Patents
Literature
629 results about "Model image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
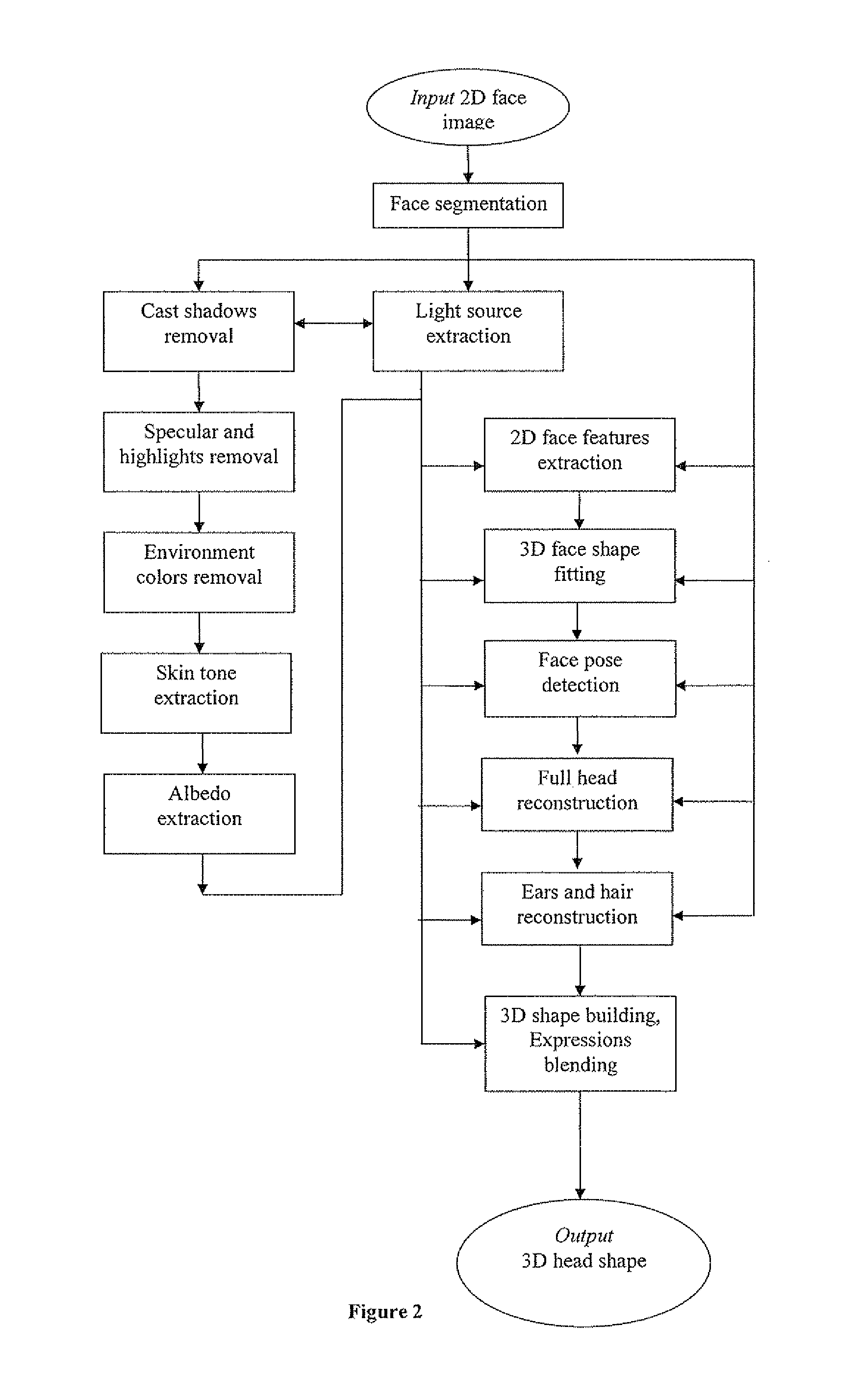
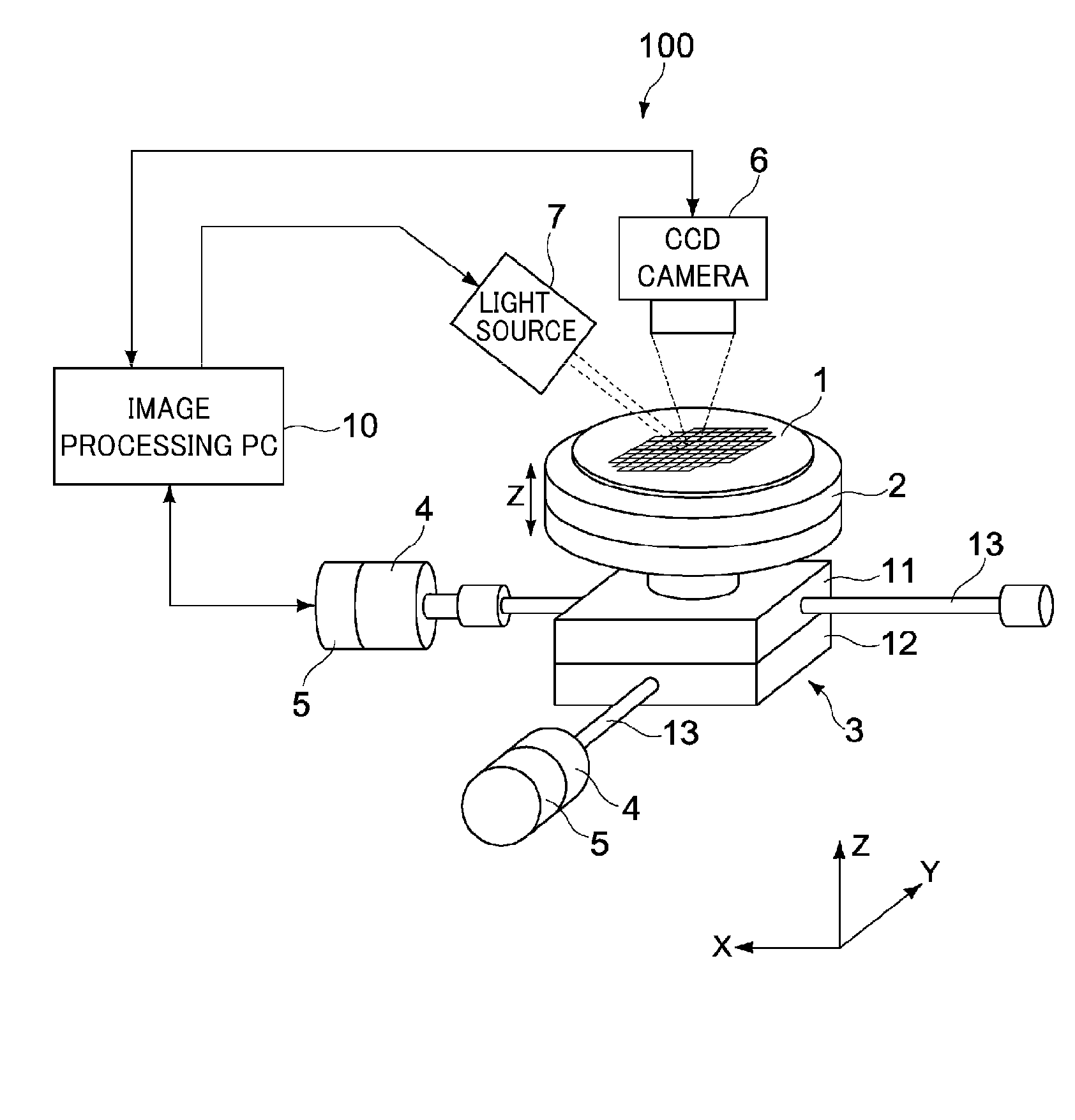
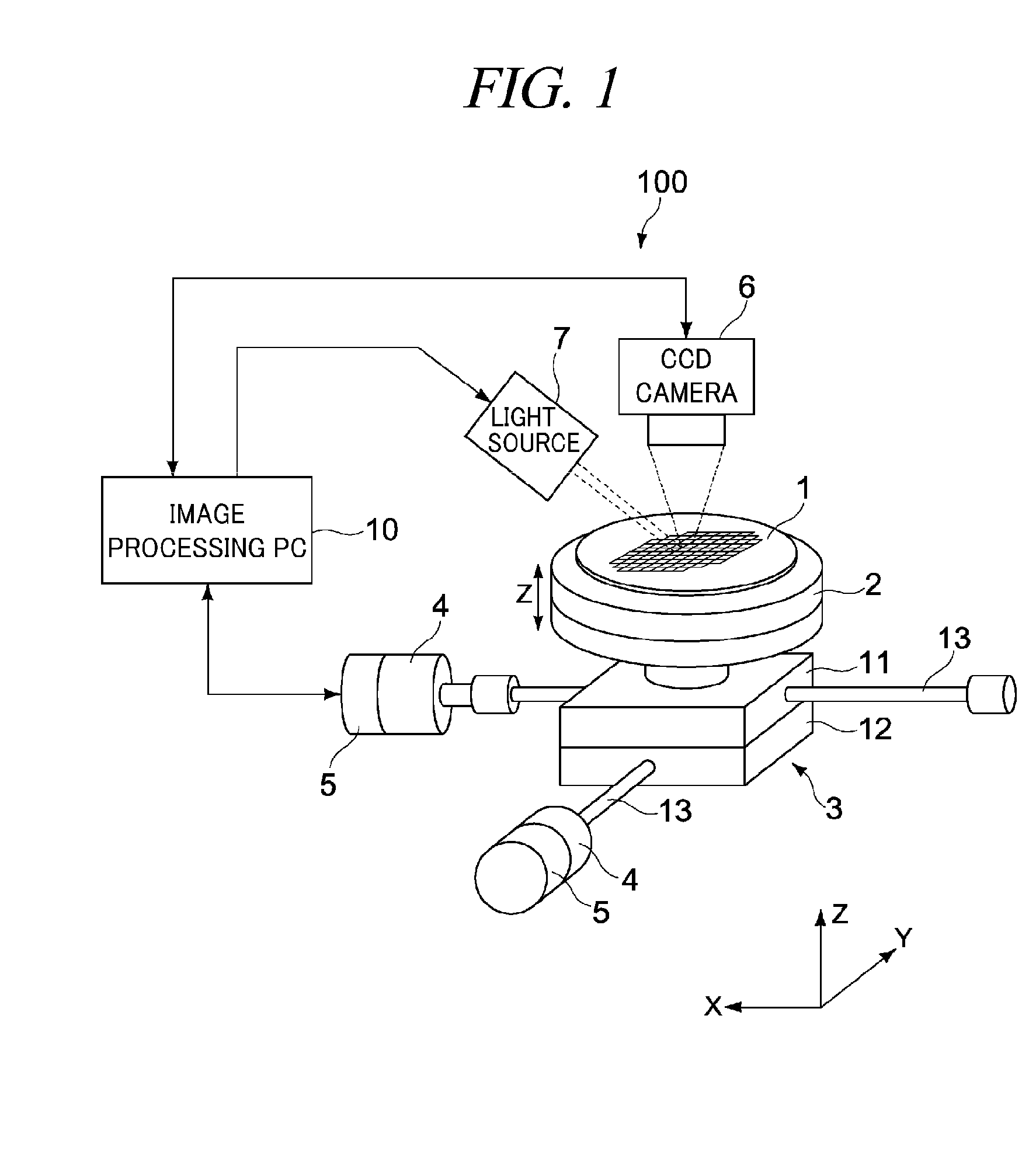
Method and system for processing captured image information in an interactive video display system
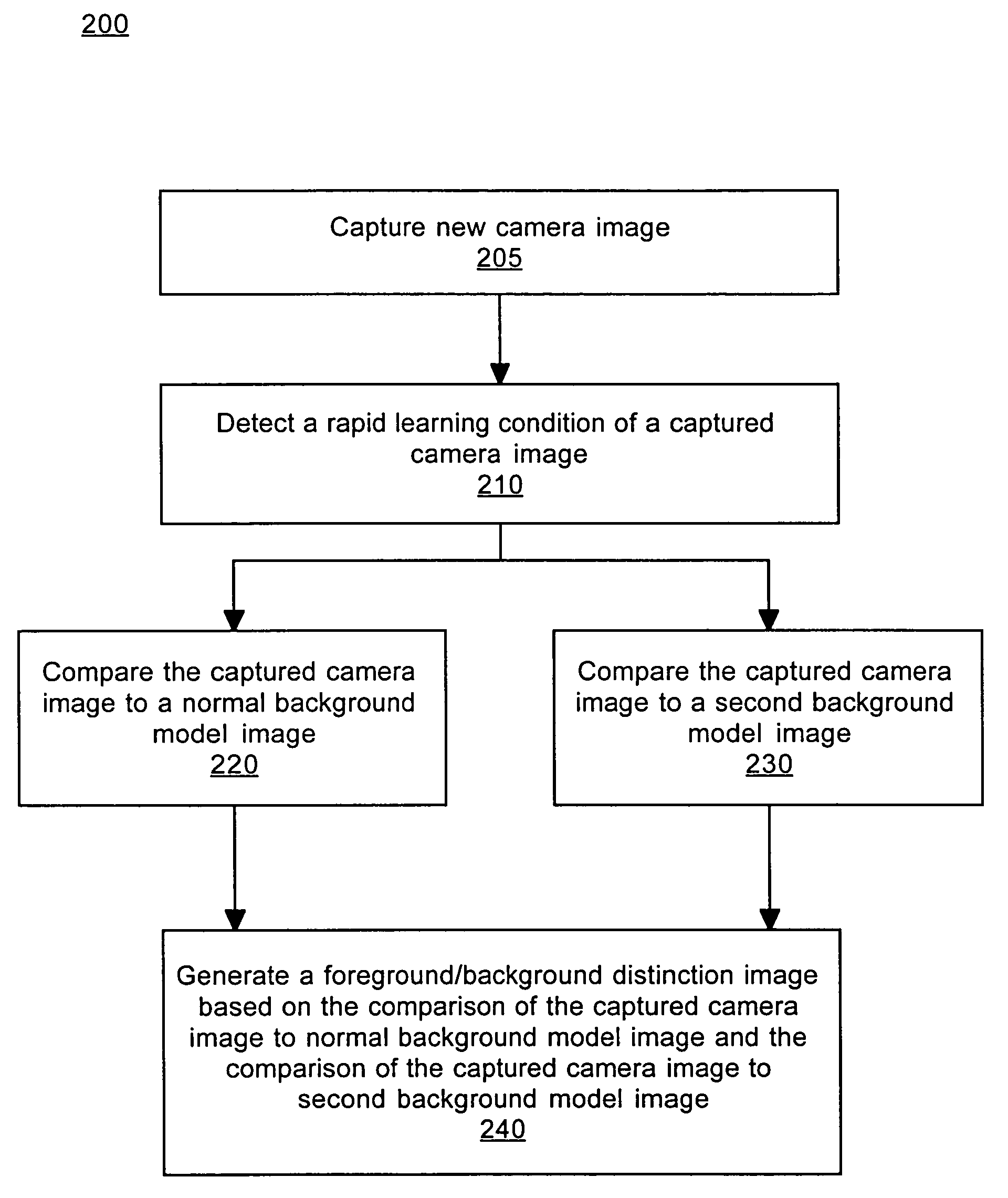
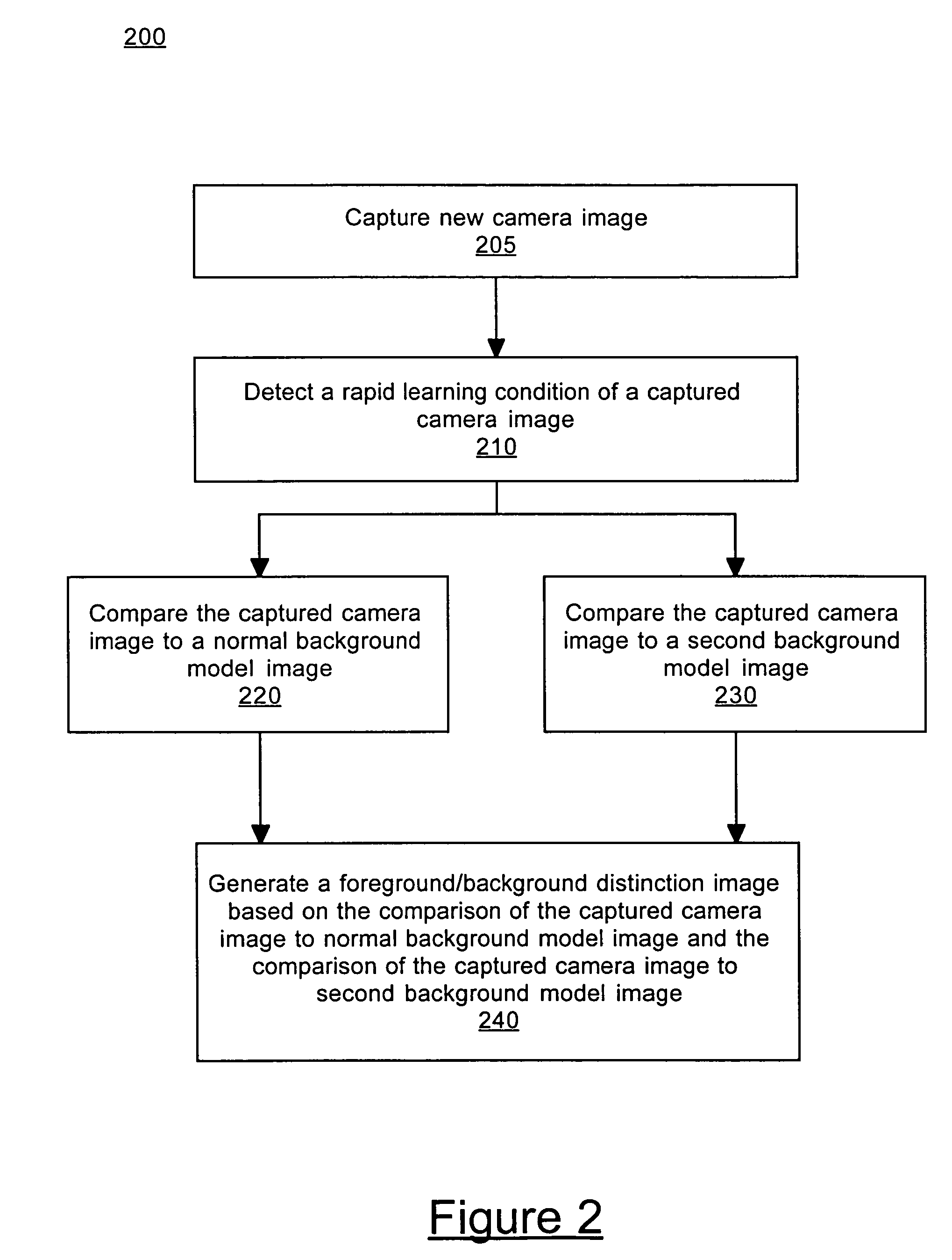
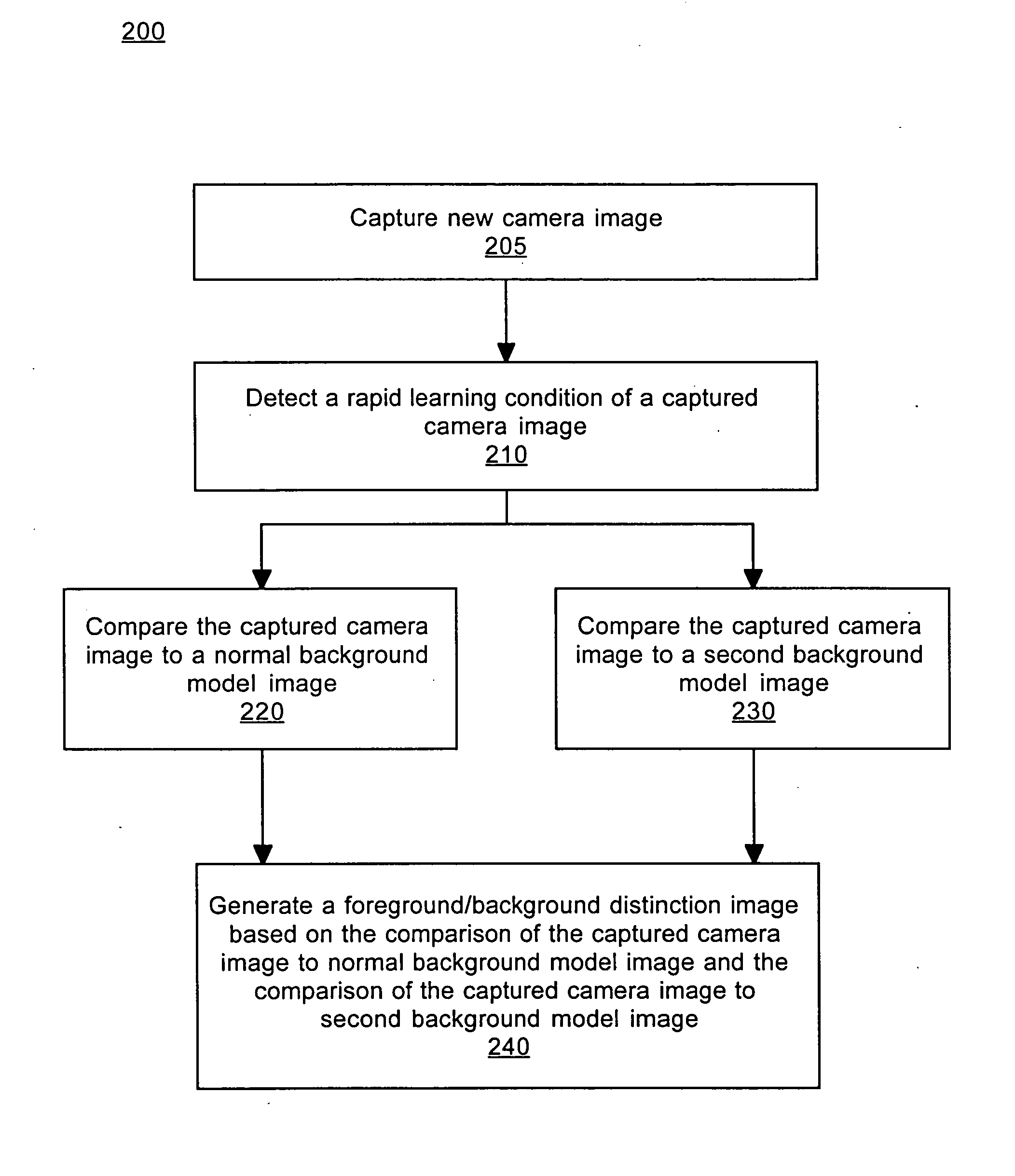
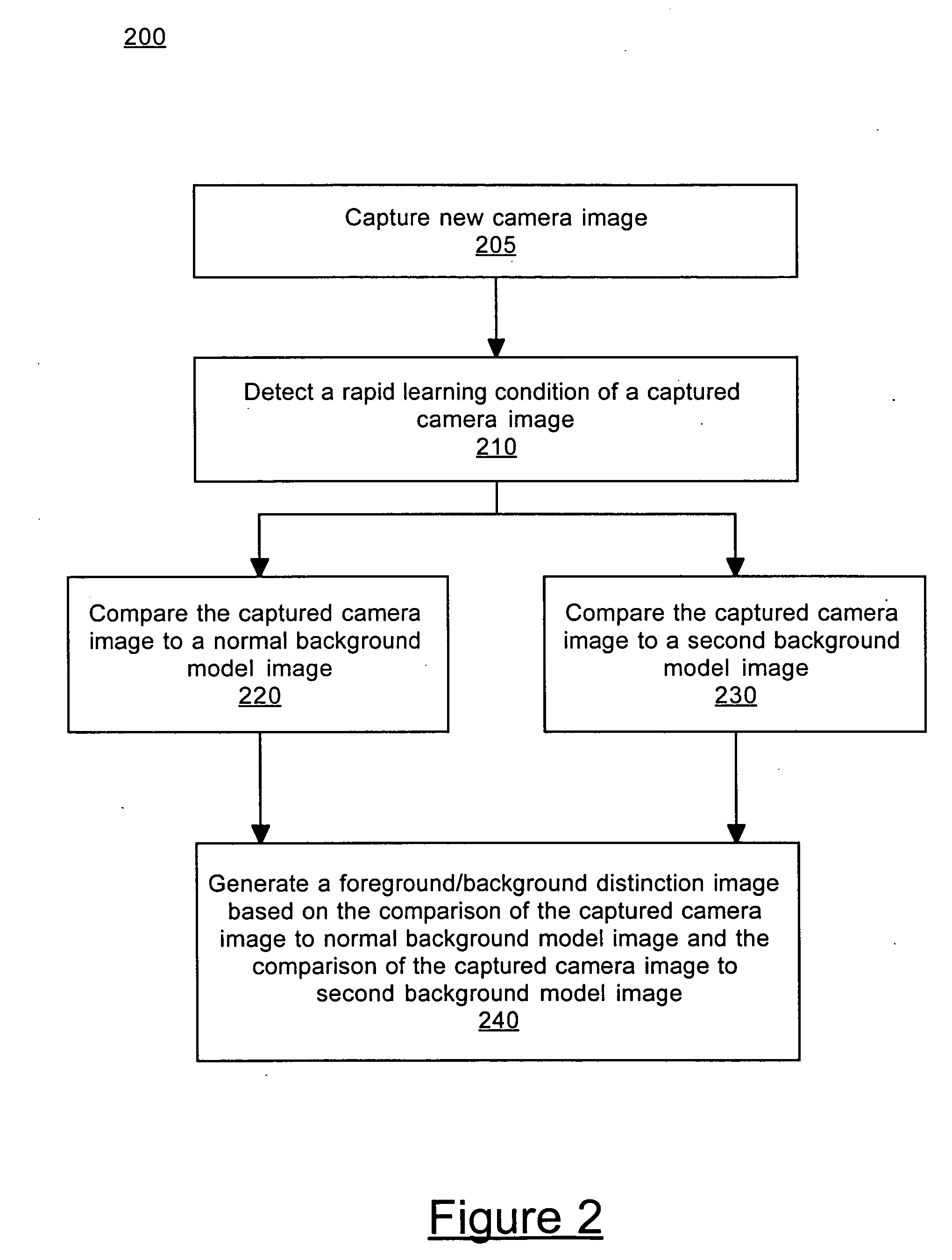
A method and system for processing captured image information in an interactive video display system. In one embodiment, a special learning condition of a captured camera image is detected. The captured camera image is compared to a normal background model image and to a second background model image, wherein the second background model is learned at a faster rate than the normal background model. A vision image is generated based on the comparisons. In another embodiment, an object in the captured image information that does not move for a predetermined time period is detected. A burn-in image comprising the object is generated, wherein the burn-in image is operable to allow a vision system of the interactive video display system to classify the object as background.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
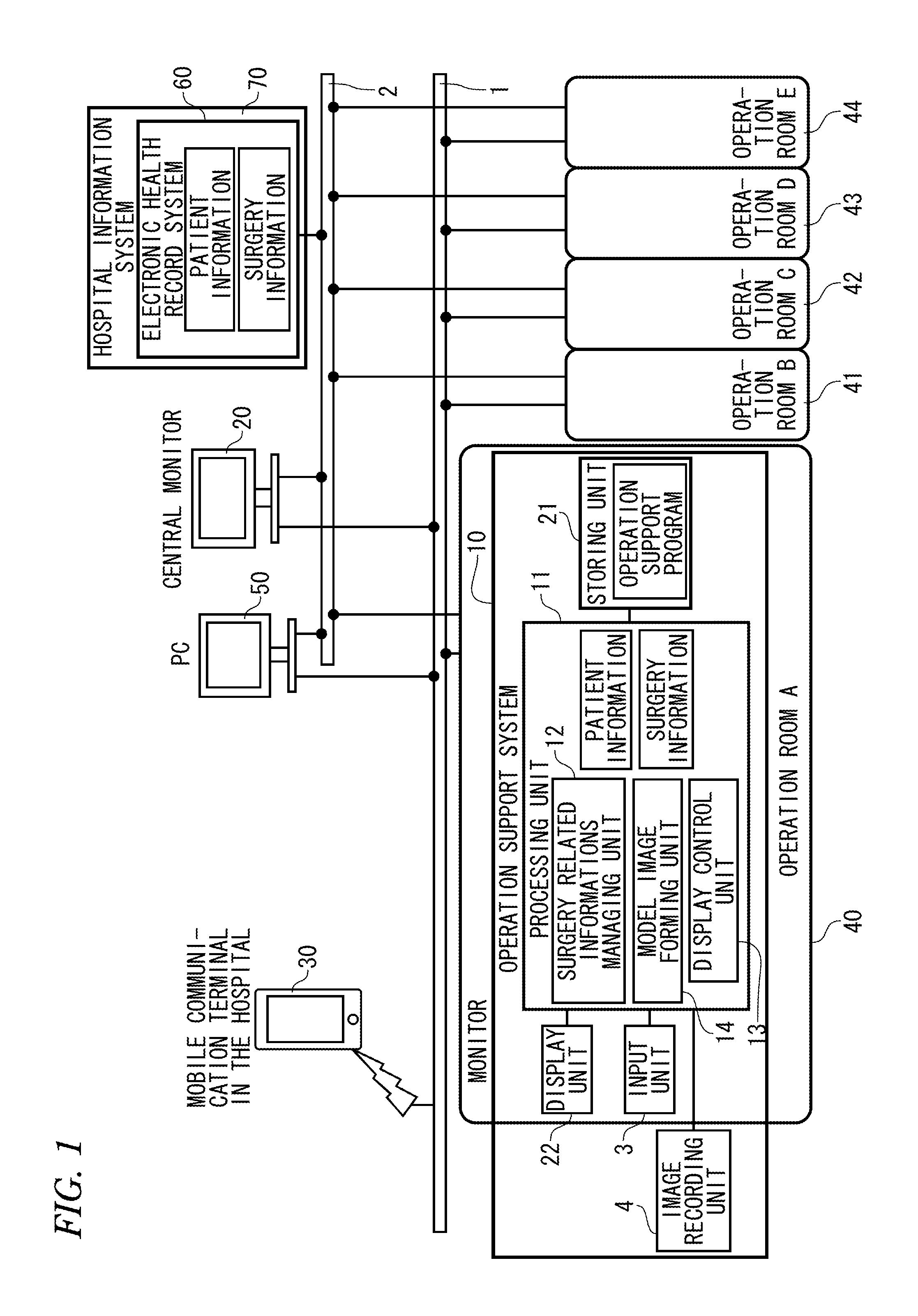
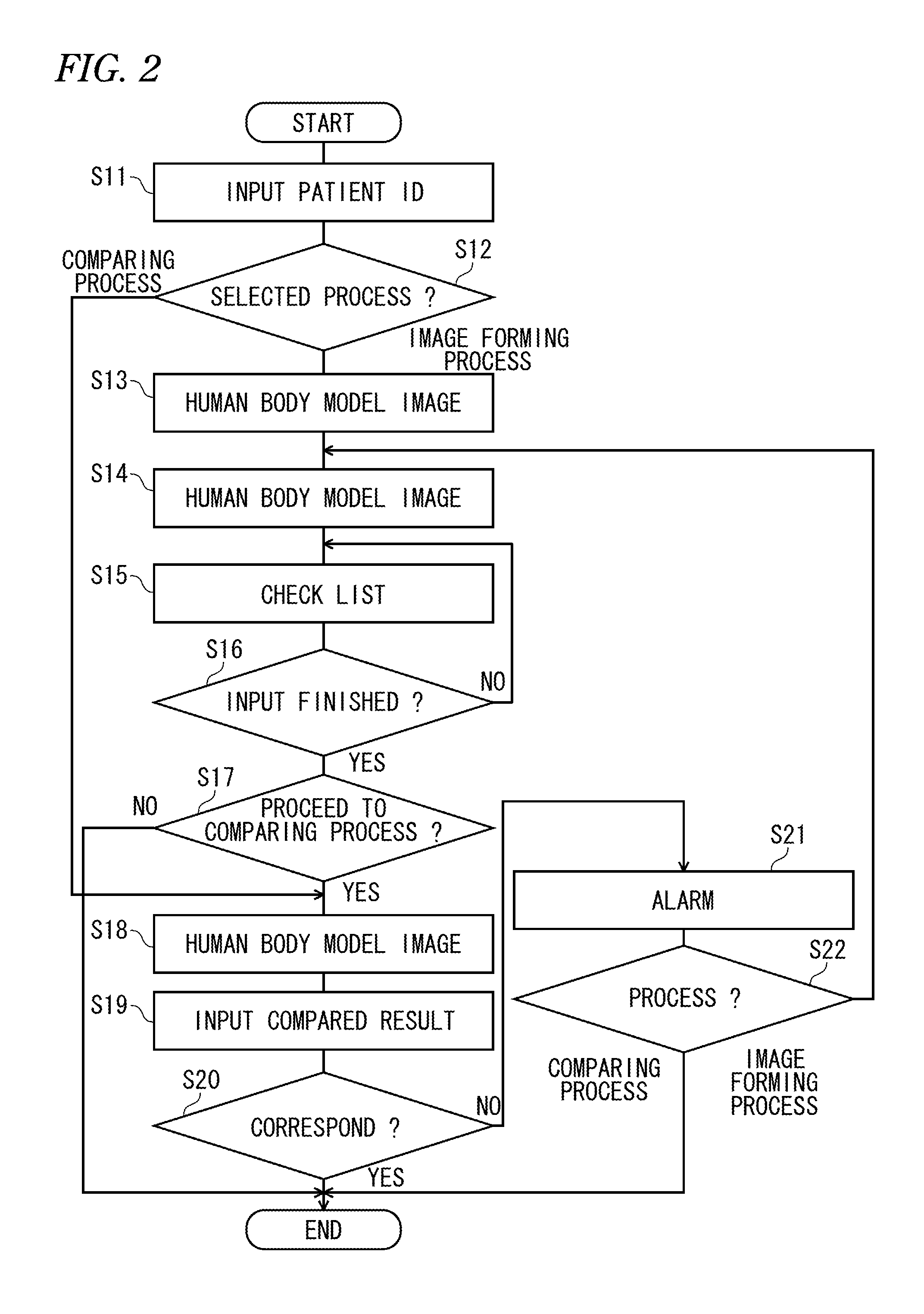
Operation support system
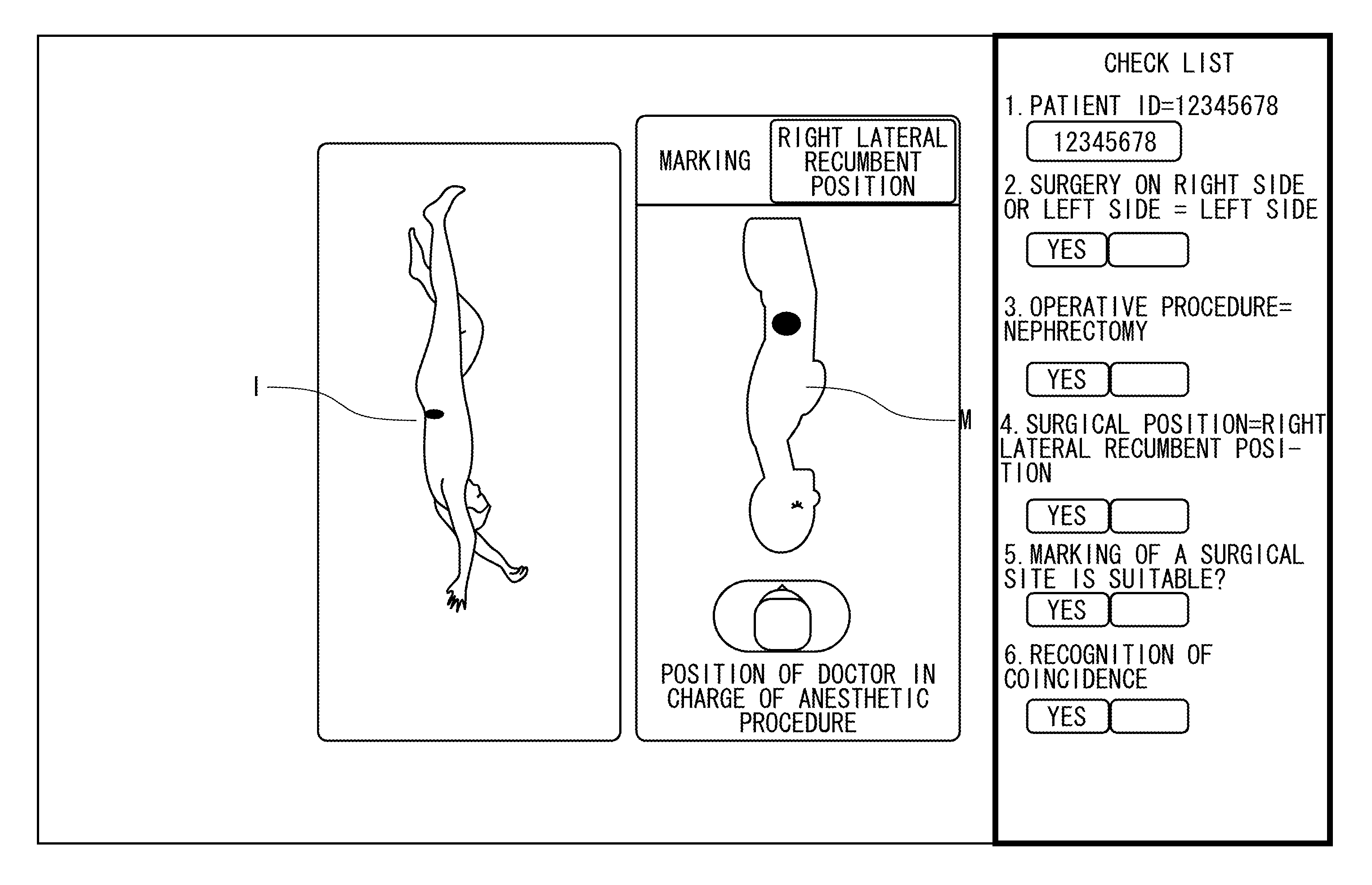
InactiveUS20140092089A1Reduce medical errorsReduce errorsMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical siteSurgical positions
To reduce medical mistakes, for instance, a surgical site is mistaken for another part. An operation support system includes a model image forming unit which applies a mark to a surgery site of a corresponding surgical position in accordance with inputted surgery information including an operative procedure, a surgery on right side or left side and the surgical position to form a human body model image and a display control unit which displays the human body model image formed by the model image forming unit on a display unit.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
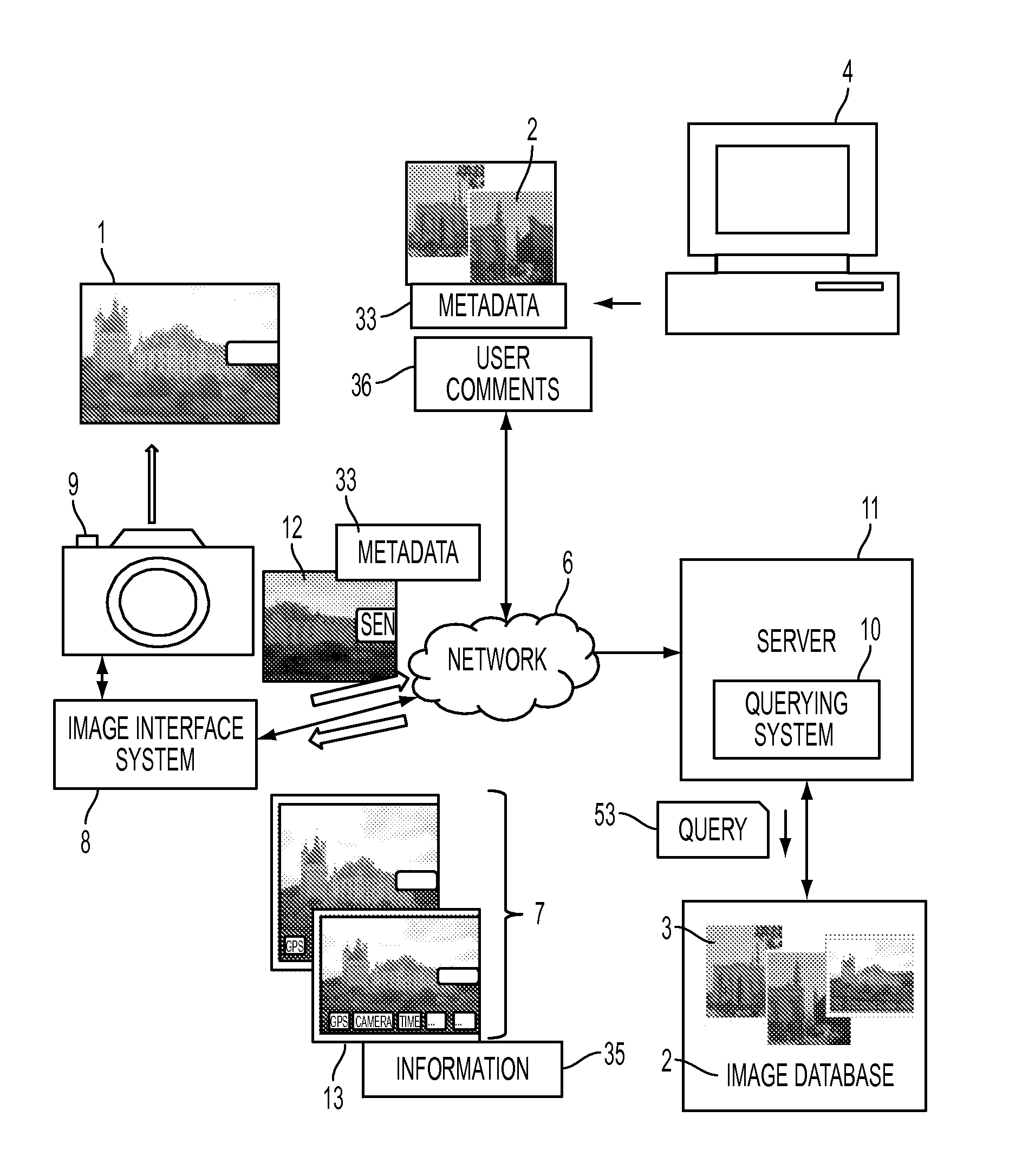
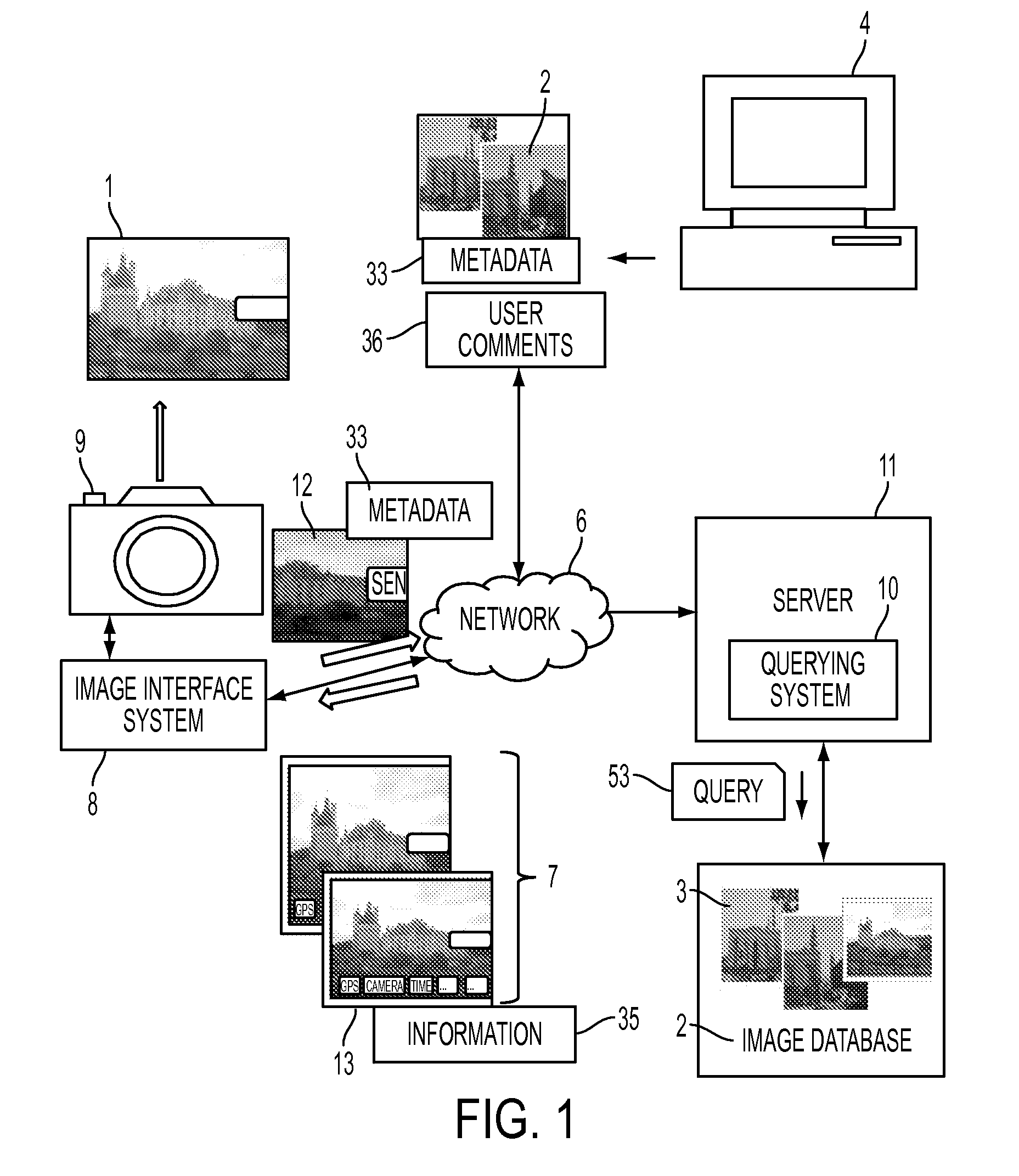
Photography assistant and method for assisting a user in photographing landmarks and scenes
ActiveUS20110314049A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsImage retrievalLandmark
A method and system to help photographers to take better quality pictures of landmarks and scenes are disclosed. A user is guided with examples of existing quality images, which are extracted from a database, of the same or similar landmarks or scenes. The method includes taking a query photograph that may include an image associated with a GPS location and other metadata, and using information extracted from the image to retrieve existing, similar images. The images retrieved may be ordered according to different criteria. When a user selects one as a model image, the user is provided with assistance for taking a target photograph of similar quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
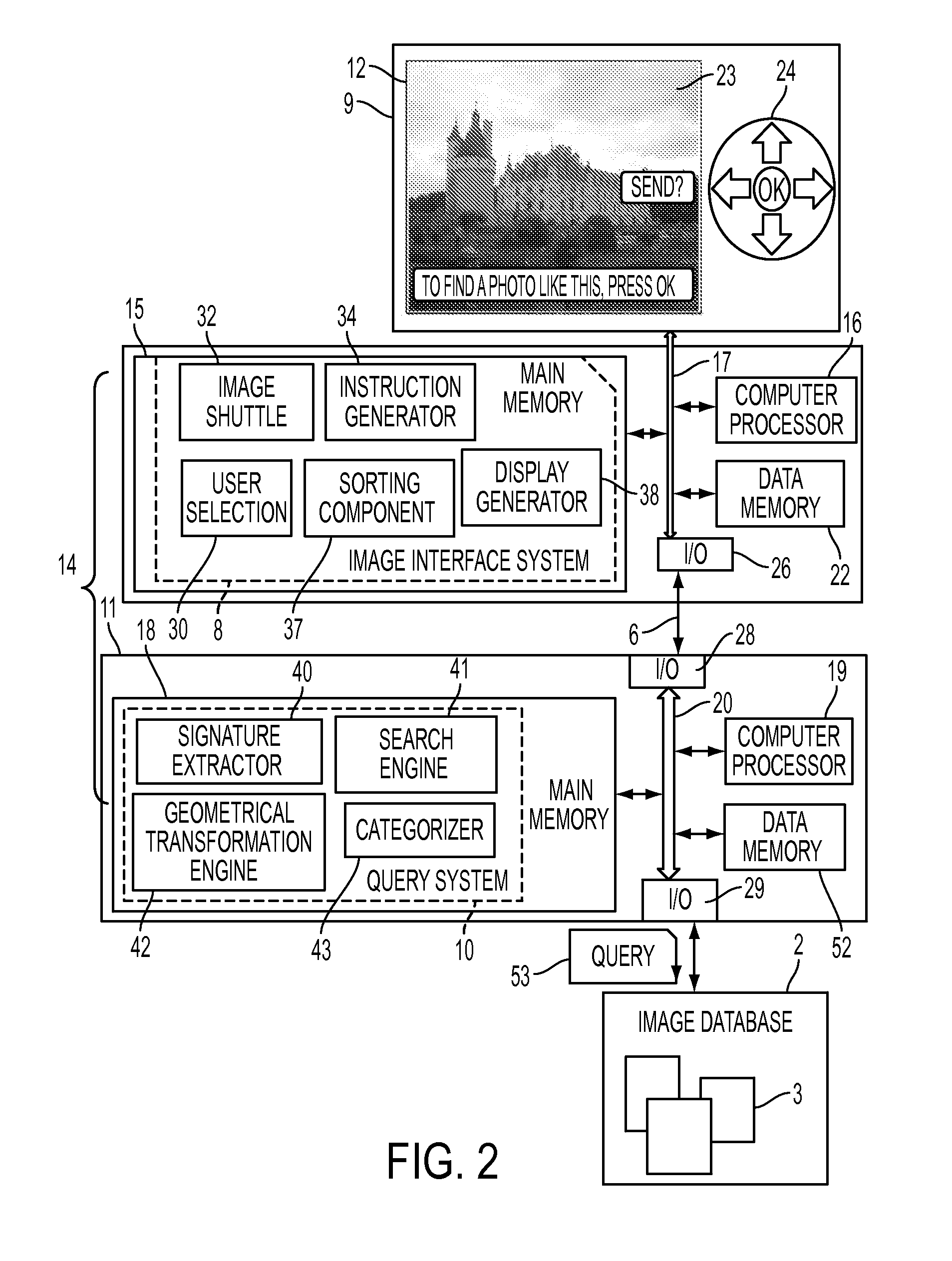
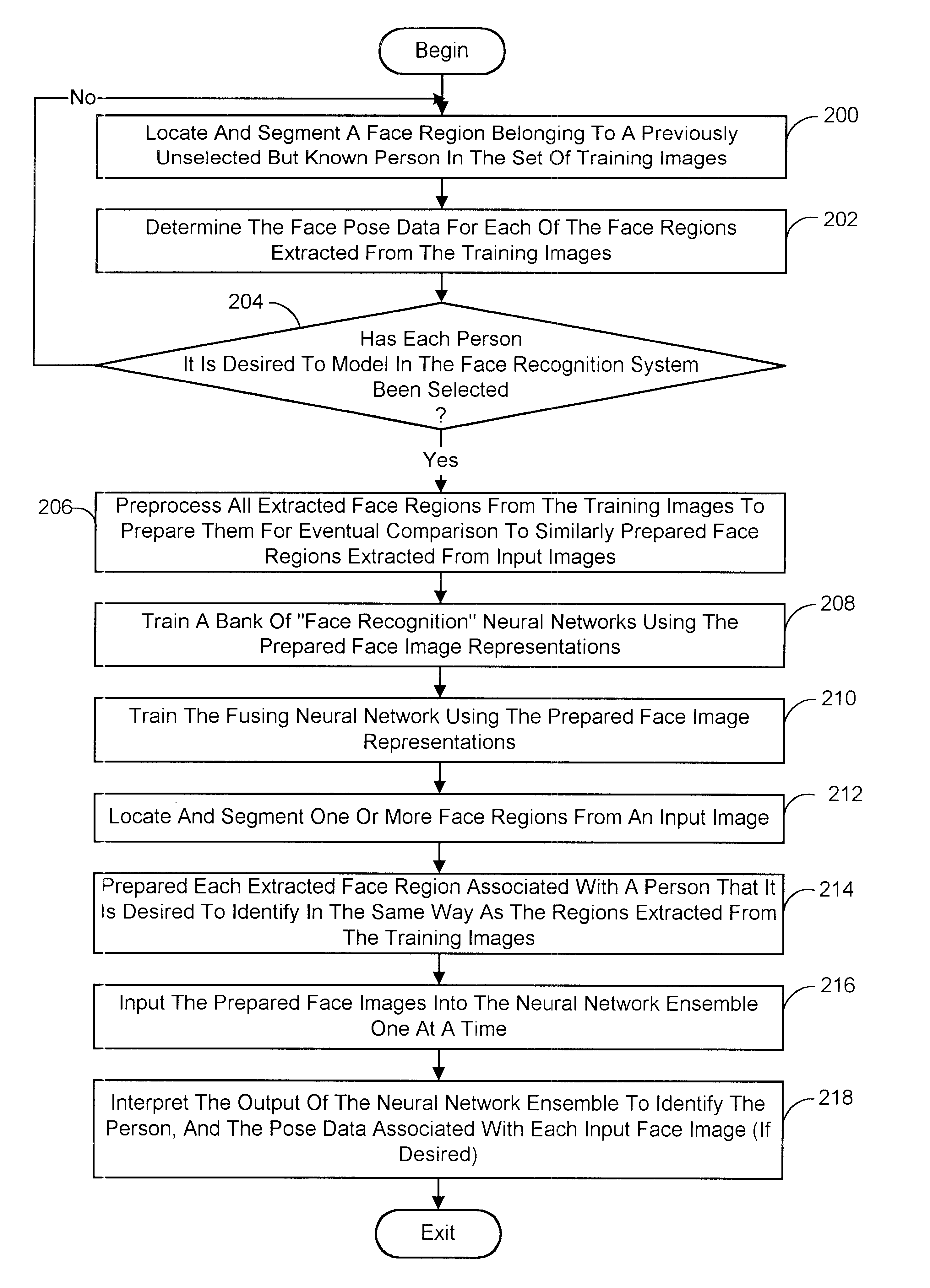
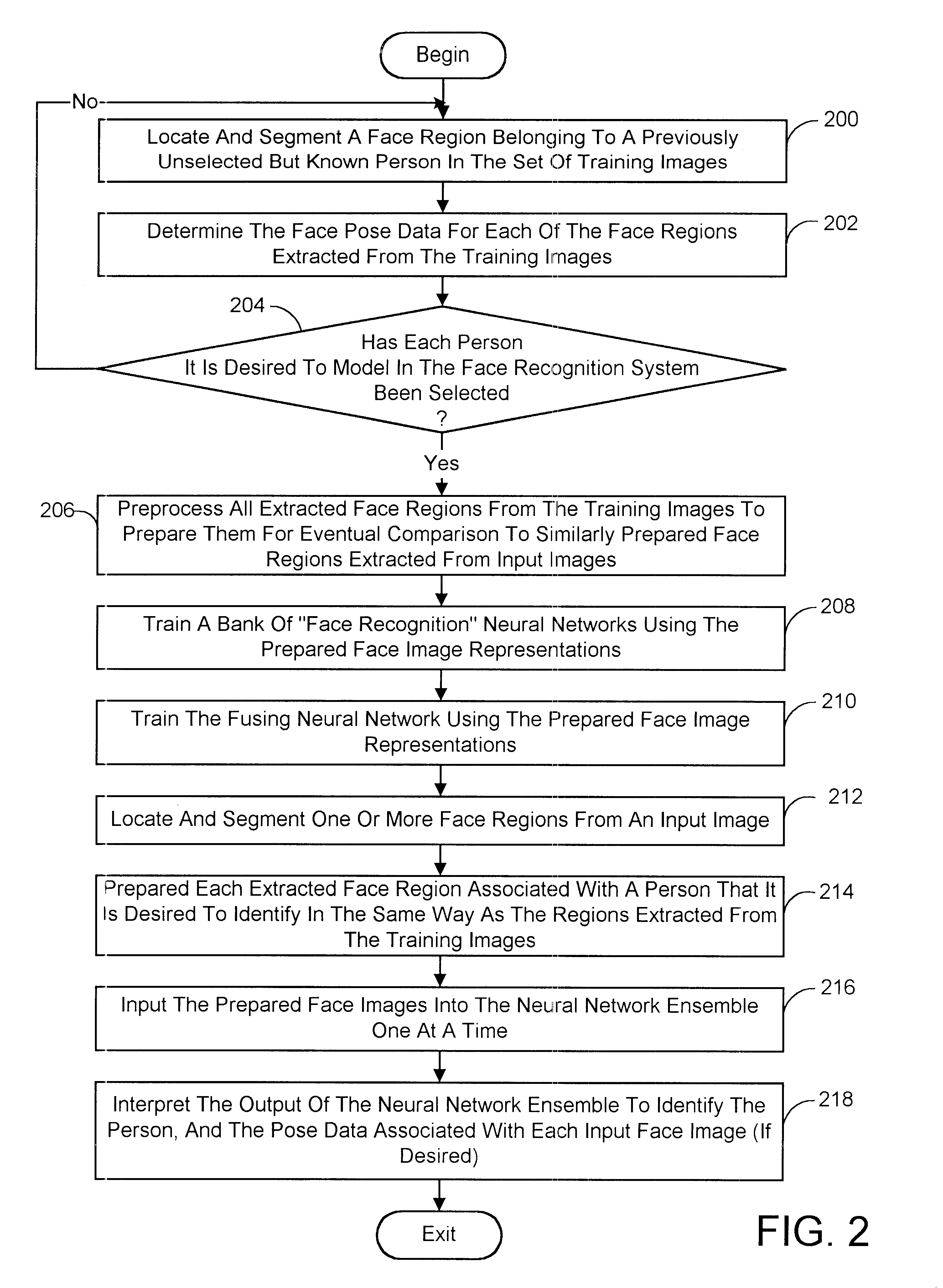
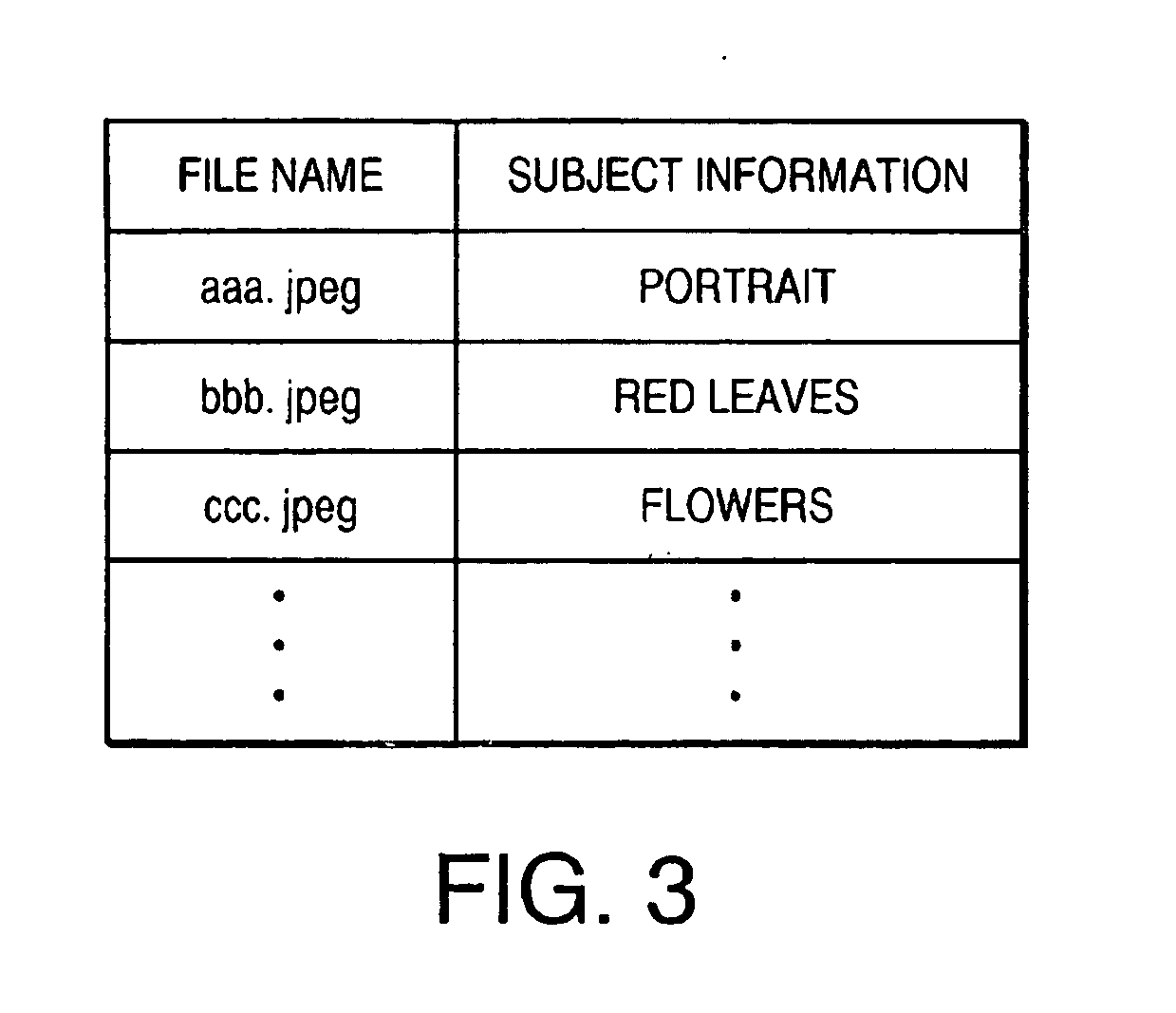
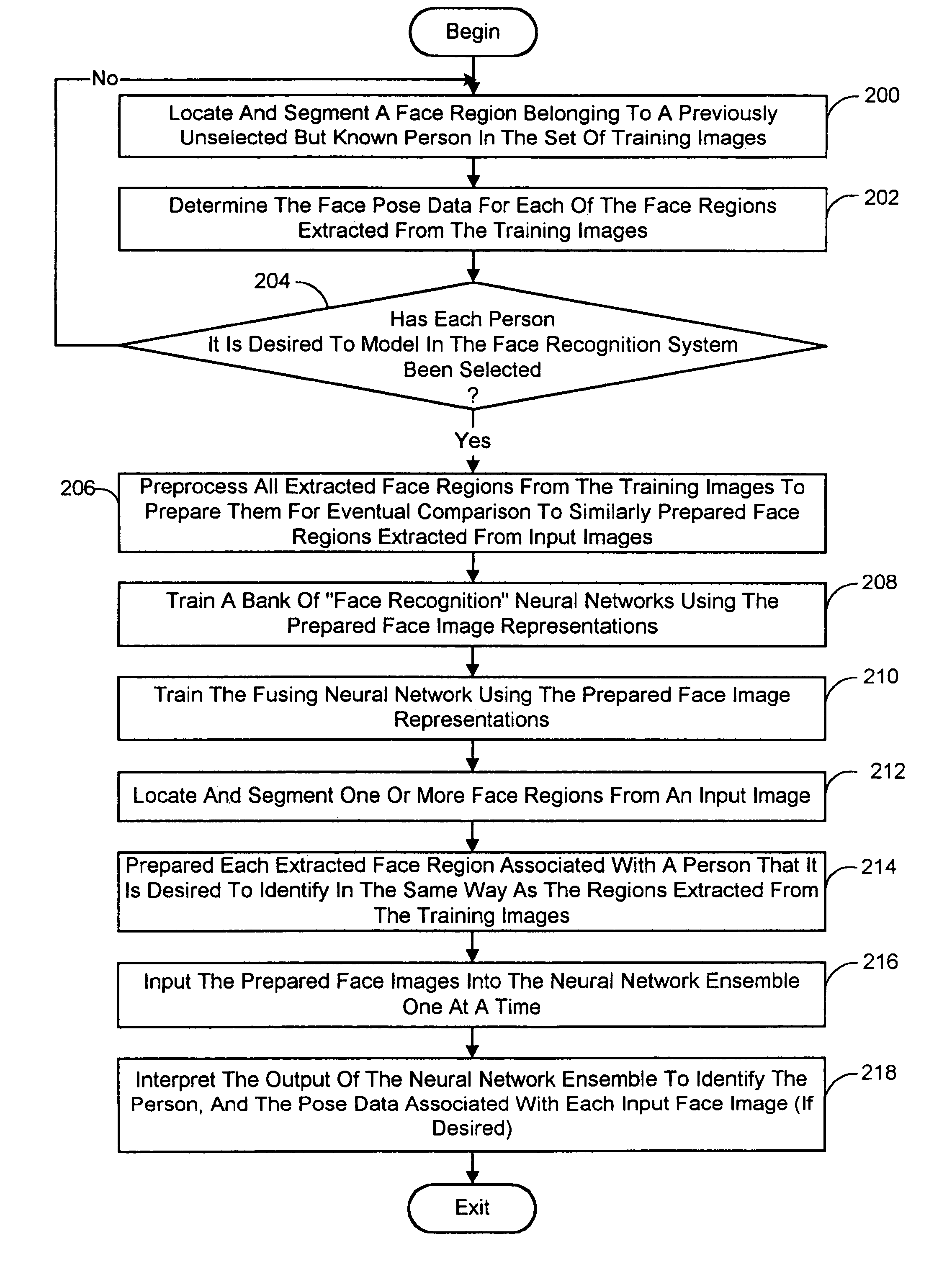
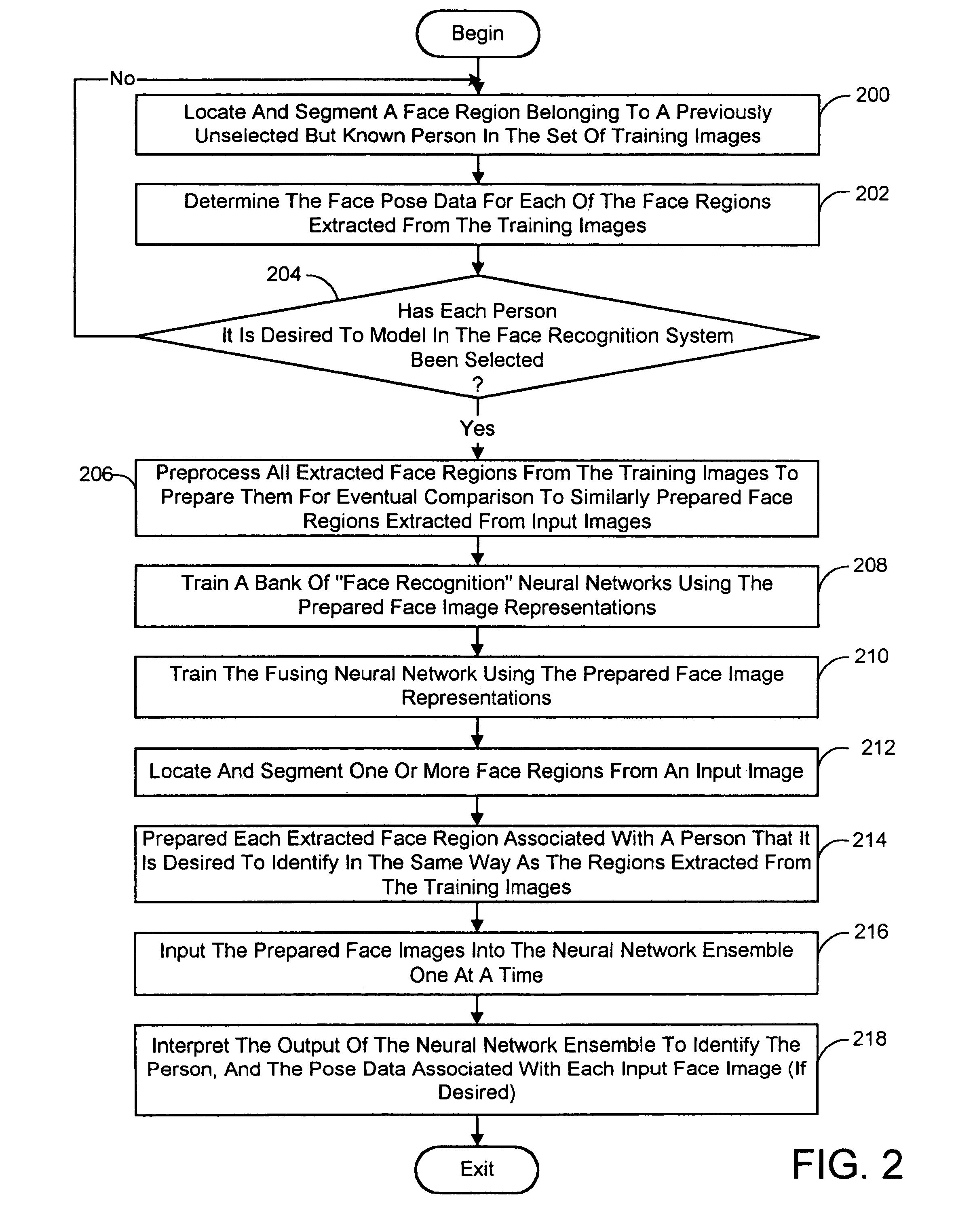
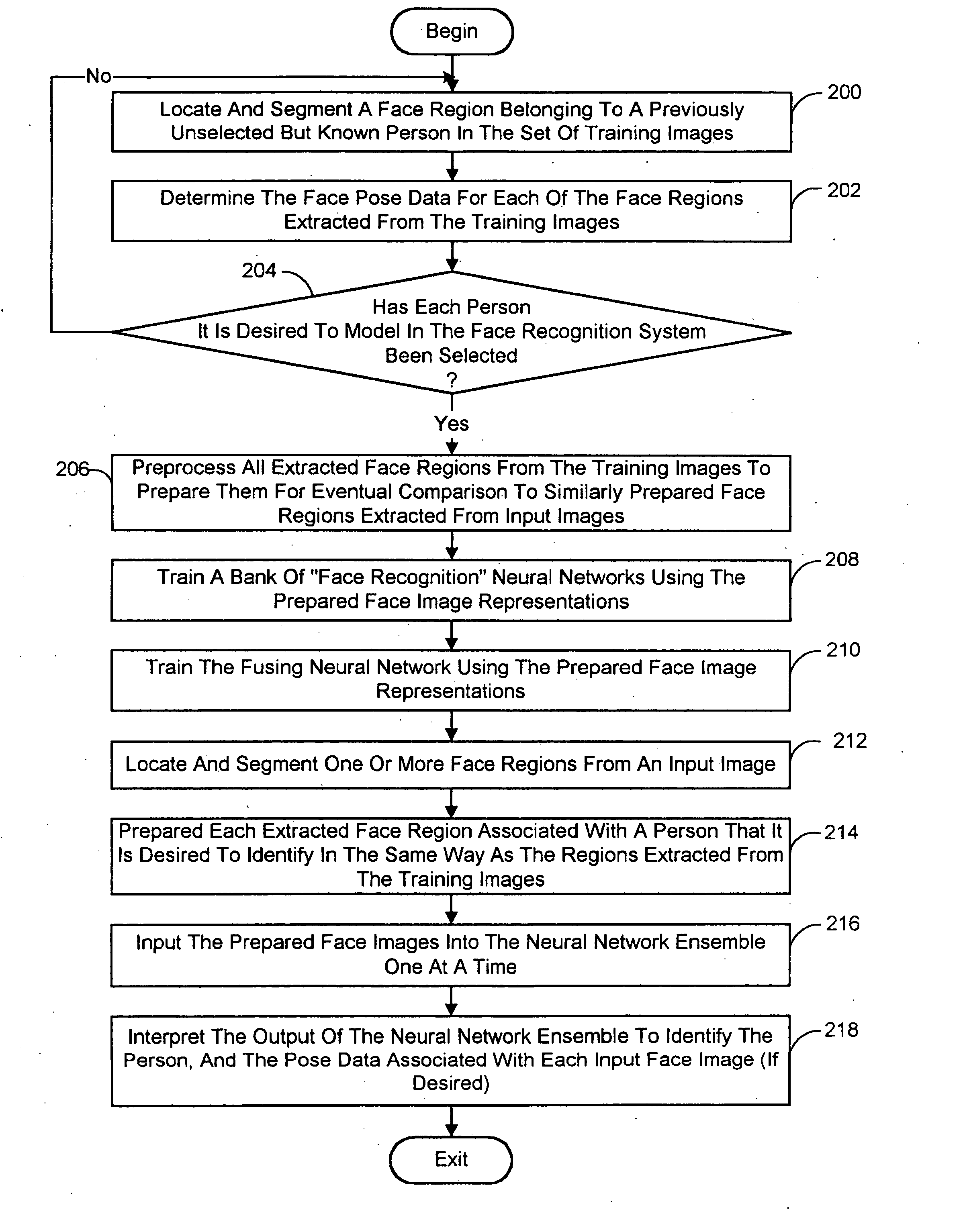
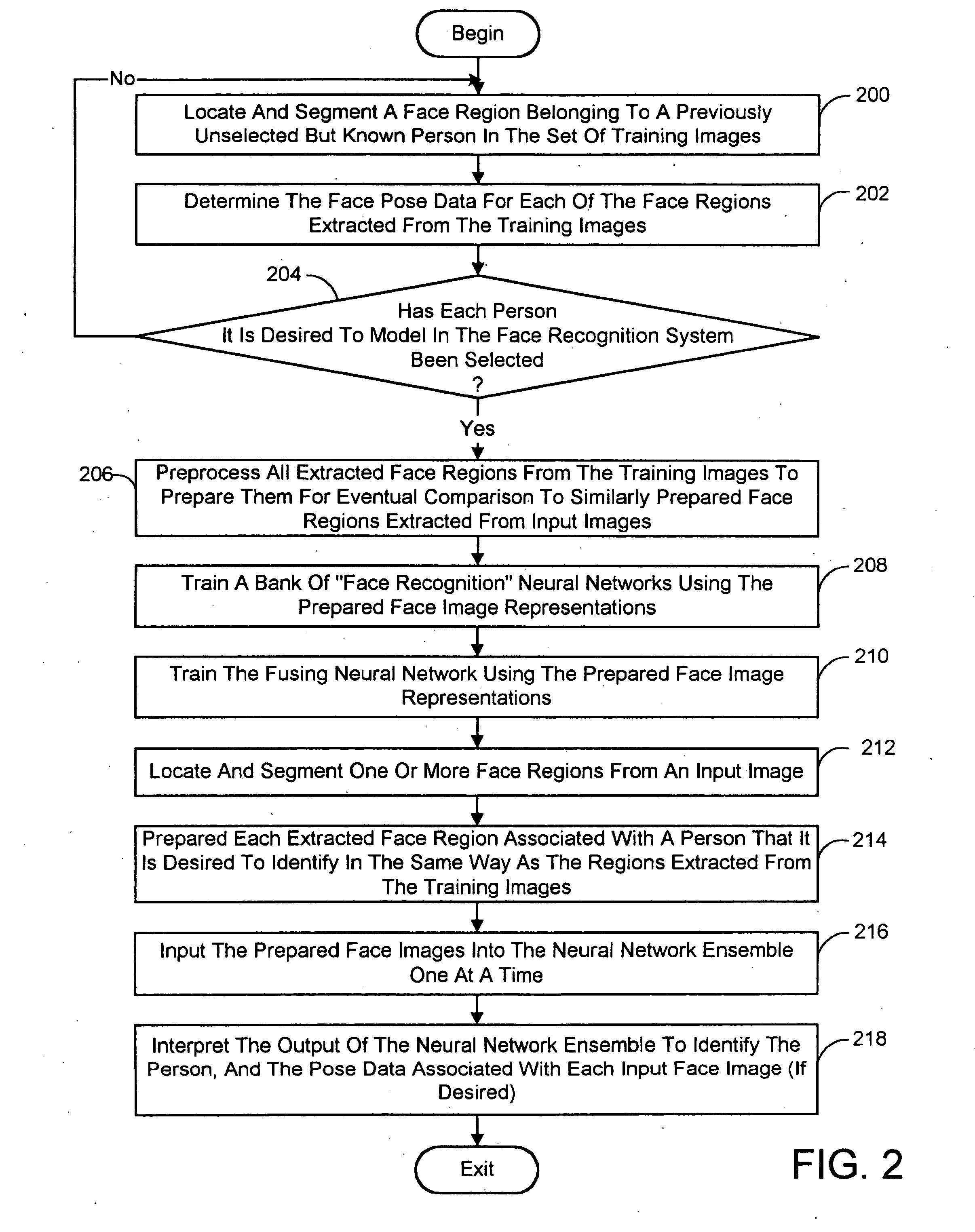
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a person's face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Image capturing apparatus and image capturing method
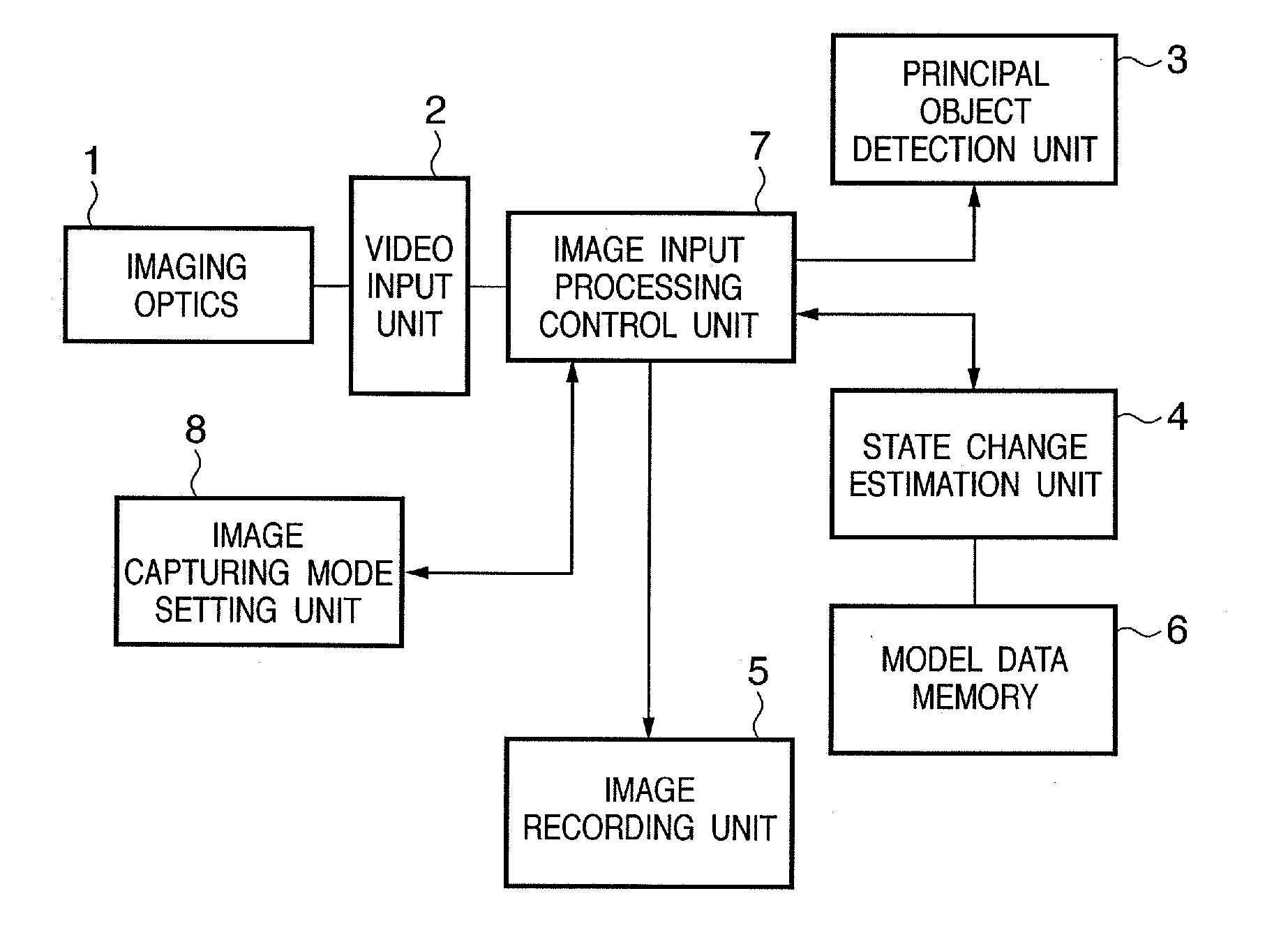
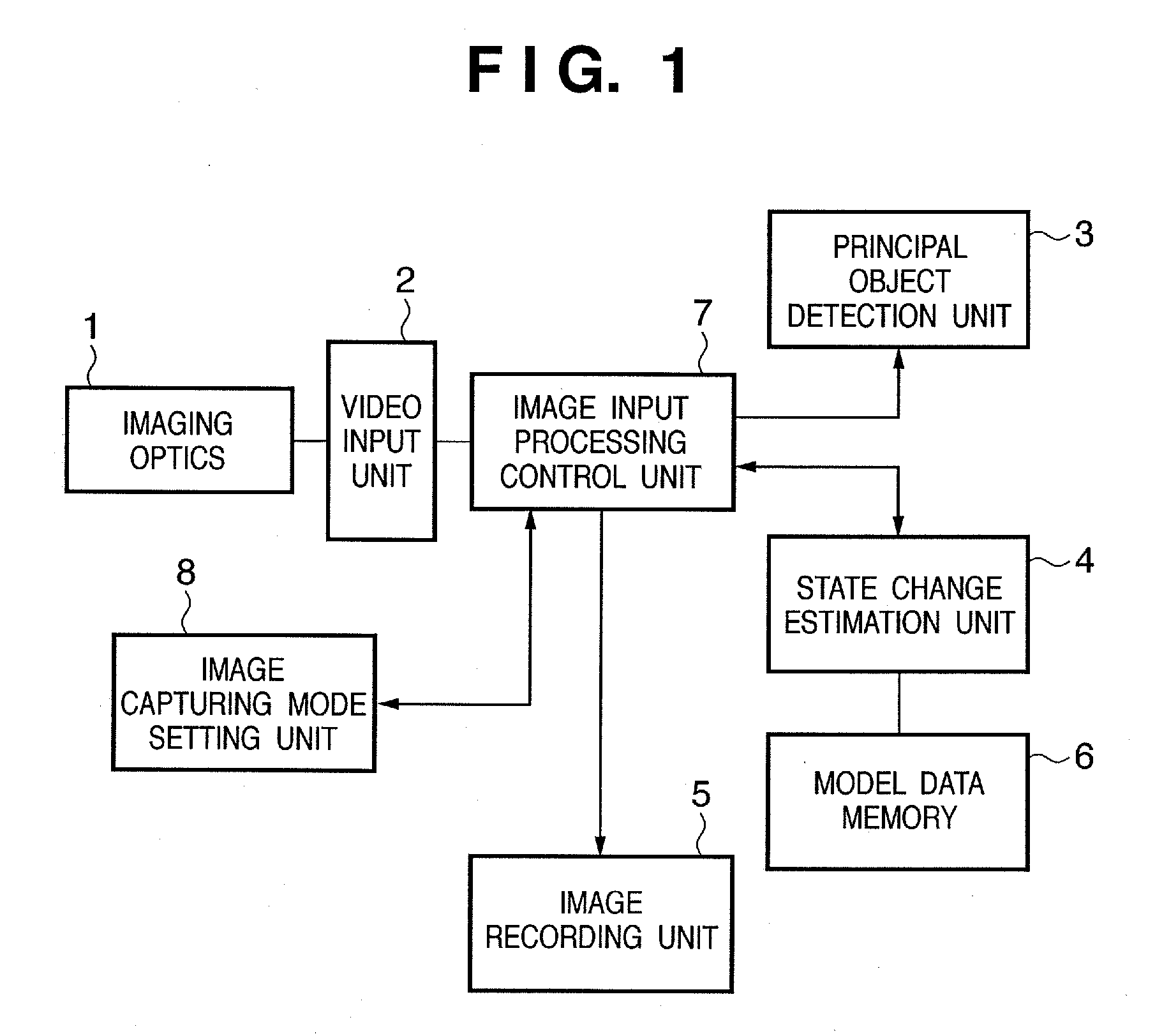
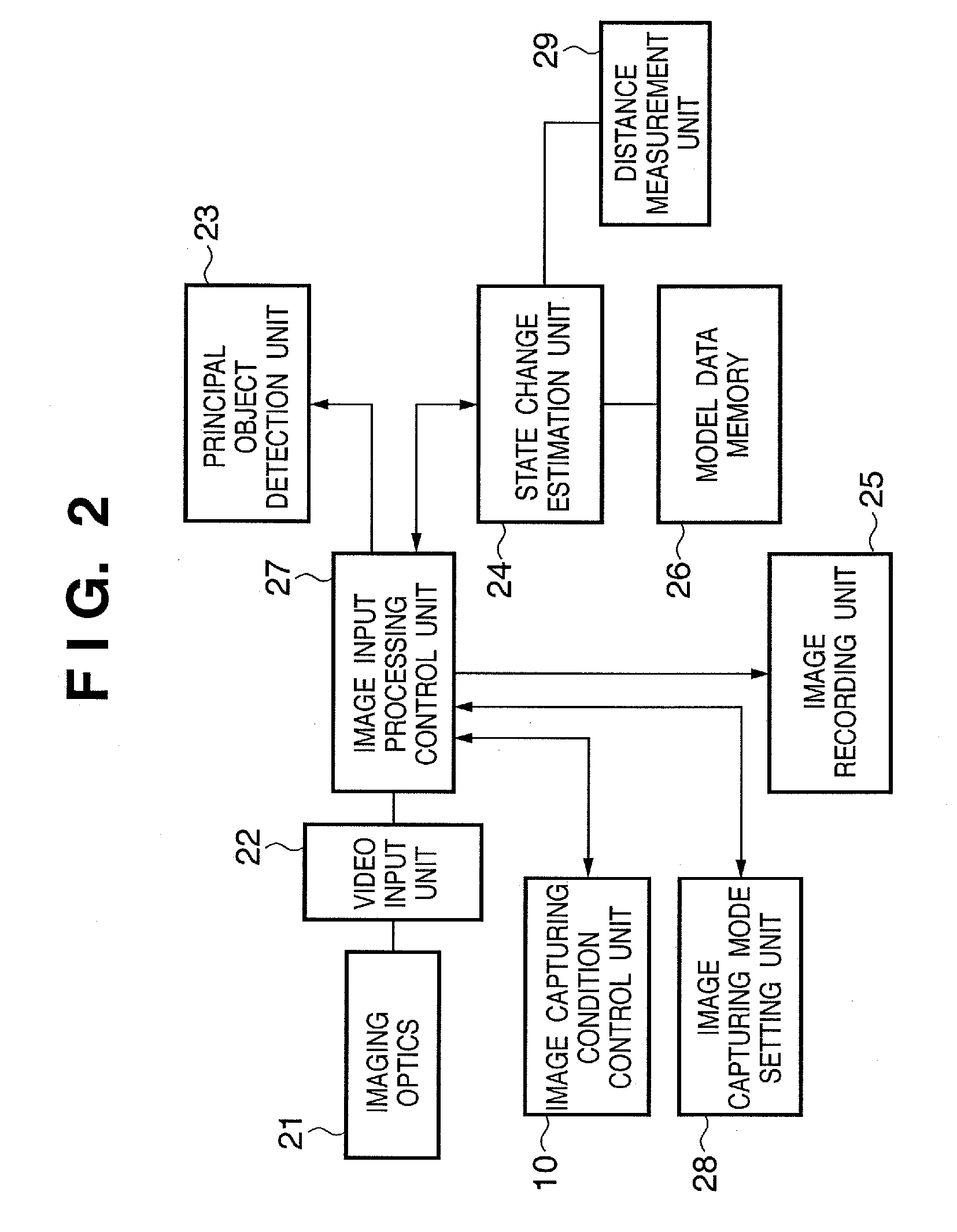
InactiveUS20070025722A1Photo opportunity can be missedTelevision system detailsImage analysisState variationImage recording
In an image capturing apparatus, a video input unit (2) captures the image of an object and sequentially acquires image data associated with the image capturing, a model data memory (6) stores model data associated with the first feature quantity calculated from a feature point of the object in a model image, a principal object detection unit (3) calculates the second feature quantity from a feature point of the object in the acquired image data, a state change estimation unit (4) estimates, on the basis of the second feature quantity and the model data, the timing when the object satisfies a predetermined condition, and an image input processing control unit (7) stores the image data corresponding to the estimated timing in an image recording unit (5). This configuration makes the image capturing apparatus acquire an image in a more proper state without large-capacity memory.
Owner:CANON KK
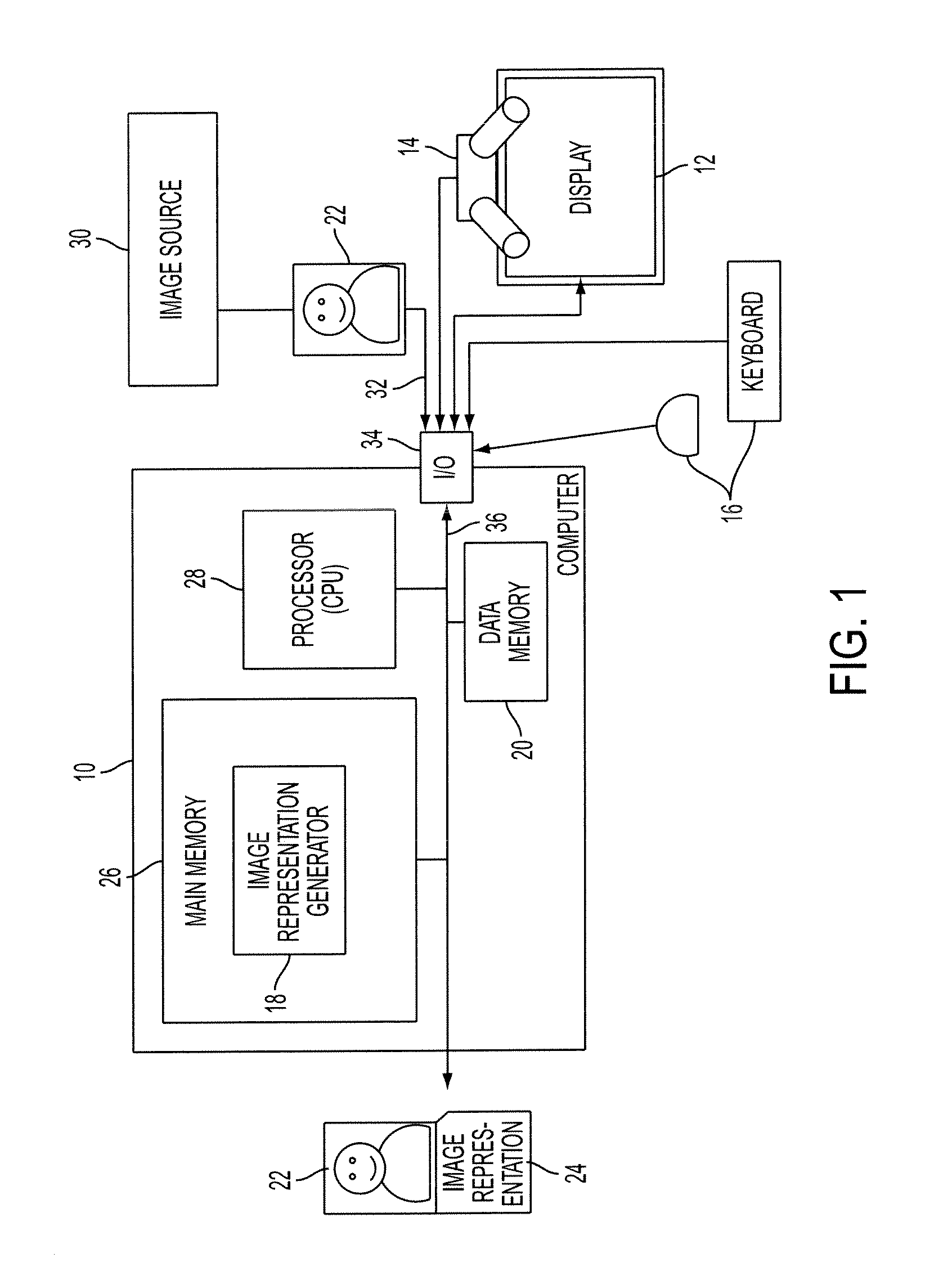
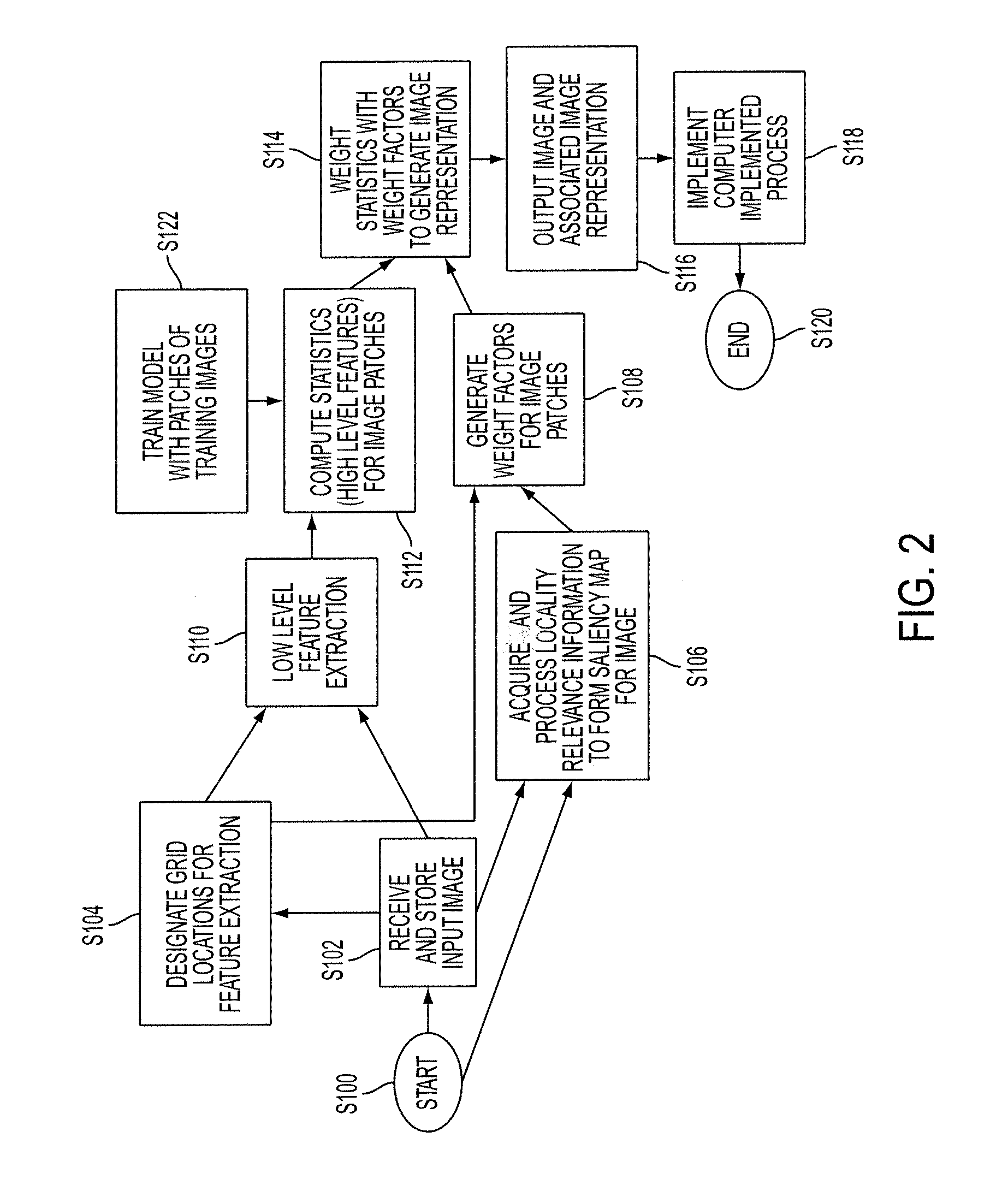
Modeling images as sets of weighted features
ActiveUS20100189354A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPosition dependentDigital image
An apparatus, method, and computer program product are provided for generating an image representation. The method includes receiving an input digital image, extracting features from the image which are representative of patches of the image, generating weighting factors for the features based on location relevance data for the image, and weighting the extracted features with the weighting factors to form a representation of the image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
System and method for intraoperative guidance of stent placement during endovascular interventions
A method for guiding stent deployment during an endovascular procedure includes providing a virtual stent model of a real stent that specifies a length, diameter, shape, and placement of the real stent. The method further includes projecting the virtual stent model onto a 2-dimensional (2D) DSA image of a target lesion, manipulating a stent deployment mechanism to navigate the stent to the target lesion while simultaneously acquiring real-time 2D fluoroscopic images of the stent navigation, and overlaying each fluoroscopic image on the 2D DSA image having the projected virtual stent model image, where the 2D fluoroscopic images are acquired from a C-arm mounted X-ray apparatus, and updating the projection of the virtual stent model onto the fluoroscopic images whenever a new fluoroscopic image is acquired or whenever the C-arm is moved, where the stent is aligned with the virtual stent model by aligning stent end markers with virtual end markers.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Method and system for processing captured image information in an interactive video display system
A method and system for processing captured image information in an interactive video display system. In one embodiment, a special learning condition of a captured camera image is detected. The captured camera image is compared to a normal background model image and to a second background model image, wherein the second background model is learned at a faster rate than the normal background model. A vision image is generated based on the comparisons. In another embodiment, an object in the captured image information that does not move for a predetermined time period is detected. A burn-in image comprising the object is generated, wherein the burn-in image is operable to allow a vision system of the interactive video display system to classify the object as background.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
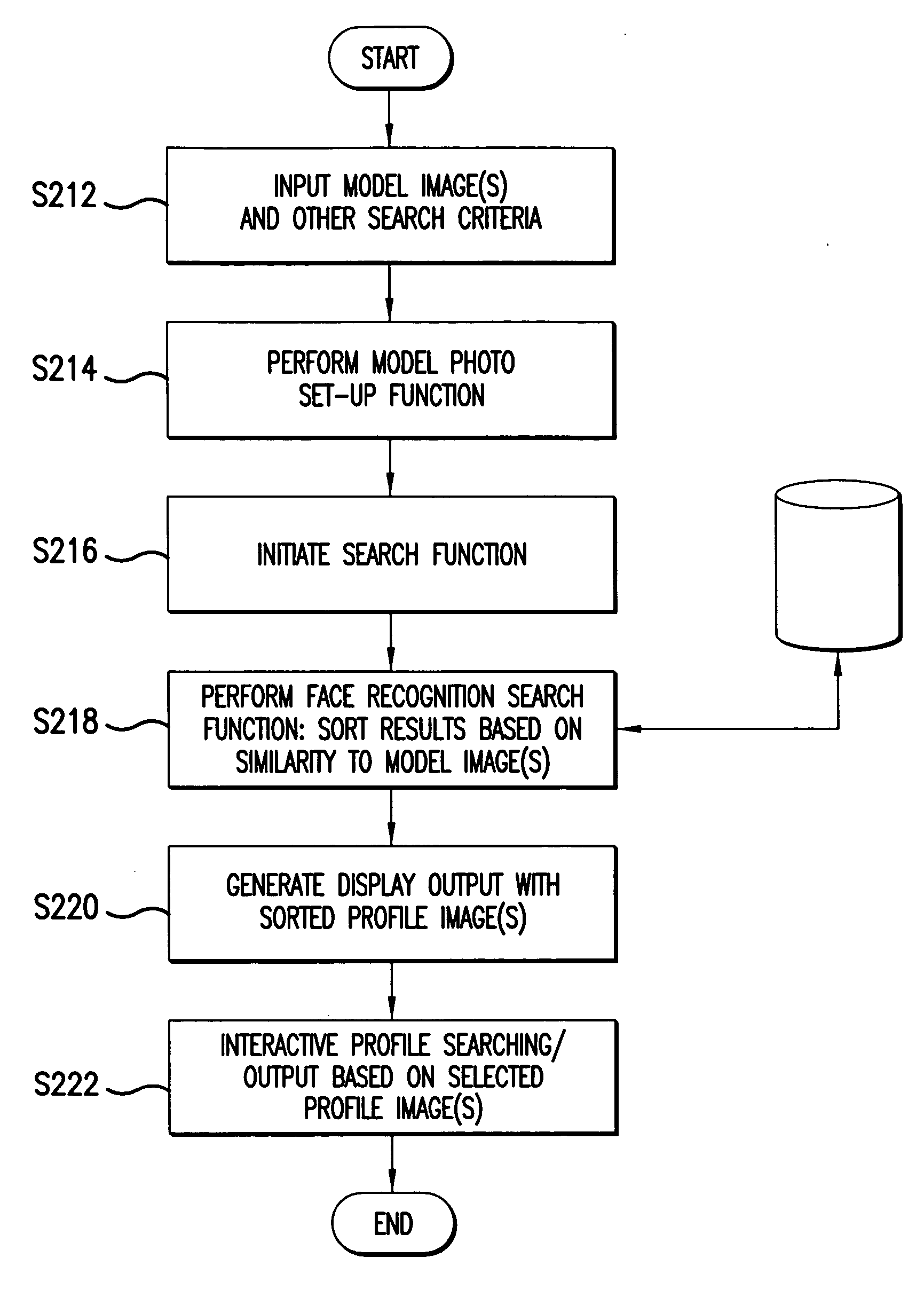
System and method applying image-based face recognition for online profile browsing
InactiveUS20060018522A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionView based
A computer-implemented method provides an online dating service in which users browse profiles of other participants using face recognition. The method comprises: inputting a model image including a face of a person, the model image representing a profile browsing preference for a user; accessing a plurality of profile images, the profile images corresponding to different participants of the online dating service; performing face recognition to determine similarity of the model image to the plurality of profile images, thereby identifying profile images that resemble the model image; outputting a display view showing a result of the face recognition, the display view including at least one profile image resembling the model image; and providing additional profile information associated with a profile image in the display view based on input browsing commands.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
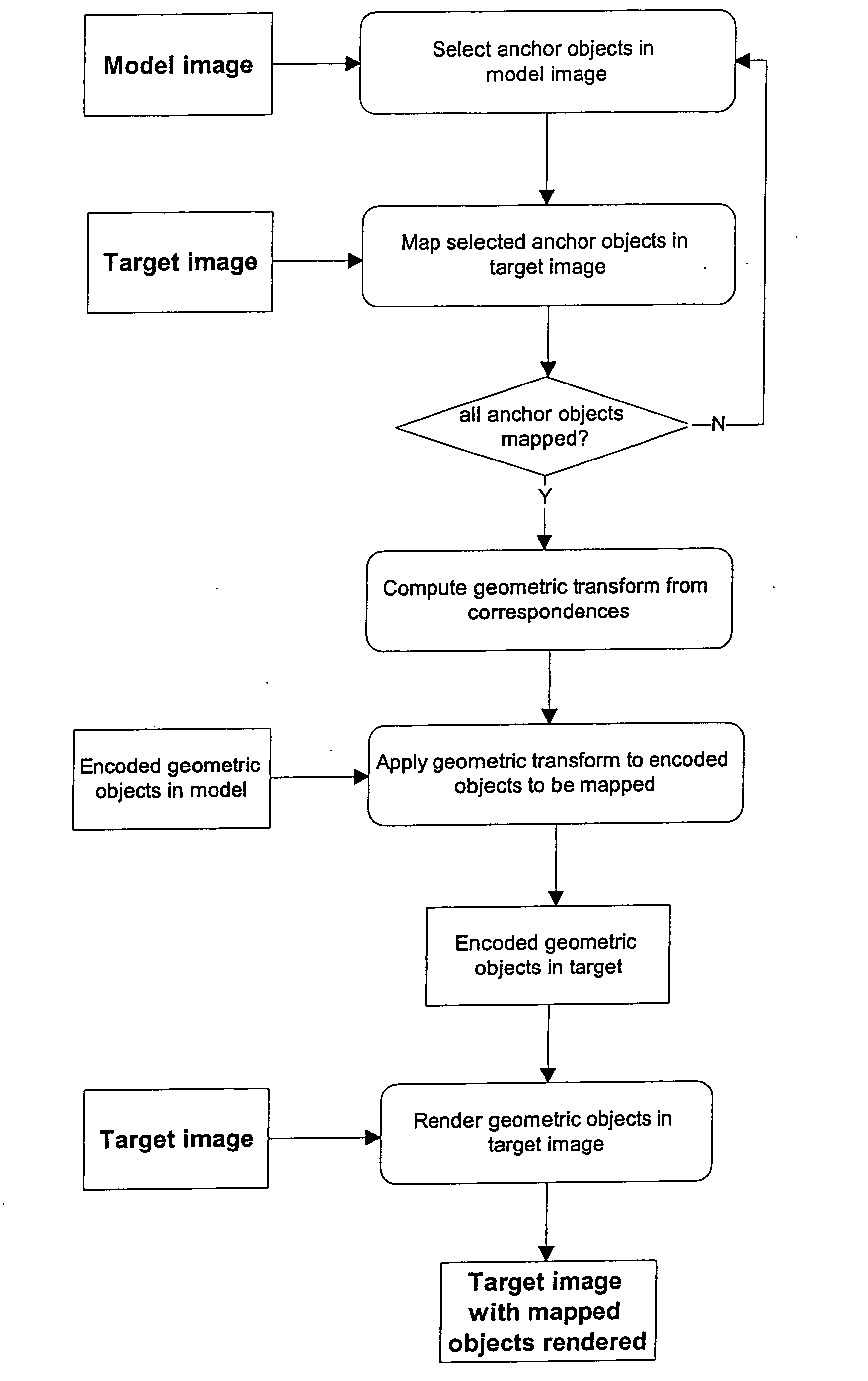
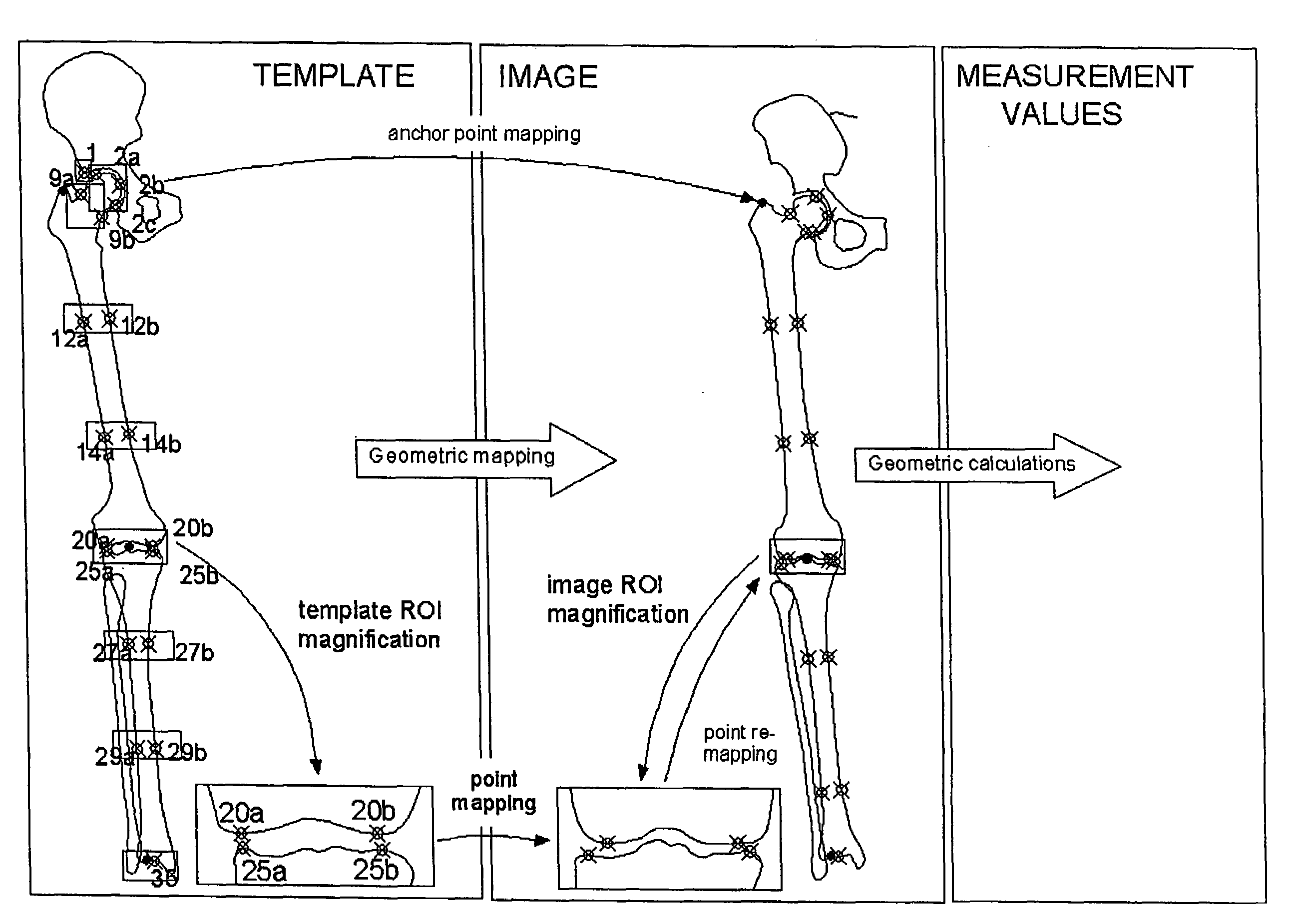
Method for automatically mapping of geometric objects in digital medical images
ActiveUS20050259882A1Precise positioningReduce the numberImage enhancementImage analysisMethod selectionDigital image
A method of mapping geometrical objects to a digital image. At least one anchor point in a model is selected and mapped to the digital image. A geometric transformation is computed on the basis of at least one correspondence between an anchor object and a corresponding mapped object, and the calculated geometric transformation is applied to at least one geometric object thereby mapping it from the model image to a corresponding mapped position in the digital image.
Owner:AGFA NV
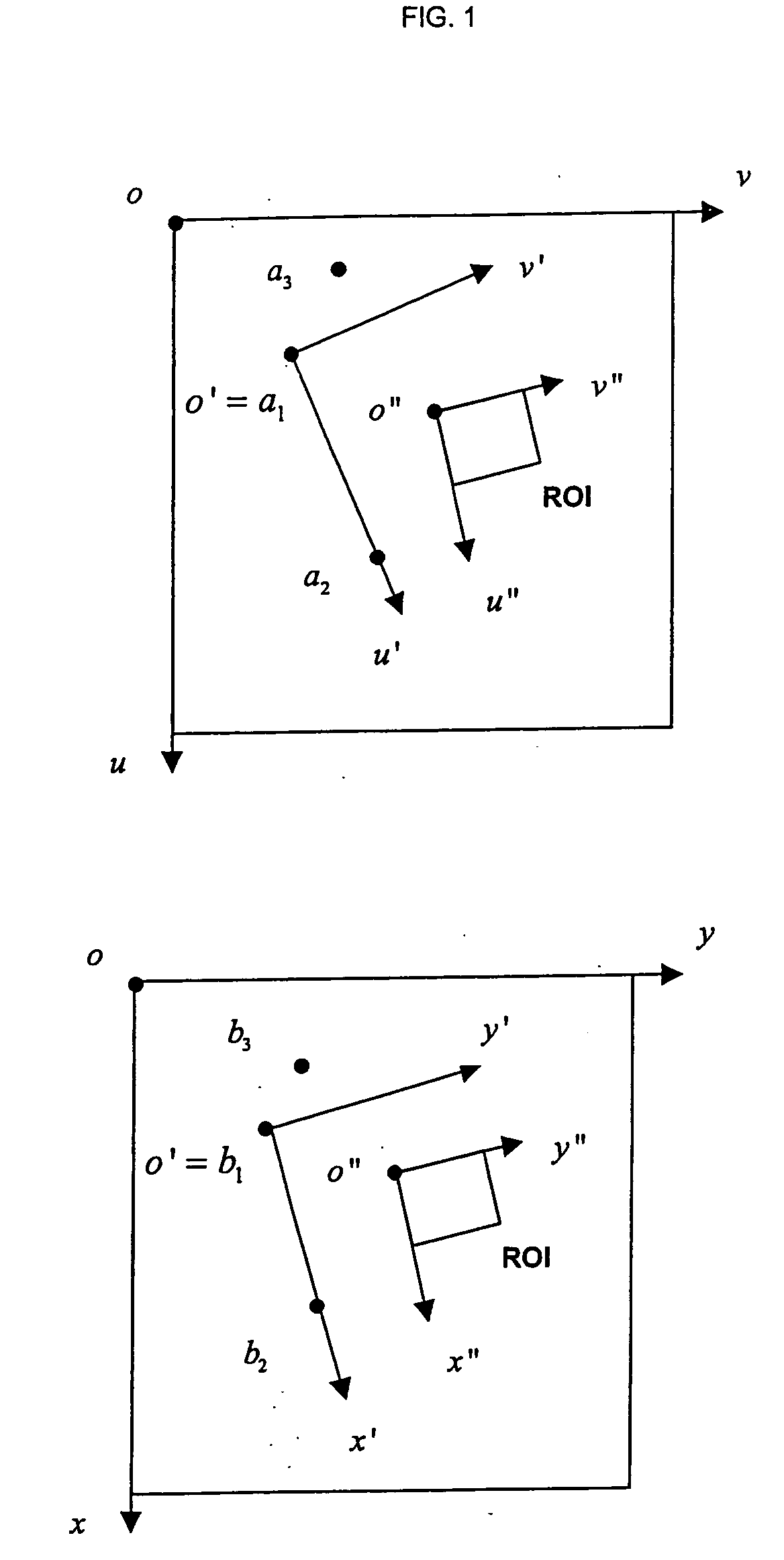
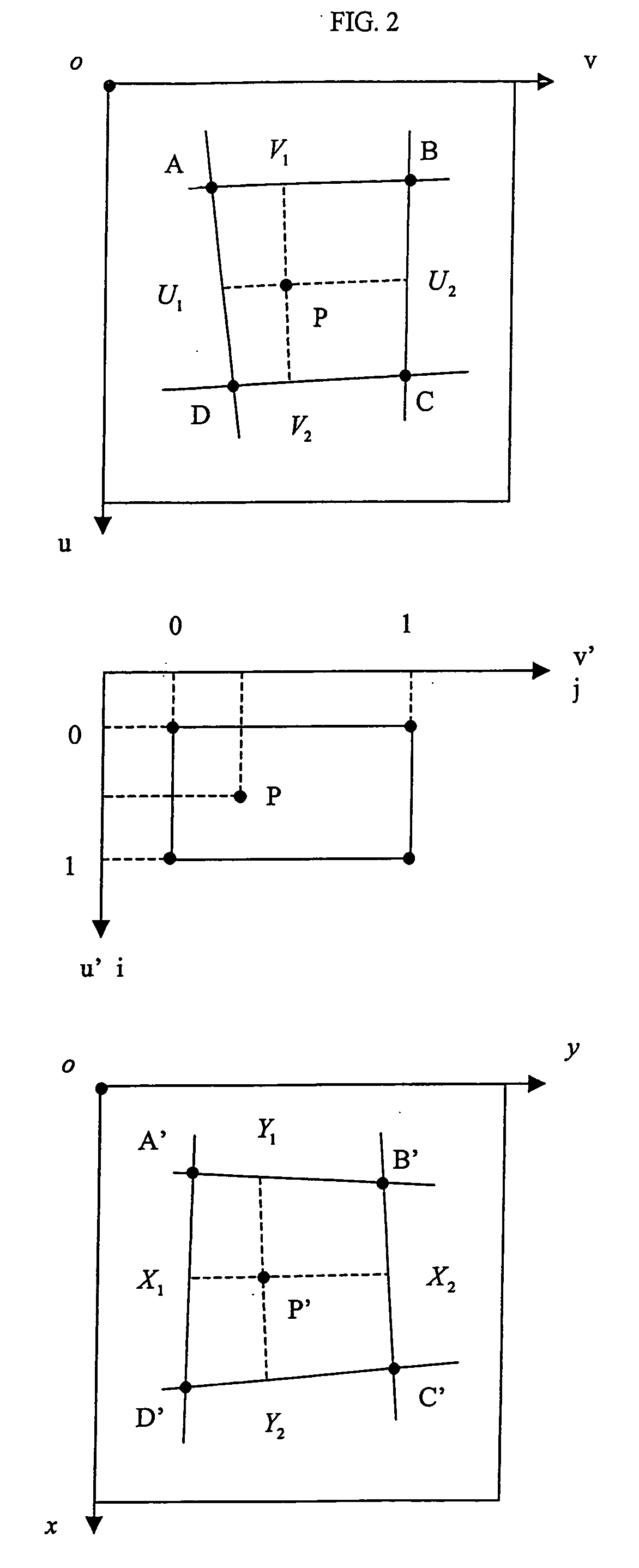
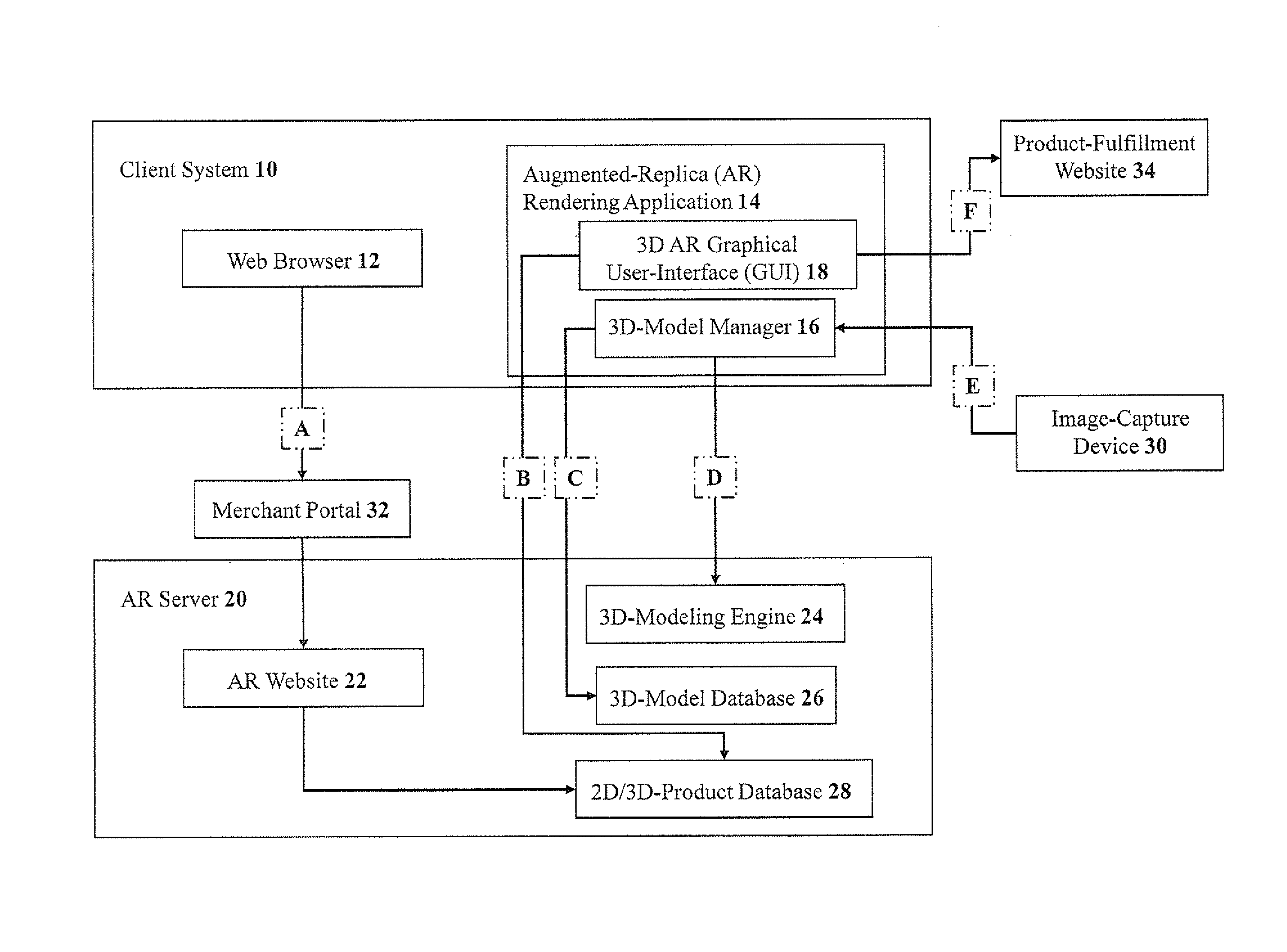
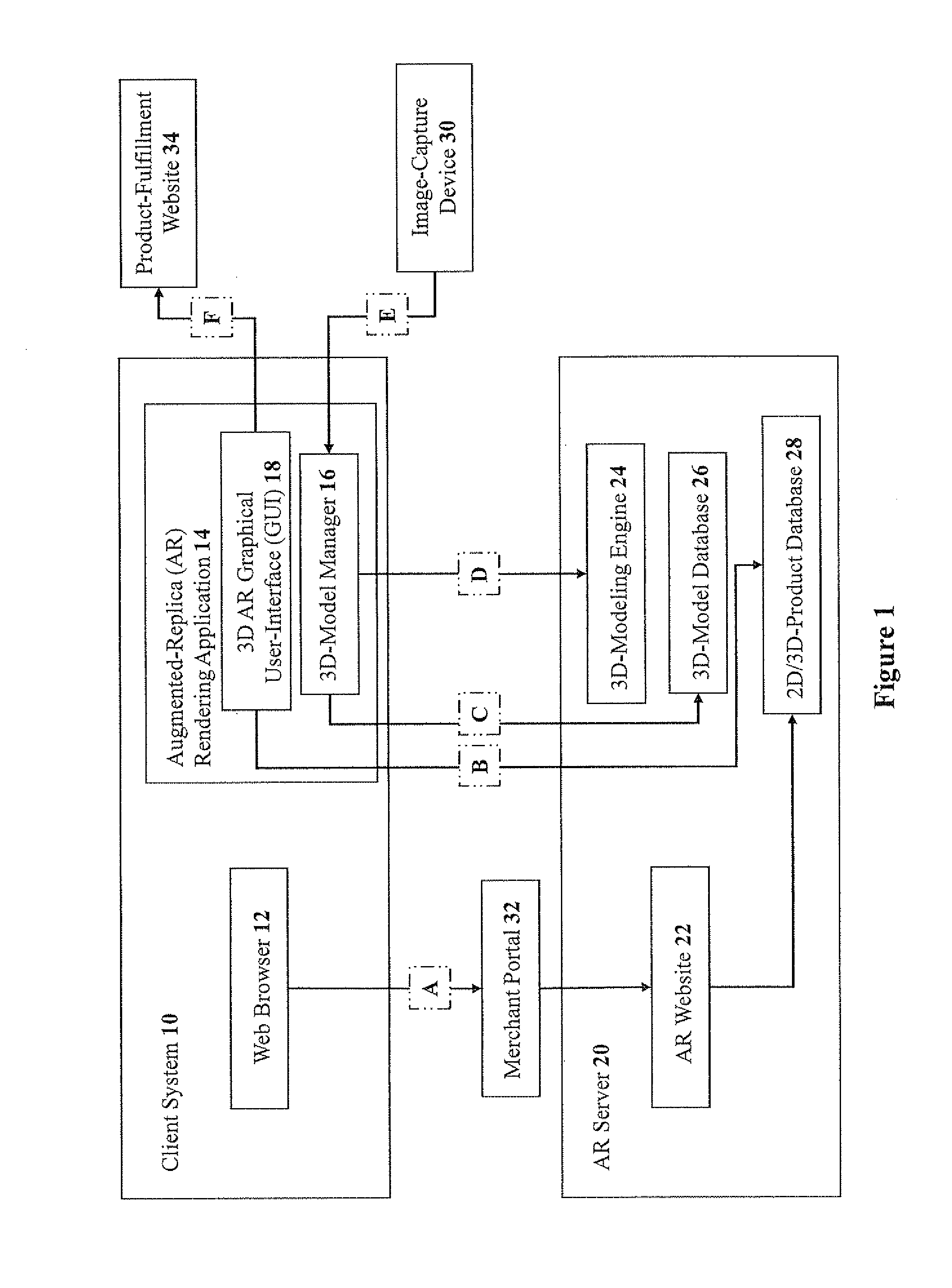
Methods and systems for three-dimensional rendering of a virtual augmented replica of a product image merged with a model image of a human-body feature
ActiveUS20110234581A1Time and cost-effectiveSpectales/gogglesCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman body3D modeling
A system for rendering a merged virtual 3D augmented replica of a 3D product image and a 3D model image of a body part. A 3D modeling engine transforms an acquired 2D image of a body part into a 3D augmented replica thereof. A GUI enables the merging, displaying and manipulating of the 3D product image and the 3D augmented replica of a body part.
Owner:AR ES TECH
Information Processing Device, Information Processing Method, and Program
ActiveUS20080013836A1Stable detection of objectImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInformation processing
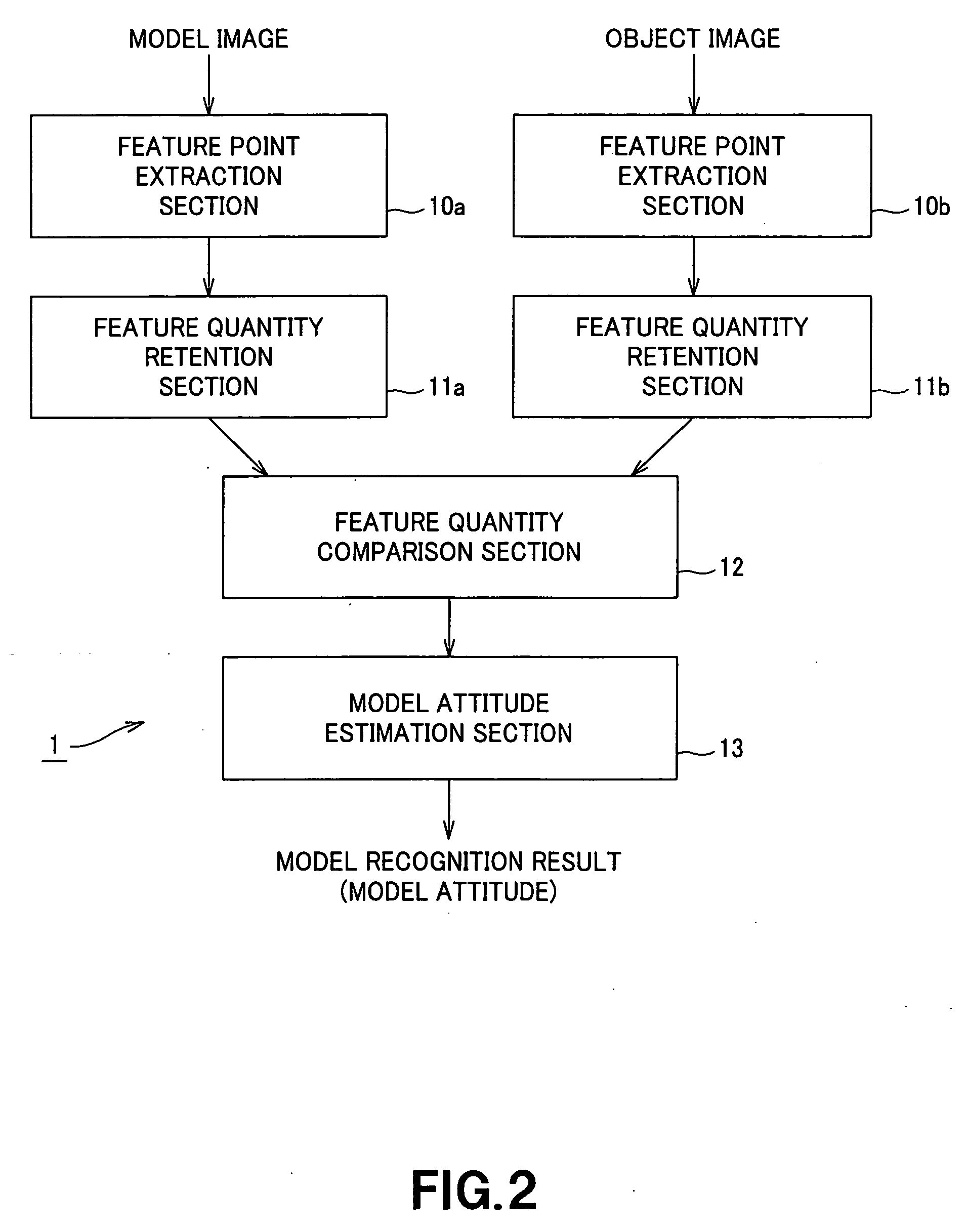
Disclosed herein an information processing device that compares an input image with a model image, the device including: a storage; an object feature point extractor; and a feature comparator.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for automatically mapping of geometric objects in digital medical images
ActiveUS7394946B2Precise positioningReduce the numberImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageAnchor point
A method of mapping geometrical objects to a digital image. At least one anchor point in a model is selected and mapped to the digital image. A geometric transformation is computed on the basis of at least one correspondence between an anchor object and a corresponding mapped object, and the calculated geometric transformation is applied to at least one geometric object thereby mapping it from the model image to a corresponding mapped position in the digital image.
Owner:AGFA NV
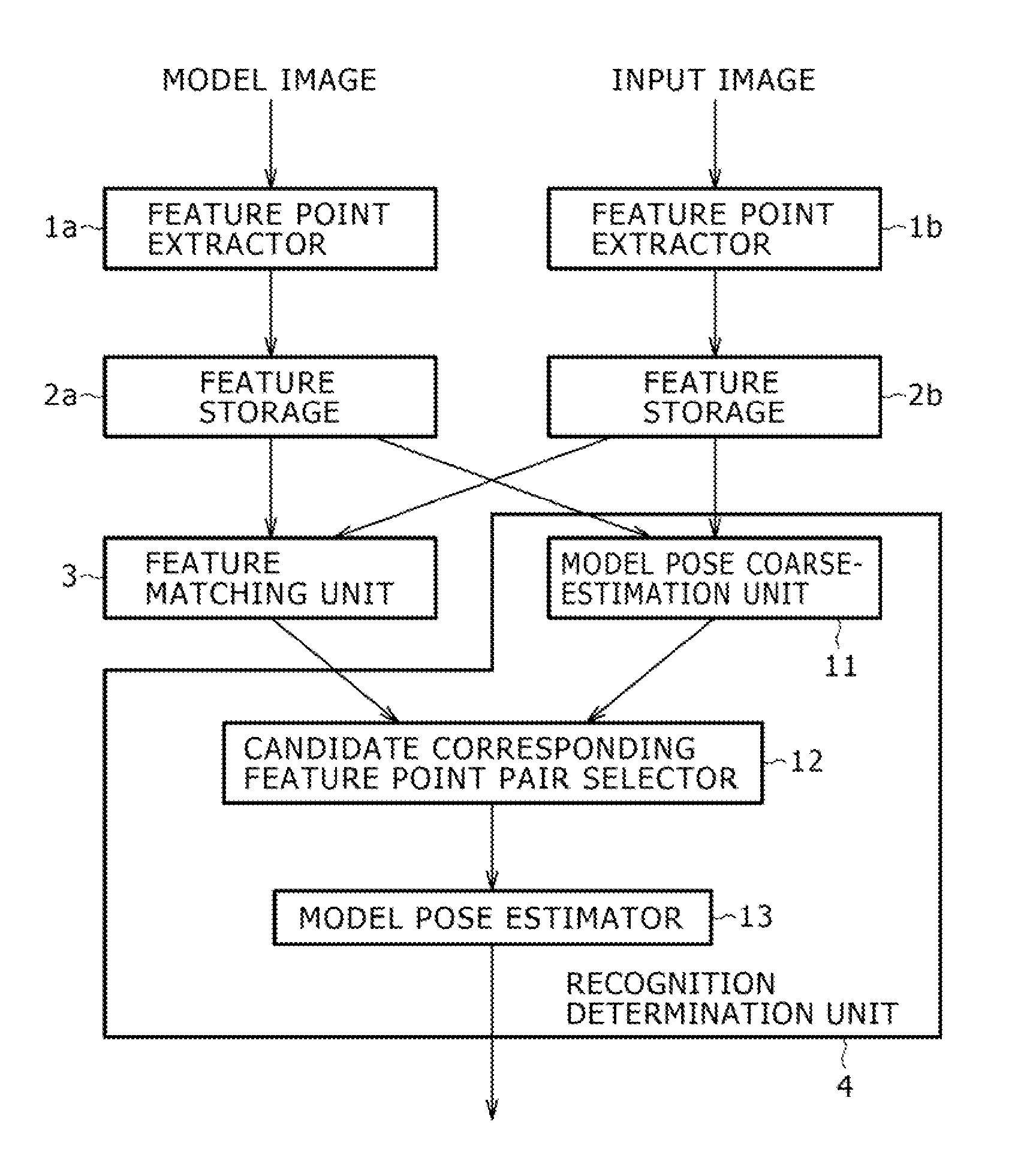
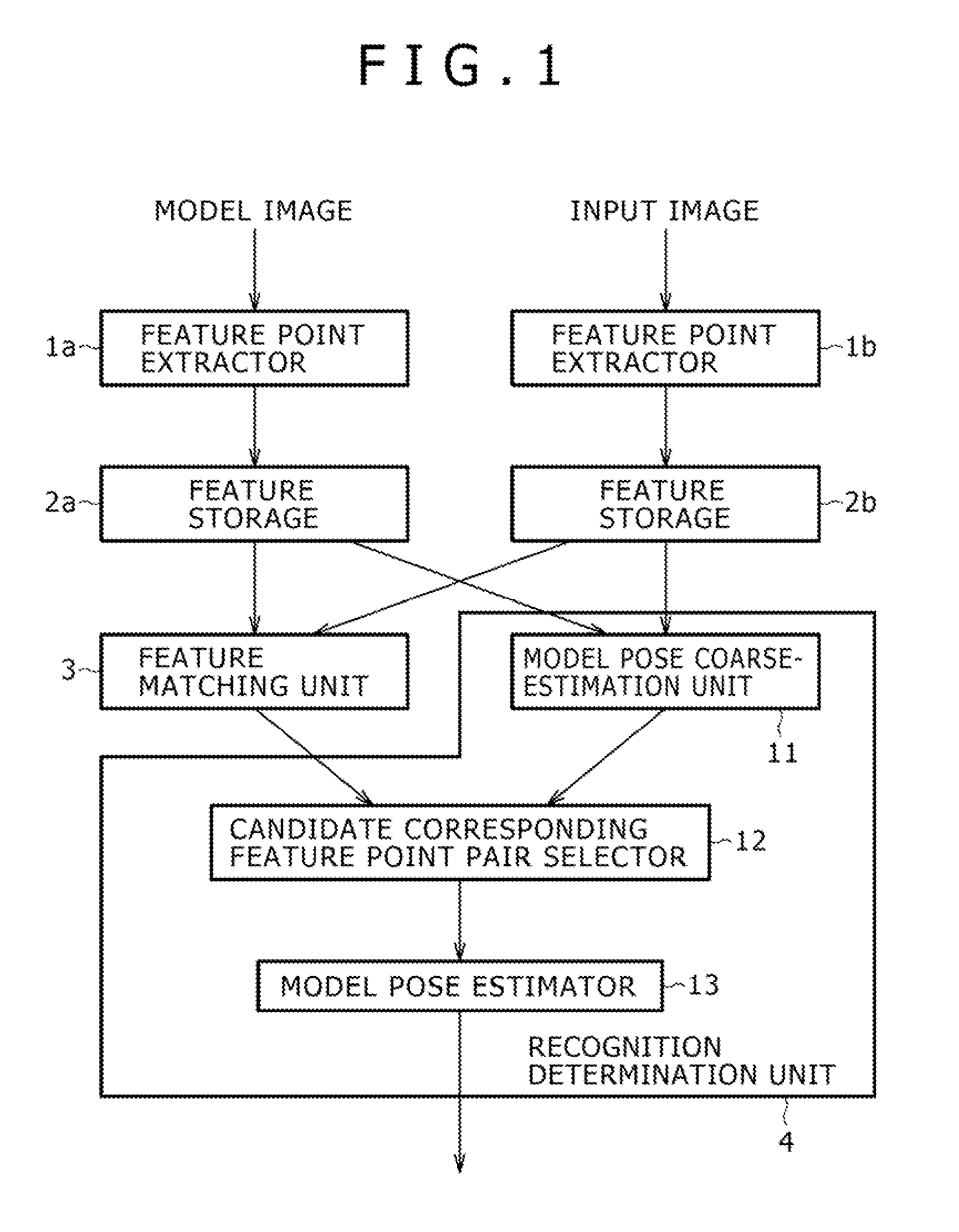
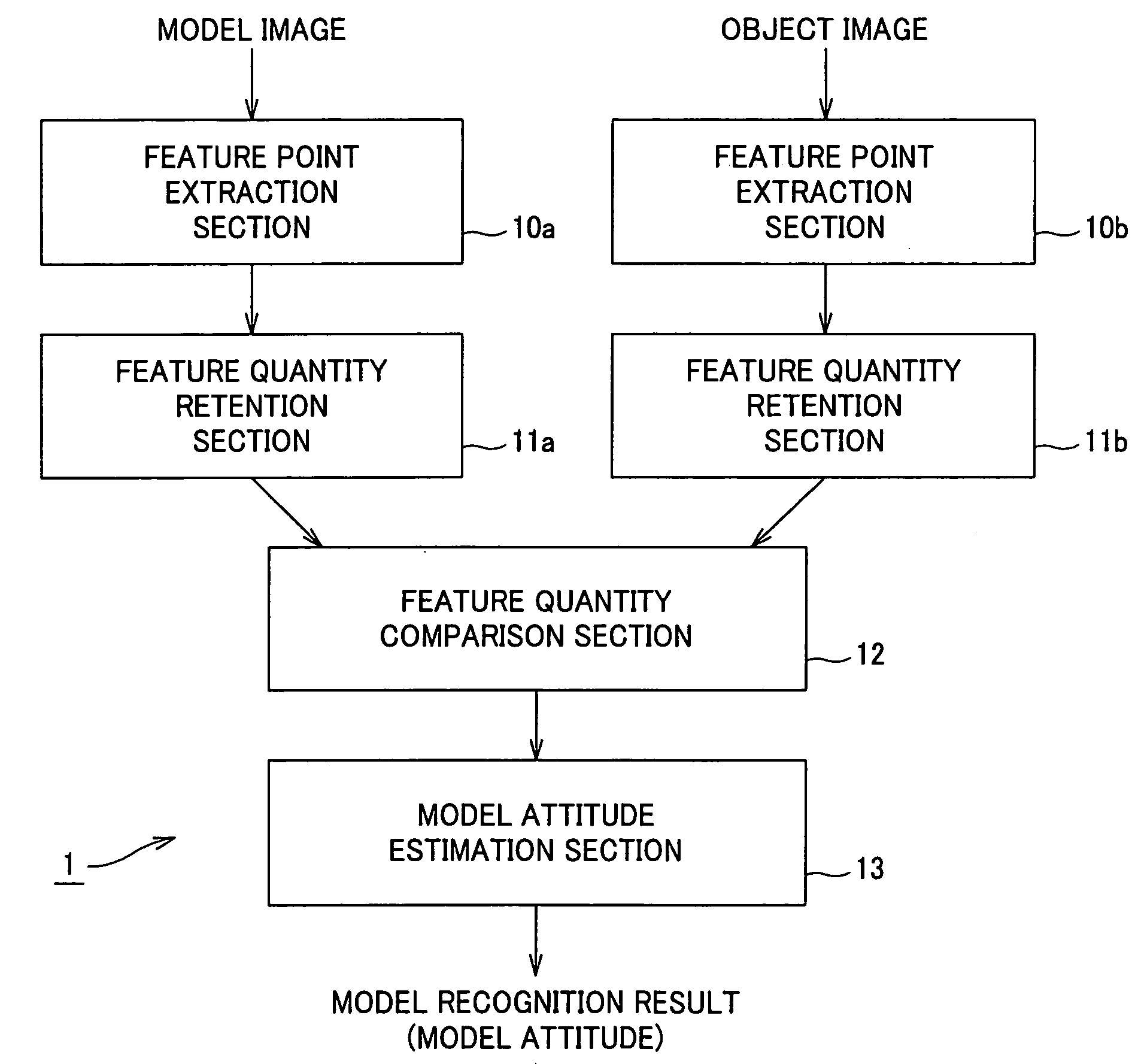
Image recognition device and method, and robot device
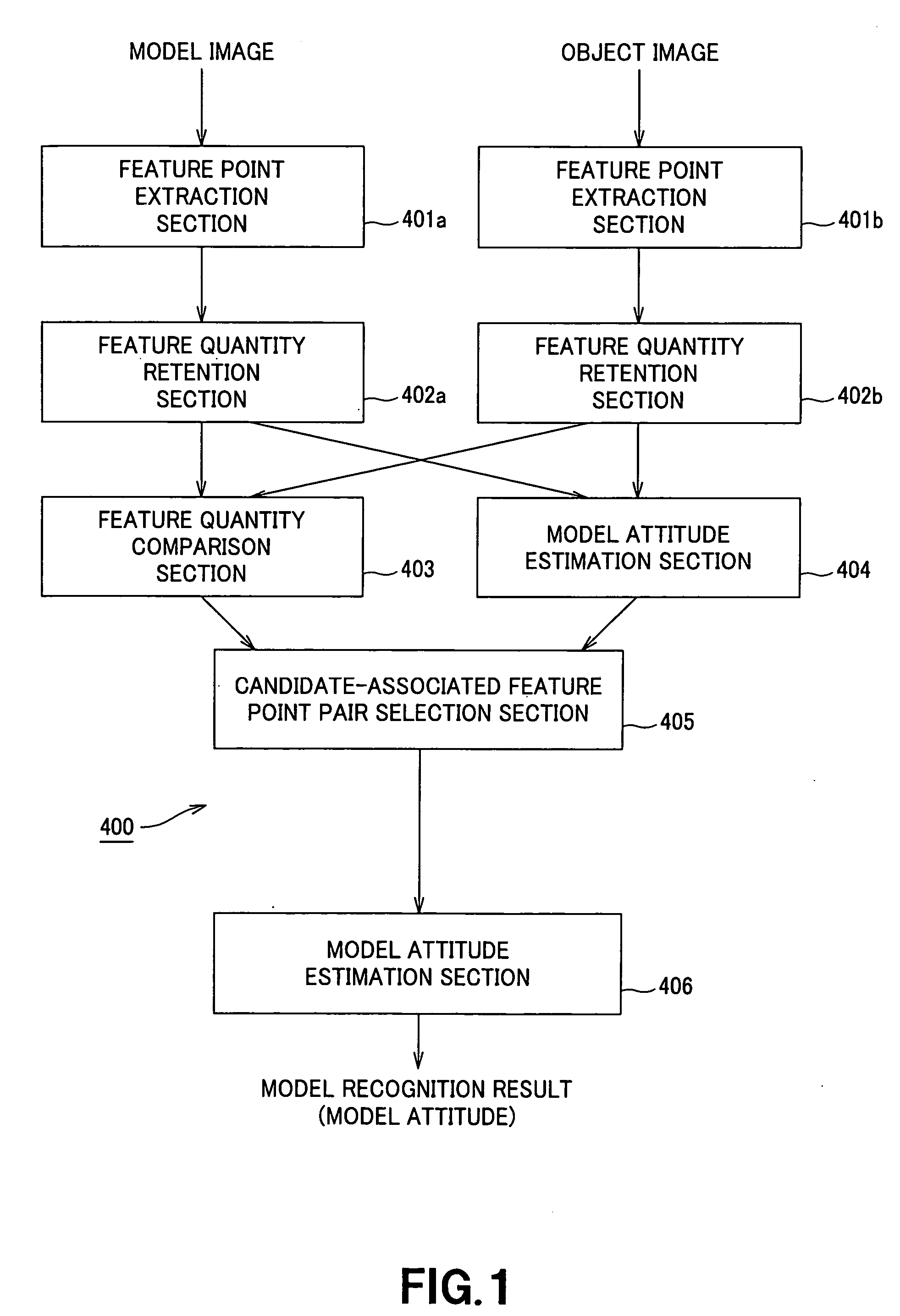
InactiveUS20050213818A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTransformation parameterRelevant feature
In an image recognition apparatus (1), feature point extraction sections (10a) and (10b) extract feature points from a model image and an object image. Feature quantity retention sections (11a) and (11b) extract a feature quantity for each of the feature points and retain them along with positional information of the feature points. A feature quantity comparison section (12) compares the feature quantities with each other to calculate the similarity or the dissimilarity and generates a candidate-associated feature point pair having a high possibility of correspondence. A model attitude estimation section (13) repeats an operation of projecting an affine transformation parameter determined by three pairs randomly selected from the candidate-associated feature point pair group onto a parameter space. The model attitude estimation section (13) assumes each member in a cluster having the largest number of members formed in the parameter space to be an inlier. The model attitude estimation section (13) finds the affine transformation parameter according to the least squares estimation using the inlier and outputs a model attitude determined by this affine transformation parameter.
Owner:SONY CORP
Digital camera having subject judgment function
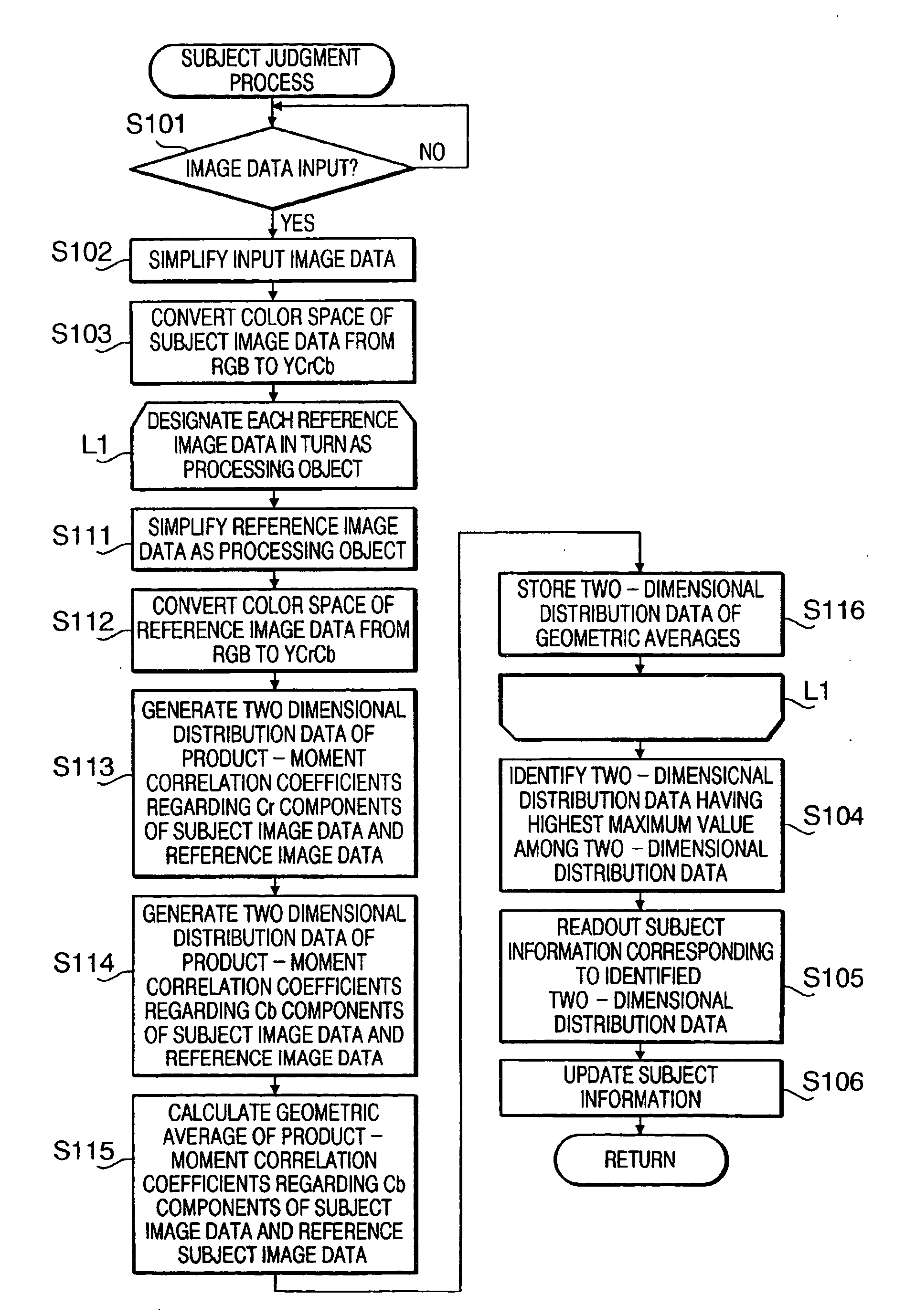
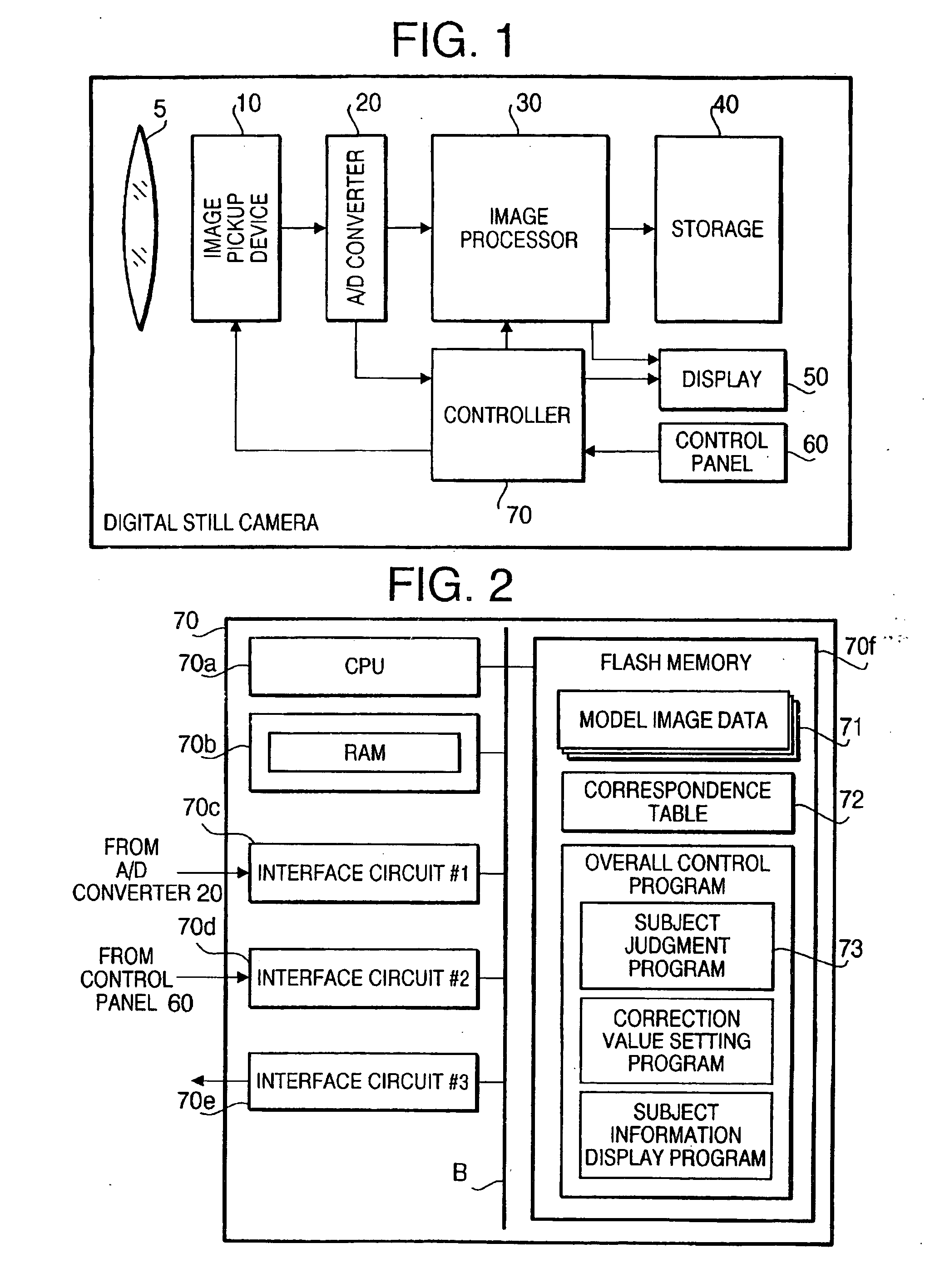
InactiveUS20050089218A1Reduce in quantityReduce loadTelevision system detailsImage analysisCorrelation coefficientStill camera
A subject judgment program is capable of reducing the calculation load on a computer functioning as a device for judging the subject in a subject image. In a controller of a digital still camera, when a CPU running the subject judgment program (stored in a flash memory) obtains image data from an A / D converter via a first interface circuit, the CPU generates two-dimensional distribution data of product-moment correlation coefficients for each of model image data stored in the flash memory by successively calculating the product-moment correlation coefficient between the model image data and each part of the obtained image data, identifies a piece of model image data corresponding to two-dimensional distribution data having the highest maximum value, and thereby identifies subject information which has been associated with the identified model image data.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
InactiveUS7127087B2Sure easyElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEigenfaceRecognition system
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a persons face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
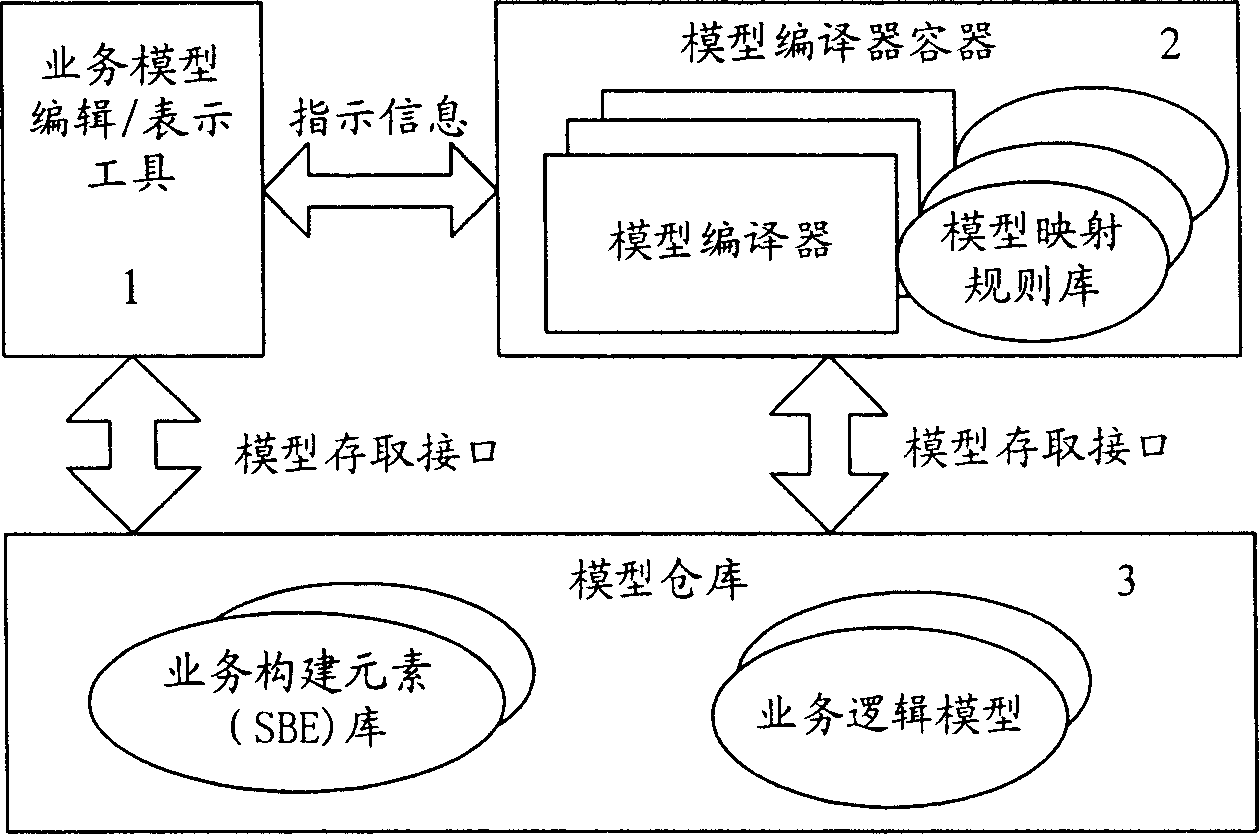
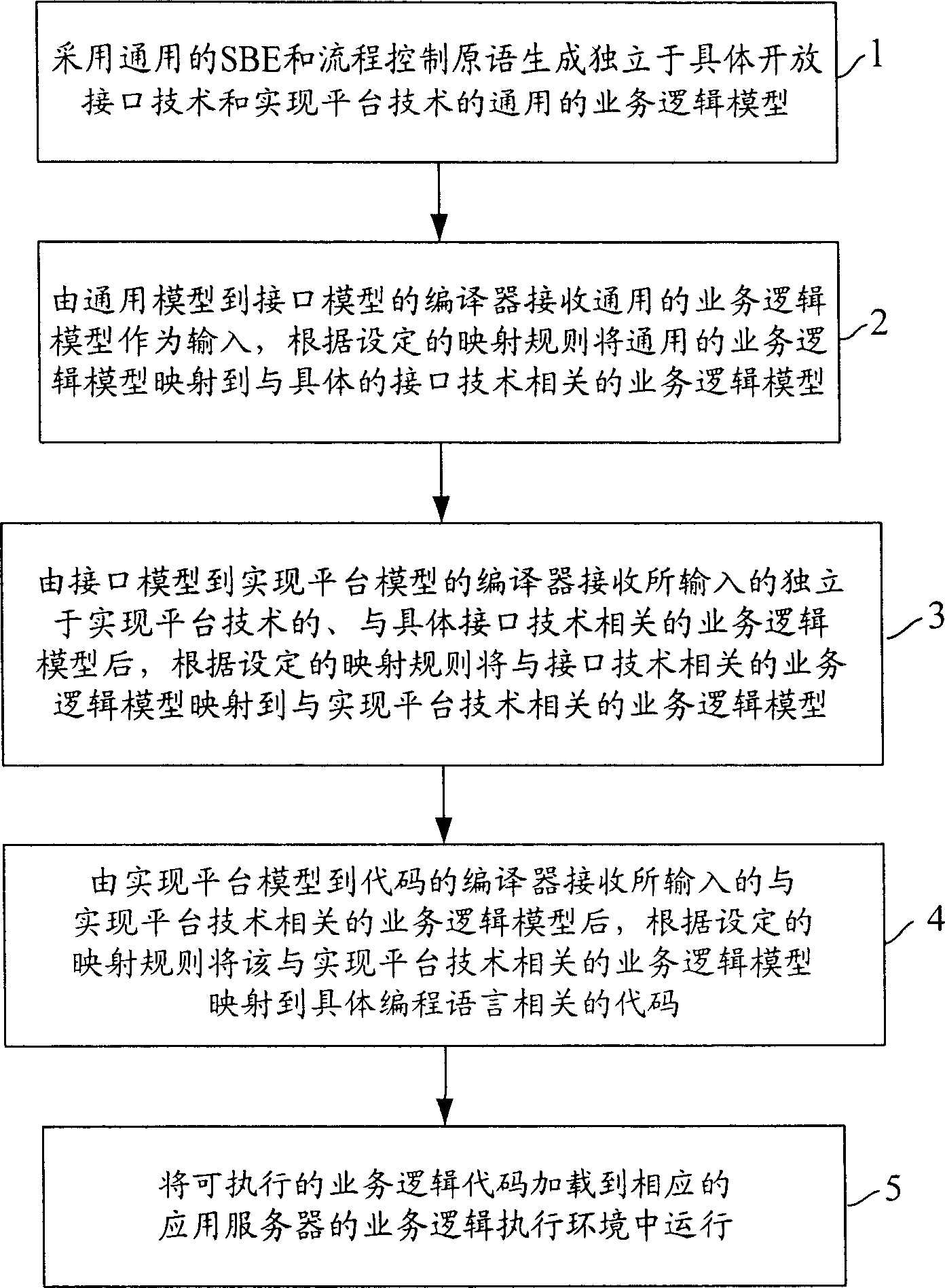
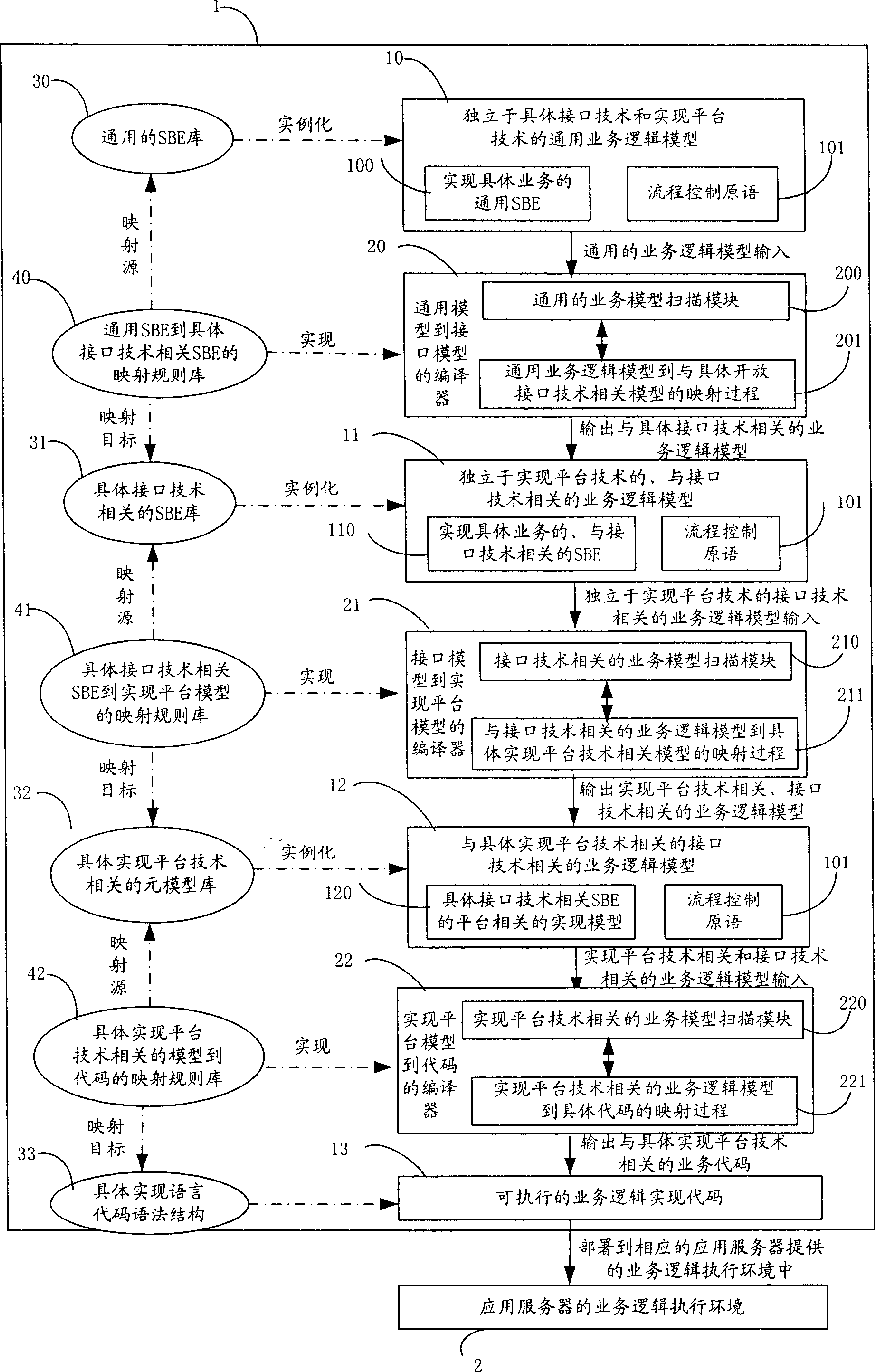
Model driven fused business generating method adapt to different interfaces and platform technique
InactiveCN1767537AHigh transplantabilityImprove reusabilityTransmissionService modelComputer architecture
This invention relates to a method and a system for generating telecommunication merging services suitable for different interfaces and platforms, in which, the system is composed of service model edit / express tools, a model decoder container and various kinds of model decoders and related model image rule library stationed in it and model storage storehouse and information interaction among the components is realized via a standard interface. The method includes: generating a general service model independent of the concrete interface technology and the platform technology then carrying out images from the general technology model to the concrete interface technology related model , to the model for realizing platform technology, then to the codes realized to the program languages then arranging the executive service logic to an available service.
Owner:YIFENG COMM EQUIP YANGZHOU
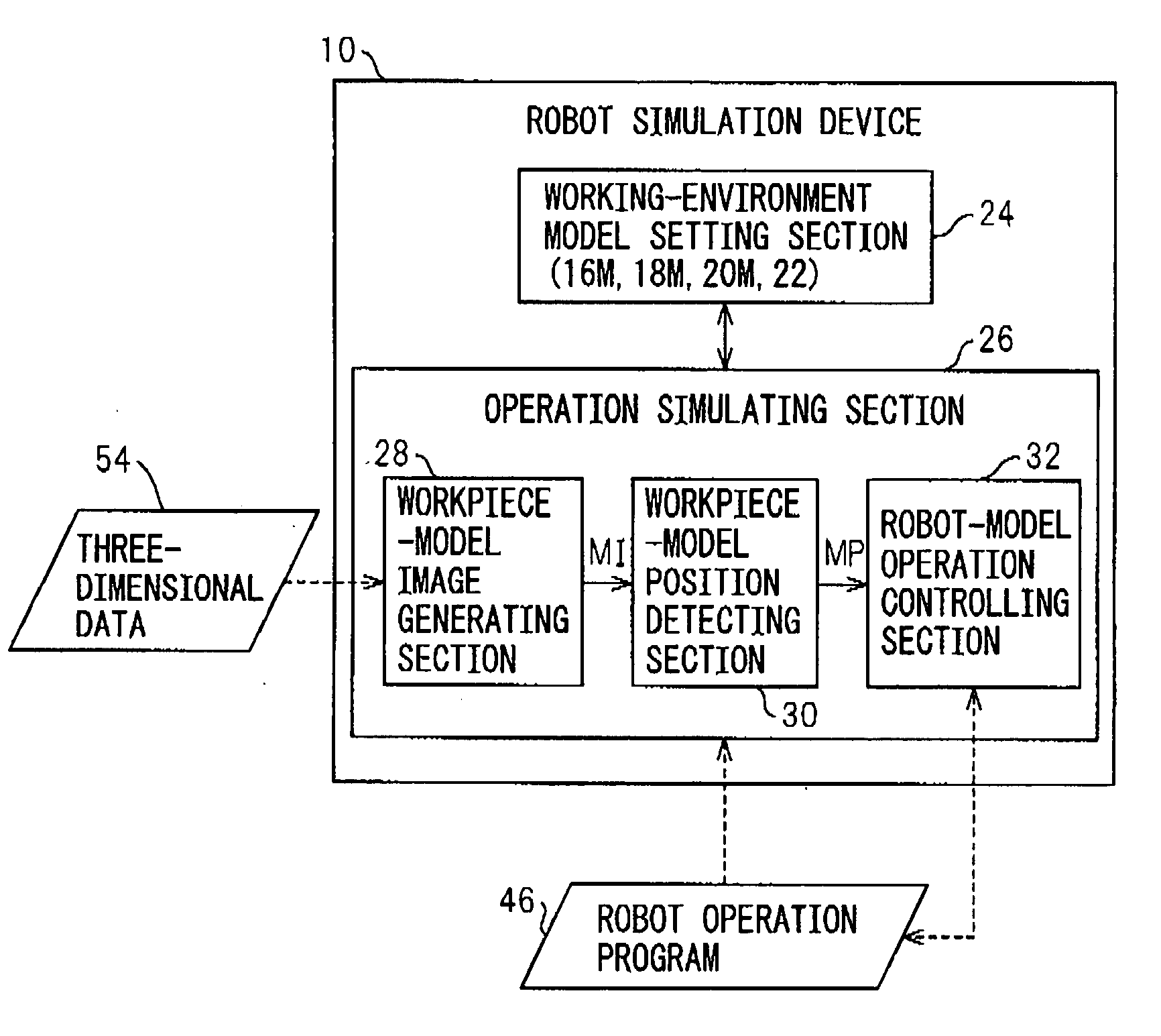
Device, program, recording medium and method for robot simulation
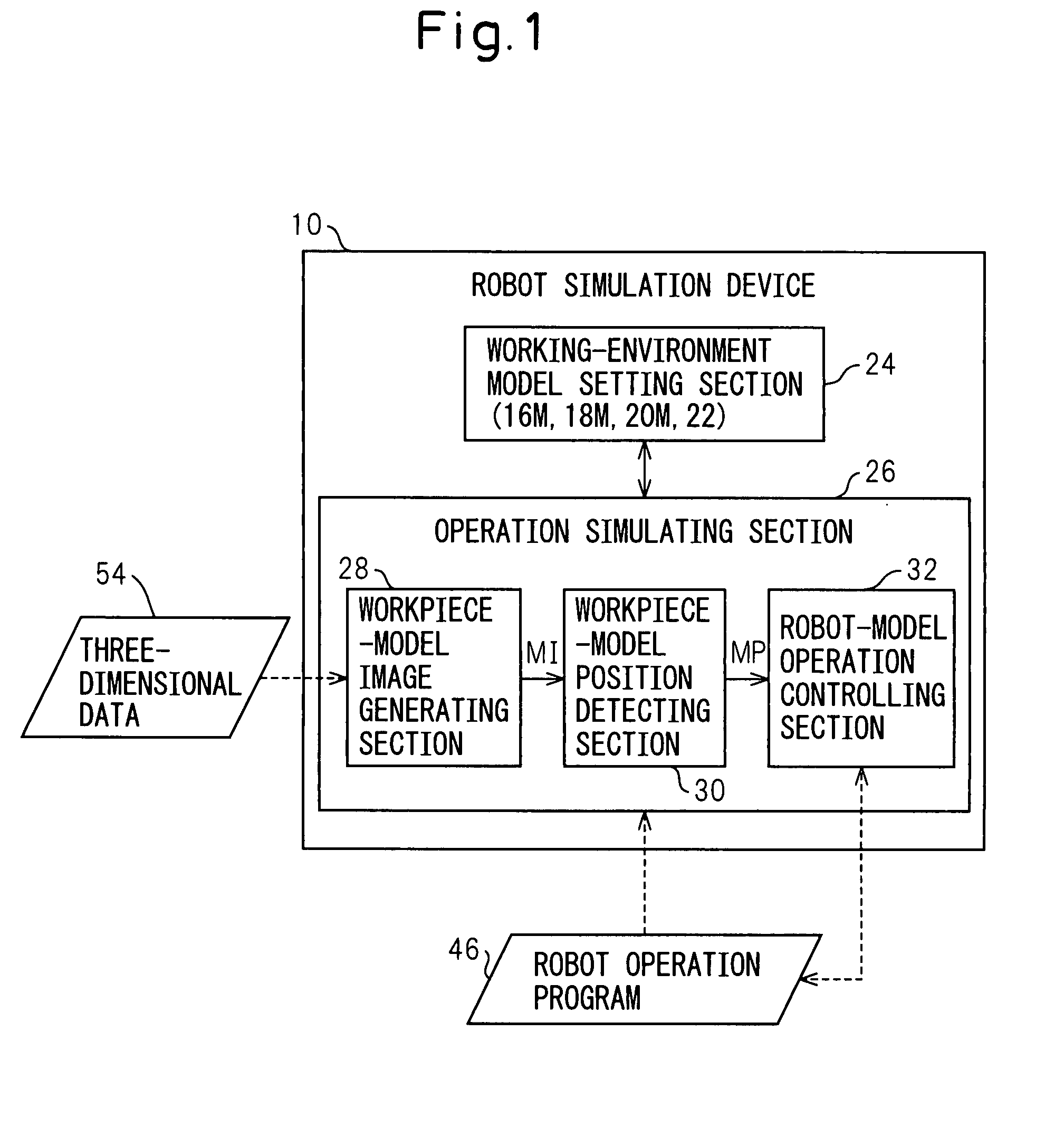
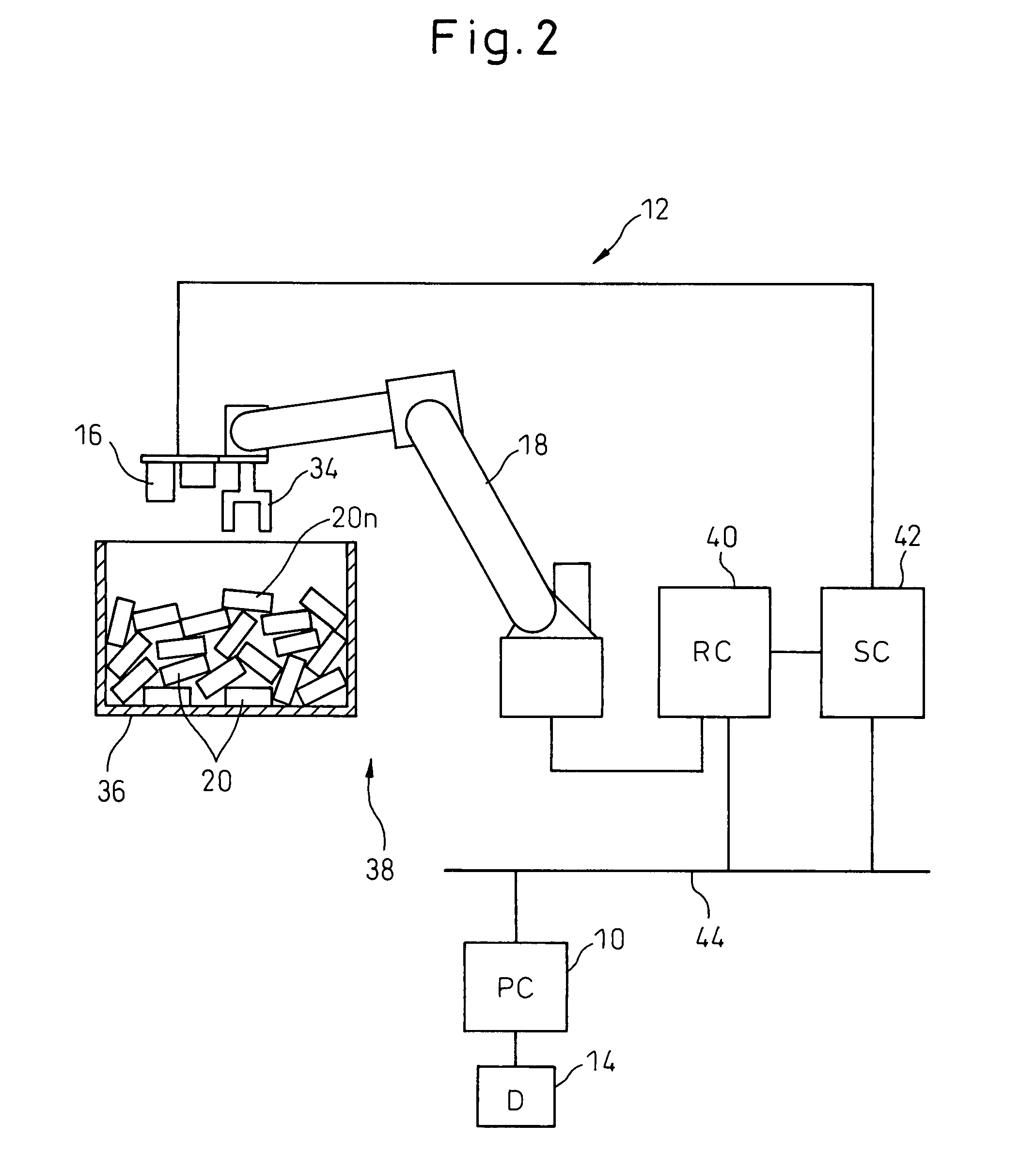
InactiveUS20070213874A1Quick calculationEasy to operateProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocation detectionSimulation
A robot simulation device for simulating an operation of a robot having a vision sensor in an off-line mode. The device includes a working-environment model setting section for arranging a sensor model, a robot model and a plurality of irregularly piled workpiece models in a virtual working environment; and an operation simulating section for allowing the sensor model and the robot model to simulate a workpiece detecting operation and a bin picking motion. The operation simulating section includes a workpiece-model image generating section for allowing the sensor model to pick up the workpiece models and generating a virtual image thereof; a workpiece-model position detecting section for identifying an objective workpiece model from the virtual image and detecting a virtual position thereof; and a robot-model operation controlling section for allowing the robot model to pick out the objective workpiece model based on the virtual position.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Pose-invariant face recognition system and process
InactiveUS20050147292A1Sure easyElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisEigenfaceRecognition system
A face recognition system and process for identifying a person depicted in an input image and their face pose. This system and process entails locating and extracting face regions belonging to known people from a set of model images, and determining the face pose for each of the face regions extracted. All the extracted face regions are preprocessed by normalizing, cropping, categorizing and finally abstracting them. More specifically, the images are normalized and cropped to show only a persons face, categorized according to the face pose of the depicted person's face by assigning them to one of a series of face pose ranges, and abstracted preferably via an eigenface approach. The preprocessed face images are preferably used to train a neural network ensemble having a first stage made up of a bank of face recognition neural networks each of which is dedicated to a particular pose range, and a second stage constituting a single fusing neural network that is used to combine the outputs from each of the first stage neural networks. Once trained, the input of a face region which has been extracted from an input image and preprocessed (i.e., normalized, cropped and abstracted) will cause just one of the output units of the fusing portion of the neural network ensemble to become active. The active output unit indicates either the identify of the person whose face was extracted from the input image and the associated face pose, or that the identity of the person is unknown to the system.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
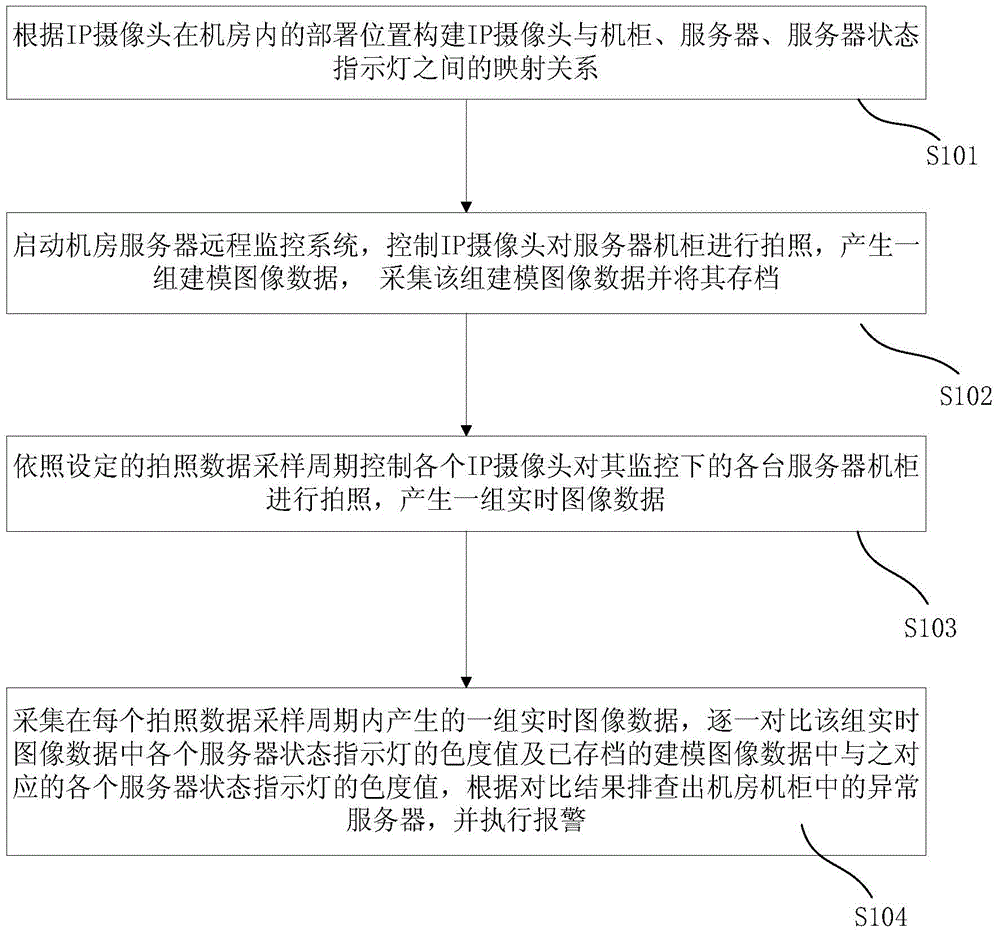
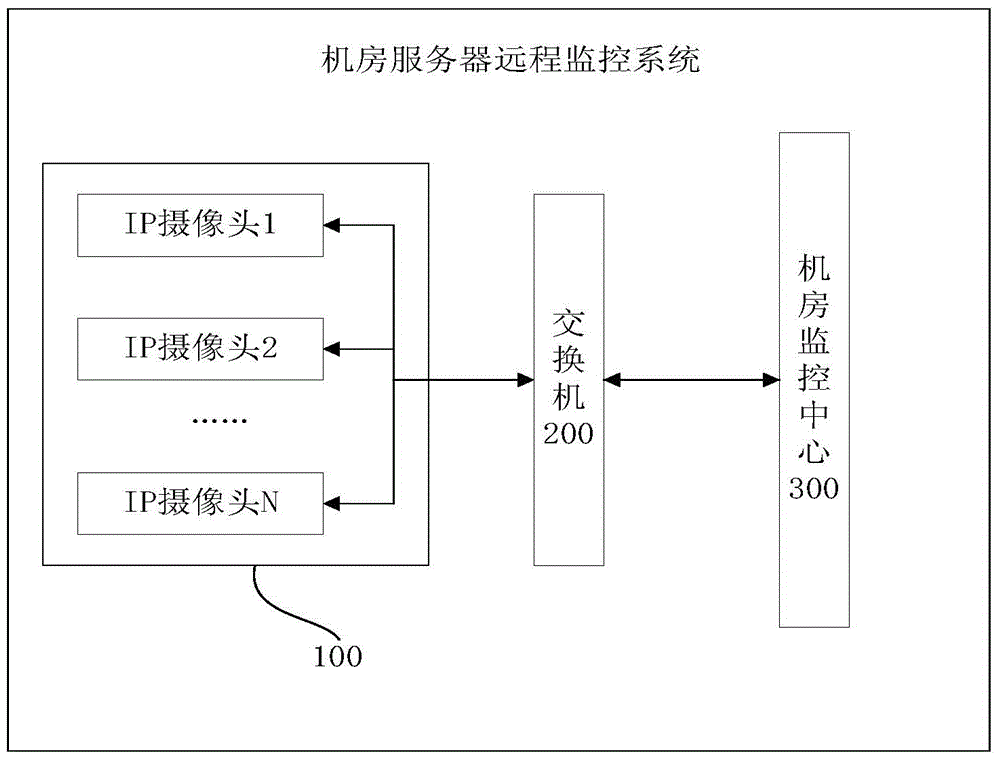
Machine room server remote monitoring method and system
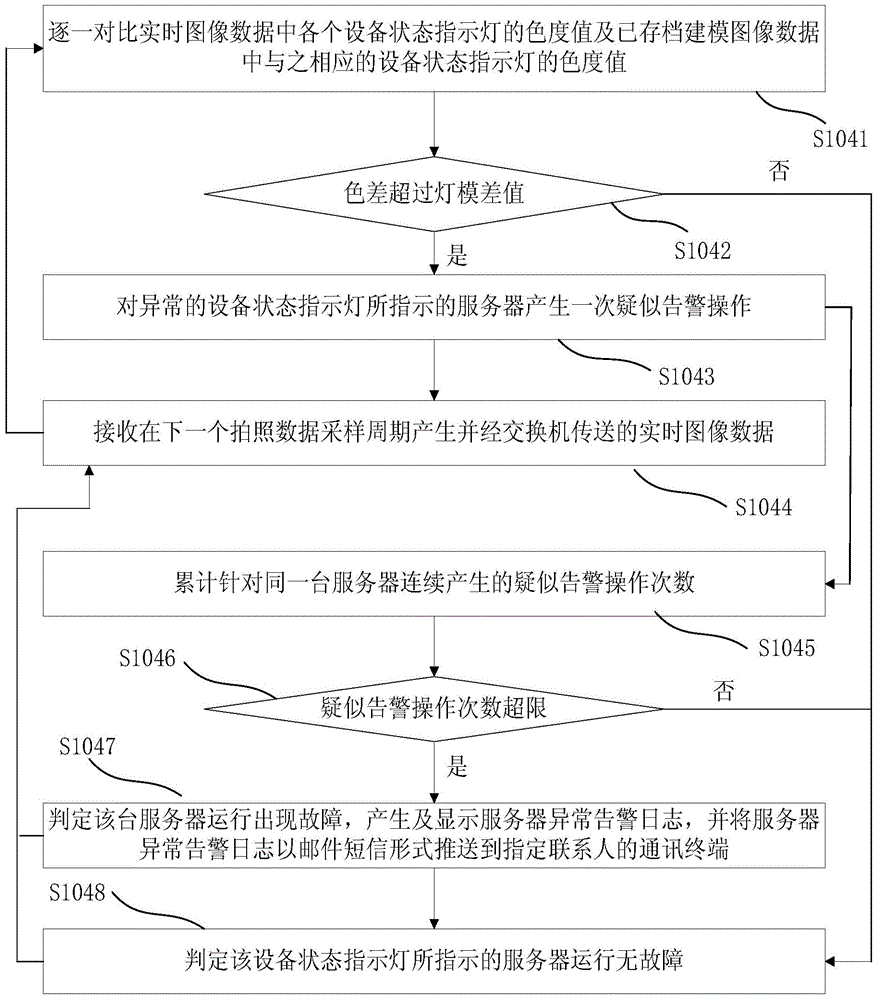
ActiveCN105100732AImprove troubleshooting efficiencyRealize remote monitoringClosed circuit television systemsAlarmsData acquisitionFault analysis
The invention discloses a machine room server remote monitoring method and system. The system comprises a plurality of IP cameras, a switch and a machine room monitoring center, wherein the IP cameras are used for receiving a shooting data acquisition command, and performing shooting on equipment state indicator lights in a machine room to generate a group of modeling image data; and the machine room monitoring center is used for acquiring and saving the group of modeling image data in advance, controlling each IP camera to perform shooting on server cabinets monitored by each IP camera according to a set shooting data sampling period, acquiring a group of real-time image data, comparing the chromatic value of each equipment state indicator light in the group of real-time image data with the chromatic values of corresponding equipment state indicator lights in the saved modeling image data one by one, checking abnormal servers in the machine room according to comparison results, and executing alarming. Through adoption of the machine room server remote monitoring method and system, accurate history image data which can be inquired is provided in order to perform server fault analysis and processing, and the server fault checking efficiency can be increased greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN INFOTECH TECH
Camera apparatus, photographing method and a storage medium that records method of photographing
ActiveUS7321391B2Television system detailsGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Shutter
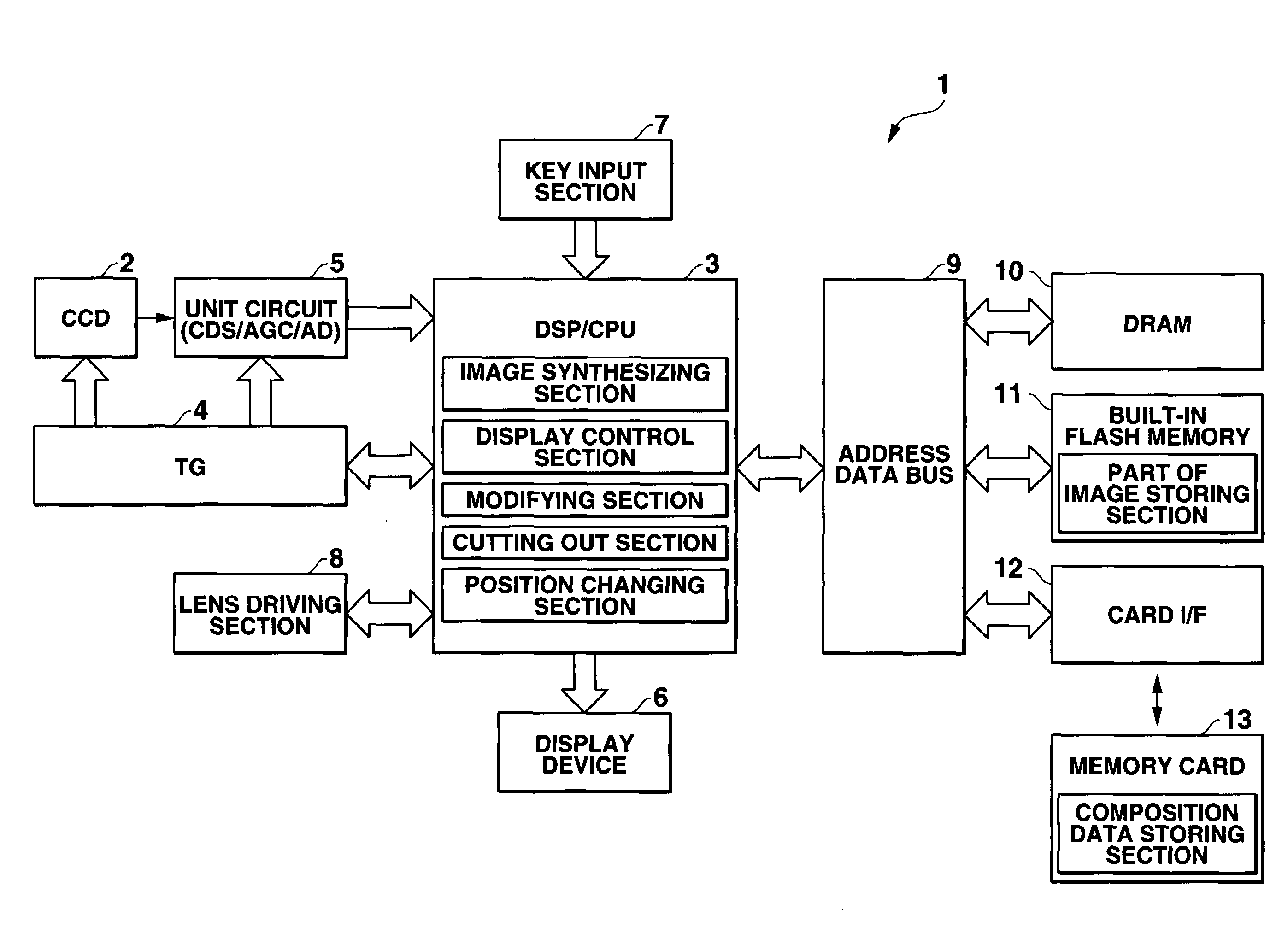
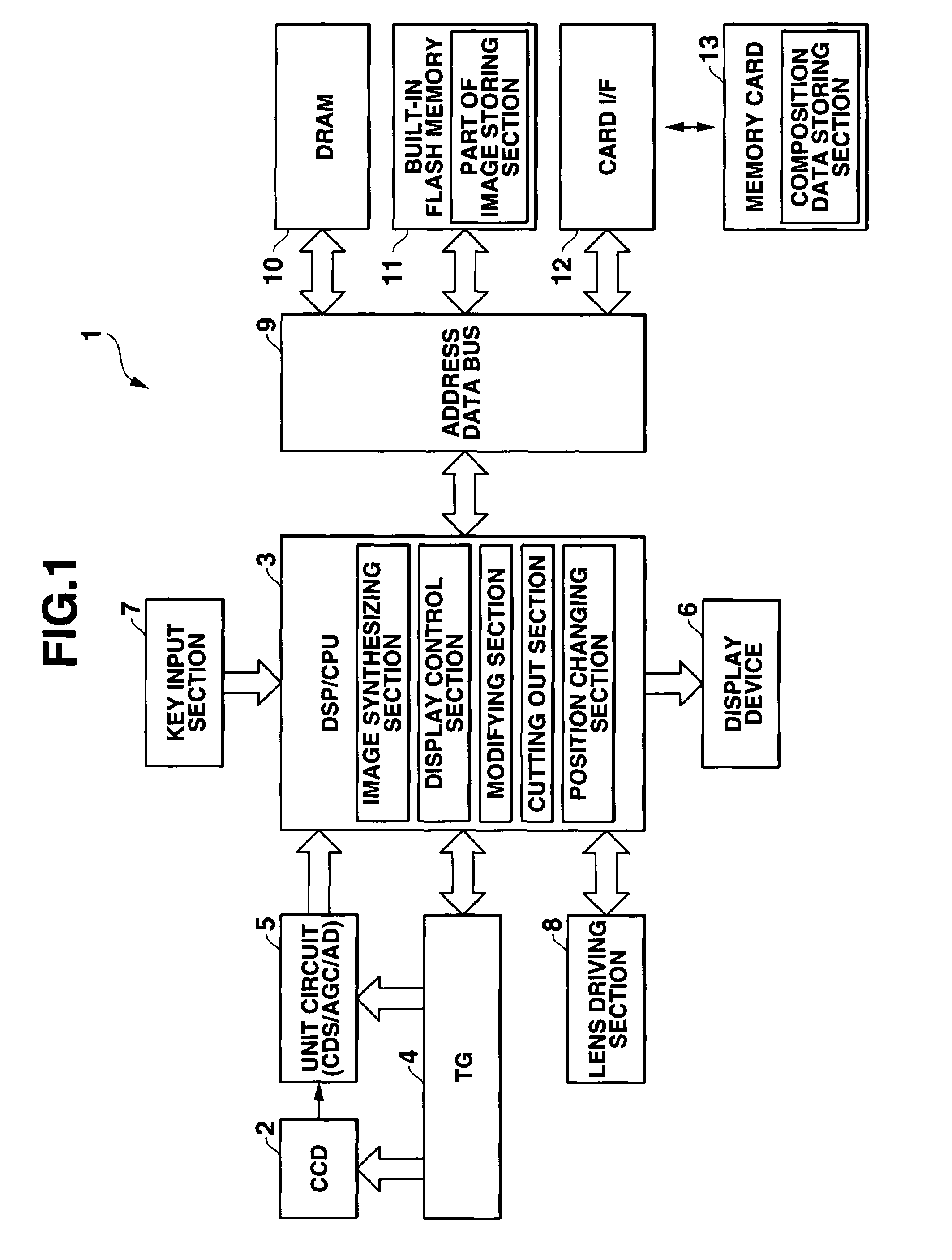
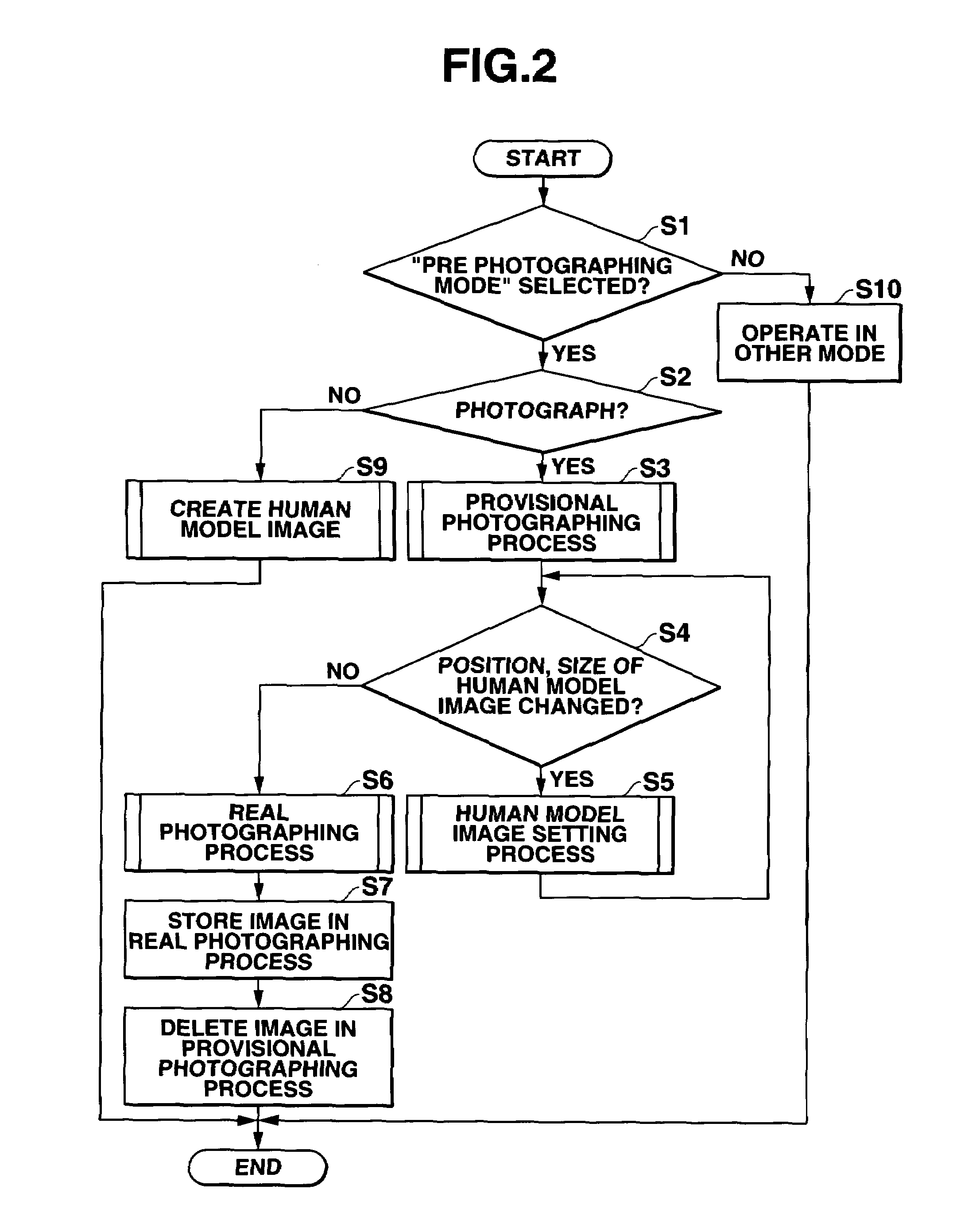
A camera has a provisional photographing mode in which a human model image is displayed on a through image in an overlapping manner on a display, and the user moves the human model image to a desired position in the through image and records a composition indicating image representing the conditions of the through image with the human model image at the desired position. After the provisional photographing process, the through image is synthesized with the recorded composition indicating image in a semi transparent manner, to display a synthesized image in place of the through image on the display. When a shutter is operated, a normal photographing process is performed to record an image.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
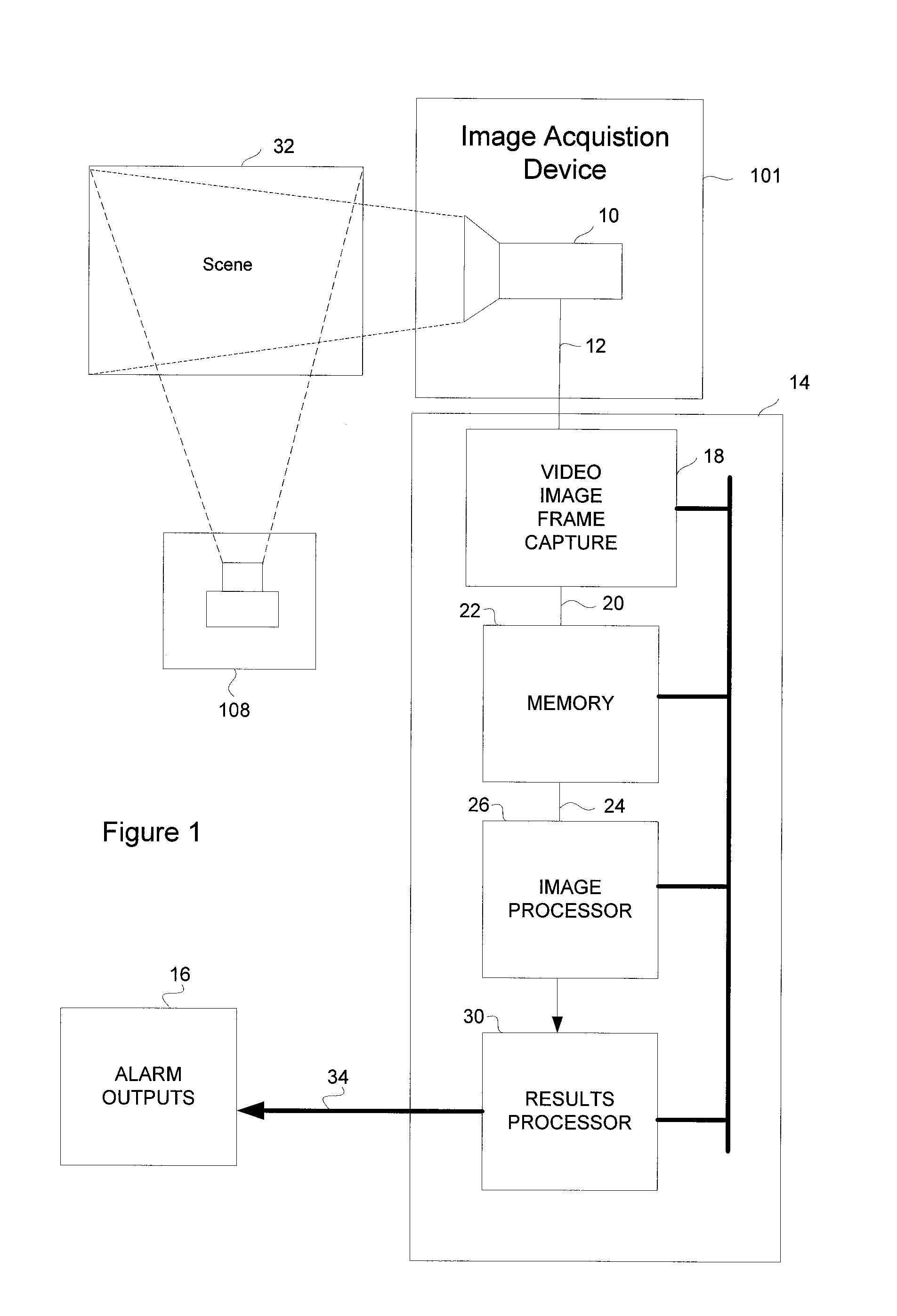
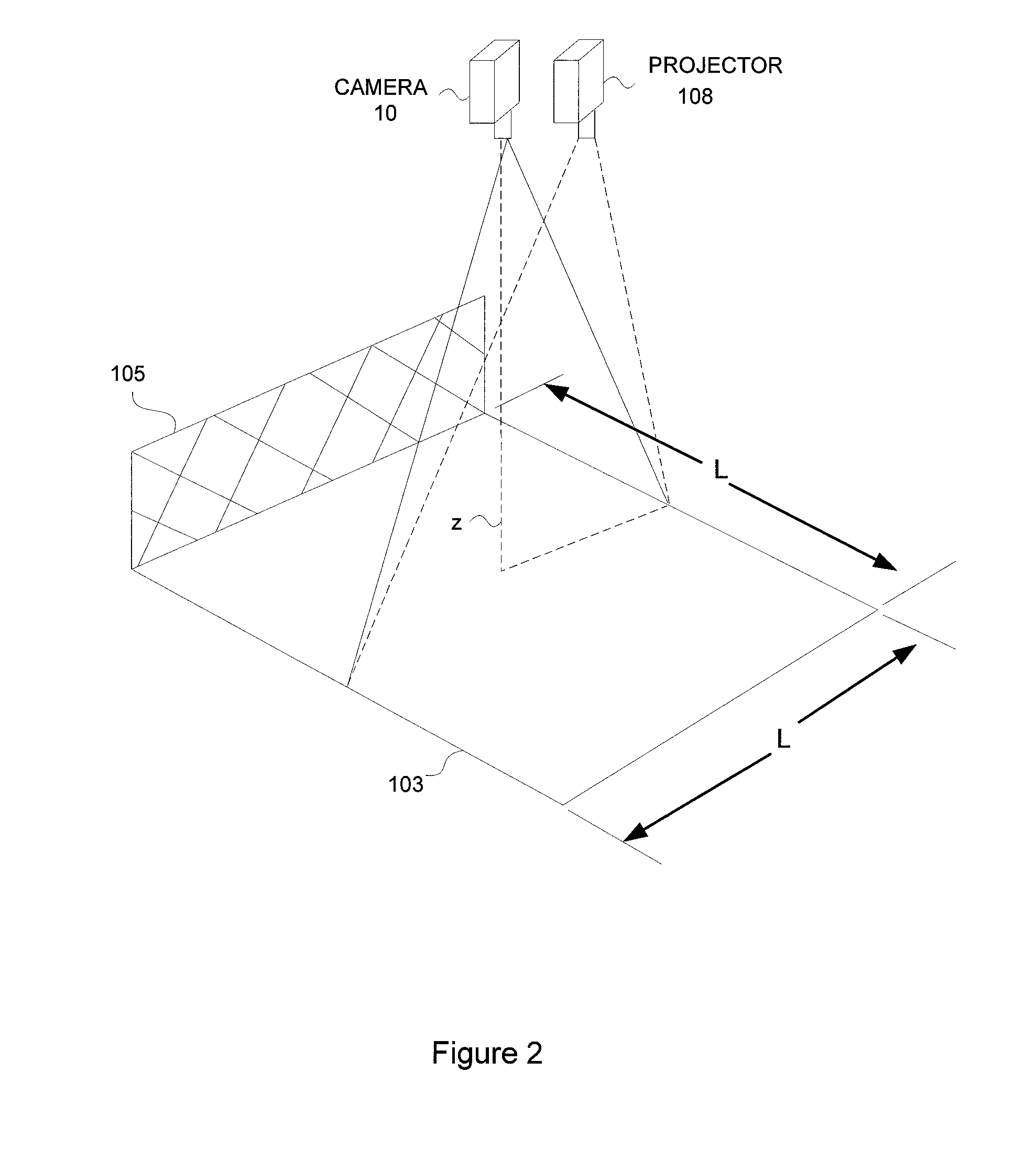
Video safety detector with projected pattern
InactiveUS7167575B1Simple methodAvoid false alarmCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsCamera imageMachine vision
A two-dimensional (2-D) machine-vision safety-solution involving a method and apparatus for performing high-integrity, high efficiency machine vision. A known structured lighting texture pattern is projected upon a target area. A model image of the pattern on an empty target field is stored during an initial training step. The machine vision safety solution digitally interprets a camera image of the light reflected by the objects in the target area to detect and characterize a pattern in the image. The pattern characterization is then processed to determine if a distortion of the characterization factors is larger than a predetermined threshold, and results in an alarm condition.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
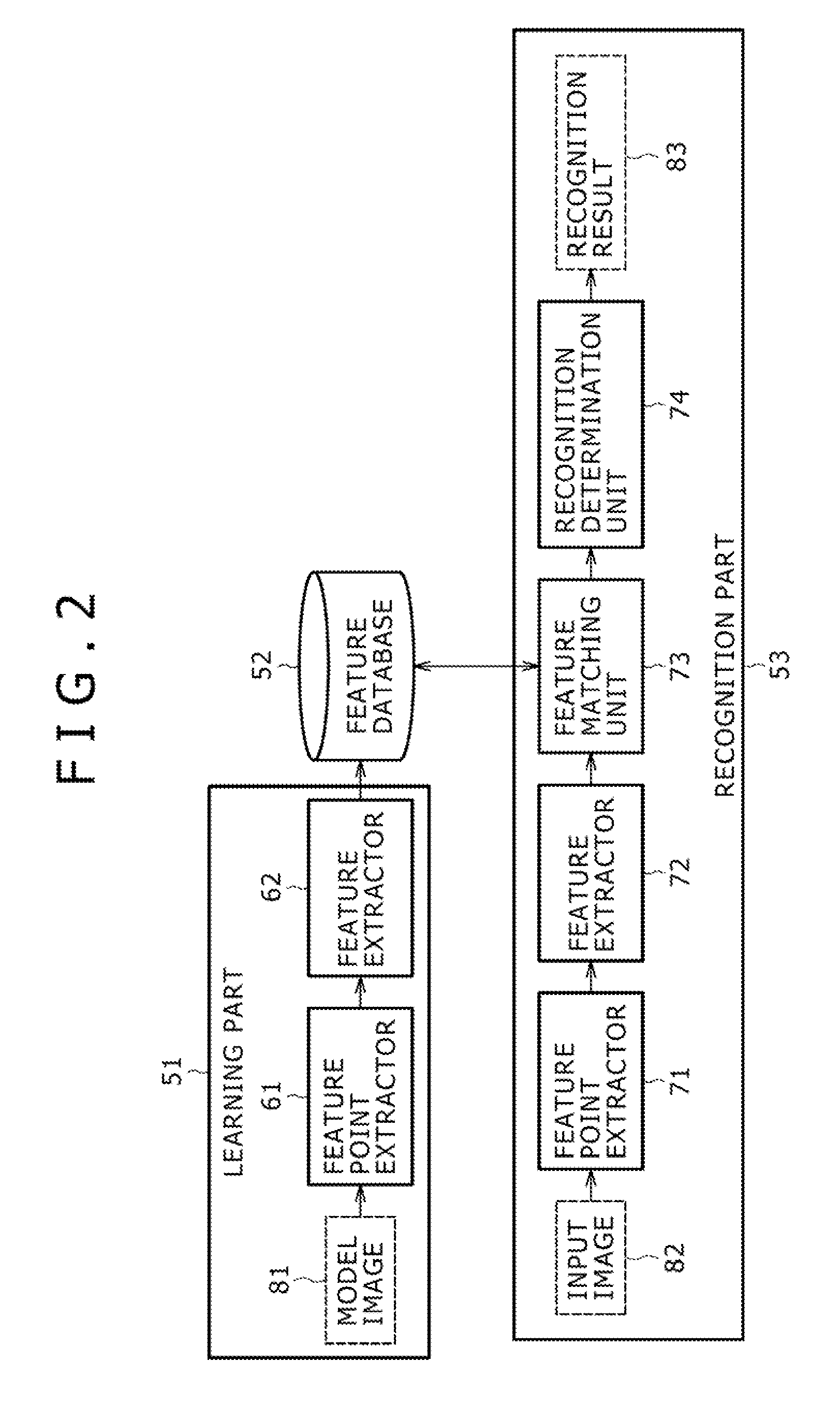
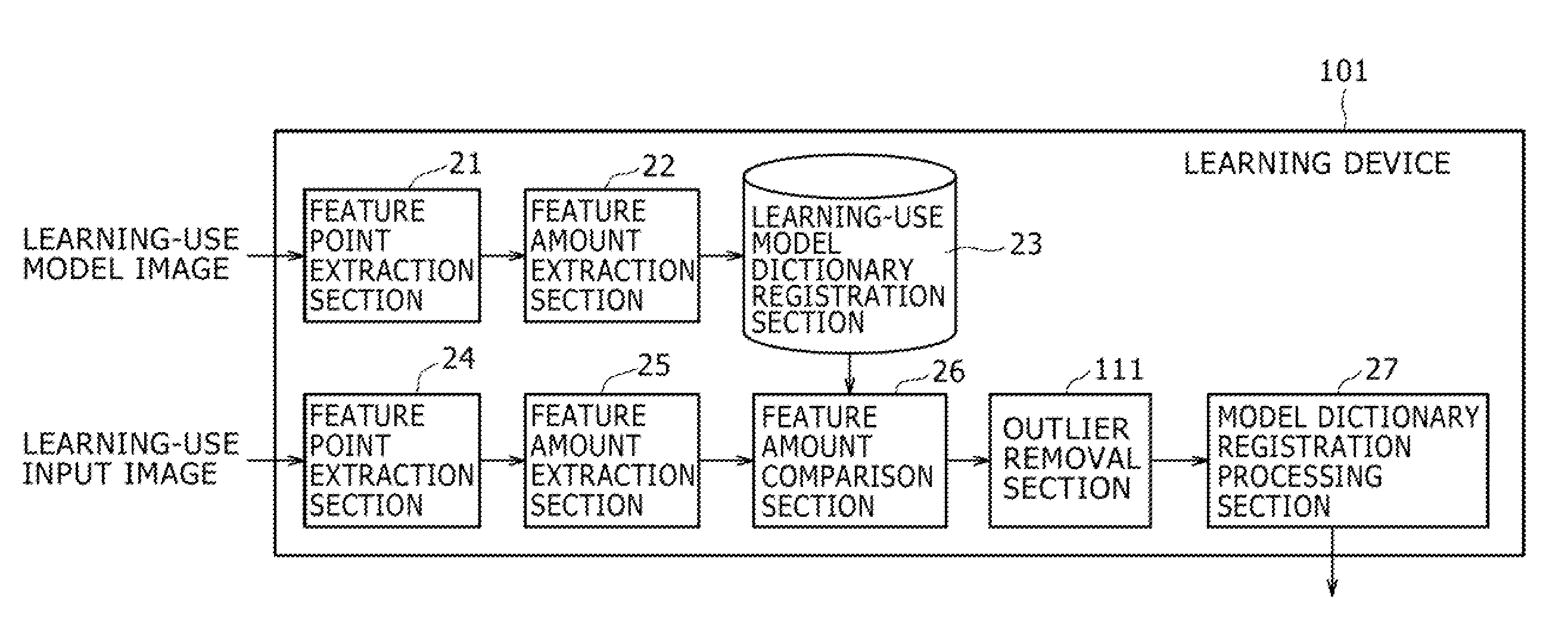
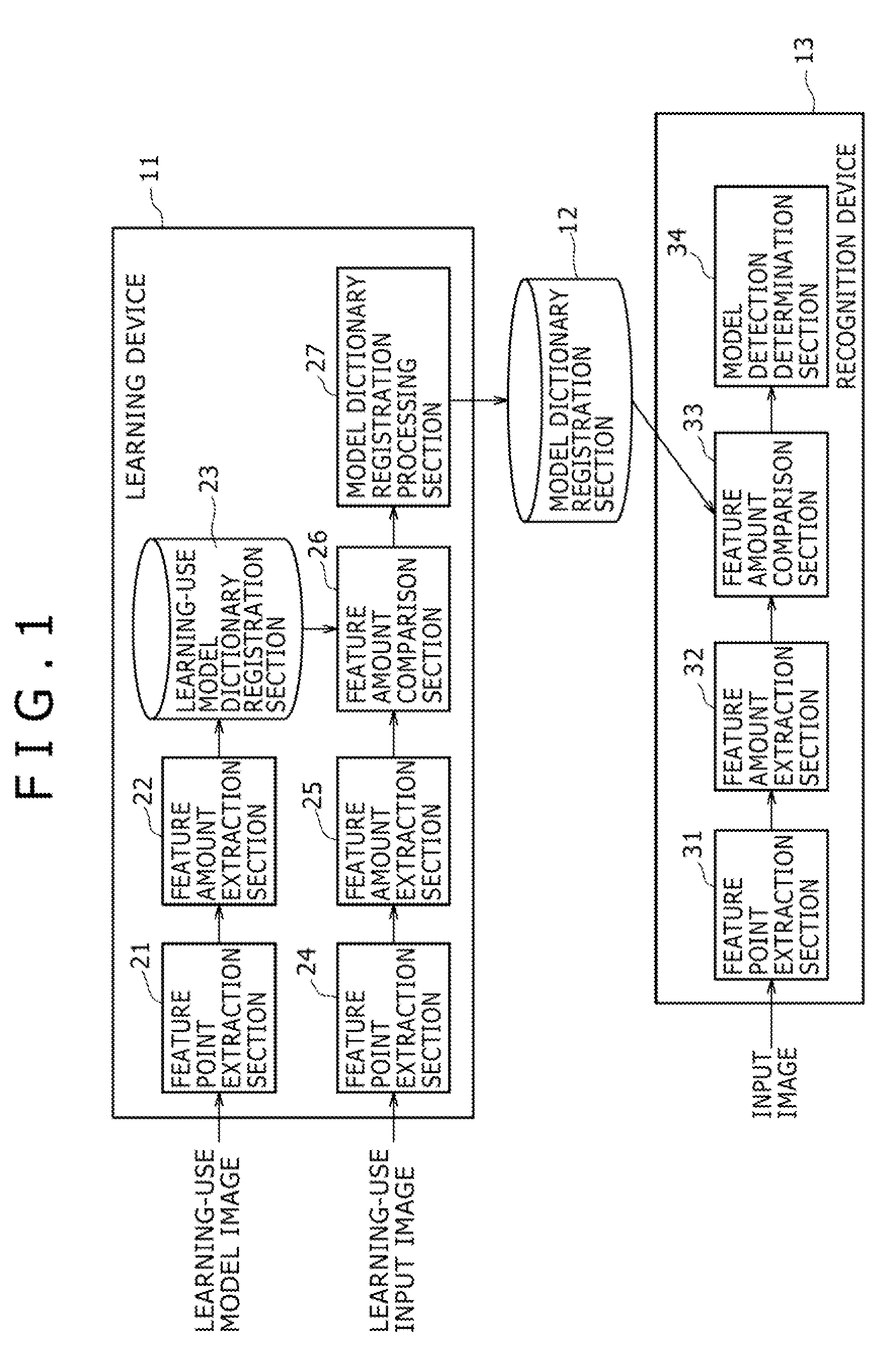
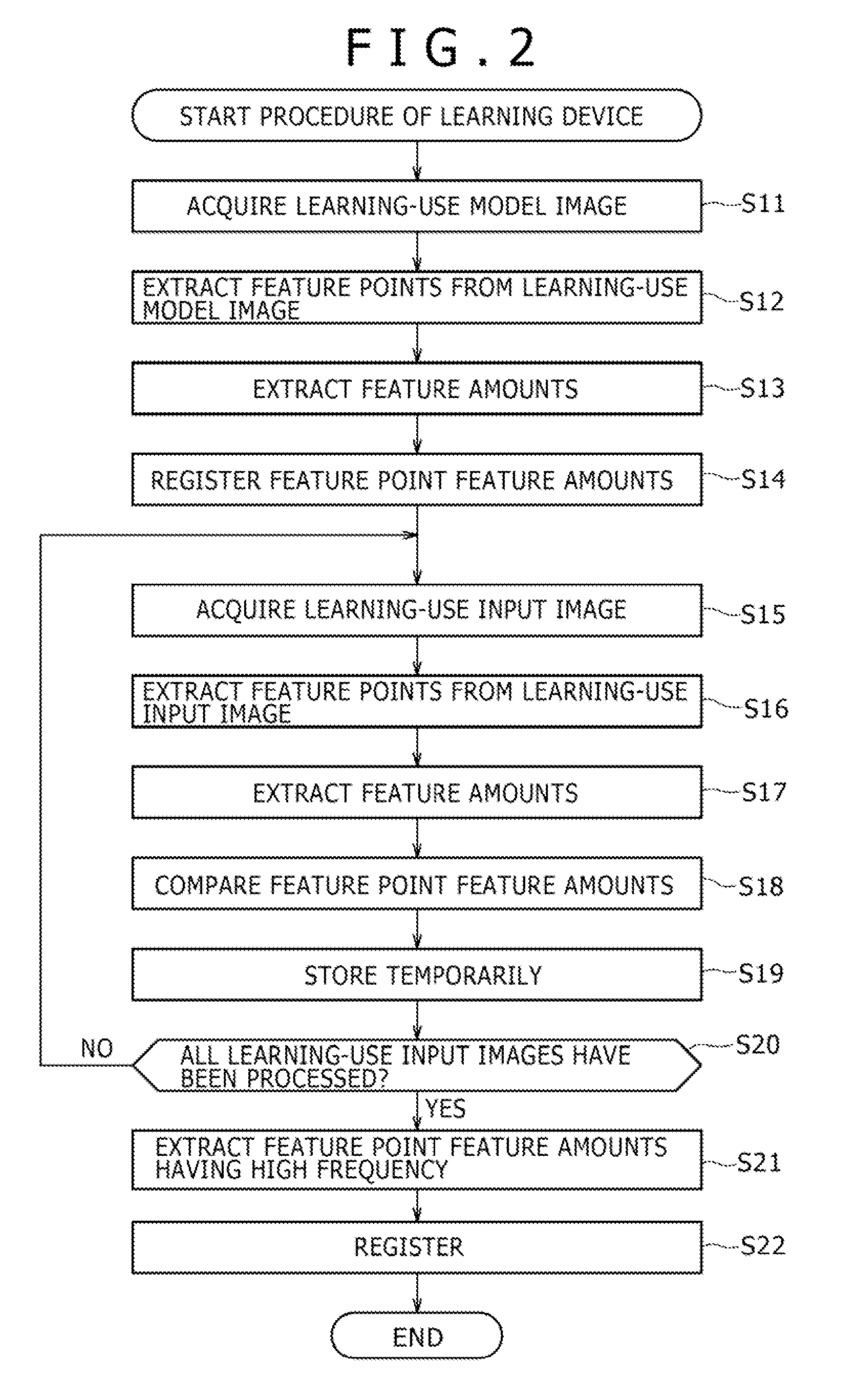
Image Processing System, Learning Device and Method, and Program
ActiveUS20090041340A1Improve recognitionImprove recognition accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingProcedure technique
The present invention relates to an image processing system, a learning device and method, and a program which enable easy extraction of feature amounts to be used in a recognition process. Feature points are extracted from a learning-use model image, feature amounts are extracted based on the feature points, and the feature amounts are registered in a learning-use model dictionary registration section 23. Similarly, feature points are extracted from a learning-use input image containing a model object contained in the learning-use model image, feature amounts are extracted based on these feature points, and these feature amounts are compared with the feature amounts registered in a learning-use model registration section 23. A feature amount that has formed a pair the greatest number of times as a result of the comparison is registered in the model dictionary registration section 12 as the feature amount to be used in the recognition process. The present invention is applicable to a robot.
Owner:SONY CORP
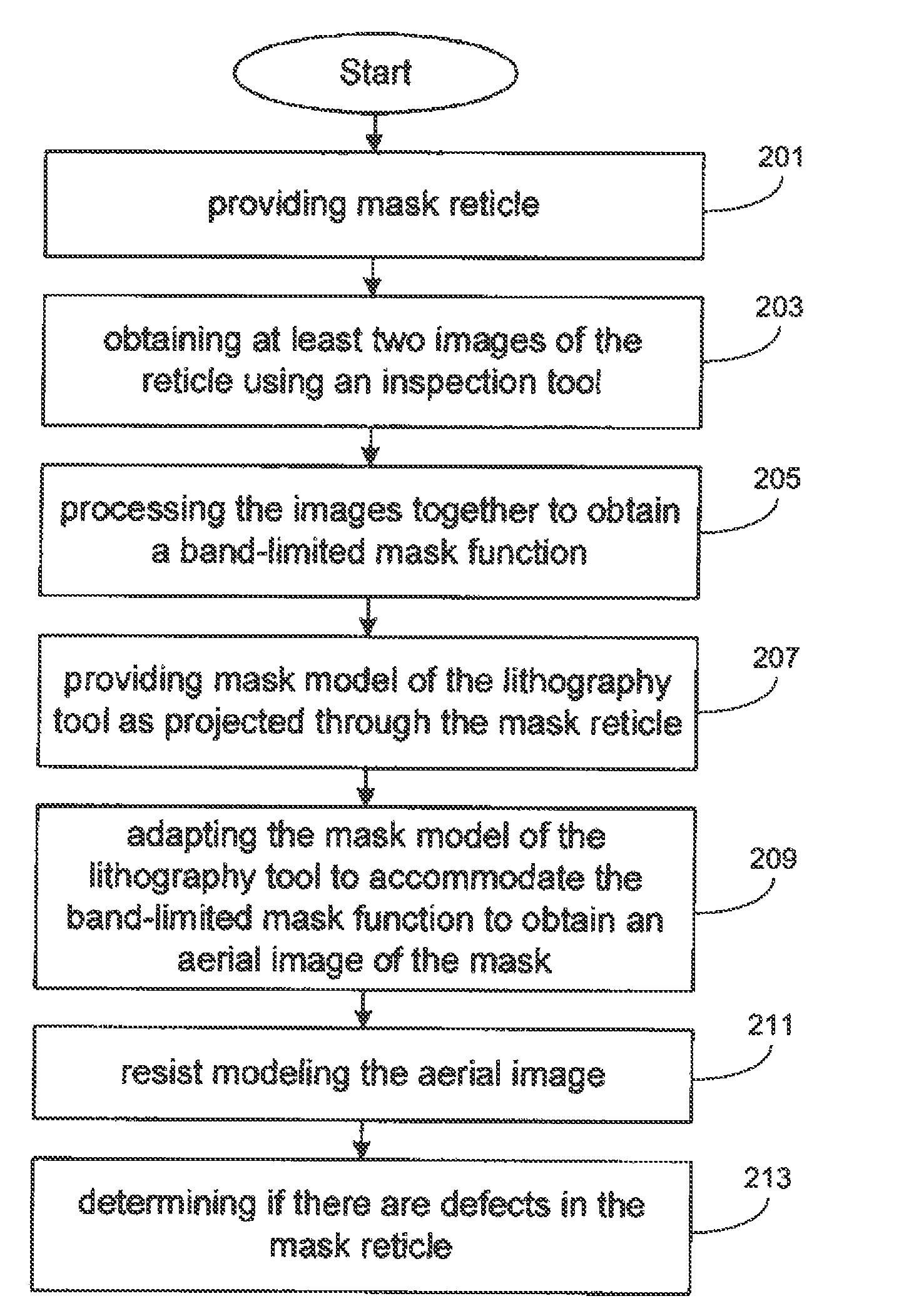
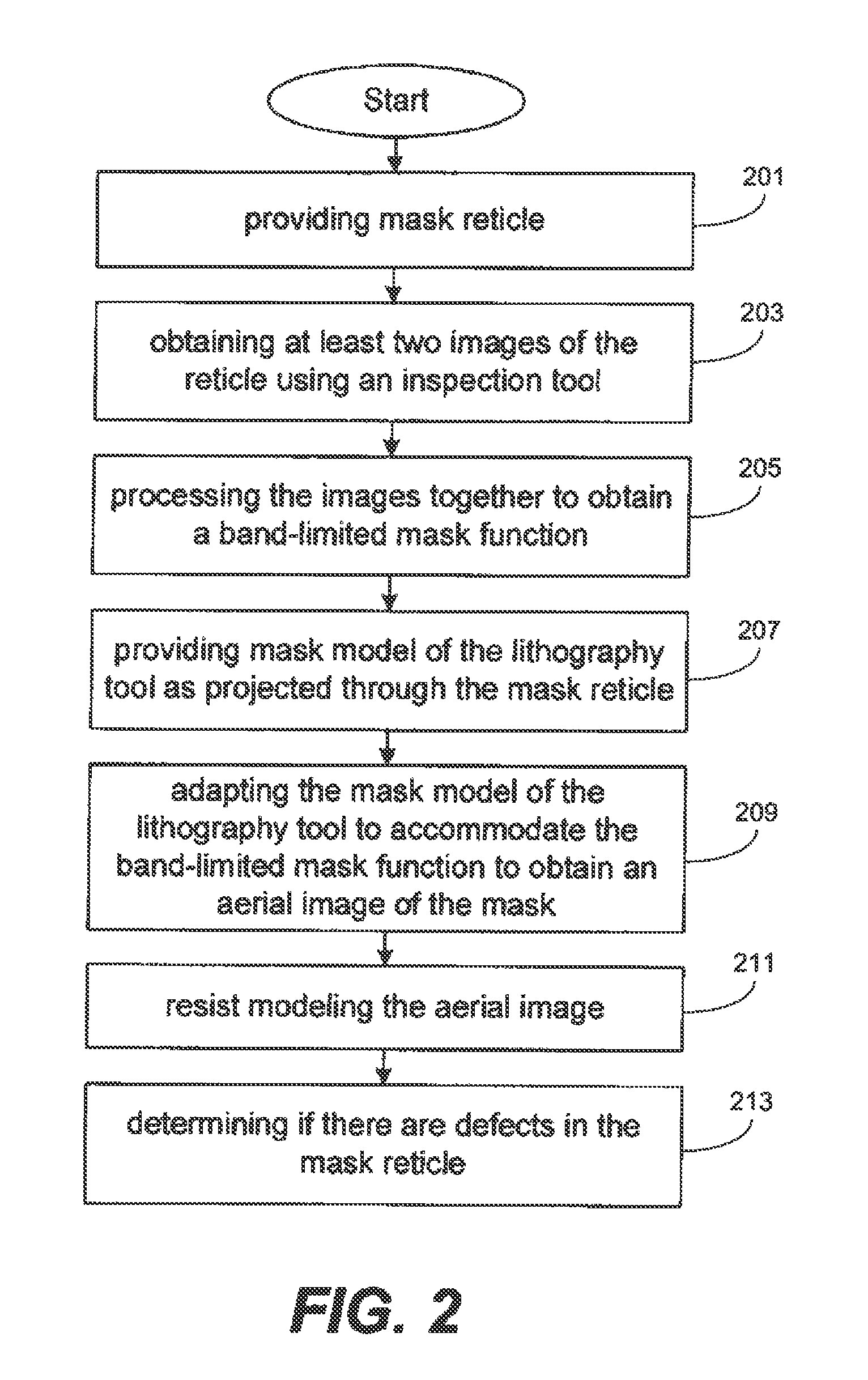
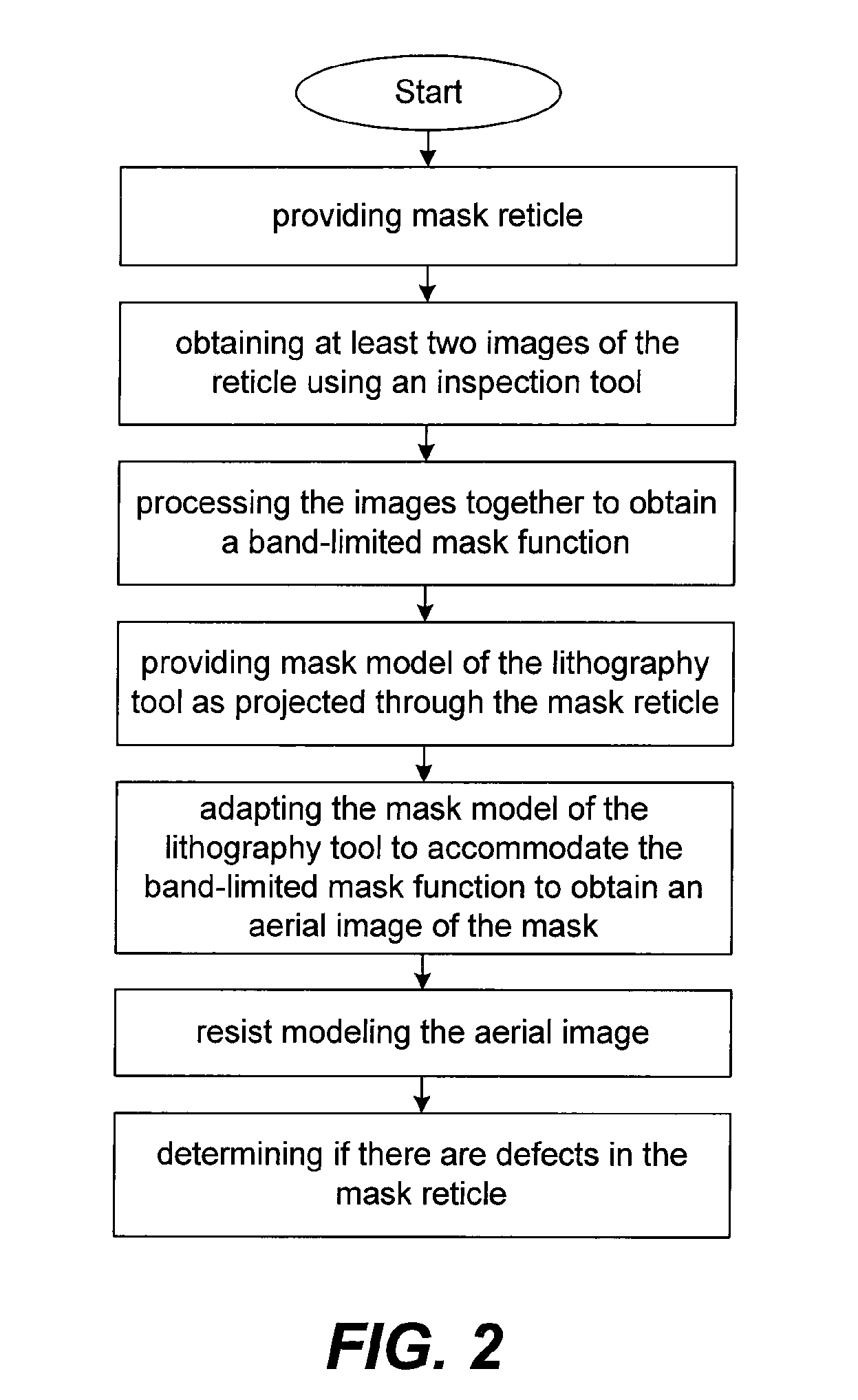
Method for detecting lithographically significant defects on reticles
ActiveUS7873204B2Character and pattern recognitionOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPattern recognitionResist
A method for identifying lithographically significant defects. A photomask is illuminated to produce images that experience different parameters of the reticle as imaged by an inspection tool. Example parameters include a transmission intensity image and a reflection intensity image. The images are processed together to recover a band limited mask pattern associated with the photomask. A model of an exposure lithography system for chip fabrication is adapted to accommodate the band limited mask pattern as an input which is input into the model to obtain an aerial image of the mask pattern that is processed with a photoresist model yielding a resist-modeled image. The resist-modeled image is used to determine if the photomask has lithographically significant defects.
Owner:KLA CORP
Defect detecting apparatus, defect detecting method, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program therefor
InactiveUS20100074516A1Highly accurate and efficient detectionAccurately determineImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingProtein chip
A defect detecting apparatus captures an image of a protein chip formed on each die of a wafer with a low magnification for every first division region obtained by dividing each die in plurality; stores each obtained image as an inspection target image together with an ID for identifying each first division region; creates a model image for every first division region by calculating an average luminance value of pixels of each inspection target image; extracts a difference between the model image and each inspection target image as a difference image; determines presence of a defect by extracting a Blob having an area larger than a preset value from the difference image; captures a high-magnification image of every second division region; creates a model image again and extracts a Blob; and determines the kind of the defect based on a feature point of the defect.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
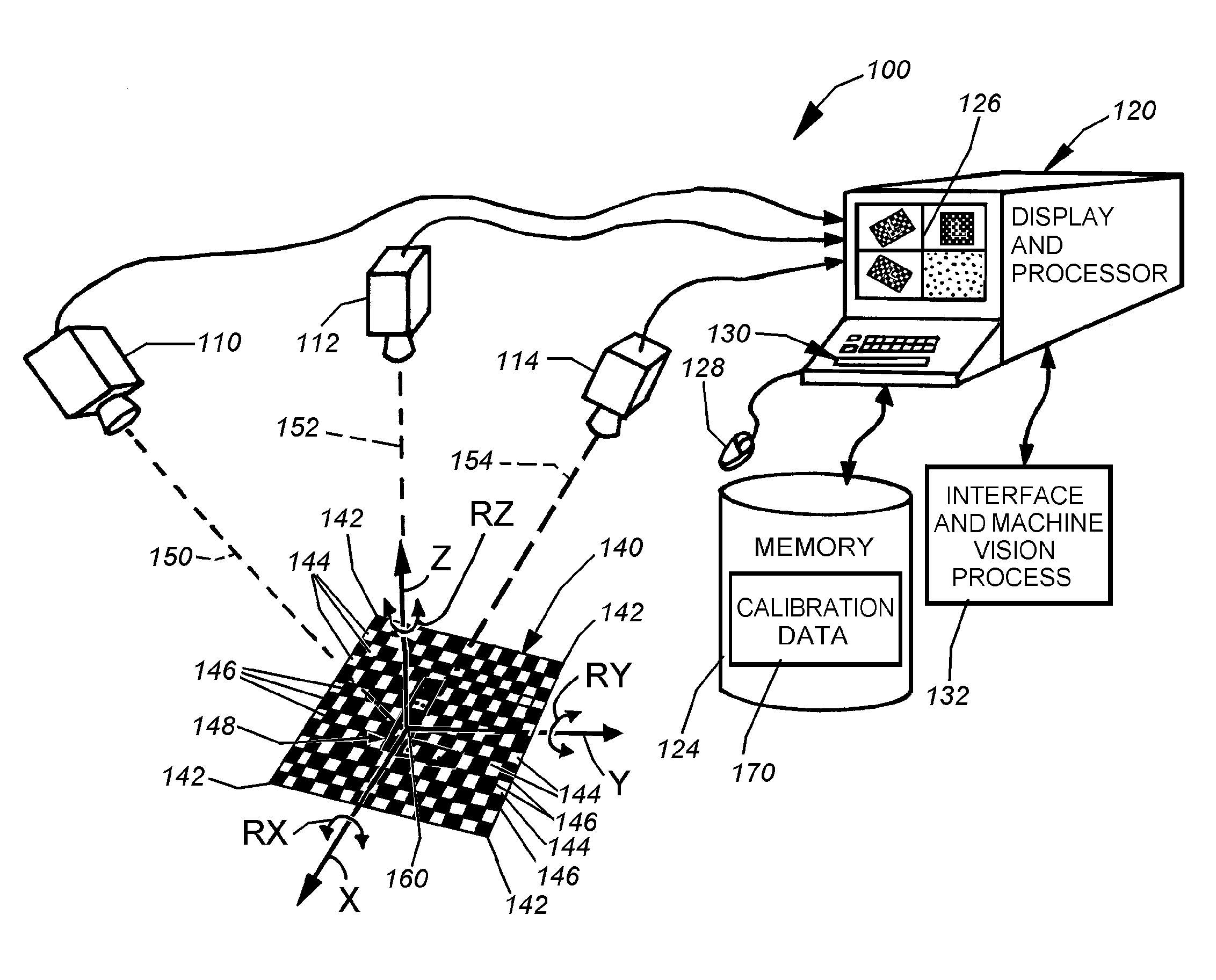
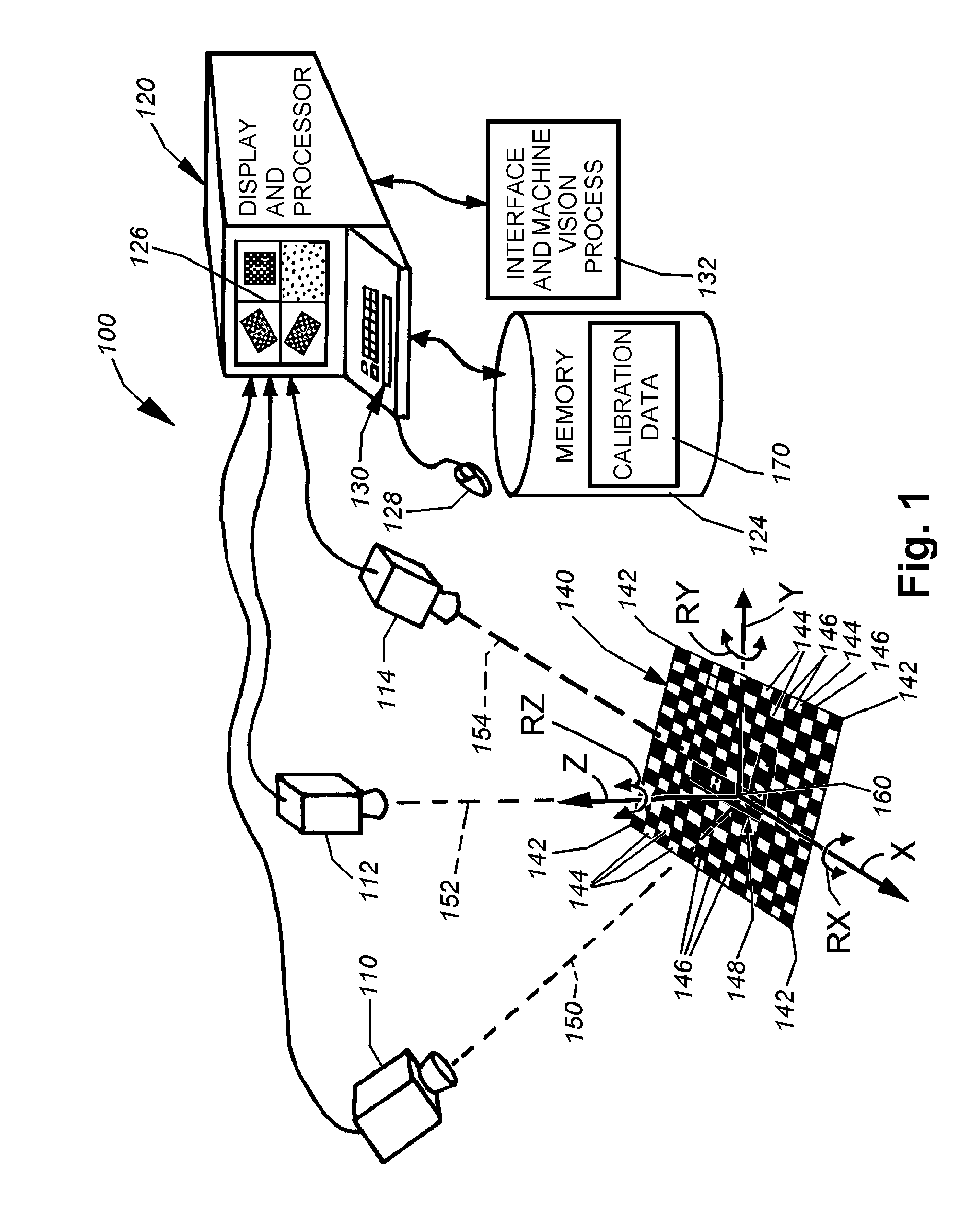
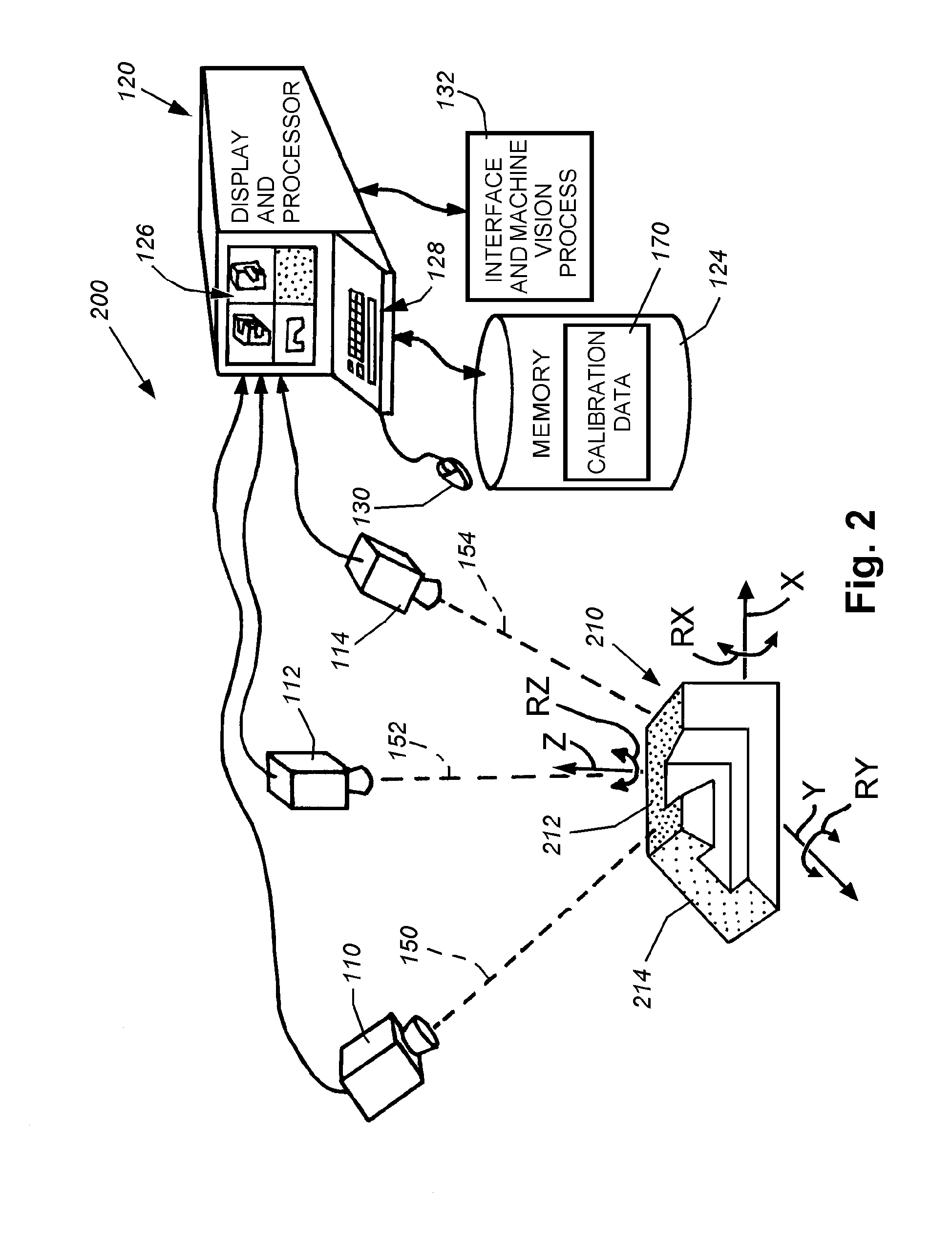
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
ActiveUS20080298672A1Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVision processing
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Method for detecting lithographically significant defects on reticles
ActiveUS20080170773A1Character and pattern recognitionOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPattern recognitionResist
A method for identifying lithographically significant defects. A photomask is illuminated to produce images that experience different parameters of the reticle as imaged by an inspection tool. Example parameters include a transmission intensity image and a reflection intensity image. The images are processed together to recover a band limited mask pattern associated with the photomask. A model of an exposure lithography system for chip fabrication is adapted to accommodate the band limited mask pattern as an input which is input into the model to obtain an aerial image of the mask pattern that is processed with a photoresist model yielding a resist-modeled image. The resist-modeled image is used to determine if the photomask has lithographically significant defects.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
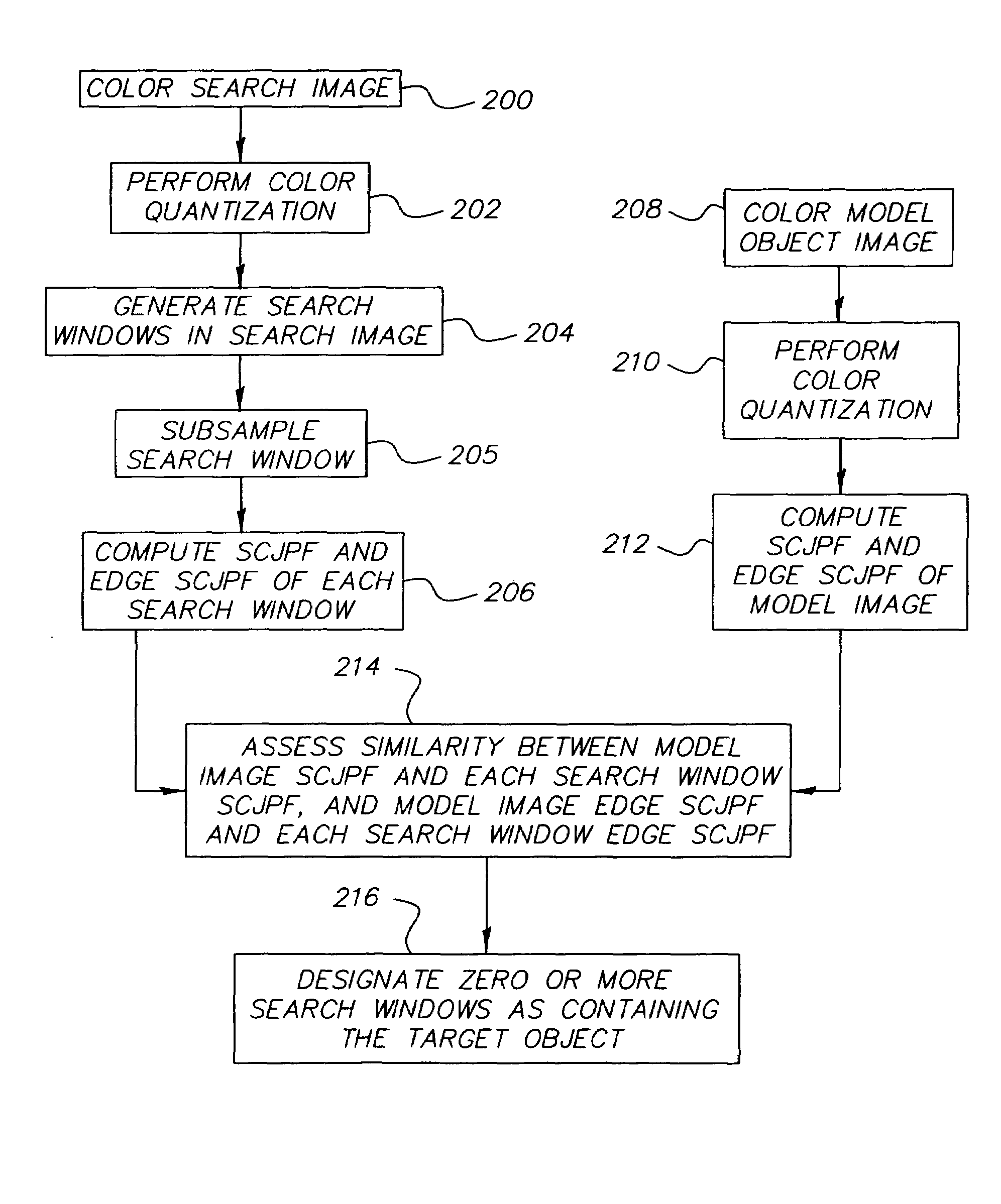
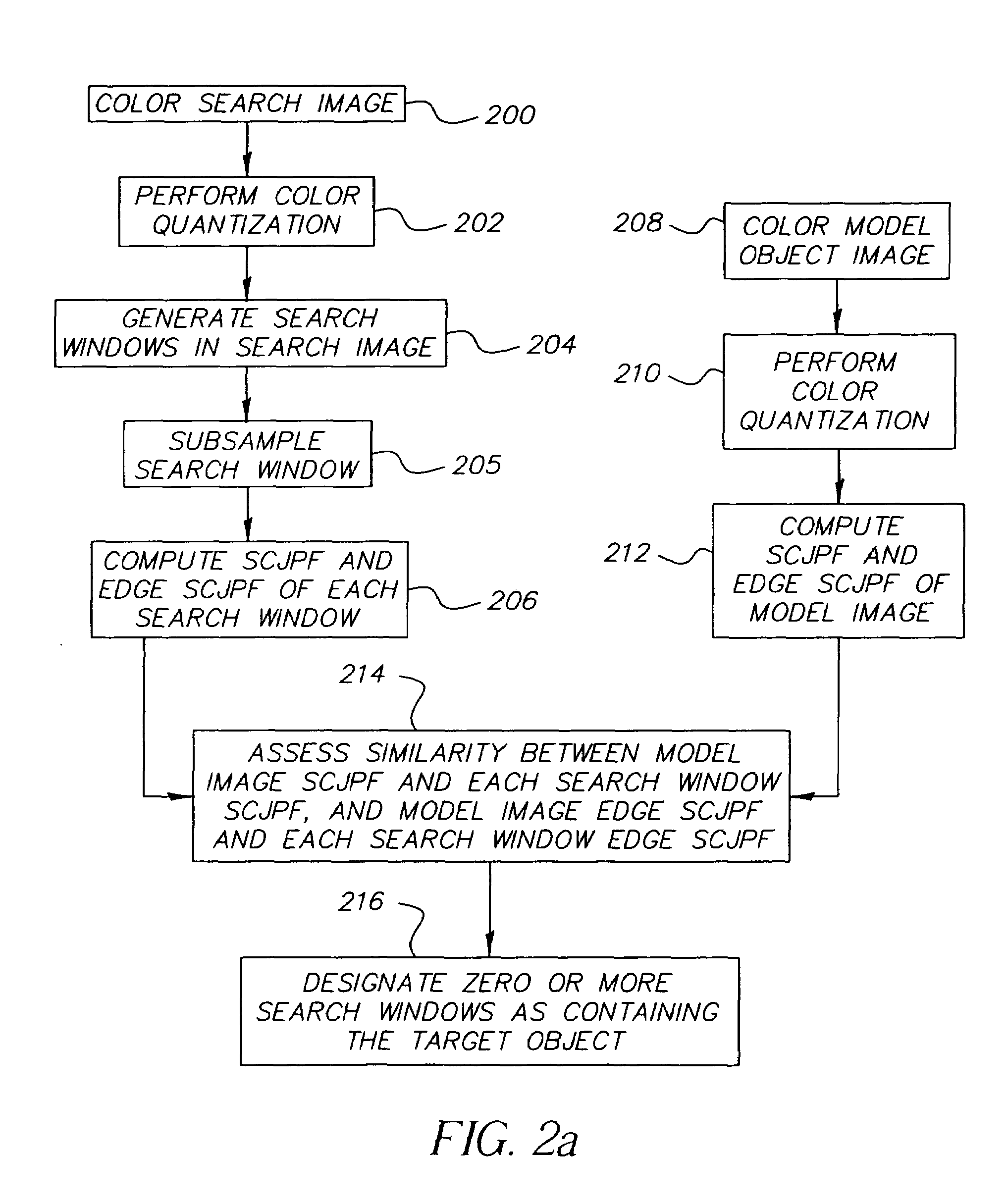
Method for detecting color objects in digital images
InactiveUS7263220B2Improve the detection rateLower detection rateImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCo-occurrenceDigital image
A method for detecting an object in a digital image including the steps of performing color quantization on a model image including the object and on a search image that potentially includes the object, generating a plurality of search windows, computing spatial-color joint probability functions of each model and search image, where the color co-occurrence edge histogram is chosen to be the spatial-color joint probability function, assessing the similarity of each search image to the model, and designating search windows as containing the target object.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Image enhancement apparatus and method
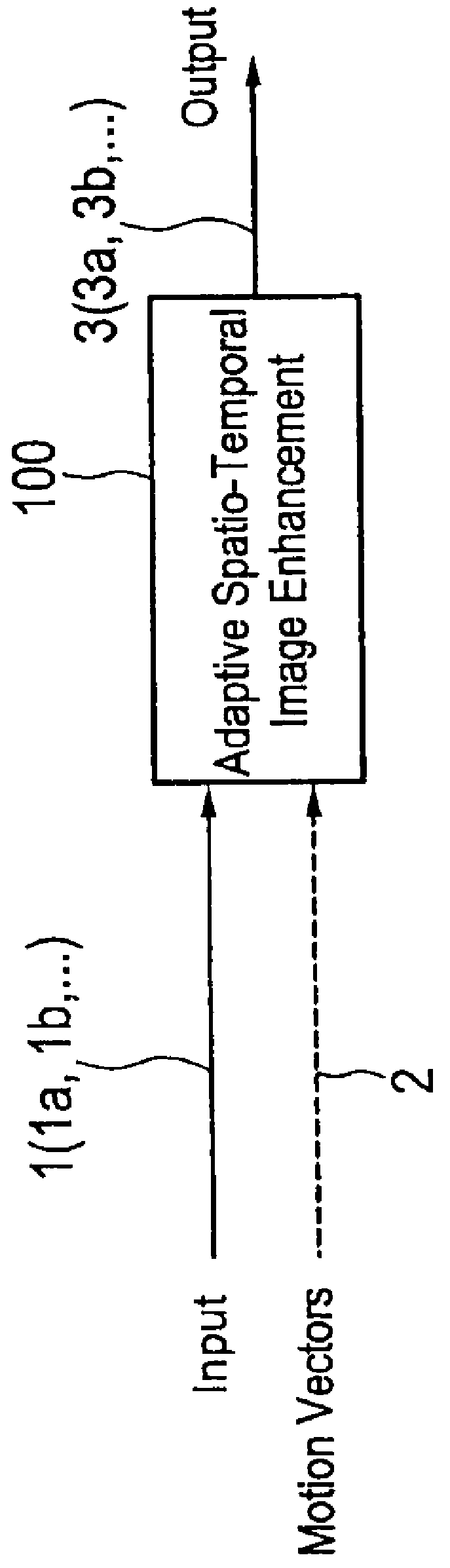
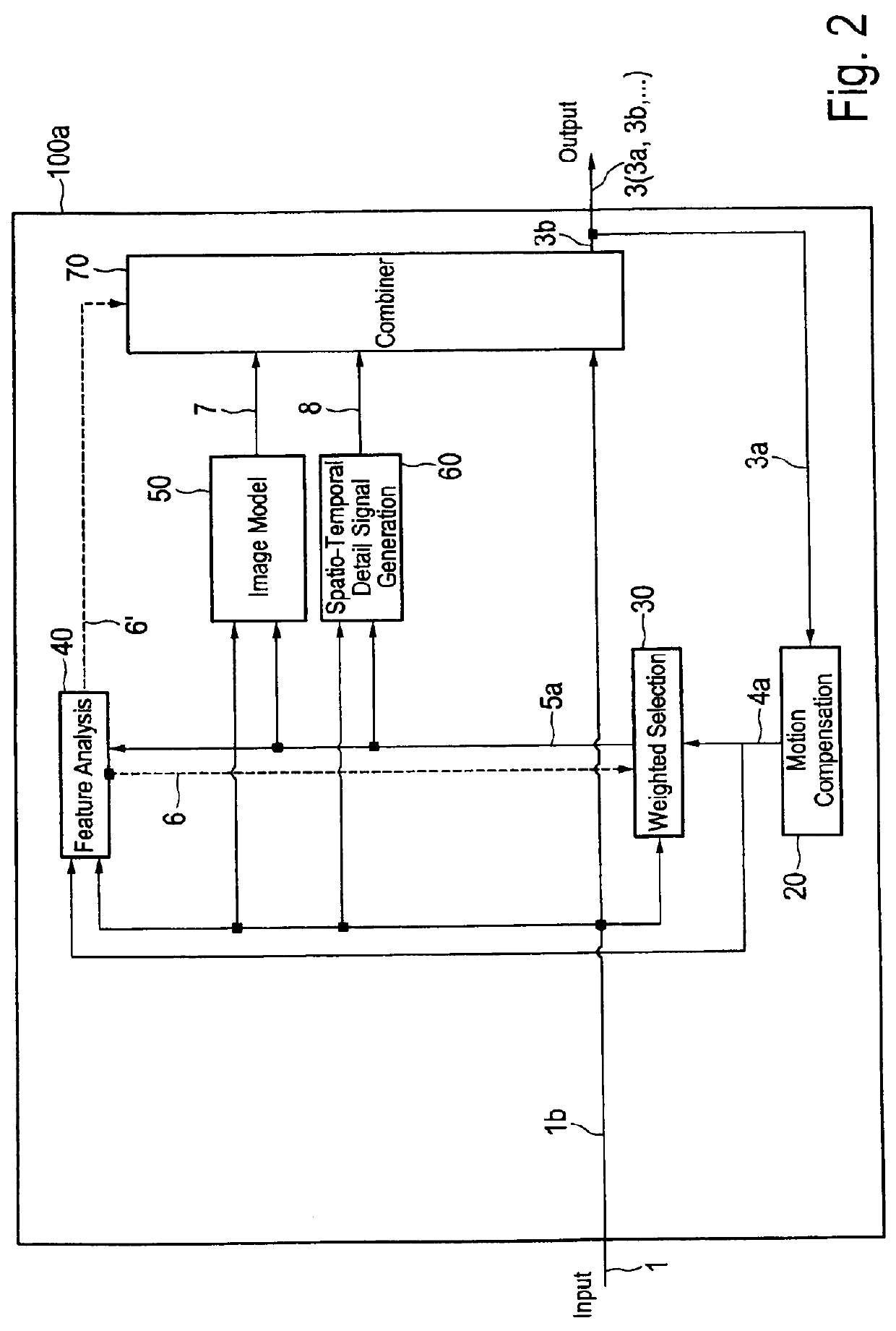
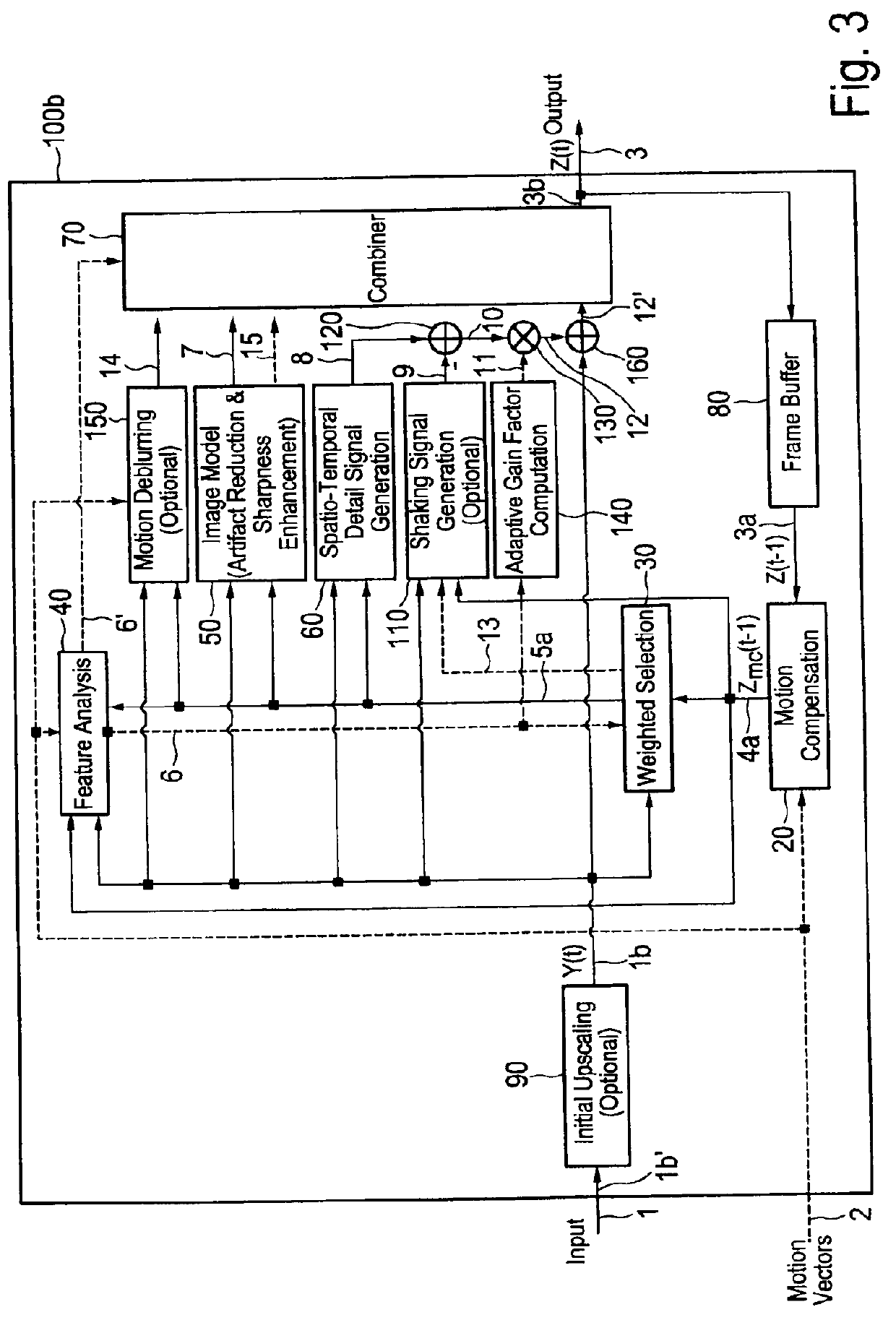
ActiveUS20120219229A1High resolutionReduce artefactImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionSpacetime
The present invention relates to an image enhancement apparatus for enhancing an input image of a sequence of input images. To provide the ability to increase the resolution of an input image and / or to temporally reduce artefacts and / or noise in an input image, the apparatus comprises a motion compensation unit, a weighted selection unit, a feature analysis unit, an image model unit configured to generate a modelled image by applying an image model on said input image and / or said weighted selection image, a spatio-temporal detail signal generation unit configured to generate a detail signal from said input image and said weighted selection image, and a combination unit configured to generate said enhanced output image from said input image, said detail signal and said modelled image.
Owner:SONY CORP
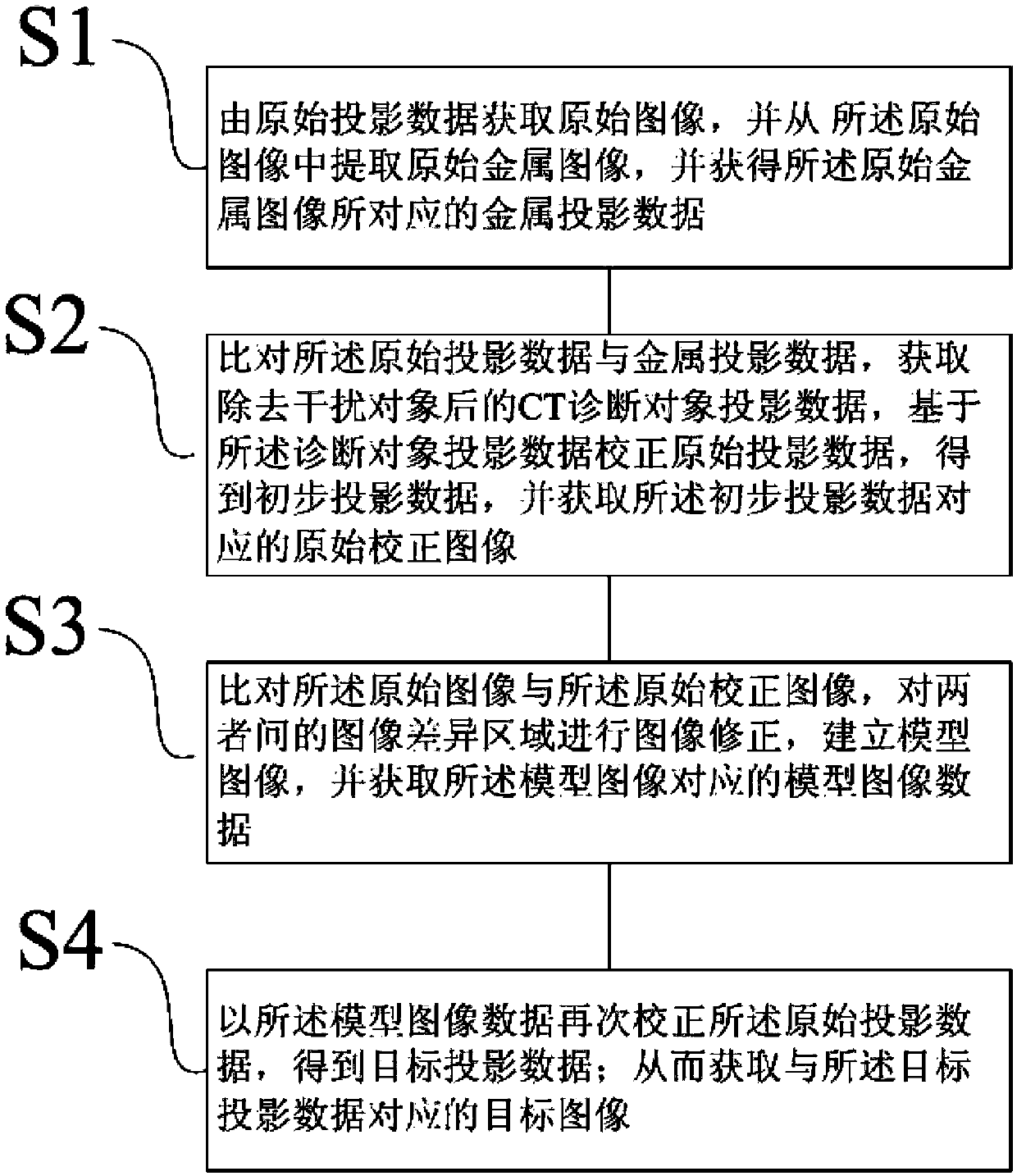
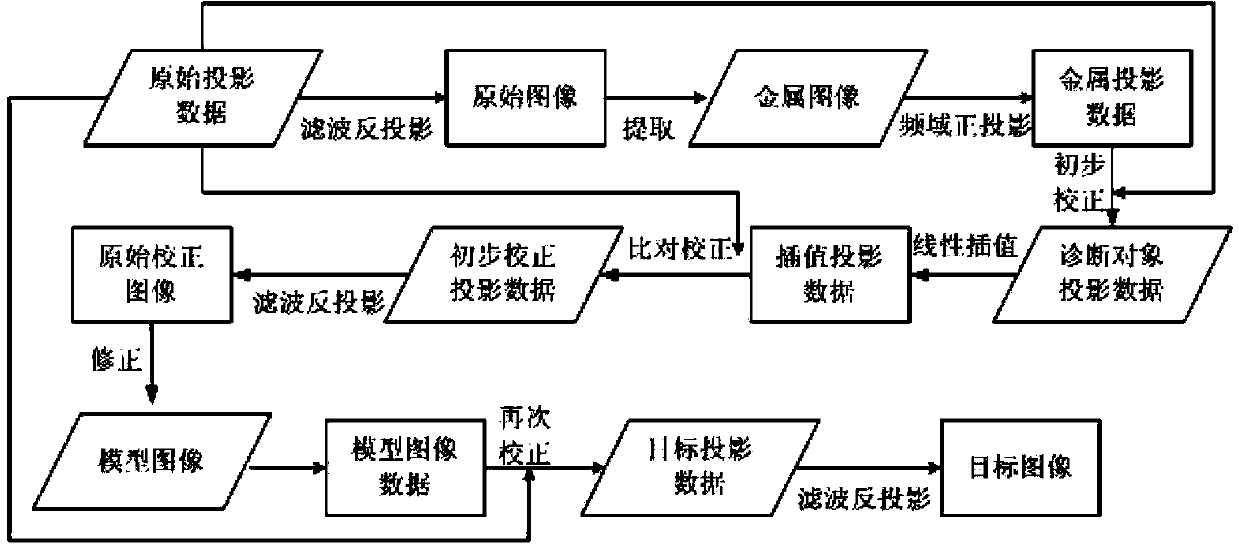
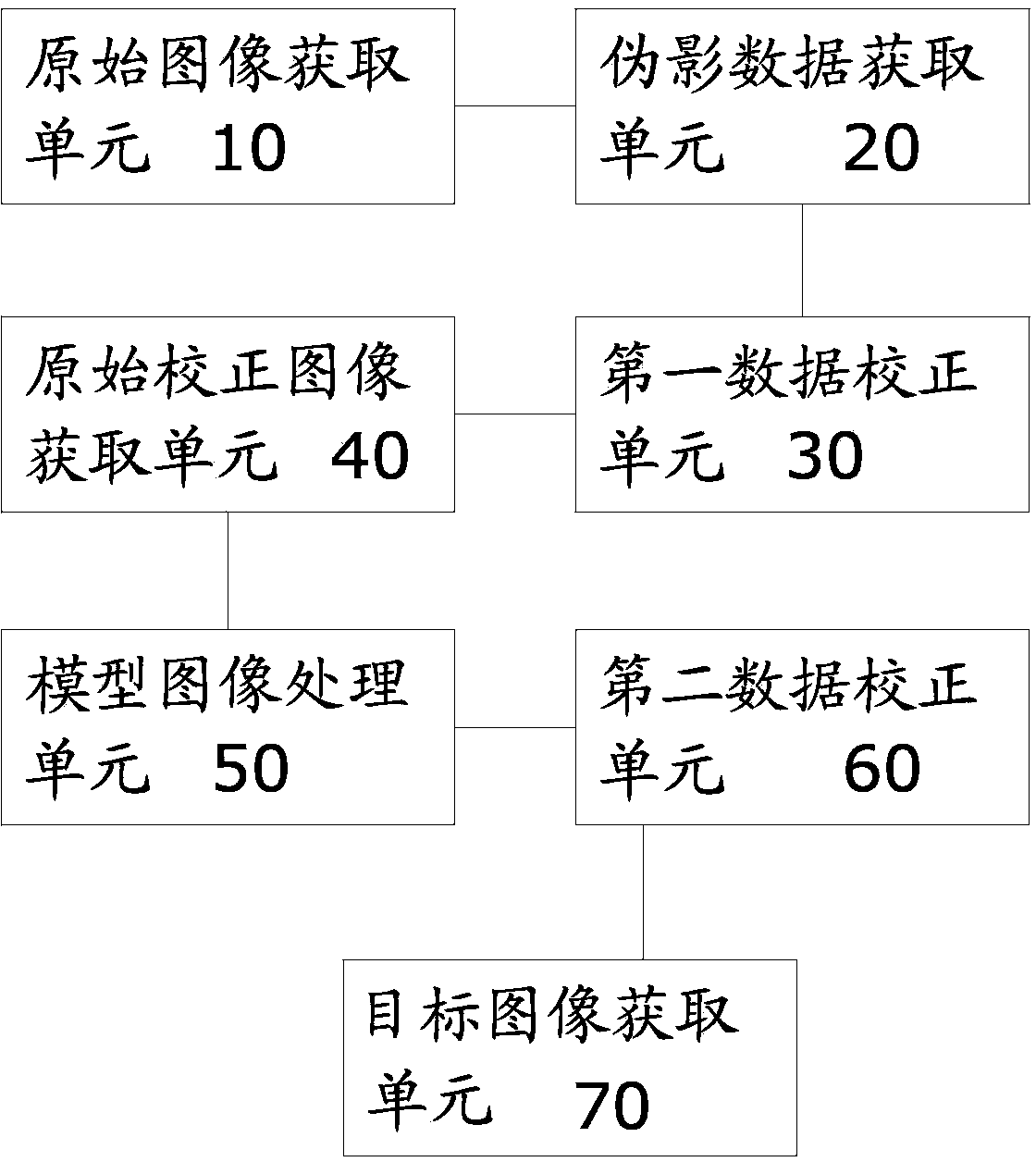
Computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method, device and computerized tomography (CT) apparatus
ActiveCN103679642AGuaranteed Spatial ResolutionLow contrast capabilityImage enhancementComputerised tomographsMetal ArtifactImage resolution
The invention provides a computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method, a computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction device and a computerized tomography (CT) apparatus. The computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method comprises the following steps that: a metal projection range caused by an interference object is determined according to an original image corresponding to original projection data; diagnosis object projection data after the removal of the interference object are obtained based on metal projection data in the metal projection range, and after that, the original projection data are corrected and a model image is constructed based on the diagnosis object projection data; and secondary correction is performed on the original projection data according to the projection data of the model image, and reconstruction is performed based on corrected target projection data and according to clinically-used scanning and image construction conditions so as to obtain a metal artifact-free target image, and therefore, the purpose of metal artifact correction can be achieved. According to the computerized tomography (CT) image metal artifact correction method of the invention, the original projection data are adopted as a correction object, and therefore, the spatial resolution and low-contrast ability of a processed image can be ensured; and the original projection data completely contain all information of the interference object, and therefore, the introduction of a new artifact can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com