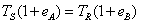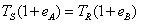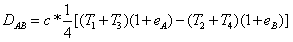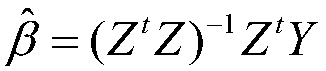Patents
Literature
196 results about "Clock offset" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clock Offset - offset of the clock is a delay of a given clock source, it might be known, or unknown. Offset can be measured in time units or phase degree.
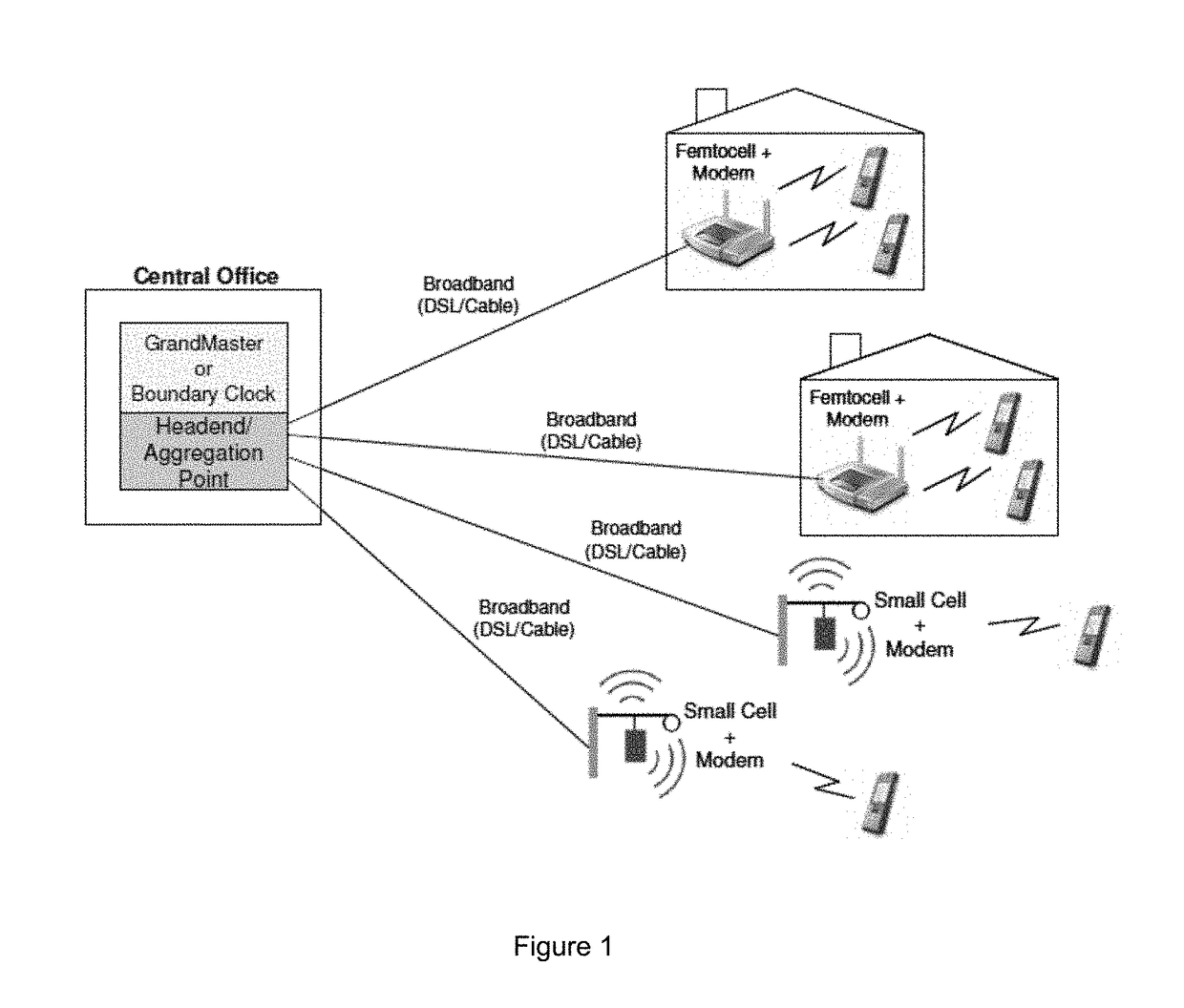
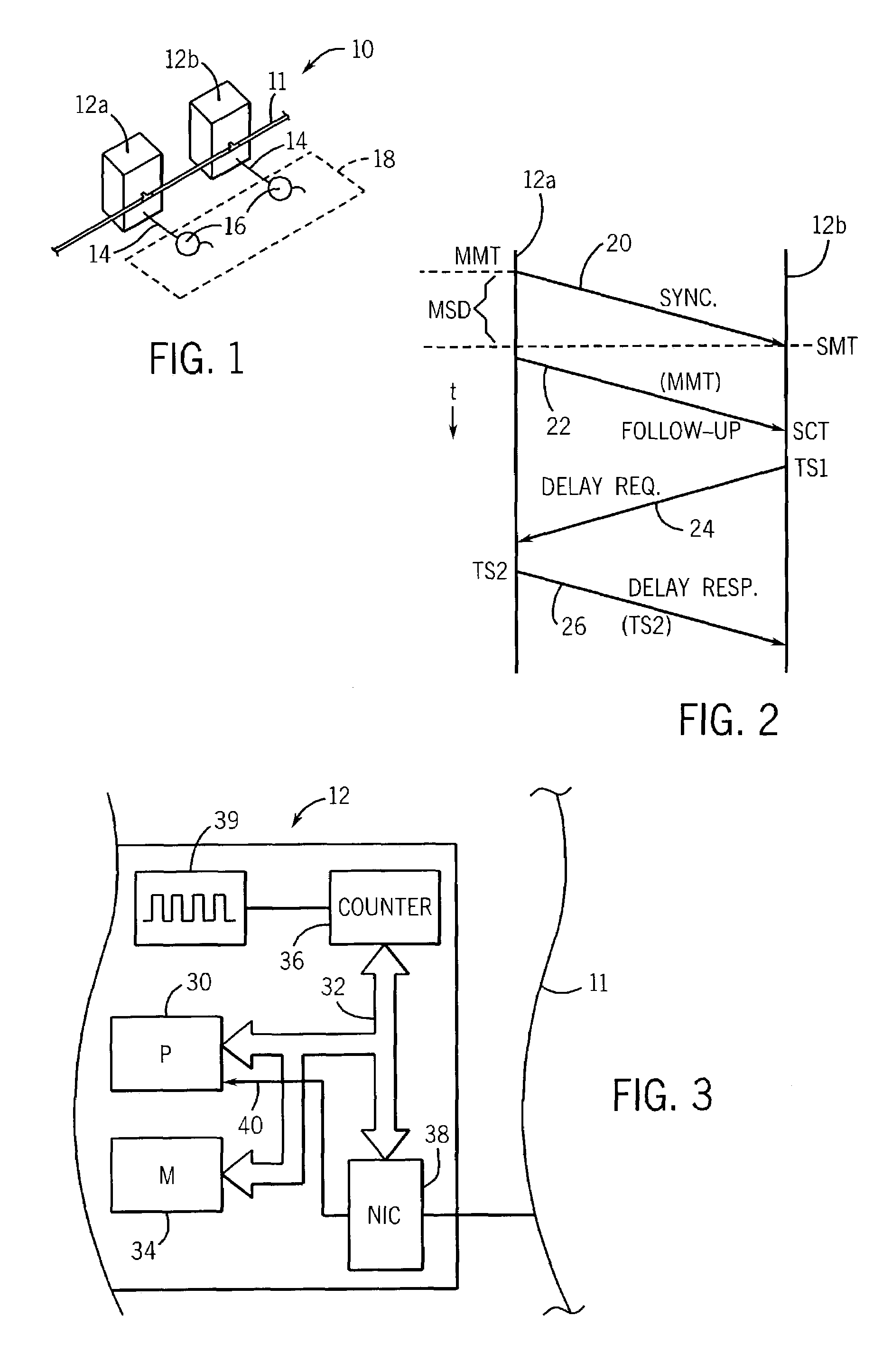
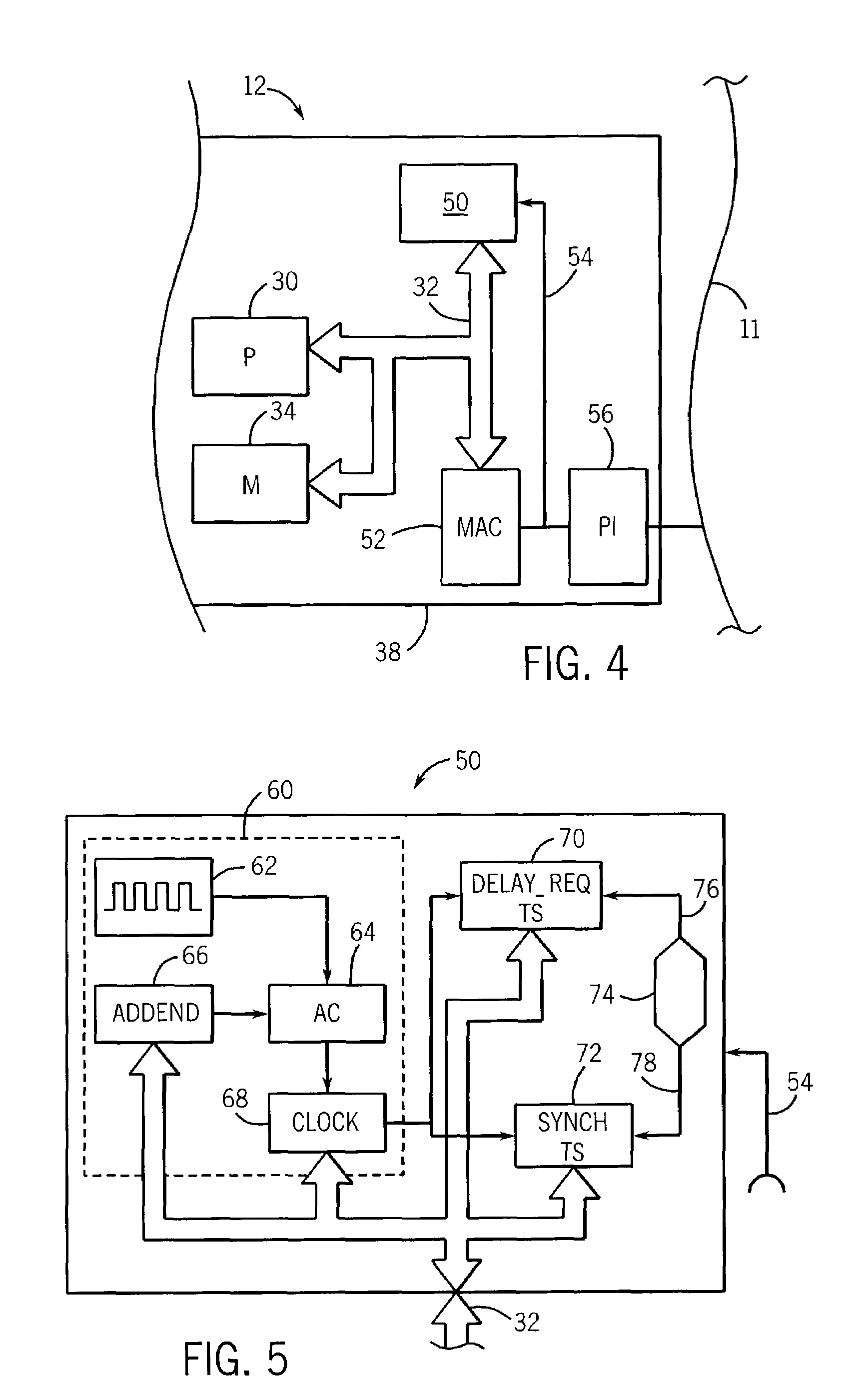
Synchronization for femto-cell base stations
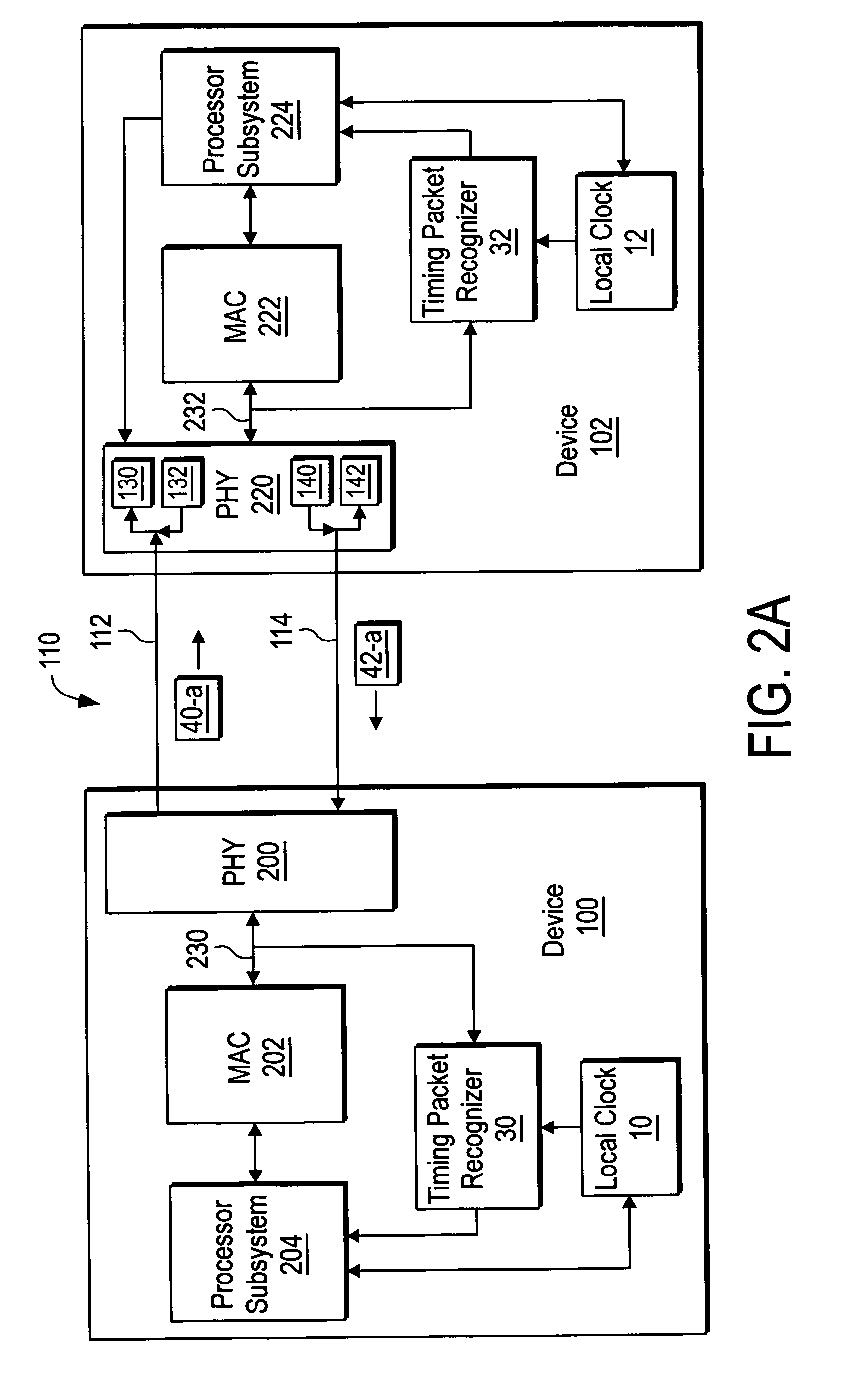
Timing synchronization between base stations of uncoordinated communication networks includes obtaining timing synchronization information from one base station, and adjusting a clock of the other station in response to the synchronization information. The timing synchronization information can be identified from a strongest synchronization signal from nearby uncoordinated base stations. The timing synchronization can accommodate clock offsets and frequency offsets.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
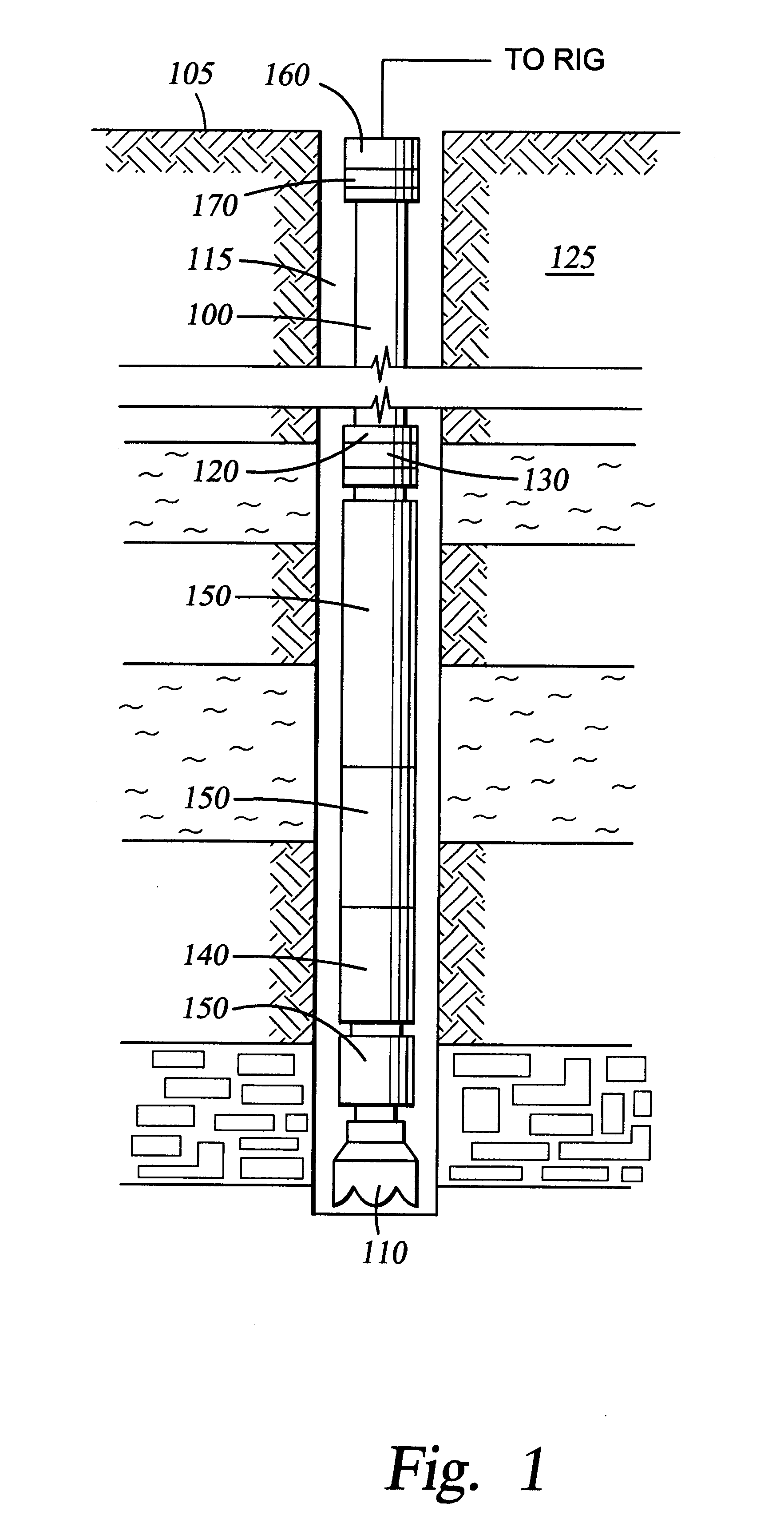
Method for compensating for remote clock offset
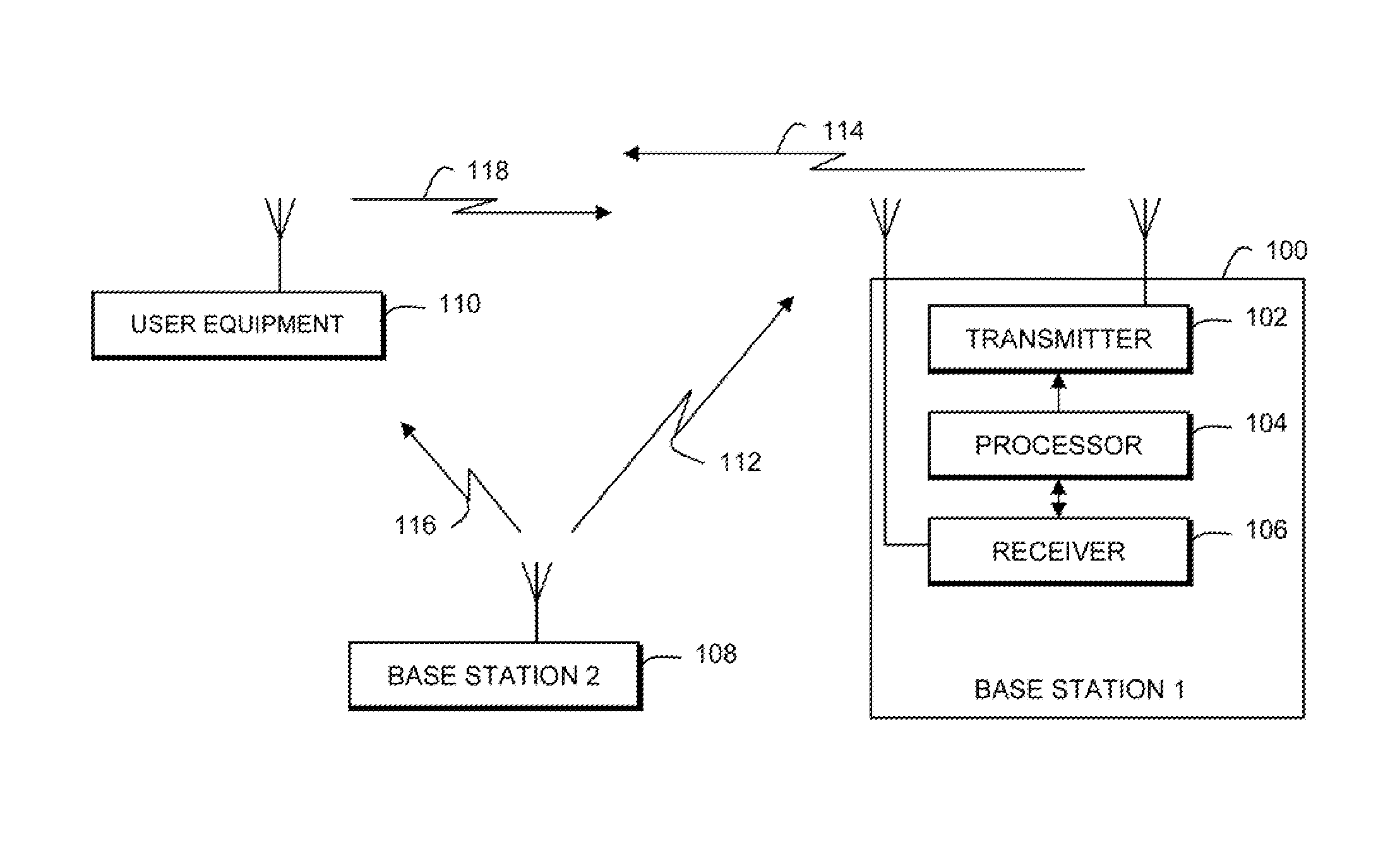
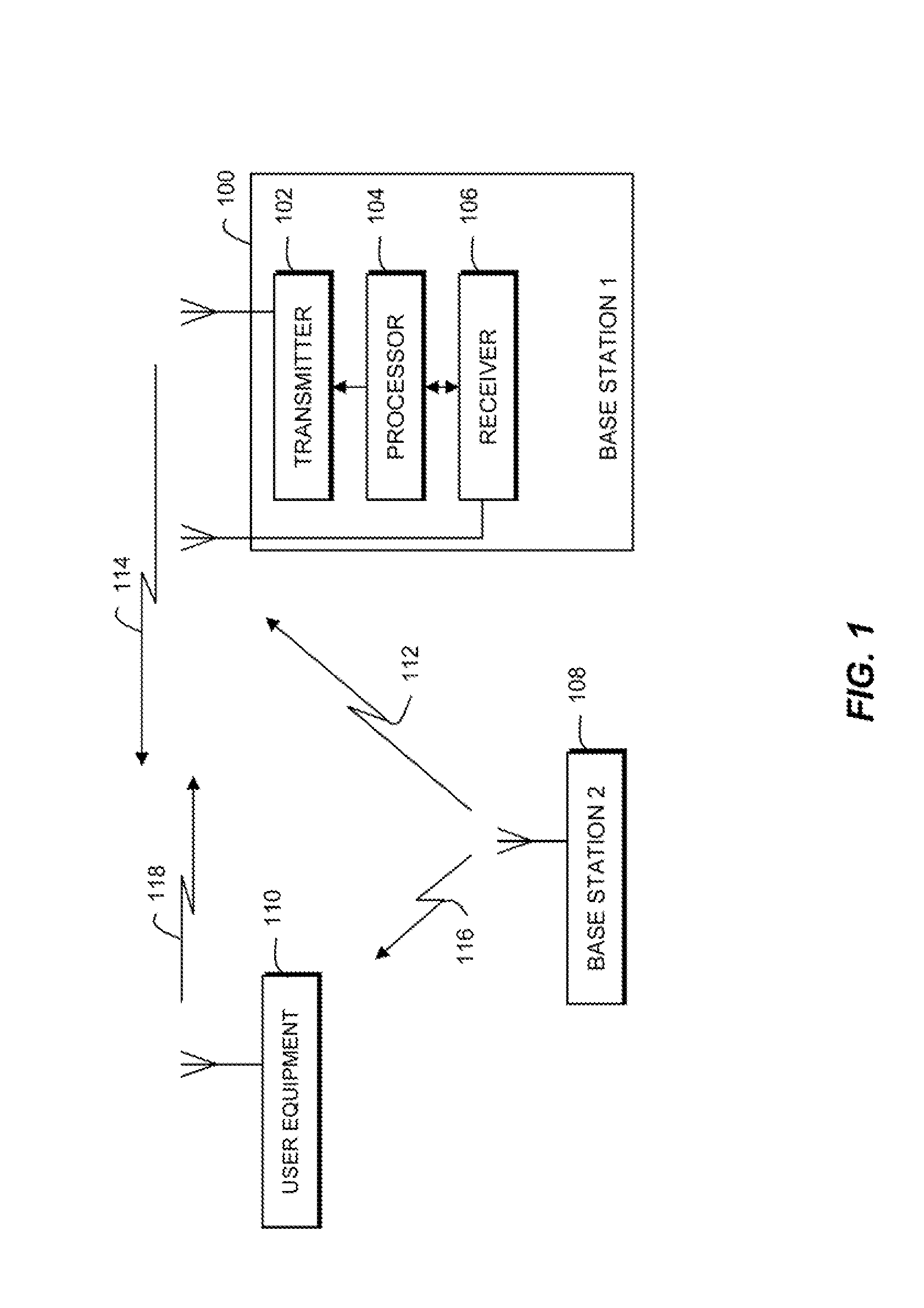
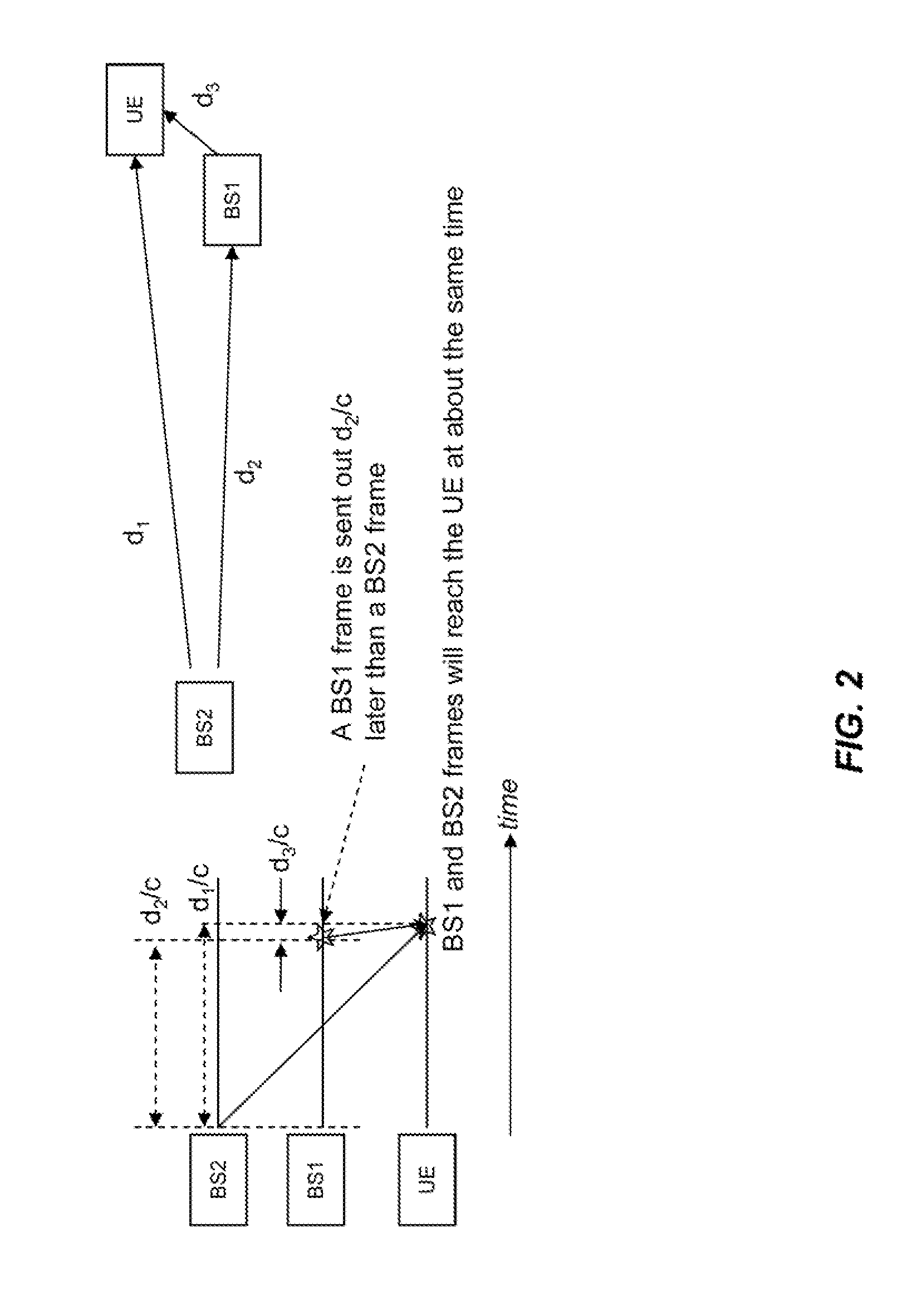
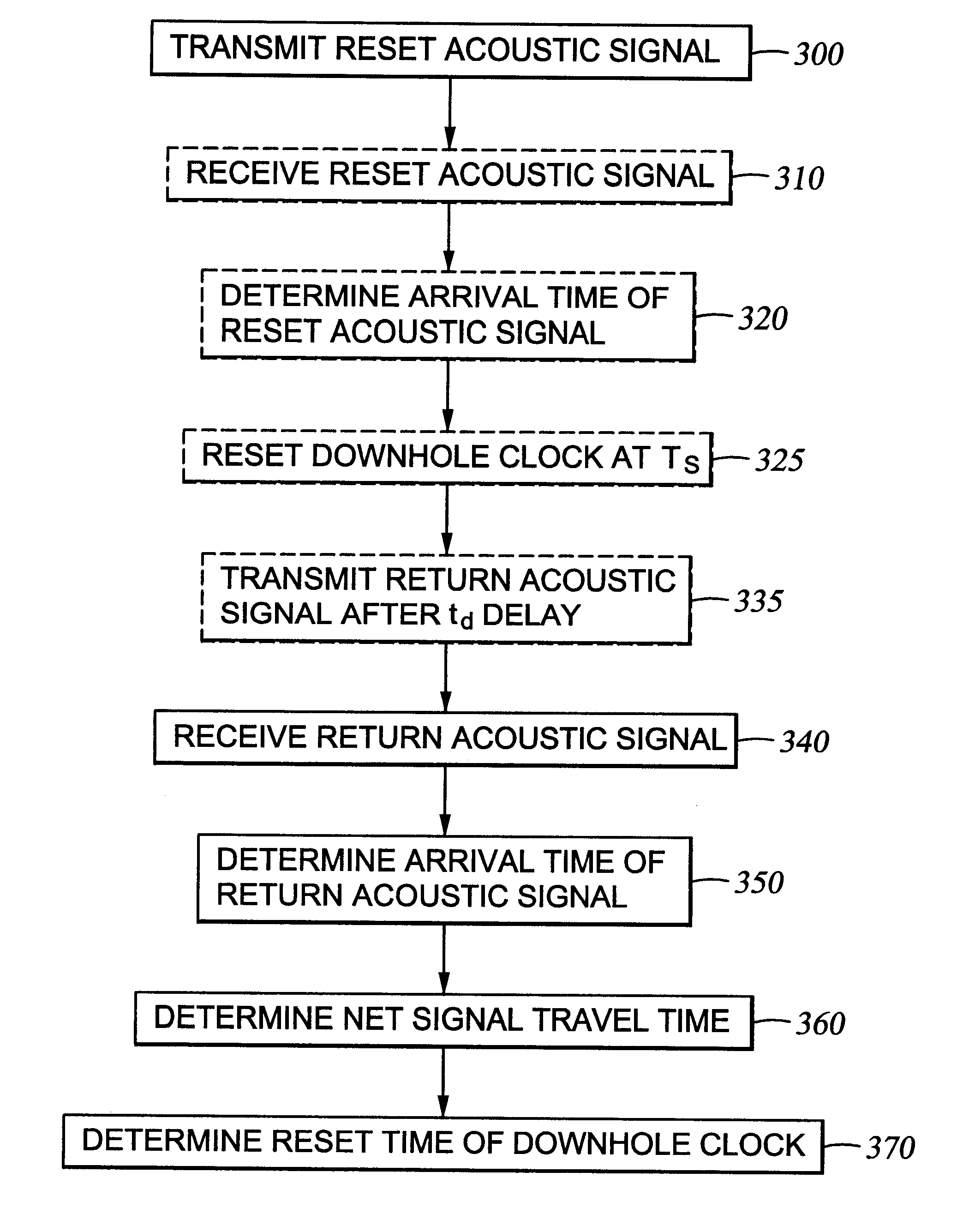
A system is disclosed for synchronizing a clock in a well containing a drill string with a clock located near the surface of the well. The system includes devices for transmitting and receiving a pair of acoustic signals between locations associated with each clock and processing those signals. The system determines the time of arrival of each acoustic signal by analyzing the shape of a function of the acoustic signal chosen from a group of functions suitable to determine a clock offset with millisecond accuracy.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Corrrecting time synchronization inaccuracy caused by asymmetric delay on a communication link
ActiveUS20070147562A1Time-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementPropagation delayTelecommunications link
Techniques for correcting time synchronization inaccuracy caused by asymmetric delays on a communication link. Time synchronization according to the present techniques includes determining an asymmetry in a propagation delay on a communication link used by a first device and a second device to exchange timing information and incorporating the asymmetry into a determination of a clock offset between the first and second devices.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Clock filter dispersion
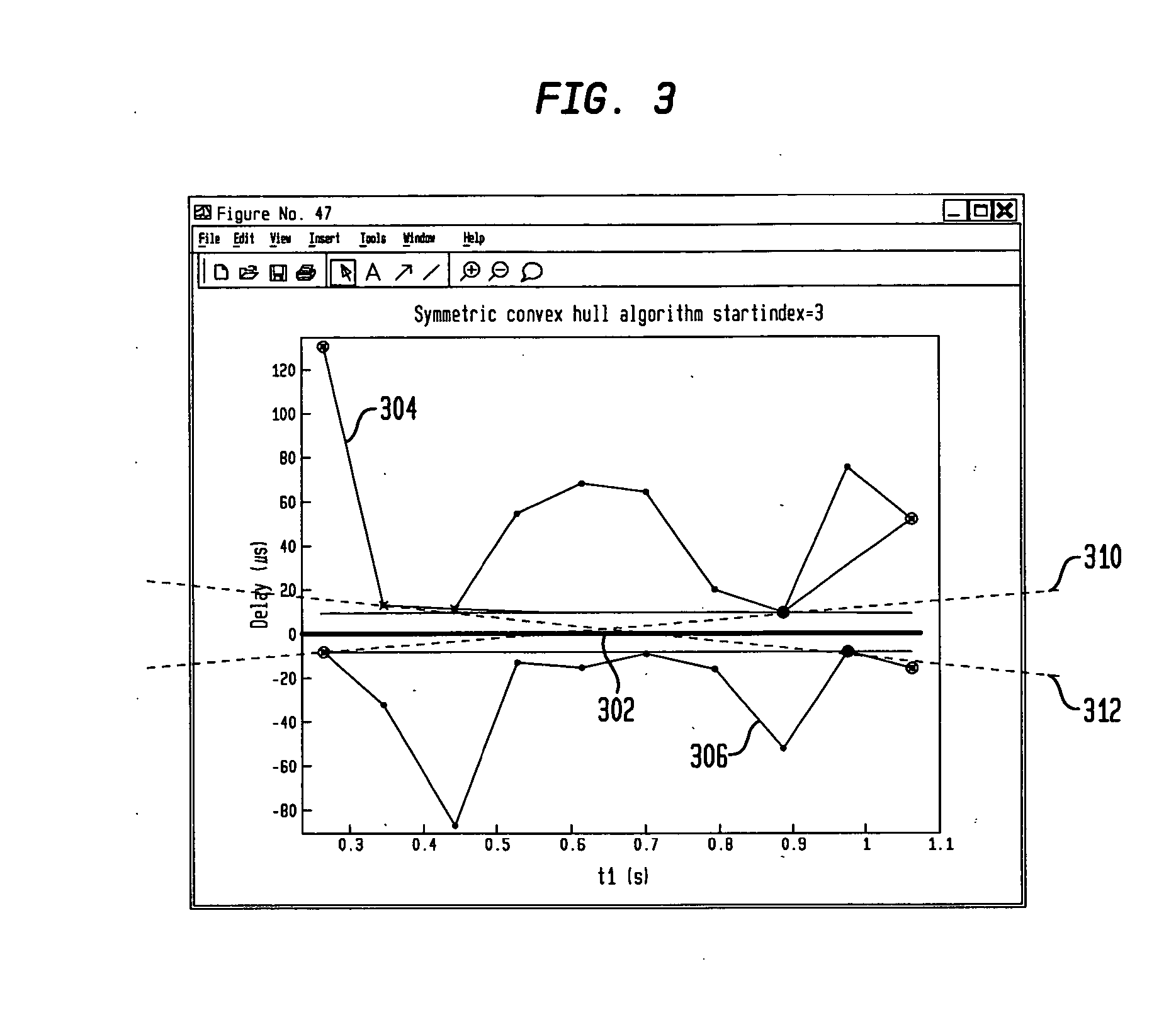
Disclosed are a method and system to estimate the maximum error in the clock offset and skew estimation between two clocks in a computer system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a first set of data values representing a forward delay between the first and second clocks, and obtaining a second set of data values representing a negative backward delay between the first and second clocks. The method comprises the further step of forming a lower convex hull for said first set of data values, and forming an upper convex hull for said second set of data values. First and second parallel lines are formed between the upper and lower convex hulls, and these parallel lines are used to estimate the worst case error for the offset, skew rate and dispersion of said first and second clocks.
Owner:IBM CORP
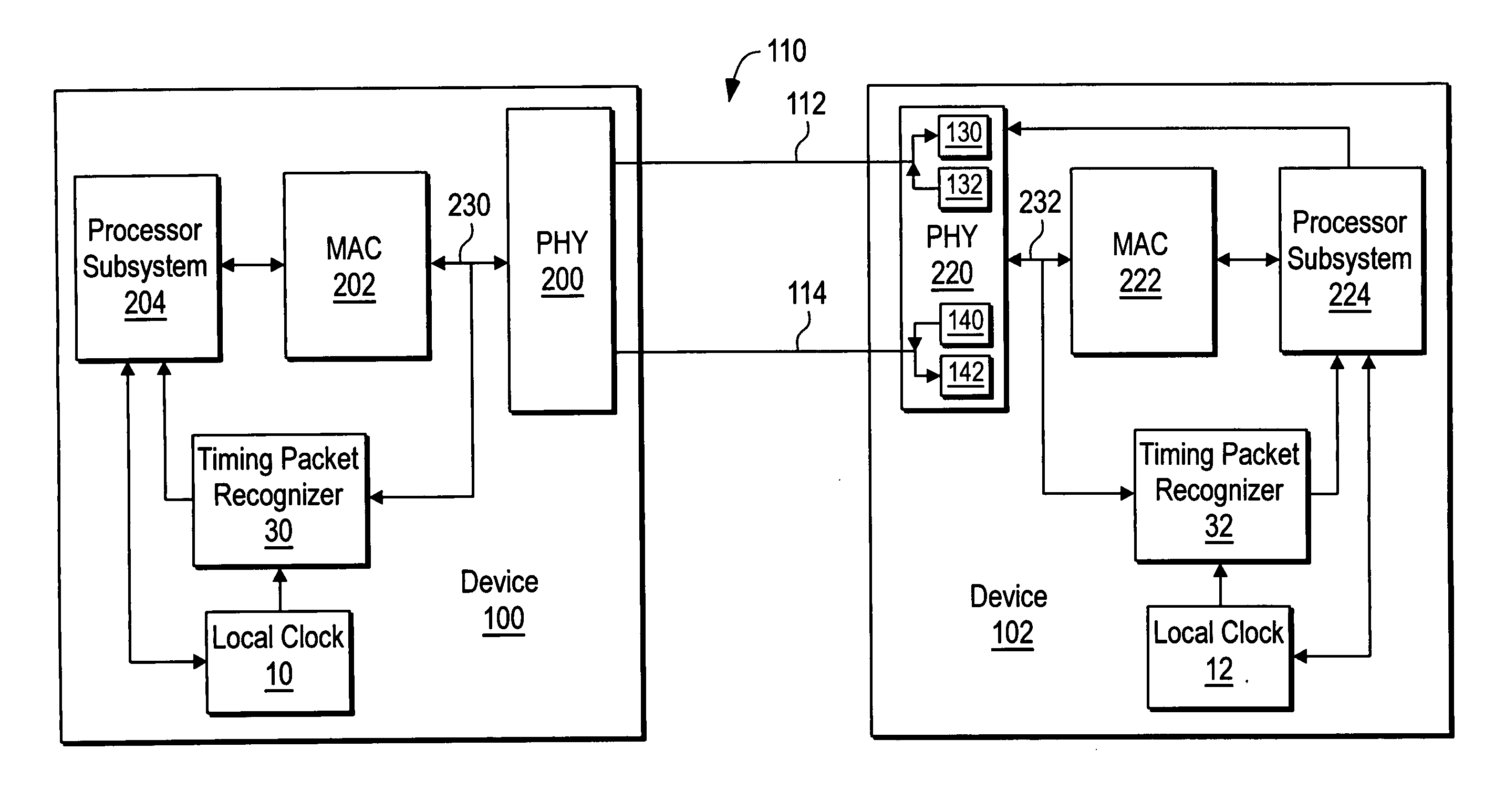
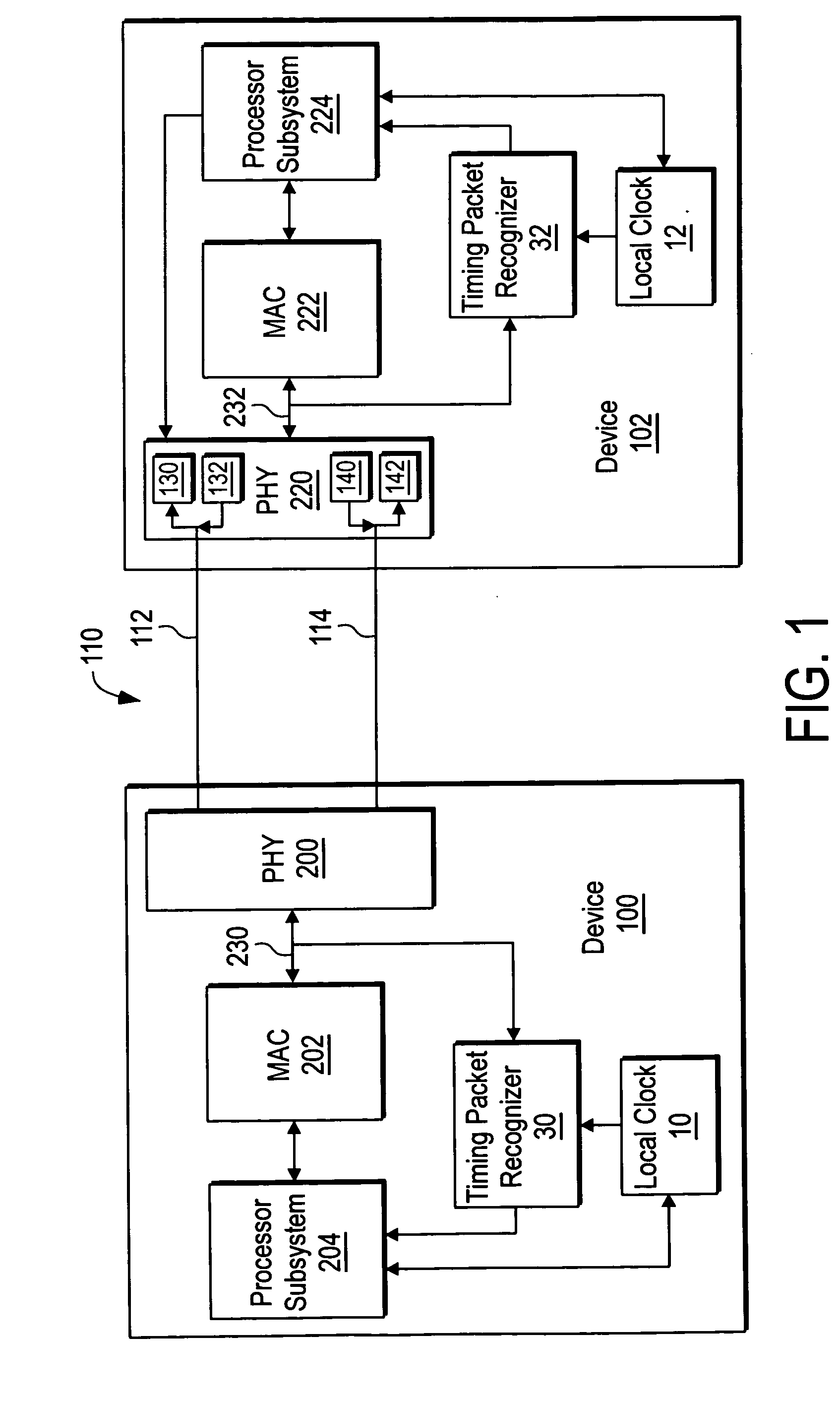
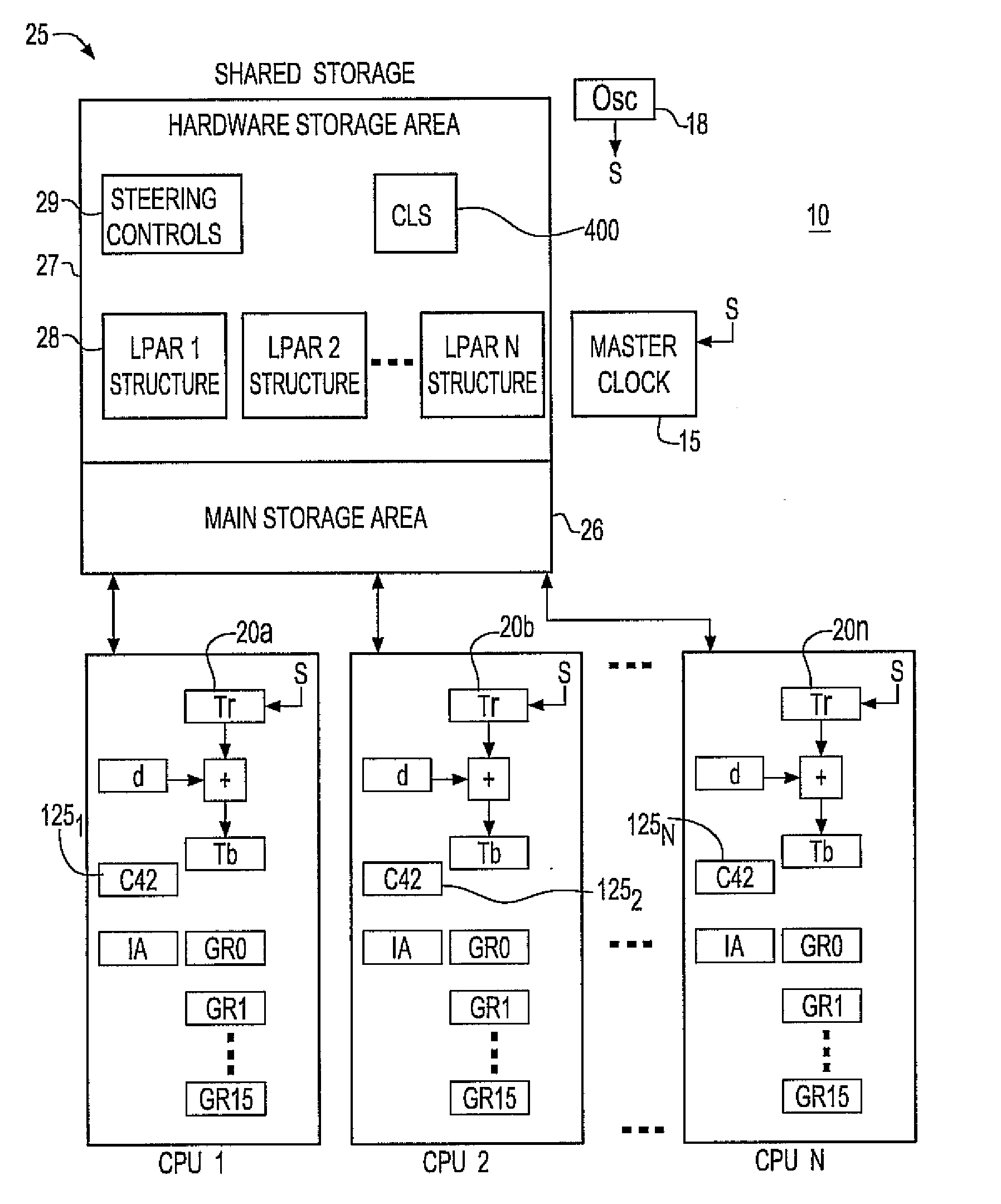
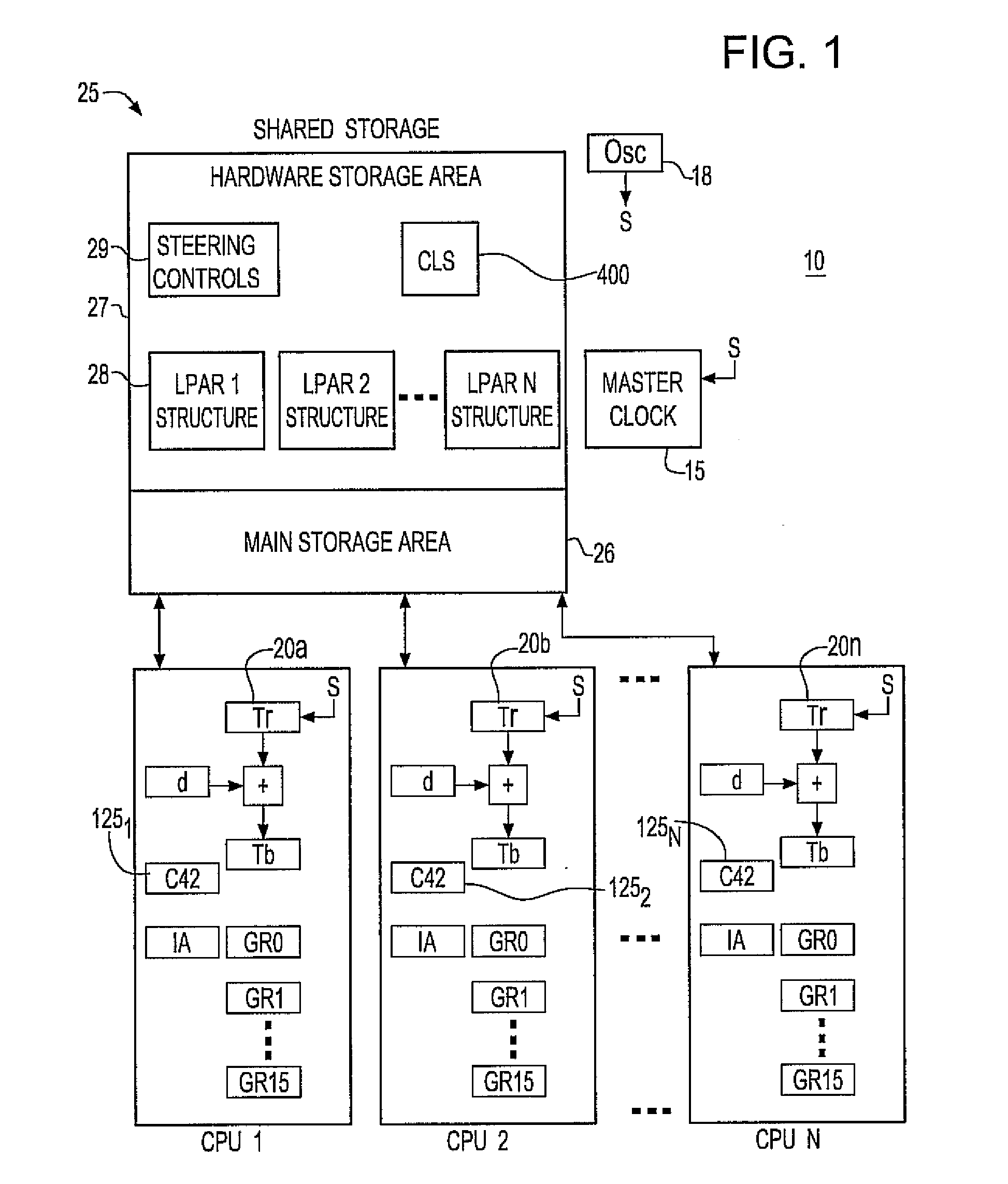
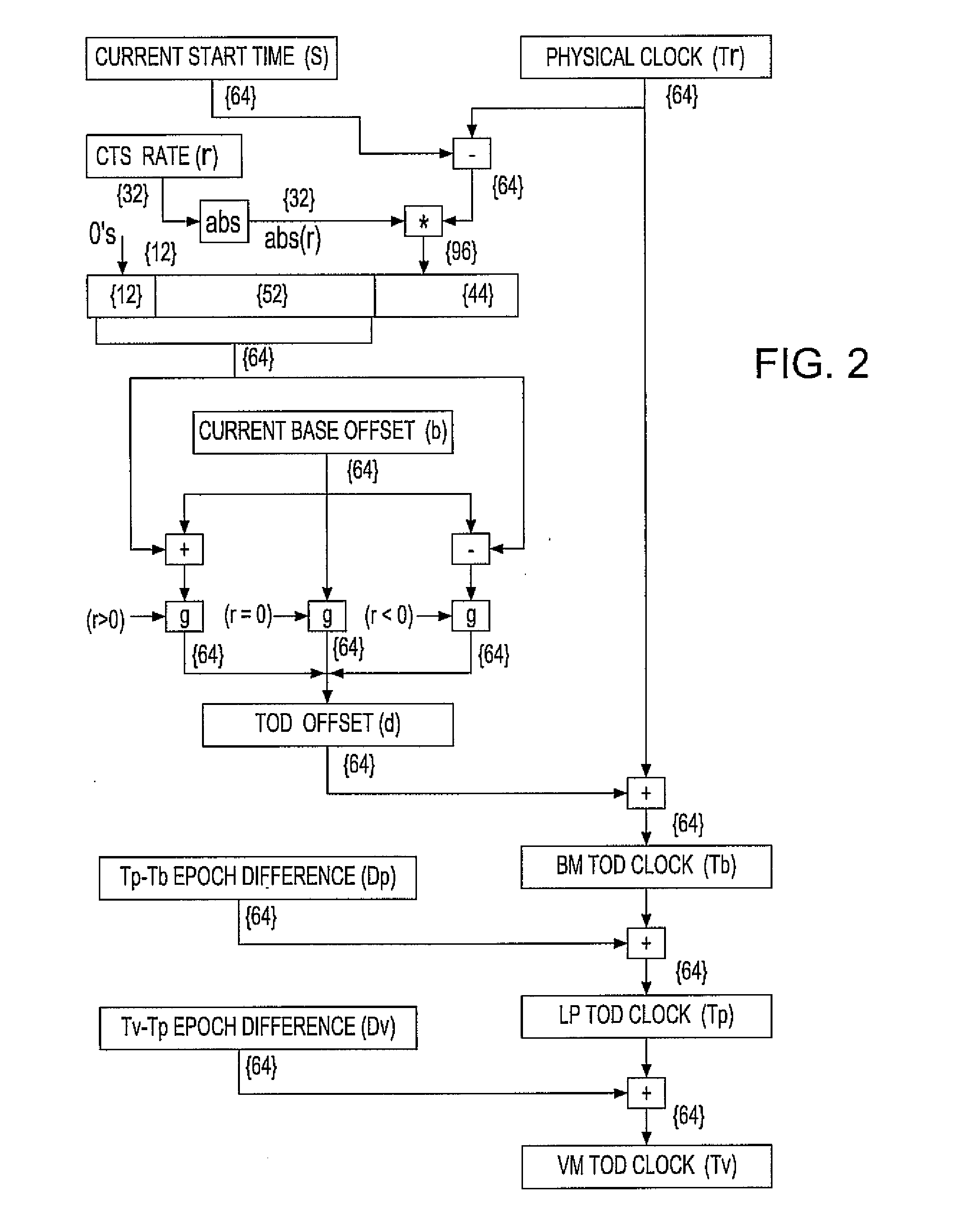
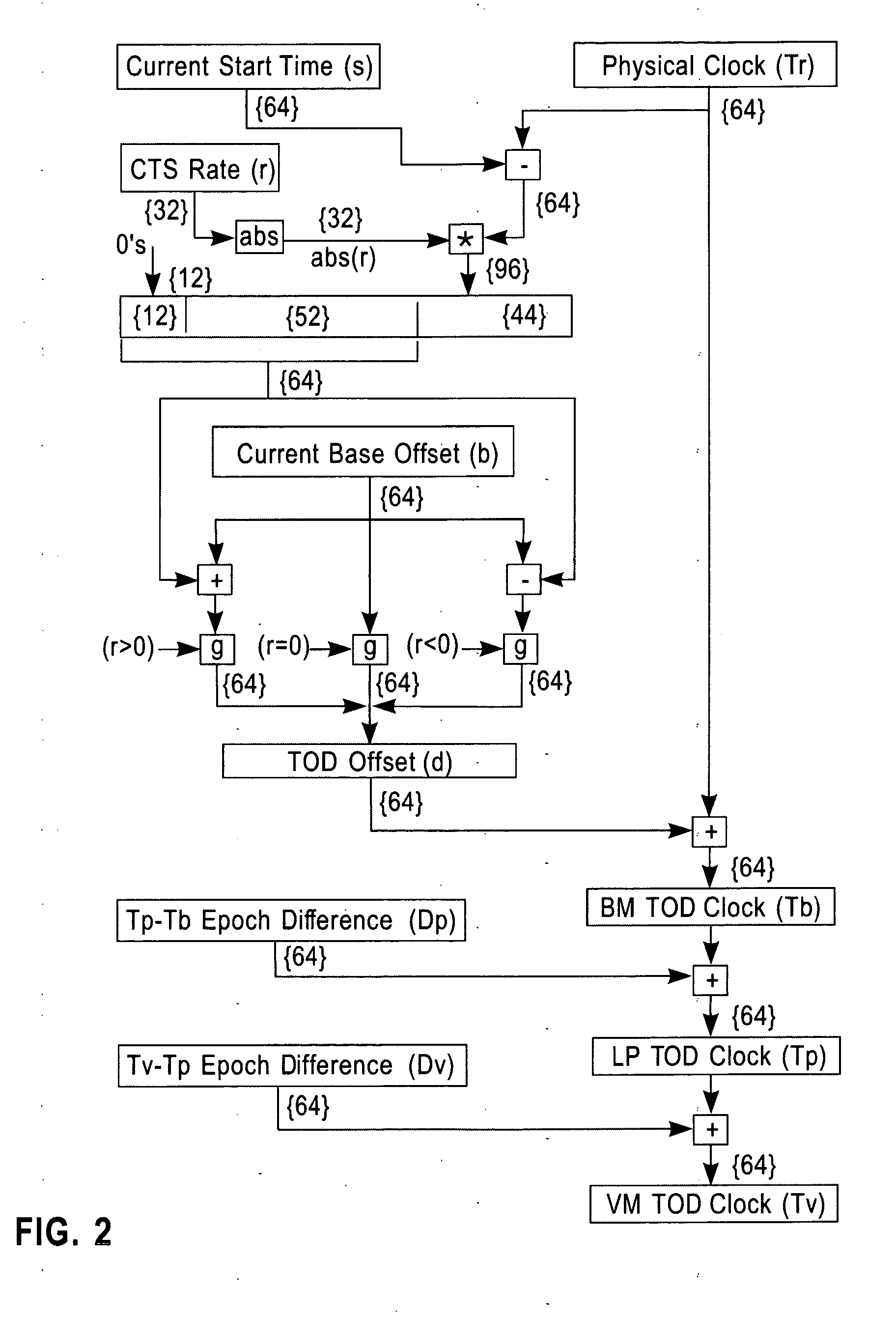
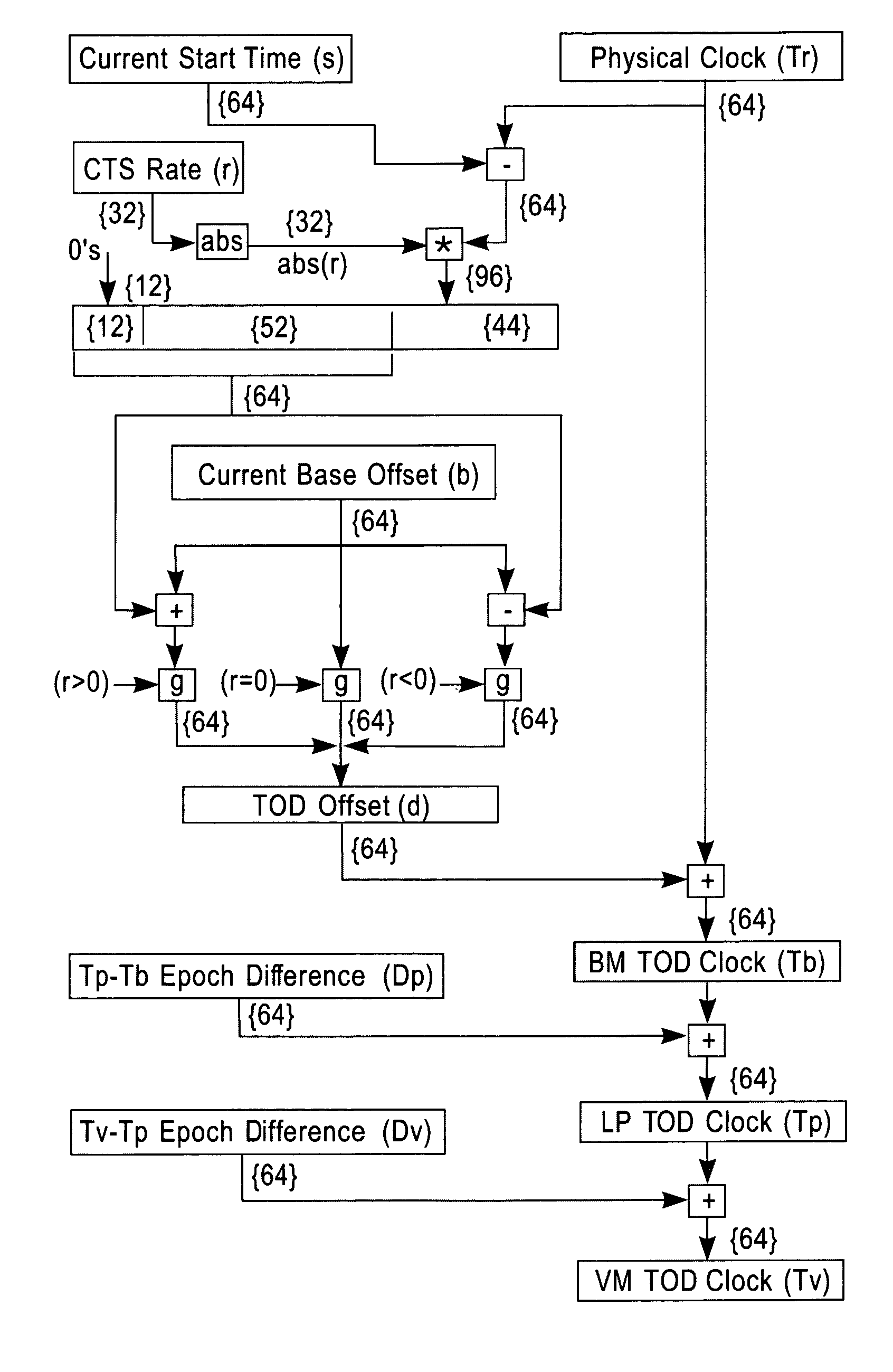
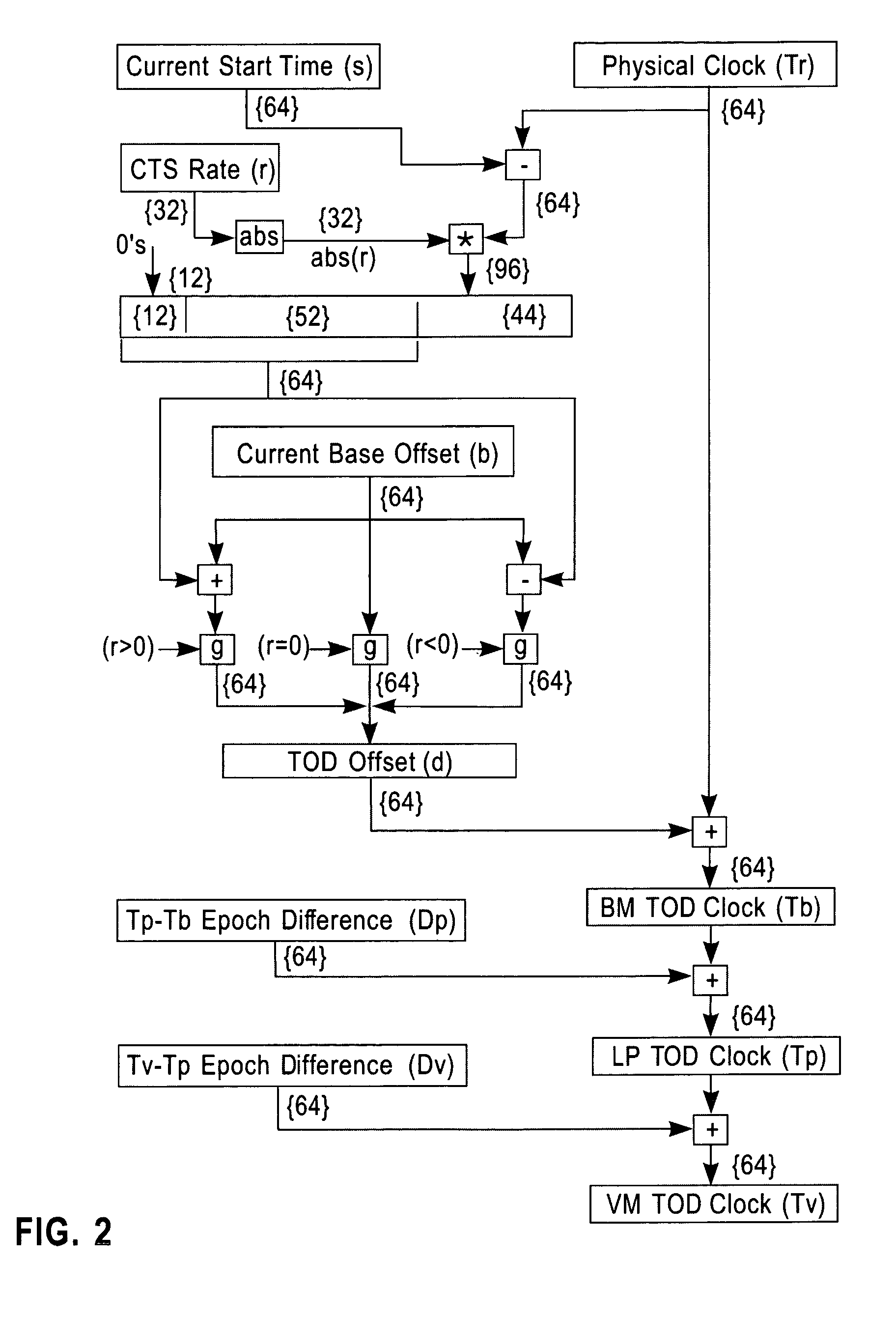
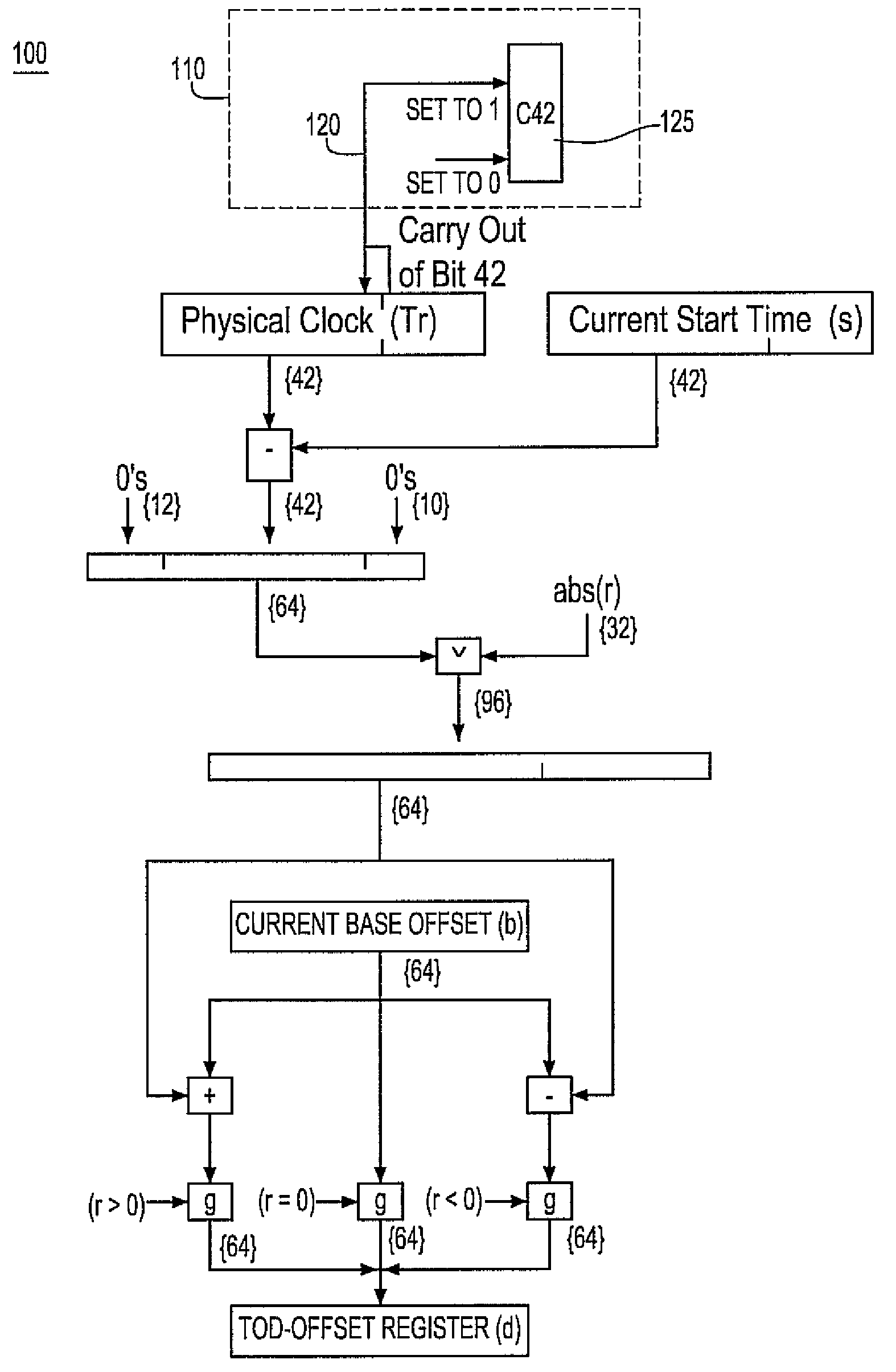
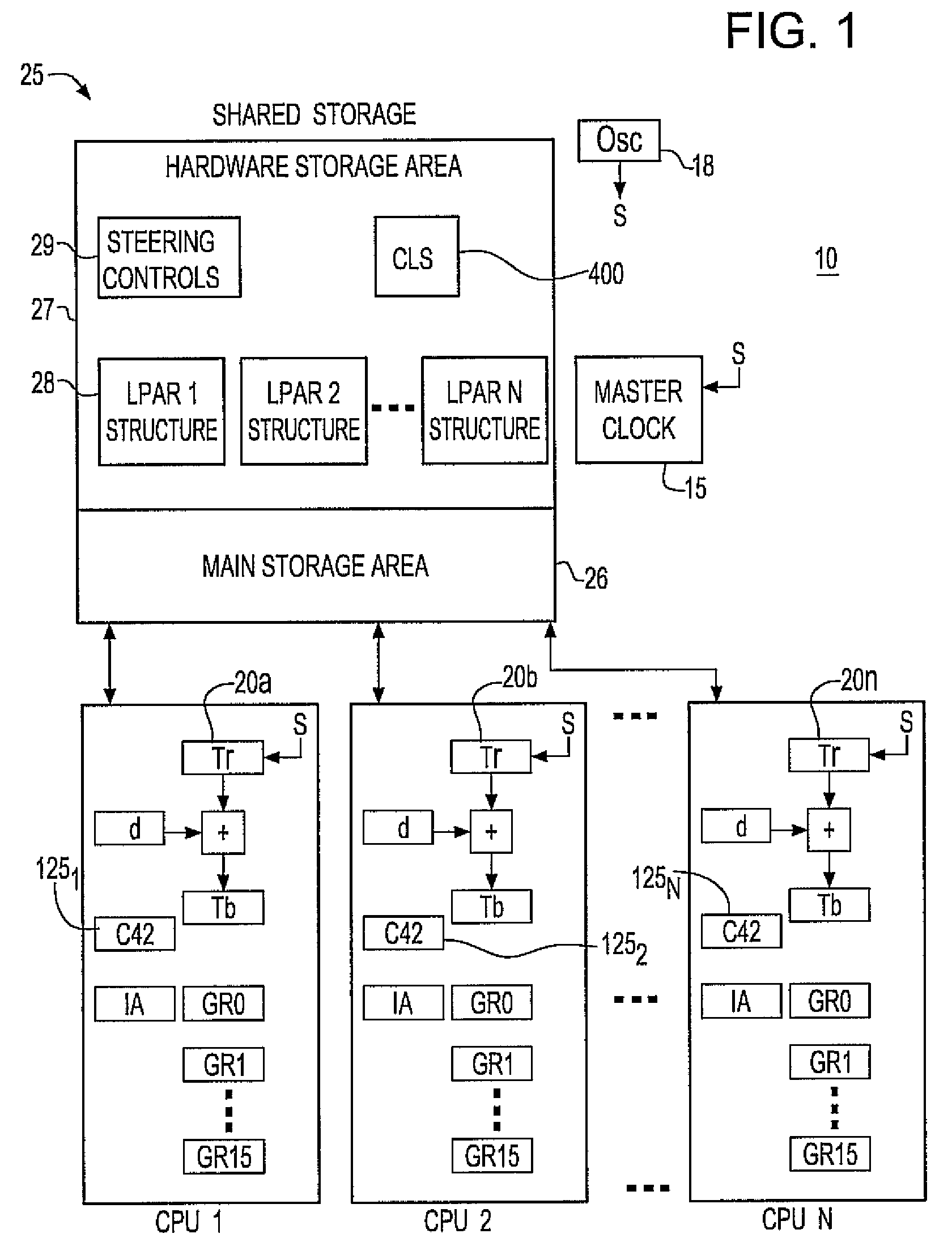
Synchronization signal for tod-clock steering adjusment
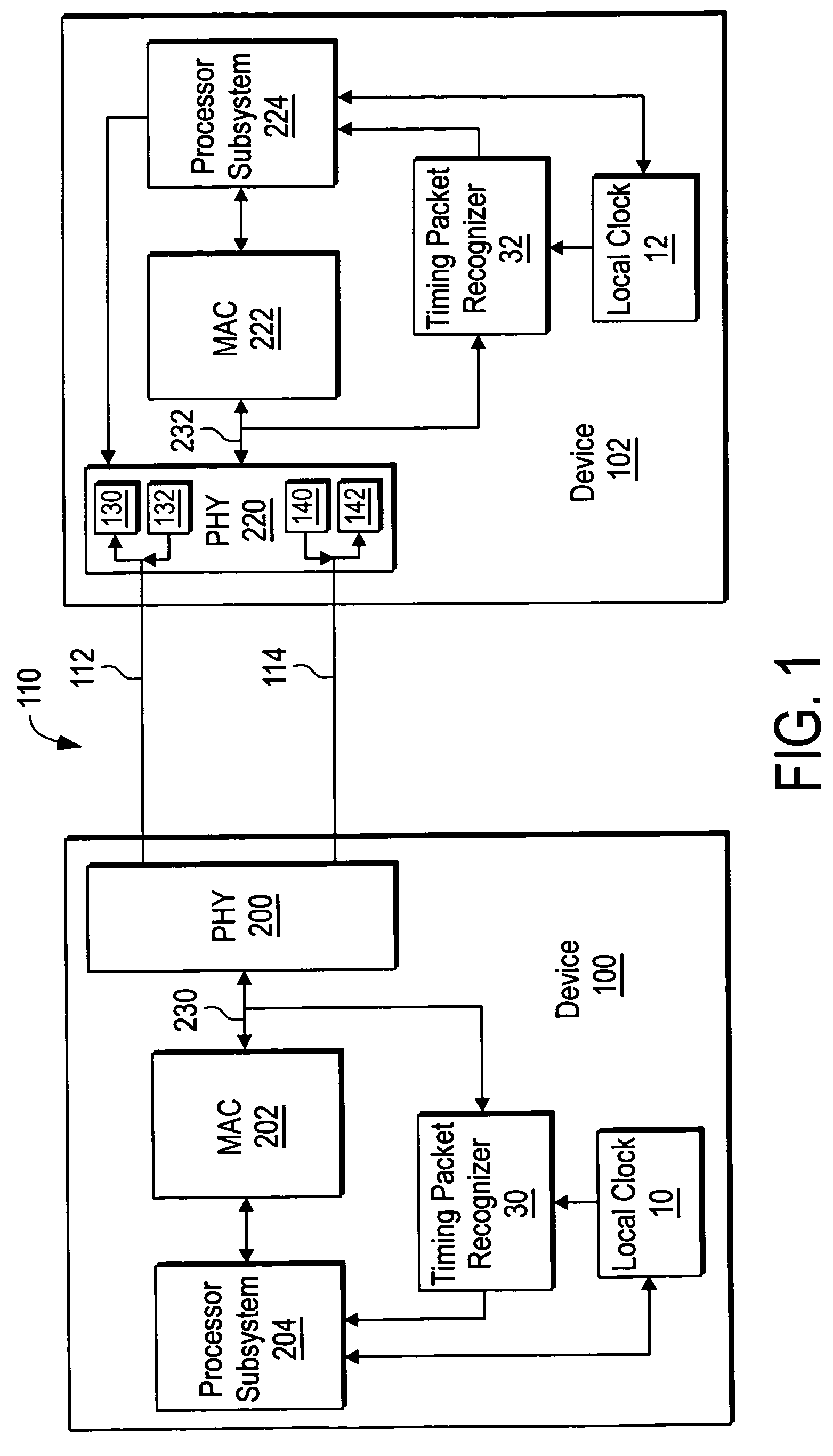
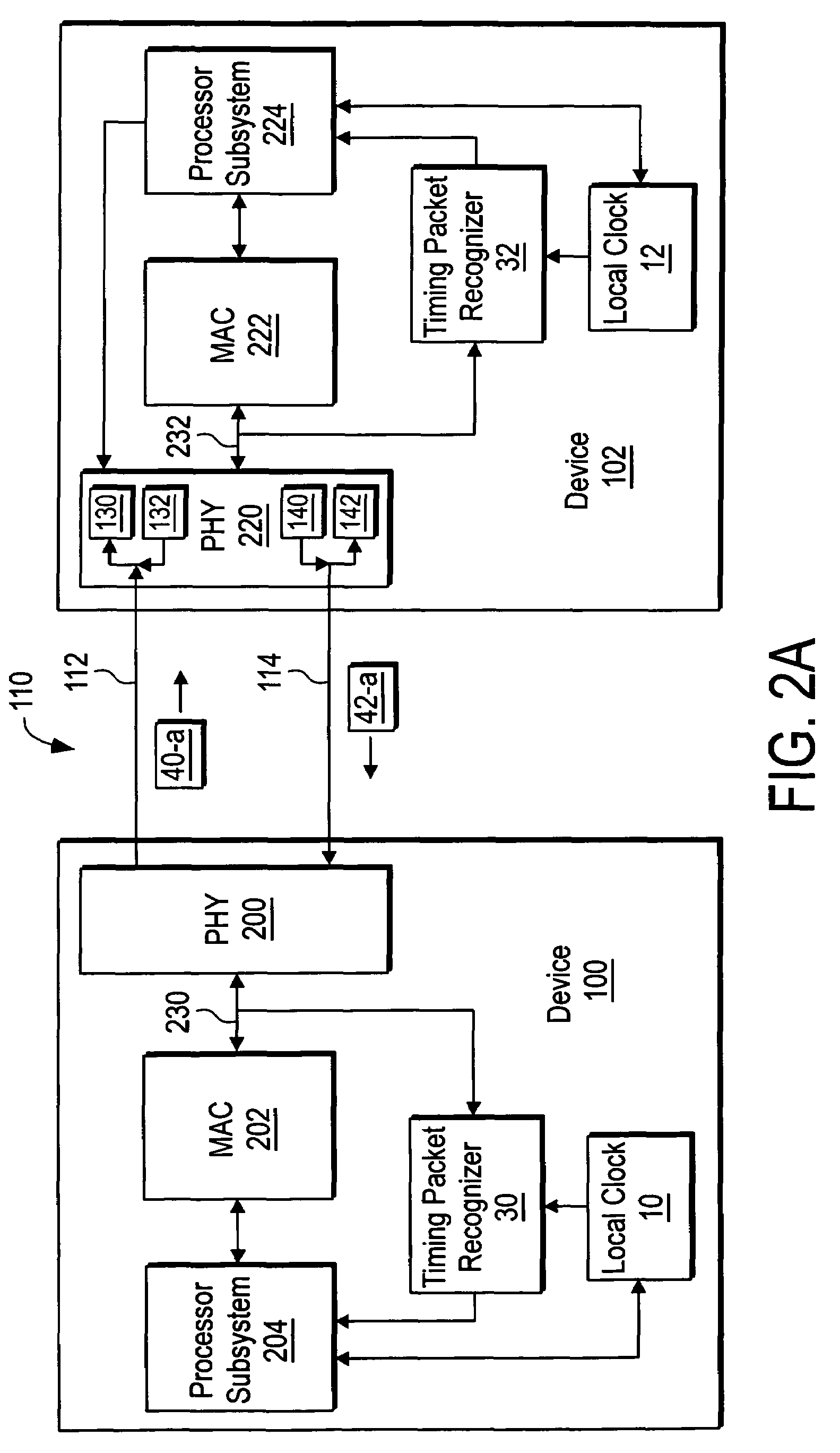
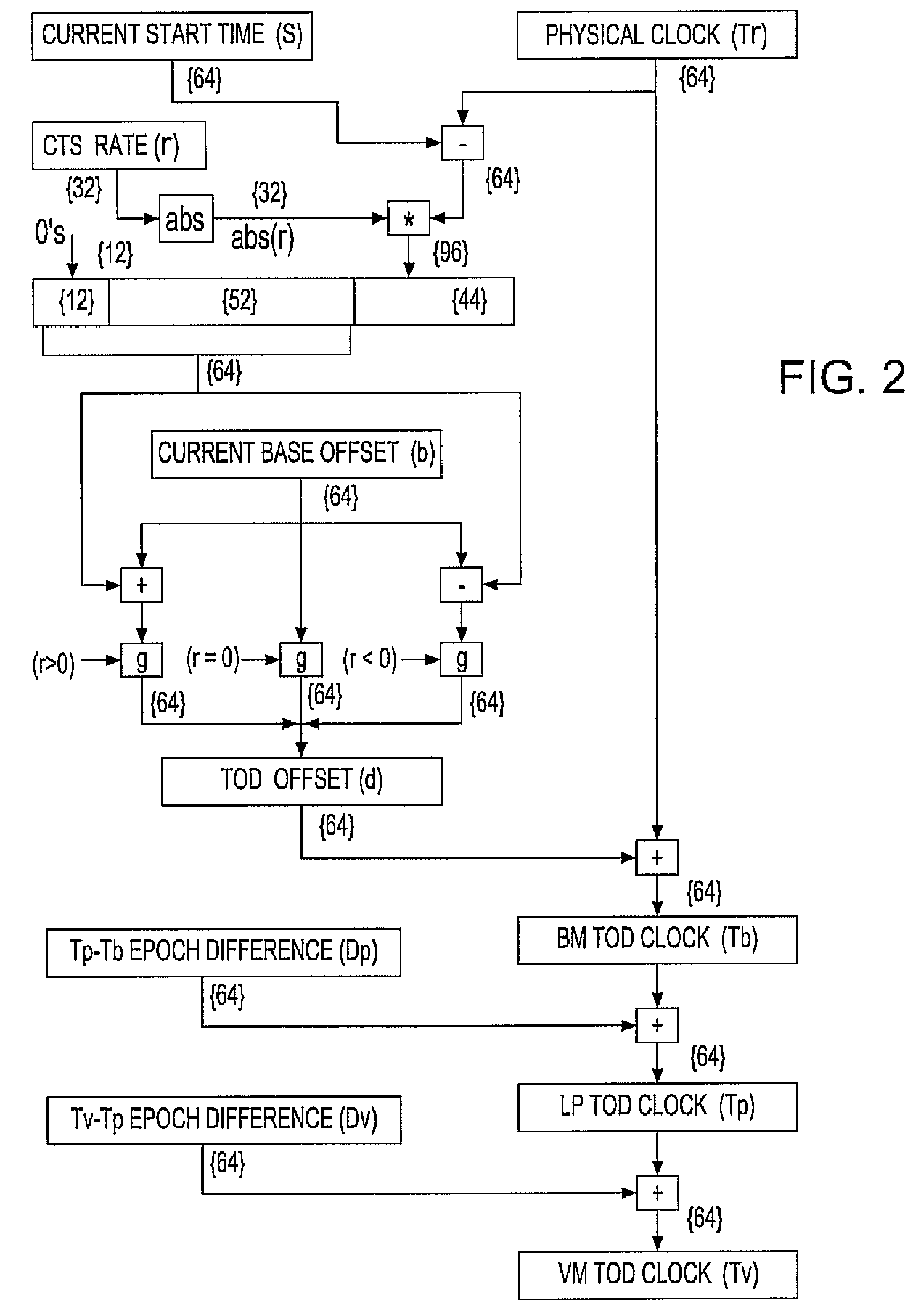
InactiveUS20080072097A1Minimize overheadAvoids a further carry propagatingError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksComputer hardwareClock offset
A system, method and computer program product for synchronizing adjustment of a time of day (TOD) clock for a computer system having multiple CPUs, each CPU having an associated physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepping to a common oscillator, and an associated logical TOD clock. The method includes detecting propagation of a carry at a pre-determined bit position of the physical clock associated with a CPU in the computer system; and, updating, in response to the detecting of the pre-determined bit position carry, a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD clock value (Tb) for use by a CPU in the system. In this manner, each CPU computes a new logical TOD clock value in synchronization—the new logical TOD clock value taking effect simultaneously for the multiple CPUs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Correcting time synchronization inaccuracy caused by asymmetric delay on a communication link
ActiveUS7602873B2Time-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementPropagation delayTelecommunications link
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
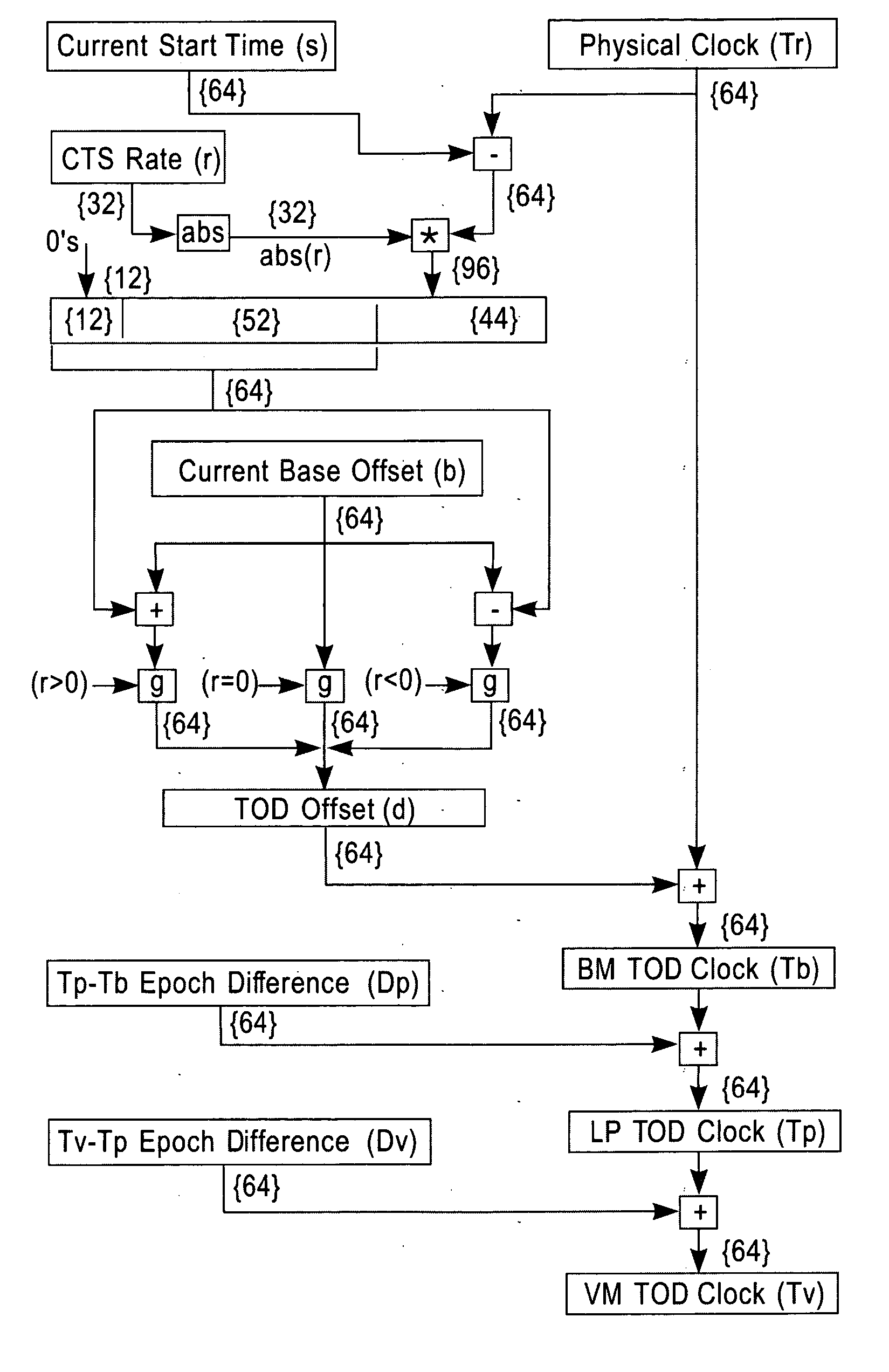
System and method for TOD-clock steering
ActiveUS20070061605A1Minimize overheadError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksClock offsetTime of day
A system, method and computer program product for steering a time-of-day (TOD) clock for a computer system having a physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepped to a common oscillator. The method includes computing a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical-clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD-clock value (Tb), where the logical TOD-clock value is adjustable without adjusting a stepping rate of the oscillator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for adjusting a time of day clock without adjusting the stepping rate of an oscillator
ActiveUS7356725B2Minimize overheadError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksClock offsetComputerized system
A system, method and computer program product for steering a time-of-day (TOD) clock for a computer system having a physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepped to a common oscillator. The method includes computing a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical-clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD-clock value (Tb), where the logical TOD-clock value is adjustable without adjusting a stepping rate of the oscillator.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
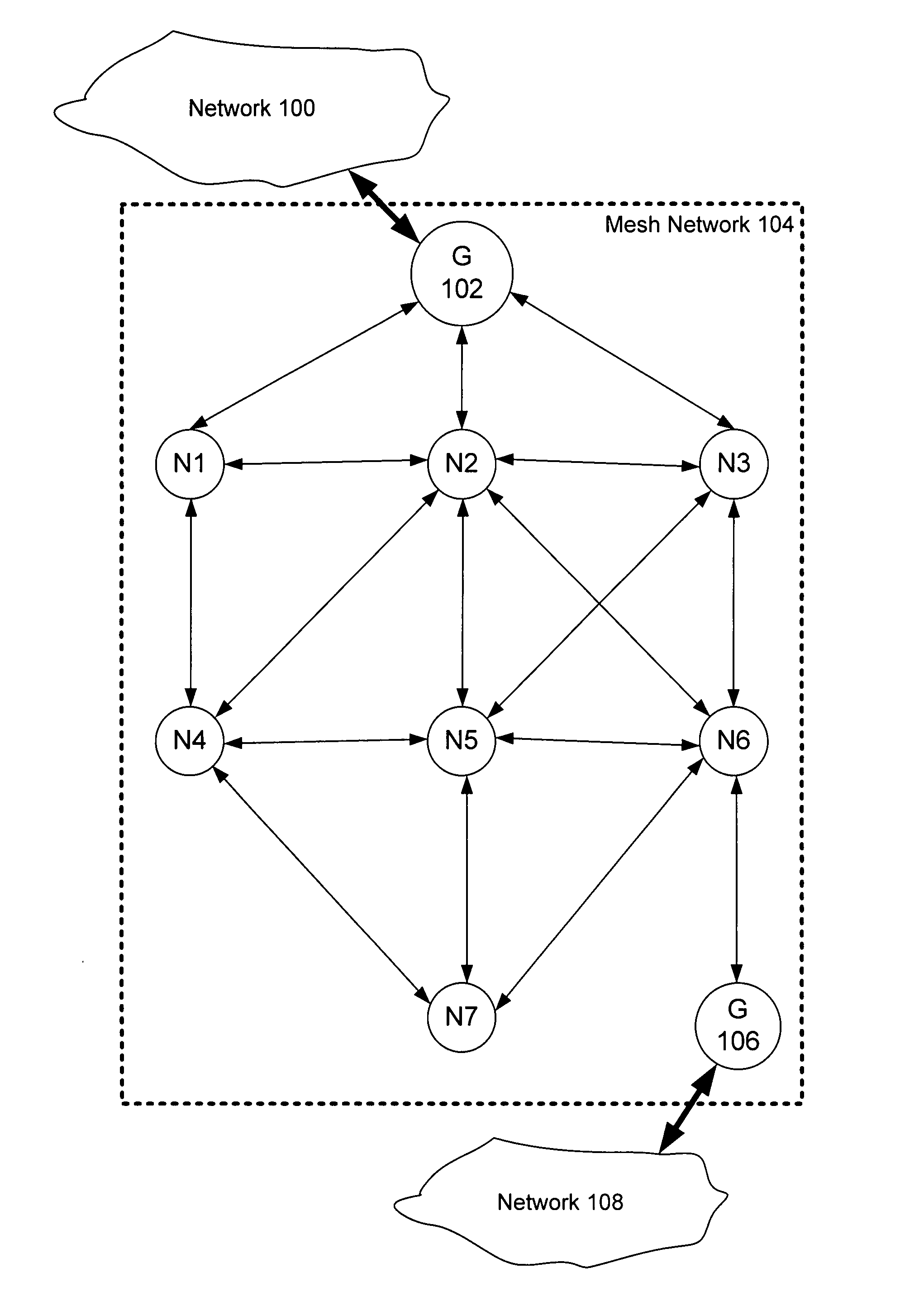
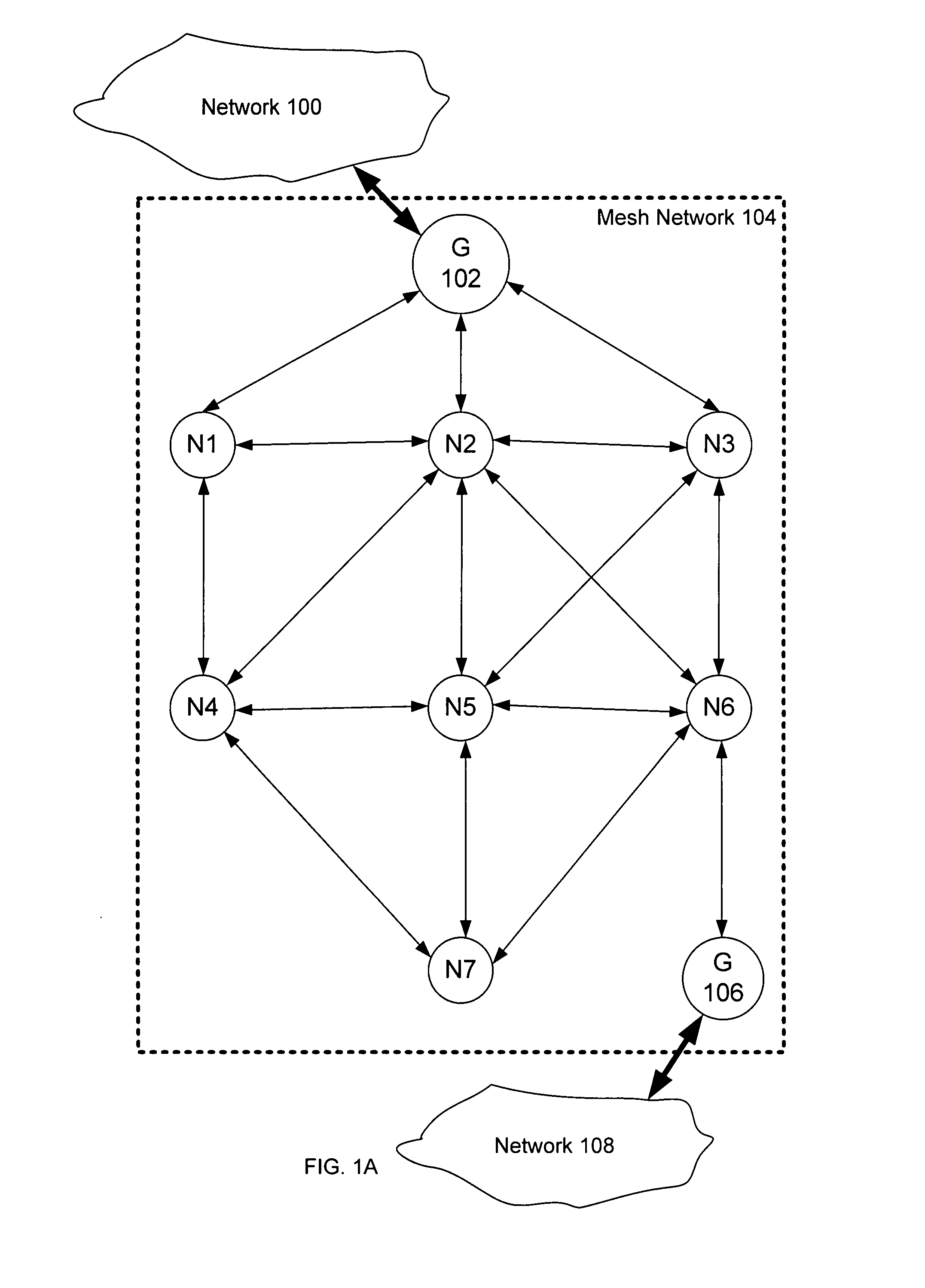
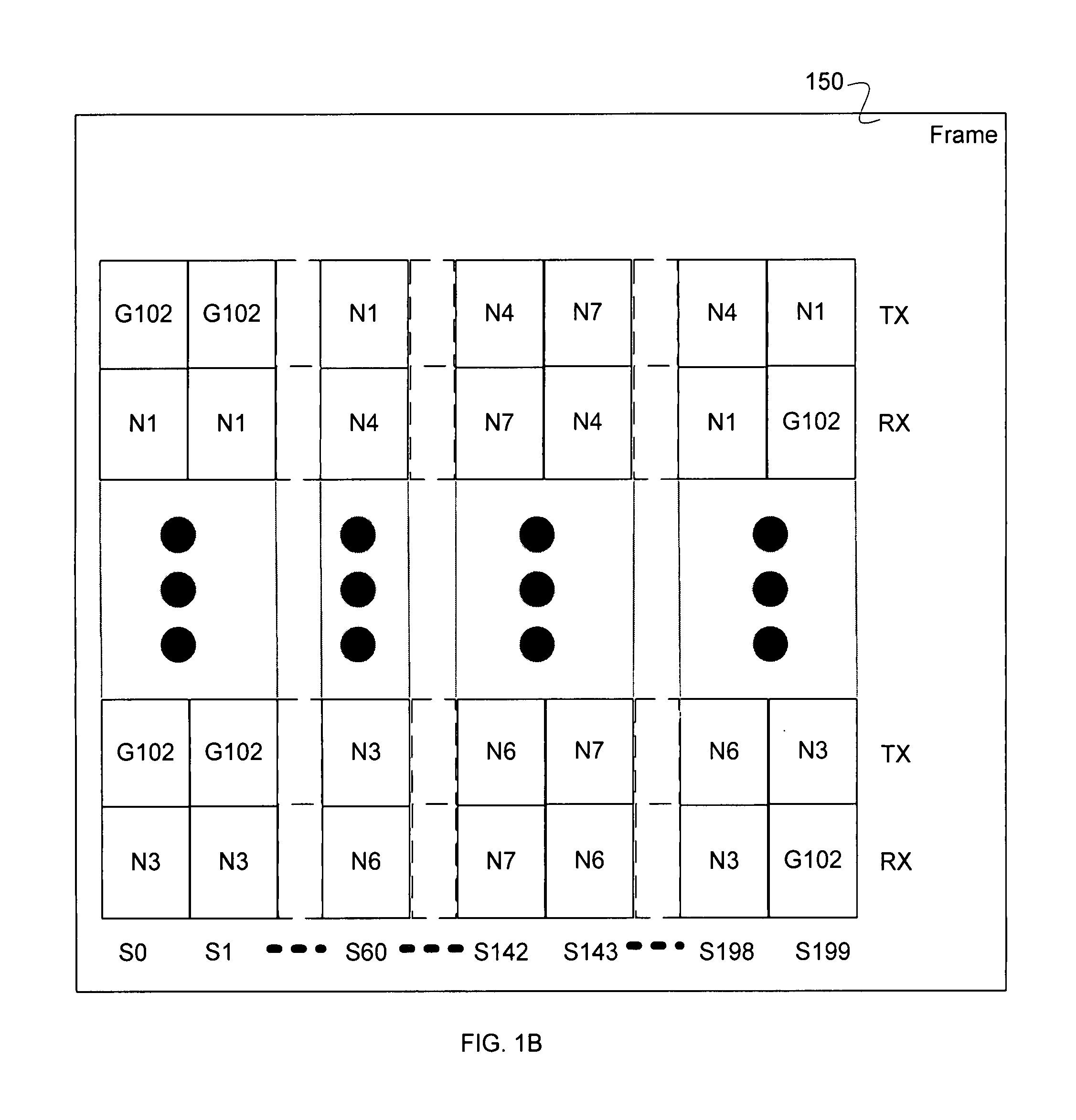
Adaptive timing synchronization for mesh networks
Timing synchronization for mesh networks is disclosed. A temperature calibration data is received. A plurality of previously stored calibration values each corresponding to different temperatures is adjusted based at least in part on the received temperature calibration data. A temperature measurement is received. A first clock offset is determined based at least in part on the adjusted plurality of previously stored calibration values and the temperature measurement.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
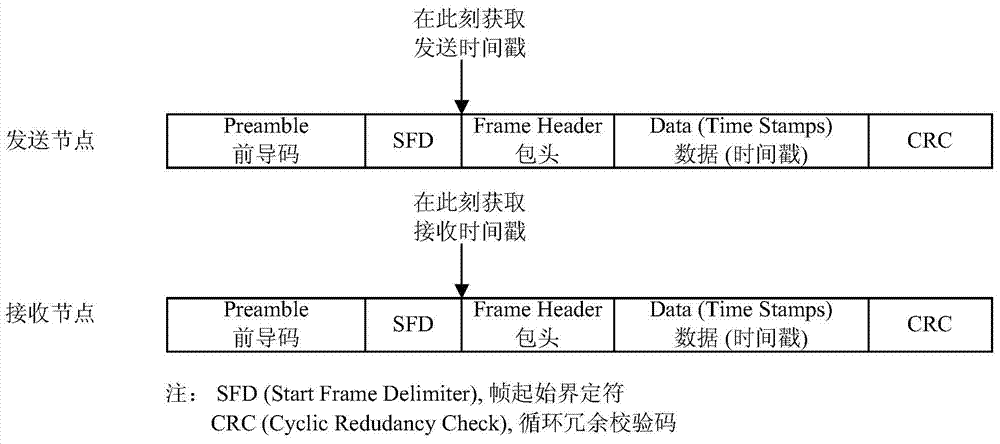
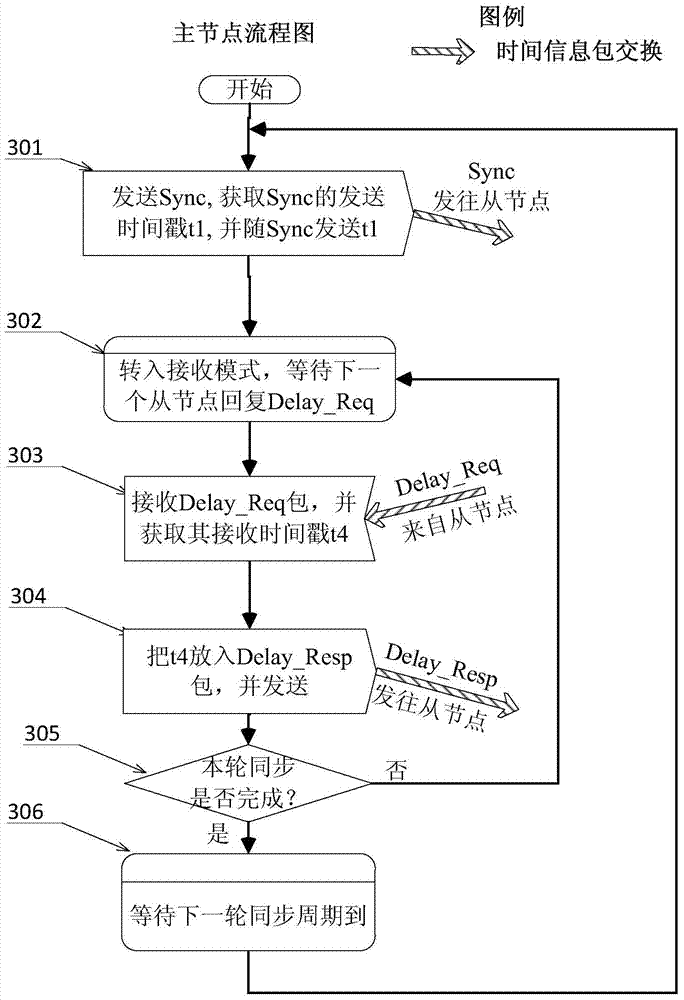
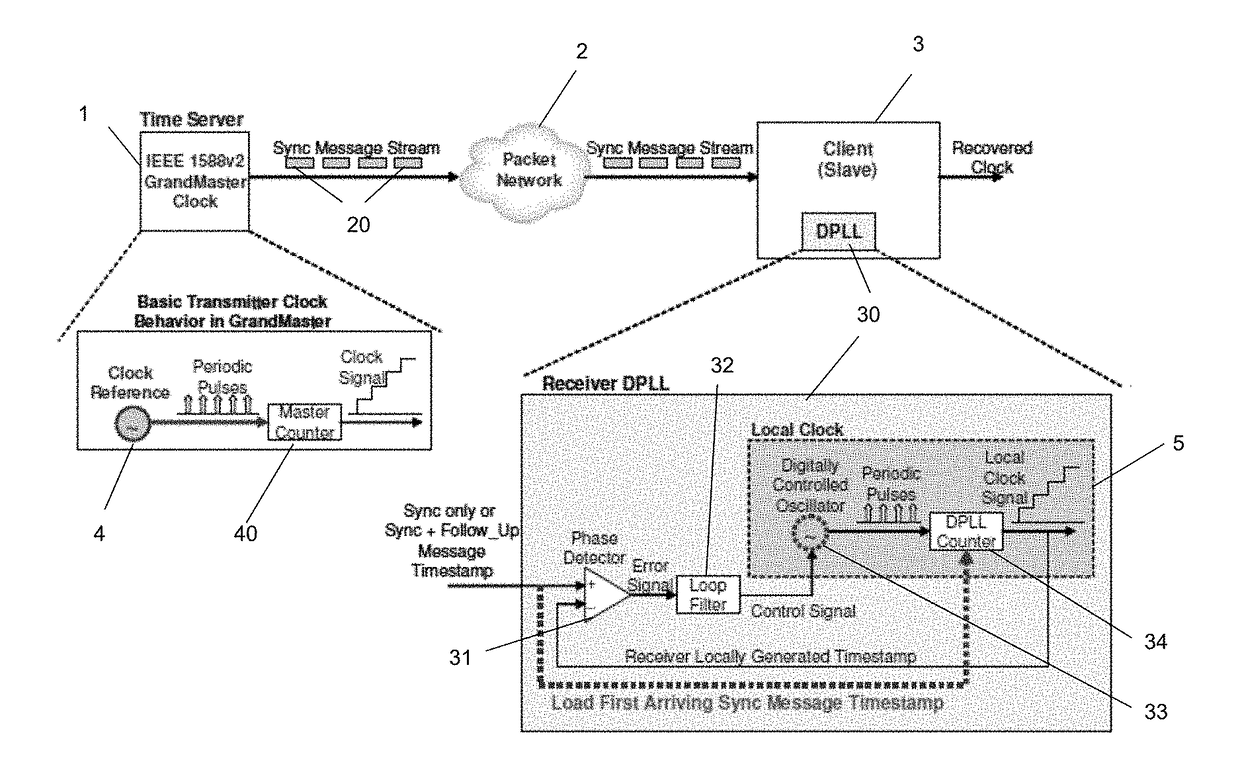
Improved method for time synchronization based on IEEE 1588 PTP mechanism for wireless network
InactiveCN104507156ATime synchronizationTime Synchronization Time for Synchronization MechanismSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexClock offsetEngineering
The invention relates to an improved method for time synchronization based on an IEEE 1588 PTP mechanism for a wireless network. The method is characterized by monitoring and intercepting a time information packet of the other adjacent nodes and a main node while exchanging according to the IEEE 1588 PTP mechanism during a time synchronization packet exchanging process under the condition of complying with an IEEE 1588 PTP time information packet exchange mechanism, thereby realizing a slave-slave synchronizing mechanism. The solution is used for expanding the IEEE 1588 PTP master-slave synchronization and can acquire much more time information; under the condition of utilizing the information redundancy acquired from the slave-slave synchronizing mechanism, a linear regression method is adopted for a slave node, so that the estimation for clock offset and frequency shift is more accurate and reliable; the influences caused by dissymmetry of main-secondary paths and insufficient accuracy of timestamp are weakened; the high-precision and high-reliability time synchronization is realized in the wireless network.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method and device for calibrating local clock based on satellite time service
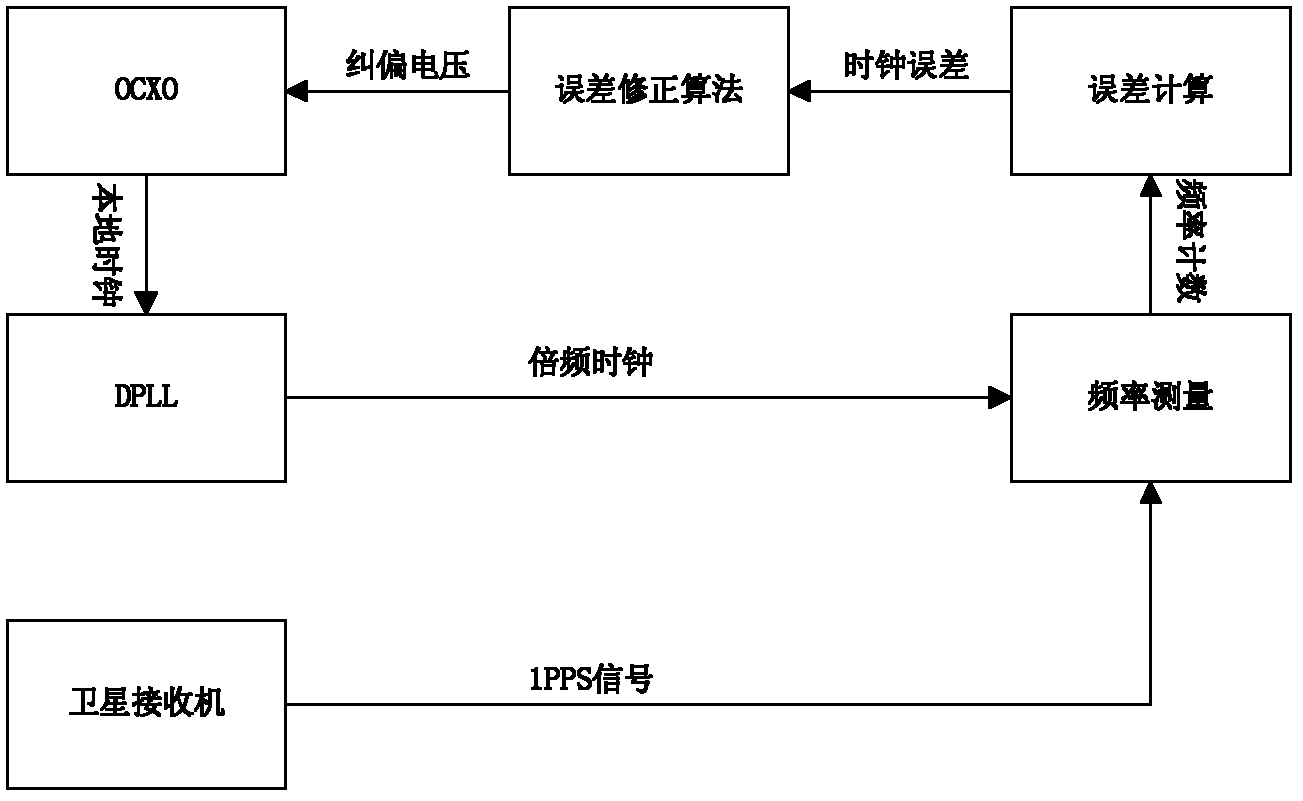
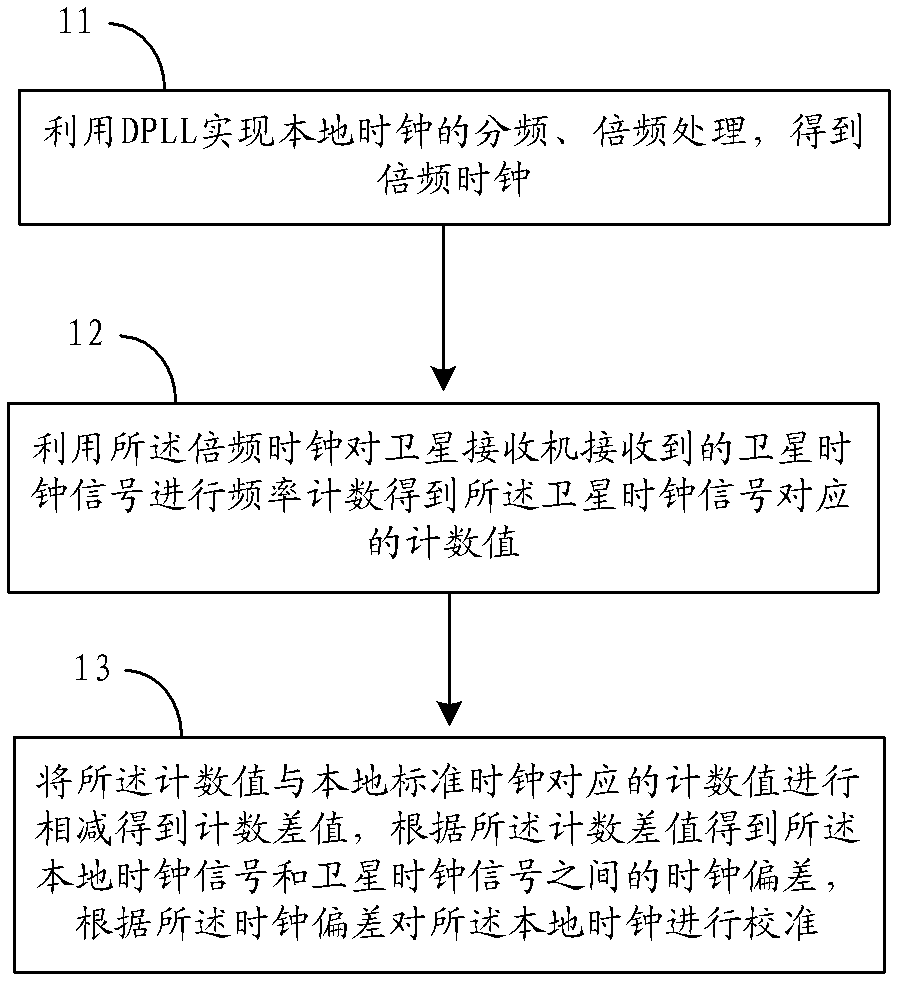
ActiveCN102566410AGet biasSynchronous motors for clocksSetting time indicationClock offsetEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for calibrating a local clock based on satellite time service. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: performing frequency multiplication on a local clock signal by using a digital phase-locked loop to acquire a frequency multiplication clock; performing frequency counting on a satellite clock signal received by a satellite receiver by using the frequency multiplication clock to acquire a count value corresponding to the satellite clock signal, and subtracting the count value from a count value corresponding to a local standard clock to acquire a count difference value; and acquiring clock offset between the local clock signal and the satellite clock signal according to the count difference value, and calibrating the local clock according to the clock offset. By the method and the device provided by the embodiment of the invention, the satellite clock signal is subjected to frequency counting through the frequency multiplication clock, so that the offset between the local clock signal and a clock signal output by a global positioning system (GPS) / Beidou satellite navigation system can be quickly acquired, and input parameters can be provided for a local clock control algorithm.
Owner:华力智芯(成都)集成电路有限公司
Method for cell search under effect of high clock offset
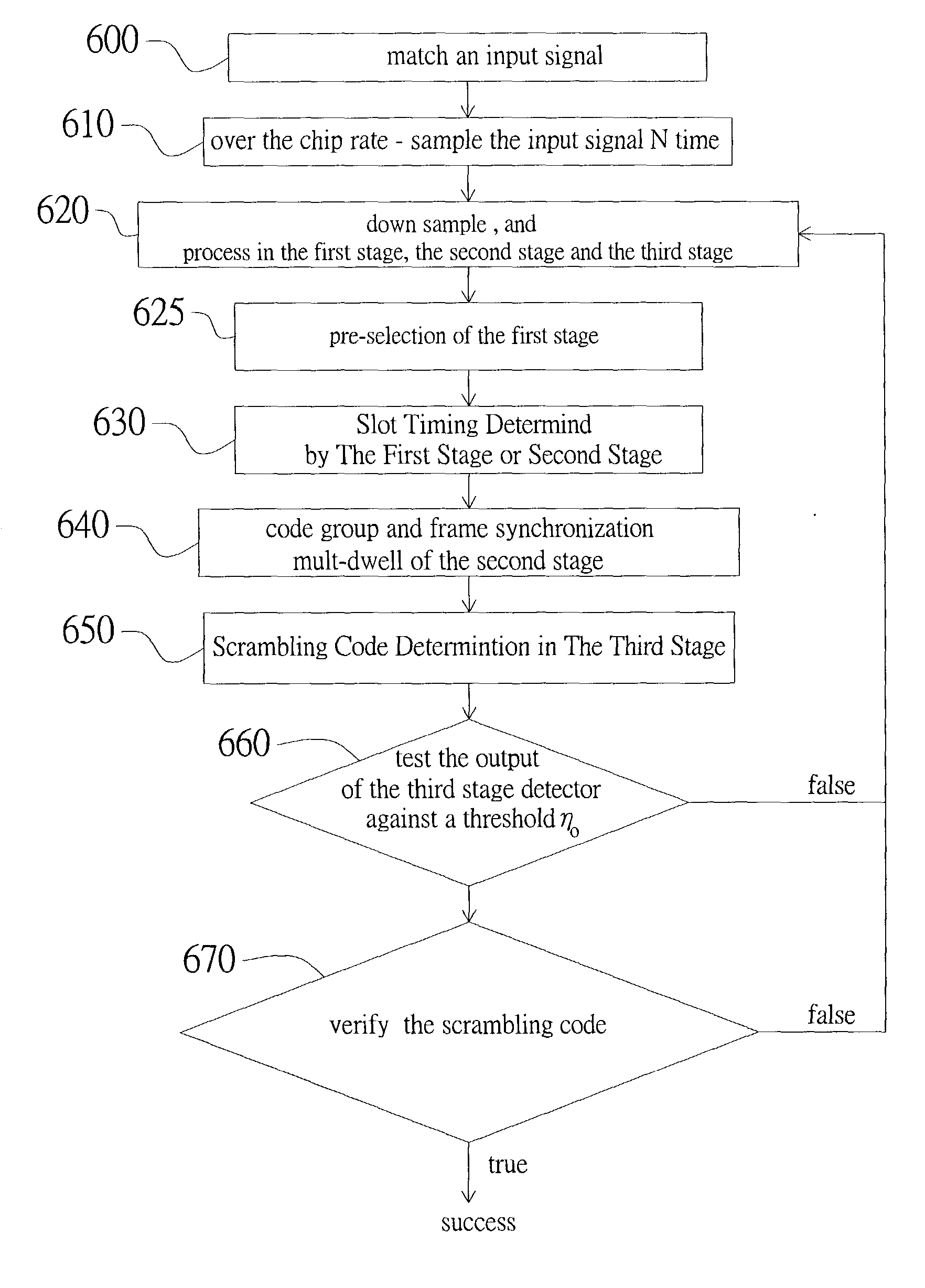
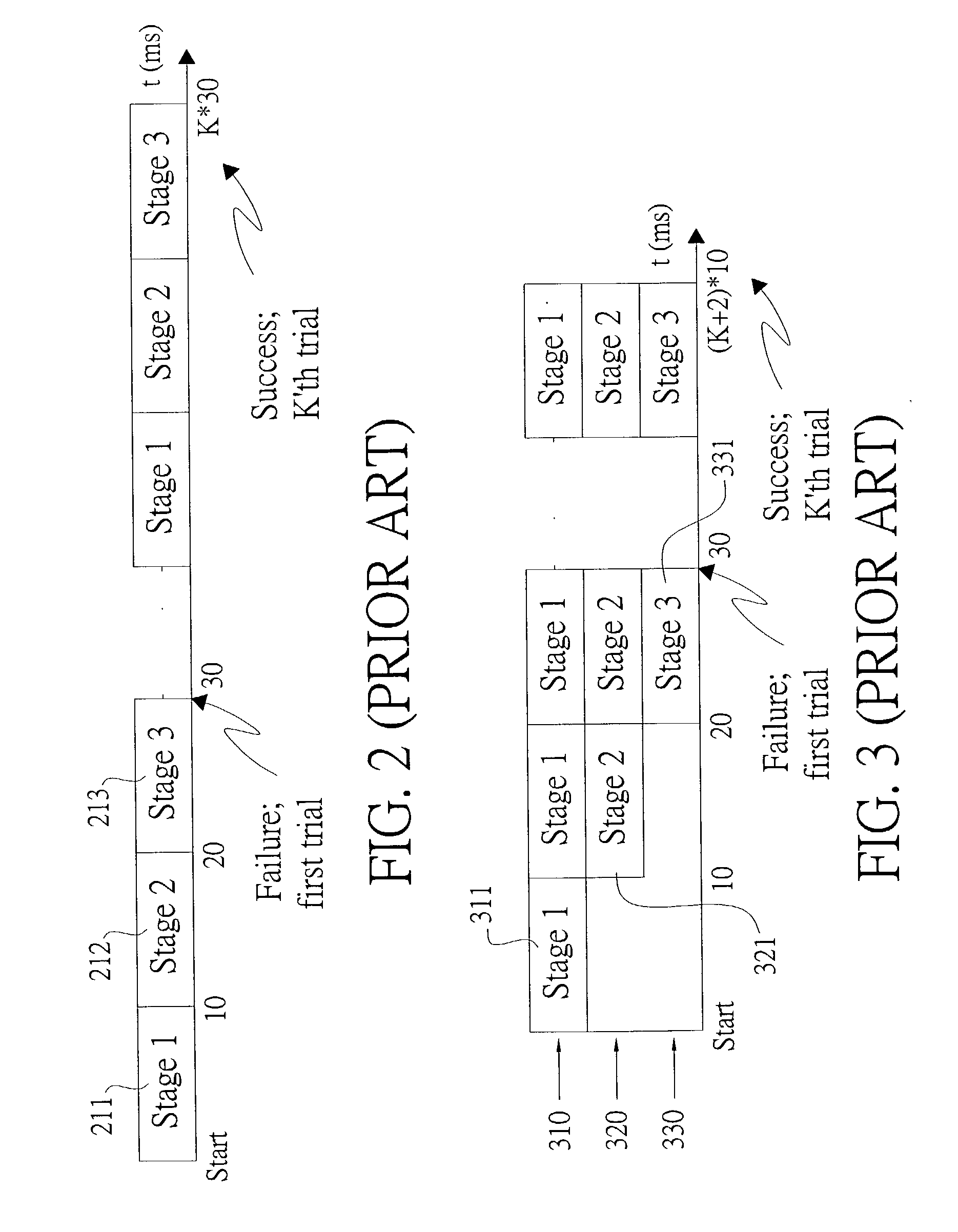
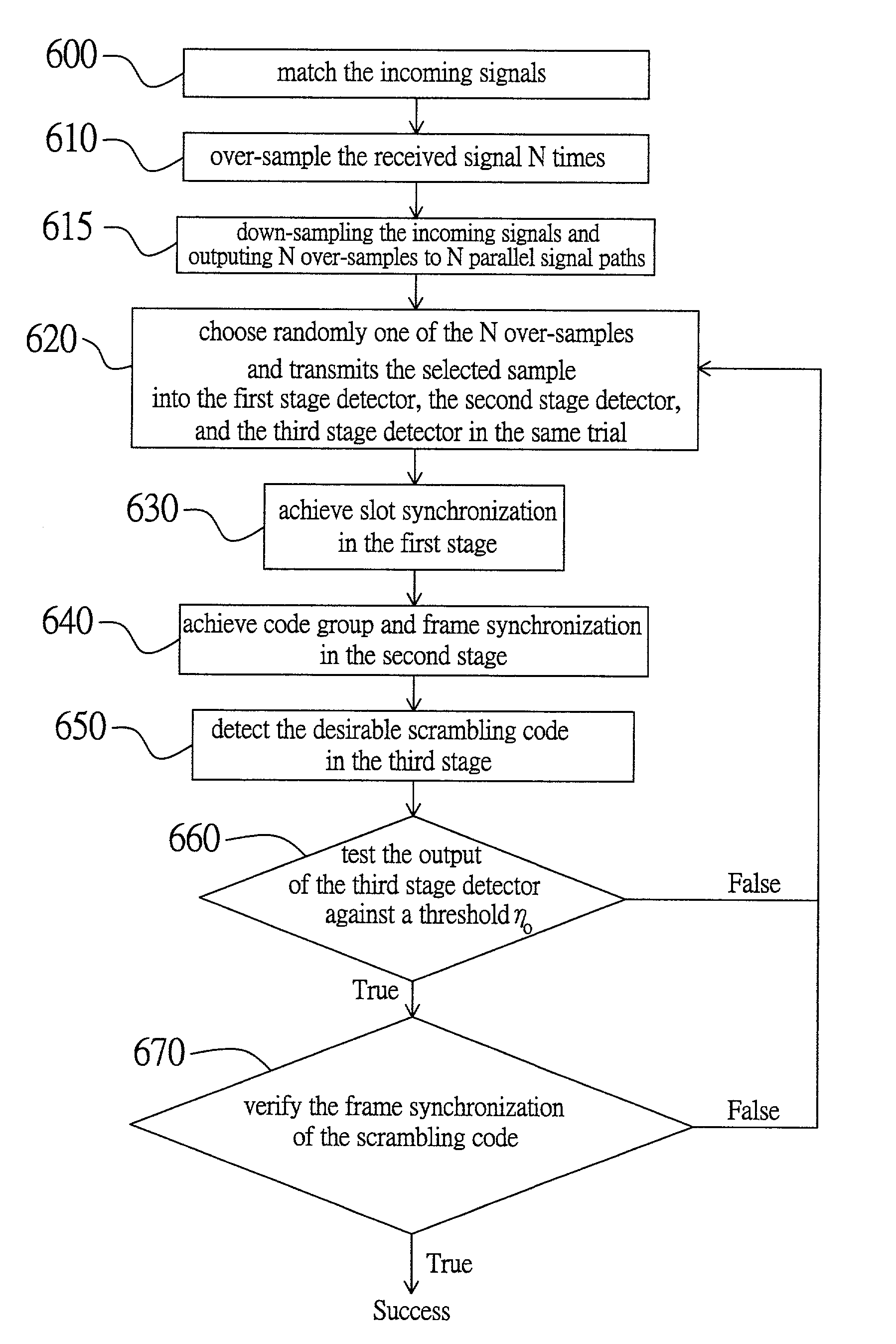
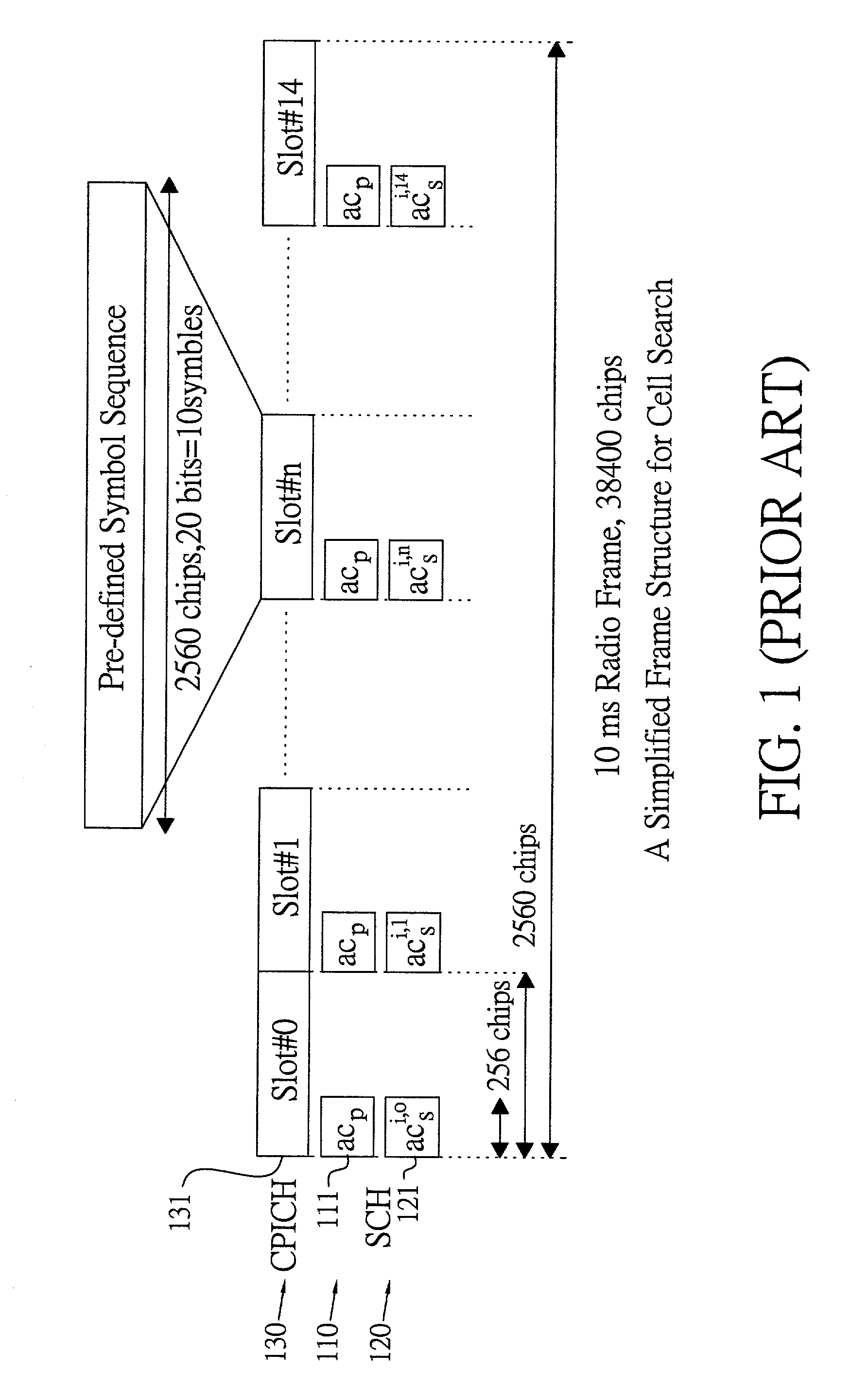
InactiveUS20030193922A1Performance degradation can be reducedHigh clock offsetTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionThree stageClock offset
The present invention discloses a cell search method for a CDMA system, using a three-stage cell search. The method comprises matching an incoming signal from the base station, wherein the frequency of the incoming signal having an uncertain range; over-sampling the incoming signal N times against a chip rate and outputting the N over-samples; down-sampling the incoming signal and outputting N over-samples to a first stage, a second stage and a third stage. The first stage further comprises selecting a first group of slot boundaries as a first group of candidates after pre-selection, and the first group of candidates transmitting to a deciding selection stage of the first stage and the second stage to be continuously processed. The cell search method of the present invention can be used to reduce the effect of clock offset on the performance of cell search and to accomplish fast cell search.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
System for determining position over a network
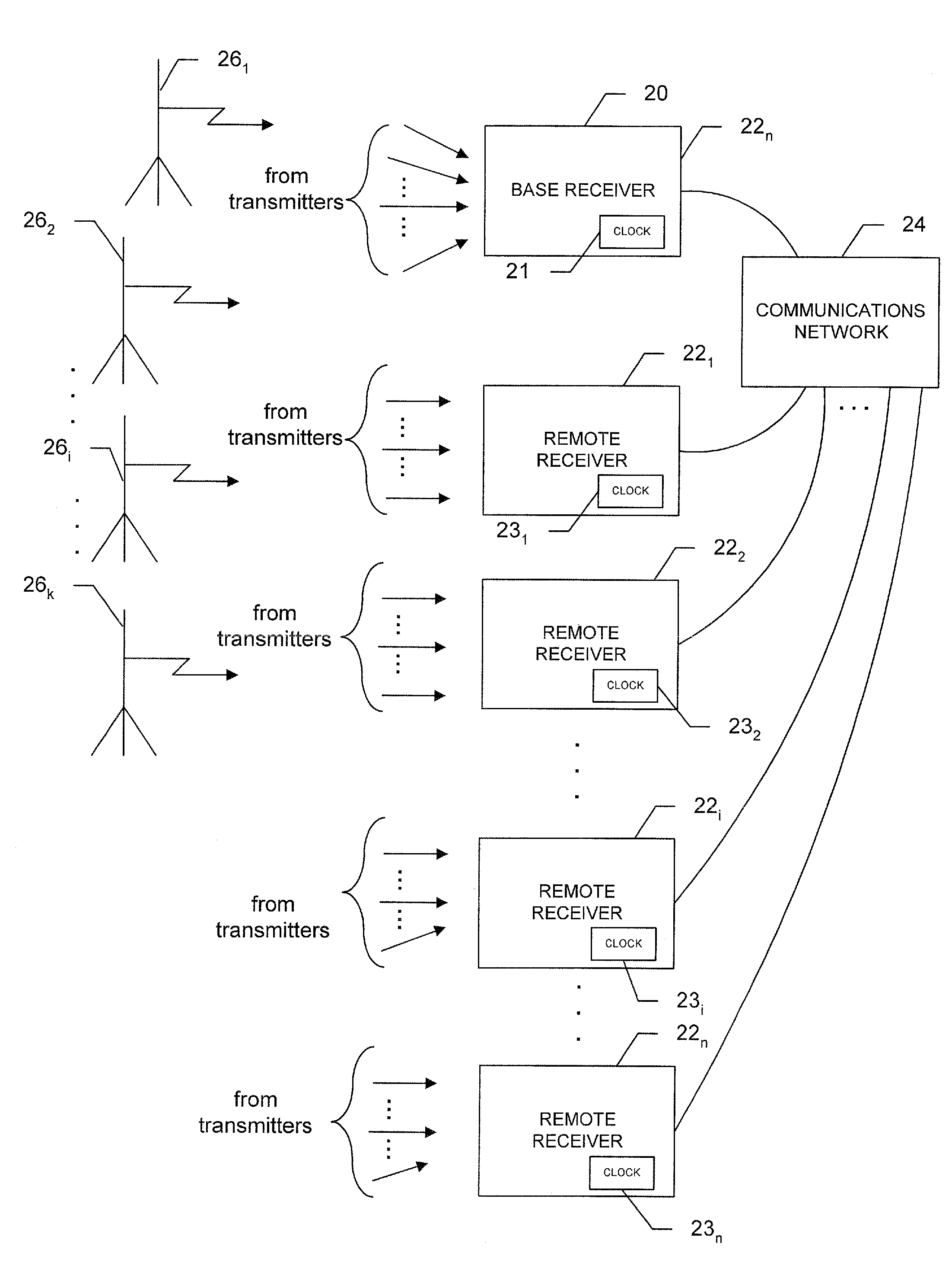
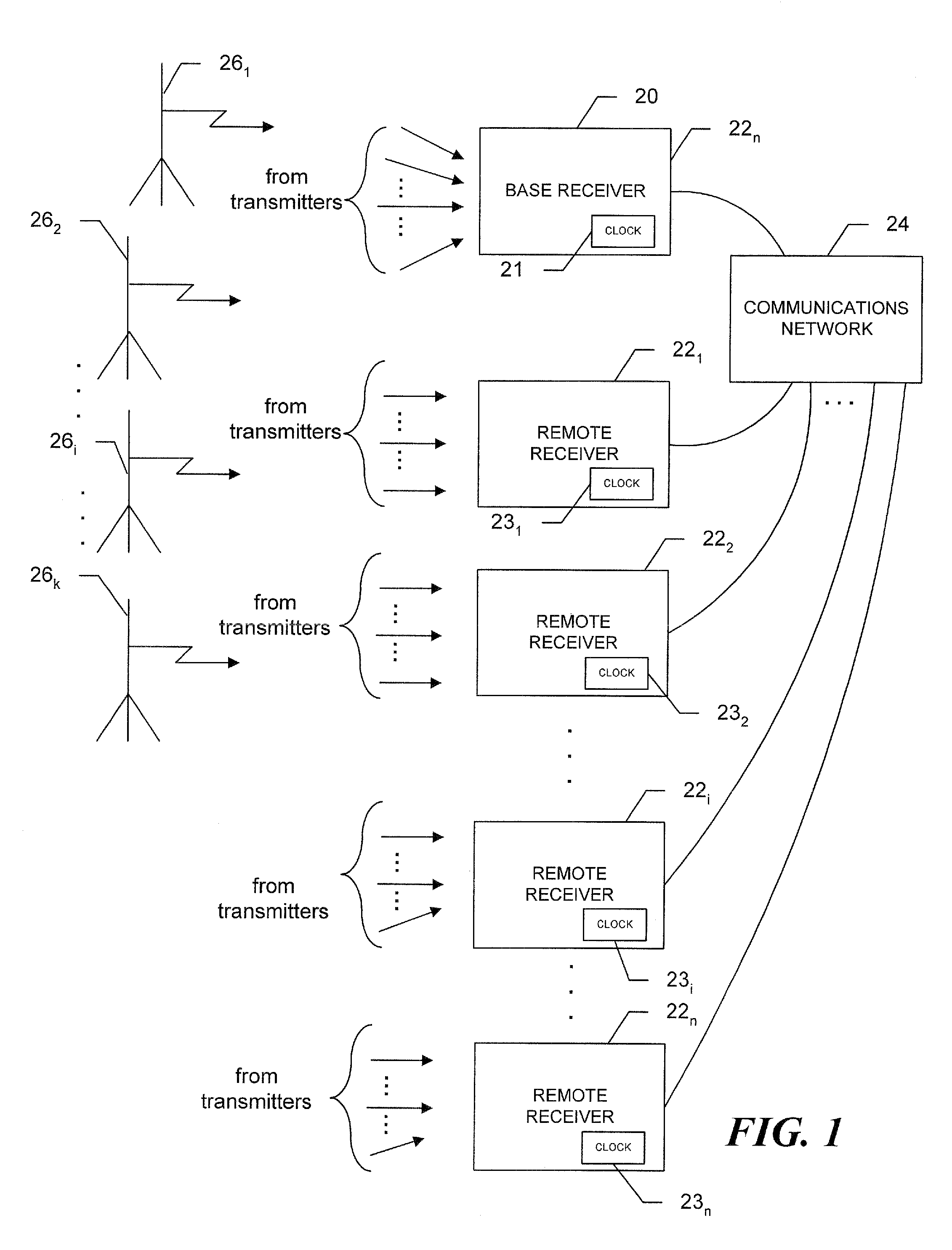
ActiveUS20090121940A1Accurate locationDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationClock offsetNetwork on
A system to determine position, frequency and clock offsets over a network utilizing signals of opportunity transmitted by one or more transmitters with known locations, the system includes a base receiver with a clock and a known position that determines ranges to the transmitters, takes a series of samples of the signals of opportunity and time tags the series with times of receipt, calculated times of transmission based on the calculated ranges, or both. The base receiver transmits the time tagged series and, as appropriate, computed ranges to the remote receivers. A given remote receiver saves and time tags samples of the signals of opportunity, correlates the time-tagged series with the saved samples, and calculates a time offset as a time difference of the times of receipt at the remote receiver and either the time of receipt at the base receiver or the time of transmission calculated at the base receiver. The remote receiver calculates position based on the time offsets, and as appropriate, the ranges provided by the base receiver. The elevations of the remote receivers may be calculated as part of the position calculations, determined iteratively based on constraining the Z coordinate to an average elevation, or determined from differences in air pressure sensor readings at the base and remoter receivers.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
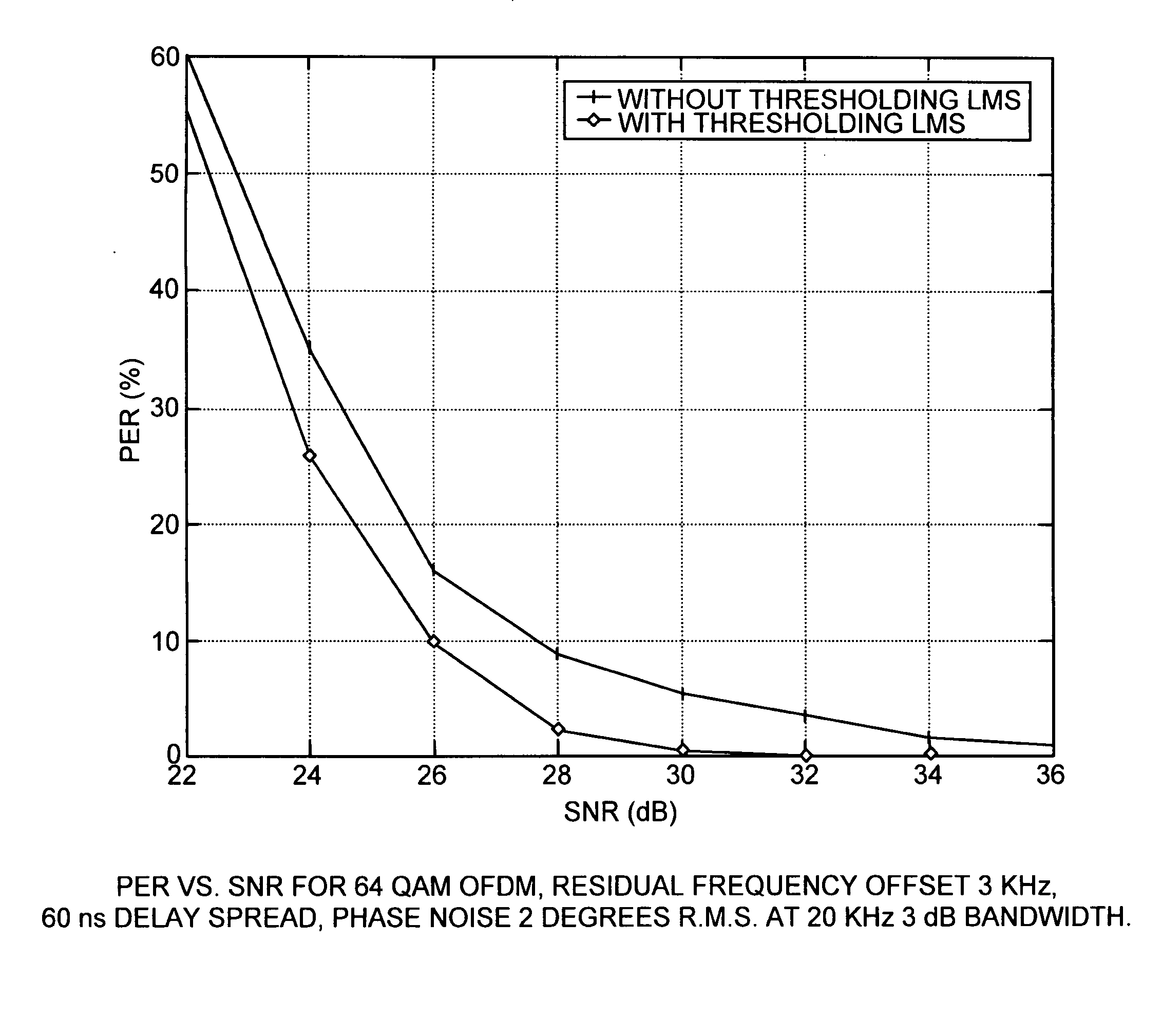
Novel receiver architecture for pilot based OFDM systems
InactiveUS20090073869A1Robust and cost-effectiveEfficient use ofMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexPhase noiseClock offset
The invention relates to a novel methodology and apparatus for clock-offset compensation and common-phase offset correction in Frequency Division Multiplixing based wireless local area network (WLAN) environment, such as an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) environment. A curve fit, such as a threshold-based, least mean squares (LMS) fit of phase of the pilot sub-carriers in each OFDM symbol is used to estimate and counteract the rotation of the data sub-carriers due to residual frequency offset, low frequency phase noise, and clock offset. The invention is particularly well suited to wireless channels with multipath where pilots typically undergo frequency-selective fading. The thresholding LMS is implemented in a hardware-efficient manner, offering cost advantages over a weighted-LMS alternative. Additionally, the invention uses a unique phase-feedback architecture to eliminate the effects of phase wrapping, and avoid the need to refine channel estimates during packet reception.
Owner:EDGEWATER WIRELESS SYST
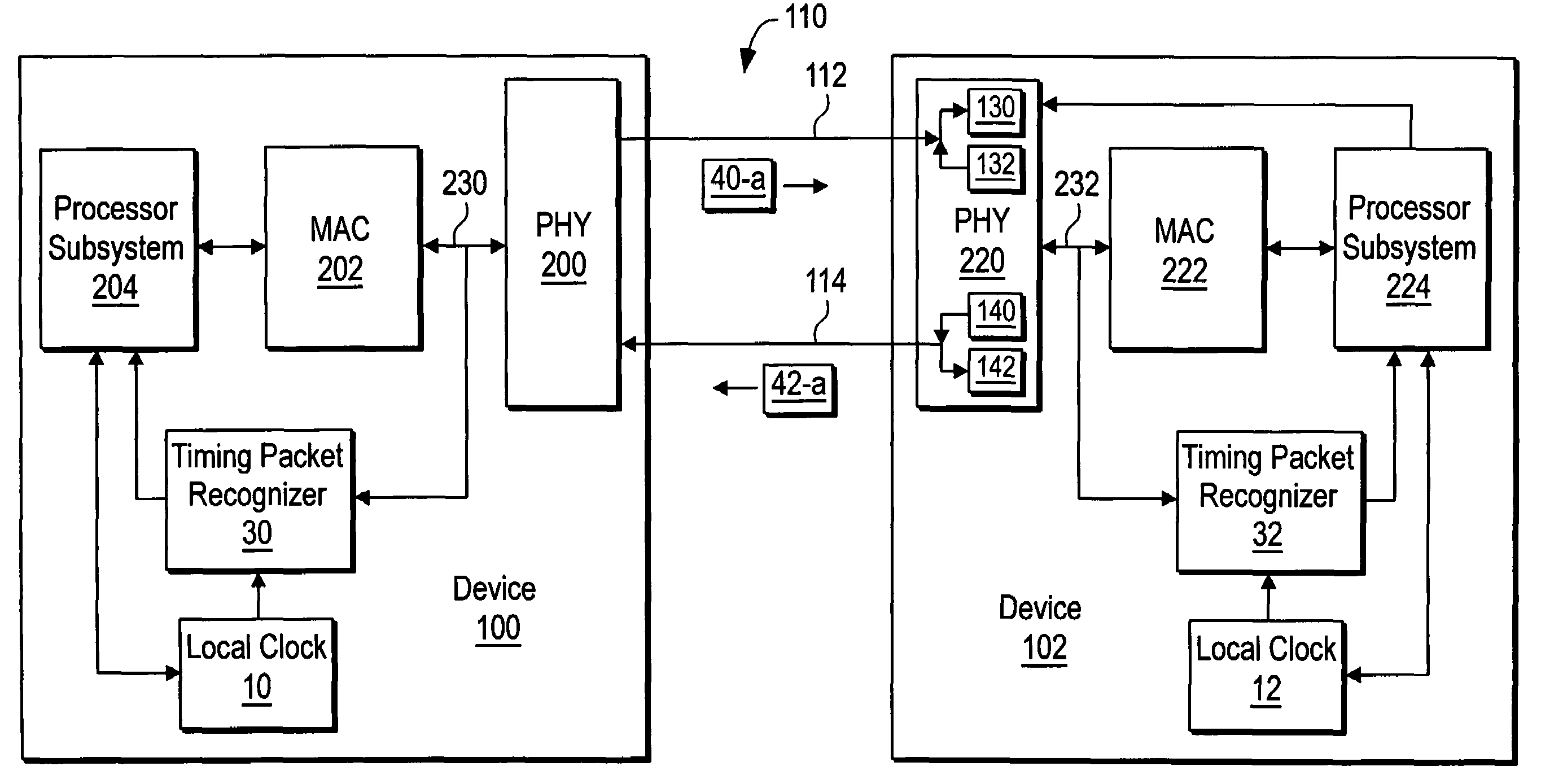
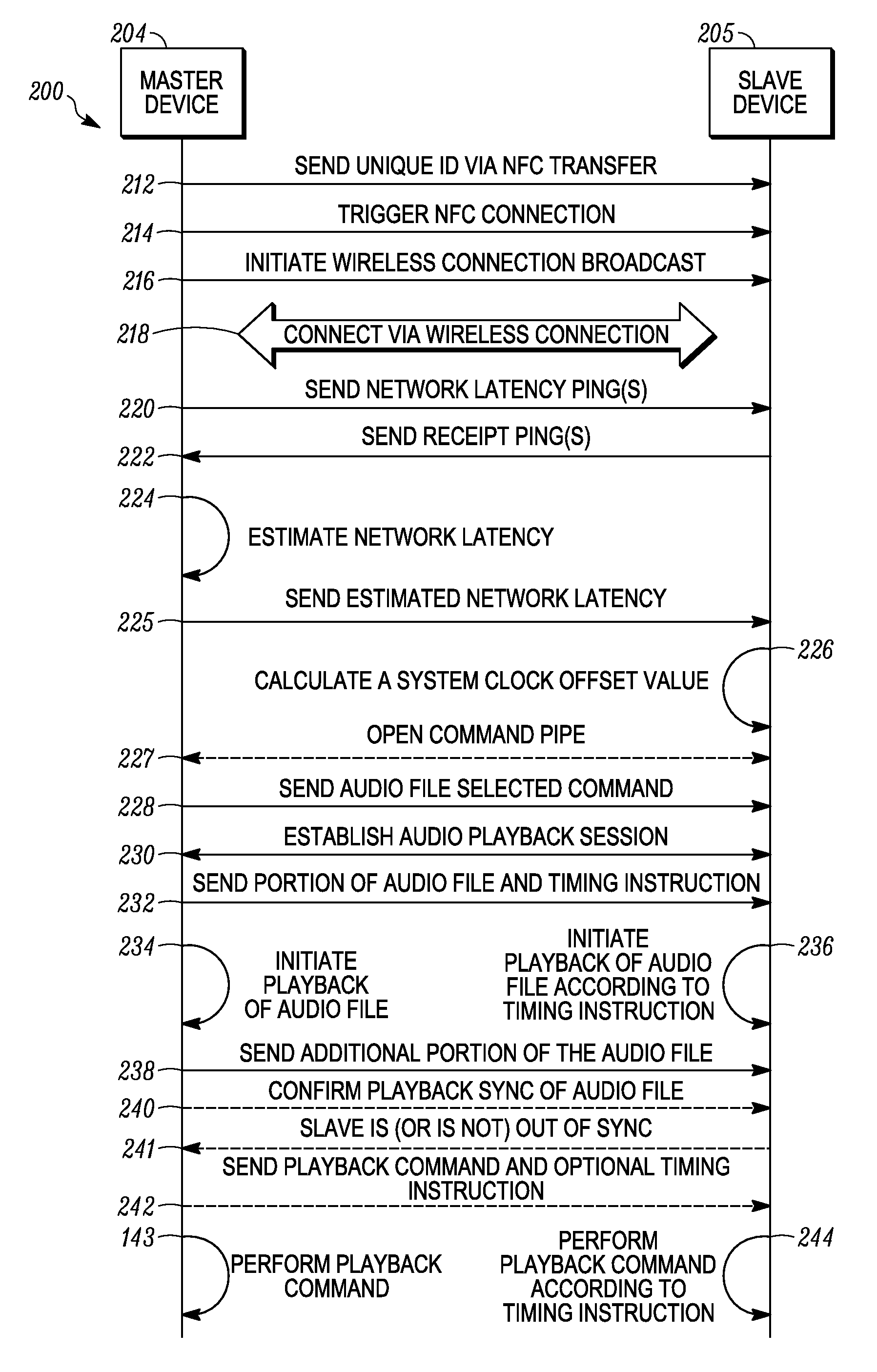
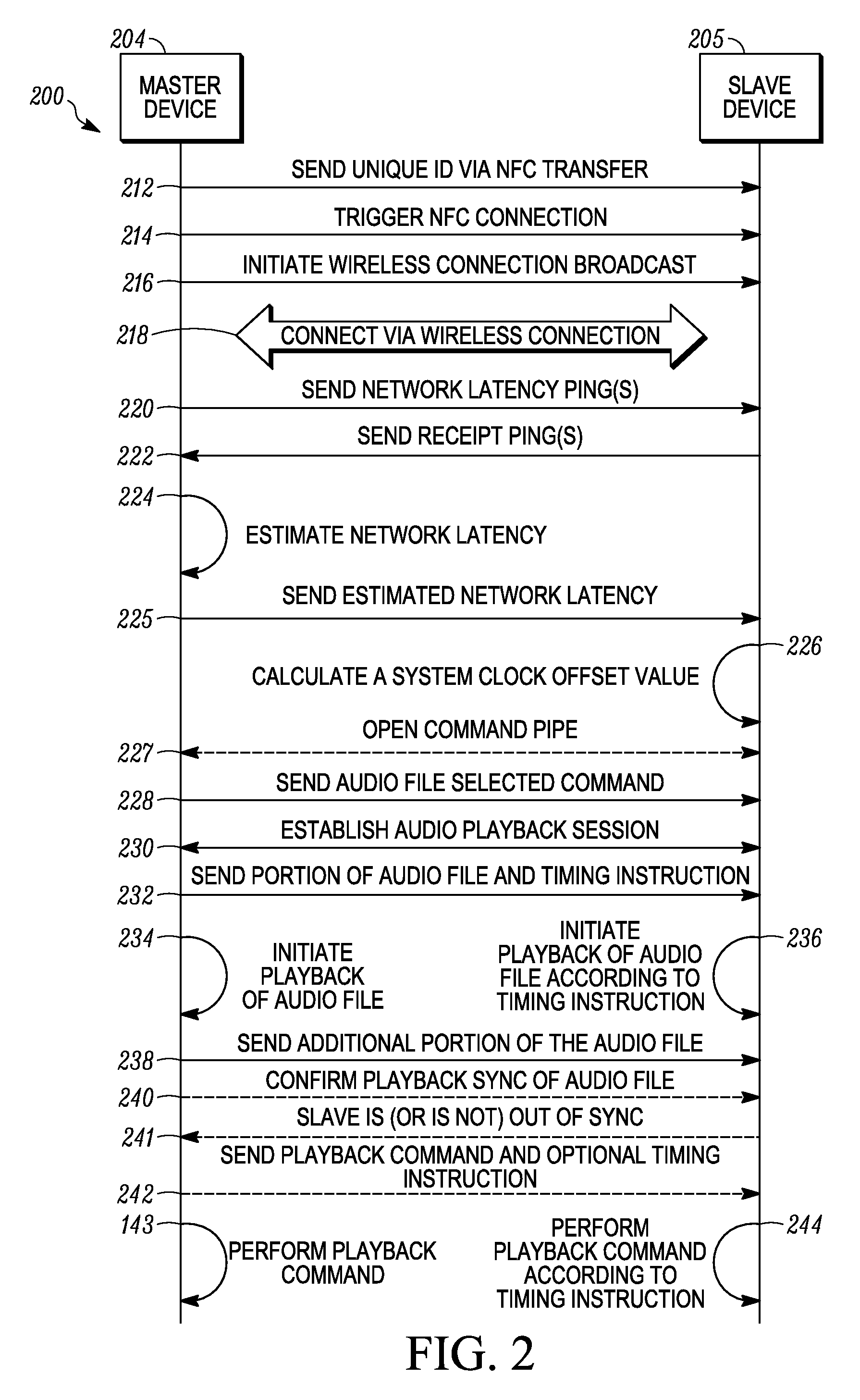
Systems and methods for syncronizing multiple electronic devices
Embodiments are provided for syncing multiple electronic devices for collective audio playback. According to certain aspects, a master device connects (218) to a slave device via a wireless connection. The master device calculates (224) a network latency via a series of network latency pings with the slave device and sends (225) the network latency to the slave device. Further, the master devices sends (232) a portion of an audio file as well as a timing instruction including a system time to the slave device. The master device initiates (234) playback of the portion of the audio file and the slave devices initiates (236) playback of the portion of the audio file according to the timing instruction and a calculated system clock offset value.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and devices for synchronization using linear programming
This invention relates to methods and devices for synchronization using linear programming, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a two-dimensional linear programming technique for estimating clock offset and skew, particularly from two-way exchange of timing messages between a master and a slave device. Some embodiments include a skew and offset adjustable free-running counter for regenerating the master time and frequency at the slave device.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
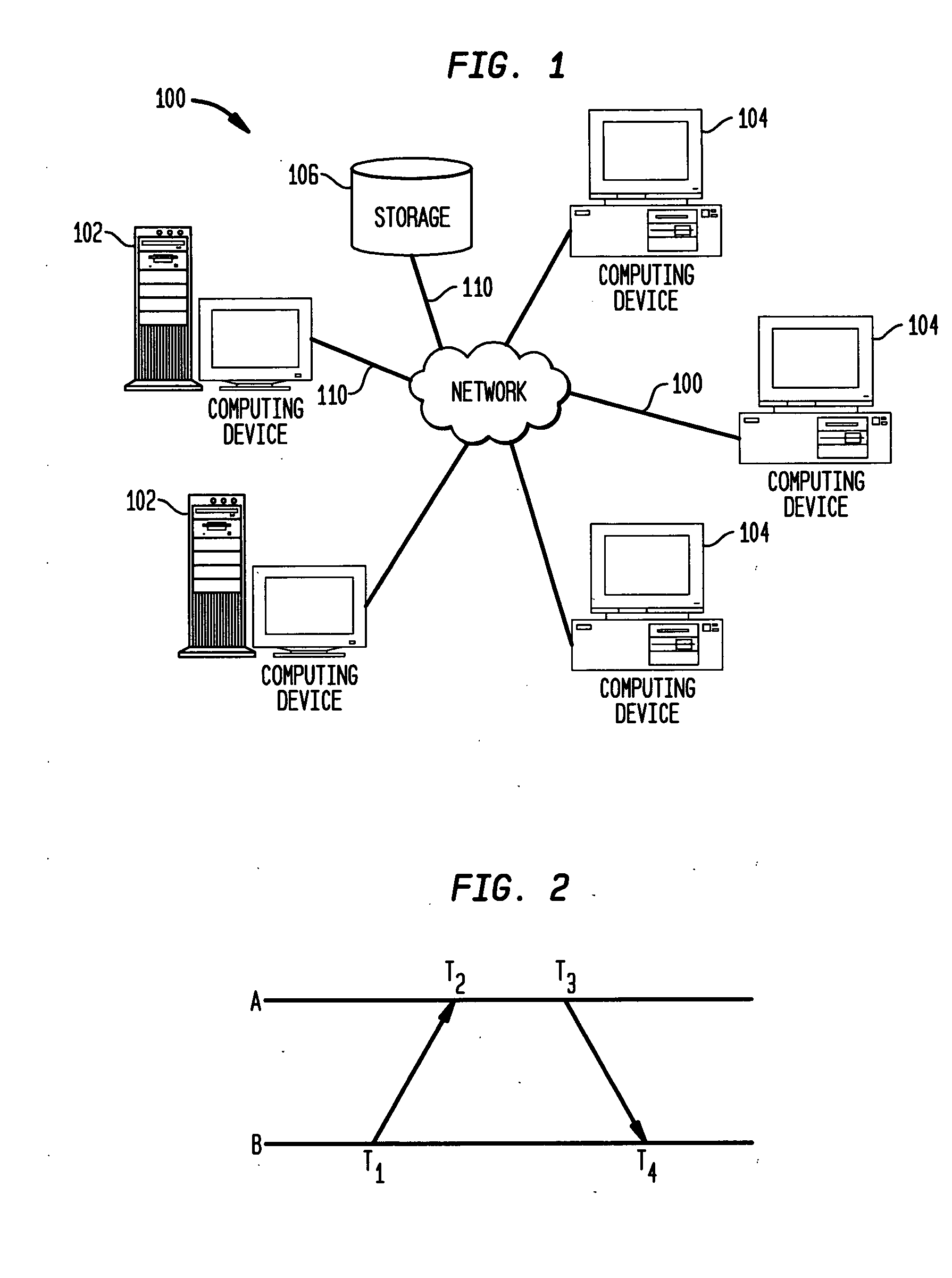
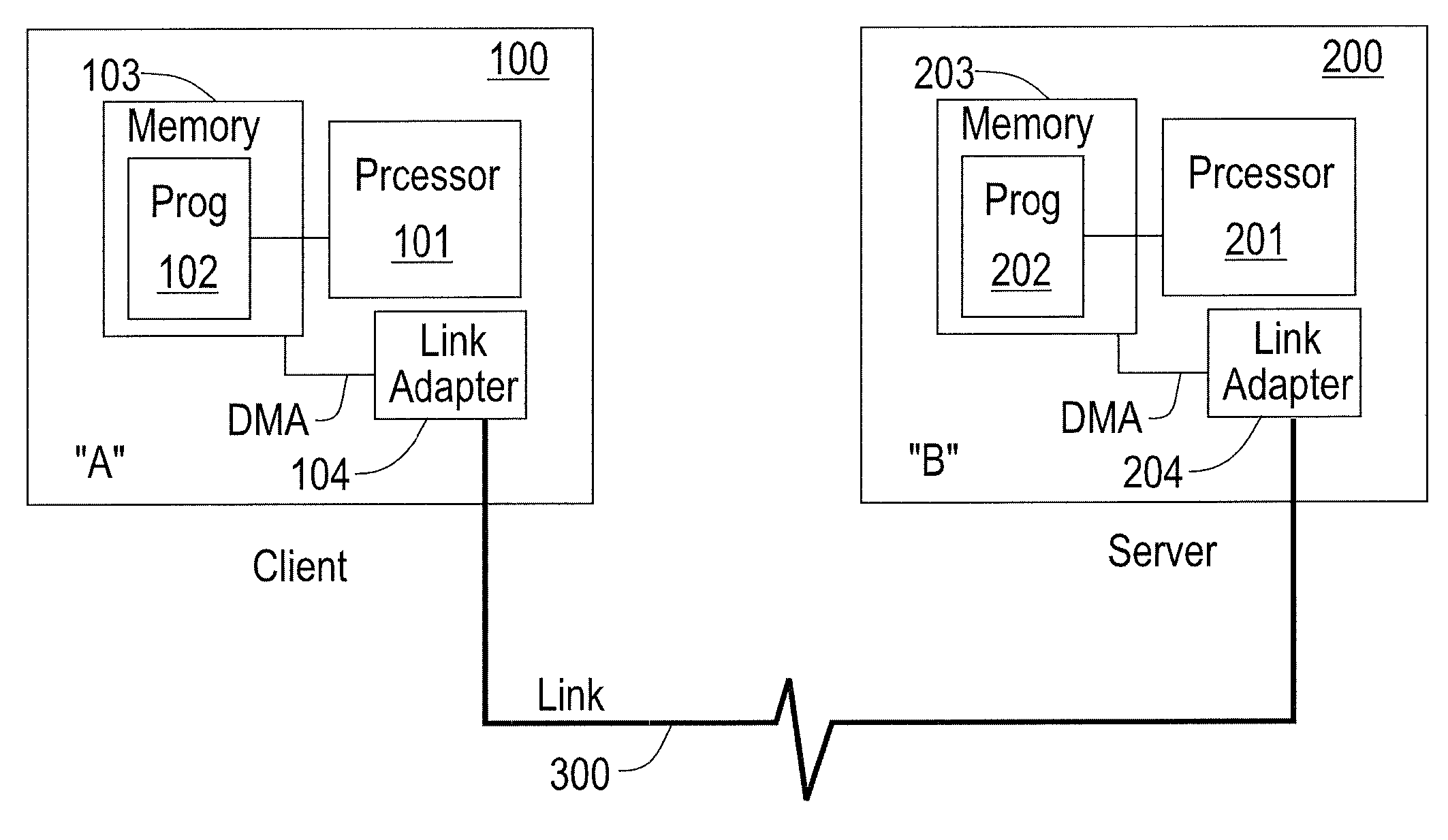
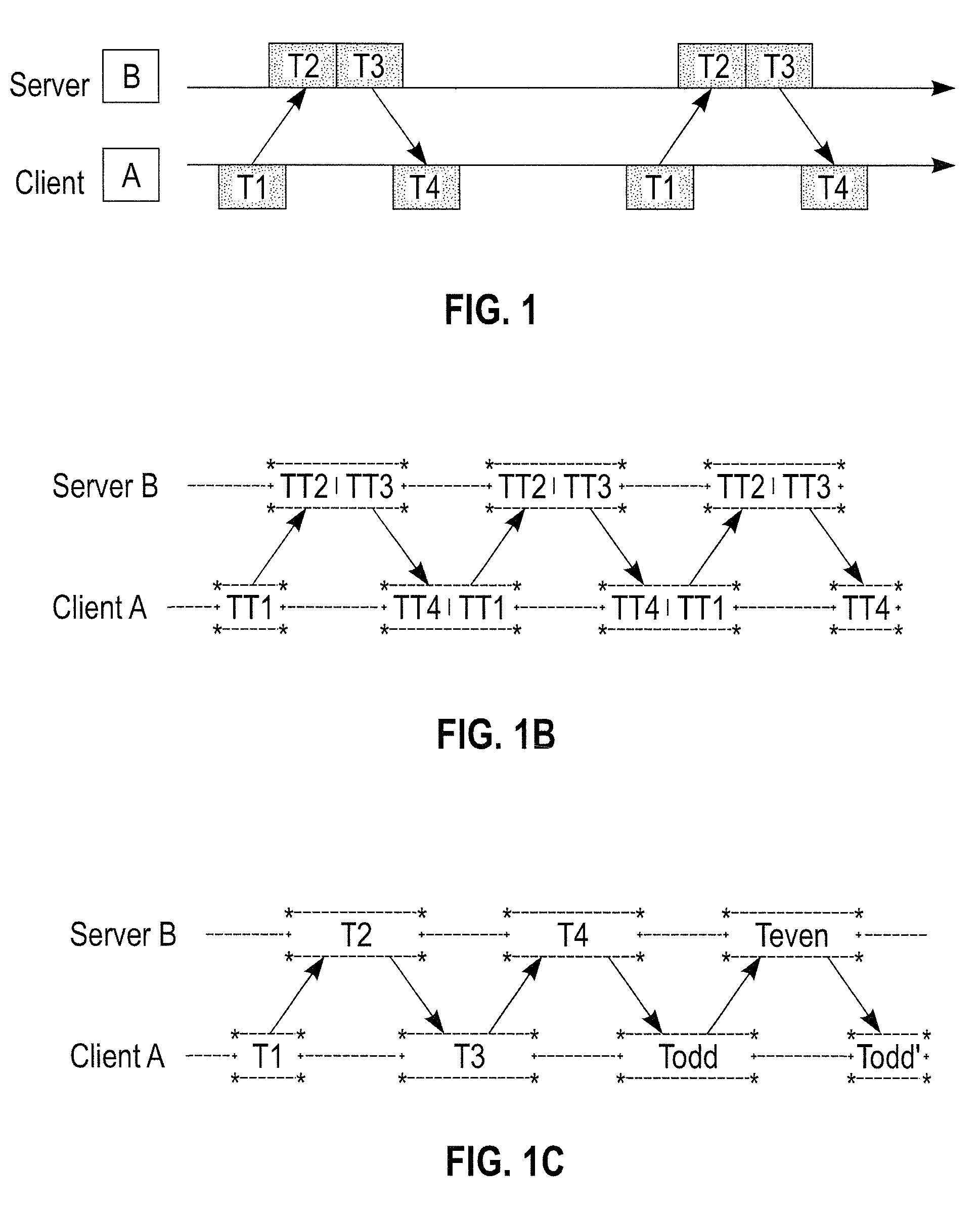
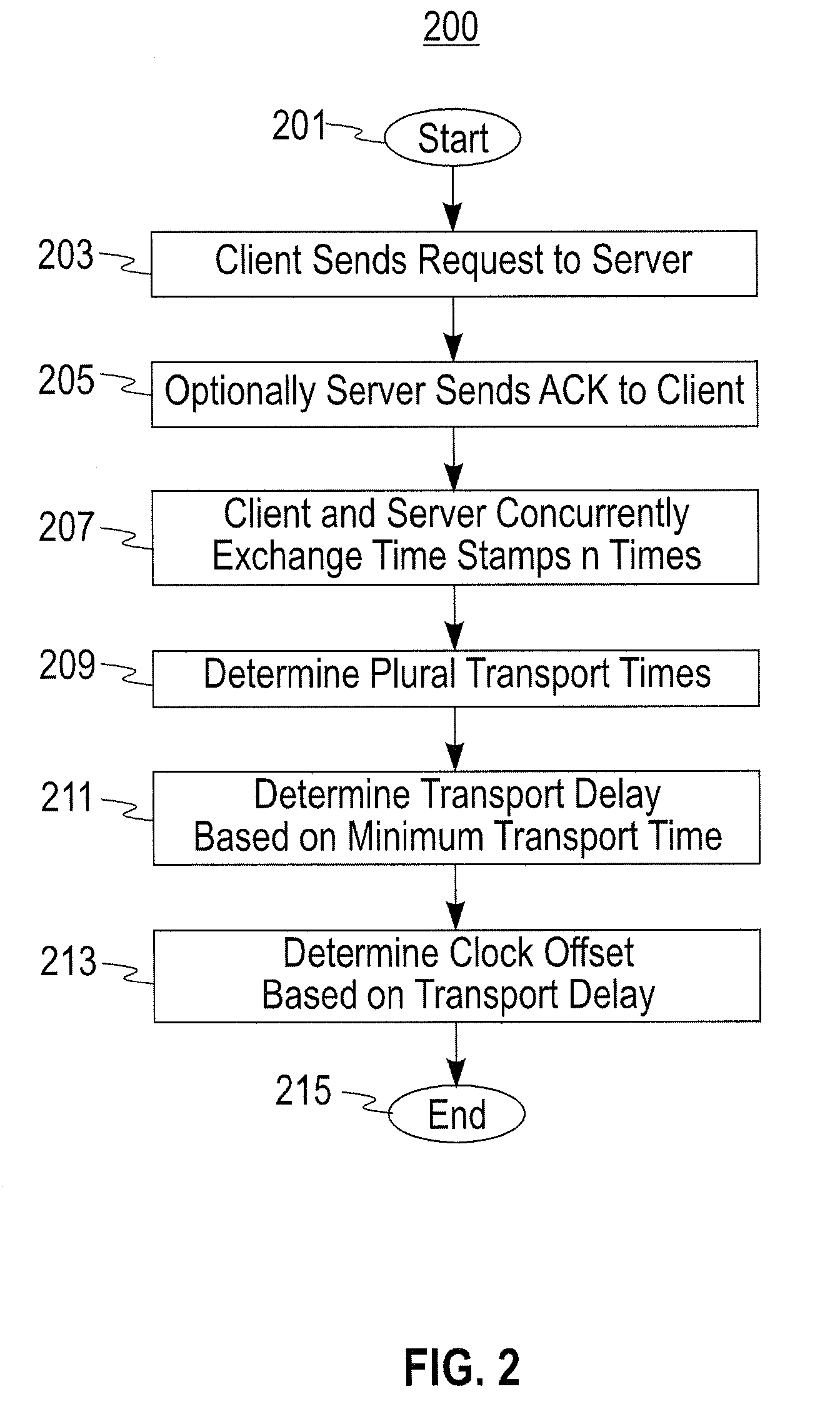
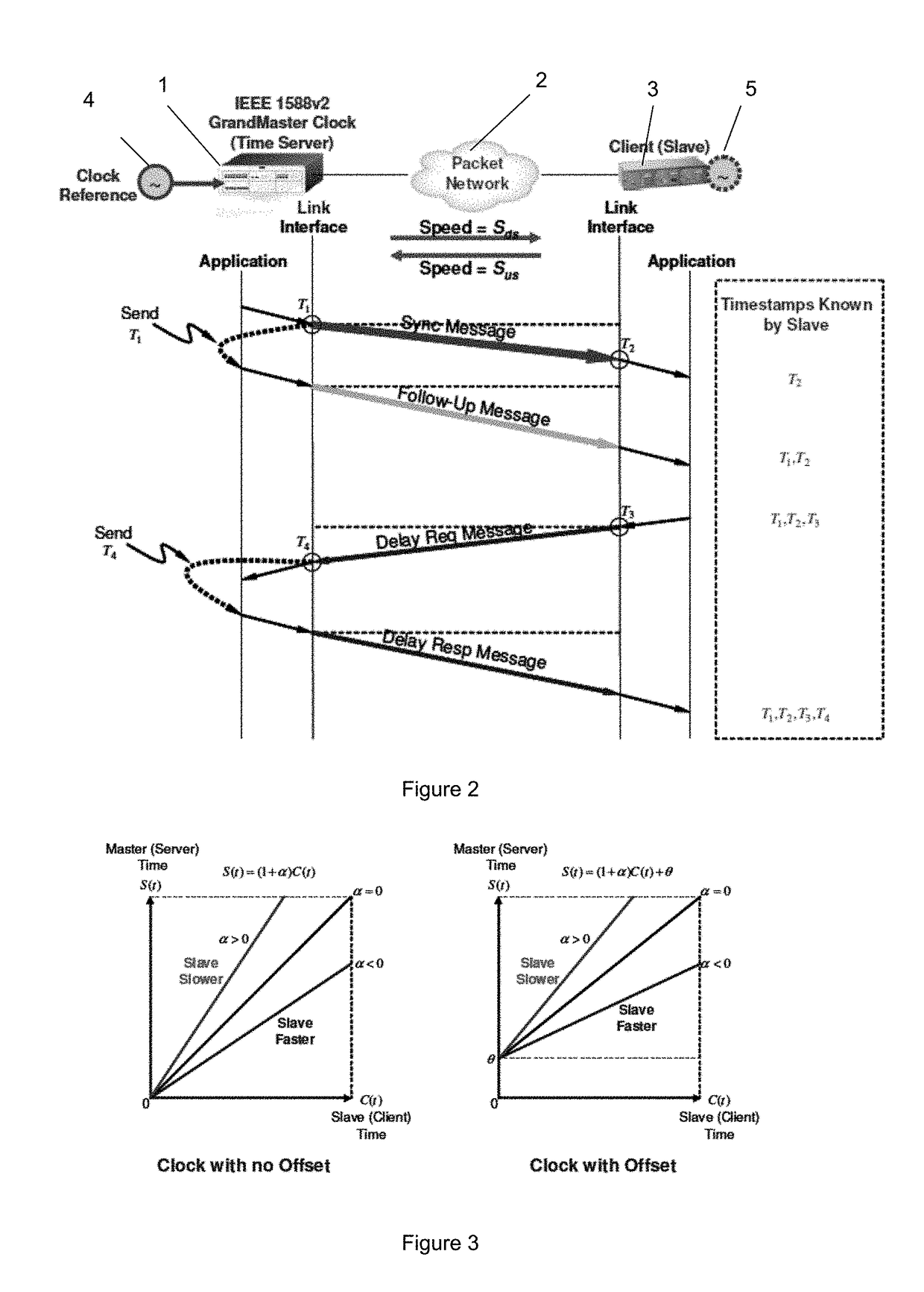
Robust Jitter-Free Remote Clock Offset Measuring Method
A clock offset between a client and a server is measured by: (a) the client sending a request to the server; (b) upon receiving the request in step (a), the server optionally sending a server acknowledgement to the client; (c) upon the client receiving the server acknowledgement in step (b) or directly, if no acknowledgement was used, each of the client and the server proceeding to concurrently exchange their respective timestamps with each other a multiplicity (n) of times, thus forming a multiplicity (n) of timestamp exchanges; and (d) determining a plurality of apparent forwards and backwards delays based on the multiplicity (n) of timestamp exchanges. The preferred apparent forwards and backwards delays are then selected based on the minimum values (for each direction) determined in (d) above. The clock offset between client and server is then determined based on the preferred apparent forwards and backwards delays.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Methods and systems for estimating offset and skew using linear programming
This invention relates to methods and systems for estimating offset and skew using linear programming. Embodiments of the invention relate to methods and systems which apply linear programming principles to links with asymmetric transmission rates which are estimated from an exchange of timing messages (for example under IEEE 1588 PTP). Further embodiments provide for the estimation of clock offsets using linear programming techniques when the skew is known or estimated.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
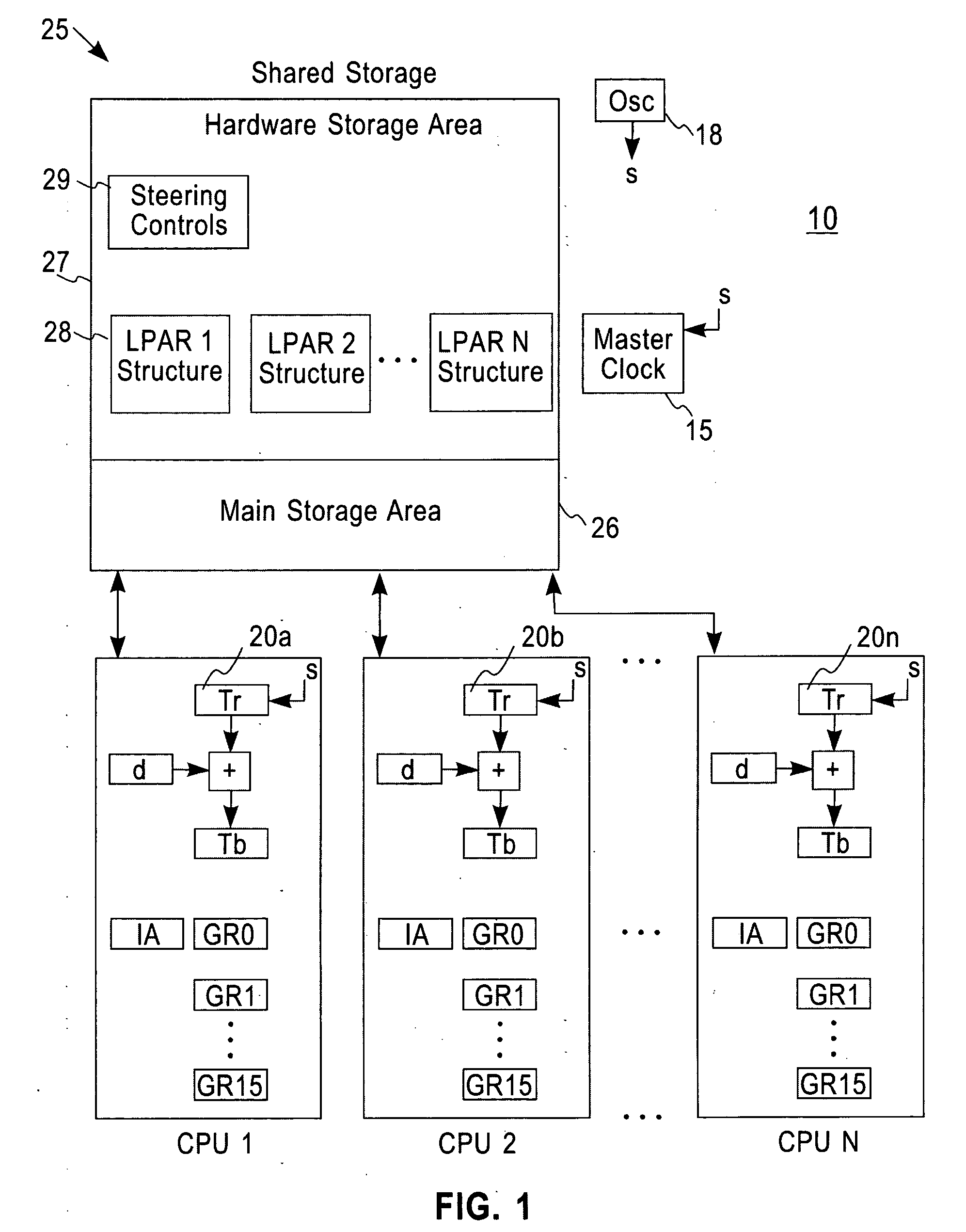
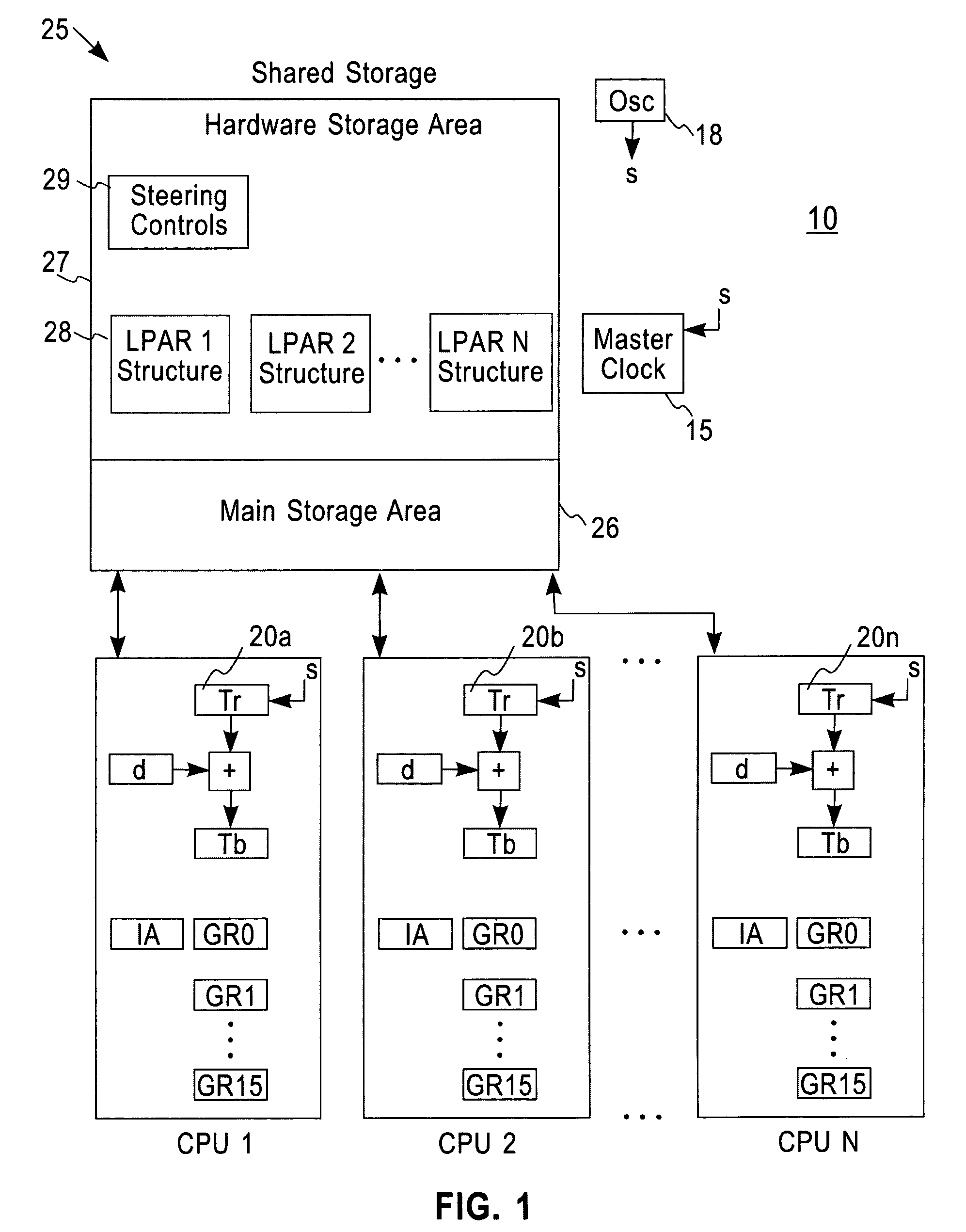
Simultaneously updating logical time of day (TOD) clocks for multiple cpus in response to detecting a carry at a pre-determined bit position of a physical clock
InactiveUS7617410B2Avoids a further carry propagatingMinimize overheadError detection/correctionSynchronous motors for clocksComputer hardwareClock offset
A system, method and computer program product for synchronizing adjustment of a time of day (TOD) clock for a computer system having multiple CPUs, each CPU having an associated physical clock providing a time base for executing operations that is stepping to a common oscillator, and an associated logical TOD clock. The method includes detecting propagation of a carry at a pre-determined bit position of the physical clock associated with a CPU in the computer system; and, updating, in response to the detecting of the pre-determined bit position carry, a TOD-clock offset value (d) to be added to a physical clock value (Tr) value to obtain a logical TOD clock value (Tb) for use by a CPU in the system. In this manner, each CPU computes a new logical TOD clock value in synchronization—the new logical TOD clock value taking effect simultaneously for the multiple CPUs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Clock offset estimation with bias correction
ActiveUS7023884B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingClock offset
A new algorithm for clock offset estimation for resources distributed across a network (such as the Internet). By exchanging a sequence of time-stamped messages between pairs of network nodes and separately estimating variable delays for each message direction, present inventive embodiments provide estimates for clock offset between node pairs and the bias of such estimates, thereby to permit more accurate correction. Present inventive algorithms operate in a variety of peer and server network configurations while providing significant improvement in convergence speed and accuracy.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Advanced global navigation satellite systems (gnss) positioning using precise satellite information
A method is provided for estimating parameters useful to determine the position of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receiver or a change in the position thereof. The method includes the steps of: obtaining at least one GNSS signal received at the GNSS receiver from each of a plurality of GNSS satellites; obtaining, from at least one network node, precise satellite information on: (i) the orbit or position of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites, and (ii) a clock offset of at least one of the plurality of GNSS satellites; identifying, among the obtained GNSS signals, a subset of at least one GNSS signal possibly affected by a cycle slip, the identified subset being hereinafter referred to as cycle-slip affected subset; and estimating parameters useful to determine the position of the GNSS receiver or a change in the position of the GNSS receiver using at least some of the obtained GNSS signals which are not in the cycle-slip affected subset, and the precise satellite information.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Fast frequency adjustment method for synchronizing network clocks
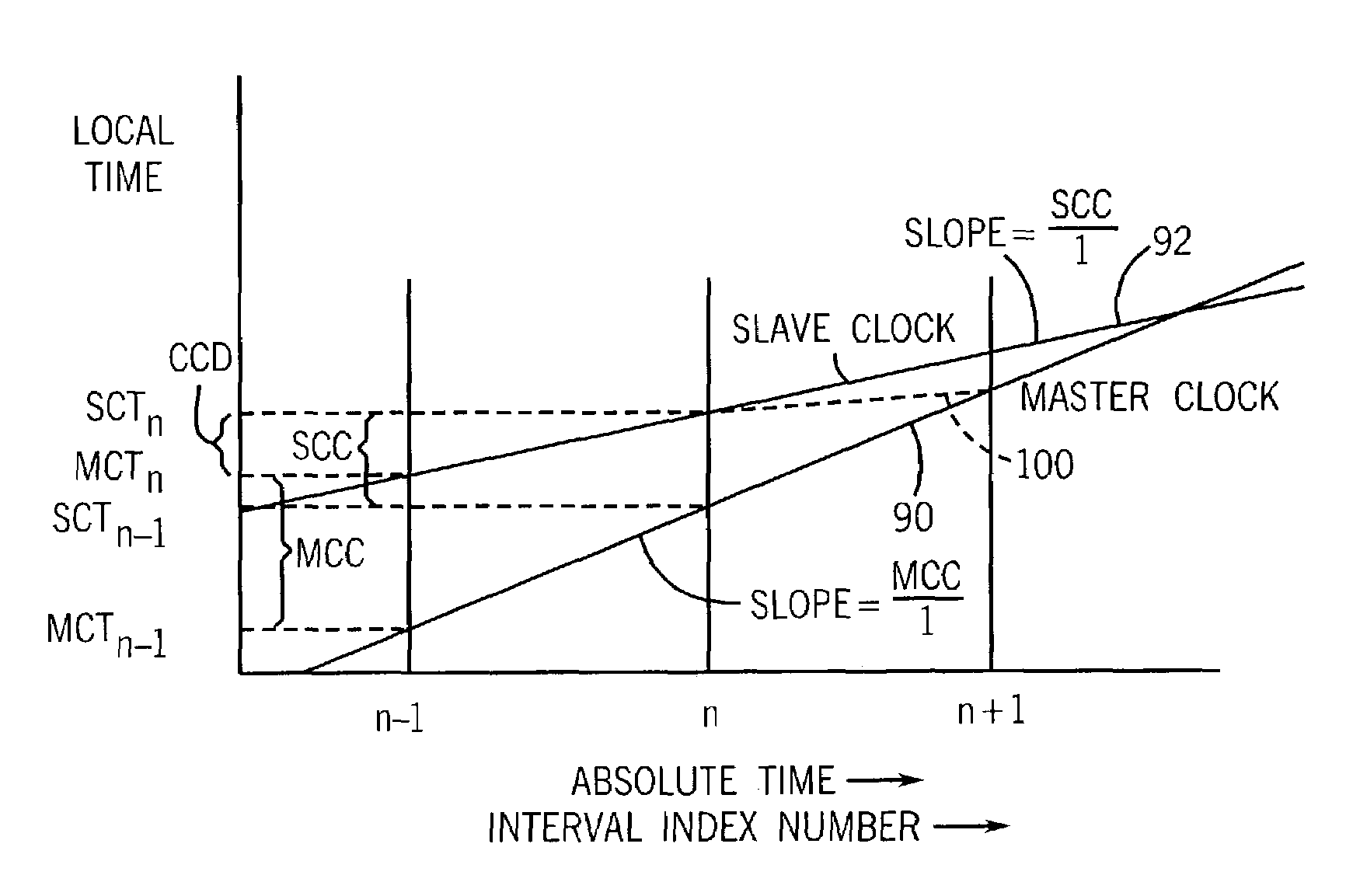
ActiveUS7379480B2Eliminate jumpingEasy to controlTime-division multiplexNetwork clockSynchronization networks
A method of precisely synchronizing clocks held in separate nodes on a communication network is provided that adjusts clock frequency based on a measure of relative clock rates and absolute clock offsets. In one embodiment, clock convergence is obtained with one synchronization session.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Deception jamming signal detection method based on single receiver
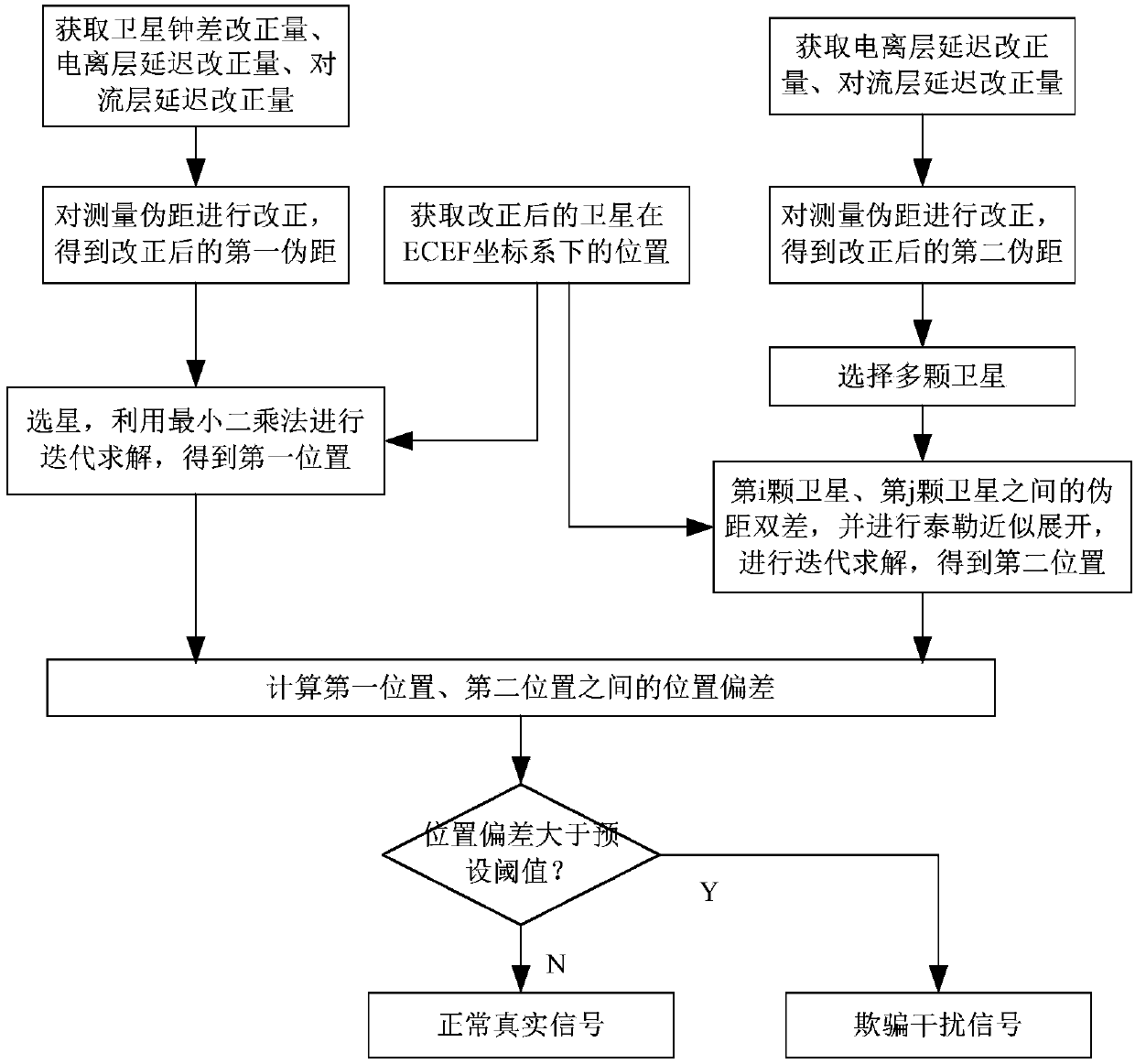
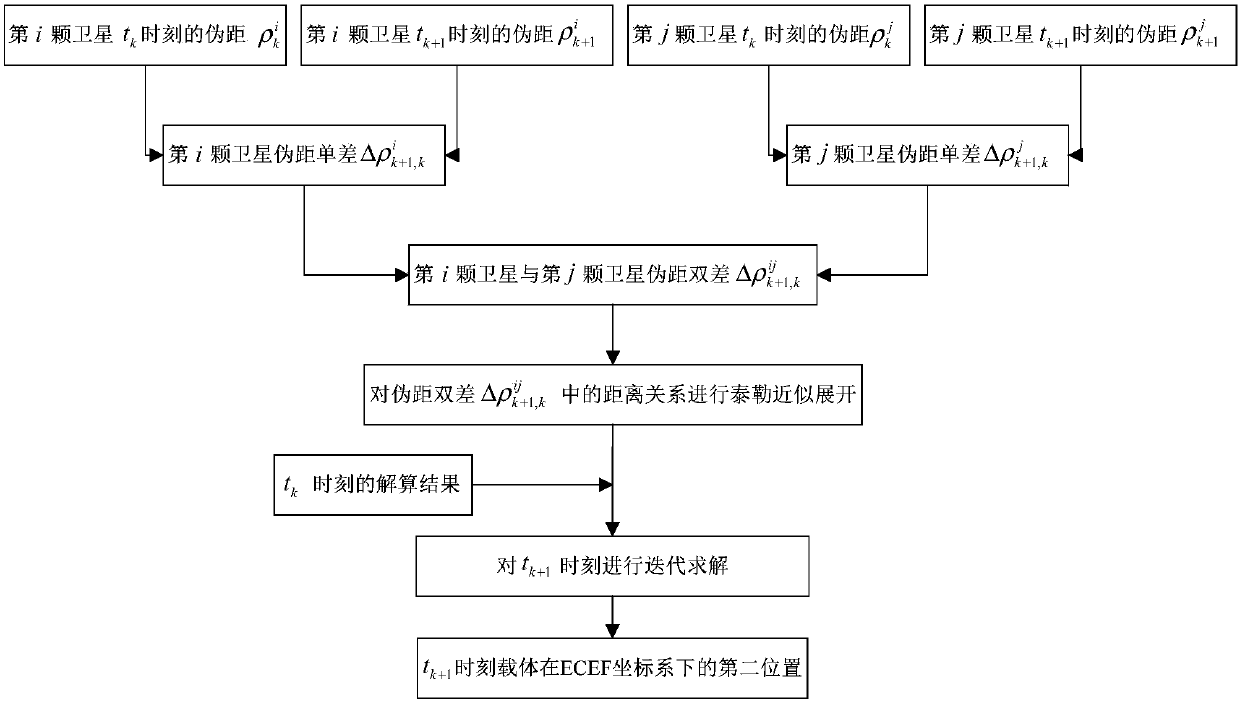
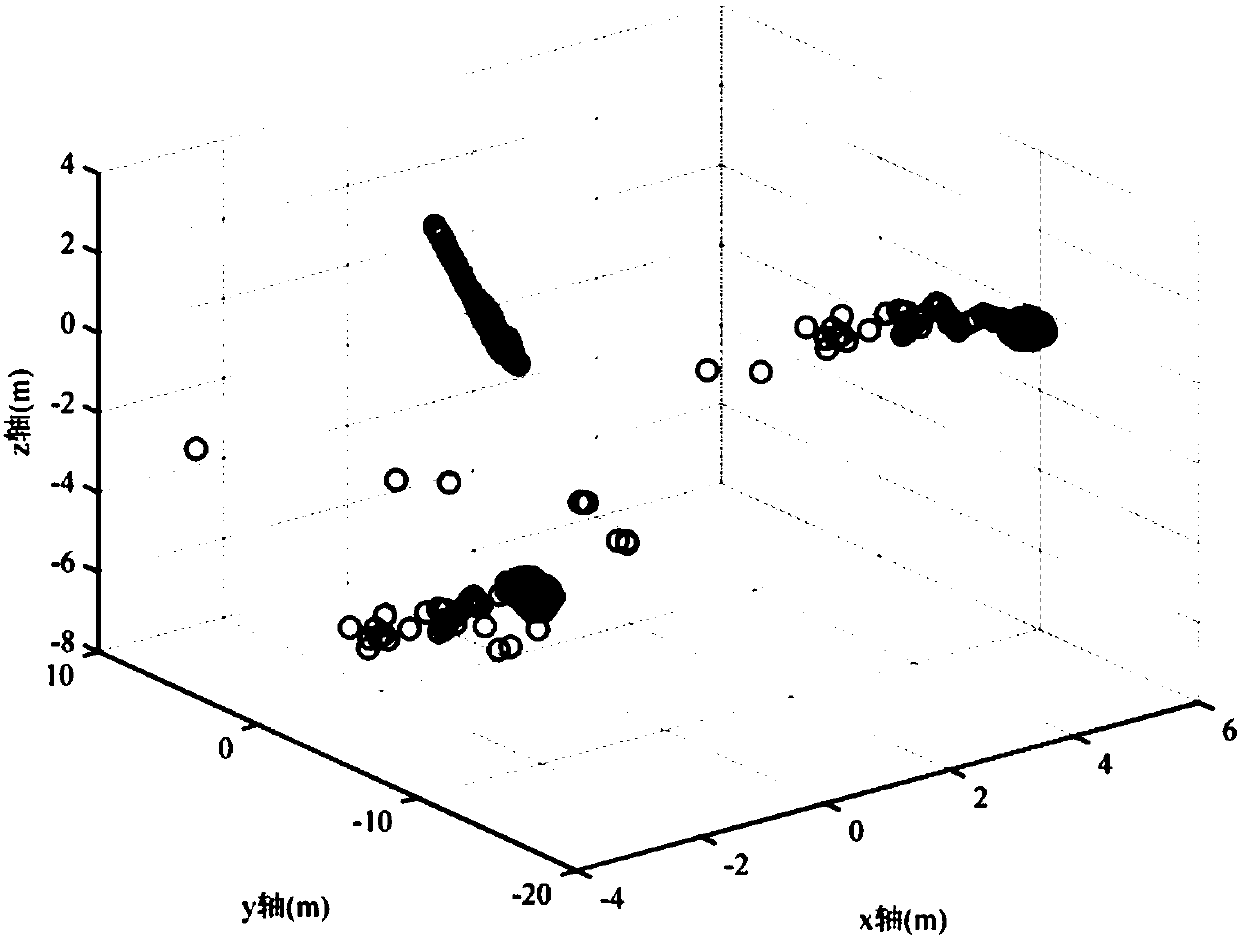
ActiveCN107621645ALower requirementThe implementation process is simpleSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereNatural satellite
The invention discloses a deception jamming signal detection method based on a single receiver. The method comprises steps: the position of a satellite after correction under an ECEF coordinate systemis acquired, satellite clock offset correction, ionosphere delay correction and troposphere delay correction are used to correct a measured pseudo range to obtain a pseudo range after correction, a least square method is used for iterative solution, the first position of a carrier under the ECEF coordinate system is obtained, and based on a pseudo range double difference model of the satellite, Taylor's approximation is carried out for iterative solution to obtain the second position of the carrier under the ECEF coordinate system; and according to whether the position offset between the first position and the second position is larger than a preset threshold, whether the currently-received signals are the deception jamming signals is judged. The detection is realized by only requiring the single receiver or a single antenna and the pseudo range measurement information, requirements on equipment are low, the algorithm is simple and efficient, the realization process is simple, and themethod is applicable to generation-type deception jamming and forward-type deception jamming.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
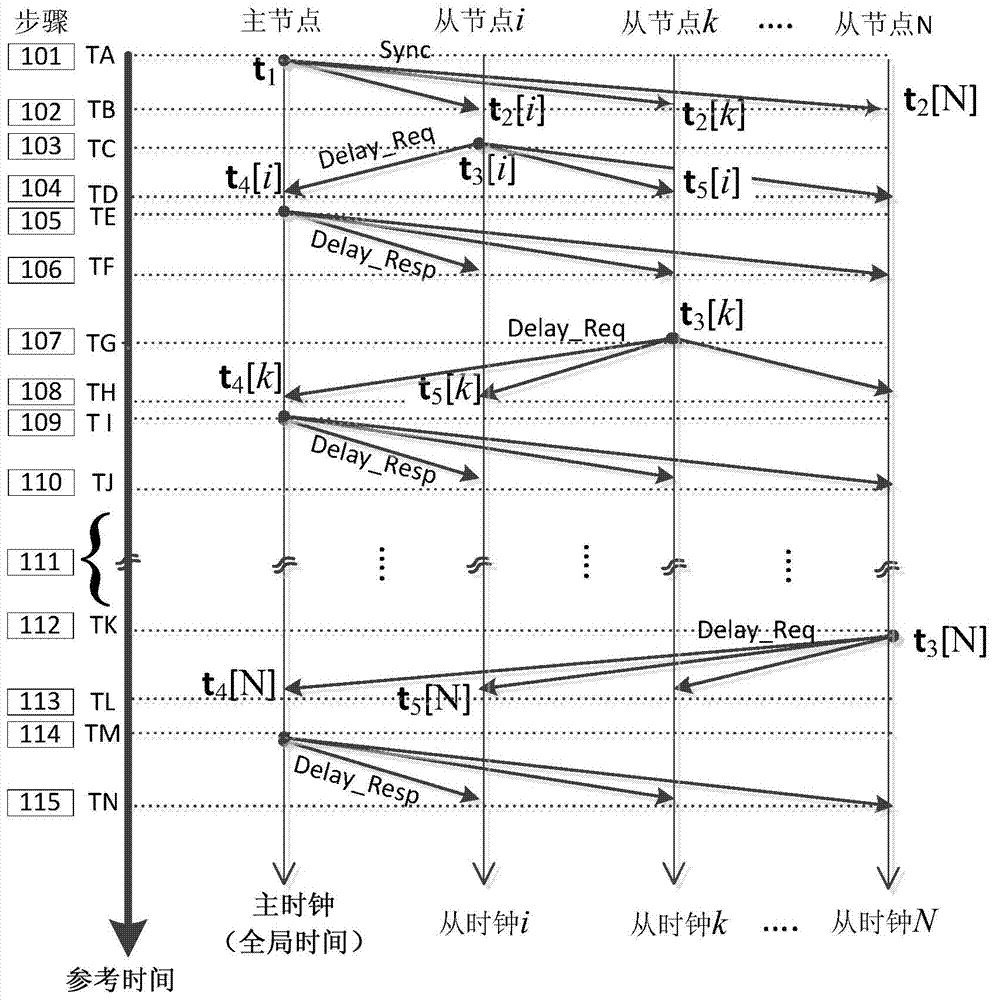
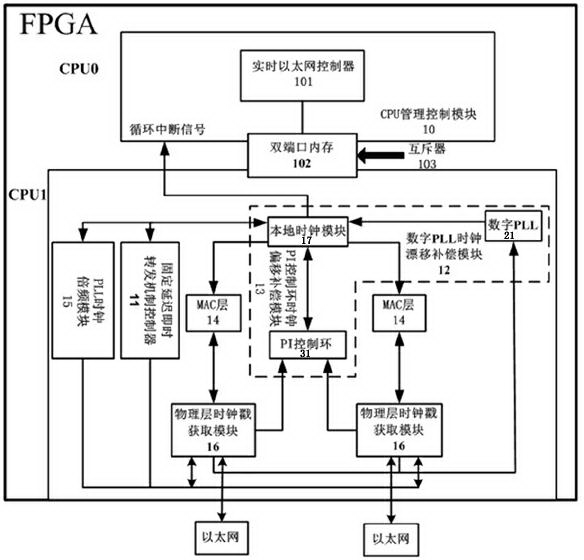
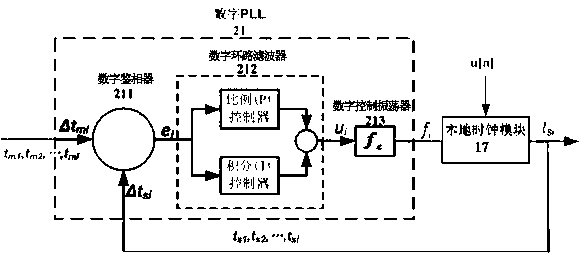
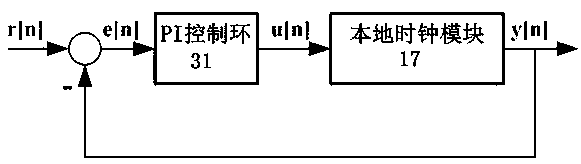
Time synchronization protocol system based on chain industrial Ethernet and synchronization method
ActiveCN103812592AImprove minimum recognition accuracyReduce measurement errorTime-division multiplexObservational errorClock drift
The invention discloses a time synchronization protocol system based on a chain industrial Ethernet and a synchronization method, and belongs to the technical field of communication. Measuring errors are decreased by the aid of a fixed-delay instant forwarding mechanism controller and a PLL (phase locking loop) frequency multiplication module output high-frequency clock, clock drift compensation is realized by the aid of a digital PLL clock drift compensation module, clock offset compensation is realized by the aid of a PI (proportional-integral) control ring clock offset compensation module, modules are obtained by the aid of a physical layer clock timestamp, and the influence of random physical link delay on clock timestamp acquiring accuracy is decreased. Random variables affecting chain Ethernet clock synchronization accuracy are limited or cut down, and the clock synchronization accuracy is improved.
Owner:南京航浦机械科技有限公司
Wireless ranging node and wireless ranging method
The invention discloses a wireless ranging node and a wireless ranging method. The wireless ranging node comprises a central processing unit, a Chirp signal radio frequency unit, a radio frequency front end unit, a power supply unit, a sensor unit and a data communication unit. The Chirp signal radio frequency unit is used for mutual conversion between digital signals and radio-frequency signals, the radio frequency front end unit is used for amplifying and filtering Chirp signals, the power supply unit is used for supplying a working power supply, and the sensor unit is used for providing node information. According to the wireless ranging node, the sensor unit informs the central processing unit of a motion state of the whole node, and the central processing unit controls the whole node to enter a working state with low power consumption at a proper moment. The wireless ranging method improves ranging accuracy of SDS-TWR through the characteristic that an actual time interval for continuously sending data two times between two nodes is equal to a time interval for continuously receiving the same data two times and through the method of figuring out clock offset of the two nodes with a time deviation formula of the SDS-TWR method.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method and apparatus for cell search for W-CDMA with effect of clock offset
The invention discloses a cell search method for a CDMA system for a three-stage cell search procedure. The cell search method have the steps of matching incoming signals; over-sampling the incoming signals N times against a chip rate; down-sampling the incoming signals and outputting N over-samples (Y1(k), Y2(k), YN(k)) to N parallel signal paths; choosing randomly a sample of the N over-samples; and transmitting the sample chosen randomly from the N over-samples into a first stage process, a second stage process and a third stage process to accomplish a trial. The invention significantly reduces the effect of clock offset so as to accomplish fast cell search.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Clock calibration method of wireless meter reading system and clock calibration method of distributed system
InactiveCN102129219AResolve Clock SkewGuaranteed Clock AccuracyAcoustic time signalsVolume indication and recording devicesStart timeClock offset
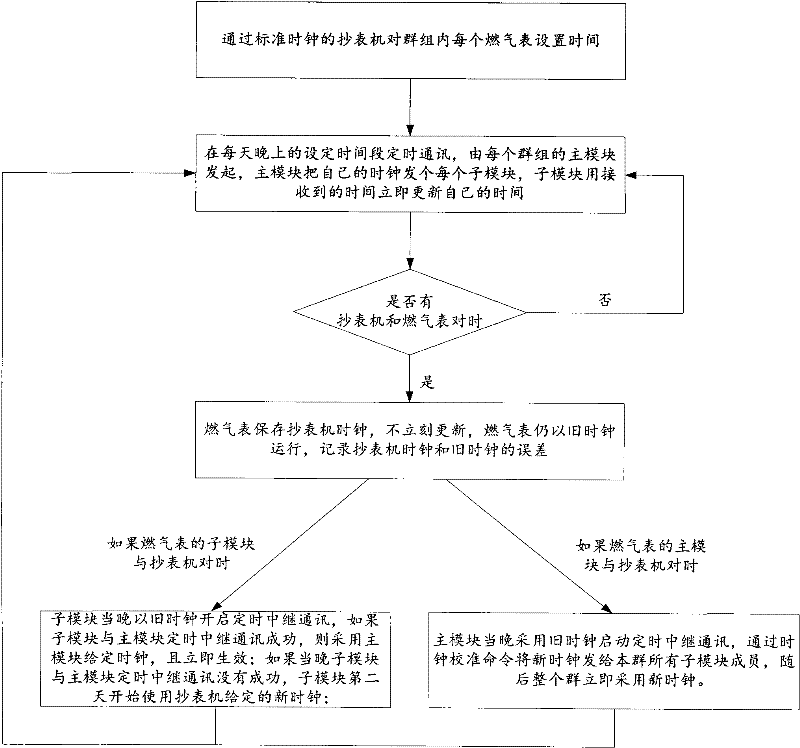
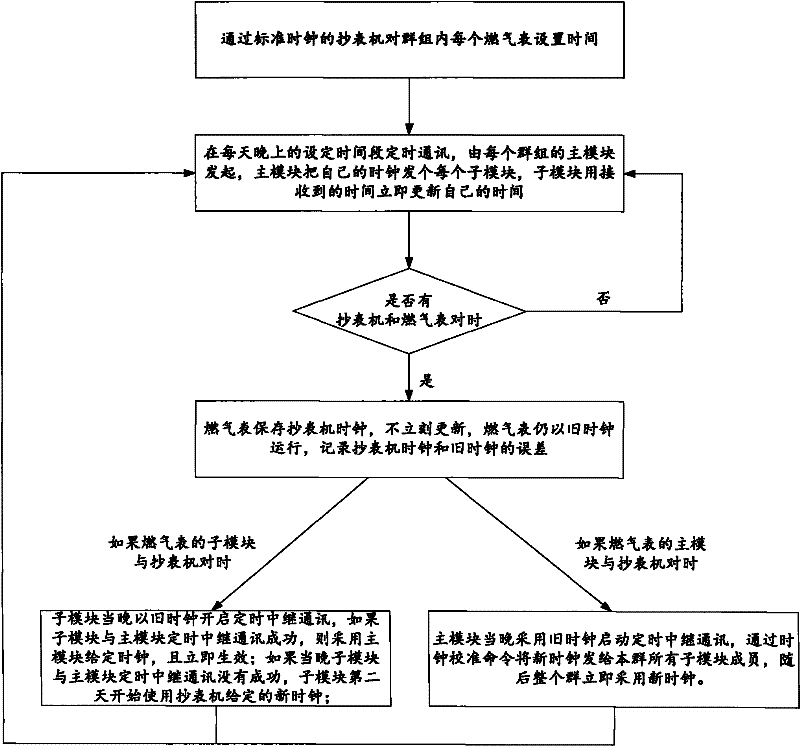
The invention discloses a clock calibration method of a wireless meter reading system. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out timed communication for time calibration in a set time interval, wherein a main module of each group initiates the timed communication and sends self time to each submodule, and the submodule immediately updates individual time with the received time; synchronizing time between a hand-held meter reading machine with a standard clock and a meter body, storing the clock of the hand-held meter reading machine by the meter body, and recording the offset between the clock of the hand-held meter reading machine and a old clock, wherein the meter body still operates with a old clock without immediate update; synchronizing time between the hand-held meter reading machine and the main module in each group; starting timed relay communication by each main module by adopting the old clock in a time calibration interval right after time synchronization, and sending a new clock to all submodule members in the group through a clock calibration command, wherein the new clock is subsequently adopted in the whole group. The clock calibration method of the wireless meter reading system, which is proposed by the invention, can be used for eliminating clock offset in the groups of the meter body to ensure the clock accuracy in the groups and effectively avoid timed communication conflicts.
Owner:上海复展智能科技股份有限公司
Clock synchronization simplified information exchange method applied to wireless sensor network
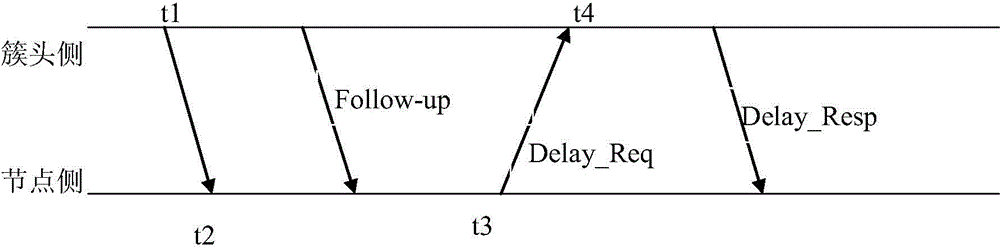
InactiveCN104918319AReduce overheadThin Computing CycleSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesRecording durationLine sensor
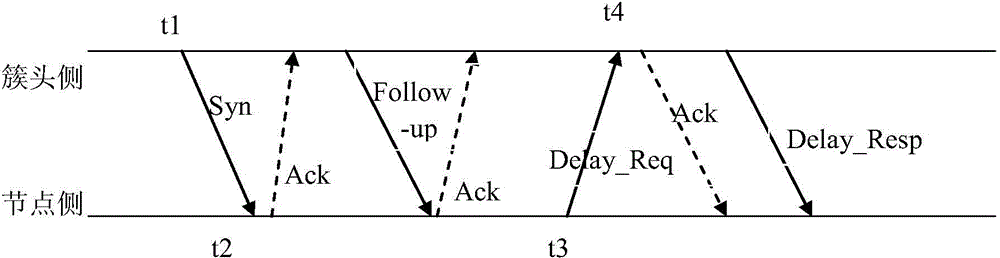
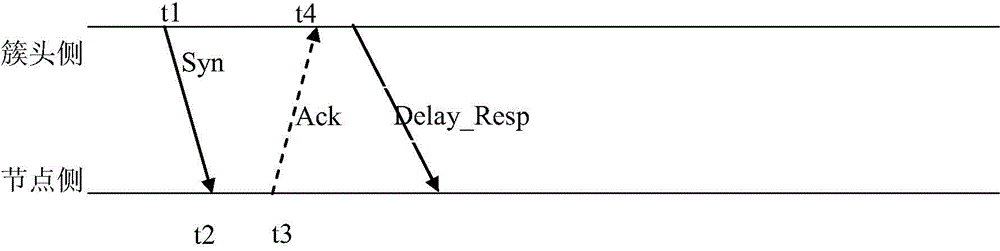
The invention provides a clock synchronization simplified information exchange method applied to a wireless sensor network. The method comprises steps: a cluster head side sends a message and records a time stamp t1, and a node side receives the message and records a time stamp t2; the node side sends and feeds back the message adn records a time stamp t3; the cluster head side receives the feedback message and records a time stamp t4; the cluster head side combines the time stamps t1 and t4 into a data packet and sends the data packets to the node side; according to the time stamps t2 and t3 and t1 and t4 analyzed from the data packet, the node side calculates clock offset for local clock calibration. The method is simple, synchronization time is greatly reduced, realization is convenient, an IEEE1588 accurate clock synchronization protocol and an IEEE802.15.4 wireless sensor network protocol are combined, at least two message sending and receiving times are saved during each time synchronization process, reliability is high, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
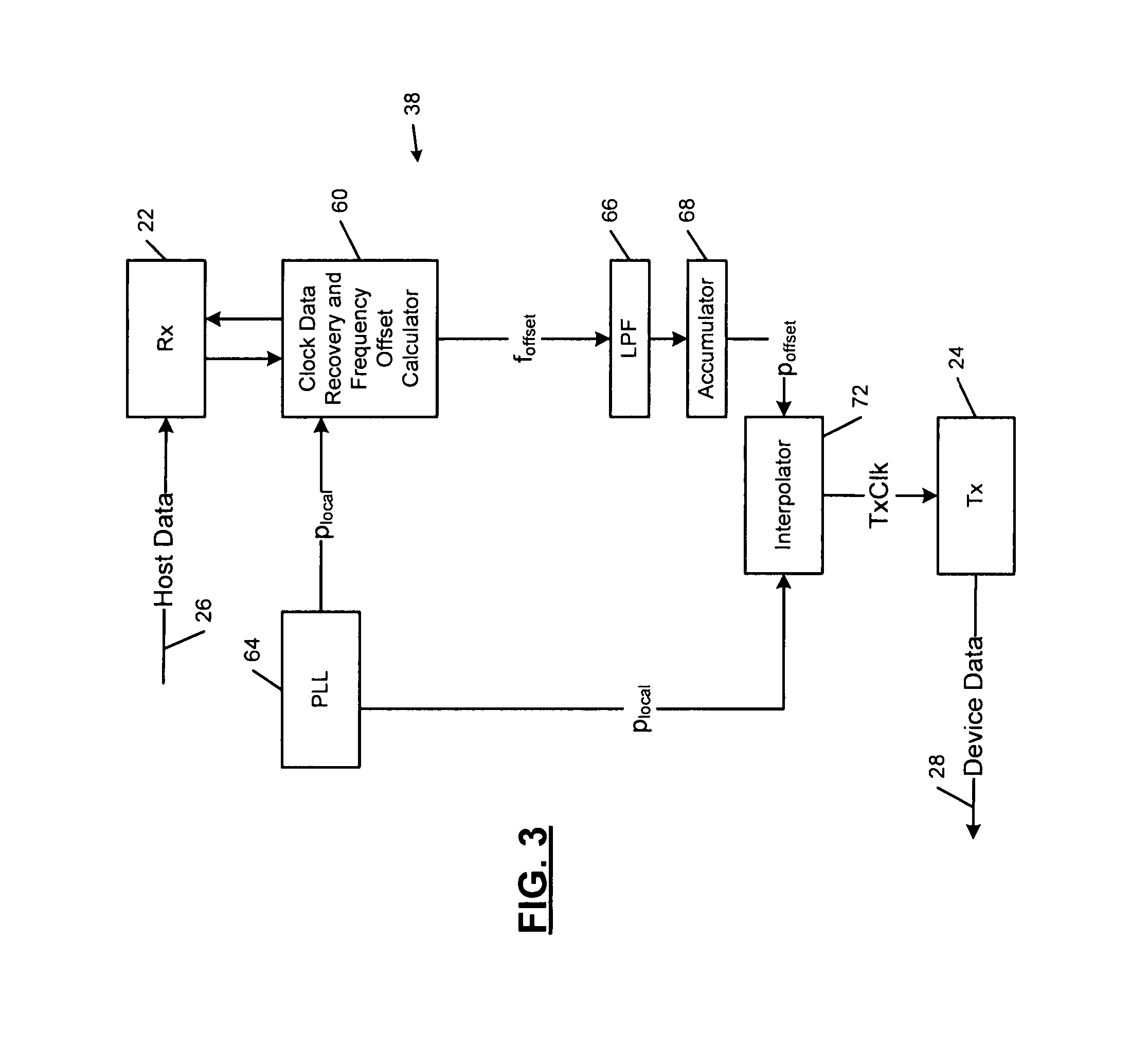
Clock offset compensator
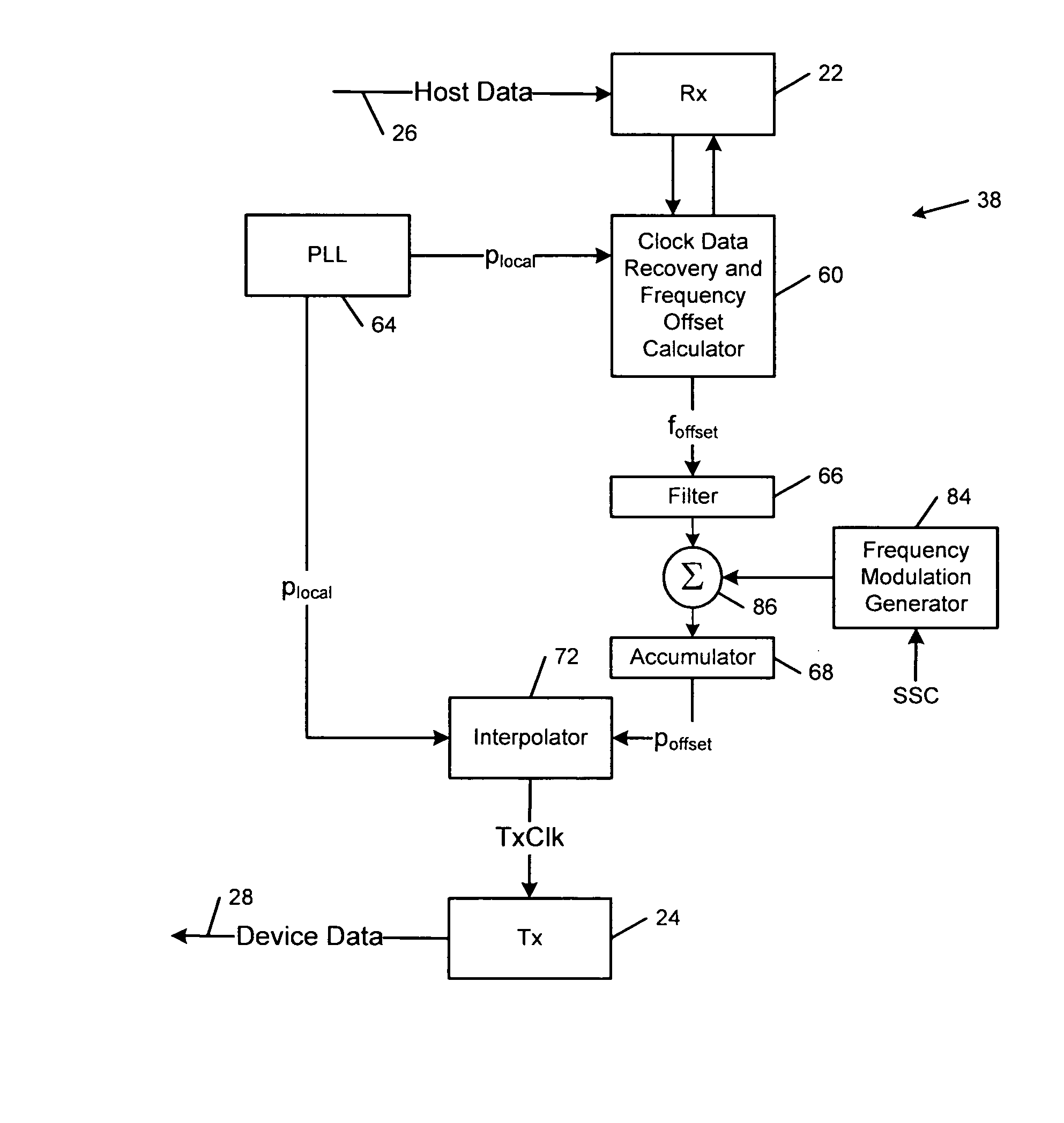
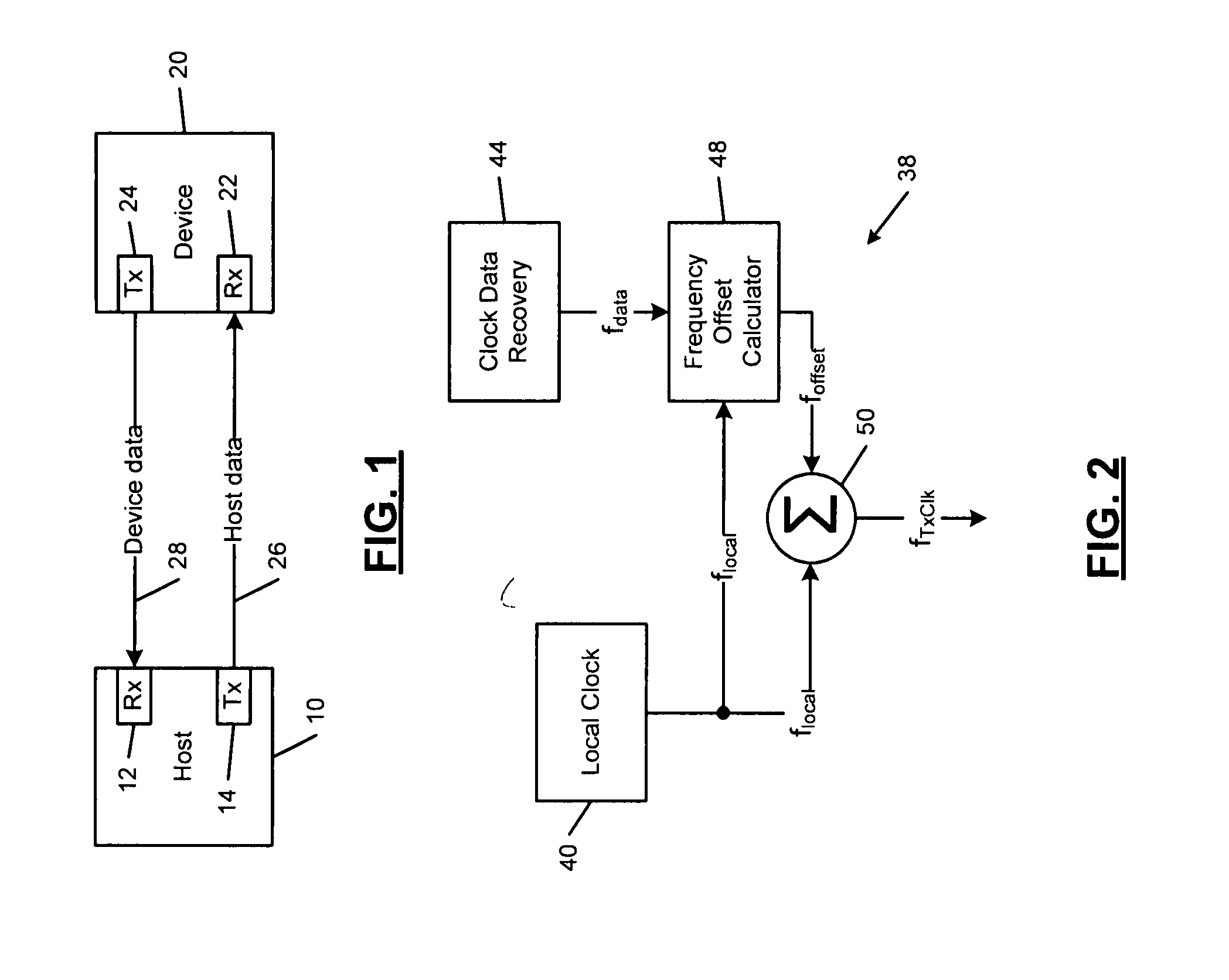
A device comprises a transmitter, a receiver and a clock generator that generates a local clock frequency. A clock recovery circuit communicates with the receiver and recovers a host clock frequency from data received from a host by the receiver. A frequency offset circuit communicates with the clock recovery circuit and the clock generator and generates a frequency offset based on the clock frequency and the recovered host clock frequency. A frequency compensator compensates a frequency of the transmitter using the frequency offset.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
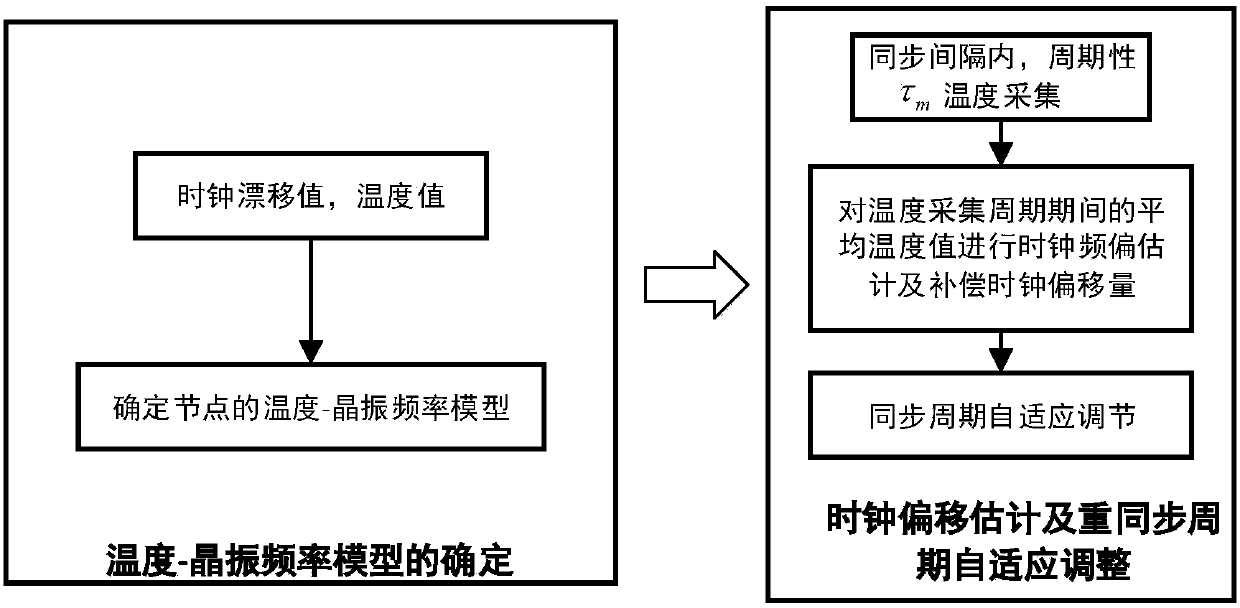
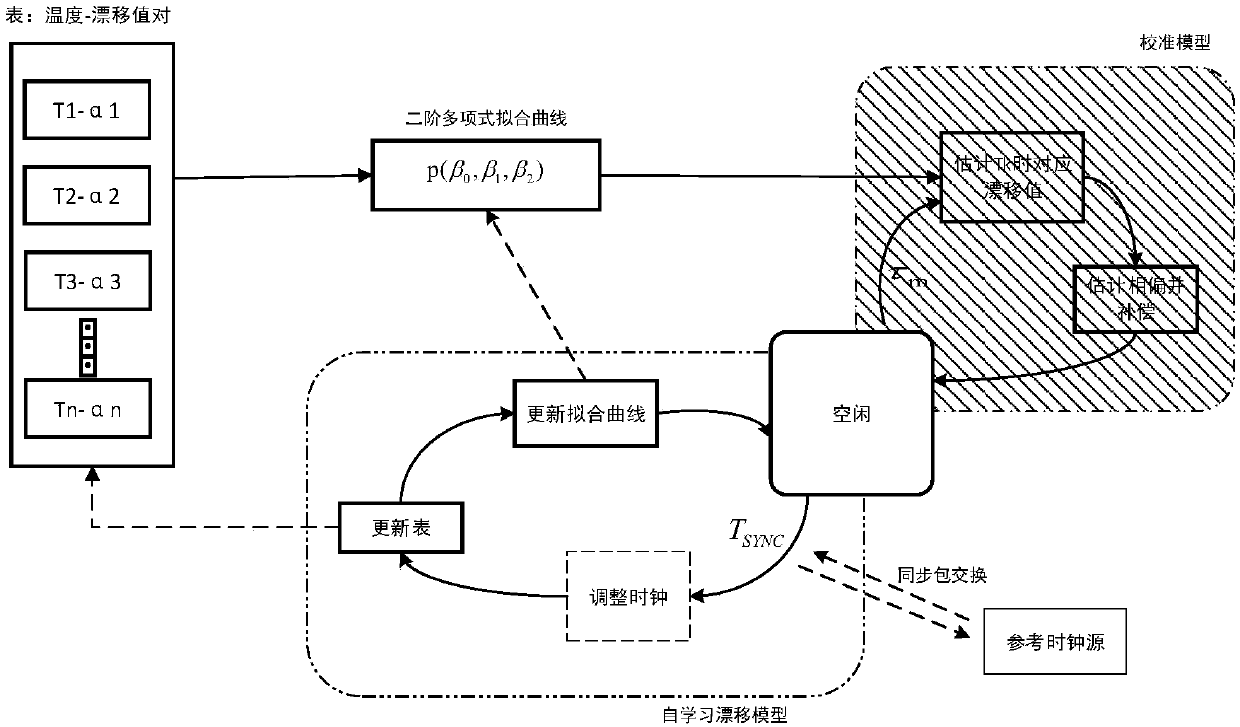
Adaptive time synchronization method based on temperature compensation
ActiveCN108449791AImprove performanceImprove energy efficiencySynchronisation arrangementSynchronous motors for clocksClock driftWireless mesh network
The invention relates to an adaptive time synchronization method based on temperature compensation, belonging to the technical field of wireless sensor networks. In consideration of the large influence of the environmental temperature on a clock crystal oscillator frequency, the method includes the following steps: firstly, a temperature-crystal oscillator frequency model is established by using the correlation between the clock drift and temperature, and nodes can compensate for the offset of a clock according to the temperature changes under the model to improve the accuracy of synchronization between the nodes; and secondly, in the case that the network delay is a Gaussian model, and in combination with the relevant theory of probability time synchronization, the nodes can compensate for the current time according to a maximum synchronization error allowed by the network and the accumulated clock offset, and estimate a corresponding resynchronization interval. According to the method, the nodes can reduce the energy consumption to the greatest extent on the basis of meeting the specific synchronization accuracy, and the network load can be reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com