Patents
Literature
233 results about "Carrier-to-noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, the carrier-to-noise ratio, often written CNR or C/N, is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a modulated signal. The term is used to distinguish the CNR of the radio frequency passband signal from the SNR of an analog base band message signal after demodulation, for example an audio frequency analog message signal. If this distinction is not necessary, the term SNR is often used instead of CNR, with the same definition.
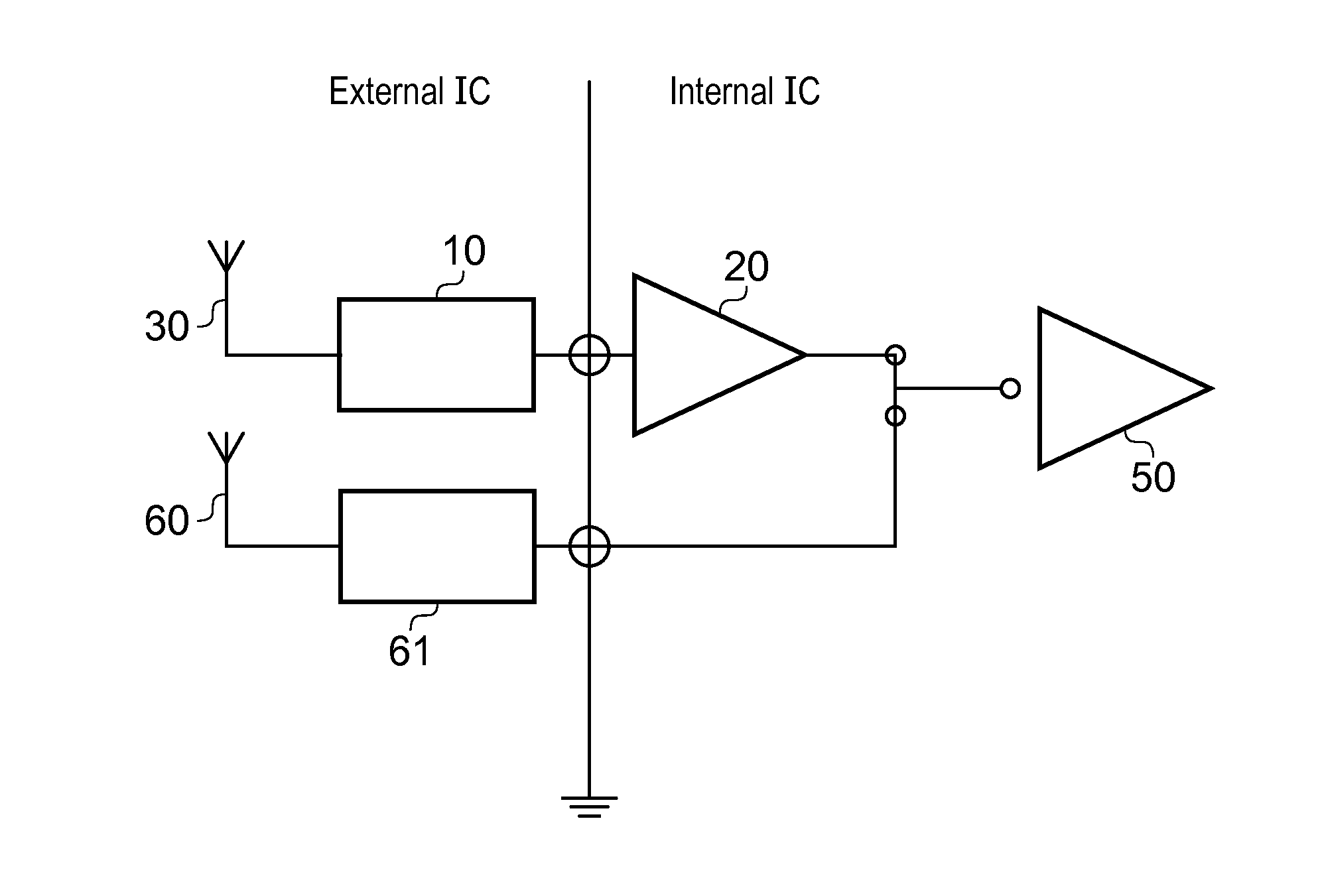
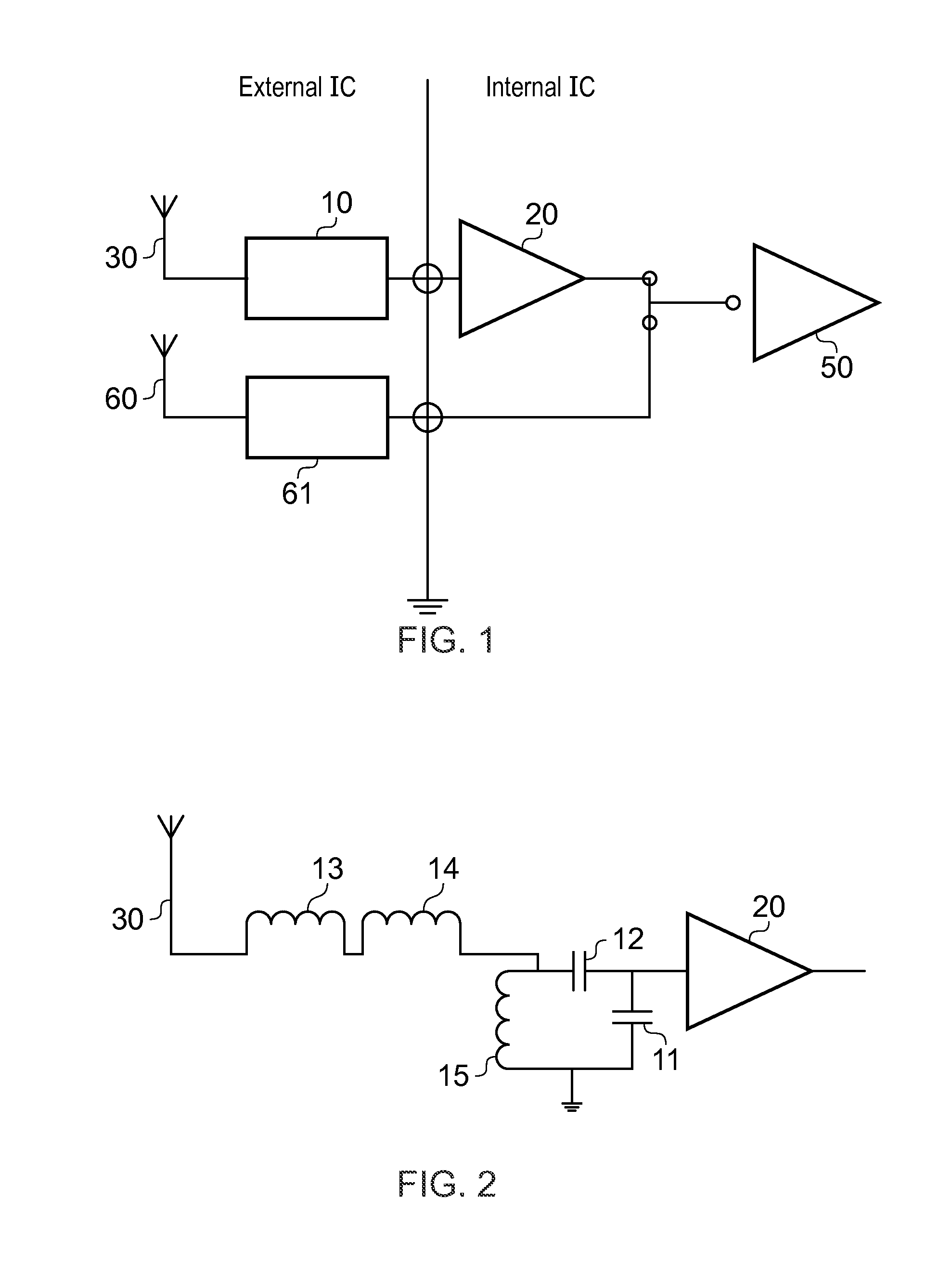
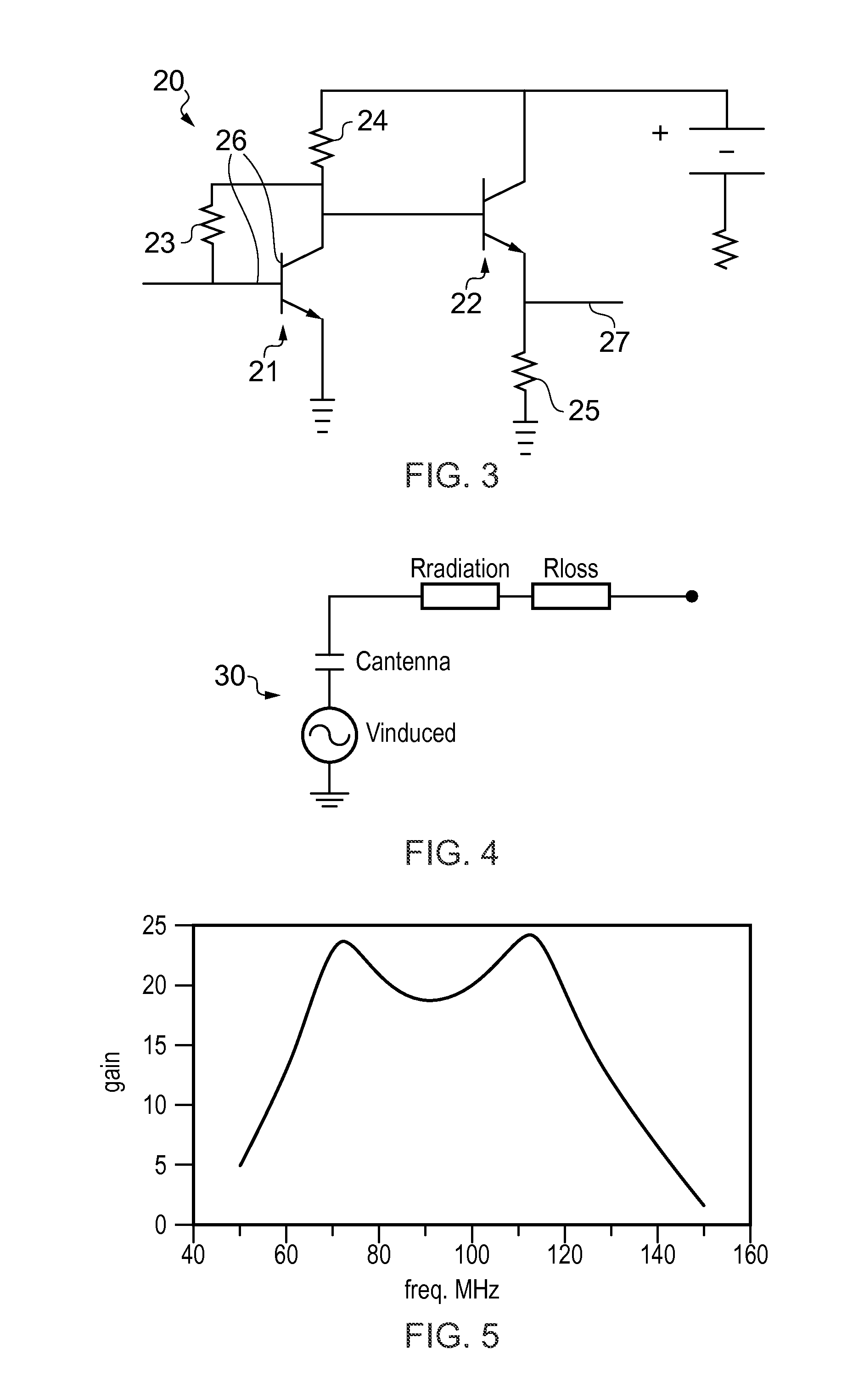
Apparatus comprising a broadcast receiver circuit and provided with an antenna
ActiveUS20110028114A1Meet the requirementsMore powerTransmissionBroadcast domainAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to an apparatus 1 comprising a broadcast receiver circuit, an embedded antenna for receiving broadcast signals and a tuning circuit coupled between the antenna and the receiver circuit, which tuning circuit comprises a filter circuit coupled to ground, wherein the tuning circuit is designed to have a first resonance at a first frequency below a broadcast band of interest, and a second resonance at a second frequency above the broadcast band and wherein the tuning circuit comprises an amplifier with an output to the receiver circuit and with an input to the filter circuit, and wherein the tuning circuit is provided with a carrier to noise ratio (CNR) which is substantially fiat across the broadcast band.
Owner:NXP BV
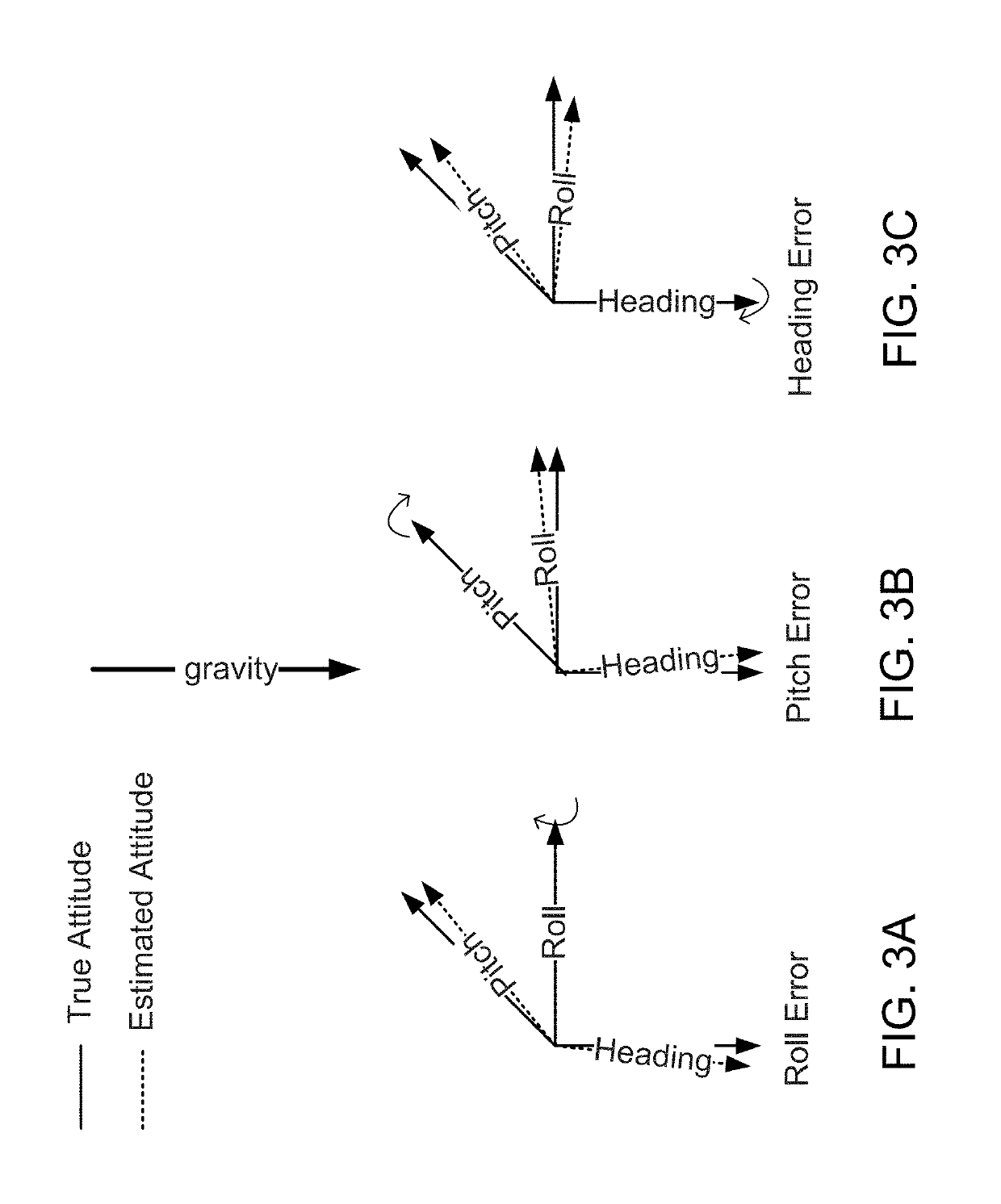
Method and system for attitude determination of a platform using global navigation satellite system and a steered antenna
InactiveUS7397422B2Reduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDirectional antennaMarine navigation
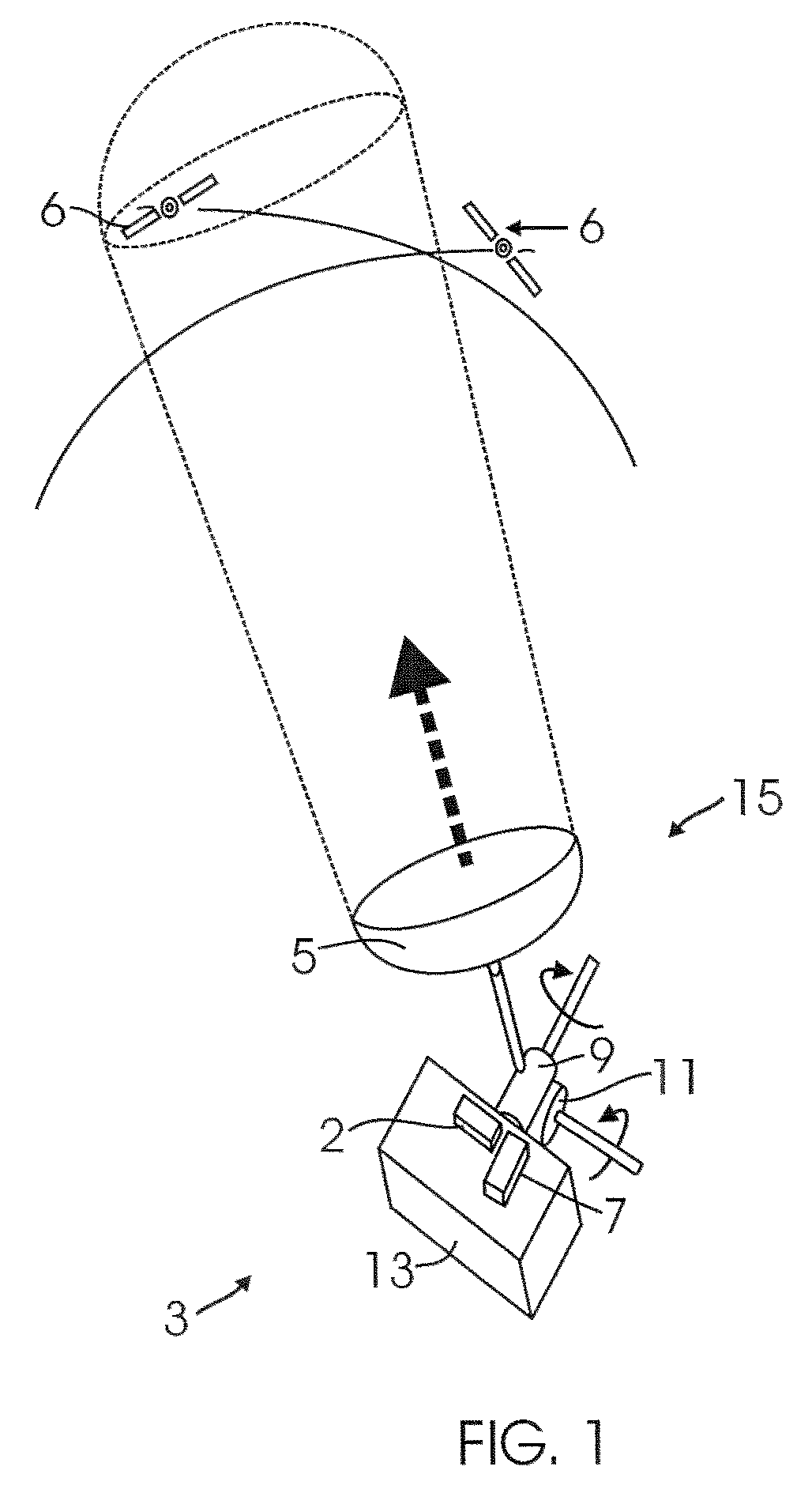
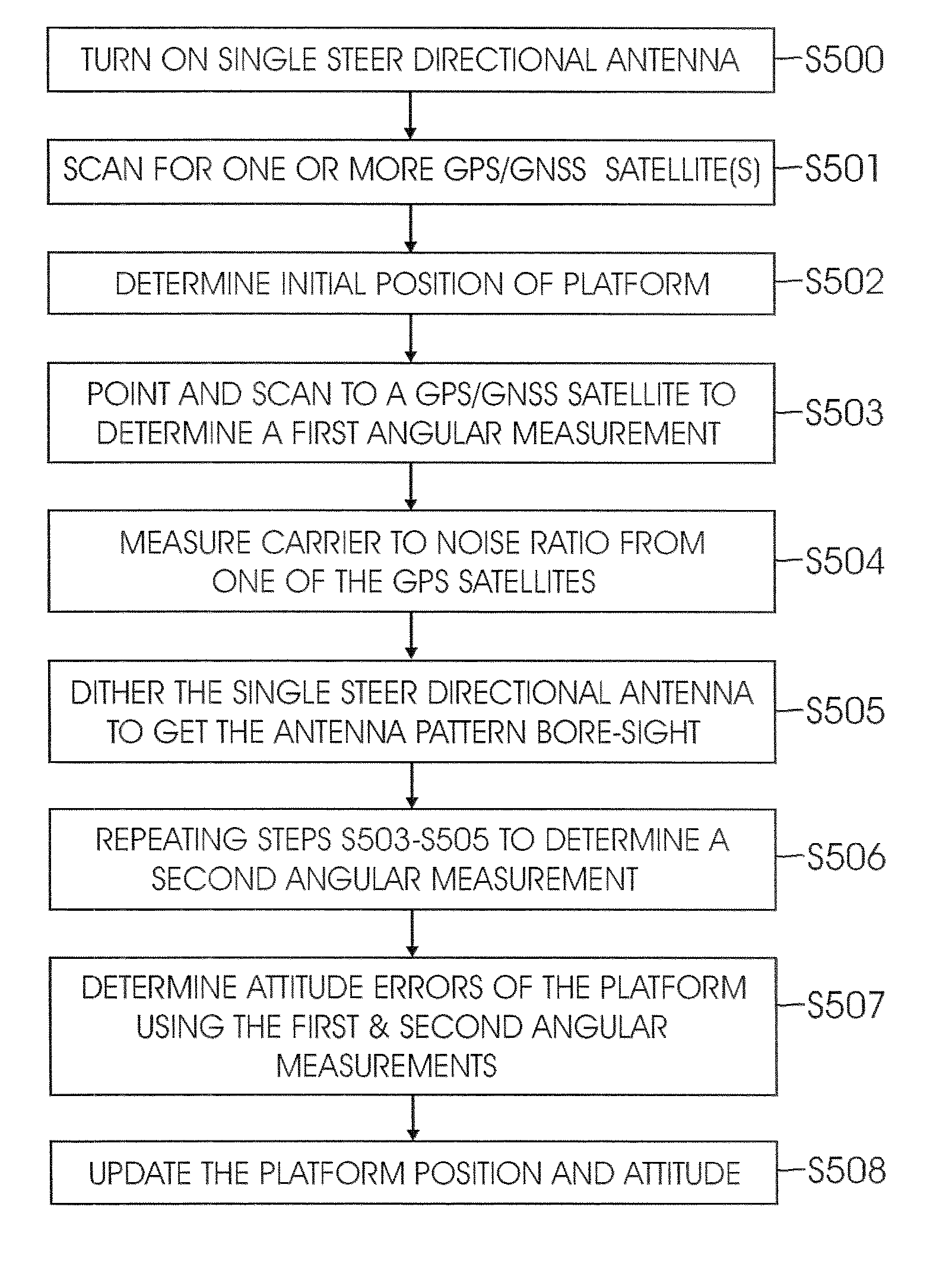
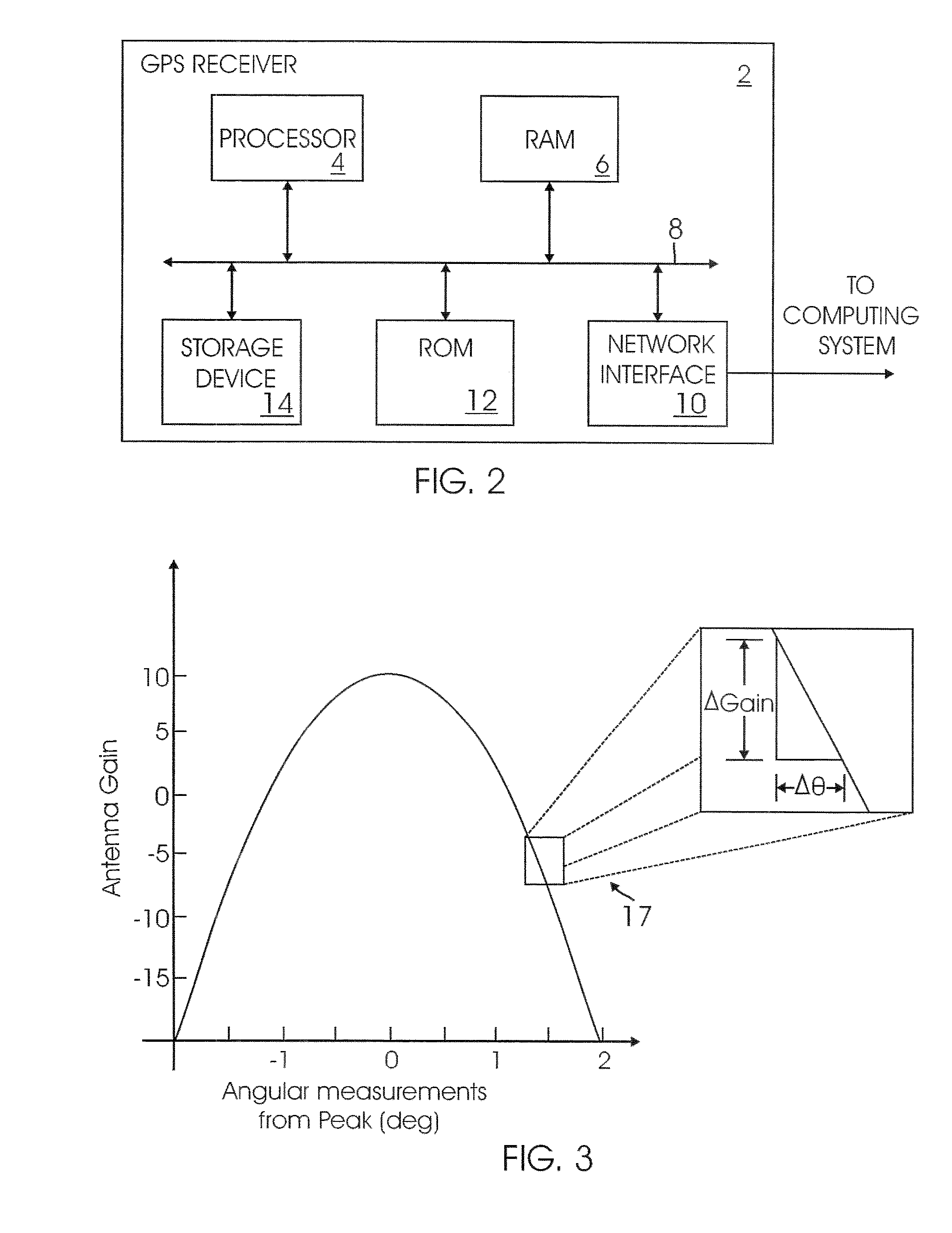
A system and method for determining the attitude of a platform is provided. The method includes: (a) Searching and scanning for one or more GPS satellite(s) to determine initial platform position; wherein a single directionally steered antenna scans for the GPS / GNSS satellite; (b) pointing and scanning the antenna to GPS / GNSS satellite to determine a first angular measurement of a direction of a GPS / GNSS signal; (c) measuring carrier to noise ratio of the GPS / GNSS satellite; (d) dithering the single directionally steered antenna to obtain an angular measurement relative to an antenna pattern bore-sight reference; (e) repeating steps (b)-(d) to determine a second angular measurement of the direction of a second GPS signal; (f) determining the attitude error of the platform using the first and second angular measurements; (g) updating the platform position and attitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
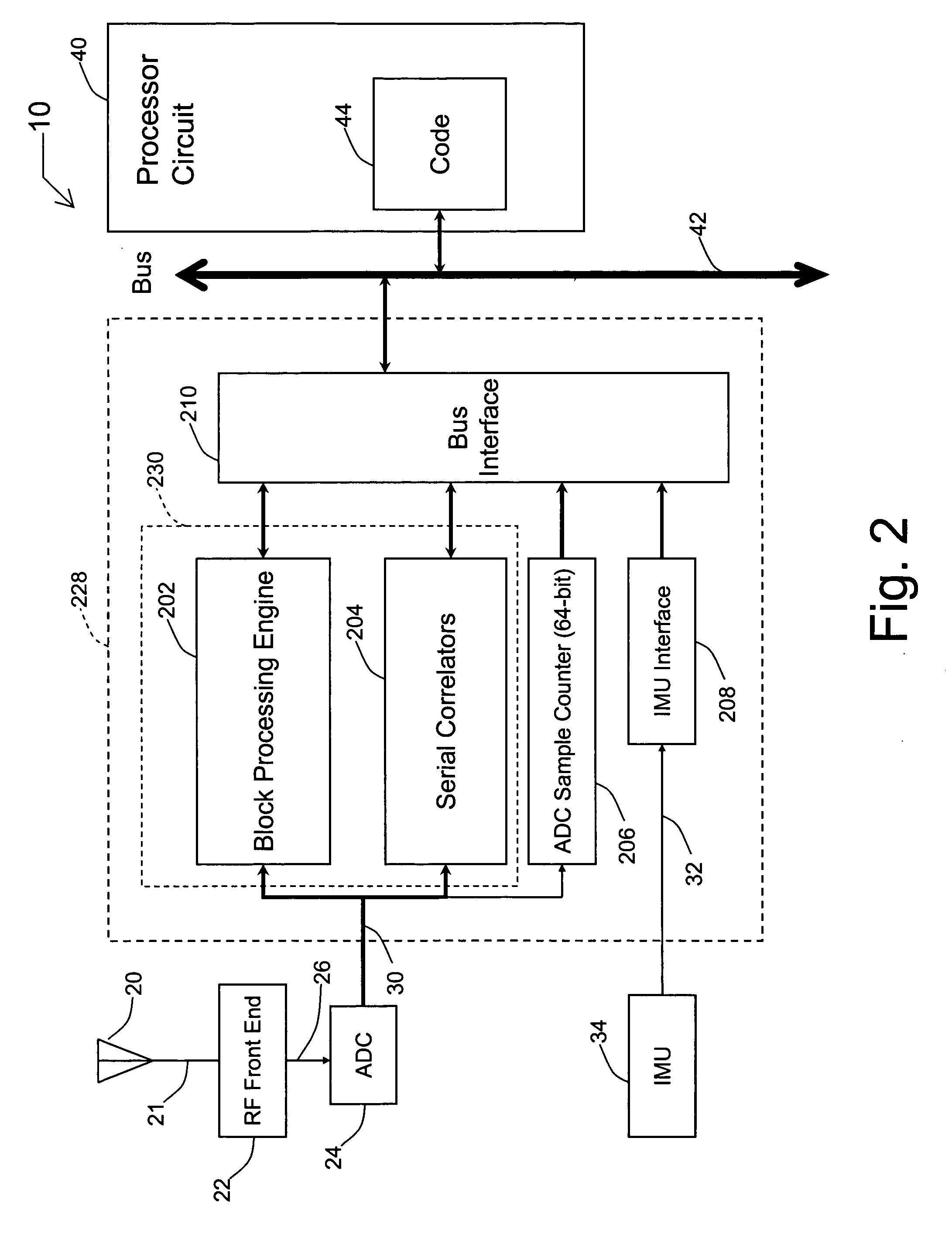
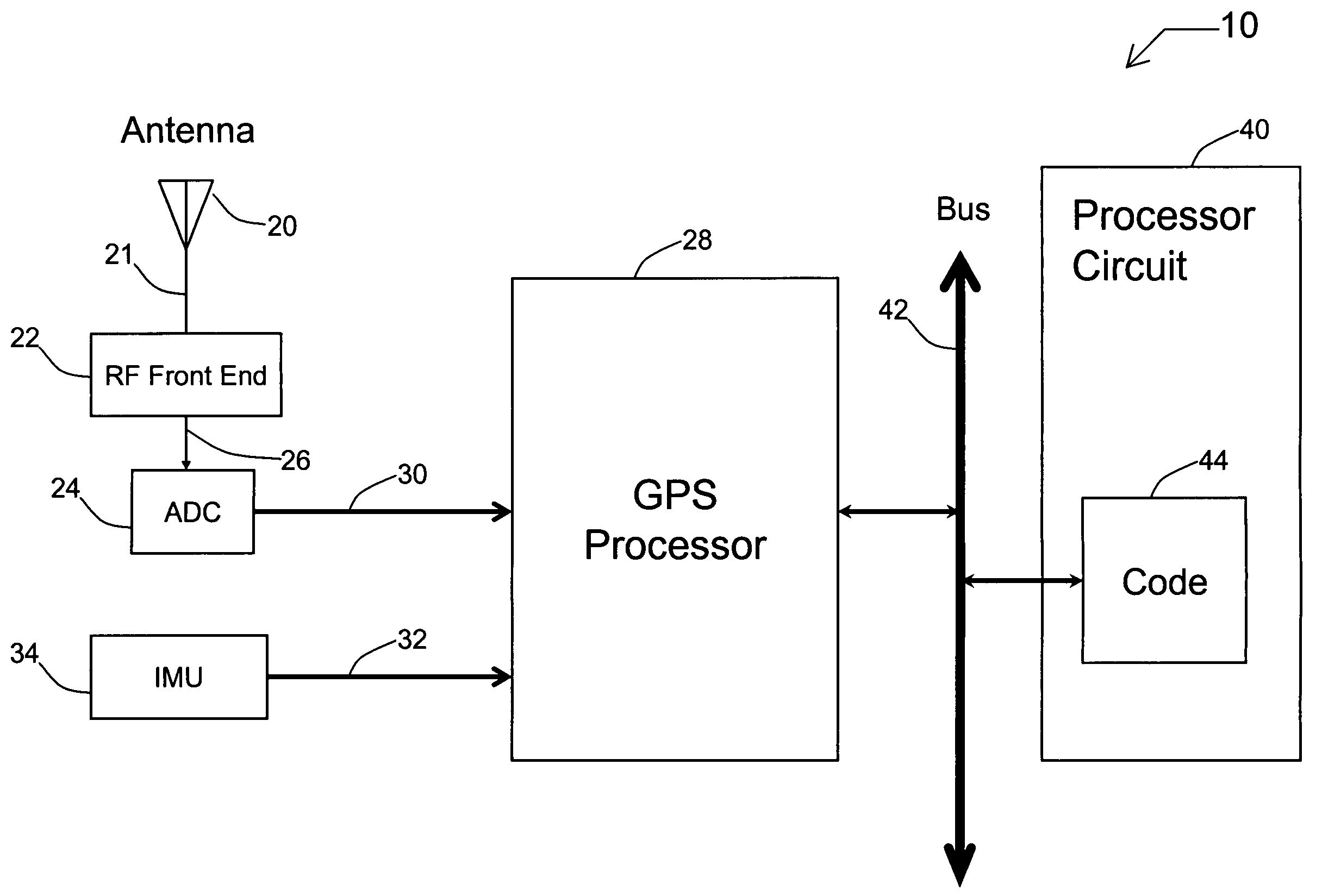
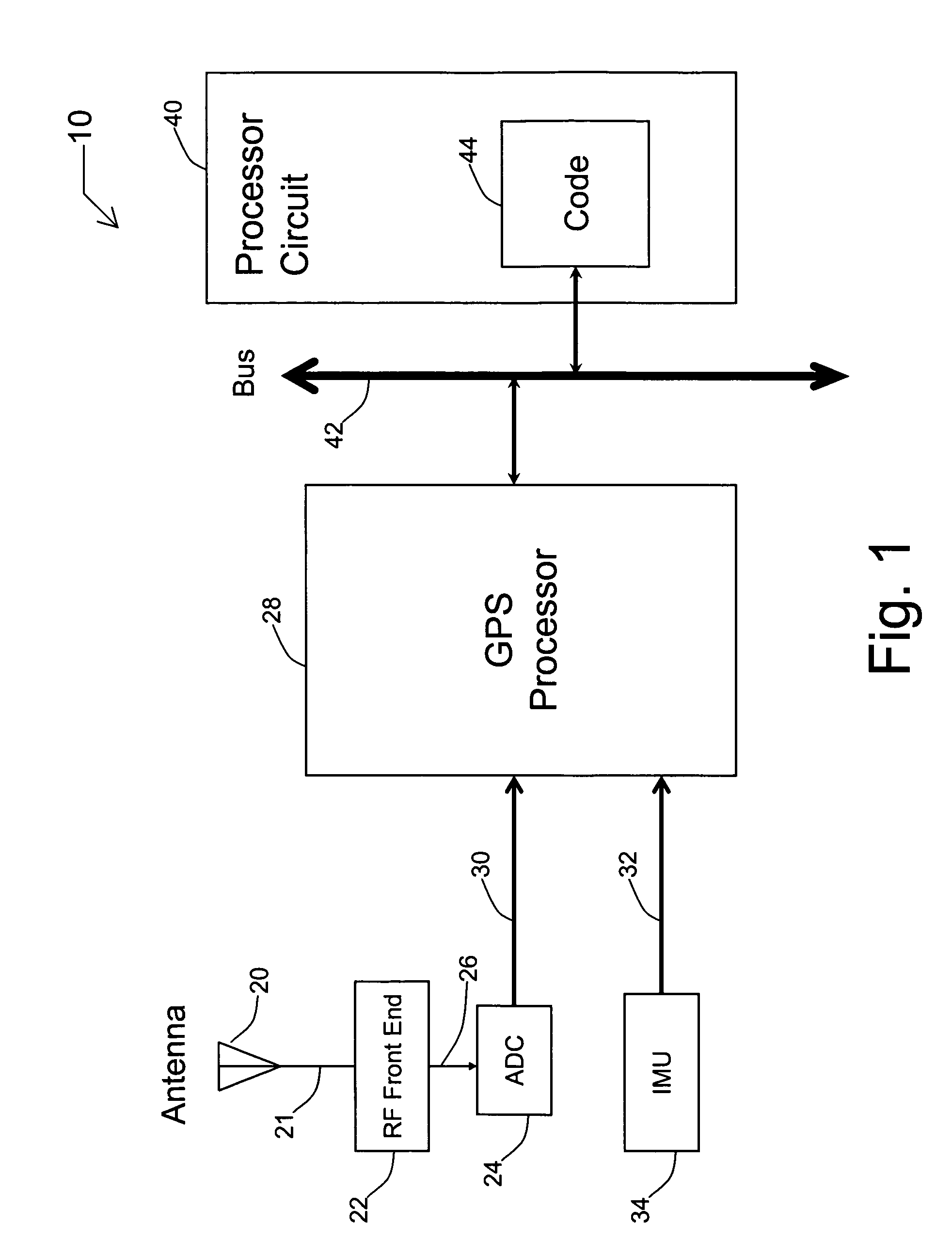
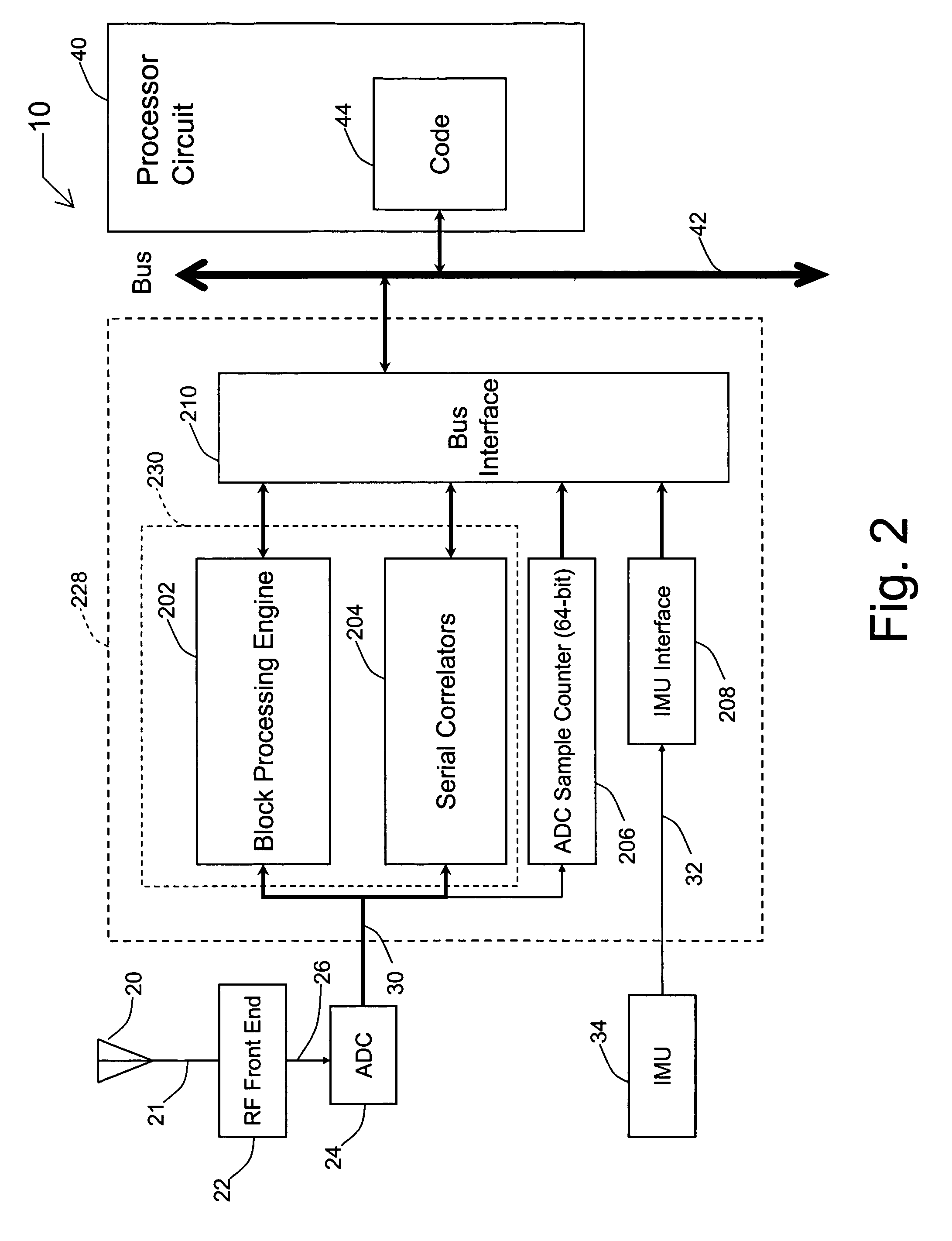
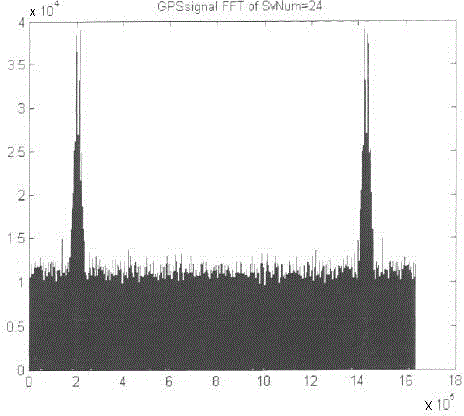
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
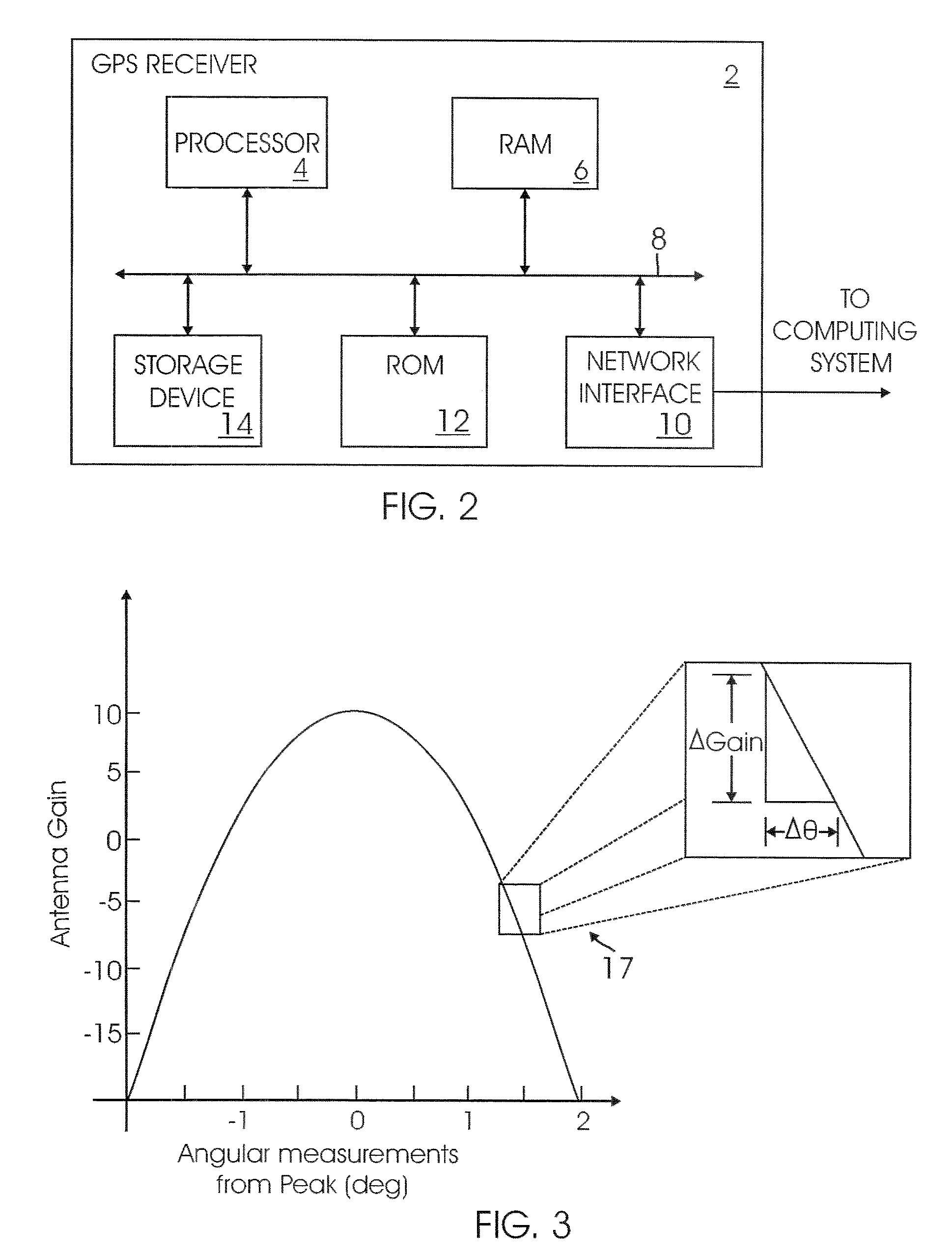
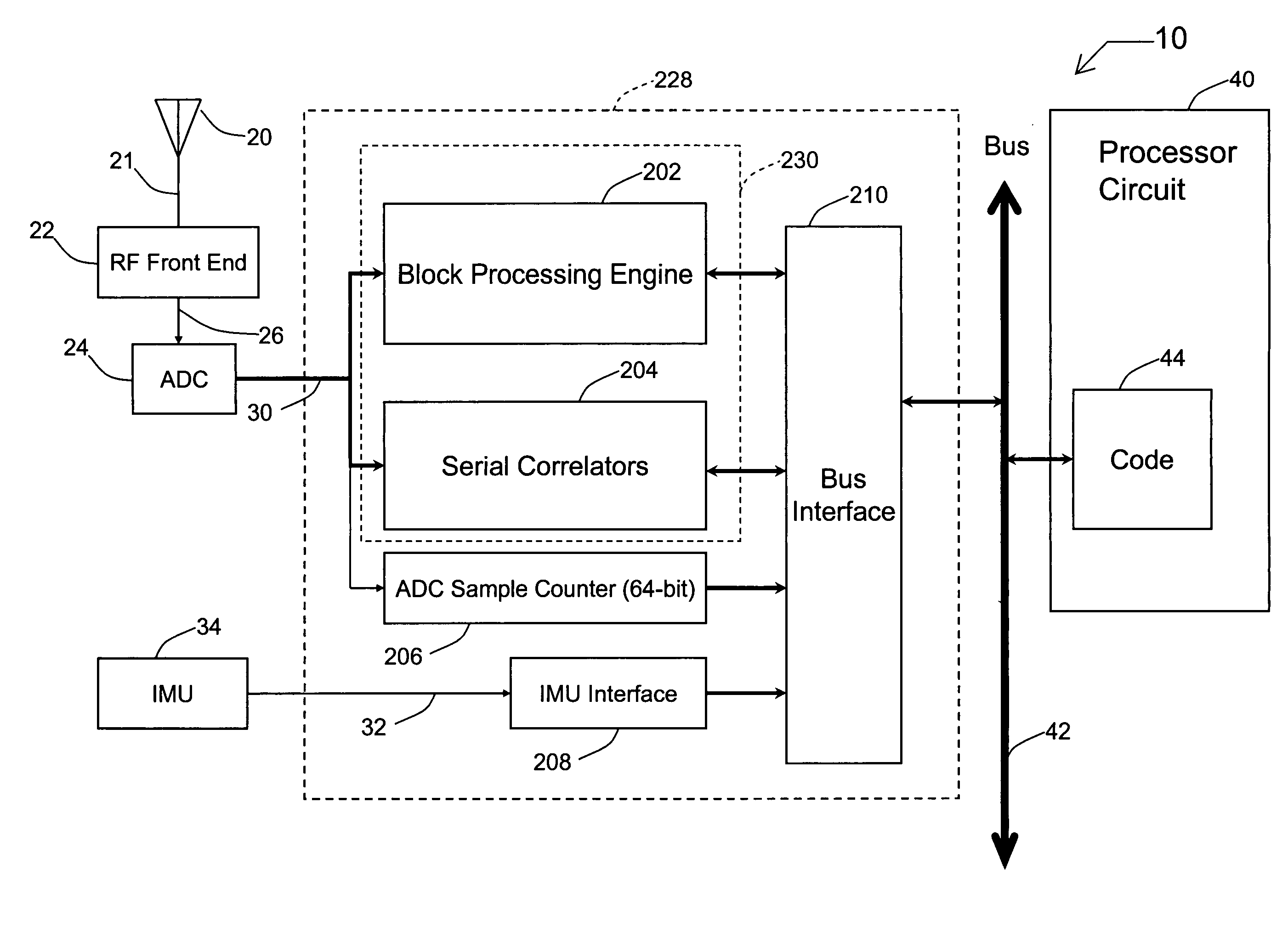
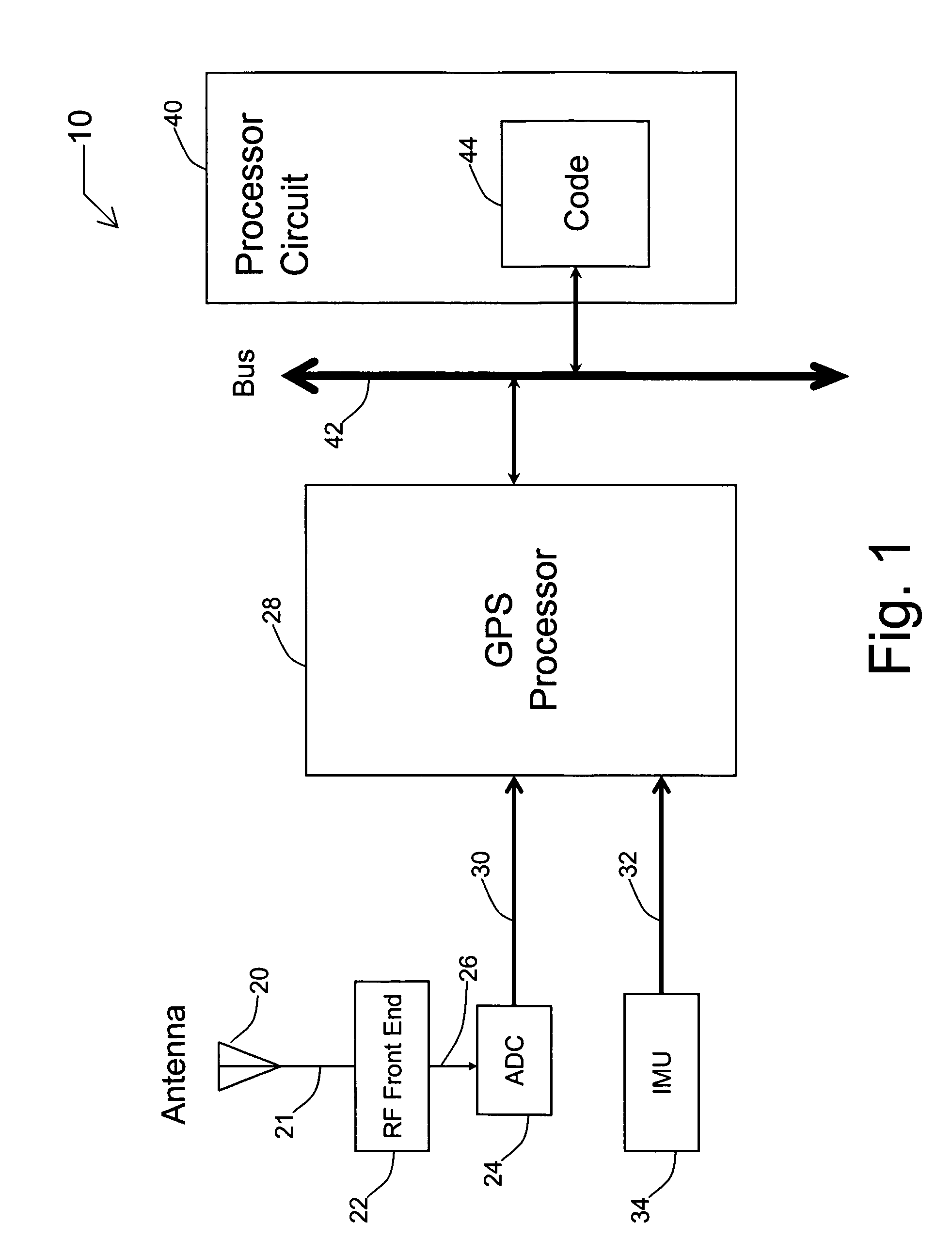
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
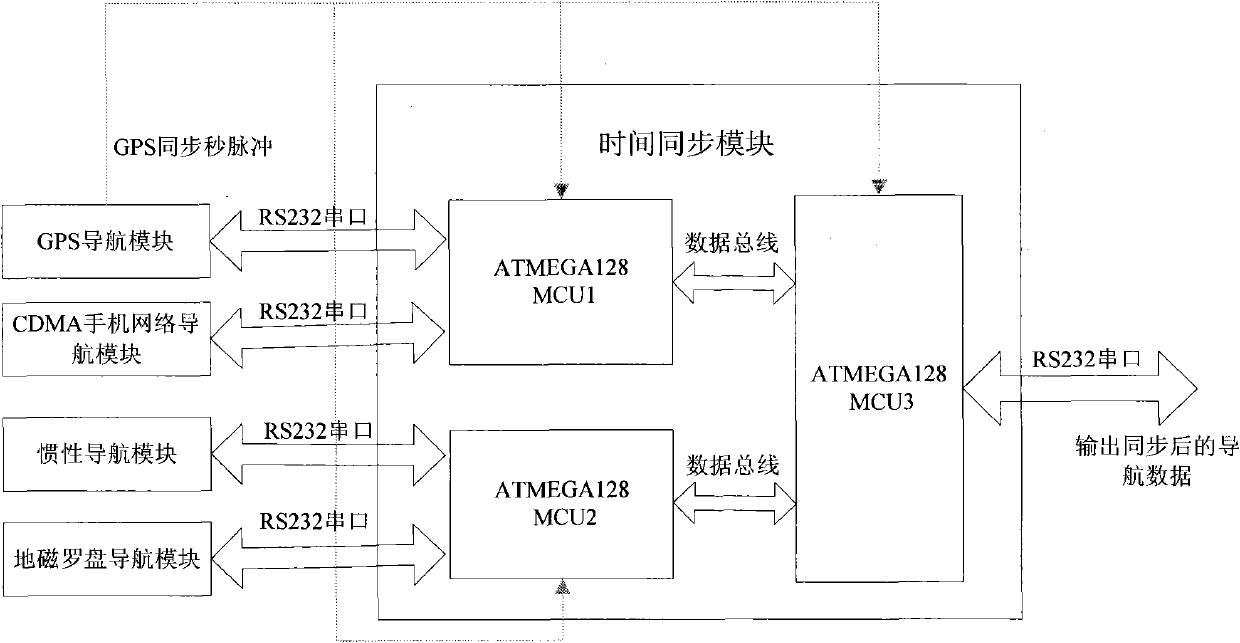
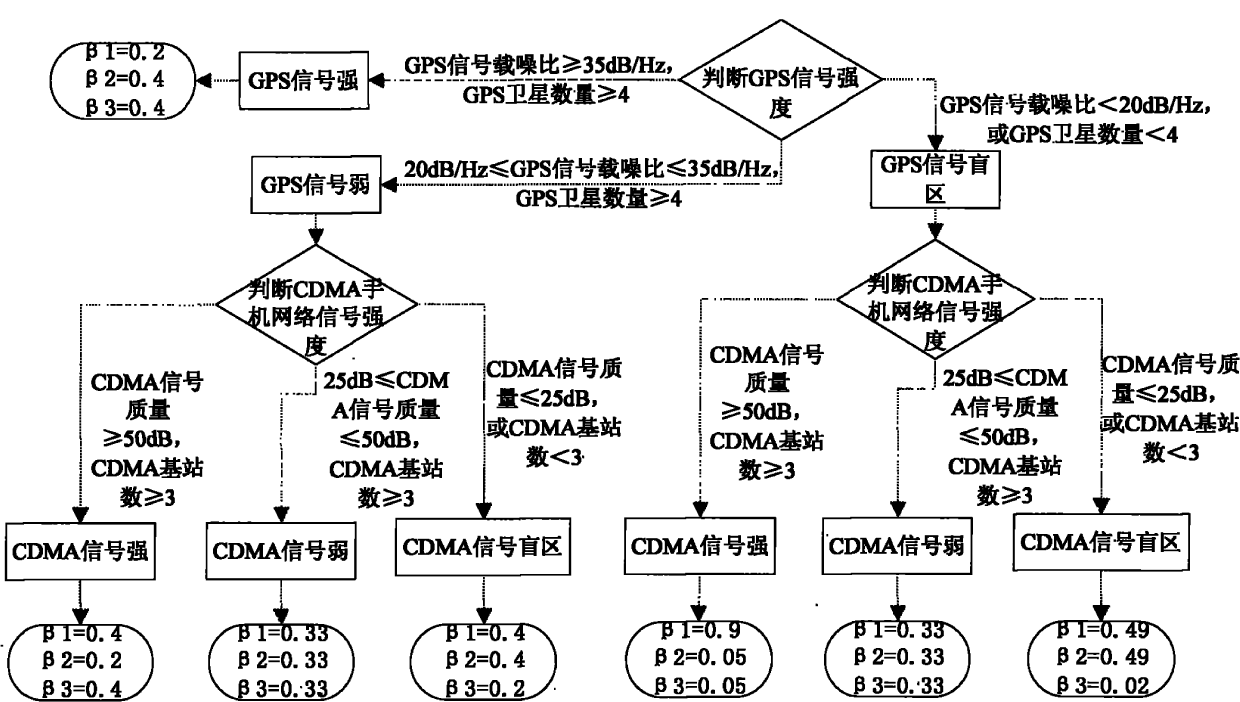
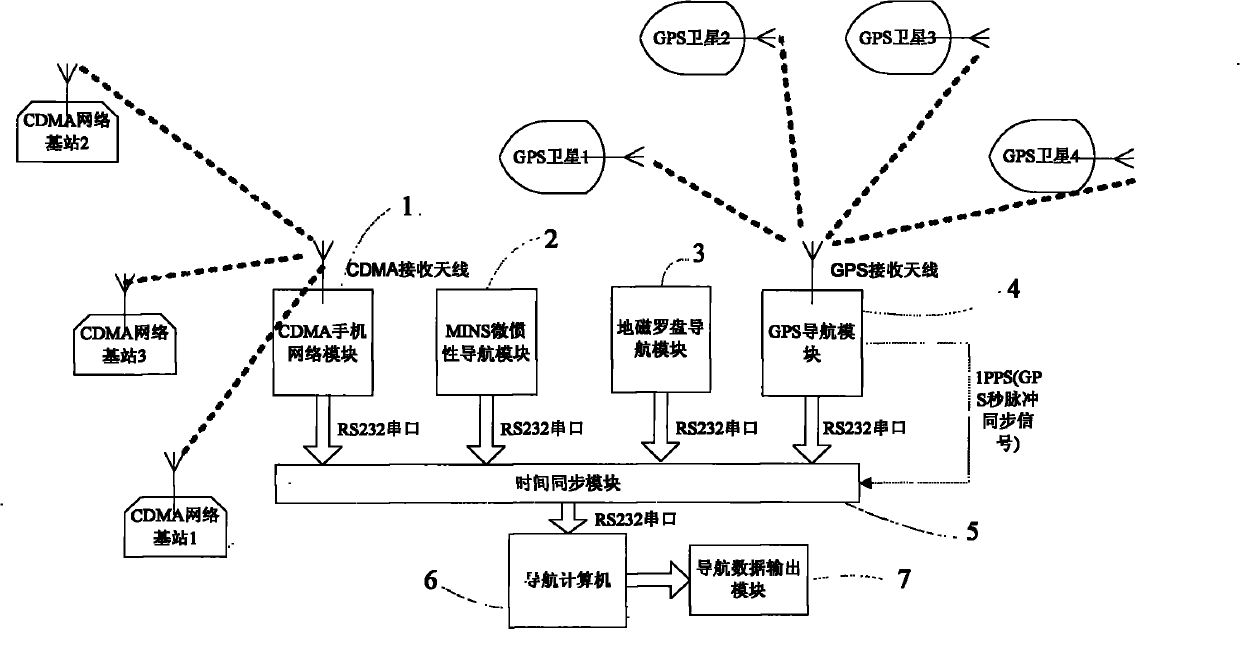
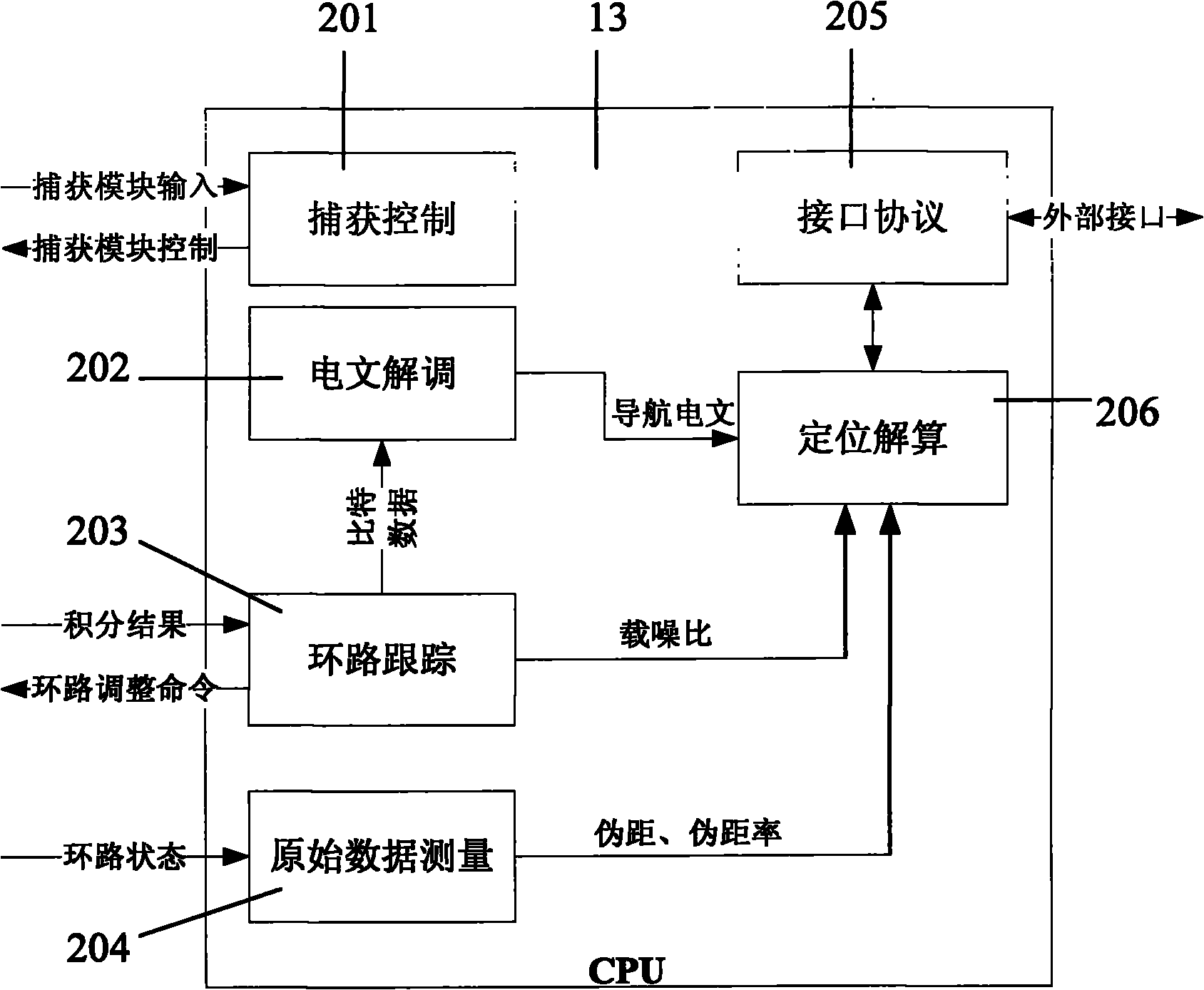
Combined navigation unit and implementing method thereof
ActiveCN101867868AOvercome the lack of normal positioningReduce volumePosition fixationLocation information based serviceData displaySignal quality
The invention discloses a combined navigation unit and an implementing method thereof. The unit comprises an MINS, a geomagnetic compass heading system, a GPS, and a CDMA mobile phone network positioning system. The method comprises that: a navigation computer synchronously receives navigation data of the GPS, dead reckoning data of the MINS, data of the CDMA mobile phone network positioning system and data of the geomagnetic compass heading system from four RS232 serial ports by utilizing a time synchronization module, and performs real-time and adaptive combined navigation according to the carrier-to-noise ratio of GPS signals and the quality of CDMA mobile phone network signals; and finally, the navigation computer displays the final navigation data in real time through a navigation data display module. The combined navigation unit has the advantages of small volume, low power consumption, low cost, complete functions, plenty interfaces, and capacity of completely meeting the requirements on medium and low-precision positioning and orientation of urban ground transportation, navigation, small intelligent robots and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
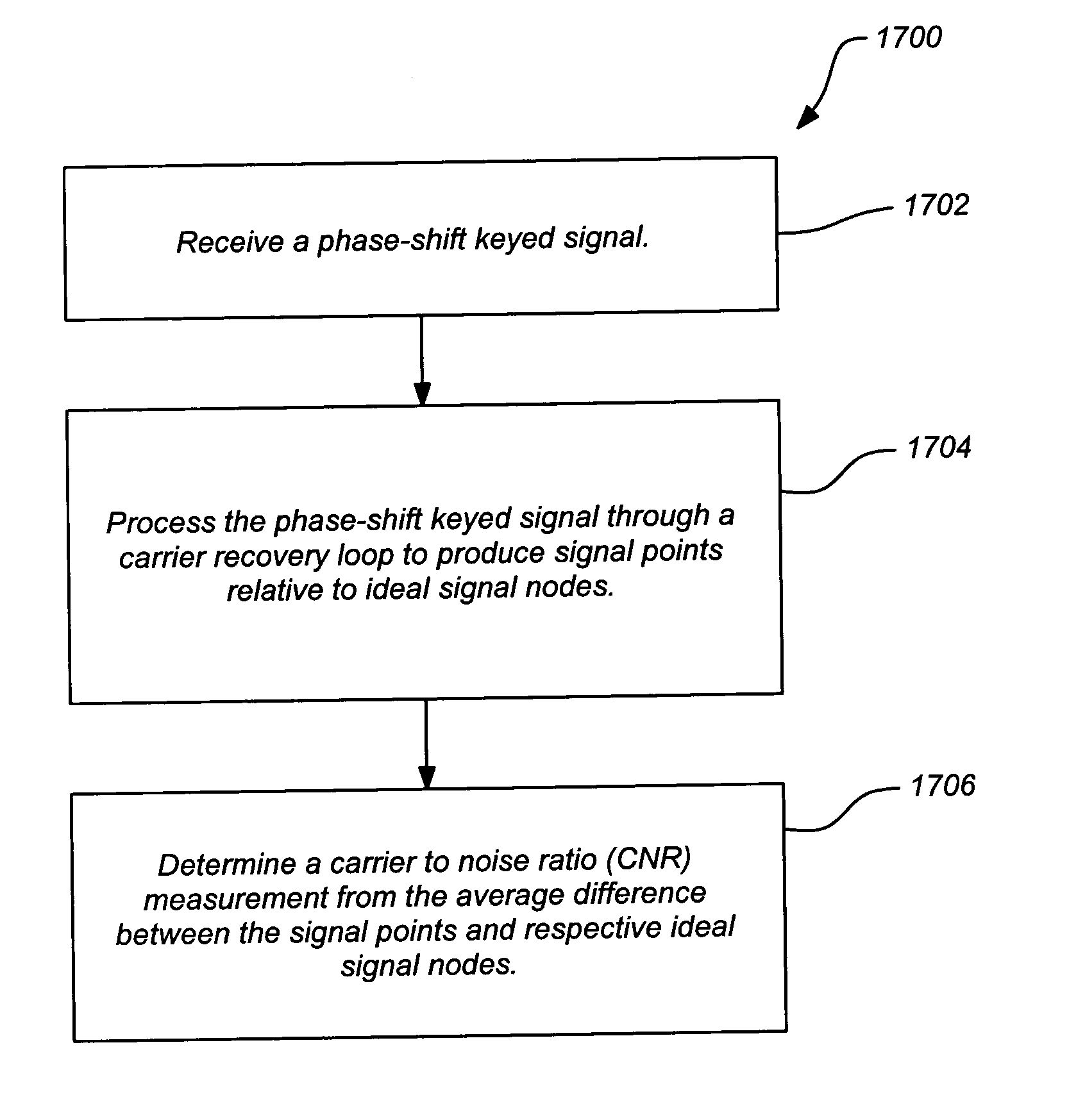
Carrier to noise ratio estimations from a received signal
InactiveUS20050008100A1Good signal cancellationTelevision system detailsReceivers monitoringA d converterEngineering
Techniques for measuring the carrier to noise ratio (CNR) in a received digital signal are disclosed. The methods can operate on a received digital signal, such as a layered modulation signal used in a satellite television system. The CNR measurement can be made at the output of a carrier recovery loop or a timing recovery loop in a demodulator. Alternately, the CNR measurement can be made when the received signal is digitized in an analog to digital (A / D) converter at base-band by the demodulator.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
New method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on satellite selecting algorithm in multimode satellite navigation system
InactiveCN103592658AReduce operational complexityHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingLoop bandwidthClock correction
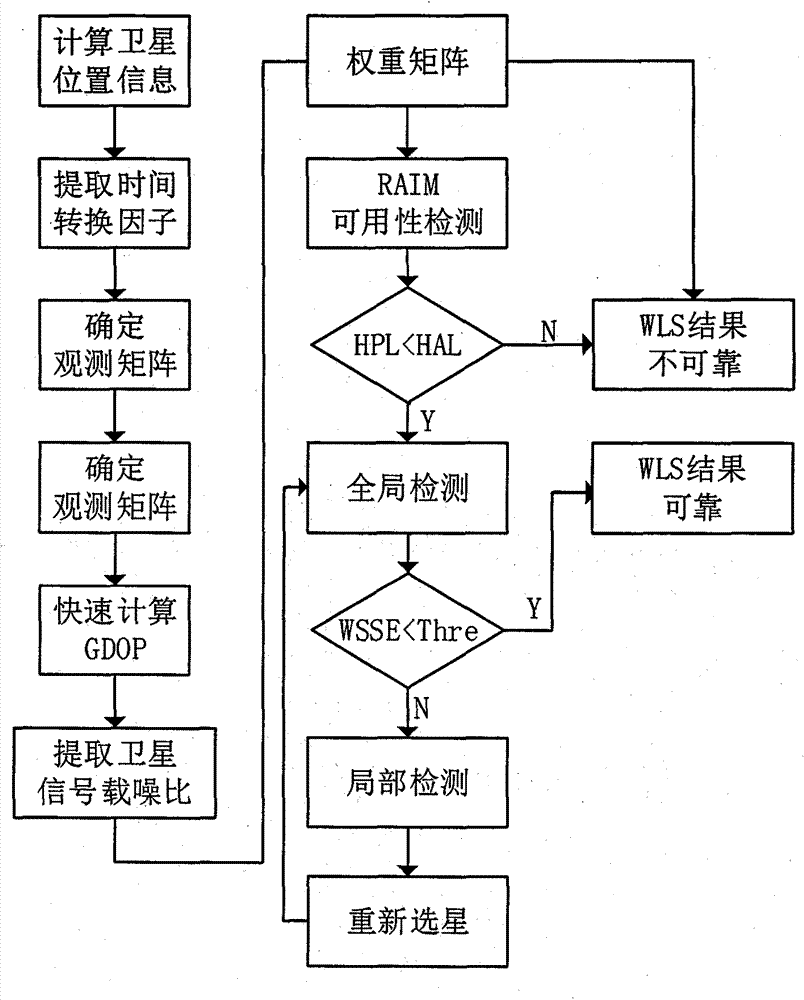
The invention discloses a new method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on a satellite selecting algorithm in a multimode satellite navigation system. The method comprises the steps of first determining space position information of satellites according to a navigation message and eliminating satellites with a small elevation angle according to a shielding angle; determining an observation matrix including only one clock correction item according to clock correction conversion factors in the navigation message; selecting p satellites from N visible satellites so as to be used for positioning calculation of a receiver, acquiring a satellite combination, which enables the GDOP (geometric dilution of precision) to be minimum, through the satellite selecting algorithm to act as calculating satellites, and determining a weight matrix in WLS (weighted least squares) according to parameters such as the carrier-to-noise ratio, the loop bandwidth, pre-check integral time and the like of satellite signals; carrying out RAIM availability detection according to a false alarm rate and a missed alarm rate which are preset by the receiver, and calculating a pseudo-range residual error threshold value after positioning according to the false alarm rate and a degree of freedom in Chi-squared distribution; carrying out global detection at first, then carrying out local monitoring in a circumstance that a fault satellite exists, determining calculation satellites again through satellite selection, and finally carrying out positioning calculation through selecting satellite combinations within the threshold value. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, high in fault recognition rate, not only applicable to multi-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, but also applicable to single-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, thereby providing new ideas for carrying out RAIM by a modern GNSS (global navigation satellite system).
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Satellite signal vector tracking method based on SINS/GPS deep integration data fusion
InactiveCN101666868AImplement vector trackingImprove tracking performanceBeacon systems using radio wavesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInformation processingVector tracking
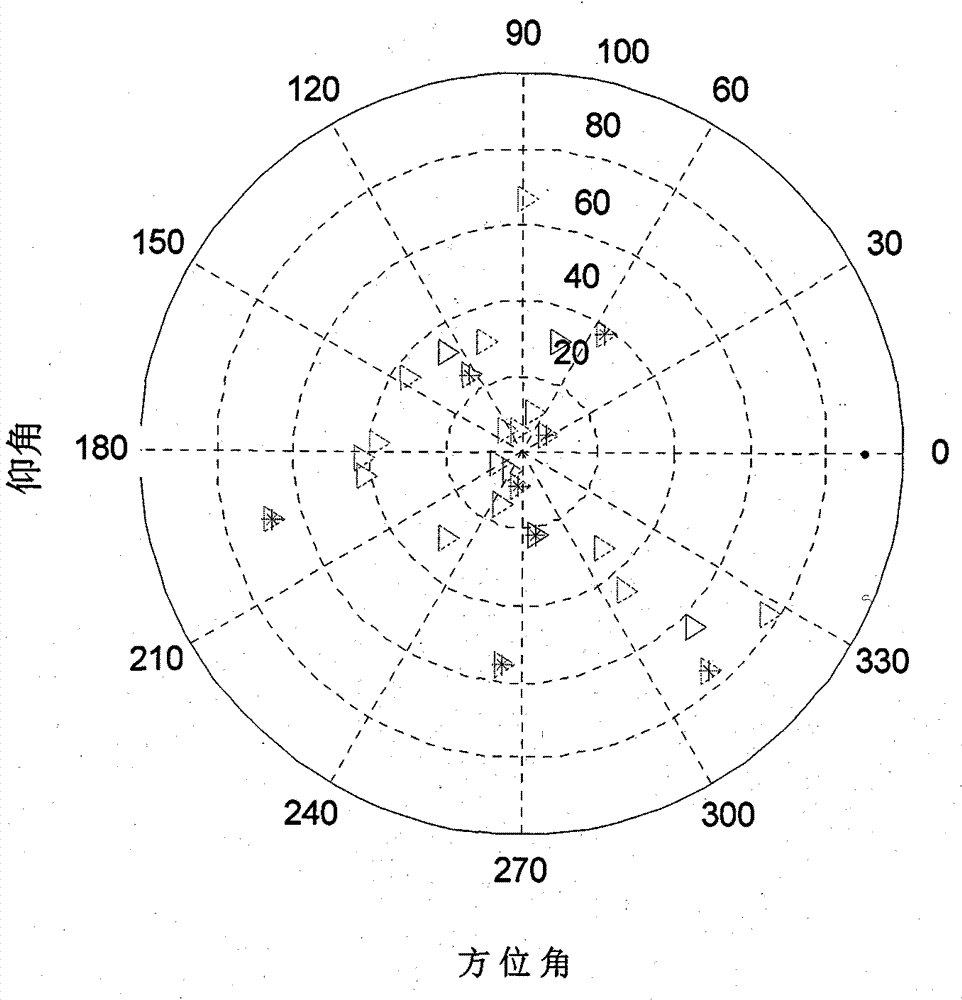
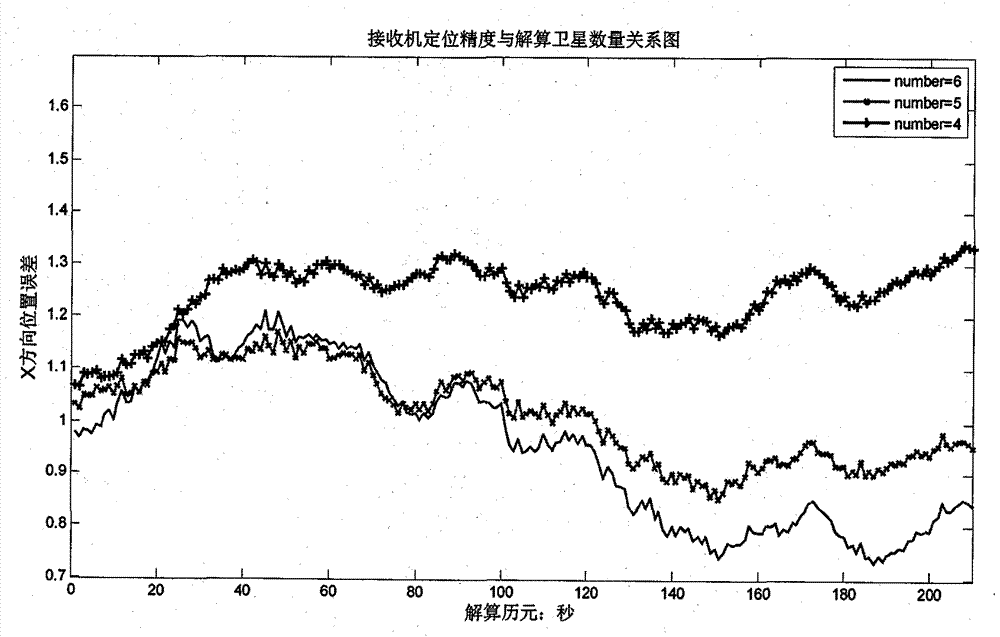
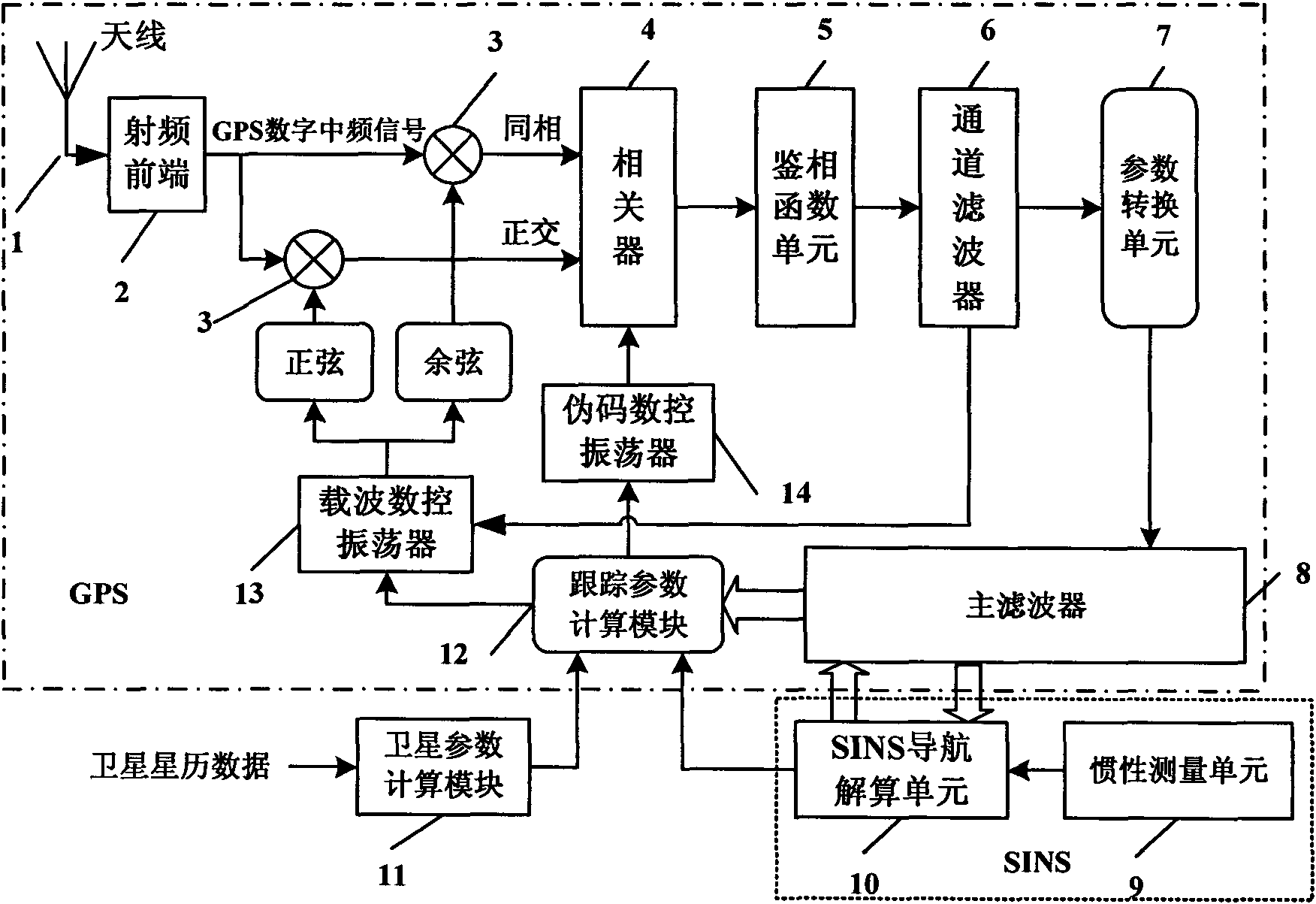
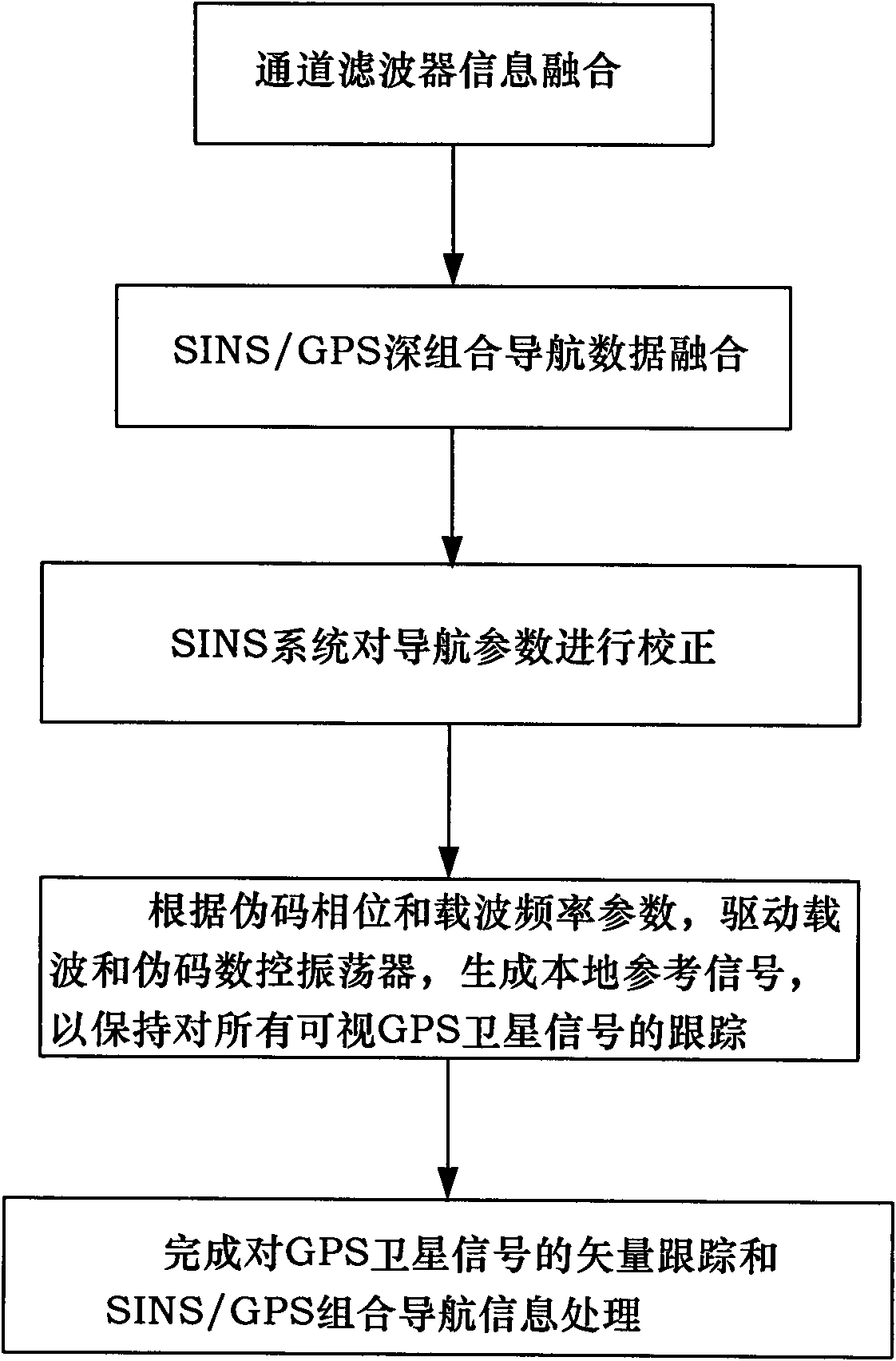
The invention discloses a satellite signal vector tracking method based on SINS / GPS deep integration data fusion. In the method, compensation is carried out on inertia element errors through channel filter information fusion, SINS / GPS deep integration navigation data fusion and an SINS system based on an SINS / GPS deep integration navigation system; and position and speed parameters of a current computation period are corrected to obtain accurate navigation parameters and generate local inference signals as well as keep the tracking for all visual GPS satellite signals; and a loop formed by channel filters and a main filter is utilized to complete the vector tracking and integration navigation information processing to the GPS satellite signals. The invention has excellent noise inhibitioncapacity and dynamic tracking performance, can ensure the navigation accuracy and the reliability of an integration system during the temporary interruption of the GPS satellite signals, and can maintain better pseudo code phase and carrier frequency tracking property in an environment with low carrier-to-noise ratio.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and system for attitude determination of a platform using global navigation satellite system and a steered antenna
InactiveUS20080068263A1Reduce noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalMarine navigation
A system and method for determining the attitude of a platform is provided. The method includes: (a) Searching and scanning for one or more GPS satellite(s) to determine initial platform position; wherein a single directionally steered antenna scans for the GPS / GNSS satellite; (b) pointing and scanning the antenna to GPS / GNSS satellite to determine a first angular measurement of a direction of a GPS / GNSS signal; (c) measuring carrier to noise ratio of the GPS / GNSS satellite; (d) dithering the single directionally steered antenna to obtain an angular measurement relative to an antenna pattern bore-sight reference; (e) repeating steps (b)-(d) to determine a second angular measurement of the direction of a second GPS signal; (f) determining the attitude error of the platform using the first and second angular measurements; (g) updating the platform position and attitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Apparatus and method for matching compressed video data under wireless fading environment
ActiveUS20070195893A1Smooth transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningControl signalCarrier signal
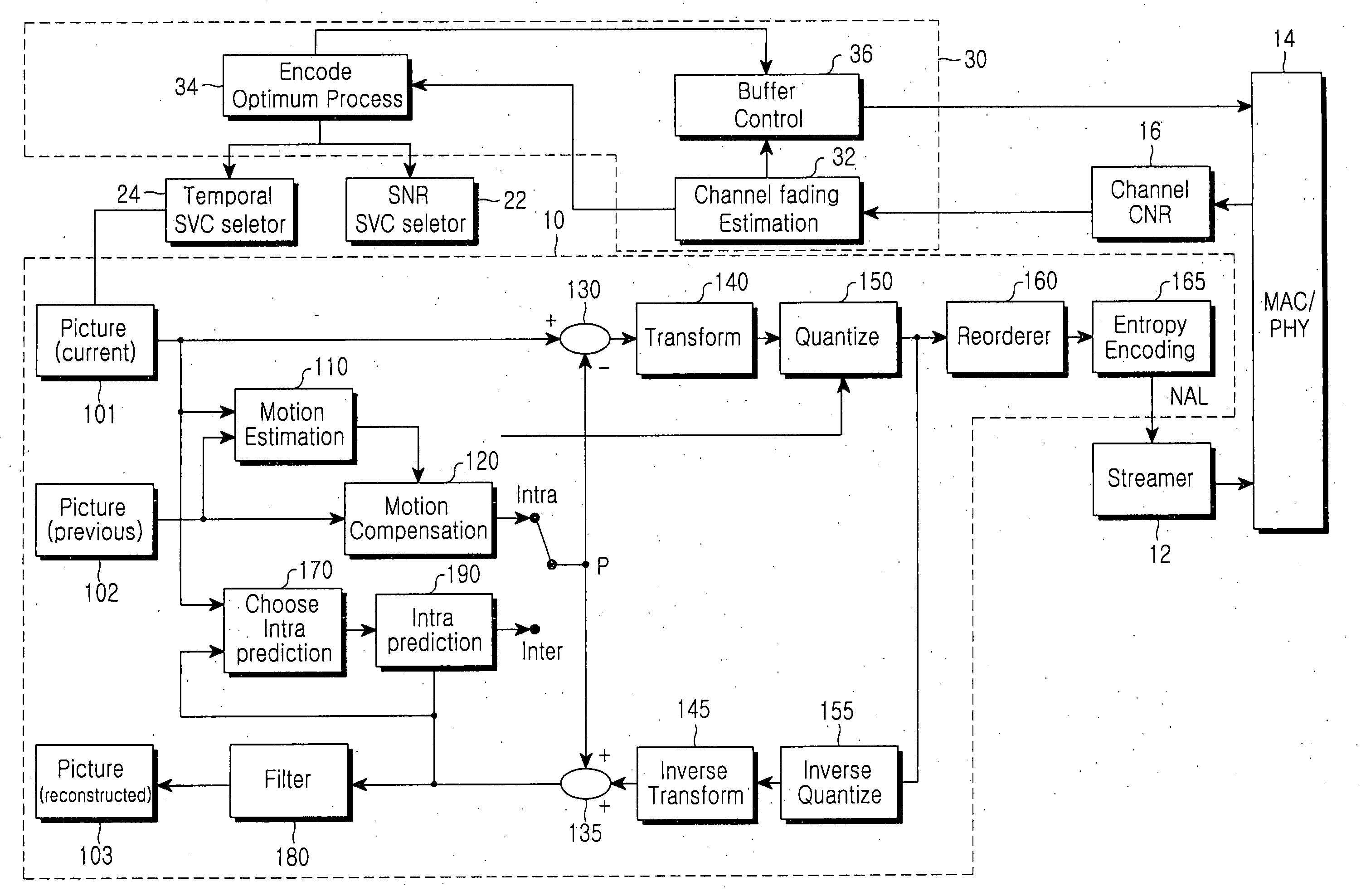
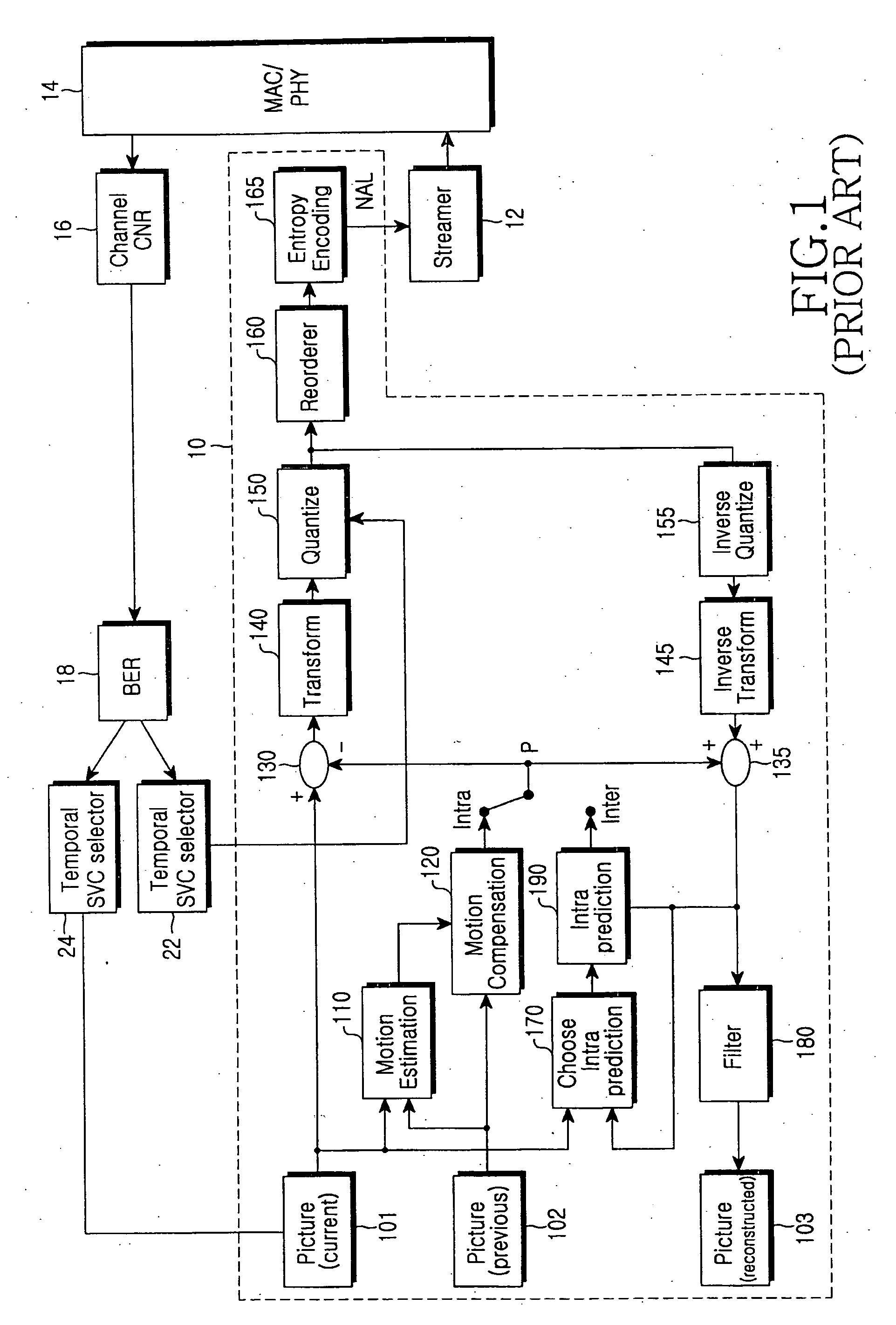
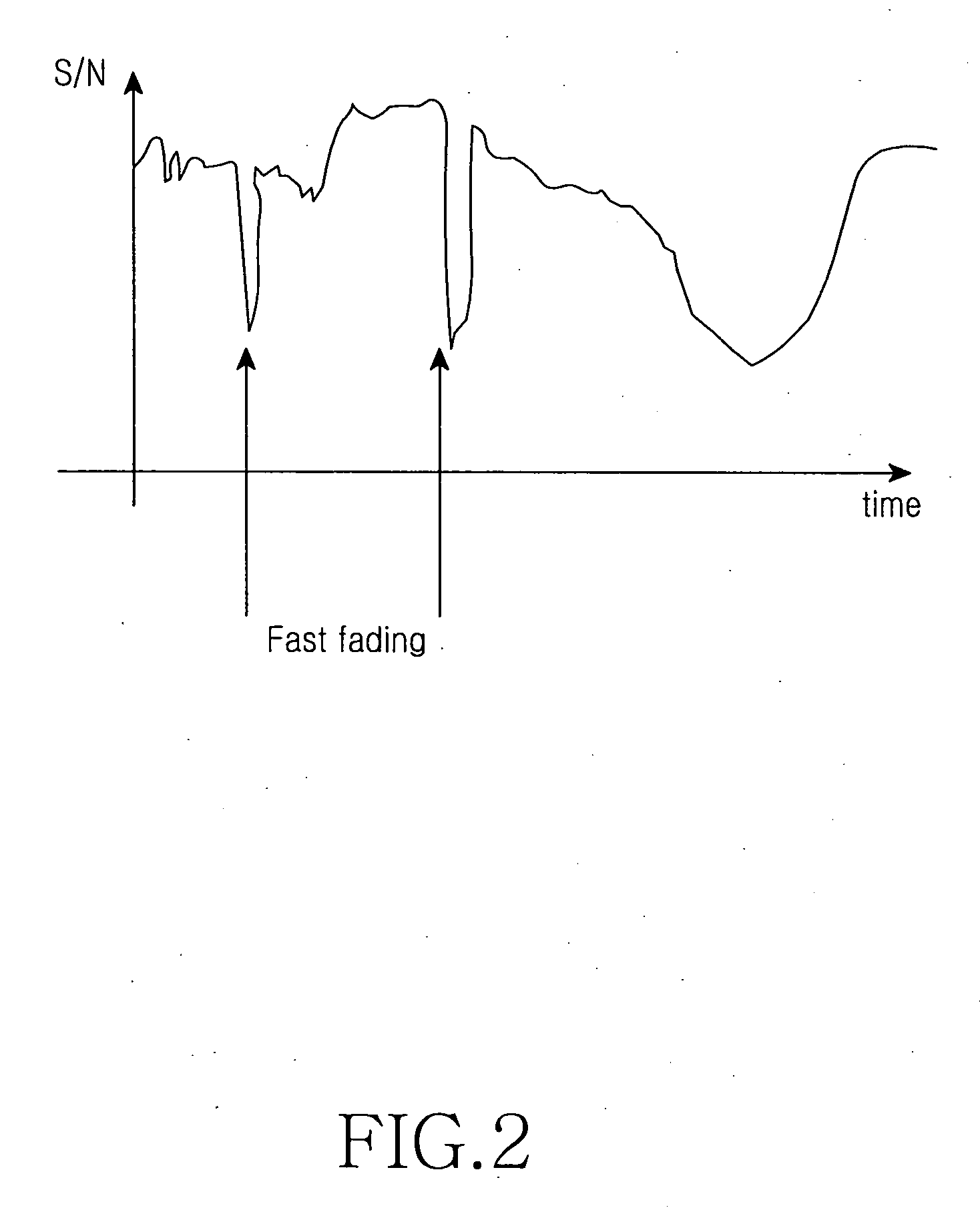
A method and apparatus for matching compressed video data under a wireless fading environment are disclosed. The apparatus includes an encoder for encoding and outputting the video data as a compressed bit stream, a channel error measurement unit for measuring Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) or Carrier-to-Noise Ratio (CNR) of a wireless channel, and an encoder optimization module for determining if the current fading is slow fading or fast fading. A control signal is output to reduce a frame transmission ratio or to change the quality of the vide data if it is determined that the current fading is slow fading. Another control signal is output to adjust the size of a data output buffer of the wireless channel if it is determined that the current fading is fast fading. The apparatus also includes a temporal Scalable Video Coding (SVC) selector 24 and an SNR SVC selector 22 for selecting the frame transmission ratio or the bit rate according to the control signal output from the encoder optimization module, to provide a frame selection signal or a bit rate selection signal to the encoder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
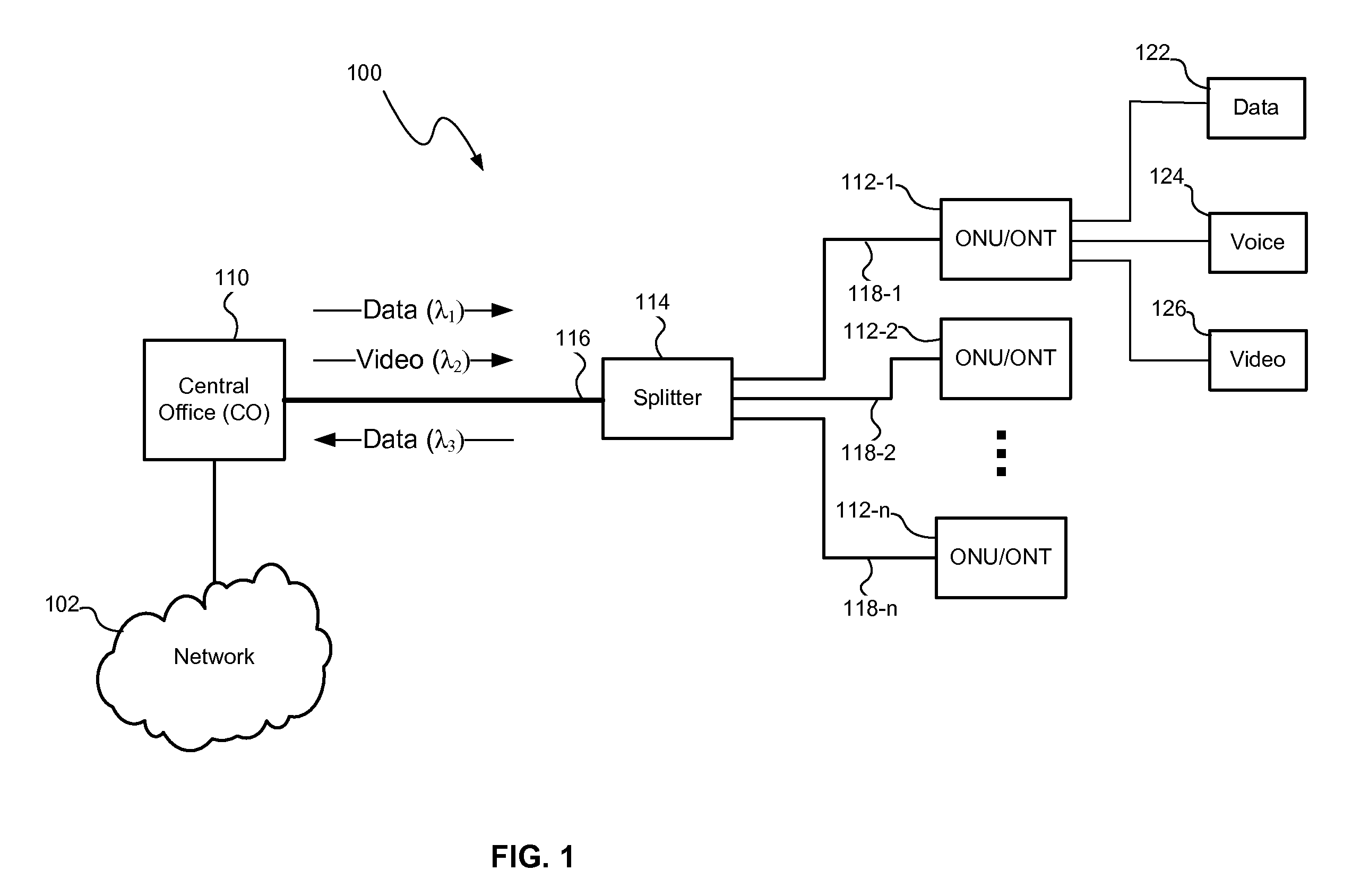
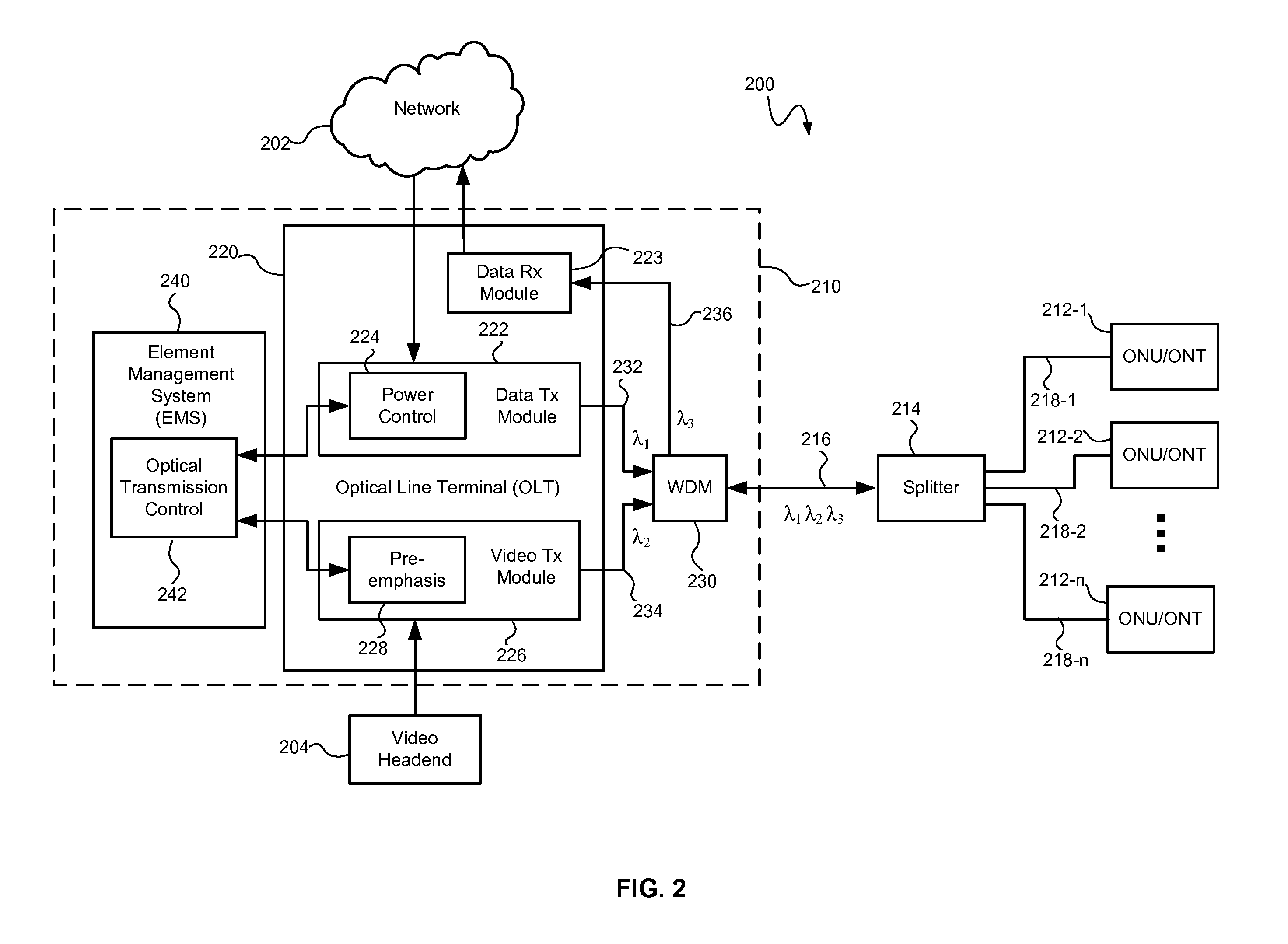
Controlling optical signal transmission to reduce optical signal degradation
InactiveUS20080031621A1Transmission monitoringOptical multiplexStimulate raman scatteringRayleigh backscattering
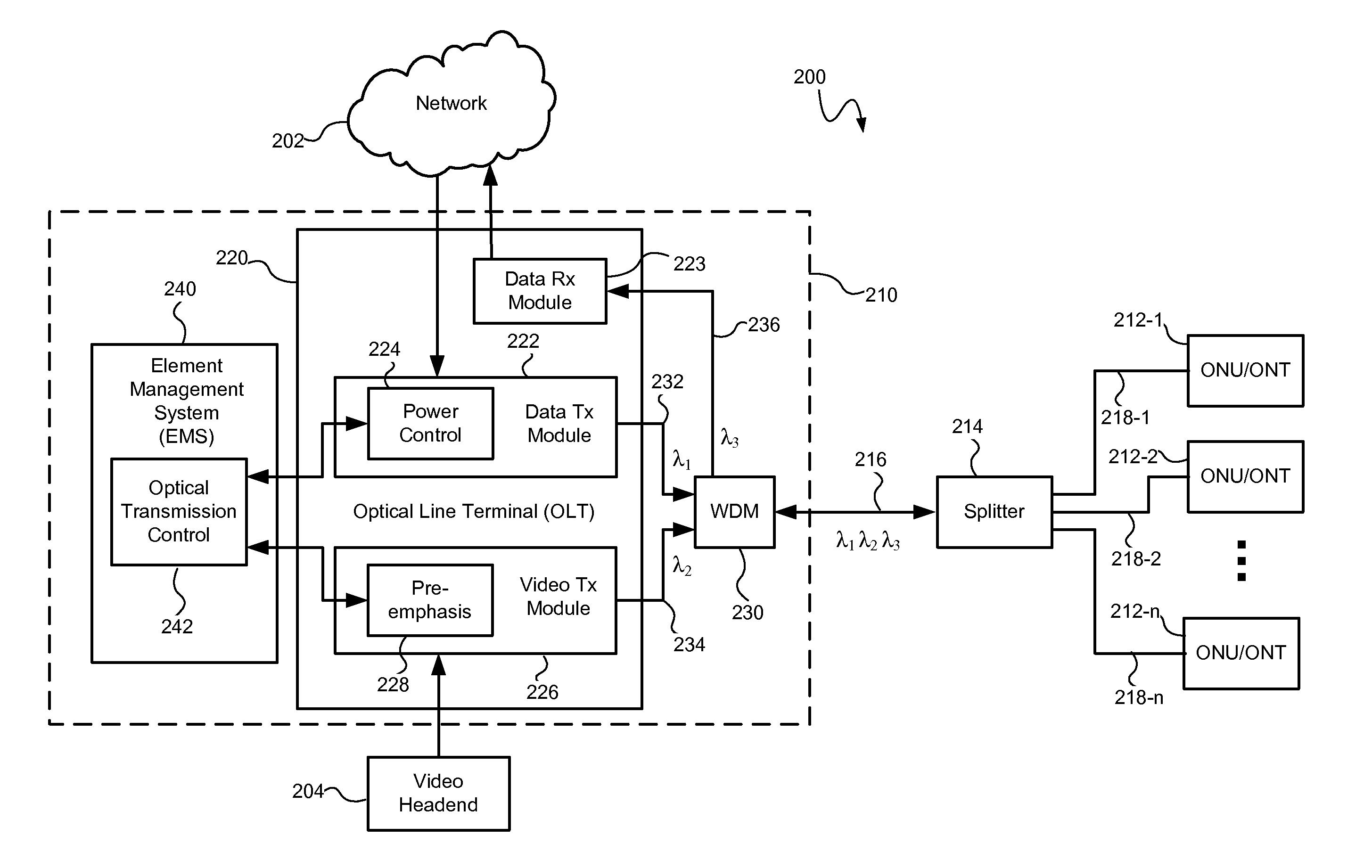
An optical transmission system and method may control optical signal transmission in an optical network, such as a passive optical network (PON), to reduce degradation of one or more optical signals traveling over the same optical waveguide. In particular, optical signal transmission may be controlled to reduce carrier to noise ratio (CNR) degradation of an optical signal (e.g., a multichannel video signal) resulting from the effects of stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and / or double Rayleigh backscattering (DRBS). The CNR degradation may be reduced by controlling transmission of one or more of a plurality of optical signals in the optical network based on various parameters affecting the contribution to CNR degradation by SRS and / or DRBS and affecting the performance of the optical transmission system. The optical signal transmission may be controlled by adjusting a preemphasis and / or transmitted power of the optical signal(s).
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Virtual watch plate based pointer reading identifying method
ActiveCN105091922AReduce labor intensityAvoid human errorInstrumentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Machine vision
The invention discloses a GNSS carrier loop circuit tracking method based on a stochastic resonance algorithm. According to the invention, the signal to noise ratio of receiving signals is increased by integral accumulation and multiplication feedback treatment on input signals; rough tracking of frequency of the receiving signals is performed by utilizing a second-order frequency locking loop; and precise tracking is performed on the signals subjected to rough tracking by adopting a third-order phase locking loop. Therefore, precise carrier loop circuit tracking on the GNSS signals is realized in a low carrier-to-noise ratio. According to the invention, an advantage of the stochastic resonance algorithm in an aspect of improving the signal to noise ratio and an advantage of anti-interference and robustness of the cooperation of the second order frequency locking loop and the third-order phase locking loop are integrated effectively. The method is simple in hardware implementation and stable in signal tracking, and can realize stable and reliable tracking of highly dynamic satellite signals by a receiver in a severe environment.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
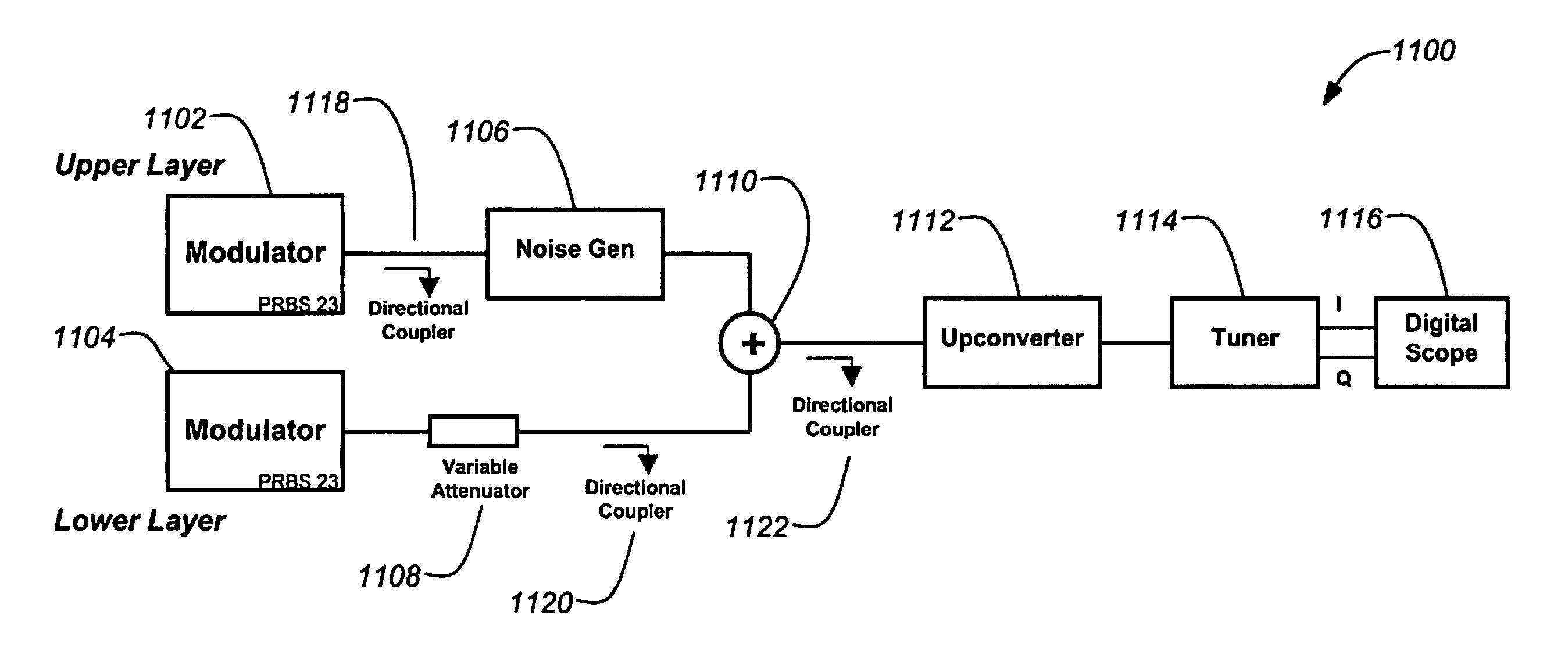
Method and apparatus for layered modulation
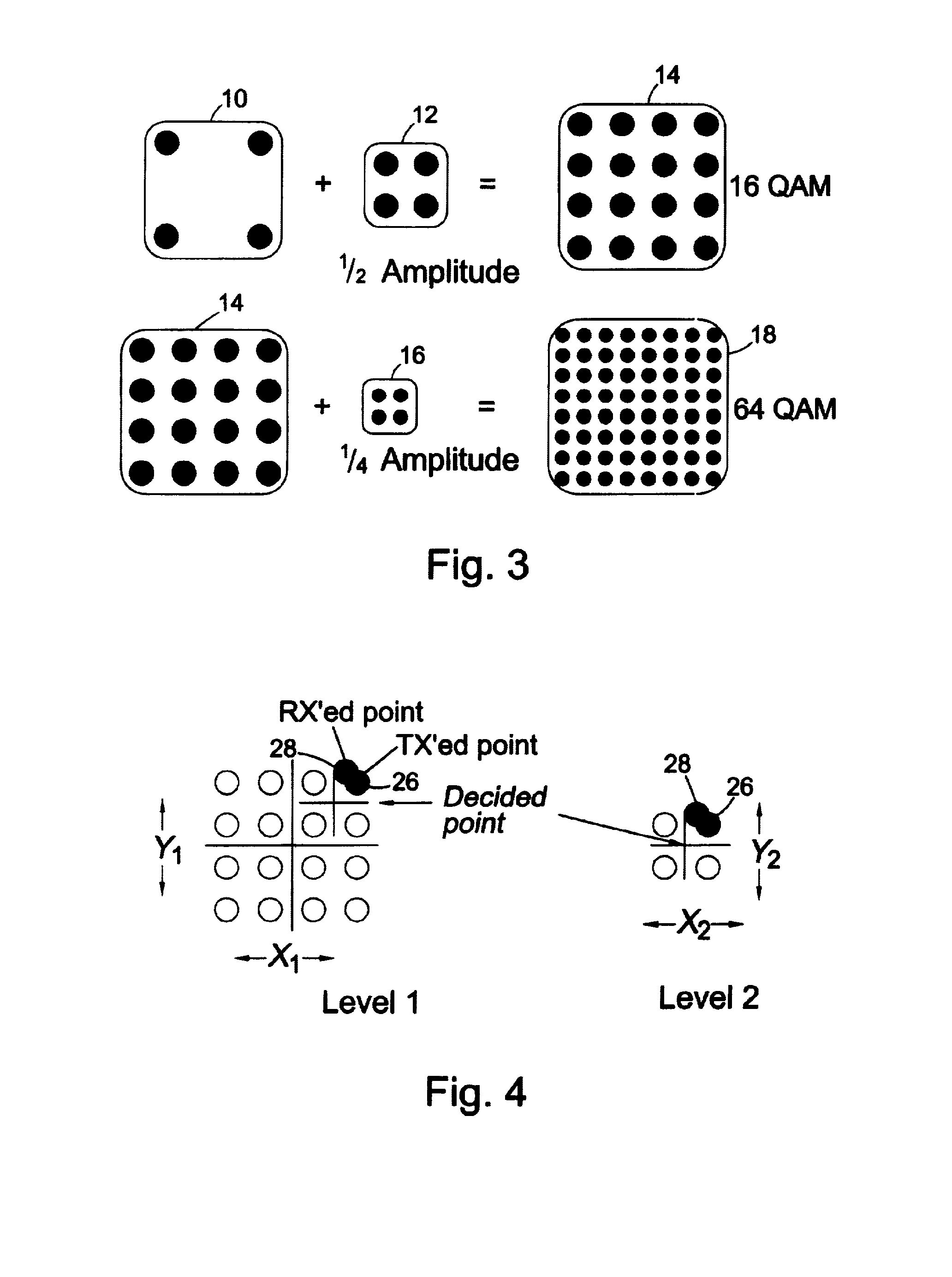
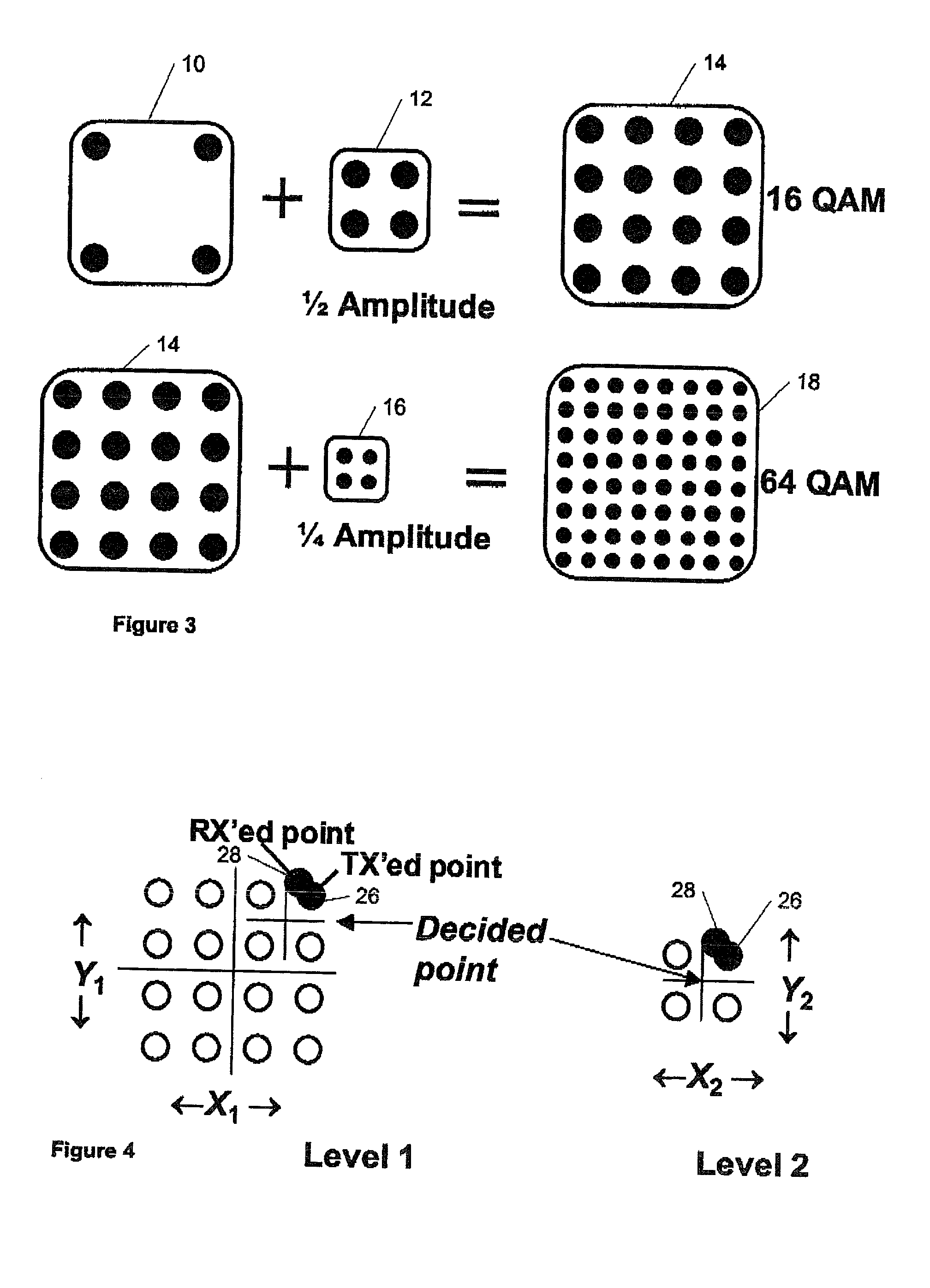
InactiveUS20060050805A1Improve carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR)Enhance layeringError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase-modulated carrier systemsComputer scienceSignal processing
Improvements to a layered modulation (LM) implementation are disclosed. The present invention discloses two implementations of LM, using single and multiple transponders per signal frequency, respectively. Layered hierarchical 8PSK (H-8PSK) is a special case of LM. By re-encoding the high-priority (HP) portion of an H-8PSK signal, LM can improve carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR) of a H-8PSK signal. LM can be computer-simulated and a two-layered signal can be sequentially demodulated with a predicted CNR performance. An LM signal can be simulated 10 using live signals for off-line processing. In addition, a signal processing apparatus can process in real time LM signals emulated from live satellite signals.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Method and apparatus for reducing power consumption in GNSS receivers
ActiveUS20110037650A1Reduce power consumptionKeep for a long timeSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalEngineering
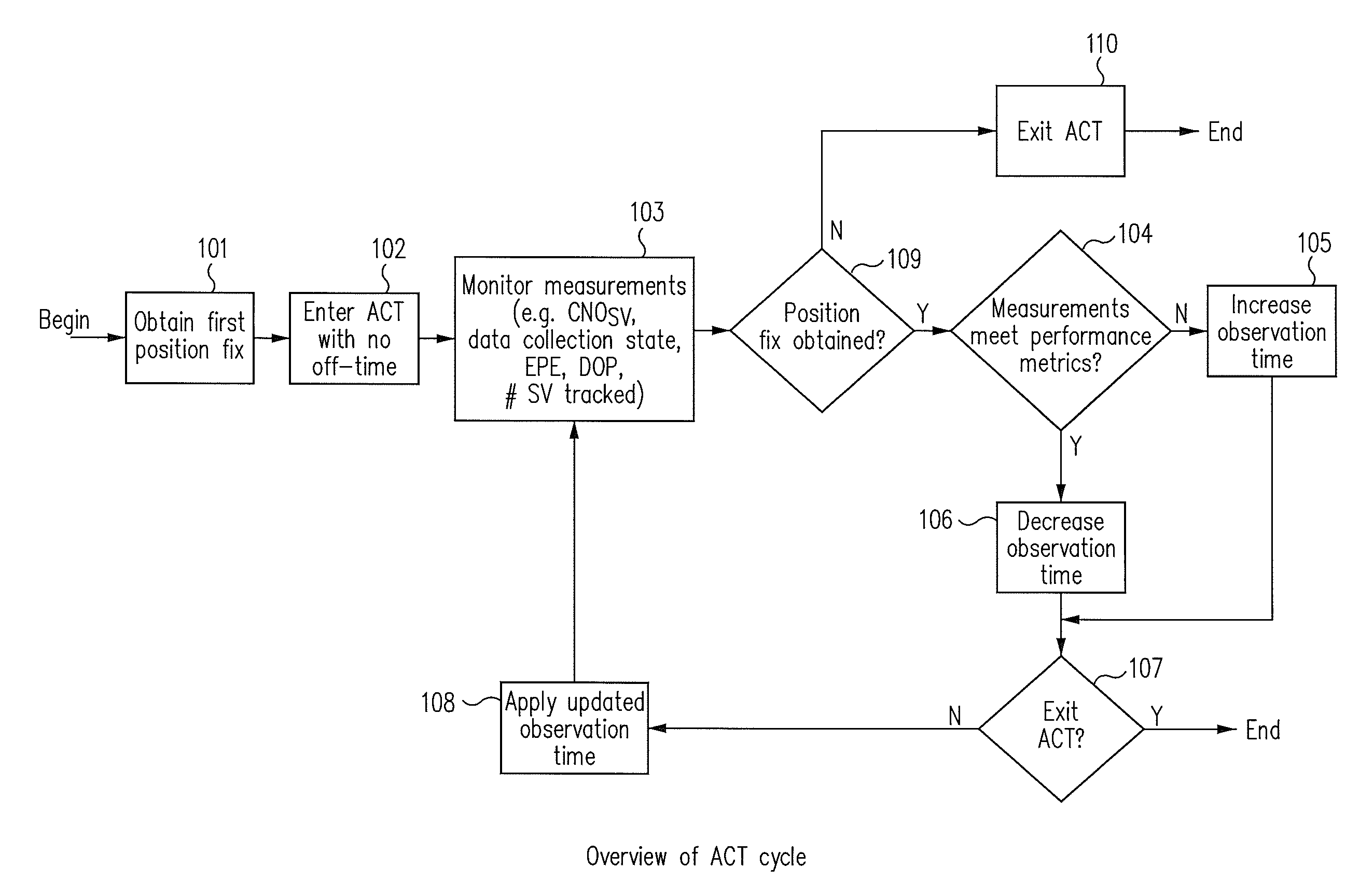
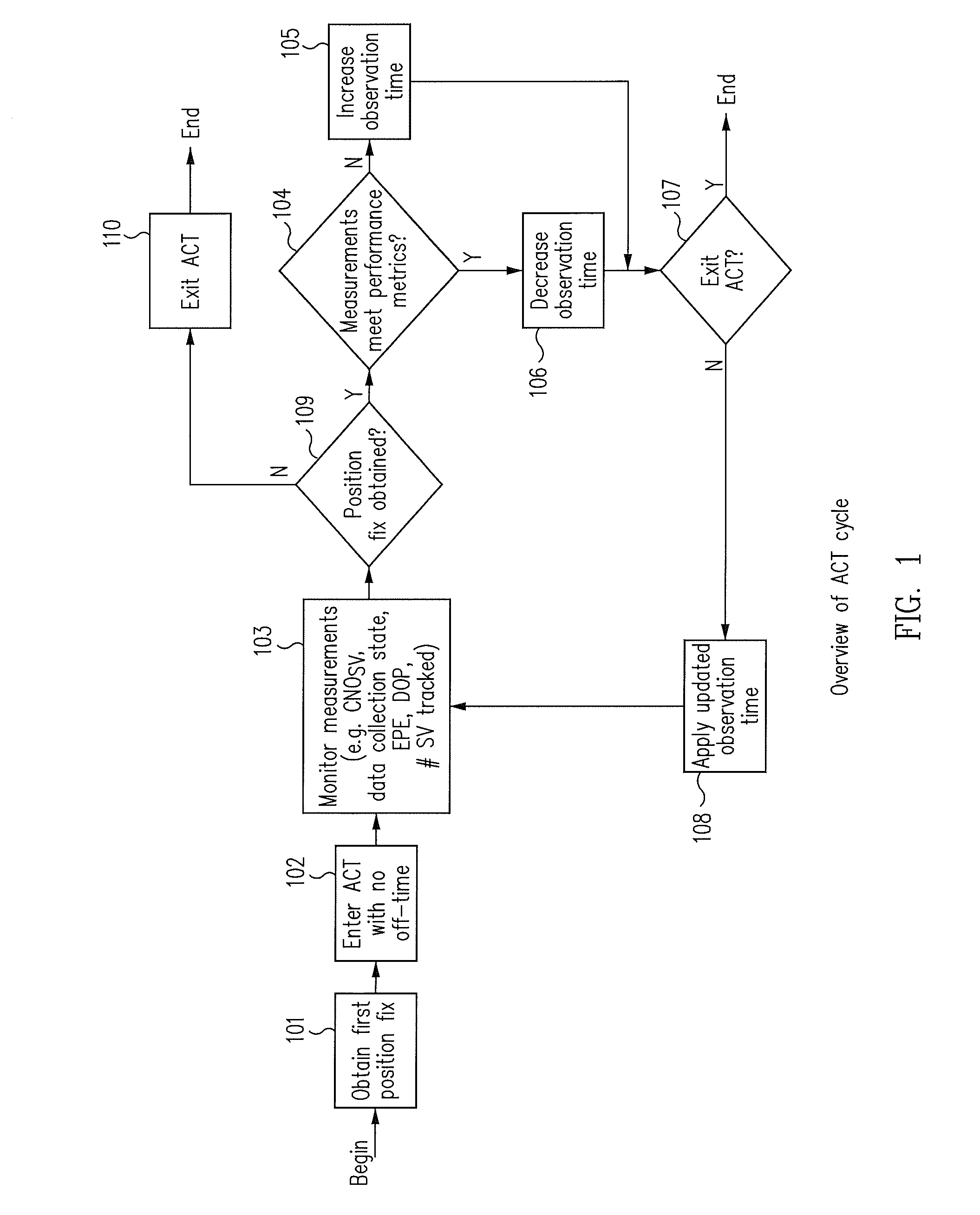
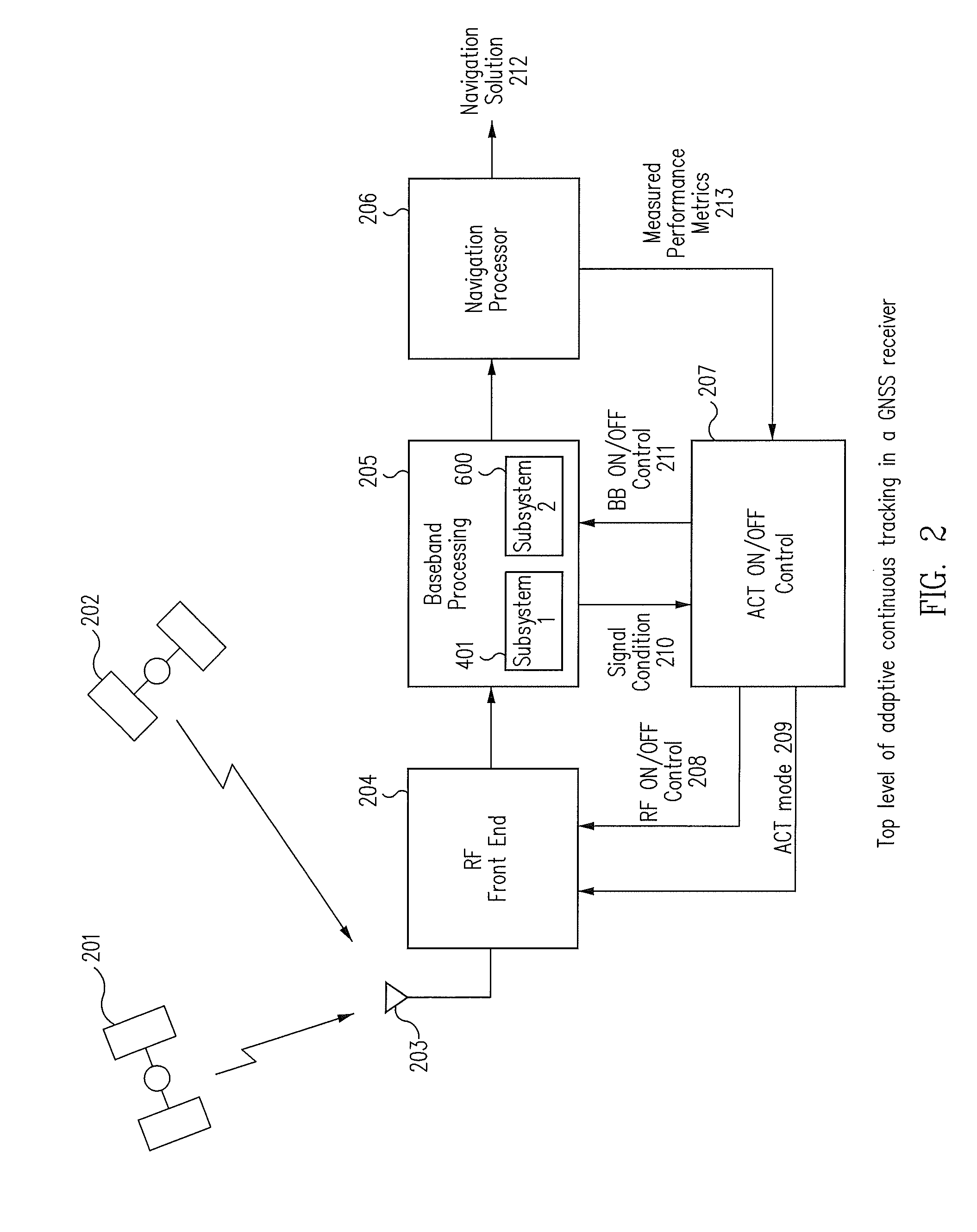
Systems and methods are disclosed herein to use what is referred to as adaptive continuous tracking (ACT) to reduce the power consumption of GNSS receivers. In GNSS receivers, performance as measured by position accuracy is a function of the observation time of the satellites. A longer observation time translates into more reliable range measurements and demodulated data, and ultimately into better positioning accuracy of the receivers. However, a longer observation time also means more power consumption. ACT allows satellite observation time to be tuned to the desired positioning performance by dynamically adjusting the on time period of the receivers while maintaining a minimum performance metric. The performance metric may be formed from a combination of the estimated position error, the horizontal dilution of precision (HDOP), the data collection state, and the receiver operating environment as characterized by the carrier to noise ratio (CN0). ACT cyclically switches on / off the radio frequency (RF) front-end and also cyclically enables / disables the baseband hardware of the receivers to reduce power consumption while allowing the receivers to meet the minimum performance metric and ensuring continuous satellite tracking, continuous positioning fix operation, multiplexed GNSS operation, and continuous data collection.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for detecting observed quantity validity in navigation receiver
ActiveCN105044737ASolve the problem of positioning stabilitySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalEngineering
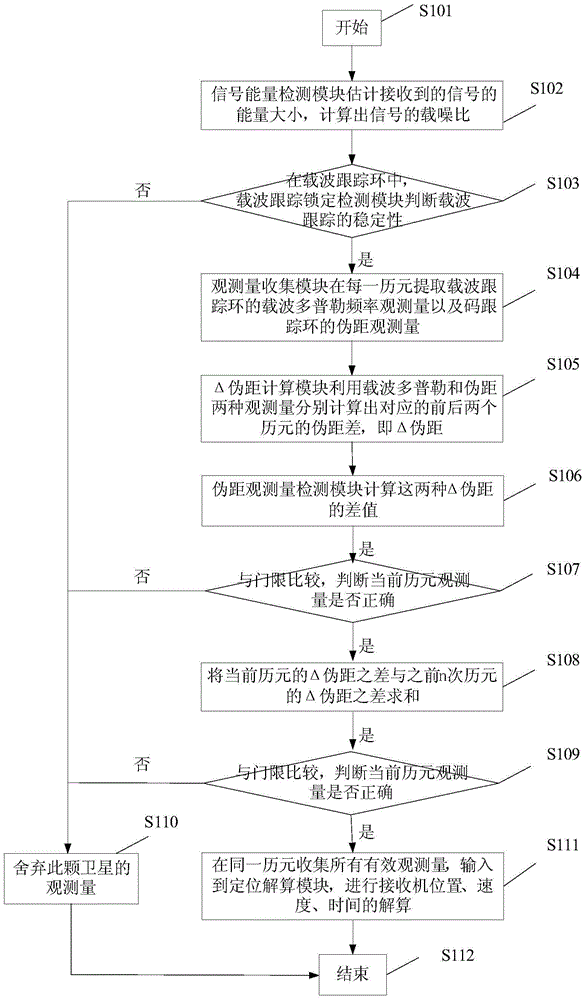
A method for detecting observed quantity validity in a navigation receiver mainly includes: S1. calculating a carrier-to-noise ratio of a signal; S2. judging stability of carrier tracking; S3. Extracting carrier Doppler frequency observed quantity of a carrier tracking loop and pseudo-range observed quantity of a code tracking loop in each epoch; S4. utilizing the two kinds of observed quantity to calculate a pseudo-range difference of corresponding two successive epoch respectively; S5. calculating a difference value of the pseudo-range differences and comparing with a threshold, thereby judging whether pseudo-range observed quantity of the current epoch is correct; S6. summing a difference of delta pseudo ranges of the current epoch and differences of delta pseudo ranges of n previous epochs, comparing with a threshold, and judging whether pseudo range observed quantity is correct; and S7. performing the abovementioned steps on each satellite which keeps tracking, collecting all signals of satellites whose observed quantity is judged to be correct, and inputting the signals to a positioning resolving module. The method provided by the invention does not need redundant information, and solves the problem of positioning stability of a receiver in complex environment with a relatively small calculated amount.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Methods and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data over a communications network in the presence of interference
InactiveUS7177371B1Reduce noiseReduce the amplitudeError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmitter specific arrangementsLow data rateData rate
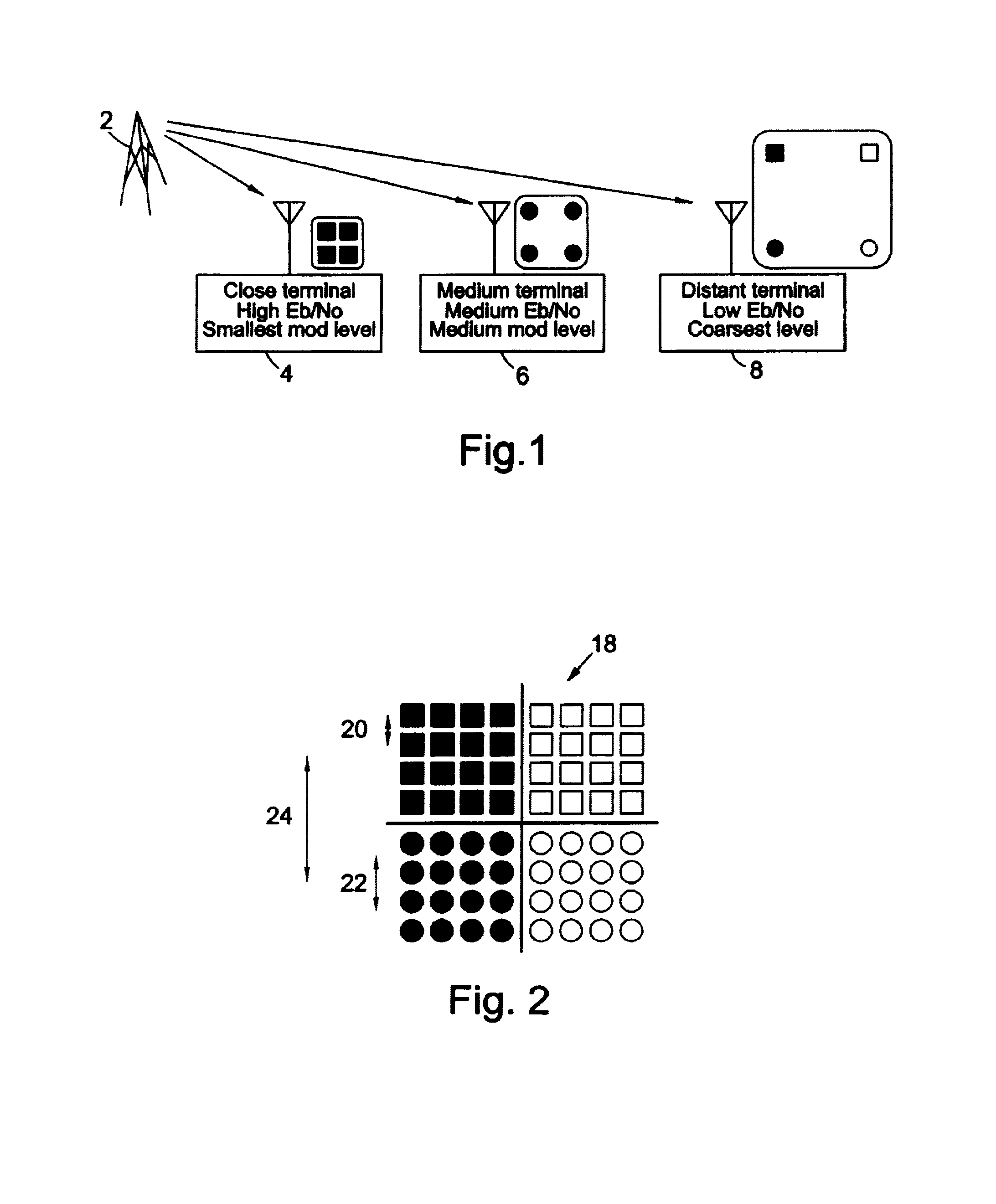
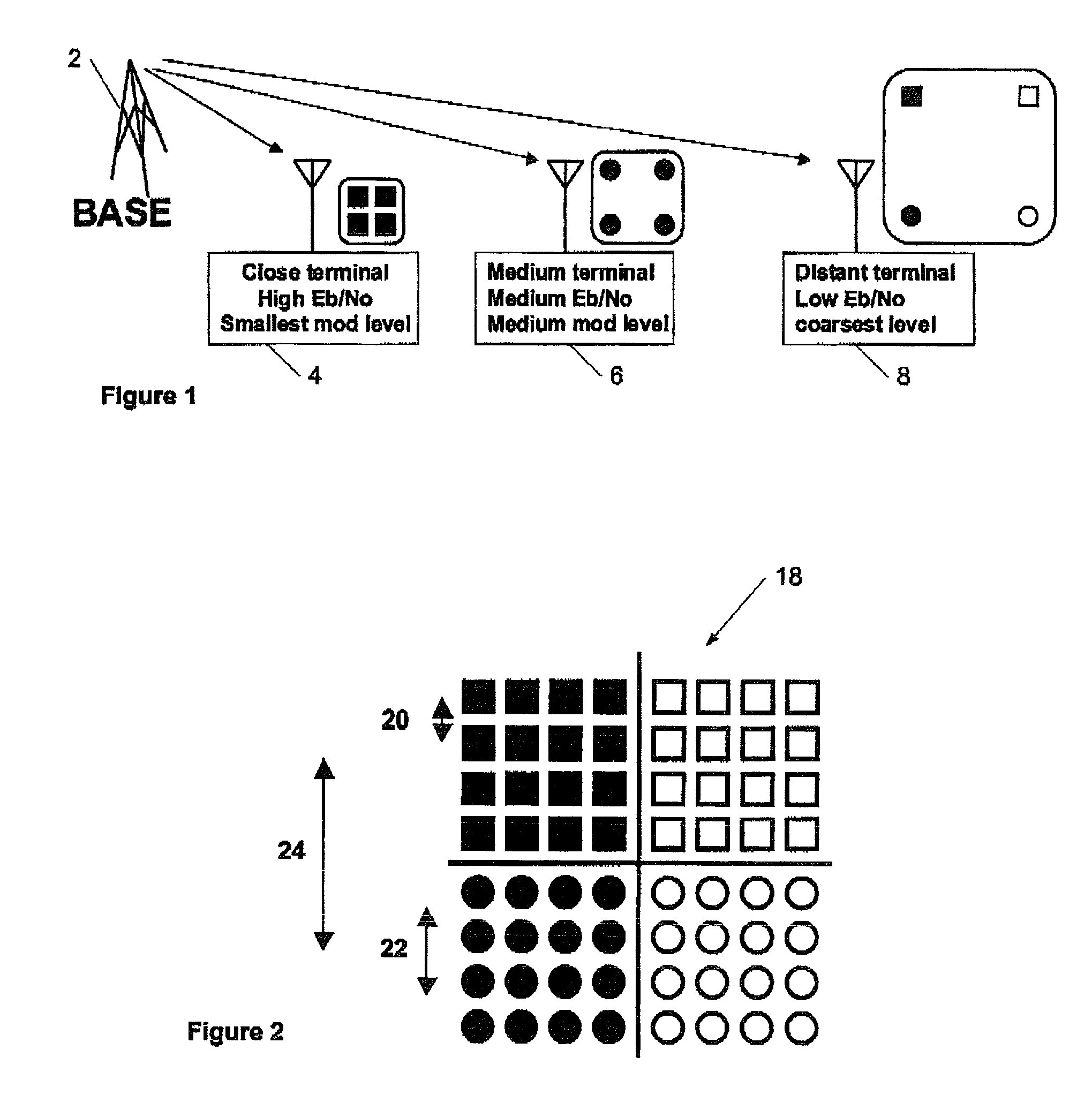
It is becoming increasingly important to improve data throughput in wireless networks. By transmitting data simultaneously at different modulation amplitudes and / or using different code strengths, terminals having different carrier to noise ratios are able to decode the different amplitude levels with varying degrees of success. This allows distant terminals to receive low data rate transmissions at high modulation levels or code rates while nearer terminals can use additional capacity in the transmission by receiving lower level modulation signals or code rates. In this way, distant terminals do not degrade overall network performance. By arranging for terminals to acknowledge receipt of data, retransmission at different modulation levels or code rates may be carried out by the base station in order to improve performance in the presence of noise without a priori knowledge of the carrier to noise ratio for a particular terminal.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
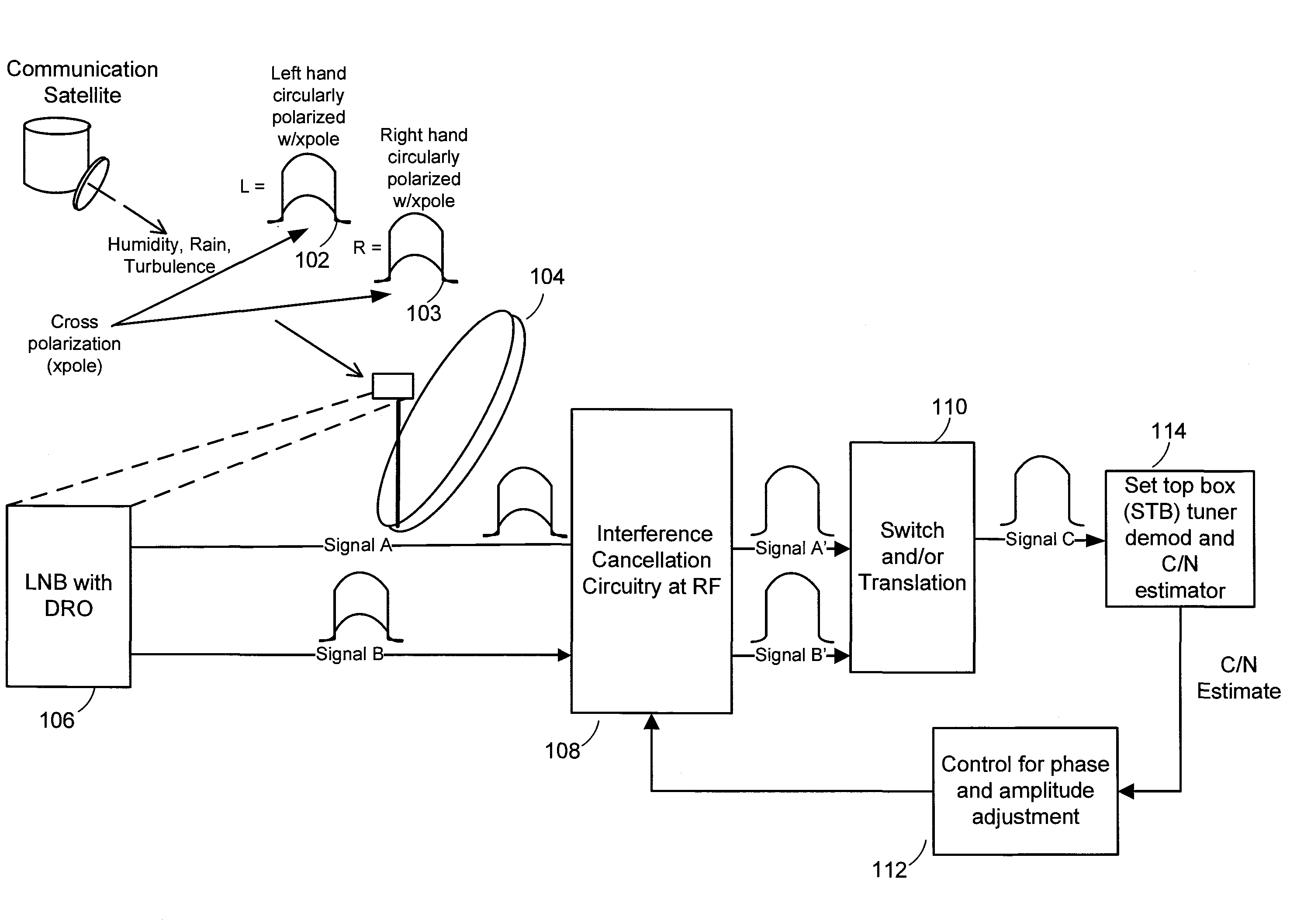
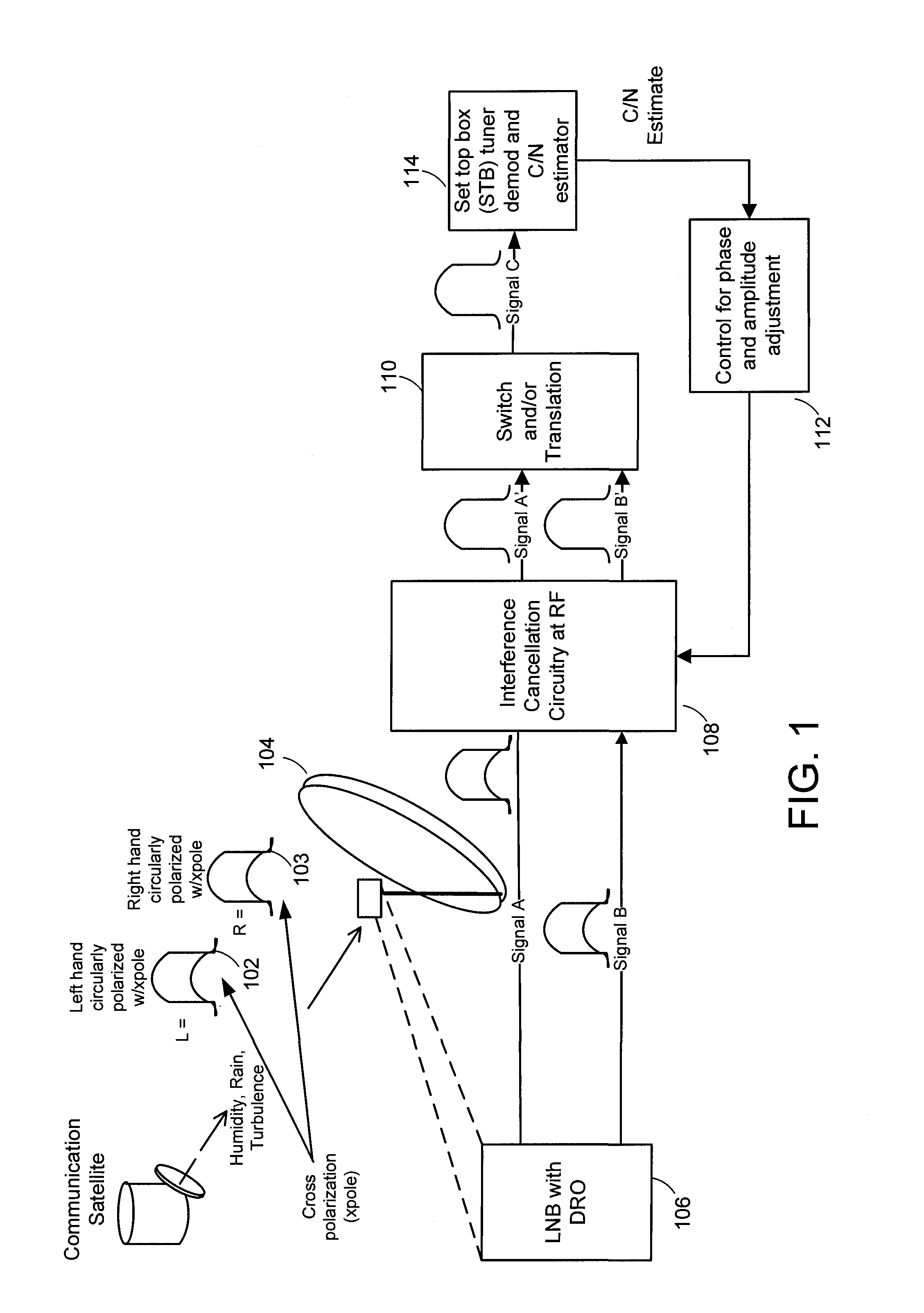
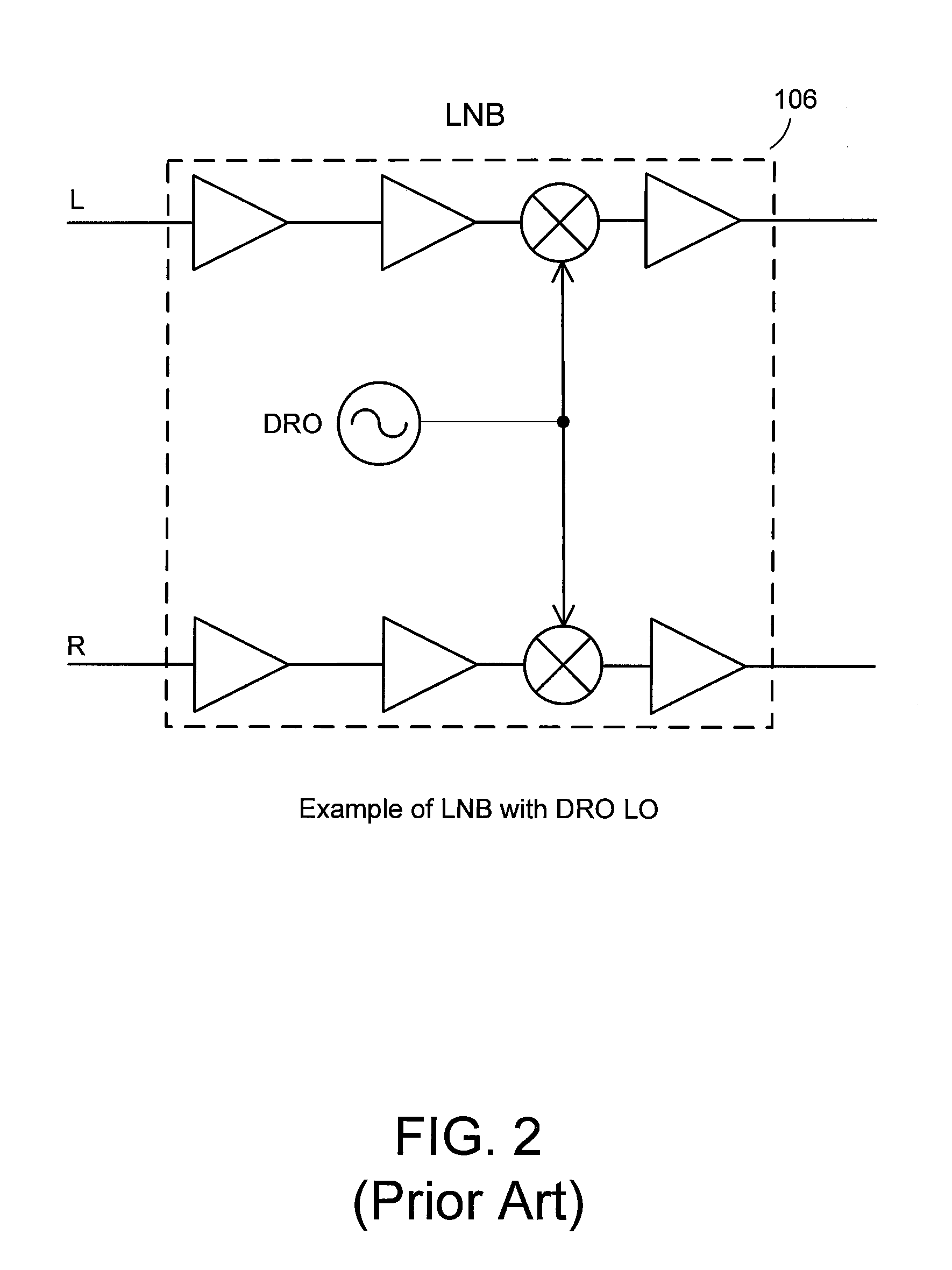
Satellite interference canceling
InactiveUS20090102706A1Interference cancellationMaximize cancellationTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionInterference eliminationEngineering
A satellite interference canceling system cancels the interference between two or more signals received by a satellite receiver. The signals can be two signals experiencing cross polarization interference or signals that experience interference from other satellite signals. Gain and phase are applied to the received signals and then combined with the other signals to result in cancellation by subtraction. The gain and phase values needed to cancel the interference are derived from measurements of carrier-to-noise ratio (C / N) as an indication of the interference level. The C / N can be measured in the set-top box indoor unit. Coherency restoration is performed in receivers that downconvert the signals before performing interference cancellation.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Recording medium having super-resolution near-field structure and method and apparatus for reproducing the same
InactiveUS20050009260A1Improve carrier-to-noise ratioMaterial nanotechnologyInformation arrangementNanoparticleOptoelectronics
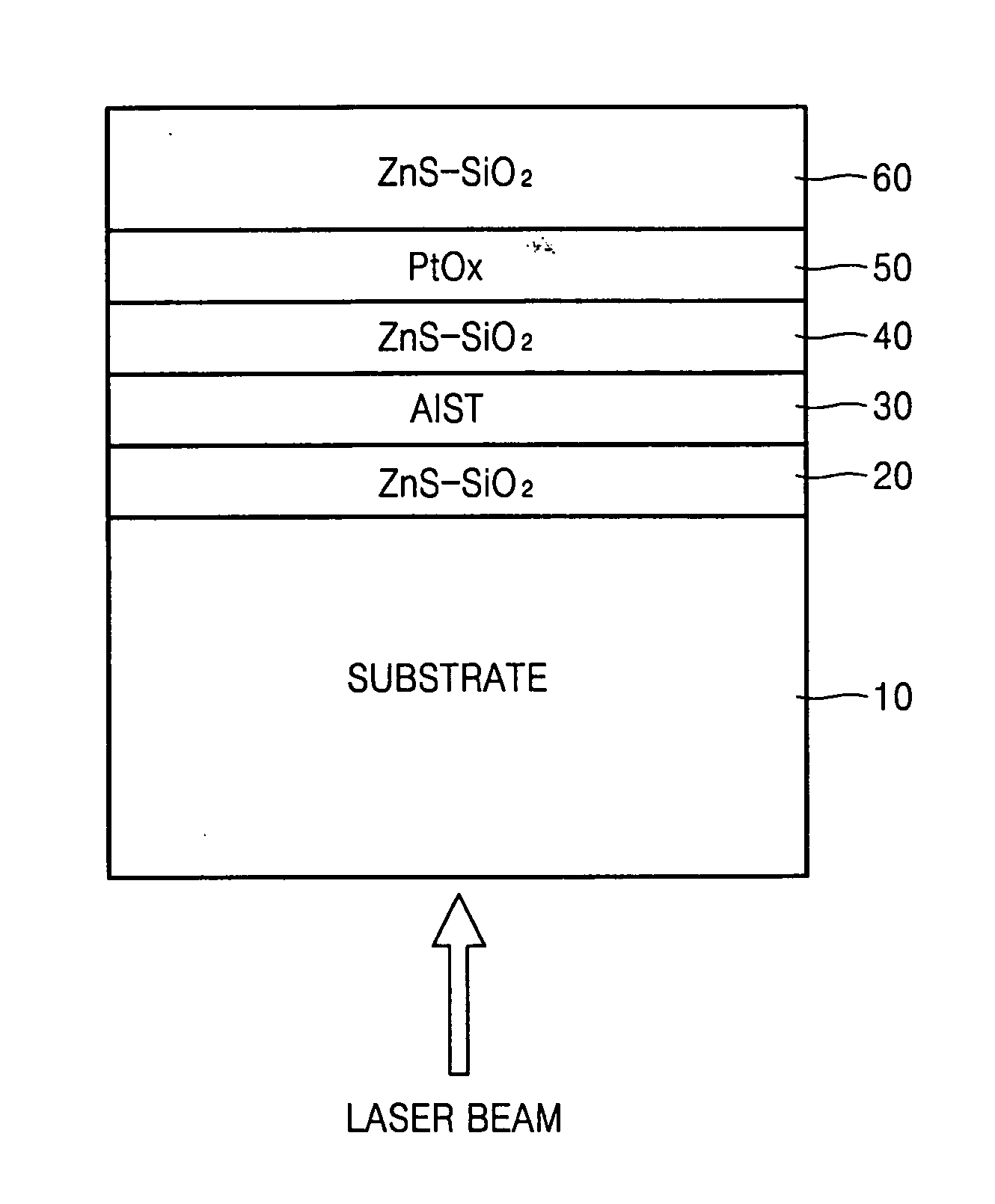
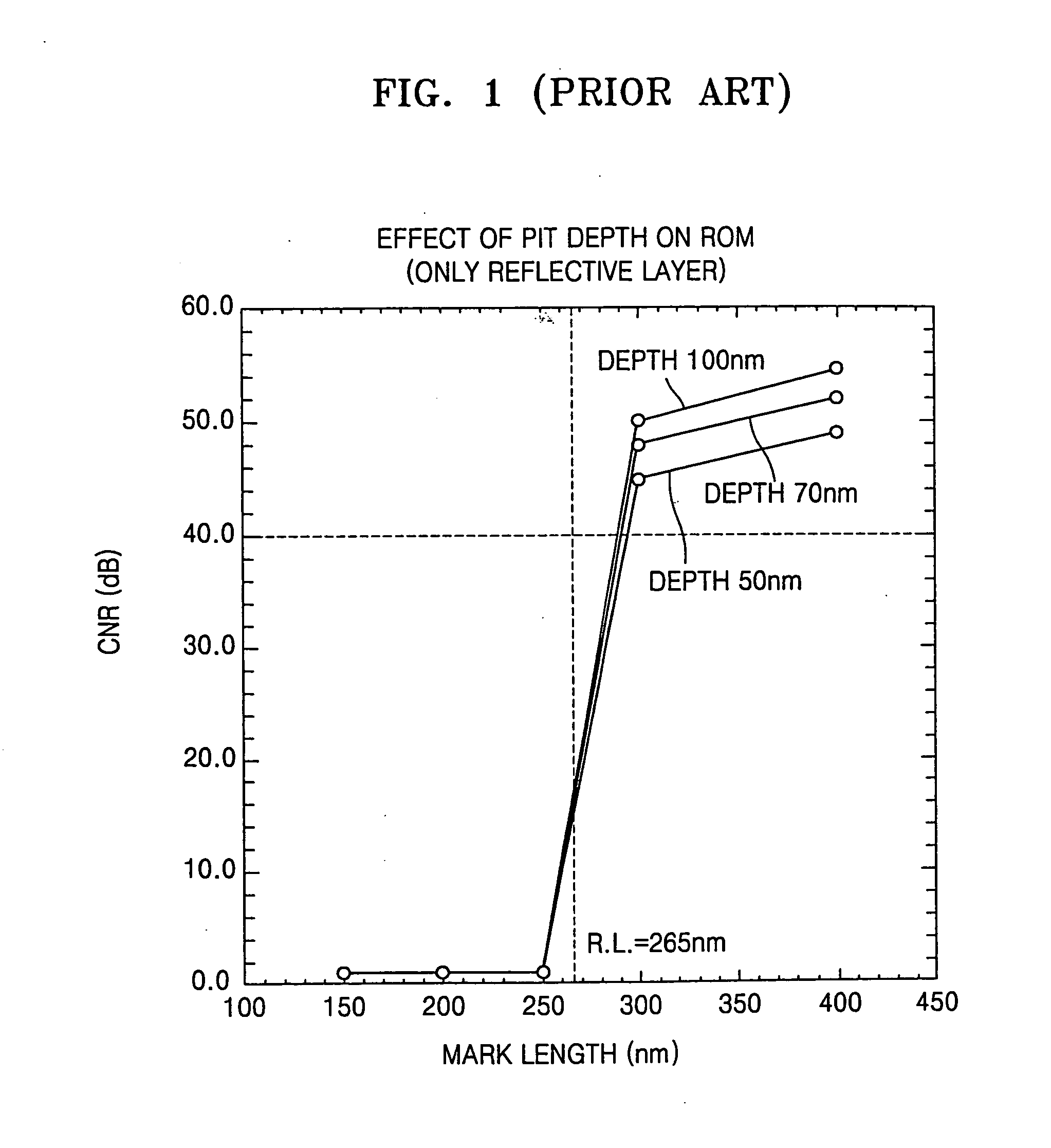
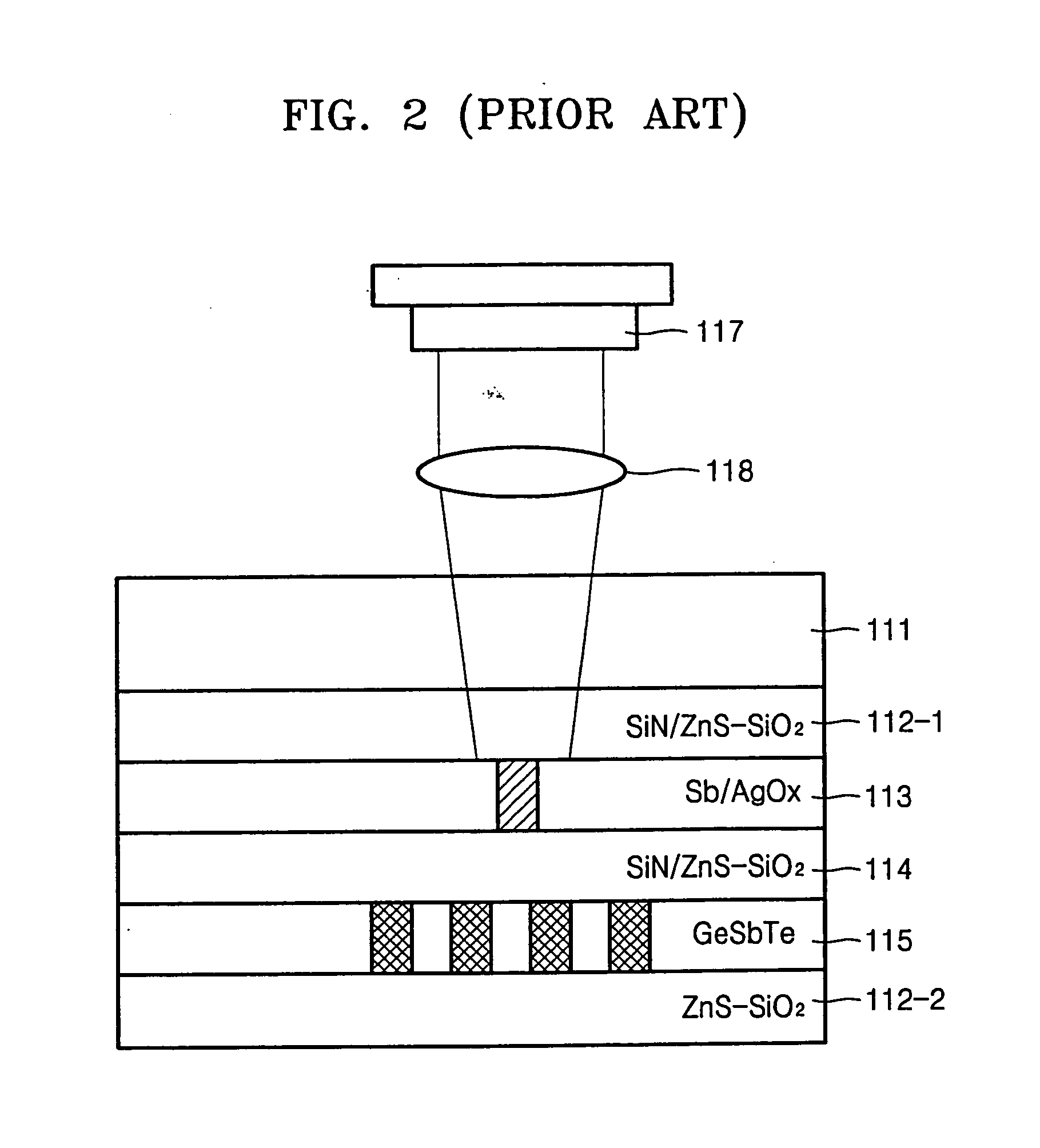
A read-only recording medium for achieving a carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR) using a super-resolution near-field structure (Super-RENS) on which information has been prerecorded includes a substrate having the information recorded on its surface, a reflective layer formed from a phase change material on the substrate, a first dielectric layer formed on the reflective layer, and a mask layer formed from metal oxide or nanoparticles on the first dielectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Optical modulating transmission method and system
InactiveCN1581756AImprove bit error rate performance indicatorsOvercoming Carrier-to-Noise Ratio LimitationsWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Data signal
The method includes following steps: first, at sending end, processing of transform with physical character is carried out for data signal including original information of pilot tone modulation so as to generate signal of pilot tone modulation, then transmission is carried out; at receiving end, original signal of pilot tone modulation is recovered after processing of transform is carried out at receiving end in physical character opposite to sending end. The system includes information destination unit, modulation unit, spread spectrum unit, electro-optical conversion unit, optical fiber, optical-electro conversion unit, signal extraction unit, de-spread unit, and demodulation unit. The invention raises performance of error rate overcomes restriction of carrier-to-noise ratio. Thus, signal of pilot tone modulation can be recovered under bad SNR.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
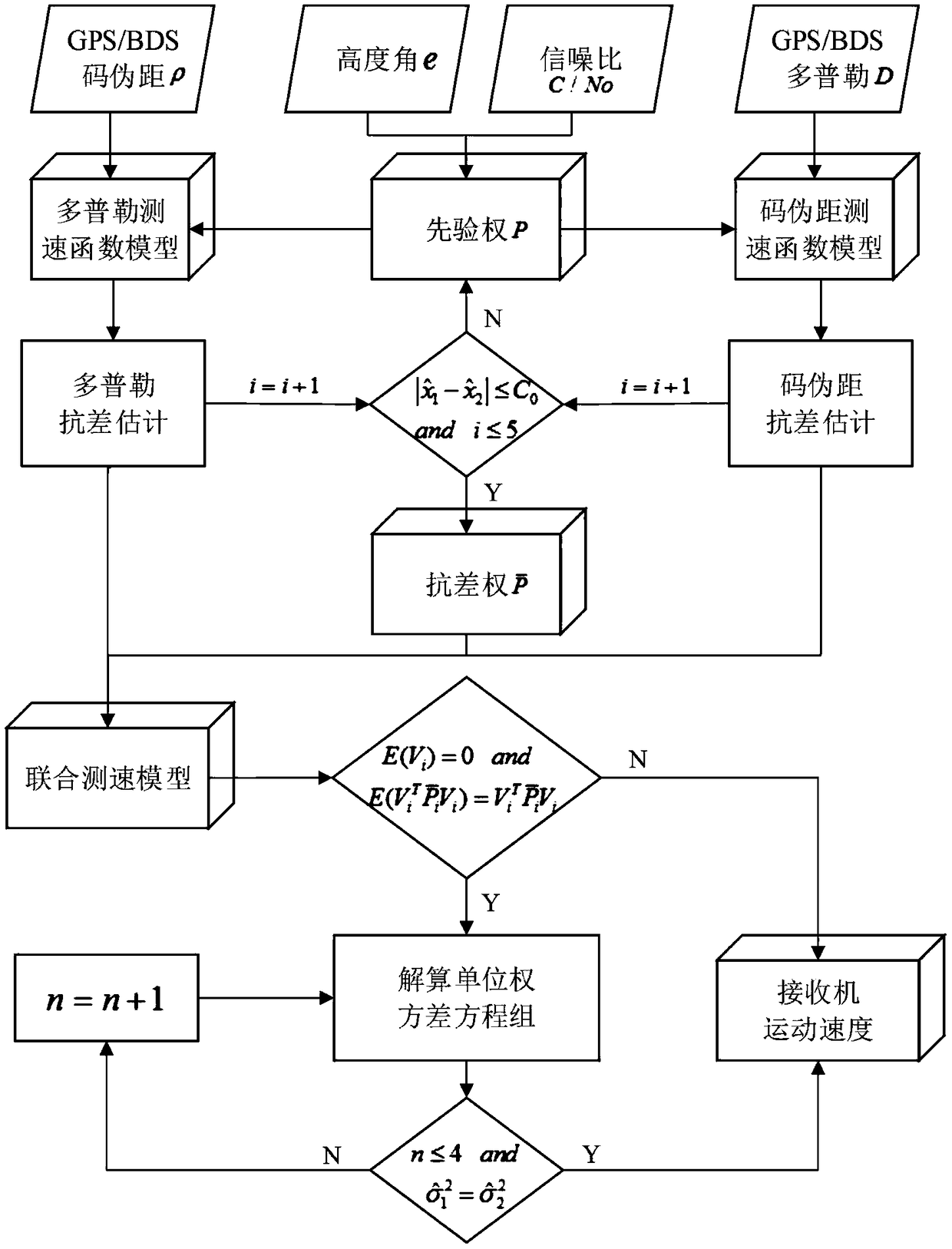
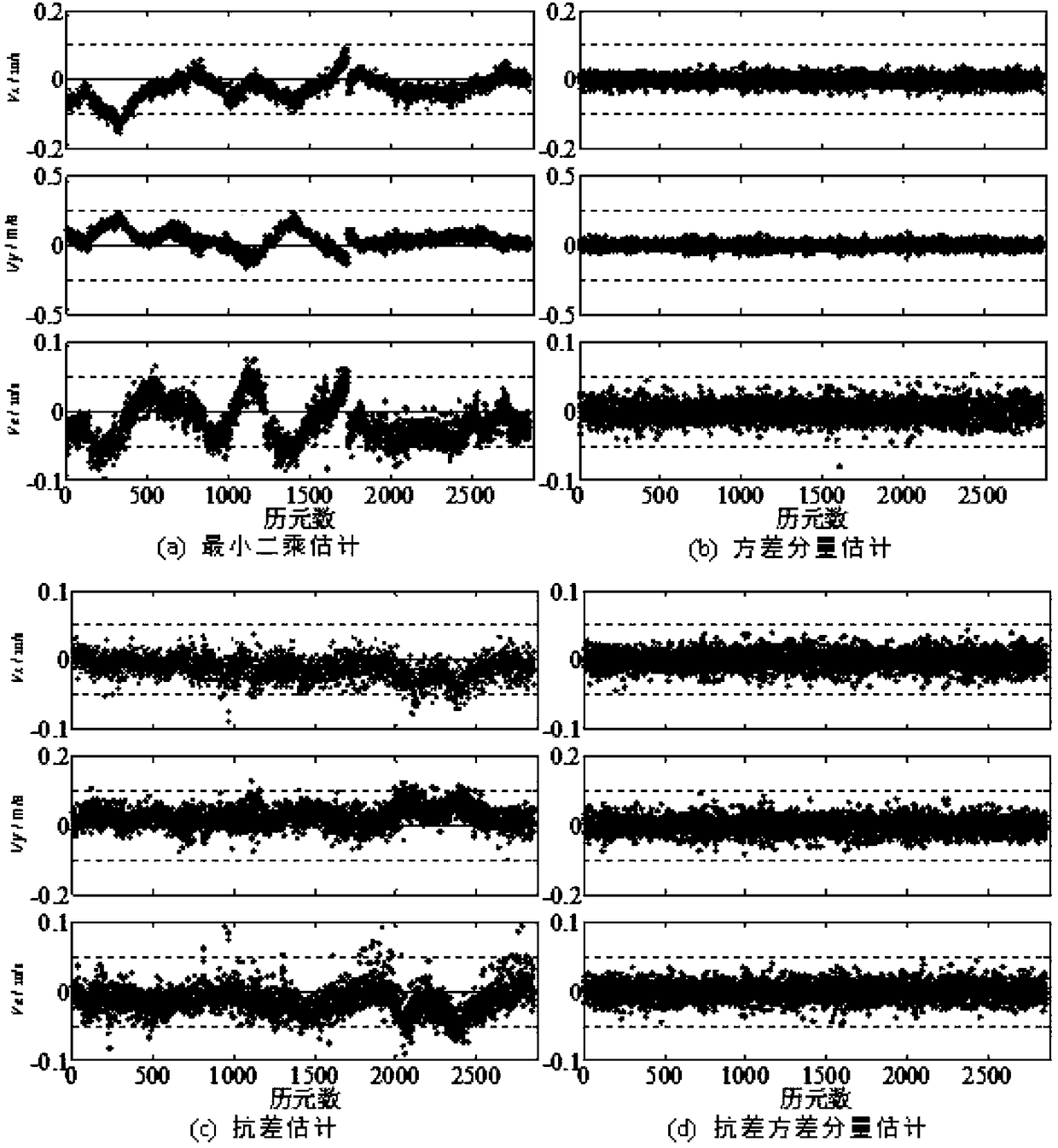
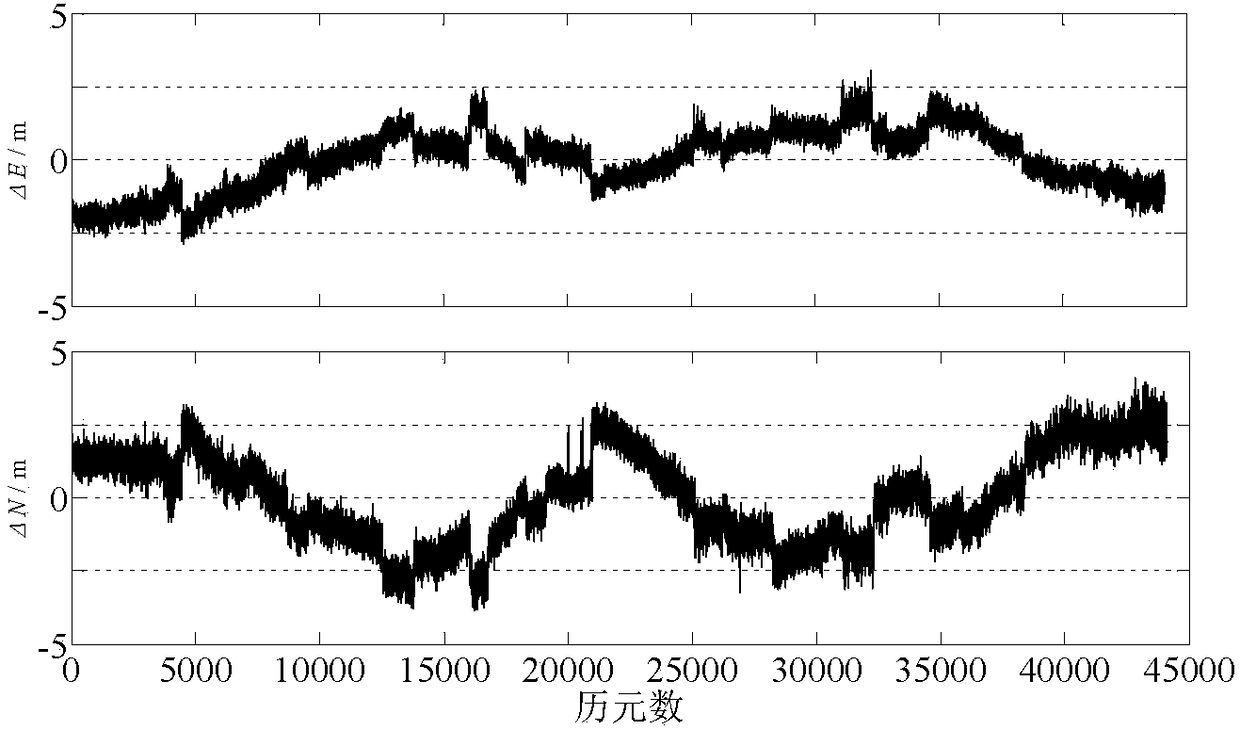
Code pseudo-range/Doppler combined speed measurement method based on robust variance assembly estimation and application thereof
ActiveCN109459778AImprove robustnessImprove stabilitySatellite radio beaconingEstimation methodsLeast squares
The invention discloses a code pseudo-range / Doppler combined speed measurement method based on robust variance assembly estimation, which comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively establishing a speed measurement function model and a random model by adopting observation information such as code pseudo-range, Doppler, carrier-to-noise ratio, satellite altitude angle and the like, then adopting a least square robust estimation method to obtain a robust random model capable of inhibiting the influence of gross error, and finally combining a speed measurement function model of code pseudo-range and Doppler with the robust random model to form a combined speed measurement model. According to the method, the limitation that the conventional single-frequency satellite receiver only uses single information to measure the speed can be broken through, the influence of observation gross error can be inhibited, and the robustness, the unbiased property and the stability of the combinedspeed measurement method can be obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for fundamental frequency extraction or detection in speech
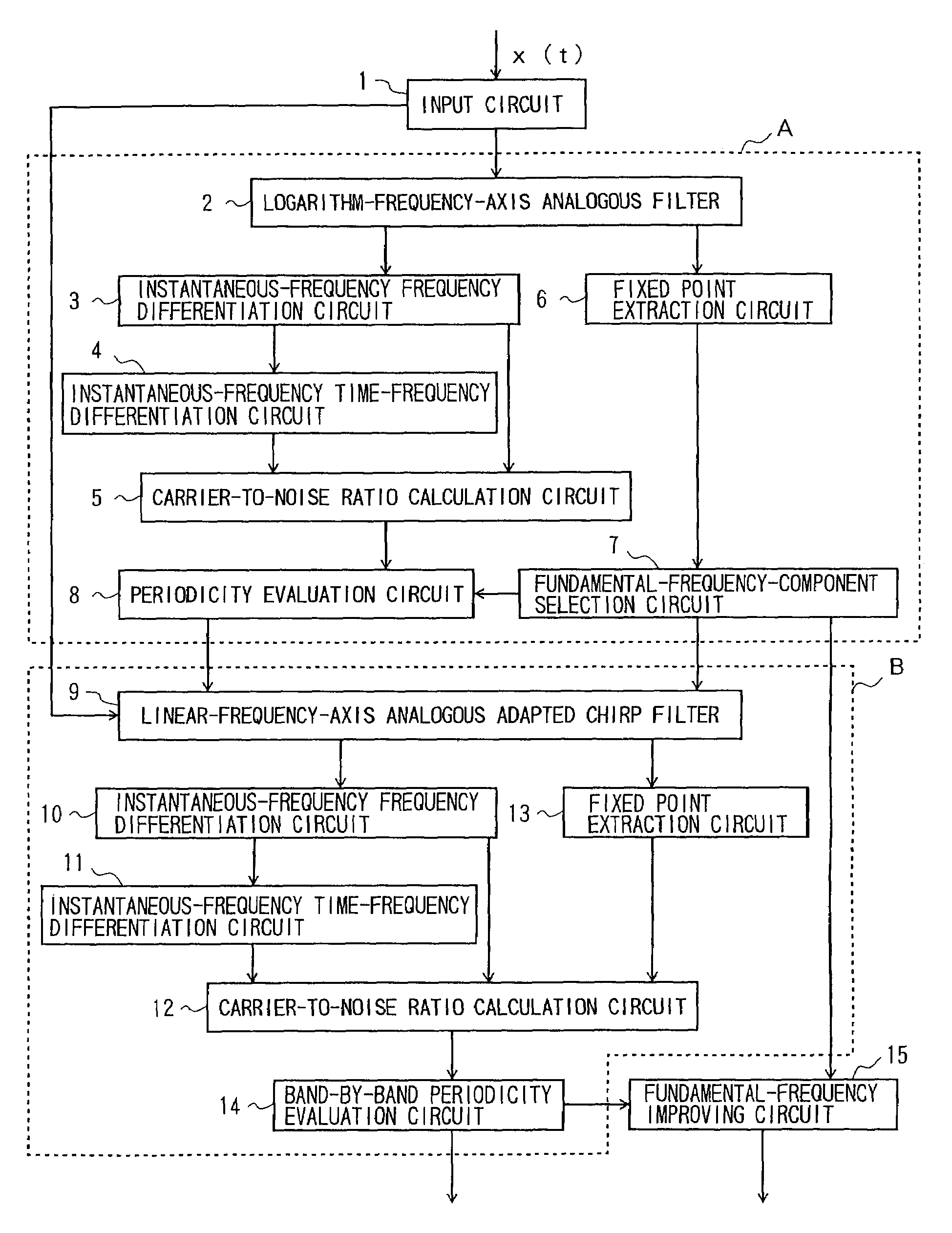
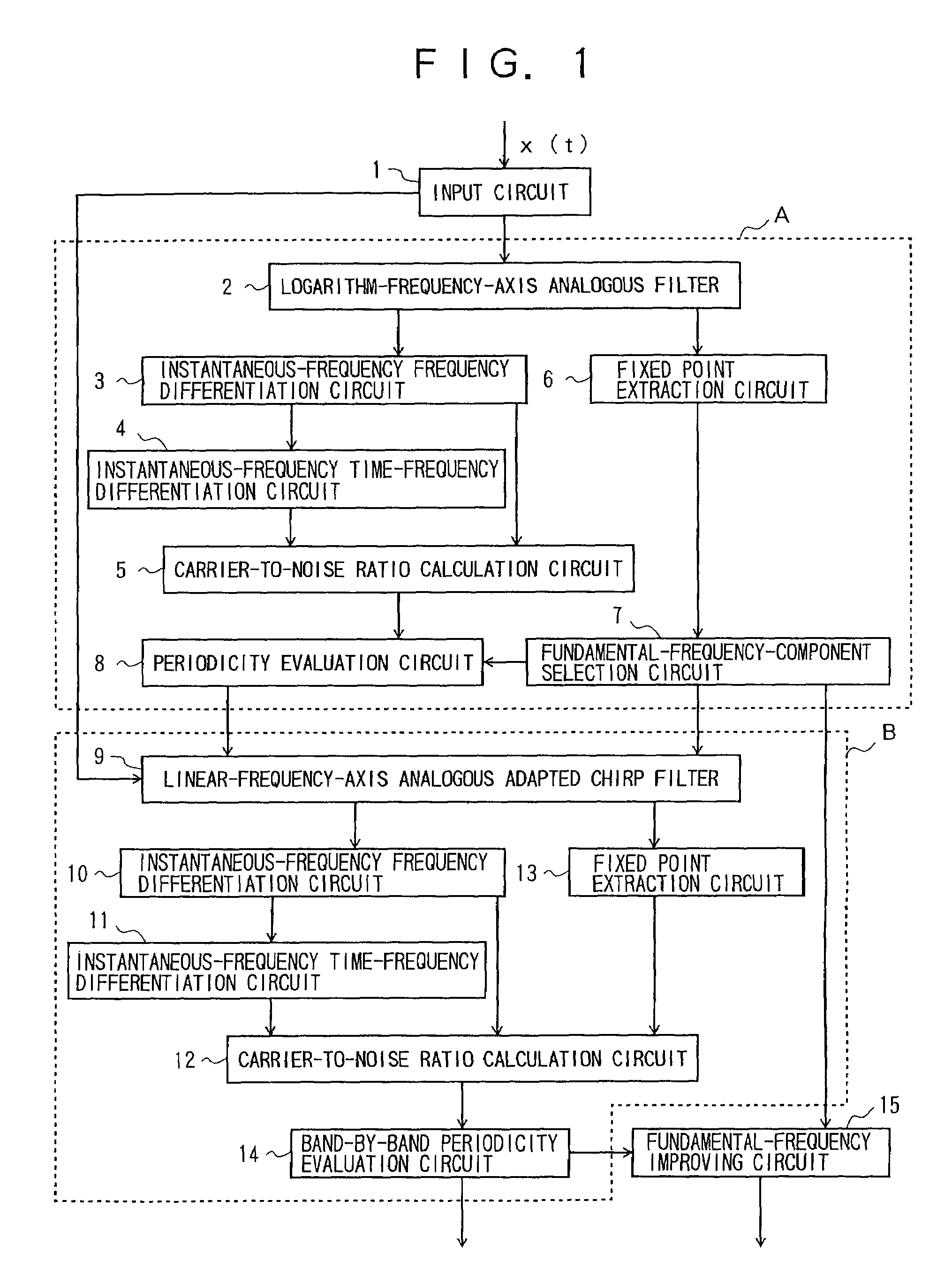
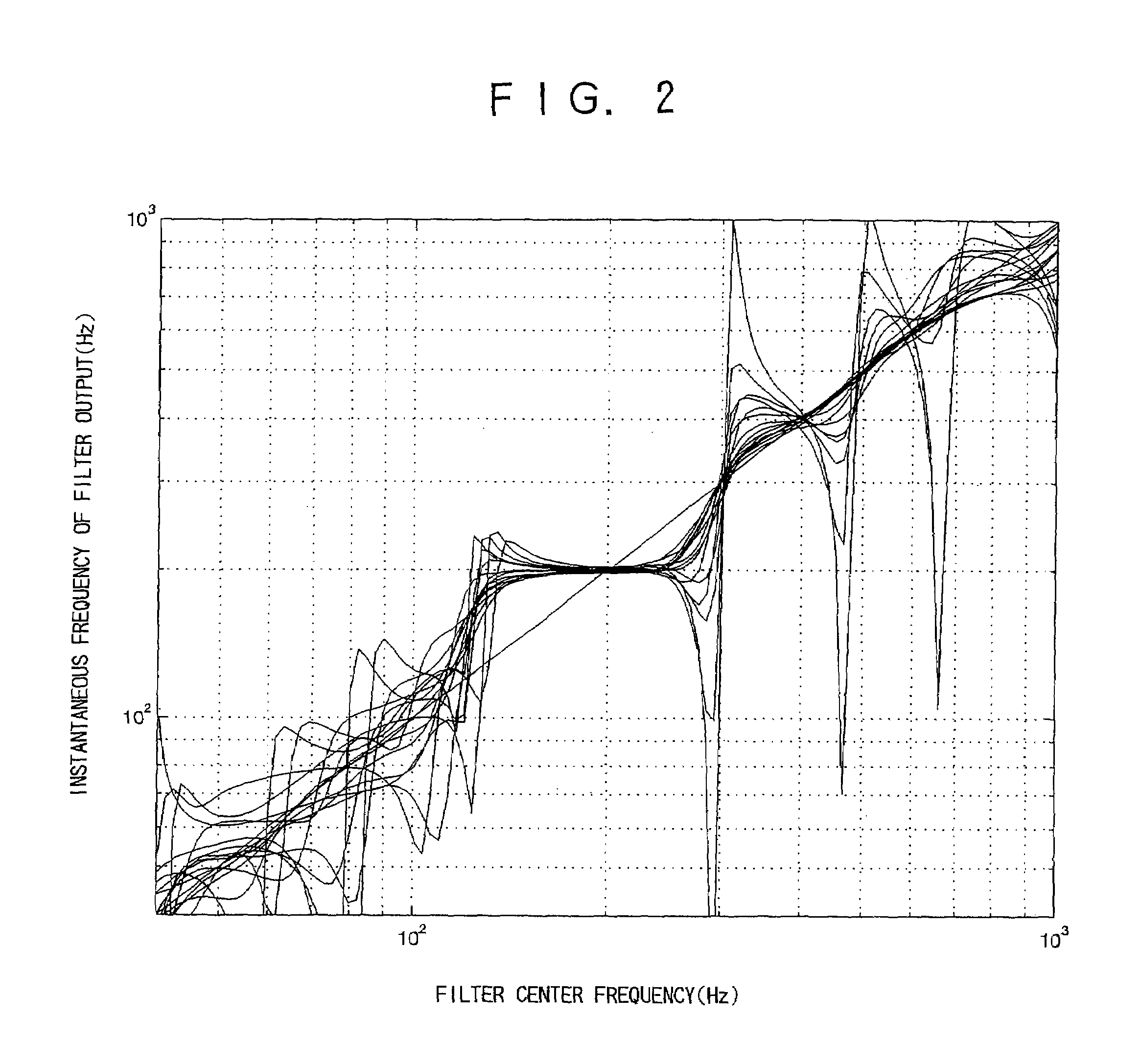
An object is to provide a method of extracting sound-source information, which method enables the characteristics of fixed points of mapping from filter center frequency to output instantaneous frequency to be detected from instantaneous data, as a value which can be interpreted quantitatively. In a method of extracting sound-source information by use of fixed points of mapping from frequency to instantaneous frequency, instantaneous frequency of each filter (2), (9) is partial-differentiated with respect to frequency by an instantaneous-frequency frequency differentiation circuit (3), (10) to thereby obtain a first value; output of each filter is partial-differentiated with respect to frequency and then with respect to time by an instantaneous-frequency time-frequency differentiation circuit (4), (11) to thereby obtain a second value; and proper weights are imparted to the first and second values and short-time weighted integration with respect to time is performed by a carrier-to-noise-ratio calculation circuit (5), (12) to estimate a carrier-to-noise ratio of each filter. Thus, a carrier-to-noise ratio is obtained, and an estimated value of evaluation value is obtained.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Transmitter with means for complementarily scaling the input and output signals of a D/A converter
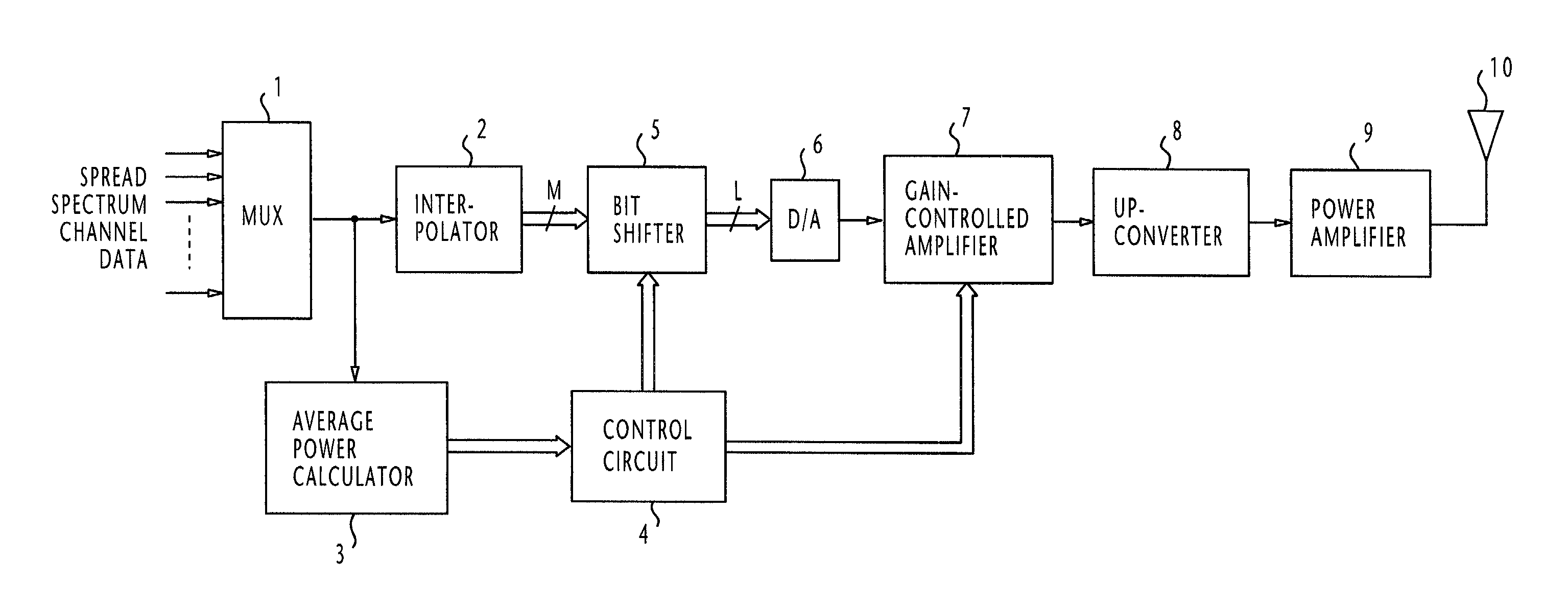
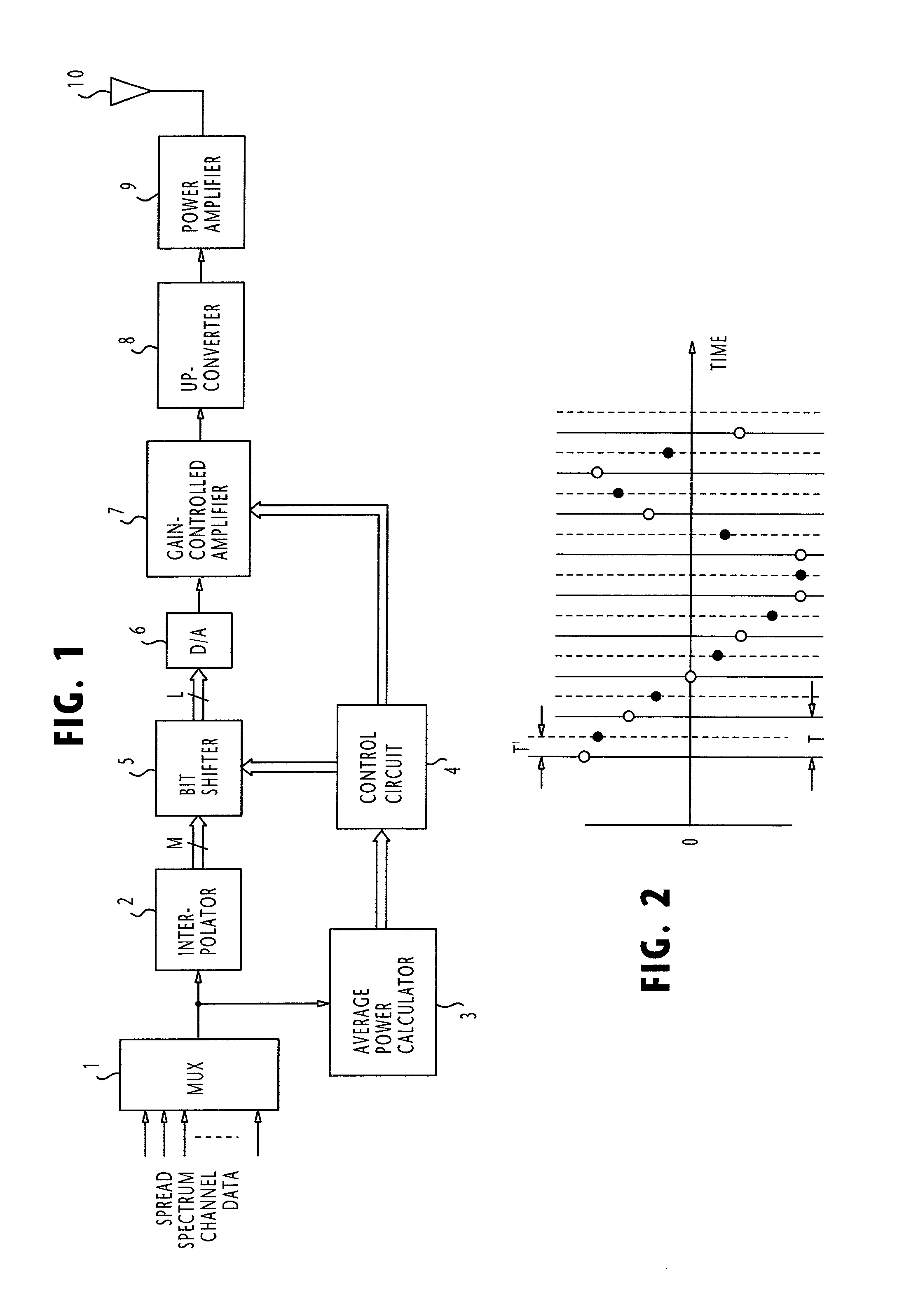
InactiveUS7027482B1Increase signal ratioRaise the ratioAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringSignal multiplexing
In a spread spectrum transmitter, a number of spread spectrum channel signals are multiplexed into a digital amplitude signal by a multiplexer, and the time-average power of the digital amplitude signal is determined by an average calculator. The digital amplitude signal is interpolated by an interpolator, scaled according to a first scale factor by a bit shifter and converted to an analog amplitude signal by a D / A converter. The analog amplitude signal is then scaled according to a second scale factor in a gain controlled amplifier. The first and second scale factors are complementarily varied by a control circuit according to the output of the average calculator so that the carrier-to-noise ratio of the transmitter is maintained substantially constant regardless of the varying power level of the multiplexed signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Satellite capturing method and device
ActiveCN103529458AReduced capture rangeImprove capture speedSatellite radio beaconingElevation angleUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a satellite capturing method and a satellite capturing device and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation. The satellite capturing method comprises the steps that multiple first satellites are obtained according to a satellite almanac and the current time; the angles of elevations of the multiple first satellites are calculated according to the satellite almanac, the current time and the coordinate positions of the equipment; satellites with the angles of elevations greater than the threshold are obtained from the multiple first satellites according to the angles of elevations of the multiple first satellites, and multiple second satellites are obtained; satellites with the angles of elevations in accordance with a preset elevation angle rule and positioning accuracy in accordance with the preset accuracy rule are obtained from the multiple second satellites according to the angles of elevations, the satellite azimuth angles and the satellite effective carrier-to-noise ratio attenuation of the multiple second satellites, and multiple third satellites are obtained; the multiple third satellites are captured. According to the satellite capturing method and the satellite capturing device, on the basis of optimum satellites, the search satellites are further optimized according to the preset elevation angle rule and the preset accuracy rule, so that the satellite capturing range is further shortened, and the satellite capturing speed is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Methods and apparatus for transmitting and receiving data over a communications network in the presence of noise
InactiveUS20030118123A1High rate dataReduce noiseError prevention/detection by using return channelAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLow data rateData rate
It is becoming increasingly important to improve data throughput in wireless networks. By transmitting data simultaneously at different modulation amplitudes and / or using different code strengths, terminals having different carrier to noise ratios are able to decode the different amplitude levels with varying degrees of success. This allows distant terminals to receive low data rate transmissions at high modulation levels or code rates while nearer terminals can use additional capacity in the transmission by receiving lower level modulation signals or code rates. In this way, distant terminals do not degrade overall network performance. By arranging for terminals to acknowledge receipt of data, re-transmission at different modulation levels or code rates may be carried out by the base station in order to improve performance in the presence of noise without a priori knowledge of the carrier to noise ratio for a particular terminal.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
High precision GNSS receiver
InactiveCN101839971AHigh positioning accuracyMitigate the effects of multipath signalsBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationOriginal dataSatellite tracking
The invention relates to a high precision GNSS receiver, which comprises a levorotatory and dextrorotary circular polarization antenna, a first radio frequency front end module and a second radio frequency front end module with a local clock, a signal following module and a CPU. The signal following module comprises a satellite capturing unit, a first satellite following unit, a second satellite following unit and an interface unit. A capturing control module, a text demodulation module, two loop following modules, two initial data measuring modules, an availability choosing module, a position resolving module and an interface protocol module are arranged in the CPU. The availability choosing module obtains the pseudo range and the carrier-to-noise ratio data of levorotatory signals and dextrorotary signals, analyzes and chooses the weak initial data of multipath signals and transmits to the position resolving module for final position resolving. The invention compares and analyzes the levorotatory signals and the dextrorotary signals, alleviates the multipath influence on data source, ensures the GNSS receiver obtains high position precision, can improve the multipath influence alleviating effect based on the traditional multipath alleviating technology, has strong structural expansibility and can realize flexible framework configuration.
Owner:遵义市华颖监测技术有限公司
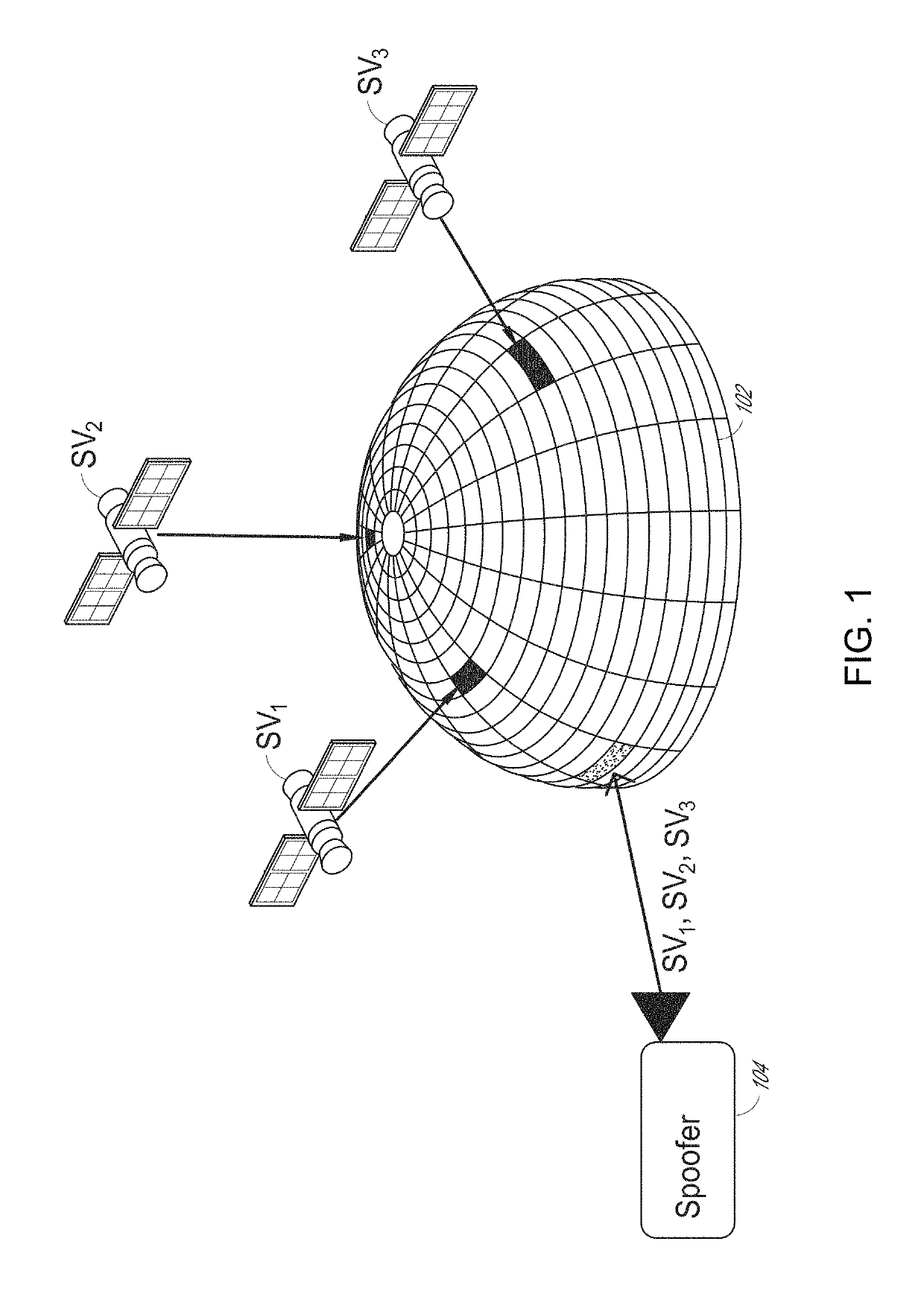
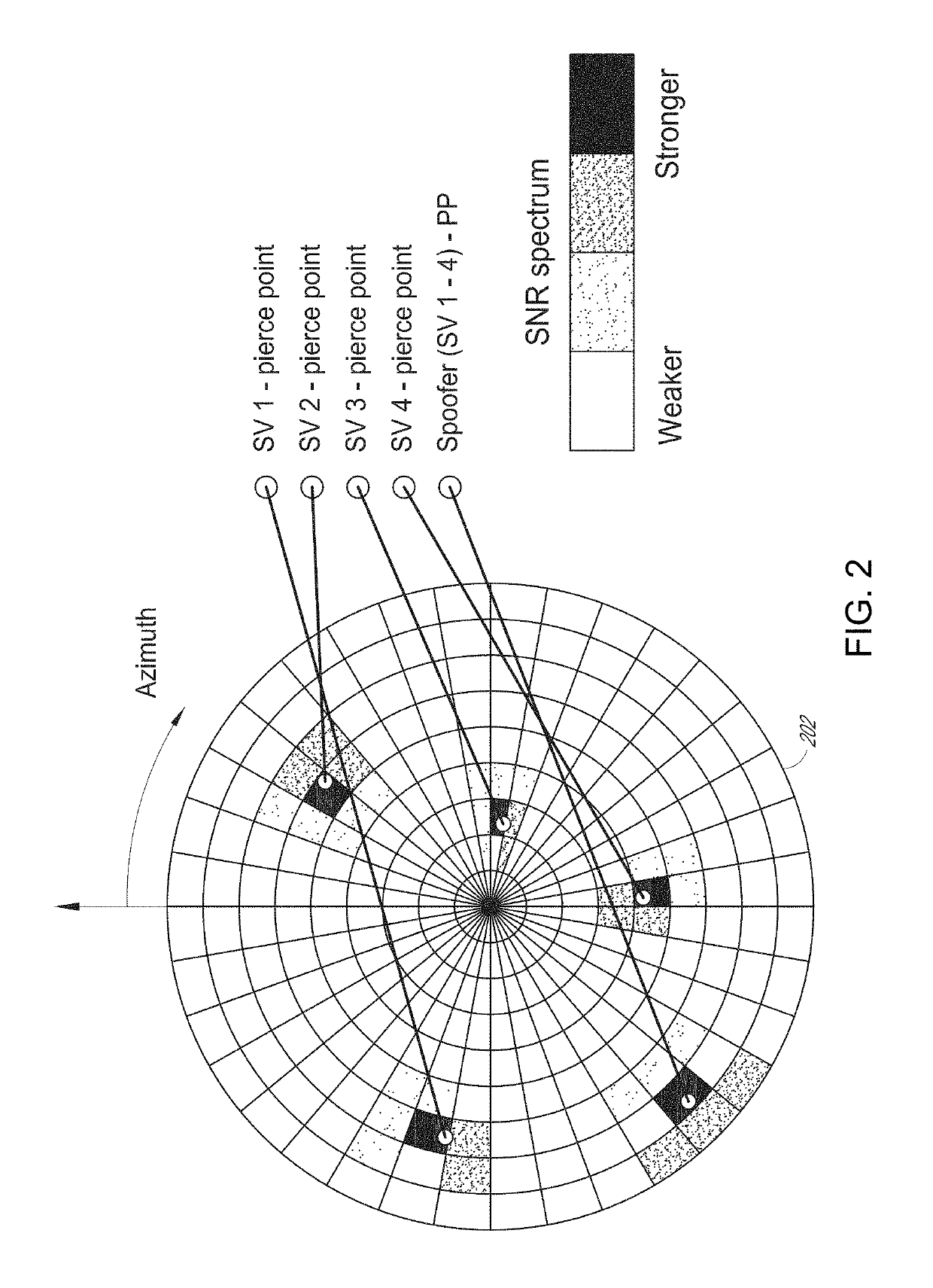
Global navigation satellite system spoofer identification technique based on carrier to noise ratio signatures
Disclosed is a technique that can provide one or more countermeasures against spoofers. A beamformer can control an antenna pattern of a CRPA to generate a survey beam. The survey beam is swept across space to determine a characteristic signature based on carrier-to-noise ratios (C / No) for particular space vehicle signals. Matching C / No signatures can be used to identify the existence of spoofers and invoke a countermeasure, such as nulling.
Owner:INTERSTATE ELECTRONICS
Broadband optical transmission system utilizing differential wavelength modulation
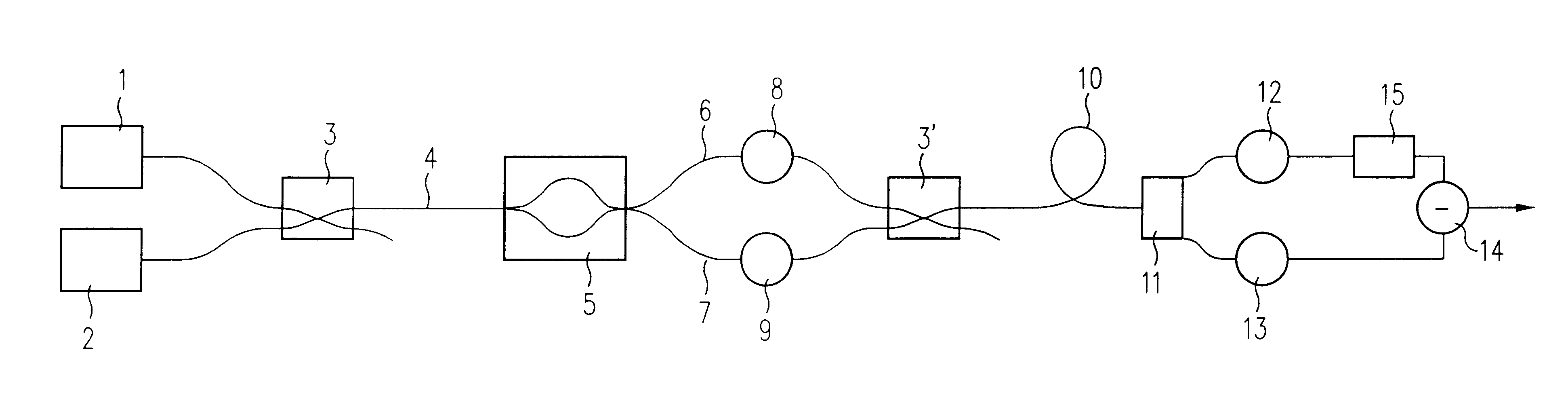
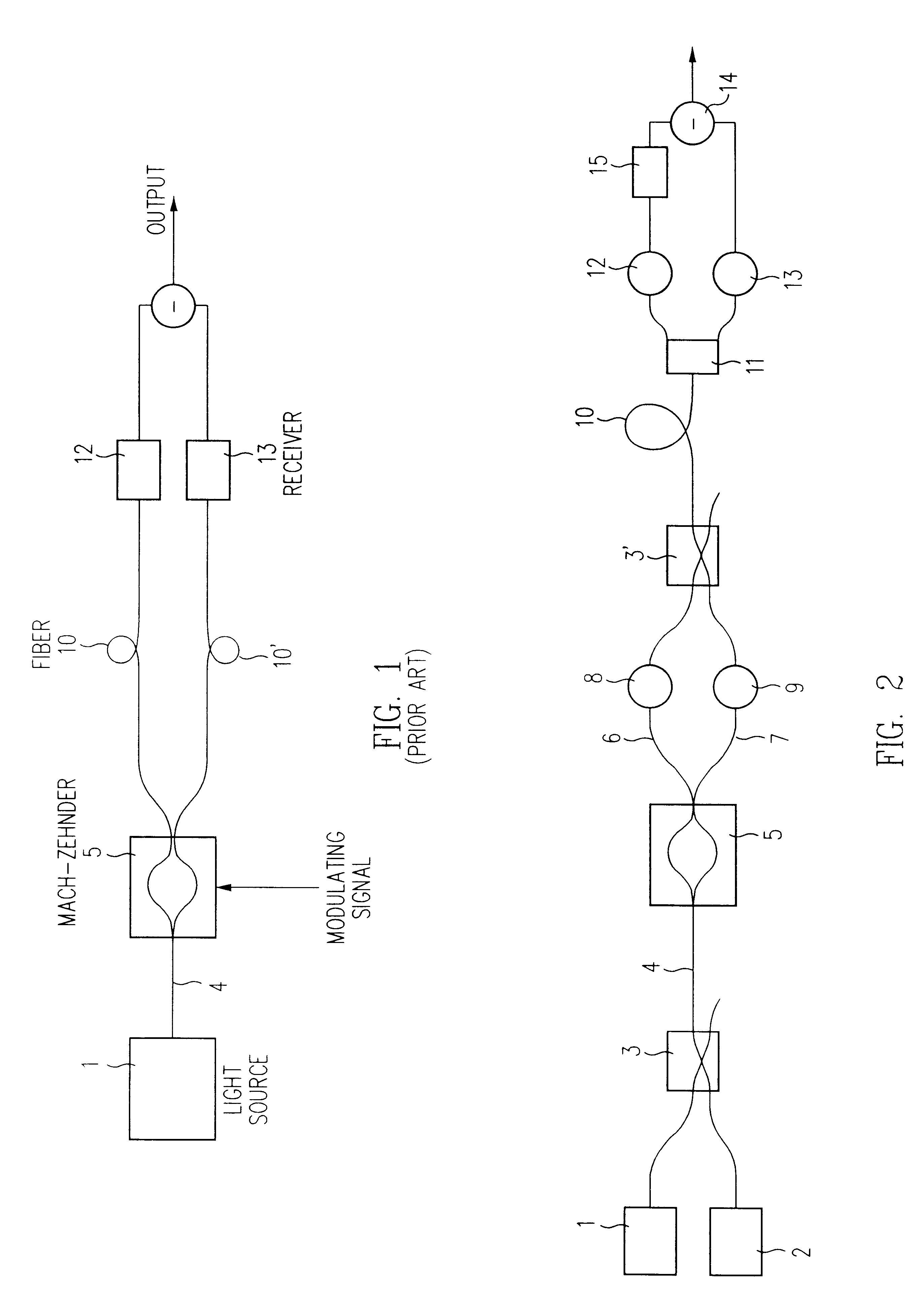
A differential method of improving the carrier to noise ratio of optically transmitted amplitude modulated signals without affecting the fidelity of the transmitted signals is disclosed. The disclosed method improves over prior art methods by utilizing a single transmission fiber transmitting two wavelengths that are modulated out of phase by a single Mach Zehnder type modulator. The received light is separated into two components at two wavelengths and each wavelength is received by a photodetector. The two photodetector outputs are differentially combined to produce an output with improved signal to noise ratio resulting in improved bit error rates in digital transmissions. The invention is also useful in fiber optic analog transmission systems such as those used to distribute AM-VSB Cable Television programming, wherein the differential method improves the carrier to noise ratio without increasing the nonlinear components in the signal.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Repeater deception type GPS (Global Position System) jamming system and jamming method thereof
InactiveCN104678406AImprove carrier-to-noise ratioOvercome the difficulty of solving the Y codeSatellite radio beaconingWireless transmissionDigital analog converter
The invention discloses a repeater deception type jamming system and a jamming method thereof. The repeater deception type jamming system comprises reconnaissance receivers, a digital analog converter, a frequency converter, a combiner, a power amplifier, a transmission system, a jammer delayer and a jamming transmitter, wherein the frequency converter comprises an up-converter and a down converter; the combiner comprises an upper combiner and a lower combiner; eight reconnaissance receivers are provided, and each reconnaissance receiver comprises a large-diameter reflector antenna and an automatic tracking system; the transmission system adopts a wire transmission mode or a wireless transmission mode; the jammer delayer is a fixed tapped delayer with a plurality of tap positions, and a delay array is composed by a CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) for each jammer delayer. The repeater deception type jamming system and the jamming method have the advantages that the jammer is small in interference emission size and light in weight, the large-diameter reflector antennas are adopted to obtain the high gain, the carrier to noise ratio of a GPS signal is improved, despreading is not needed, a sending part and a receiving part are insulated and connected by the transmission system, the insulation difficulty of the sending and the receiving is avoided, the remote transmission effect is also achieved, and a far effective jamming distance can be realized.
Owner:WUHU HANGFEI SCI & TECH
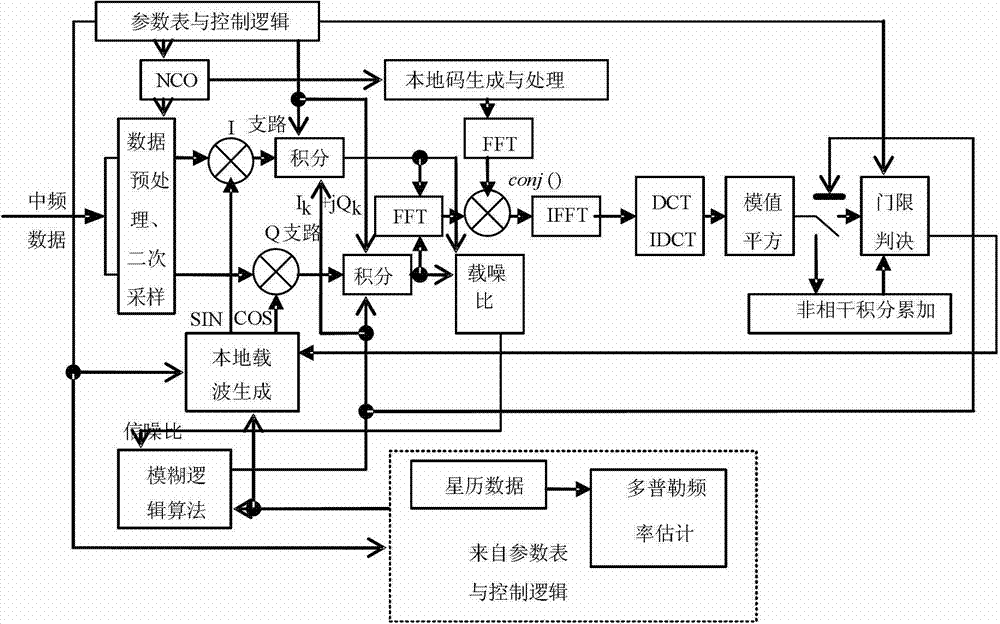
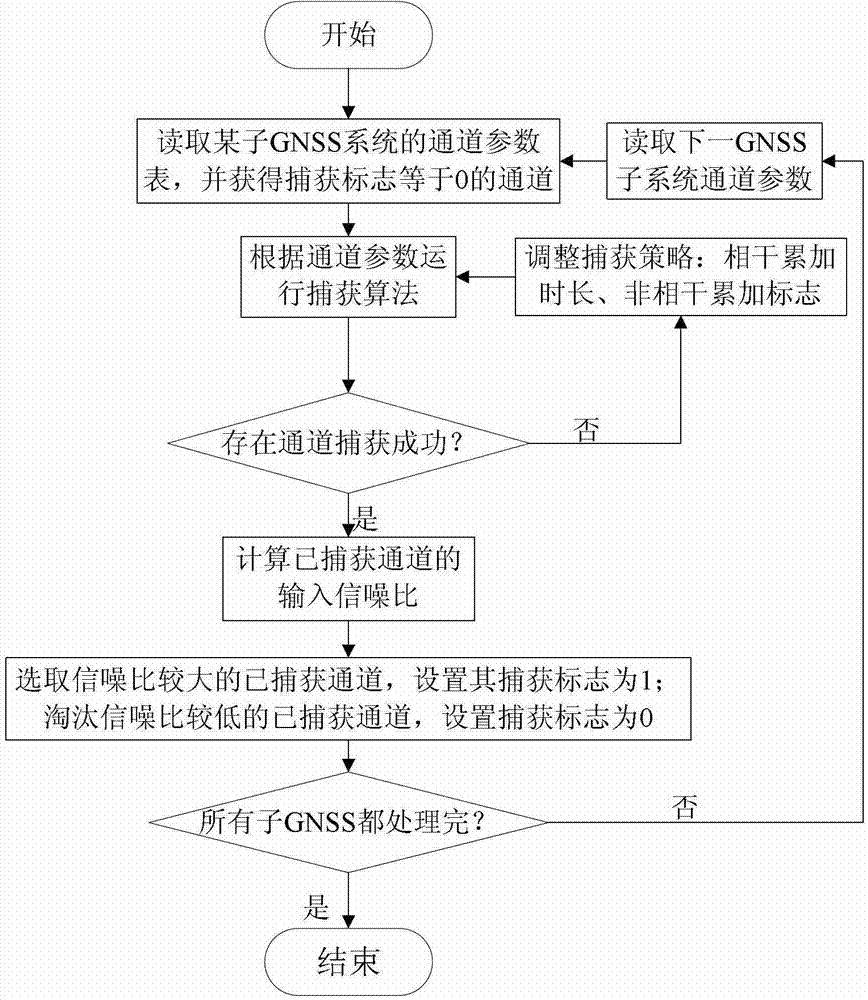
Compatibility capturing method of multi-mode GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) combination receiver
InactiveCN102890280AImprove adaptabilityImprove capture sensitivitySatellite radio beaconingIntermediate frequencyCoded element
The invention discloses a compatibility capturing method of a multi-mode GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) combination receiver. The capturing method comprises the following steps of: carrying out corresponding capture process on a satellite signal within coherent integration accumulation time and non-coherent integration accumulation time; adopting a fuzzy logic algorithm in the capture process, dynamically adjusting the coherent integration accumulation time and the non-coherent integration accumulation times according to a carrier-to-noise ratio and a carrier speed; and within the coherent integration accumulation time, carrying out the secondary sampling on a middle frequency signal of the acquired satellite signal, i.e. all data are decomposed into a plurality of groups, and the data points in each group are at one pseudo-random code element, and subsequently the Fourier transform, the Fourier inversion, the DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation), the IDCT (Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform), the mode value square and threshold judgment process are carried out. With the adoption of the capturing method, the defects that signals cannot be captured as an existing capturing method is low in sensitivity and likely to be interfered are overcome, and satellite signals can be captured normally when a GNSS signal is shielded and strong environment noise exists.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method and apparatus for laser performance enhancement
InactiveUS6181453B1Less average photo currentReduction in photo-current dependent noiseLaser detailsTransmission monitoringPretreatment methodPerformance enhancement
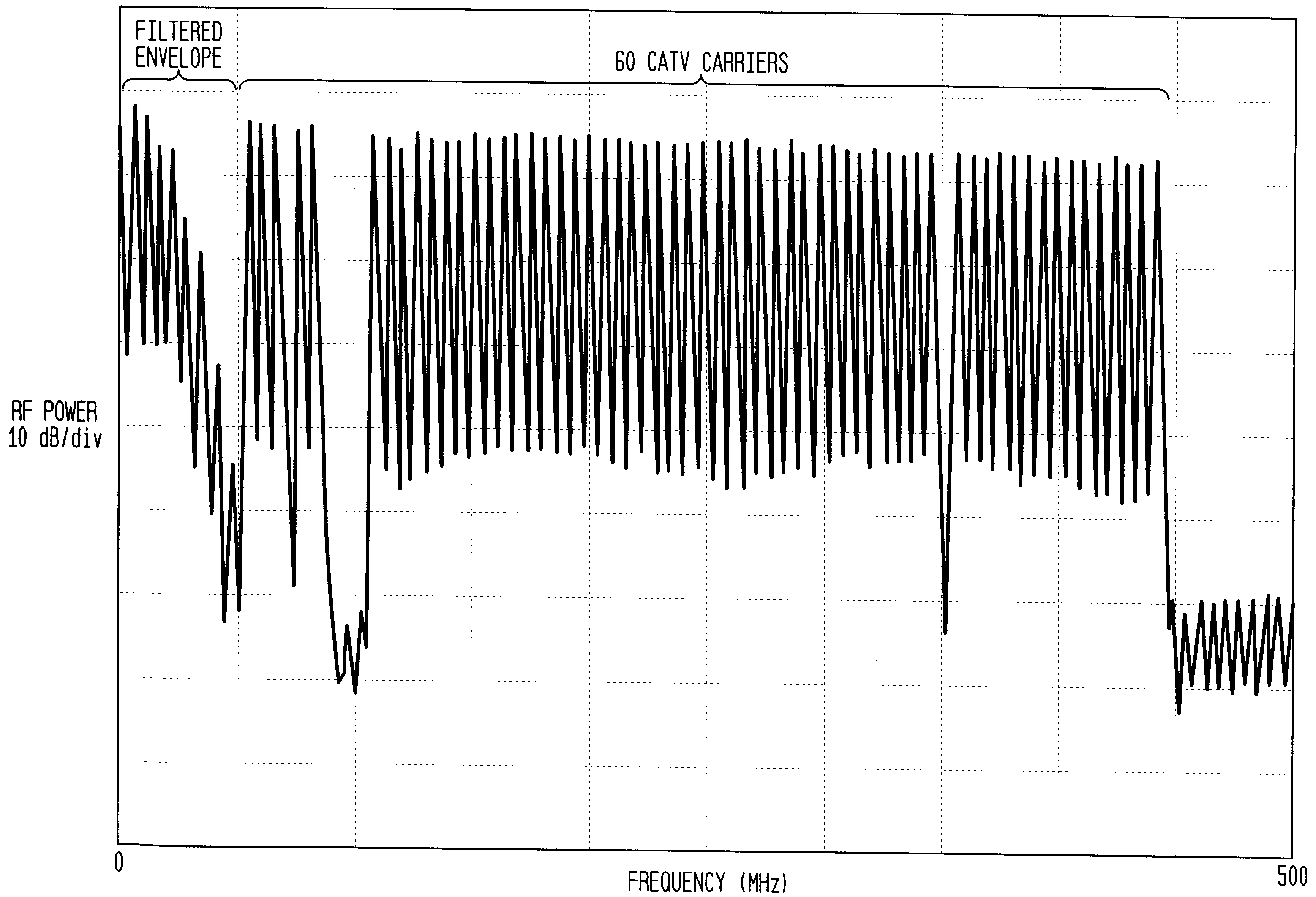
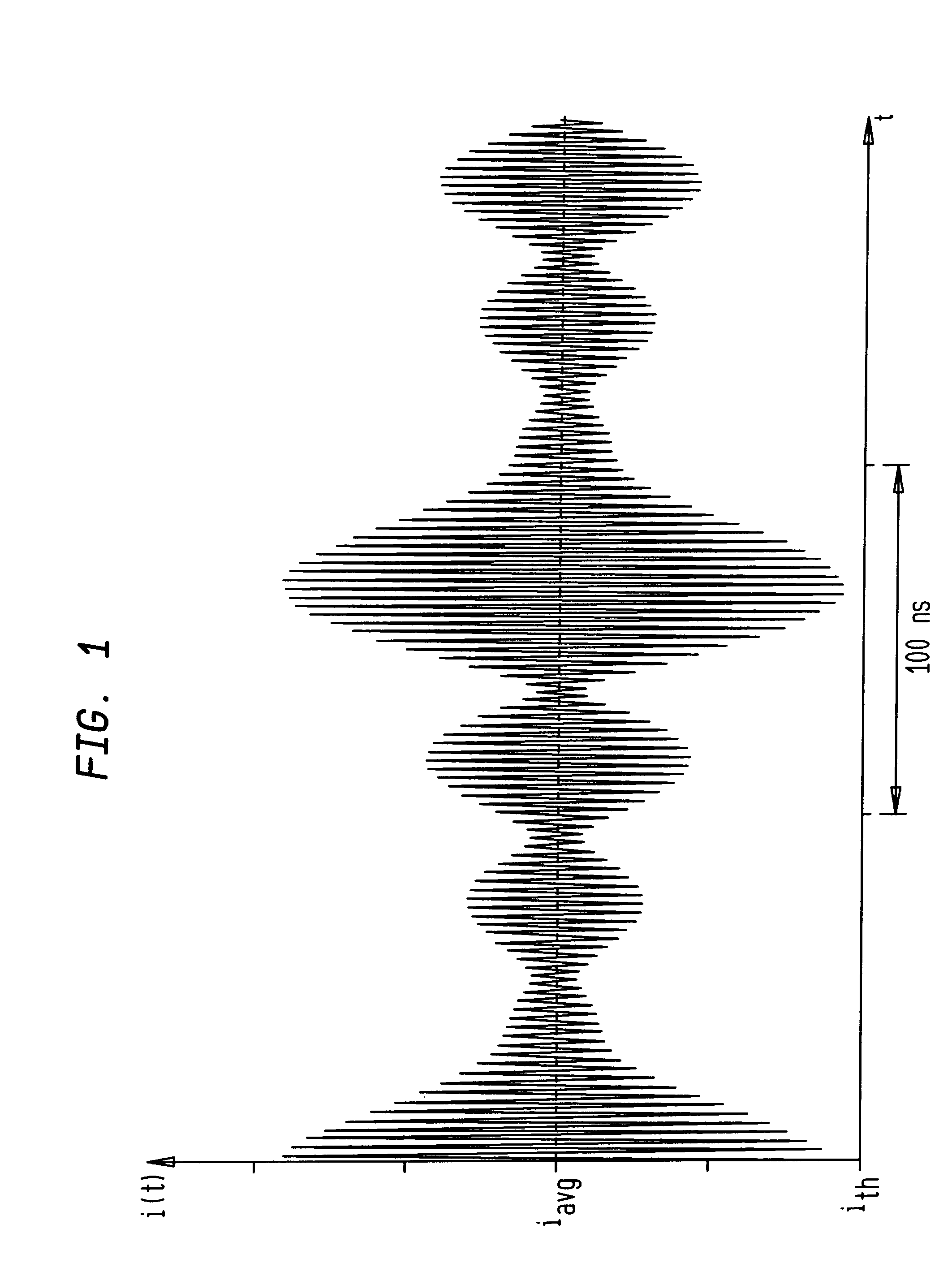
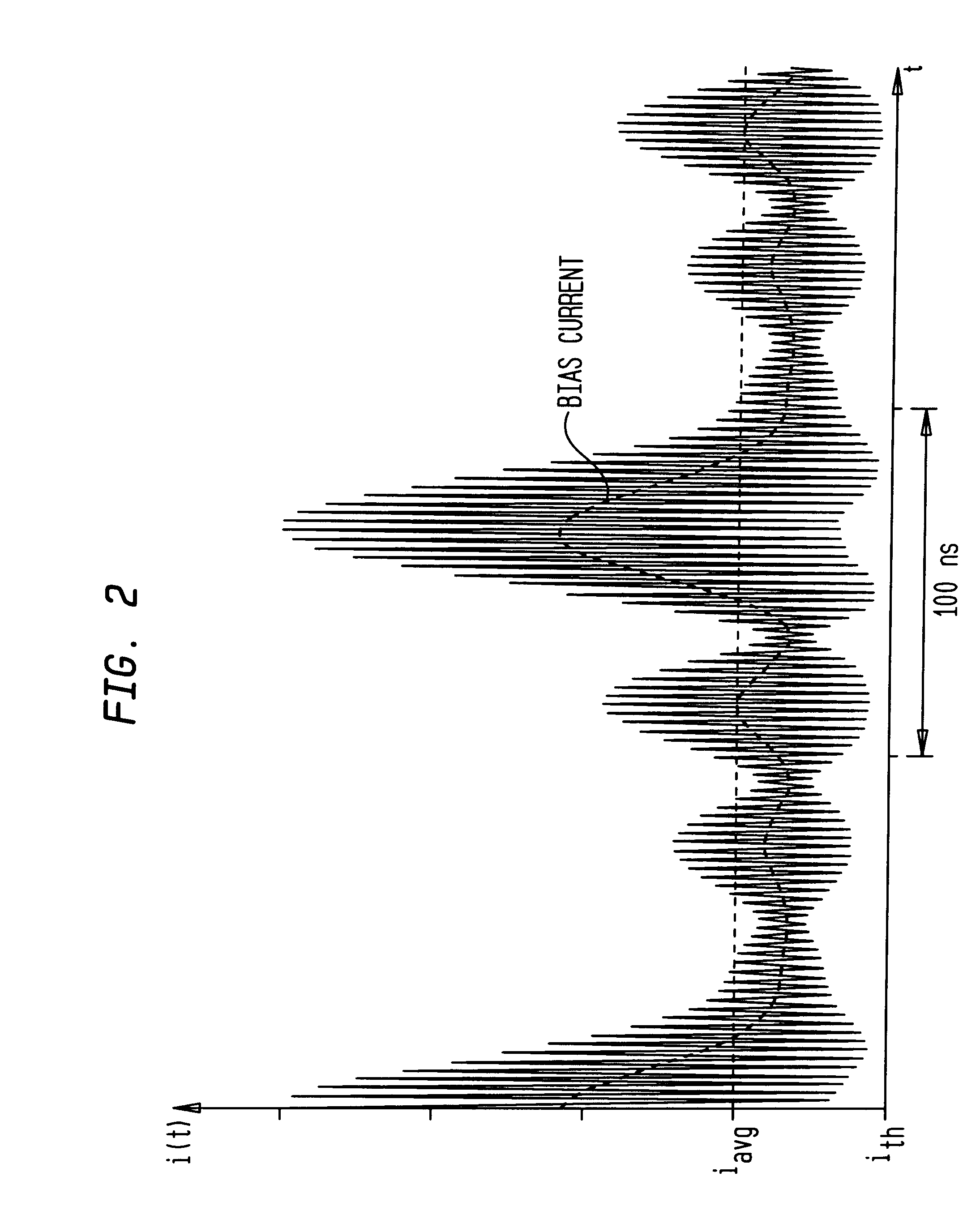
A laser bias preconditioning methodology is provided, and an implementation of that methodology, that improves the carrier-to-noise ratio of analog CATV signals sent over an optical transmission medium. The bias preconditioning methodology causes the laser bias current to be continuously varied to track an envelope of the carrier signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com