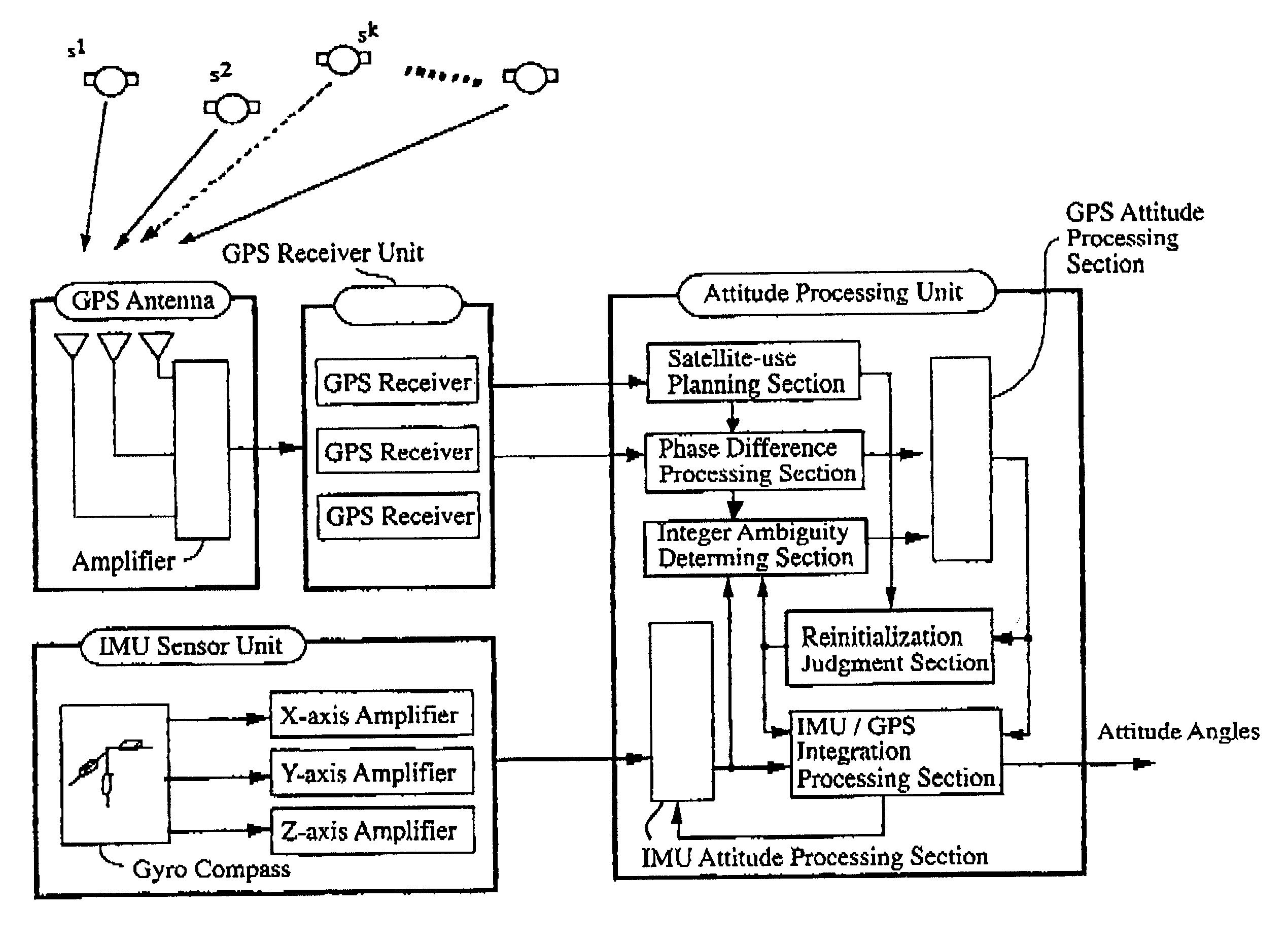
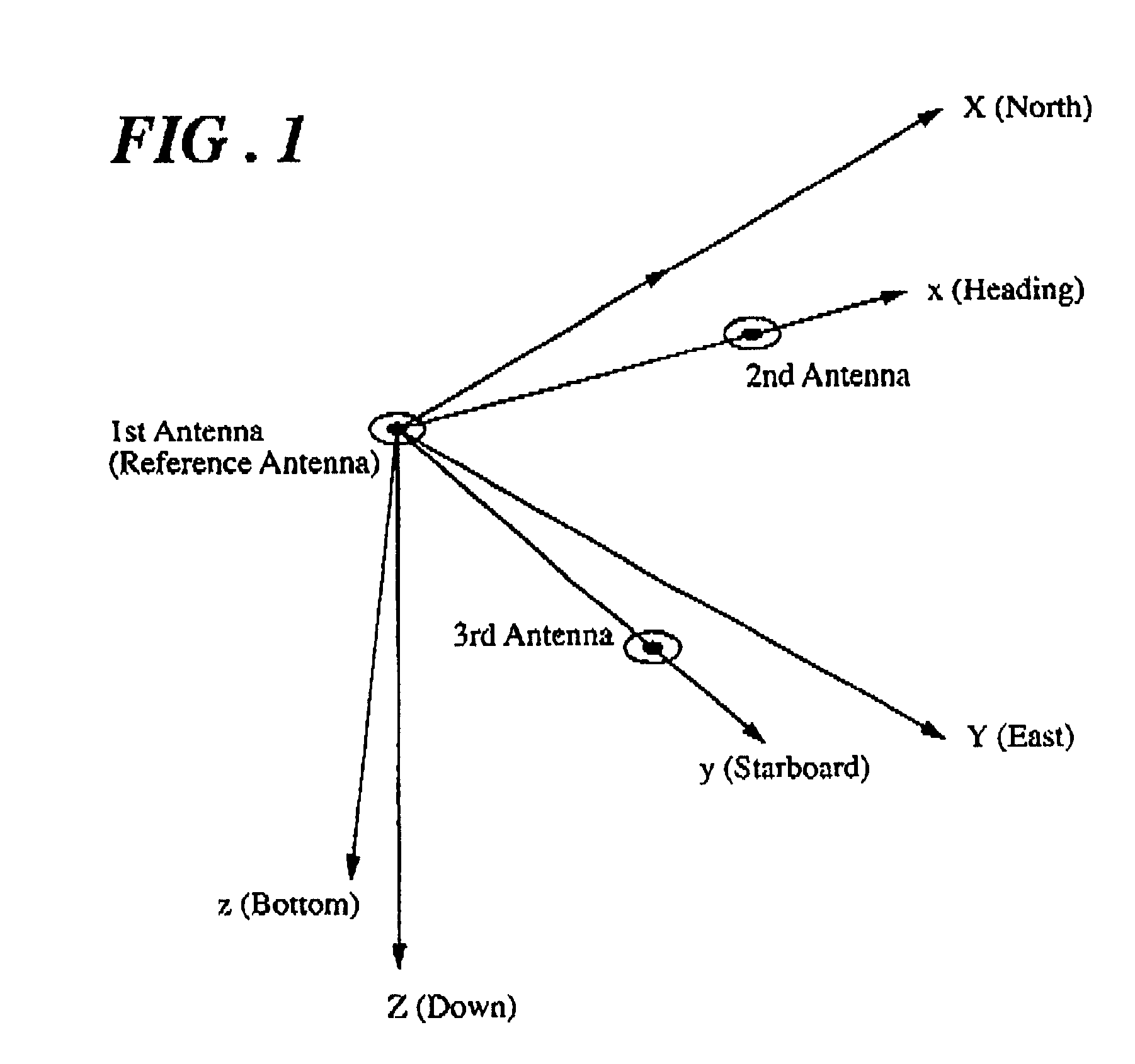
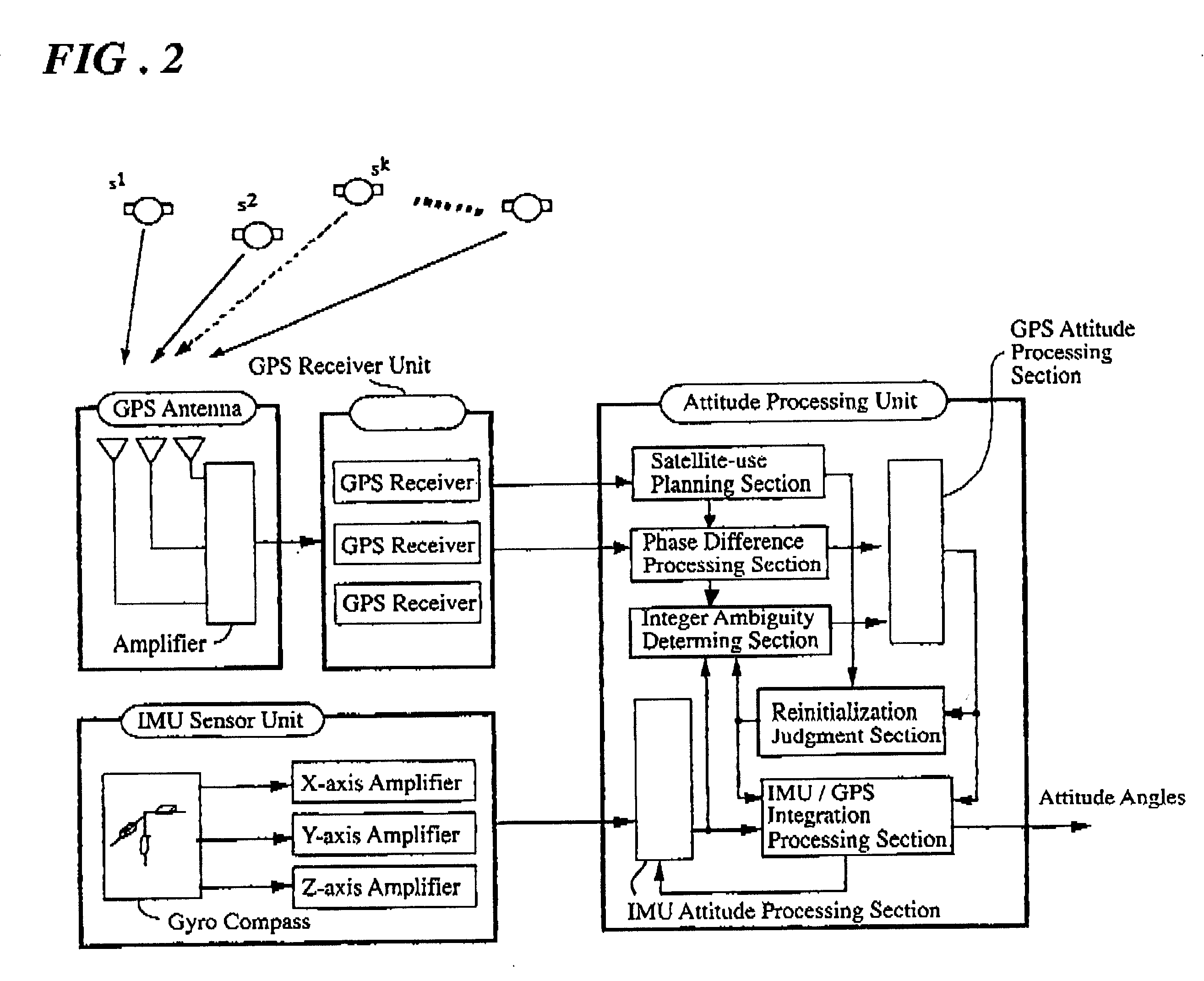
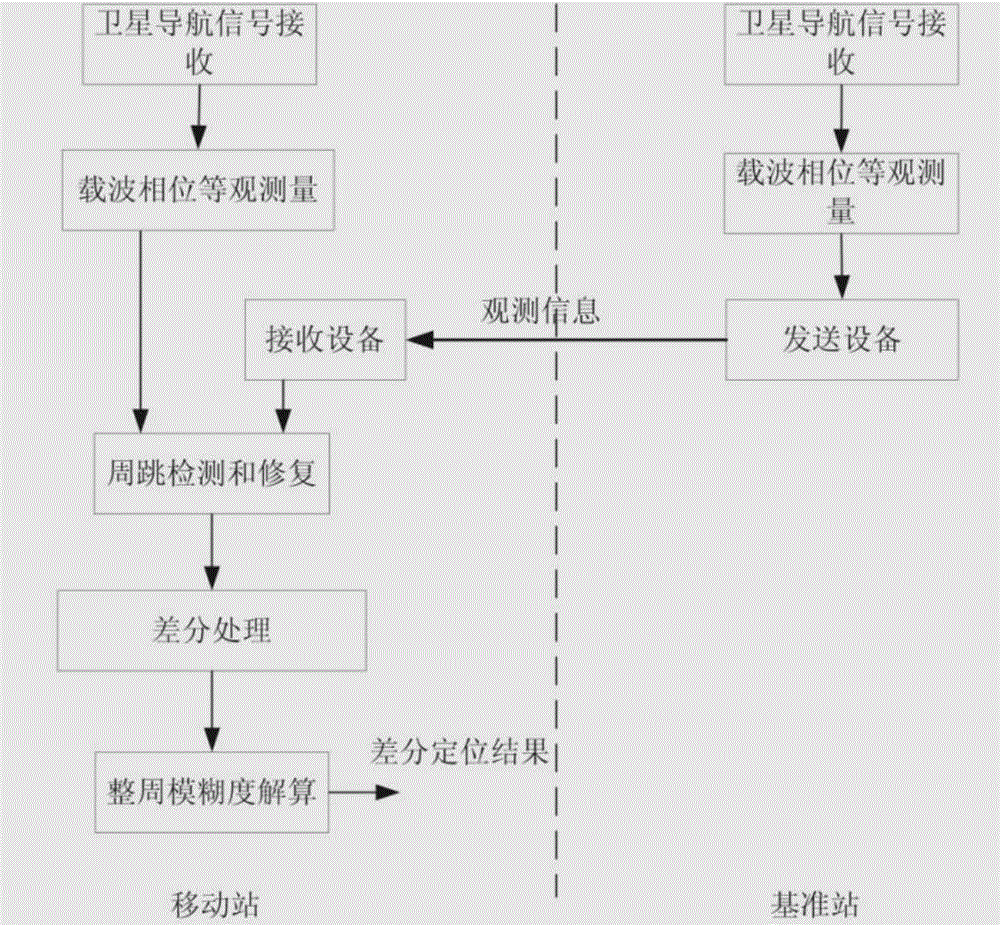
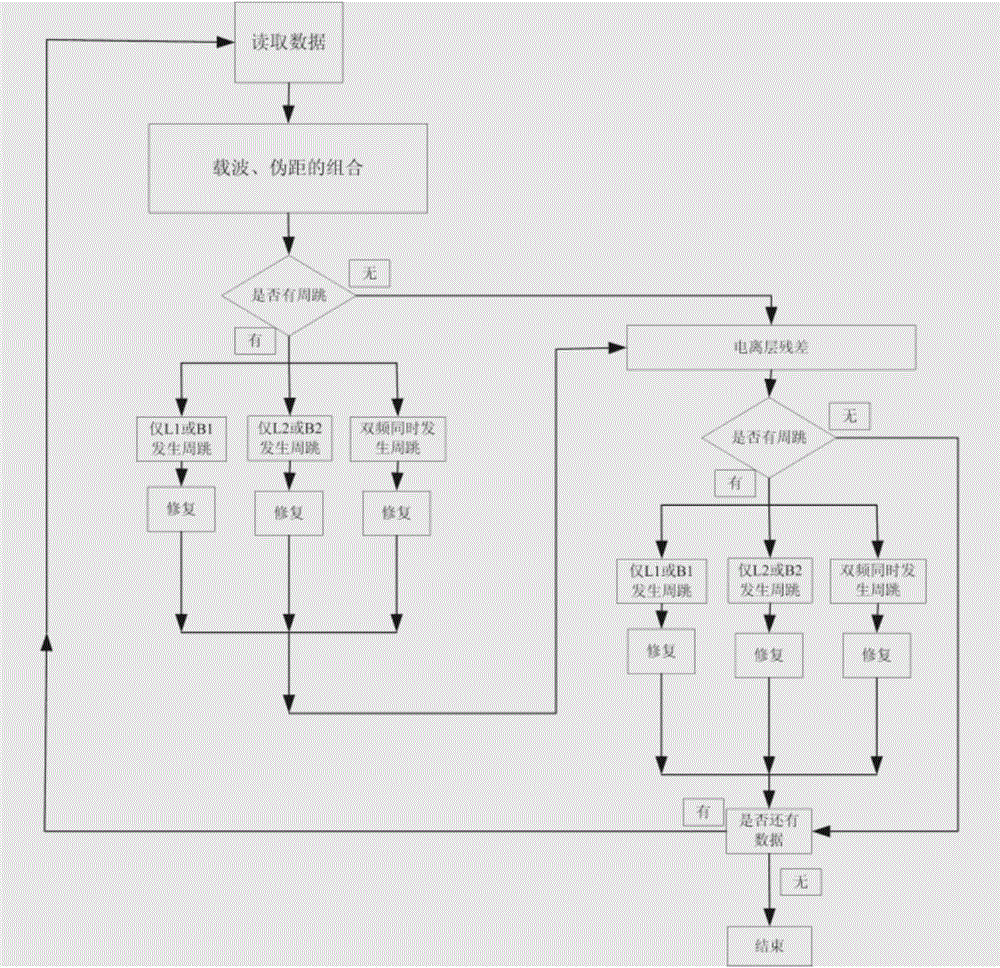
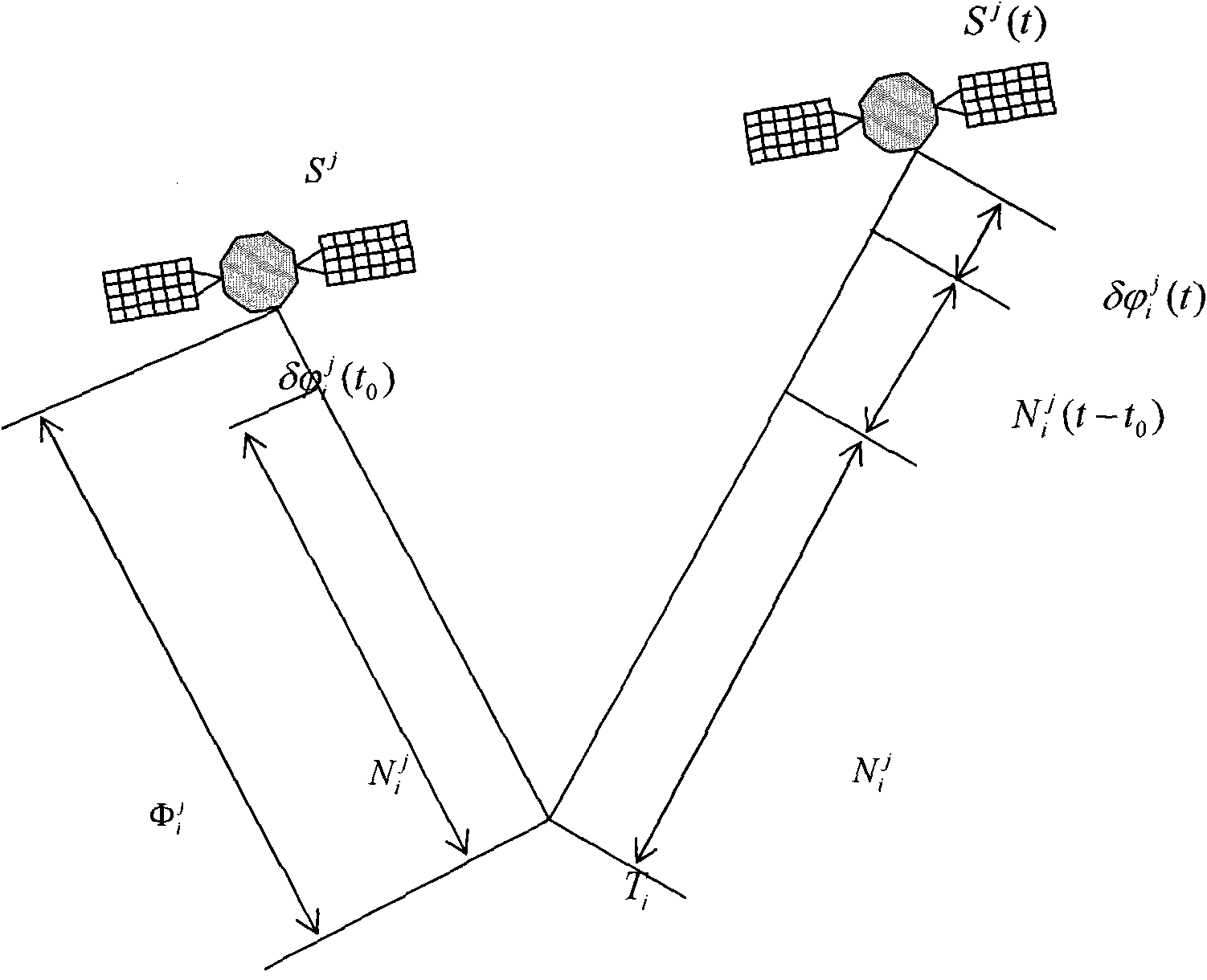
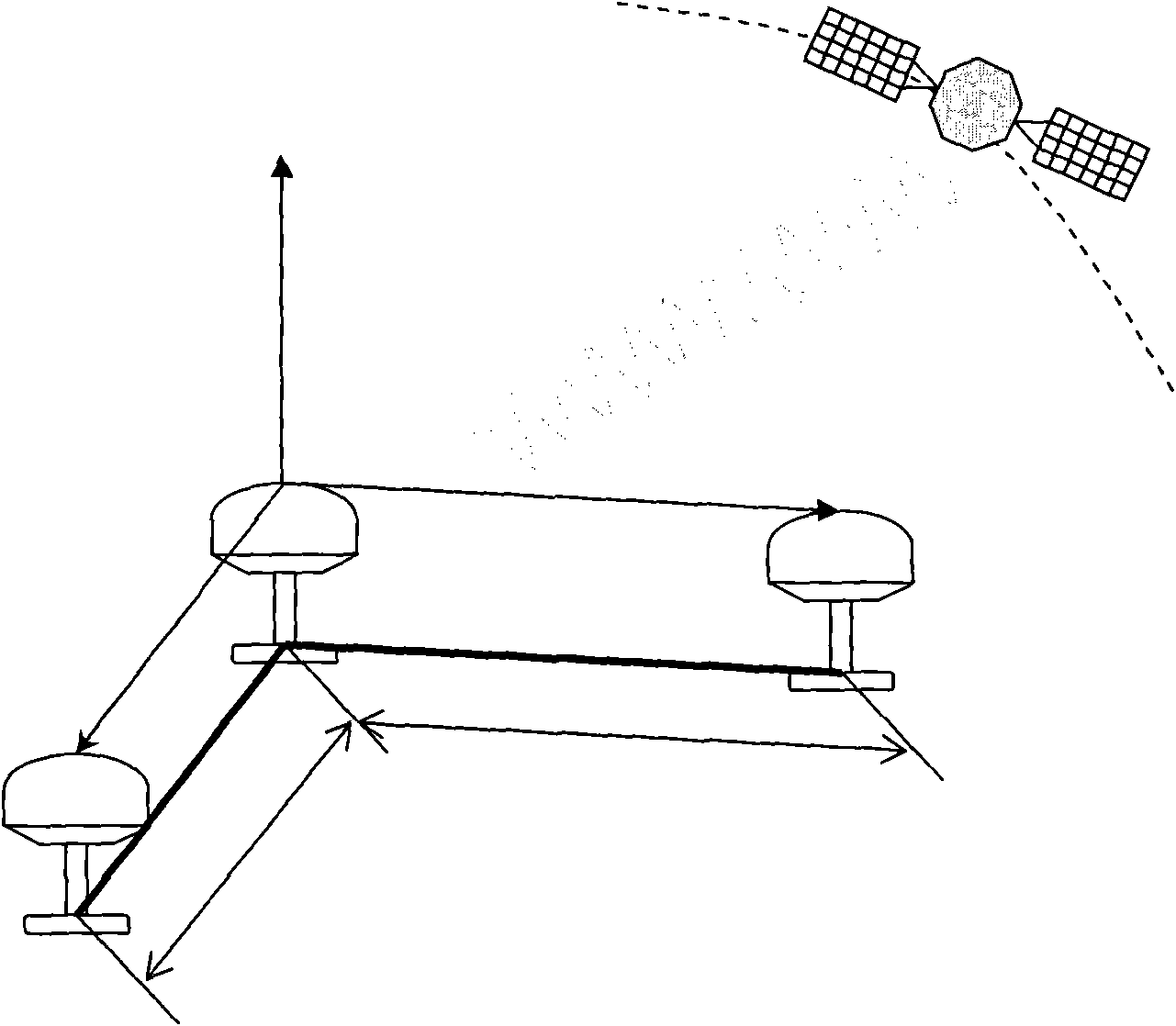
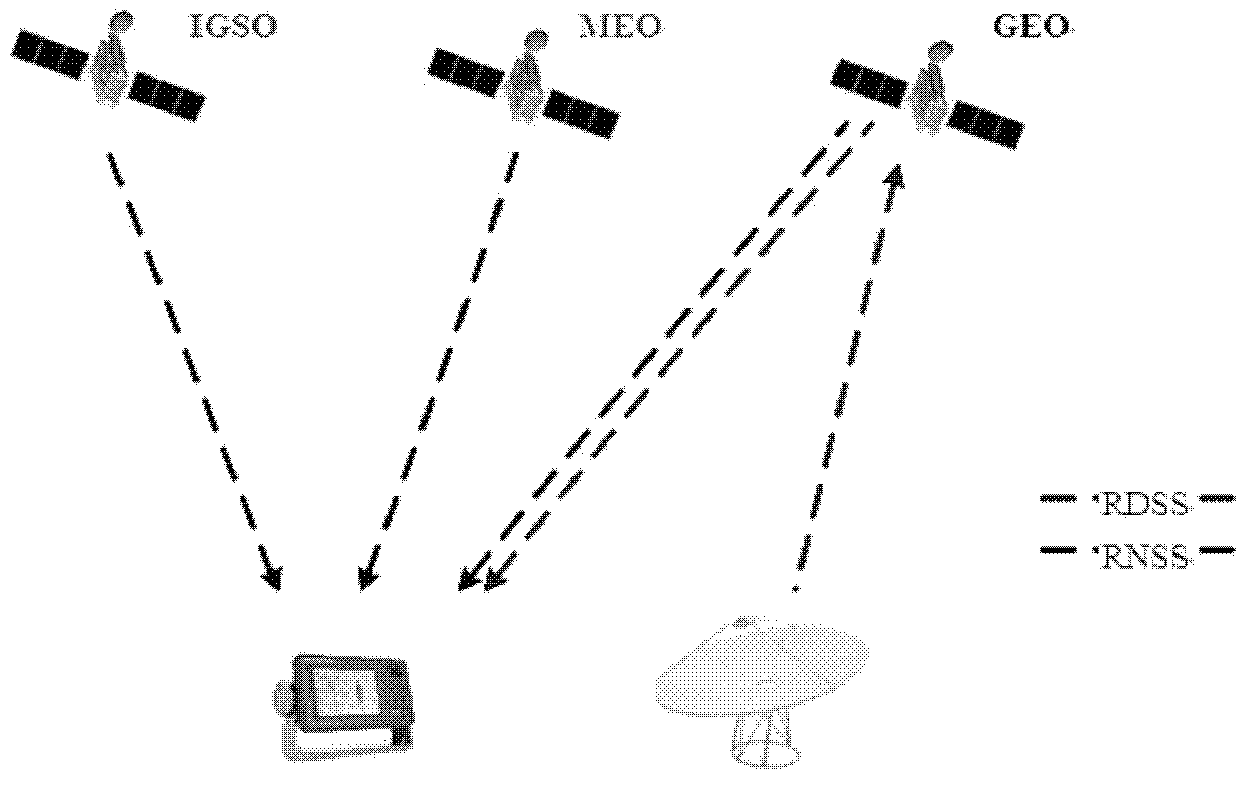
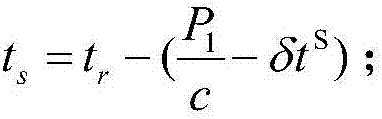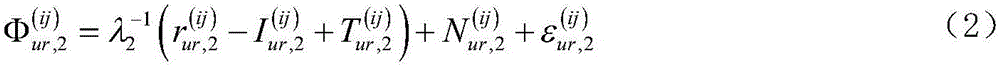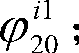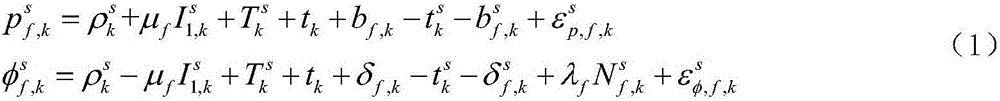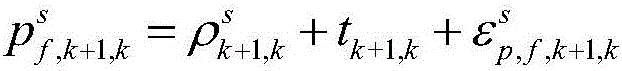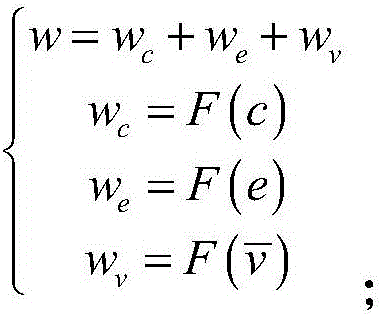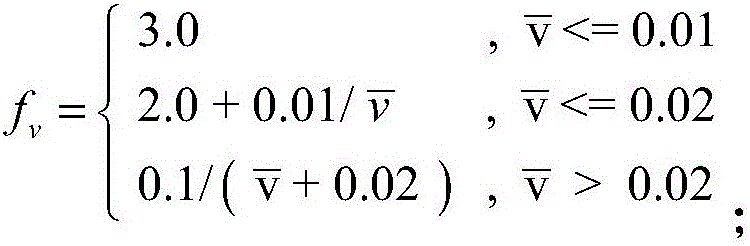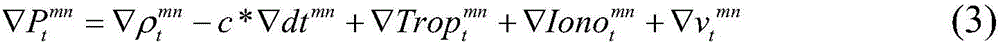Patents
Literature
266 results about "Double difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Double is an object and double is a primitive data type. See this answer for more details. The Double class wraps a value of the primitive type double in an object. An object of type Double contains a single field whose type is double. Source: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Double.html.
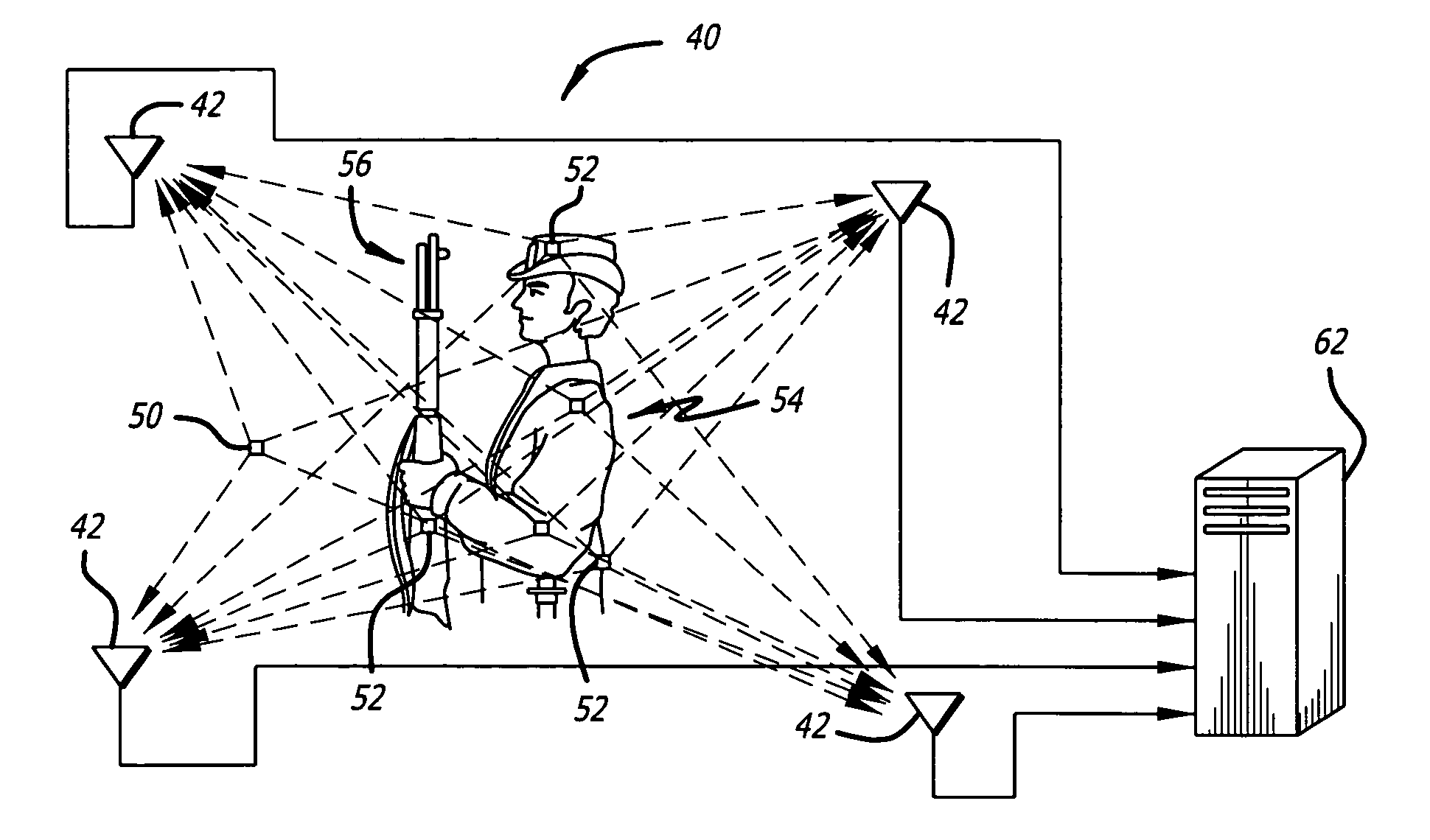
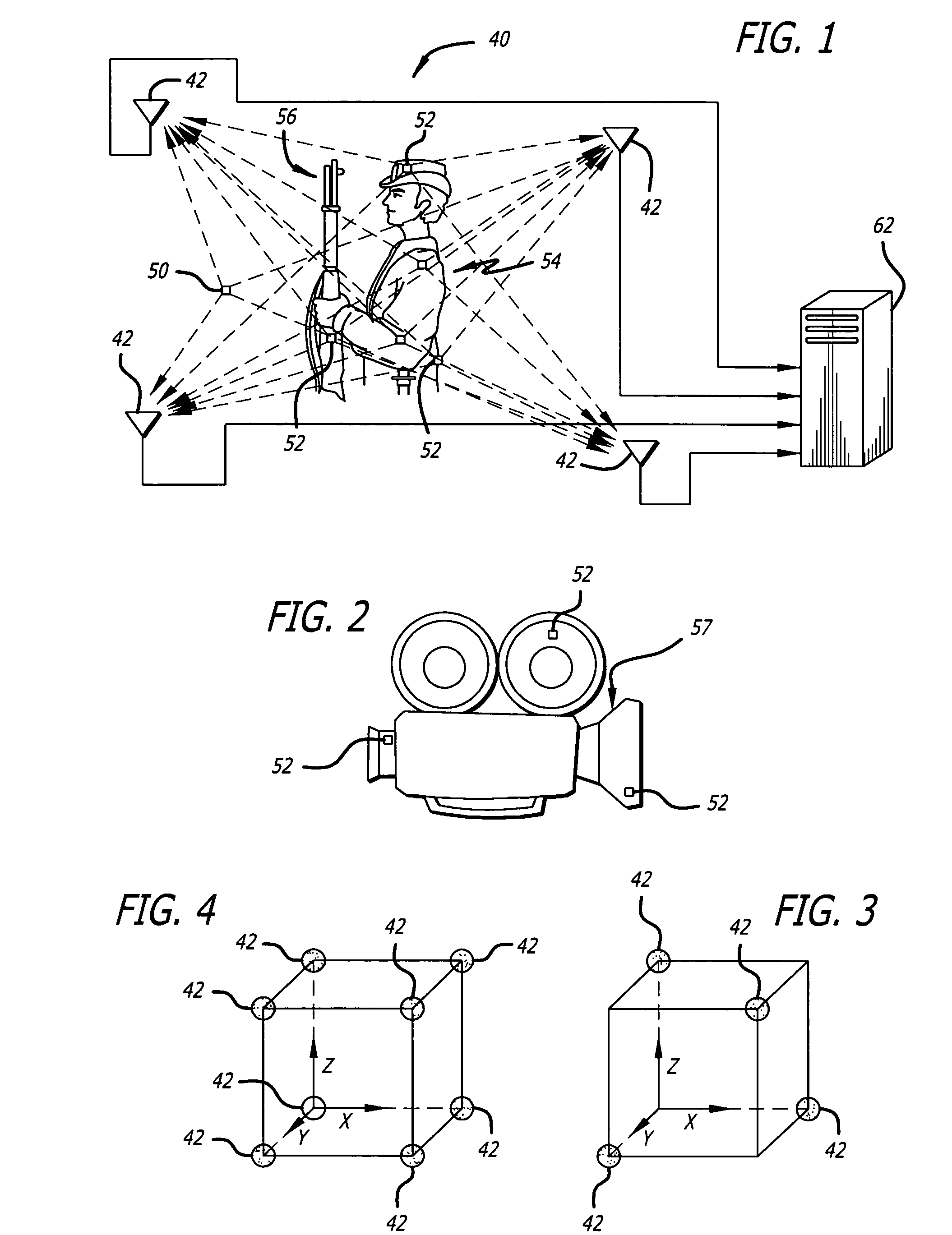
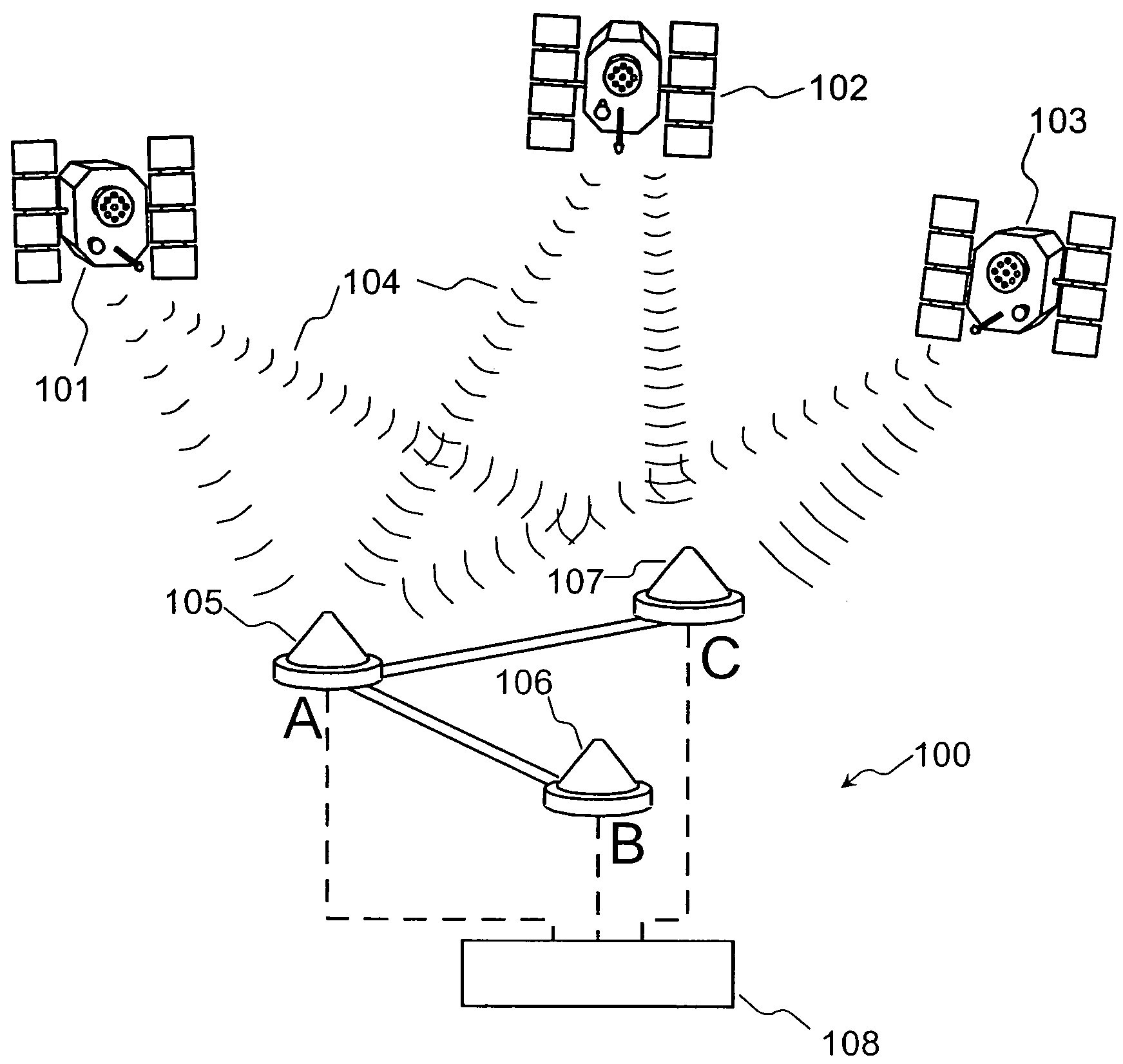
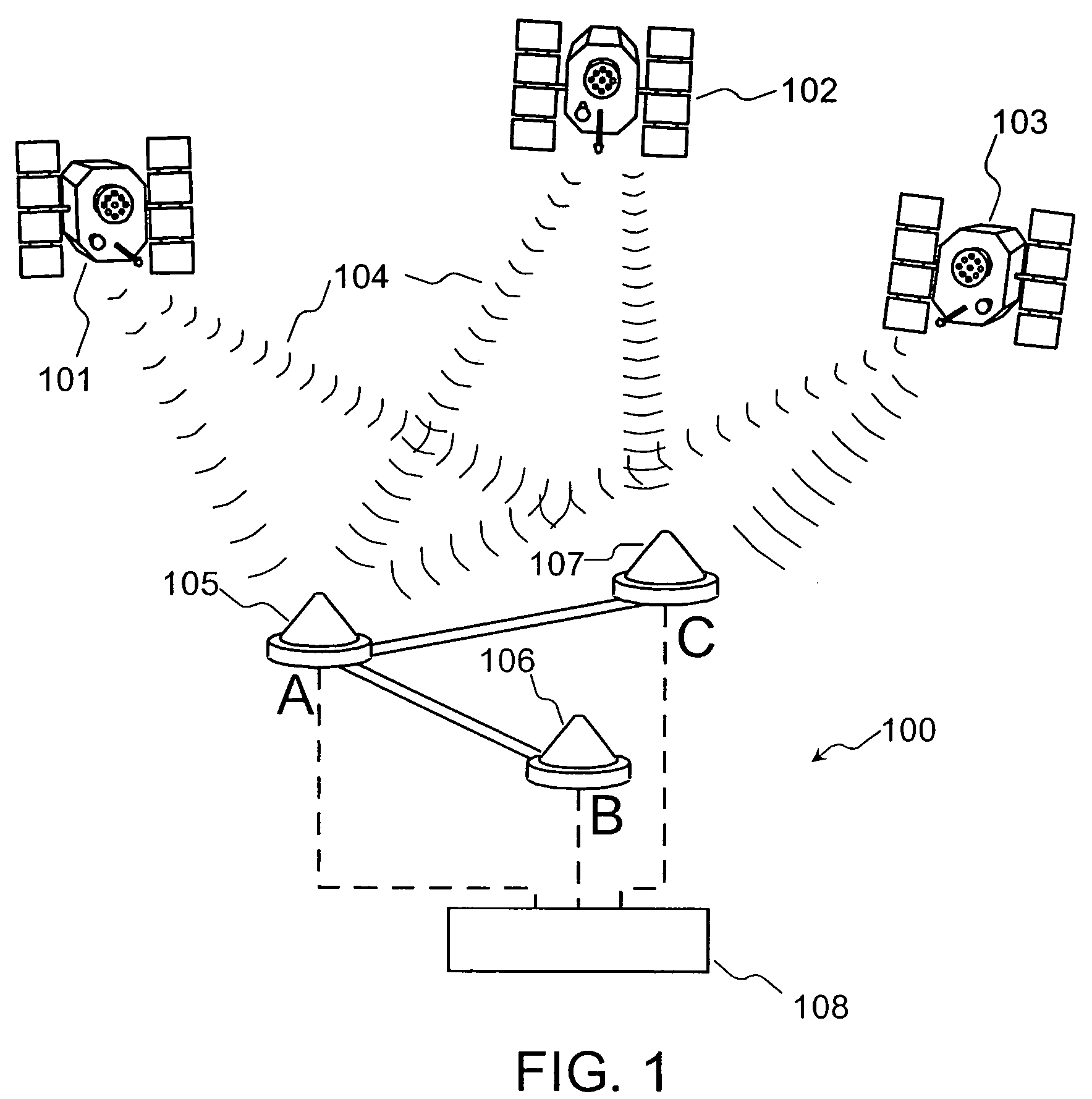
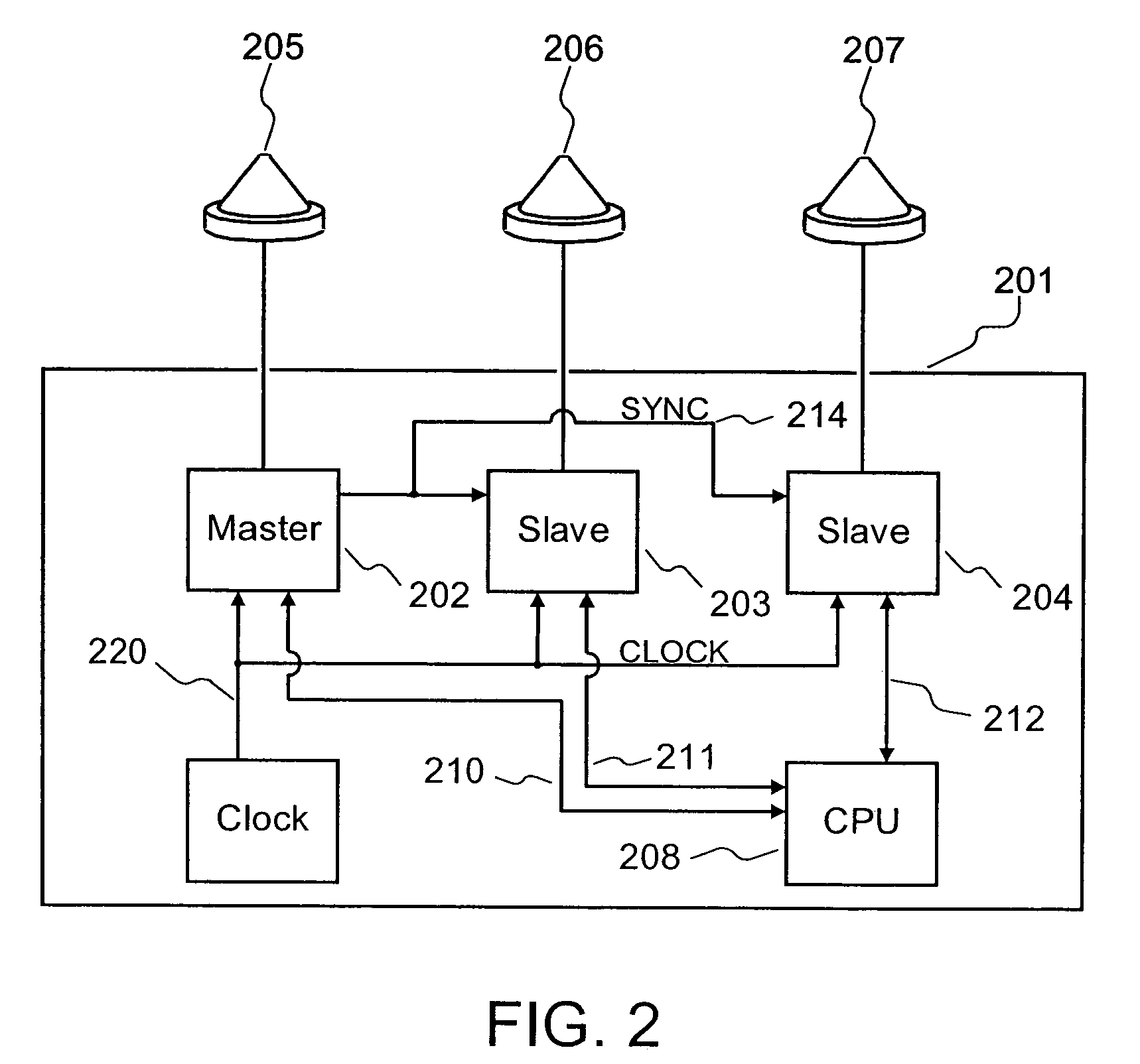
Radio frequency motion tracking system and method
InactiveUS7009561B2Desirable effectReducing manual correlatingDirection finders using radio wavesCode conversionDouble differenceHandling system
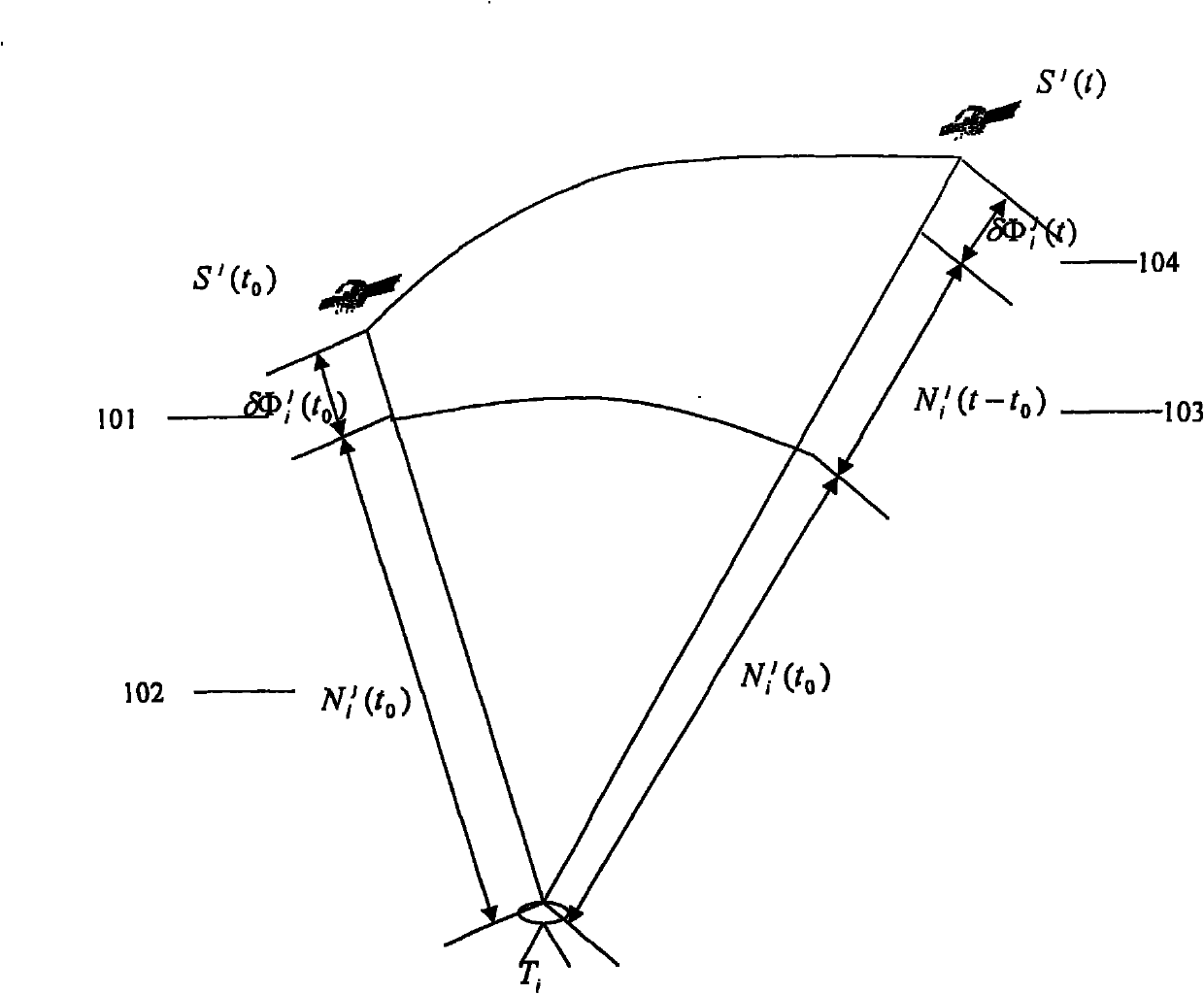
A radio frequency (RF) motion capture system includes stationary sensor receivers, one or more transmitter marker tags on one or more objects to be tracked within a capture zone, at least one stationary reference tag transmitter, and a processing system for processing the received signals. The individual tags transmit burst of spread-spectrum RF signals. The transmitted signals include a common sync code, and a tag identification code that is unique to each tag. By computing double differences of pseudoranges, clock terms are cancelled out allowing the processing system to precisely determine the location of each tag as it moves through the capture zone without the need to synchronize clocks between sensors and tags. The system can be used for RF match moving.
Owner:MENACHE
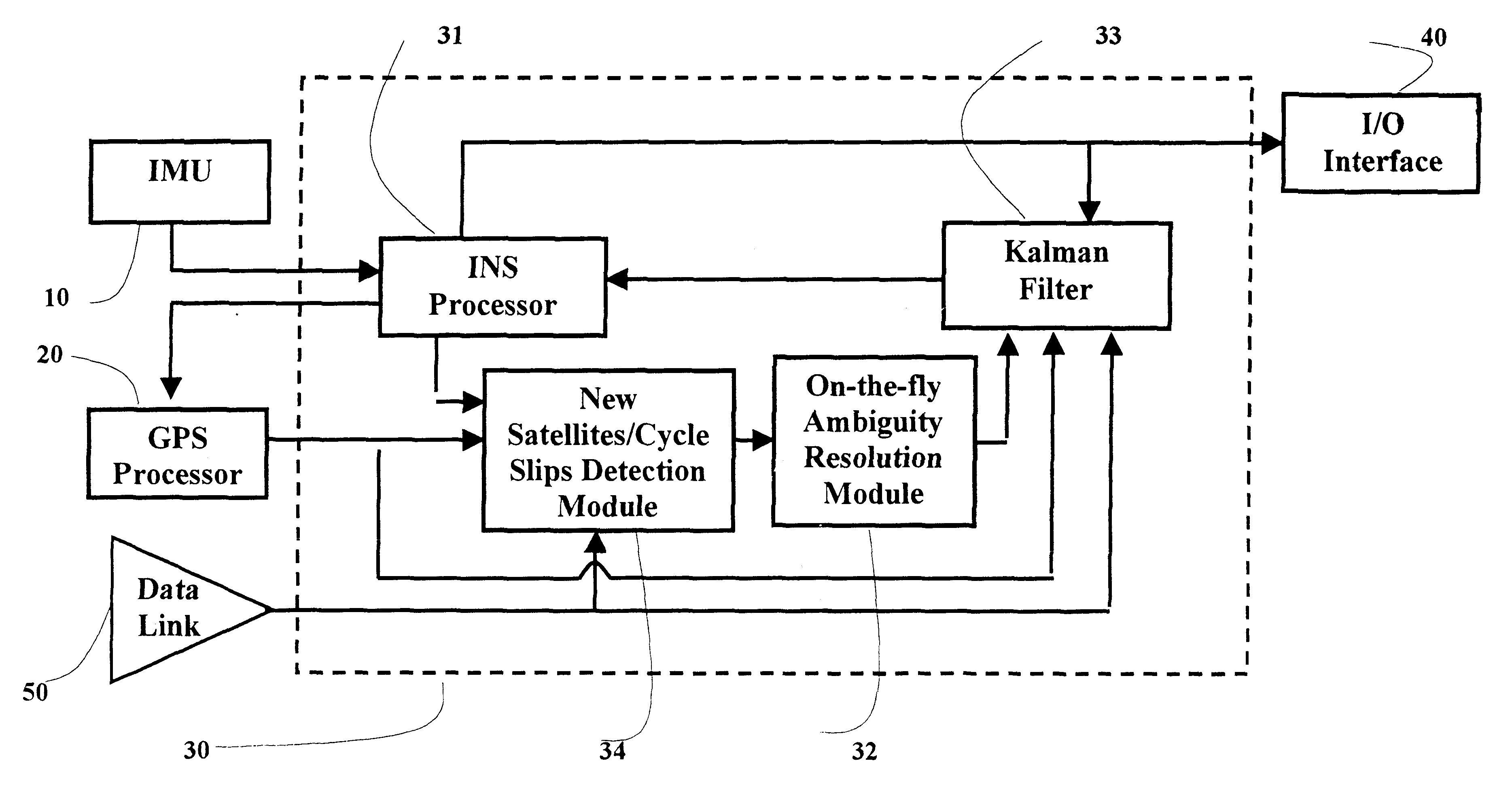
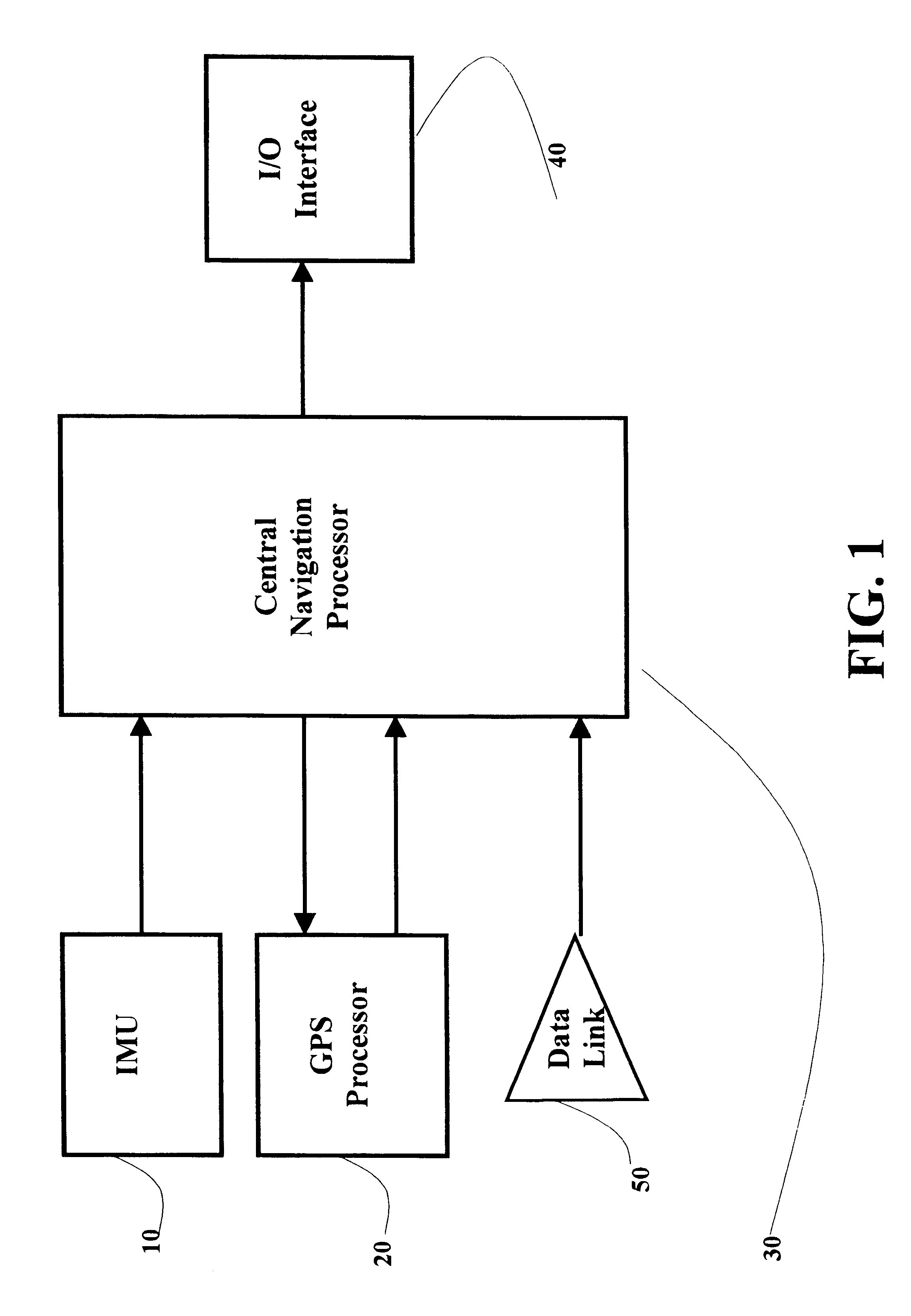
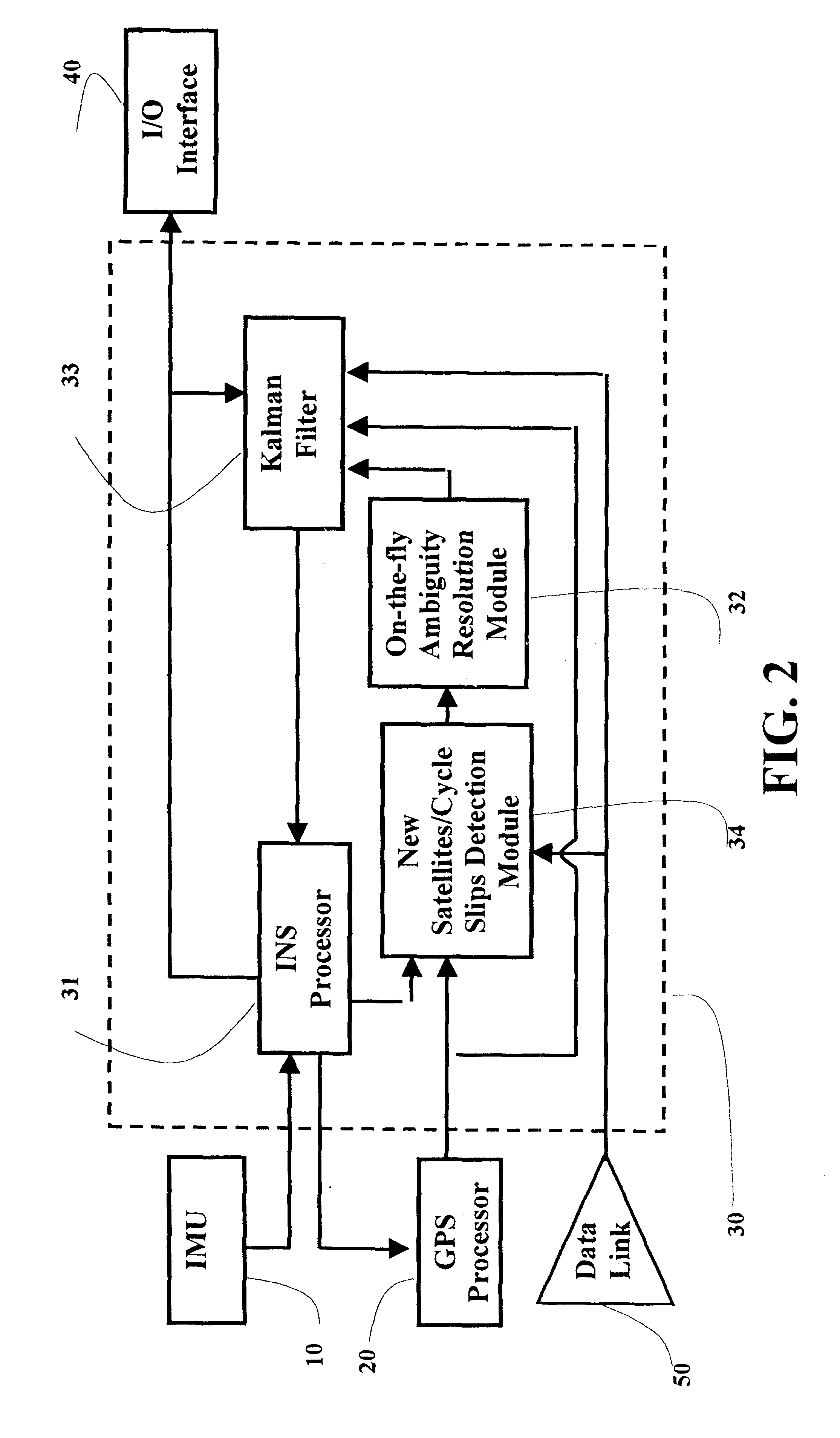
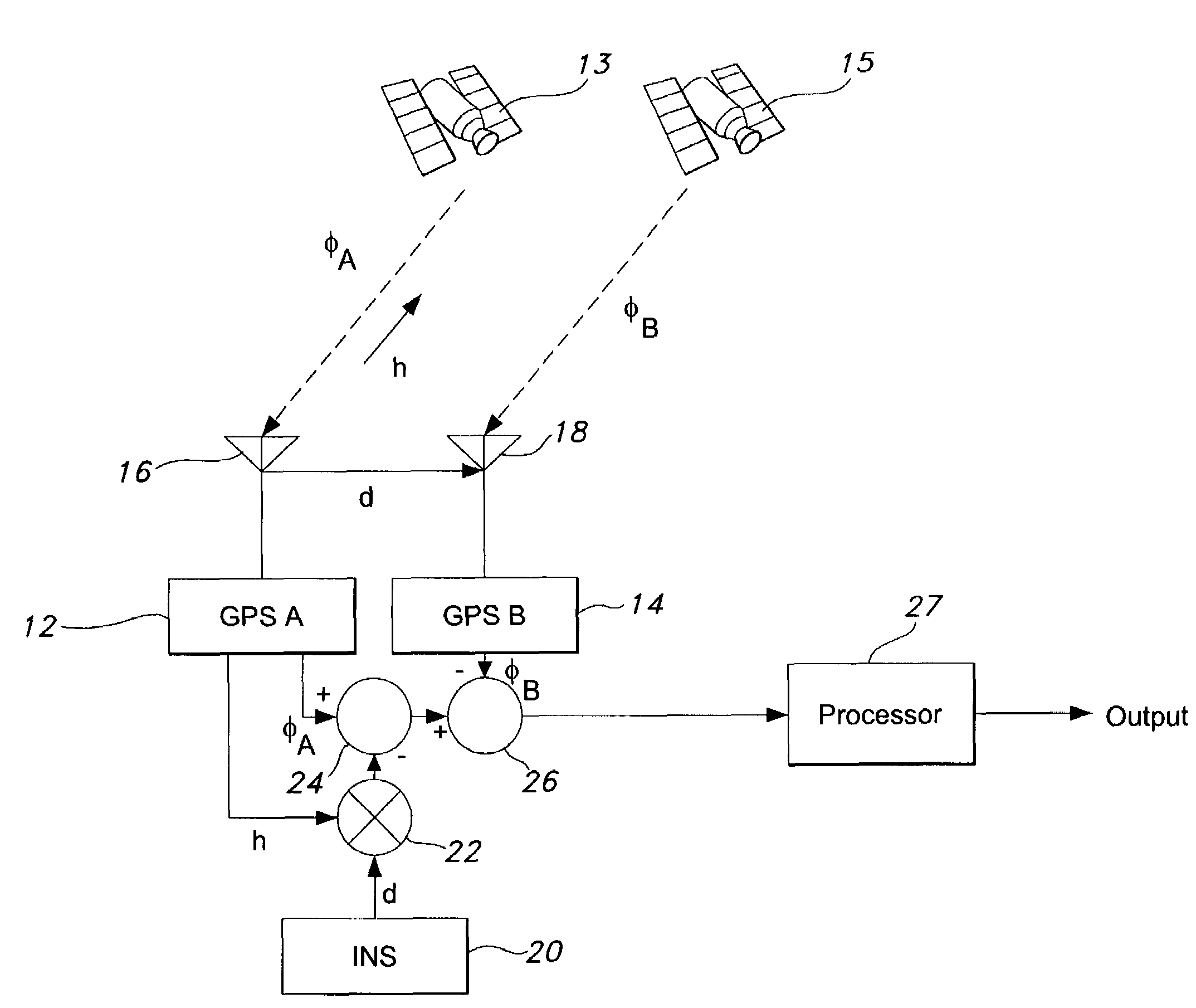
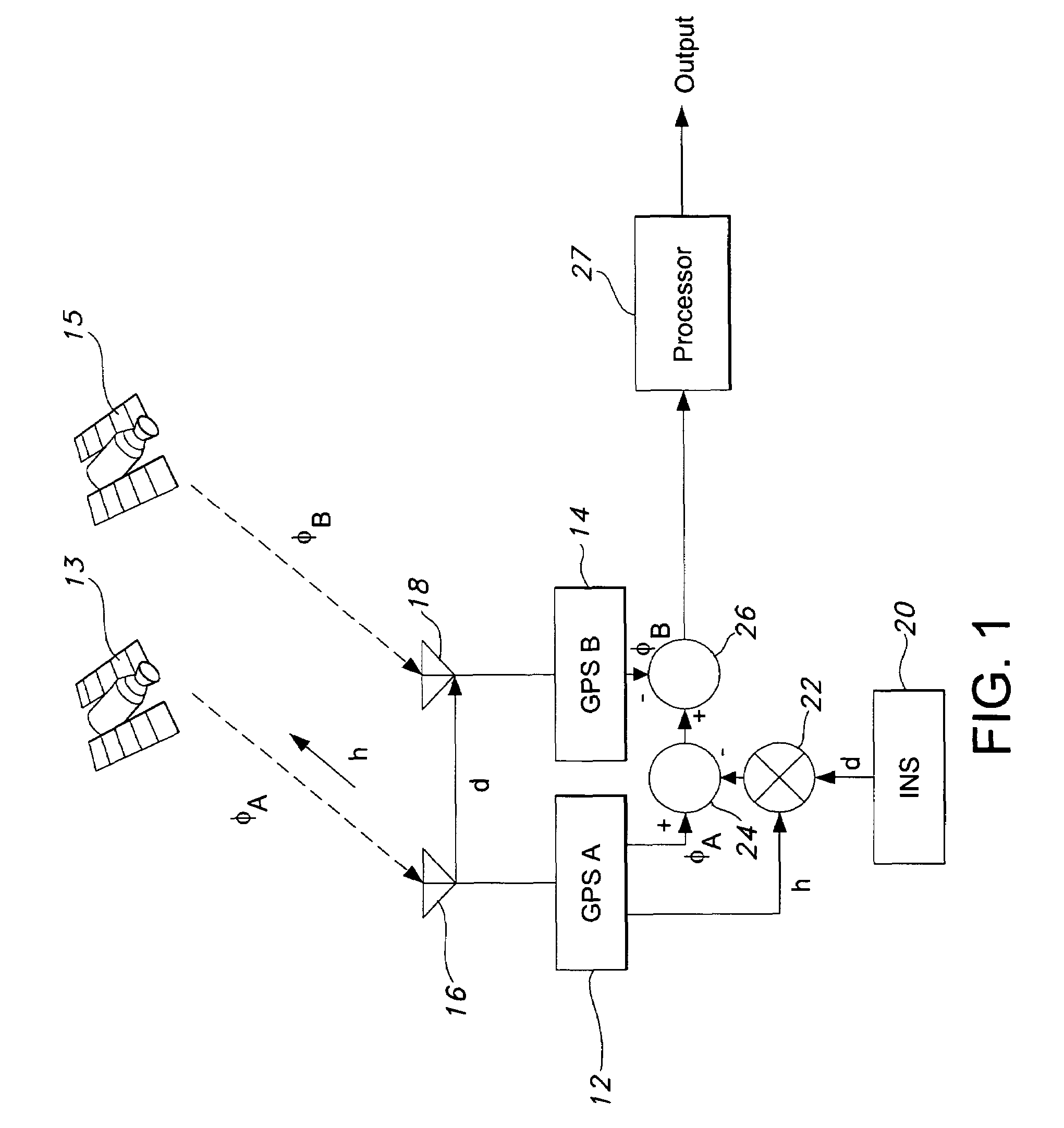
Real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS
InactiveUS6496778B1Improve performanceLow costPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceFully coupled
A real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS can substantially solve the problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial navigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time. In the present invention, the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. However, integer ambiguities have to be resolved for high accuracy positioning. Therefore, in the present invention a new on-the-fly ambiguity resolution technique is disclosed to resolve double difference integer ambiguities. The real-time fully-coupled GPS / IMU vehicle positioning system includes an IMU (inertial measurement unit), a GPS processor, and a data link which are connected to a central navigation processor to produce a navigation solution that is output to an I / O (input / output) interface.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
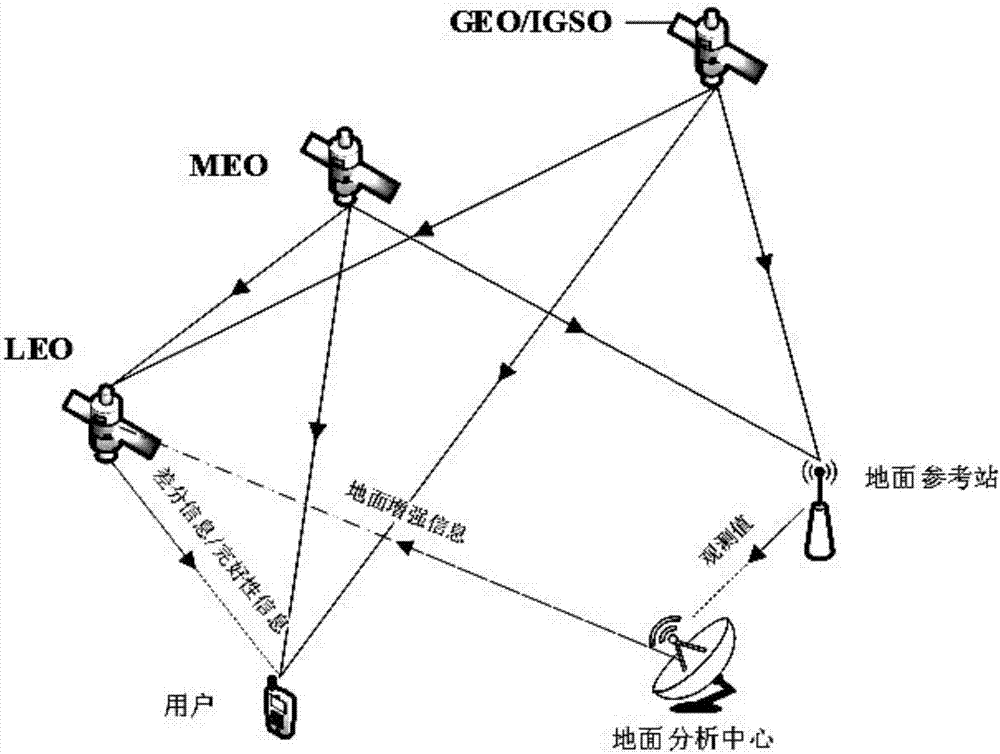
Low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method
ActiveCN107229061ARapid positioningRealize Differential Positioning ServiceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention belongs to the satellite navigation and positioning technical field and discloses a low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method. A low earth orbit satellite is utilized to broadcast the observation data and real-time orbit data of the satellite-borne GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver of the low earth orbit satellite to the ground; and after receiving the differential information broadcasted by the low earth orbit satellite, a ground receiver generates a double-difference observation value consisting of the differential information and a local GNSS observation value and performs pseudorange-based moving base station DGNSS (Differential Navigation Satellite System) positioning and carrier phase-based moving base station RTK (Rea-time kinematic) positioning. According to the positioning method of the invention, the global mobile low earth orbit satellite platform is adopted as a reference station, so that real-time precision differential positioning service in the whole world can be realized, and the method does not depend on the distribution of ground reference stations; and a user can realize differential real-time precise positioning just through using a single receiver, and therefore, the method is free of operating range restrictions, and data communication links are not required to be considered.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus
InactiveUS6611228B2Improve reliabilityShorten the timePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceReference antenna
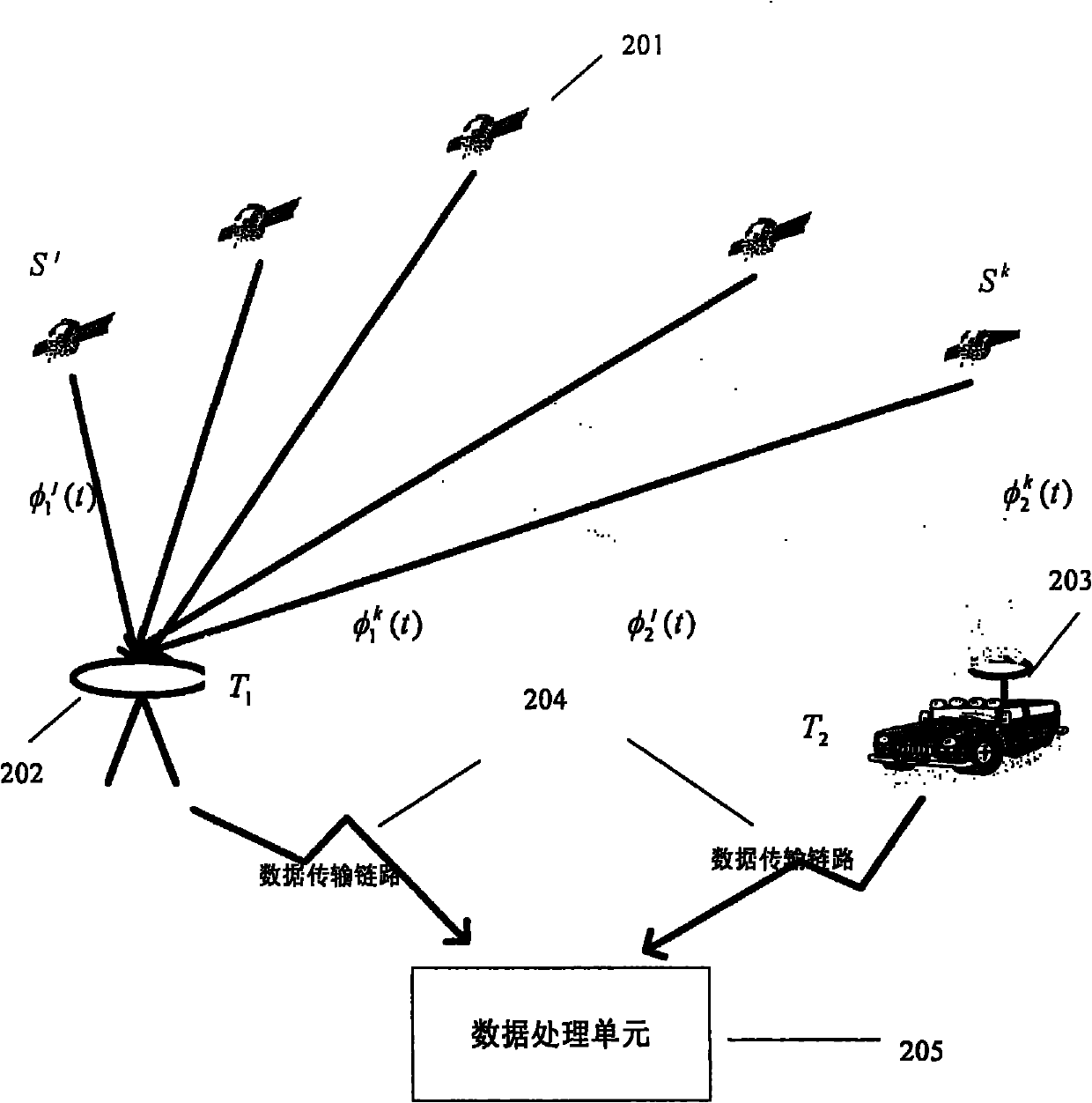
A carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus comprises a plurality of antennas of which at least one is installed on a mobile unit. The apparatus determines the position of each antenna other than one antenna used as a reference antenna relative to the reference antenna by receiving radio signals transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with the multiple antennas, observing a single difference phase or a double difference phase, and calculating an integer ambiguity of the single difference phase or the double difference phase. The apparatus judges that the integer ambiguity has been incorrectly determined if the position of any of the antennas relative to the reference antenna (or the angle of a flat plane formed by those two antennas) falls out of a preset range in which the relative position (the angle of the flat plane) falls under normal conditions.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
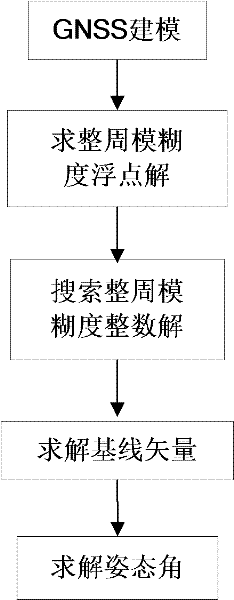
Attitude determination exploiting geometry constraints
A method and system for determining at least one attitude angle of a rigid body. The method comprising: receiving a plurality of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) satellite signals with a plurality of antennas; establishing at least one pair of antennas such that each antenna of the plurality of antennas is included in at least one antenna pair; computing single- or double-difference phases corresponding to one or more GNSS satellites for each of the pairs of antennas; and constructing a single Differential Carrier Phase Attitude (DCPA) equation based on known geometry constraints of each of the pairs of antennas. The method also includes determining a solution for the DCPA equation based on a cost function, the solution yielding at least one integer ambiguity value and the at least one attitude angle.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
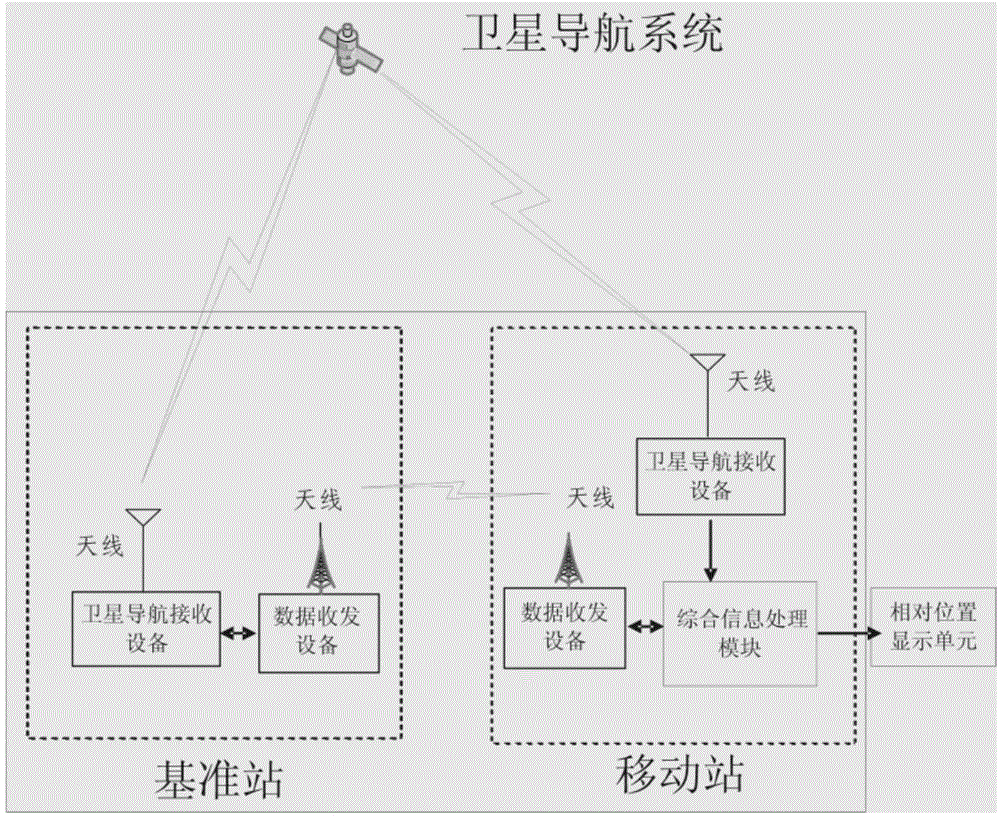
Relative positioning device for satellite navigation and carrier phase cycle-slip repairing method of device
InactiveCN104570011AHigh frequencyReduce resource requirementsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInformation processing
The invention provides a relative positioning device for satellite navigation and a carrier phase cycle-slip repairing method of the device. A satellite navigation antenna on a base station receives a navigation signal, outputs ephemerides and observed quantities of all satellites through a satellite navigation receiver and sends the ephemerides and the observed quantities to a mobile station; the mobile station receives data sent by the base station and outputs the data to a comprehensive information processing module, a satellite navigation antenna on the mobile station receives the navigation signal and outputs the ephemerides and the observed quantities of all the satellites through the satellite navigation receiver, the comprehensive information processing module performs gross error processing on data output by the base station and the mobile station, carrier phase cycle-slip detection and repairing are finished, a double-difference observation equation is established through carrier phase double-difference processing, the whole-cycle ambiguity is resolved, and relative positioning information is output. With the adoption of the device and the method, the cycle-slip can be detected and repaired in real time, outliers can be marked out in real time, meanwhile, the cycle-slip occurrence frequency can be determined, high-precision relative positioning can be realized, and the availability of a system is guaranteed.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Method for measuring attitude of carrier by using additional constraint condition of GPS system
The invention relates to a method for measuring attitude of a carrier by using an additional constraint condition of a satellite, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a linearization carrier phase double-difference model for each baseline of an attitude measuring system, and determining the integer ambiguity; expanding a search space, and determining a trigonometric function constraint and a base length constraint; substituting a constraint condition containing the maximum boundary and the minimum boundary into a search process to obtain an upper bound and a lower bound of a formula ambiguity candidate value; performing a comparison according to the boundaries obtained in the search process and an original constraint, and selecting a smaller boundary as the boundary of the ambiguity; and selecting ambiguity candidate values, wherein if the ambiguity candidate values are more than one, two groups of the ambiguity candidate values with the minimum residual errors are selected to perform a verification of the next step, and the candidate values passing through a significance test are fixed solutions of the integer ambiguity. The attitude of the carrier is obtained by further using an attitude measurement algorithm through the fixed solutions. The method has the advantages of reducing the search times, reducing influences caused by noises and significantly improving the measuring accuracy and the success ratio.
Owner:周迅
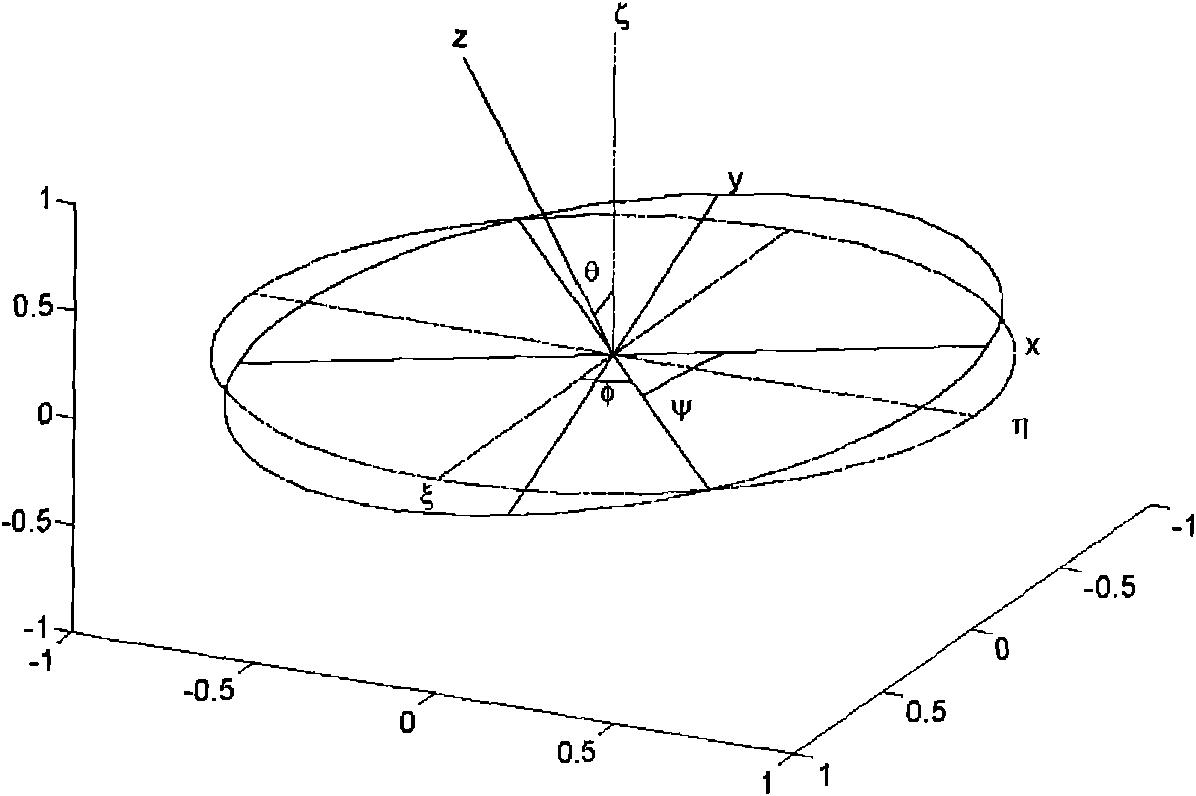
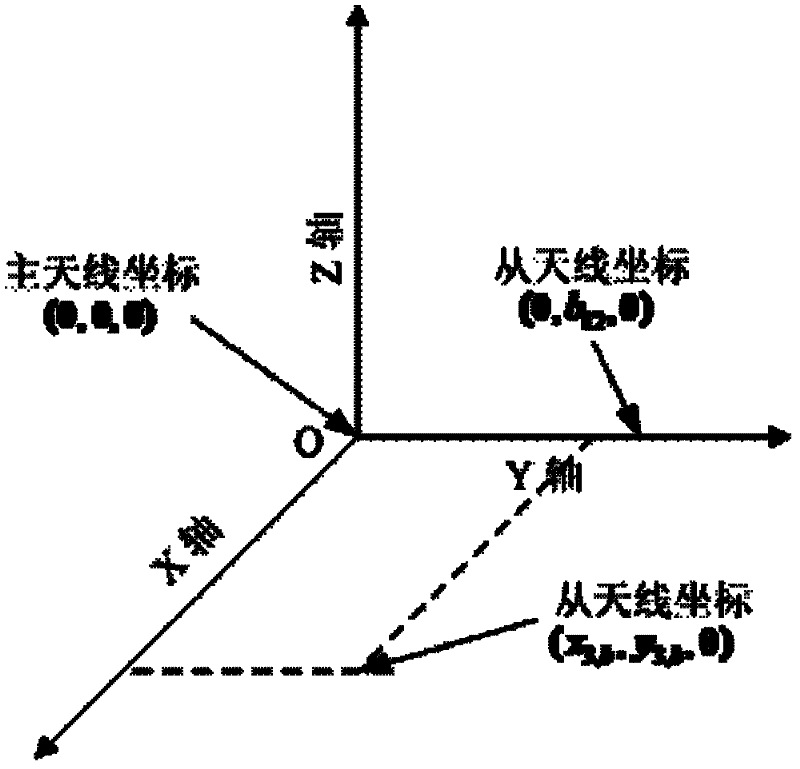
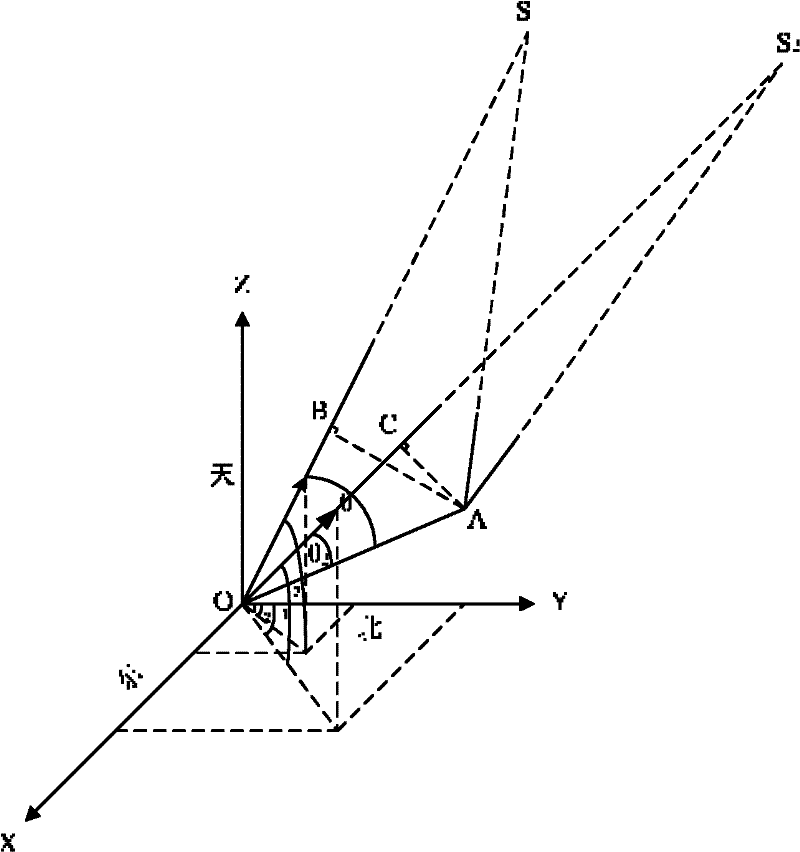
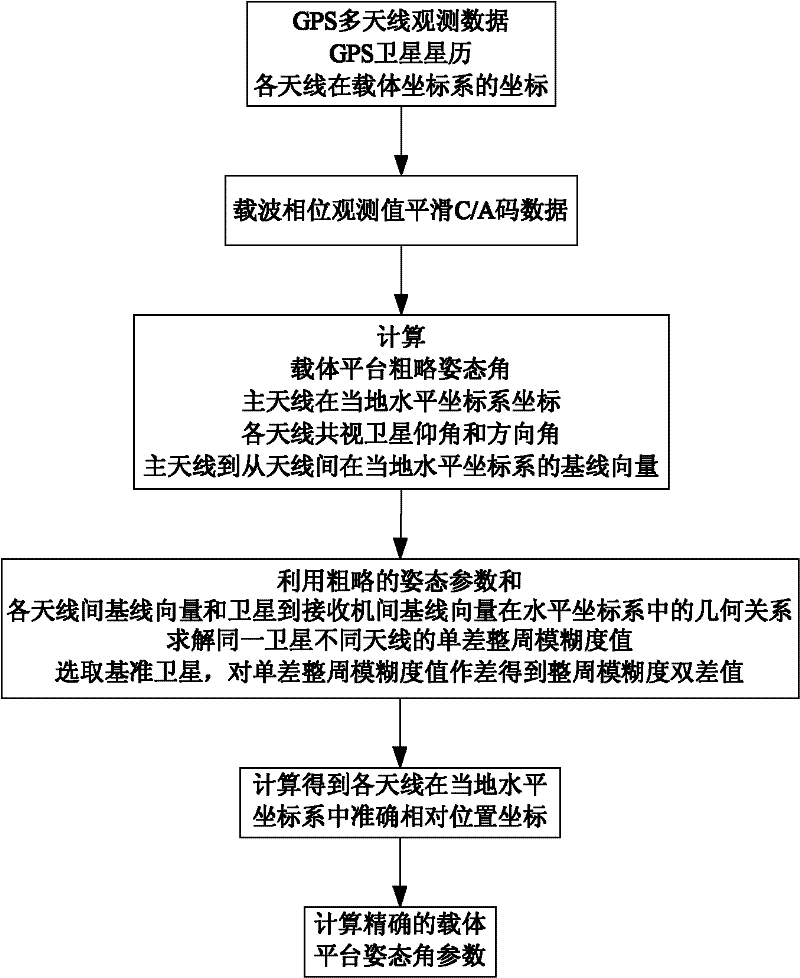
GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method
The invention aims at providing a GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly GPS multi-antenna observation data, a GPS satellite ephemeris and the coordinates of antennas on a carrier coordinate system are collected; a smoothing procedure is carried out to C / A code observation data with a carrier wave phase observed value; a carrier platform rough attitude angle, the coordinate of the main antenna in a local horizontal coordinate system, the shared vision satellite elevation angles and direction angles of the antennas and the baseline vector from the main antenna to subordinated antennas in the local horizontal coordinate system are calculated; based on the geometry relations of the baseline vectors among the antennas and the baseline vectors from the satellite to a receiver in the horizontal coordinate system, the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value of different antennas of the same satellite is solved; a reference satellite is selected and a difference operation is carried out to the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value to obtain an integer cycle fuzziness double difference value; the integer cycle fuzziness double difference value obtained is substituted into a carrier wave phase double difference model to obtain accurate coordinate components of the antennas and based on the coordinate components of the antennas, accurate attitude parameters are solved so as to realize GPS multi-antenna attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) triple-frequency motion-to-motion positioning method
ActiveCN101710179AImprove calculation accuracyHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceLow noise
The invention relates to a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) triple-frequency motion-to-motion positioning method. In the original epoch, the triple-frequency precision single-point positioning technology is adopted to obtain the coordinates of two movable carriers, one of the two movable carries is selected as the reference station for the triple-frequency double-difference position, the triple-frequency double-difference positioning technology is adopted to calculate the baseline component of the two movable carriers and the integer ambiguity resolution of the double-difference carrier phase, and the baseline component of the two movable carriers and the integer ambiguity resolution of the double-difference carrier phase are used as the constraint conditions for the triple-frequency precision single-point positioning in the subsequent epochs to improve the single-point position precision and the convergence speed thereof. The geometry-Base TCAR ambiguity resolution fixation method is adopted to calculate the triple-frequency integer ambiguity resolution. The three irrelevant combination observation values of the triple-frequency non-ionizing layer and the long wave-length and low noise carrier are adopted to detect and repair the cycle slip of the original observation data.
Owner:威海五洲卫星导航科技股份有限公司
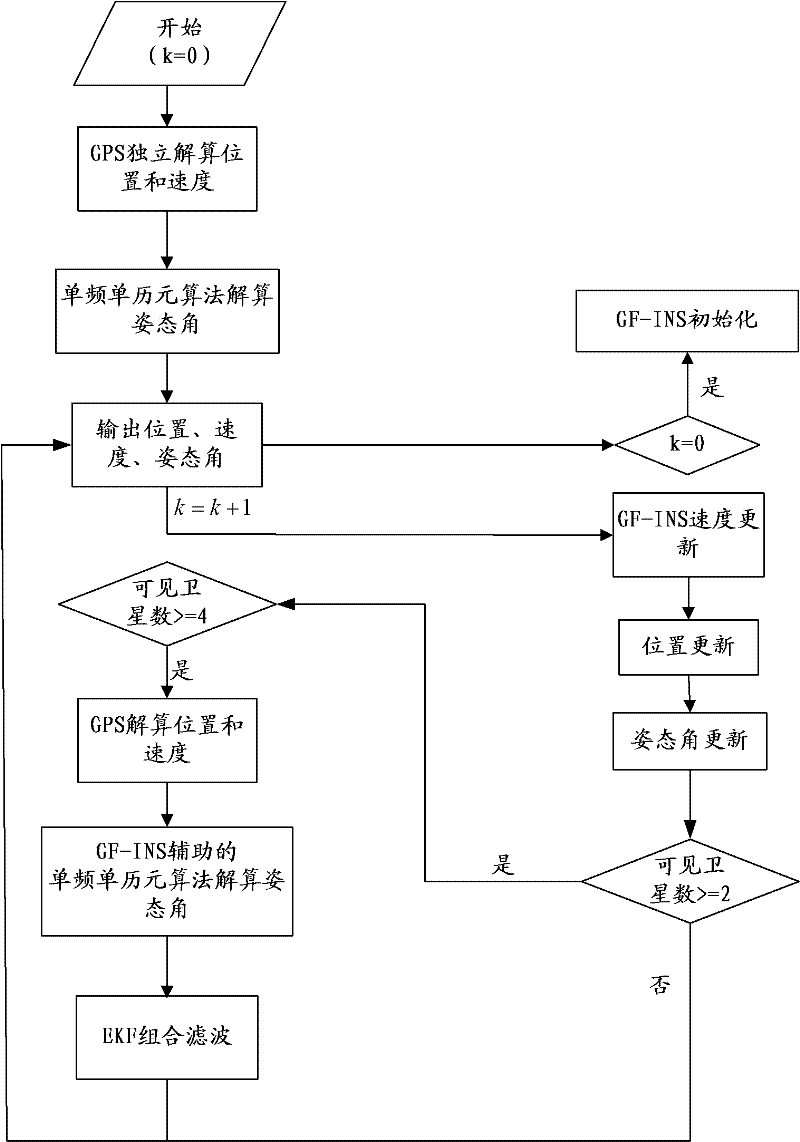
Multiple-antenna GPS(Global Positioning System)/GF-INS (Gyroscope-Free-Inertial Navigation System) depth combination attitude determining method
InactiveCN102508275ALow costSolve problems that need to be assisted by external informationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAnti jamming
The invention discloses a multiple-antenna GPS(Global Positioning System) / GF-INS (Gyroscope-Free-Inertial Navigation System) depth combination attitude determining method. The method comprises the following steps: when a multiple-antenna GPS / GF-INS system operates for the first time, the GPS independently work to independently resolve position, speed and an attitude angle firstly; after the GPS stably works, the position, speed and attitude angle of the GF-INS are initialized according to the position, speed and a carrier attitude angle, which are output by the GPS; and after the GF-INS is initialized, navigation calculation is performed normally, wherein the multiple-antenna GPS / GF-INS system outputs the position, the speed and the attitude angle according tp a preset method. The multiple-antenna GPS / GF-INS depth combination attitude determining method has simple structure, and the search successful rate of a GPS double-difference complete-cycle ambiguity can be greatly improved so as to improve the attitude measurement precision of the GPS system and the navigation precision and the anti-jamming capability of the whole combined navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for detecting and restoring cycle slip of GPS (Global Positioning System) carrier phase under dynamic environment
InactiveCN102116867ASmall amount of calculationSimple calculationSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceGps receiver
The invention discloses a method for detecting and restoring the cycle slip of a GPS (Global Positioning System) carrier phase under dynamic environment, comprising the steps of: carrying out difference kalman filtering calculation by utilizing a double-difference code pseudo-range observed quantity so as to obtain two epoch GPS receiver coordinates; constructing a carrier phase cycle slip detection equation by utilizing the two epoch GPS receiver coordinates and two epoch double-difference carrier phase observed quantities, calculating the equation and computing a residual error RMS (Root Mean Square) value; comparing the residual error RMS value with a set threshold, if the residual error RMS is greater than the set threshold, determining that the cycle slip occurs, selecting a satellite combination with the minimum residual error as a combination without the cycle slip by taking five satellites as a combination so as to restore the cycle slip, and then ending; if the residual error RMS value is less than or equal to the set threshold, comparing the result deltaX of the calculated cycle slip detection equation with the set threshold, if the result deltaX is less than the set threshold, determining that no cycle slip occurs and exiting the cycle slip detection process; and if the result deltaX is greater than the set threshold, determining that the cycle slip can not be detected and quitting from the cycle slip detection process.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
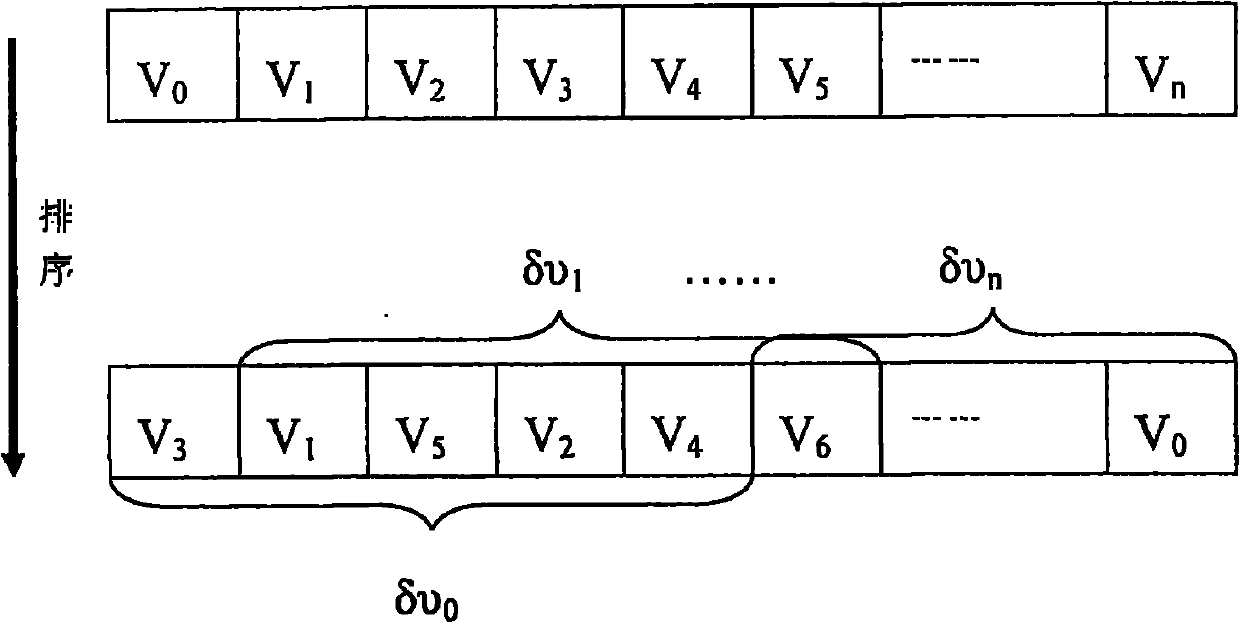
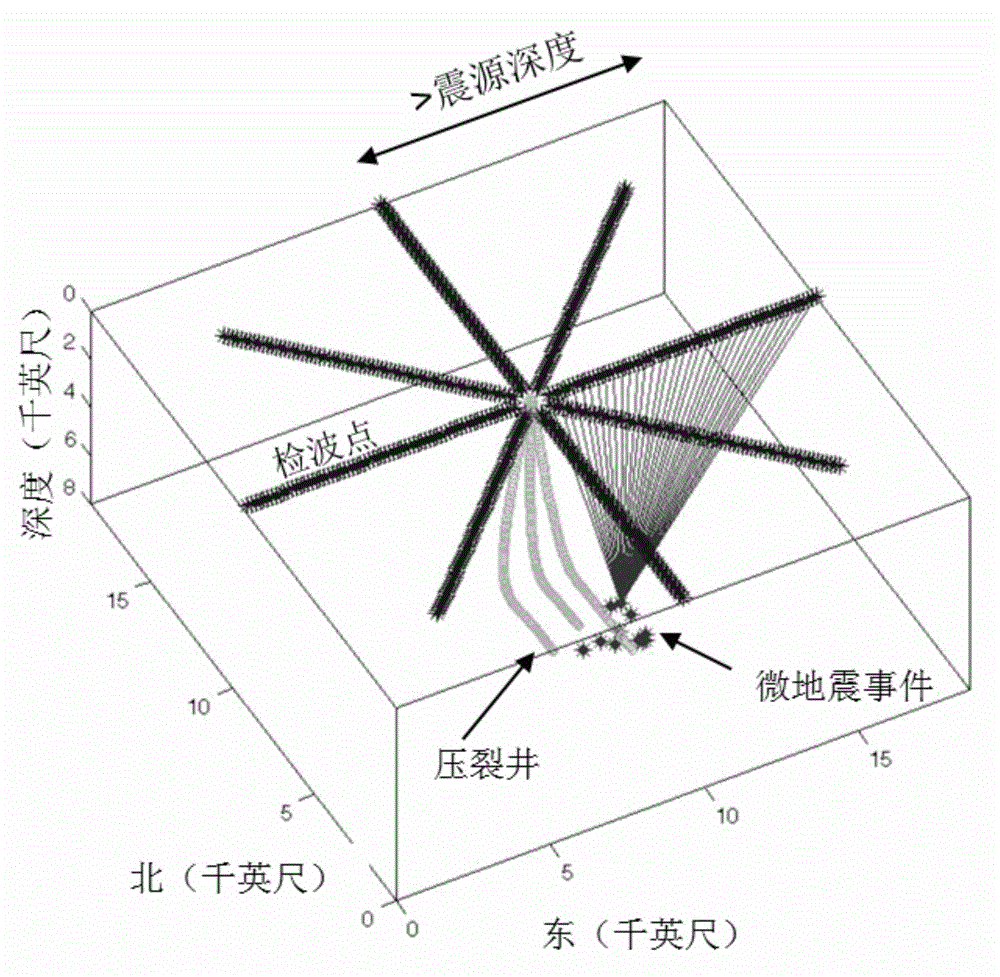
Microseism focus positioning method based on double-difference method
The invention provides a microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method, and belongs to the field of geophysical prospecting of petroleum. The microseism focus positioning method selects a perforation event as the main event, and picks the observation travel time for a microseism event, and can determine the relative distance between the perforation and the microseism event by calculating the residual error (double difference) between the observation travel time of the perforation and the microseism event and the theoretically calculated travel time difference. The microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method is high in operation speed and efficiency, and is easy for local convergence. As the microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method has the relative main event, the relative positioning accuracy is higher and the microseism focus positioning method is not limited by the spacial scale. The microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method offsets the error caused by changes of the speed of the near surface and the stratum speed, and can improve the positioning accuracy.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dual antenna diversity method to detect GPS signal tampering
ActiveUS7310062B1Readily availableLow costPosition fixationBeacon systemsDouble differenceGps receiver
A method of detecting GPS signal tampering uses two GPS receivers. A first receiver measures carrier phases of two or more satellite signals and of a tampered signal. A second receiver measures carrier phases of the two or more satellite signals and the tampered signal. A baseline vector between the receiver antennas is measured. Direction cosine vectors of the two or more satellite signals are computed and a dot product is computed from the baseline vector to translate measurements made at antennas of the GPS receivers to a virtual zero baseline condition. The carrier phase measurements are double differenced to obtain double difference residuals. A test statistic of the double difference residuals is computed and tested for phase coherency. An inconsistency in measured signals is flagged when there is an inconsistency in phase coherence indicating the tampered signal is present.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
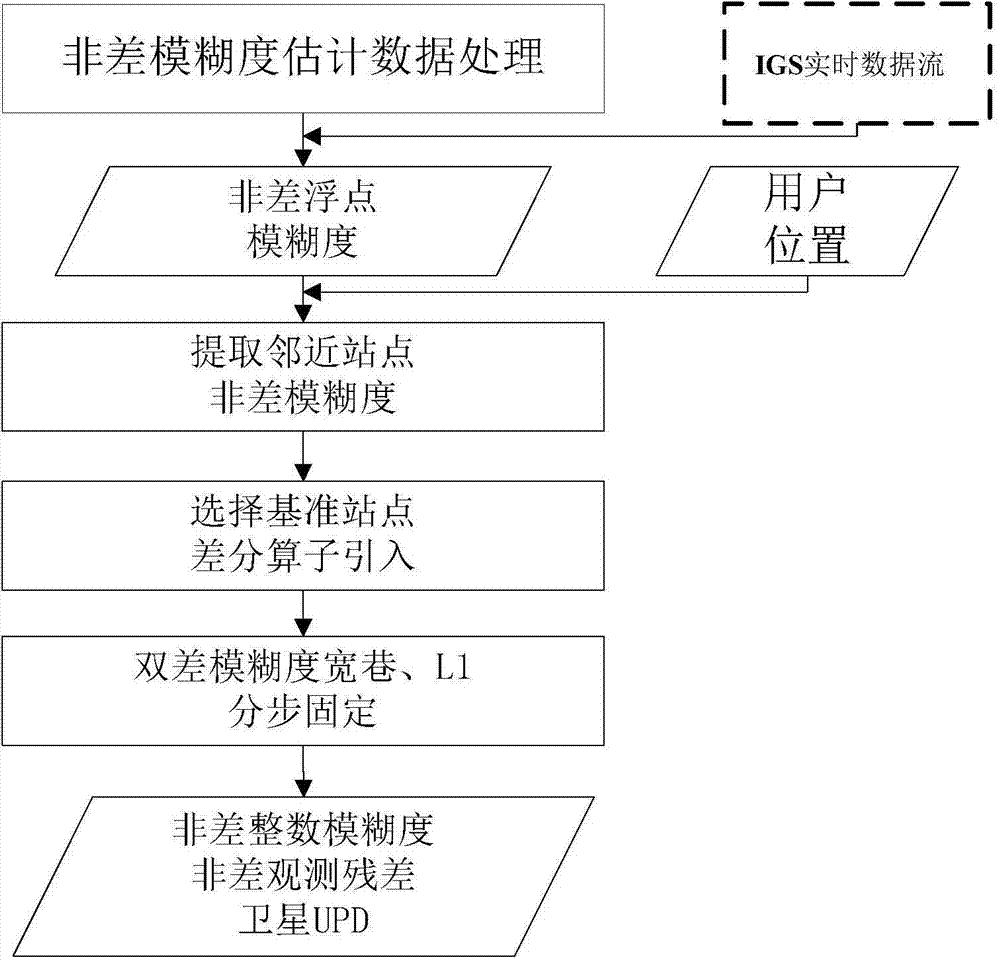
Network RTK (real-time kinematic) ambiguity resolution method based on un-differential uncombined model
ActiveCN104502935AIncreased degree of robustnessImprove solver performanceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a network RTK (real-time kinematic) ambiguity resolution method based on an un-differential uncombined model. The un-differential uncombined model is used to estimate single-station un-differential ambiguity of a whole network, a satellite clock is used as an unknown parameter, and a real-time satellite clock bias product is added as a pseudo-observable; according to a user's position, un-differential ambiguity of stations adjacent to the user is extracted, one of the adjacent stations is selected as a reference station, integer features of double-difference ambiguity are acquired by reduction through difference operators, double-difference ambiguity results with the integer features are acquired by a single epoch method. The network RTK (real-time kinematic) ambiguity resolution method based on the un-differential uncombined model has the advantages that capacity of calculation for large-scale reference station networks can be effectively improved, the influence of barometric error and length upon double-difference ambiguity fixing is weakened, the double-difference model is less ill-conditioned, difference resistance of the model and ambiguity fixing success rate are increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for detecting and repairing cycle slip by utilizing BeiDou three-frequency observed quantity
InactiveCN102650692ALong wavelengthReduce noiseVoltage-current phase angleSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNoise detection
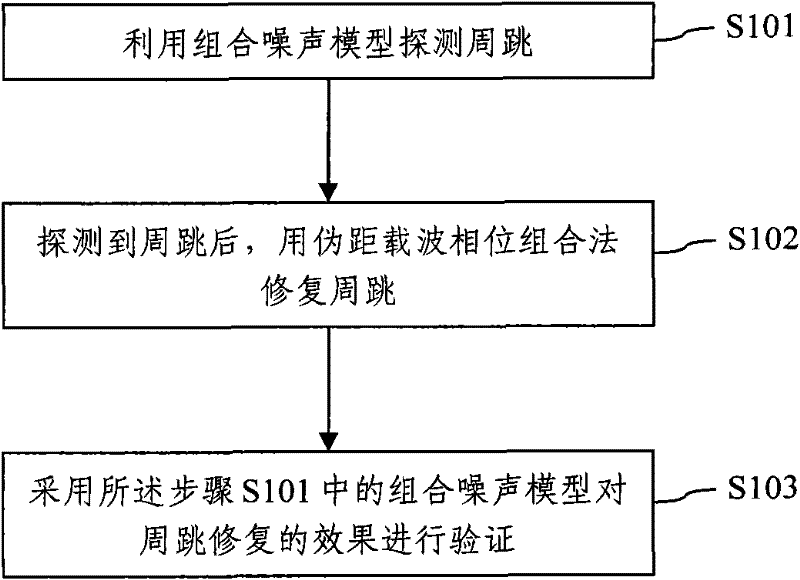
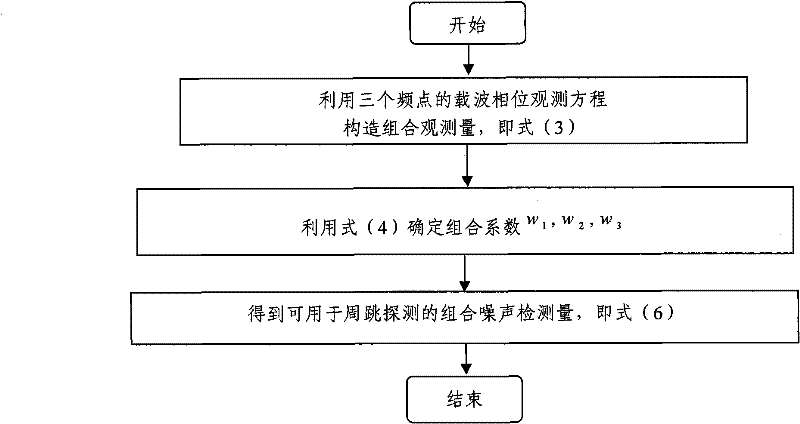
The invention discloses a method for detecting and repairing a cycle slip by utilizing a BeiDou three-frequency observed quantity. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, performing linear combination by utilizing the three-frequency observed quantity under the condition of providing a three-frequency signal by a BeiDou satellite navigation system, and constructing a combination noise detection quantity by selecting proper combination coefficients to detect the cycle slip; 2, after the cycle slip is detected, calculating and screening to obtain three sets of combination coefficients with superior performance in a pseudo-range carrier phase combination method, and calculating and repairing the cycle slip by utilizing the pseudo-range carrier phase combination method; and 3, finally, performing verification on a cycle-slip repairing effect by utilizing the combination noise detection quantity. The method for detecting and repairing the cycle slip is not related to the motion state of a carrier, can be used for reliably detecting and repairing the minimum cycle slip of which the time of losing lock reaches up to 30 seconds and can be used for detecting and repairing the cycle slip by the zero-difference, single-difference or double-difference carrier phase observed quantity when static measurement or dynamic measurement is performed.
Owner:中国人民解放军61081部队
Long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing
ActiveCN105372691AHigh precisionOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
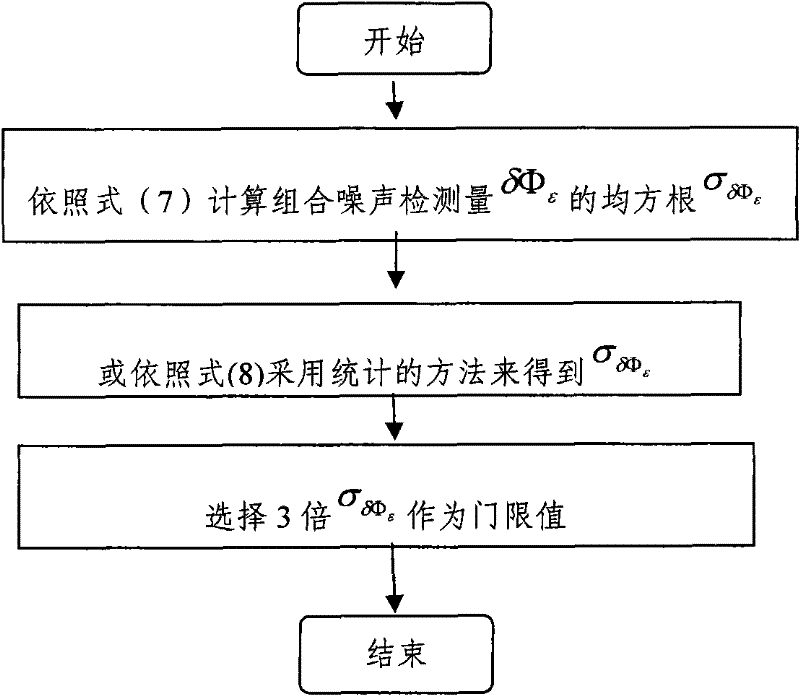
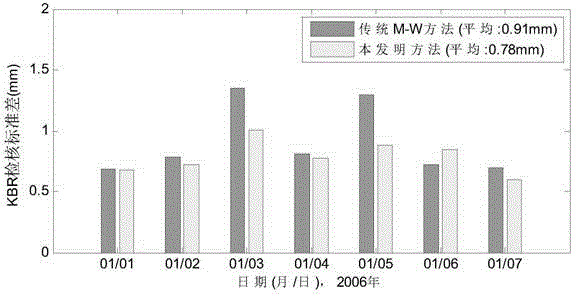
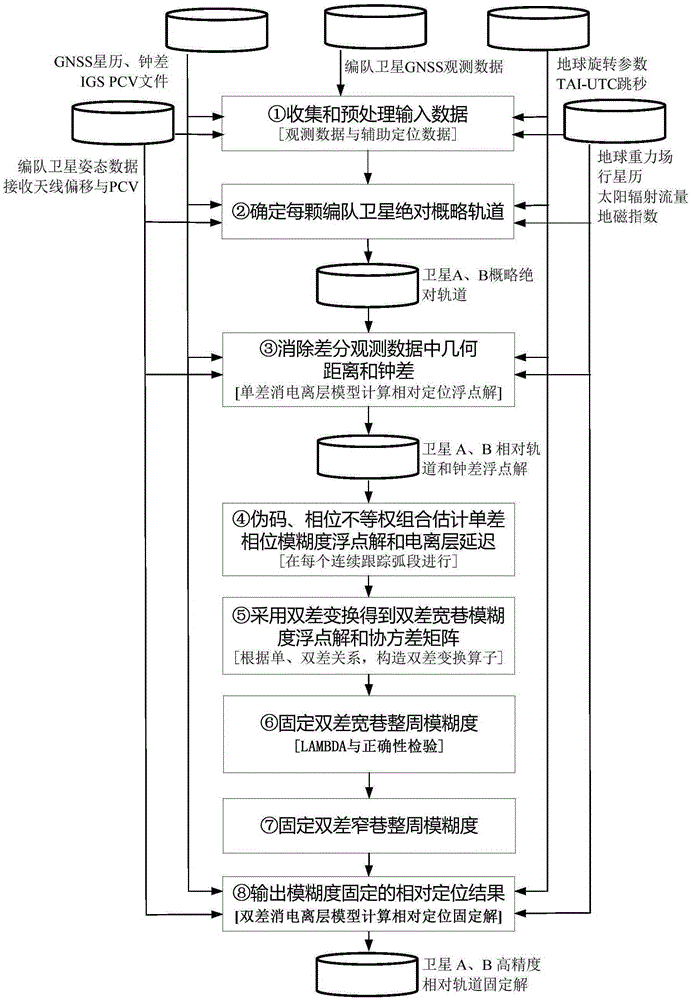
A long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing is provided in order to improve the success rate of ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of relative positioning results. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: first, collecting and pre-processing input data, and determining the absolute general orbit of a formation satellite; then, eliminating the geometric distance and clock error in differential observation data, estimating a single-difference phase ambiguity float solution and a single-difference ionosphere delay parameter, carrying out double-difference transform to get a double-difference wide-lane ambiguity float solution and a covariance matrix, and fixing the double-difference wide-lane integer ambiguity and the double-difference narrow-lane integer ambiguity; and finally, outputting the relative positioning result of ambiguity fixing. By adopting the method of the invention, the problem that ambiguity fixing strongly depends on a pseudo code with low observation precision due to equally-weighted pseudo code and phase processing in M-W combination in the traditional method is avoided, the success rate of long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of final relative positioning results are improved, calculation is stable, and the reliability of relative positioning results is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for realizing high-precision location based on Big Dipper system civil carrier phase combination
ActiveCN103837879AOvercome limitationsFast Ambiguity ResolutionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceObservational error
The invention discloses a method for realizing high-precision location based on Big Dipper system civil carrier phase combination. The method comprises the steps of calculating the original user position and utilizing the original user position to calculate the GEO superwide lane whole circle ambiguity; taking the integer of the observed quantity of GEO superwide lane combination, calculating the GEO wide lane whole circle ambiguity (img file='DDA00002471851000011.TIF' wi='160' he'='47' / ), calculating the error of double difference observed quantity of the GEO superwide lane combination, and determining the searching range of the ambiguity of a GEO wide lane; conducting dimensionality reduction search on the GEO wide lane whole circle ambiguity (img file='DDA00002471851000012.TIF' wi='134' he'='47' / ) to obtain the accurate value of the GEO wide lane whole circle ambiguity; selecting an MEO / IGSO satellite to initially calculate the wide lane whole circle ambiguity; utilizing the ambiguity combined relationship between a superwide lane and a wide lane to obtain the double difference ambiguity on a B1 frequency point, a B2 frequency point and an S frequency point; utilizing the sum of the double difference ambiguity on the B1 frequency point, the B2 frequency point and the S frequency point to receive carrier phase of machine measurement and conduct planet base double difference location, and calculating the high precision position of a user. Through the method, the purpose of quick high precision location of Big Dipper carrier phases is achieved.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving resolving success rate of medium and long baseline GPS integral cycle fuzziness
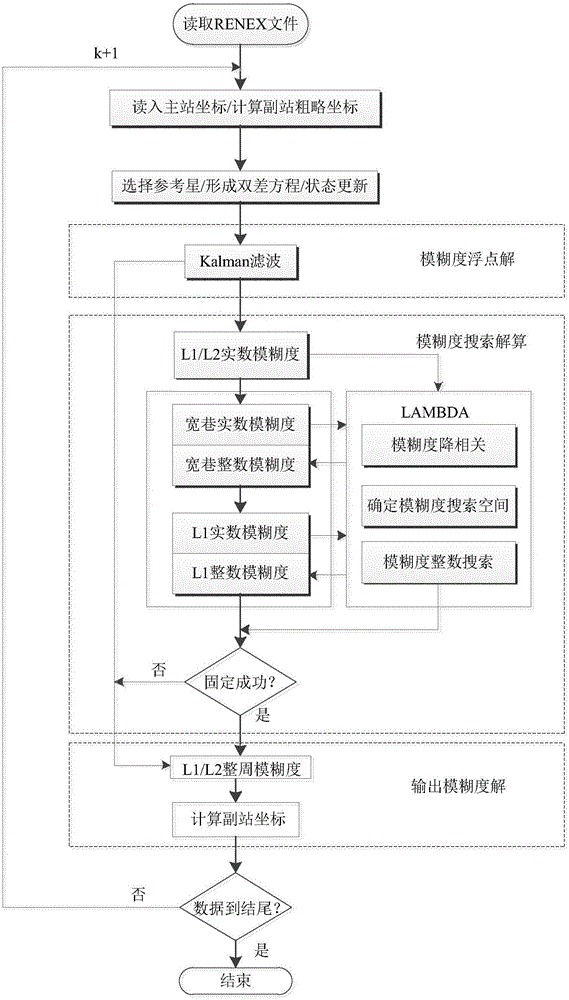
ActiveCN105842721AImprove fixation efficiencyQuick solveSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterDouble difference
The invention provides a method for improving resolving success rate of medium and long baseline GPS integral cycle fuzziness, and aims to provide a method with advantages of high fuzziness real solution precision and high success rate. The method is realized through a technical solution which is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of setting an elevation mask angle by means of monitoring and measuring software, acquiring rough coordinates of a main measurement station and an auxiliary measurement station, and extracting useful observation data; selecting a reference satellite, comparing observation data of the main measurement state with the observation data of the auxiliary measurement station, establishing a double-difference observation equation by means of the observation data of the main measurement station and the auxiliary measurement station, performing state updating and parameter estimation on an observed equation by means of a Kalman filter, and solving a fuzziness float solution; then, converting the fuzziness float solutions of GPS double-difference carrier L1 and L2, and forming a vector set which comprises a wide lane integral cycle fuzziness and a carrier L1 fuzziness; searching the wide lane integral cycle fuzziness by means of a LAMBDA algorithm, obtaining the integer solution of the wide lane integral cycle fuzziness after fixation, and finally determining the success rate of the resolved fuzziness through a preset threshold, and confirming a correctly resolved integral cycle fuzziness.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Method for improving fixed correct rate of network RTK double-difference wide lane ambiguity
ActiveCN108415049AReduce the impactHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention provides a method for improving fixed correct rate of network RTK double-difference wide lane ambiguity. The method comprises the following steps of 1, data preparation, namely receivingreal-time observing data, satellite ephemeris and coordinate information of a GNSS reference station; 2, performing real-time ionosphere product calculation, namely performing non-difference precisesingle-point positioning according to coordinate information and satellite coordinate of the reference station, and calculating a non-difference real-time ionosphere delay value of a satellite signalpropagation path; and 3, performing baseline double-difference wide lane ambiguity calculation, wherein the step 3 comprises a procedure 3.1, forming a double-difference observing value by the observing data of two reference stations, and correcting a double-difference ionosphere residual item by means of the non-difference real-time ionosphere delay value calculated by the step 2; procedure 3.2,calculating a floating point solution of the double-difference wide lane ambiguity; and procedure 3.3, performing rounding on the floating point solution of the double-difference wide lane ambiguity for obtaining a double-difference wide lane ambiguity. The method improves correct rate in understanding the baseline double-difference wide lane ambiguity, thereby improving precision and stability ofthe network RTK.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
Real-time dynamic differential positioning method and device thereof
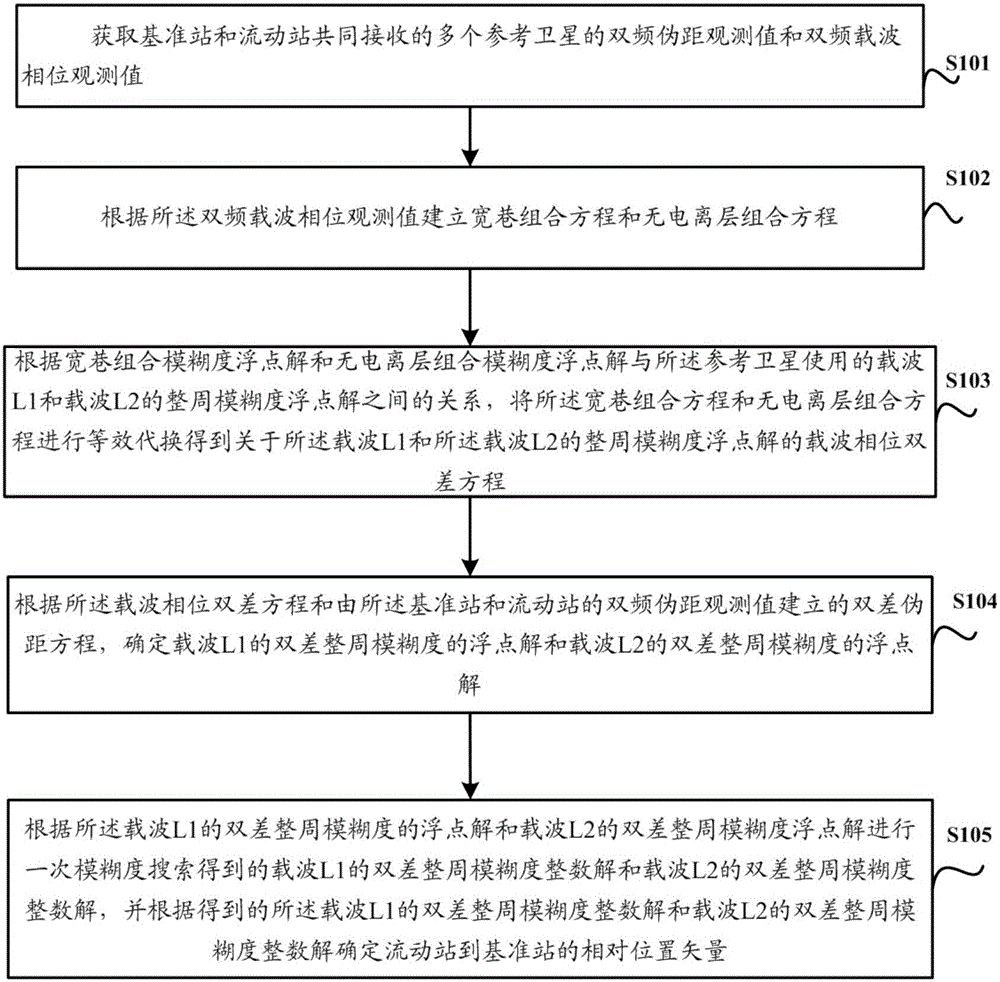
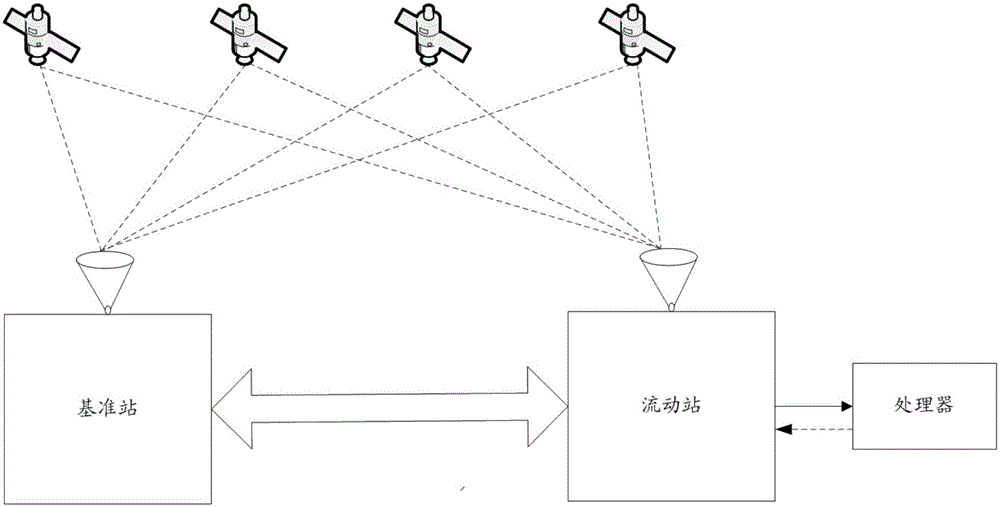
ActiveCN105158783AReduce the number of timesNo loss of positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceDual frequency
The invention discloses a real-time dynamic differential positioning method and a device thereof. The method comprises the steps of acquiring dual-frequency pseudo-range observed values and dual-frequency carrier-phase observed values from a plurality of reference satellites received by means of a reference station together with a moving station; figuring out a carrier phase double-difference equation on the who-cycle ambiguity float solutions of a carrier L1 and a carrier L2 through the equivalent substitution of a wide-lane composite equation and an ionosphere-free composite equation; according to a double-difference pseudo-range equation established based on the carrier phase double-difference equation and the dual-frequency pseudo-range observed values received by the reference station and the moving station, determining a float solution for the double-difference who-cycle ambiguity of the carrier L1 and a float solution for the double-difference who-cycle ambiguity of the carrier L2. The ambiguity searching operation is conducted only once during the entire positioning process, so that the number of the ambiguity searching operation is effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the real-time dynamic differential positioning efficiency is improved on the condition of the loss-free positioning precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIJI INFORMATION TECH
Method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values
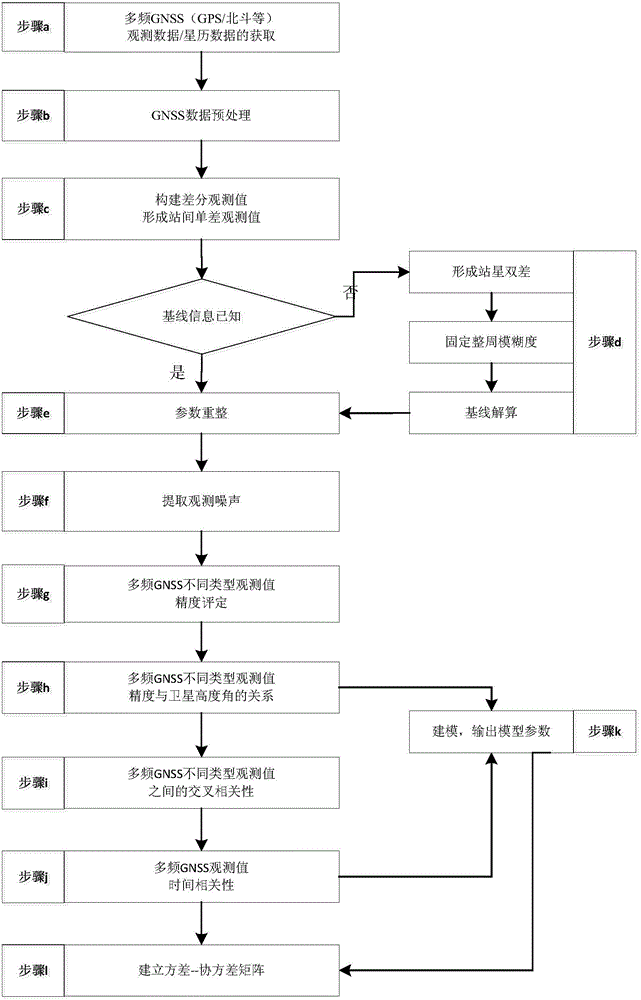
InactiveCN104102822ASimple calculationHigh speedSatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention relates to a method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring multi-frequency GNSS observed data, and preprocessing the data; constructing a single difference observation equation to form an intersite single difference observed value; performing parameter reforming on the single difference observation equation according to a base line and fixed double-difference ambiguity; taking the average value of single difference observed values of single-epoch multiple satellites as the least square solution of the reformed parameter, and subtracting the least square solution from the single different observed value of each satellite to obtain single difference observation noise; calculating the accuracy of non-difference observed values of single-epoch multi-frequency GNSS different-type observed values, cross-correlation coefficients of the different-type observed values and temporal correlation coefficients of the same-type observed values by utilizing the extracted observation noise; obtaining a relation between the accuracy of the observed value of each satellite and an elevating angle; modeling, outputting model parameters and establishing a variance-covariance matrix. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simple calculating process, reliability and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
UWB (ultra wide band) wireless positioning method based on double-difference duplex
InactiveCN106879067AReduce mistakesImprove time utilizationPosition fixationWireless communicationDouble differenceBroadband
Owner:GUANGZHOU TUGUIYAO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
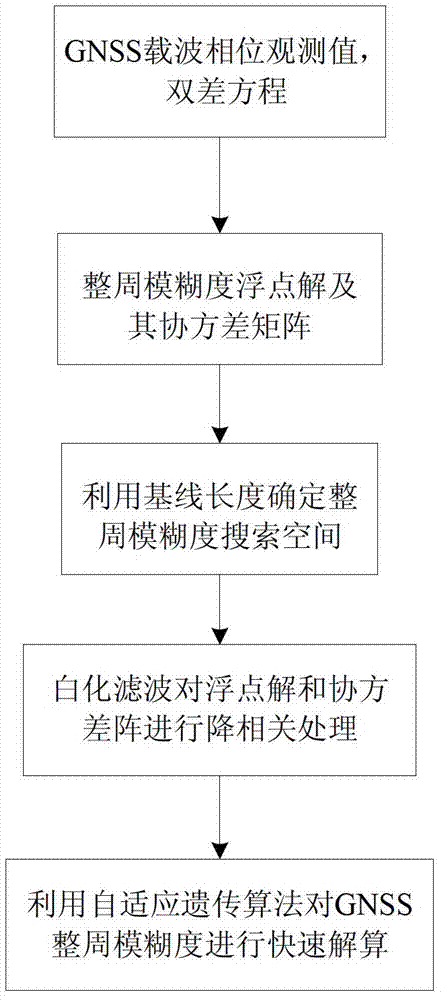
Adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) integer ambiguity acquisition method
InactiveCN102736094AReduce correlationAvoid complex calculationsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInteger ambiguity
The invention discloses an adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS integer ambiguity acquisition method. The method includes the following steps: step 1: acquiring the observed data of a GNSS carrier phase, and establishing a double-difference observation equation for the GNSS carrier phase; step 2: according to the double-difference observation equation obtained in step 1, utilizing the least square method to acquire the float solution and corresponding covariance matrix of GNSS integer ambiguity; step 3: utilizing known base length as a constraint condition to determine the search space of integer ambiguity; step 4: utilizing the whitening filter method to decorrelate the float solution and covariance matrix of integer ambiguity obtained in step 2; step 5: according to anobjective function, determining a fitness function, determining each operating parameter in the adaptive genetic algorithm, finally, introducing the adaptive genetic algorithm into fast solution on integer ambiguity, and searching the optimal solution of integer ambiguity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-antenna attitude determining method based on Beidou system
ActiveCN107102346AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceCarrier signal
The invention provides a multi-antenna attitude determining method based on a Beidou system. With the establishment and improvement of the Beidou satellite regional navigation system, the use of the Beidou satellite system for high-precision attitude determination has become one of the hot spots in the field of navigation. The method is based on the realization of the Beidou receiver hardware embedded platform and based on the three-antenna carrier phase data simultaneously observed by the Beidou receiver, the double-difference model is constructed and finally the high-precision attitude information is obtained. The present invention mainly makes innovation and improvement of the satellite selection strategy, the cycle slip detection method, the rough error rejecting and fuzziness calculation method, the base line verification method in the attitude determination flow. The method is highly modularized, supports various platforms, is particularly suitable for the embedded receiver platform, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Attitude angle direct resolving method based on global position system (GPS) carrier wave double-difference equation
InactiveCN102998690AReduce intermediate processReduce estimation errorSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceCarrier signal
The invention provides an attitude angle direct resolving method based on a global position system (GPS) carrier wave double-difference equation. The attitude angle direct resolving method mainly comprises building a carrier wave double-difference equation, guiding carrier attitude information into the carrier wave double-difference equation and solving an attitude angle by utilizing nonlinear least squares. The attitude angle direct resolving method can effectively reduce or eliminate short base line public errors, achieves high-precision resolving, can directly resolve the attitude angle by leading the attitude angle information into the double-difference equation, greatly reduces intermediate evaluated errors, evaluates the attitude angle by utilizing the nonlinear least squares method, improves system resolving speed, finishes real-time resolving of the attitude information and is more suitable for real-time carrier attitude measuring.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
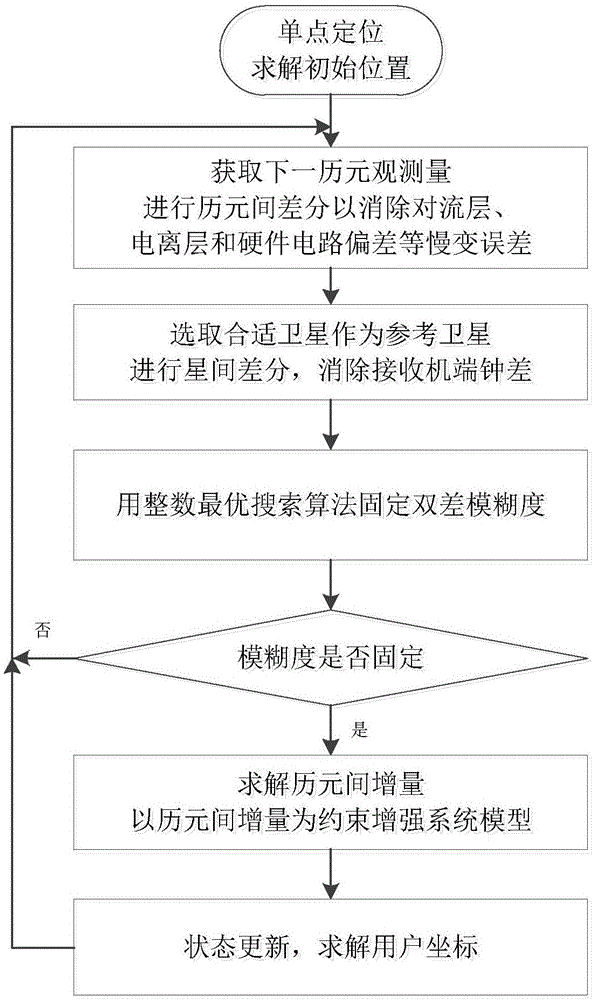
Positioning method based on epoch-satellite difference constraint
ActiveCN106772478AMake up for inaccurate problemsHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation and positioning, and relates to a positioning method based on epoch-satellite difference constraint. The positioning method enhances the intensity of a satellite navigation system model and improves the convergence speed of a system. The positioning method provided by the invention comprises the steps that (1) observation acquired by a receiver is used for precise single point positioning to acquire the initial solution of the position of a user; (2) the observation of two adjacent epochs is used for first difference to acquire single difference observation; and (3) a satellite is selected as a reference satellite, and second difference between satellites is carried out on the single difference observation acquired in the step (2) to acquire double difference observation. According to the method proposed by the invention, epoch-satellite difference is carried out the original observation of the receiver; the whole-week characteristic of double difference ambiguity is recovered; and accurate inter-epoch position increment is acquired.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Carrier phase difference positioning method and device and single-frequency receiver
ActiveCN106646565AImprove fixation efficiencyAvoid cycle slip problemSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
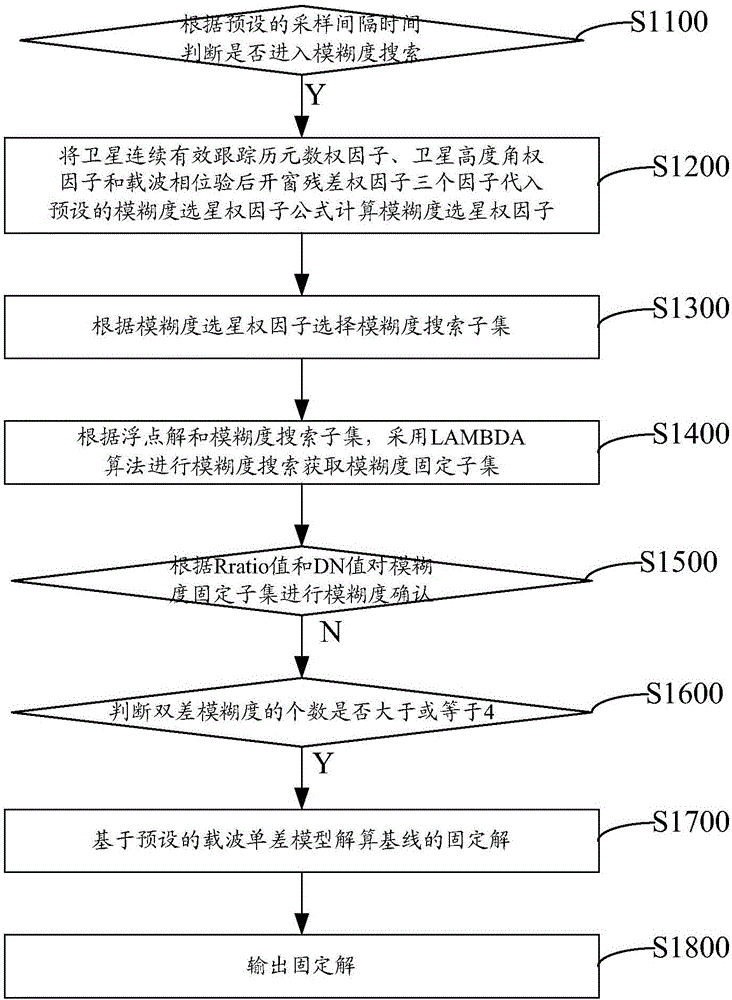
The invention relates to a carrier phase difference positioning method and device and a single-frequency receiver, and the method comprises the steps: judging whether to carry out the ambiguity search or not according to a preset sampling time interval; substituting a satellite continuous and effective tracking epoch number weight factor, a satellite elevation weight factor and a carrier phase posterior windowing residual error weight factor into a preset ambiguity satellite selection weight factor formula if the ambiguity search is carried out, and calculating a ambiguity satellite selection weight factor; selecting a ambiguity search subset according to the ambiguity satellite selection weight factor; carrying out the ambiguity search through employing an LAMBDA algorithm, and obtaining an ambiguity fixed subset; respectively judging whether the obtained ratio value and DN value are greater than a preset first threshold value and a preset second threshold value or not, and carrying out the ambiguity confirmation of the ambiguity fixed subset; judging whether the number of double-difference ambiguities is greater than or equal to 4 or not if the obtained ratio value and DN value are greater than the preset first threshold value and the preset second threshold value; solving a fixed solution of a base line based on a preset carrier single-difference model if the obtained ratio value and DN value are not greater than the preset first threshold value and the preset second threshold value; and outputting the fixed solution. The method can enable the single-frequency receiver to carry out the RTK high-precision positioning.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HI TARGET SURVEYING INSTRUMENT CO LTD
Deception jamming signal detection method based on single receiver
ActiveCN107621645ALower requirementThe implementation process is simpleSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereNatural satellite
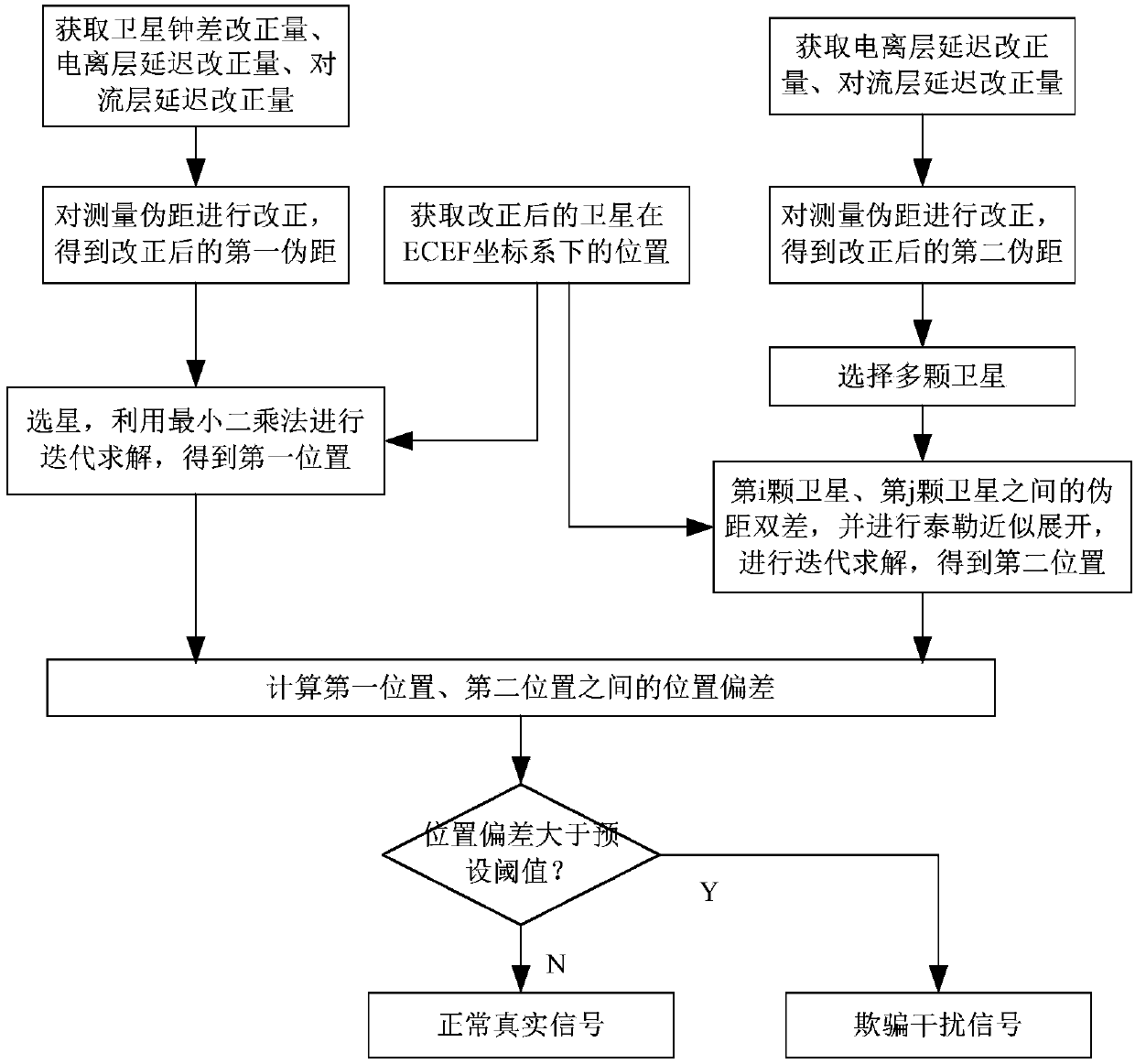
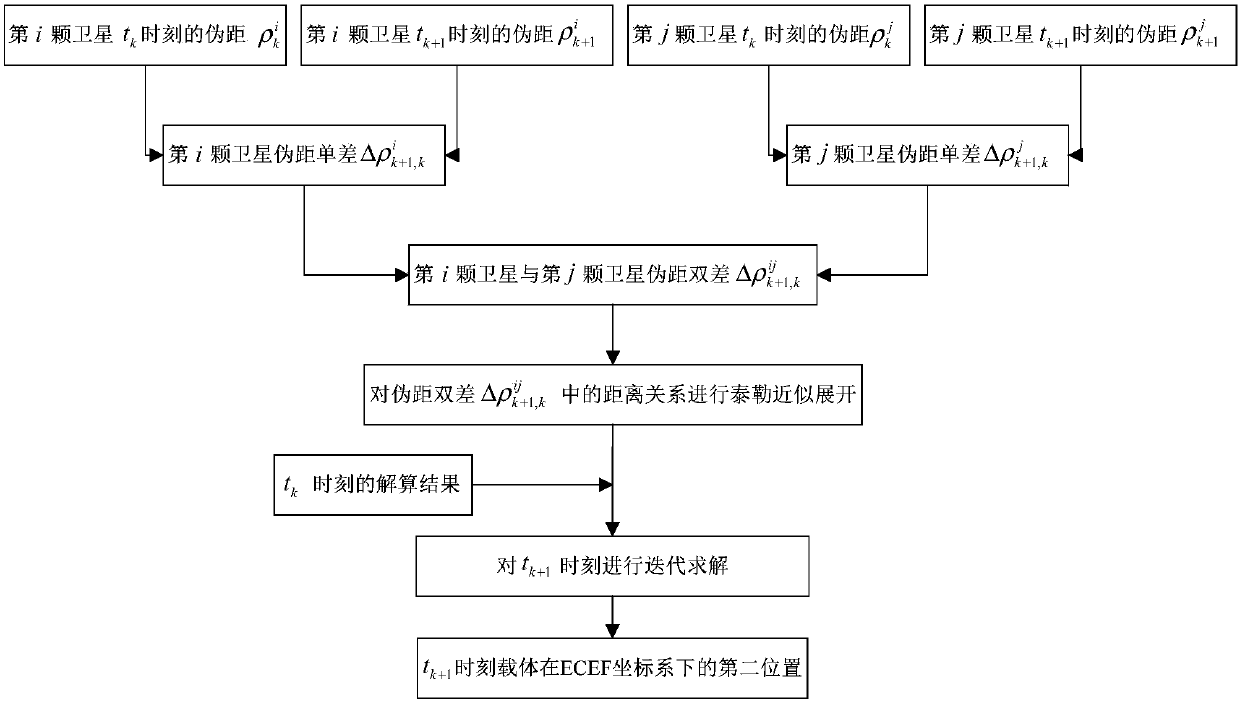
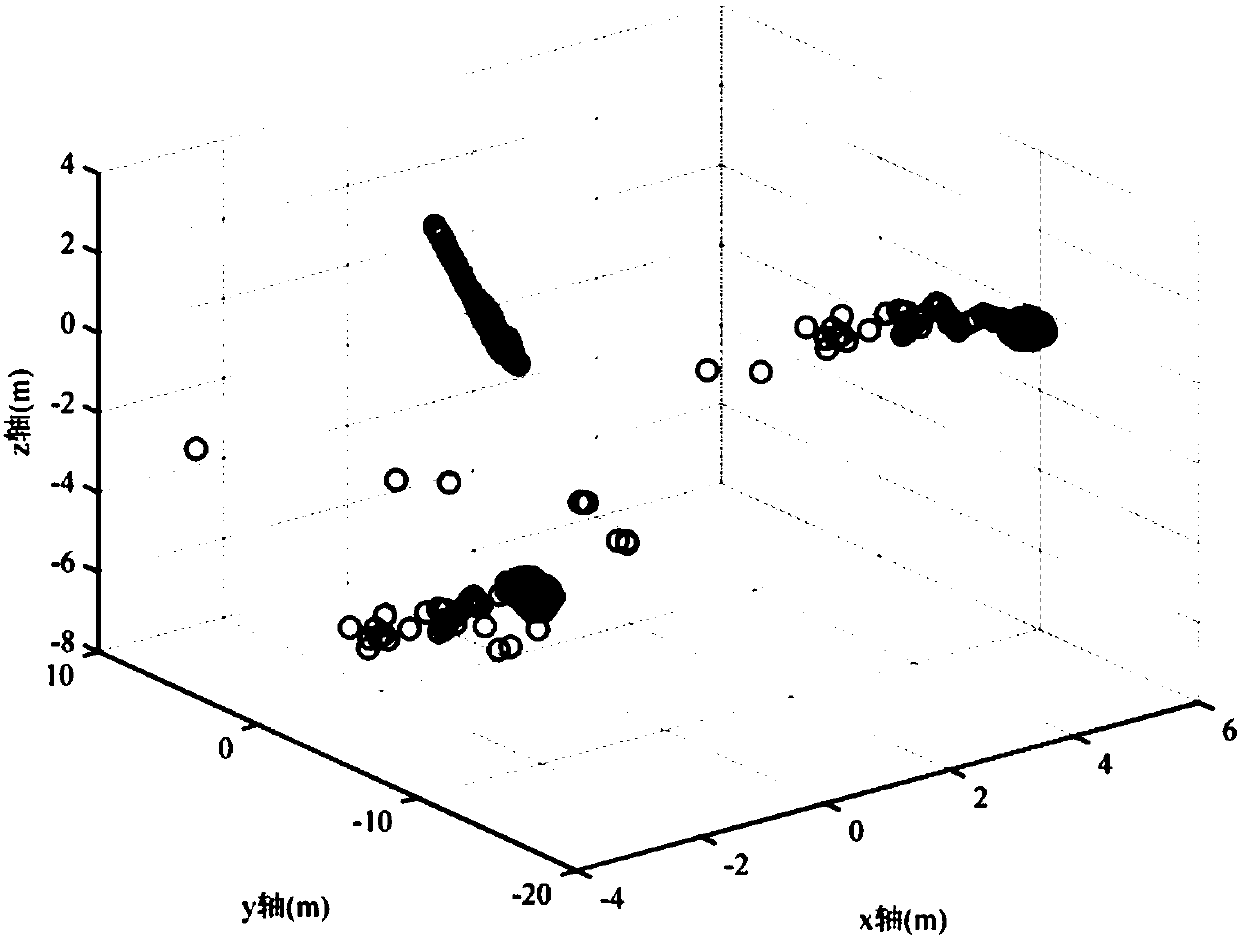
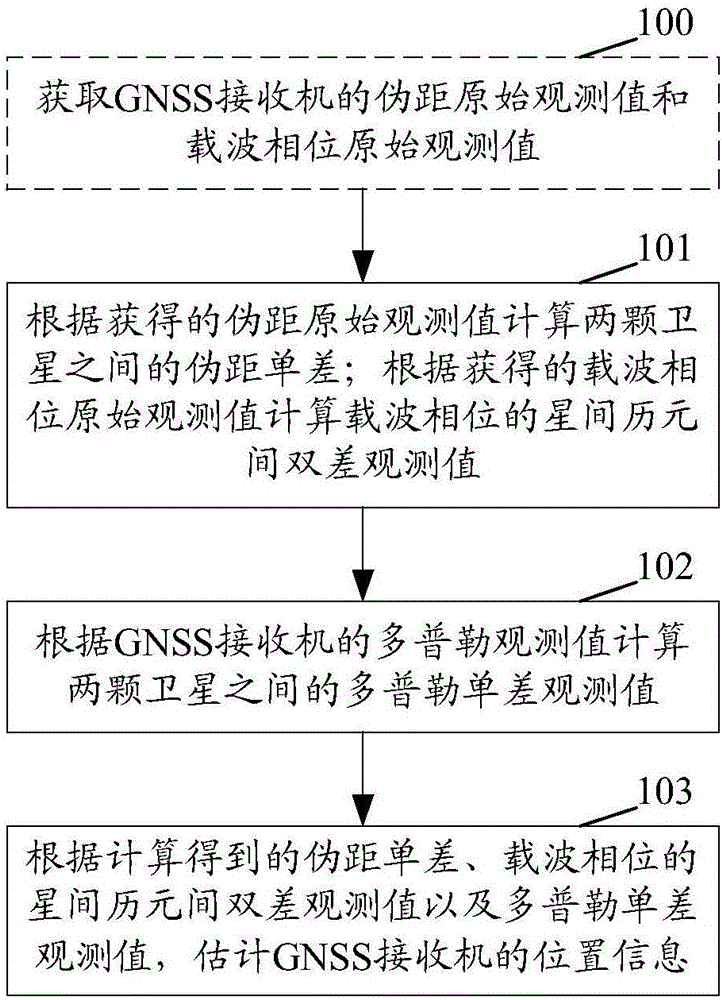
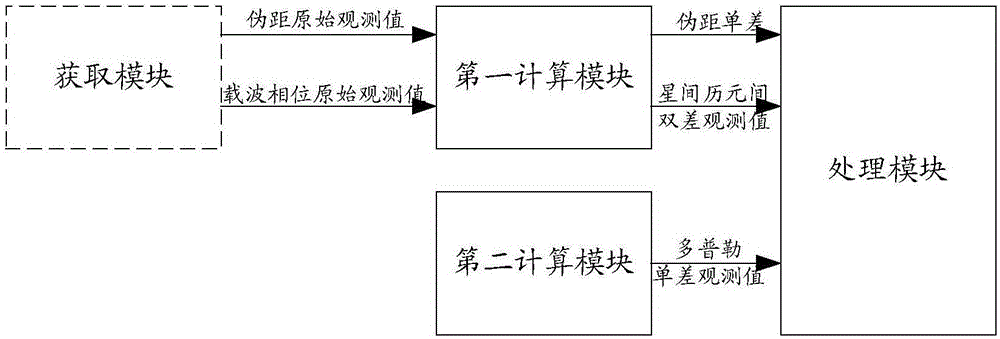
The invention discloses a deception jamming signal detection method based on a single receiver. The method comprises steps: the position of a satellite after correction under an ECEF coordinate systemis acquired, satellite clock offset correction, ionosphere delay correction and troposphere delay correction are used to correct a measured pseudo range to obtain a pseudo range after correction, a least square method is used for iterative solution, the first position of a carrier under the ECEF coordinate system is obtained, and based on a pseudo range double difference model of the satellite, Taylor's approximation is carried out for iterative solution to obtain the second position of the carrier under the ECEF coordinate system; and according to whether the position offset between the first position and the second position is larger than a preset threshold, whether the currently-received signals are the deception jamming signals is judged. The detection is realized by only requiring the single receiver or a single antenna and the pseudo range measurement information, requirements on equipment are low, the algorithm is simple and efficient, the realization process is simple, and themethod is applicable to generation-type deception jamming and forward-type deception jamming.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for positioning GNSS receiver
ActiveCN106291639AHigh positioning accuracyEasy to operateSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceExternal data
Owner:UNICORE COMM INC
Inertial navigation assisted Big Dipper single-frequency whole-cycle ambiguity calculation method under short baseline condition
InactiveCN104375157AIncrease speedHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceCarrier signal
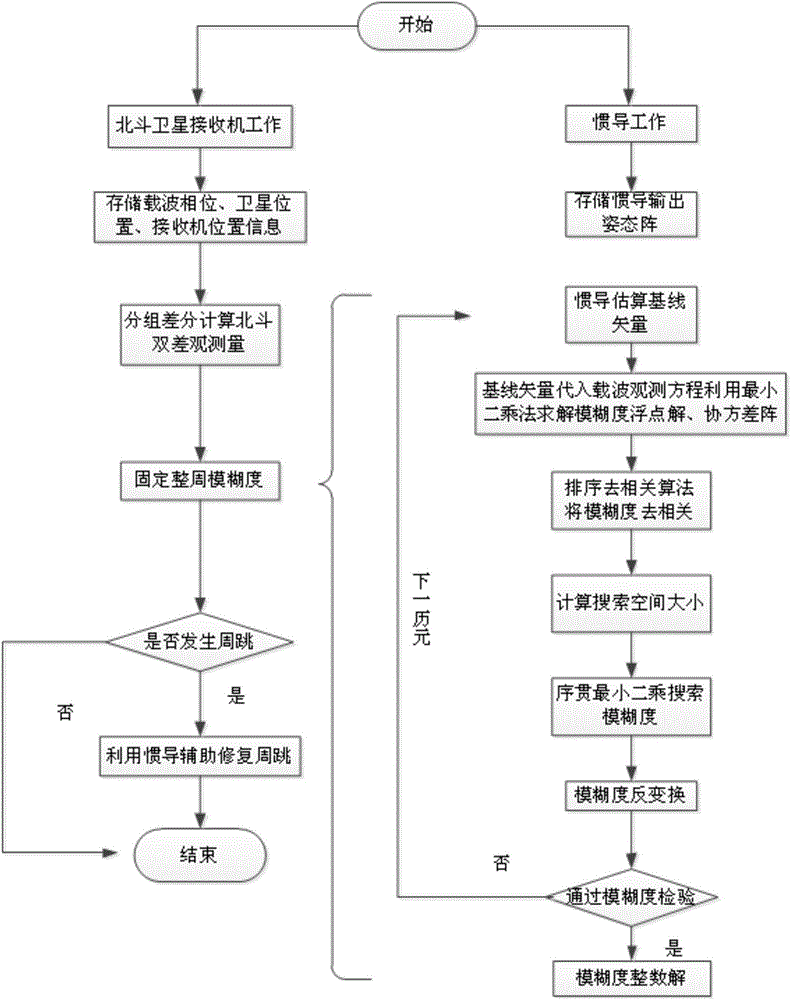
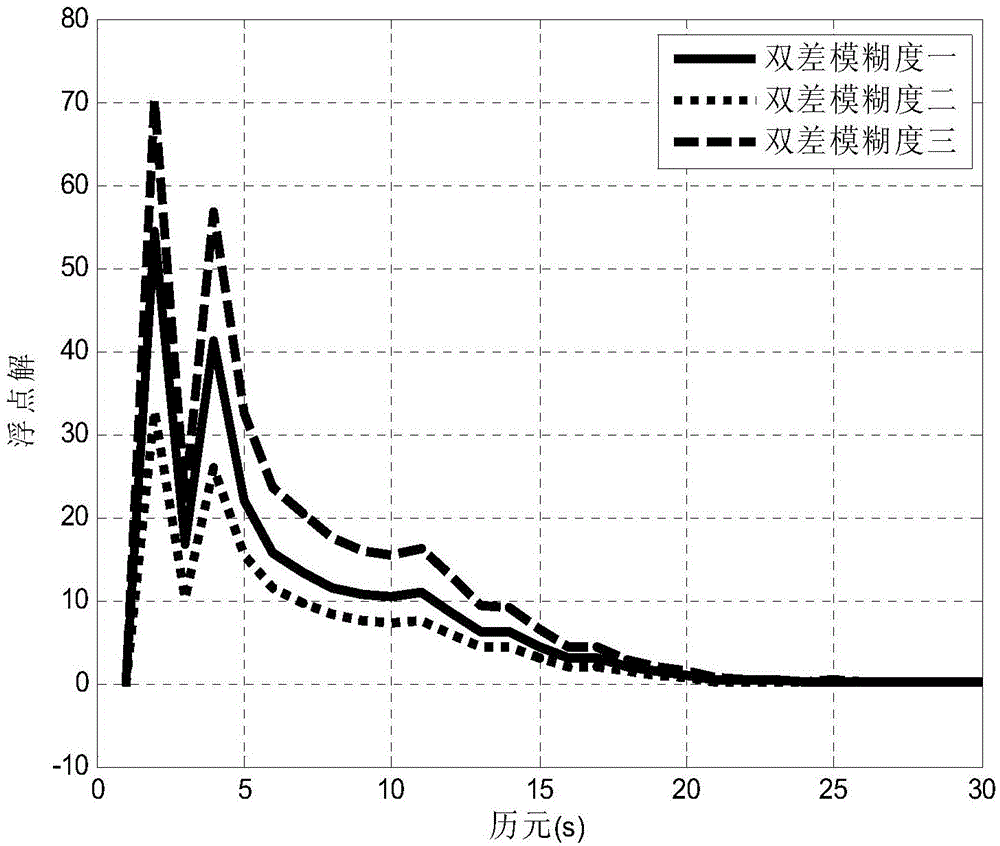
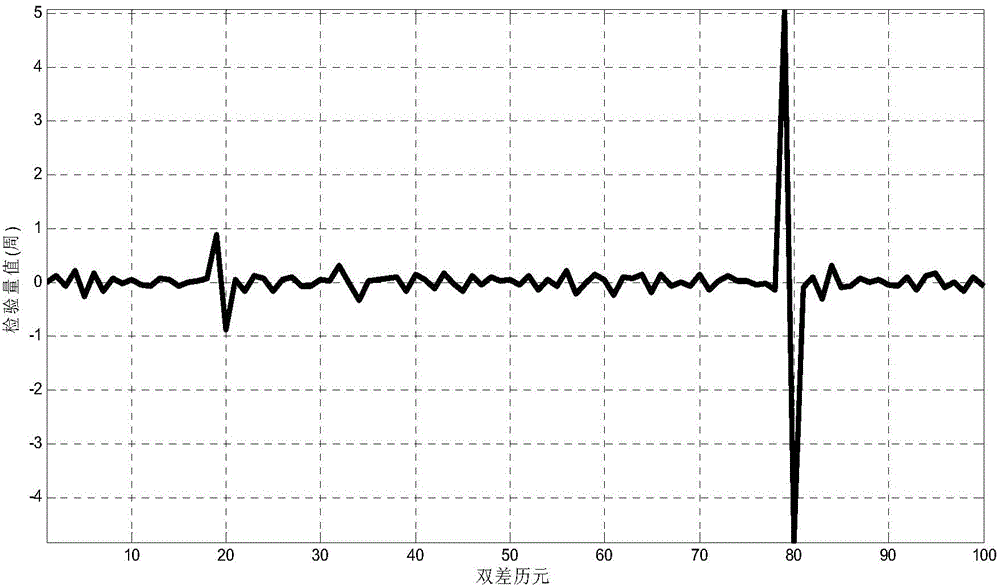
The invention discloses an inertial navigation assisted Big Dipper single-frequency whole-cycle ambiguity calculation method under the short baseline condition. The inertial navigation assisted Big Dipper single-frequency whole-cycle ambiguity calculation method comprises three steps of firstly conducting grouping difference on Big Dipper observed quantity according to the height of a Big Dipper constellation type orbit, wherein atmosphere delay errors of the Big Dipper observed quantity under the short baseline condition can be effectively eliminated; secondly, utilizing an inertial navigation output attitude matrix to estimate a baseline vector and substituting a baseline vector into a Big Dipper double-difference carrier wave observation equation, utilizing a recursive least-squares method to calculate whole-cycle ambiguity floating point solution and a covariance matrix of the floating point solution, then adopting an improved least-squares ambiguity de-correlation method to fix a whole-cycle ambiguity integer solution; finally, utilizing an inertial navigation estimated baseline vector and a Big Dipper three-difference carrier phase observed value to produce inspection amount so as to judge whether a cycle slip occurs or not, estimating and repairing a cycle slip value if the cycle slip occurs. By means of the inertial navigation assisted Big Dipper single-frequency whole-cycle ambiguity calculation method under the short baseline condition, the calculation speed and accurate of the whole-cycle ambiguity can be effectively improved, and the method is suitable for positioning and attitude fixing of a high-dynamic carrier under the condition of a single-frequency Big Dipper satellite system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com