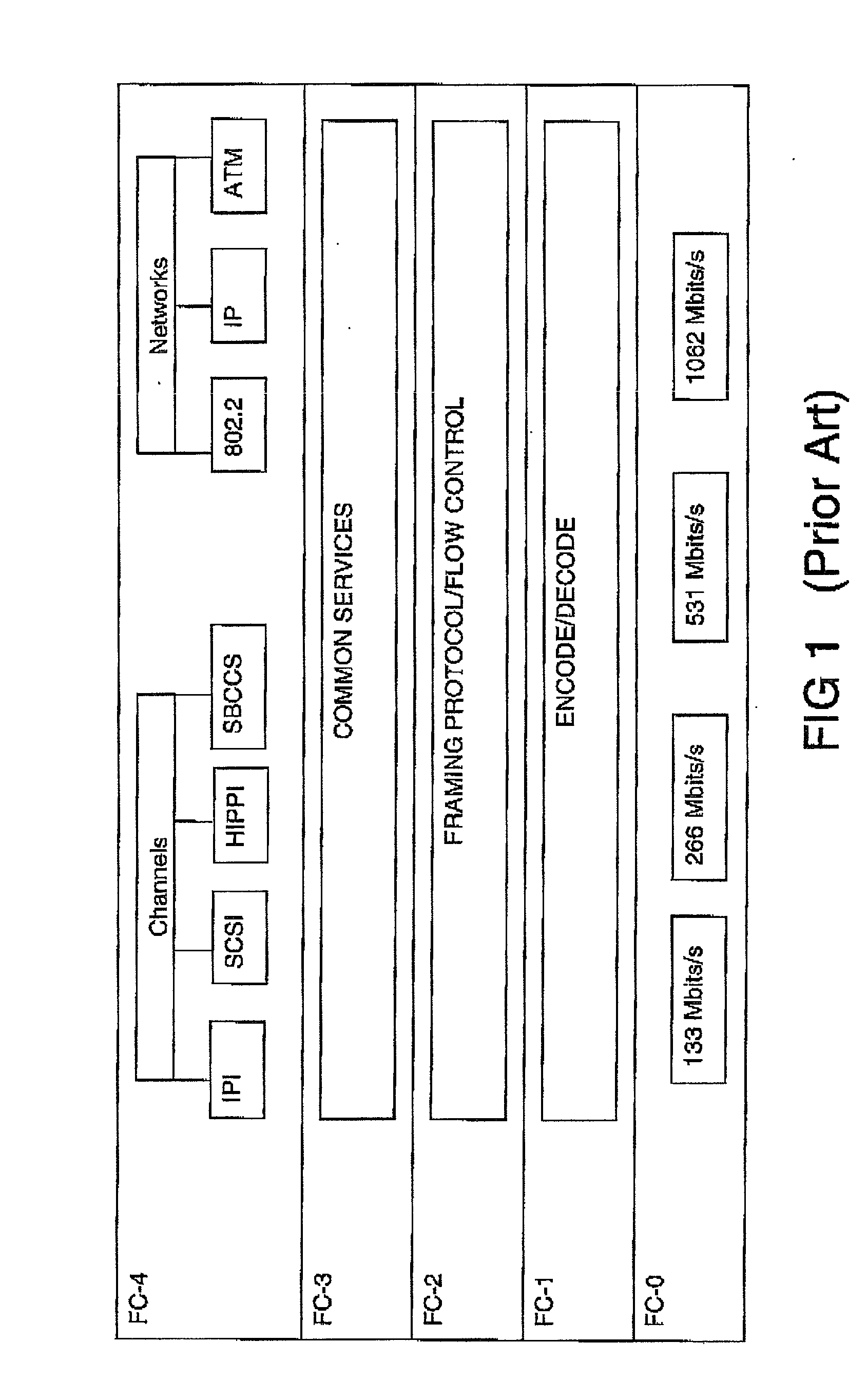
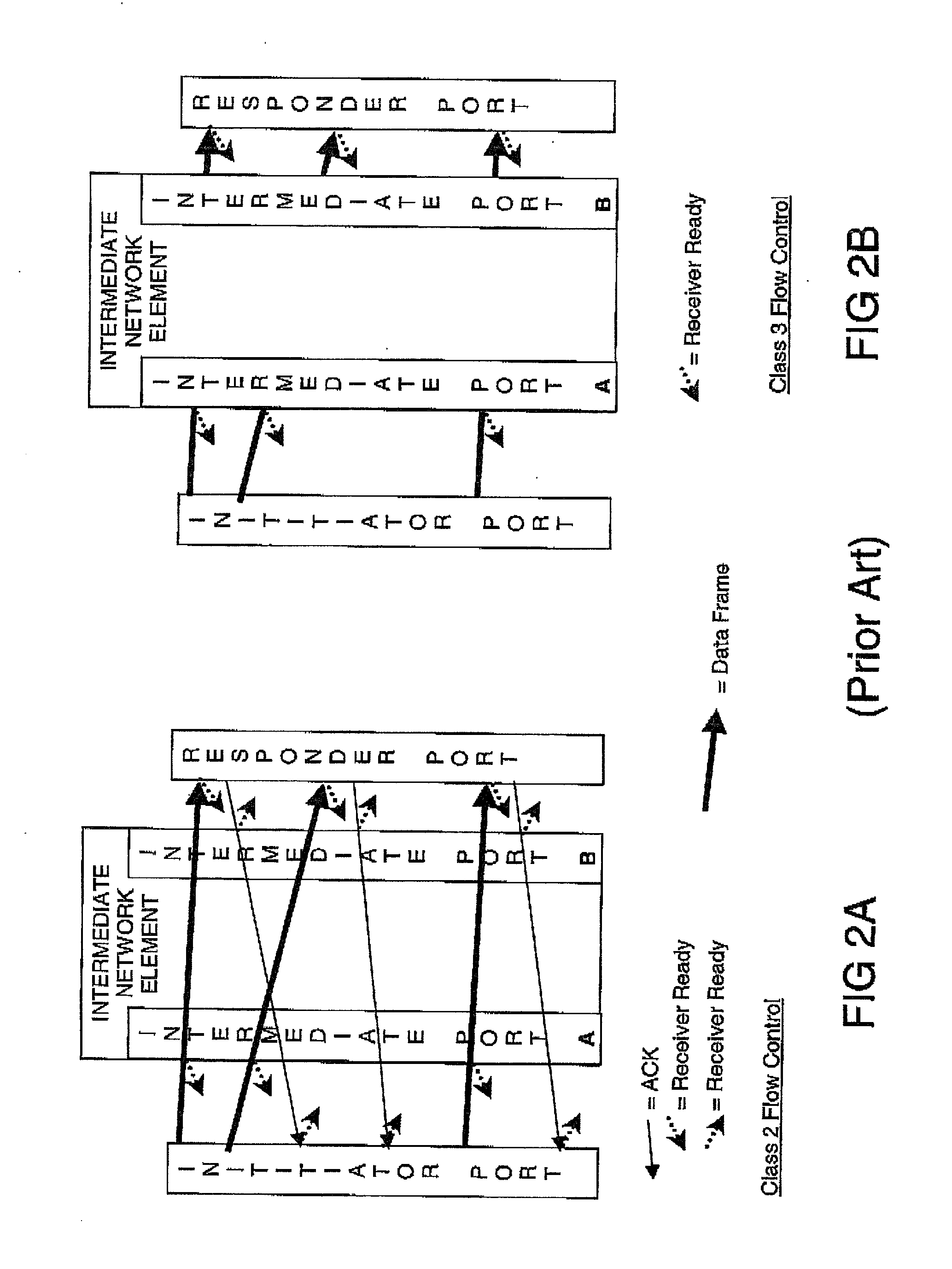
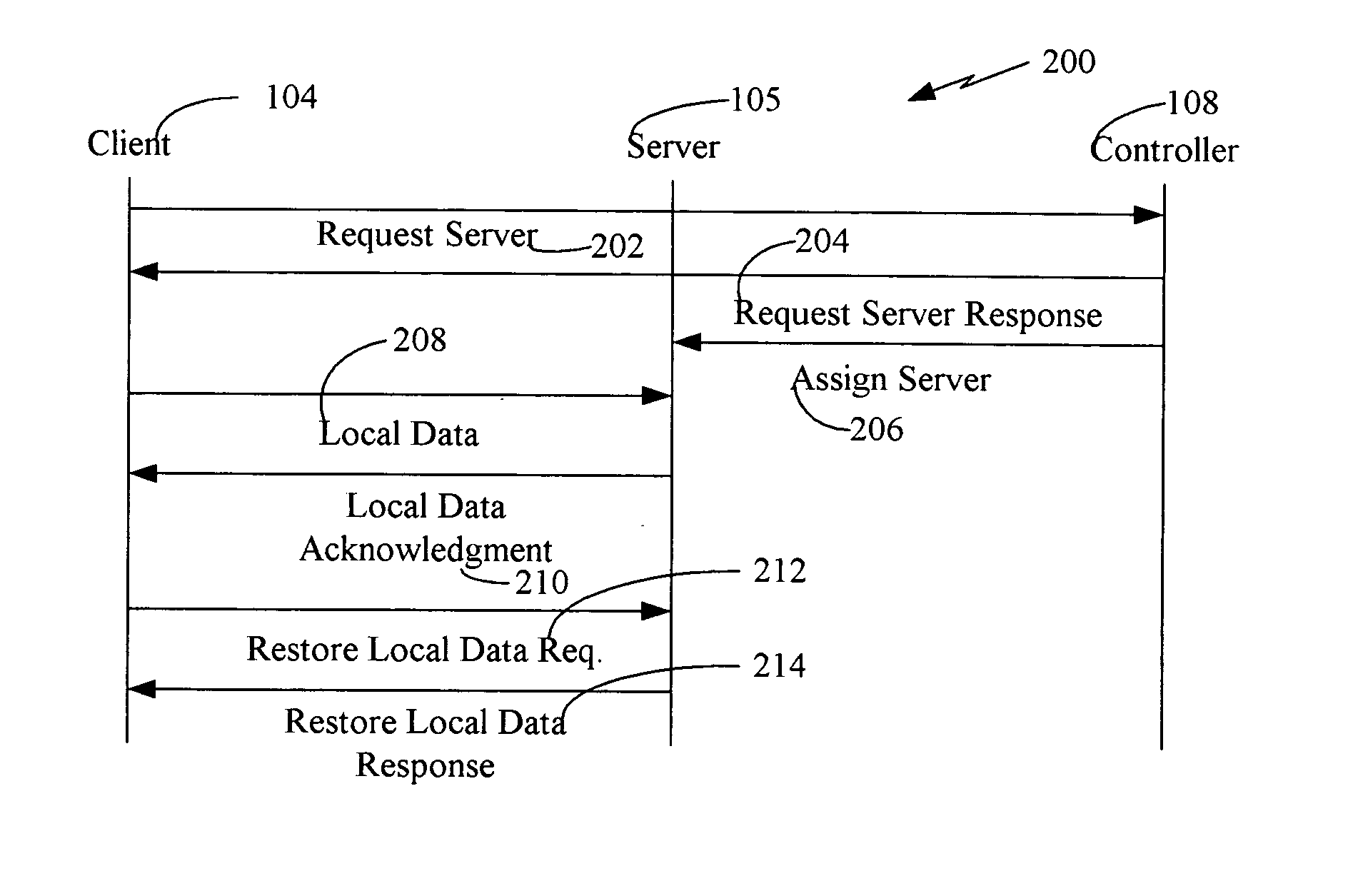
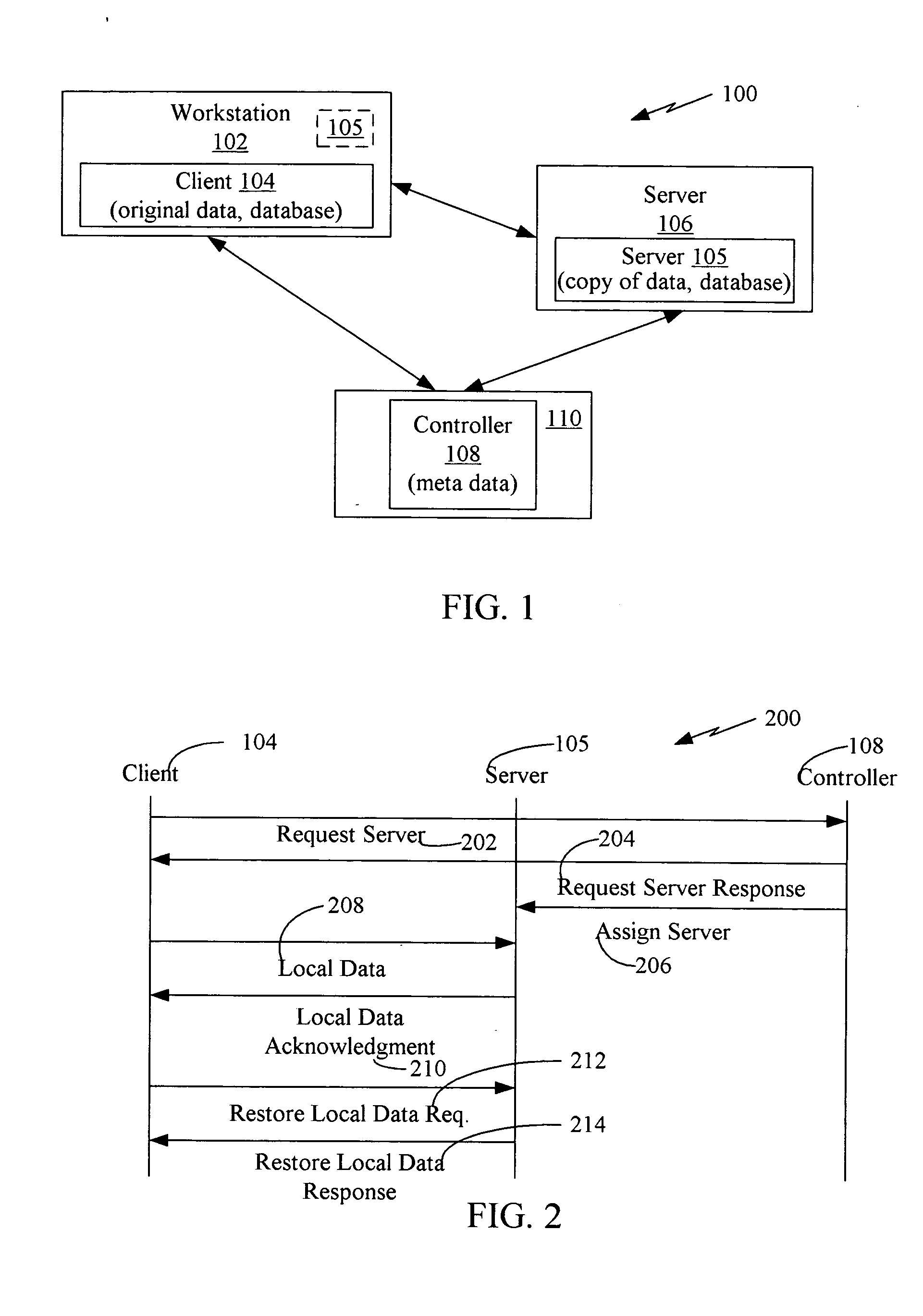
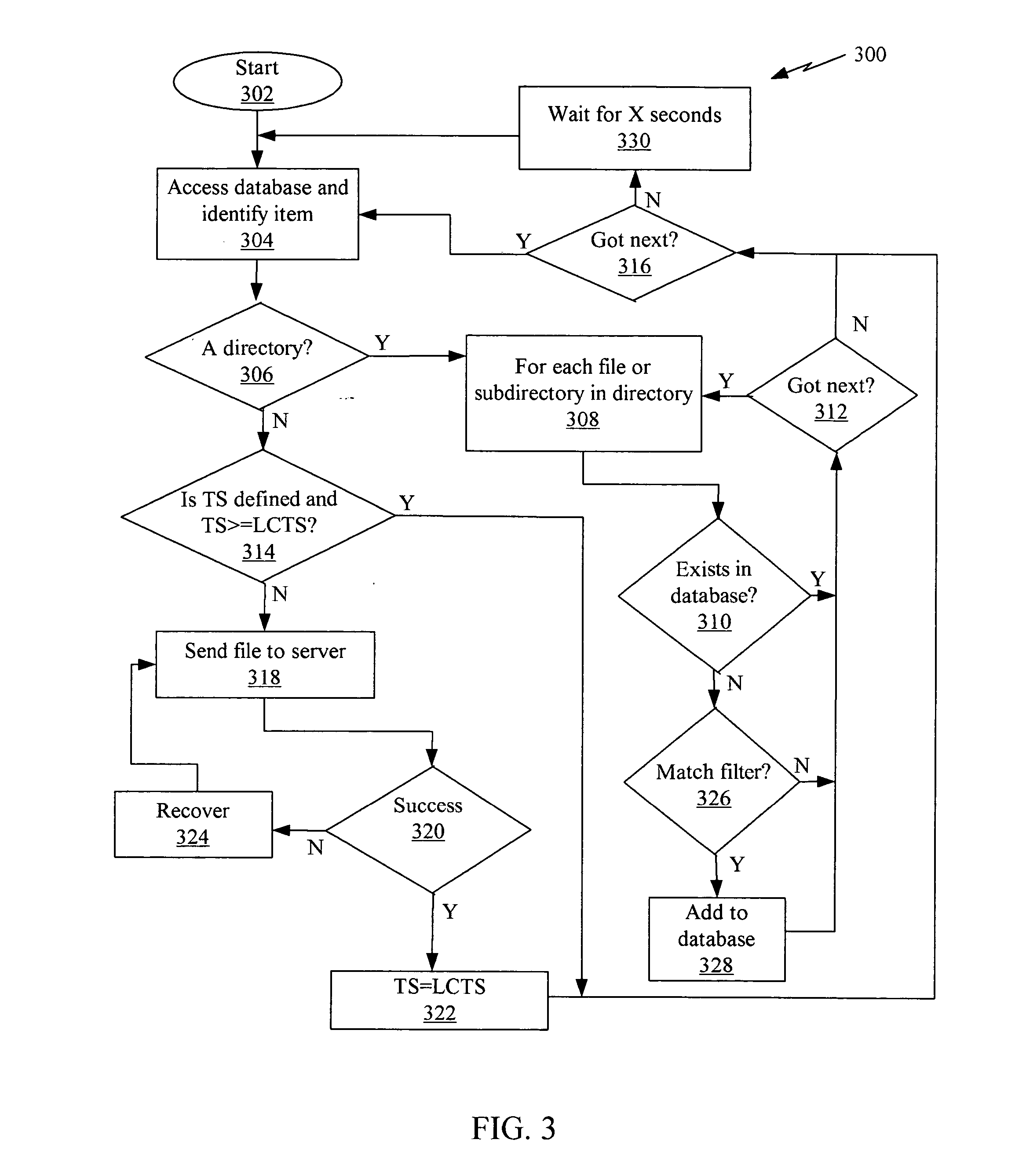
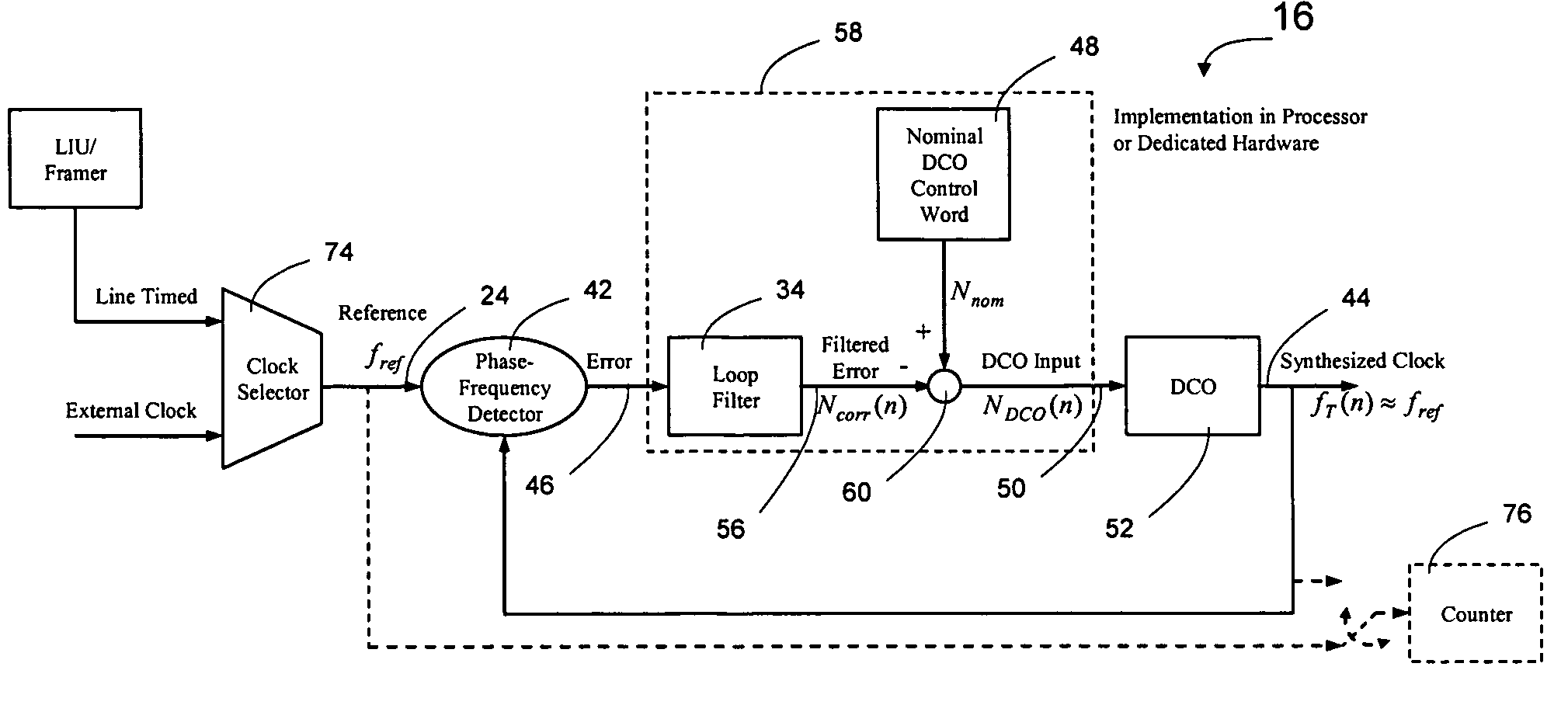
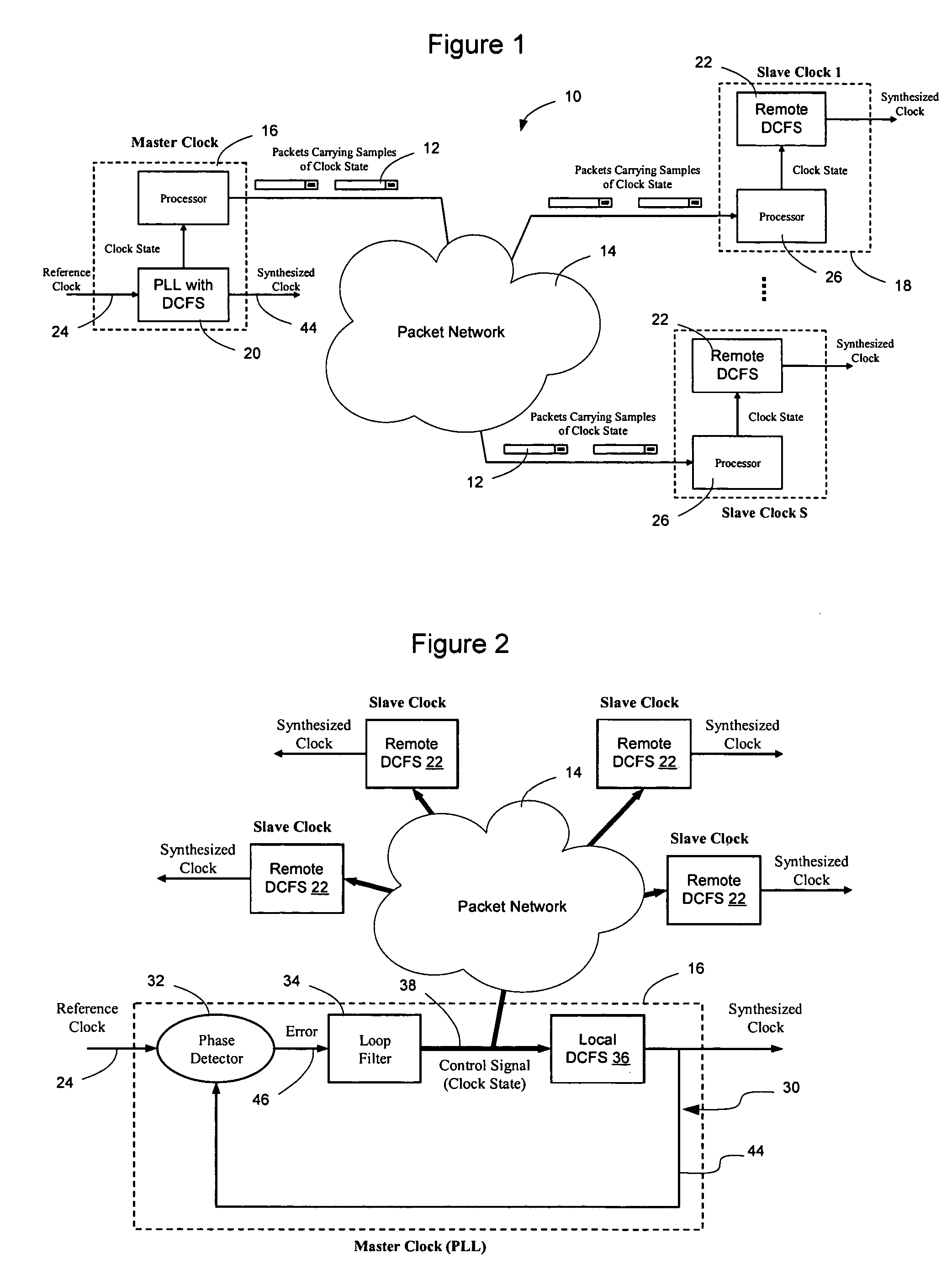
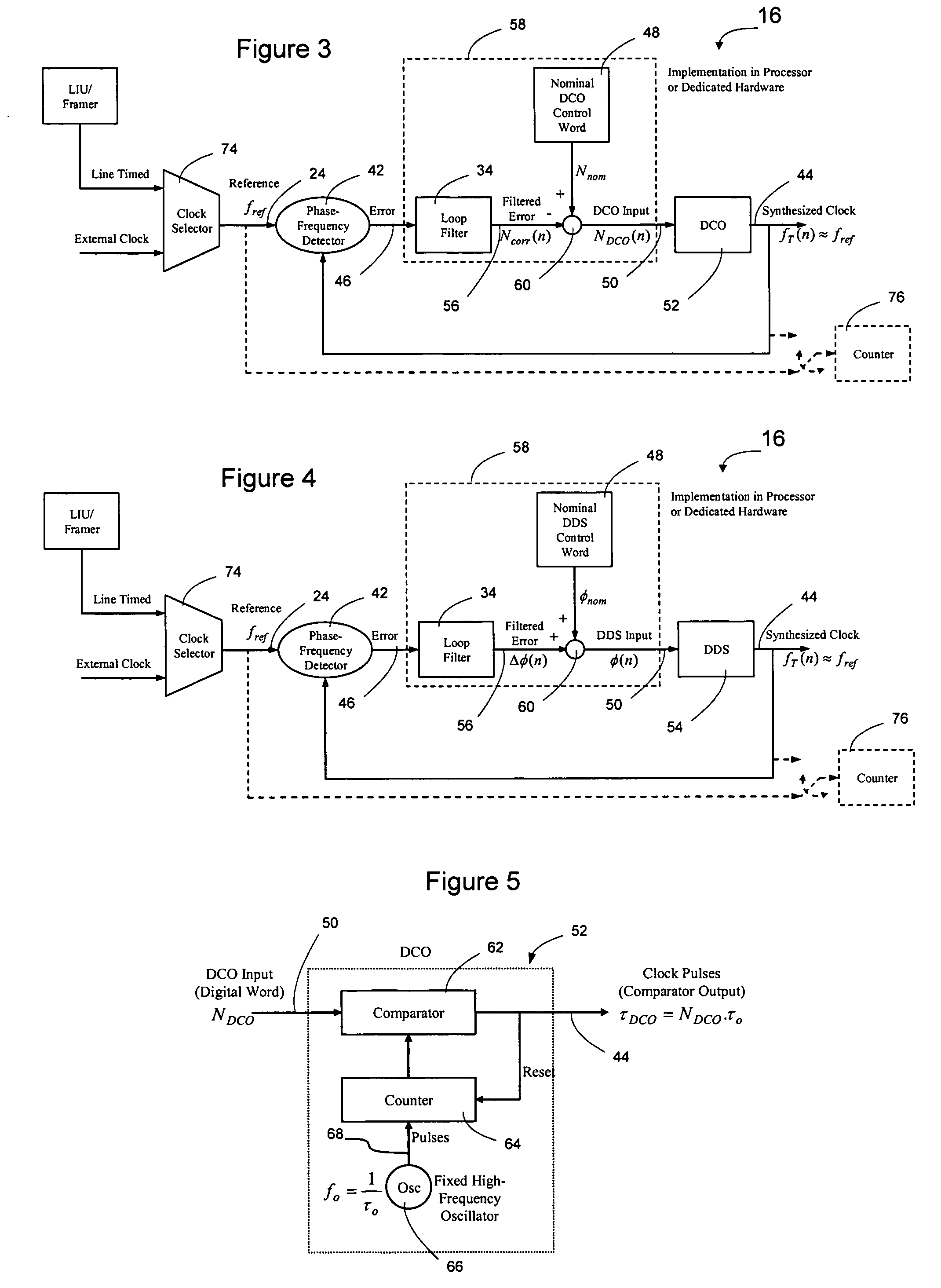
Patents
Literature
439 results about "Synchronous network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Many services running on modern digital telecommunications networks require accurate synchronization for correct operation. For example, if telephone exchanges are not synchronized, then slips will occur and degrade performance. Telecommunication networks rely on the use of highly accurate primary reference clocks which are distributed network-wide using synchronization links and synchronization supply units.
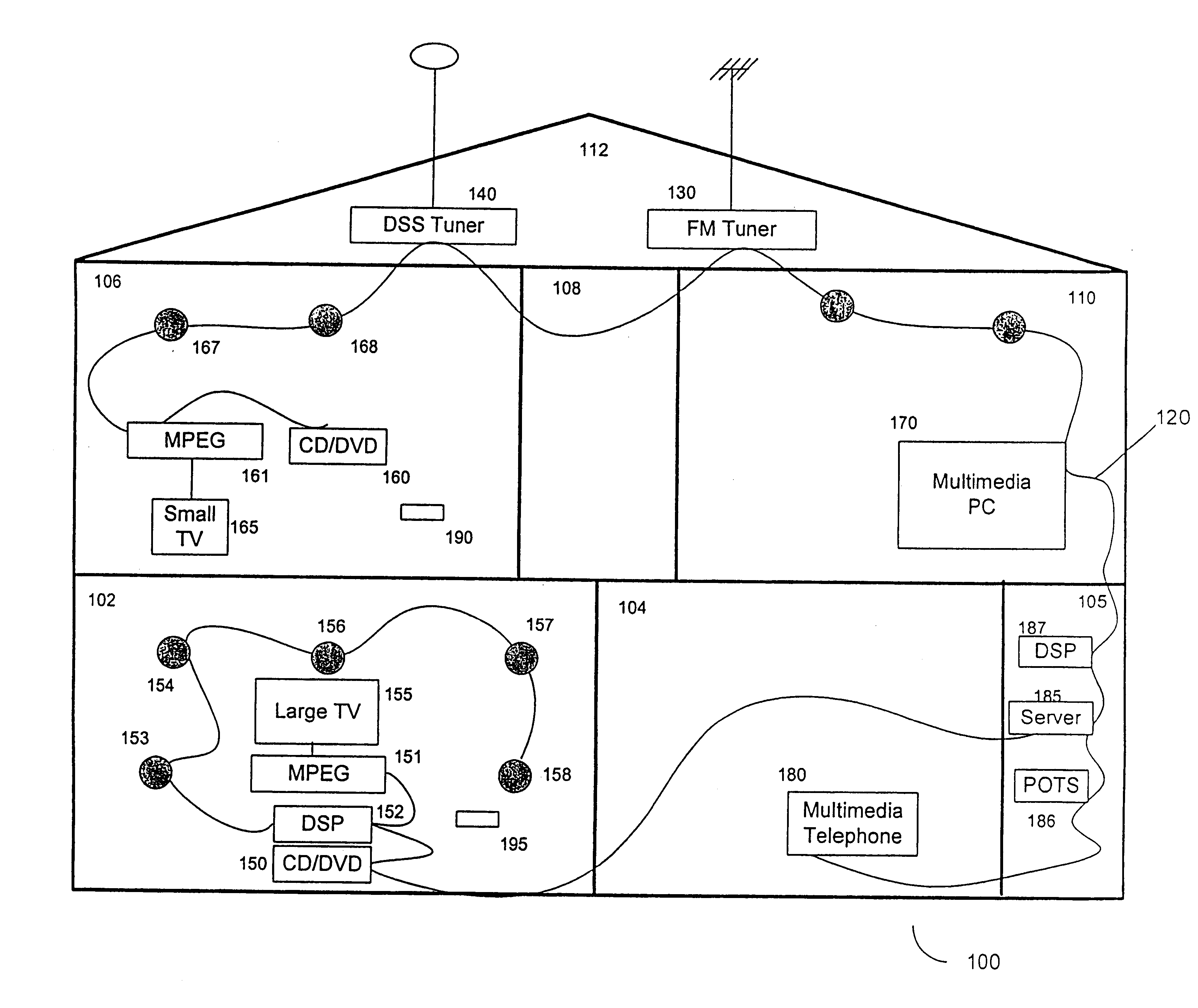
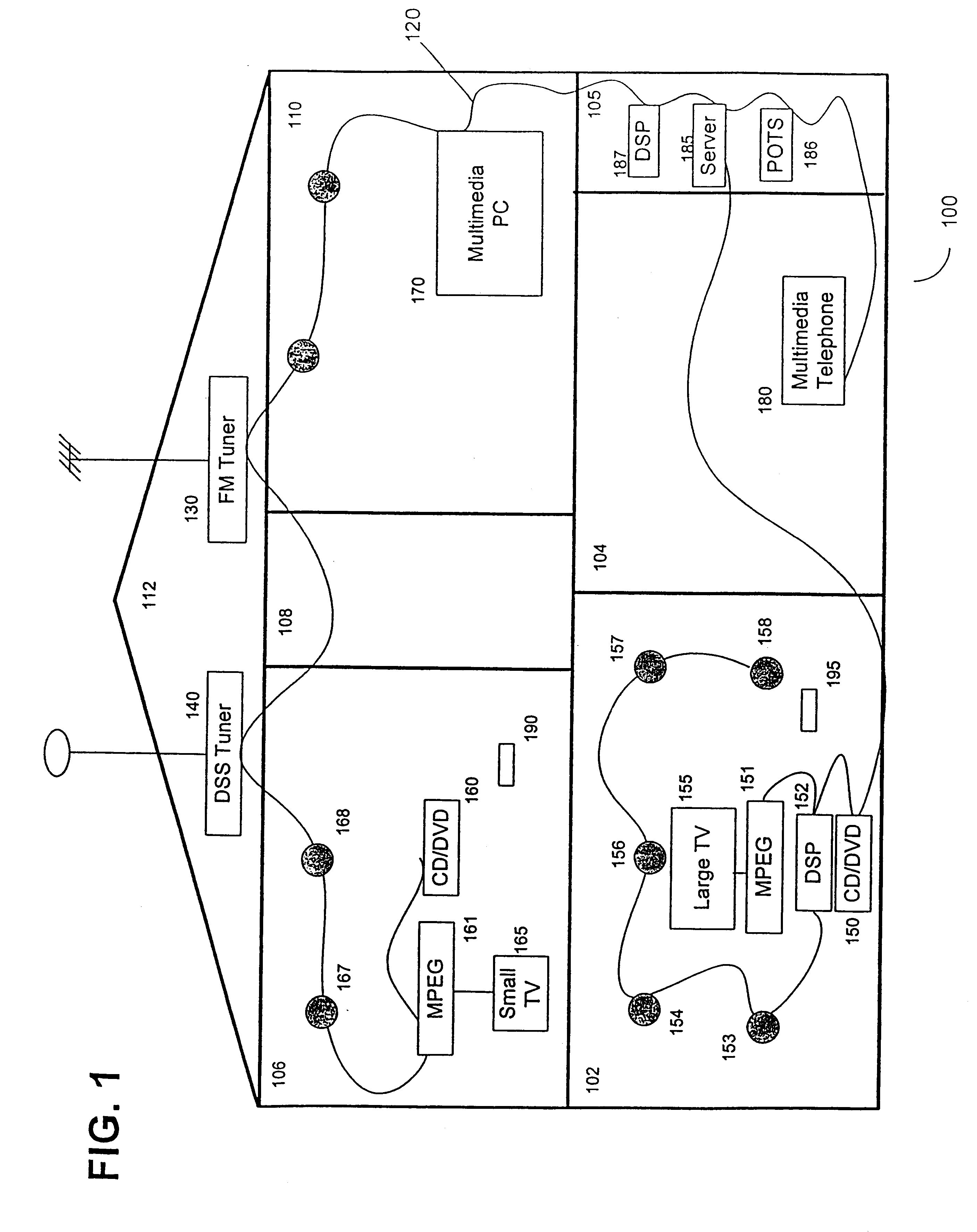
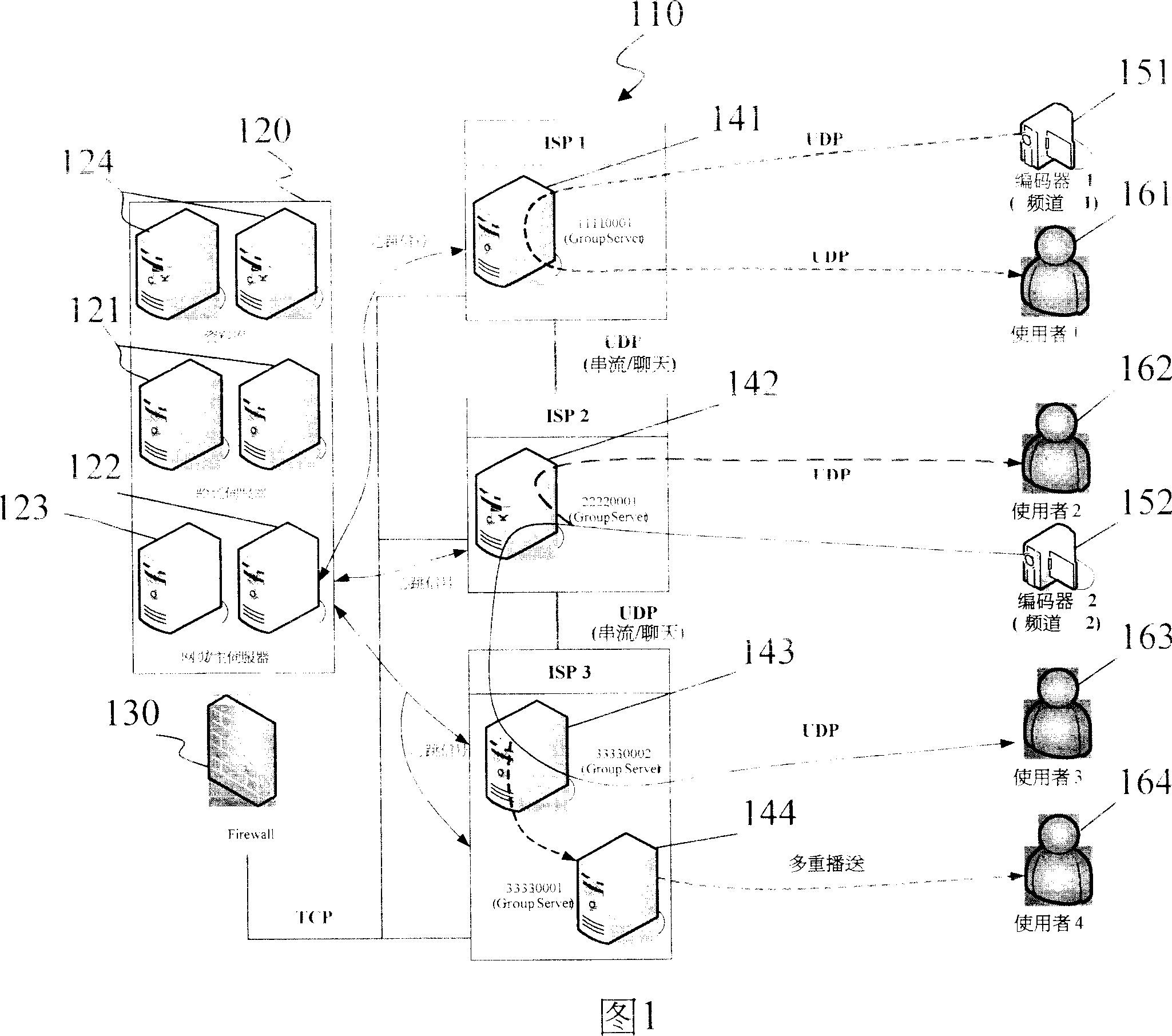
Synchronous network for digital media streams
InactiveUS6611537B1Avoid collisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexData streamNetwork clock
A network adapter for a synchronous logical ring network operates on existing physical twisted-pair telephone topologies. Information propagates around the logical ring, reaching every device on each revolution around the network. Network devices are full-duplex, transmitting and receiving information on every clock cycle. Network devices arbitrate to be elected the network clock device. By synchronizing all network devices to a single reference clock, and providing fixed frames of information propagating around the network at consistent time intervals, the logical ring network ensures that information propagates from one device to another at consistent time intervals. The fixed-length frames are divided into two independent streams: a data stream for the distribution of real-time continuous digital media streams; and a system command stream for the distribution of system commands.
Owner:CENTILLIUM COMM
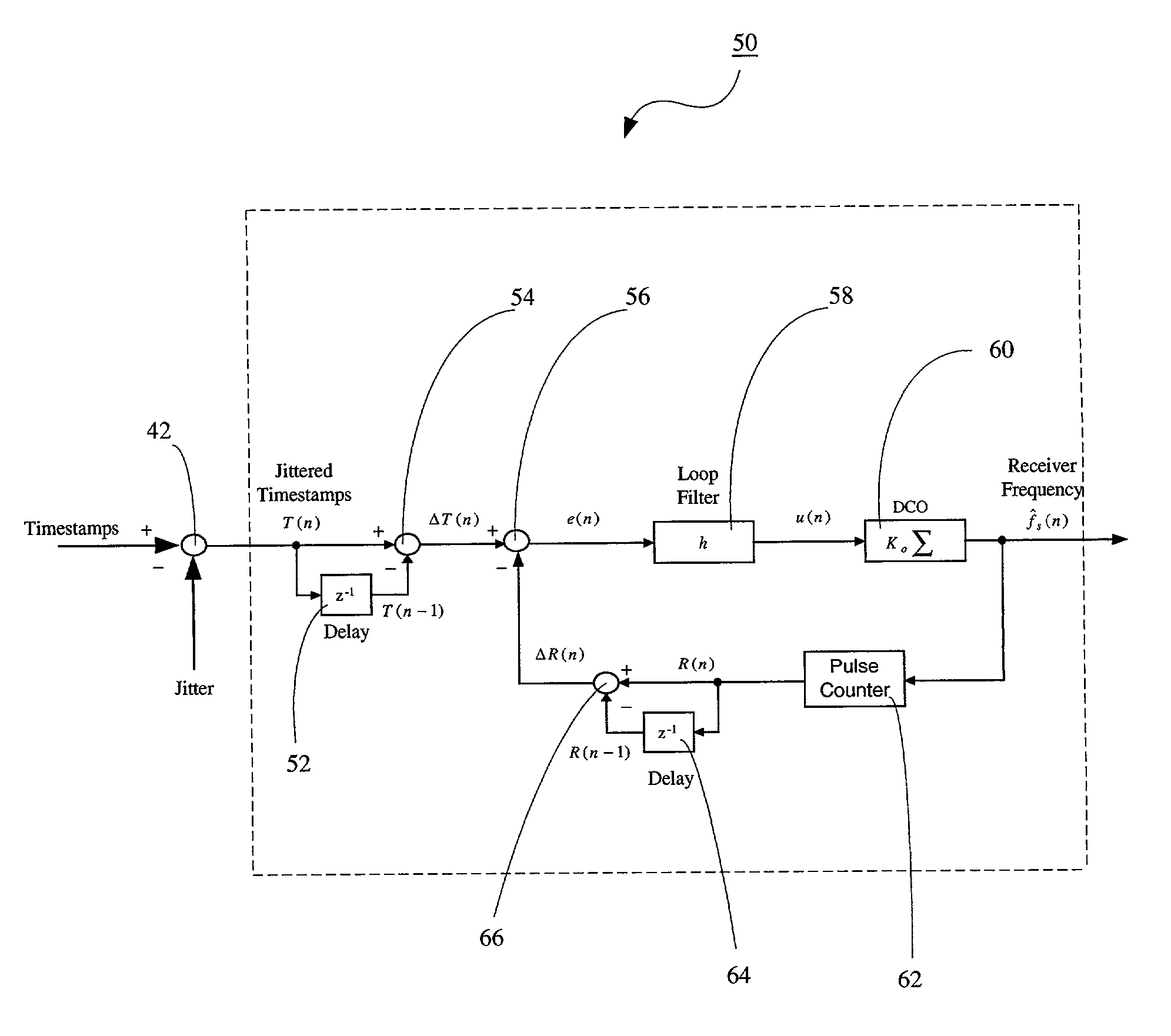
Technique for synchronizing clocks in a network
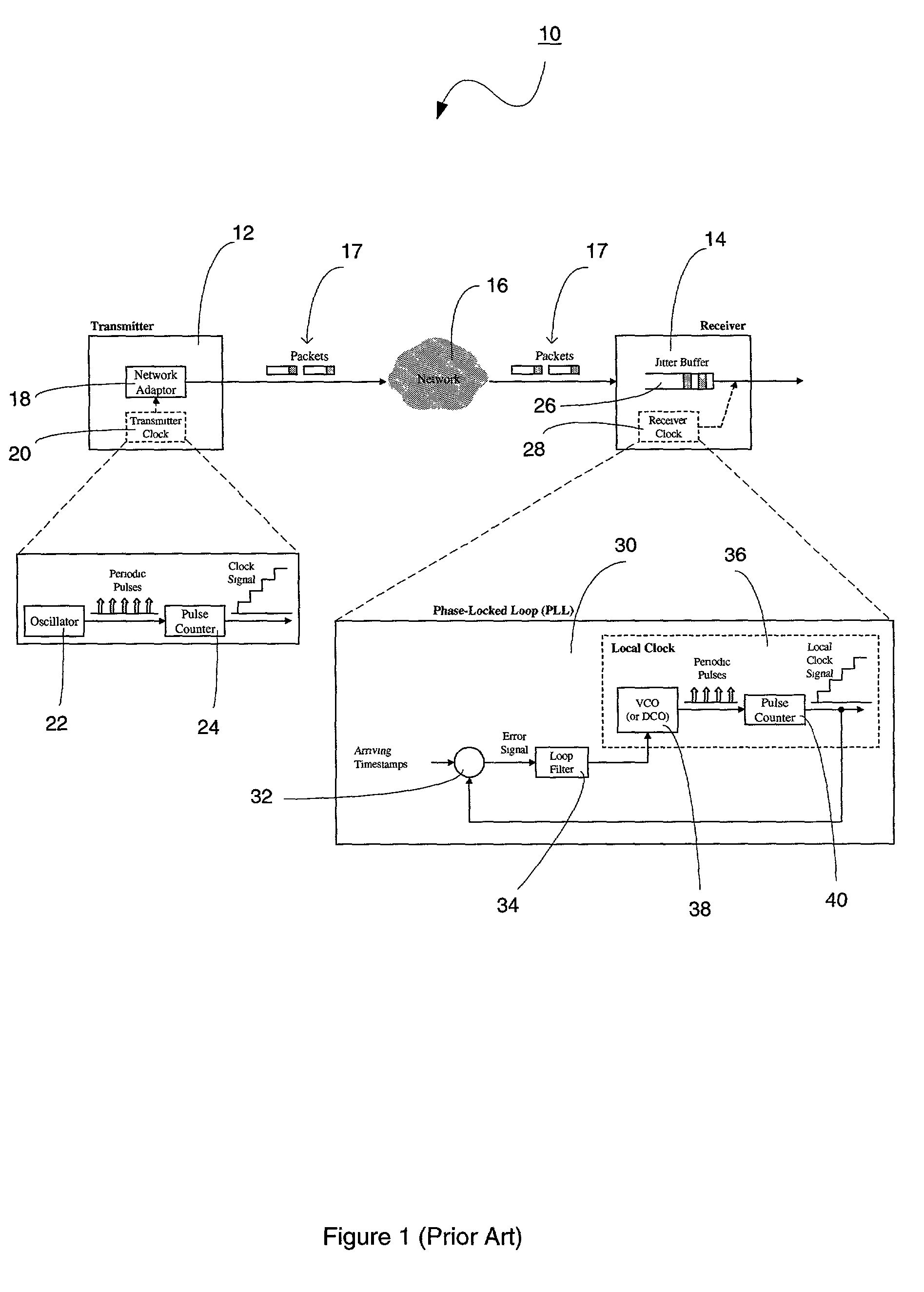
A technique for synchronizing clocks in a network is disclosed. In one exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for synchronizing clocks in a network. The method comprises receiving a first timestamp and a second timestamp, each indicating a respective time instance as determined by a first clock signal within the network. The method also comprises measuring a first time interval between the first timestamp and the second timestamp. The method further comprises generating a difference signal representing a difference between the first time interval and a second time interval, and generating a second clock signal based upon the difference signal such that the second clock signal is synchronized with the first clock signal.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Protocol and method for multi-chassis configurable time synchronization
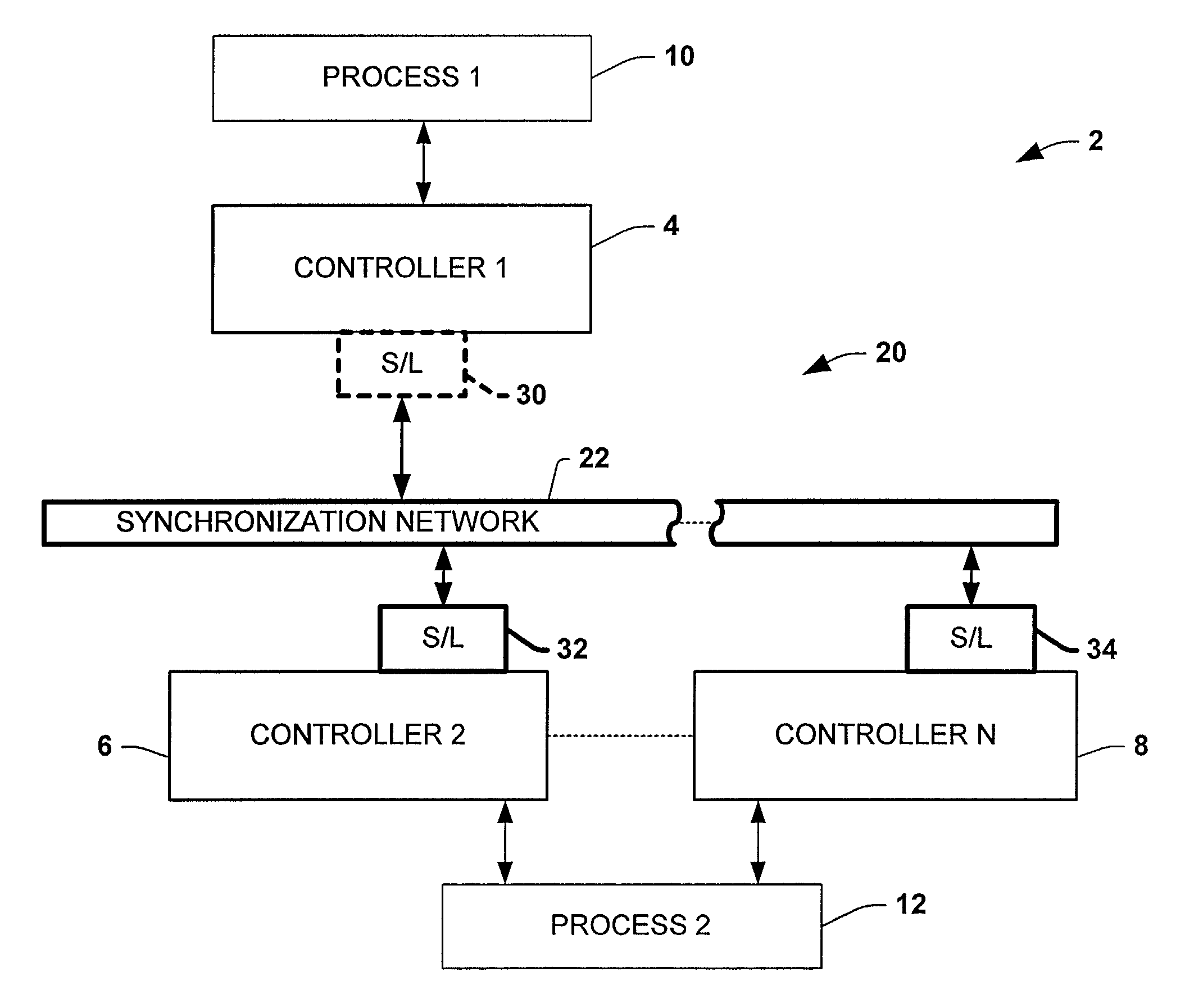
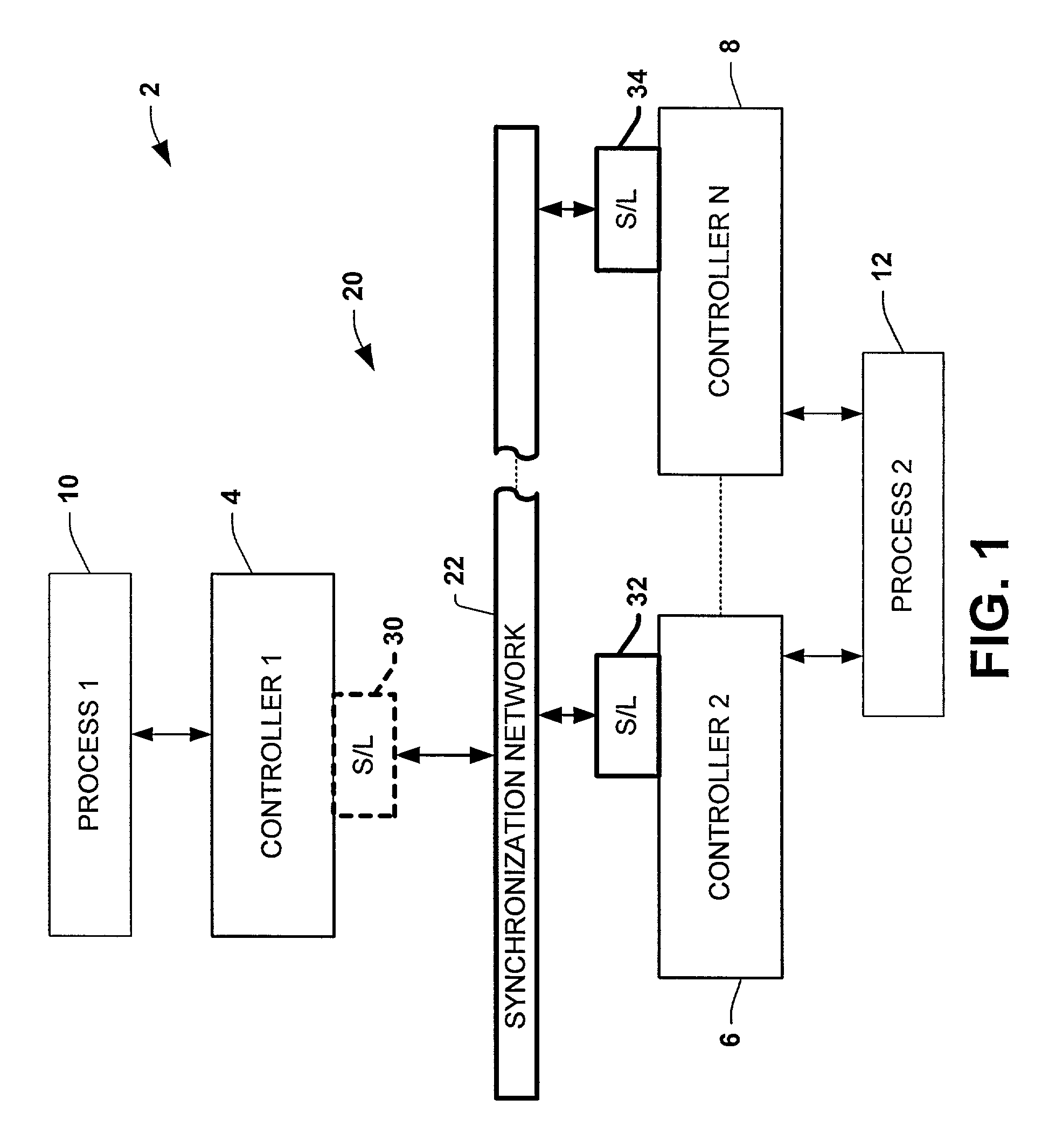
ActiveUS7007106B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionSynchronous controlControl system
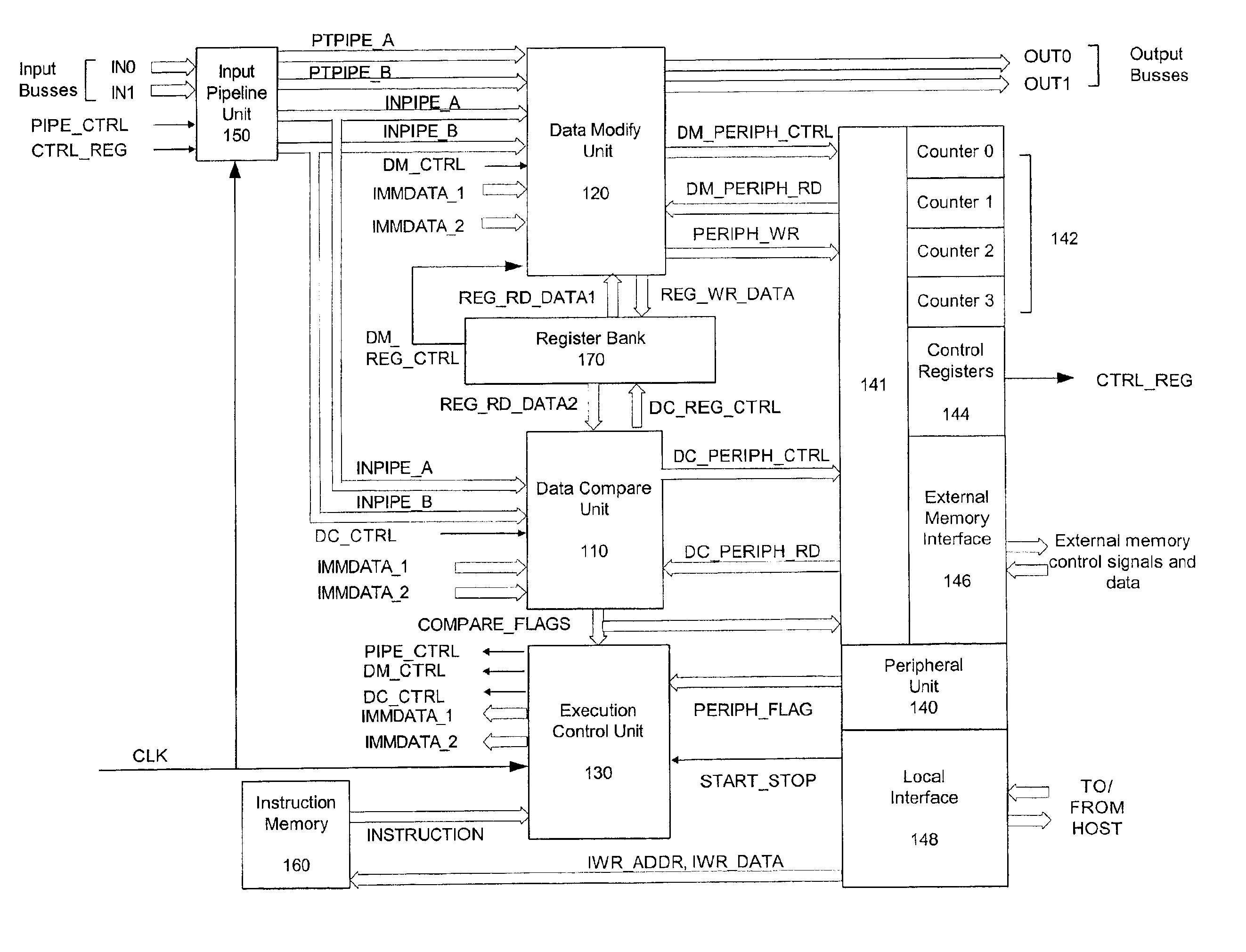
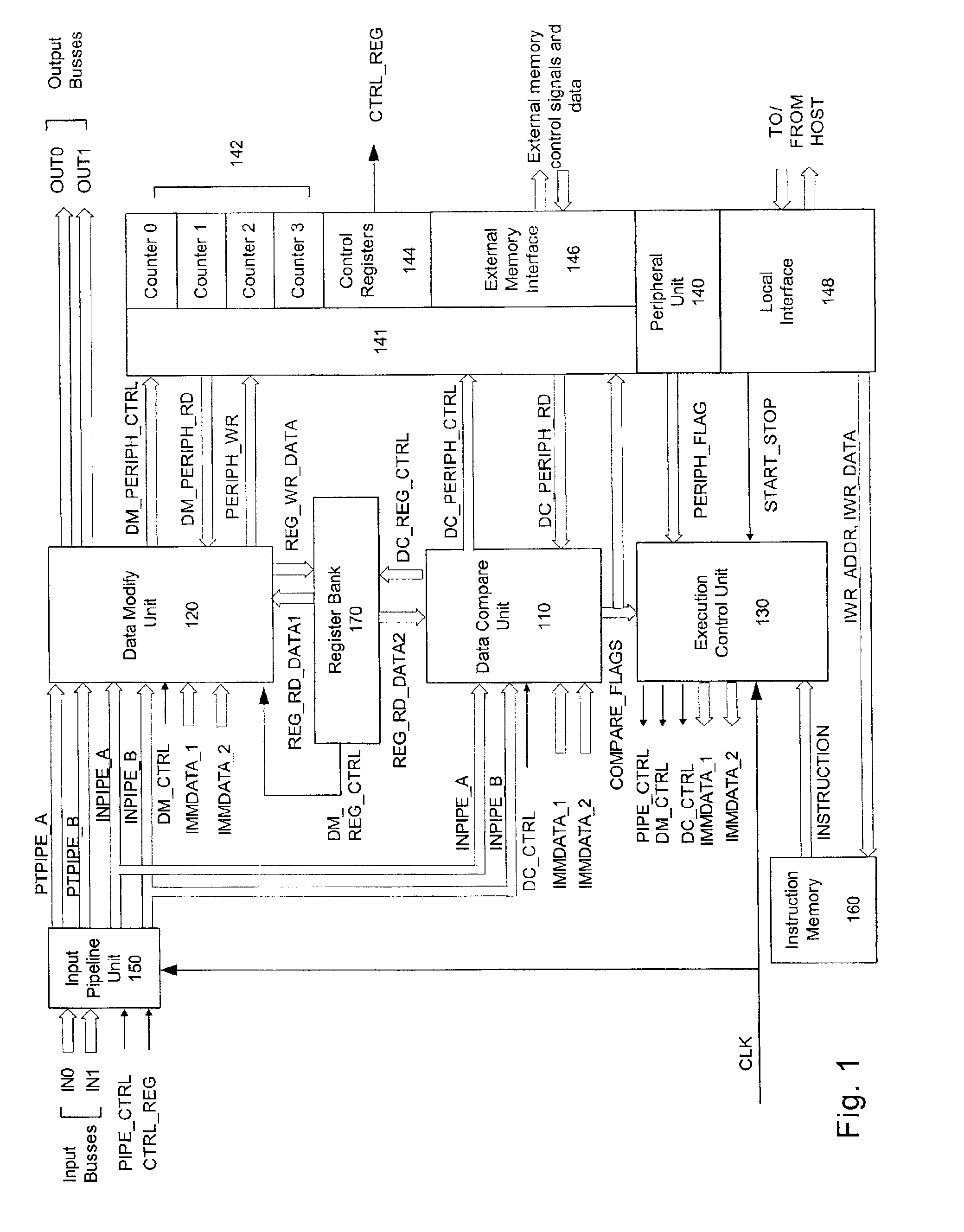
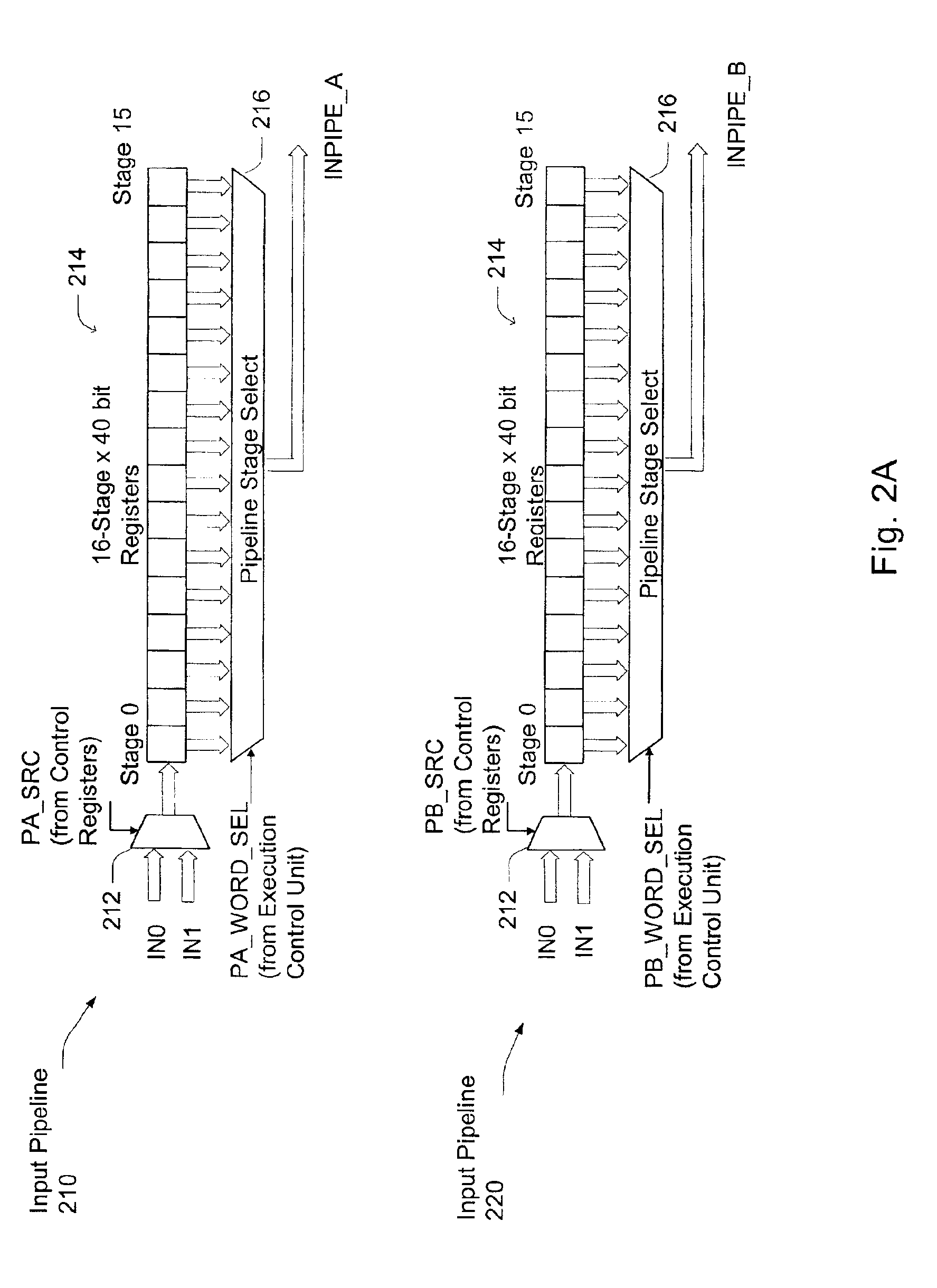
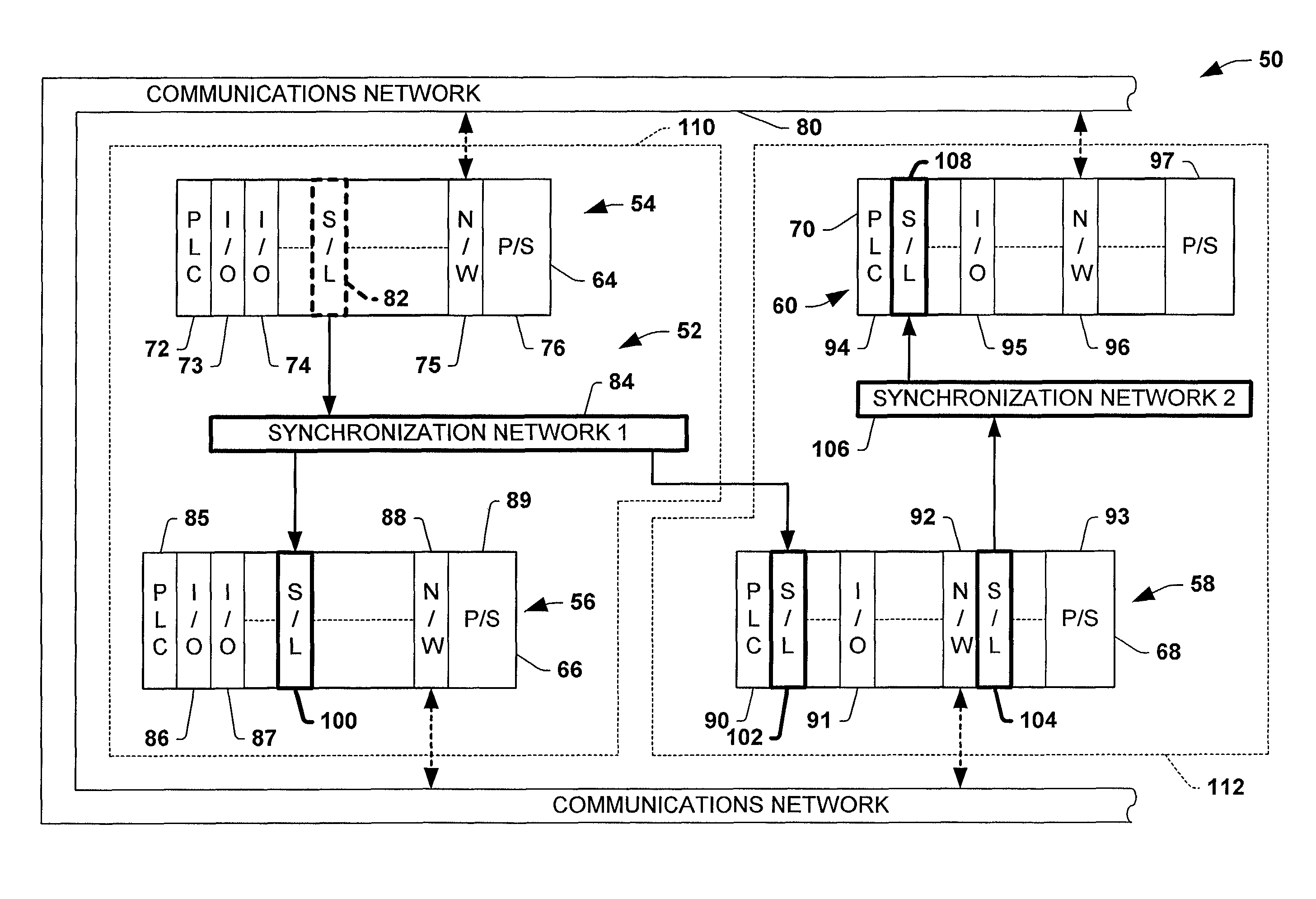
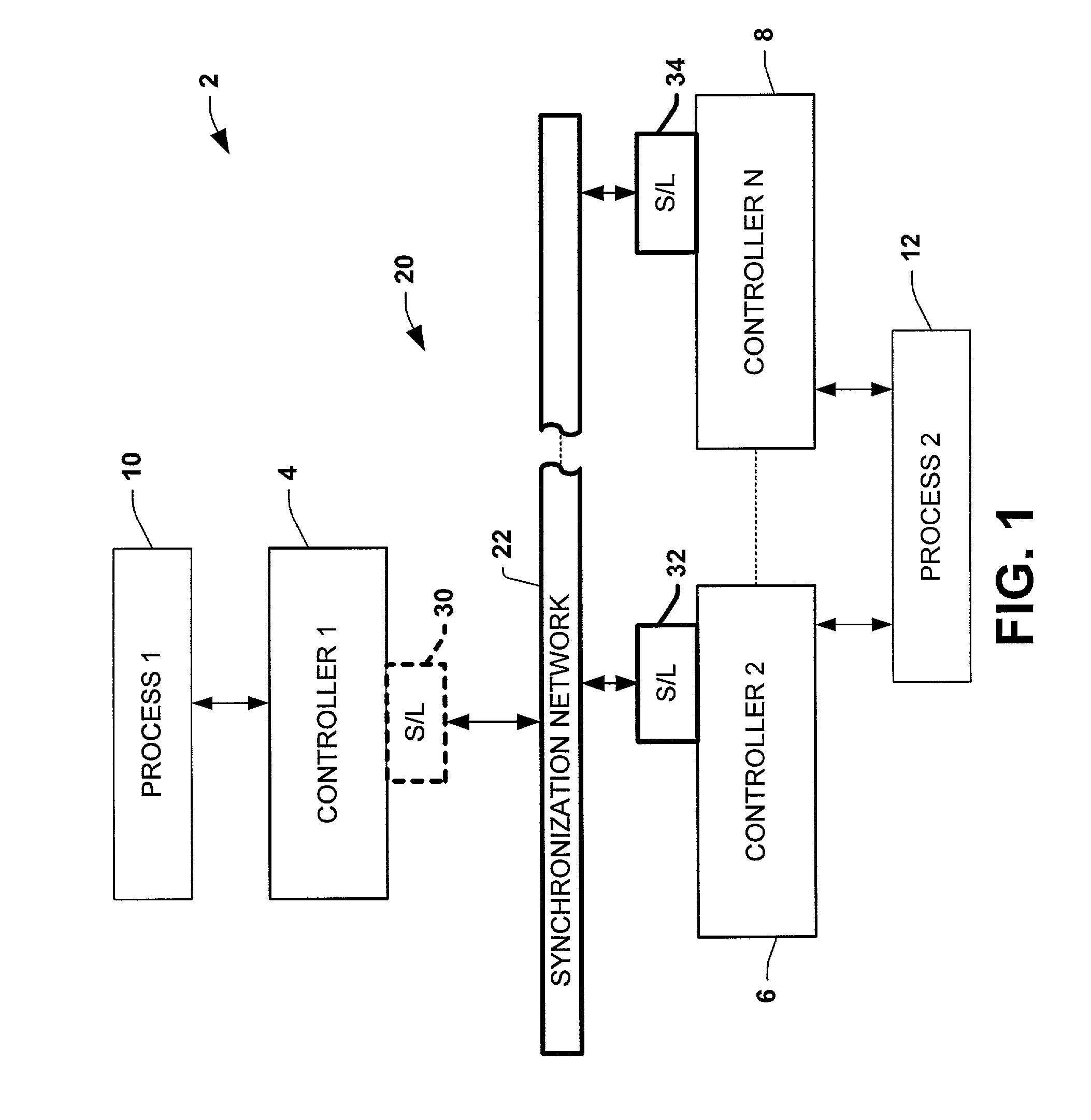
Systems and methods are disclosed for time synchronization of operations in a control system. Synchronization networks and devices are provided for transferring synchronization information between controllers in a distributed or localized control system, which is employed in order to allow operation of such controllers to be synchronized with respect to time. Also disclosed are synchronization protocols and hardware apparatus employed in synchronizing control operations in a control system.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
Desynchronized network access in m2m networks
ActiveUS20120231828A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionSynchronous network
Systems, methods, and instrumentalities are disclosed to desynchronize transmissions in group-based operations. A group user equipment (UE), e.g., a UE that is a member of a group of UEs, may be in an inactive mode. The group UE may receive a multicast message indicating that the group UE may enter an active mode. For example, the group UE may use the active mode for periodic reporting of its monitoring activity to the network. The multicast message may indicate a mechanism for the group UE to use to send an uplink transmission to the network. The group UE may send the uplink transmission to the network at a transmission time indicated by the mechanism. The transmission time may be desynchronized from other UEs in the group.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Data network with a time synchronization system
ActiveUS20090100189A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData synchronizationSynchronous network
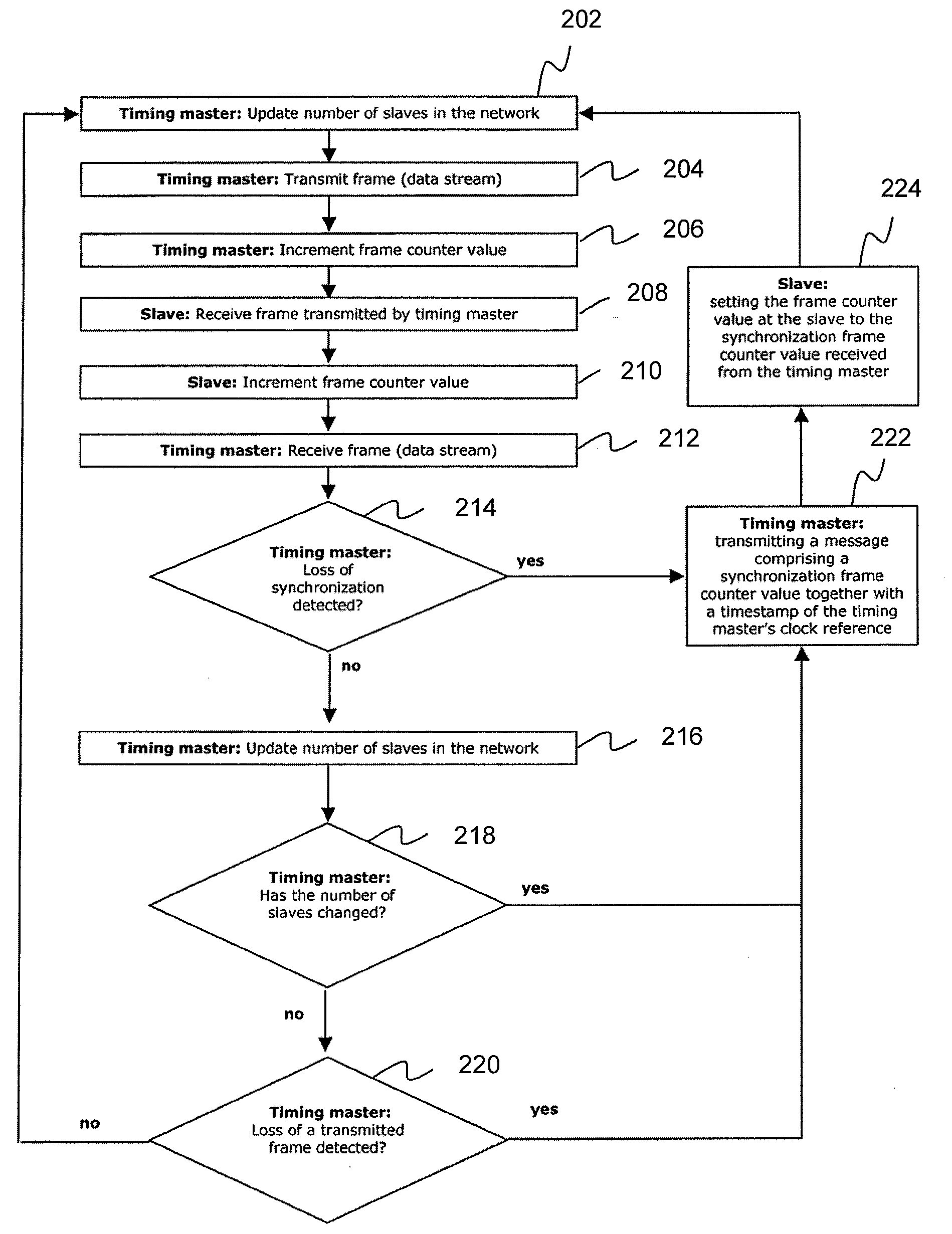
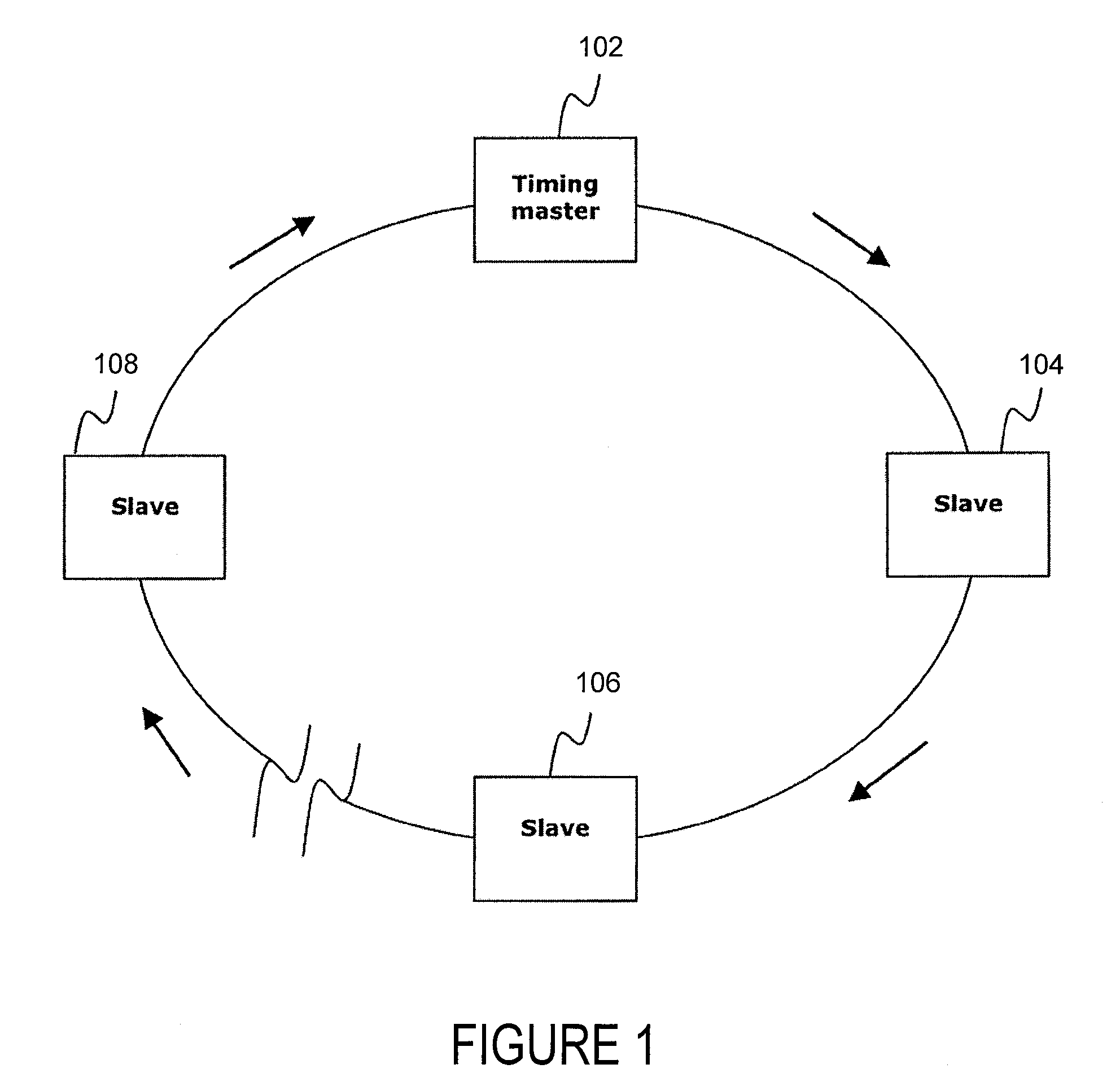
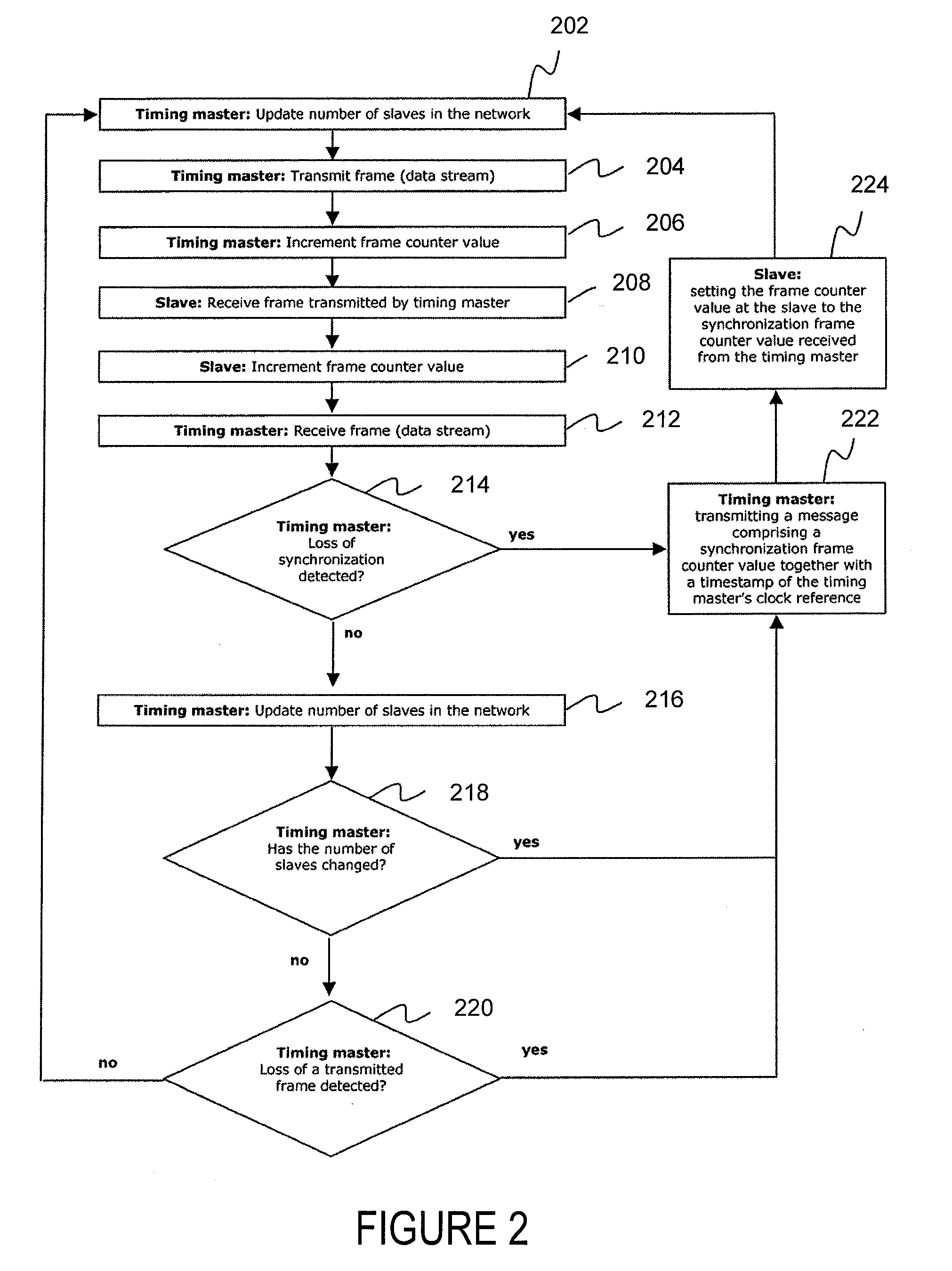
A system matches frame counter values between a timing master and one or more slave devices in a synchronous network. To detect synchronization losses, a timing master counts transmitted frames of a continuous data stream. When a synchronization loss occurs, the timing master transmits a message to the slave devices that includes a synchronization frame counter value. The message synchronizes the frame counter value of the timing master to the frame counter value of the slave devices.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Bandwidth allocation in a synchronous transmission network for packet oriented signals
InactiveUS20030074449A1Mitigate and obviateDigital computer detailsTime-division multiplexESCONSynchronous network
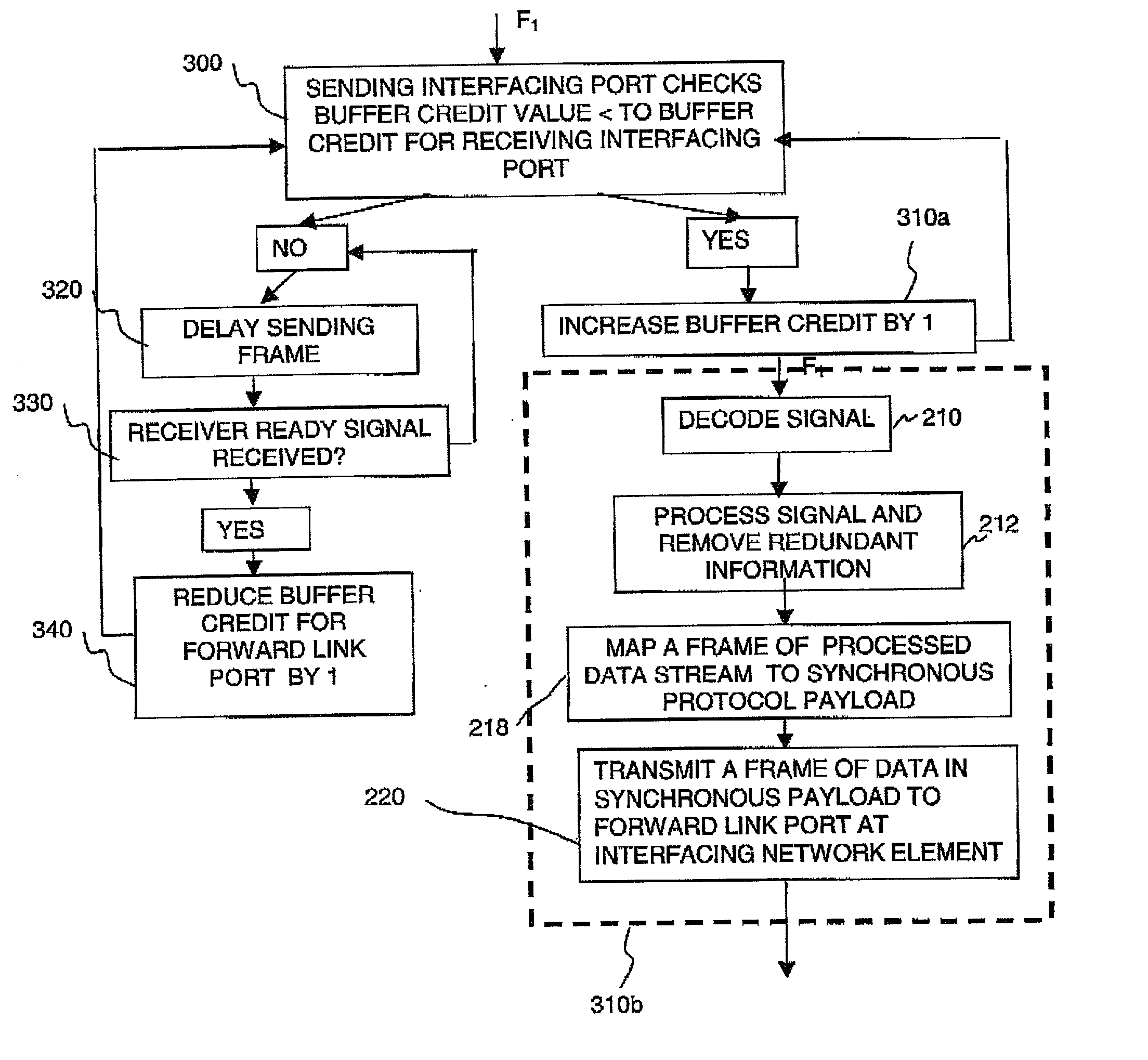
A method of transporting a packet oriented client signal which uses a buffer-to-buffer flow control mechanism over a synchronous transmission network by assigning an arbitrary synchronous payload, where the synchronous payload bandwidth may be significantly smaller than the full bandwidth of the client signal. Flow control over the synchronous network is provided by the buffer-to-buffer flow control mechanism of the client signal to automatically regulate the data throughput to ensure no data can be lost. The method is independent of the Client Signal Data Rate and the provisioned SDH / SONET bandwidth, and SDH / SONET payload which may be non-concatenated, contiguously concatenated, or virtually concatenated. In particular, the method may be used to support the transport of Fibre Channel (1G, 2G and 4G), and ESCON (200M) in a synchronous payload.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for synchronizing clock timing between network elements
Network elements may be synchronized over an asynchronous network by implementing a master clock as an all digital PLL that includes a Digitally Controlled Frequency Selector (DCFS), the output frequency of which may be directly controlled through the input of a control word. The PLL causes the control word input to the master DCFS to be adjusted to cause the output of the master DCFS to lock onto a reference frequency. Information associated with the control word is transmitted from the master clock to the slave clocks which are also implemented as DCFSs. By using the transmitted information to recreate the master control word, the slaves may be made to assume the same state as the master DCFS without requiring the slaves to be implemented as PLLs. The DCFS may be formed as a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) or as a Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS).
Owner:CIENA
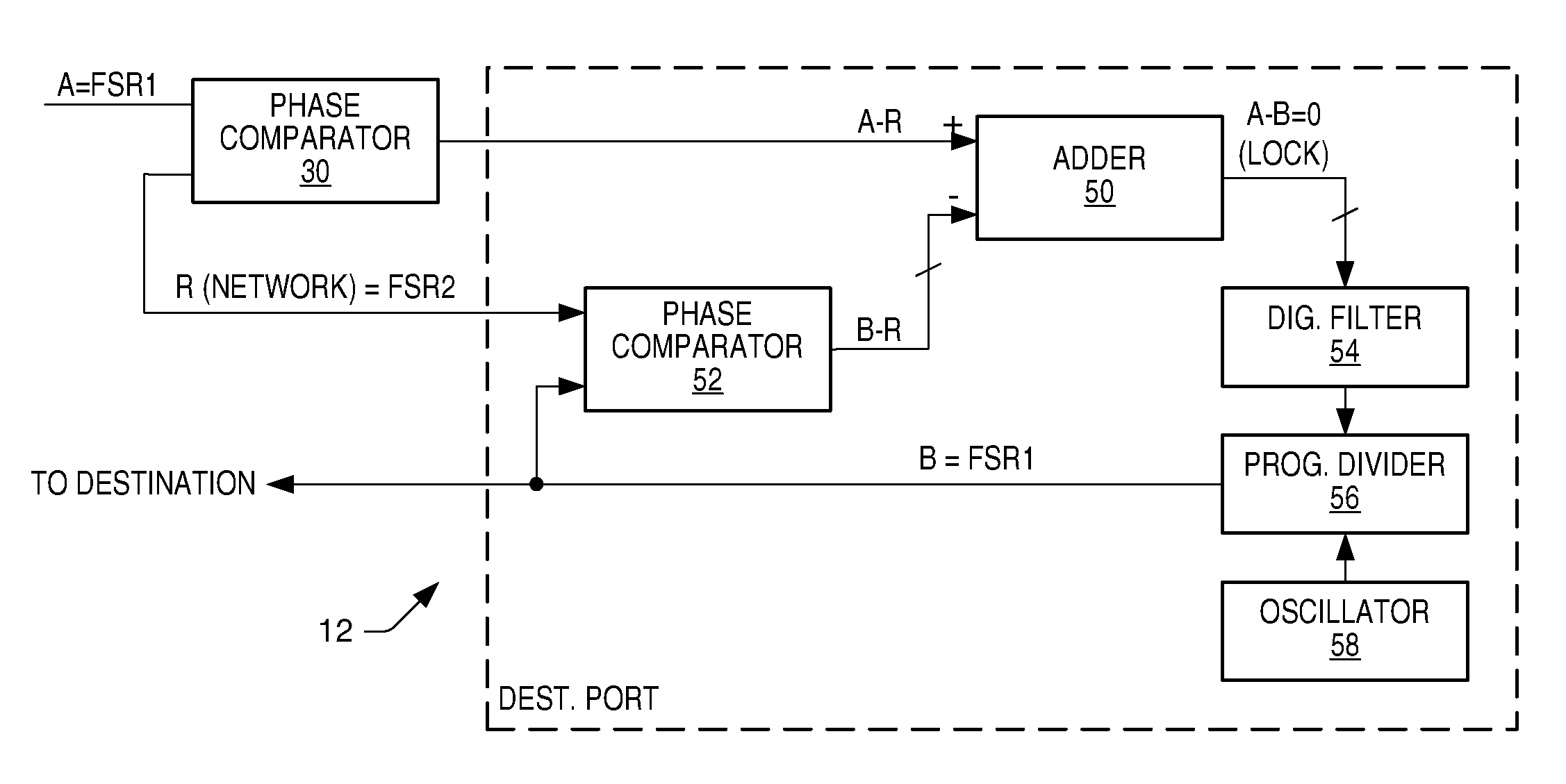
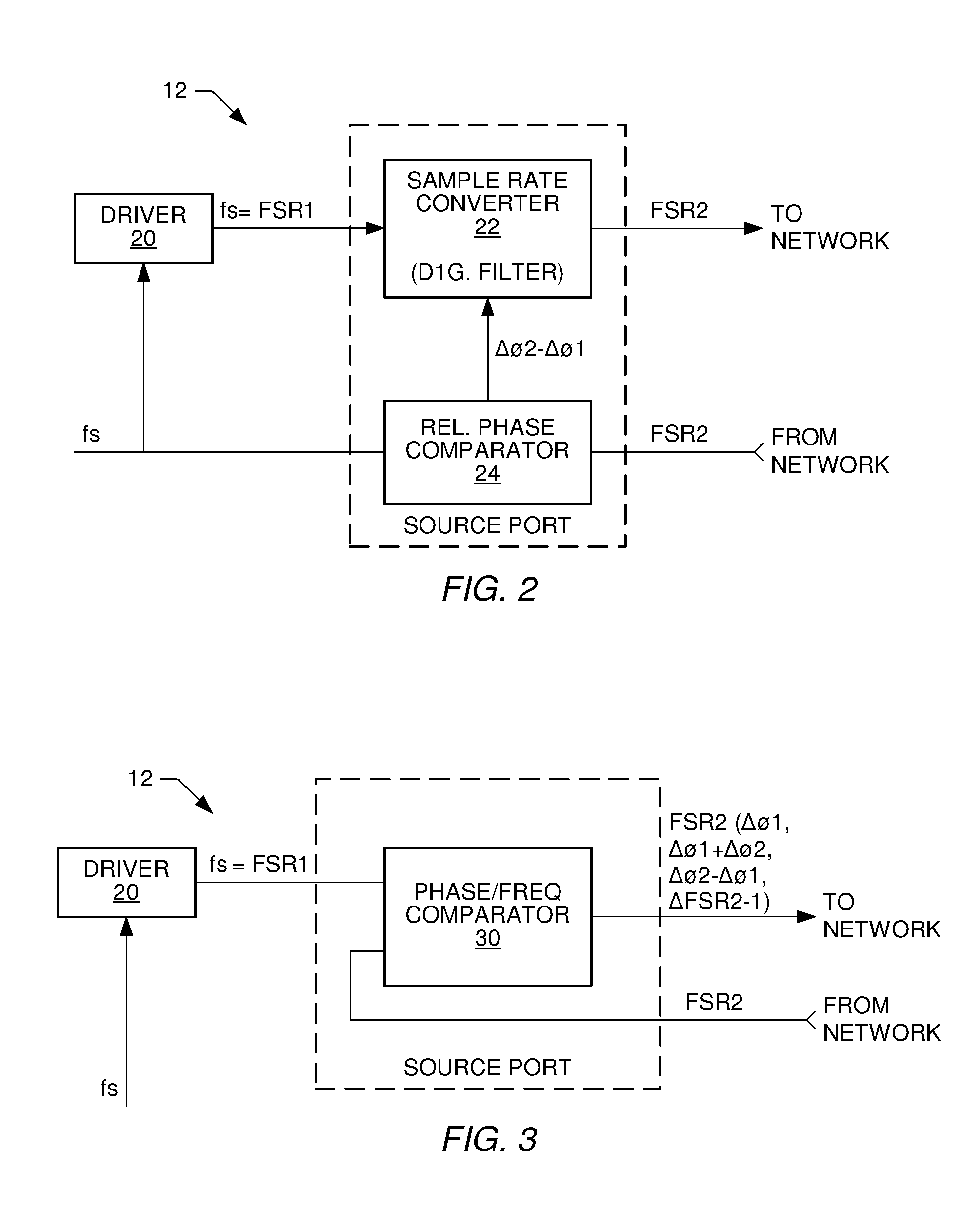
Communication system and method for sample rate converting data onto or from a network using a high speed frequency comparison technique
ActiveUS7106224B2High resolutionImprove accuracyTime-division multiplexIndividual digits conversionSample rate conversionPhase difference
A communication system, source and destination ports of the communication system, and methodology is provided for transporting data in one of possibly three different ways. Data is transported across the network at a frame sample rate that can be the same as or different from the sample rate or master clock within the source port or the destination port. If the sample rate of the source port is known, the sample rate of the destination port can be created using a PLL within the destination port and simply employing a phase comparator in the source port. The phase comparator forwards the phase or frequency difference of the network transfer rate and the source sample rate to the destination port, which then generates a local clock equivalent to the source which then compiles audio data being played at the same rate in which it was sampled at the source. Where economically feasible, sample rate conversion can be used at the source. However, sample rate conversion at the destination is preferred if the source sample rate is forwarded across the network relative to the frame transfer rate of the synchronous network. The sample rate converter simply produces a play rate from the transmitted information at the destination. Again, however, sample rate conversion compares relative phase difference changes similar to the phase difference compared in the digital PLL mode. As a further alternative, sample rates within the source and destination ports can be derived from the network frame rate using fractional dividers in the source and destination ports.
Owner:STANDRD MICROSYSTEMS CORPORATION
Multi-terminal power conversion device, multi-terminal power transfer device, and power network system
ActiveUS20120173035A1Reduce capacityIncrease volumeMechanical power/torque controlDc network circuit arrangementsNetworked systemTerminal equipment
The present invention provides a multi-terminal power conversion device, a multi-terminal power transfer device, and a power network system which allows an existing power grid to be divided into a plurality of power grids that can be interconnected together and operated stably via existing or new transmission lines. An inter-power grid asynchronous interconnection network system includes a multi-terminal power conversion device characterized by connecting together a plurality of asynchronous power grids including a bulk power grid and controlling power so that the sum of inflow power and outflow power is zero. An intra-power grid synchronous network system includes a power apparatus control terminal device with means for controlling power for a power apparatus installed in an autonomous power grid. A plurality of inter-power grid asynchronous interconnection network systems are connected to an intra-power grid synchronous network system to integrate the power control with communication control.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Synchronization of time in a mobile ad-hoc network
ActiveUS20120127977A1Reduce overheadEfficient communicationSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesObservational errorSynchronous network
Methods and systems are disclosed herein for synchronizing network time in a mobile ad-hoc network (MANET). Each node in the MANET may be synchronized with all of its neighbors for effective communications. More specifically, a local timing reference may be adjusted according to measured errors in incoming control packets so that time slotted transmissions can be scheduled without collisions with other nodes. The method and system is a low overhead protocol that only requires a small amount of data attached to each scheduled transmission avoiding the requirement for separate messaging. This may reduce the overhead of maintaining the MANET providing additional efficiency and robustness.
Owner:POWERWAVE COGNITION INC
Media flow method for transferring real-time data between asynchronous and synchronous networks
InactiveUS7126957B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationReal-time dataSynchronous motor
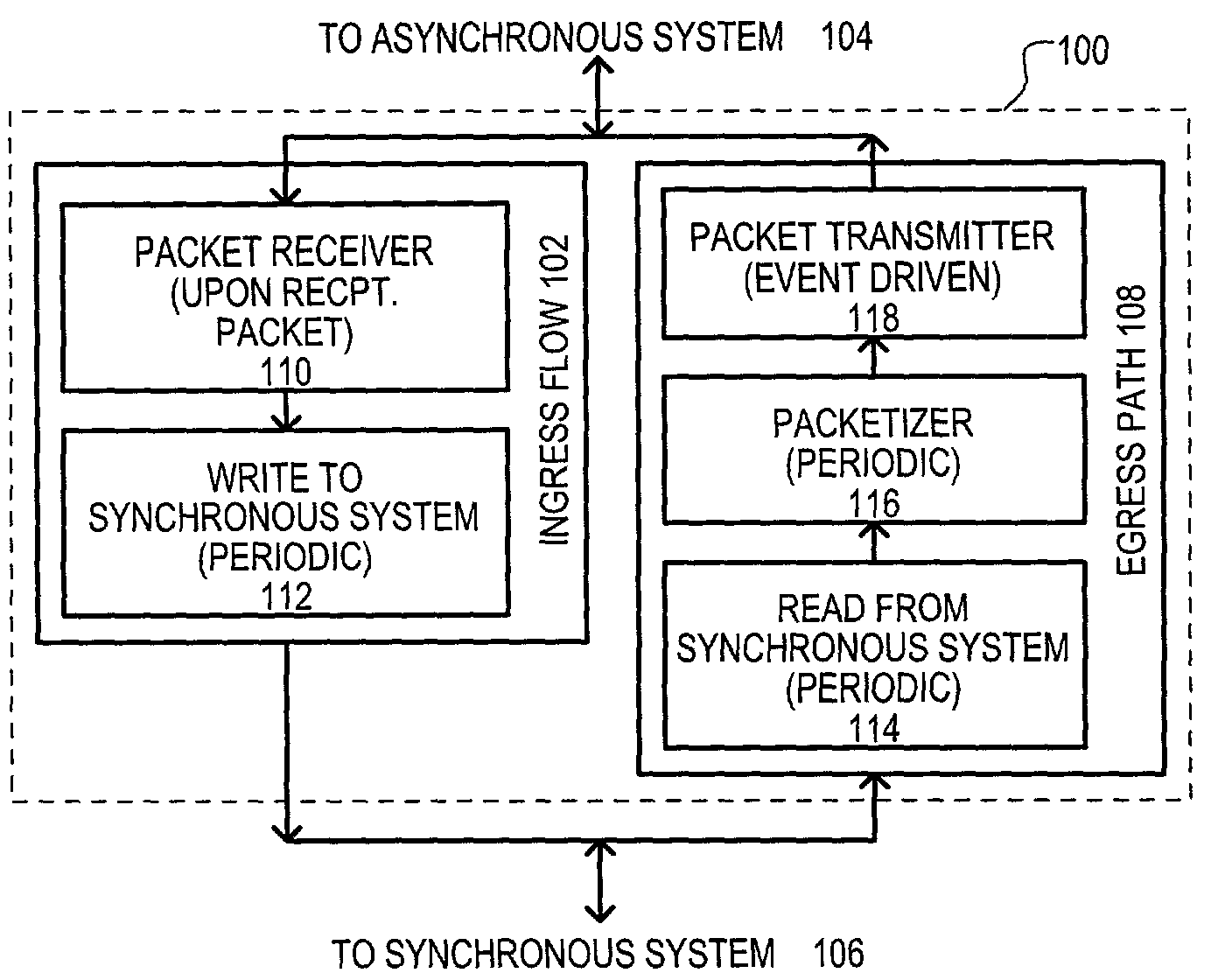
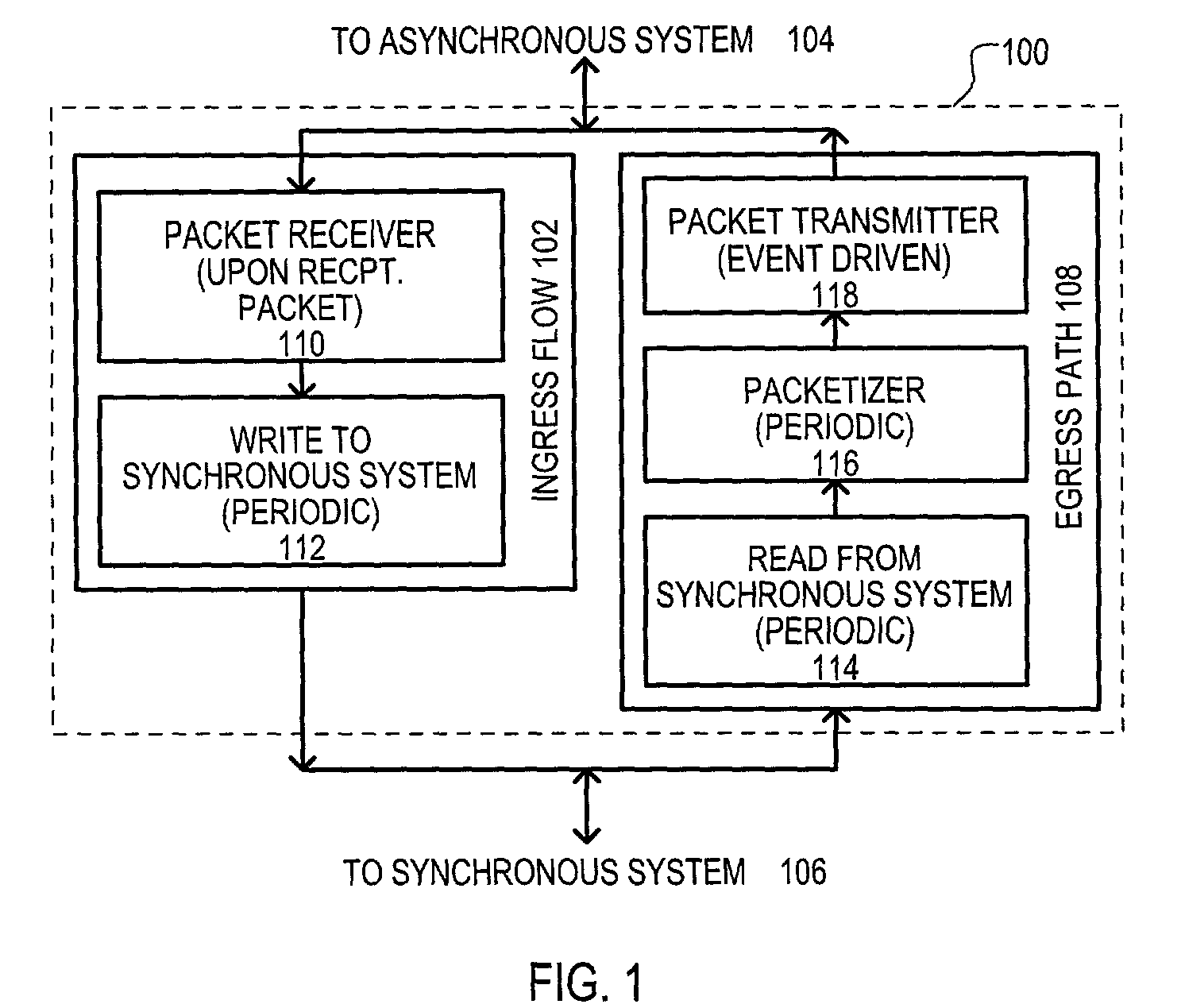
A system for transmitting real-time data between an asynchronous network (104) and a synchronous network (106) is disclosed. A method (100) may include an ingress path (102) for transmitting data from an asynchronous system (104) to a synchronous system (106), and an egress path (108) for transmitting data from a synchronous system (106) to an asynchronous system (104). An ingress path (102) may include a packet receiver (110) and write to synchronous system (112) steps. An egress path (108) may include read from synchronous system (114), packetizer (116), and packet transmitter (118) steps.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Synchronous network traffic processor
InactiveUS6880070B2Low costReduce developmentDigital computer detailsNext instruction address formationTraffic capacityWire speed
A synchronous network traffic processor that synchronously processes, analyzes and generates data for high-speed network protocols, on a wire-speed, word-by-word basis. The synchronous network processor is protocol independent and may be programmed to convert protocols on the fly. An embodiment of the synchronous network processor described has a low gate count and can be easily implemented using programmable logic. An appropriately programmed synchronous network traffic processor may replace modules traditionally implemented with hard-wired logic or ASIC.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
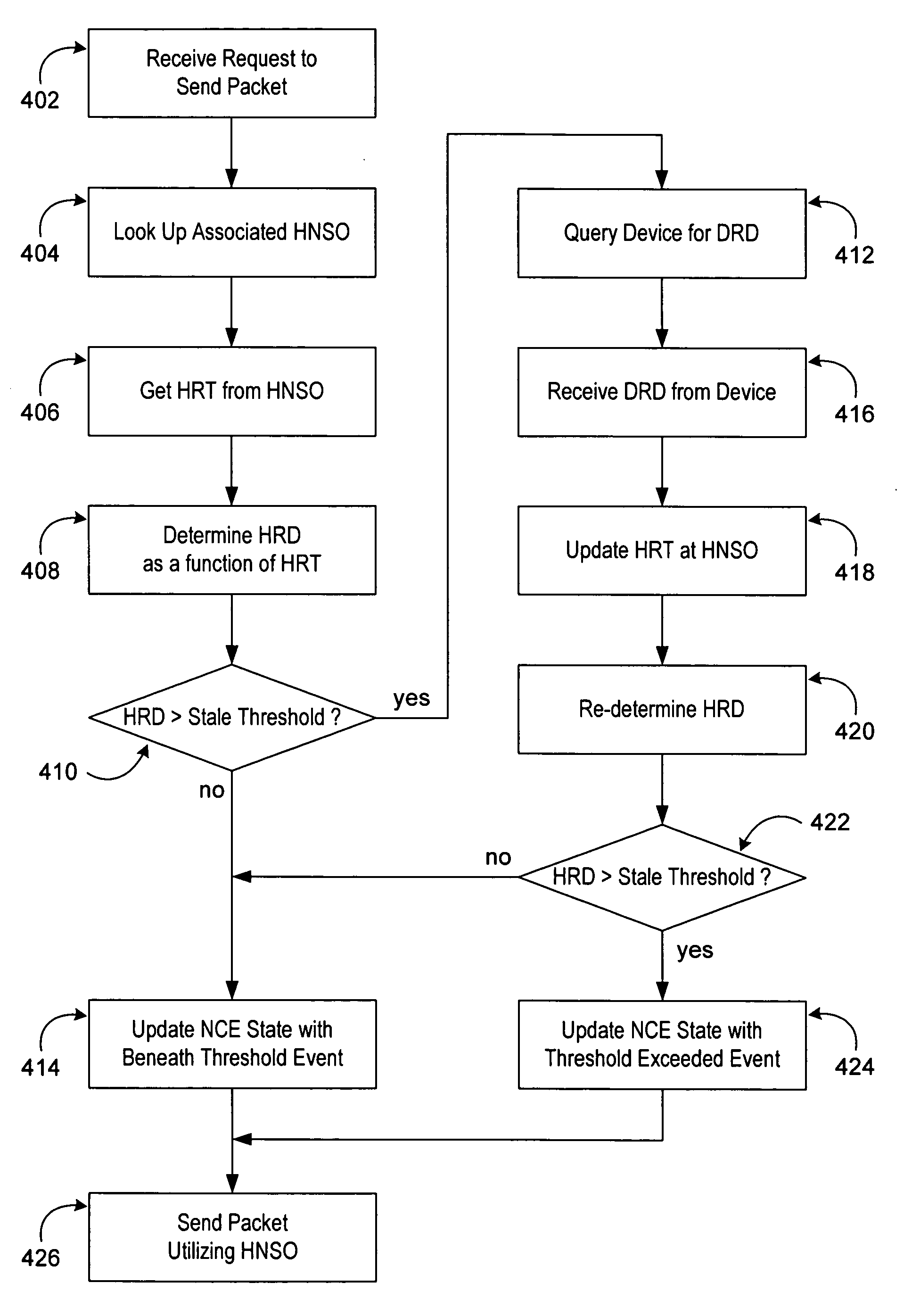
Offloaded neighbor cache entry synchronization
A method for the synchronization of network neighbor reachability between a host networking stack and a peripheral device, which offloads one or more network protocols is provided. The network neighbor reachability represents the reachability of another computer on the network. This invention enables conventional neighbor reachability to be extended to seamlessly support some network connections to a specific remote host to be offloaded to a peripheral device, while other network connections are not.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
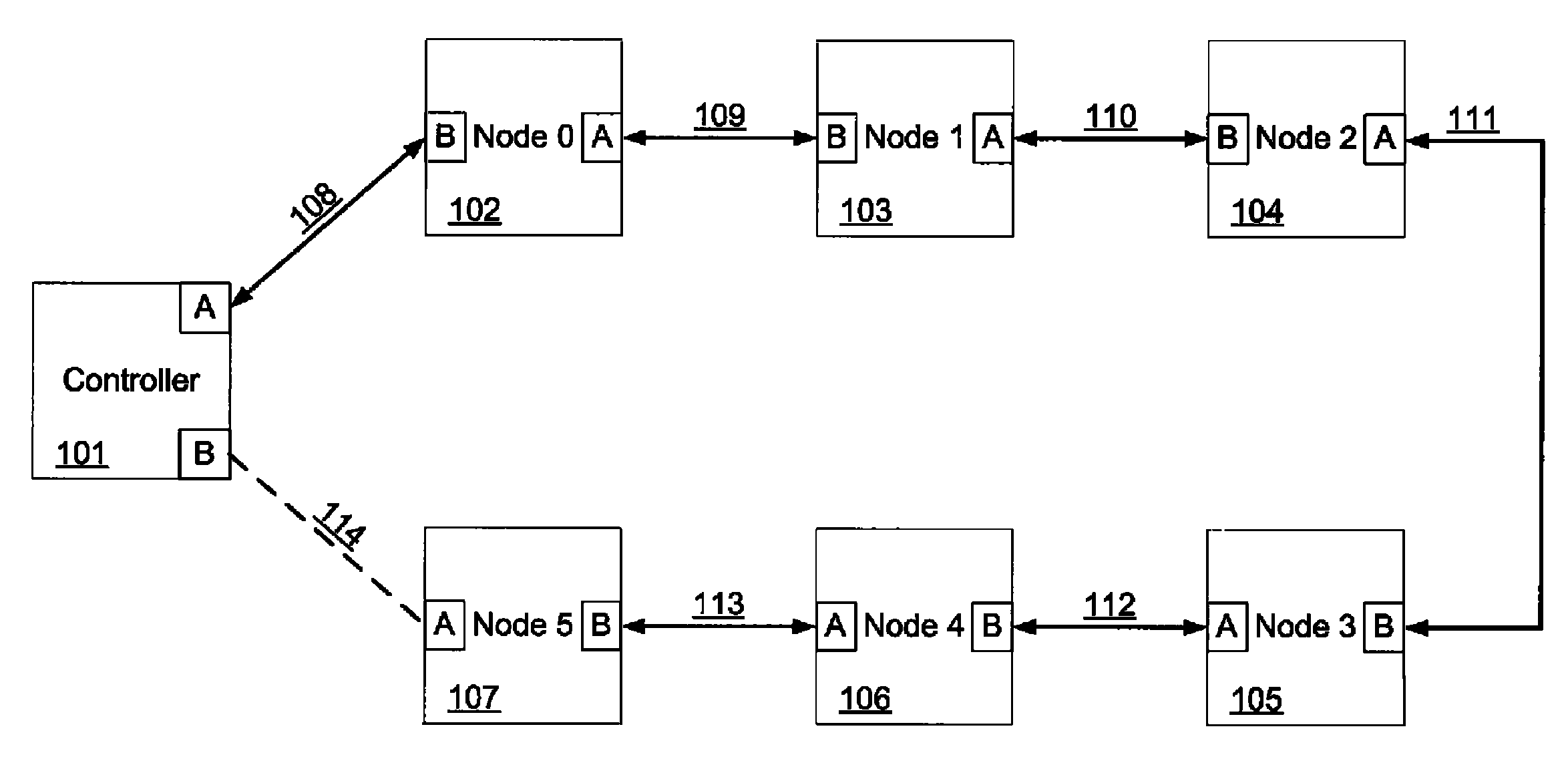
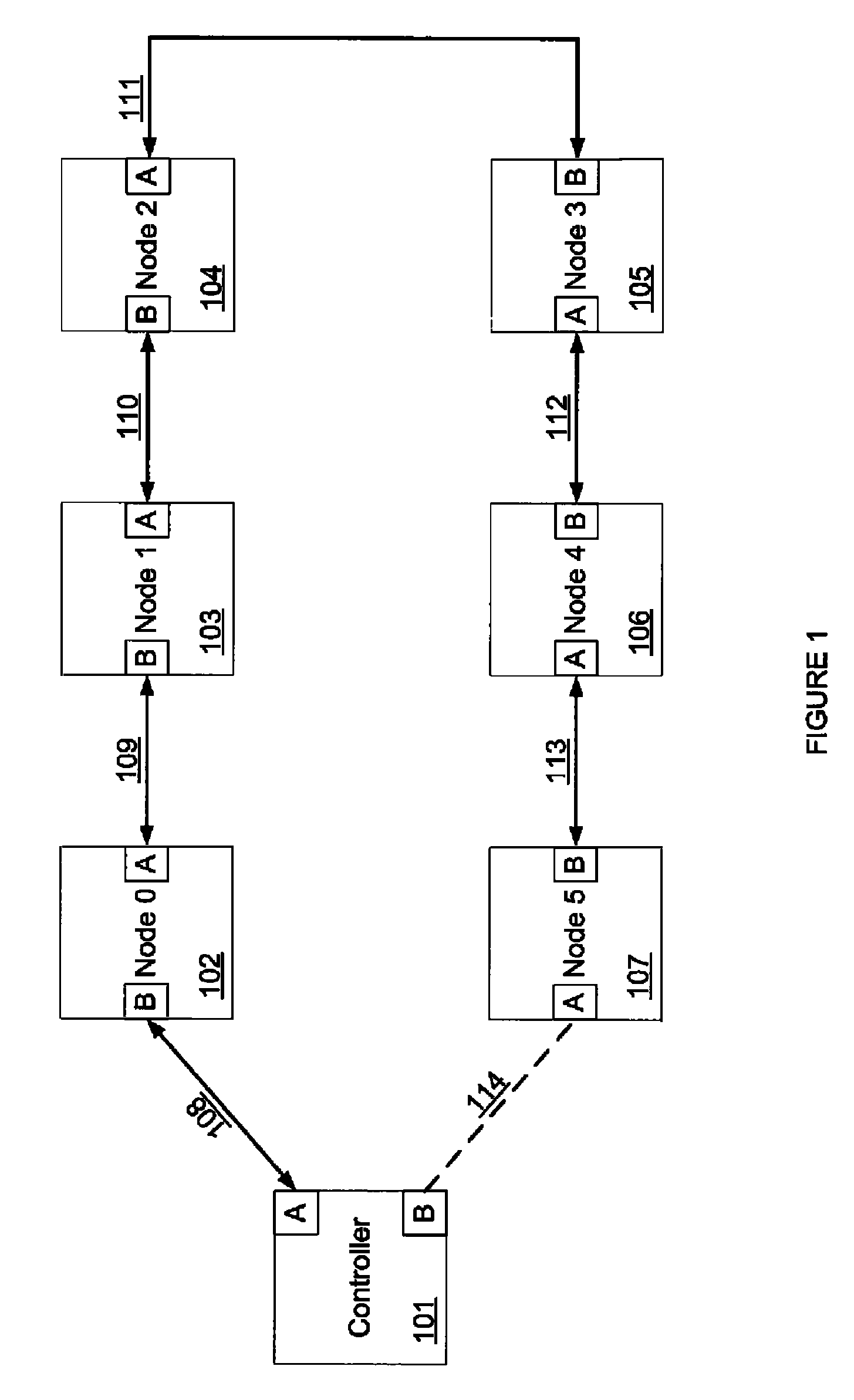
Method and system for removing and returning nodes in a synchronous network
InactiveUS8072999B1Without undue complexityEasy to attachRadio transmissionLoop networksSynchronous networkDistributed computing
A method and system for adding a node into a network operating in a cyclic state after one or more nodes have been previously removed without interrupting the synchronous traffic of the remaining nodes on the network is provided. The method includes discovering an added node by sending data to the added node in a downstream timeslot previously assigned to a removed node, the data having a delay value for scheduling a response from the added node to coincide with an upstream timeslot previously assigned to the removed node, thereby avoiding collisions with the synchronous traffic on the network; receiving the response from the added node; configuring the added node in accordance with an original configuration of the removed node; and commencing cyclic operation of the added node.
Owner:MOTION ENG
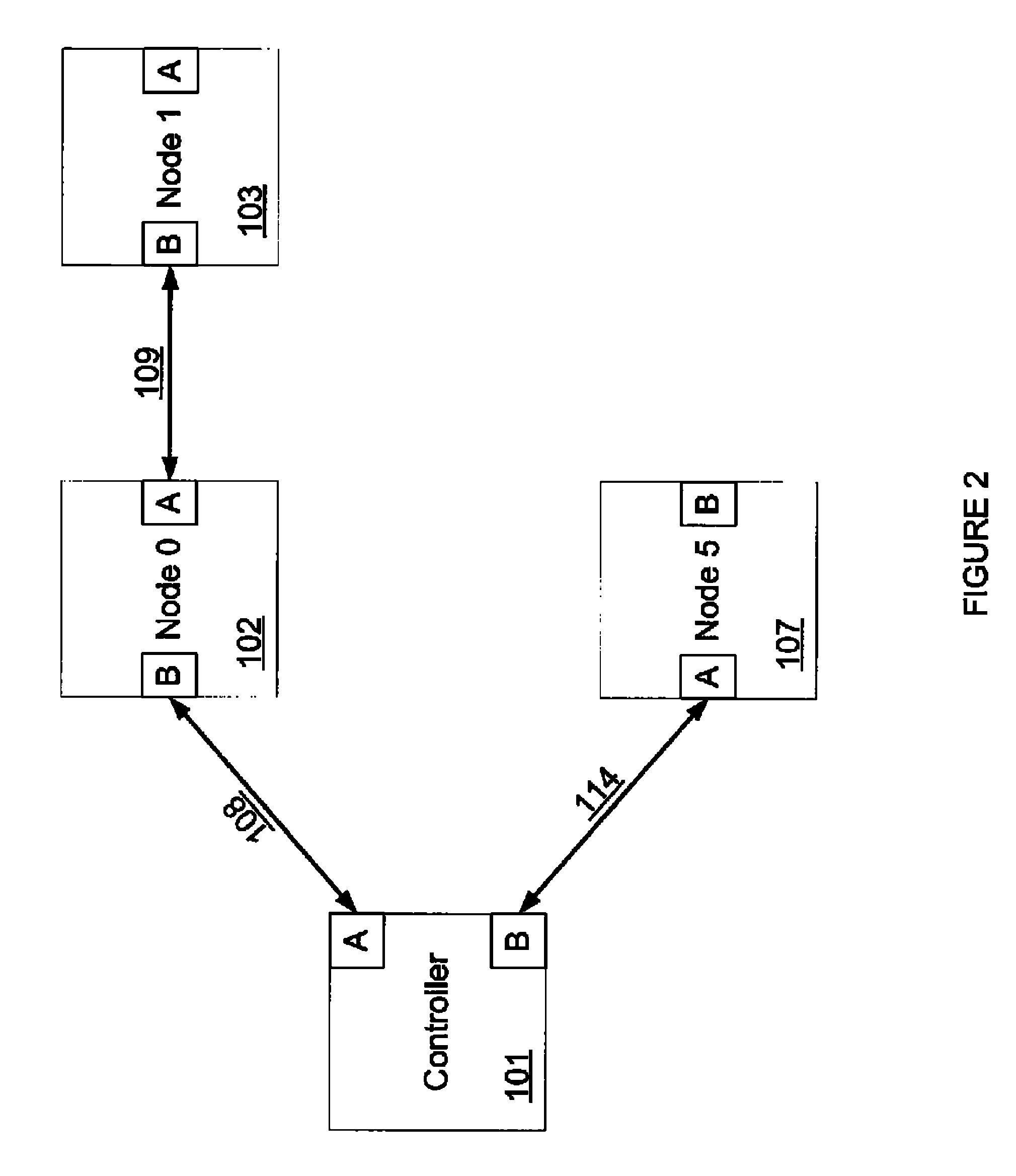
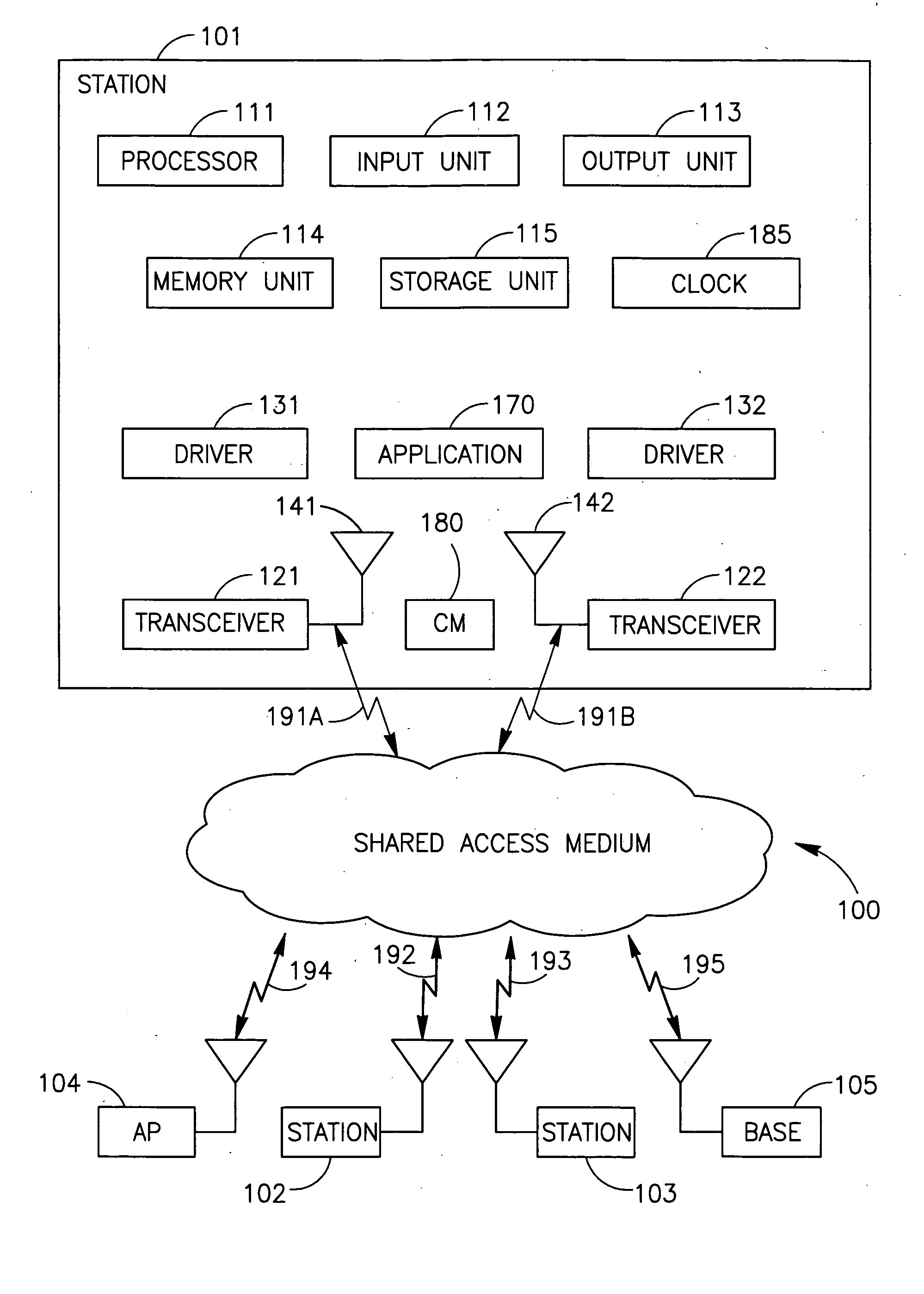
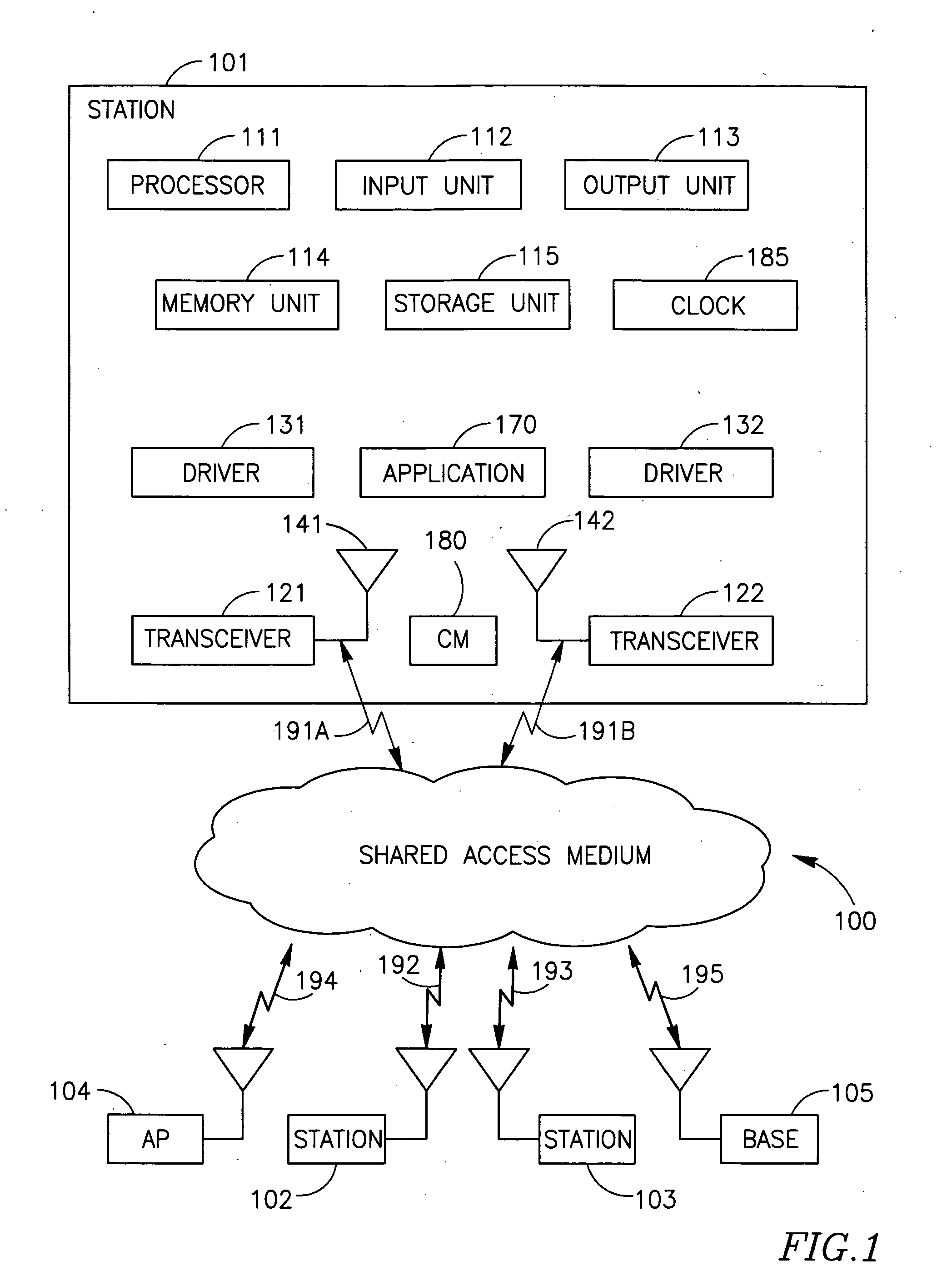
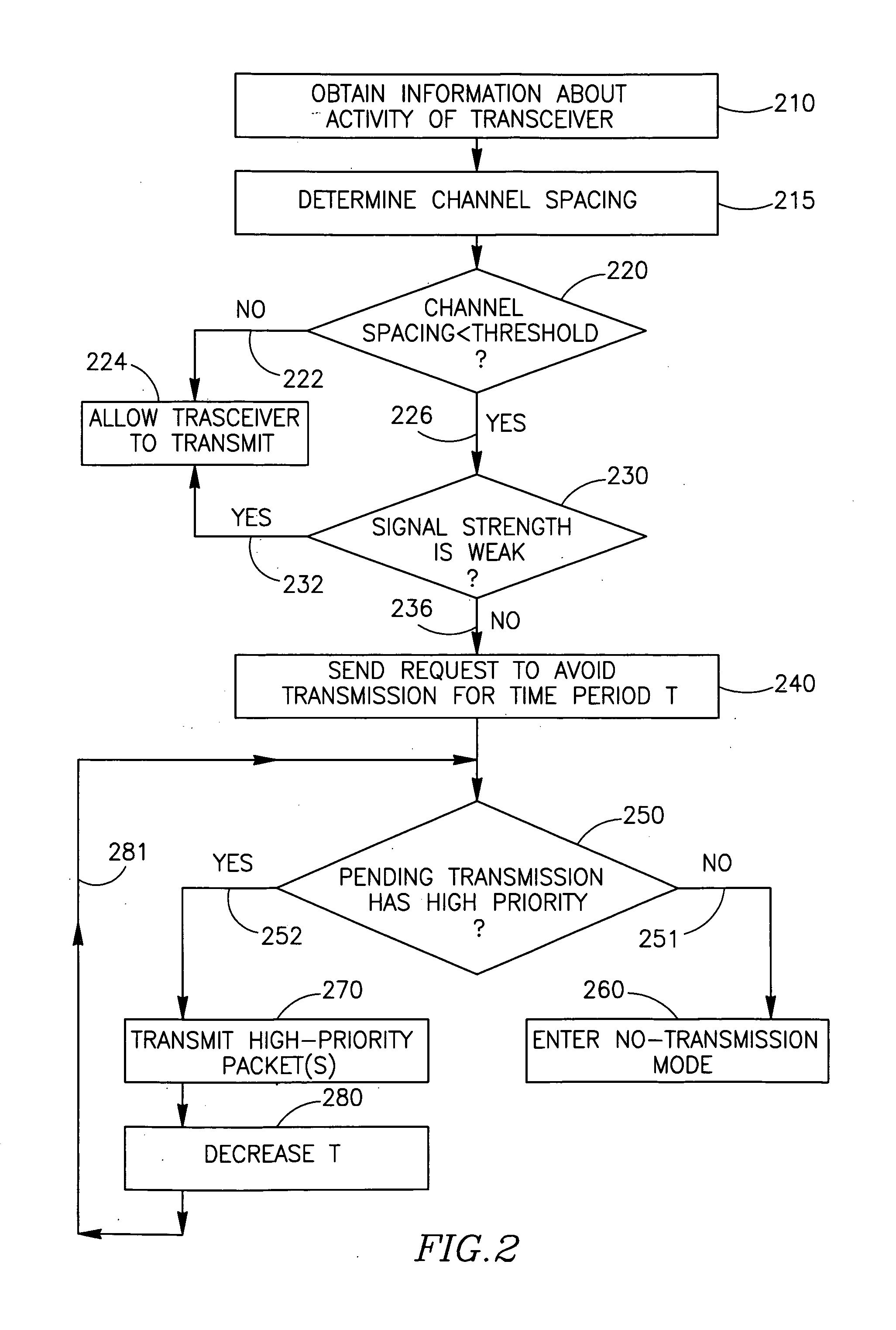
Device, system and method of coordination among wireless transceivers
ActiveUS20070080781A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexTransceiverWireless transceiver
Some embodiments of the invention provide devices, systems and methods of coordination among wireless transceivers. For example, an apparatus in accordance with an embodiment of the invention includes first and second wireless transceivers, wherein the first wireless transceiver is to enter a non-transmission mode for a pre-defined time period in response to an indication from the second wireless transceiver, and wherein one of the first and second wireless transceivers is to operate in a synchronous network and the other of the first and second wireless transceivers is to operate in a non-synchronous network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
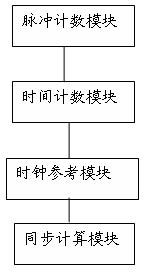
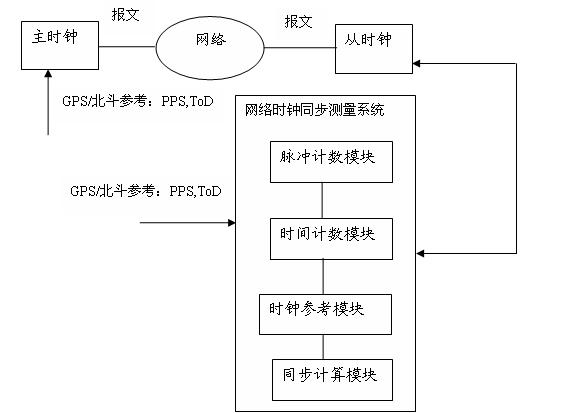
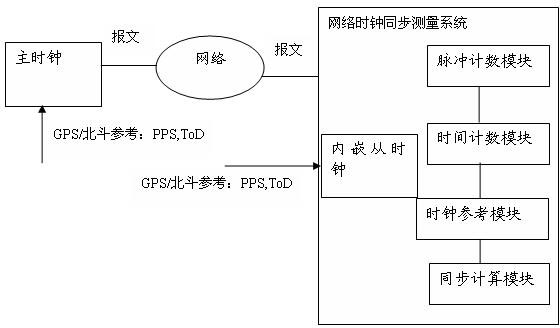
System and method for measuring network clock synchronization
The invention discloses a system for measuring network clock synchronization, is applied to the communication and smart grid fields. The system comprises a pulse countering module, a time counting module, a clock reference module and a synchronization calculation module, wherein the pulse counting module calculates pulse frequency difference between a master clock and a slave clock, the master clock is synchronous with a remote reference clock, and the slave clock is synchronous with the master clock through a network so as to be synchronous with the remote reference clock; the time counting module measures the time difference between the master clock and the slave clock; the clock reference module inputs a reference clock, and the reference clock is synchronous with the remote reference clock; and the synchronization calculating module is used for calculating network clock synchronization parameters according to the time difference and the pulse frequency difference and outputting time synchronization parameters. The system disclosed by the invention can be used for evaluating the clock frequency synchronization accuracy and the time synchronization accuracy which can be reached at each node by an IEEE1588PTP (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 1588 Peer To Peer) clock synchronous network, and important reference data is provided for clock synchronization network optimization, and performance prediction on application and equipment depending on clock synchronization.
Owner:上海奇微通讯技术有限公司
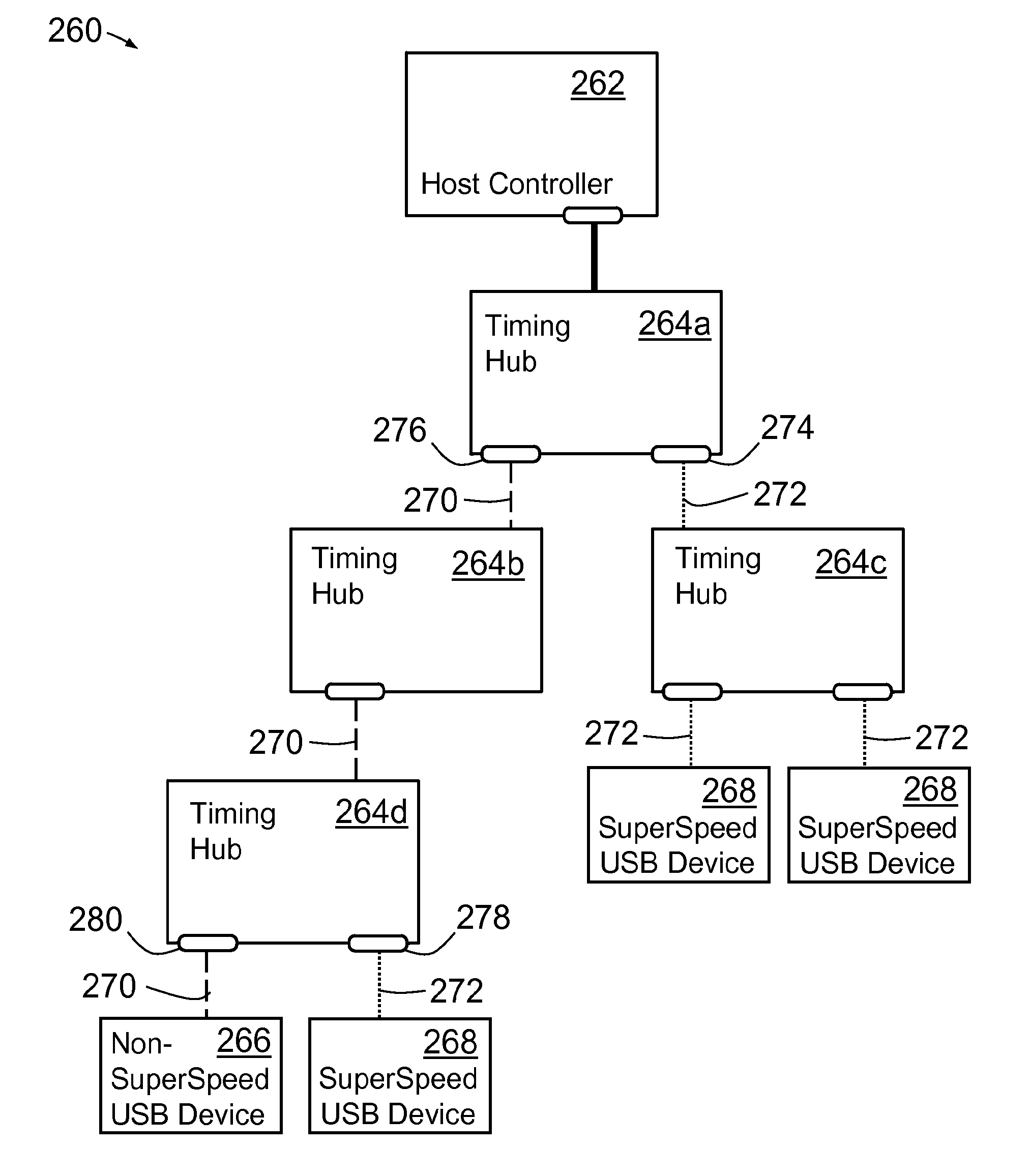
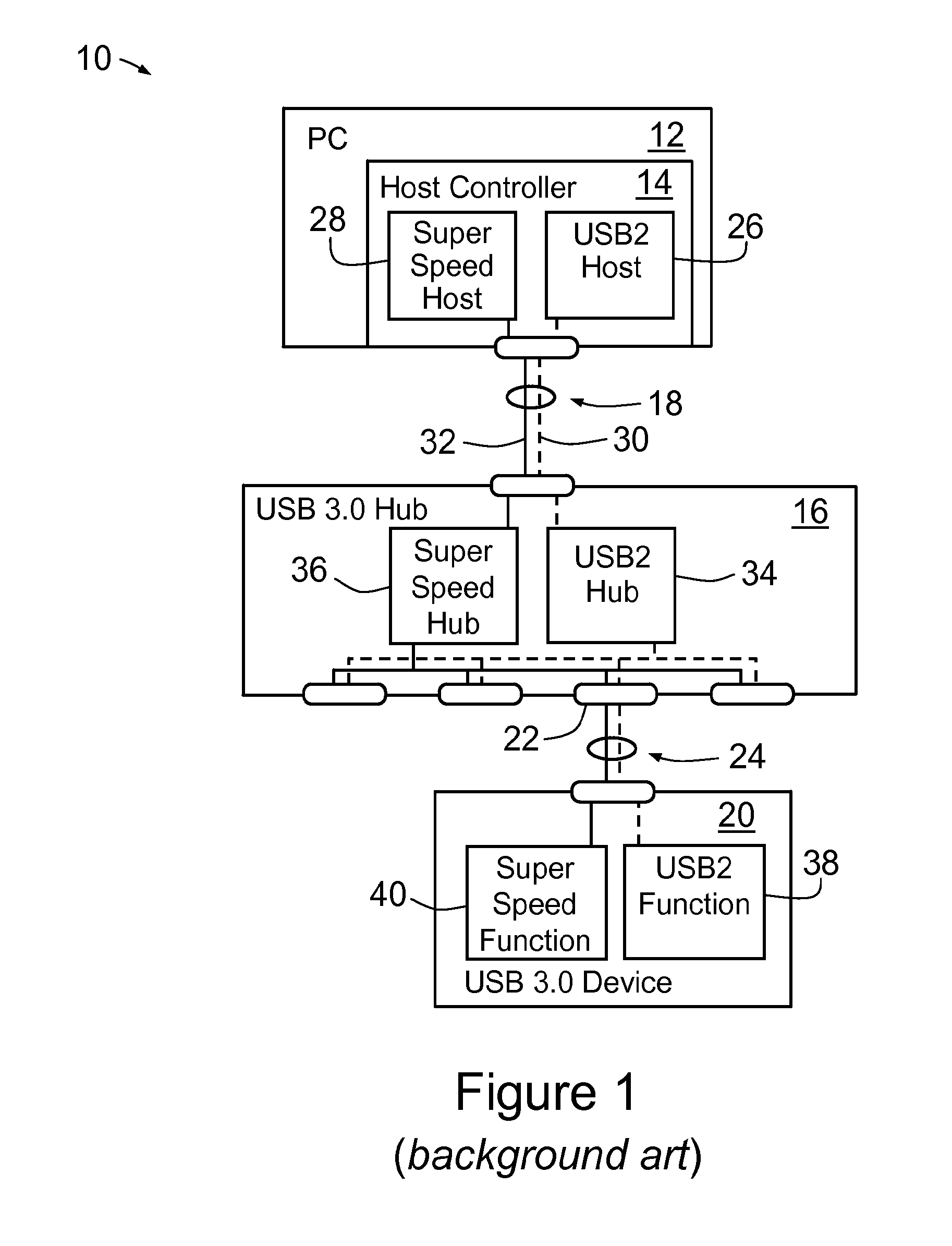
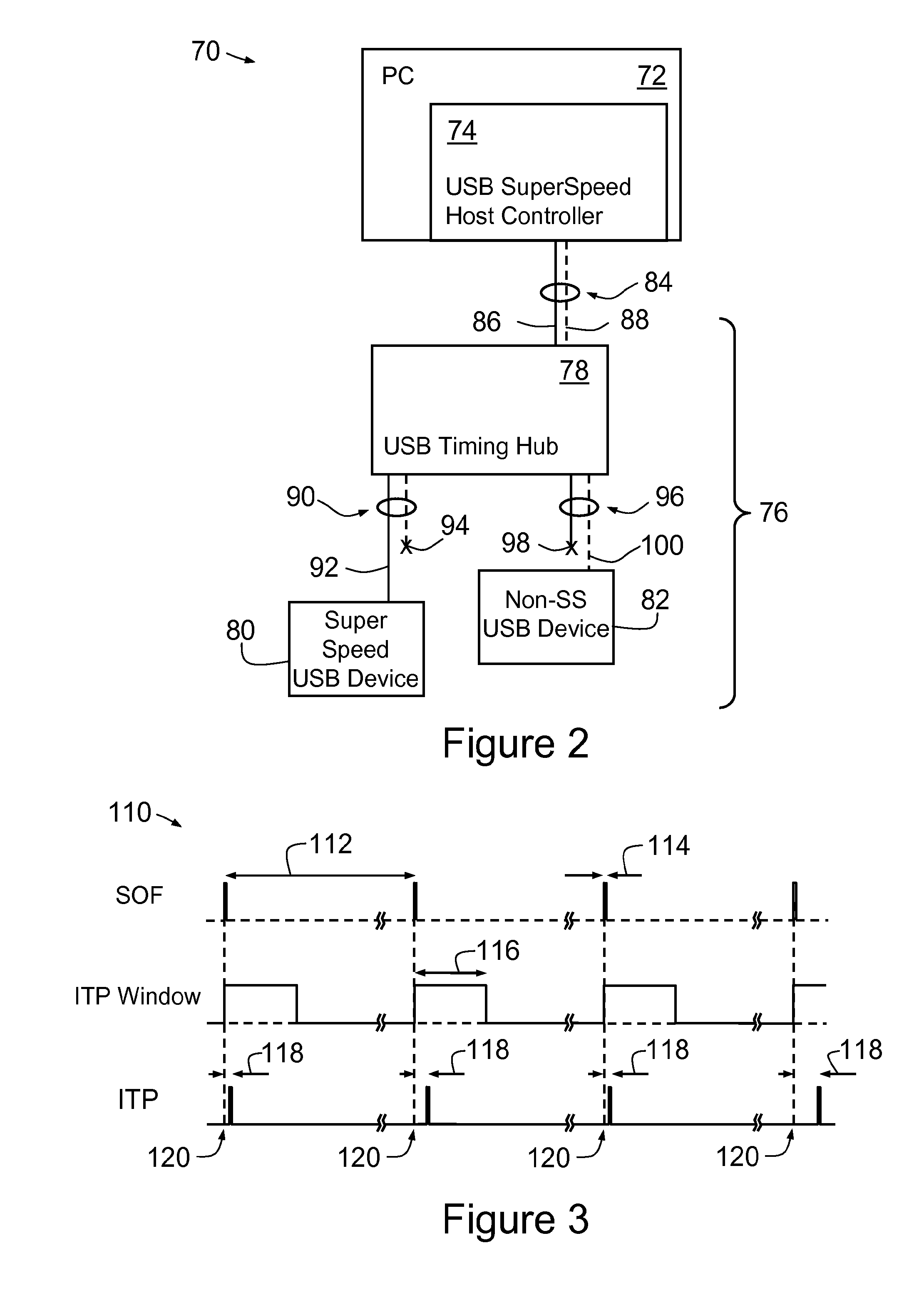
Synchronous network of superspeed and non-superspeed USB devices
InactiveUS20120066418A1Improve accuracyError detection/correctionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlSynchronous networkUSB
Owner:CHRONOLOGIC PTY LTD
Real time synchronization network based on the standard Ethernet and its operating method
InactiveCN101018115AAchieve consistencyOvercome limitationsData switching by path configurationSynchronising arrangementPresent methodSynchronous network
The disclosed real-time synchronous network based on standard Ethernet divides devices in network into the primary and slavery ones, provides a network topology for full-duplex communication in Ethernet, and presents method for primary device to automatic enumerate and configure slavery devices.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
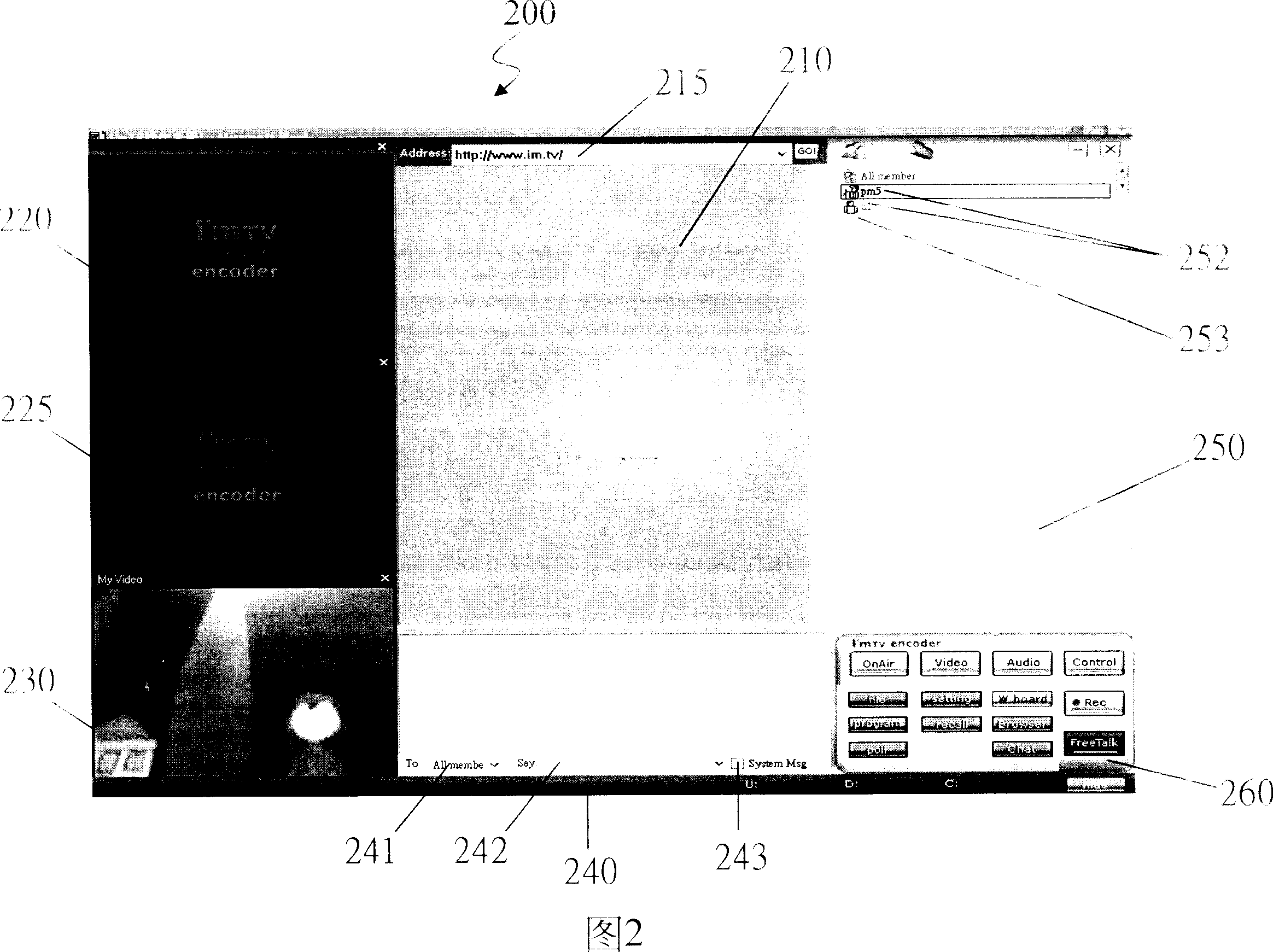
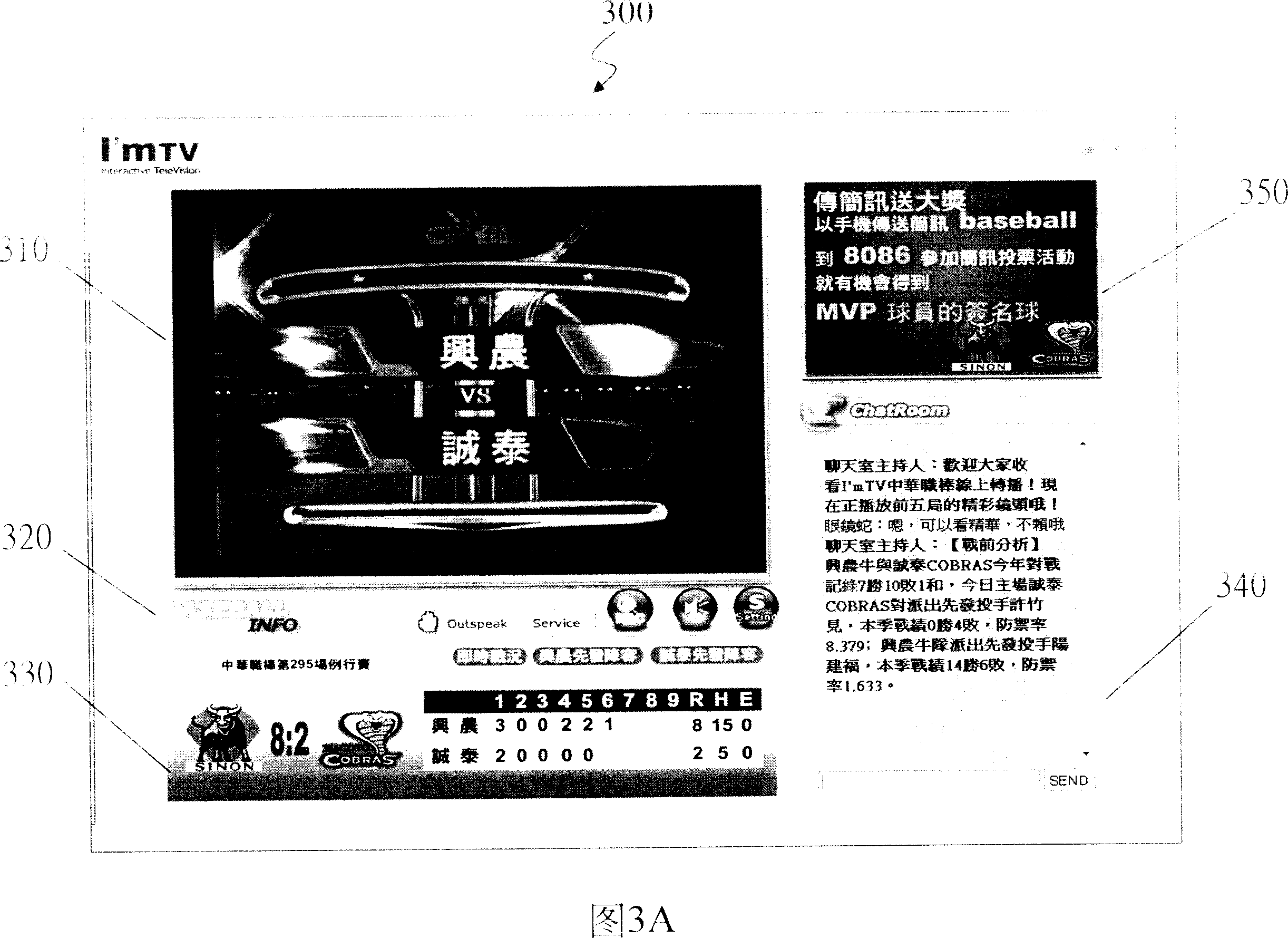
Interactive multimedia interface and display
The interactive multimedia interface provides multiple multimedia contents and services for complex user from different platforms, and let users communicate by real-time information, sound or video signal. Besides, it also provides lots of interactive tools, such as application share, synchronous network browsing, file sending, voting, conference record, and chat room; specially, there is an ad and shopping information window.
Owner:ERA DIGITAL MEDIA
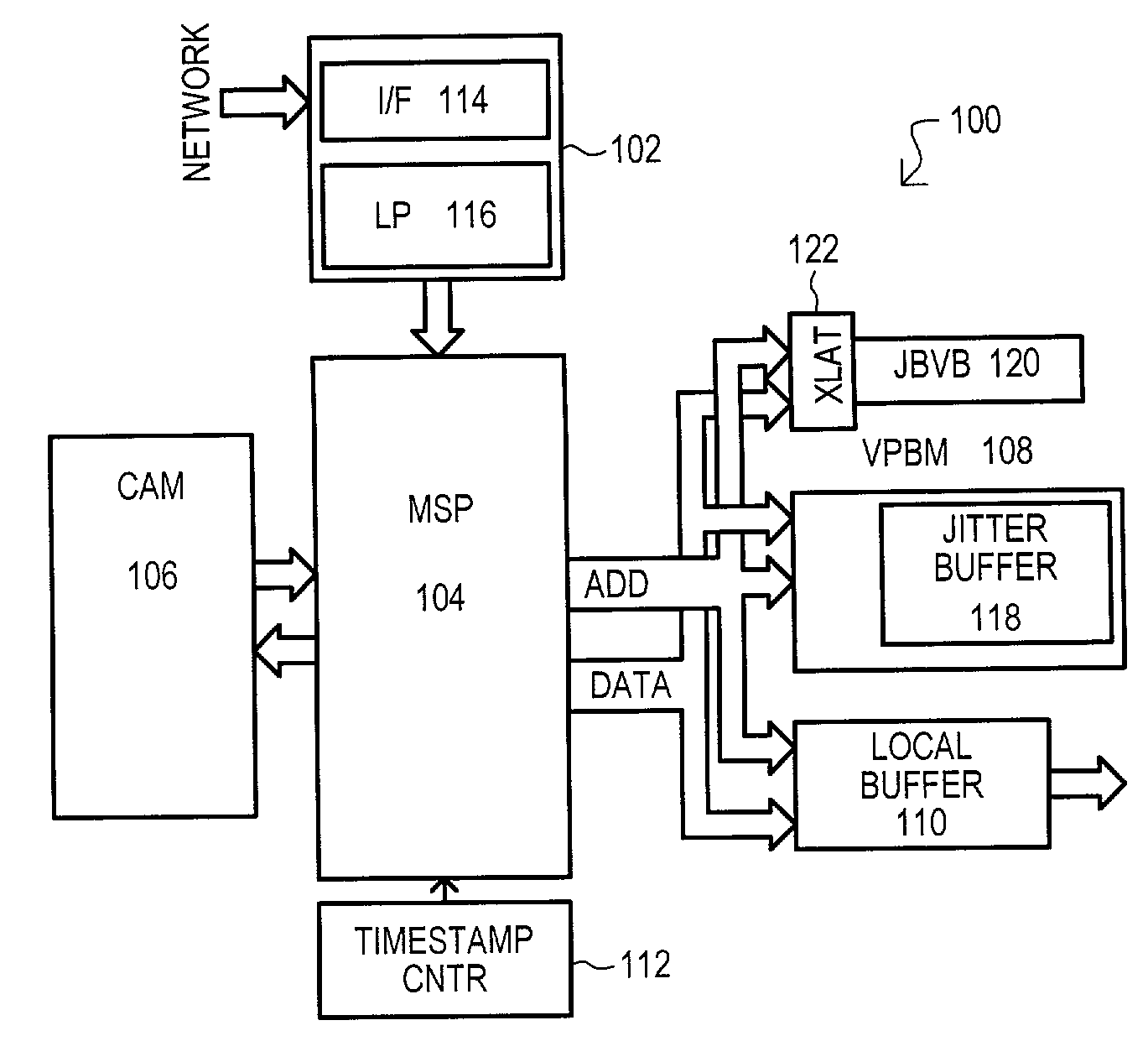
Jitter buffer state management system for data transmitted between synchronous and asynchronous data networks
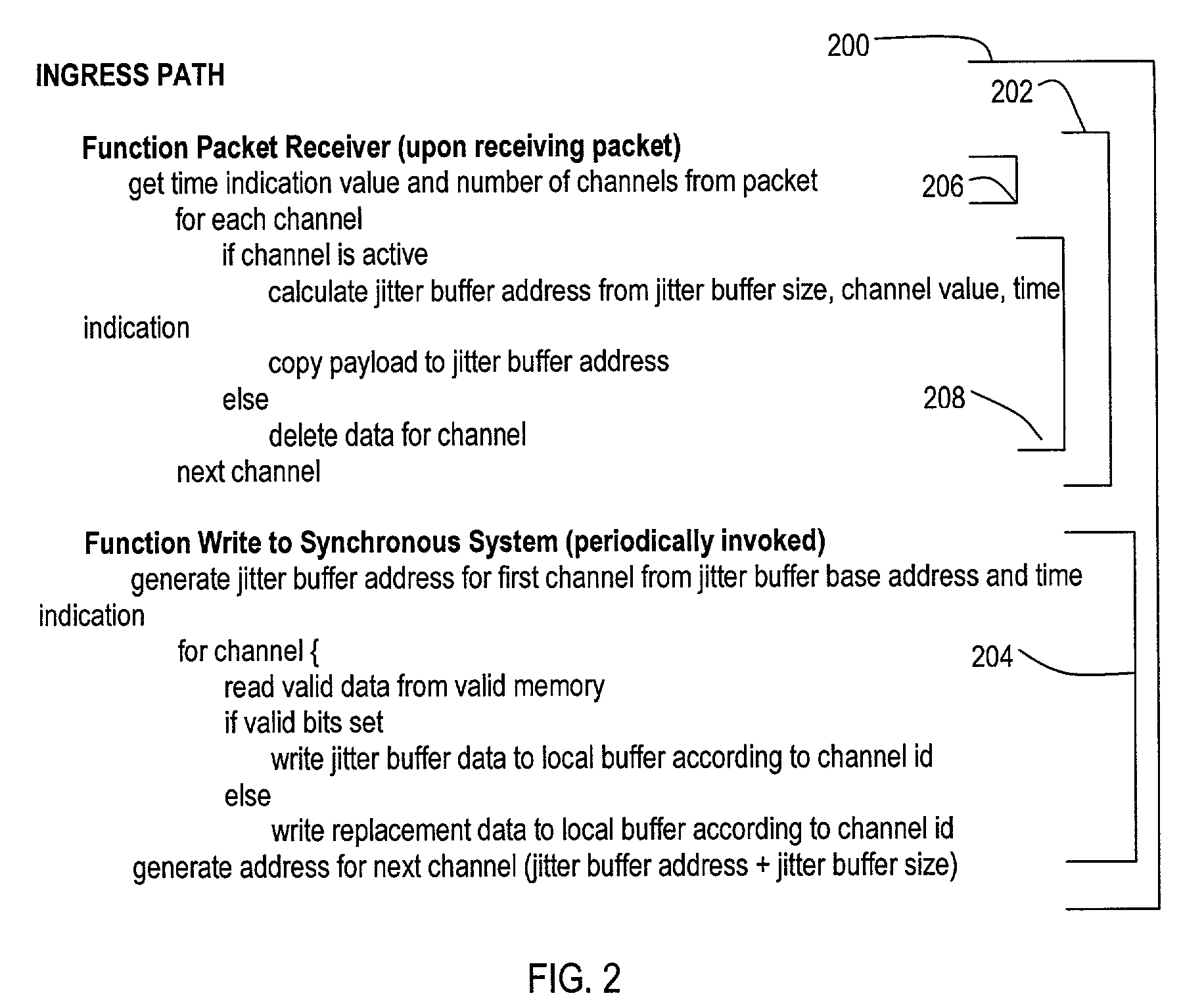
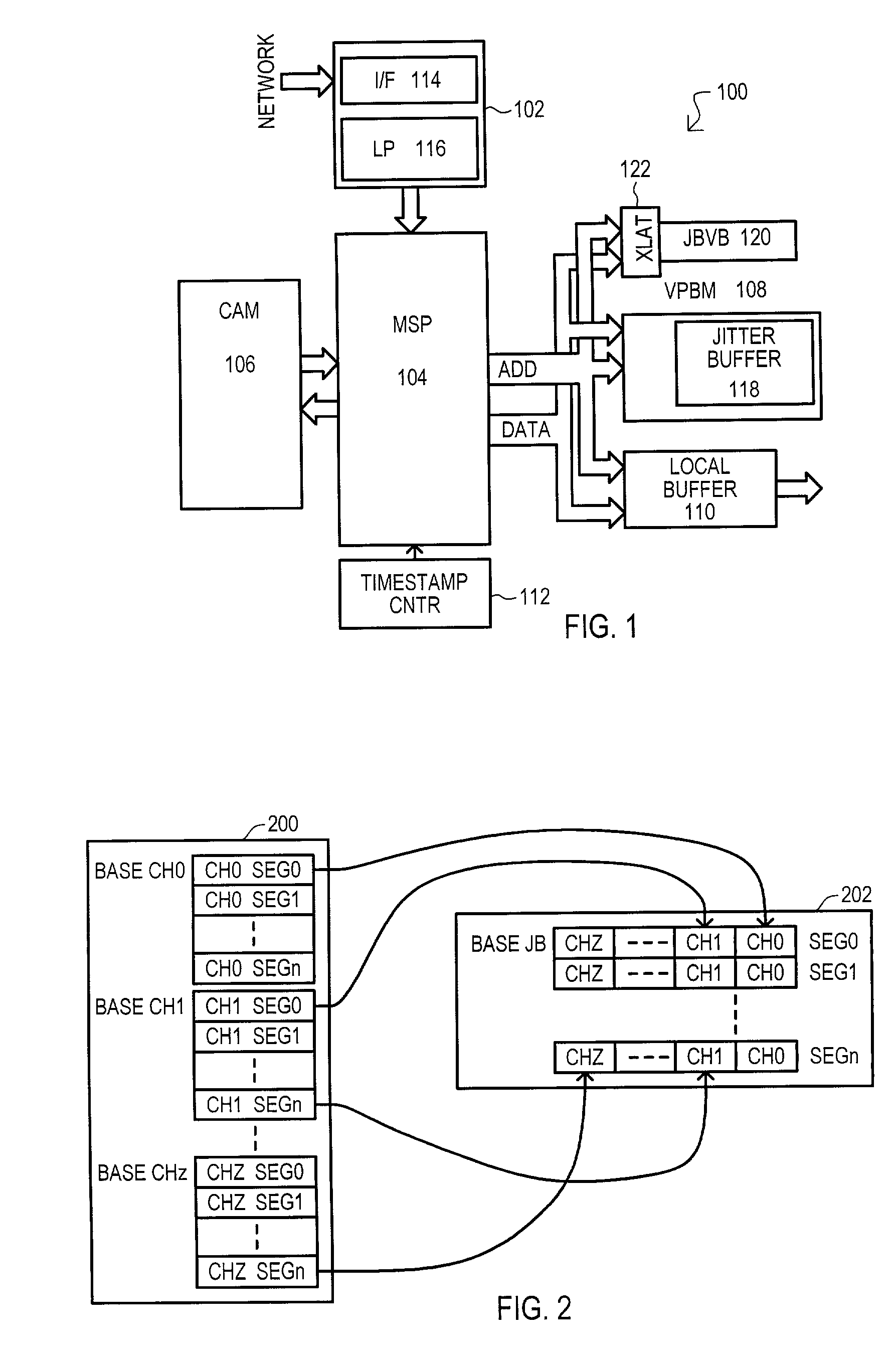
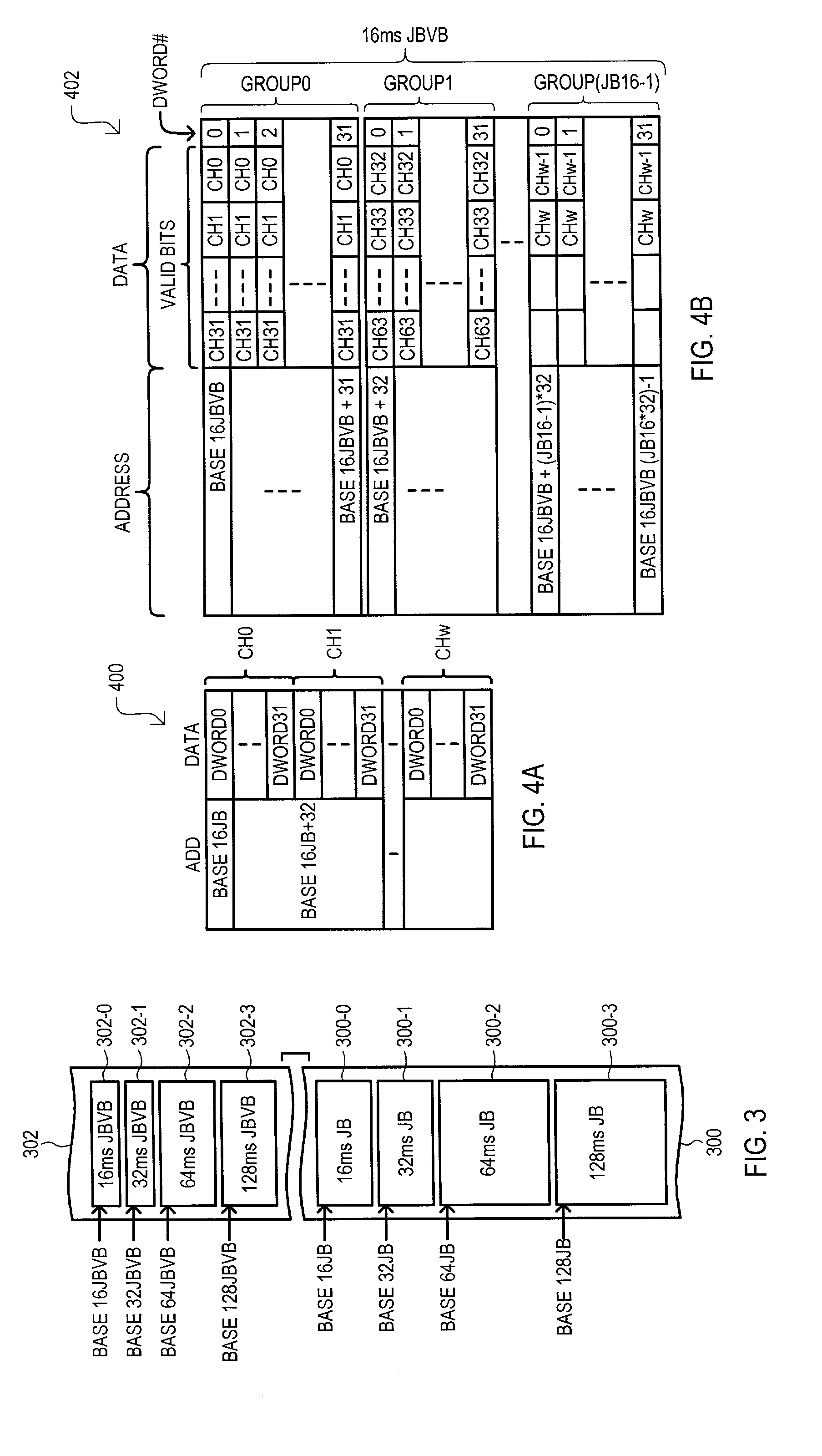
A system (100) for receiving data from an asynchronous network and transmitting such data onto a synchronous network includes a voice packet buffer memory system (108) with a jitter buffer (118) having groups of entries storing data for voice channels and jitter buffer valid bit (JBVB) memory (120) for status of a particular entry for multiple jitter buffer groups. Writing or reading data from a jitter buffer entry sets a corresponding JBVB memory bit to a valid or invalid state respectively. Jitter buffer data may be read with a corresponding state memory bit. If a corresponding JBVB memory bit is valid, data from a jitter buffer (118) may be provided as an output. If a corresponding JBVB memory bit is invalid, a loss recovery algorithm may compensate for such invalid jitter buffer data.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC +1
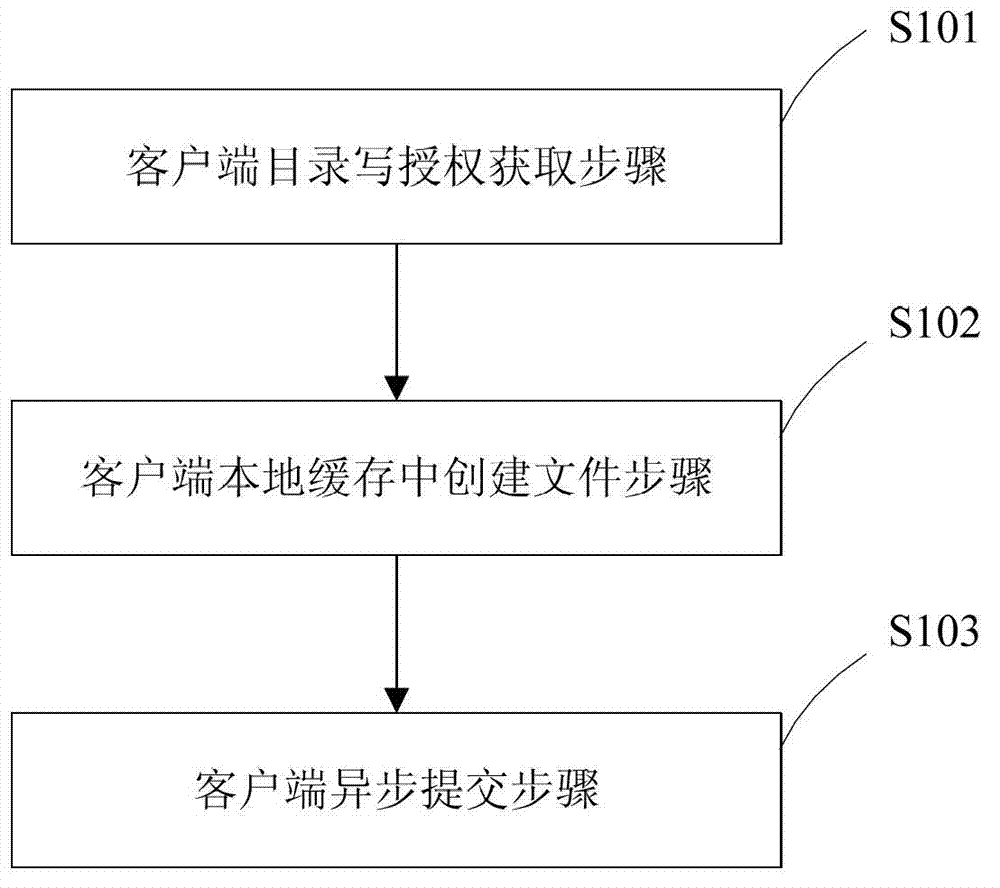
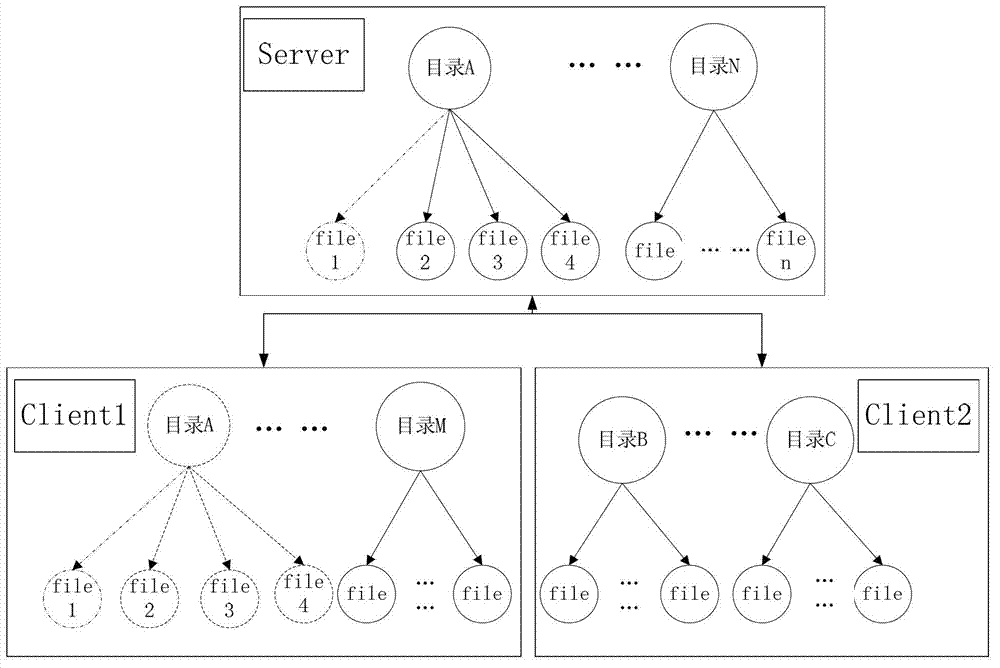
Method and system for creating files in cache of distributed file system client
ActiveCN103179185AReduce creation latencyInteraction overhead avoidanceTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed File SystemSynchronous network
The invention discloses a method and a system for creating files in cache of a distributed file system client. The method includes the steps of firstly, allowing the client to acquire catalogue writing authorization from a metadata server; secondly, allowing the client to create files in local cache; and thirdly, allowing the client to asynchronously submit the created files to the metadata server. The problem that the cost of interaction with a metadata server synchronous network fails to be effectively lowered during file creation for the distributed file system in the prior art under the scenario of application of lots of small files is solved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
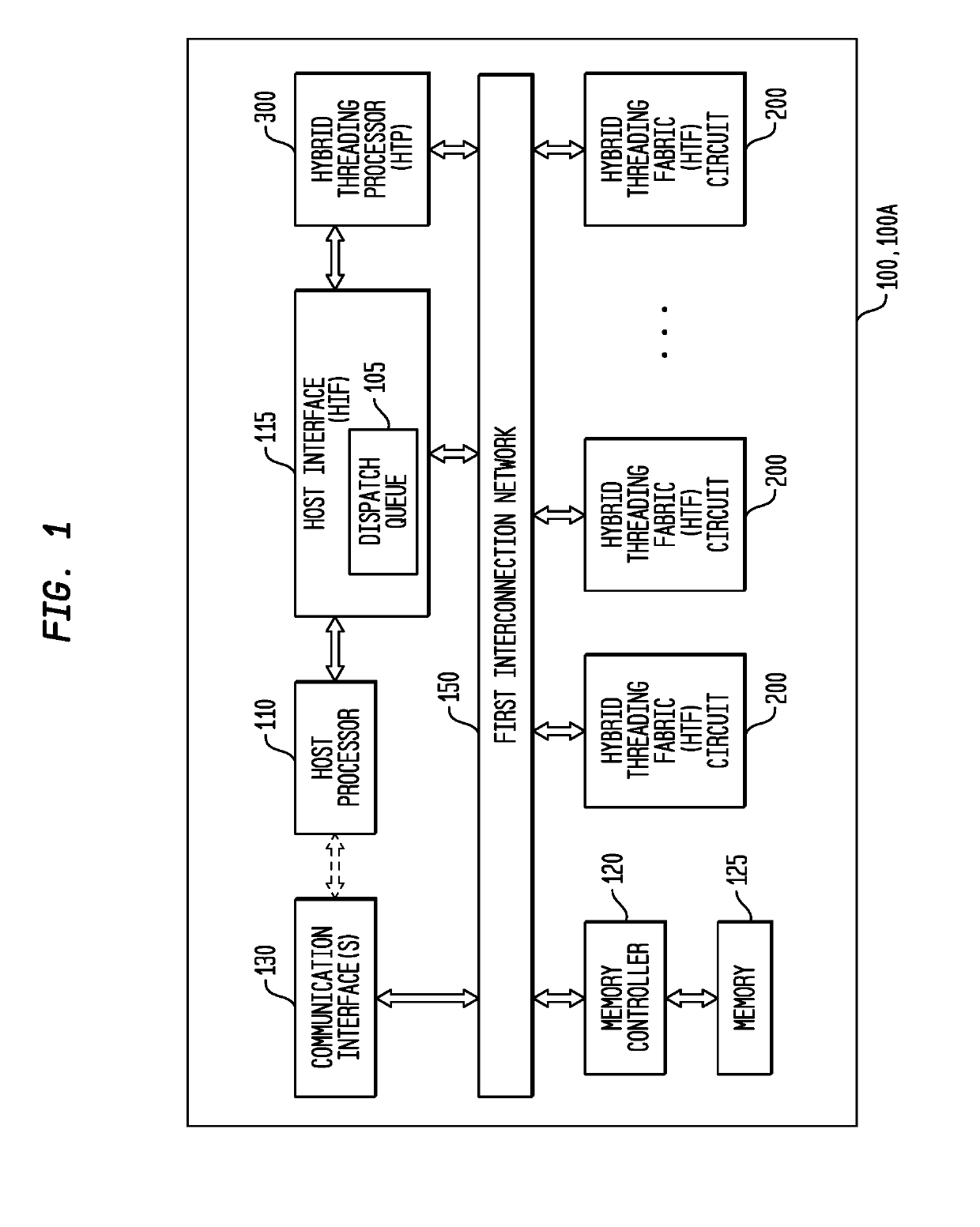
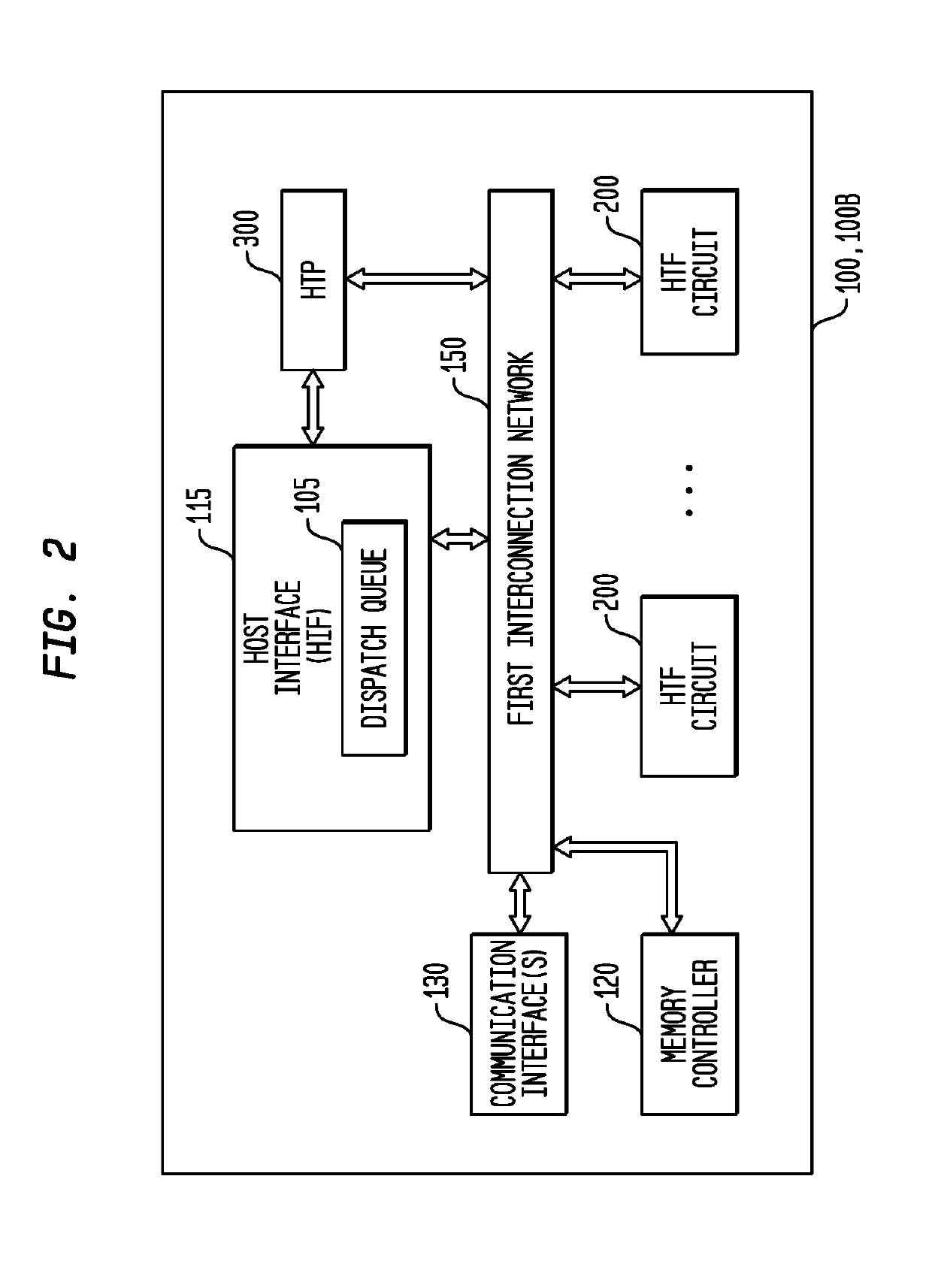
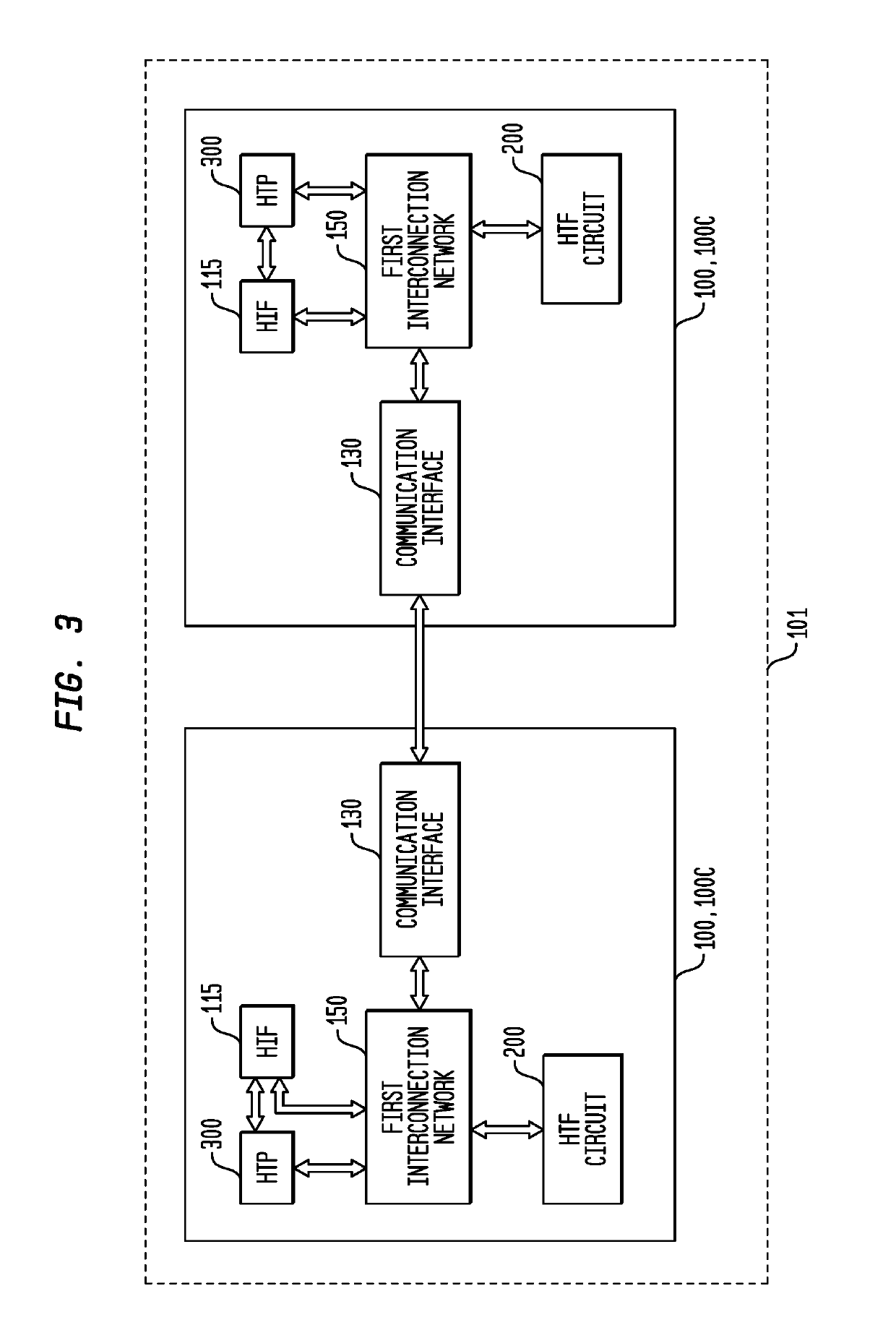
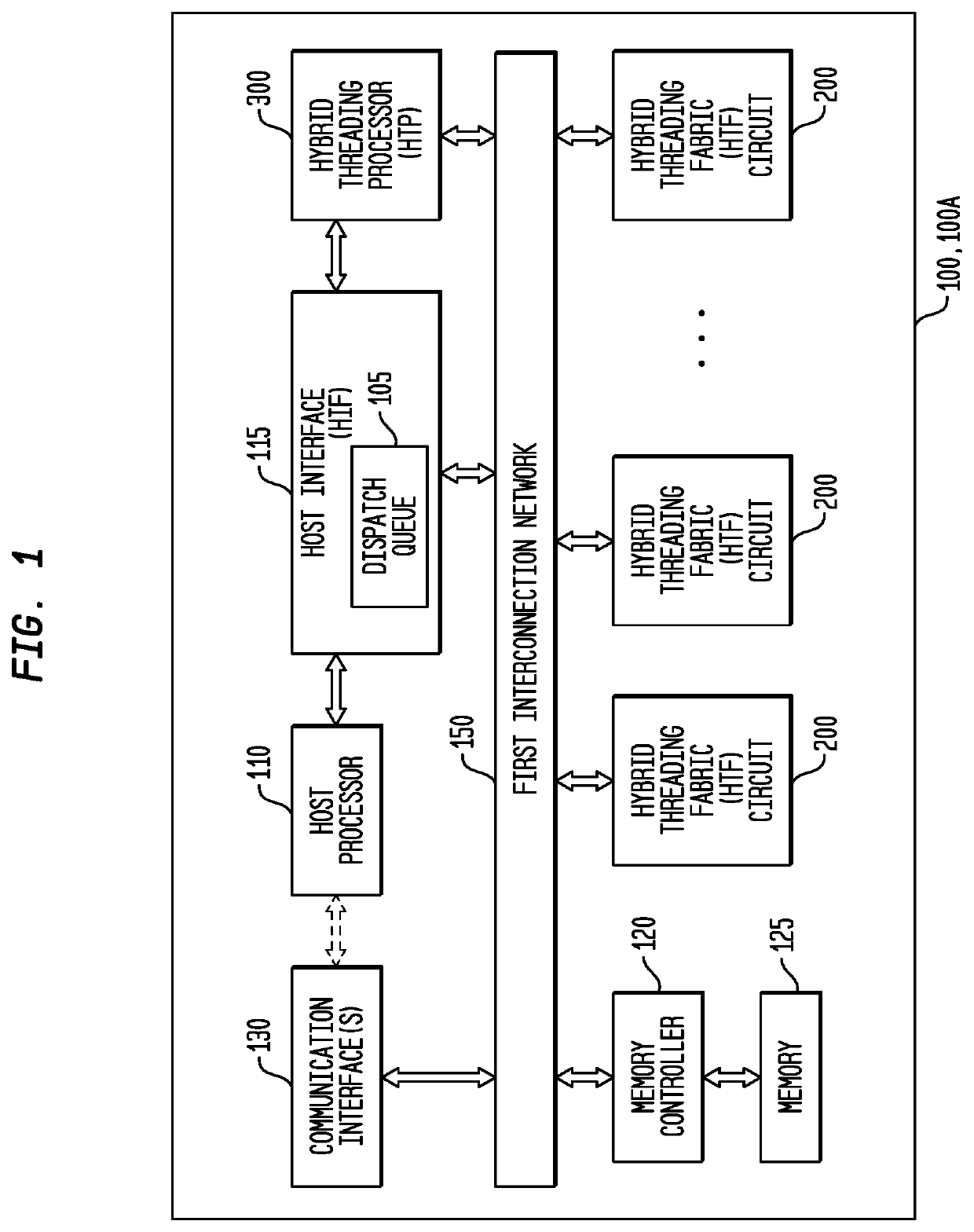
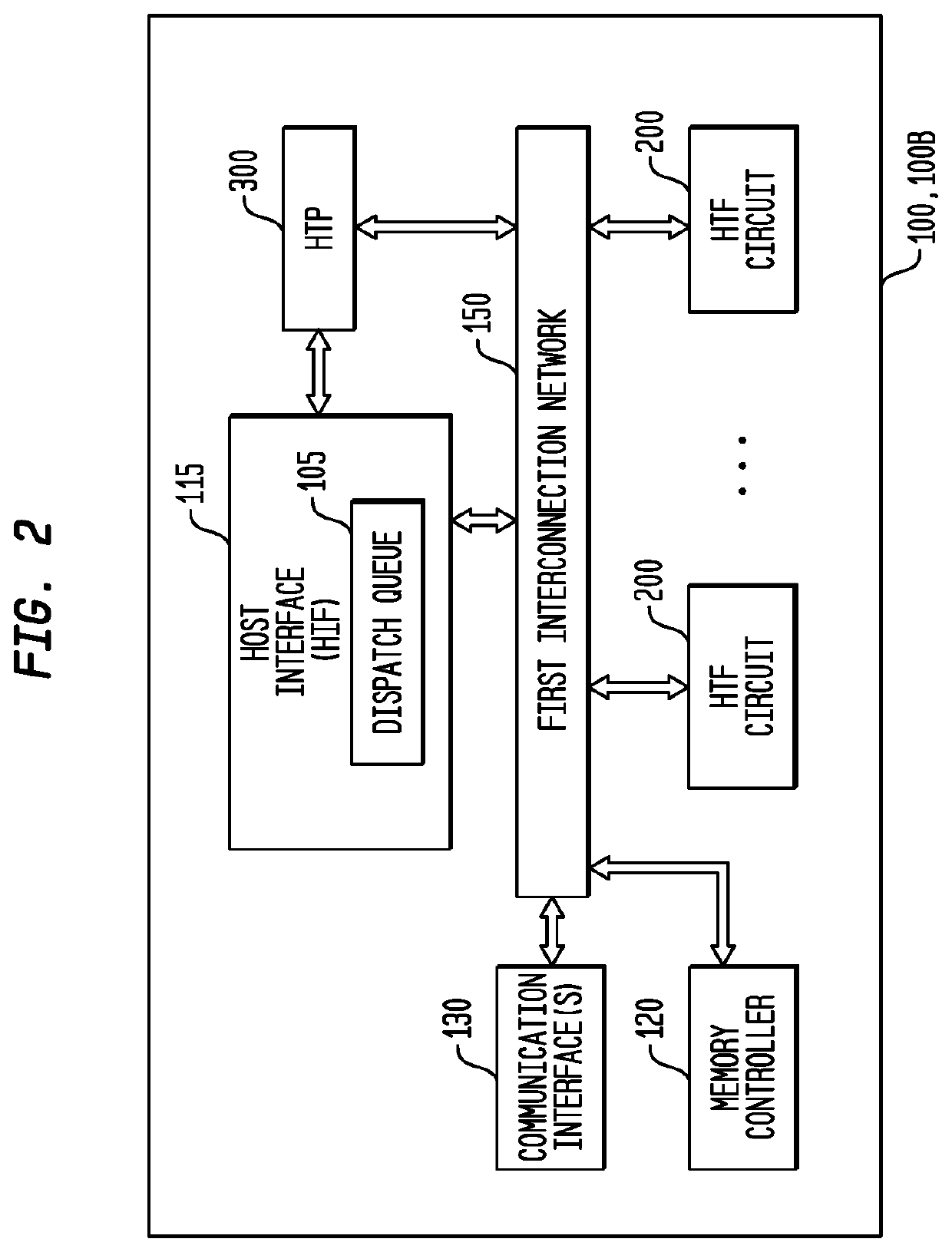
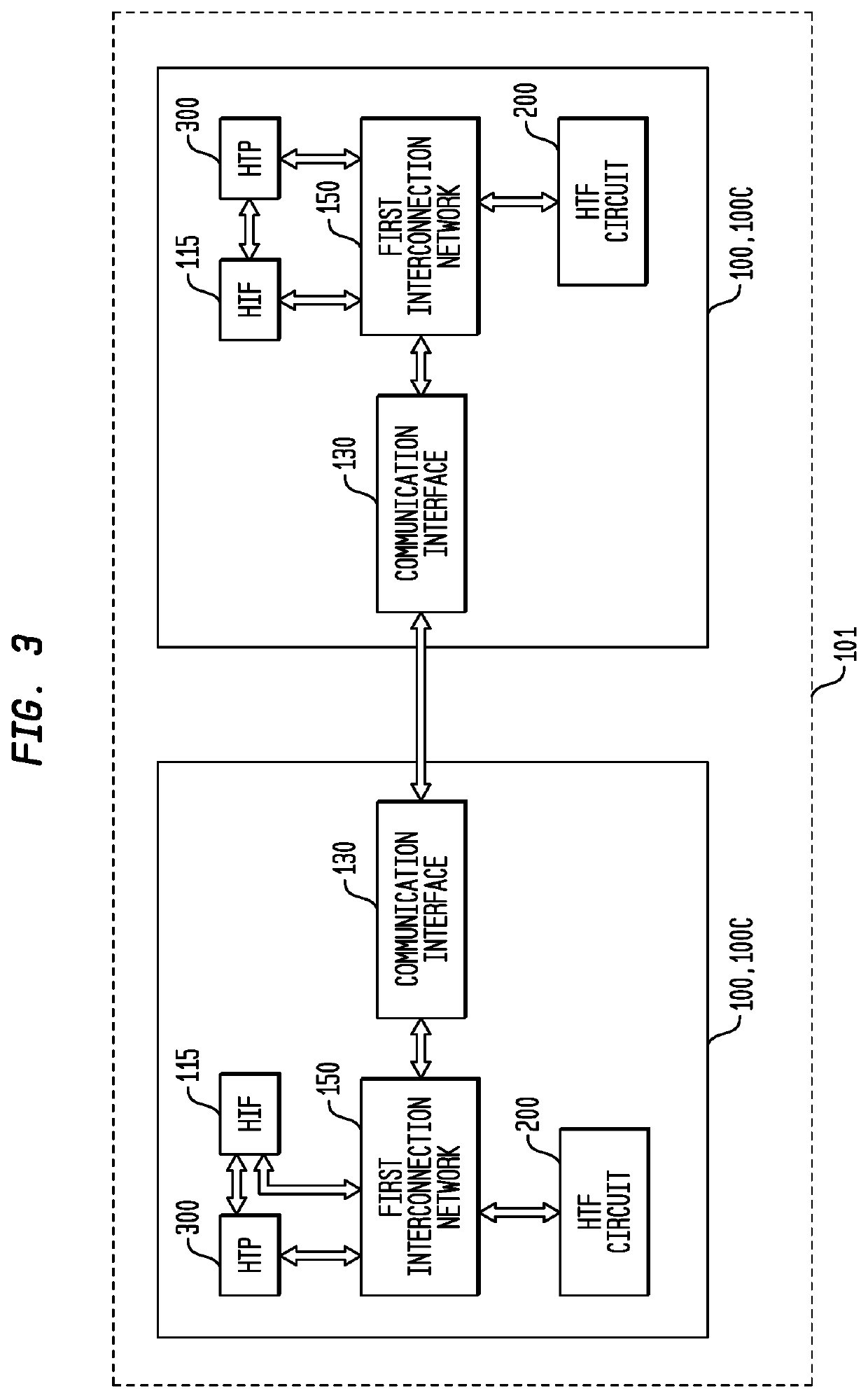
Conditional Branching Control for a Multi-Threaded, Self-Scheduling Reconfigurable Computing Fabric
ActiveUS20190303154A1Fast executionRegister arrangementsInterprogram communicationInstruction memoryInterconnection
Representative apparatus, method, and system embodiments are disclosed for configurable computing. A representative system includes an interconnection network; a processor; and a plurality of configurable circuit clusters. Each configurable circuit cluster includes a plurality of configurable circuits arranged in an array; a synchronous network coupled to each configurable circuit of the array; and an asynchronous packet network coupled to each configurable circuit of the array. A representative configurable circuit includes a configurable computation circuit and a configuration memory having a first, instruction memory storing a plurality of data path configuration instructions to configure a data path of the configurable computation circuit; and a second, instruction and instruction index memory storing a plurality of spoke instructions and data path configuration instruction indices for selection of a master synchronous input, a current data path configuration instruction, and a next data path configuration instruction for a next configurable computation circuit.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Interface between a synchronous network and high-speed ethernet
InactiveUS20070242676A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationEliminating portion of dataTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork linkSynchronous network
A method for communication includes receiving over a synchronous optical network link a flow of encapsulated Ethernet data frames. Two or more of the Ethernet data frames are concatenated to form an extended frame having a single start frame delimiter (SFD) and a single end frame delimiter (EFD) in compliance with an Ethernet standard, and the extended frame is transmitted over an Ethernet link.
Owner:CORRIGENT SYST LTD
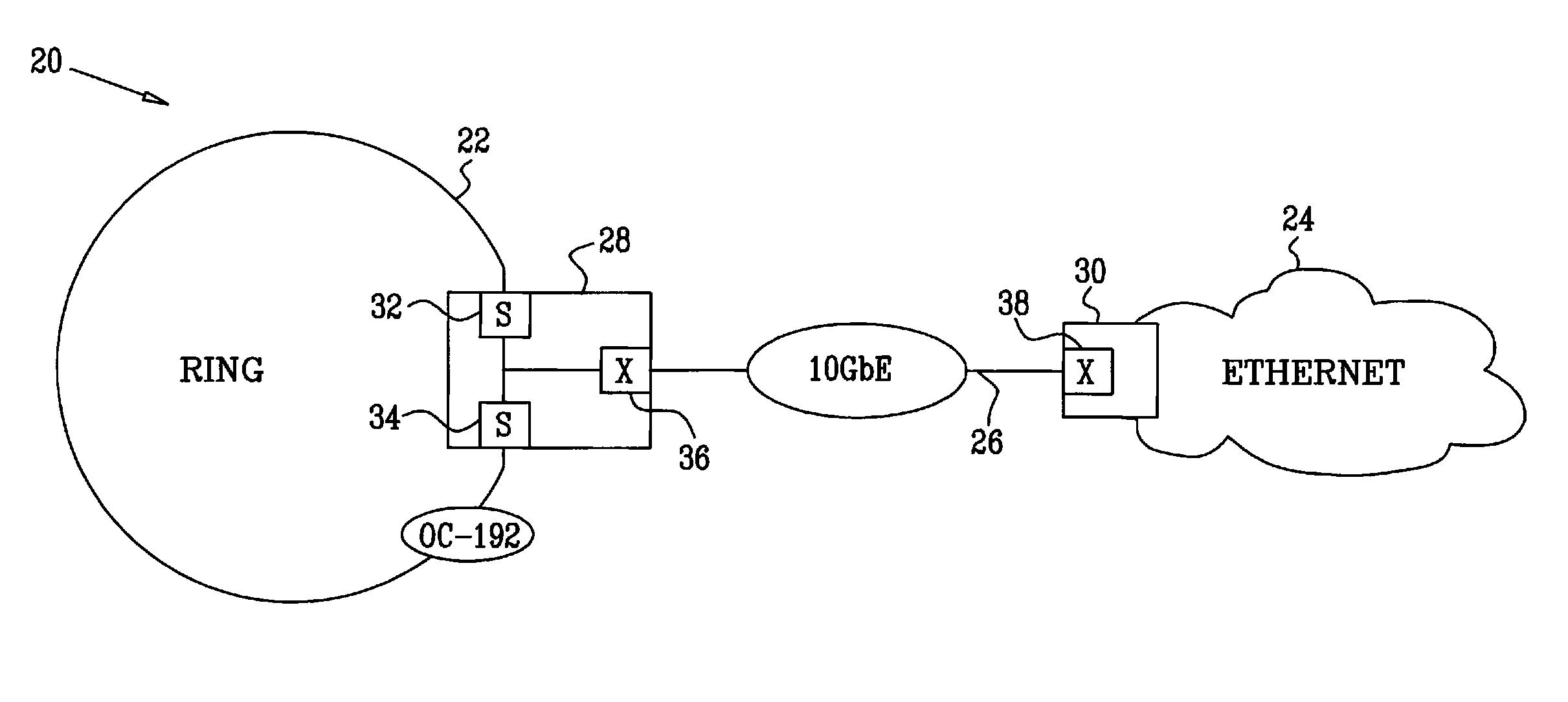
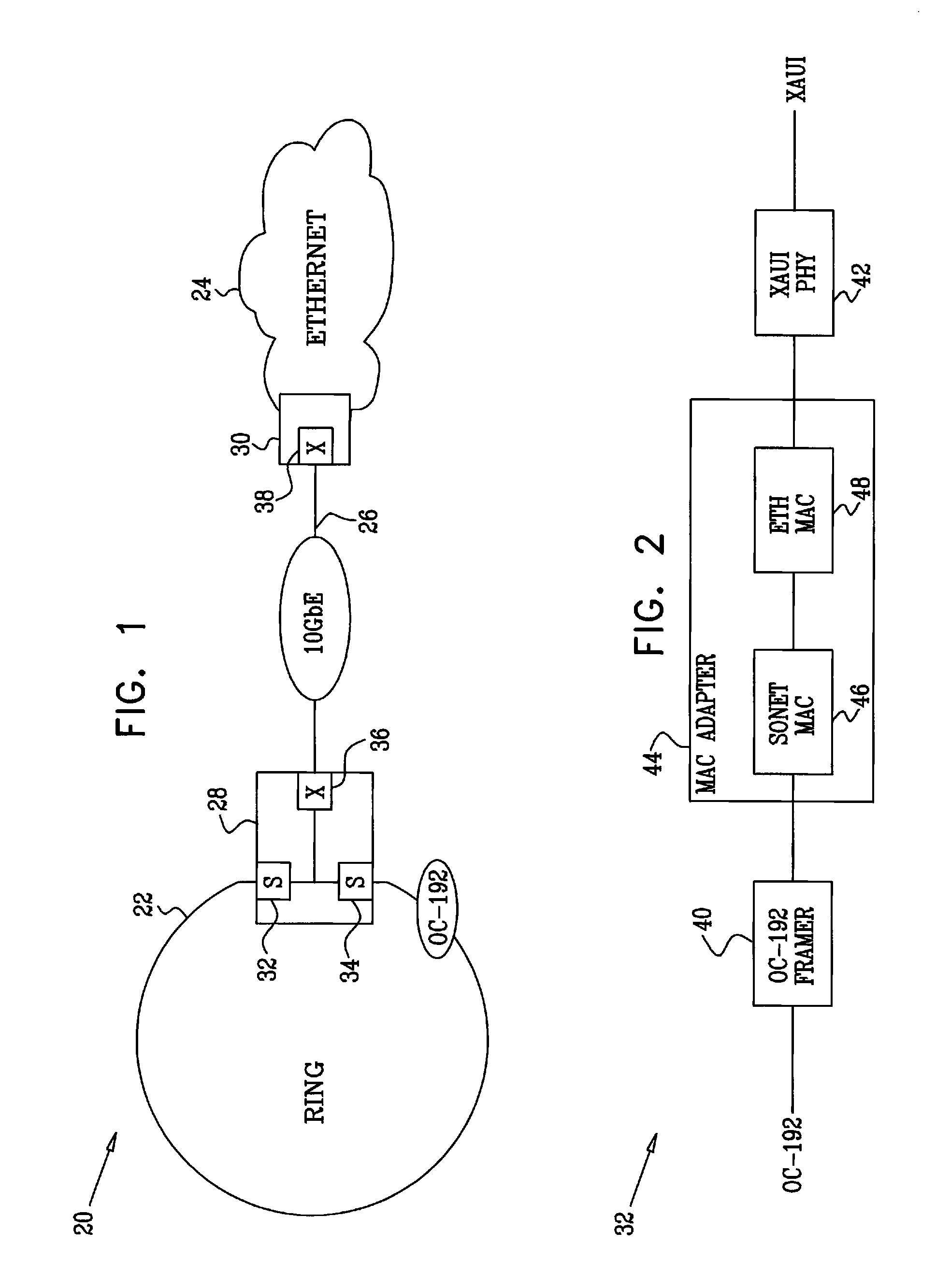
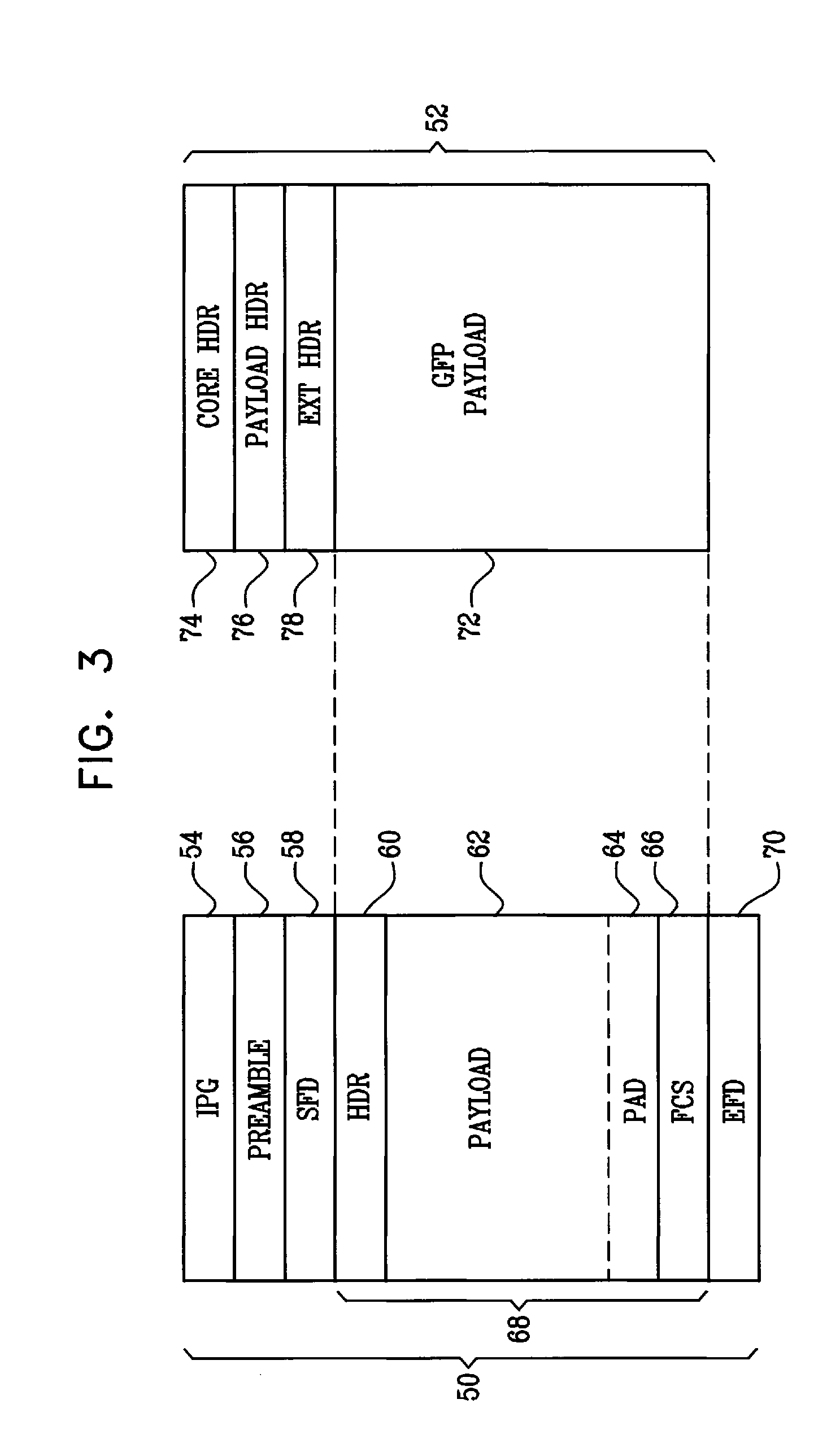
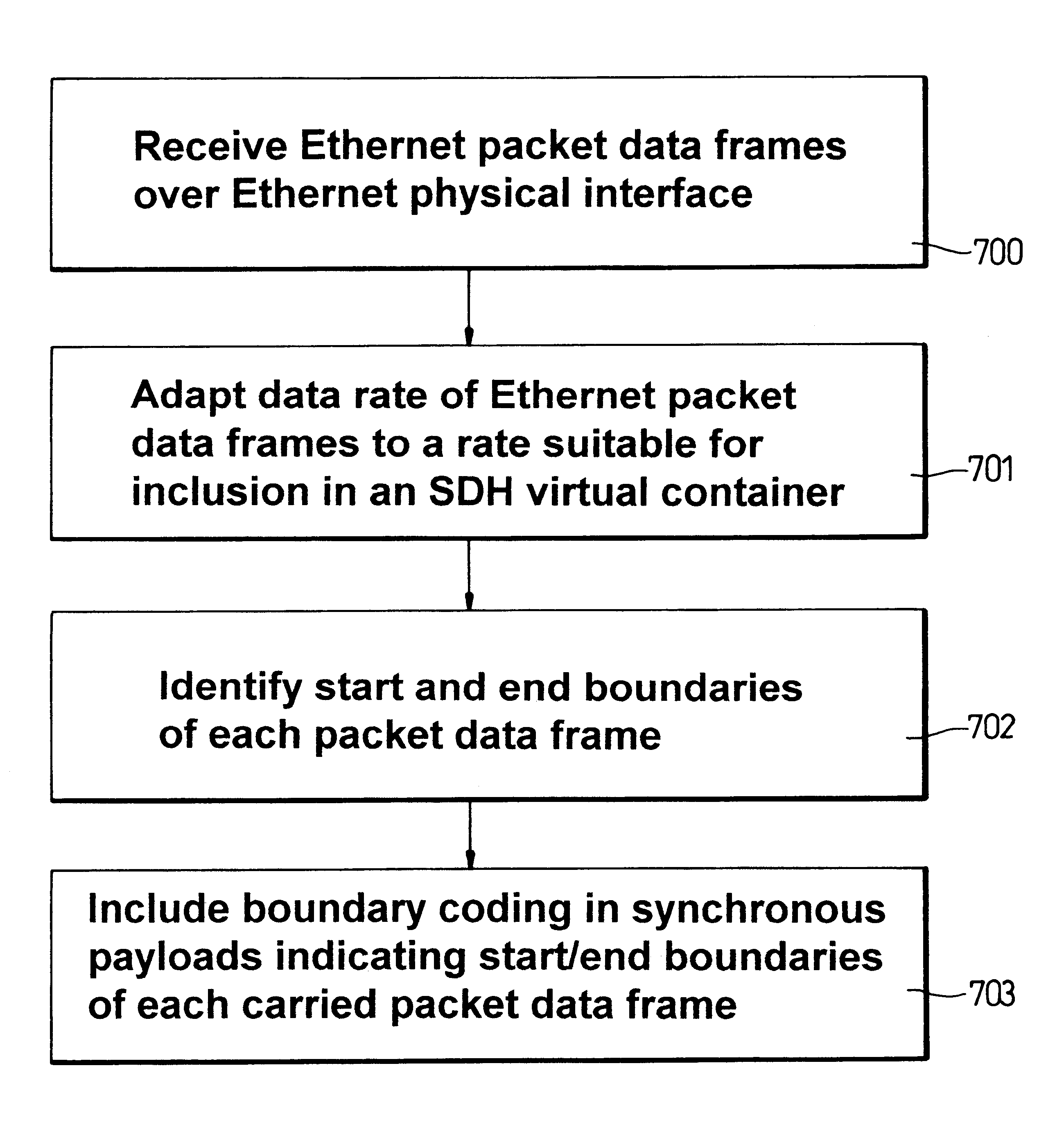
Payload mapping in synchronous networks
There is disclosed a method of carrying frame based data, eg Ethernet data, over a synchronous digital hierarchy network in order to provide local area network type functionality over a wide area network coverage. Specific embodiments disclose methods of mapping Ethernet data frames into SDH virtual containers, and distinguishing start and end boundaries of the Ethernet data frames within the virtual container payloads, by a selection of encoding methods including a segmentation, pointer methods, bit stuffing methods and byte stuffing methods. Data frames are encoded with a code which designates a boundary of each frame, and the encoded frames are input into a synchronous data channel.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
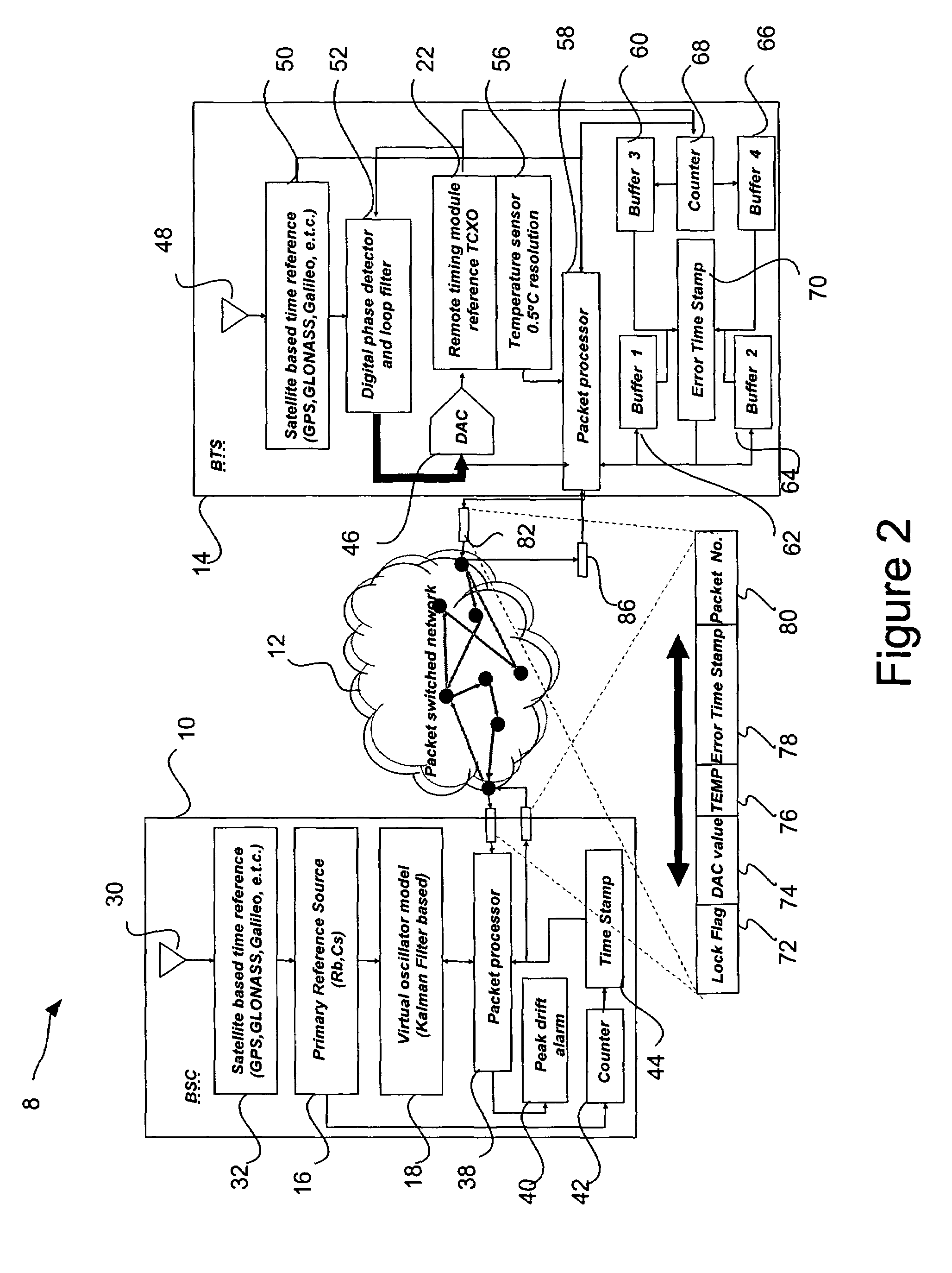
Enhanced holdover for synchronous networks employing packet switched network backhaul
ActiveUS7606541B1Automatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayTime-division multiplexCommunication unitSynchronous network
Systems and methods are disclosed to maintain synchronous communications that uses a global positioning system satellite, a primary communication unit, and a secondary communication unit. The satellite based time reference broadcasts a reference signal to the primary communication unit and the secondary communication unit. The primary communication unit contains a high quality oscillator, and operates a virtual model of a secondary oscillator which is located in the secondary communication unit. The primary and secondary units have synchronous communications with each other by using a global positioning system satellite broadcast as a reference signal. If the secondary unit loses its signal from the global positioning system, the secondary oscillator enters a holdover state and transmits a notification of the holdover state to the primary communications unit. The primary communication unit then transmits time insensitive synchronization data based upon the virtual model through the packet switched network to the secondary communications unit to maintain synchronization.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
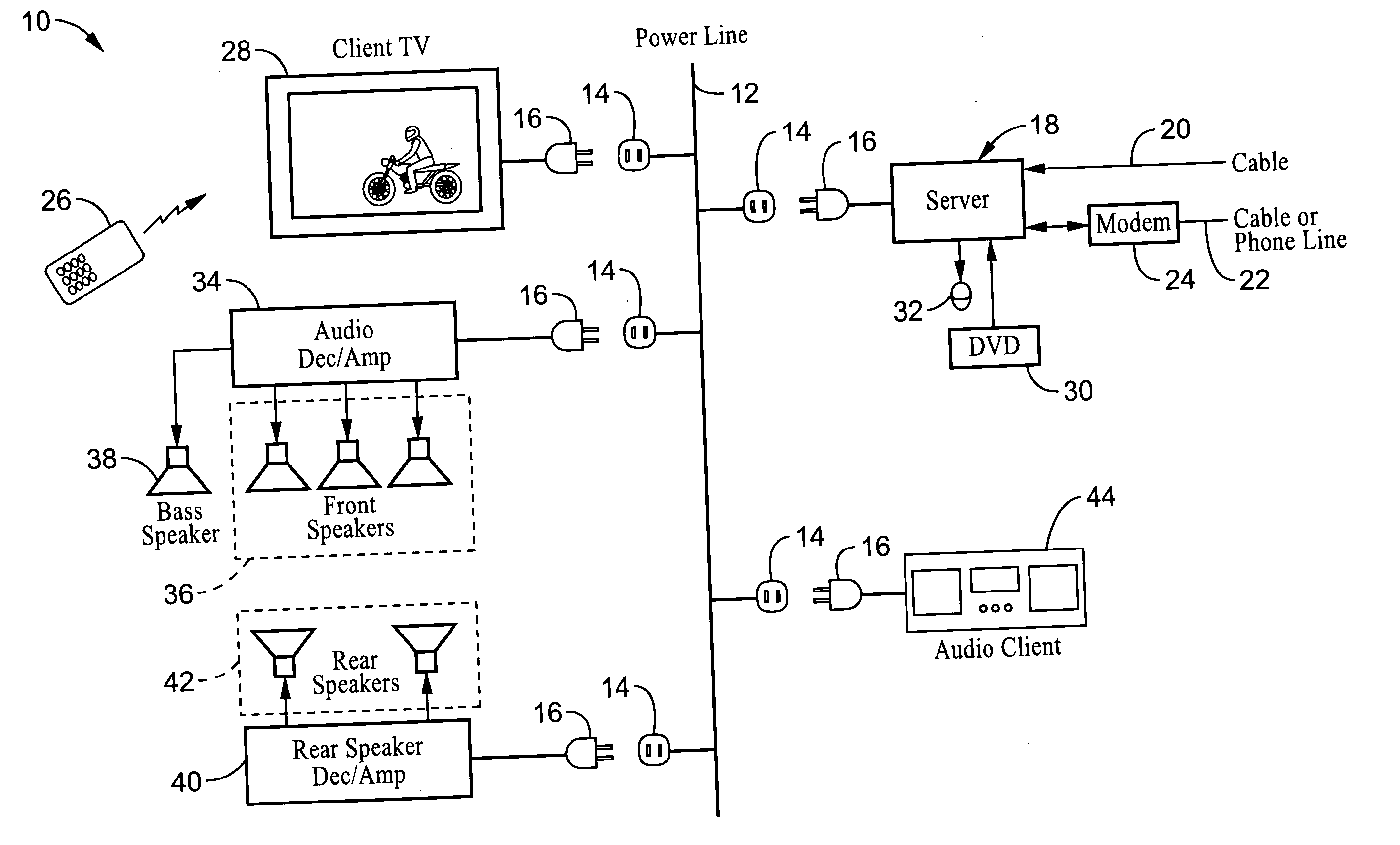
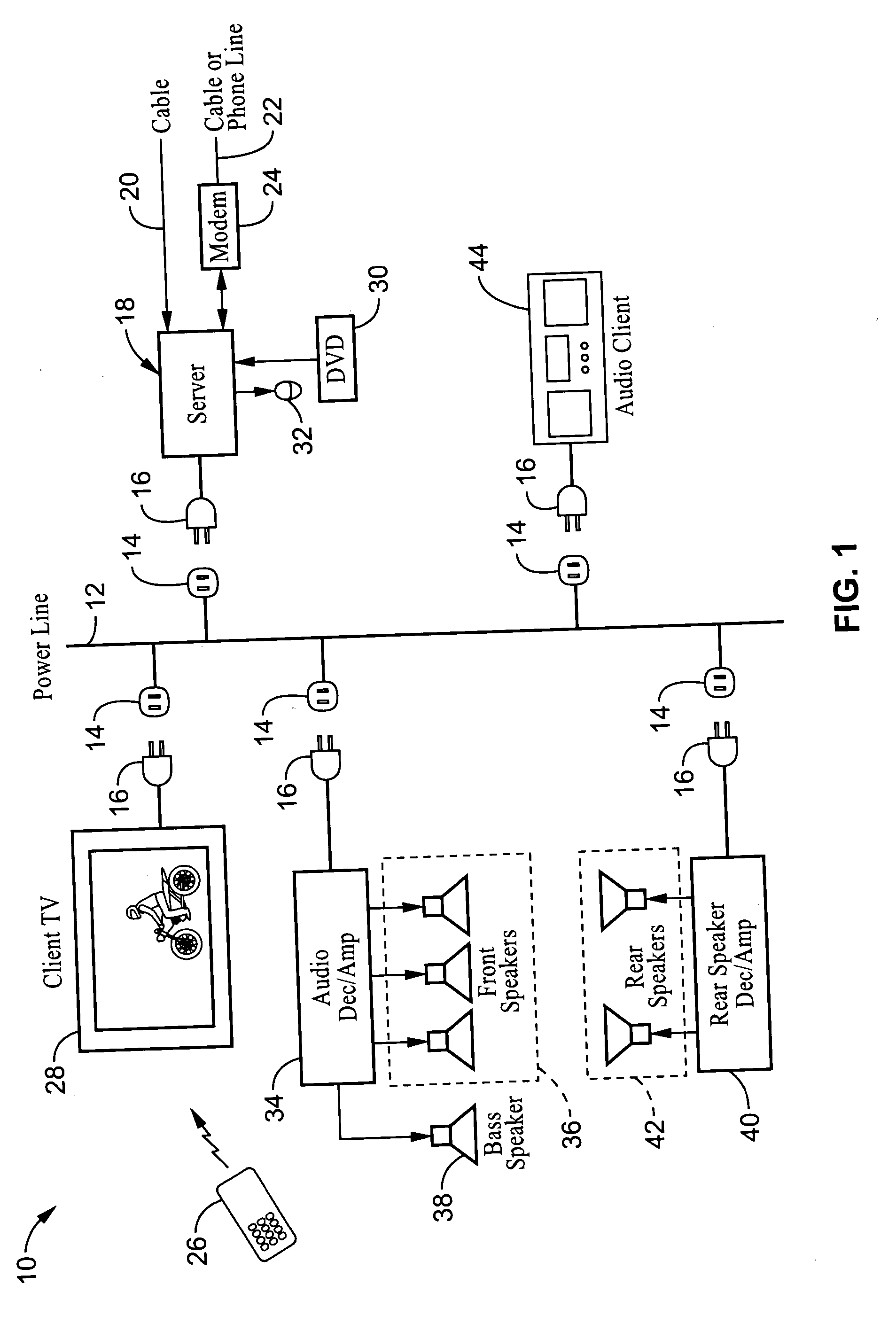
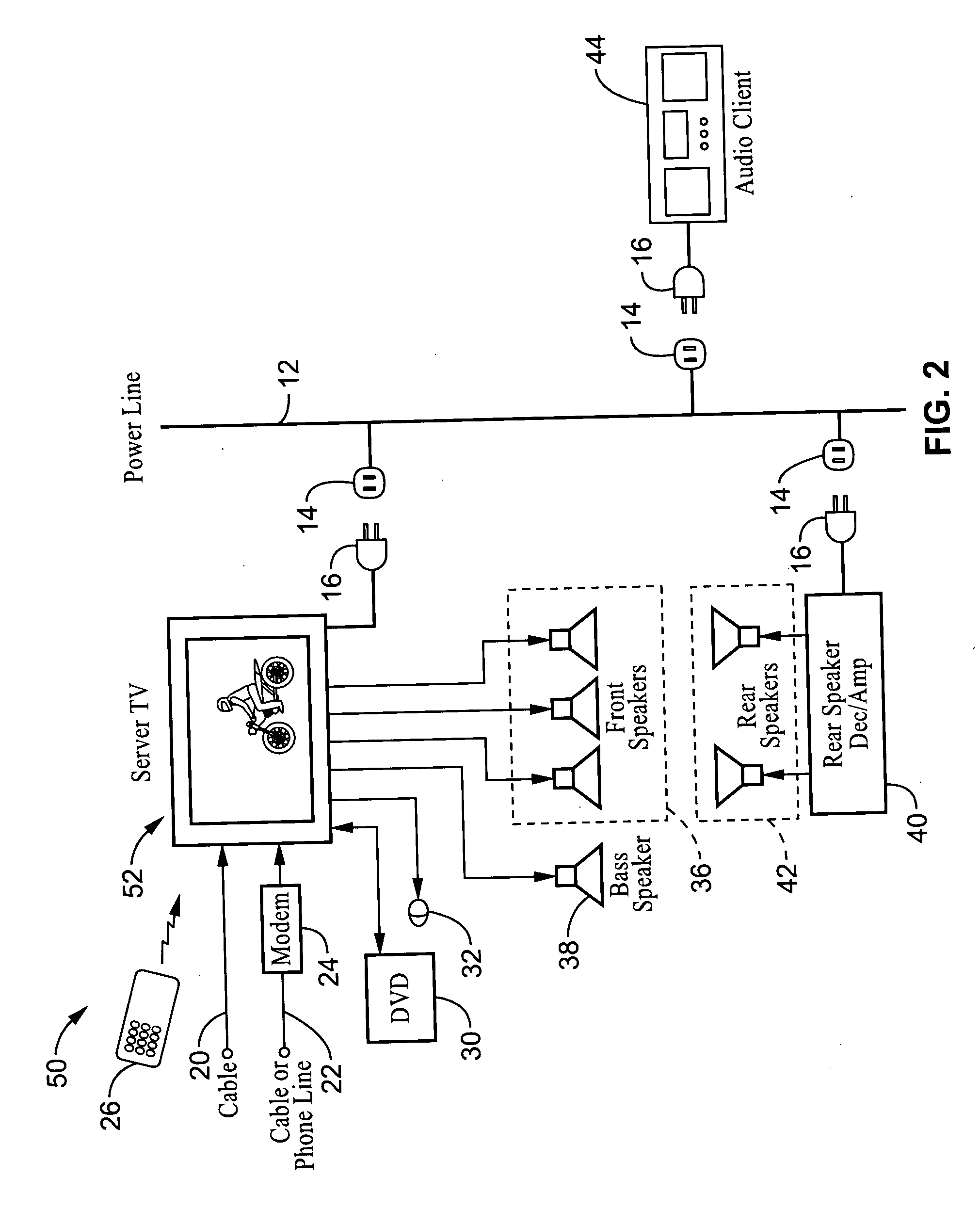
System and method for synchronizing audio-visual devices on a power line communications (PLC) network
ActiveUS20060072695A1Minimum delayMinimize divergenceTime-division multiplexWireless systems/telephoneComputer hardwareClock time
A method and apparatus for synchronizing streaming media devices within a PLC network. Output synchronization errors exceeding ˜30 ms become noticeable when multiple streaming media devices are outputting an audio stream. The present invention provides a system and method for isochronously sending periodic reference clocks from a master device to client devices coupled to the PLC network. The client devices set their clocks based on the reference clock. In addition the clients adjust their system clock time base in response to the average divergence of the system clock with the reference clock, or a count of the number of clocks between beacon frames. In this way the client clock is adjusted to closely track the server clock so that synchronization is maintained between each of the devices. Streaming audio shared between servers and client devices is thus output across the network with high fidelity due to the accurate synchronization.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Efficient loop execution for a multi-threaded, self-scheduling reconfigurable computing fabric
Representative apparatus, method, and system embodiments are disclosed for configurable computing. A representative system includes an interconnection network; a processor; and a plurality of configurable circuit clusters. Each configurable circuit cluster includes a plurality of configurable circuits arranged in an array; a synchronous network coupled to each configurable circuit of the array; and an asynchronous packet network coupled to each configurable circuit of the array. A representative configurable circuit includes a configurable computation circuit and a configuration memory having a first, instruction memory storing a plurality of data path configuration instructions to configure a data path of the configurable computation circuit; and a second, instruction and instruction index memory storing a plurality of spoke instructions and data path configuration instruction indices for selection of a master synchronous input, a current data path configuration instruction, and a next data path configuration instruction for a next configurable computation circuit.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
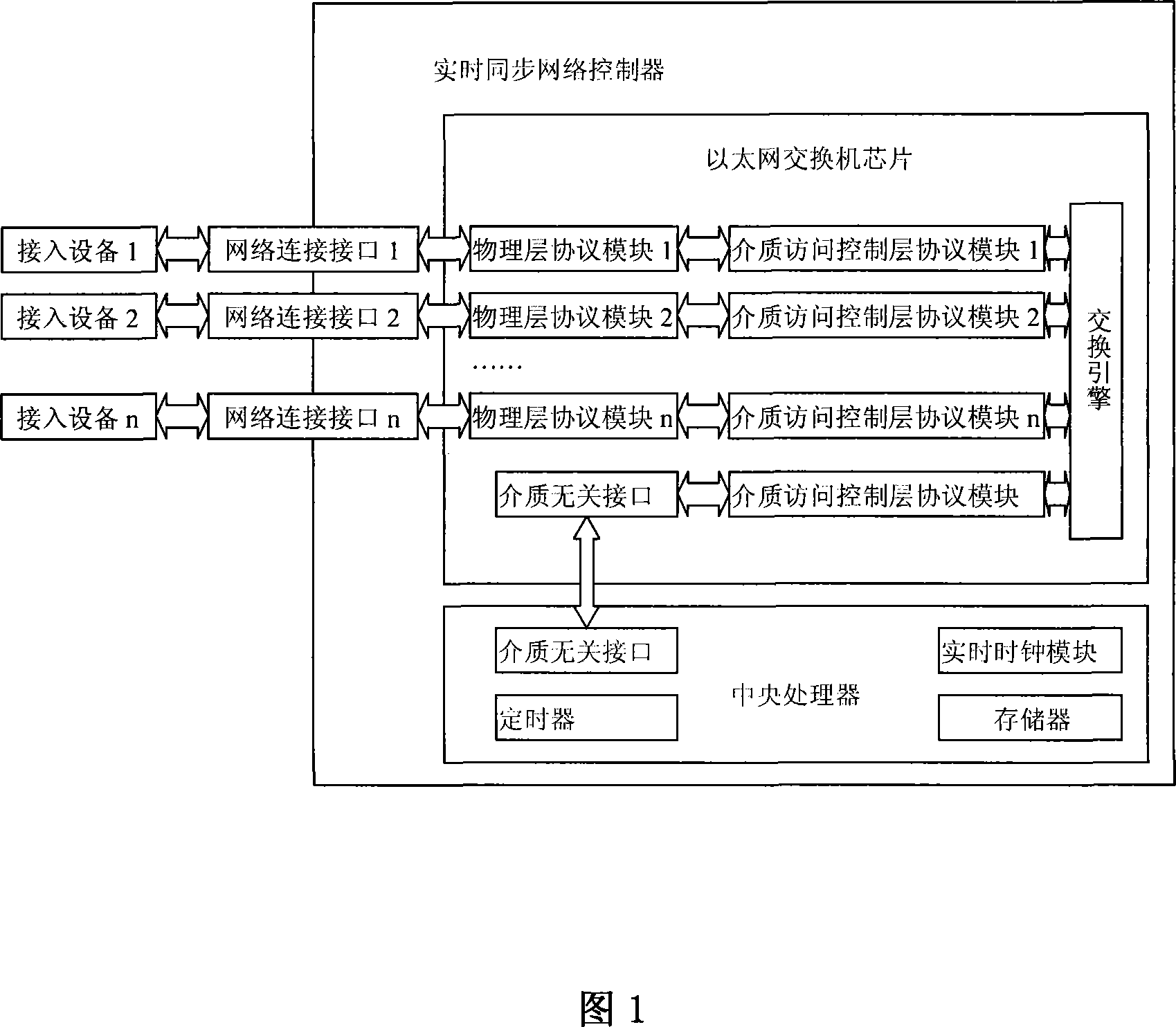
Numerical control system real-time synchronization network controller and communication control method
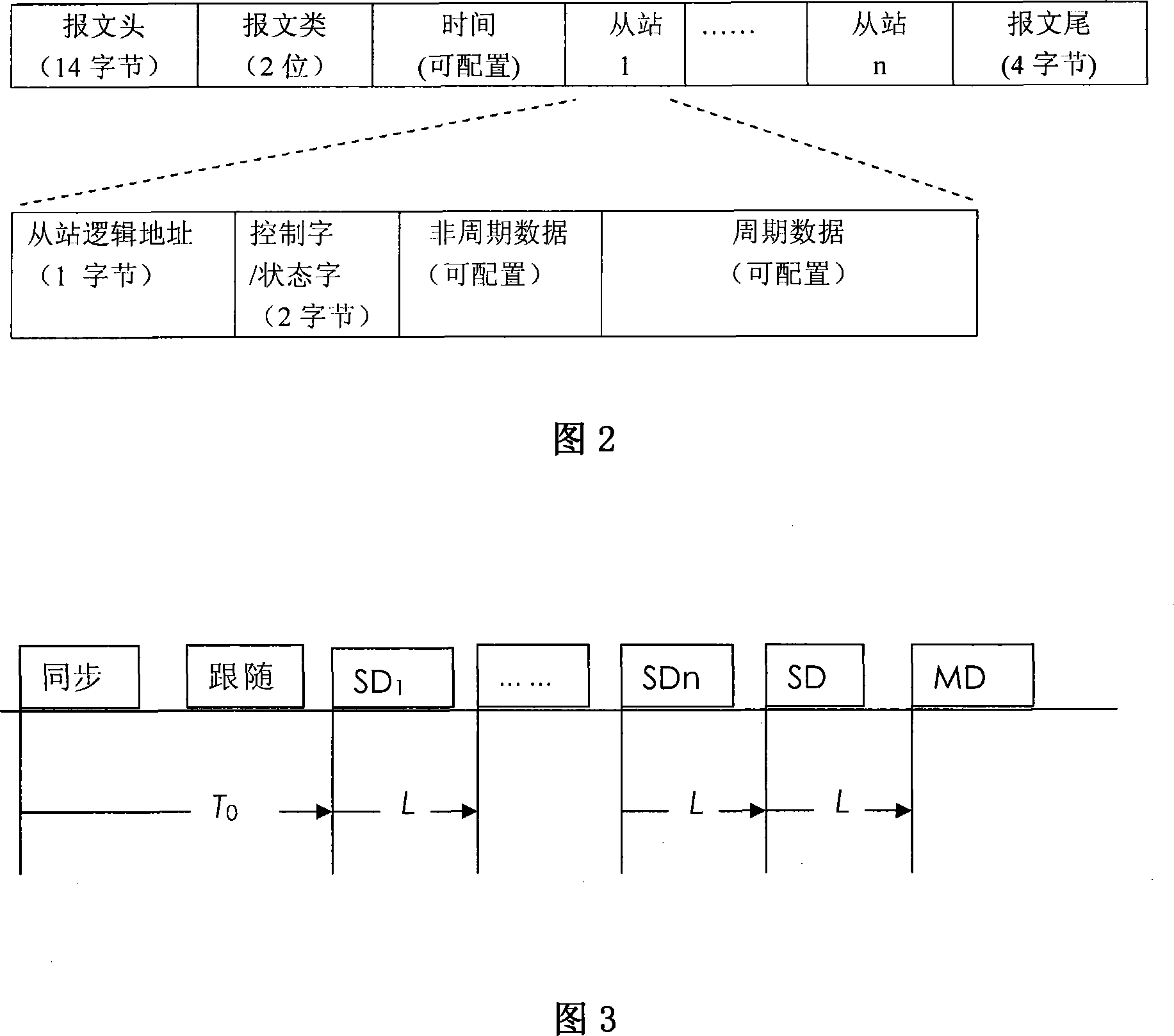
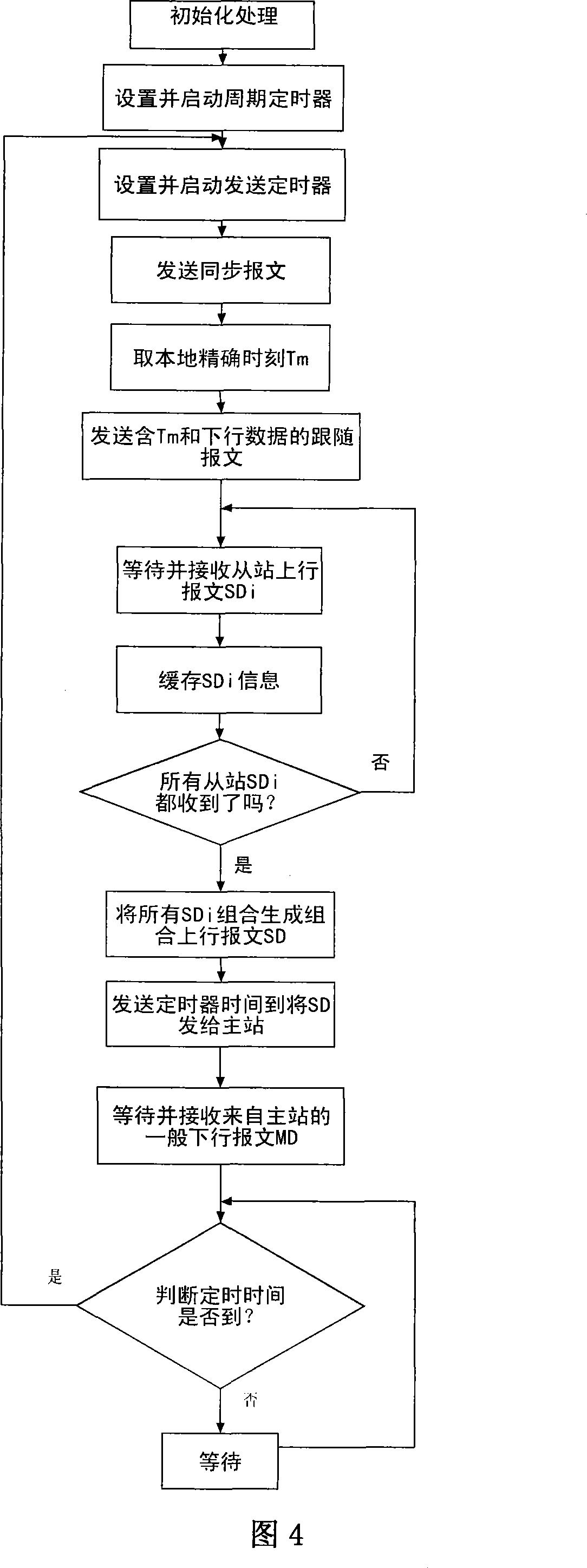
InactiveCN101083657AImprove versatilityReduce the burden onData switching networksSynchronising arrangementPrimary stationInformation transmission
Purpose of the invention is to connect the access devices at bottom layers of digital control systems, which possess Ethernet interface, to implement high synchronous information transmission in strong real time. The disclosed network controller includes chips of Ethernet exchange, CPU, and network connection interface. The communication control method includes step of system initiation, and step of communication. The step of communication repeats following communication cycle: (1) sending out synchronous message; (2) sending out follow message; (3) each slave station sends out up going message in turn; (4) sending out the combined up going message crated by assembling going messages to main station; (5) main station sends out generic down going message. Using general Ethernet chip, the invention possesses good generality. For digital control system with 16 axes, the method provides interpolation cycle being as 0.5 ms, and synchronization error less than 1 micro second.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus for multi-chassis configurable time synchronization
ActiveUS7818457B1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsControl systemSynchronous control
Systems and methods are disclosed for time synchronization of operations in a control system. Synchronization networks and devices are provided for transferring synchronization information between controllers in a distributed or localized control system, which is employed in order to allow operation of such controllers to be synchronized with respect to time. Also disclosed are synchronization protocols and hardware apparatus employed in synchronizing control operations in a control system.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com