Patents
Literature
311 results about "Sensor model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
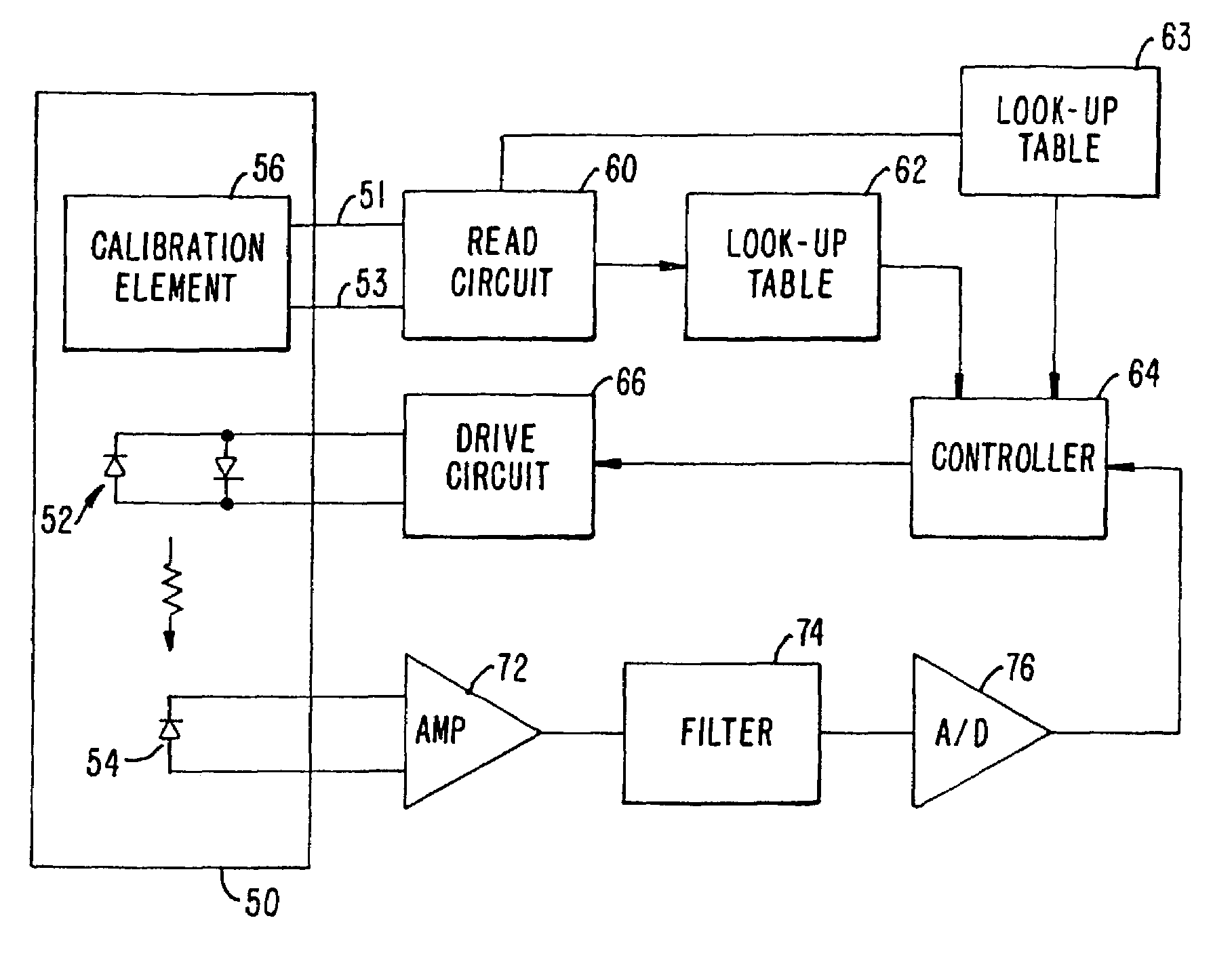
Oximeter sensor with digital memory recording sensor data
InactiveUS20020038081A1Improve abilitiesEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsMemory chipDriving current
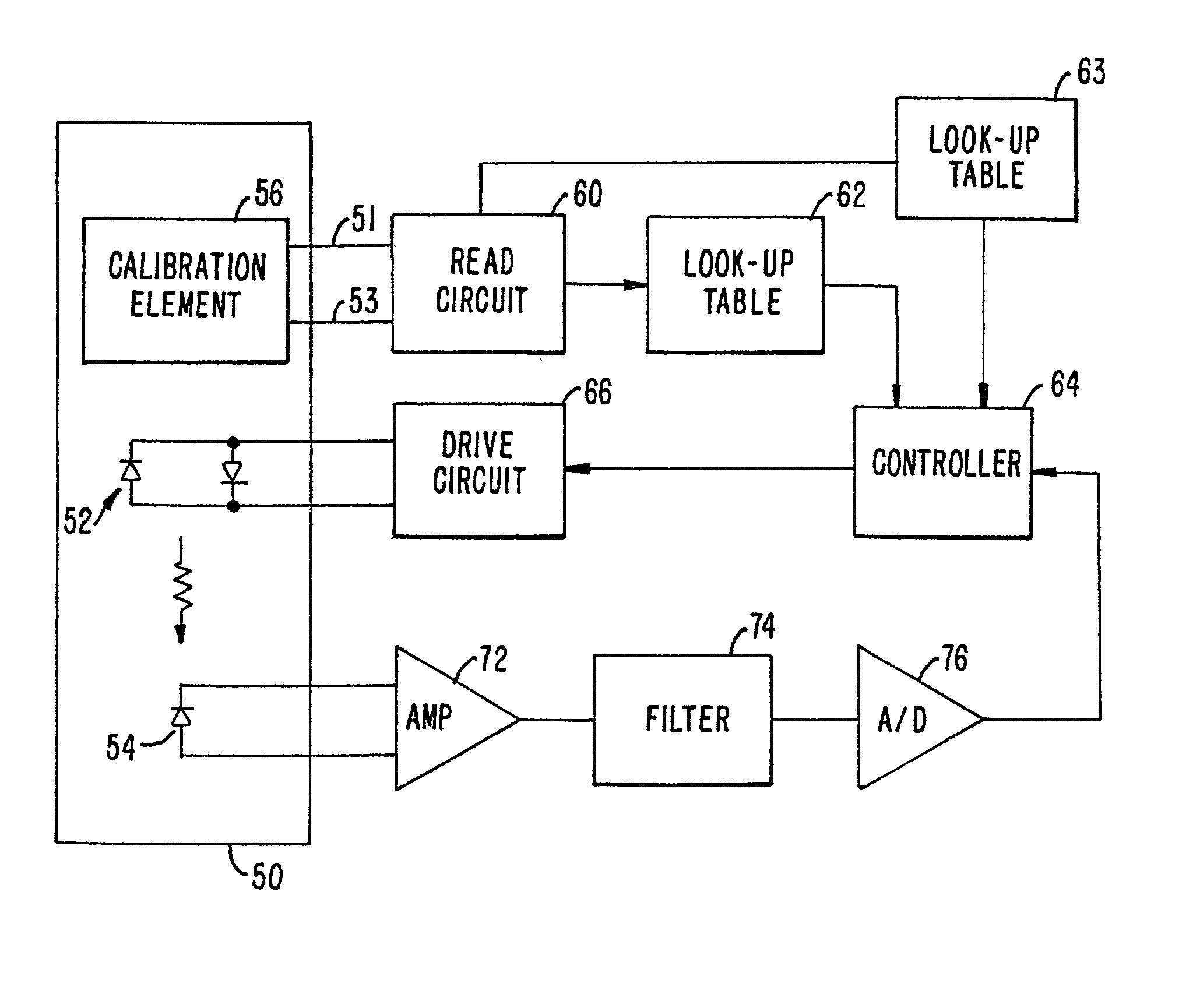
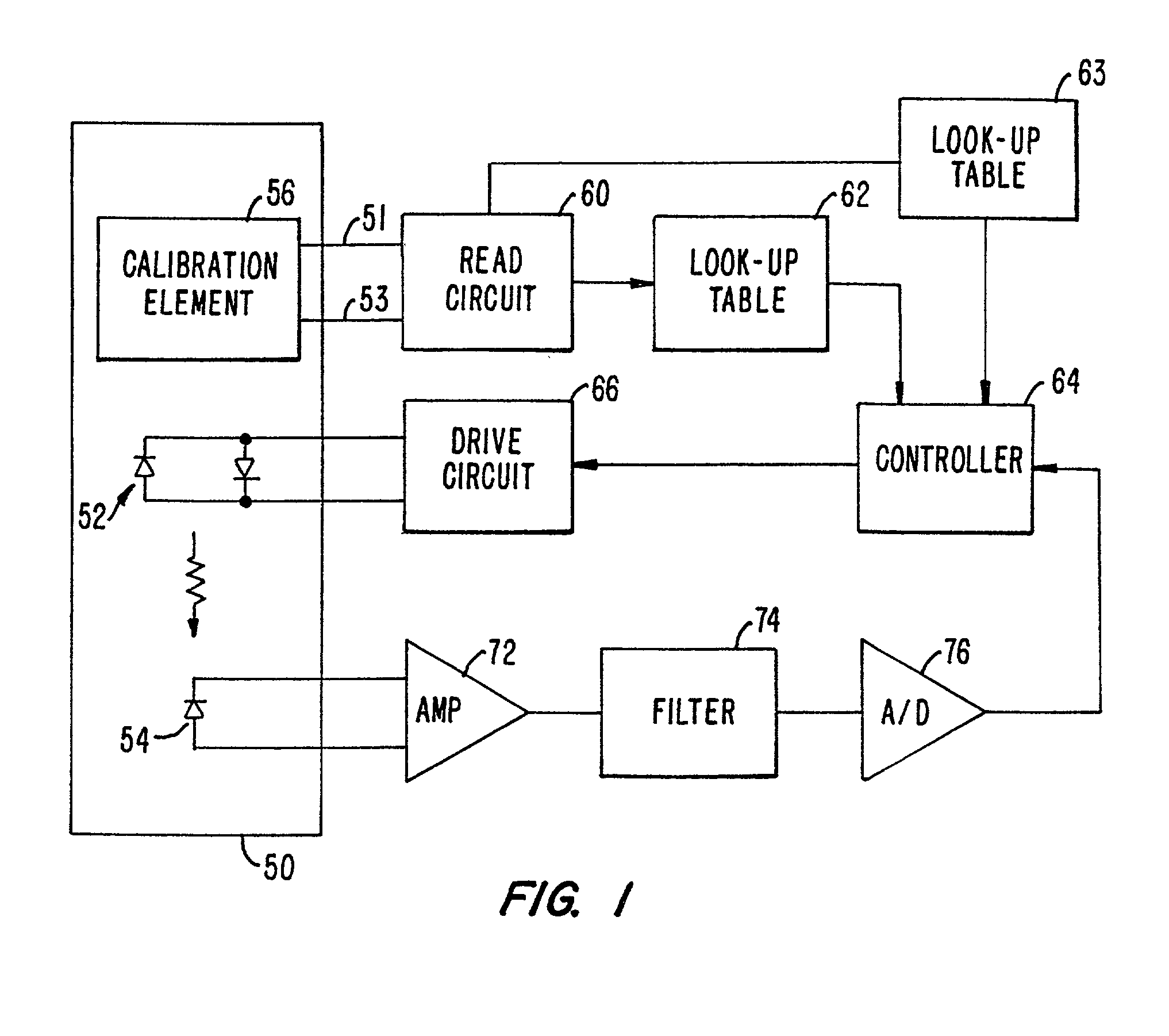
The present invention provides a memory chip for use in an oximeter sensor, or an associated adapter or connector circuit. The memory chip allows the storing of different data to provide enhanced capabilities for the oximeter sensor. In addition to providing unique data to store in such a memory, the invention describes unique uses of data stored in such a memory. The data stored in the memory chip may include information relating to use of the oximeter sensor. For example, the memory chip may encode a sensor model identification that can be displayed on a display screen when the sensor is connected to an oximeter monitor. The memory may also encode a range of operating parameters such as light levels over which the sensor can function or a maximum drive current. The operating parameters are read and interpreted by a controller circuit to control the pulse oximetry system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
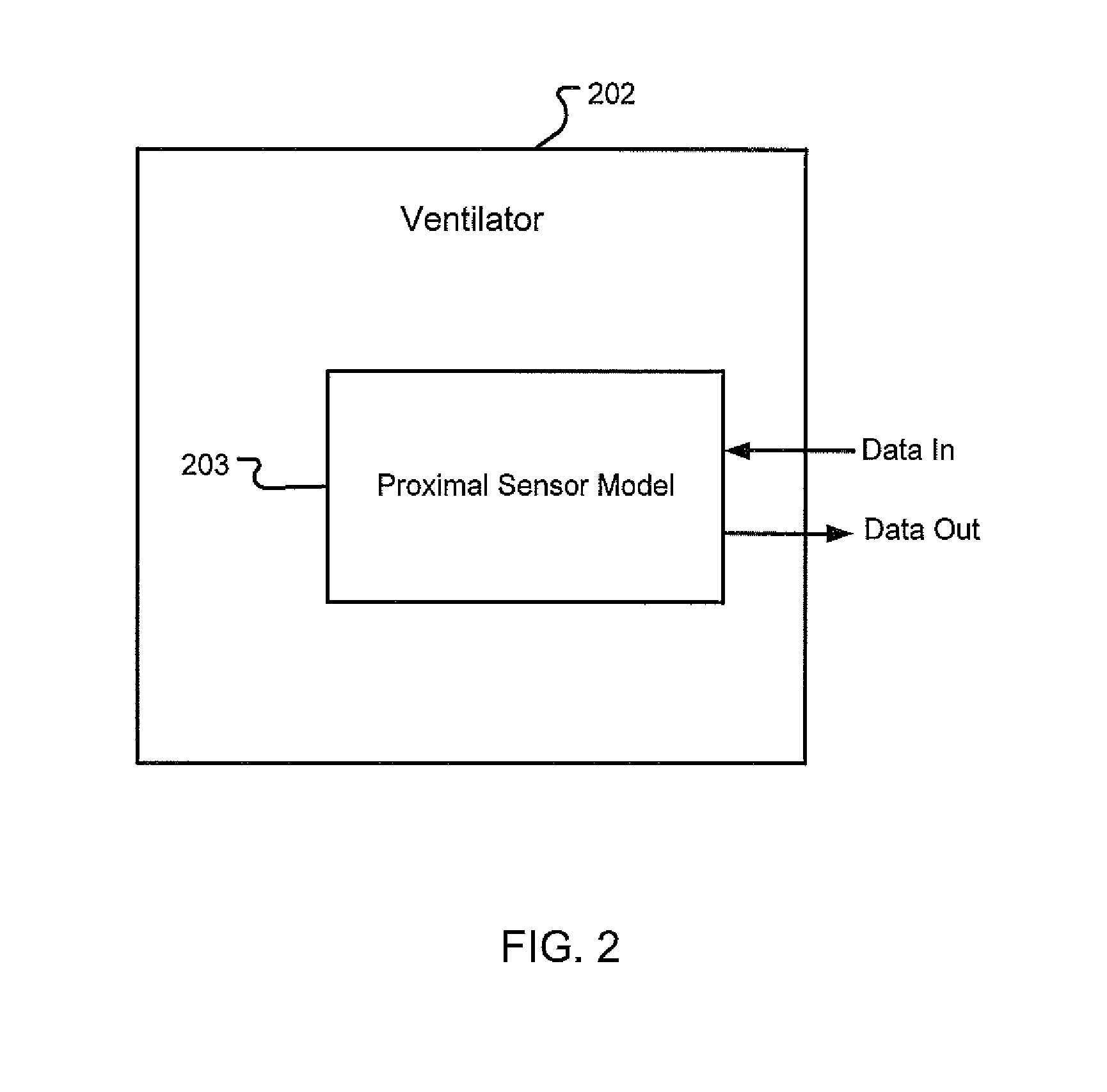
Sensor Model
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
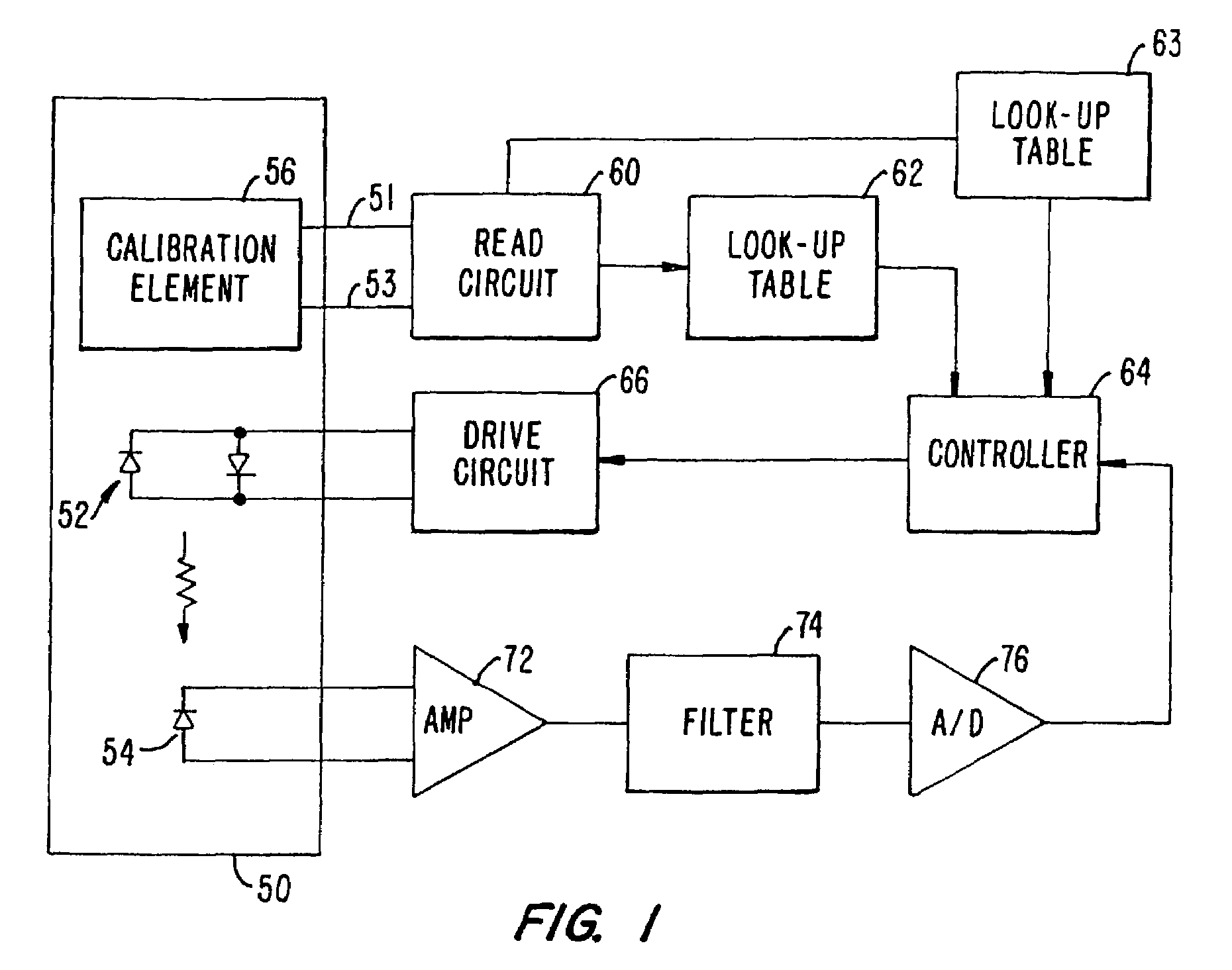
Oximeter sensor with digital memory recording sensor data
The present invention provides a memory chip for use in an oximeter sensor, or an associated adapter or connector circuit. The memory chip allows the storing of different data to provide enhanced capabilities for the oximeter sensor. In addition to providing unique data to store in such a memory, the invention describes unique uses of data stored in such a memory. The data stored in the memory chip may include information relating to use of the oximeter sensor. For example, the memory chip may encode a sensor model identification that can be displayed on a display screen when the sensor is connected to an oximeter monitor. The memory may also encode a range of operating parameters such as light levels over which the sensor can function or a maximum drive current. The operating parameters are read and interpreted by a controller circuit to control the pulse oximetry system.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
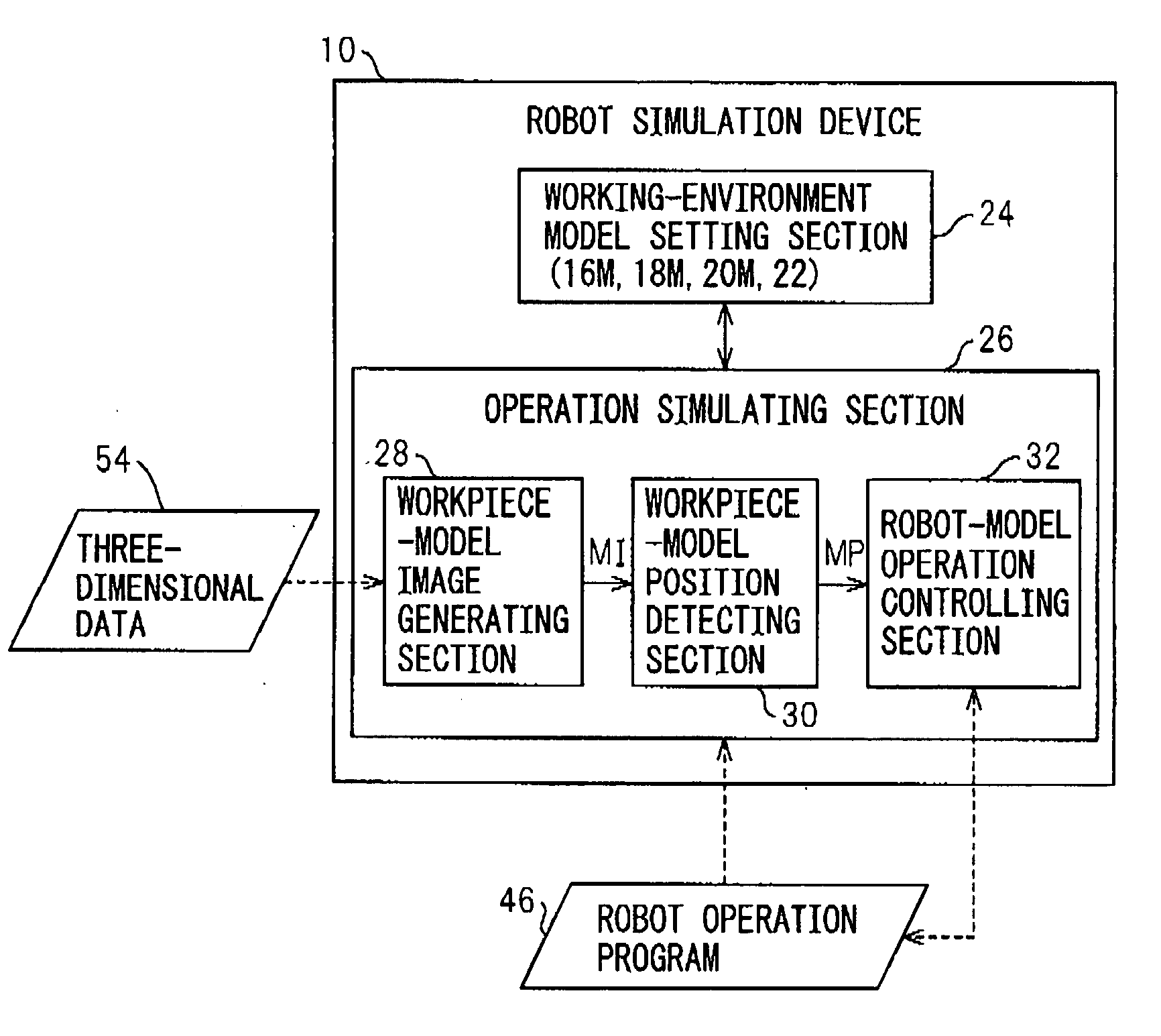
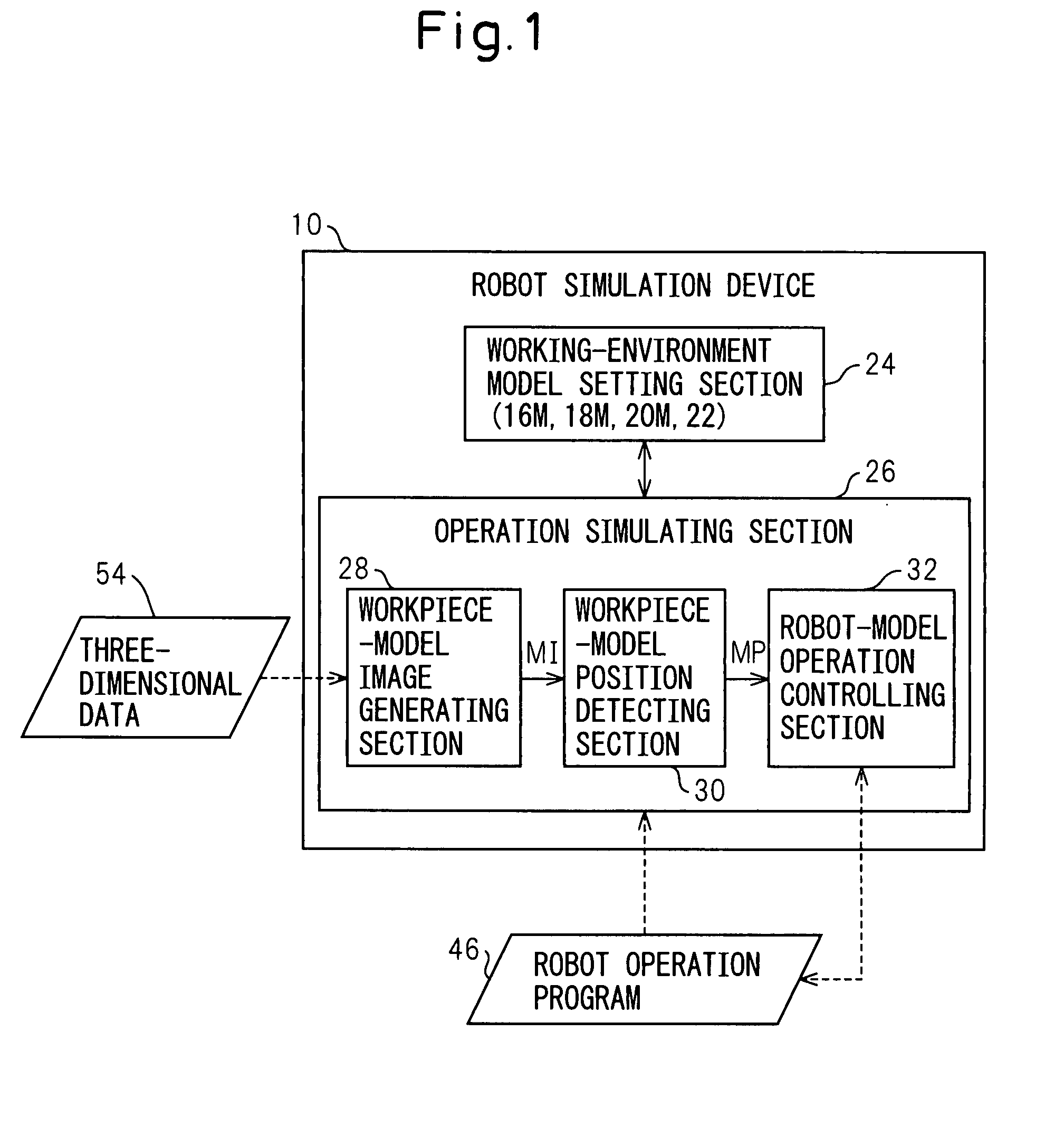
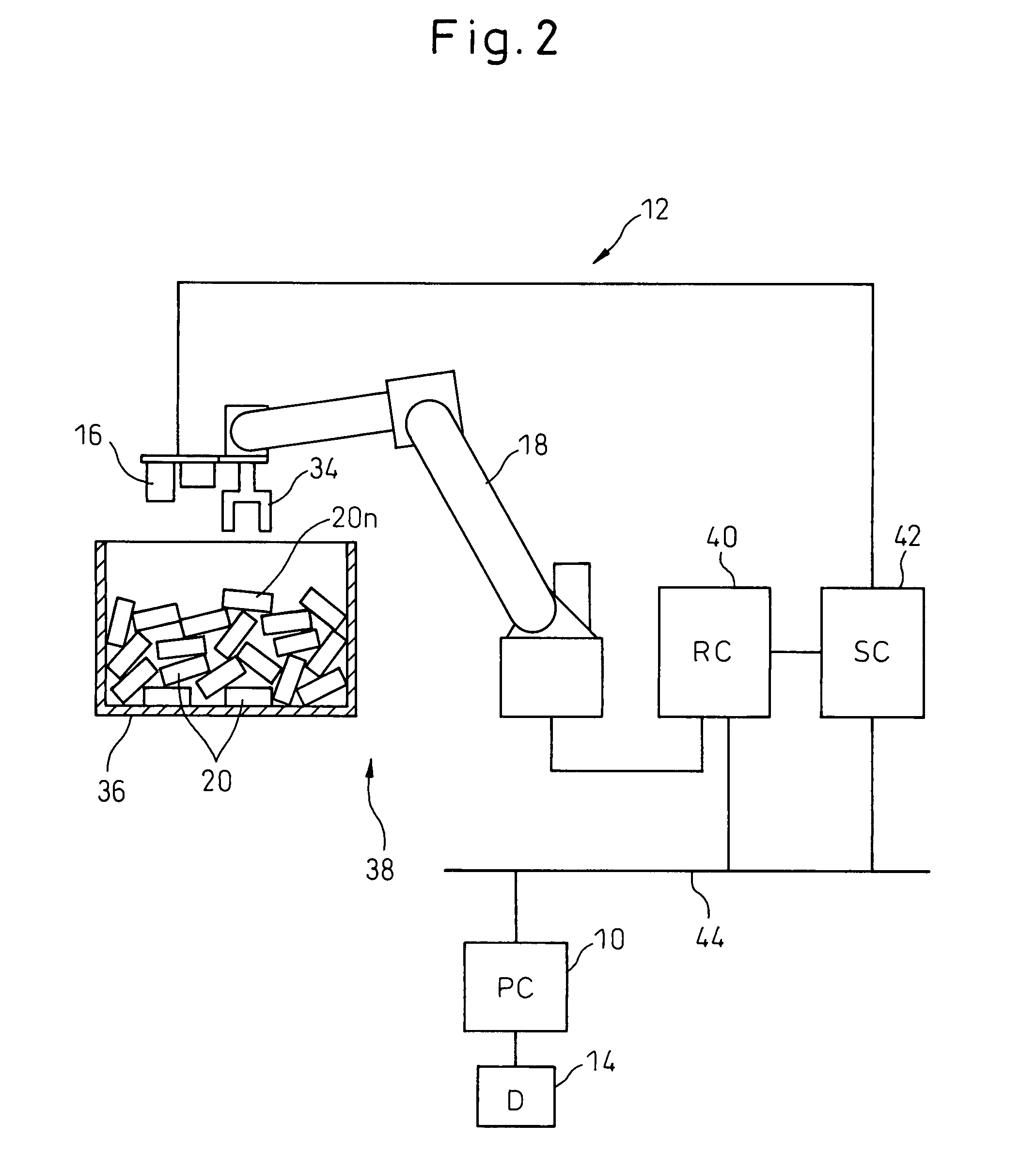
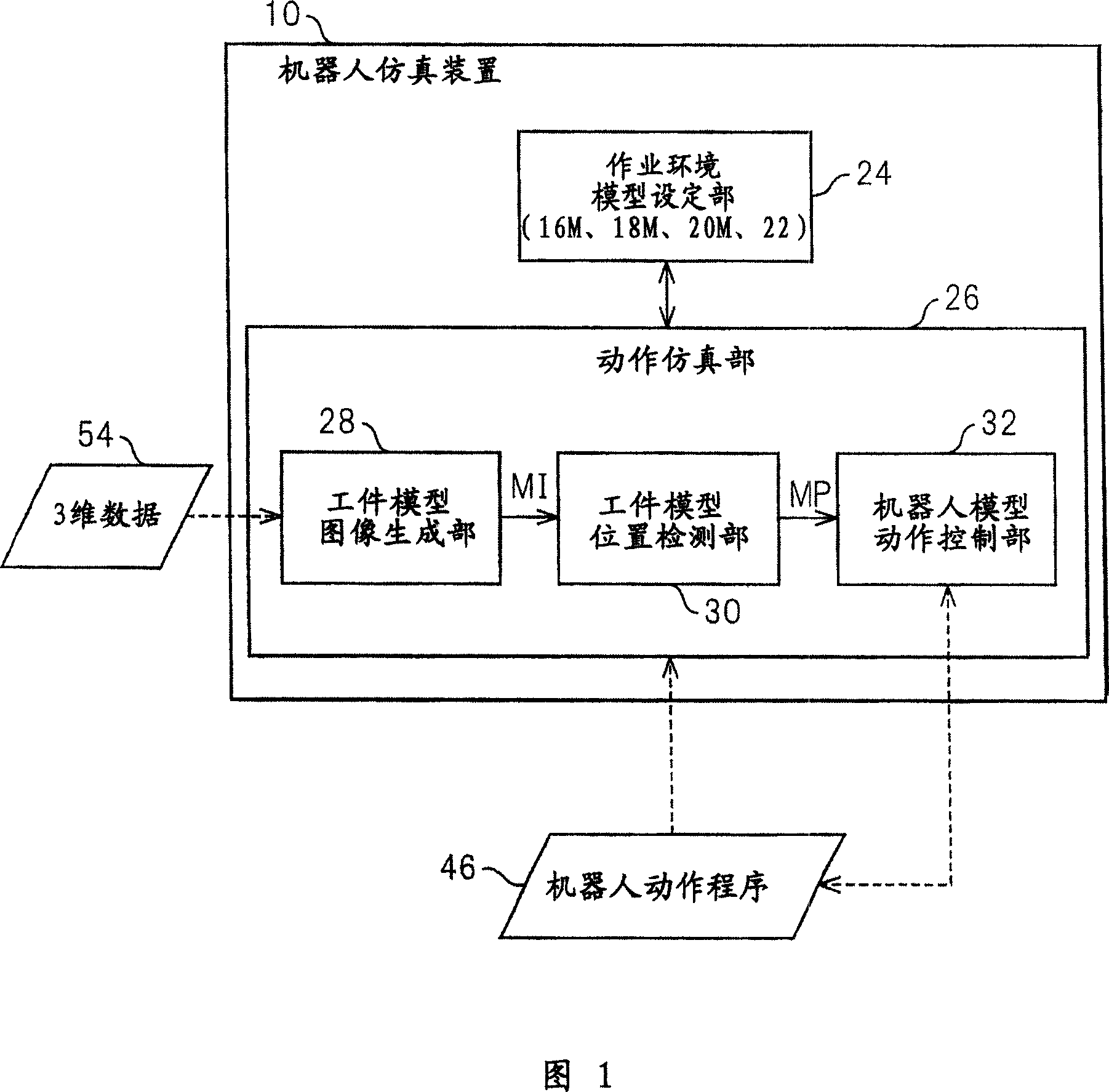
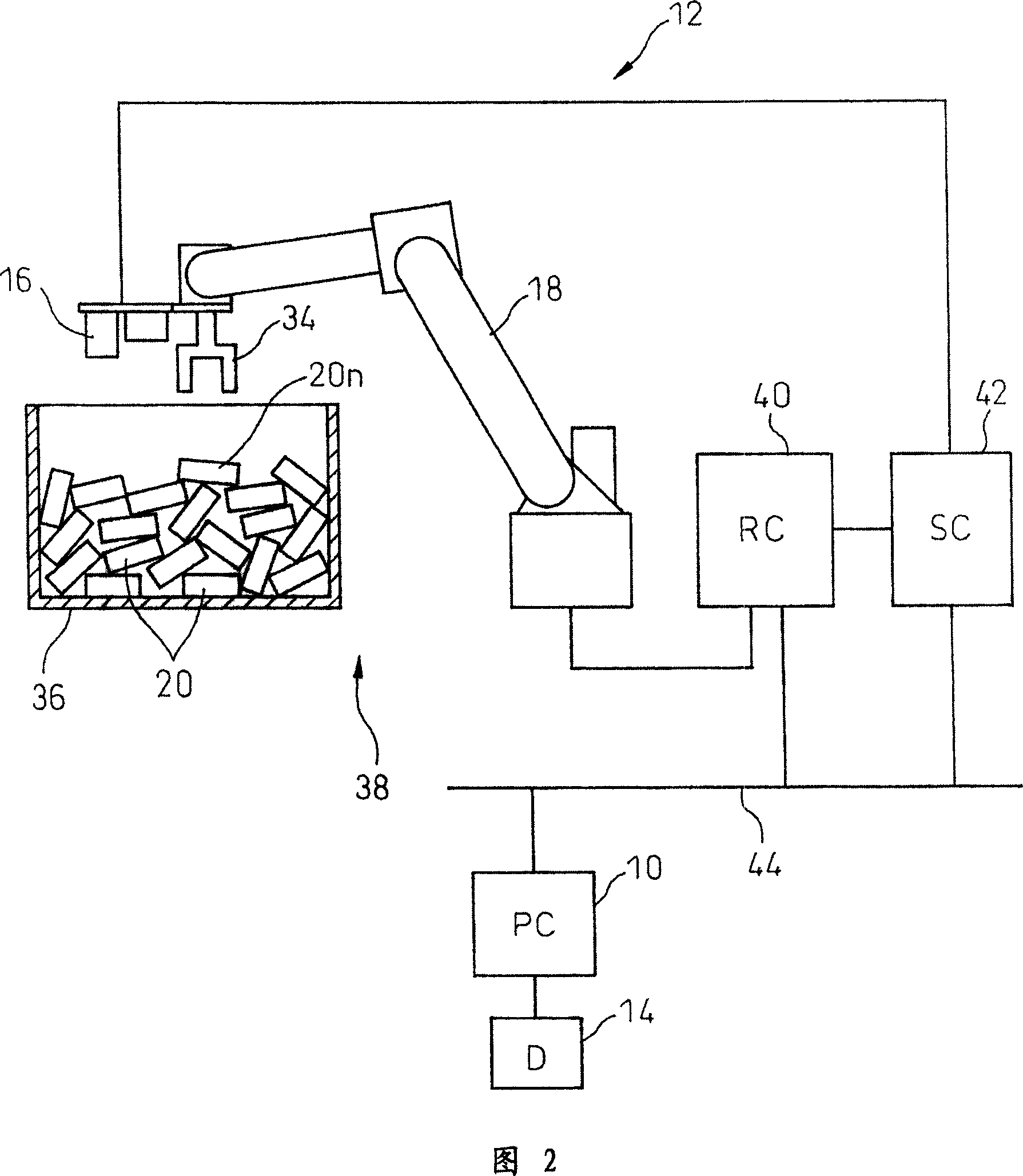
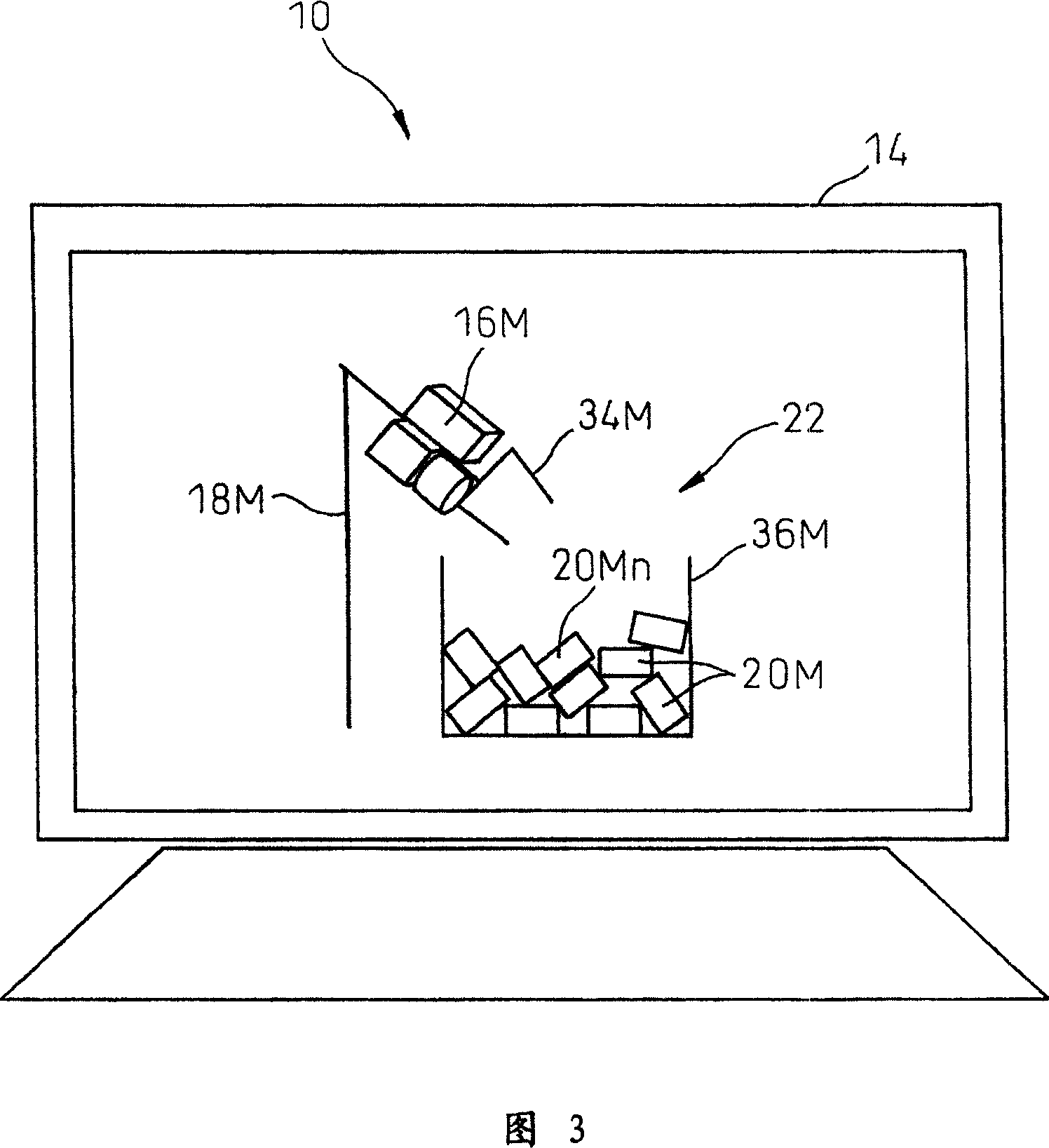
Device, program, recording medium and method for robot simulation
InactiveUS20070213874A1Quick calculationEasy to operateProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocation detectionSimulation
A robot simulation device for simulating an operation of a robot having a vision sensor in an off-line mode. The device includes a working-environment model setting section for arranging a sensor model, a robot model and a plurality of irregularly piled workpiece models in a virtual working environment; and an operation simulating section for allowing the sensor model and the robot model to simulate a workpiece detecting operation and a bin picking motion. The operation simulating section includes a workpiece-model image generating section for allowing the sensor model to pick up the workpiece models and generating a virtual image thereof; a workpiece-model position detecting section for identifying an objective workpiece model from the virtual image and detecting a virtual position thereof; and a robot-model operation controlling section for allowing the robot model to pick out the objective workpiece model based on the virtual position.
Owner:FANUC LTD
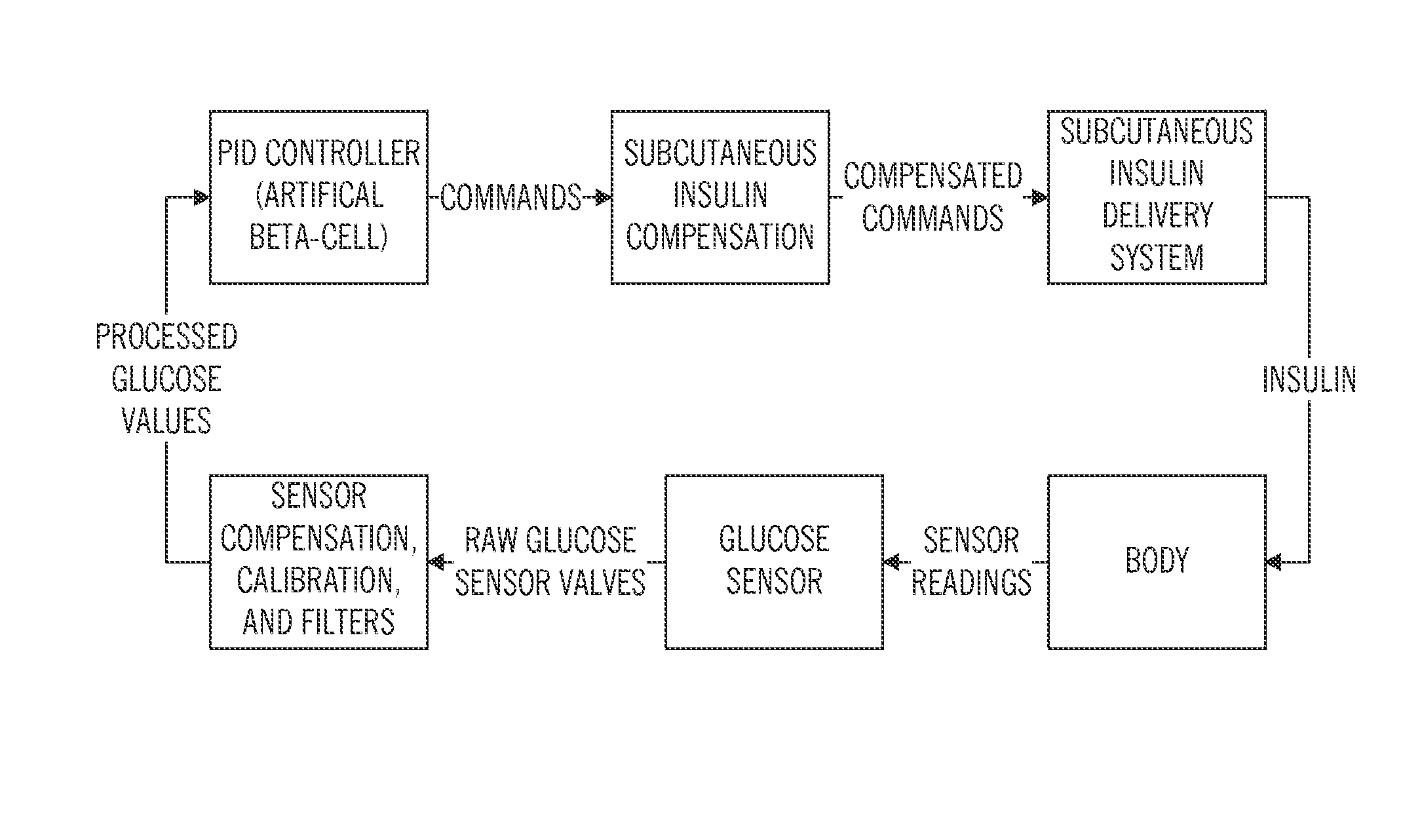
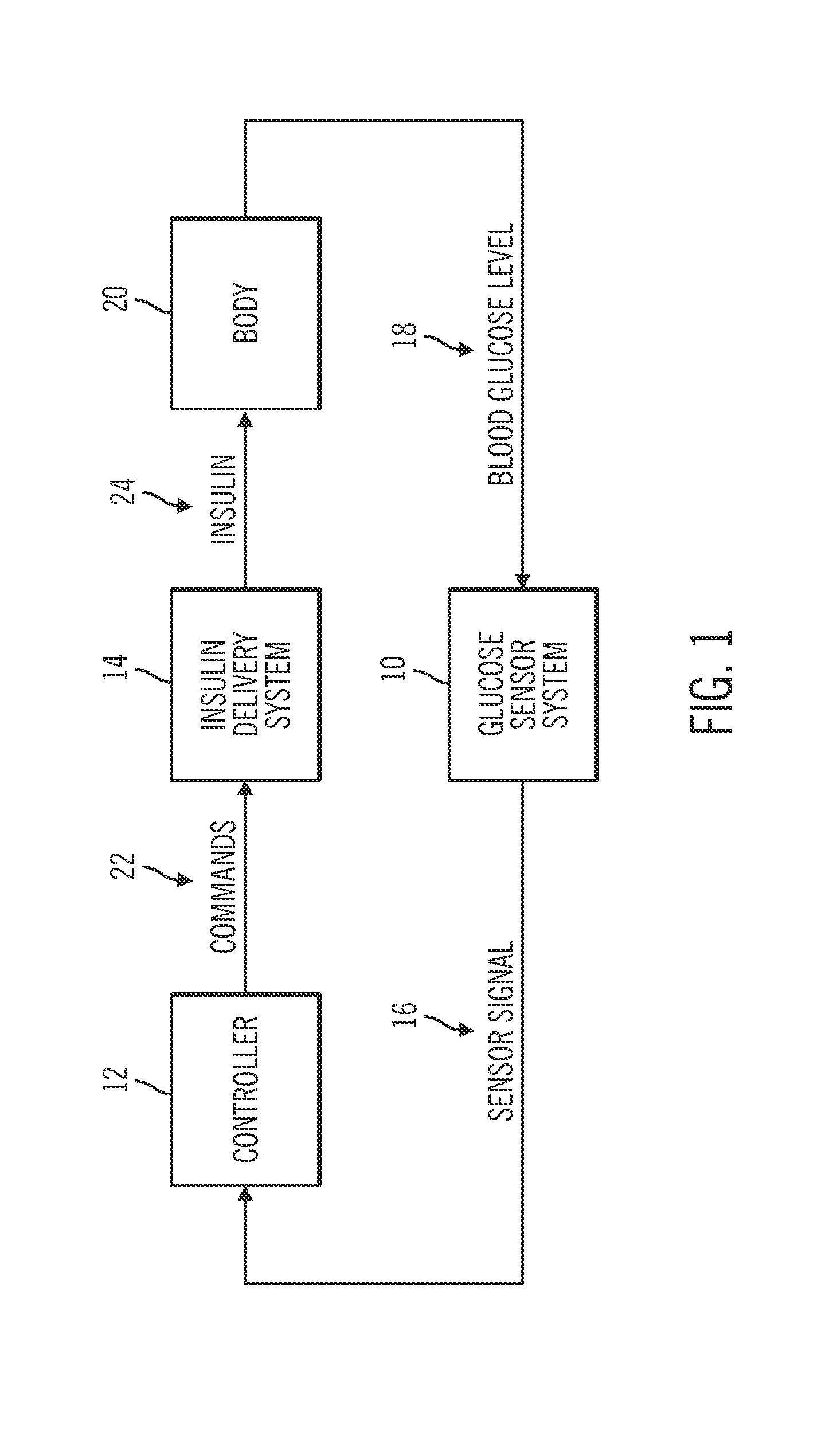
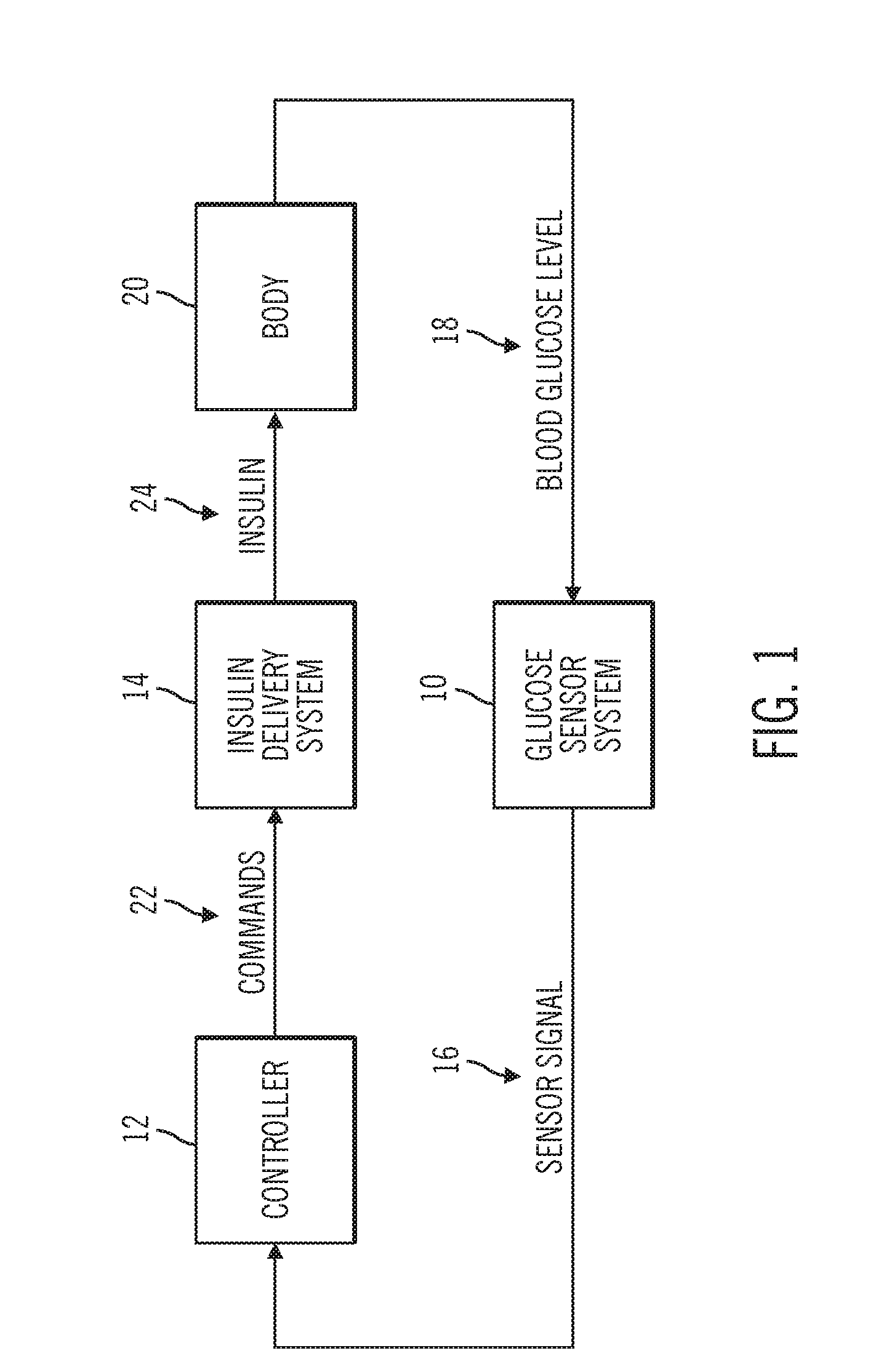
Sensor model supervisor for a closed-loop insulin infusion system
InactiveUS20140066884A1Well formedMedical simulationDrug and medicationsInsulin infusionGlucose sensors
An electronic device includes a processor architecture and a memory element that stores instructions that, when executed by the processor architecture, perform a method of controlling an insulin infusion device for a user. The method operates the device in a closed-loop mode to deliver insulin to the user, obtains current insulin-delivered data and current glucose sensor data for the user, and processes historical insulin-delivered data and historical sensor data, to obtain predicted sensor glucose values for a historical time period. The method continues by calculating a difference between the current sensor glucose value and a predicted current sensor glucose value for the most recent sampling period. An alert is generated when the difference exceeds a threshold error amount.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
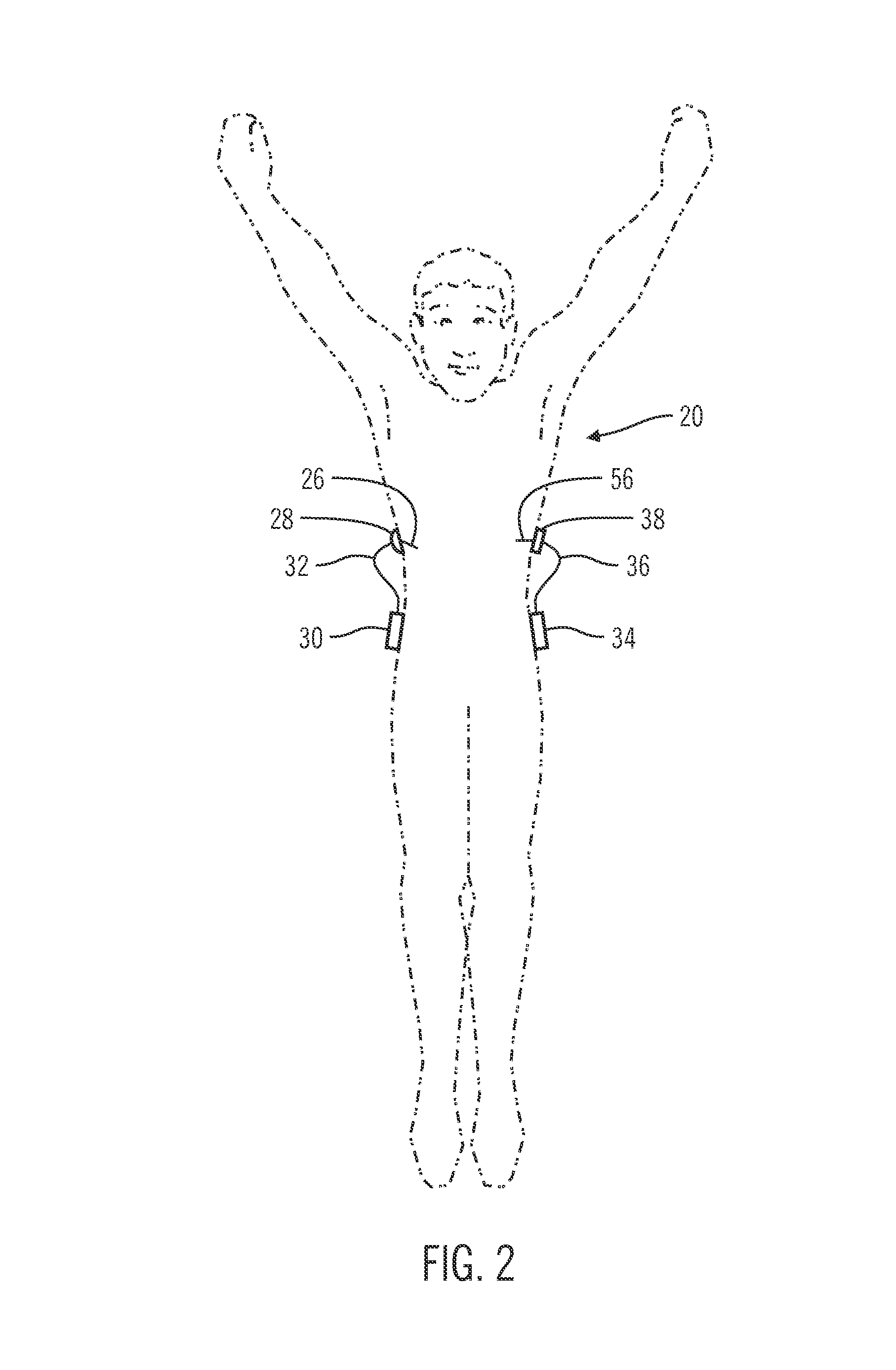
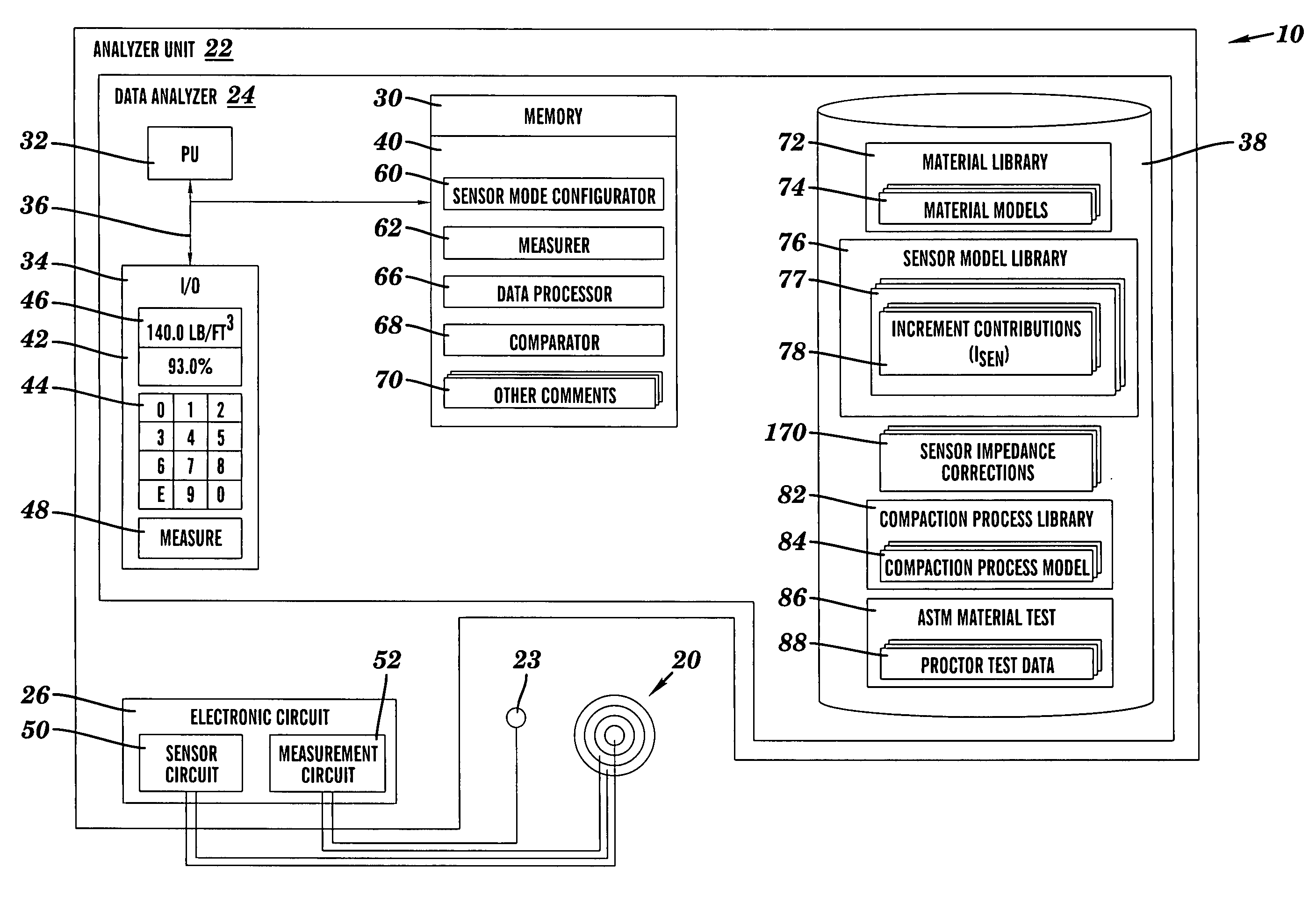
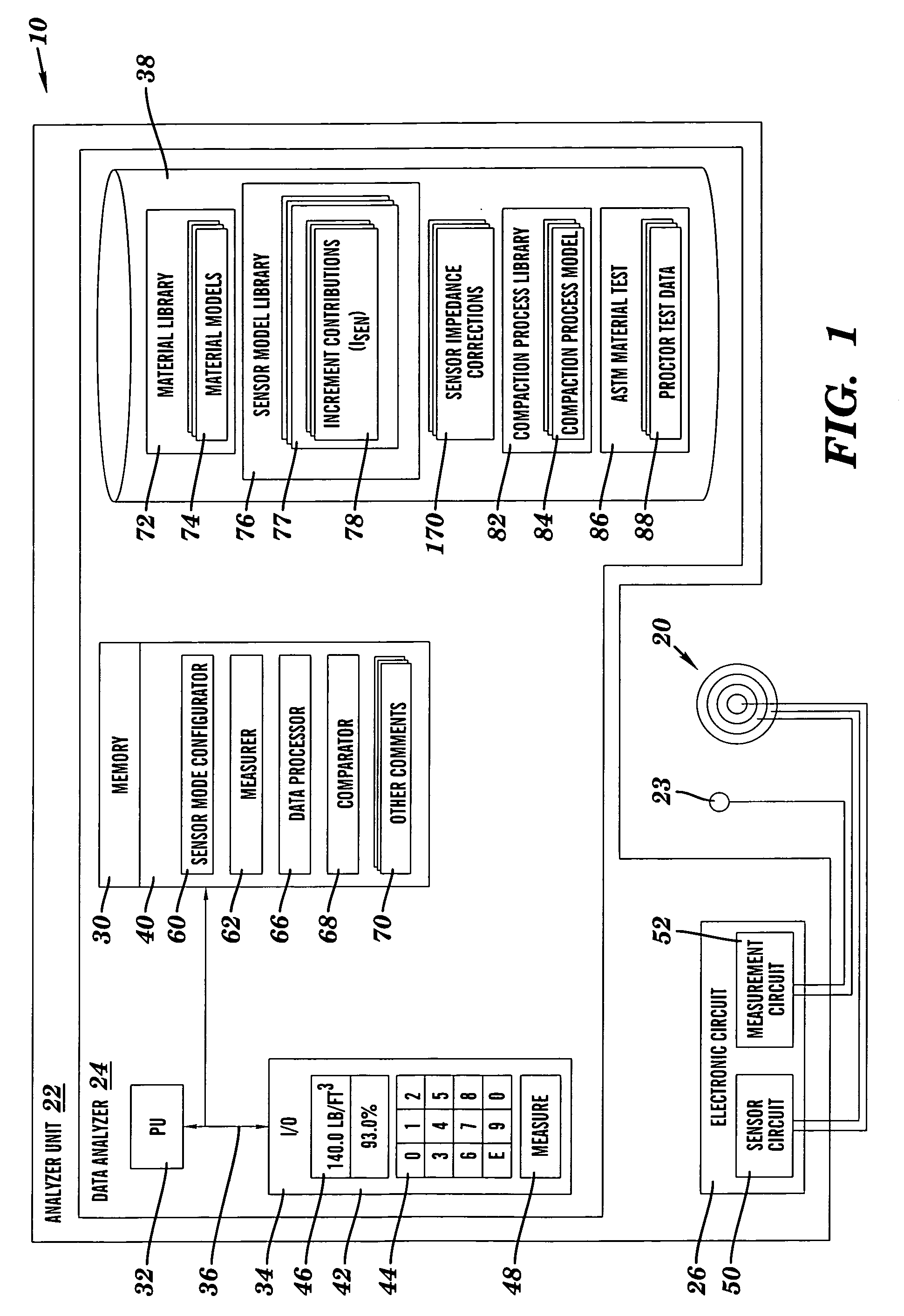
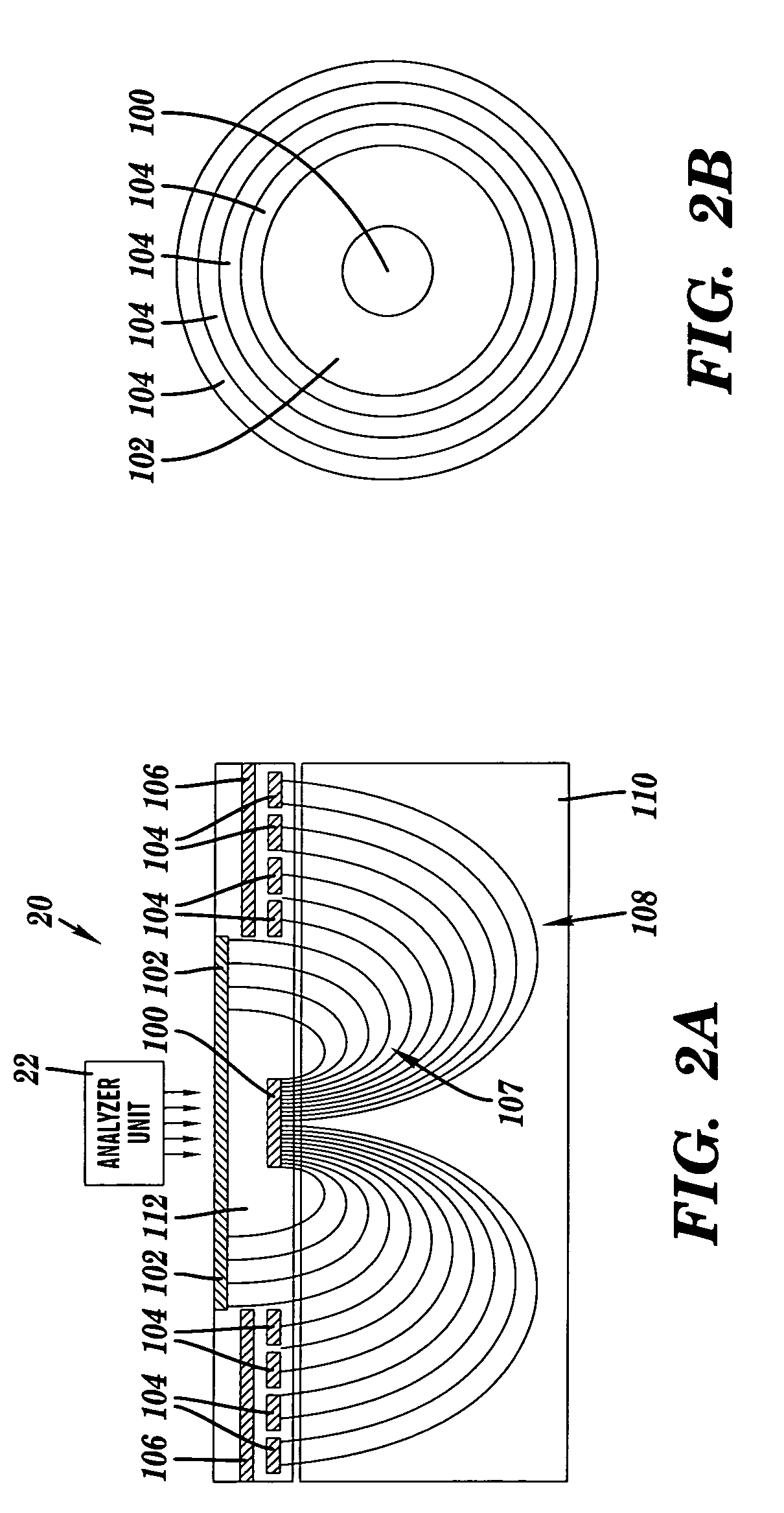
Material analysis including density and moisture content determinations
Owner:TRANSTECH SYST
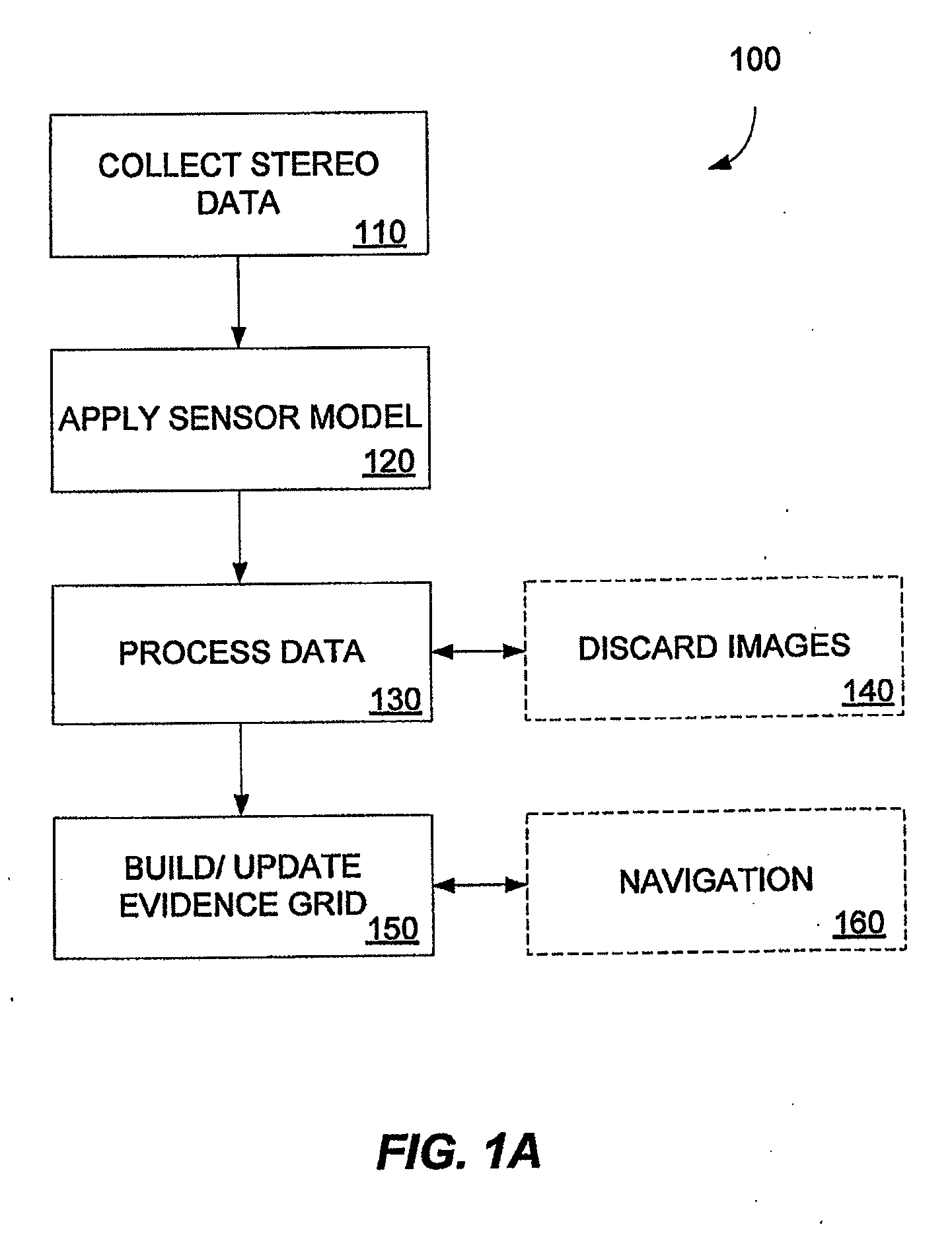
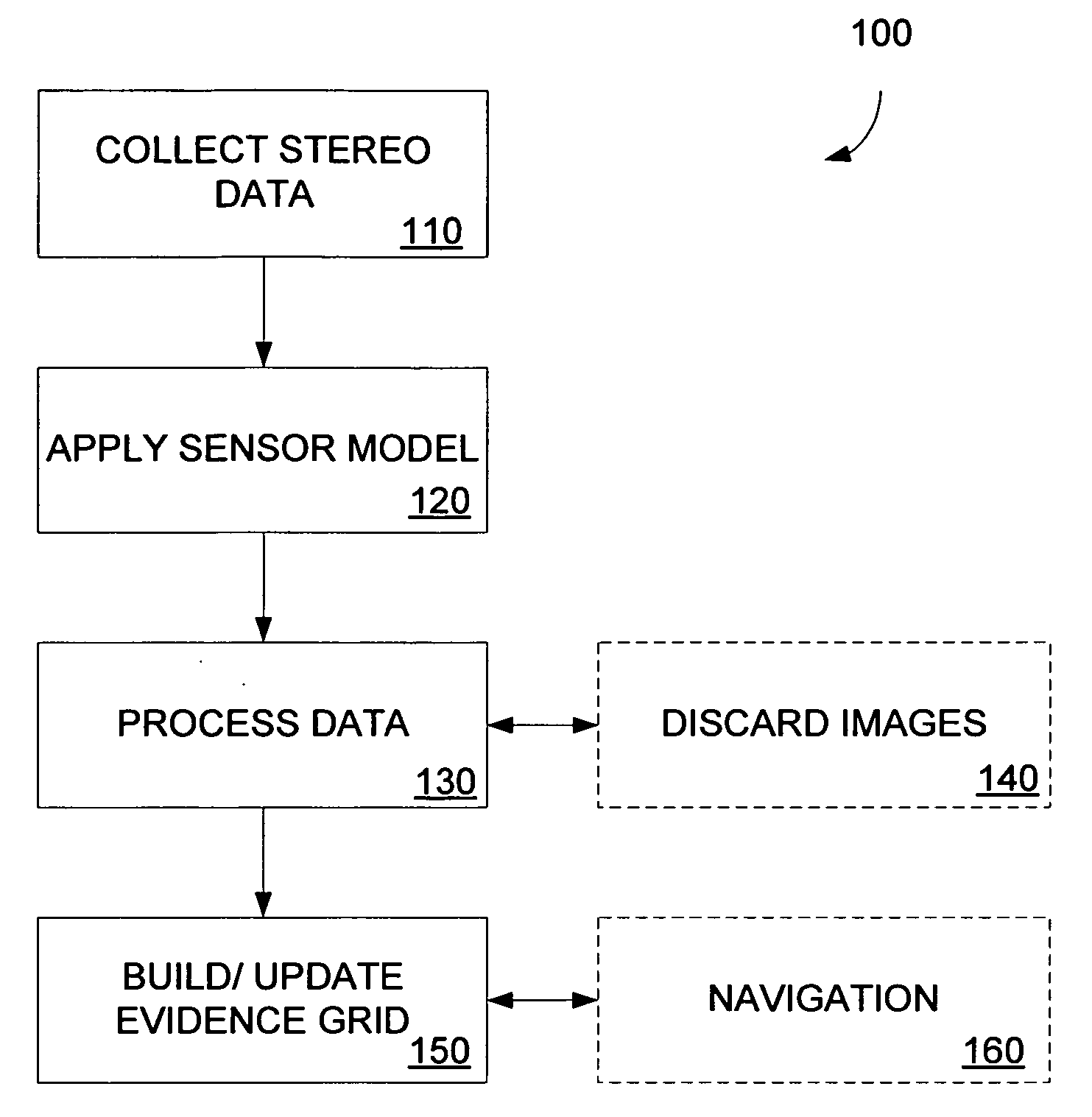
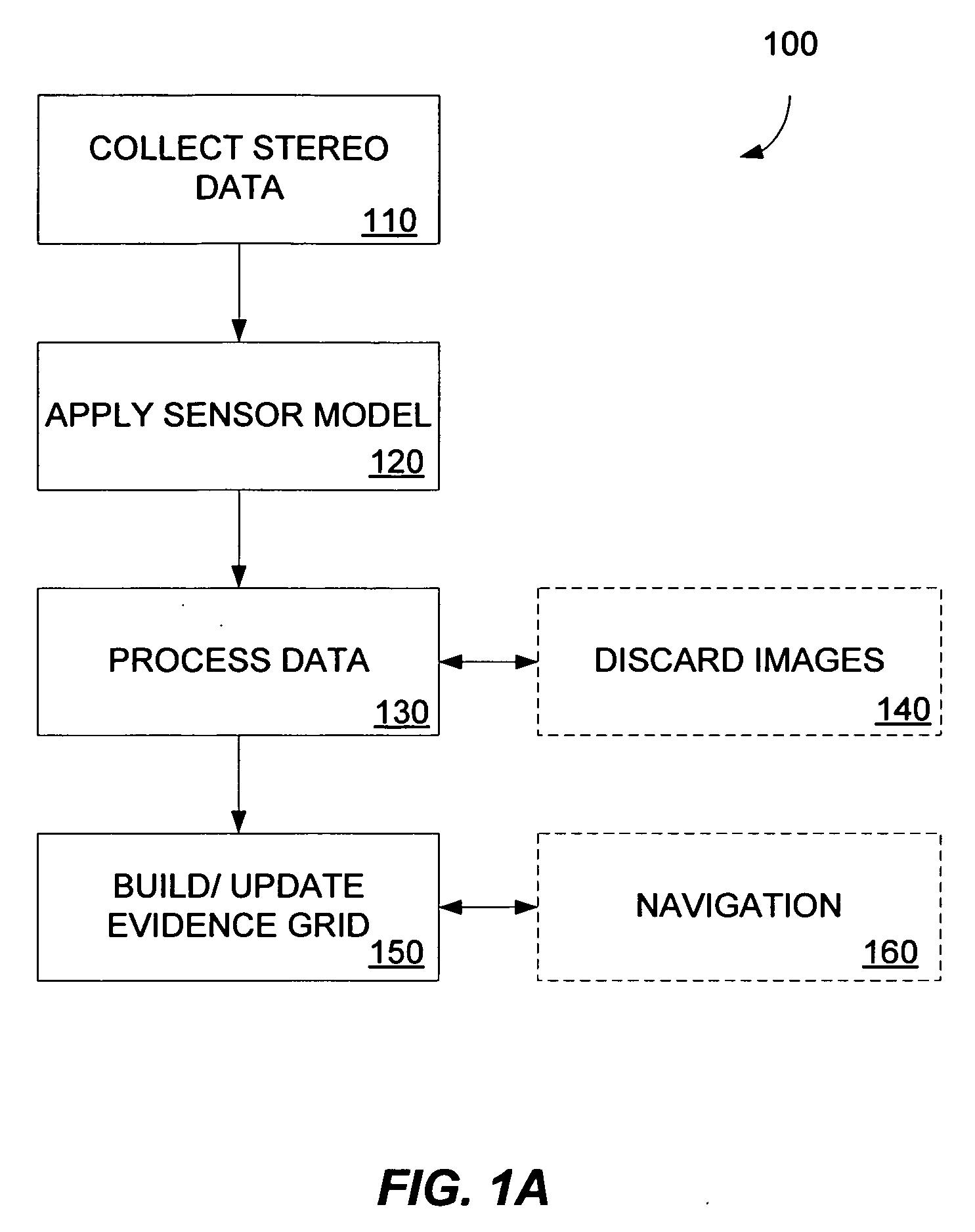
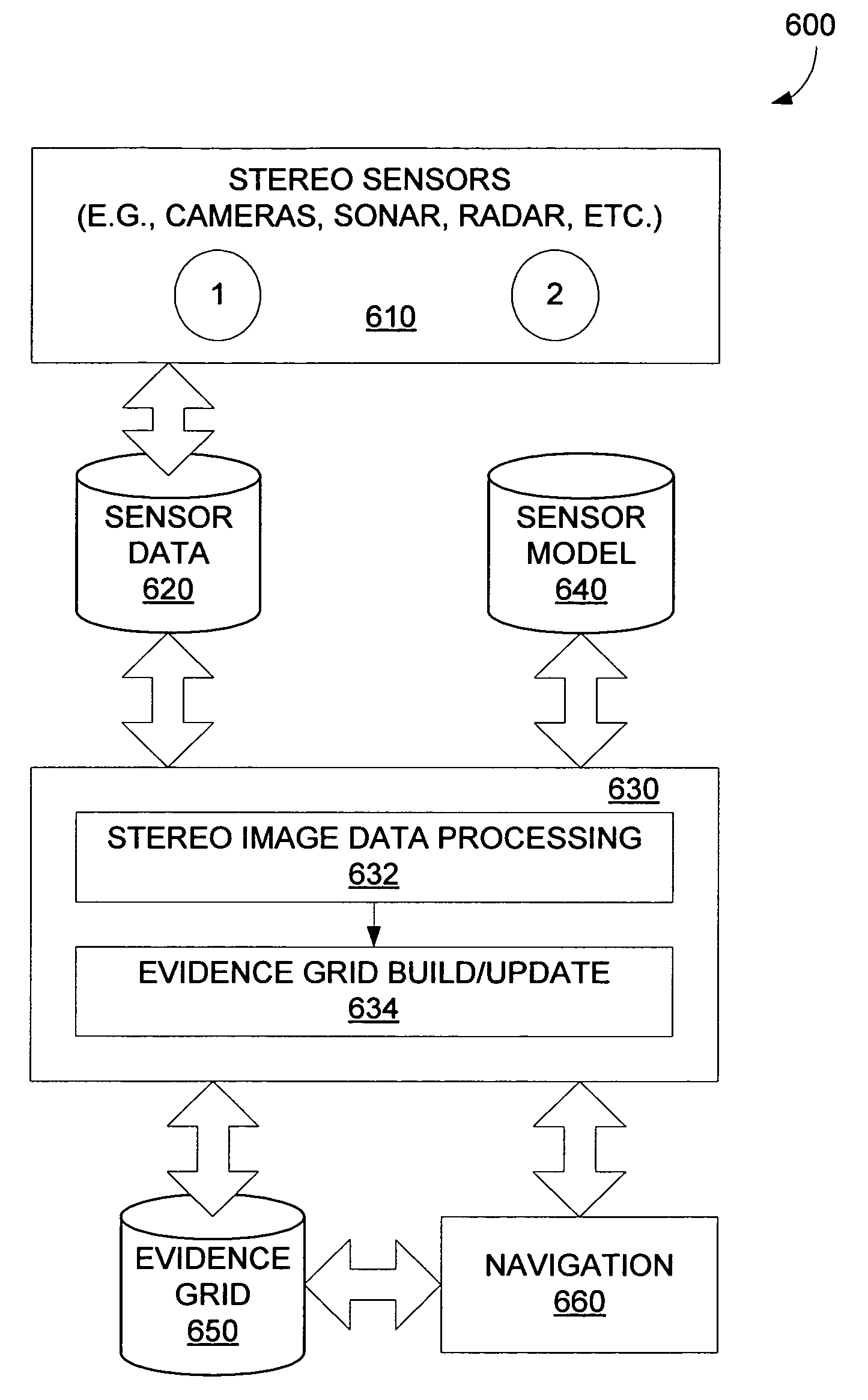
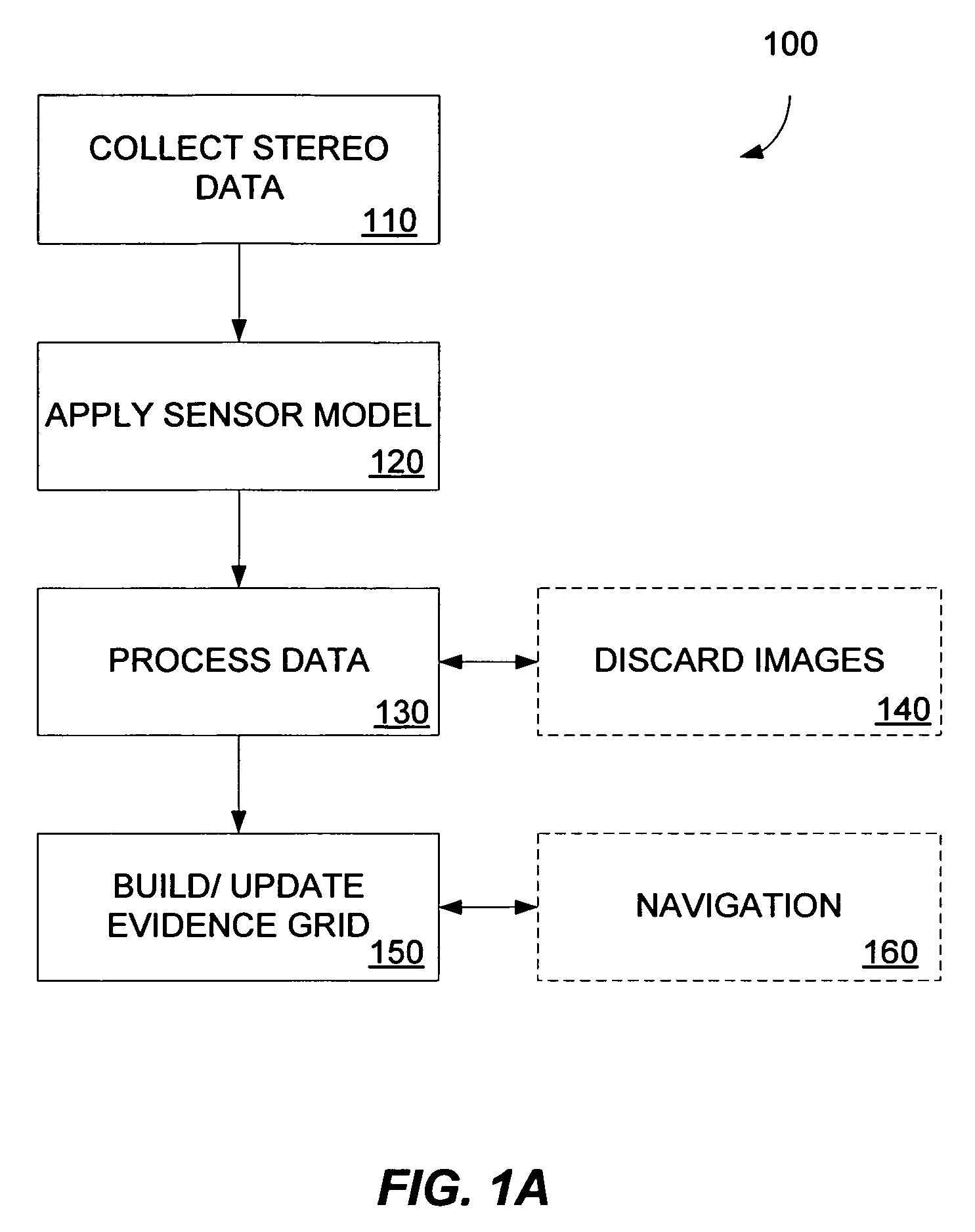
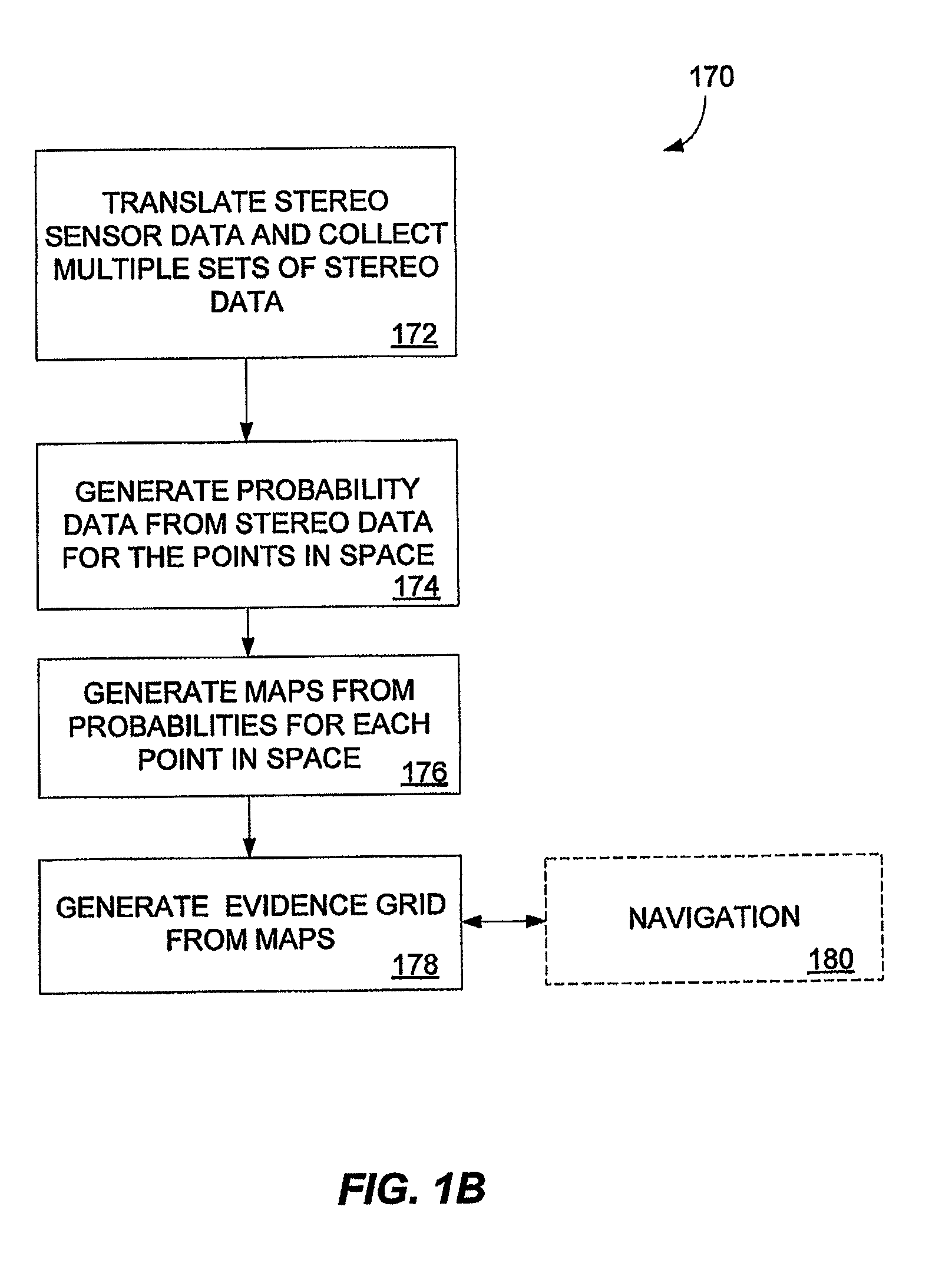
Multidimensional evidence grids and system and methods for applying same
ActiveUS20090119010A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemSensor model
Mapping, localization, and navigation systems for use with a mobile unit are provided that use a sensor model with adjustable parameters. The system includes range sensors configured to collect range data and a data storage system having stored therein an evidence grid representing an environment and a sensor model comprising adjustable parameters representing inaccuracies of the range sensors. A grid engine adjusts the adjustable parameters based on received range data from the range sensors. A navigation module can direct the mobile unit though the environment using the evidence grid, received range data, and adjustable parameters. The grid engine can also locate the mobile unit within the environment by using the adjusted sensor model parameters to compare the received range data against the evidence grid.
Owner:SEEGRID CORPORATION
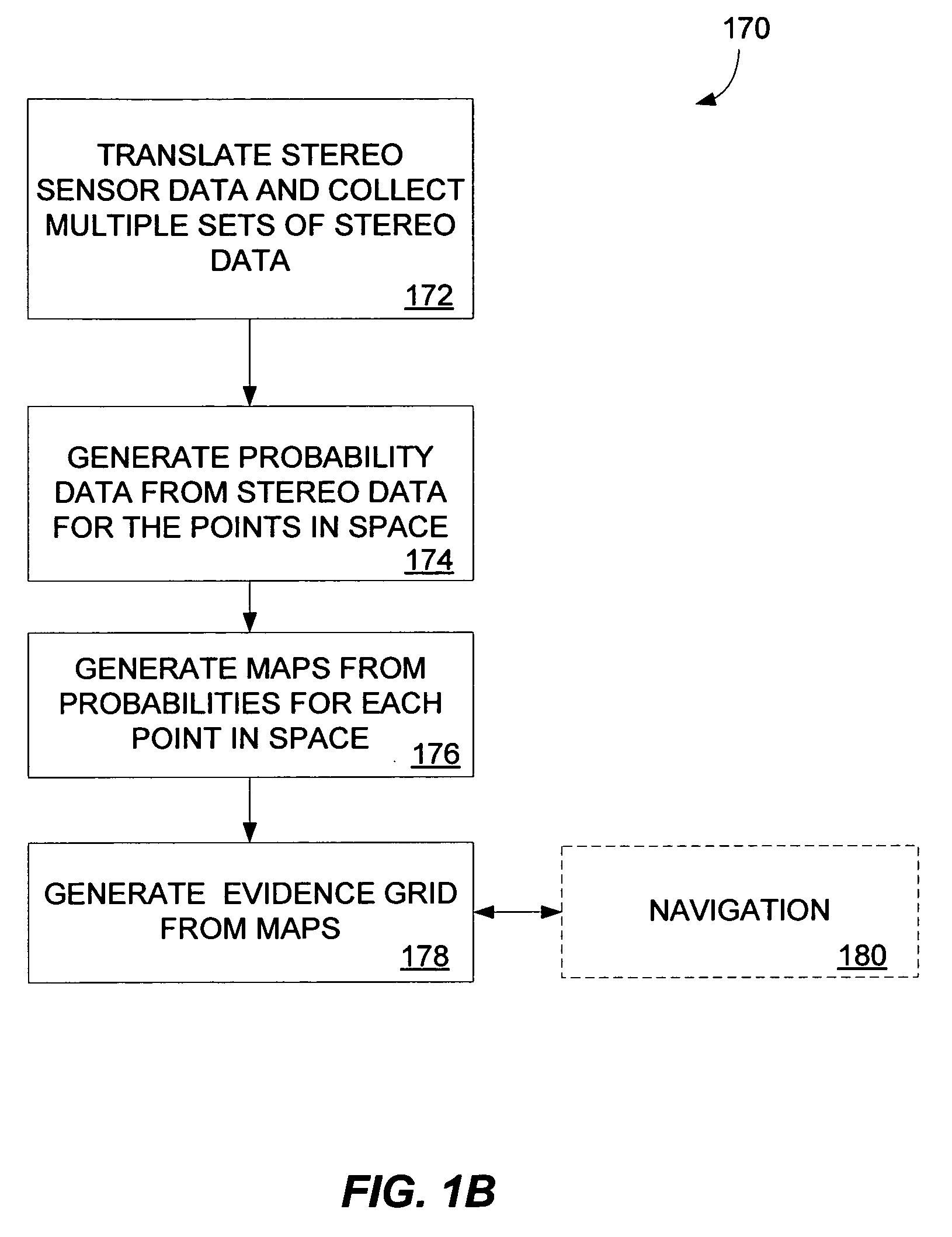
Multidimensional evidence grids and system and methods for applying same
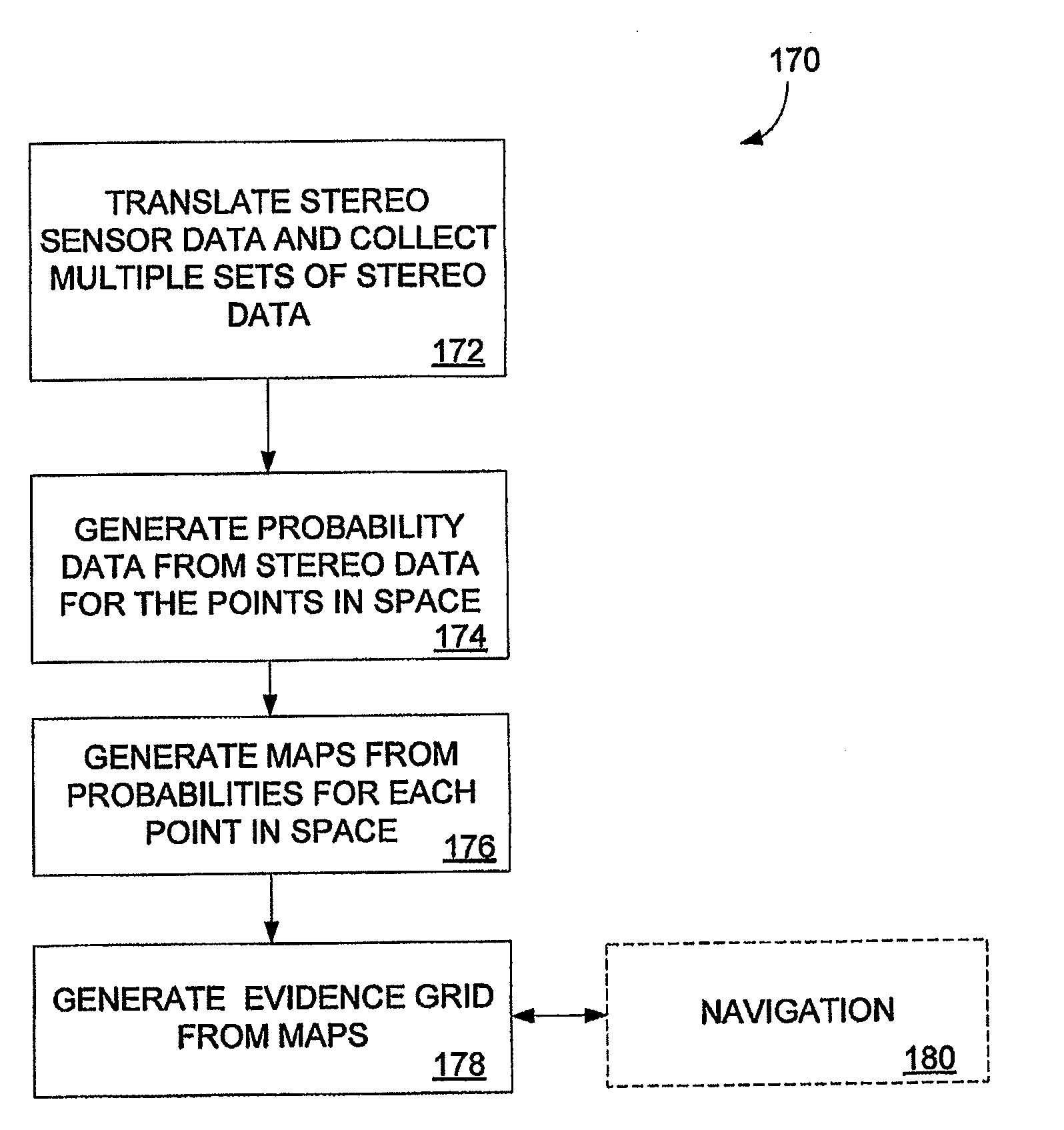
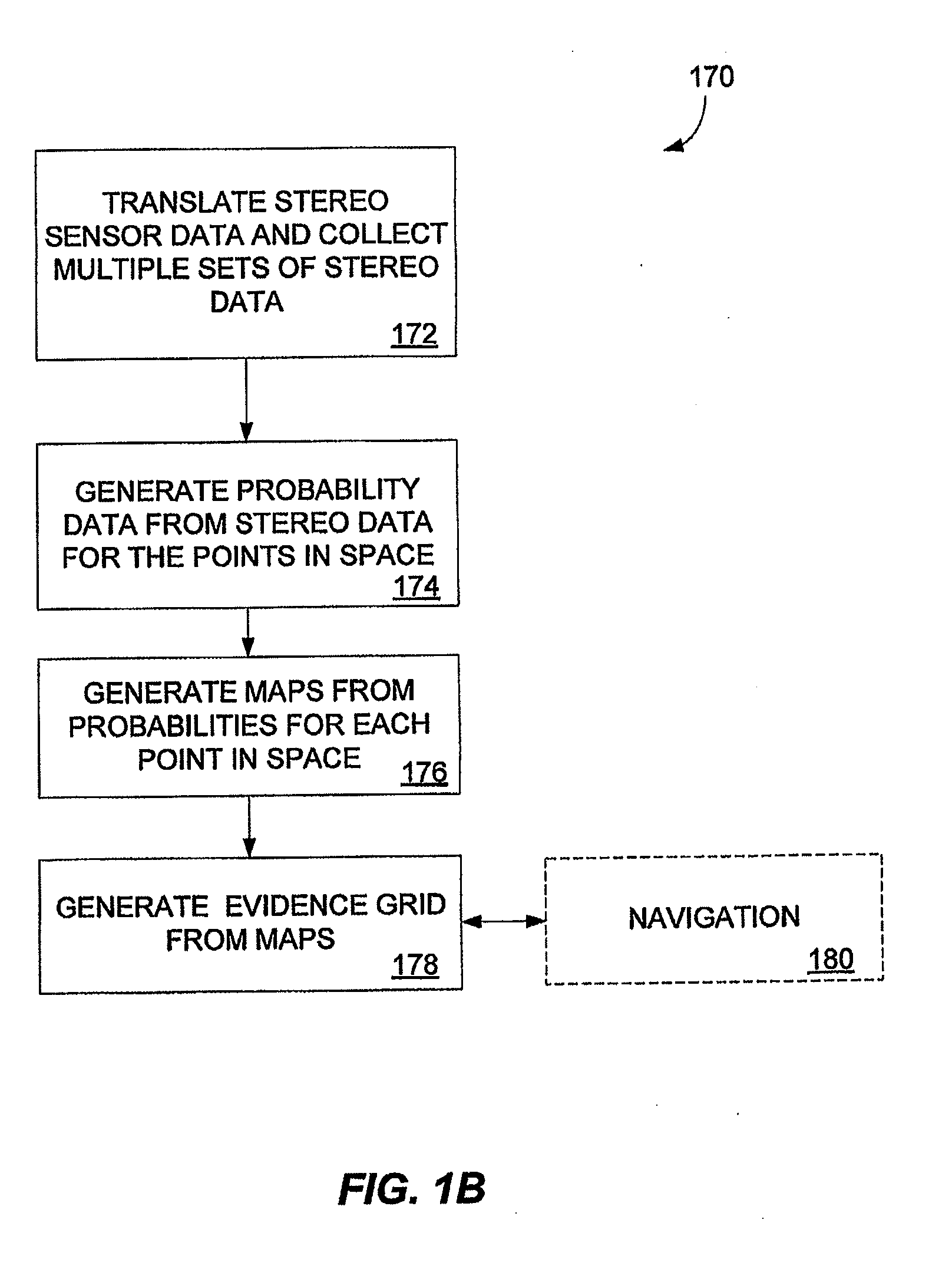
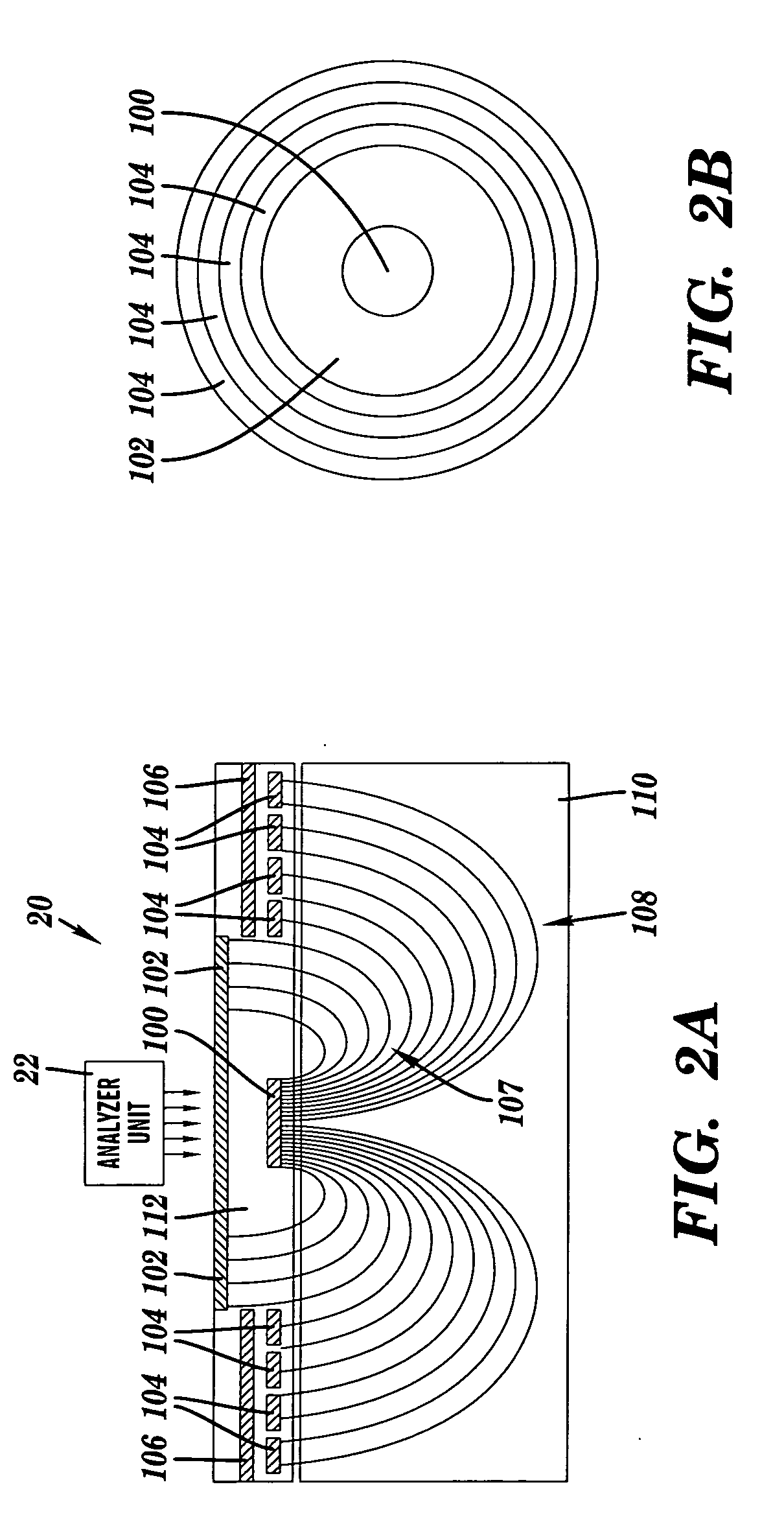
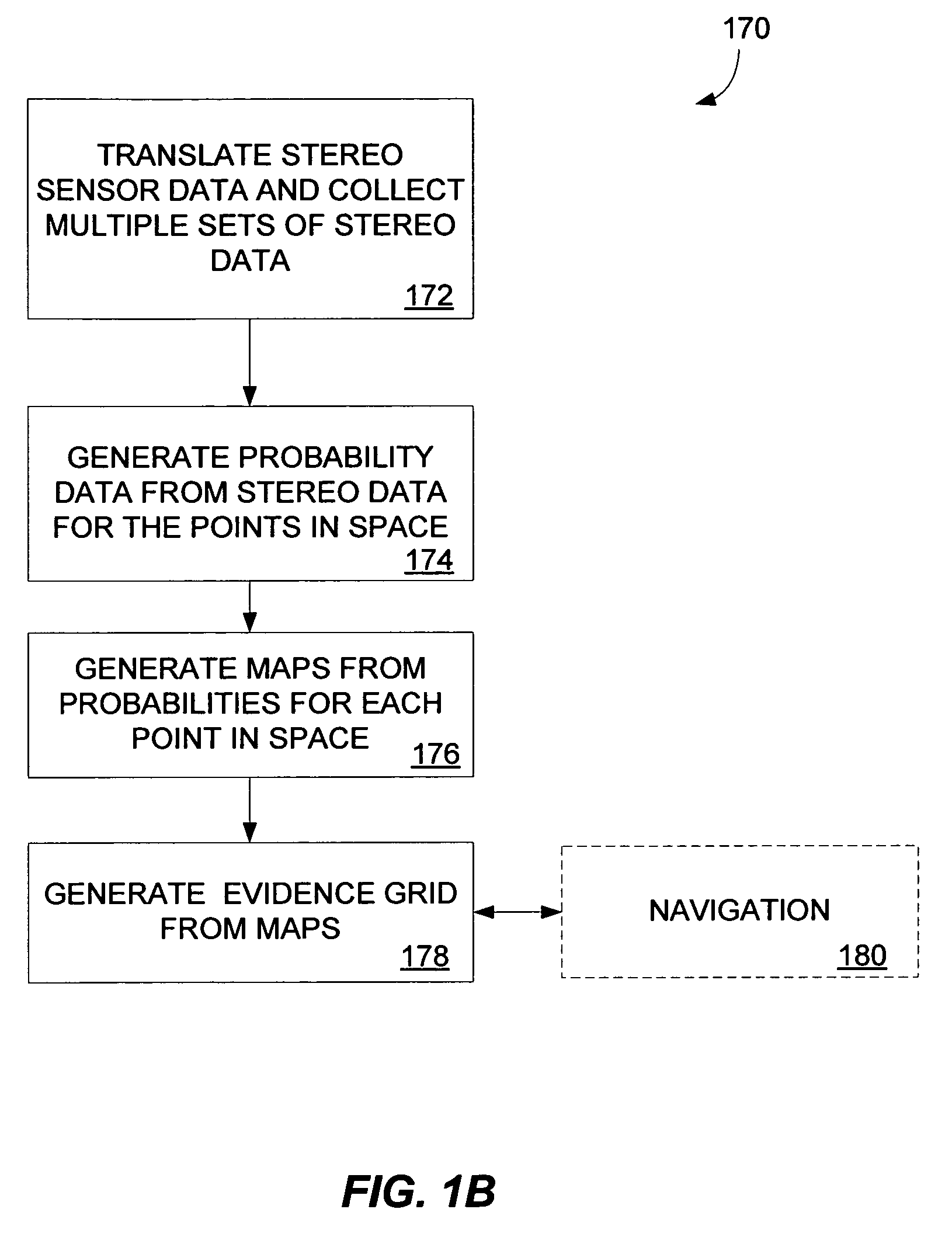
ActiveUS20060178828A1Instruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelStereo image
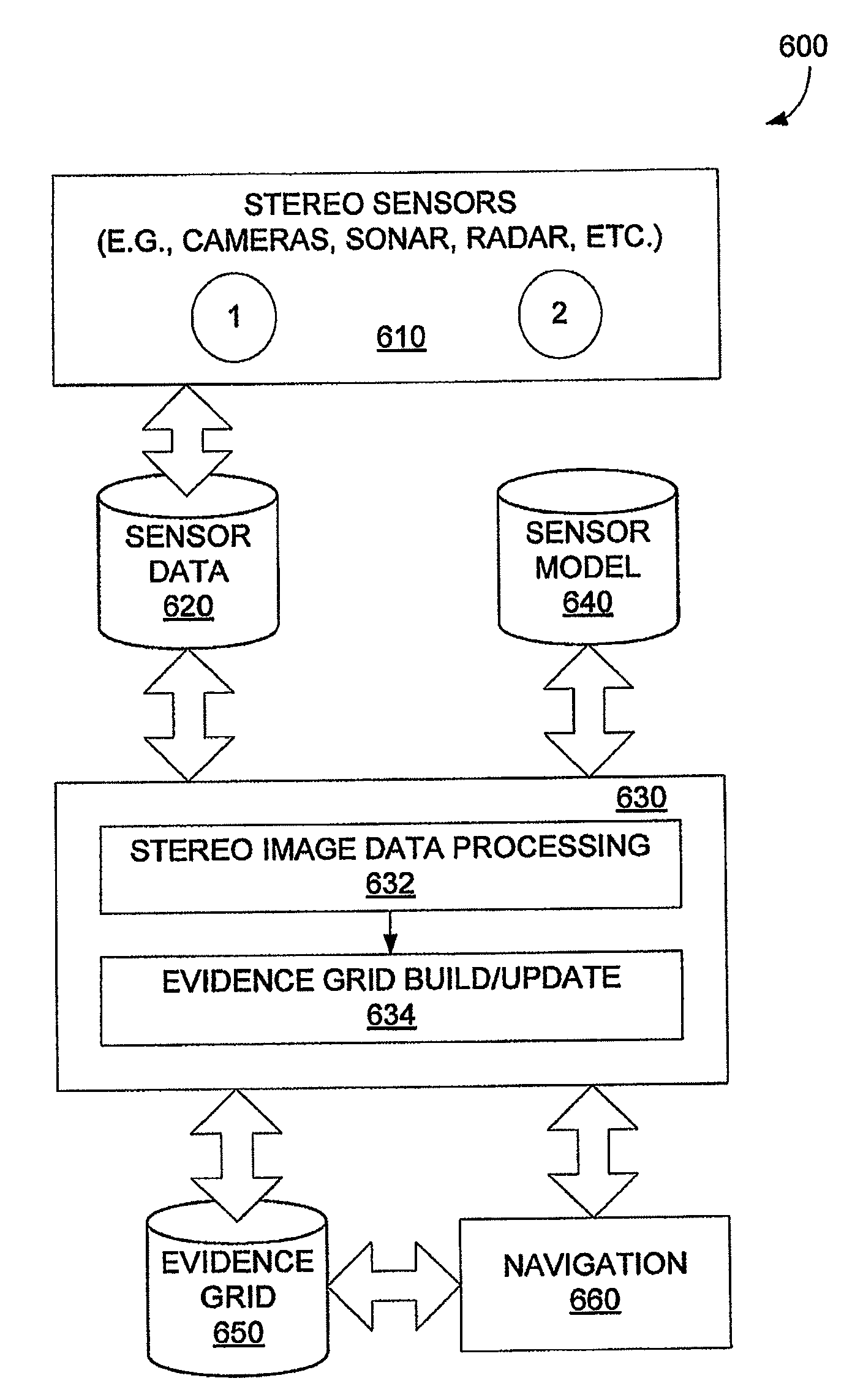
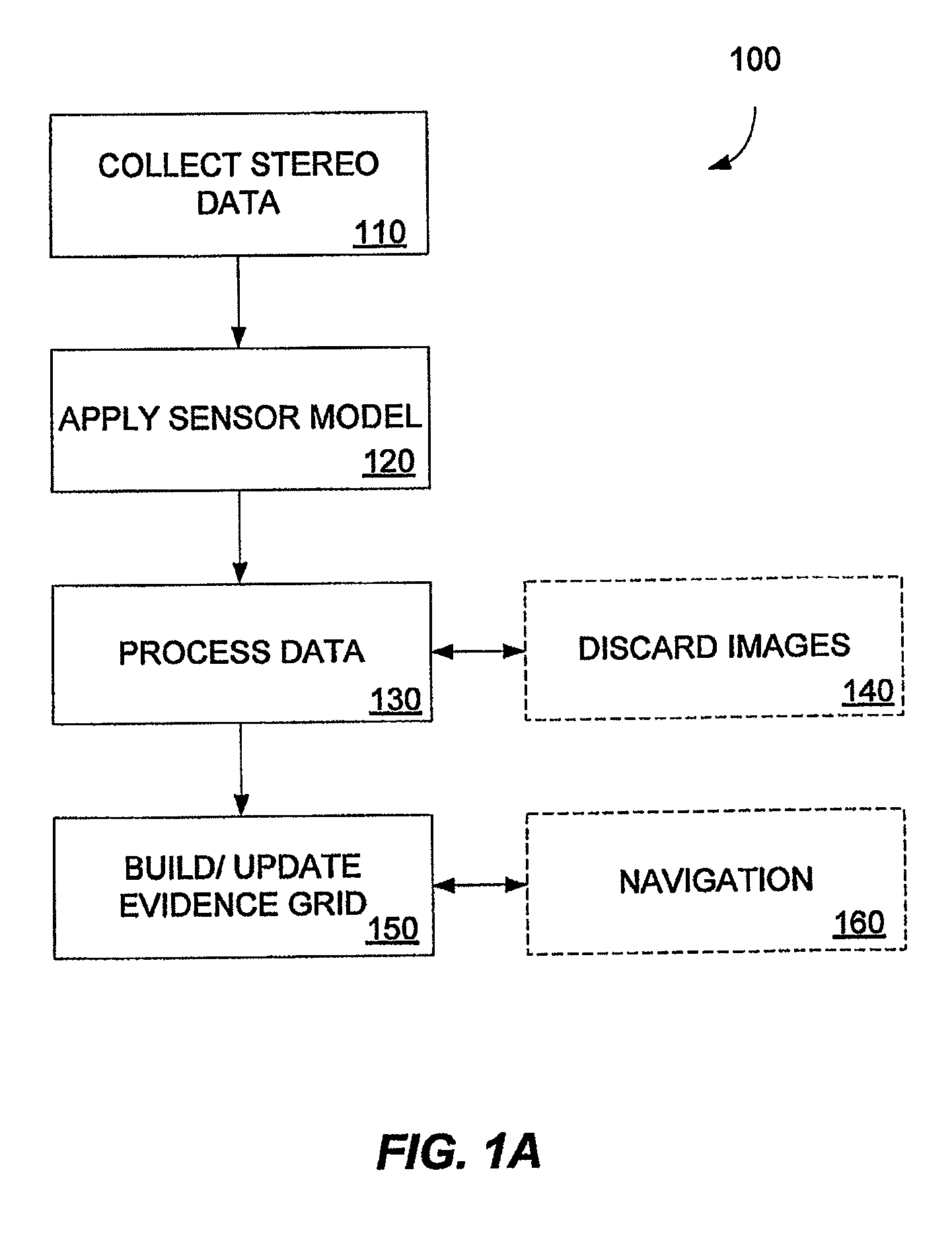
A method of generating an evidence grid representing an environment comprises the steps of collecting a set of stereo images at multiple locations within the environment using stereo sensors, and processing the set of stereo images to determine occupancy and distance data associated with each point in space represented in the set of stereo images; applying a sensor model to each point in space to determine a probability of occupancy of each voxel representing each point in space; and generating an evidence grid of the environment by combining the probabilities for each voxel.
Owner:SEEGRID CORPORATION
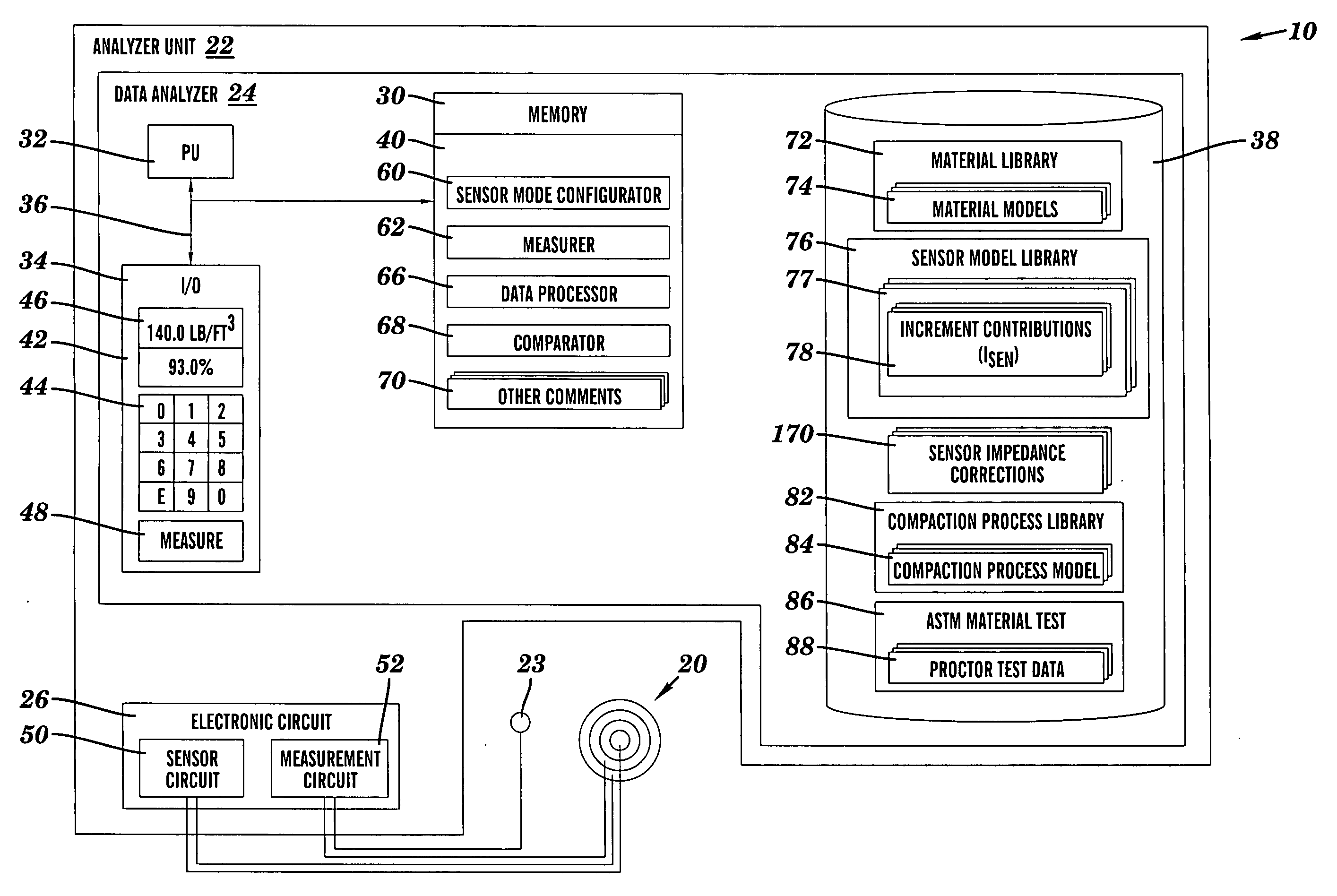
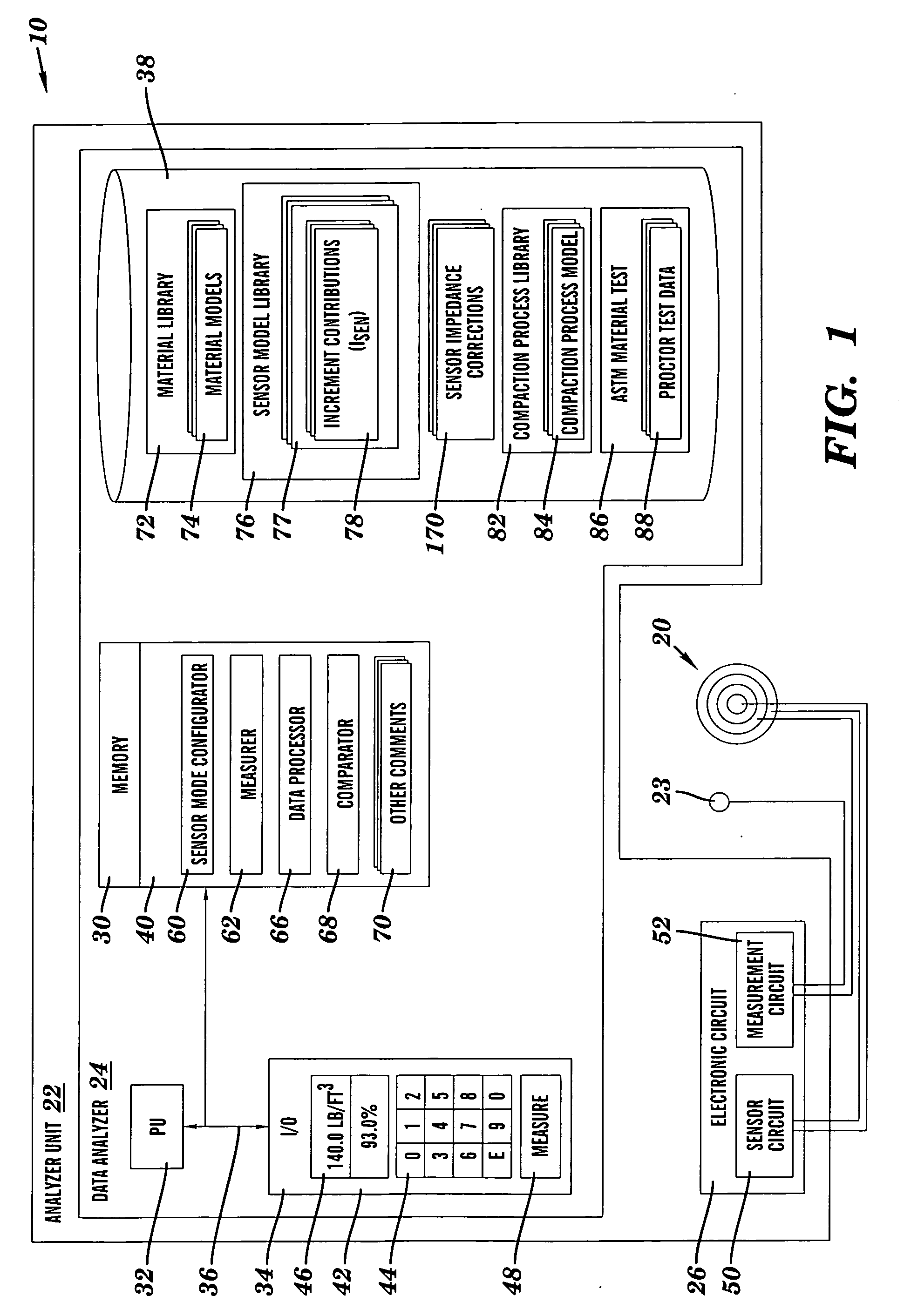
Material analysis including density and moisture content determinations
ActiveUS20050267700A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceNuclear monitoringEngineeringContent determination
A system, method and program product for determining the in-place engineering properties such as density and moisture content of many varieties of engineering materials, are disclosed. The invention also includes a database, material model and sensor model for use with the above-described aspects. In one embodiment, the invention determines a compaction indication of the material based on an effect of impedance characteristics of the material on an electrical field, and corrects the compaction indication for at least one of a sensor depth-sensitivity inaccuracy and a compaction process inaccuracy. The compaction indication is determined based on a material model, and the corrections are based on mathematical and empirical models of the compaction process and the sensor.
Owner:TRANSTECH SYST
Multidimensional evidence grids and system and methods for applying same
ActiveUS7446766B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlVoxelStereo image
A method of generating an evidence grid representing an environment comprises the steps of collecting a set of stereo images at multiple locations within the environment using stereo sensors, and processing the set of stereo images to determine occupancy and distance data associated with each point in space represented in the set of stereo images; applying a sensor model to each point in space to determine a probability of occupancy of each voxel representing each point in space; and generating an evidence grid of the environment by combining the probabilities for each voxel.
Owner:SEEGRID CORPORATION
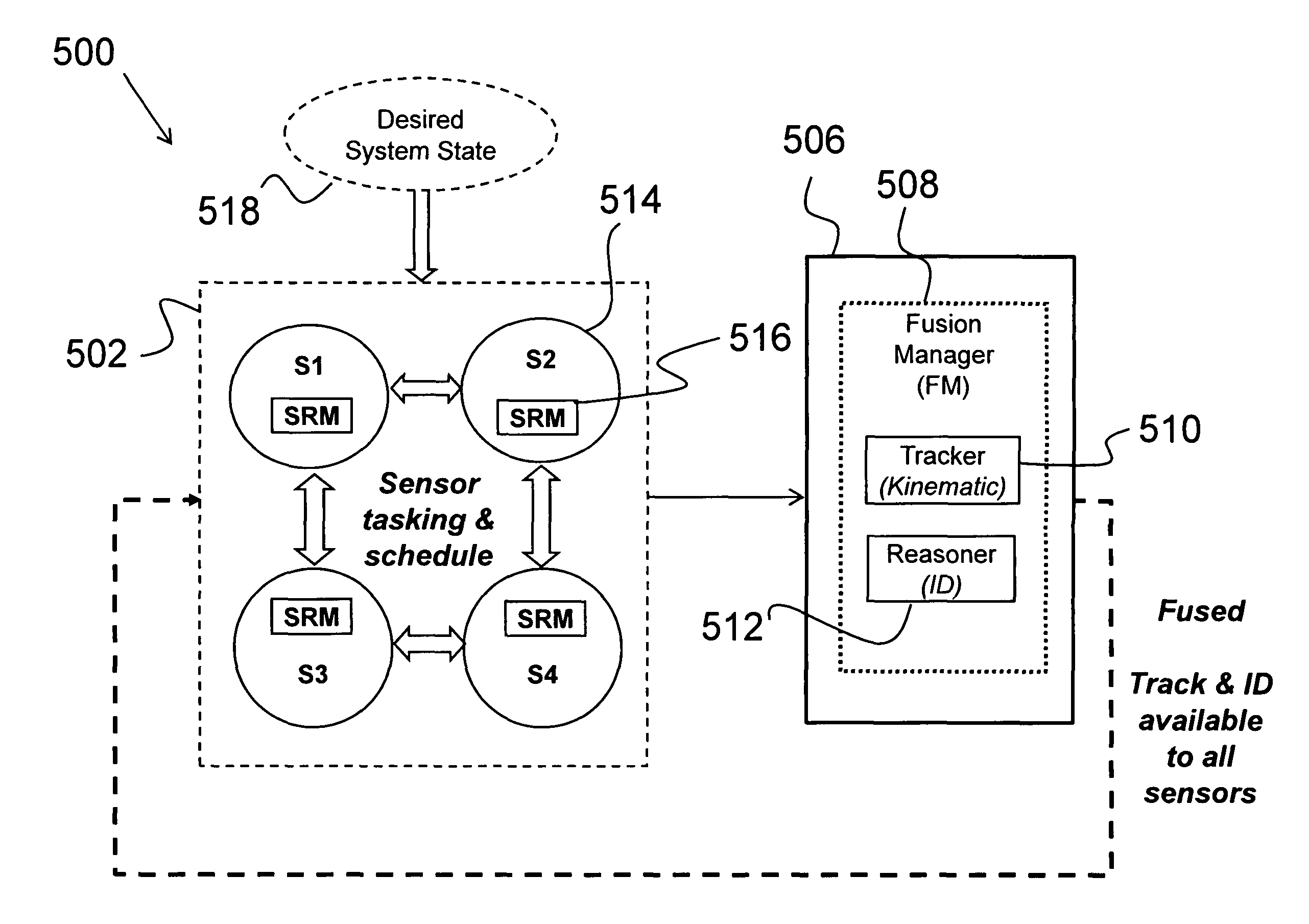
System for allocating resources to optimize transition from a current state to a desired state
ActiveUS8458715B1Easy to operateProgramme controlTesting/calibration apparatusResource allocation systemsEngineering
Described is a Distributed Resource Allocation System (DRAS) for sensor control and planning. The DRAS comprises an information framework module that is configured to specify performance goals, assess current performance state, and includes sensor models to achieve the performance goals. The DRAS is configured to further allocate the sensors to achieve the performance goals. Once allocated, the DRAS then reassesses the current performance state and continues reallocating the sensors until the current performance state is most similar to the performance goals.
Owner:HRL LAB
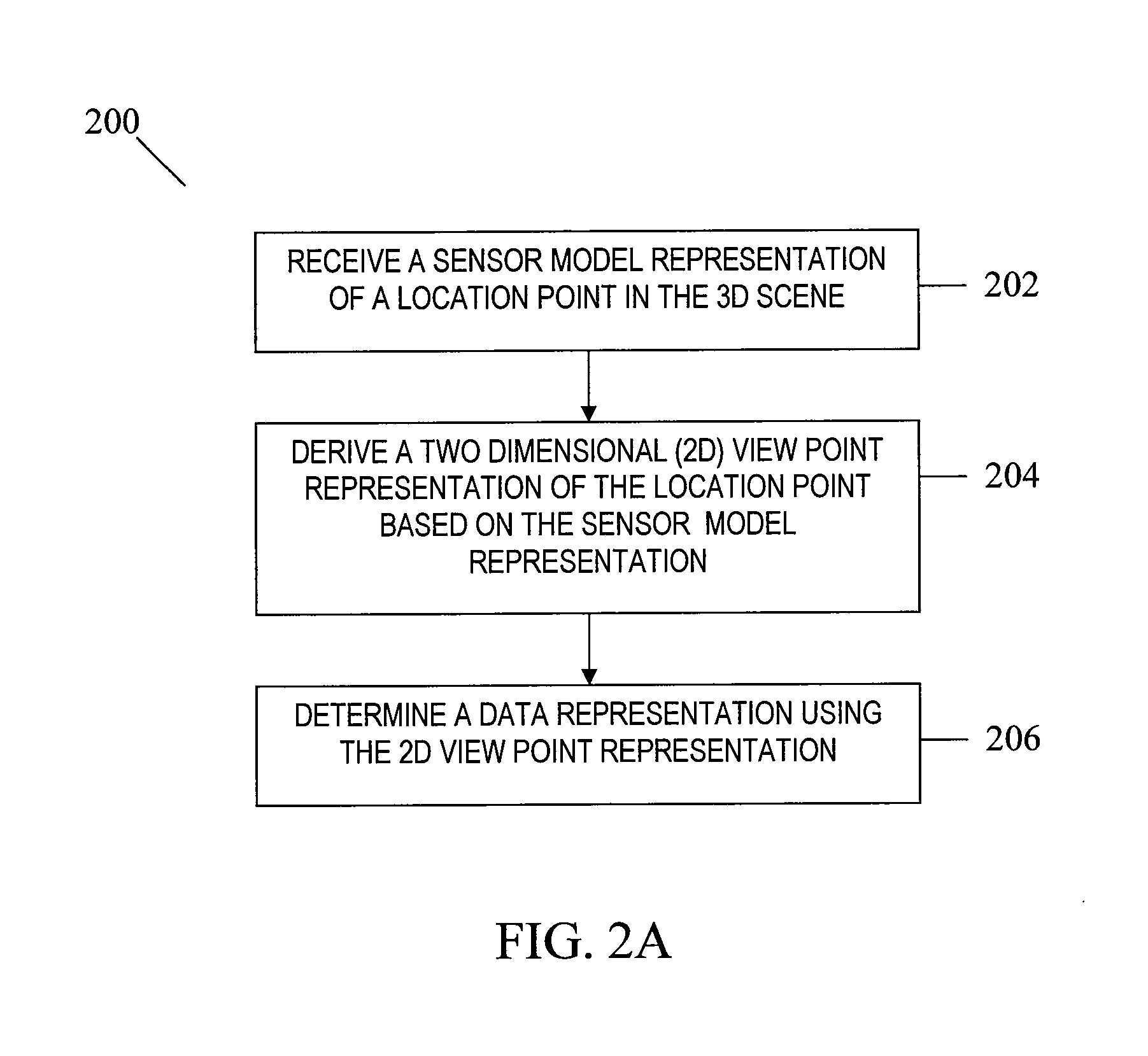
View Point Representation for 3-D Scenes
Techniques are described for deriving information, including graphical representations, based on perspectives of a 3D scene by utilizing sensor model representations of location points in the 3D scene. A 2D view point representation of a location point is derived based on the sensor model representation. From this information, a data representation can be determined. The 2D view point representation can be used to determine a second 2D view point representation. Other techniques include using sensor model representations of location points associated with dynamic objects in a 3D scene. These sensor model representations are generated using sensor systems having perspectives external to the location points and are used to determine a 3D model associated with a dynamic object. Data or graphical representations may be determined based on the 3D model. A system for obtaining information based on perspectives of a 3D scene includes a data manager and a renderer.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
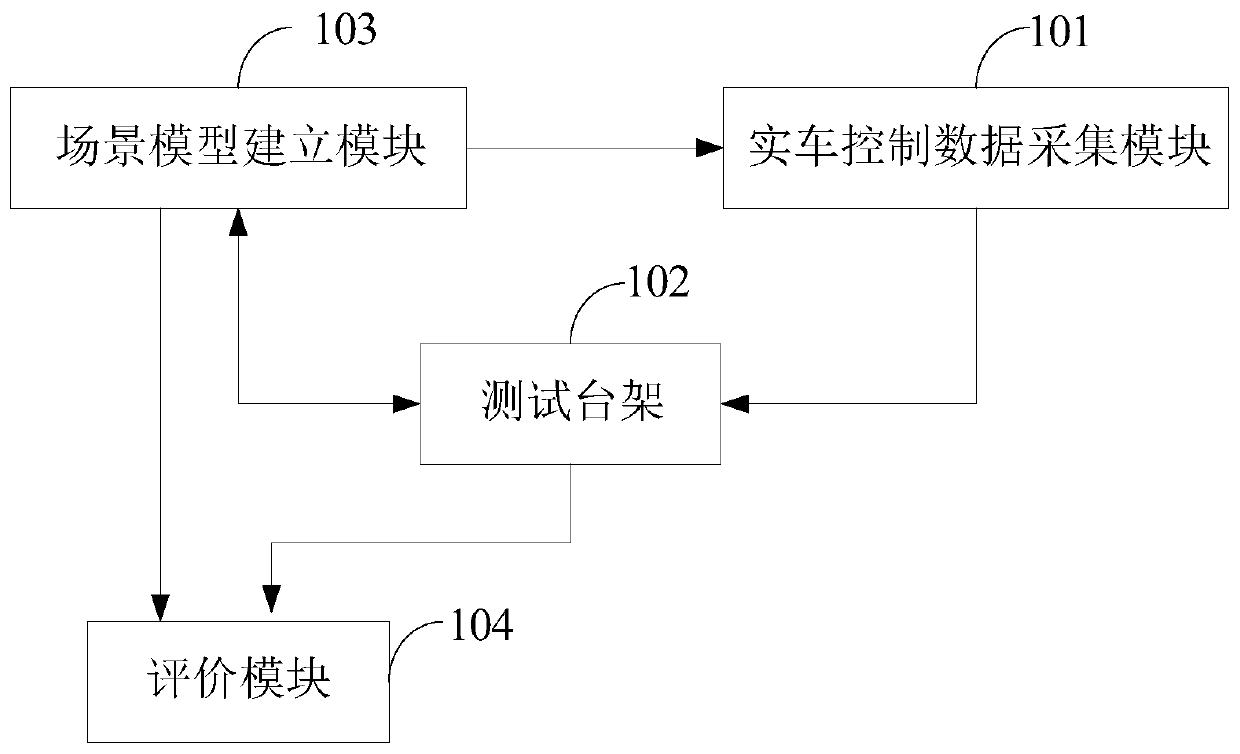
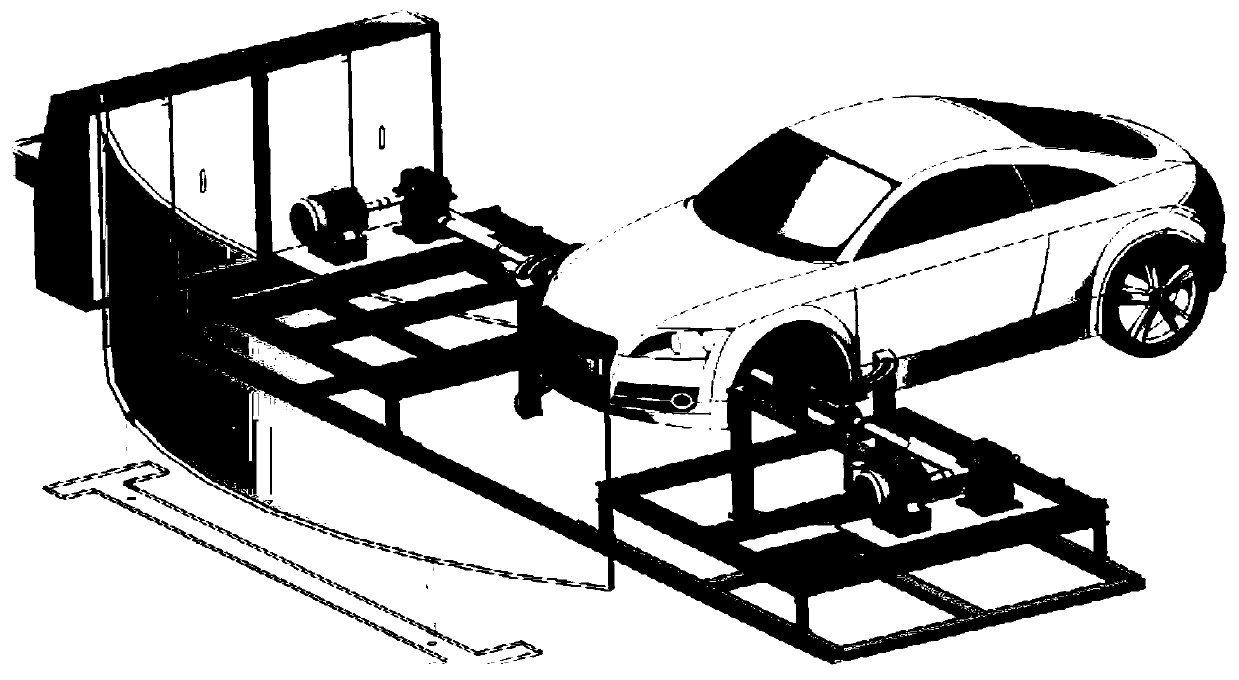
Test method, device and system for automatic driving vehicle
ActiveCN110160804AReliable identification abilityReliable timeVehicle testingSimulator controlVehicle dynamicsEngineering
The invention relates to a test system for an automatic driving vehicle. A real vehicle data collection module is used for collecting control data; a test bench is used for generating a reaction forceaccording to the control data and scene information and obtaining state data of an automatic driving vehicle according to the reaction force; a scene model establishing module is used for establishing a traffic scene model, a traffic flow model, an automatic driving vehicle dynamics model and an environment perception sensor model and obtaining position data of the automatic driving vehicle; andan evaluation module is used for calculating a return value for evaluating the running state of the automatic driving vehicle according to the position data and the state data. By combining the test bench with a scene model comprising traffic flow data, the environment recognition capability, the dangerous condition recognition response time and the processing mode of the automatic driving vehiclecan be more truly tested, and the safety and the stability of the autonomous recognition capability under a complex traffic environment can be more truly tested.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiprocessor real-time simulation platform
InactiveCN101320524AStrong computing powerAchieve sharingCosmonautic condition simulationsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationReal-time simulationSpace environment
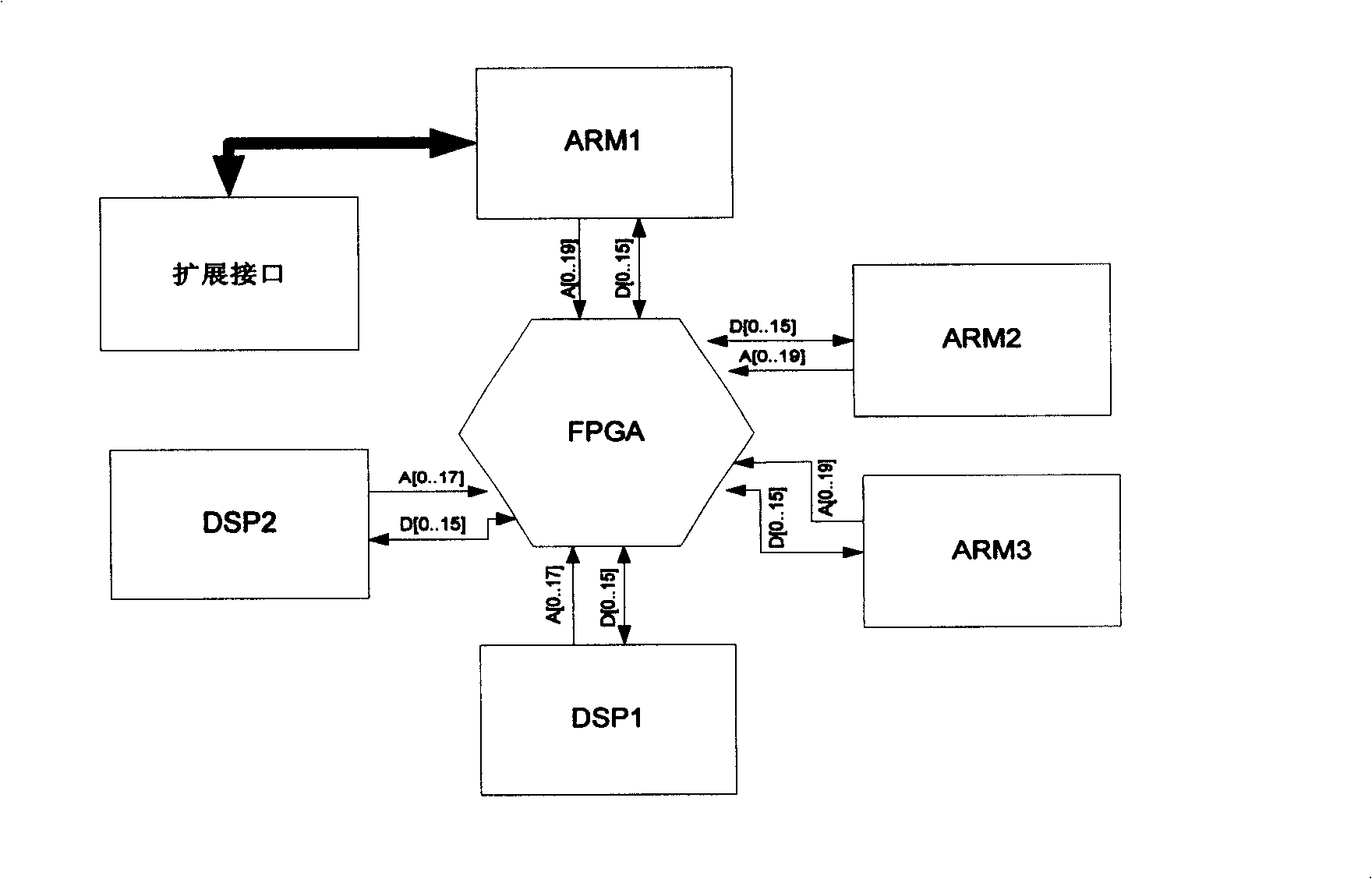
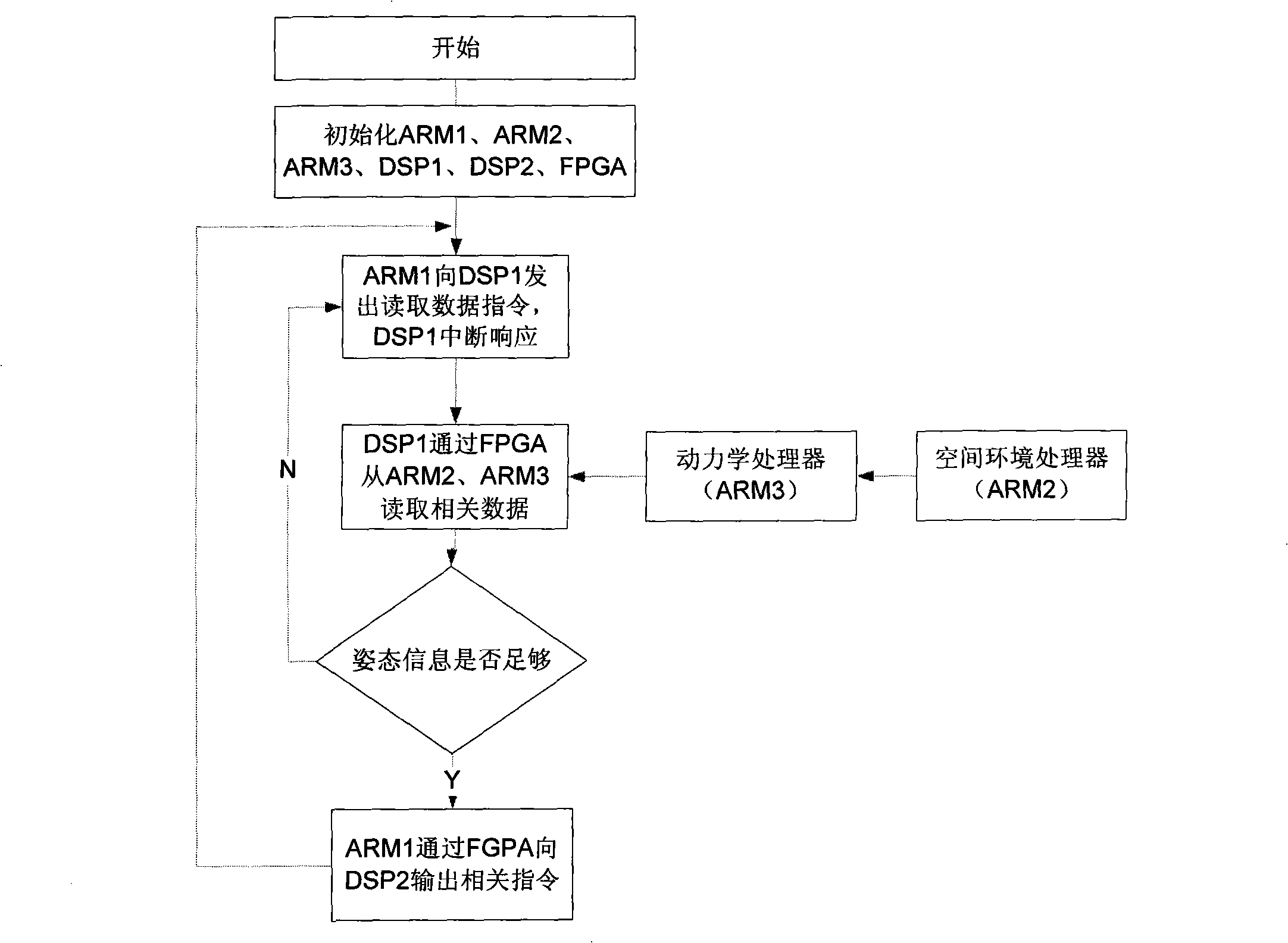
The present invention relates to a multi-processor satellite real-time simulation platform which consists of three or more than three ARM processors, and two or more than two DSP processors with an FPGA as an intermediate memory. The ARM1 is used as the computer of the simulation satellite control center; the ARM2 is used in the space environment of the simulation satellite; the ARM3 is used for the kinetic calculation of the satellite; the DSP1 is used for completing the calculation of a sensor model; the DSP2 is used for completing the calculation of an actuating mechanism; the ARM1 sends data to the DSP1 so as to acquire instructions; the DSP1 sends the acquired data instructions to the ARM2 and the ARM3, fetches relevant data from the FPGA, and transmits the data to the ARM1; the ARM1 completes the calculation according to the read data, and acquires the corresponding attitude orbital parameters; if the parameters satisfy the requirements, the satellite enters the normal mode; if the parameters do not satisfy the requirements, the ARM1 sends control instructions to the DSP2 so as to control the actuating mechanism; the DSP2 transmits the corresponding data to the ARM2 and the ARM3 through the FPGA after completing the calculation, until the attitude orbit can satisfy the corresponding requirements. The platform simplifies the complexity of the system, lowers the difficulty of the simulation, and improves the real-time performance of the simulation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Object inspection with referenced volumetric analysis sensor
InactiveUS20130028478A1Using subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansCharacter and pattern recognitionNon destructiveVolume analysis
A positioning method and system for non-destructive inspection of an object include providing at least one volumetric analysis sensor having sensor reference targets; providing a sensor model of a pattern of at least some of the sensor reference targets; providing object reference targets on at least one of the object and an environment of the object; providing an object model of a pattern of at least some of the object reference targets; providing a photogrammetric system including at least one camera and capturing at least one image in a field of view, at least a portion of the sensor reference and the object reference targets being apparent on the image; determining a sensor spatial relationship and an object spatial relationship; determining a sensor-to-object spatial relationship of the at I act one volumetric analysis sensor with respect to the object; repeating the steps and tracking a displacement of the volumetric analysis sensor and the object.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
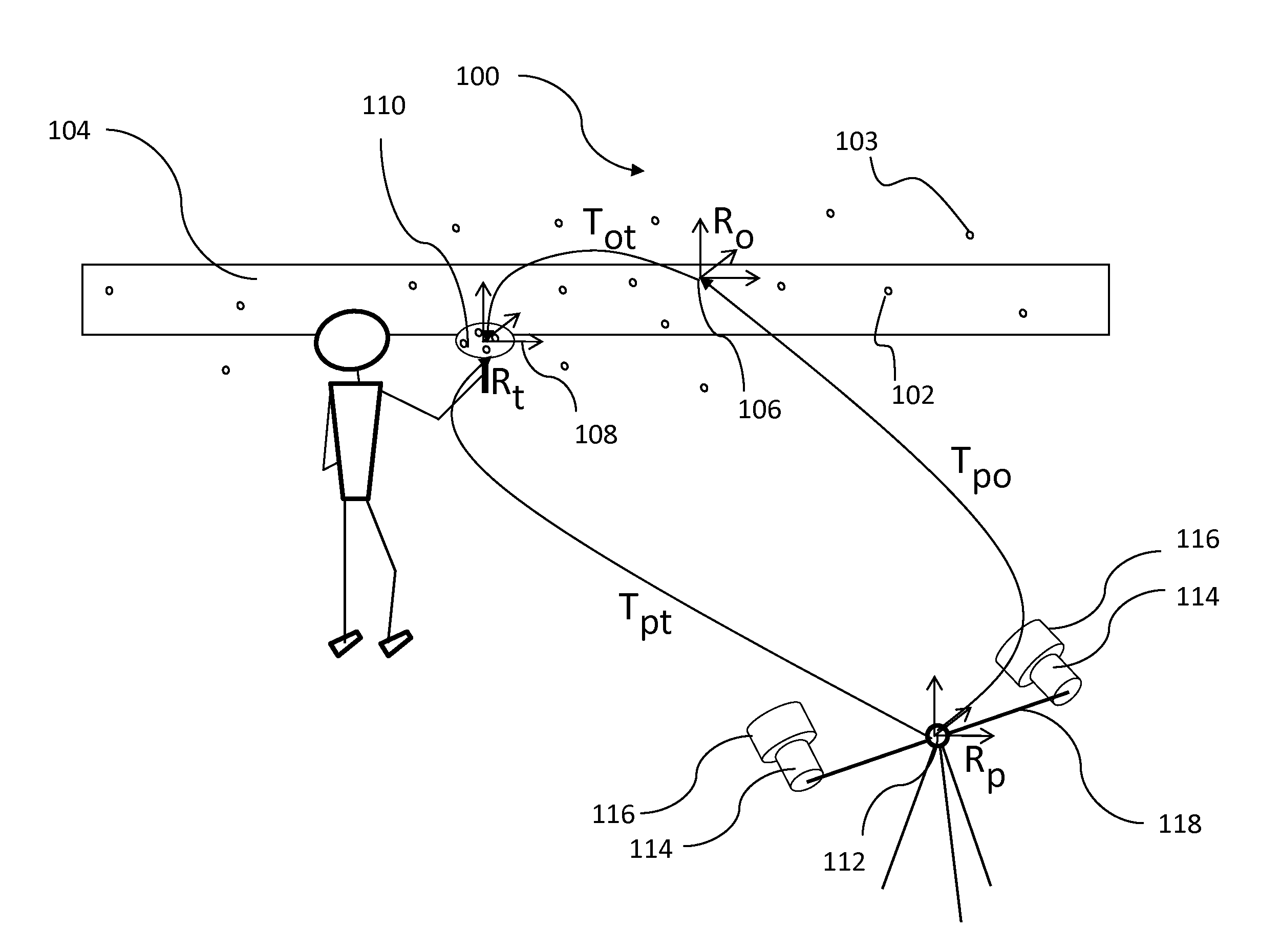
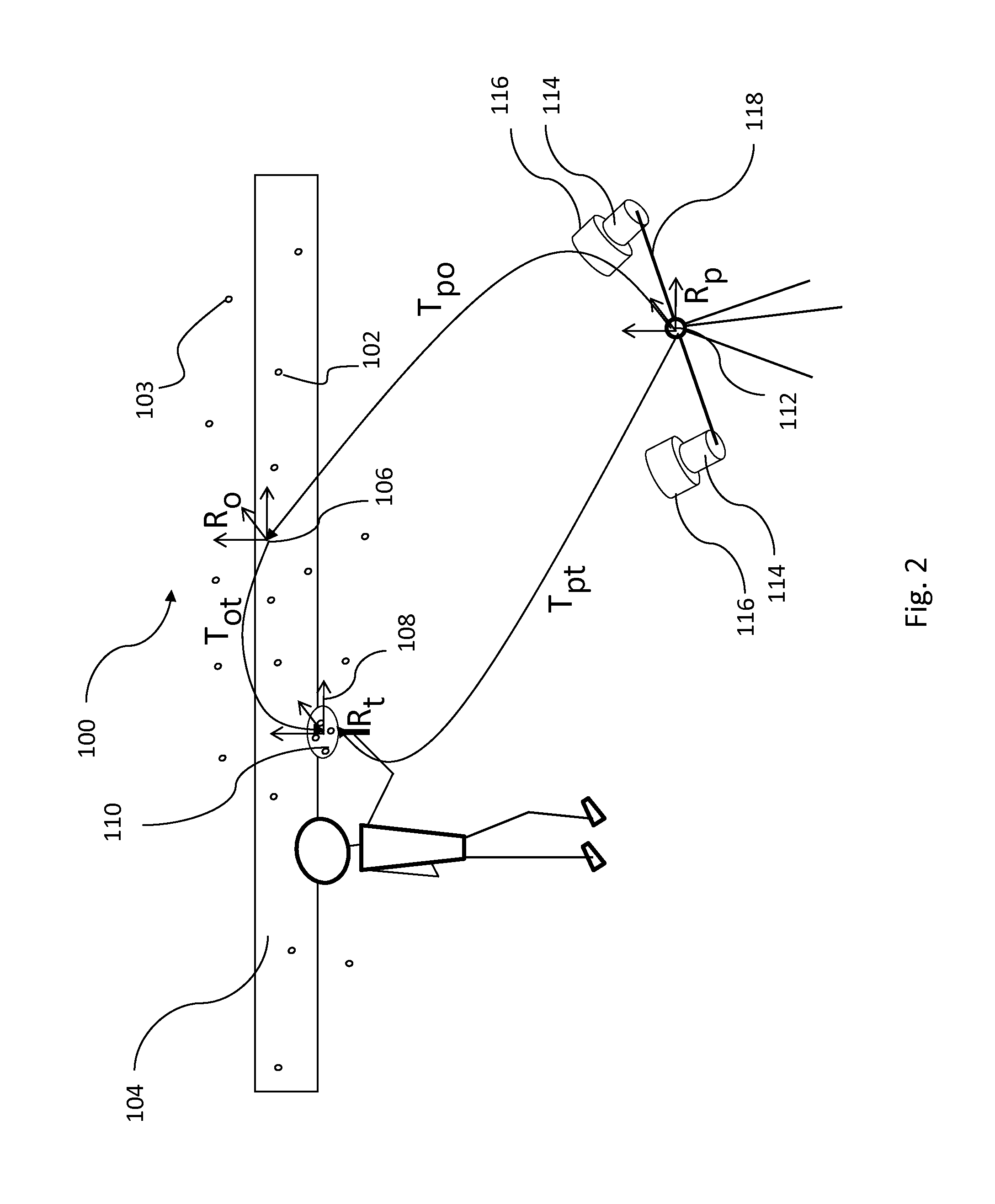
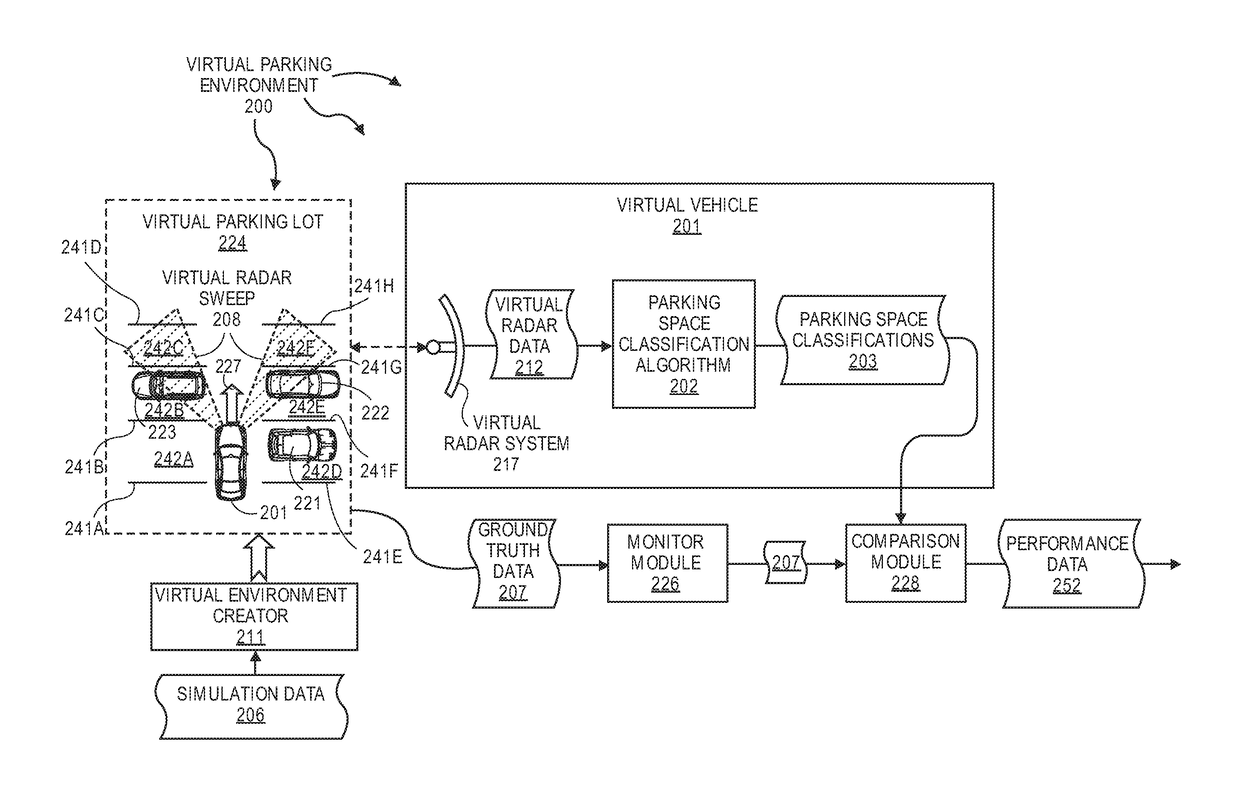
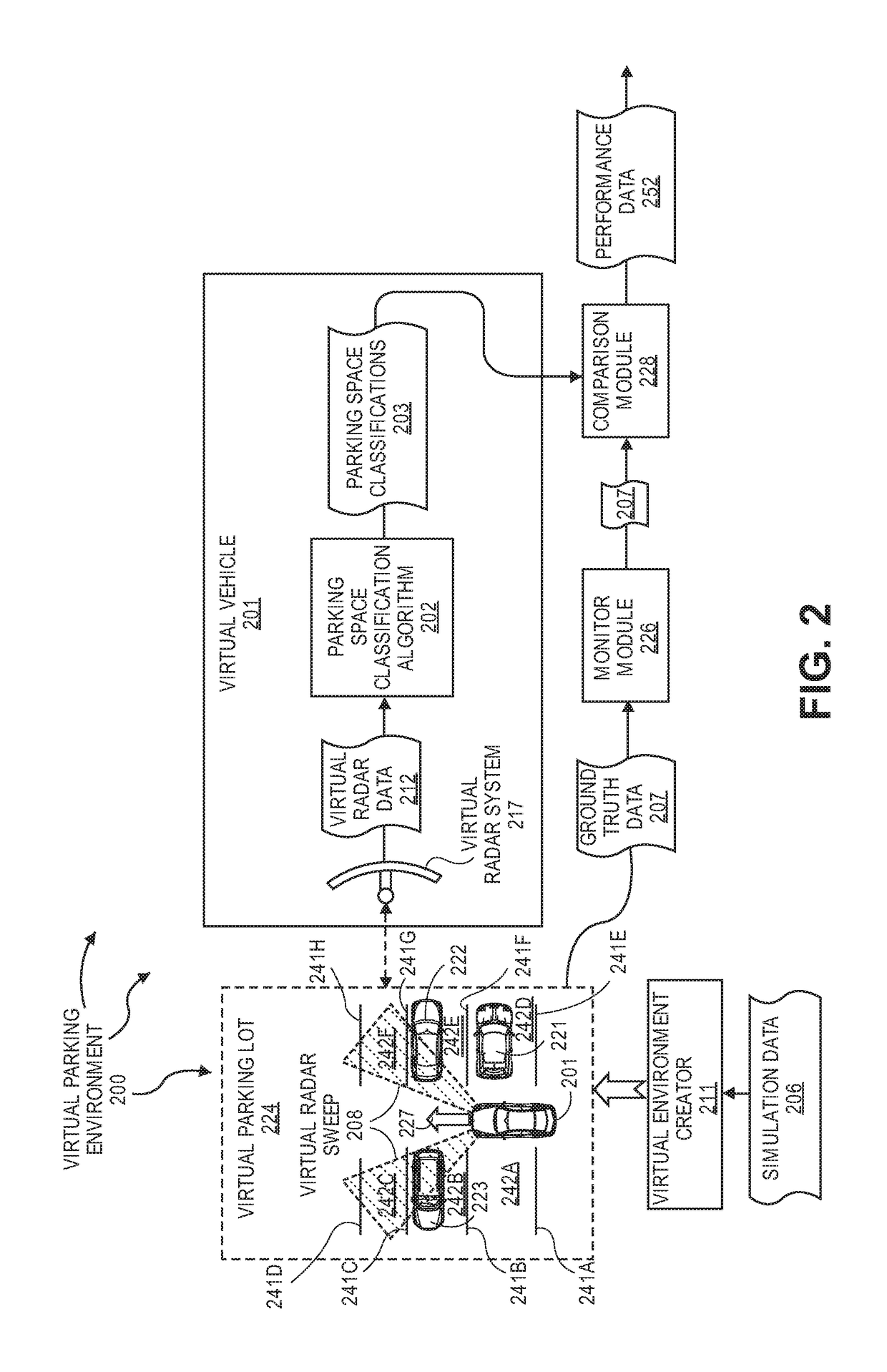
Using Virtual Data To Test And Train Parking Space Detection Systems
InactiveUS20180025640A1Indication of parksing free spacesCharacter and pattern recognitionVirtualizationGround truth
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for using virtual data to test and train parking space detection systems. Aspects of the invention integrate a virtual driving environment with sensor models (e.g., of a radar system) to provide virtual radar data in relatively large quantities in a relatively short amount of time. The sensor models perceive values for relevant parameters of a training data set. Relevant parameters can be randomized in the recorded data to ensure a diverse training data set with minimal bias. Since the driving environment is virtualized, the training data set can be generated alongside ground truth data. The ground truth data is used to annotate true locations, which are used to train a parking space classification algorithms to detect the free space boundaries.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sensor model supervisor for a closed-loop insulin infusion system
An insulin infusion device includes a processor architecture, and a memory element that stores executable instructions to perform a method of controlling delivery of insulin to a user. The method operates the device in a closed-loop mode to deliver insulin, obtains patient-specific parameters for a current time sample, and estimates a plasma insulin value and a blood glucose value for the user based on at least some of the patient-specific parameters. The estimating is also based on a previously estimated plasma insulin value obtained for a previous time sample, and a previously estimated blood glucose value obtained for the previous time sample. A predicted sensor glucose value is generated for the current time sample, and the closed-loop mode or a safe basal mode is selected for controlling operation of the insulin infusion device in accordance with the selected mode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Systems and methods for characterizing the coverage of ad hoc sensor networks
InactiveUS7091902B2Simple and intuitive wayAccurate measurementTesting/calibration apparatusPosition fixationQuality of serviceGraphics
Owner:MAJANDRO LLC
Off-line programming system and method of optical visual sensor with linear structure for welding robot
InactiveCN101973032AIntuitive detection statusIntuitive display of detection statusManipulatorInteractive graphicsSimulation
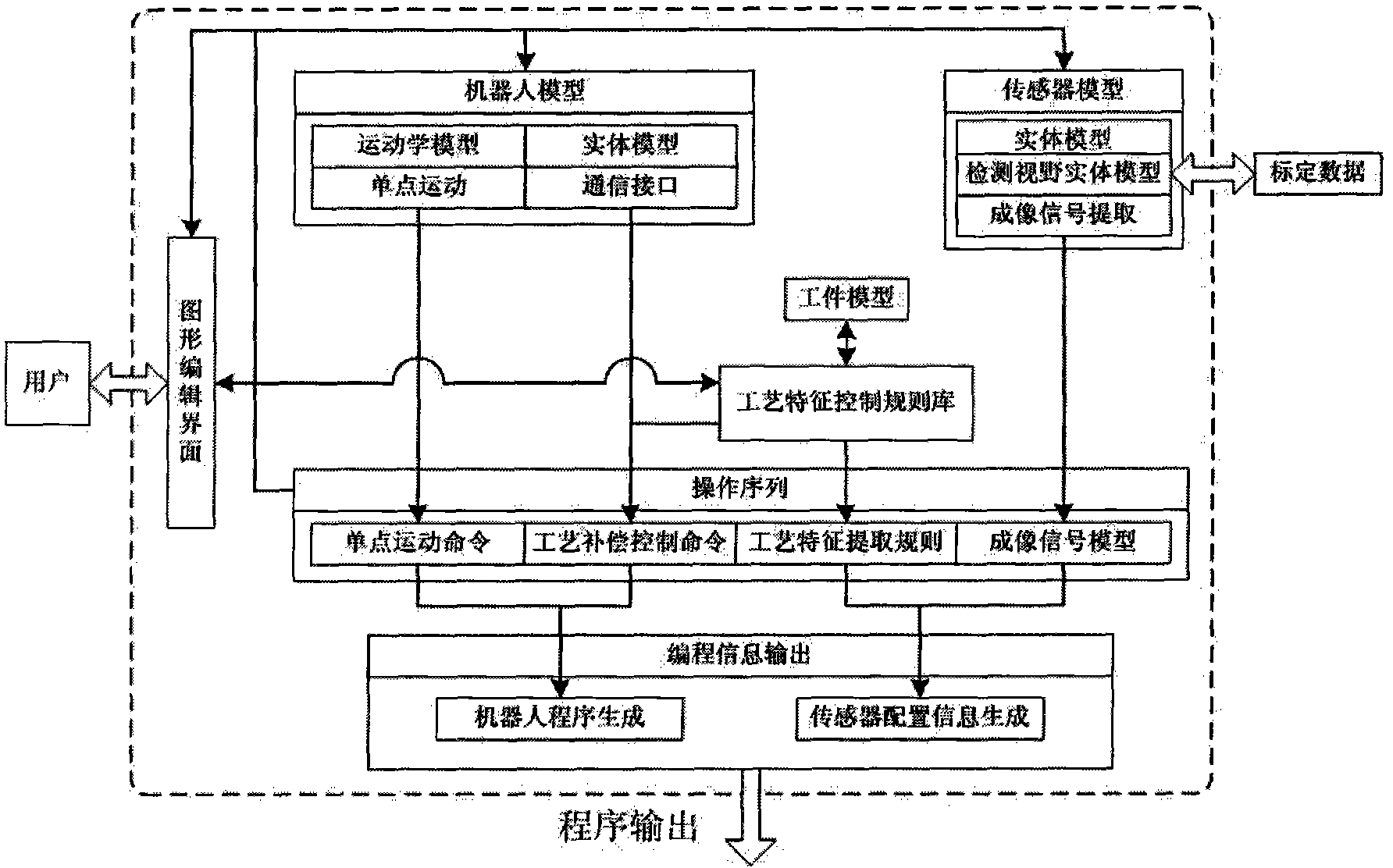
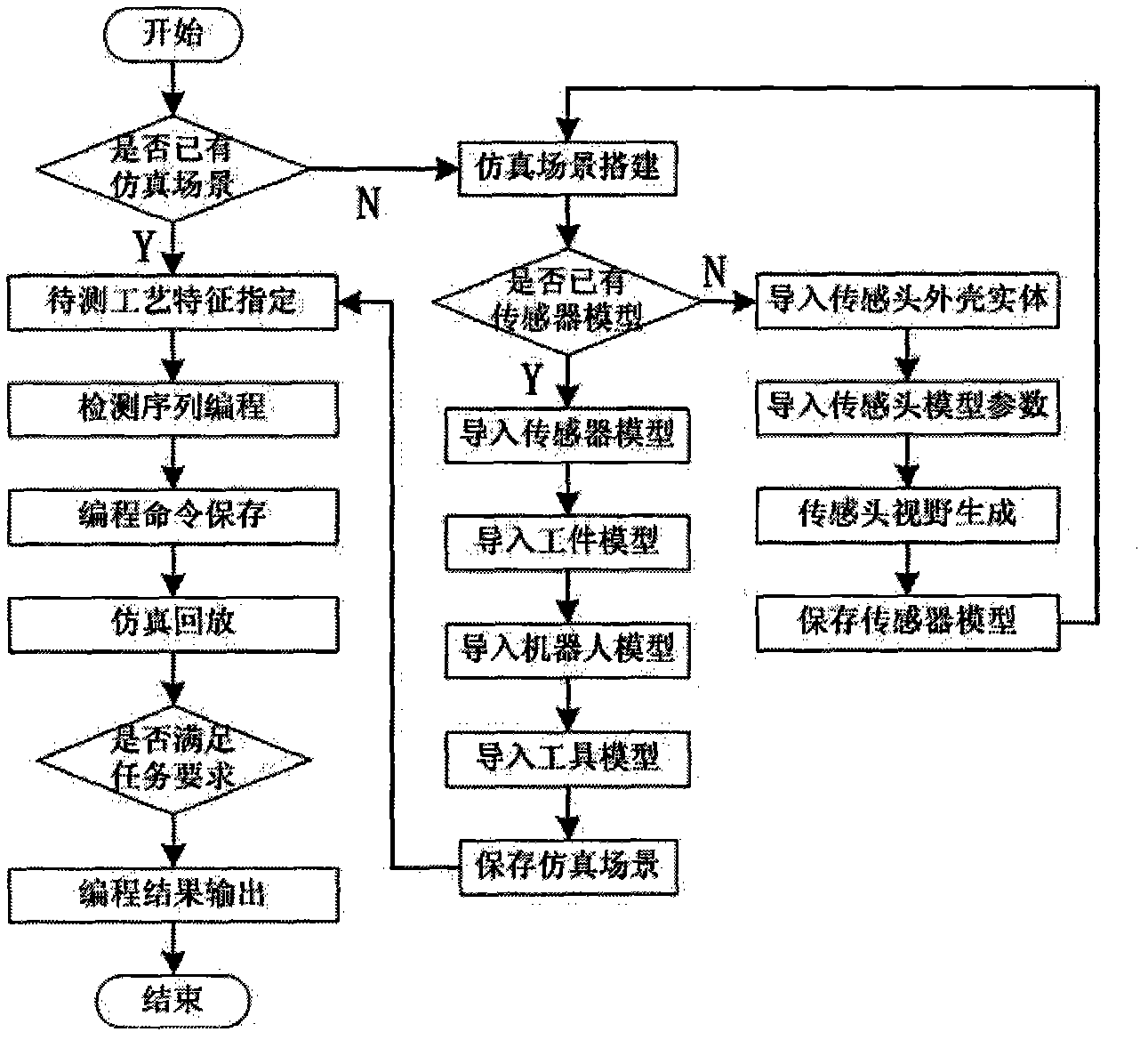
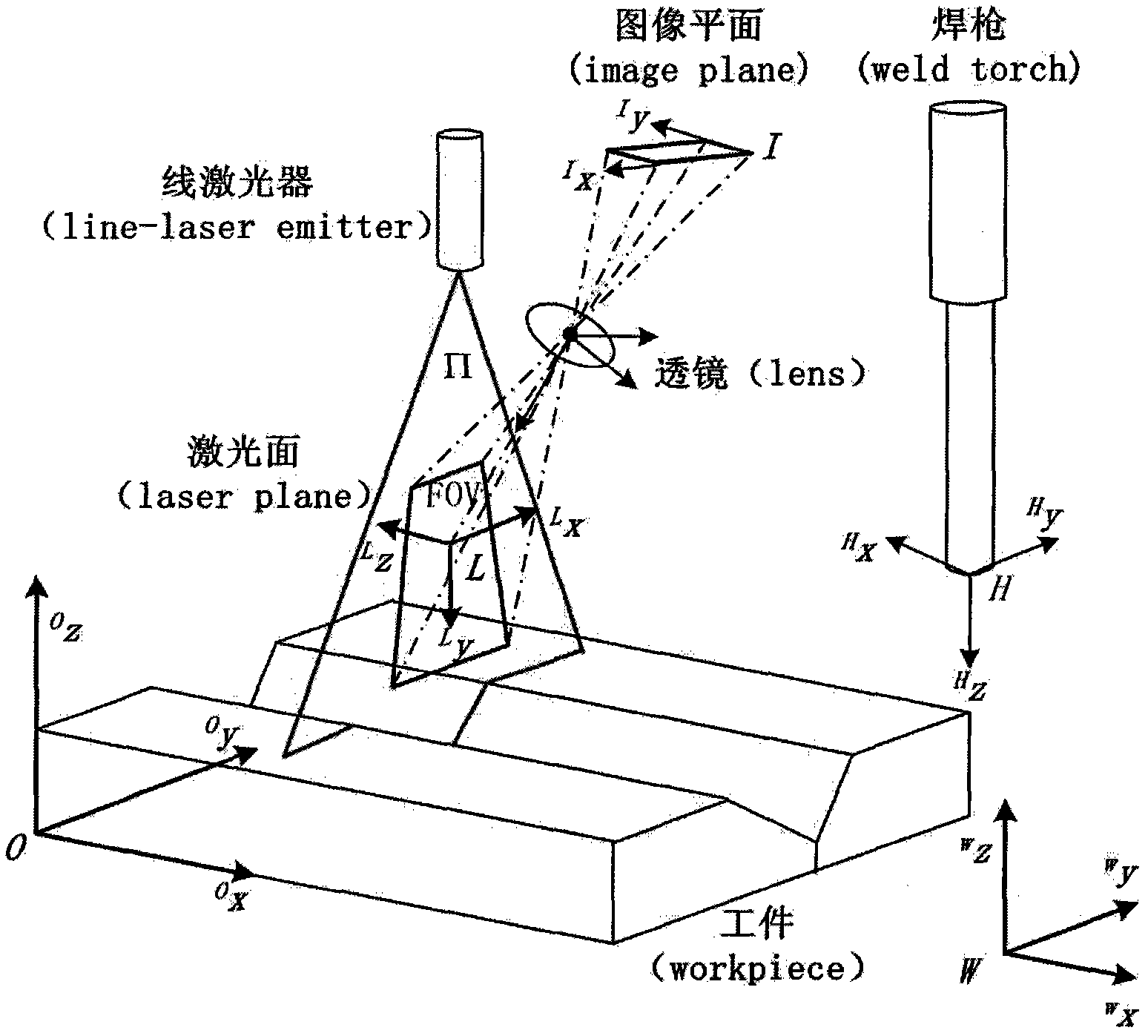
The invention relates to an off-line programming system and method of an optical visual sensor with a linear structure for a welding robot. The system comprises a sensor model, a robot model, a process control rule base, a graphic editing interface, an operation sequence module and a programming information output, wherein the sensor model is used for simulating a sensor imaging process to acquire a view model and simultaneously completing detection view substantiation to be convenient for user graphic programming; the robot model is used for simulating the single-point motion of the robot and providing communication interface information of connecting sensor input signals; the process control rule base is used for providing process feature extraction rules for different welding tasks andcontrol command related information of processes; the graphic editing interface is used for interactive graphic programming between a user and a system; the operation sequence module is used for saving the information of a series of detection points, wherein the information comprises single-point motion commands, process compensation control commands, process feature extraction rules and imaging signal model information; and the programming information output is used for outputting the program text of the robot and the configuration information text of the sensor system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
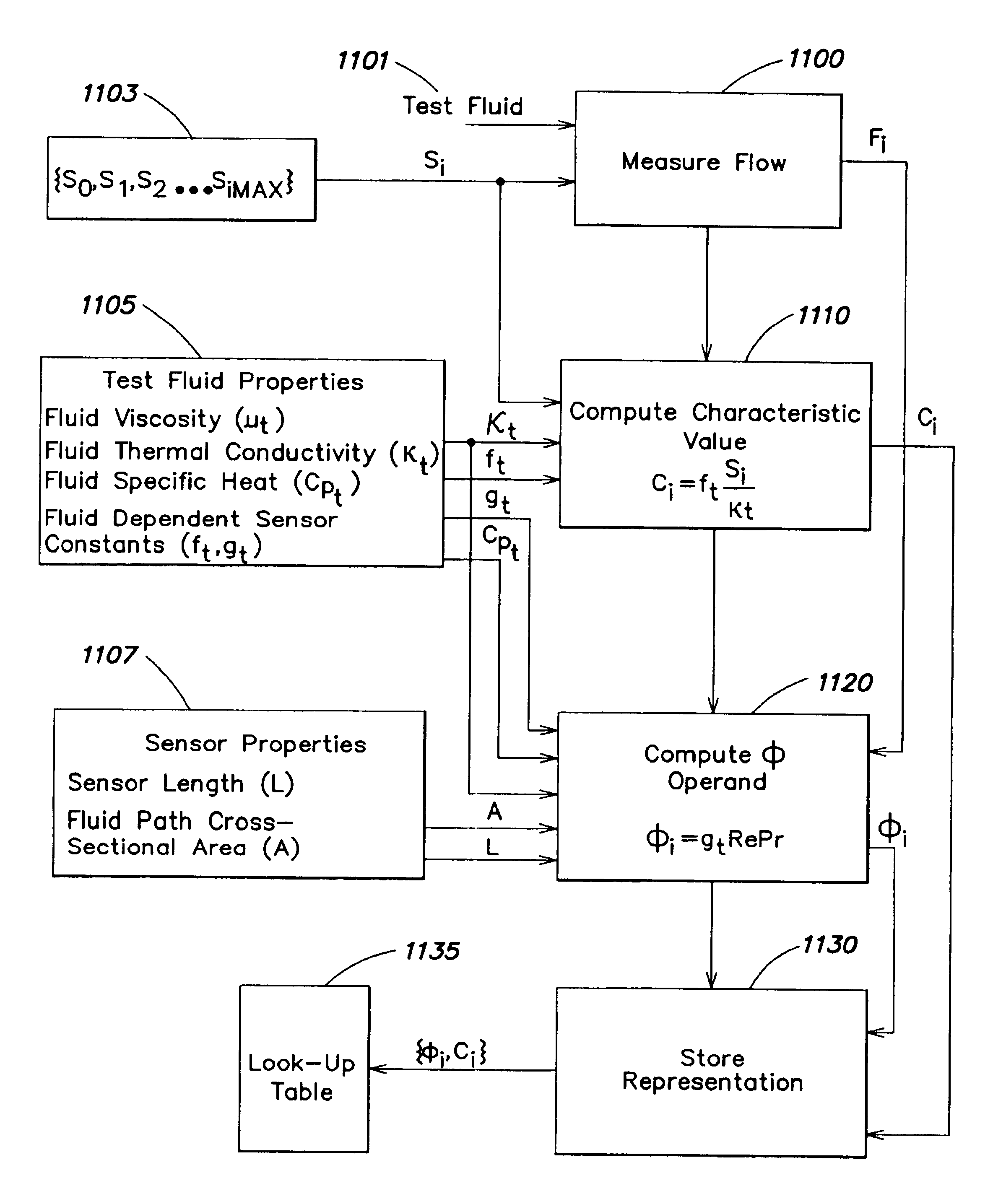
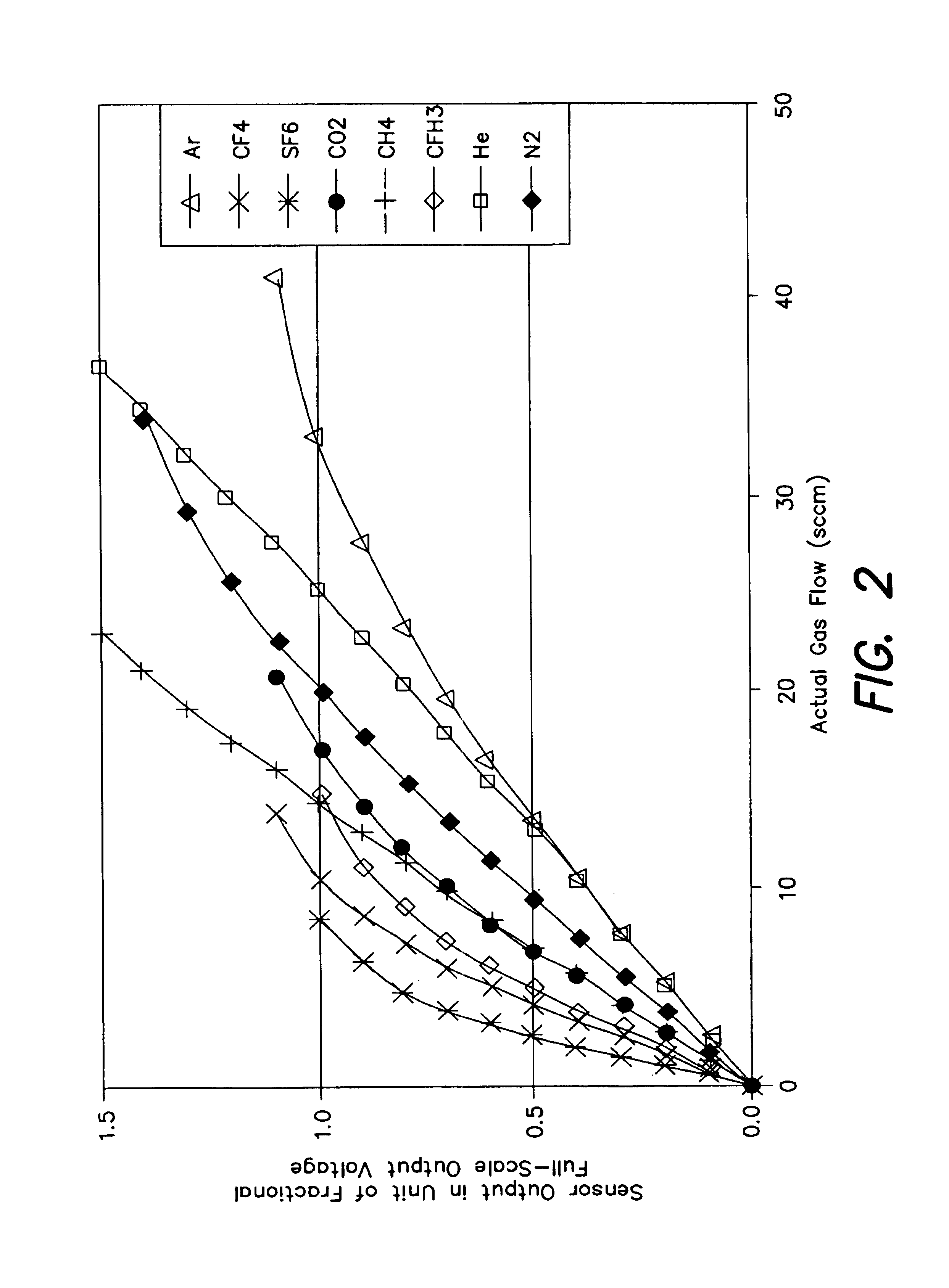
Flow sensor signal conversion
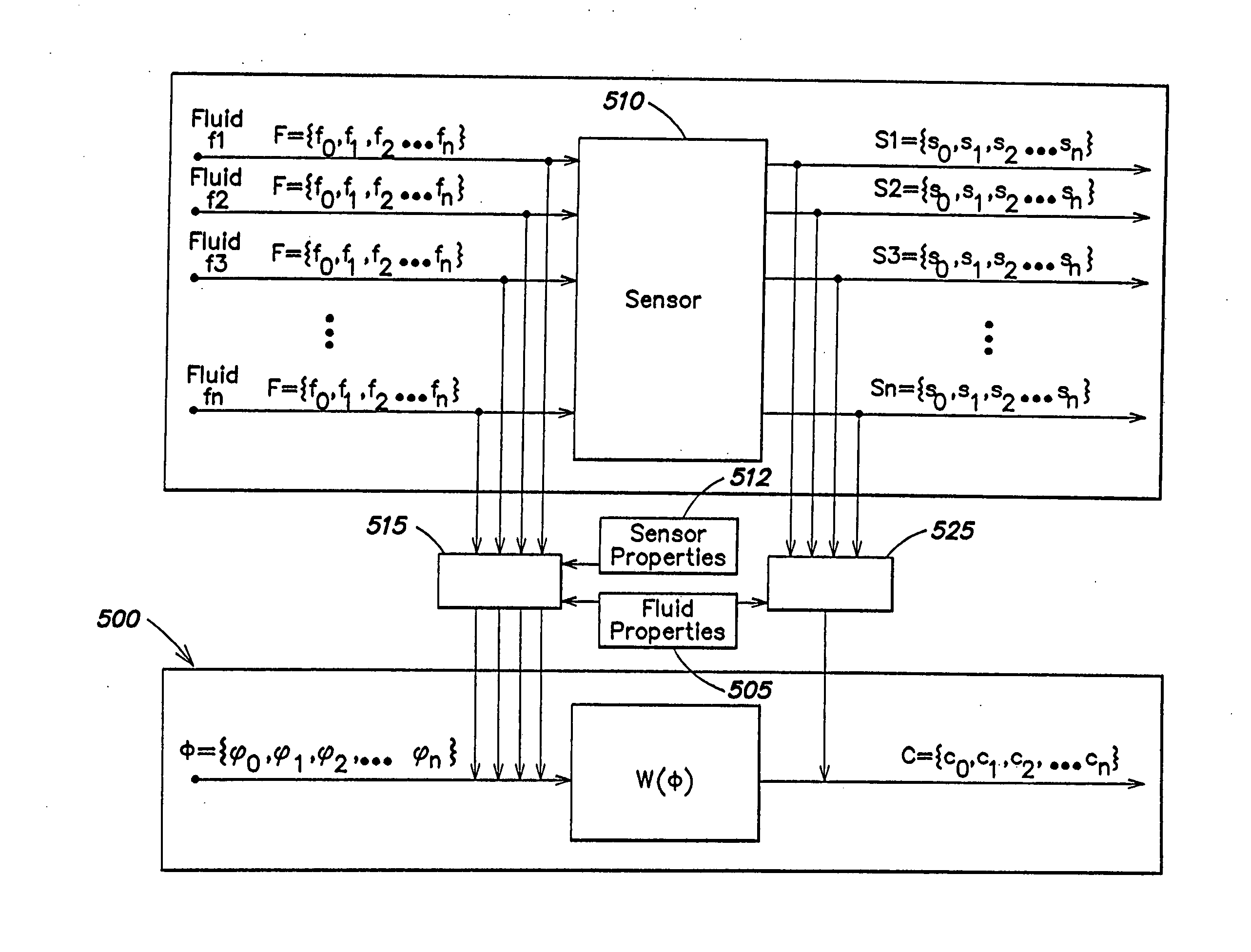
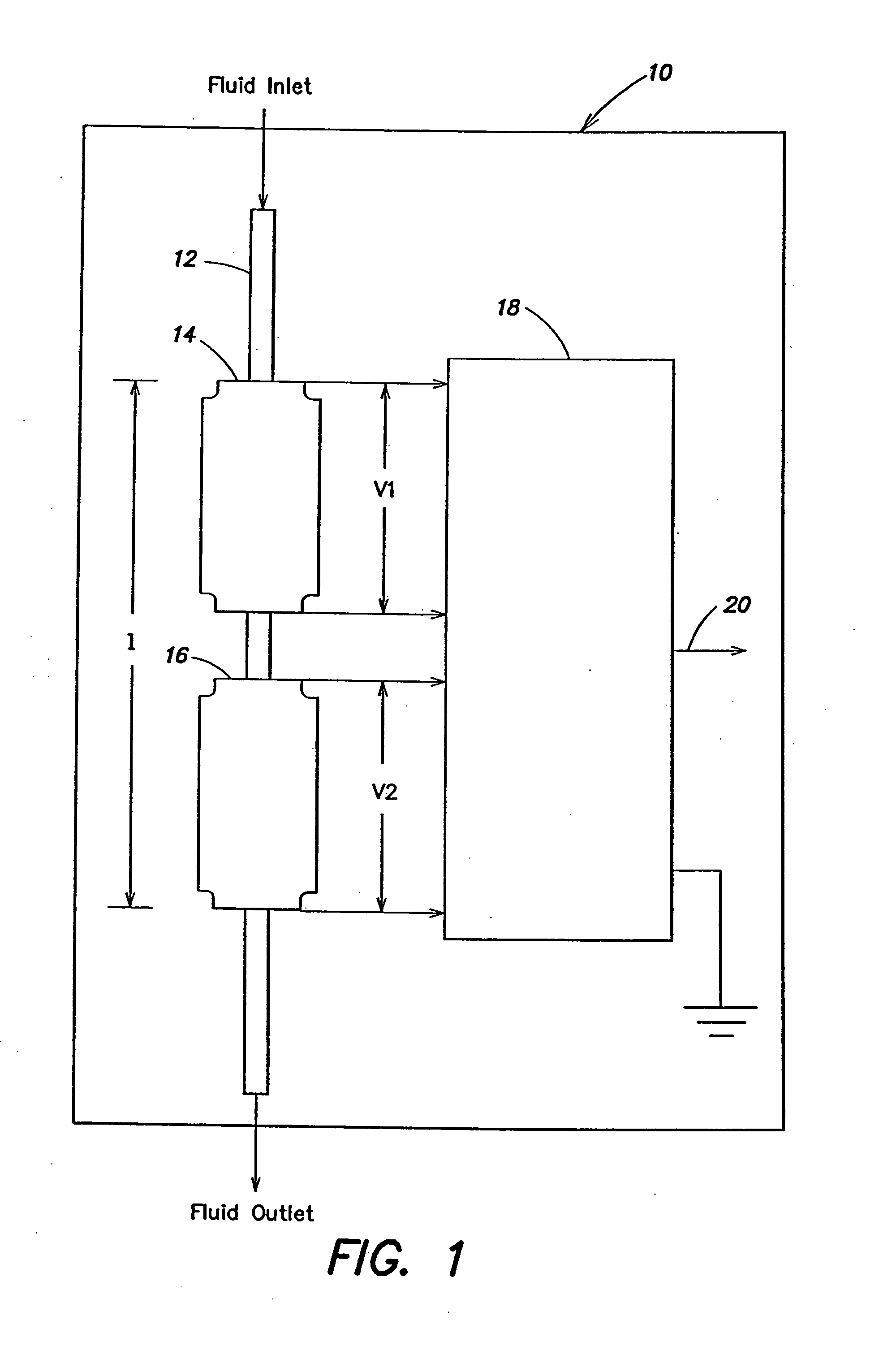
InactiveUS20050126306A1Facilitates accurately determining flow rateVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsVolume flow proportion measurementStream flowSensor model
A method of obtaining at least one representation of a characteristic function of a sensor from a test fluid during calibration of the sensor according to a sensor model having a transfer function operating on flow rate, at least one sensor property and at least one fluid property and employing the at least one representation of the characteristic function to determine flow rates through the sensor during operation with an arbitrary fluid.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
Multidimensional evidence grids and system and methods for applying same
ActiveUS8427472B2Road vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionModel parametersNavigation system
Mapping, localization, and navigation systems for use with a mobile unit are provided that use a sensor model with adjustable parameters. The system includes range sensors configured to collect range data and a data storage system having stored therein an evidence grid representing an environment and a sensor model comprising adjustable parameters representing inaccuracies of the range sensors. A grid engine adjusts the adjustable parameters based on received range data from the range sensors. A navigation module can direct the mobile unit though the environment using the evidence grid, received range data, and adjustable parameters. The grid engine can also locate the mobile unit within the environment by using the adjusted sensor model parameters to compare the received range data against the evidence grid.
Owner:SEEGRID CORPORATION
Multi-chaos system based method of encrypting images related to plaintext
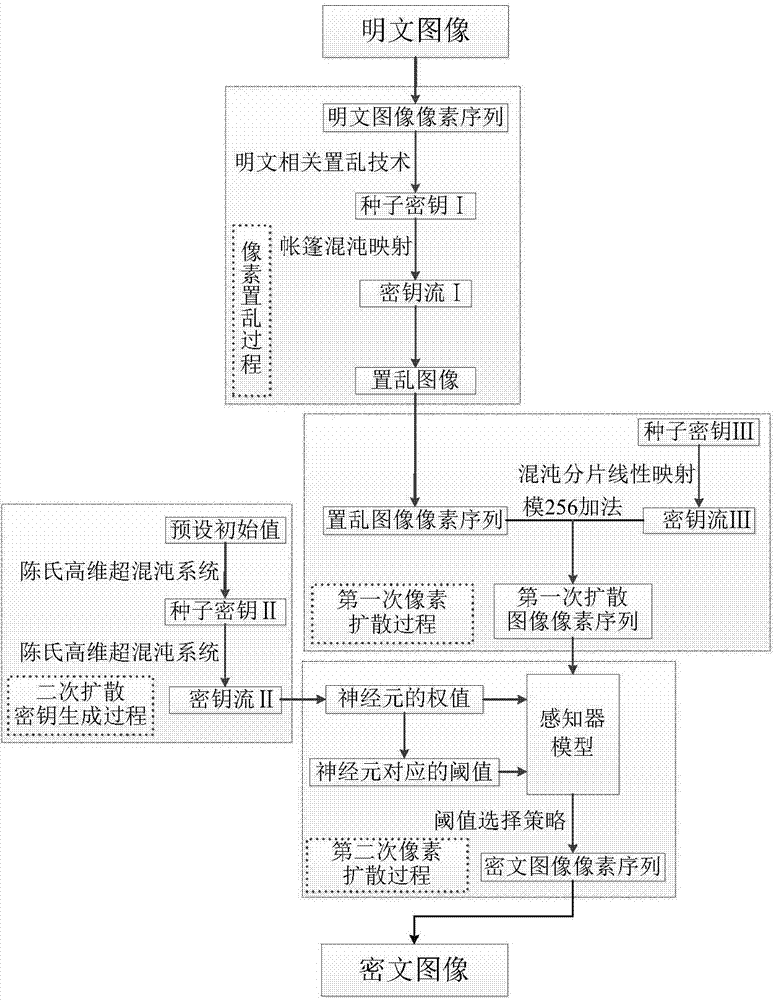
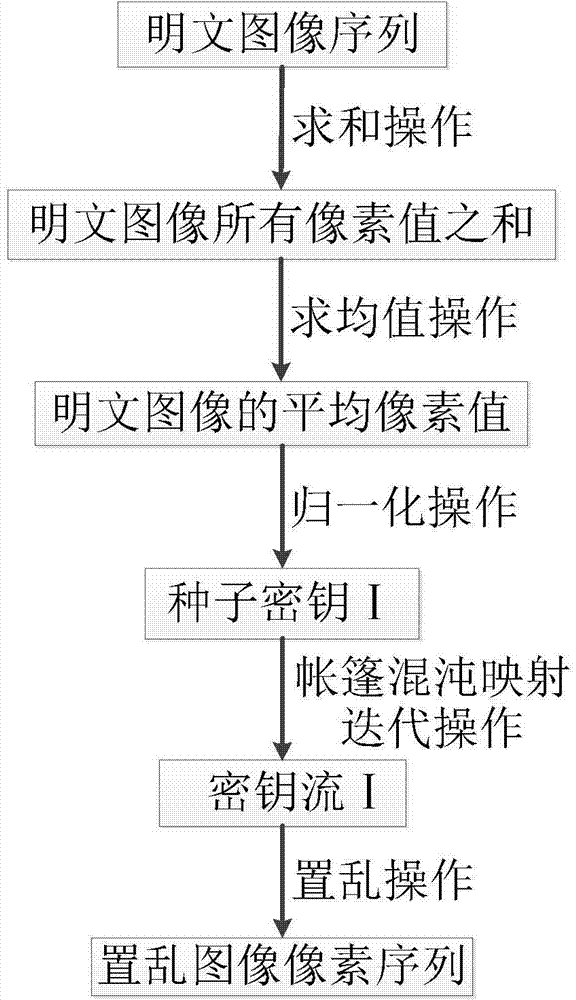
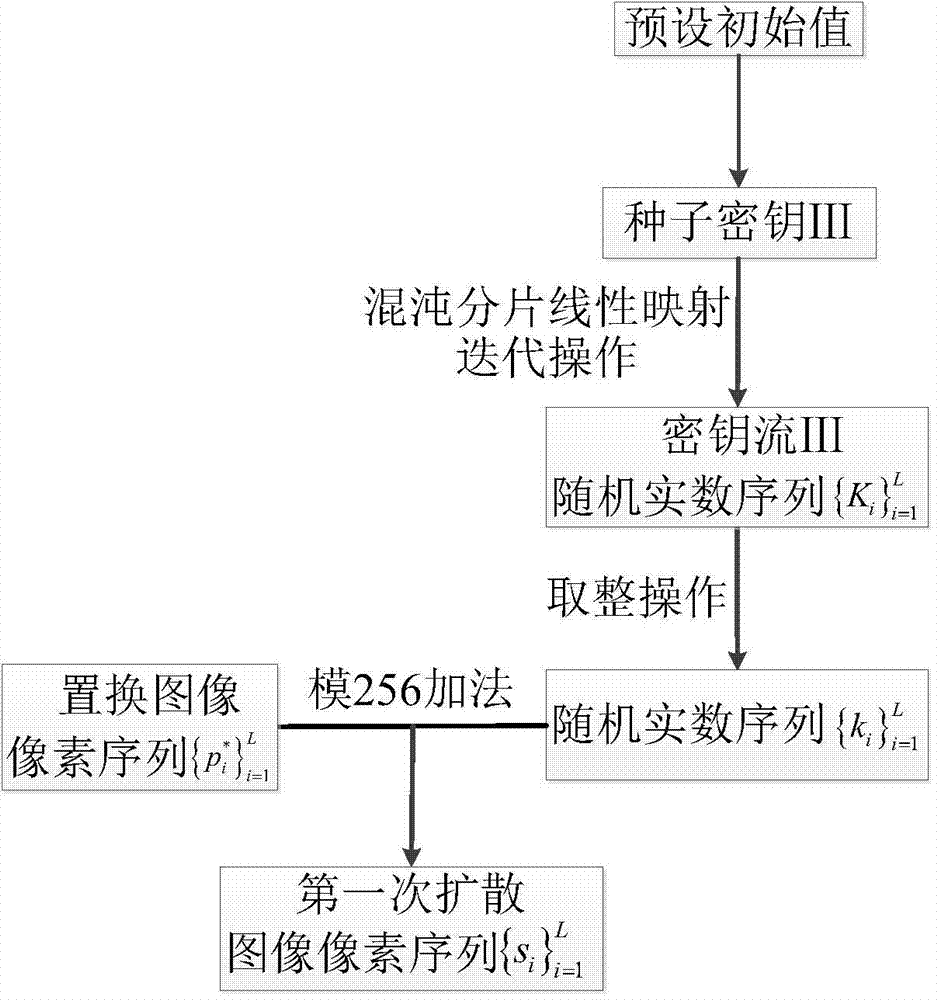
ActiveCN104751403AReduce correlationEnsure safetyImage data processing detailsPlaintextInformation processing
The invention provides a multi-chaos system based method of encrypting images related to plaintext and belongs to the field of information security. The method combining the plaintext-related scrambling technique, the multi-chaos system and a sensor model includes: scrambling plaintext images by means of the plaintext related scrambling technique based on tent chaotic mapping, subjecting the images to primary diffusion by means of chaotic piecewise linear mapping, and performing secondary diffusion by the combination of a Chen's high-dimensional hyper-chaotic system and the sensor model to finally generate ciphertext images. The algorithm structure of scrambling, diffusion and diffusion is used, relevance between the plaintext and keys is established, key space is enlarged, scrambling effect is better, diffusion degree is higher, and the ability to resist common attacks, such as exhaustive attack, statistical attach and differential attach is achieved. The method is applicable to image information processing and implementation of encryption techniques of other multimedia messages and also applicable to hardware static encryption and industrial productions, such as computer receiving or transmitting ports.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device, program, recording medium and method for robot simulation
ActiveCN101034418ACalculate cycle time quicklyLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationVirtual position
A robot simulation device for simulating an operation of a robot having a vision sensor in an off-line mode. The device includes a working-environment model setting section for arranging a sensor model, a robot model and a plurality of irregularly piled workpiece models in a virtual working environment; and an operation simulating section for allowing the sensor model and the robot model to simulate a workpiece detecting operation and a bin picking motion. The operation simulating section includes a workpiece-model image generating section for allowing the sensor model to pick up the workpiece models and generating a virtual image thereof; a workpiece-model position detecting section for identifying an objective workpiece model from the virtual image and detecting a virtual position thereof; and a robot-model operation controlling section for allowing the robot model to pick out the objective workpiece model based on the virtual position.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method for rigorous reshaping of stereo imagery with digital photogrammetric workstation
InactiveUS6064760AAccurate removalCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTerrainTriangulation
A method for rigorously reshaping a pair of overlapping digital images using a Digital Photogrammetric Workstation (DPW) is disclosed. The overlapping images are imported into the DPW as a pair of originally distorted images having an associated sensor model. The original images are triangulated to adjust sensor parameters. Orthophotos are created with a flat digital terrain matrix (DTM) to leave terrain displacements within themselves, and according to a sensor model and formula for exact projective computations. The orthophotos are aligned by rotation, and interior orientation coordinates of the equivalent vertical frame images are determined. The orthophotos are imported as a pair of overlapping equivalent vertical frame images according to the interior orientation coordinates. A digital terrain model is generated in the DPW using the overlapping equivalent vertical frame images. Another orthophoto is produced using the digital terrain model to remove the measured terrain displacements. In an alternative embodiment, the equivalent vertical frame images are aligned by using the classical pair-wise rectification method or by separately rotating each image without aligning the orthophotos by rotation during their creation. In each embodiment, the sensor model of the original distorted images is dissociated from the orthophotos for subsequently greater distribution and usage of the stereo imagery.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES CORPS OF ENGINEERS AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF
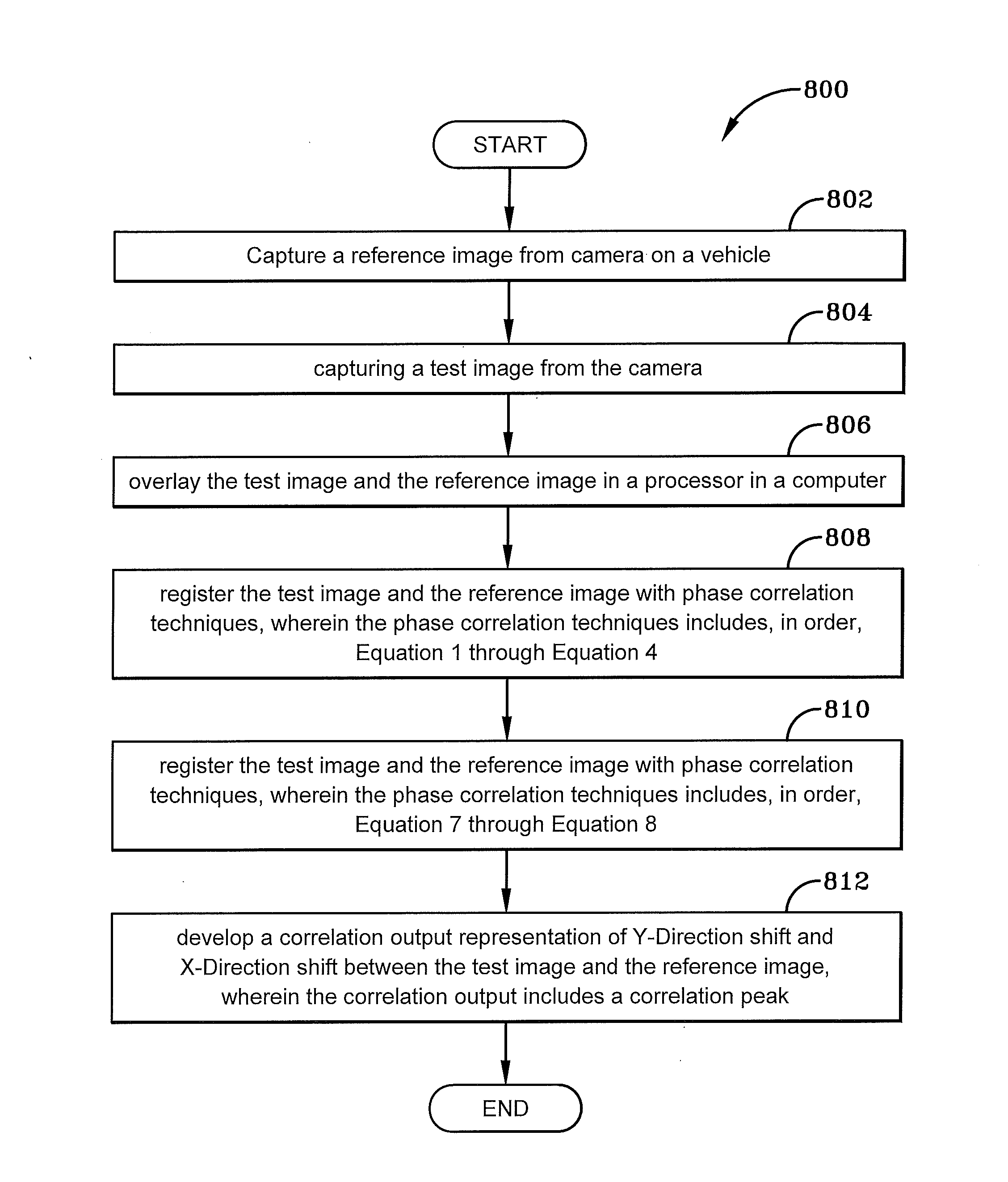
Enhanced phase correlation for image registration
An image registration system and method for matching images having fundamentally different characteristics. One exemplary feature of the system and method includes the use of an enhanced phase correlation method combined with a coarse sensor model to hypothesize and match a custom match metric to determine a best solution. The system and method may be operated on a non-transitory computer-readable medium storing a plurality of instructions which when executed by one or more processors causes the one or more processors to perform the image registration method utilizing the enhanced phase correlation.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
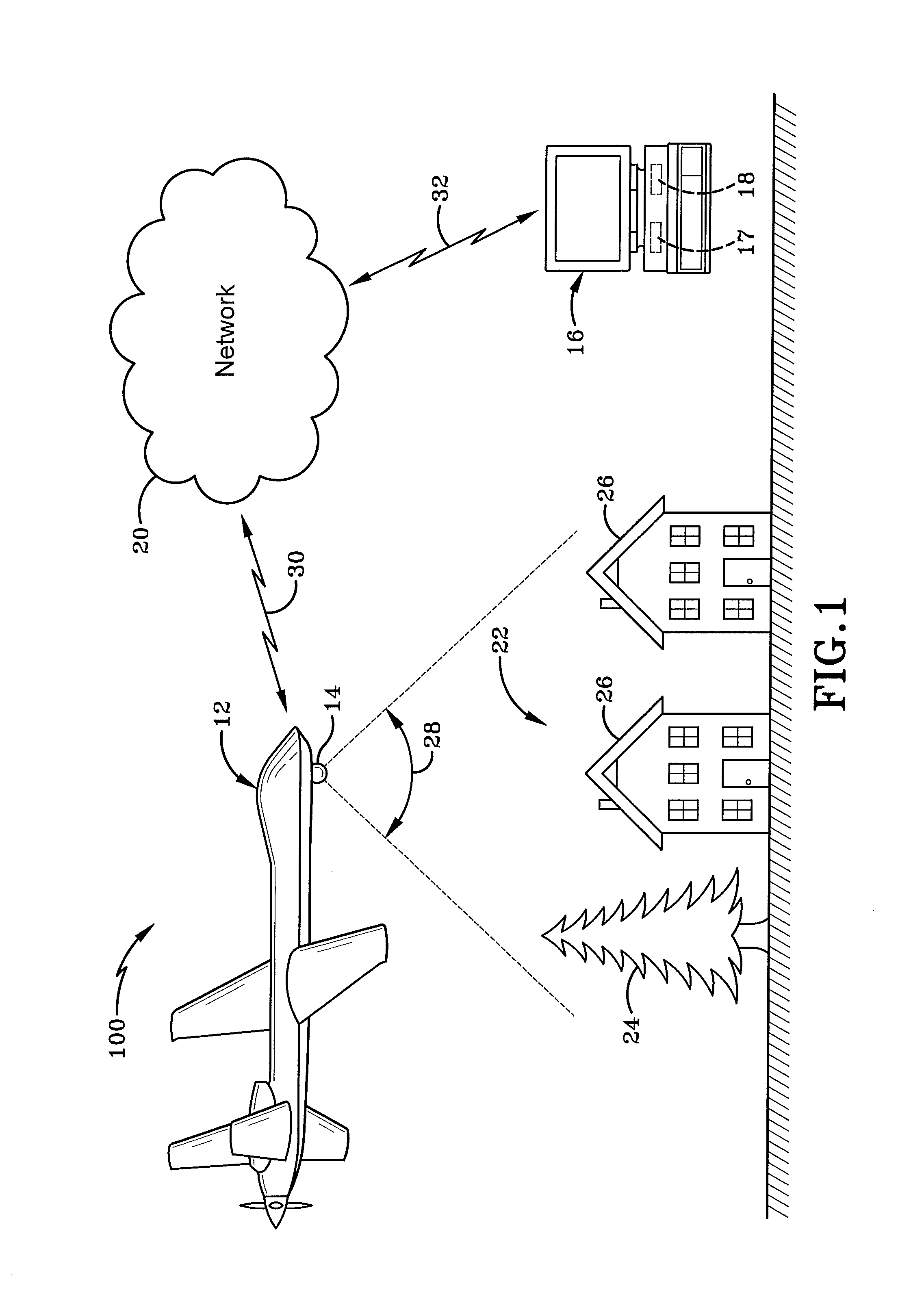
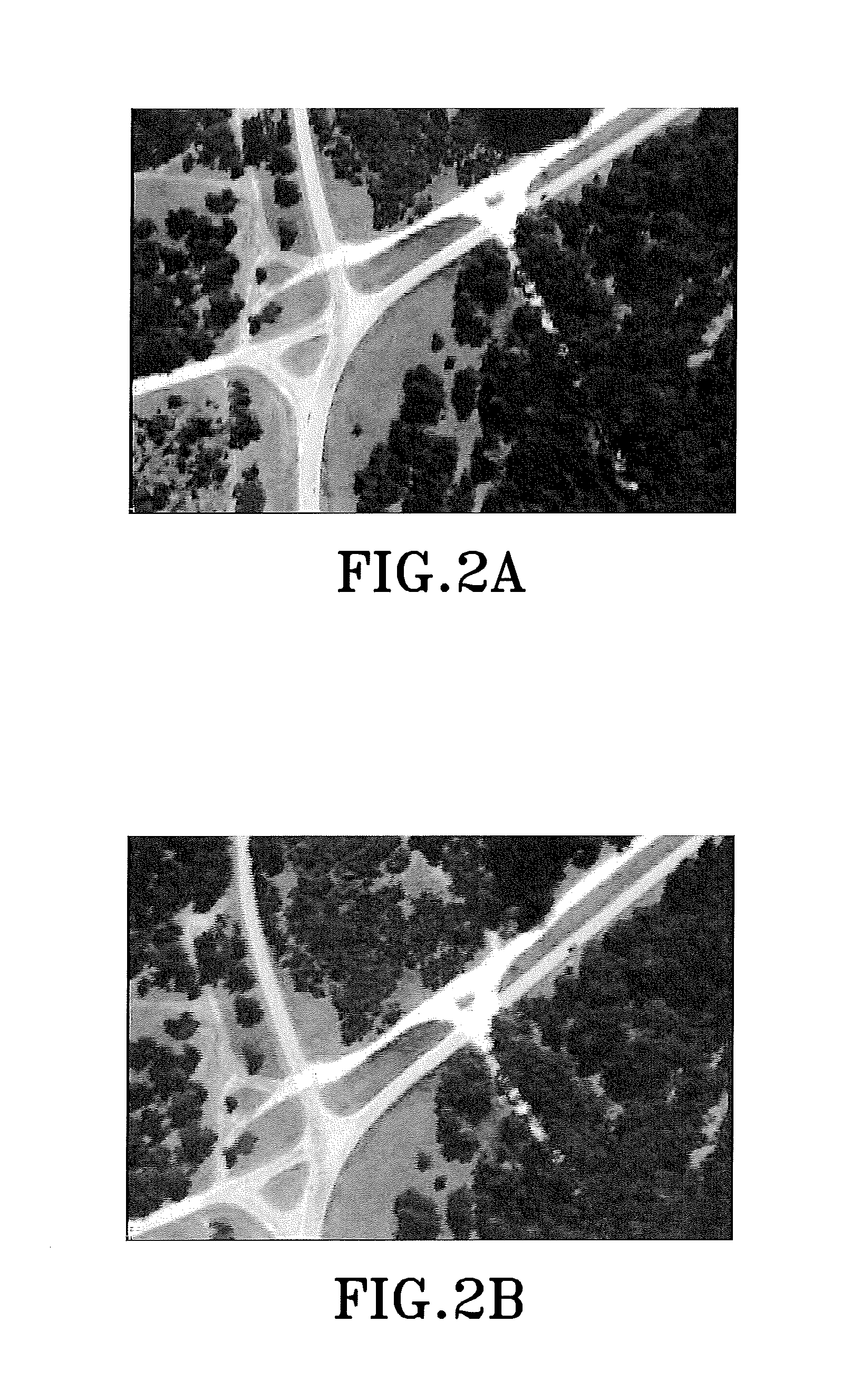
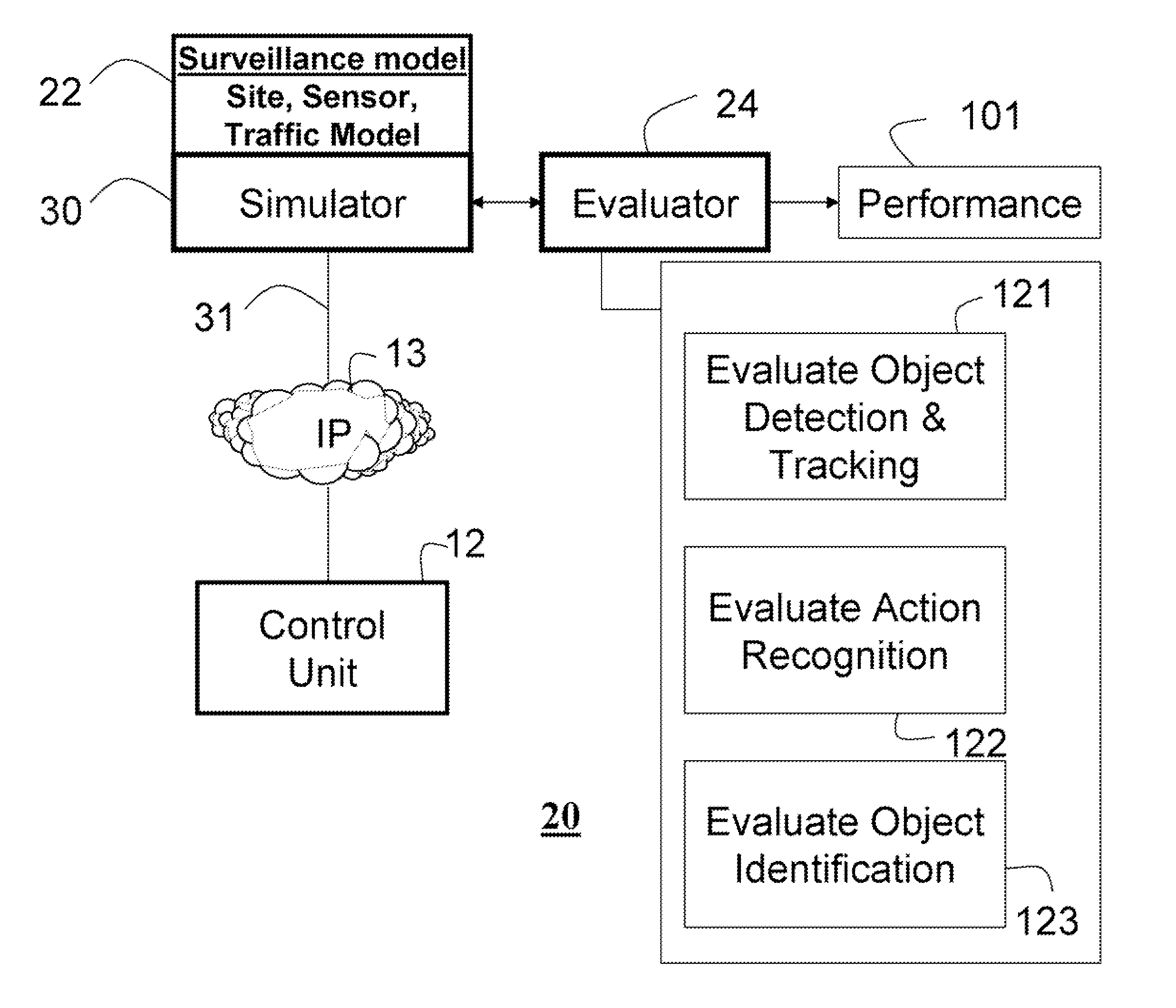
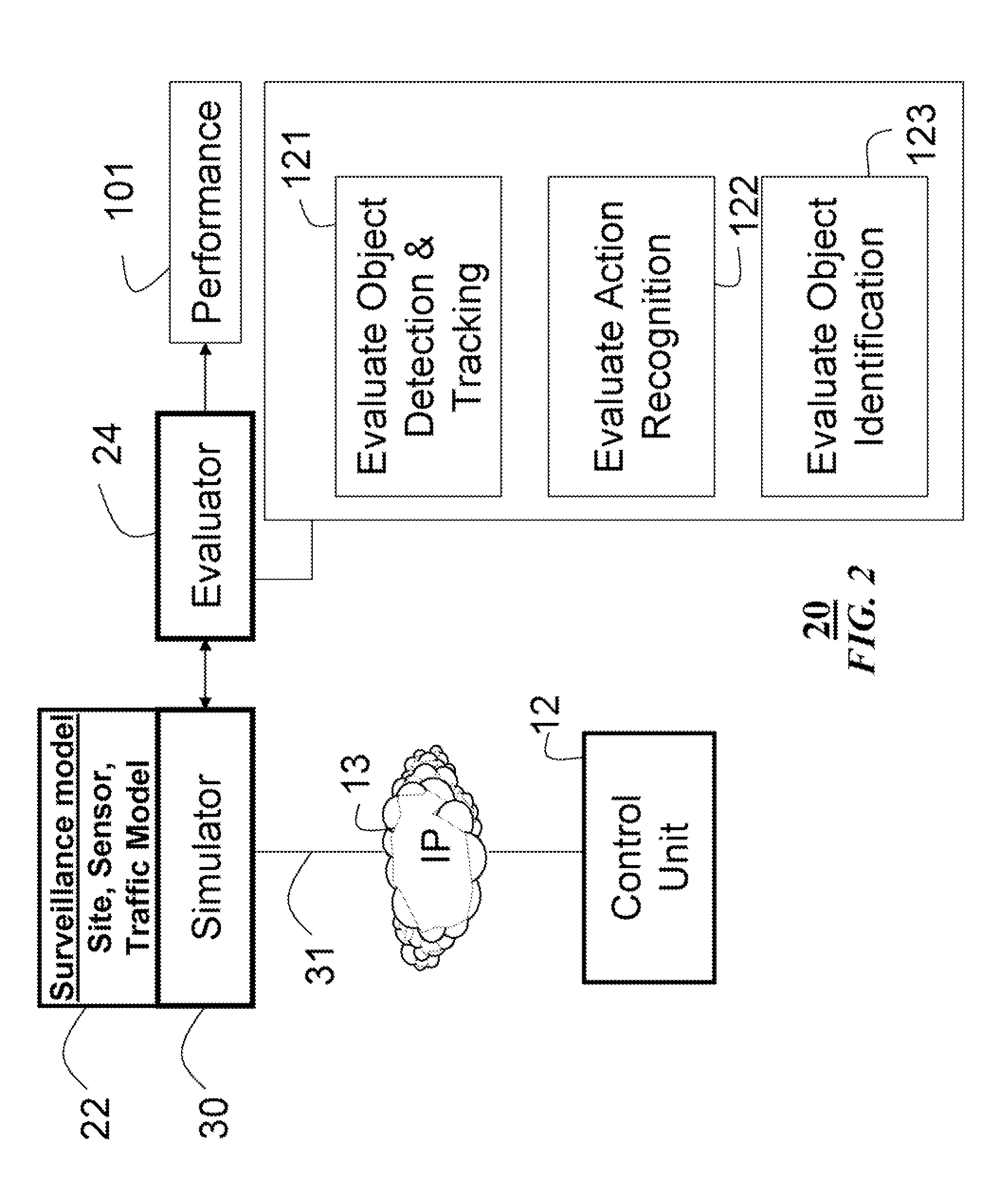
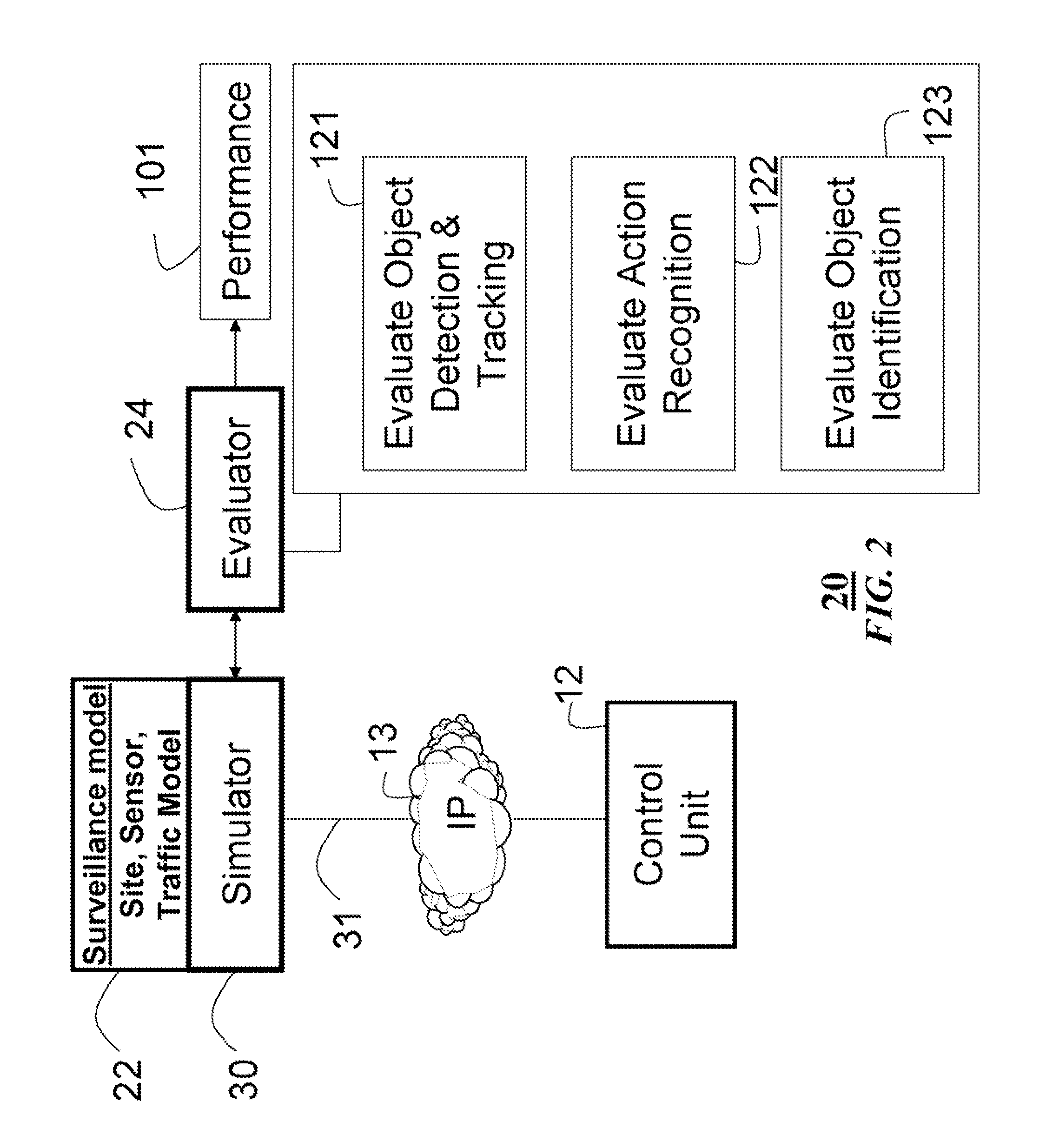
System and method for measuring performances of surveillance systems
A computer implemented method measures a performance of surveillance system. A site model, a sensor model and a traffic model are selected respectively from a set of site models, a set of sensor models, and a set of traffic models to form a surveillance model. Based on the surveillance model surveillance signals are generated. Performance of the surveillance system is evaluated according to qualitative surveillance goals and the surveillance signals to determine a value of a quantitative performance metric of the surveillance system.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and system for charge sensing with variable gain, offset compensation, and demodulation
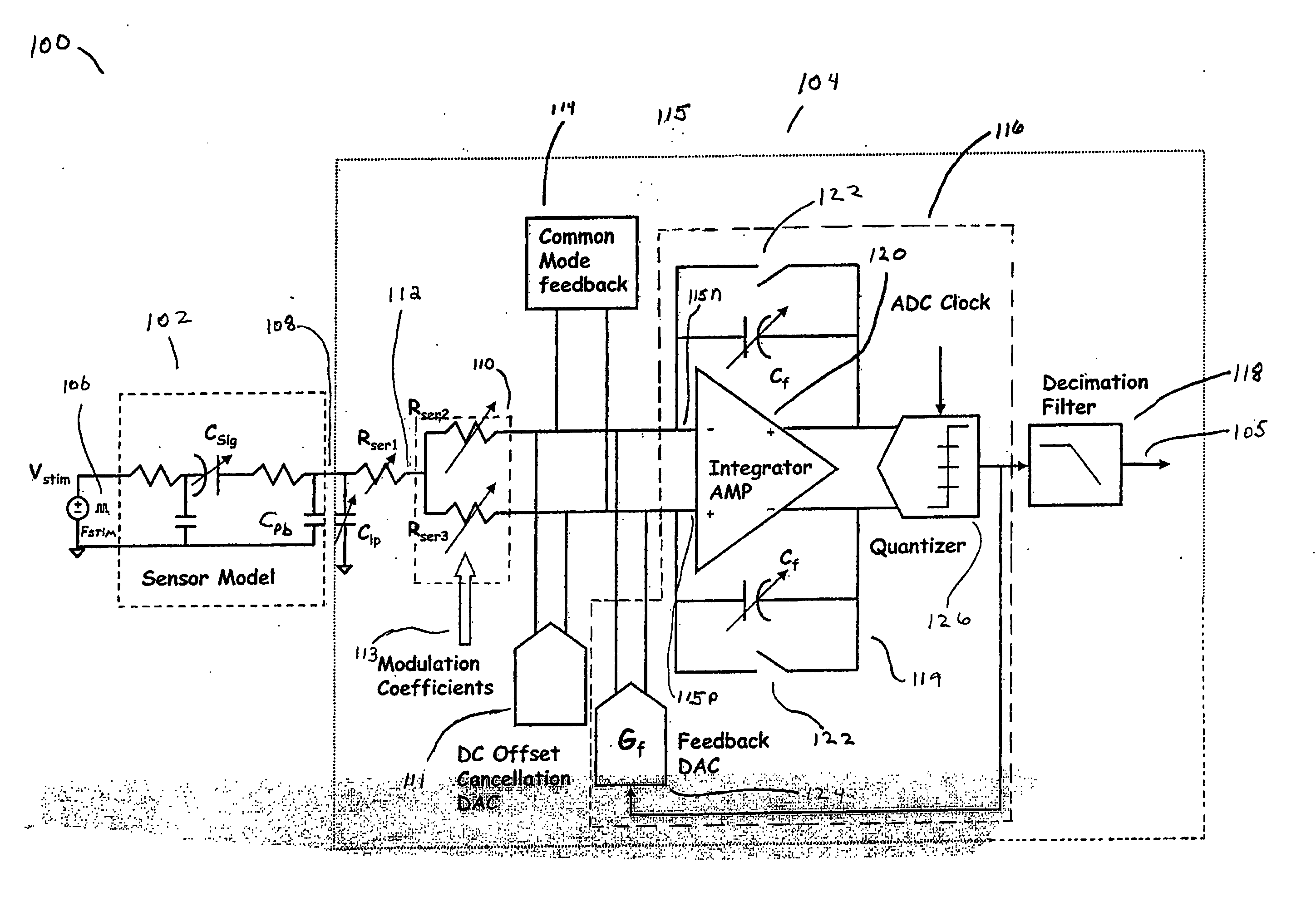
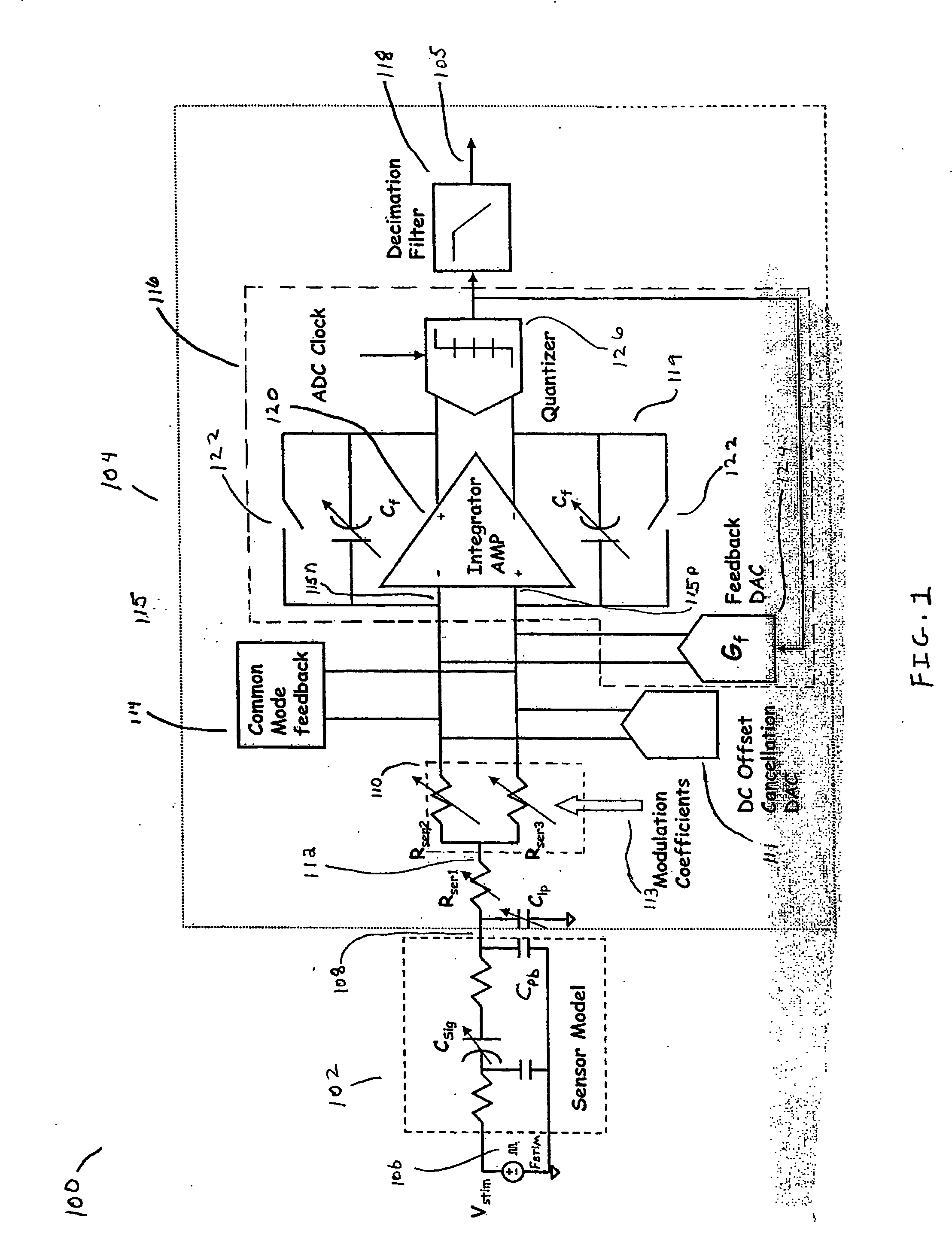
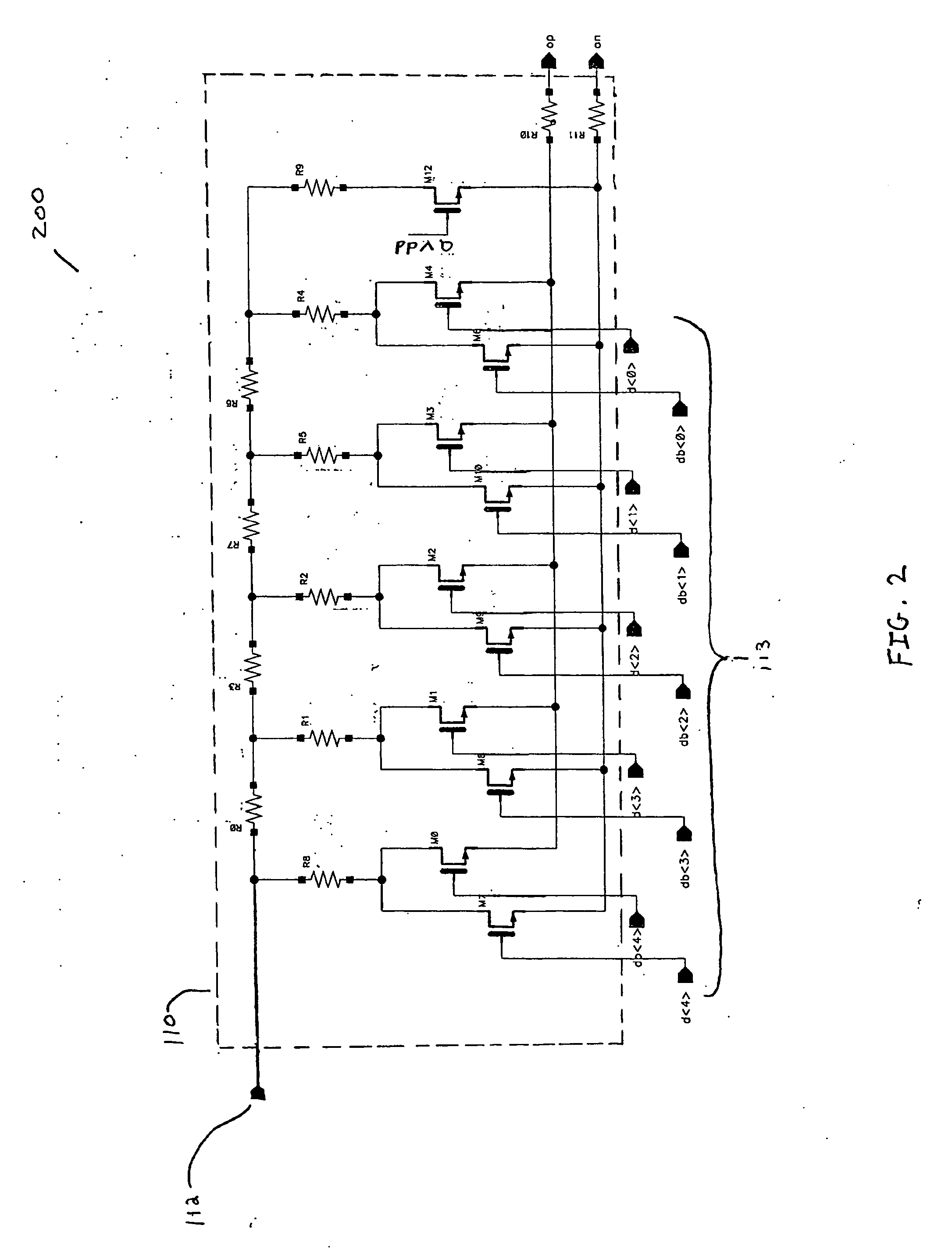
InactiveUS20050238123A1Acceleration measurementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsOffset cancellationEngineering
Provided are a method and system for digitizing a sensor model output signal. The system includes a filter, a demodulator coupled to the filter, a DC offset cancellation mechanism coupled to the demodulator, and an analog to digital converter (ADC). The ADC is directly coupled to the demodulator and the DC offset cancellation mechanism.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Flow sensor signal conversion
InactiveUS7043374B2Facilitates accurately determining flow rateVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsVolume flow proportion measurementComputer scienceSensor model
A method of obtaining at least one representation of a characteristic function of a sensor from a test fluid during calibration of the sensor according to a sensor model having a transfer function operating on flow rate, at least one sensor property and at least one fluid property and employing the at least one representation of the characteristic function to determine flow rates through the sensor during operation with an arbitrary fluid.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT
System and Method for Measuring Performances of Surveillance Systems
InactiveUS20080126031A1Computation using non-denominational number representationAnimationSite modelTraffic model
A computer implemented method measures a performance of surveillance system. A site model, a sensor model and a traffic model are selected respectively from a set of site models, a set of sensor models, and a set of traffic models to form a surveillance model. Based on the surveillance model surveillance signals are generated. Performance of the surveillance system is evaluated according to qualitative surveillance goals and the surveillance signals to determine a value of a quantitative performance metric of the surveillance system.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
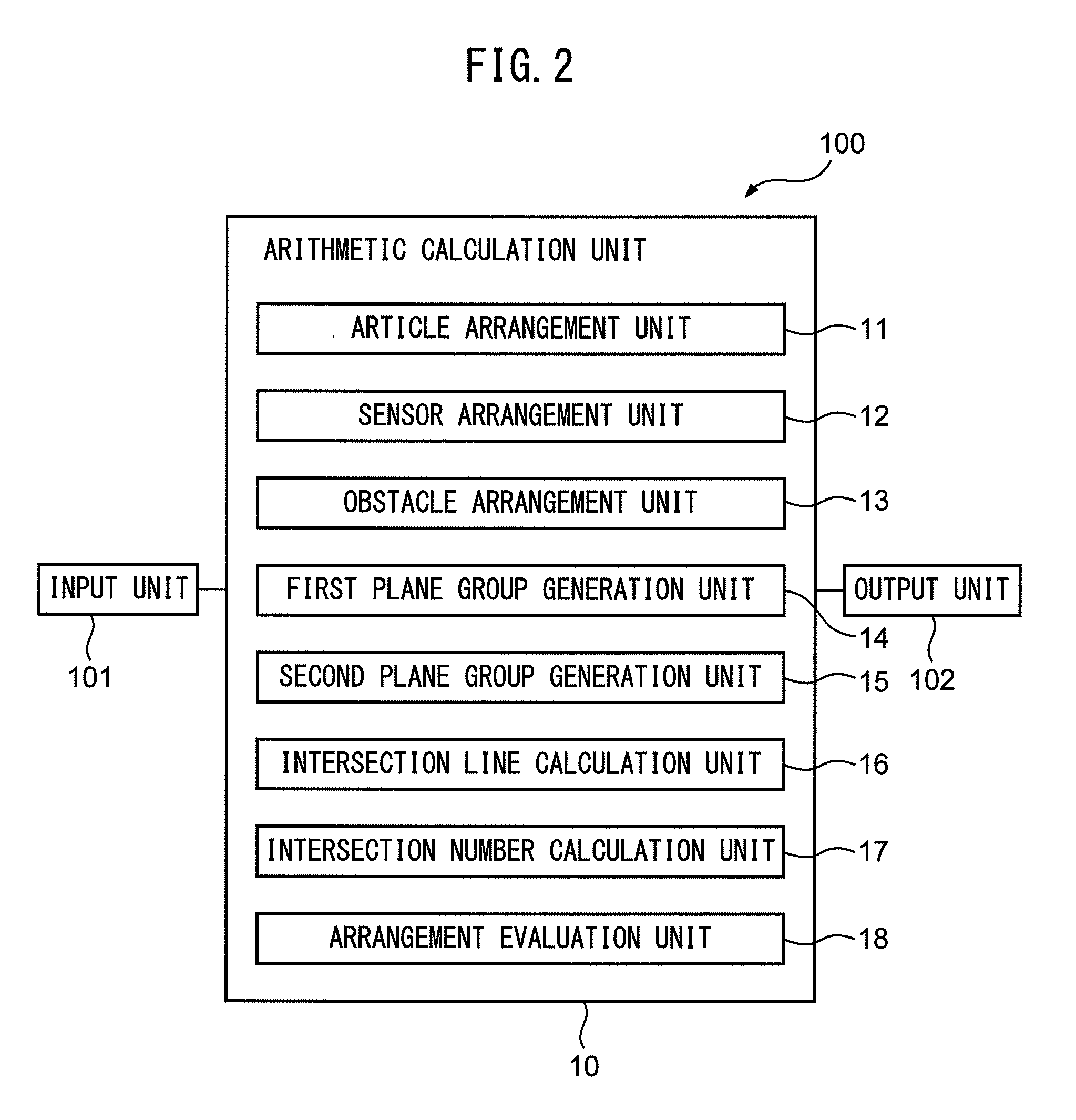
Arrangement evaluation apparatus for evaluating arrangement position of range sensor
An arrangement evaluation apparatus of a range sensor comprises an article arrangement unit which arranges an article model, a sensor arrangement unit which arranges a sensor model, a first plane group generation unit which generates a plurality of first planes including division lines obtained by dividing a virtual plane, a second plane group generation unit which generates a plurality of second planes by boundary surfaces of stripe pattern light projected from the projector model, an intersection line calculation unit which calculates intersection lines between the first planes and the second planes, and an intersection number calculation unit which counts the number of intersection points between the intersection lines and the surface of the article model.
Owner:FANUC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com