Patents
Literature
351 results about "Broadcast control channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
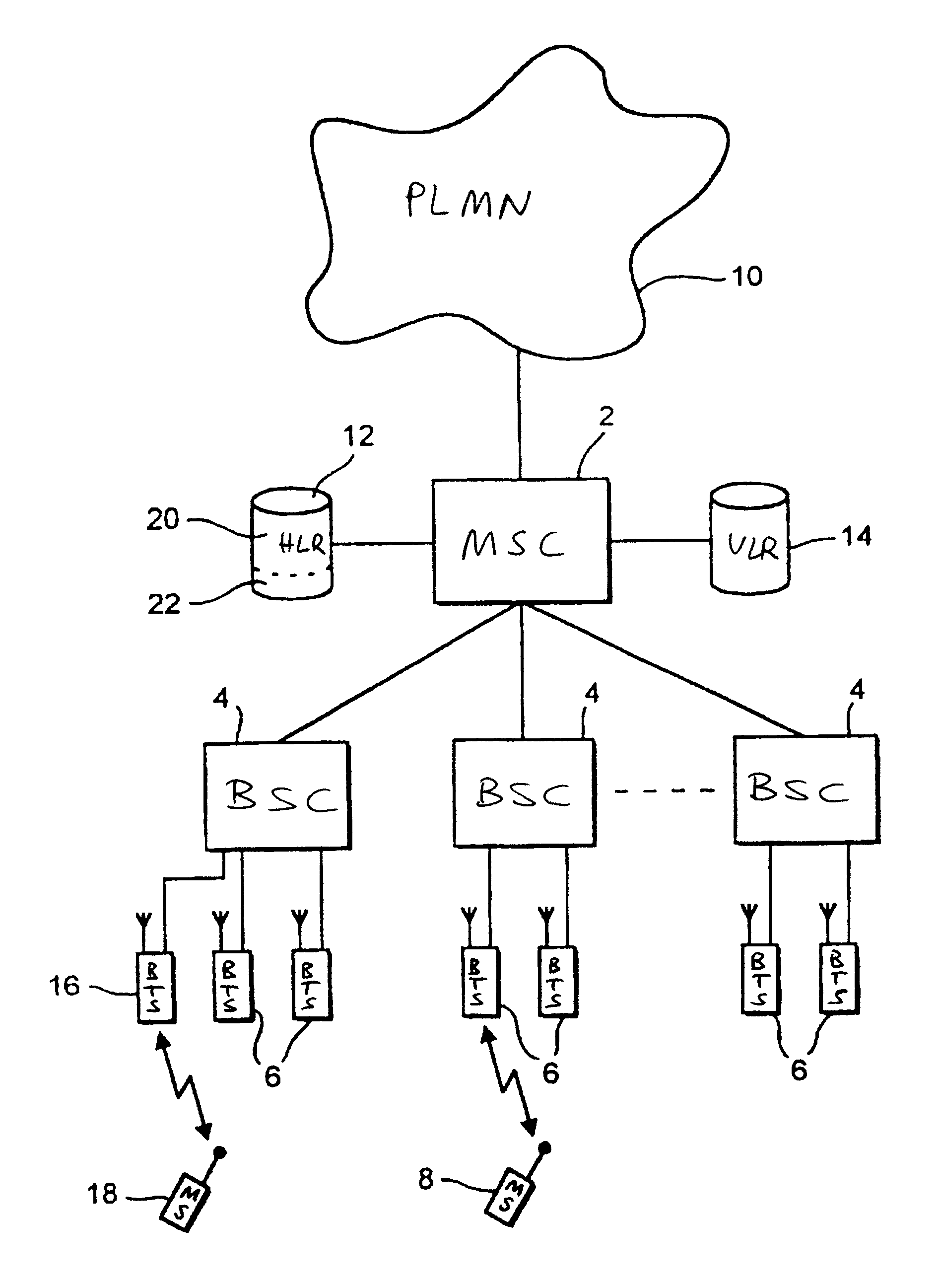
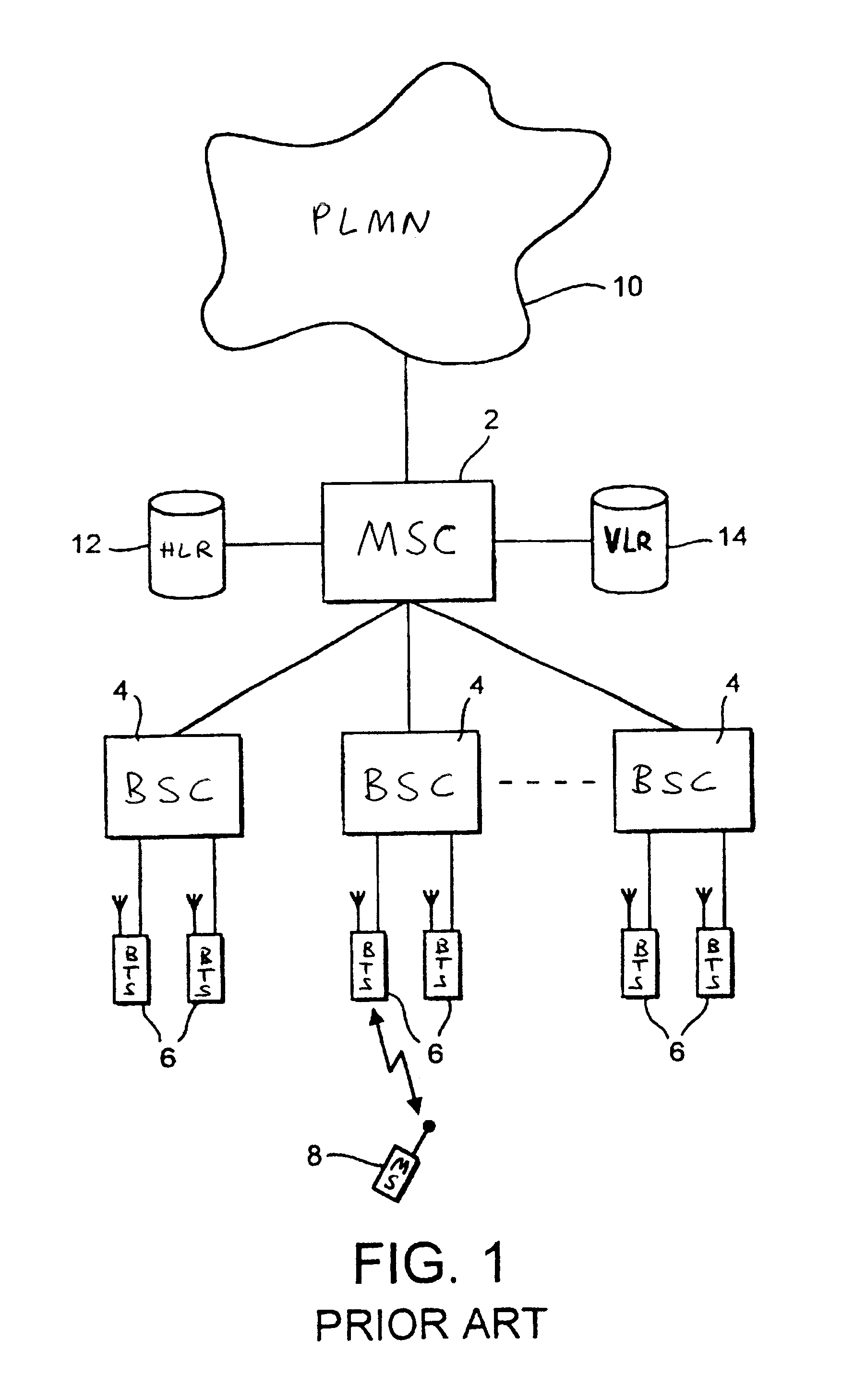
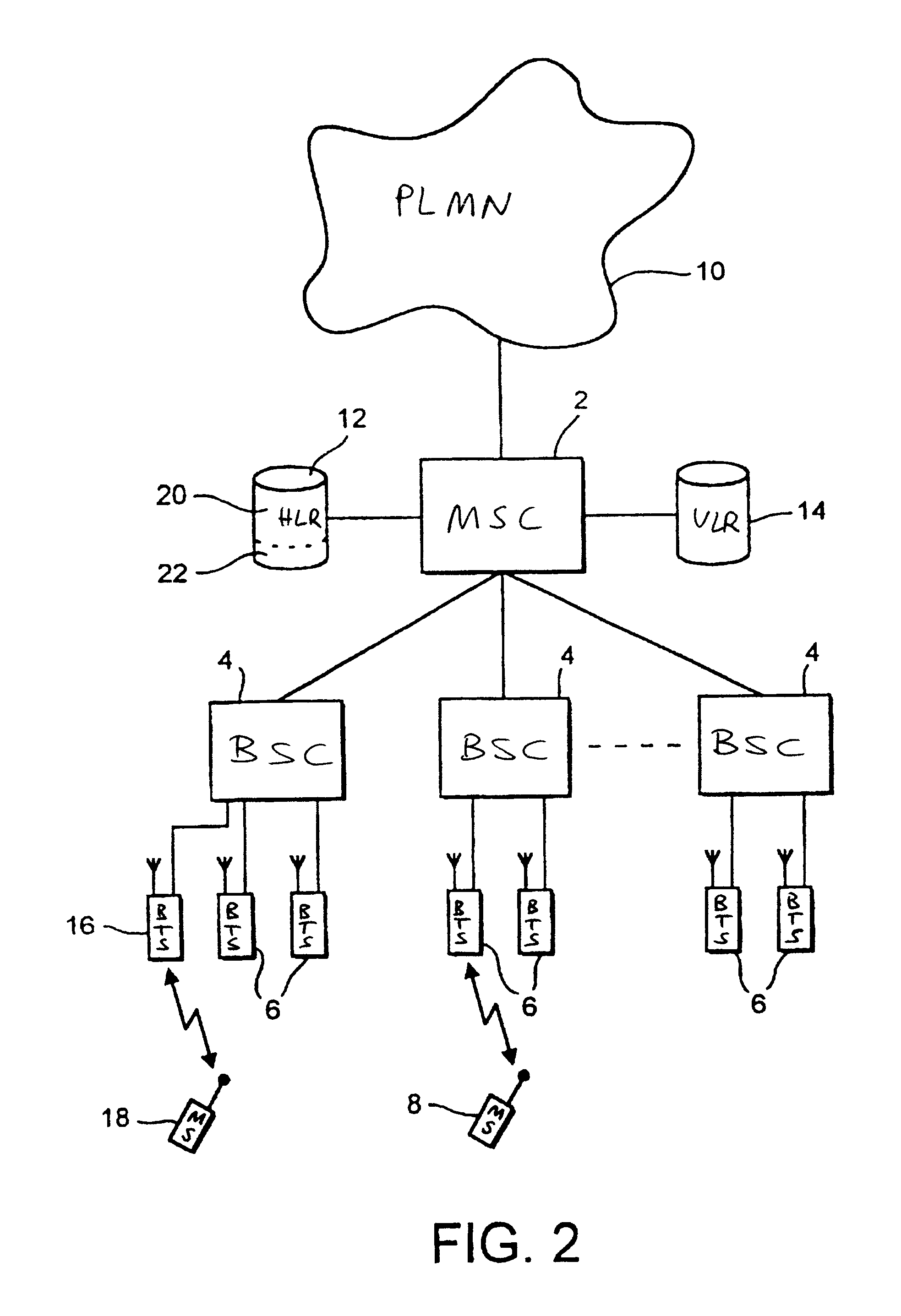
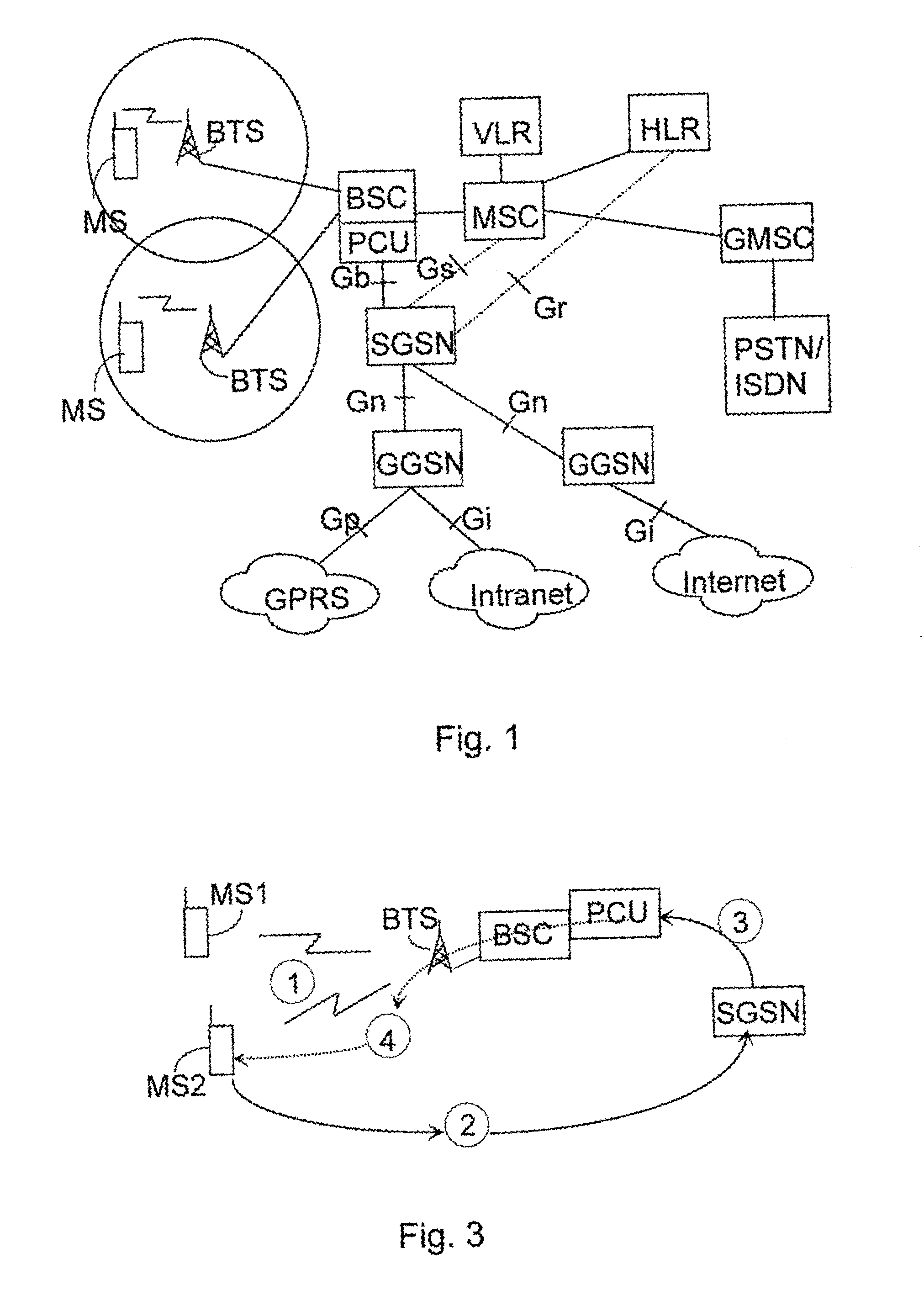
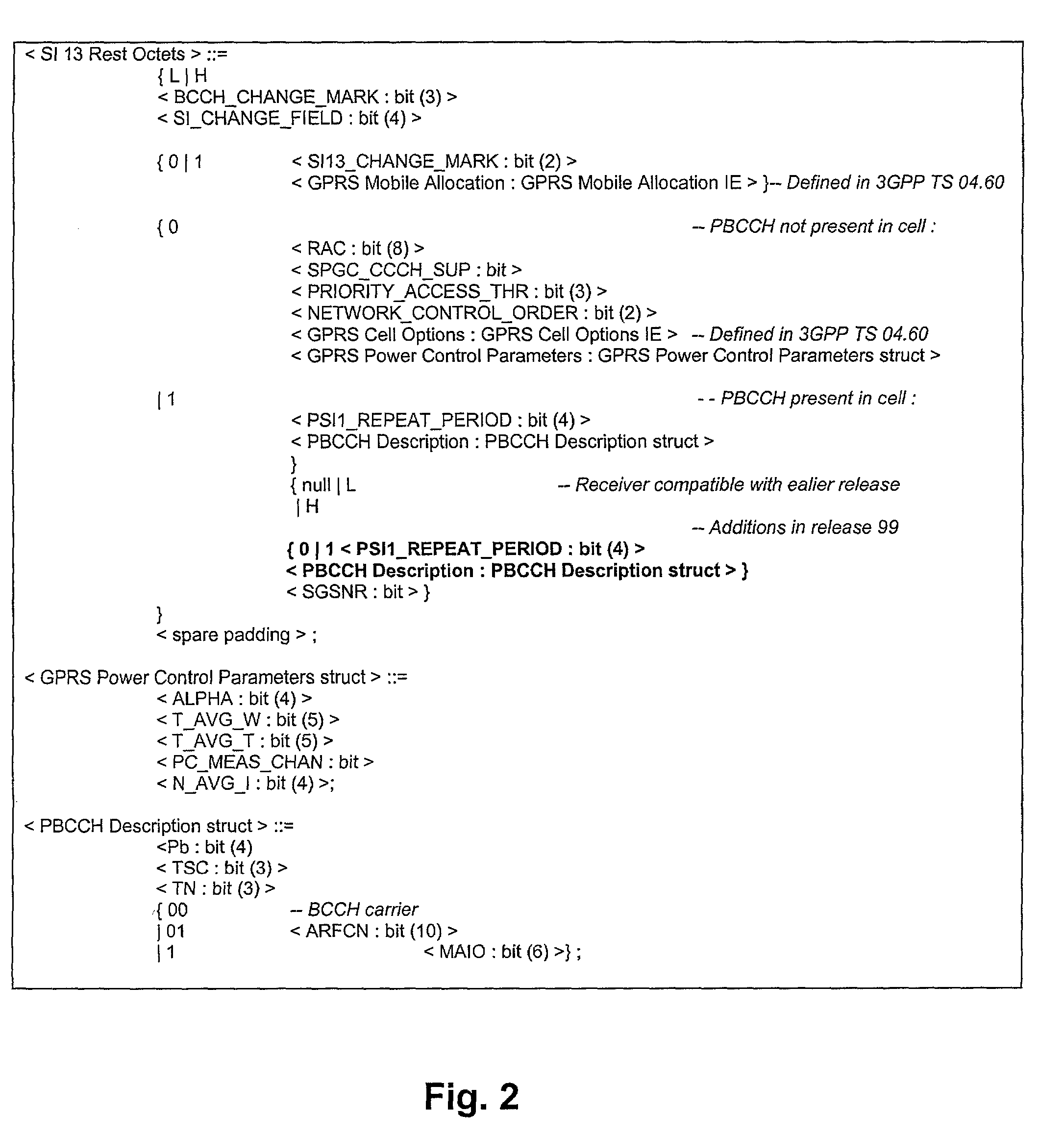
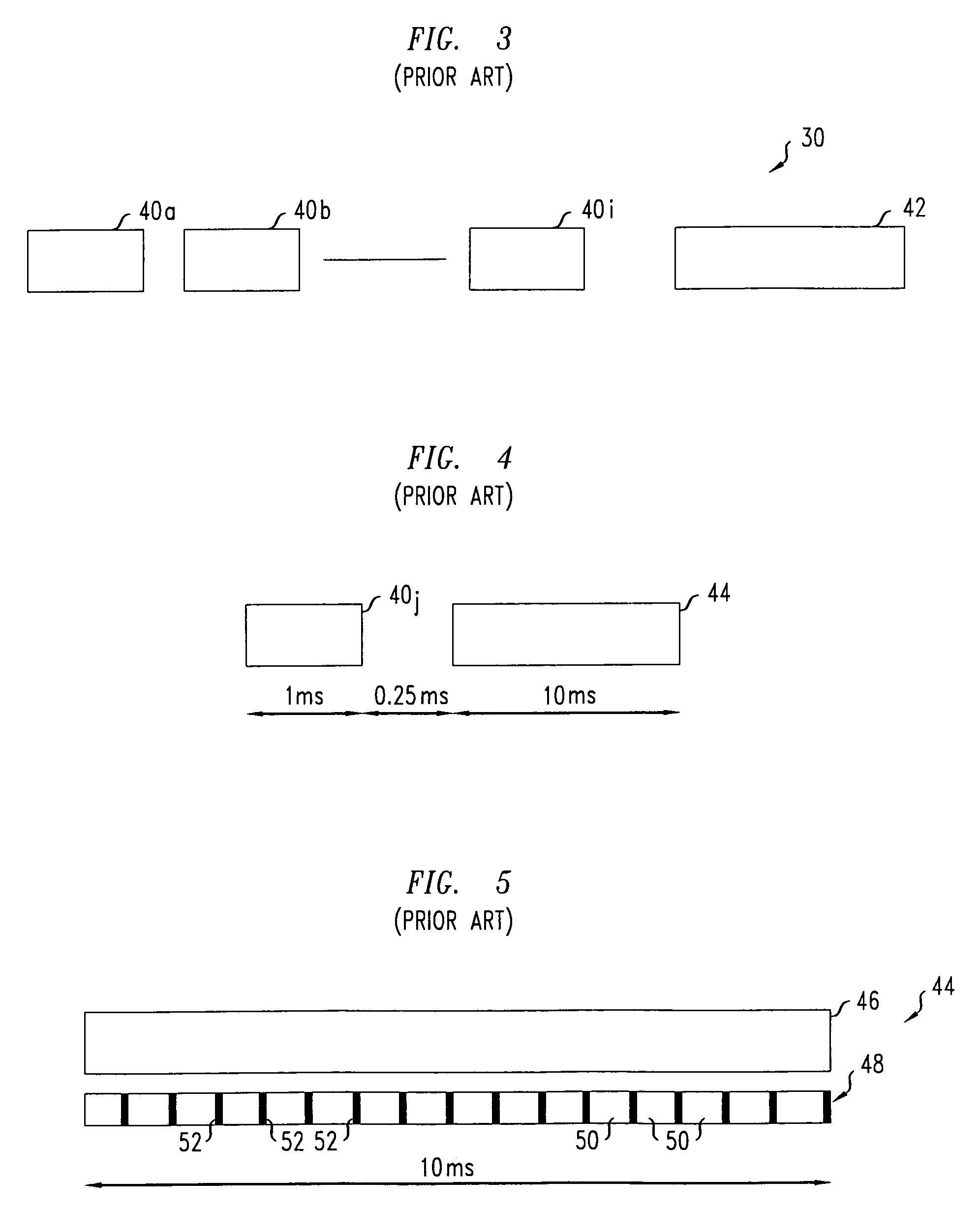
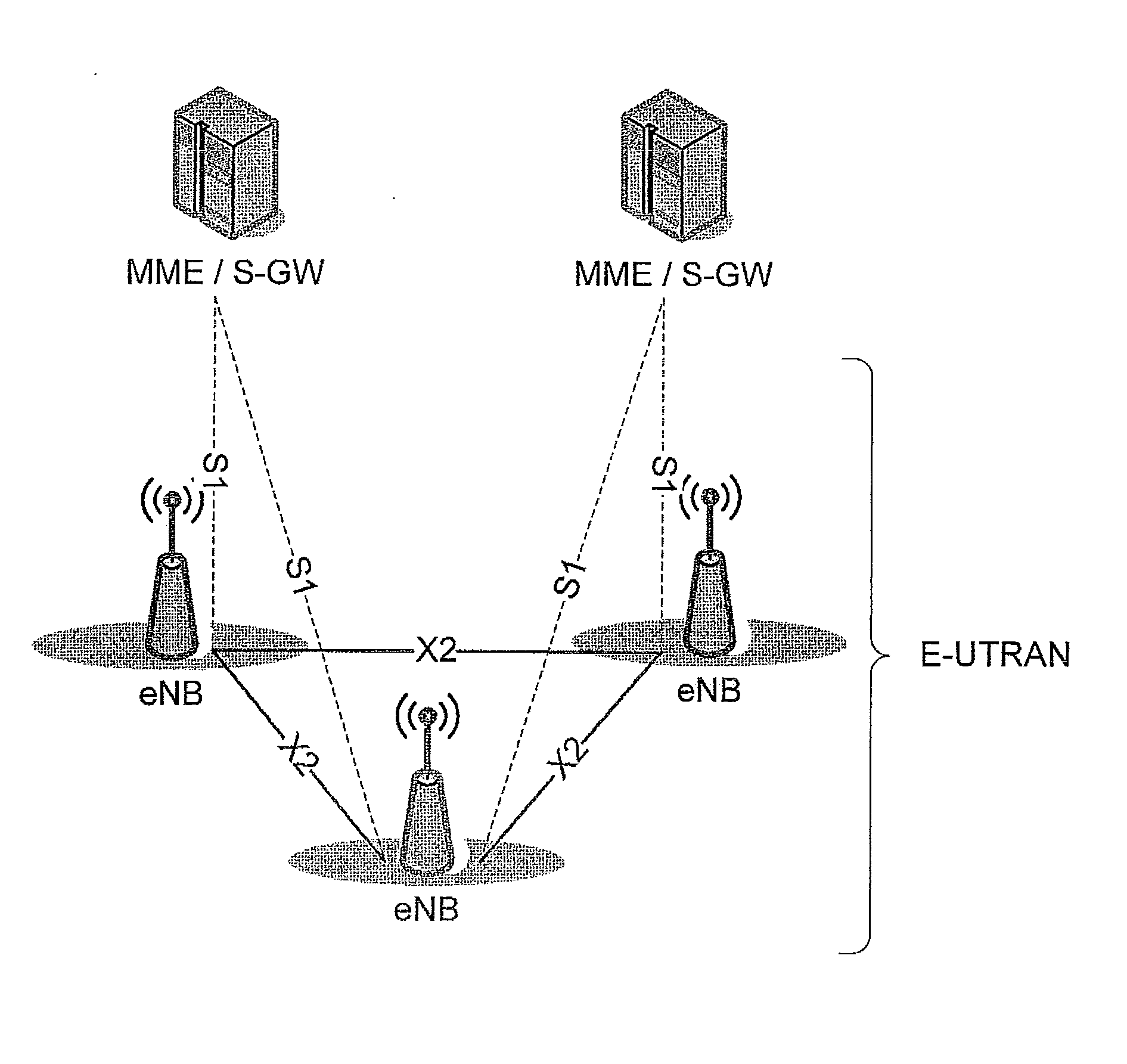
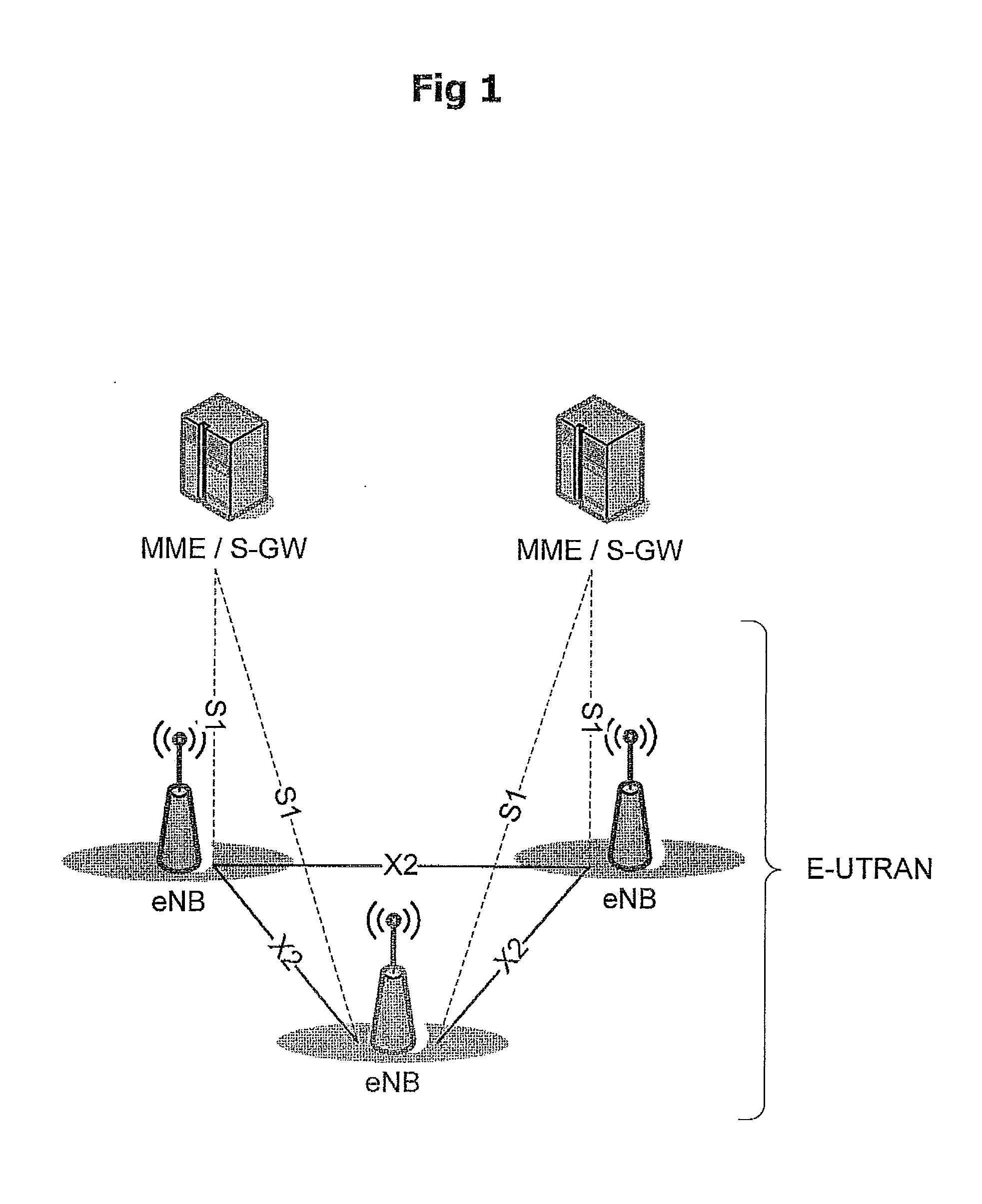
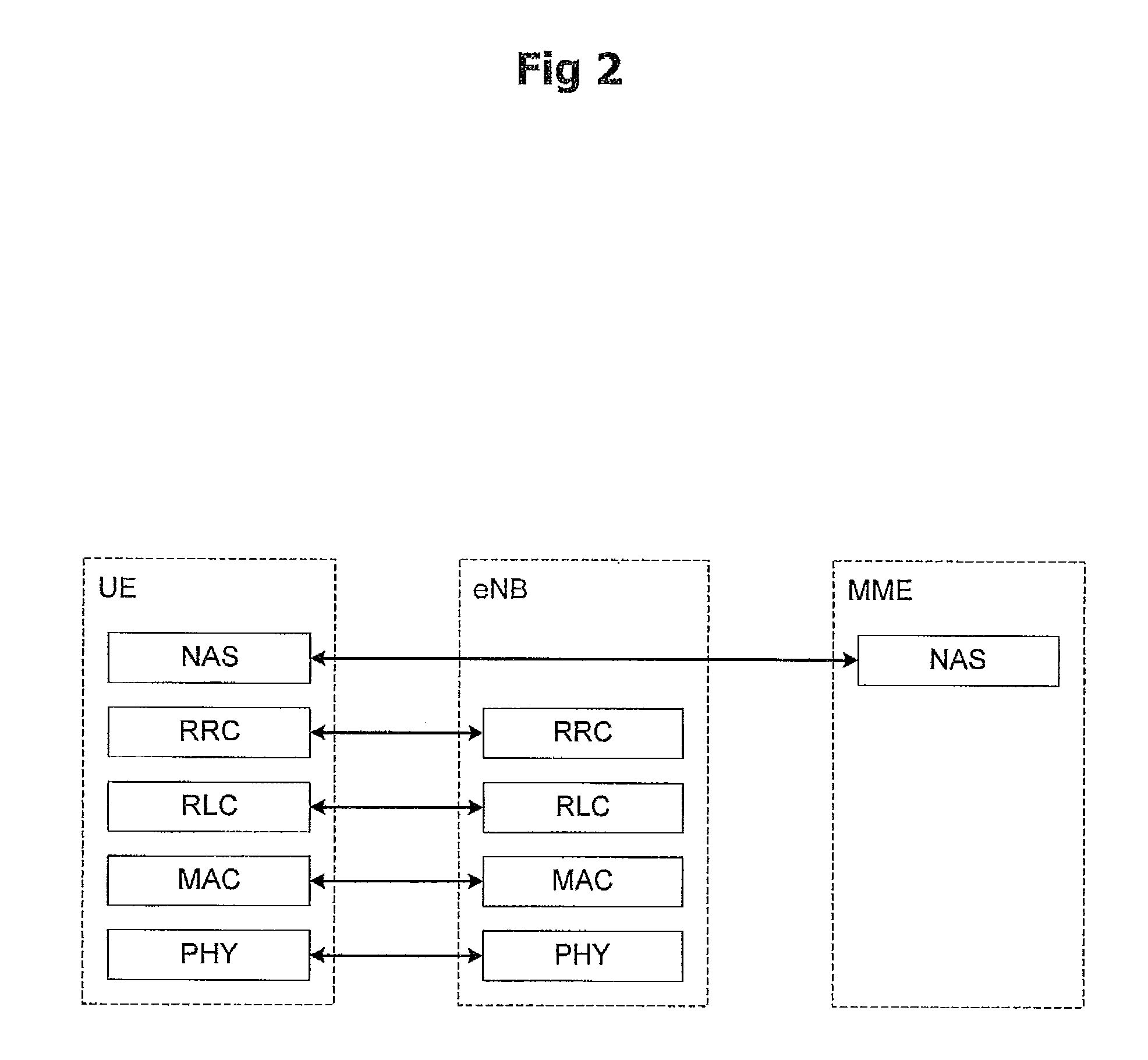
A broadcast control channel (BCCH) is a point to multipoint, unidirectional (downlink) channel used in the Um interface of the GSM cellular standard. The BCCH carries a repeating pattern of system information messages that describe the identity, configuration and available features of the base transceiver station (BTS). These messages also provide a list of absolute radio-frequency channel numbers (ARFCNs) used by neighboring BTSs. This message pattern is synchronized to the BTS frame clock. The minimum BCCH message set is system information messages 2–4, although other messages are normally present. The messages themselves are described in 3GPP Technical Specification 44.018.
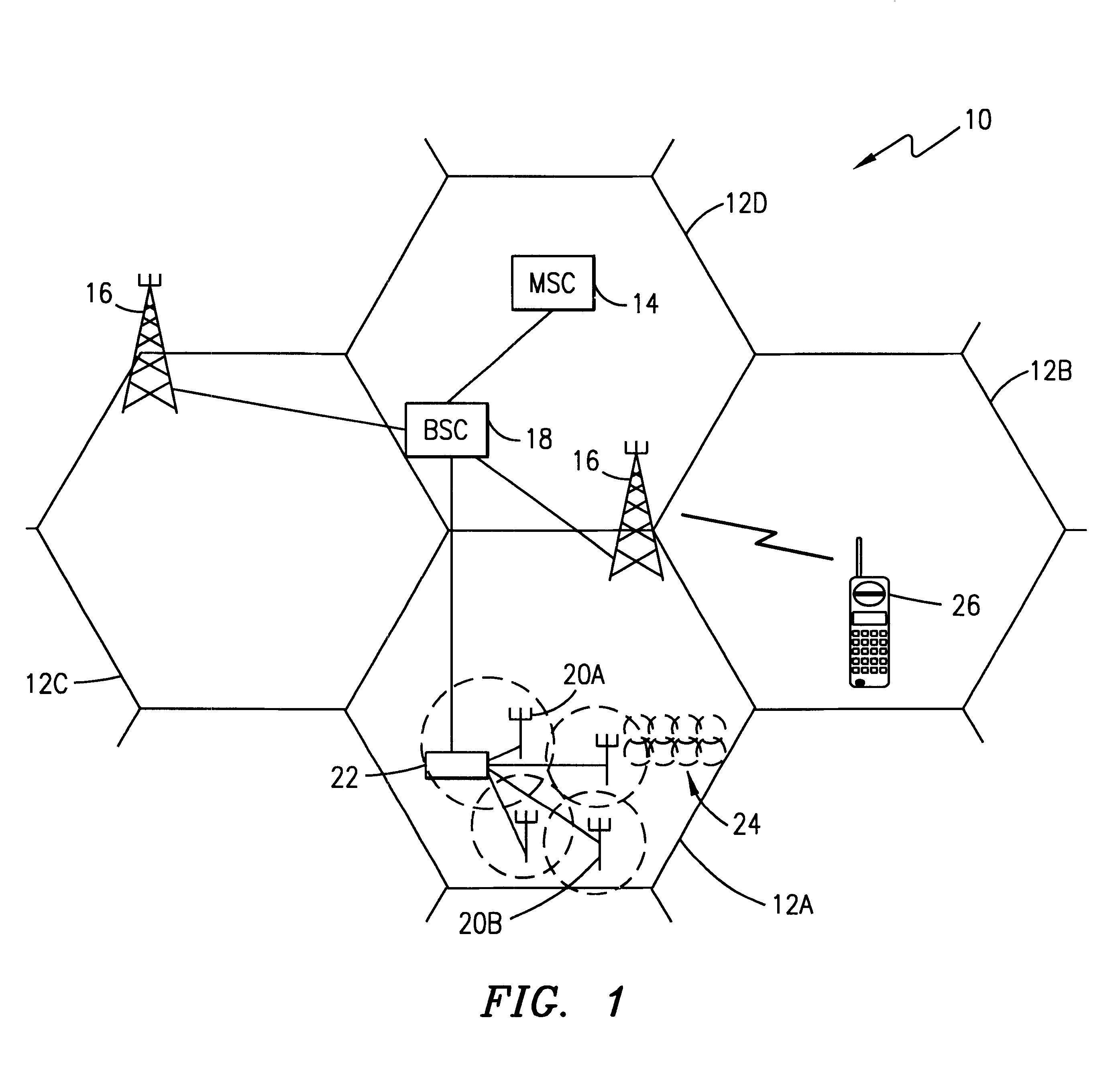
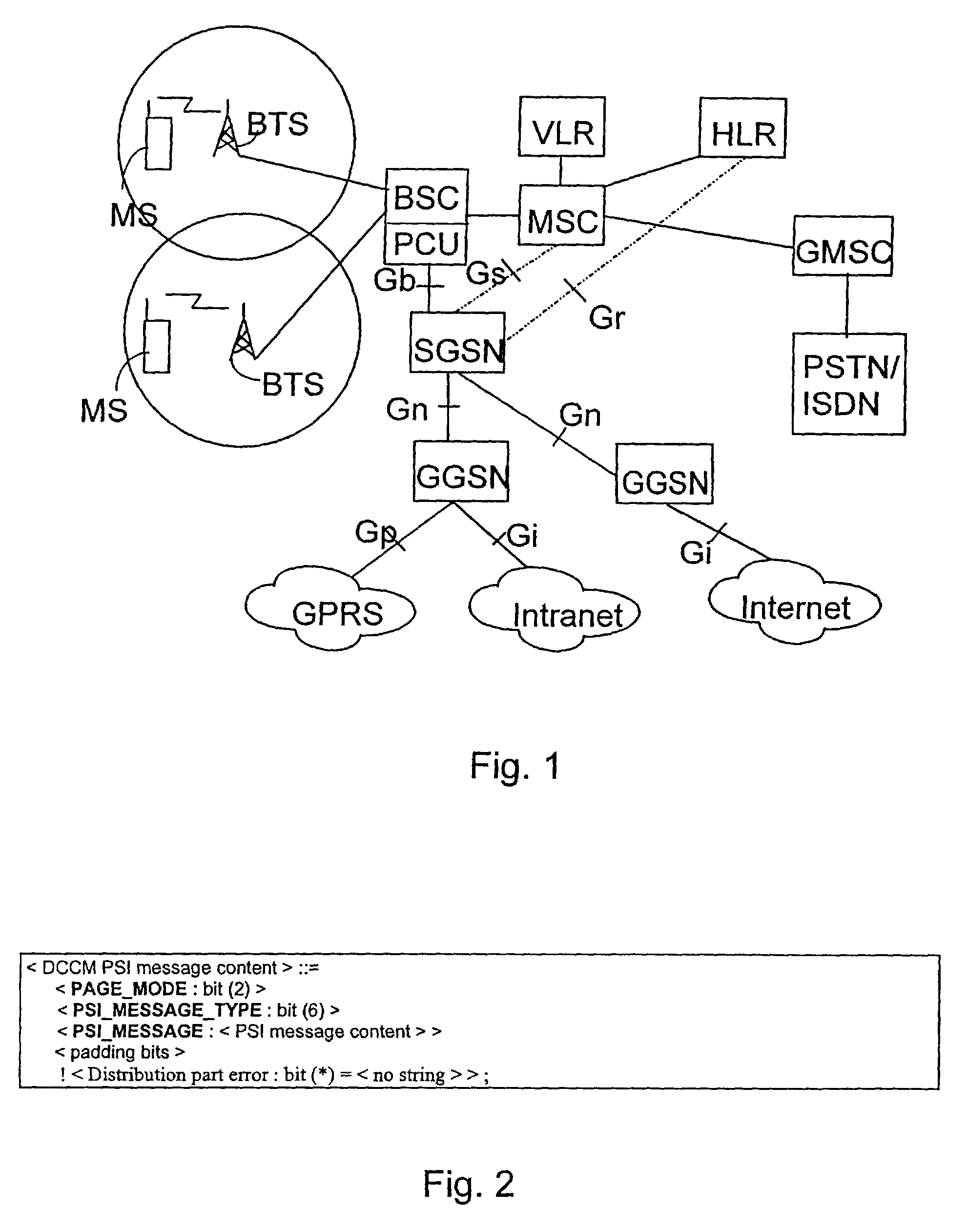
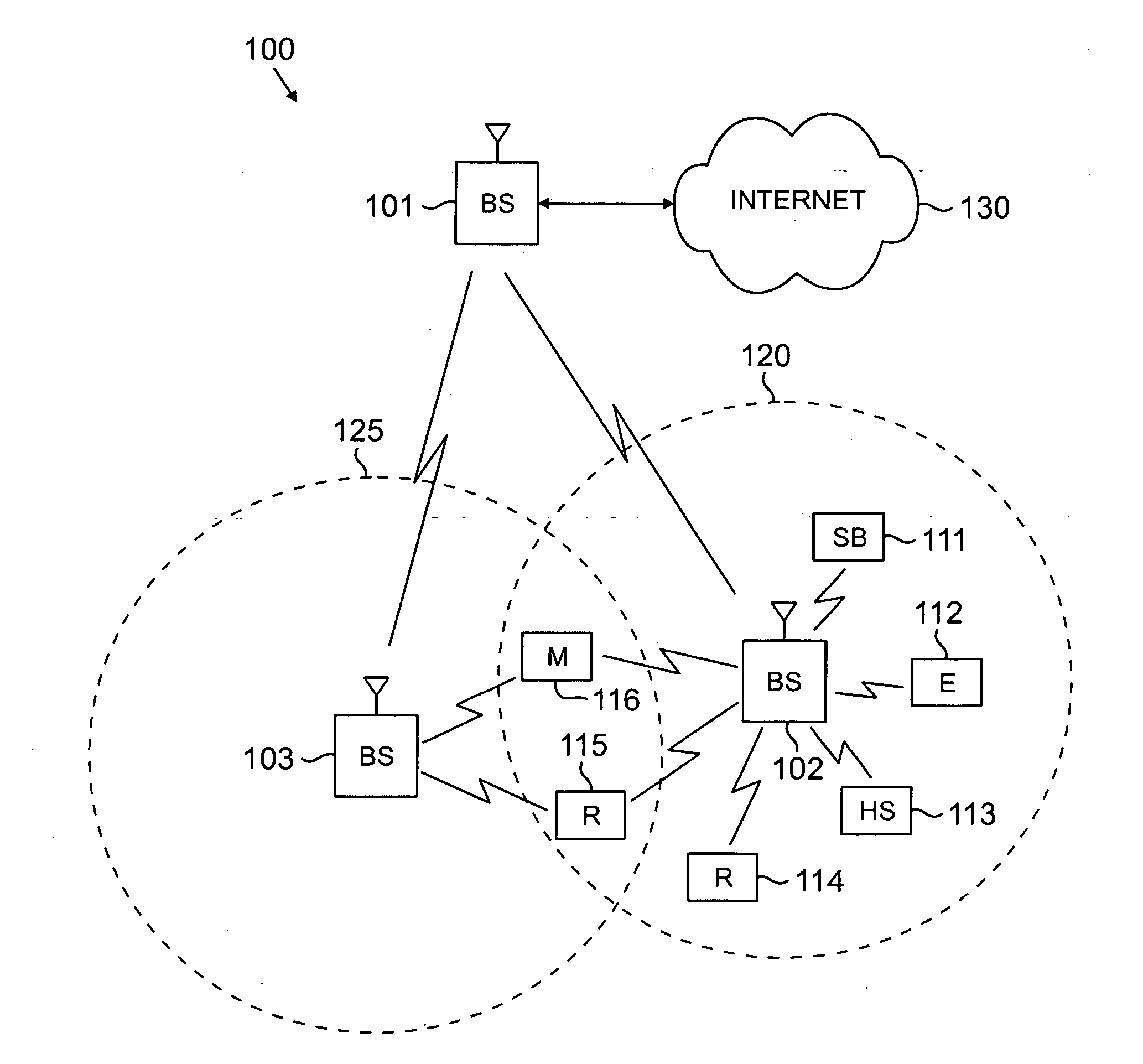
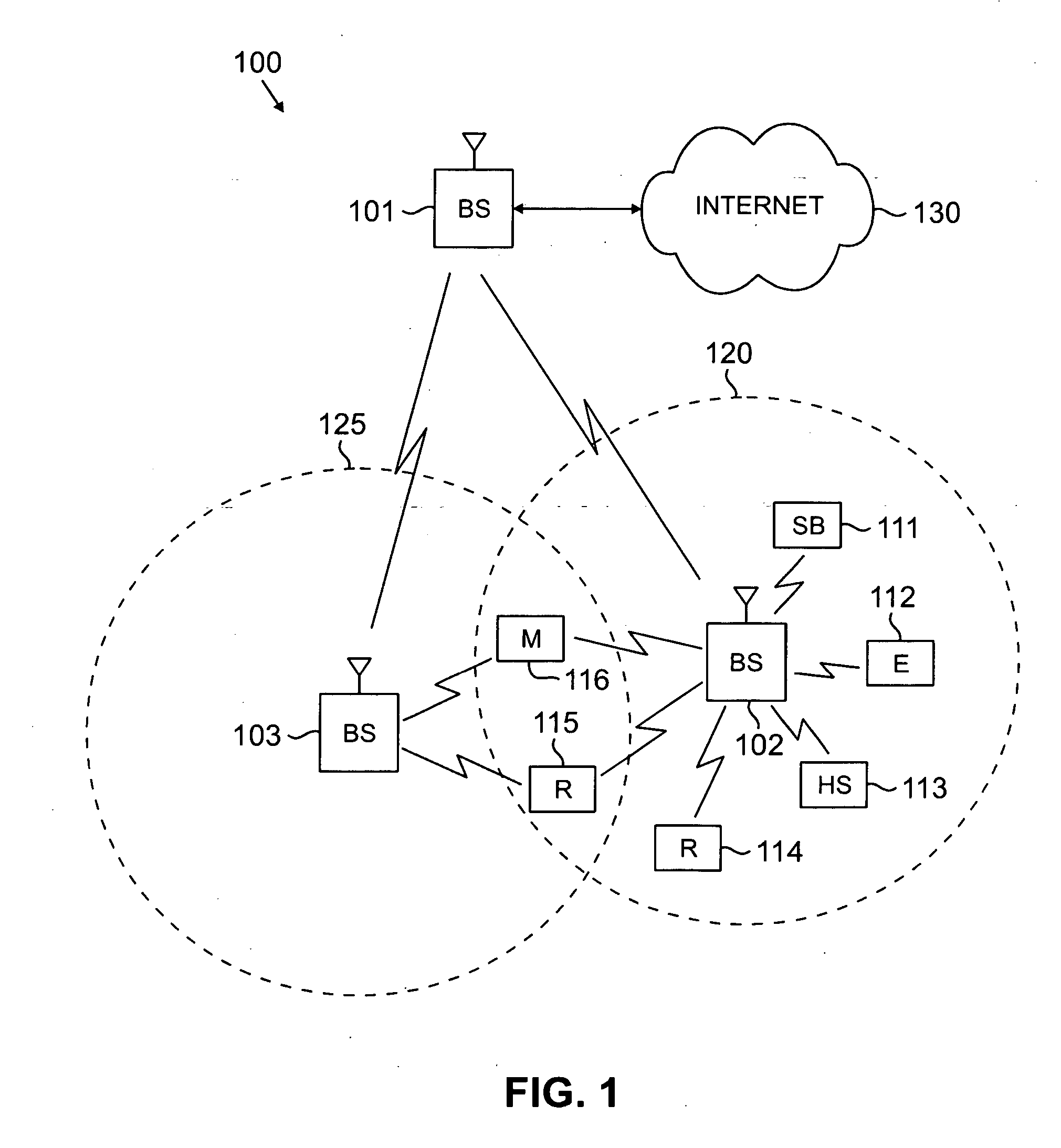
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS20010036810A1Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
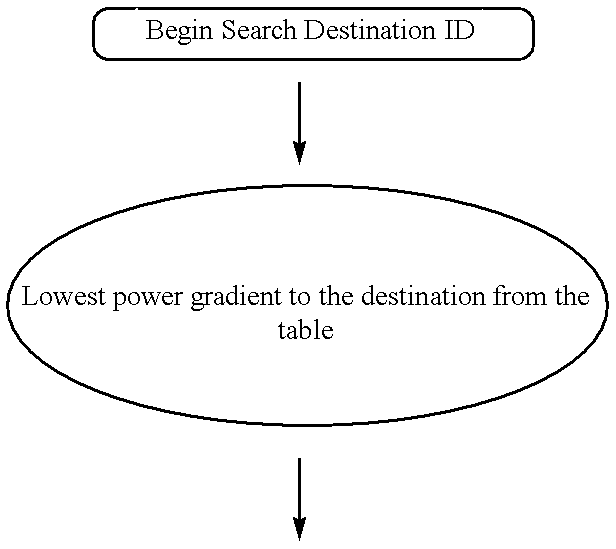
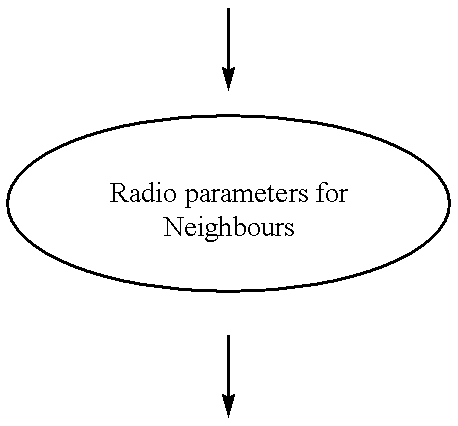
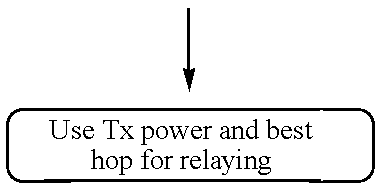
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Mobile communications system having a cellular communications network comprising a public network portion and a private network portion using a common radio interface protocol
InactiveUS6826414B1Easy to distinguishReduce congestionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemPrivate network
A public mobile communications network is configured in accordance with an established protocol which includes a private network portion to which only a selected set of mobile stations have access. The selected set of mobile stations has a private network identity code which is different from a public network identity code. A base transceiver station of the private network portion broadcasts the private network identity code on its broadcast control channel. A mobile switching center prevents public subscriber mobile stations from registering via the private network portion, while the private subscriber mobile stations are allowed to register over the entire network.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS6785510B2Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Method and system for autonomously allocating frequencies to a radio system sharing frequencies with an overlapping macro radio system
InactiveUS6405048B1Avoid co-channel interferenceMaximize radio spectrum usageAssess restrictionFrequency-division multiplexCellular radioCommunications system
A system and a method to automatically select a frequency set in a low-tier radio communication system, sharing frequencies with an overlapping high-tier cellular radio system, that minimally interferes with the high-tier system employing frequency hopping is described. The present invention makes use of the broadcast information that is transmitted by the high-tier radio base stations on their broadcast control channels (BCCH), which contains not only the BCCH carrier frequencies of surrounding cells, but also information regarding the frequencies applied in the considered cell for frequency hopping traffic channels. With this broadcast information, the low-tier system can derive the frequency planning of the high-tier system, and can then derive a frequency set for low-tier usage that minimally interferes with the overlapping high-tier system. The advantage with this technique is that only measurements on BCCH carriers have to be performed, which are non-hopping, have a constant transmit power, and have a continuous (non-bursty) signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transmitting control messages on control channels of packet data network
InactiveUS7209459B2Connection managementData switching by path configurationNetwork onMobile station
A method for transmitting control messages of a packet data network in a telecommunications system which includes at least one cell, in which the control messages are arranged to be transmitted on a circuit-switched broadcast control channel, a packet-switched broadcast control channel and a traffic channel. In addition, the telecommunications system includes at least one mobile station which supports the packet data network and is arranged to listen to at least one of the broadcast control channels. First control messages to be transmitted on a packet-switched channel of the packet data network are transmitted to the mobile stations in the cell encapsulated inside a second control message if the cell supports the transmission of the connection set-up parameters of the packet data network on both a circuit-switched broadcast control channel and a packet-switched broadcast control channel.
Owner:RPX CORP
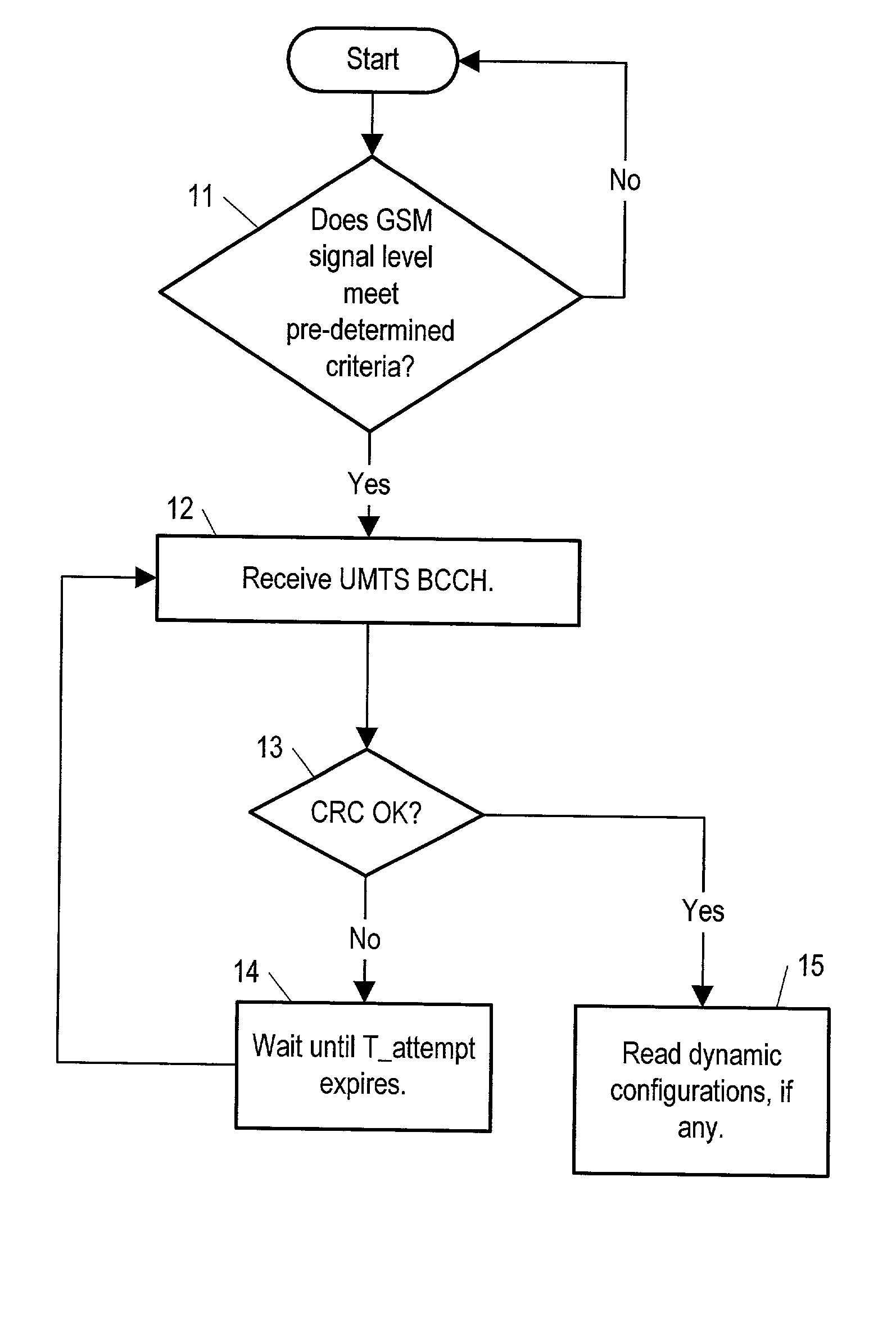
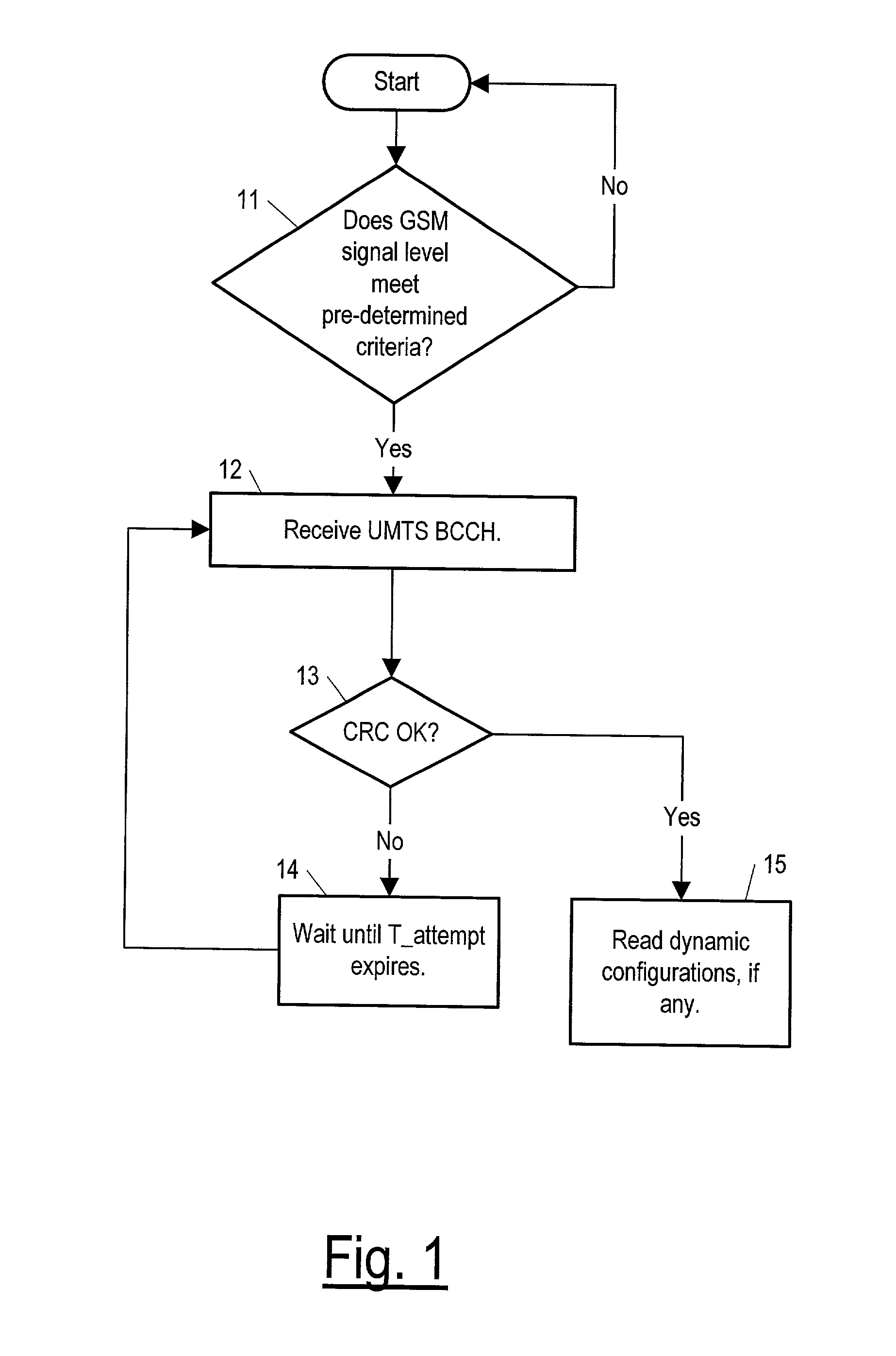
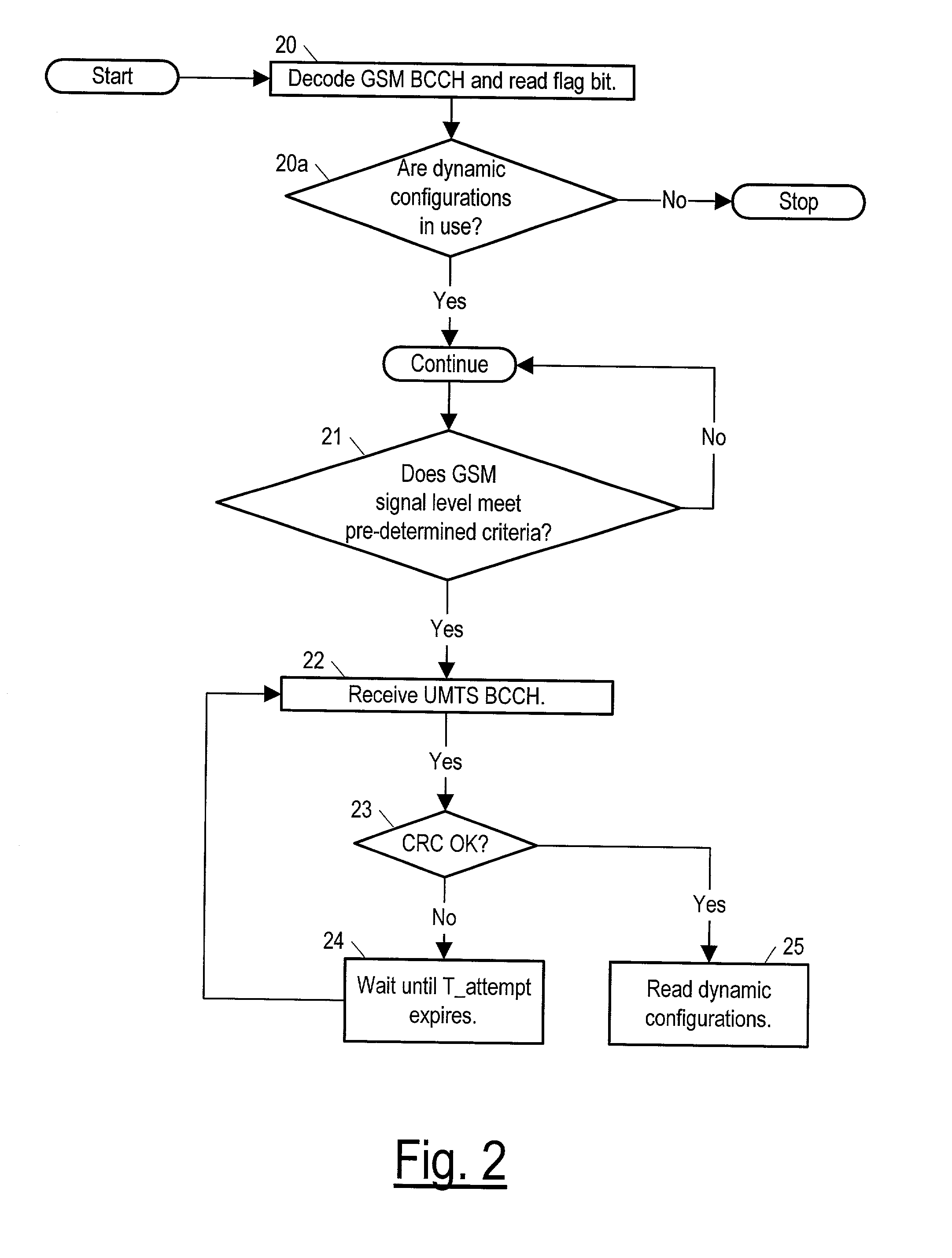
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving dynamic configuration parameters in a third generation cellular telephone network
InactiveUS20020128035A1Reduce power consumptionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemControl signal
A method for a mobile station and a base station to which the mobile is being handed over, and corresponding apparatuses for use by the mobile and the base station. The method for use by the mobile station is for determining whether dynamic configurations are in use by the base station to which the mobile is being handed over, and the method for use by the base station is for determining whether to use a dynamic configuration (if the base station uses dynamic configurations) or to switch to a static preconfiguration in communicating with the mobile. The base station to which the mobile is being handed over is of one wireless communication system (such as the UTRA wireless communication system) and the base station doing the handing over is of another type (such as GSM). Both base stations are assumed to broadcast control signals on a respective broadcast control channel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for fast cold start of a GPS receiver in a telecommunications environment
InactiveUS7215967B1Reduce startup timeImprove performanceActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBroadcastingGSM
A telecommunications system and method for rapid start-up of a Global Position System (GPS) receiver integrated with a mobile terminal is disclosed. The location of a reference GPS receiver associated with a Base Transceiver Station (BTS) within the cell that the mobile terminal is currently located is used as the local position estimate for that mobile terminal. The GSM TDMA frame numbers are first correlated with the GPS clock signal. Optionally, this correlation is adjusted using the adaptive frame alignment mechanism. This local position estimate is used to ascertain the location of the GPS receiver. The correlation data is then sent to the GPS-capable mobile terminal through the Short Messaging Service (SMS) cell broadcast facility or the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) facility of the GSM network to enable the built-in GPS receiver to calculate its position relatively quickly.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Sending transmission format information on dedicated channels
InactiveUS7161971B2Information transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex code generationBroadcast channelsRadio channel
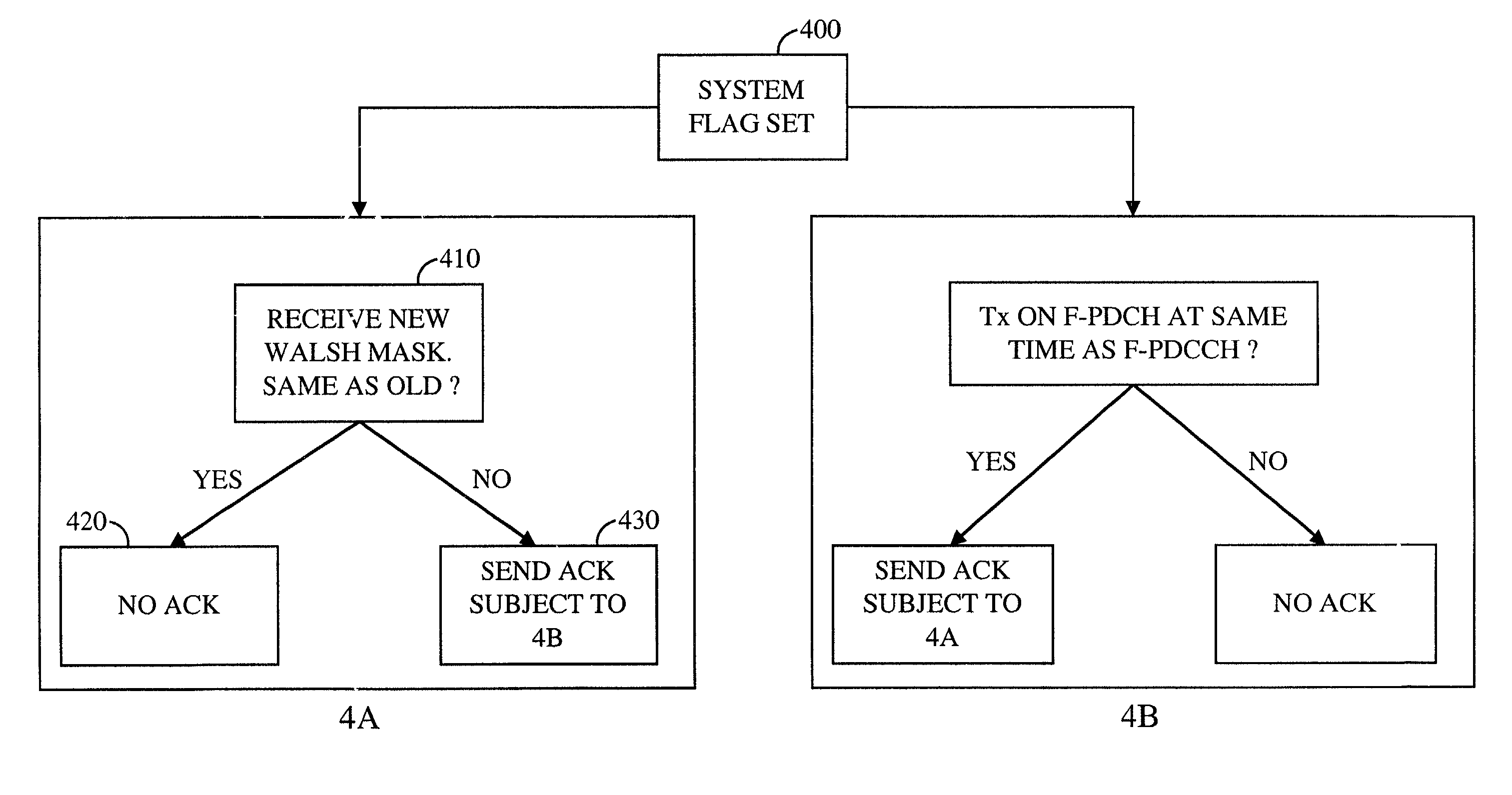
Transmissions on the dedicated channel are encoded using a set of paramaters that are picked from a large selection of potential parameters. If the remote station does not know the particular set of parameters that were used by a base station, then the remote station would have to attempt to decode the transmission using every set of parameters, until the transmission is decoded correctly. This is an inefficient methodology. Hence, transmission format information is typically transmitted on a broadcast channel so that a remote station could receive the transmission format information. However, the broadcast channel has reliability problems. New methods and apparatus are presented to allow a base station to determine an overlapping set of Walsh code sequences that can be used to send the transmission format information on the dedicated channel, rather than a broadcast channel. Using the overlapping set allows the remote station to decode the information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Transmitting connection set-up parameters in packet data network
InactiveUS7020481B2Easy to separateConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork onMobile station
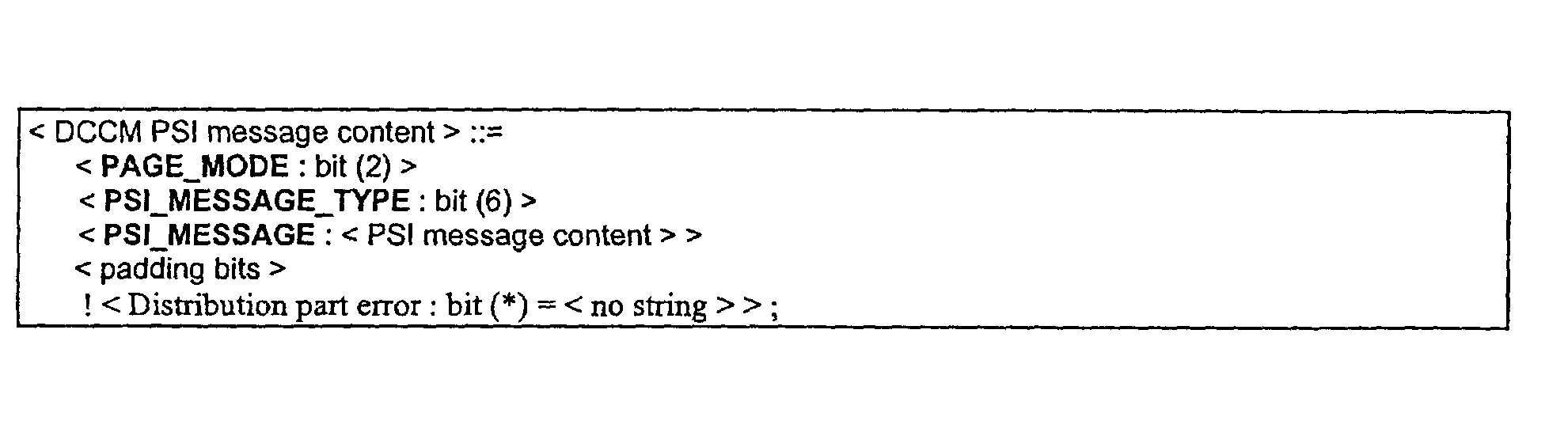
A method for transmitting connection set-up parameters of a packet data network on broadcast control channels in a telecommunications system, which comprises at least one cell, which uses a circuit-switched and a packet-switched broadcast / common control channel. At least one mobile station supports the packet data network and is arranged to listen to at least one of said broadcast / common control channels. The connection set-up parameters of the packet data network are transmitted to mobile stations in the cell on both broadcast control channels, if the cell supports the transmission of the connection set-up parameters of the packet data network on both broadcast control channels. The mobile station transmits to the packet data network a DCCM indication, if the mobile station is capable of receiving control messages on both common control channels, and the telecommunications system is directed to transmit control messages to the mobile station on one of the common control channels.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and apparatus for system access in system using beamforming
ActiveUS20150208443A1Valid choiceSynchronisation arrangementSpatial transmit diversityBroadcastingBroadcast control channel
The present invention relates to an method and an apparatus for upward access, and the method for upward access according to one embodiment of the present invention can comprise the steps of: receiving, from a base station, a synchronization QO channel, a broadcasting control channel and a secondary reference signal; selecting a transmission beam which transmits an upward access signal by using received results from at least one of the synchronization channel, the broadcasting control channel and the QO secondary reference signal; transmitting the upward access signal by using the selected transmission beam; and receiving, from the base station, an access response and initial set-up information of the control channel as a response for the upward access signal. According to the one embodiment of the present invention, the upward access steps can efficiently perform a beam selection.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Broadcast scheme for a multi-carrier wireless network
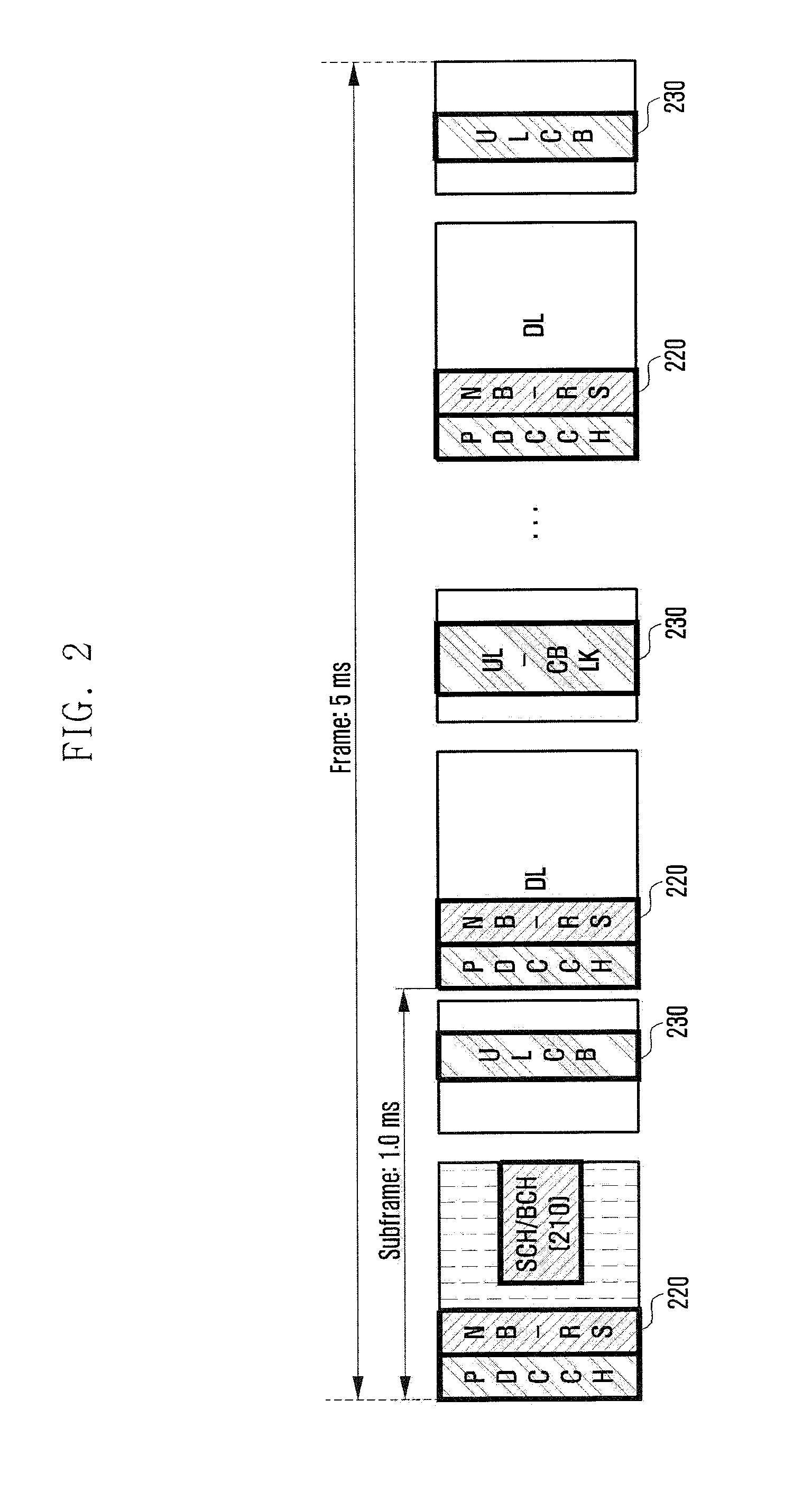
A base station for use in an OFDM / OFDMA wireless network. The base station transmits system-specific broadcast control channel (BCCH) information in a first group of time-frequency slots and transmits cell-specific BCCH information in a second group of time-frequency slots. The time-frequency slots in the first group are orthogonal to the time-frequency slots in the second group. The base station transmits the system-specific BCCH information in the same time-frequency slots as a neighboring base station. The neighboring base station transmits cell-specific BCCH information in a third group of time-frequency slots that may or may not be orthogonal to the time-frequency slots in the second group.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
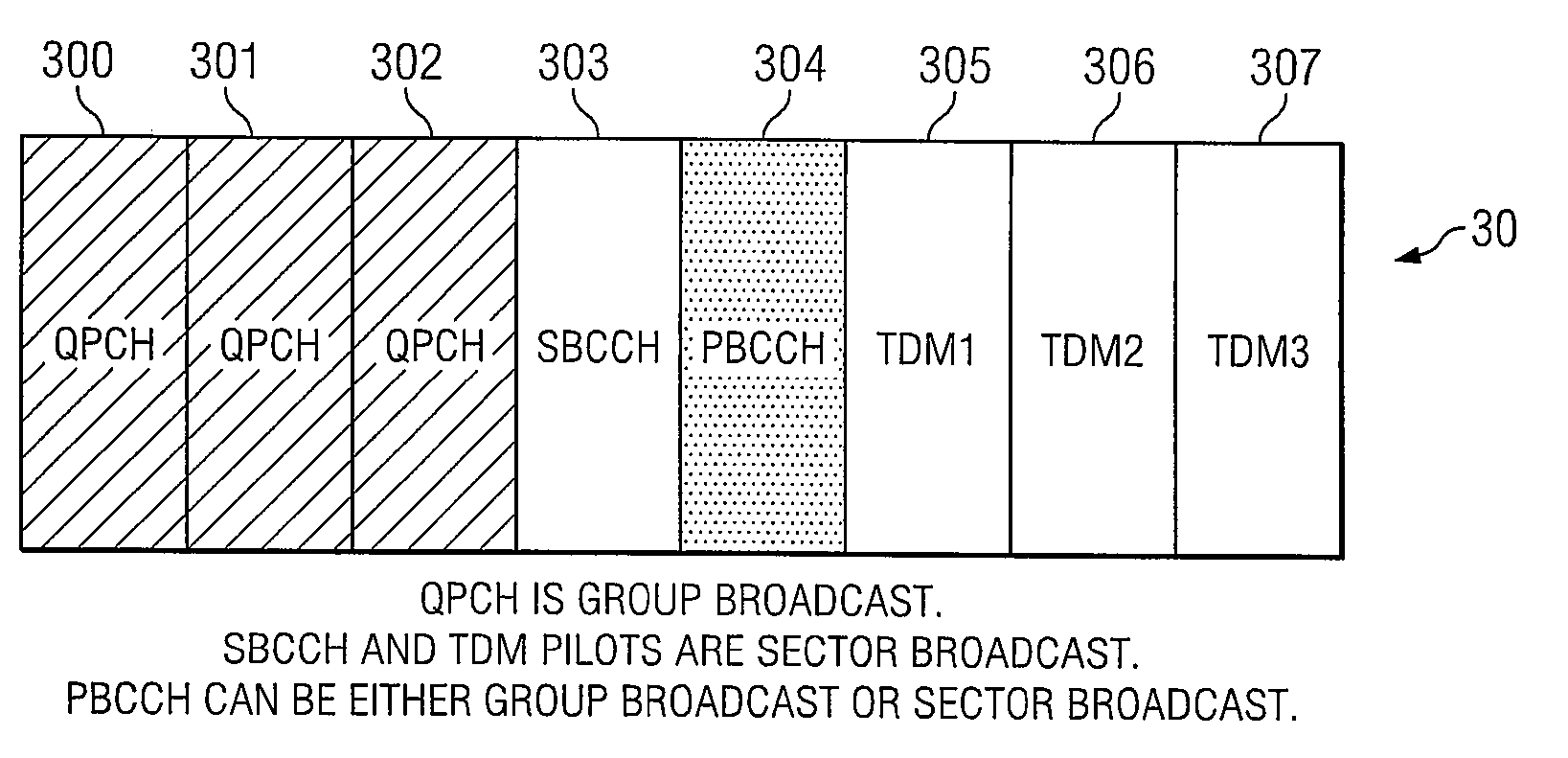
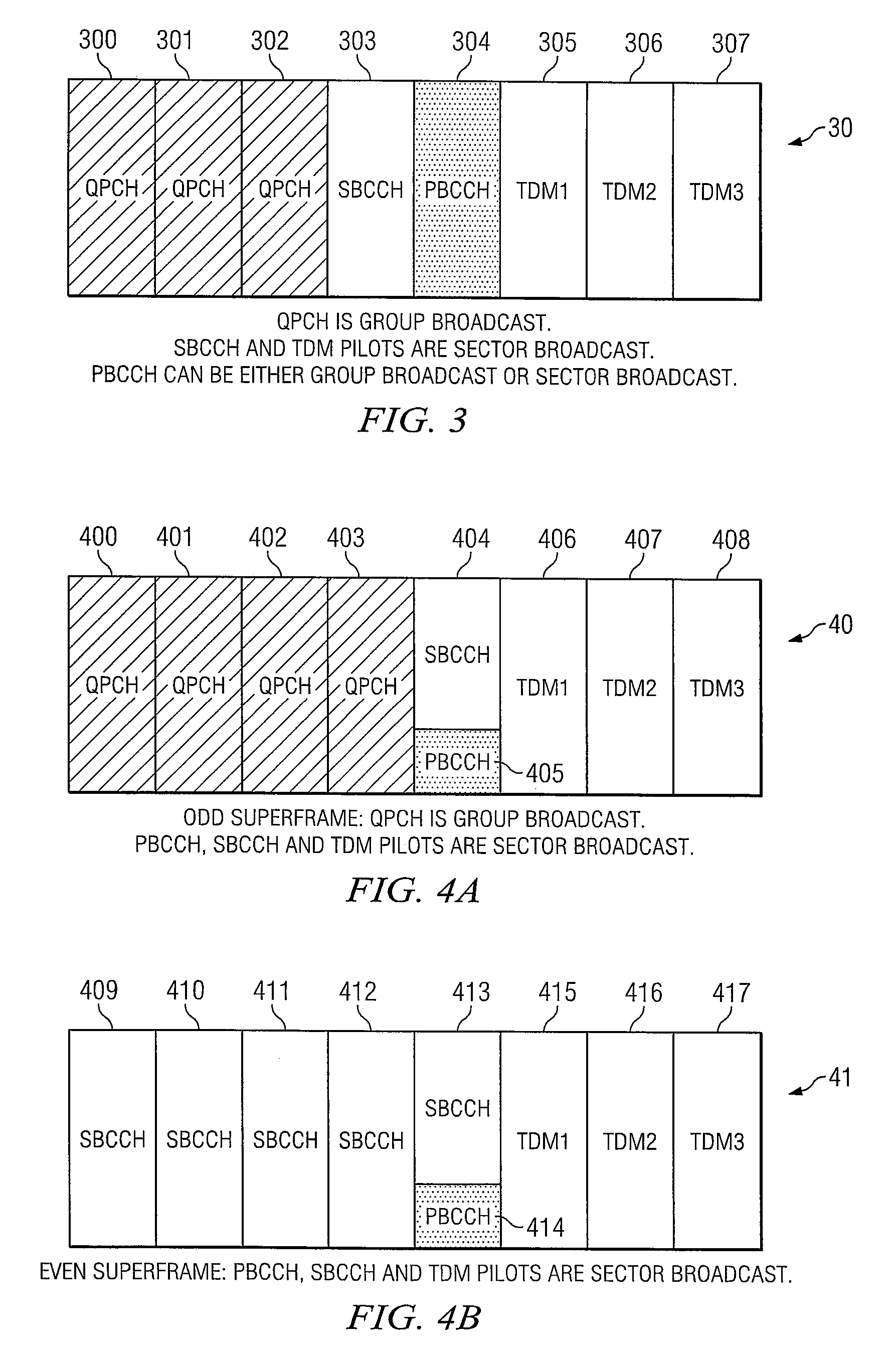
Transmitting Page and Broadcast Control Channel through the Same Time Frequency Resources across the Sectors in a Wireless Communications System
ActiveUS20080056188A1Improve performanceMacro diversityBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemBroadcasting
The present invention describes transmitting the page channel, which may comprise a quick page channel and a regular page channel, and the broadcast control channel, which conveys the system information, through the same time-frequency resources across the sectors of a wireless communications network.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
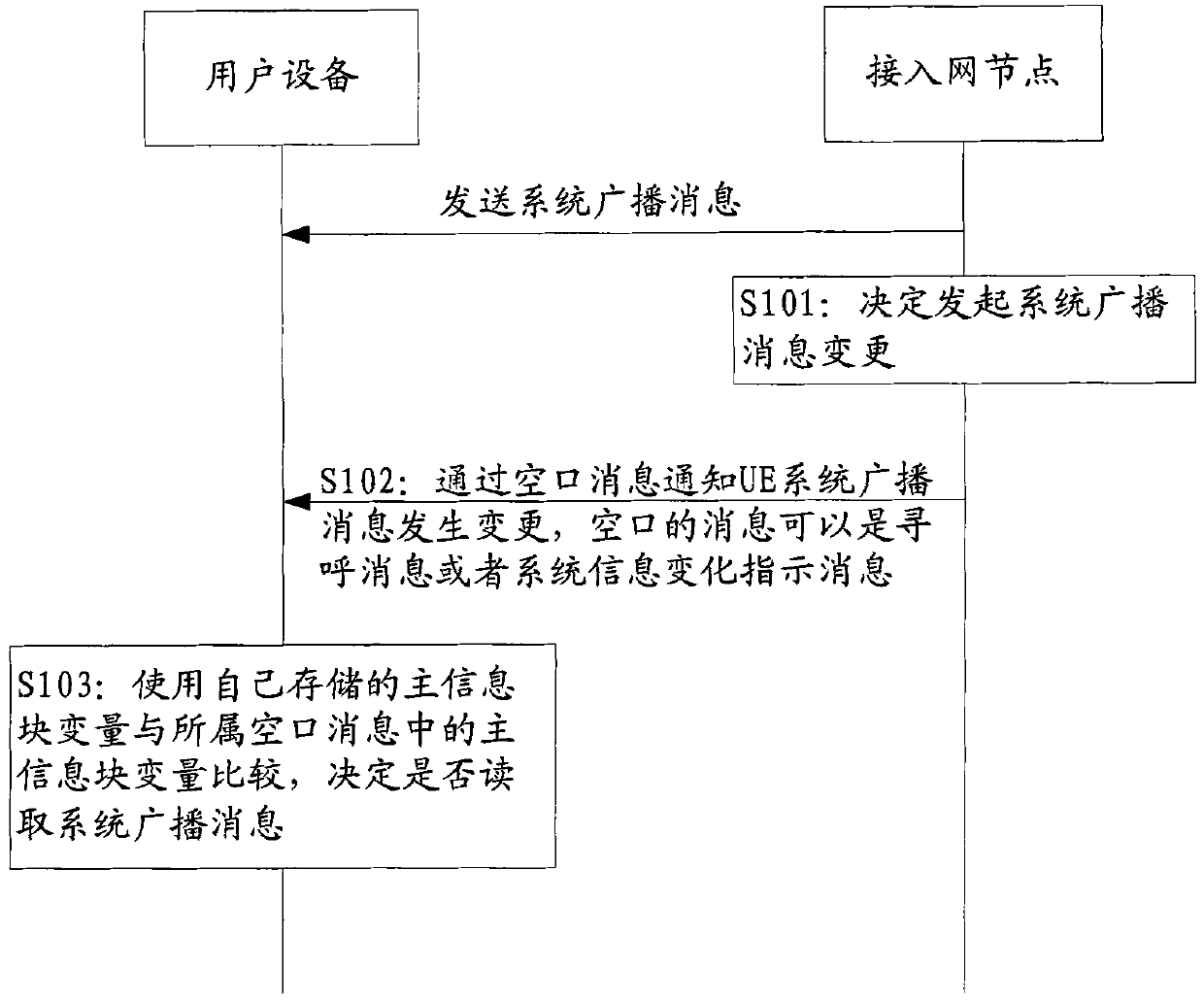
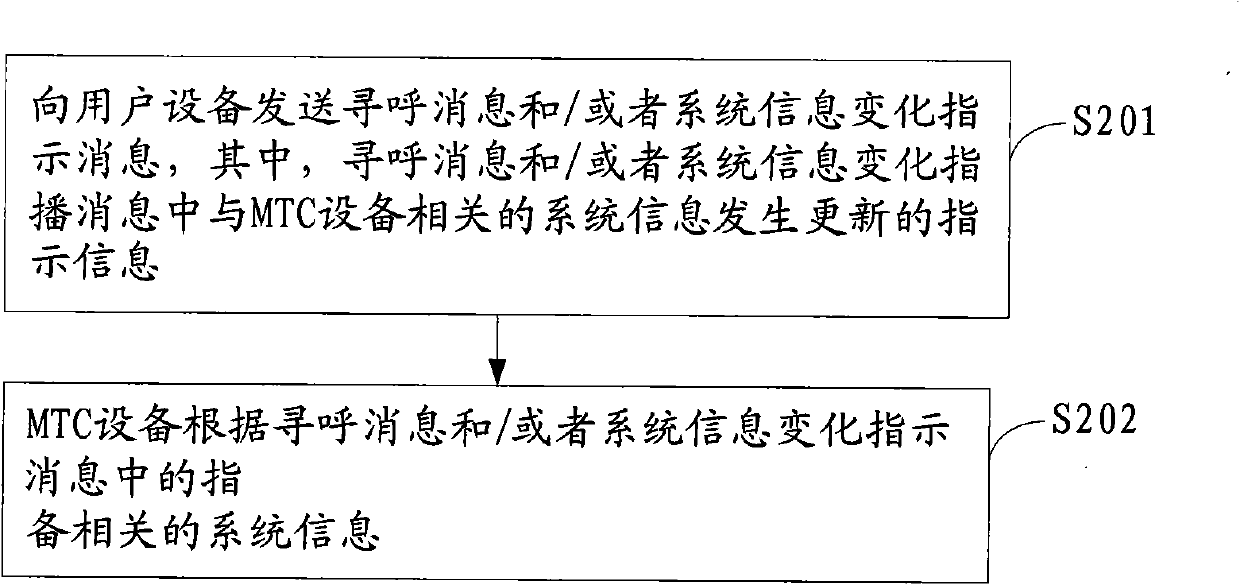
Method and equipment for notifying and reading system broadcast message update
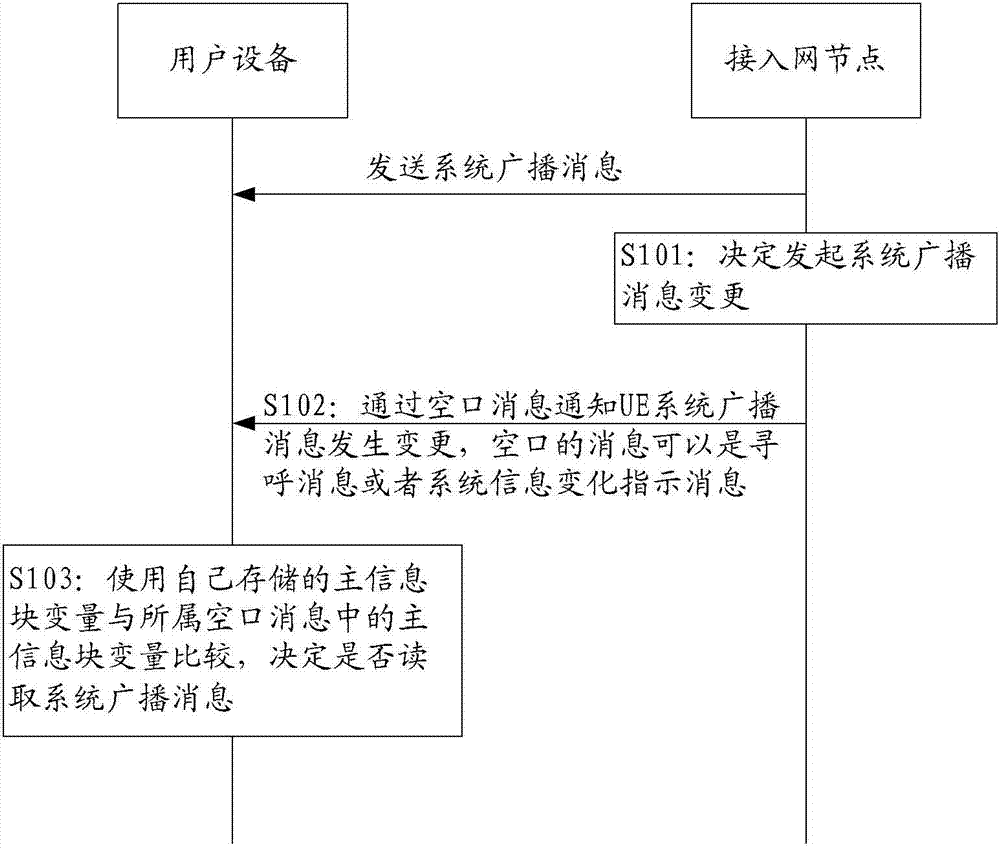
ActiveCN102026372ASolve the impactEfficiently obtainedWireless communicationBroadcast control channelSystem information
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and equipment for notifying and reading system broadcast message update, which relate to the field of communication and can solve the problem of influence on non machine type communication (MTC) equipment when the system broadcast message related with MTC equipment is changed. The provided method for reading the updated system broadcast message comprises the following steps of: receiving page message and / or system information change indicating message, wherein the page message and / or the system information change indicating message comprise indicating information on the update of the system information related with the MTC equipment in the system broadcast message; and determining that user equipment is the MTC equipment, reading a broadcast control channel according to the indication of the indicating information, and acquiring the updated system information related with the MTC equipment in the system broadcast message.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
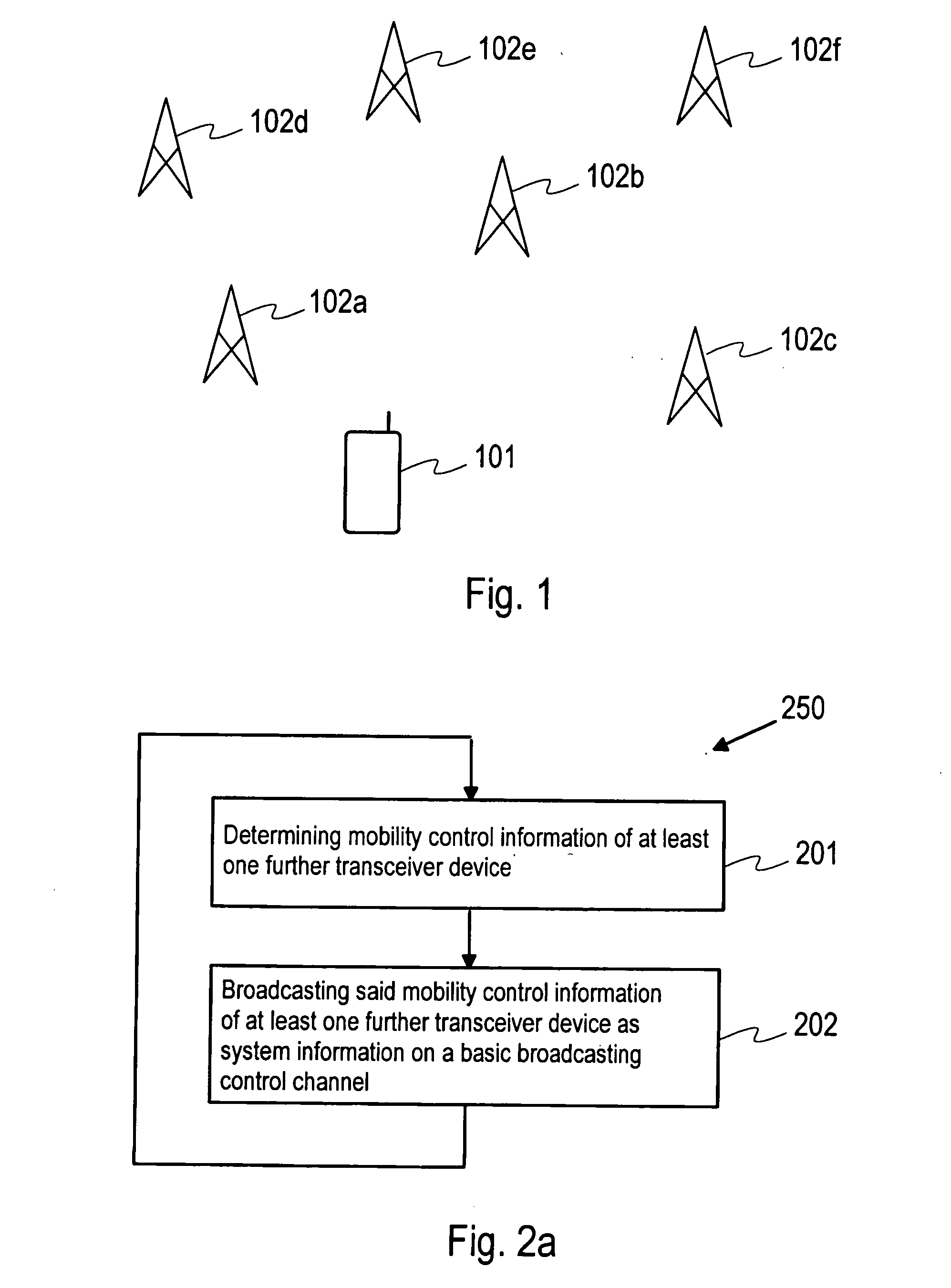
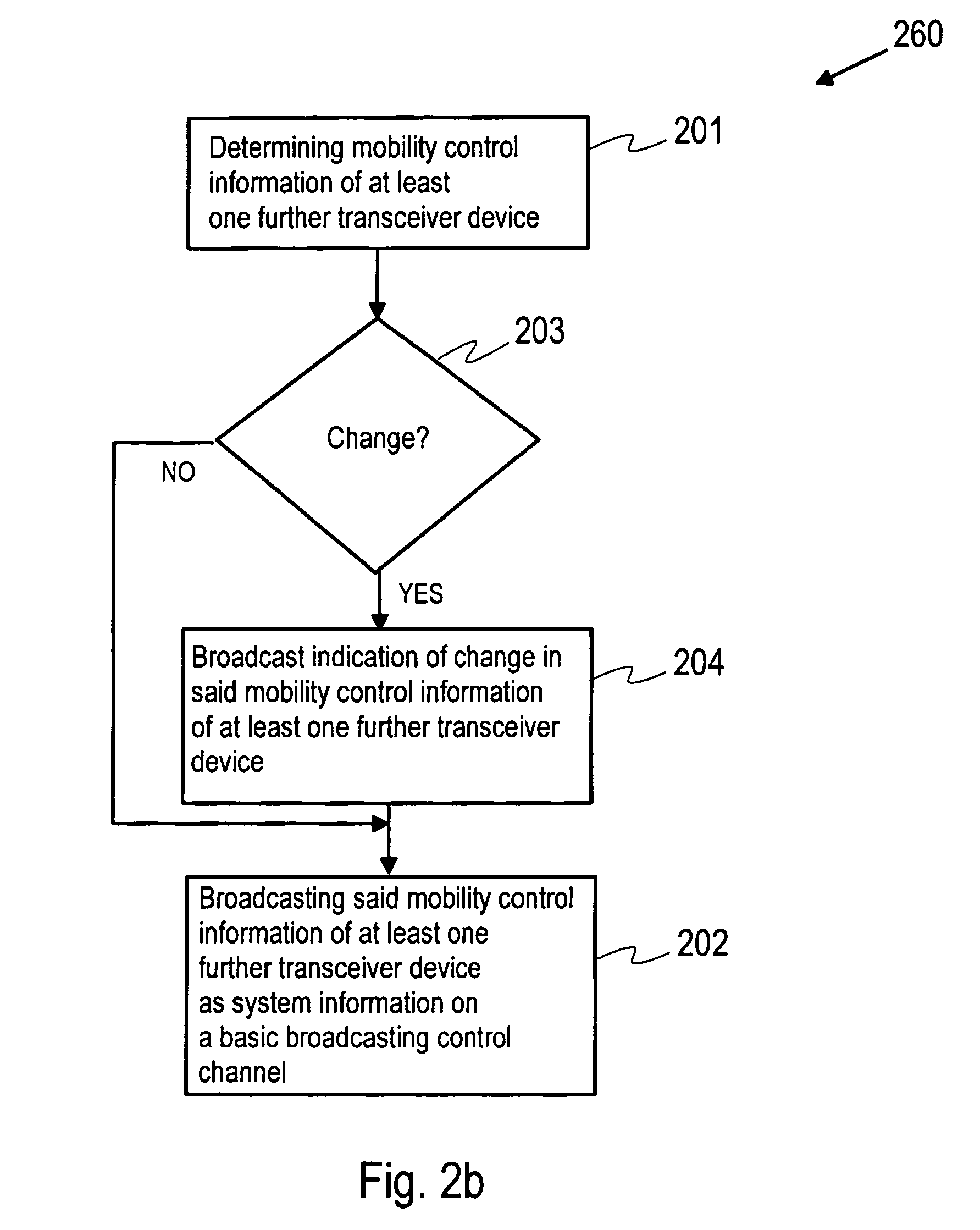
Providing mobility control information to a communications device
InactiveUS20060068780A1Assess restrictionBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemTransceiver
A method for providing mobility control information to a communications device includes determining, for a transceiver device of a communication system, mobility control information of at least one further transceiver device and broadcasting system information from the transceiver device on a basic broadcast control channel, wherein the system information comprises the mobility control information of the at least one further transceiver device.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Apparatus and method for positioning mobile station
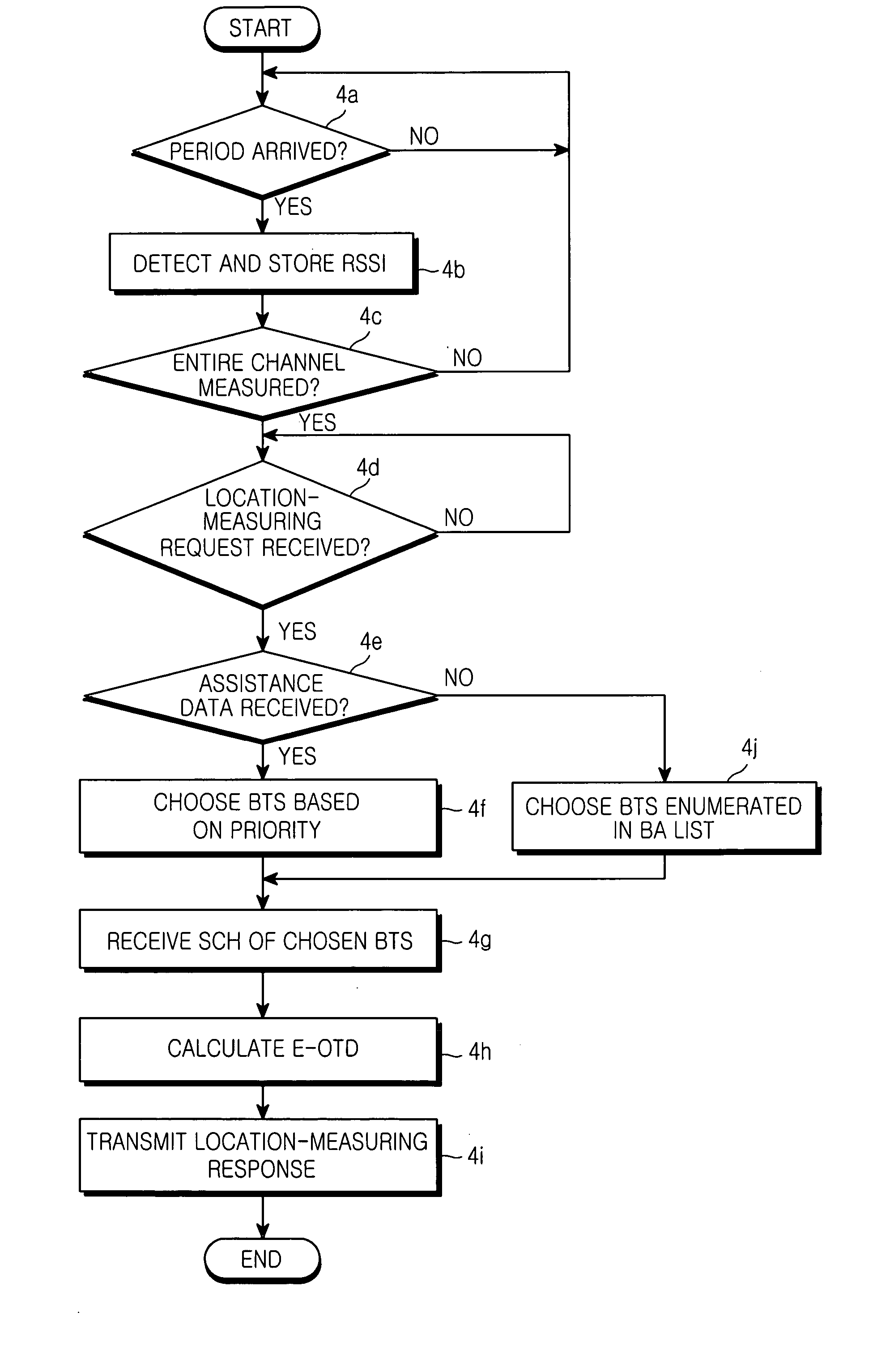
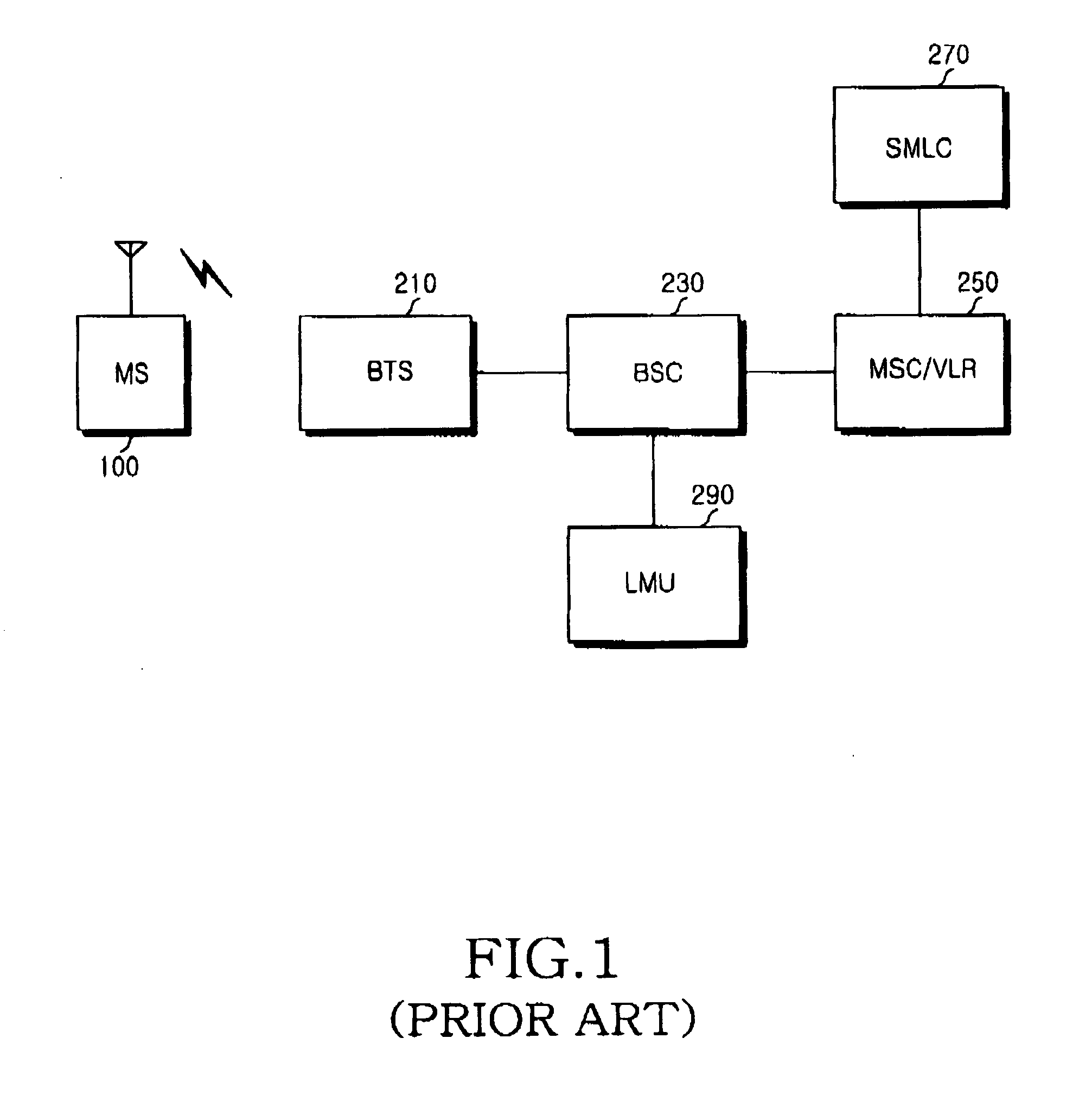
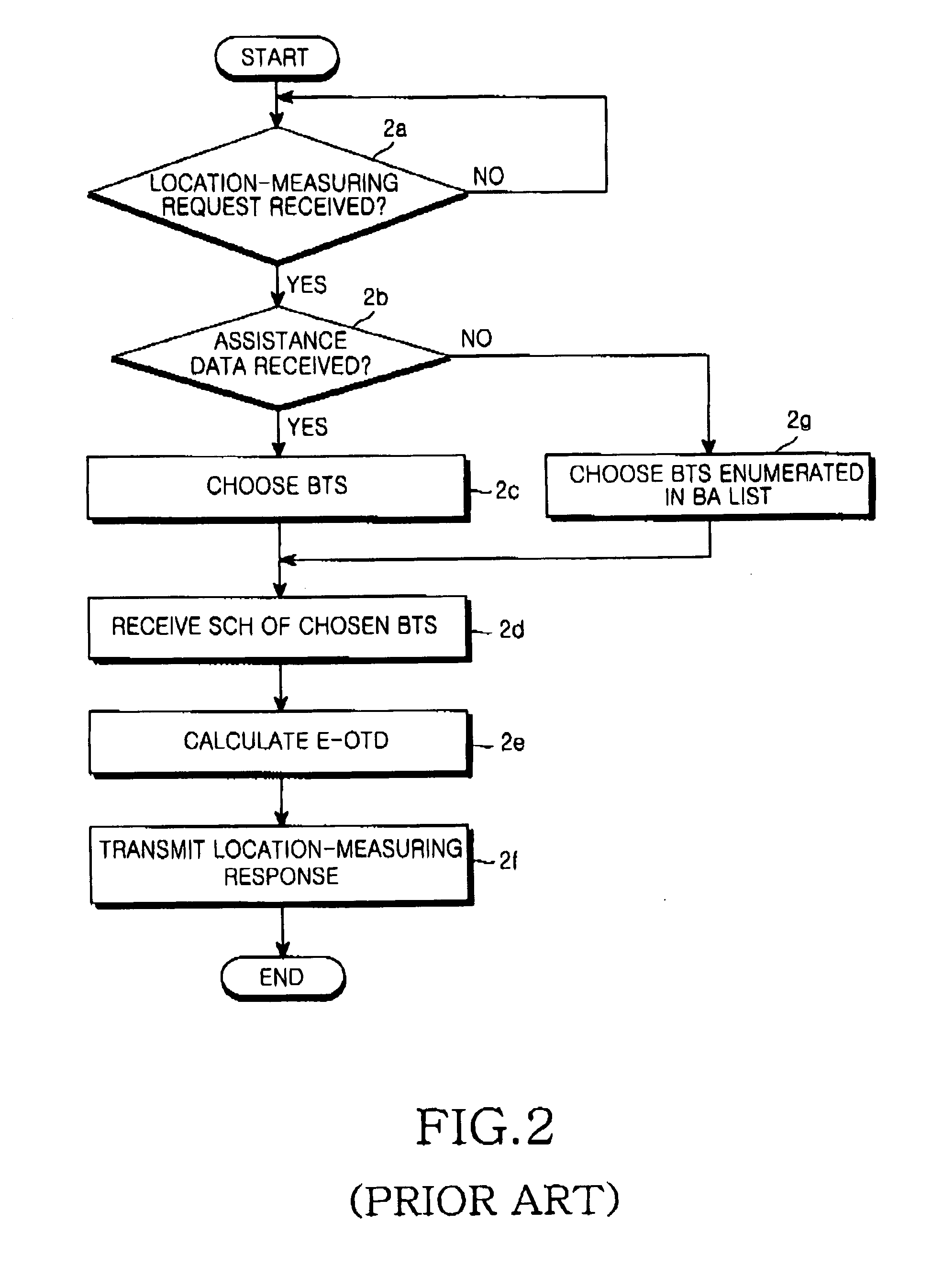
ActiveUS20050136938A1Accurately calculate locationEfficient receptionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationMobile stationBroadcasting
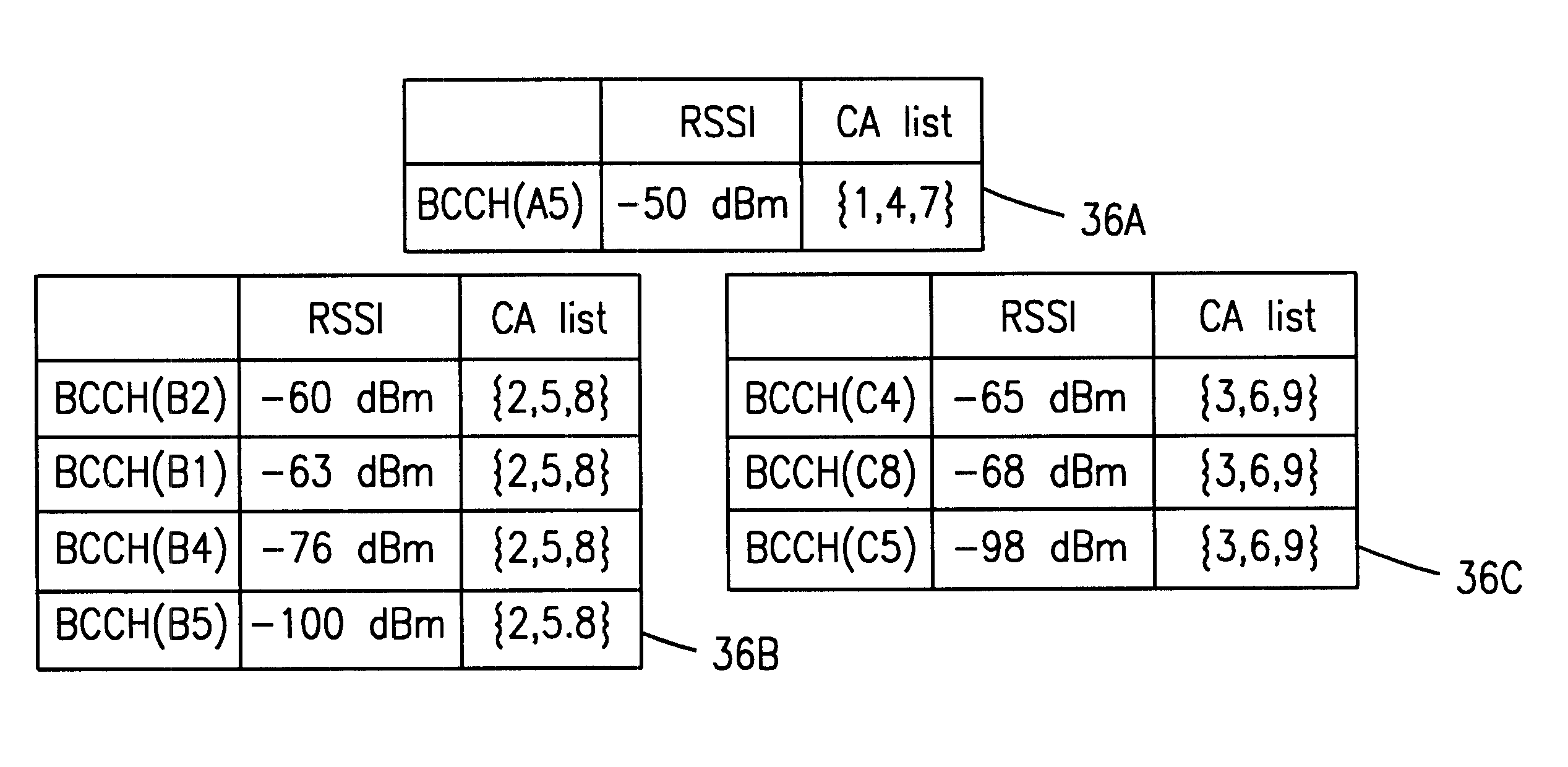
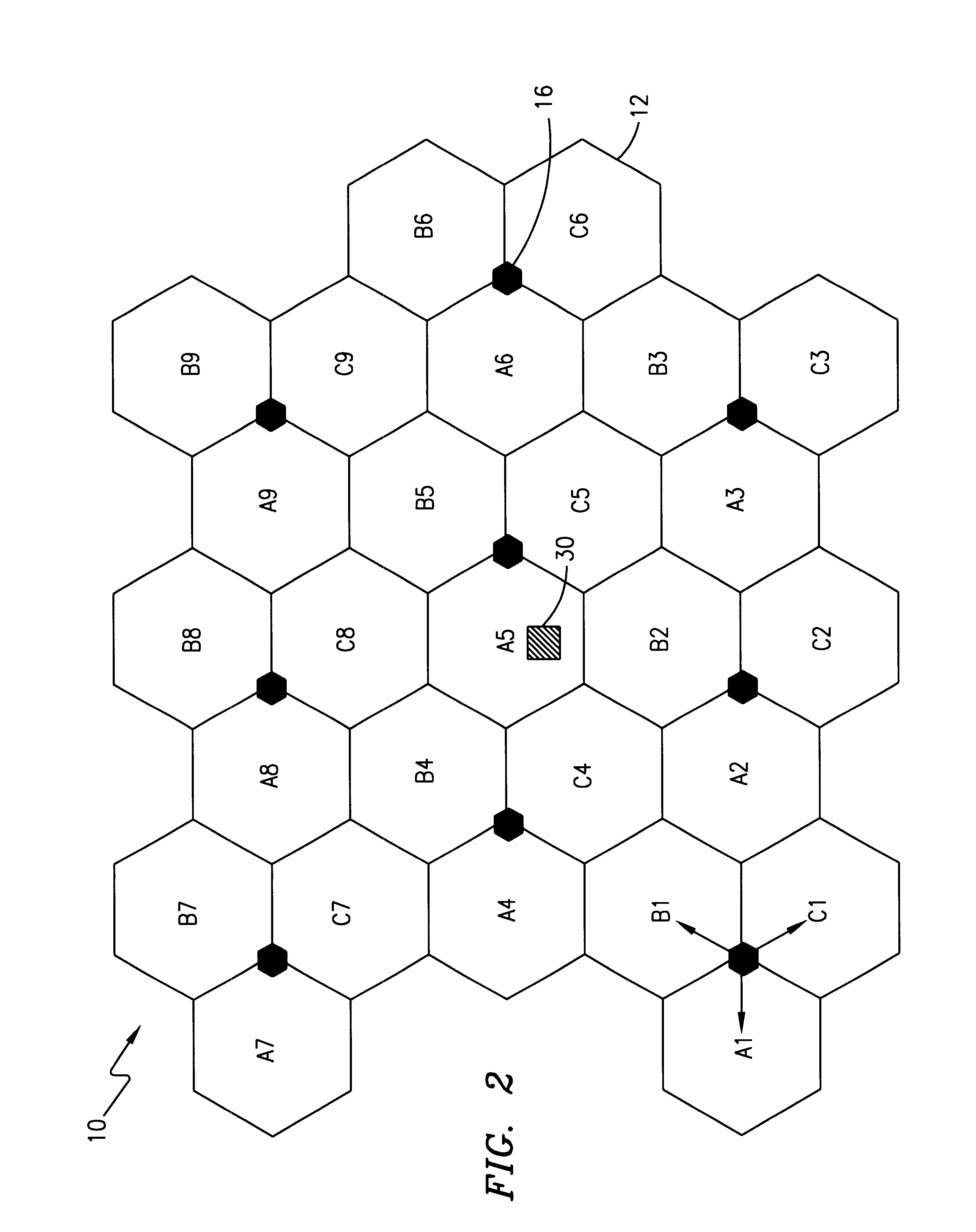
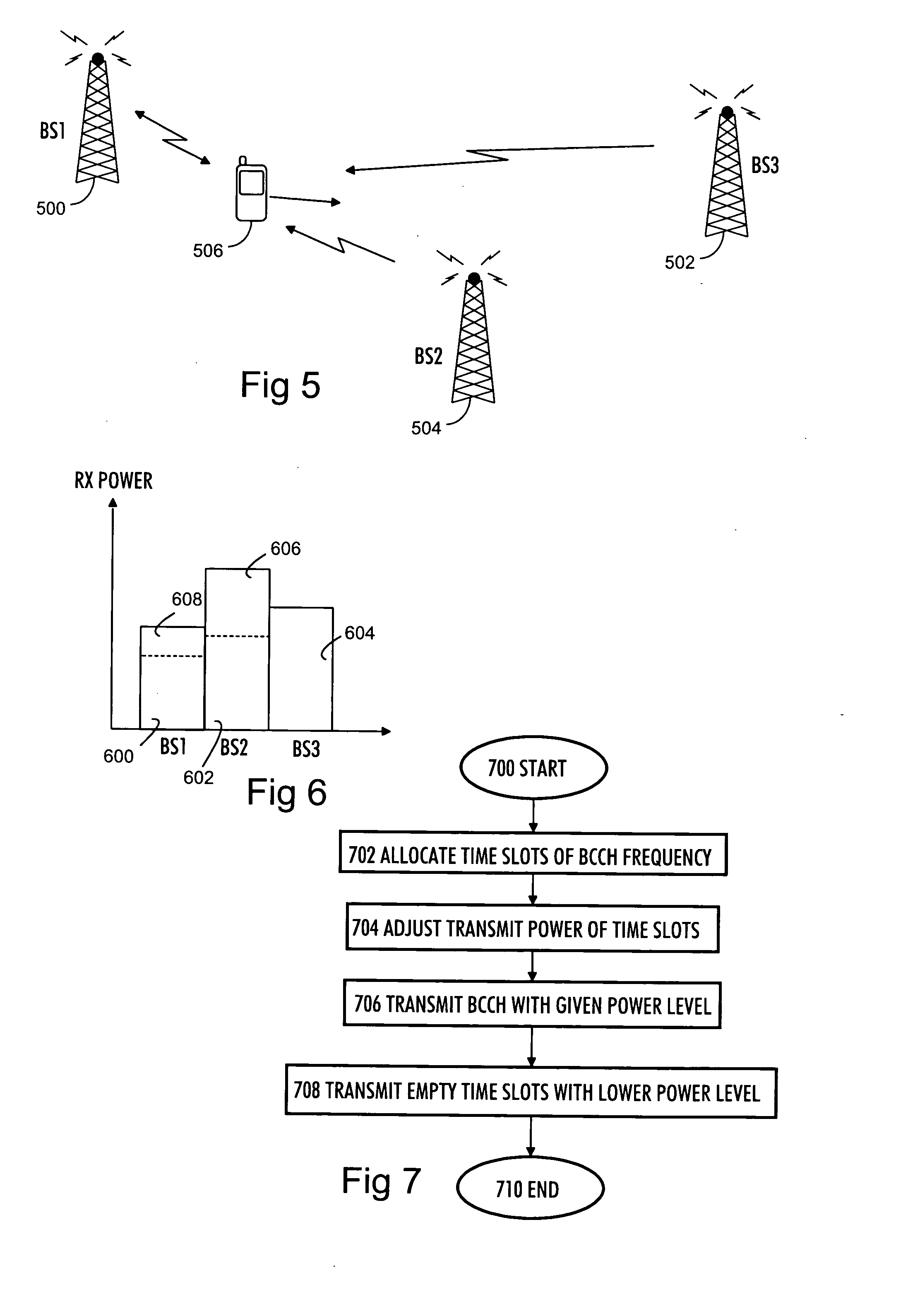
An apparatus and a method for calculating an enhanced observed time difference from a mobile station and transmitting the enhanced observed time difference to a servicing mobile location center for a location-based service are provided. The apparatus comprises means for receiving a location-measuring request and assistance data from the servicing mobile location center; means for choosing a base transceiver station, the synchronization channel of which is to be measured, based on response time detected from the location-measuring request and a predetermined priority; and means for calculating an enhanced observed time difference for the chosen base transceiver station and transmitting a location-measuring response, including the calculation result, to the servicing mobile location center. A first priority is assigned to an overlap between a channel list included in the assistance data and a list of a number of nearby cells and a second priority is assigned to a broadcast control channel allocation list except the channel list included in the assistance data and the list of nearby cells.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
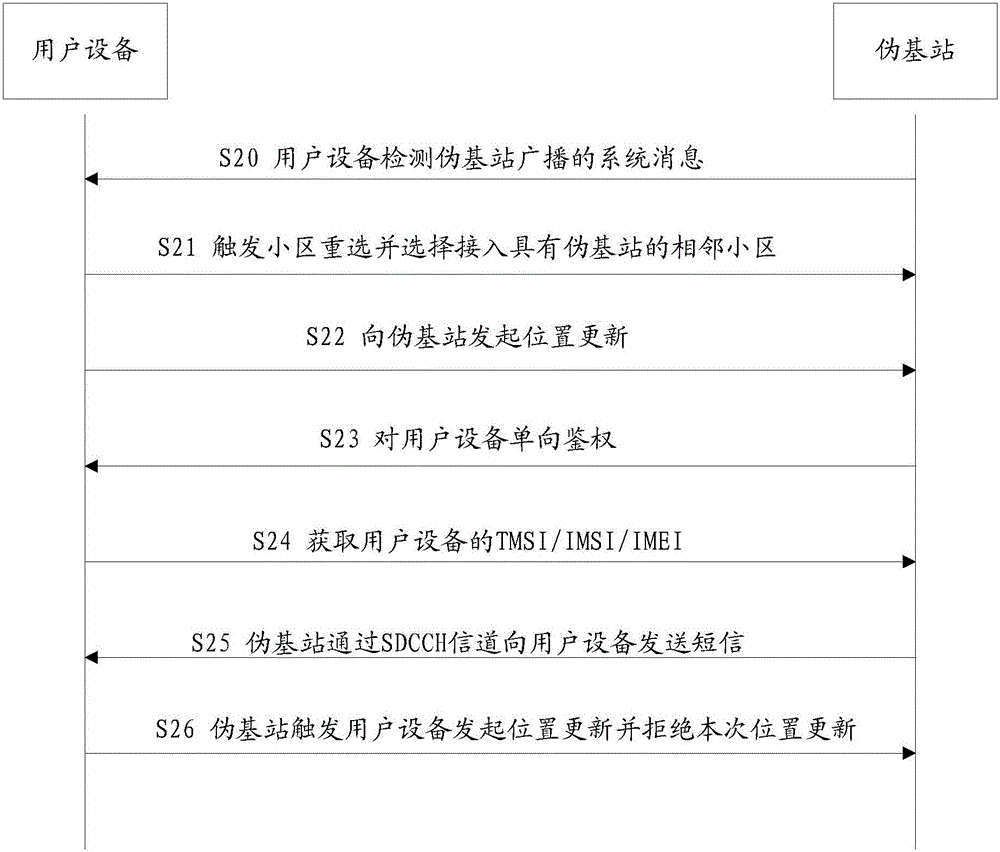
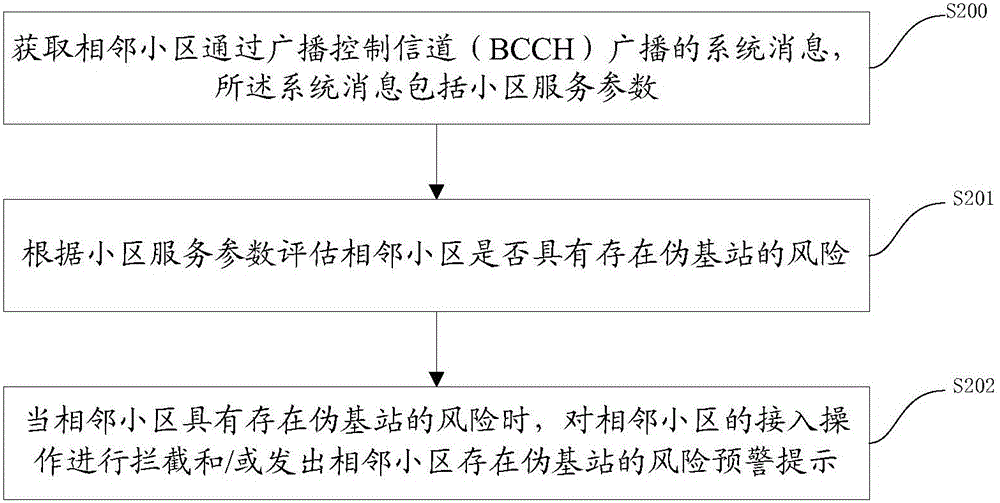
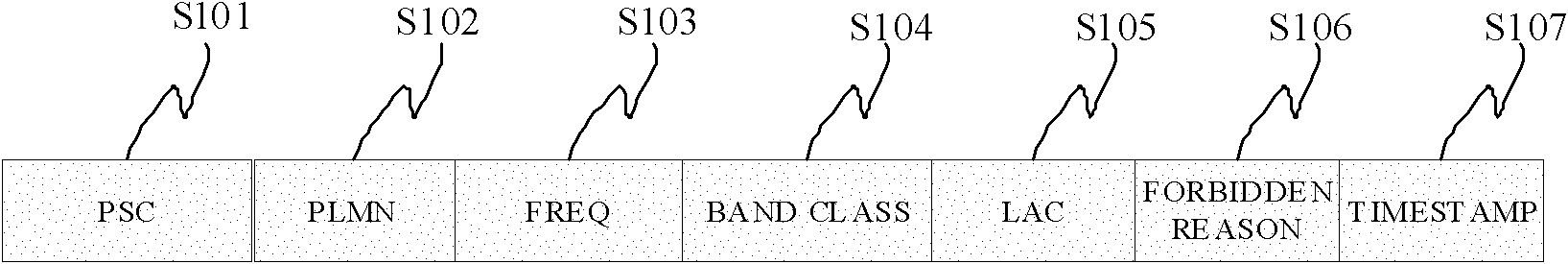
Method and device for recognizing pseudo base-station
The invention discloses a method and device for recognizing a pseudo base-station. The method comprises the steps that system information, broadcast through a broadcast control channel (BCCH), of a neighbor cell is acquired, wherein the system information comprises cell service parameters; whether the neighbor cell has the risk that the pseudo base-station exists or not is evaluated according to the cell service parameters; if yes, an access operation of the neighbor cell is intercepted, and / or a risk early warning prompt that the neighbor cell has the pseudo base-station is given out. By detecting the cell service parameters of the neighbor cell, the purposes of recognizing and avoiding the pseudo base-station are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Power efficient wireless transmission
InactiveUS20070191051A1Increase capacityImprove service qualityEnergy efficient ICTPower managementWireless transmissionPower efficient
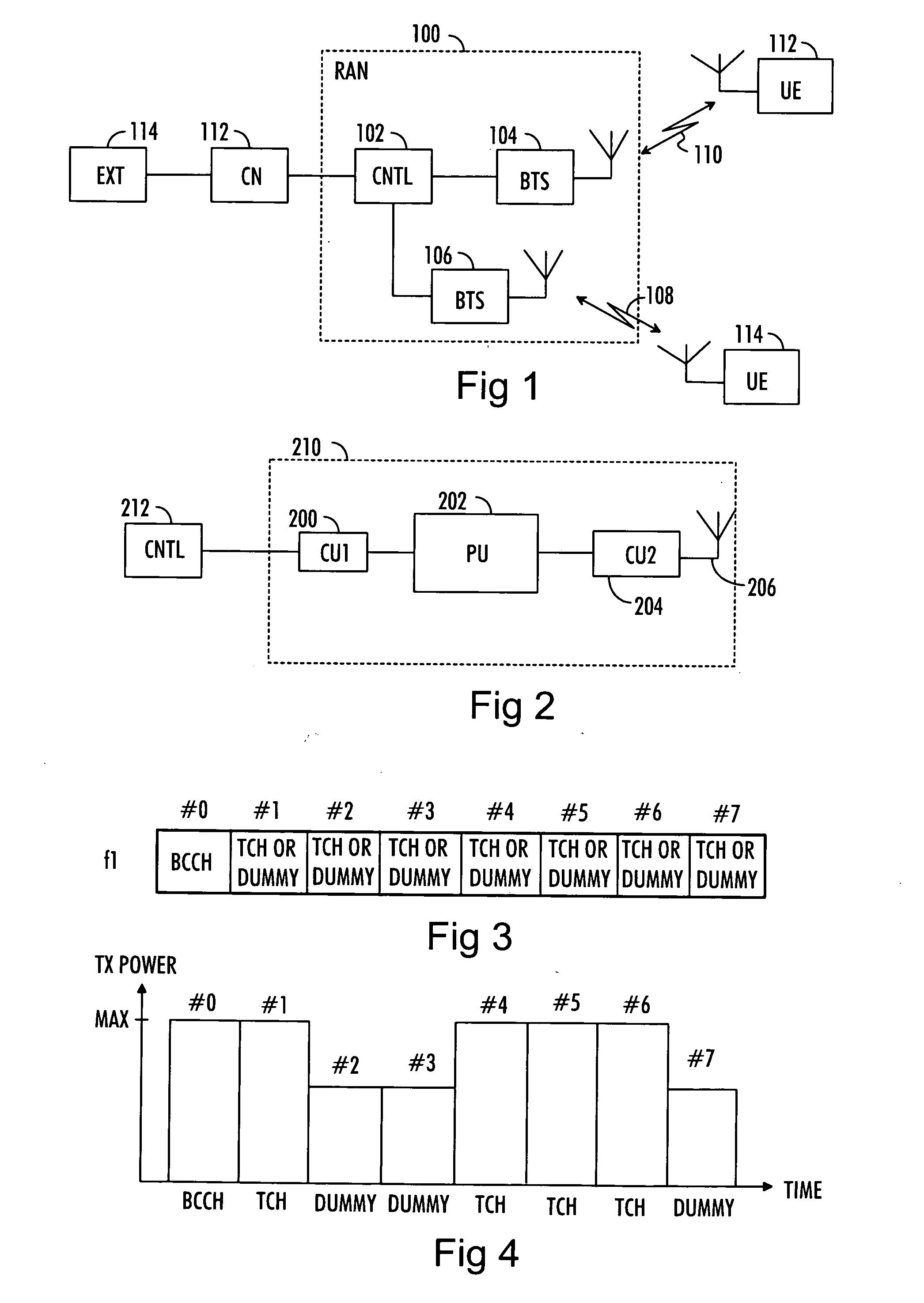
A solution for power efficient transmission in a wireless telecommunication system is provided. The telecommunication system utilizes a time slot based data transmission scheme. According to the provided solution, at least a portion of time slots is allocated to a broadcast control channel on a given frequency and to at least one different channel. The transmit power levels of the time slot or time slots allocated to another channel or other channels than the broadcast control channel are then adjusted on the basis of contents of the time slots. The broadcast signal is then transmitted with a given transmit power level on a time slot allocated to the broadcast control channel, and a signal or signals on other time slots are transmitted with the adjusted transmit power level.
Owner:RPX CORP
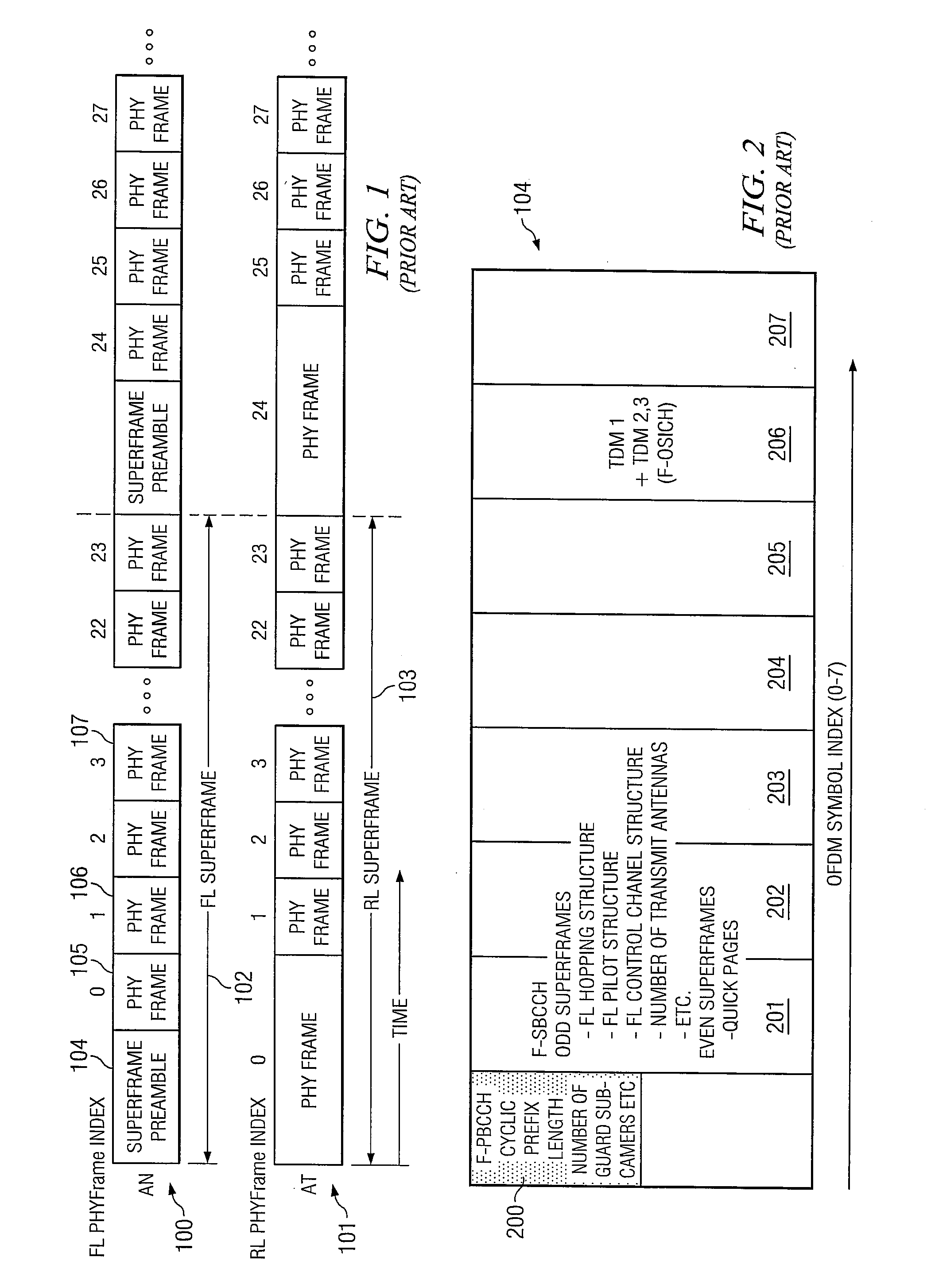
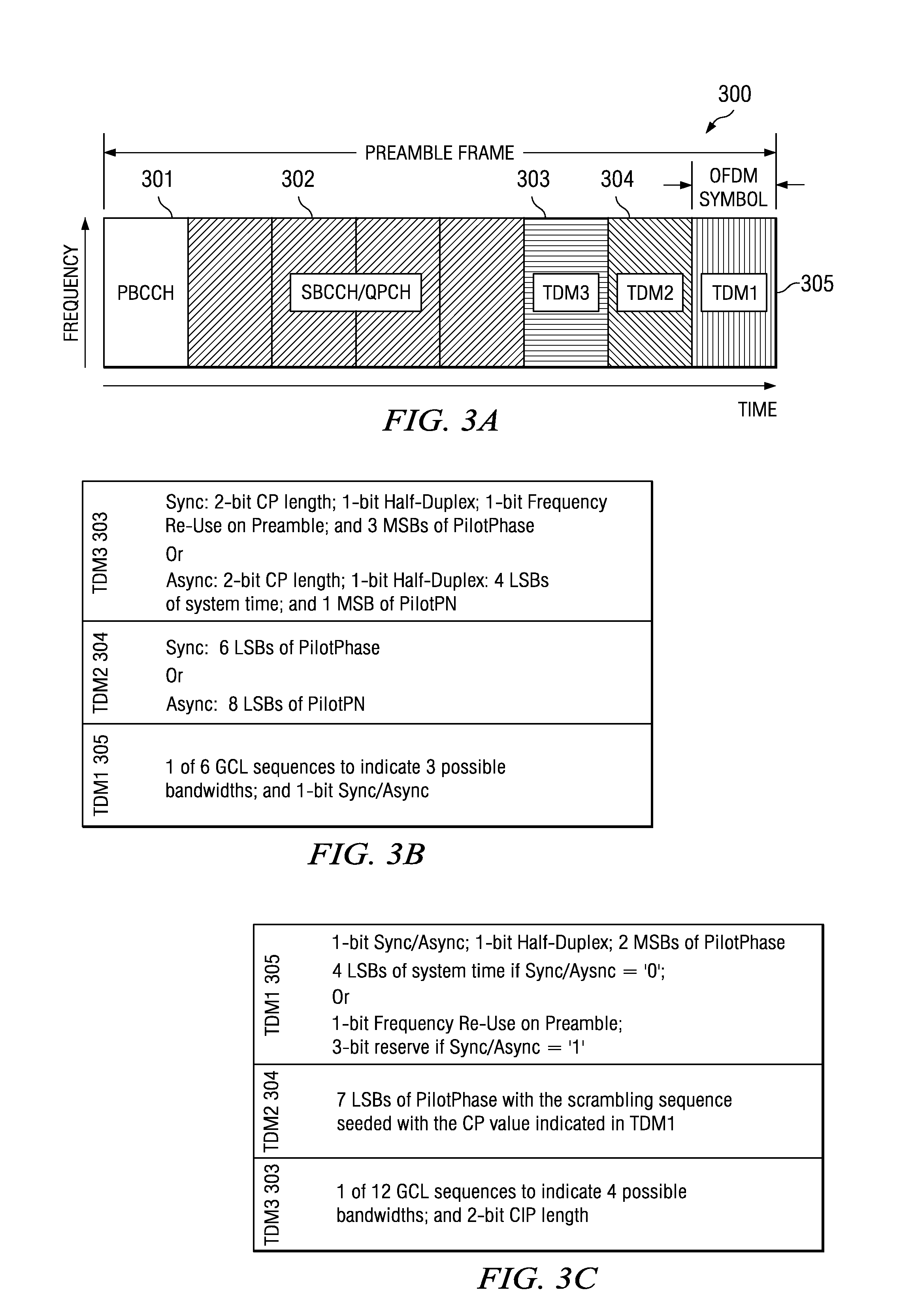
Method and Apparatus for Achieving System Acquisition and Other Signaling Purposes Using the Preamble in an OFDM Based Communications System
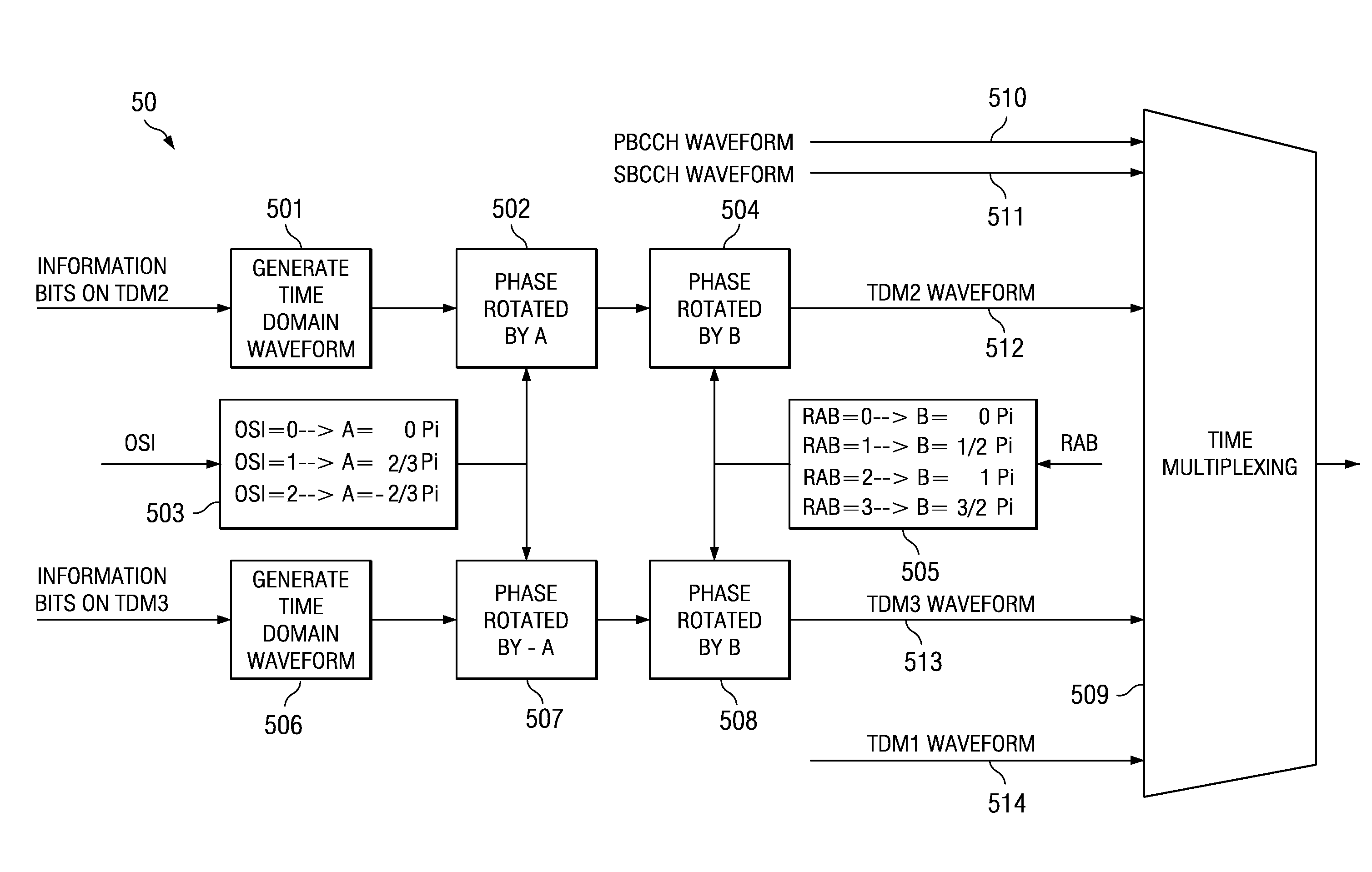
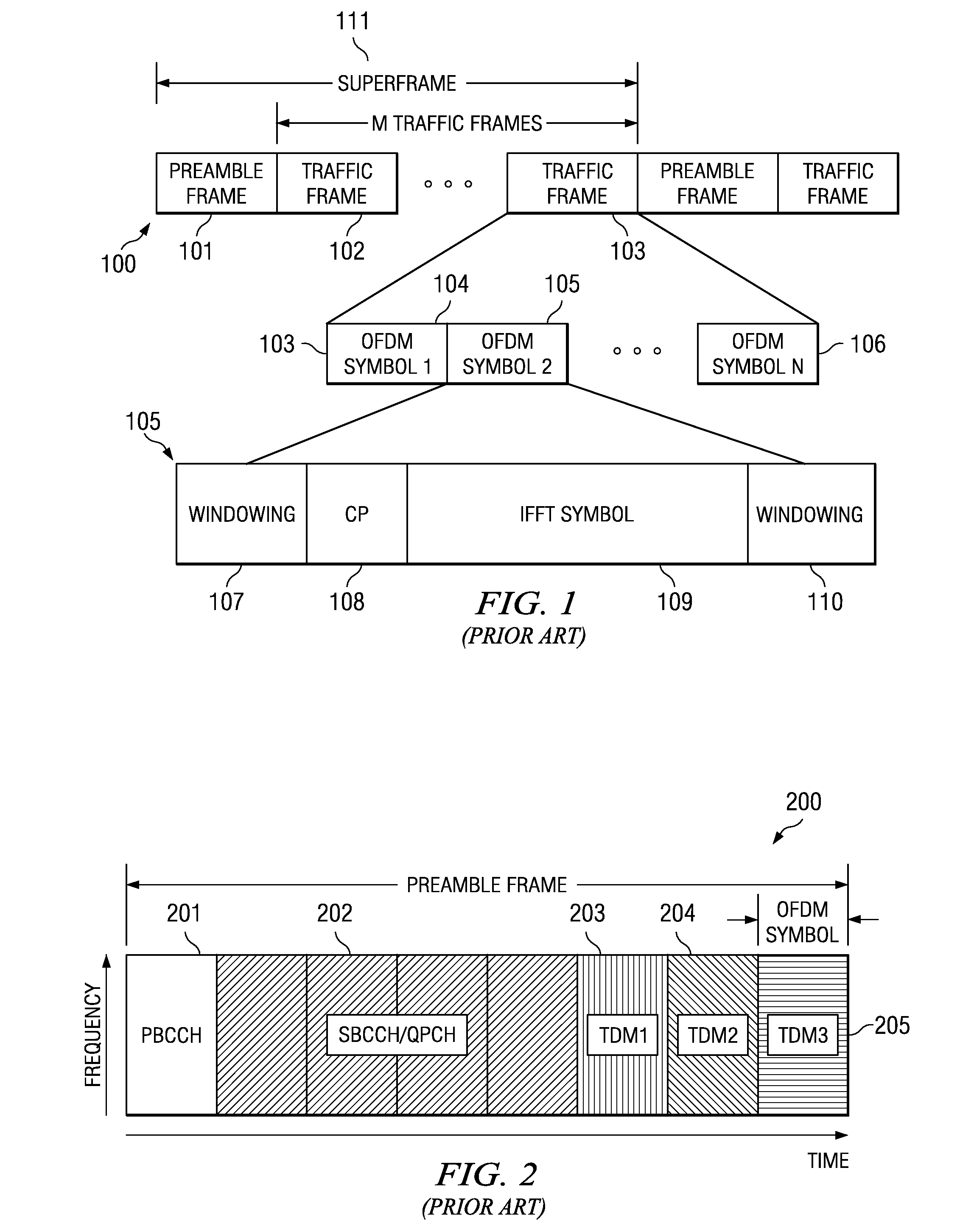
In the system acquisition process system information is non-coherently detected using correlation of reconstructed and received preamble signals, such as the primary broadcast control channel (PBCCH) and the acquisition pilots (TDM1, TDM2, and TDM3). The phase correlation signals between the correlated signals of PBCCH and TDM2 or TDM3 and between the correlated signals of TDM2 and TDM3 are combined to decode other sector interference (OSI) information and the like. Acquisition is also made more efficient by taking advantage of predictable information based on system synchronicity. The sync / async bit is included in at least one of the acquisition pilots. The mobile then uses knowledge of system synchronicity to more efficiently detect the additional information in the superframe preamble.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method of monitoring a broadcast channel for a page at a mobile communication device
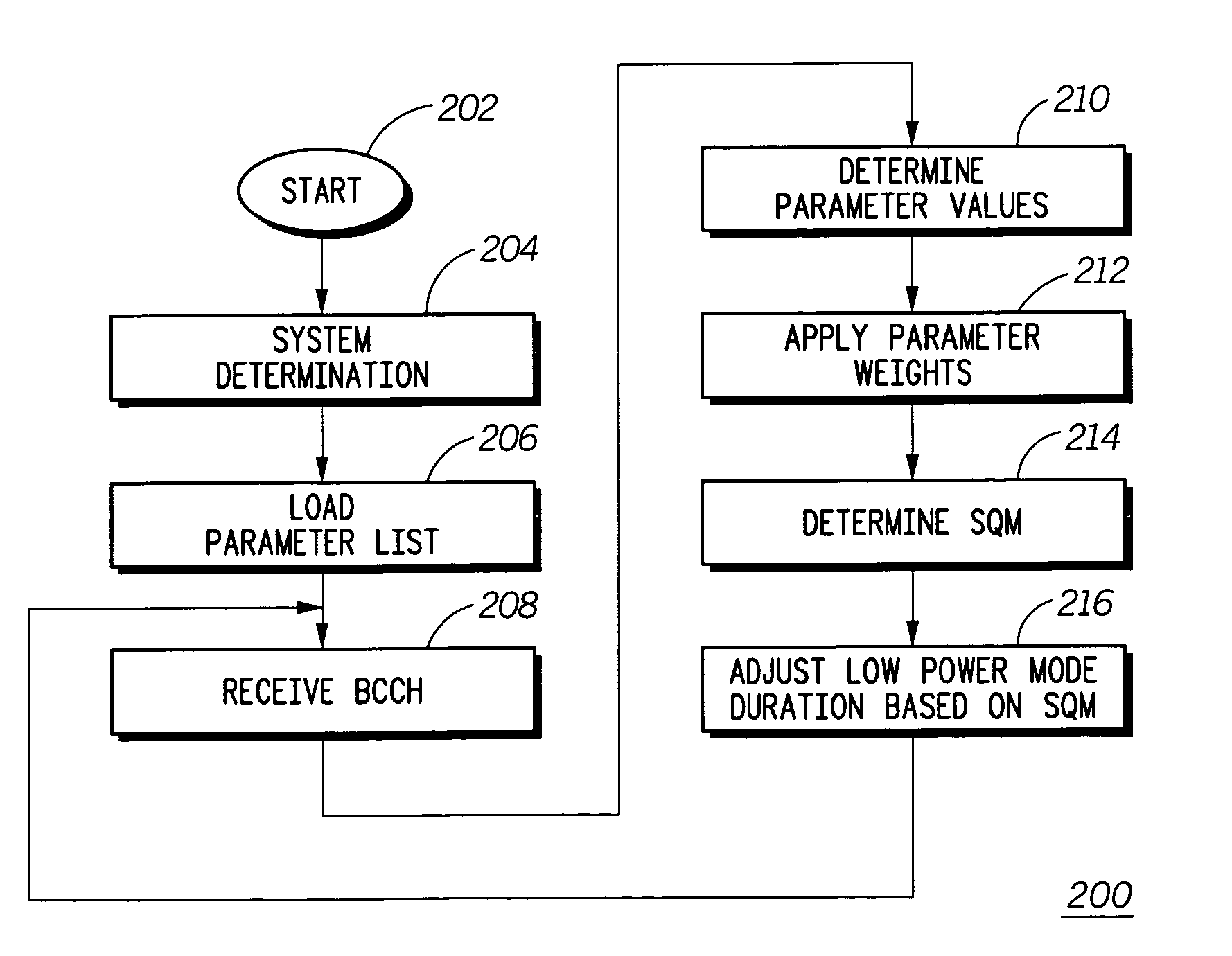
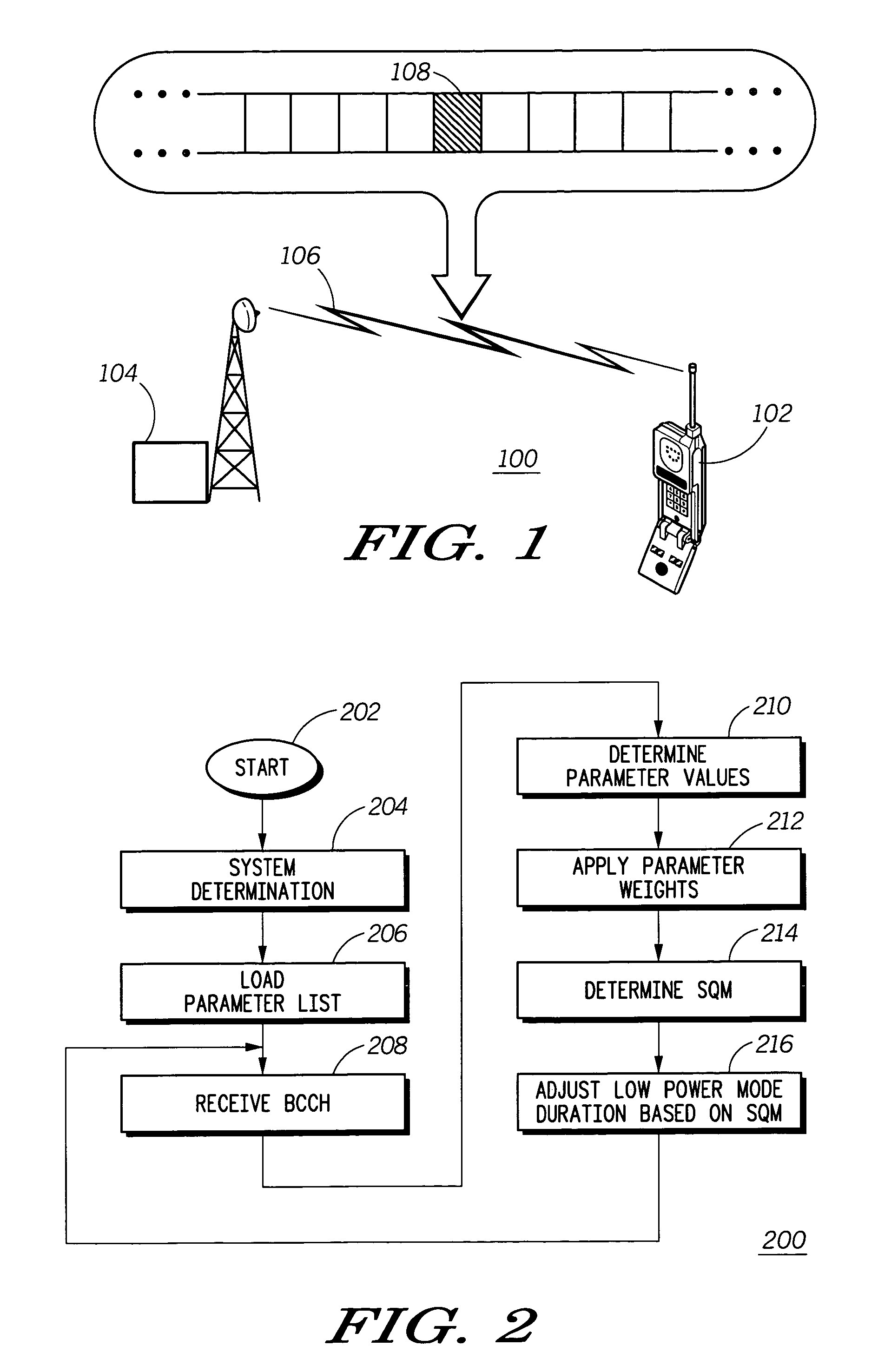
InactiveUS7047050B1Extension of timeSacrificing operating effectivenessPower managementEnergy efficient ICTBroadcast channelsBattery charge
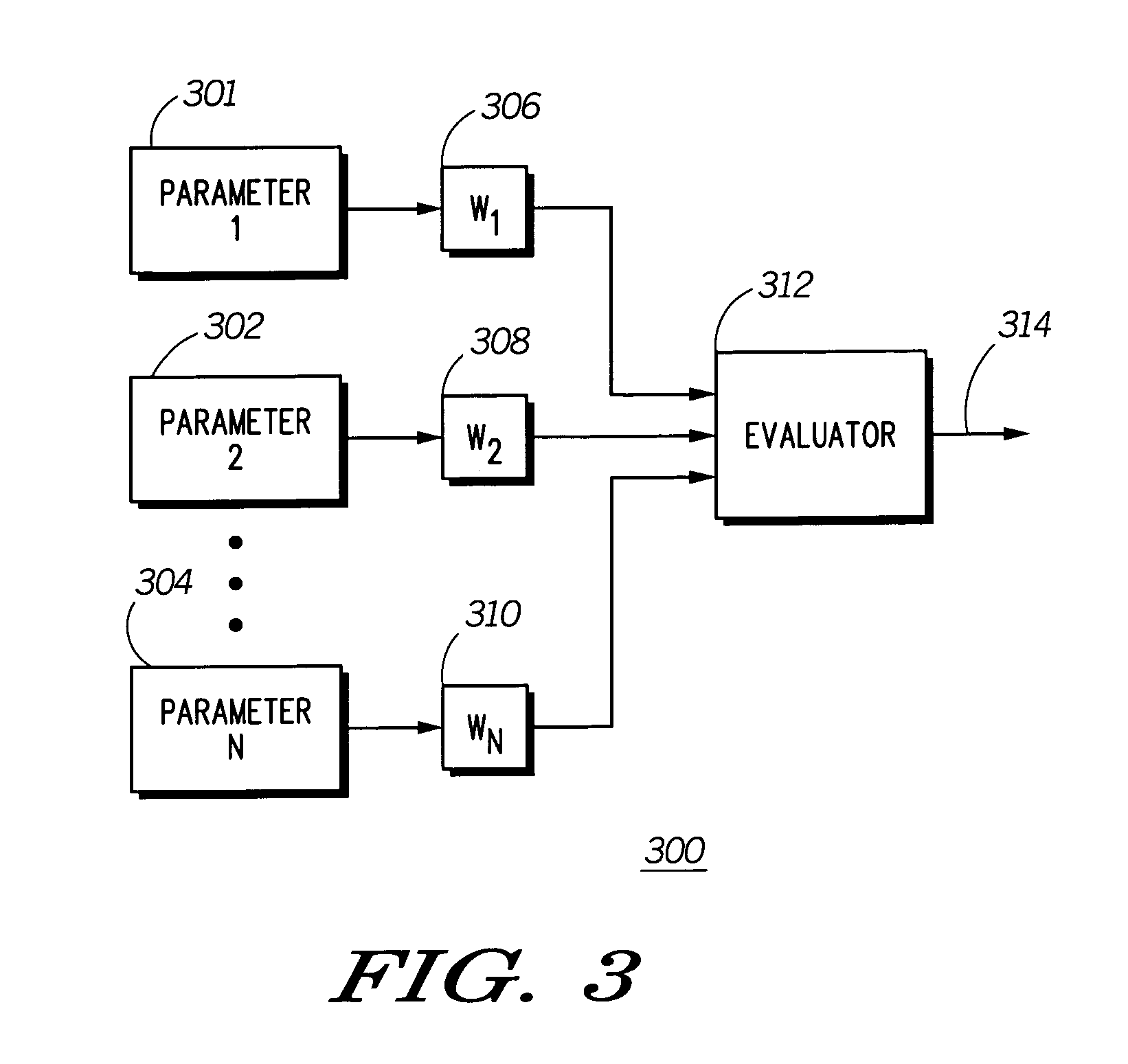
A mobile communication device (102) receives information in a broadcast control channel (108) including a page message (108). The mobile communication device measures certain parameters (210) of the control channel, such as received signal strength, channel quality, and the present automatic gain setting. These parameters are scored and weighted (300) to produce a signal quality metric (314) to determine the duration of time the mobile communication device can remain in a low power state to conserve battery charge before checking for page alert message in the broadcast control channel next.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Wireless subscriber terminal programming using a broadcast control channel
InactiveUS6885862B1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBroadcast channelsProgram segment
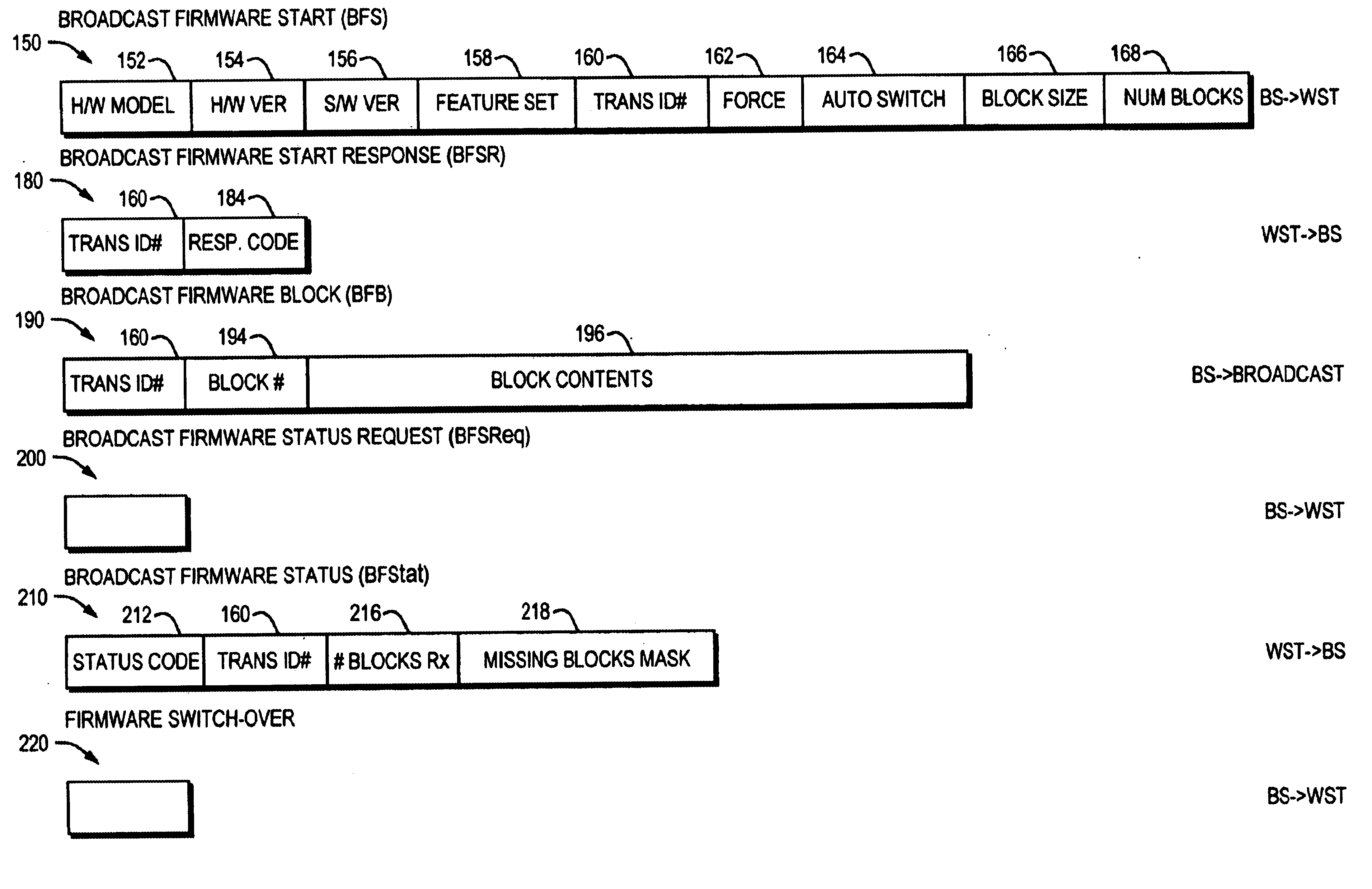
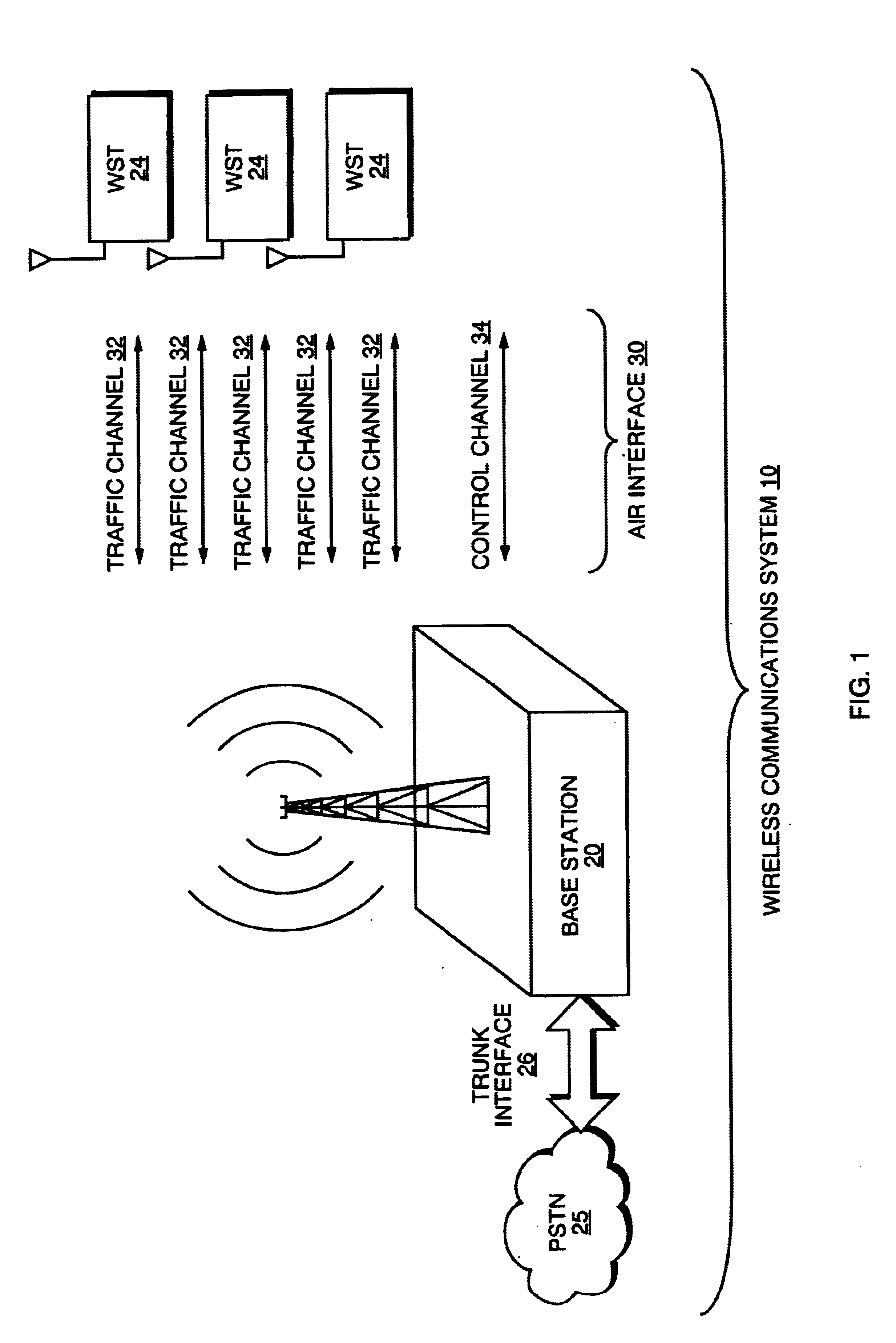
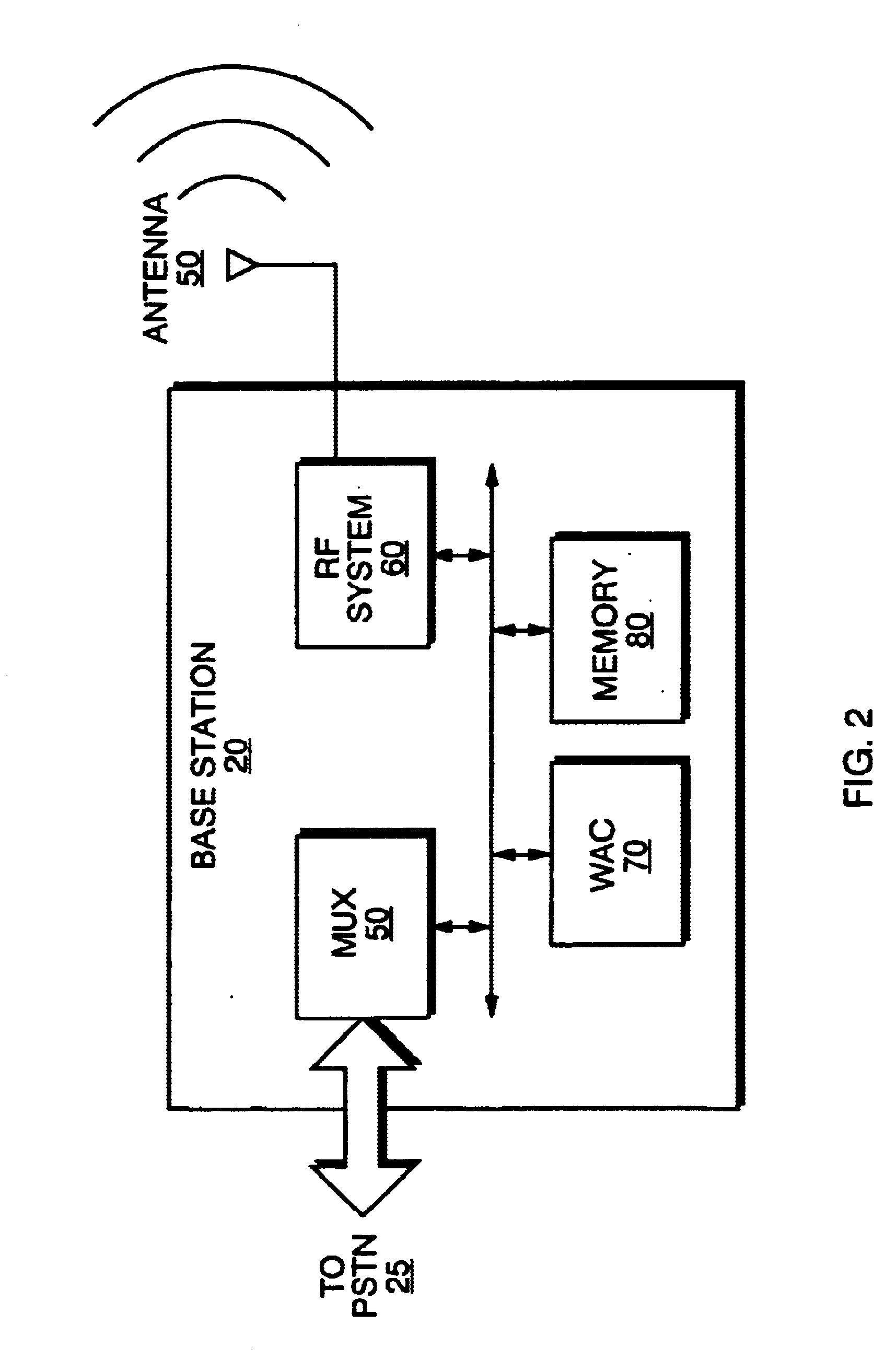
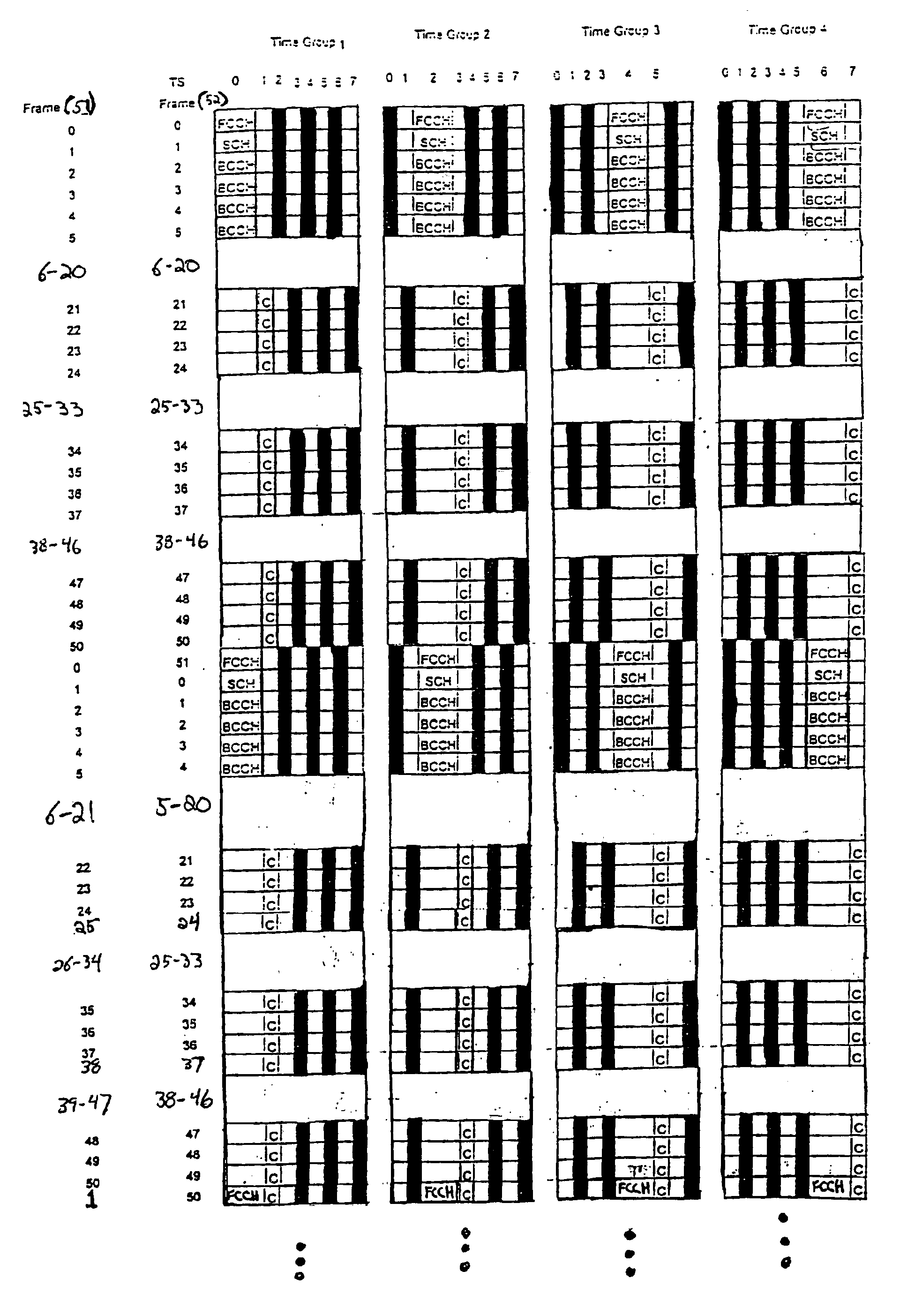
The invention is a system for programming wireless subscriber terminals (WST's) using a broadcast channel of a wireless communication system. In accordance with the invention, a control program, for controlling operation of the WST, is updated using a series of messages transmitted from a base station over a broadcast control channel to one or more WST's simultaneously. Each message in the series contains a segment of the control program, and the series of messages is interleaved with other control data on the broadcast control channel in order to avoid interference with other call activities. When a WST identifies a message as containing a control program segment, the WST stores the segment. Once a complete control program has been received, control of the WST can be transferred to the new control program. Receipt of the broadcast transmission is subject to interruption for a variety of reasons, e.g., a WST is powered off, a WST moves outside the range of a base station, other radio signals or noise interfere with the broadcast signal, or a call is received by a WST, which then transfers to a voice channel. Thus the base station arbitrates the re-transmission of missing program segments by polling individual WST's using control channels, and retransmitting missing segments. The system also preferably provides non-volatile storage of a partial program within each WST so that the WST's need not receive an entire program in a single session.
Owner:HARRIS STRATEX NETWORKS CANADA ULC
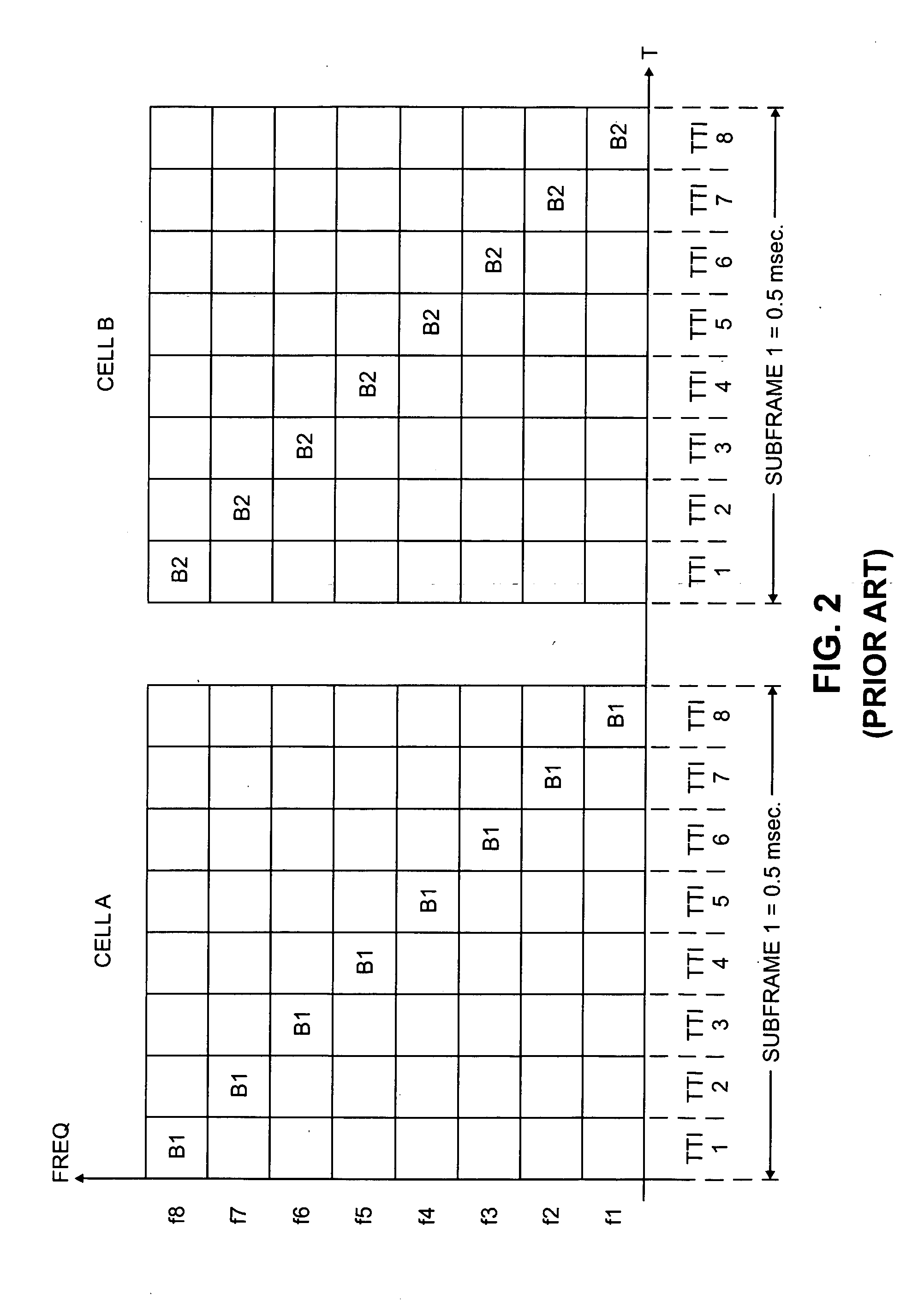
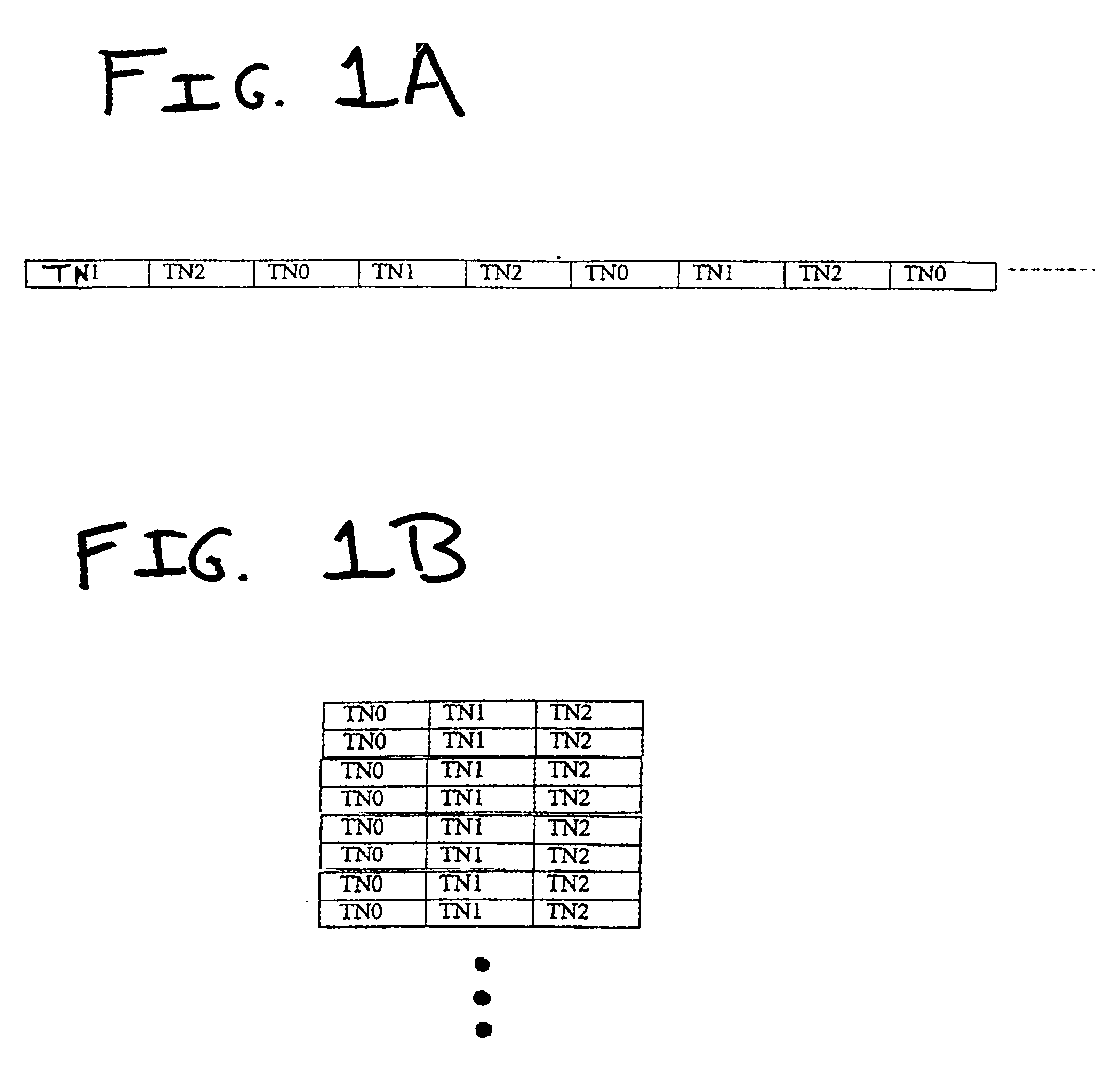
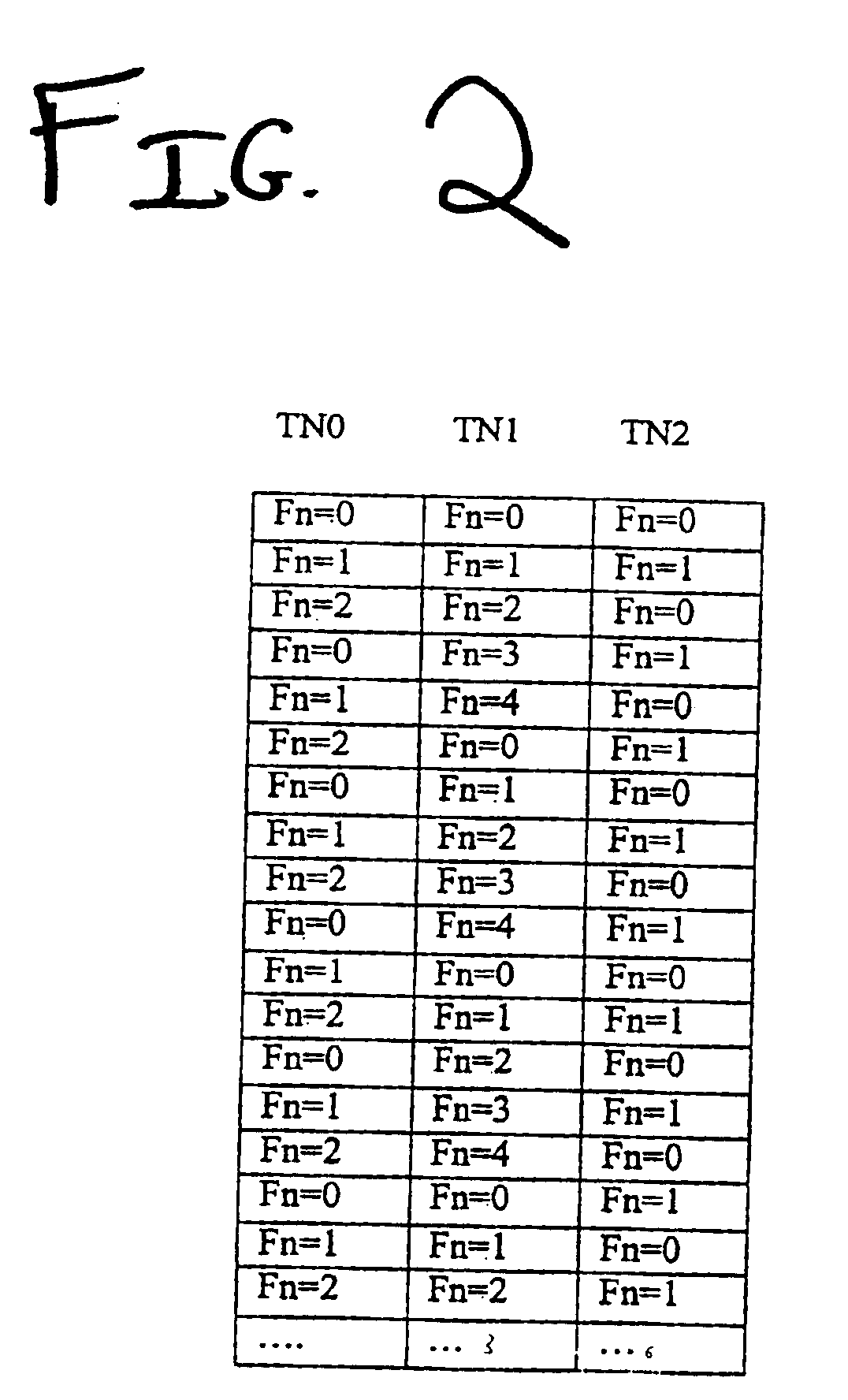
Channel sharing by diverse multiframes in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS6879573B1Great frequency reuseEasy to implementTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemAir interface
A wireless communication system and method provide air interface channels using diverse multiframe types on a single frequency carrier. Physical channels for a single frequency carrier are defined as time slots, a series of consecutive time slots define a frame, and a plurality of multiframe types are defined for the single frequency carrier as including different numbers of consecutive frames. By multiplexing a plurality of multiframe types onto a single frequency carrier, diverse channels types such as traffic channels, broadcast control channels, and common control channels can be accommodated on the same frequency carrier to enable efficient utilization of frequency resources. In one exemplary implementation, a first multiframe type is defined as having x consecutive frames, a second multiframe type is defined as having y consecutive frames, and a third multiframe type is defined as having z consecutive frames. Thus, the frame number for the first multiframe type is counted modulus x, the frame number for the second multiframe type is counted modulus y, and the frame number for the third multiframe type is counted modulus z. The first, second, and third multiframe types are further assigned to different time slots. For example, if a frame is defined as having three time slots, the first multiframe type may be assigned to the first time slot, the second multiframe type may be assigned to the second time slot, and the third multiframe type may be assigned to the third time slot.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
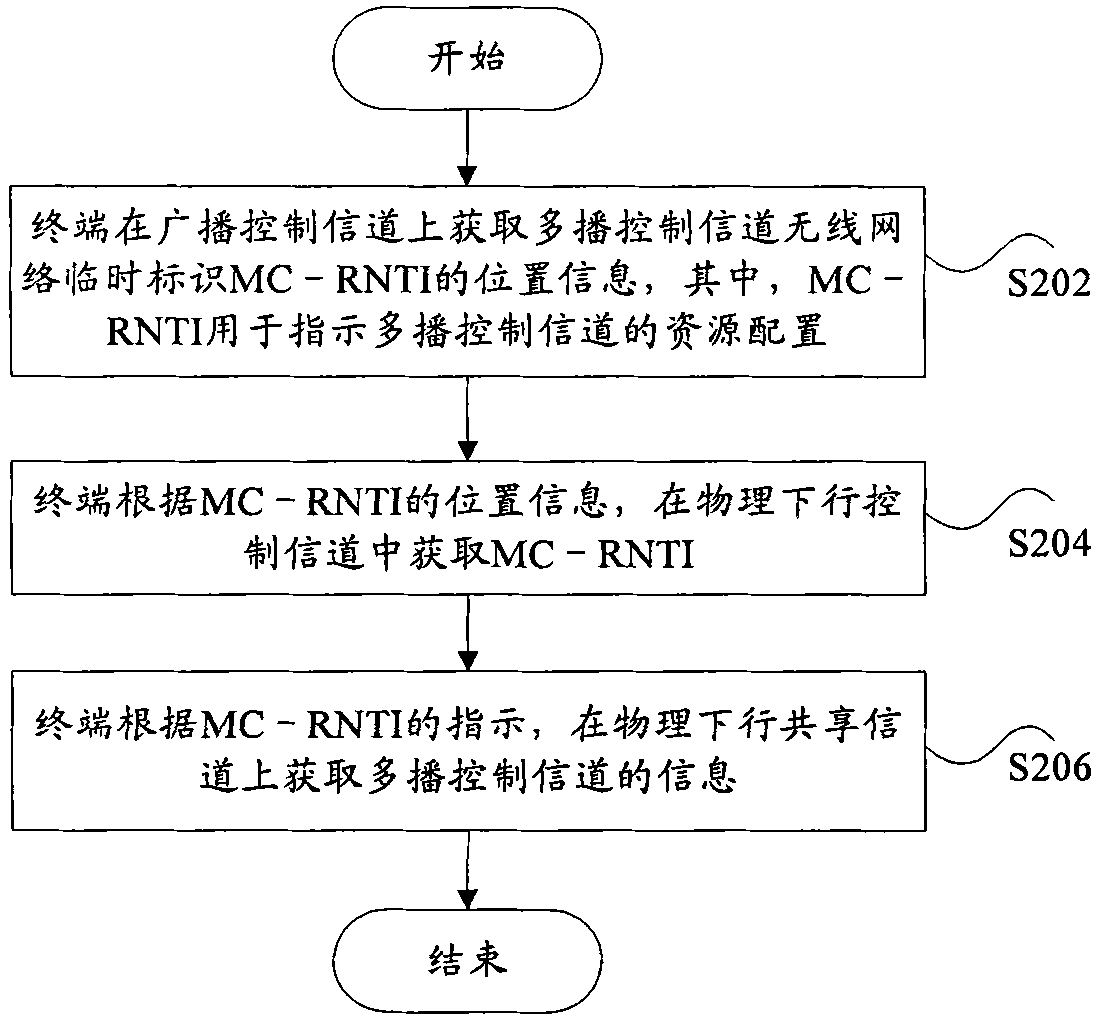
Method and terminal for indicating resources
InactiveCN101841773AImprove service efficiencySolve the problem of not being able to accurately obtain MCCH location informationEnergy efficient ICTBroadcast service distributionRadio networksService efficiency
The invention discloses a method and a terminal for indicating resources. The method comprises the steps that: the terminal acquires position information of a multicast control channel radio network temporary identity MC-RNTI which is used for indicating resource allocation of a multicast control channel on a broadcast control channel; and the terminal acquires the MC-RNTI in a physical downlink control channel according to the position information of the MC-RNTI. By the information indication of the MC-RNTI, the terminal can acquire the resource position of an MCCH in the single-cell or multi-cell mode so as to acquire control information related to a multicast service, simplify the complexity of a system, reduce power consumption of the terminal and improve the service efficiency of an MBMS.
Owner:ZTE CORP
System information block transmission method and apparatus
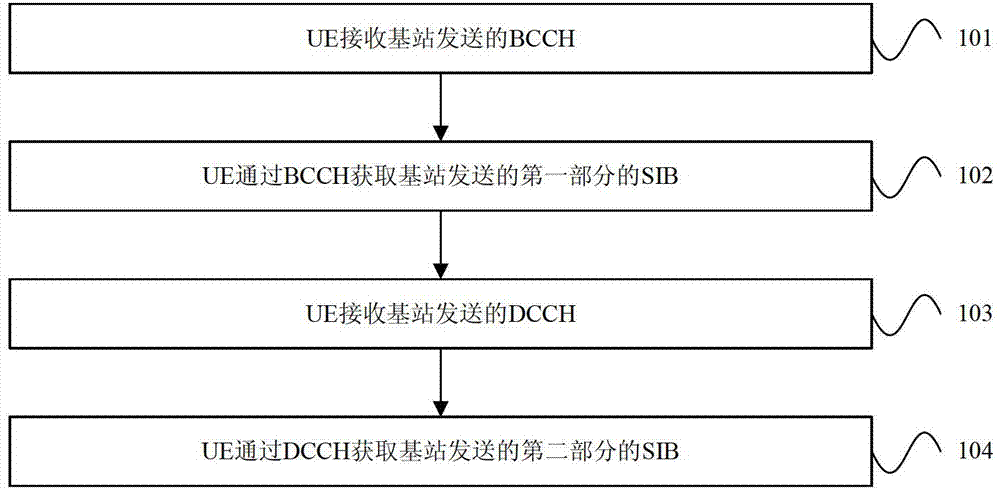
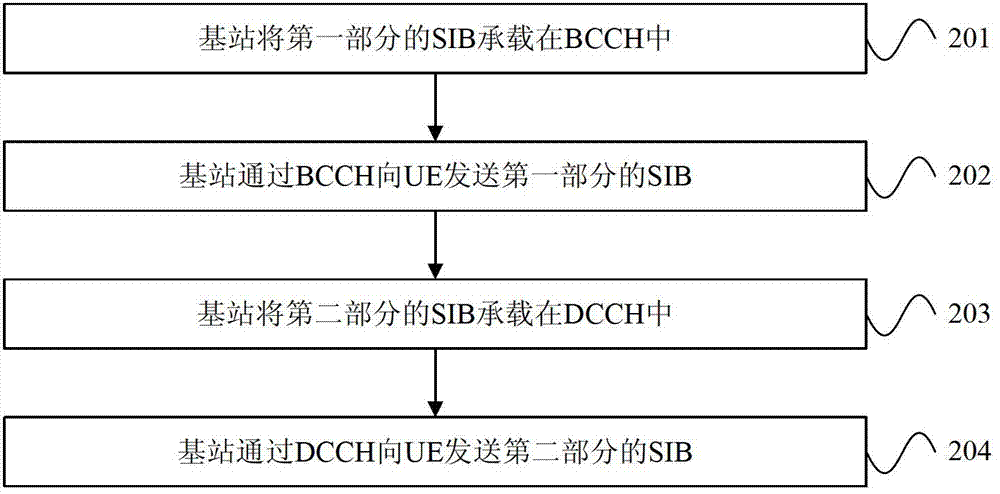
ActiveCN103534970AReduce transfer timeImprove transmission efficiencyError preventionWireless communicationAccess networkBroadcast control channel
Embodiments of the invention provide block transmission method and apparatus of system information, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: user equipment UE receives a broadcast control channel BCCH sent from a base station; the BCCH acquires a system information block SIB of a first part sent by the base station; the DCCH acquires SIB of a second part sent from the base station, wherein, the sum of the SIB of the first part and the SIB of the second part is integrated system broadcast information; DCCH acquires SIB of the second part sent from the base station. The system information block is transmitted by BCCH and DCCH respectively, thereby minimizing transmission time of SIB and improving transmission efficiency of SIB, minimizing time for UE to read SIB, and reducing time for accessing network, and improving user experience and improving success rate of service initiation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Uplink acknowledgment channel in wireless communication
ActiveUS20080137605A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission control/equalisingBroadcast control channelBroadcasting
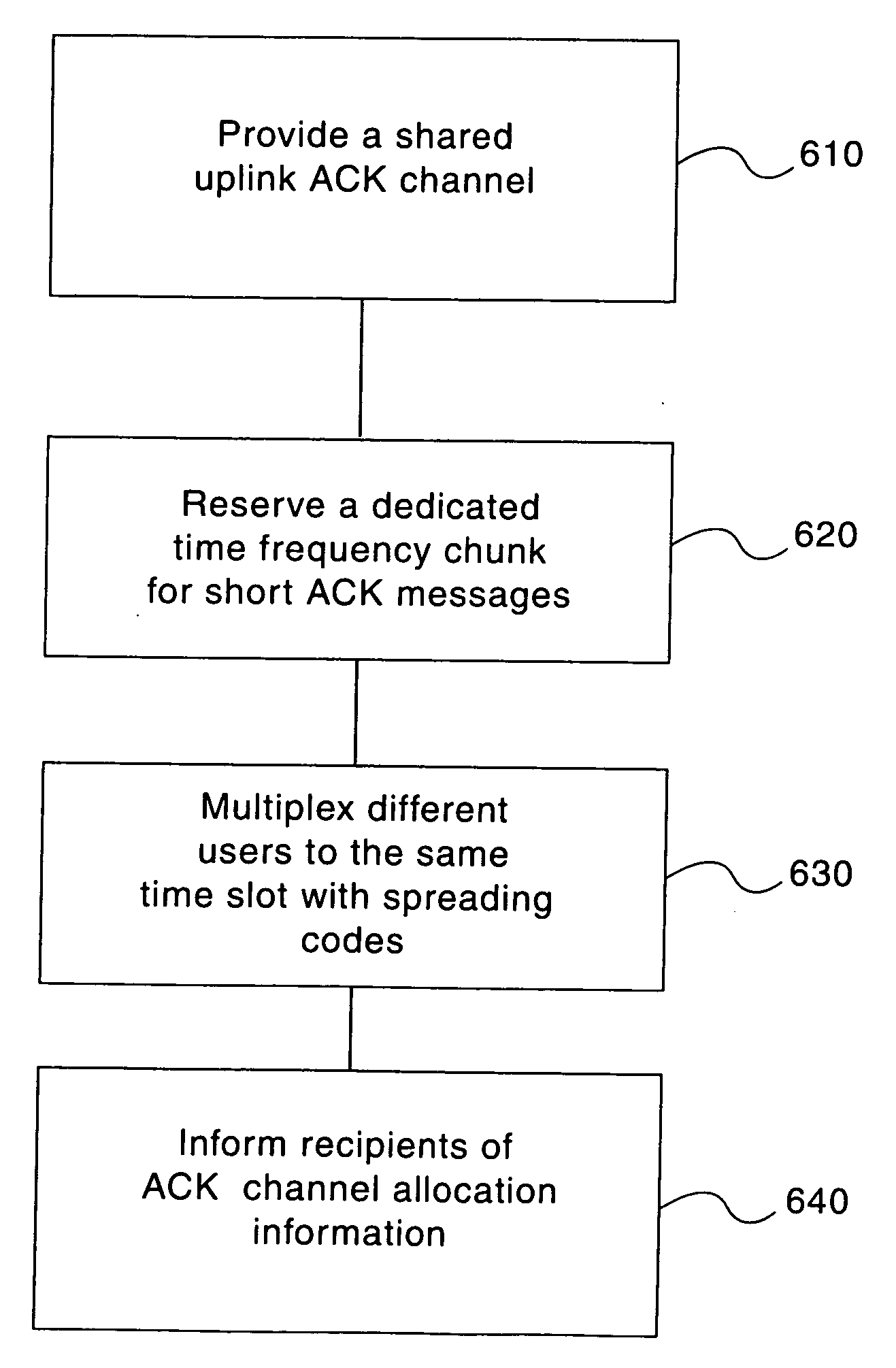
A shared uplink acknowledgment (ACK) channel can be communicated to the payload recipient. The shared uplink ACK channel information can be communicated in the payload message or in a broadcast control channel. Reserving a dedicated time-frequency chunk for these short ACK messages and multiplexing different users to the same time slot with spreading codes having good cross-correlation properties can be used to accomplish such a shared uplink ACK channel.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
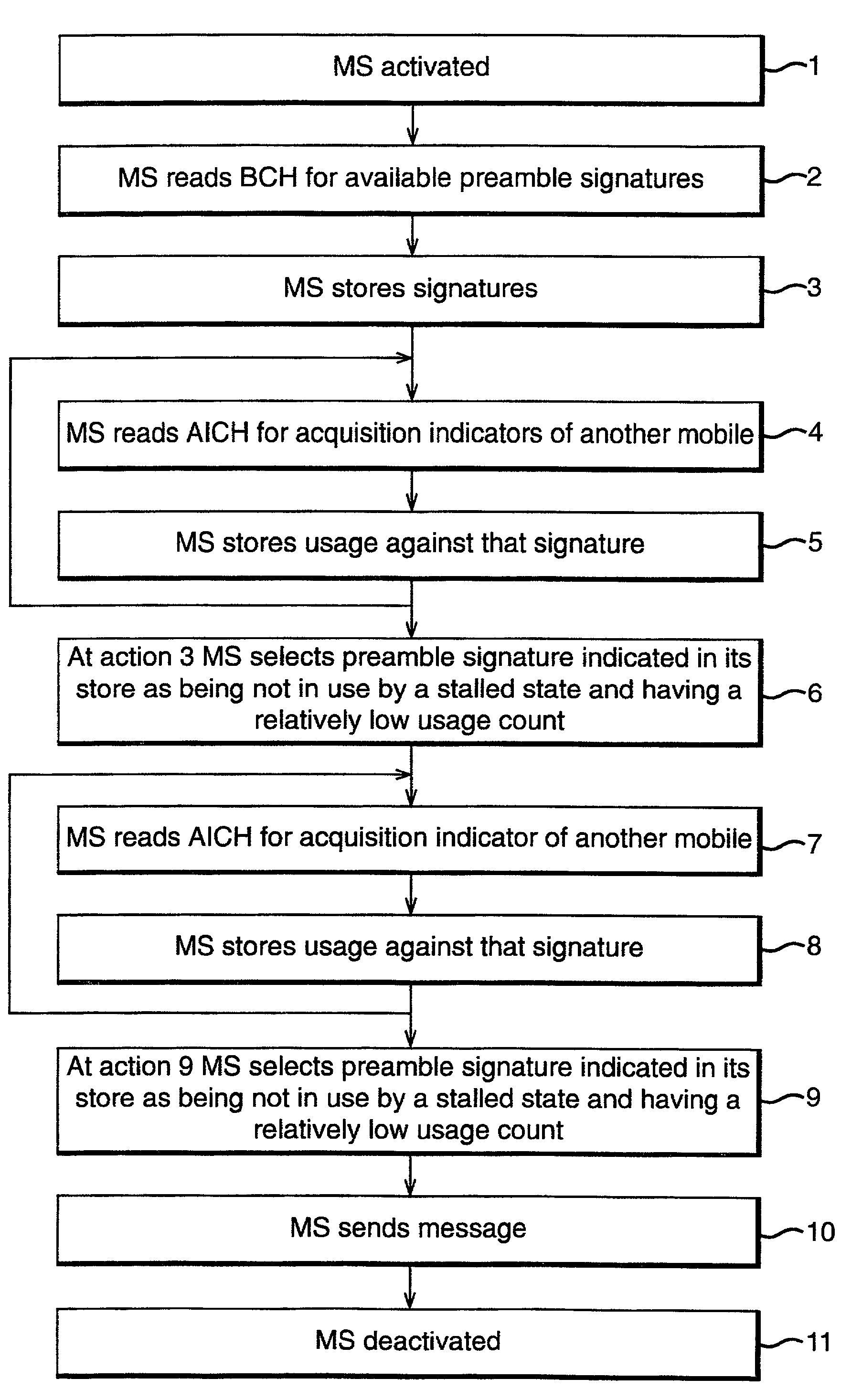
Message access for radio telecommunications system
InactiveUS6992998B1Improve efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementBroadcast control channelBroadcasting
A mobile for use in the UMTS is arranged, on activation to read the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) for all available preamble signatures; to store the signatures in its processor; to read the Acquisition Indication Channel (AICH) for acquisition indicators sent to other mobiles; to store usage of other mobiles against each signature; and to select when required a signature the recorded usage of which is unlikely to cause collisions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
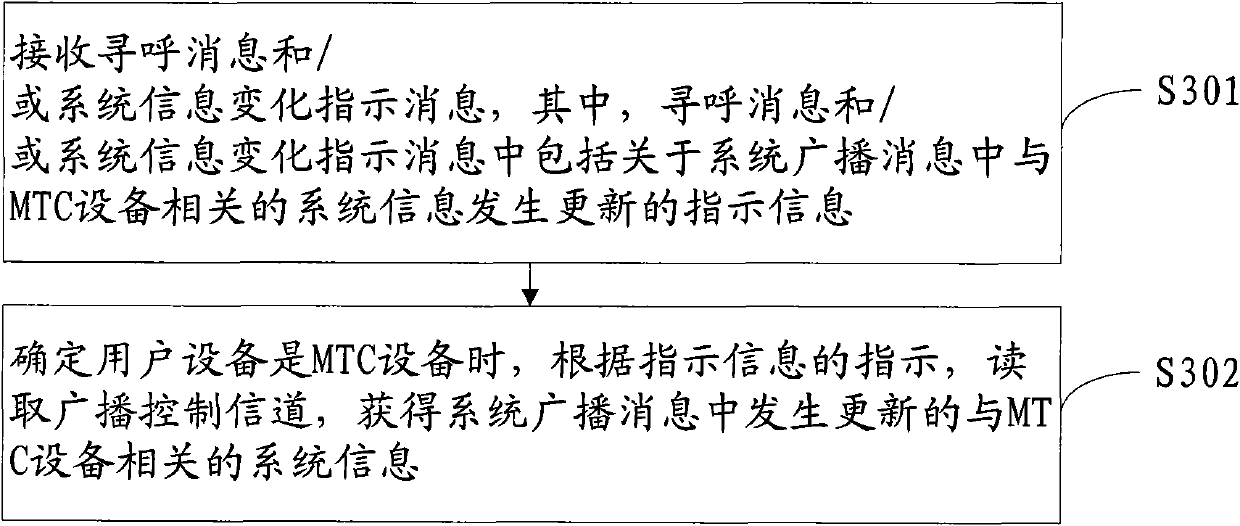
Notifying and reading method and device of update of system broadcast message
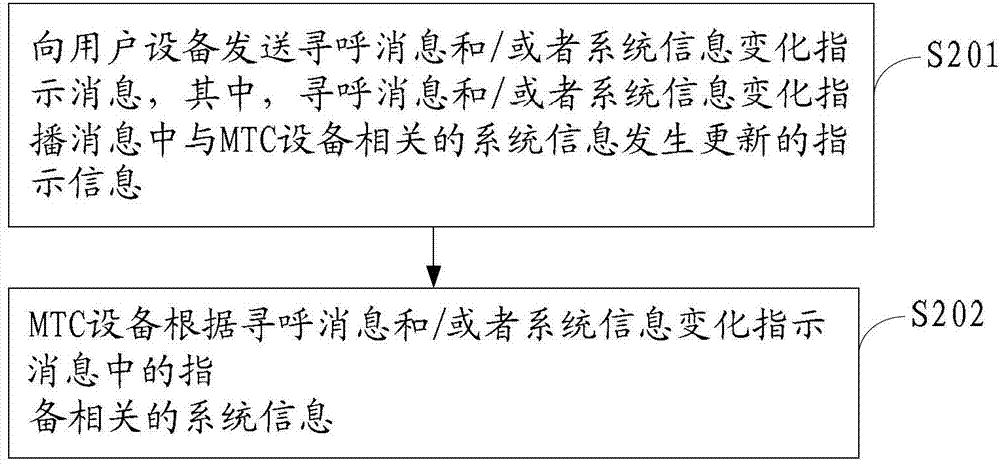
ActiveCN103209481ASolve the impactEfficiently obtainedWireless communicationBroadcast control channelBroadcasting
The embodiment of the invention provides a notifying and reading method and device of the update of a system broadcast message, relates to the field of communication, and can solve the problem of the influence of the change of the system broadcast message associated to an MTC (Multimedia Telephone Communication) device to a non-MTC device. The reading method of the updated system broadcast message includes receiving a paging message and / or a system information change instruction message which include instruction information of the update of system information related to the MTC device about the system broadcast message; and reading a broadcast control channel to obtain the updated system information related to the MTC device in the system broadcast message according to the instruction of the instruction message when a user device is judged to be the MTC device.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and terminal for measuring cells
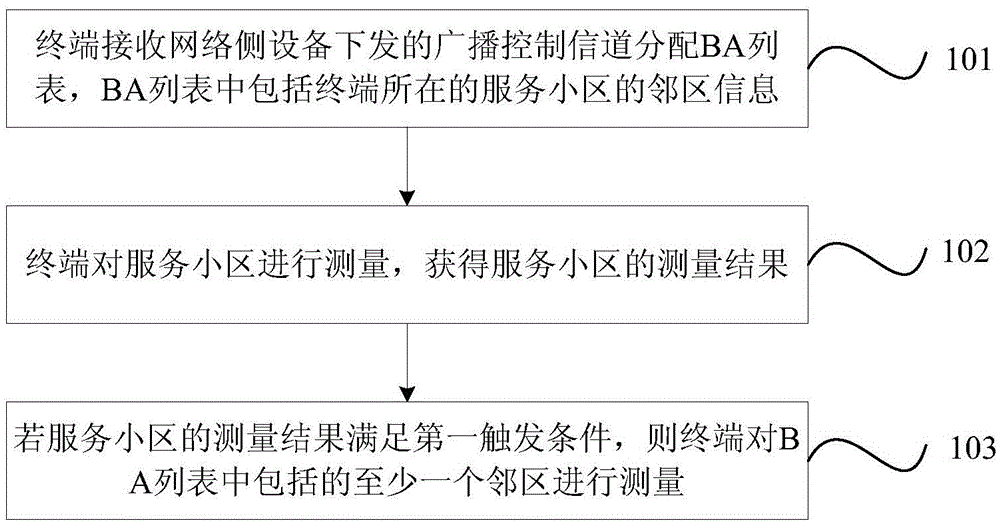
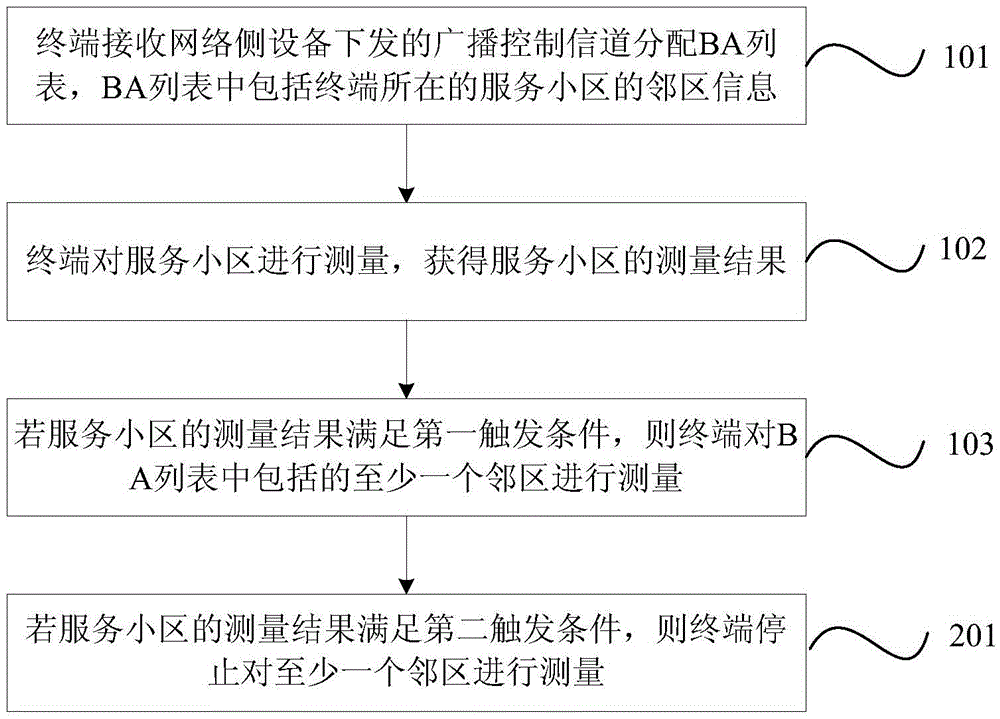
InactiveCN105493551AAvoid frequent measurementsReduce consumptionPower managementHigh level techniquesBroadcast control channelComputer science
The invention provides a method and a terminal for measuring cells. The method comprises following steps: the terminal receives broadcast control channel distribution BA list issued by a network side device, wherein the BA list comprises information of cells adjacent to the service cell where the terminal locates; the terminal performs measurement to the service cell to obtain measurement results of the service cell; if the measurement results of the service cell satisfy a first triggering condition, then at least one of adjacent cells included in the BA list is measured by the terminal. According to the cell measurement method provided by one embodiment of the invention, through measuring the terminal service cell, when the measurement results satisfy the triggering condition, the measurement of adjacent cells is enabled so that frequent measurement of adjacent cells is avoided, and electric energy consumption of the terminal is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
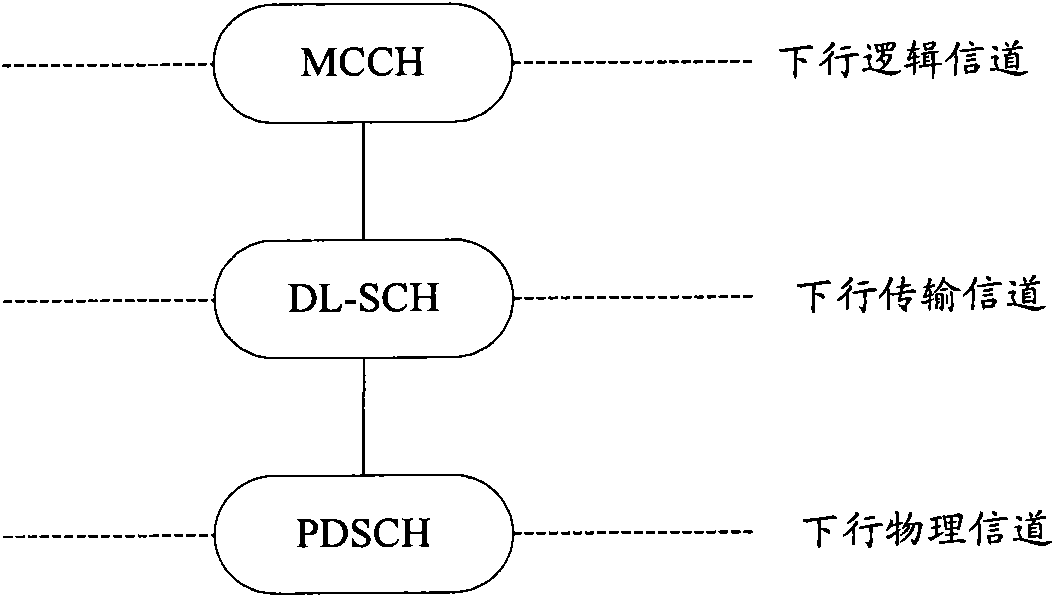
Method and system for realizing multimedia broadcast multicasting service
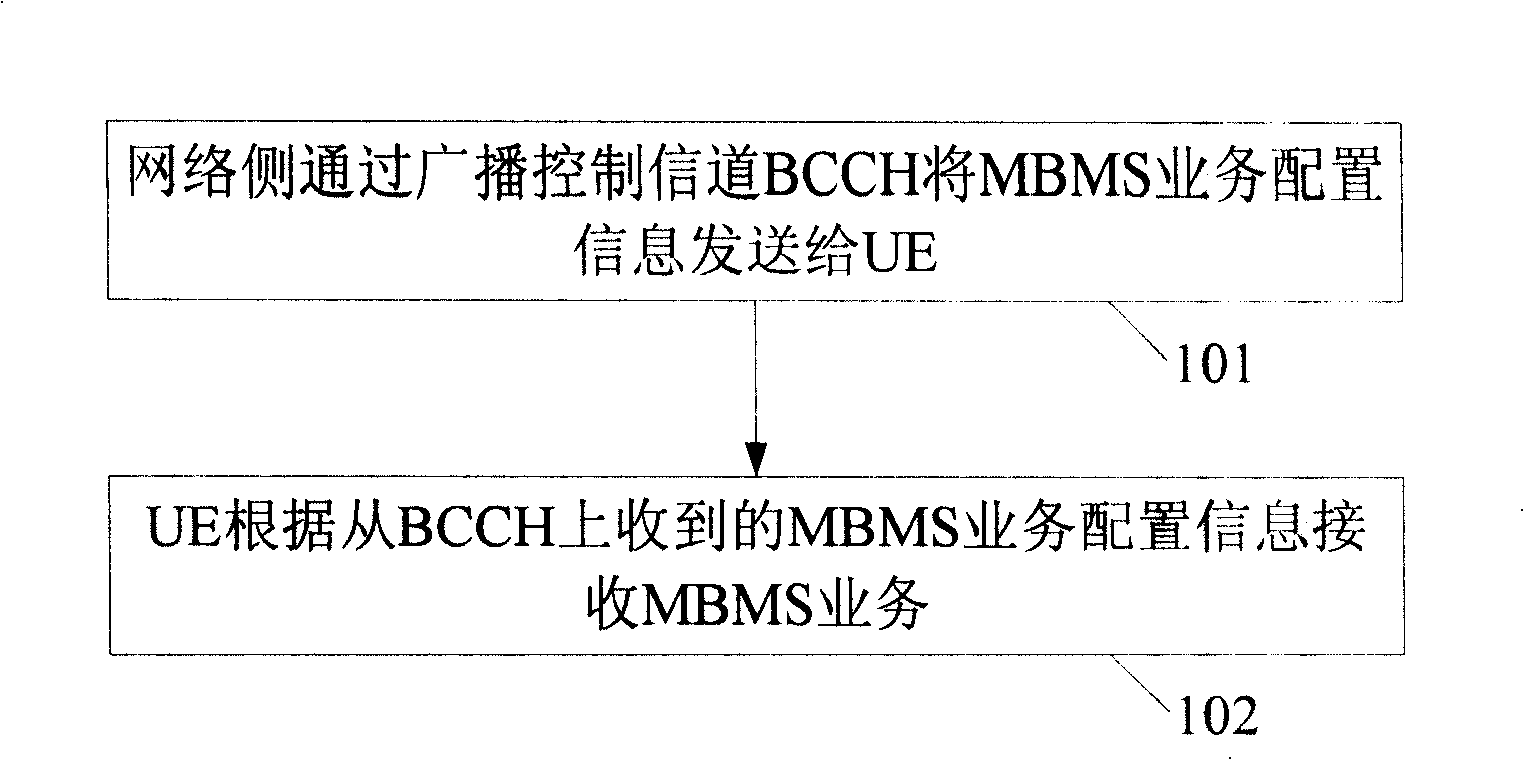
ActiveCN101257649ASimple processReduce implementation complexitySpecial service provision for substationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceService configuration
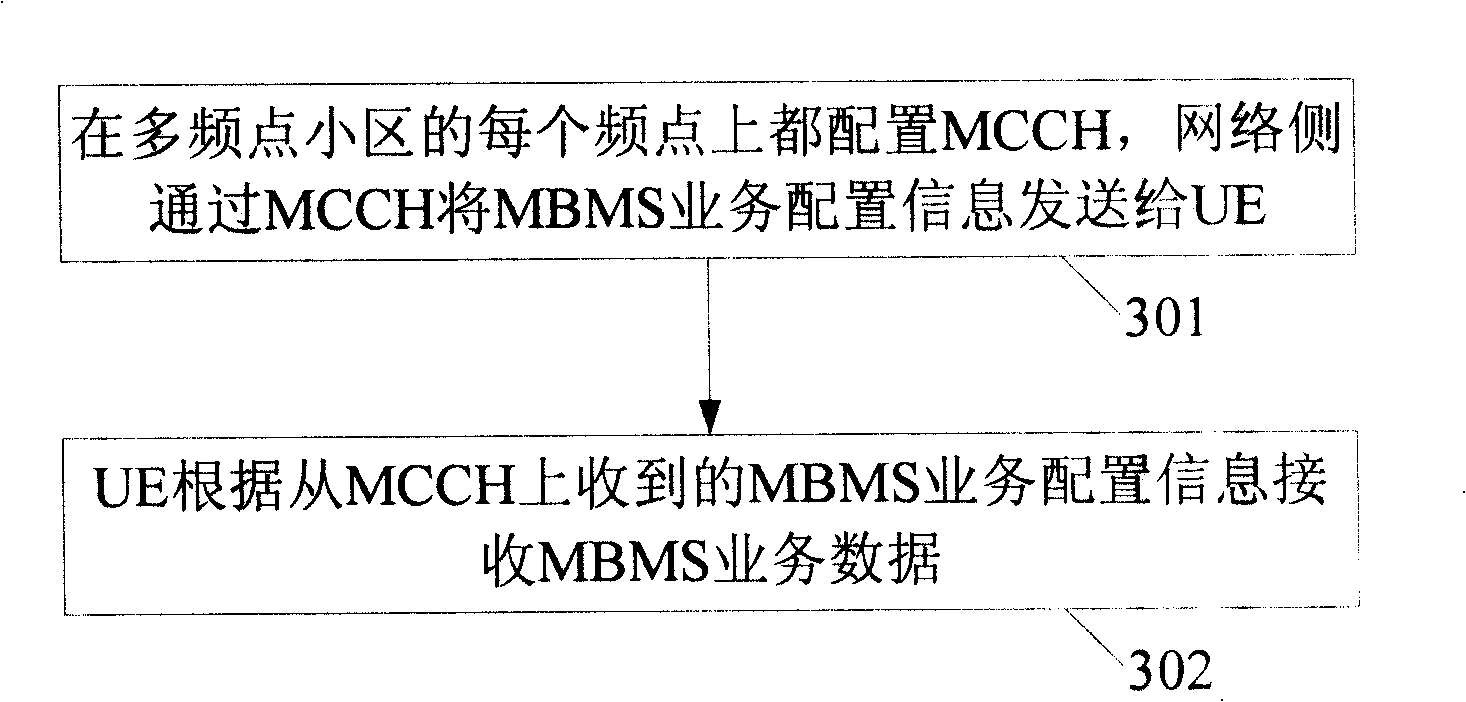
The present invention provides a method and system for implementing multimedia broadcast multicast service, capable of reducing implementation complexity of MBMS. The method includes that: network side transmit the MBMS service configuration information to UE through broadcast control channel MCCH, UE receives MBMS service according to the received MBMS service configuration information from MCCH.In addition, the invention also provides another two methods and system for implementing multimedia broadcast multicast service, which implements MBMS service on the basis of supporting multi-frequency point characteristics.The method includes that: MCCH is configured on each frequency point of multi-frequency point cell, network side transmit the MBMS control information to UE through MCCH, UE receives MBMS service according to the received MBMS control information from MCCH.Or, MCCH is configured on main frequency point of multi-frequency point cell, network sides transmit the MBMS control information to UE through MCCH of main frequency point, UE receives MBMS service according to the received MBMS control information from MCCH of main frequency point.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
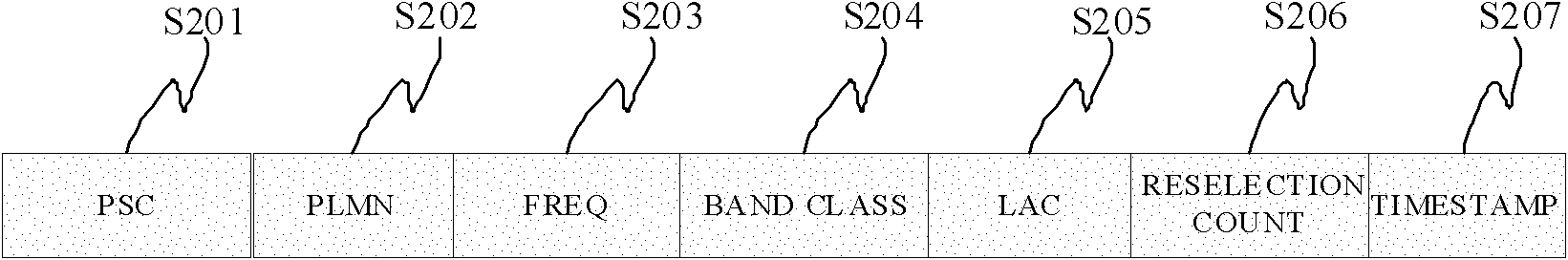
Method for controlling cell reselection and wireless communication terminal
ActiveCN101984711AAvoid decodingImprove operational efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceStandby power
The invention provides a method for controlling cell reselection and a wireless communication terminal. The method for controlling cell reselection comprises the following steps: the resident number of cells per unit time is recorded to judge whether frequent reselection is performed; and if so, a frequent reselection protection strategy is started to record the cells with lower priorities in an inhibited reselection cell list, thus the terminal can reside in the cell with higher service quality or with more stable signal level as far as possible. By adopting the method for controlling cell reselection, the problem that the broadcast control channel (BCCH) information is decoded by the mobile terminal as the target cell is inhibited or not accessed can be avoided, the standby power can be reduced, the operating efficiency of protocol stack can be increased; and the reselection parameter can be adjusted dynamically according to the wireless environment, the frequent reselection problem caused by the frequent fluctuation of the electrical level of the cell can be avoided, and the quality of wireless communication service and the user experience can be increased.
Owner:杭州平治信息技术股份有限公司
Method of receiving a disaster warning message using scheduling information included in system information within mobile communication system
ActiveUS20090239498A1Efficiently receiving a warning messageMinimum delayEmergency connection handlingAssess restrictionCommunications systemMobile communication systems
Disclosed is a method of receiving a warning message in wireless communication system. A terminal (UE) receives system information through a control channel such as a Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH), and receives a warning message through a downlink channel according to scheduling information related to the warning message included in the system information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com