Patents
Literature
4530 results about "Clock synchronization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clock synchronization is a topic in computer science and engineering that aims to coordinate otherwise independent clocks. Even when initially set accurately, real clocks will differ after some amount of time due to clock drift, caused by clocks counting time at slightly different rates. There are several problems that occur as a result of clock rate differences and several solutions, some being more appropriate than others in certain contexts.
Source-clock-synchronized memory system and memory unit
InactiveUS6034878ALarge data storage capacity per memoryImprove installation densityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankComputer module
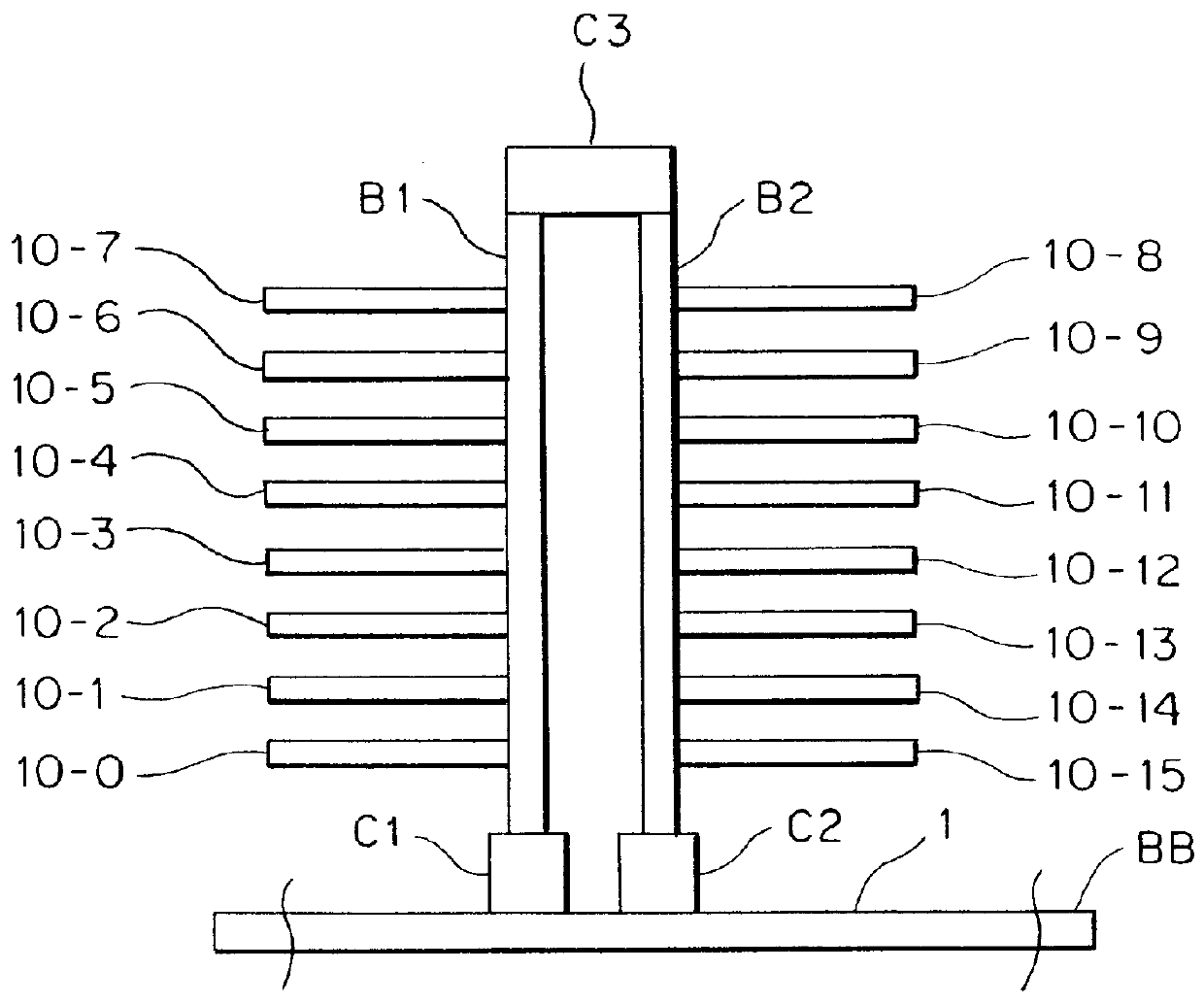
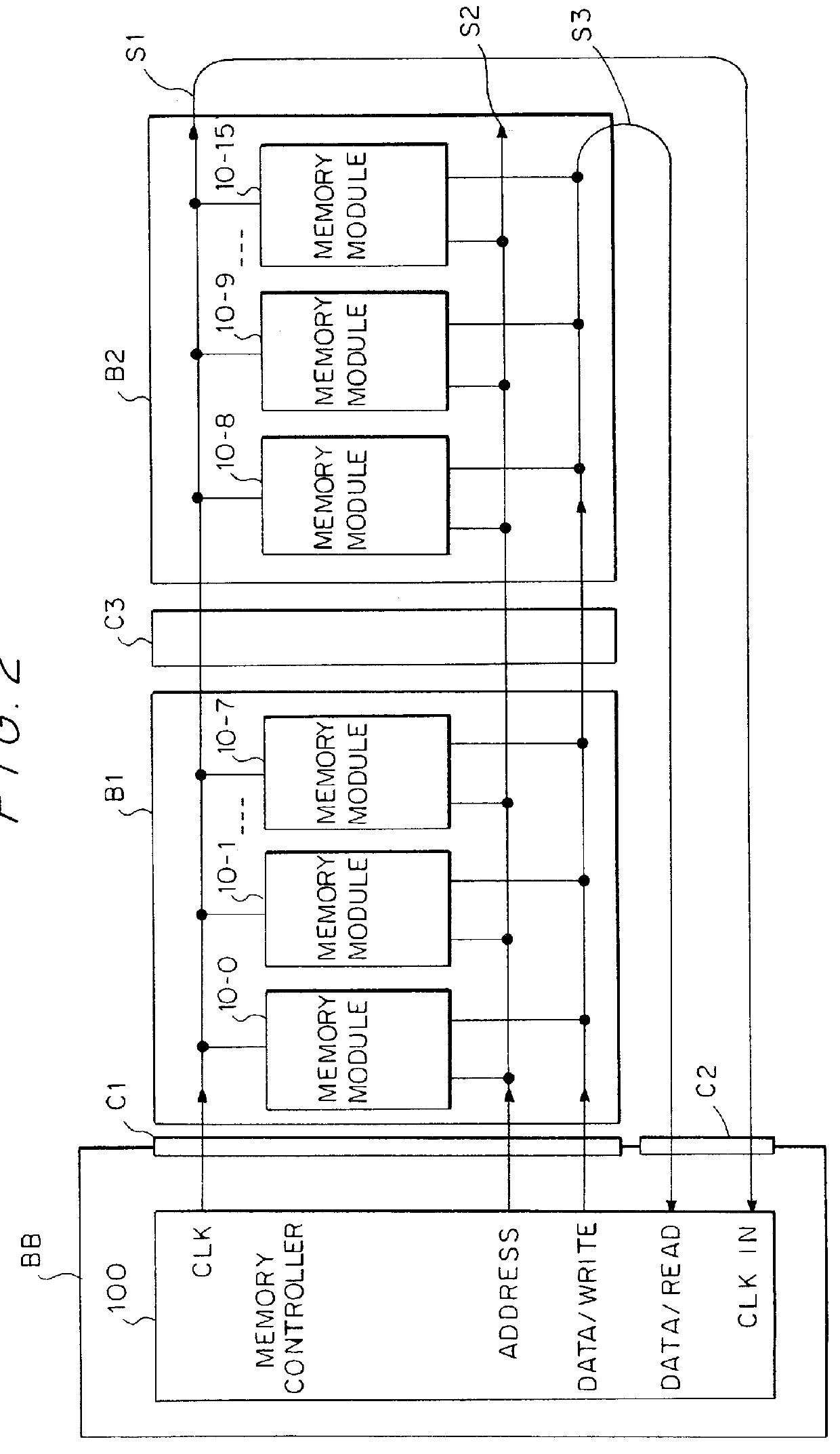
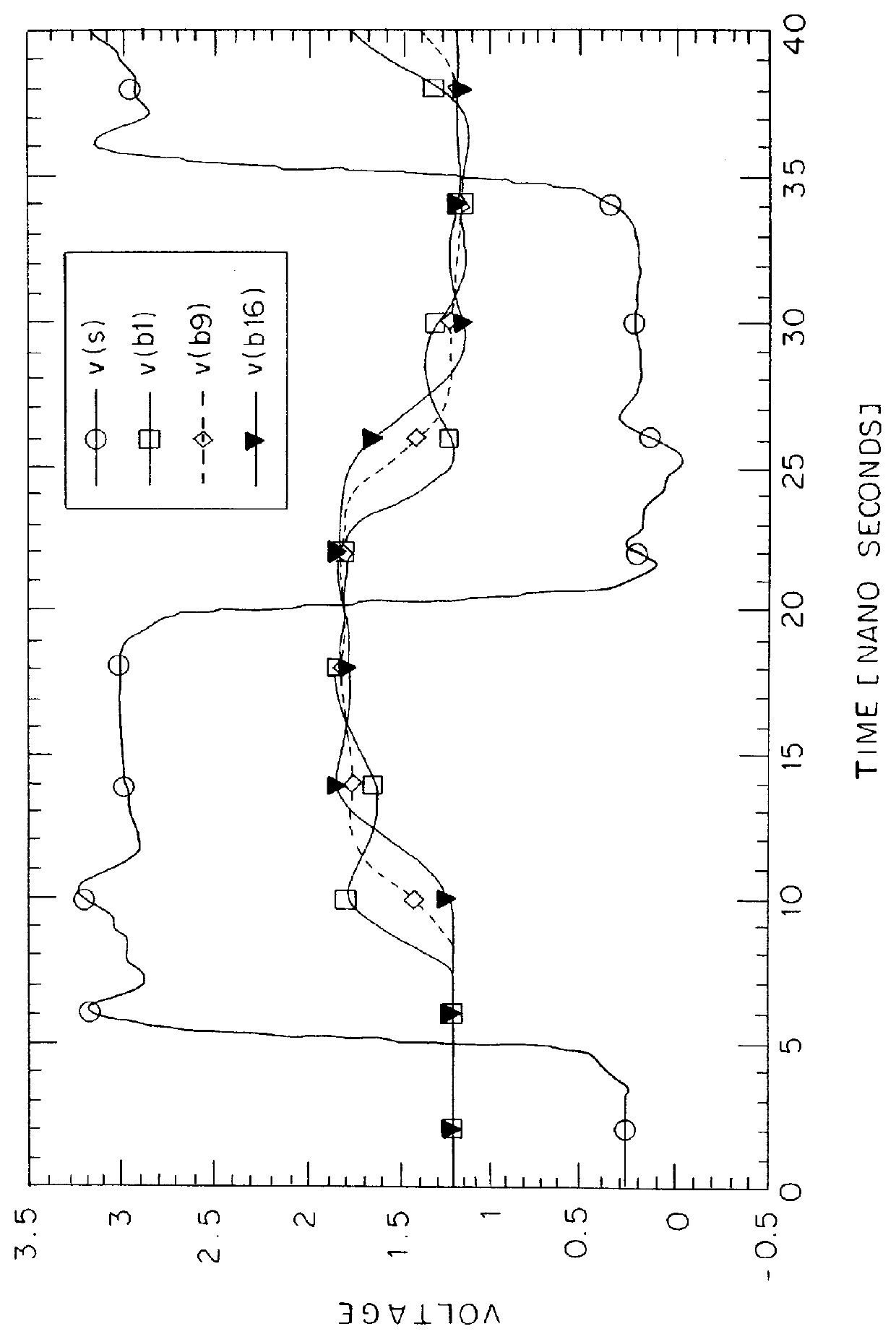
A source-clock-synchronized memory system having a large data storage capacity per memory bank and a high mounting density. The invention includes a memory unit having a first memory riser board B1 mounted on a base board through a first connector C1 and a second memory riser board B2 mounted on the base board BB through a second connector C2. The first memory riser board has a plurality of first memory modules mounted on the front surface thereof and the second memory riser board has a plurality of second memory modules mounted on the front surface thereof. The first and second memory riser boards are arranged in such a way that the back surface of the first memory riser board faces the back surface of the second memory riser board. The invention further includes a board linking connector for connecting signal lines on the first memory riser board to corresponding signal lines on the second memory riser board.
Owner:DELTA KOGYO CO LTD +1
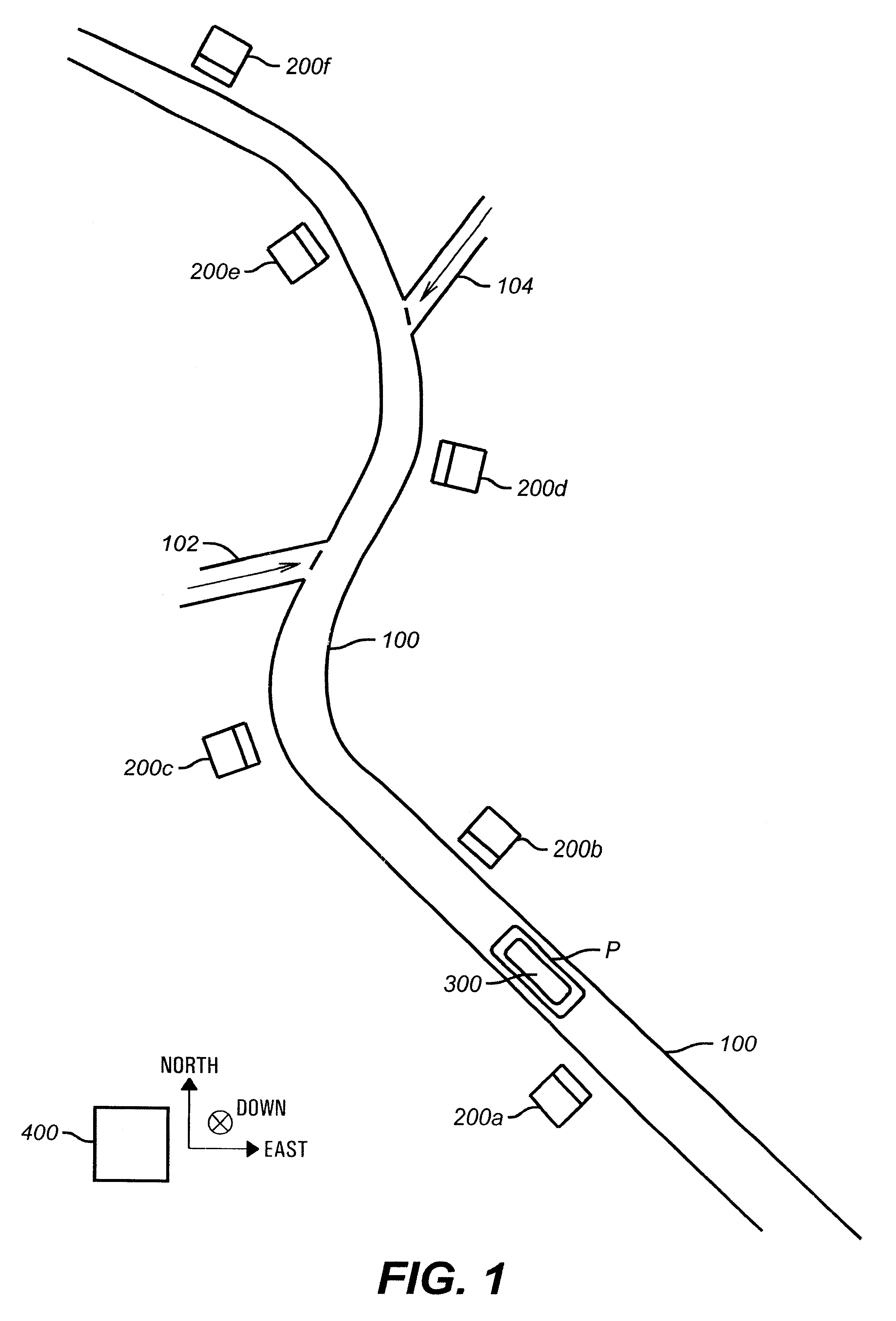
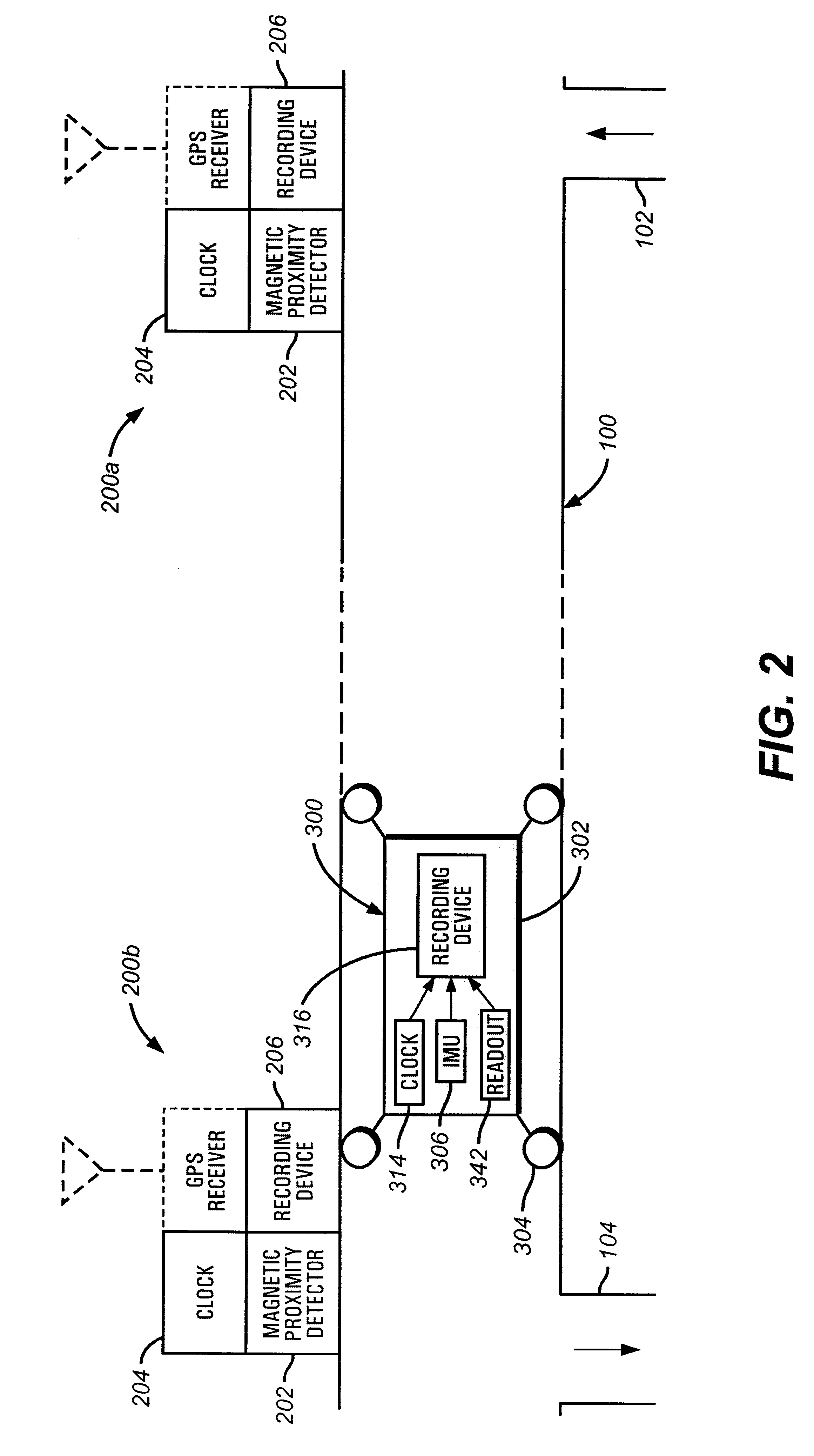
Method and apparatus for determining location of characteristics of a pipeline
InactiveUS6243657B1High degreeHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksKaiman filterComputerized system
A pipeline inspection and defect mapping system includes a pig having an inertial measurement unit and a pipeline inspection unit for recording pig location and defect detection events, each record time-stamped by a highly precise onboard clock. The system also includes several magloggers at precisely known locations along the pipeline, each containing a fluxgate magnetometer for detecting the passage of the pig along the pipeline and further containing a highly precise clock synchronized with the clock in the pig. The locations of the various magloggers are known in a north / east / down coordinate system through a differential global positioning satellite process. Finally, a postprocessing off-line computer system receives downloaded maglogger, inertial measurement, and odometer data and through the use of several Kalman filters, derives the location of the detected defects in the north / east / down coordinate frame. Consequently, a task of identifying sites for repair activity is much simplified.
Owner:PIPELINE INTEGRITY INT INC FORMERLY BRITISH GAS INSPECTION SERVICES INC +1
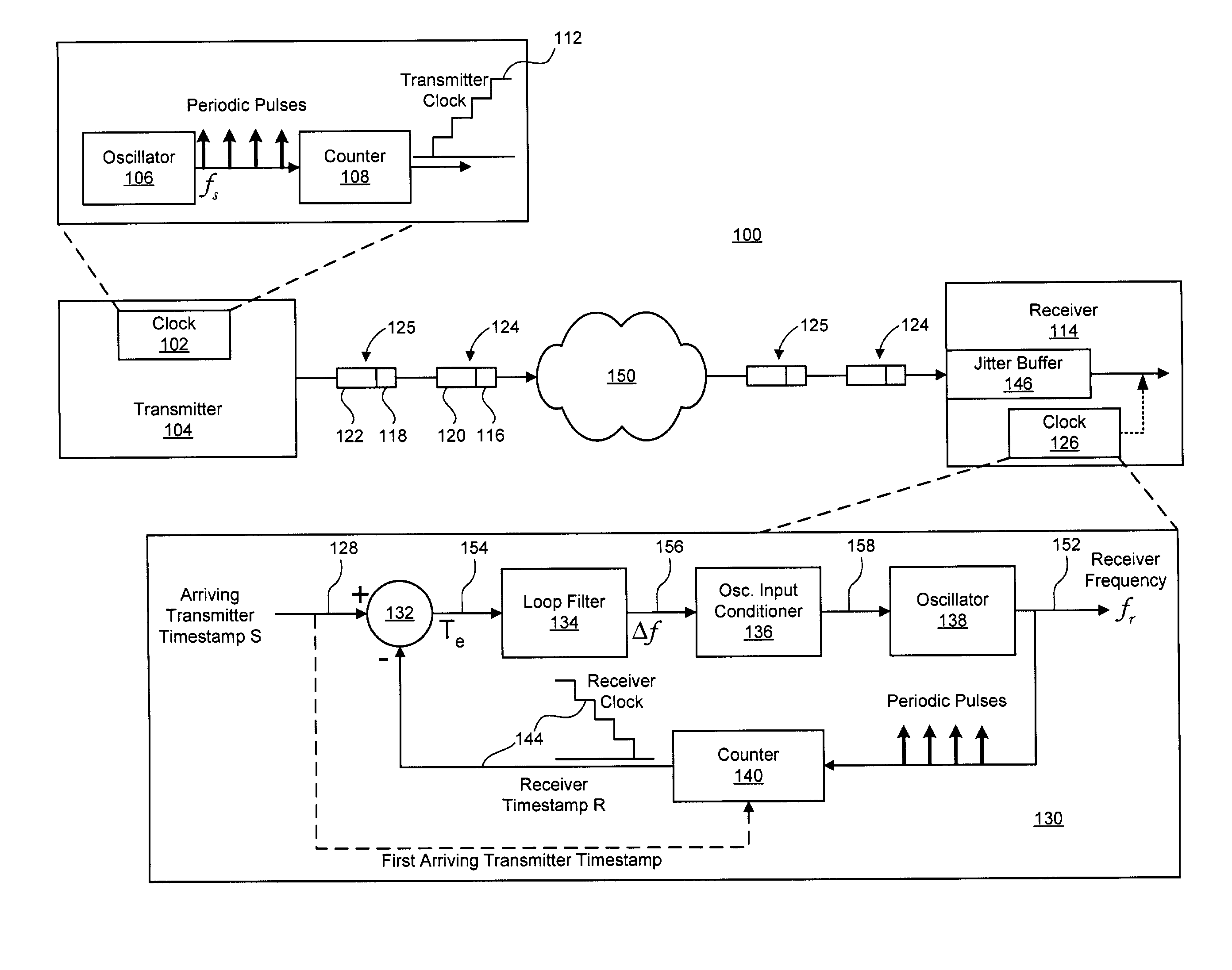
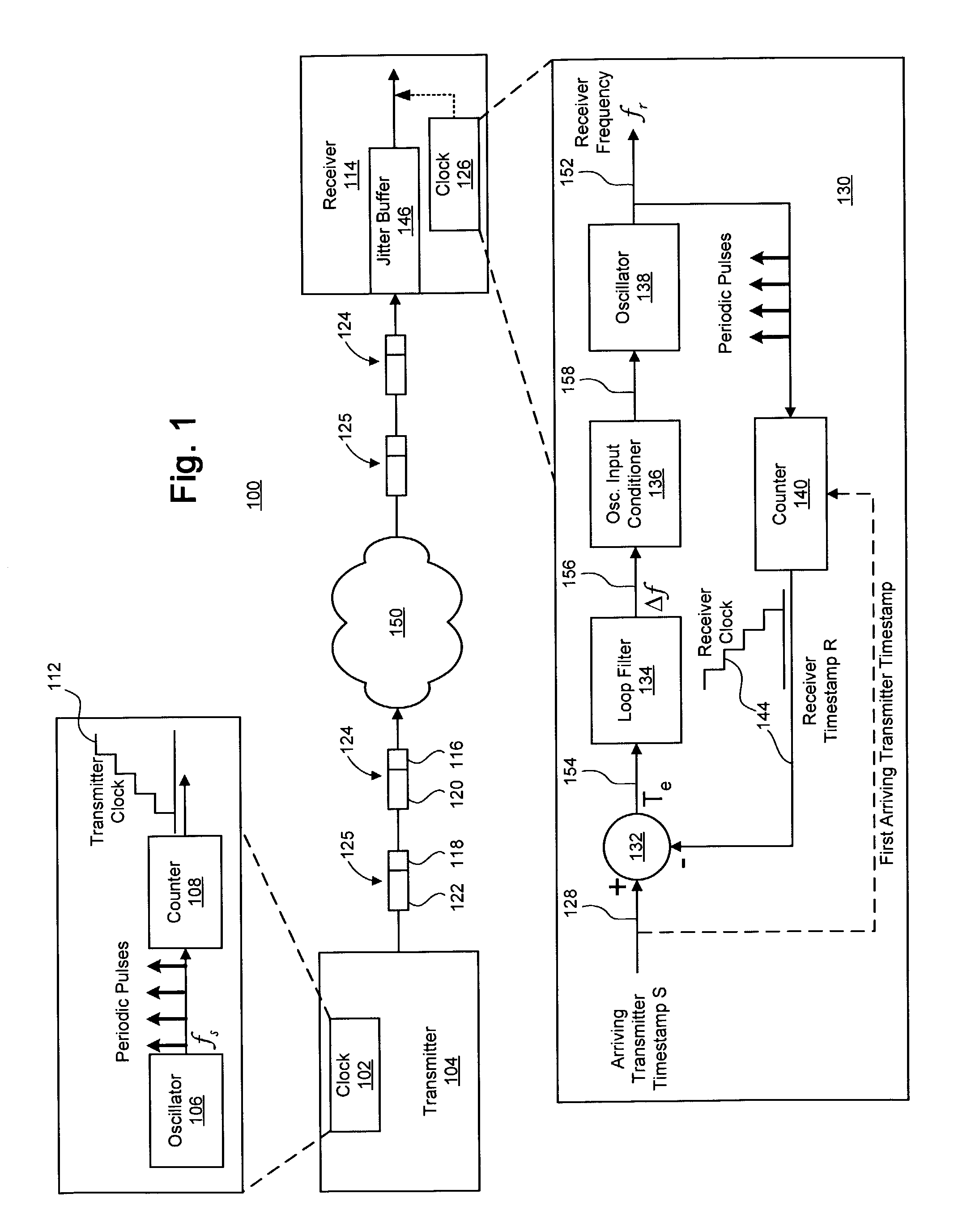
Clock recovery using a double-exponential smoothing process
A system and method for synchronizing a local clock to a reference clock using a linear model of the clock error between the local clock and the reference clock is disclosed. In one embodiment, a double-exponential smoothing process is used in conjunction with the linear model to estimate a frequency offset by which the frequency of an oscillator of the local clock is adjusted. Also disclosed herein is a phased-lock loop (PLL) adapted to synchronize a local clock with a reference clock using the double-exponential smoothing process, as well as a system implementing the PLL for timing the playout of data received from a transmitter.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Clock recovery using a direct smoothing process
ActiveUS7130368B1Guaranteed maximum utilizationPulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsClock recoveryLinear model
A system and method for synchronizing a local clock to a reference clock using a linear model of the error between the local clock and the reference clock is disclosed. In one embodiment, a direct smoothing process is used in conjunction with the linear model to estimate a frequency offset by which the frequency of an oscillator of the local clock is adjusted. Also disclosed herein is a phased-lock loop (PLL) adapted to synchronize a local clock with a reference clock using the direct smoothing process, as well as a system implementing the PLL for timing the playout of data received from a transmitter.
Owner:CIENA
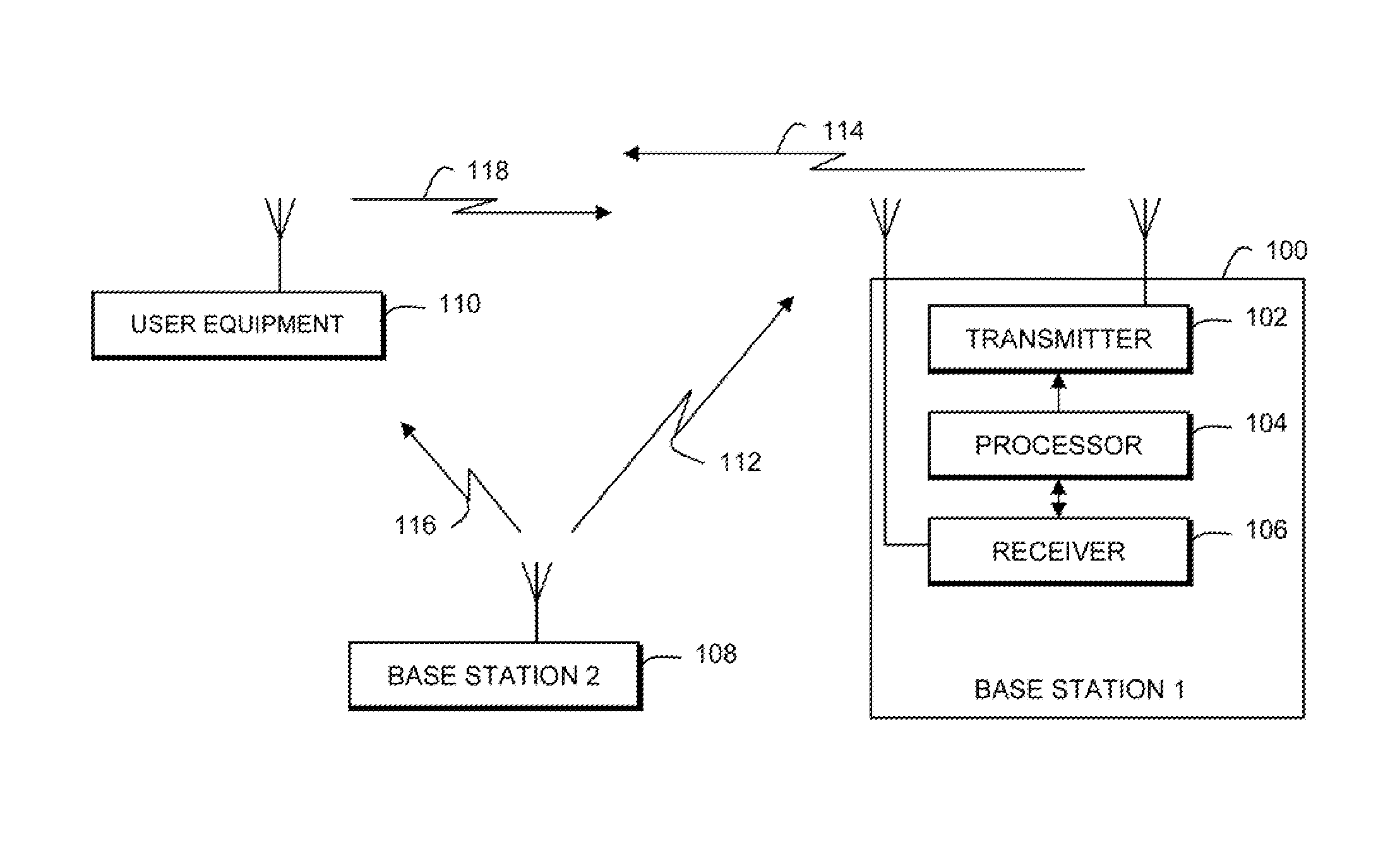
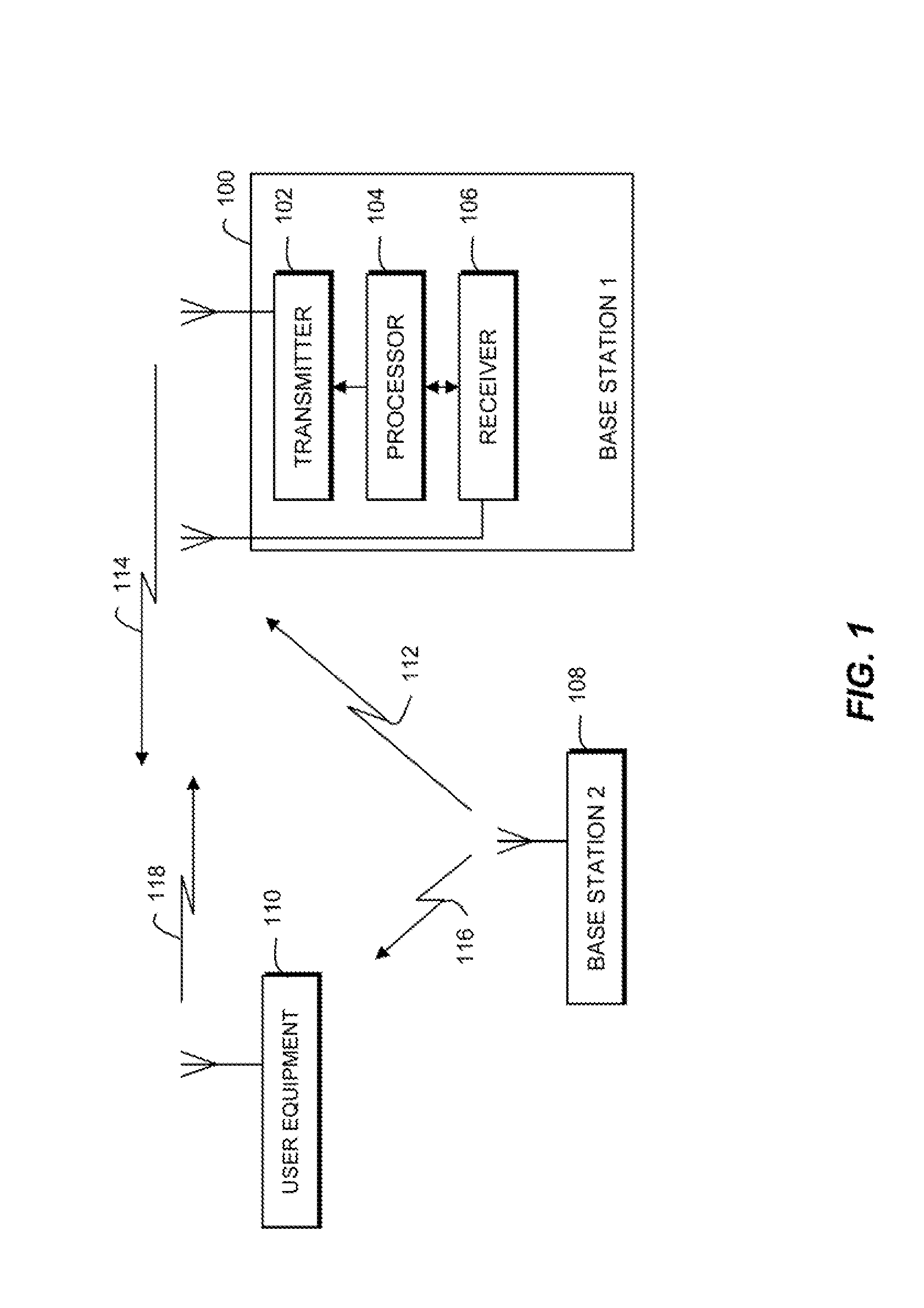
Synchronization for femto-cell base stations
Timing synchronization between base stations of uncoordinated communication networks includes obtaining timing synchronization information from one base station, and adjusting a clock of the other station in response to the synchronization information. The timing synchronization information can be identified from a strongest synchronization signal from nearby uncoordinated base stations. The timing synchronization can accommodate clock offsets and frequency offsets.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
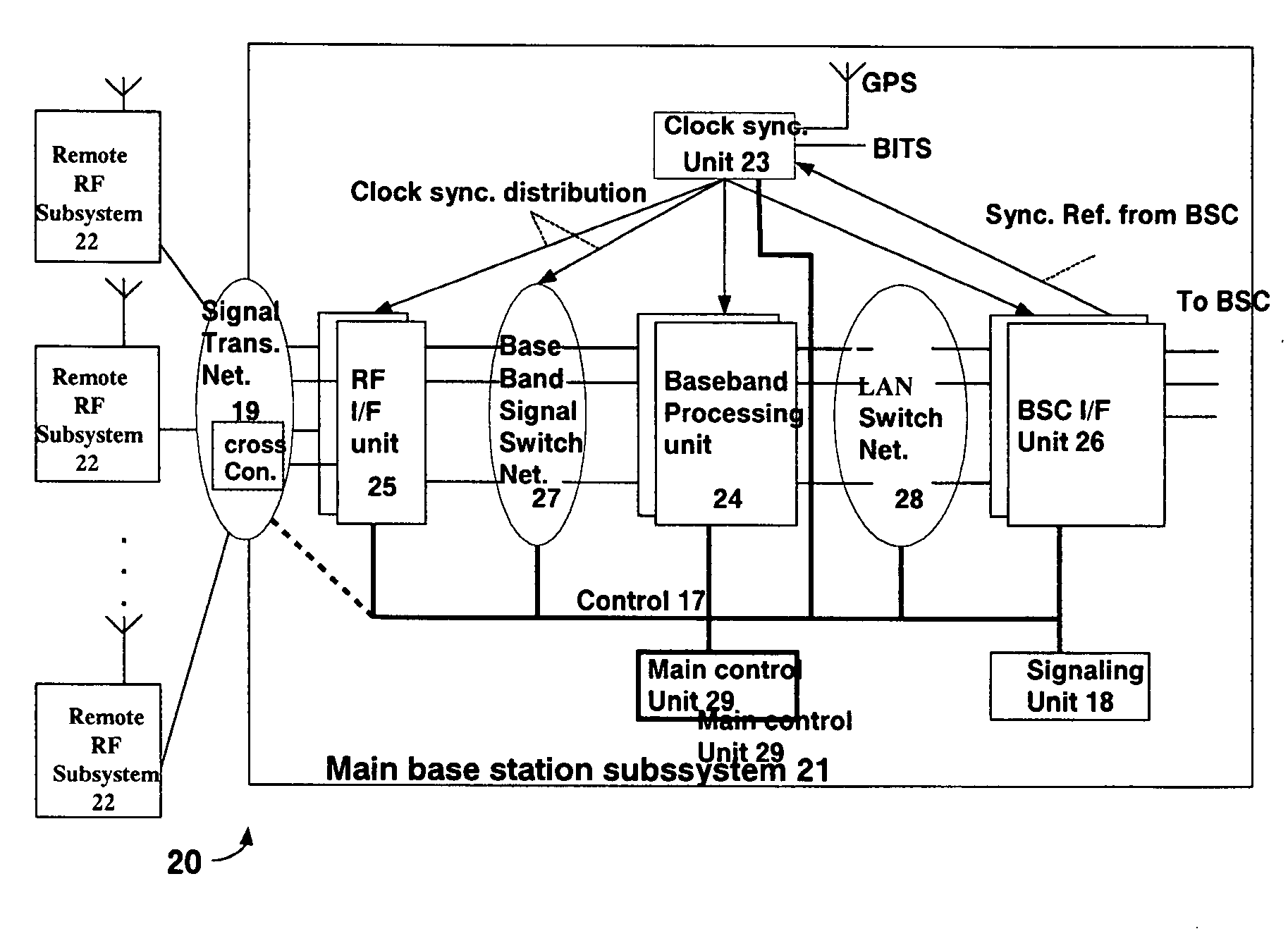
Centralized base station system based on advanced telecommunication computer architecture platform
InactiveUS20090149221A1Type of reductionSaving slotSubstation equipmentTransmissionNetwork switchControl switch
A centralized base station system based on ATCA, comprising a main base station subsystem and one or more remote radio frequency subsystems, the main base station subsystem comprising: one or more shelves based on ATCA platform, each shelf comprising at least one control switch module of ATCA board form; one or more base station controller interface module; a signaling module; one or more baseband processing modules; one or more remote radio frequency interface modules; a first switch network comprising first switch network shelf back board BASE interface link, a control switch module and a first network switch unit; a second switch network comprising a shelf back board FABRIC interface link, a control switch module and a second network switch unit; a clock synchronization network comprising a shelf back board clock synchronization bus, a control switch module and a clock unit; and a signal transmission network, wherein the second network switch unit and the clock unit are further connected to the first network switch unit, one of the control switch modules of all the shelves is the main control module.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
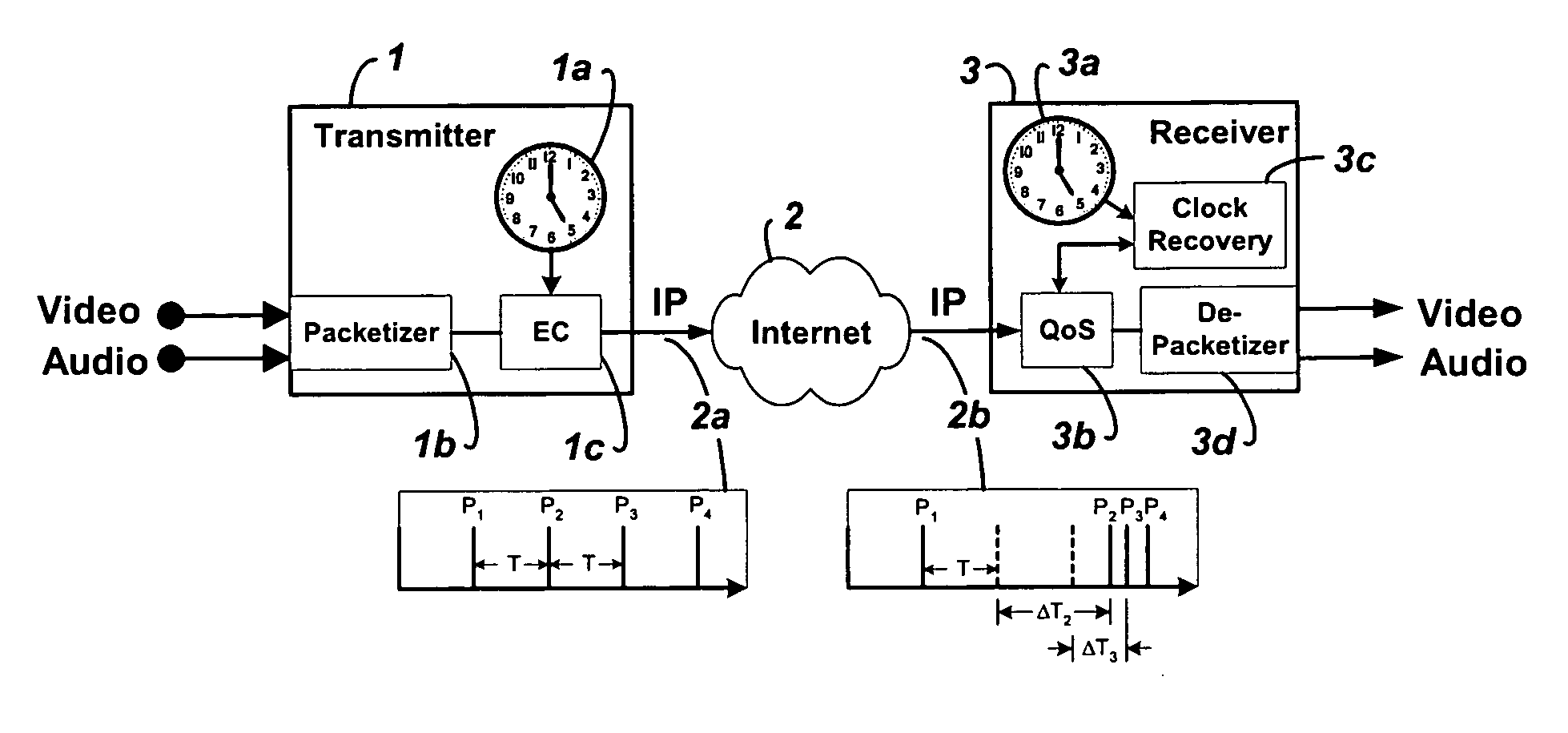
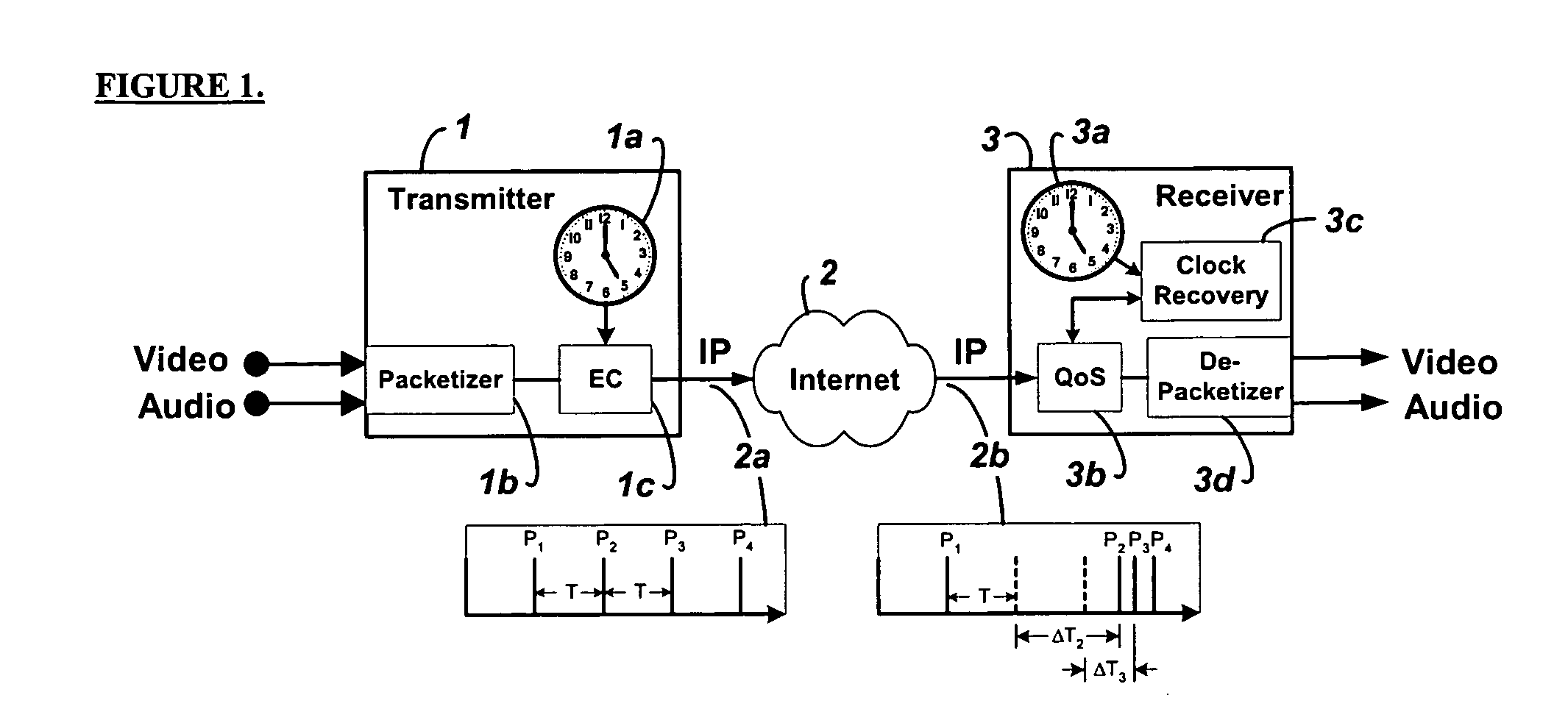
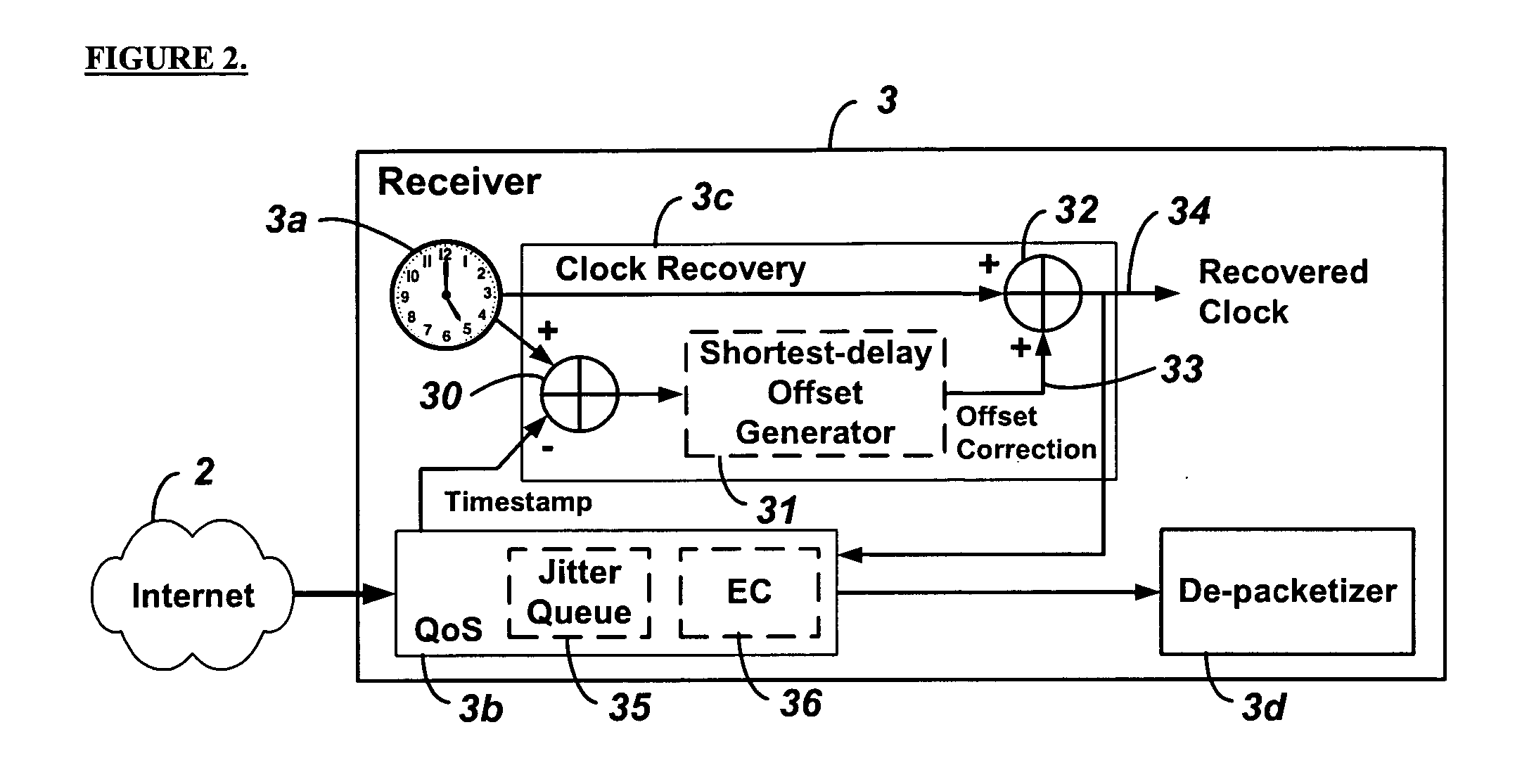
System and method for clock synchronization over packet-switched networks
ActiveUS20060013263A1Easy to replaceImprove abilitiesTime-division multiplexTransmissionQuality of serviceThe Internet
Embodiments of the invention enable the synchronization of clocks across packet switched networks, such as the Internet, sufficient to drive a jitter buffer and other quality-of-service related buffering. Packet time stamps referenced to a local clock create a phase offset signal. A shortest-delay offset generator uses a moving-window filter to select the samples of the phase offset signal having the shortest network propagation delay within the window. This shortest network propagation delay filter minimizes the effect of network jitter under the assumption that queuing delays account for most of the network jitter. The addition of this filtered phase offset signal to a free-running local clock creates a time reference that is synchronized to the remote clock at the source thus allowing for the transport of audio, video, and other time-sensitive real-time signals with minimal latency.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
Method to synchronize playback of multicast audio streams on a local network
A method is provided for synchronizing the playback of a digital audio broadcast on a plurality of network output devices using a microphone near a source, embedded control codes, and the audio patterns from the network output devices. An optional, additional manual adjustment method relies on a graphical user interface for adjustment and audible pulses from the devices which are to be synchronized. Synchronization of the audio is accomplished with clock synchronization of the network output devices. The digital audio broadcast from multiple receivers does not present to a listener any audible delay or echo effect.
Owner:GATEWAY
Digital audio compensation
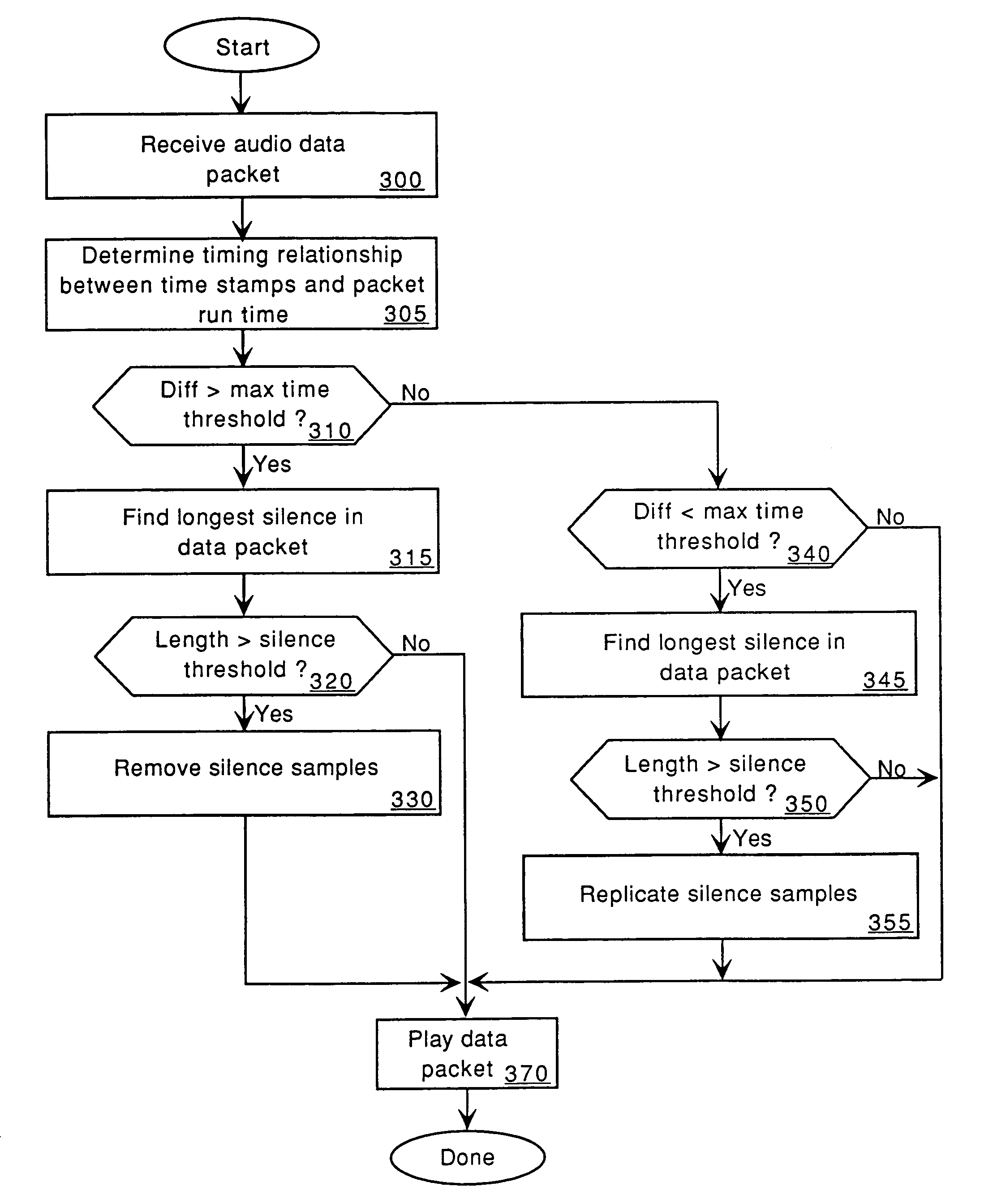
A method and apparatus for audio compensation is disclosed. If audio input components and audio output components are not driven by a common clock (e.g., input and output systems are separated by a network, different clock signals in a single computer system), input and output sampling rates may differ. Also, network routing of the digital audio data may not be consistent. Both clock synchronization and routing considerations can affect the digital audio output. To compensate for the timing irregularities caused by clock synchronization differences and / or routing changes, the present invention adjusts periods of silence in the digital audio data being output. The present invention thereby provides an improved digital audio output.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
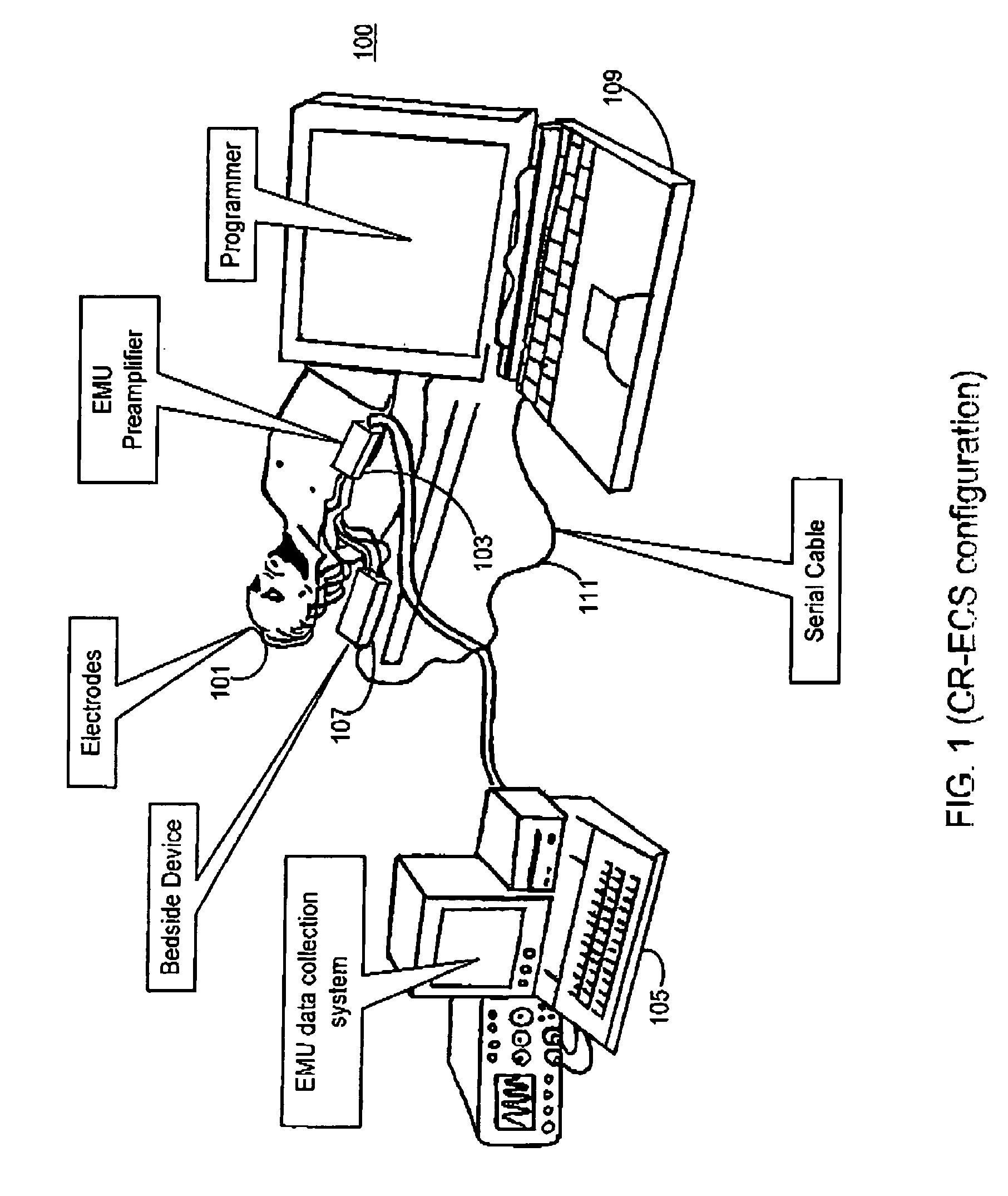
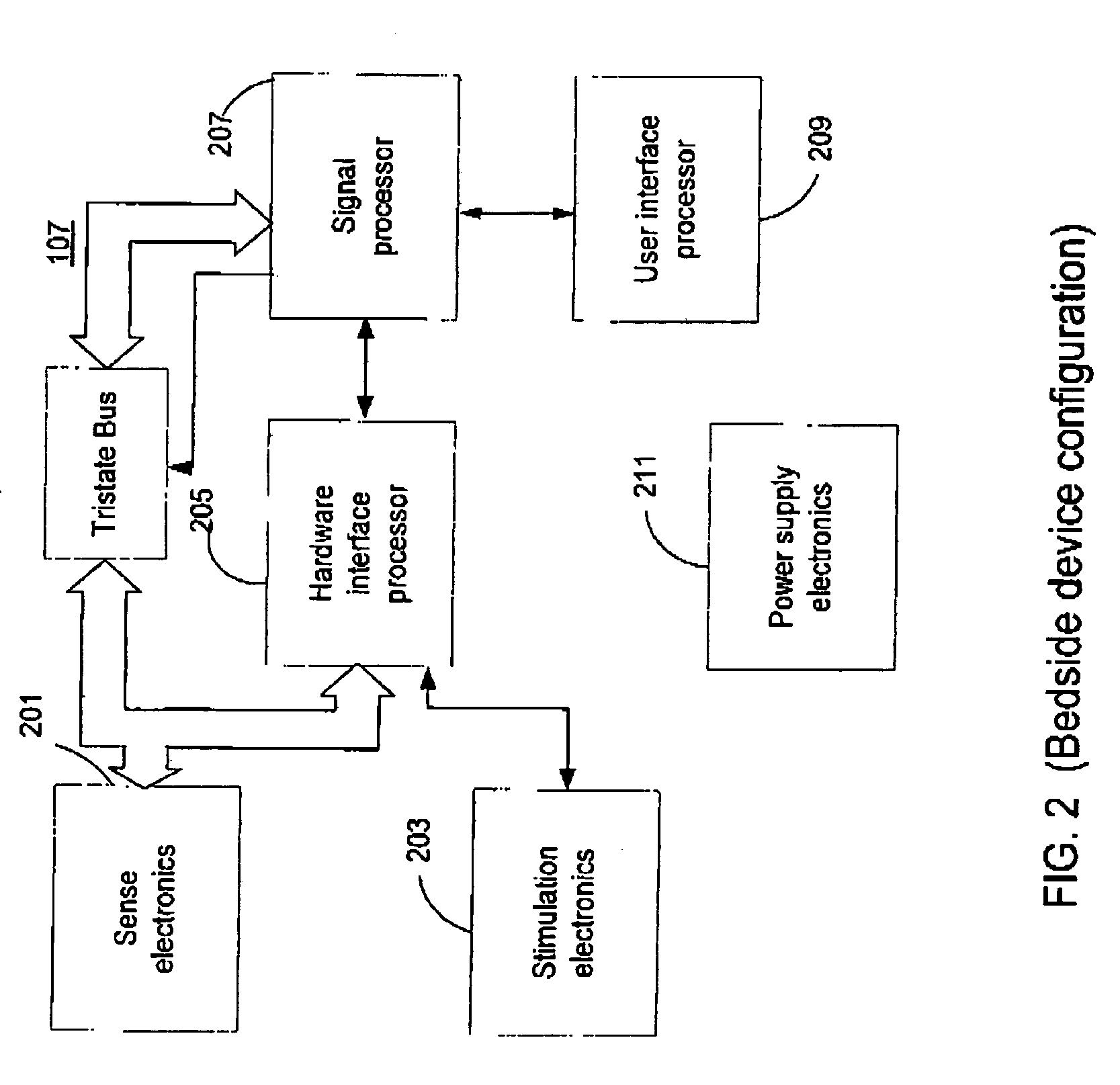
Synchronization and calibration of clocks for a medical device and calibrated clock
Apparatus and method support the synchronization and calibration of a plurality of clocks in a medical device system that may provide treatment to a patient with a nervous system disorder. The plurality of clocks, which may be located at different components of the medical device system, includes a first clock and a second clock. The second clock may be synchronized to a first clock by disabling a run mode operation and setting the second clock to a selected time. When a reference time of the first clock approximately equals the selected time, the second clock enables the run mode operation. Additionally, a drift time that is indicative of a time difference between the first clock and the second clock is determined. If the drift time is greater than a predetermined amount, an indication to resynchronize the first and second clocks is provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
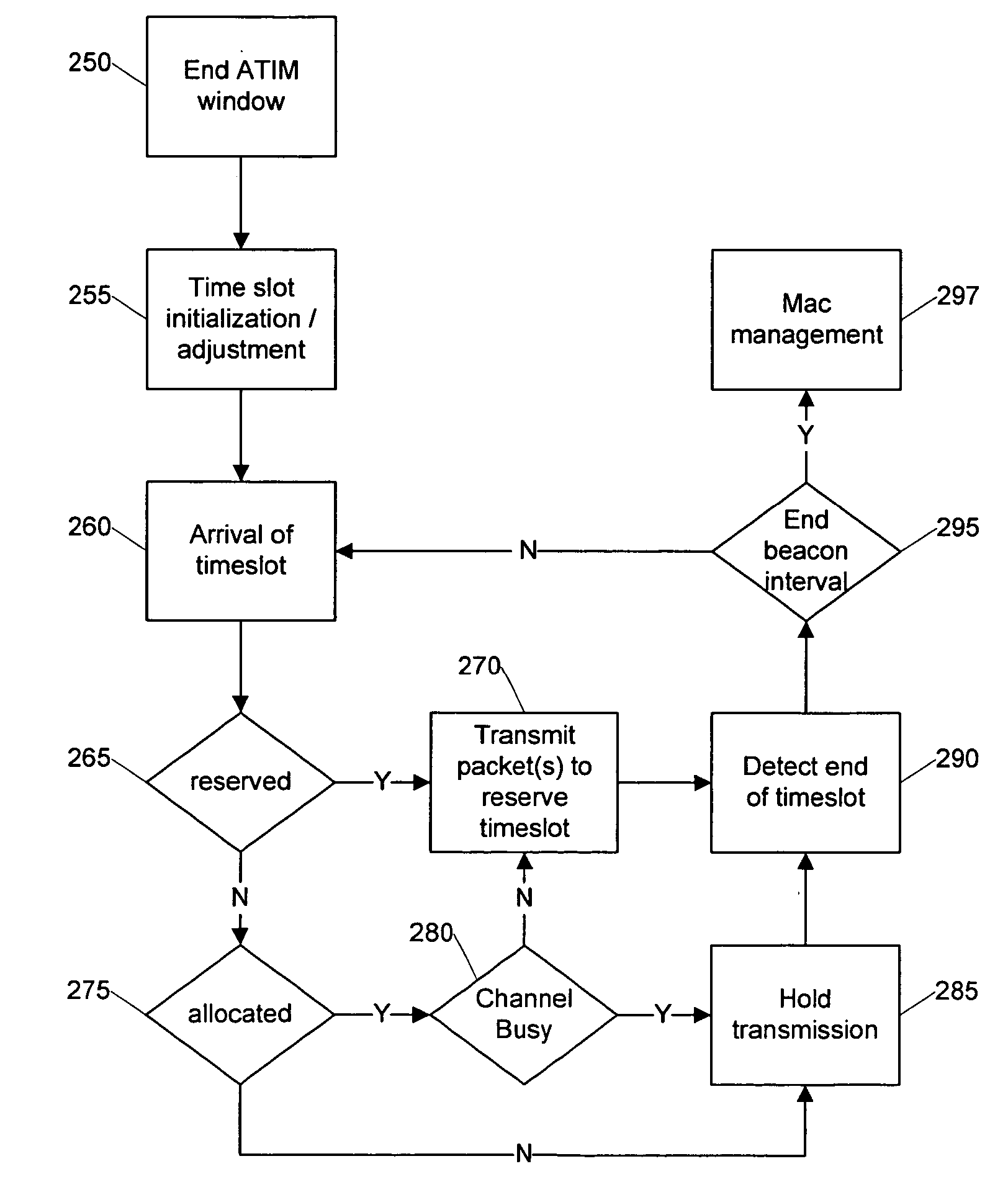
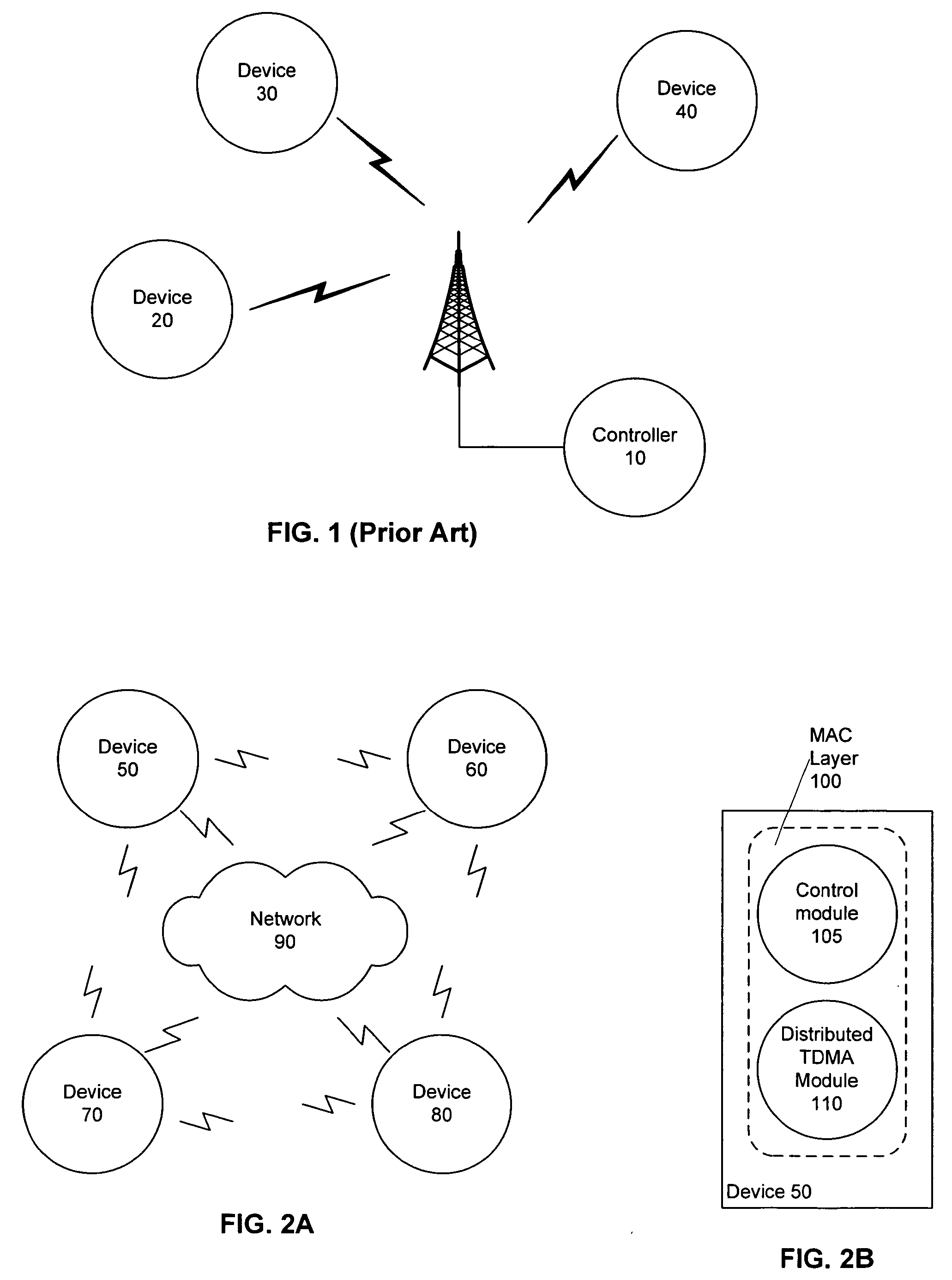
Distributed TDMA for wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20050201340A1Optimizing bandwidth usageFree communicationSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceWireless mesh network
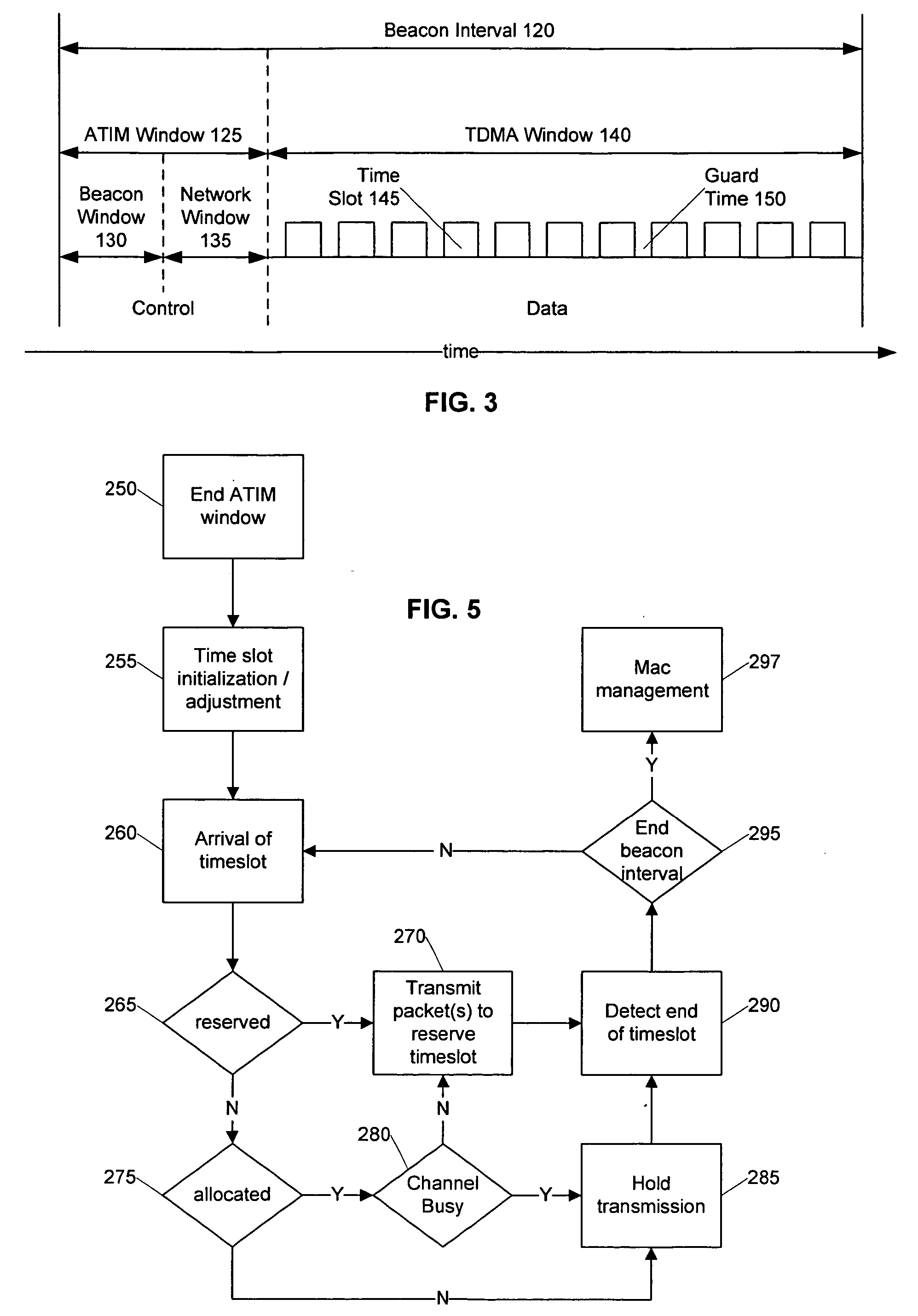
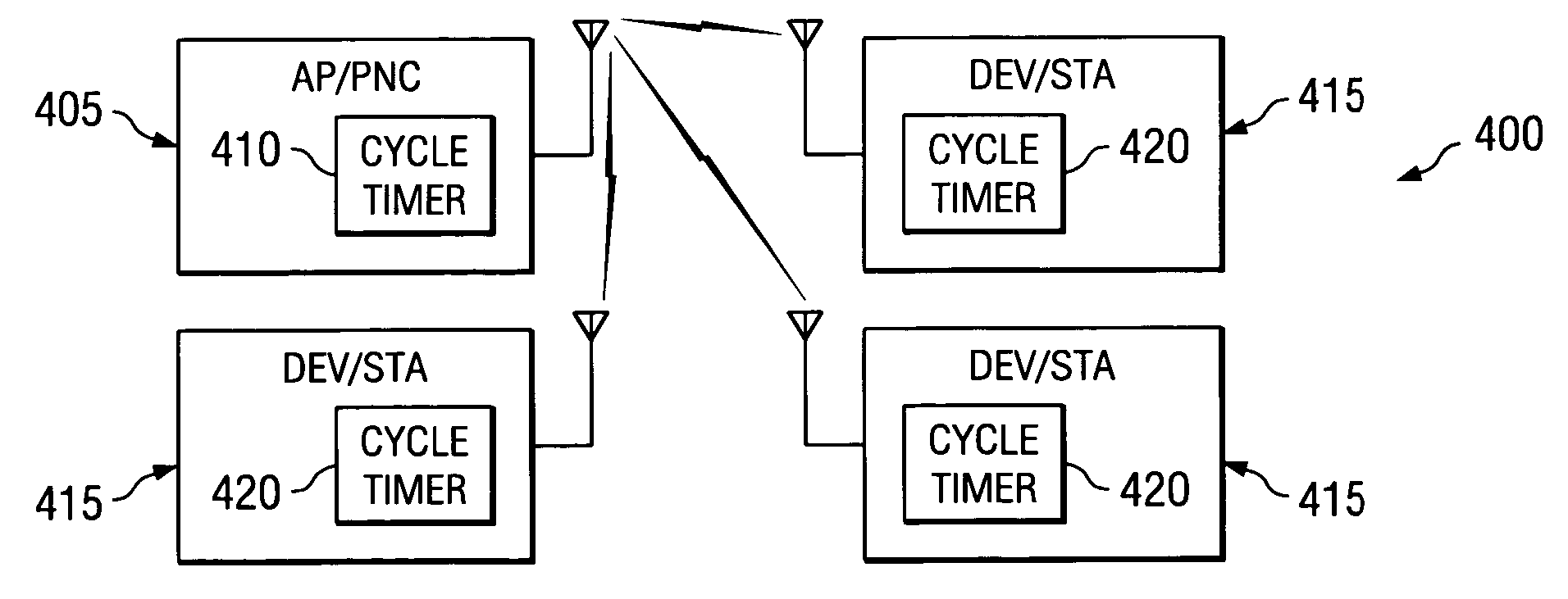
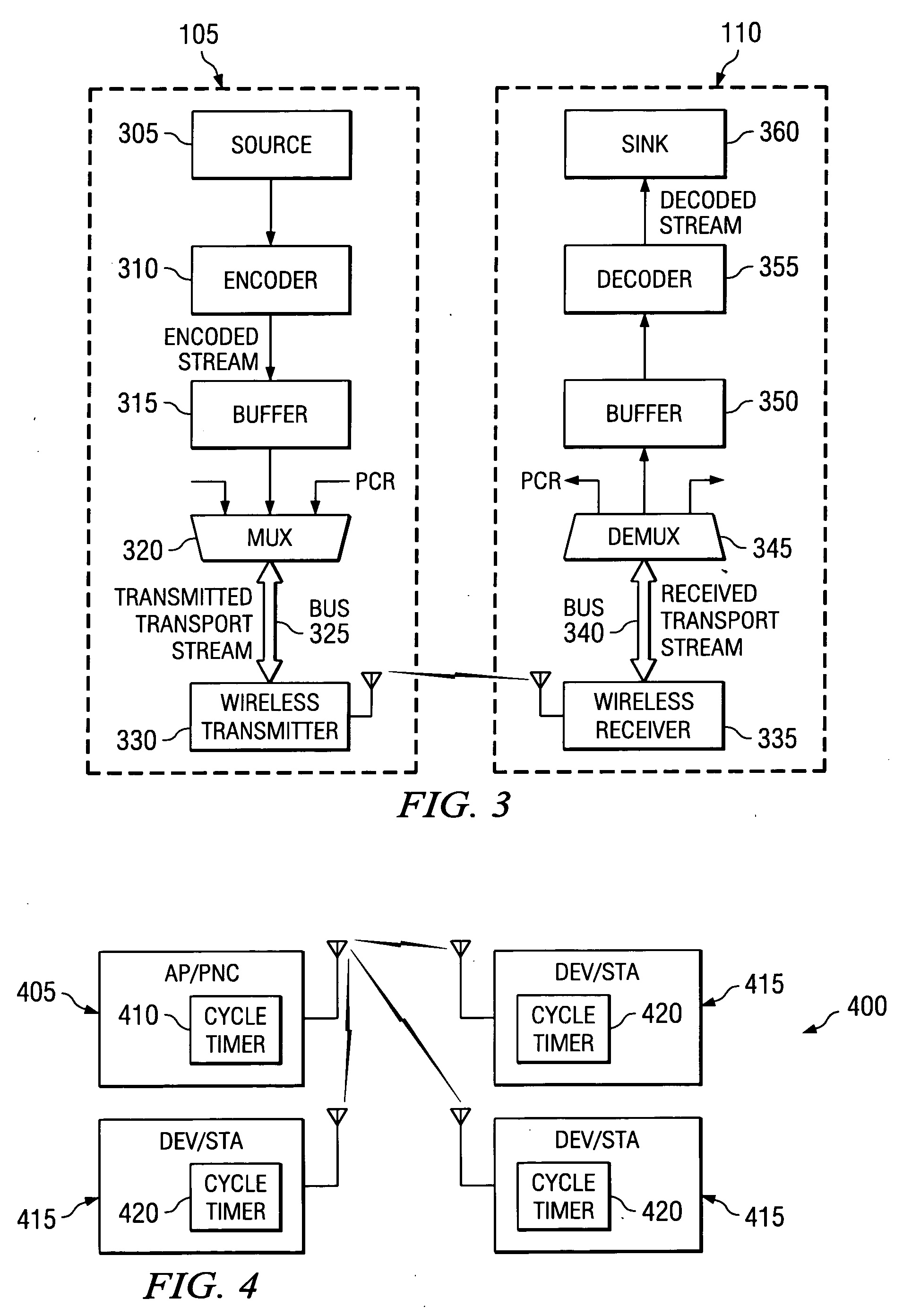
Systems and methods are provided that facilitate distributed TDMA communication amongst nodes in an ad hoc wireless network without the need for centralized management and control. A wireless communication device includes a MAC layer that is configured to synchronize its local clock from a beacon frame that is sent by another node in the ad hoc network. After synchronizing its clock to the ad hoc network, the device identifies a timeslot for transmission. When the timeslot arrives, the device senses the channel to determine if there is traffic and if there is no traffic, the device reserves the timeslot by transmitting. In this fashion, a plurality of timeslots can be divided amongst the devices in the ad hoc wireless network for optimized collision free communication using distributed TDMA. This distributed TDMA communication can also be applied across multiple channels in a wireless network to significantly increase bandwidth and quality-of-service.
Owner:COMMWORKS SOLUTIONS LLC +1
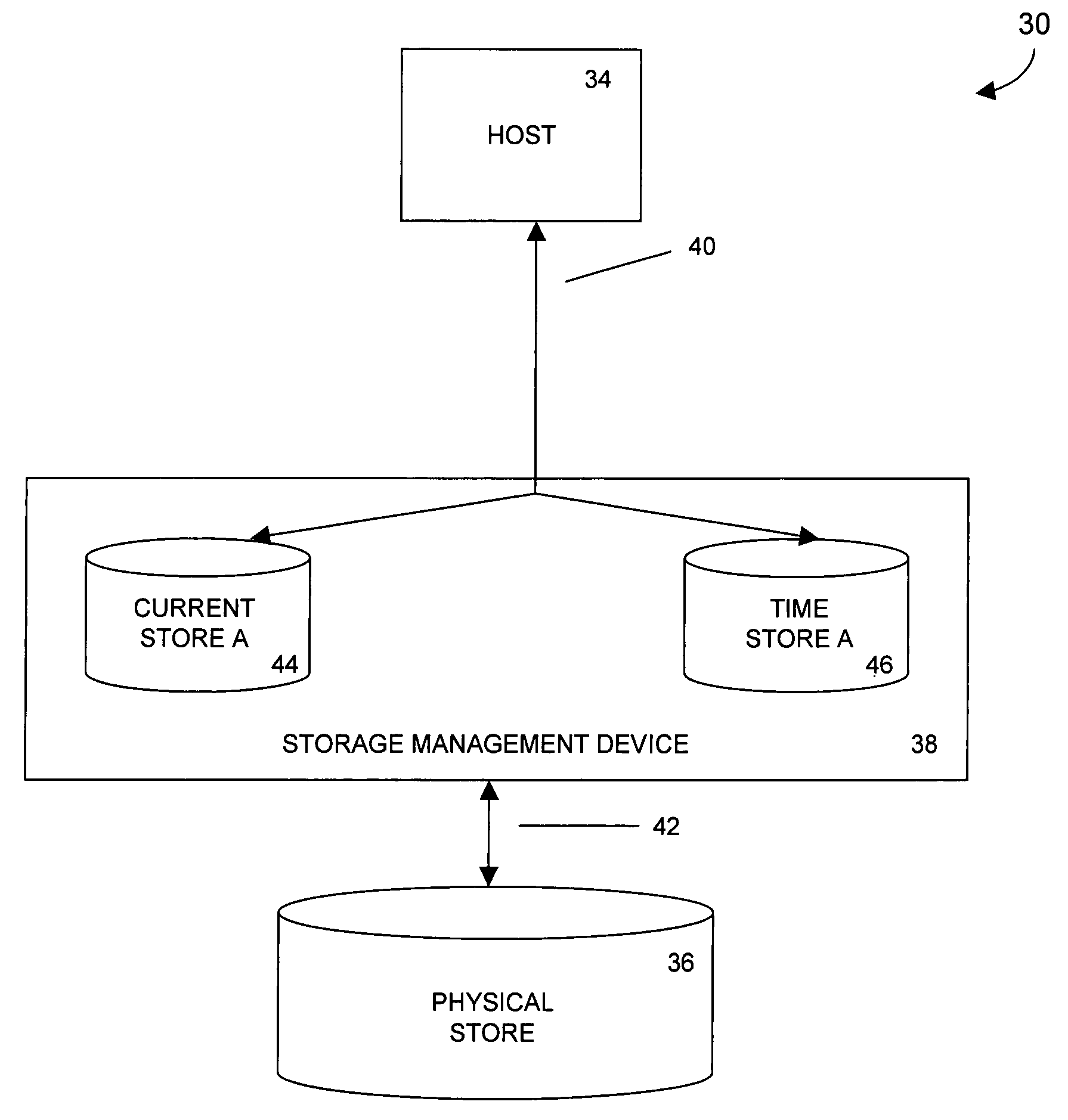
Bypassing an intermediate synchronization server of a three tiered synchronization system
InactiveUS7634519B2Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationData storeSynchronization system
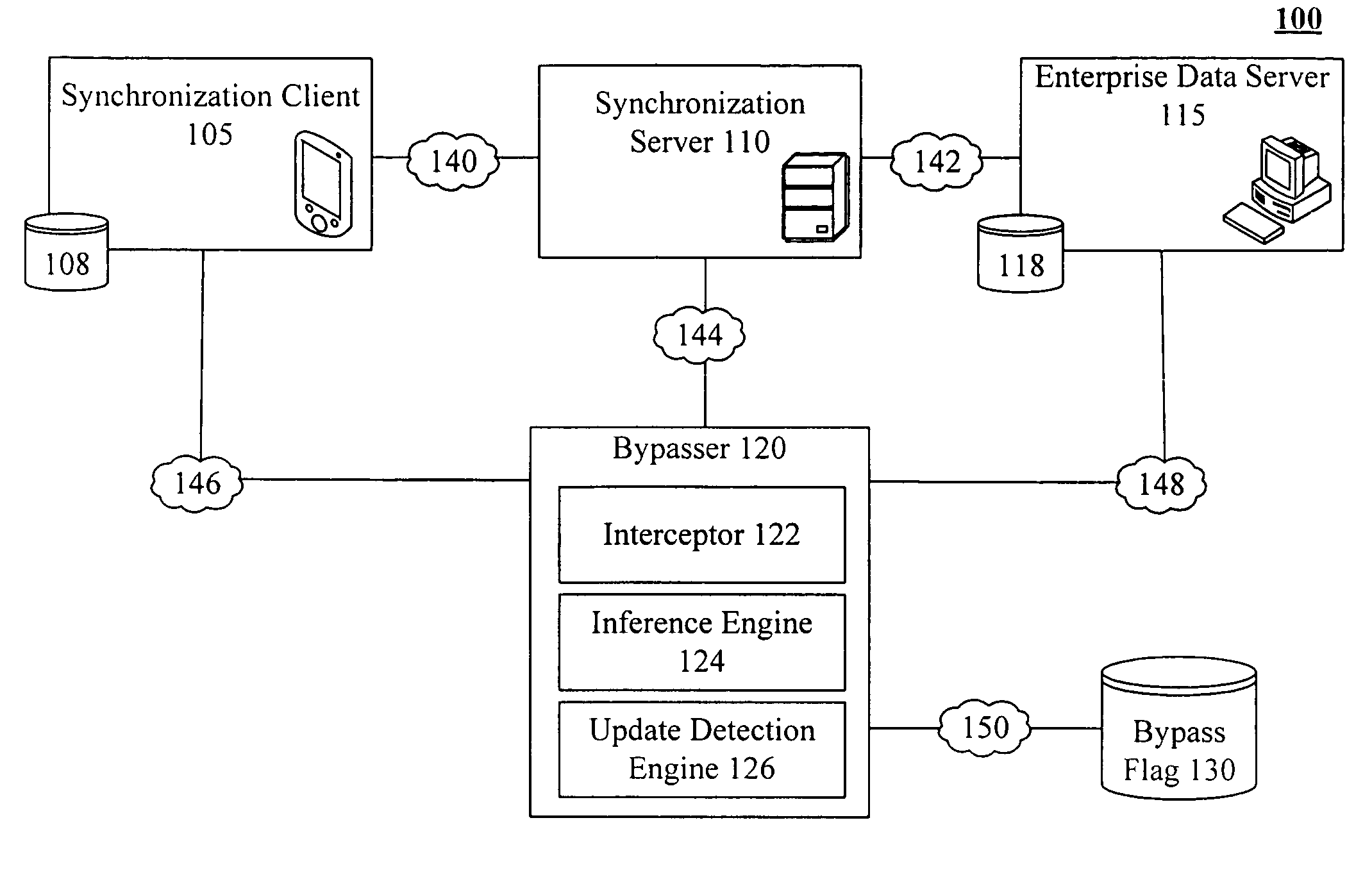
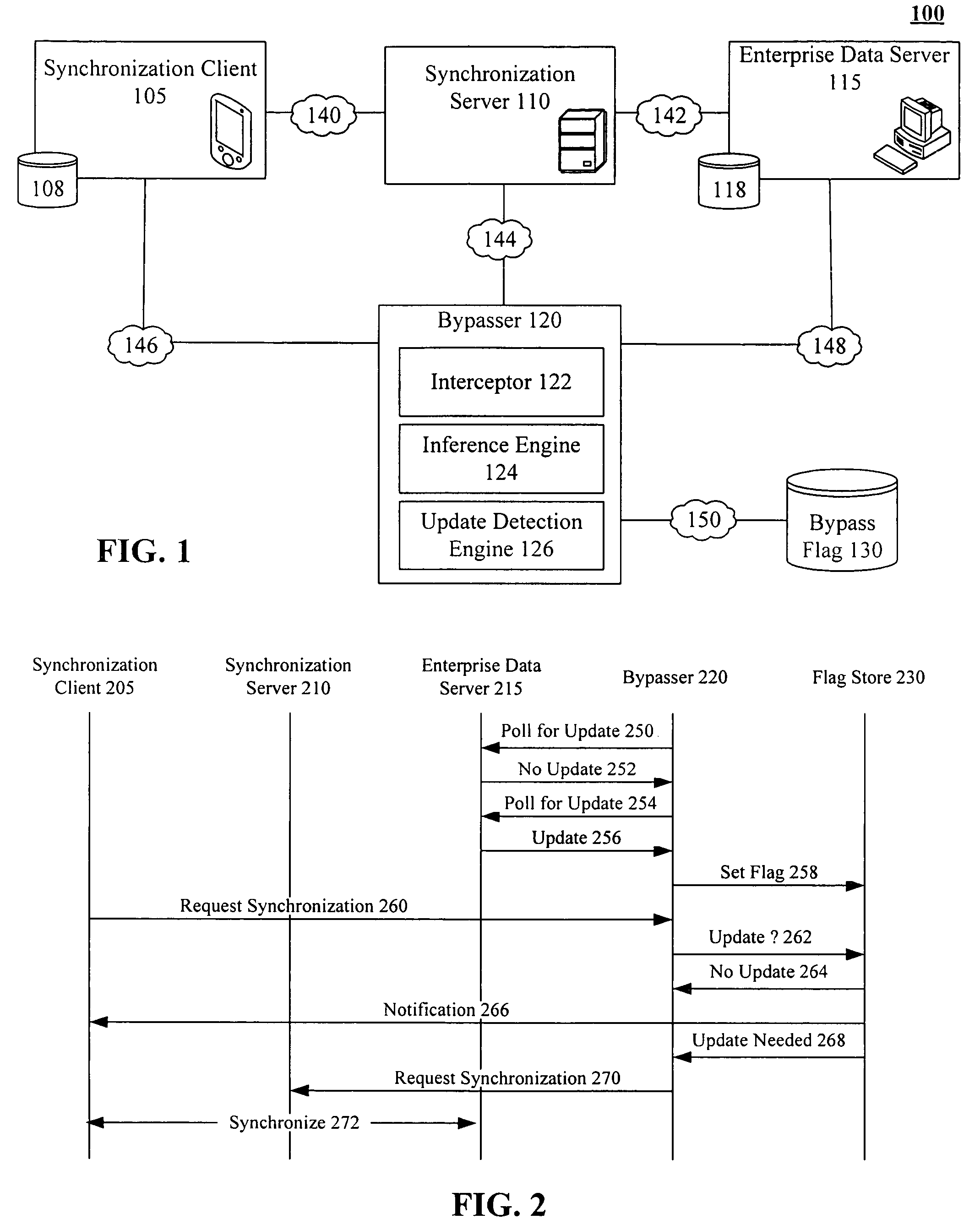
A bypasser configured to operate within a three tiered synchronization system. The bypasser can include an interceptor and an inference engine. The interceptor can intercept synchronization requests before a synchronization event involving a synchronization server is initiated. The inference engine can determine if the data store and the another data store are to be synchronized and can selectively initiate the synchronization event based on the determination of the inference engine. For example, when the inference engine determines that synchronization is not to occur, the bypasser can convey a notification that no update is needed to the source of an intercepted synchronization request without requiring the synchronization server to process the synchronization request. When the inference engine determines that synchronization is to occur, the bypasser can convey an intercepted synchronization request to the intermediate synchronization server for processing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
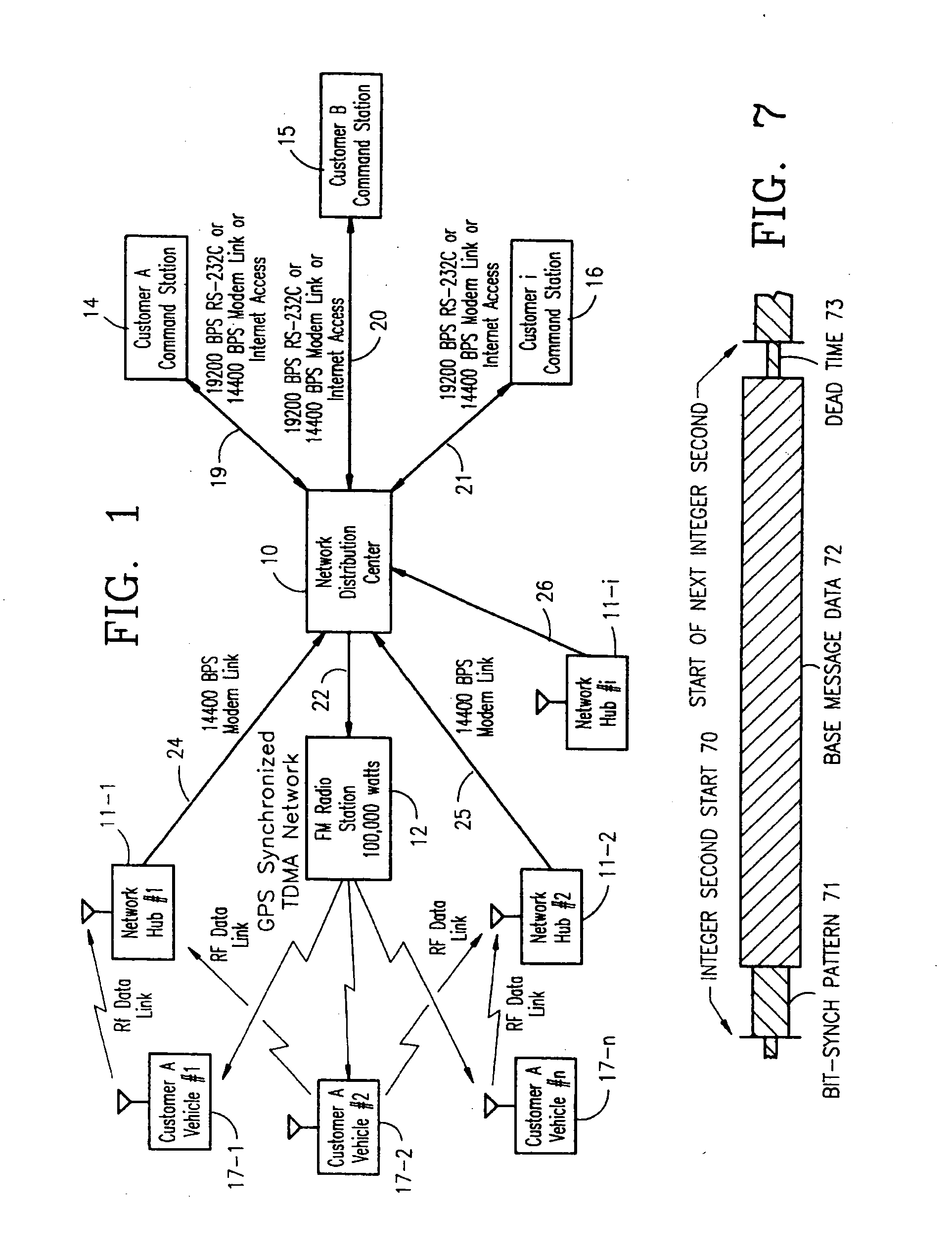
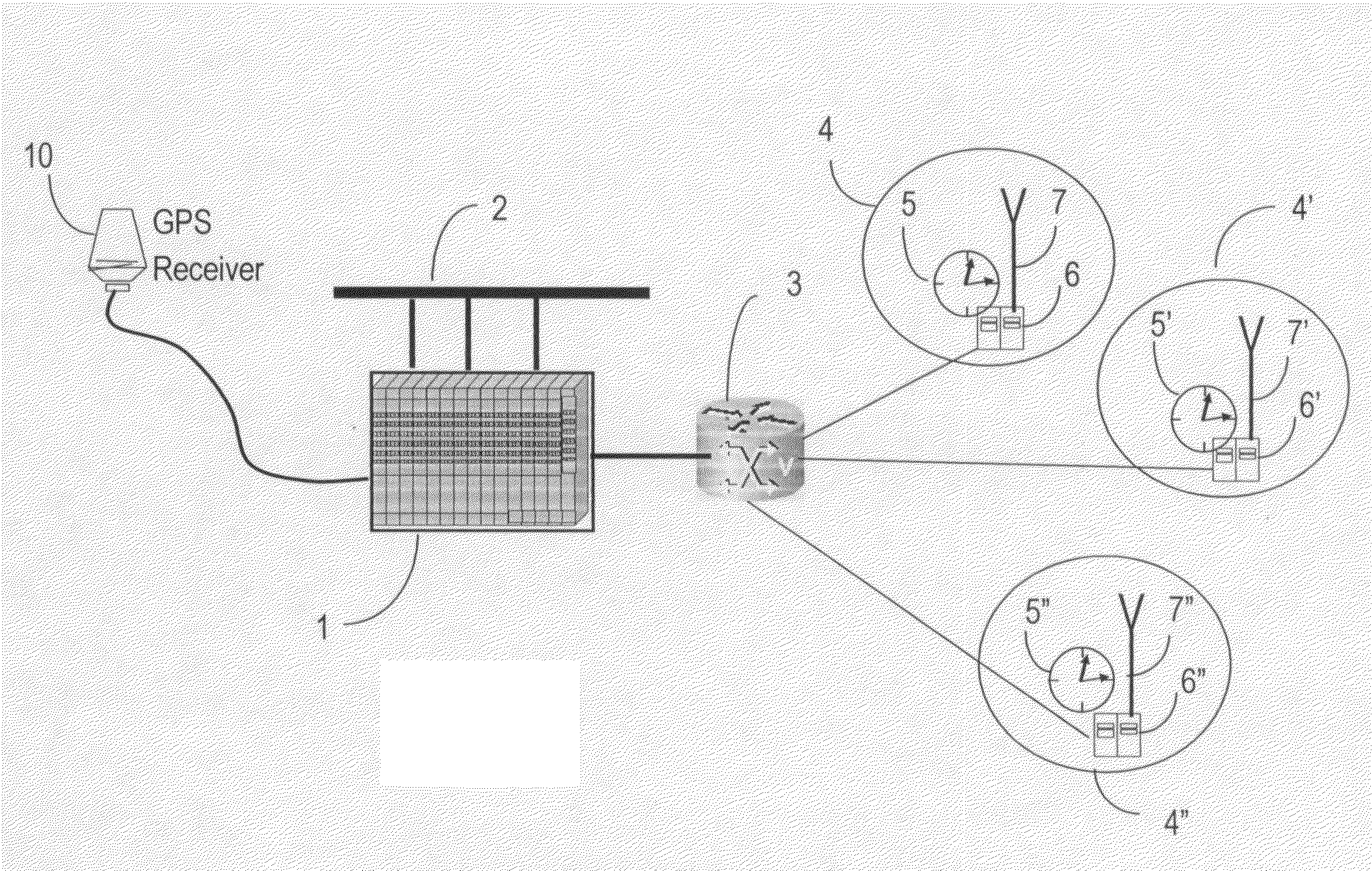
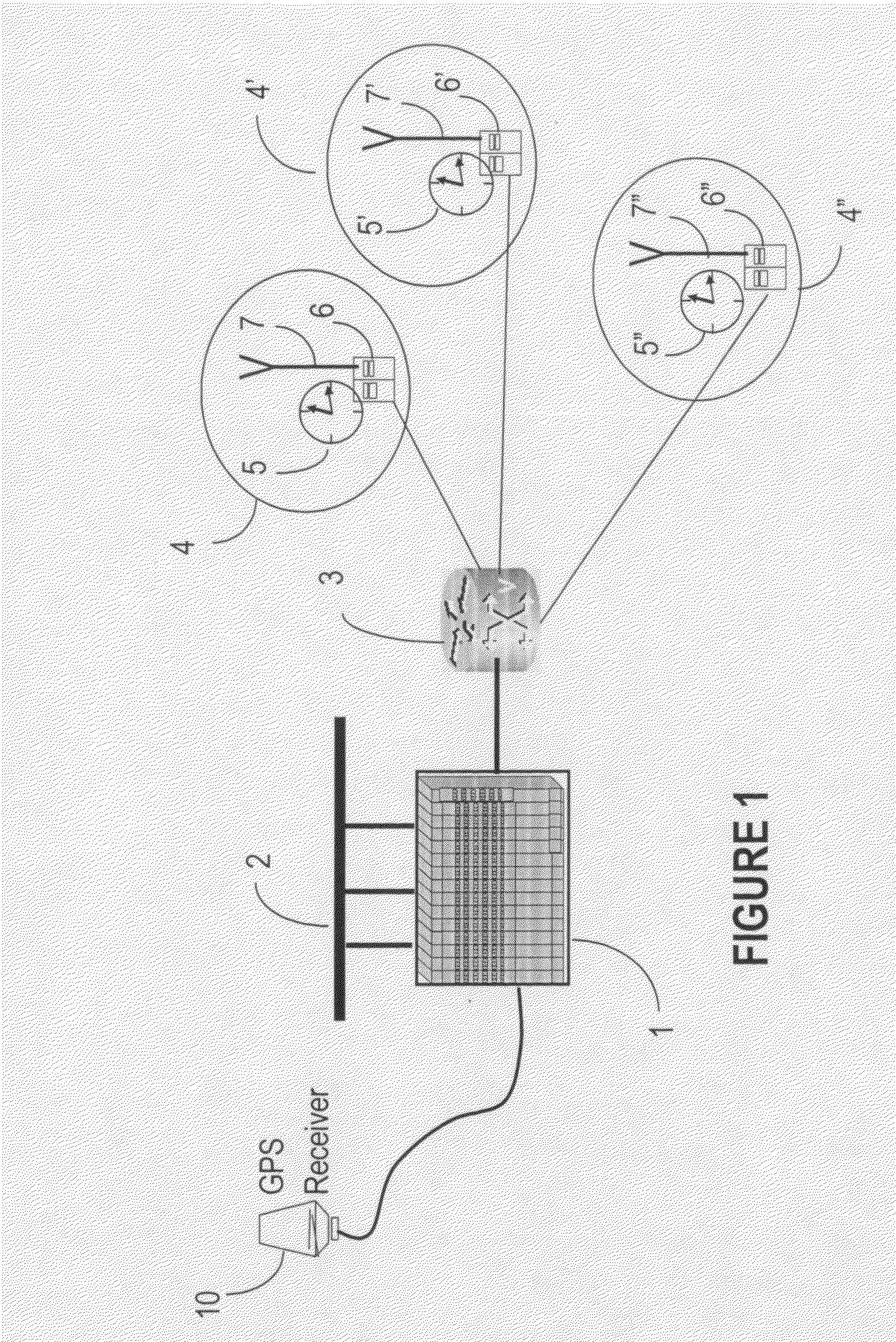
Vehicle tracking, communication and fleet management system
InactiveUS20060142913A1Management moreEfficient and reliableVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesFleet managementEngineering
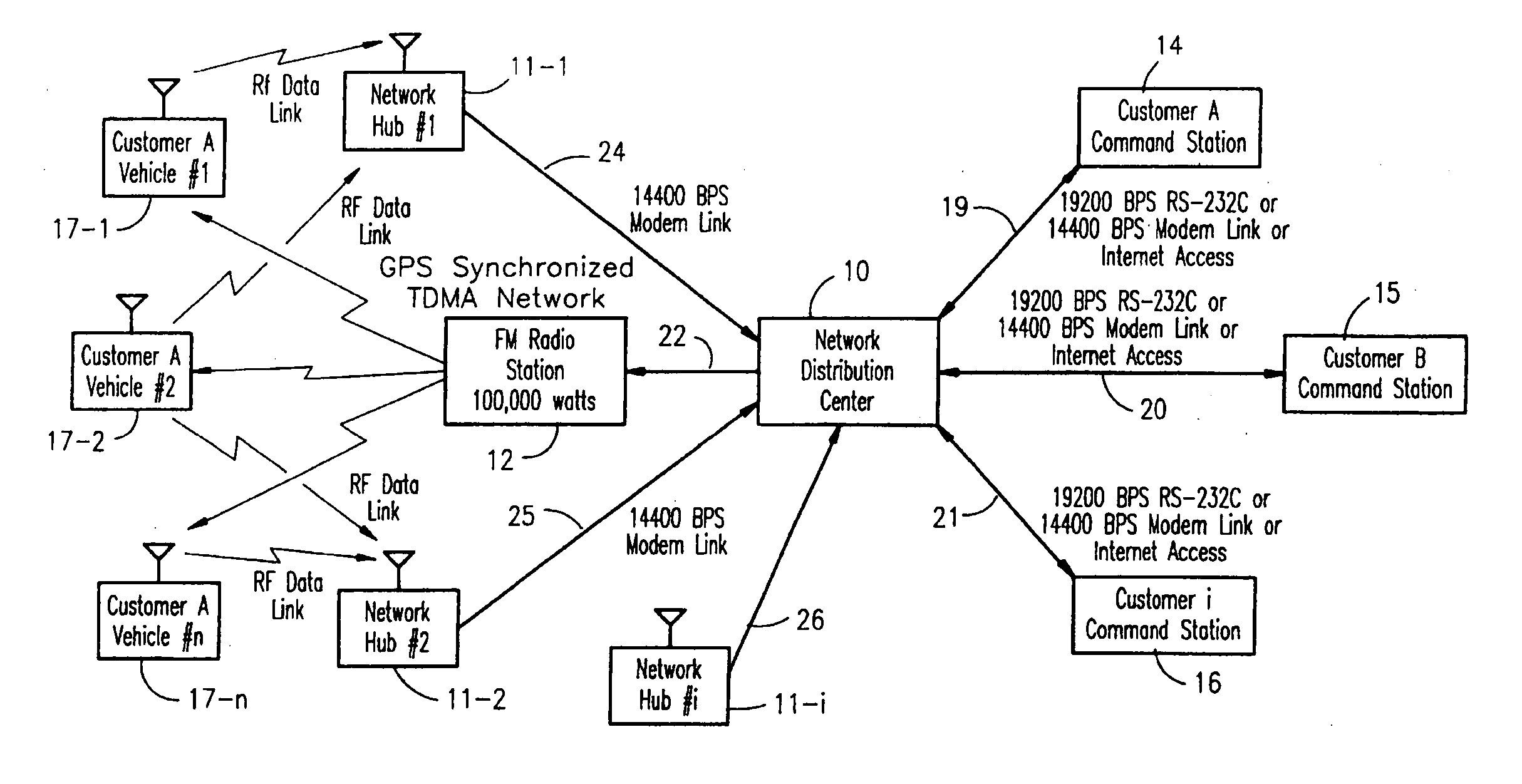
A vehicle fleet management information system identifies location and direction of movement of each vehicle in a fleet in real-time, and automatically reports such information, as well as status of predetermined events in which the vehicle is engaged, directly to the fleet manager. Each fleet vehicle has an assigned time slot to transmit its reporting information over a communications network without interfering with transmissions from other vehicles in their own respective time slots. A timing control phase lock loop (PLL) provides precise time synchronization for timing corrections from a global positioning system (GPS) based time reference. A dual band full-duplex interface of the network has TDMA on one-half and broadcast on the other half. Microprocessor time processing units in components of the network perform precise clock synchronization. Space diversity performed on received vehicle transmitted messages avoids data corruption. Different vehicles have different periodic transmission intervals, by dynamically allocating the slots for various update rates. Auxiliary reporting slots enable prompt reporting of important data by the respective vehicle transmitters independent of the slower periodic transmission intervals.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
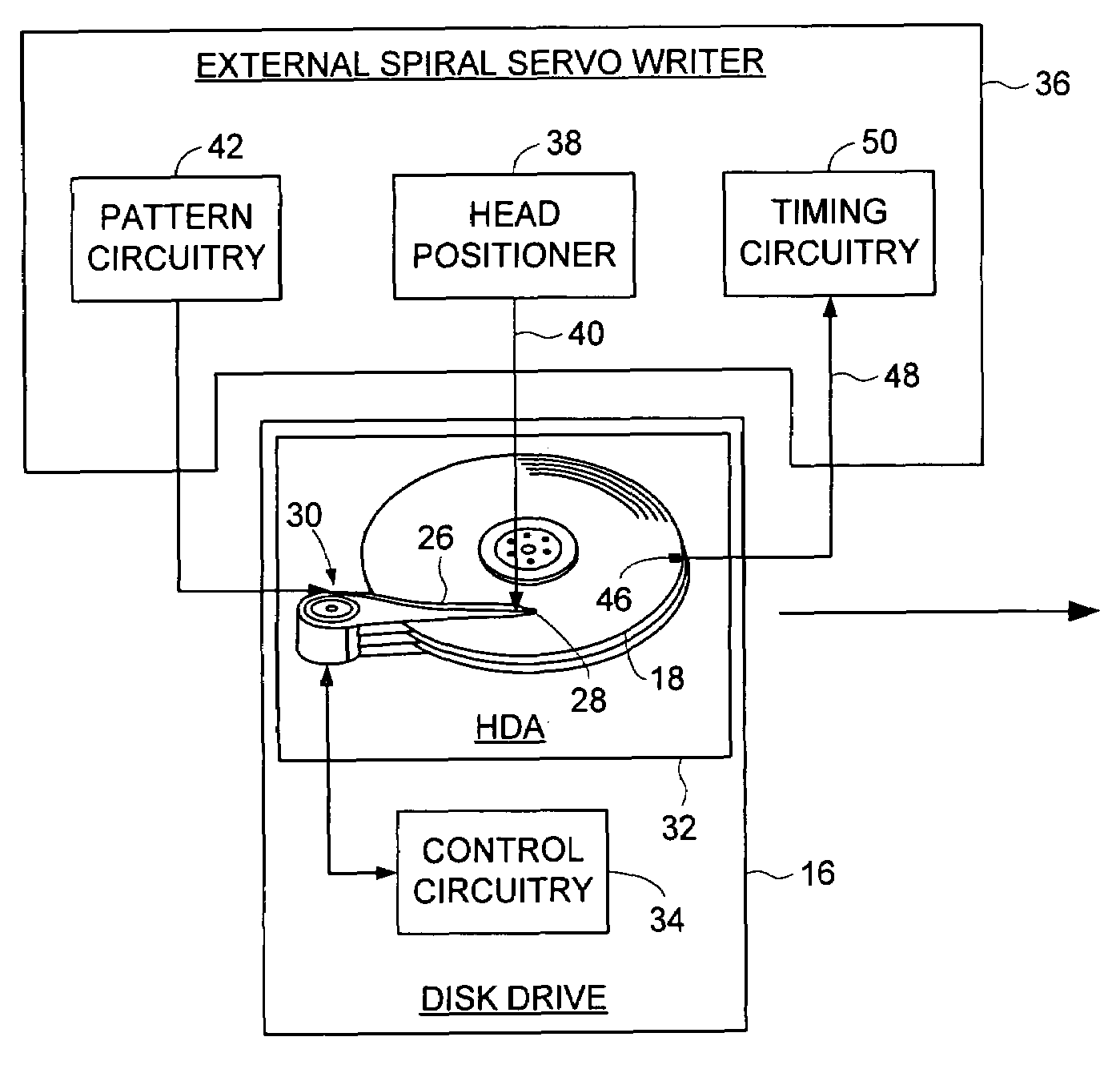
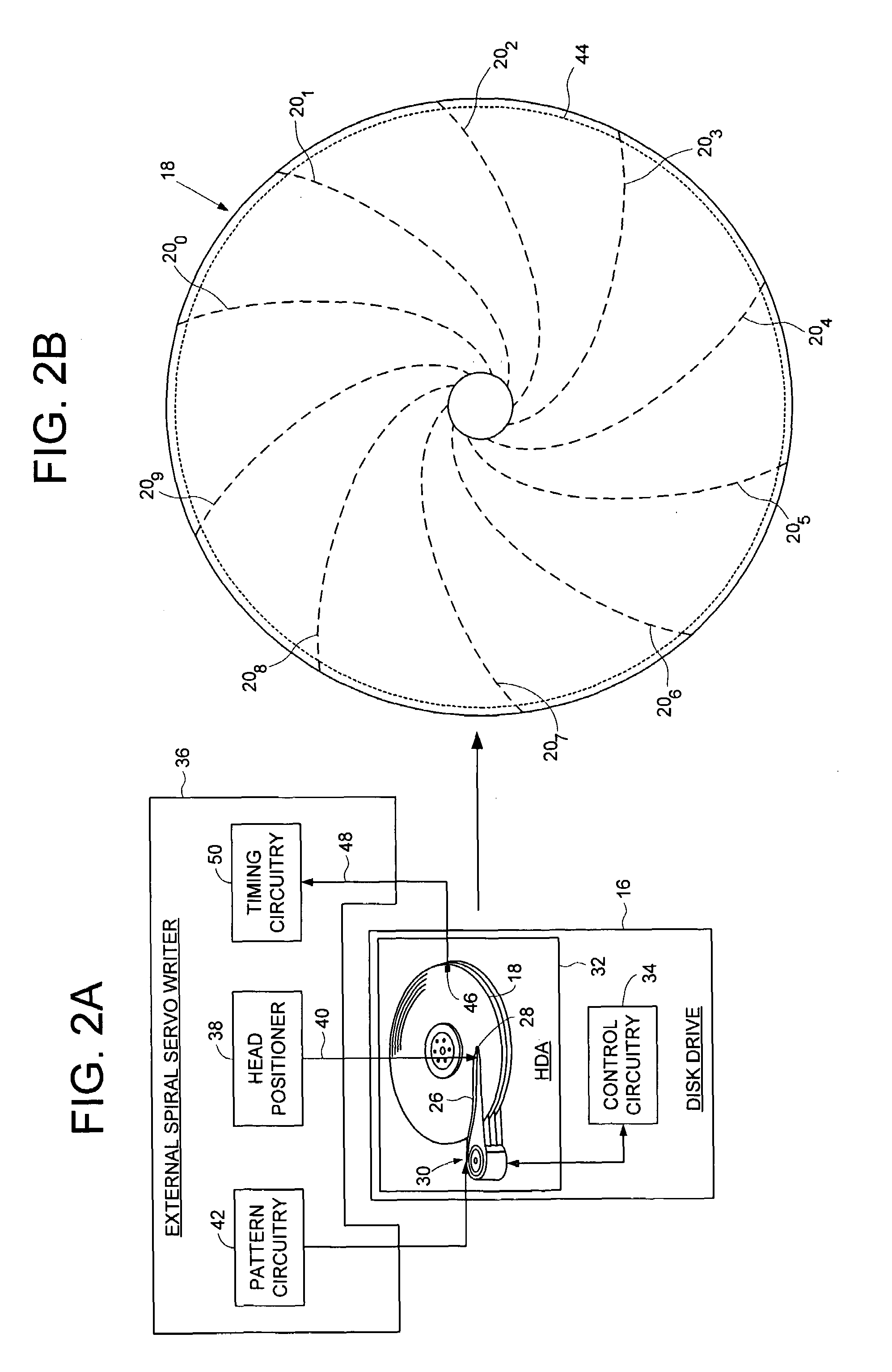
Servo writing a disk drive by synchronizing a servo write clock to a high frequency signal in a spiral track
InactiveUS6943978B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl theoryControl circuit
A method of writing product servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive is disclosed. A plurality of spiral tracks are written to the disk, wherein each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark. During the product servo writing process, the sync marks in the spiral tracks are read to generate a coarse timing recovery measurement, and the high frequency signal in the spiral tracks is read to generate a fine timing recovery measurement. The coarse and fine timing recovery measurements are processed to synchronize a servo write clock used to write the product servo sectors to the disk. In one embodiment the control circuitry within the disk drive synchronizes the servo write clock by reading the spiral tracks, and in an alternative embodiment an external product servo writer synchronizes the servo write clock by reading the spiral tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Apparatus and method for performing uplink synchronization in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20120300752A1Reduce overheadSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemMobile station
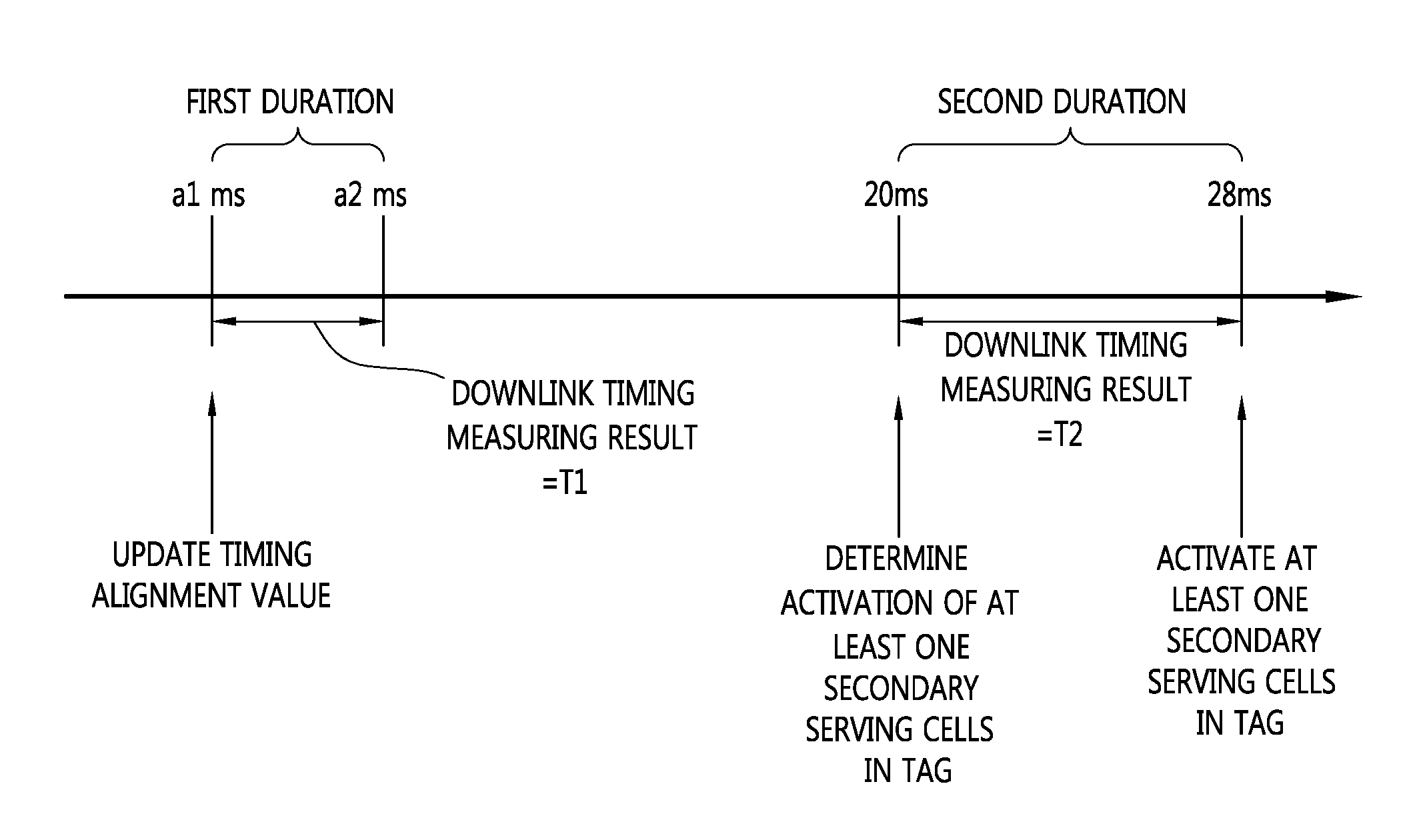
This specification relates to an apparatus and method for performing random access in a wireless communication system. This specification discloses a mobile station, including a reception unit for receiving TAG configuration information on which at least one serving cell configured in the mobile station is classified as a Timing Alignment Group (TAG) from a base station and a transmission unit for transmitting a random access preamble to the base station on one representative serving cell within the TAG. In accordance with this specification, a procedure of obtaining a TAV for a serving cell in order to secure and maintain uplink timing synchronization becomes clear, the time taken to obtain uplink synchronization for a serving cell may be reduced, and overhead due to excessive random access attempts may be reduced by obtaining a TAV for a plurality of serving cells through one random access procedure.
Owner:APPLE INC
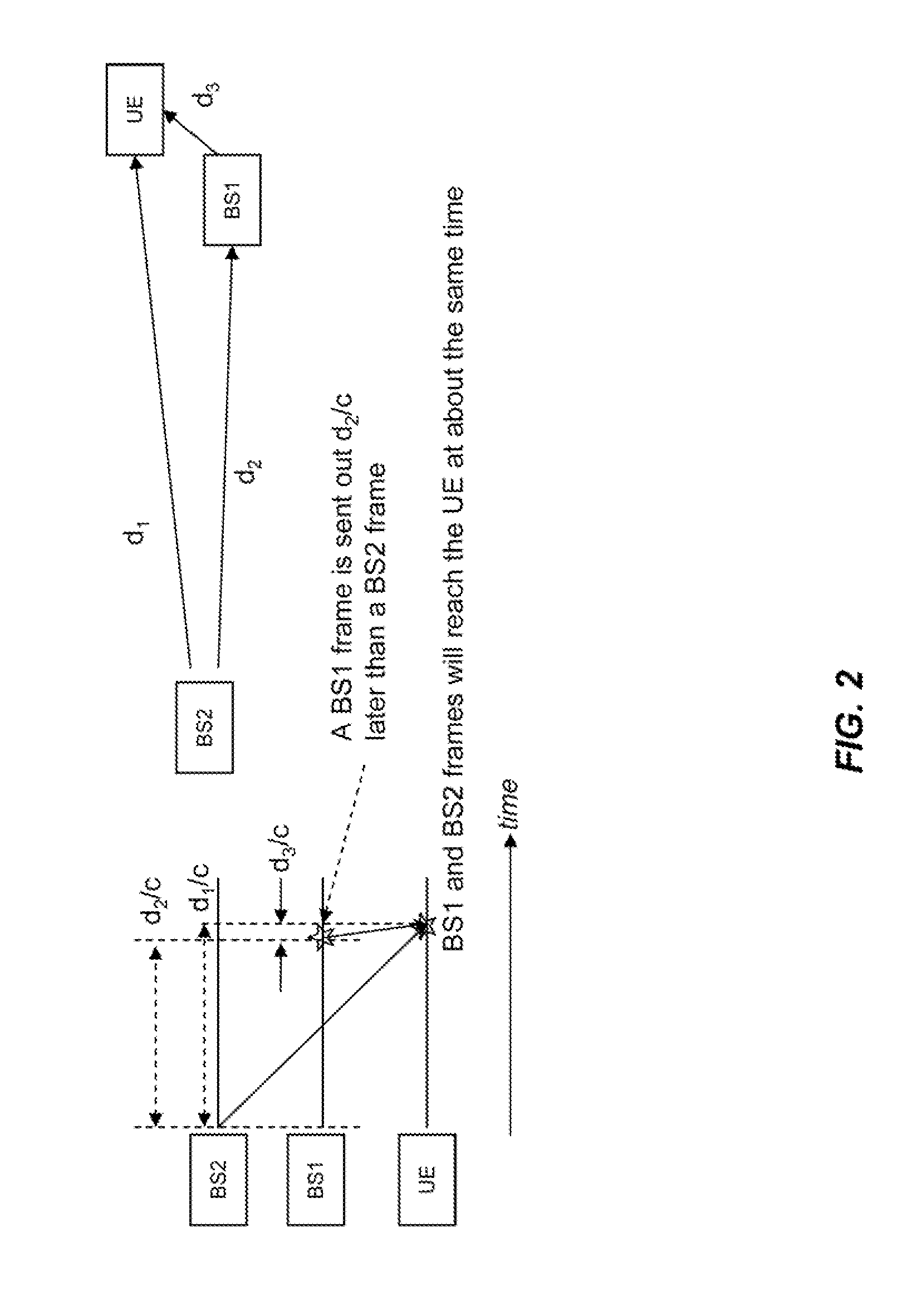
Audio and video clock synchronization in a wireless network
ActiveUS20050259754A1Need can be replacedEnabling synchronizationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningCommunications systemTimestamp
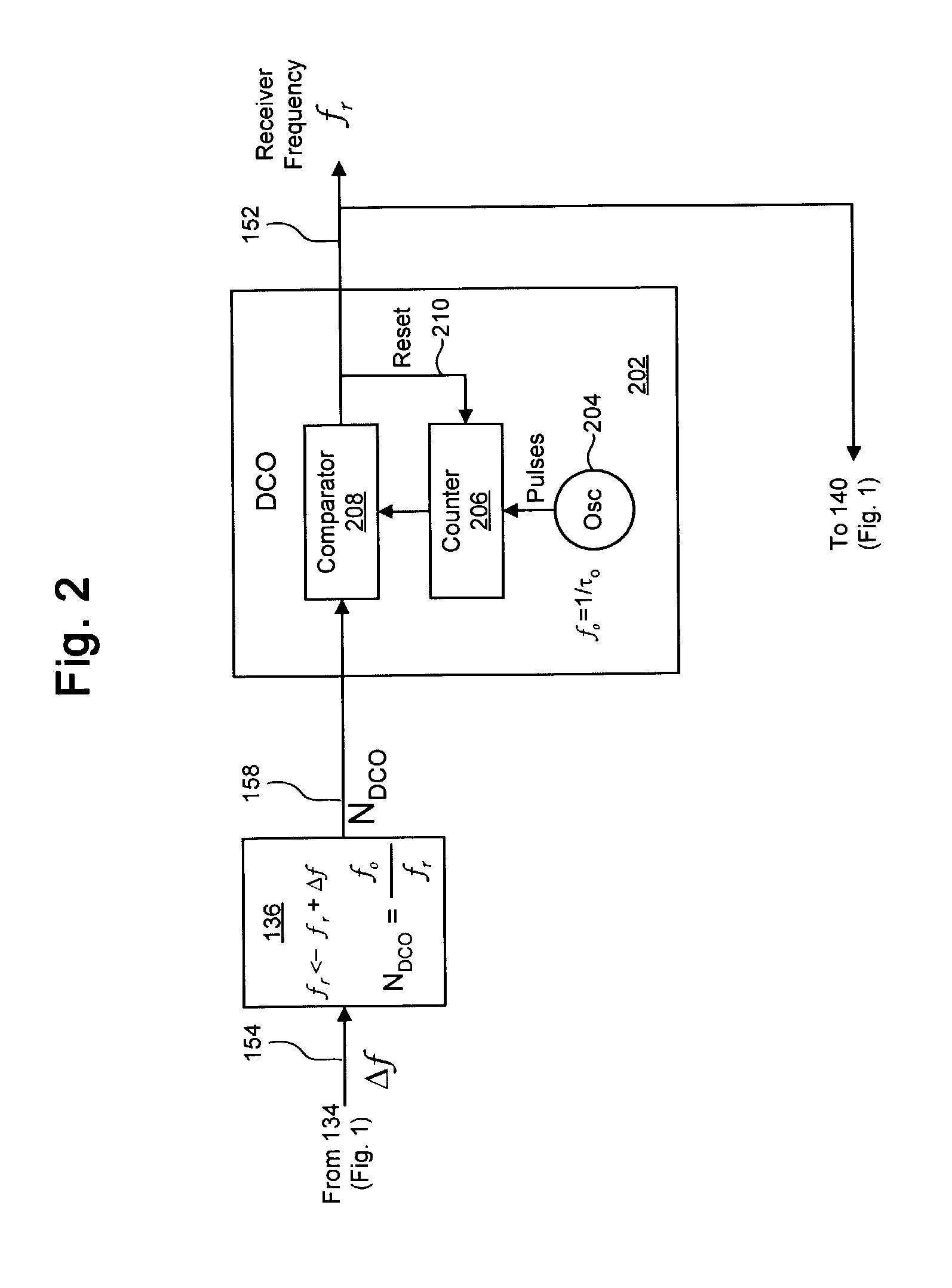
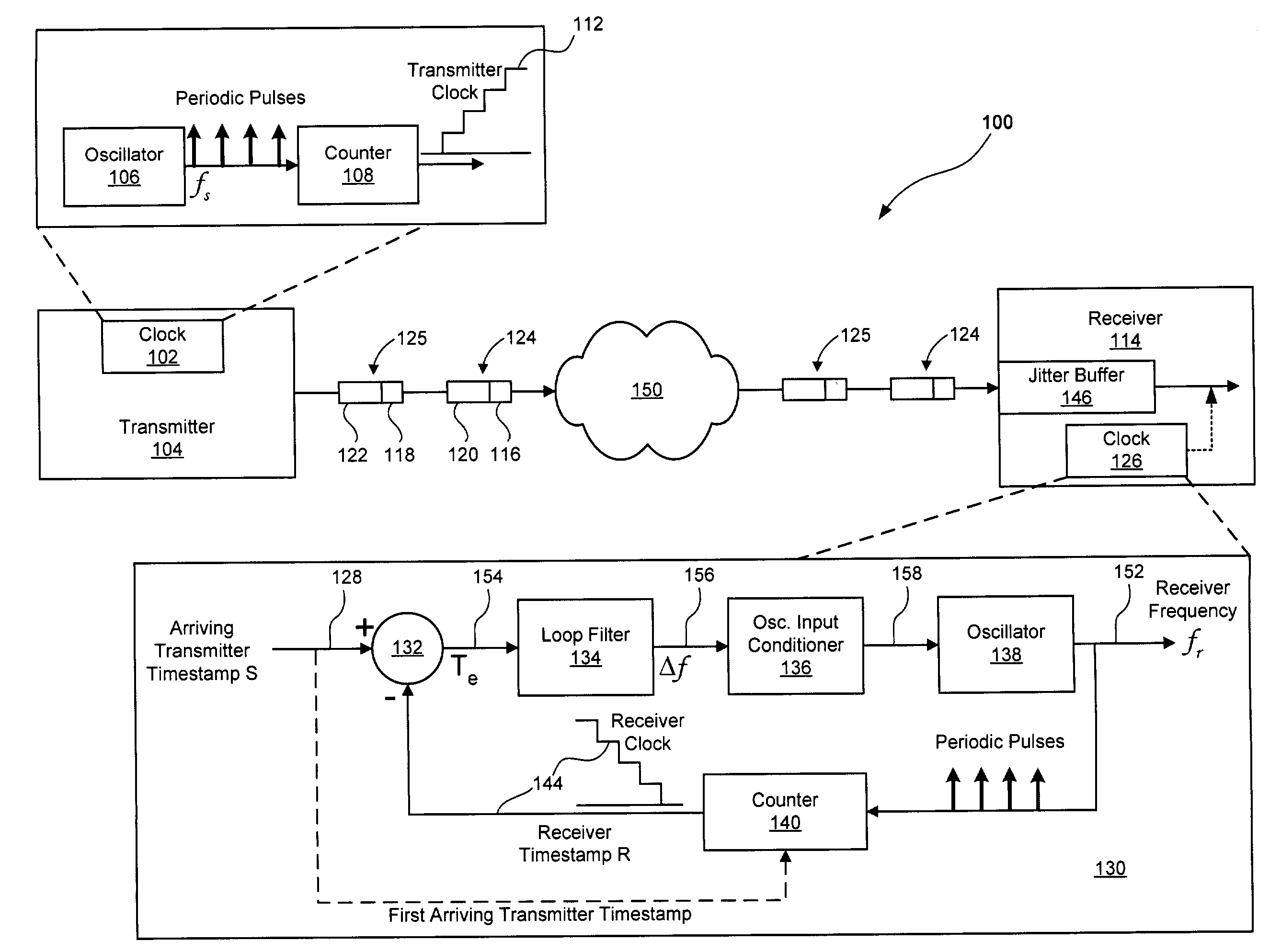
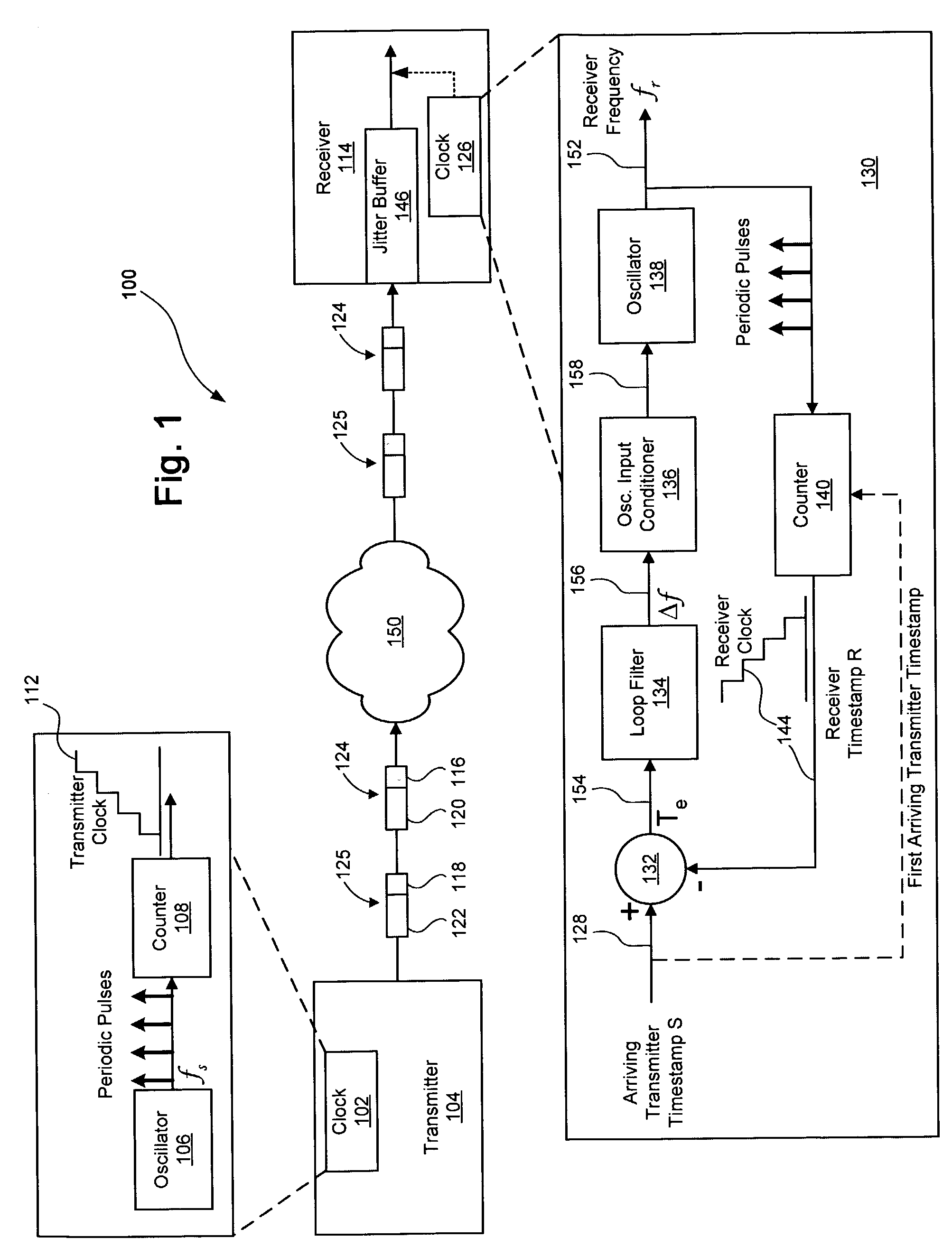
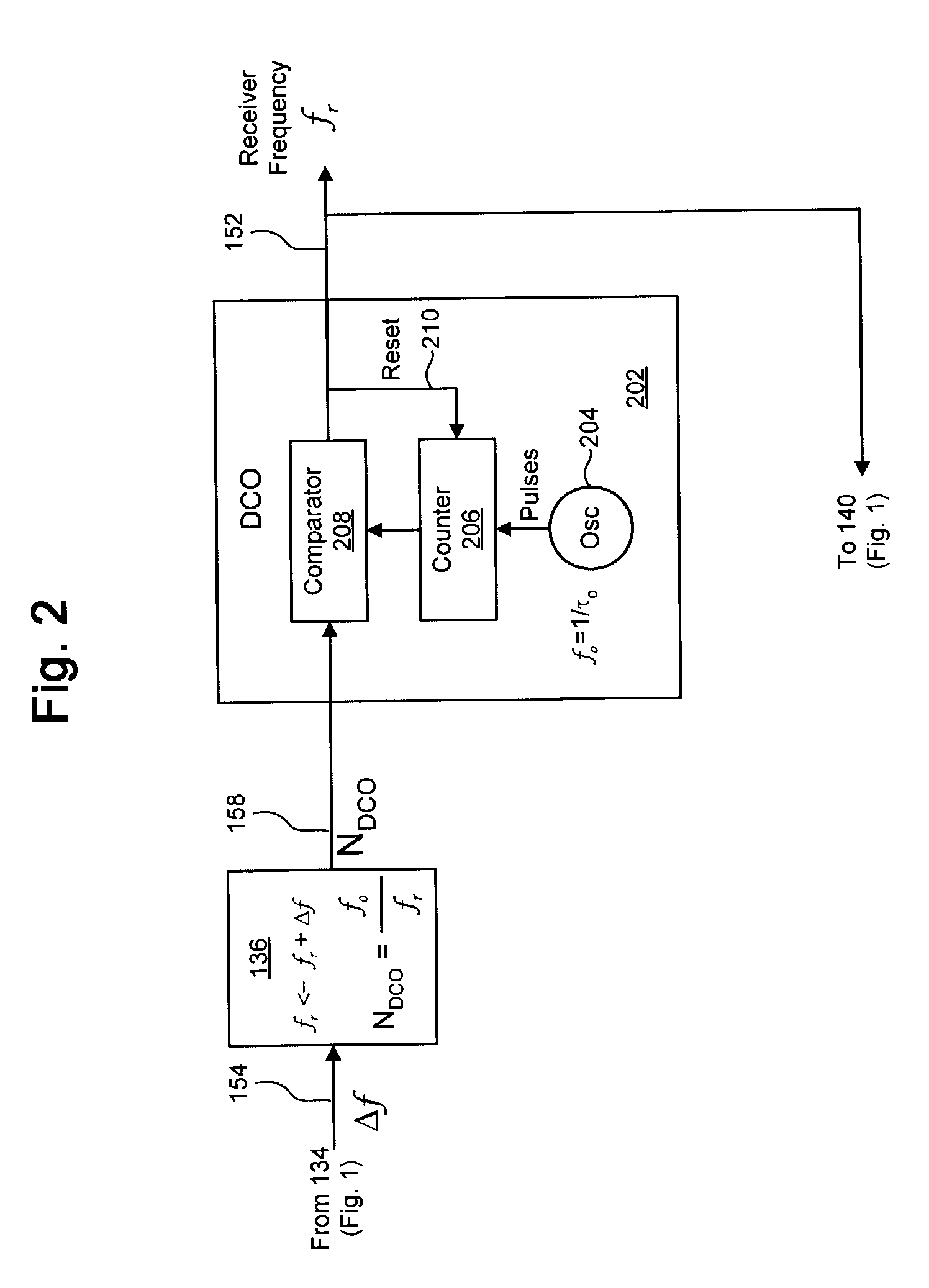
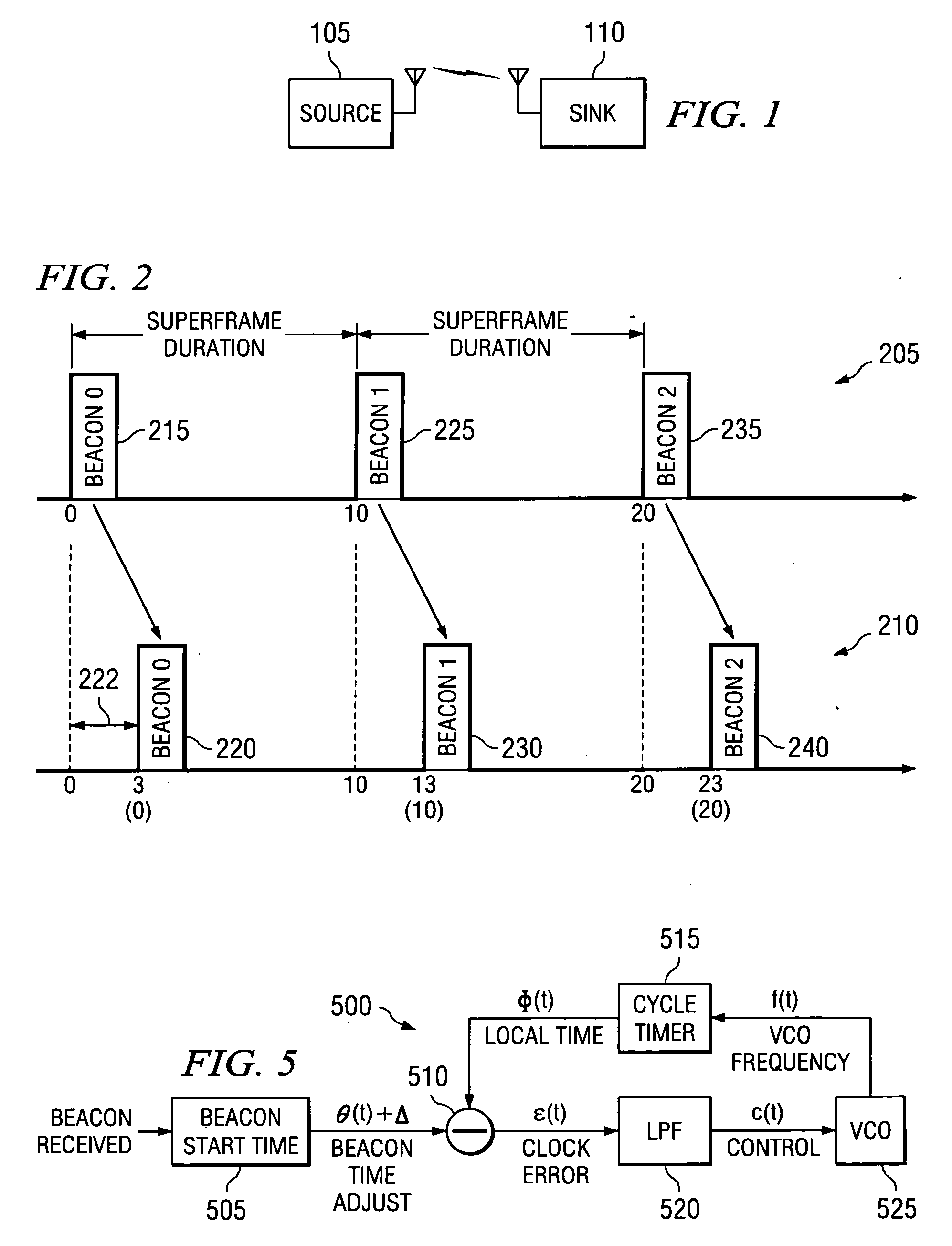
System and method for synchronizing clocks and maintaining packet timing relationships in a wireless communications system. A preferred embodiment further comprises periodically synchronizing local clocks at a transmitter and a receiver to a clock reference, adding a timestamp to each application packet at a transmitter of a wireless network, setting the timestamp to a value of a local time at the transmitter plus a link delay, buffering a received packet at a receiver, and releasing the buffered packet to an application level when a value of a local time at the receiver equals the timestamp value in the packet. This can help to ensure that the timing relationships between data packets present at a transmitter is maintained at a receiver, regardless of transport delays (waiting, transmission and processing) incurred by the data packets.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Device and method for selecting power down exit
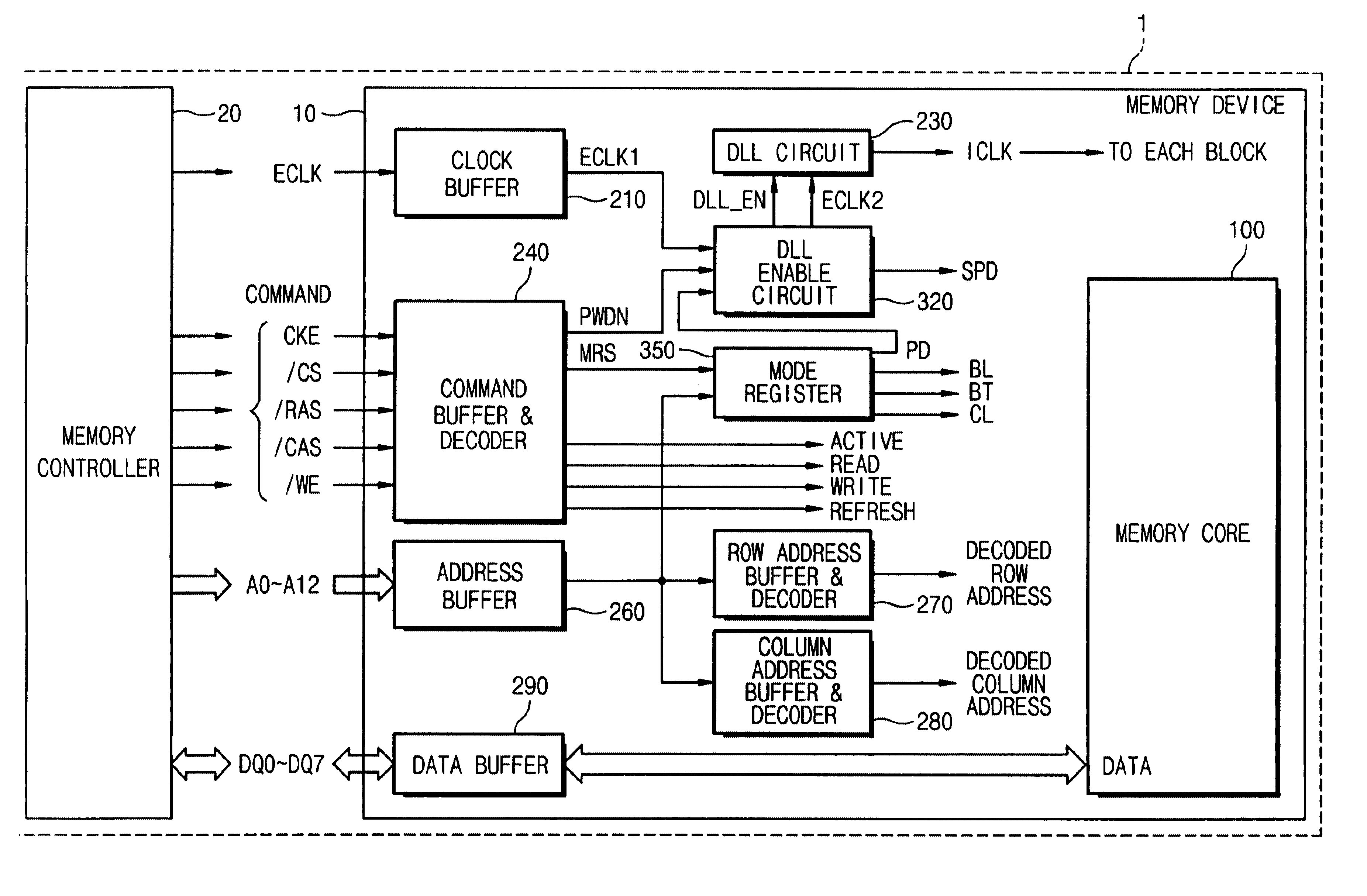
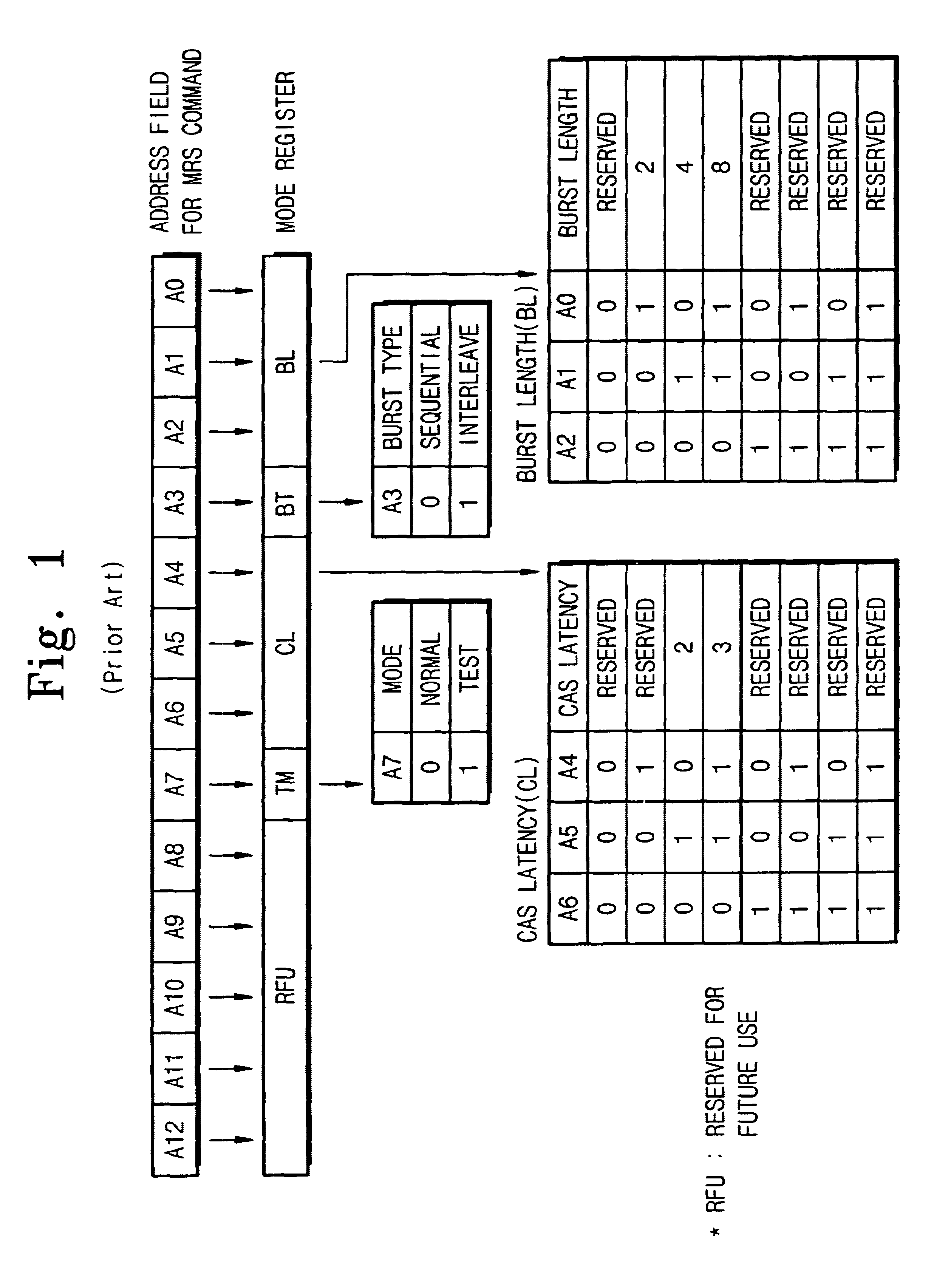
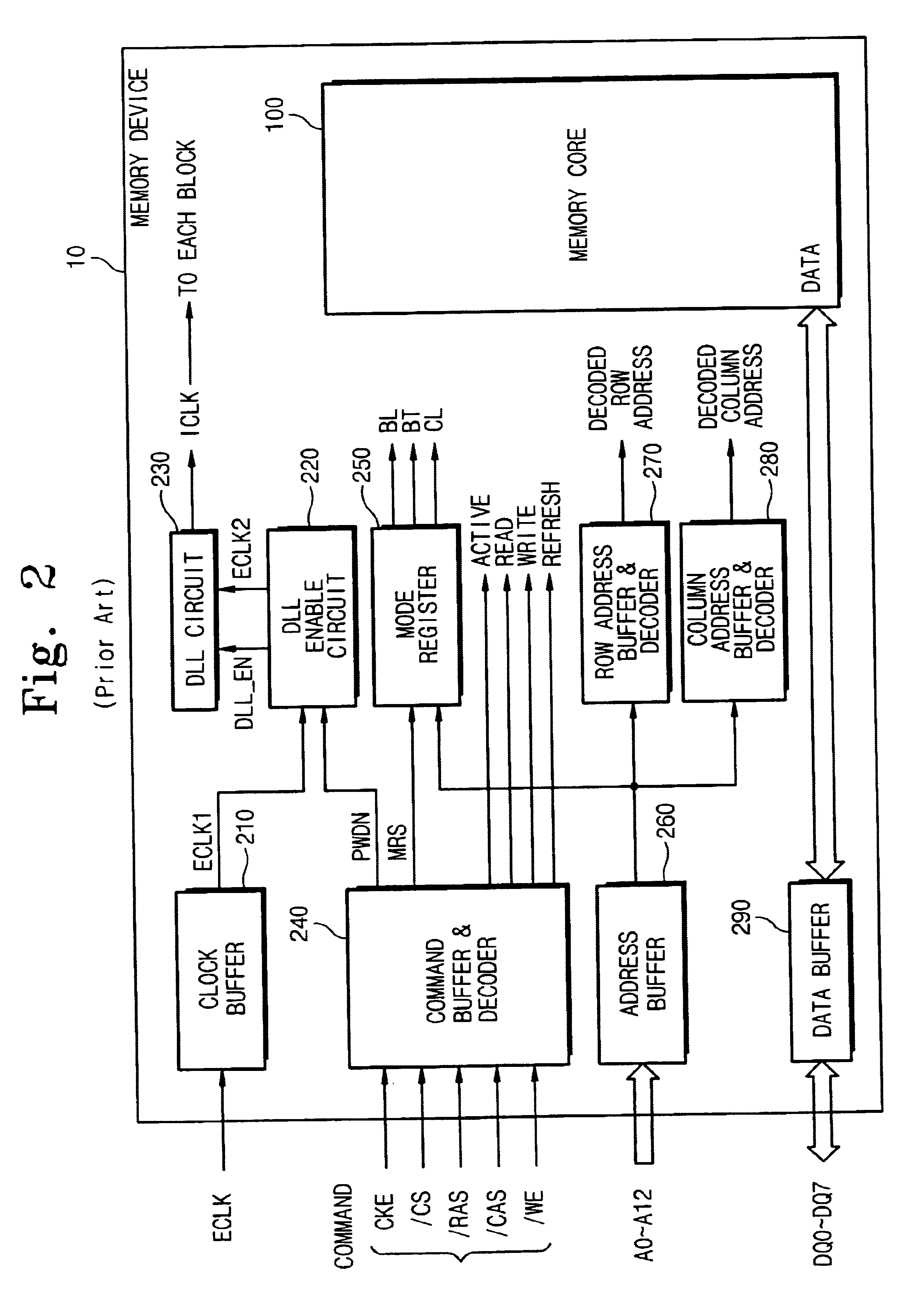
A semiconductor integrated circuit and a memory device capable of selecting power-down exit speed and power-save modes and method thereof are provided. The memory device includes a command decoder for generating a power-down signal in response to a power-down command, a mode register (MRS) for storing power-down exit information, a clock synchronization circuit such as a DLL or PLL circuit for generating an internal clock signal synchronized with an external clock signal, and a controller for controlling the DLL or PLL circuit. At power-down exit of the memory device, the power-down exit information can be selected between a fast wakeup time and a slow wakeup time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
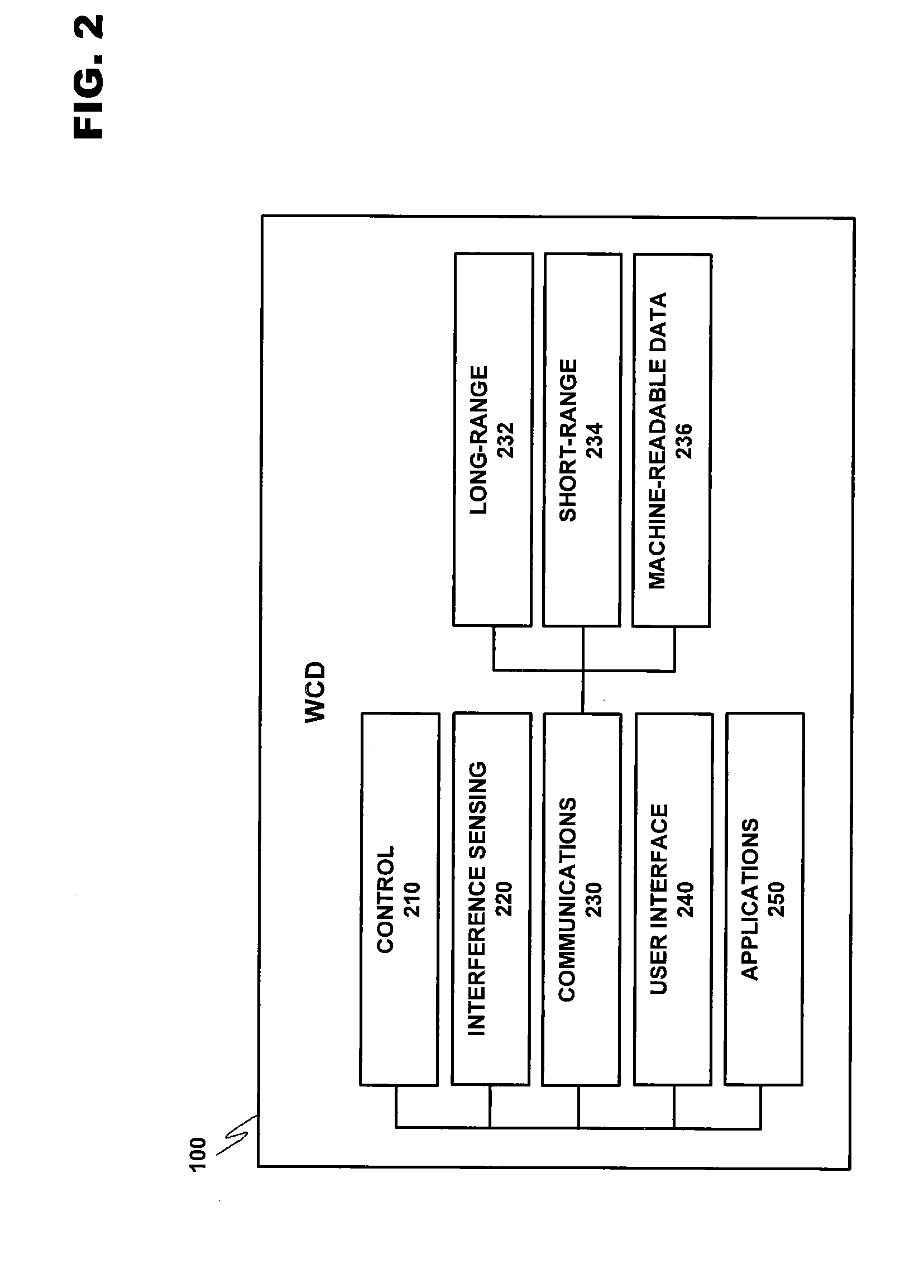
Multiradio scheduling including clock synchronization validity protection
ActiveUS20080043714A1Fast transferImmune from any communication overheadTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionModem deviceControl system
A system for managing the simultaneous operation of a plurality of radio modems in a single wireless communication device (WCD). The multiradio control may be integrated into the WCD as a subsystem responsible for scheduling wireless communications by temporarily enabling or disabling the plurality of radio modems within the device. The multiradio control system may comprise a multiradio controller (MRC) and a plurality dedicated radio interfaces. Further, clock synchronization protection between the multiradio system controller, other modems and wireless communication devices with whom the wireless device is communicating may further be implemented as a protective measure to ensure a valid clock synchronization between all devices internal and external to the primary wireless device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
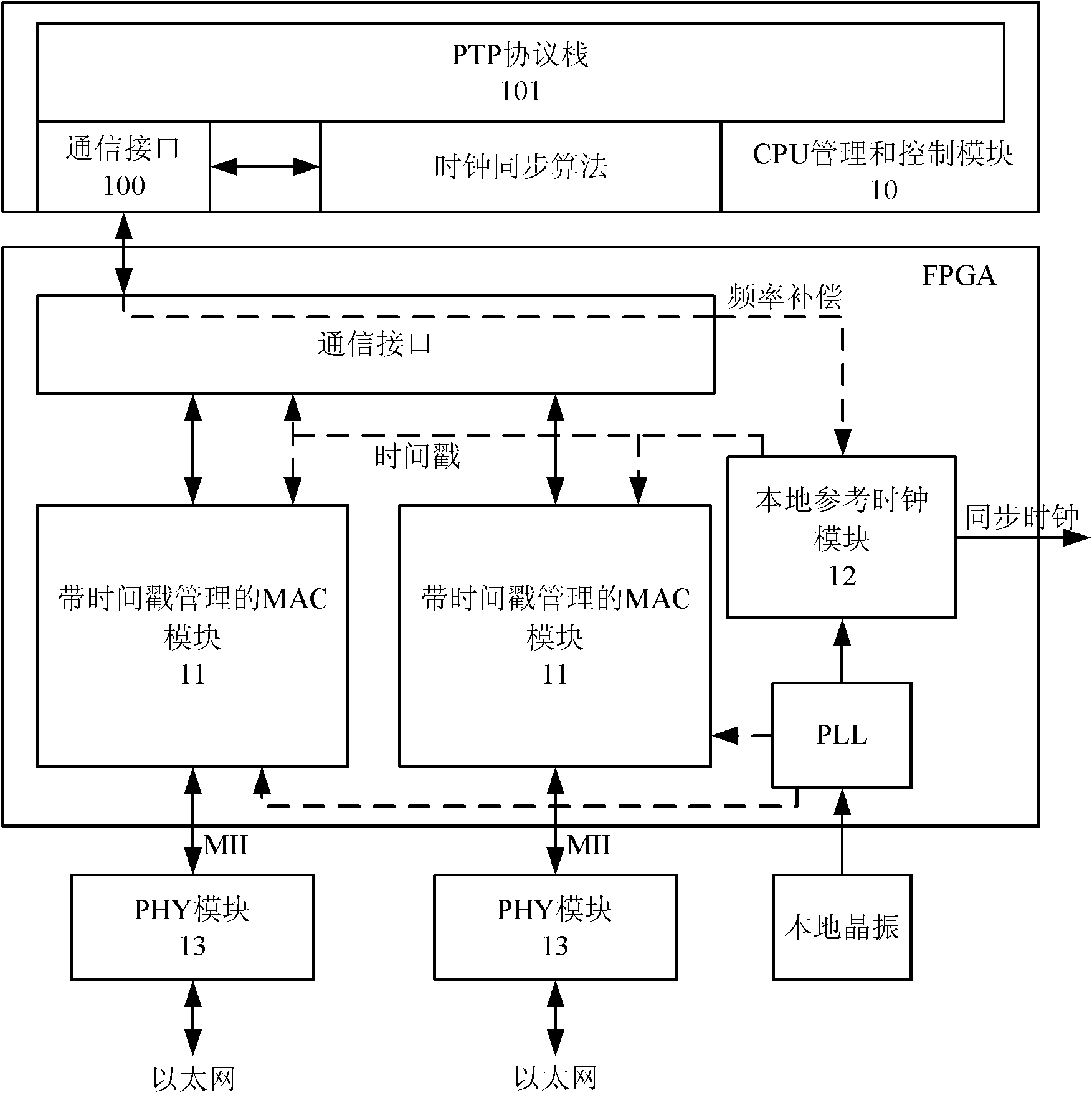
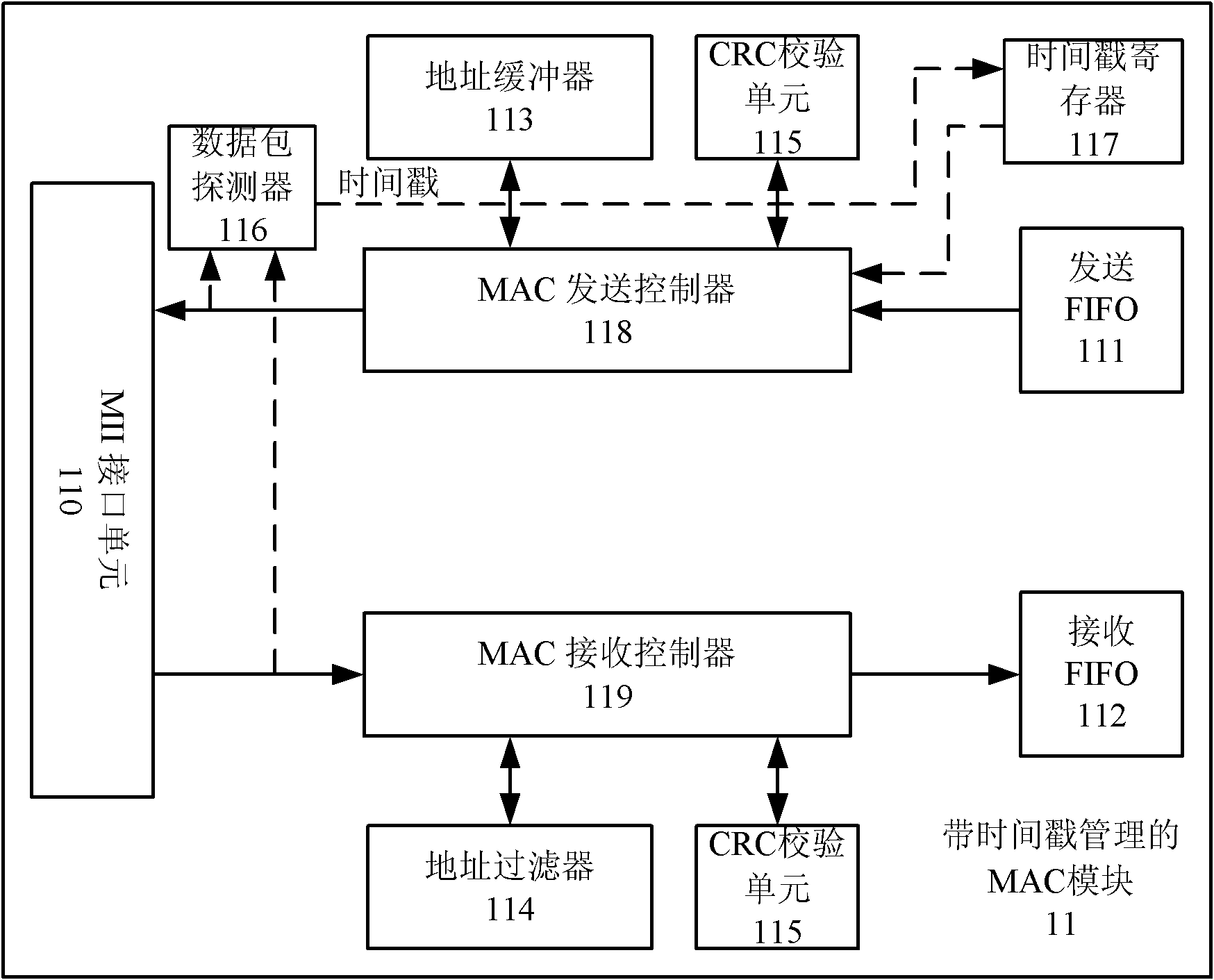
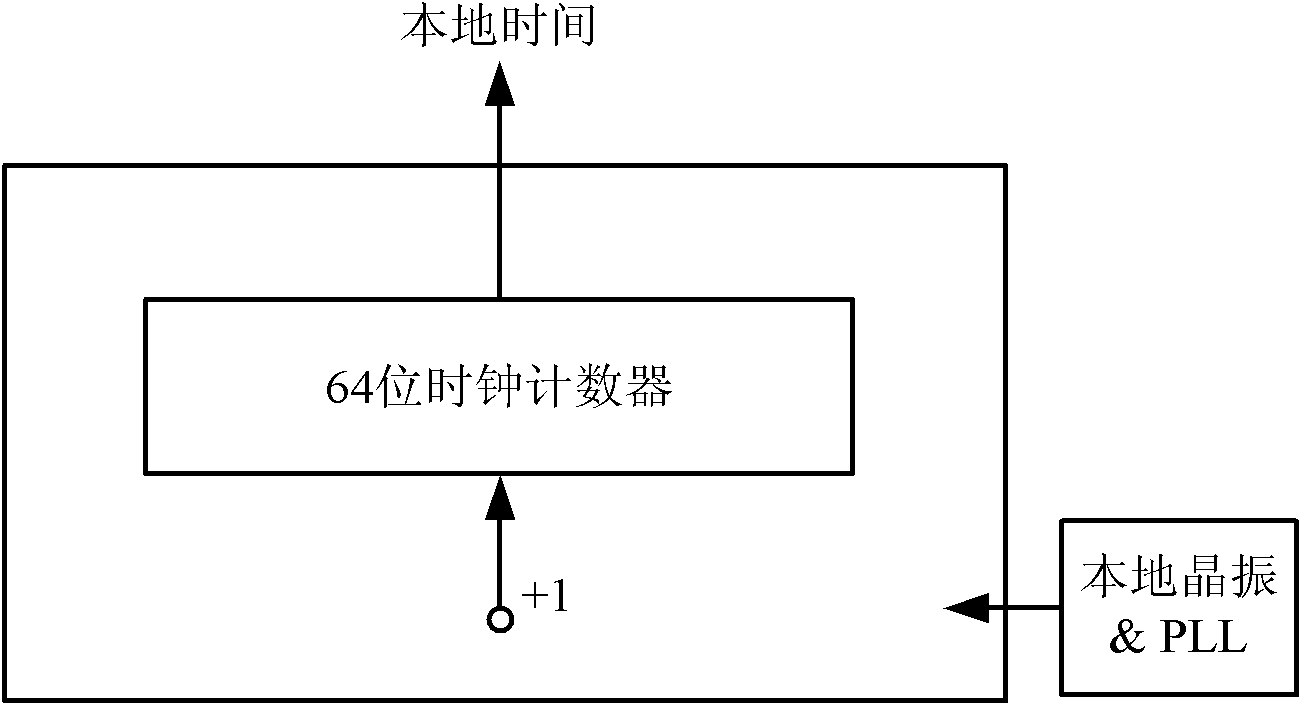
IEEE1588 based accurate clock synchronization protocol system and synchronization method thereof
ActiveCN101977104ASave communication bandwidthImprove real-time performanceSynchronising arrangementBus networksInformation transmissionTimestamp
The invention relates to an IEEE 1588 based accurate clock synchronization protocol system and a synchronization method thereof, belonging to the technical field of network information transmission. By adopting the invention, a main clock carries an accurate timestamp while sending a synchronization message, and a follow message is not required to be sent, thus greatly reducing communication bandwidth required for realizing clock synchronization. Meanwhile a frequency adjustable clock counter is constructed, and clock synchronization algorithm is combined, so as to realize frequency compensation function and achieve high accuracy clock synchronization requirement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Synchronization of network nodes
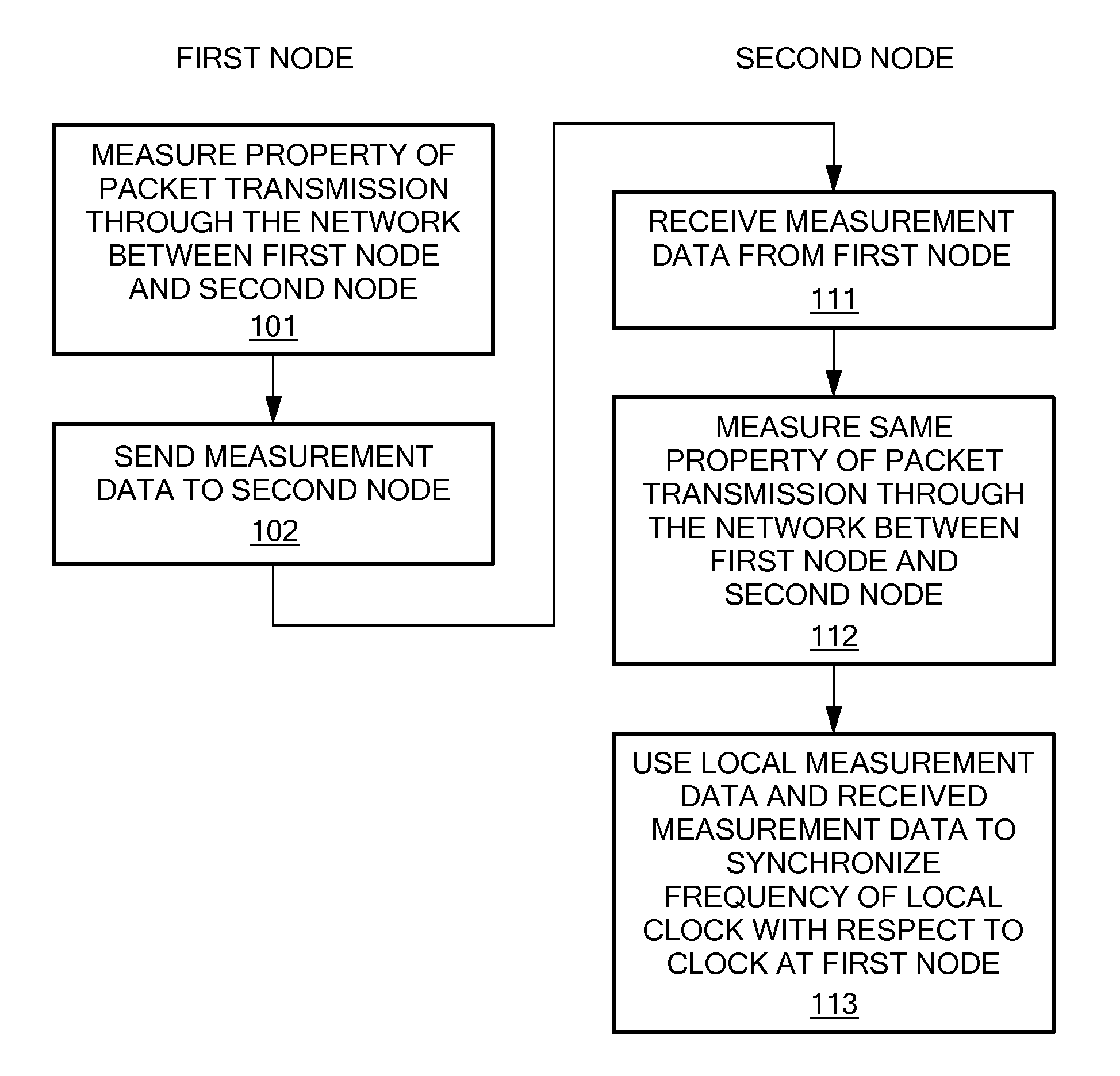
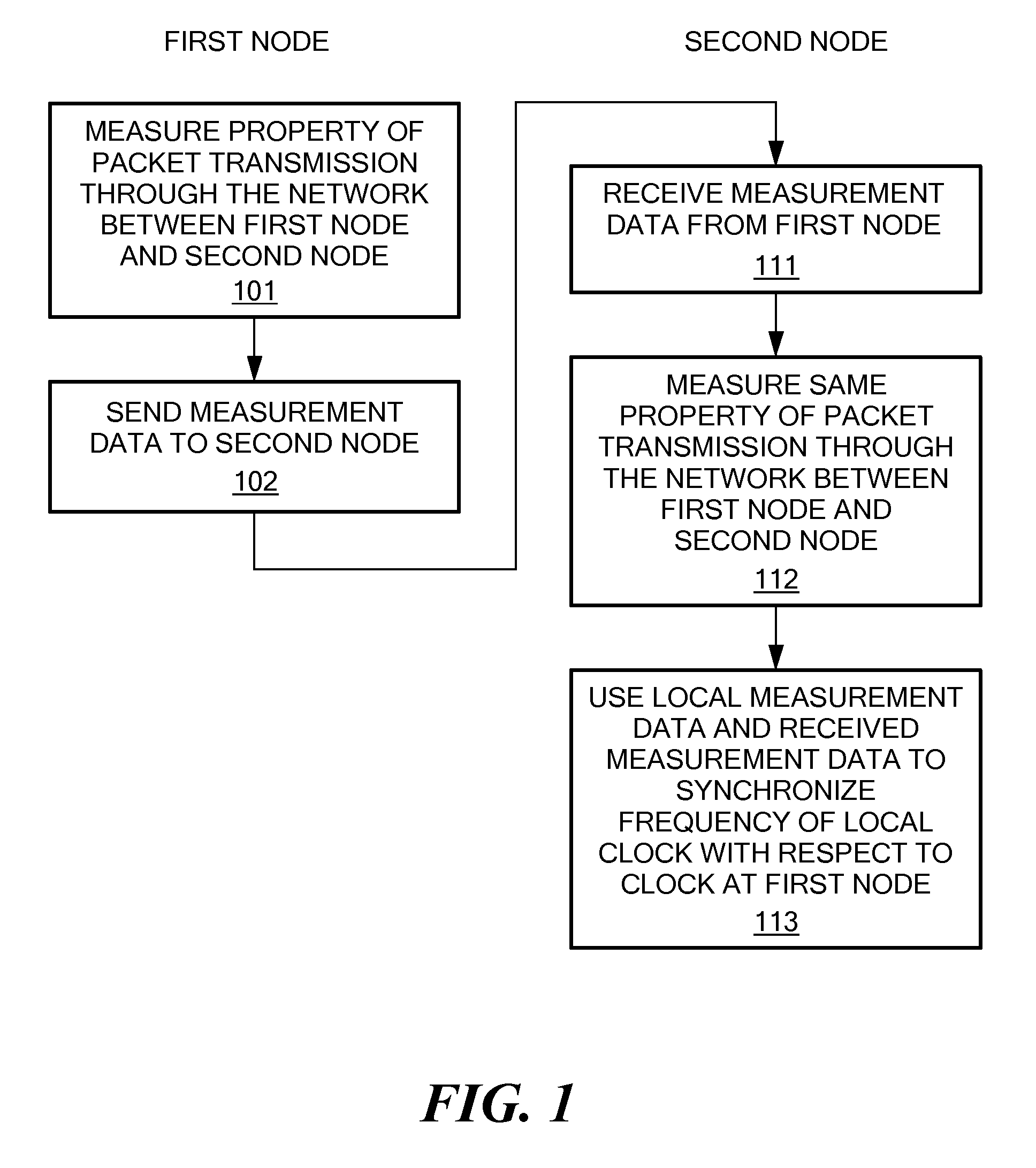
ActiveUS20090147806A1Improve accuracyAccurate correctionTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionComputer scienceClock synchronization
A method and apparatus are provided to achieve frequency synchronization between a first clock at a first node and a second clock at a second node of a packet-carrying communications network. At the first node: a property of packet transmission through the network between the first node and the second node is measured; and the measurement of the property is sent to the second node. At the second node, the same property of packet transmission through the network between the first node and the second node is measured. The measurement of the property made at the first node and the measurement of the property made at the second node are used to synchronize the frequency of the second clock with respect to the first clock.
Owner:CIENA
RFID tracking of anesthesiologist and patient time
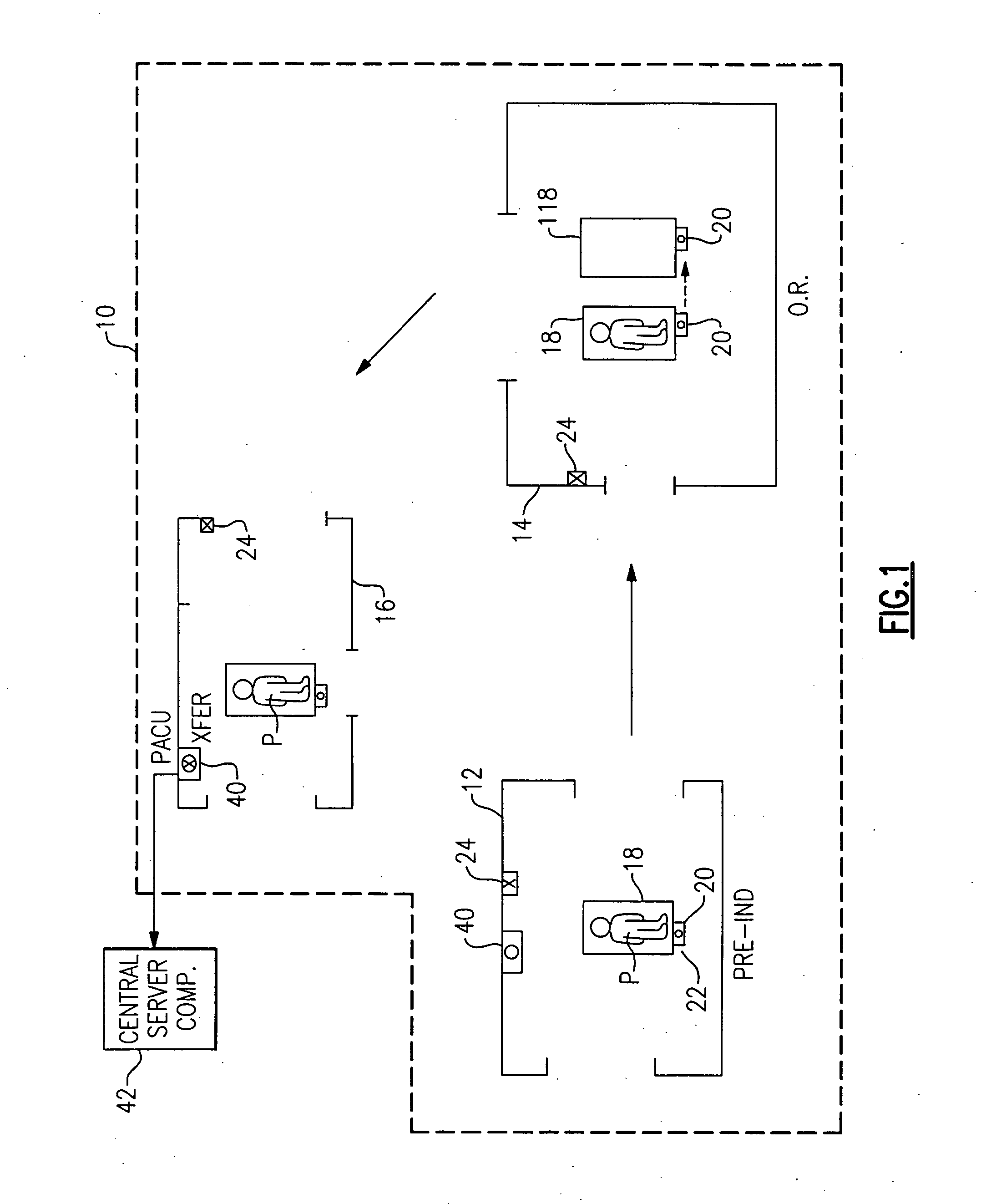
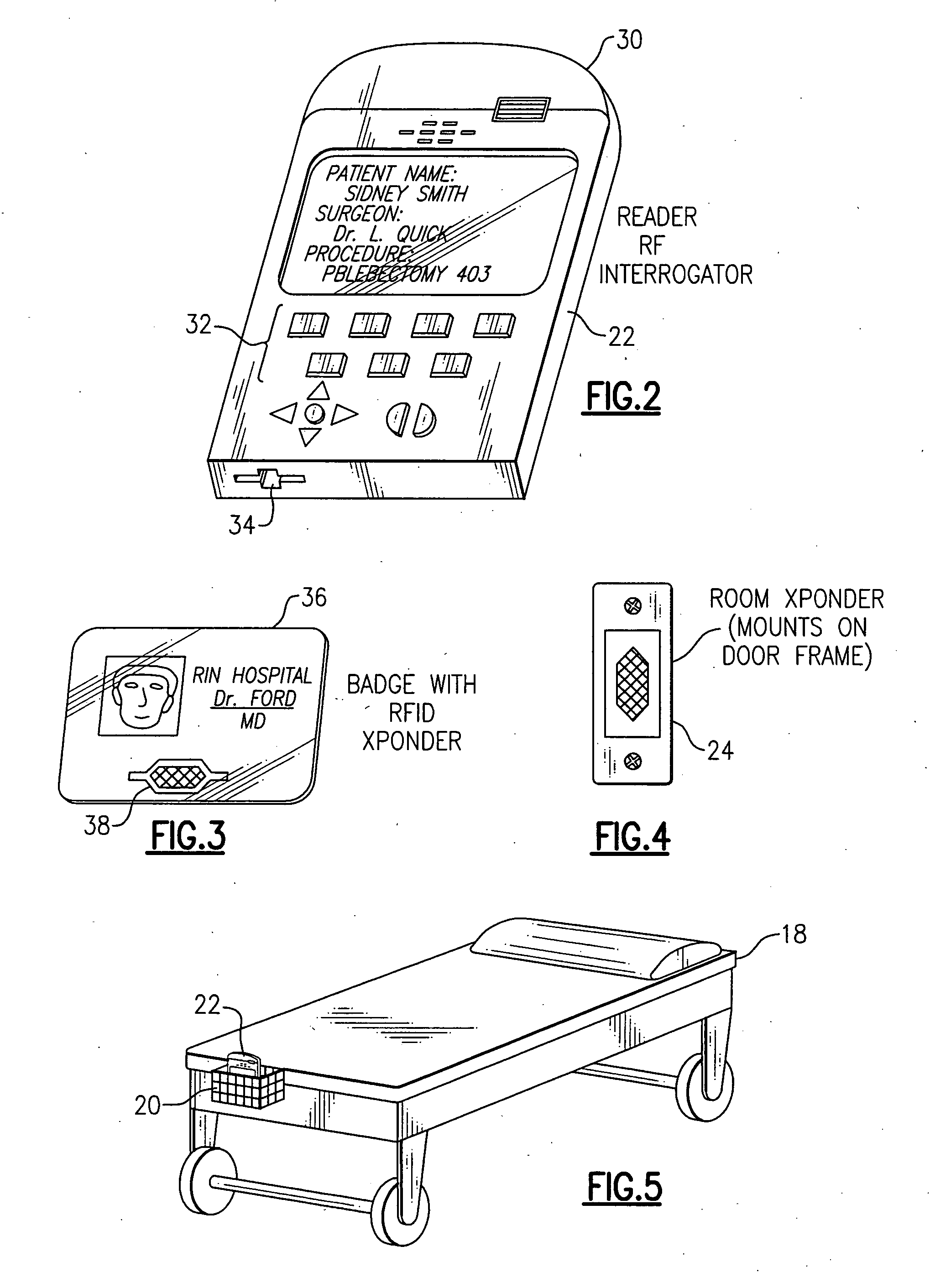
InactiveUS20050149358A1Simple methodNot easy to copyElectric signal transmission systemsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHand heldOperating theatres
RFID-based system for tracking billable anesthesiology time in a surgical environment employs hand-held RFID reader devices that record and store timed anesthesia events for each surgical patient. Each patient is assigned a reader device, uploaded with patient data. Each anesthesiology professional has an identifying RFID transponder, and room transponders are located on wall or doorway of each room in the surgical suite. A download cradle is used for downloading the patient data collected during surgery to a central computer. The reader devices are synchronized to a high-accuracy clock, eliminating time accounting problems associated with concurrency and discontinuous time.
Owner:SACCO LISA M +1
Dual clocked synchronous memory device having a delay time register and method of operating same
InactiveUS6035365AFast readWrite quicklyEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor registerDelay-locked loop
A synchronous memory device having at least one memory section which includes a plurality of memory cells. The memory device comprises a register to store a value which is representative of a delay time after which the memory device responds to a read request and clock receiver circuitry to receive first and second external clock signals. The memory device also includes an output driver(s) to output data on a bus, in response to a read request and in accordance with the delay time, wherein a first portion of the data is output synchronously with respect to the first external clock signal and a second portion of the data is output synchronously with respect to the second external clock signal. The memory device may include a delay locked loop to generate internal clock signal(s) using the external clock signal(s). The output drivers output data on the bus in response to the internal clock signal(s). The memory device may include input receiver circuitry, coupled to the bus, the receive the read request, wherein the read request is sampled from the bus synchronously with respect to the first external clock signal.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
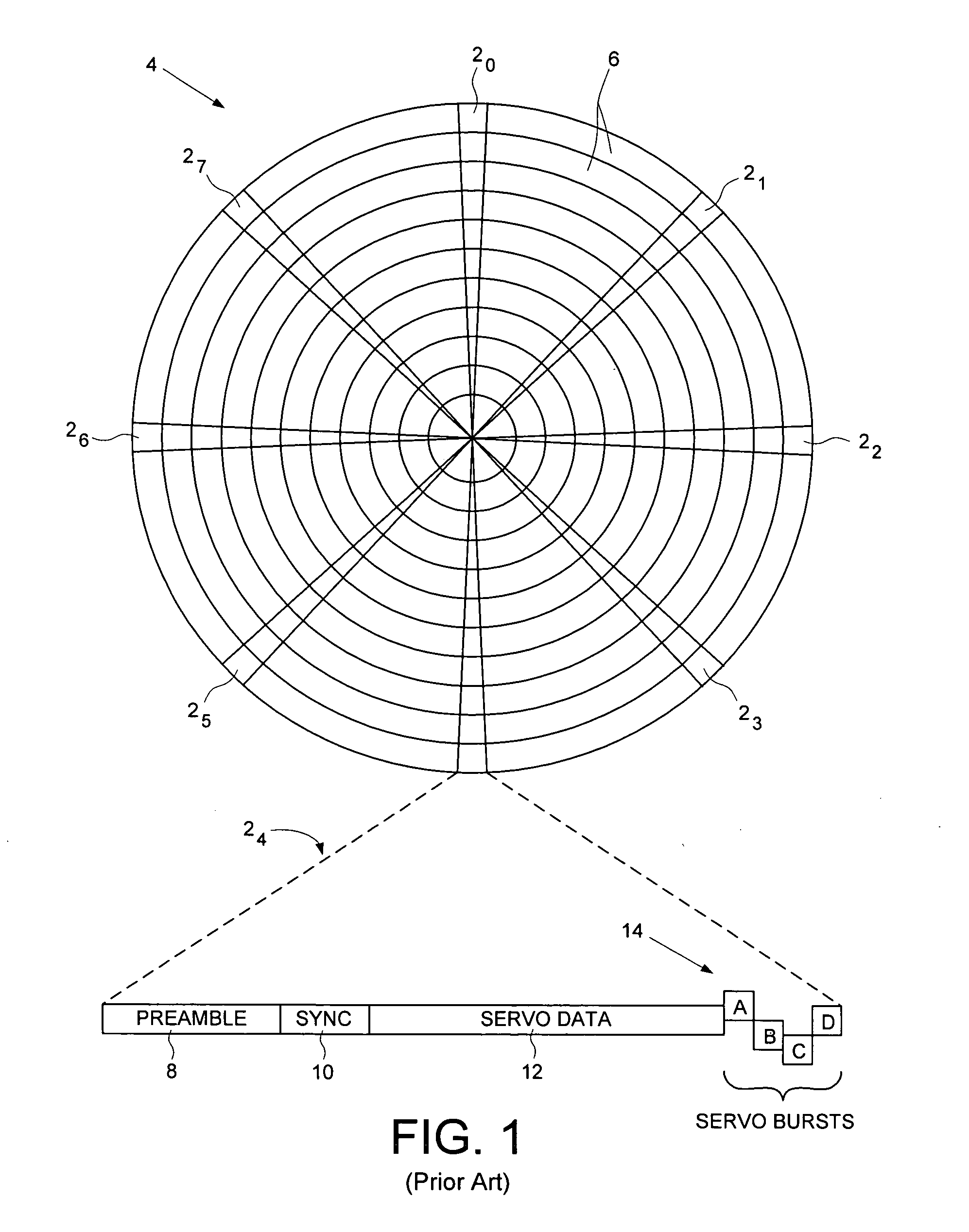
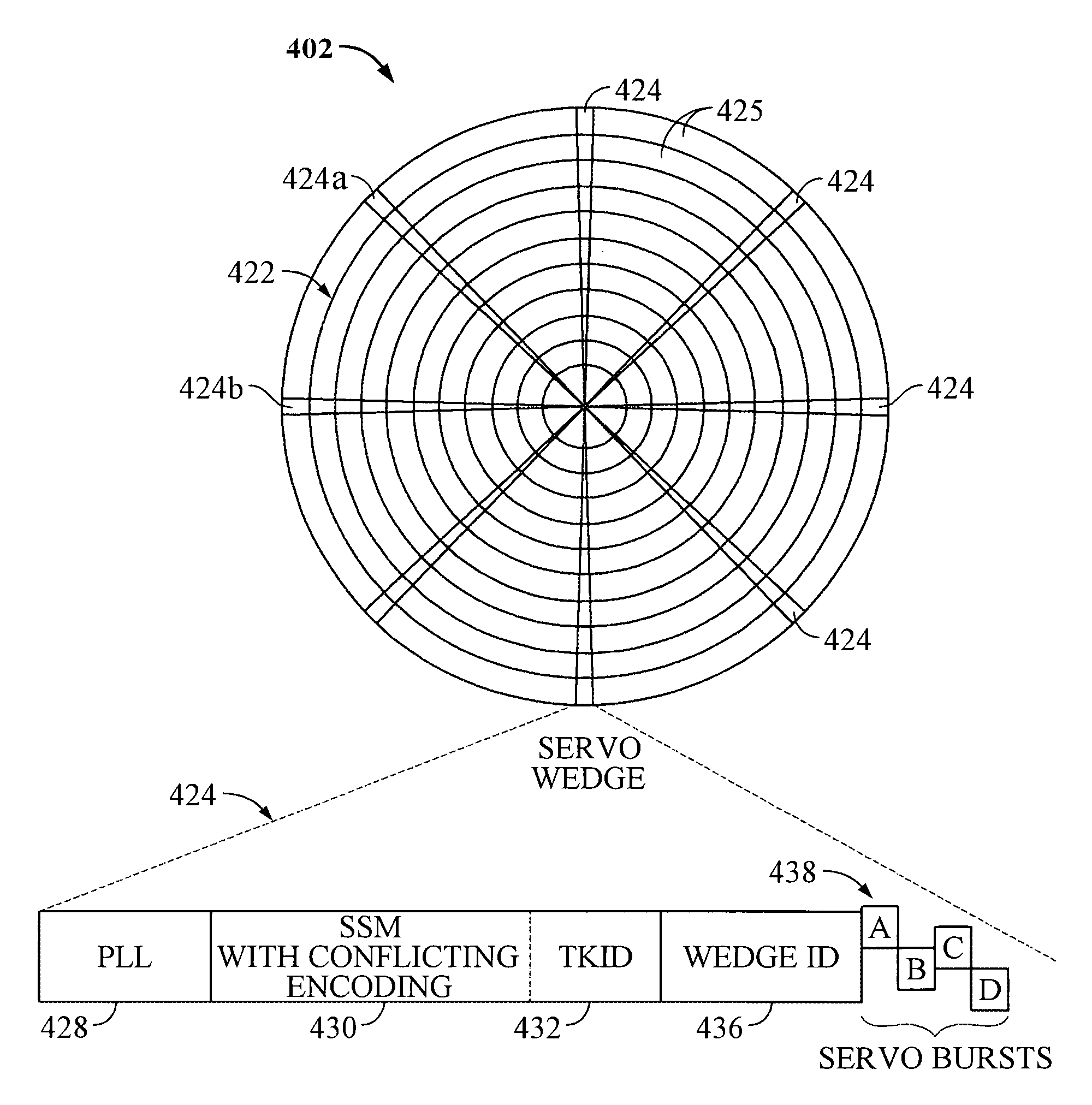
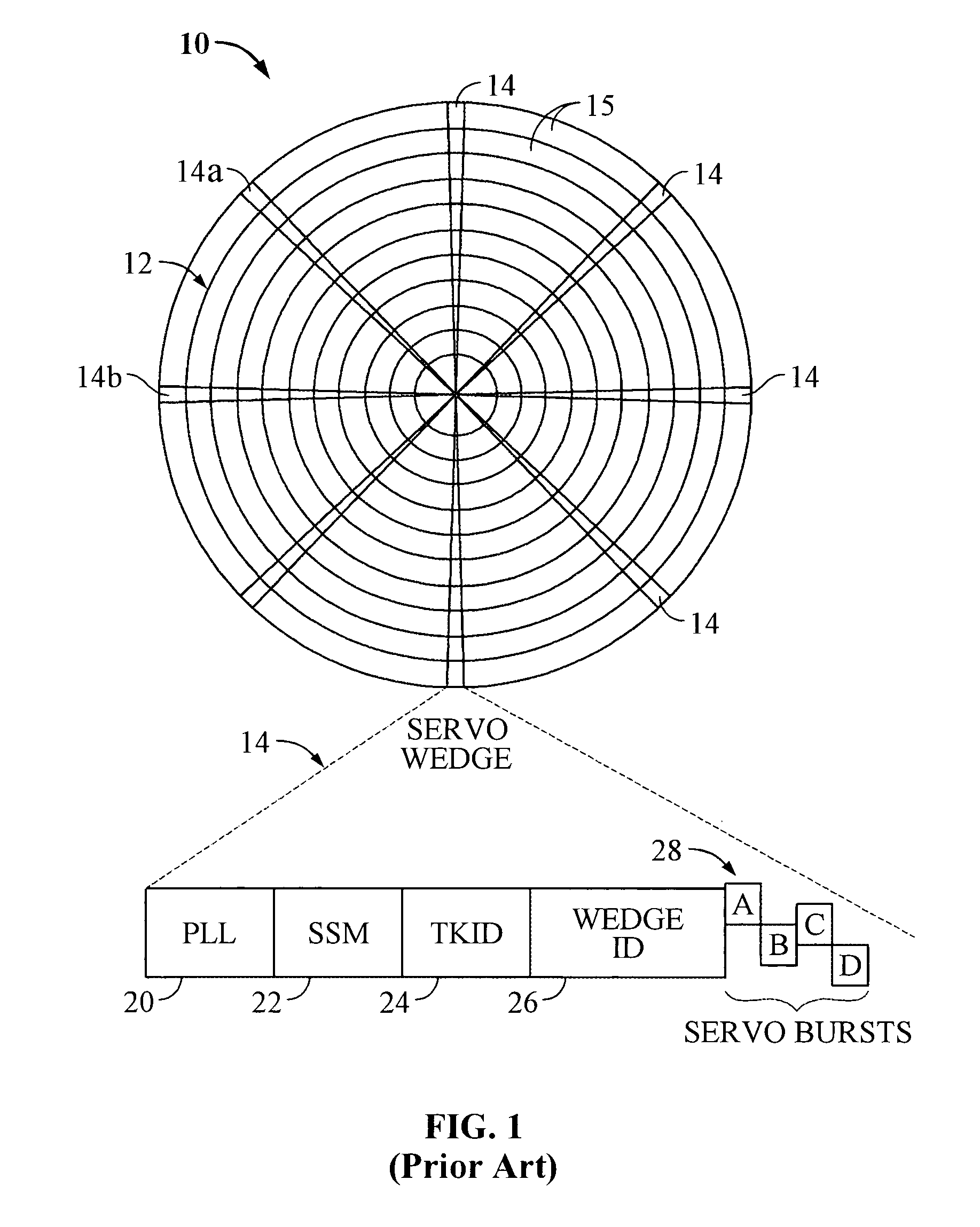
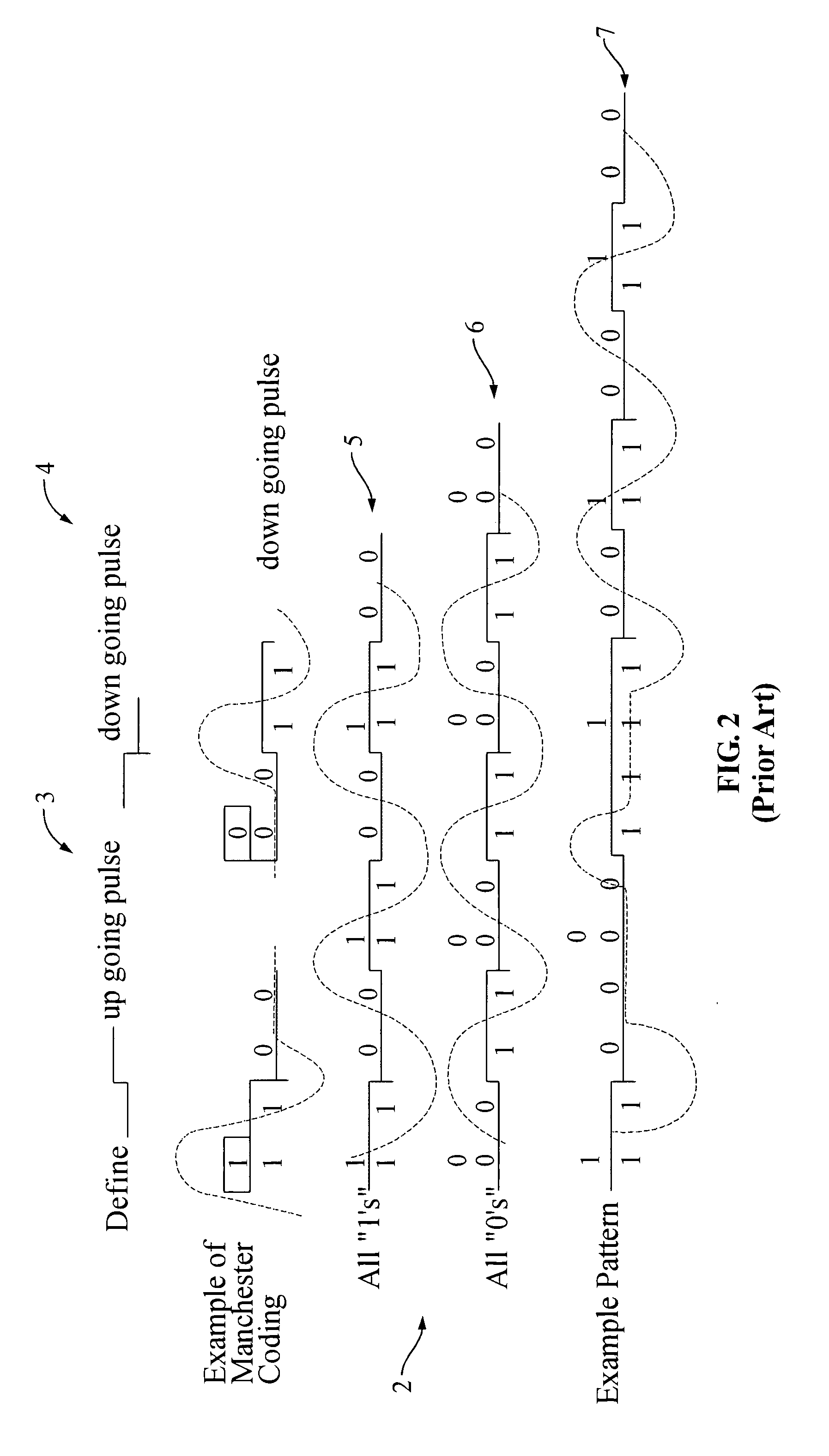
Servo synchronization based on a servo synch mark that conflicts with self-clocking encoding algorithms
InactiveUS6934104B1Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageEncoding algorithmComputer science
Disclosed is a rotatable media storage device (RMSD) that performs servo synchronization based on a servo synch mark (SSM) that conflicts with self-clocking encoding algorithms. The RMSD includes a disk having a plurality of tracks wherein each track comprises a plurality of data regions interspersed between servo wedges. The servo wedges comprise a servo synch mark field including a servo synch mark (SSM) and a track identification field including a track identifier (TKID). The TKID is encoded in accordance with a self-clocking encoding algorithm whereas the SSM is encoded in accordance with a second algorithm that conflicts with the self-clocking encoding algorithm of the TKID. Thus, the SSM is prevented from being decoded as a portion of the TKID.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Apparatus for performing uplink synchronization in multiple component carrier system and method therefor
InactiveUS20130100938A1Synchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsUplink transmissionCarrier signal
There are provided an apparatus for performing uplink synchronization in a multiple component carrier system and a method thereof. The method includes determining whether a timing advance value for adjusting uplink timing of a secondary serving cell is valid, entering a transmission holding mode in which the secondary serving cell holds uplink transmission, and determining a releasing condition of releasing the transmission holding mode is satisfied. The timing advance value is secured and the validity of the timing advance value is determined so that it is possible to prevent uplink interference from being generated due to a difference in timing advance values and to prevent capability from deteriorating due to the uplink interference.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
Radio communication semiconductor integrated circuit, data processing semiconductor integrated circuit and portable device
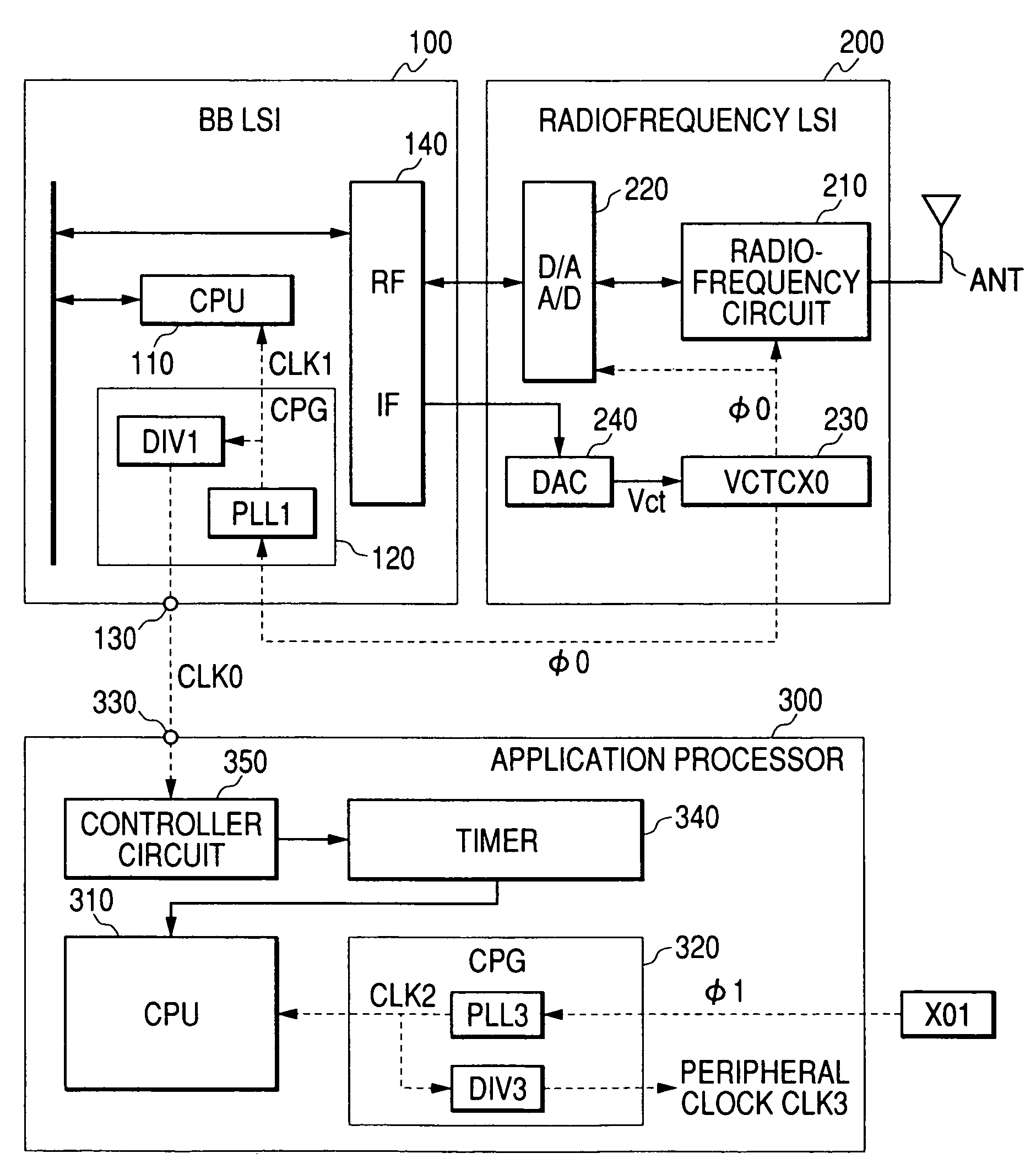
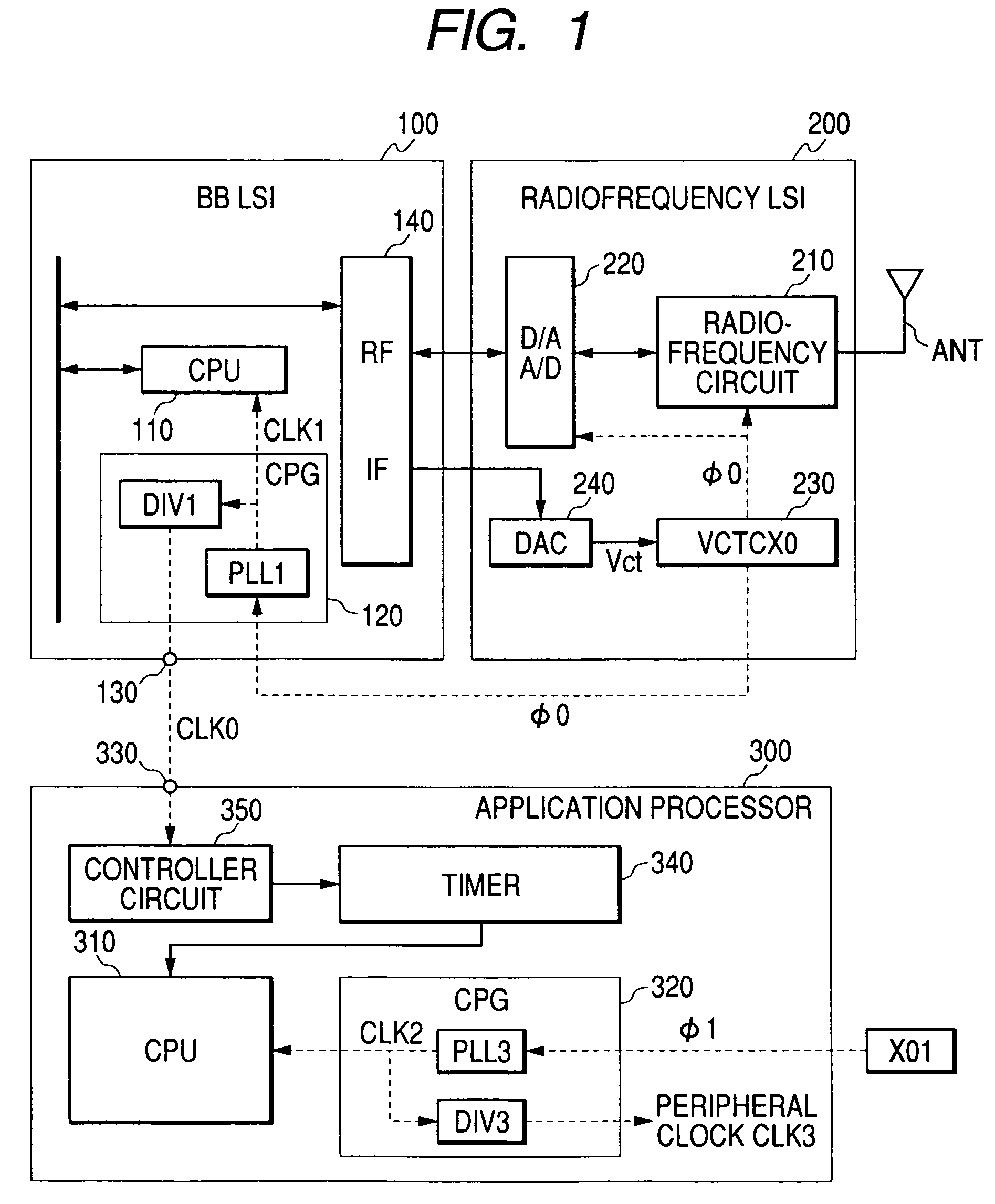
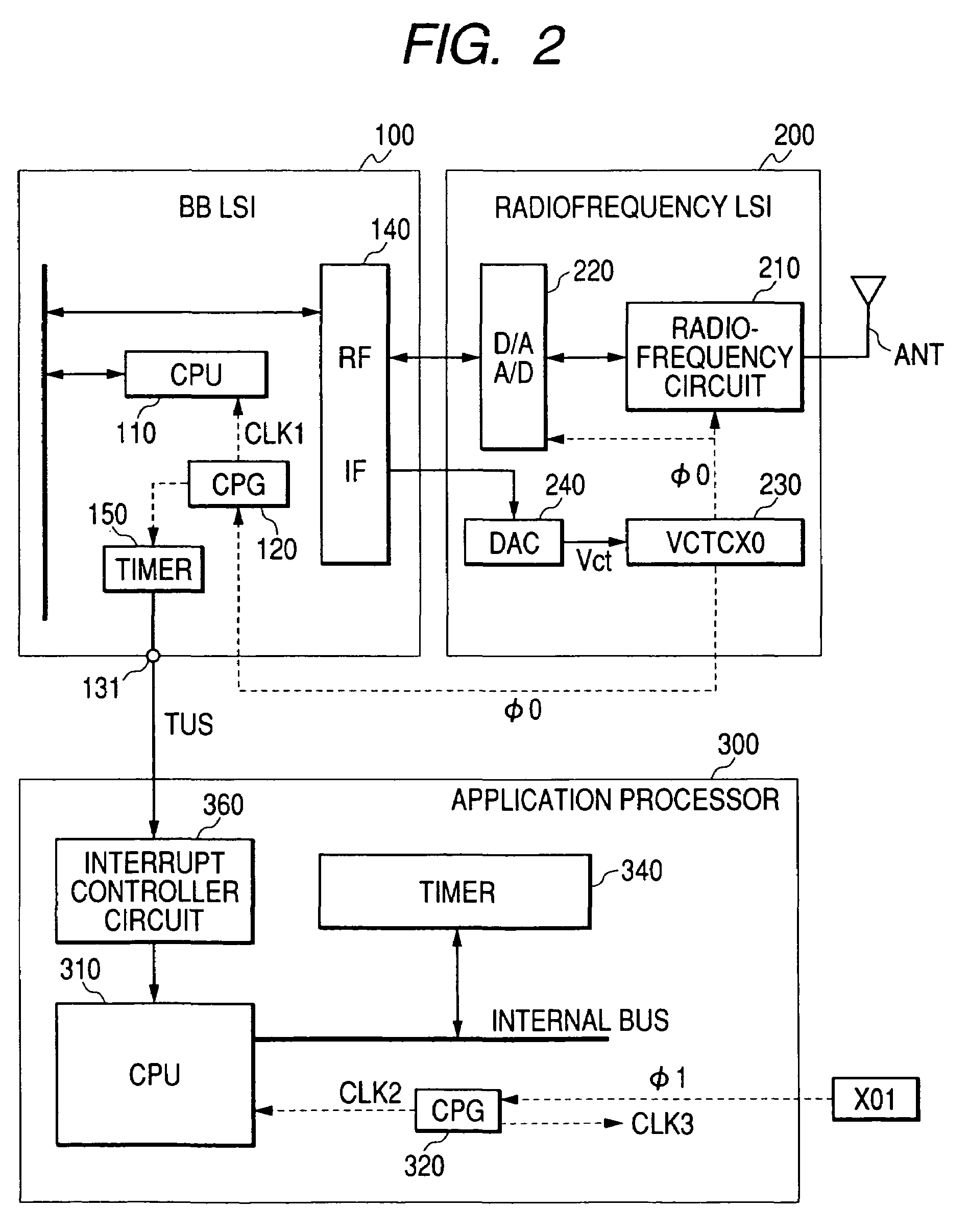
ActiveUS7444168B2Without lowering performanceAutomatic frequency control detailsData switching by path configurationEngineeringApplication processor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
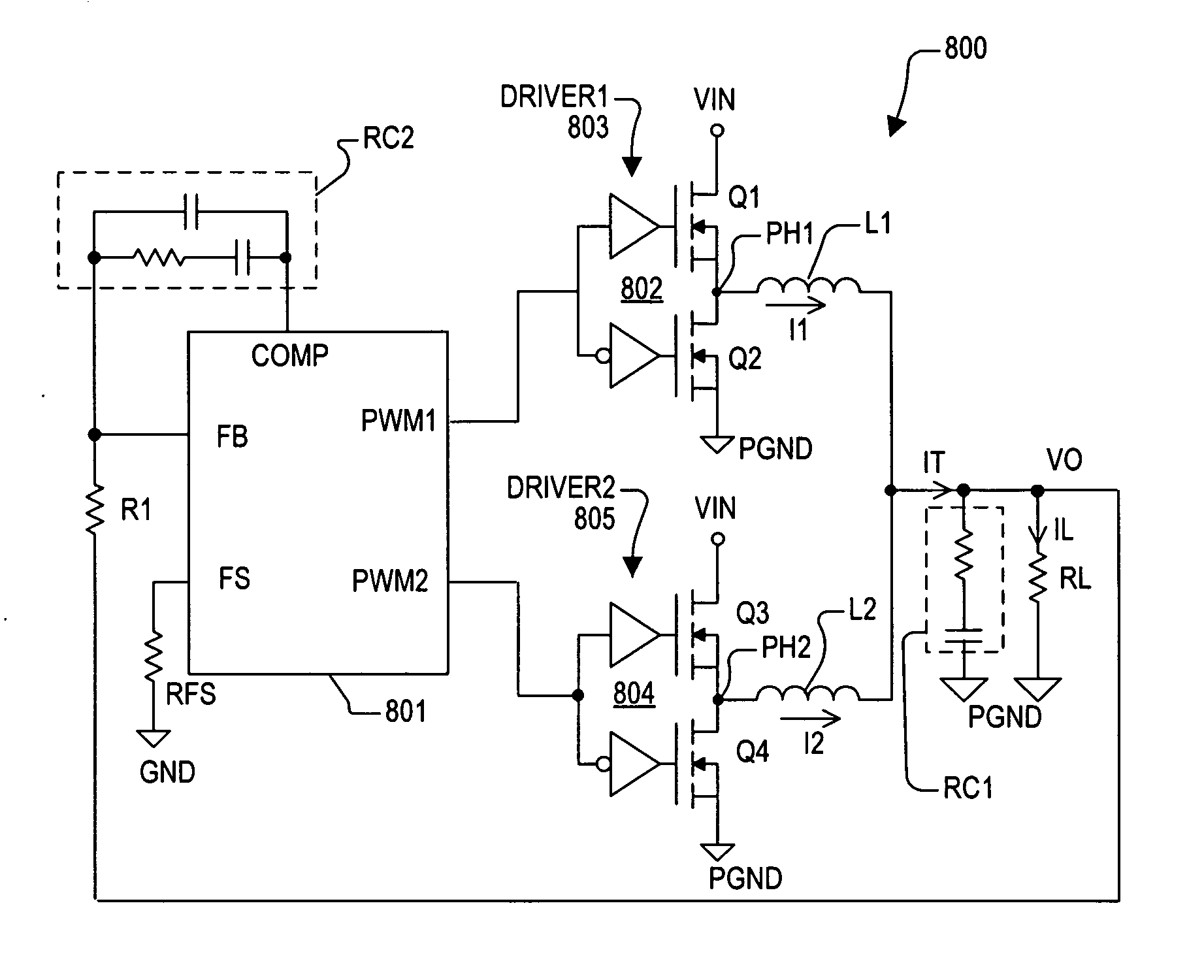
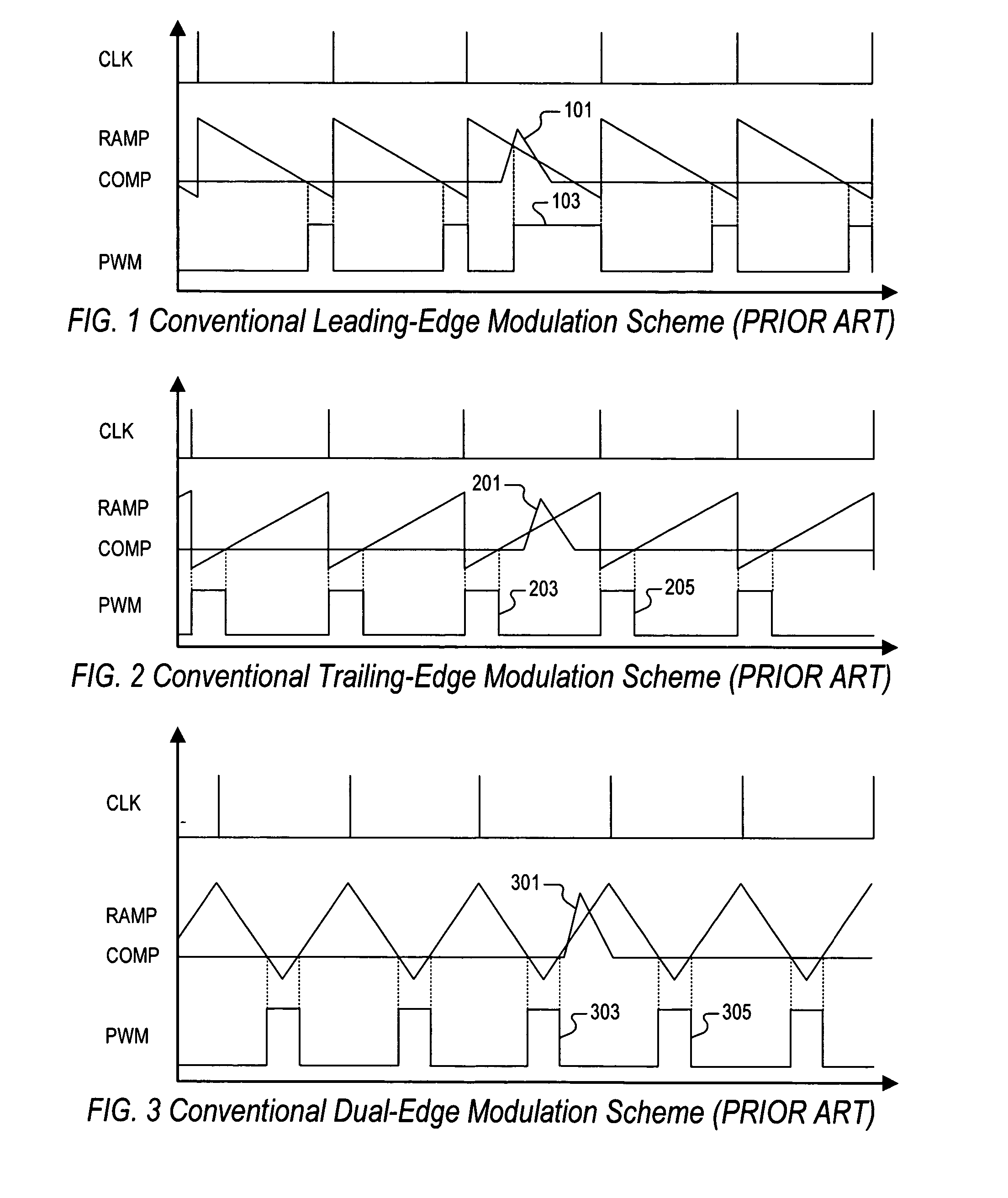
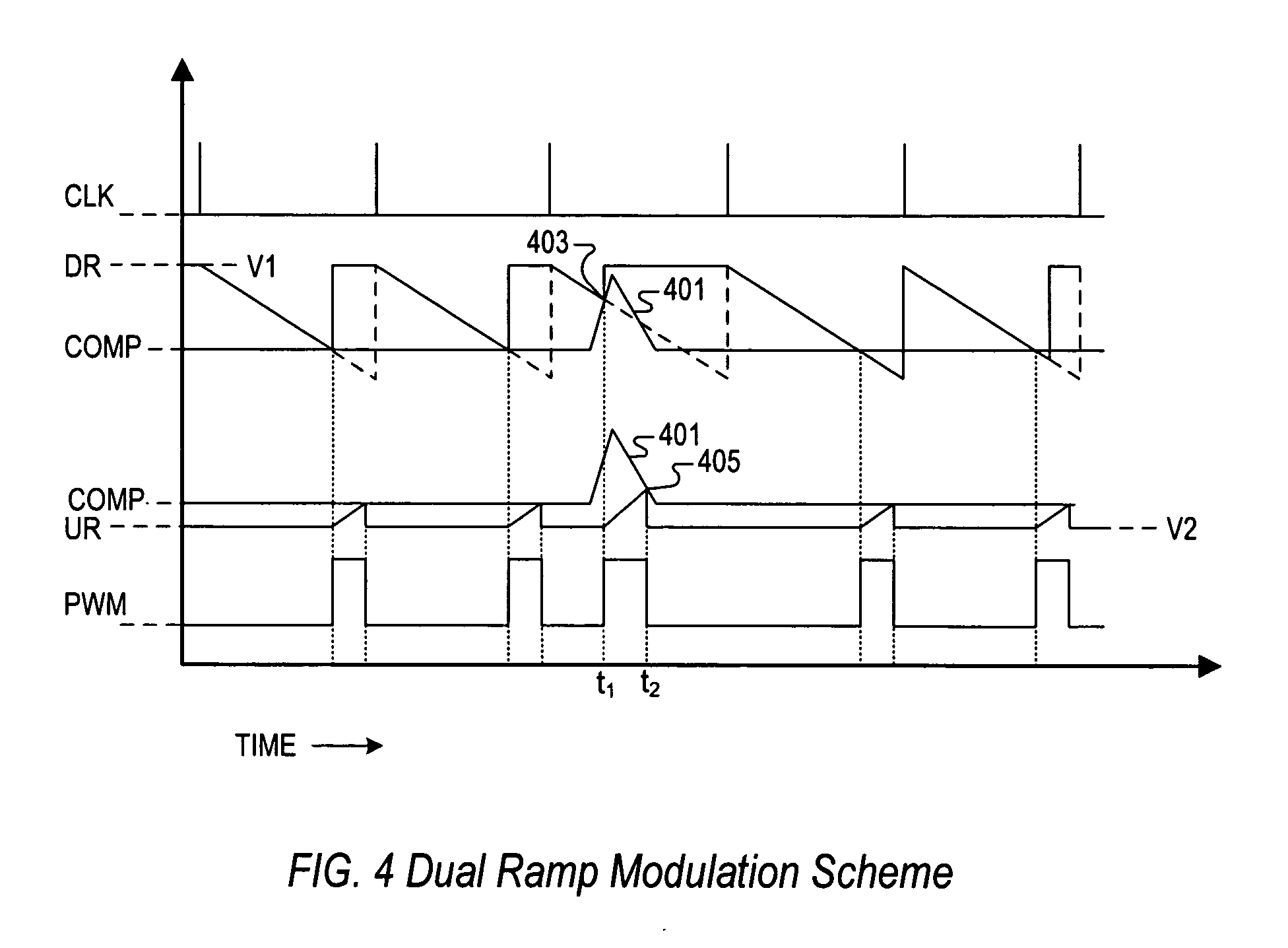
PWM controller with dual-edge modulation using dual ramps
ActiveUS20070013356A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLeading edgePulse control
A dual-edge modulation controller including first and second ramp circuits, first and second comparators, an error amplifier and pulse control logic. The first ramp circuit provides a leading-edge ramp synchronous with a clock. The error amplifier compares a feedback signal with a reference and provides a compensation signal. The first comparator compares the leading-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a set signal. The second ramp circuit provides a trailing-edge ramp that begins ramping when the set signal is asserted. The second comparator compares the trailing-edge ramp with the compensation signal and asserts a reset signal. The pulse control logic asserts a PWM signal when the set signal is asserted and de-asserts the PWM signal when the reset signal is asserted. The controller may control multiple phases with current balancing. The slew rate of the ramps may be adjusted based on the number of PWM signal asserted.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Systems and methods for distributing GPS clock to communications devices
ActiveUS20090231191A1Good quality VoIP serviceFew dropped frameTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork serviceUser equipment
A method for synchronizing network elements to a global clock derived from the GPS clock acquired by a plurality of base stations. The global clock is distributed to controllers of various networks, and from there to network access devices. The network access devices further distribute the global clock to various wire-line and local wireless networks and from there, to the users served by these networks. The user equipment is enabled with a simple clock discipliner that adjusts the local clock to the global clock, resulting in a reliable synchronization across the converged communication networks.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Systems and methods for synchronizing the internal clocks of a plurality of processor modules
ActiveUS20060047989A1Promote recoveryData storage is convenientMechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksComputer architectureMulti processor
In a multiprocessor system that includes a plurality of processor modules, each one of which includes its own internal clock, one of the plurality of processor modules is designated as a master processor module having a master internal clock. Each other processor module is designated as a slave processor module having a slave processor module internal clock. Each slave processor module synchronizes its internal clock with the master internal clock.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Communication method, communication system, transmission method, transmission apparatus, receiving method and receiving apparatus
InactiveUS20070296859A1Maintain compatibilityTransmission easilyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCommunications systemComputer science
A communication method of transmitting video data which may include a predetermined number of bits as a unit from a source device to a sink device in sync with pixel clock and using individual transmission lines for respective color data or the like, may include preparing video data for three-dimensional display including the video data for a left eye and the video data for a right eye; forming the data for the left eye and for the right eye including the predetermined number of bits per pixel respectively; adding one of the data for the left eye and data for the right eye to the other thereof per pixel; forming the data of one pixel including twice the predetermined number of bits and transmitting the data at a timing in sync with the pixel clock; and transmitting the data for three-dimensional display from the source device to the sink device.
Owner:SONY CORP
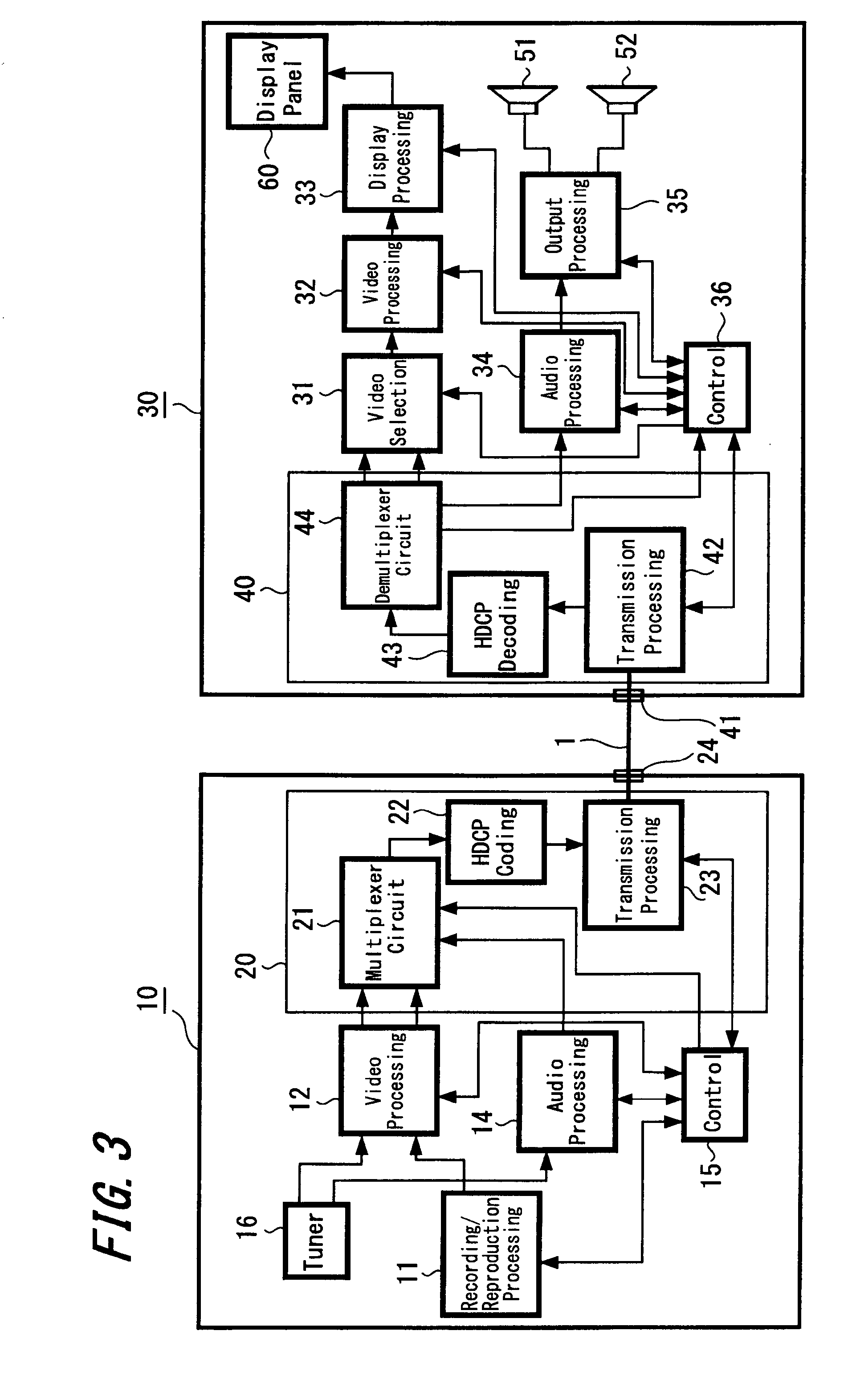
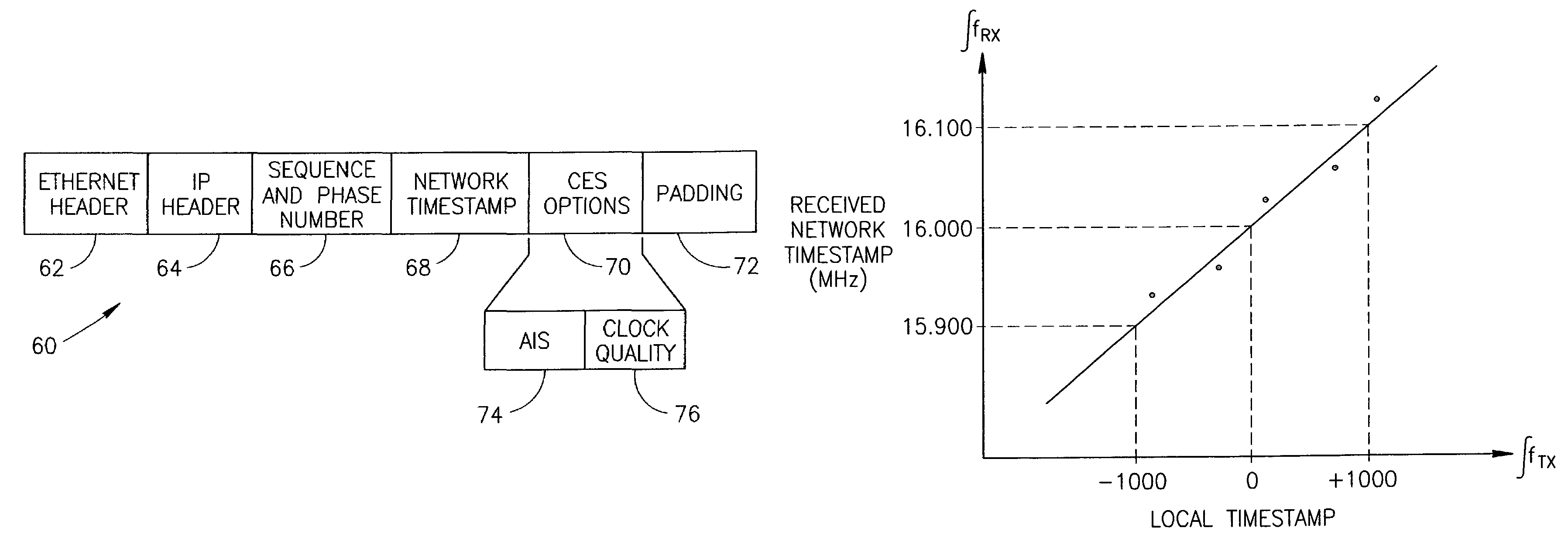
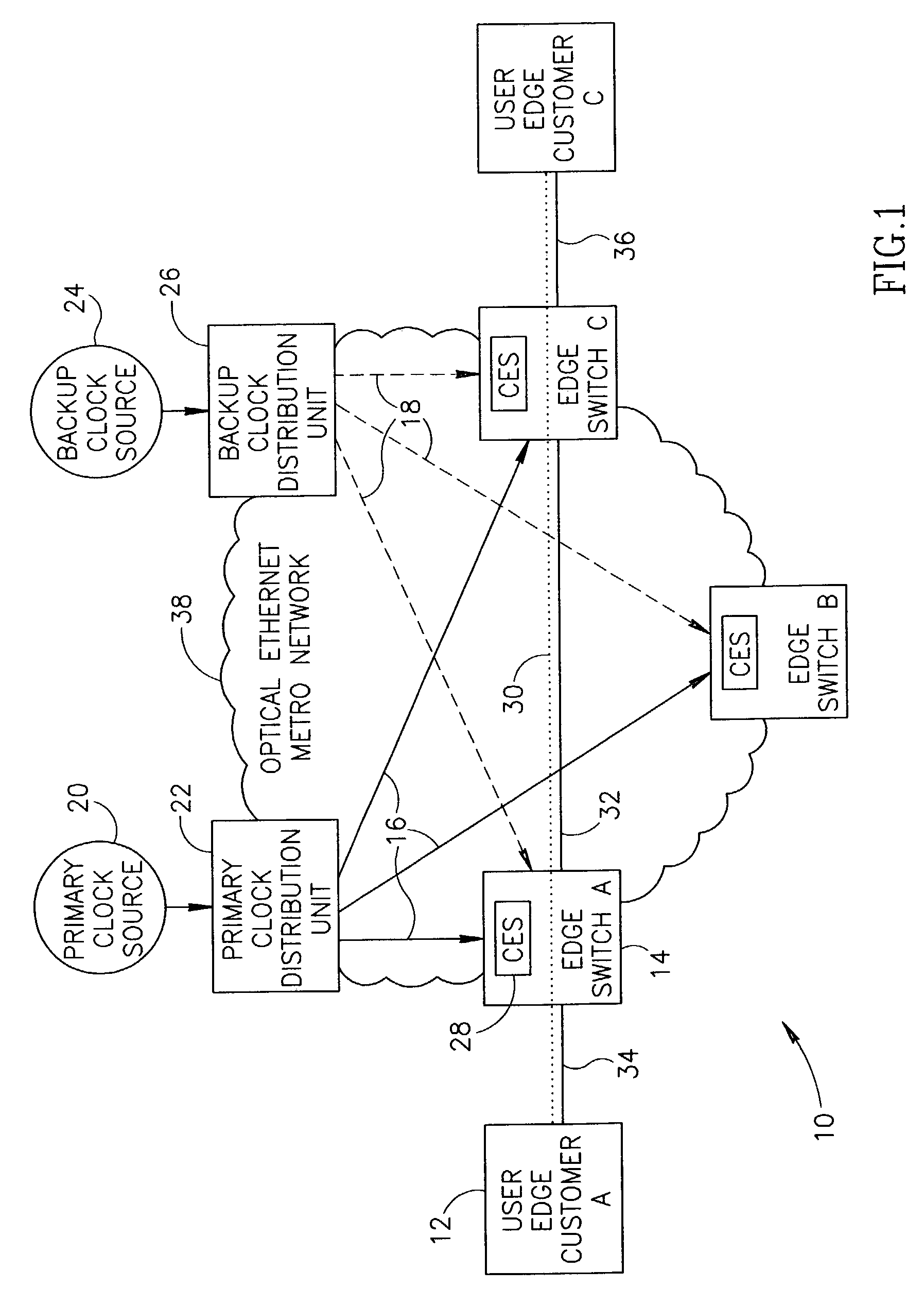
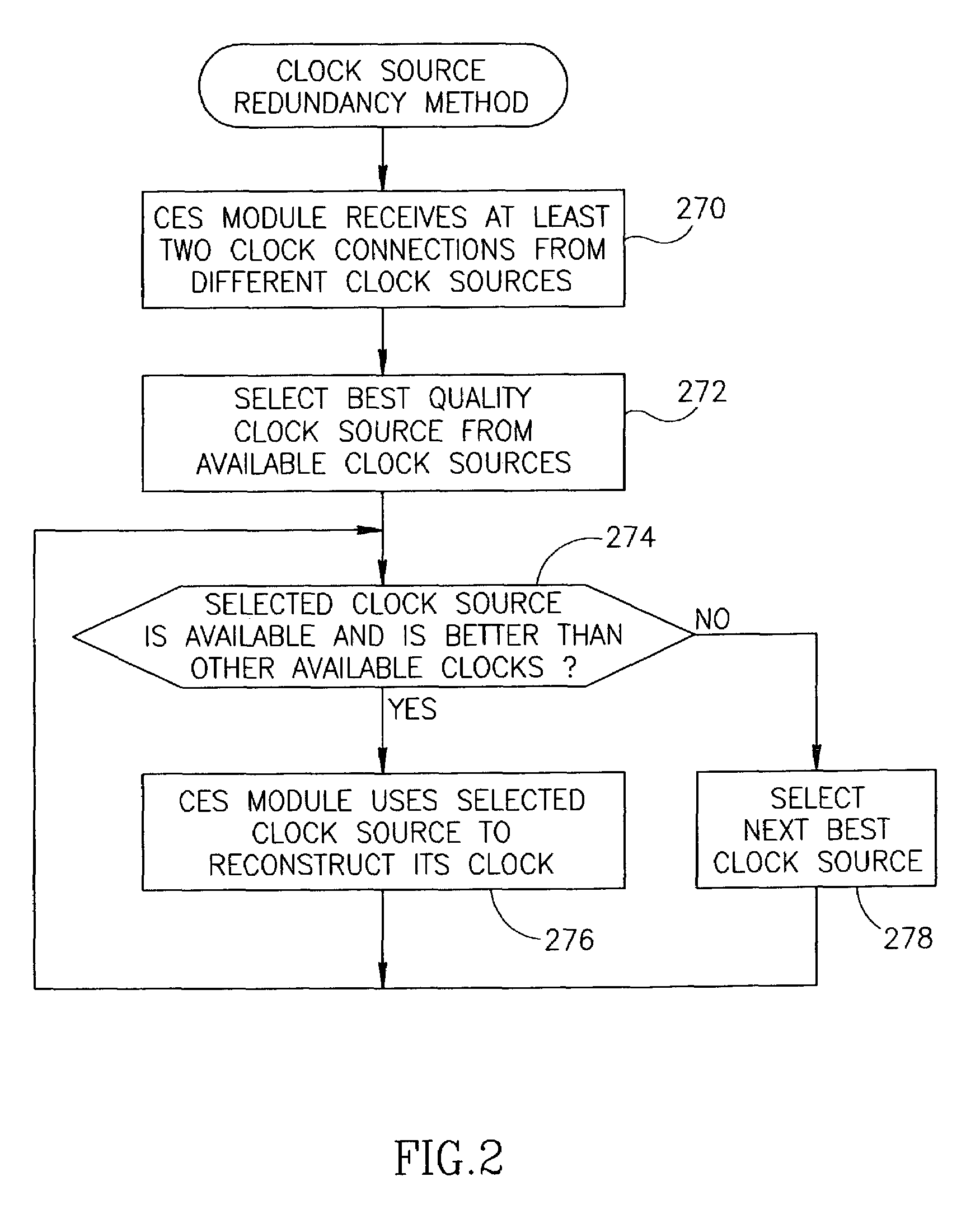
Centralized clock synchronization for time division multiplexed traffic transported over Ethernet networks
InactiveUS7613212B1Improve accuracyImprove clock reliabilityTime-division multiplexTransmissionTraffic capacityAsynchronous network
A centralized clock distribution mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The centralized clocking mechanism of the present invention distributes a high accuracy central clock source to a plurality of CES modules over an Ethernet network. Clock synchronization information based on a high quality clock reference source is distributed to circuit emulation service (CES) modules in the network. CES modules receive the clock synchronization information and use it to reconstruct a local clock. A plurality of clock distributors provide clock redundancy whereby each CES module selects the best clock source to use in reconstructing the local clock.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com