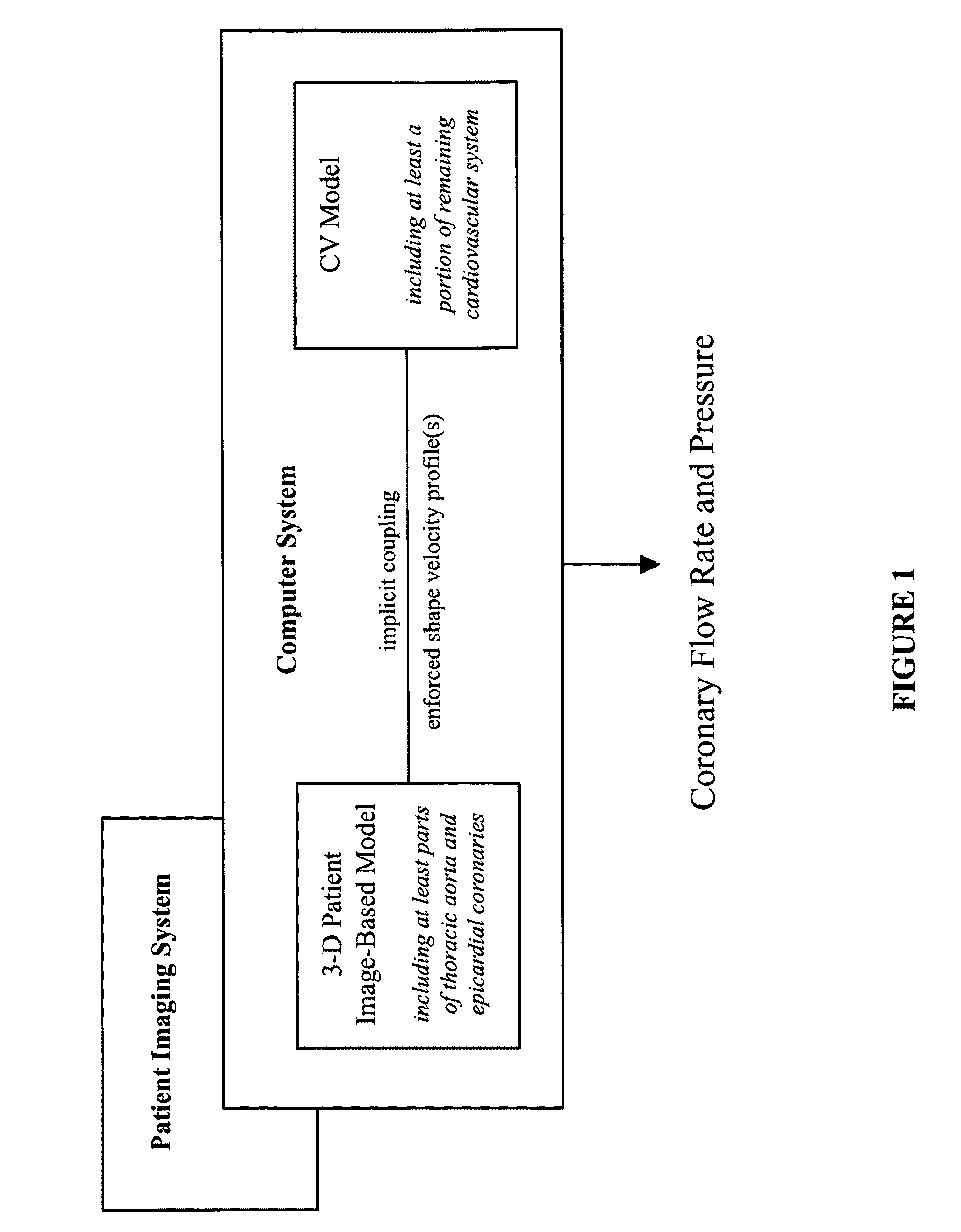
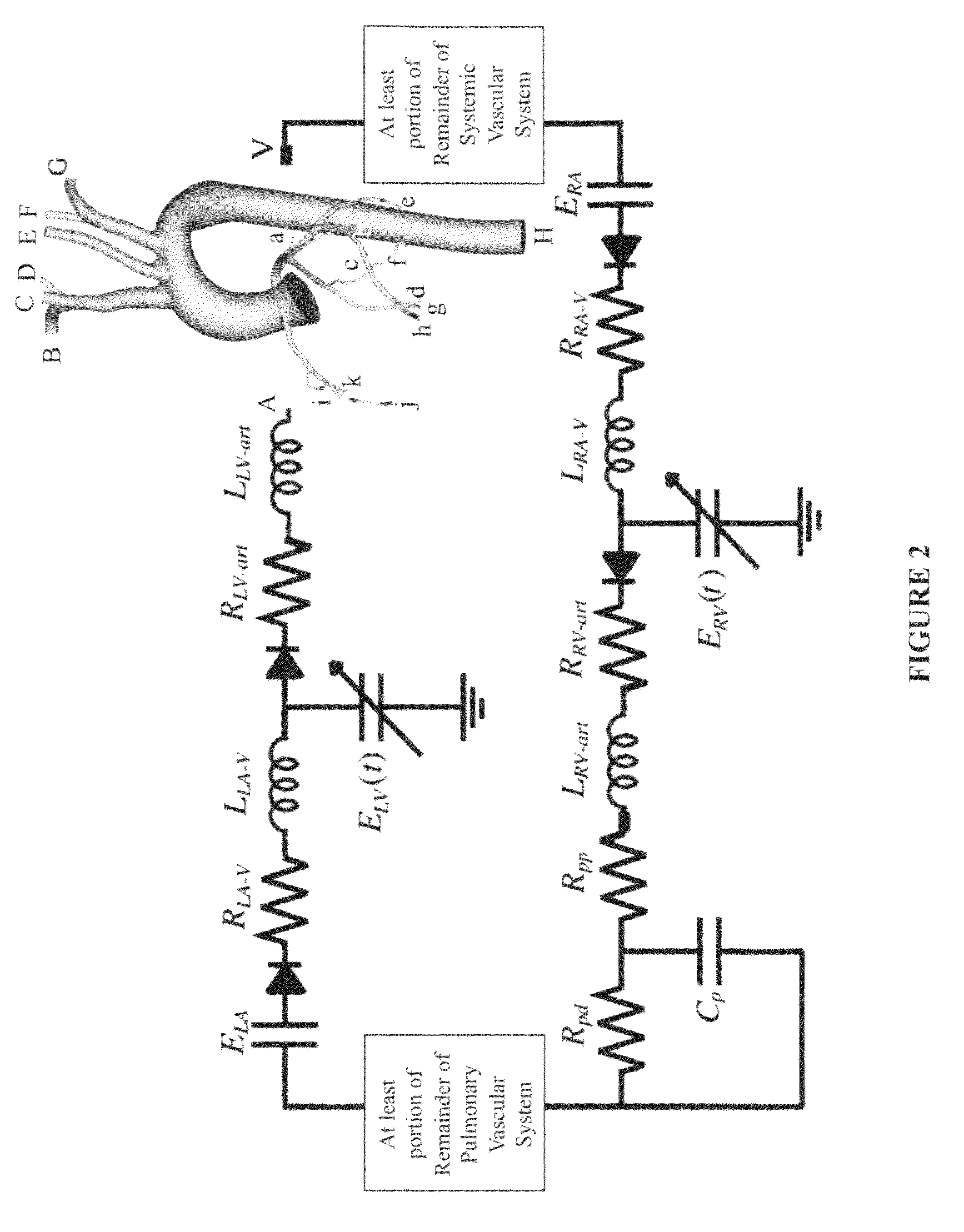
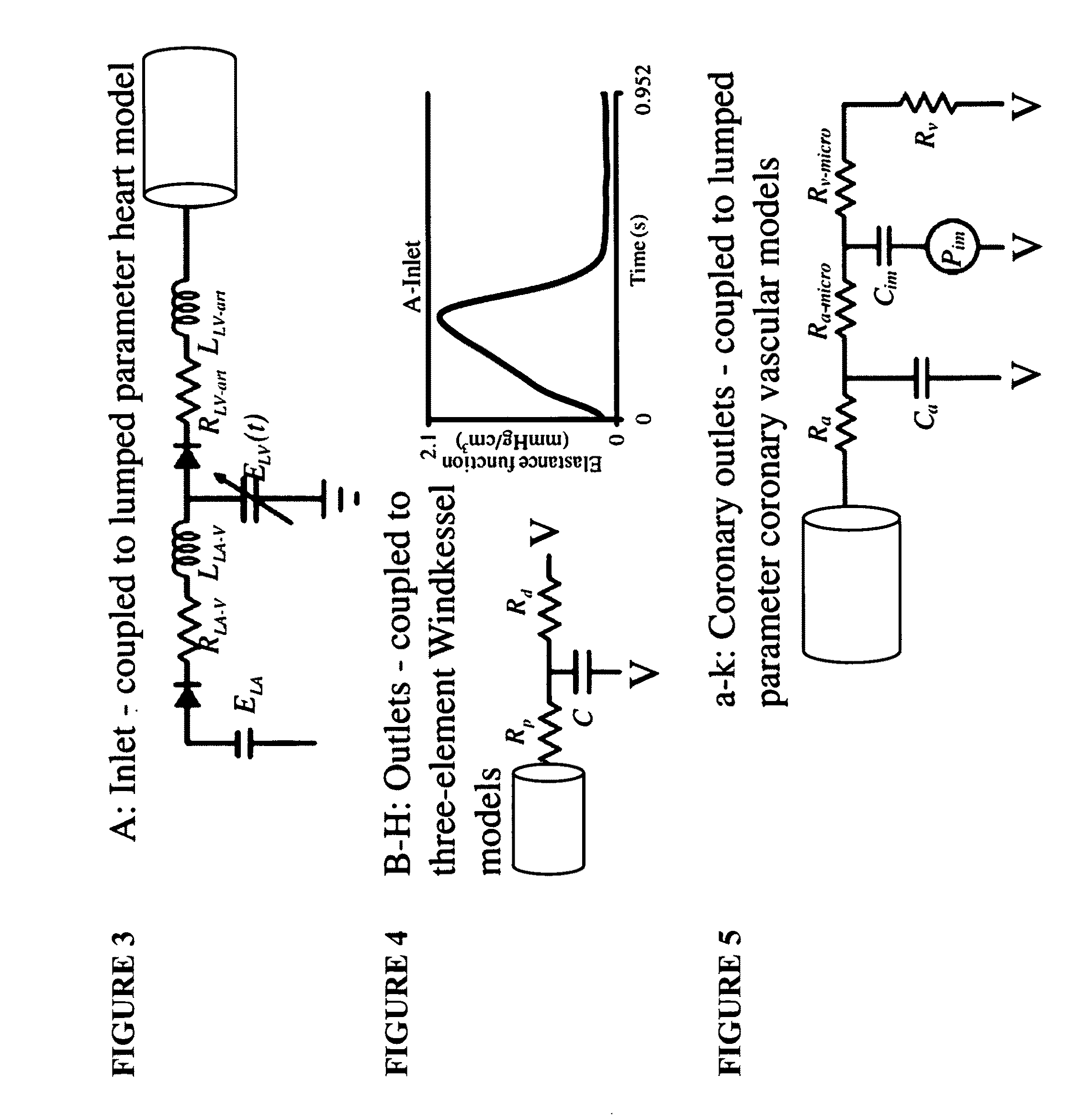
Patient-specific hemodynamics of the cardio vascular system
ActiveUS20100241404A1Minimize model instabilityMore benefitMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesInstabilityRetrograde Flow
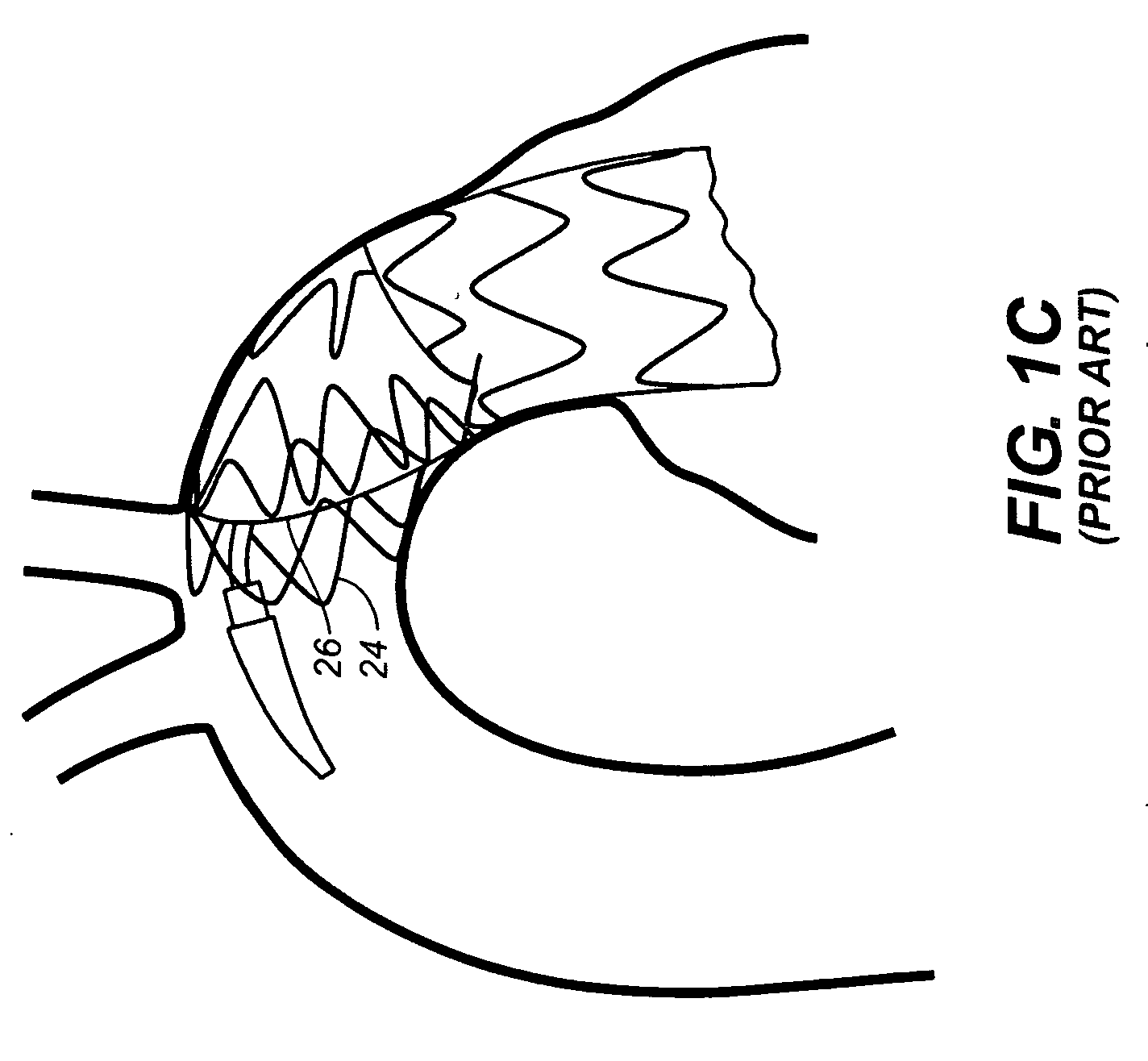
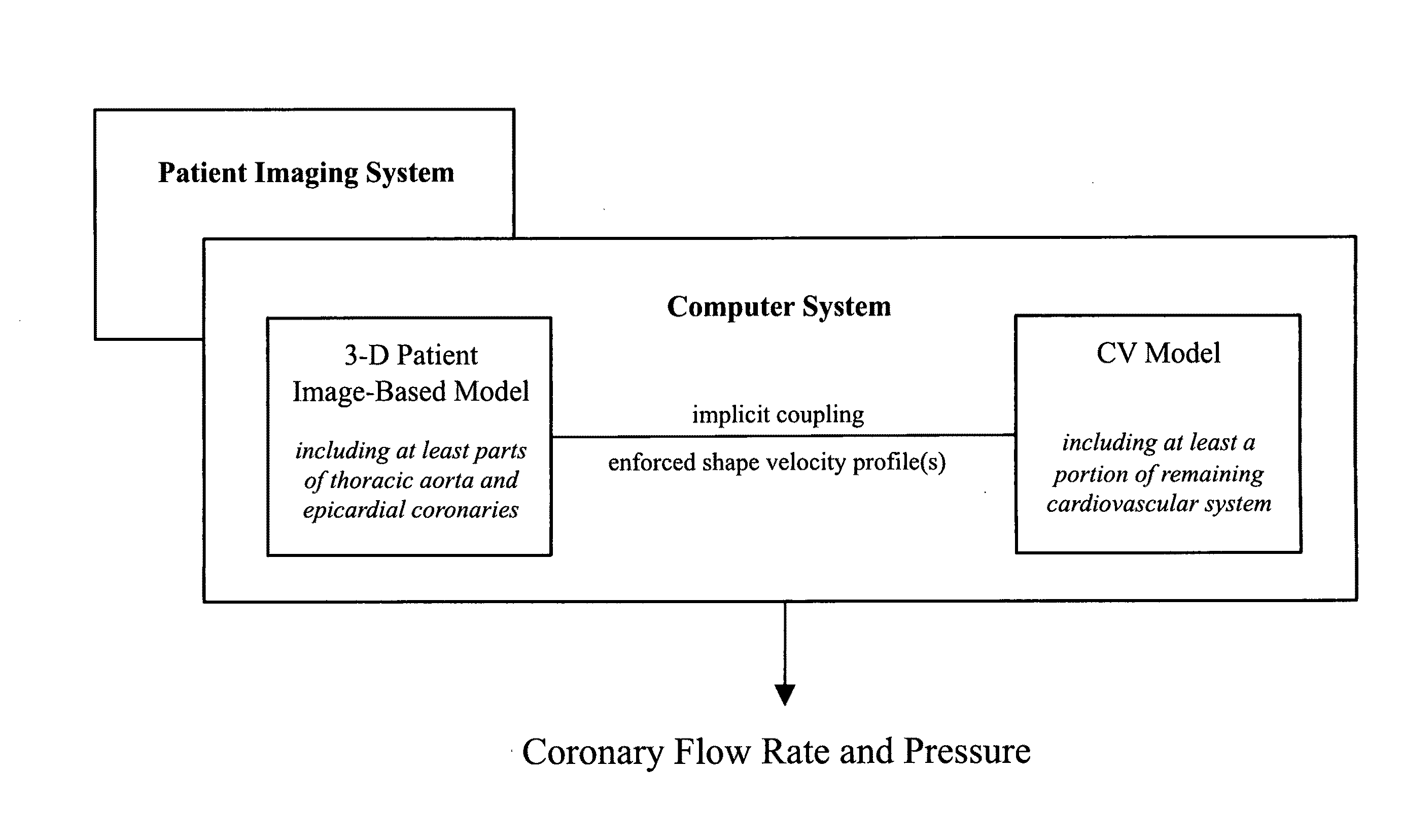
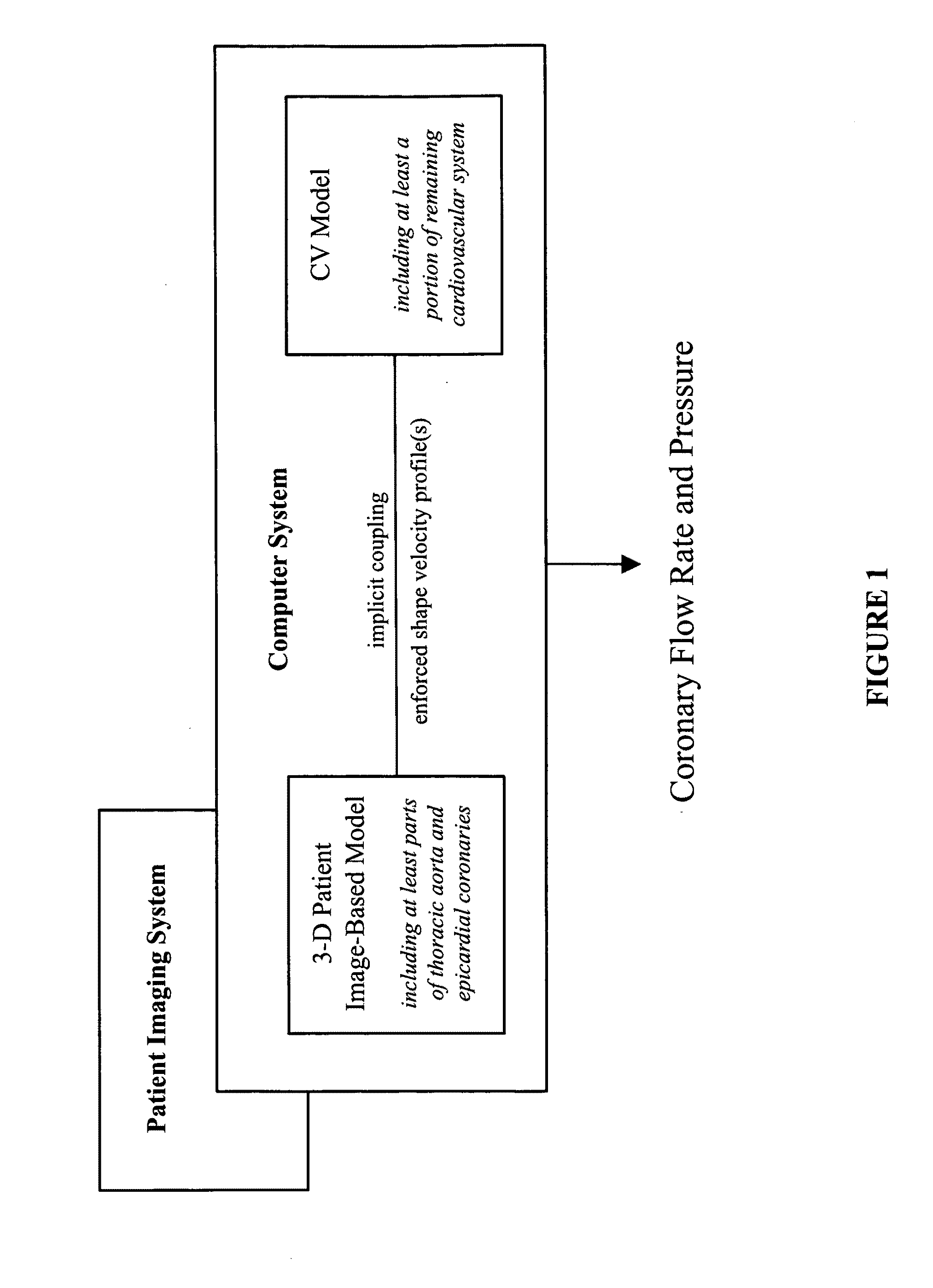
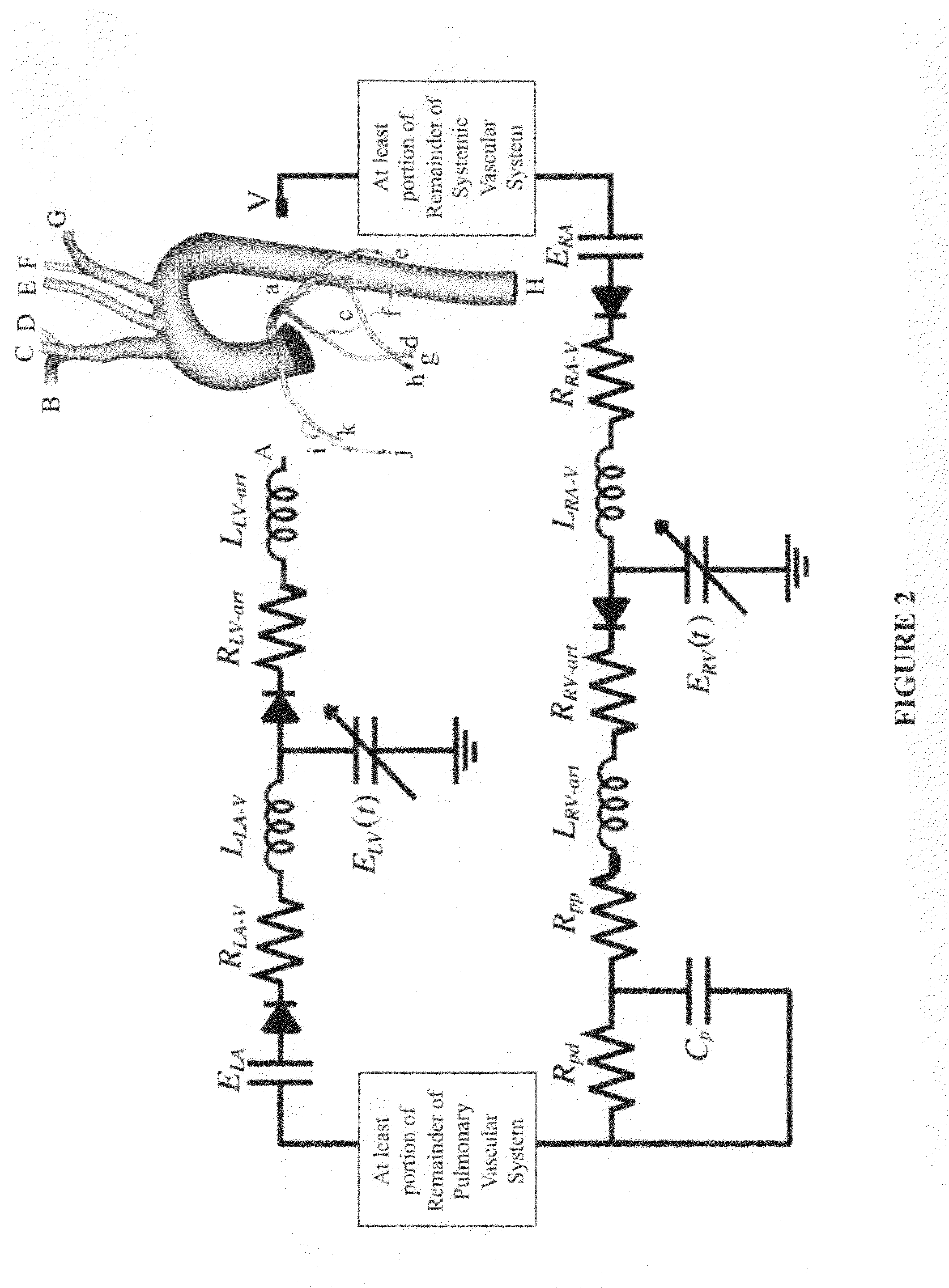
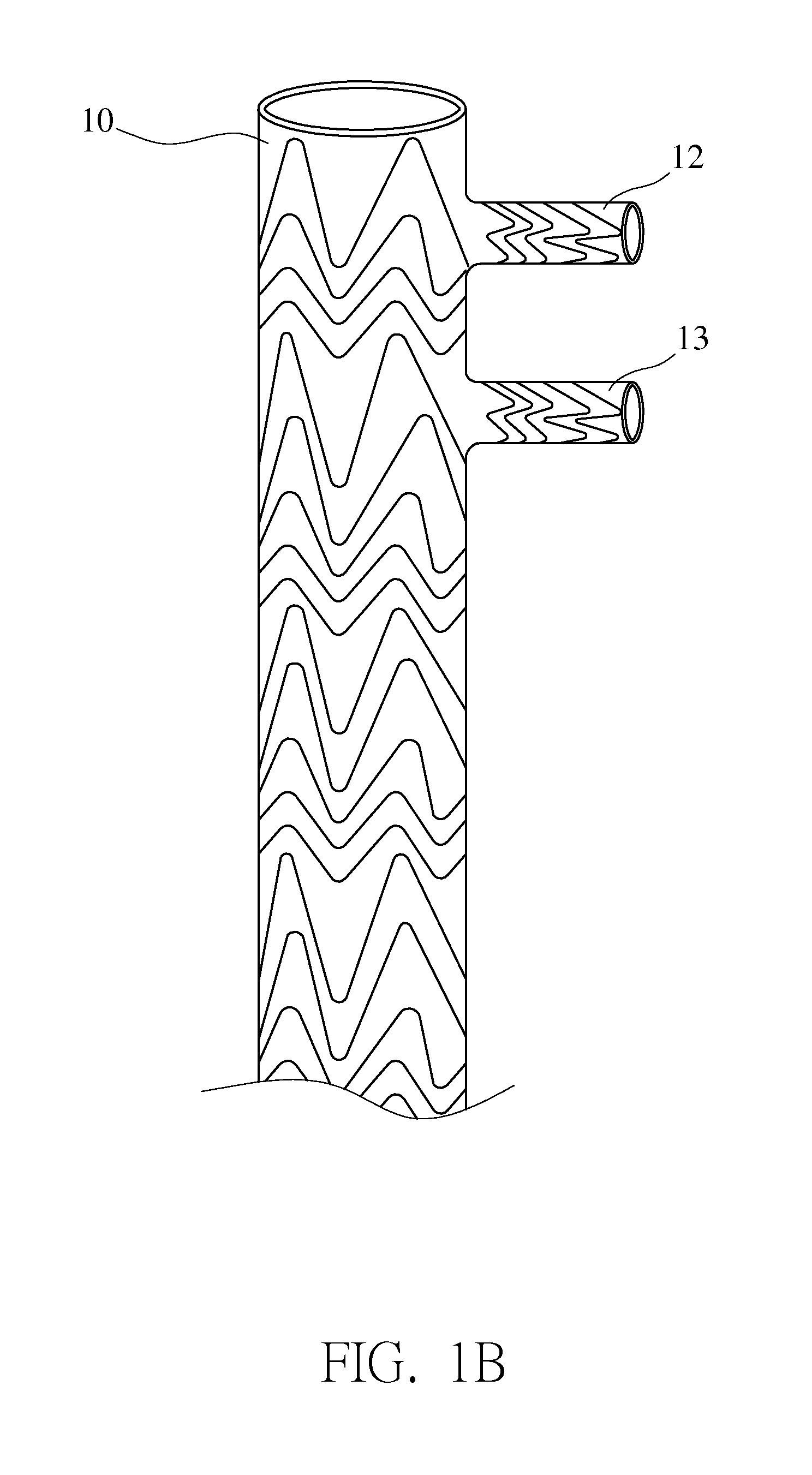
A noninvasive patient-specific method is provided to aid in the analysis, diagnosis, prediction or treatment of hemodynamics of the cardiovascular system of a patient. Coronary blood flow and pressure can be predicted using a 3-D patient image-based model that is implicitly coupled with a model of at least a portion of the remaining cardiovascular system. The 3-D patient image-based model includes at least a portion of the thoracic aorta and epicardial coronaries of the patient. The shape of one or more velocity profiles at the interface of the models is enforced to control complex flow features of recirculating or retrograde flow thereby minimizing model instabilities and resulting in patient-specific predictions of coronary flow rate and pressure. The invention allows for patient-specific predictions of the effect of different or varying physiological states and hemodynamic benefits of coronary medical interventions, percutaneous coronary interventions and surgical therapies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
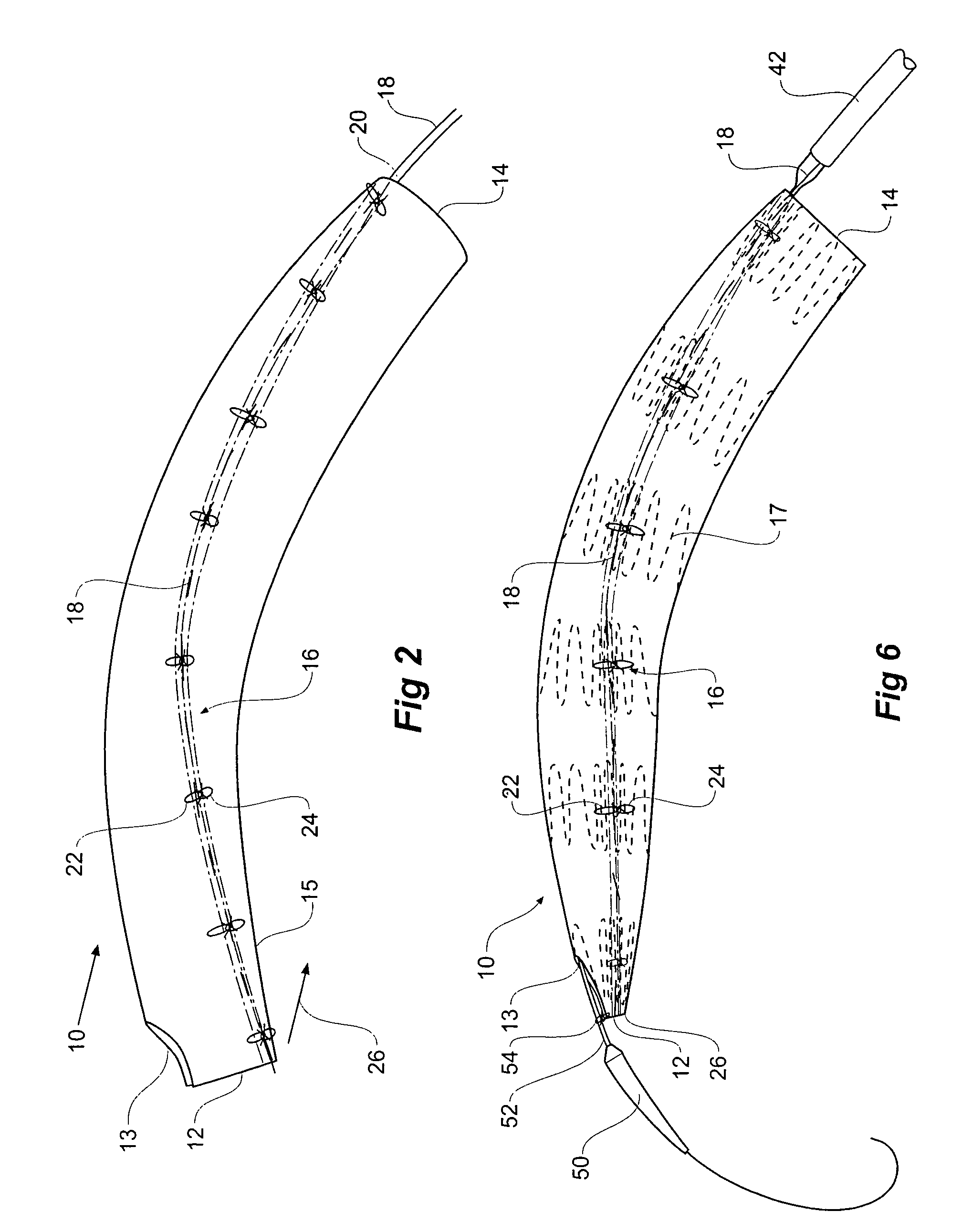
Stent grafts for the thoracic aorta
ActiveUS20080294234A1Reduce the overall diameterReduce distanceStentsBlood vesselsThoracic aortaStent grafting
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
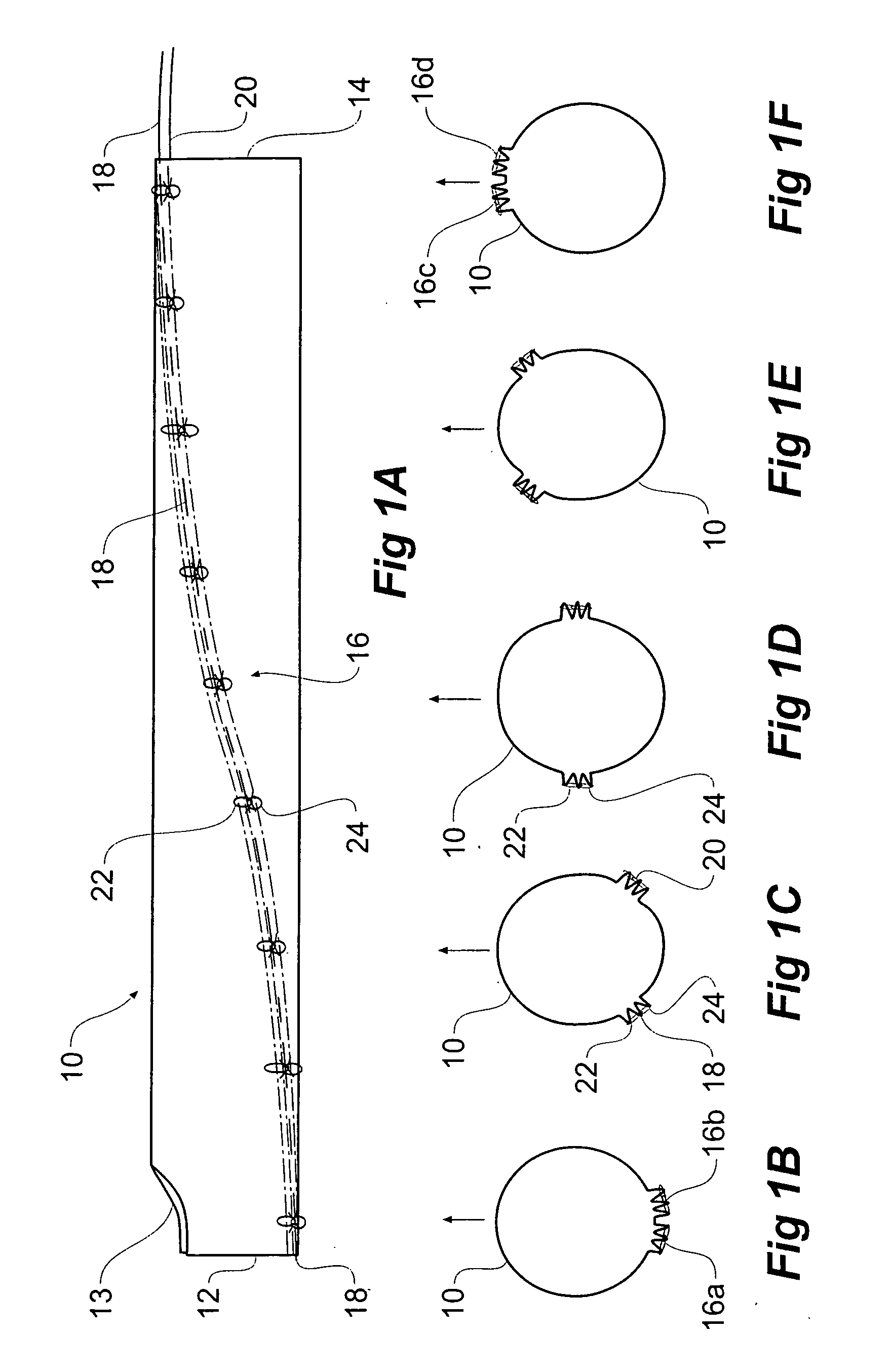
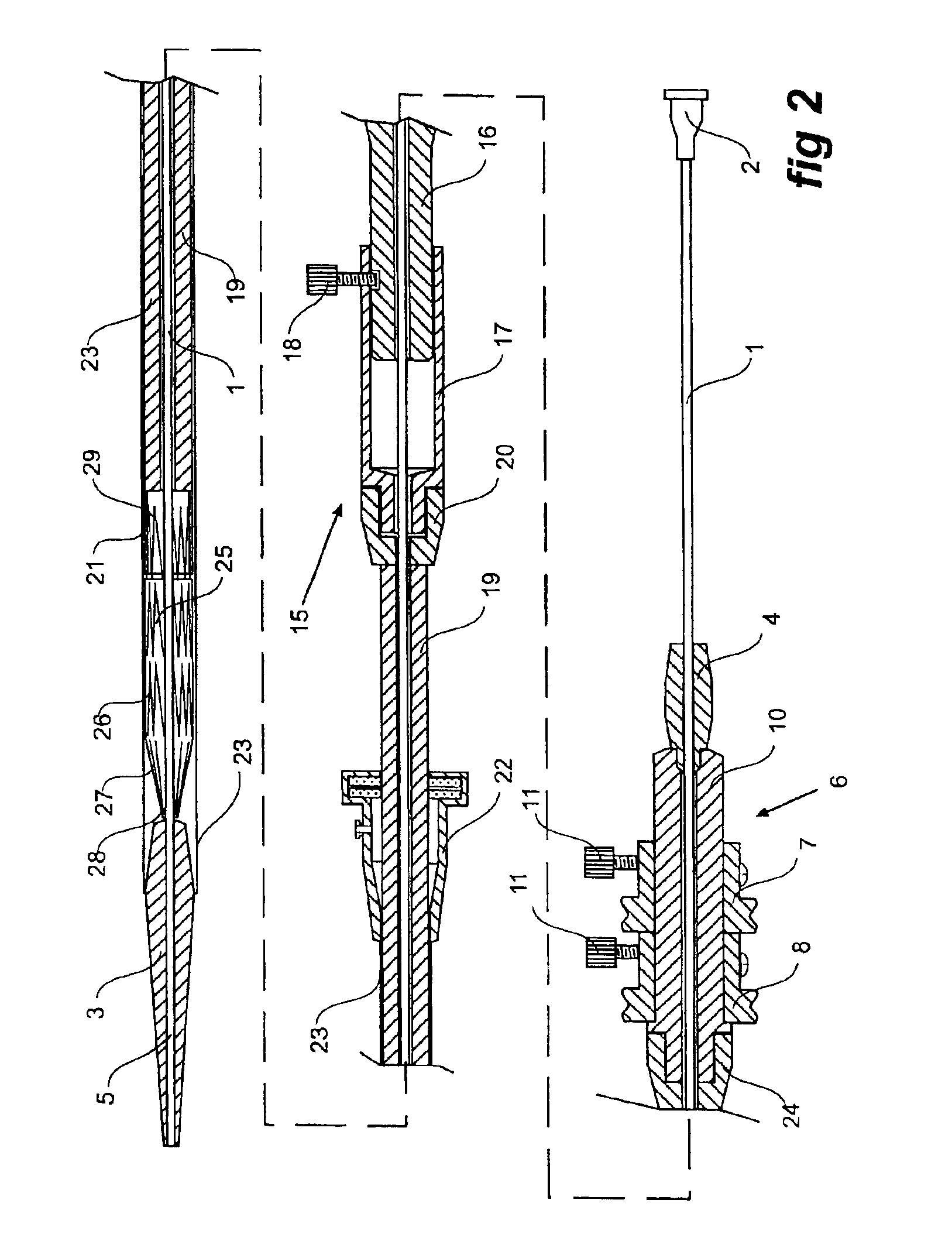
Thoracic aortic stent graft deployment device
ActiveUS6939370B2Prevent movementPrevent forward movementStentsEar treatmentThoracic aortaStent grafting
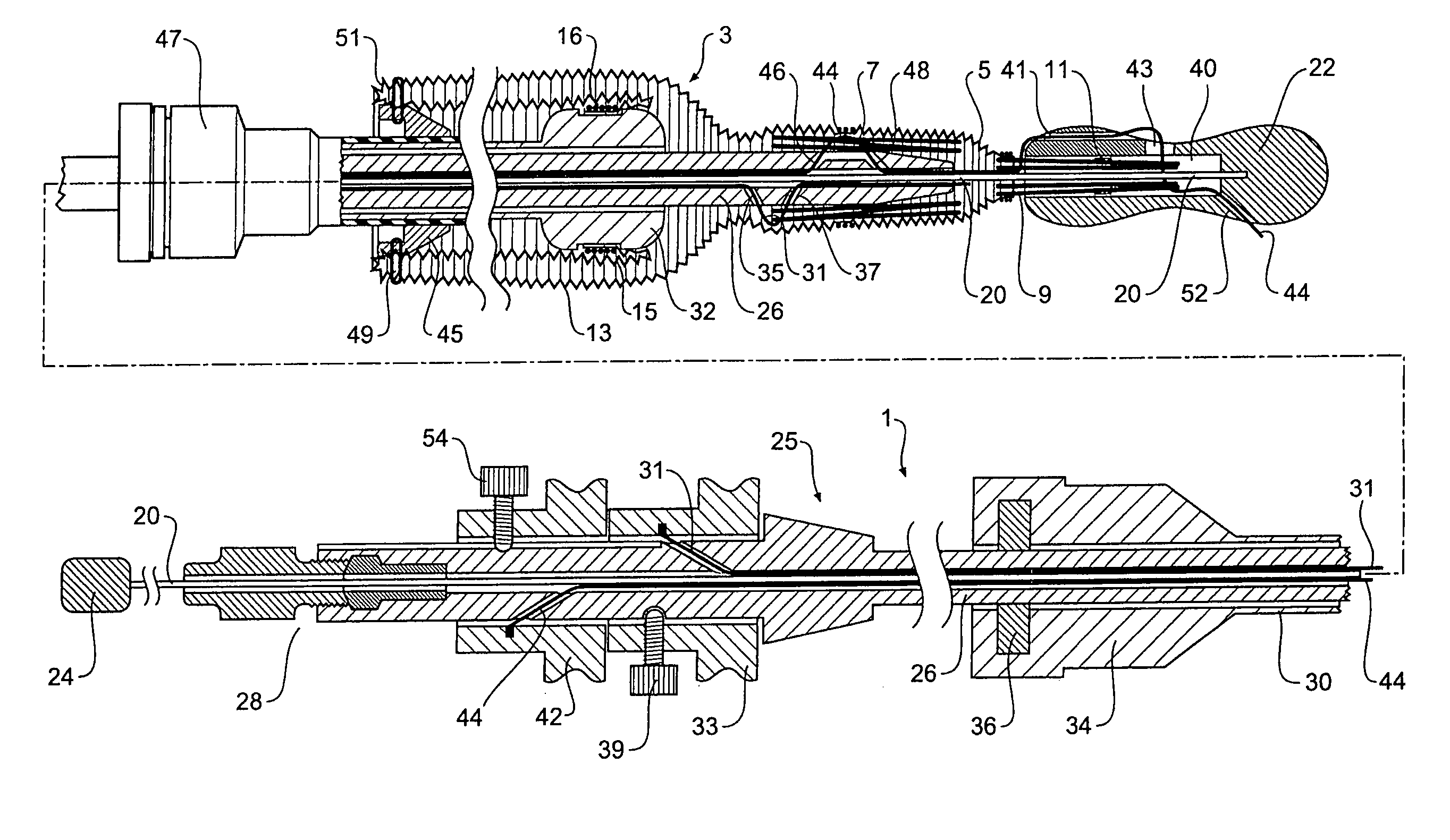
A stent graft deployment device adapted for release of a distal end (29) of a stent graft (25) before the proximal end (27) of the stent graft (25). The arrangement (15) allows movement of at least part of the deployment catheter (23) independently of movement of a proximal end release mechanism has a fixed handle (16) associated with a trigger wire release mechanism (6) and a sliding handle (17) to which the deployment catheter and a capsule (21) are fixed. The sliding handle (17) is mounted on the fixed handle (16) and can slide longitudinally with respect to the fixed handle (16).
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
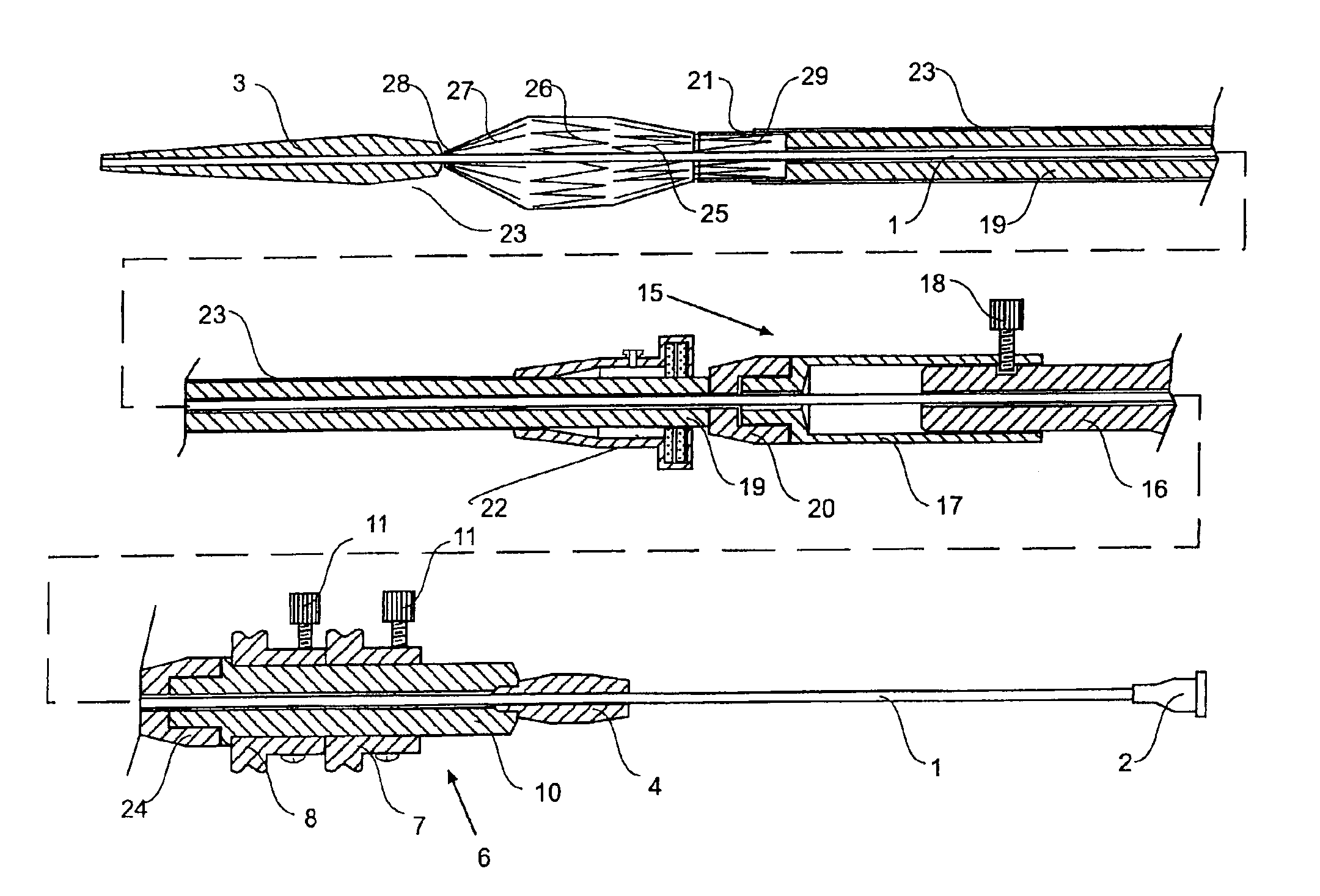
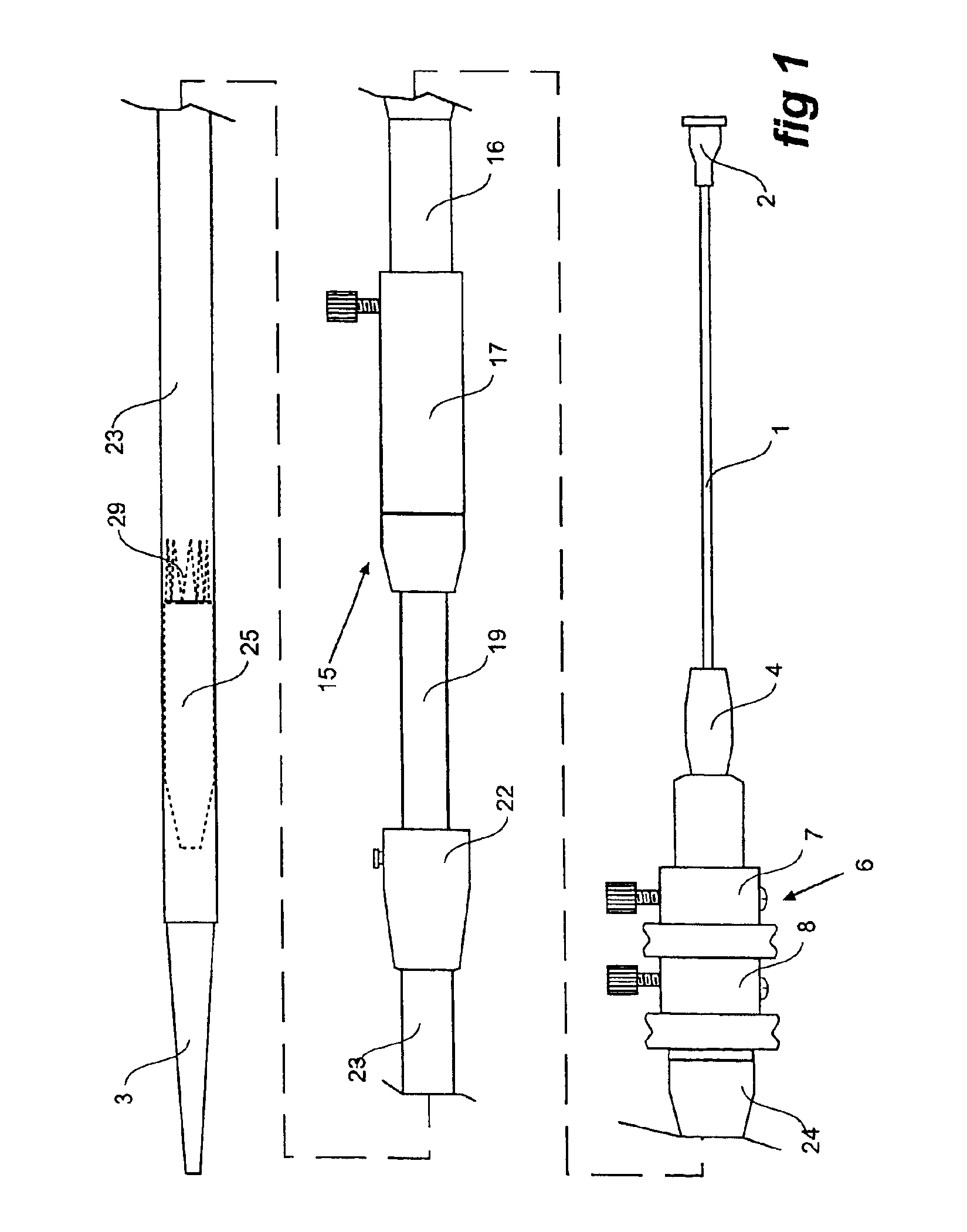
Vascular graft and deployment system
A vascular graft includes a main portion and a branch portion that is coupled to the main portion by an articulating joint. The vascular graft may be inserted into the thoracic aorta with the branch portion positioned within a branch vessel and the main portion positioned within the thoracic aorta. The graft may be deployed within a deployment apparatus comprising an outer member and an inner member and a pusher. The main graft portion may be housed within the inner member while the branch graft portion is housed within the space between the inner and outer members. The inner member may have a longitudinal groove for allowing the articulating joint to pass by when the branch graft portion is deployed.
Owner:DOUGLAS MYLES
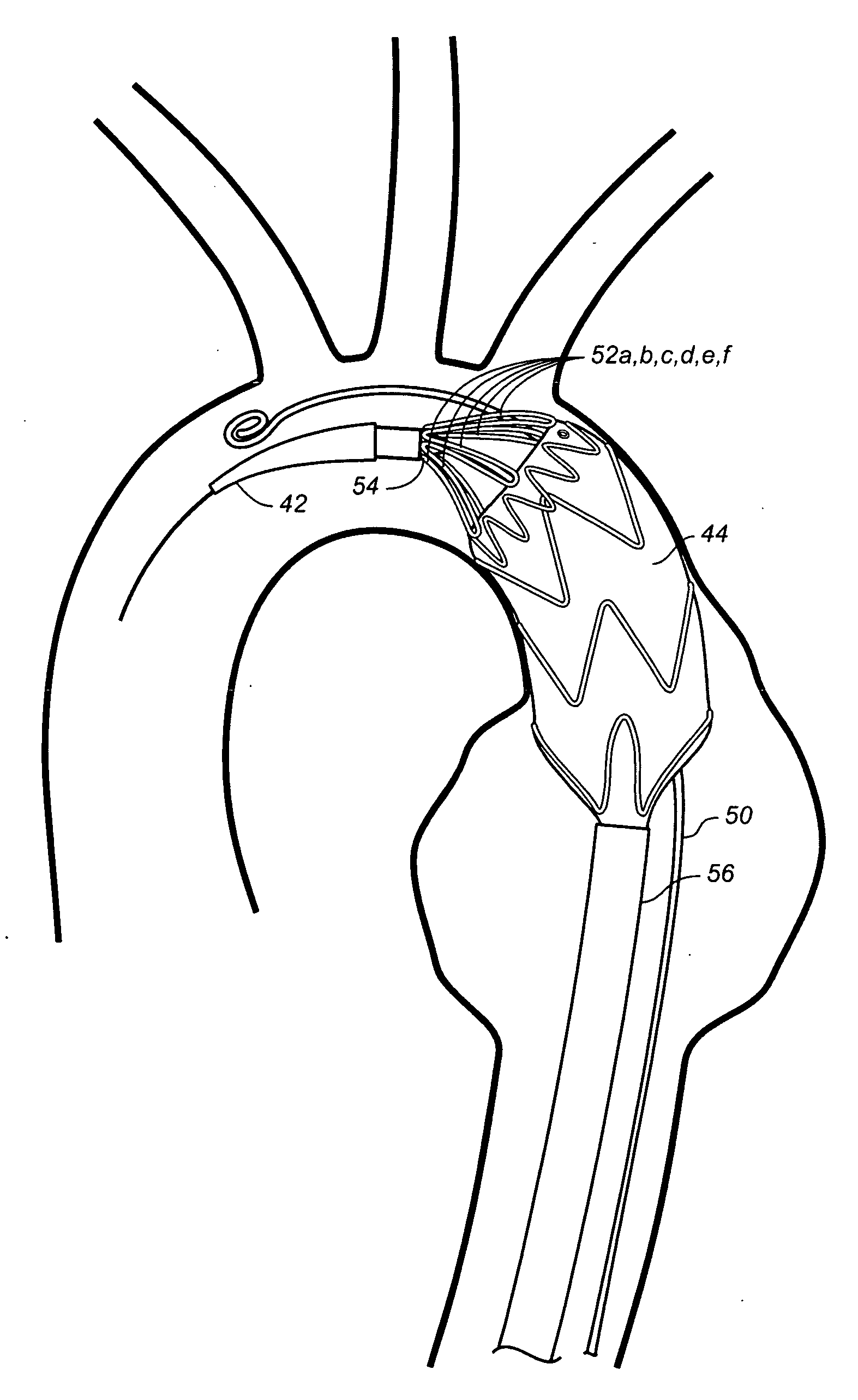
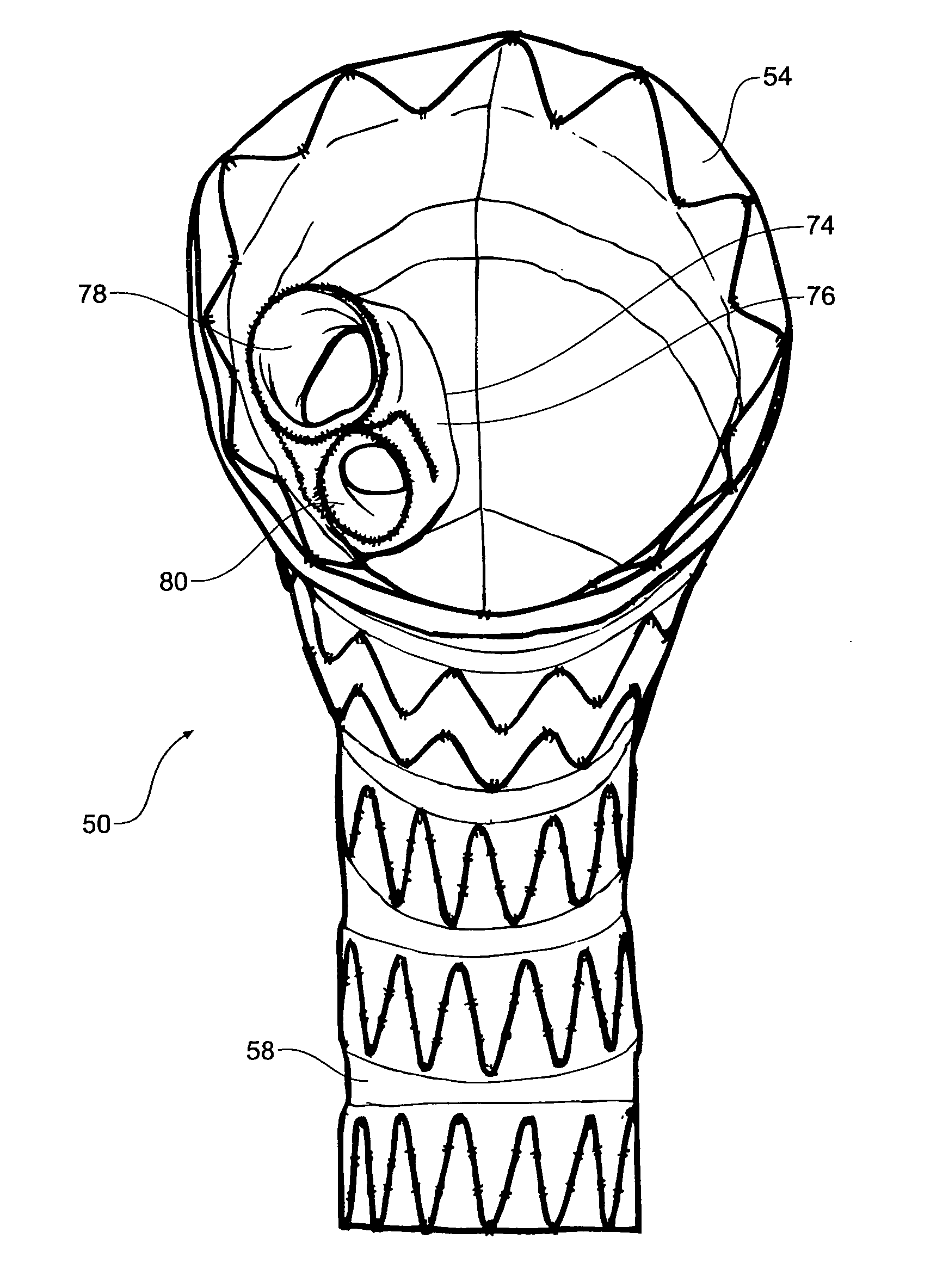
Centering for a TAA
A stent graft is deployed by a steerable catheter delivery system having a integral tip capture release mechanism. The steering mechanism provides for a locked interference with a distal lock at the distal end of the delivery catheter. The configuration allows for selective circumferentially distributed release of one half or less of the number of crowns of a proximal spring which are captured by a tip capture mechanism so that new positioning of the stent graft can be verified and assured before full release of all proximal spring crowns is done. In this way, one or more steering elements of a catheter can be maintained in tension until catheter position is verified and acceptable stent graft position is achieved. This apparatus and method is particularly useful for deploying stent graft in curved passages such a thoracic aorta.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
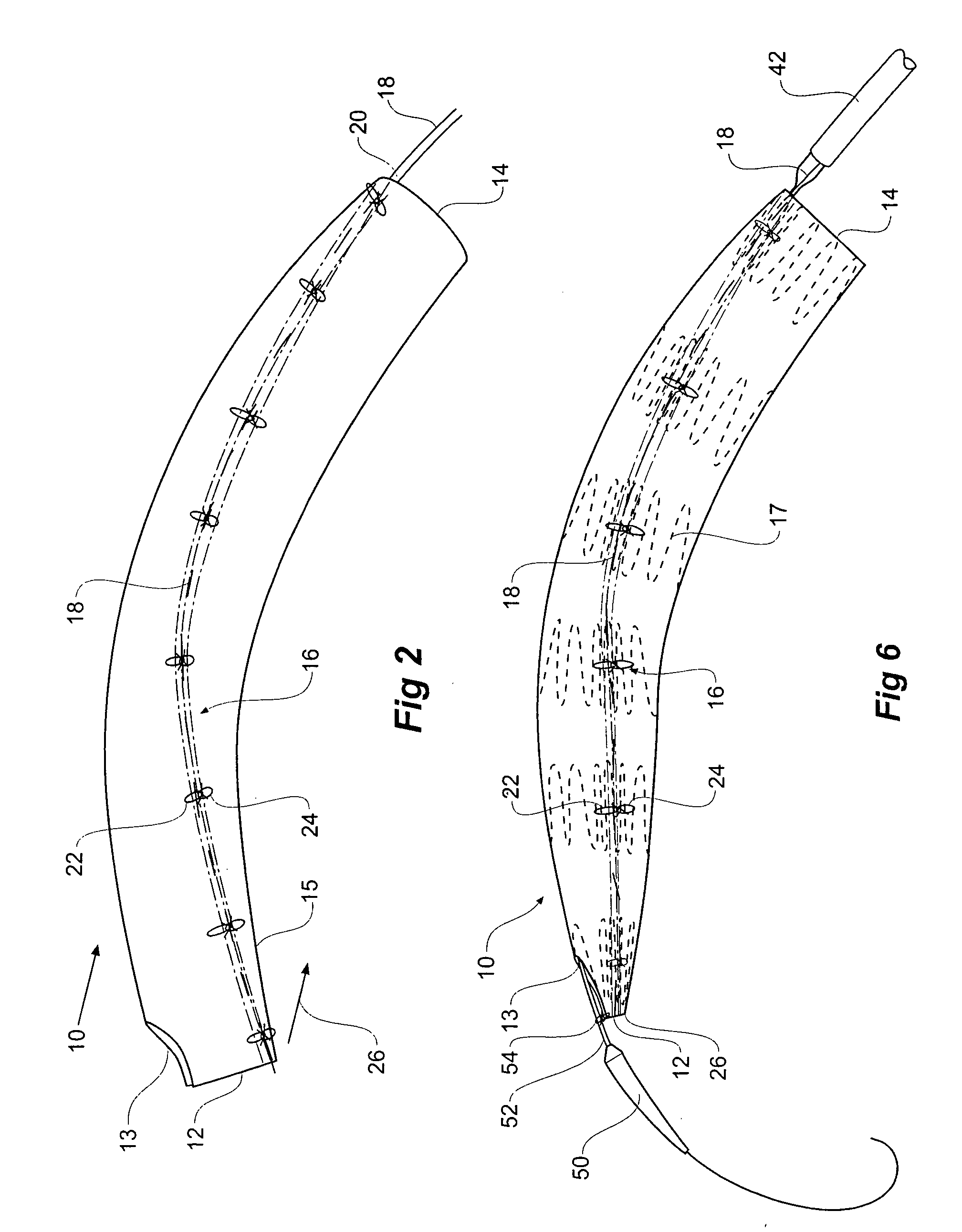
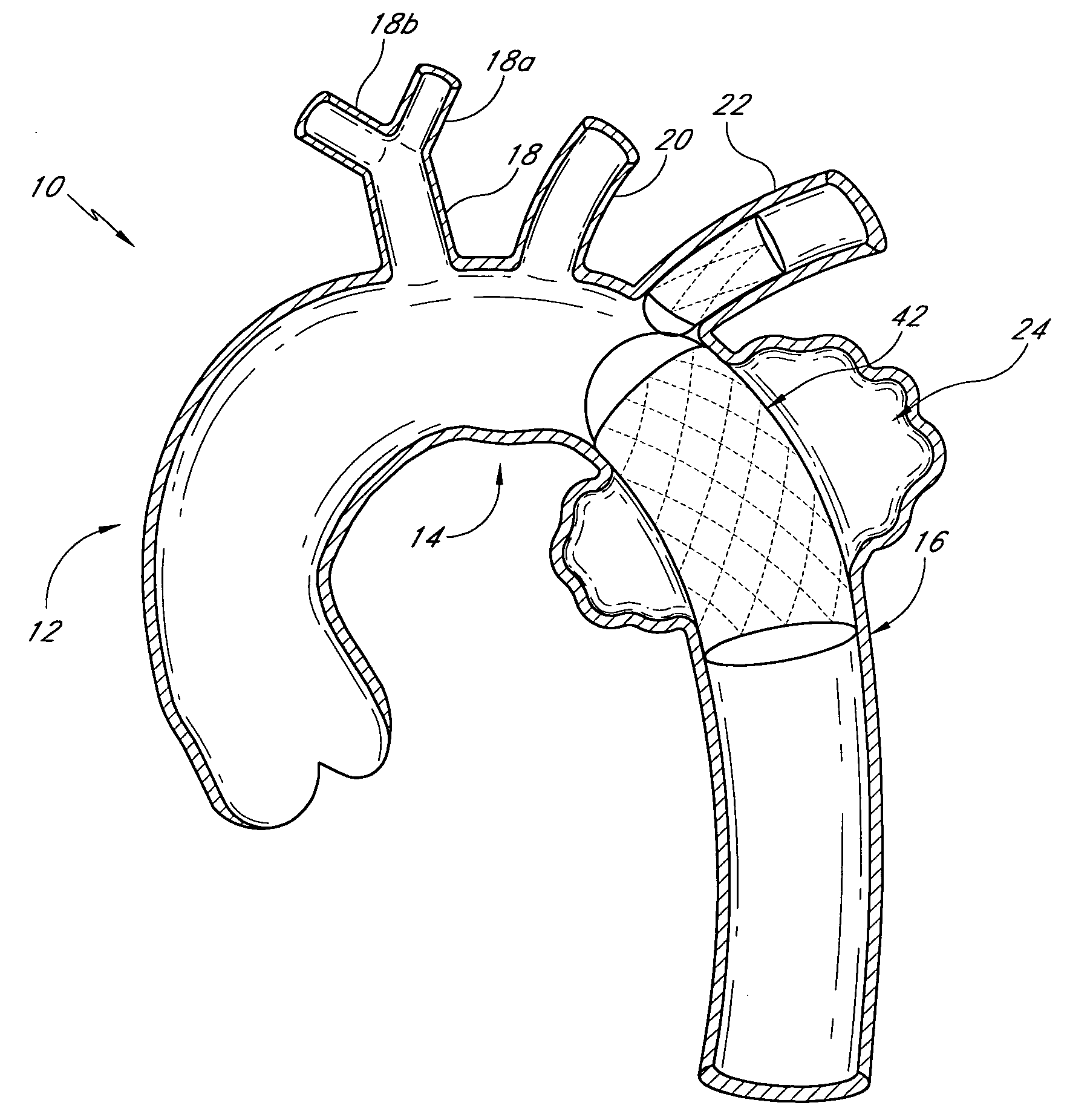
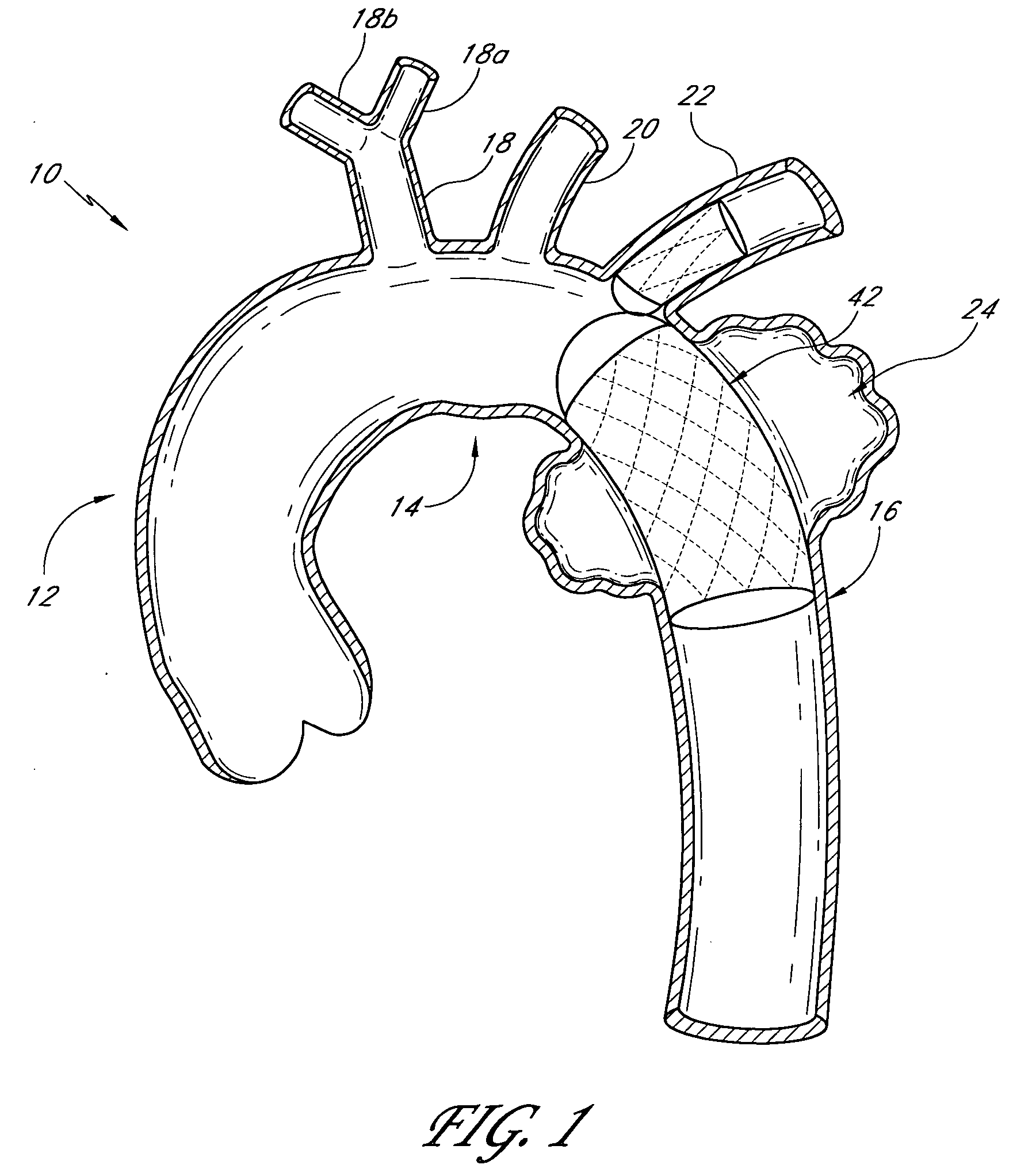
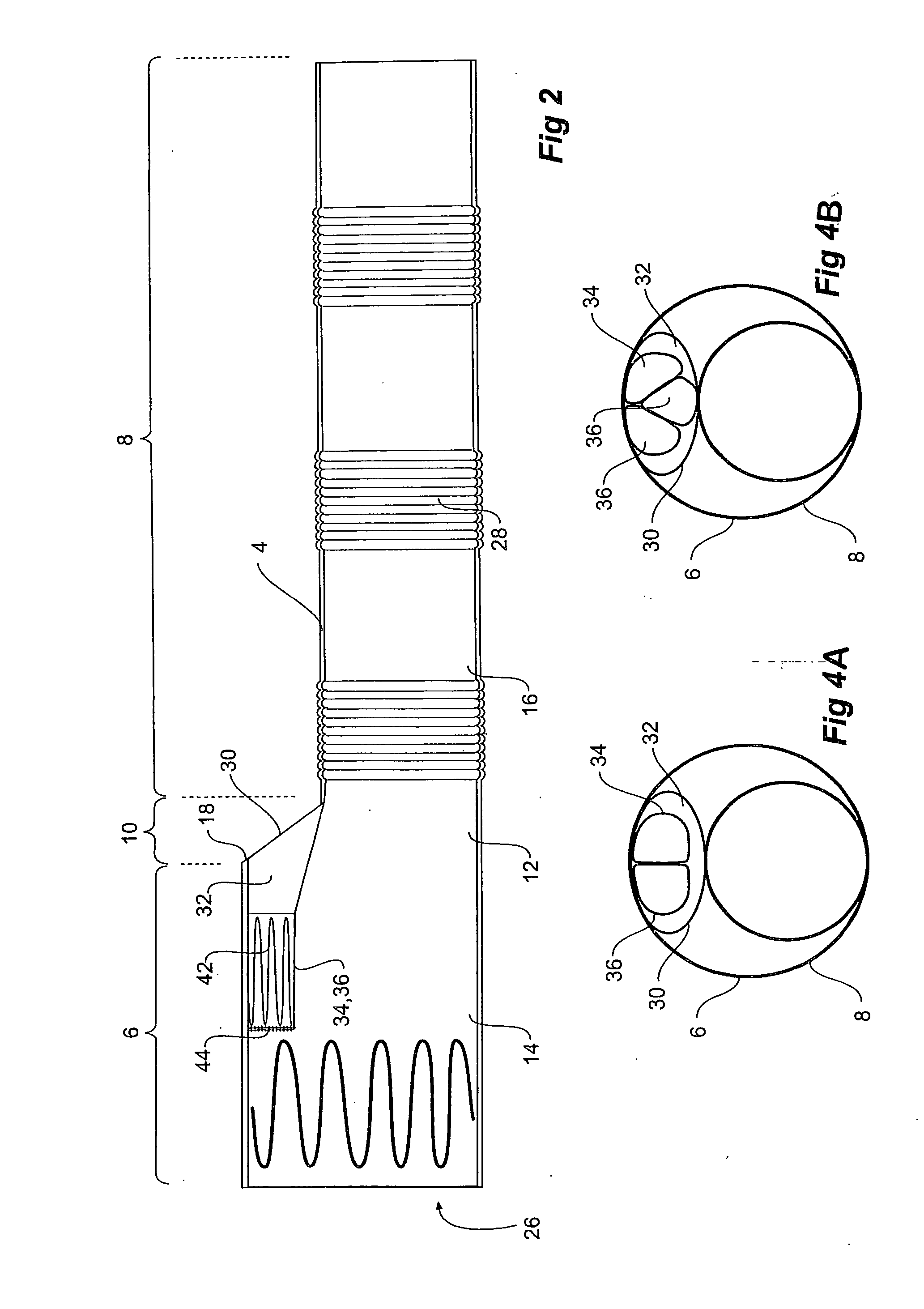
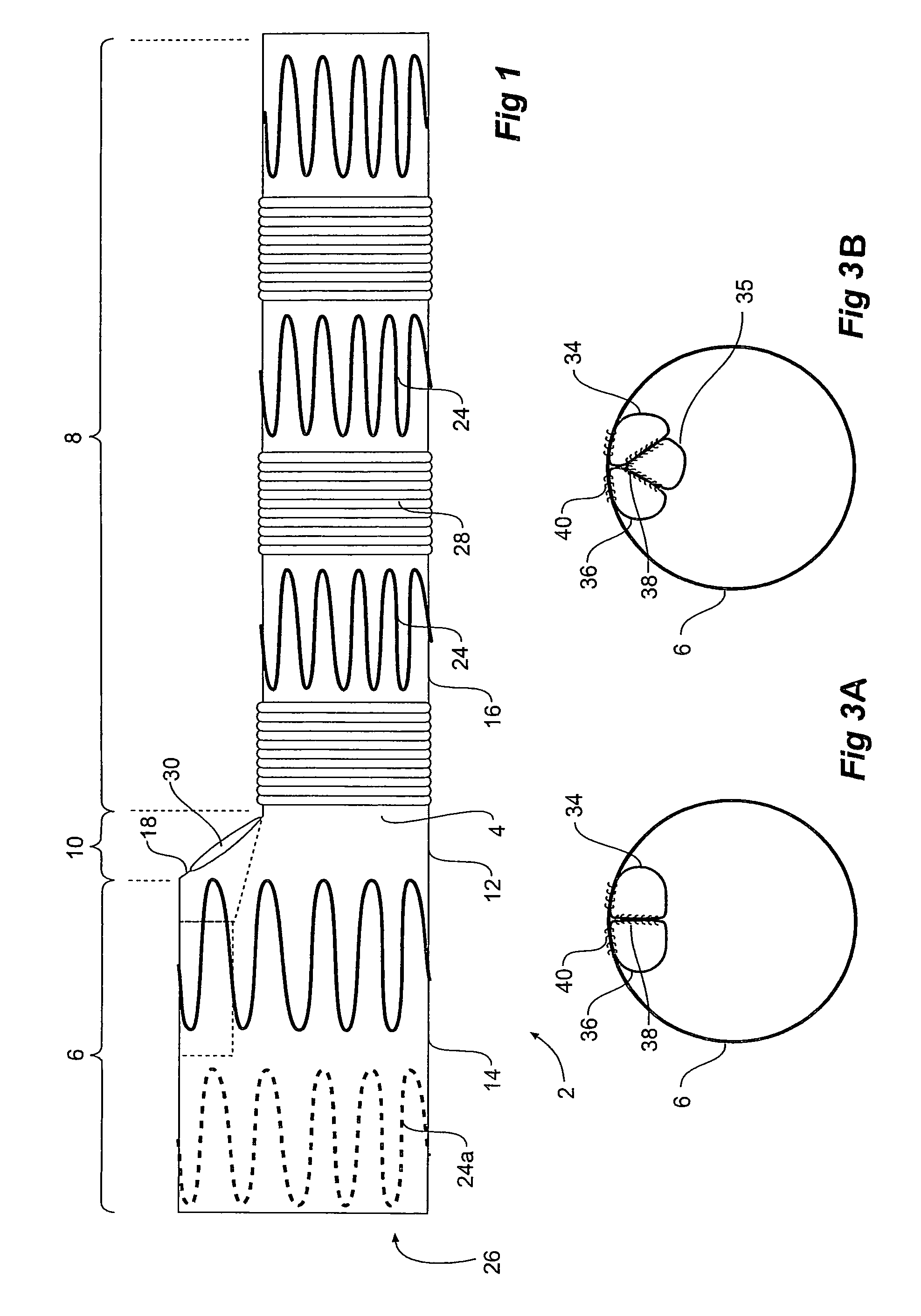
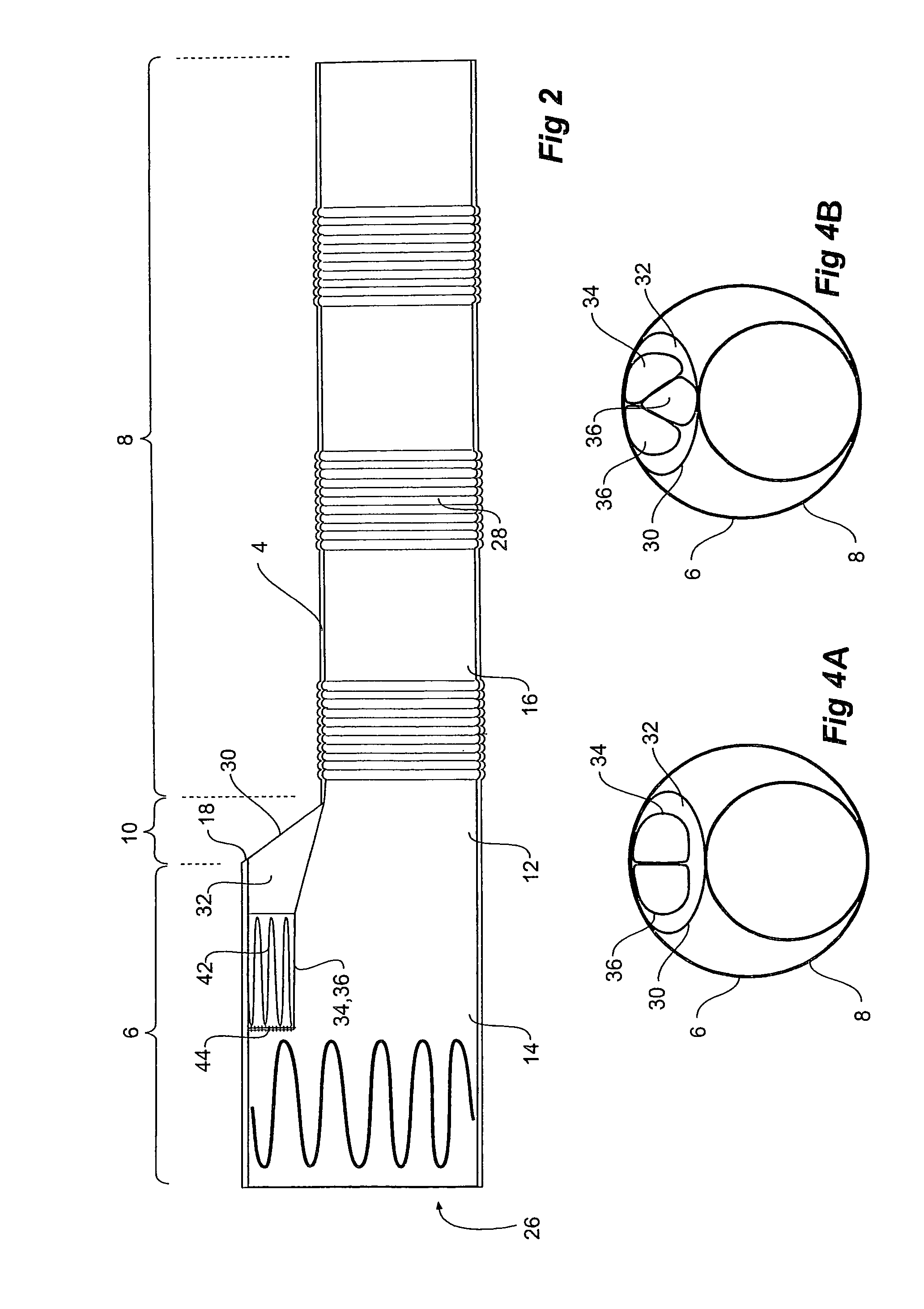
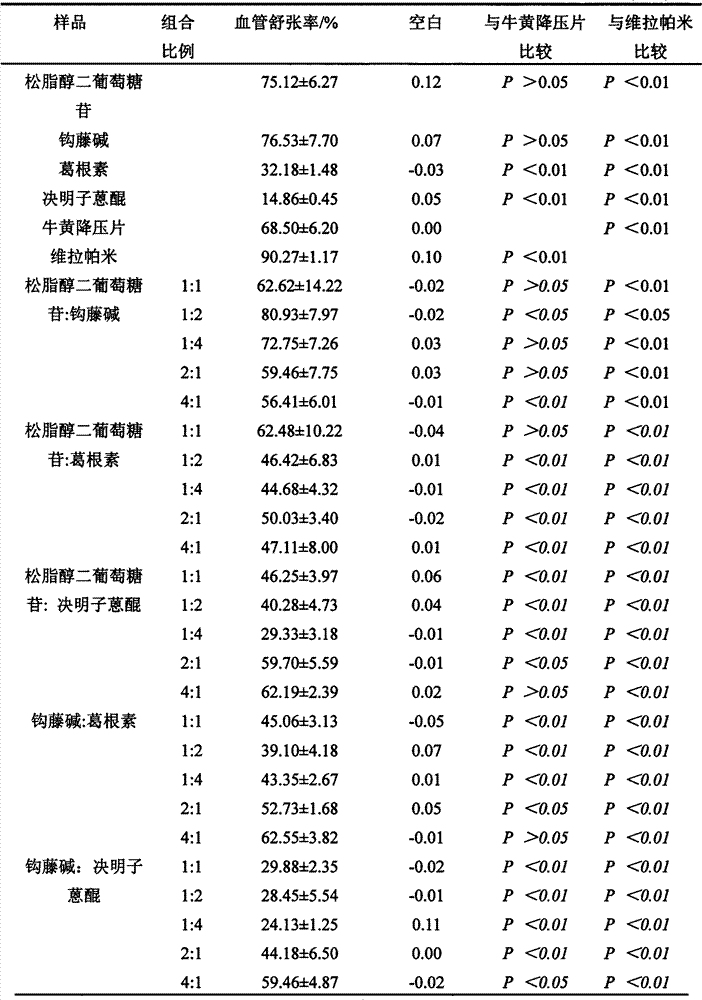
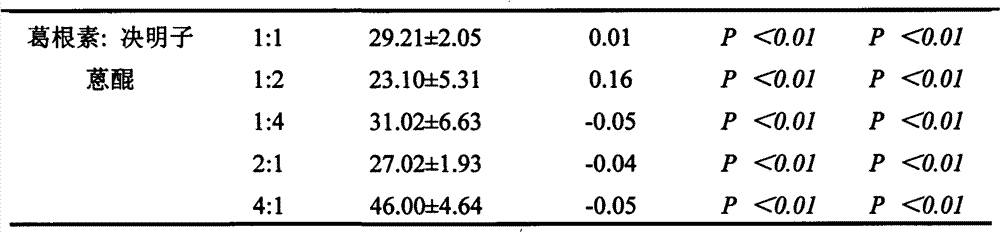
Thoracic aorta stent graft with access region
ActiveUS20110257731A1Allow for flexibility of stentAllow flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsAscending aortaThoracic aorta
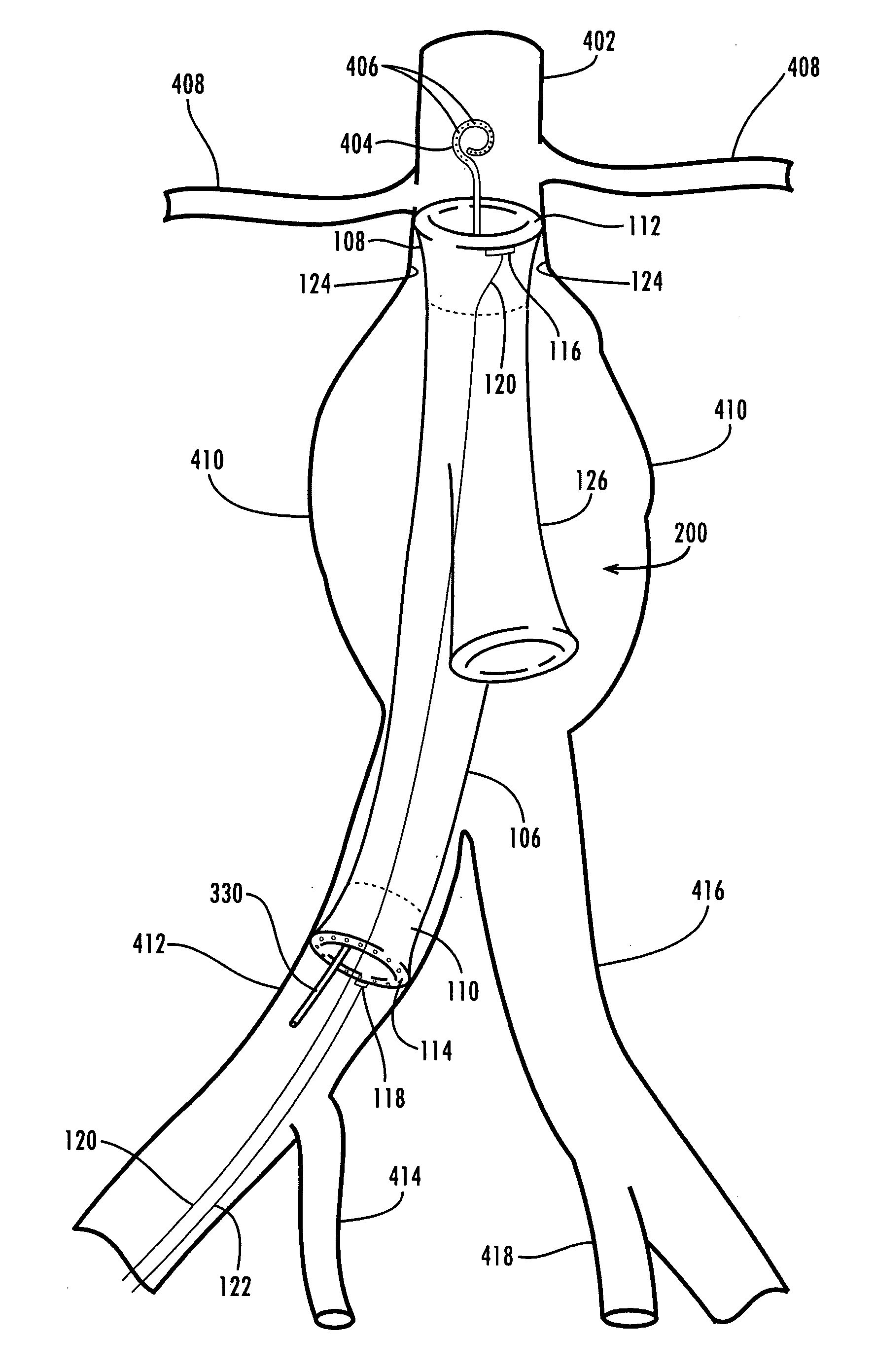
A stent graft (2) for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a first tubular body portion (6) with a first lumen therein for placement in the ascending aorta of a patient and a second tubular body portion (8) to extend along the thoracic arch and down the descending aorta. The second tubular body portion is of a lesser diameter than the first tubular body portion. There is a step portion (10) between the first body portion and the second body portion. The step portion is joined to and continuous with the first portion and the second portion. A first side of each of the first body portion, the step portion and the second body portion are substantially aligned so that there is a step (18) defined on a second side opposite to the first side of the body portion. There is an aperture (30) in the step portion and an internal tube (32) extending from the aperture towards the first body portion. The internal tube is divided along part of its length into at least two smaller internal tubes (34, 36) with the smaller internal tubes opening into the first lumen.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
Vascular graft and deployment system
A vascular graft includes a main portion and a branch portion that is coupled to the main portion by an articulating joint. The vascular graft may be inserted into the thoracic aorta with the branch portion positioned within a branch vessel and the main portion positioned within the thoracic aorta. The graft may be deployed within a deployment apparatus comprising an outer member and an inner member. The outer member may include an area of increased flexibility that corresponds to the articulating joint.
Owner:DOUGLAS MYLES
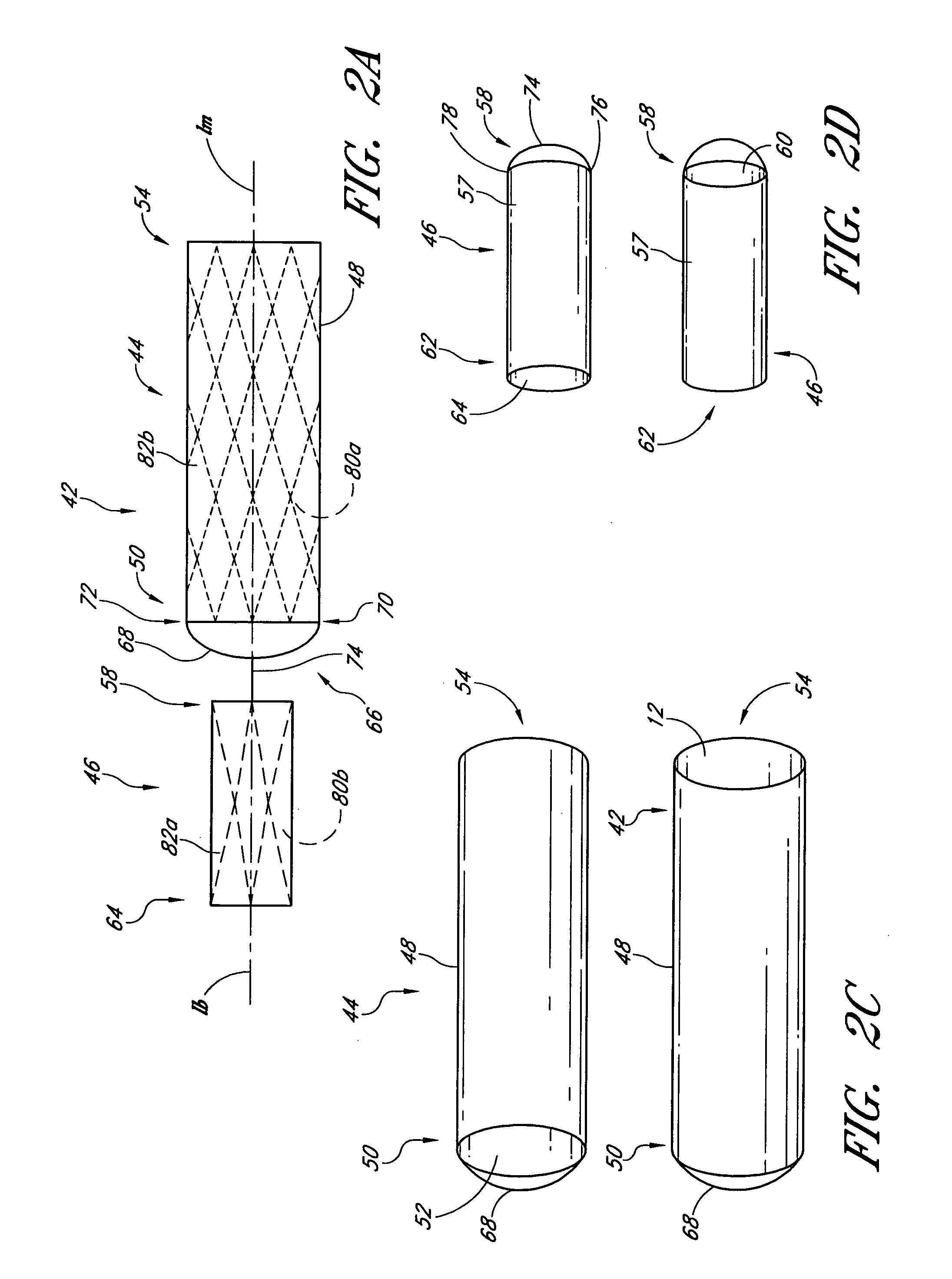
Sealable endovascular implants and methods for their use
The present invention is directed towards sealable and repositionable endovascular implant grafts, and methods for their use for the treatment of aortic aneurysms and other structural vascular defects. Sealable, repositionable endograft systems for placement in a blood vessel are disclosed, in which endograft implants with circumferential sealable collars and variable sealing devices upon deployment achieve a desired controllable seal between the collar and the vessel's inner wall. Embodiments of endovascular implants according to the present invention may further be provided with retractable retention tines or other retention devices allowing an implant to be repositioned before final deployment. An endograft system according to the present invention further comprises a delivery catheter to allow placement through a peripheral arteriotomy site, and of sufficient length to allow advancement into the thoracic or abdominal aorta.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
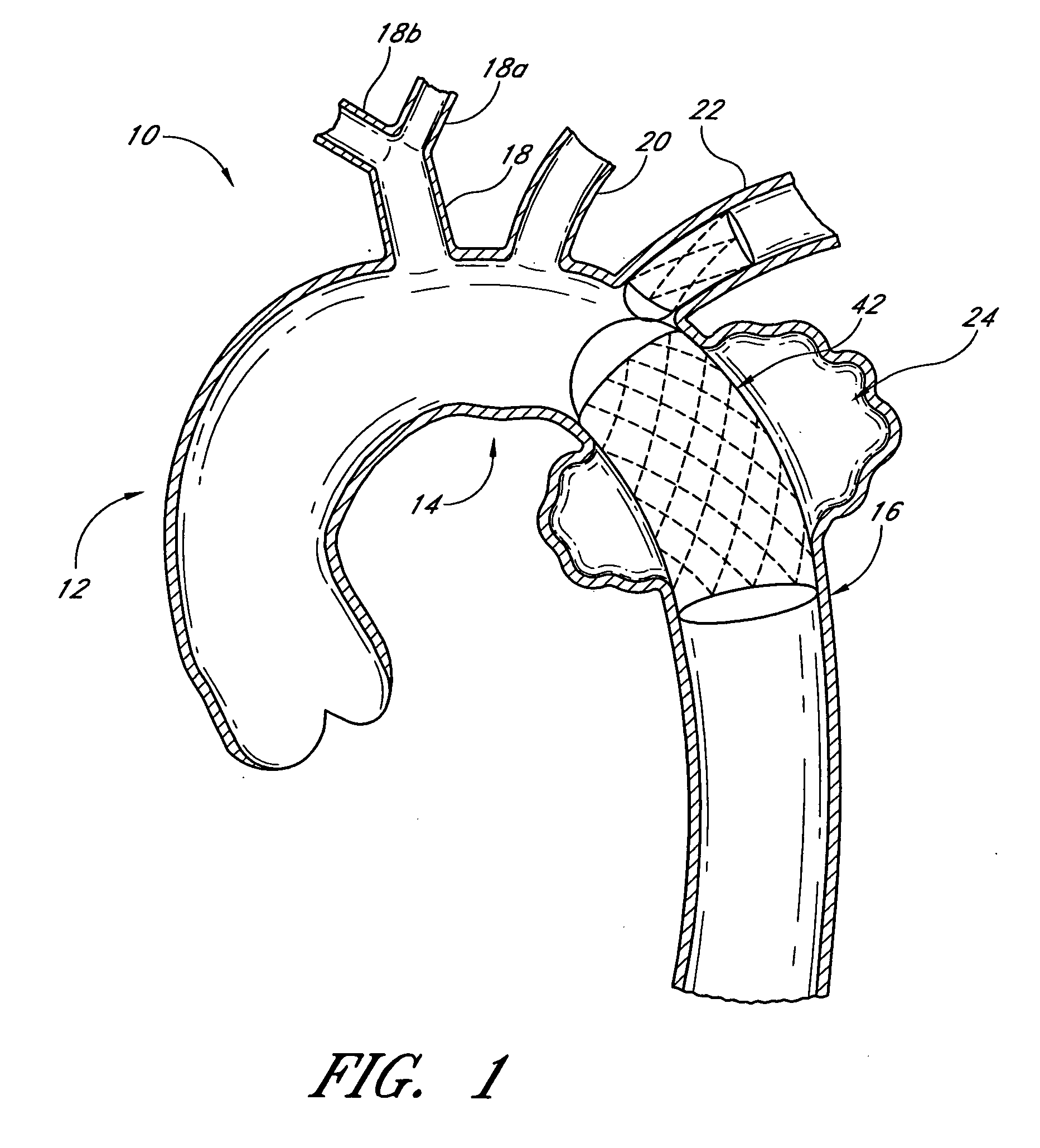
Device and method for treating thoracic aorta
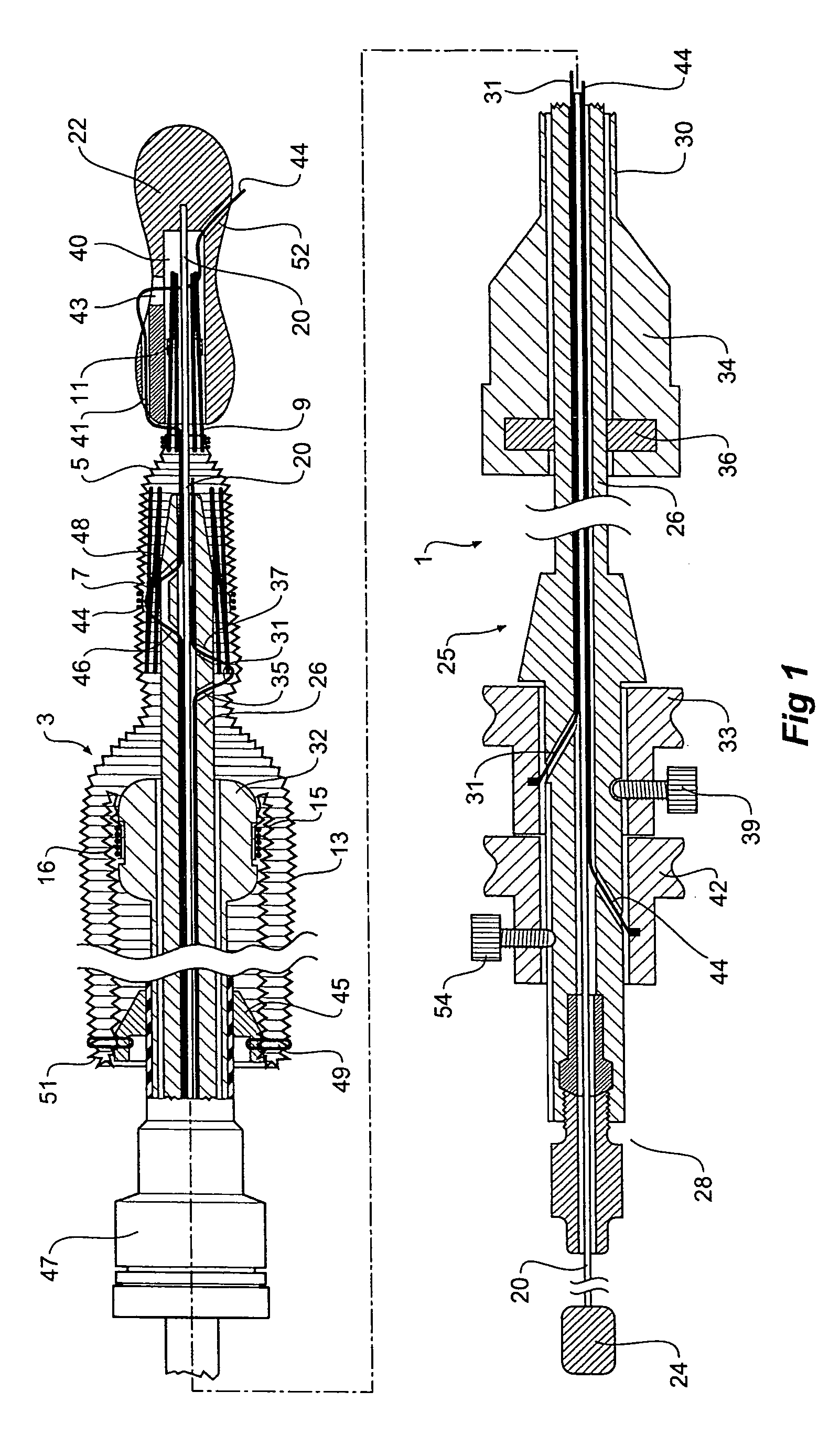
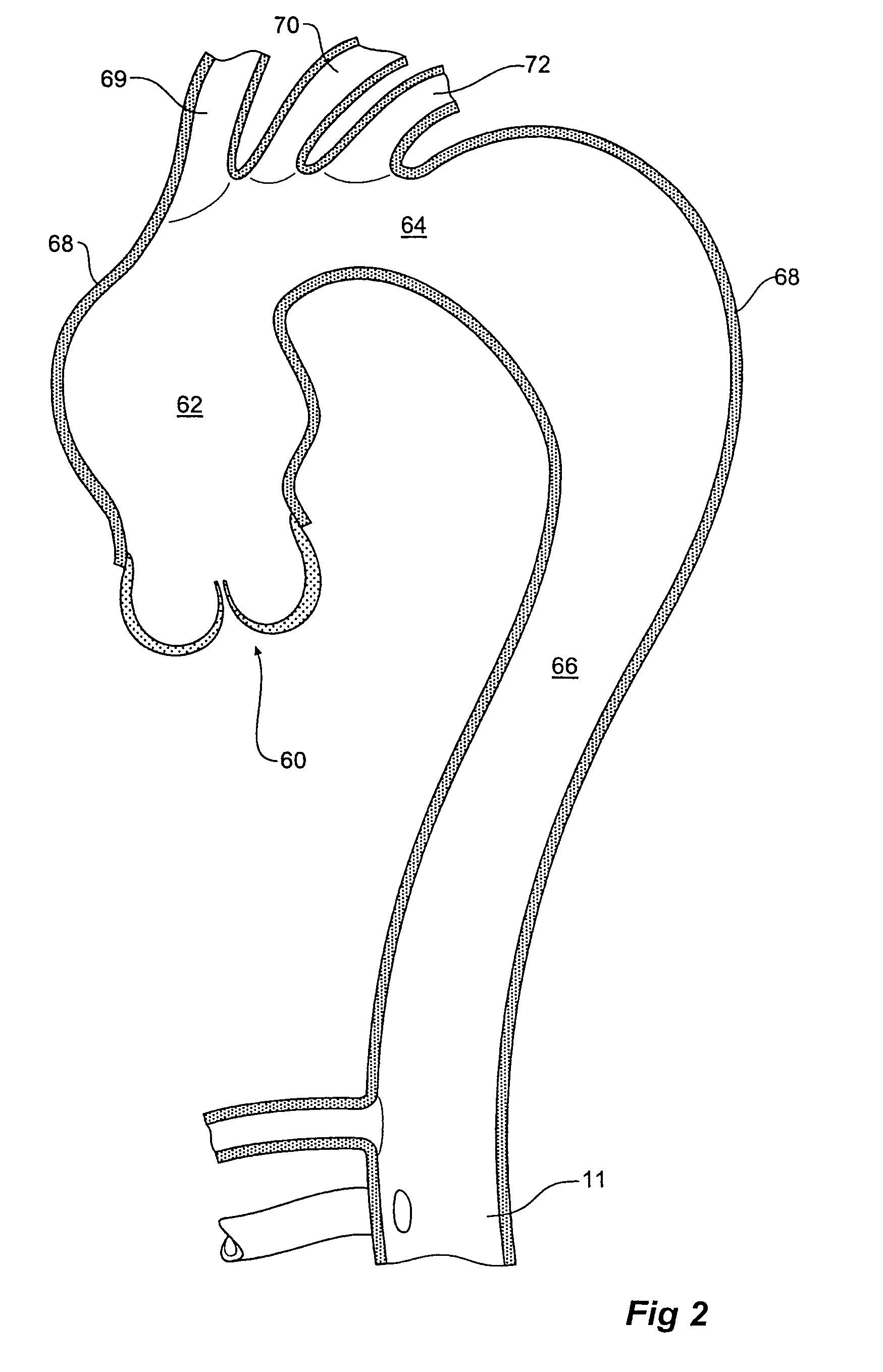
A prosthesis, introducer device and a method for repair of an aortic aneurysm which is positioned at least partially in the ascending aorta (62). The prosthesis (3) has a proximal end (15) and a distal end (5) and is formed from a biocompatible material, the proximal end is adapted to be surgically fastened adjacent and around the aortic heart valve (60) of a patient and the distal end is adapted to extend into the descending aorta (66). The distal end has a distally extending exposed self-expanding stent (9). The introducer device can be deployed through an incision (75) in the thoracic arch (64) and extend down the descending aorta to place the distal end of the prosthesis first and then removed so that the proximal end of the prosthesis can be sutured in place around the aortic heart valve (60).
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +2
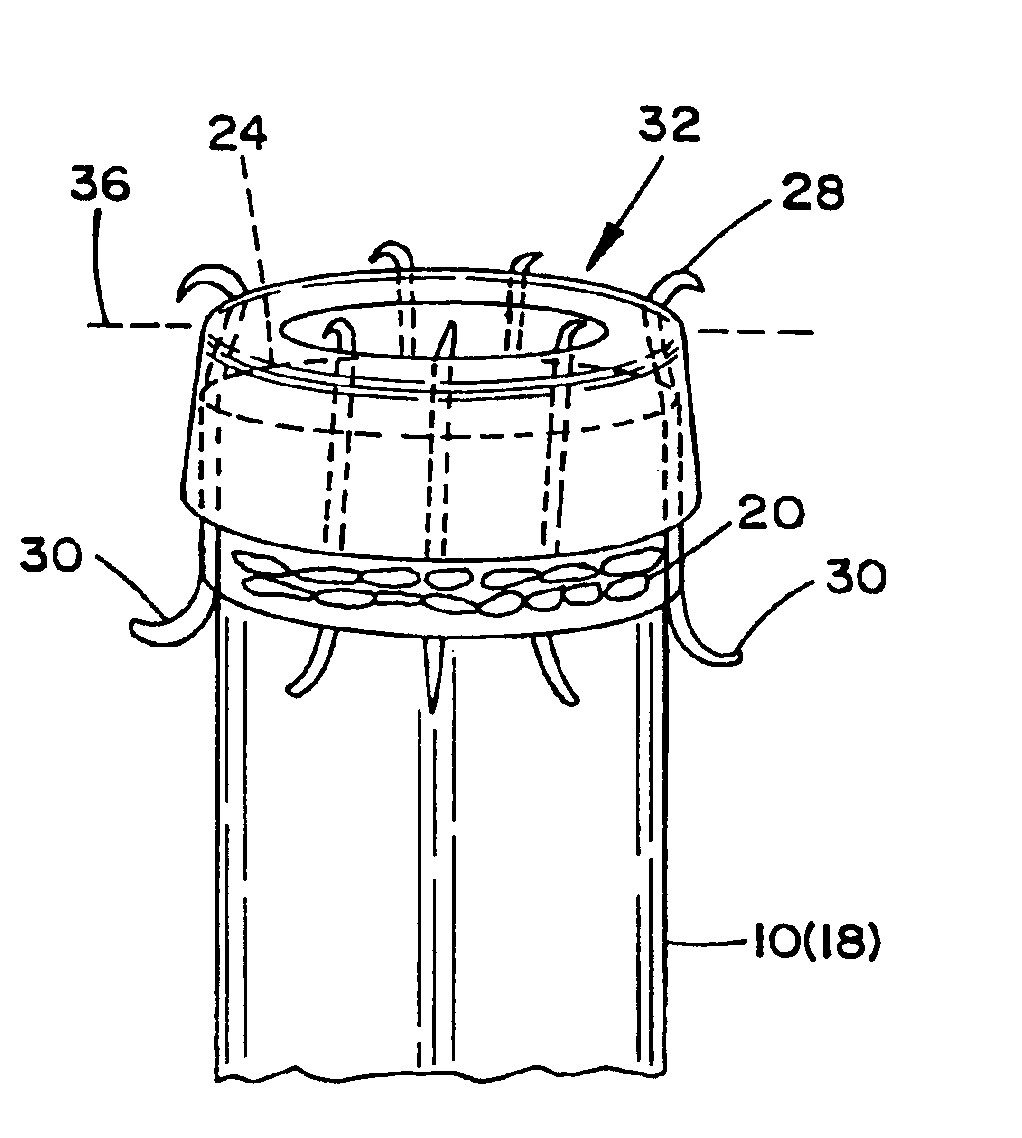
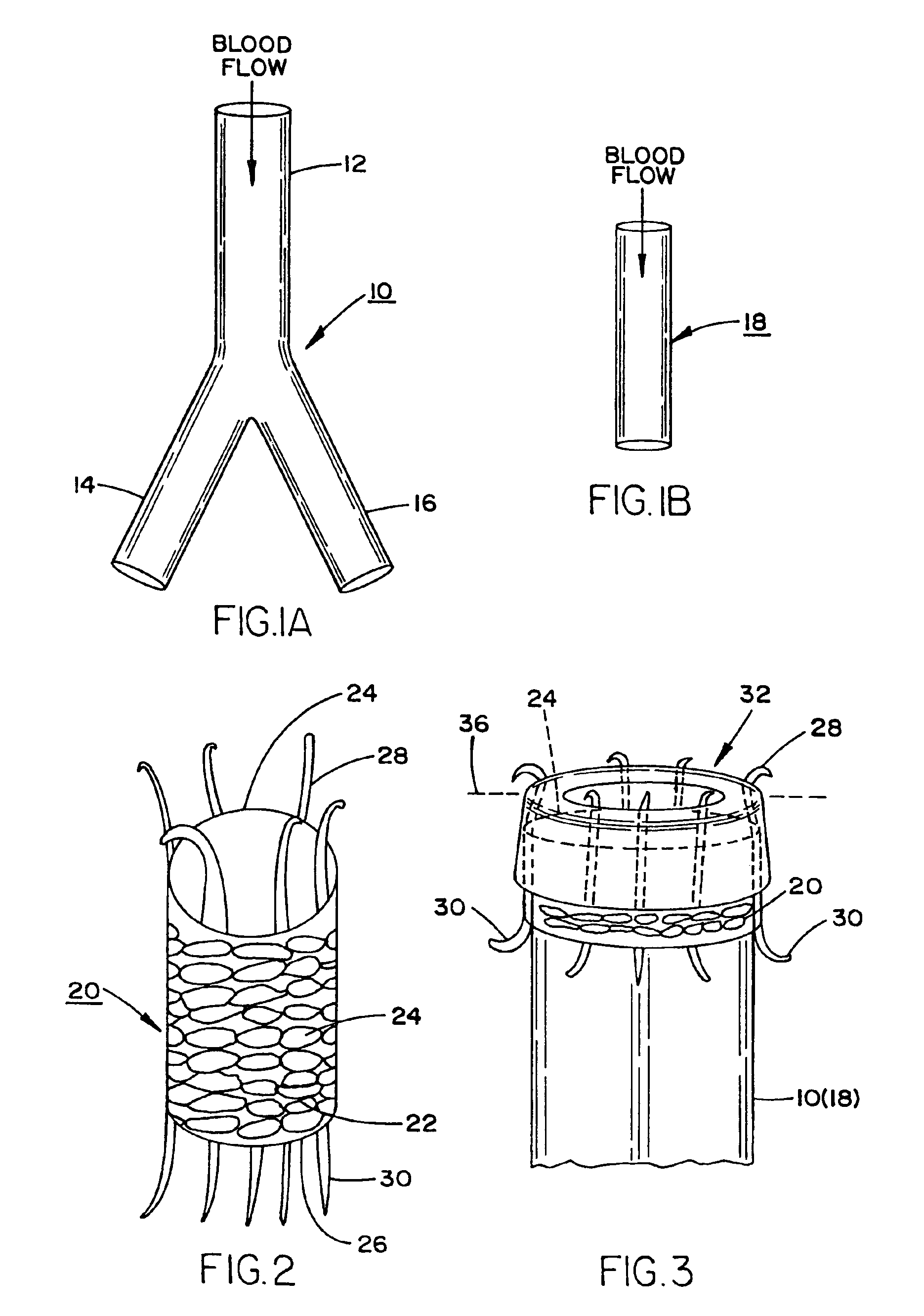
Prosthesis for the repair of thoracic or abdominal aortic aneurysms and method therefor
An prosthesis for the repair of thoractic or abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) and a method for utilizing the prosthesis. Furthermore, an arrangement and method is provided for the repair of aortic aneurysms incorporating a device for the placement of the prosthesis in the corporeal lumen or body vessel of a patient, and wherein the prosthesis comprises a graft facilitating the exclusion of the aneurysm, and also provides for anastomotic structure for the attachment of the prosthesis in a laparoscopic surgical procedure.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Sealable endovascular implants and methods for their use
The present invention is directed towards sealable and repositionable endovascular implant grafts, and methods for their use for the treatment of aortic aneurysms and other structural vascular defects. Sealable, repositionable endograft systems for placement in a blood vessel are disclosed, in which endograft implants with circumferential sealable collars and variable sealing devices upon deployment achieve a desired controllable seal between the collar and the vessel's inner wall. Embodiments of endovascular implants according to the present invention may further be provided with retractable retention tines or other retention devices allowing an implant to be repositioned before final deployment. An endograft system according to the present invention further comprises a delivery catheter to allow placement through a peripheral arteriotomy site, and of sufficient length to allow advancement into the thoracic or abdominal aorta.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
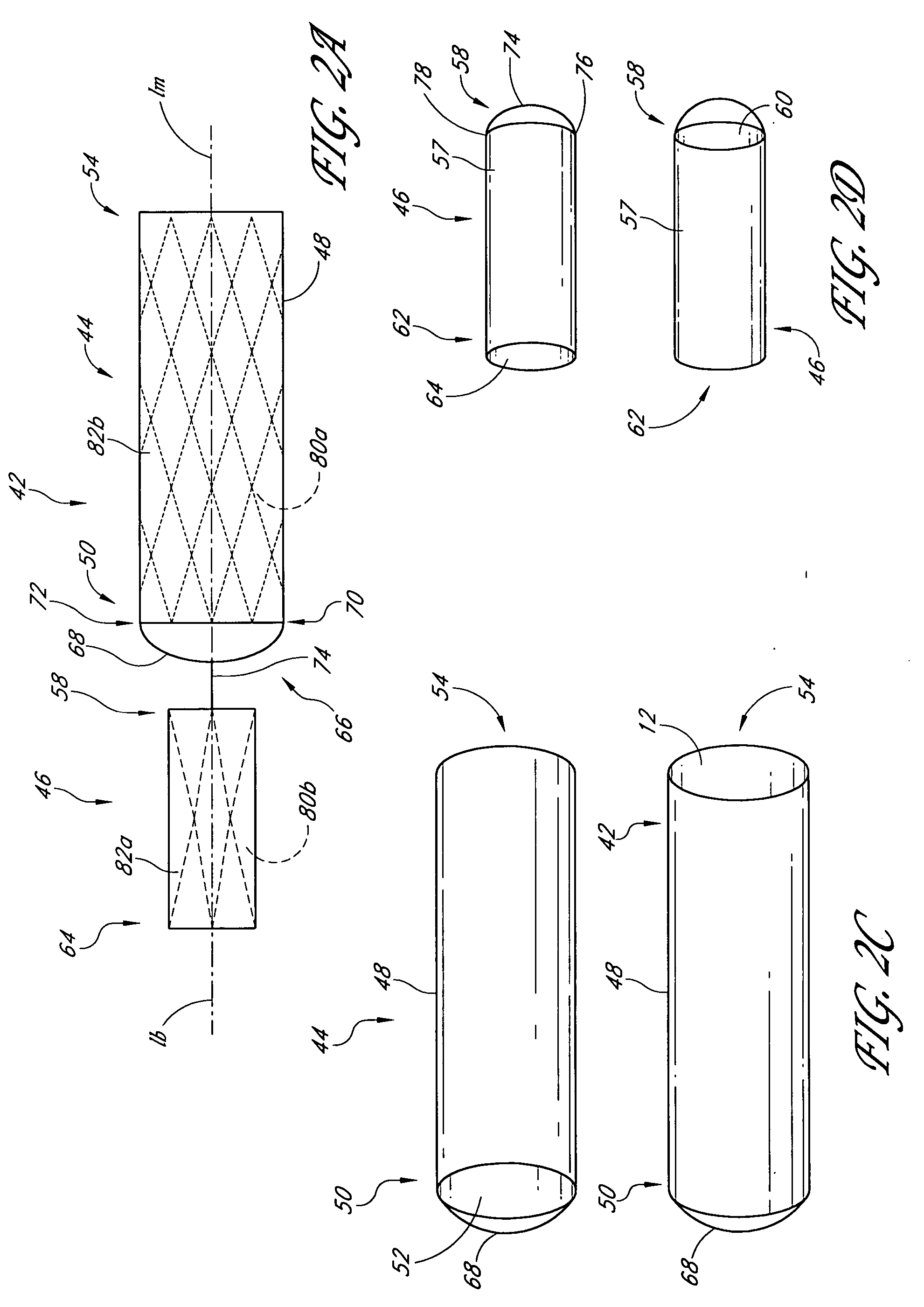
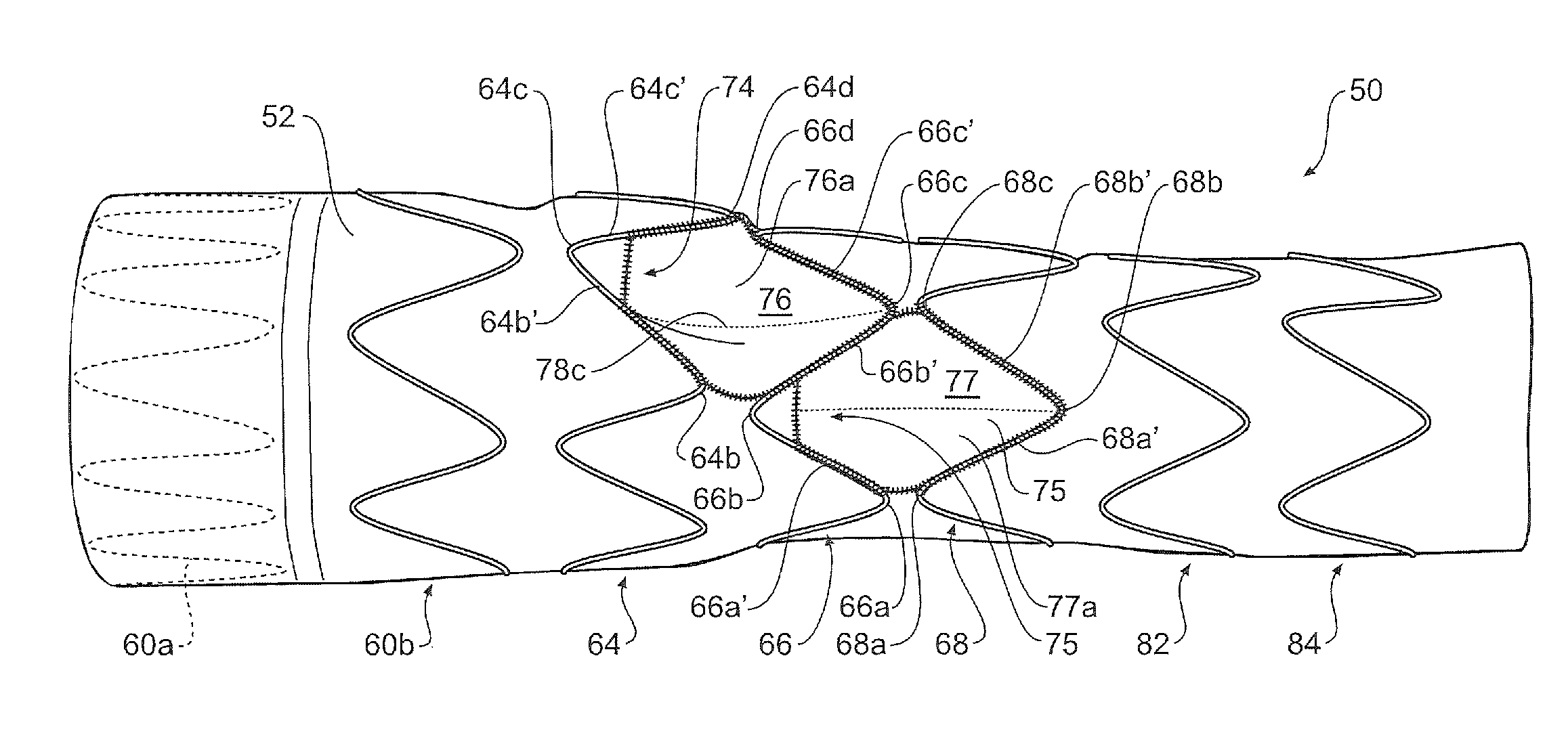
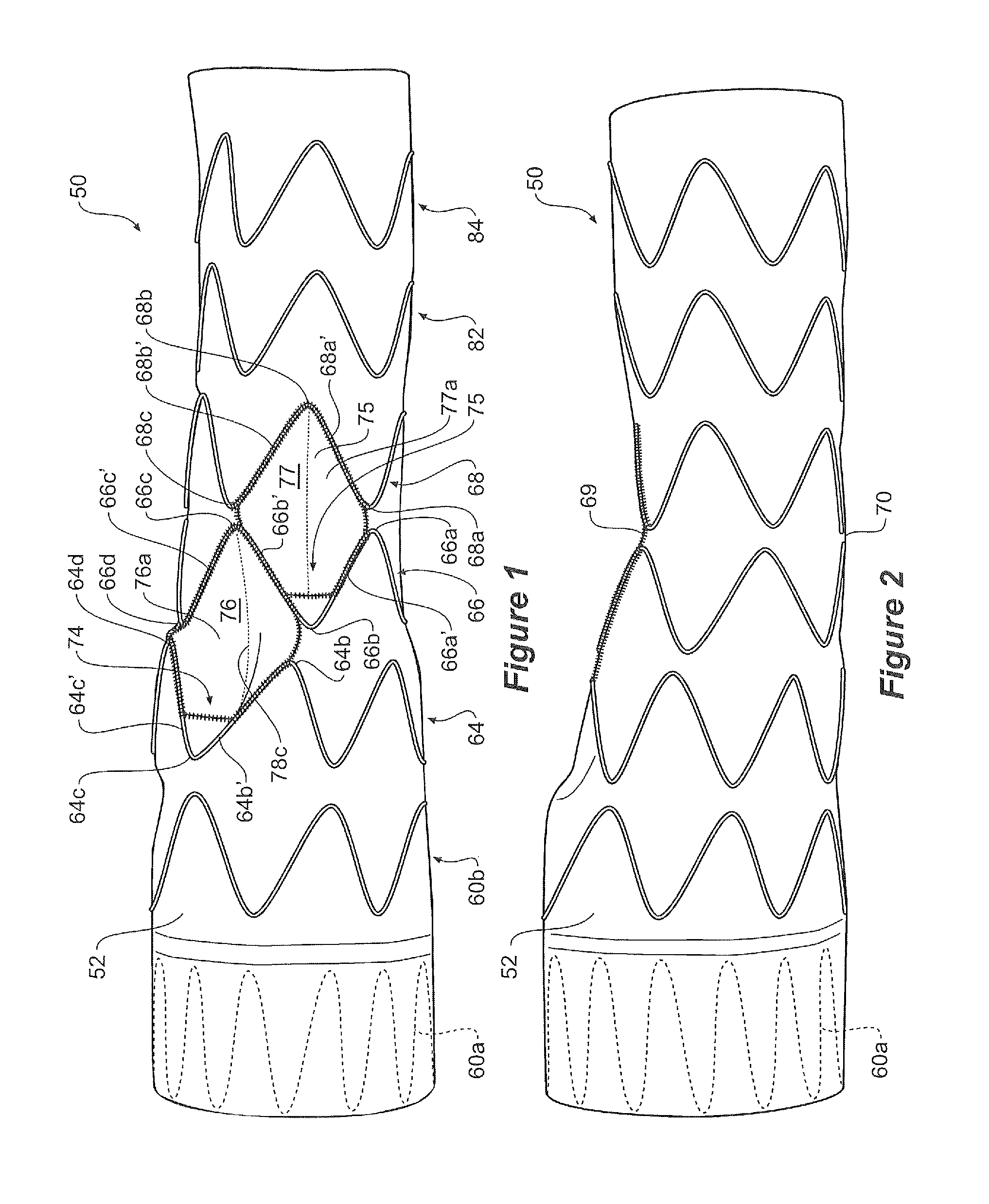
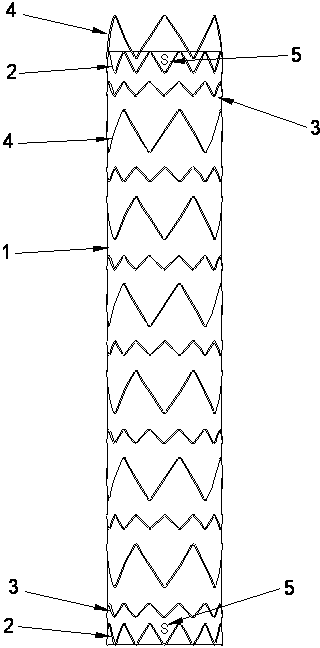
Thoracic aorta stent graft
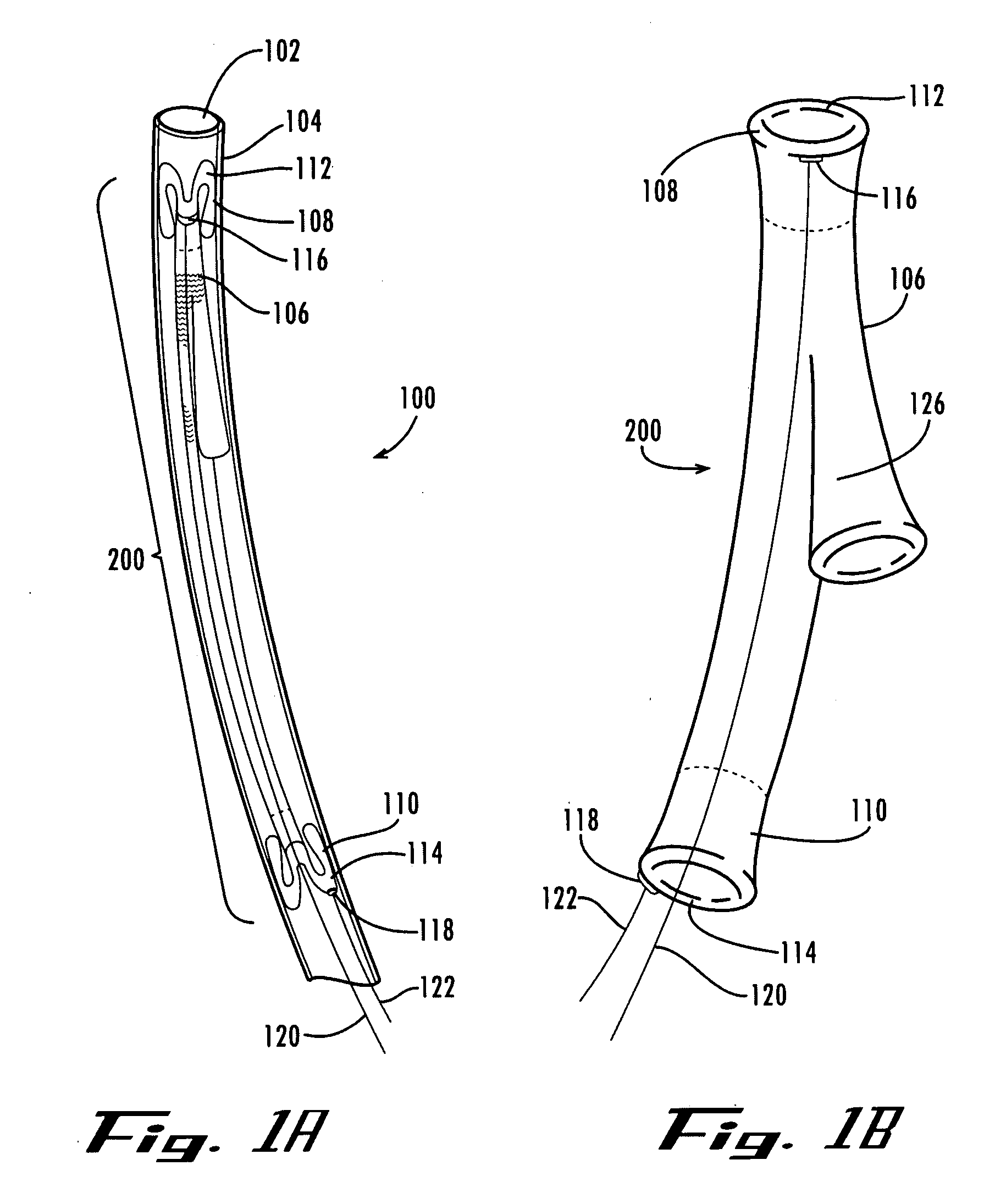
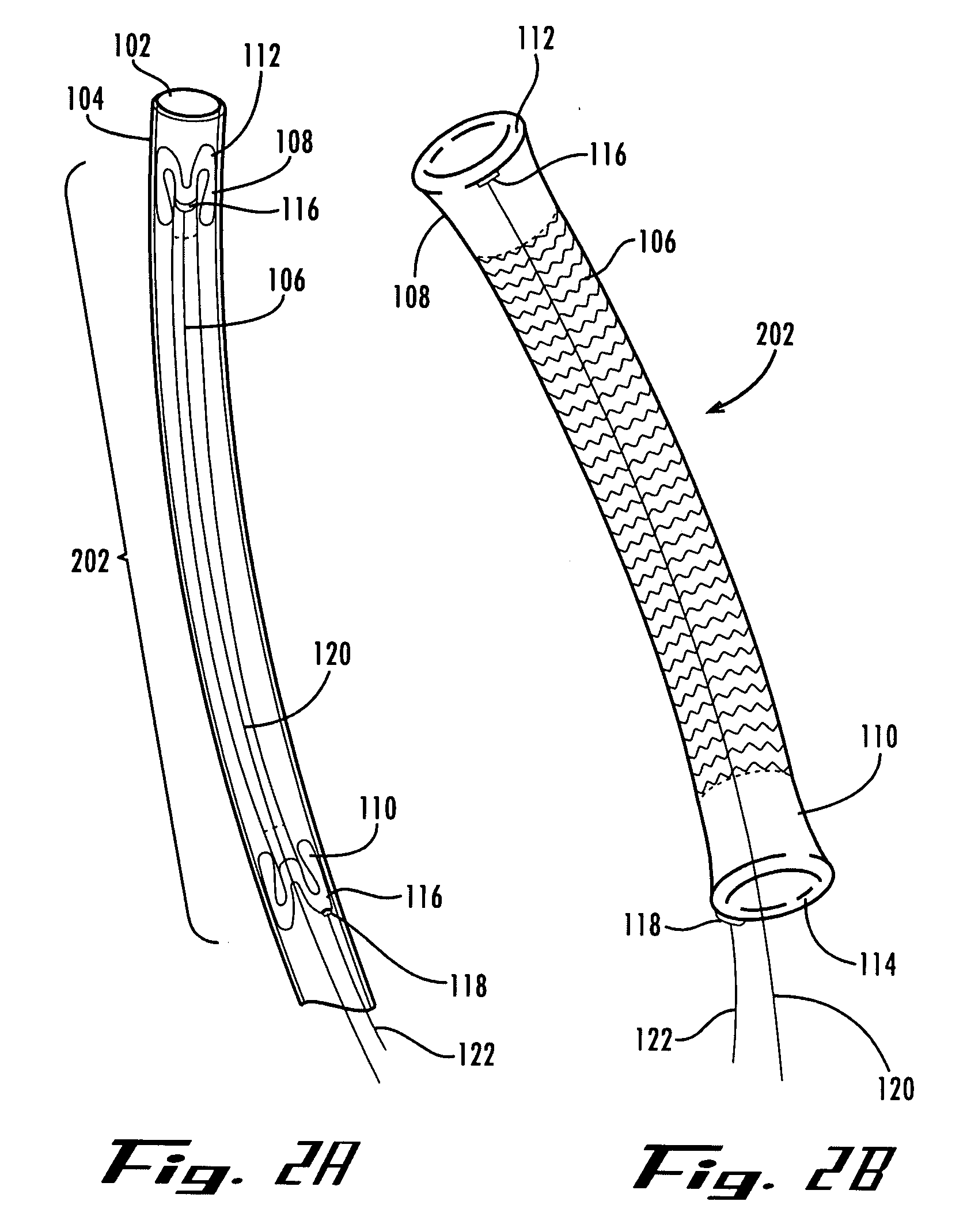
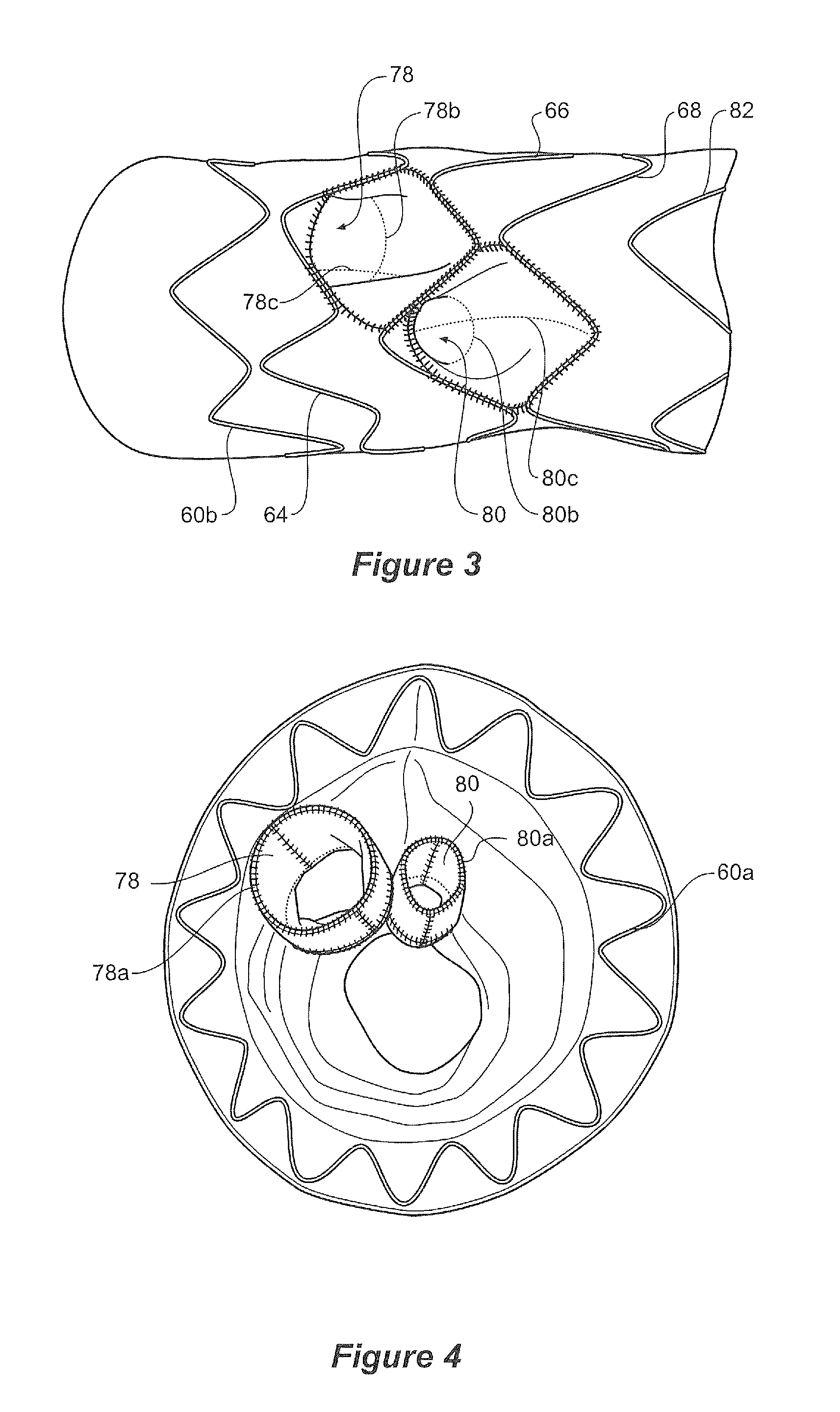
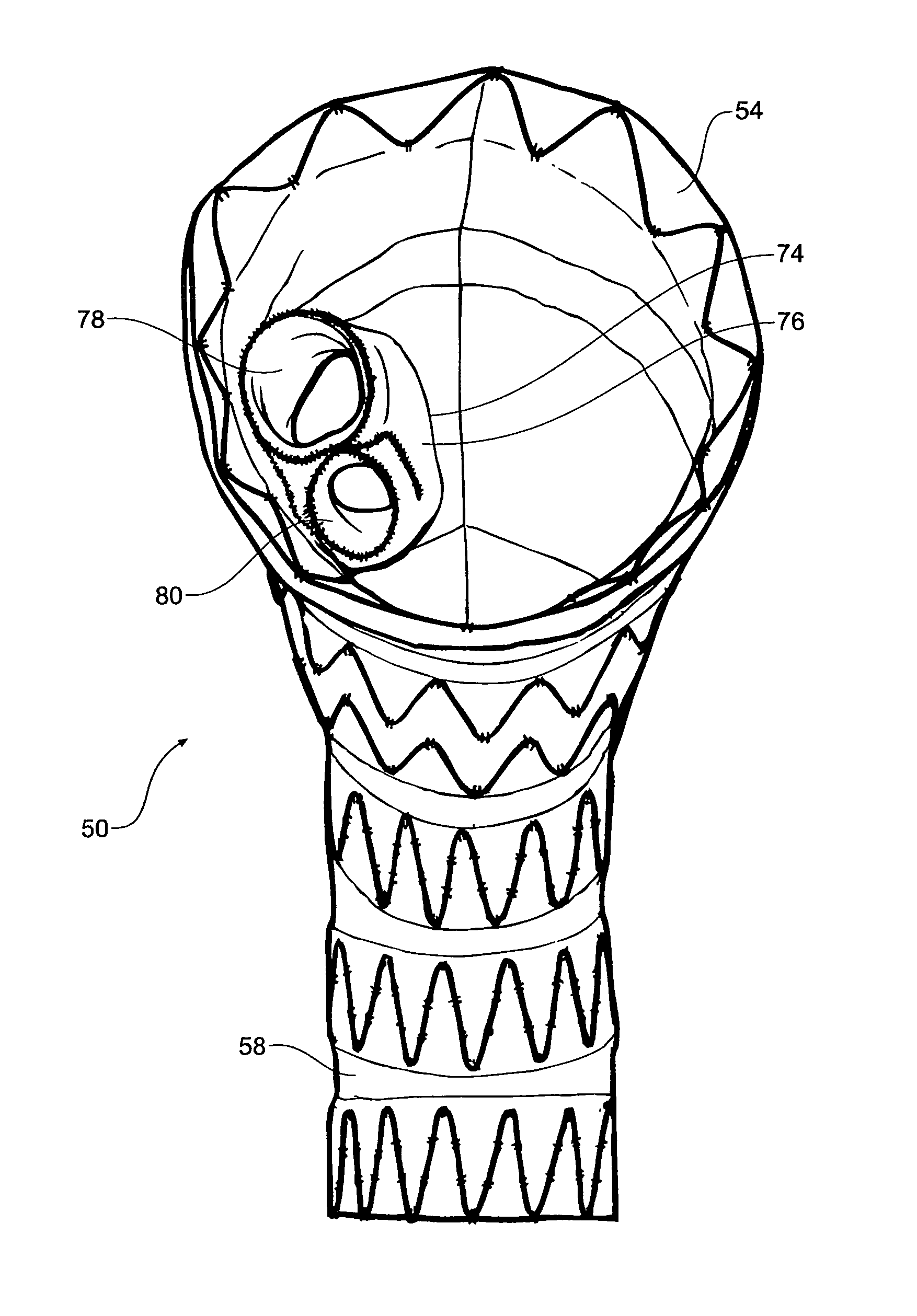
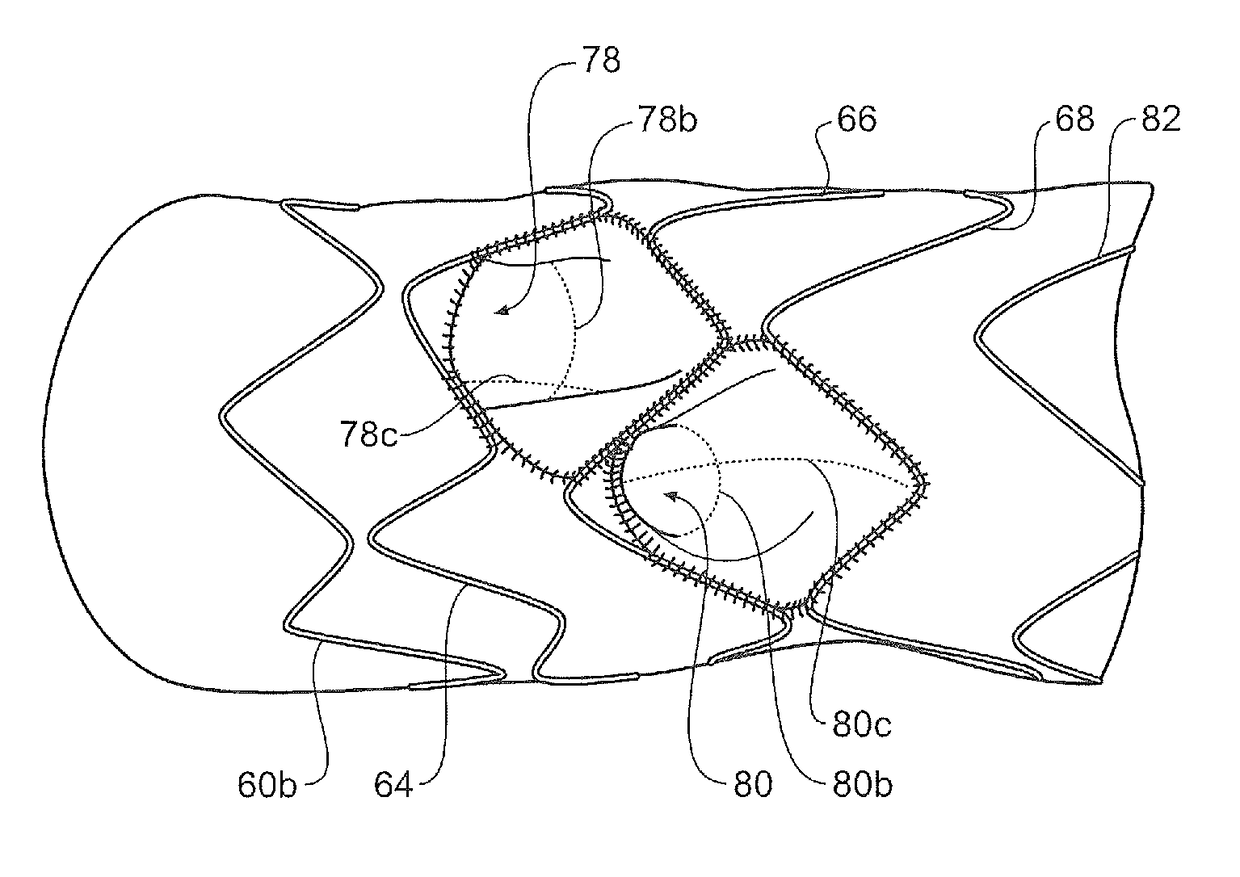
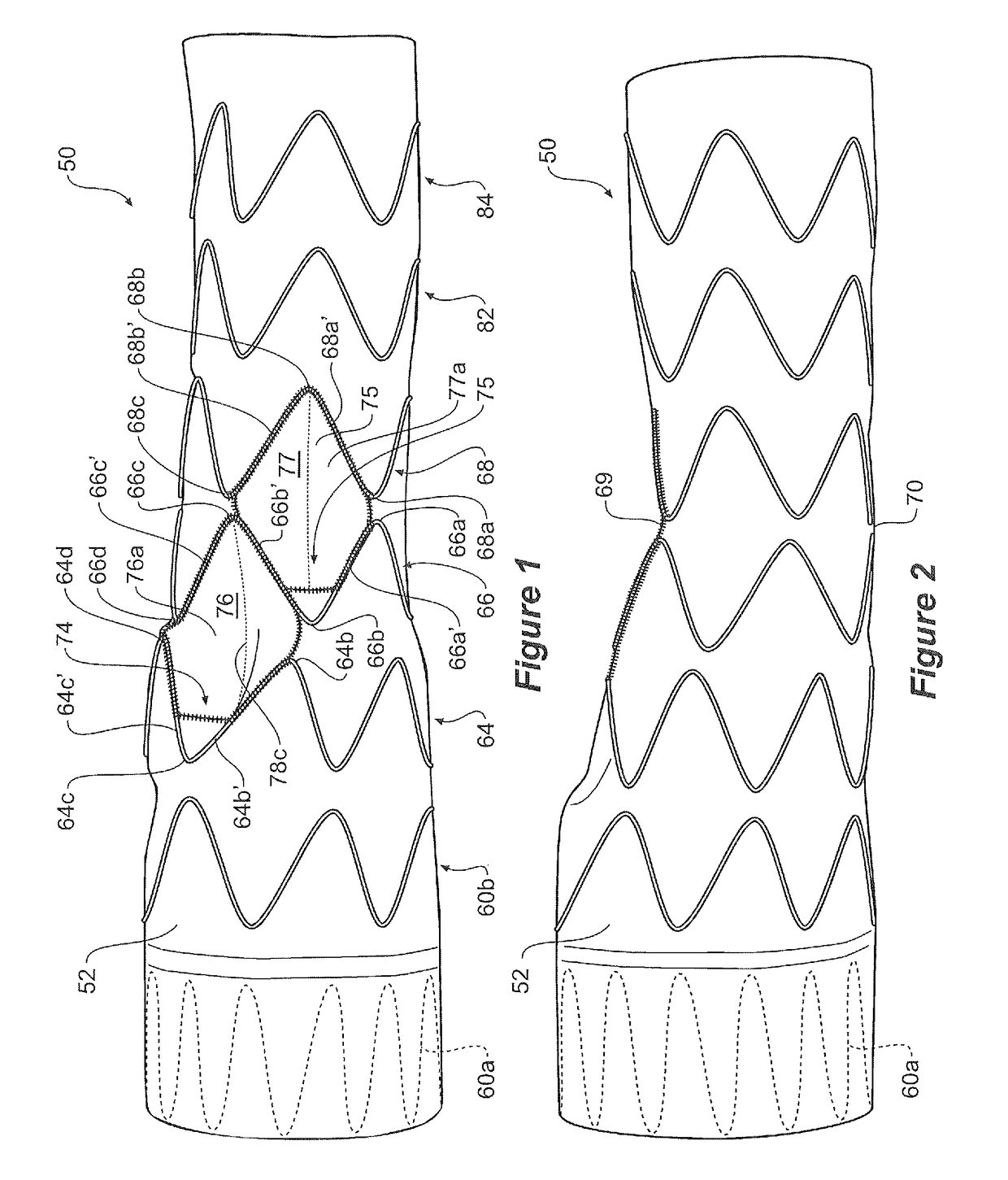
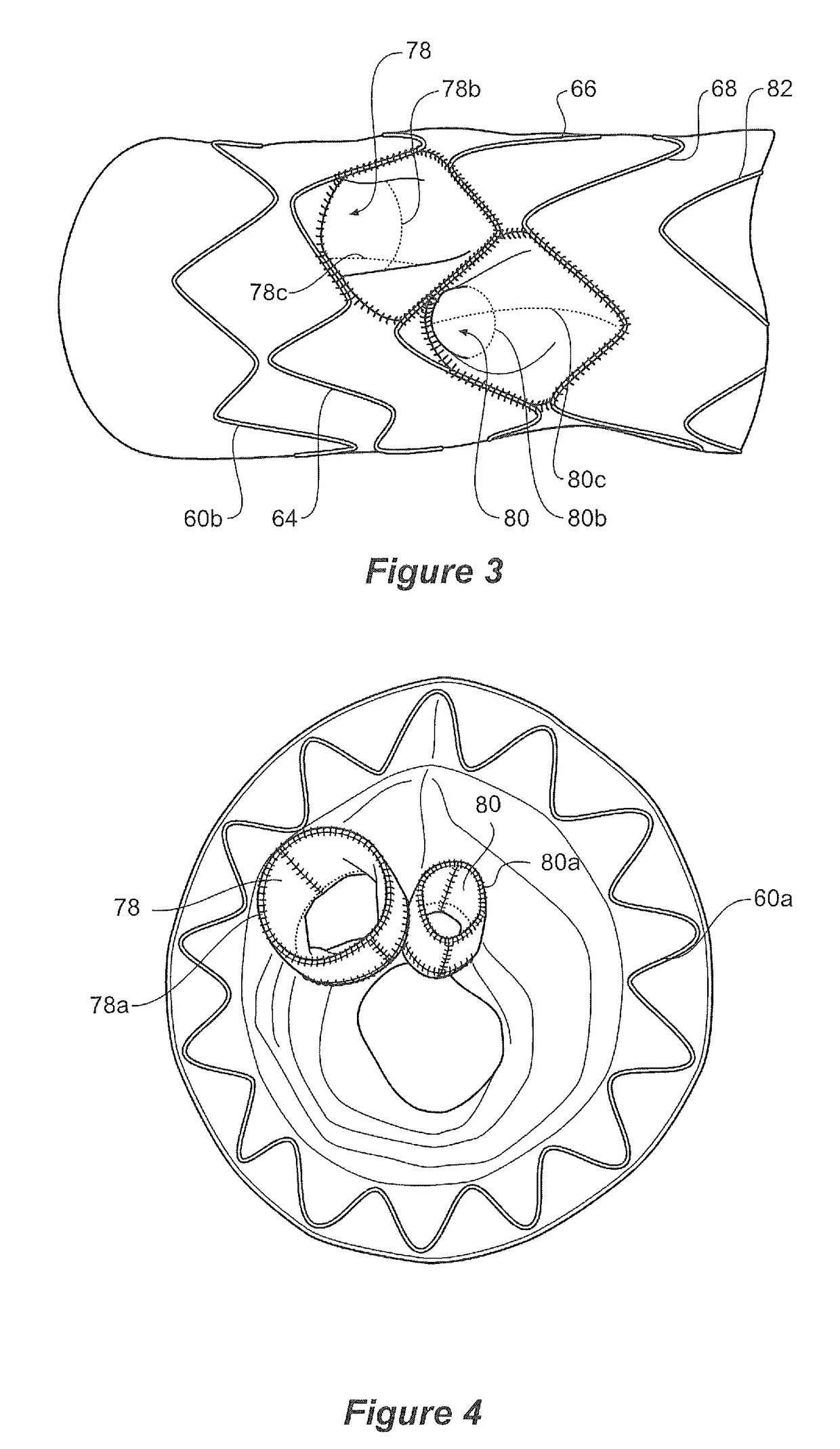
A stent graft for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a tubular body defining a main lumen therethrough, a plurality of zig zag stents along the tubular body, each of the stents comprising a plurality of struts and bends, the bends being between adjacent struts. At least a first stent and an adjacent second stent having at least a pair of adjacent bends on the first stent aligned with an adjacent pair of bends on the second stent, whereby a first pair of adjacent struts of the first stent and a second pair of adjacent struts of the second adjacent stent together define a diamond shape region. A recess is within the diamond shaped region with the recess extending into the lumen of the tubular body. A fenestration extending into the tubular body within the recess in the diamond shaped region and a graft tube leading from the fenestration into the main lumen. There can be one, two or three diamond shaped regions, recesses, fenestrations and graft tubes Proximally of the or each diamond shaped region the tubular body has a first diameter, distally of the diamond shaped region the tubular body has a second diameter and in the region of the tubular body around the diamond shaped region the tubular body has a third diameter, the first diameter being greater than the second diameter and both the first and second diameter being greater than the third diameter whereby a central region is defined which will allow circumferential blood flow during an operation out of the graft tube into the recess and then into the central region.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Thoracic aorta stent graft with access region
A stent graft (2) for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a first tubular body portion (6) with a first lumen therein for placement in the ascending aorta of a patient and a second tubular body portion (8) to extend along the thoracic arch and down the descending aorta. The second tubular body portion is of a lesser diameter than the first tubular body portion. There is a step portion (10) between the first body portion and the second body portion. The step portion is joined to and continuous with the first portion and the second portion. A first side of each of the first body portion, the step portion and the second body portion are substantially aligned so that there is a step (18) defined on a second side opposite to the first side of the body portion. There is an aperture (30) in the step portion and an internal tube (32) extending from the aperture towards the first body portion. The internal tube is divided along part of its length into at least two smaller internal tubes (34, 36) with the smaller internal tubes opening into the first lumen.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
Vascular graft and deployment system
A vascular graft includes a main portion and a branch portion that is coupled to the main portion by an articulating joint. The vascular graft may be inserted into the thoracic aorta with the branch portion positioned within a branch vessel and the main portion positioned within the thoracic aorta. The graft may be deployed within a deployment apparatus comprising an outer member and an inner member and a pusher. The main graft portion may be housed within the inner member while the branch graft portion is housed within the space between the inner and outer members. The inner member may have a longitudinal groove for allowing the articulating joint to pass by when the branch graft portion is deployed.
Owner:DOUGLAS MYLES
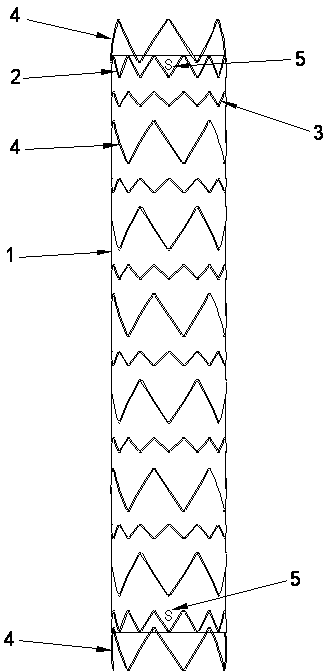
Thoracic aorta stent graft
A stent graft for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a tubular body defining a main lumen therethrough, a plurality of zig zag stents along the tubular body, each of the stents comprising a plurality of struts and bends, the bends being between adjacent struts. At least a first stent and an adjacent second stent having at least a pair of adjacent bends on the first stent aligned with an adjacent pair of bends on the second stent, whereby a first pair of adjacent struts of the first stent and a second pair of adjacent struts of the second adjacent stent together define a diamond shape region. A recess is within the diamond shaped region with the recess extending into the lumen of the tubular body. A fenestration extending into the tubular body within the recess in the diamond shaped region and a graft tube leading from the fenestration into the main lumen. There can be one, two or three diamond shaped regions, recesses, fenestrations and graft tubes Proximally of the or each diamond shaped region the tubular body has a first diameter, distally of the diamond shaped region the tubular body has a second diameter and in the region of the tubular body around the diamond shaped region the tubular body has a third diameter, the first diameter being greater than the second diameter and both the first and second diameter being greater than the third diameter whereby a central region is defined which will allow circumferential blood flow during an operation out of the graft tube into the recess and then into the central region.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Related ingredient combination with function of relaxing vessels in traditional Chinese medicine for reducing blood pressure
InactiveCN102727762AAvoid side effectsOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderVascular ringAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to the related ingredient combination with the function of relaxing vessels in traditional Chinese medicine for reducing blood pressure which is commonly used clinically. The invention utilizes modern traditional Chinese medicine theory and provides a related ingredient combination with definite ingredient, controllable quality and precise curative effect by animal model tests for reducing blood pressure. The related ingredient combination can be used for relaxing vessels, treating hypertension and improving hypertension complication. The commonly used traditional Chinese medicine relates to eucommia ulmoides, rhizoma gastrodiae, rhizoma chuanxiong, salviae miltiorrhizae, Astragalus mongholicus, root of kudzu vine, uncaria, radix stephaniae tetrandrae, red flower, radix scutellariae, selfheal, semen cassiae, dogbane leaf, hawthorn, radix achyranthis bidentatae, sophora flower, pseudo-ginseng, motherwort, chrysanthemum, lotus plumule, evodia, cape jasmine fruit, epimedium and caltrop which are included in Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2010 edition). The related ingredients are active ingredients which are extracted from single traditional Chinese medicine. Each traditional Chinese medicine provides one or several active ingredients. The combination study comprises the following steps of combining 2-6 active ingredients with different mechanisms in proportion, screening by utilizing rat thoracic aorta vascular rings and spontaneous hypertension rat models and determining the optimum combination proportion.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Thoracic aortic stent structure
InactiveUS20120123526A1Complicated and difficult to operateStentsBlood vesselsThoracic aortaInsertion stent
A thoracic aortic stent structure, including a main stent having at least one sub-stent which is formed as a piece on the main stent; and a membrane covering the main stent and the at least one sub-stent, and having at least one side-opening corresponding to a free end of the at least one sub-stent. The membrane compresses the main stent and the at least one sub-stent, which causes diameter of the main stent and the at least one sub-stent narrower. Upon removing the membrane, the main stent and the at least one sub-stent can extend to reconstruct a vascular pathway. The thoracic aortic stent is able to simplify the process, of placement, save time and provide easy operation.
Owner:KO PO JEN +2
Method for determining cardiovascular information
ActiveUS9405886B2Minimizes instabilityMore benefitMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesInstabilityRetrograde Flow
A noninvasive patient-specific method is provided to aid in the analysis, diagnosis, prediction or treatment of hemodynamics of the cardiovascular system of a patient. Coronary blood flow and pressure can be predicted using a 3-D patient image-based model that is implicitly coupled with a model of at least a portion of the remaining cardiovascular system. The 3-D patient image-based model includes at least a portion of the thoracic aorta and epicardial coronaries of the patient. The shape of one or more velocity profiles at the interface of the models is enforced to control complex flow features of recirculating or retrograde flow thereby minimizing model instabilities and resulting in patient-specific predictions of coronary flow rate and pressure. The invention allows for patient-specific predictions of the effect of different or varying physiological states and hemodynamic benefits of coronary medical interventions, percutaneous coronary interventions and surgical therapies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Covered stent for aortic dissection surgery, conveying device and use method
InactiveCN106214287AAvoid punctureEnsure blood supplyStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionArcus aortae
The invention discloses a covered stent for aortic dissection surgery, a conveying device and a use method. The stent comprises a body which is a covered stent body. The stent is a conical stent with the diameter gradually reduced from the cardiac proximal portion to the thoracic aorta distal portion. An exposed portion is arranged on the lower portion of the body of the stent and is not covered. Three balloon dilatation stents are connected to the upper edge of the middle of the body. A protective gasket made from polytetrafluoroethylene is arranged at the near end of the body. The three balloon dilatation stents are provided with three catheters respectively. Each catheter is about 2 m long. The conveying device comprises a conveying sheath, the body of the stent is compressed in the conveying sheath, and the three balloon dilatation stents on the middle section of the body are compressed in the conveying sheath. A conveying sheath system is provided with an apex, and notches are formed in the tip end of the conveying sheath system for the body of the stent and guide wires and the catheters of the three balloon dilatation stents. The invention provides the covered stent for aortic dissection surgery. The stent is used for minimally invasive surgery treatment of Stanford A type aortic dissection with a wound among three branch vessels on the arcus aortae, avoids injuries caused by thoracotomy, and can be directly used for intra-cardiac wound occlusion.
Owner:杨威
Thoracic aorta covered stent
ActiveCN102824237AImprove flexibilityNot easy to twistStentsBlood vesselsThoracic aortaCovered stent
The invention relates to a thoracic aorta covered stent, which is used for treating aneurysm of thoracic aorta and dissecting aortic aneurysm in minimally invasive surgeries. The thoracic aorta covered stent comprises a cover and a stent composed of a plurality of cylindrical single rings, wherein the cover is adhered to the stent to form a tubular cover; the plurality of cylindrical single rings are in wave patterns; a supporting frame is arranged at the near end of the stent; and each cylindrical single ring comprises a first type cylindrical single ring and a second type cylindrical single ring which are distributed at intervals on the tubular cover; the amount of the waveforms of the first type cylindrical single ring is not less than that of the second type cylindrical single ring; and the waveform of the first type cylindrical single ring is less than that of the second type cylindrical ring.
Owner:BEIJING PERCUTEK THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Stent grafts for the thoracic aorta
ActiveUS8377113B2Precise positioningDifficult to withdrawStentsBlood vesselsThoracic aortaInsertion stent
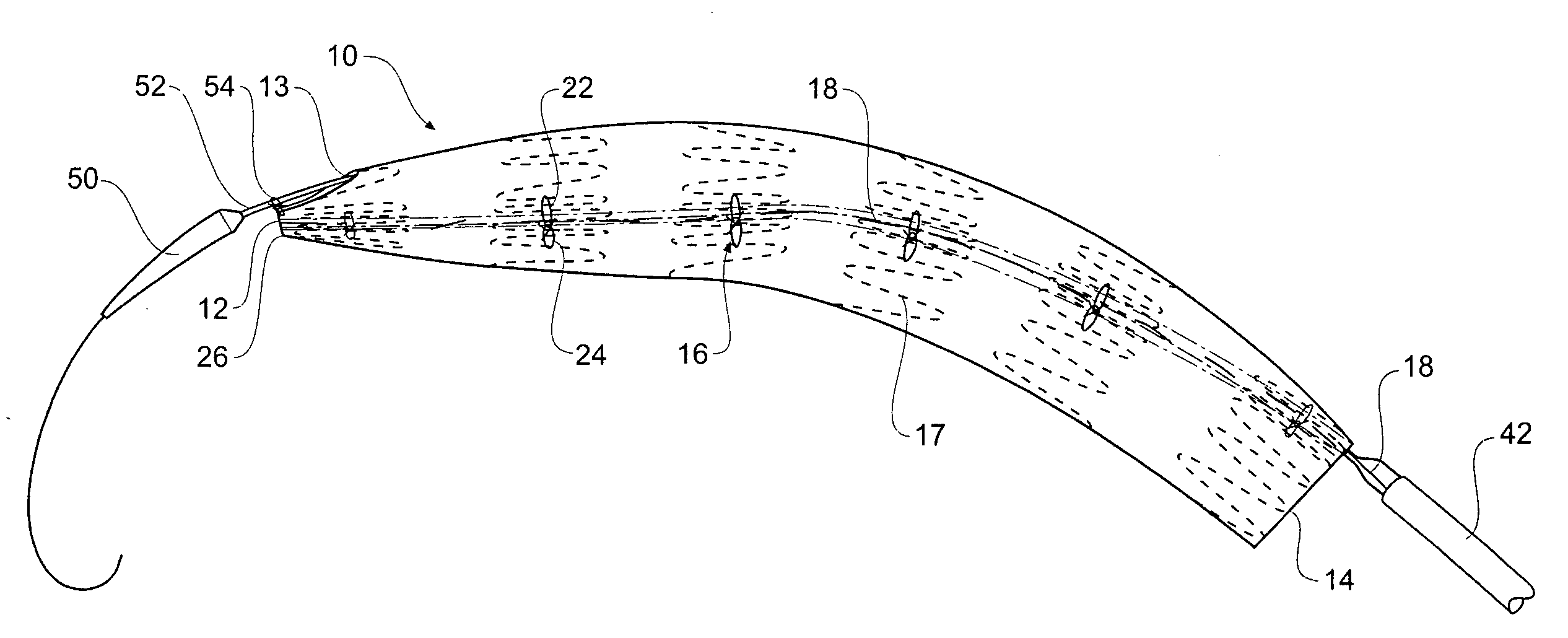
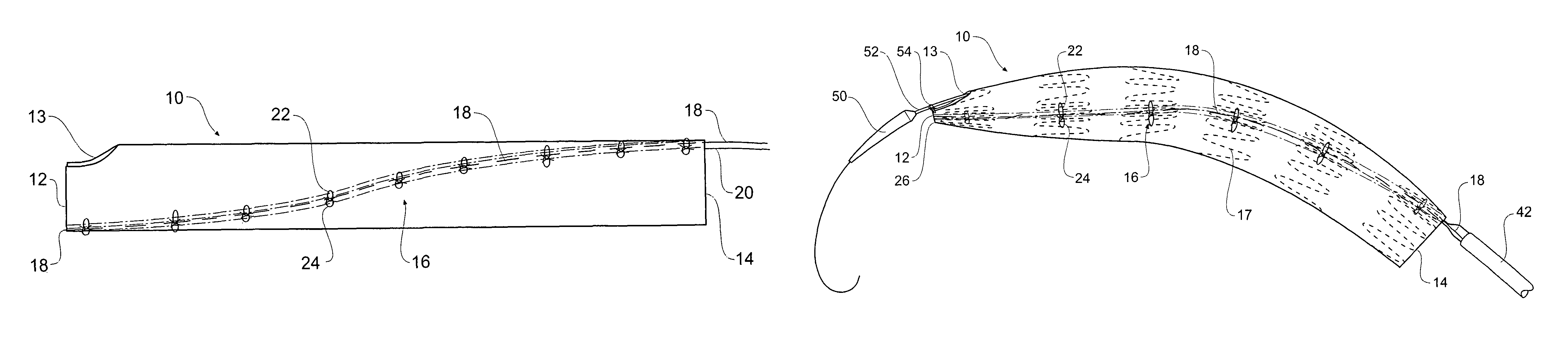
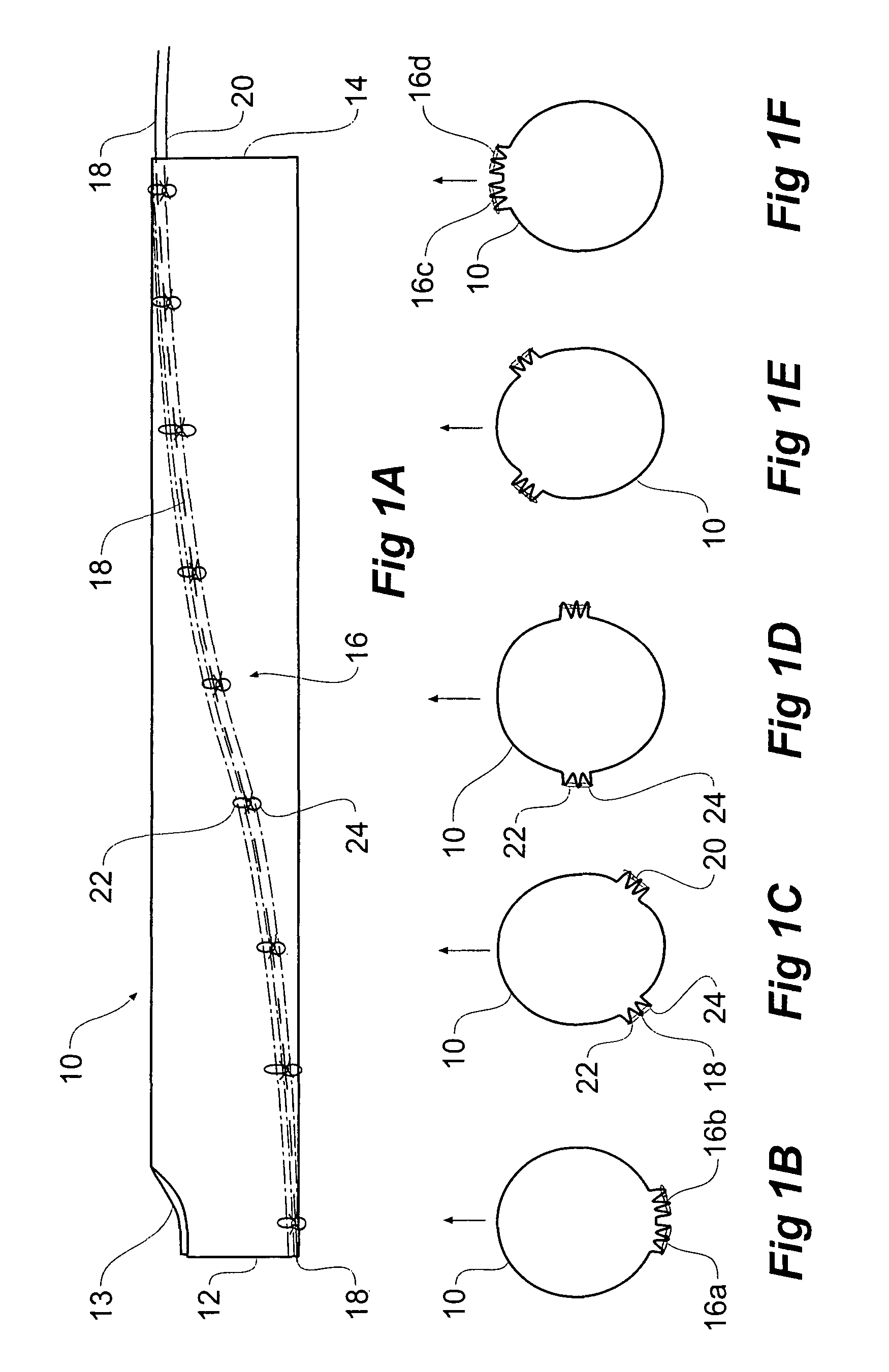
A method of temporarily reducing the diameter of a stent graft (10) and a stent graft with its diameter reduced. The stent graft has a tubular body and self expanding stents. The method comprising extending a release wire (18, 20) part helically along the graft material tube from substantially one side of the graft material tube at one end (14) of the graft material tube to substantially the opposite side of the graft material tube at the other end (12) of the graft material tube along the stent graft and stitching the release wire into the graft material tube, at each of a number of positions along the release wire looping flexible threads (22, 24) around the release wire and extending the flexible threads laterally around the circumference of the stent graft in each direction to a position away from the release wire, engaging the first flexible threads into the graft material or around struts of the stent, and drawing the ends of the thread together and tying ends of the thread to thereby temporarily reduce the overall diameter of the stent graft.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
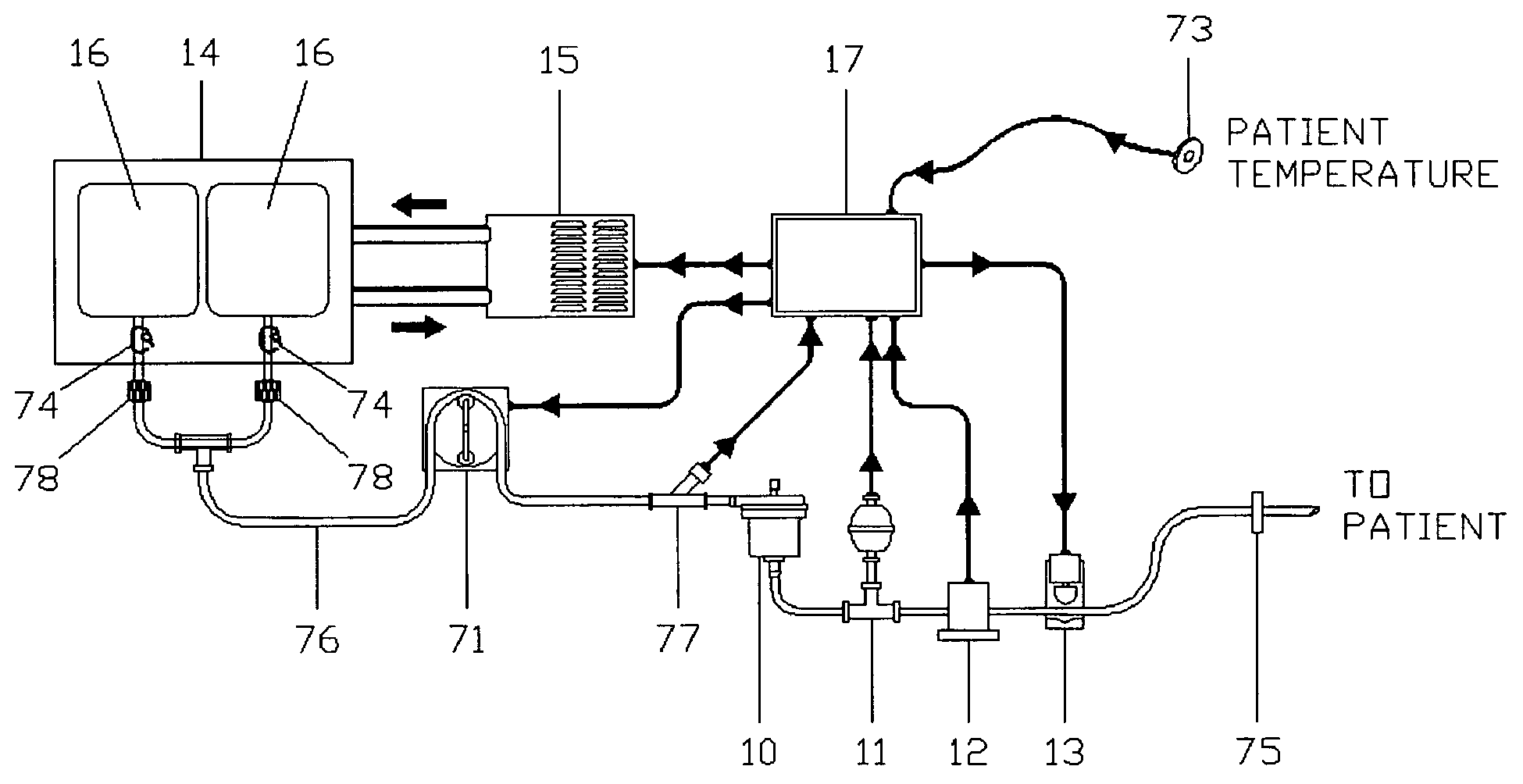
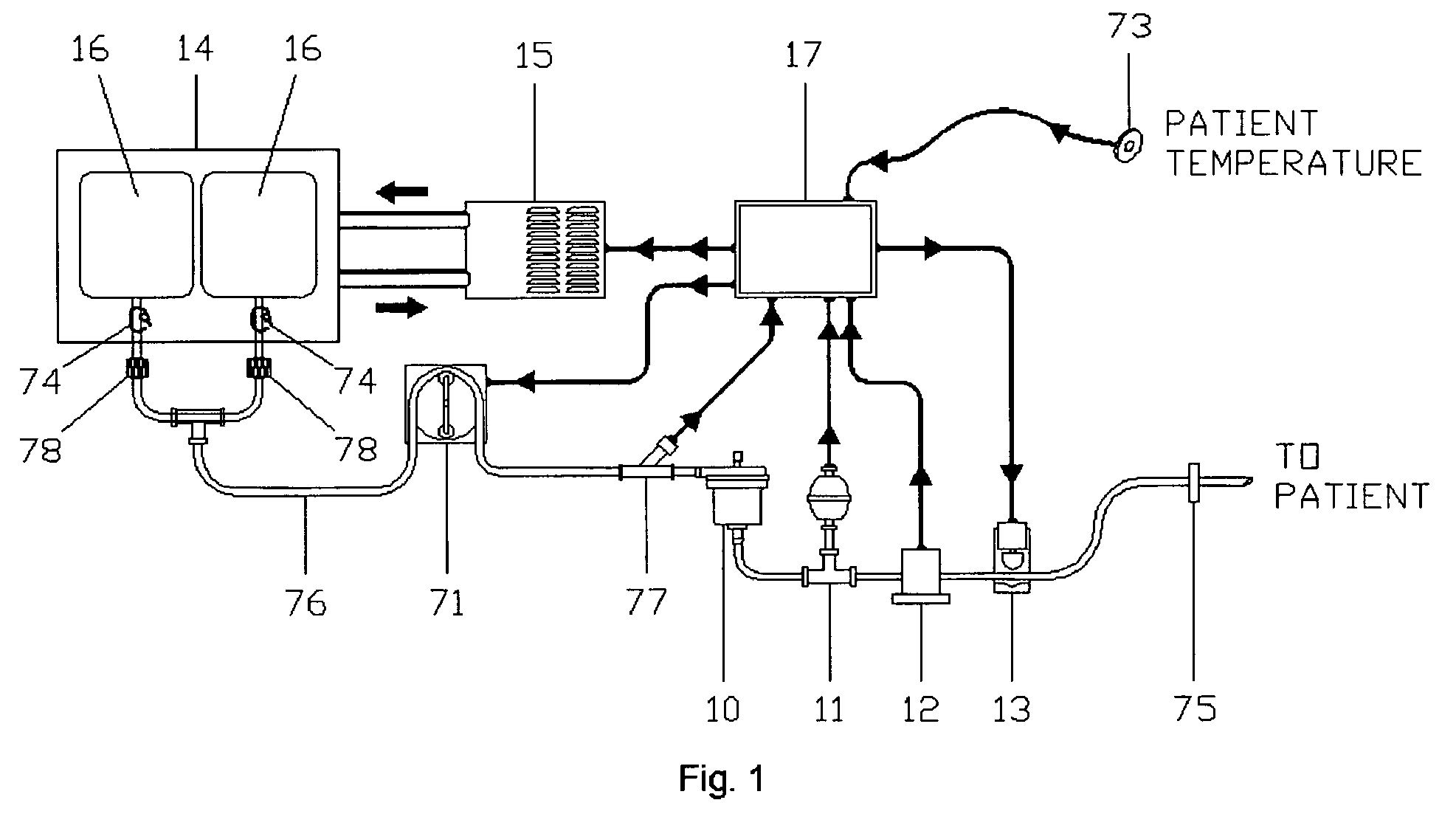
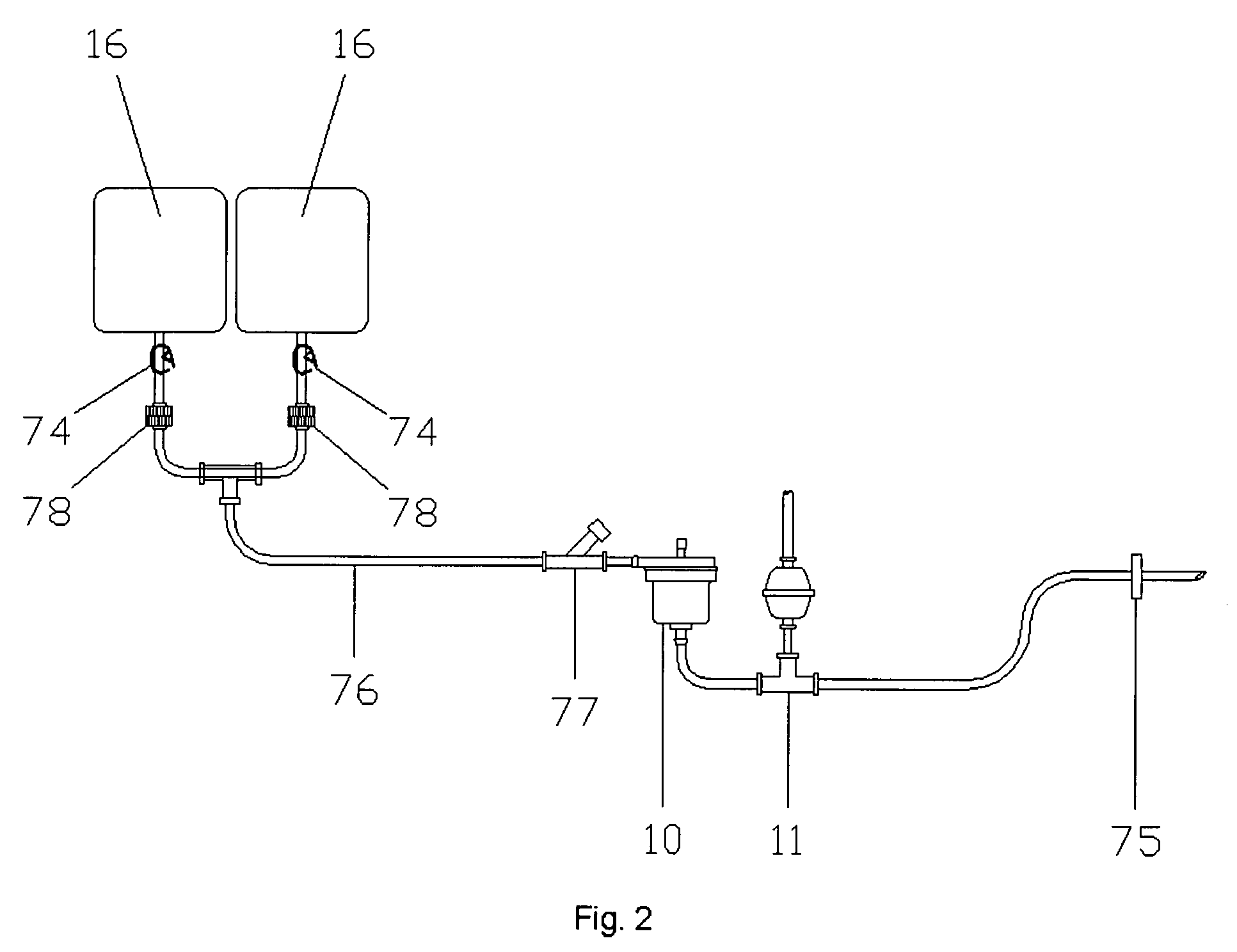
Apparatus and Method for Inducing Suspended Animation Using Rapid, Whole Body, Profound Hypothermia
InactiveUS20080312723A1Increase chances of survivalGood effectTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingThoracic aortaProper treatment
Disclosed is a transportable apparatus that maintains a large volume of a cold solution at a preset low temperature and rapidly delivers it to an irresuscitable patient's thoracic aorta at a preset and controlled flow rate, while monitoring pressure and eliminating the introduction of air embolisms into the patient, for the purpose of inducing profound hypothermia and suspended animation until proper treatment of the patient is available. The induction of suspended animation is intended for preservation of viability of the brain, heart, and organs for subsequent repair and resuscitation or for organ harvesting. The procedure may be performed by emergency personnel on the scene of an accident and / or while the patient is being transported in an emergency vehicle, or while in a hospital.
Owner:ARDIEM MEDICAL
Thoracic aorta ventricular assist system
An implantable heart assist system, includes a pumping chamber formed of a flexible material and being adapted to be placed in fluid connection with the aorta and a pump system comprising a first rigid member, a second rigid member spaced from the first rigid member so that at least a portion of the pumping chamber may be positioned between the first rigid member and the second rigid member, a drive system comprising a motor, an extending member comprising a threaded section operatively connecting the first rigid member and the second rigid member and a nut in operative connection with the threaded section. The motor is adapted to rotate either the extending member or the nut relative to the other to convert rotary motion of the motor to linear motion to cause the second rigid member to move toward the first rigid member or away from the first rigid member. The heart assist system further includes a controller or a control system in operative connection with the drive system and controlling the motor. Movement of the second rigid member toward the first rigid member results in compression of the pumping chamber, and movement of the second rigid member away from the first rigid member causes expansion of the pumping chamber.
Owner:VASCOR INC
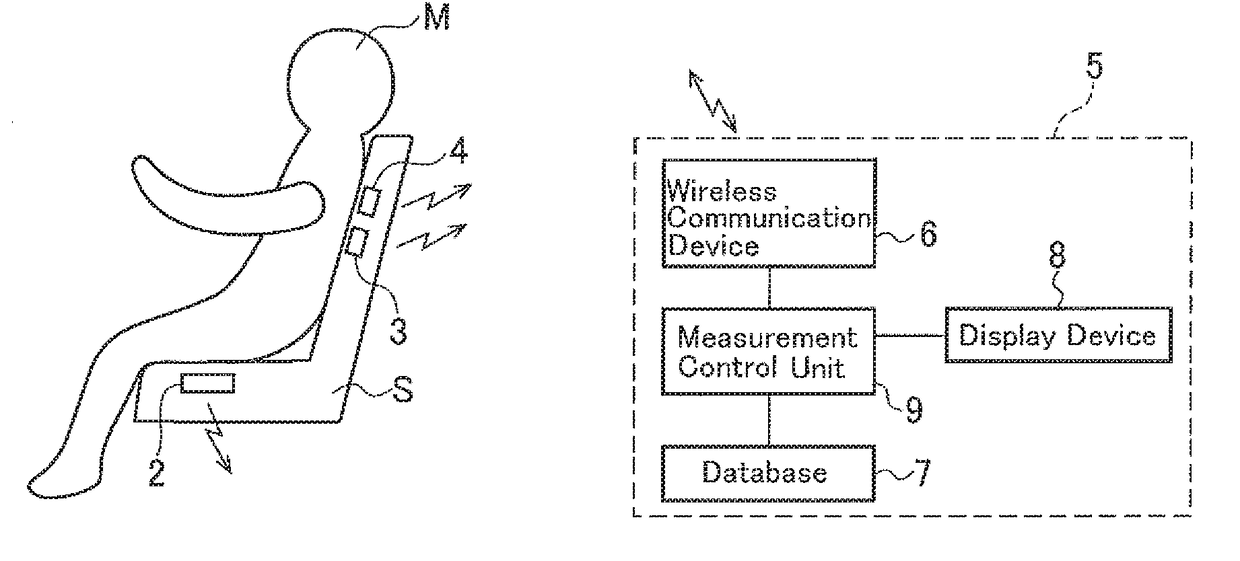
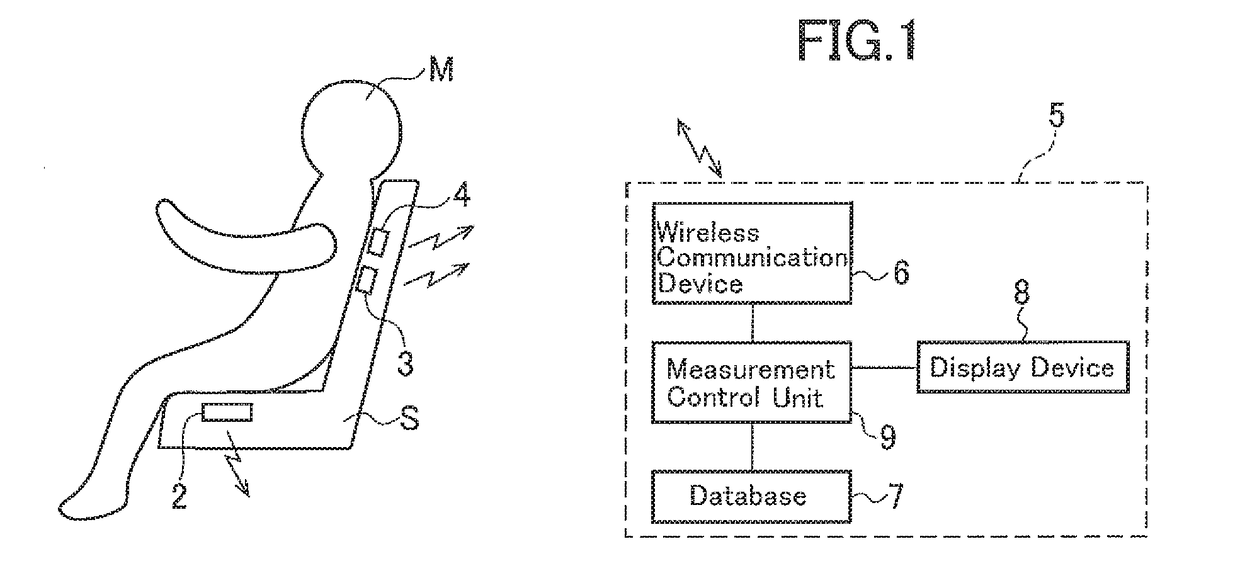
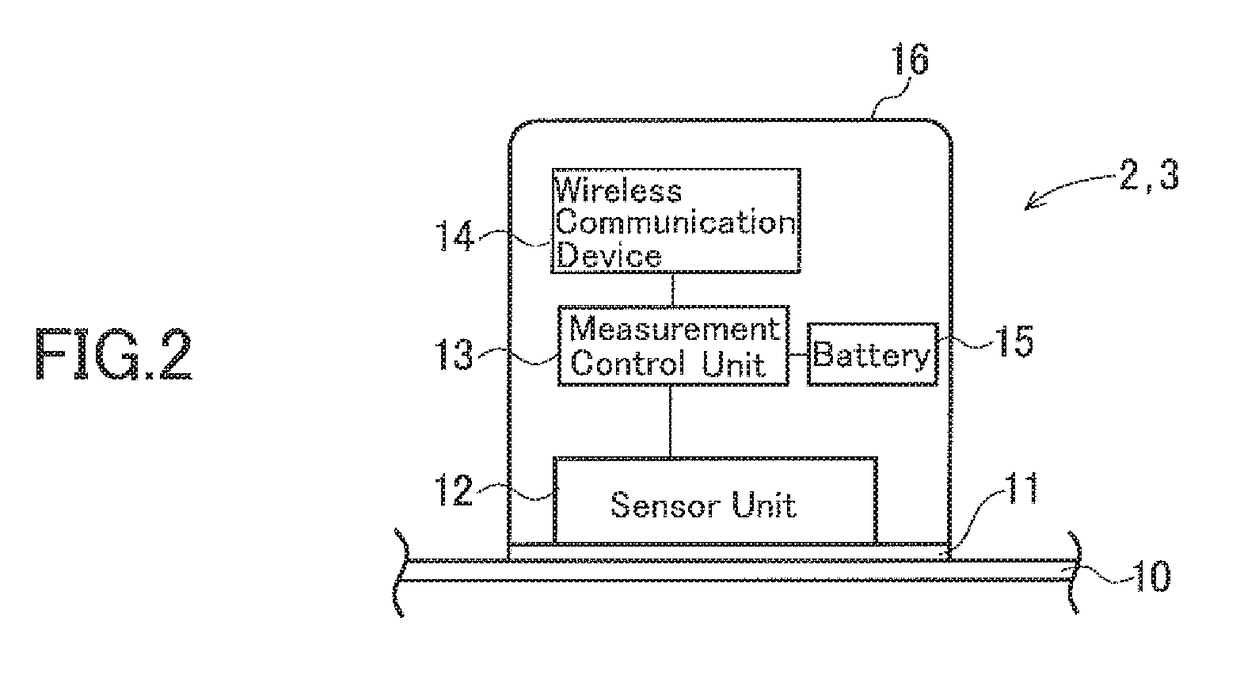
Biological-information detecting apparatus, seat with backrest, and cardiopulmonary-function monitoring apparatus
InactiveUS20170150929A1Reduce the burden onImprove accuracyCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationThoracic aortaBlood pressure
A biological-information detecting apparatus includes a first blood-flow measuring device provided at a seat surface of a seat, the first blood-flow measuring device measuring a condition of a blood flow of a popliteal artery of a measurement subject seated in the seat, a second blood-flow measuring device provided at a back of the seat, the second blood-flow measuring device measuring a condition of a blood flow of a thoracic aorta of the measurement subject, and a blood-pressure calculation device determining a pulse-wave propagation velocity and a degree of arteriosclerosis from blood flow data acquired by the first blood-flow measuring device and blood flow data acquired by the second blood-flow measuring device and calculating blood pressures of the popliteal artery and the thoracic aorta of the measurement subject based on the pulse-wave propagation velocity and the degree of arteriosclerosis.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC +1
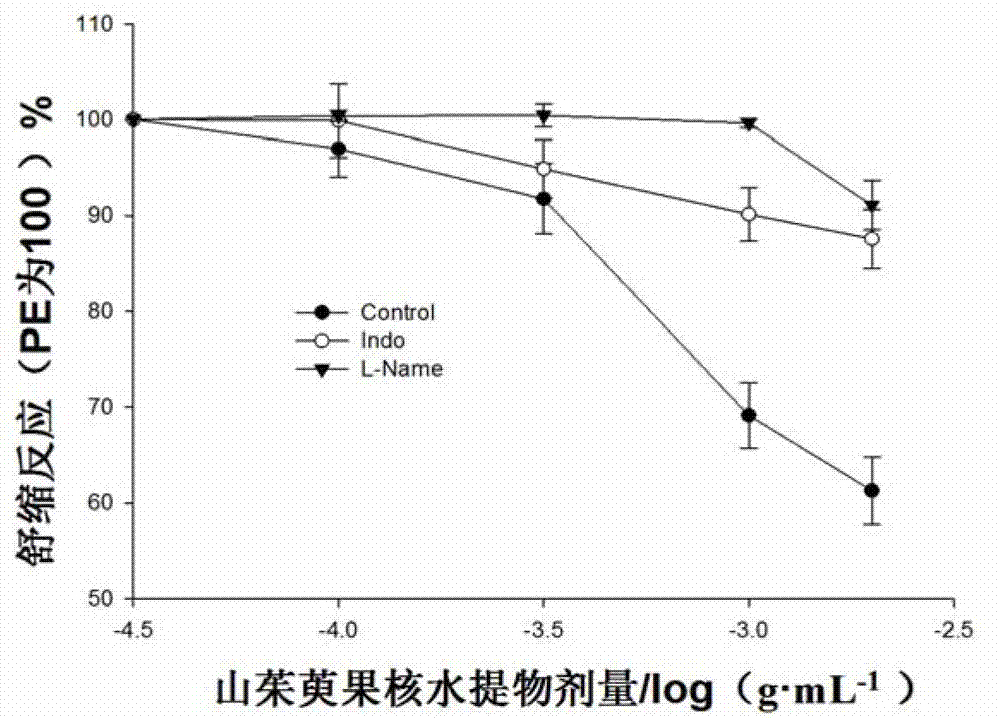
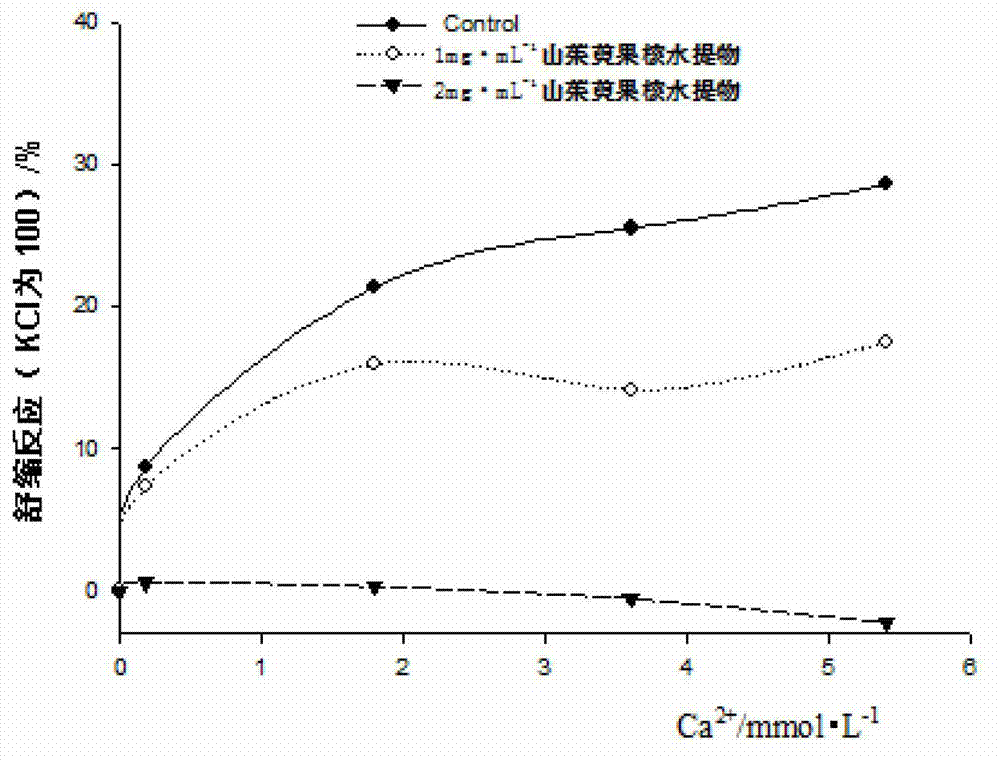
Cornel kernel water extract and application thereof
InactiveCN103110685ASimple stepsEasy to operateFood preparationCardiovascular disorderThoracic aortaActive component
The invention discloses a cornel kernel water extract and application of the cornel kernel water extract in preparing a thoracic aorta ring diastole composite and a hypotensive composite, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The extraction method of the cornel kernel water extract comprises the following steps of: taking dried cornel kernels; smashing into powder of 20-100 meshes; adding water to the kernel powder, and then uniformly mixing; standing at normal temperature for 20-28 hours, and then heating to boil for 20-50 minutes; and filtering to obtain filter liquor, and then concentrating the filter liquor at 40-60 DEG C. The extraction method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the cornel kernel extract by adopting an water extraction method and has the advantages of simple step and easiness in operation. The cornel kernel water extract obtained by adopting the extraction method is proved through experiments to play a role of isolated vascular ring diastole, can be used as the active component contained in arterial diastole drug and food or health-care products and can also be used as the active component contained in hypotensive drug and food or health-care products.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
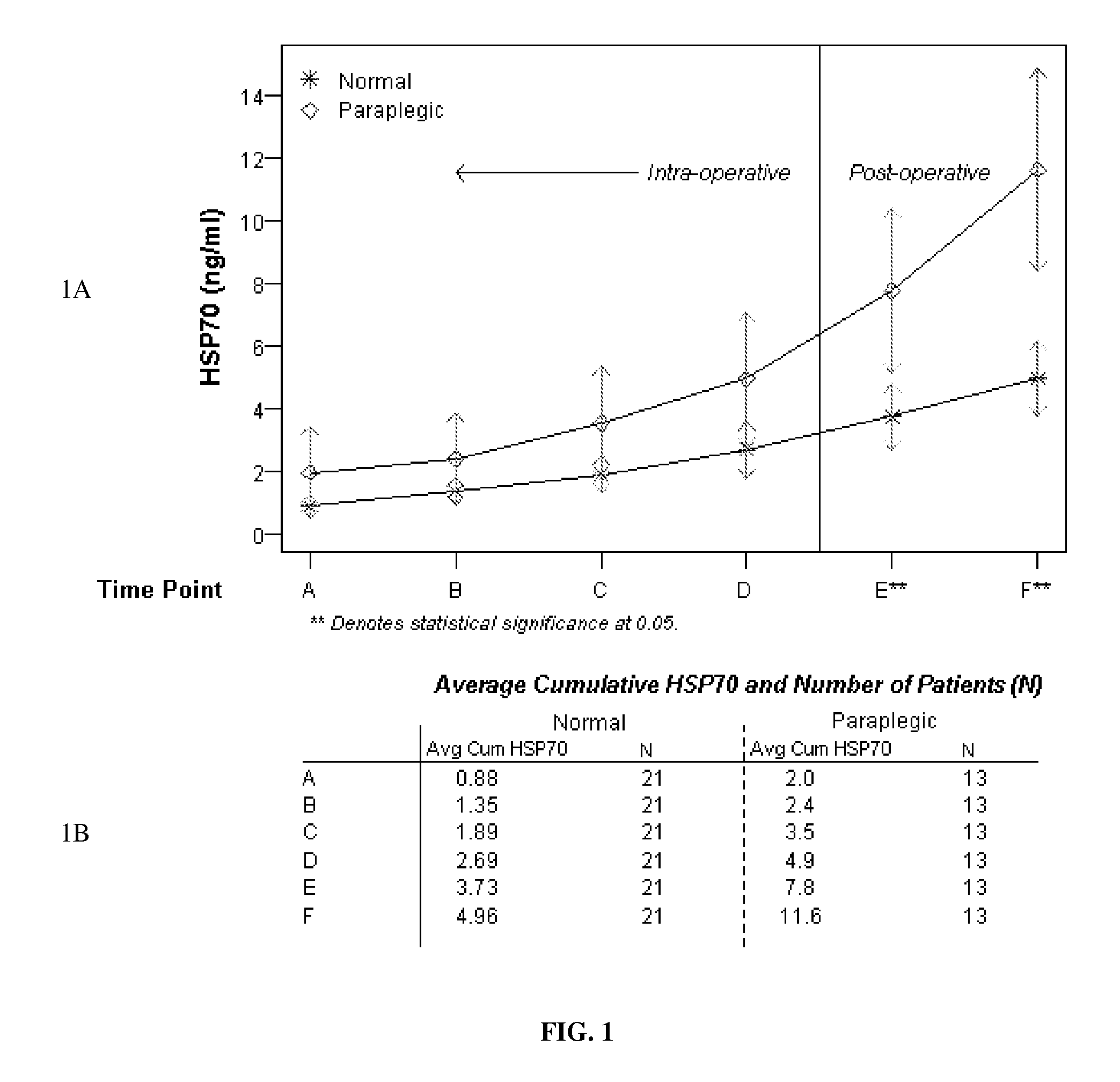
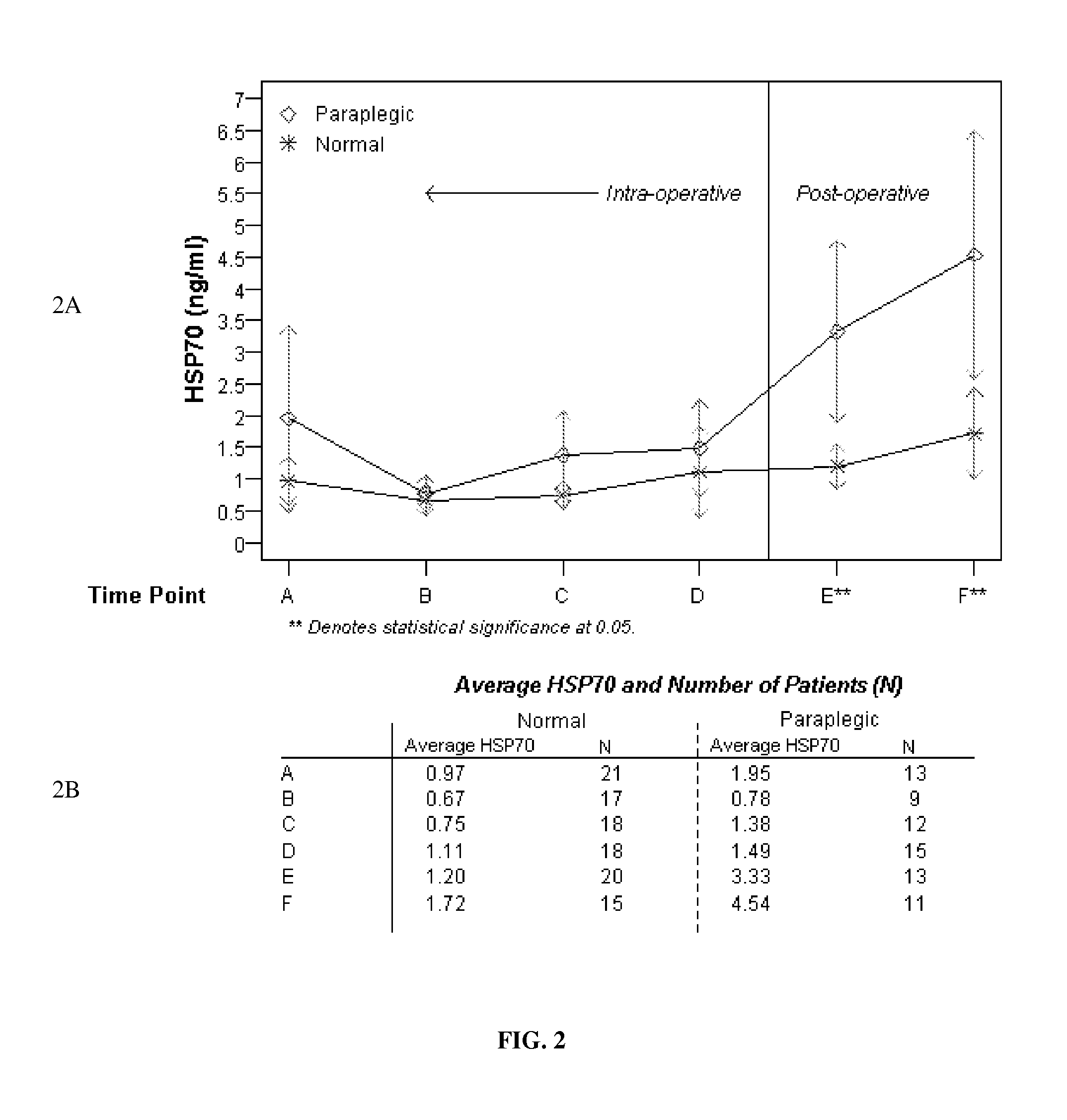
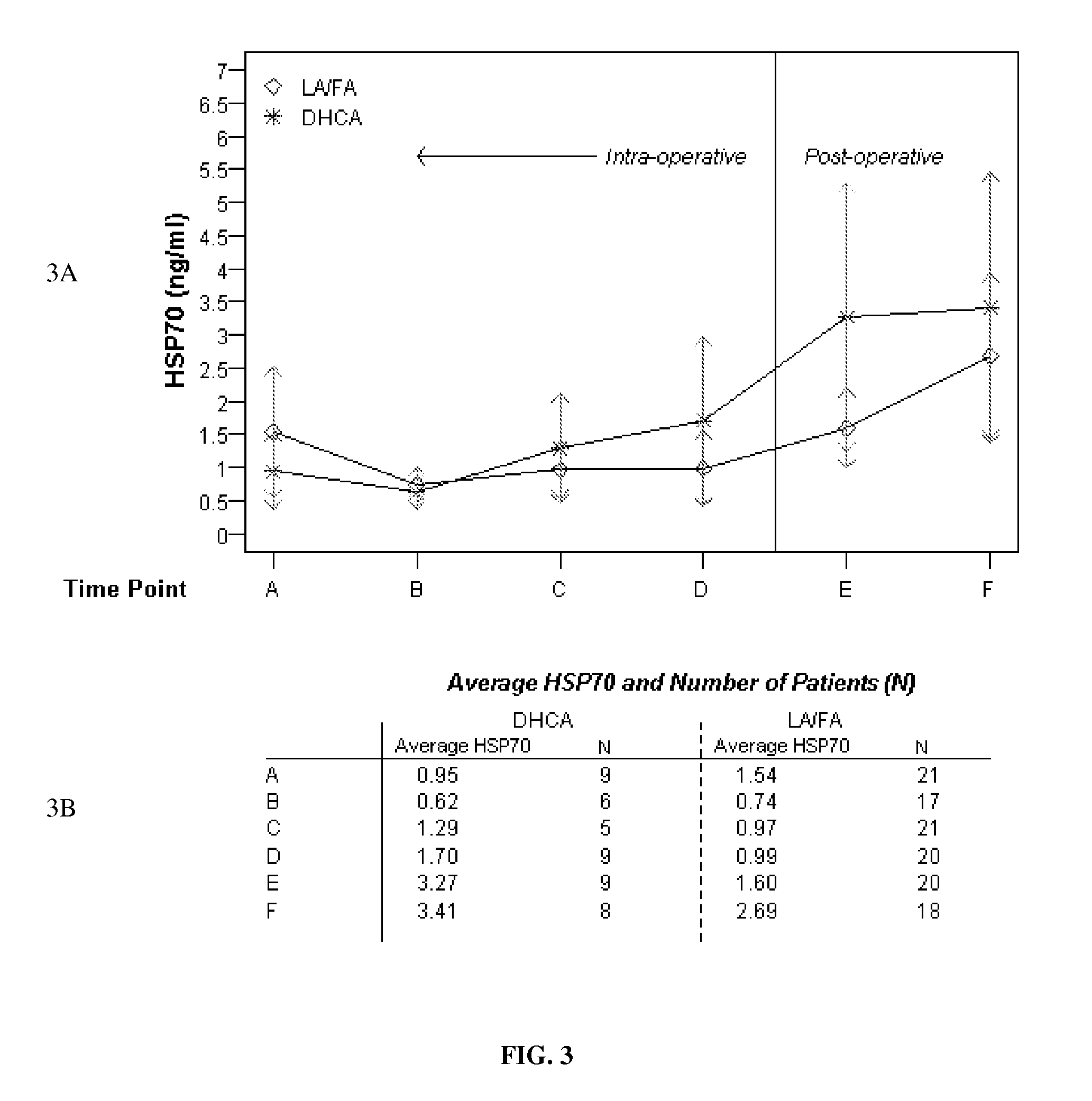
Elevation of Induced Heat Shock Proteins in Patient's Cerebral Spinal Fluid: A Biomarker of Risk/Onset of Ischemia and/or Paralysis in Aortic Surgery
Provided are methods for intra-operatively predicting, detecting or diagnosing the risk or onset of spinal cord ischemia and / or associated permanent paralysis in a patient, based upon the stress-induced elevation of levels of heat shock proteins, specifically HSP70 and / or HSP27 in the cerebral spinal fluid of the patient, as measured during thoracic-aorta surgery, particularly thoracic aneurysm repair surgery, that will permit intra-operative medical intervention to try to prevent or attenuate severe, and often fatal, complications. Further provided are kits, assay devices and methods of analyzing biomarker data for use in pre-, intra- or post-operatively detecting the stress-induced elevations of the measured levels of HSP70 and / or HSP27, and the biomarker itself.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
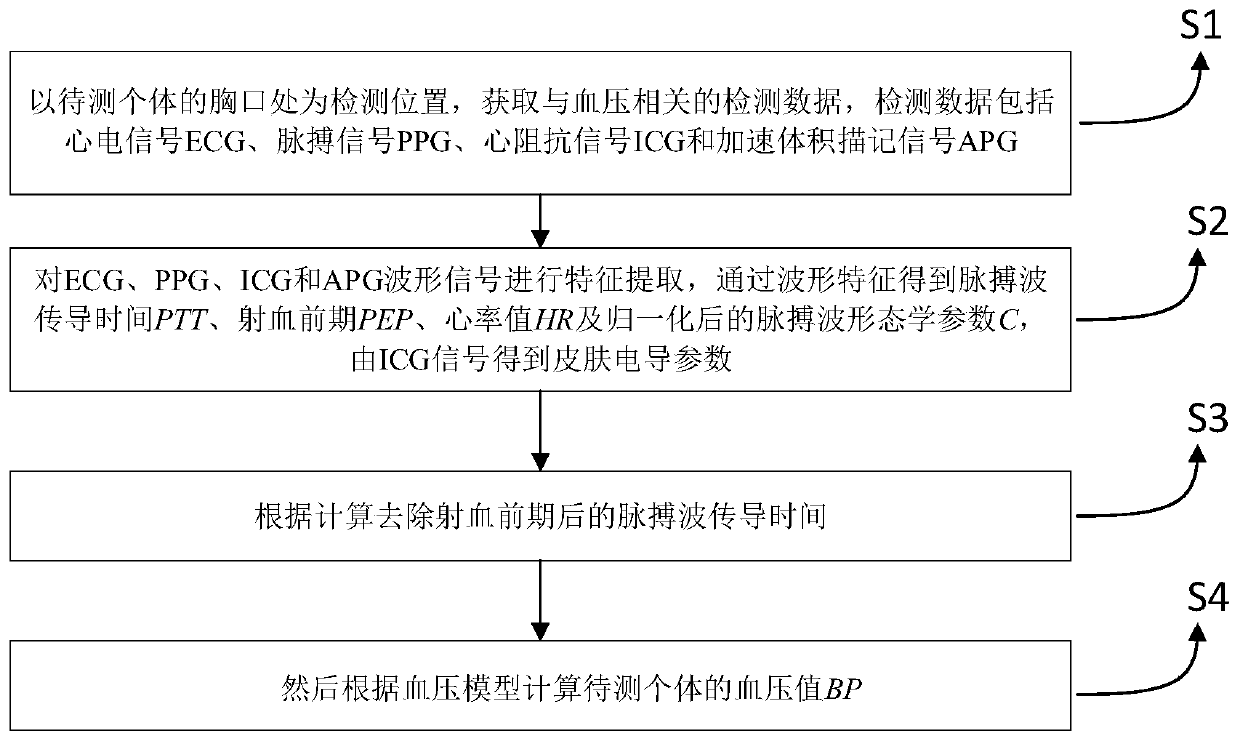
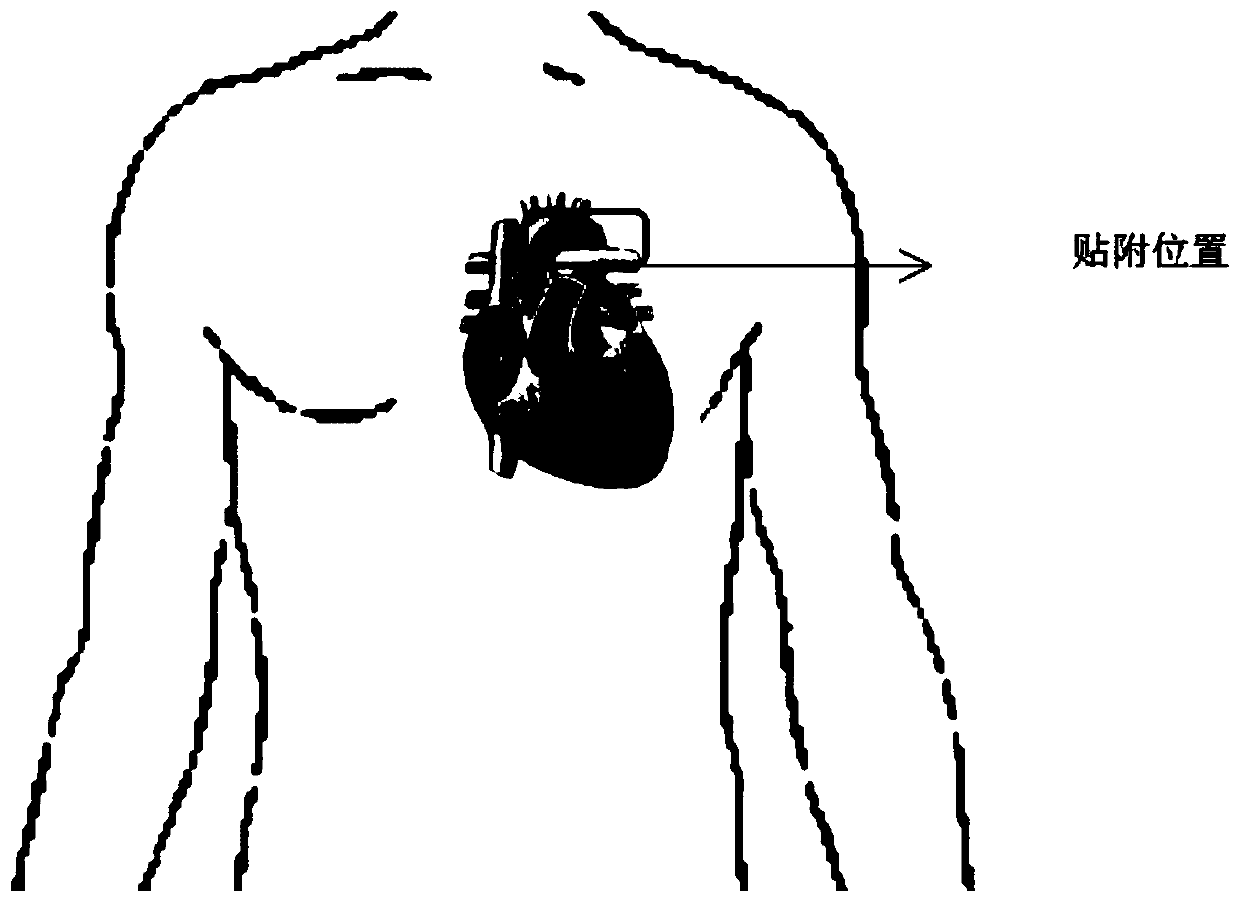
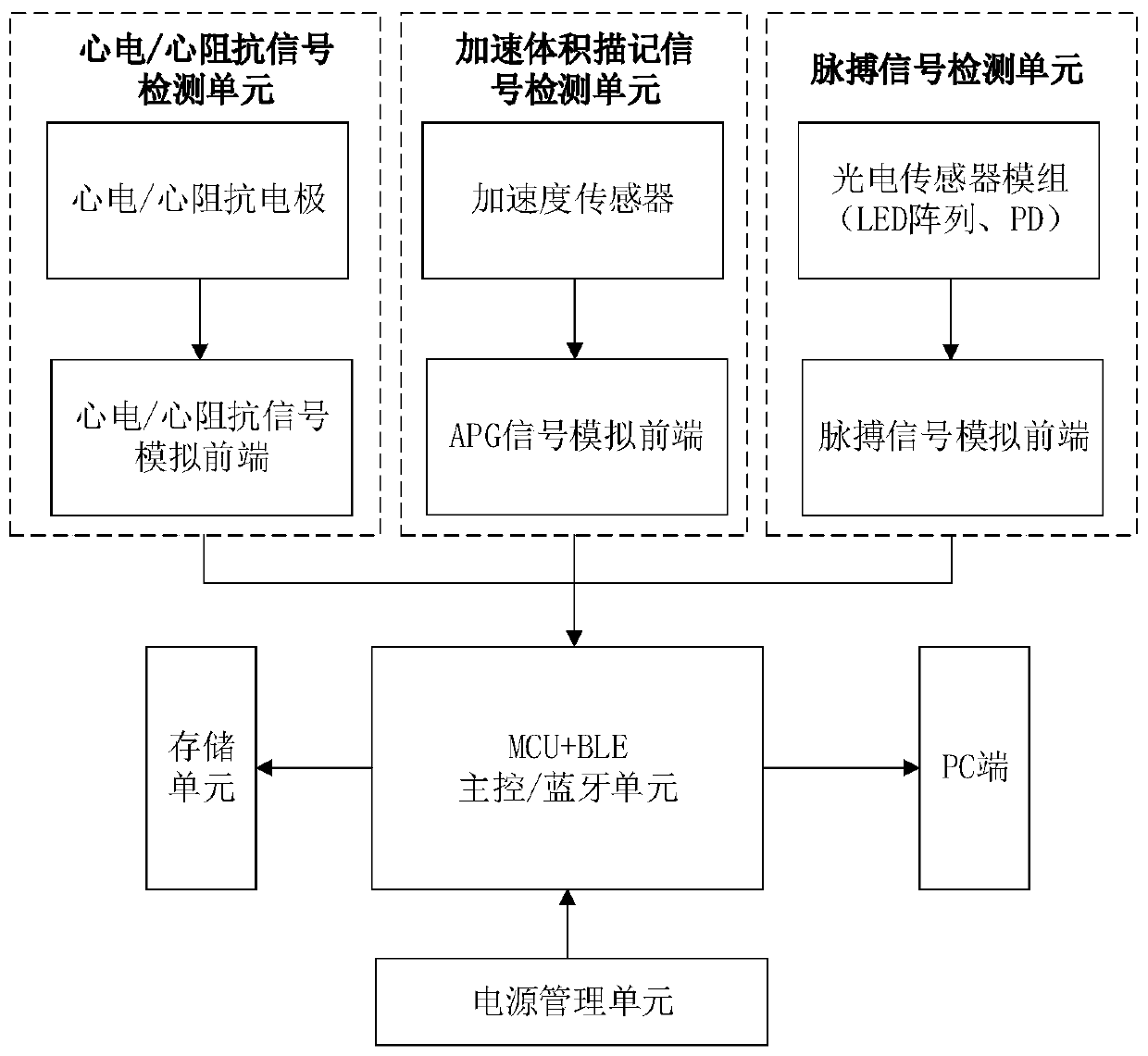
Chest non-invasive blood pressure detection method based on pulse wave conduction time
ActiveCN110292370AAccurate Aortic Blood PressureFitting results are accurateDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic aortaPulse wave
The invention discloses a chest non-invasive blood pressure detection method based on pulse wave conduction time and belongs to the field of non-invasive blood pressure monitoring methods. The problemthat a time parameter, namely the blood pre-ejection period, is ignored in pulse wave conduction time PTT in traditional detection approaches is considered in the method, correspondingly the measurement position is fixed to an outlet of the thoracic aorta, the cardiac ejection period PEP is obtained through electrocardio signals ECG and aorta acceleration tracing signals APG, the influence of PEPin PTT is removed, the more accurate pulse wave conduction time PTT' is obtained, the detected conduction time is more proximate to the actual conduction time, and it is ensured that accurate aorta blood pressure can be obtained. Meanwhile, according to the method, by taking the defect that the accuracy of traditional non-invasive blood pressure detection is not ideal into consideration, a bloodpressure model is improved, and the heart rate HR, the pulse wave morphological parameter C and the skin conductance rho are added, so that a model fitting result is more accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for extracting water-insoluble collagen from thoracic aorta of pig
ActiveCN104805165ATo achieve the effect of removing impuritiesEasy to purifyConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsWater insolubleHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for preparing water-insoluble collagen by using thoracic aortas of pigs as raw materials through process steps such as degreasing, impurity removal, enzyme hydrolysis, salt induced precipitation and dialysis. The process steps of the method are simple, safe and easy to operate, the cost is low and the purity of the obtained product is high. Compared with water-soluble collagen, the in-vivo degradation speed of the water-insoluble collagen obtained by the invention is reduced, the blood coagulation speed is faster and the water-insoluble collagen can be used for stopping wound bleeding or preparing other medical biological materials.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Thoracic aorta ventricular assist system
ActiveUS20160022888A1Minimizing creationHigh viscosityElectrocardiographyControl devicesLinear motionThoracic aorta
An implantable heart assist system, includes a pumping chamber formed of a flexible material and being adapted to be placed in fluid connection with the aorta and a pump system comprising a first rigid member, a second rigid member spaced from the first rigid member so that at least a portion of the pumping chamber may be positioned between the first rigid member and the second rigid member, a drive system comprising a motor, an extending member comprising a threaded section operatively connecting the first rigid member and the second rigid member and a nut in operative connection with the threaded section. The motor is adapted to rotate either the extending member or the nut relative to the other to convert rotary motion of the motor to linear motion to cause the second rigid member to move toward the first rigid member or away from the first rigid member. The heart assist system further includes a controller or a control system in operative connection with the drive system and controlling the motor. Movement of the second rigid member toward the first rigid member results in compression of the pumping chamber, and movement of the second rigid member away from the first rigid member causes expansion of the pumping chamber.
Owner:VASCOR INC
Centering for a TAA
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com