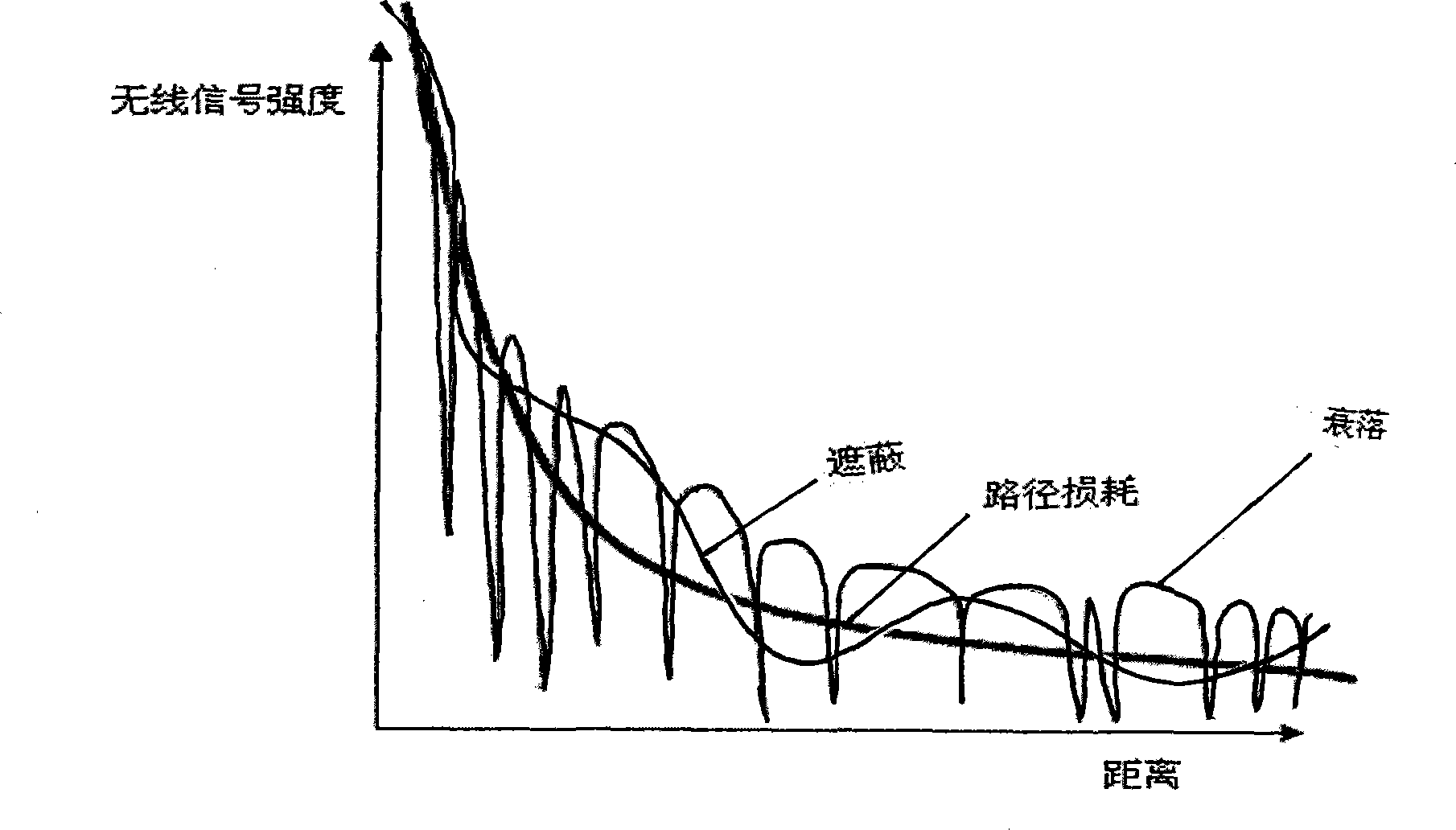
Patents
Literature
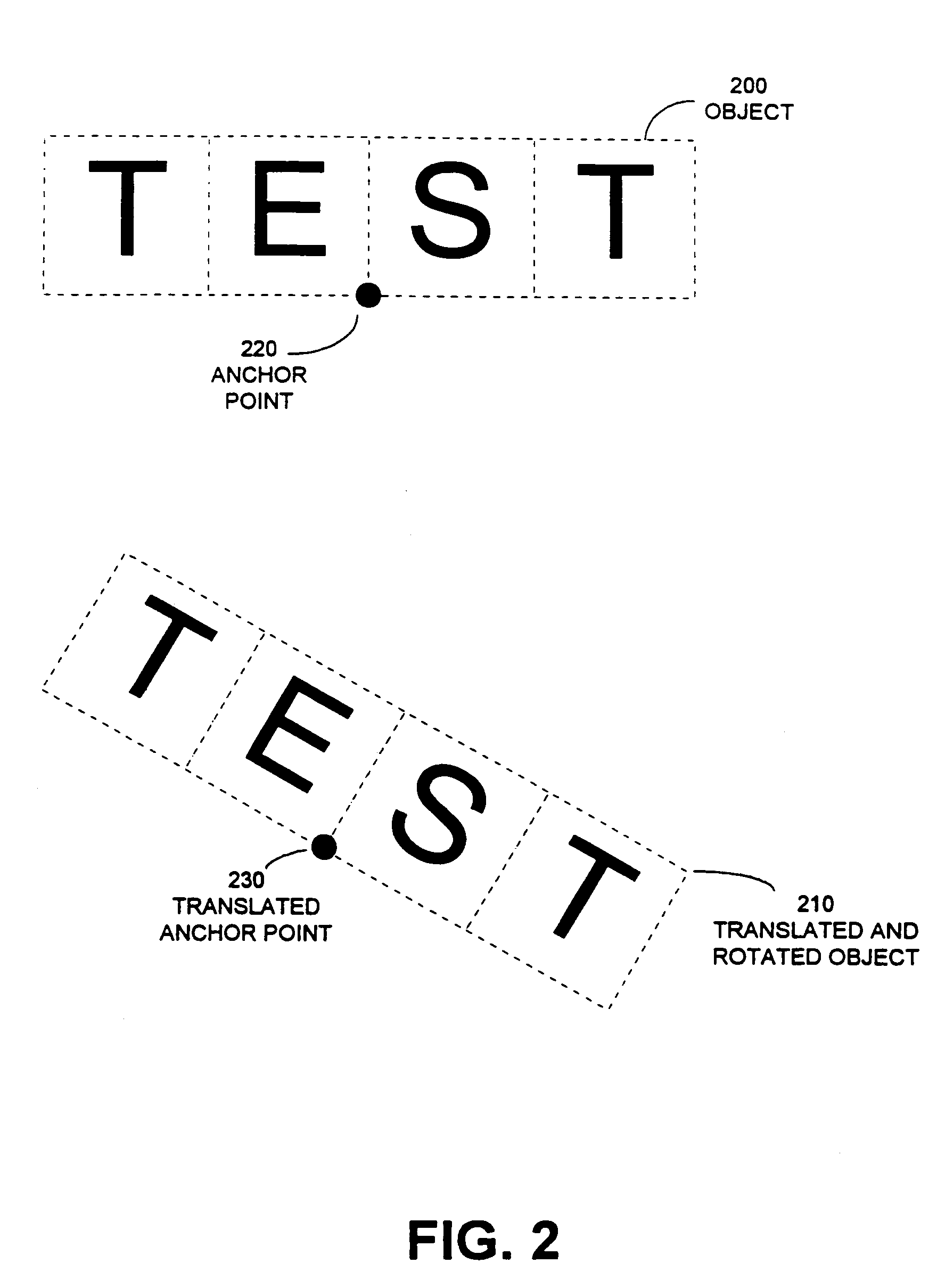
2923 results about "Anchor point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
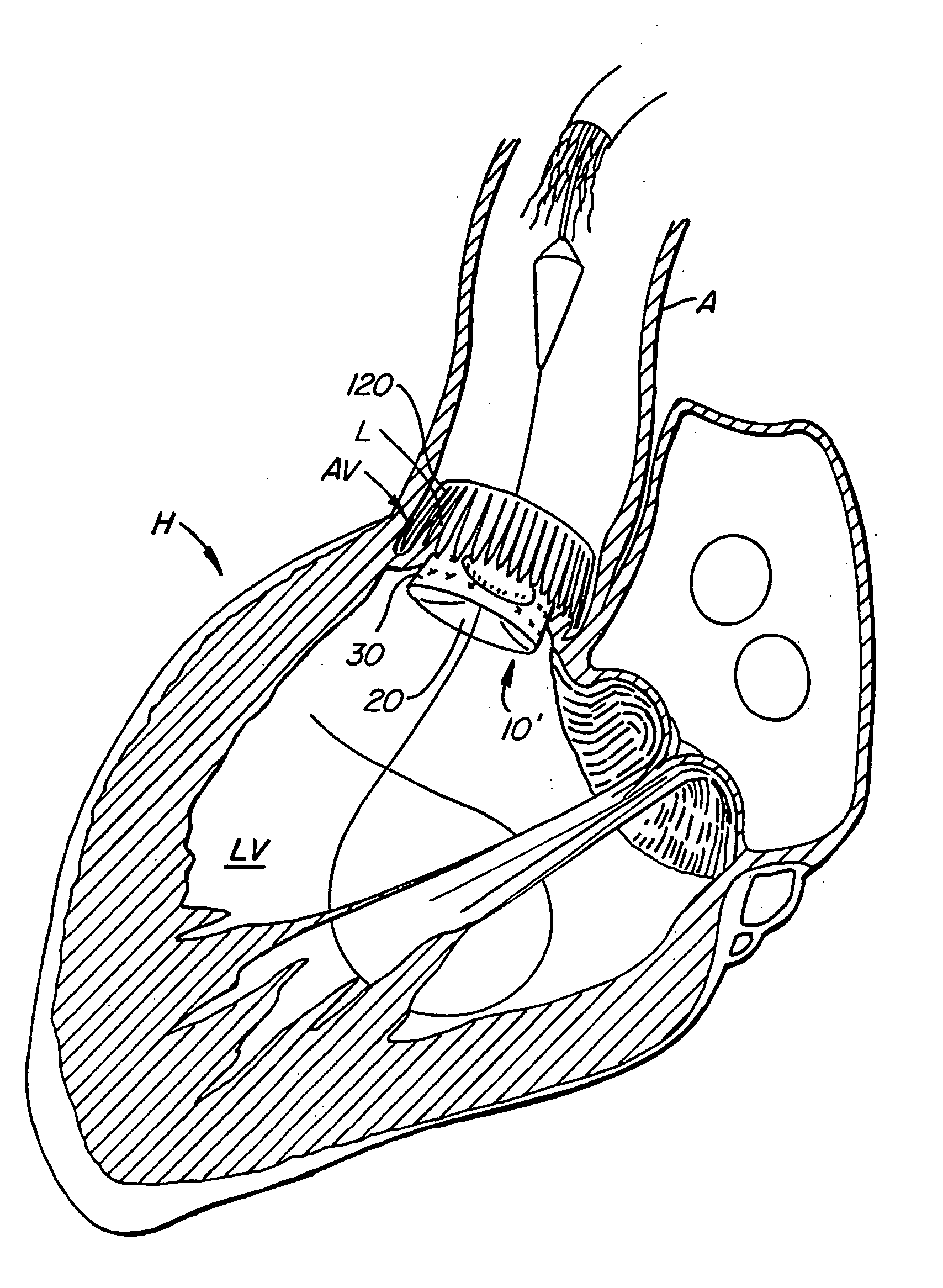
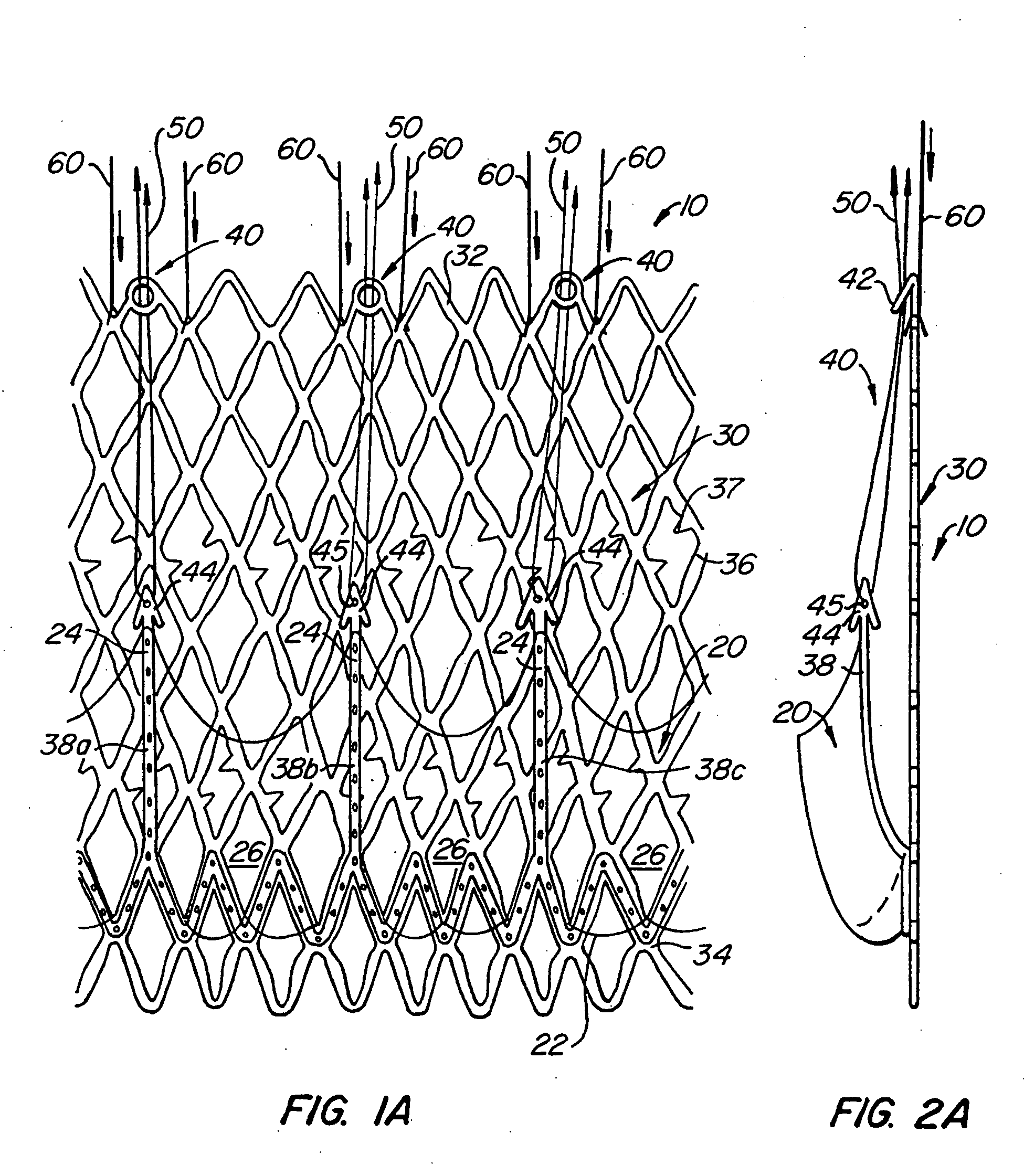
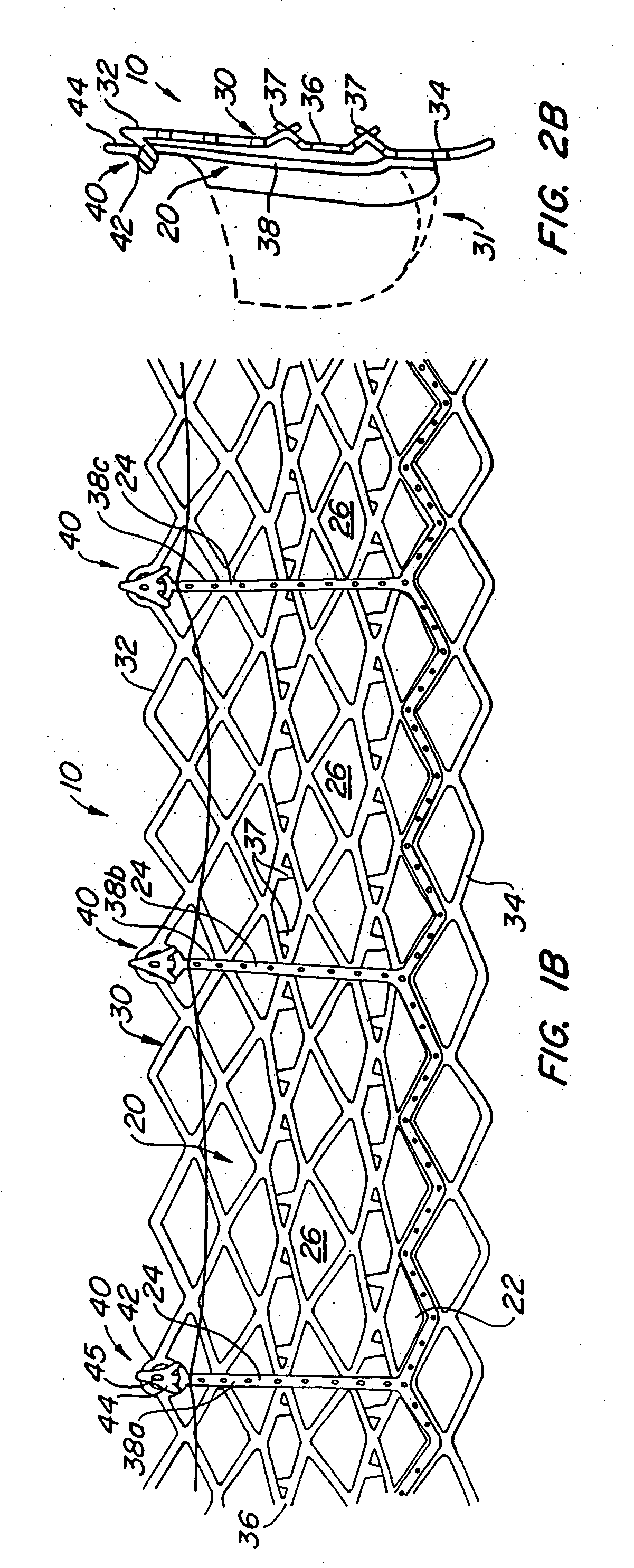
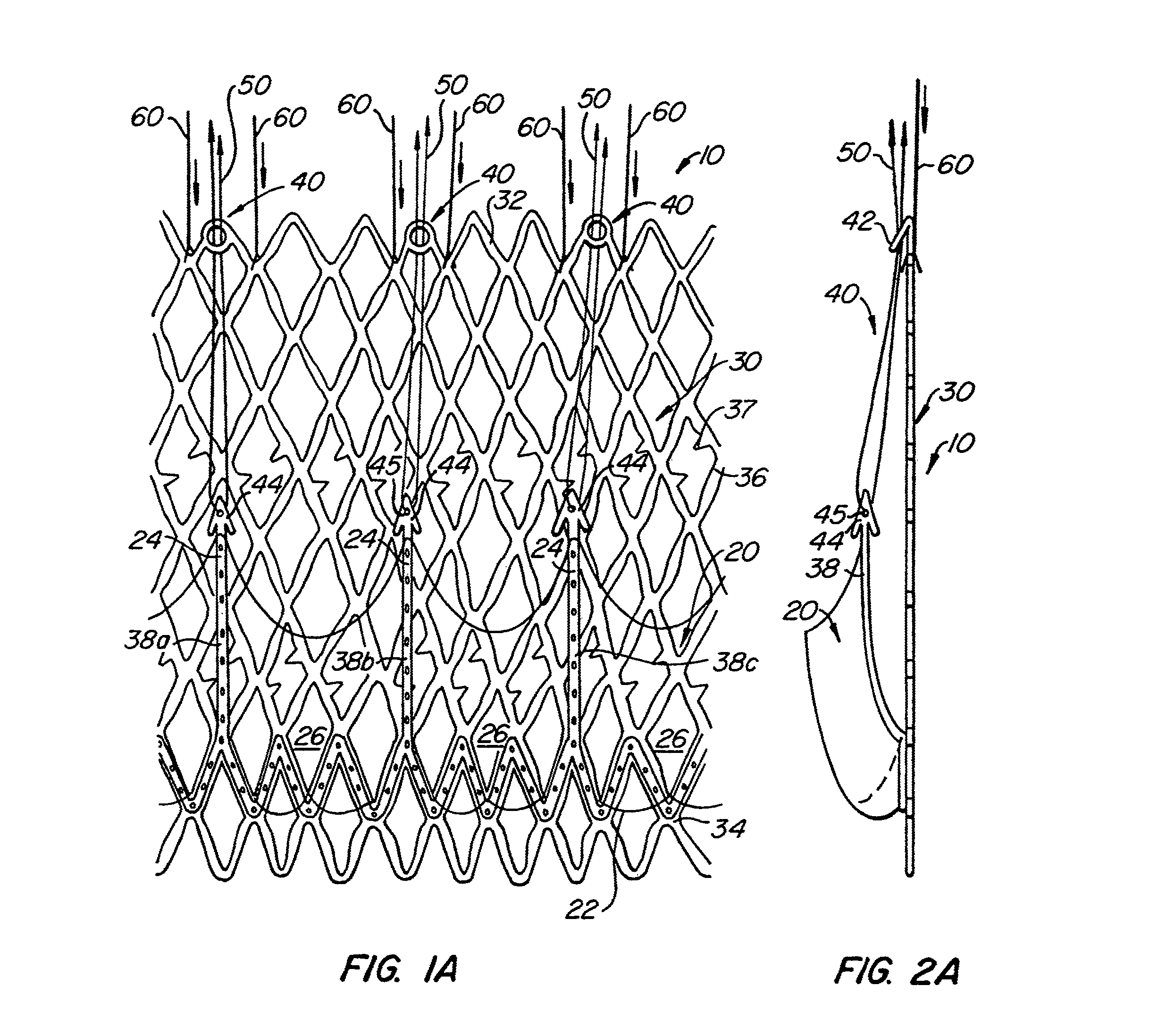
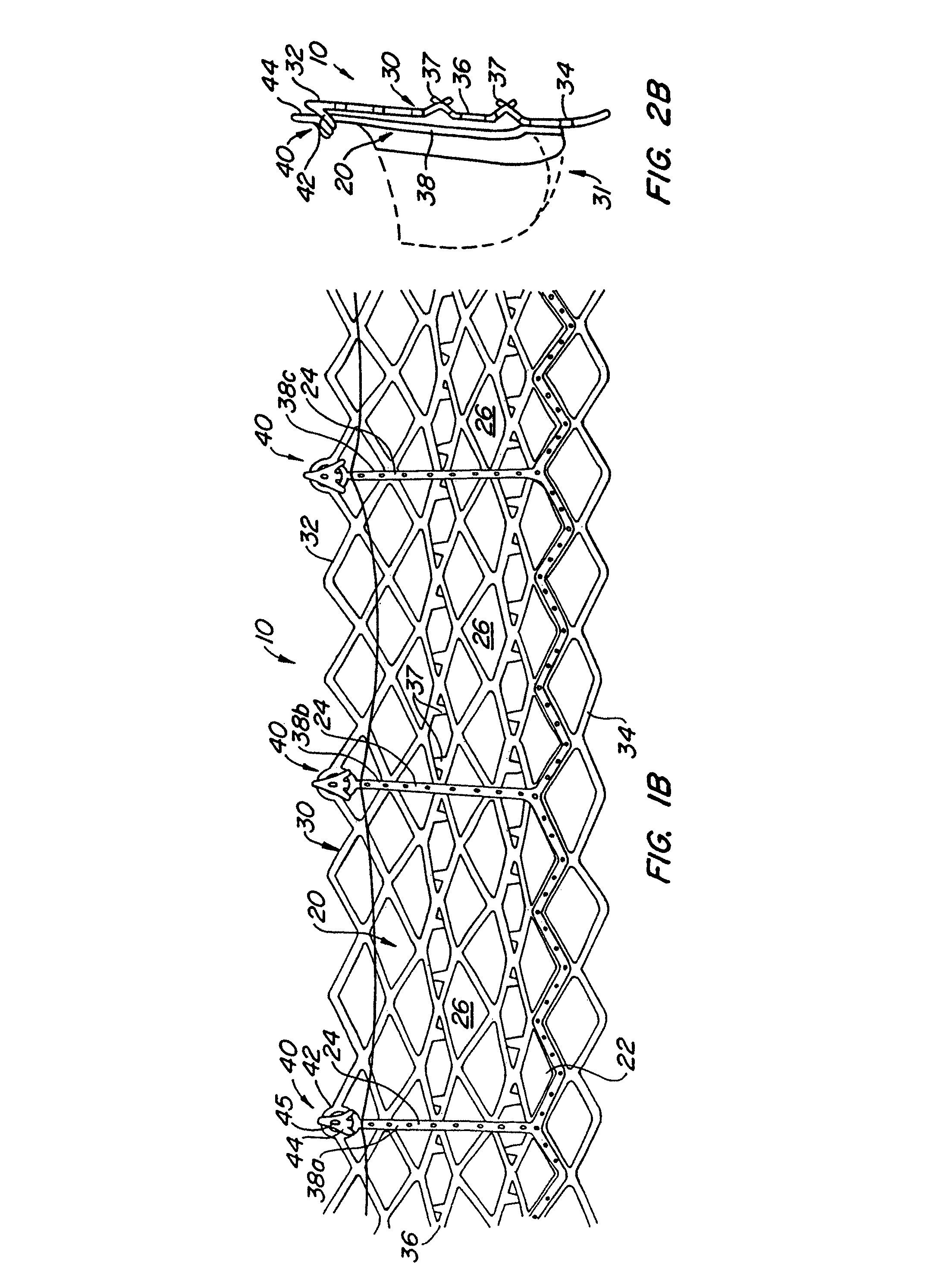
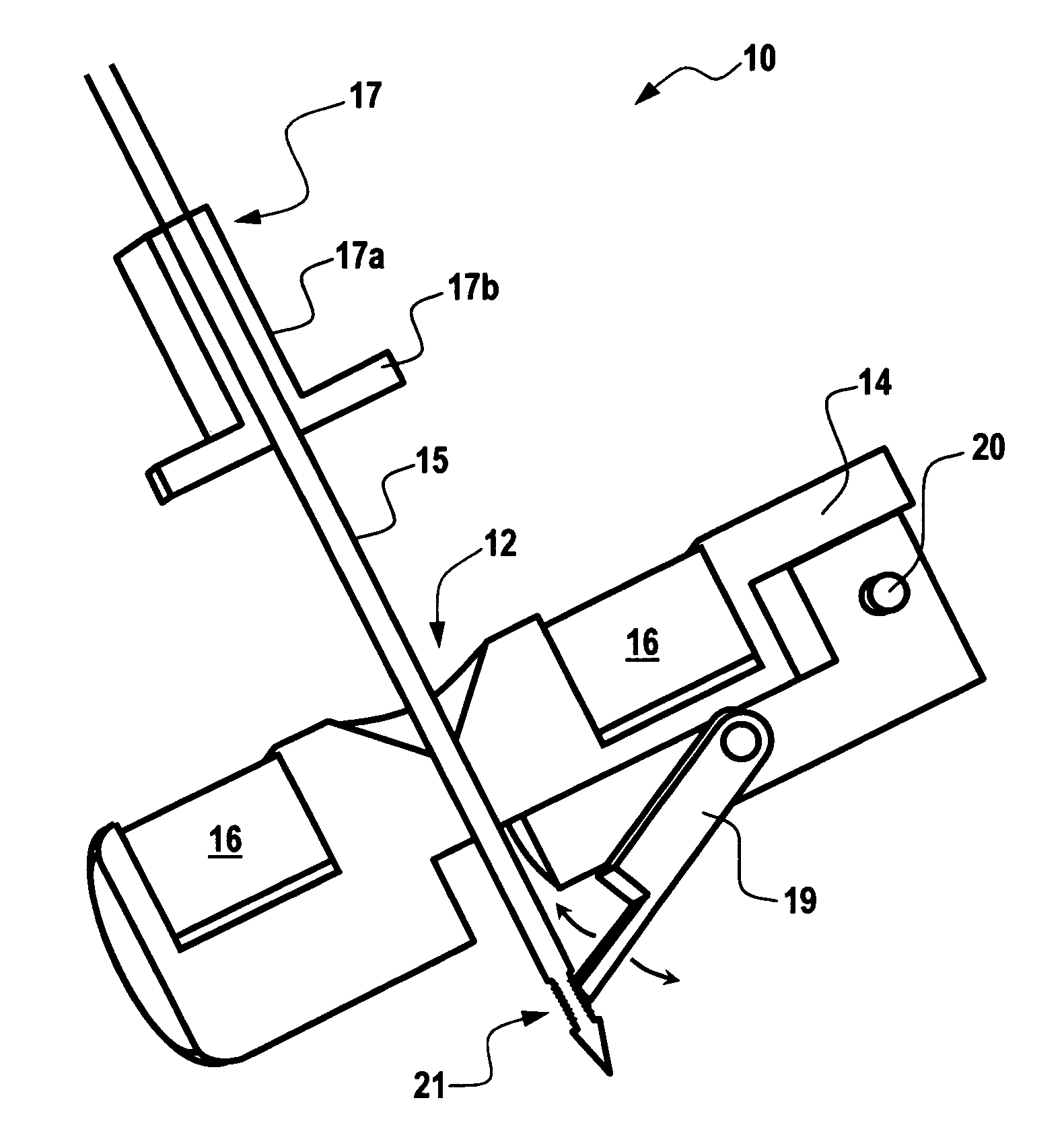
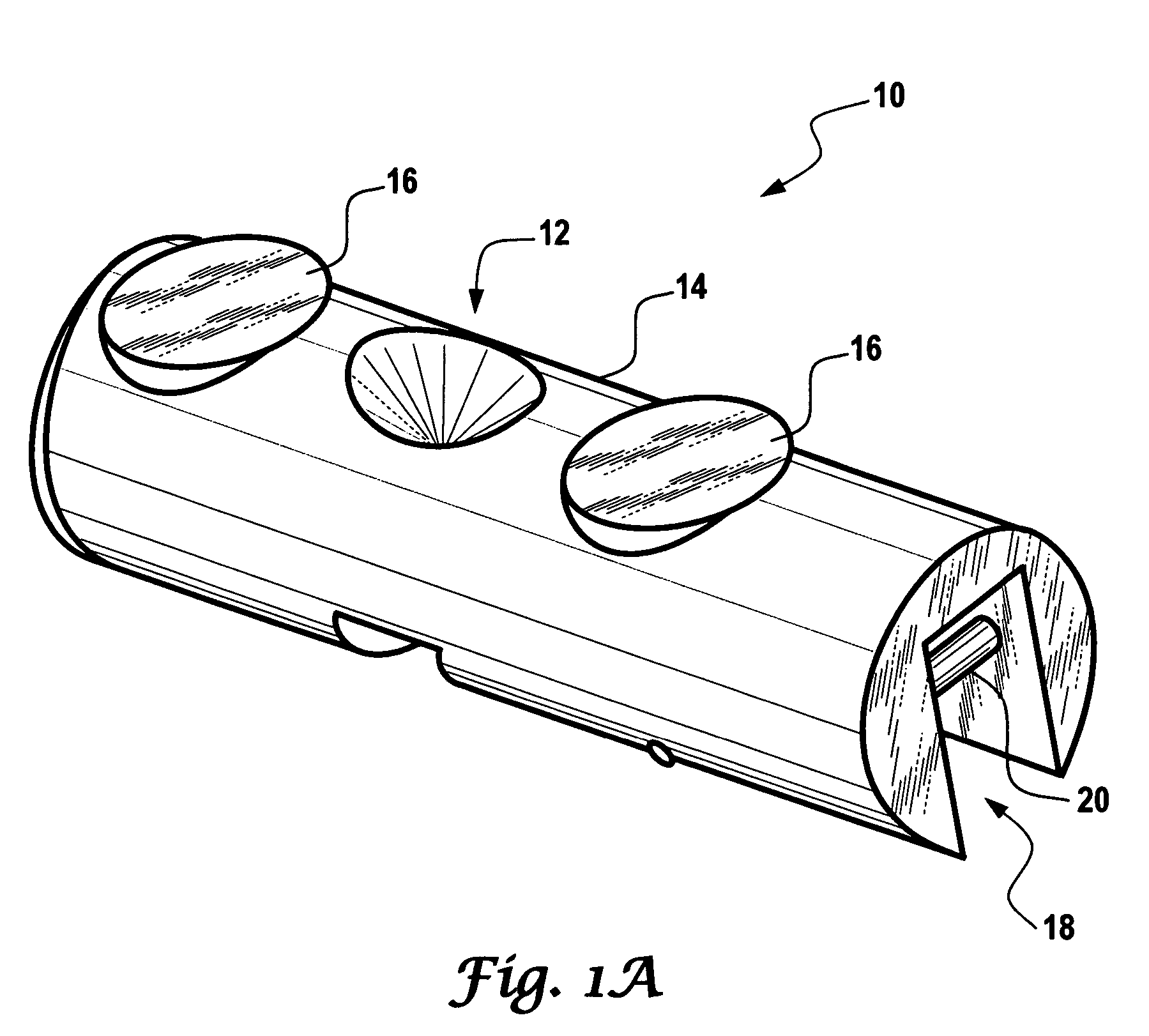
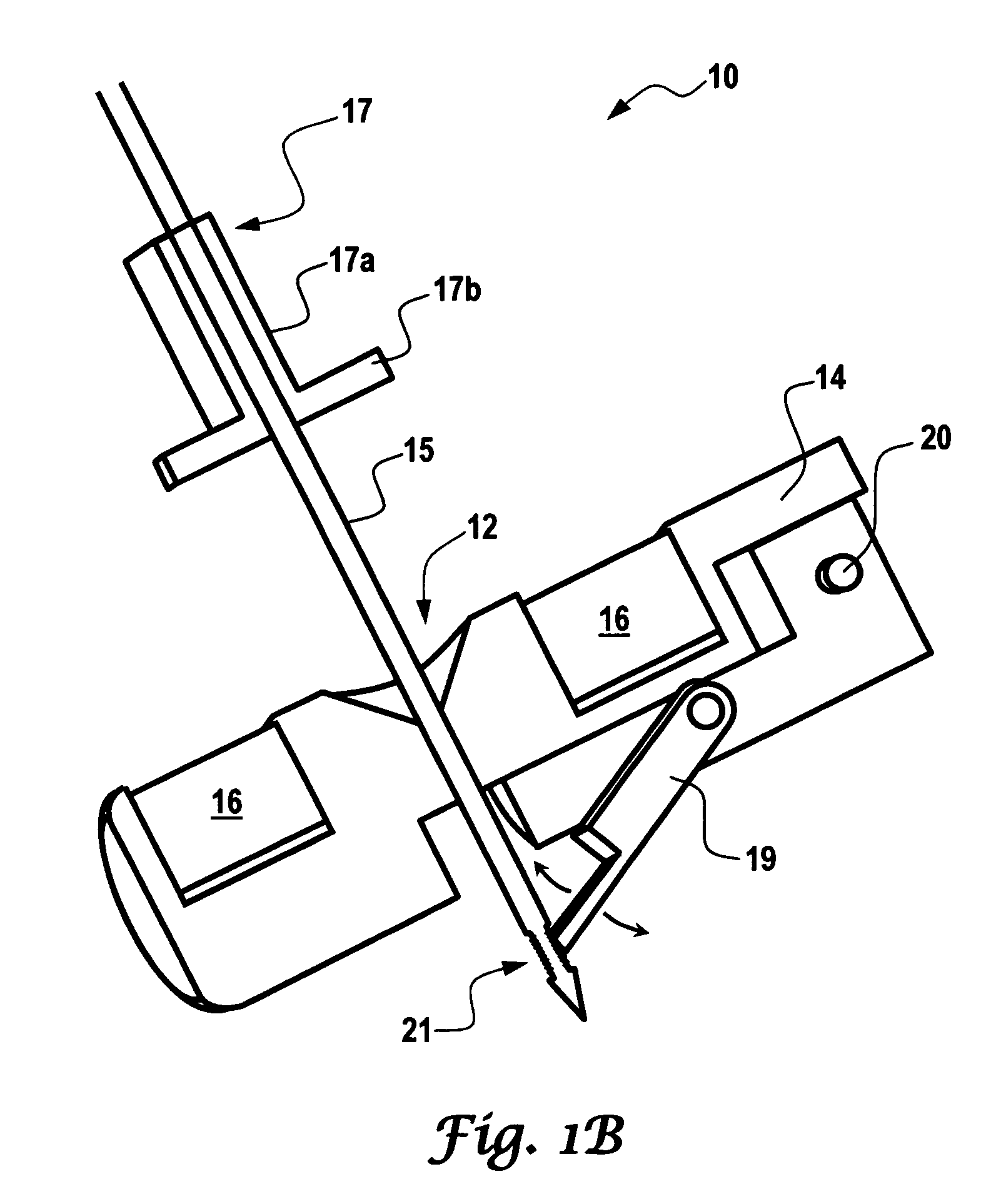
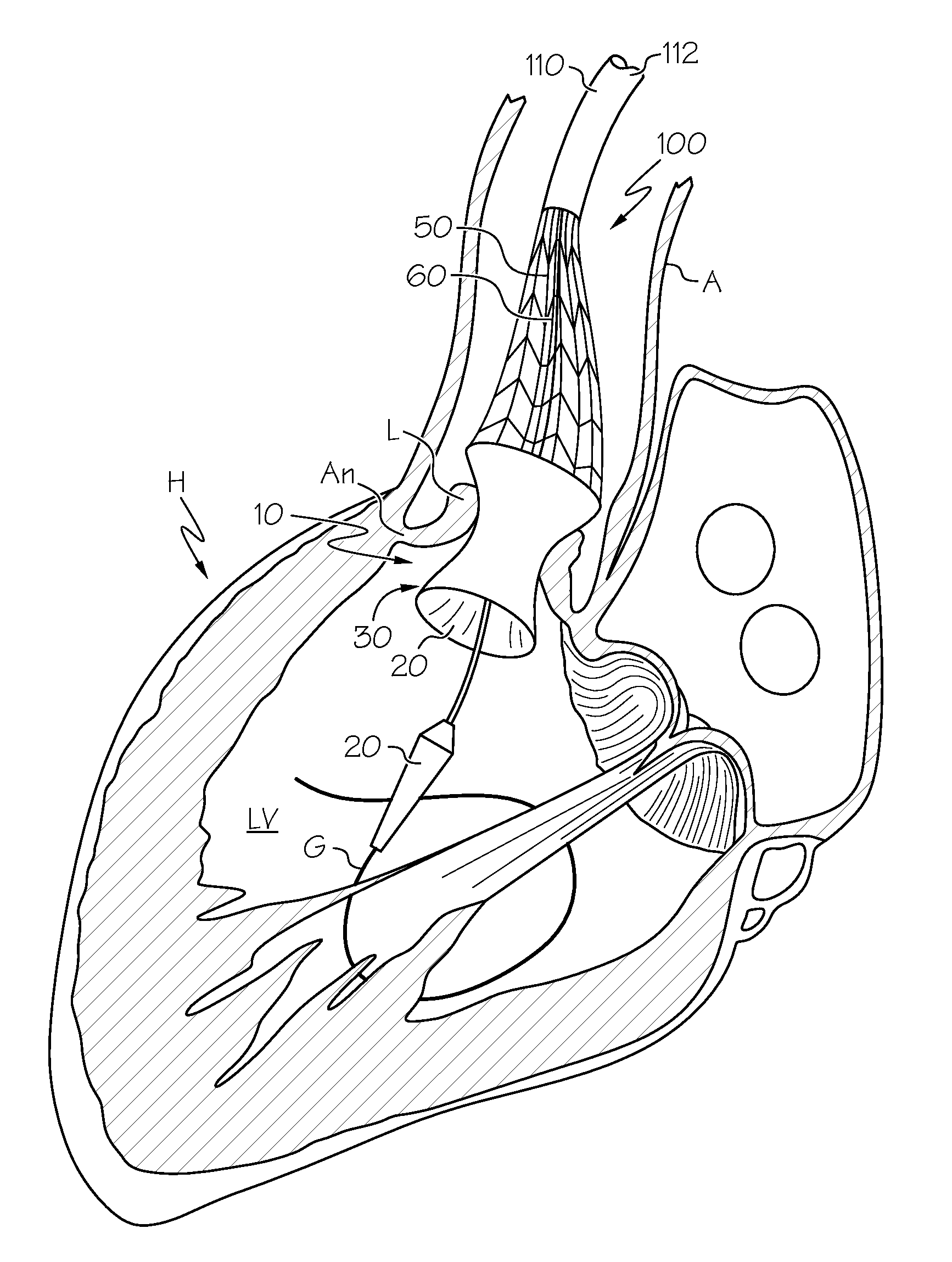
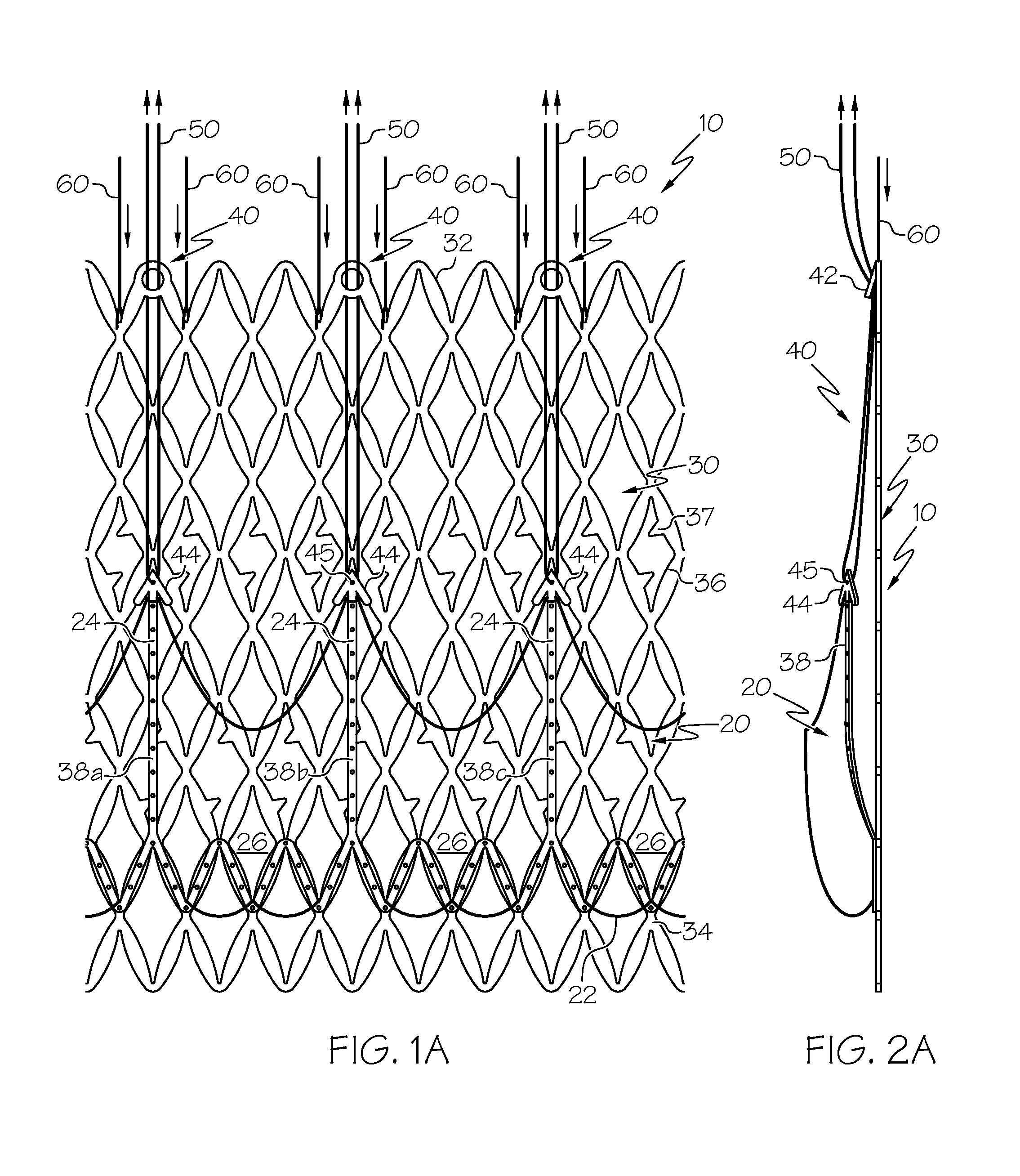
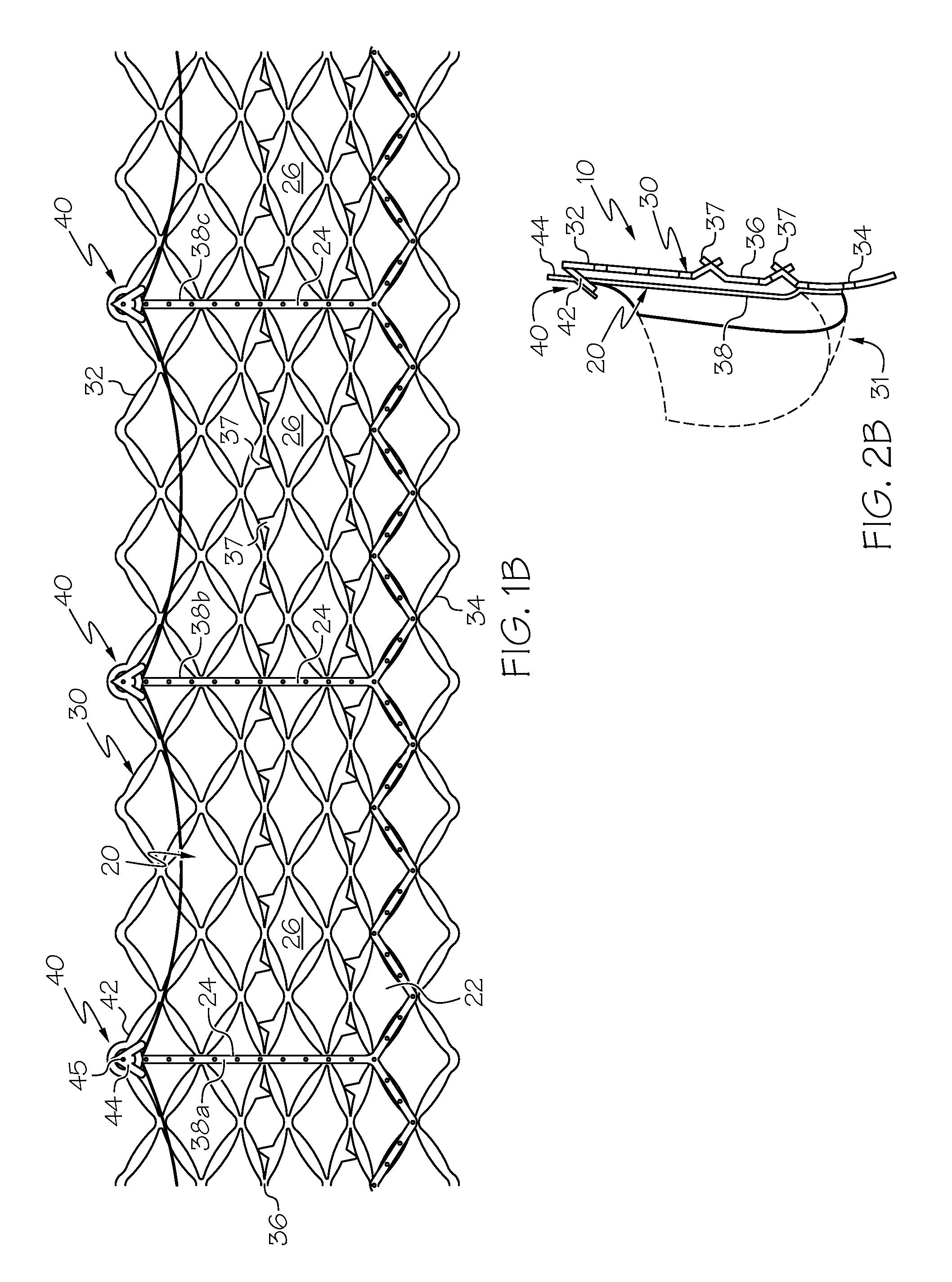
Repositionable heart valve and method
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Repositionable heart valve method
A method for percutaneously replacing a heart valve of a patient. In some embodiments the method includes the steps of percutaneously delivering a replacement valve and an expandable anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve in an unexpanded configuration; expanding the anchor to a deployed configuration in which the anchor contacts tissue at a first anchor site; repositioning the anchor to a second anchor site; and deploying the anchor at the second anchor site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
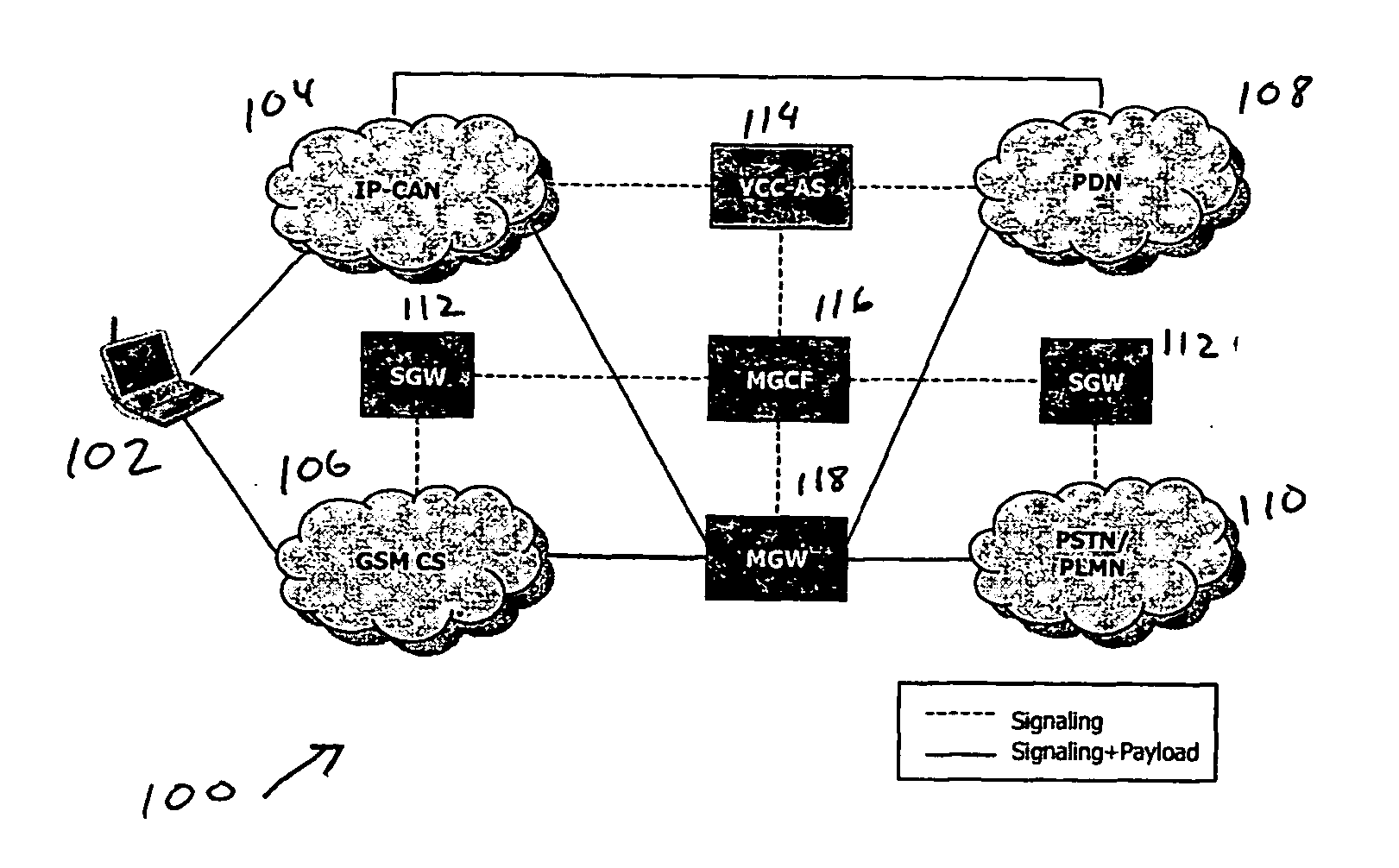
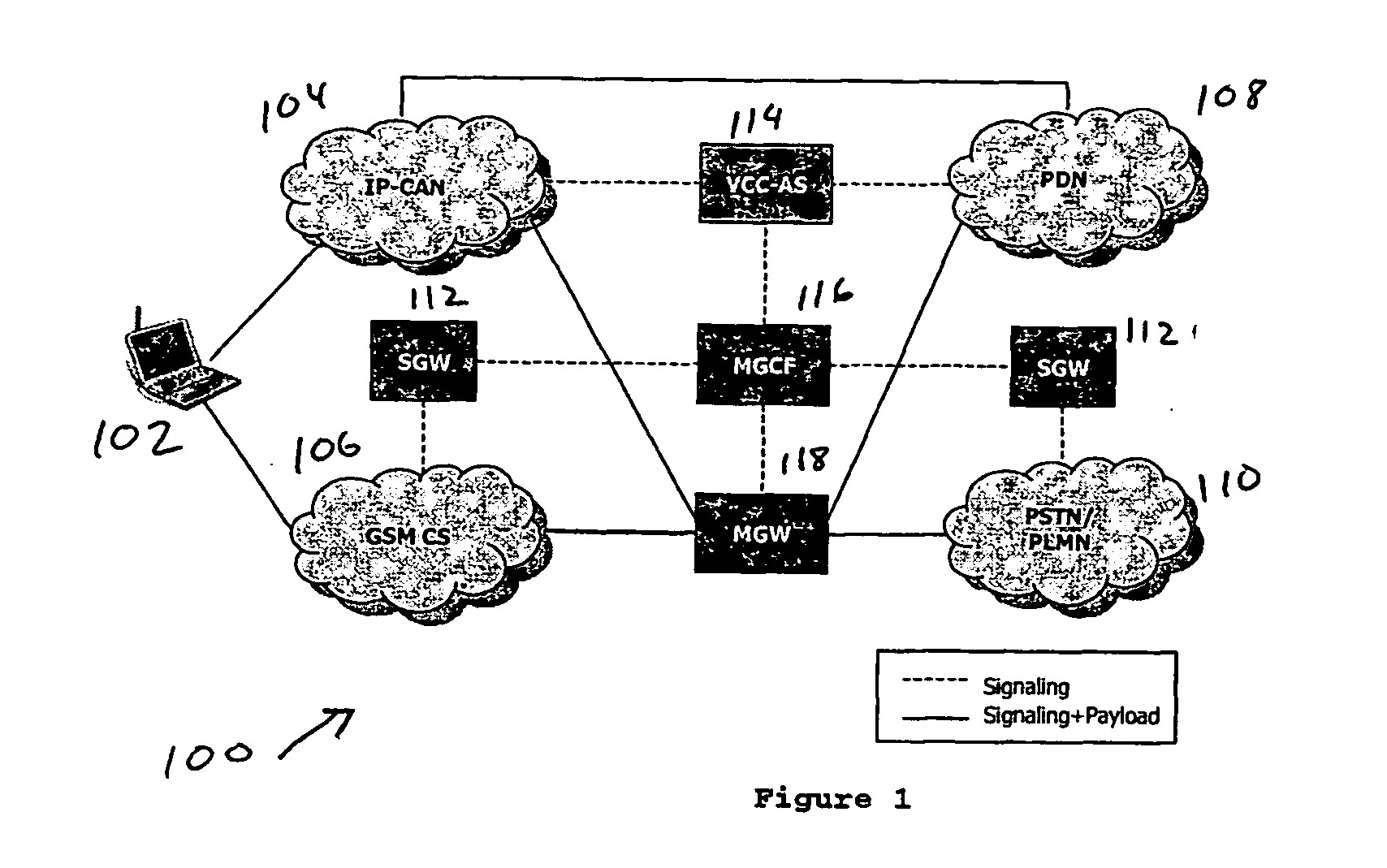
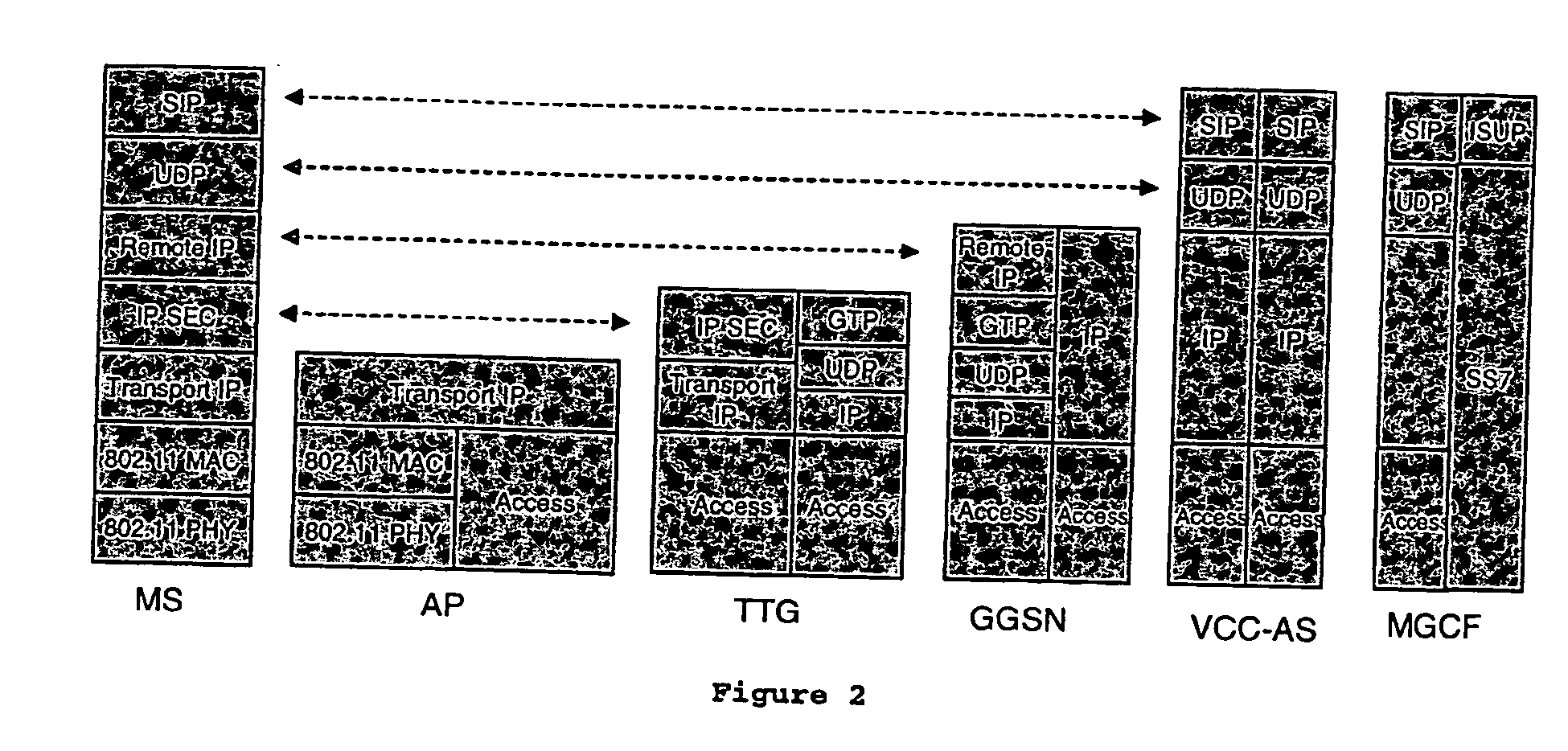
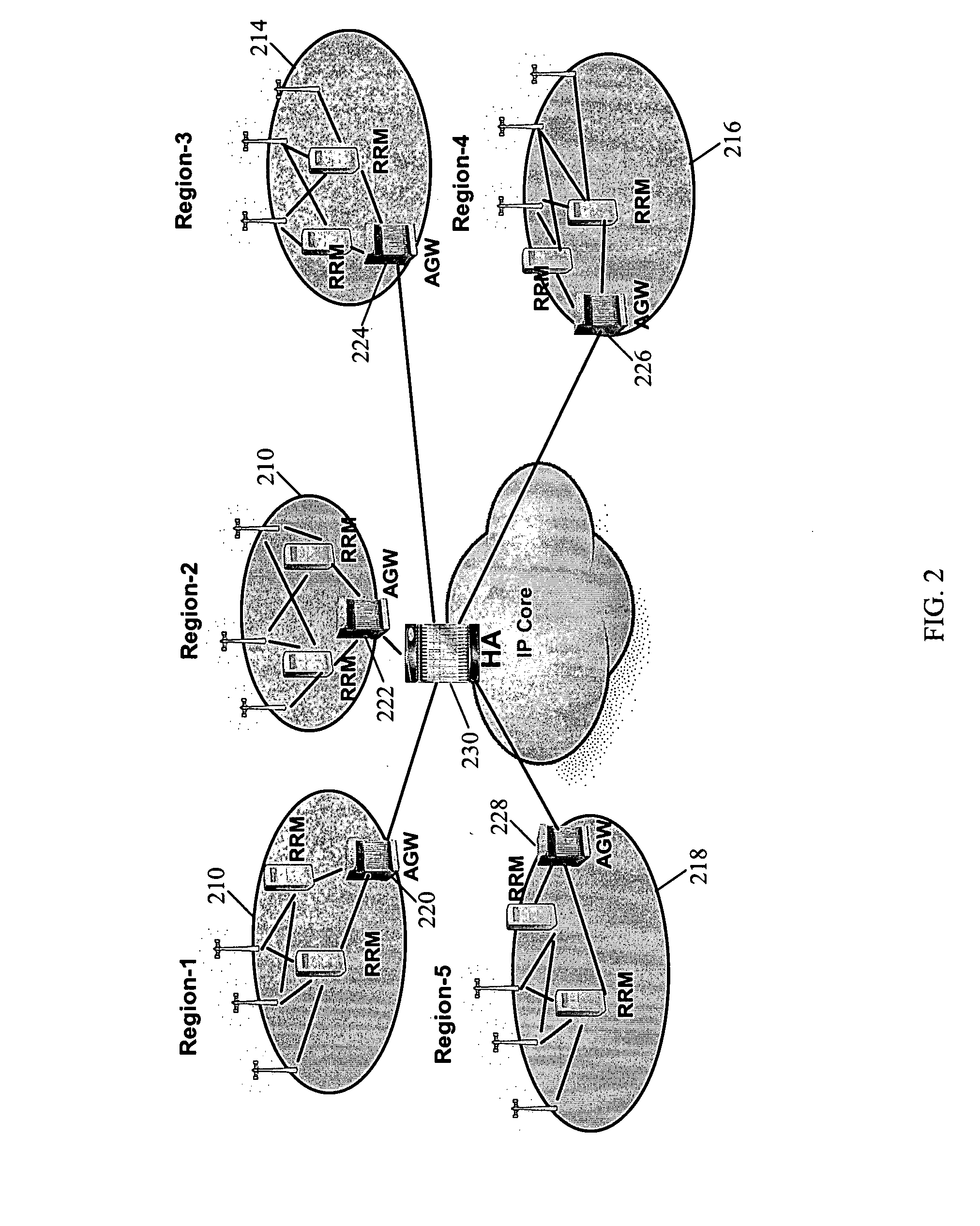
Voice call continuity application server between IP-CAN and CS networks
InactiveUS20070014281A1Accurate processingMultiplex system selection arrangementsConnection managementAccess networkApplication server
A system and method for continuous voice calls when a user switches between packet data and circuit switched access networks. In one example embodiment, the present innovations include an interworking system that supports voice call continuity for a user that moves between IP-CAN and CS networks (e.g., PSTN or GSM). In one example embodiment, the present innovations comprise a voice call continuity application server (VCC-AS) that serves as an anchor point for a voice call (i.e., it is the node from which a handover is initiated) and controls and handles voice calls to and from the user equipment (UE) regardless of the access network.
Owner:INTELLINET TECH
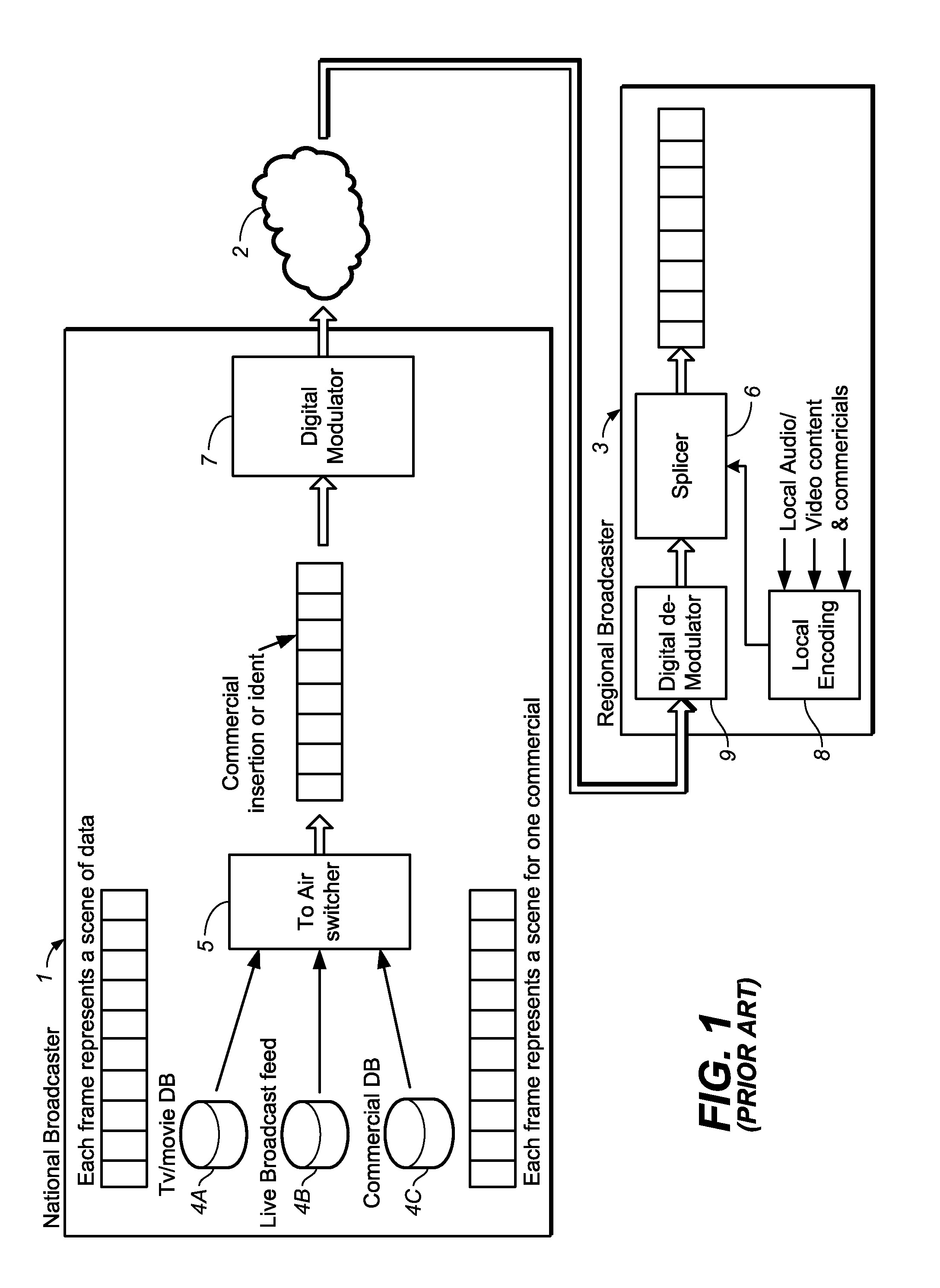
System and method for sampling based elimination of duplicate data
ActiveUS20070255758A1Overcome disadvantagesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionData setFile comparison
A technique for eliminating duplicate data is provided. Upon receipt of a new data set, one or more anchor points are identified within the data set. A bit-by-bit data comparison is then performed of the region surrounding the anchor point in the received data set with the region surrounding an anchor point stored within a pattern database to identify forward / backward delta values. The duplicate data identified by the anchor point, forward and backward delta values is then replaced in the received data set with a storage indicator.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Process for anchoring connecting elements in a material with pores or cavities and connecting elements therefor
InactiveUS6913666B1Easy to reachReduce disadvantagesRivetsCylinder headsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
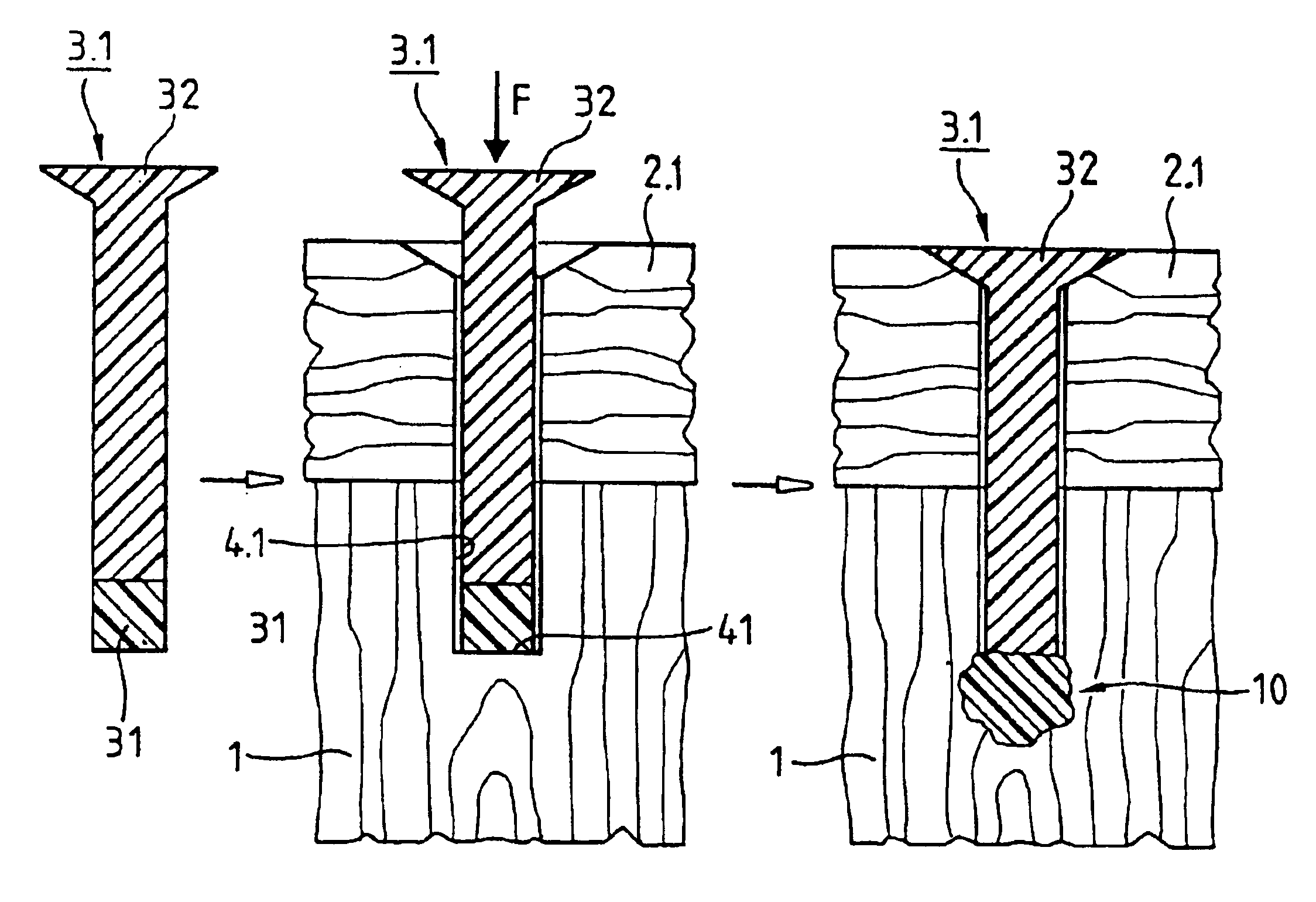
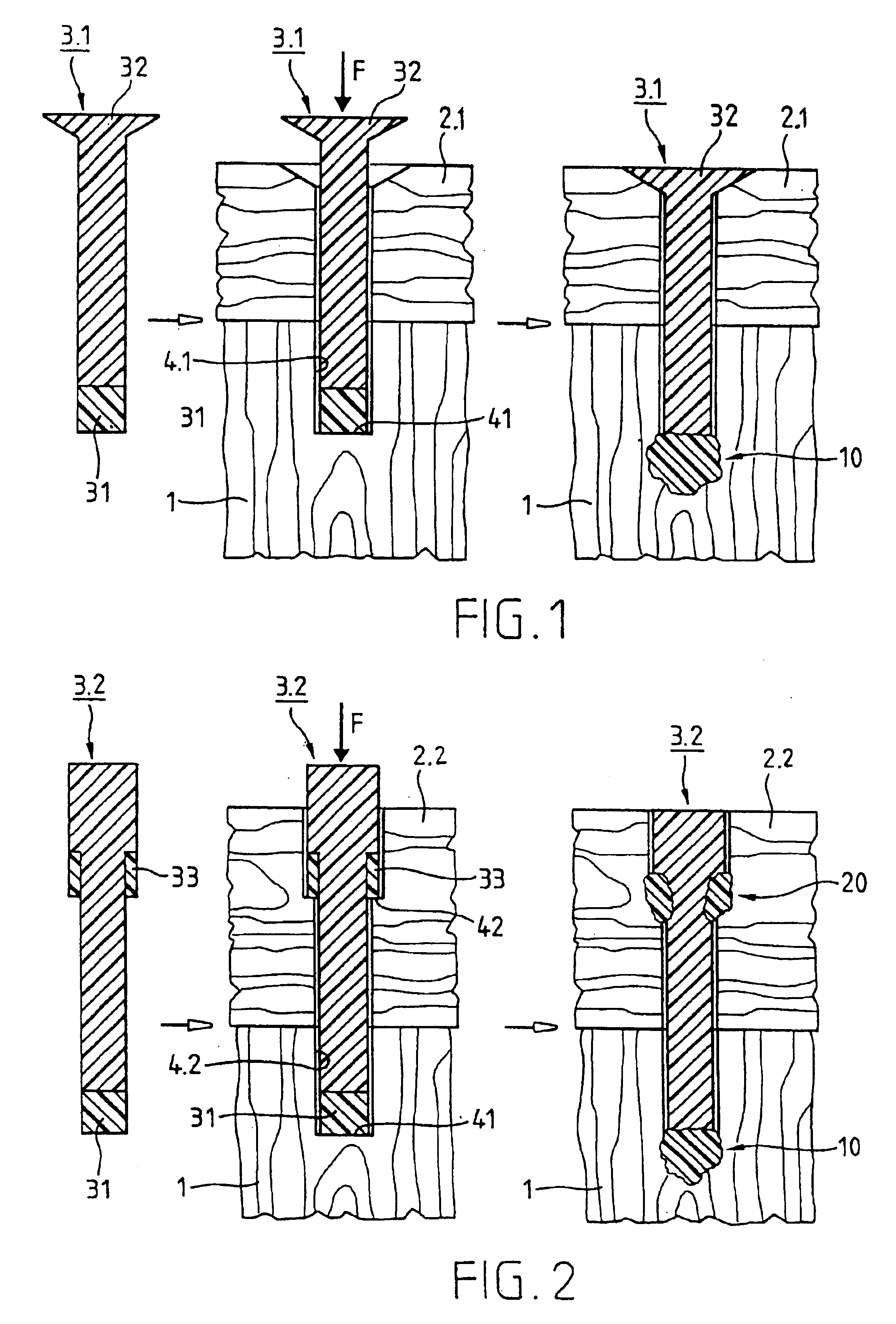
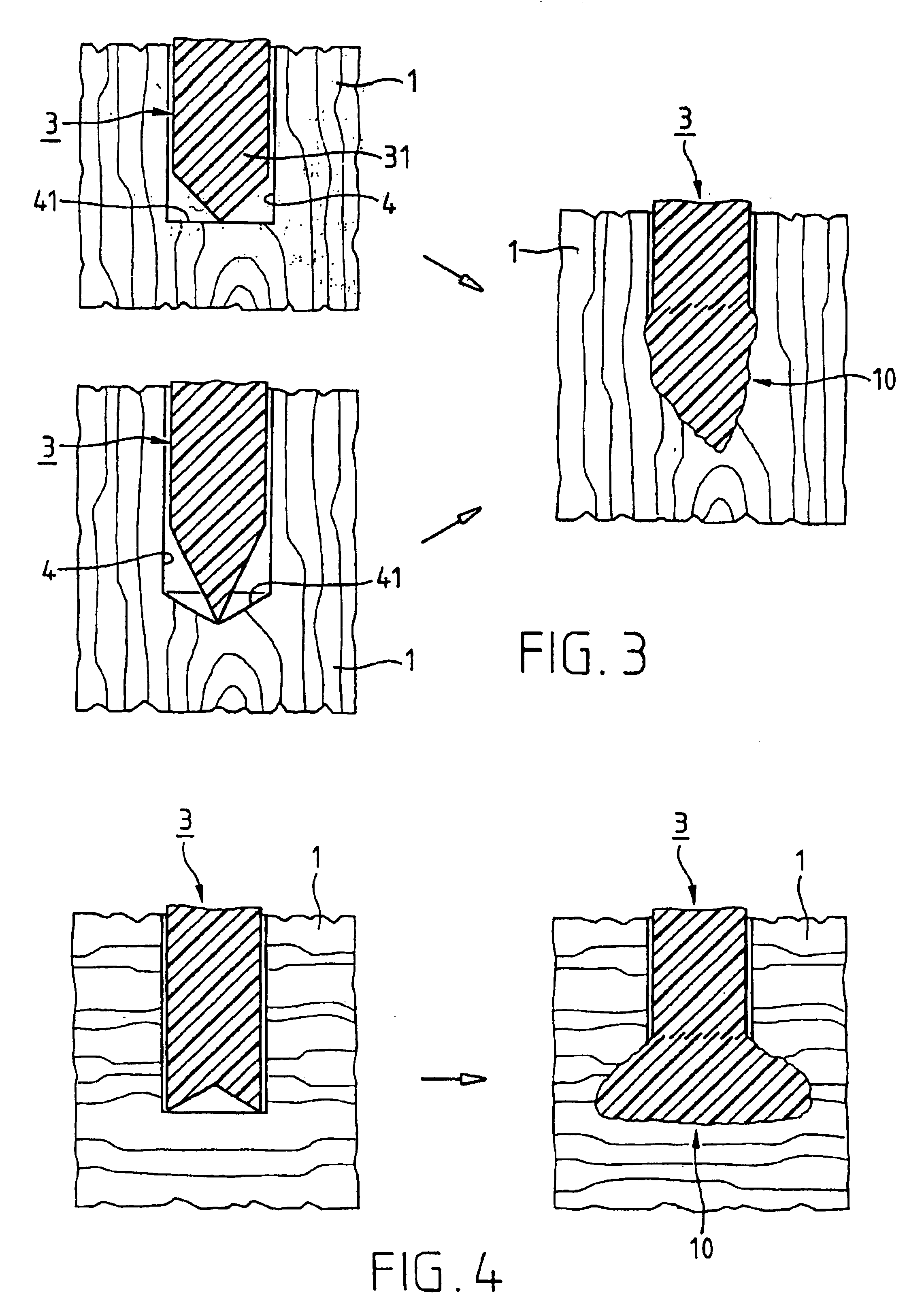
A joining pin (3.2) with which two parts (1 and 2) made from a porous material, particularly wood or a wood-like material, are to be joined together, is anchored in the porous material at predetermined anchoring points (31, 33). For this purpose, a bore (4.2) with a closed inner end (41) is made in the parts (1 and 2). The shape of this bore (4.2) is so matched to the joining pin (3.2) that it can be introduced substantially without force expenditure into the bore and is positionable in a first position. At least one predetermined anchoring point (31, 33) between the joining pin (3.2) and the wall of the bore (4.2) is formed when pressure is built up by pressing the joining pin (3.2) with a pressing force (F) more deeply into the bore to a second position. Energy is supplied in a planned manner to the joining pin (3.2) so that at the predetermined anchoring points (31, 33) the thermoplastic material of the joining pin (3.2) is plasticized. The locally plasticized plastic material is pressed by the local pressure into the porous material of the parts and forms local, macroscopic anchors (10, 20). The joining pin (3.2) is, e.g., made entirely from a thermoplastic material and the energy for plasticizing is supplied thereto by ultrasonic vibration.
Owner:WOODWELDING
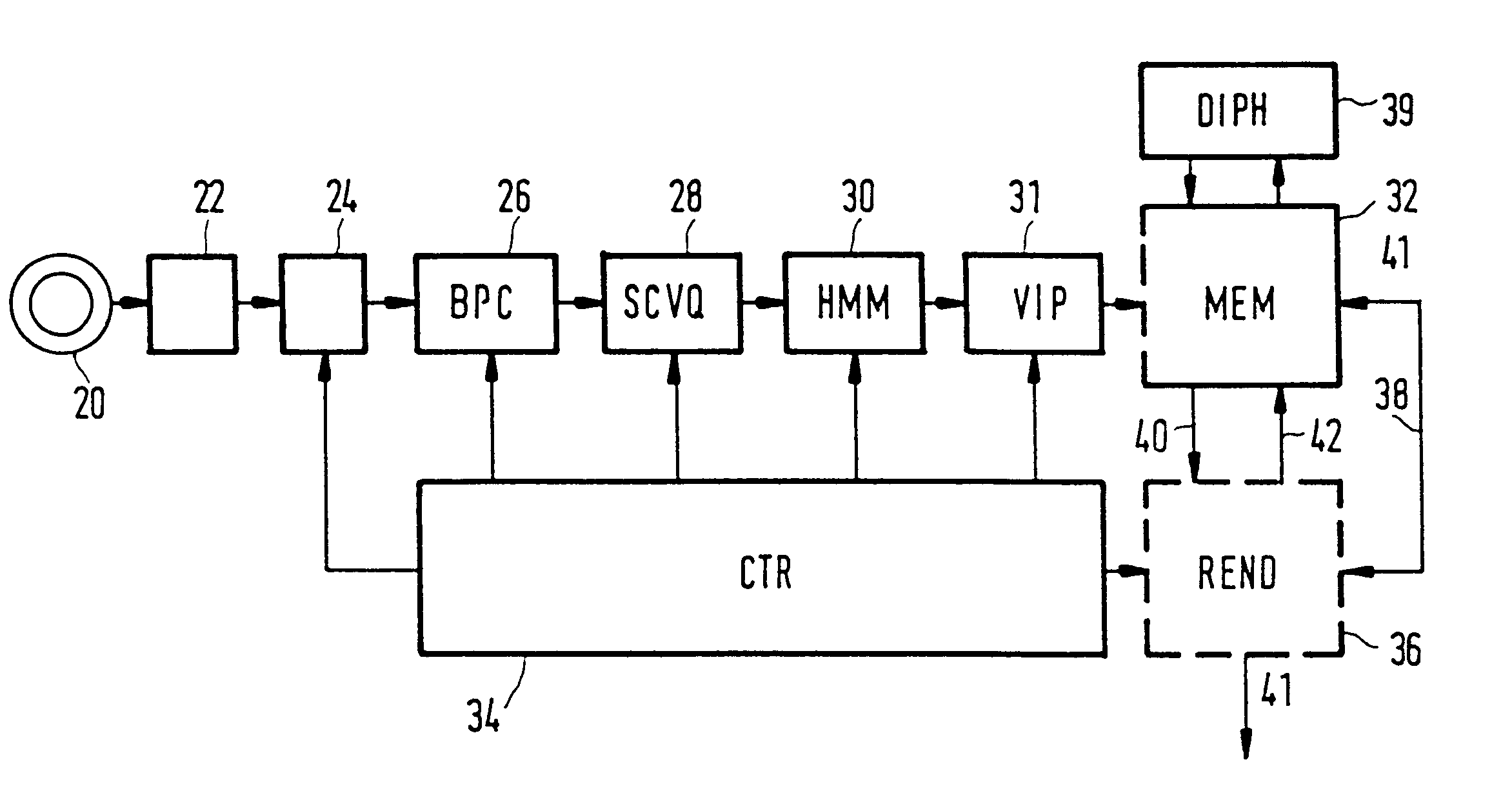
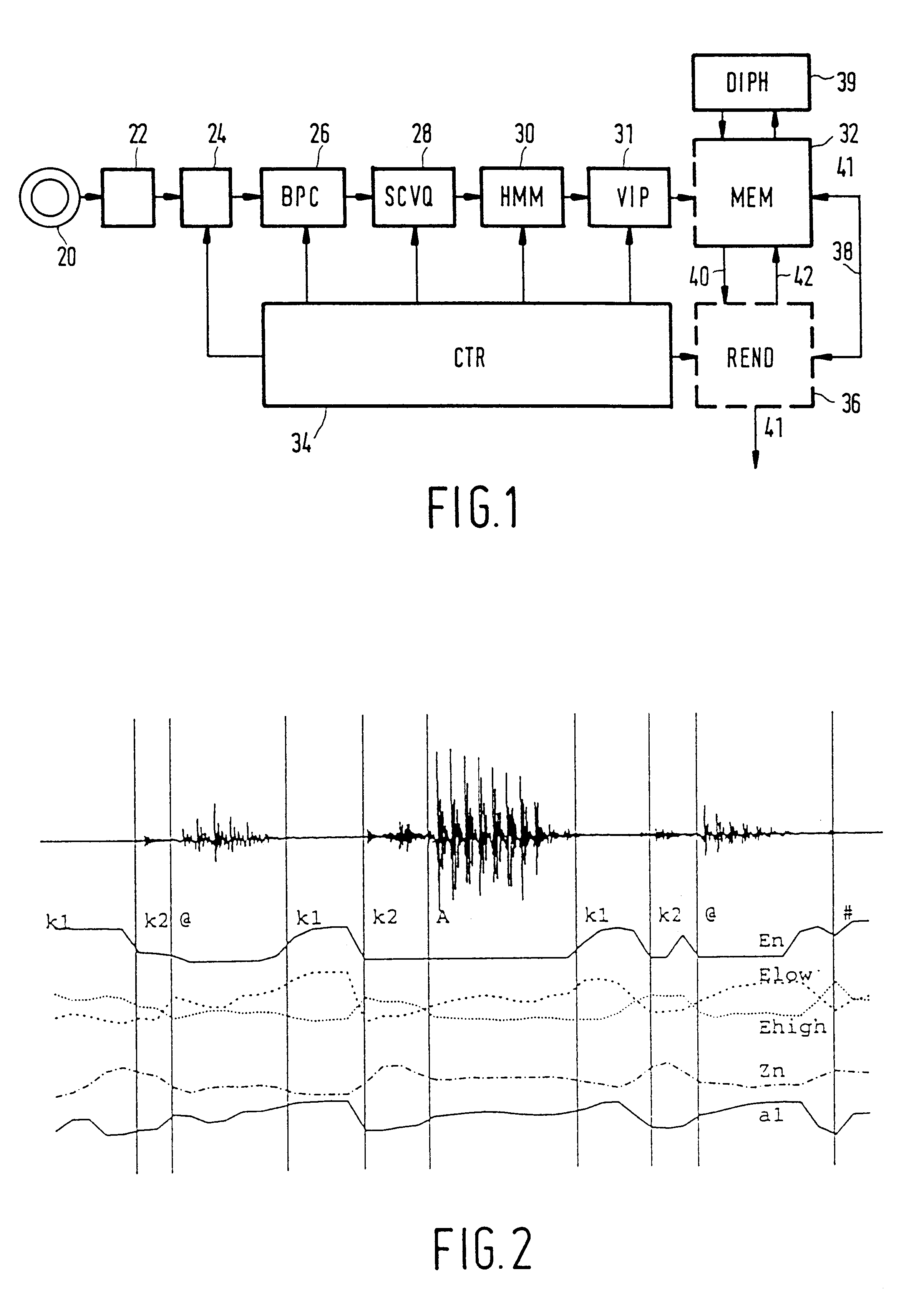
Method and apparatus for automatic speech segmentation into phoneme-like units for use in speech processing applications, and based on segmentation into broad phonetic classes, sequence-constrained vector quantization and hidden-markov-models
InactiveUS6208967B1Straightforward and inexpensiveDigital computer detailsBiological modelsAutomatic speech segmentationSpoken language
For machine segmenting of speech, first utterances from a database of known spoken words are classified and segmented into three broad phonetic classes (BPC) voiced, unvoiced, and silence. Next, using preliminary segmentation positions as anchor points, sequence-constrained vector quantization is used for further segmentation into phoneme-like units. Finally, exact tuning to the segmented phonemes is done through Hidden-Markov Modelling and after training a diphone set is composed for further usage.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
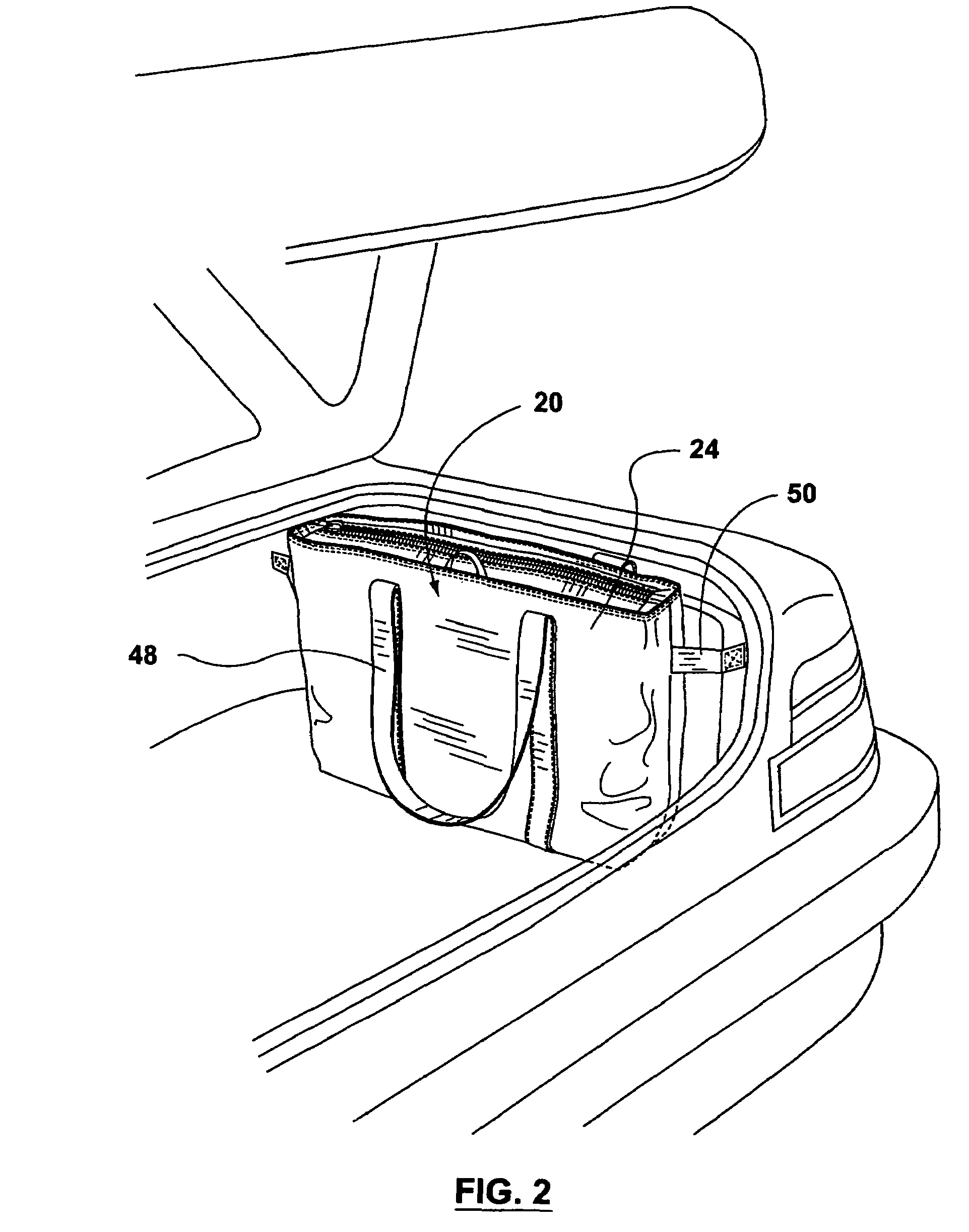
Insulated bag with lifting apparatus
A soft sided insulated cooler bag has a base and side panels. The base includes a rigid or semi-rigid reinforcement or batten that serve to provide a relatively hard or stiff edge about which the bag can be panel folded over on itself. The upper edge of the bag has a length that is as great as half the periphery of the bottom panel. The bag can be collapsed to a flat position and then panel folded to a storage position. Retainers are provided to keep the bag in the storage position. The bag has lifting apparatus, which may be strap. The straps may be anchored to the bag at a plurality of anchor points, some of which may be sliding keepers, such that the handle can be moved to a first position in which the bag may be held in a predominantly up-and-down orientation, and to a second position in which the bag may be held in a predominantly flat or horizontal position.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INNOVATIONS
Surgical anchor and system
InactiveUS20050165449A1Good flexibilityReduce morbiditySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsHuman bodyEngineering
The present invention is a device and system for manipulating a surgical tool at an intended location, e.g., a confined or inaccessible space, which includes a surgical anchor having at least one opening, wherein the opening provides a catch for a pin; and at least one anchor point to position and orient a surgical tool inside a human body. The apparatus and system of the present invention allows for the use of multiple intra-abdominal surgical tools inserted through a single incision.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Surgical anchor and system
InactiveUS7429259B2Good flexibilityReduce morbiditySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsEngineeringSingle incision
The present invention is a device and system for manipulating a surgical tool at an intended location, e.g., a confined or inaccessible space, which includes a surgical anchor having at least one opening, wherein the opening provides a catch for a pin; and at least one anchor point to position and orient a surgical tool inside a human body. The apparatus and system of the present invention allows for the use of multiple intra-abdominal surgical tools inserted through a single incision.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
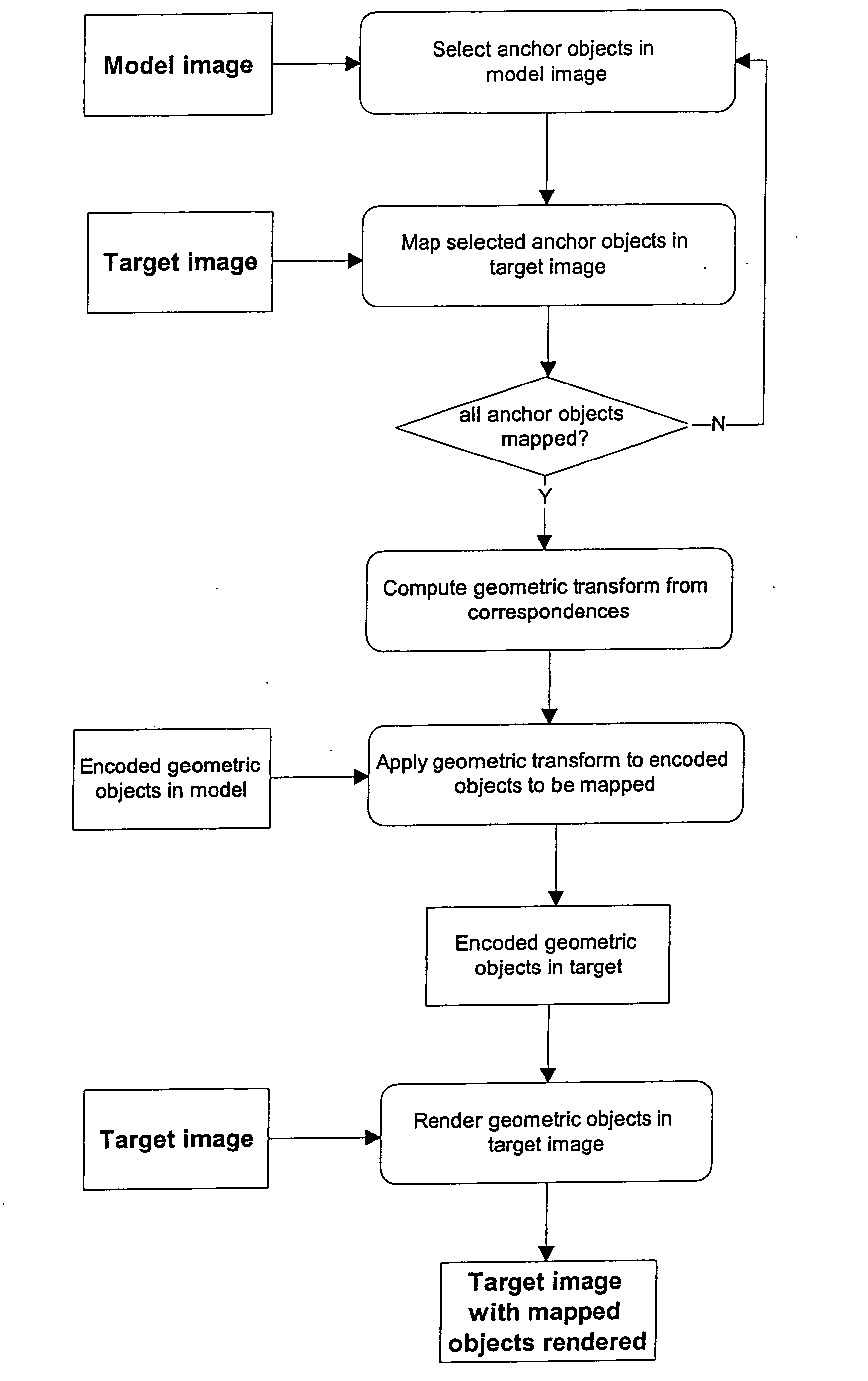
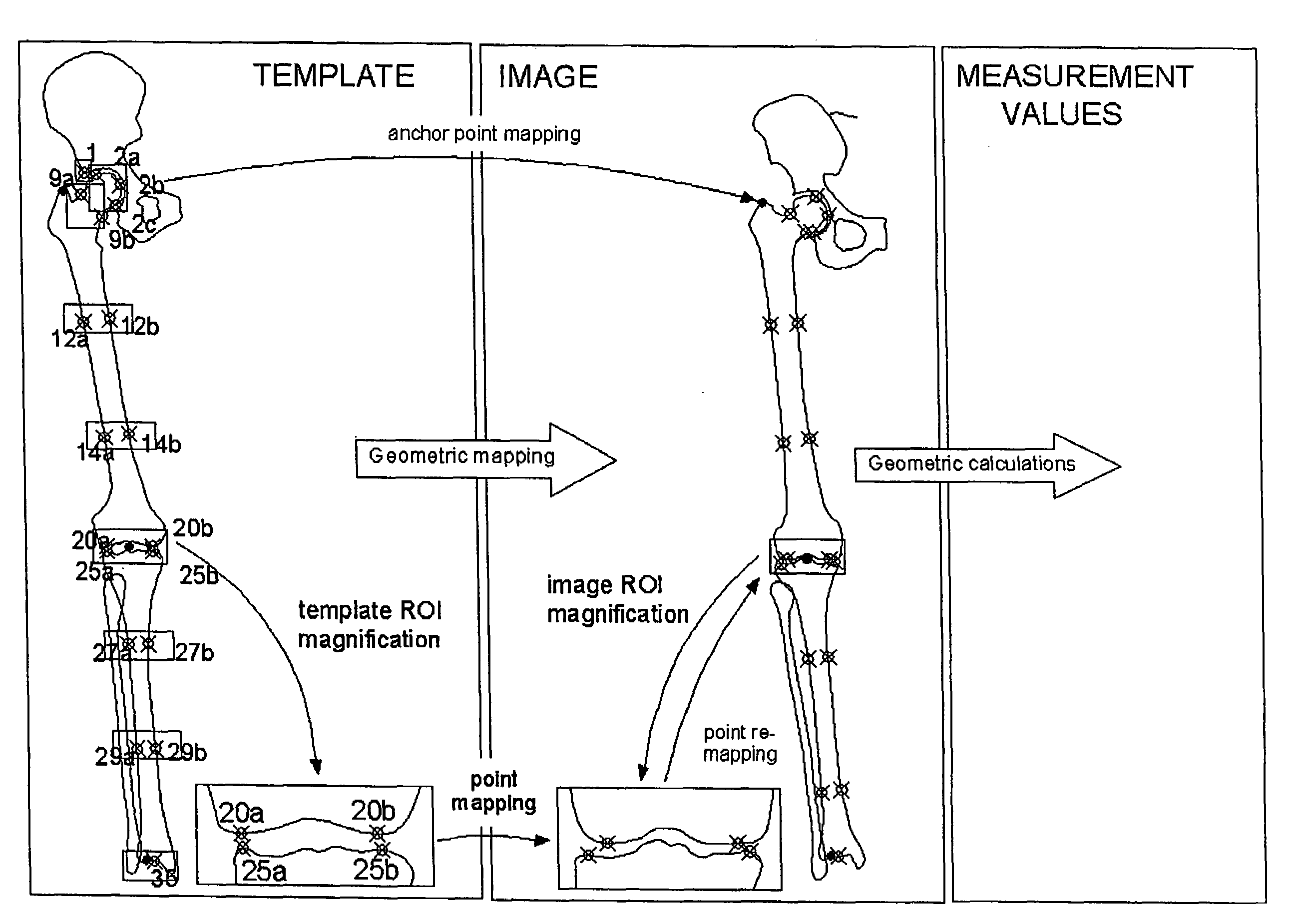
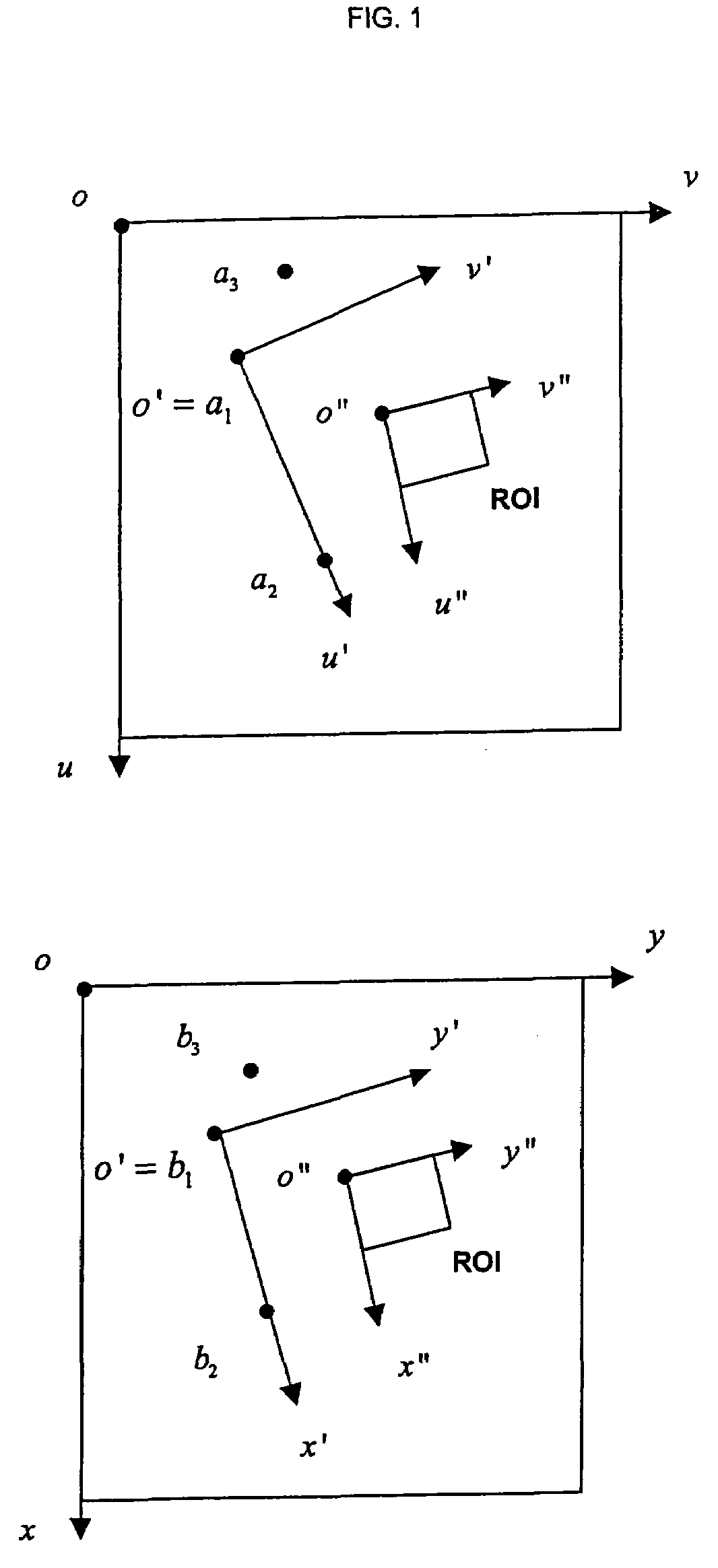
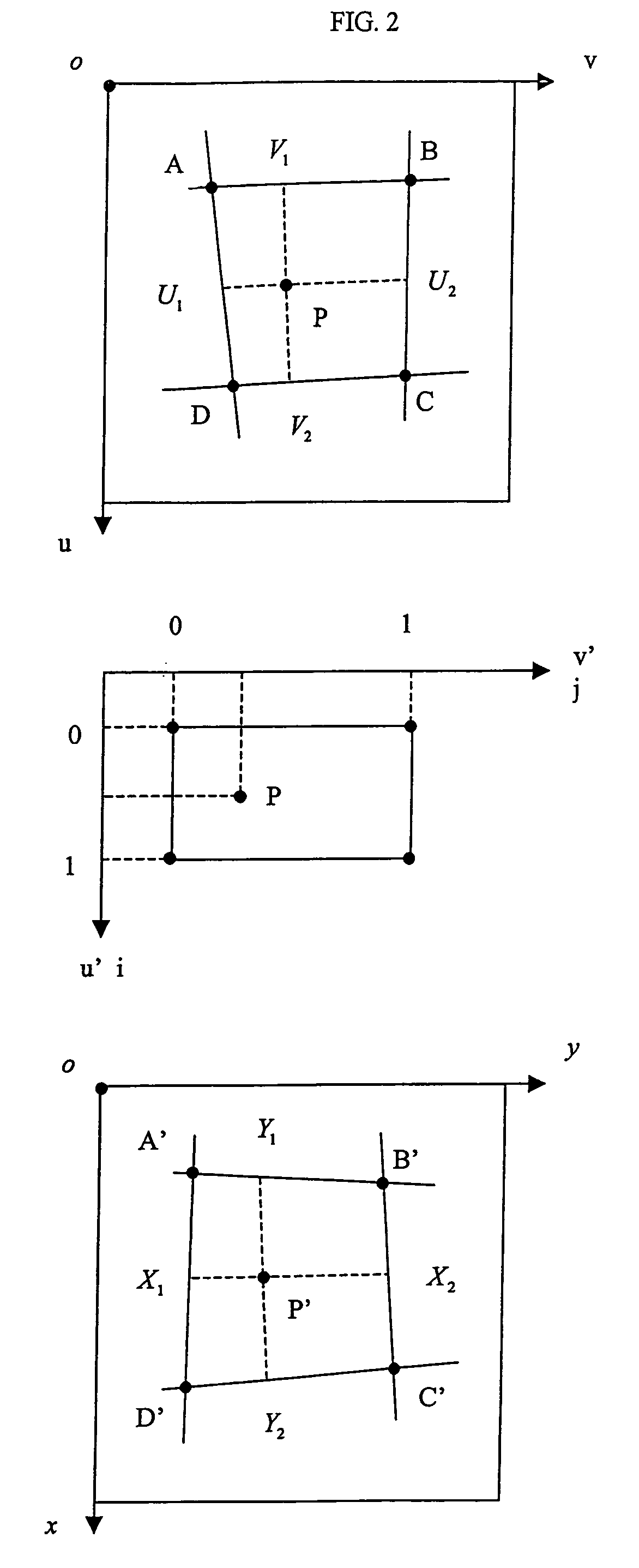
Method for automatically mapping of geometric objects in digital medical images
ActiveUS20050259882A1Precise positioningReduce the numberImage enhancementImage analysisMethod selectionDigital image
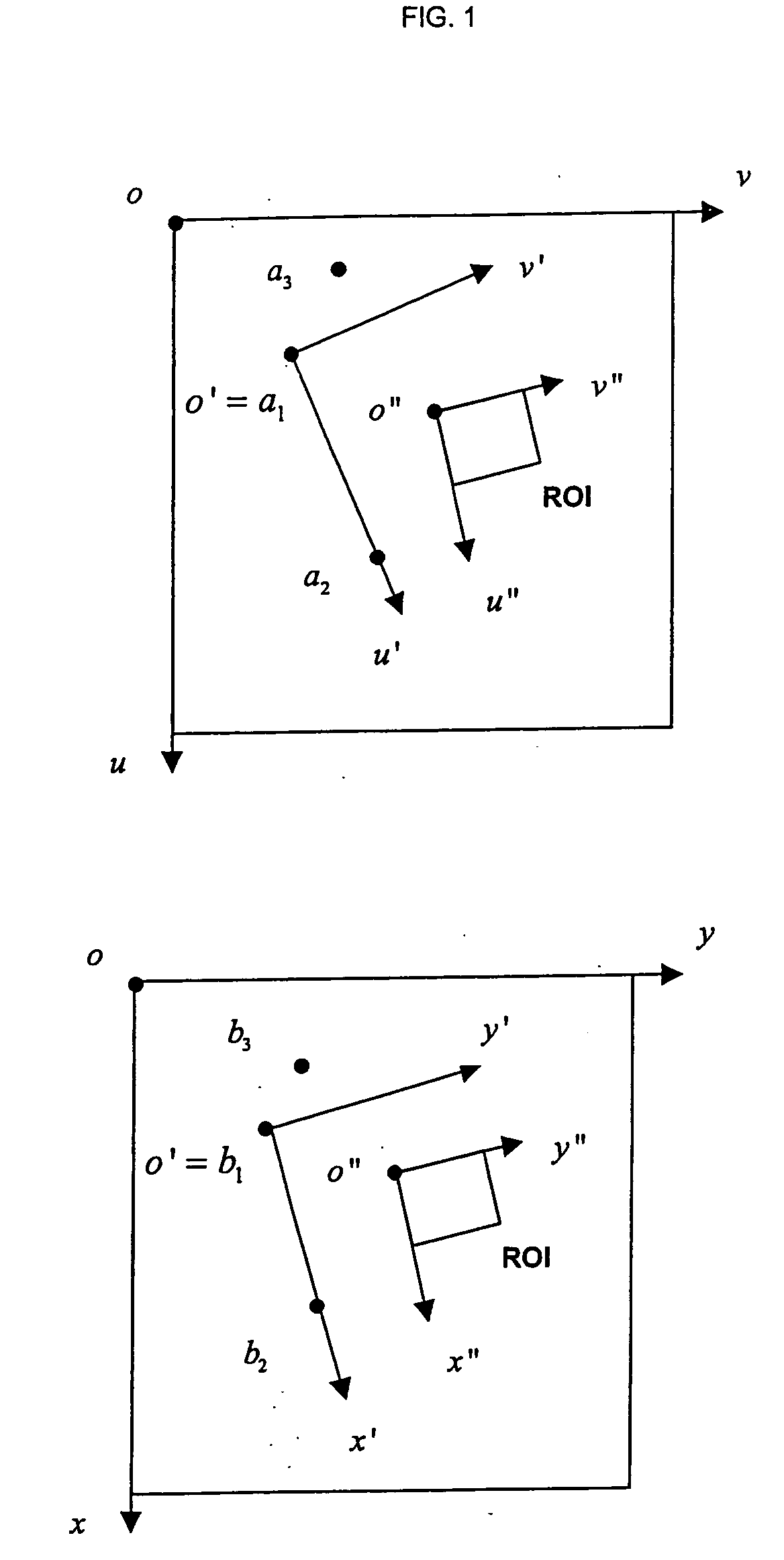
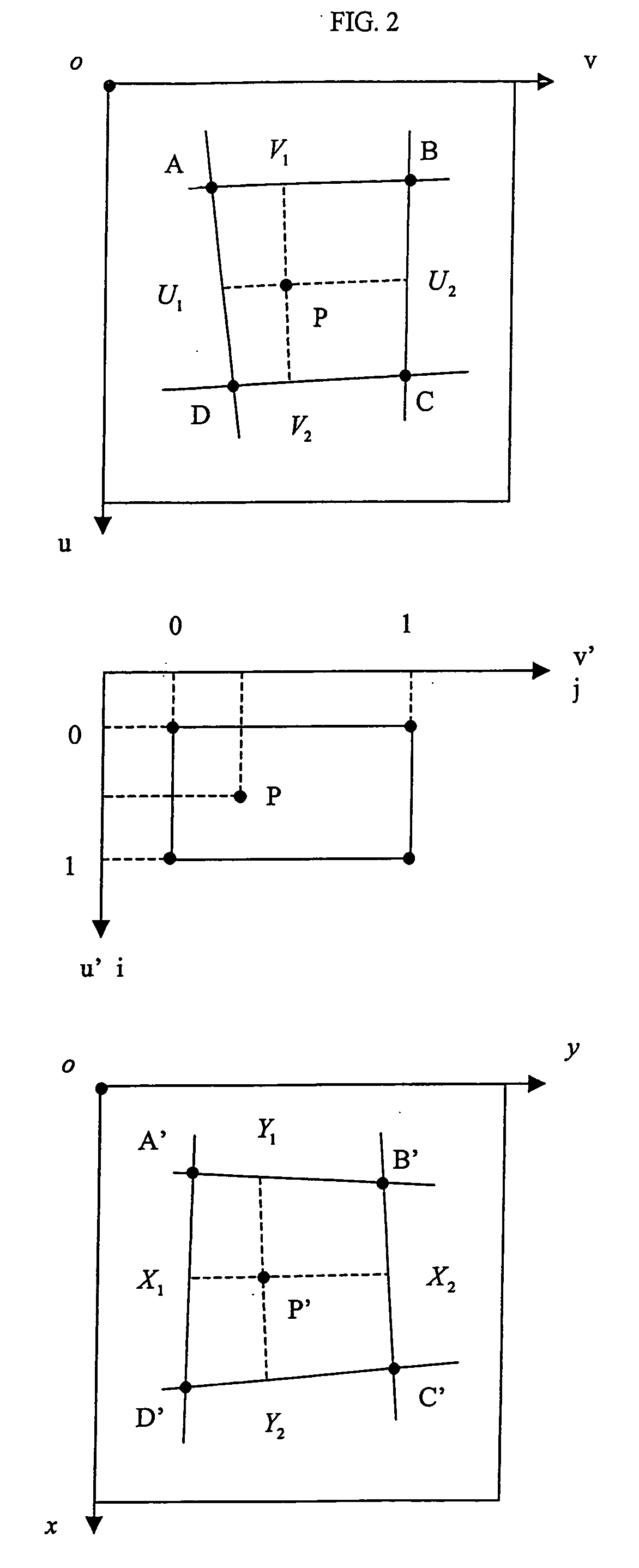
A method of mapping geometrical objects to a digital image. At least one anchor point in a model is selected and mapped to the digital image. A geometric transformation is computed on the basis of at least one correspondence between an anchor object and a corresponding mapped object, and the calculated geometric transformation is applied to at least one geometric object thereby mapping it from the model image to a corresponding mapped position in the digital image.
Owner:AGFA NV
System and method for traffic localization
ActiveUS20070253371A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsLocalization system
Systems and methods for bridging packet flows to bypass call legs and / or tunnels are provided. A tunnel initiator, which can be an access gateway, a foreign agent, and a mobility anchor point, for example, provides a bypass for certain packets that have a destination serviced by the same tunnel initiator. The bridge allows the packets to bypass a backhaul loop and reduces latency and frees bandwidth for other purposes in the network. The bridging can be implemented in a tunnel initiator for mobile to mobile packet flows, mobile to land line packet flows, and land line to mobile packet flows. Route optimization can also be provided in certain embodiments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
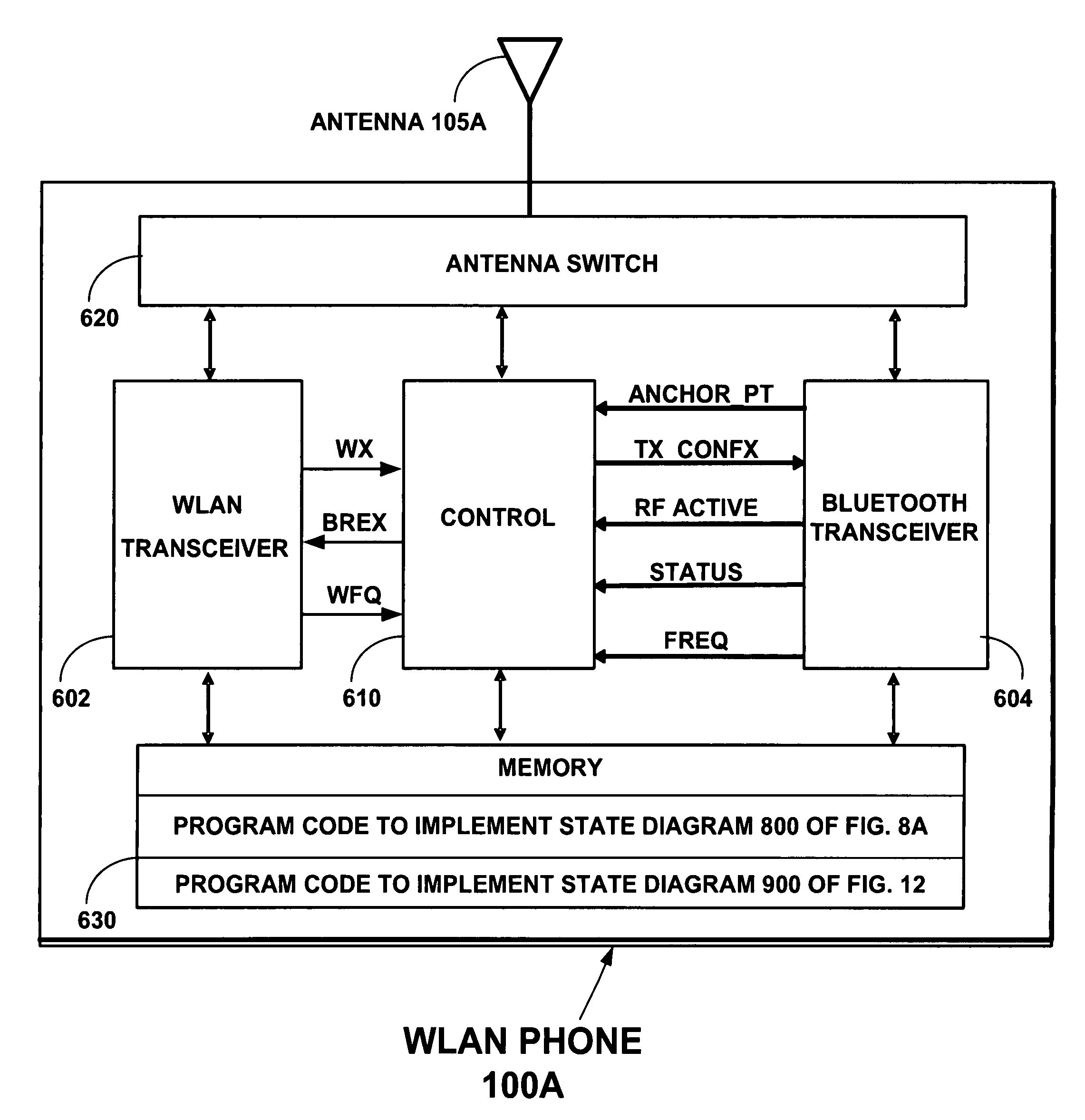
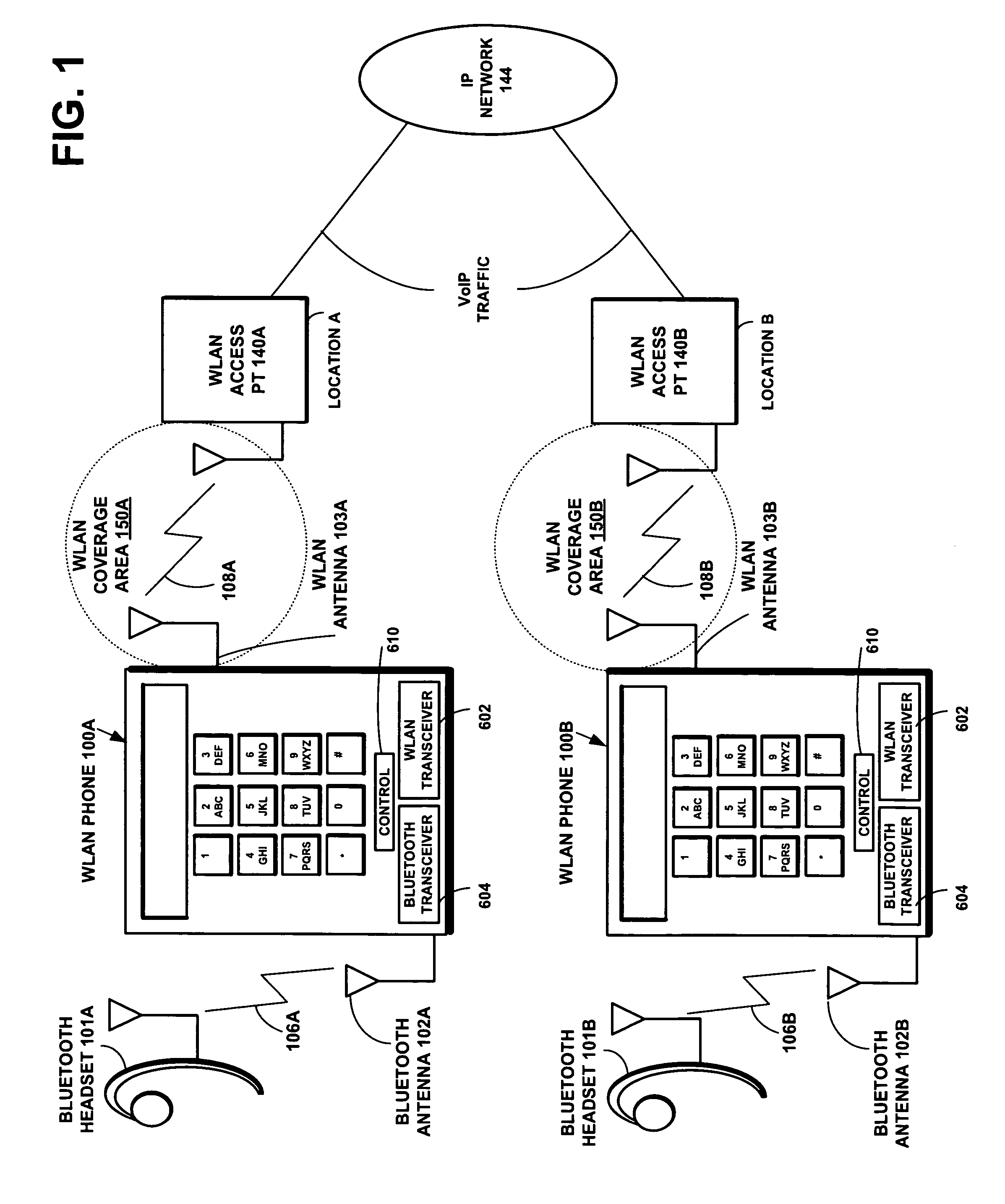
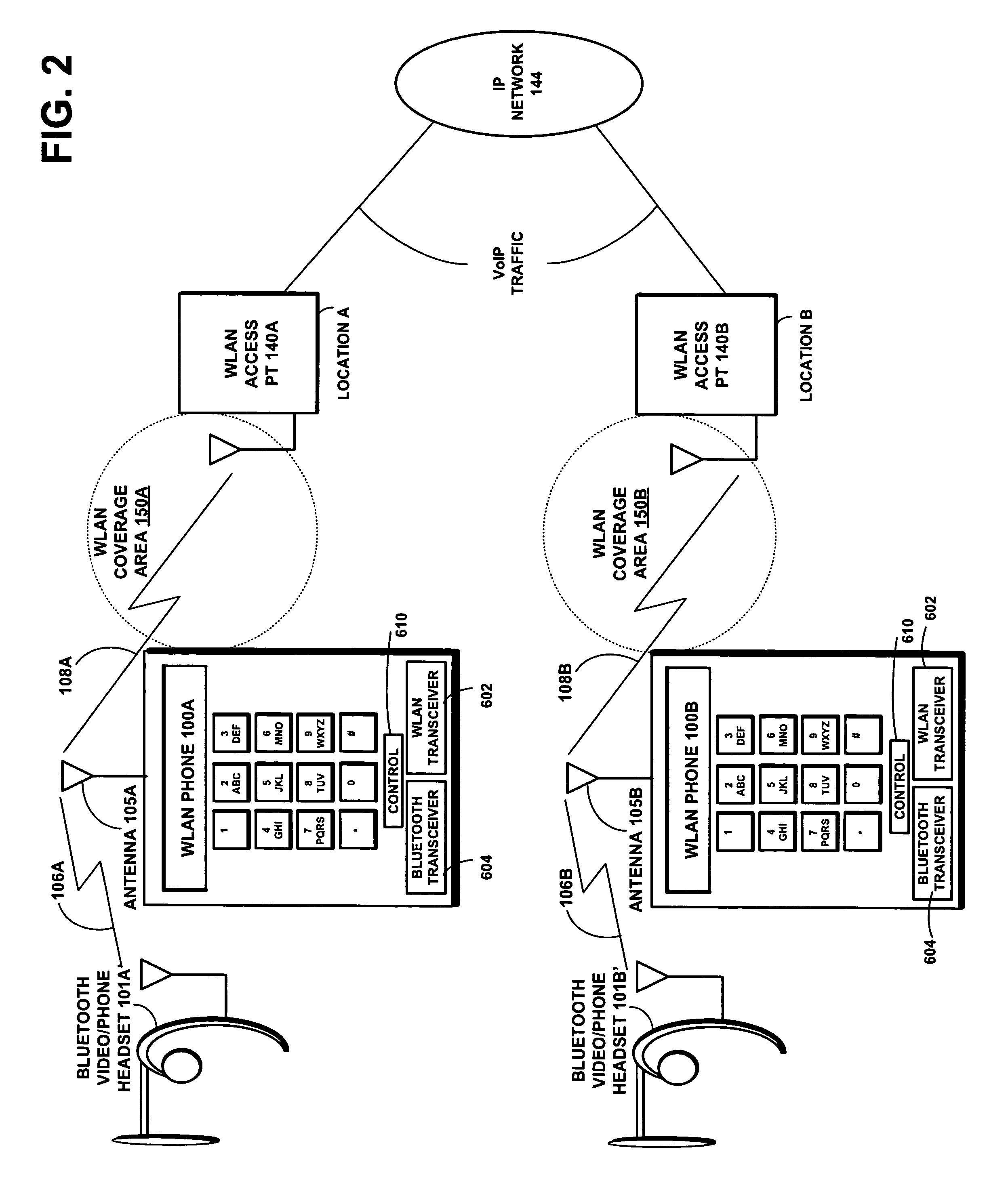
Method and system for VoIP over WLAN to Bluetooth headset using ACL link and sniff for aligned eSCO transmission
ActiveUS7454171B2Reduce distractionsRaise priorityCordless telephonesError preventionTraffic capacityNetwork packet
The invention solves the problem of reducing interference in simultaneous wireless LAN (WLAN) and Bluetooth signal handling, especially in voice over IP communications via a WLAN telephone to a Bluetooth headset. The invention sets up a voice link between the terminal and the headset by establishing sniff anchor points in the ACL link for assigning relative priorities to the WLAN and Bluetooth ACL packet traffic. A higher priority is assigned to WLAN packet traffic when it collides with original Bluetooth ACL packet traffic during a sniff anchor point. Thereafter, a higher priority is assigned to the terminal's retransmission of aborted Bluetooth ACL packets and the headset's response ACL packets in available Bluetooth slots following the anchor point.
Owner:III HLDG 3
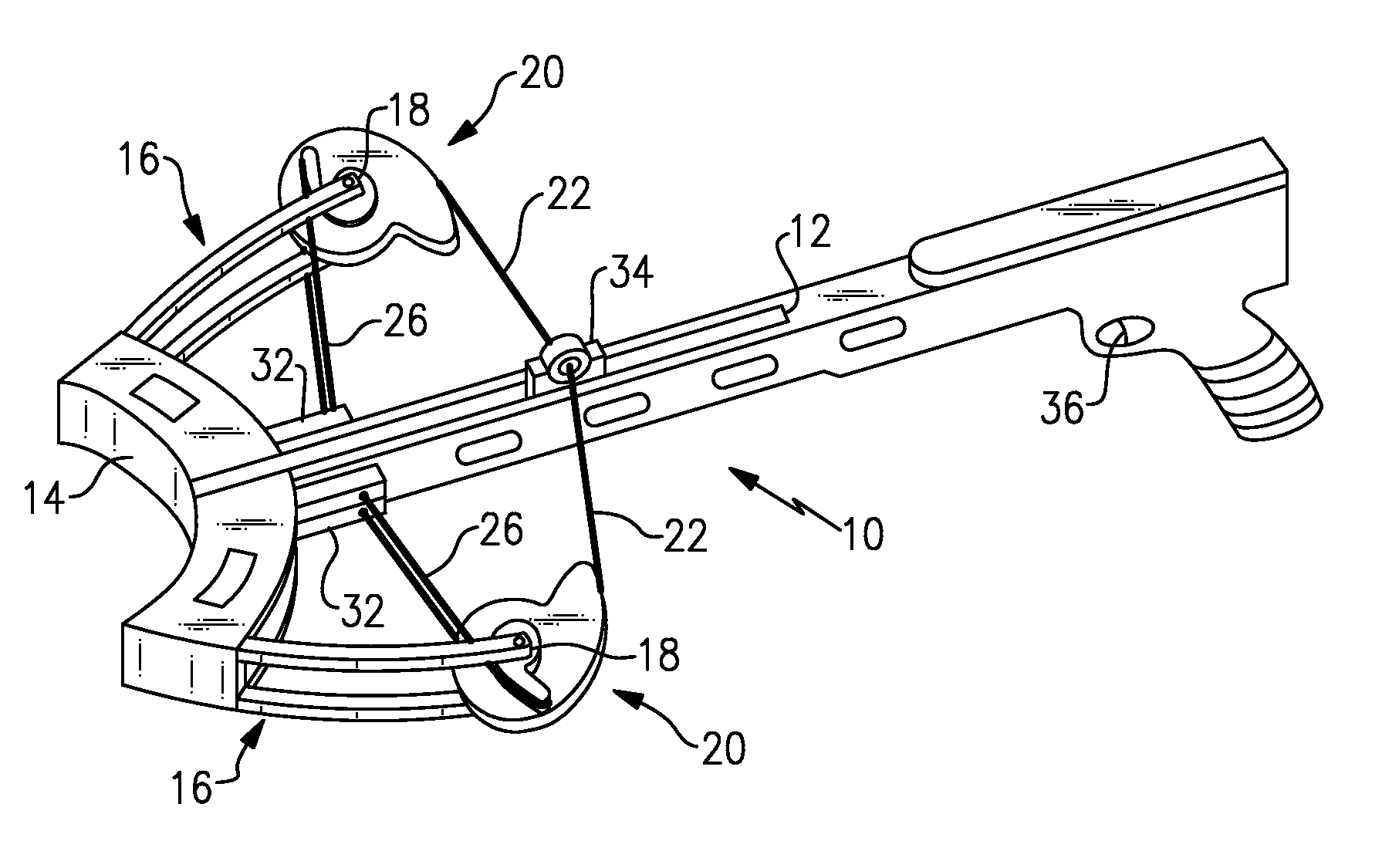
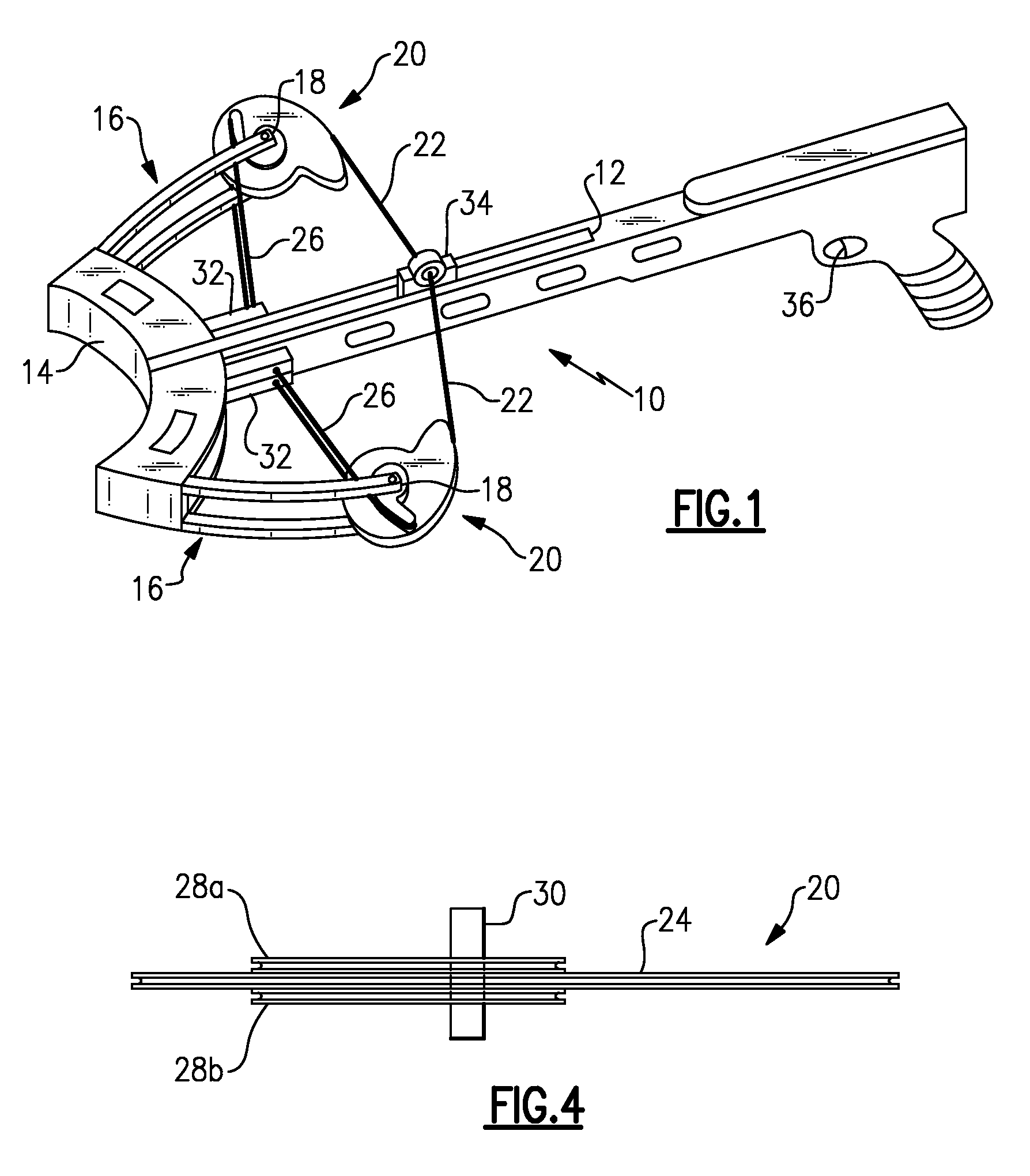
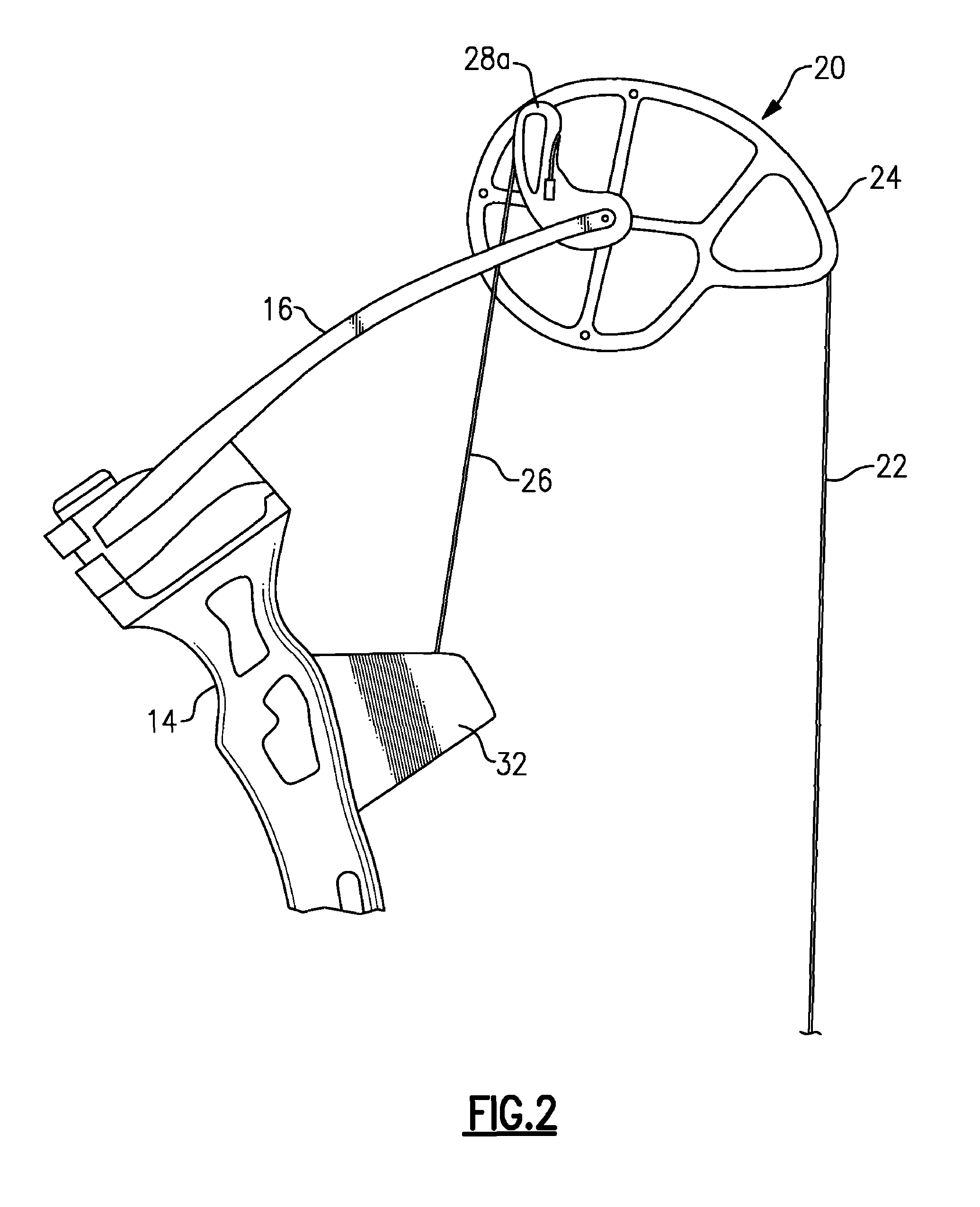
Bowstring cam arrangement for compound crossbow
A compound bow or crossbow employs bowstring cams with bowstring cam grooves and power cord cam grooves. Preferably a pair of generally identical power cord cam grooves are positioned axially above and below the bowstring cam groove. The power cords are anchored to a fixed anchor point, e.g., a pylon, on the near end of the riser or on the near side of the crossbow bar or stock. The power cords do not cross over to the other limb. The reduction in the number of cam wheels and pulleys and in the number of strings or cords results in greater efficiency and higher transfer of energy from the bow to the arrow or bolt. There is no drop-off in pull weight at full draw. The bolt or arrow accelerates throughout the travel of the bowstring, resulting in significantly higher velocity.
Owner:RAVIN CROSSBOWS
Method for automatically mapping of geometric objects in digital medical images
ActiveUS7394946B2Precise positioningReduce the numberImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageAnchor point
A method of mapping geometrical objects to a digital image. At least one anchor point in a model is selected and mapped to the digital image. A geometric transformation is computed on the basis of at least one correspondence between an anchor object and a corresponding mapped object, and the calculated geometric transformation is applied to at least one geometric object thereby mapping it from the model image to a corresponding mapped position in the digital image.
Owner:AGFA NV
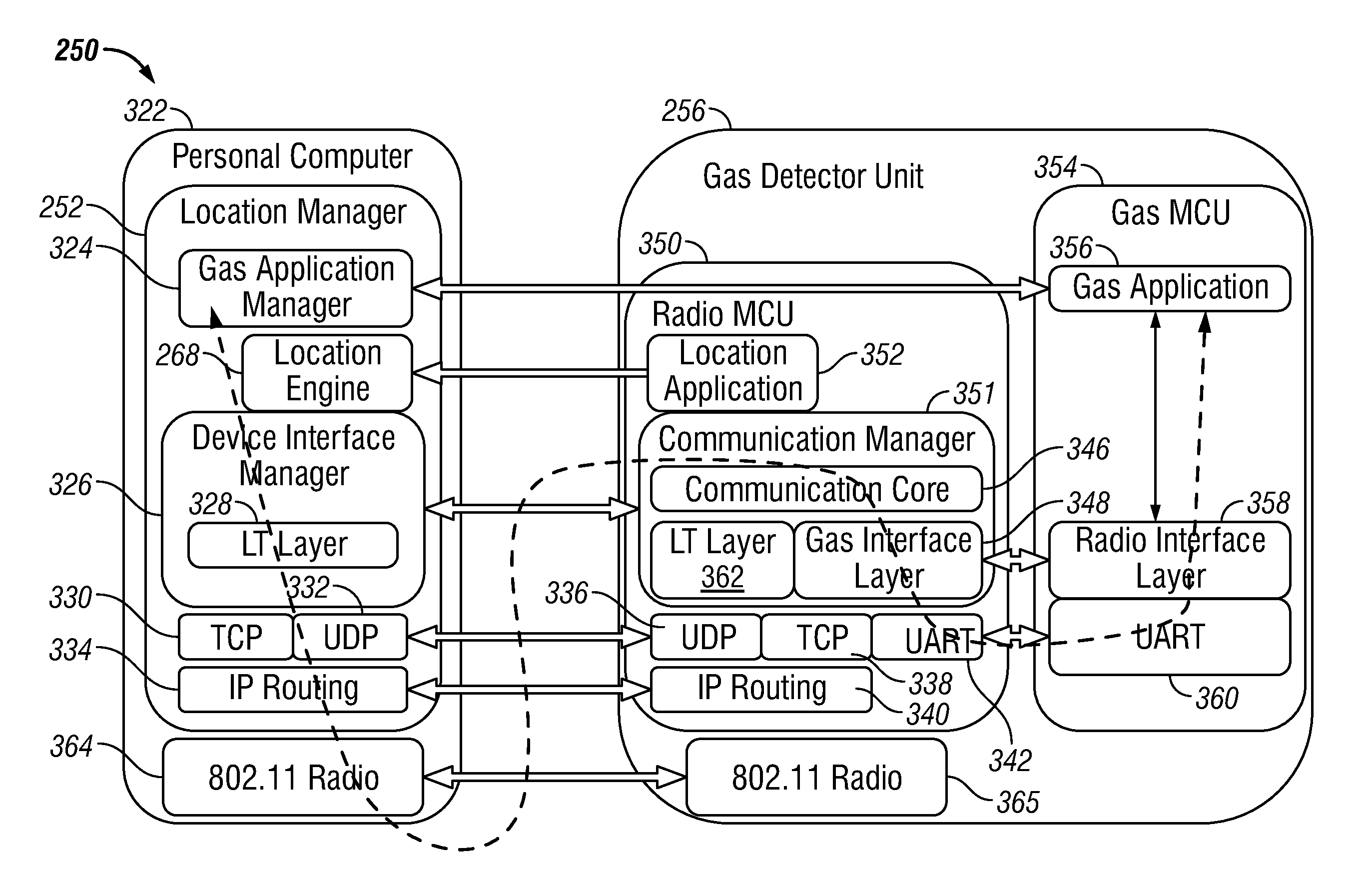
Wireless location-based system and method for detecting hazardous and non-hazardous conditions
ActiveUS20110161885A1Efficient accessError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsTime informationGraphical user interface
A wireless location-based gas detection system and method includes a gas detector for wirelessly detecting location information associated with a hazardous gas event. The gas detector includes one or more remote gas sensors that monitor for the occurrence of a gas event and wirelessly communicates information with respect to the location of the event in association with time information to a server or location manager. A wireless communication device in association with one or more location anchor points periodically and under event conditions, transmits the location information and the gas concentration level. A location engine calculates an estimated location of the gas detector based on information received from the wireless communication device and provides the location data to the location manager. The location manager records the gas concentration level, the estimated location, and the time information and stores this information within a database. A graphical user interface is provided for visualizing the current and historical information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
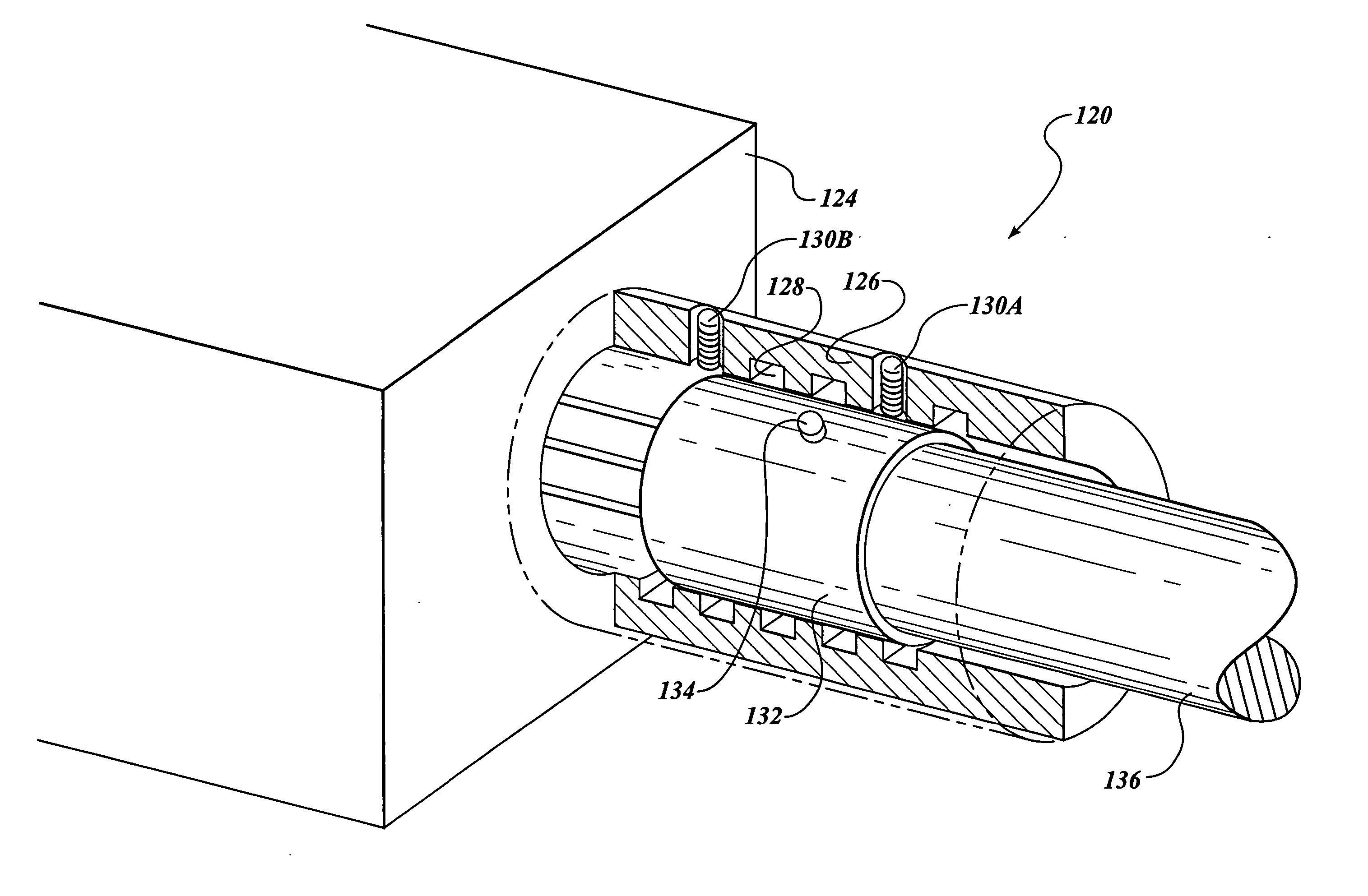
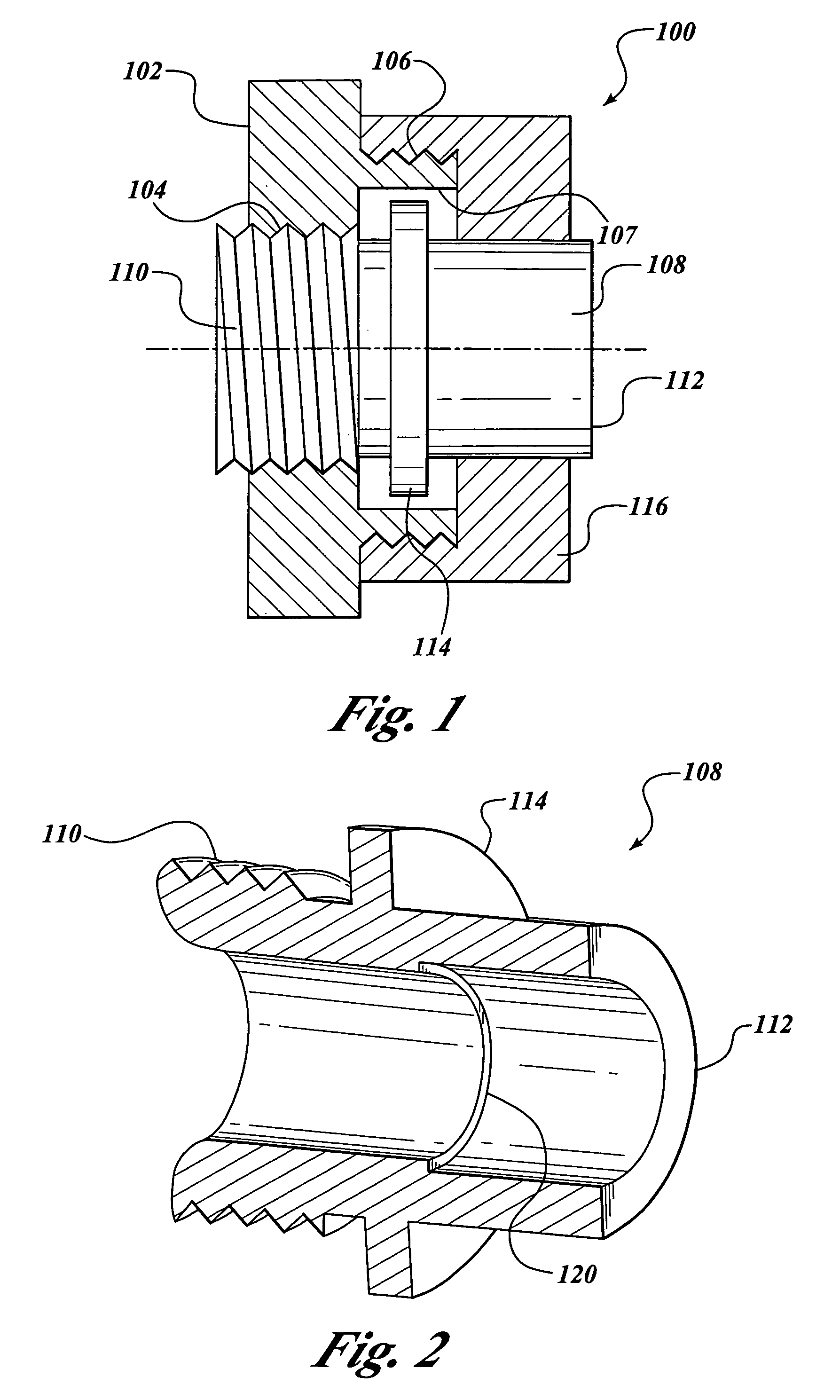
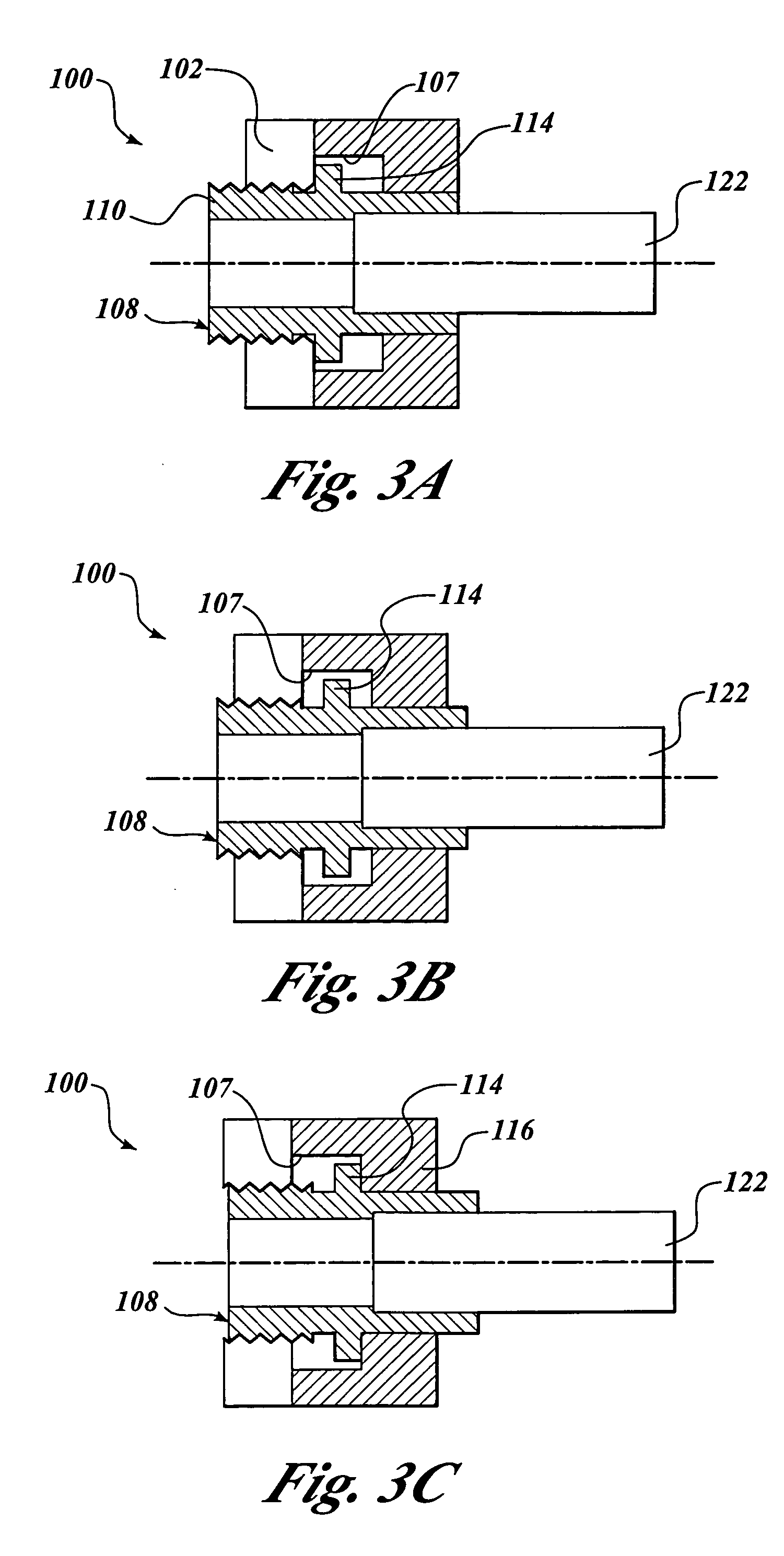
Selectively rotatable shaft coupler
The present invention is a system for dissipating loops in an elongated medical device having one end secured to an anchor point, such as a housing. The system includes a selectively rotatable shaft coupler that connects a shaft to the anchor point that allows a limited amount of shaft rotation during use, but which sets a restriction on the maximum amount of shaft rotation. In another embodiment, the invention provides a shaft coupling system for connecting a proximal end of an endoscope shaft to an object without the use of adhesives or fasteners. In another embodiment, the invention provides a rotatable shaft coupling system for rotatably coupling a first and second shaft segment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
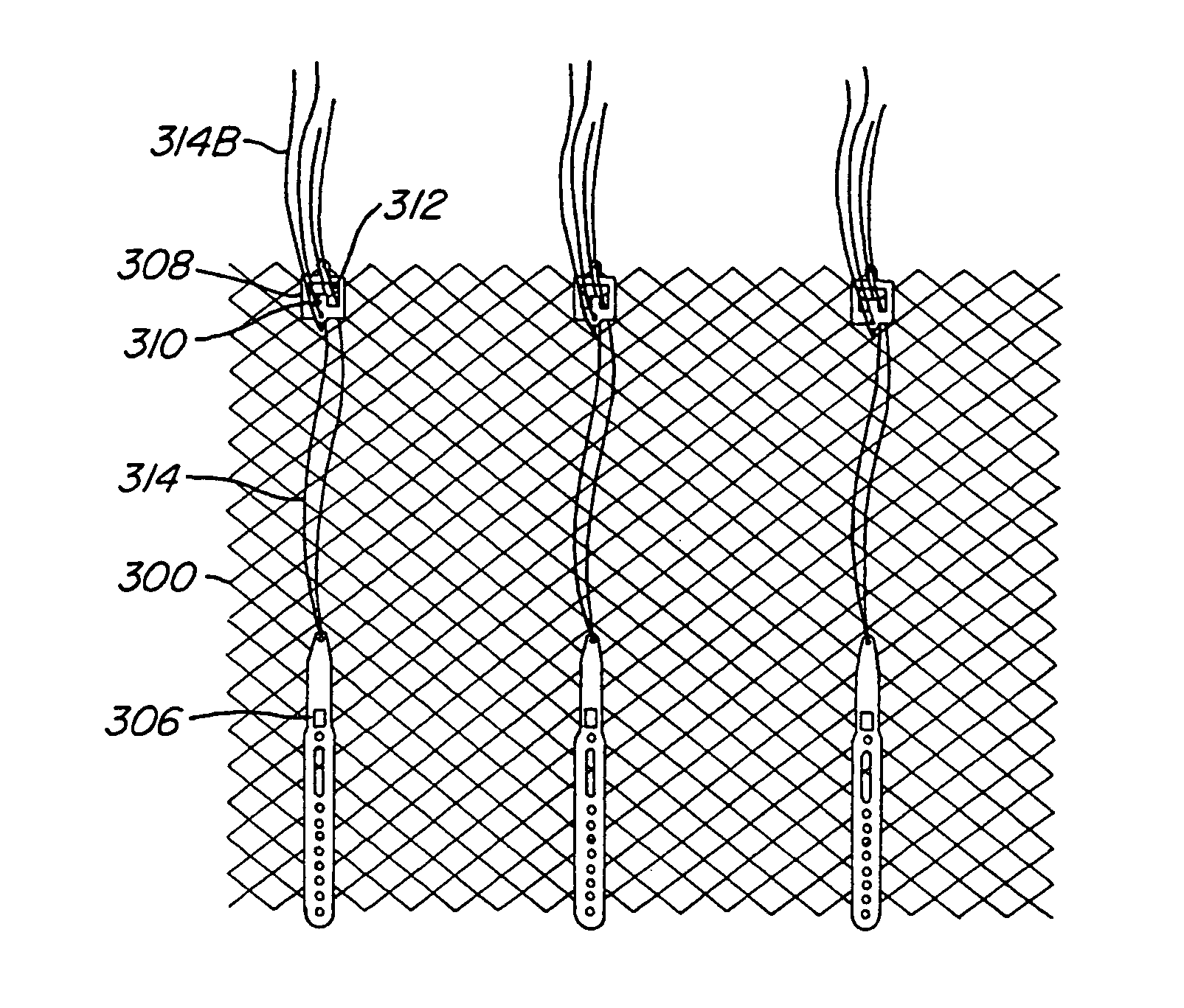
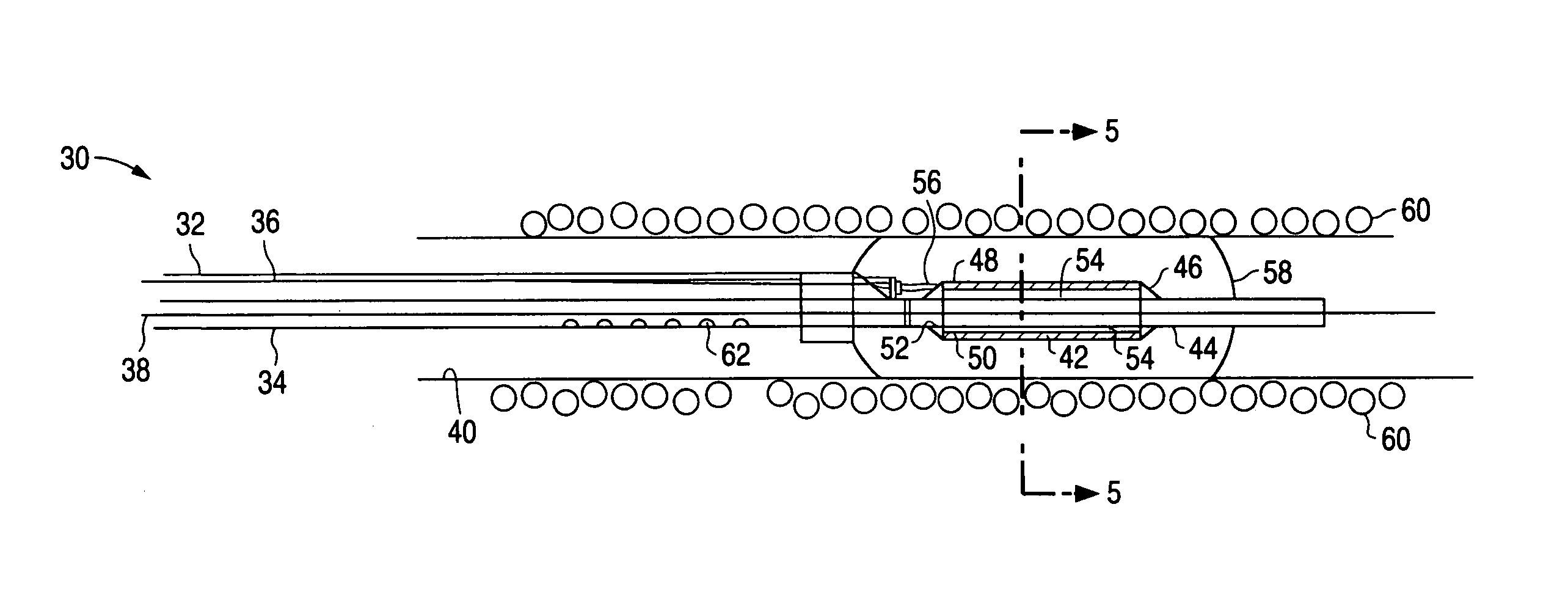
Medical assembly with transducer for local delivery of a therapeutic substance and method of using same
A medical assembly is used to deliver a therapeutic substance to a treatment area. The medical assembly comprises a catheter having a distal end and a proximal end, a transducer supported by at least a portion of the distal end of the catheter assembly, and a delivery lumen mounted on the catheter for delivery of a therapeutic substance. Support for the transducer is provided at a preselected number of anchoring points, wherein an inner surface of the transducer is positioned at a preselected distance from an outer surface of the catheter. The preselected distance defines a gap that is occupied by a low density material such as a gas which reflects acoustic pressure waves directed toward the gap by a transducer when a voltage is applied to the transducer. The reflected pressure wave increases the energy in the system, enhancing transport of therapeutic substances from the delivery lumen to the surrounding tissues and / or cells to be treated. The medical assembly may optionally be used in conjunction with both macroporous and microporous balloons. The medical assembly may optionally be modified so that a plurality of transducers are used, wherein the distal end of a transducer is positioned at a preselected distance from the proximal end of an adjacent transducer.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
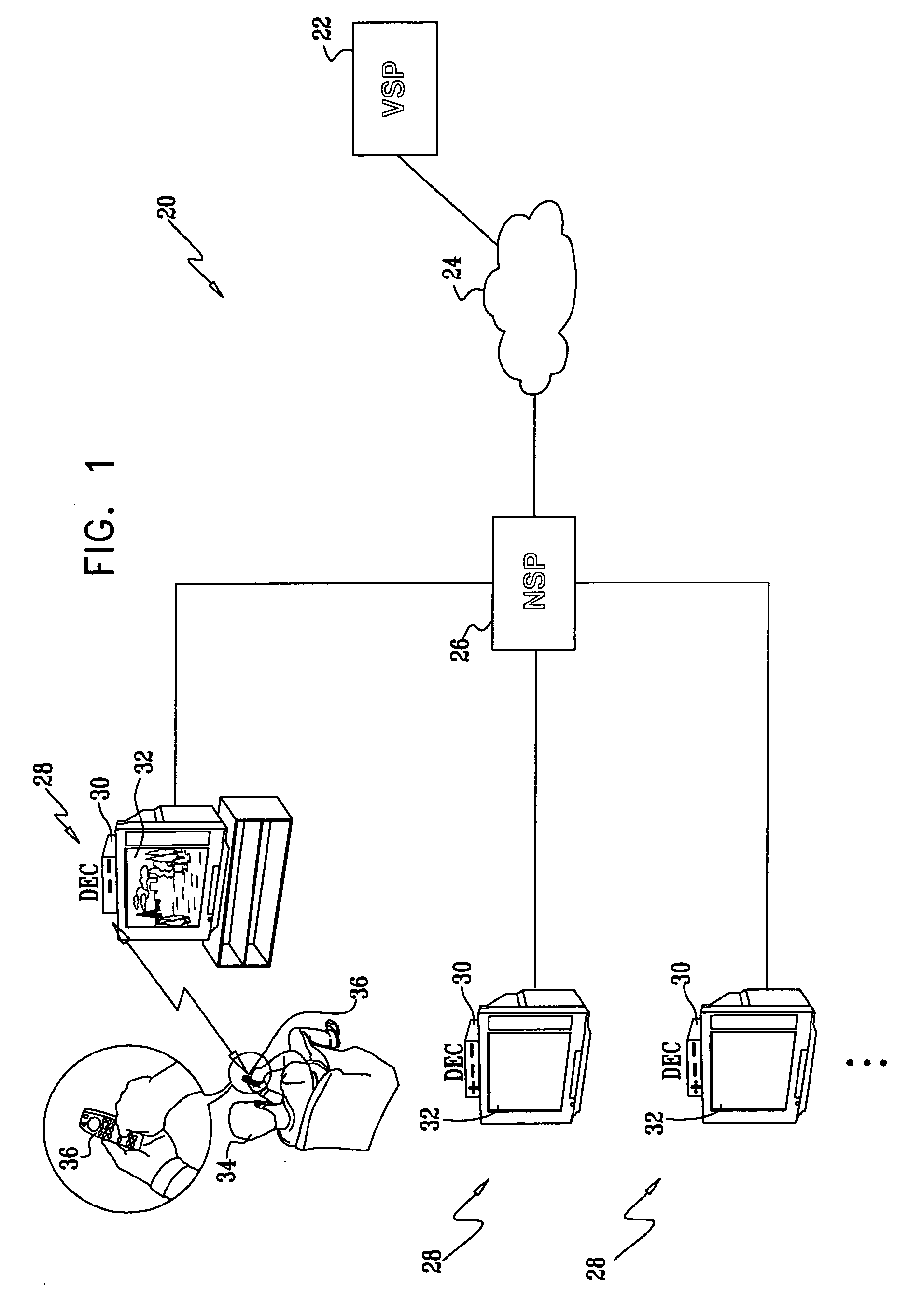
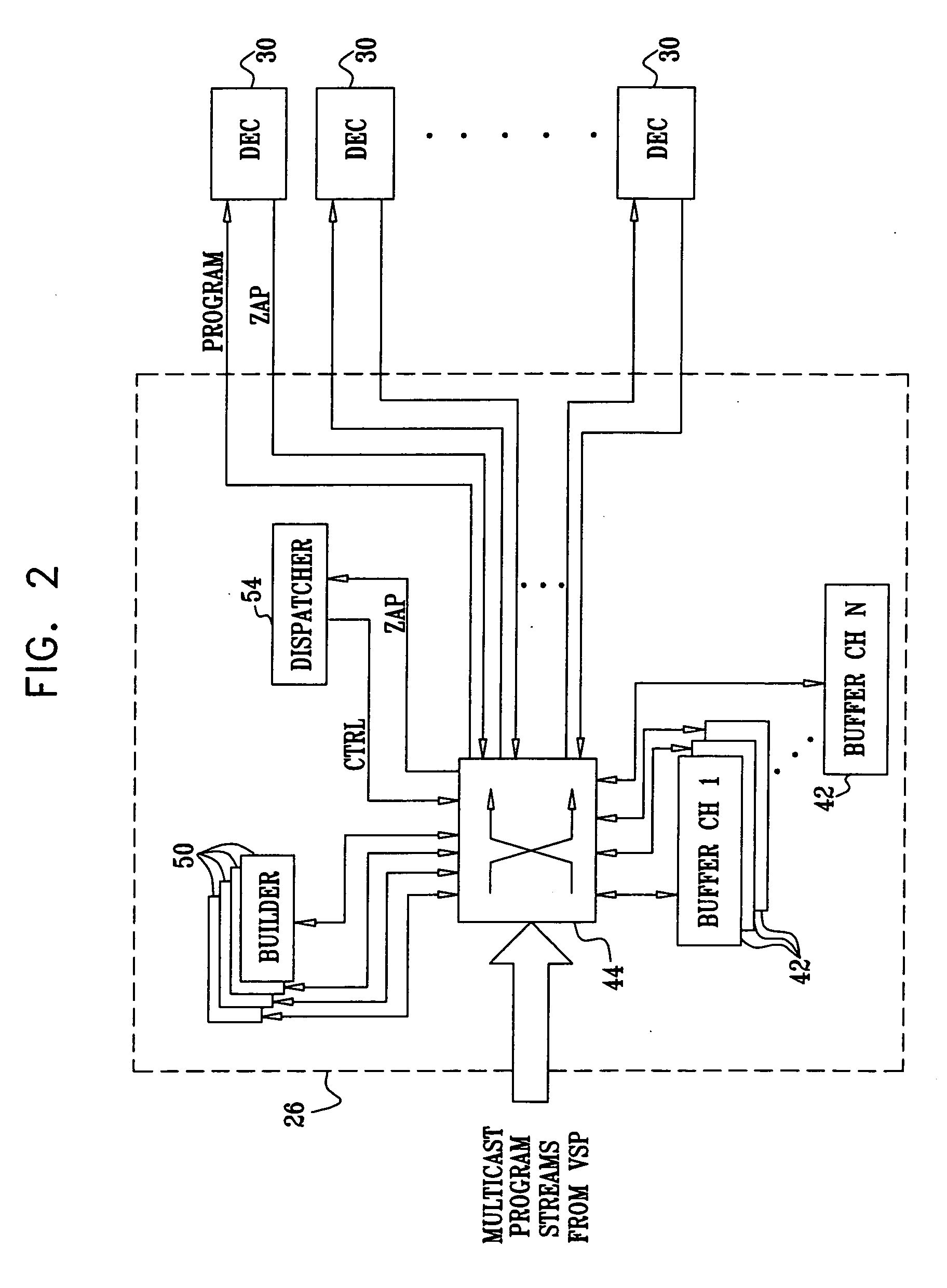
Fast channel switching for digital TV
InactiveUS20060143669A1Shorten the timeReduce delaysTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionDigital videoClient-side
A method for digital video distribution includes transmitting a multicast stream over a network. Upon receiving, at a time subsequent to a first anchor point and prior to a second anchor point in the multicast stream, a request from a client to begin receiving the multicast stream, a boost stream is generated, including at least a portion of the video data in the frames between the first and second anchor points. The boost stream is transmitted to the client during an interval between the time at which the request was received and the second anchor point in the multicast stream, so as to cause the client to display the video data beginning from the first anchor point. Upon completing transmission of the boost stream, the multicast stream is transmitted to the client beginning from the second anchor point.
Owner:BITBAND TECH
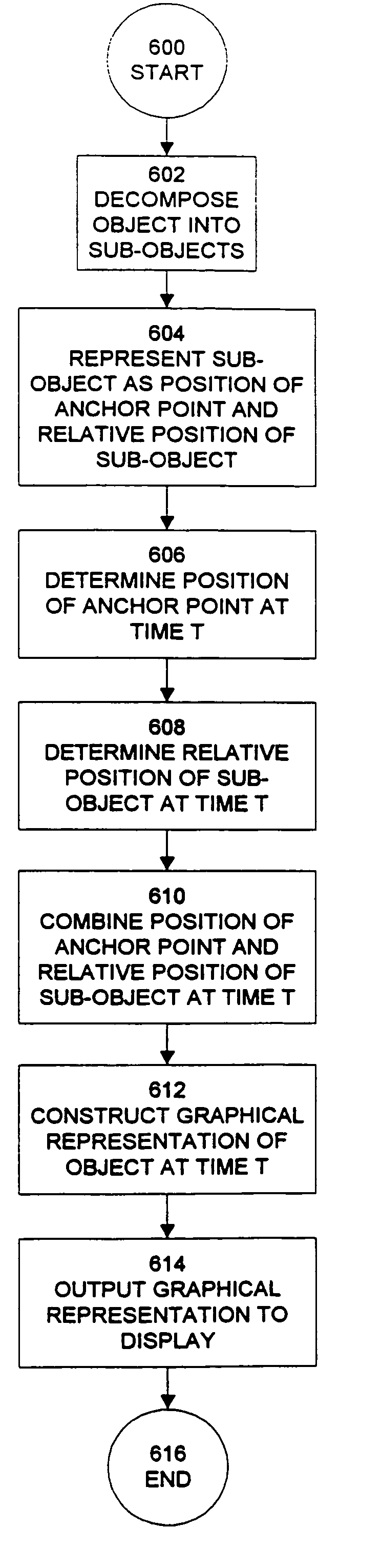
Methods and apparatus for supporting and implementing computer based animation
The present invention provides a method for hierarchically decomposing a visual or audio object within an animation into plurality of objects which can be individually edited to achieve particular animation effects. For example, a graphical object may be decomposed into a plurality of graphical sub-objects, each of which is inherits an anchor point from the original object, or is given an original anchor point distinct from the original object. Each sub-object also includes a relative position for the sub-object relative to the anchor point. The path of the anchor point is combined with relative positions of the sub-objects to produce an animation for the object as a whole. This decomposition technique can greatly increase computational efficiency of an animation. It also provides for inheritance of attributes between objects and descendent sub-objects. The objects may support functions, or behaviors, such as morphing or motion blurring. The present invention additionally provides a flexible grouping operation to facilitate modifications to a group of objects. When a first type of modification is made to an attribute of an object in a group, this change is applied to corresponding attributes of other objects in the group. When a second type of modification is made to an attribute of an object in a group, the change only applies to the selected object or objects, and not to other objects in the group. The present invention allows objects to be manipulated on servers which are connected to a display via the Internet.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
Tire comprising a measurement device
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Mesh based frame processing and applications
ActiveUS20050249426A1Reduce computing costImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionFrame basedMotion vector
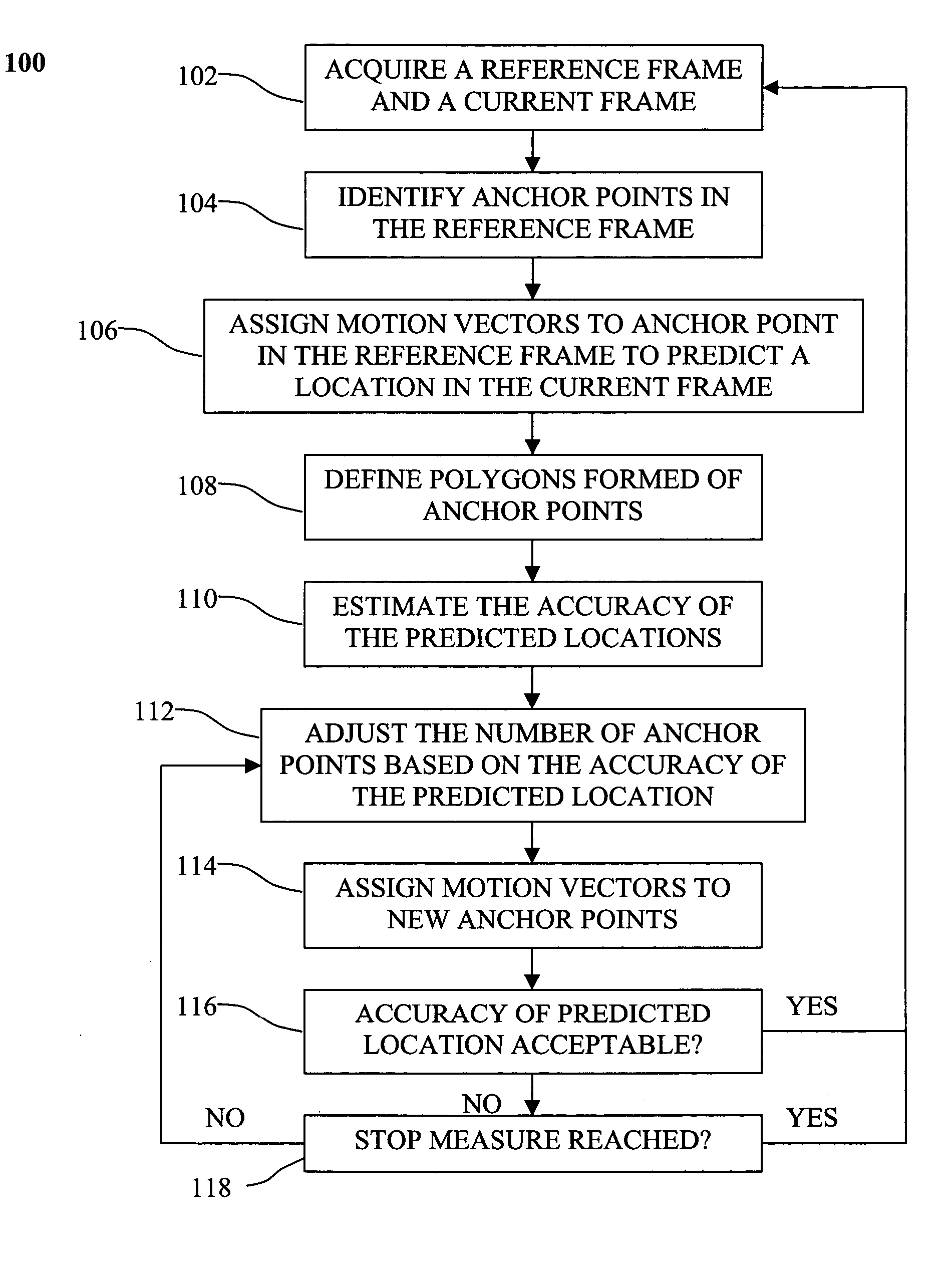
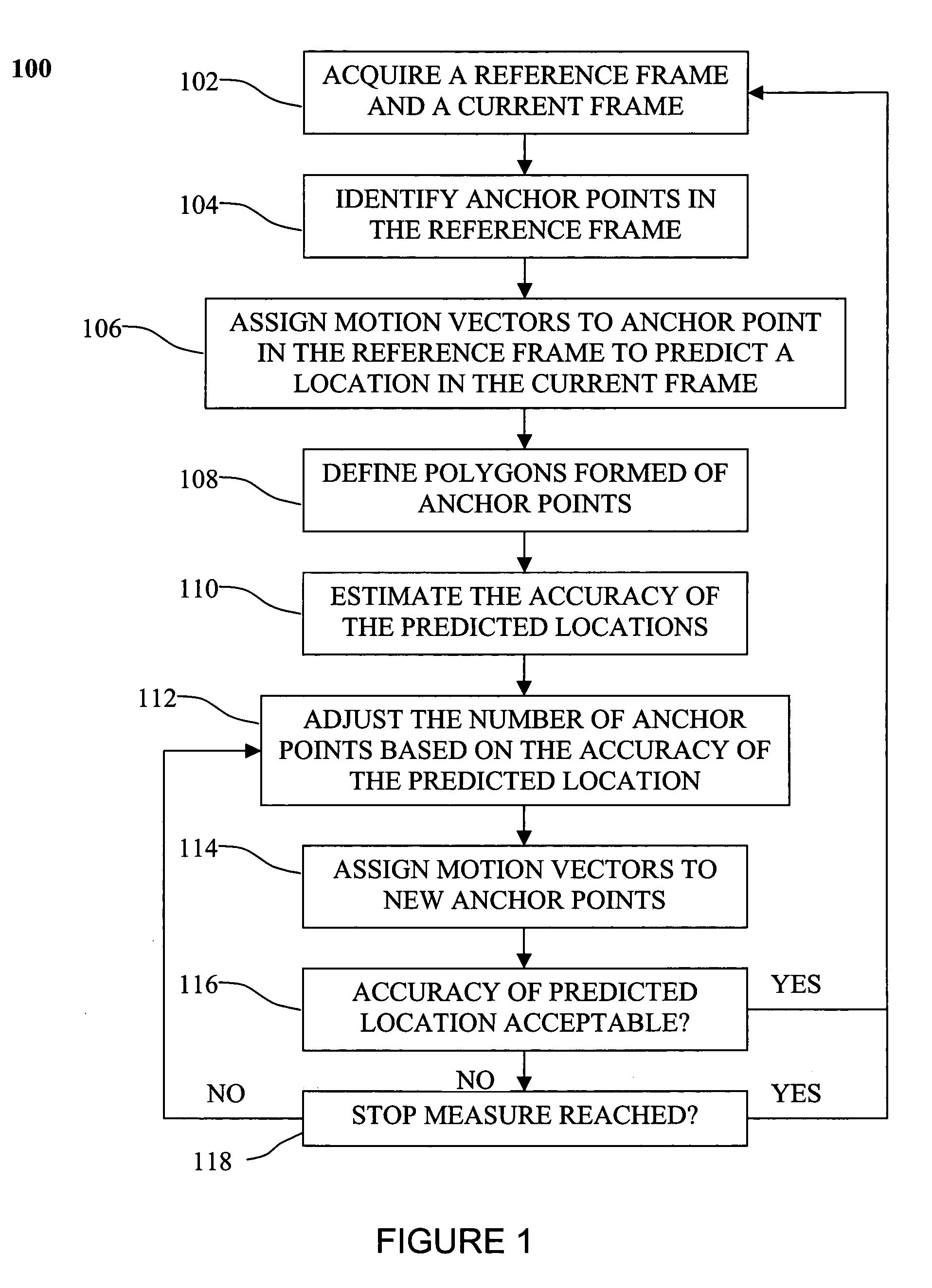
A method of processing sequential frames of data comprises repeating the following steps for successive frames of data: acquiring at least a reference frame containing data points and a current frame of data points; identifying a set of anchor points in the reference frame; assigning to each anchor point in the reference frame a respective motion vector that estimates the location of the anchor point in the current frame; defining polygons formed of anchor points in the reference frame, each polygon containing data points in the reference frame, each polygon and each data point contained within the polygon having a predicted location in the current frame based on the motion vectors assigned to anchor points in the polygon; for one or more polygons in the reference frame, adjusting the number of anchor points in the reference frame based on accuracy of the predicted locations of data points in the current frame; and if the number of anchor points is increased by addition of new anchor points, then assigning motion vectors to the new anchor points that estimate the location of the anchor points in the current frame.
Owner:INTELLIVIEW TECH
Wheeled system for coolers
ActiveUS9278704B2Improve mobilityDiminished access to and useLuggageOther accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CATES JOHN DAVID
System and method for data format transformation
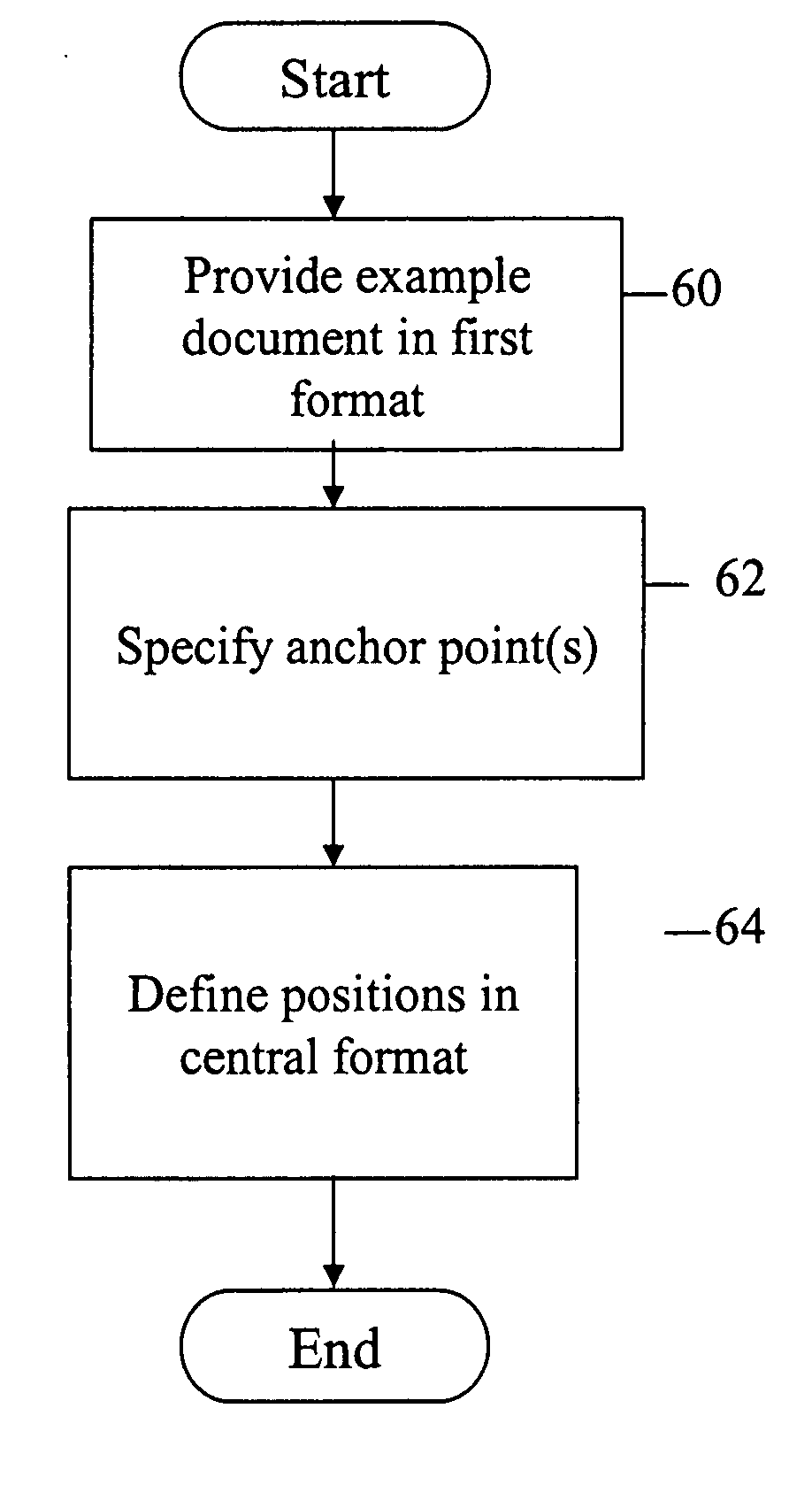
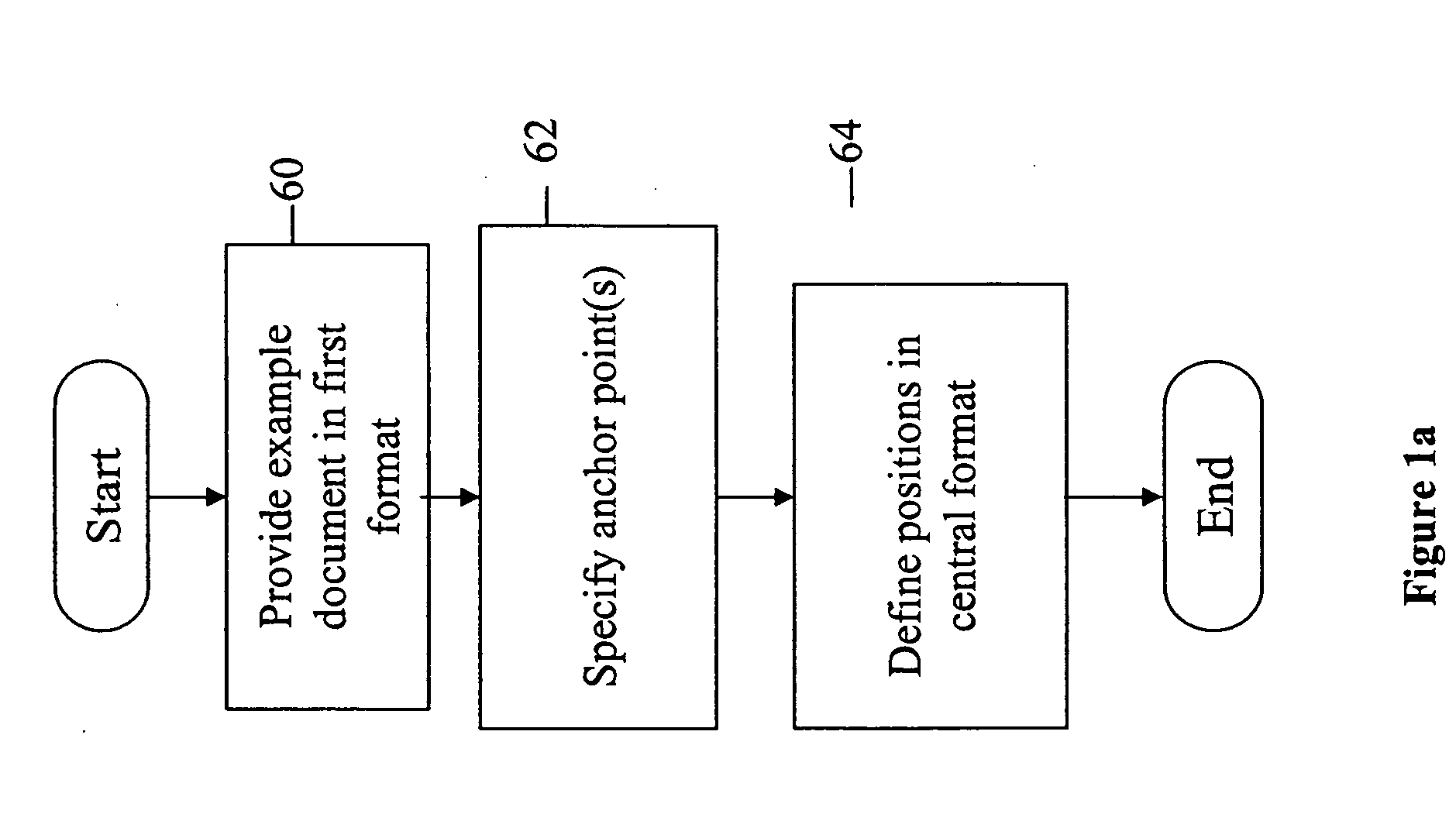
ActiveUS20060007466A1Easy to operateEfficient executionDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsMarking outDocument format
A method for defining a document format transformation process for documents similar to an example document includes the following steps. An example document is provided in a first format. At least one anchor point is then specified within the example document. The anchor points serve to mark out regions of data within the example document. Positions are then defined for respective regions within a central format. During the transformation process, the data extracted from each region is transferred into the respective position. The method enables transforming documents similar to the example document into the central format.
Owner:INFORMATICA CORP
Device for strengthening, training, and rehabilitating isolated muscle groups using elastic resistance elements
ActiveUS7608026B1Good adhesionEasy detachmentSnap fastenersResilient force resistorsMuscle groupEngineering
An exercise device, for use in strengthening, training, and rehabilitating the body, using at least two harnesses and at least one elastic element. The harnesses are attached to the body and have mating clips attached to them to establish anchor points. The elastic element has a pair of clip receptacle for attaching to the mating elements and has an elastic cord extending therebetween. When the clip receptacles are secured to the mating clips at a pair of anchor points, body movements relative to the anchor points are resisted by the elastic elements.
Owner:NICASSIO JESSE
Mechanical structures and implants using said structures
A deformable medical implant, comprising: a body defining at least two anchor points, which body is adapted to be deformed so that the two anchor points are moved relative to each other; at least two elongate extensions, each extension fixed to one anchor point; a bridge coupling at least two of said extensions to each other; and at least two hinges defined on at least one of said extensions, two of said at least two hinges having different preferred bending directions and being defined on one extension.
Owner:EXISTENT
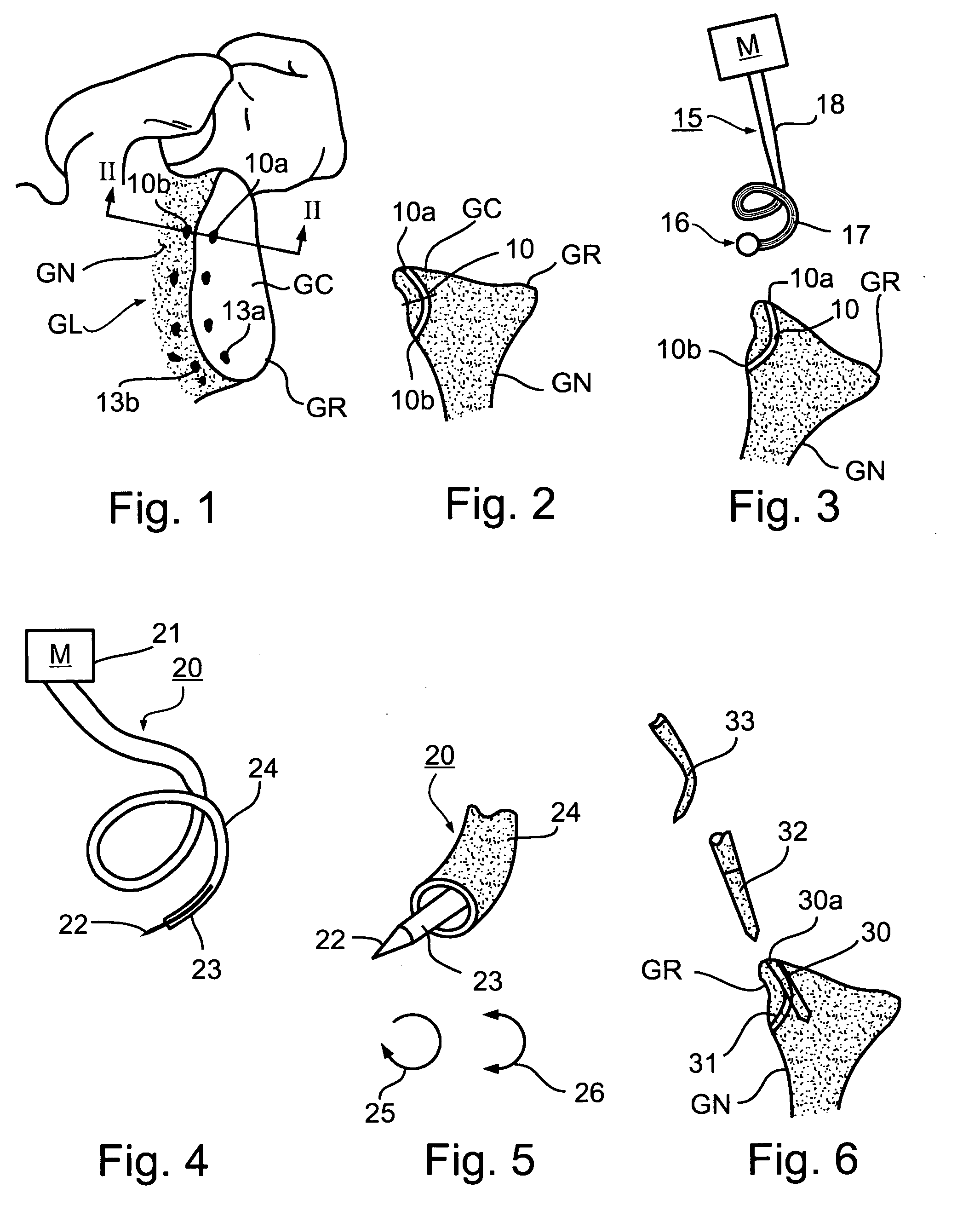
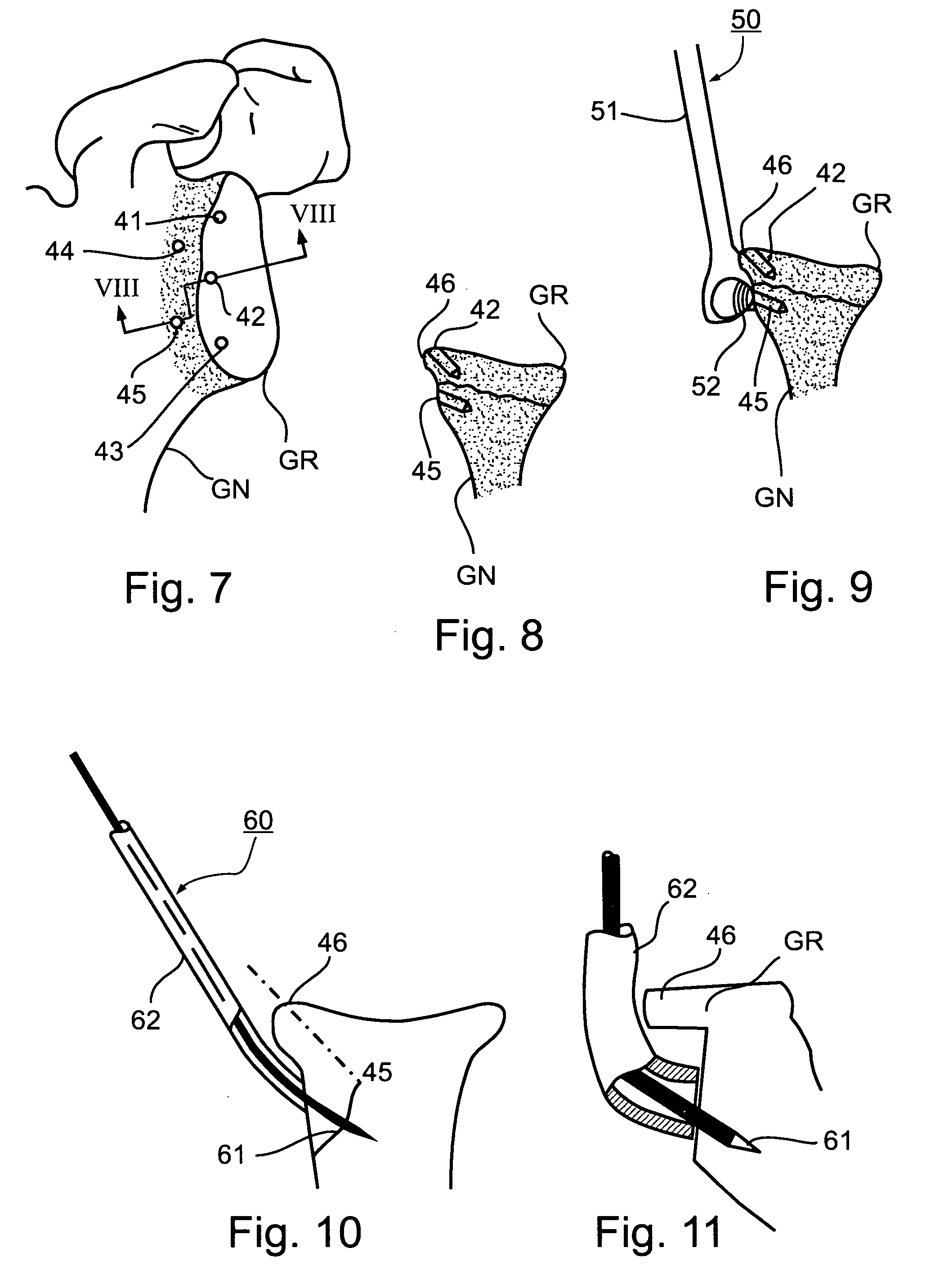
Method and Apparatus for Repairing Separations in the Capsular Labrum Structure
InactiveUS20080275453A1Increase the areaStrong tissue-to-bone reattachmentLigamentsMusclesGlenoid neckEngineering
A method of repairing separations in the capsular labrum structure, in which the head of the humerus bone separates from the glenoid cavity of the glenoid, by: producing a first plurality of anchor points in an anterior face of the rim of the glenoid; producing a second plurality of anchor points in a corresponding anterior face of the neck of the glenoid; and utilizing the first and second plurality of anchor points for attaching the tendons to the glenoid. Also described is an apparatus for use in repairing separations in a capsular labrum structure including a drill guide having a proximal end formed with a handle, and a distal end formed with a surface configured for engaging a posterior face of the neck of the glenoid to properly fix the position of the drill guide with respect to the glenoid. The drill guide is formed with a passageway sized and configured for receiving a drill for drilling a bore through the neck of the glenoid, with the entry point of the drill at the posterior face of the glenoid neck, and the exit point of the drill at the anterior face of the glenoid neck slightly spaced from the glenoid rim.
Owner:T MEDICAL PRODS A PARTNERSHIP
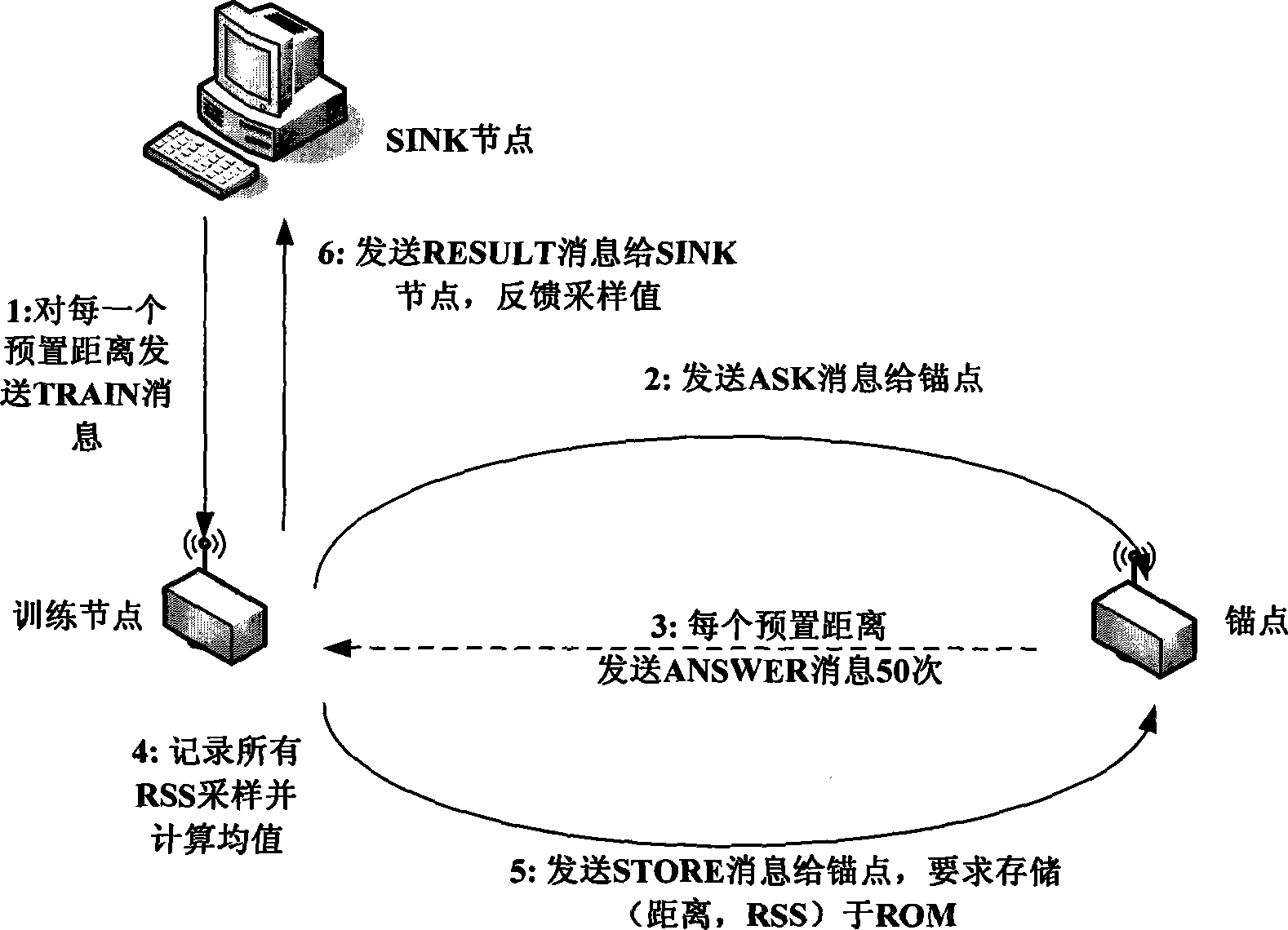
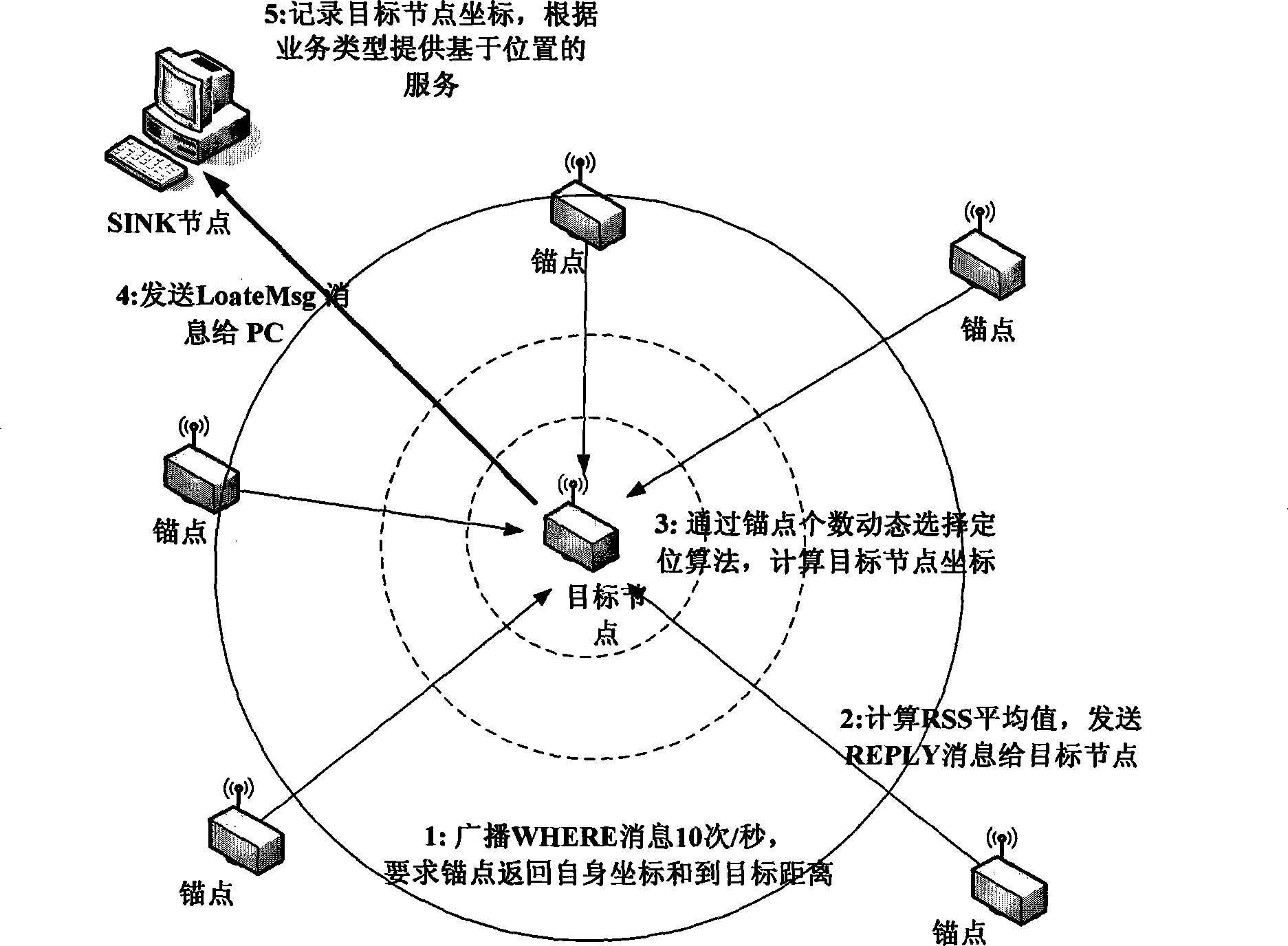
Node indoor locating method based on wireless signal strength in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101247650AReduce communication consumptionSmall amount of calculationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless mesh networkAnchor point
The present invention belongs to node self-localization field in large-scale wireless sensor network, and discloses a node indoor localization method based on wireless signal intensity, which main includes: getting relationship curve of signal intensity and distance, and putting forward concept of effective wireless signal intensity (Effective RSS, ERSS); obtaining coordinates of target node by selecting localization arithmetic (ERSS filter + maximum likelihood estimation, triangle localization, approximate location estimation) according with anchor point amount through distance between anchor point and target by training RSS curve; providing alerting service by using physics coordinate, providing navigation service according with route arithmetic and address chain by using sign coordinate (for example in hall). Precisely localization of indoor target can be realized in condition of low-cost, simple initial configuration, and a plurality of services based on location can also be provided.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
Repositionable Heart Valve and Method
A method for percutaneously replacing a heart valve of a patient. In some embodiments the method includes the steps of percutaneously delivering a replacement valve and an expandable anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve in an unexpanded configuration; expanding the anchor to a deployed configuration in which the anchor contacts tissue at a first anchor site; repositioning the anchor to a second anchor site; and deploying the anchor at the second anchor site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
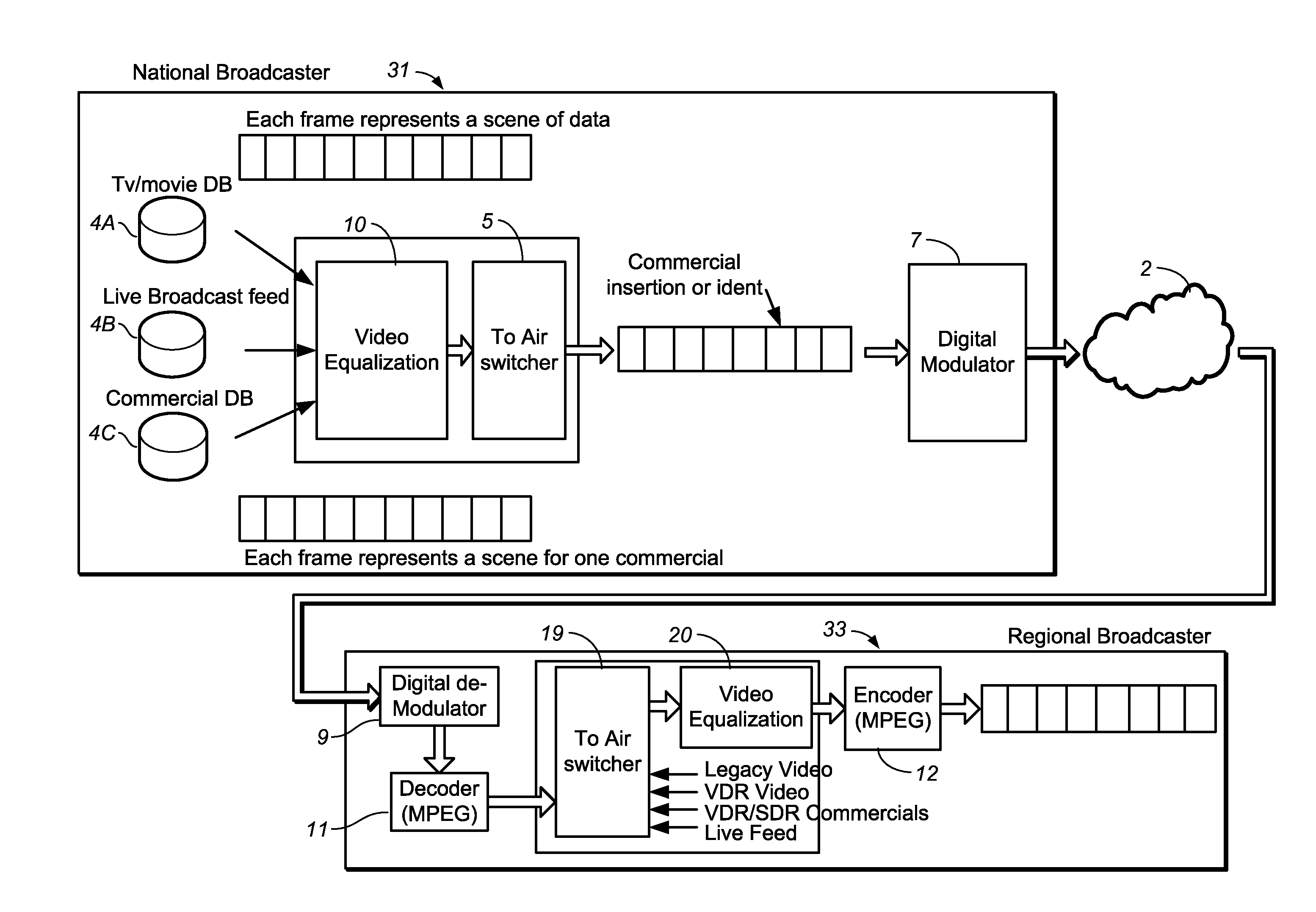
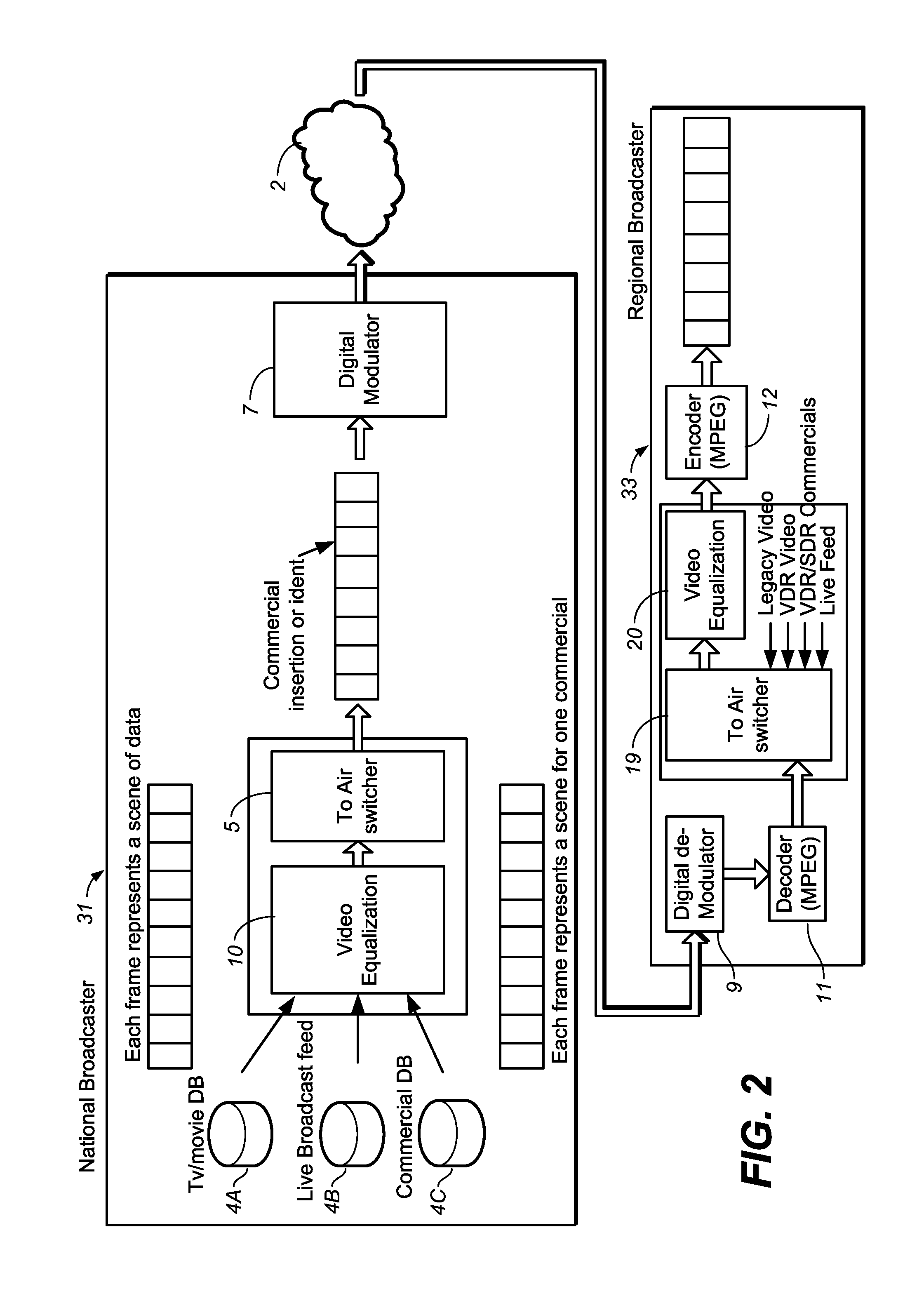
Method and system for video equalization
ActiveUS20150042890A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsStandard dynamic rangeGray level
Video equalization including performing equalization such that a sequence of images have dynamic range (optionally other characteristics) that is constant to a predetermined degree, where the input video includes high and standard dynamic range videos and images from both. Equalization is performed with a common anchor point (e.g., 20% gray level, or log mean of luminance) input video and the equalized video, and such that the images determined by the equalized video have at least substantially the same average luminance as images determined by the input video. Other aspects are systems (e.g., display systems and video delivery systems) configured to perform embodiments of the equalization method.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
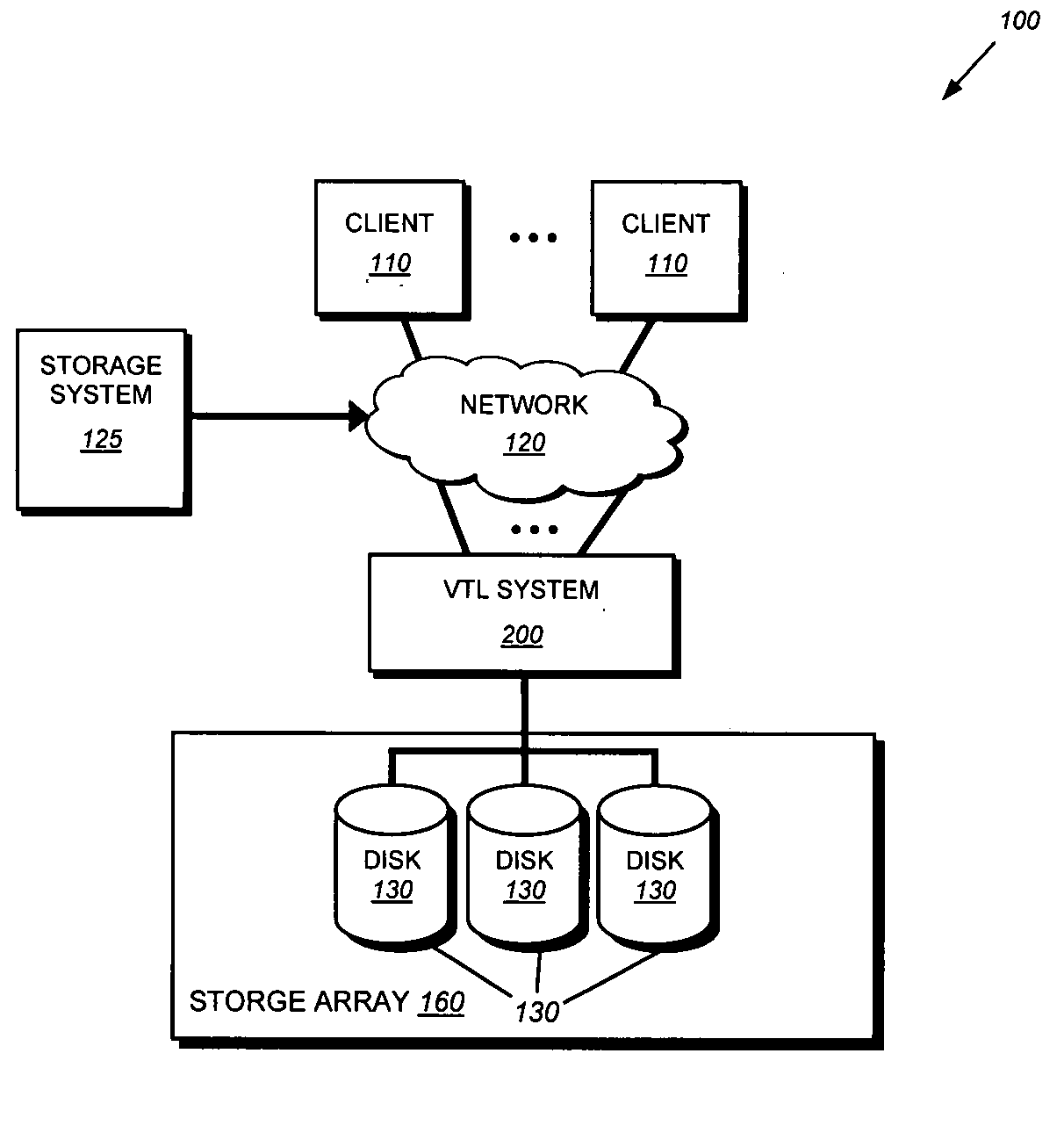
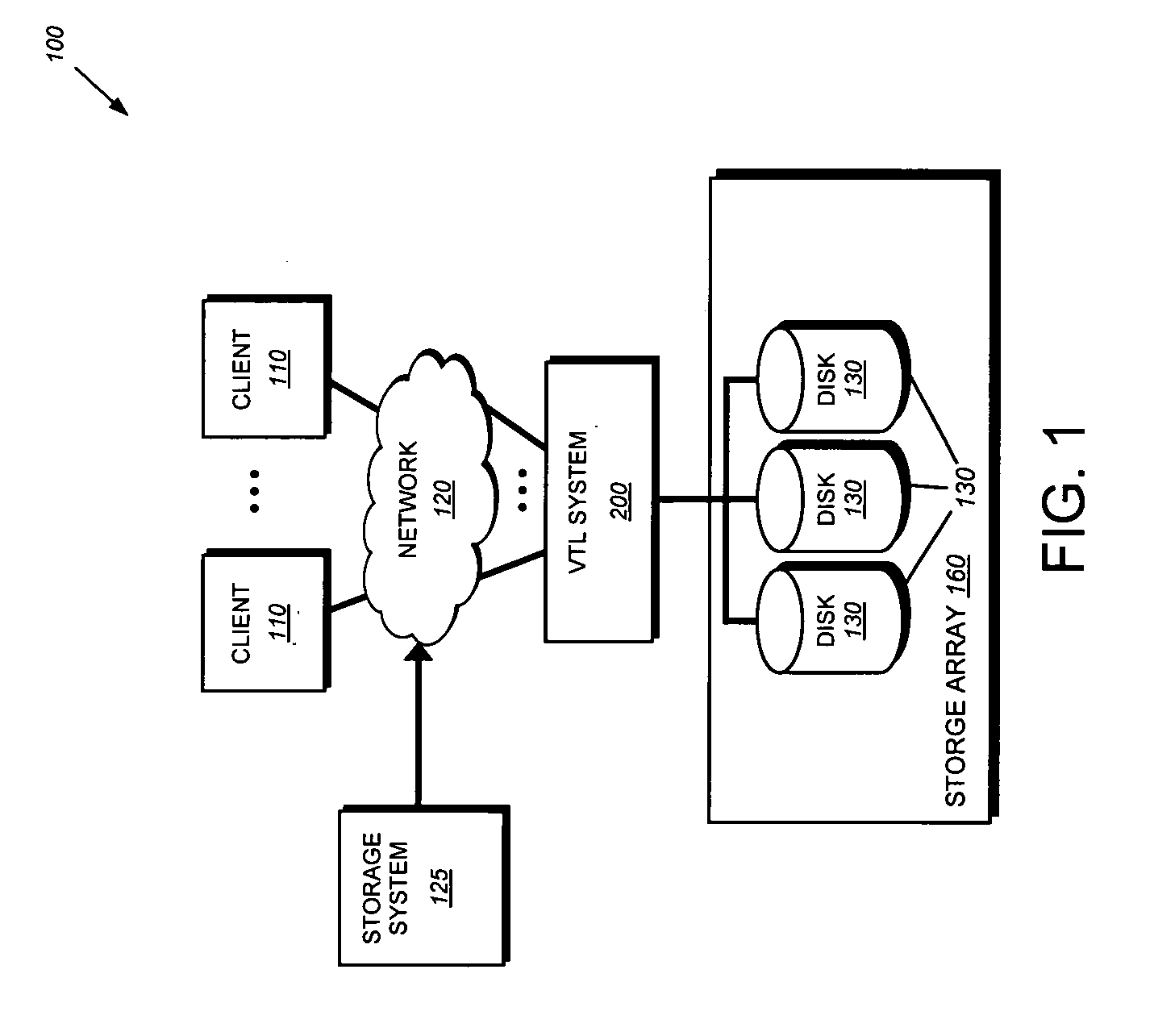
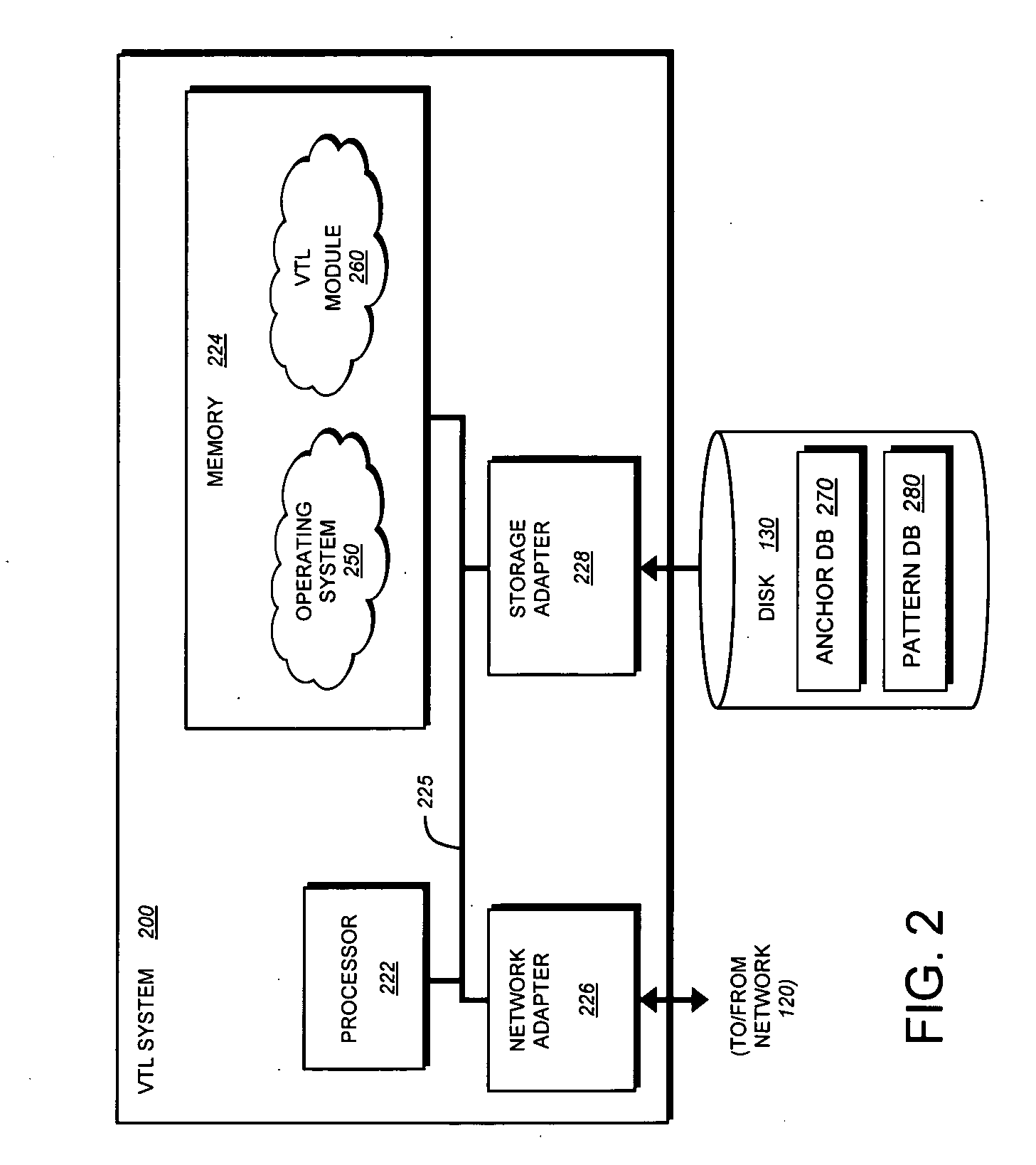
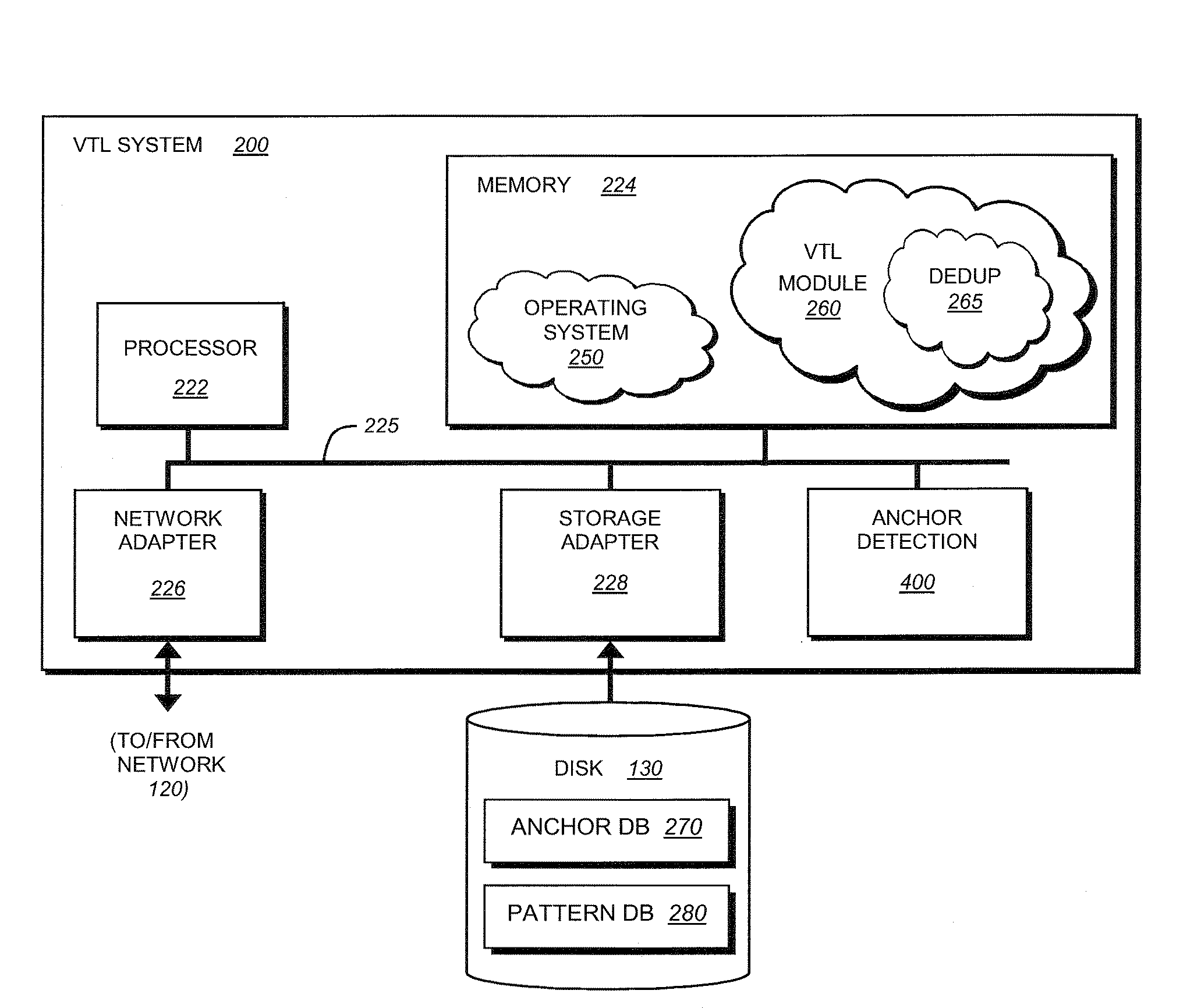
System and method for accelerating anchor point detection
ActiveUS20080301134A1Reduce loadQuick identificationDigital data information retrievalCode conversionComputer hardwareData stream
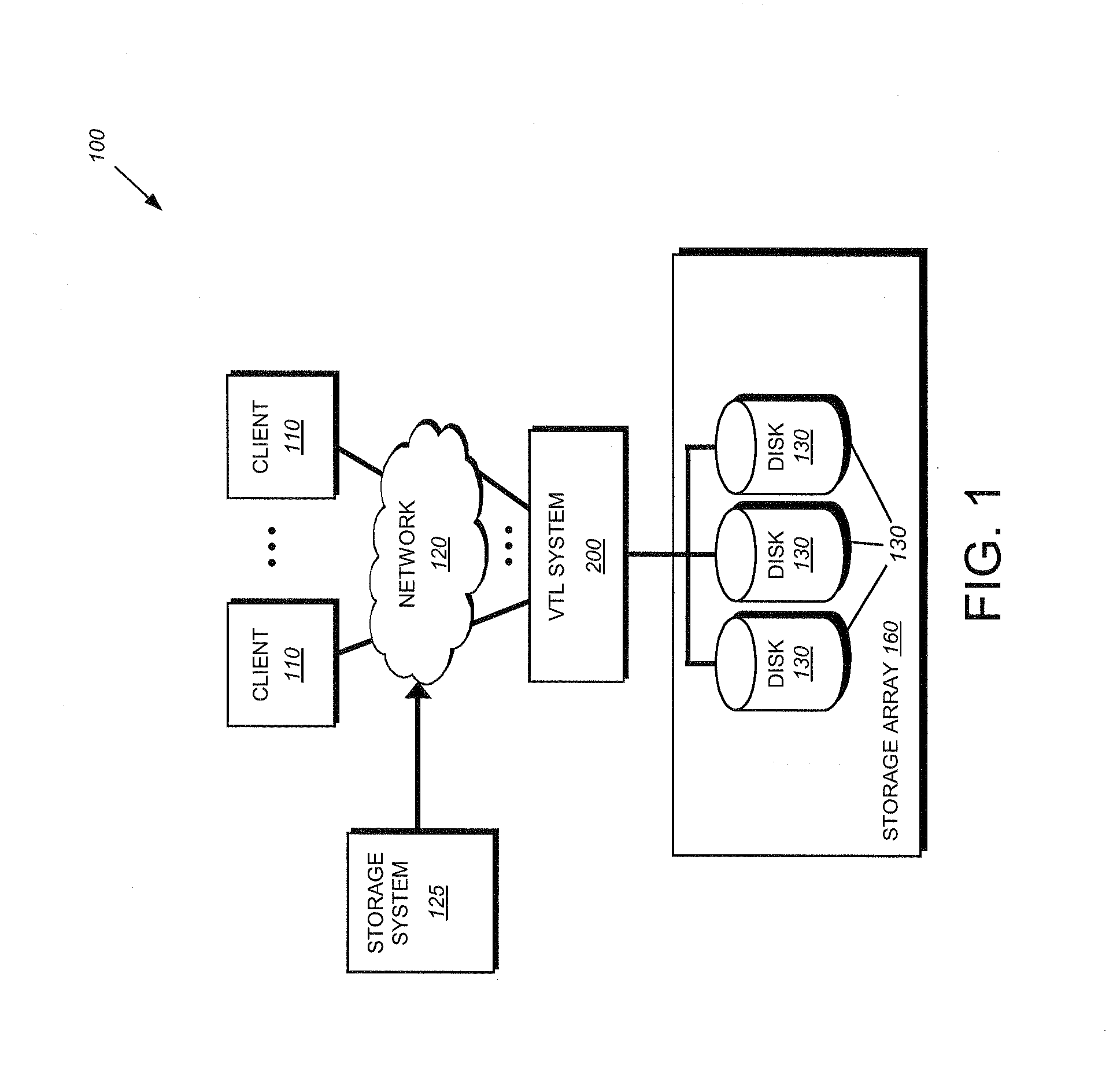
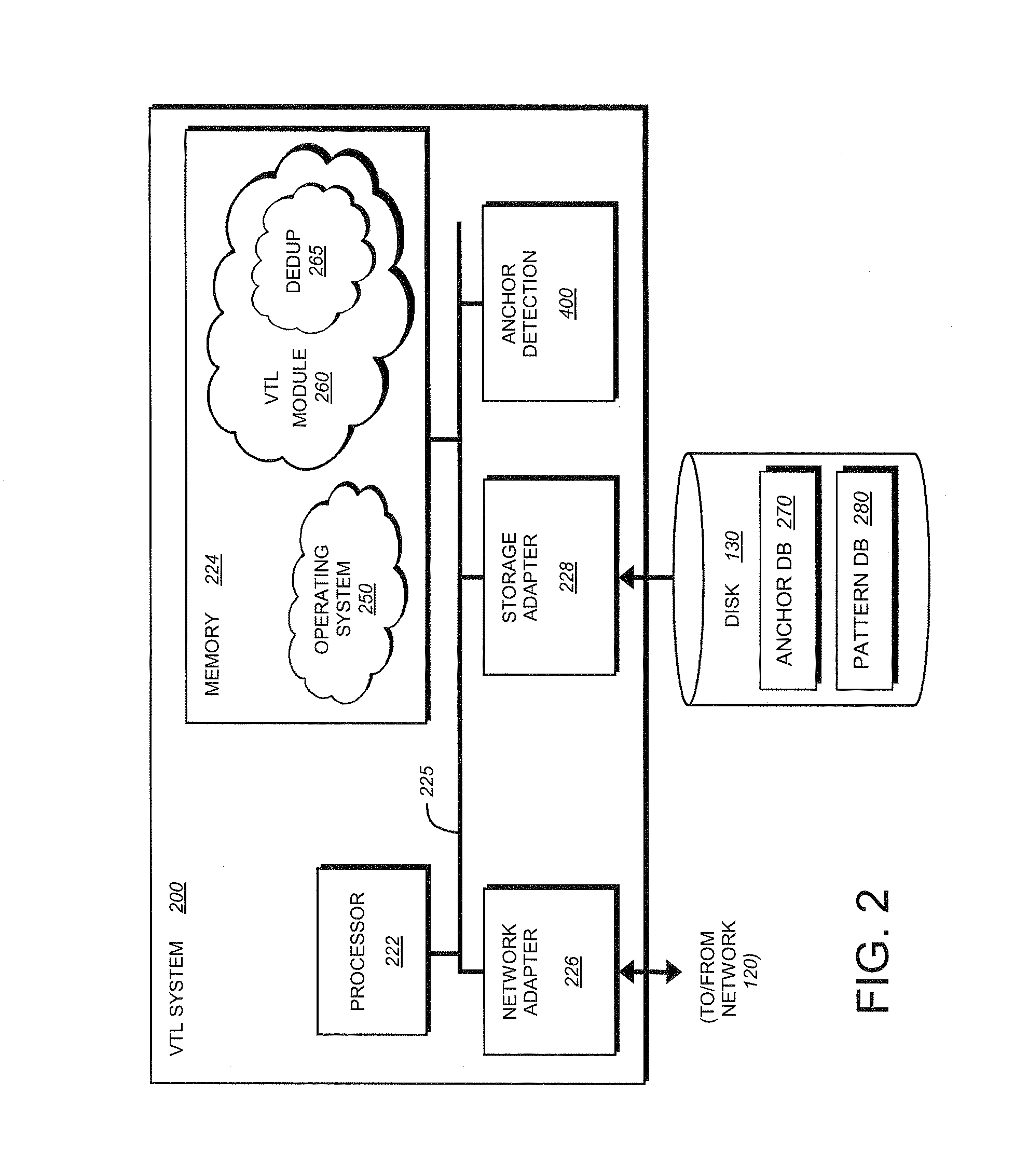
A sampling based technique for eliminating duplicate data (de-duplication) stored on storage resources, is provided. According to the invention, when a new data set, e.g., a backup data stream, is received by a server, e.g., a storage system or virtual tape library (VTL) system implementing the invention, one or more anchors are identified within the new data set. The anchors are identified using a novel anchor detection circuitry in accordance with an illustrative embodiment of the present invention. Upon receipt of the new data set by, for example, a network adapter of a VTL system, the data set is transferred using direct memory access (DMA) operations to a memory associated with an anchor detection hardware card that is operatively interconnected with the storage system. The anchor detection hardware card may be implemented as, for example, a FPGA is to quickly identify anchors within the data set. As the anchor detection process is performed using a hardware assist, the load on a main processor of the system is reduced, thereby enabling line speed de-duplication.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com