Patents
Literature
6555 results about "Transmission time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication networks, the transmission time, is the amount of time from the beginning until the end of a message transmission. In the case of a digital message, it is the time from the first bit until the last bit of a message has left the transmitting node.
Billing system for information dispersal system
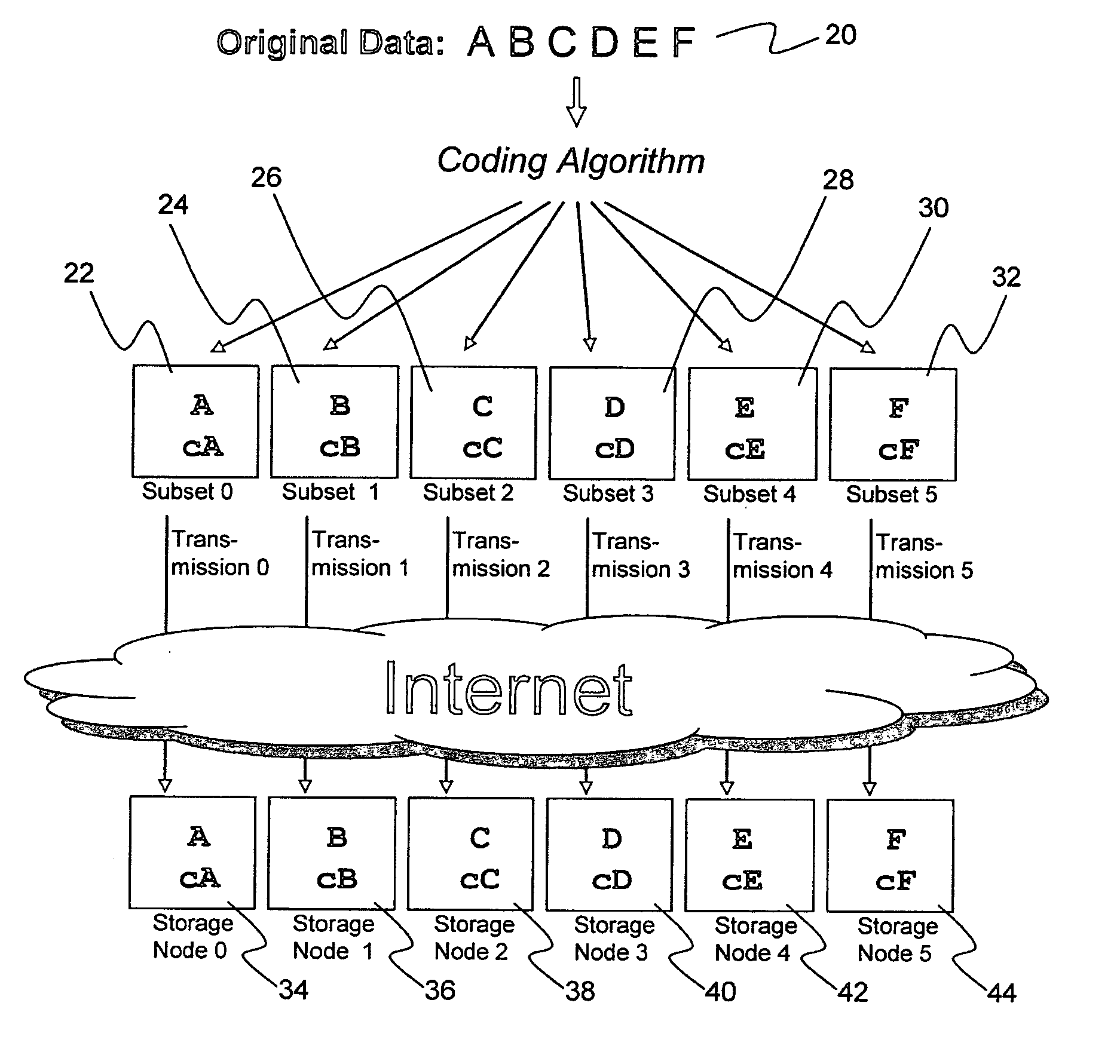
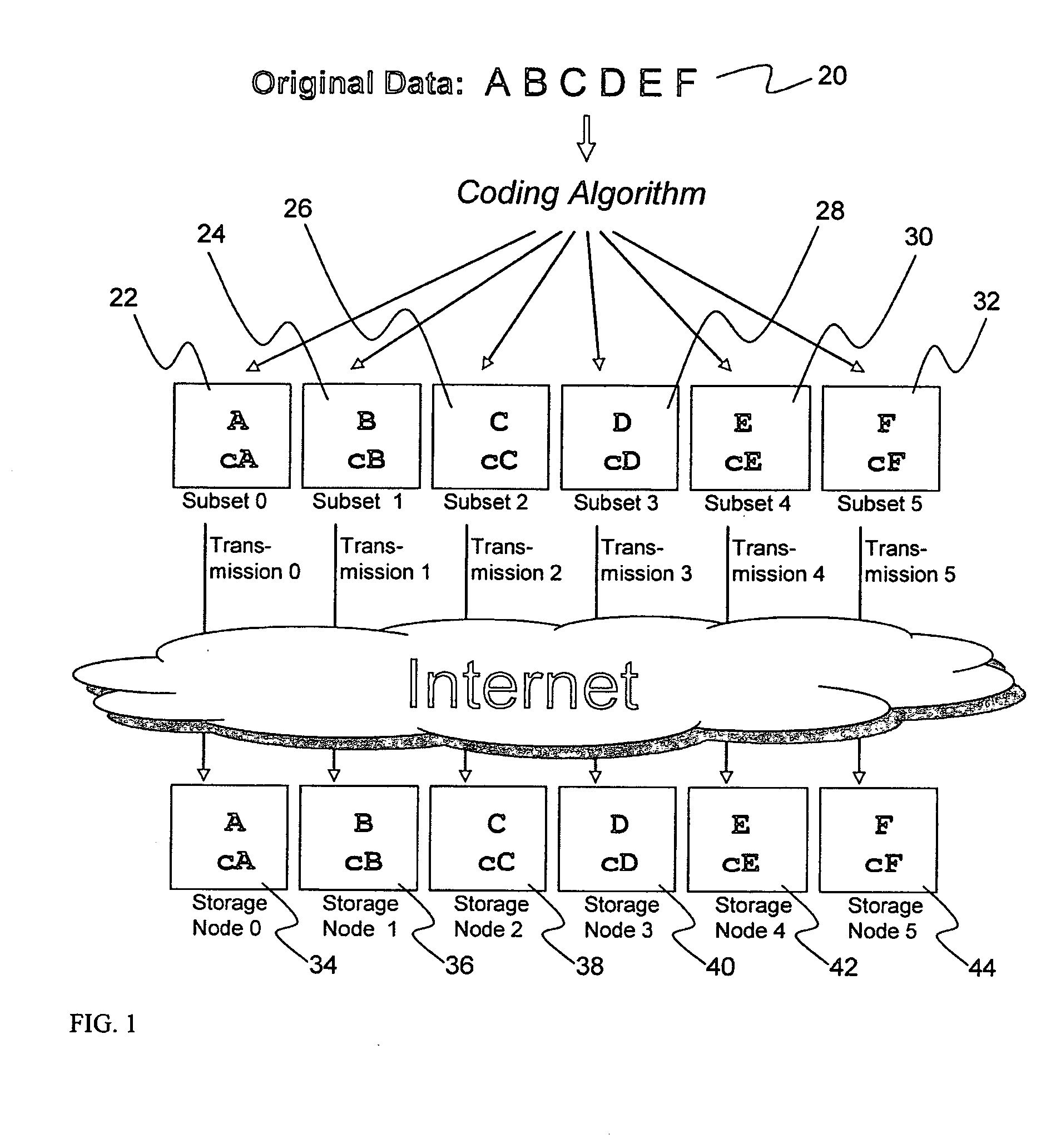
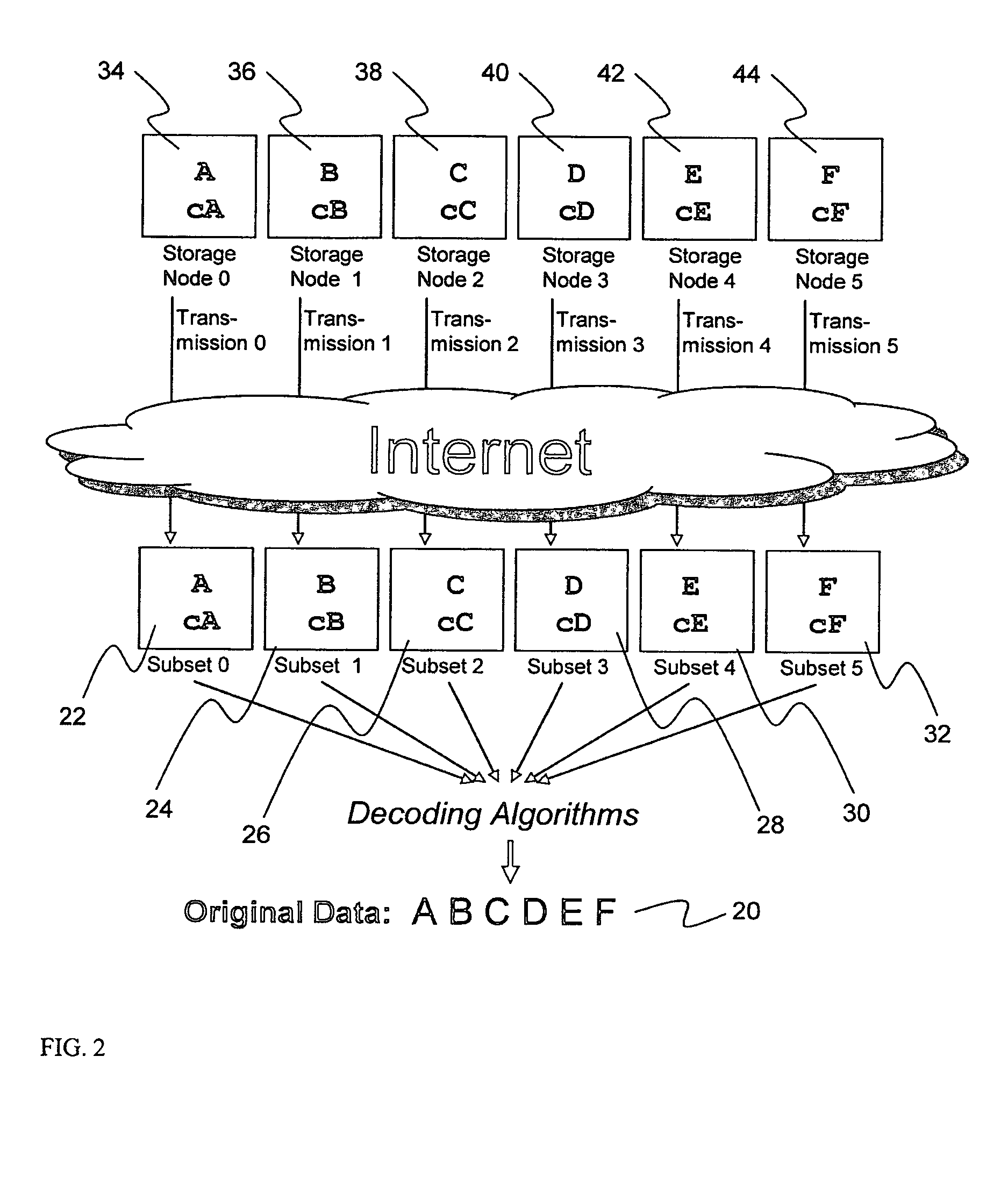
ActiveUS20070174192A1Less usableLess recognizableFinanceComputer security arrangementsInformation dispersalOriginal data
A billing process is disclosed for a information dispersal system or digital data storage system. In one embodiment of the invention, the original data to be stored is separated into a number of data “slices” or shares in such a manner that the data in each subset is less usable or less recognizable or completely unusable or completely unrecognizable by itself except when combined with some or all of the other data subsets. These data subsets are stored on separate digital data storage devices as a way of increasing privacy and security. As dispersed file shares are being stored or removed from a grid of distributed storage locations, a set of metadata tables are created, separate from the dispersed file share storage, to maintain information about the original data size of each block, file or set of file shares dispersed on the grid. The original data size information in these separate metadata tables is used to determine usage information based upon the original file size even though the file has been dispersed onto a storage grid that contains file slices who size may not relate to the original file size and the file slices may have been compressed by the system in order to reduce storage space or improve transmission time. As such, the billing process is able to enable a broad range of commercial billing options for billing for commercial data services on an information dispersal grid.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
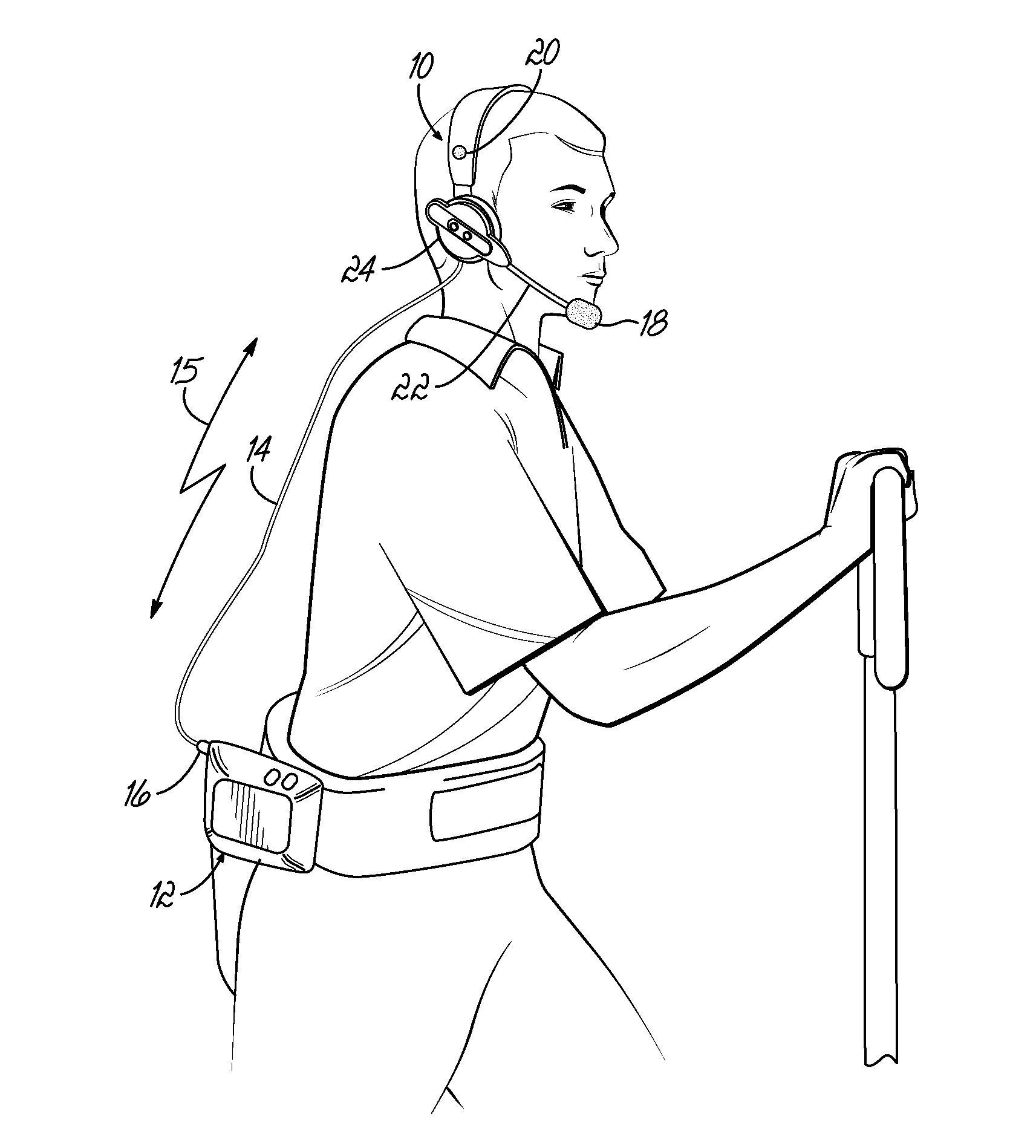
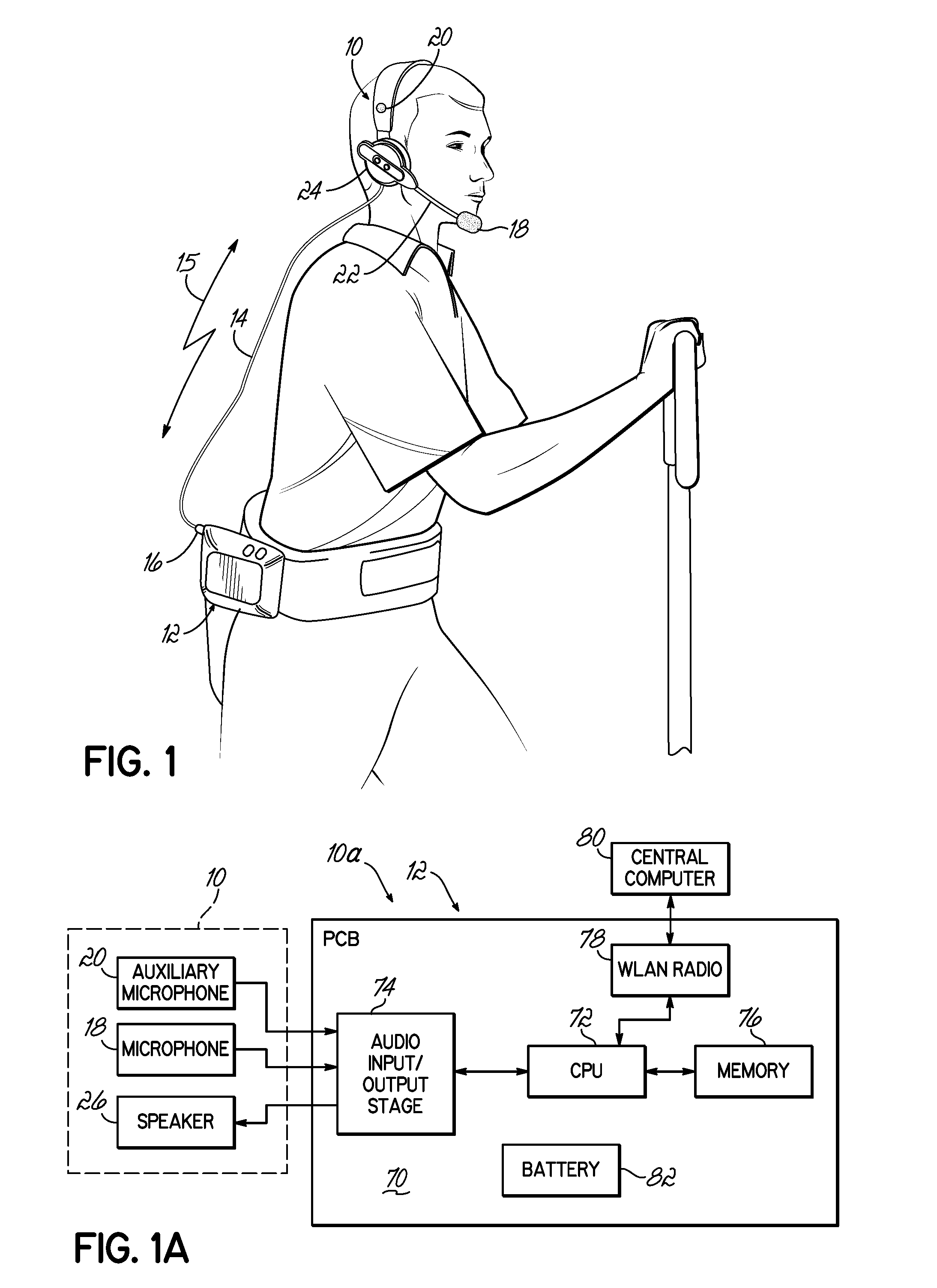
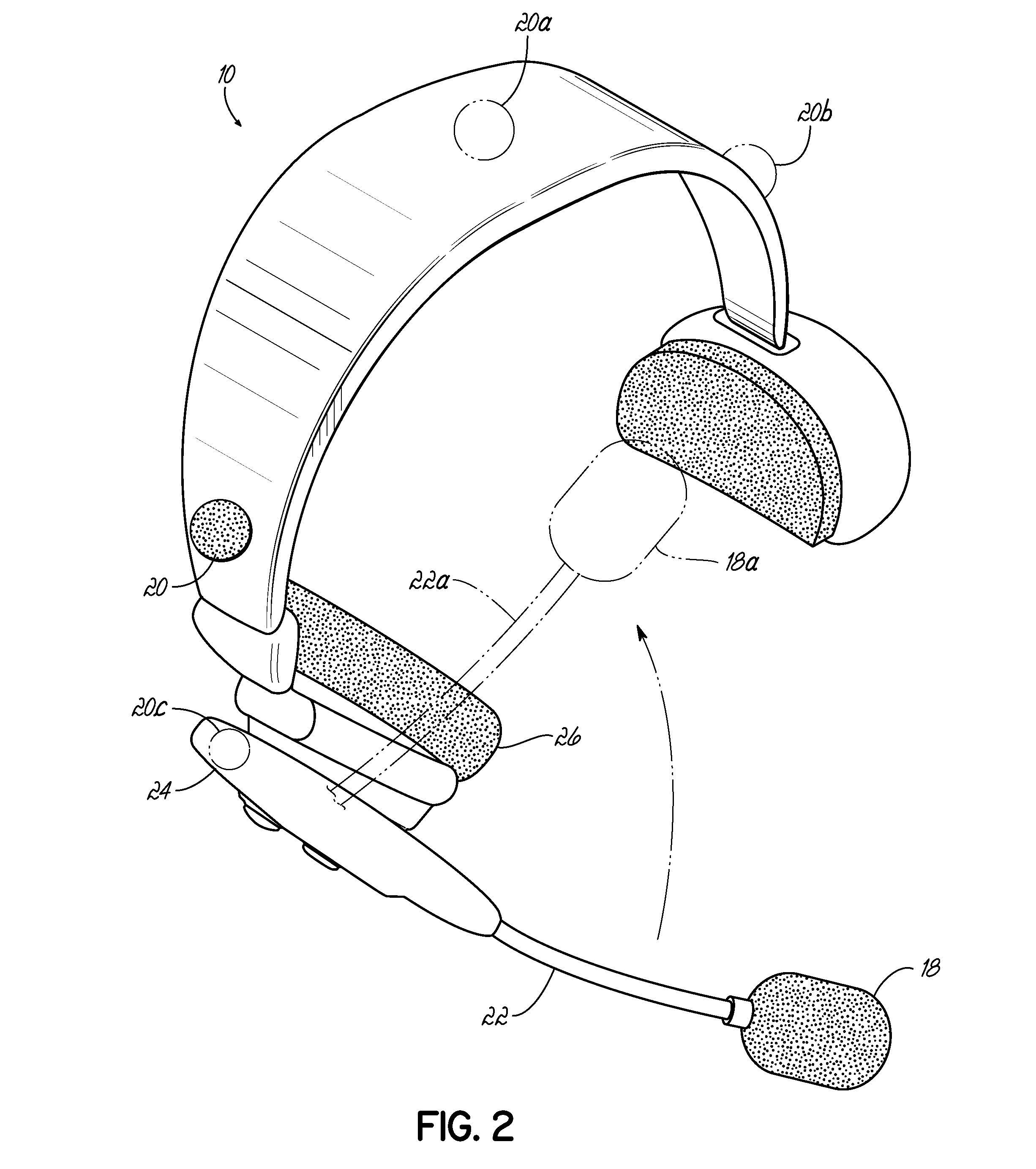
System and method for improving speech recognition accuracy in a work environment
Apparatus and method that improves speech recognition accuracy, by monitoring the position of a user's headset-mounted speech microphone, and prompting the user to reconfigure the speech microphone's orientation if required. A microprocessor or other application specific integrated circuit provides a mechanism for comparing the relative transit times between a user's voice, a primary speech microphone, and a secondary compliance microphone. The difference in transit times may be used to determine if the speech microphone is placed in an appropriate proximity to the user's mouth. If required, the user is automatically prompted to reposition the speech microphone.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
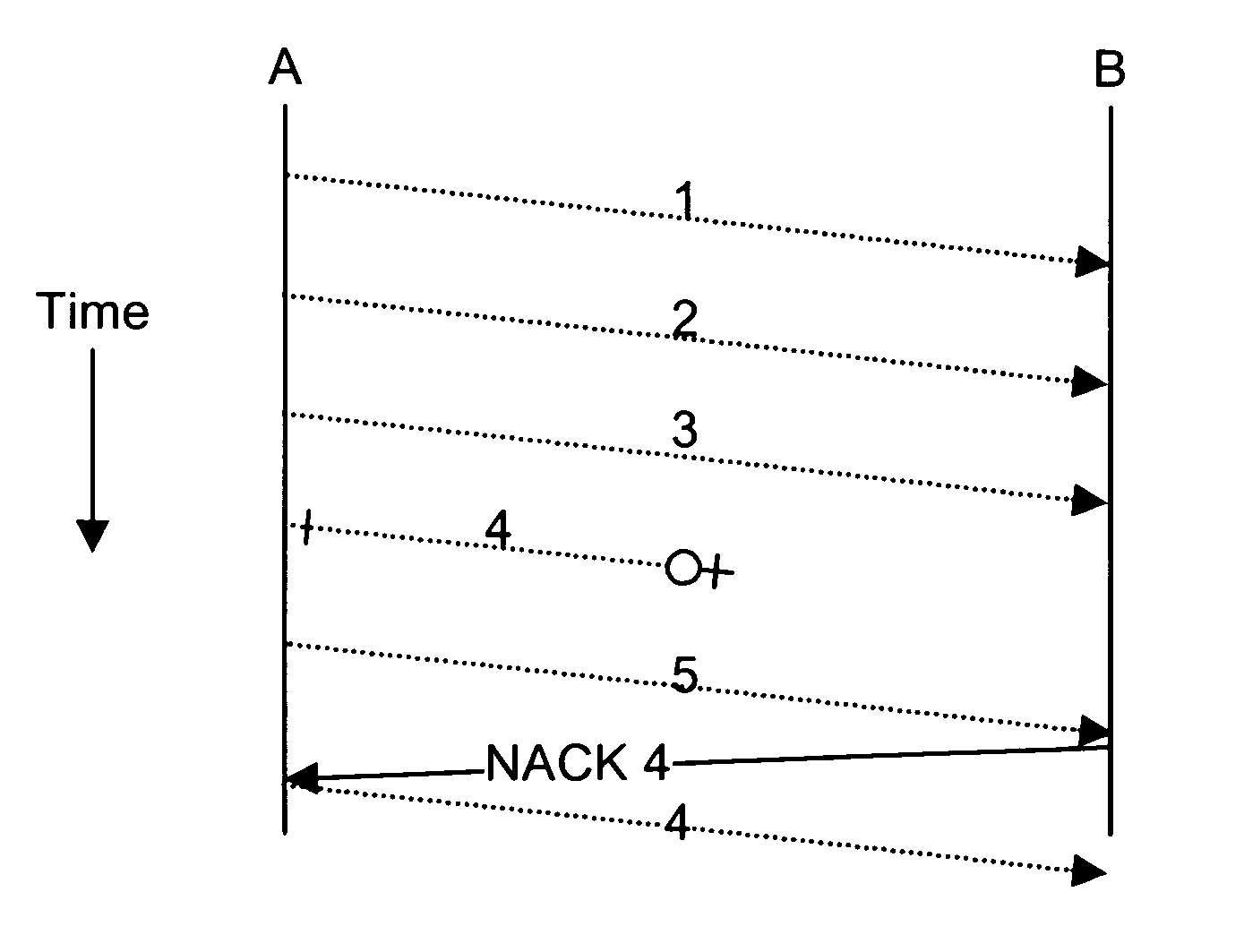
System and method for a negative acknowledgement-based transmission control protocol
InactiveUS7035214B1Shorten the lengthError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowTraffic capacity
A system and method for transmitting data in a data communications network, using a transmission control protocol, to provide reduced acknowledgment control traffic, error recovery and congestion control. A communications link is established between a transmitter and a receiver. Setting the communications link includes setting a network congestion window to an initial length. A sequence, or stream, of data packets is sent from the transmitter to the receiver. The receiver detects any missing packets, by examining the sequence numbers of the incoming packets, and sends negative acknowledgments, generally no more than four, to the transmitter identifying the missing data packet. When the transmitter receives a negative acknowledgment, it decreases the length of the congestion window, and re-transmits the missing packet. Detection and use of round-trip time, re-transmission time-out are provided.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method for transmitting time information via a data packet network
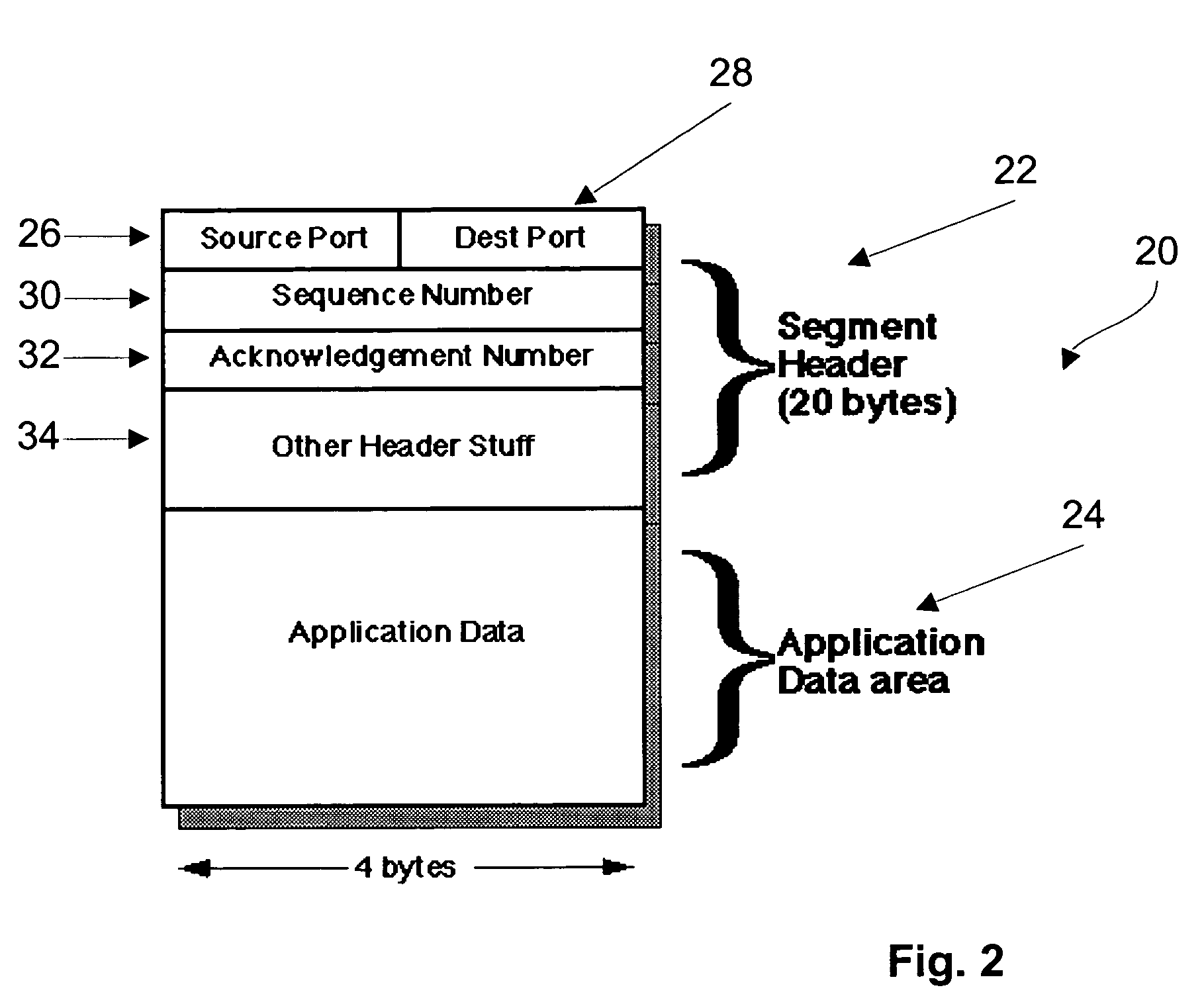
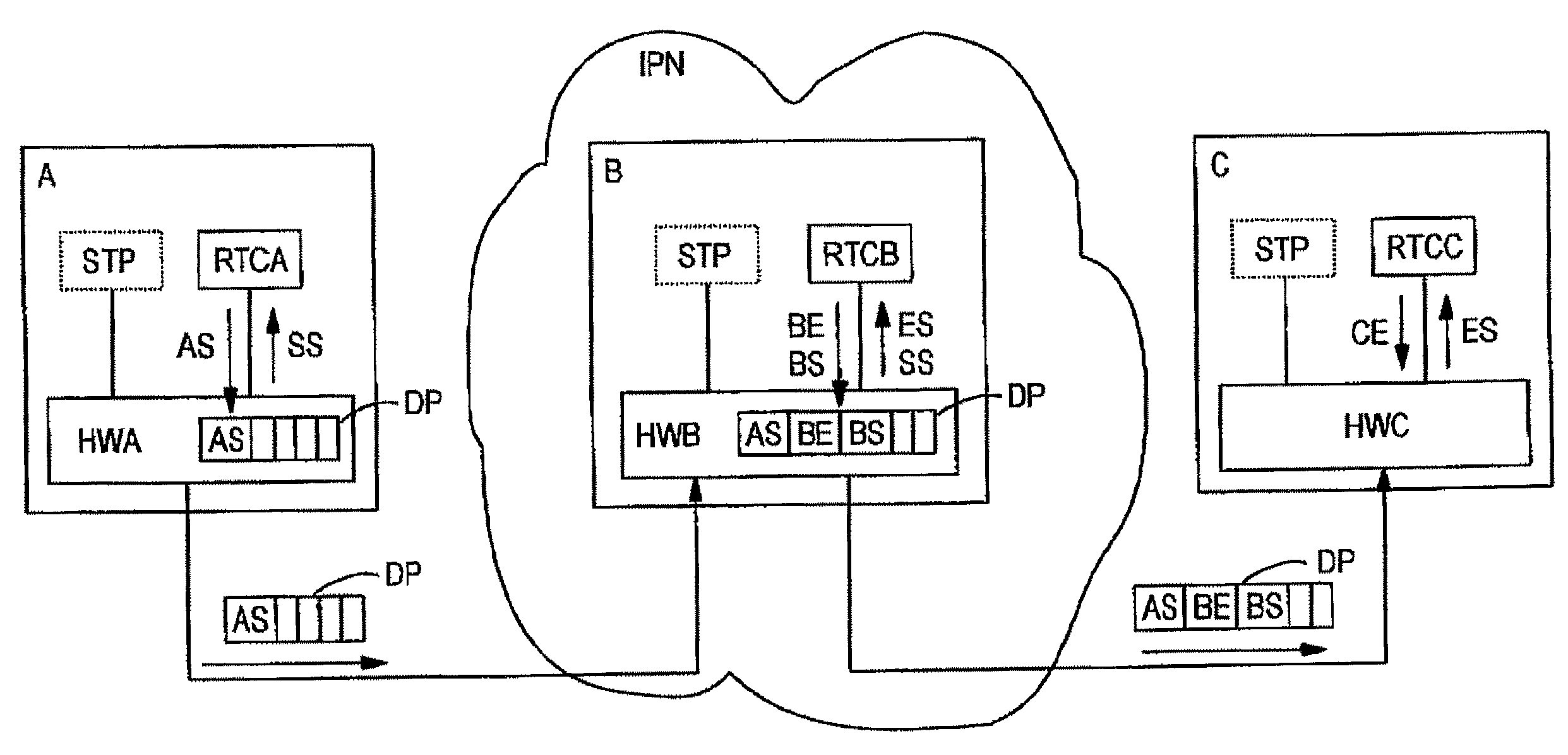
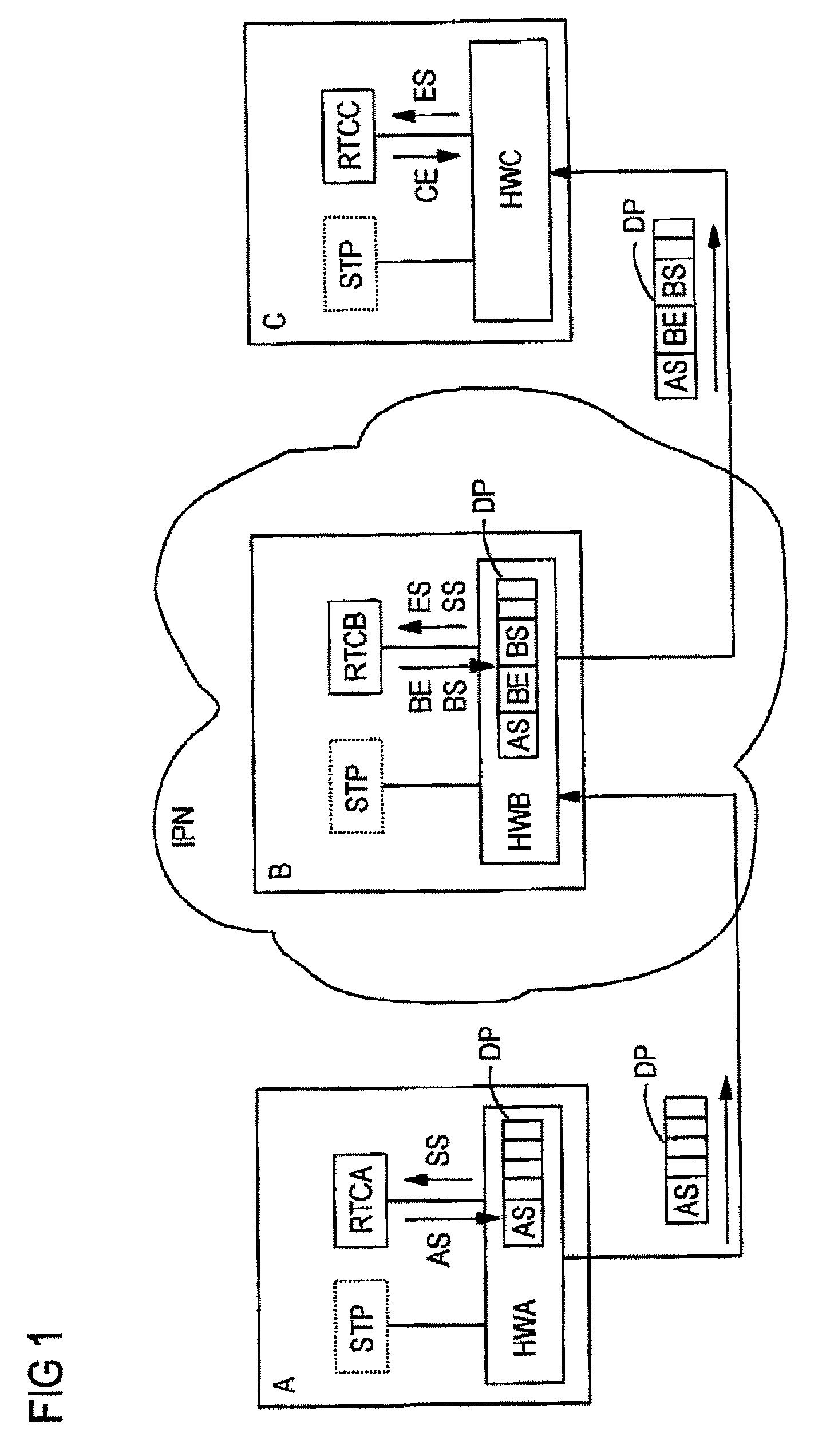
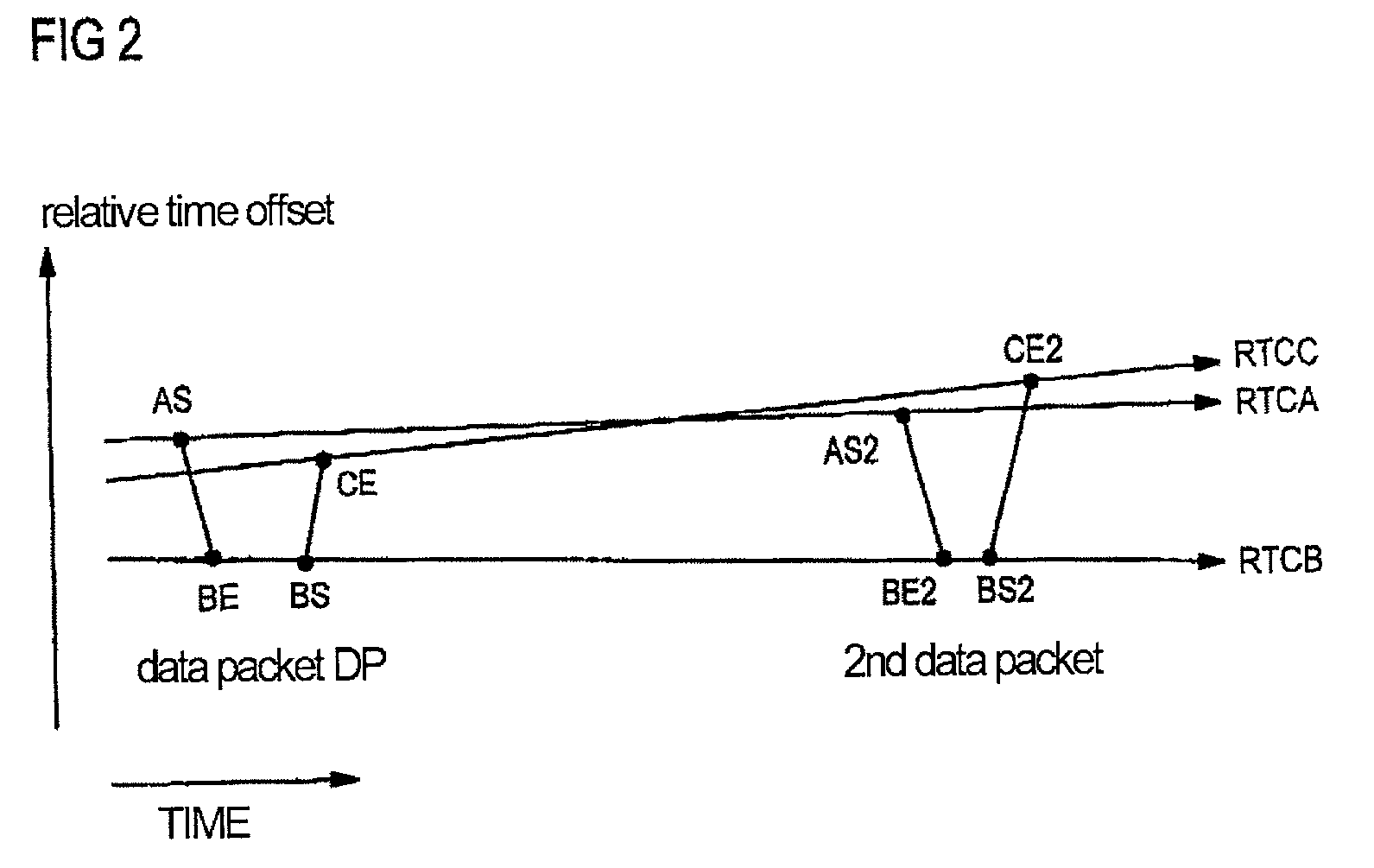
InactiveUS7372846B2Accurate timingHigh synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTemporal informationNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
Time information which is to be transmitted via a data packet network is called up from a time information source and is transmitted to a data packet transmission module. The data packet transmission module controls the transmission time of a data packet in which the time information is transmitted via the data packet network. The transmission time and the calling of the time information are aligned with respect to one another in time by a transmission signal which is generated by the time information source or by the data packet transmission module and indicates the transmission time.
Owner:RINGCENTRAL INC
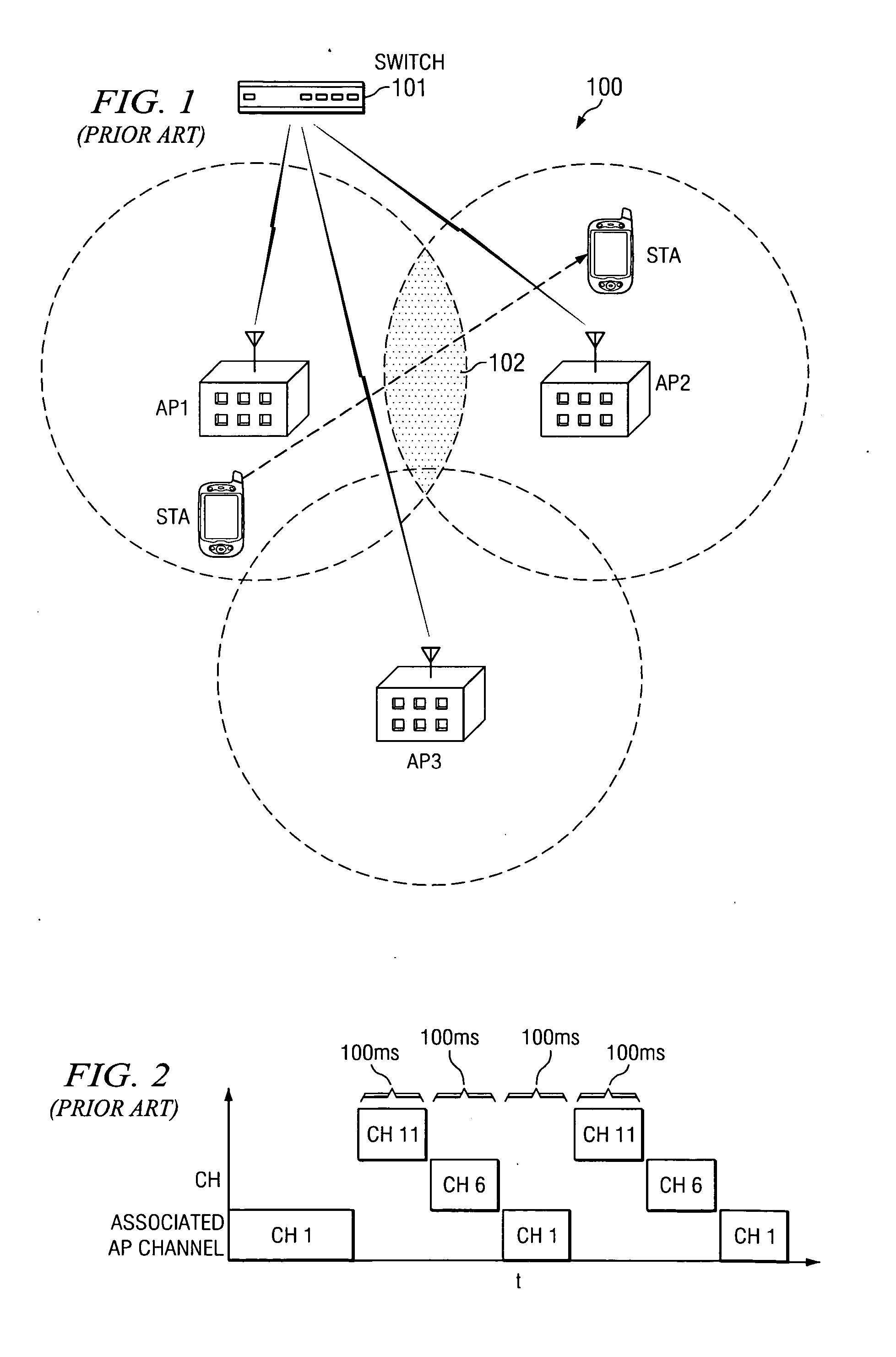
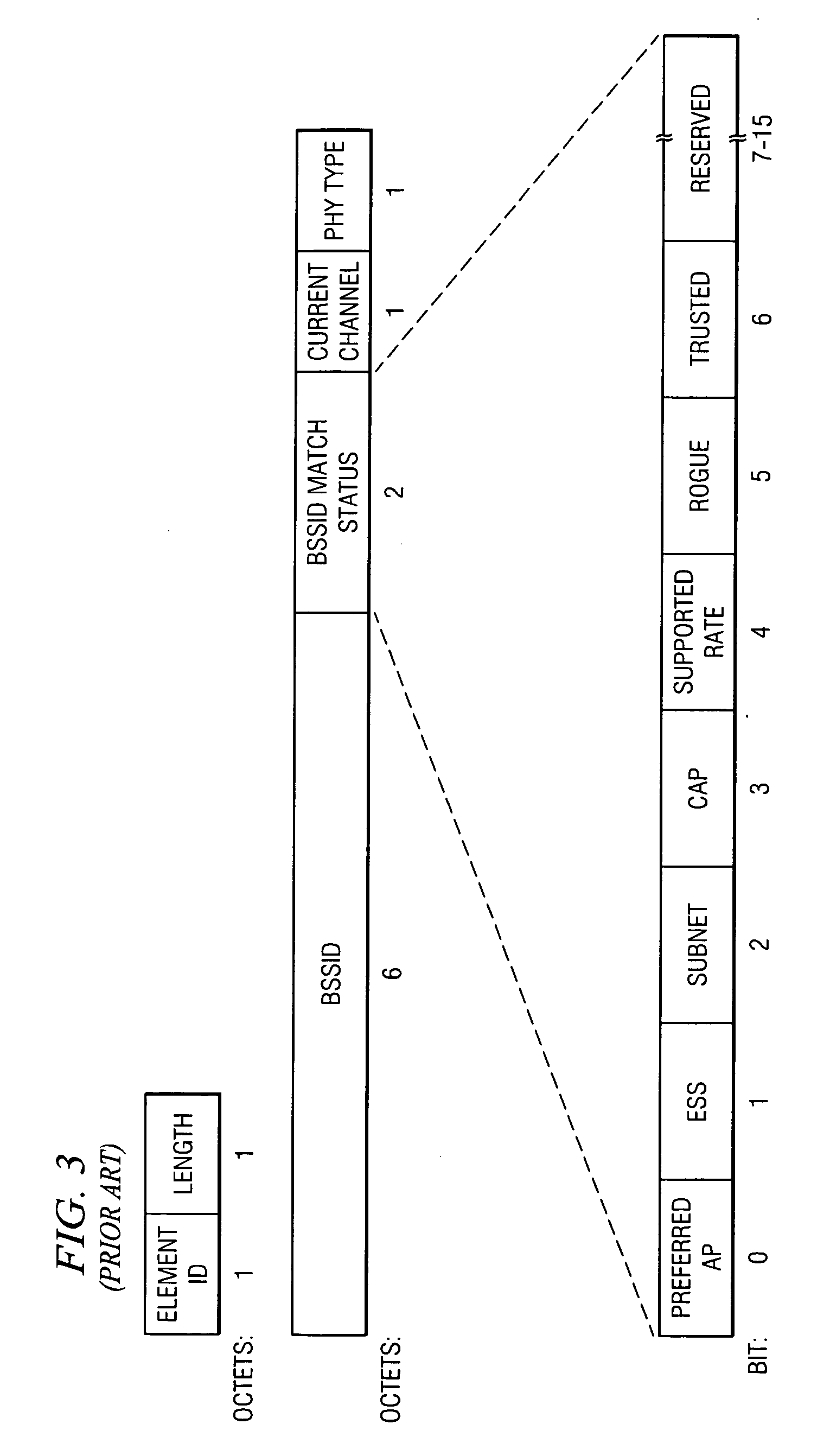
Wireless access point simultaneously supporting basic service sets on multiple channels
InactiveUS20050124294A1Create efficientlyImprove economyData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionTime segmentBasic service
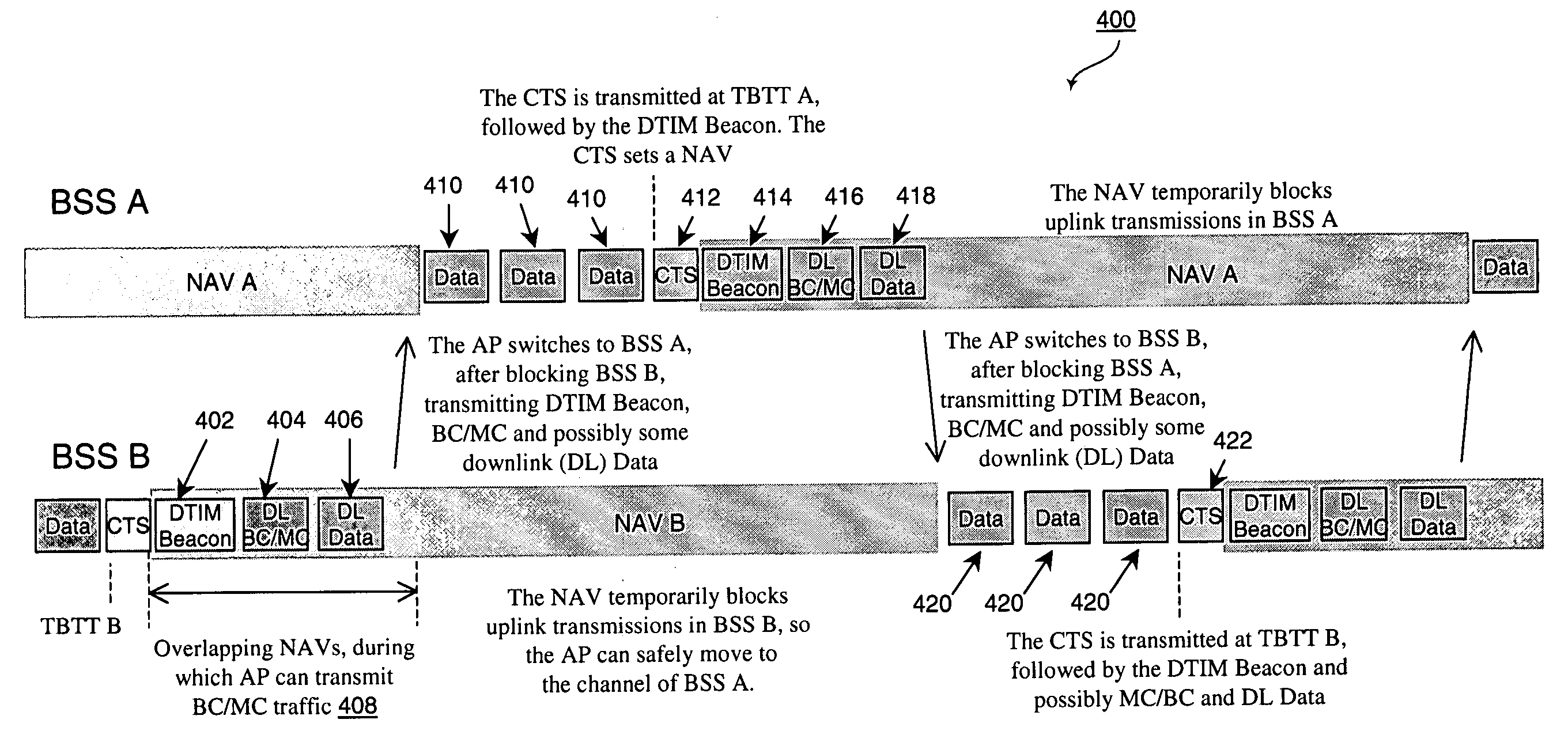
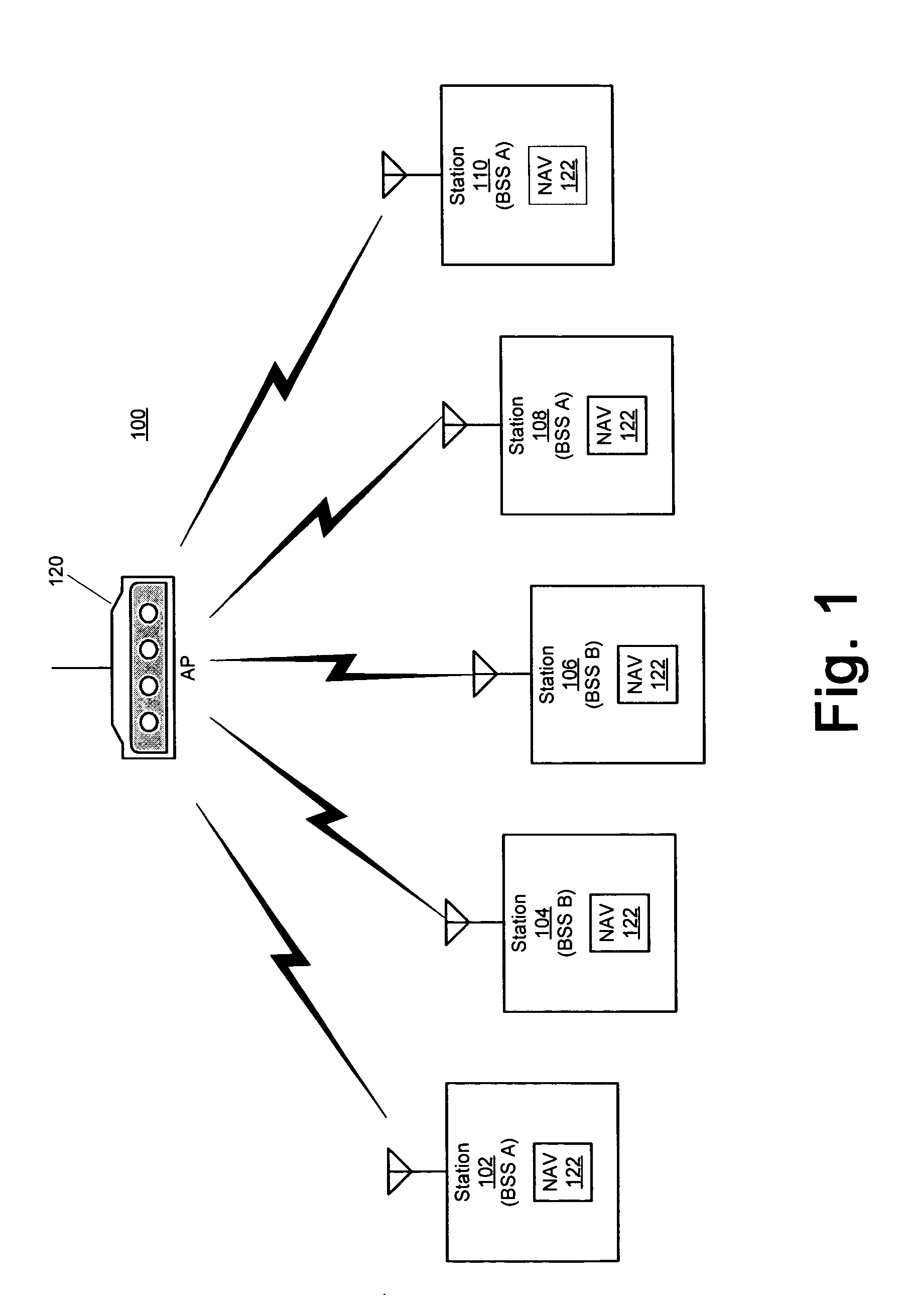
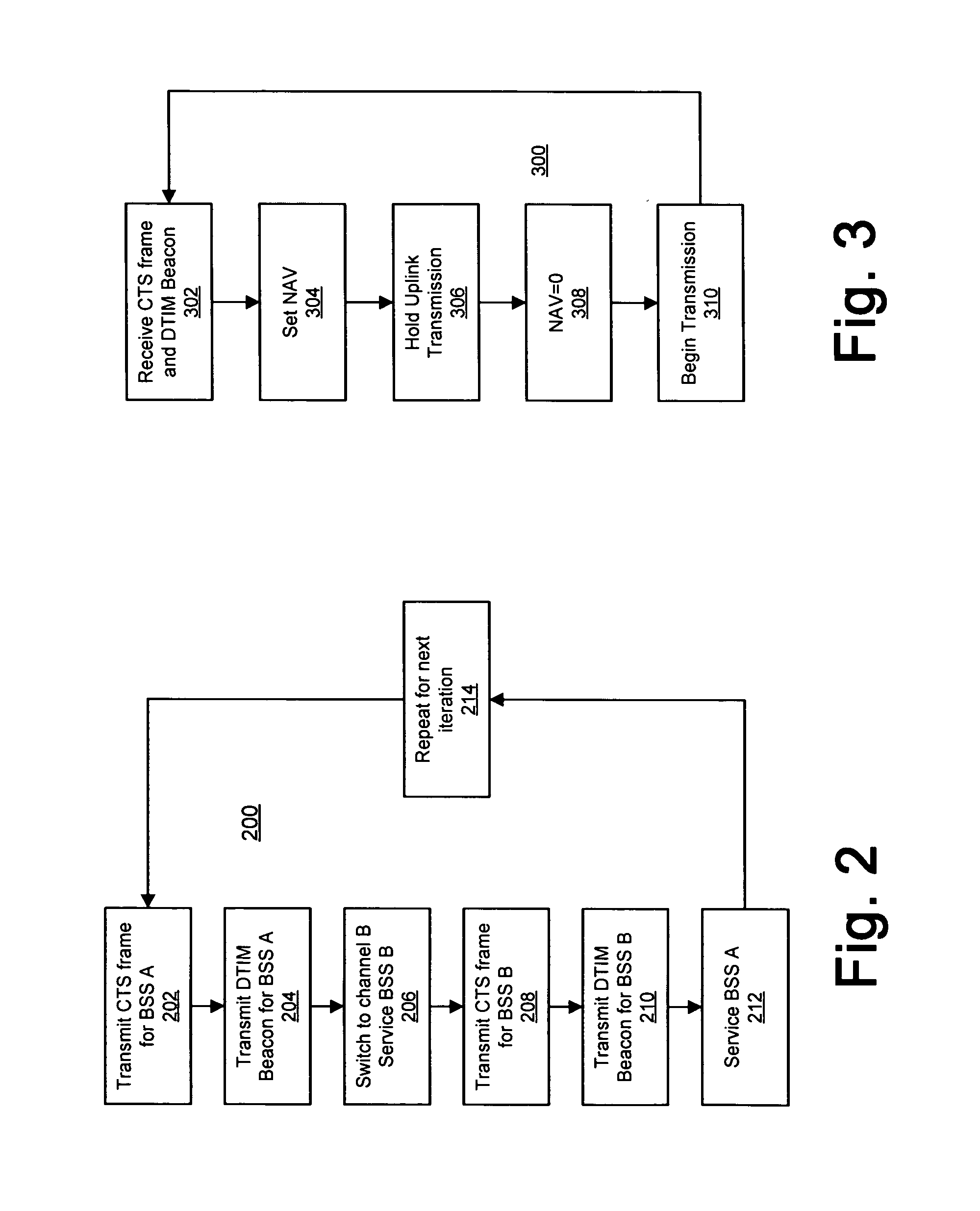
The present invention provides a technique for an access point (AP) to maintain a basic service set (BSS) on two or more channels simultaneously by temporarily blocking one BSS and servicing the other BSS while the other BSS is blocked, thereby providing an efficient way to create a dual cell AP with only a single radio. In an embodiment of the invention, a method for servicing a first set of wireless stations operating on a first channel of an access point and a second set of wireless stations operating on a second channel of the access point comprises transmitting, at a first time, a first frame from the access point to the first set of wireless stations via the first channel, the first frame having duration data directing the first set of wireless stations to cease transmitting until a second time represented by the duration data and servicing the second set of wireless stations via the second channel of the access point for at least a part of a time period between the first time and the second time. The method further comprises transmitting, at the second time, a second frame from the access point to the second set of wireless stations via the second channel, the second frame having duration data directing the second set of wireless stations to cease transmitting until a third time represented by the duration data of the second frame and servicing the first set of wireless stations via the first channel of the access point for at least a part of a time period between the second time and the third time. The method also may comprise transmitting a Delivery Transmission Indication Map (DTIM) frame prior to transmitting each of the first and second frames. The transmission of the DTIM frame preferably occurs substantially simultaneously with a Target Beacon Transmission Time (TBTT) of the access point.
Owner:GLOBESPANVIRATA
Telecommunication and multimedia management method and apparatus
InactiveUS8321581B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork conditionsMediaFLO
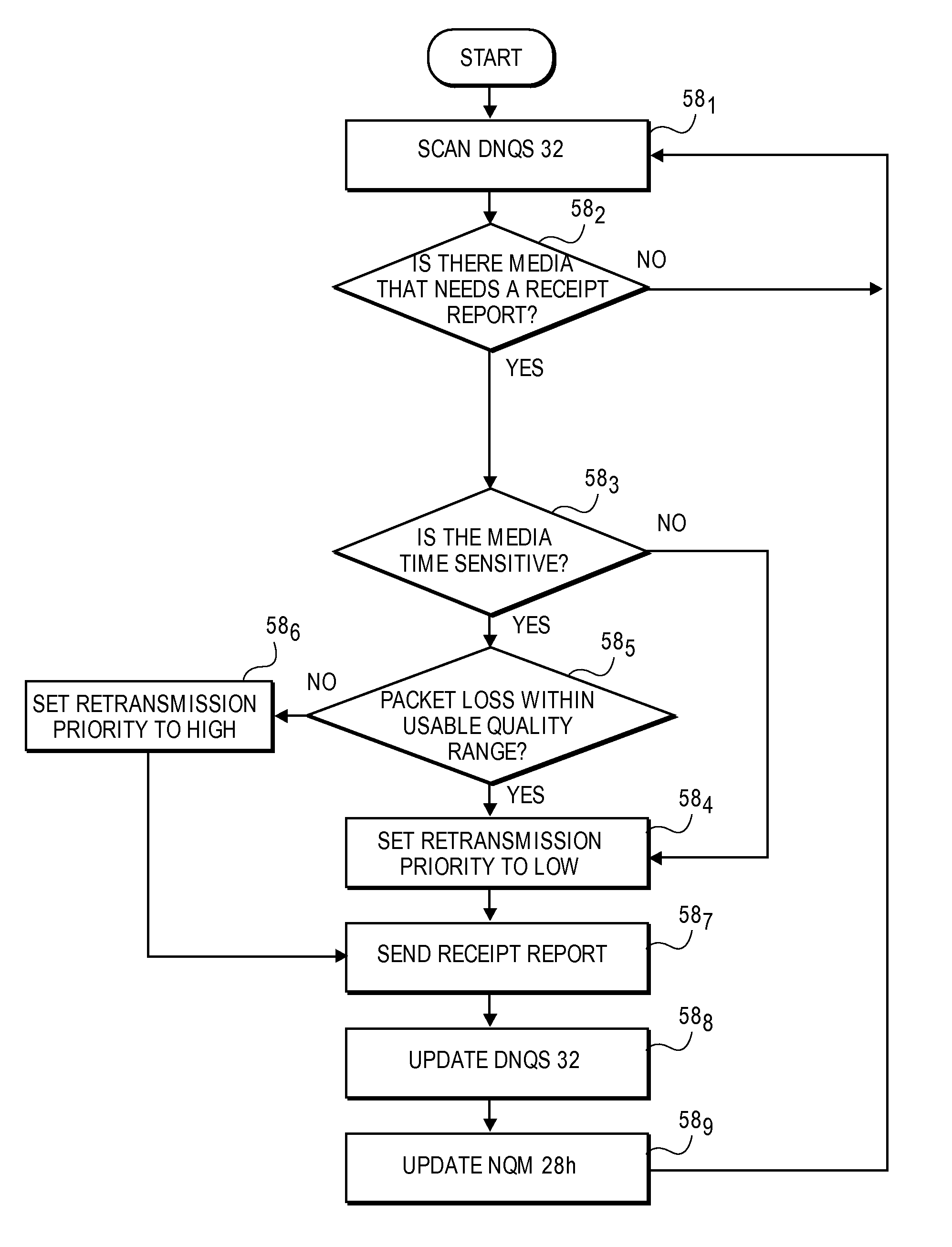
A method for reliably transferring media over a network from a sending node to a receiving node. The method includes ascertaining at the sending node if the media to be transmitted is either time-sensitive or not time-sensitive. For media ascertained as non time-sensitive, the media is transmitted by adjusting the rate of transmission at the sending node based on network conditions. As the non time-sensitive media is received, the receiving node generates one or more low priority requests for the retransmission of any missing non time-sensitive media lost during the transmission. The method also includes transmitting the time-sensitive media from the sending node to the receiving node. As the time-sensitive media is received, the receiving node ascertains if a predetermined acceptable network transmission loss level is met. If met, the receiving node generates one or more low priority requests for the retransmission of any missing time-sensitive media lost during transmission. The sending node retransmits the missing time-sensitive and non time-sensitive media in response to the low priority requests when bandwidth on the network becomes available in excess of what is needed for the transmission of time-sensitive media.
Owner:VOXER IP
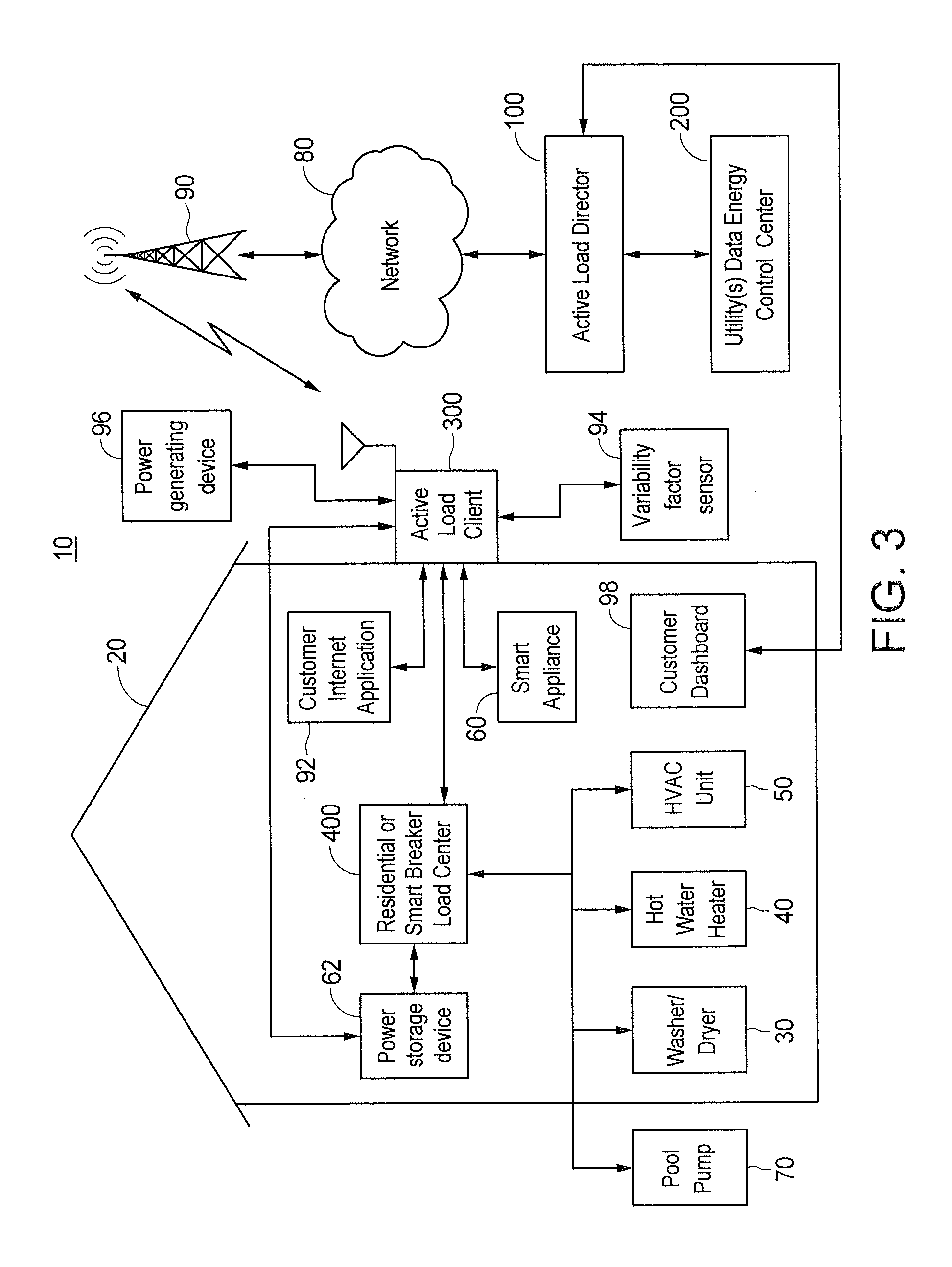
Apparatus and Method for Controlling Communications to and from Utility Service Points
ActiveUS20110029655A1Special service provision for substationData processing applicationsFixed positionComputer science
An apparatus and method control transmission of messages over a fixed bandwidth link from fixed position communication devices to a central controller in a load management system. The messages include information relating to electric power consumption by power consuming devices located at service points that include the communication devices. In one embodiment, the central controller determines an identifier associated with each communication device, a reporting period during which the messages are to be transmitted by the communication devices, and transmission increments within the reporting period. The controller allocates each transmission increment to a respective group of communication devices. The controller then determines a transmission time for a message from a particular communication device based on the identifier for the particular device, a duration of a transmission increment allocated to a group of communication devices that includes the particular device, and a quantity of communication devices in the particular device's group.
Owner:LANDISGYR INNOVATIONS INC +1
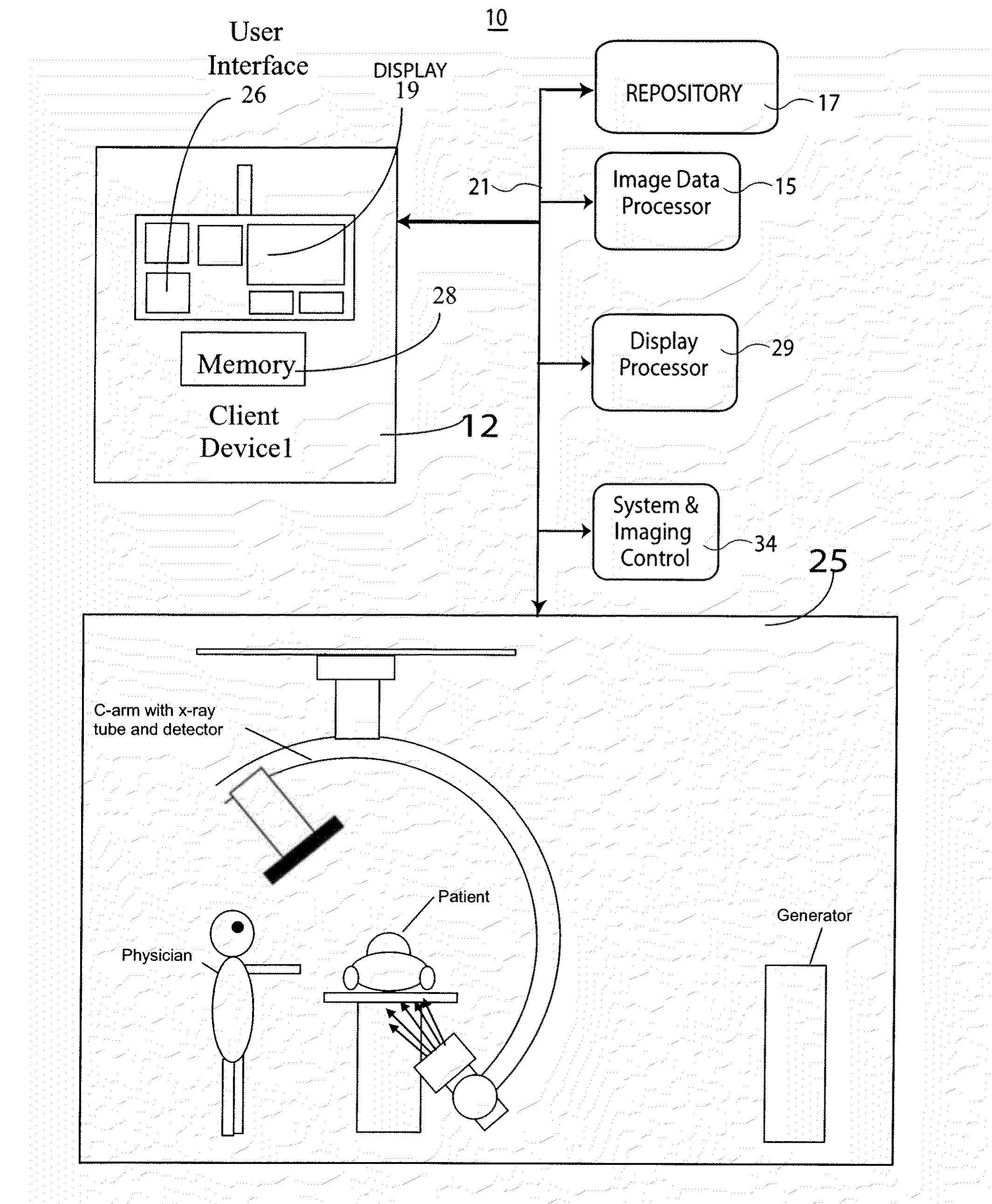
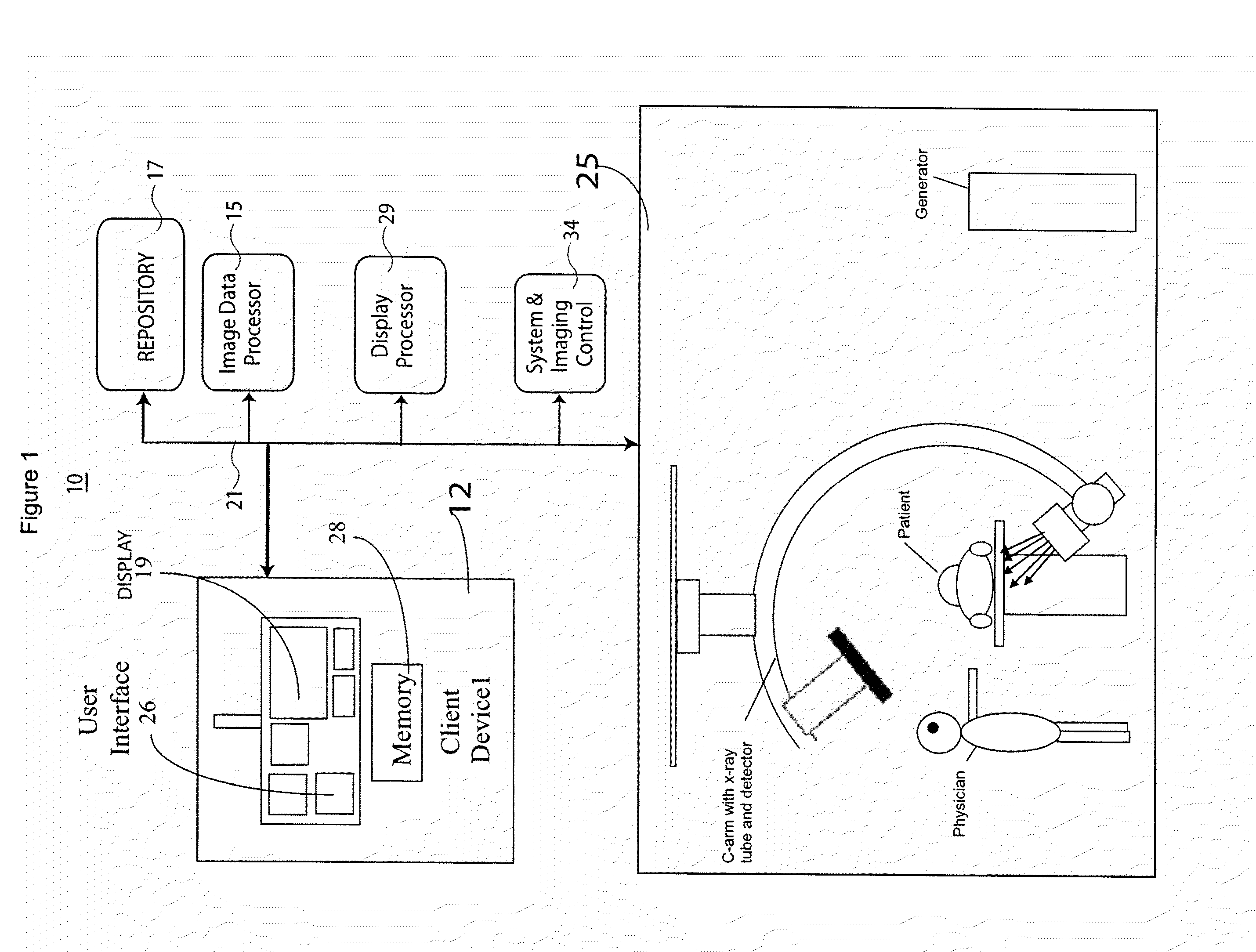
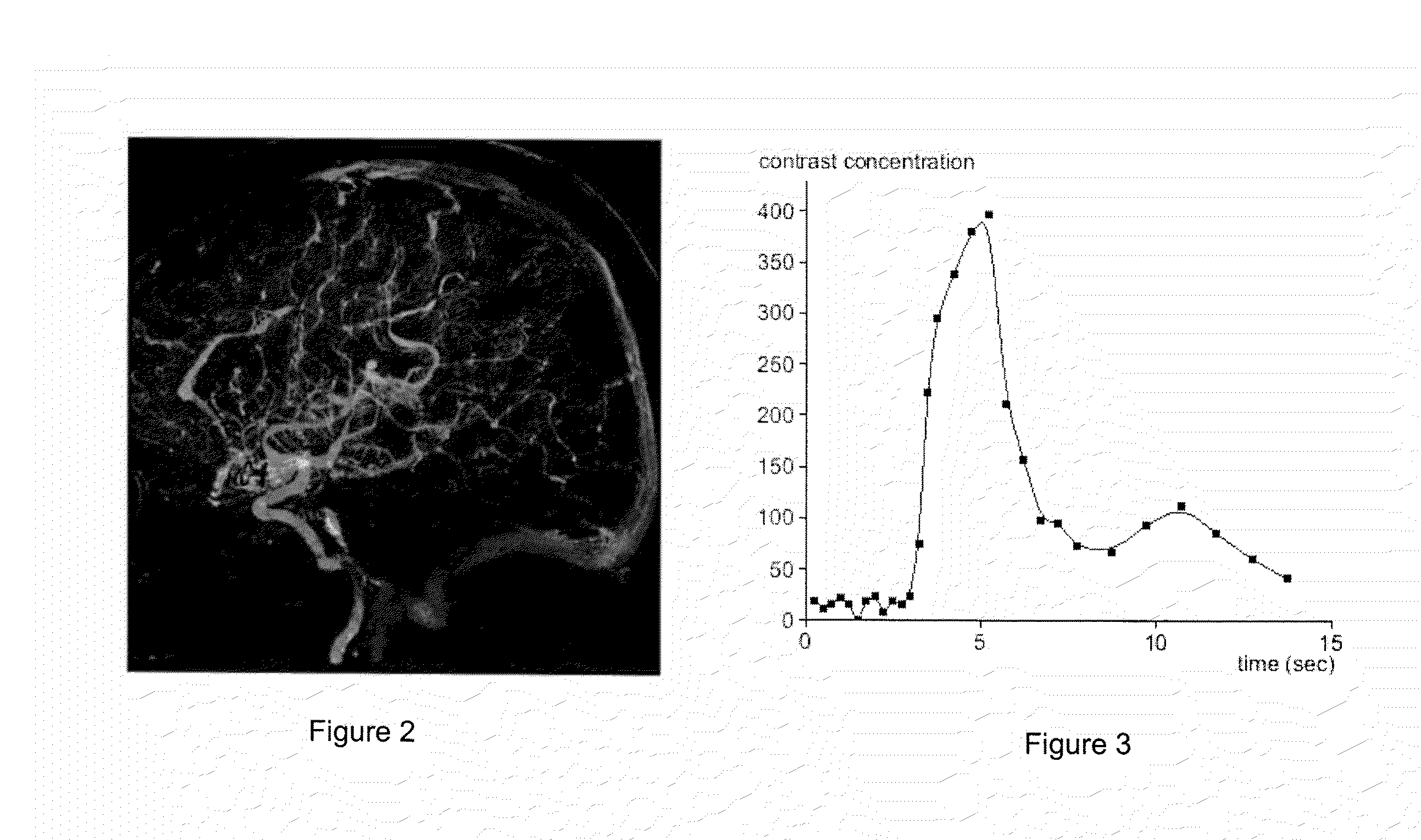
System for Processing Medical Image data to Provide Vascular Function Information
A system creates a visually (e.g., color) coded 3D image that depicts 3D vascular function information including transit time of blood flow through the anatomy. A system combines 3D medical image data with vessel blood flow information. The system uses at least one repository for storing, 3D image data representing a 3D imaging volume including vessels, in the presence of a contrast agent and 2D image data representing a 2D X-ray image through the imaging volume in the presence of a contrast agent. An image data processor uses the 3D image data and the 2D image data in deriving blood flow related information for the vessels. A display processor provides data representing a composite single displayed image including a vessel structure provided by the 3D image data and the derived blood flow related information.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Desynchronized network access in m2m networks
ActiveUS20120231828A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionSynchronous network
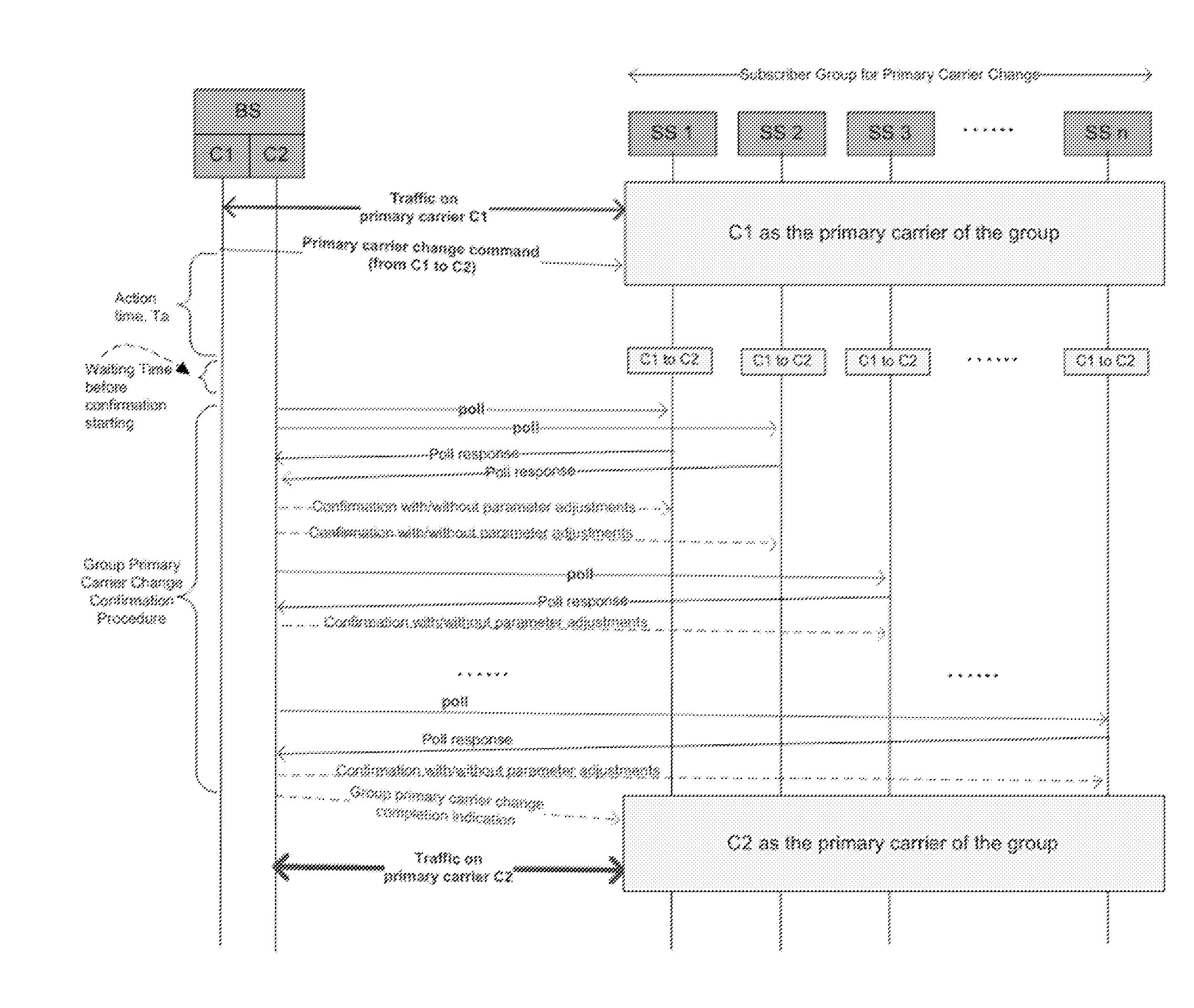
Systems, methods, and instrumentalities are disclosed to desynchronize transmissions in group-based operations. A group user equipment (UE), e.g., a UE that is a member of a group of UEs, may be in an inactive mode. The group UE may receive a multicast message indicating that the group UE may enter an active mode. For example, the group UE may use the active mode for periodic reporting of its monitoring activity to the network. The multicast message may indicate a mechanism for the group UE to use to send an uplink transmission to the network. The group UE may send the uplink transmission to the network at a transmission time indicated by the mechanism. The transmission time may be desynchronized from other UEs in the group.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Distributed channel allocation method and wireless mesh network therewith
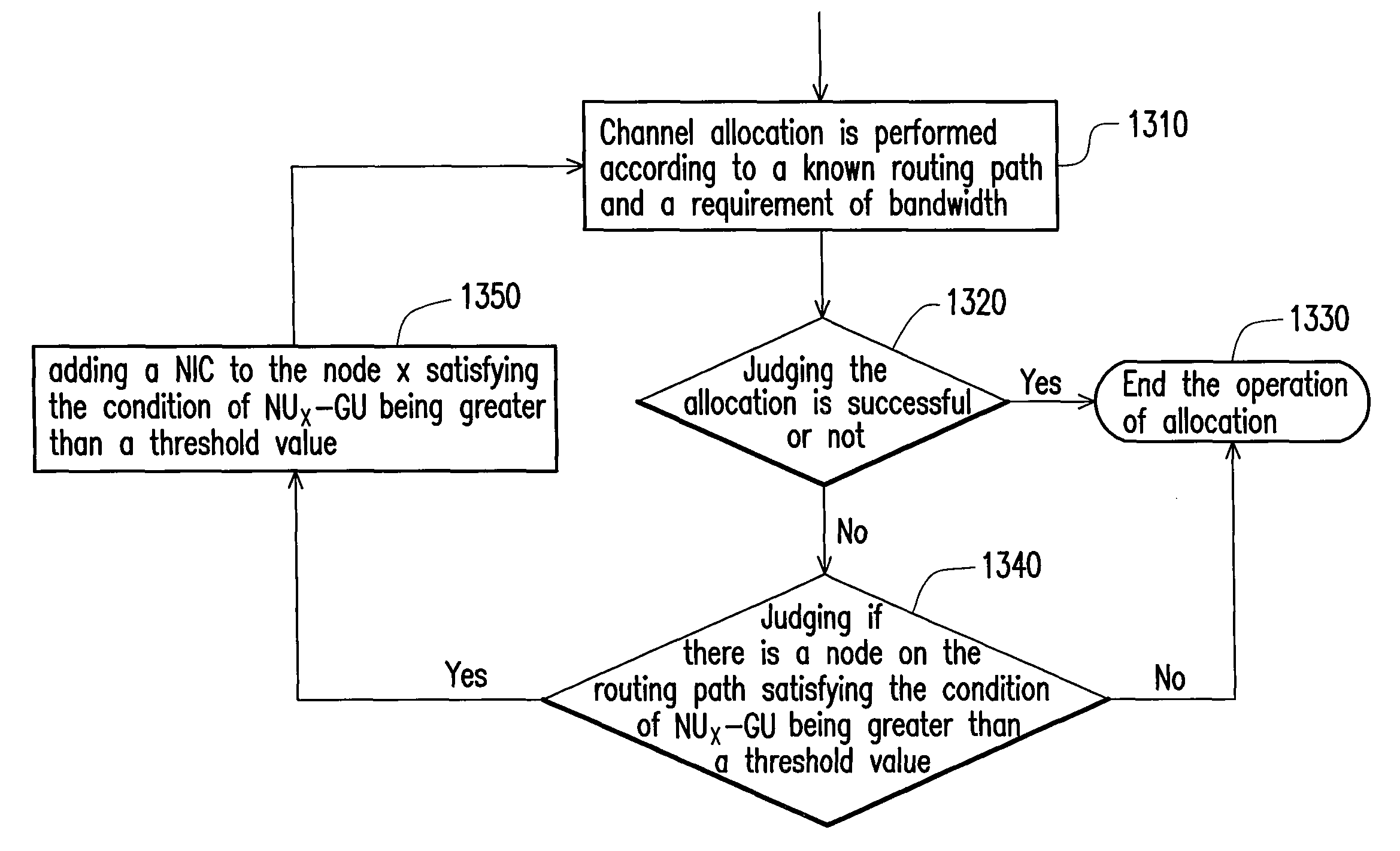
InactiveUS8059593B2Avoid interferenceGuaranteed bandwidthRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesWireless mesh networkDistributed computing
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for transmitting channel quality information in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
InactiveUS20050201474A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionAsynchronous cdmaAsynchronous communication
A method and apparatus for efficiently transmitting channel quality information in an OFDM communication system using dynamic channel allocation and adaptive modulation, and determining parameters required for time-division channel quality information transmission in an asynchronous CDMA communication system are provided. In the OFDM communication system in which a plurality of subcarriers are allocated to a plurality of UEs, the subcarriers are divided into a plurality of subcarrier groups each having at least one subcarrier. Each of the UEs determines and transmits the channel quality information of each of the subcarrier groups according to predetermined transmission parameters at transmission time points that do not overlap with those of other UEs. A Node B dynamically allocates the subcarriers to the UEs and their corresponding modulation schemes according to the channel quality information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Secure network system and method for transfer of medical information
InactiveUS7028182B1Data processing applicationsComputer security arrangementsCombined usePublic network
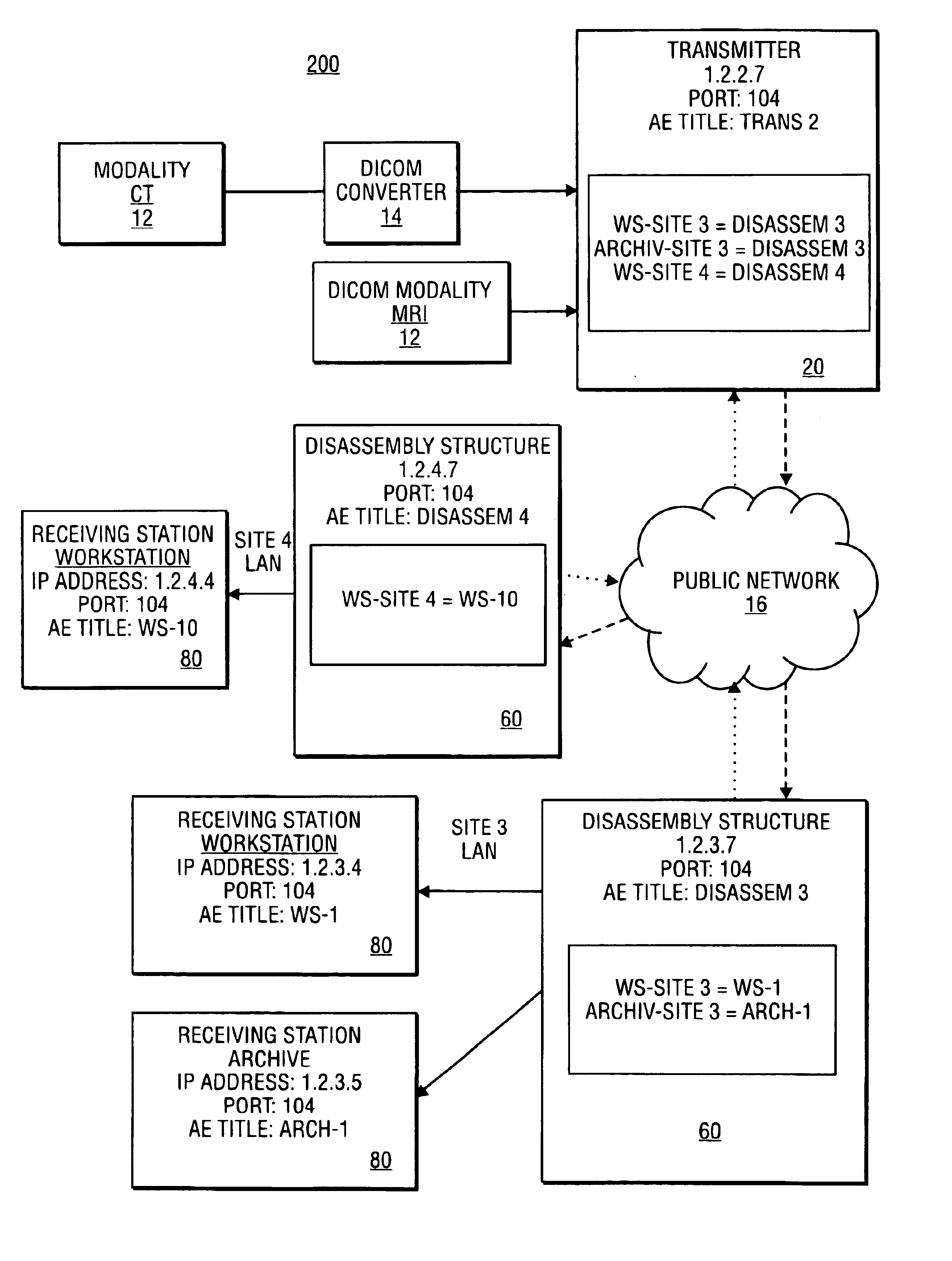
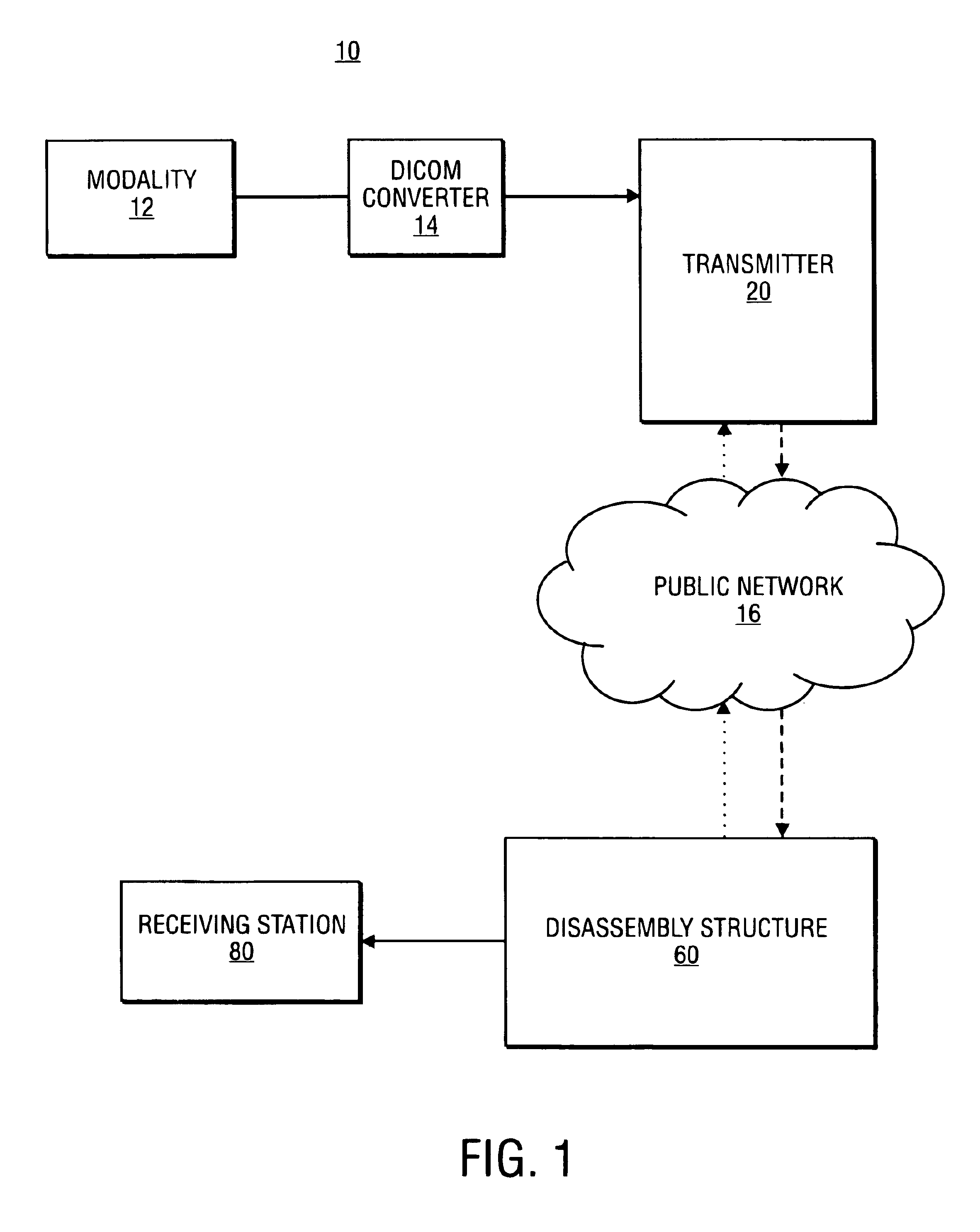
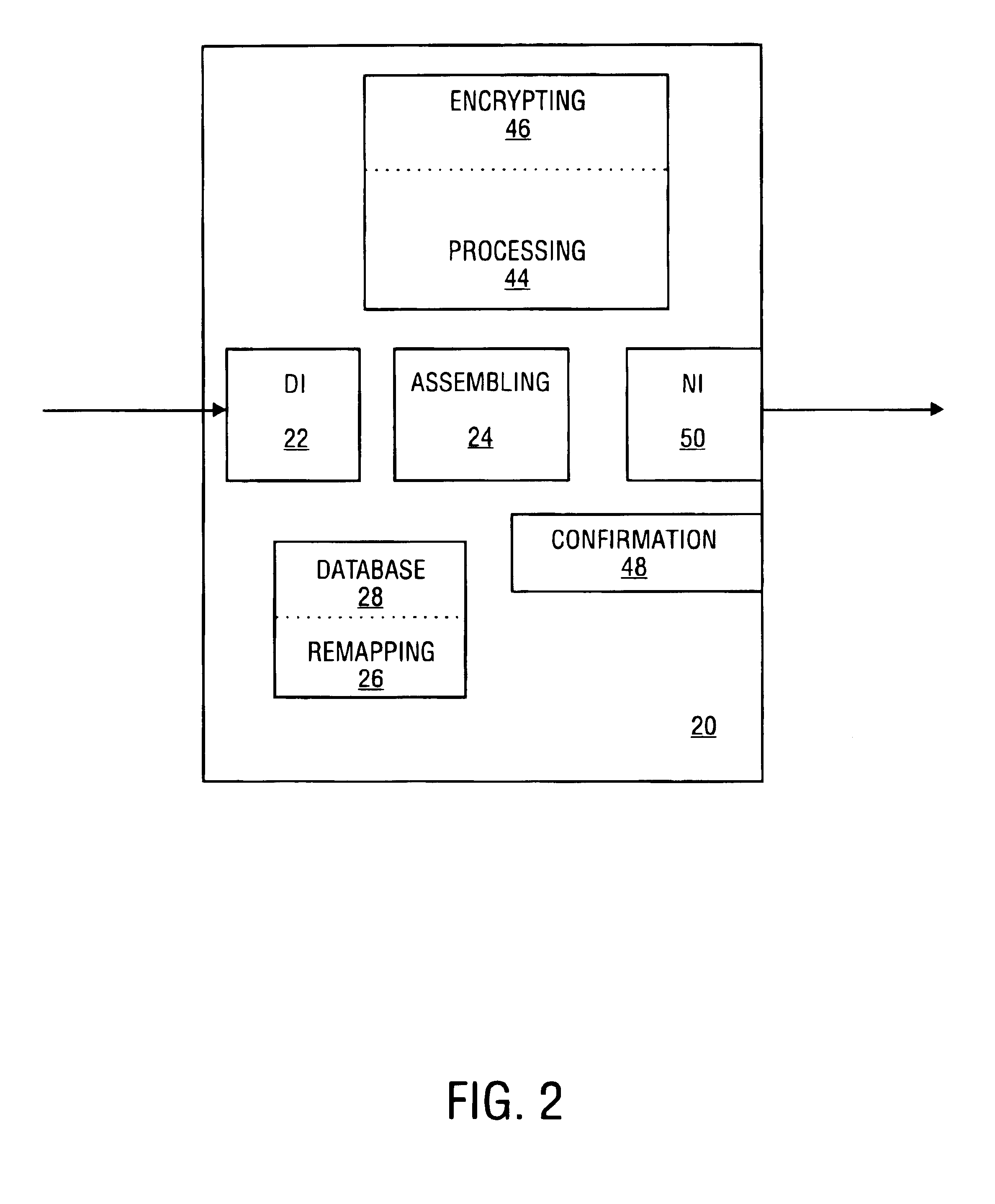
The assembly and communication of medical information from a variety of modalities to remote stations through a public network is provided for by the combined use of a transmitter and disassembly structure. The transmitter includes an assembly unit for gathering data into packets and a processing unit to provide security for transfer. The disassembly structure reconfigures the data for relay to a receiving station. Mechanisms are provided for conserving the transfer time from transmitter to disassembly structure.
Owner:NEXSYS ELECTRONICS
Beacon signaling in a wireless system
InactiveUS6985498B2Improve and optimize system performanceImprove throughputPower managementFrequency diversityEngineeringData transmission
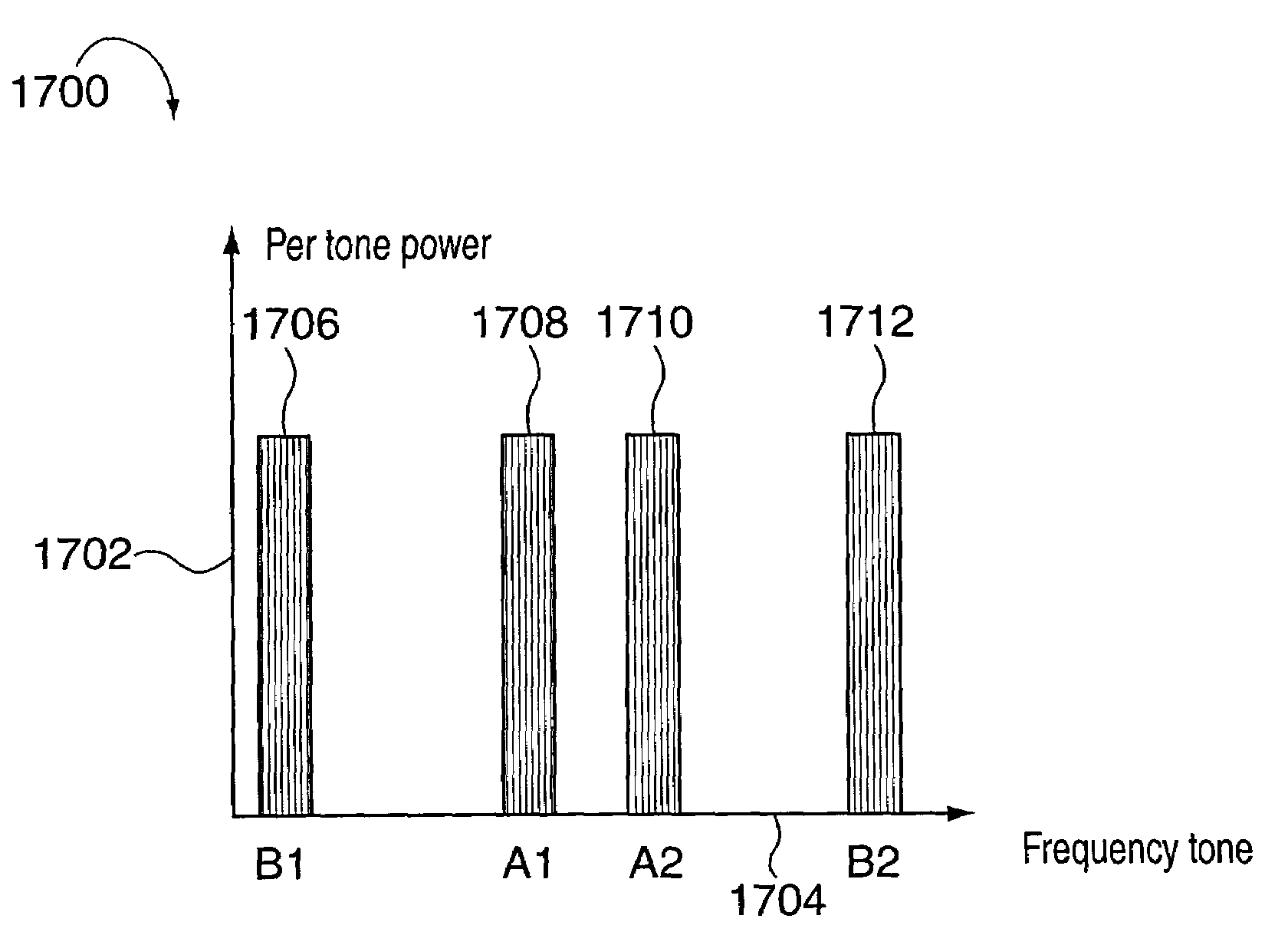
A few high power tones used for synchronization and / or other purposes are transmitted in a FDM system during a period of time, e.g., a symbol transmission time period. During normal data transmission symbol periods signals are transmitted using at least 10 tones, e.g., per symbol time. Less than 5 high power signals are transmitted in a symbol time with at least 80% the maximum total transmitter power transmitted being allocated to the high power signals where the maximum total transmitter power is determined from a period of time which may includes one or more data and / or high power tone transmission periods. When the high power tones are transmitted at most 20% of transmitter power is available for transmitting other tones with the power normally being distributed among multiple tones. Normally some tones which would be transmitted in a symbol time go unused during transmission of the high power signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems and methods for efficient hand-off in wireless networks
InactiveUS20060268756A1Freeing network capacityReduce eliminateAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkFrequency spectrum
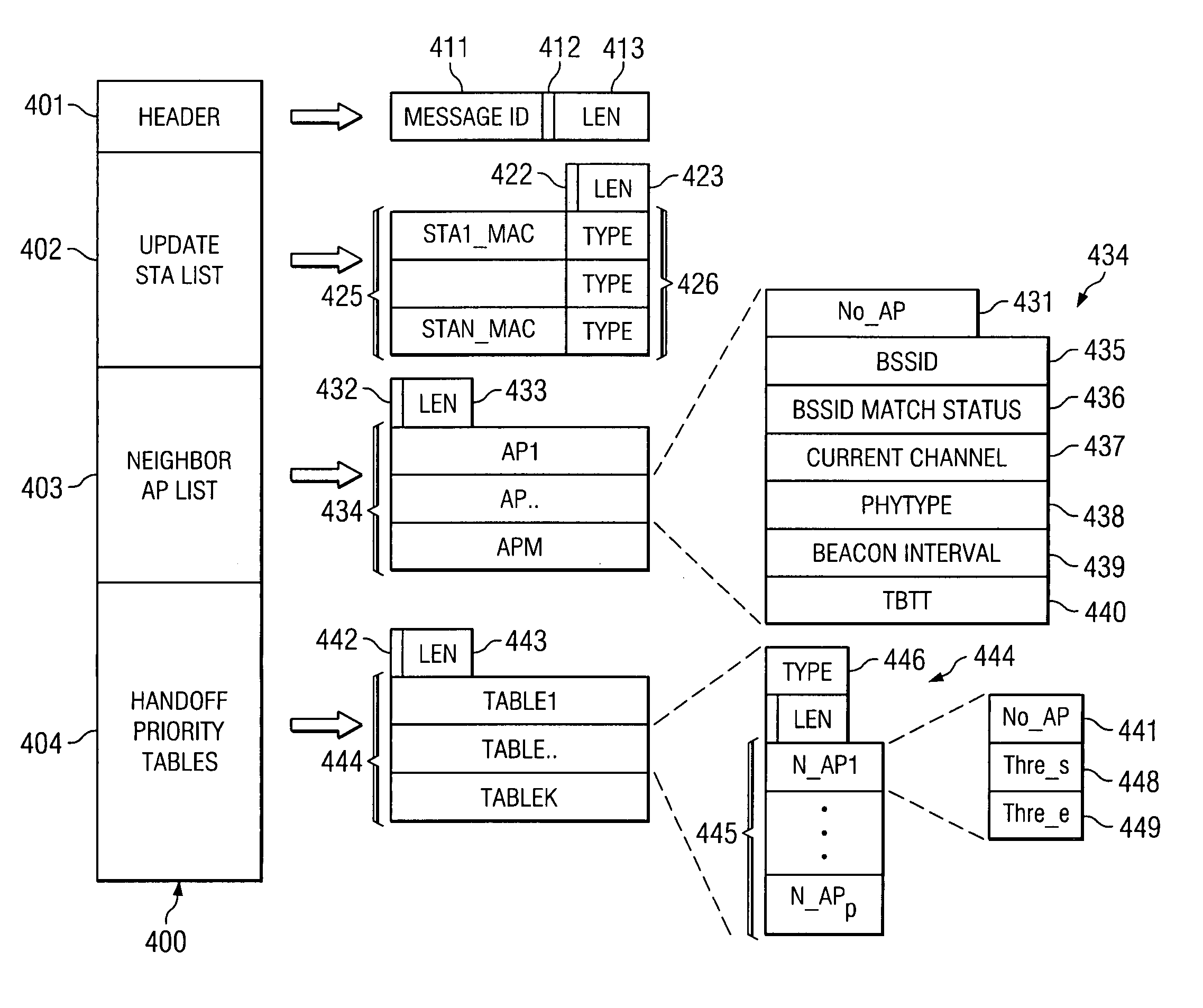
Embodiments of systems and methods for efficient hand-off in a wireless network employ a neighbor report which may include, in addition to more convention information about neighboring access point, search thresholds, target beacon transmission time of neighboring access points, and execution thresholds. The present systems and methods also provide a mechanism of updating neighbor report and its elements. A faster and lower spectrum cost active search scheme based on sending a null packet may also be used by the systems and methods.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
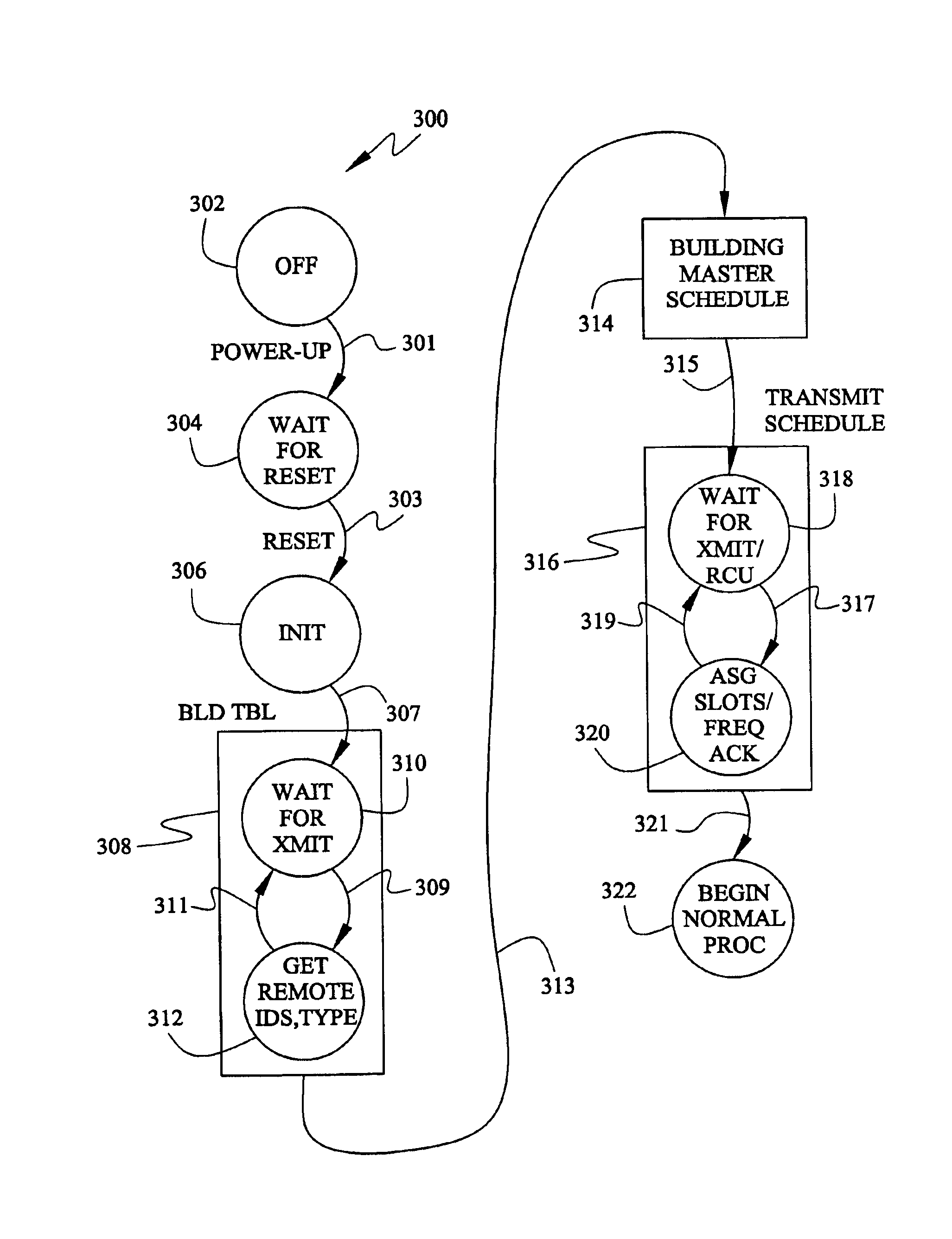
Wireless control network with scheduled time slots
InactiveUS6901066B1Easy to optimizeImprove update rateTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsElectric testing/monitoringWireless controlMonitoring system
A building monitoring system is disclosed that includes a bi-directional radio link between a master and a number of remote units, wherein the master unit schedules the transmission times of the remote units to avoid collisions.
Owner:HONEYWELL INC
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks
InactiveUS20090011713A1Distance can be measured is lengthenEnhanced distance estimateSatellite radio beaconingTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsSignal strength
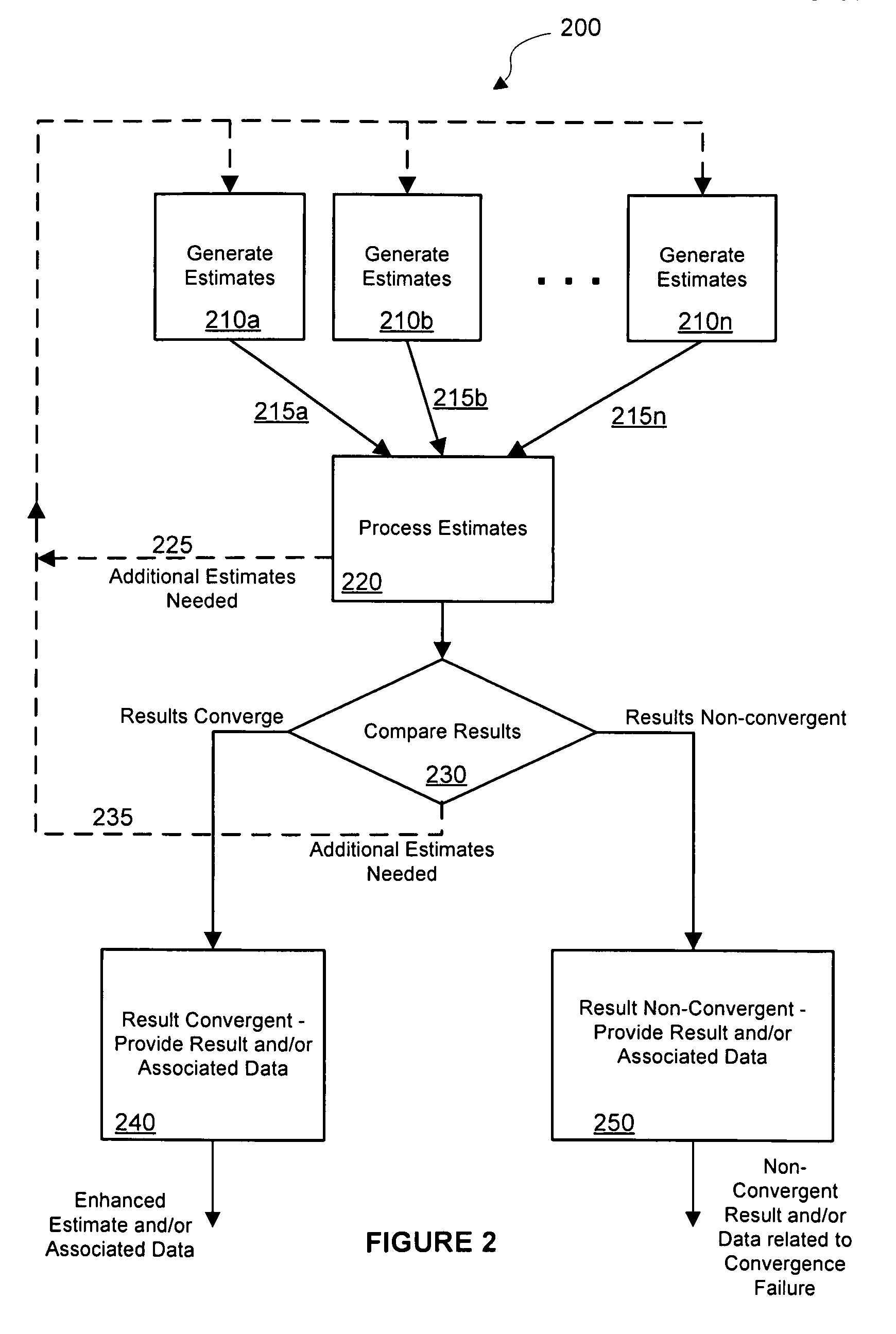
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks are disclosed. A method for measuring distance between nodes or devices in a wireless network comprises estimating a distance between network devices based on a first distance measurement method, estimating the distance based on a second distance measurement method, and processing the first and second distance estimates to determine convergence and to generate an enhanced distance measurement. Additional distance estimates may be combined to further improve accuracy. Convergence information may be provided indicating whether two or more distance estimates converge. In some implementations, the first distance estimate may be generated by a transmission time estimation method, the second distance estimate may be generated by a received signal strength distance estimate, the two estimates may be combined by averaging to generate an enhanced distance estimate, and the difference between the estimates may be compared to a threshold to determine whether the estimates have sufficiently converged to within a desired convergence range.
Owner:PROXIMETRY
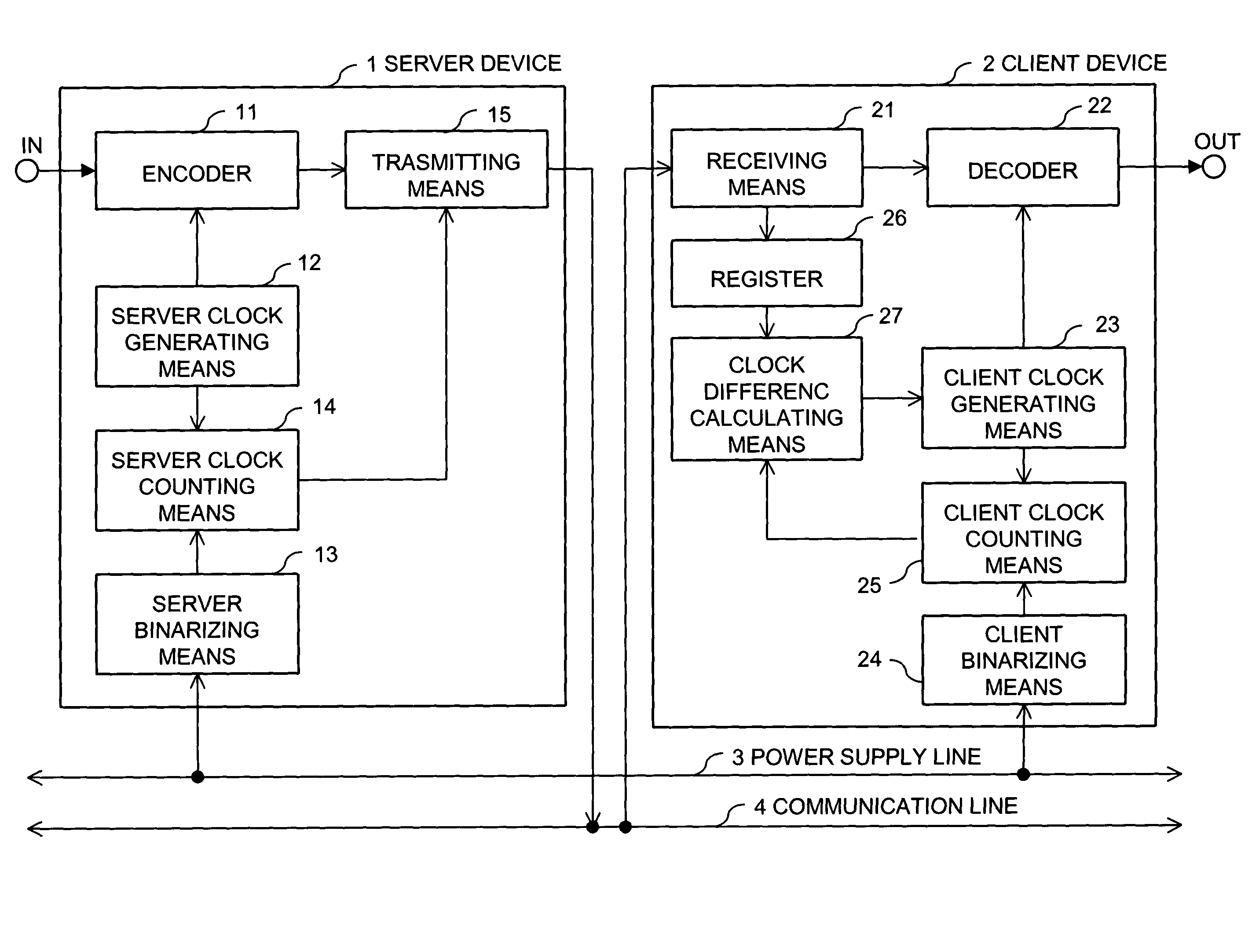
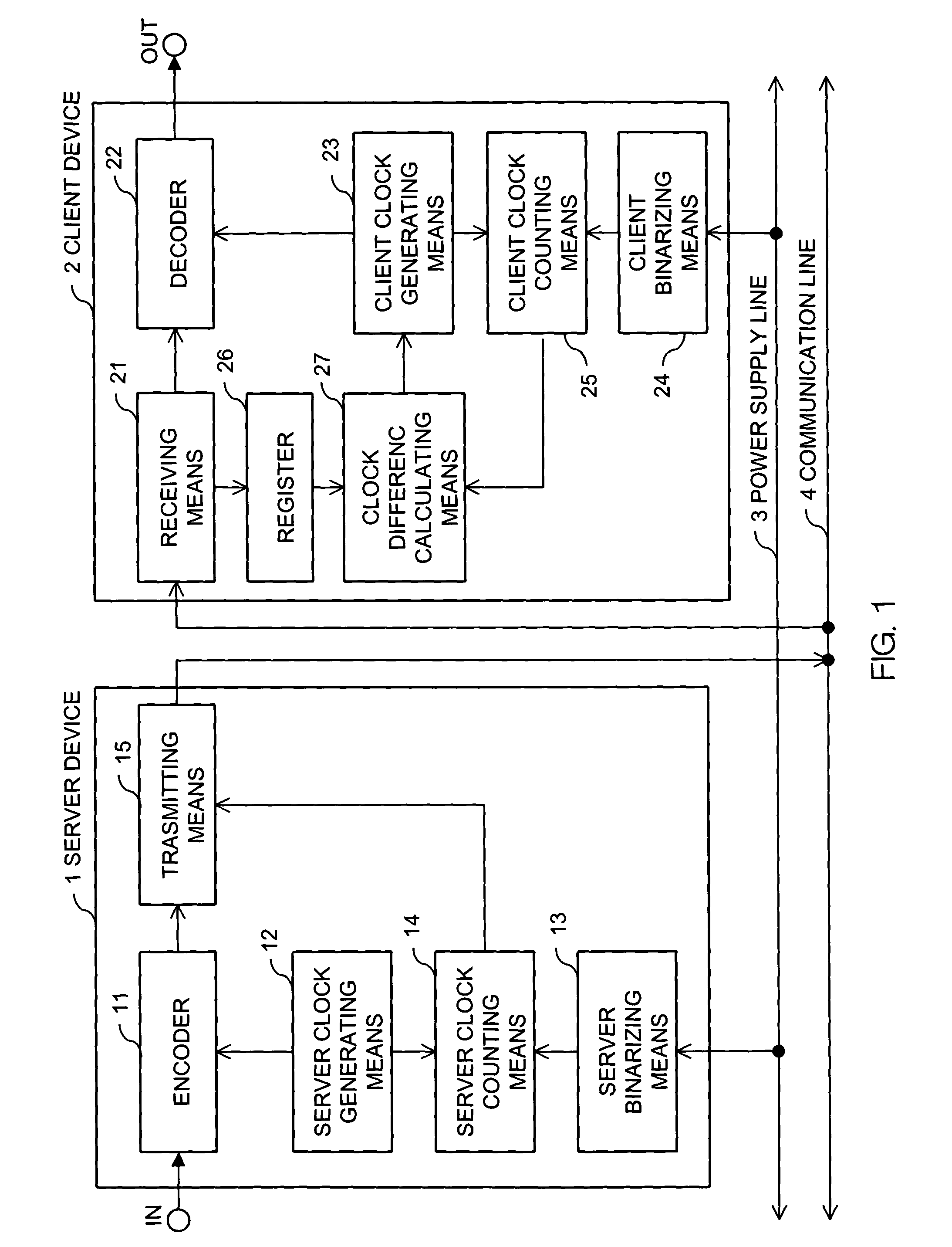
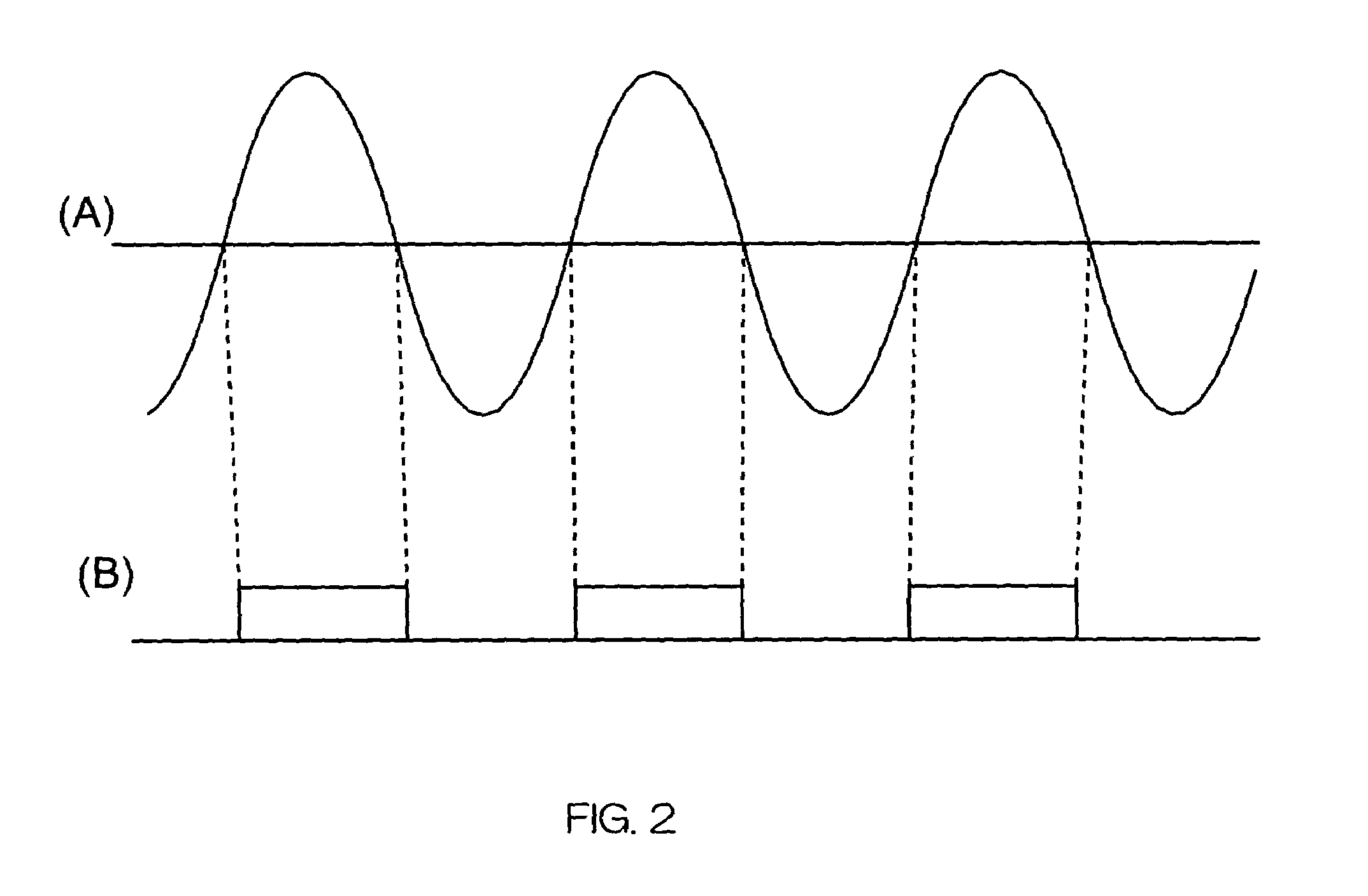
Synchronizing clock signals of server and client devices in a network system based on power source synchronous pulse signal
InactiveUS7263110B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData transmission timeNetworked system
In a network system, clock signals of a server device and a client device are synchronized with each other without having any influence of a change and a delay of the transmission time of data. Therefore, in the network system in which the client device receives and reproduces information transmitted from the server device, the server device counts the number of clock pulses of a server clock signal used to compress and encode information on the basis of a power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with a power source frequency. The server device outputs information showing the counted clock pulse number and the compressed and encoded information to the client device. The client device counts the number of clock pulses of a client clock signal used to decode and decompress the compressed and encoded information on the basis of the power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with the power source frequency. The client device conforms the frequency of the client clock signal to the frequency of the server clock signal on the basis of the clock difference between the clock pulse number received from the server device and the counted clock pulse number.
Owner:D & M HOLDINGS INC
Time division multiple access over broadband modulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6891841B2Accurate resolutionBroadband local area networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime division multiple accessBurst transmission
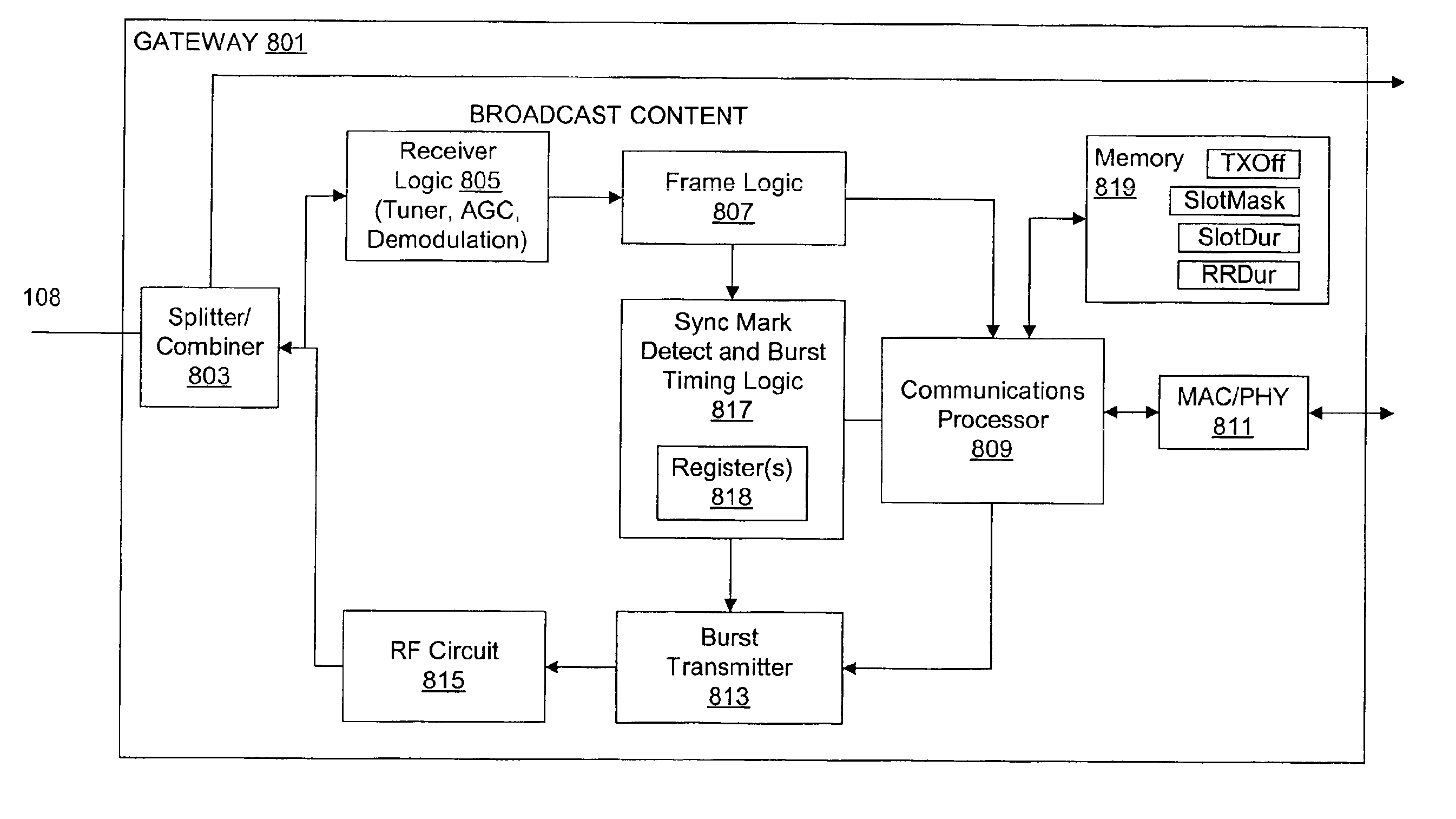
A communication system is disclosed for providing dedicated bandwidth to at least one subscriber location for transmitting to a common point of distribution via an HFC network. In an embodiment of the invention, the communication system includes a channel interface module and at least one gateway coupled across the HFC network. The channel interface module is located at the point of distribution and includes a transmitter that transmits a windowing signal via the HFC network. The gateway is located at a subscriber location and includes a processor that encapsulates subscriber data into data cells suitable for burst transmission, receive logic that receives the windowing signal, timing logic that indicates burst transmission times only at programmed time slots within each of repeating transmission windows based on the windowing signal and a predetermined transmission timing offset, and a burst transmitter that burst transmits subscriber data cells in a predetermined upstream frequency channel when indicated by the timing logic.
Owner:INCEPTIA +1
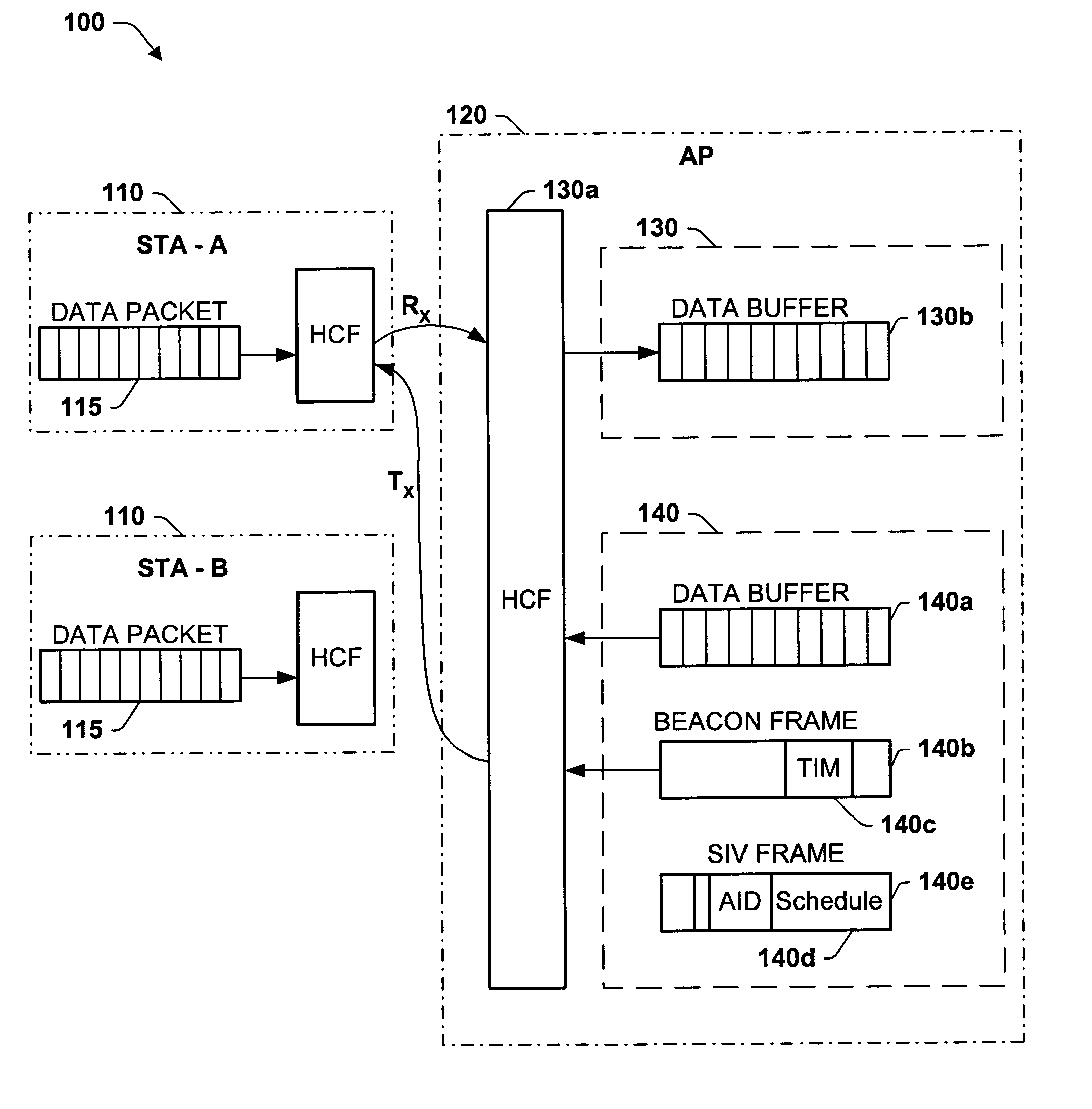
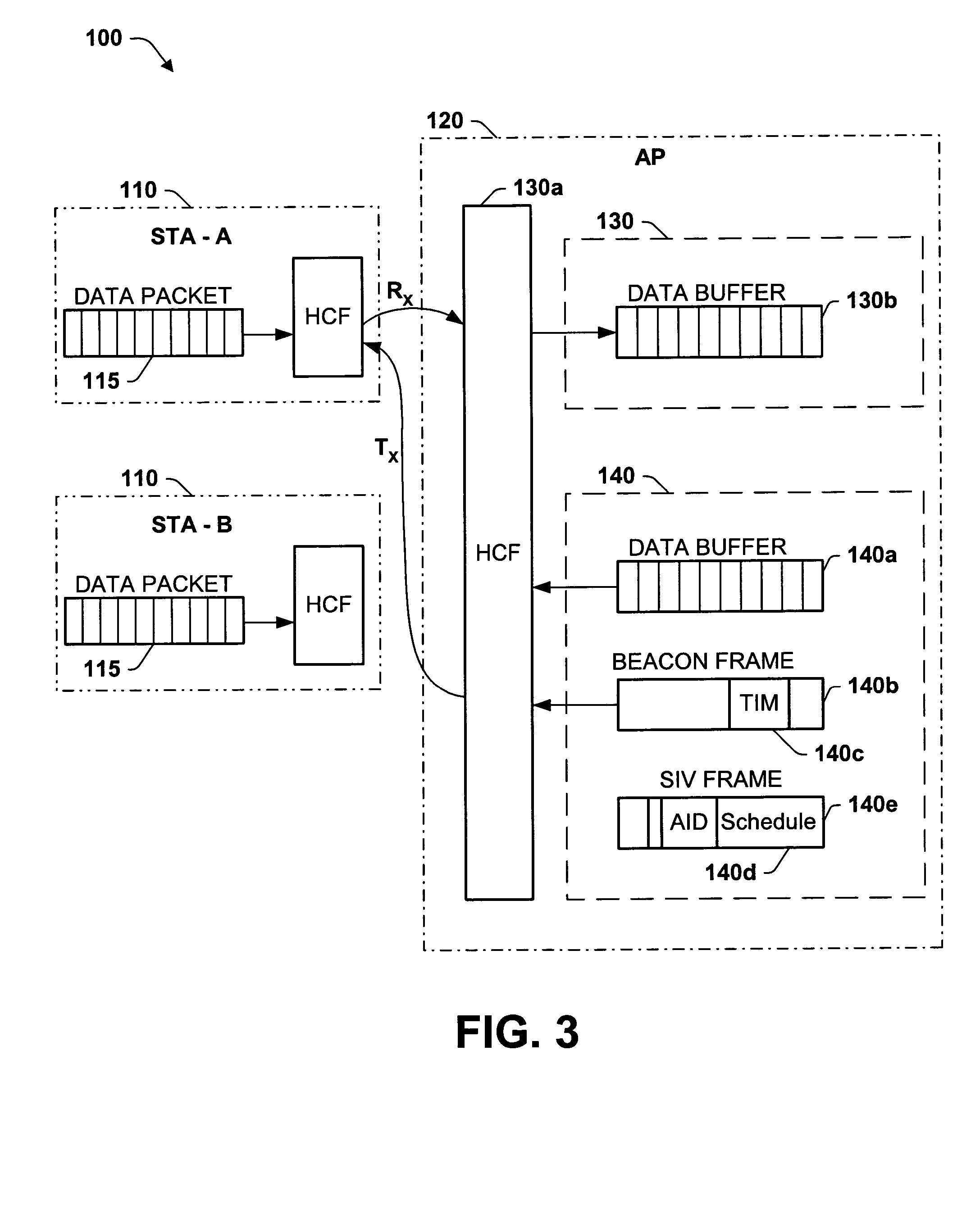
Optimal power saving scheduler for schedule information vector
ActiveUS20050003794A1Minimize timeSave powerEnergy efficient ICTError preventionSorting algorithmData transmission time
A new system and method is described, utilizing a scheduler based on a transmission time calculation and prioritizing algorithm. The system utilizes a Schedule Information Vector (SIV) protocol for saving power in wireless local area networks. The system comprises an access point having a priority queue, one or more stations, an SIV frame comprising an association ID for identifying one of the stations and a scheduled wake-up time for the identified station. An algorithm is employed for calculating the transmission time of downlink data for the stations. The access point originates and transmits to the one or more stations the SIV frame of the scheduled wake-up times. The current data to be transmitted to each station is accessed by the algorithm to determine the total transmission time to each station. A priority queue in the access point is ordered from the shortest to the longest transmission, assigning the highest priority to the shortest power save transmission to minimize the total power consumption of the network.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
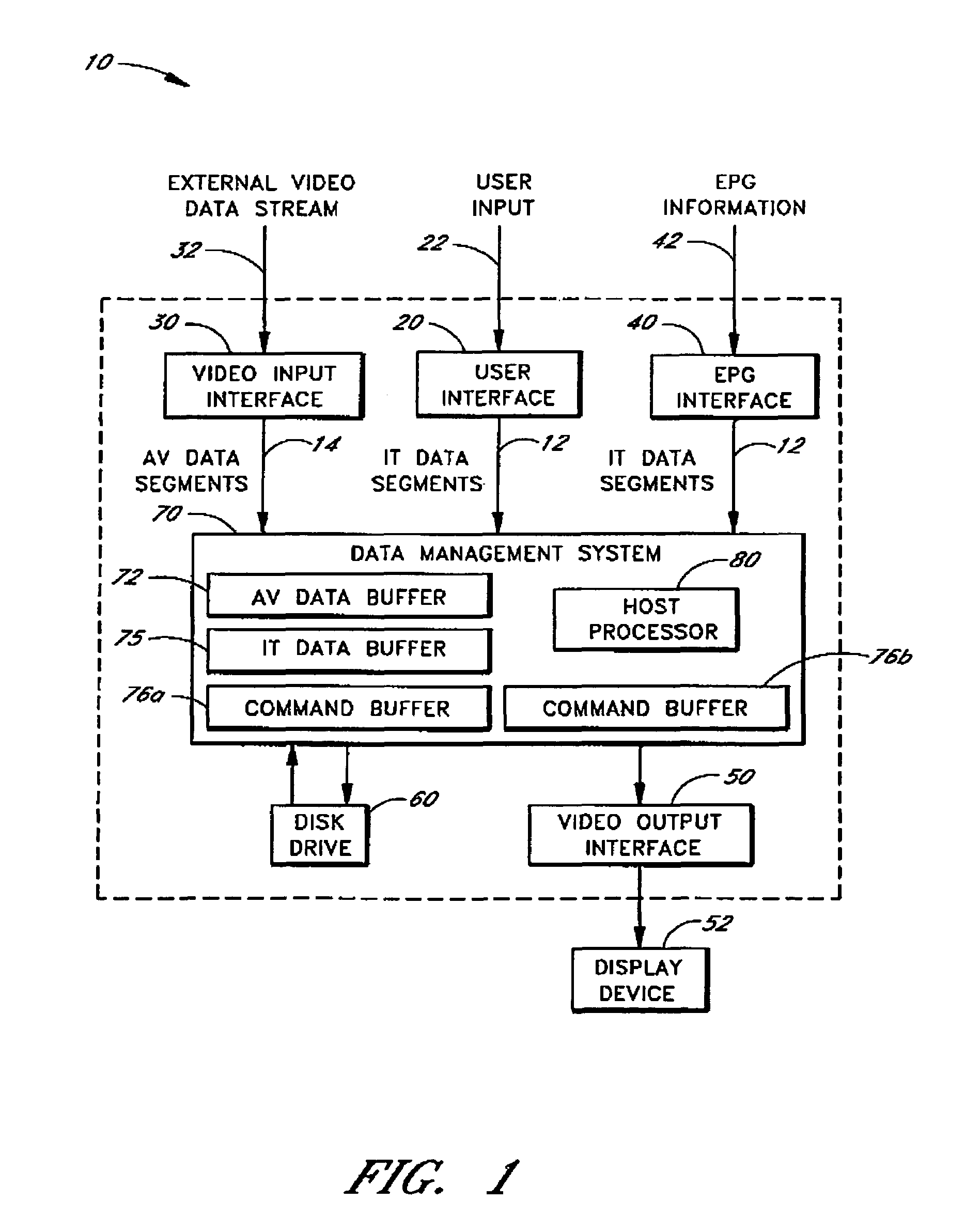
Video recording system utilizing storage redundancy to transfer non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segments while transferring time-critical, error-tolerant streaming data segments at a required data transfer rate
InactiveUS7133600B1Maintaining data transfer bandwidthEasy transferTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsStreaming dataData segment
The present invention may be regarded as a video recording system and method of transferring a non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segment stored on a disk drive, which is responsive to a set of data transfer commands generated by a host processor and which is operating in a mode optimized for transferring time-critical, error-tolerant streaming data segments stored or to be stored on the disk drive. The method includes sending a sequence of data transfer commands generated by the host processor to the disk drive to transfer a respective sequence of time-critical, error-tolerant streaming data segments at a required data transfer rate. The method further includes selectively interposing a first data transfer command into the sequence of data transfer commands, the first data transfer command initiating a first transfer of the non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segment from a first storage location. The method further includes transmitting a data transfer error signal generated by the disk drive to the host processor, the data transfer error signal having a state that indicates whether any data transfer errors have occurred with respect to the first transfer of the non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segment. The method further includes selectively interposing a second data transfer command into the sequence of data transfer commands, the second data transfer command initiating a second transfer of the non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segment from a second storage location, thereby utilizing storage redundancy to achieve an accuracy required for the non-time-critical, error-intolerant data segment while maintaining the required data transfer rate of the sequence of time-critical, error-tolerant data segments.
Owner:KEEN PERSONAL MEDIA +1
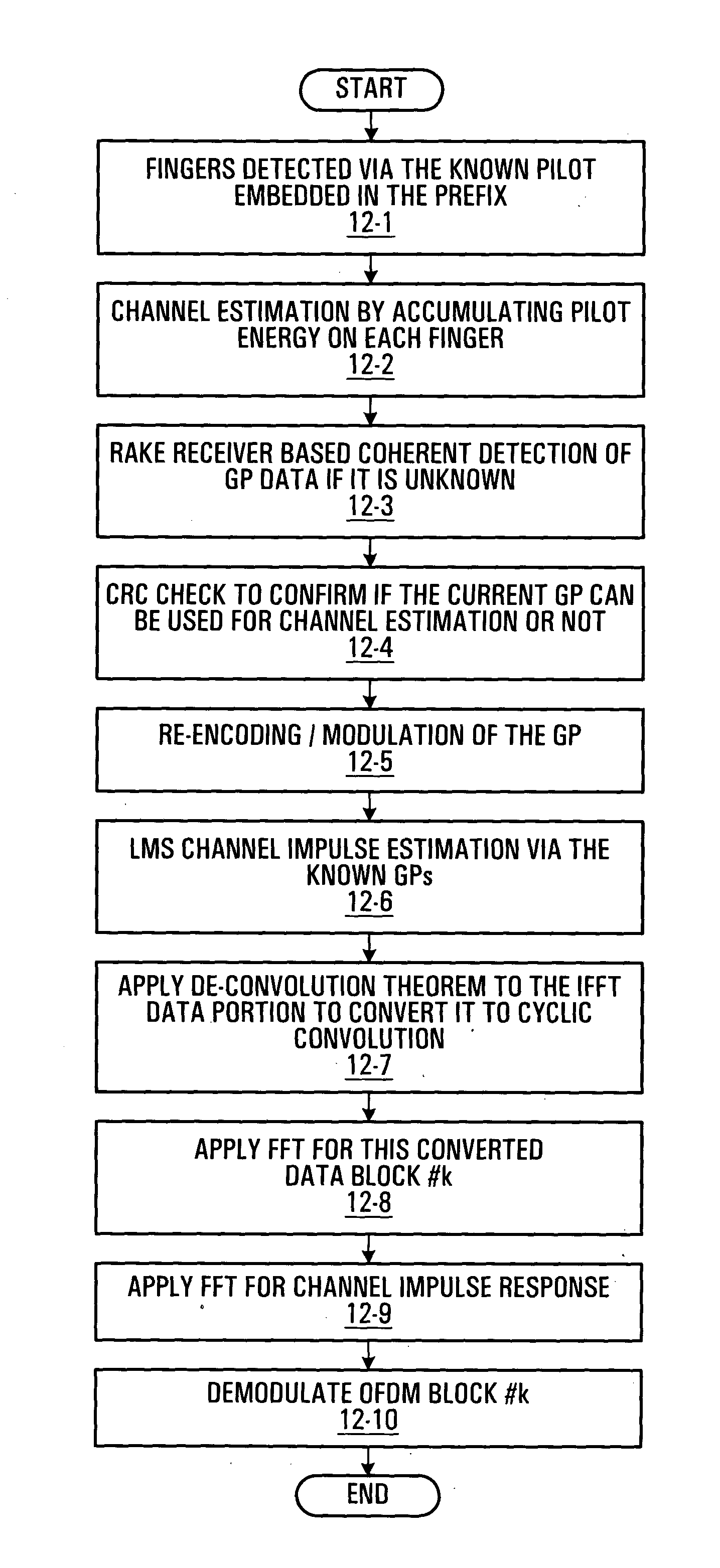
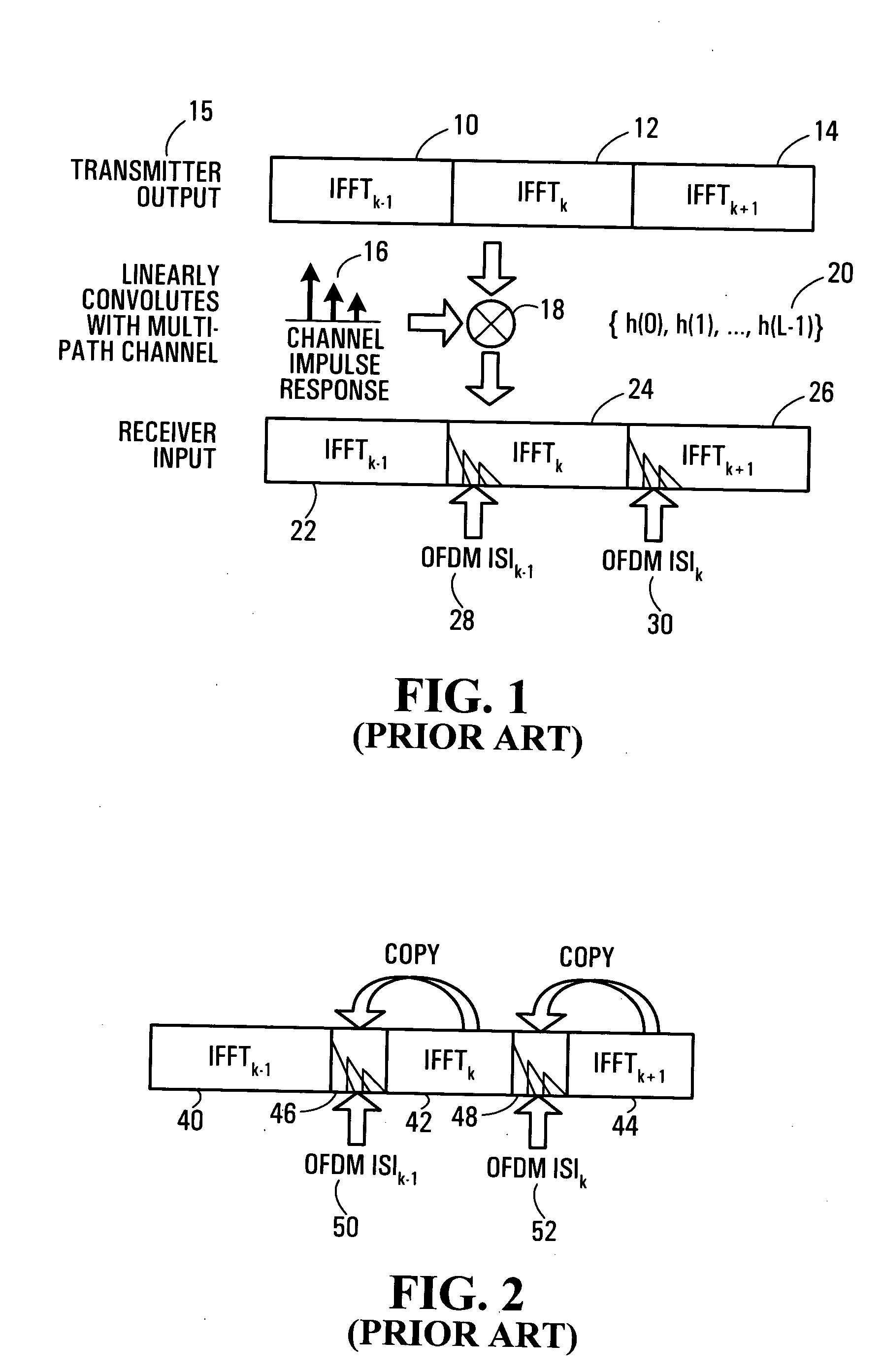
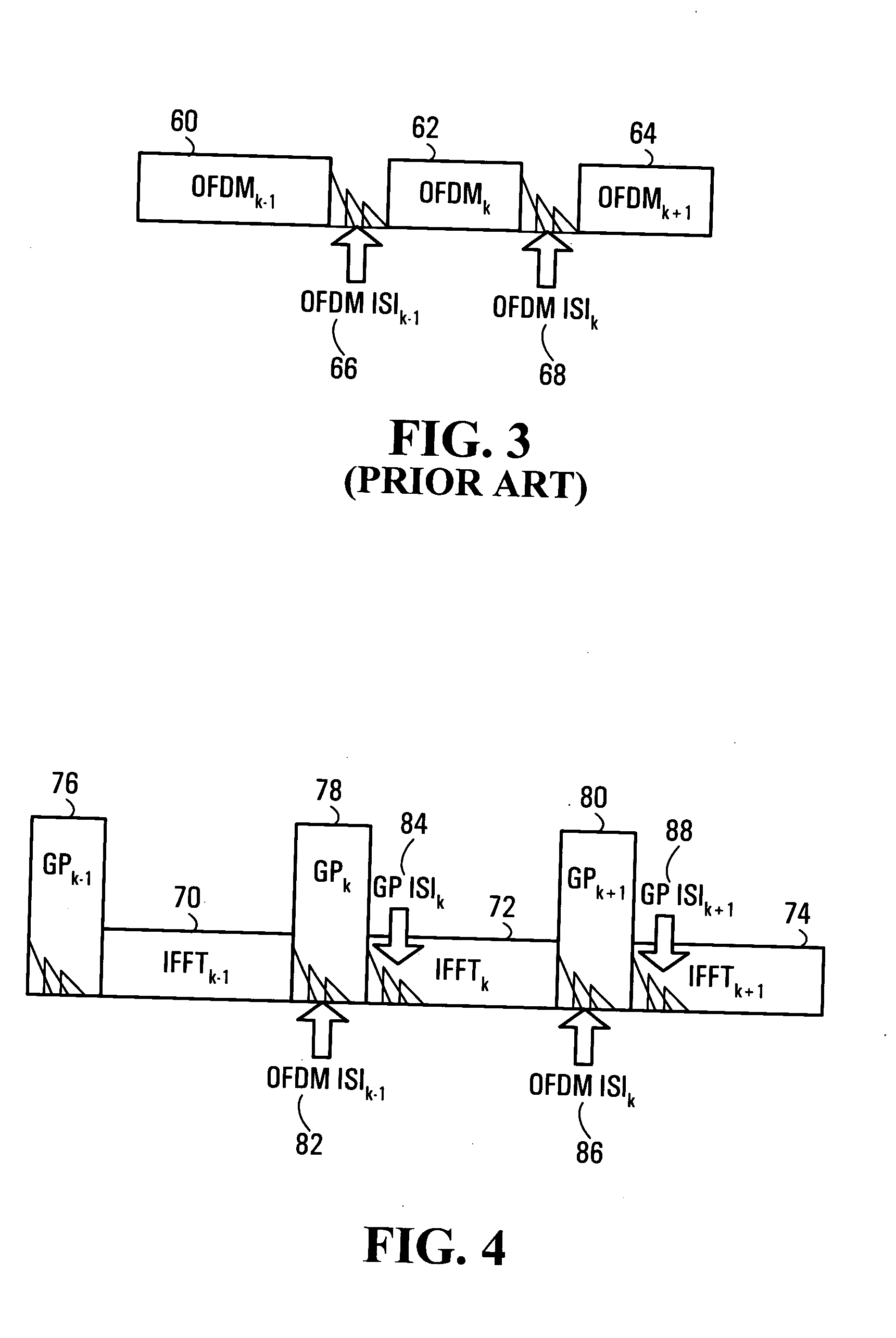
OFDM system and method employing OFDM symbols with known or information-containing prefixes
ActiveUS20050030886A1Multi-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Systems and methods for transmitting and receiving OFDM symbols are provided which enable the otherwise wasted transmission time normally used as a prefix for each OFDM symbol to contain useful information. At the receiver, the received signal is processed to convert received OFDM symbols from a linear convolution with the channel to a cyclic convolution.
Owner:APPLE INC
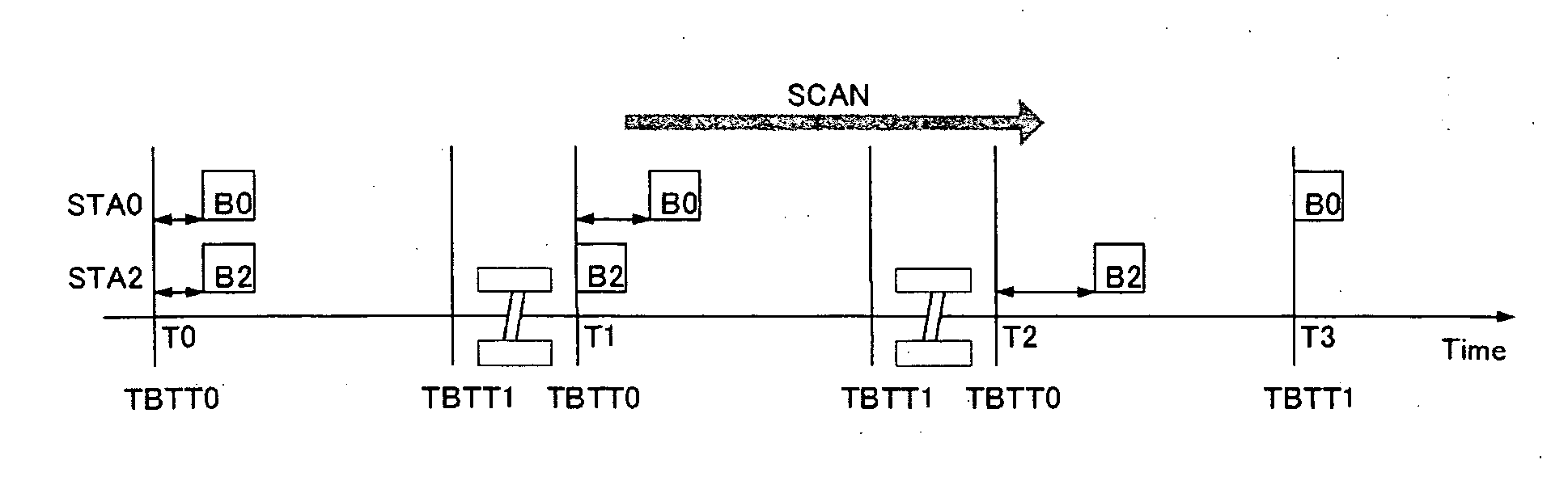
Radio communication system, radio communication apparatus, radio communication method, and computer program
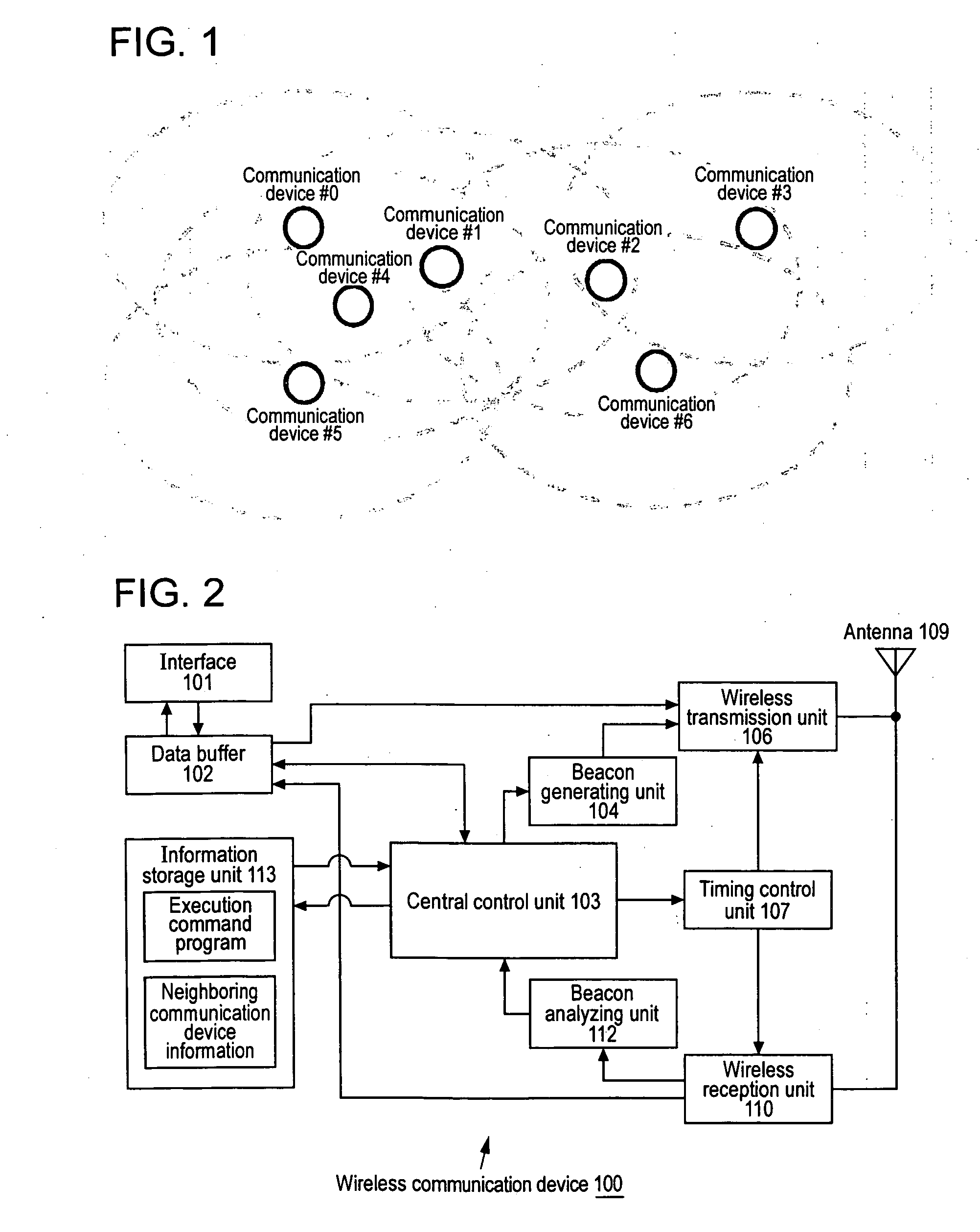
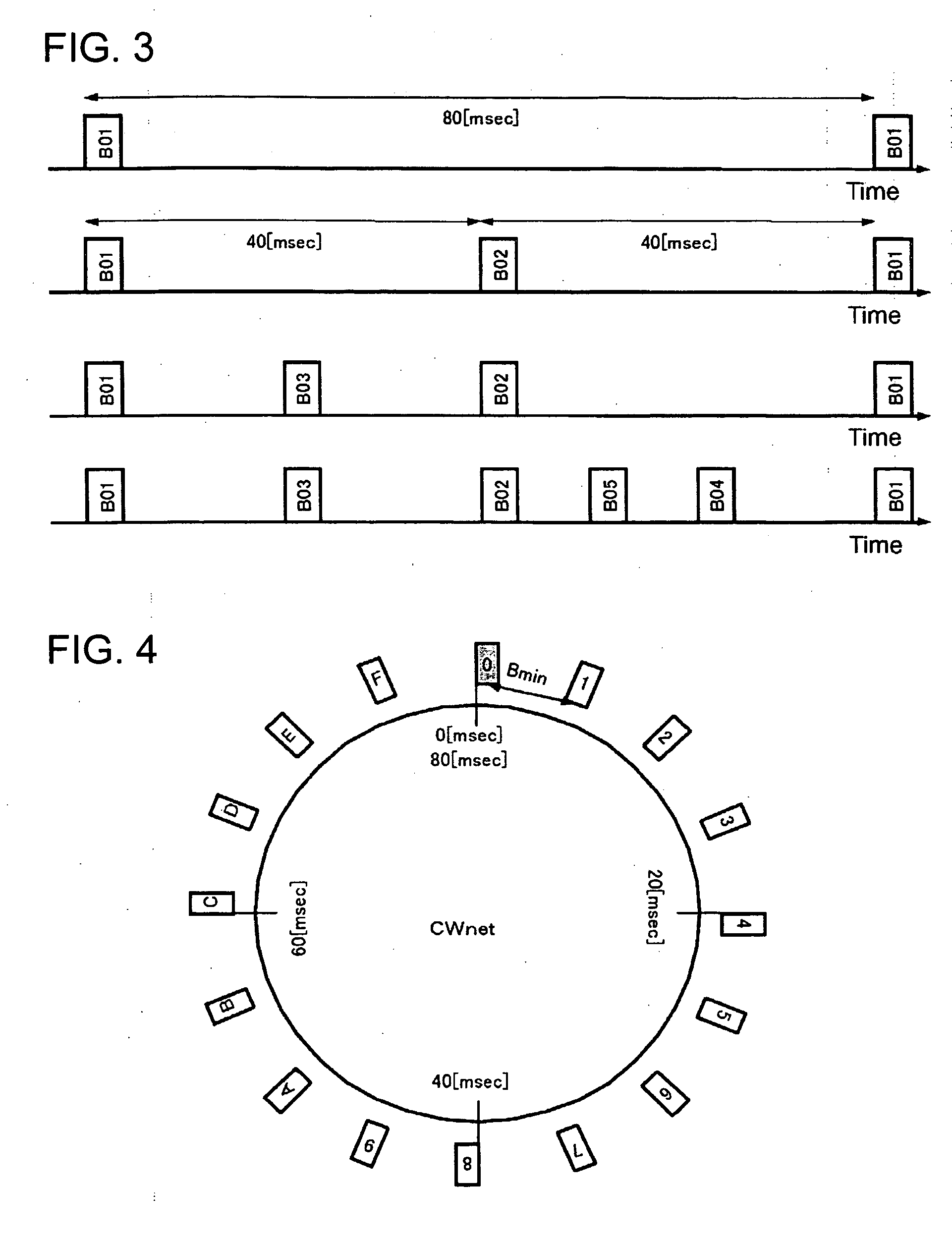
ActiveUS20070165589A1Avoid collisionCollision of beacon can be avoidedSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionRadio waveTransmission time
An autonomously dispersed type wireless network is suitably formed with communication stations avoiding collision of beacons transmitted one to another. In the event that the range of reach of airwaves change and a receivable state is created and beacons collide, a communication station changes the beacon transmission position of itself in response to receiving a beacon from another station at a timing immediately prior to transmission to its own beacon. Also, in the event that beacon collision is exposed due to emergence of a new communication which can perform reception from two systems out of airwave range of each other, the newly-participating station requests one of the communication stations of which the beacons are colliding to change the beacon transmission timing.
Owner:SONY CORP
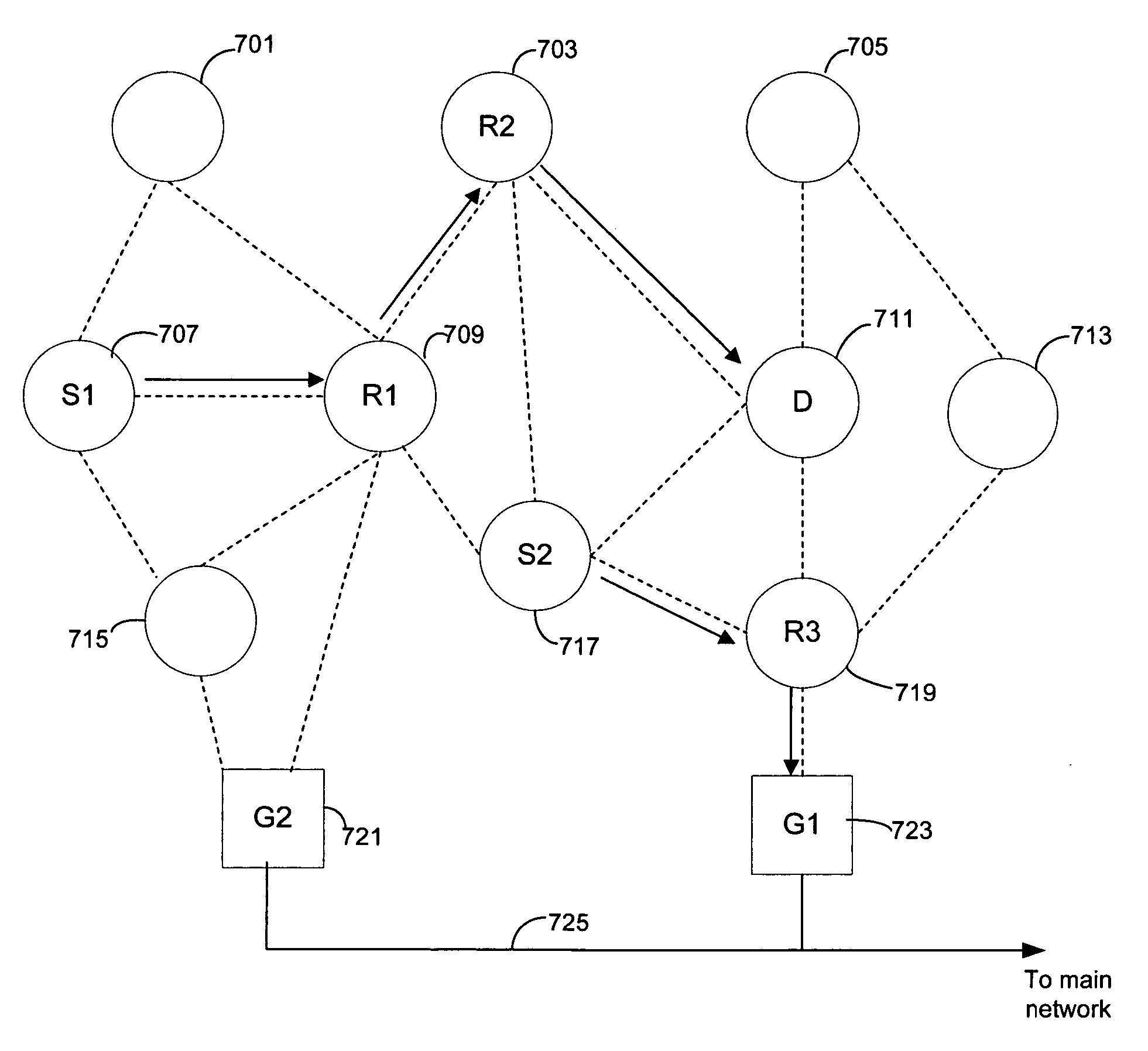
System and method for link quality routing using a weighted cumulative expected transmission time metric
A system and method for link quality routing uses a weighted cumulative expected transmission time path metric. A system for routing in a multi-hop ad hoc network, and a method for measuring the link quality of a route in the network, include assignment of a weight to a link in accordance with an expected transmission time of a packet over the link, and a combining of individual link weights for a route into a path metric. The path metric accounts for interference among links that use a shared channel. In the calculation of the path metric, the expected transmission times of links that interfere with one another are added, while the expected transmission times for non-interfering links are considered separately.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for radio communication in a wireless local area network and transceiving device
InactiveUS8423084B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsNetwork packetDirectional antenna
Method for radio communication in a wireless local area network and transceiving device refers to wireless local area networks (WLAN) consisting of a multitude of transceiving devices of users (14, 15, 16 . . . N). Simultaneous scanning by their antenna beams in different directions by the transceiving devices (with the transceiving devices being in reception mode) and transmission of an omnidirectional signal in the form of calibration signal and data package by one of the transceiving devices of the network (with the transceiving device being in transmission mode), reception of the signal by the transceiving devices operating in reception mode and subsequent orientation of their antenna beams in the direction of signal source. The recognition and orientation is performed during the period of reception of the calibration signal. The Method increases the range of a WLAN, reduces the transmission time and improves quality and reliability of communication. Each transceiving device (1) includes at least one directional antenna (3) featuring a controllable directional pattern, switched-over by unit (4), reception / transmission mode switch (5), receiver (8), transmitter (10) and controller (11). Additionally a unit for signal detection (13) is incorporated in the device.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Radio over fiber system and method for controlling transmission time
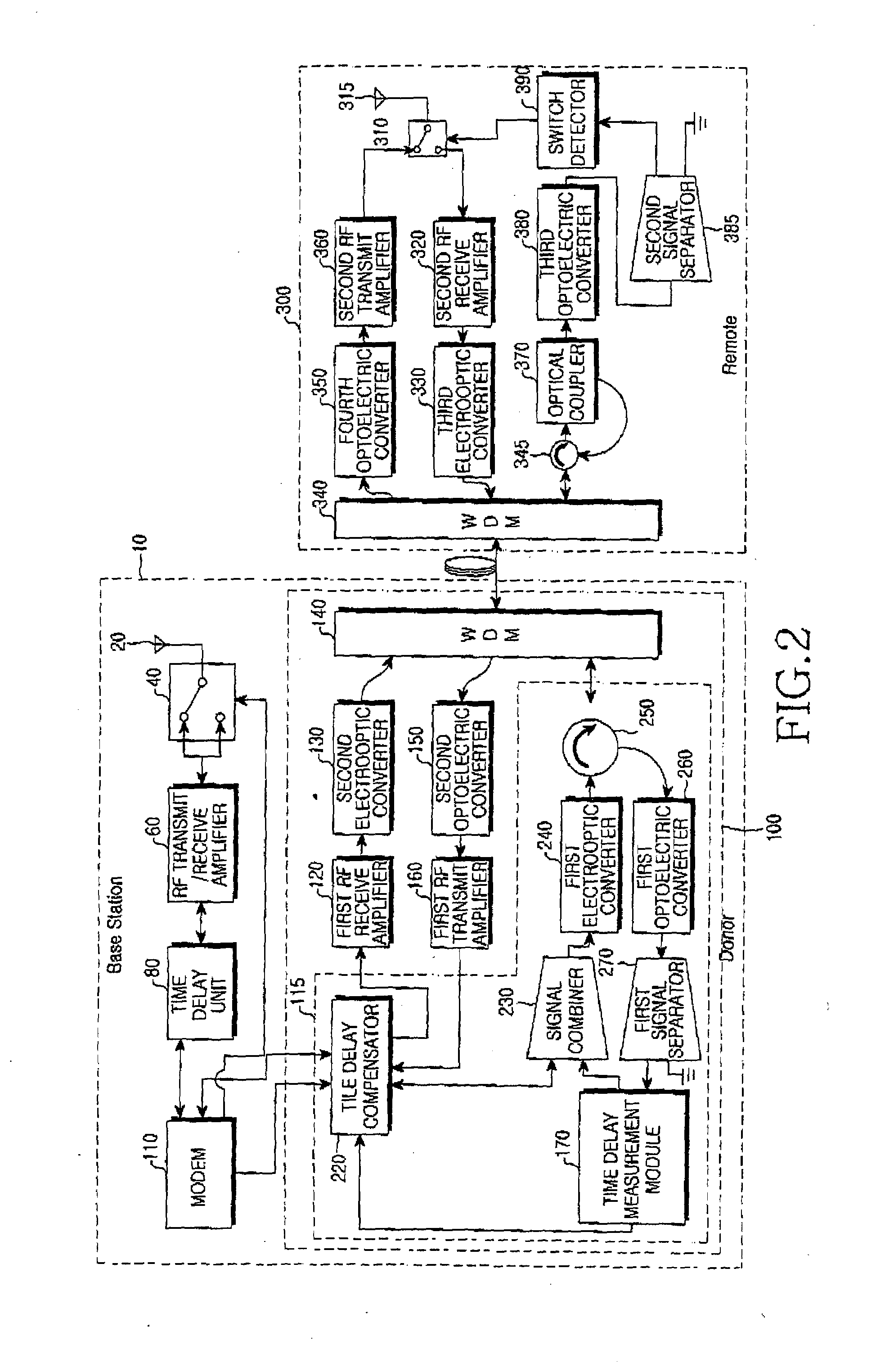
InactiveUS20080056167A1Improve performanceRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic repeatersRadio over fiberCommunications system
A radio-over-fiber (RoF) system and method for controlling a transmission time is provided. In a Time Division Duplex (TDD) wireless communication system comprising a Base Station (BS) having a donor and a remote connected thereto via am optical fiber, upstream and downstream Radio Frequency (RF) signals are transmitted and received, and by reliably transmitting a switch control signal to the remote and simultaneously compensating for a transmission time delay occurring in the optical cable, time synchronization of the upstream and downstream RF signals transmitted and received via antennas of the BS and the remote is controlled, thereby efficiently increasing the performance of a TDD wireless service system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
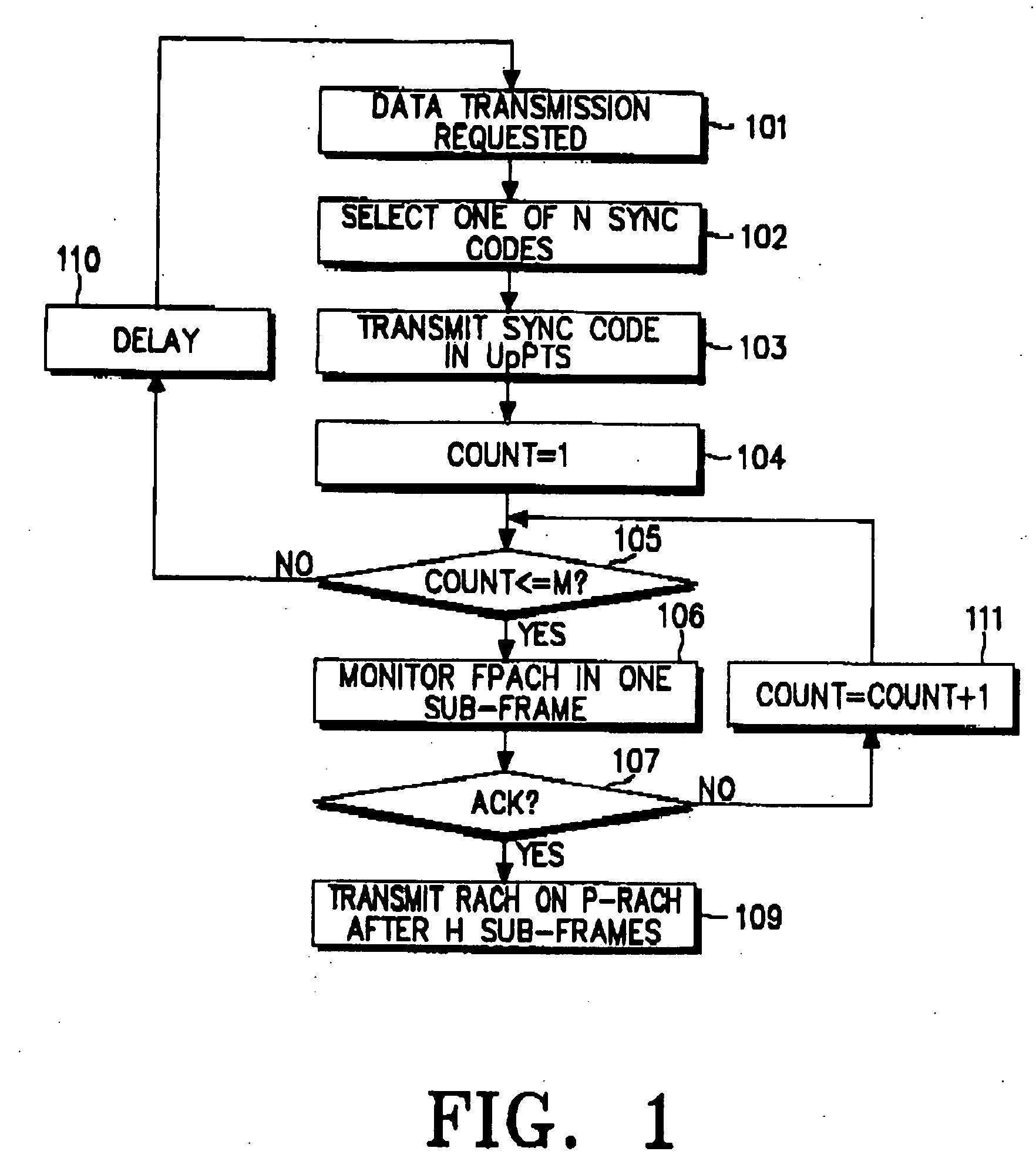
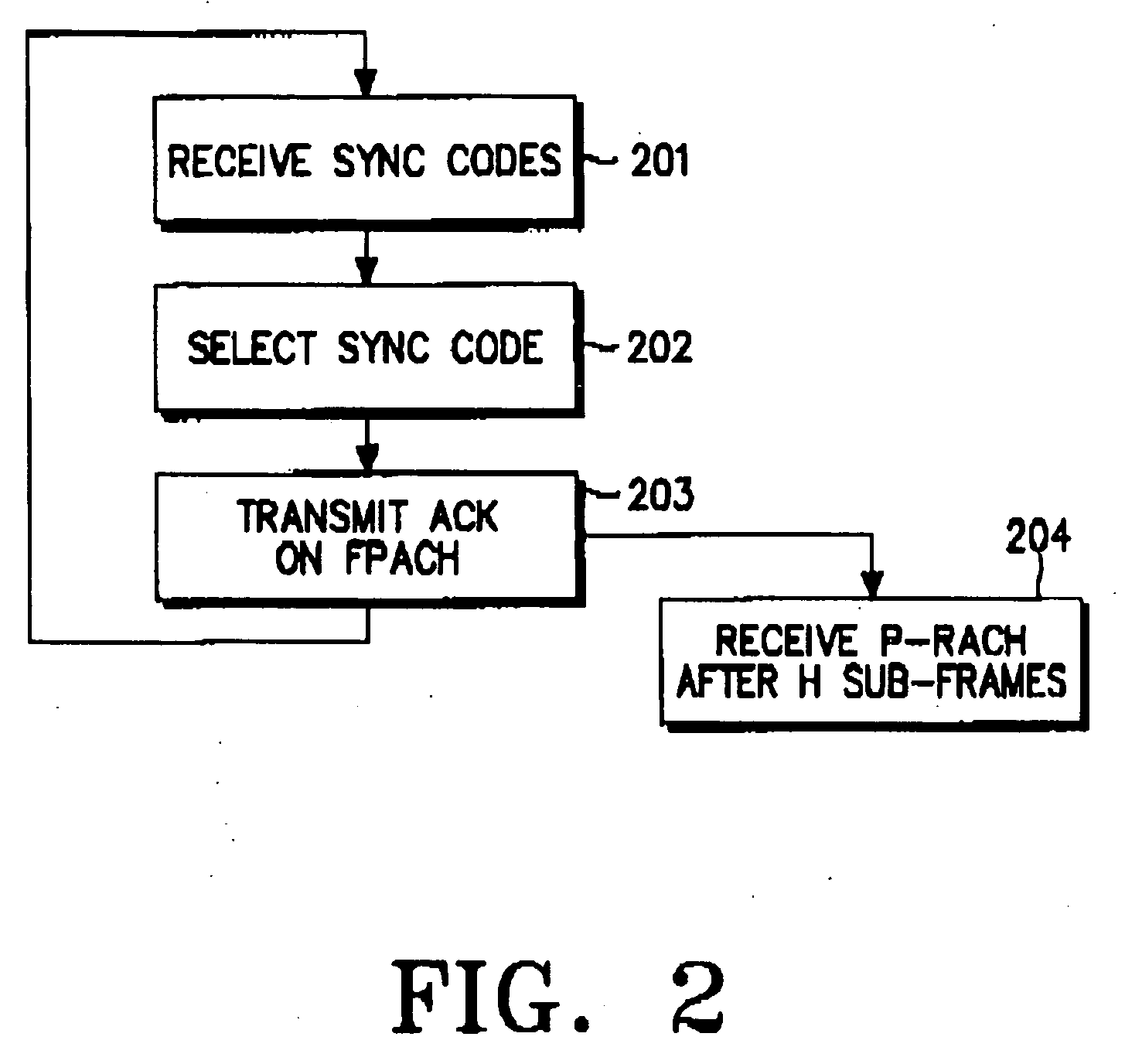
Method of assigning an uplink random access channel in a CDMA mobile communication system
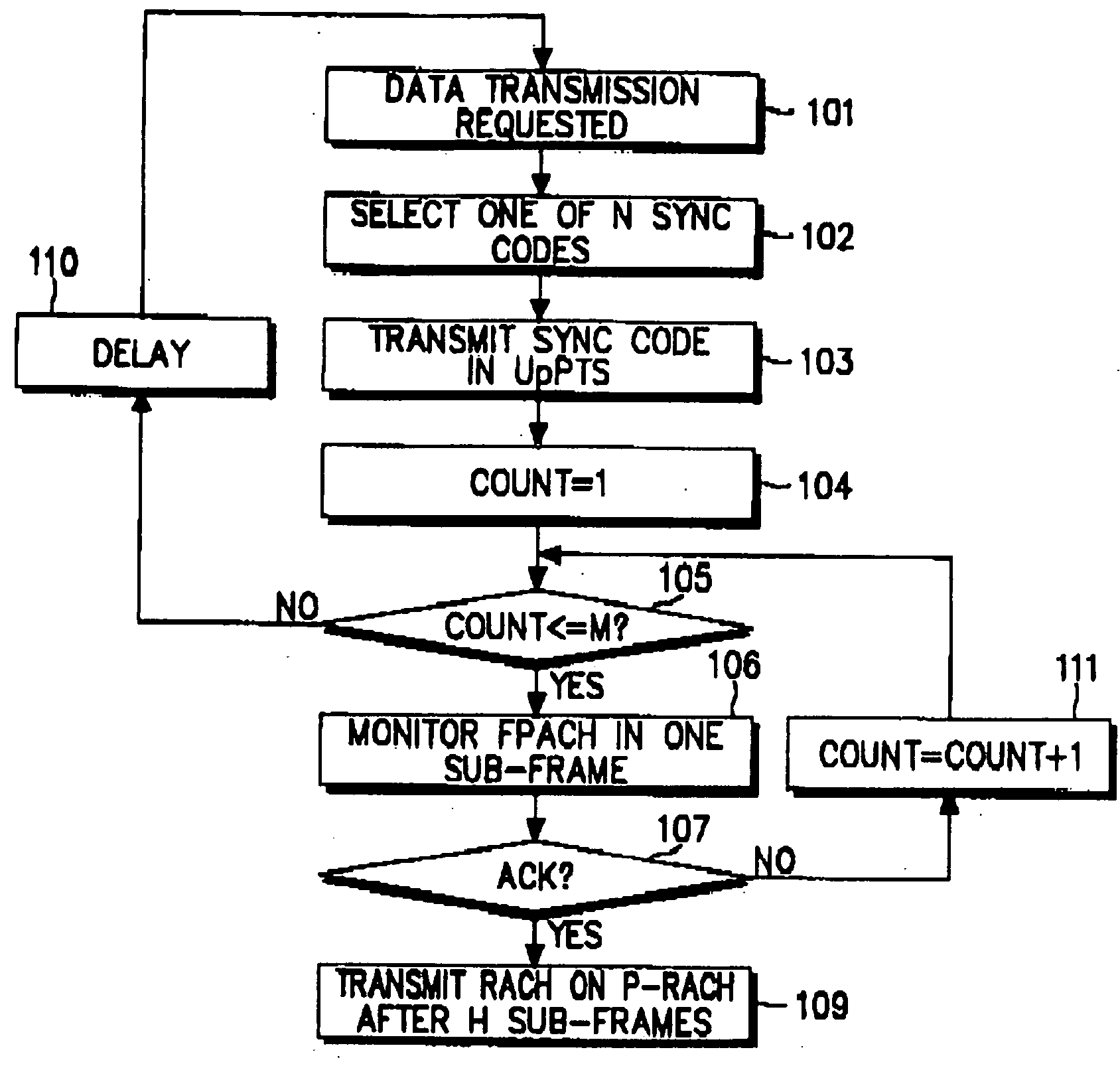
ActiveUS20070274278A1Easy to useMinimize timePower managementSynchronisation arrangementData transmission timeRandom-access channel
Disclosed is an uplink random access procedure in an NB-TDD (Narrow Band Time Division Duplexing) system. To achieve an acknowledgement for data transmission from a UTRAN (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network), a UE selects one of a plurality of sync codes by which the UTRAN identifies UEs that request data transmission and transmits the selected sync code in a time slot of a sub-frame to the UTRAN. Then, the UE receives the sync code information, information about the arrival time of the sync code, time update information indicating a variation in the transmission time of data, and power information indicating an adjustment to a power gain in the UE from the UTRAN on an FPACH (Fast Physical Access Channel). The UE transmits the data on a P-RACH (Physical Random Access Channel) mapped from the FPACH according to the time update information and the power information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimizing batch size for prefetching data over wide area networks
ActiveUS20100174823A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWide area networkTransmission time
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Digital telecommunication system with selected combination of coding schemes and designated resources for packet transmission based on estimated transmission time
InactiveUS6363425B1Quantity minimizationAir interface efficientlyError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionForward error correctionMajorization minimization
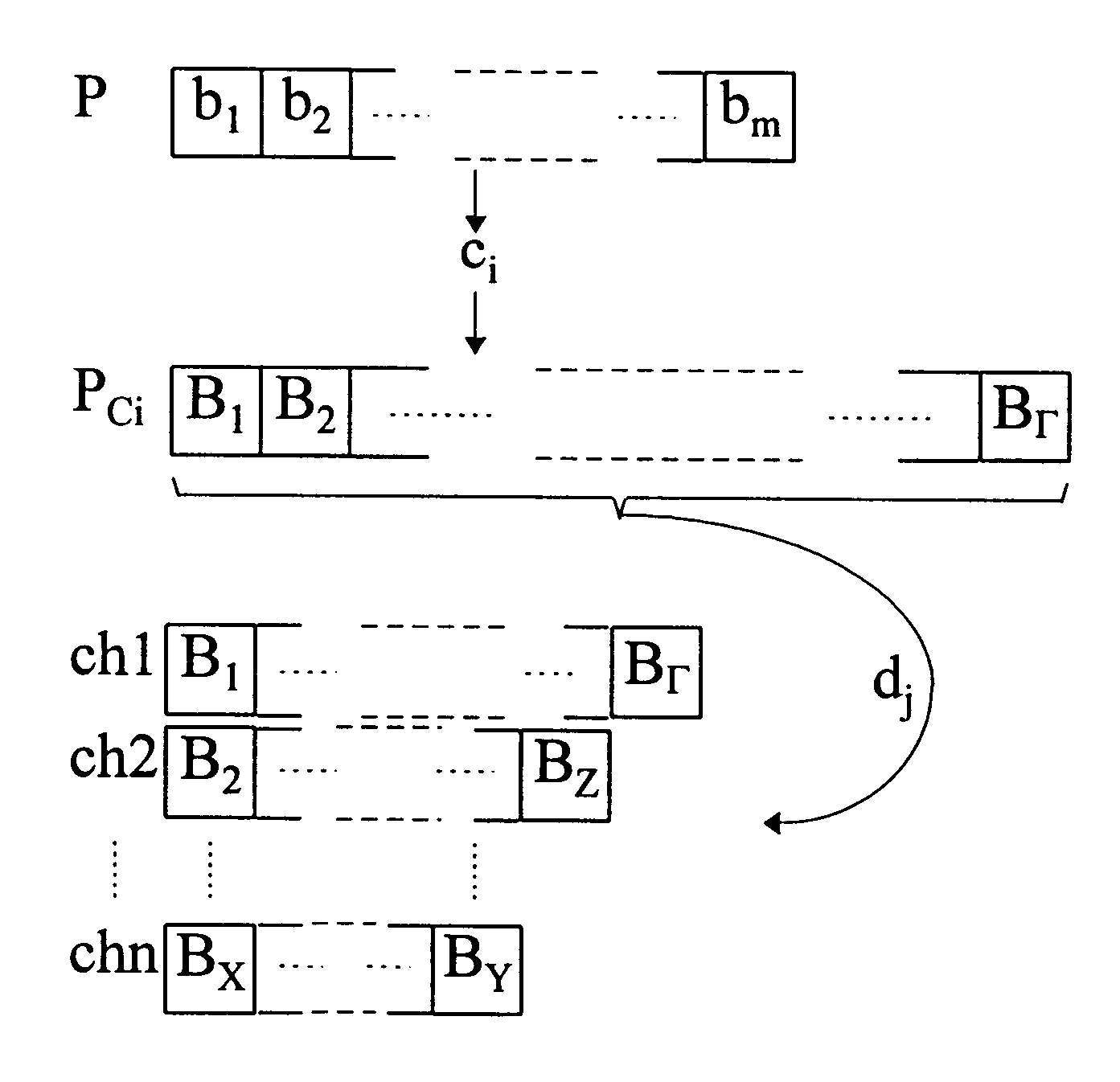
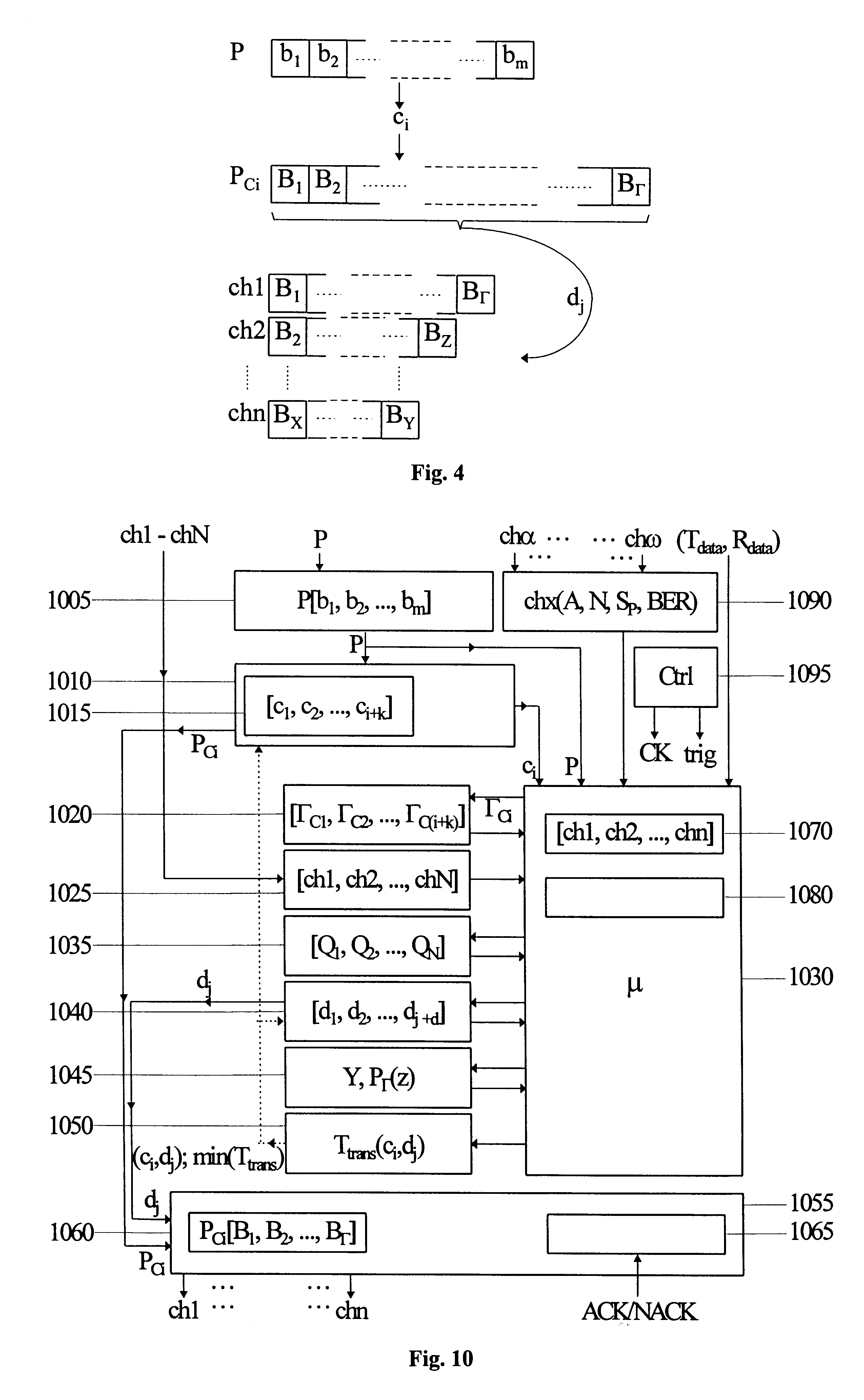
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for communicating packet information in a digital telecommunications system. Through the invention is selected a set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn) from an available amount of resources. Every packet (P) is forward error correction encoded into an encoded packet (Pci), via one of at least two different coding schemes (ci), prior to being transmitted to a receiving party, over the designated communication resources (ch1-chn). An estimated transmission time is calculated for all combinations of coding scheme (ci) and relevant distribution (dj) of the encoded data blocks (B1-BΓ), in the encoded packet (Pci) over the set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn), and the combination (ci,dj) is selected, which minimises the estimated transmission time.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for adding advertising information in flow media
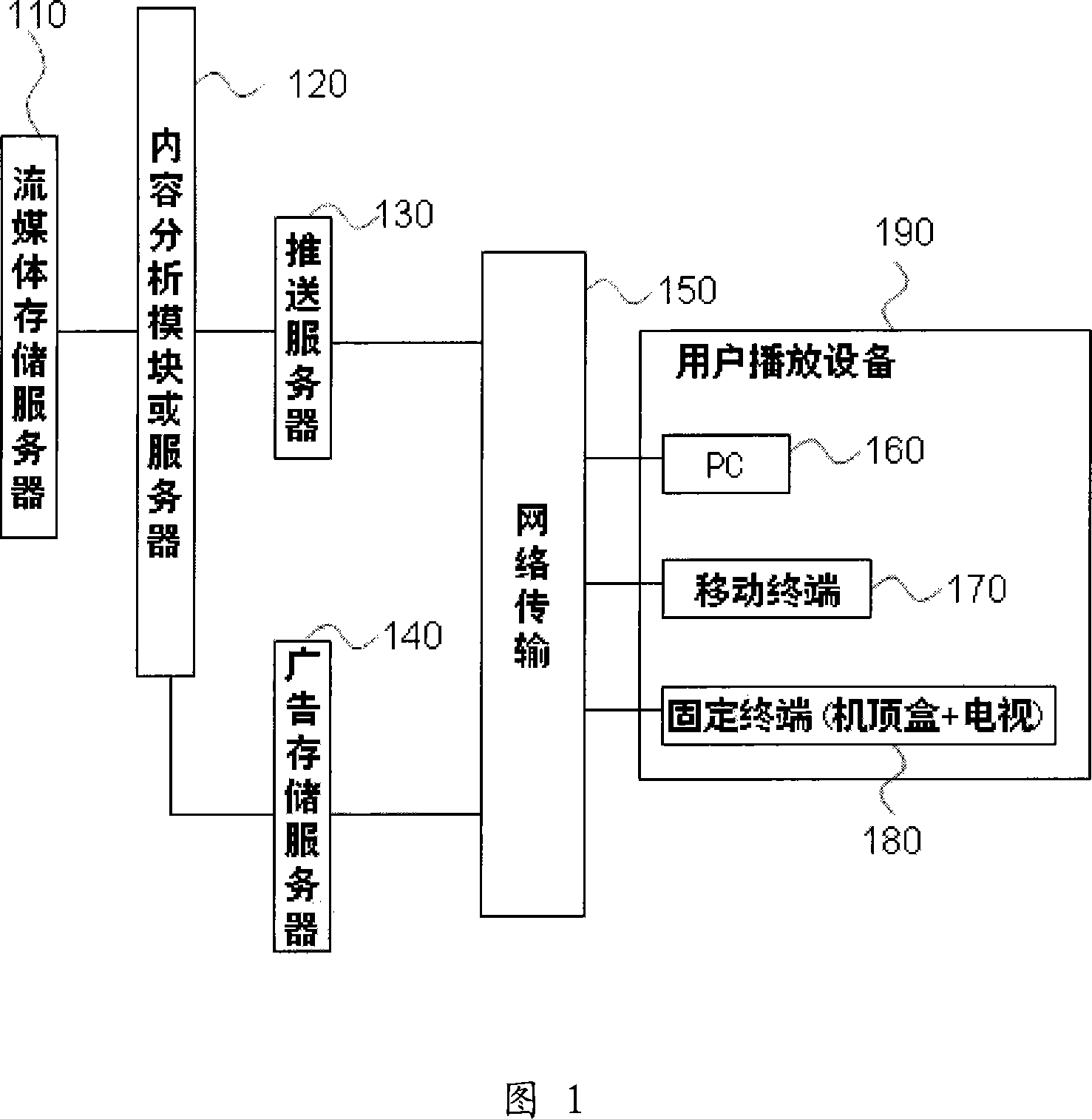
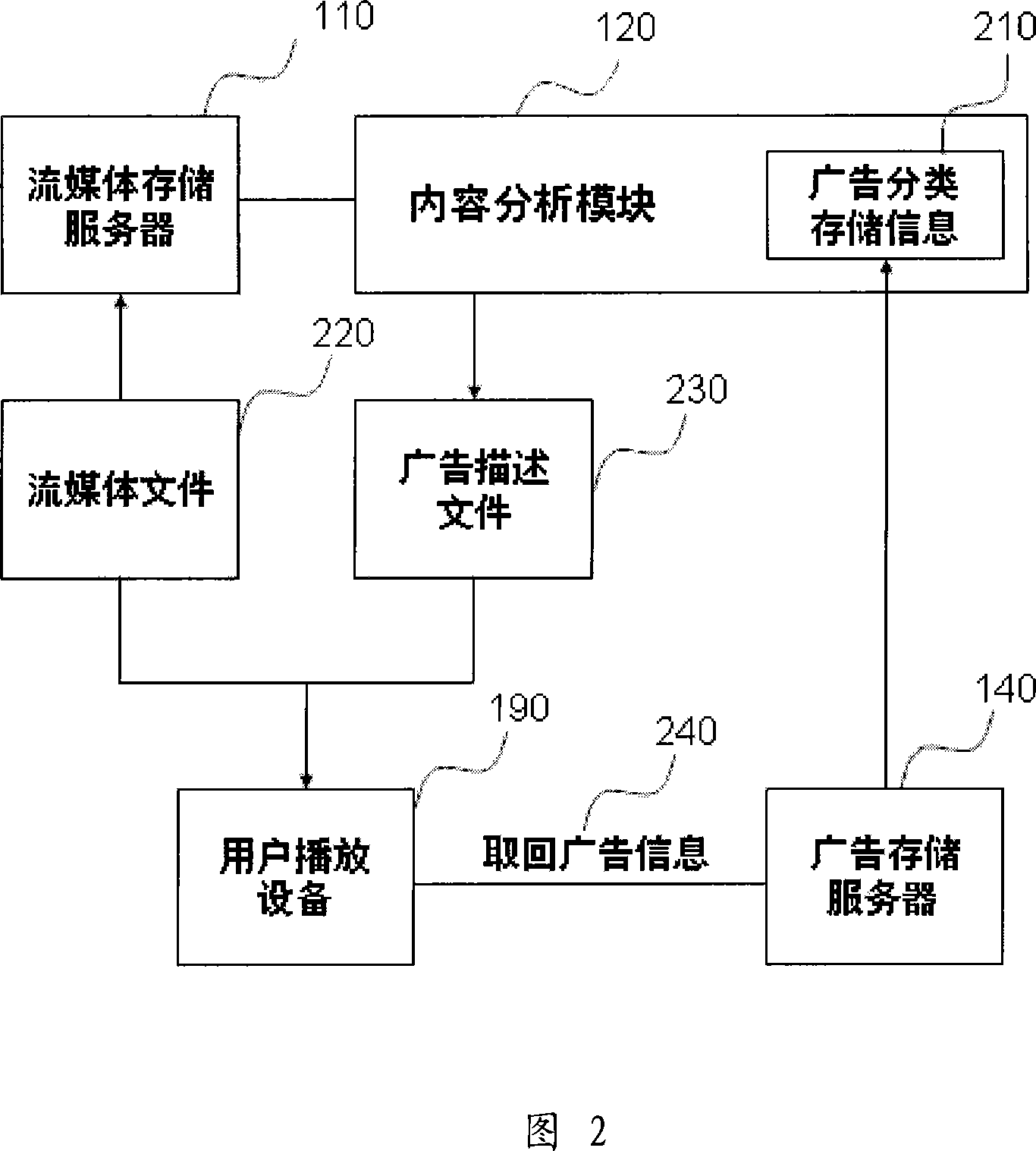
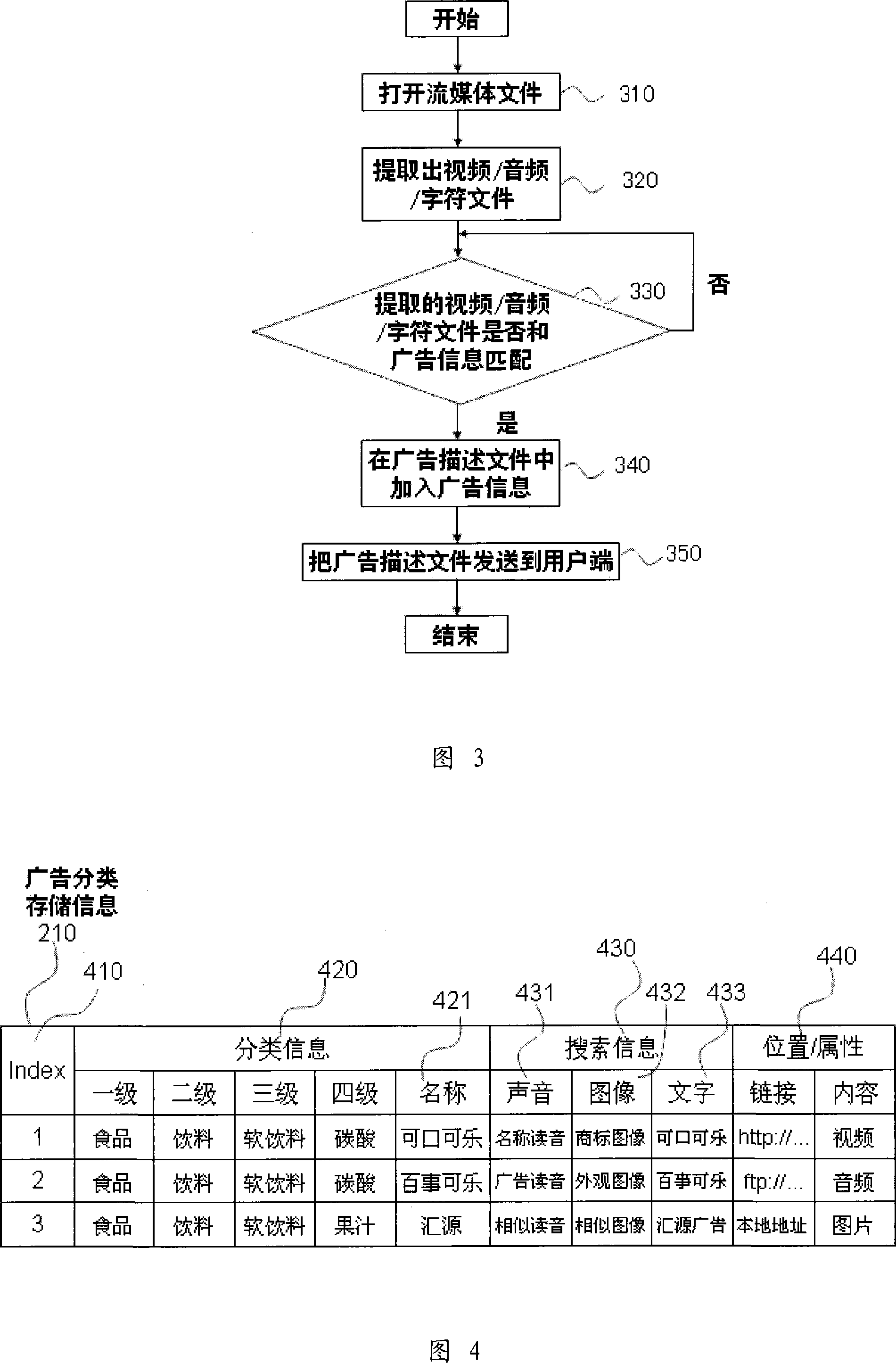
ActiveCN101072340AAccurate advertisingImprove the delivery effectPulse modulation television signal transmissionSelective content distributionWorld Wide WebTransmission time
The relativity between advertisement (ad) information and content of stream media or transmission objects or transmission time / place often exists so as to make users receive contents of ad or auxiliary information easily. The invention needs to process stream files based on content, and adds more ad information. Then, through network, the processed media files are sent to users. When adding ad information, the method expands current ad search information first to form sorted stored information of ad. Then, the method recognizes contents of video, audio, and caption in stream media files. If the searched contents of ad are accorded with recognized results, then ad information of stream media is added to form ad description file. Finally, ad description file and stream media files together are sent to user end. Parsing the ad description file, user retrieves and plays the ad information from ad storage server.
Owner:孟智平
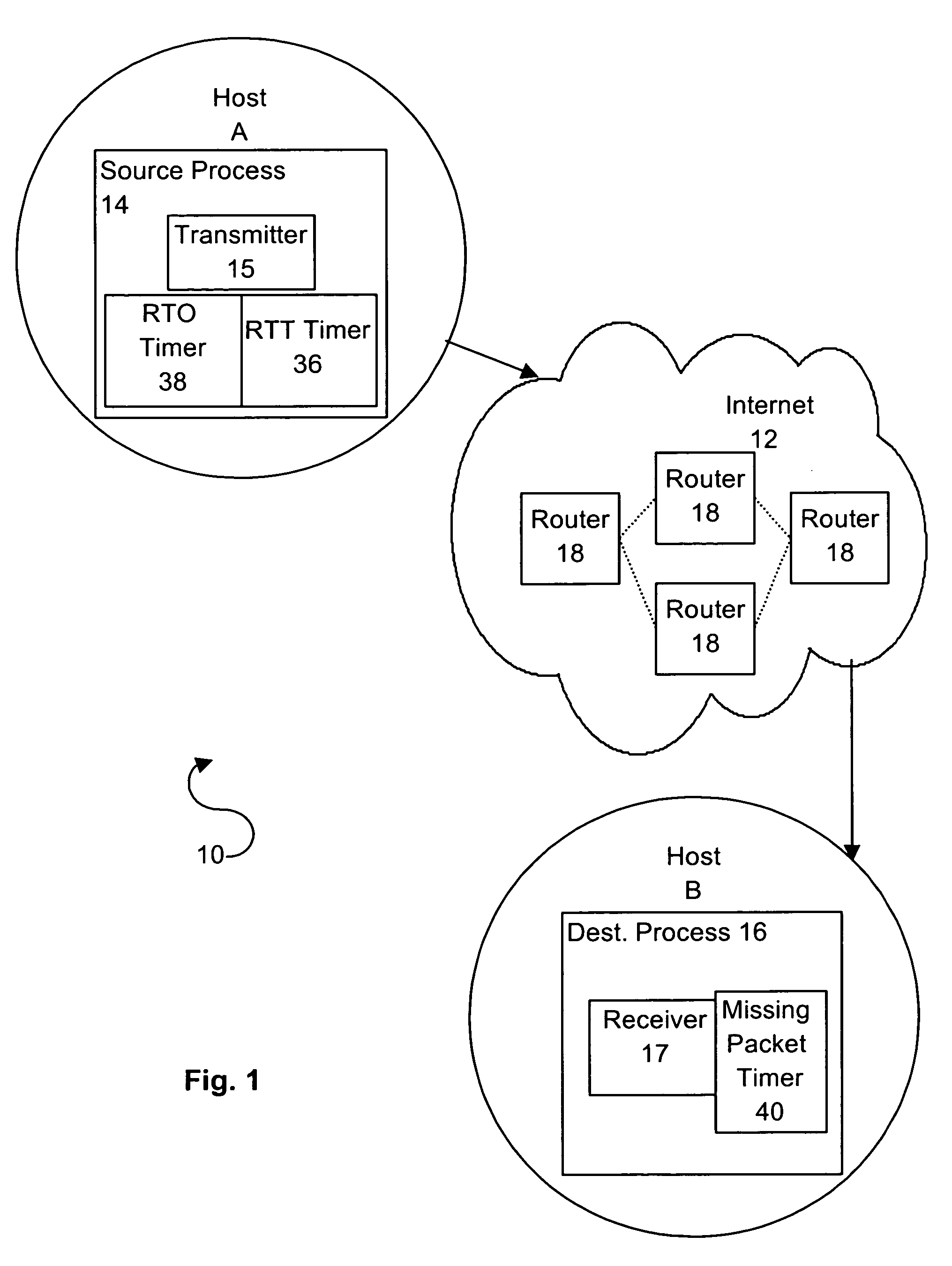
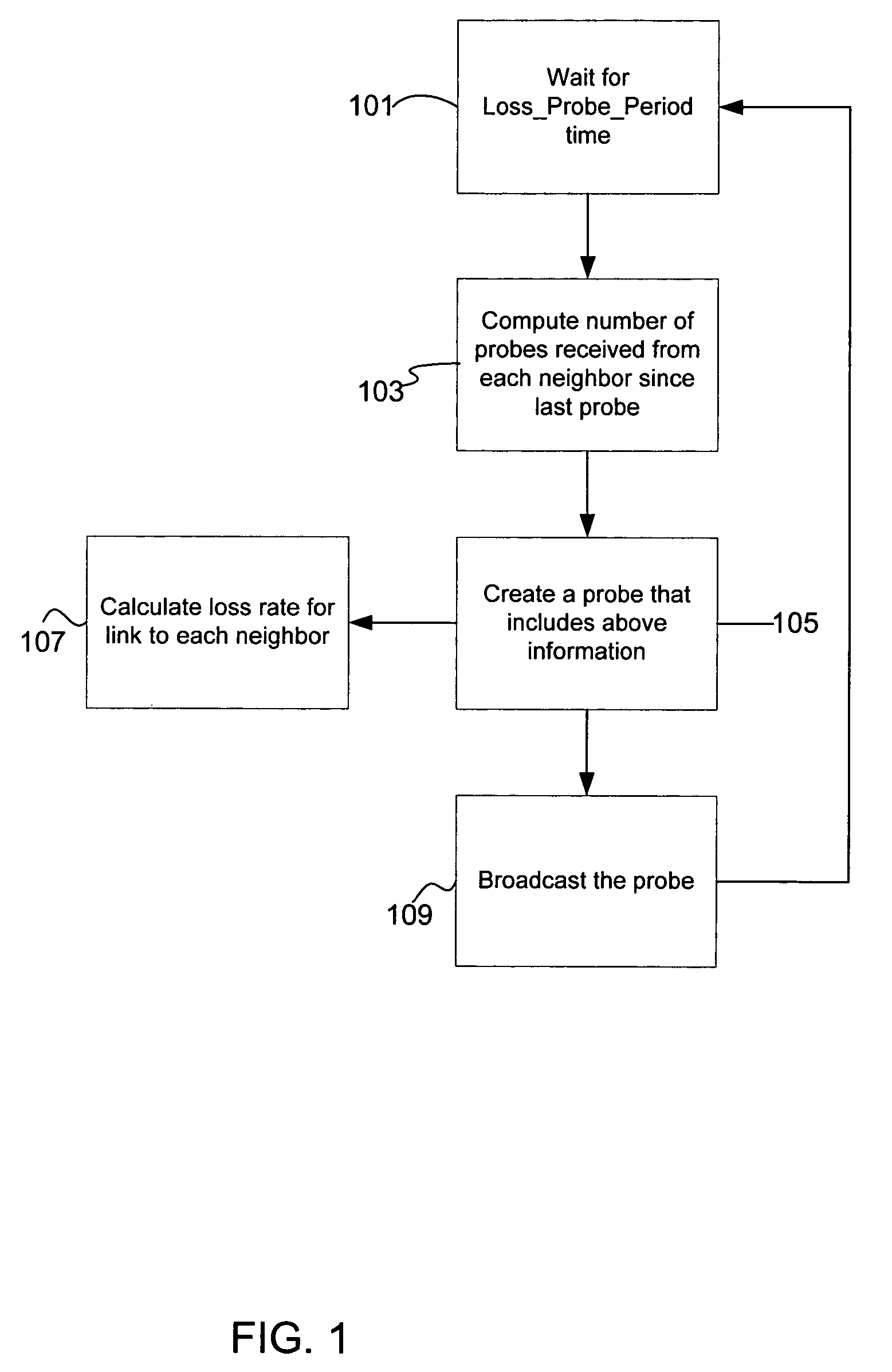
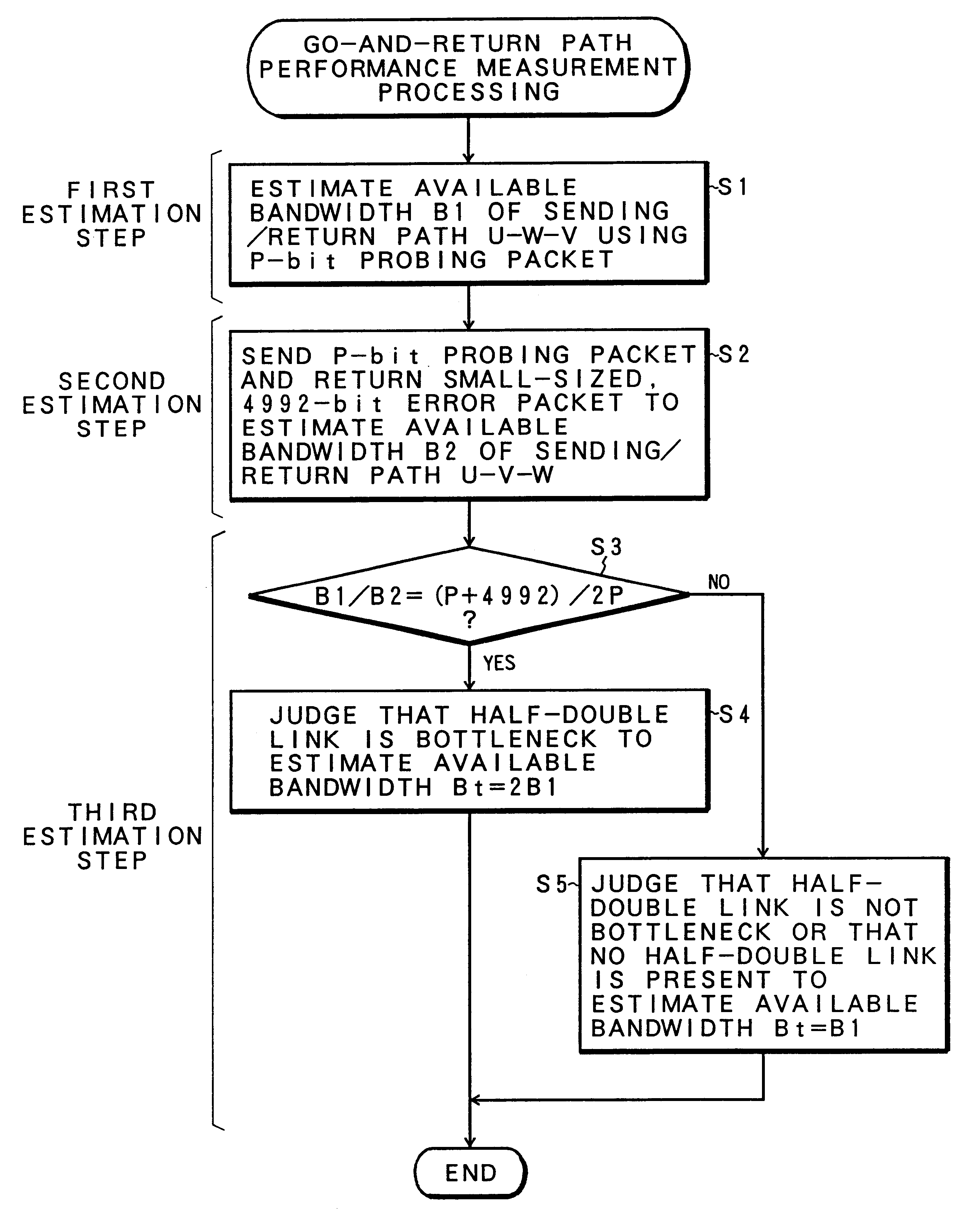
Method of and apparatus for measuring network communication performances, as well as computer readable record medium having network communication performance measuring program stored therein
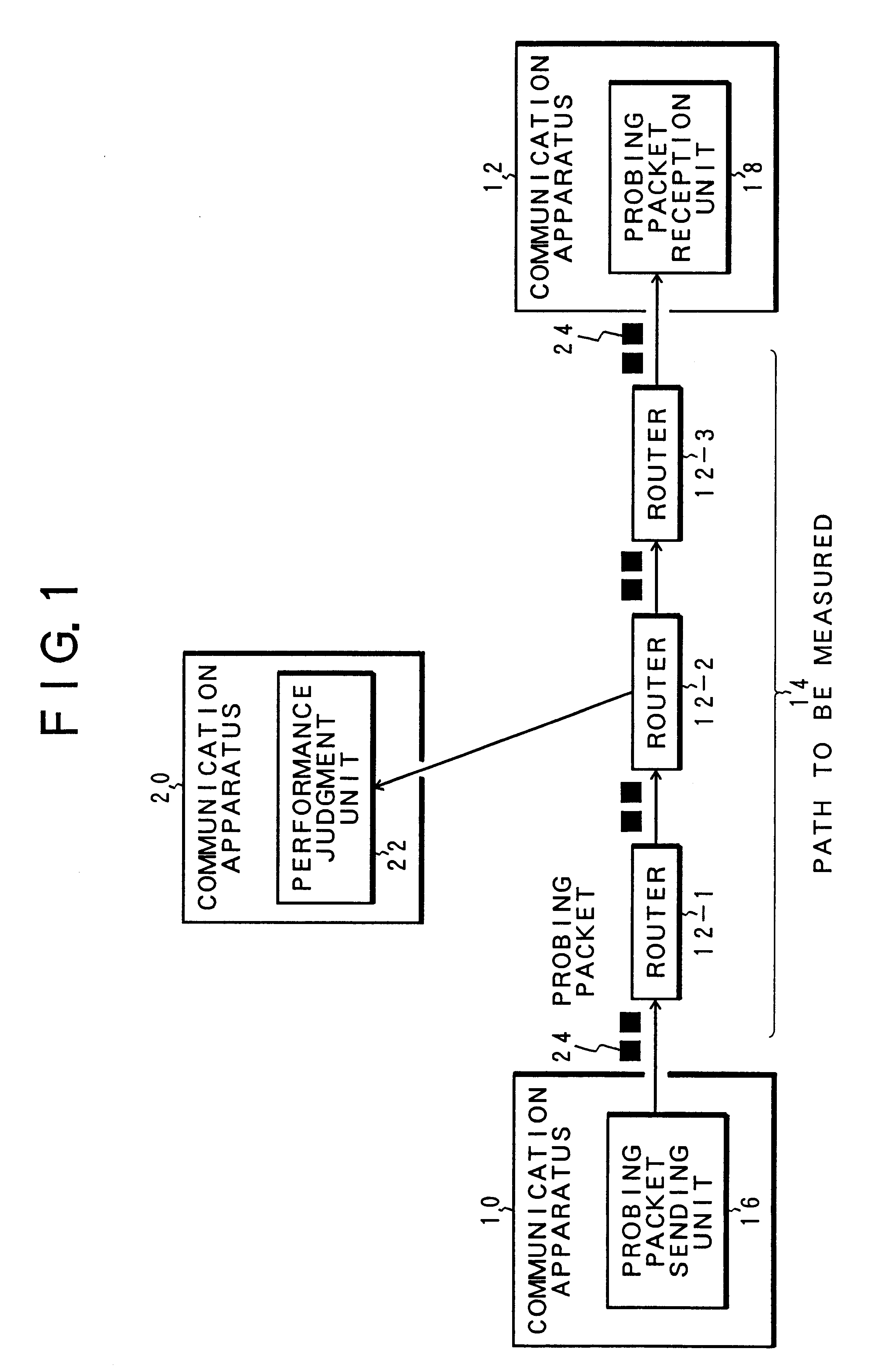
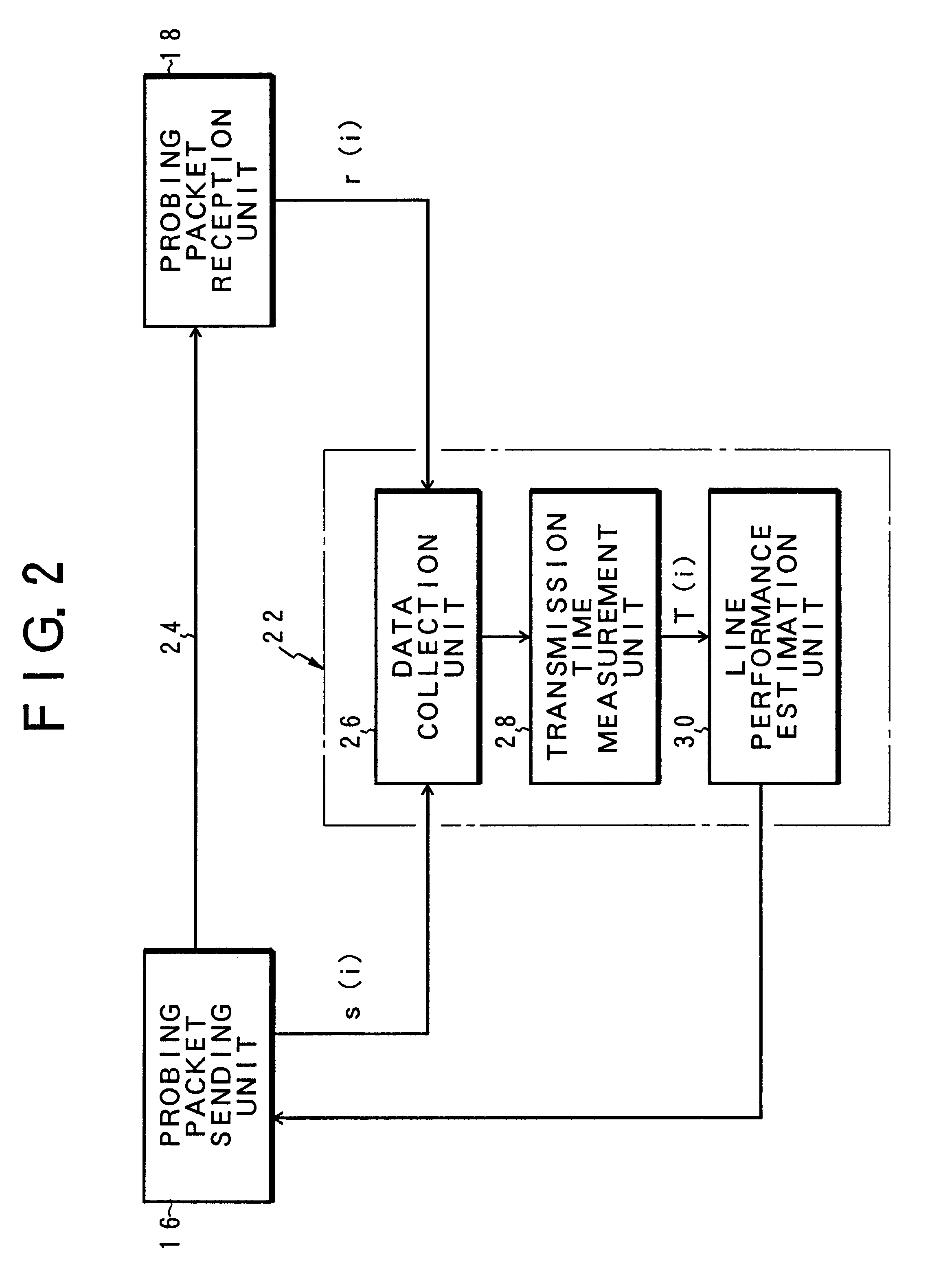
InactiveUS6614763B1Rapid available width measurementAccurate estimateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork communicationPacket transmission
Measurement packets are sent at equi-intervals from a sending unit into a network path. The probing packets are received by a reception unit, which measures the packet transmission time to estimate an available bandwidth of a network path from a parameter Q indicative of a correlation in the packet transmission time between adjacent packets.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com