Patents
Literature
566 results about "Phase correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
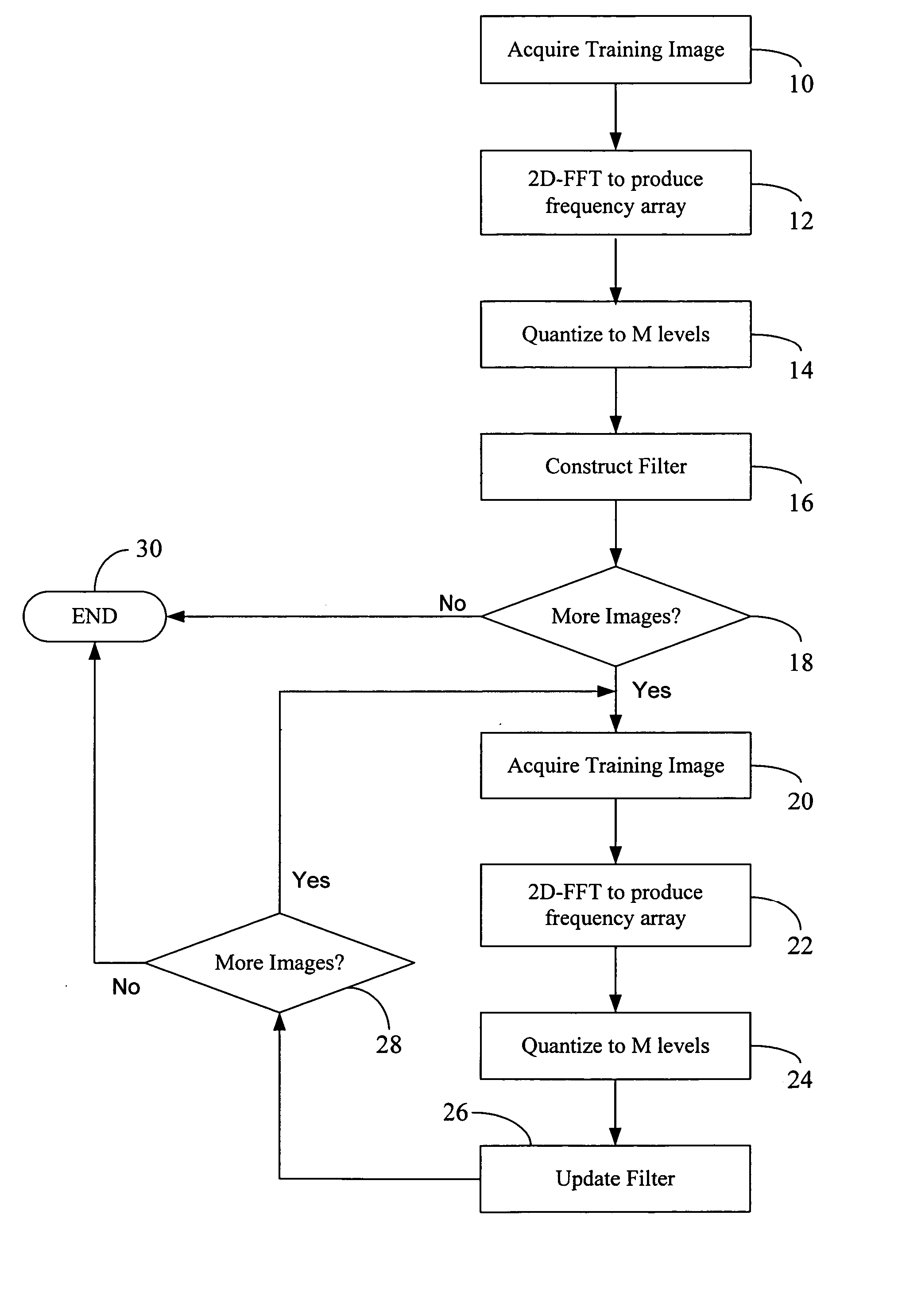
Phase correlation is an approach to estimate the relative translative offset between two similar images (digital image correlation) or other data sets. It is commonly used in image registration and relies on a frequency-domain representation of the data, usually calculated by fast Fourier transforms. The term is applied particularly to a subset of cross-correlation techniques that isolate the phase information from the Fourier-space representation of the cross-correlogram.
Apparatus, method and system for performing phase-resolved optical frequency domain imaging
ActiveUS20060279742A1Reduce the impactWeakening rangePhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsPhase correlationTime changes
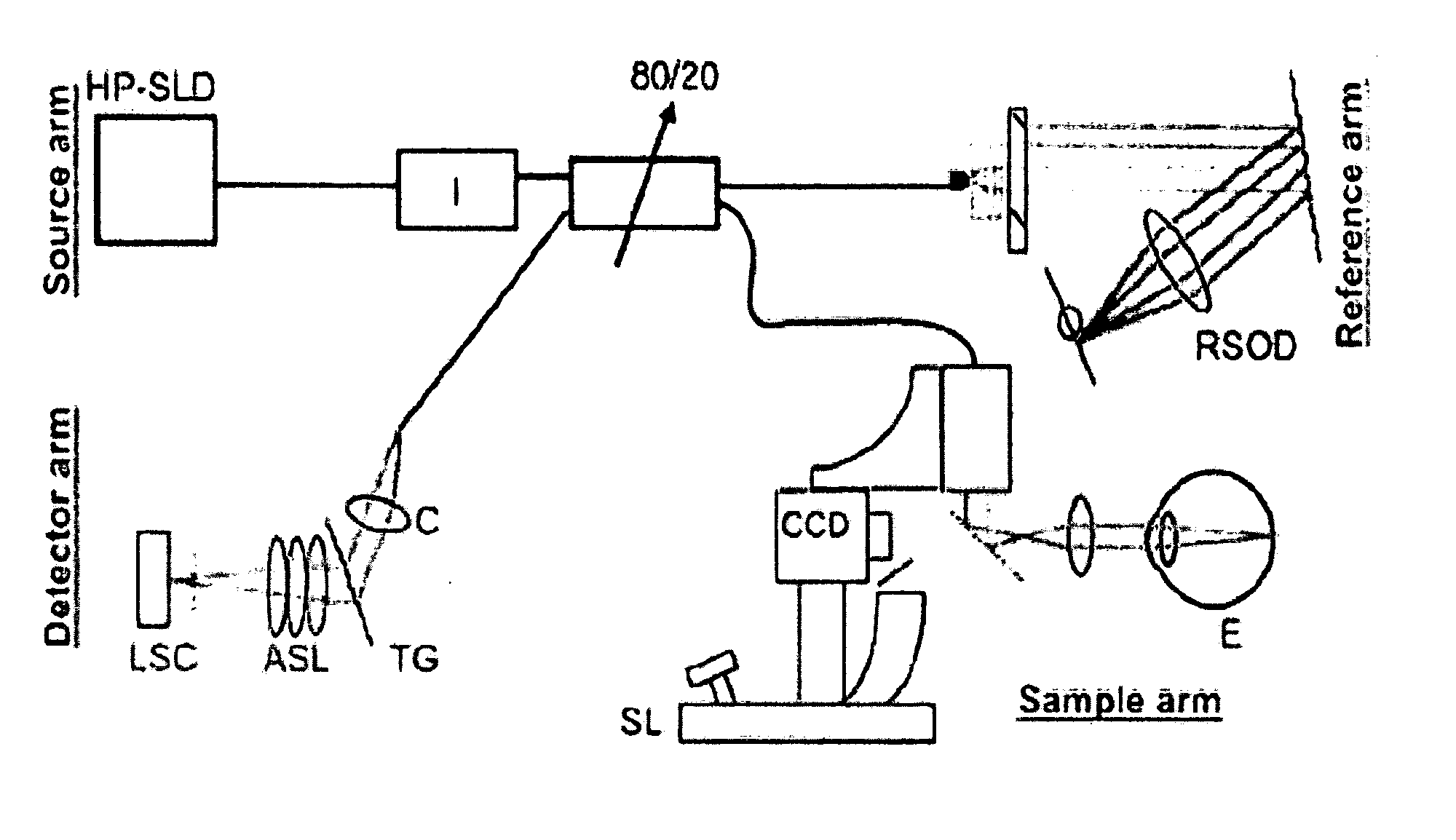
Apparatus, system and method are provided which utilize signals received from a reference and a sample. In particular, a radiation is provided which includes at least one first electromagnetic radiation directed to the sample and at least one second electromagnetic radiation directed to the reference. A frequency of the radiation varies over time. An interference can be detected between at least one third radiation associated with the first radiation and at least one fourth radiation associated with the second radiation. It is possible to obtain a particular signal associated with at least one phase of at least one frequency component of the interference, and compare the particular signal to at least one particular information. Further, it is possible to receive at least one portion of the radiation and provide a further radiation, such that the particular signal can be calibrated based on the further signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
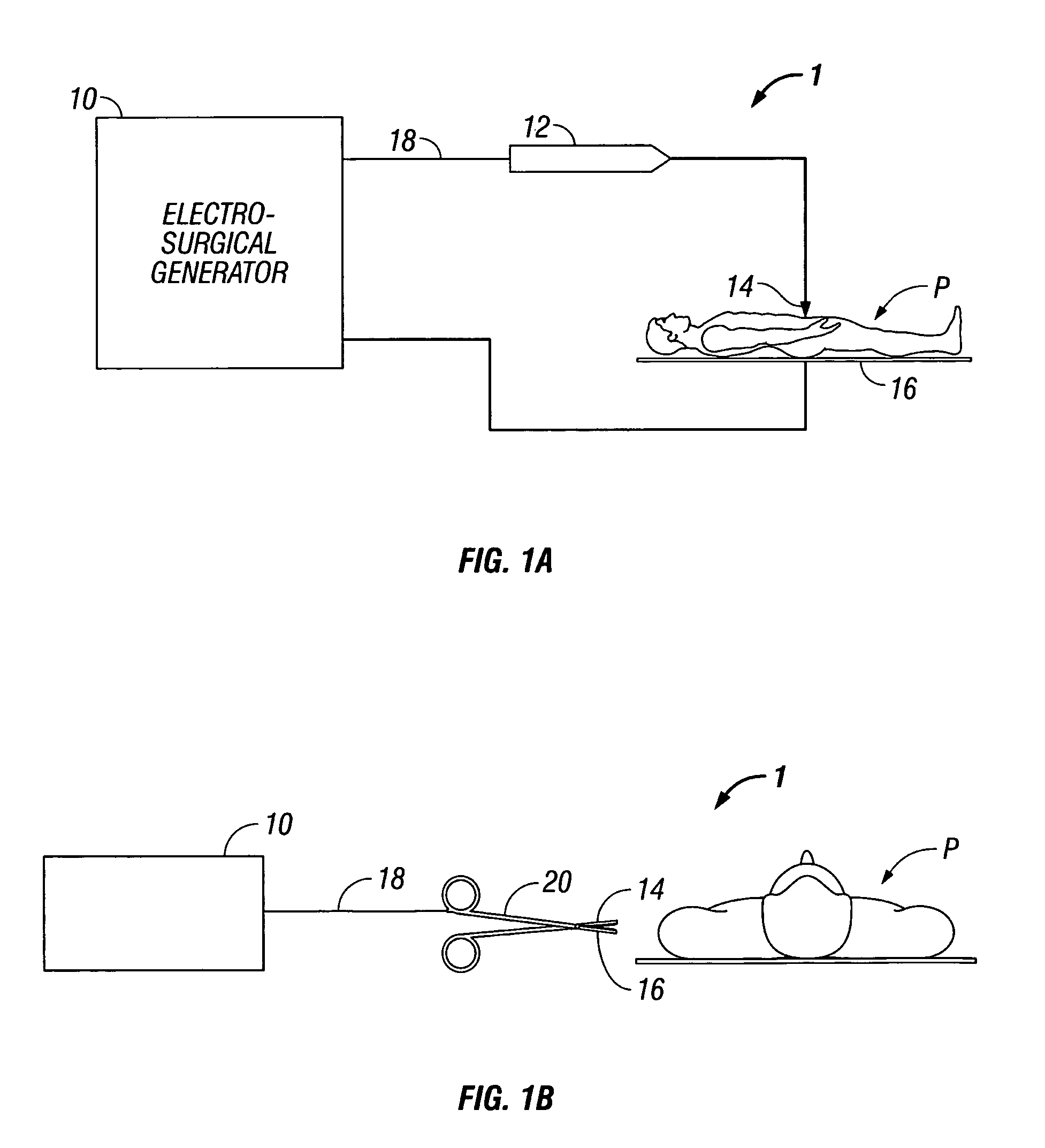
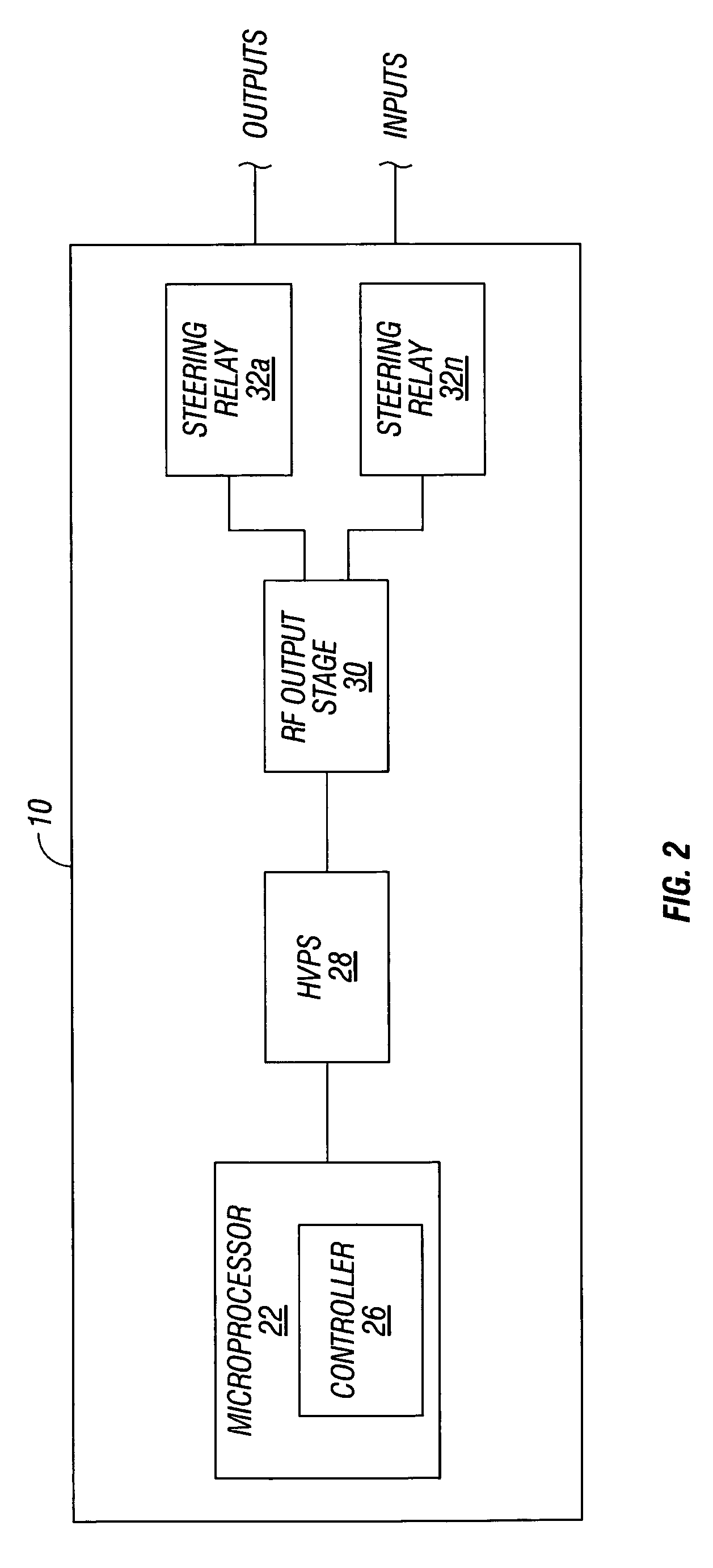
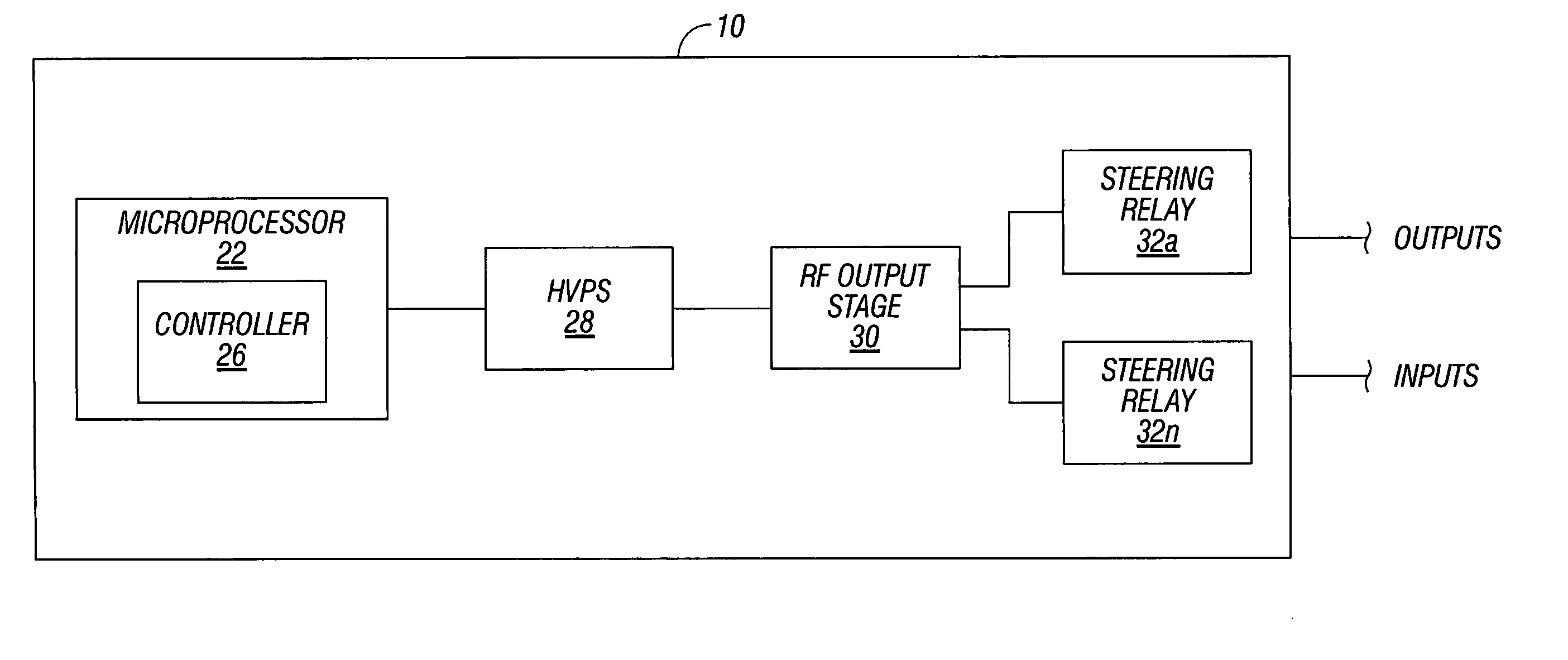
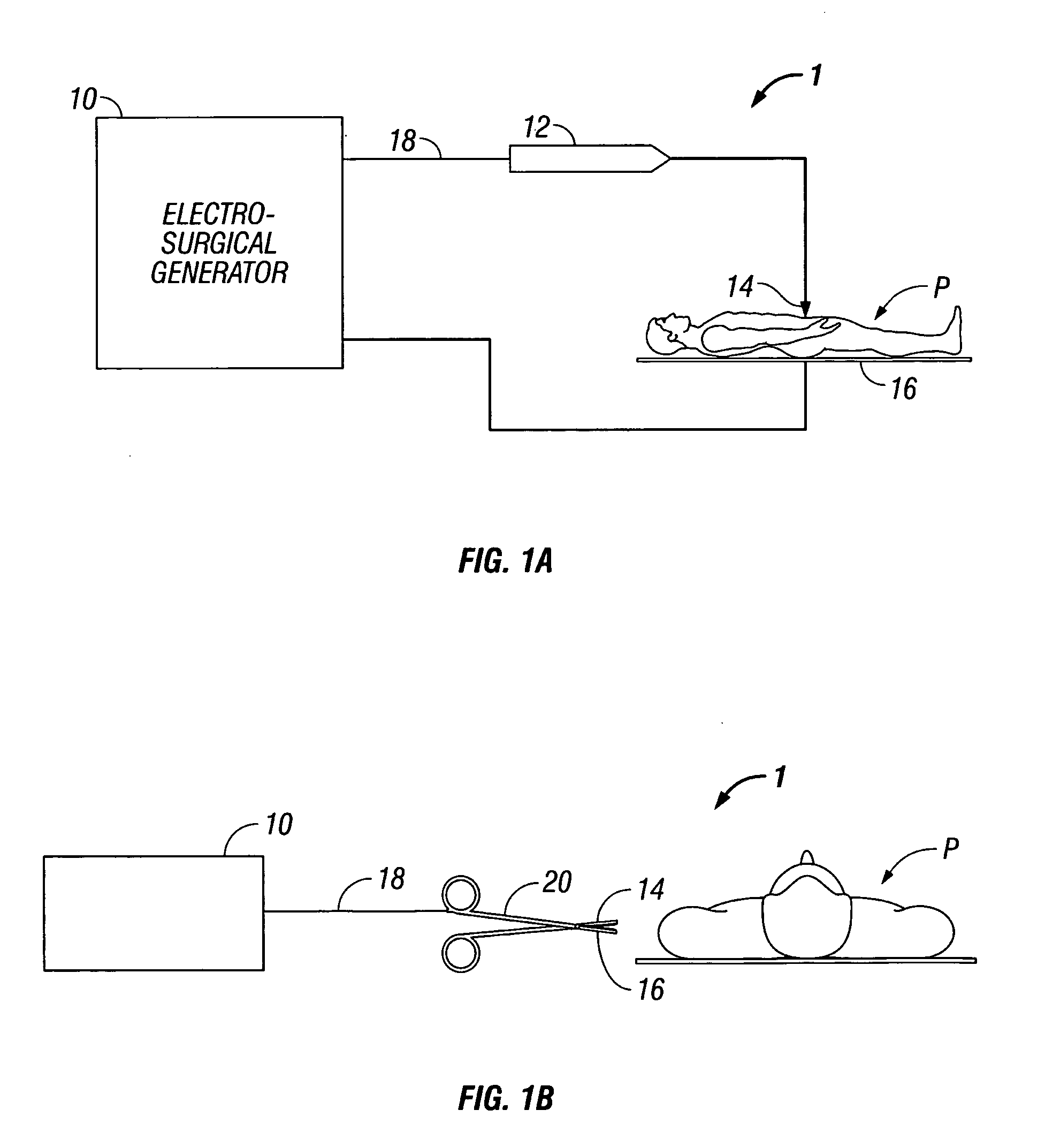
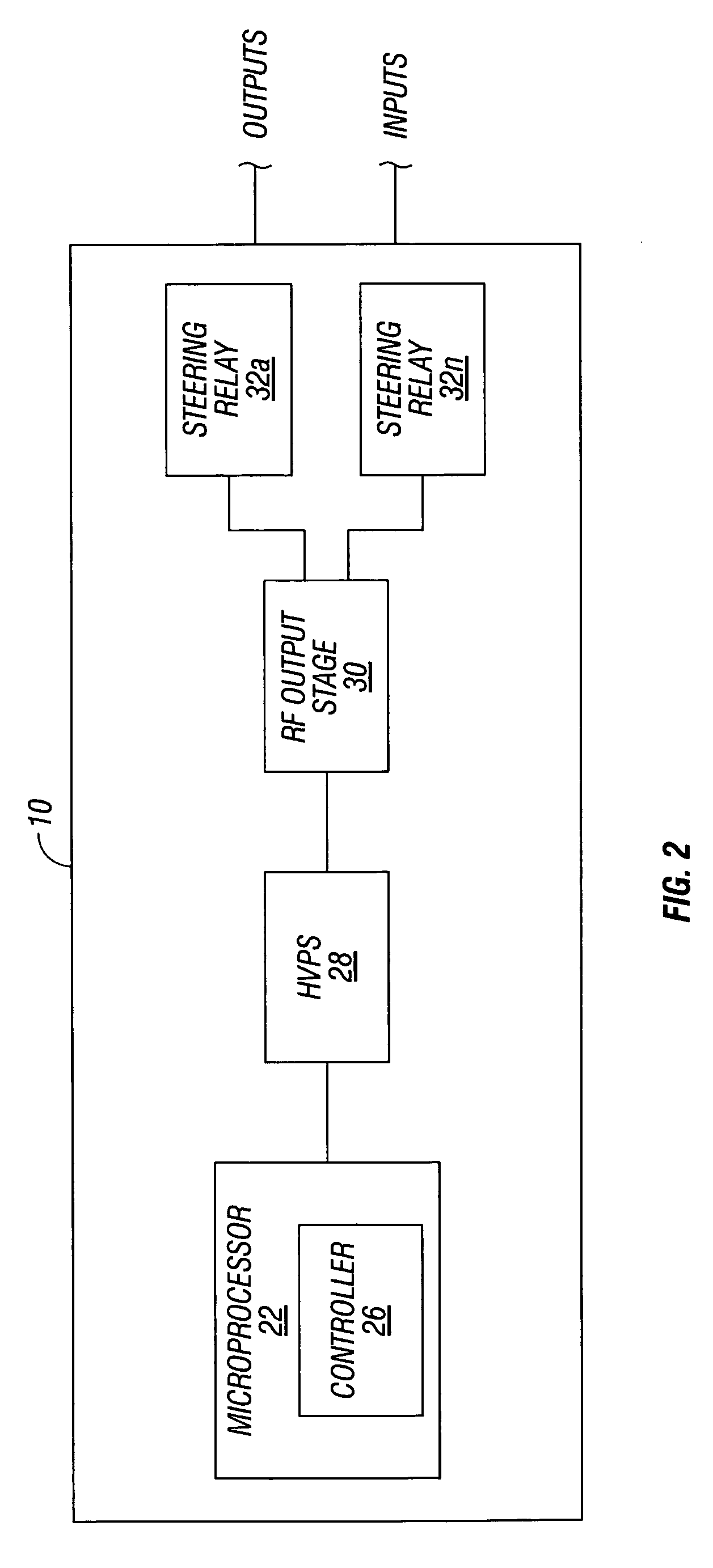
Dual synchro-resonant electrosurgical apparatus with bi-directional magnetic coupling
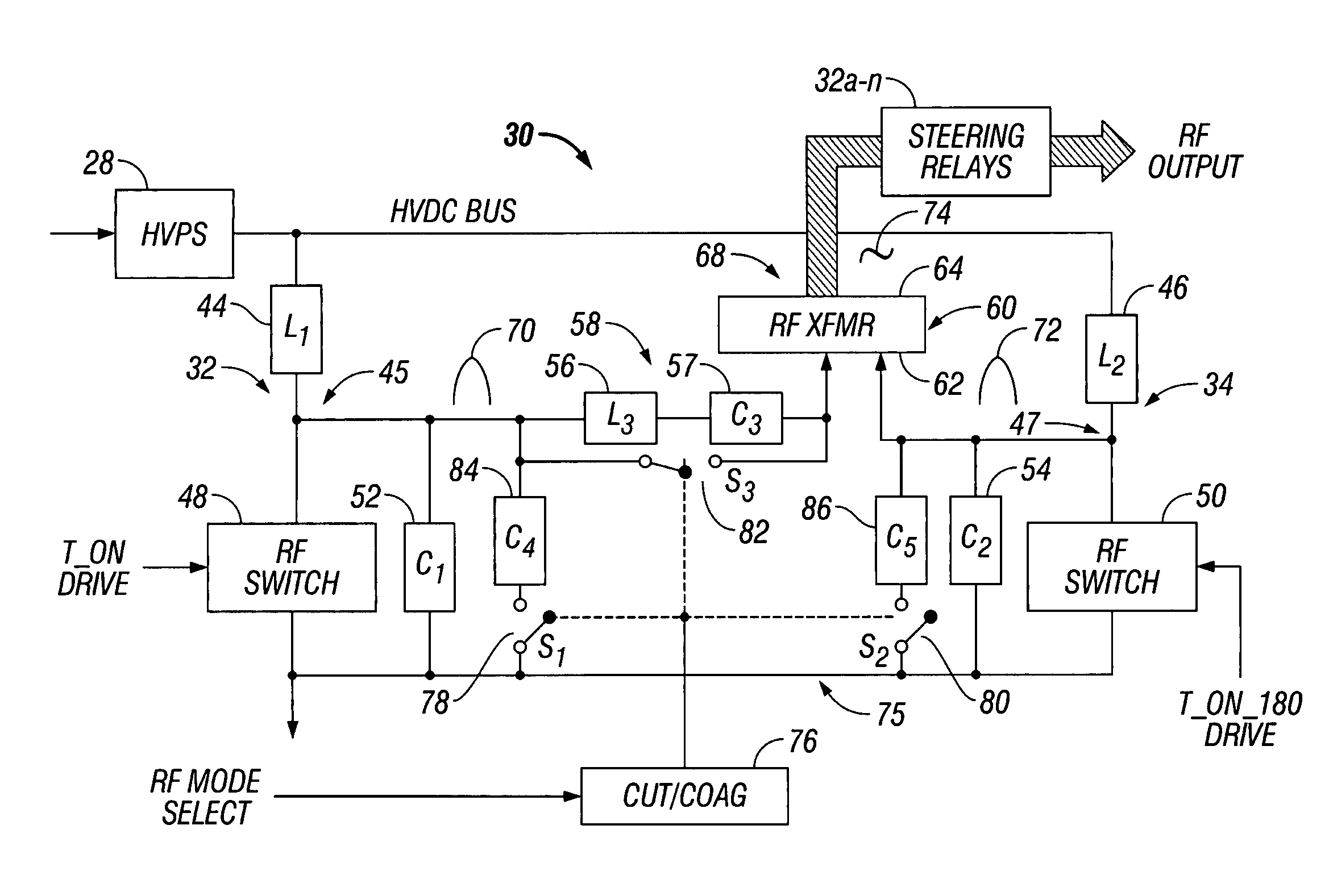
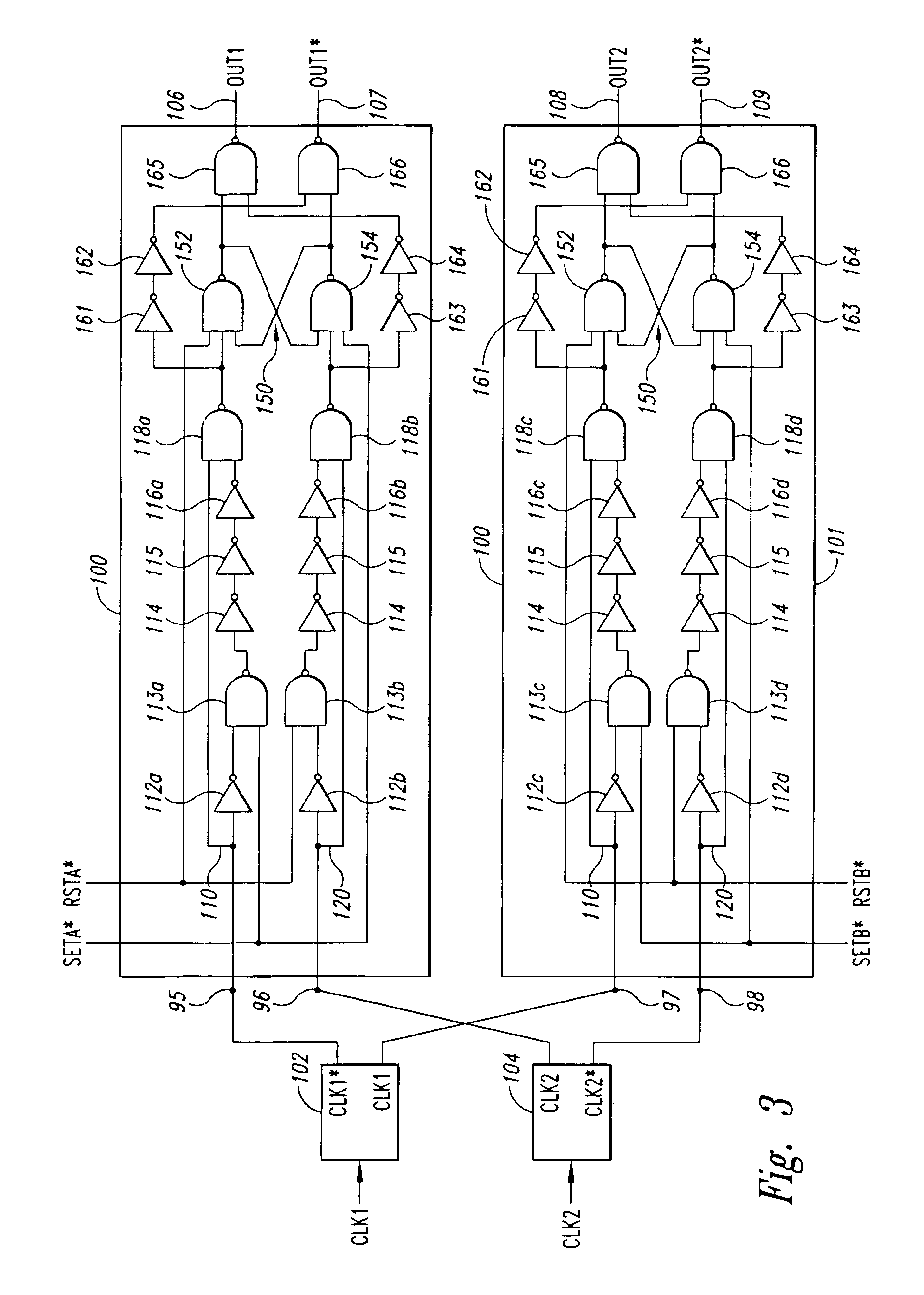
ActiveUS7513896B2Controlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingPhase correlationTransformer
An electrosurgical generator is disclosed, which includes an RF output stage connected to a DC power supply and first and second connections. The first connection includes a first switching component and a first parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit. The second connection includes a second switching components and a second parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit. The first and second switching components are configured to open and close at a predetermined frequency based on a phase-correlated dual drive signal emitted by a driver and are in a 180 degree out-of-phase relationship. The first parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit is further configured to produce a first half-sinusoidal waveform and the second parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit is configured to produce a second half-sin half-sinusoidal waveform. The RF output stage further includes a transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding and a series inductor-capacitor resonant circuit, which are configured to generate a sinusoidal waveform.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
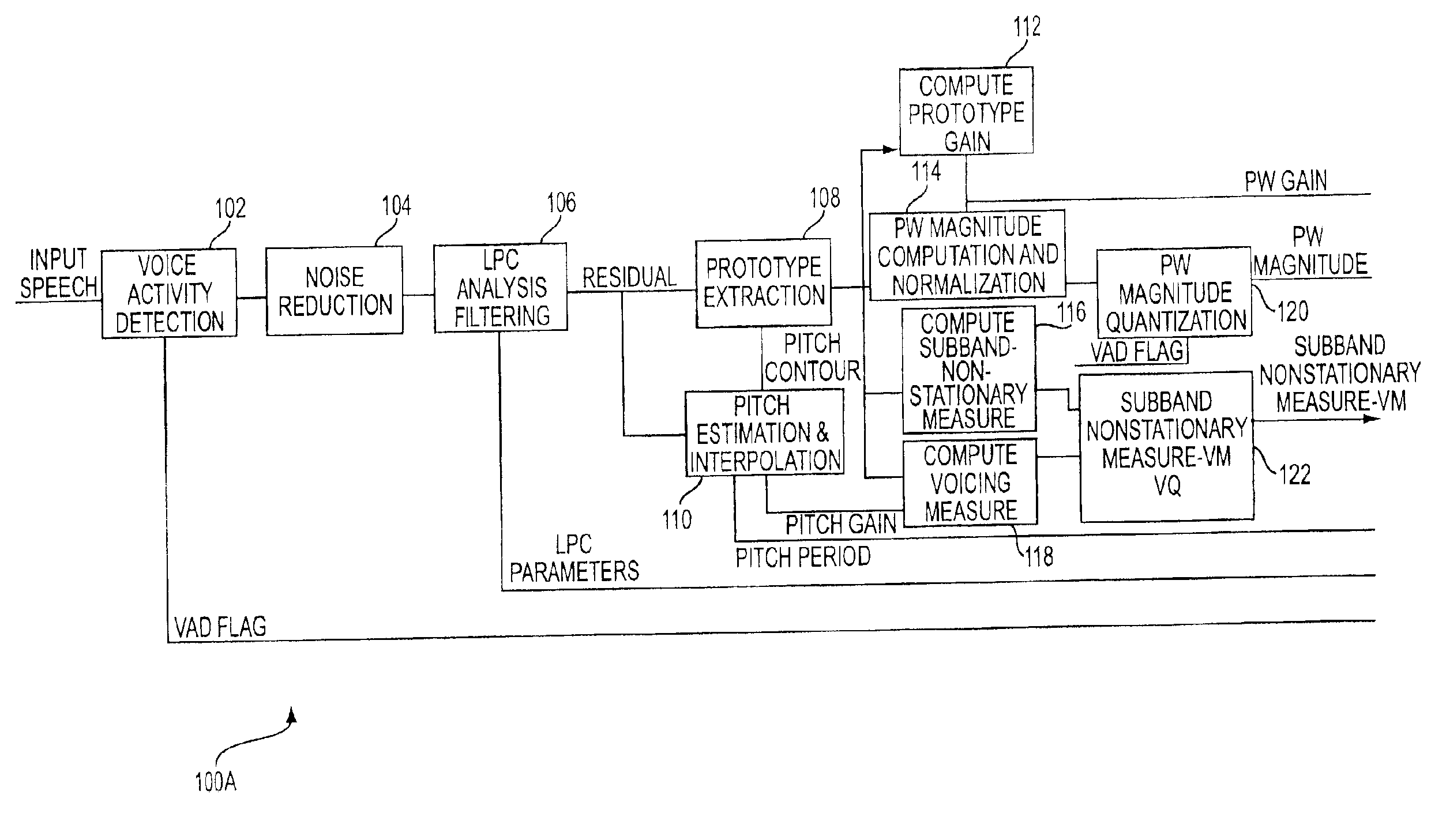
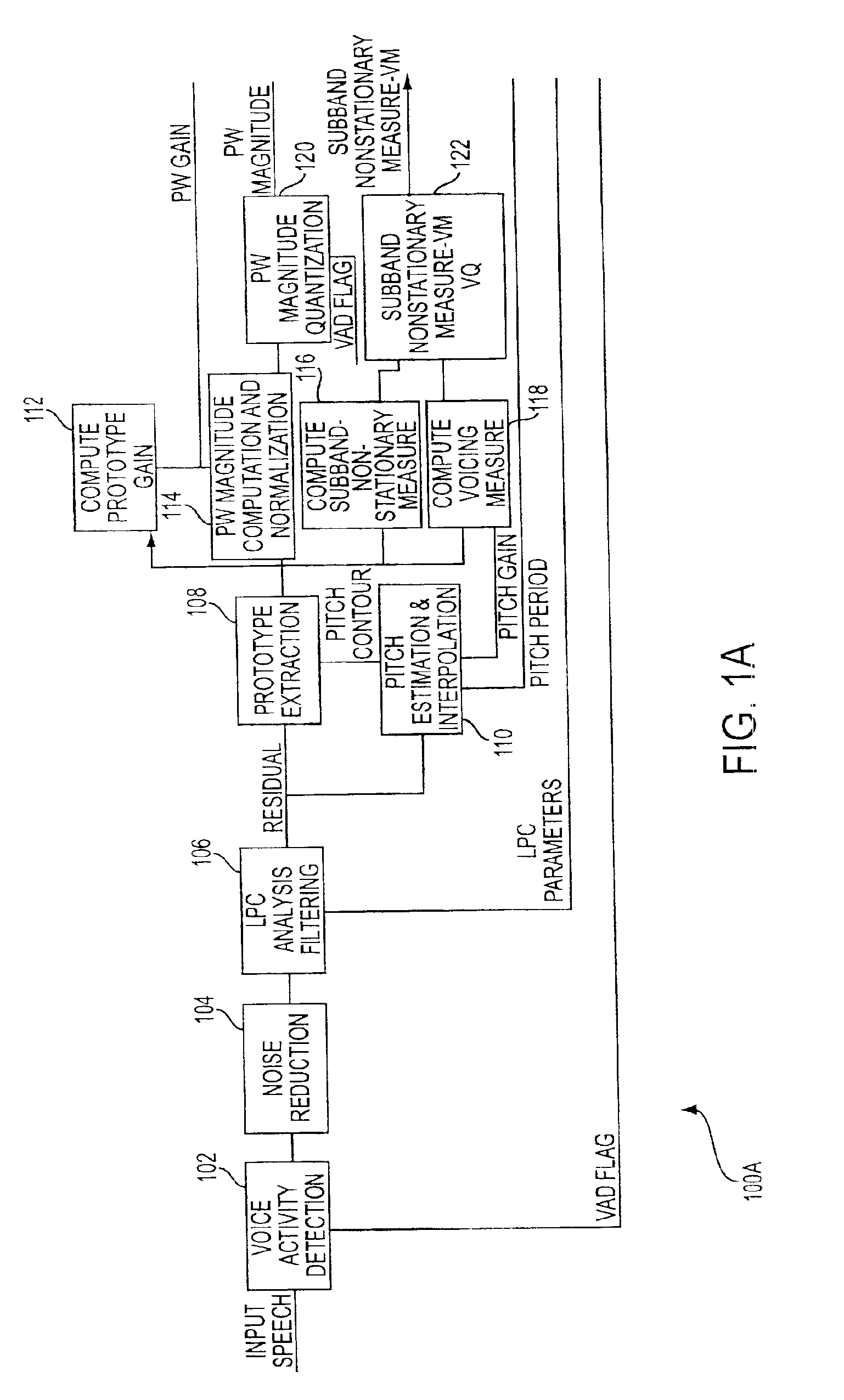
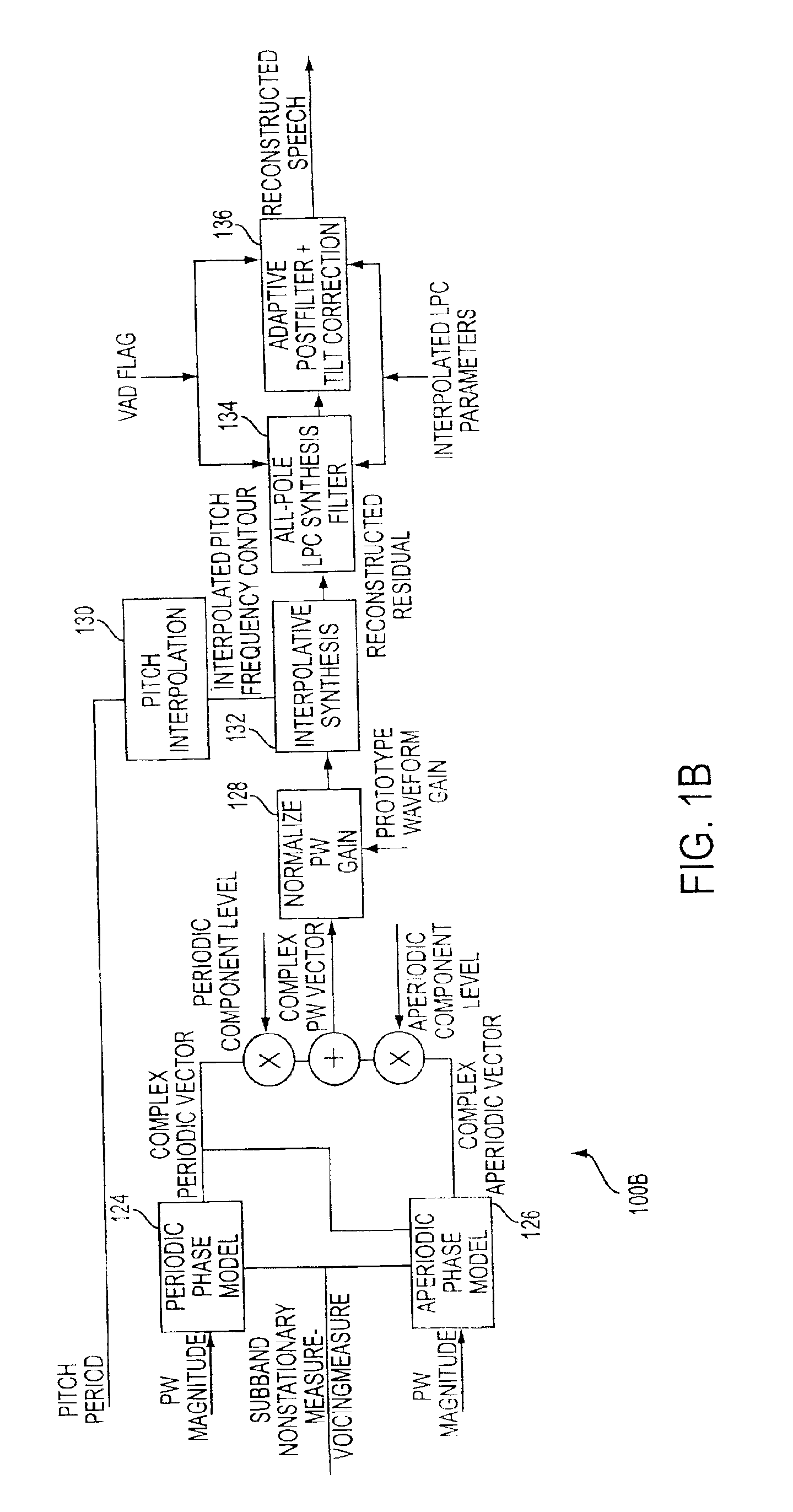
Prototype waveform phase modeling for a frequency domain interpolative speech codec system
A system and method is provided that employs a frequency domain interpolative CODEC system for low bit rate coding of speech which comprises a linear prediction (LP) front end adapted to process an input signal that provides LP parameters which are quantized and encoded over predetermined intervals and used to compute a LP residual signal. An open loop pitch estimator adapted to process the LP residual signal, a pitch quantizer, and a pitch interpolator and provide a pitch contour within the predetermined intervals is also provided. Also provided is a signal processor responsive to the LP residual signal and the pitch contour and adapted to perform the following: provide a voicing measure, where the voicing measure characterizes a degree of voicing of the input speech signal and is derived from several input parameters that are correlated to degrees of periodicity of the signal over the predetermined intervals; extract a prototype waveform (PW) from the LP residual and the open loop pitch contour for a number of equal sub-intervals within the predetermined intervals; normalize the PW by a gain value of the PW; encode a magnitude of the PW; and separate stationary and nonstationary components of the PW using a low complexity alignment process and a filtering process that introduce no delay. The ratio of the energy of the nonstationary component of the PW to that of the stationary component of the PW is averaged across 5 subbands to compute the nonstationarity measure as a frequency dependent vector entity. A measure of the degree of voicing of the residual is also computed using openloop pitchgain, pitch variance, relative signal power, PW correlation and PW nonstationarity in low frequency subbands. The nonstationarity measure and voicing measure are encoded using a 6-bit spectrally weighted vector quantization scheme using a codebook partitioned based on a voiced / unvoiced decision. At the decoder, a stationary component of PW is reconstructed as a weighted combination of the previous PW phase vector, a random phase perturbation and a fixed phase vector obtained from a voiced pitch pulse.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
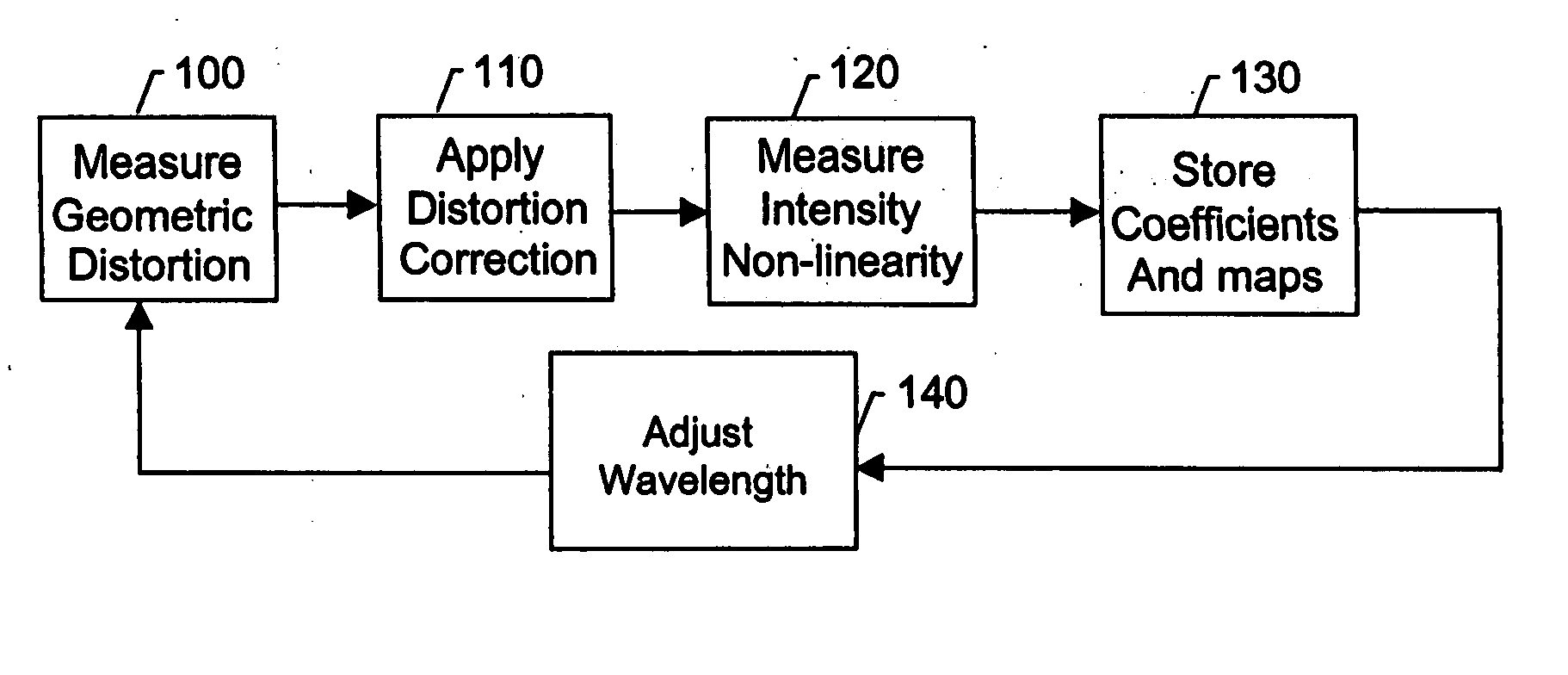
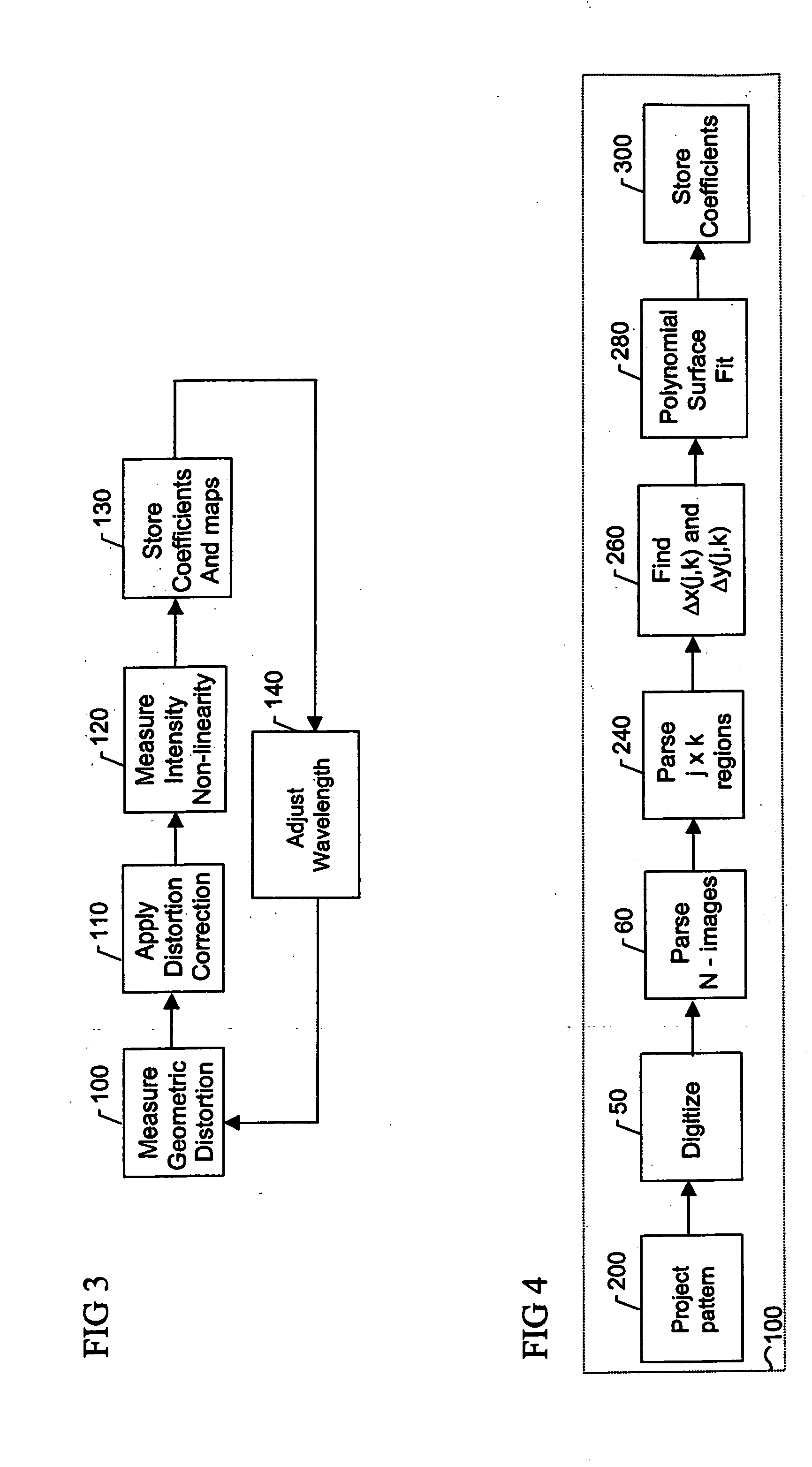
Calibration and error correction in multi-channel imaging
ActiveUS20050083531A1Reducing phase-dependent systematic measurement errorMeasure can be takenImage enhancementOptical measurementsPhase correlationPath length
A multi-channel imaging system is calibrated by measuring the geometric distortion in each sub-image, generating corresponding correction factors, and applying such factors to correct subsequent image data. In addition, intensity transfer-function arrays are measured at each pixel, and further used to correct for system and detector nonlinearities and nonuniformity between images. The procedure is repeated over a range of wavelengths to produce a complete set of correction coefficients and transfer functions. When the system is used for interferometric phase measurements, multiple measurements are preferably taken and a random phase offset in the reference path length is introduced at each measurement. The multiple phase data so derived are then averaged to reduce phase-dependent systematic measurement errors.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
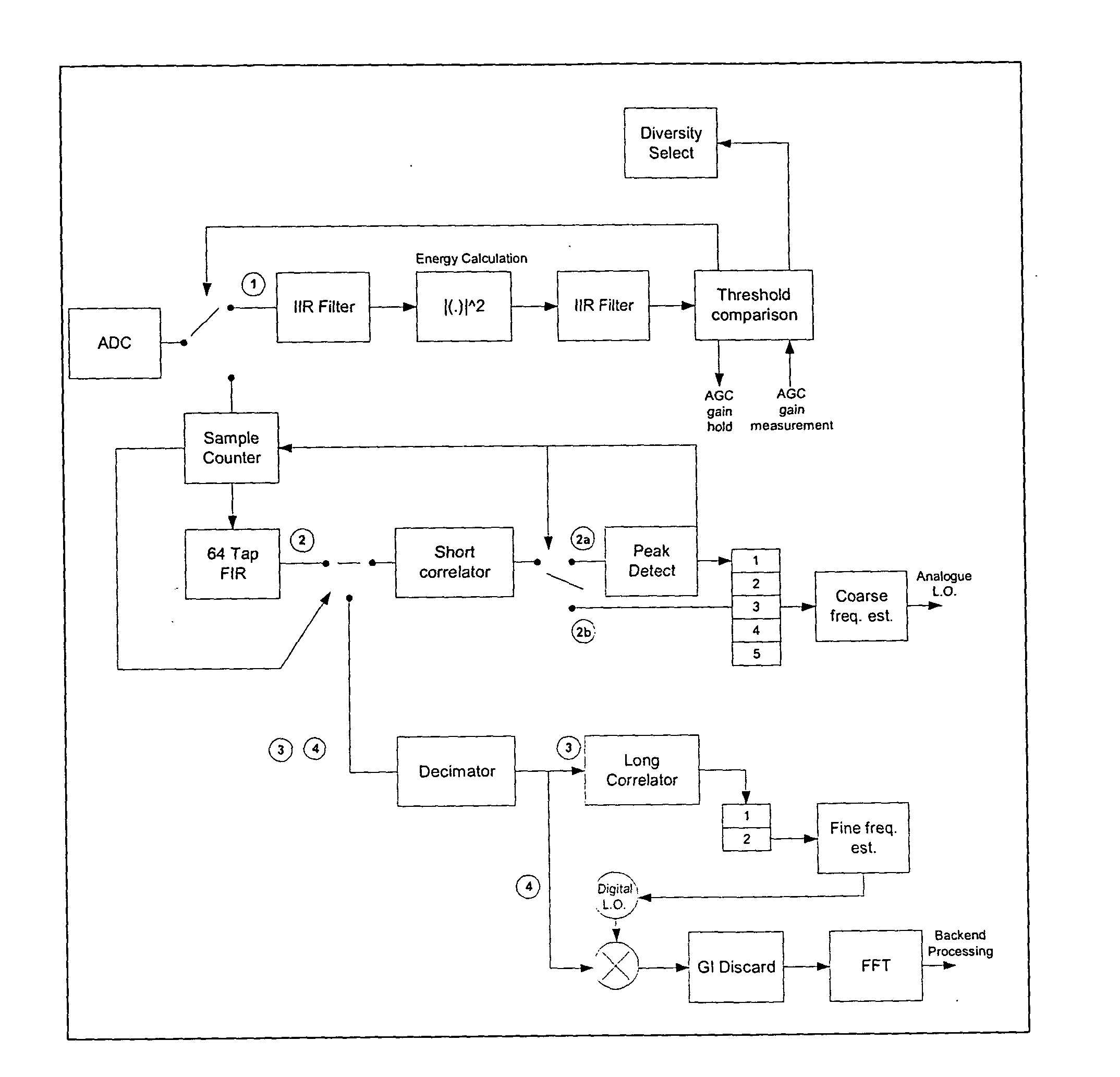
Method for amplitude insensitive packet detection
ActiveUS20050058227A1High outputEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase correlationComputer science
The invention relates generally to the field of wireless communications and more particularly to a method of and device for detecting the presence of a received data packet in a digital receiver. The present invention proposes a simplified method of correlation by removing dependency on the amplitude fluctuations while at the same time maintaining phase relevancy. The key advancement involves mapping the complex quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) preamble to a quantized phase shift keying (PSK) constellation before application to a matched complex correlator. The proposed process essentially “amplitude normalizes” the input signal without the use or complexity associated with a divider. This simplified normalization scheme makes the packet detection algorithm robust against amplitude variations in the input signal, while still allowing for good correlation output. In applications where interference is superimposed on the I / Q input signals, the invention improves the detection capability over automatic gain control (AGC) normalization methods.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
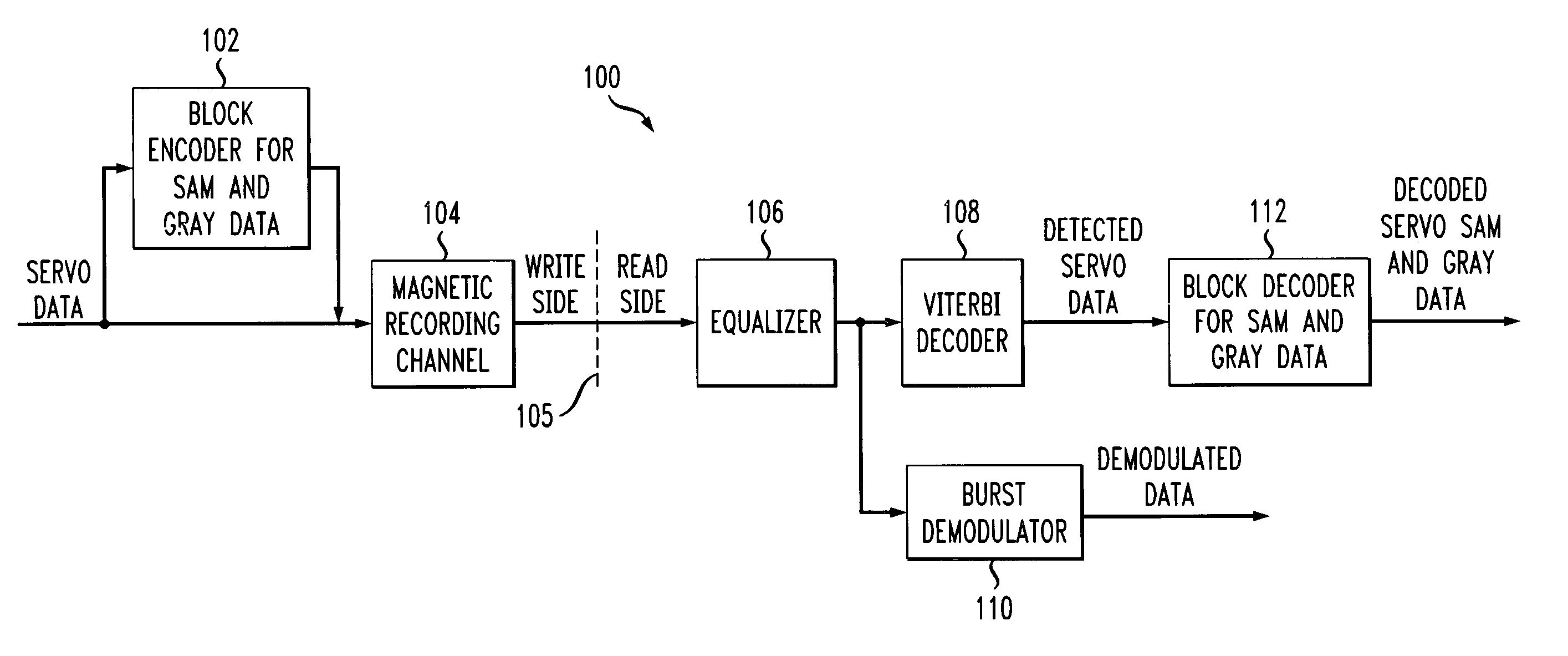
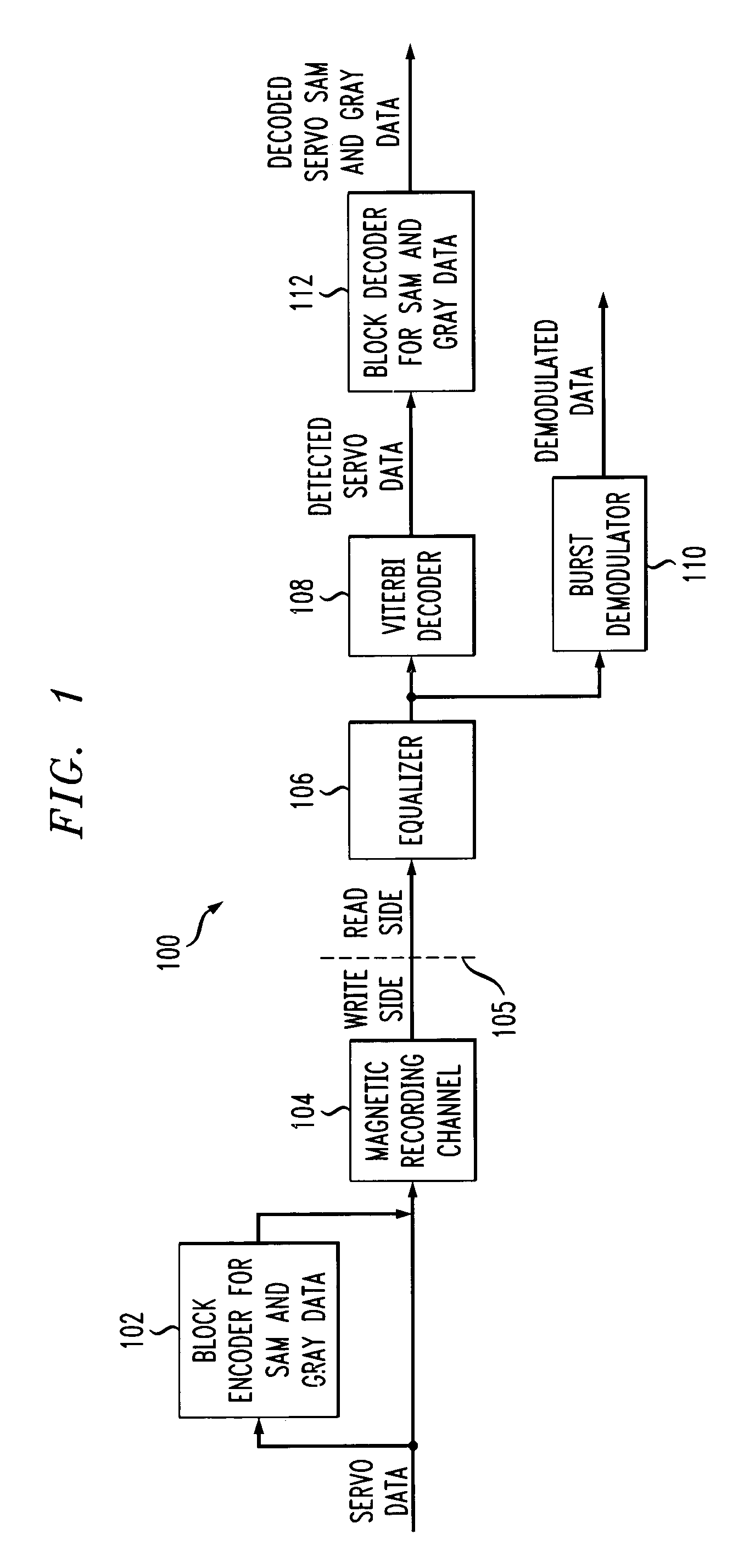
Servo data detection in the presence or absence of radial incoherence using digital interpolators
ActiveUS7082005B2Improve performanceSeek time increaseModification of read/write signalsRecord information storagePhase correlationData storing
Techniques for detecting data, such as servo data, from input or incoming data read from a transmission medium, such as magnetic recording medium, in the presence or absence of radial incoherence. In one illustrative recording medium-based aspect of the invention, such a technique for detecting data from input data stored on a recording medium comprises the following steps. First, one or more samples are interpolated from one or more samples which have been generated from the input data at a given symbol rate. The one or more interpolated samples have one or more phases associated therewith which differ from a phase associated with the one or more samples generated at the given symbol rate. Then, an optimum or best phase is selected from the symbol rate phase and the one or more interpolated phases such that at least a portion of the one or more samples associated with the optimum phase are identified as representative of detected data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
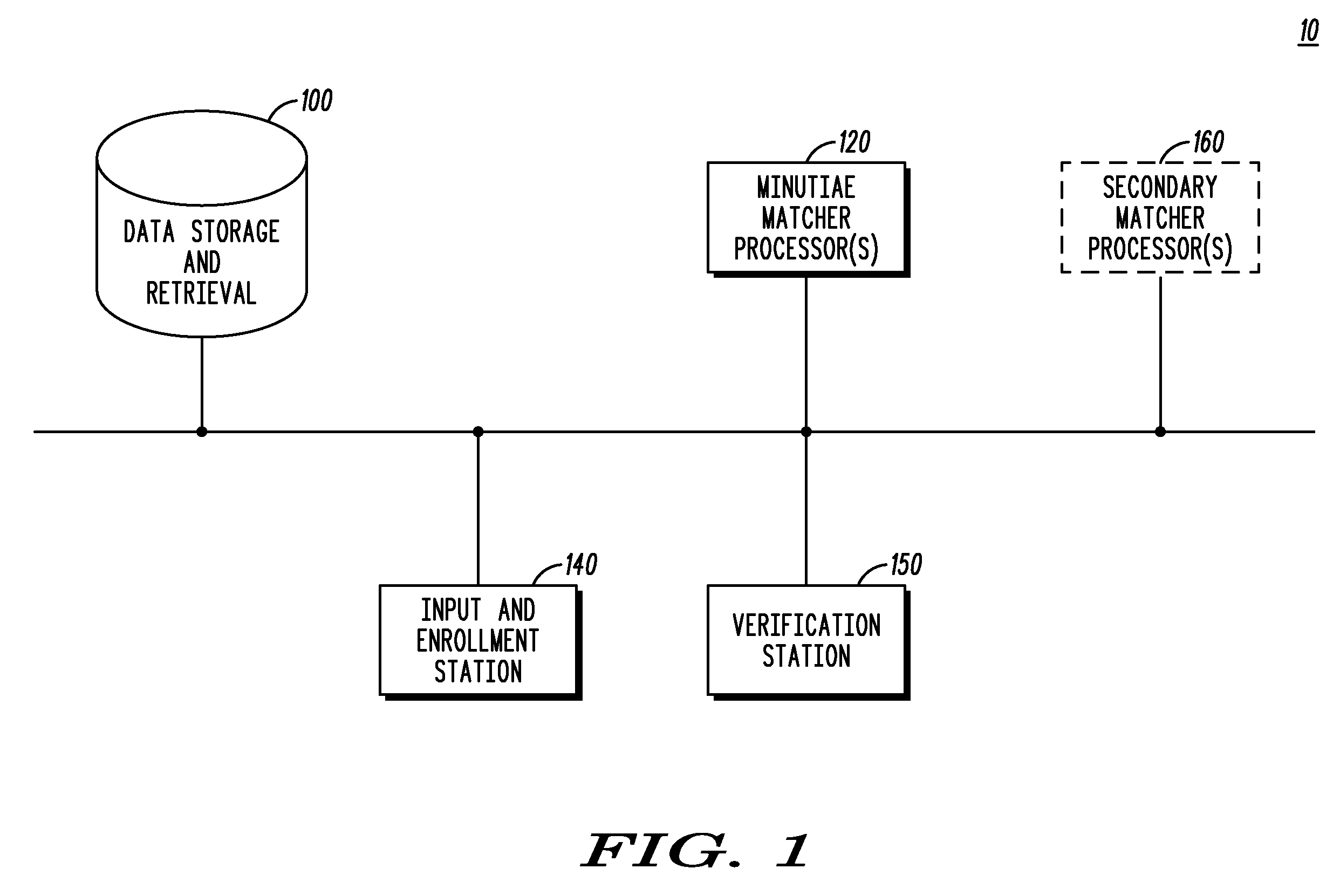
Match filters for a real time fingerprint sensor and verification system
InactiveUS6111671AAcquiring/reconising fingerprints/palmprintsOptical elementsPhase correlationSpatial light modulator
A real time fingerprint verification system includes a recording device and a verification device each having a fingerprint scanner for generating a flat, dimensionally undistorted, high contrast, fingerprint image, and an intensity sensitive, spatial light modulator (SLM) for receiving and transforming the flat fingerprint image into a planar, coherent light image. In the recording device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint from the SLM is Fourier transformed, and input into a microscope objective lens system which expands the Fourier transformed beam image sufficiently to allow mechanical blocking of its central portion or order, whereupon it is directed to interact as an object beam with a reference beam from the particular coherent light source to record a holographic matched filter. In the verification device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint is Fourier transformed and input into a microscope objective lens system to allow similar mechanical blocking of its central portion or order whereupon it is directed to interrogates a previously recorded holographic matched filter of a fingerprint image as an object beam for determining a match or not between the respective recorded and interrogating images. The spatial light modulator (SLM) in both the respective recording and verification devices enables phase correlation (optical path length determination) of one device to another device. X-Y alignment and rotational orinentation of the respective real time image and holographic matched filter image is accomplished by jittering (orbiting and angularly oscillating) either the interrogating object beam, real time, relative to the matched filter or visa versa.
Owner:ADVANCED PRECISION TECH
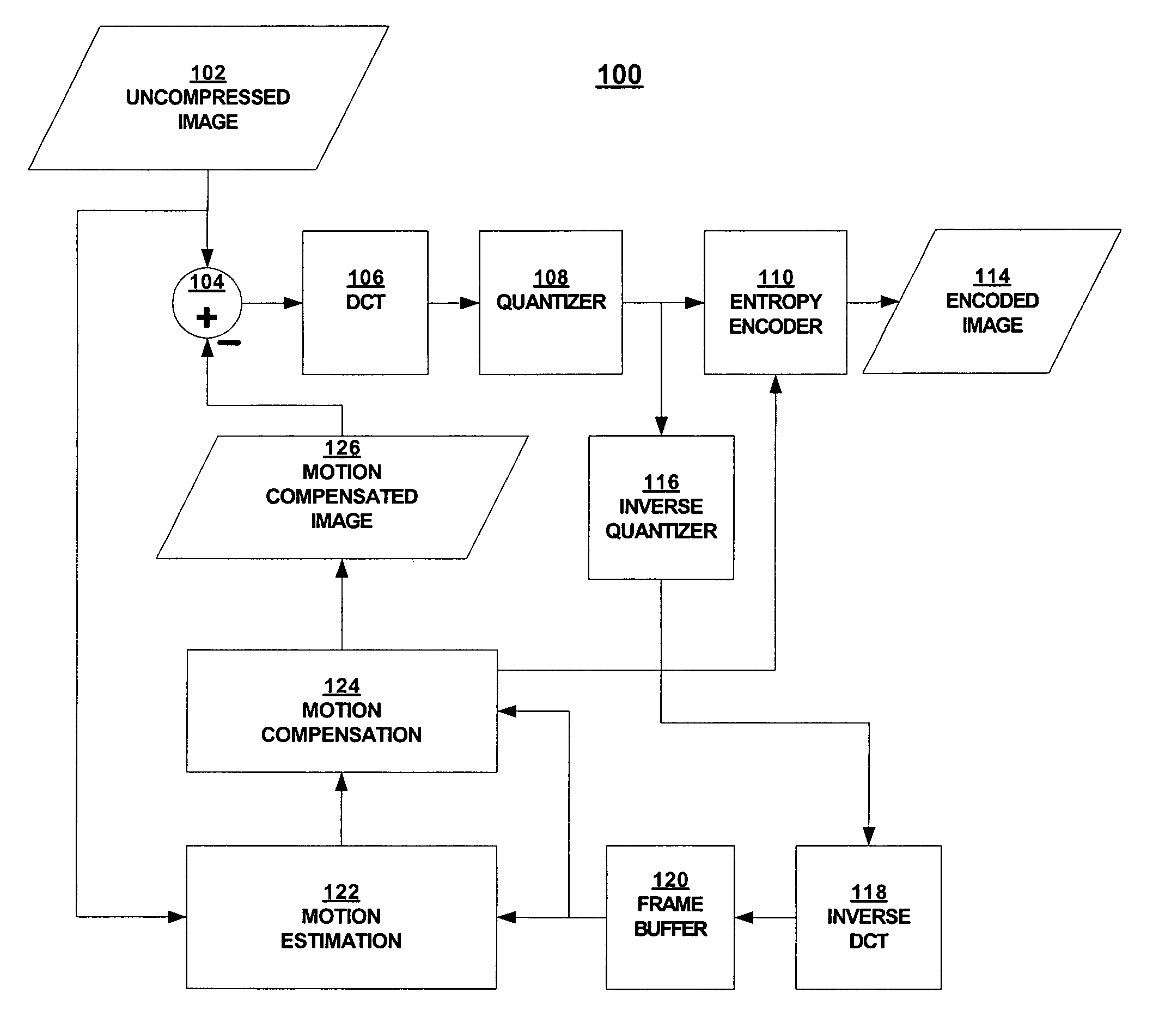
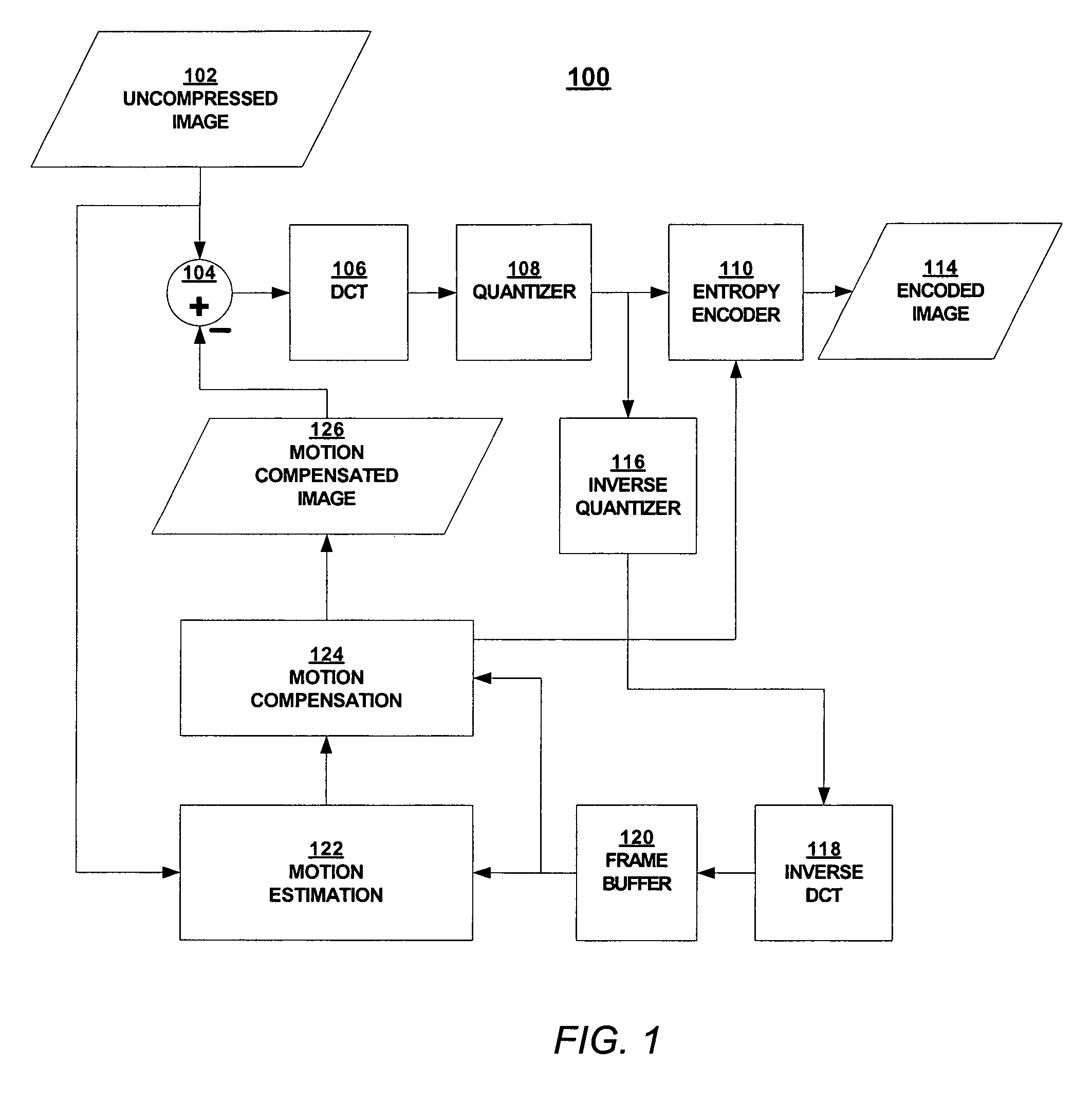
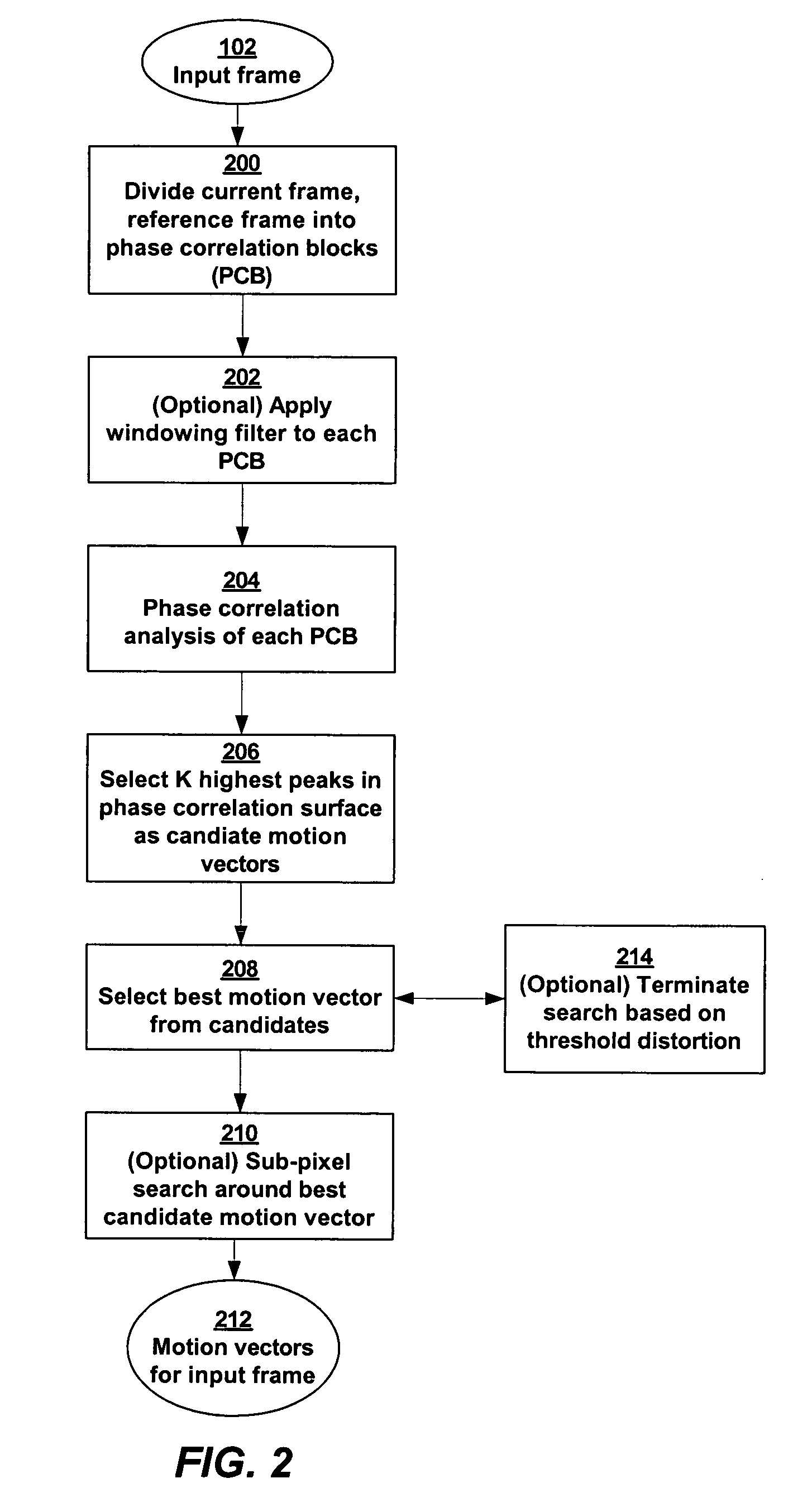
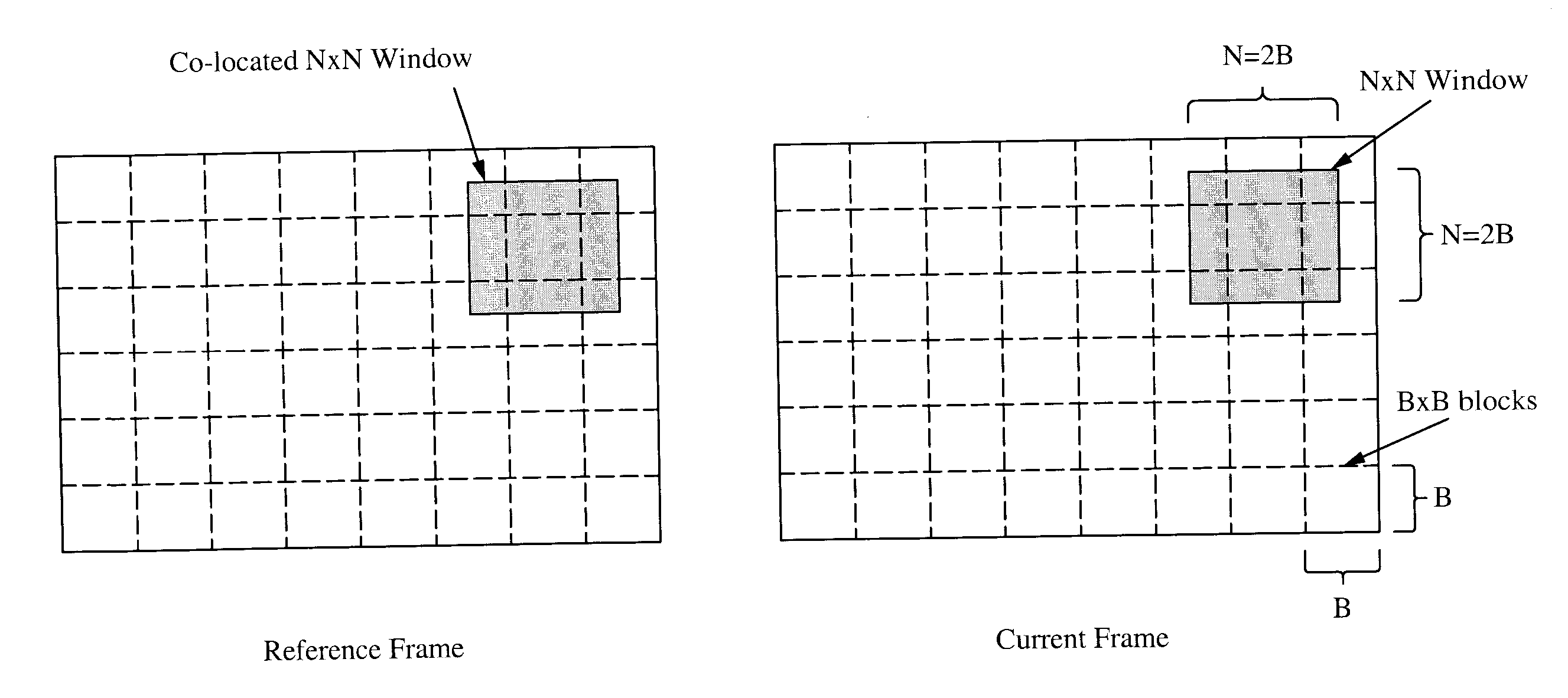
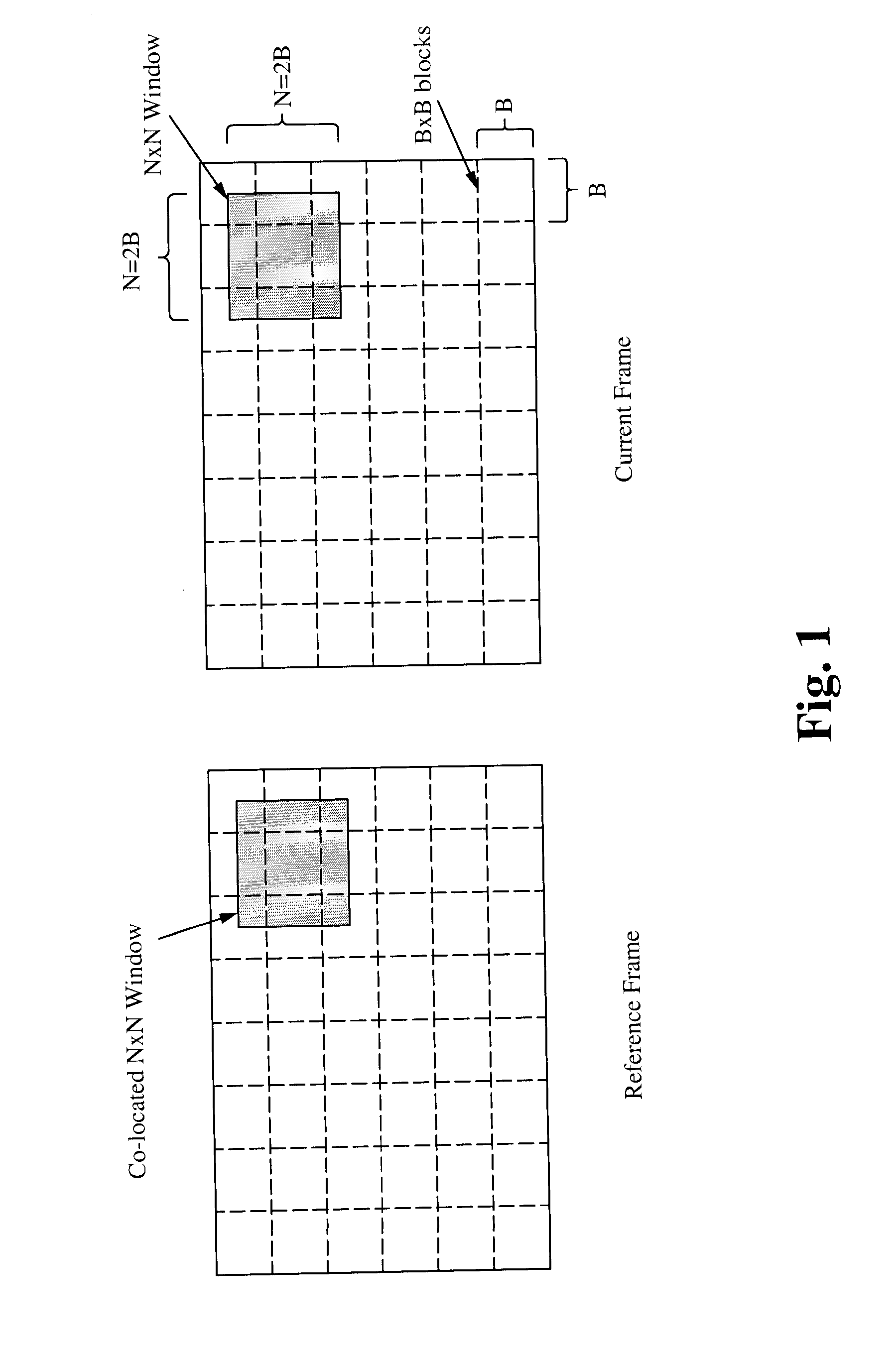
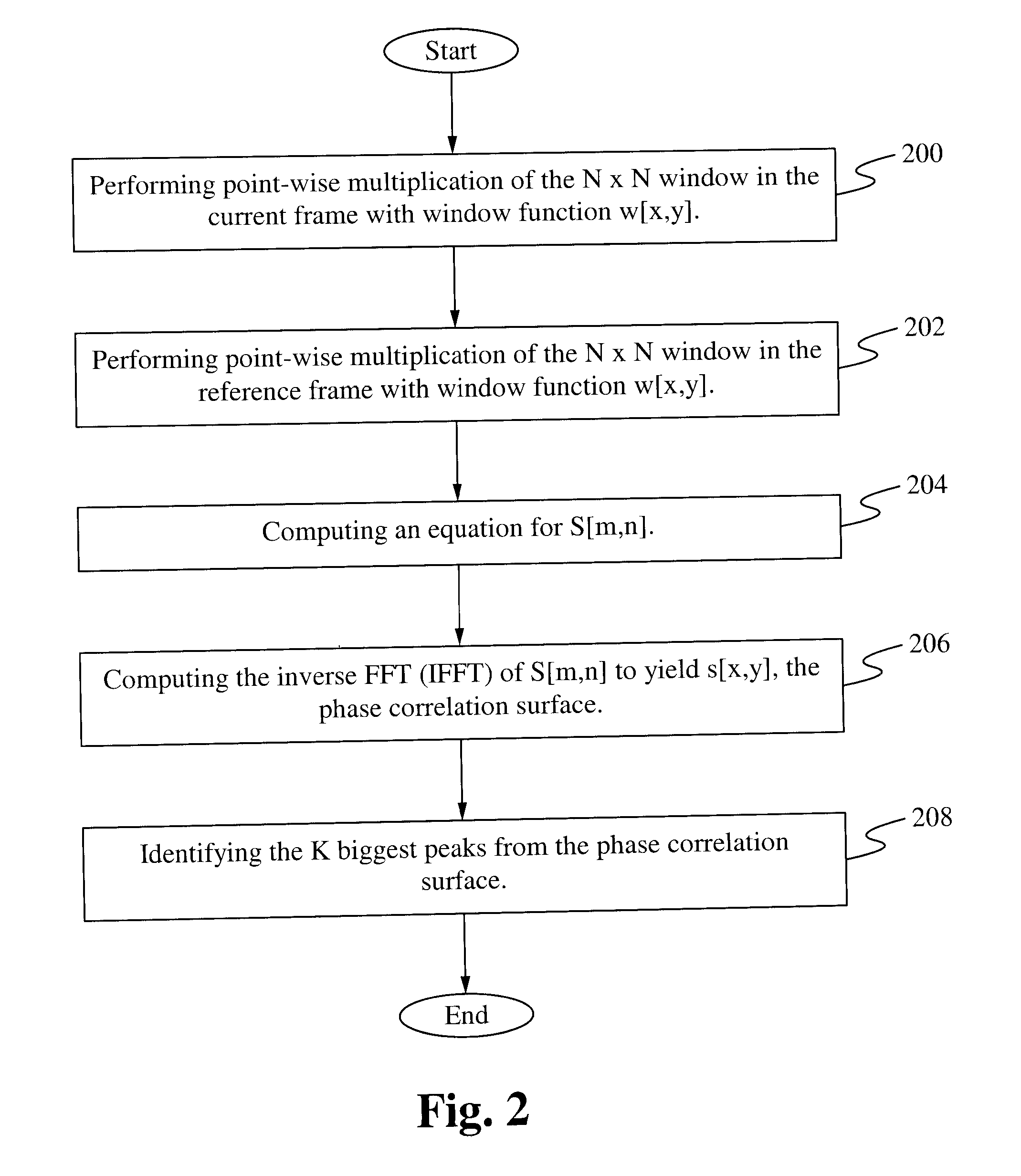
Phase correlation based motion estimation in hybrid video compression
InactiveUS7751482B1Easily scaledColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPhase correlationMotion vector
Motion vectors for encoding a predicted frame relative to a reference frame are determined from a phase correlation of corresponding regions of the predicted frame and reference frame. Peaks in the phase correlation are identified, and the location of the peaks are used as candidate motion vectors. From this limited set of candidate motion vectors, the best motion vectors for predicting blocks within each region can be readily identified.
Owner:VBRICK SYST
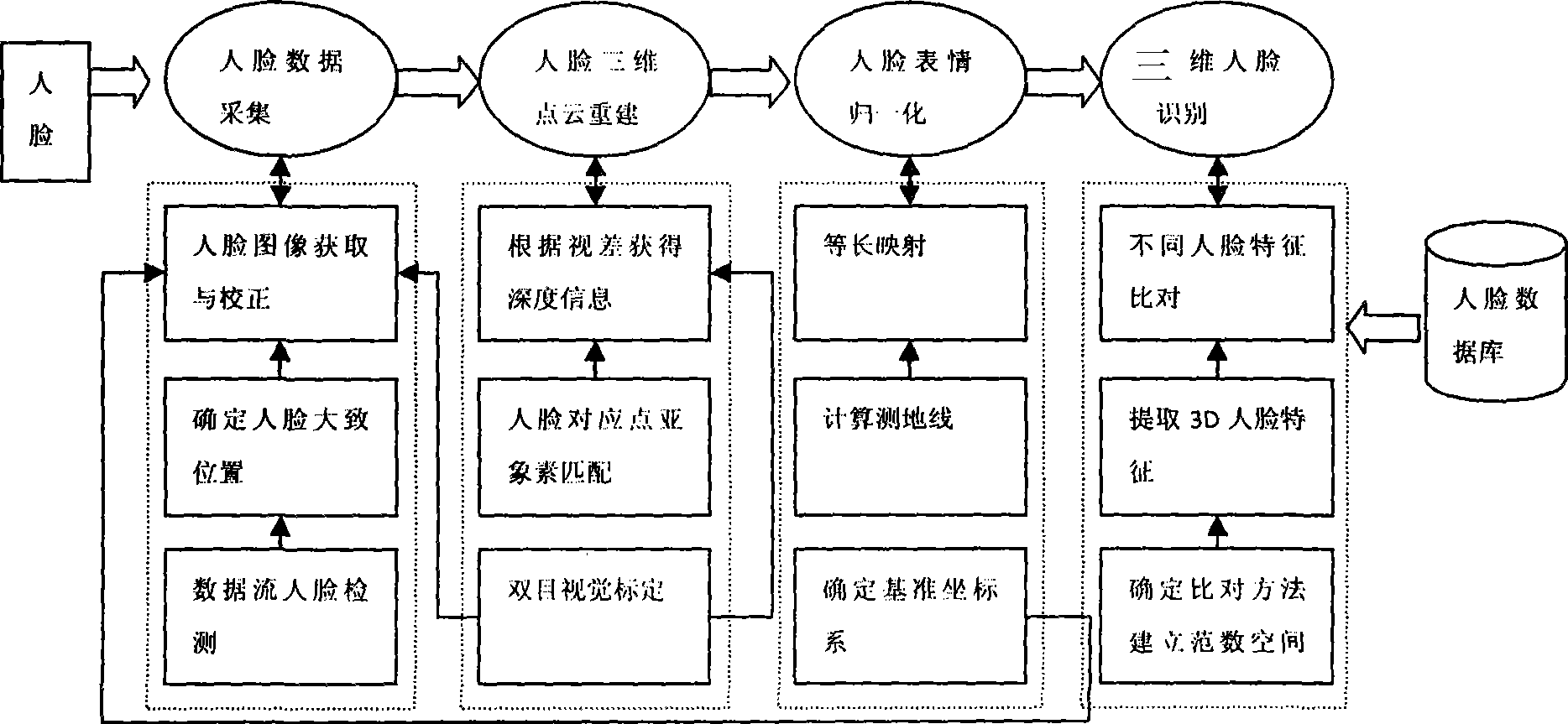
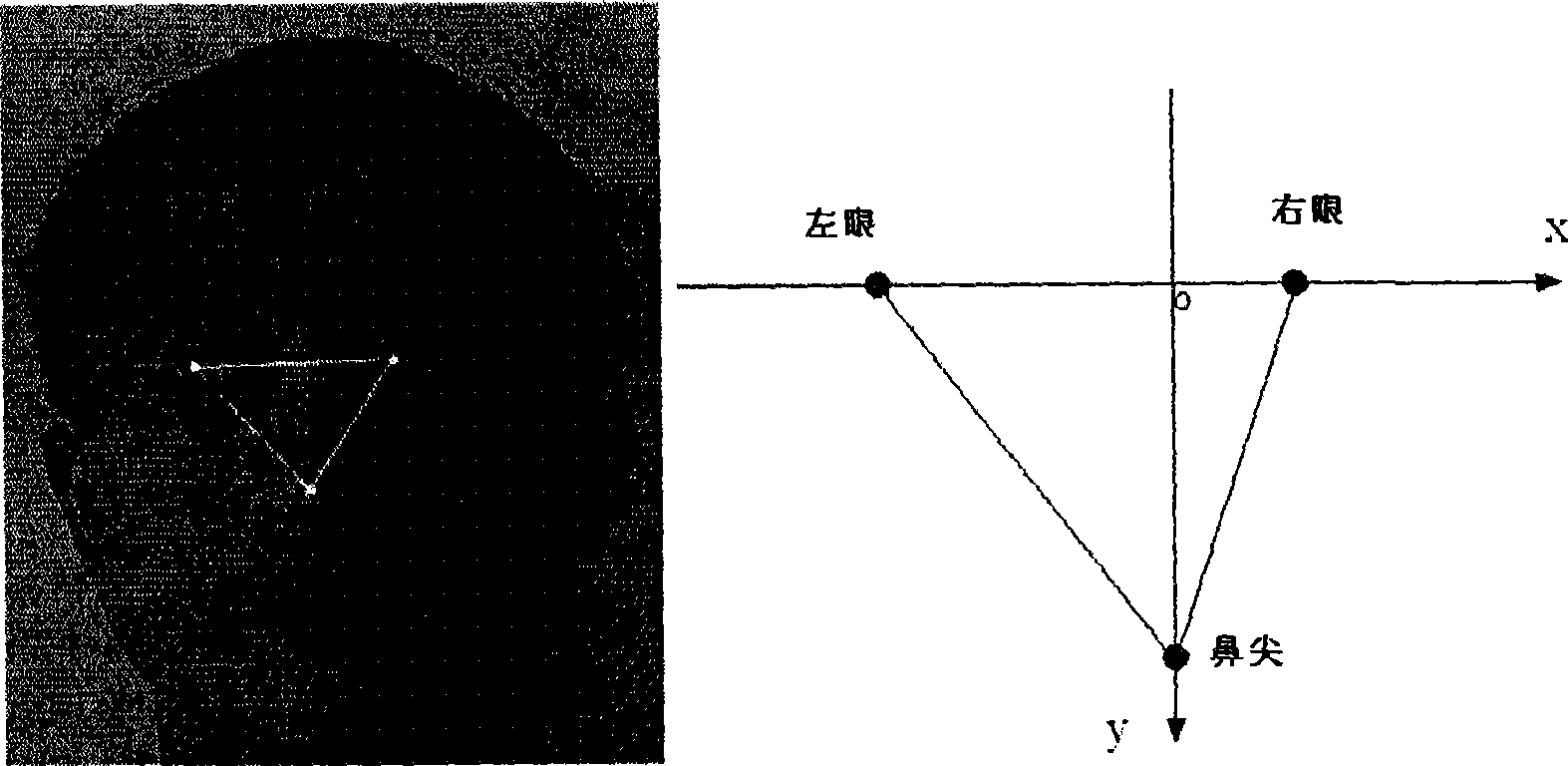
Rapid three-dimensional face identification method based on bi-eye passiveness stereo vision
InactiveCN101398886AShorten the lengthFast 3D recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correlationPoint cloud
The invention discloses a fast 3D face identifying method based on double-eye passive solid sight, which includes the following steps: 1) a non-contact short shaft parallel binocular stereo vision system is built by applying two high-definition digital cameras; 2) after system calibration is finished, face detection and collection based on a haar-AdaBoost sorting machine is carried out on a preview frame image for obtaining corresponding upper and lower stereoscopic vision graph pairs and estimating a sight difference; image correction is carried out on a face area for obtaining the upper and lower stereoscopic vision graph pairs vertical to the polar lines inside and outside the area; 3) the accurate location on the eyes and a spex nasi is captured by applying a Bayesian and the haar-AdaBoost sorting machines as well as point cloud 3D information for building a benchmark triangle; 4) the corresponding sub pixels in the middle and small areas are matched by applying the pyramidal parallel search solid graph of a phase relevant arithmetic based on a complex wavelet; 5) pose normalizing and hole filling are carried out on the faces under different poses by applying the built benchmark triangle; 6) expression normalization is carried out on different faces based on the suppose that the surface geodesic distance of the face is invariable; 7) the 3D faces after normalization are identified by utilizing the arithmetic. The method has the beneficial effects of: mainly solving the problems of being hard to fast and automatically obtain the passive stereoscopic vision and identifying the 3D point cloud information of the dense and accurate face under different poses and expressions, thus leading the 3D face identifying process to be faster, more hidden, safer and more reliable.
Owner:杭州大清智能技术开发有限公司
Dual synchro-resonant electrosurgical apparatus with bi-directional magnetic coupling
ActiveUS20070173810A1Inhibit transferControlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingPhase correlationTransformer
An electrosurgical generator is disclosed, which includes an RF output stage connected to a DC power supply and first and second connections. The first connection includes a first switching component and a first parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit. The second connection includes a second switching components and a second parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit. The first and second switching components are configured to open and close at a predetermined frequency based on a phase-correlated dual drive signal emitted by a driver and are in a 180 degree out-of-phase relationship. The first parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit is further configured to produce a first half-sinusoidal waveform and the second parallel inductor-capacitor resonant circuit is configured to produce a second half-sin half-sinusoidal waveform. The RF output stage further includes a transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding and a series inductor-capacitor resonant circuit, which are configured to generate a sinusoidal waveform.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
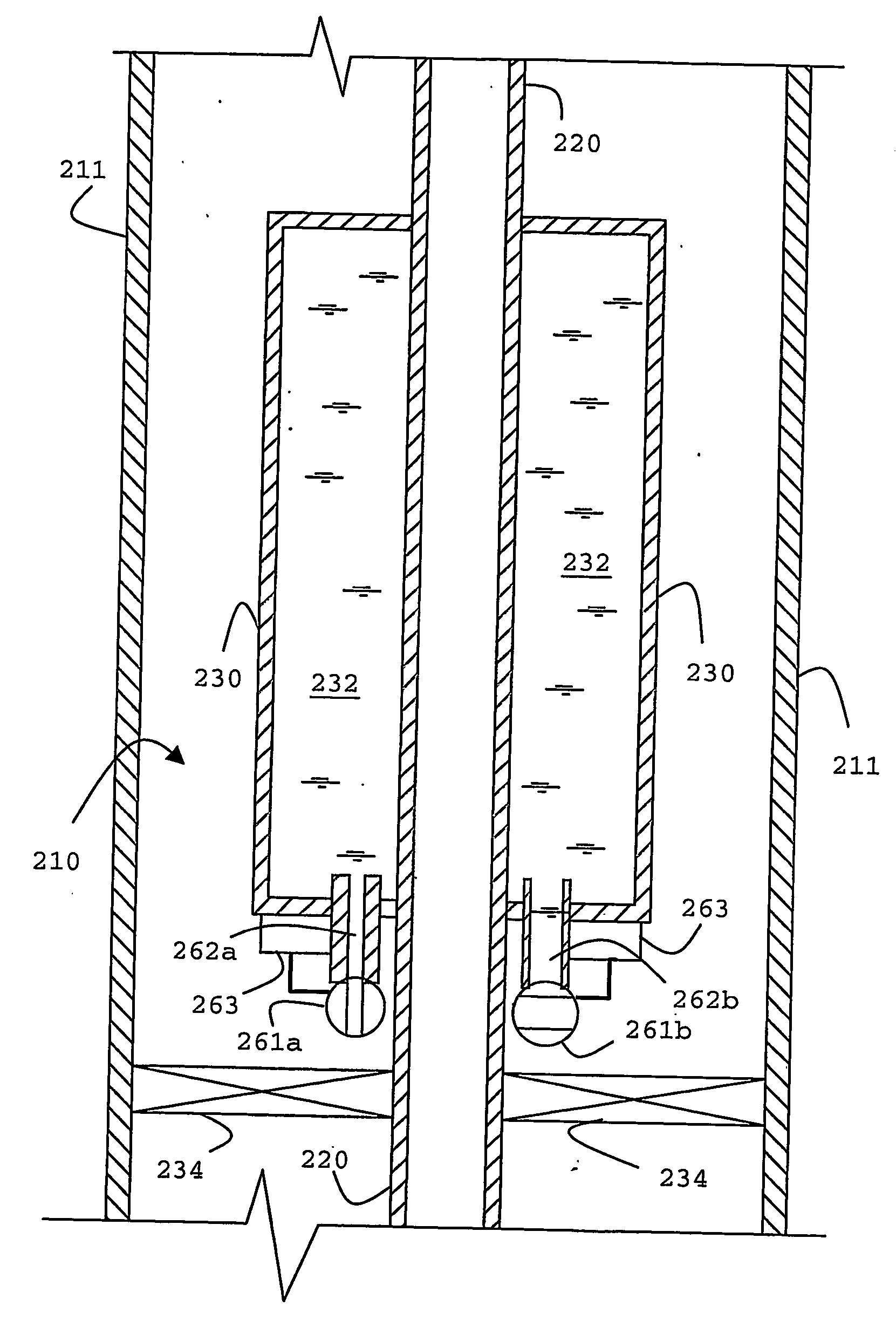
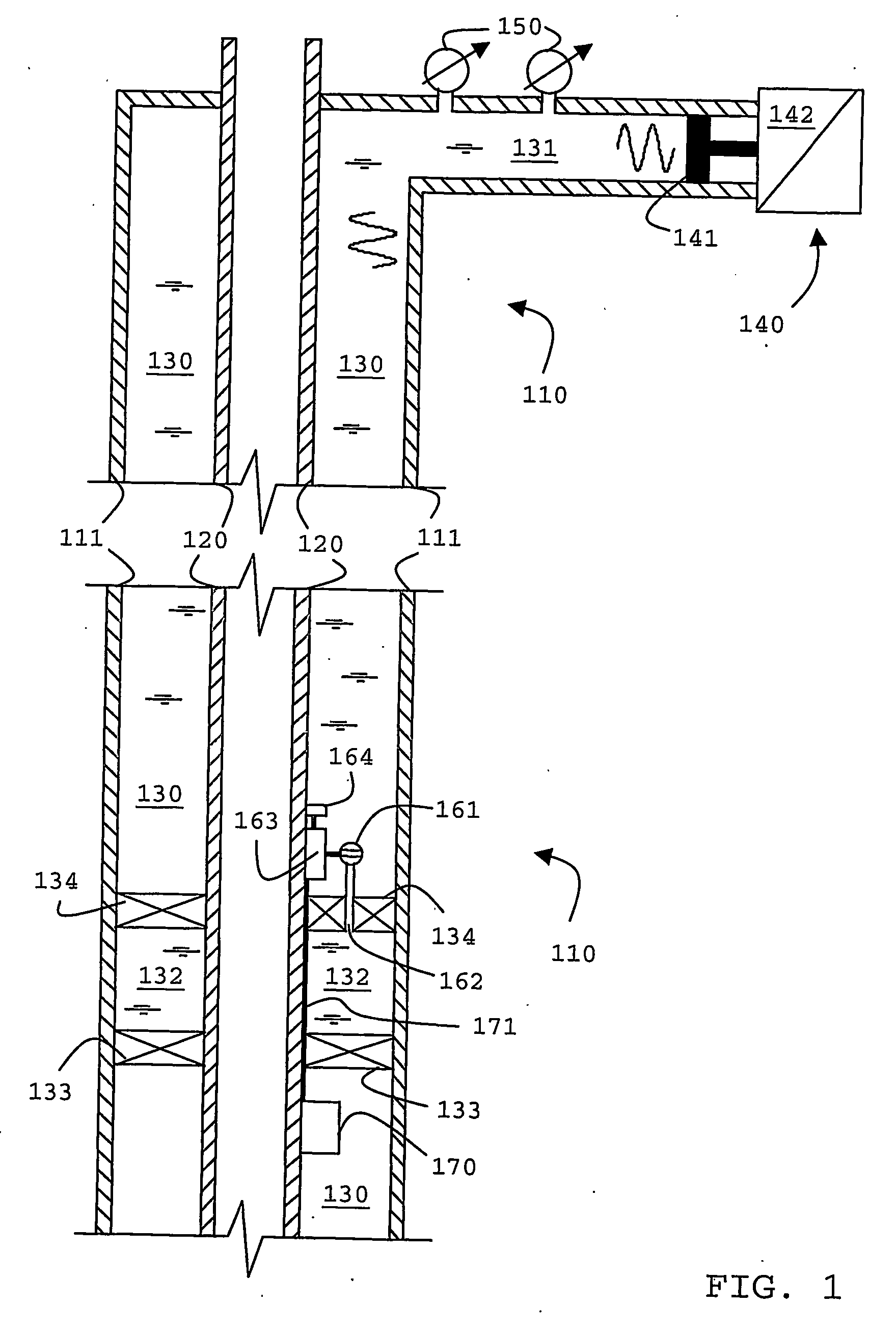
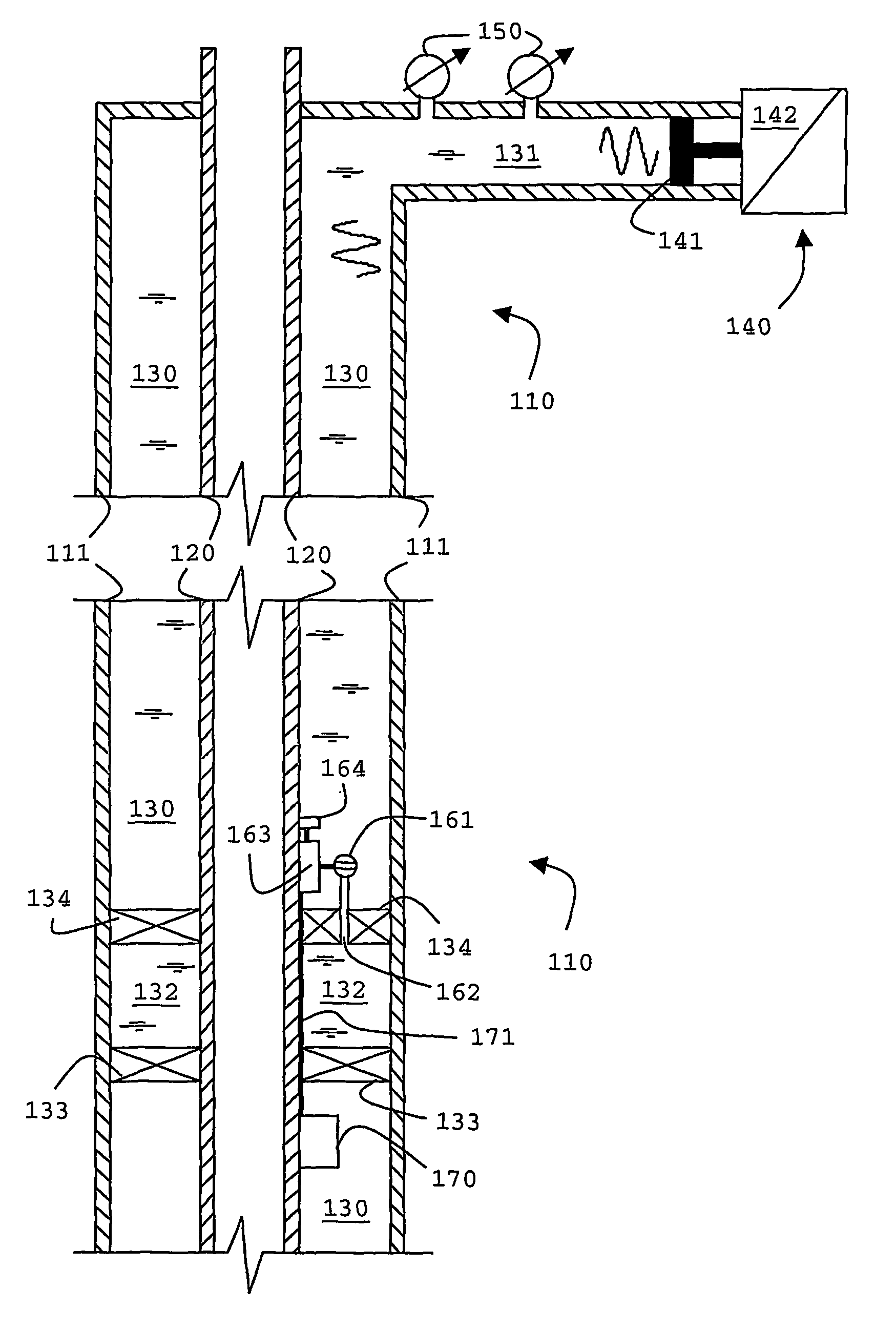
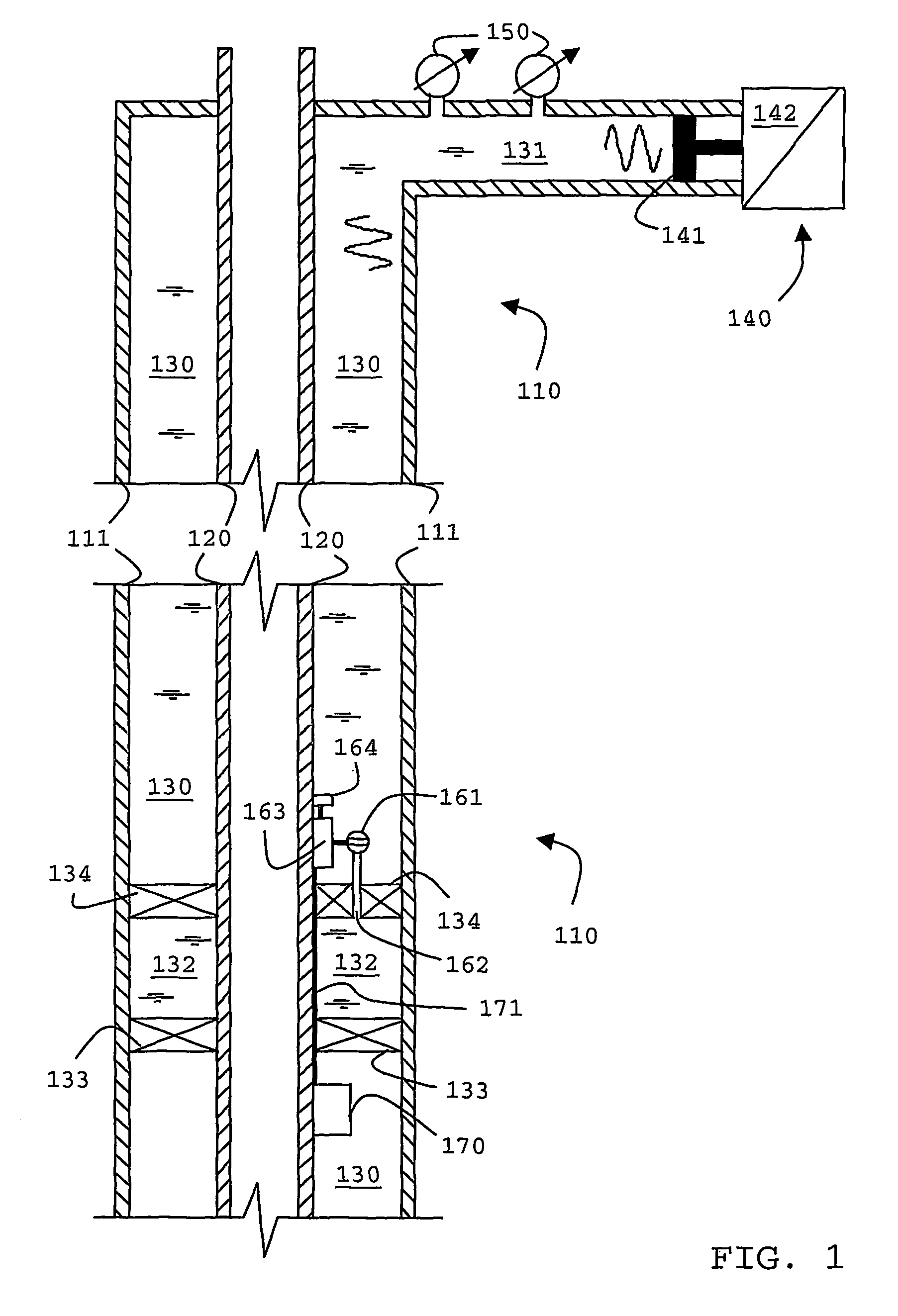
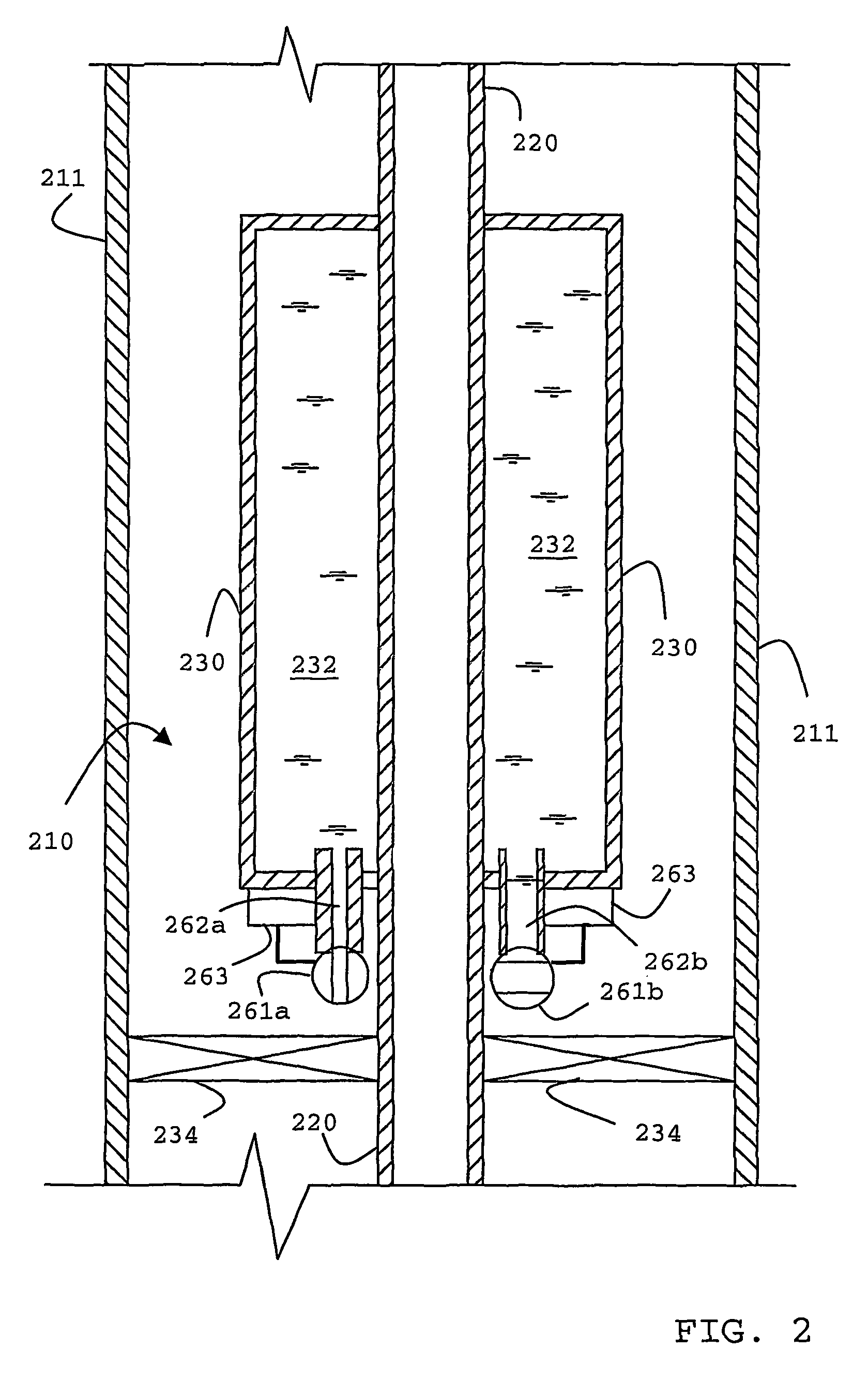
Borehole telemetry system
An acoustic telemetry apparatus and method for communicating encoded digital data from a down-hole location through a borehole to the surface is described including an acoustic channel terminated at a down-hole end by a reflecting terminal (133, 134), an acoustic wave generator (140) located at the surface and providing an acoustic wave carrier signal through said acoustic, channel, a modulator (162, 163) located down-hole to modulate amplitude and / or phase of said carrier wave in response to an encoded digital signal and one or more sensors (150) located at the surface adapted to detect amplitude and / or phase related information of acoustic waves traveling within said acoustic channel to determine the encoded digital data.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for phase correlation holographic drive
InactiveUS6909529B2Record information storageSystems characterised by carrier structurePhase correlationHolographic storage
A holographic storage apparatus for recording data in a holographic medium includes at least one light source for generating a reference beam and a signal beam. The reference beam is preferably a phase beam of unchanging phase content. The apparatus also includes a holographic medium placed in a path of the reference beam and a path of the signal beam. The holographic medium has a first face and both the reference beam and the signal beam enter the holographic medium through the first face. The holographic medium also includes a data reflective surface. The reference beam and the signal beam interfere in the holographic medium to create a hologram only after at least one of the reference beam and the signal beam have reflected off of the data reflective surface.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
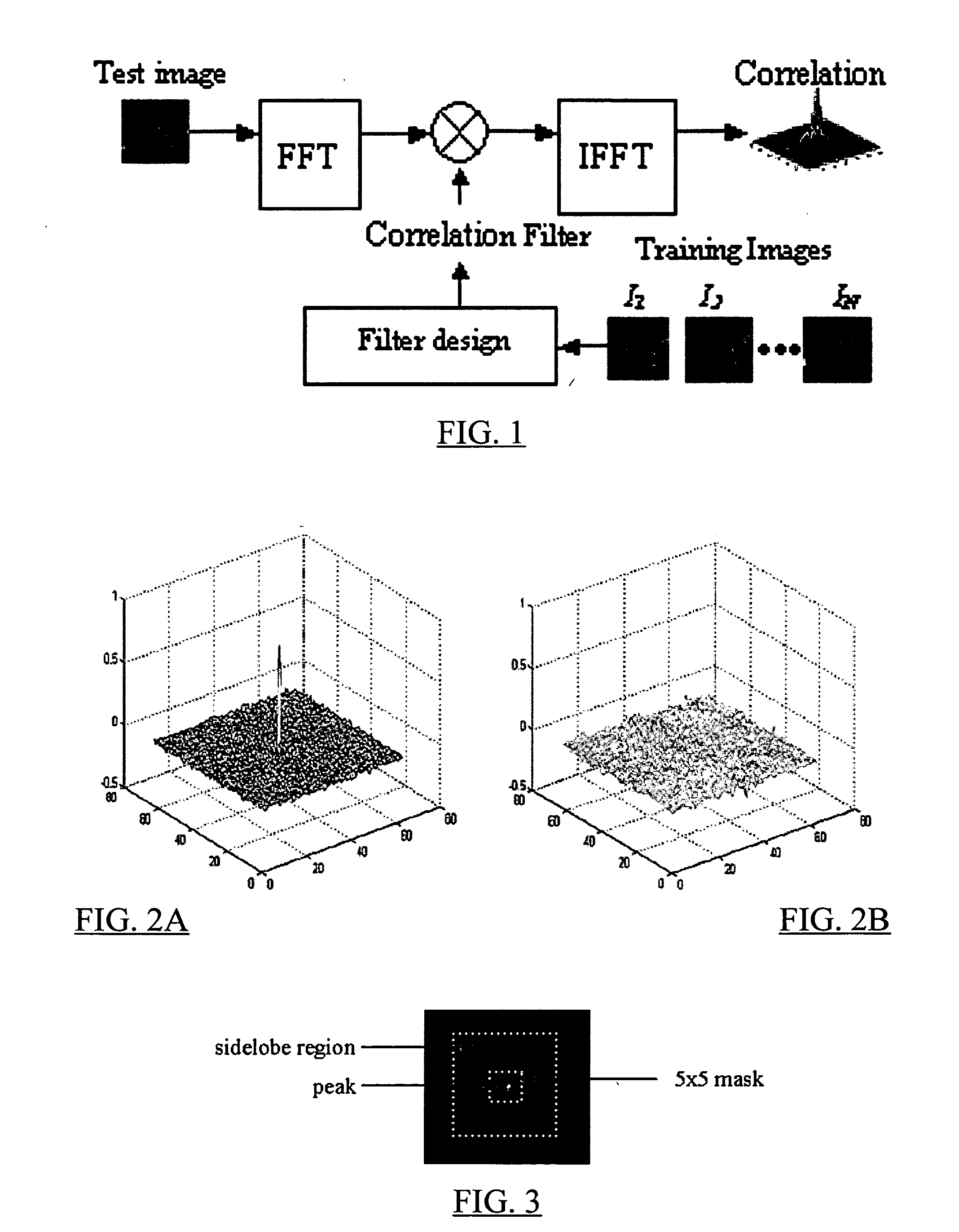
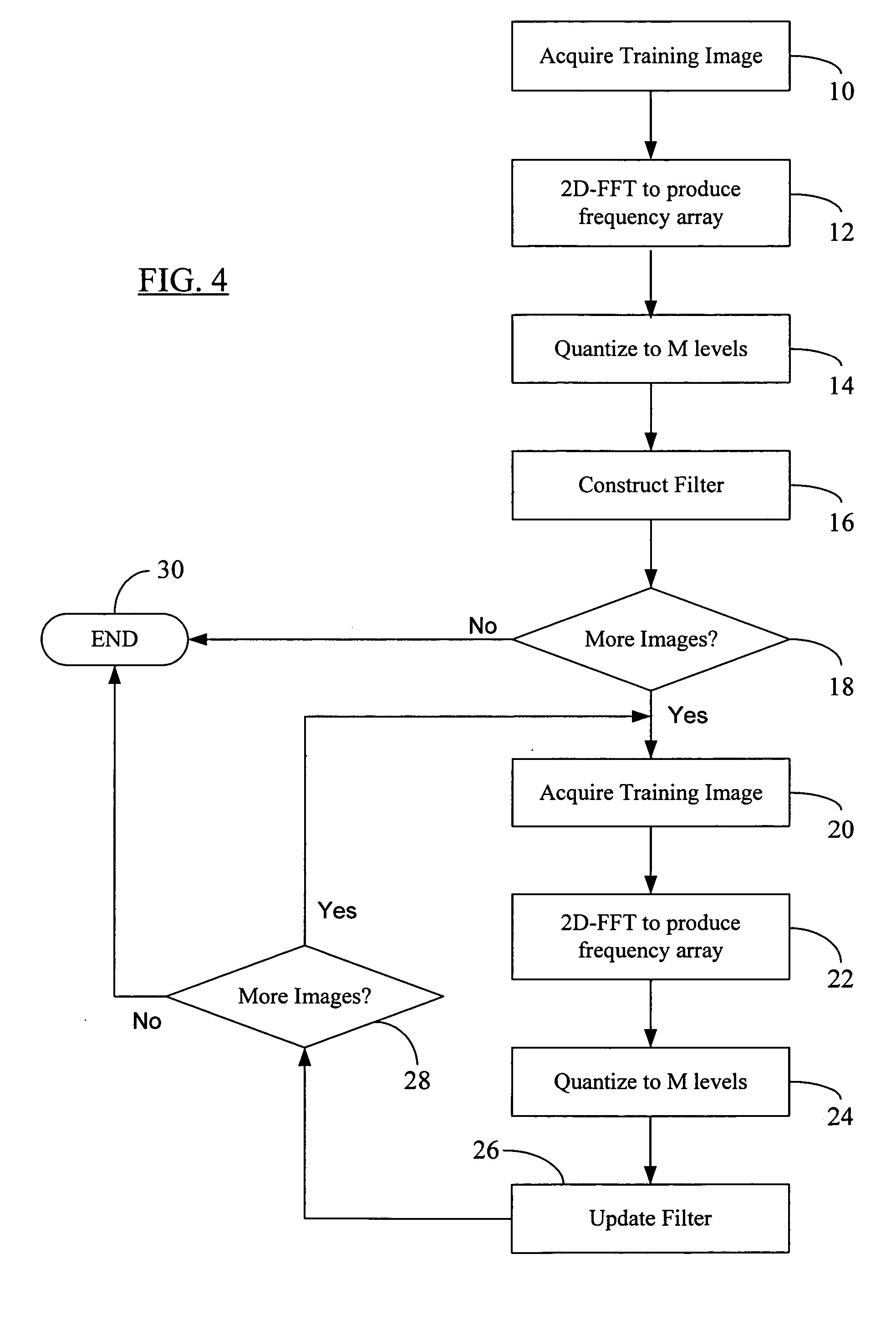
Reduced complexity correlation filters
InactiveUS20050018925A1Reduce storageReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correlationPattern recognition
A methodology is described to reduce the complexity of filters for face recognition by reducing the memory requirement to, for example, 2 bits / pixel in the frequency domain. Reduced-complexity correlations are achieved by having quantized MACE, UMACE, OTSDF, UOTSDF, MACH, and other filters, in conjunction with a quantized Fourier transform of the input image. This reduces complexity in comparison to the advanced correlation filters using full-phase correlation. However, the verification performance of the reduced complexity filters is comparable to that of full-complexity filters. A special case of using 4-phases to represent both the filter and training / test images in the Fourier domain leads to further reductions in the computational formulations. This also enables the storage and synthesis of filters in limited-memory and limited-computational power platforms such as PDAs, cell phones, etc. An online training algorithm implemented on a face verification system is described for synthesizing correlation filters to handle pose / scale variations. A way to perform efficient face localization is also discussed. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Method and system for imaging an object
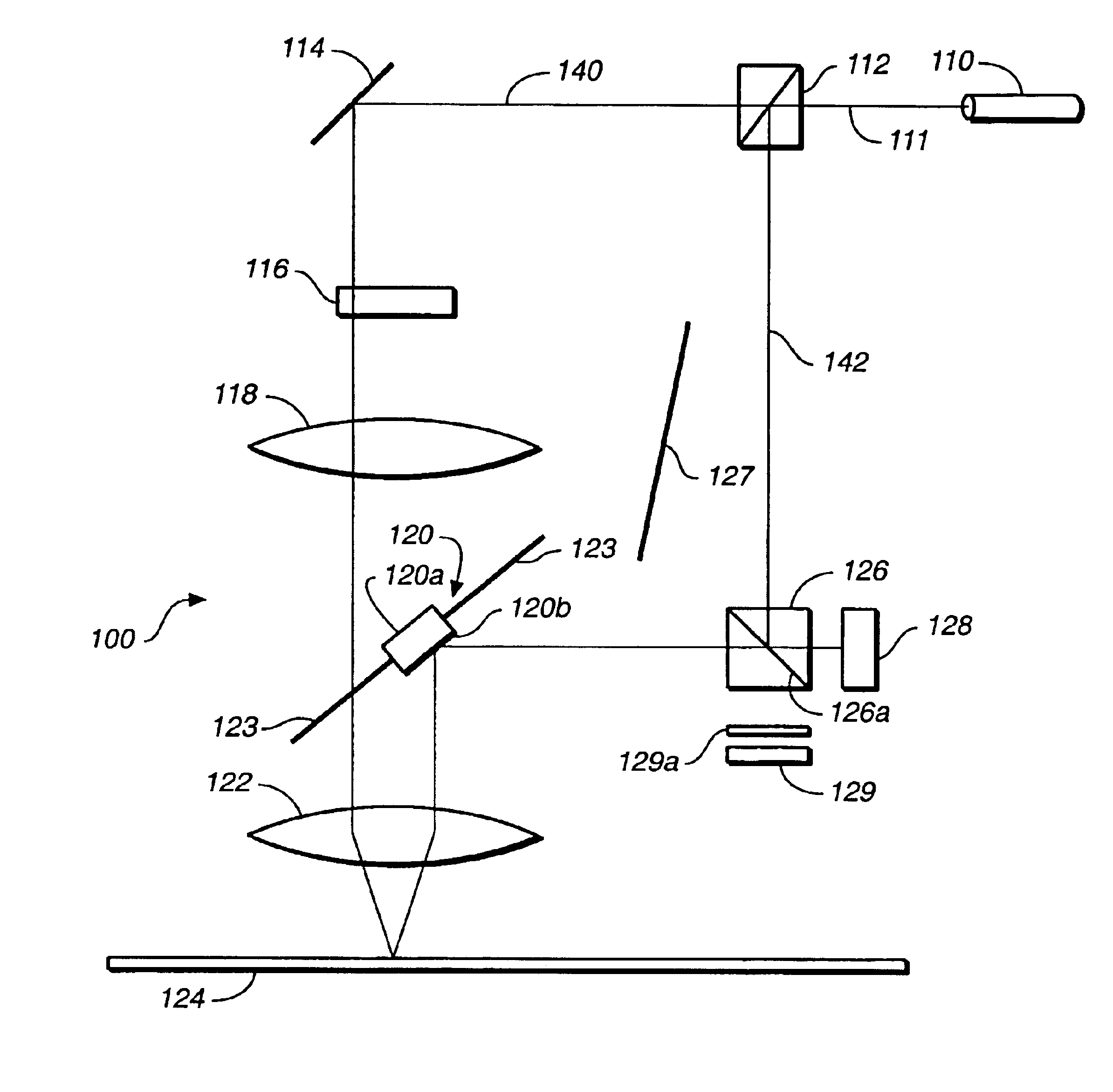
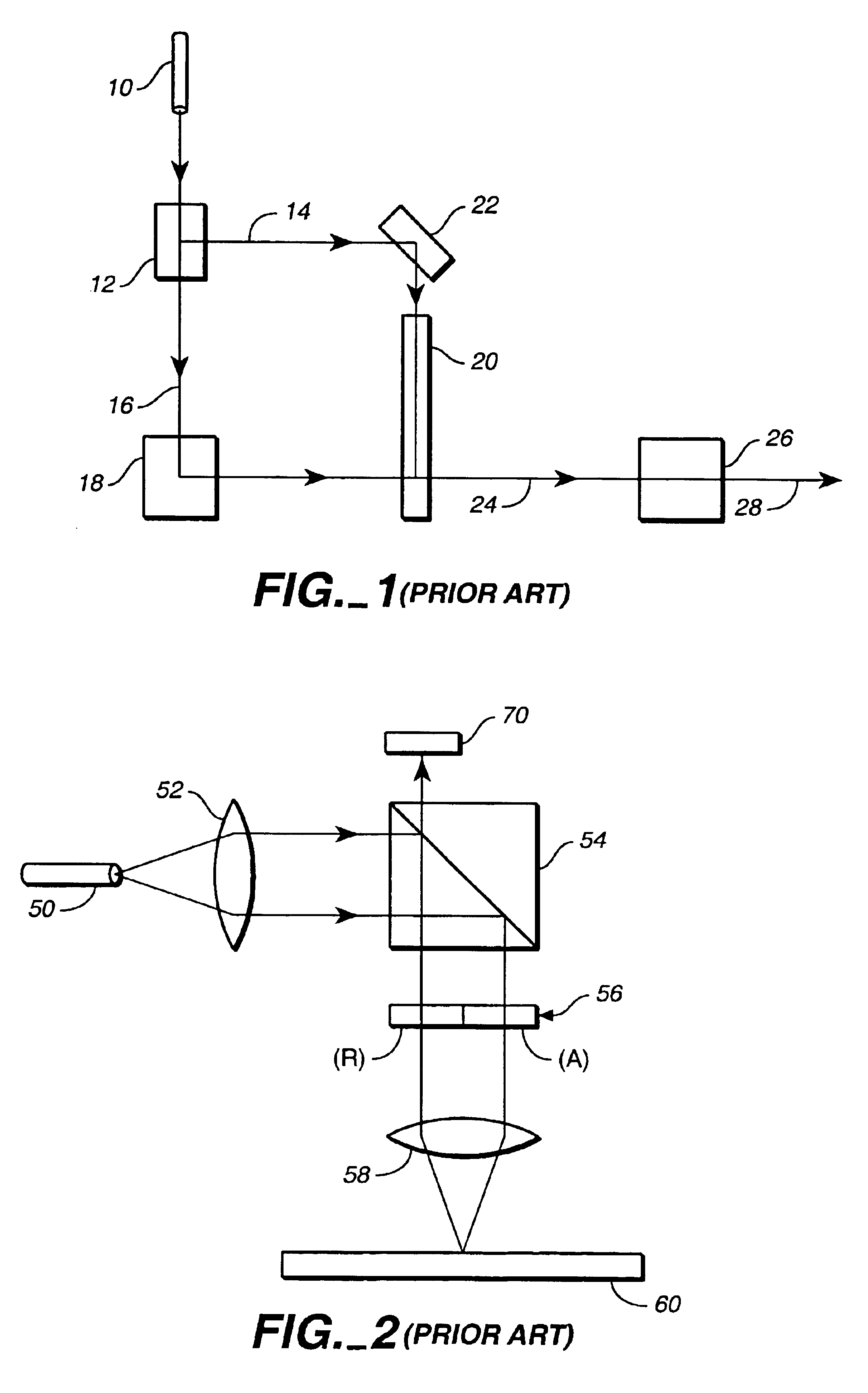
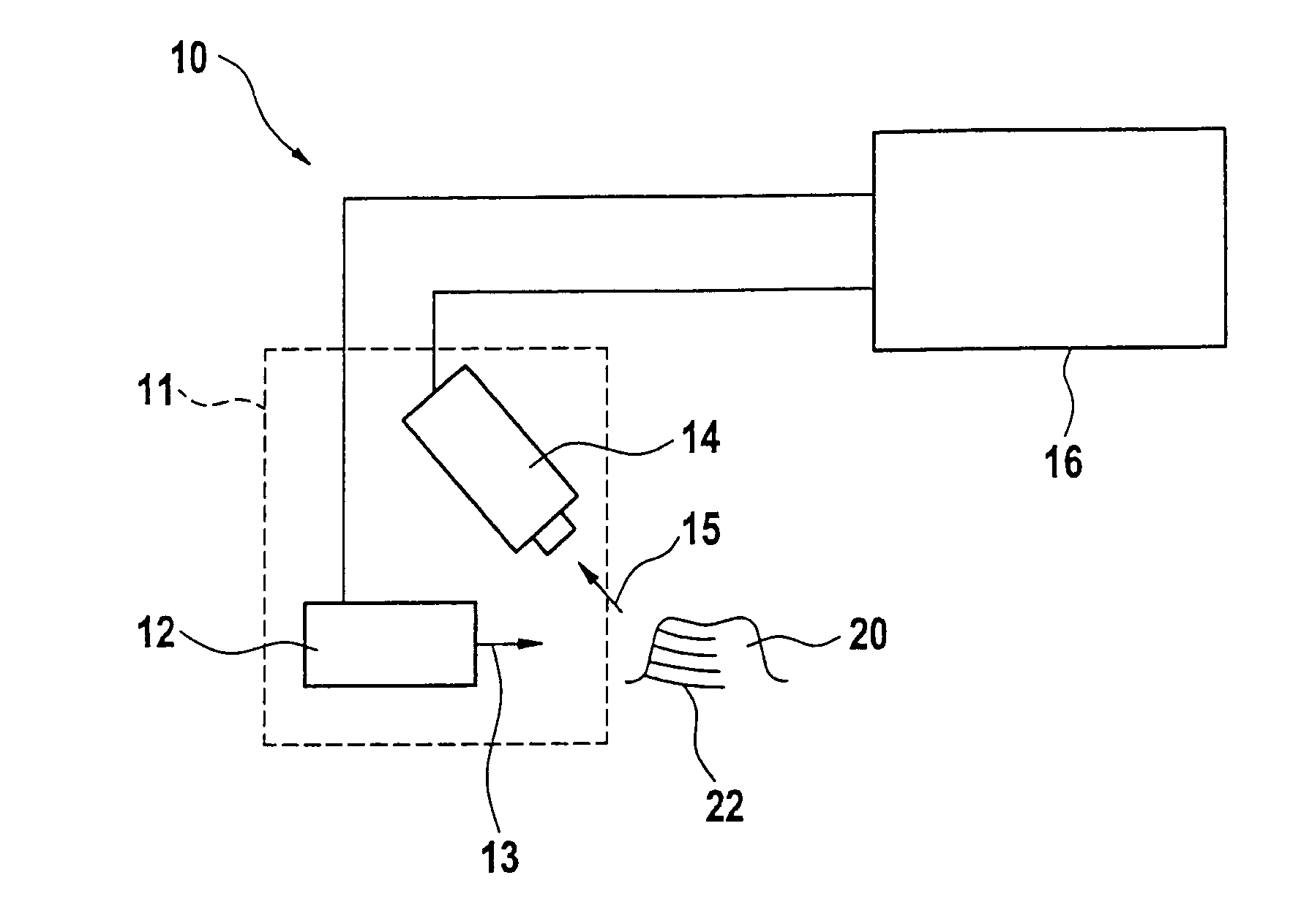
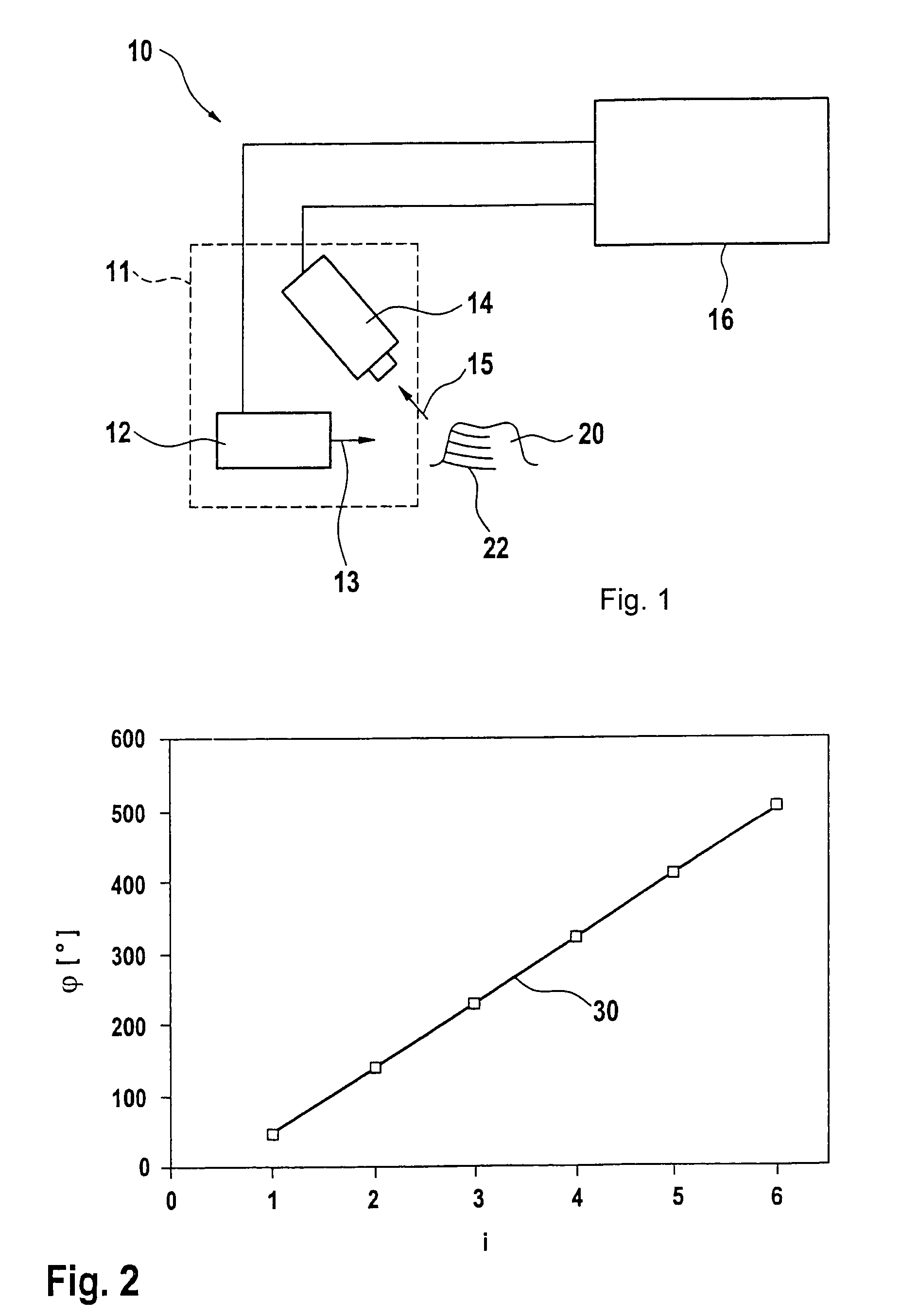
ActiveUS7522764B2Easy to calculateFree-hand recordingDental toolsCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera imageMethod of images
In a method of imaging an object, for dental purposes, comprises:a) projecting a striped pattern on to the object to be imaged,b) recording the projected striped pattern as a basic image (Ri) with a camera, steps a) and b) being carried out at a number of different positions of the phase relationship of the striped pattern, andc) computing an image of the object from the plurality of mutually out-of-phrase basic camera images. Provision is made for suppression of periodic disturbances in that, in step c),c1) at least two groups of basic images (R1, R2, . . . , Rn; R2, R3, . . . , Rn+1) are formed from the basic camera images (R1, . . . , Rm),c2) a phase related image (Pj) of the object to be imaged (20) is computed from each group of basic images (R1, R2, . . . , Rn; R2, R3, . . . , Rn+1),c3) the computed phase related images (P1, P2) are averaged such that a phase related image (P) having a reduced amount of noise is formed, and thatc4) an image of the object is computed from the phase related image (P) having a reduced amount of noise.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for generating a phase dependent control signal
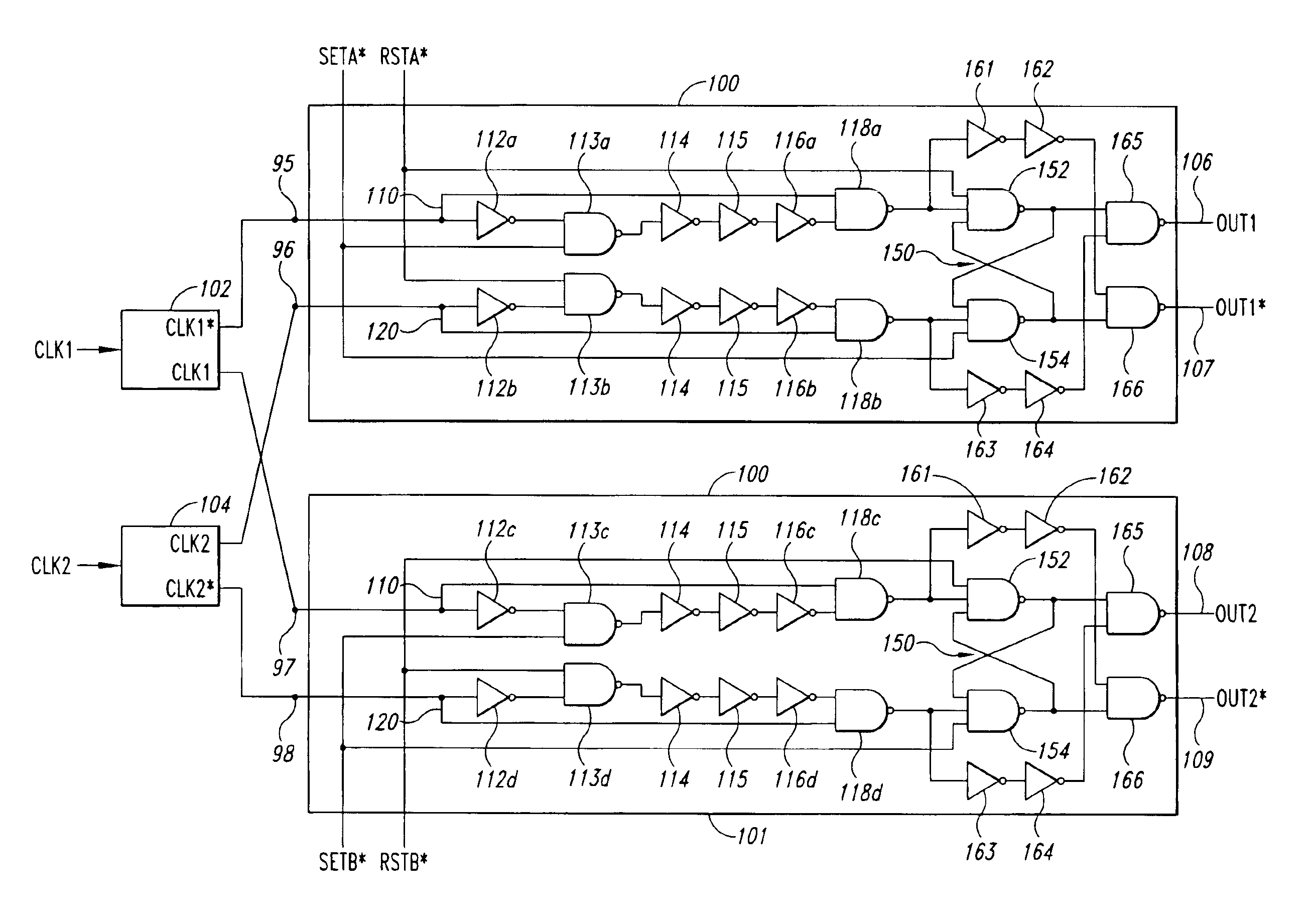
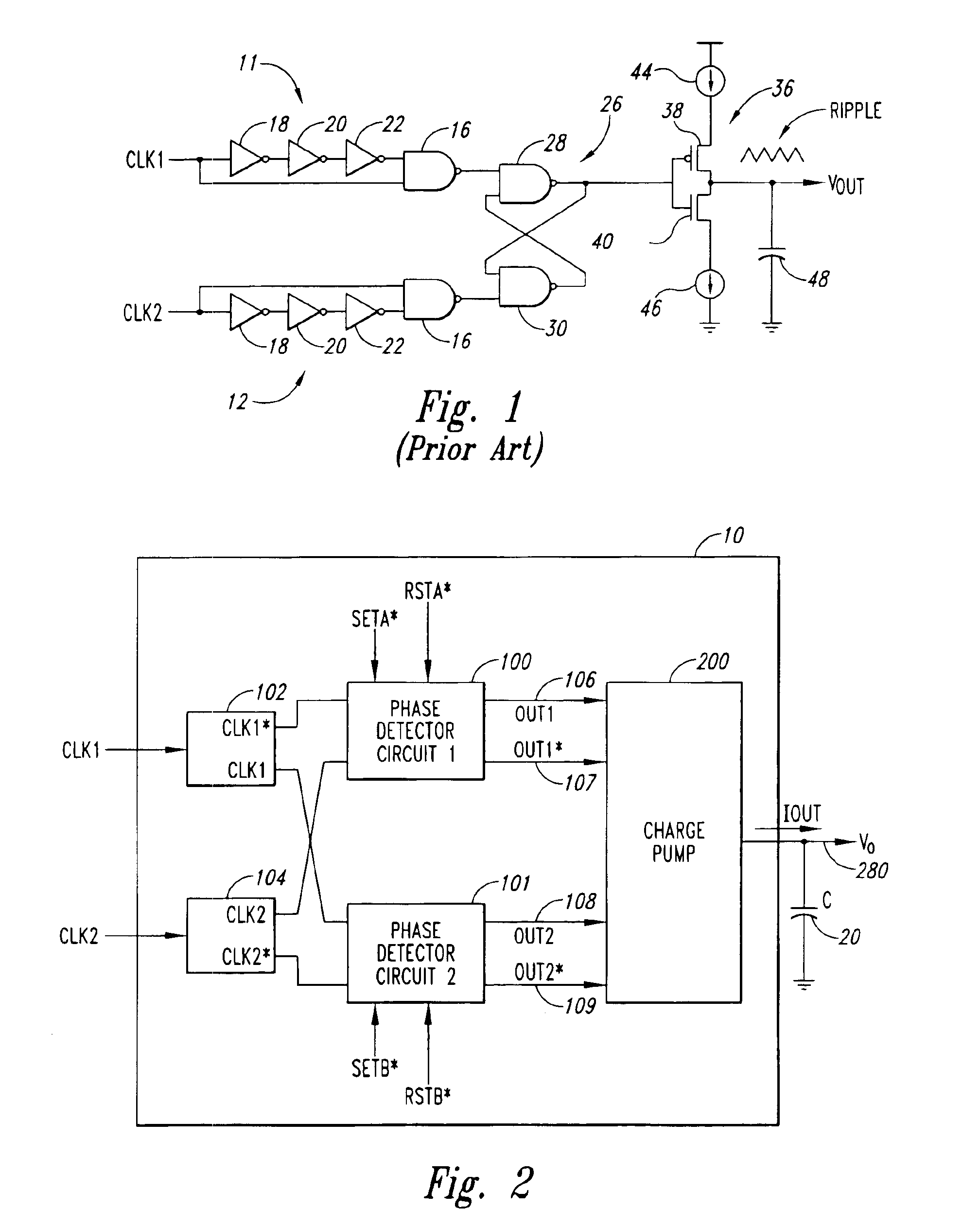
InactiveUS6952462B2Avoid problemsPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase detectorPhase correlation
A phase detector generates a phase dependent control signal according to the phase relationship between a first and second clock signal. The phase detector includes first and second phase detector circuits receiving the first and second clock signals and generating select signals having duty cycles corresponding to the phase relationship between the clock edges of the first and second clock signals. The phase detector also includes a charge pump that receives select signals from the phase detector circuits and produces an increasing or decreasing control signal when the first and second clock signals do not have the predetermined phase relationship, and a non-varying control signal when the first and second clock signals do have the predetermined phase relationship. The control signal may be used to adjust the delay value of a voltage-controlled delay circuit in order to adjust the phase relationship between the first and second clock signals to have a predetermined phase relationship.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Borehole telemetry system
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
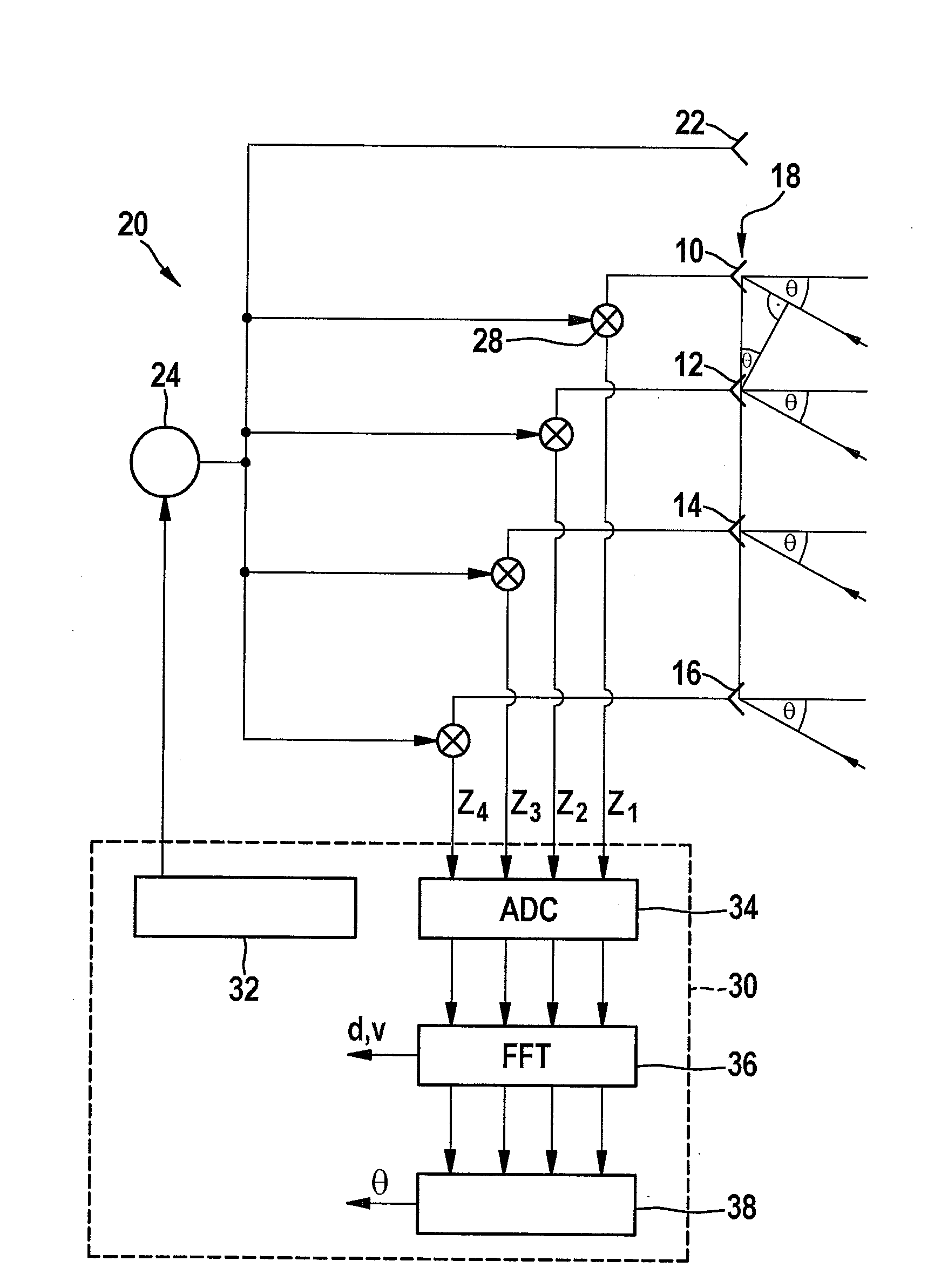
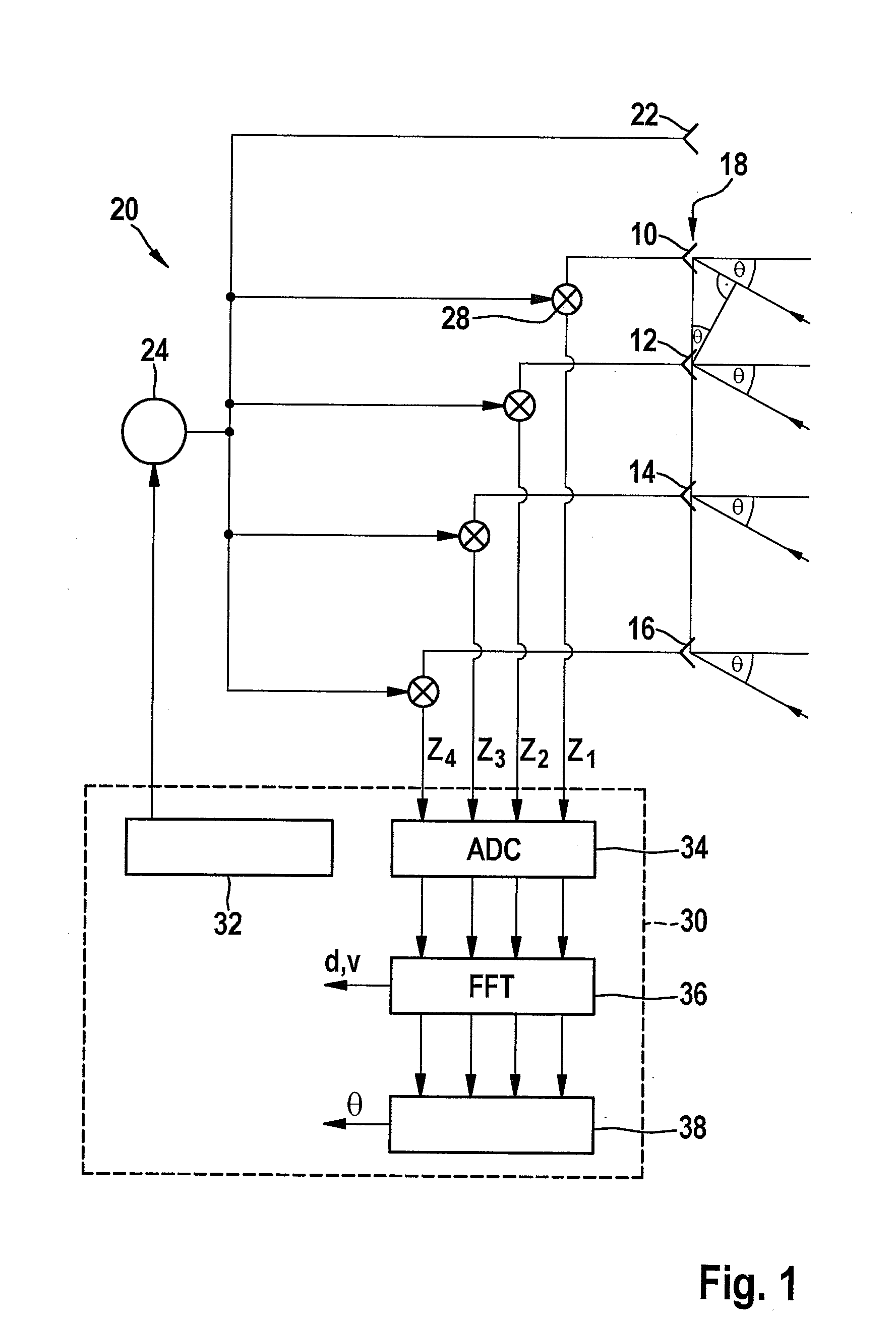
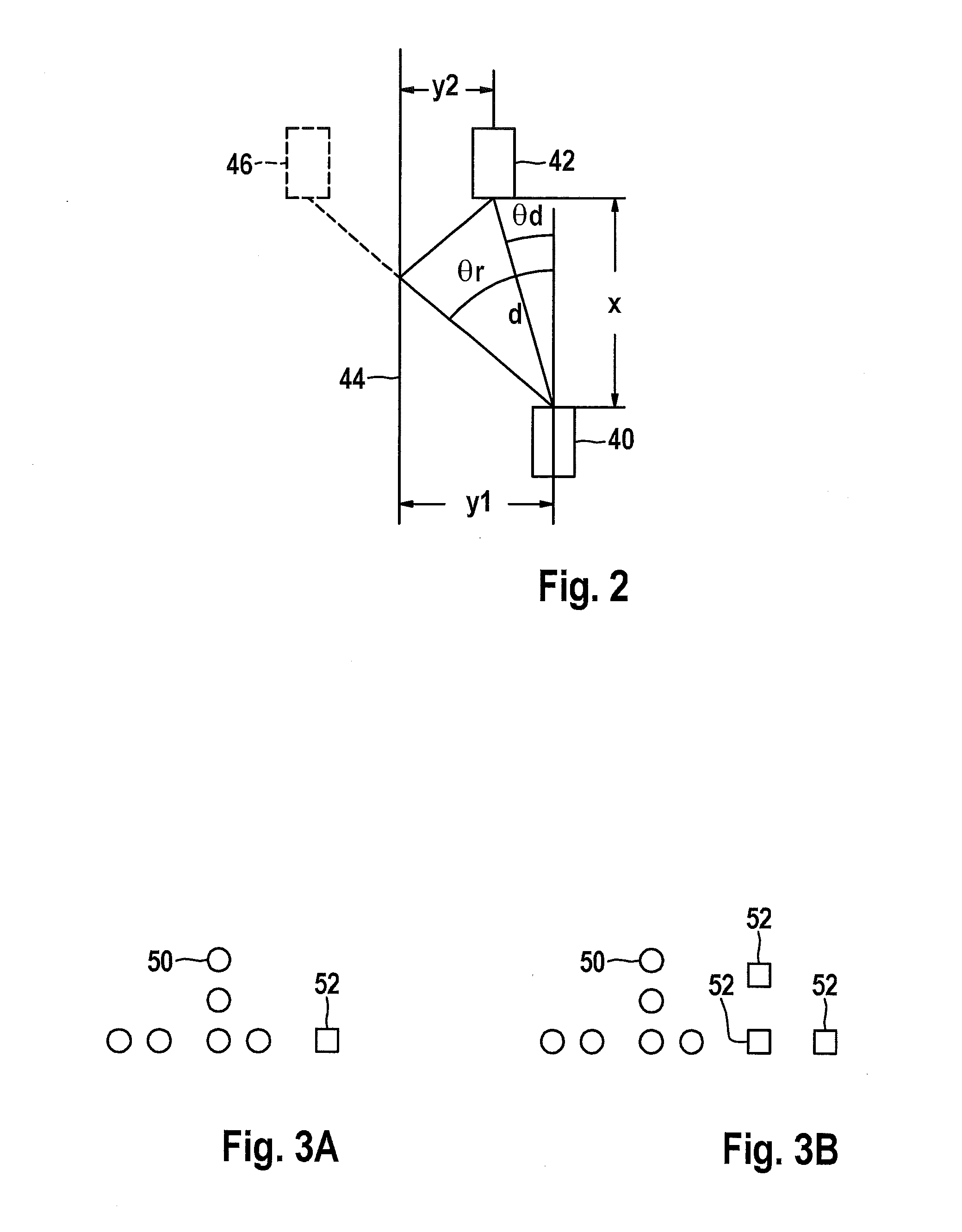
Method for angle estimation and radar sensor for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20150204972A1Simpler and accurate estimationLow computational costAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase correlationRadar
A method for a radar sensor for a motor vehicle, for angle estimation of radar targets based on an antenna diagram that indicates, for various configurations of radar targets, pertinent amplitudes and / or phase correlations between signals which are obtained for the relevant configuration in multiple evaluation channels of the radar sensor, wherein for a single real target, the occurrence of a number n of apparent targets, which are caused by reflection of the signal coming from the real target from elongated objects, is modeled mathematically; a correlation between the location angle of the real target and the location angles of the apparent targets is calculated; and to estimate the location angle of the real target, a multi-target estimate is performed in an n-dimensional search space and the search is limited to a sub-space that is determined by the calculated correlation.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method to estimate segmented motion
InactiveUS20110176013A1Narrow spaceEfficient managementTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPhase correlationAlgorithm
A method to estimate segmented motion uses phase correlation to identify local motion candidates and a region-growing algorithm to group small picture units into few distinct regions, each of which has its own motion according to optimal matching and grouping criteria. Phase correlation and region growing are combined which allows sharing of information. Using phase correlation to identify a small number of motion candidates allows the space of possible motions to be narrowed. The region growing uses efficient management of lists of matching criteria to avoid repetitively evaluating matching criteria.
Owner:SONY CORP
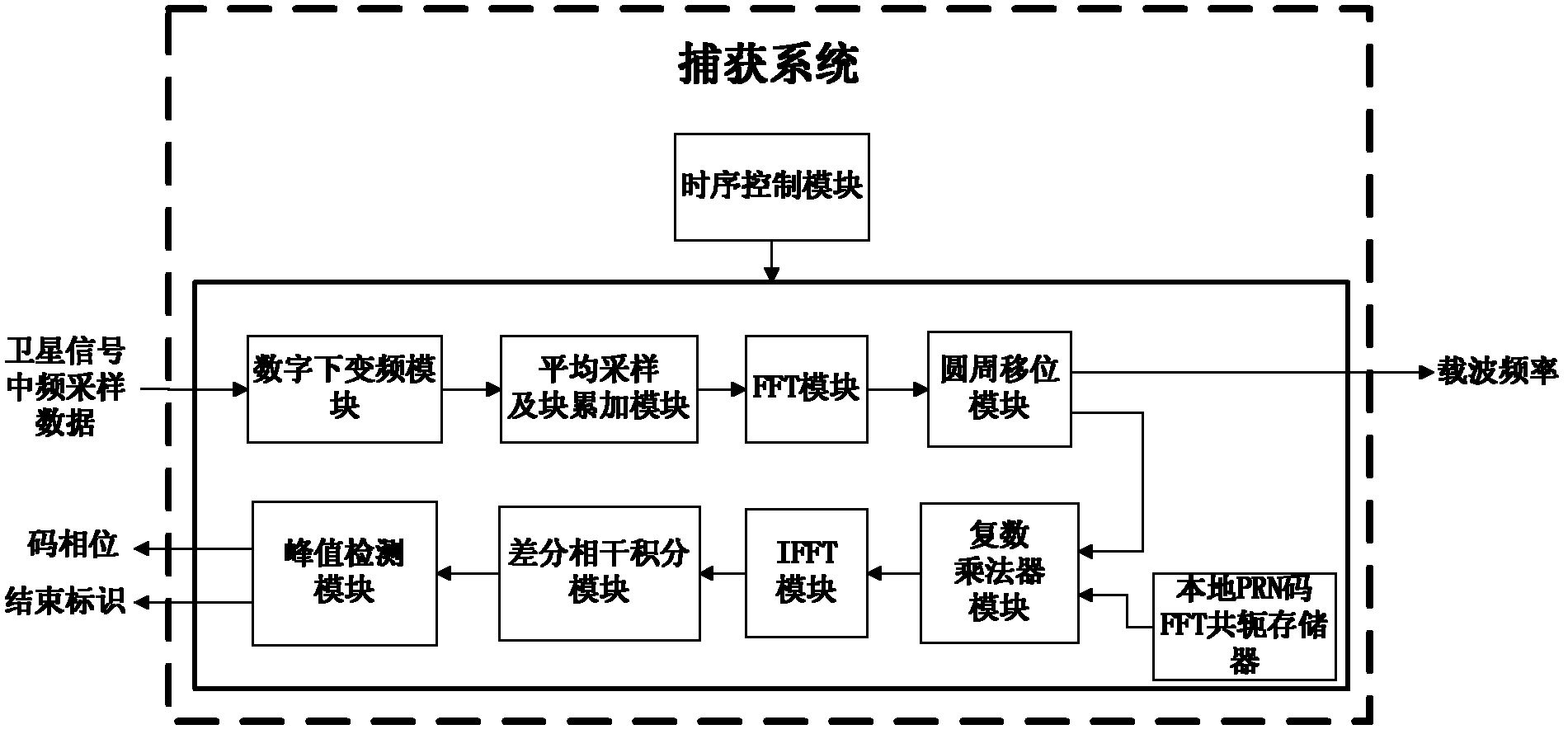
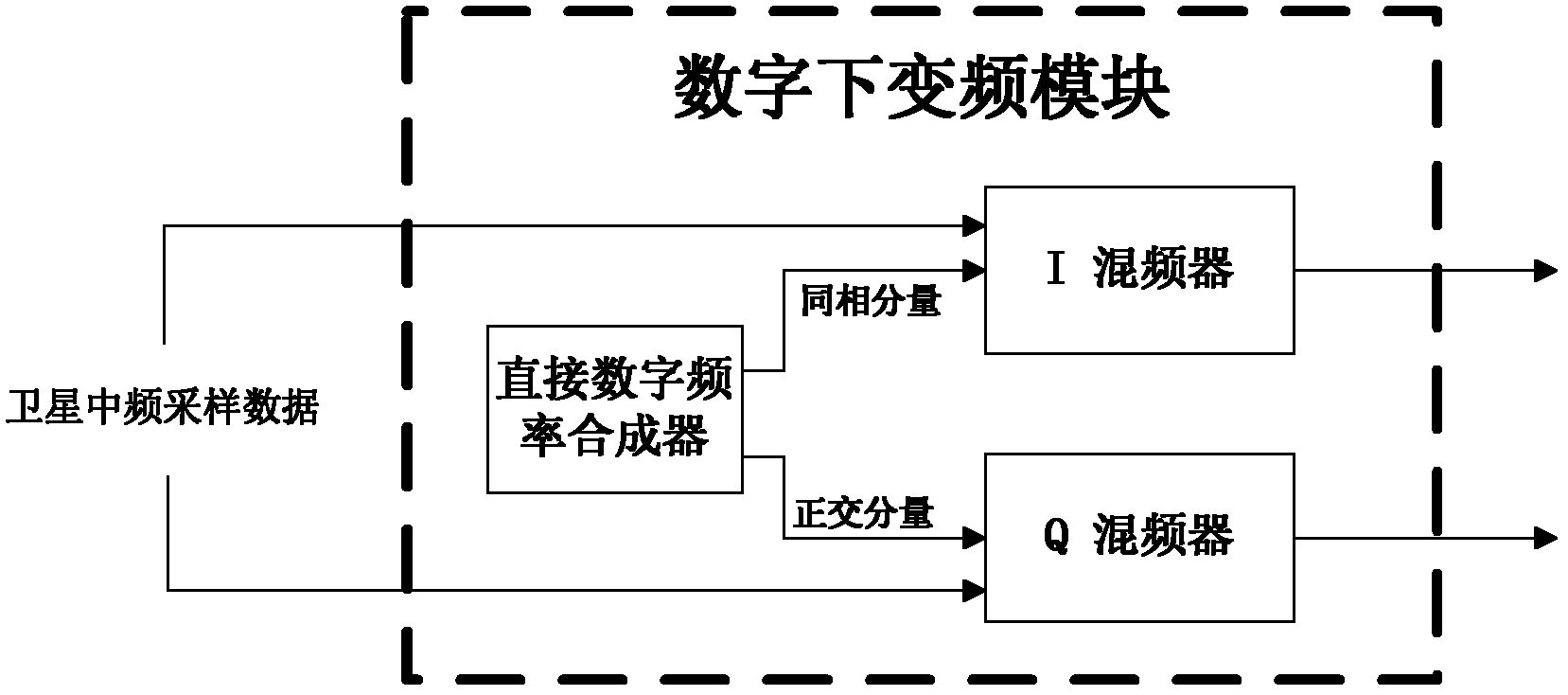
High-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and system
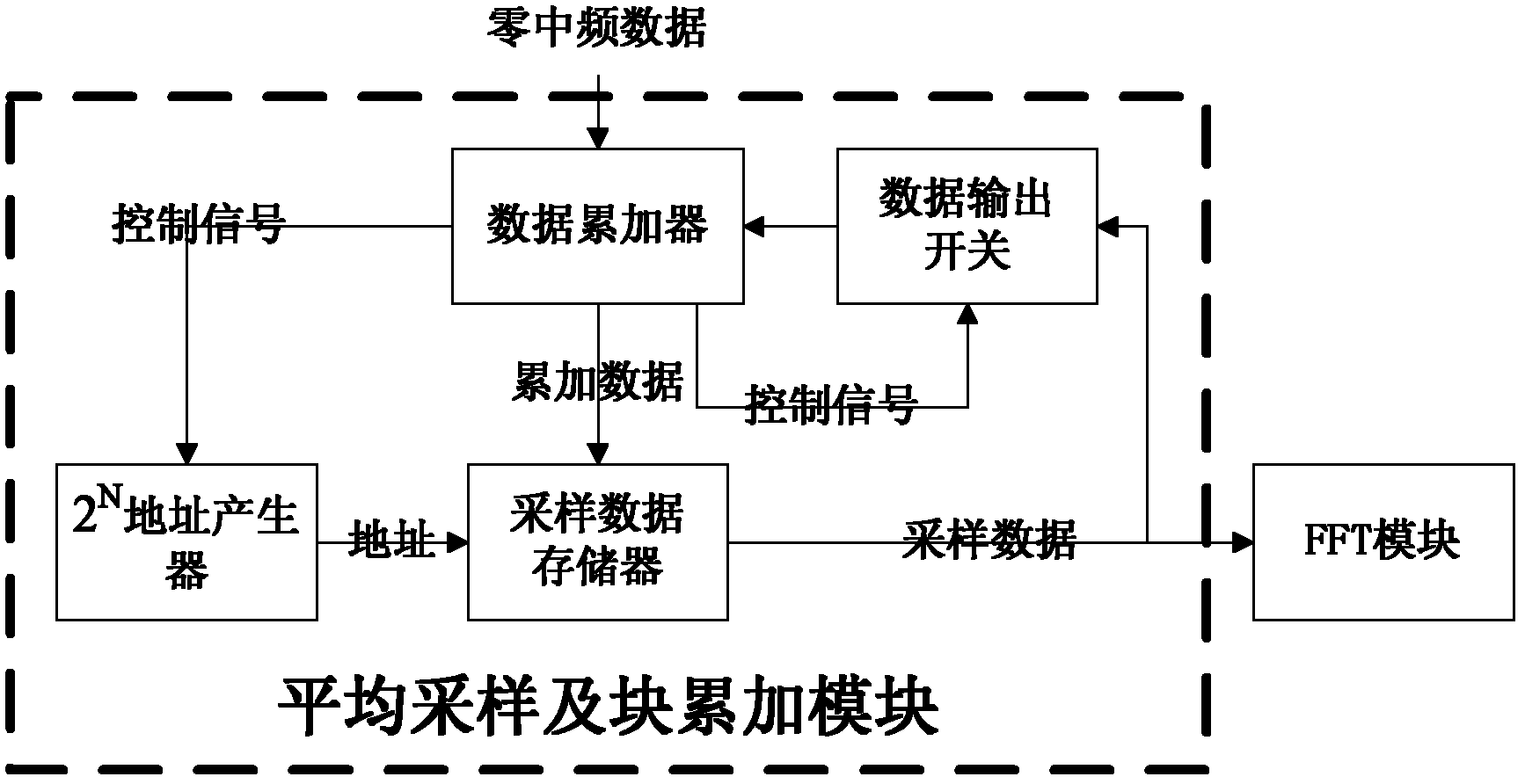
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and a system. The system comprises a digital down-conversion module, an average sampling and block accumulation module, an FFT (fast Fourier transform) module, a circumference shifting module, a local PRN (pseudo random noise) code FFT conjugate memory, a complex multiplier module, an IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) module, a differential coherence integration module, a peak detection module and a sequential control module. The digital down-conversion module realizes digital down-conversion operation for satellite digital intermediate frequency signals; the average sampling and block accumulation module averagely samples satellite data and completes a block accumulation function; the FFT module searches code phase frequency domains; the circumference shifting module utilizes Doppler circumference shifting search to replace frequency compensation; the local PRN code FFT conjugate memory stores a local PRN code FFT conjugate result; the complex multiplier module realizes signal de-spreading; the IFFT module calculates different code phase coherence results; the differential coherence integration module accumulates differential coherence energy of de-spread satellite signals; the peak detection module realizes signal capturing output; and the sequential control module controls timing sequence of the various modules of the system. Weak signal capturing speed and sensitivity of a satellite navigation receiver are improved, and parameters can be configured flexibly.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Autonomous navigation, guidance and control using LDRI
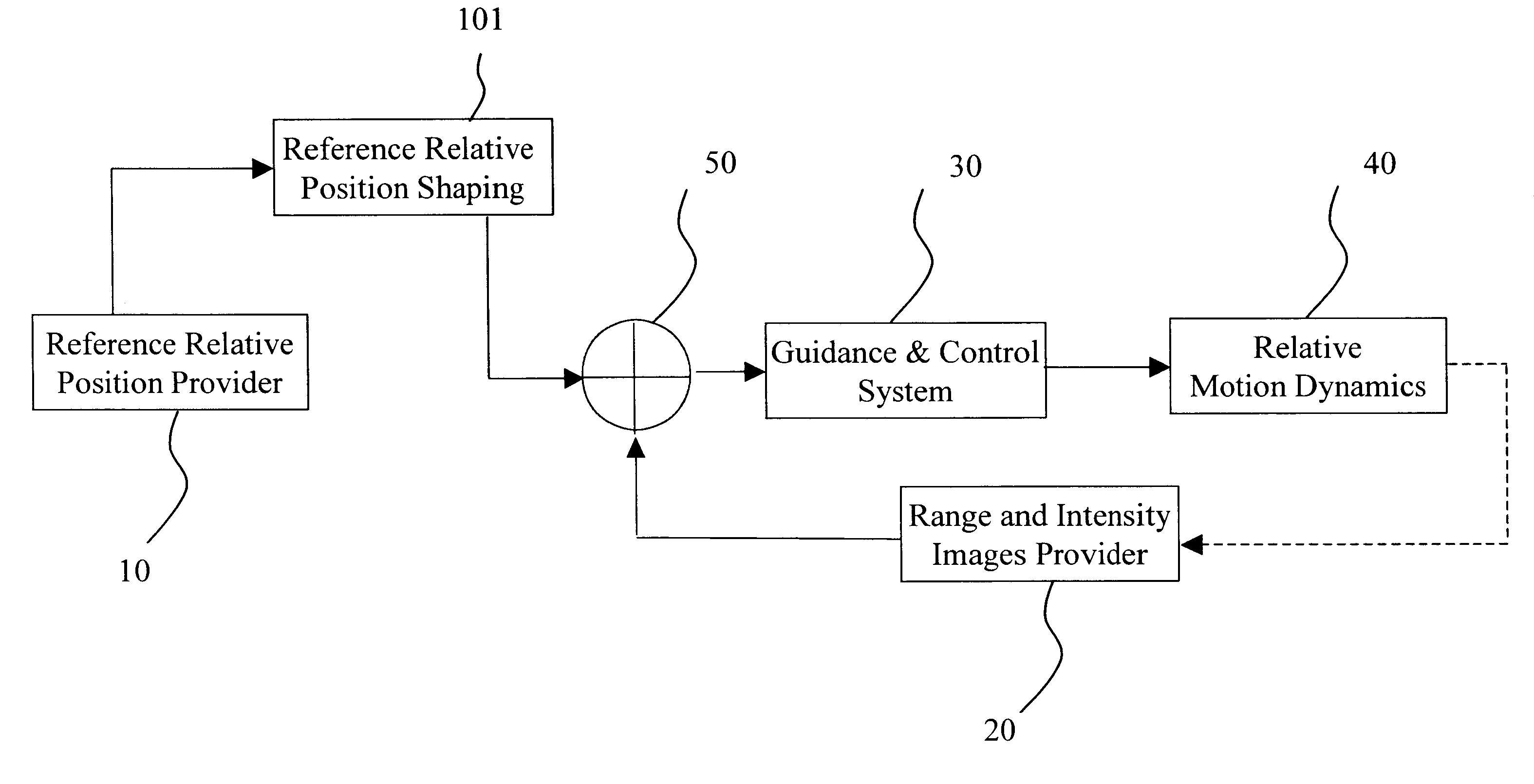
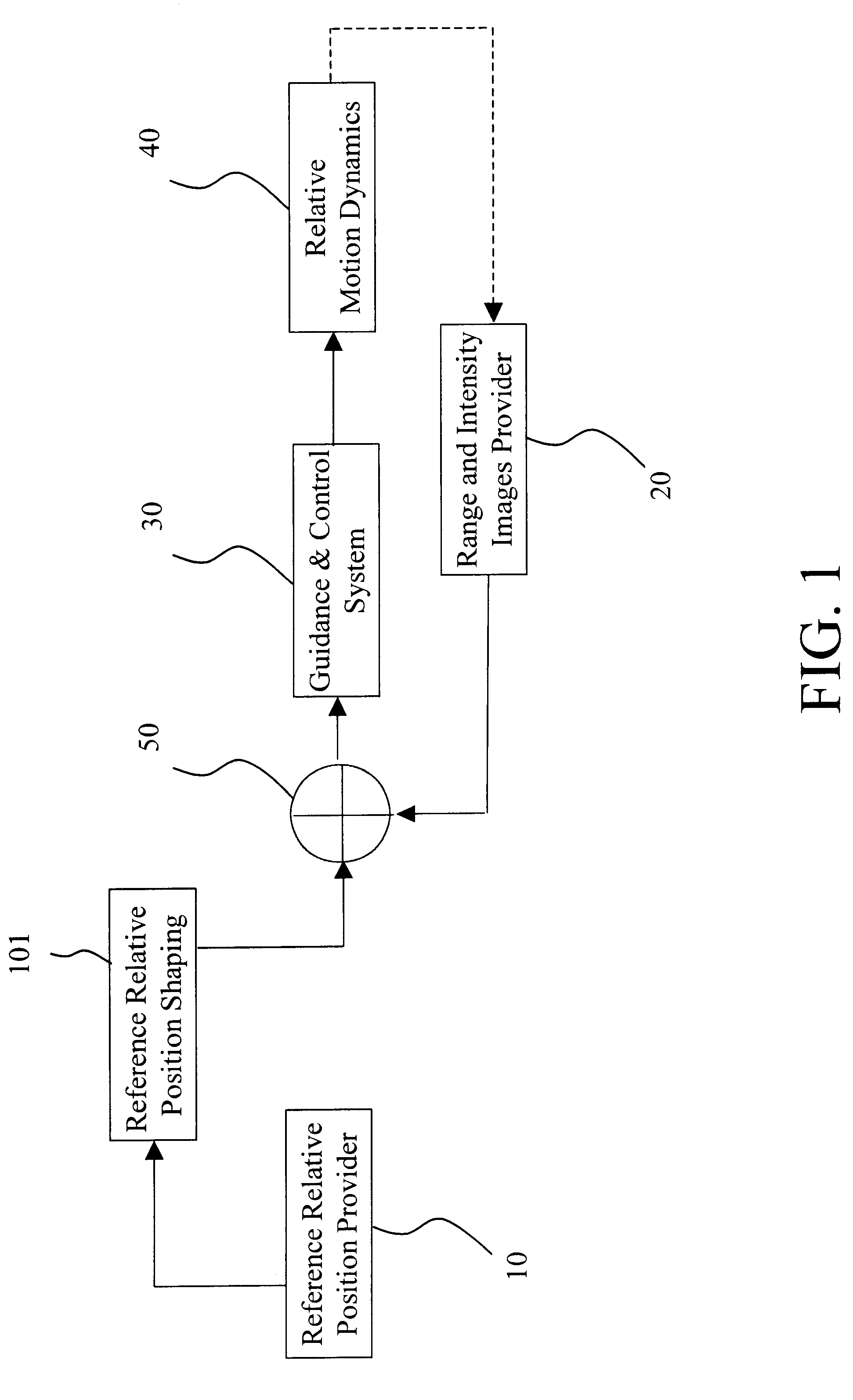
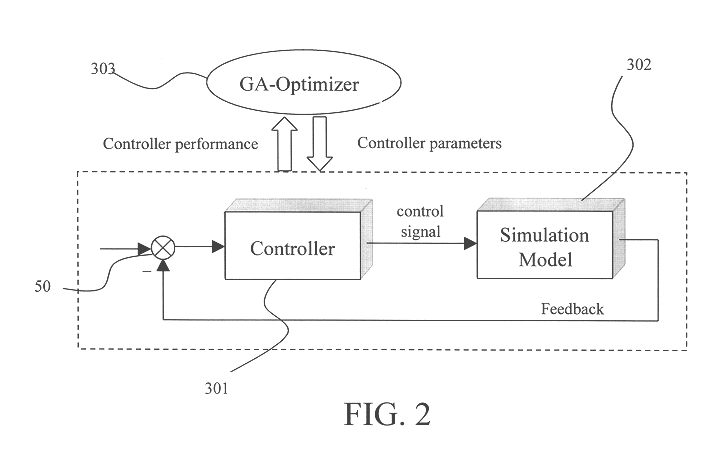
An autonomous navigation, guidance, and control process for docking and formation flying by utilizing the laser dynamic range imager (LDRI) and key technologies, including fuzzy logic based guidance and control, optical flow calculation (including cross-correlation, phase-correlation, and image differential), software design and implementation, and verification methods. The autonomous navigation, guidance, and control process includes the steps of providing an expected reference position relative to a target; generating a carrier position and attitude relative to said target by a Range and Intensity Images Provider; producing a relative position and attitude error; and producing control commands from said relative position and attitude error for relative motion dynamics.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
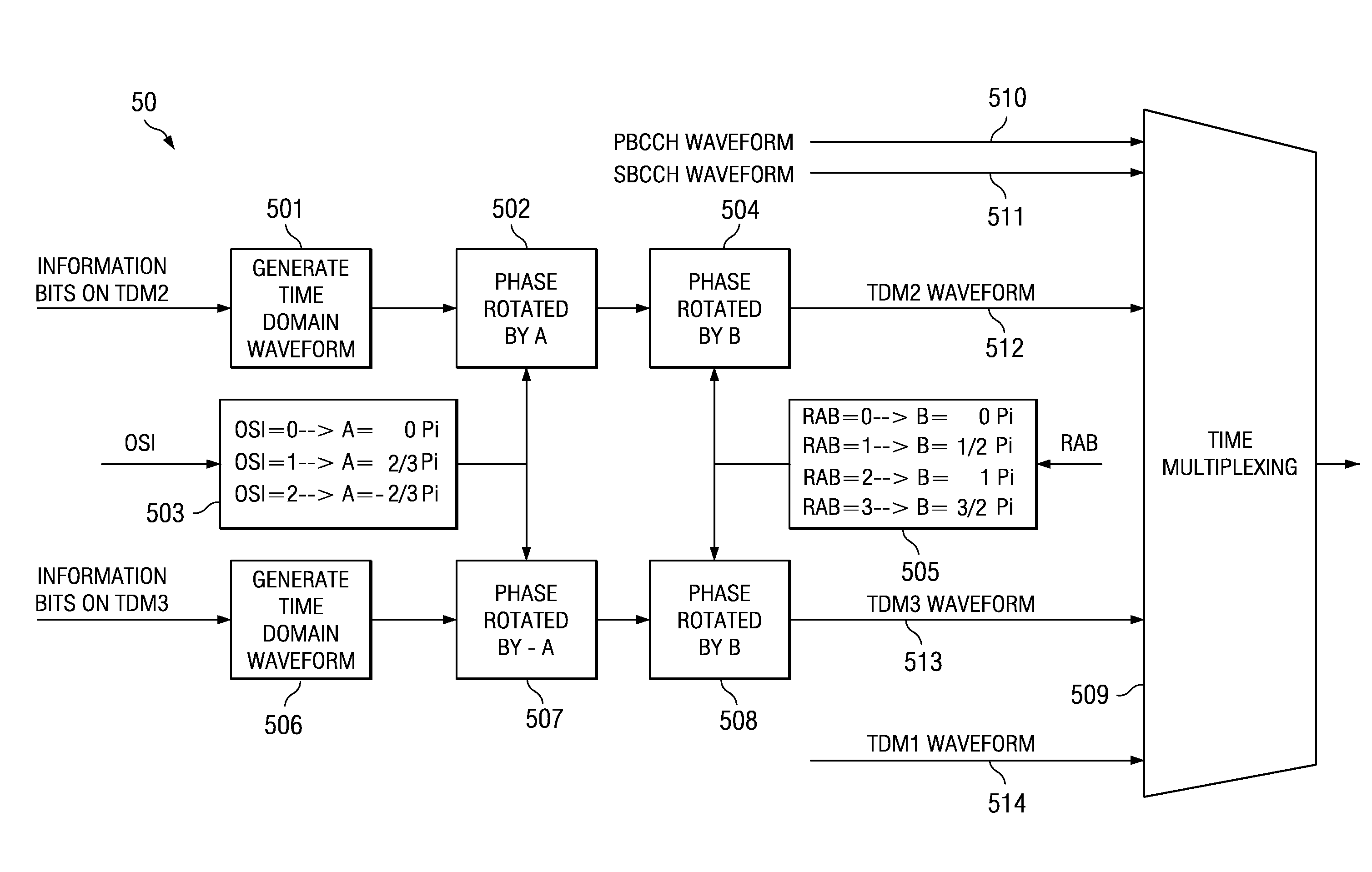
Method and Apparatus for Achieving System Acquisition and Other Signaling Purposes Using the Preamble in an OFDM Based Communications System
In the system acquisition process system information is non-coherently detected using correlation of reconstructed and received preamble signals, such as the primary broadcast control channel (PBCCH) and the acquisition pilots (TDM1, TDM2, and TDM3). The phase correlation signals between the correlated signals of PBCCH and TDM2 or TDM3 and between the correlated signals of TDM2 and TDM3 are combined to decode other sector interference (OSI) information and the like. Acquisition is also made more efficient by taking advantage of predictable information based on system synchronicity. The sync / async bit is included in at least one of the acquisition pilots. The mobile then uses knowledge of system synchronicity to more efficiently detect the additional information in the superframe preamble.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
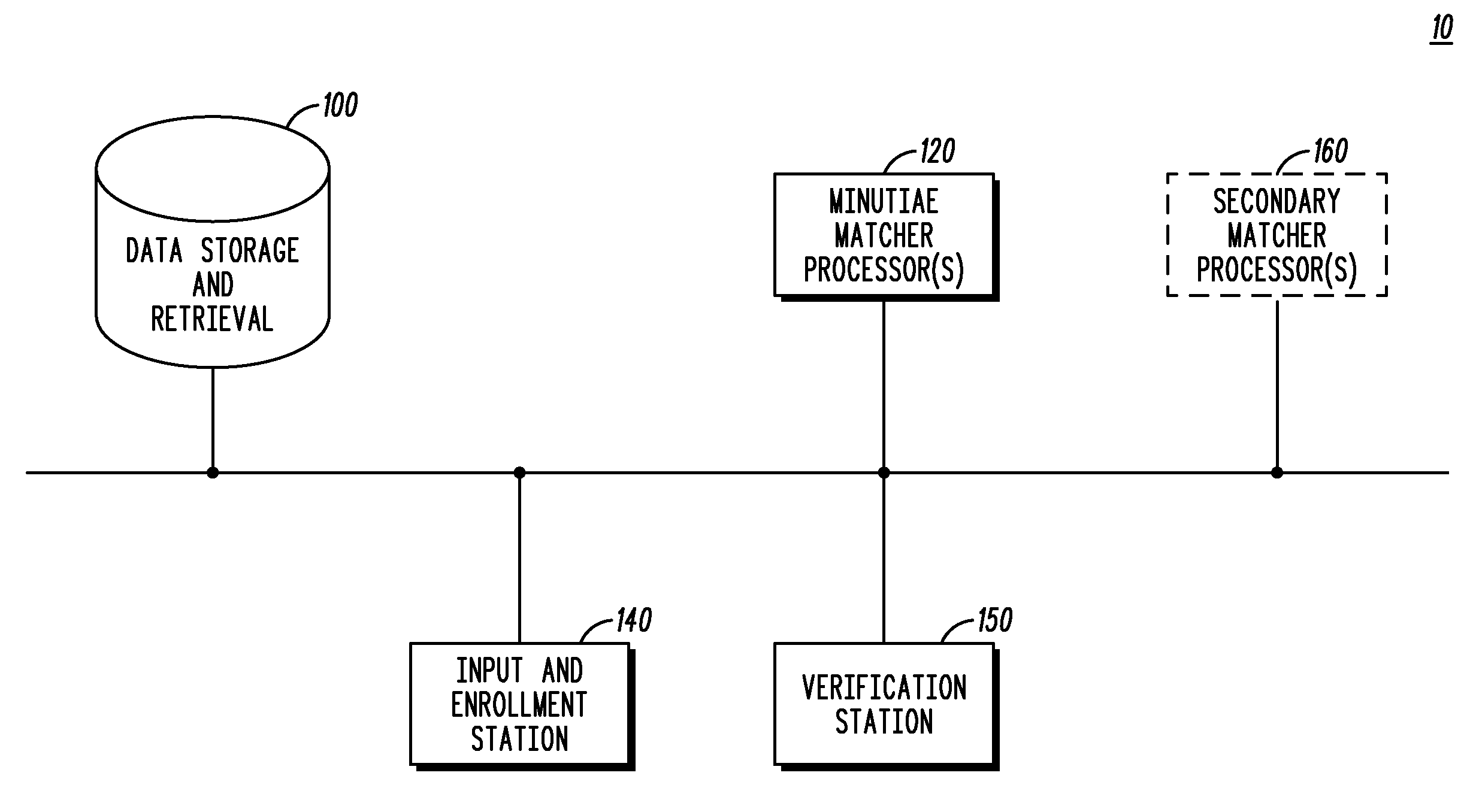
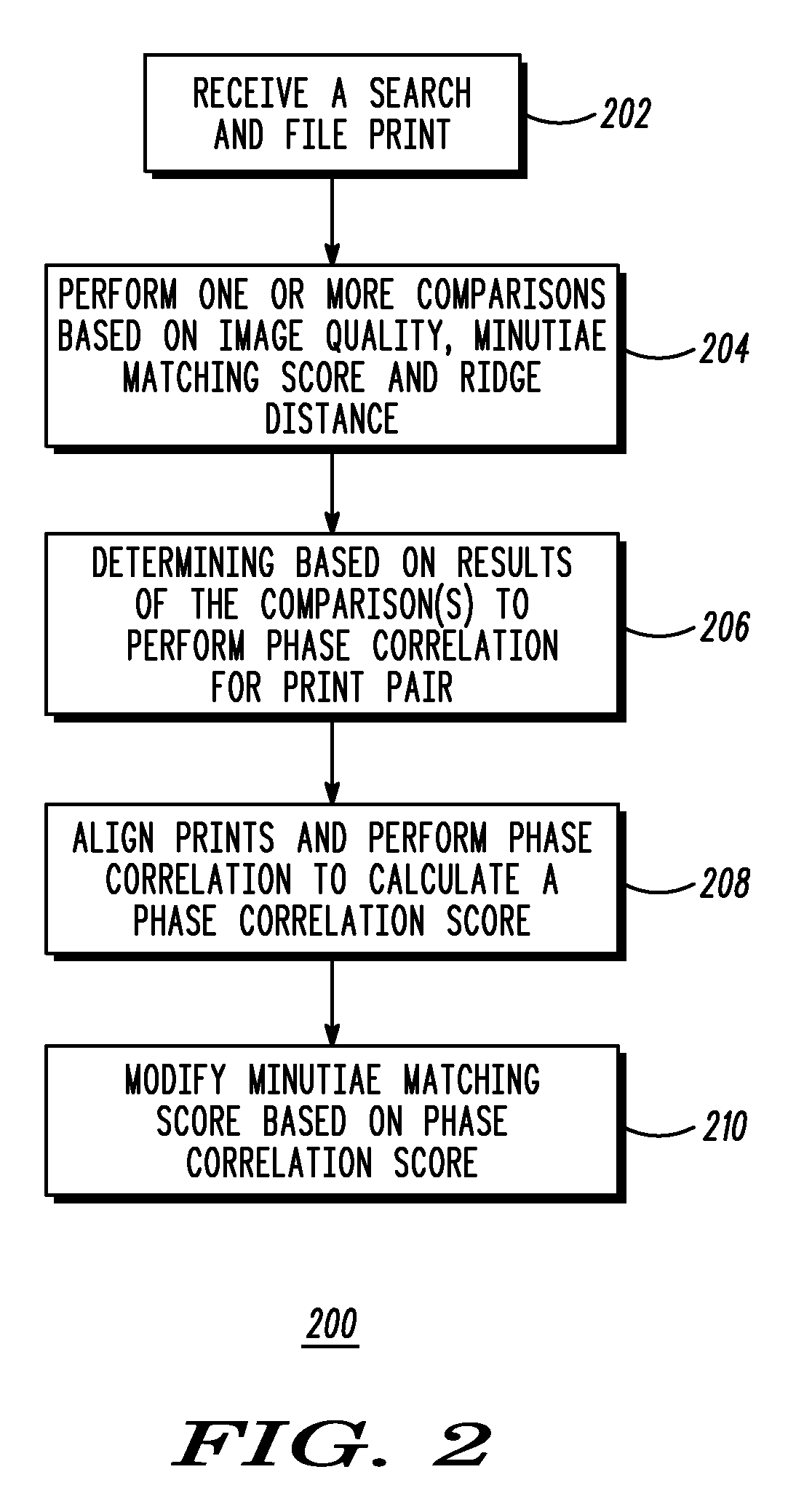
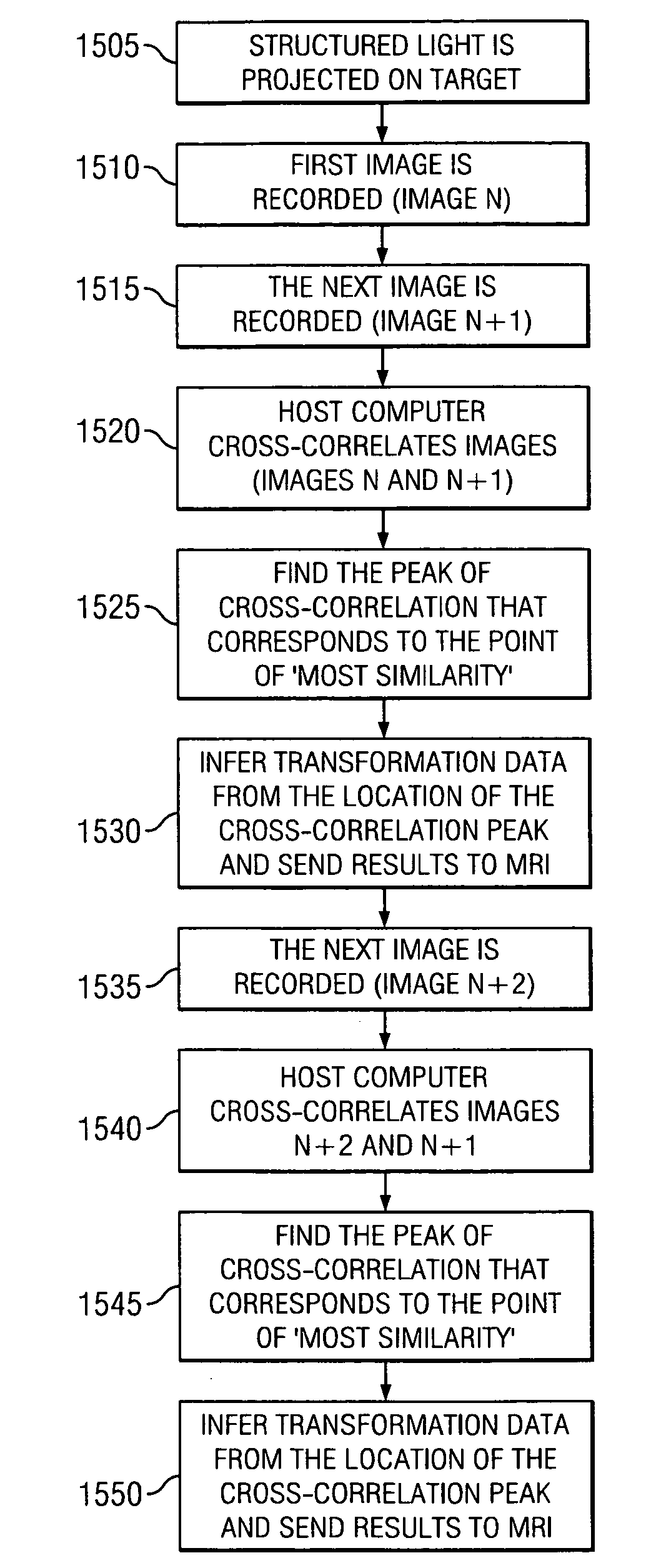
Print matching method and system using phase correlation
A system includes an interface receiving a search and file print and a processing device. The processing device performs a method that includes: performing at least one of a first comparison of quality of the search and file prints to a quality threshold, a second comparison of a minutiae matching score for the search and file prints to a minutiae matching score threshold, and a third comparison of a ridge distance of the search and file prints to a ridge distance threshold; determining that a phase correlation between the search and file prints is to be performed based on results of the at least one of the first, second and third comparisons; aligning the search and file prints and performing the phase correlation to calculate a phase correlation score; and modifying the minutiae matching score based on the calculated phase correlation score.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
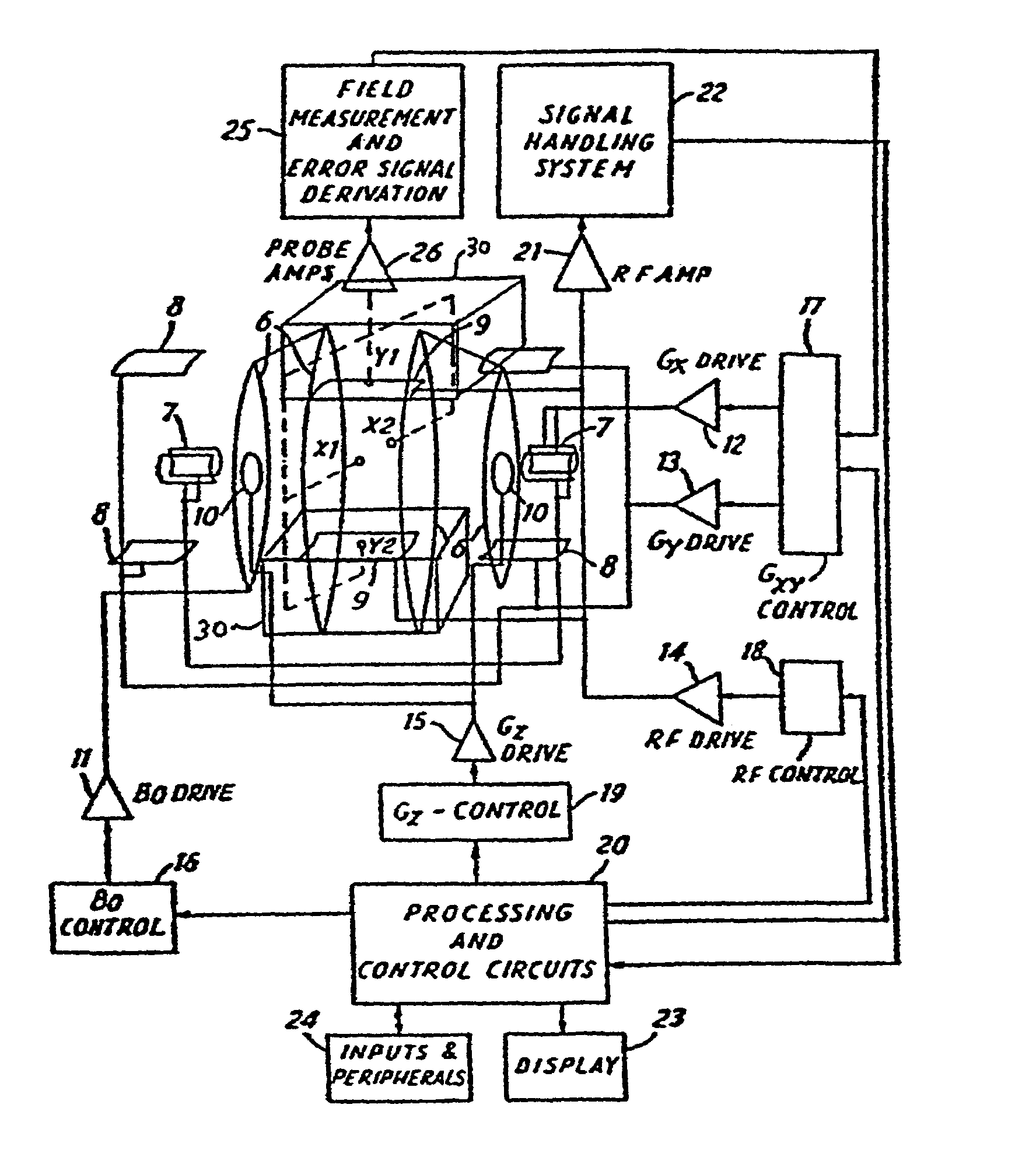
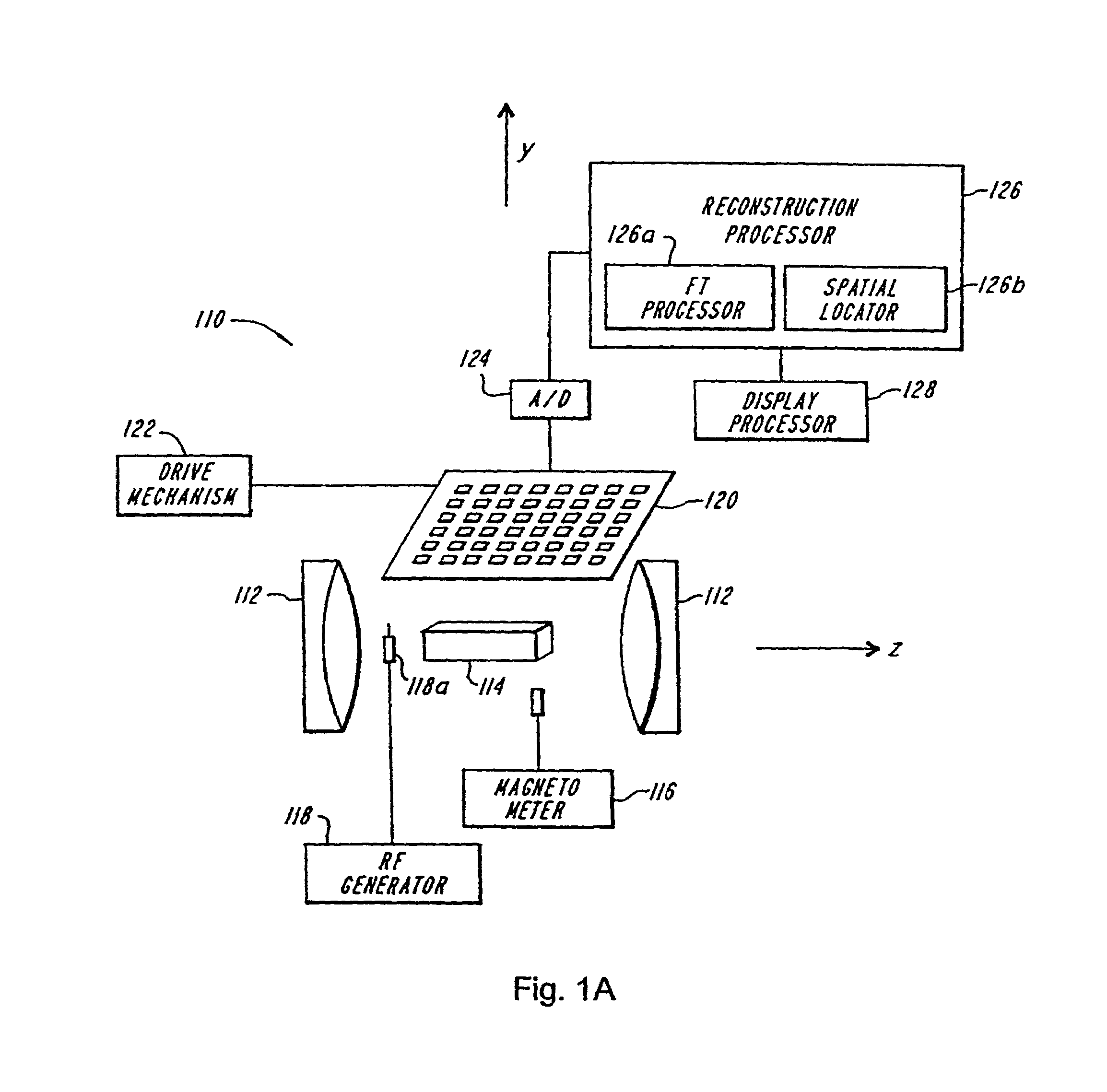
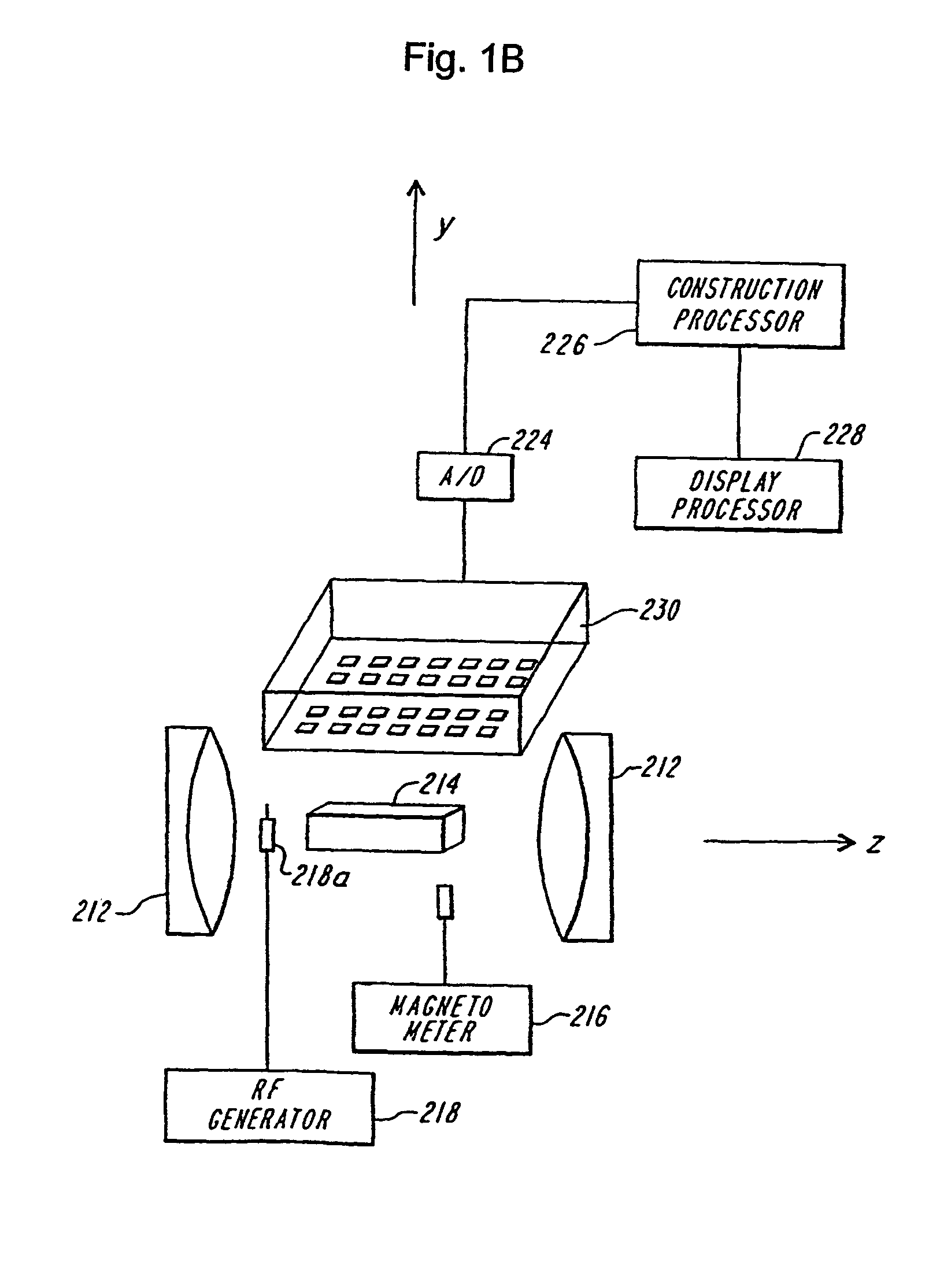
4 dimensional magnetic resonance imaging
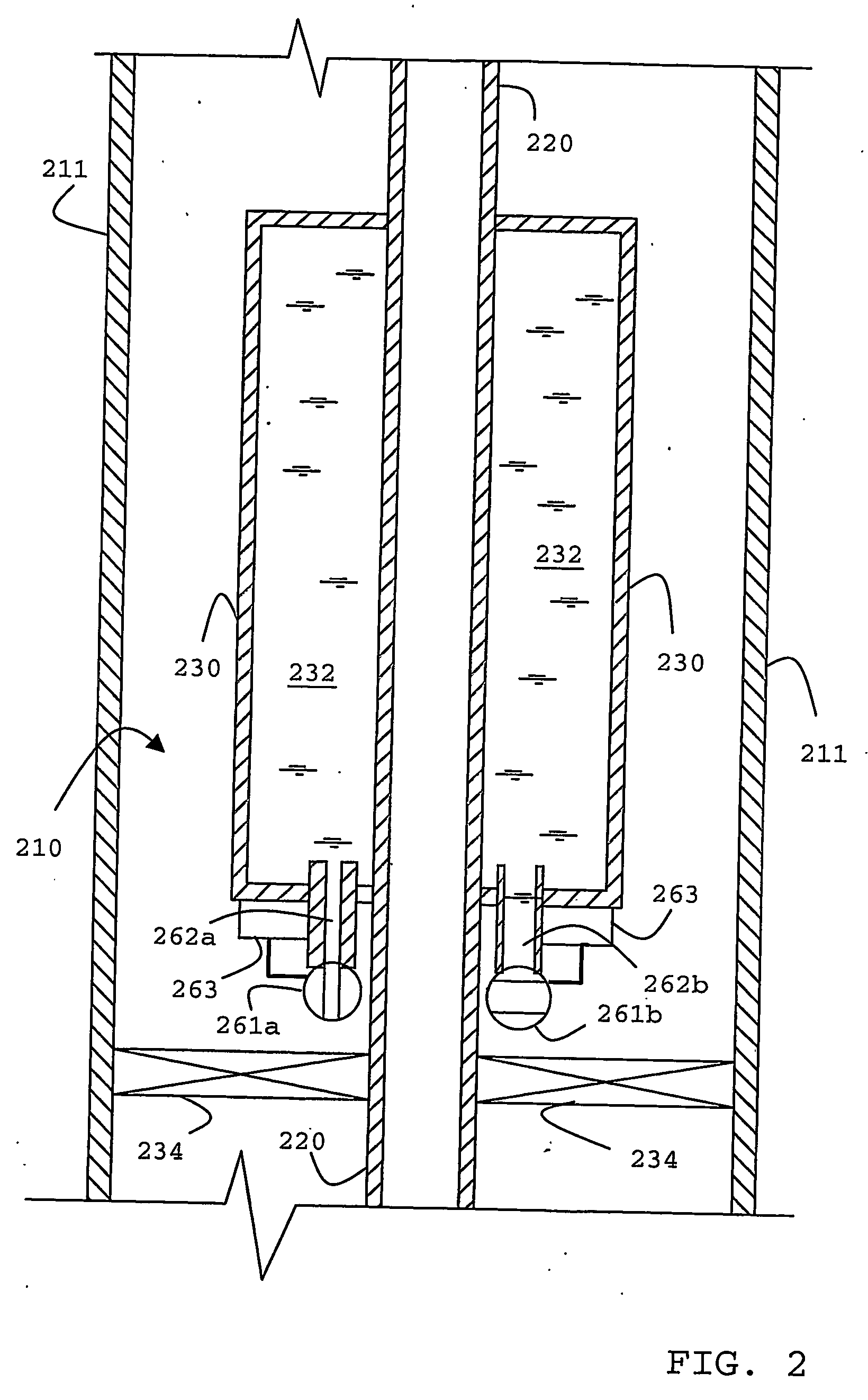
InactiveUS7382129B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correlationVoxel
Provided are apparatus and methods for forming a multidimensional image of inanimate or animate objects which utilize a magnetization source (112) to magnetize a volume of an object to be imaged, a radiation source (118) for applying a radiation field to the object to be imaged, an output signal detector (120) for producing output signals in response to the secondary radiation at a plurality of spatial locations outside of the object as a function of time, processors (126, 126a and 126b) for determining a plurality of Fourier components, for associating the Fourier components due to each voxel (14) by phase, and for converting each set of components into a voxel location, and an image processor (128) for producing an image.
Owner:MILLS RANDELL L
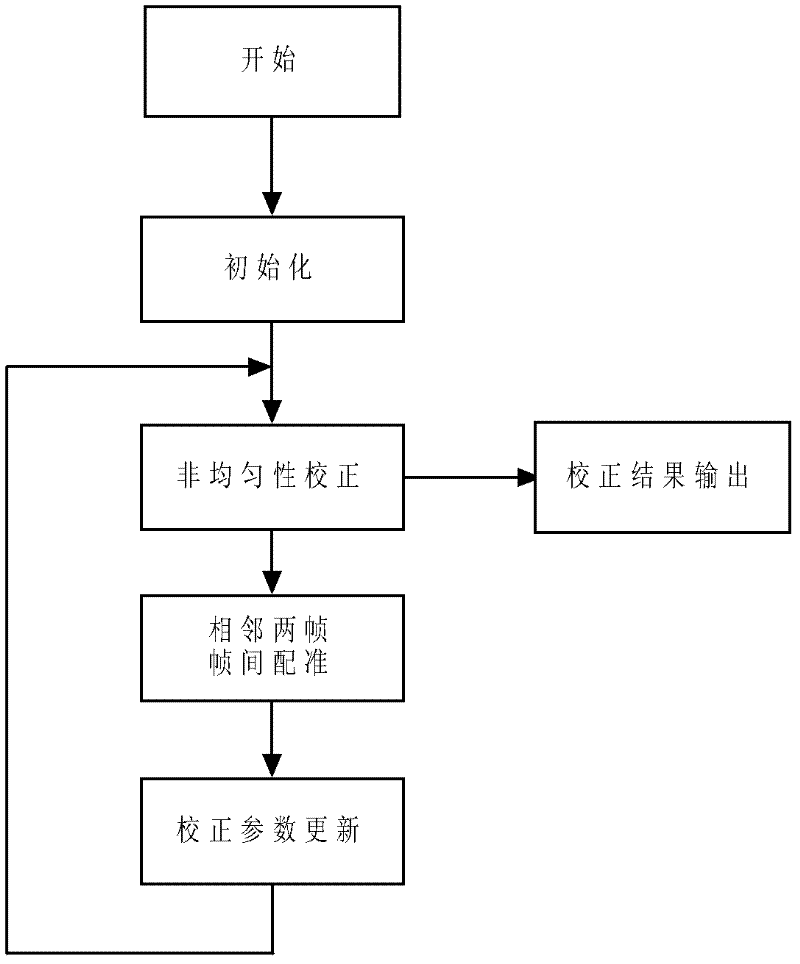
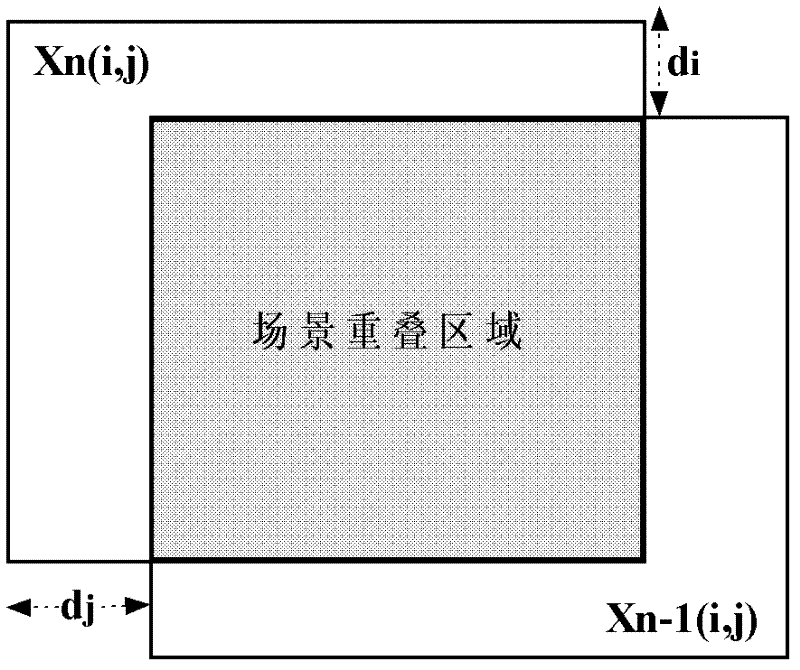
Rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method
InactiveCN102538973APrevent erroneous updatesBug update avoidanceRadiation pyrometryPhase correlationSteep descent
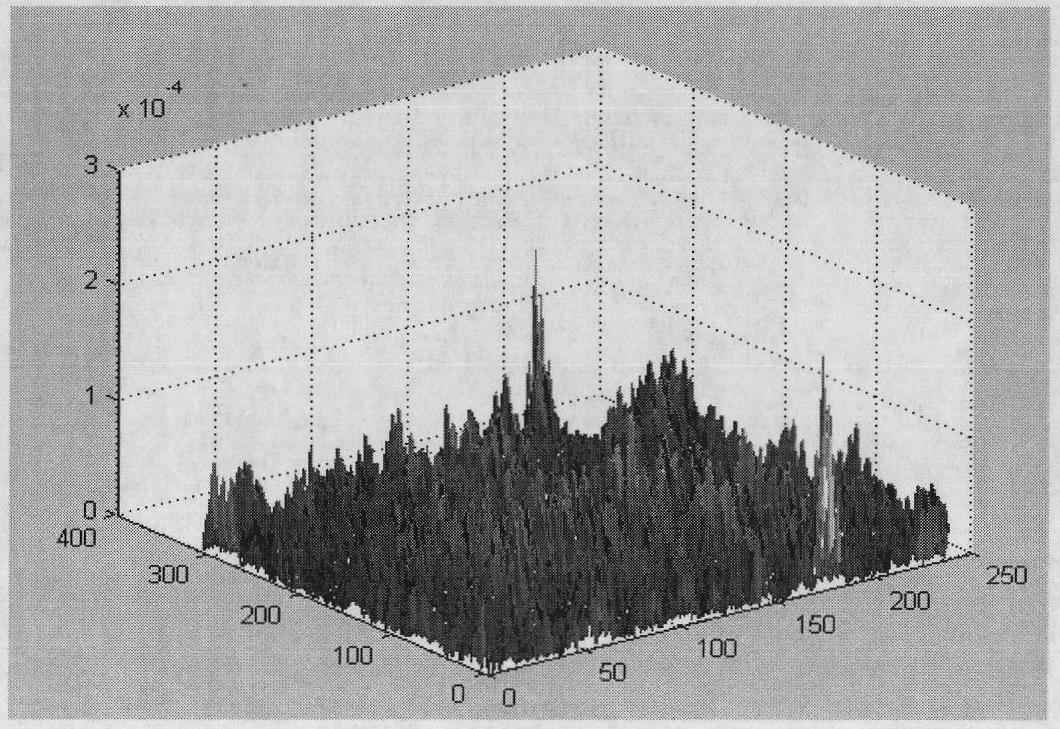
The invention discloses a rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method, wherein the aim of non-uniformity correction is achieved by minimizing interframe registration error of two adjacent images. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: initializing gain and offset correction parameters and acquiring an uncorrected original image; acquiring a new uncorrected original image, and carrying out non-uniformity correction on the new uncorrected original image and the previous uncorrected original image by utilizing the current non-uniformity correction parameters; obtaining relative displacement, scene correlation coefficient and interframe registration error of two corrected images by utilizing an original point masking phase correlation method; and updating correction parameters along the negative gradient direction by adopting a steepest descent method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high correction accuracy, fast convergence speed, no ghost effect and low calculated amount and storage content and is especially applicable to being integrated into an infrared focal plane imaging system, and the effect of improving imaging quality, environmental suitability and time stability of an infrared focal plane array is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
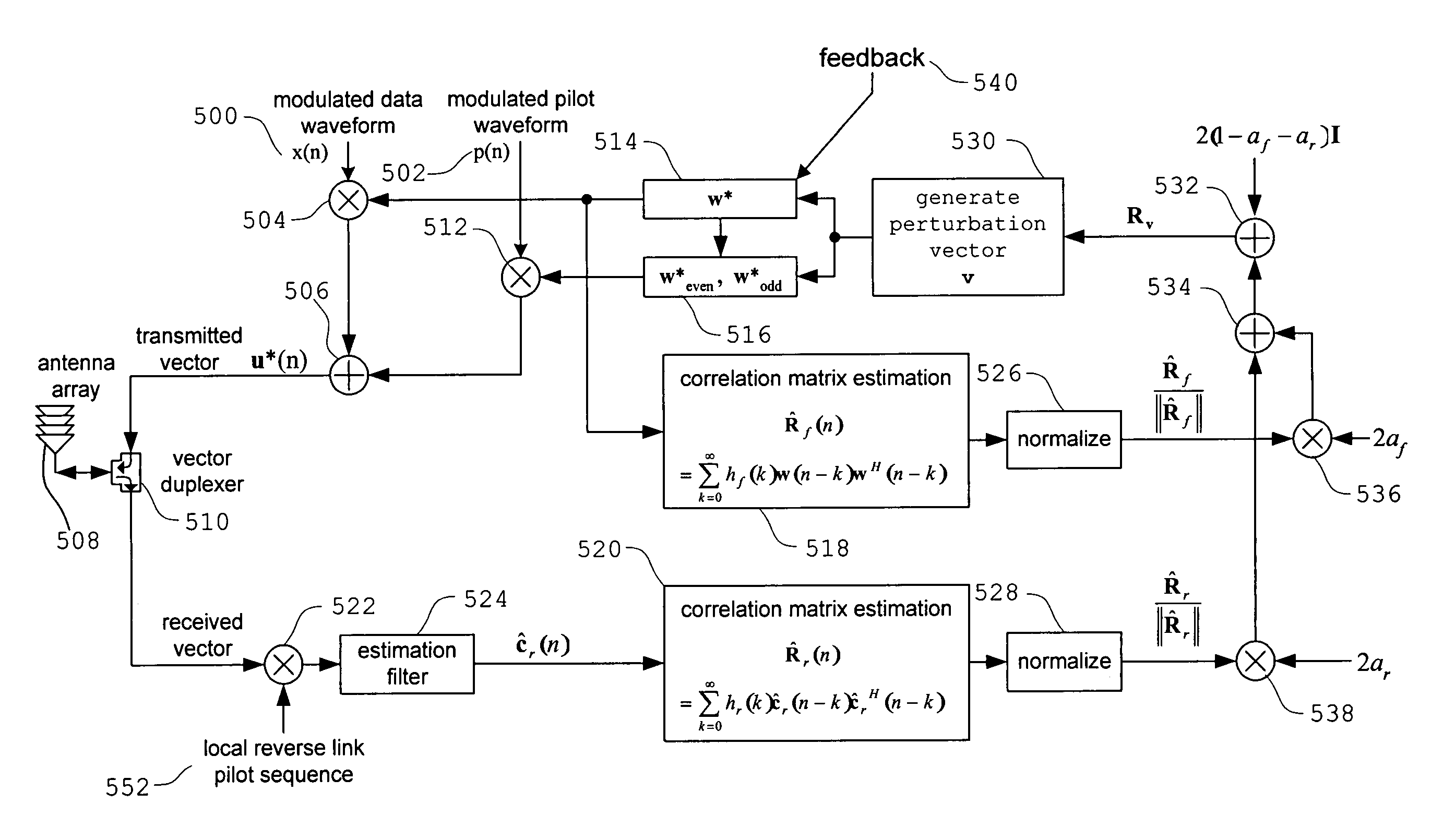
Method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel correlations in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7236538B1Improves weight vector trackingDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPhase correlationGradient estimation
A novel method and apparatus for improving transmit antenna weight tracking using channel vector element to element correlations in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The present channel autocorrelation tracking technique utilizes the observation that tracking can be improved when a channel gain vector contains correlated elements. In a first embodiment of the autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing a perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimate and a perturbation autocorrelation matrix to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a second embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention extracts a coarse gradient estimate by utilizing eigendecompositions, perturbation vector autocorrelation matrix estimates, and perturbation autocorrelation matrices to update TxAA weight vectors accordingly. In a third embodiment of the channel autocorrelation tracking technique, the present invention reduces the phase change that can occur at receivers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
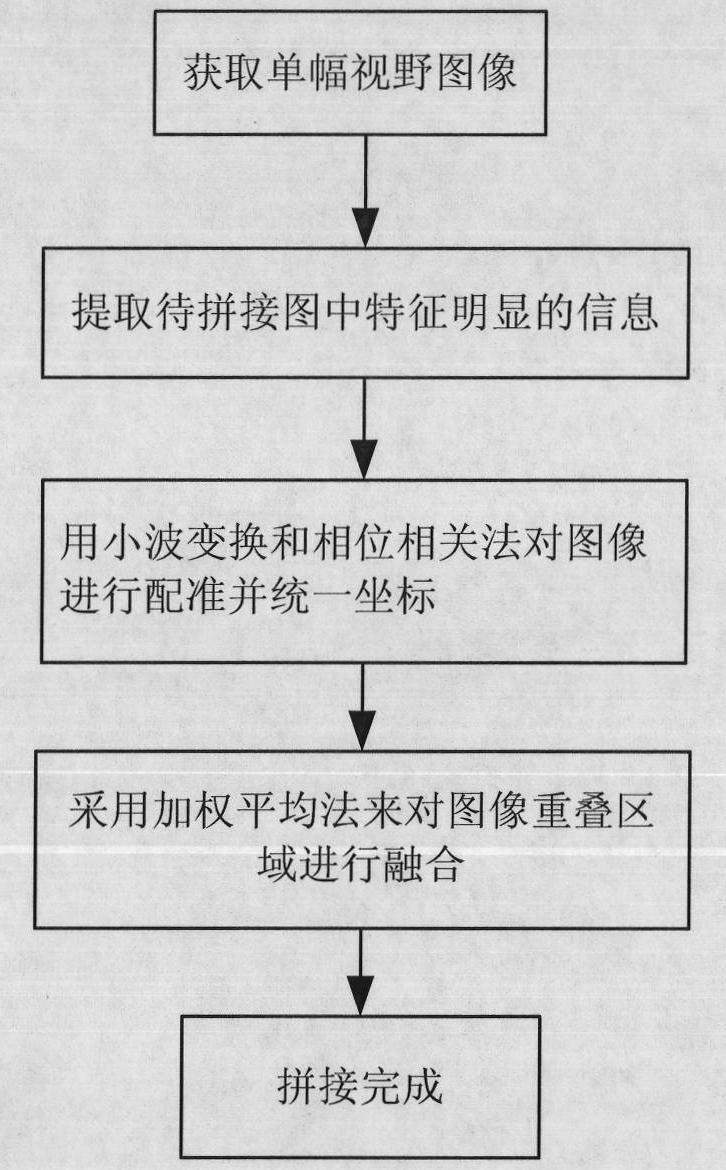
Fast image splicing method
InactiveCN101840570AAchieve integrationQuick stitchingImage enhancementImage analysisPhase correlationComputation complexity
The invention discloses a fast image splicing method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) acquiring a single-breadth field image; (2) extracting characteristic information in an image to be spliced; (3) performing two-dimensional wavelet transform on the image to be spliced to obtain high-frequency coefficients reflecting the profile of change in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction of the image, and realizing overlapped position alignment in combination with a phase correlation method; and (4) adopting a weighted mean method to fuse overlapped areas of the image to finish the splicing. In the method, low-energy coefficients reflecting the gradual change of illumination are removed by performing the two-dimensional wavelet transform on the image and then the high-frequency coefficients reflecting the profile of the change in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction of the image are obtained, which can effectively reduce calculation complexity; and simultaneously, the fast and accurate overlapped position alignment is realized in combination with the phase correlation method and the fusion of the image is realized by adopting the weighted mean method so as to realize the fast and accurate splicing of PCB images of various specifications and various colors.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and method for tracking movement of a target
InactiveUS20090039886A1Optical detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correlationMedical imaging
Owner:VETERANS AFFAIRS US GOVT AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF +1
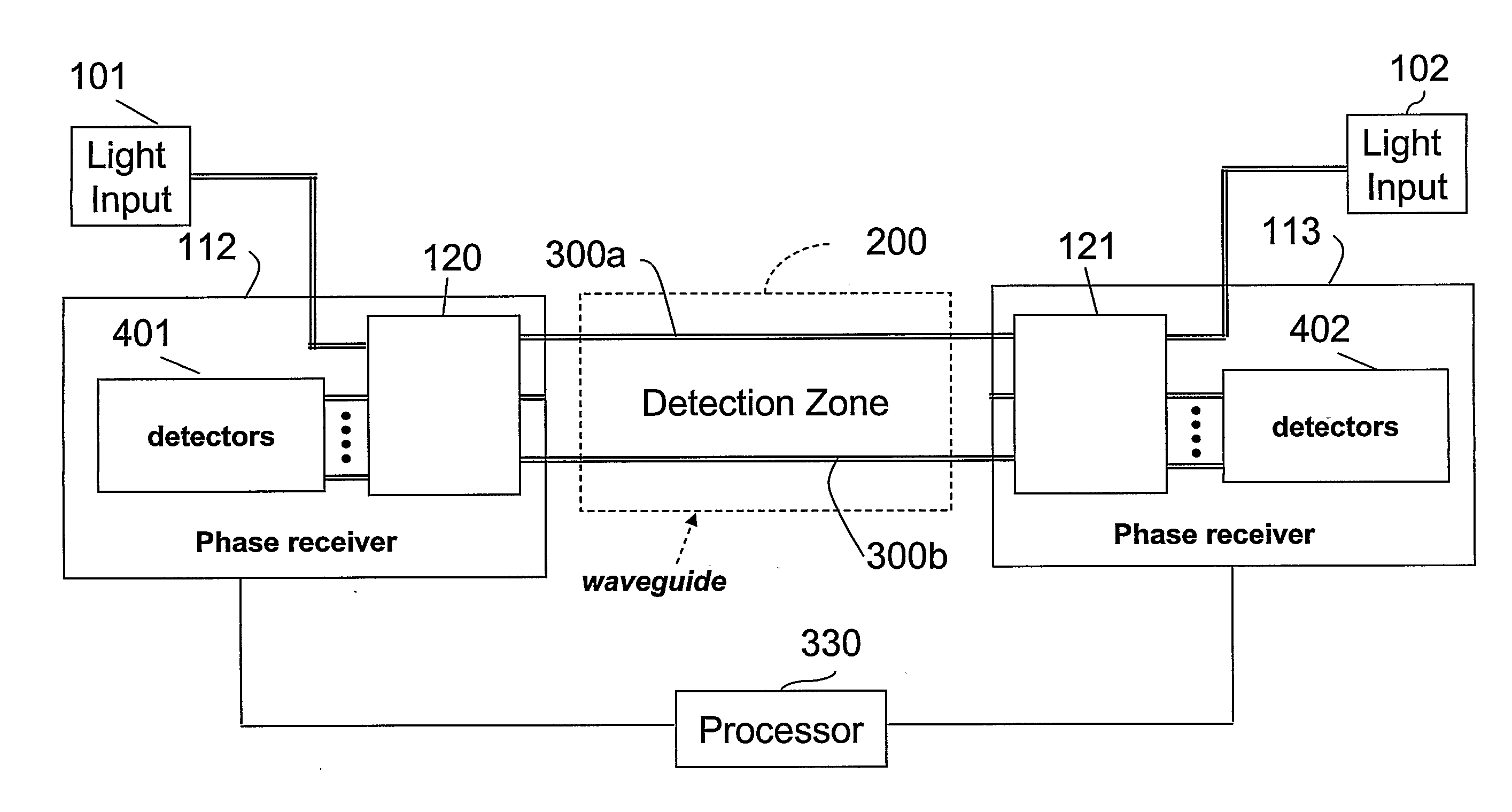
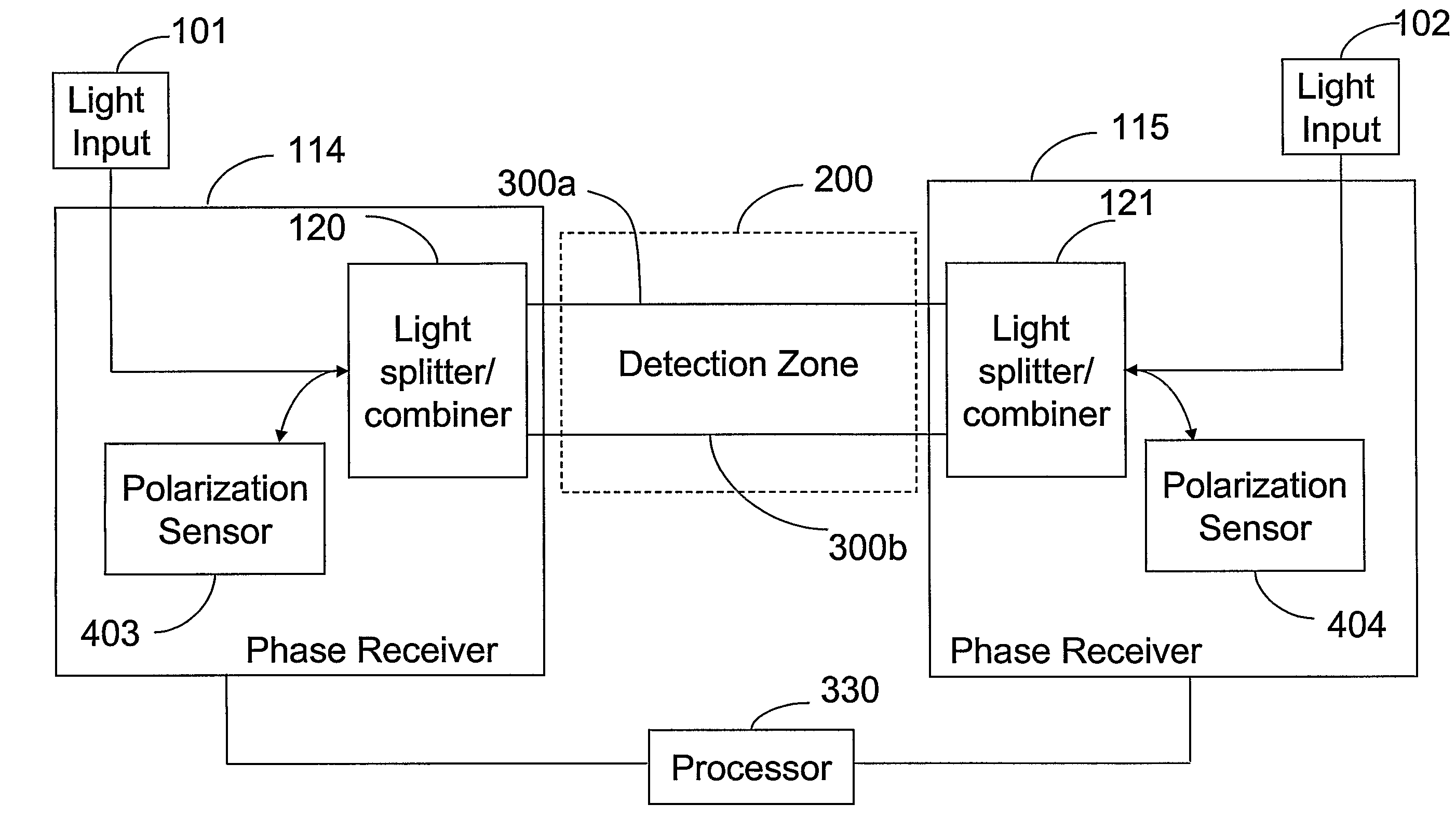
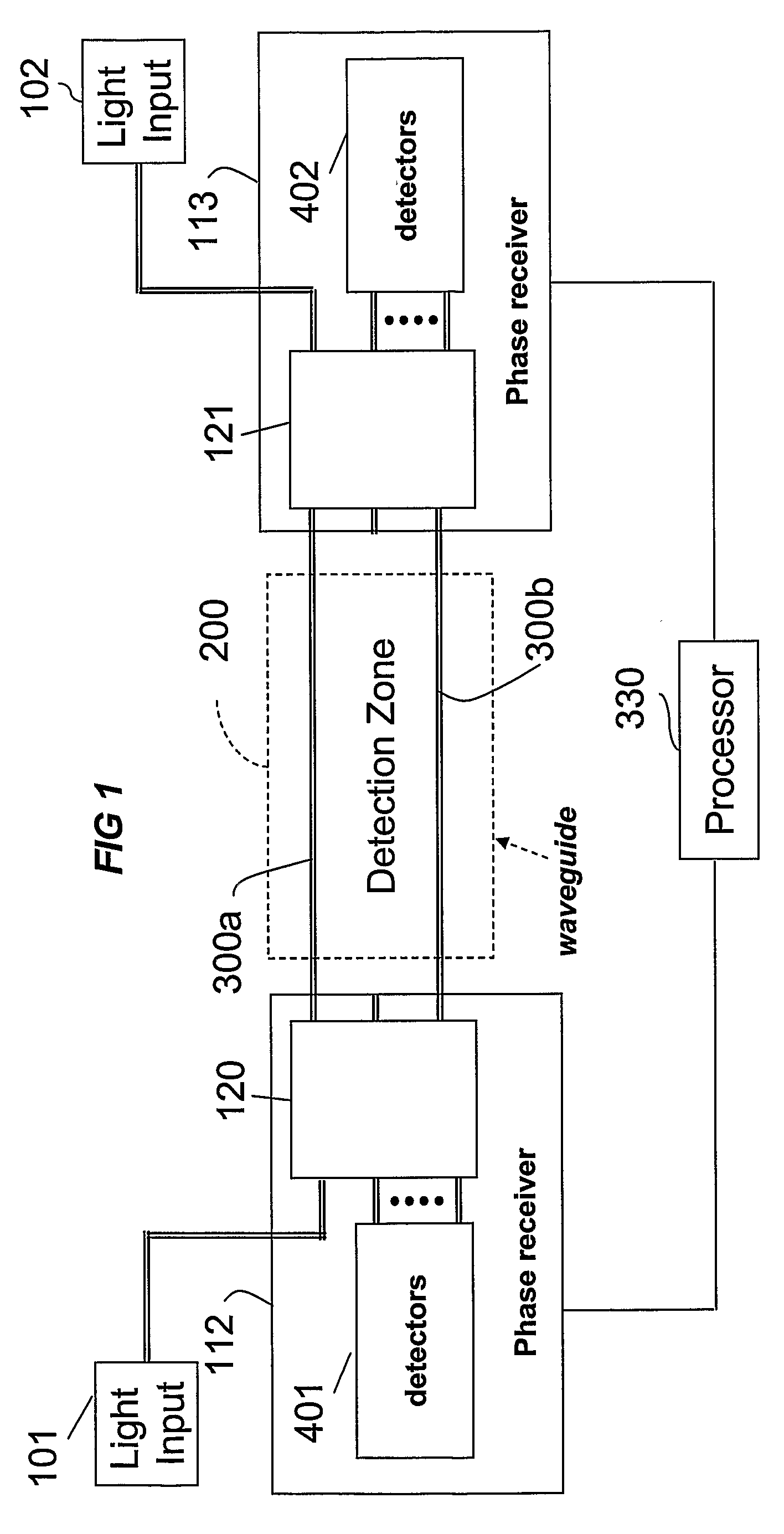
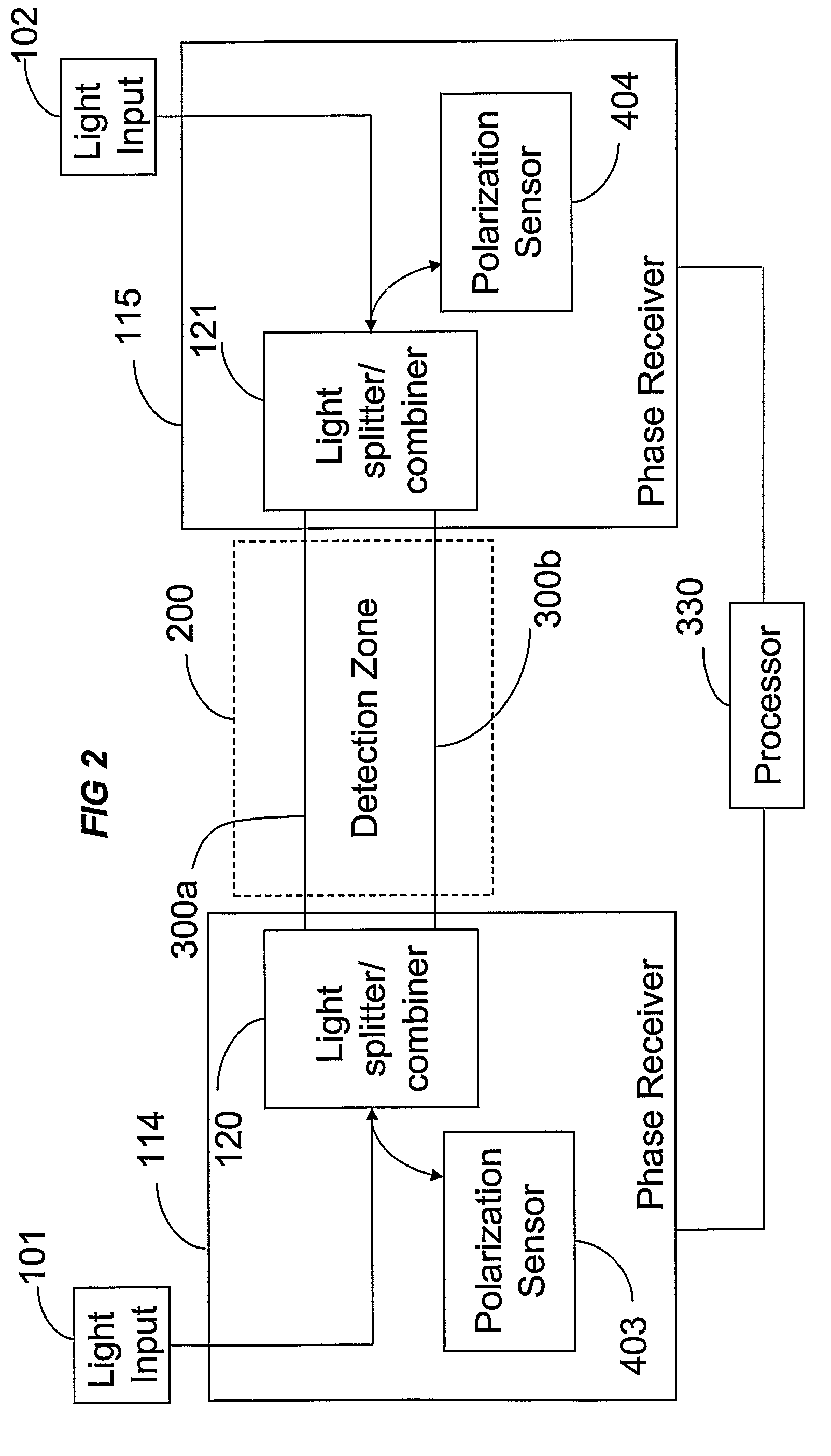
Phase Responsive Optical Fiber Sensor
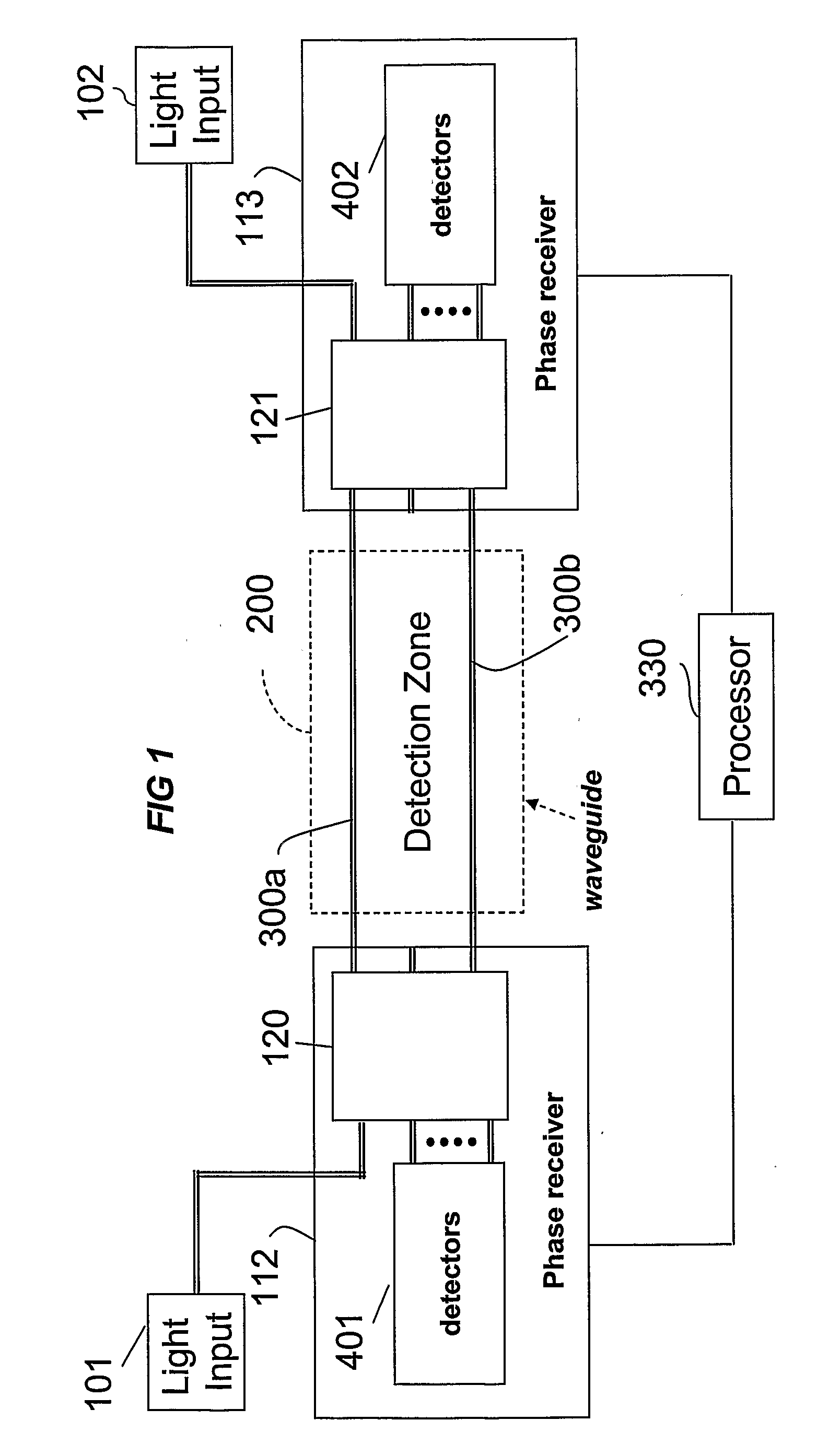
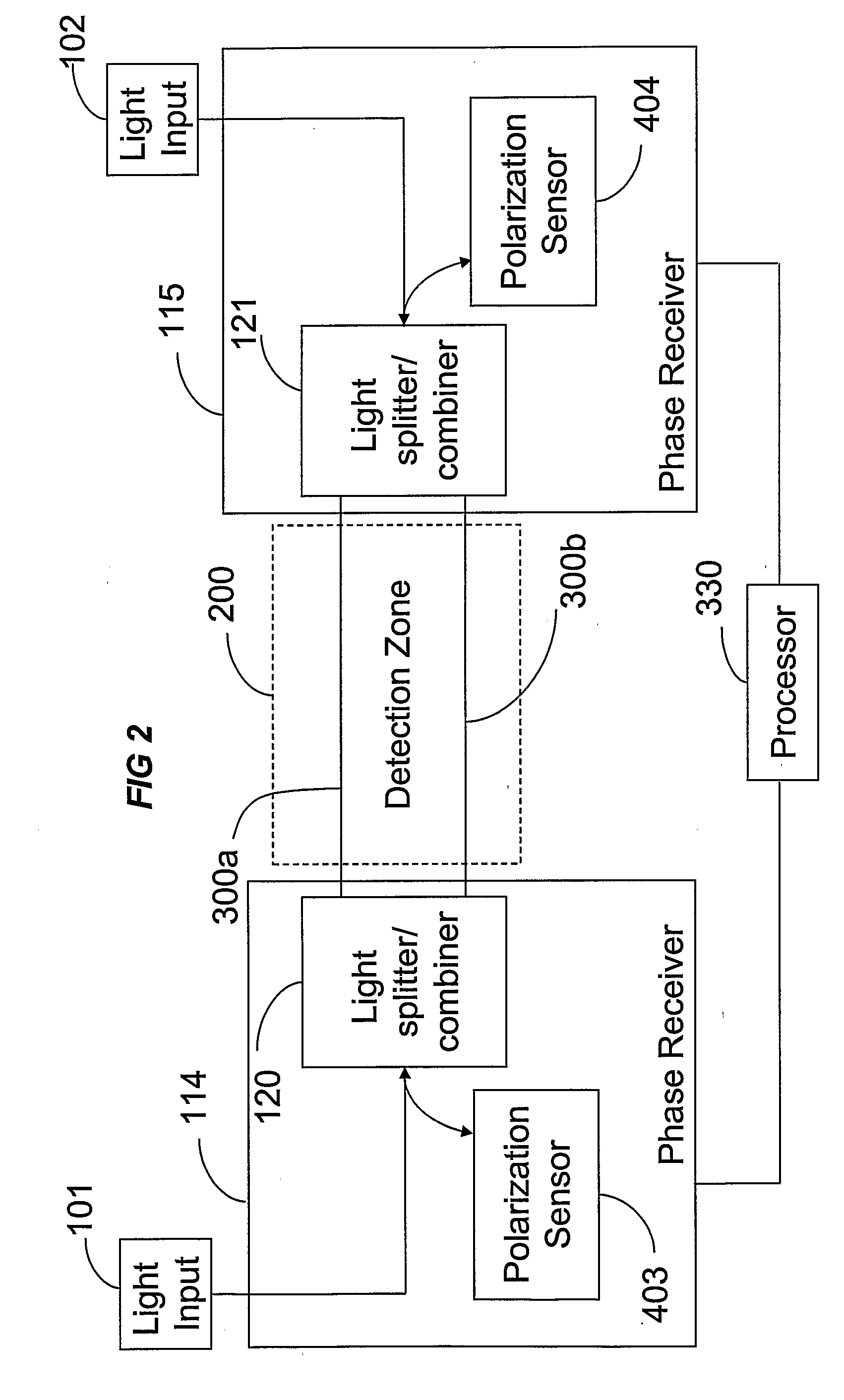
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
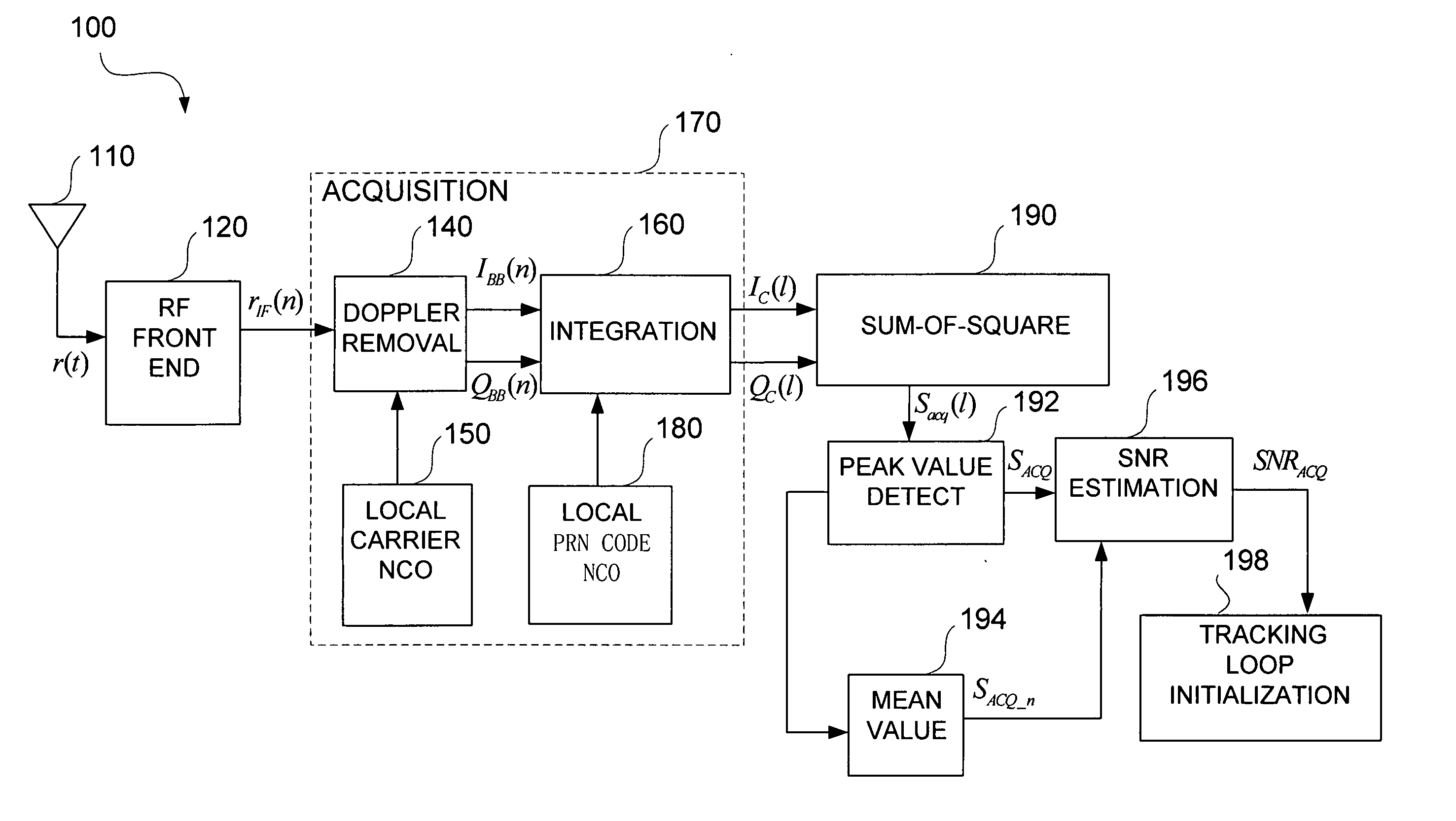
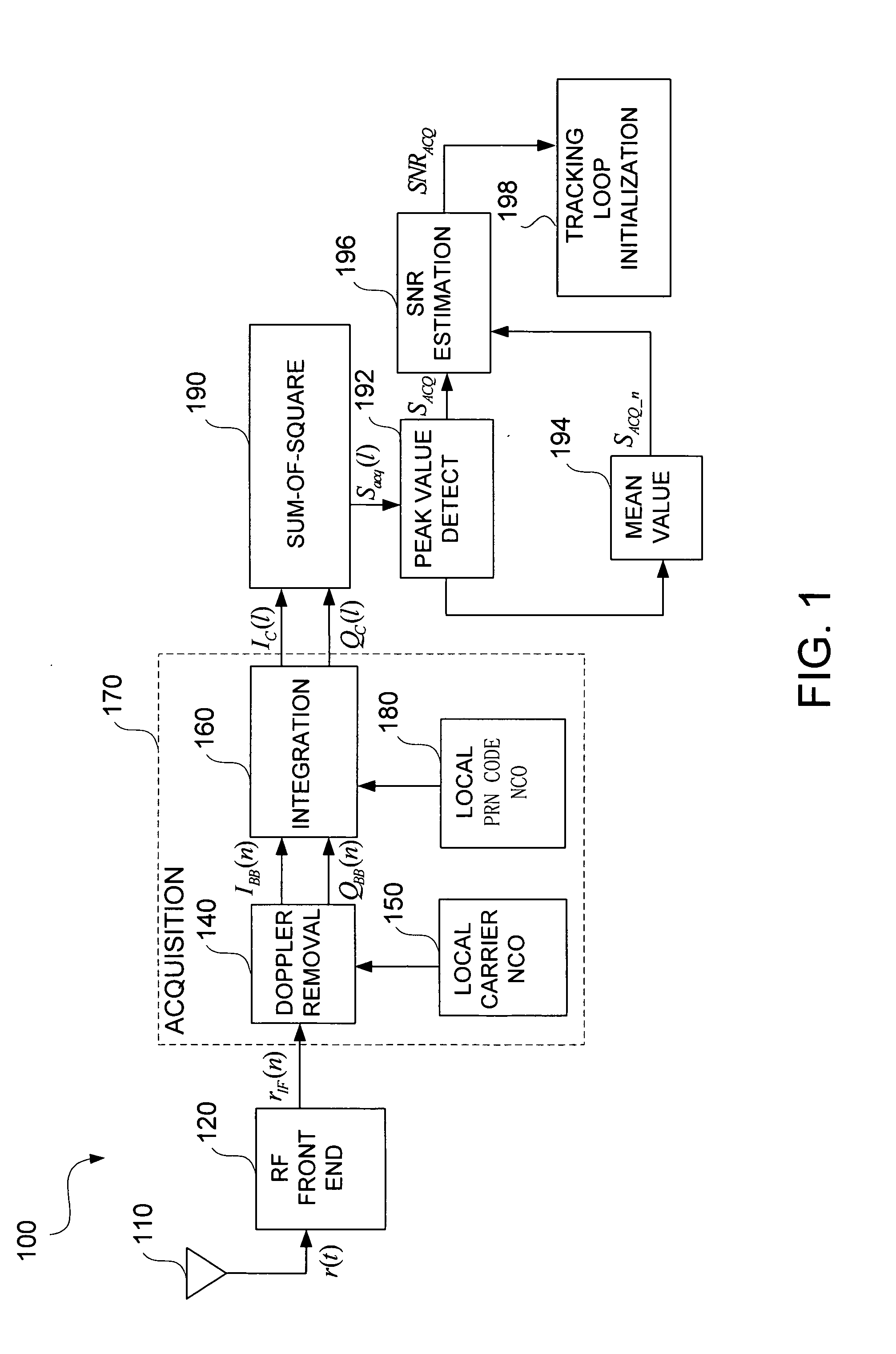
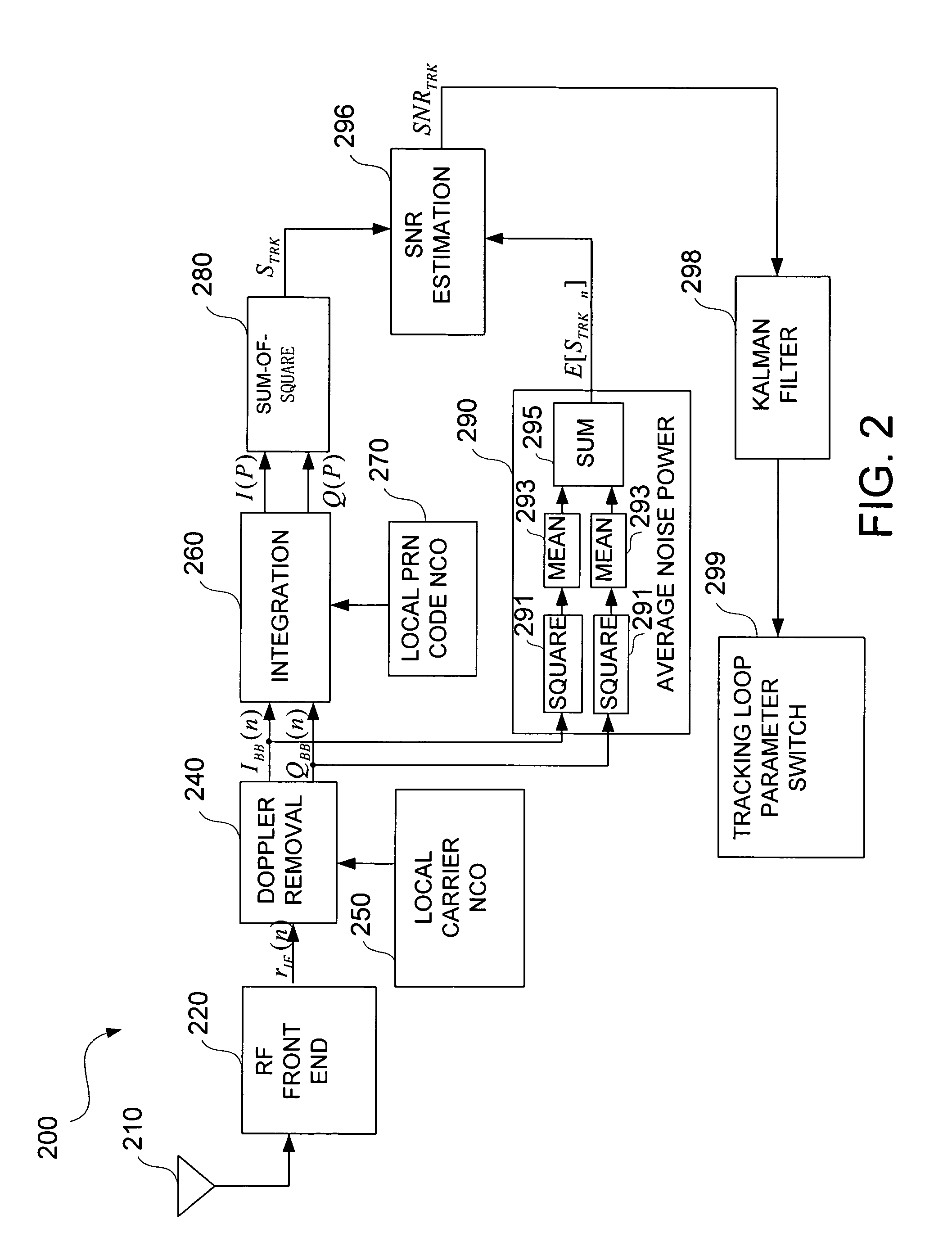
Apparatus and method for determining GPS tracking loop parameter based on SNR estimation
ActiveUS20070201539A1Direction finders using radio wavesError preventionPhase correlationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method for estimating signal quality of a spread spectrum signal is provided. The method includes squaring a plurality of in-phase correlation results and a plurality of quadrature correlation results, summing each squared in-phase correlation result and the corresponding correlation result to obtain a plurality of sum-of-square values, detecting a peak value among the plurality of sum-of-square results, calculating an average of non-peak values among the plurality of sum-of-square results. The peak value is regarded as a signal power value, while the averaged non-peak values are regarded as an average noise power value. A signal-to-noise ratio is then calculated based on the signal power value and the average noise power value. A method for determining the parameters for the tracking loop is also provided. The method includes estimating the signal-to-noise ratio of the spread spectrum signal, and determining the tracking loop parameters based on the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
Phase responsive optical fiber sensor
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com