Patents
Literature
213 results about "Balloon dilatation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
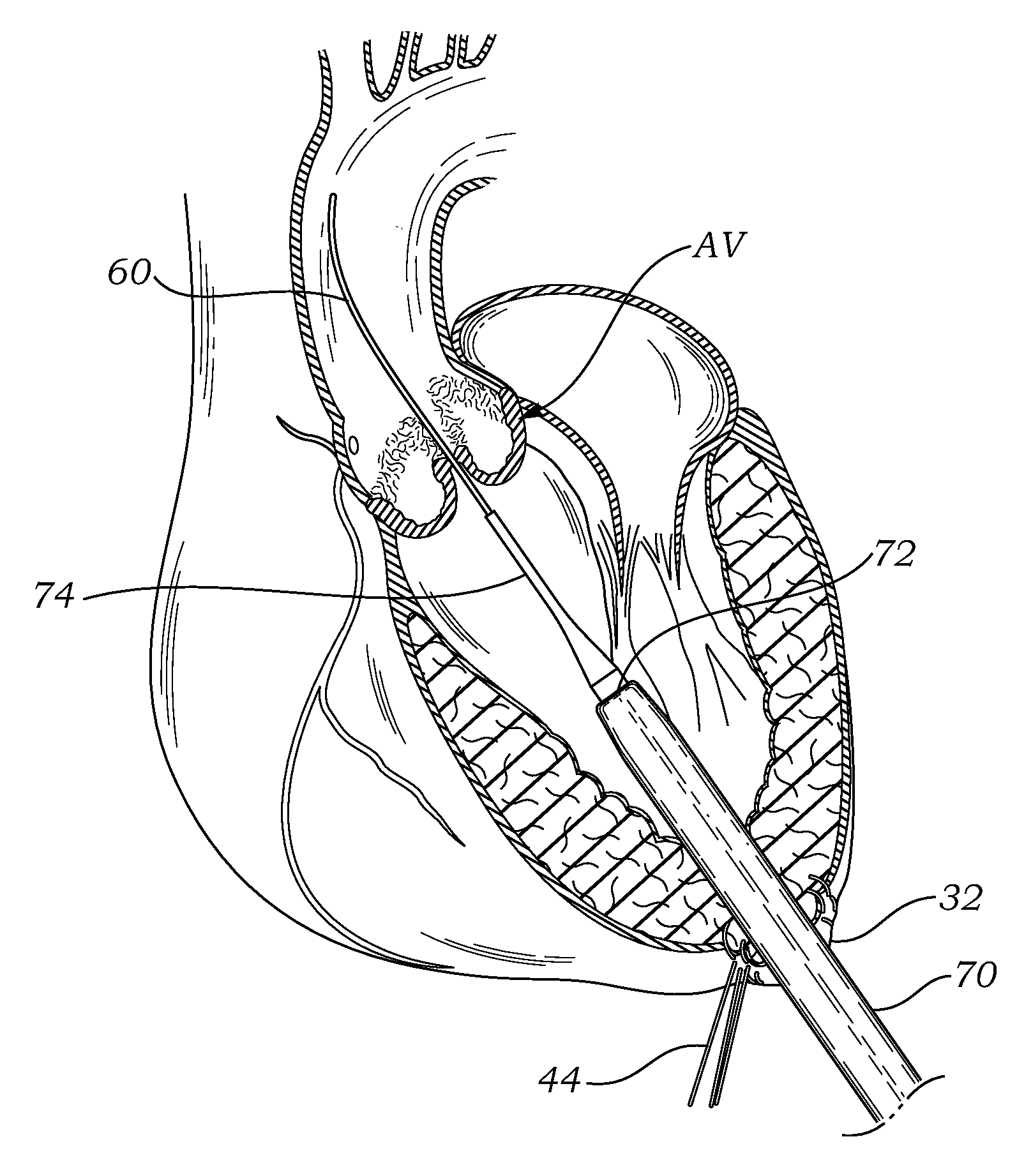
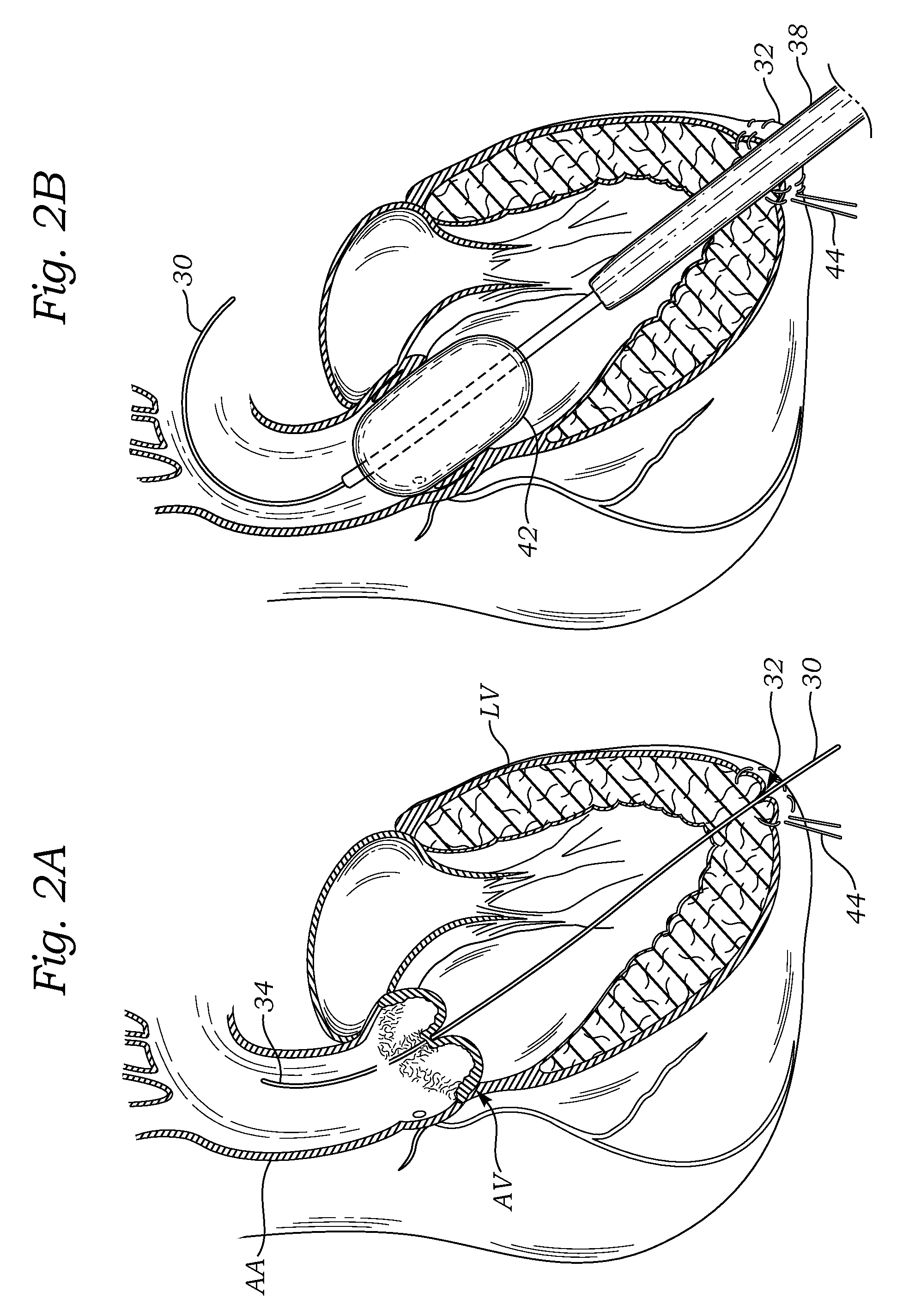
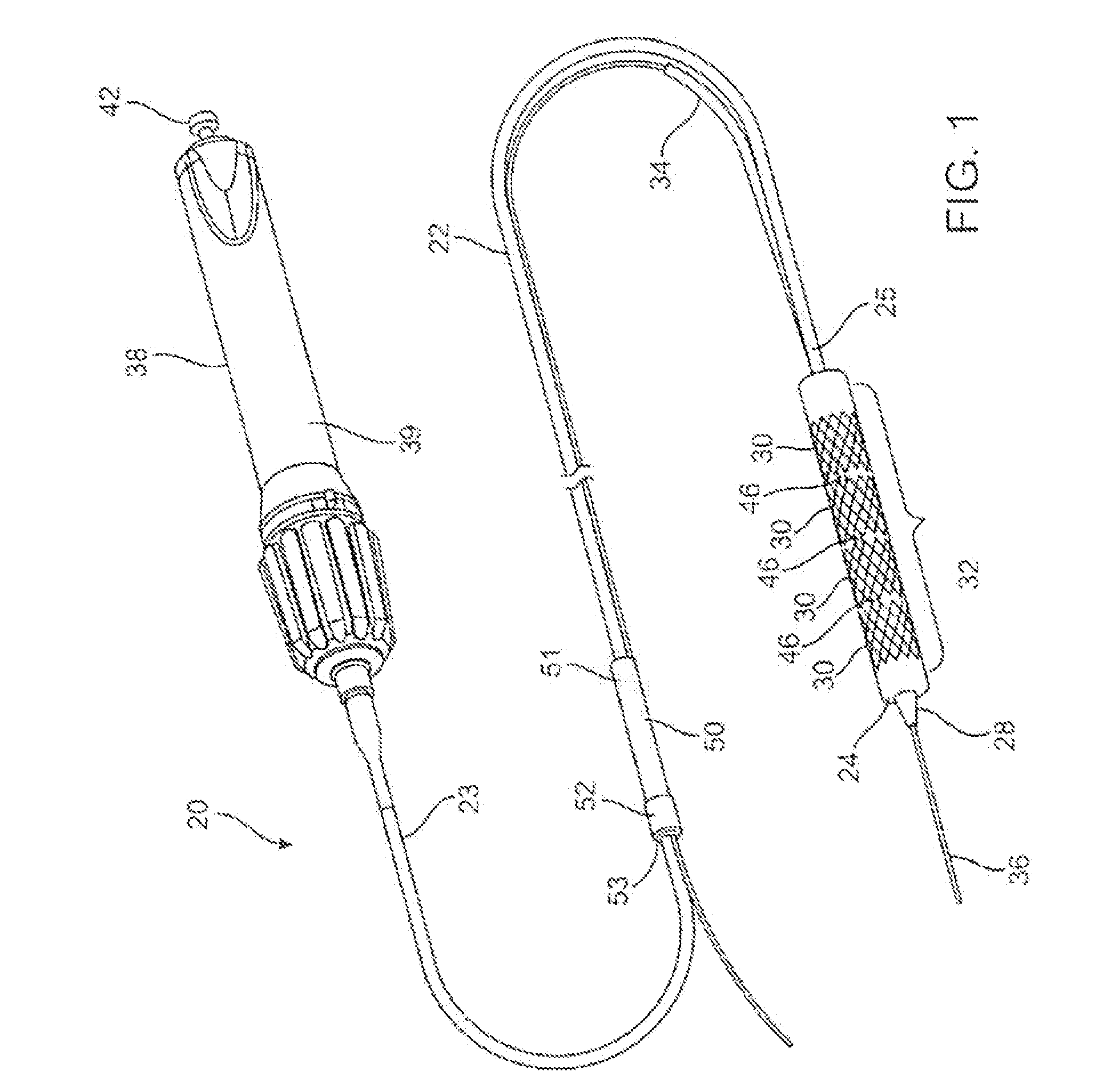
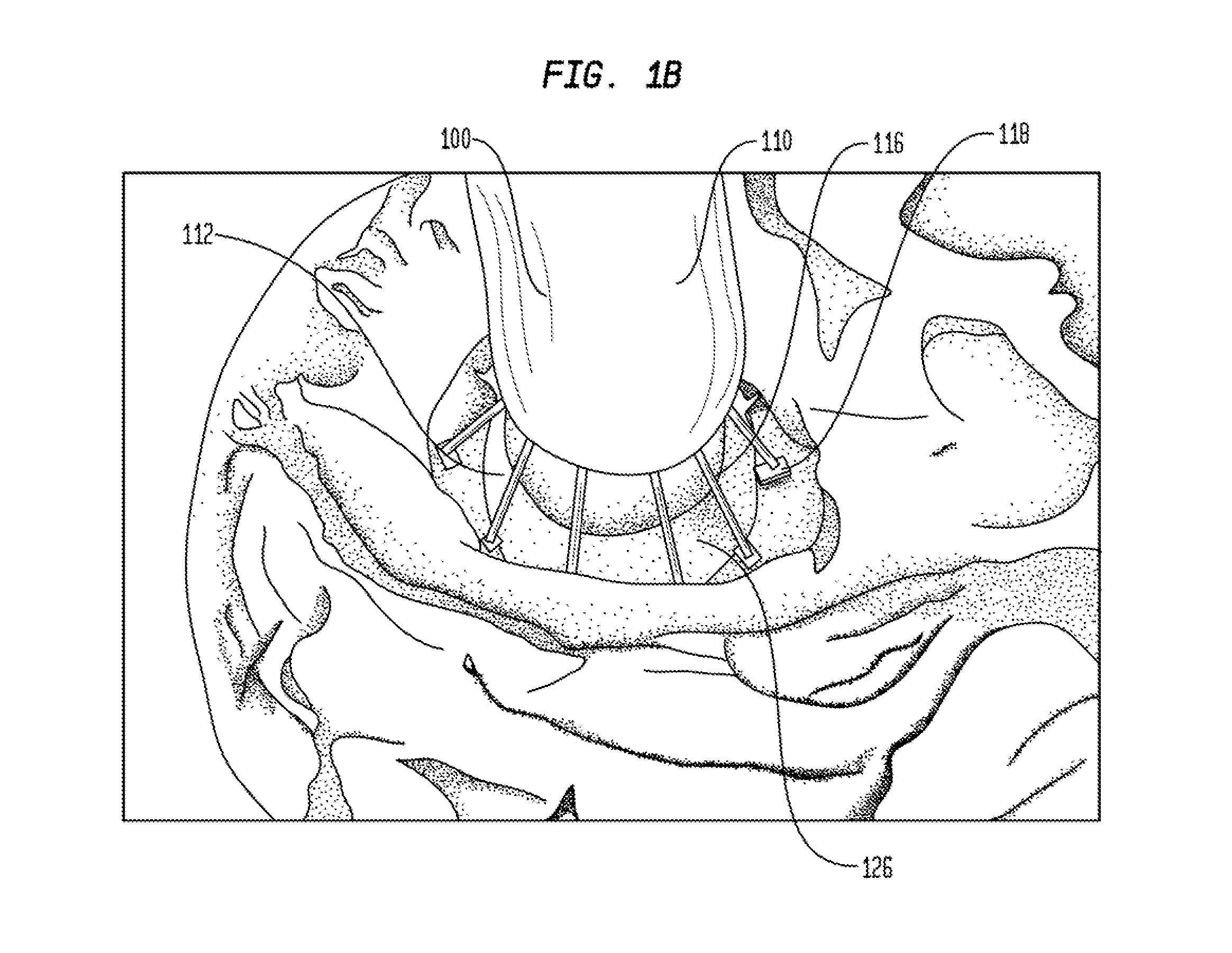
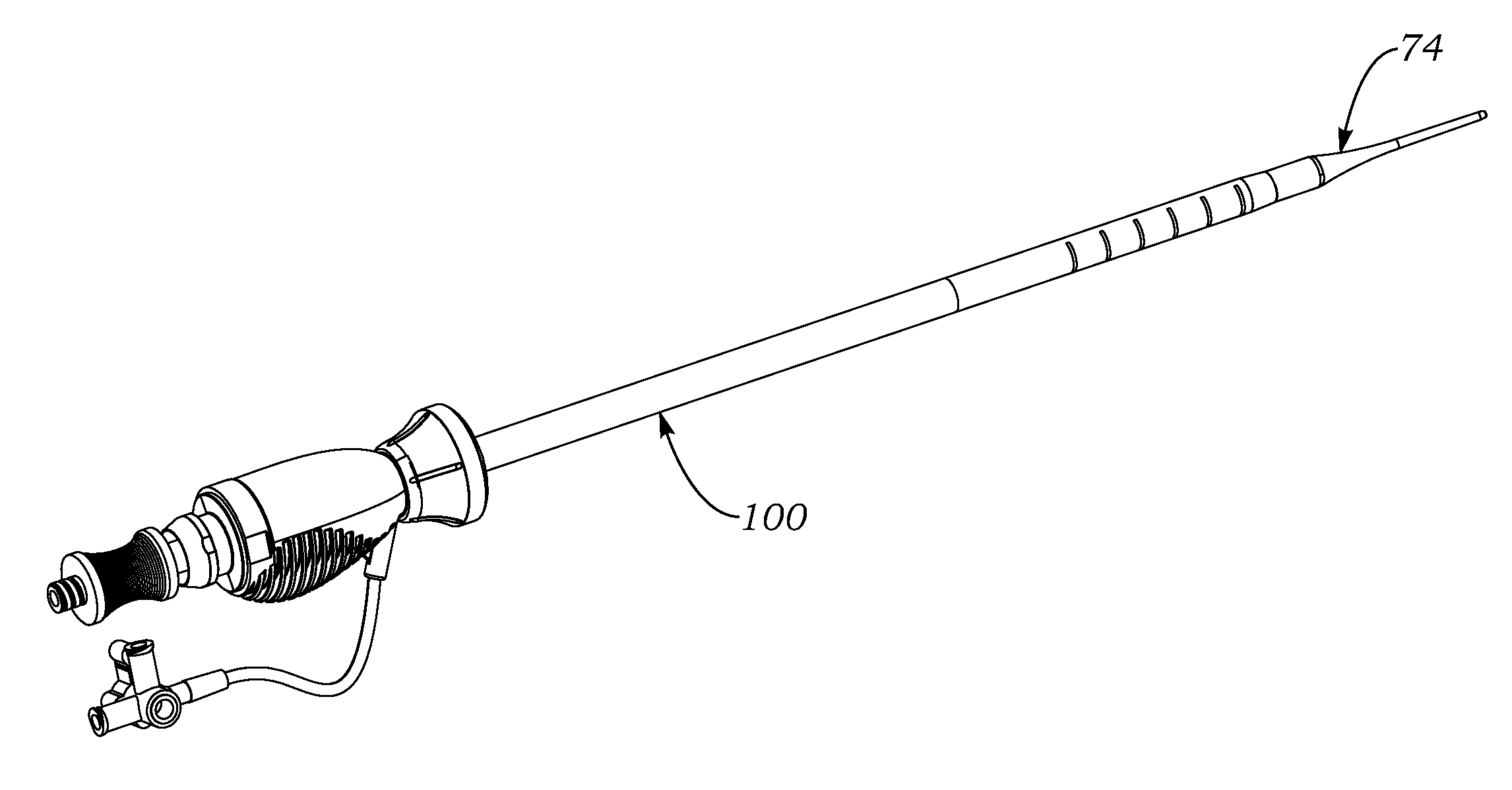
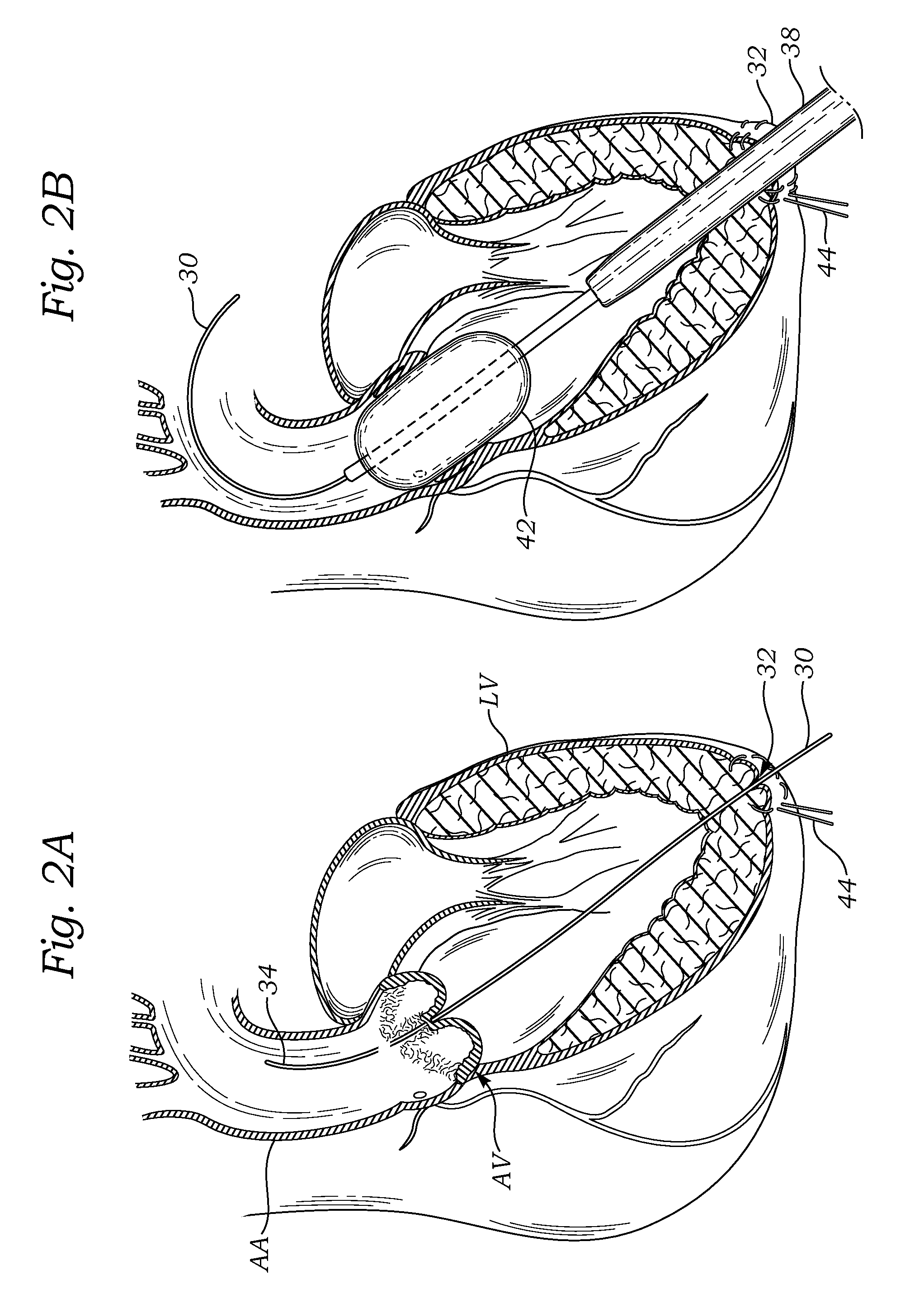
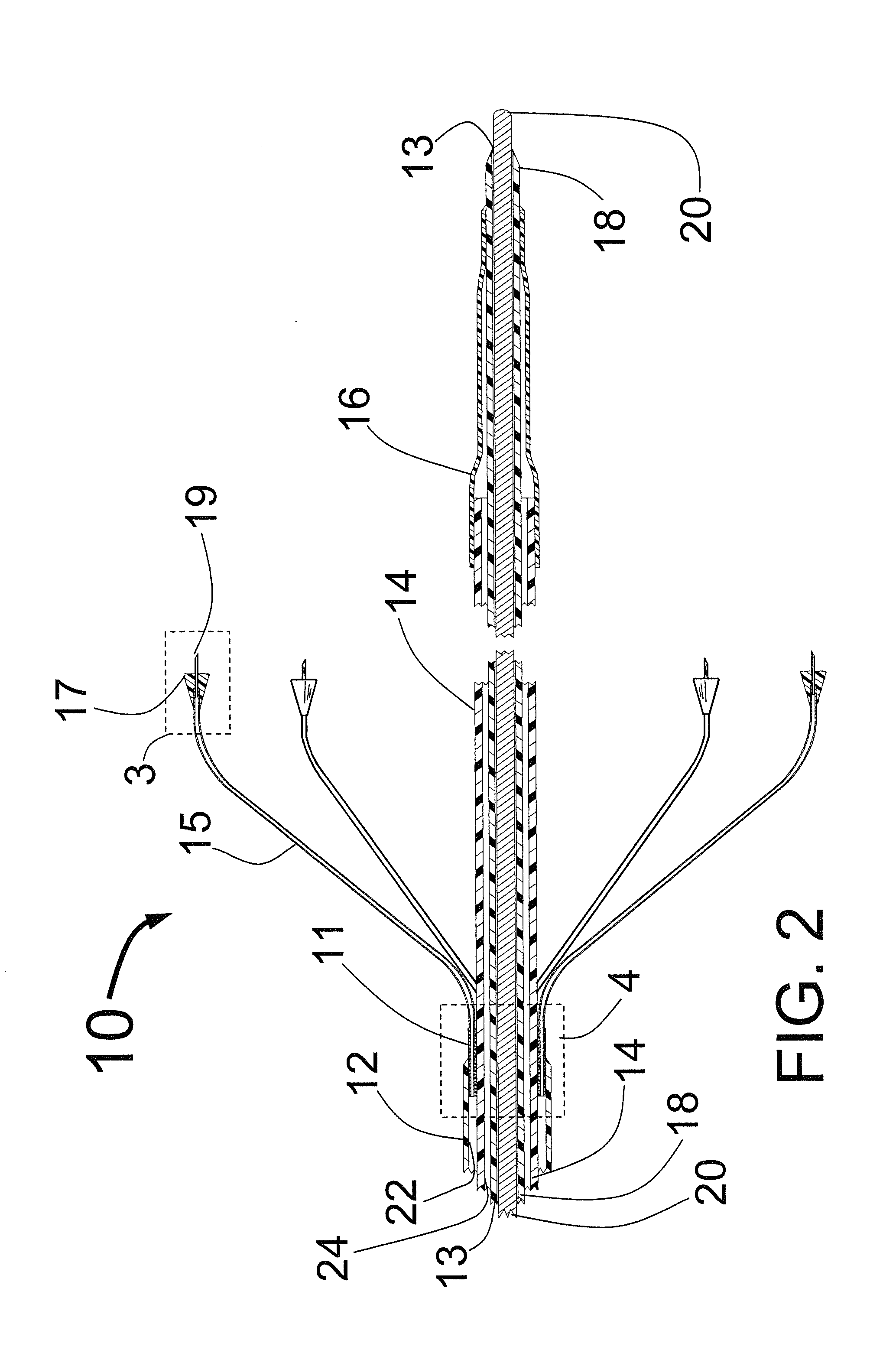
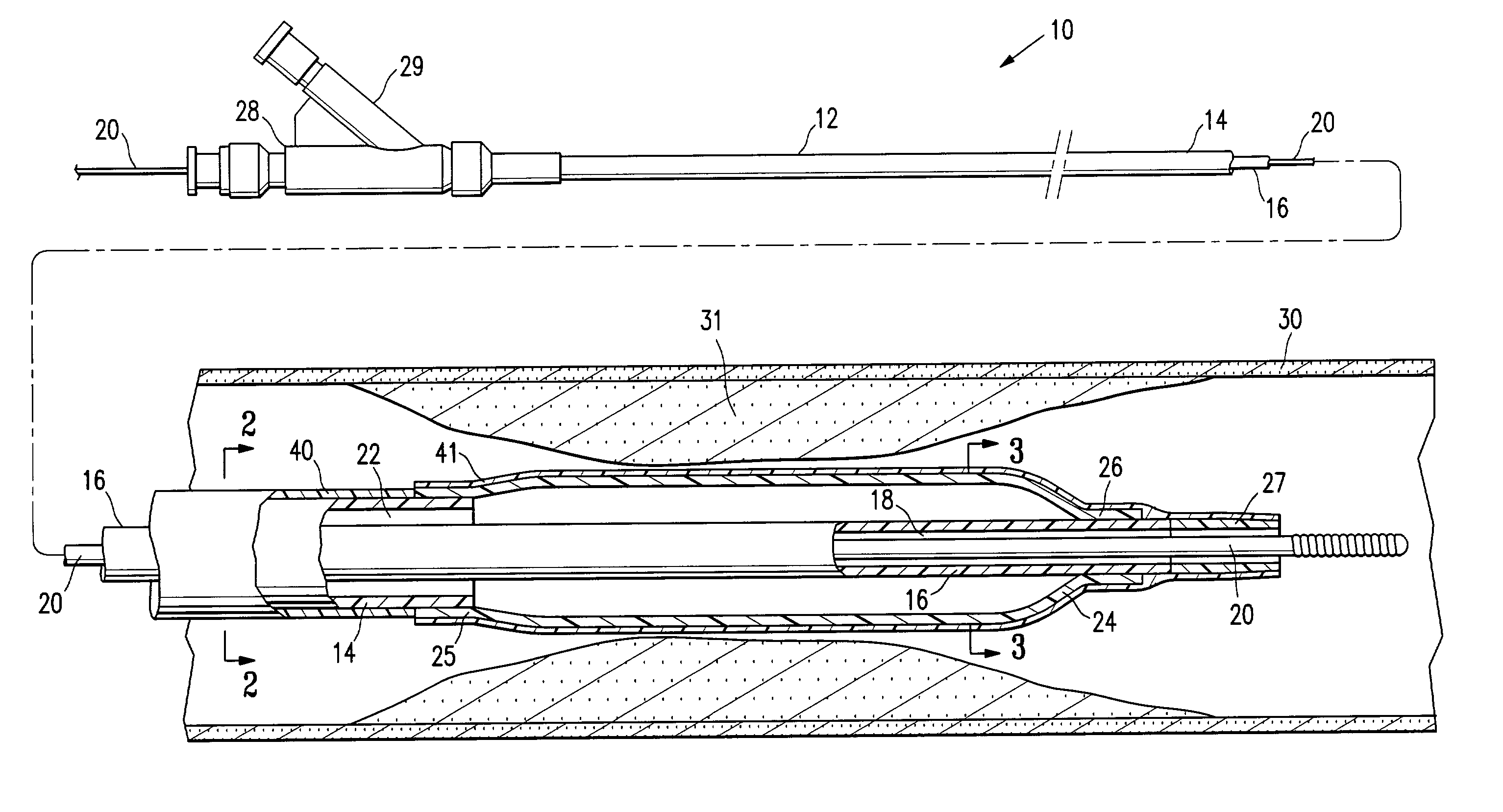
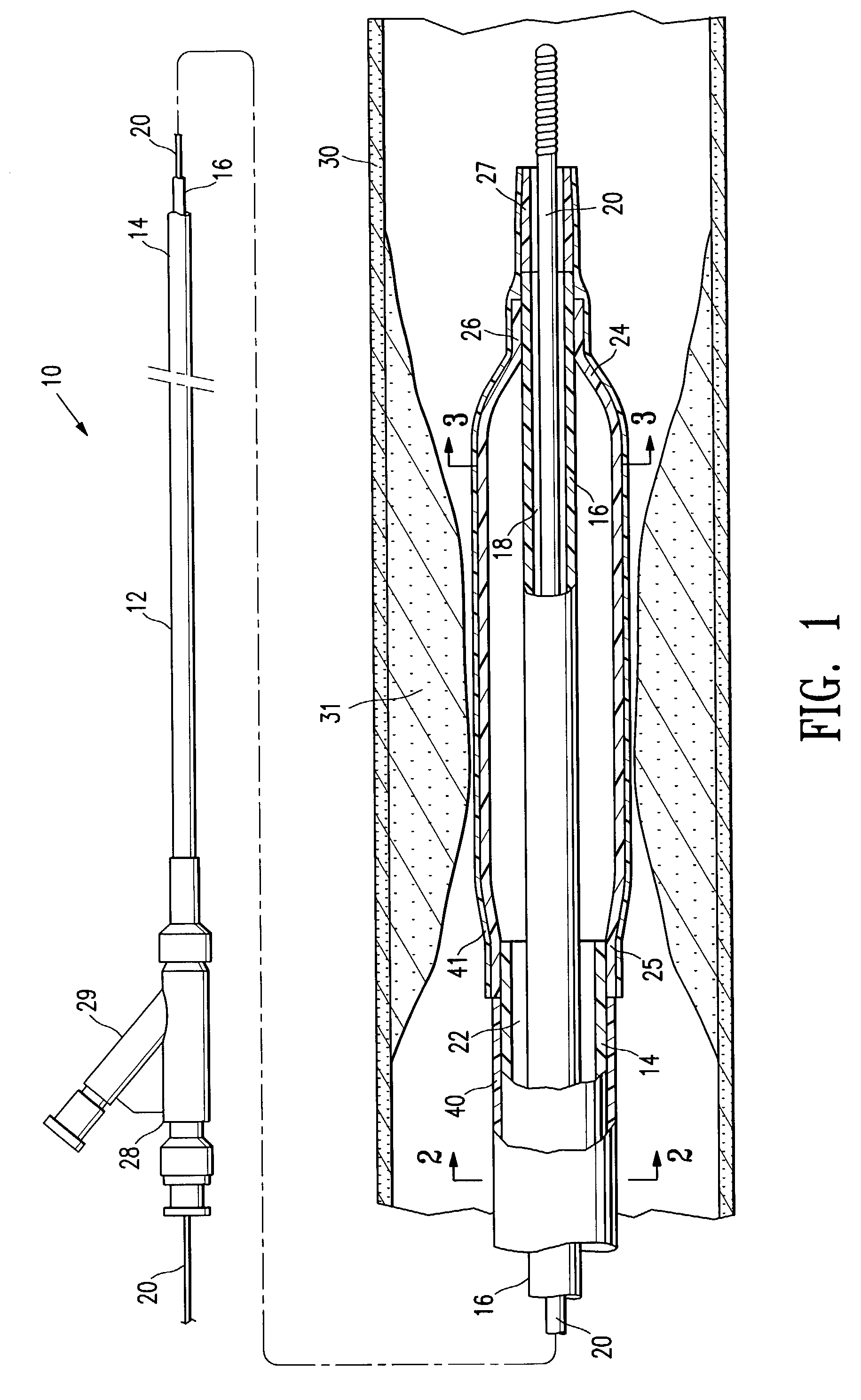
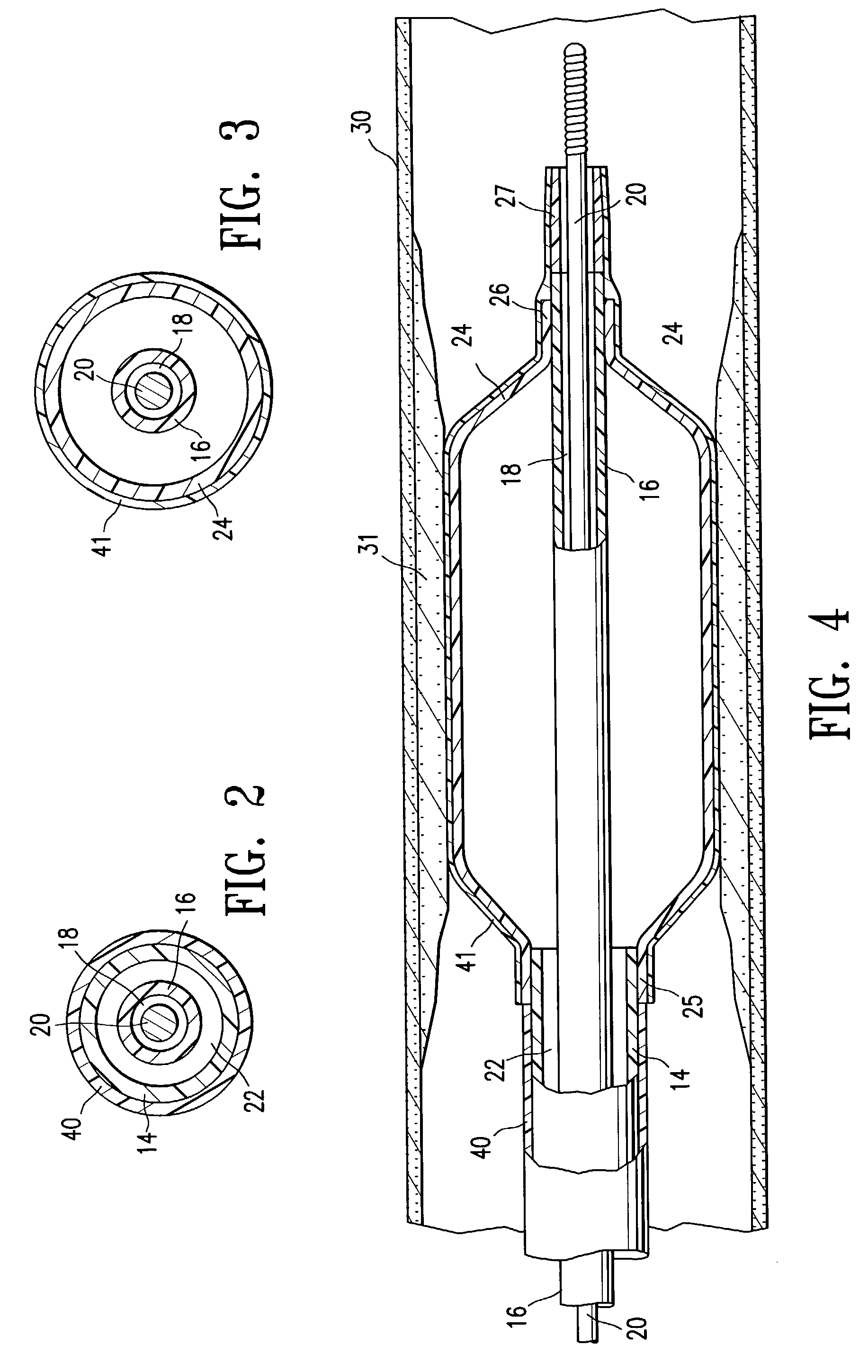
Transapical delivery system for heart valves
ActiveUS20110015729A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveProsthetic heart
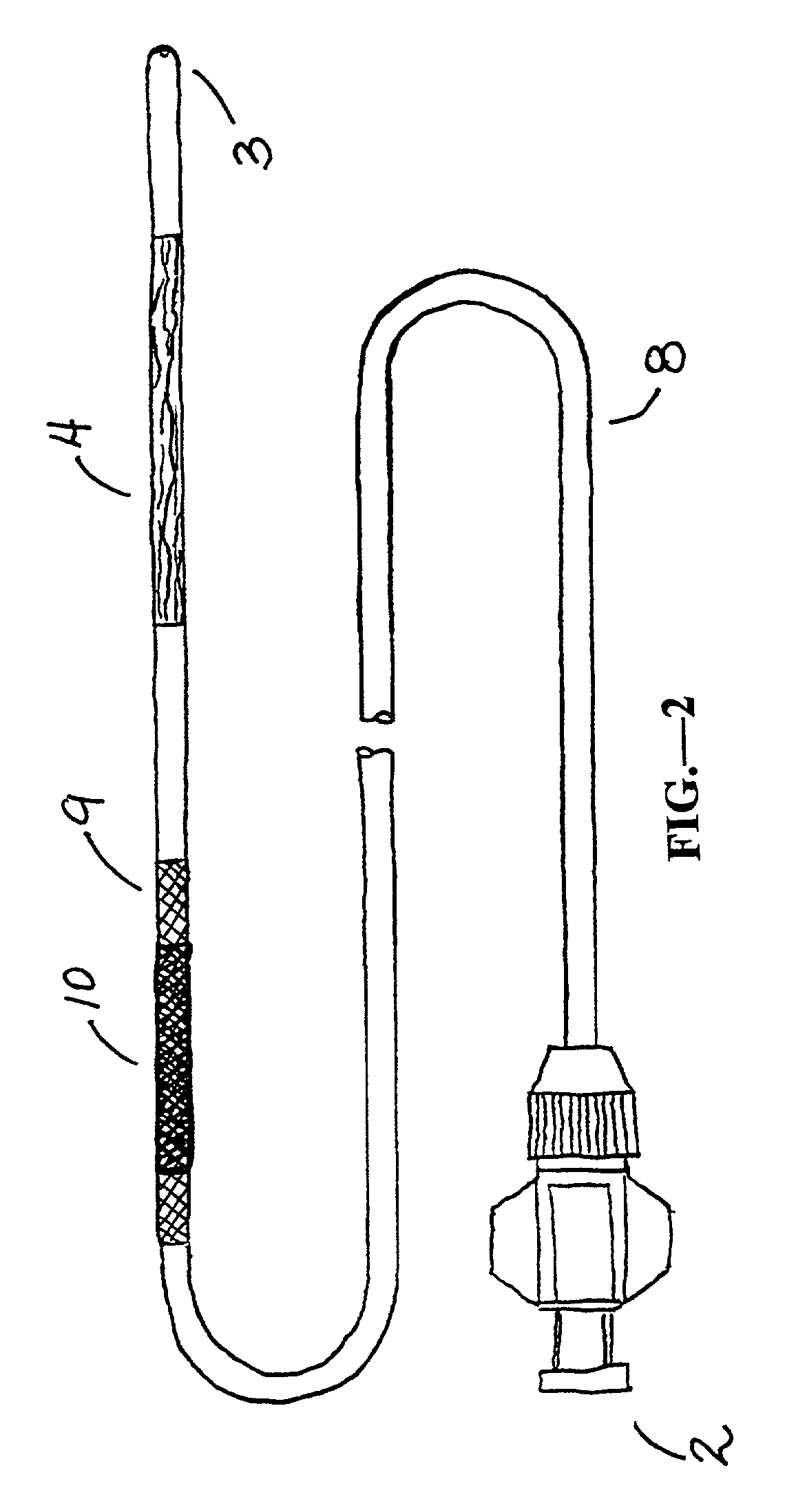
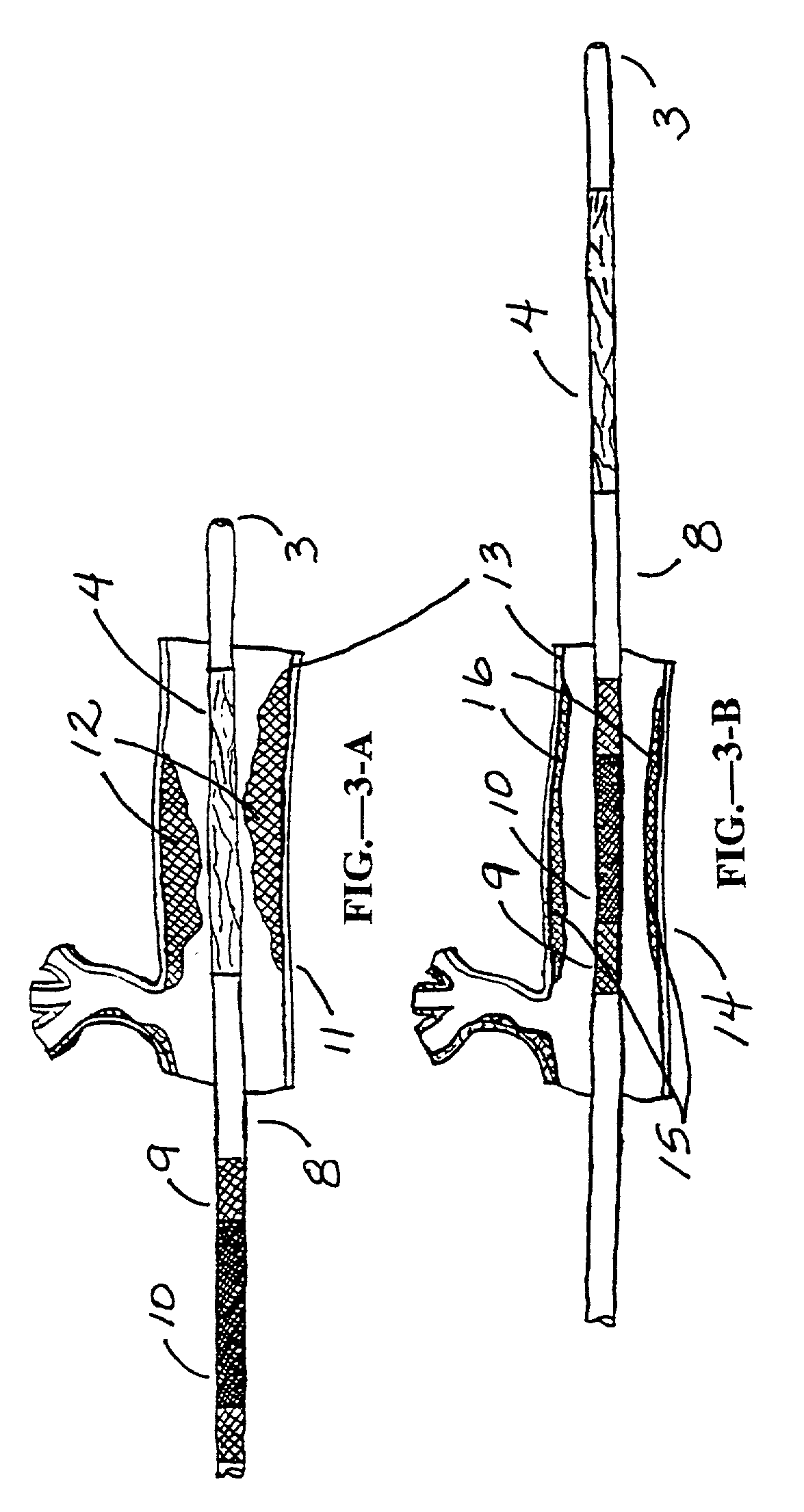
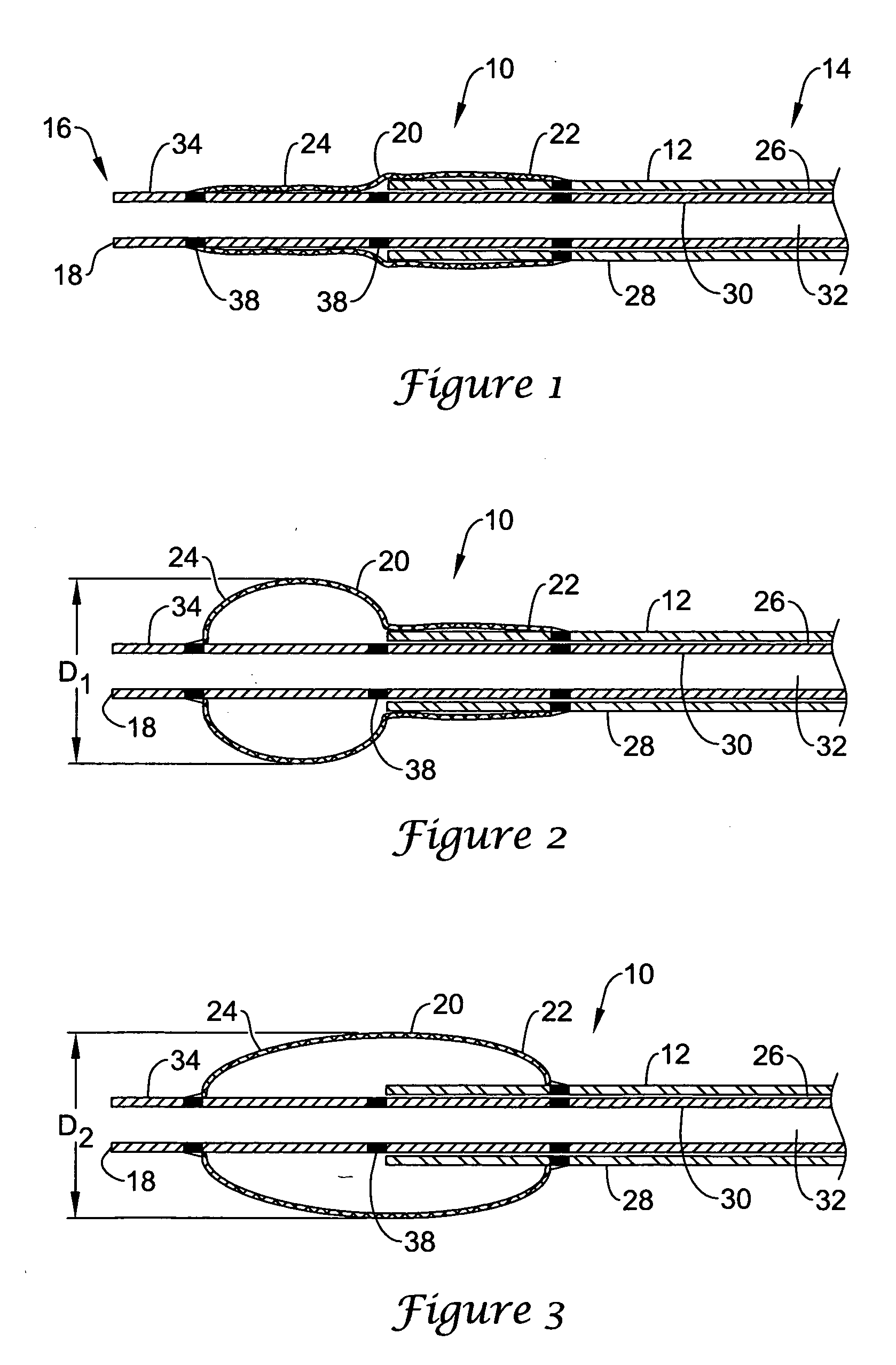
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a delivery catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve to the aortic annulus in an antegrade fashion through an introducer passing into the left ventricle through its apex. The introducer may have a more floppy distal section than a proximal section to reduce trauma to the heart wall while preserving good operating field stability. The delivery catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to a distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A trigger in a catheter handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment, while a slider in the handle controls retraction of a valve pusher. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
System for deploying balloon-expandable heart valves
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
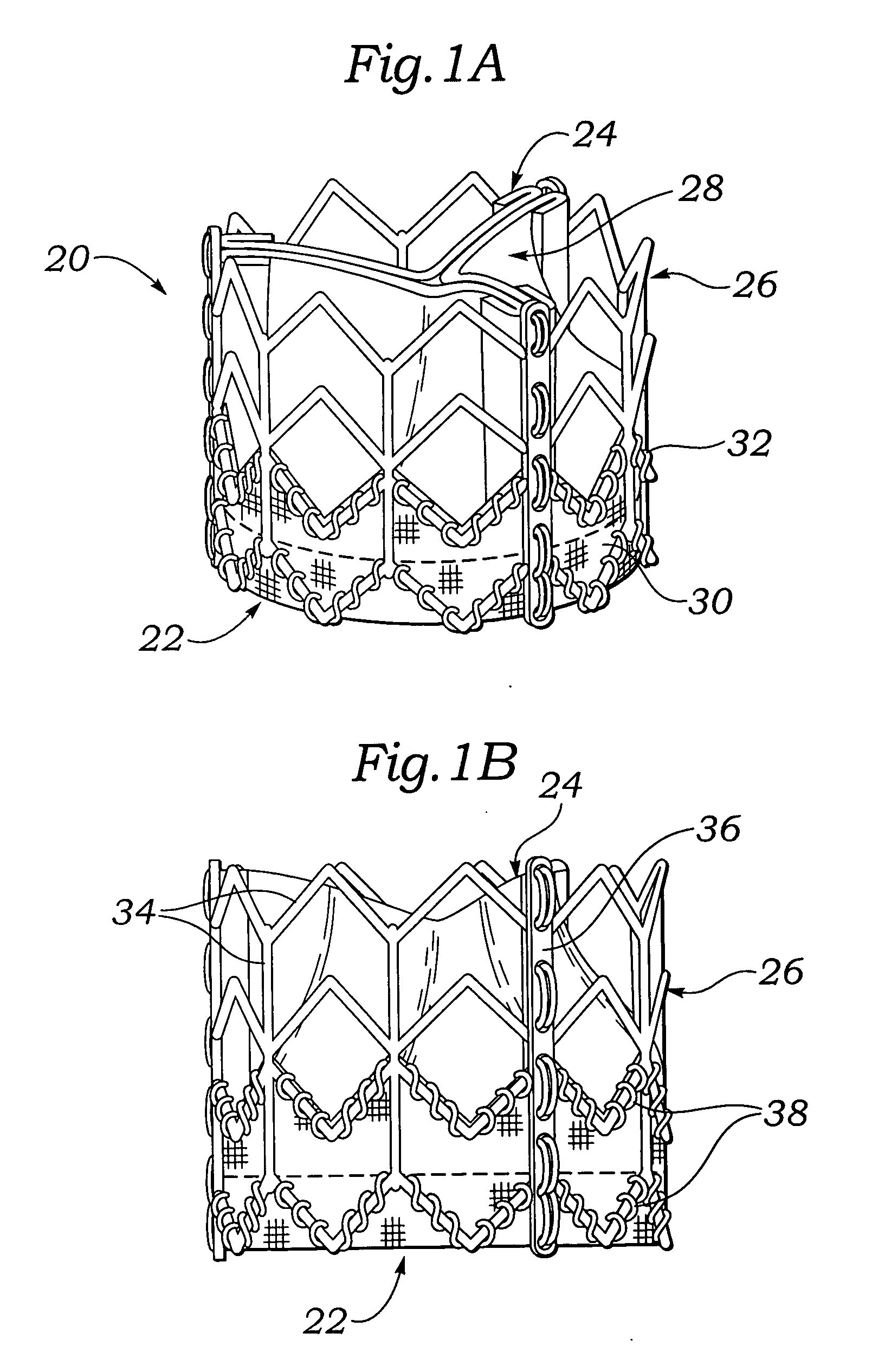
Percutaneous valve prosthesis and system and method for implanting same
InactiveUS20090306768A1Minimizes gradientIncrease the areaHeart valvesBlood vesselsInsertion stentBalloon dilatation
A heart valve prosthesis includes a cylindrical valve cage stent constructed to be implanted percutaneously in the planar axis of a native valve annulus, an elastic and compressible, multi-leaflet valve insertable percutaneously into the body, and an attachment mechanism for attaching the valve to the superior rim of the valve cage stent. The valve can be of a bi-leaflet or a tri-leaflet type and includes a valve frame made from a memory metal and a tissue cover attached to the valve frame. The valve cage stent is self-expanding or balloon expandable, made respectively from memory metal or stainless steel but otherwise structurally the same.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Stent system for preventing restenosis
A system for treating a body lumen is disclosed. The system comprises an outer stent and an inner stent disposed within the lumen of the outer stent. At least one end of the inner stent extends outside of the lumen of the outer stent, so that the end of the inner stent contacts and conforms to the body lumen wall that is adjacent the end of the outer stent. A coating can be disposed on a surface, preferably the outer surface, of the inner stent. The coating contains a therapeutic substance that may be released into the body lumen wall to help in preventing restenosis. Also disclosed is a stent having a balloon-expandable portion connected to a self-expanding portion. Methods for deploying the system and the stent are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Adjustable-length drug delivery balloon
ActiveUS20090105686A1Inhibit and prevent restenosisDesirable lengthStentsBalloon catheterProsthesisBalloon dilatation
A drug or agent coated balloon having a length which is adjustable in vivo is described herein. The balloon is configured to be coated or coatable with one or more drugs where the coating may be applied prior to advancement into a patient body or prior to balloon expansion within the patient body. The length of the expandable portion of the balloon is adjustable to approximate a length of the tissue region to be treated. Moreover, the drug-coated balloon may be used alone or it may be utilized to deploy luminal prostheses having one or more linked or otherwise coupled segments.
Owner:JW MEDICAL SYSTEMS LTD
Prosthesis Seals and Methods for Sealing an Expandable Prosthesis
InactiveUS20140350668A1Good strength against burstingHigh riskStentsHeart valvesInsertion stentProsthesis
Embodiments of the present disclosure are related to devices and techniques for para-valve sealing of an expandable stent-valve implanted using a catheter. In some embodiments, a stent-valve is provided which comprises a seal sleeve / cuff containing material that swells when contacted by blood. A piercing tool may be included and used to permit a user to puncture the sleeve / cuff prior to introduction into a patient's body. In some embodiments, the sleeve / cuff has an integral tubular structure configured to withstand balloon expansion of the stent-valve during or after implantation.
Owner:SYMETIS
Stent graft loading and deployment device and method
An endoluminal prosthesis includes a tubular graft, an expandable annular support structure and a restraining mechanism restraining the prosthesis in a collapsed configuration in which the annular support structure is compressed to a low profile. The restraining mechanism holds the annular support structures in the collapsed configuration until the prosthesis is positioned for deployment. The restraining mechanism is then released to allow the annular support structures to expand into conforming engagement with the inner wall of a lumen in which the prosthesis is to be deployed. A feature according to the invention provides a balloon catheter onto which the prosthesis is loaded for deployment where the balloon is expanded to provide a radial force to release the restraining mechanism. Another feature provides for a restraining member that breaks upon application of the radial force to release the annular support structure from its constrained configuration. Another feature of the invention provides for independent and / or sequential release of the annular support members. Various types of annular support members attached to tubular grafts in a variety of manners may be used in accordance with the invention. The invention may be used in tubular grafts for endoluminal placement within a body lumen, including blood vessels, and for the treatment of abdominal and other aneurysms.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Apparatus and method for treating venous reflux
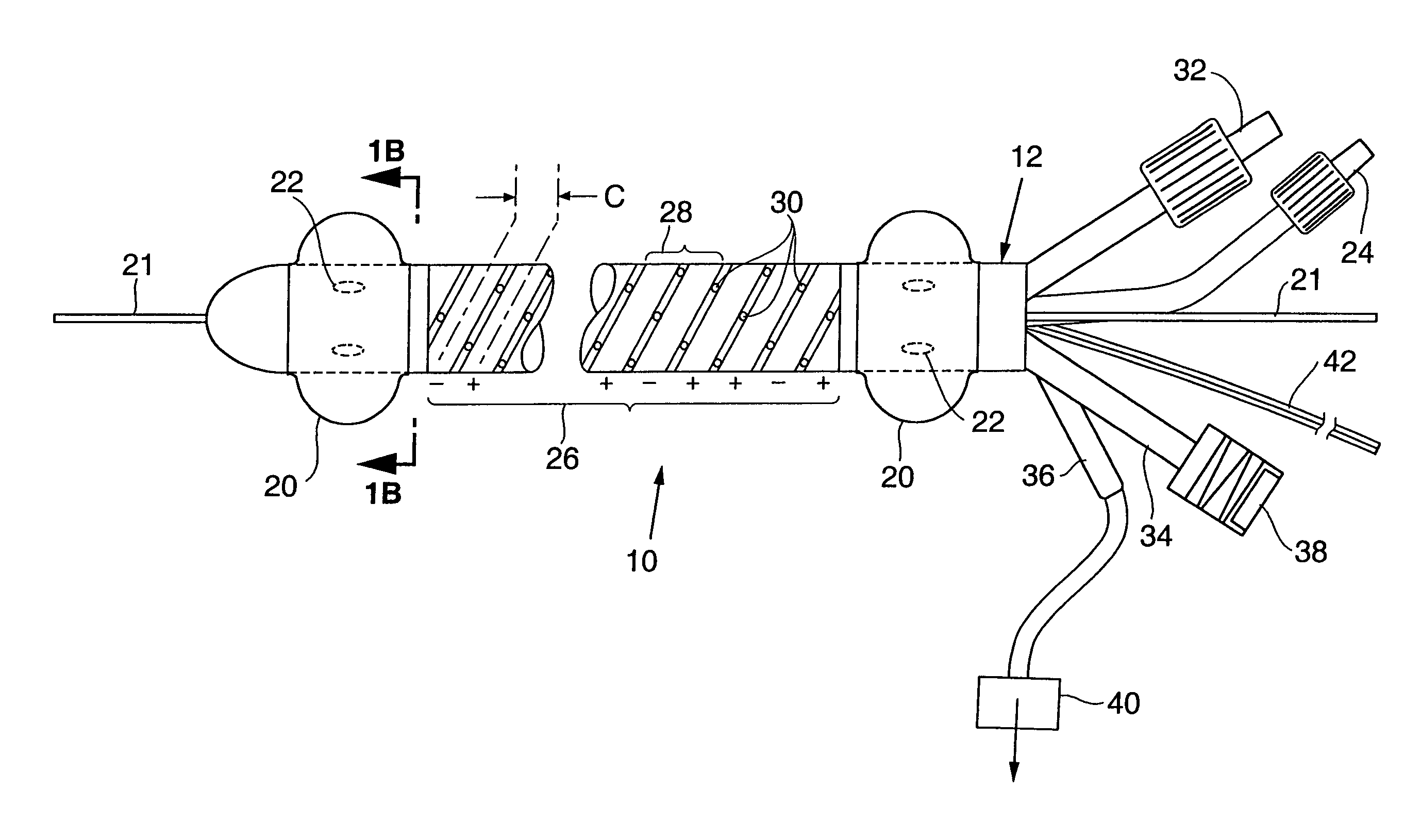
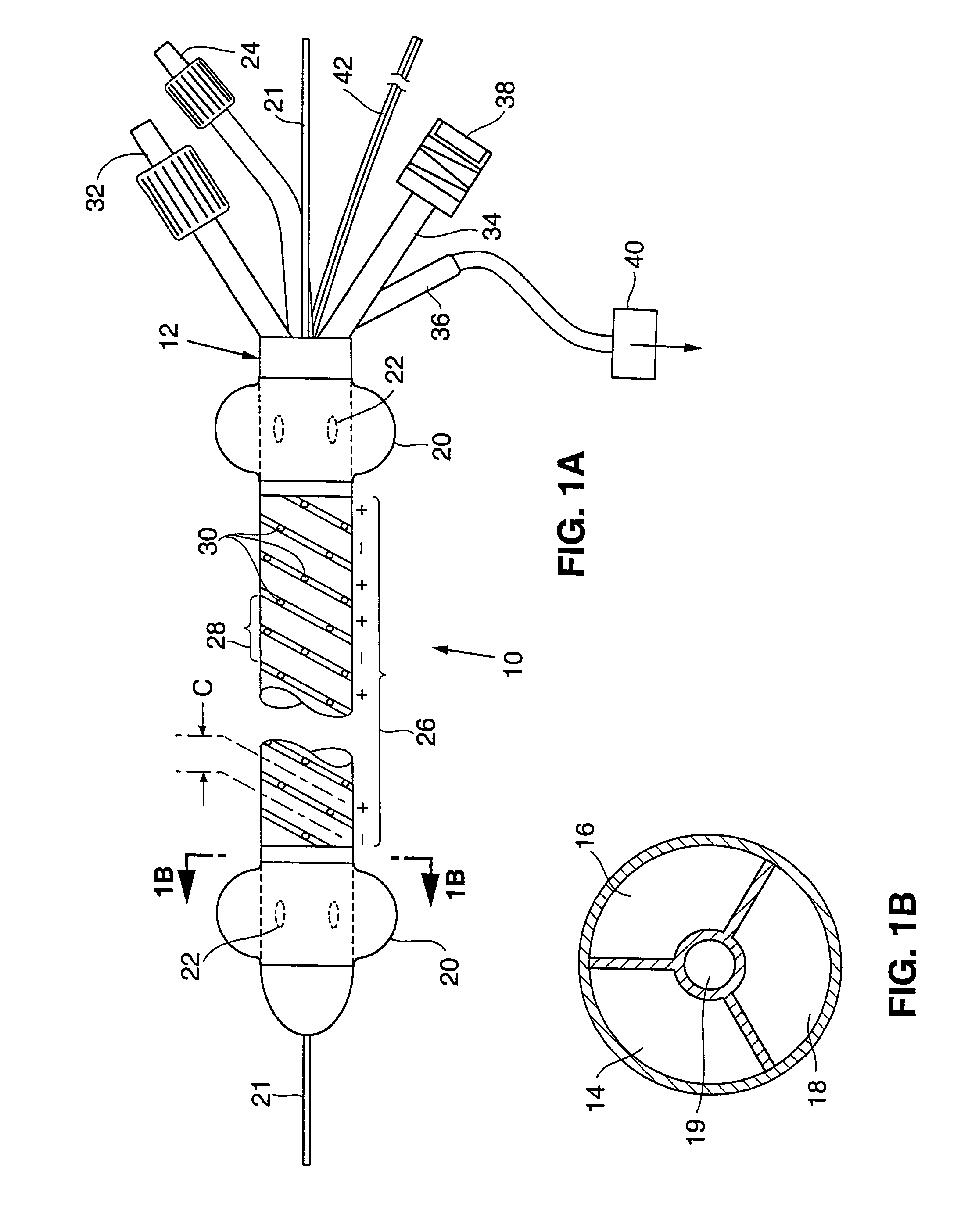
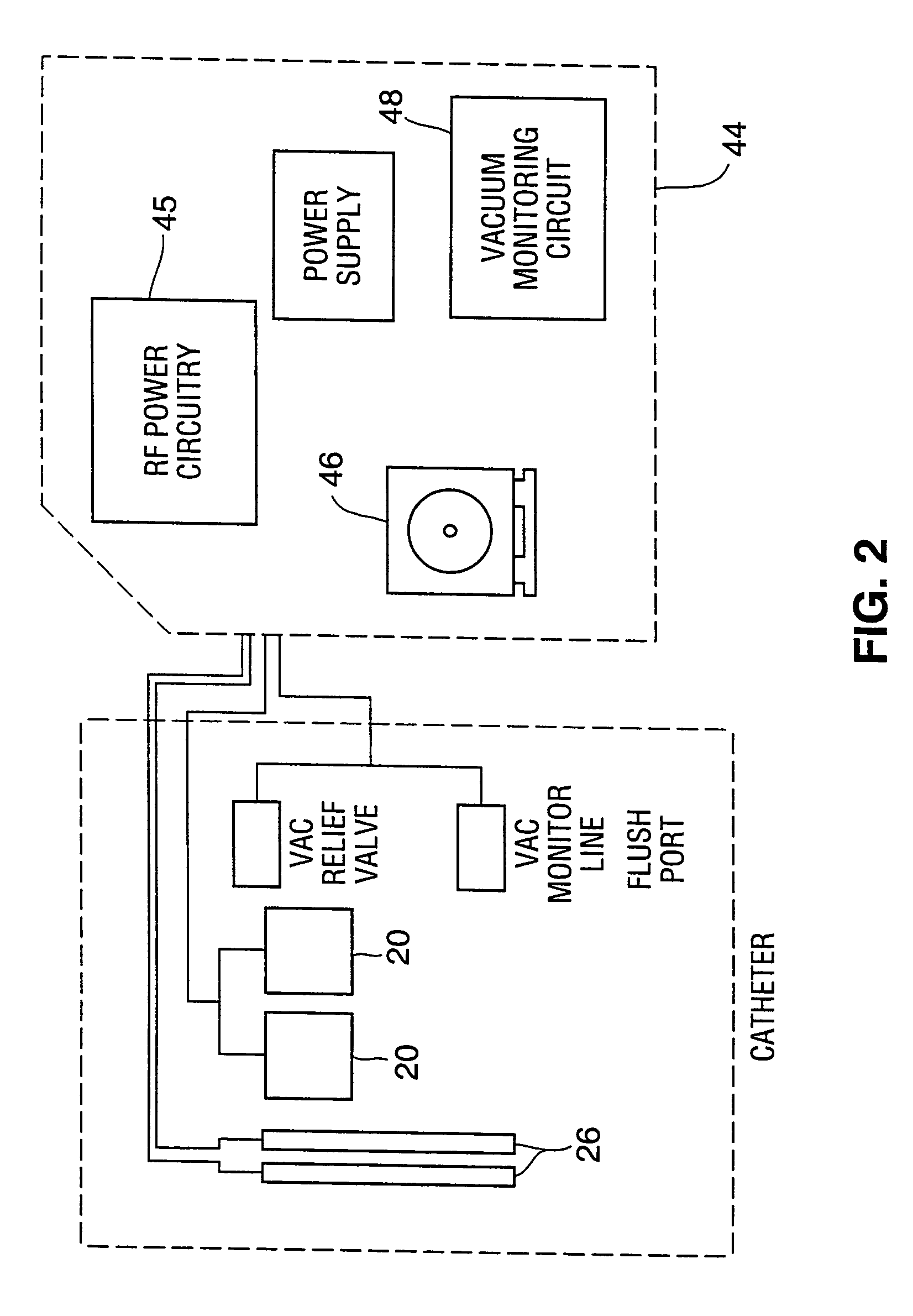
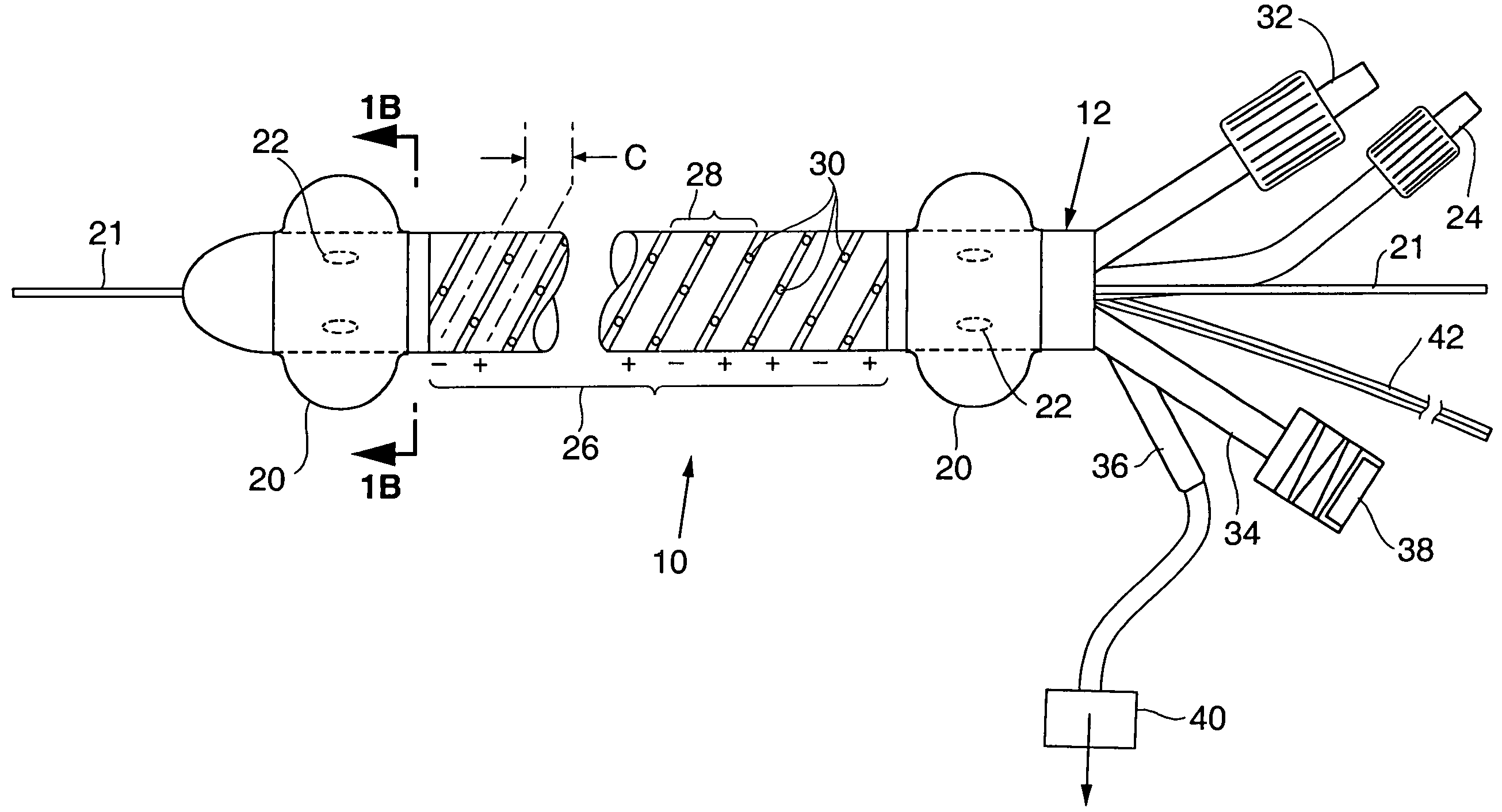
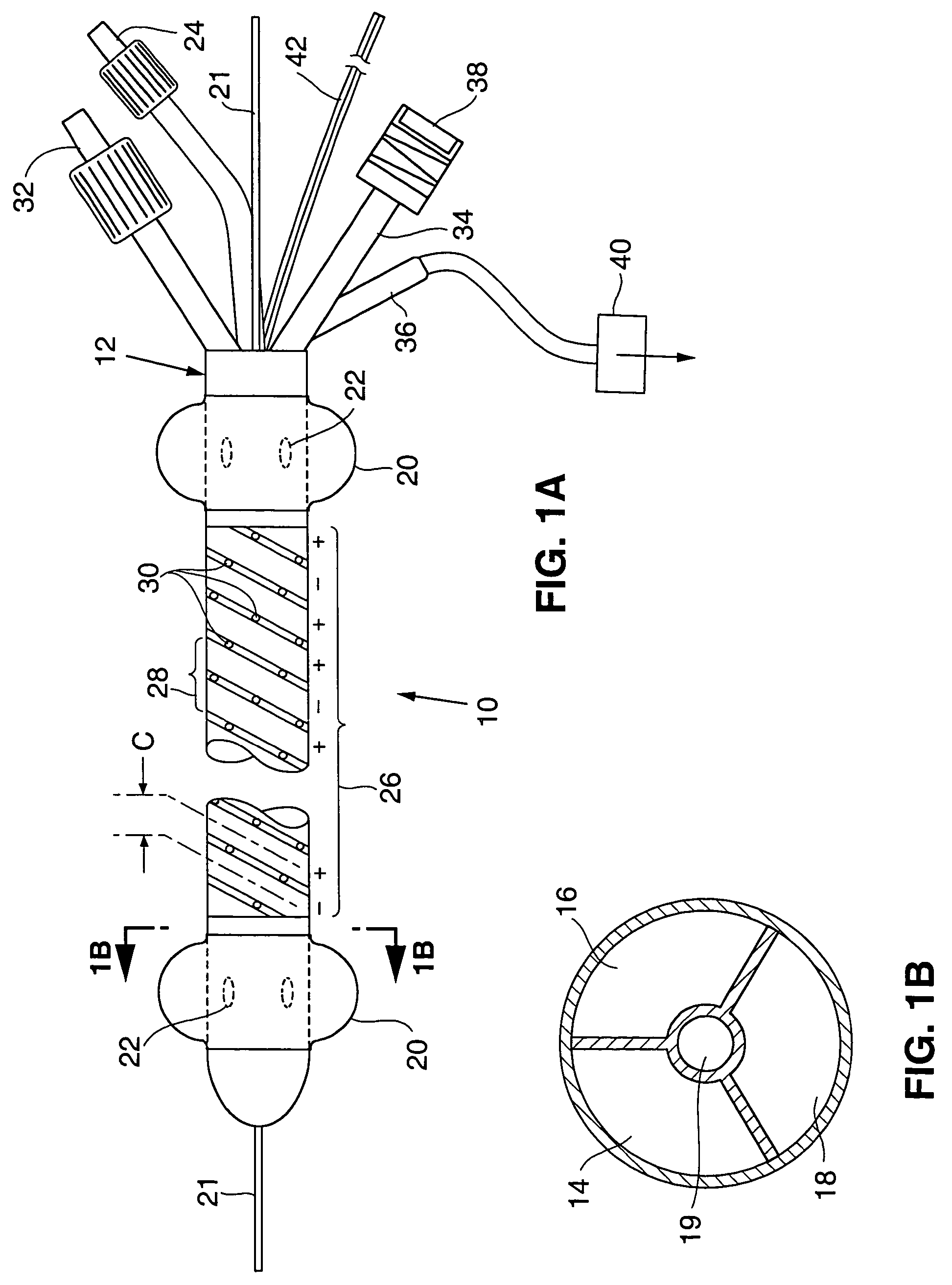
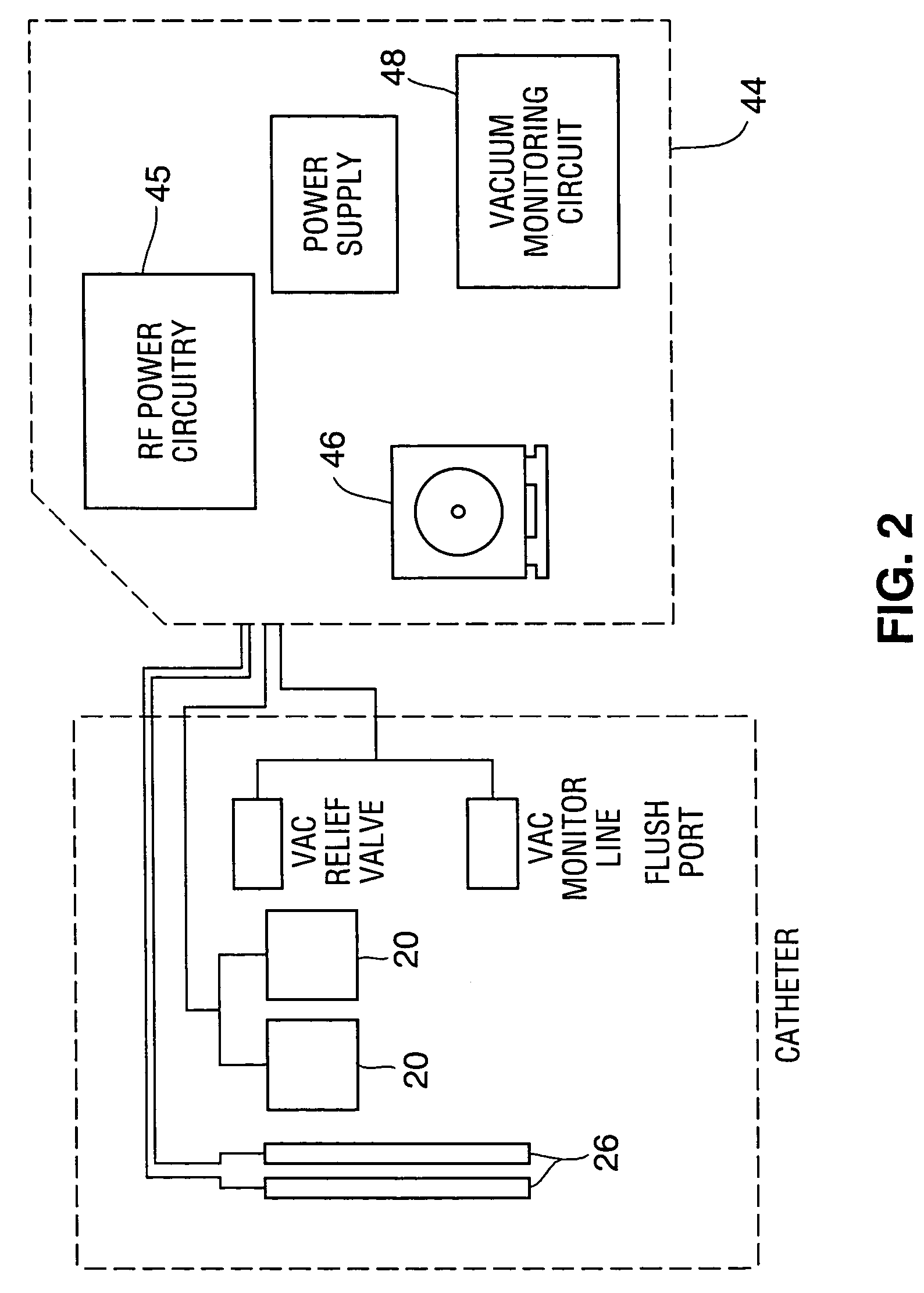
Disclosed is an ablation method and apparatus used to close veins for treatment of venous insufficiency disease. The apparatus includes a catheter proportioned for insertion into a vein, a pair of inflatable balloons spaced apart on the catheter body, and an ablation electrode array disposed between the balloons. According to the disclosed method, the catheter is introduced into the vein to be treated and the balloons are distended. Blood is flushed and aspirated from the site between the balloons. RF power is applied to the electrode array, causing scarring of the vessel walls and eventual sealing of the vein.
Owner:CYTYC SURGICAL PRODS
Apparatus and method for treating venous reflux
Owner:CYTYC SURGICAL PRODS
Inflatable minimally invasive system for delivering and securing an annular implant
InactiveUS20130123910A1Reduce the overall diameterIncrease the diameterSuture equipmentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatationBiomedical engineering
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Transapical delivery system for heart valves
ActiveUS20110015728A1Facilitate positioning of valveHelp positioningStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveProsthetic heart
A delivery system and method for delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. The system includes a delivery catheter having a steering mechanism thereon for delivering a balloon-expandable prosthetic heart valve to the aortic annulus in an antegrade fashion through an introducer passing into the left ventricle through its apex. The introducer may have a more floppy distal section than a proximal section to reduce trauma to the heart wall while preserving good operating field stability. The delivery catheter includes a deflecting segment just proximal to a distal balloon to facilitate positioning of the prosthetic heart valve in the proper orientation within the aortic annulus. A trigger in a catheter handle may be coupled to a deflection wire that actuates the deflecting segment, while a slider in the handle controls retraction of a valve pusher. The prosthetic heart valve may be installed over the existing calcified leaflets, and a pre-dilation valvuloplasty procedure may also be utilized.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Combination self-expandable, balloon-expandable endoluminal device
An endoluminal device, such as a stent or a vena cava filter, comprising at least one superelastic section and at least one plastically deformable section. The superelastic section may comprise, for example, a superelastic grade of nitinol, whereas the plastically deformable section may comprise, for example, gold, platinum, tantalum, titanium, stainless steel, tungsten, a nickel alloy, a cobalt ally, a titanium alloy, or a combination thereof. Each plastically deformable section may merely comprise a constrained portion of the superelastic section comprising a plastically deformable material, such as gold. The device enables deployment by a method comprising introducing the device into a body lumen with the device radially constrained in a first configuration having a first diameter; allowing the device to self-expand into a second configuration having a second diameter less than or equal to a fully-self-expanded diameter; and then optionally “fine-tuning” the device by forcibly expanding the device into a third configuration having a third diameter in a range between the second diameter and less than or equal to a fully-forcibly-expanded diameter. The superelastic and plastically deformable sections may be tubular sections placed end-to-end, such that the plastically deformable section can be conformed to fit a tapered section of a lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
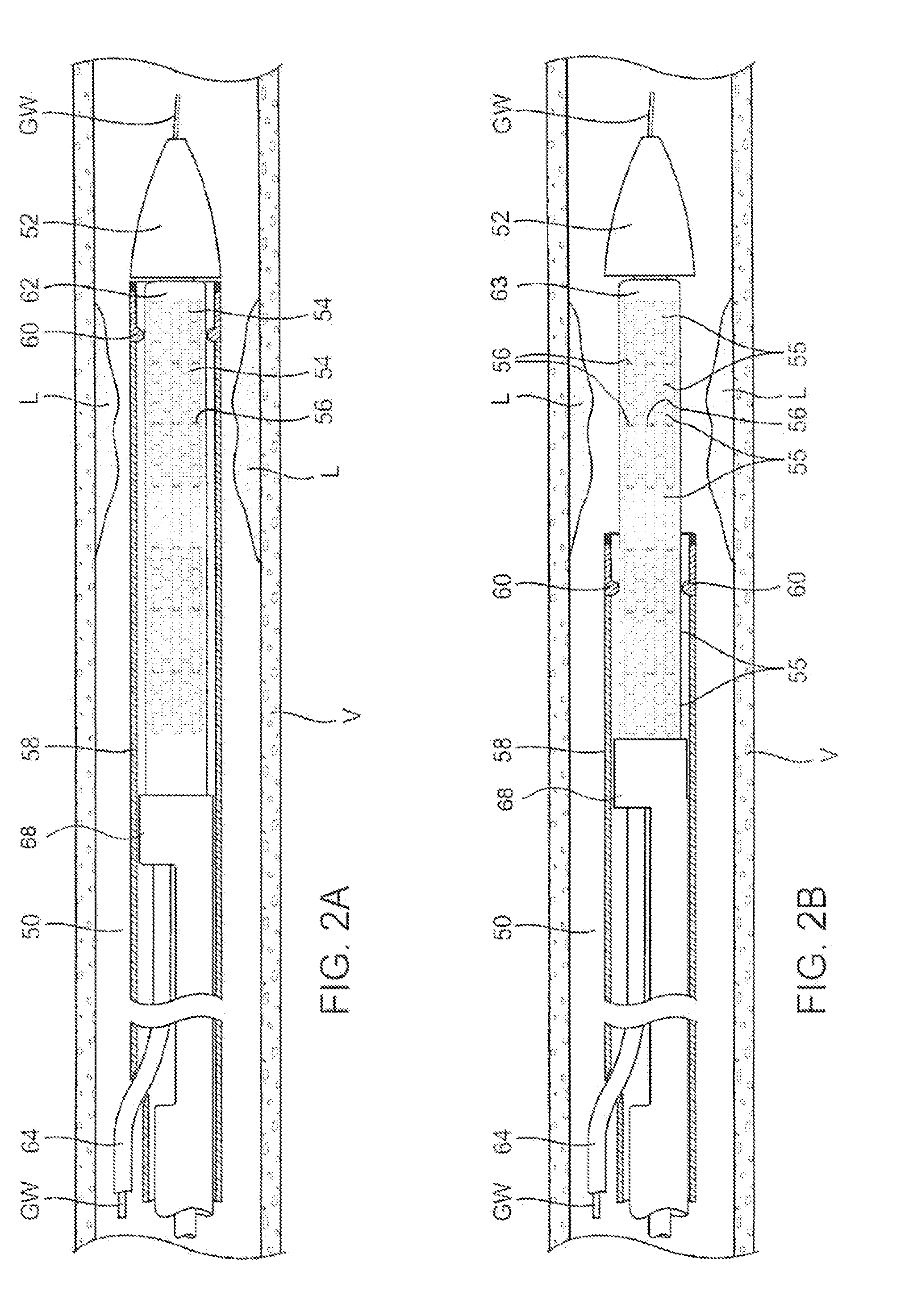
Occlusion balloon catheter with longitudinally expandable balloon
ActiveUS7198632B2Increase expansionConstant radial expansionStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterBalloon dilatation
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Expandable tip atherectomy method and apparatus
InactiveUSRE36764E1Reducing circumferenceConvenient introductionCannulasExcision instrumentsAtherectomyBalloon dilatation
A device for removing obstructions from vessels or small openings in the body, comprising a rotatable ablator tip which is guided to the obstruction in a reduced diameter configuration, expanded and rotated to remove the obstruction, and contracted to remove the device from the body. The variably expandable abrasive tip coil in one embodiment of the invention is actuated by a piston means disposed within the coil. A pair of collars is attached to the ends of the coil, and the piston effects relative longitudinal axial movement of the collars and, hence, the respective ends of the coil tip. When the ends of the coil tip are so moved with respect to one another, expansion and contraction of the diameter of the coil tip results. In another embodiment of the invention, the expansion tip coil is actuated by an expandable and contractible bellows means disposed within the coil, instead of the piston means. In another embodiment of the invention, the expansion and contraction of the coil tip are effected by longitudinal axial movement of an internal coil attached to one end of the coil tip, within an outer coil attached to the other end of the coil tip. In another embodiment of the invention, expansion and contraction of the coil tip are effected by an inflatable balloon disposed within the coil tip. The balloon expansion means enlarges preferably at the central portion of the coil to make a bulge. +RR The questions raised in reexamination request No. 90 / 003,360, filed Mar. 15, 1994, and 90 / 003,723 filed Feb. 14, 1995, have been considered and the results thereof are reflected in this reissue patent which constitutes the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 307 as provided in 37 CFR 1.570(e).
Owner:ZACCA NADIM M
Stent and stent delivery system for ostial locations in a conduit
ActiveUS7632302B2Improve radial strengthMaintaining dilated diameter of the renal vesselStentsBlood vesselsBalloon dilatationRenal vessels
Owner:EV3
Intravascular folded tubular endoprosthesis
InactiveUS20080132996A1Accurately determinePrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsThree vesselsFocal line
A bifurcated or straight intravascular folded tubular member is deliverable percutaneously or by small cutdown to the site of a vascular lesion. Its inserted state has a smaller nondeployed diameter and a shorter nondeployed length. The intravascular tubular member has a folded tubular section that is unfolded following insertion into the blood vessel. The length of the intravascular folded tubular member is sized in situ to the length of the vessel lesion without error associated with diagnostic estimation of lesion length. The folded tubular member is self-expandable or balloon-expandable to a larger deployed diameter following delivery to the lesion site. An attachment anchor can be positioned at the inlet or outlet ends of the intravascular folded tubular member to prevent leakage between the tubular member and the native vessel lumen and to prevent migration of the tubular member. The attachment anchor has a short axial length to provide a more focal line of attachment to the vessel wall. Such attachment is valuable in attaching to a short aortic neck in the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The attachment anchor can have barbs which are held in a protected conformation during insertion of the tubular member and are released upon deployment of the attachment anchor. The intravascular tubular member can be formed of woven multifilament polymeric strands with metallic strands interwoven along with them. Double weaving is incorporated to prevent leakage at crossover points.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM J +1
Dilating and support apparatus with disease inhibitors and methods for use
A dilating and support apparatus with disease inhibitors and methods for use is disclosed that is particularly useful for repairing and / or serving as a conduit for body passageways that require reinforcement, dilatation, disease prevention or the like. Such apparatuses are utilized to deliver a therapy, that therapy being from a family of devices, drugs, or any of a variety of other elements to a specific location within the body. The instant disclosure provides a system of combining a novel radial deployment and / or drug delivery therapy with existing balloon dilatation therapy into one device. This combination will yield a significant decrease in cost to the healthcare system as well as providing a therapy to the patient with increased safety and efficacy. Further, the instant invention provides a novel and improved platform for synthetic / tissue interface between the device and the body.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
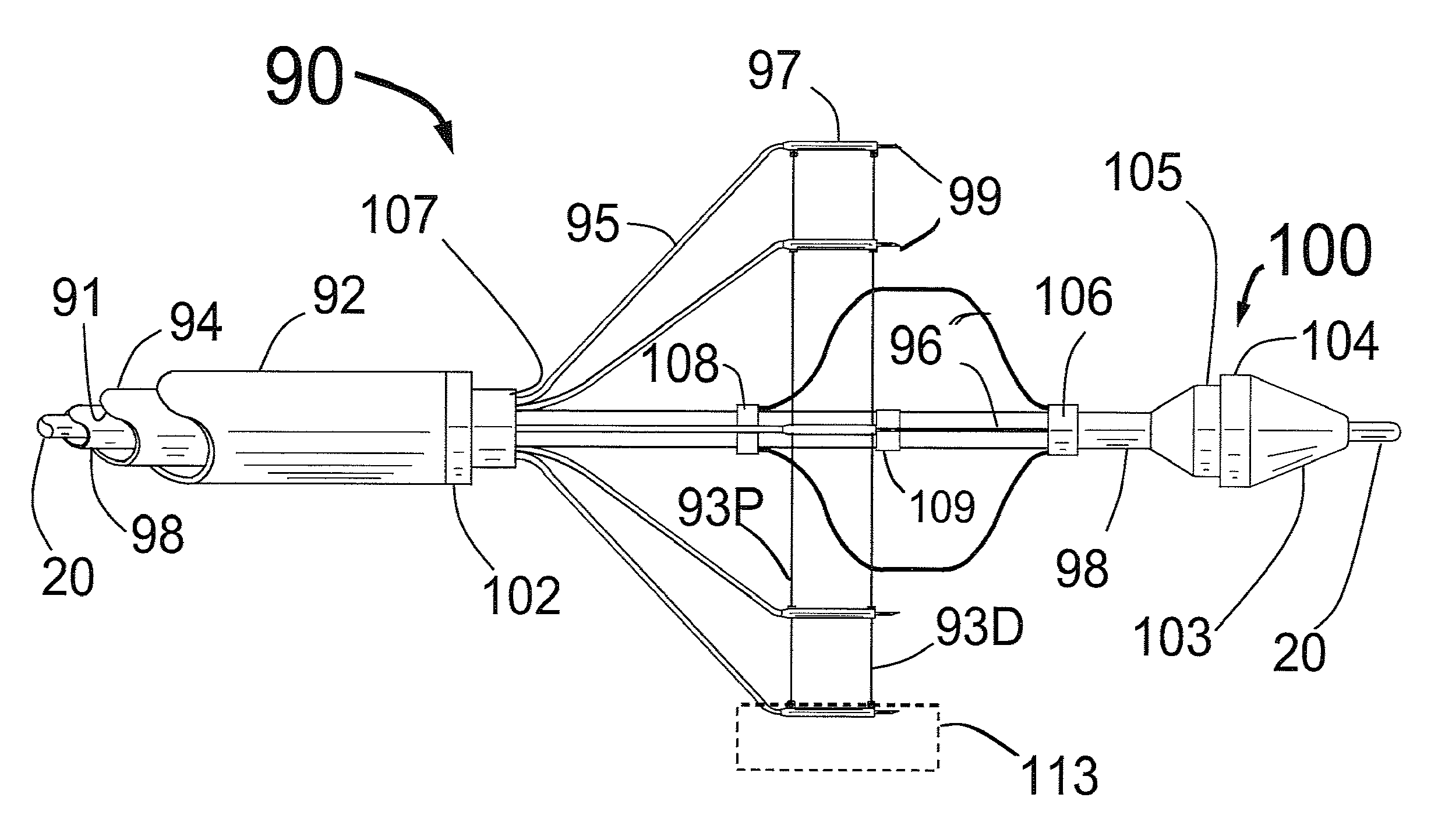
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271301A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeIntravenous devicesSurgical instruments for heatingCapital equipmentLeft atrium
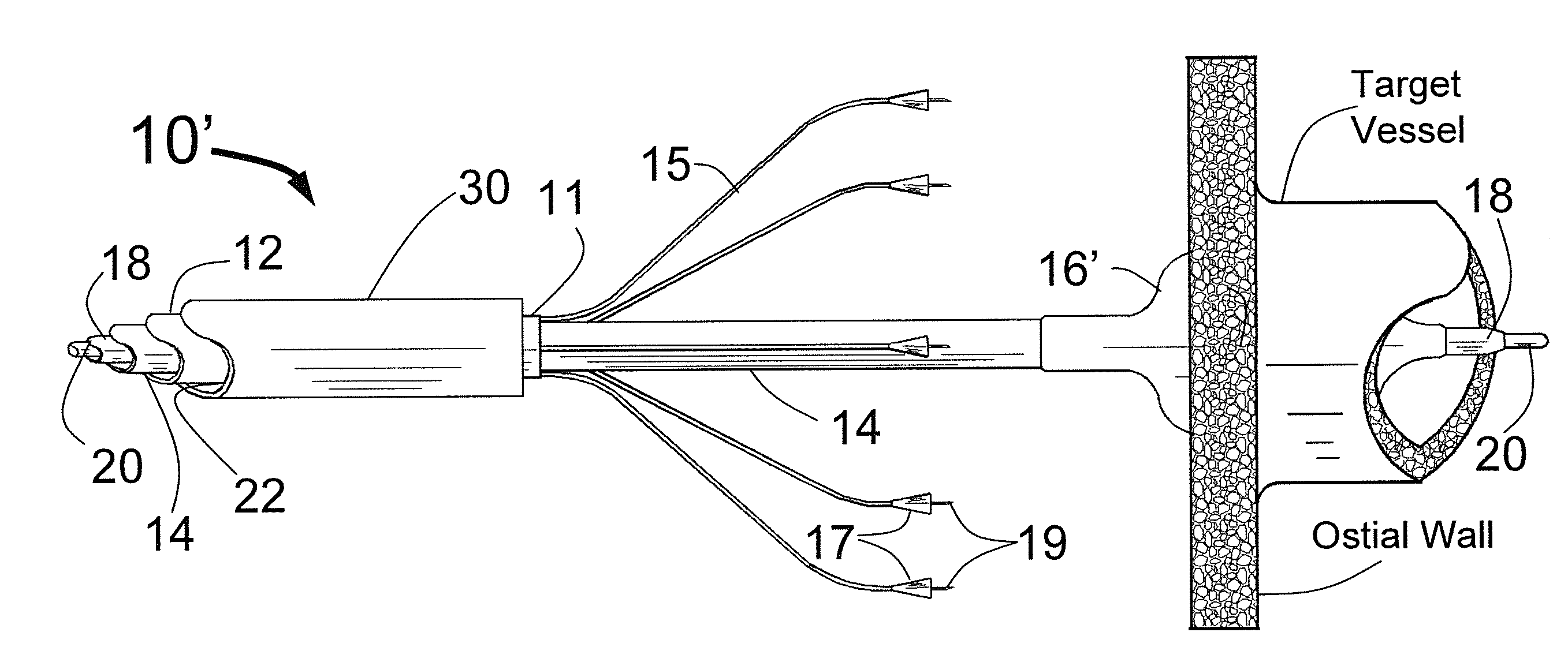
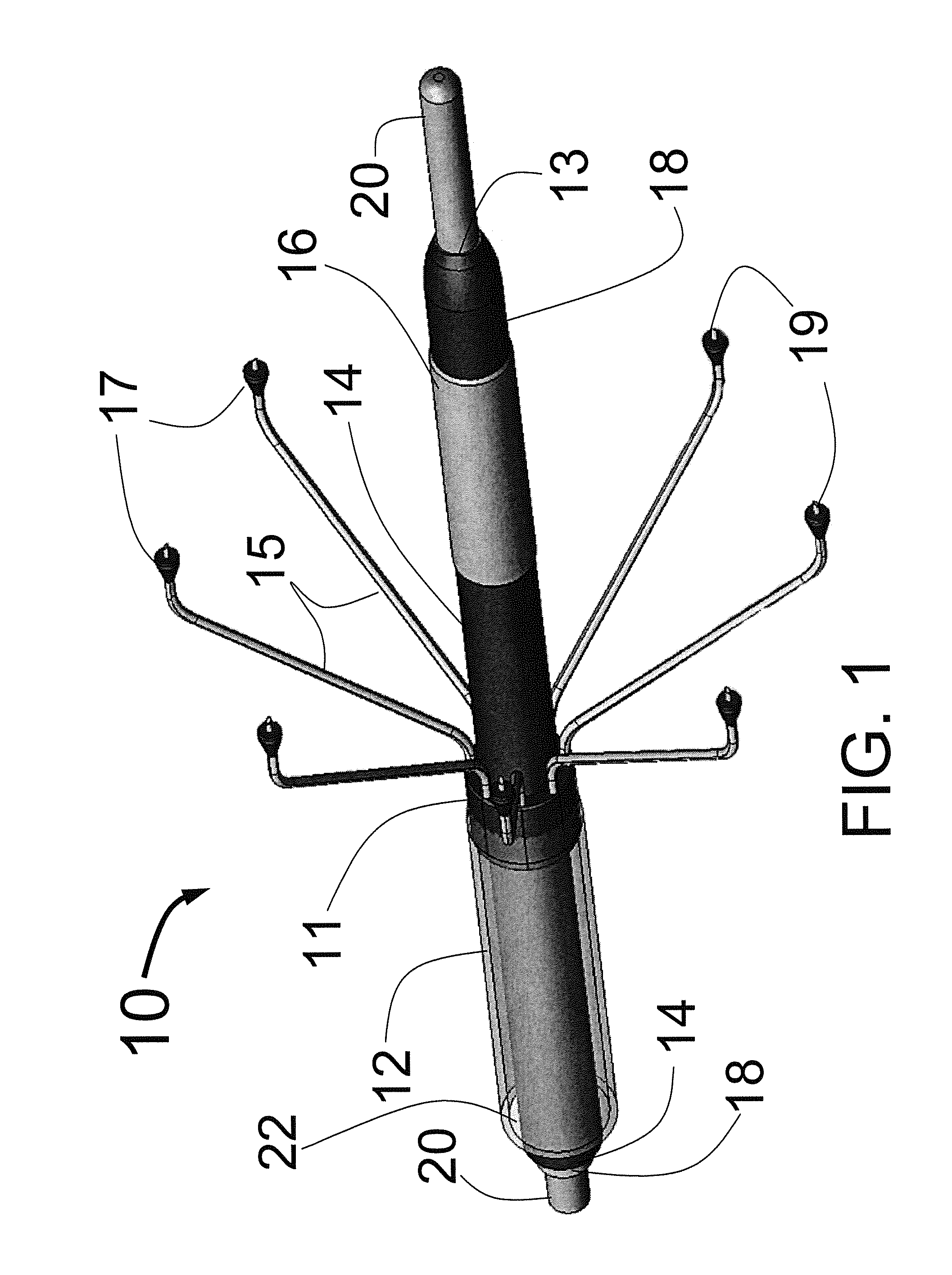
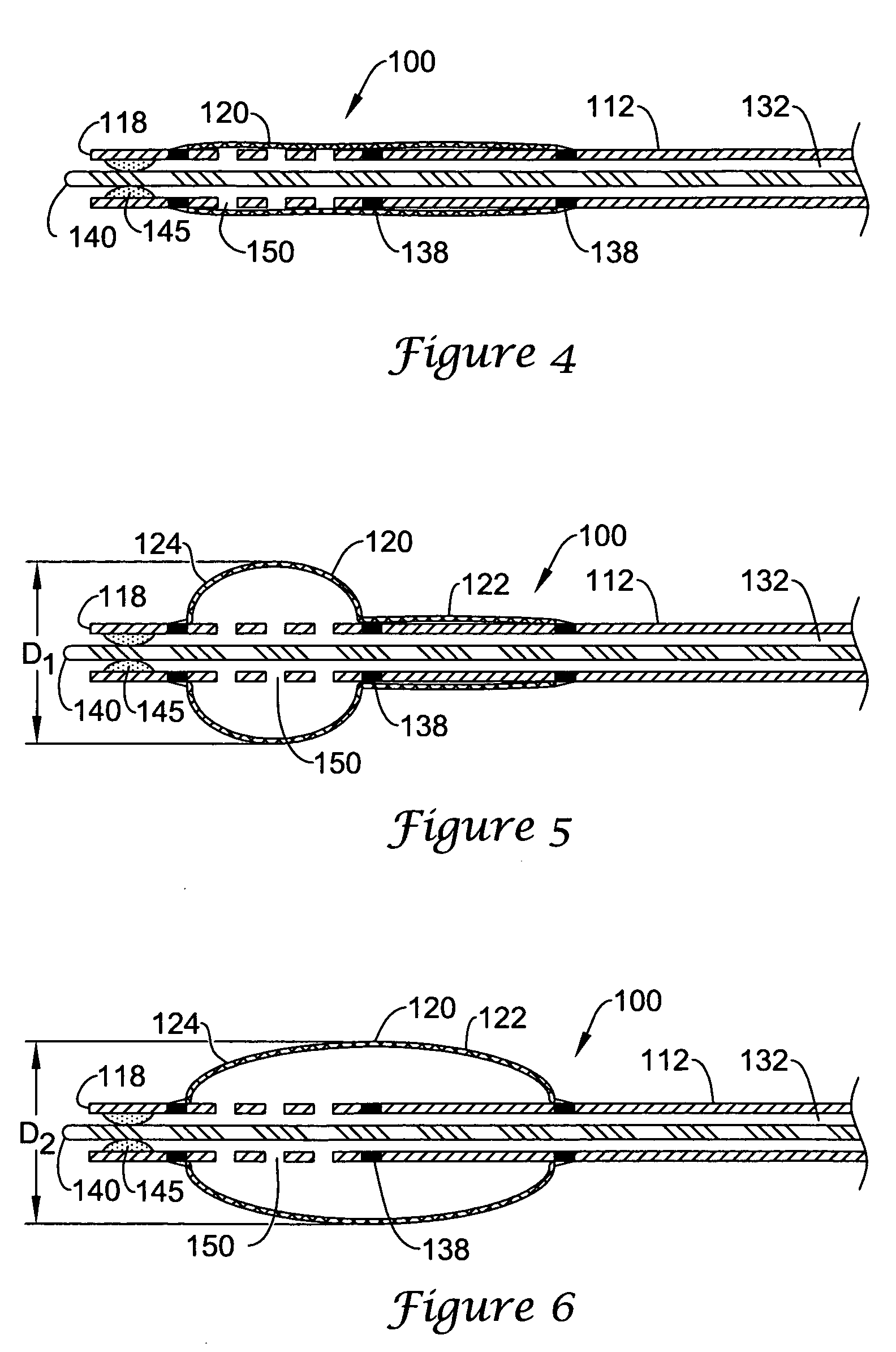
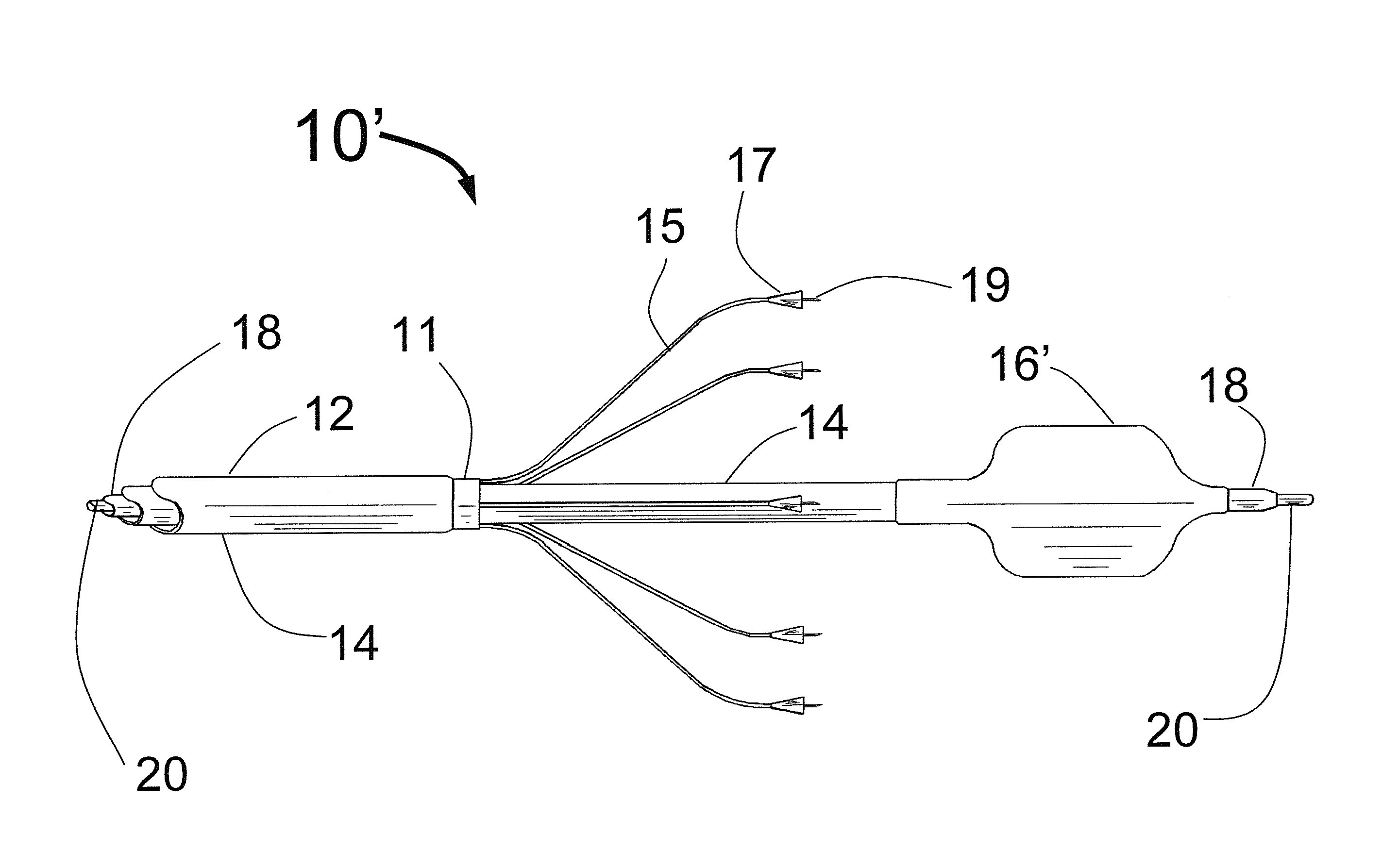
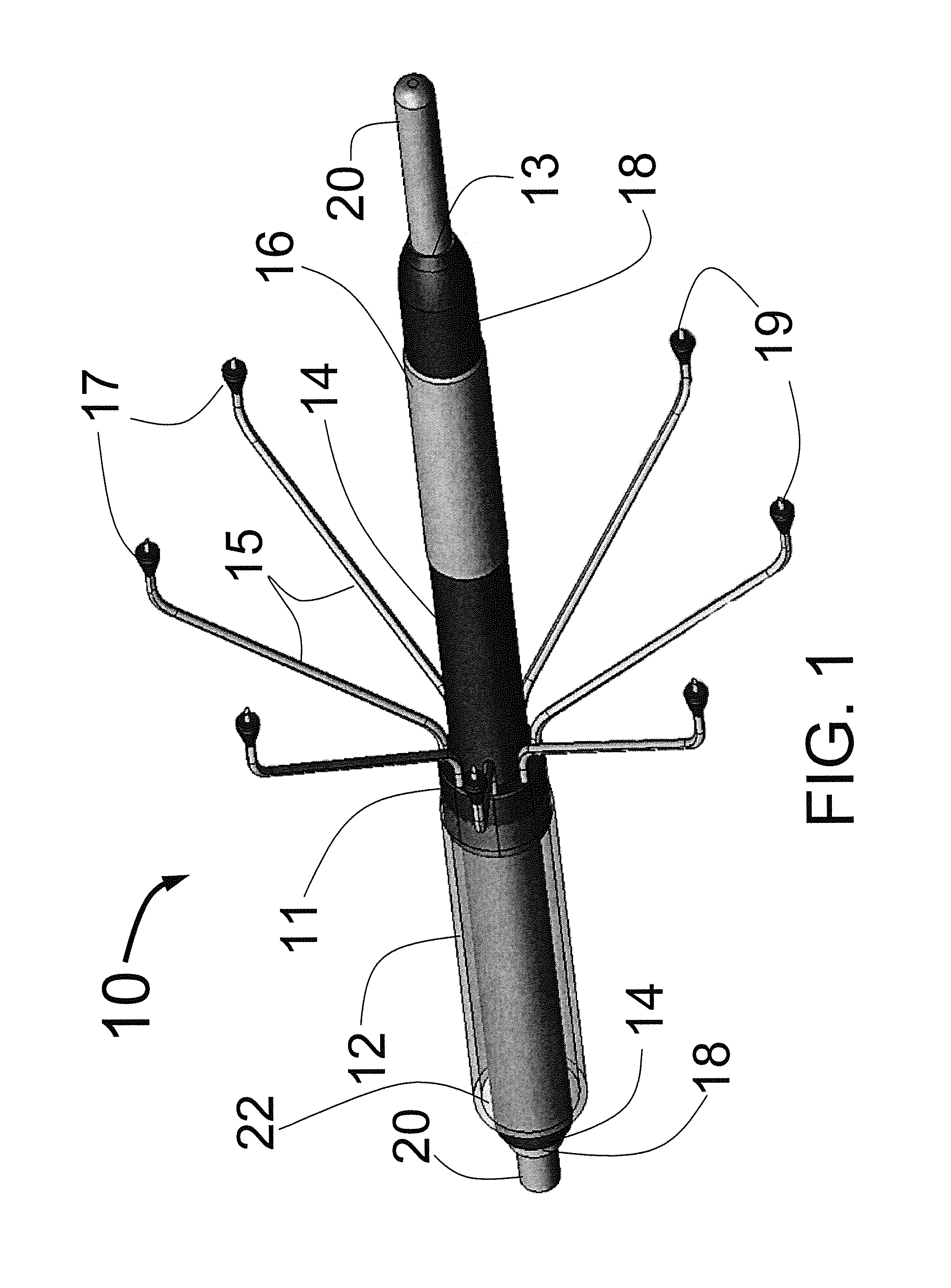
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium. The present invention also has application to ablating tissue around the ostium of a renal artery for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Inflatable minimally invasive system for delivering and securing an annular implant
InactiveUS20110093062A1Alter positionAlter sizeSuture equipmentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatationBiomedical engineering
A delivery device for an annular implant that includes a balloon expansion mechanism and an annular implant having an adjustable dimension. The balloon expansion mechanism includes an inflation tube attached to a non-occluding balloon collar which is supported by trusses radially extending from a trocar. The annular implant further includes a flexible ring core, contiguous coiled spacers, and anchoring blocks. The flexible ring core is adjusted via a cinching mechanism. The anchoring blocks are spaced along the ring core by the contiguous coiled spacers, which keeps the distance between each pair of anchoring blocks equidistant as the ring core diameter is manipulated by the device user. The annular implant can also include gunbarrel elements housed in the trocar. Each gunbarrel element contains a gunbarrel pusher which drives an attachment element into the annular implant and annular tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Hybrid amorphous metal alloy stent
InactiveUS20060178727A1Inhibit and decrease cell proliferationReduce restenosisStentsSurgeryMetal alloyBalloon dilatation
An expandable stent is provided, wherein the stent is advantageously formed of at least one amorphous metal alloy and a biocompatible material. The stent is formed from flat metal in a helical strip which is wound to form a tubular structure. The tubular structure is not welded but rather is wrapped or coated with a biocompatible material in order to maintain the amorphous metal in its tubular configuration. Said stent can be balloon expanded or self expanding.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Dilating and support apparatus with disease inhibitors and methods for use
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Device and method for tacking plaque to blood vessel wall
A plaque tack device for treating atherosclerotic occlusive disease is formed as a thin, annular band of durable, flexible material having a plurality of barbs or anchoring points on its outer periphery for preventing it from being dislodged. The plaque tack may be used with a balloon angioplasty procedure or as a de novo treatment for blood vessel blockage to reopen the vessel lumen for desired blood flow. It has a width that is small relative to its diameter, to minimize the amount of foreign structure placed in the blood vessel. One or more tacks may be applied in positions along a plaque accumulation site as needed to stabilize the site and / or hold pieces of plaque out of the way of blood flow. The barbs of the tack may be pressed into the plaque and / or blood vessel walls by balloon expansion. Related methods of deployment and delivery devices are provided for insertion of the plaque tack in a compressed state into the blood vessel and expanding it back to its annular shape for holding plaque against the blood vessel walls.
Owner:INTACT VASCULAR
Device and method for tacking plaque to blood vessel wall
ActiveUS20090157159A1Few structuresLimiting bending stressStentsBlood vesselsBalloon dilatationAnchor point
A plaque tack device for treating atherosclerotic occlusive disease is formed as a thin, annular band of durable, flexible material having a plurality of barbs or anchoring points on its outer periphery for preventing it from being dislodged. The plaque tack may be used with a balloon angioplasty procedure or as a de novo treatment for blood vessel blockage to reopen the vessel lumen for desired blood flow. It has a width that is small relative to its diameter, to minimize the amount of foreign structure placed in the blood vessel. One or more tacks may be applied in positions along a plaque accumulation site as needed to stabilize the site and / or hold pieces of plaque out of the way of blood flow. The barbs of the tack may be pressed into the plaque and / or blood vessel walls by balloon expansion. Related methods of deployment and delivery devices are provided for insertion of the plaque tack in a compressed state into the blood vessel and expanding it back to its annular shape for holding plaque against the blood vessel walls.
Owner:INTACT VASCULAR
Occlusion balloon catheter with longitudinally expandable balloon
ActiveUS20050197668A1Increased longitudinal expansionConstant radial expansionStentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatationBalloon catheter
Balloon catheters such as guide catheters can be configured to provide distal occlusion, while still providing sufficient interior lumen space for device delivery. Such catheters can provide a desired level of balloon expansion, yet prevent vessel damage caused by balloon over-expansion. A catheter can include an elongate shaft having a distal region, a proximal region and a lumen extending therebetween. A balloon is inflated to a desired expansion configuration with a desired diameter. Over-inflation of the balloon causes longitudinal expansion instead of increased radial expansion, thus maintaining the diameter of the balloon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods of treating atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS20140046298A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeMedical devicesIntravenous devicesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium. The present invention also has application to ablating tissue around the ostium of a renal artery for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
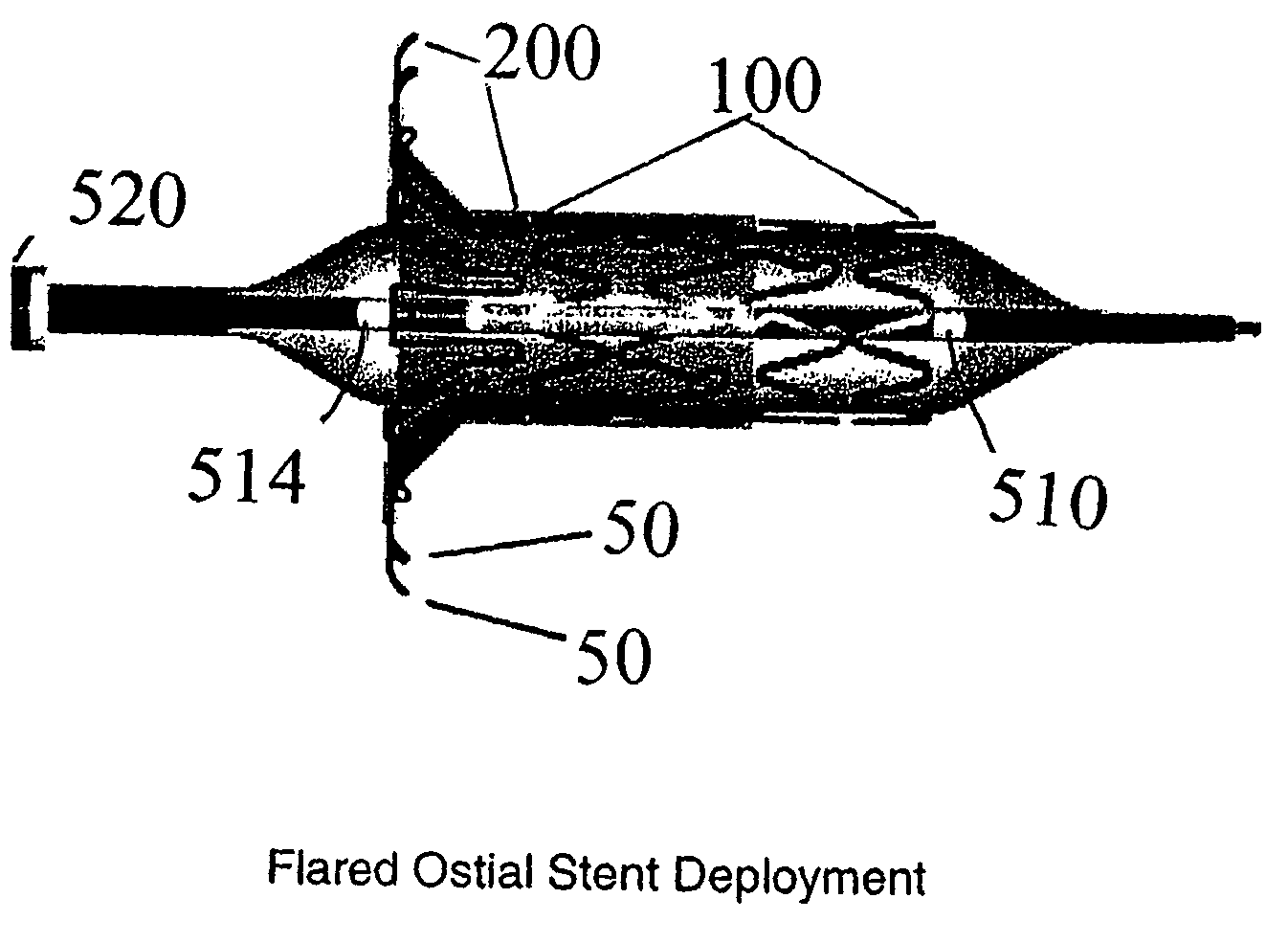
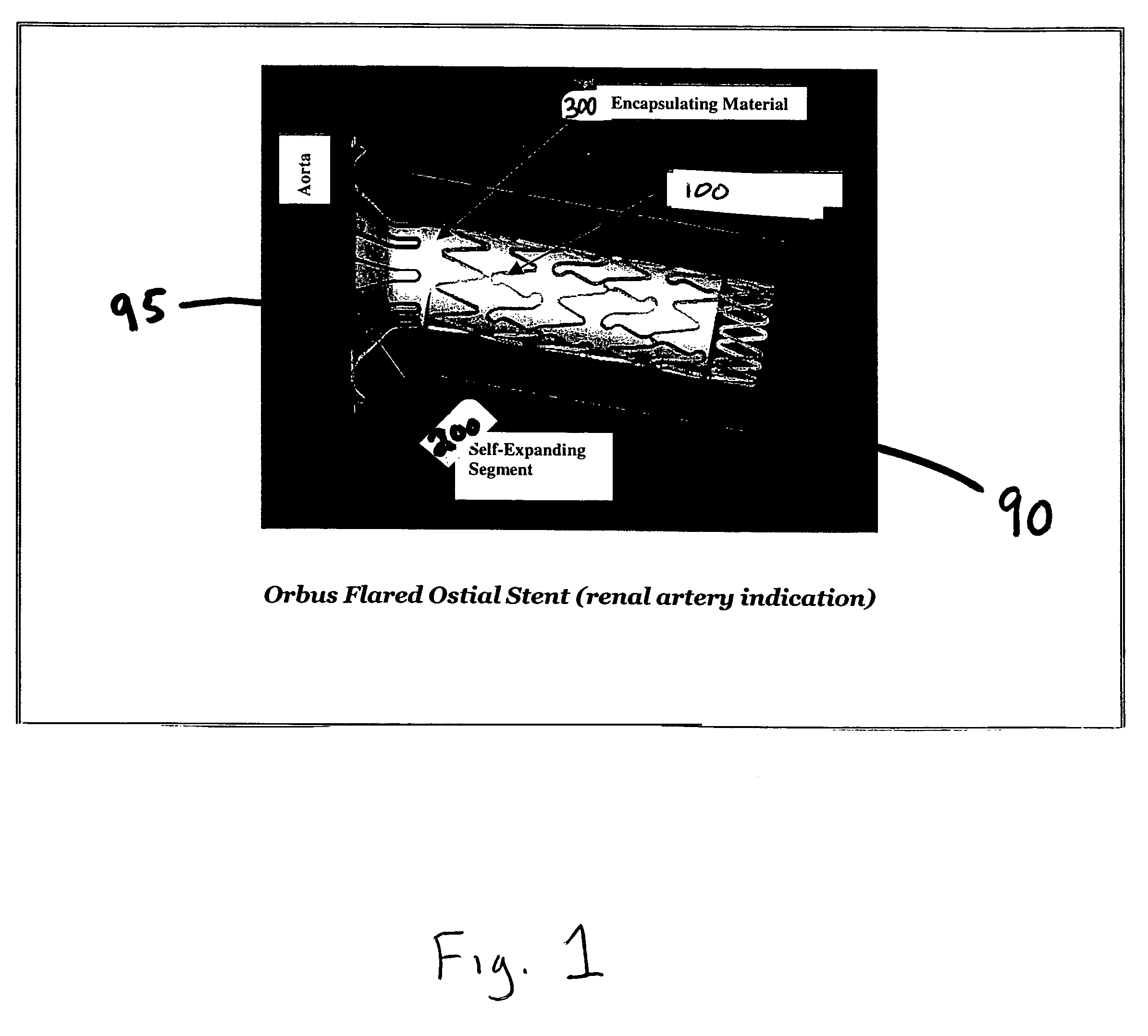
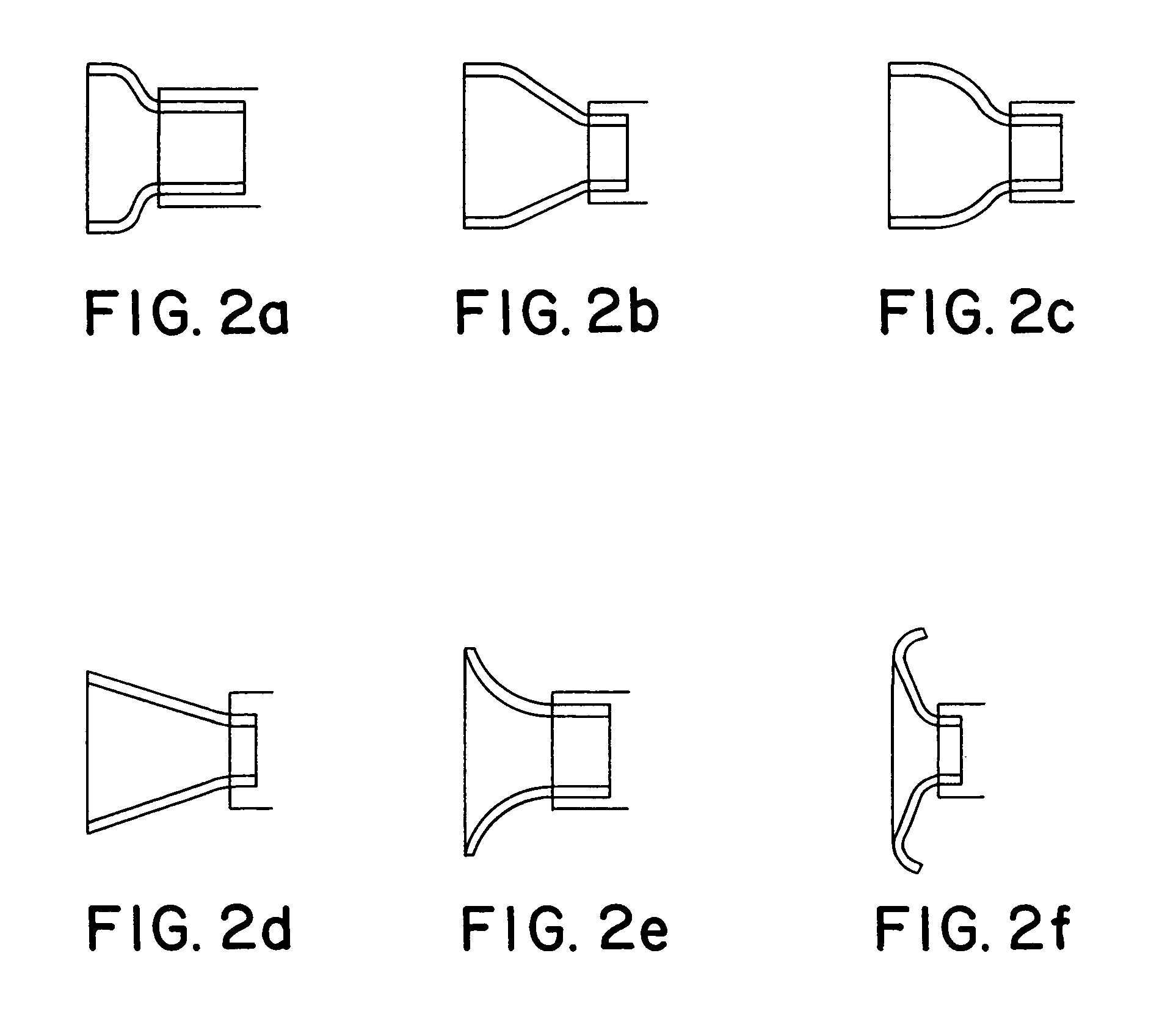
Flared ostial endoprosthesis and delivery system
An intraluminal endoprosthesis having a conically shaped first end and a tubular shaped balloon-expandable stent for a main body is disclosed. The conically shaped first end may form a flare to the main body and is particularly well suited for in ostium use. The first end is preferably self-expanding and the main body is preferably balloon-expandable. Also disclosed is a delivery device for delivering intraluminal ostial endoprosthetic devices, especially those disclosed herein, to a site for deployment. The delivery device may comprise an over-the-wire system or may comprise a rapid-exchange shuttle system. The self-expanding portion of the endoprosthesis is encapsulated in a sheath or other restraining apparatus on the delivery device. The balloon-expandable stent portion of the endoprosthesis is crimped onto a balloon delivery device. The delivery system and endoprosthesis of the present invention allow the endoprosthesis to be partially expanded and relocated if it is determined that it is not located in the proper location. To aid in positioning, the delivery device may comprise marker bands.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Reduced slippage balloon catheter and method of using same
InactiveUS7025752B2High slip angleLess lubriciousStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterBalloon dilatation
A balloon catheter having a balloon with a reduced slippage lubricious coating, and a method of performing a medical procedure such as a balloon dilatation procedure in a patient's blood vessel. The second coating (i.e., the balloon coating) is lubricious to facilitate movement of the catheter in the patient's body lumen, yet has sufficiently low lubricity such that the slippage of the inflated balloon from a desired site within the blood vessel is reduced compared to a balloon coated with the first lubricious coating.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS9237925B2Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesFiberCapital equipment
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Viewing System for Control of Ptca Angiograms
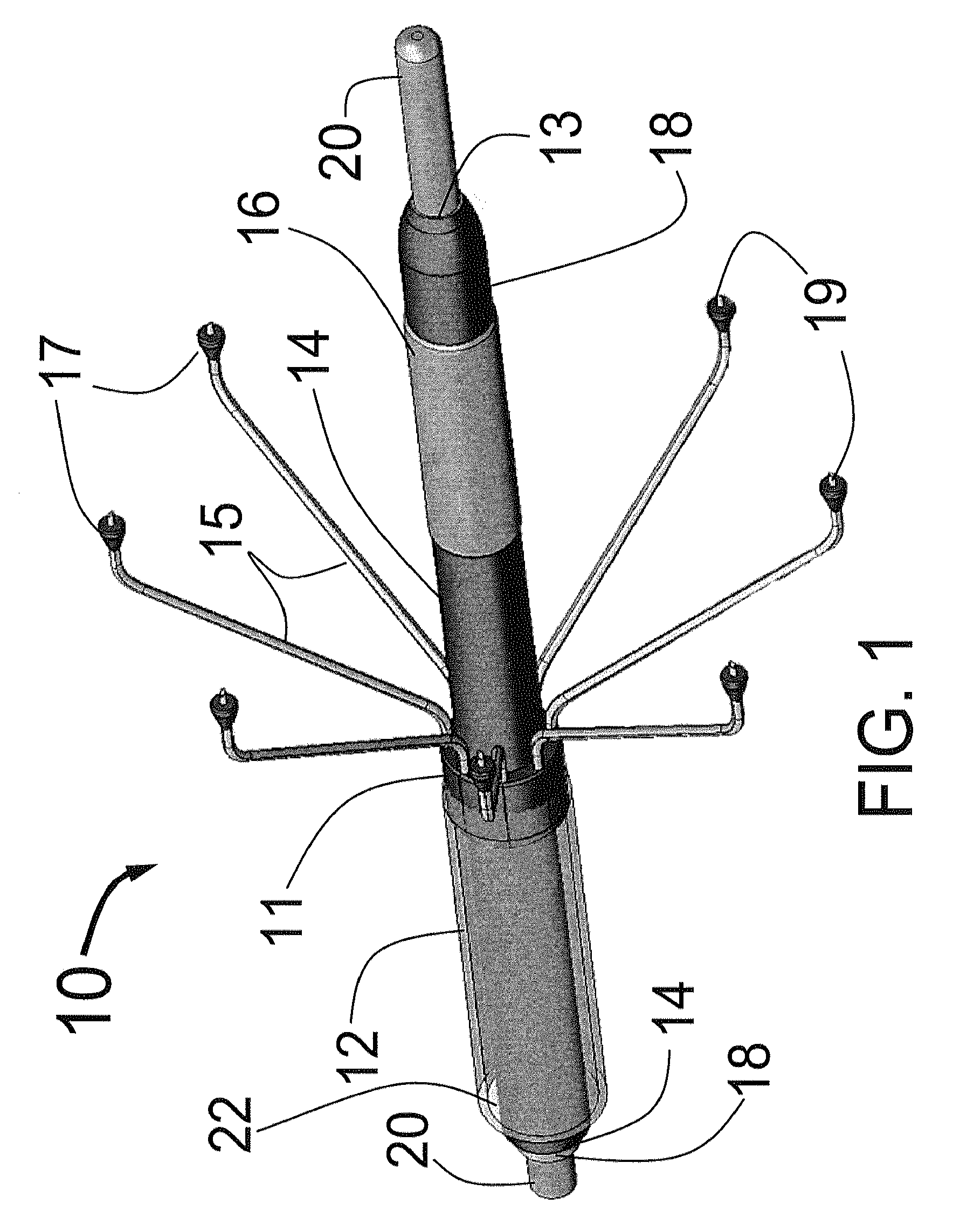
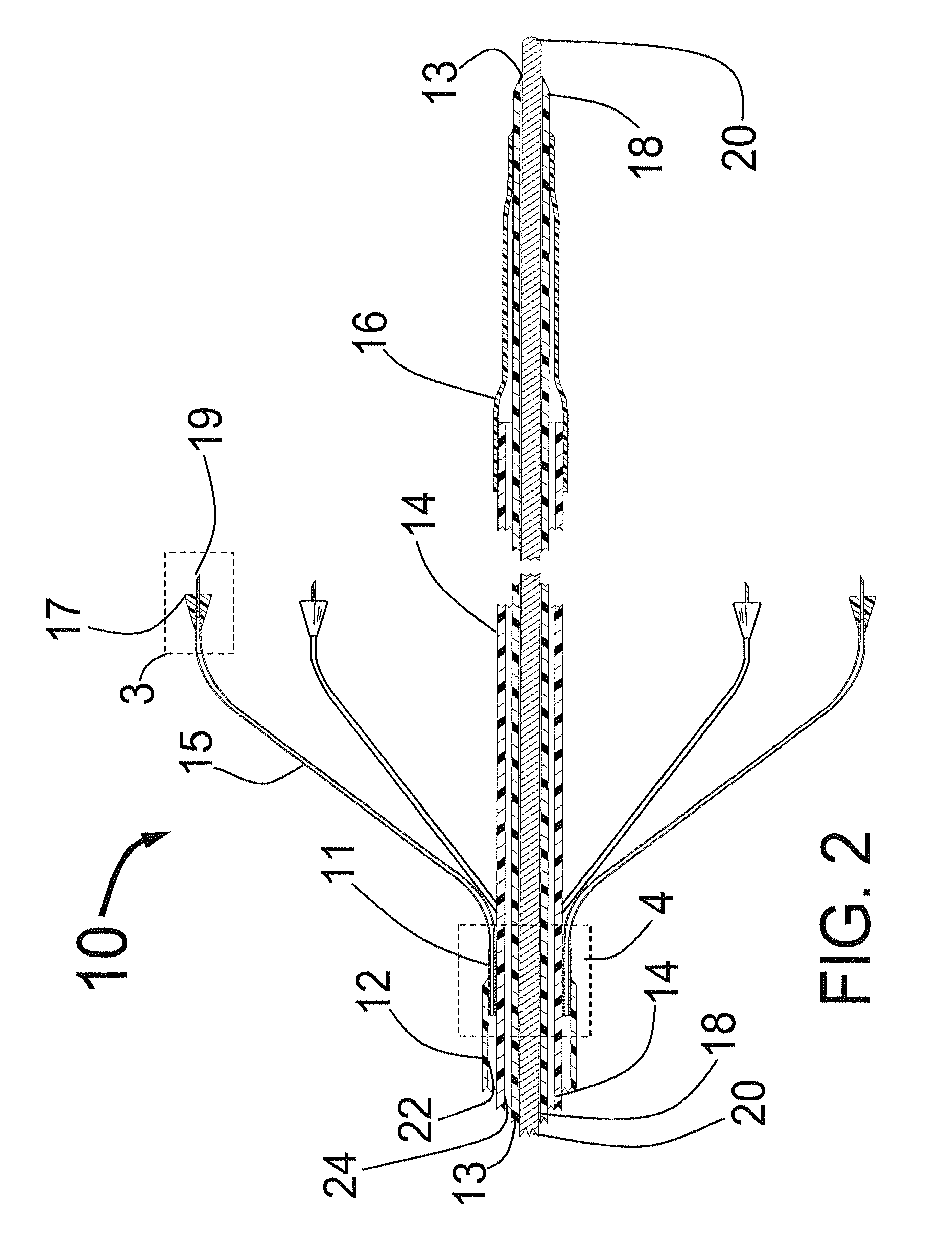
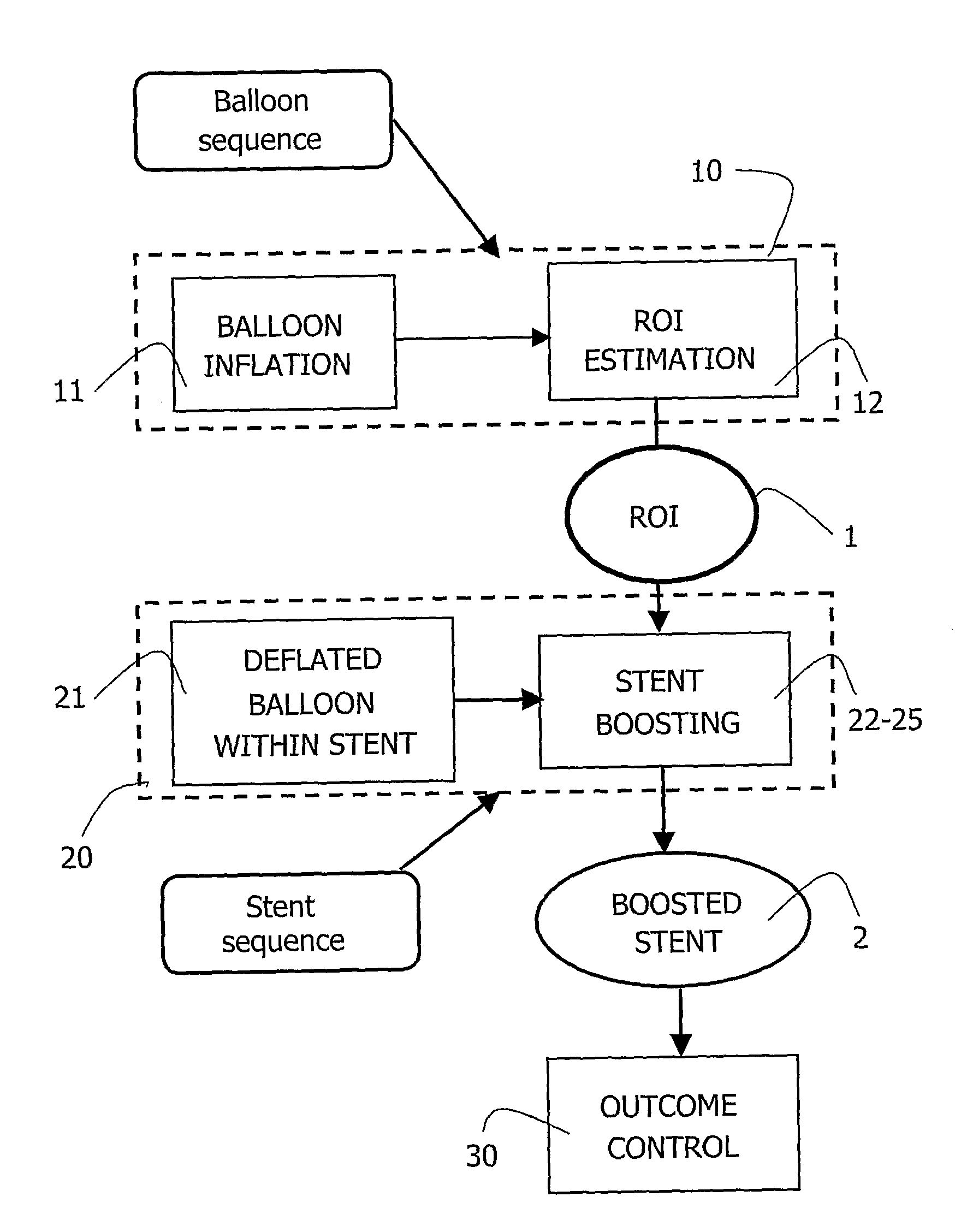
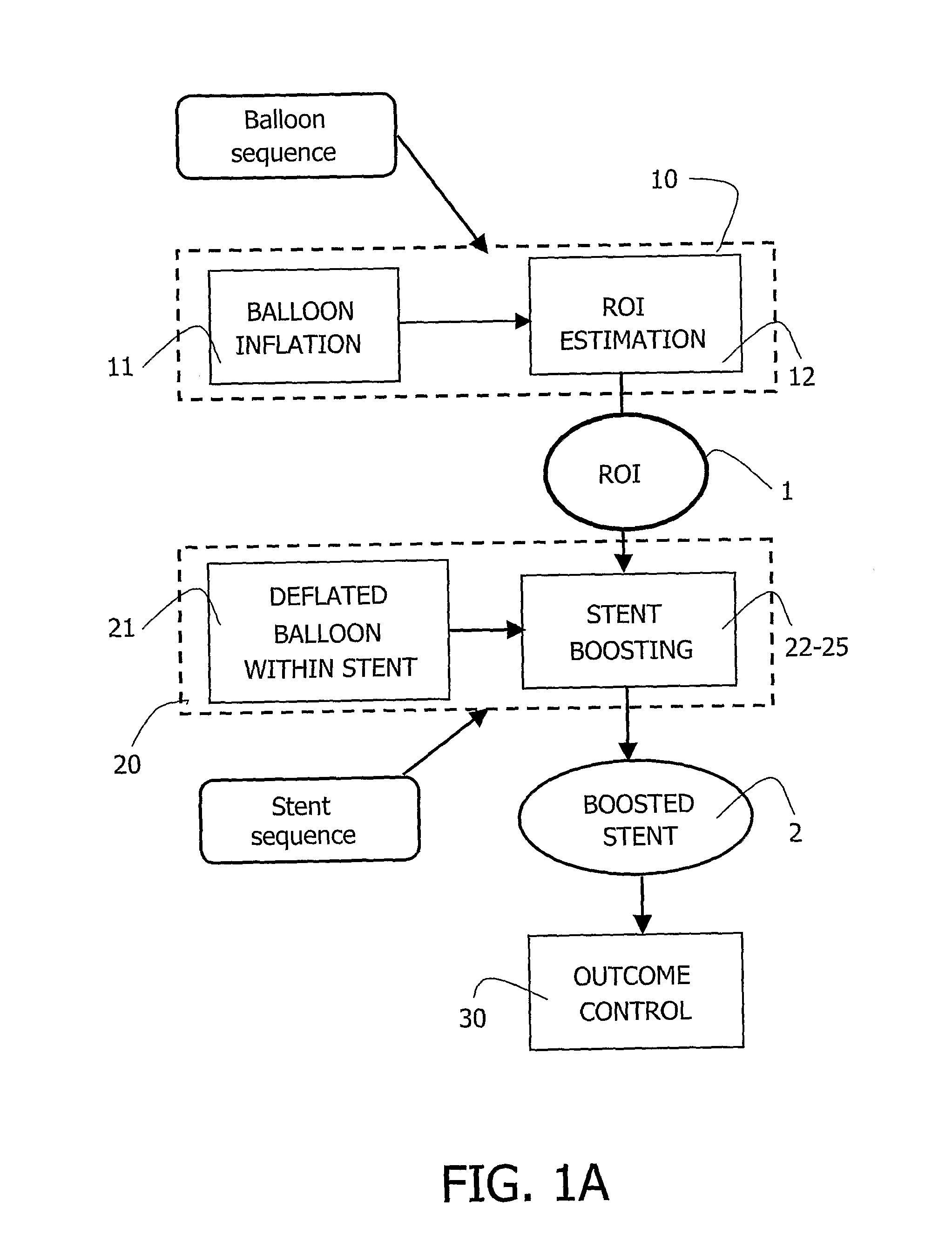
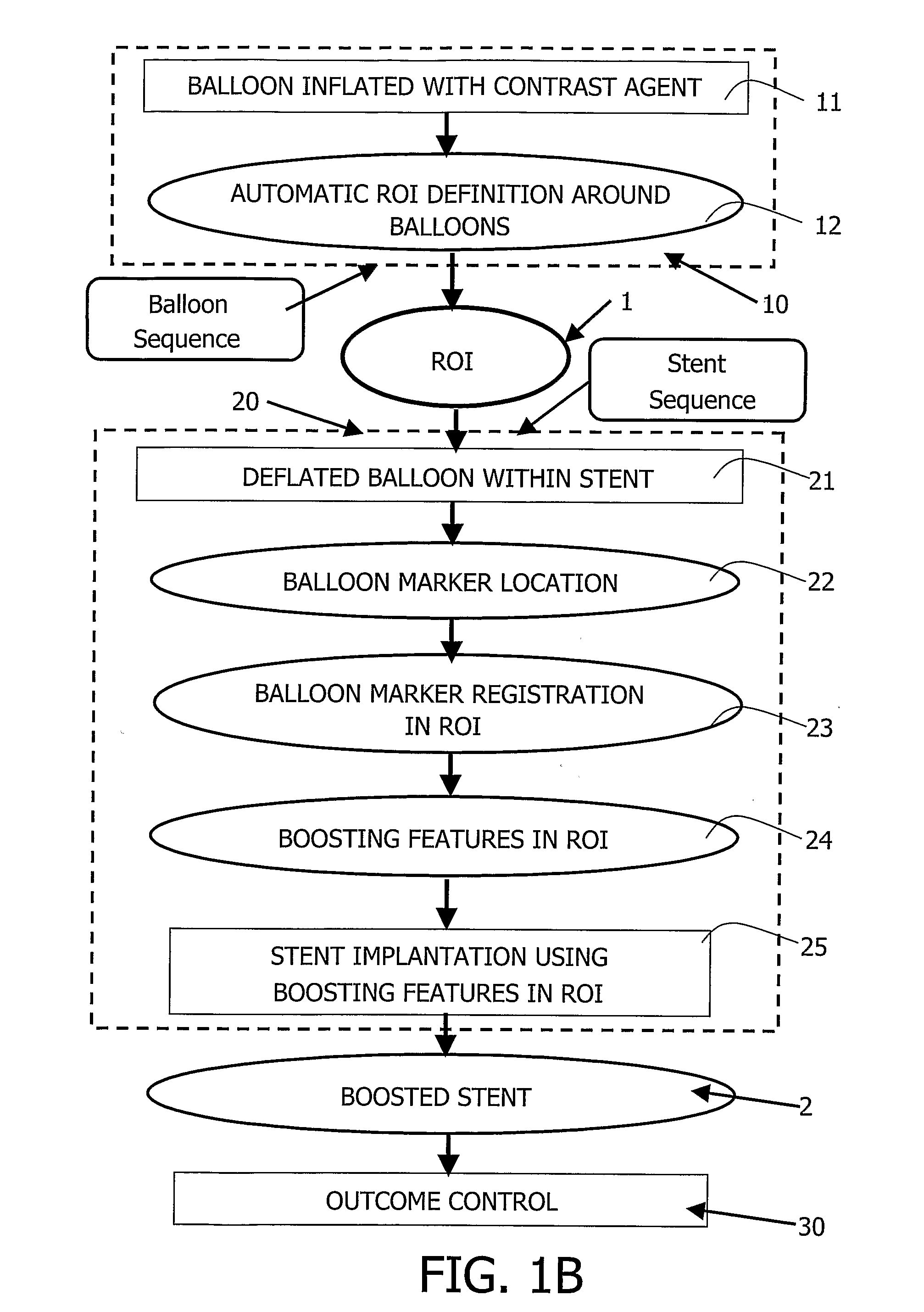
A medical viewing system for processing and displaying a sequence a sequence of medical angiograms representing a balloon, moving in an artery, this system comprising extracting means for automatically extracting balloon image data in a phase of balloon expansion, and computing means for automatically defining and storing coordinates of a Region of Interest (ROI) based on the expanded balloon image data, located around the expanded balloon; and display means for displaying the images. Contrast agent may be used as agent of balloon expansion. The system may have means to detect and keep track of balloon markers and means to look around those markers for further balloon image data extraction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20160235464A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com