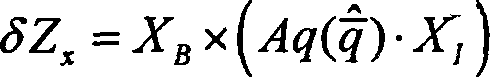Patents
Literature
812 results about "Attitude determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition Attitude determination . The characterization of an object’s position in space, be it a vehicle or a measuring instrument, requires the knowledge of both its location and attitude (viz. orientation) with respect to a reference frame.
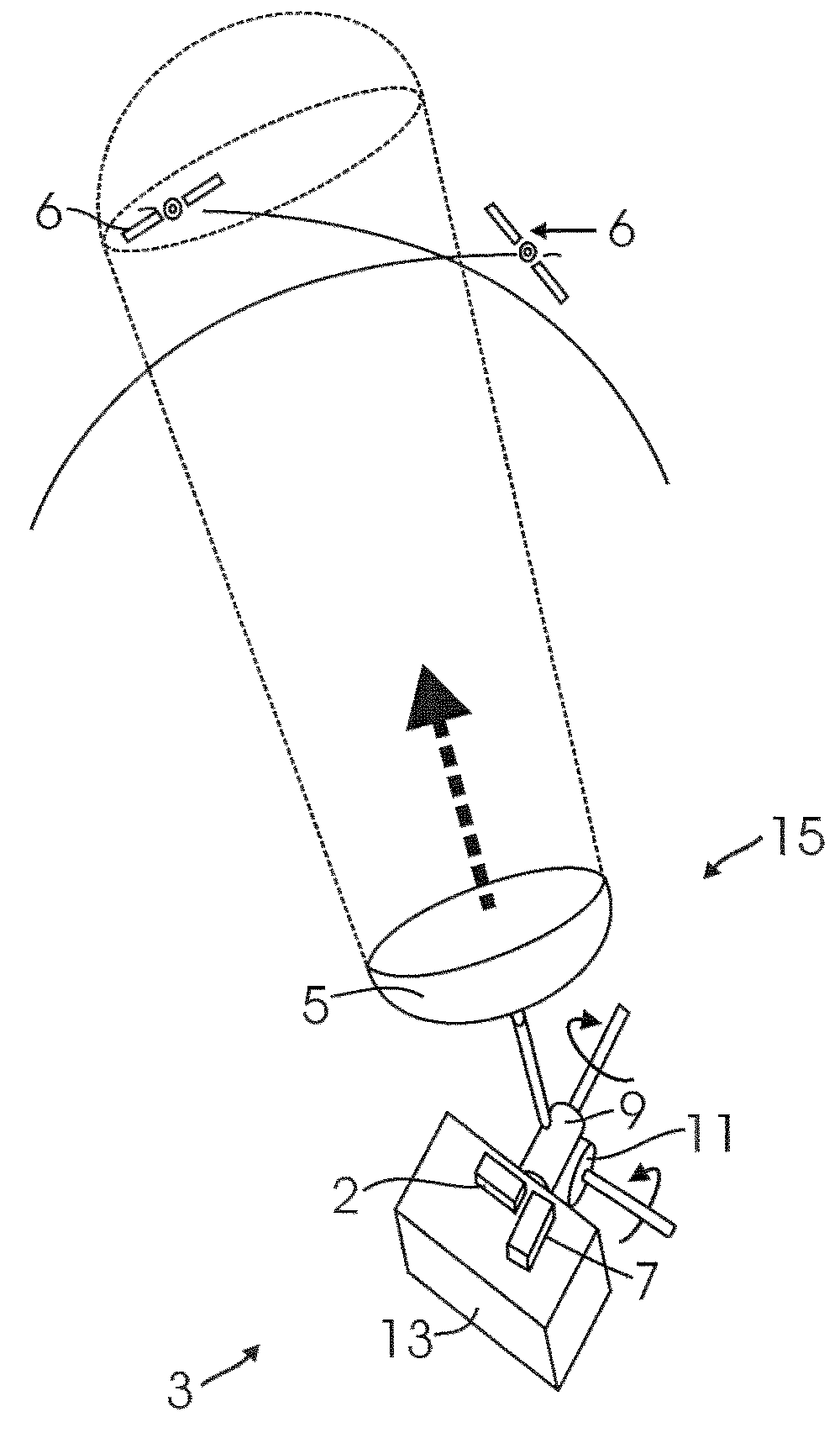
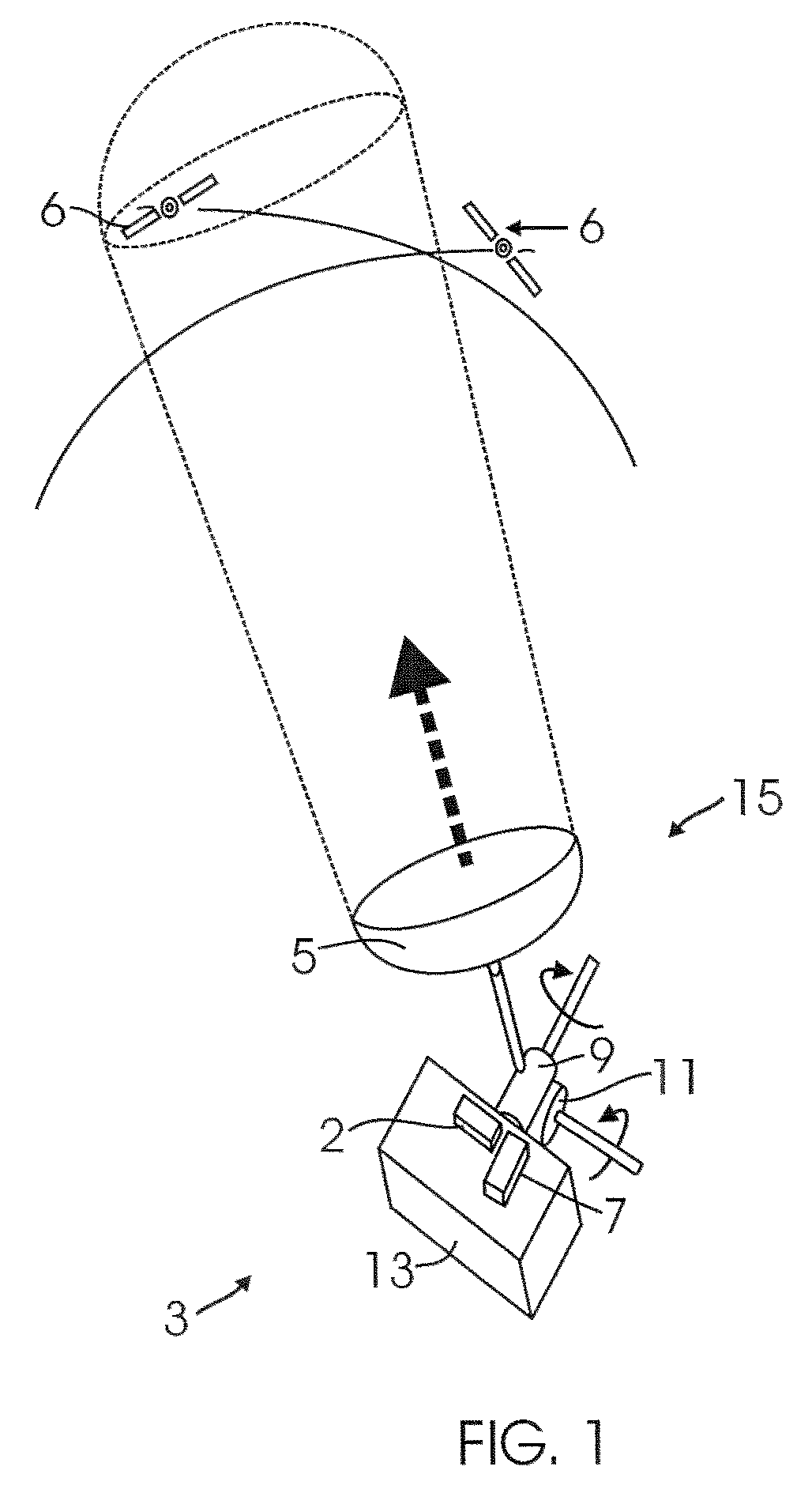
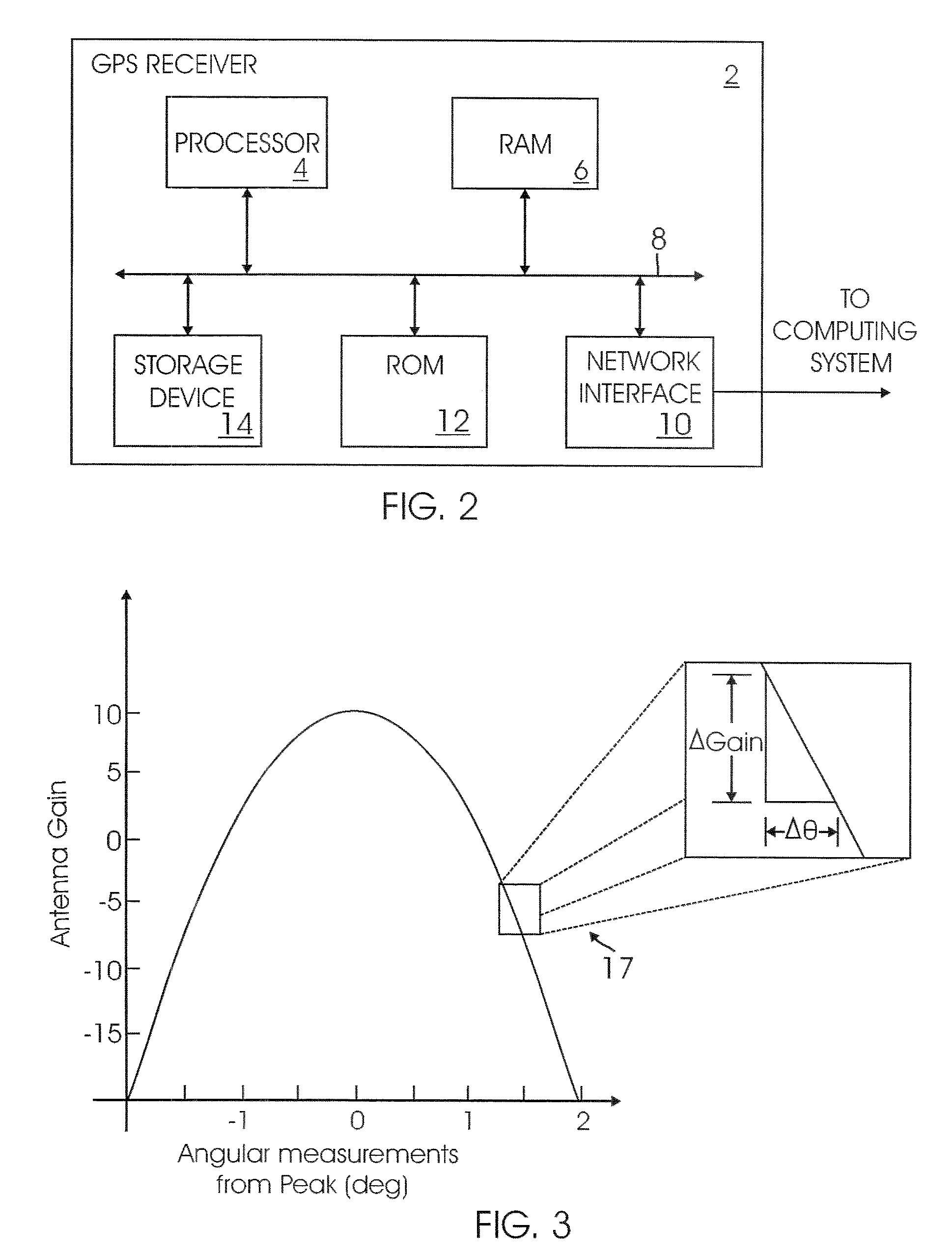
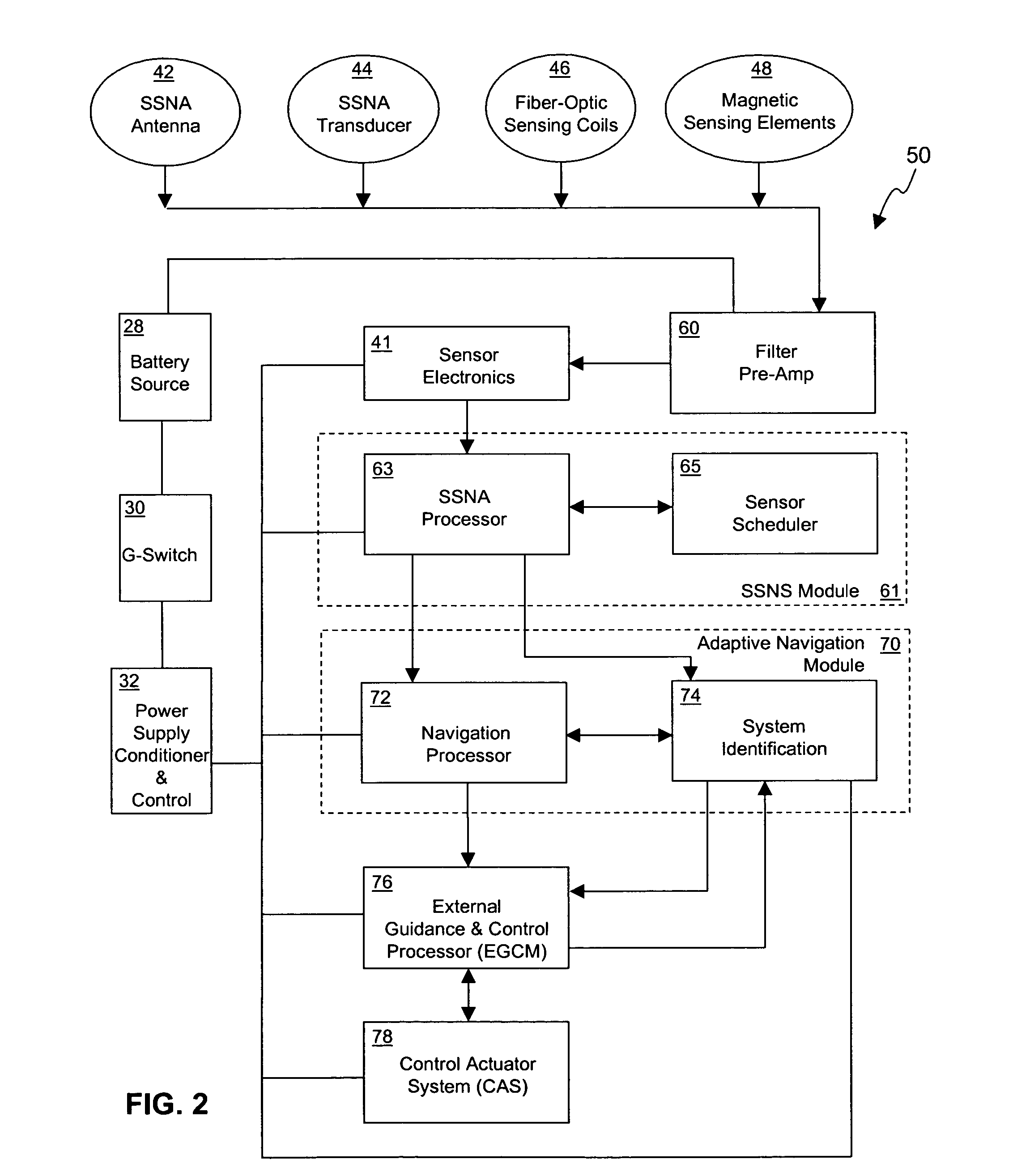
Method and system for attitude determination of a platform using global navigation satellite system and a steered antenna
InactiveUS7397422B2Reduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDirectional antennaMarine navigation
A system and method for determining the attitude of a platform is provided. The method includes: (a) Searching and scanning for one or more GPS satellite(s) to determine initial platform position; wherein a single directionally steered antenna scans for the GPS / GNSS satellite; (b) pointing and scanning the antenna to GPS / GNSS satellite to determine a first angular measurement of a direction of a GPS / GNSS signal; (c) measuring carrier to noise ratio of the GPS / GNSS satellite; (d) dithering the single directionally steered antenna to obtain an angular measurement relative to an antenna pattern bore-sight reference; (e) repeating steps (b)-(d) to determine a second angular measurement of the direction of a second GPS signal; (f) determining the attitude error of the platform using the first and second angular measurements; (g) updating the platform position and attitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method
InactiveCN102538781AReduce cumulative errorHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionInertial navigation system
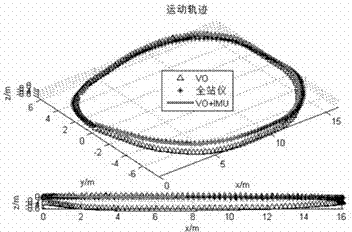
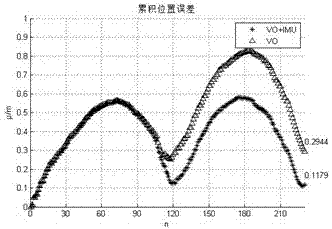
The invention discloses a machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method which comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring a mobile robot binocular camera image and triaxial inertial navigation data; distilling front / back frame image characteristics and matching estimation motion attitude; computing a pitch angle and a roll angle by inertial navigation; building a kalman filter model to estimate to fuse vision and inertial navigation attitude; adaptively adjusting a filter parameter according to estimation variance; and carrying out accumulated dead reckoning of attitude correction. According to the method, a real-time expanding kalman filter attitude estimation model is provided, the combination of inertial navigation and gravity acceleration direction is taken as supplement, three-direction attitude estimation of a visual speedometer is decoupled, and the accumulated error of the attitude estimation is corrected; and the filter parameter is adjusted by fuzzy logic according to motion state, the self-adaptive filtering estimation is realized, the influence of acceleration noise is reduced, and the positioning precision and robustness of the visual speedometer is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
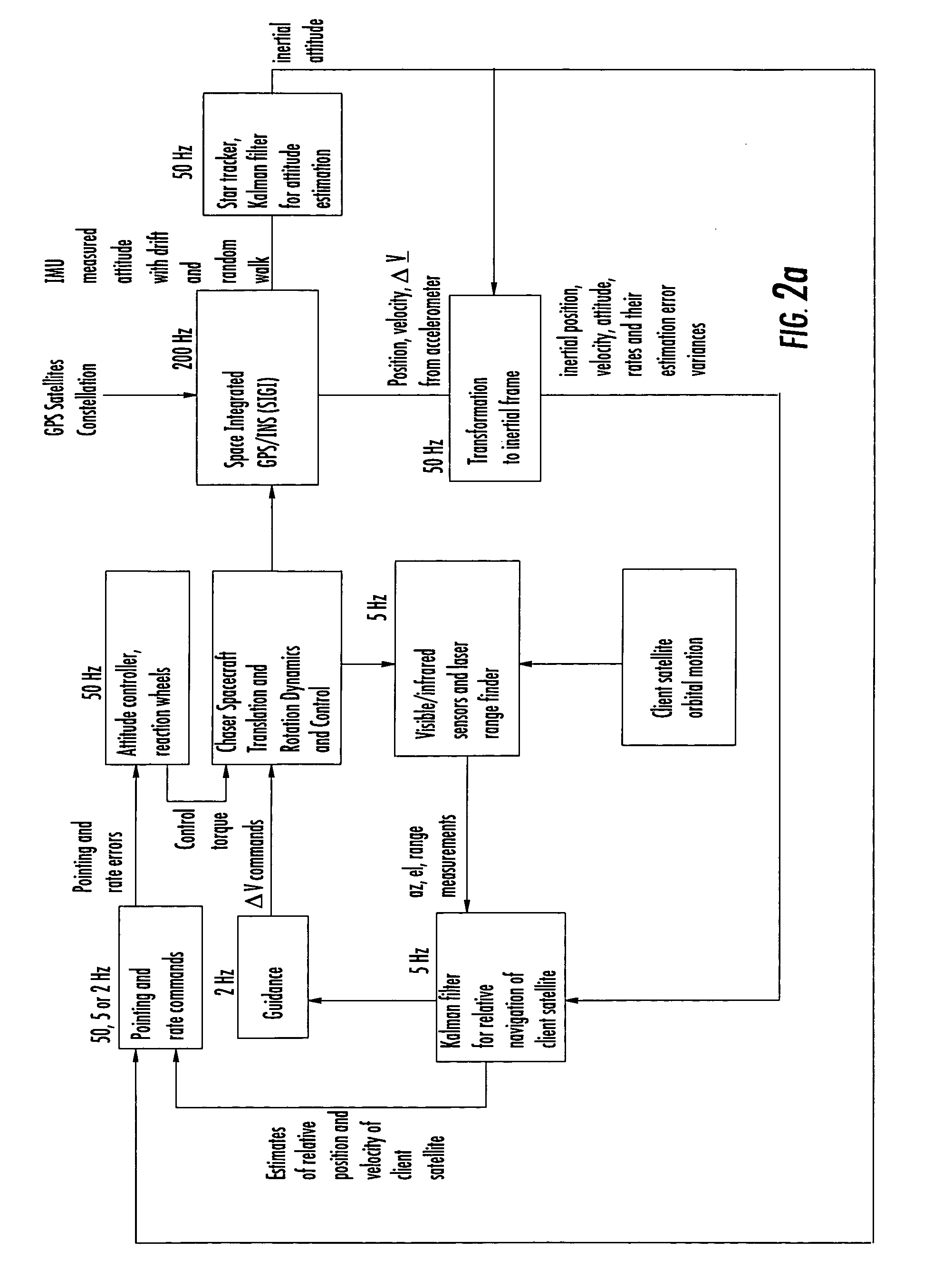
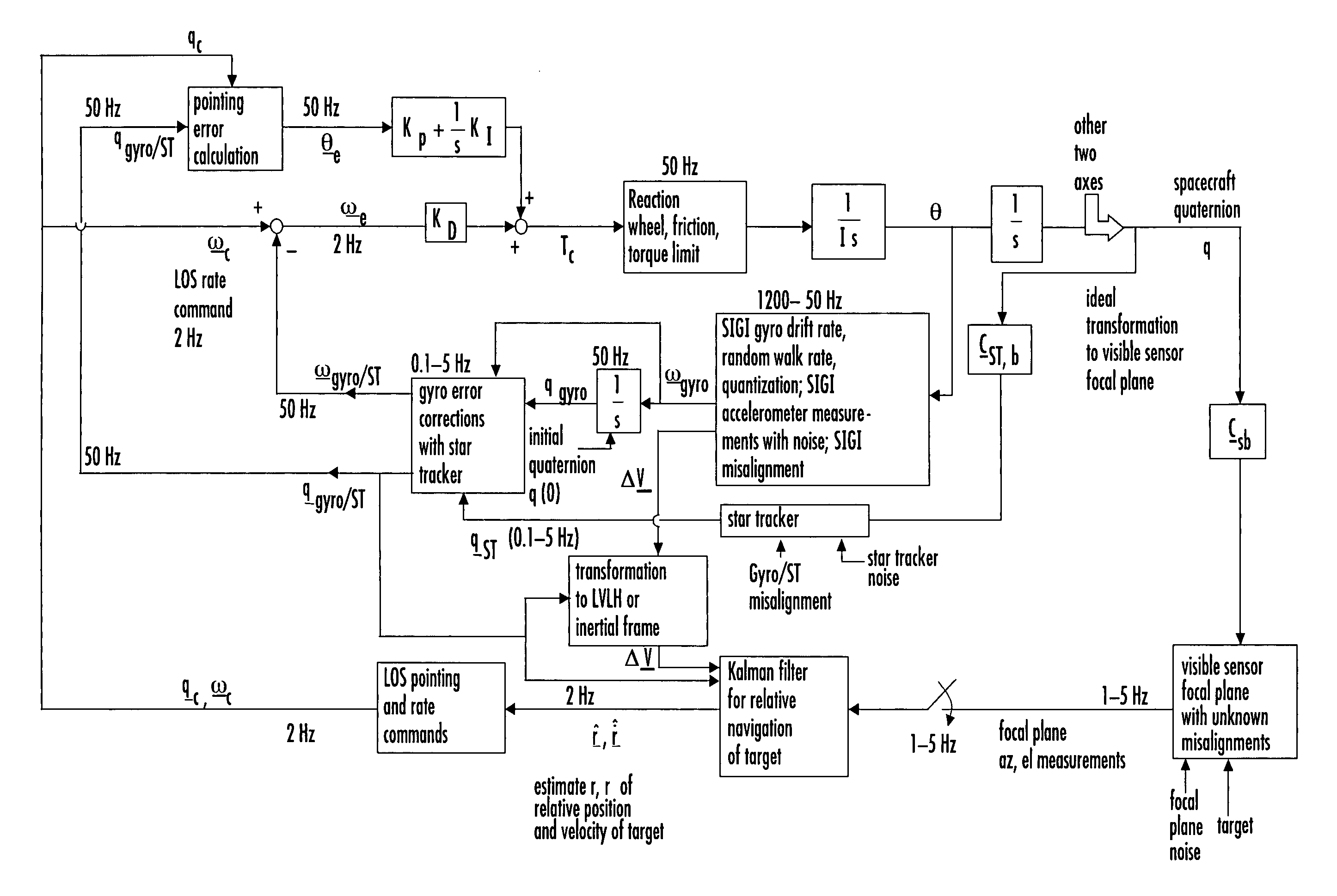
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
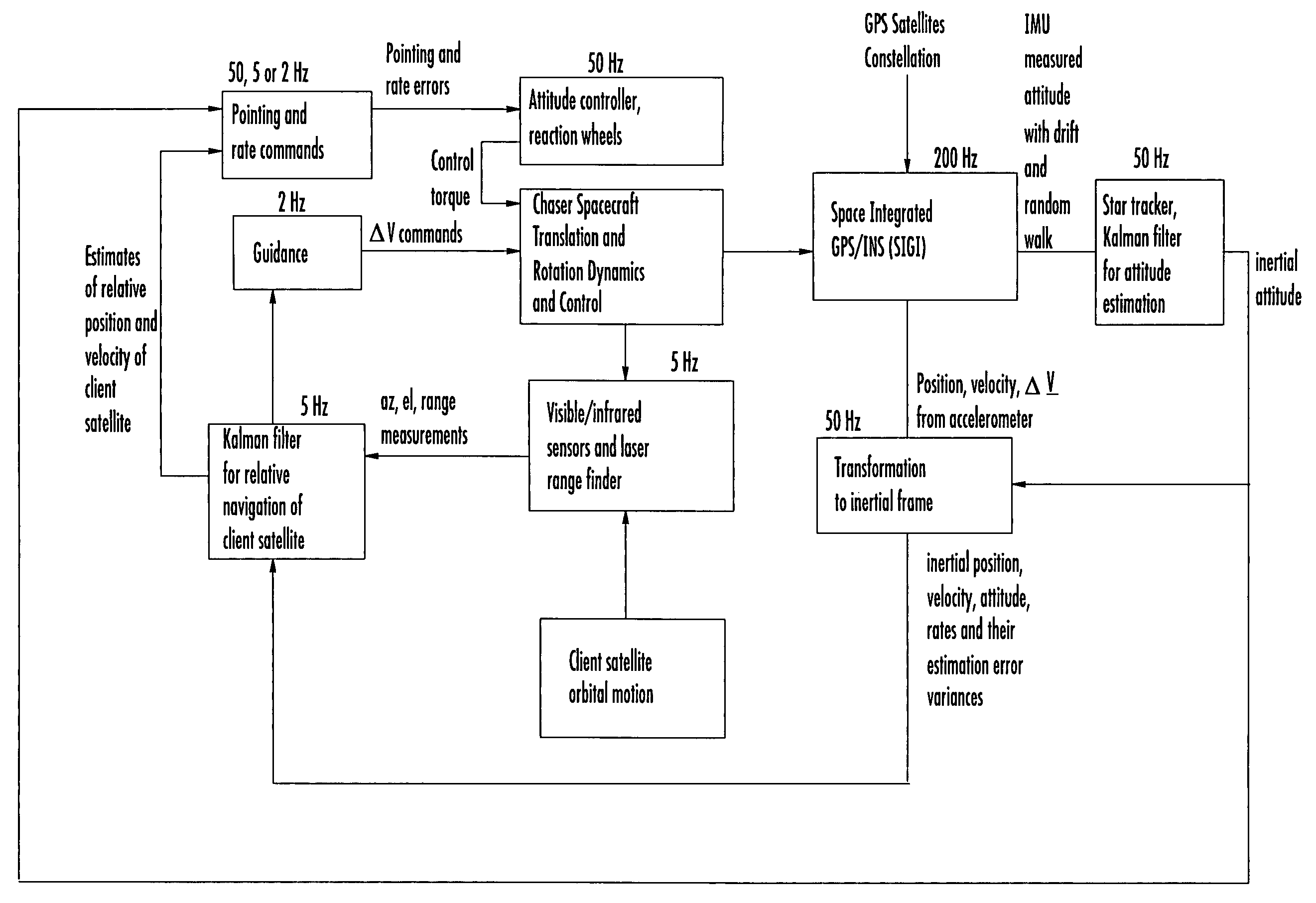
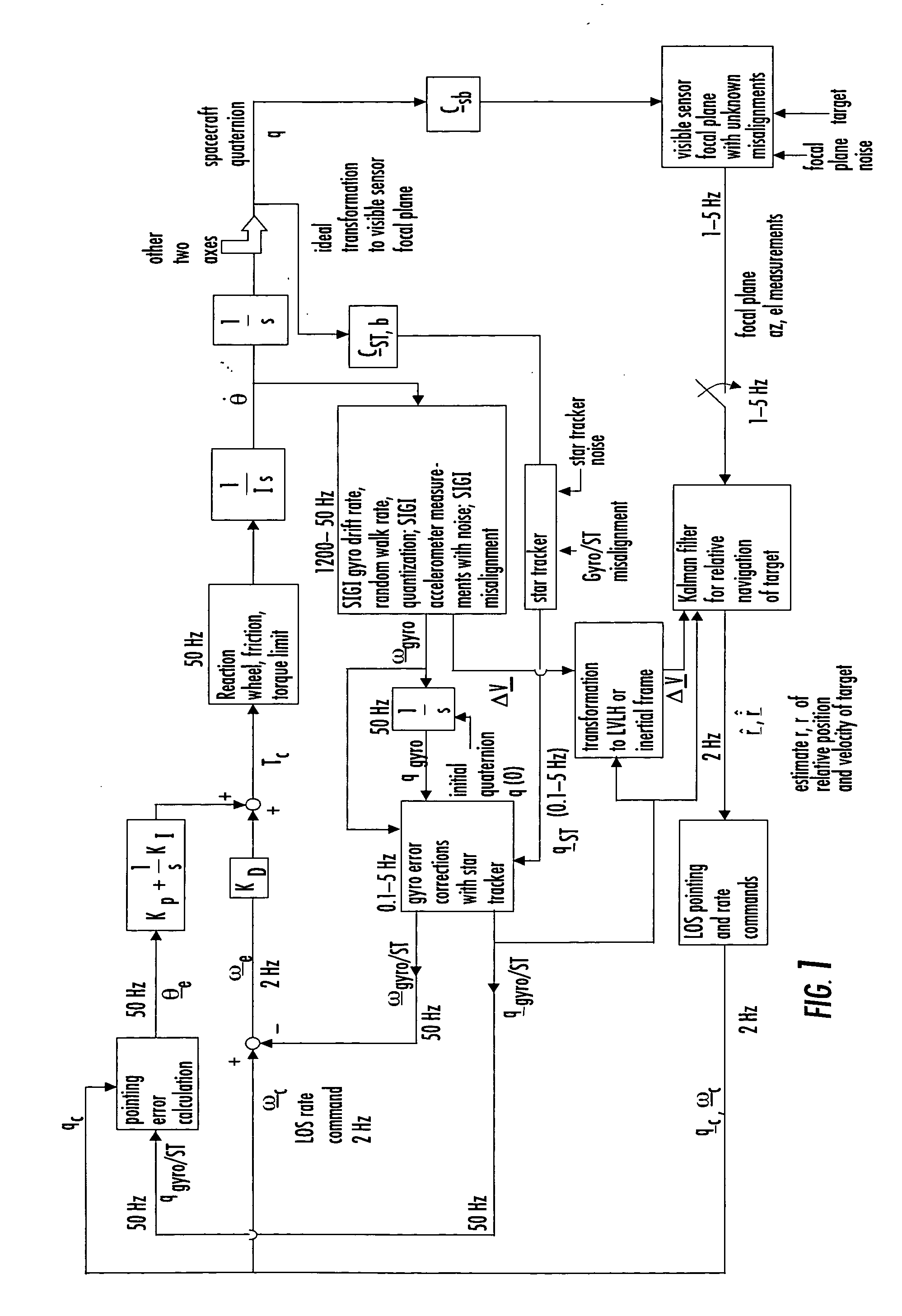
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
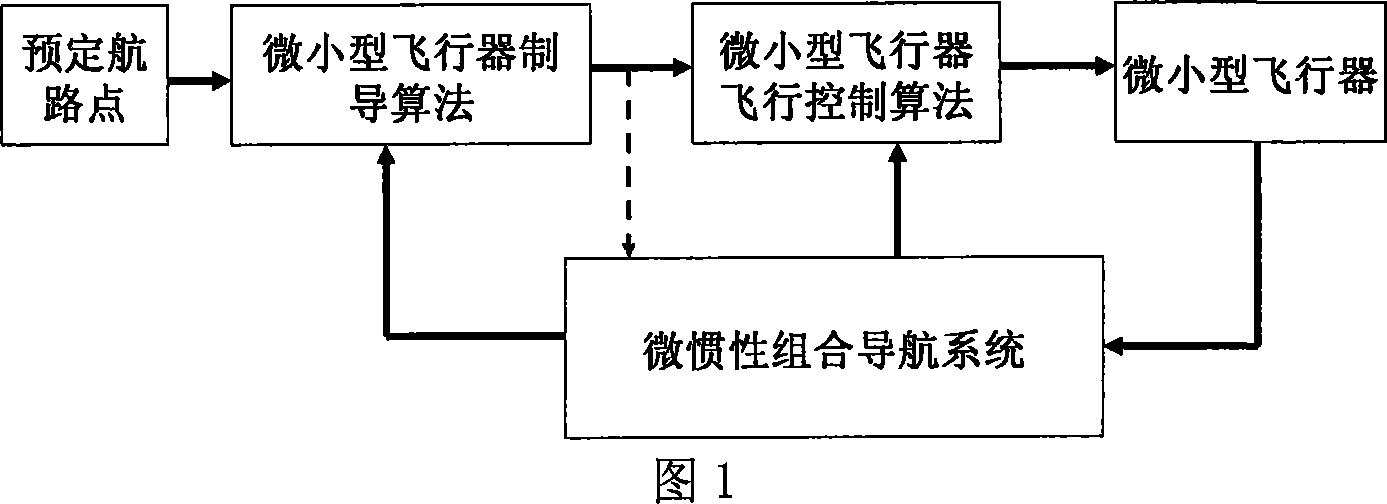
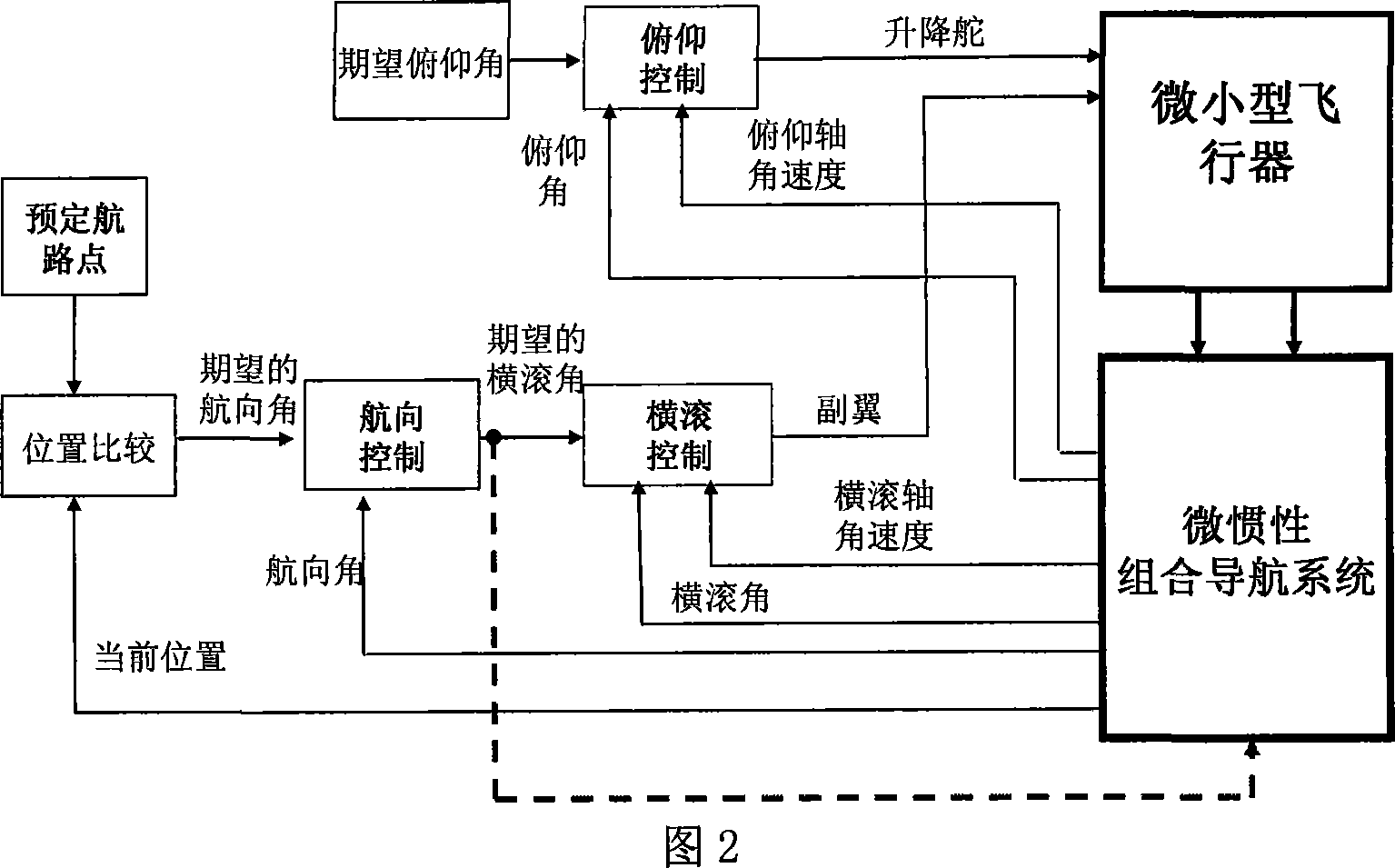
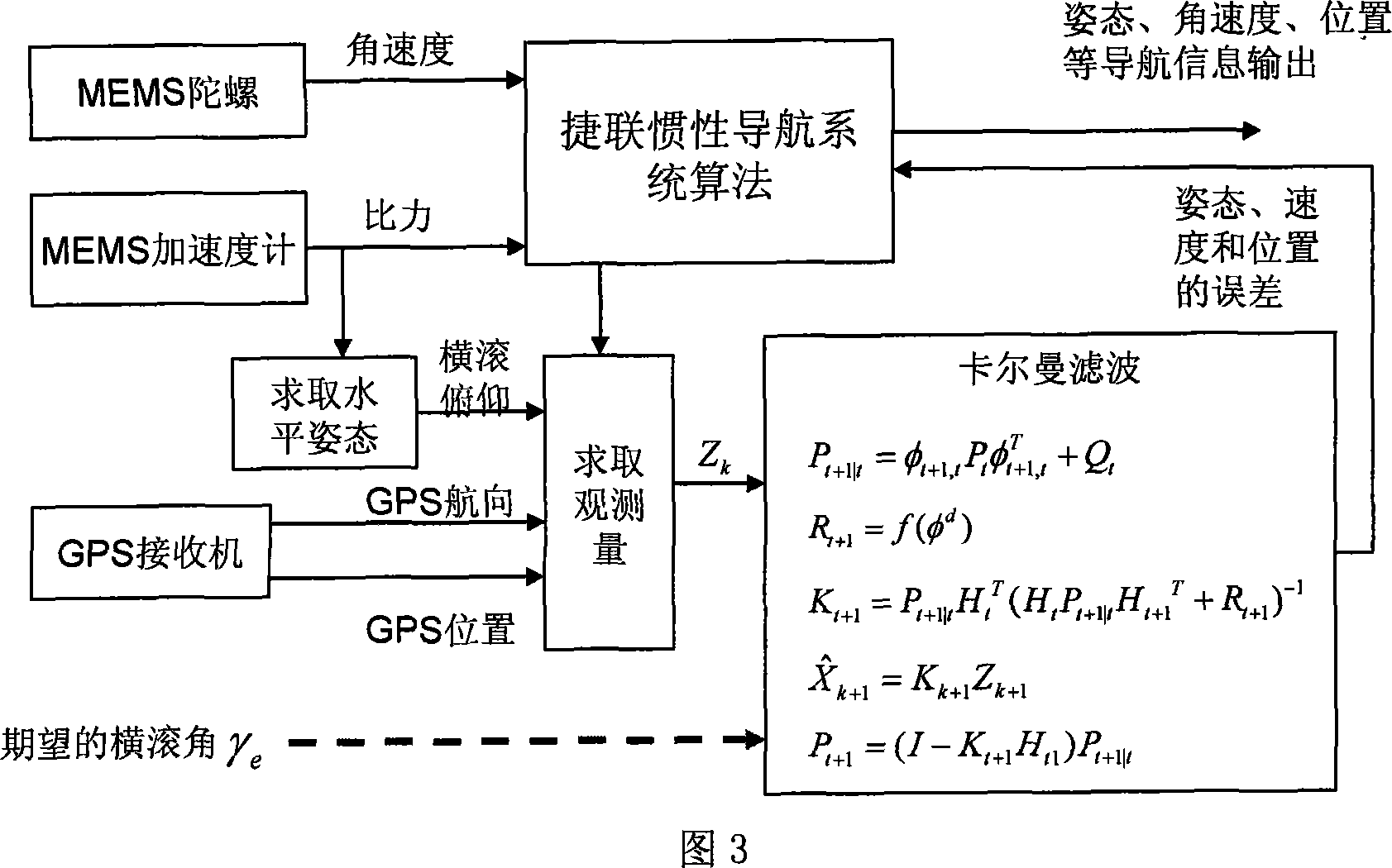
Attitude determination method of mini-aircraft inertial integrated navigation system
InactiveCN101033973AImprove flight qualityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGuidance systemAccelerometer
This invention relates to a kind of attitude definition method of micro inertia mixed navigation system of microminiature aero craft, belongs to microminiature vehicle attitude definition method. The method utilize guidance information, control Kalman filter noise matrices, to realize self-adapting adjust according to flight status; through parameter adjust to realize attitude definition of micro inertia mixed navigation system on dynamic airborne conditions; the specific process: through GNC closed loop circuit guidance algorithm, to gain aero craft barrel angle; through sensor picking, obtain vehicle rate and specific force; by strap inertial navigation algorithm to resolve out vehicle attitude, velocity and position information; by accelerometer and GPS data to count pose and position measurement information of aero craft; real-time compute horizontal attitude variance of Kalman filter observation noise matrices, through Kalman filter to estimate error of strap inertial guidance system; Amend above acquired pose, velocity and position information, and took as feedback information to import in control system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope
InactiveCN101846510AOvercome the disadvantage of error processing as zero-mean white noiseHigh precisionAngle measurementNavigation instrumentsGyroscopeZero mean
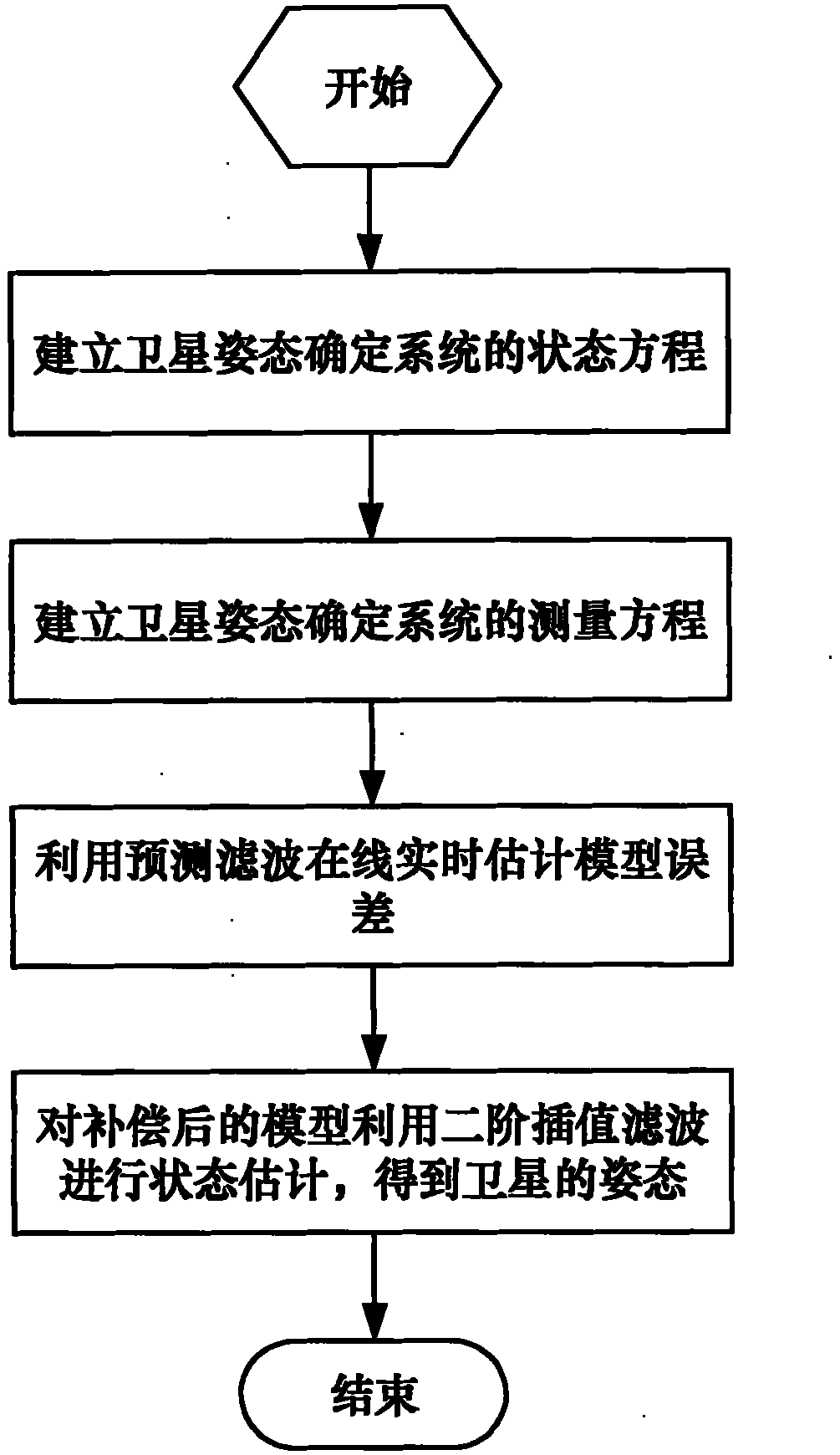
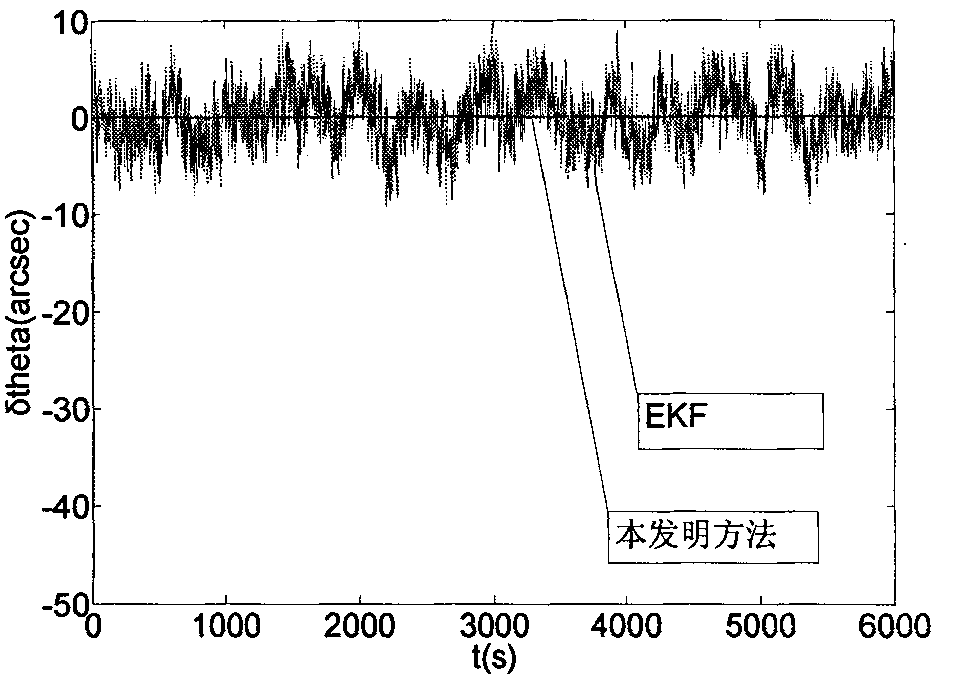
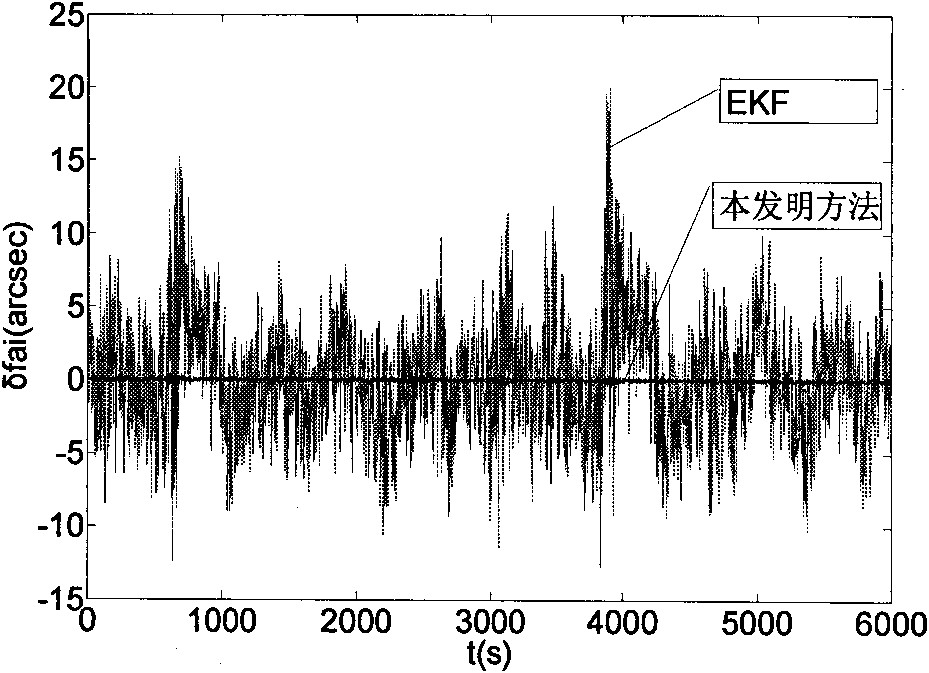
The present invention discloses a high-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope, which comprises the following steps: step 1. establishing a status equation of a satellite attitude determination system; step 2. establishing a measurement equation of the satellite attitude determination system; step 3. performing an online real-time model error estimation through predictive filtering; and step 4. performing a status estimation on a compensated model through 2-order interpolation filtering to obtain the attitude of a satellite. By applying predictive filtering to performing an online real-time model error estimation and correcting the system model, the invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the conventional estimation process that error is processed into zero-mean white noise; and in addition, the invention can process any nonlinear system and noise conditions to obtain an estimation result of higher precision and is applicable to thefield of high-precision attitude determination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
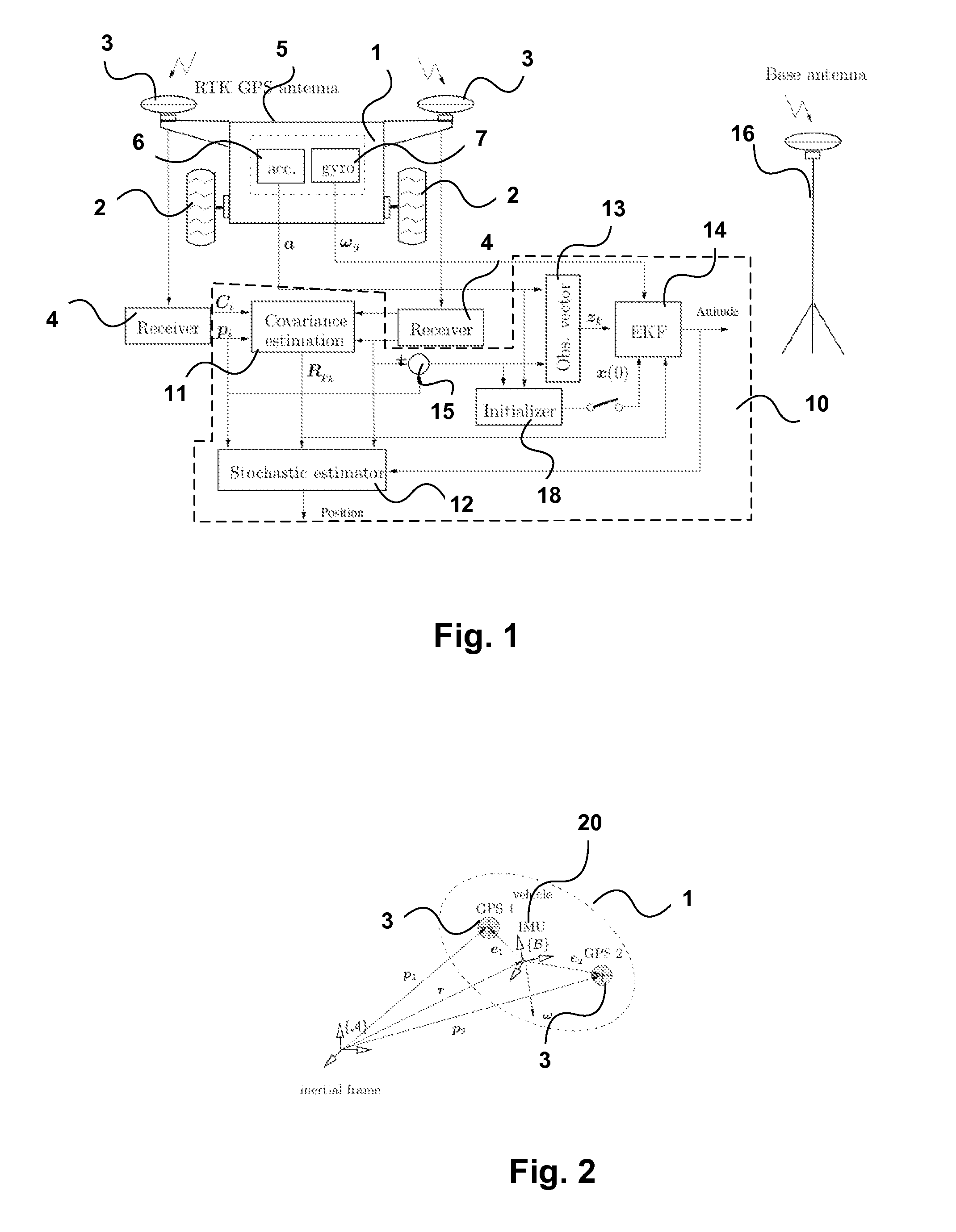
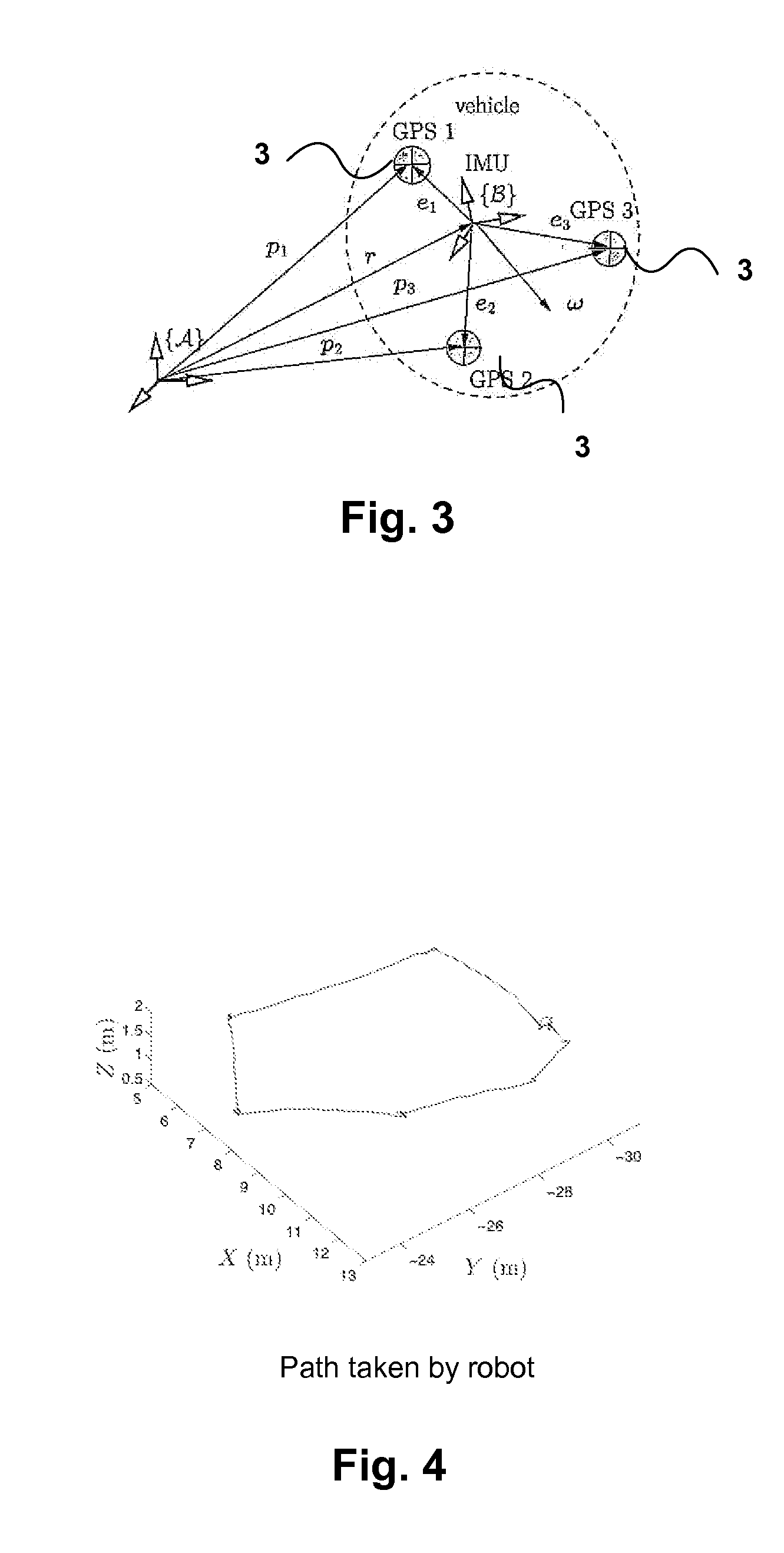
Apparatus and methods for driftless attitude determination and reliable localization of vehicles
InactiveUS20120086598A1Enhanced positional informationImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingReal Time KinematicAttitude determination
In order to determine positional information, about a mobile robot, Real Time Kinematic (RTK) Global Satellite Navigation System (GNSS) measurement data are obtained by at least two GNSS receivers mounted on the mobile robot. Estimates of the covariance matrices of the measurement data are computed. The RTK GNSS measurement data are combined according to the covariance matrices to obtain enhanced positional information. The results may be fused with data from an IMU to obtain driftless attitude and / or localization information.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
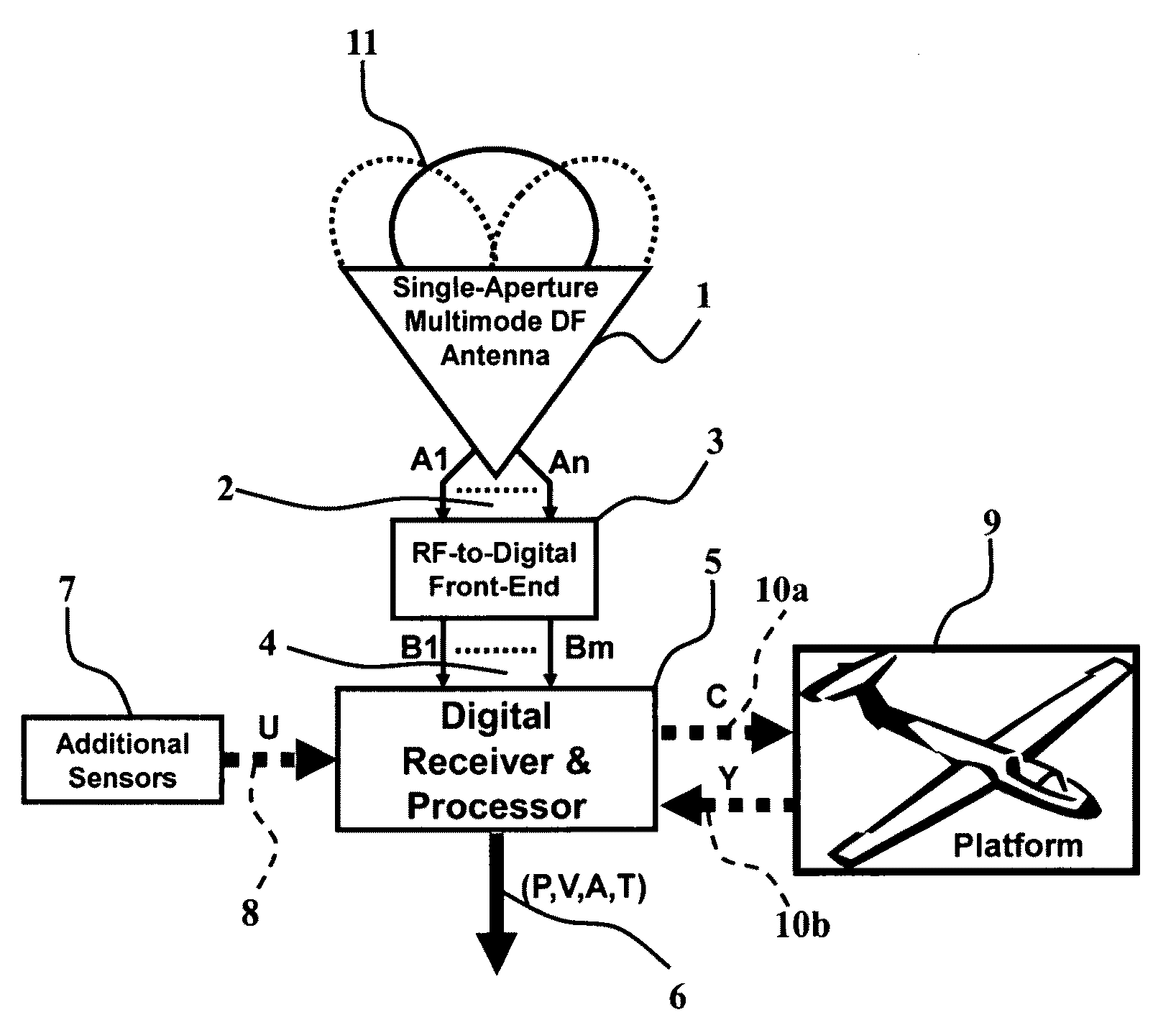
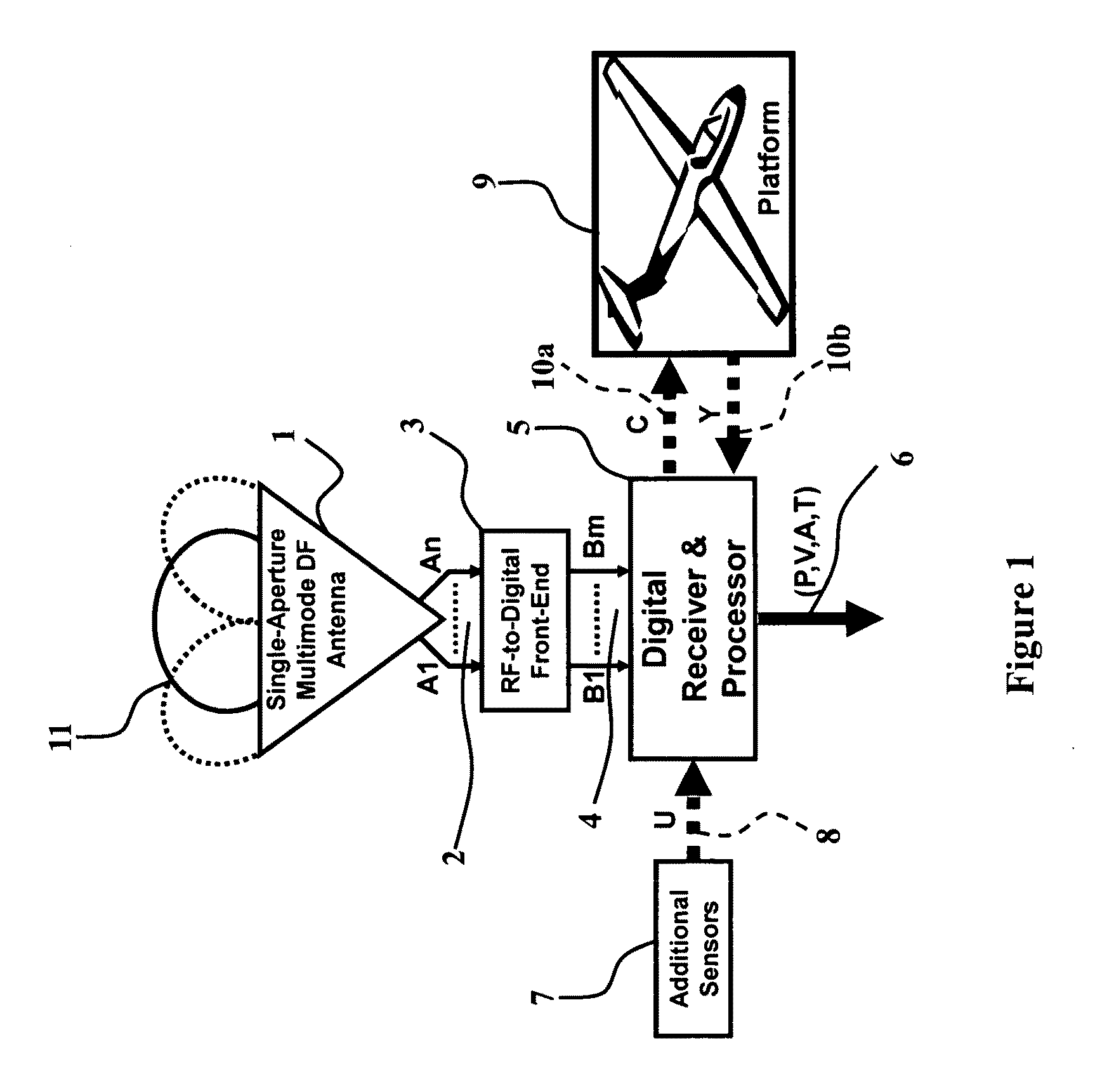
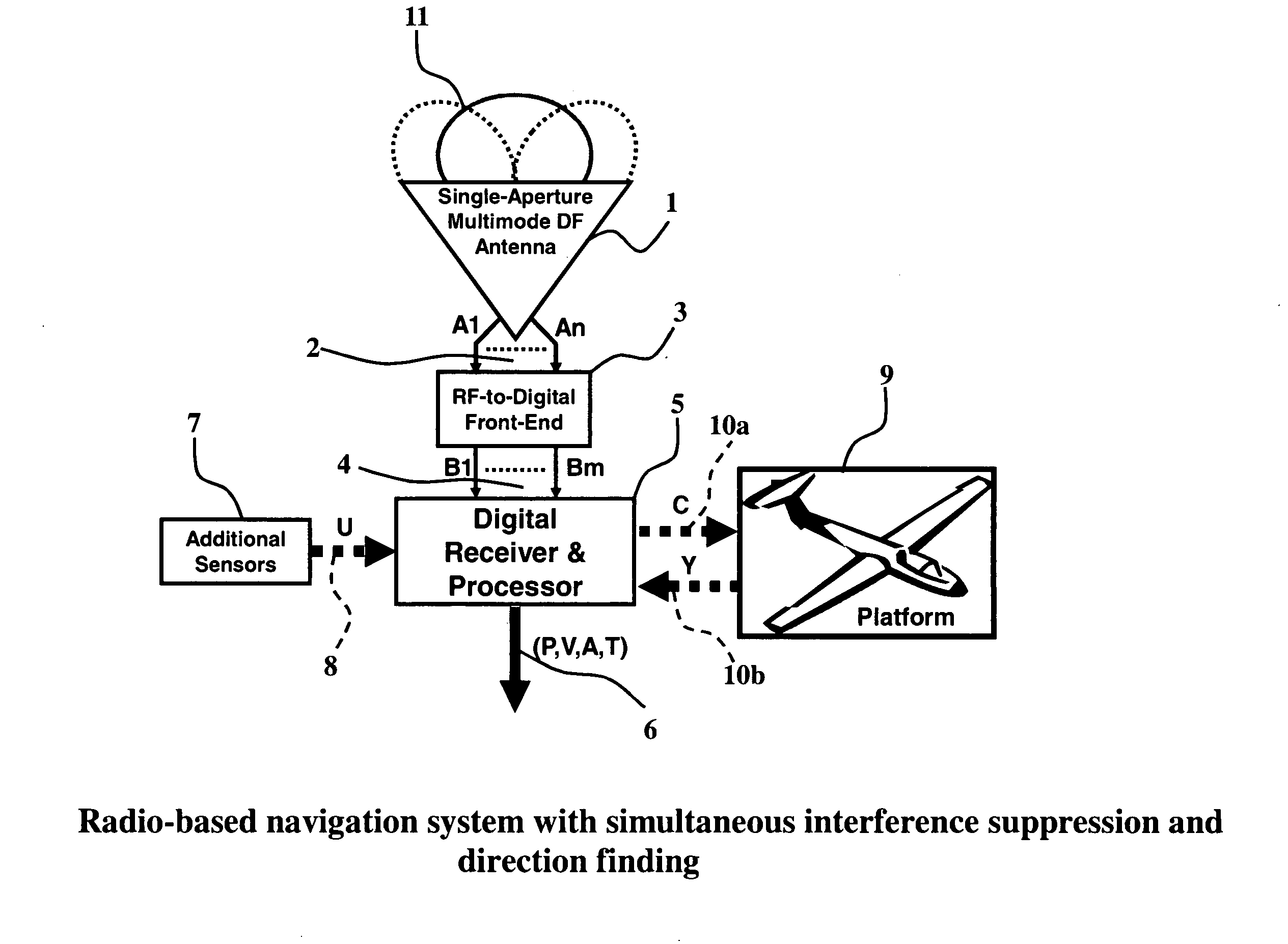
Compact single-aperture antenna and direction-finding navigation system
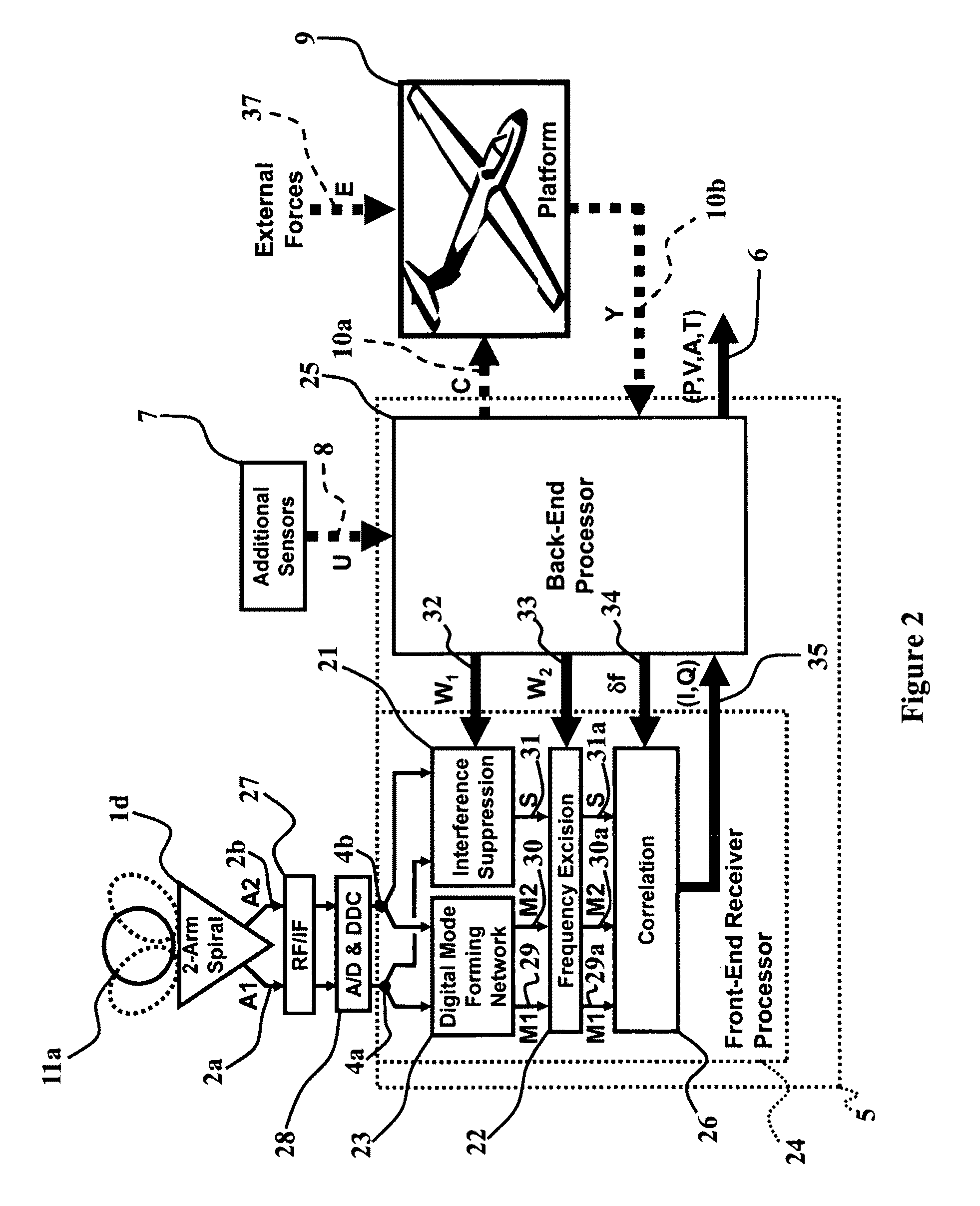
ActiveUS20100007555A1Improve attitude accuracyImprove system robustnessAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringNavigation system
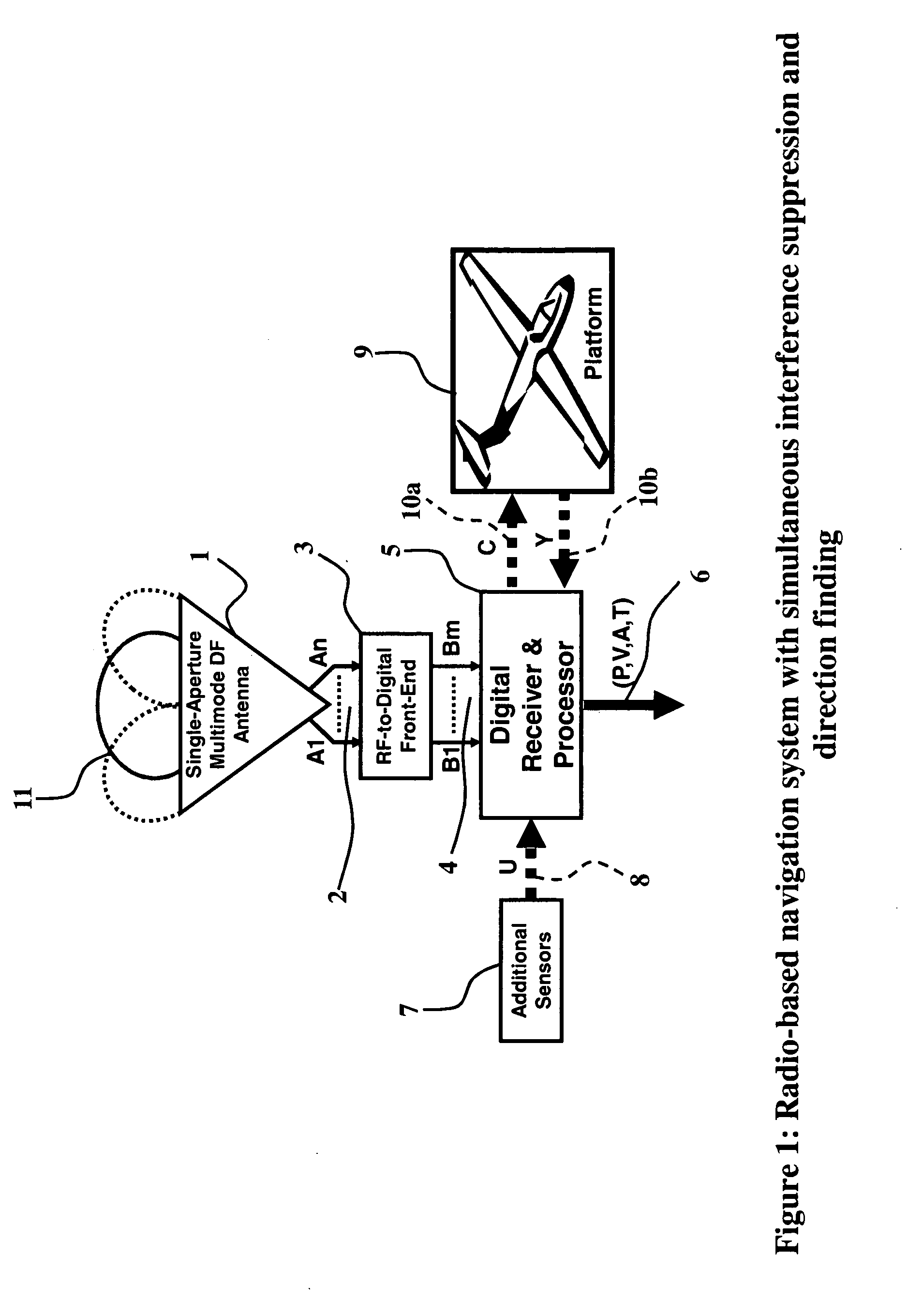
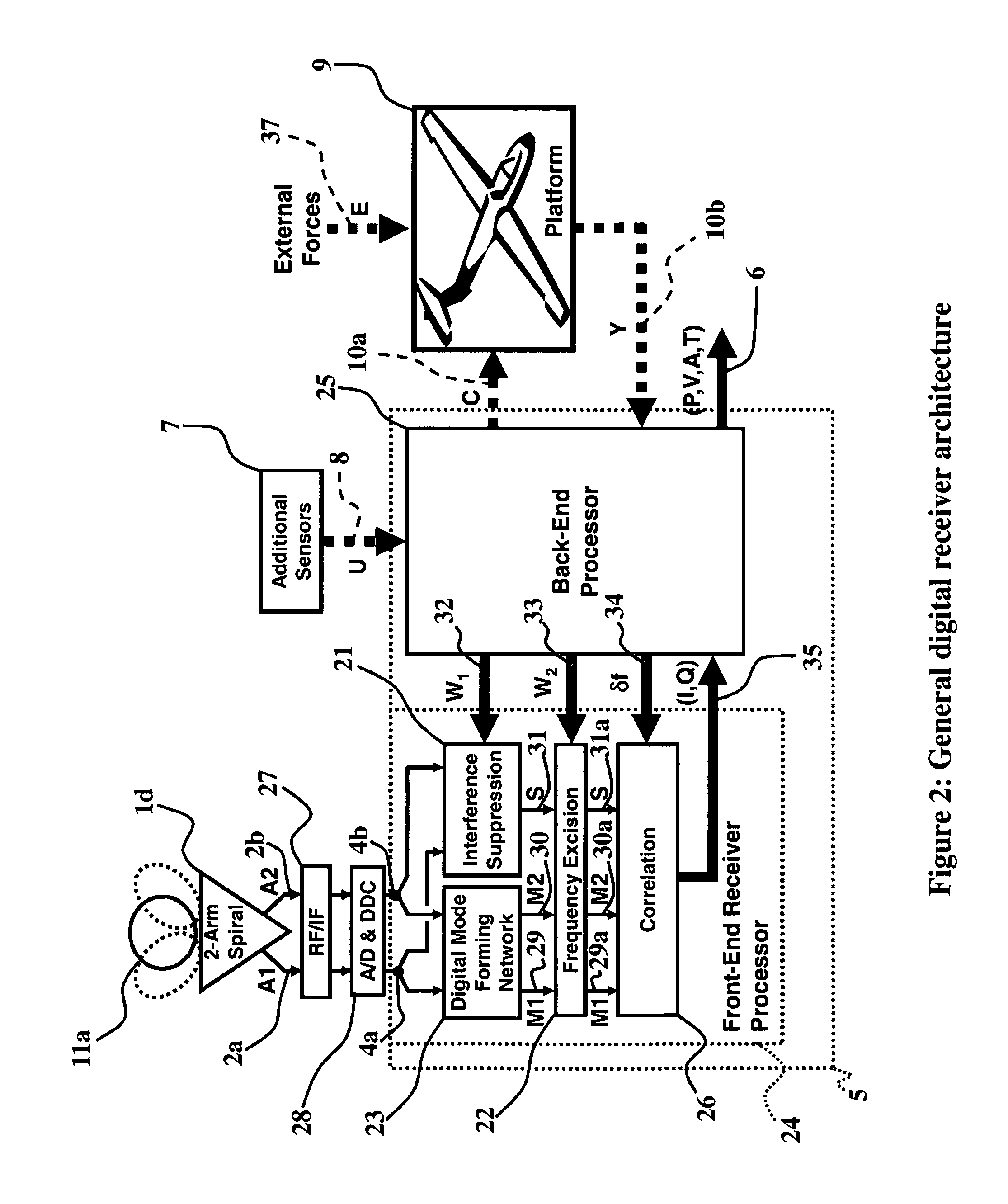
An exemplary radio-based navigation system uses a small multimode direction-finding antenna and a direction-finding receiver capable of determining platform position, velocity, attitude, and time while simultaneously providing protection against narrowband and broadband sources of interference. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals such as those from the Global Positioning System (GPS) provide attitude measurements with a compact multimode direction-finding antenna (e.g., a small two-arm spiral with improved angle-of-arrival performance over the entire hemisphere enhanced through the use of a conductive vertical extension of the antenna ground plane about the antenna perimeter and / or conductive posts placed evenly around the antenna perimeter) which provides simultaneous protection against jammers. The multimode spiral may be treated as an array of rotationally-symmetric antenna elements. The GPS receiver architecture also may be modified for direction-finding and thereby attitude determination by increasing the requisite number of input signals from one to at least two while minimizing the required number of correlators and mixers.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
Attitude determination exploiting geometry constraints
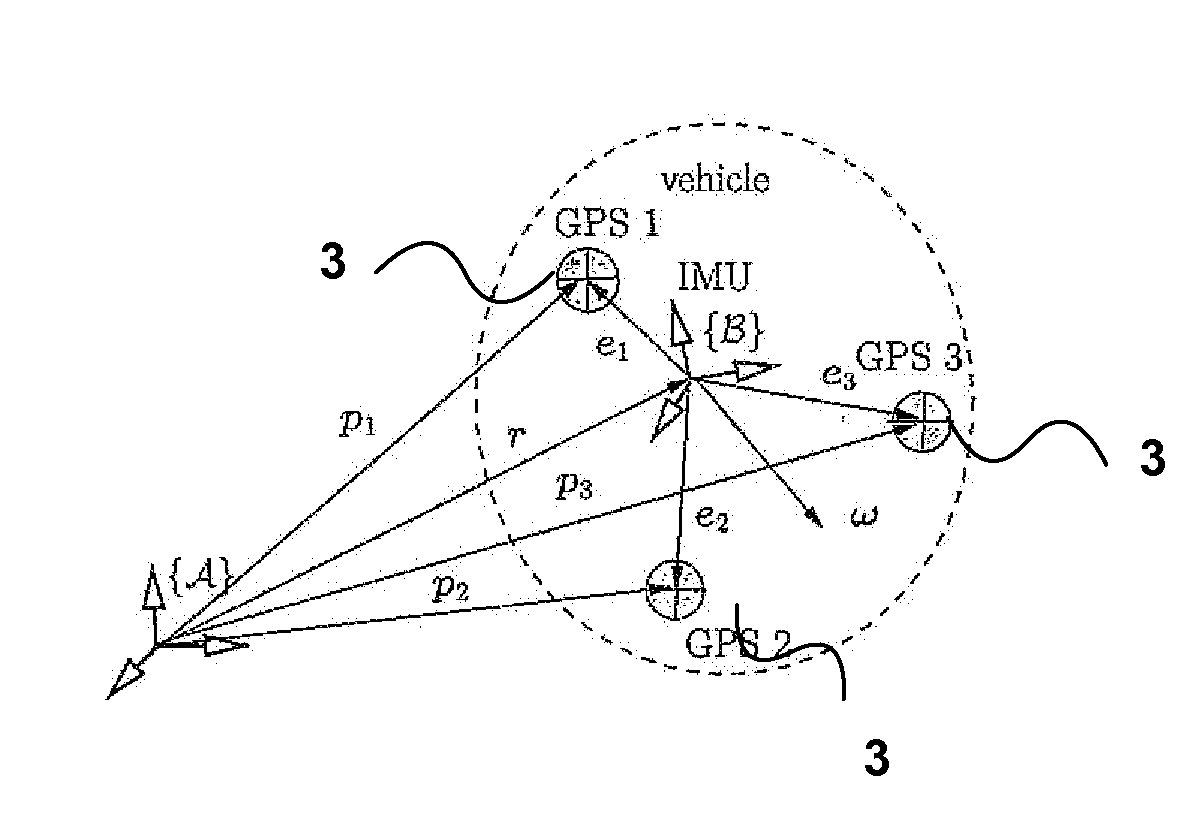
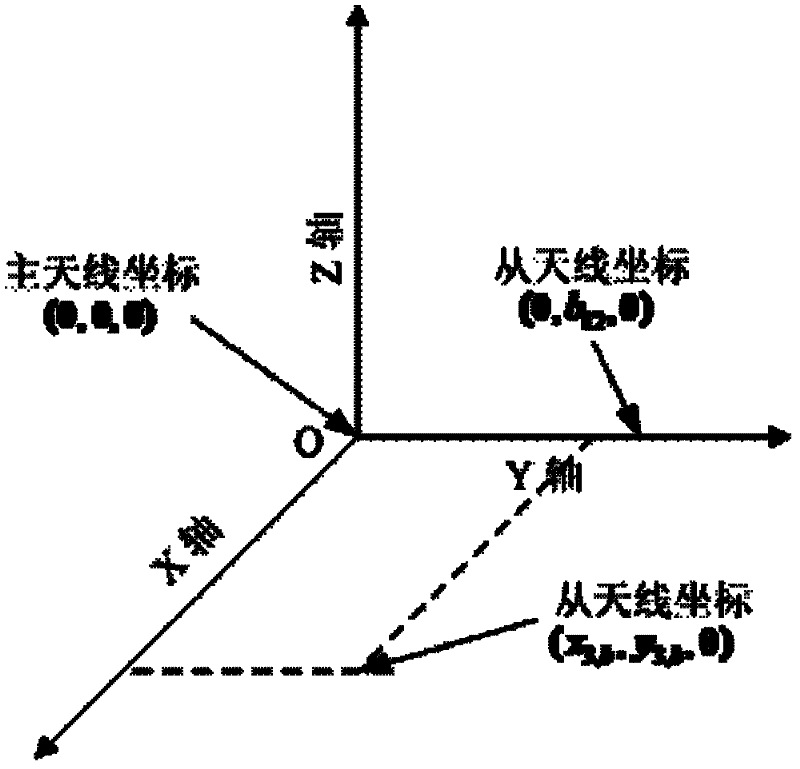
A method and system for determining at least one attitude angle of a rigid body. The method comprising: receiving a plurality of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) satellite signals with a plurality of antennas; establishing at least one pair of antennas such that each antenna of the plurality of antennas is included in at least one antenna pair; computing single- or double-difference phases corresponding to one or more GNSS satellites for each of the pairs of antennas; and constructing a single Differential Carrier Phase Attitude (DCPA) equation based on known geometry constraints of each of the pairs of antennas. The method also includes determining a solution for the DCPA equation based on a cost function, the solution yielding at least one integer ambiguity value and the at least one attitude angle.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
Target tracking method
ActiveCN105184776AStable postureEffective trackingTelevision system detailsImage enhancementThree-dimensional spaceAttitude determination
The invention discloses a target tracking method. The method comprises the steps that the high-precision three-dimensional space coordinate of a target is acquired; a high-precision positioning and attitude determination system is used to acquire the high-precision three-dimensional space coordinate and the attitude of a load in real time; according to the moving speed of the load and the geometric position relationship between a GNSS antenna and a camera in the high-precision positioning and attitude determination system, the three-dimensional space coordinate of a camera projection center is calculated; according to the three-dimensional space coordinate of the camera projection center and the three-dimensional space coordinate of the target, the target azimuth angle and the target attitude angle of the target are calculated; according to the target azimuth angle and the target attitude angle, the prediction attitude of a camera is calculated; the attitude of the camera is adjusted to the prediction attitude; and at an exposure position, the target is shot. The prediction attitude of the camera is adjusted in advance, which ensures that the attitude of the camera maintains stable in an exposure process, and a shot image is clear. The azimuth angle and the attitude angle of the camera are corresponding to the azimuth angle and the attitude angle of the target, which ensures that the target is at the middle position of the image shot by the camera.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Method for compensating star motion induced error in a stellar inertial attitude determination system
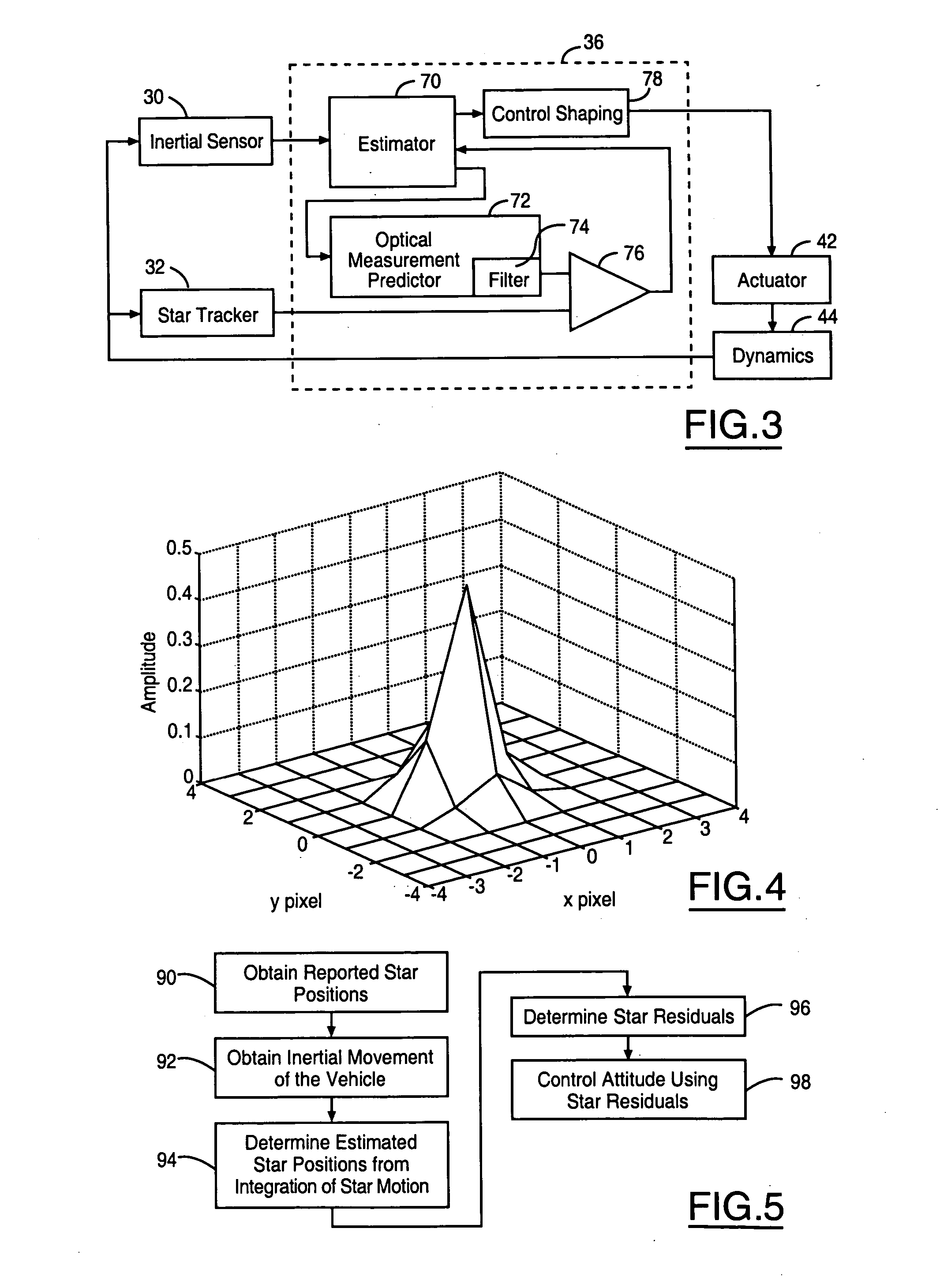
ActiveUS20080046138A1Improve attitude determination accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl signalActuator
A method for controlling an actuator of a vehicle comprises providing a dynamic condition sensor generating a vehicle movement signal and a position sensor for generating a reported position. A processor is coupled to the inertial sensor and the position sensor and comprises an estimator, a position measurement predictor having a filter, a comparator and a control shaping block, said estimator generating a vehicle position based upon the dynamic condition sensor, said position measurement predictor generating an estimated position measurement in response to the reported vehicle position and a matched frequency response to the movement signal, said control shaping block generating an actuator control signal in response to a comparison of the estimated position measurement and the reported vehicle position.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
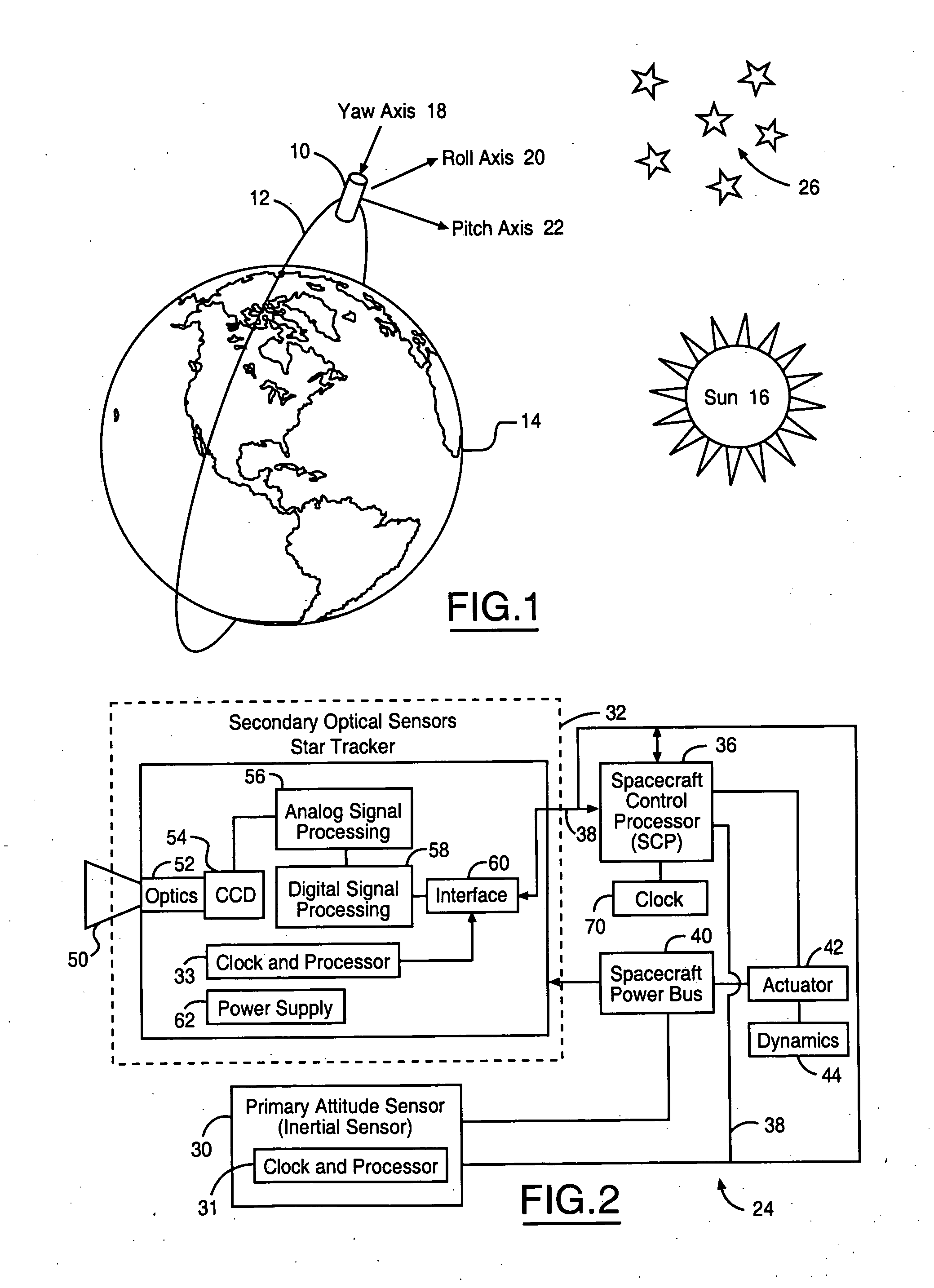
Daytime stellar imager for attitude determination
InactiveUS20060085130A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationJet aeroplaneGuidance control
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes a GPS sensor and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, position and timing information from the GPS sensor, and the catalogued star charts information to determine orientation (attitude) of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to calculate further information which may be used by a guidance control system. These systems provide efficient alternatives to inertial navigation systems when such systems are too expensive and can be used for periodic augmentation and calibration of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Spectral imaging system
InactiveUS7369229B2Increase calibration rangeAccurate detectionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull spectral imagingData acquisition
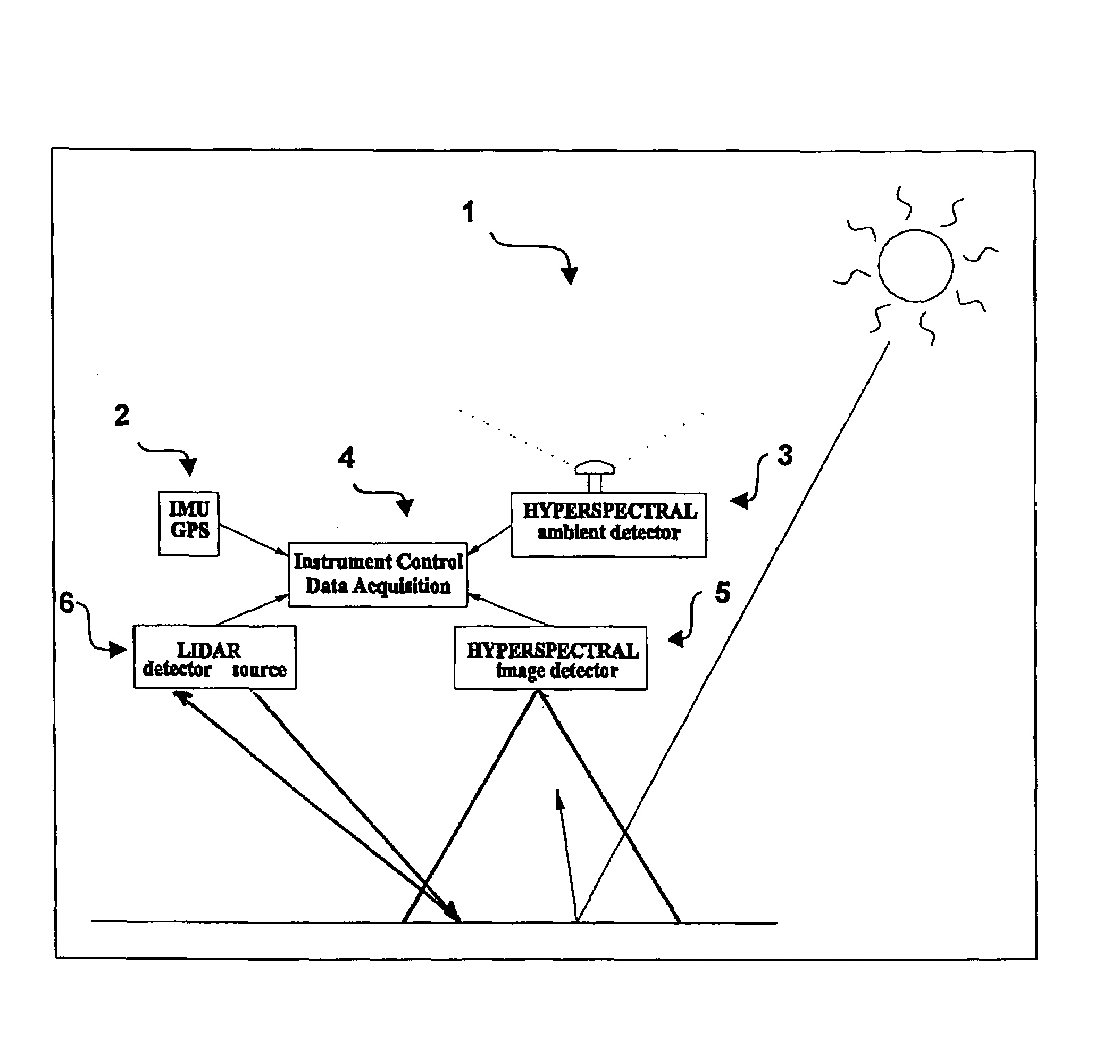
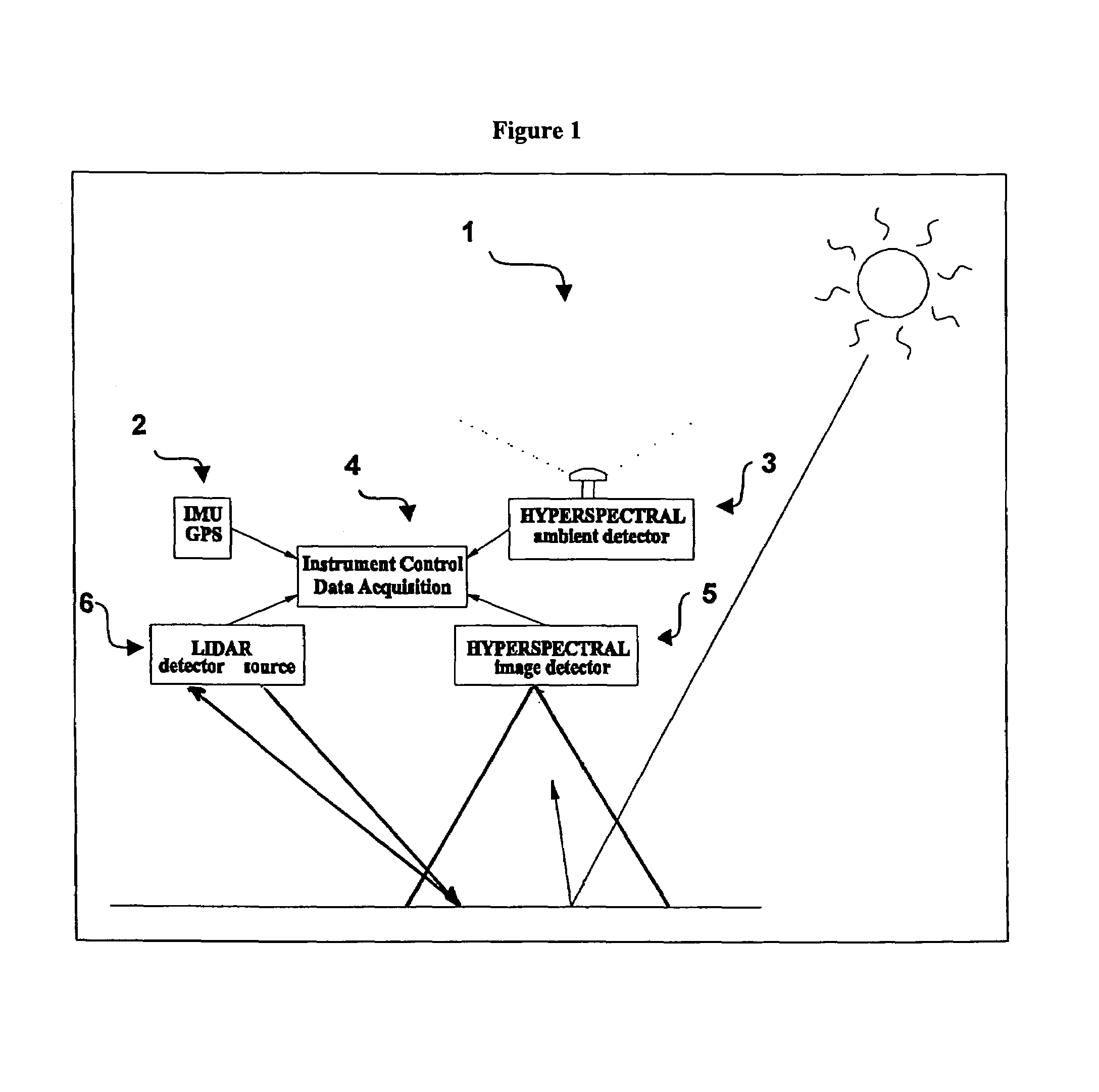
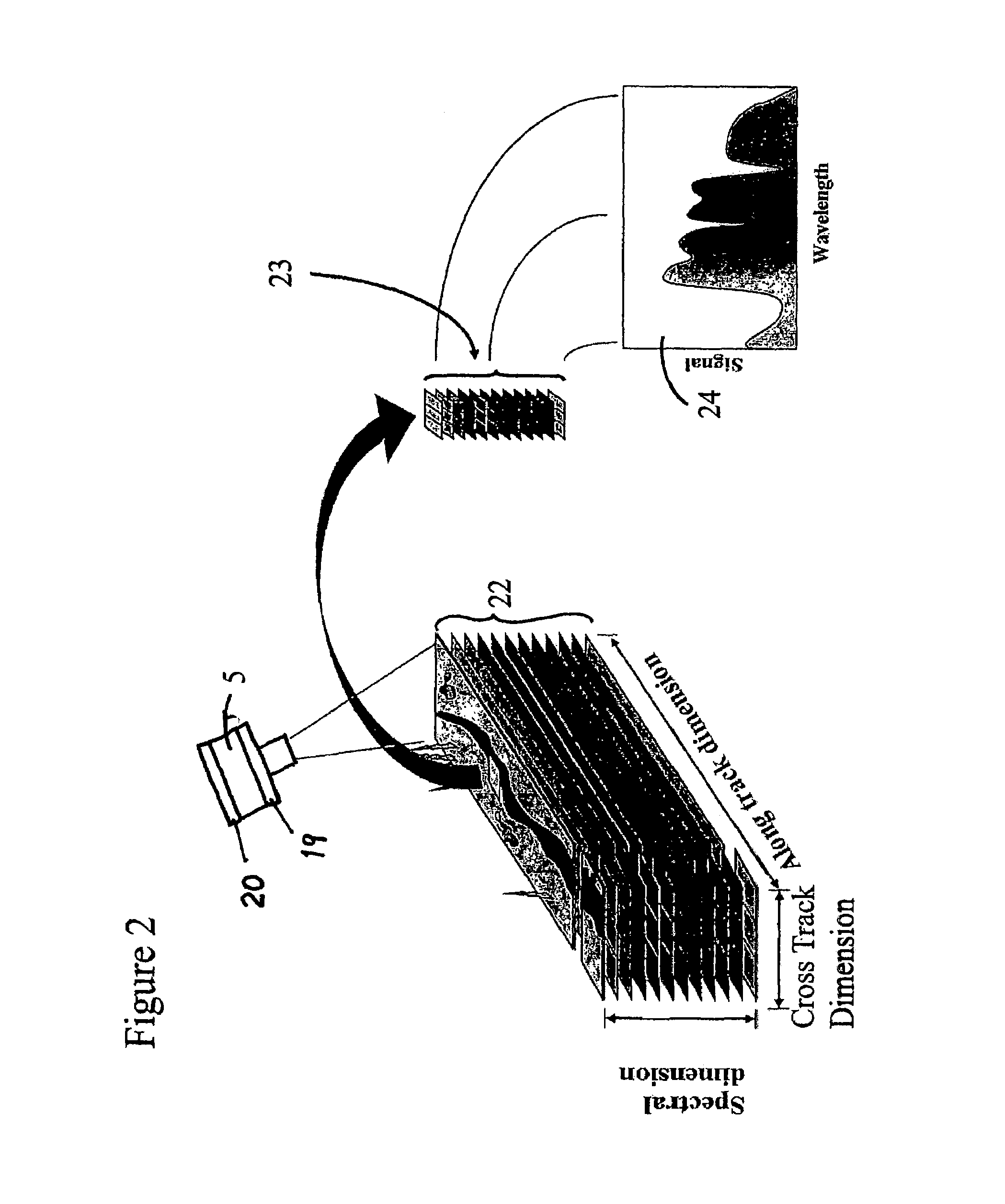
An imaging system and methods for resolving elements of interest through and obscuring environment by removing undesired signals from the intervening, obscuring environment is disclosed. A passive hyperspectral imaging sensor is calibrated and integrated into a system having a positioning and attitude detection system and an instrument control and data acquisition system that records data from sensors in a three-dimensional data cube having two spatial dimensions and a spectral dimension. Either an active detection and ranging system or a look-up-table approach or both are used to remove the noise generated by the intervening, obscuring environment from the data relevant to the elements of interest.
Owner:EATHON INTELLIGENCE
Small satellite attitude determination system and method thereof
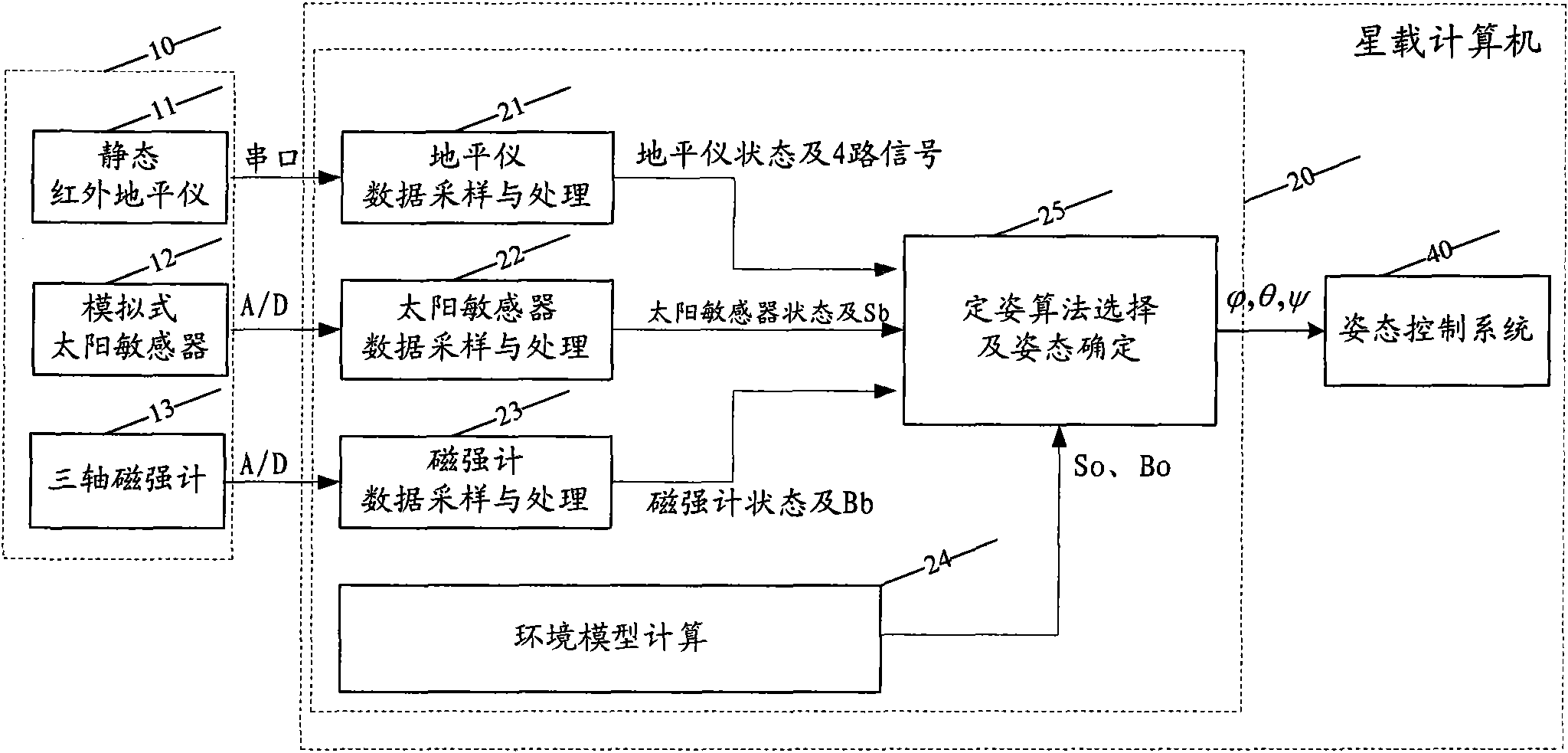
InactiveCN101556155ALow costImprove reliabilityAngle measurementNavigation instrumentsHorizonHydrology
The invention discloses a small satellite attitude determination system and a method thereof. The system comprises a plurality of attitude measuring units and a central processing unit; the central processing unit is used for collecting measurement data of the attitude measuring units, calculating environment model and selecting corresponding attitude determination algorithm according to the measurement data and the environment model, so as to determine the attitude. The central processing unit consists of a horizon sensor data sampling and processing unit, a solar sensor data sampling and processing unit, a gaussmeter data sampling and processing unit, an environment model calculating unit and an attitude determination selecting unit. The attitude determination selecting unit selects corresponding attitude determination algorithm according to data of the horizon sensor data sampling and processing unit, the solar sensor data sampling and processing unit, the gaussmeter data sampling and processing unit and the environment model calculating unit, so as to determine the attitude. The small satellite attitude determination system has low cost and simple structure; the small satellite attitude determination system also has various attitude determination algorithms, wherein, four fixed attitude determination algorithms and four Kalman filtering algorithms are designed; the algorithms can be effectively integrated and automatically alternated on the satellite to improve reliability of the system.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR MICROSATELLITES OF CAS
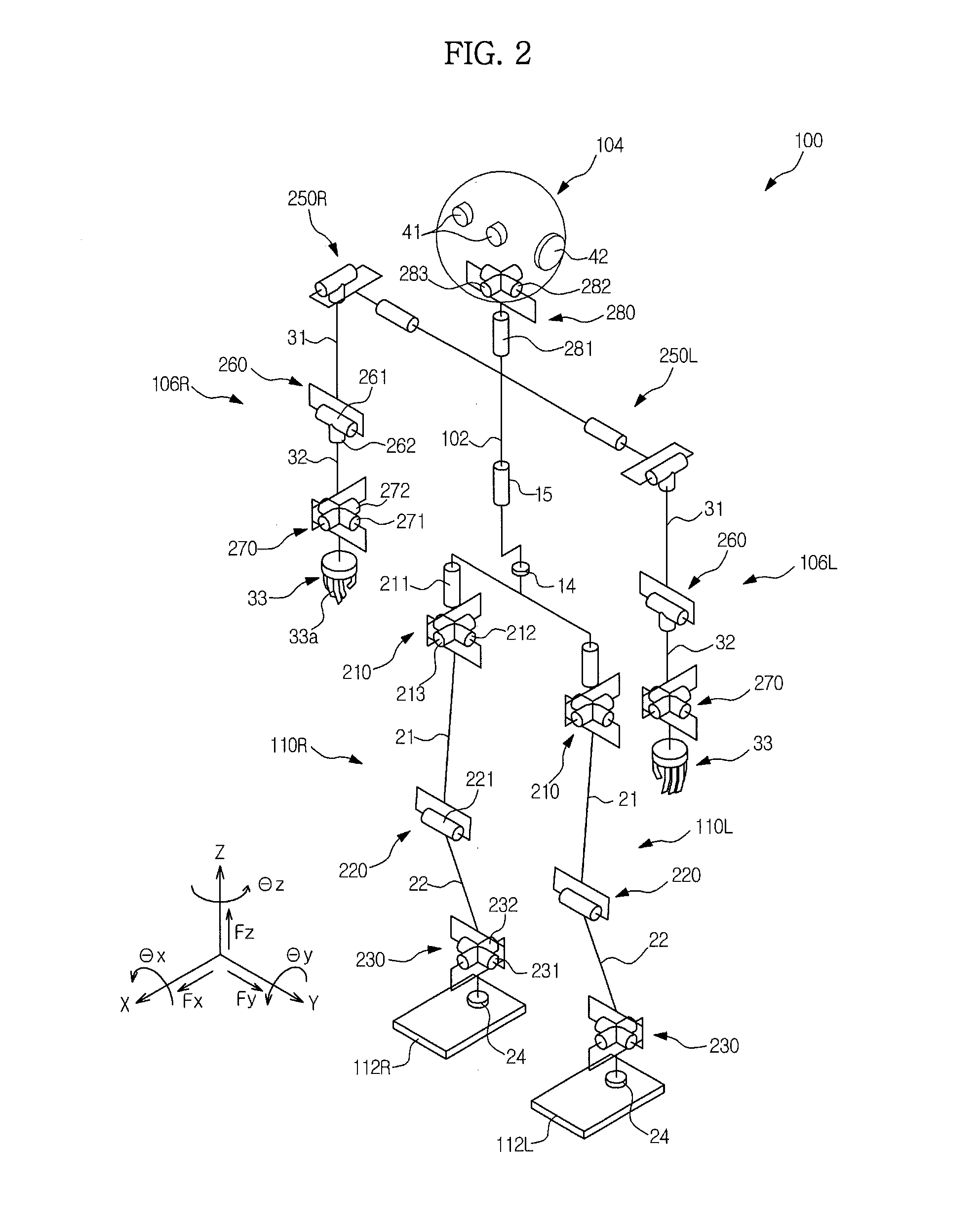
Variable surface landing platform (varslap)
In one embodiment, a variable surface landing platform (VARSLAP) includes a base for contacting a landing surface; at least 3 adjustable struts interconnected with the base, wherein each strut is bisected by a strut actuator-housing, and wherein the at least 3 adjustable struts are interconnected to a main body aerospace craft (MAC); a sensor array on the base; and an attitude determination and control system (ADCS).
Owner:CARREKER RAYMOND GEORGE
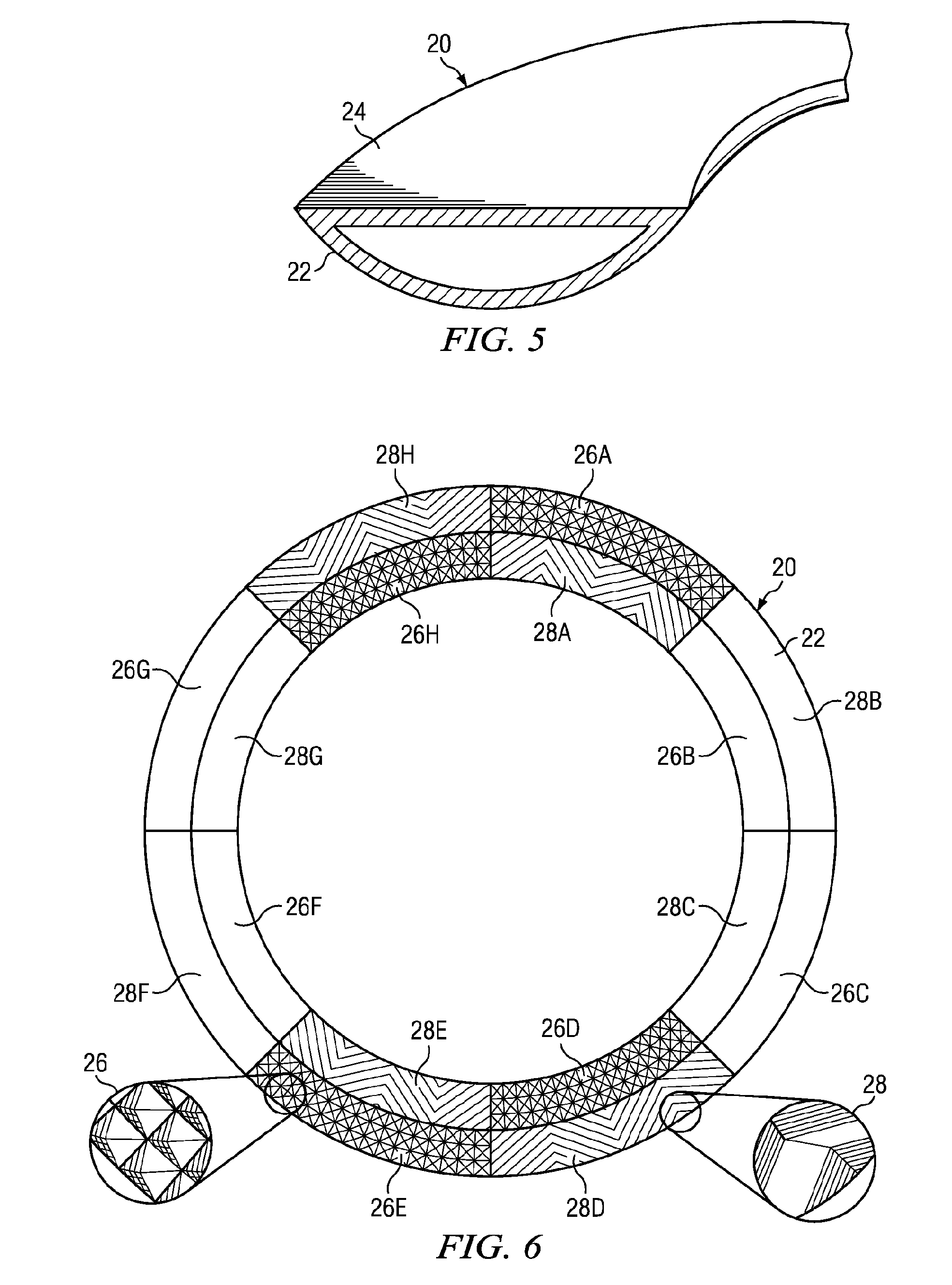
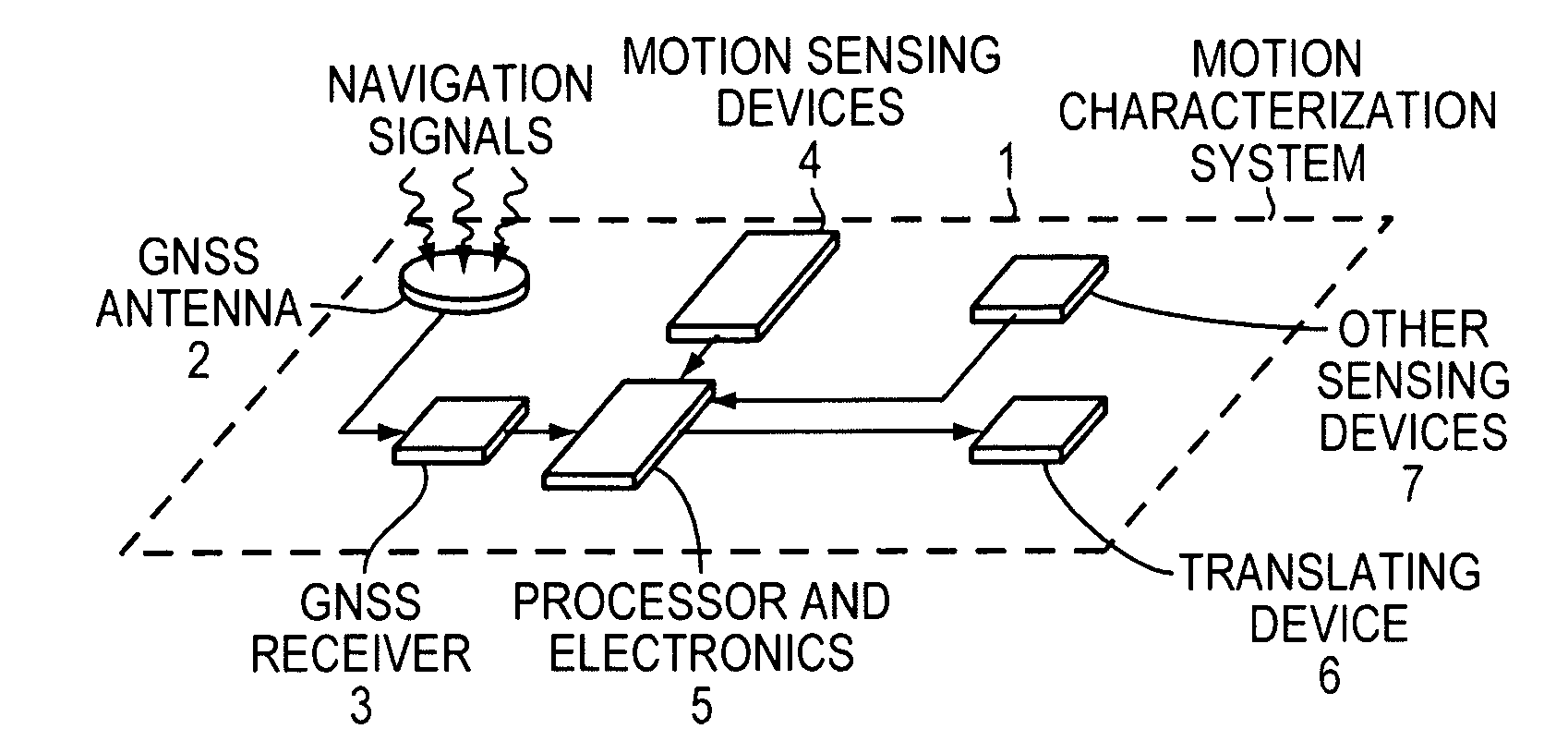
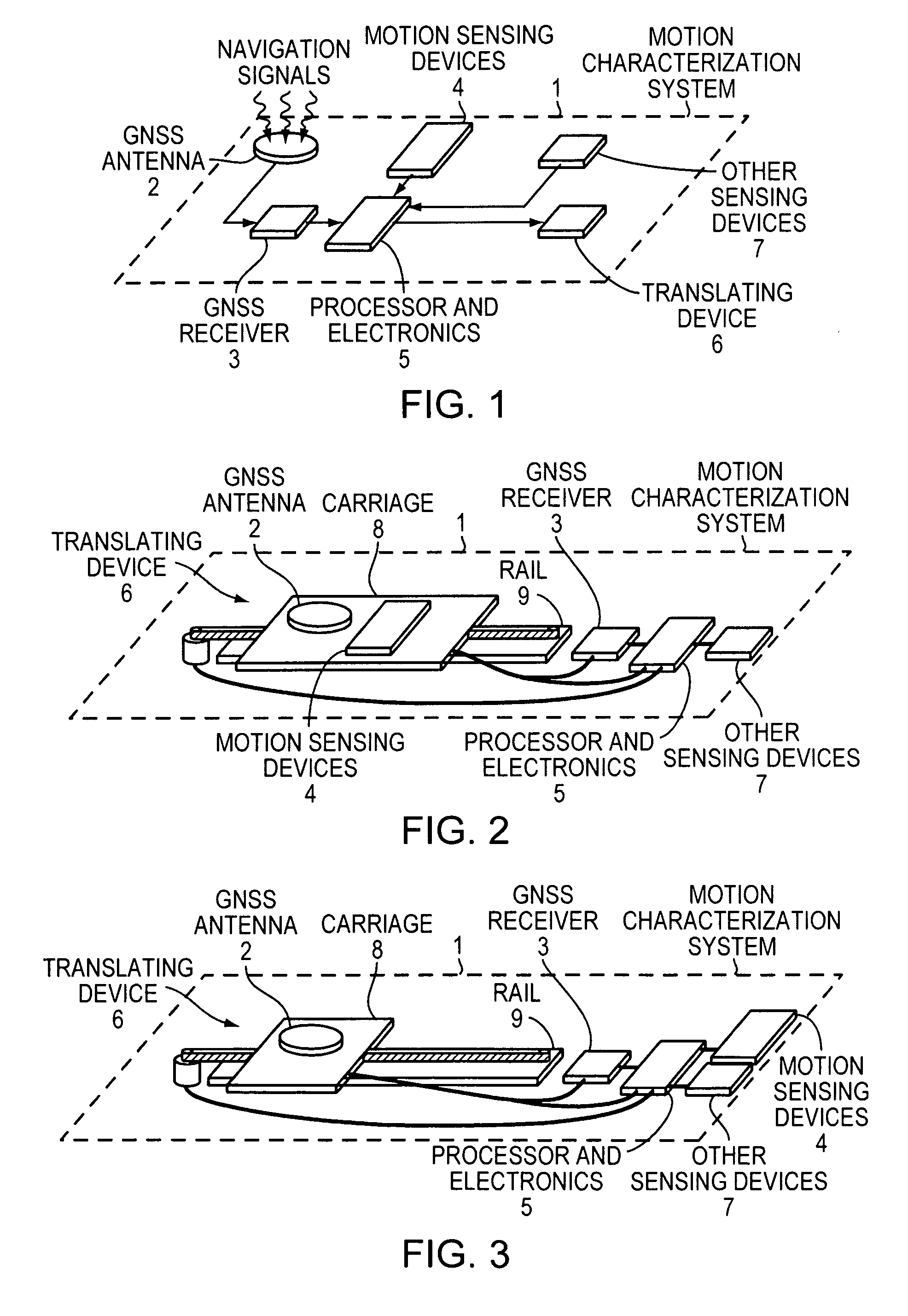
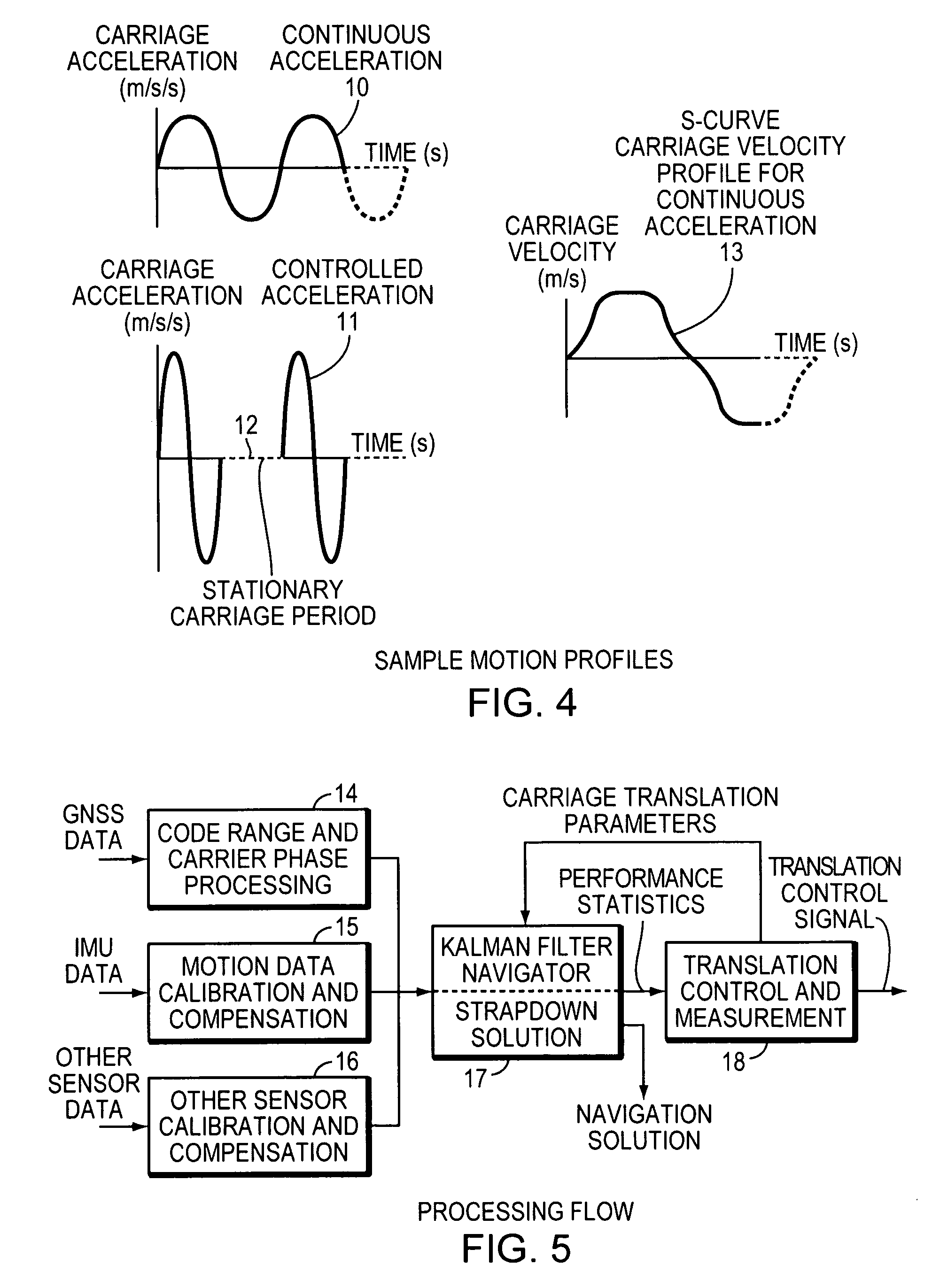
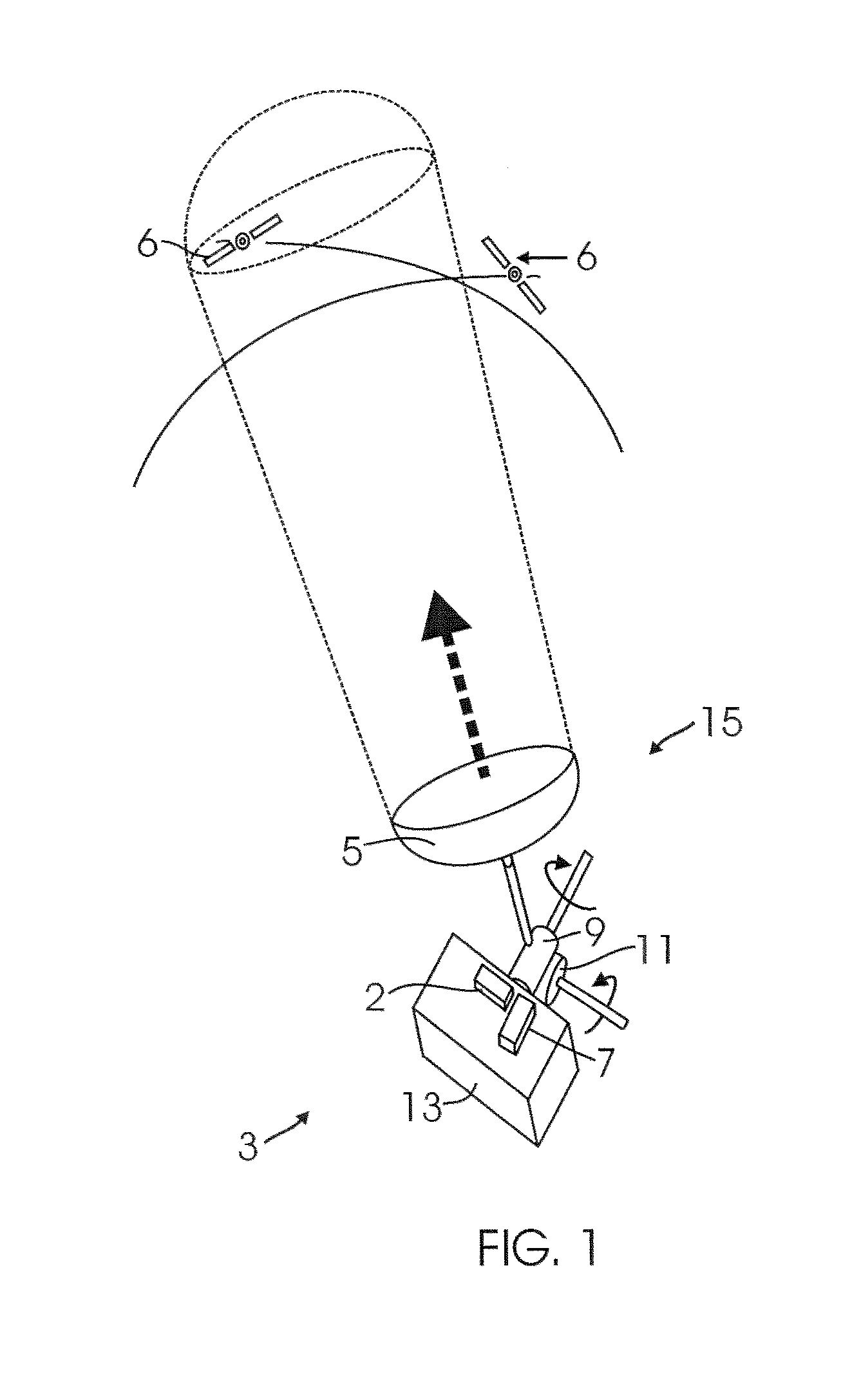
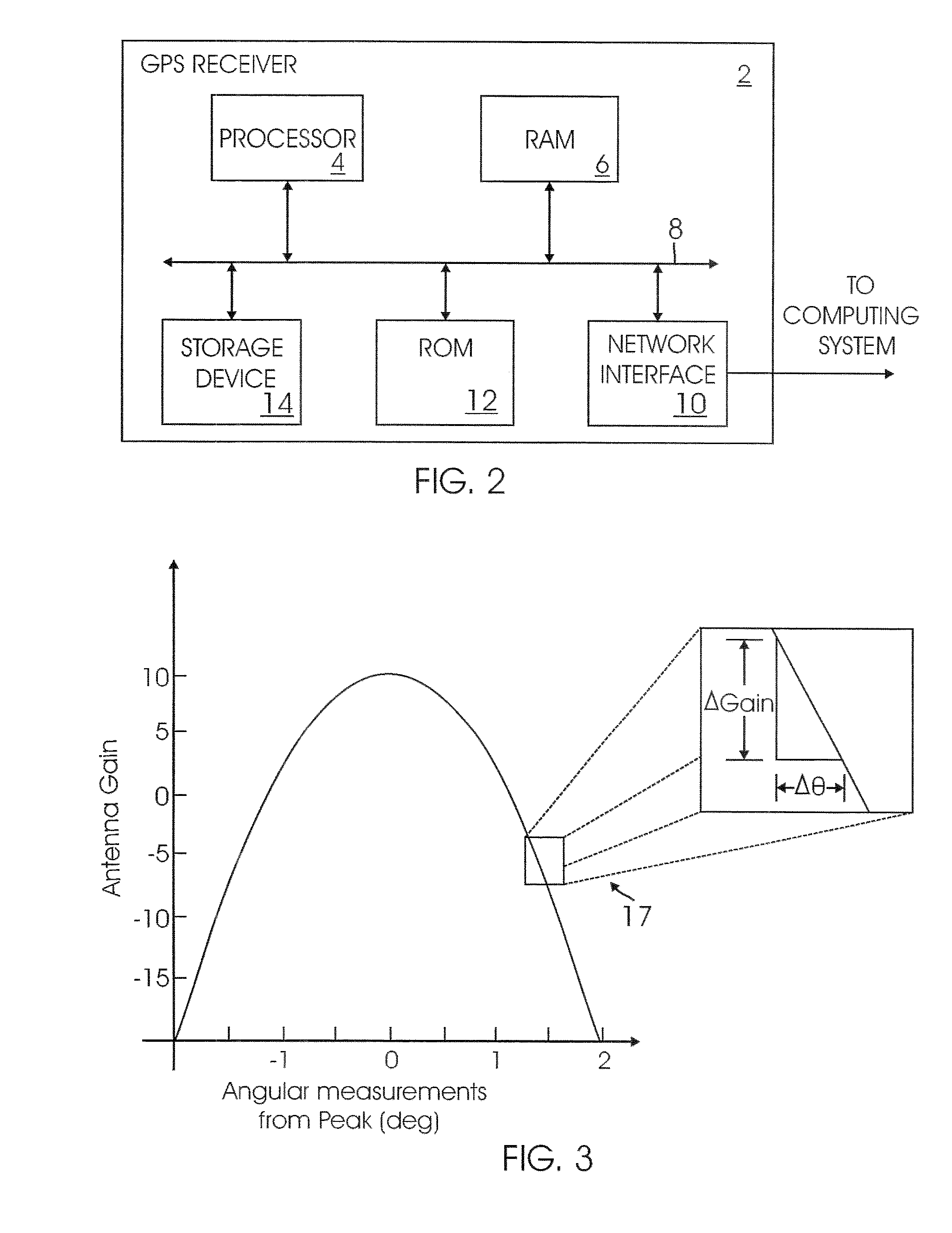
Attitude estimation using intentional translation of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) antenna
ActiveUS20090295633A1Improve accuracyImprove ObservabilityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingInertial accelerationSystem usage
A system determines three-dimensional attitude of a stationary or moving platform using signals from a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) antenna that undergoes deliberate translation, which may be occasional. The system uses single GNSS receiver, a single GNSS antenna, and inertial acceleration and / or rotation rate sensors. In one implementation, the GNSS antenna and inertial sensing components are rigidly connected and mounted to a pallet that is intentionally translated along a track as needed. In a second implementation, the GNSS antenna is mounted to a pallet, and the inertial sensing components are fixed in position. To maximize effectiveness, the track is oriented along a geometrical direction of the platform that is predominantly in a lateral direction from the gravity vector. The system achieves three-dimensional attitude accuracy that rivals interferometric GNSS systems.
Owner:WALDOAIR CORP
Decoupling control method for relative orbits and attitudes of formation satellites
InactiveCN101794154AReduce the control dimensionImprove solution efficiencyAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitAttitude control
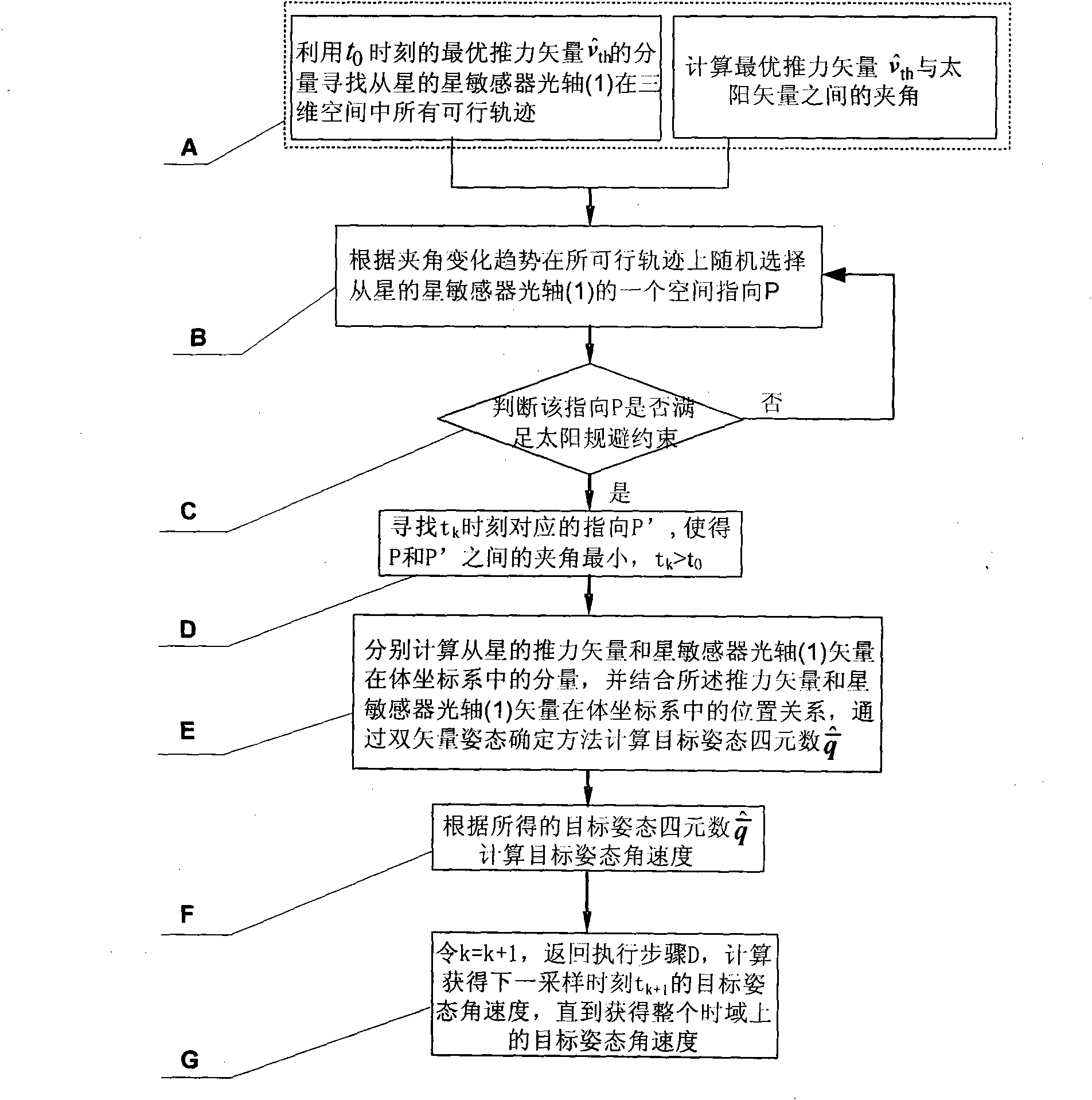
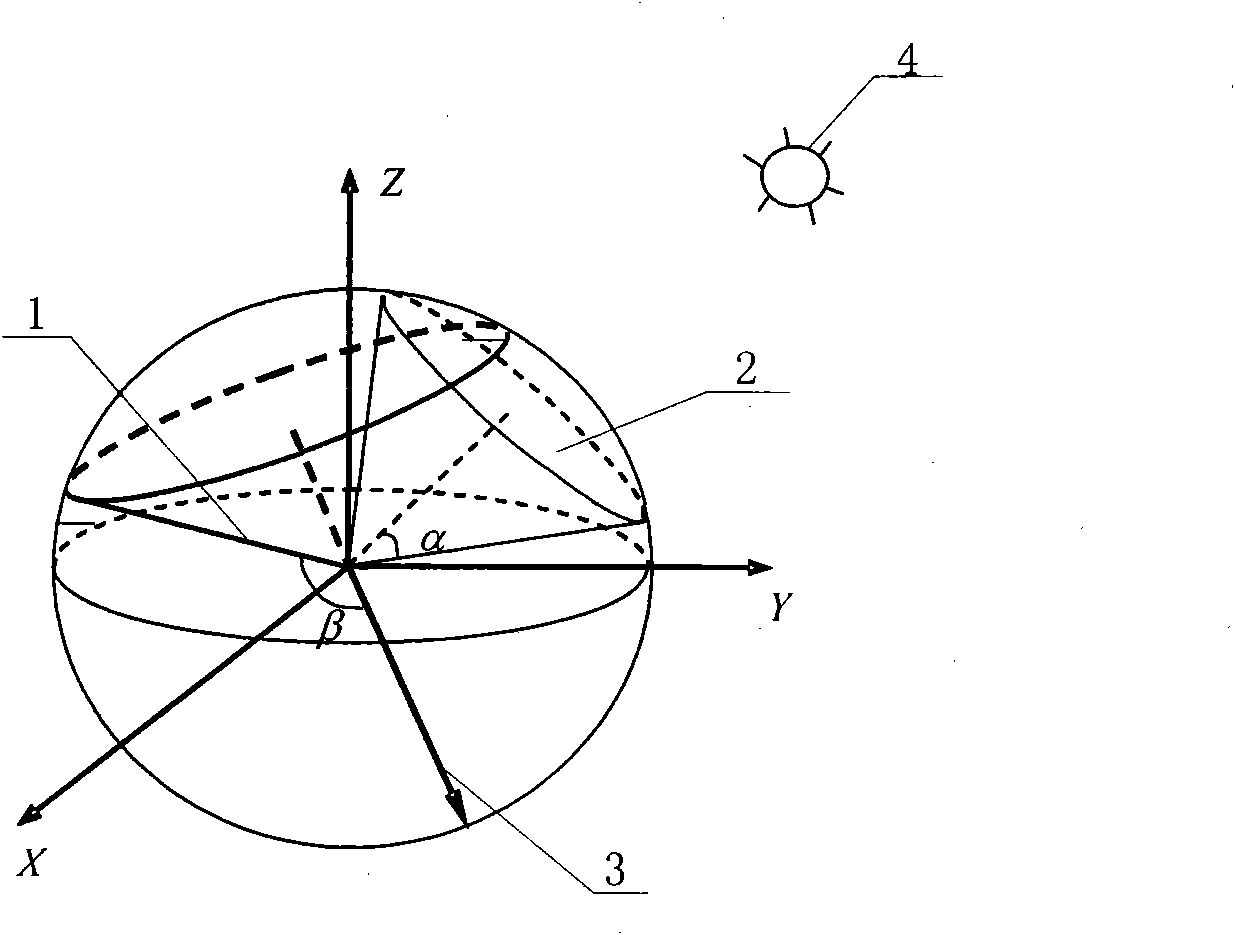
The invention discloses a decoupling control method for relative orbits and attitudes of formation satellites, relates to the technical field of the control of the orbits and attitudes of a spacecraft formation, and solves the problems of large satellite calculation amount and low orbit solving efficiency caused by high control dimension of the formation satellites due to serious coupling of the relative orbits and the attitudes of the formation satellites. The method gives two decoupling conditions at first, so that the control of the relative orbits and the attitudes can be designed independently; a thrust vector mobility decoupling constraint condition is introduced to the initialization control of the relative orbits according to satellite attitude mobility constraints indirectly; and during the optimal thrust vector attitude tracking, the possible orientation in space, which meets solar avoidance constraints, of a star sensor optical axis (1) is sought by using a geometric method, and the optimal attitude quaternion and attitude angular velocity are calculated finally by using a double-vector attitude determination algorithm. The method provides important reference value for the control of the orbits and the attitudes of the spacecraft formation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Walking control apparatus of robot and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20110178637A1Maintain balanceWalking smoothlyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl theoryIntermediate point
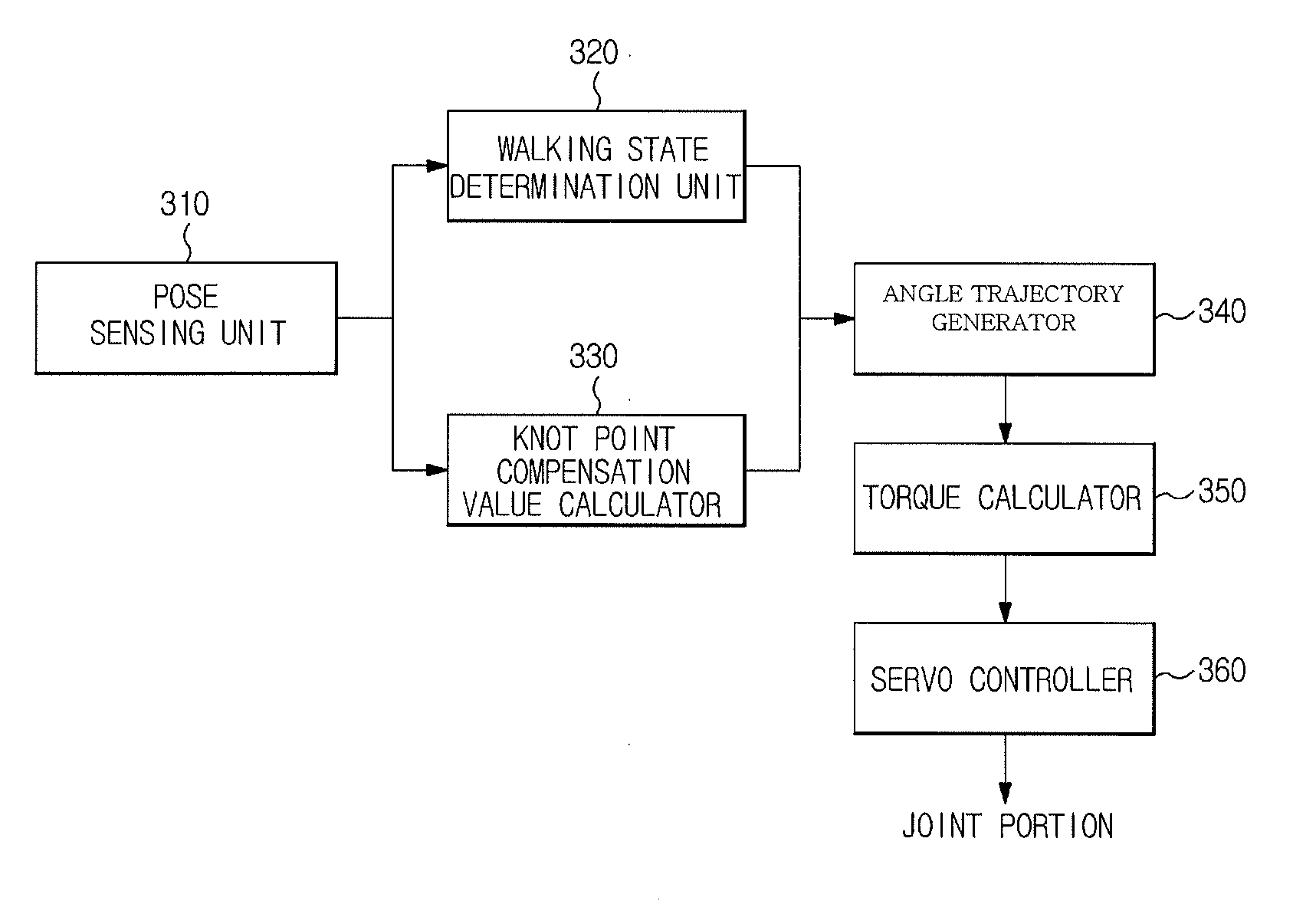
A walking control apparatus of a robot includes a joint portion provided in each of a plurality of legs of the robot, a pose sensing unit to sense the pose of the robot, a walking state determination unit to determine a walking state from the pose of the robot, a knot point compensation value calculator to determine a Center Of Mass (COM) of the robot from the pose of the robot and to calculate a knot point compensation value, a desired angle trajectory generator to generate a reference knot point of the joint portion corresponding to the walking state, to compensate for the reference knot point using the knot point compensation value so as to generate a desired knot point, and to generate a desired angle trajectory of the joint portion using the desired knot point. The knot point which is the angle command of the joint portion of each of the legs to perform the next step is compensated for based on the COM, and the compensated desired knot point is smoothly connected using the spline curve such that the robot walks similar to a human. In addition, in order to maintain balance while walking, the angle of the joint portion of the intermediate point of the current step is fed back and the knot point of the next step is predicted and adjusted, such that the robot stably and smoothly walks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
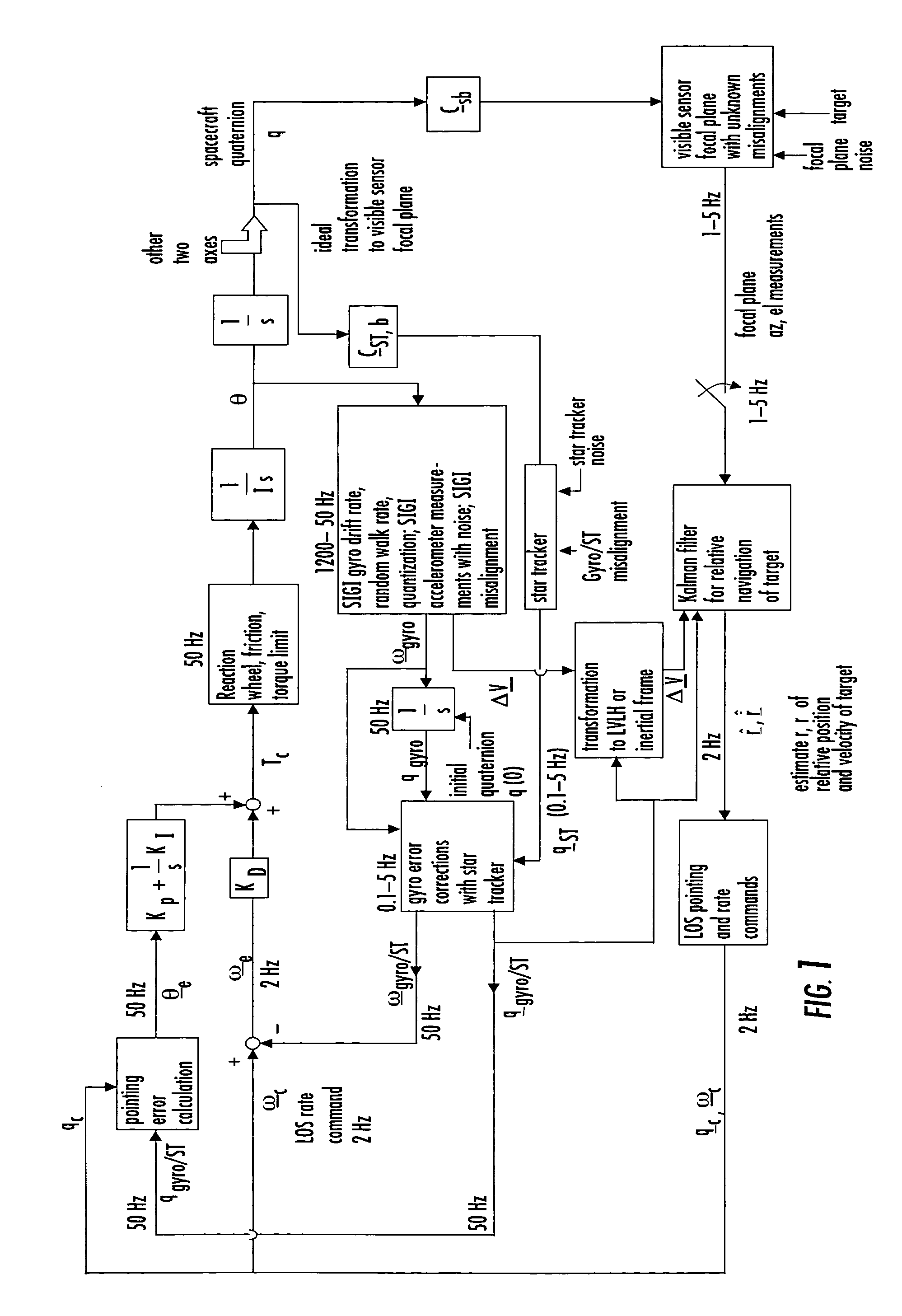
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS7142981B2Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsKaiman filterLaser ranging
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes: LOS angle measurements of the target, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system provides improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed for the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Real-time multi-target human body 2D attitude detection system and method
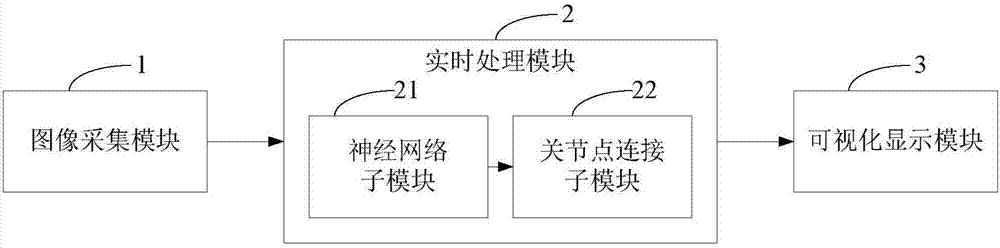
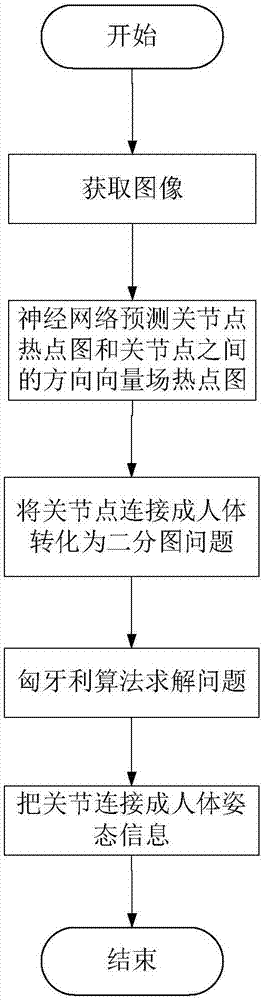
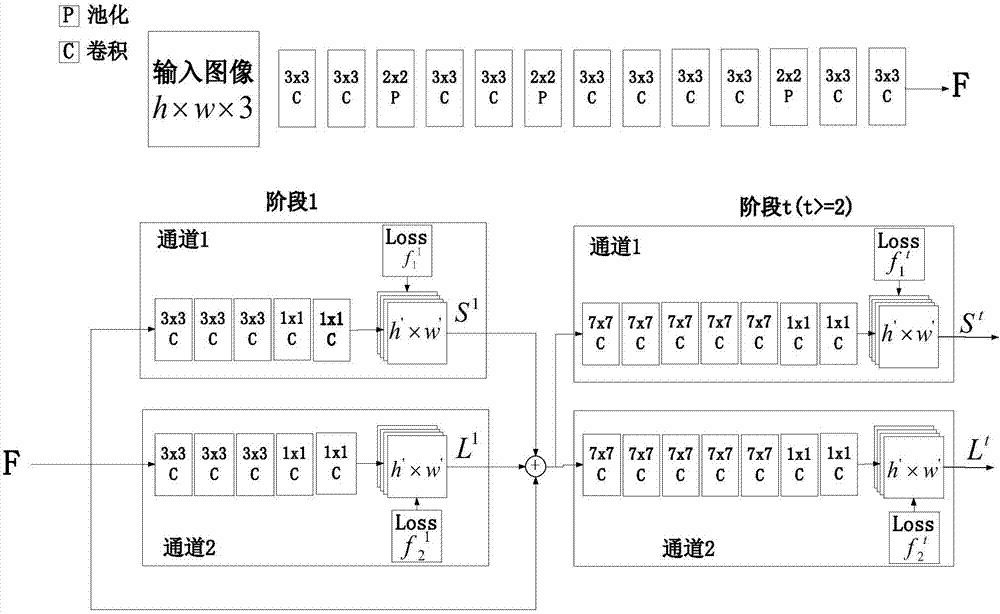
InactiveCN107886069AAccurate estimateEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHuman bodyNerve network
The invention relates to a real-time multi-target human body 2D attitude detection system and method. The system comprises an image acquisition module used for acquiring image data, a real-time processing module used for inputting the image data to the neural network for learning and prediction and generating the human body attitude information according to a hot spot map of the acquired joint point position and a hot spot map of the direction vector field among joint points, and a visual display module used for presenting the predicted human body attitude information to users in a line connection mode. The system is advantaged in that the depth learning method is utilized to encode the joint position and the position and the direction of bones formed by joints through interconnection, accurate human body 2D attitude estimation of a single image is realized, for complex people gathering conditions, multiple human body attitudes of the scene can be accurately estimated, the users are facilitated to carry out further analysis processing and mining of the human body attitudes, and next behaviors are predicted.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Star-tracker-based attitude determination for spinning spacecraft
ActiveUS20050133671A1Launch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusStar trackerAttitude determination
A method of determining the attitude of a spinning spacecraft is provided. The method includes stabilizing the spacecraft, initializing the attitude of the spacecraft using star tracker data, and estimating the attitude of the spacecraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Star sensor attitude determination method at self-determination retrieve rail controlling fault
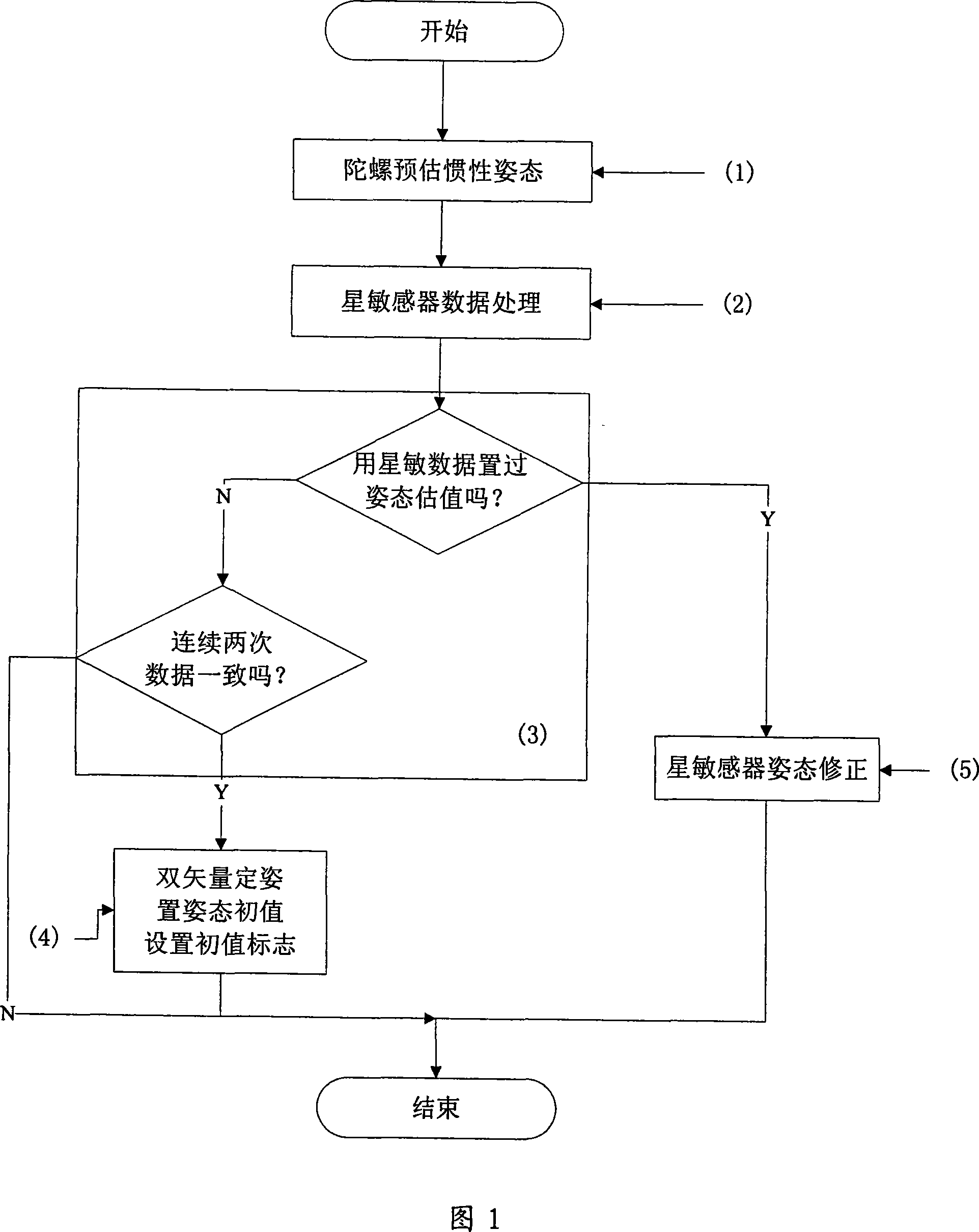
InactiveCN101214861AAccurate estimateShorten the process of failure recoverySpacecraft guiding apparatusTwo-vectorOptical axis
A star sensor attitude-determination method during the autonomous orbital control fault recovery includes: (1) predicting the satellite inertia attitude according to data measured by a gyro; (2) calculating the filtering modified innovation amount according to the inertia attitude of the satellite and the optical axis vector and the lateral axis vector under an inertial coordinate system which are measured and output by the star sensor, and calculating the error of the innovation amount between the front and the back periodicals, which is used for judging the consistency of star sensor data; (3) judging the consistency of the star sensor data; (4) fixing the attitude of the star sensor according to the two vectors; (5) introducing the star sensor which is combined with the gyro for the correction of the satellite attitude under the condition that the star sensor data arranges the initial value of the attitude estimation. The method can improves the reliability of the orbital control fault recovery, saves the time for the fault recovery and ensures that the orbital control is accurately recovered in time.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
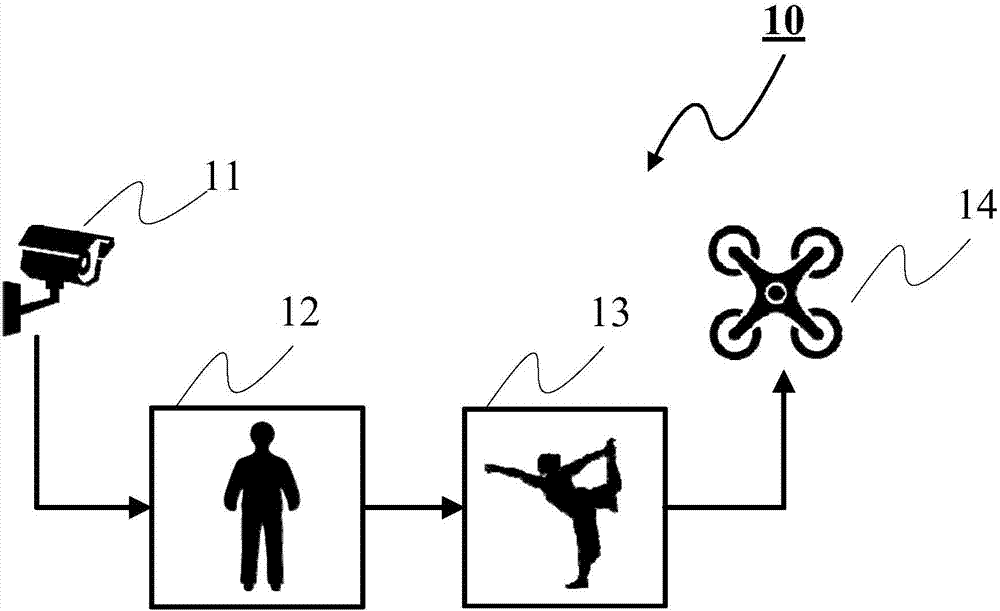
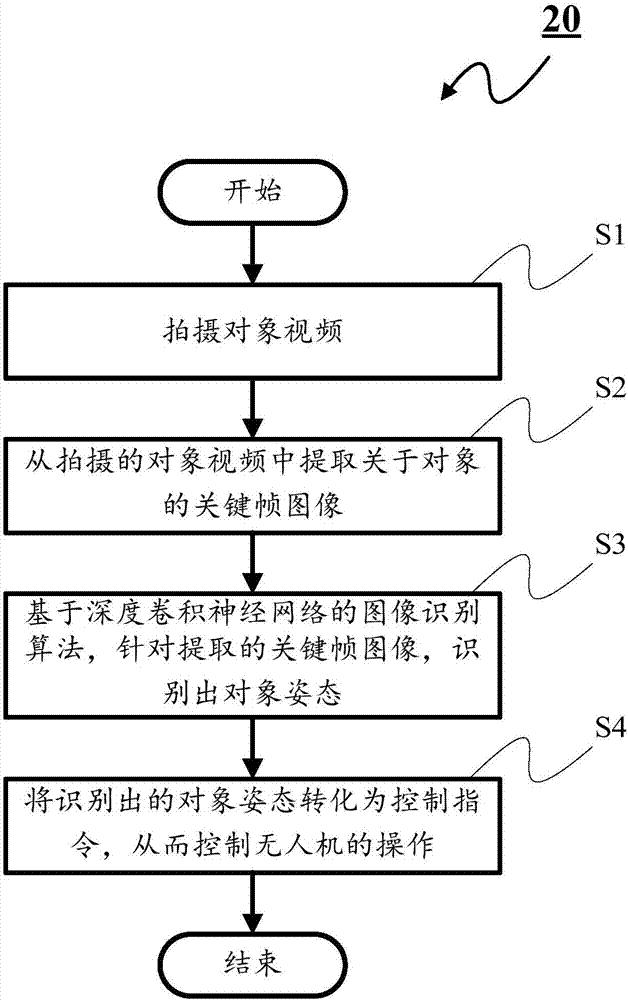
Unmanned aerial vehicle interaction apparatus and method based on deep leaning and attitude estimation
ActiveCN107239728AEasy to operateFast resultsInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementHuman bodyUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a Unmanned aerial vehicle interaction apparatus and method based on deep leaning and attitude estimation. According to the invention, the apparatus herein includes: a photographing unit which is intended for photographing a target video; a key frame extracting unit which is intended for extracting a key frame image of a target from the photographed target video; an attitude estimation unit which is intended for based on an image identifying algorithm of a deep convolutional neural network, identifying a target attitude for the key frame image; and an unmanned aerial vehicle operation and control unit which is intended for converting the identified target attitude to a control command so as to control the operation of an unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the invention, the apparatus herein controls the unmanned aerial vehicle based on human body attitude estimation so as to control the unmanned aerial vehicle in an easy manner. In addition, in the proceeding of key frame extraction and attitude estimation, by using the algorithm of the deep convolutional neural network, the apparatus can acquire the result in a faster and more accurate manner.
Owner:XILINX TECH BEIJING LTD
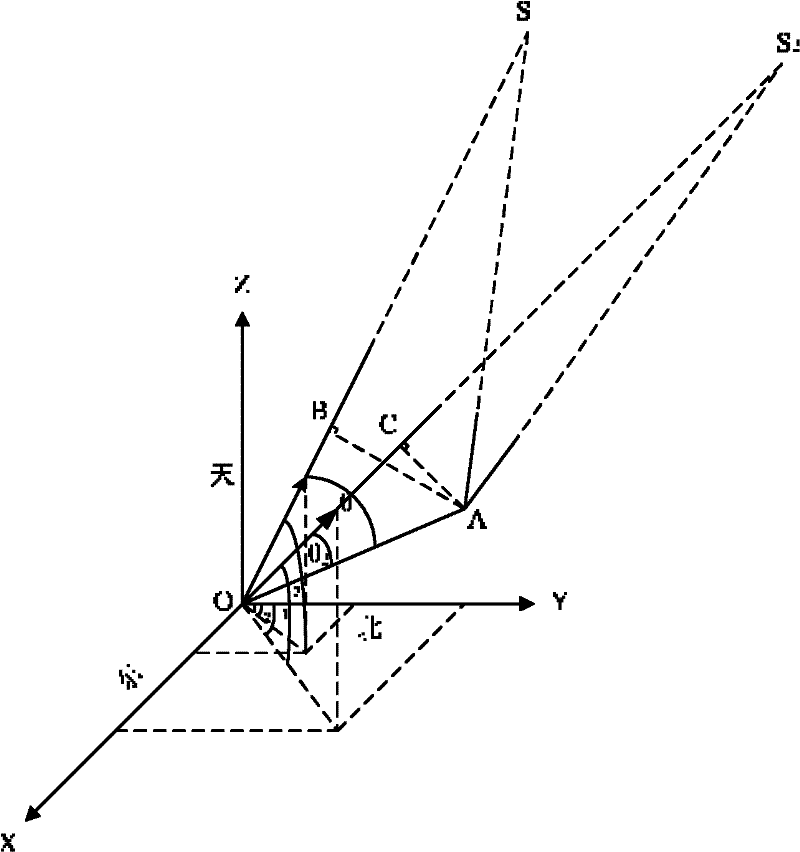
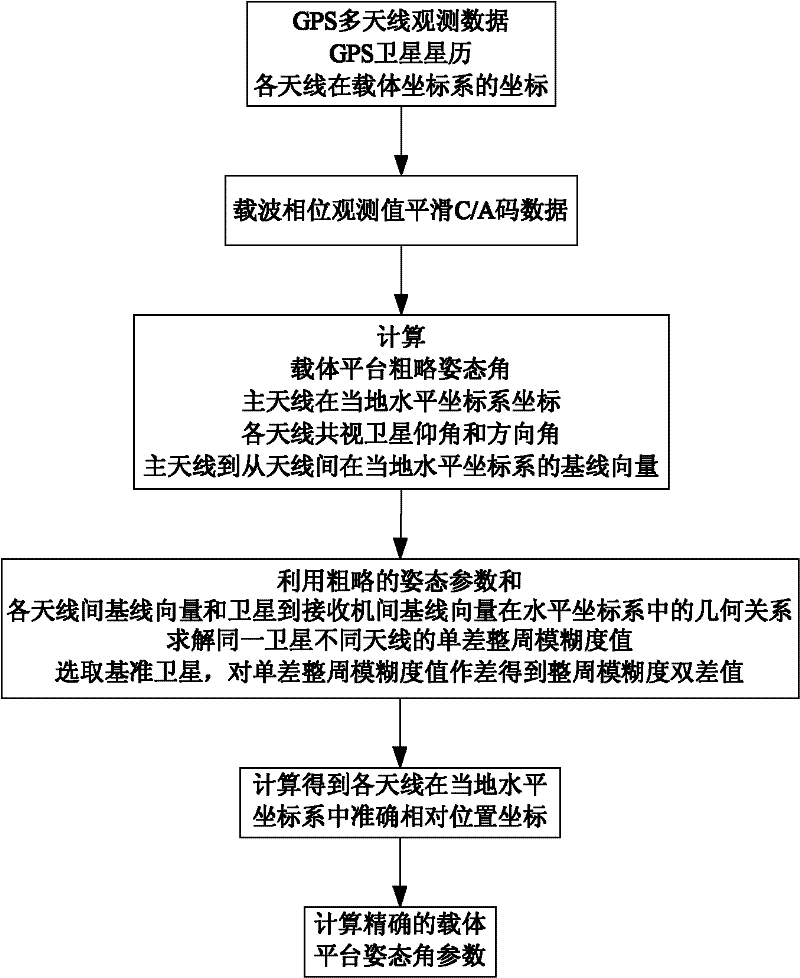
GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method
The invention aims at providing a GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly GPS multi-antenna observation data, a GPS satellite ephemeris and the coordinates of antennas on a carrier coordinate system are collected; a smoothing procedure is carried out to C / A code observation data with a carrier wave phase observed value; a carrier platform rough attitude angle, the coordinate of the main antenna in a local horizontal coordinate system, the shared vision satellite elevation angles and direction angles of the antennas and the baseline vector from the main antenna to subordinated antennas in the local horizontal coordinate system are calculated; based on the geometry relations of the baseline vectors among the antennas and the baseline vectors from the satellite to a receiver in the horizontal coordinate system, the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value of different antennas of the same satellite is solved; a reference satellite is selected and a difference operation is carried out to the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value to obtain an integer cycle fuzziness double difference value; the integer cycle fuzziness double difference value obtained is substituted into a carrier wave phase double difference model to obtain accurate coordinate components of the antennas and based on the coordinate components of the antennas, accurate attitude parameters are solved so as to realize GPS multi-antenna attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
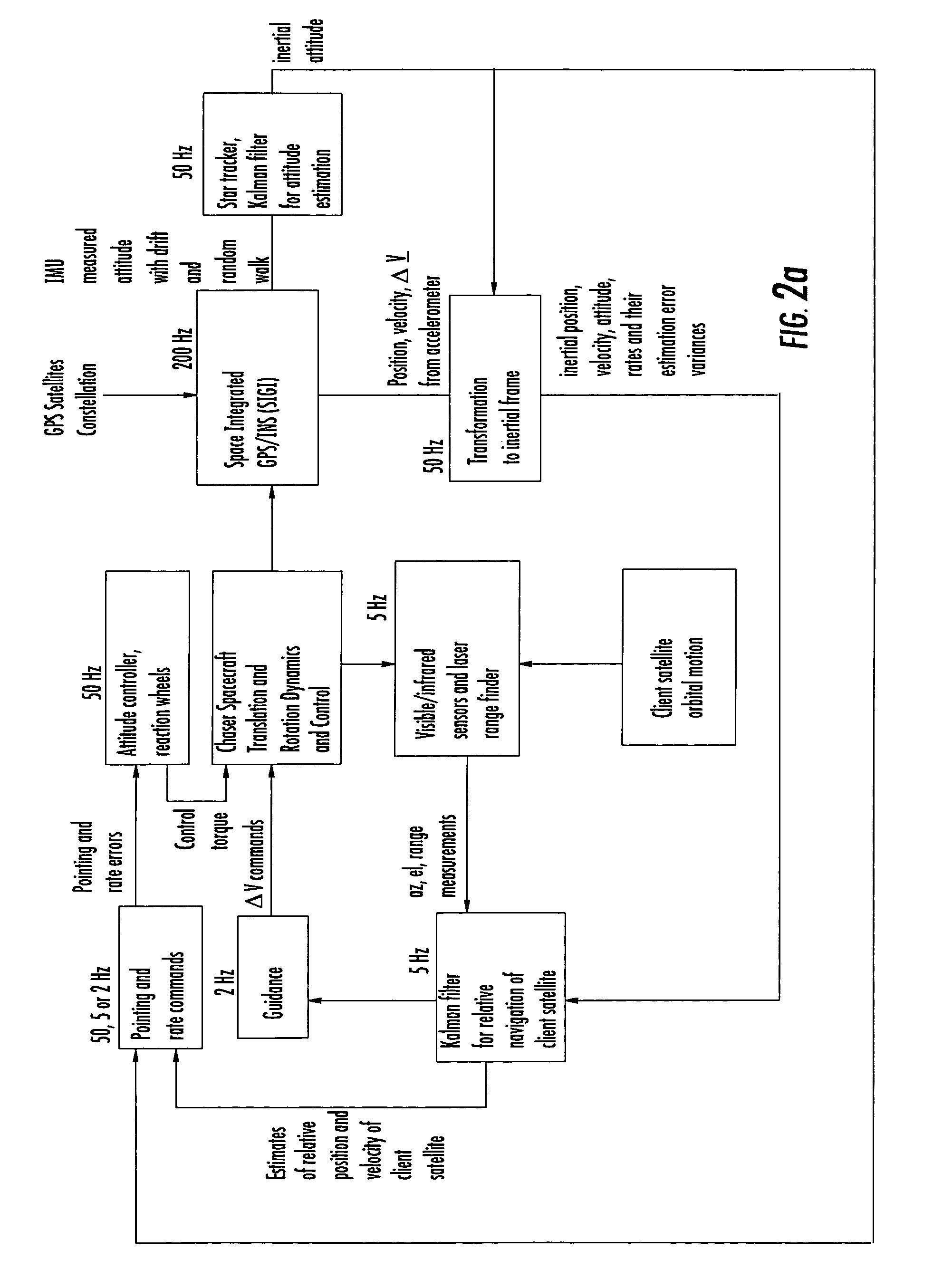
Multi-sensor guidance system for extreme force launch shock applications
InactiveUS20050040280A1Direction controllersDigital data processing detailsGuidance systemControl signal
A projectile navigation system operable within an extremely high G-shock loading environment during the launch phase may include a set of Kalman filters configured to repeatedly calculate a navigational solution by solving a set of non-linear equations of motions of the projectile utilizing a current parameter vector, position, velocity, and attitude of the projectile. The system may include a suite of solid state sensors to calibrate the Kalman filter equations. If desired, the system may also include a satellite based positioning-determining (SBPD) attitude determination system configured to update the state of the host projectile by making real time attitude measurements of the projectile, and a parameter estimator configured to estimate and update a parameter vector of the host projectile. An external guidance and control processor may be used to generate guidance and control signals, enabling real time navigation of the host projectile.
Owner:HUA CUONG TU
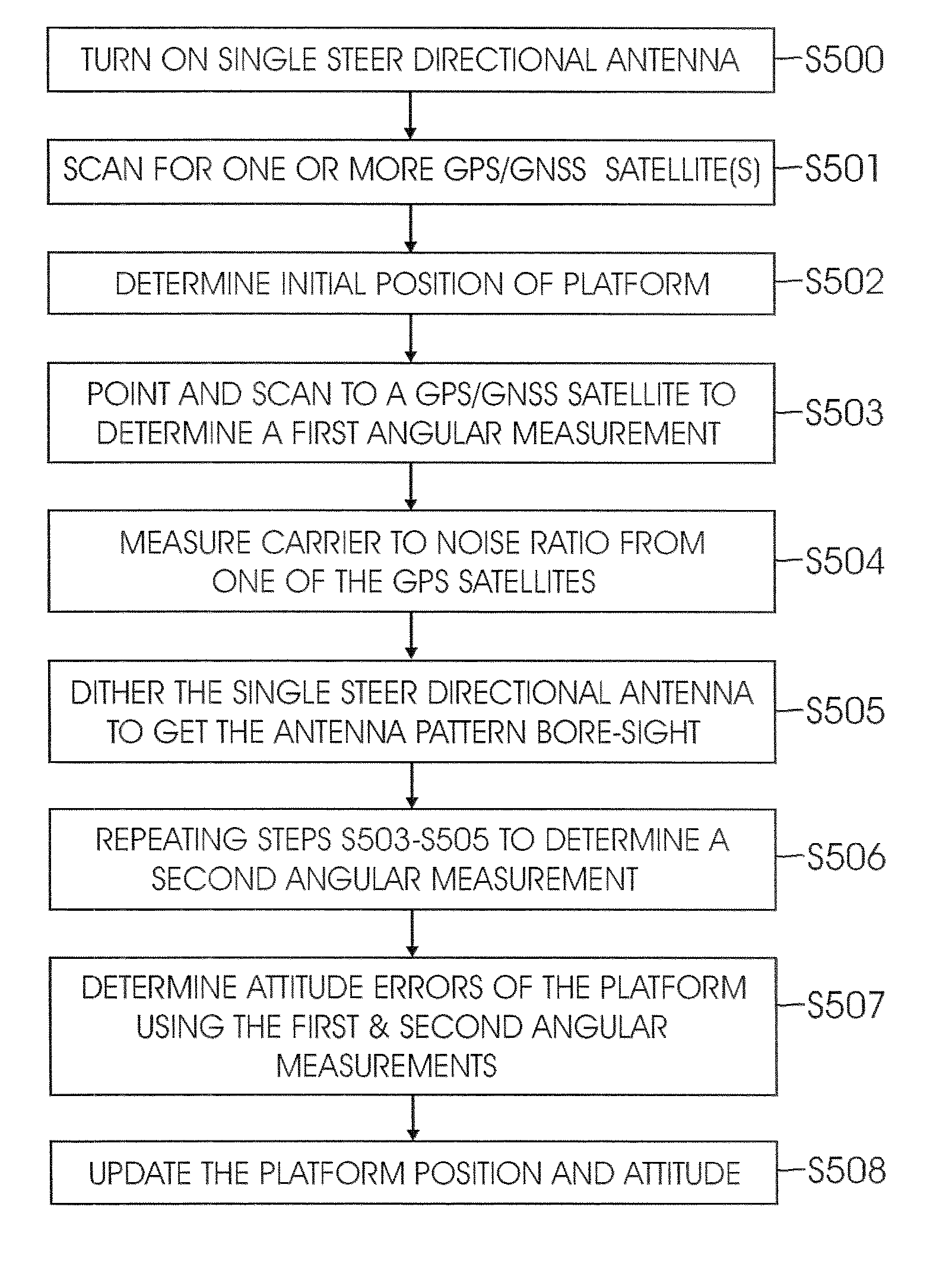
Method and system for attitude determination of a platform using global navigation satellite system and a steered antenna
InactiveUS20080068263A1Reduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalMarine navigation
A system and method for determining the attitude of a platform is provided. The method includes: (a) Searching and scanning for one or more GPS satellite(s) to determine initial platform position; wherein a single directionally steered antenna scans for the GPS / GNSS satellite; (b) pointing and scanning the antenna to GPS / GNSS satellite to determine a first angular measurement of a direction of a GPS / GNSS signal; (c) measuring carrier to noise ratio of the GPS / GNSS satellite; (d) dithering the single directionally steered antenna to obtain an angular measurement relative to an antenna pattern bore-sight reference; (e) repeating steps (b)-(d) to determine a second angular measurement of the direction of a second GPS signal; (f) determining the attitude error of the platform using the first and second angular measurements; (g) updating the platform position and attitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
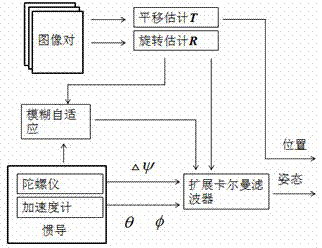
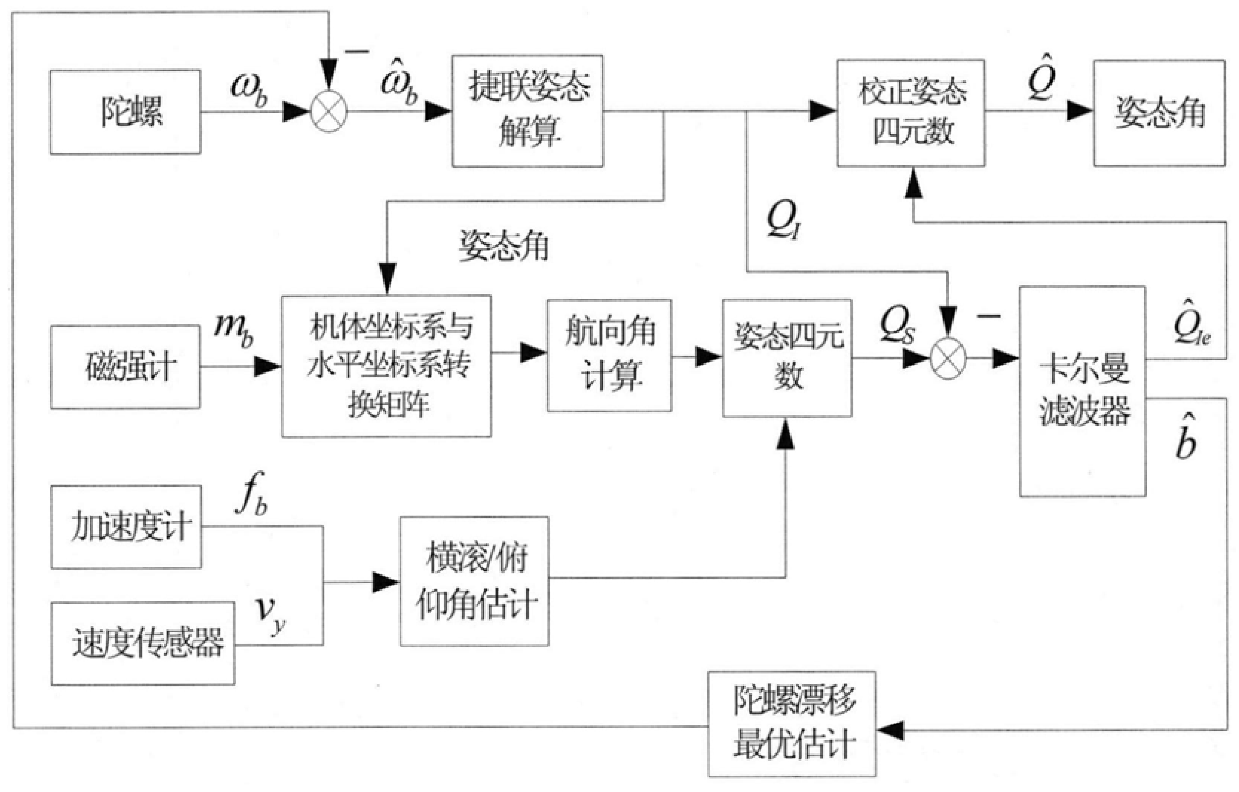
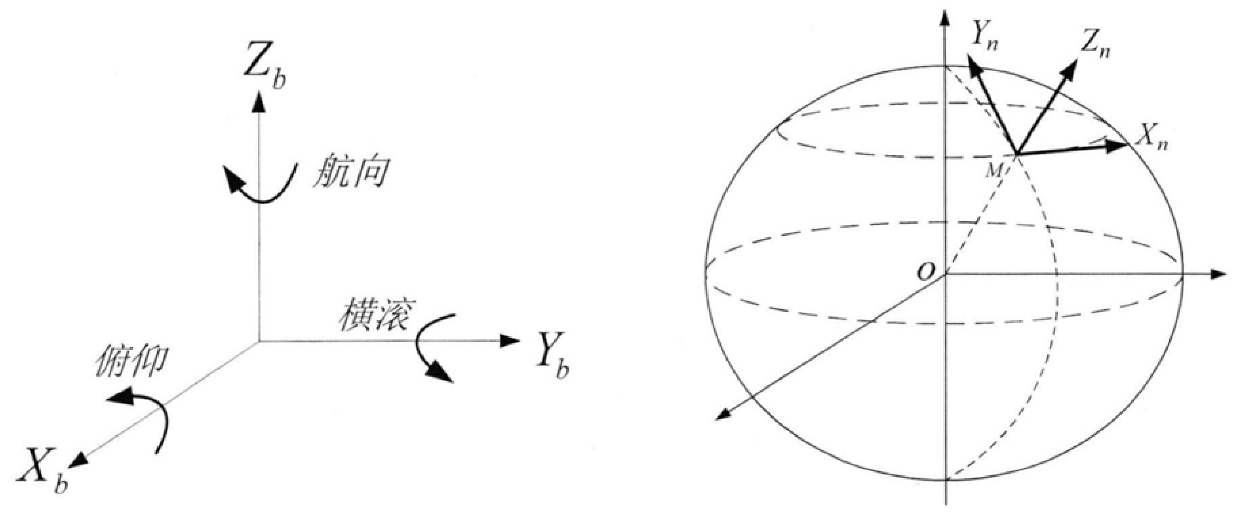
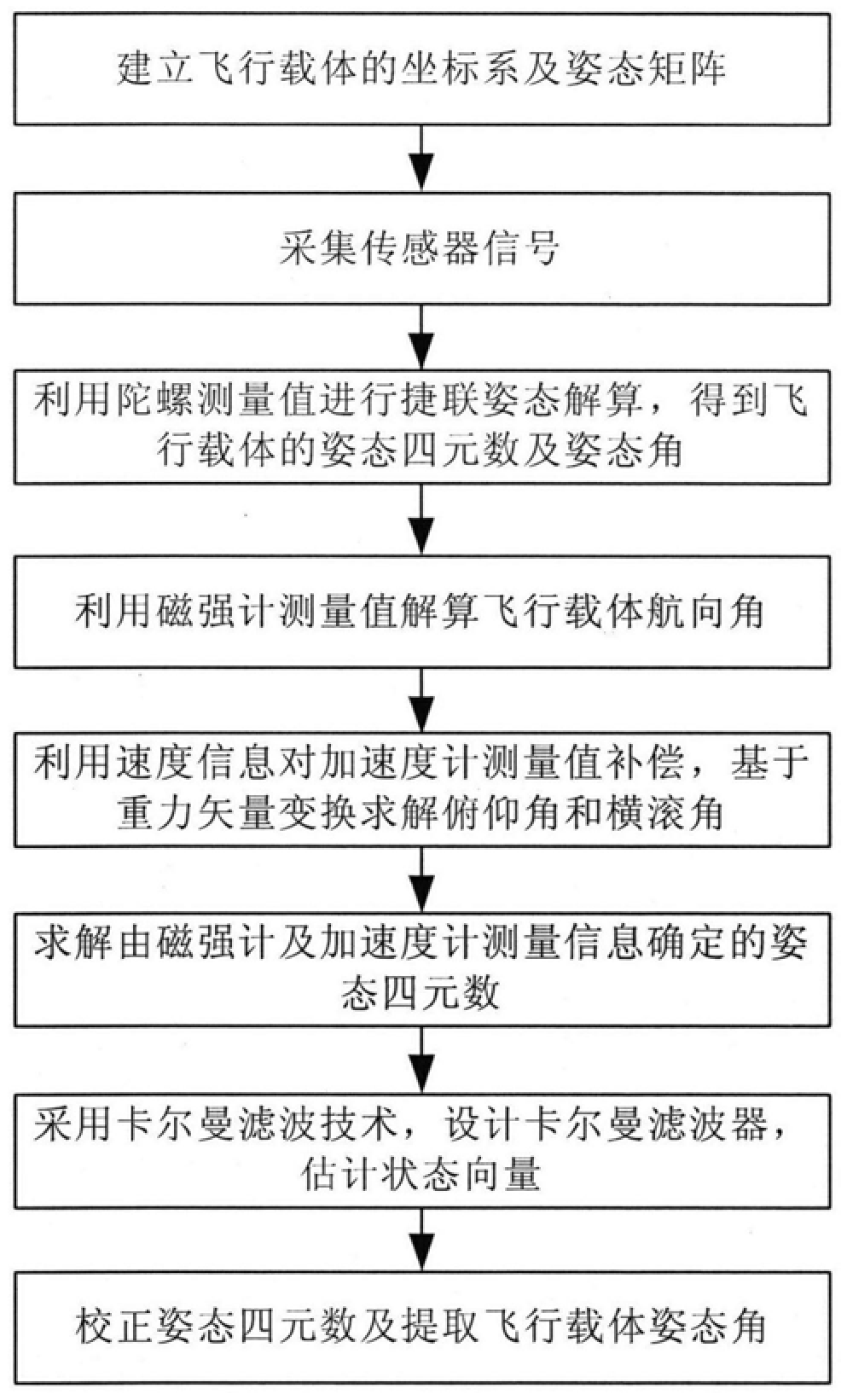
A Method for Determining the Attitude of a Flight Carrier
InactiveCN106342284BHigh measurement accuracyMeet the requirements of real-time attitude controlAttitude controlKaiman filterAccelerometer
The invention discloses a method for determining the attitude of a flight carrier, which belongs to the field of attitude measurement. The main steps include: establish the coordinate system and attitude matrix of the flight carrier; collect sensor signals; use the gyro measurements to carry out strapdown attitude calculations to obtain the attitude quaternions and attitude angles of the flight carrier; use the magnetometer measurements to calculate the flight Carrier heading angle; use speed information to compensate acceleration measurement value, solve pitch angle and roll angle; solve attitude quaternion determined by magnetometer and accelerometer information; design Kalman filter, estimate state vector; correct attitude four arity and extract attitude angle. This method combines gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers, and speed sensors to meet the requirements of real-time attitude control of the flight carrier; introduces gyroscope drift into the system state vector, estimates and corrects it in real time, and uses the measured value of the magnetometer to directly Calculate the heading angle, avoid the calculation of the geomagnetic field vector in the geographic coordinate system, and improve the accuracy of attitude determination.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Compact single-aperture antenna and navigation system
InactiveUS20080303714A1Increase hardware costIncrease in sizeAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPosition fixationEngineeringNavigation system
An exemplary radio-based navigation system uses a single-aperture multimode direction-finding antenna capable of determining platform position, velocity, attitude, and time while simultaneously providing protection against narrowband and broadband sources of interference. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-signals such as those from the Global Positioning System (GPS) provide protection against jammers while simultaneously providing attitude measurements with a compact single-aperture multimode antenna (e.g., a small two-arm spiral with improved angle-of-arrival performance over the entire hemisphere enhanced through the use of a conductive vertical extension of the antenna ground plane about the antenna perimeter and / or conductive posts placed evenly around the antenna perimeter). The multimode spiral may be treated as an array of cylindrically symmetric antenna elements. GPS receiver correlation architecture also may be modified for attitude determination by increasing the requisite number of input signals from one to at least two while minimizing the required number of correlators and mixers.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
Microelectromechanical system optical sensor providing bit image data of a viewed image
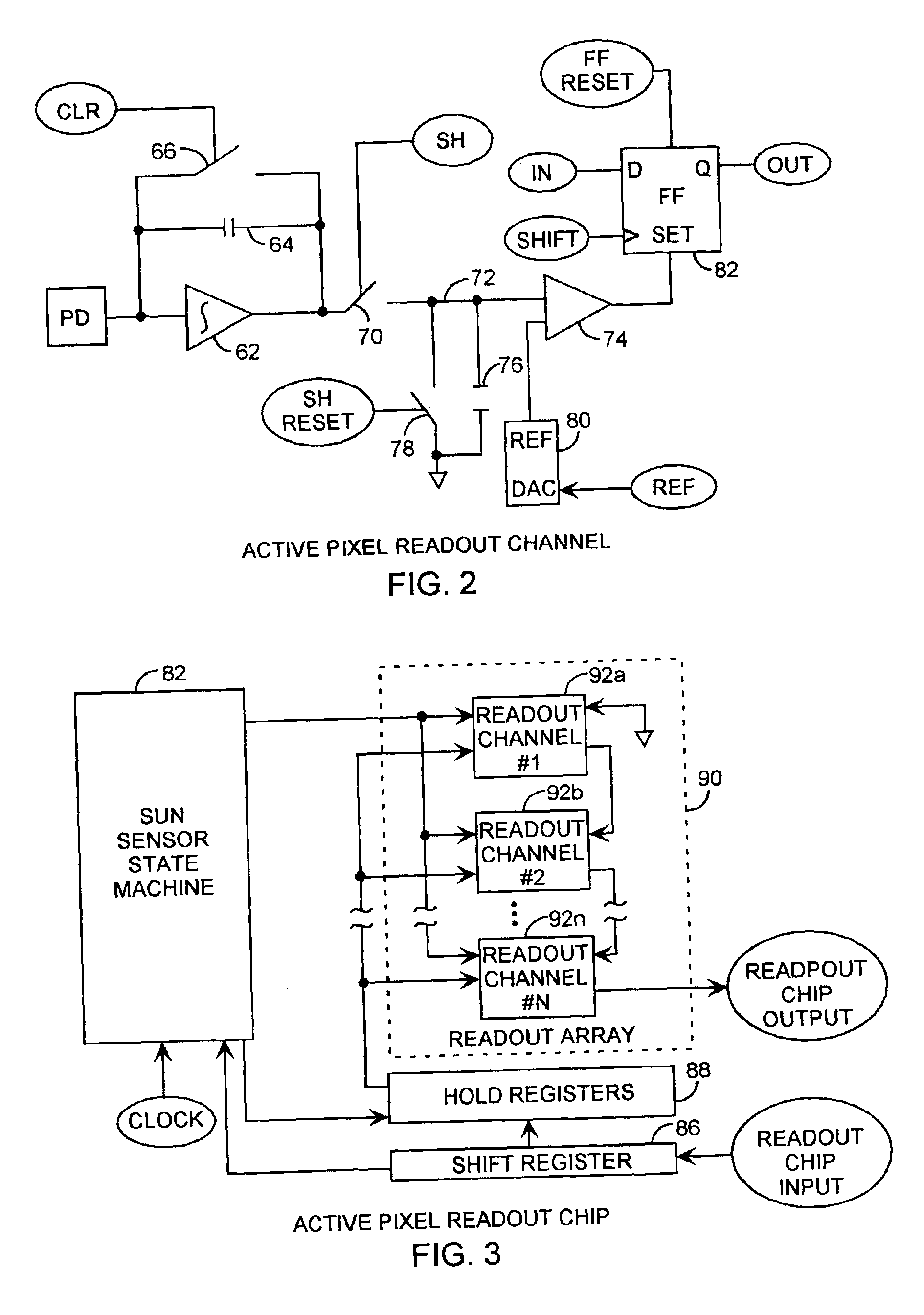
InactiveUS6861633B2Precise positioningReduce power consumptionPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationCMOS sensorSensor array
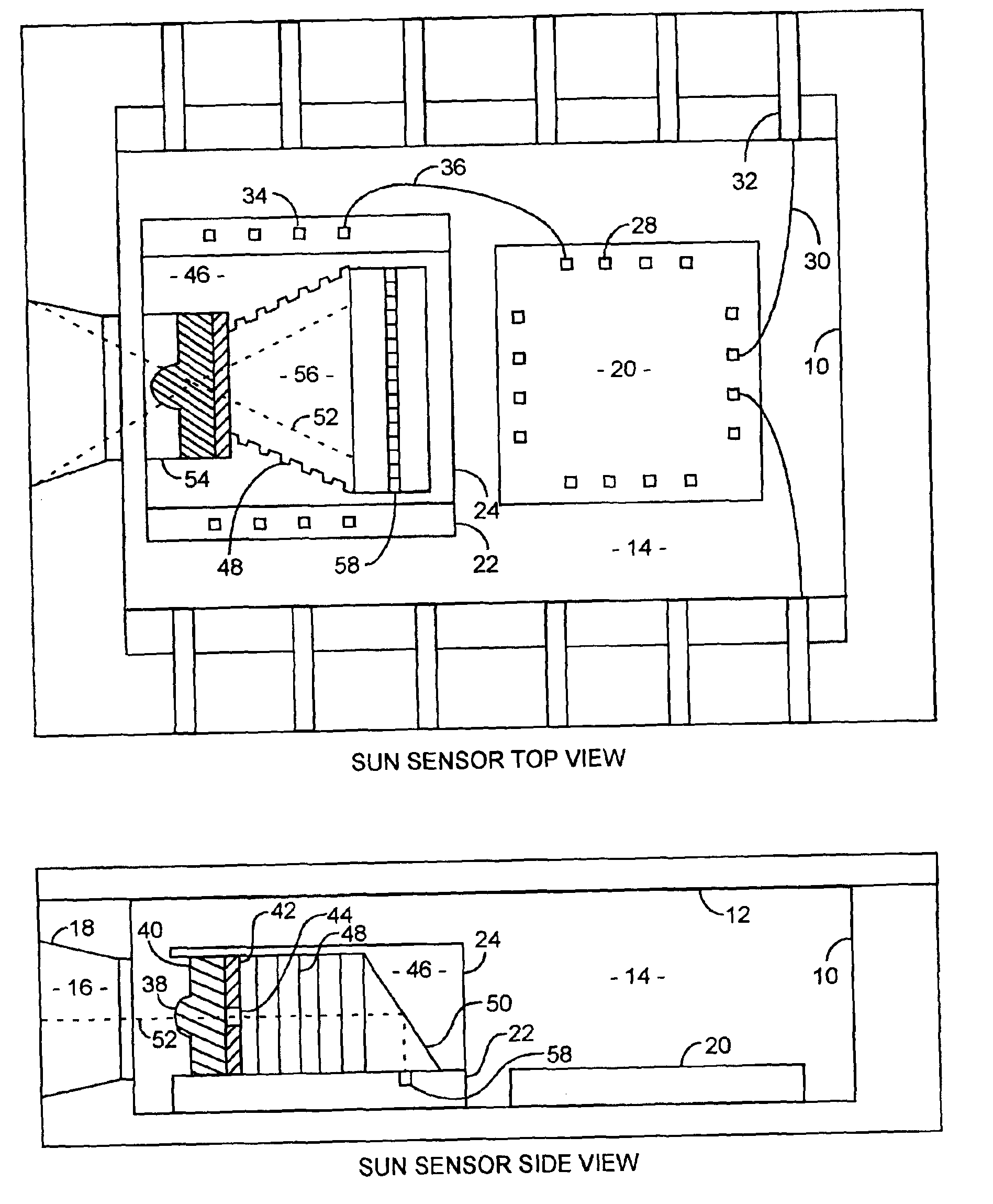
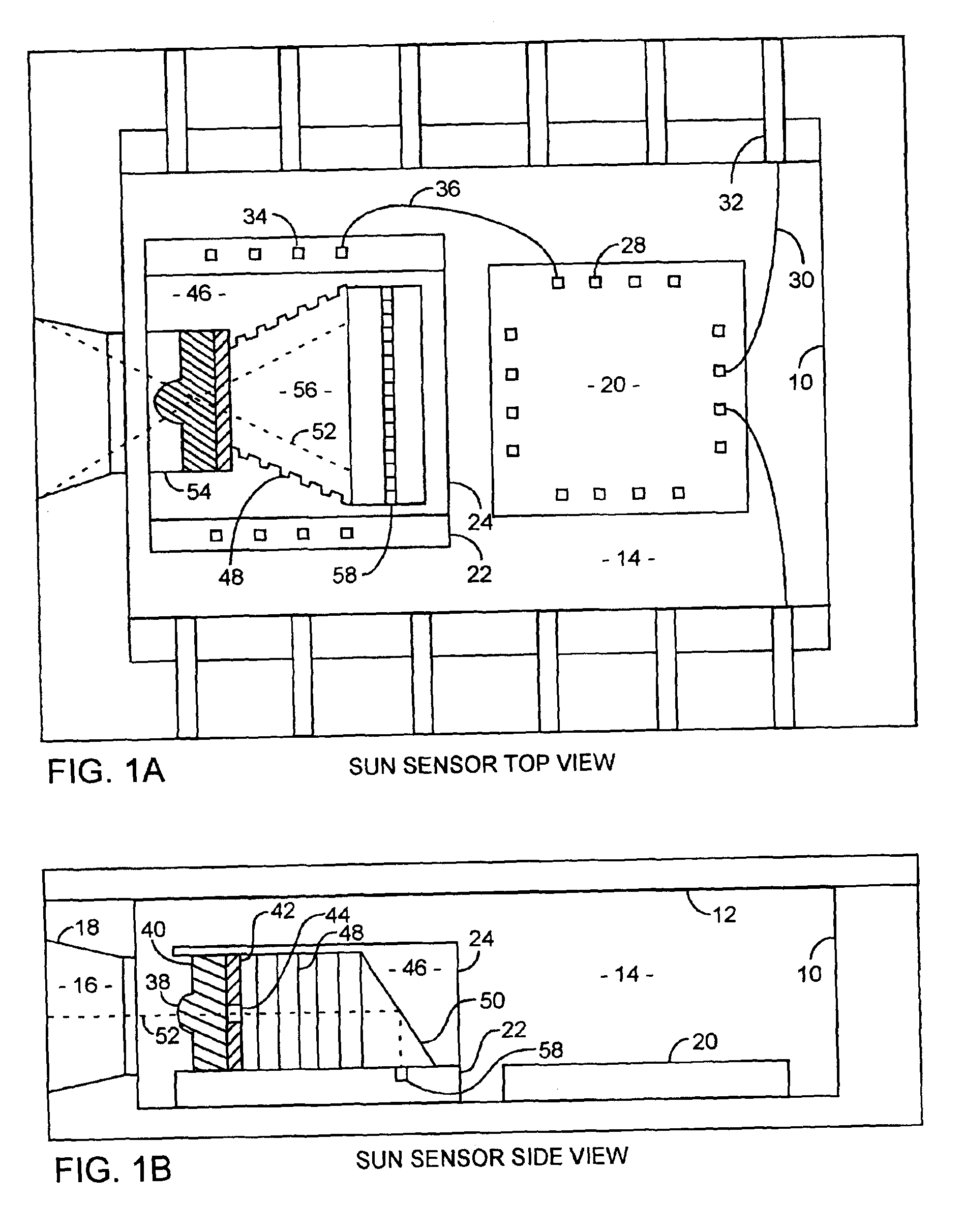
An integrated microelectromechanical system (MEMS) sun sensor includes a filter, microlens, aperture and a folded MEMS optical element combined with an active pixel sensor array to form an integrated spacecraft sun sensor in an integrated sealed package, offering lower power, smaller size and higher performance for use on spinning spacecraft useful in attitude determinations. Multiple like sun sensors can be disposed for increasing the reliability, spatial coverage or spatial resolution for a specific performance requirement.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Robust integrated precision high-speed satellite attitude determination and control system (ADCS)
ActiveUS20150219744A1Robust and efficient satellite attitude determinationRobust and efficient and controlPosition fixationColor television detailsStar trackerControl system
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods, systems, apparatus, and computer program products for providing integrated attitude determination and attitude control for slewing of a satellite. In one embodiment a method is provided. The method comprises after receiving a repointing request, selecting a guide star sample comprising one or more guide stars from a guide star catalog; determining current attitude information; selecting and retrieving at least one point spread function (PSF) image from a PSF library; estimating an expected position for at least one guide star, the at least one guide star being one of the guide stars of the guide star sample; acquiring at least one star tracker image; calculating a cross-correlation function (CCF) to determine shifts in position of the at least one guide star compared to the expected position; and determining updated current attitude information based at least in part on the determined shifts in position.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
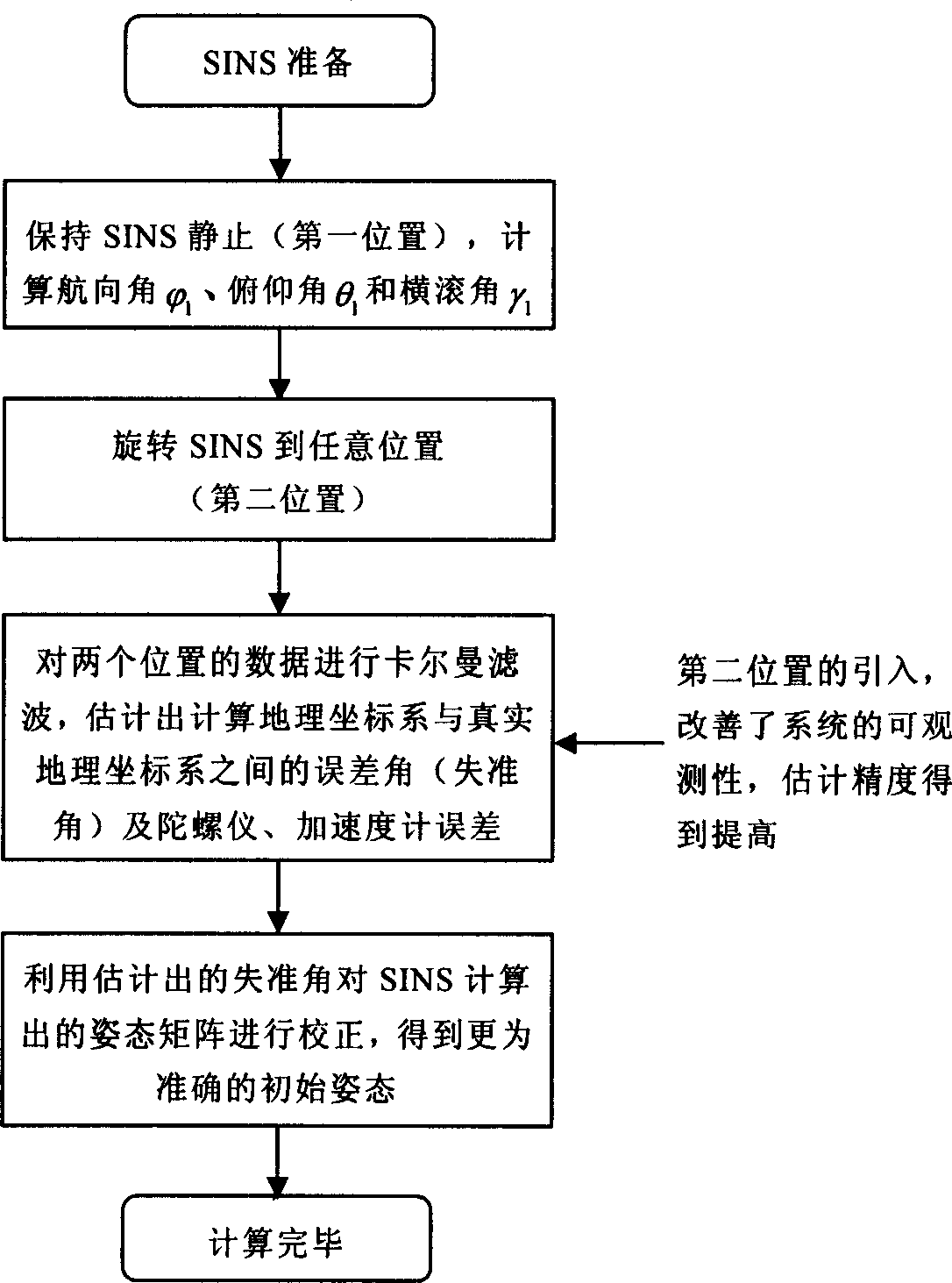
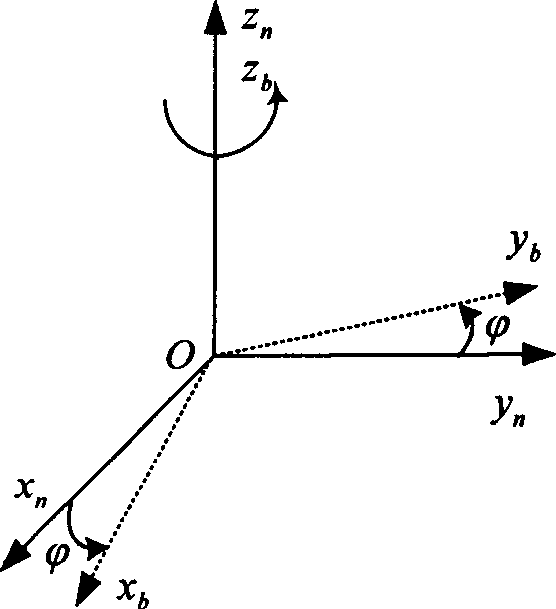
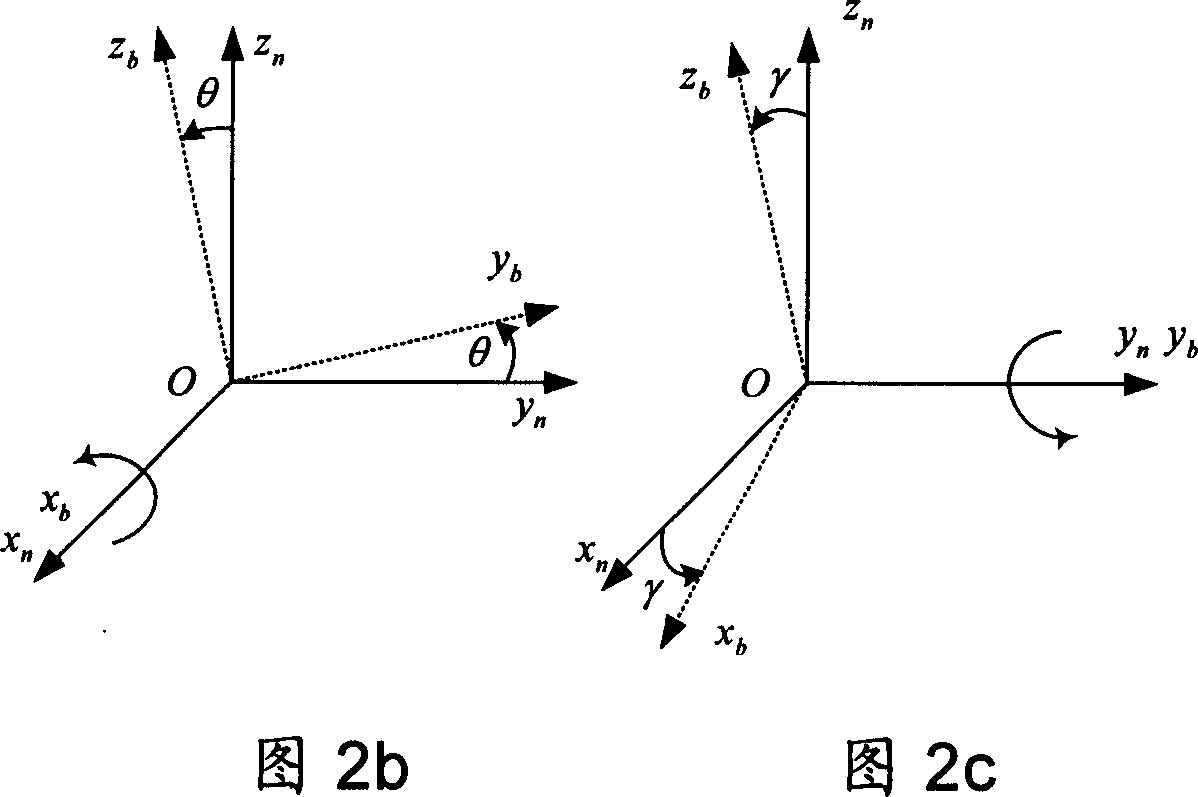
Method for determining initial status of strapdown inertial navigation system
ActiveCN1908584AImprove ObservabilityImprove filtering effectNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarth's rotationGyroscope
The initial attitude determination method for SINS comprises: rotating the SINS from initial position to any one position round arbitrary 3D axis; according to SINS output on first position and the relation of earth rotational angular velocity and acceleration of gravity, determining the initial attitude primarily; then, using Kalman filter to estimate the gyro constant drift and other values for more accurate initial attitude. This invention improves observability and precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com