Patents
Literature
84results about How to "Improve carrier-to-noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scrambled multicarrier transmission
InactiveUS20100027608A1Easy to useImprove carrier-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainGuard interval
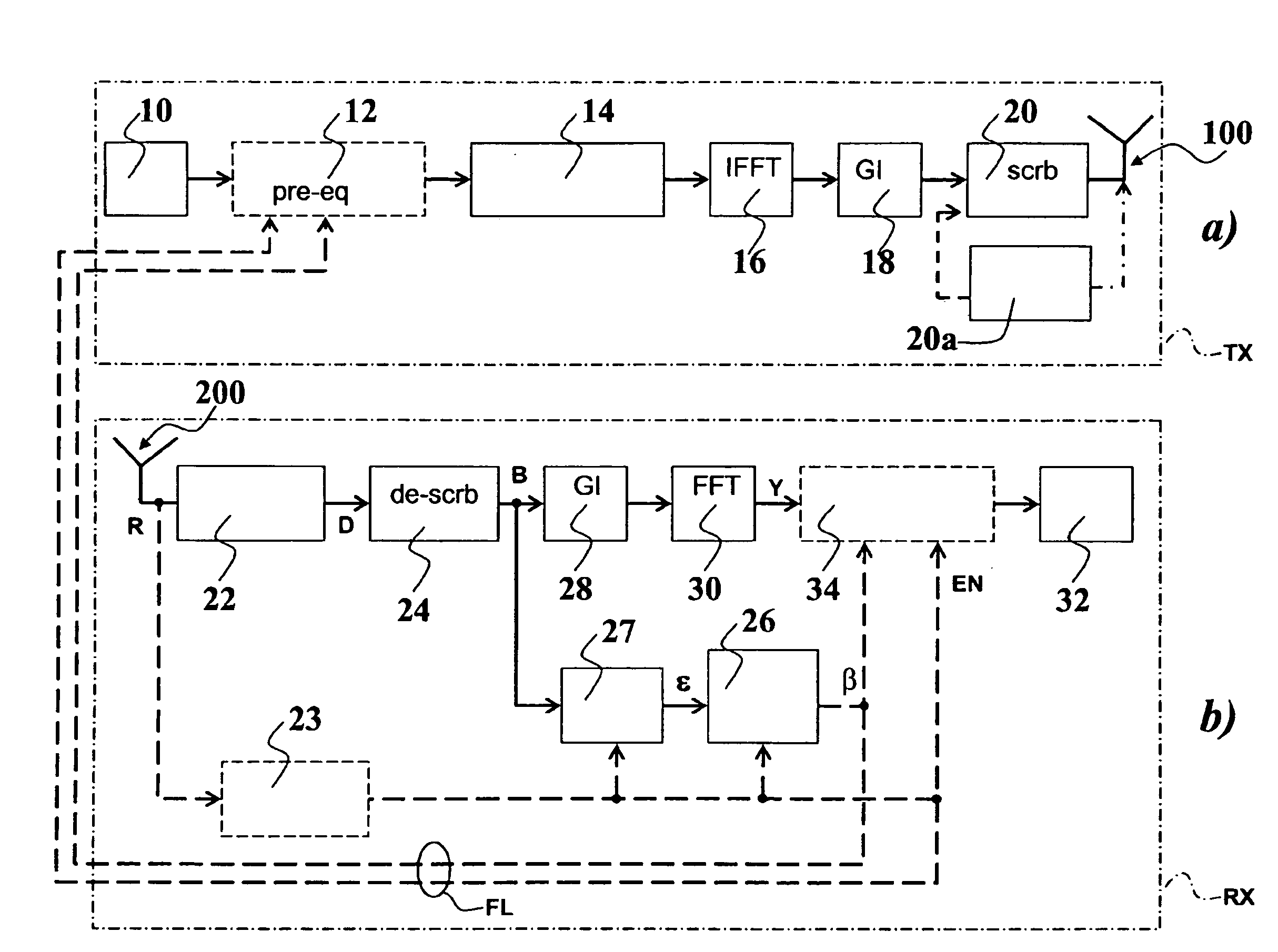
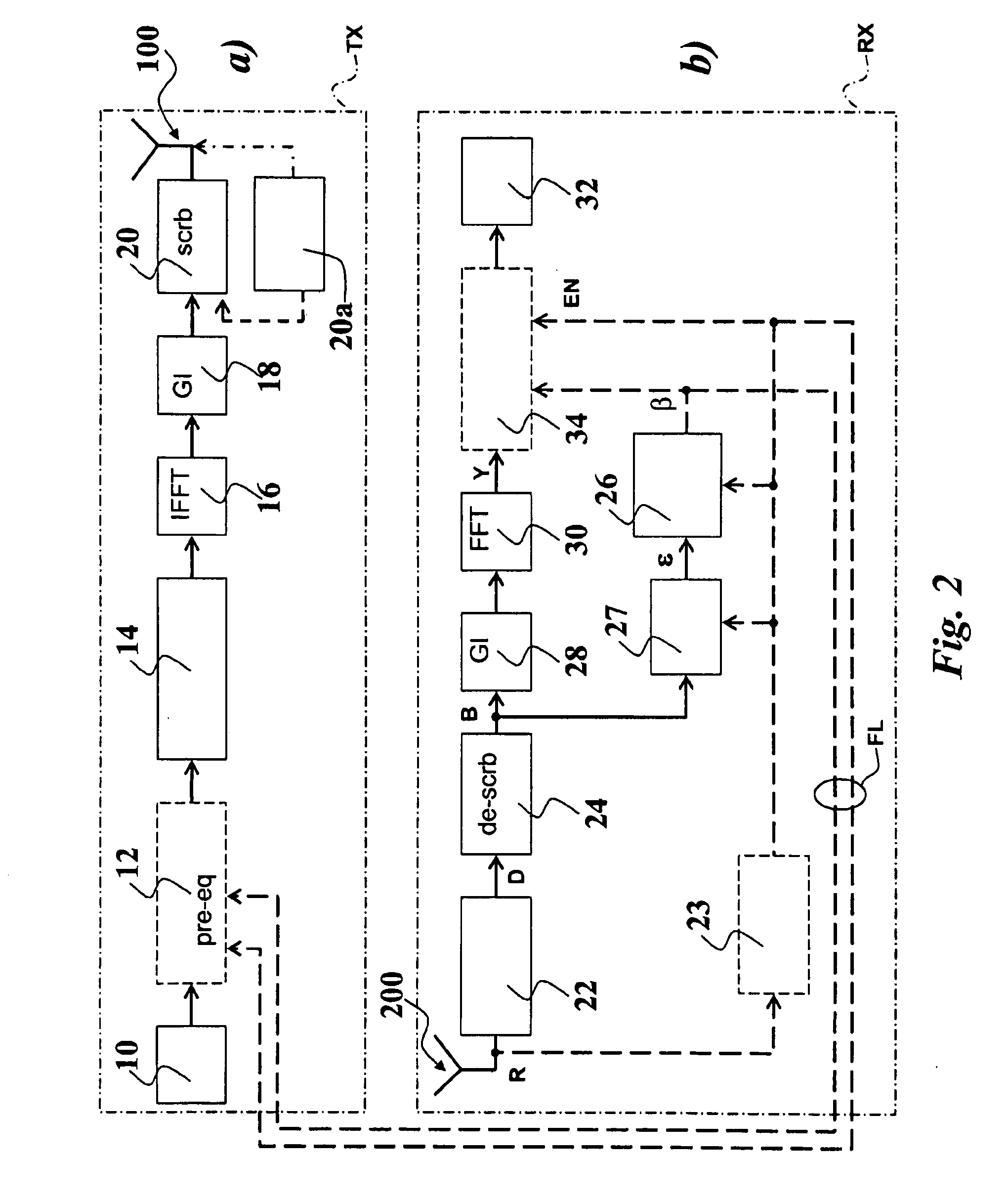
Signals (typically in the form of OFDM signals) are transmitted between one or more transmitting antennas and one or more receiving antennas. The signals transmitted are subject to addition of a guard interval before scrambling in the time domain, while the signals received are subject to removal of the guard interval after scrambling in the time domain. Preferably time-scrambling of the OFDM signal being transmitted occurs after IFFT processing and guard interval insertion, while time de-scrambling of the signal being received occurs before both guard interval removal and FFT processing. Optionally, unscrambled pilot symbols (e.g. in the form of a training sequence), can be present at regular intervals inside the signal structure. At the receiver, equalization is carried out preferably in the frequency domain.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Agile frequency converter for multichannel systems using IF-RF level exhange and tunable filters
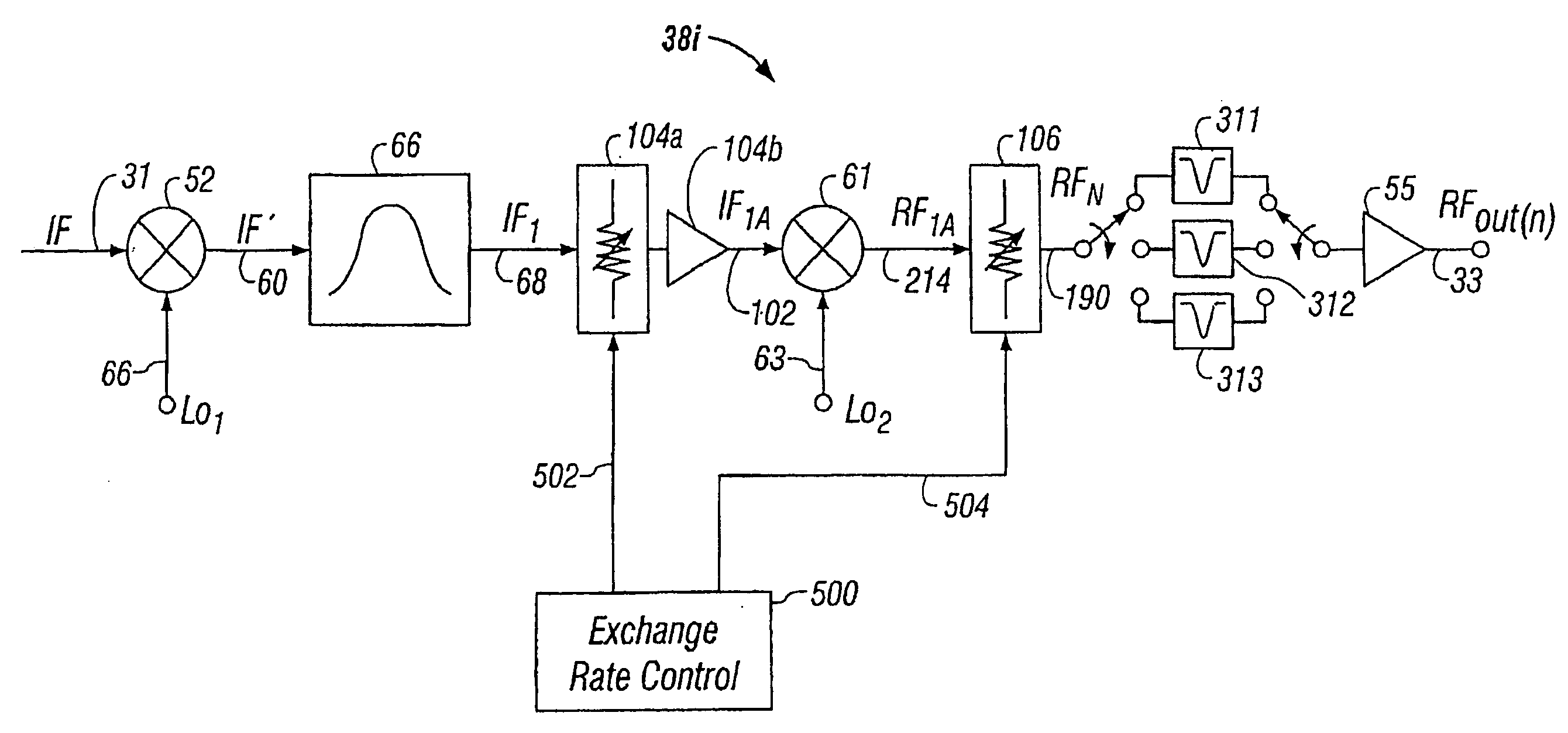
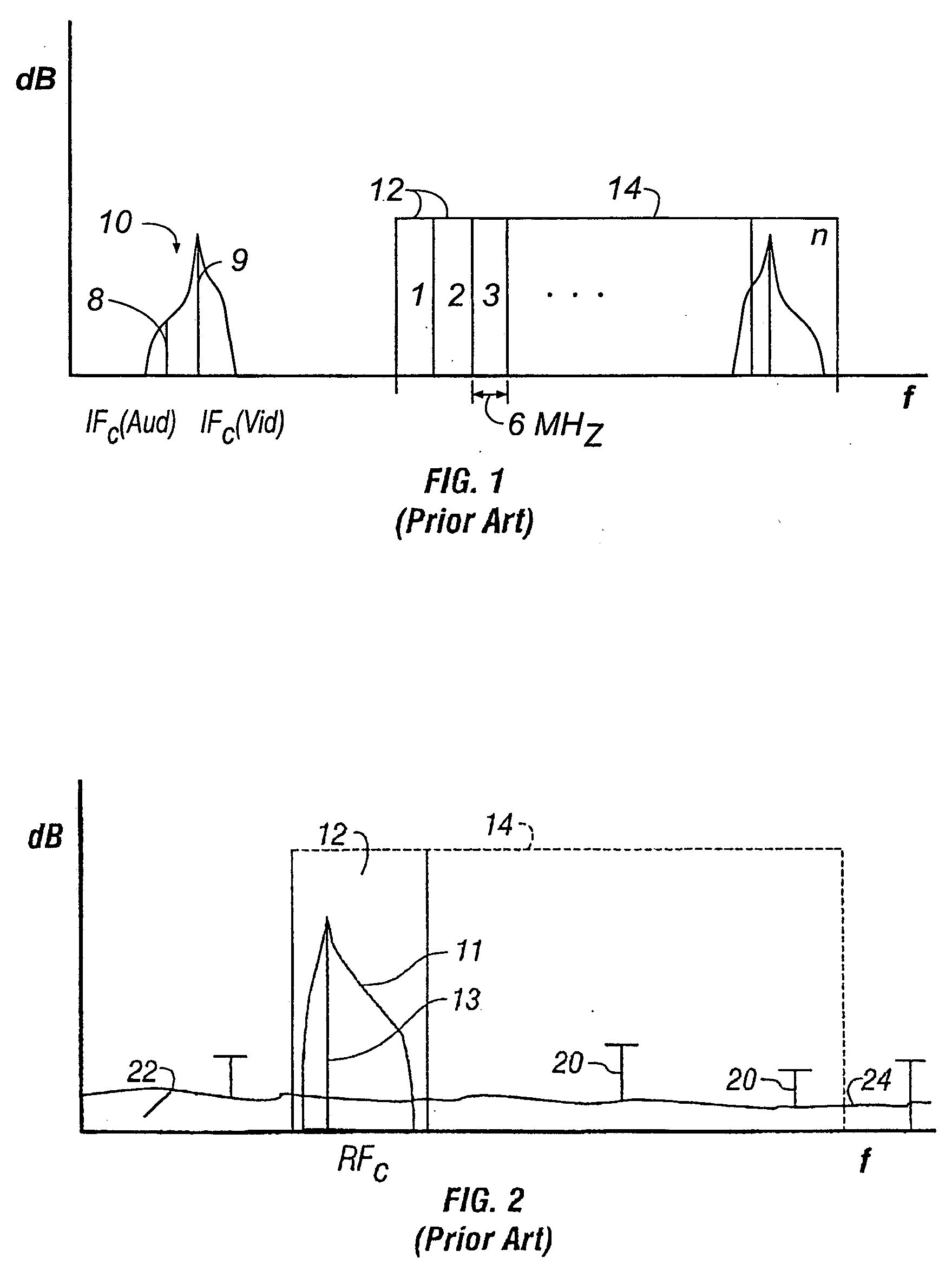
InactiveUS7003275B1Increasing unloaded QReduced insertion lossResonant long antennasFrequency-division multiplex detailsMicrocontrollerFrequency changer
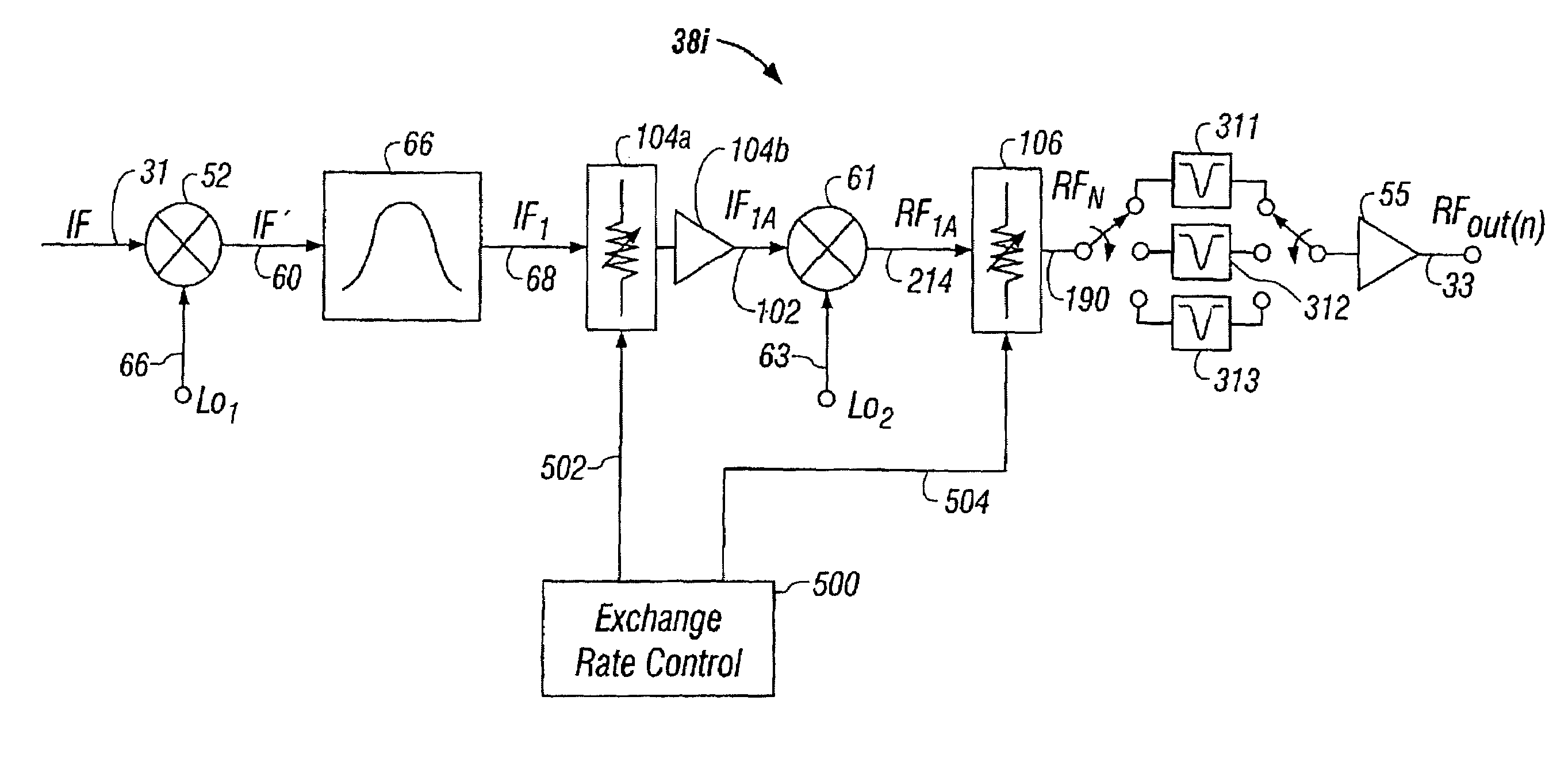
Agile frequency converter and method, IF-RF level exchange process, and notch filtering techniques. System noise and spurious levels generated by channel frequency conversion is reduced in applications requiring broadband combining of frequency converters to form multichannel composite signal. Converter employs two-stage frequency conversion process, with gain exchange system using variable pre-mixer gain and variable post-mixer attenuation to maintain constant RF output signal power level. For those few conversion frequencies where distortion component(s) cannot be filtered without degrading desired signal, IF-RF level exchange is optimized for meeting the carrier-to-distortion (C / D) ratio specifications at slight expense of noise level for that channel only, while still meeting aggregate combined carrier-to-noise (C / N) specification requirements. Optimal apportionment of level exchange for each channel depends on specific frequency rejection capability of spurious components and is matched to filtering capability and stored within non-volatile memory of a microcontroller used in the frequency converter.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
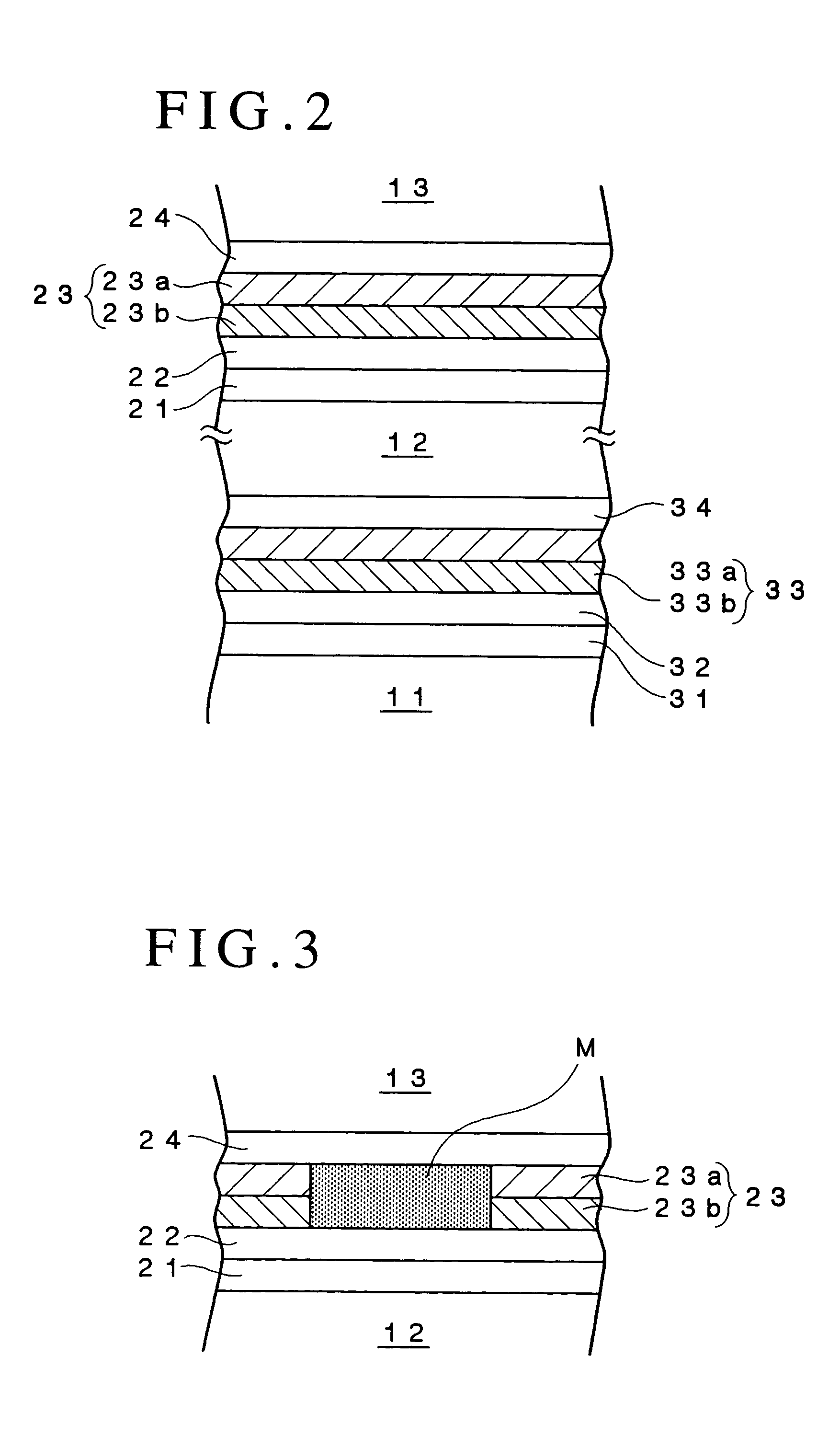
Optical information recording medium
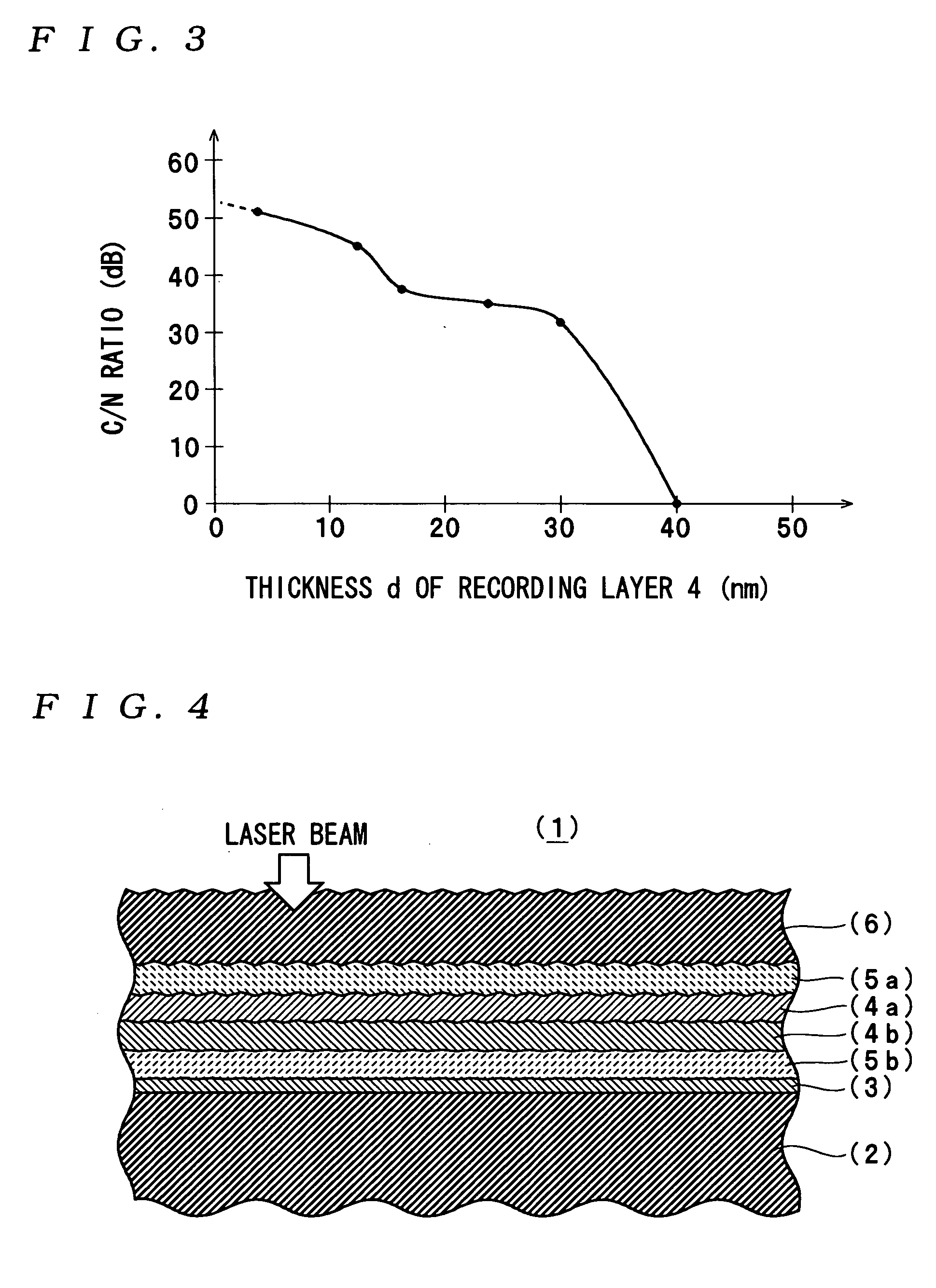
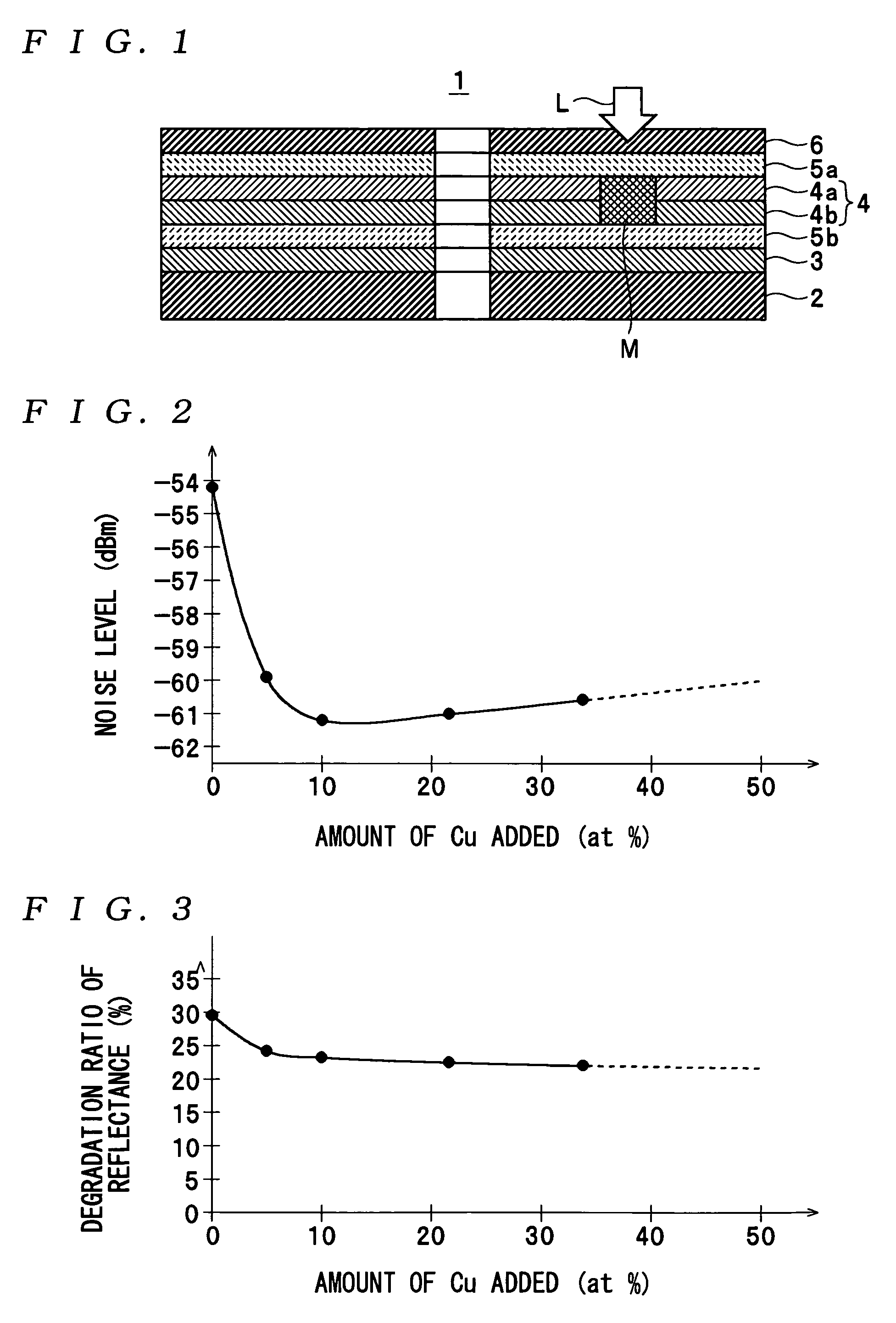
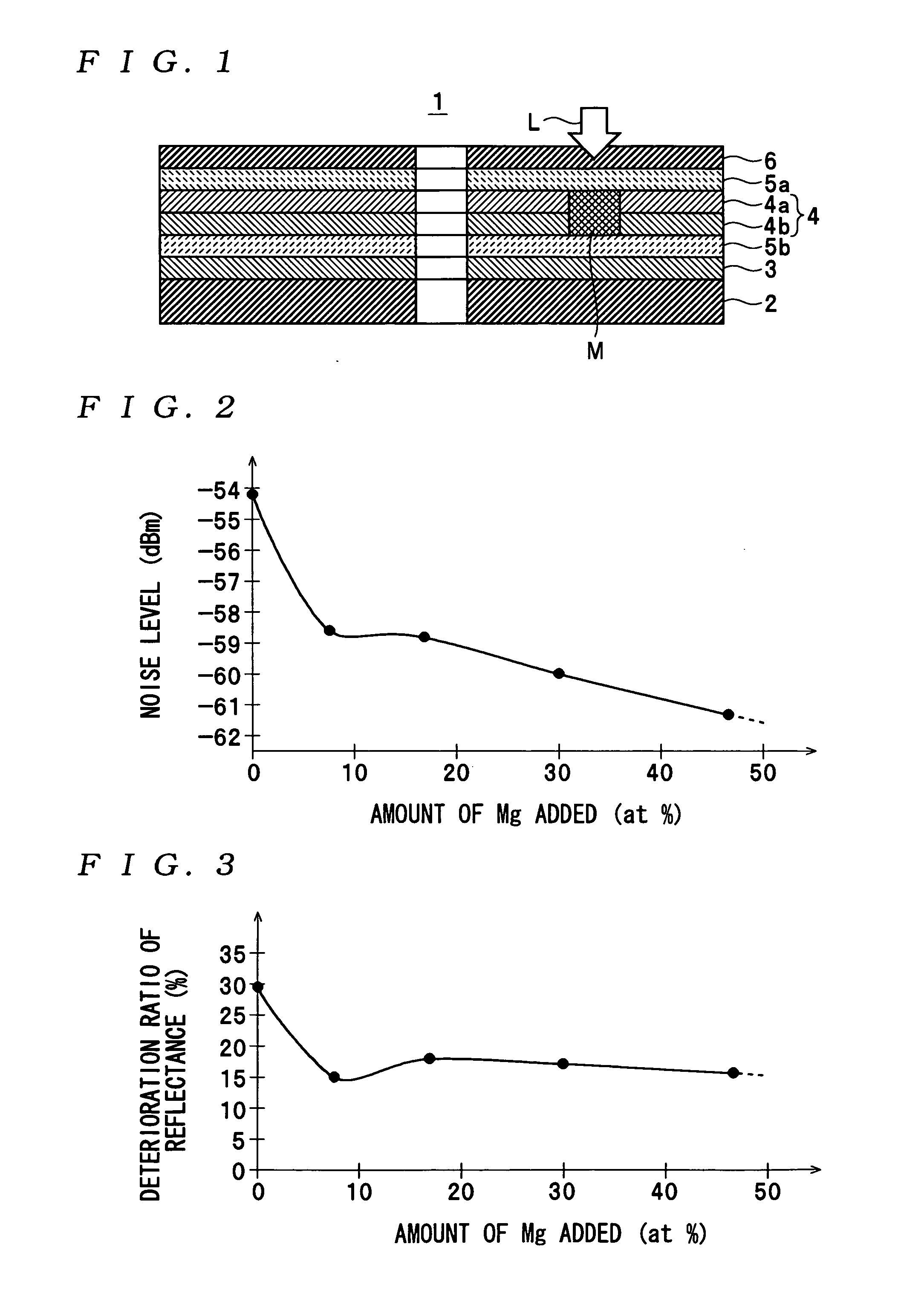
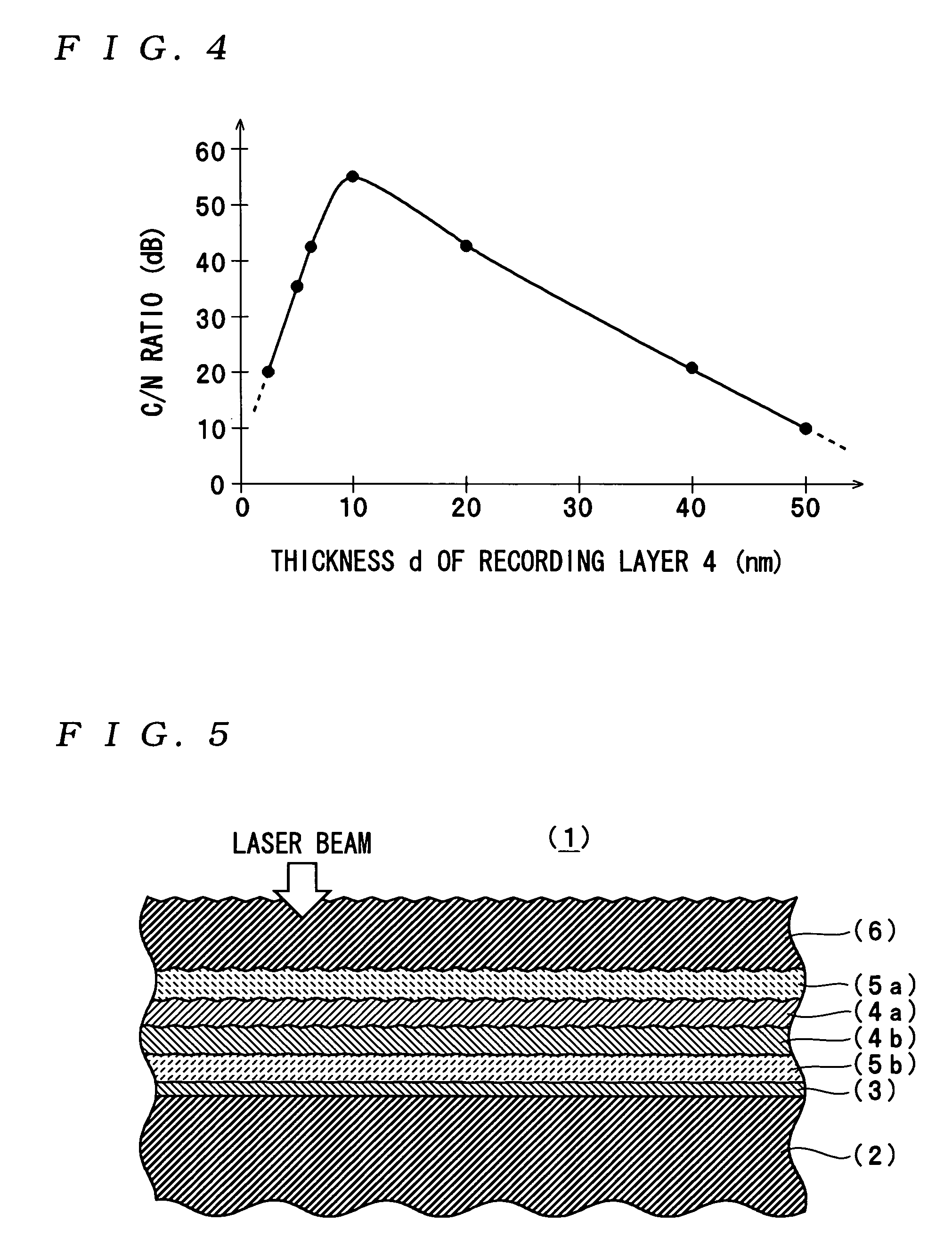
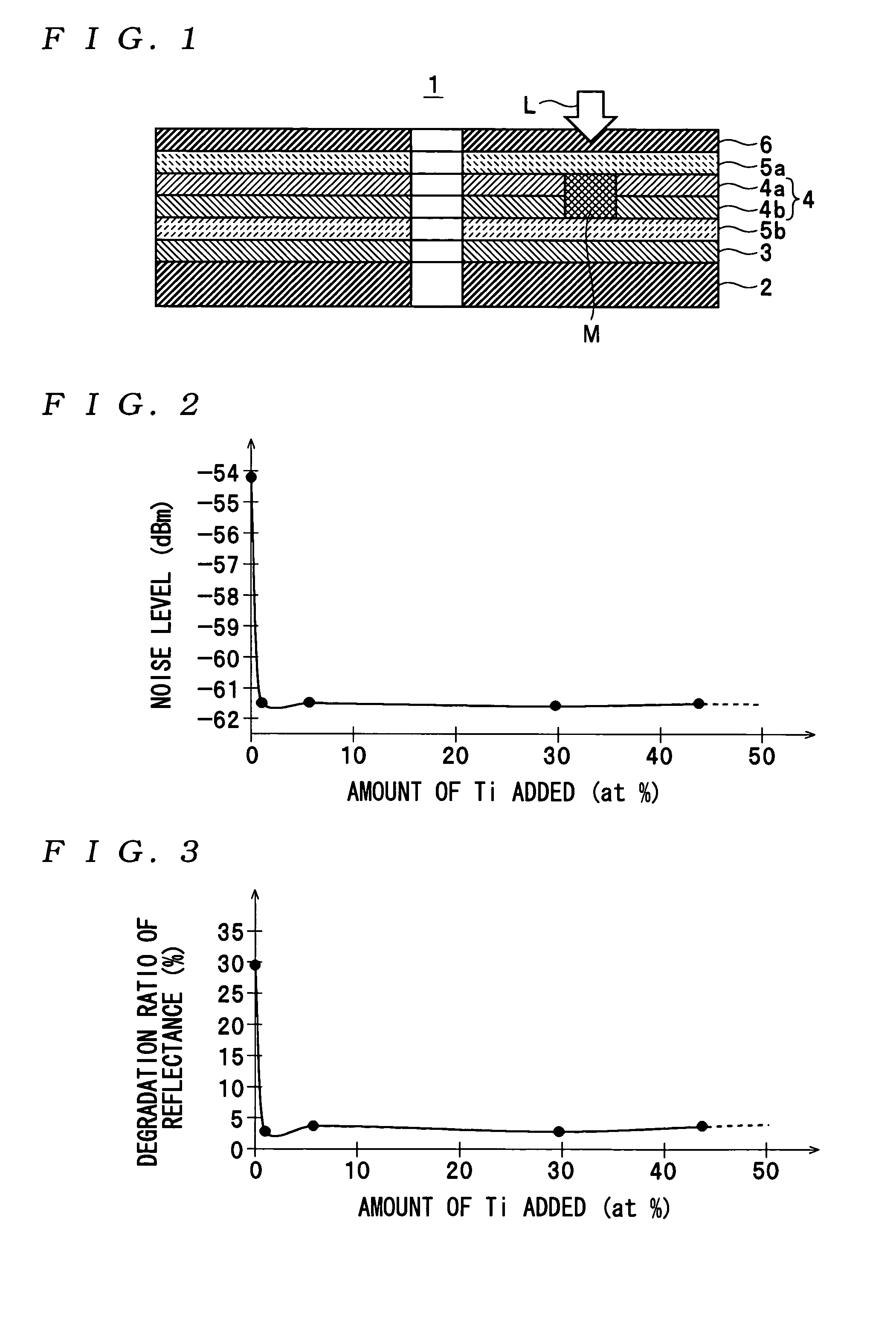
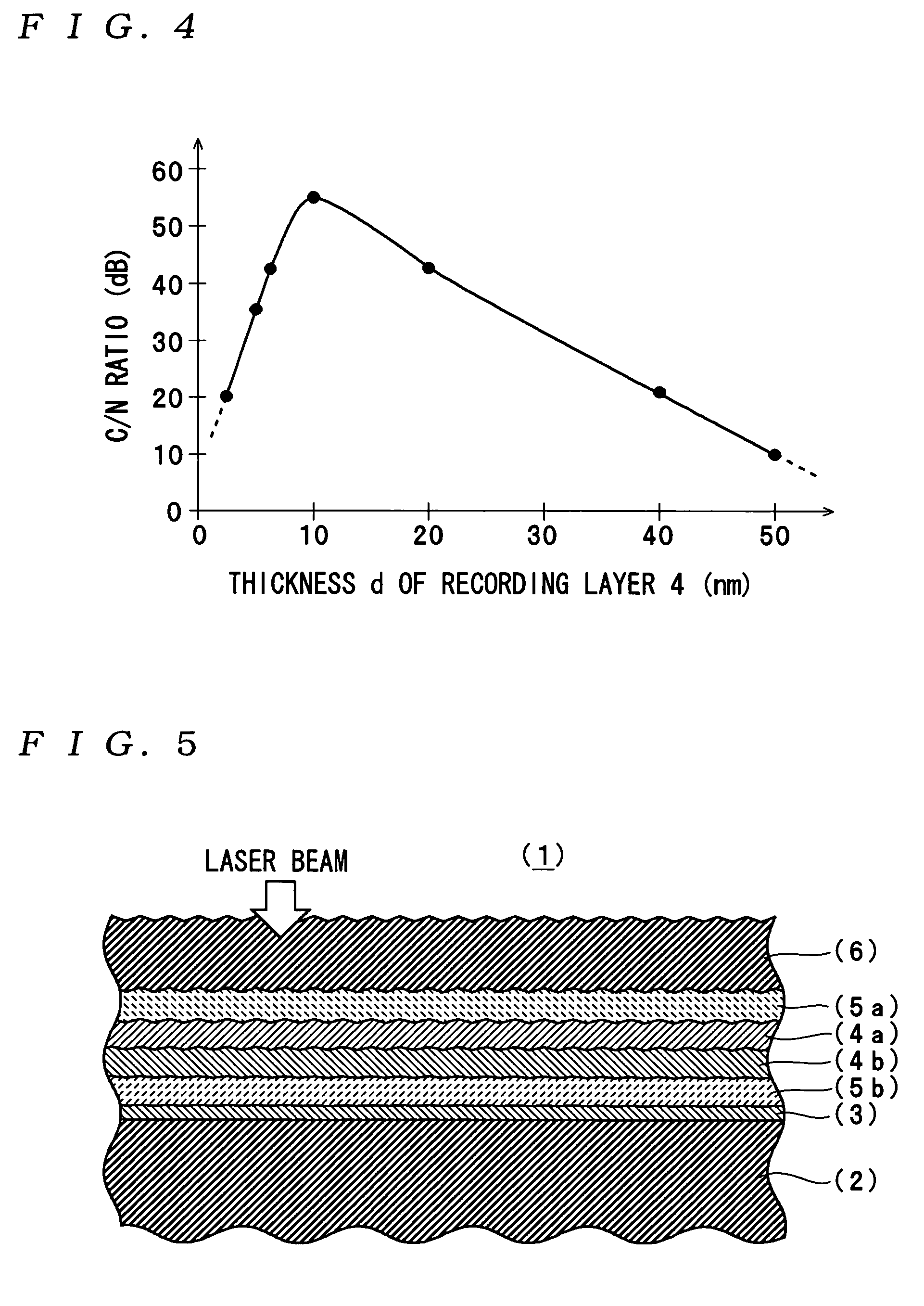
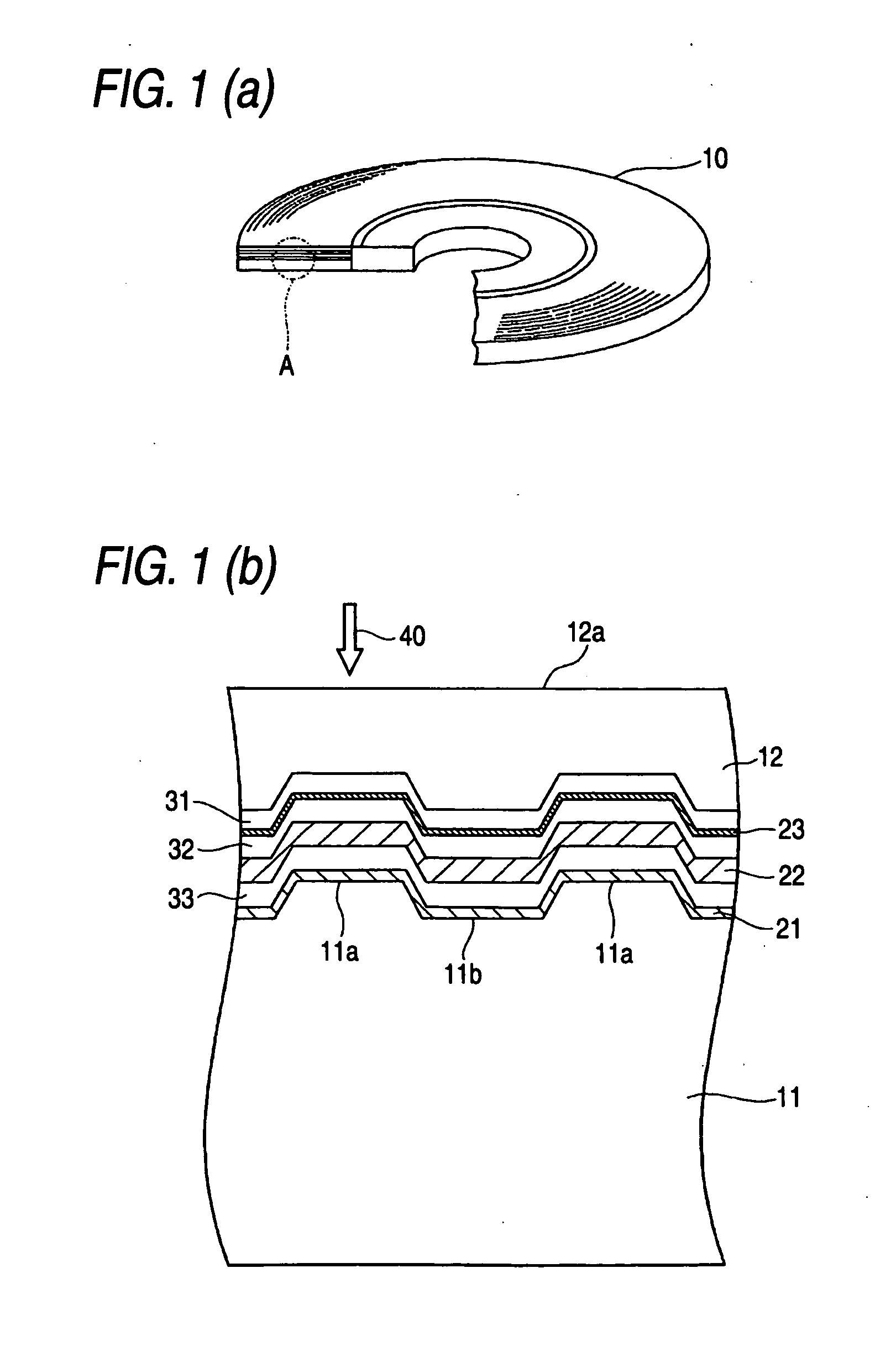
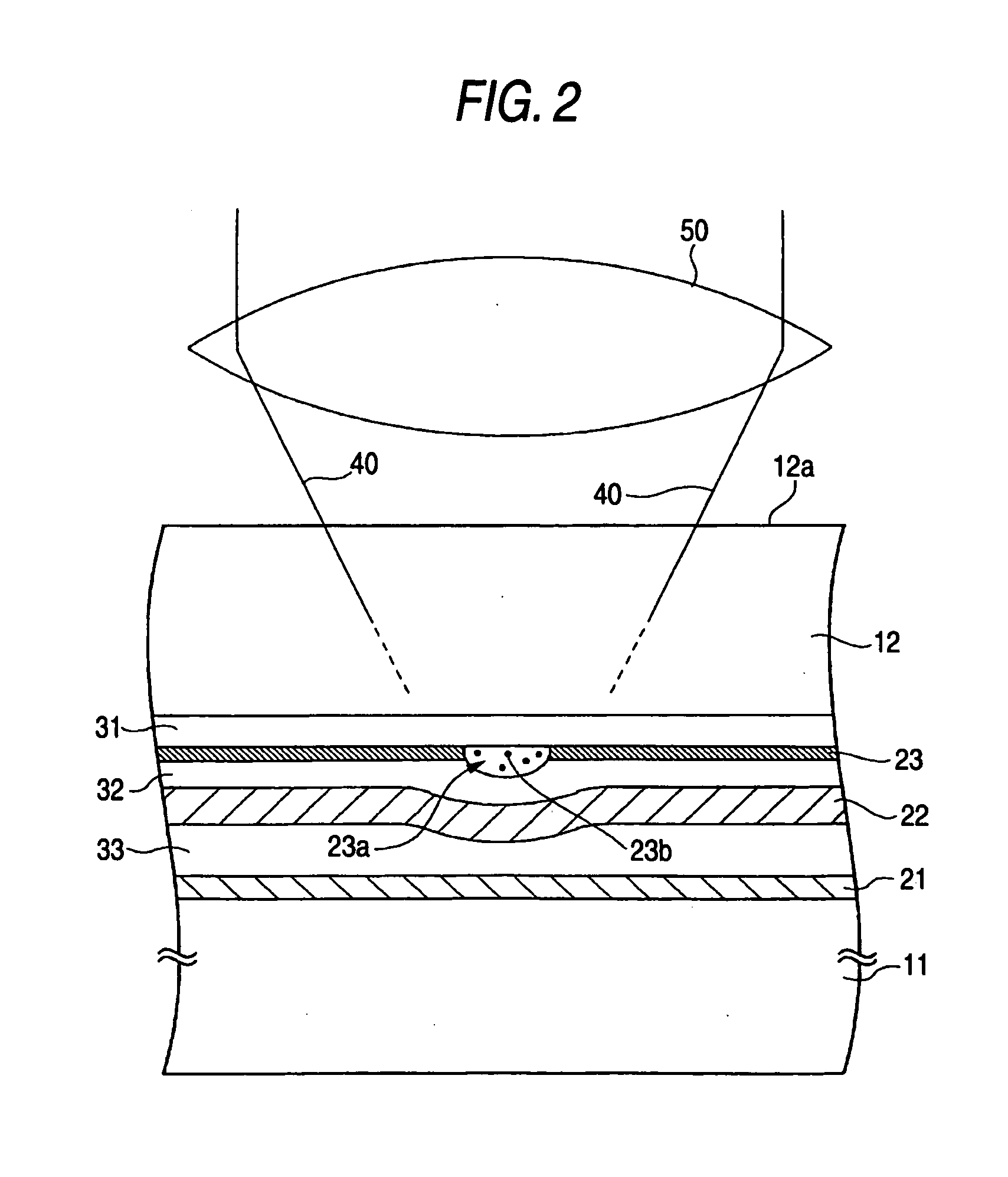
ActiveUS20050018590A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingMechanical record carriersNoise levelRecording layer
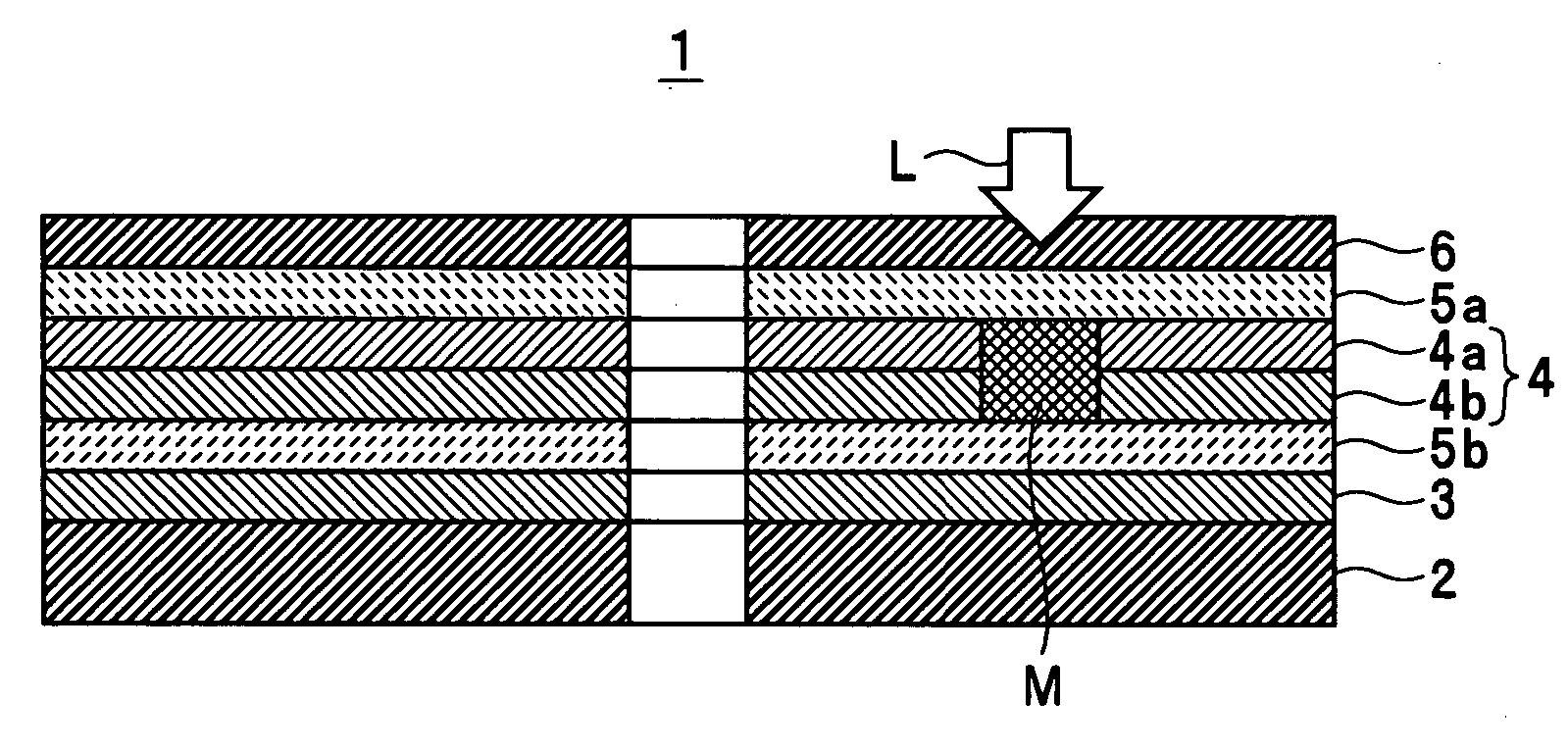
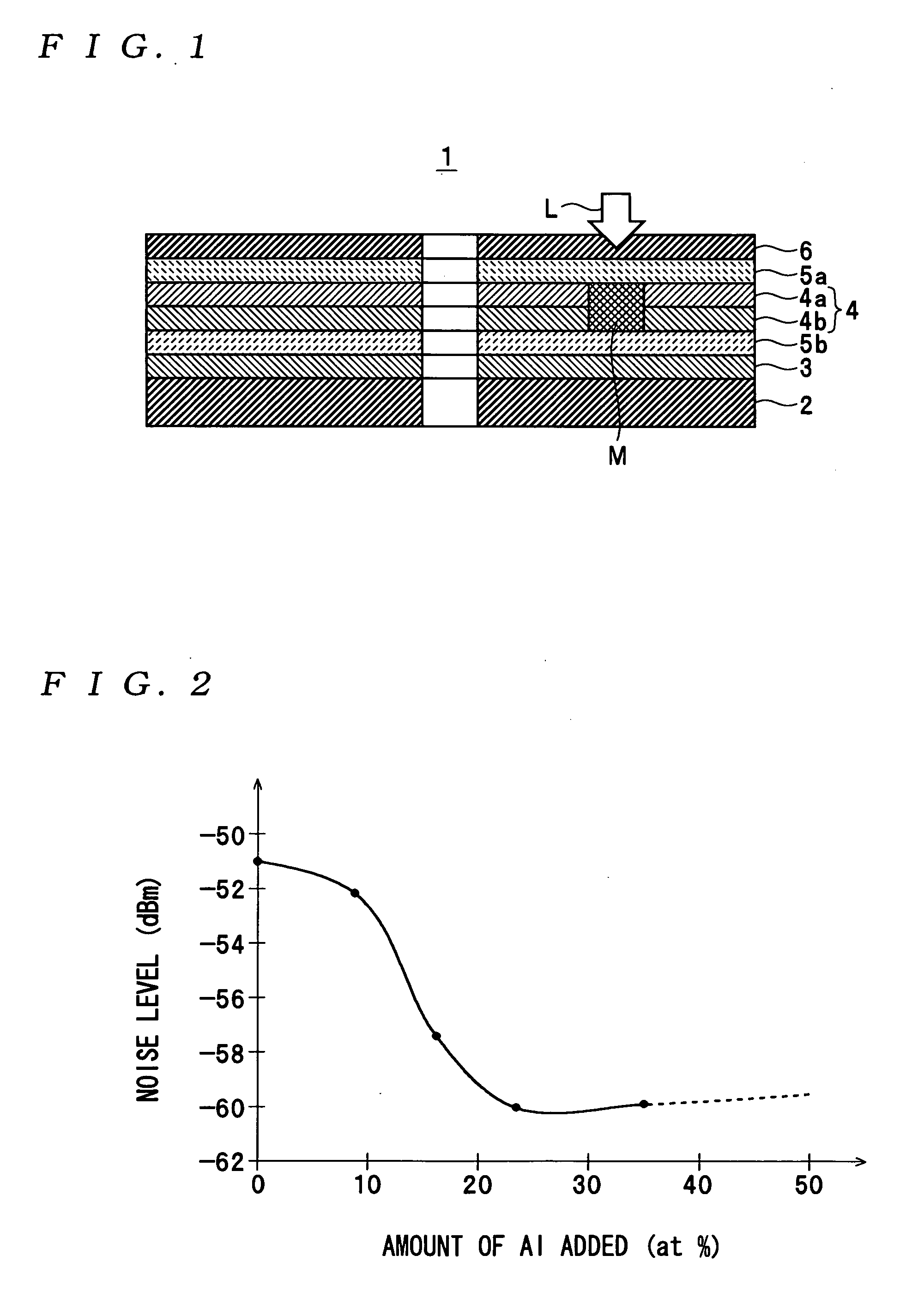
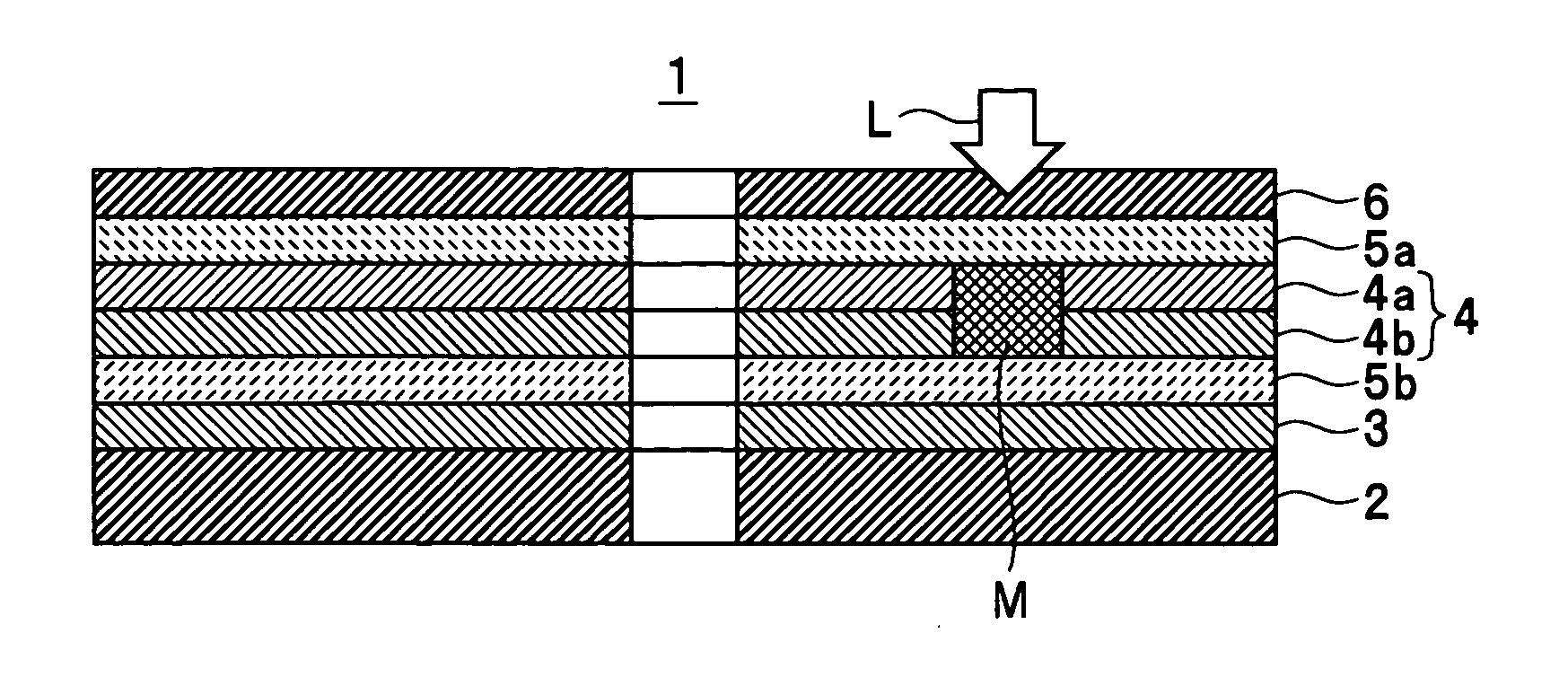
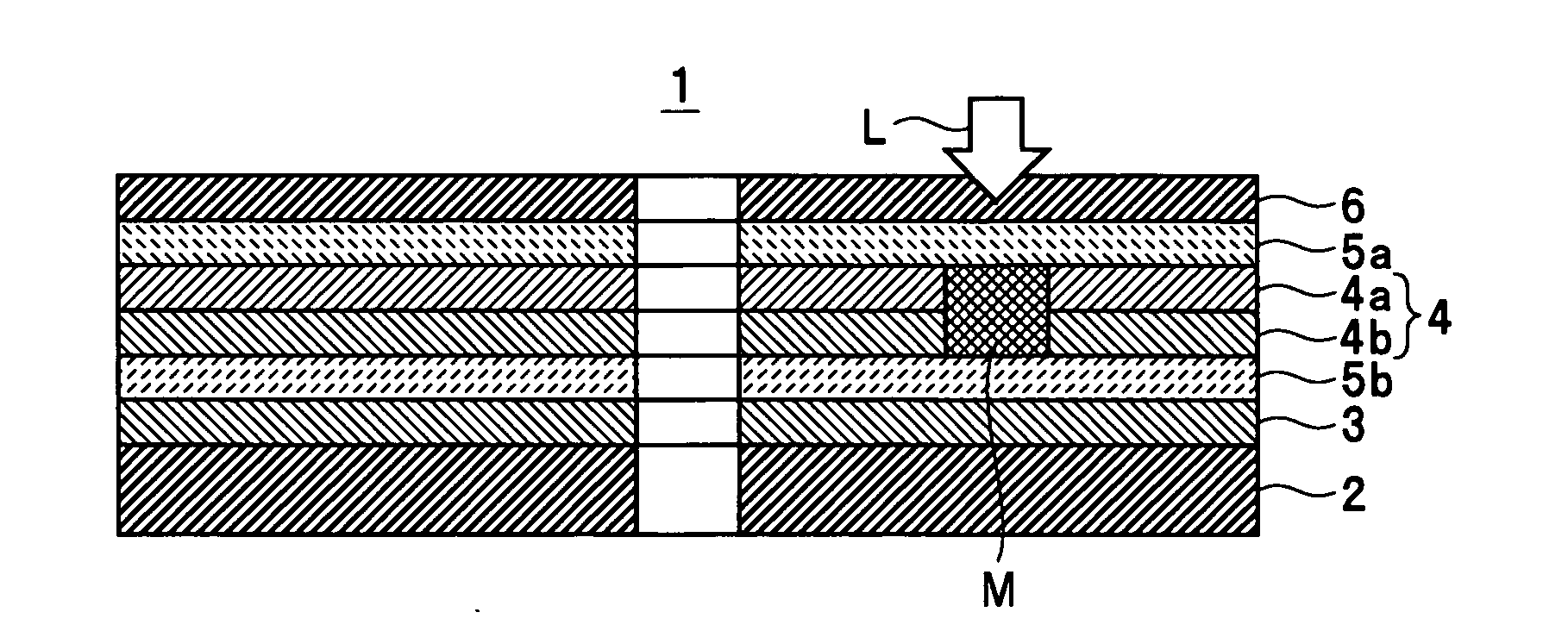
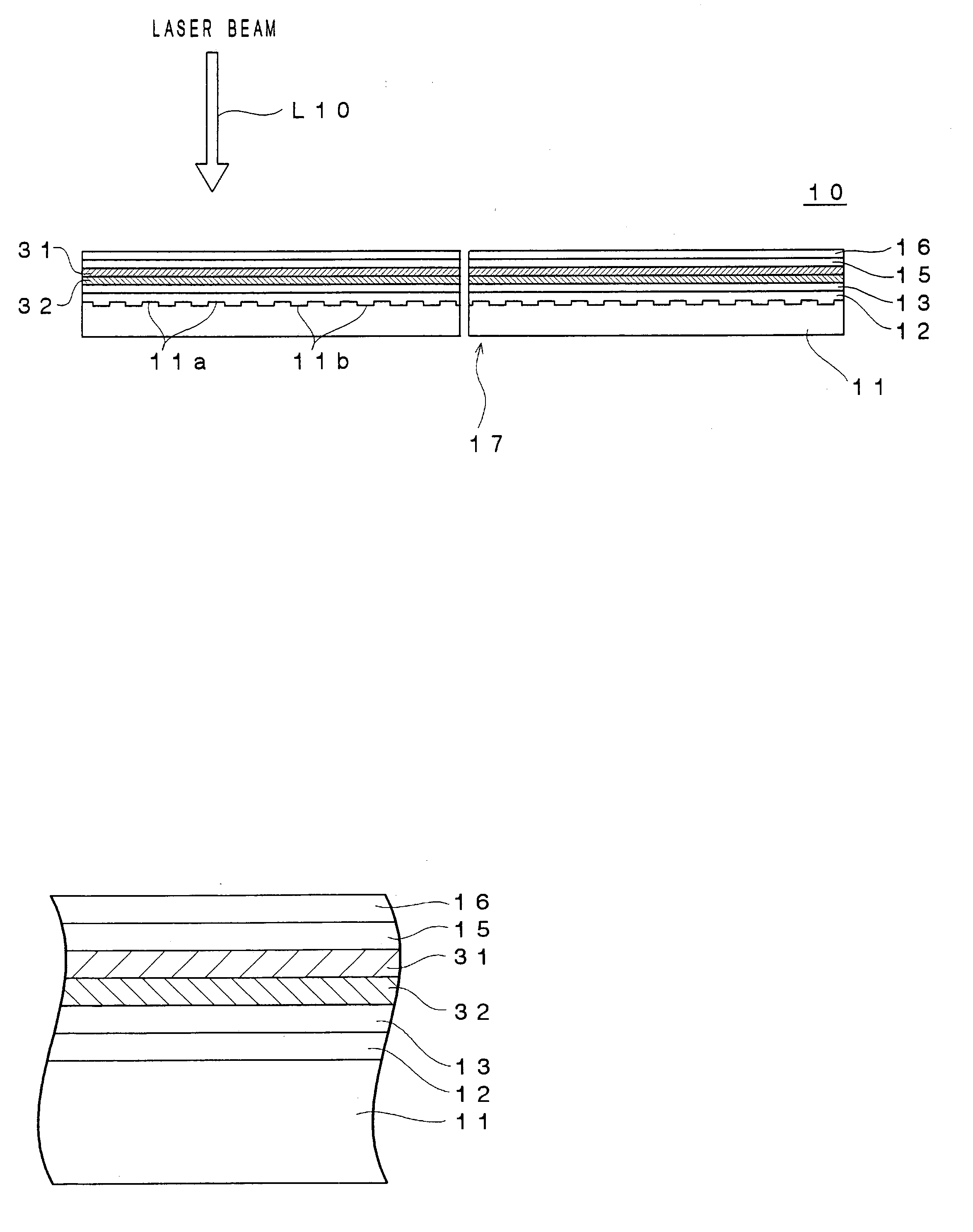
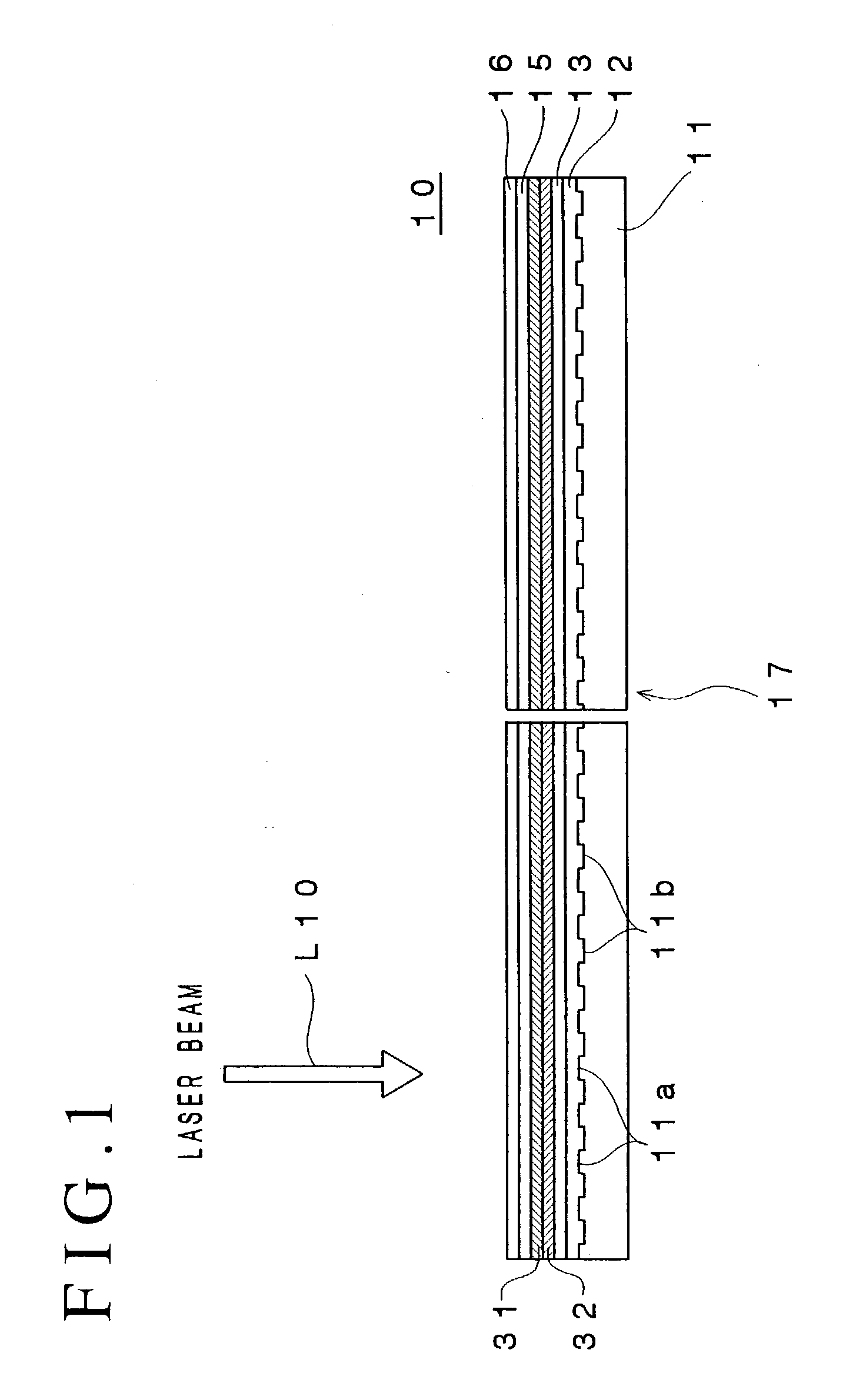
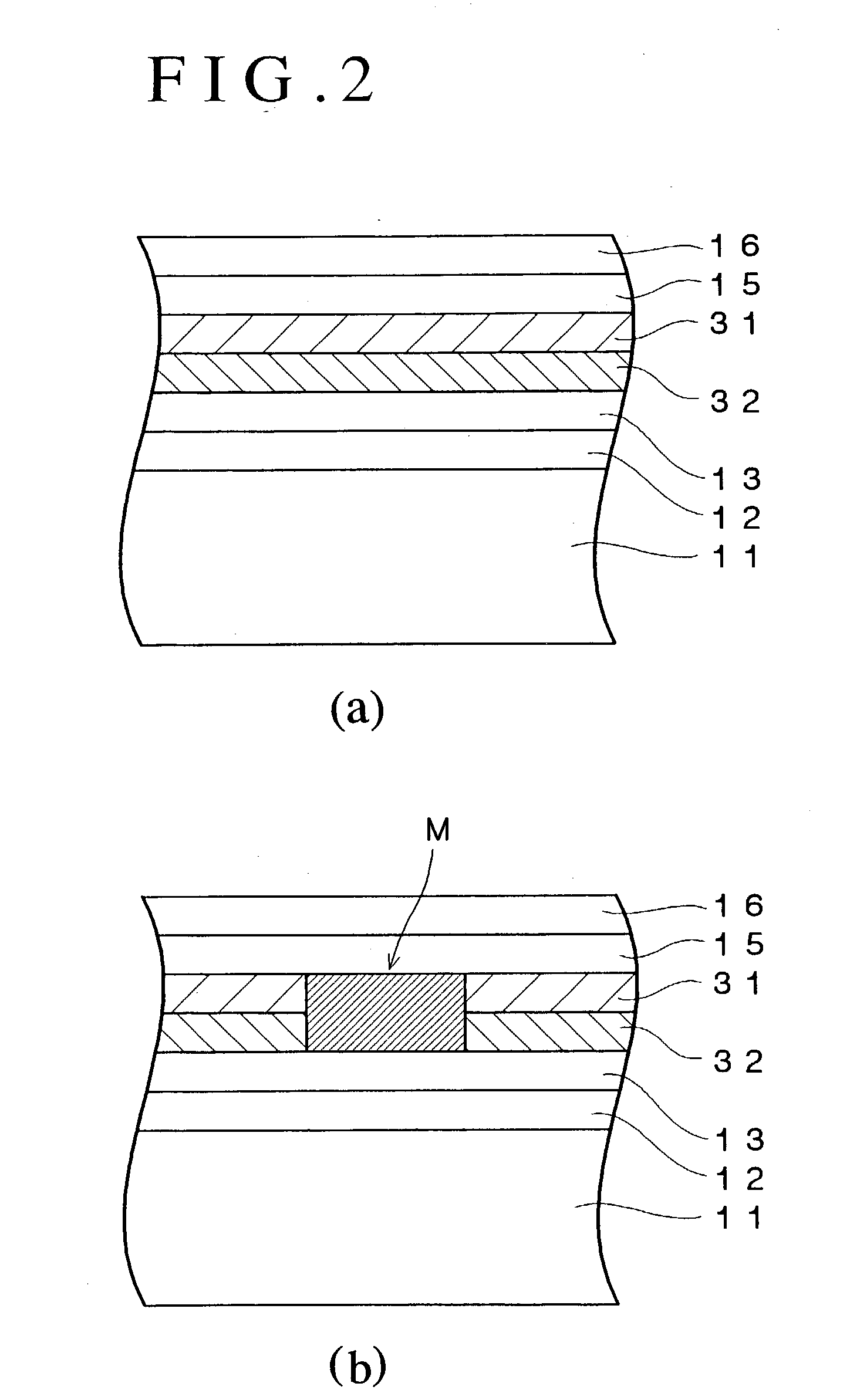
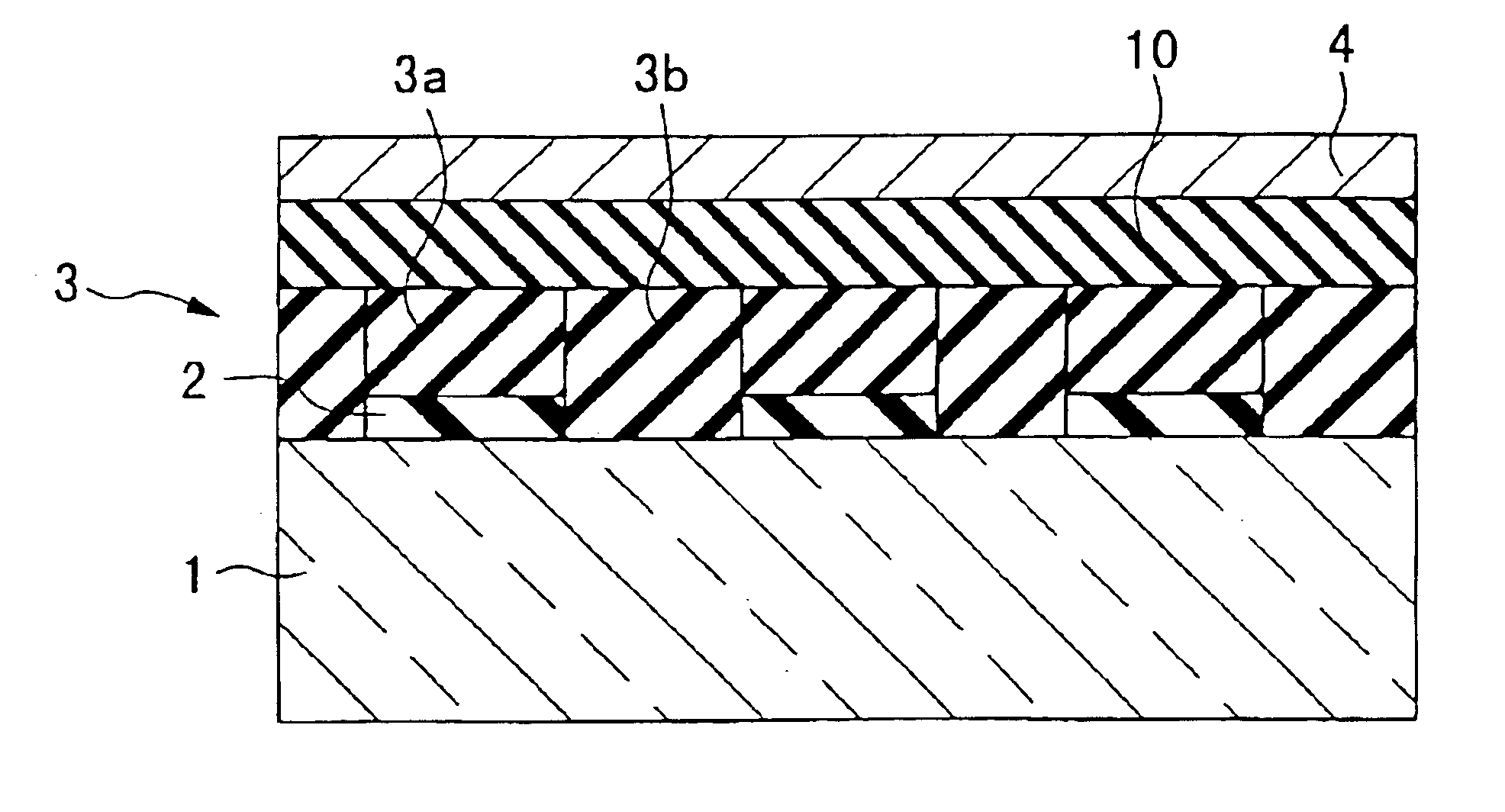
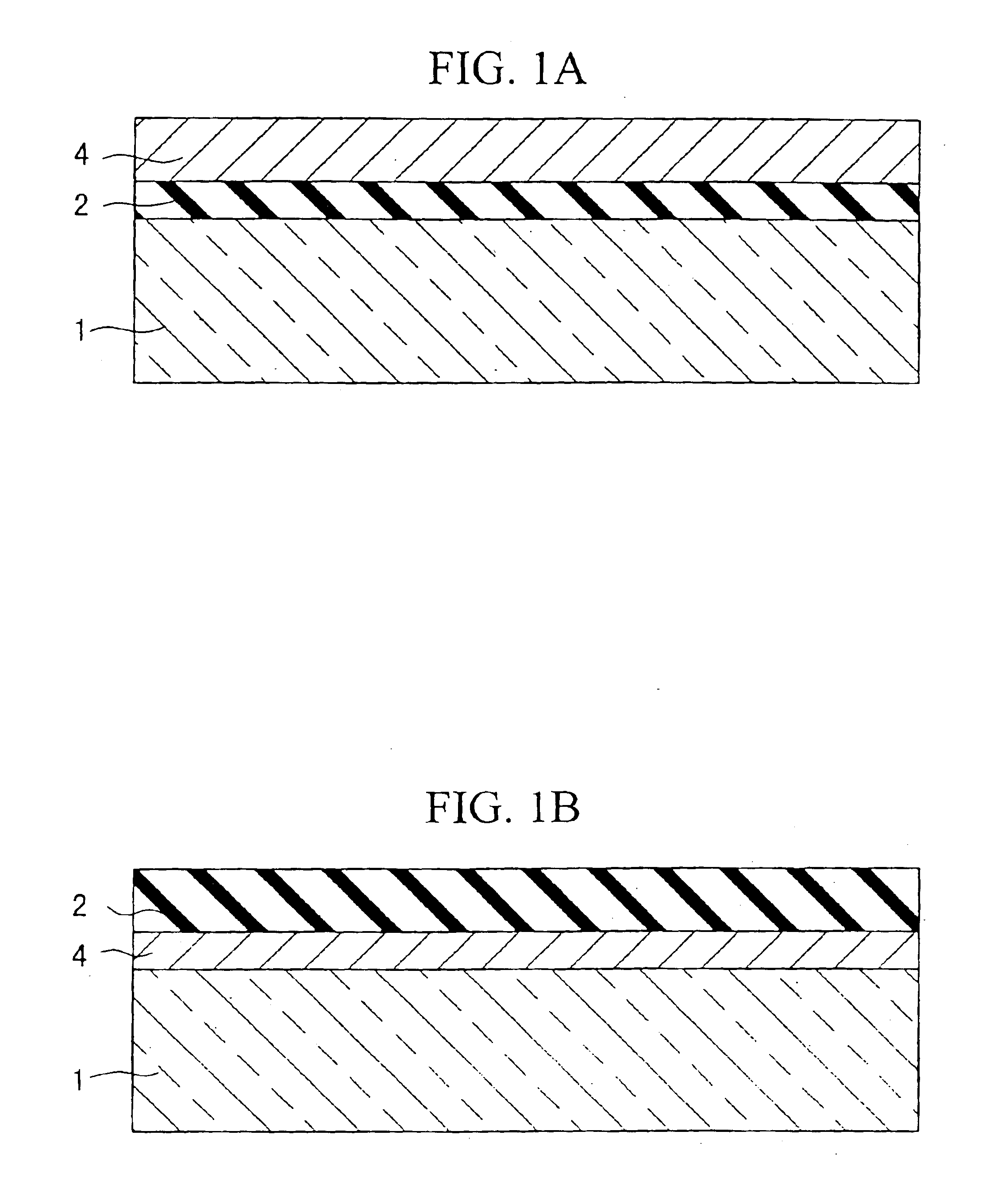
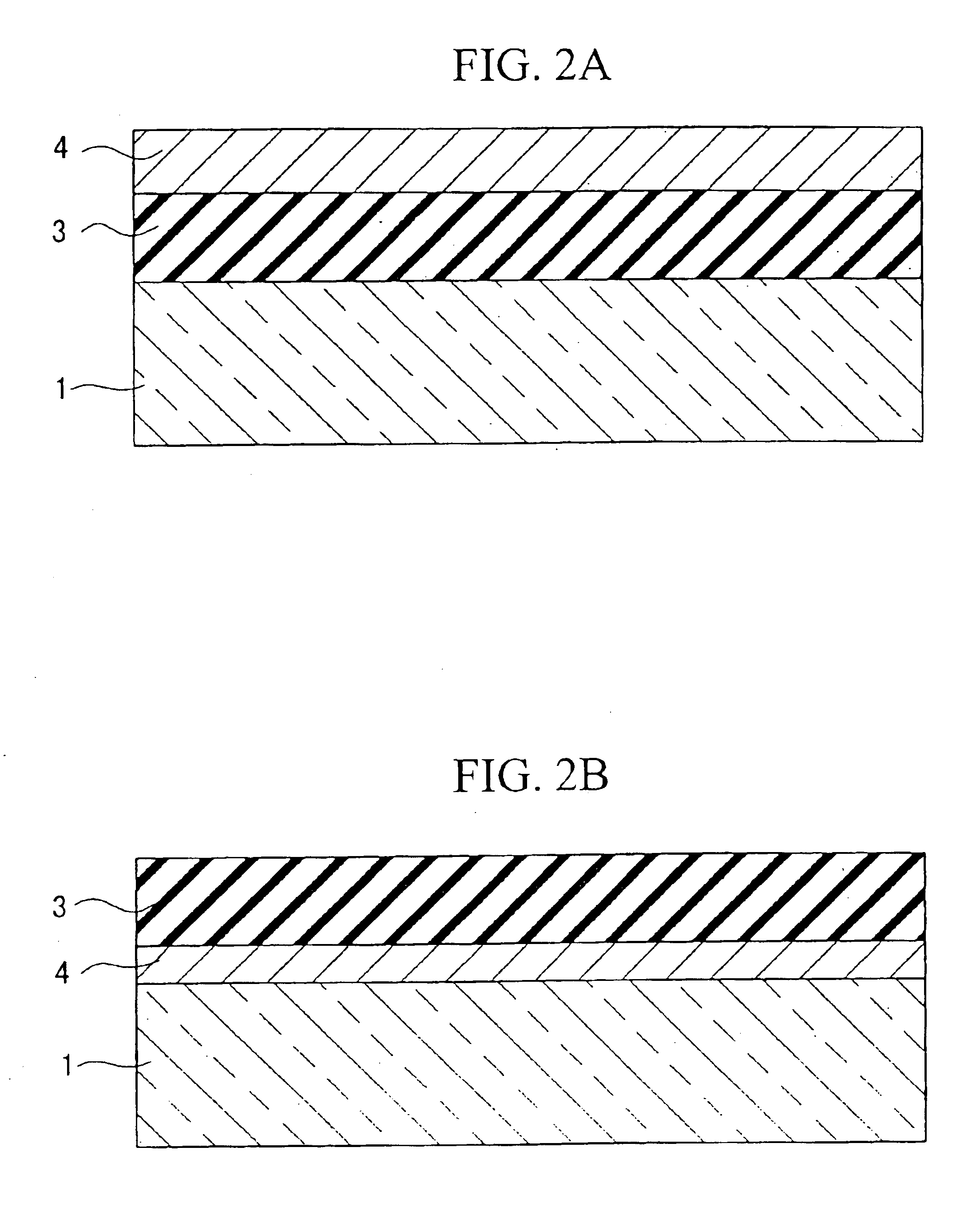
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level and improve the C / N ratio. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproducing record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as a main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Zn as a main component and having Al added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
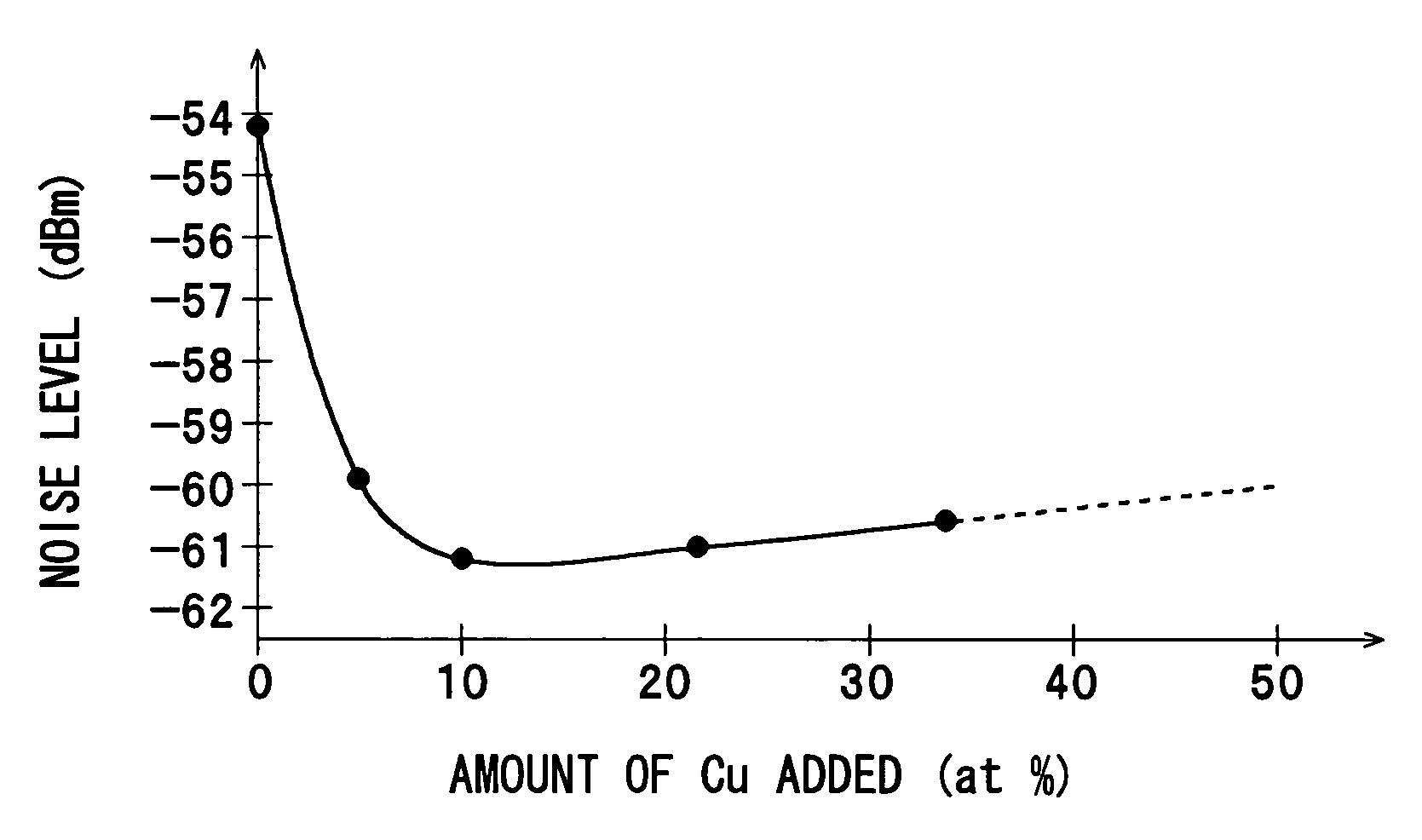
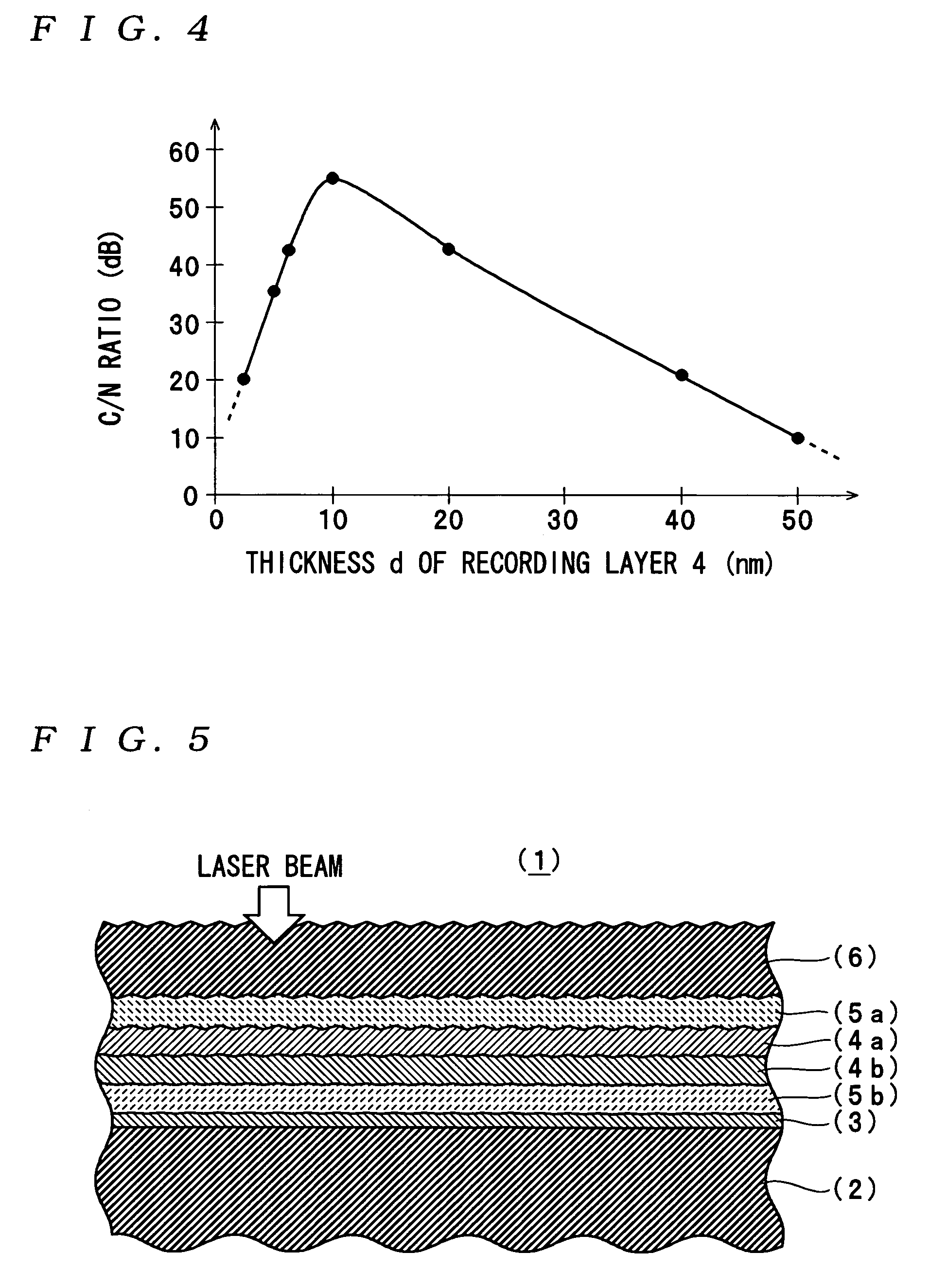
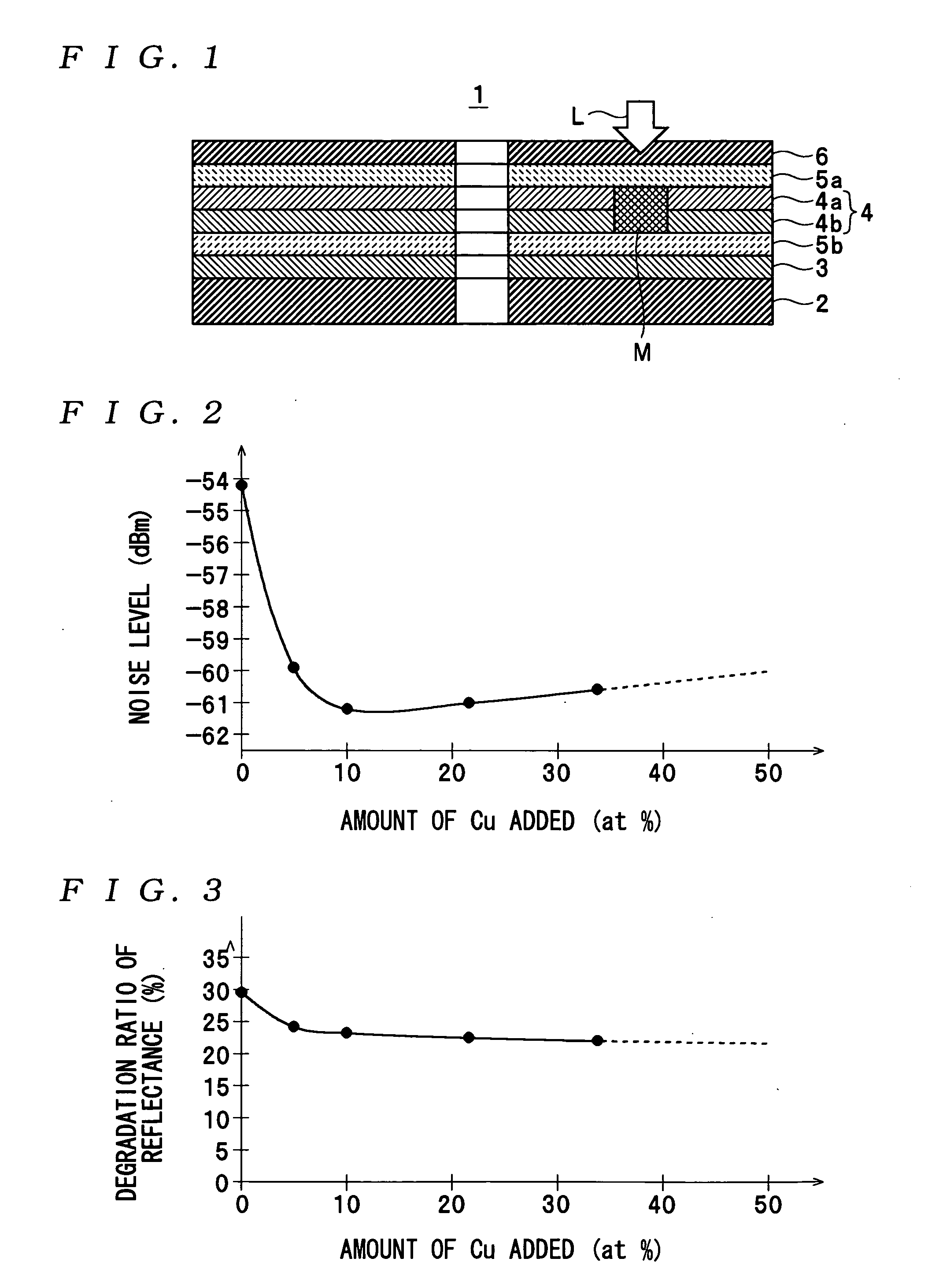
ActiveUS7166347B2Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioLayered productsRecord information storageNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level, improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as the main component and having Cu added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050047302A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingMechanical record carriersNoise levelRecording layer
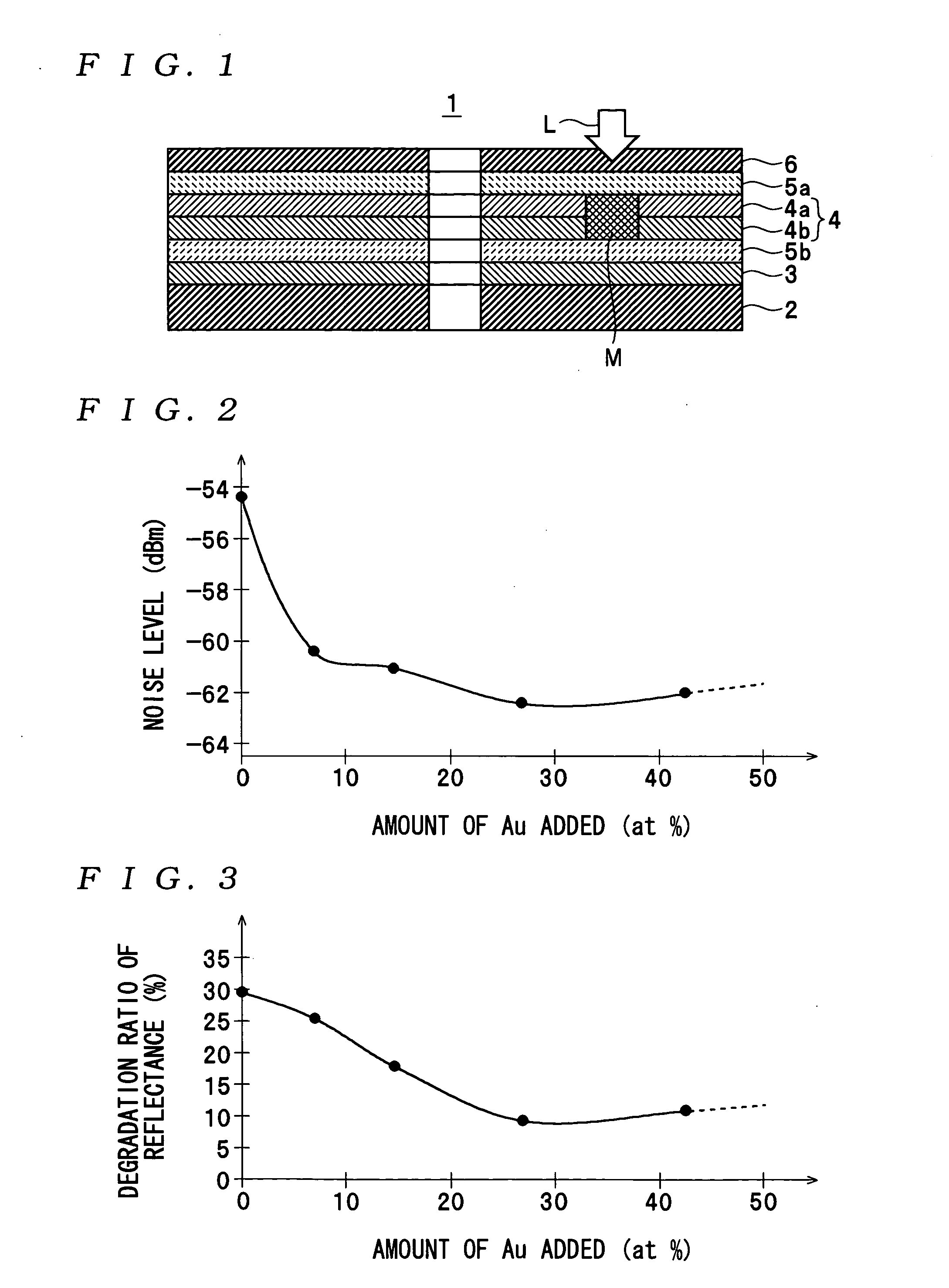
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level, improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as the main component and having Au added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS20050018592A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingMechanical record carriersNoise levelRecording layer
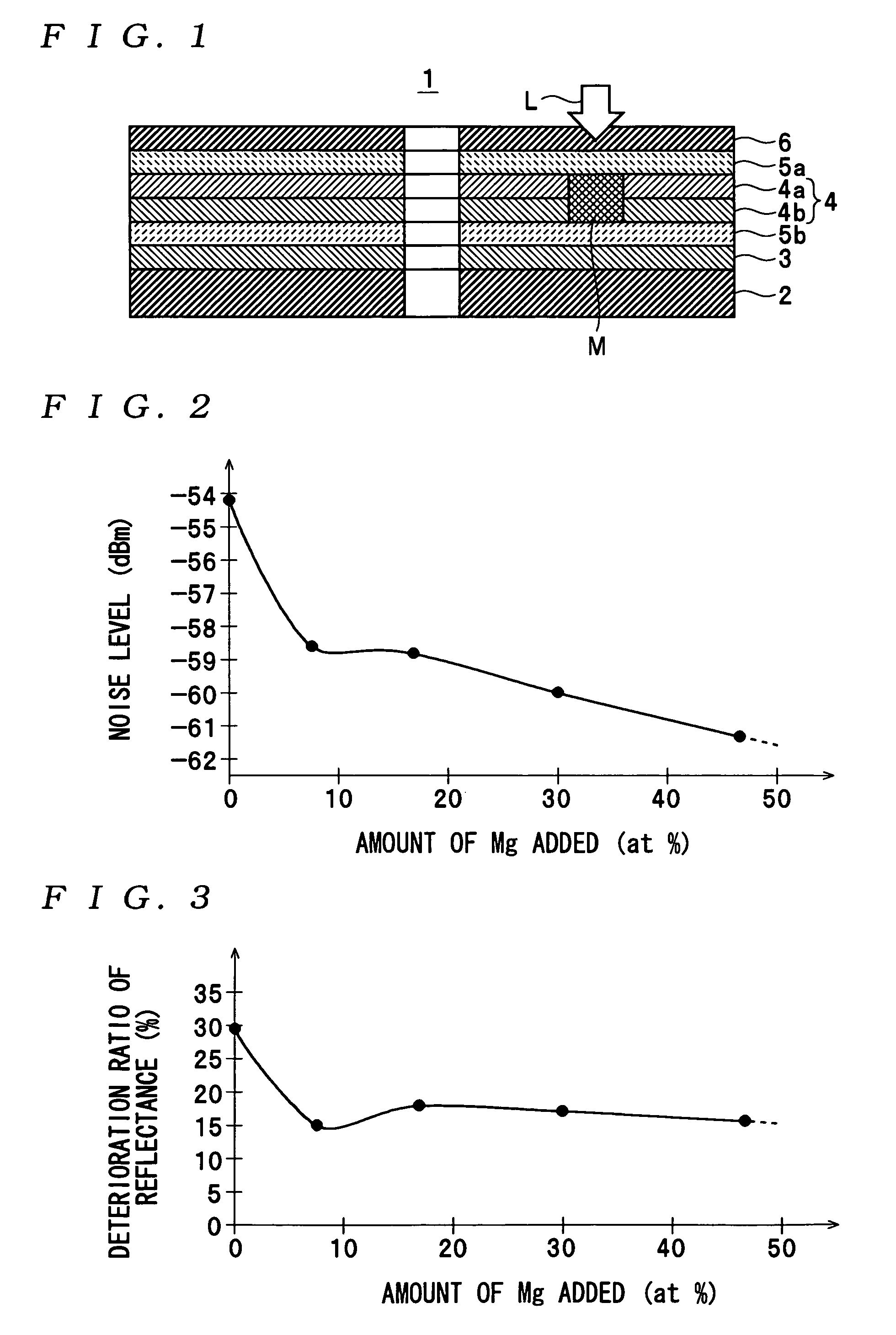
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level and improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as a main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as a main component and having Mg added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS20050048249A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioLayered productsRecord information storageNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level, improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as the main component and having Cu added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
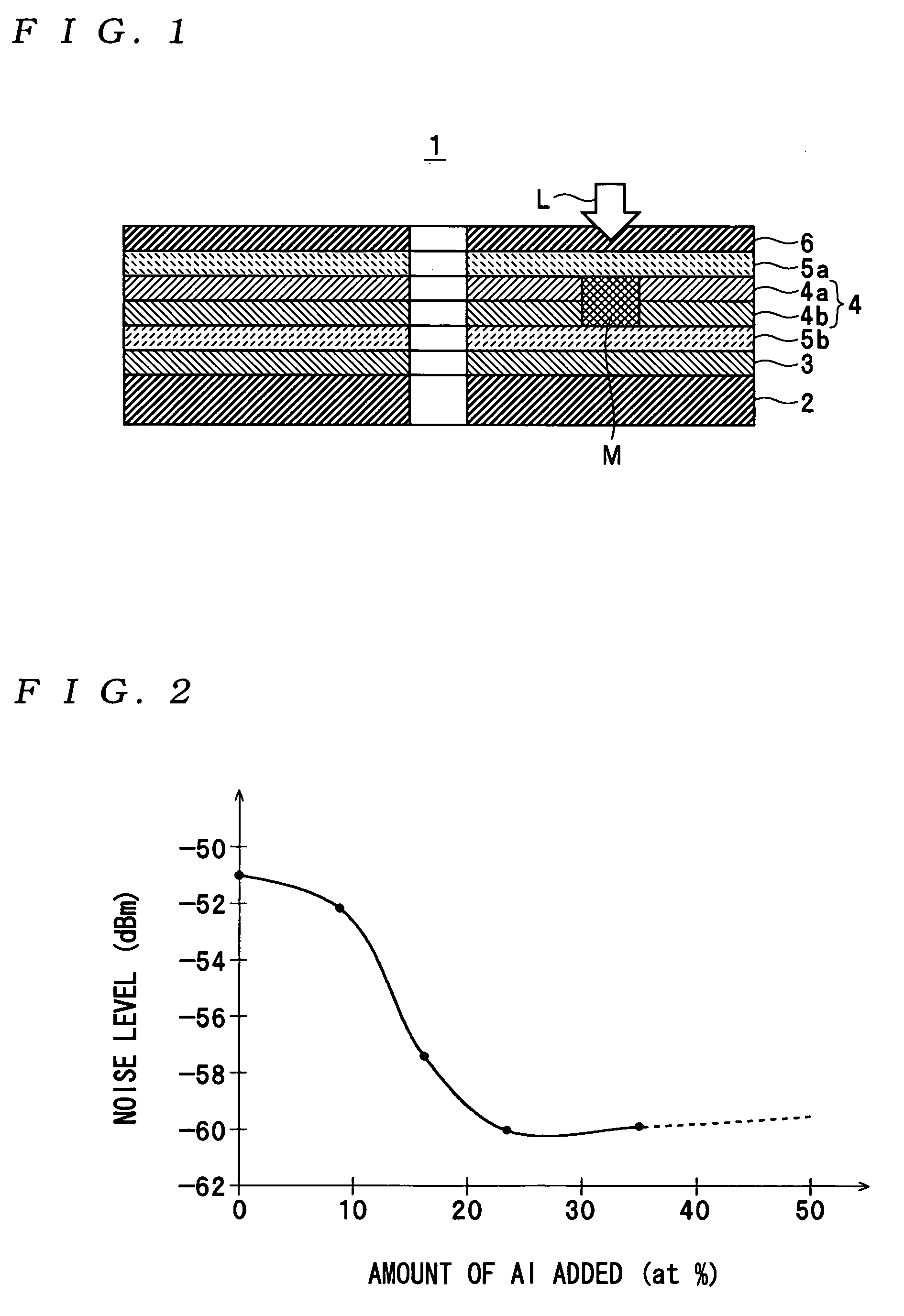
InactiveUS20030202452A1Minimal loadingHigh long-term storage reliabilityRadiation applicationsLayered productsNoise levelRecording layer
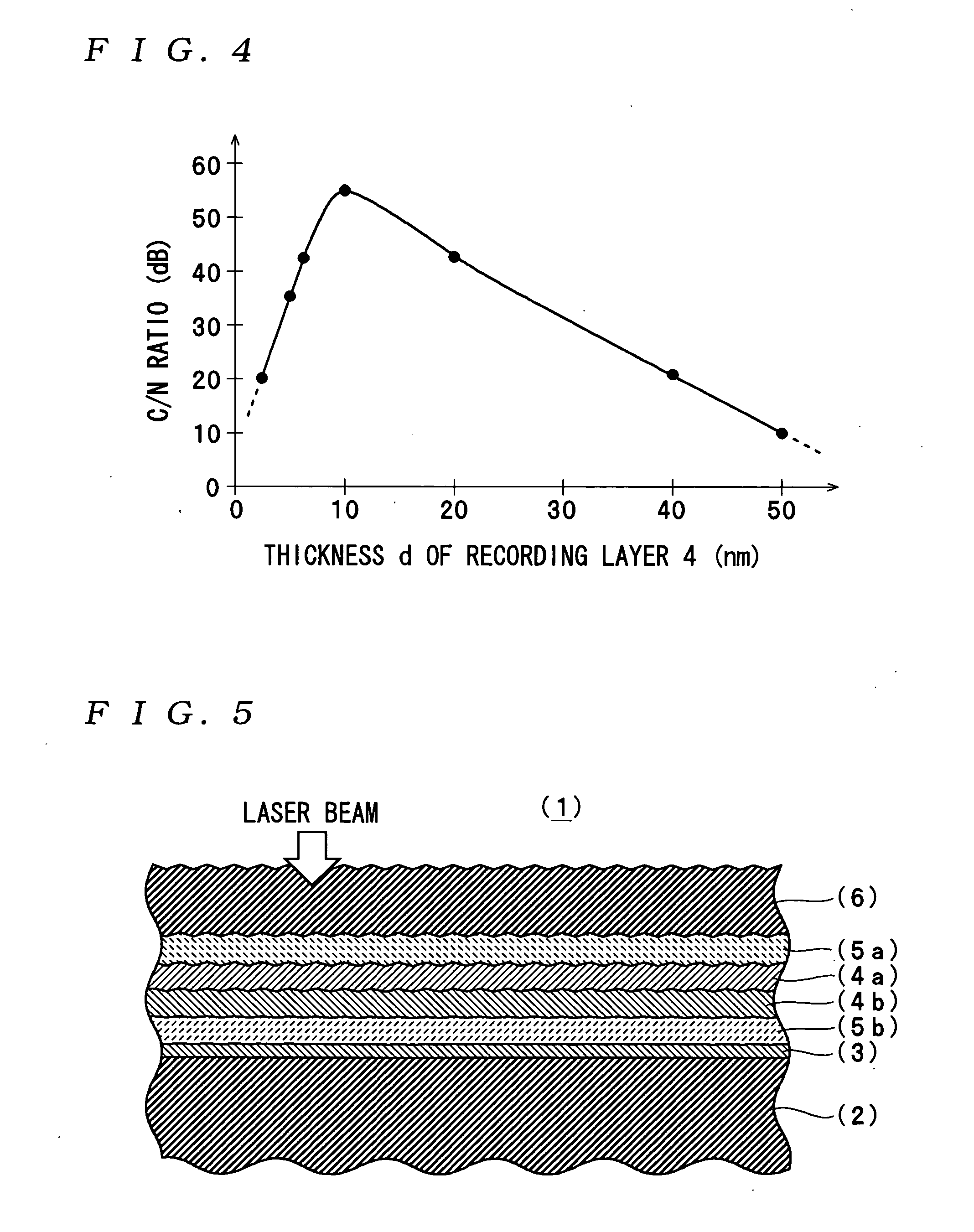
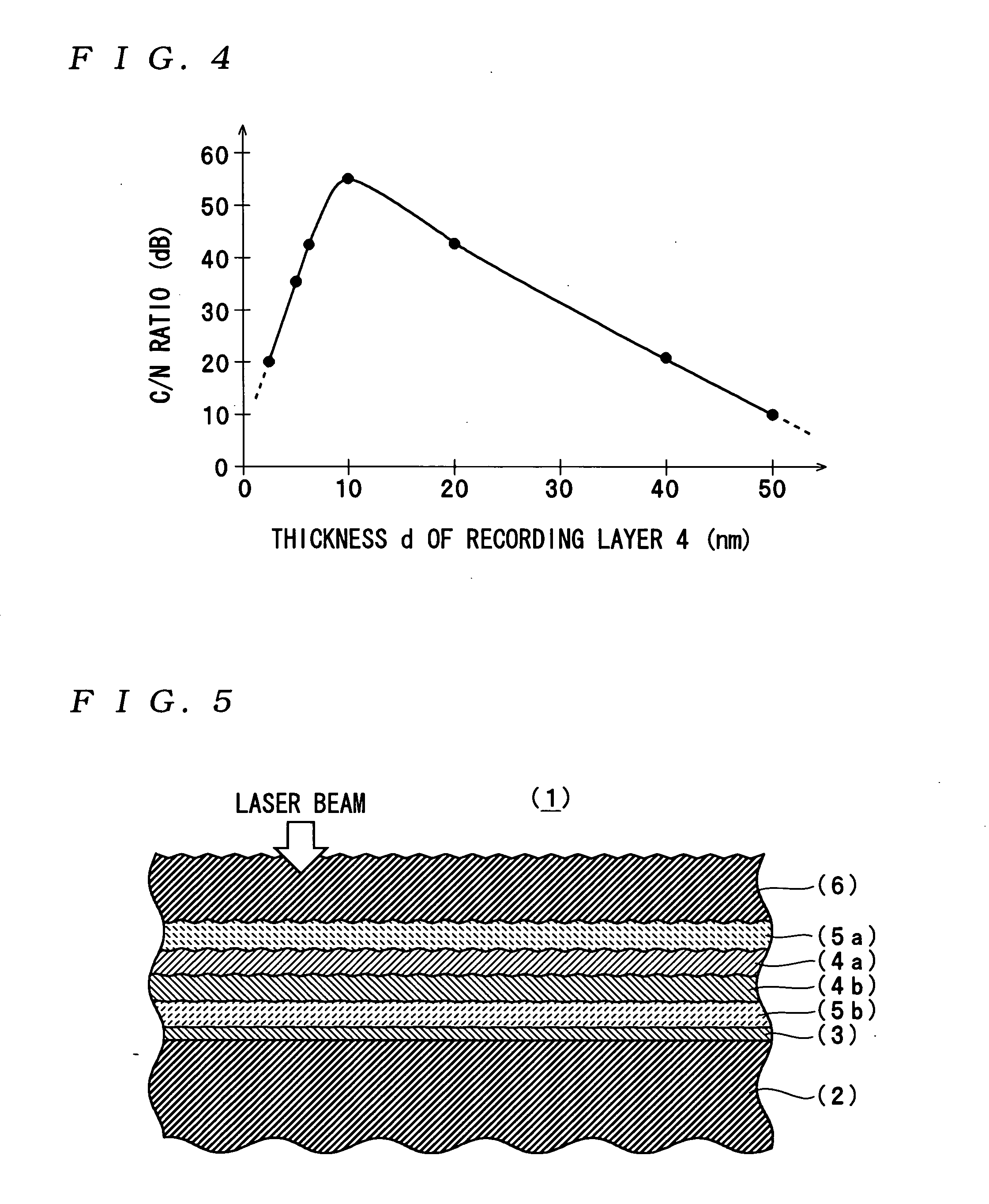
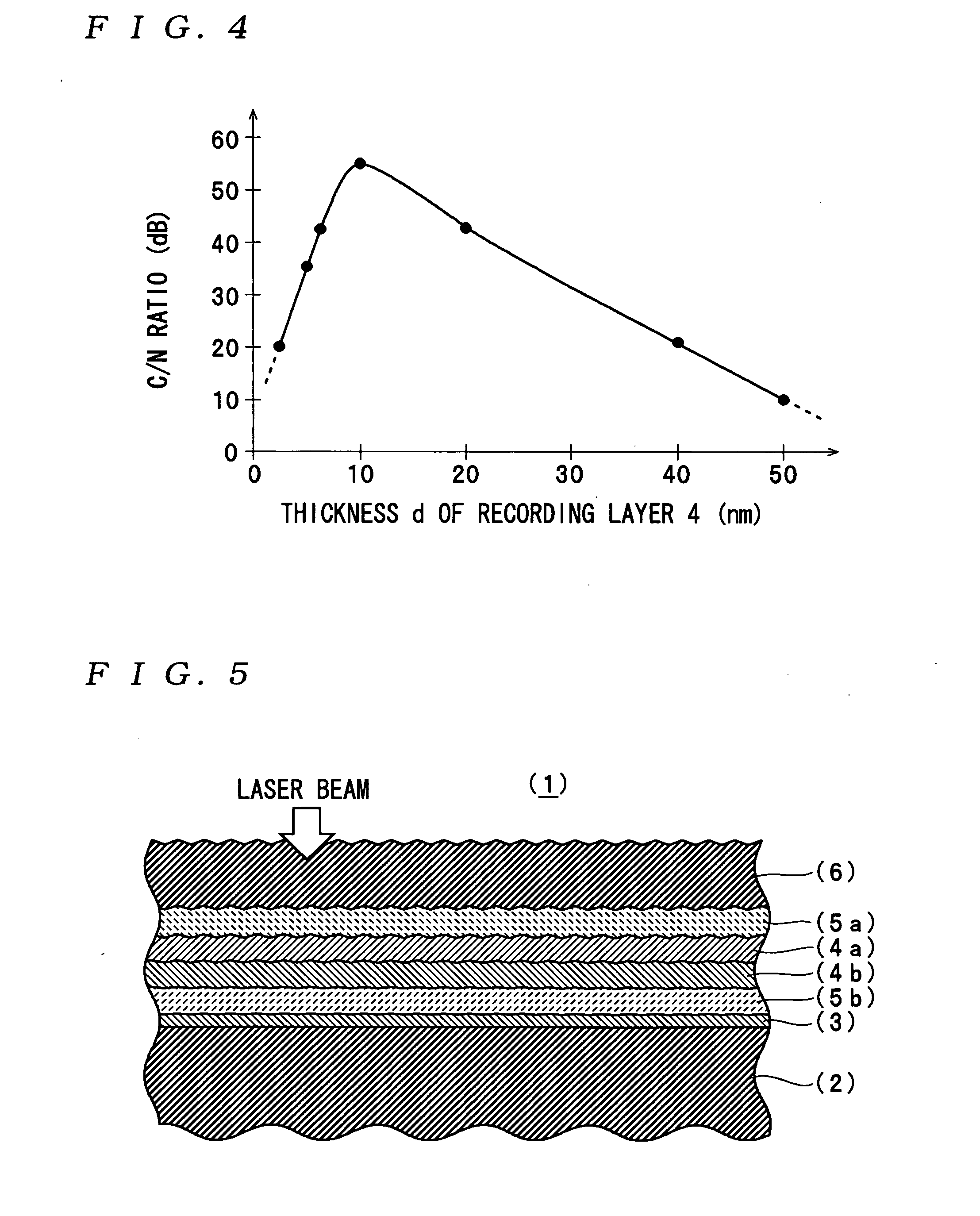
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Ge, C, Sn, Zn and Cu as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing Al as a primary component, the optical recording medium being constituted to be irradiated by a laser beam projected onto the side opposite from the substrate and the total thickness of the first recording layer and the second recording layer being equal to or thinner than 40 nm. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to decrease a noise level and improve a C / N ratio in a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS7160597B2Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingLayered productsNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level and improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as a main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as a main component and having Mg added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS7167440B2Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingLayered productsNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level, improve the C / N ratio and store record data for a long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Al as the main component and having Ti added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium and method for recording data in the same
InactiveUS20040038080A1Good signalImprove carrier-to-noise ratioRecording strategiesLayered productsRecording layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, two recording layers provided on the substrate and two dielectric layers each provided adjacent to one of the recording layers, the optical recording medium being constituted so that when it is irradiated with a laser beam having a wavelength lambda via an objective lens having a numerical aperture NA satisfying lambda / NA<=640 nm from the side opposite from the substrate, a record mark whose reflection coefficient is different from those of other regions of the recording layers is formed in the recording layers and at least a part of a region(s) of the dielectric layers adjacent to the record mark is crystallized to form a crystallized region. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reproduce a signal having excellent signal characteristics.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
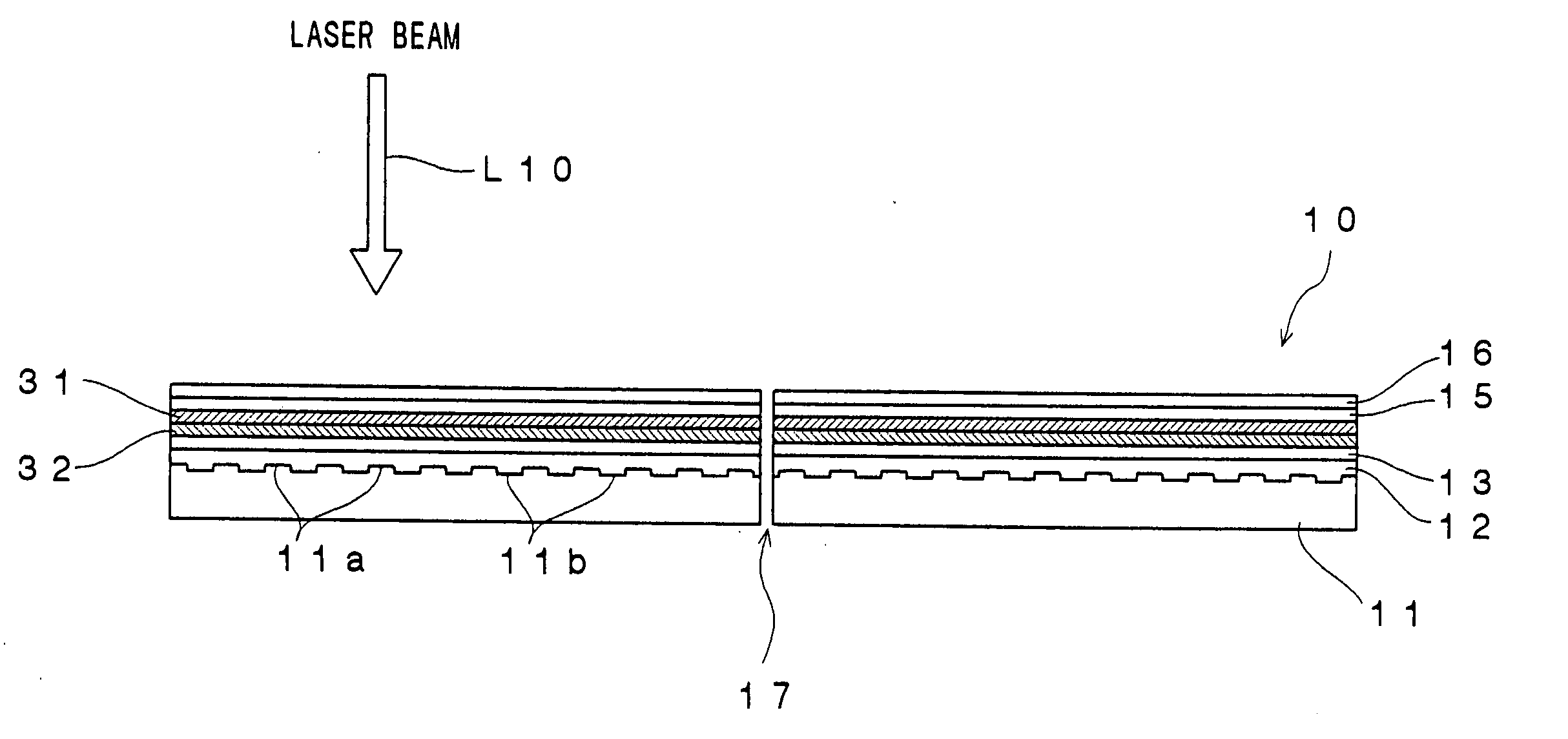
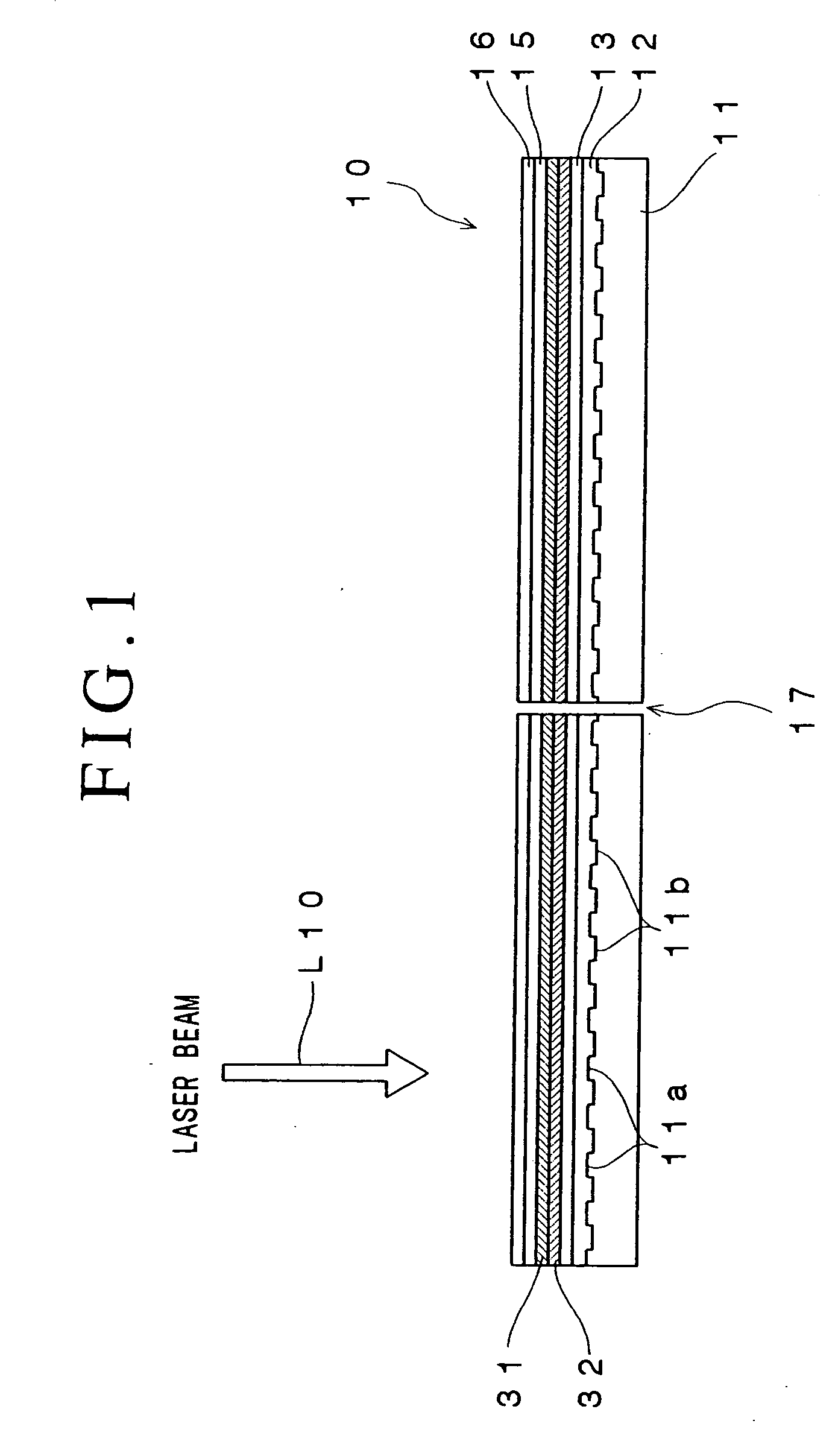
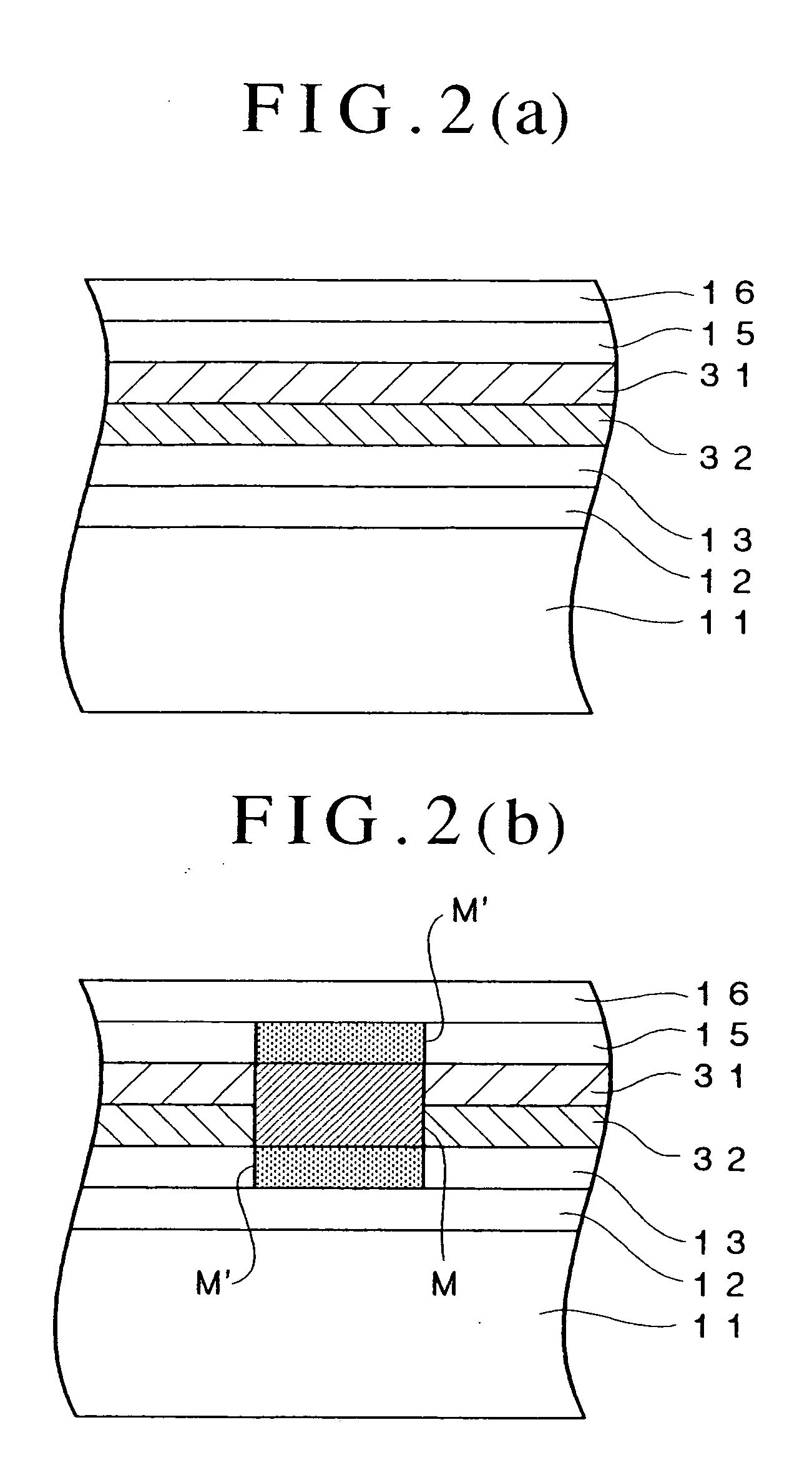
Optical recording medium and process for producing the same, method for recording data on optical recording medium and method for reproducing data from optical recording medium
InactiveUS20060161942A1Increase the number ofImprove carrier-to-noise ratioRecord information storageFlat record carrier containersOptical recordingDielectric layer
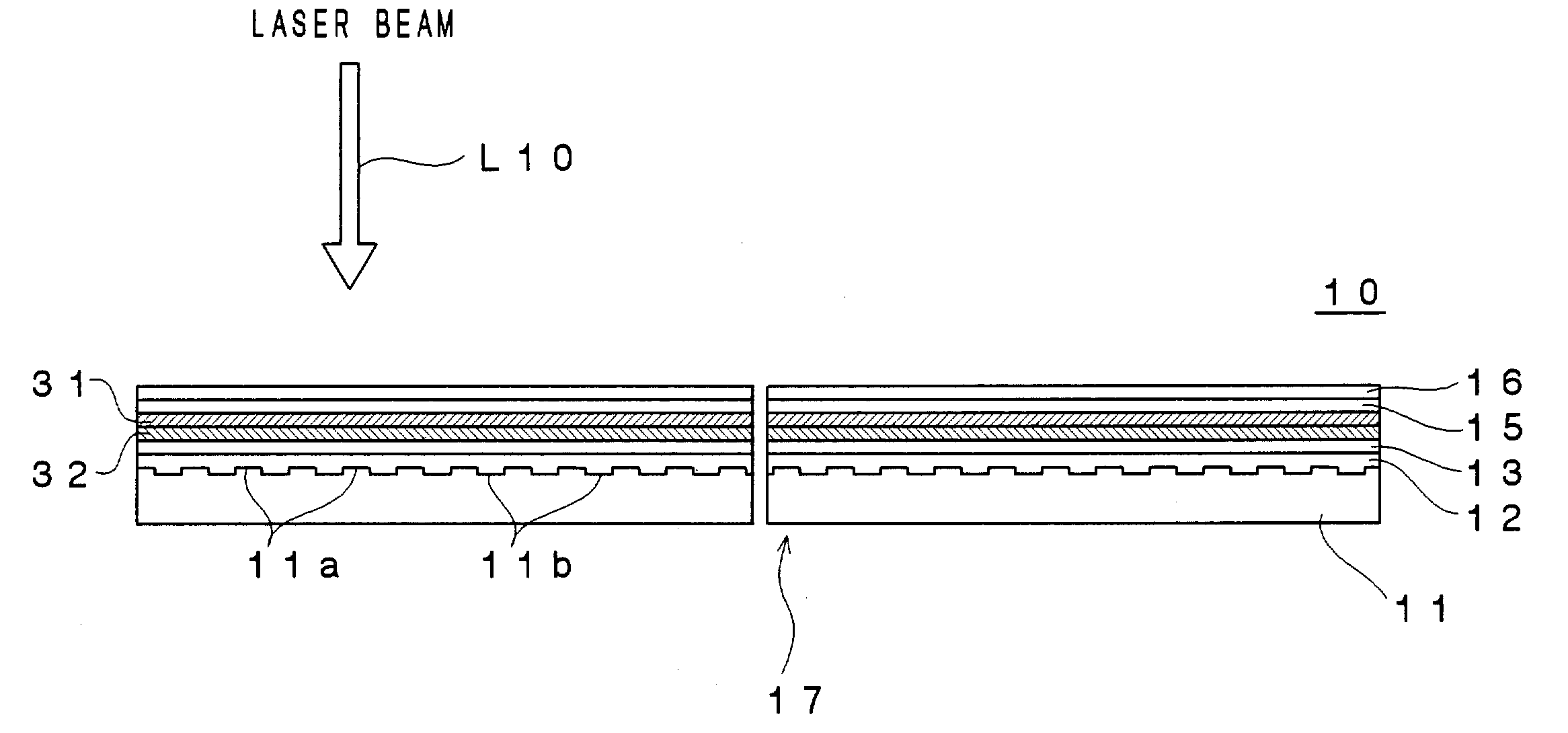
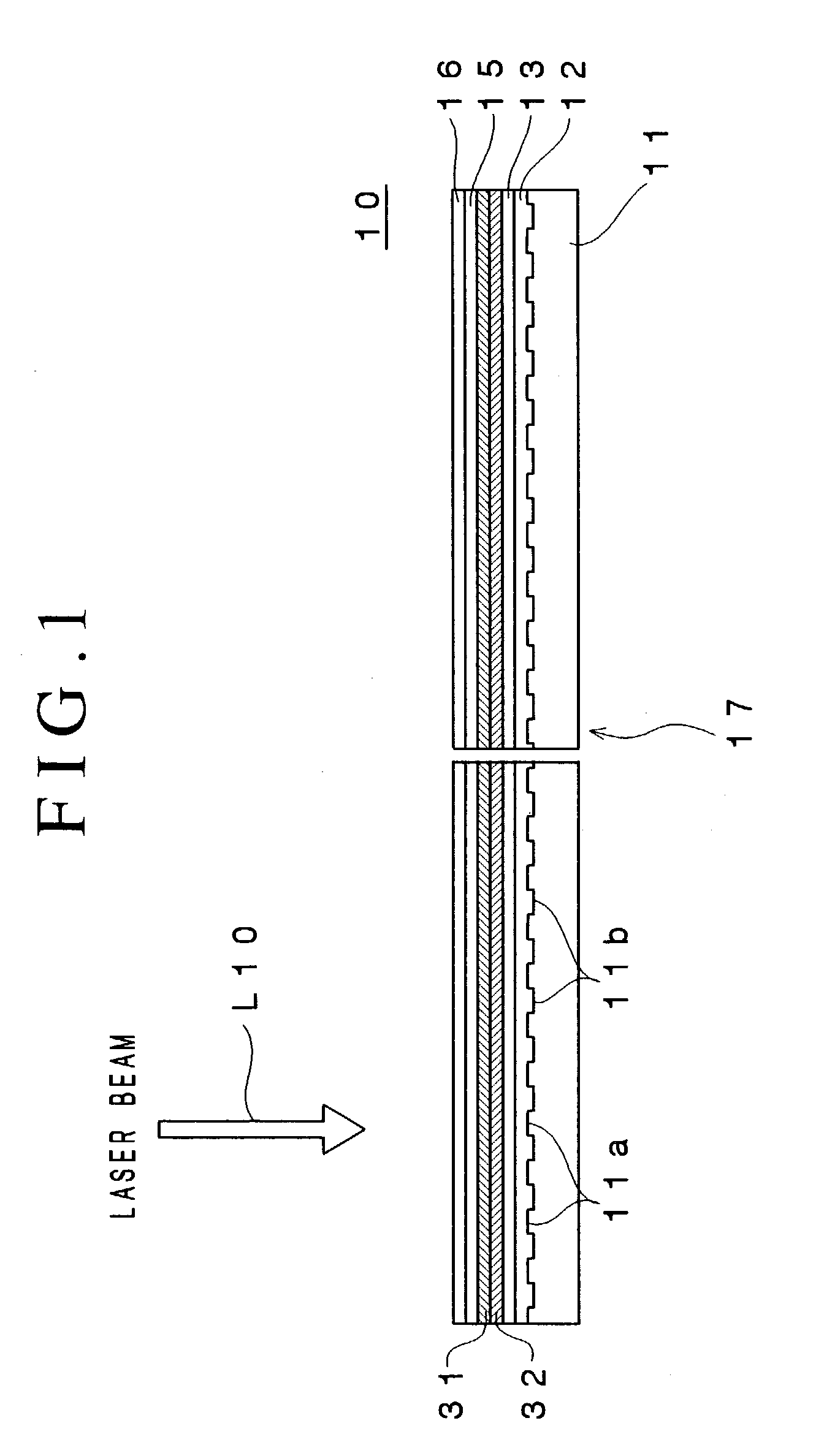
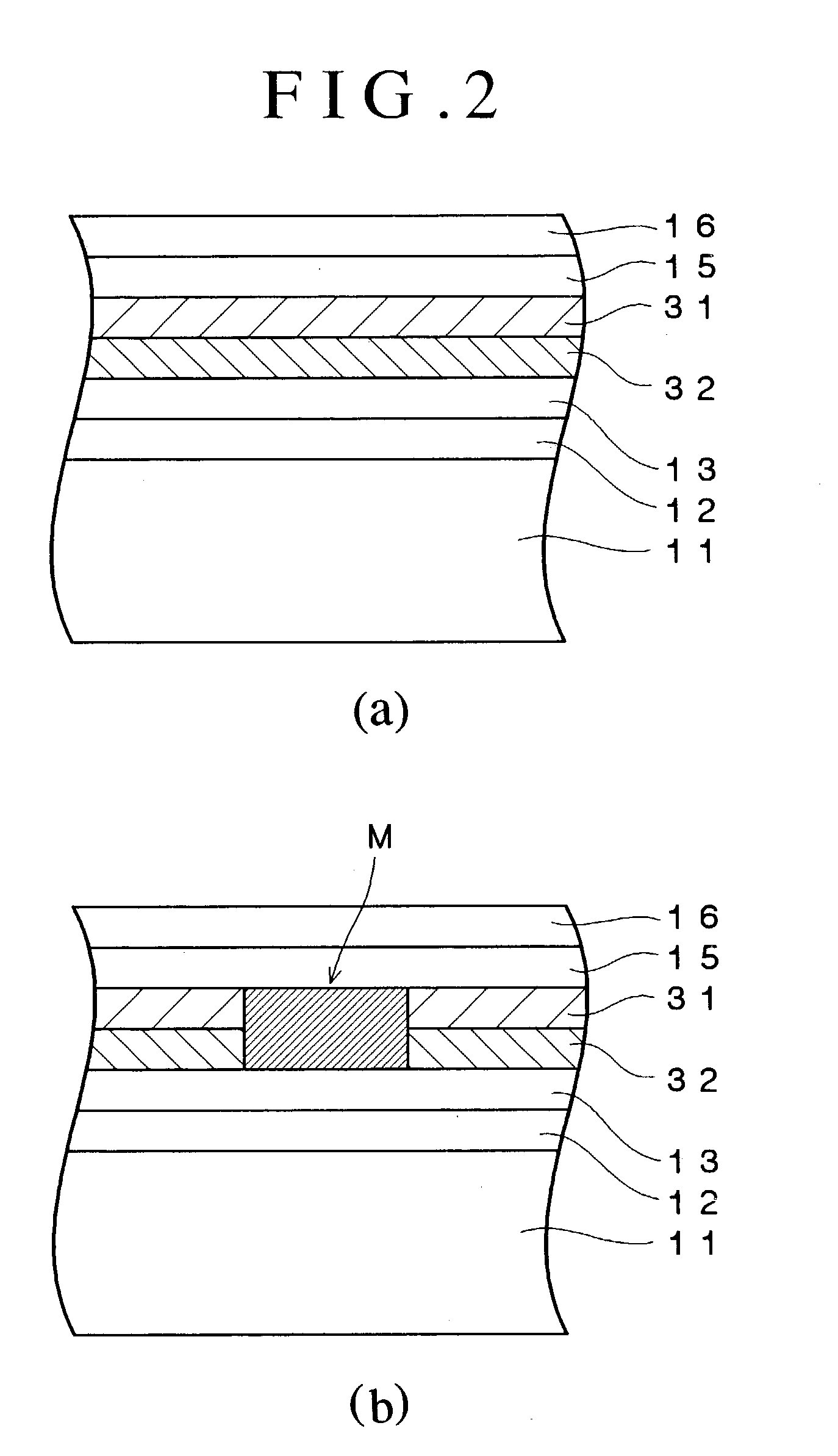
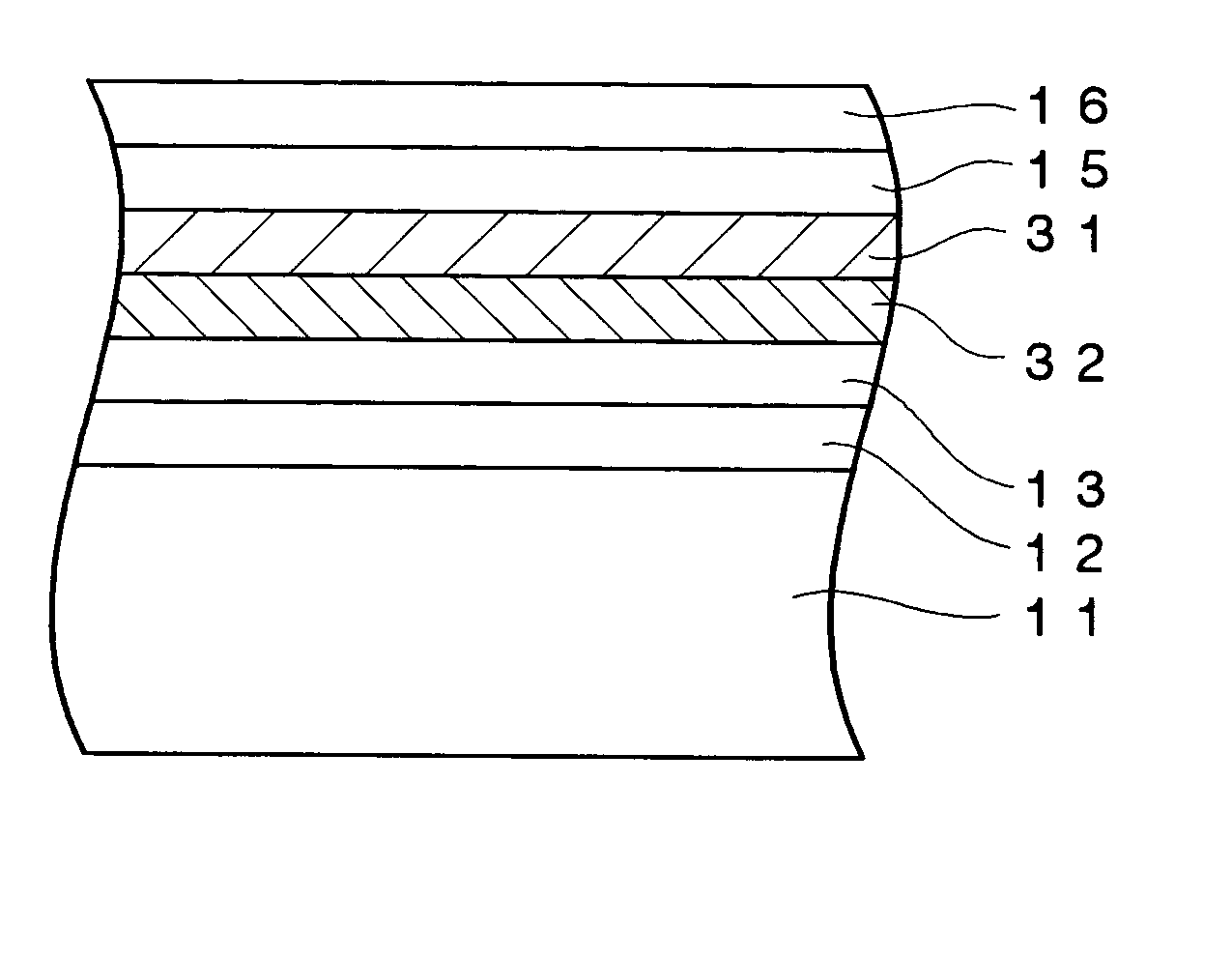
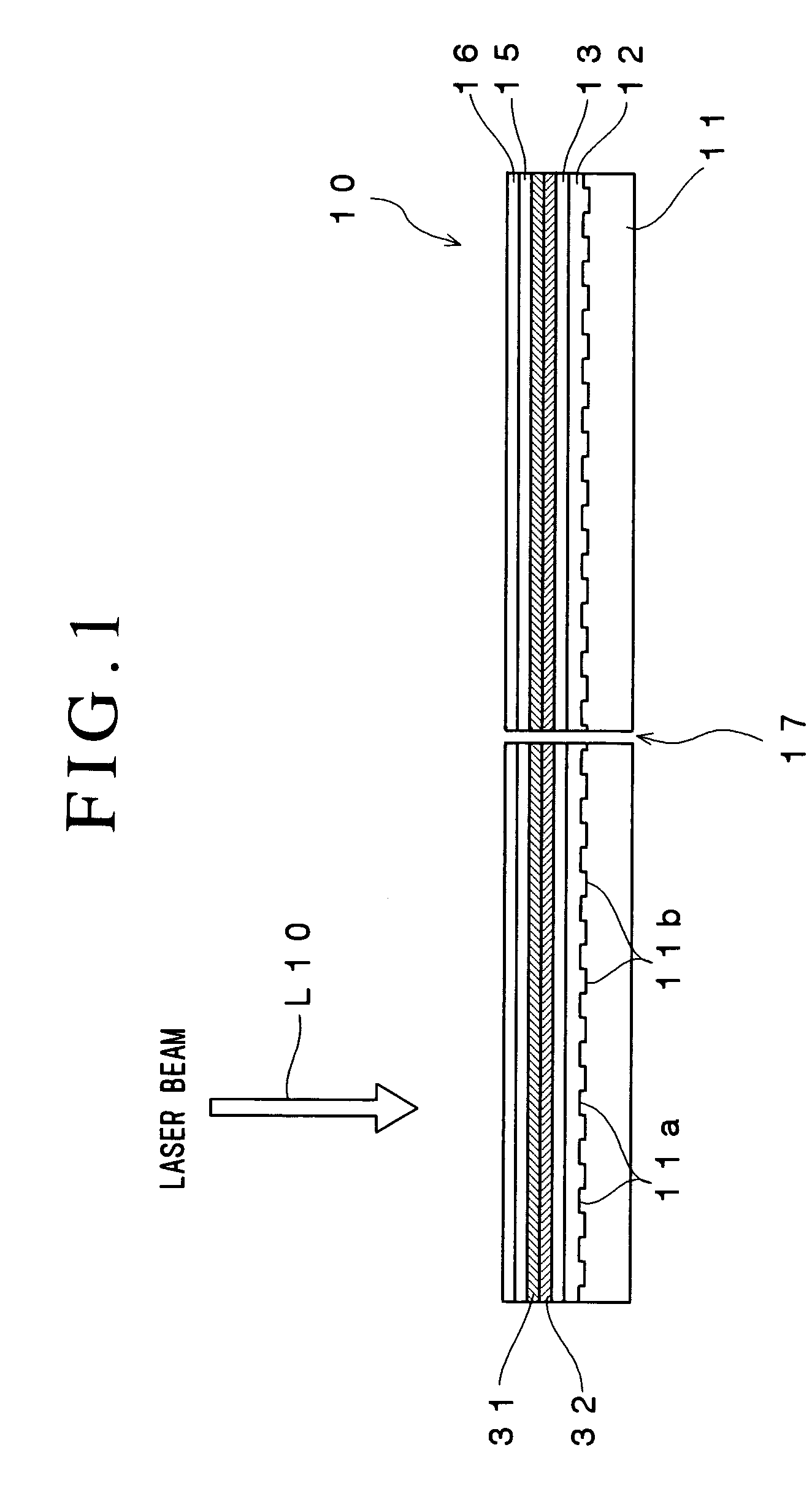
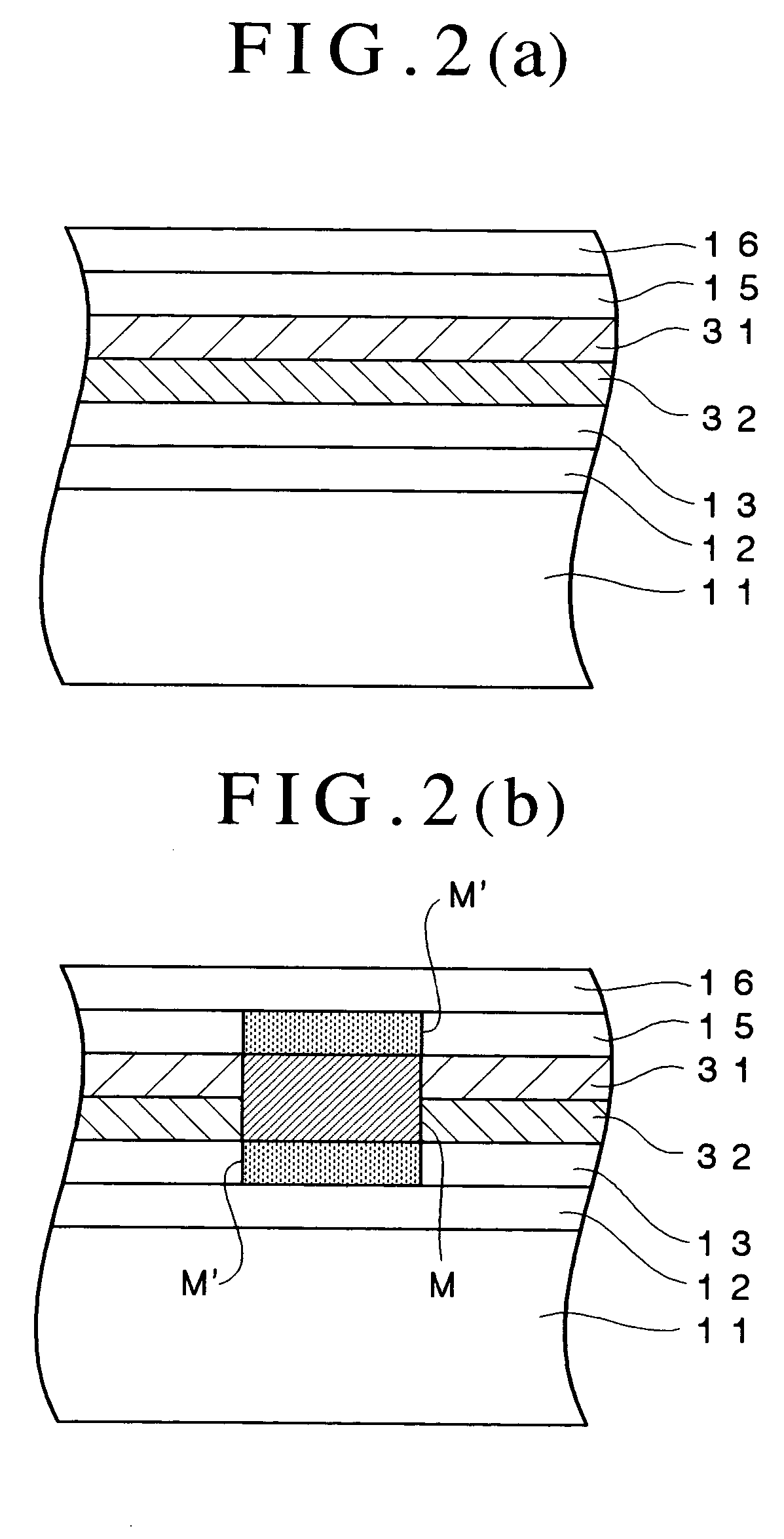
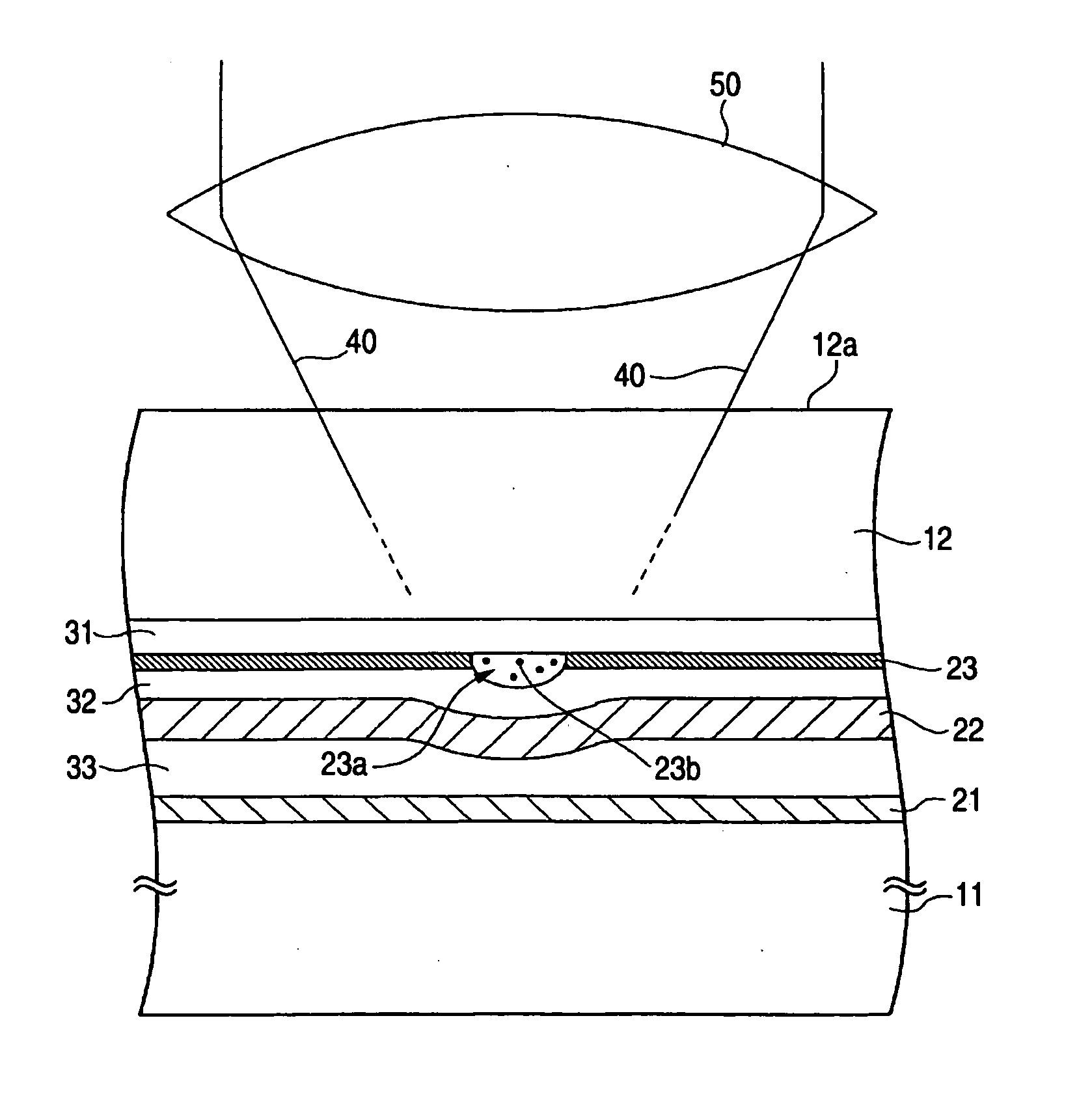
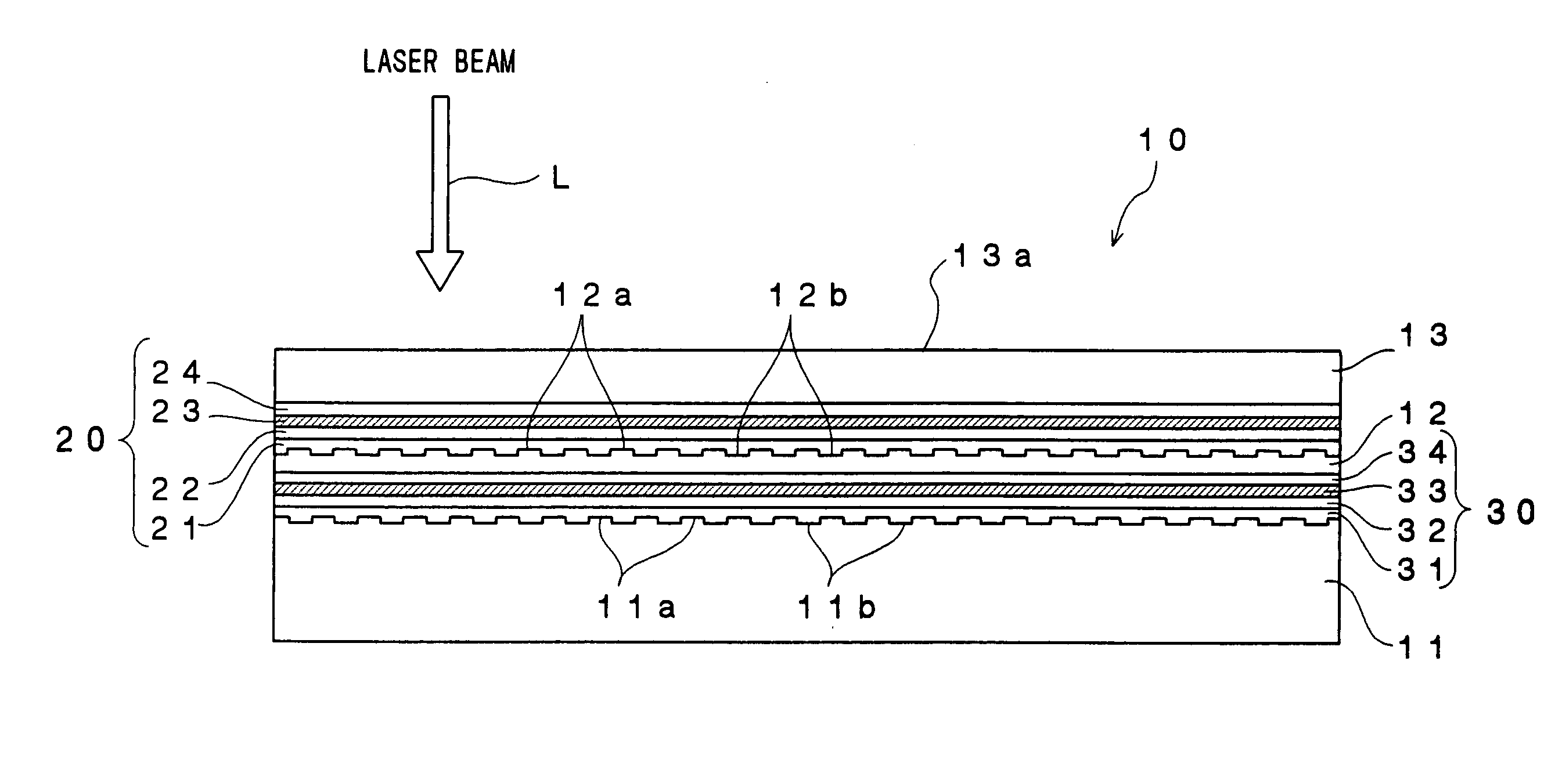
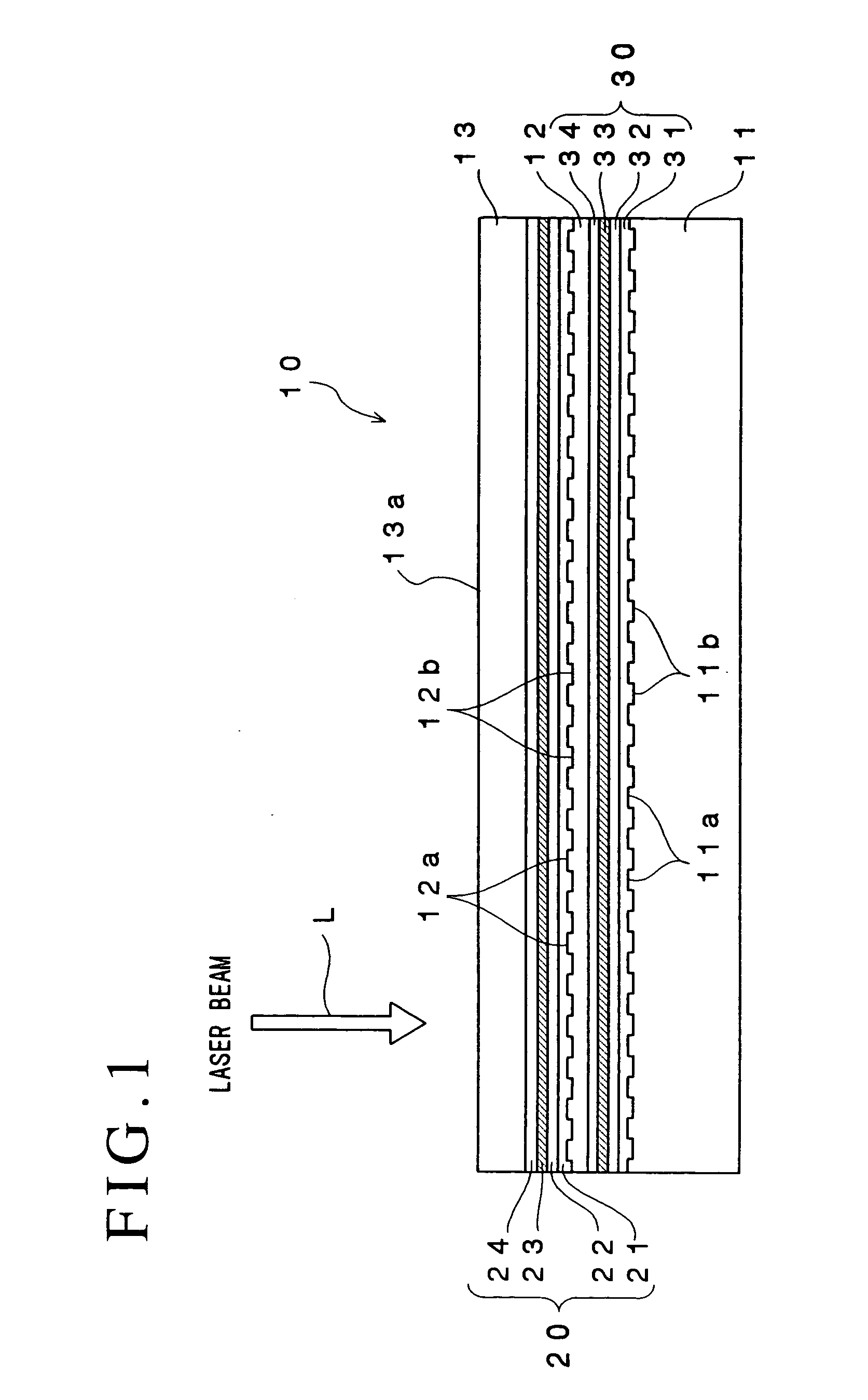
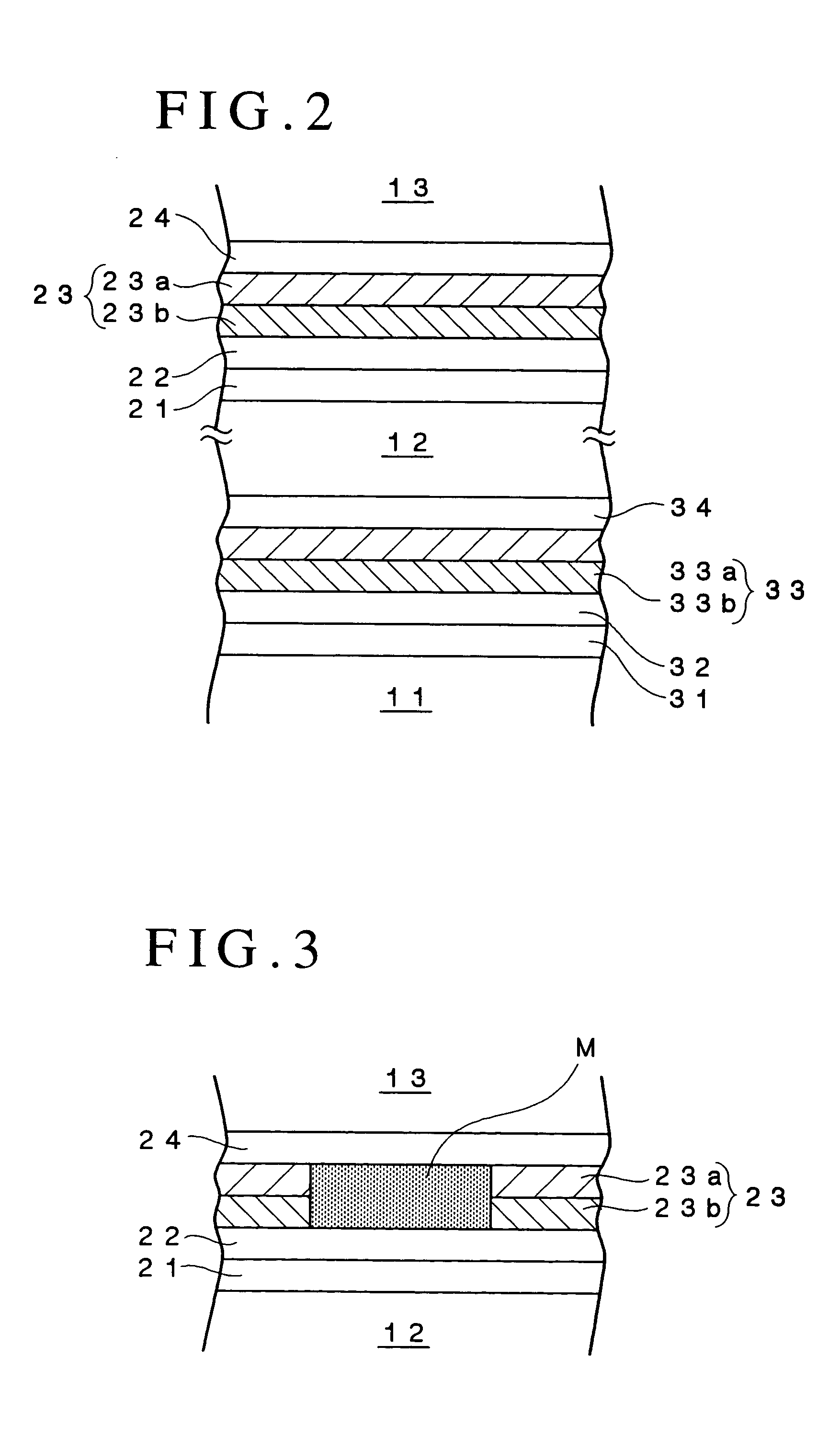
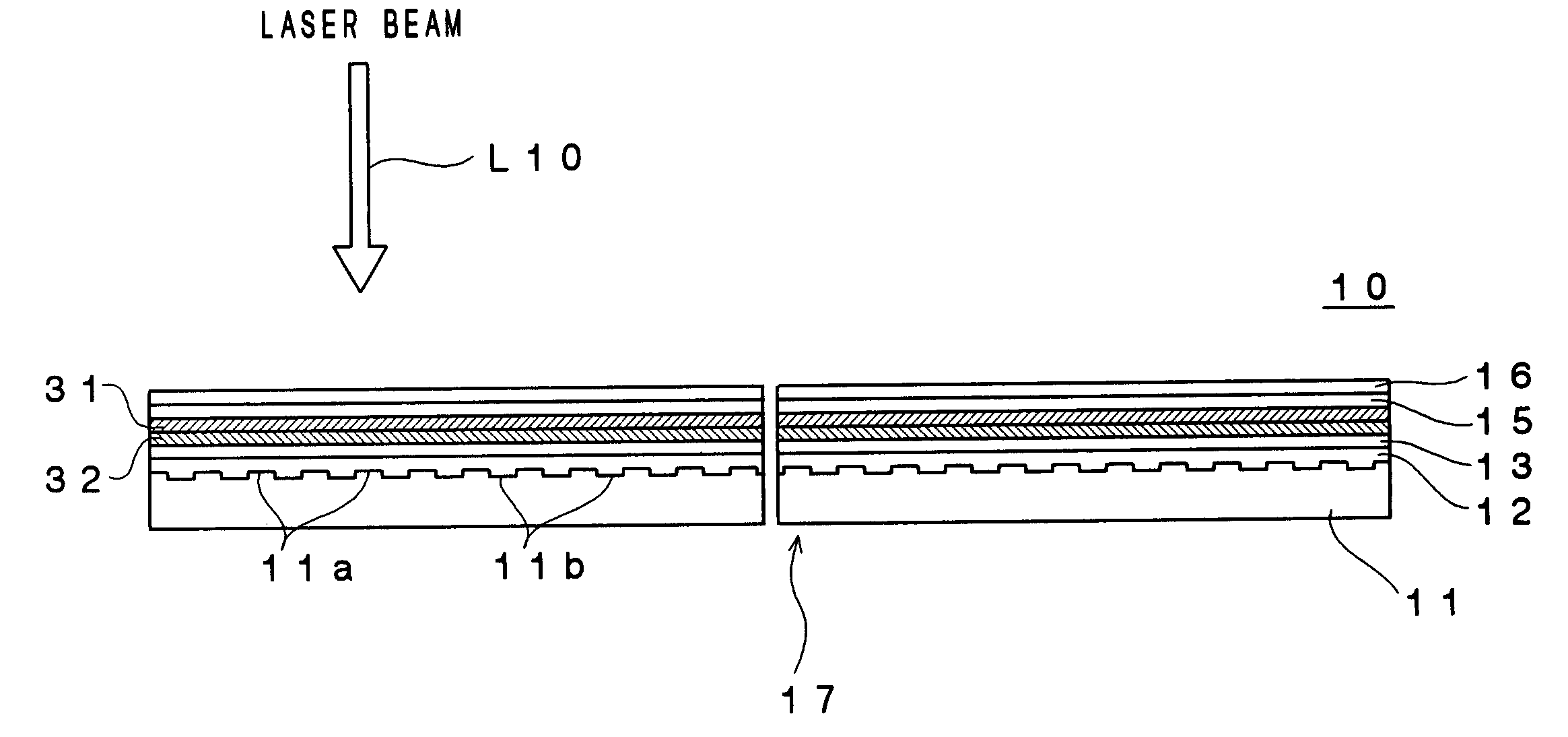
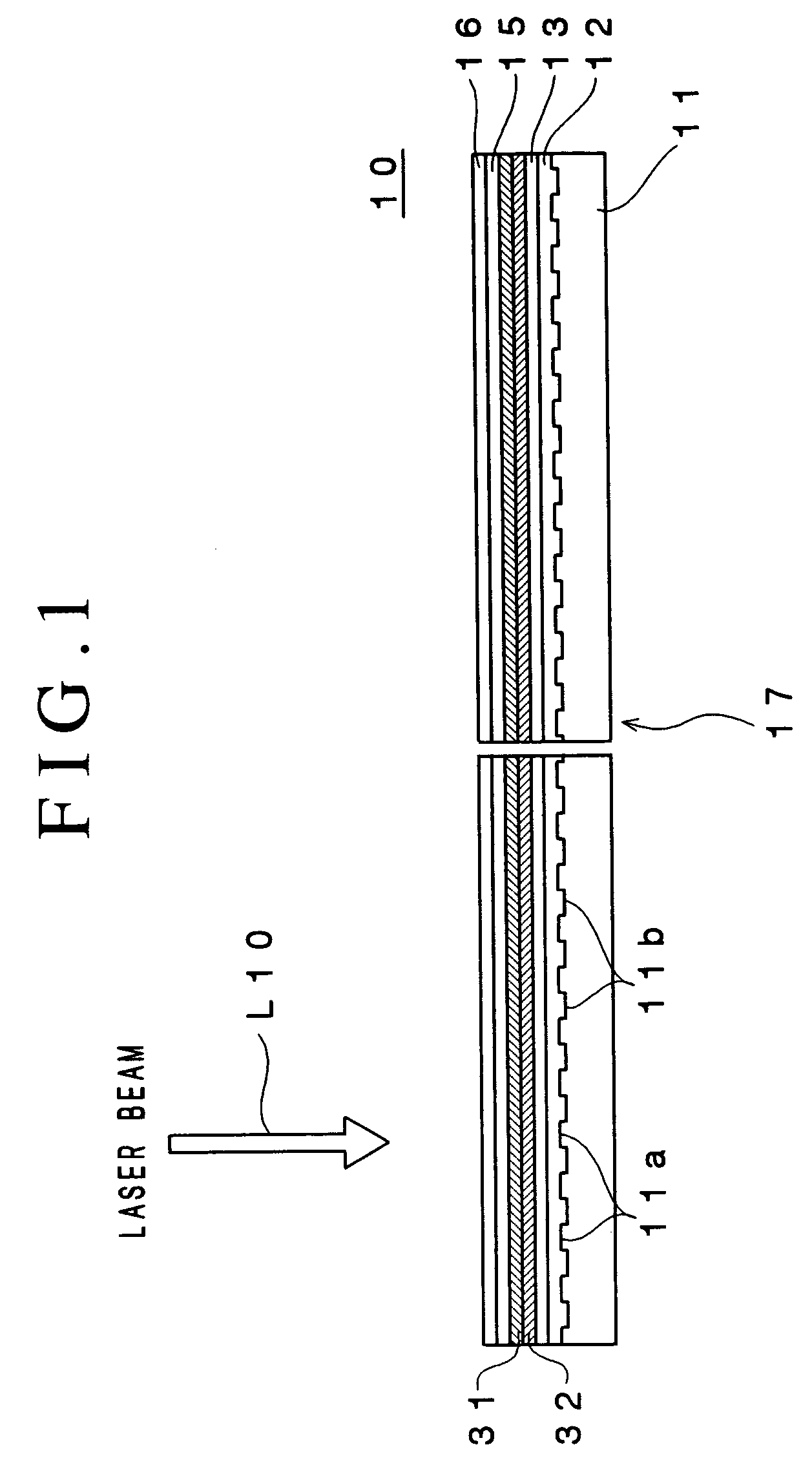
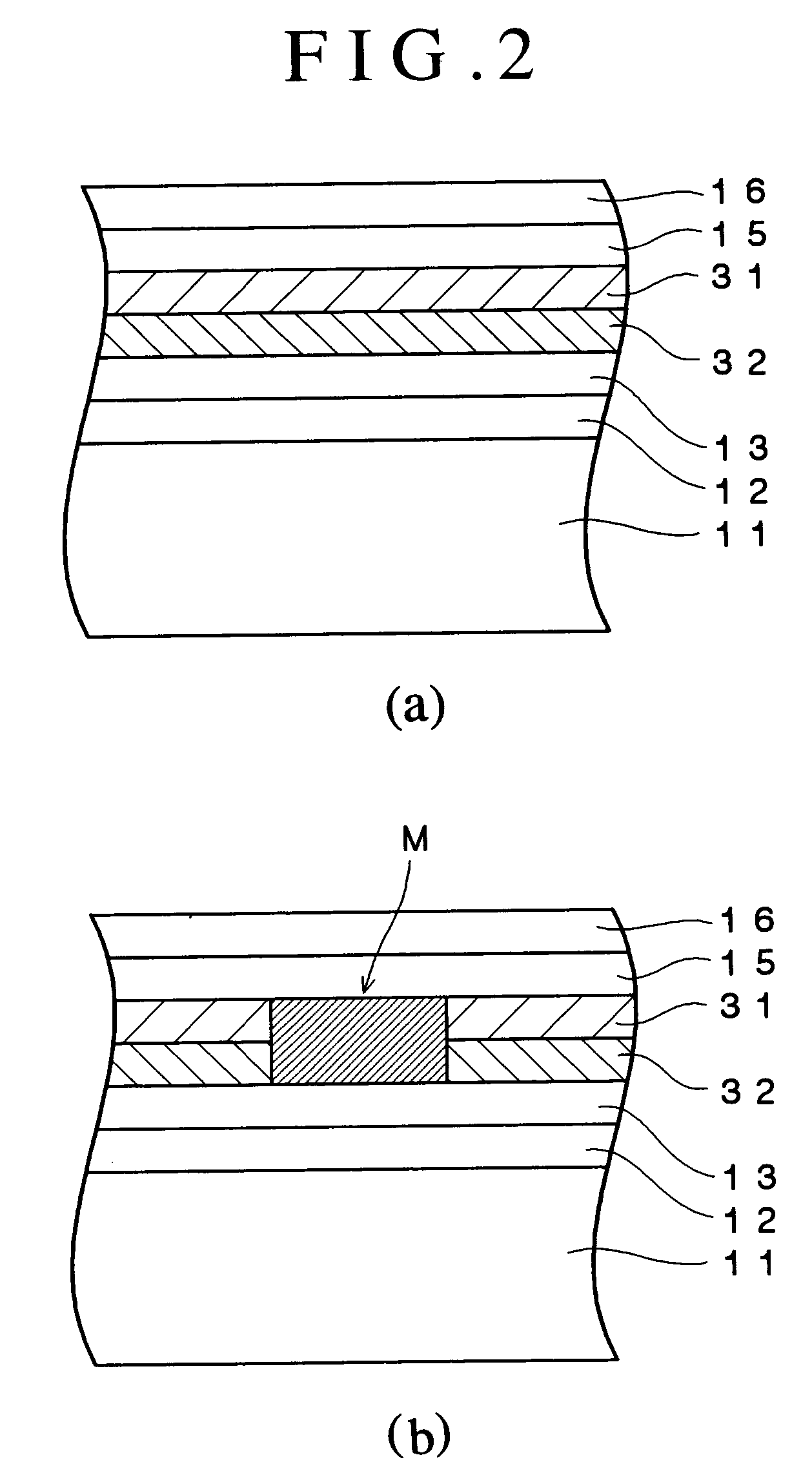
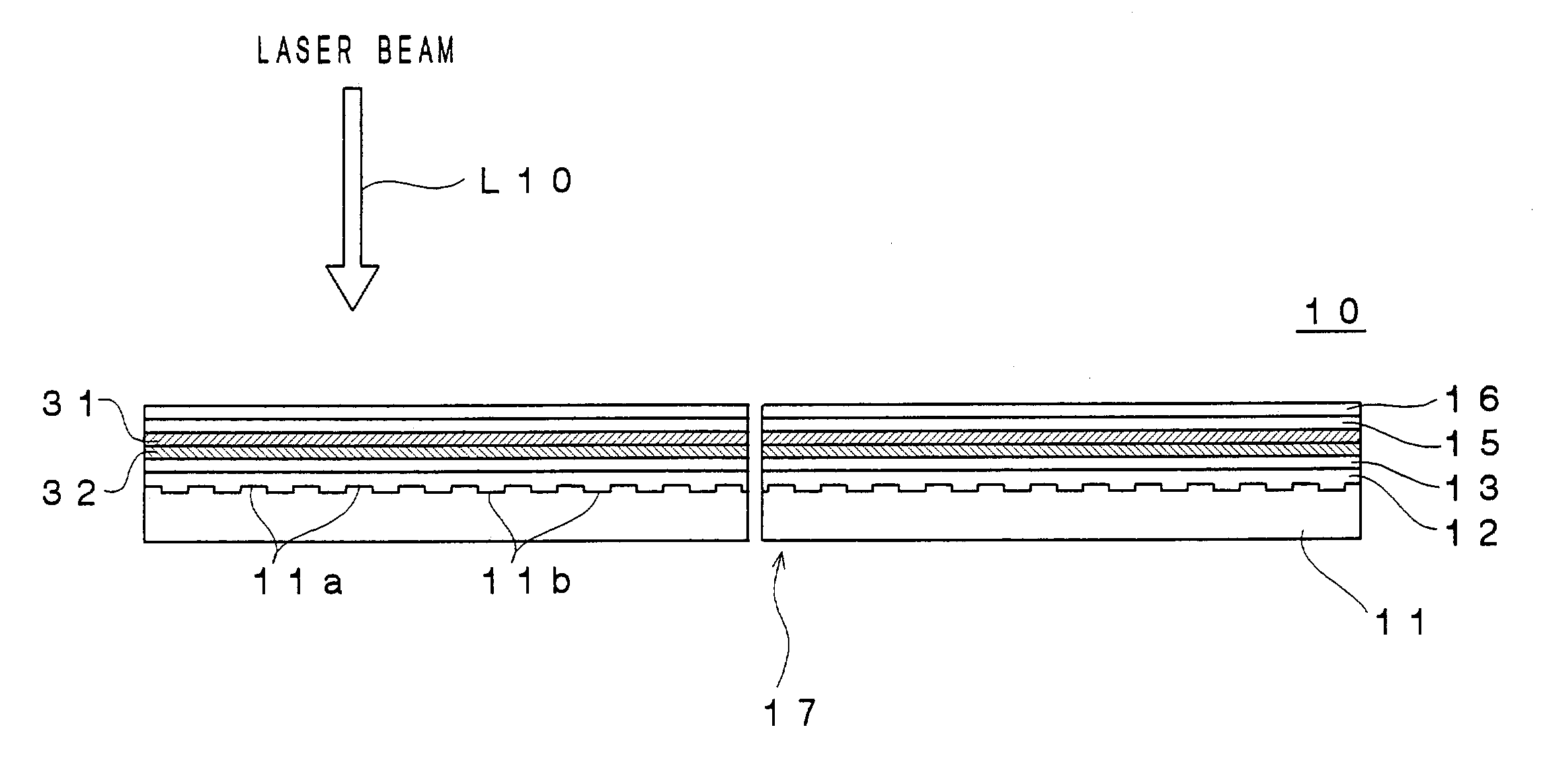
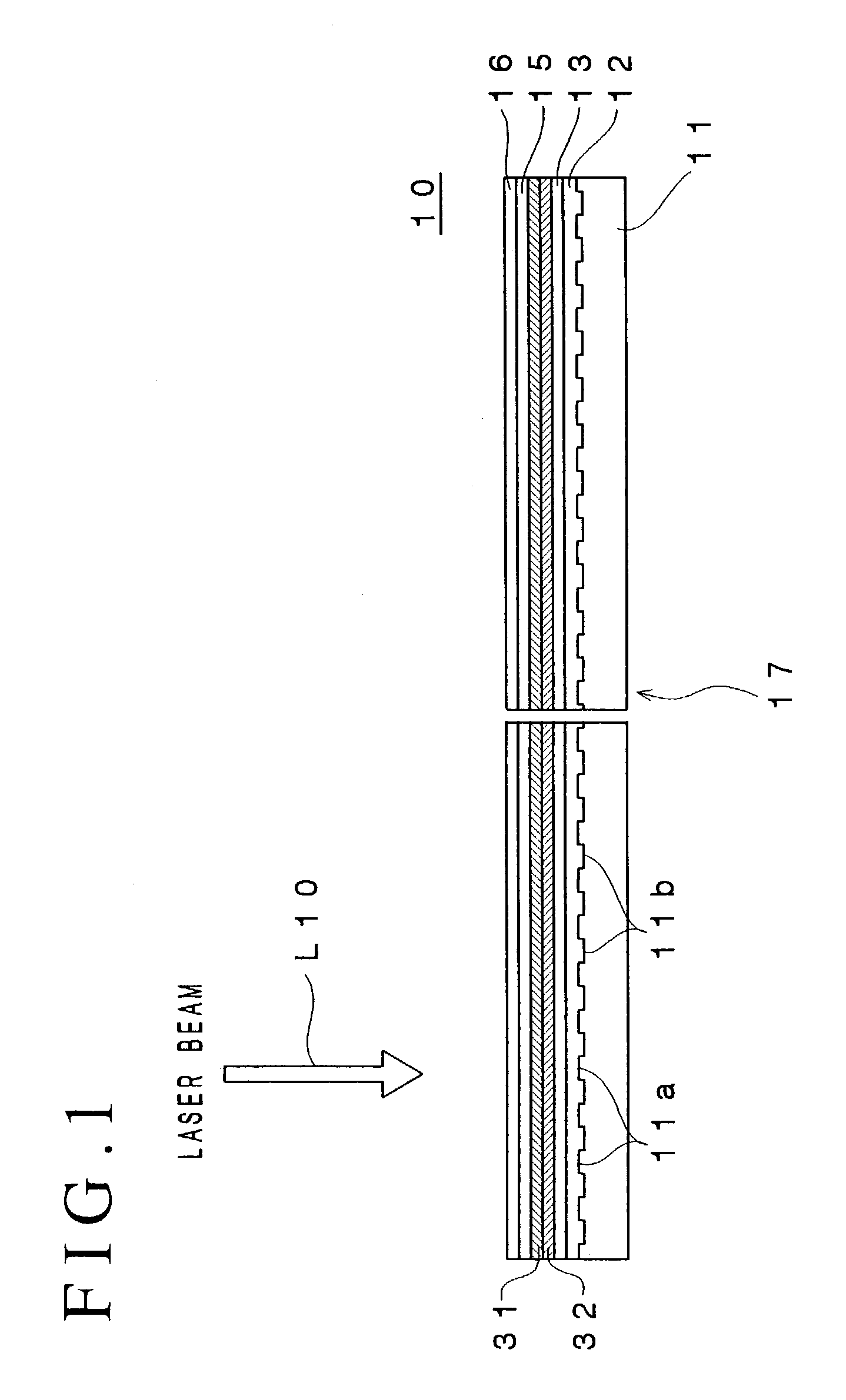
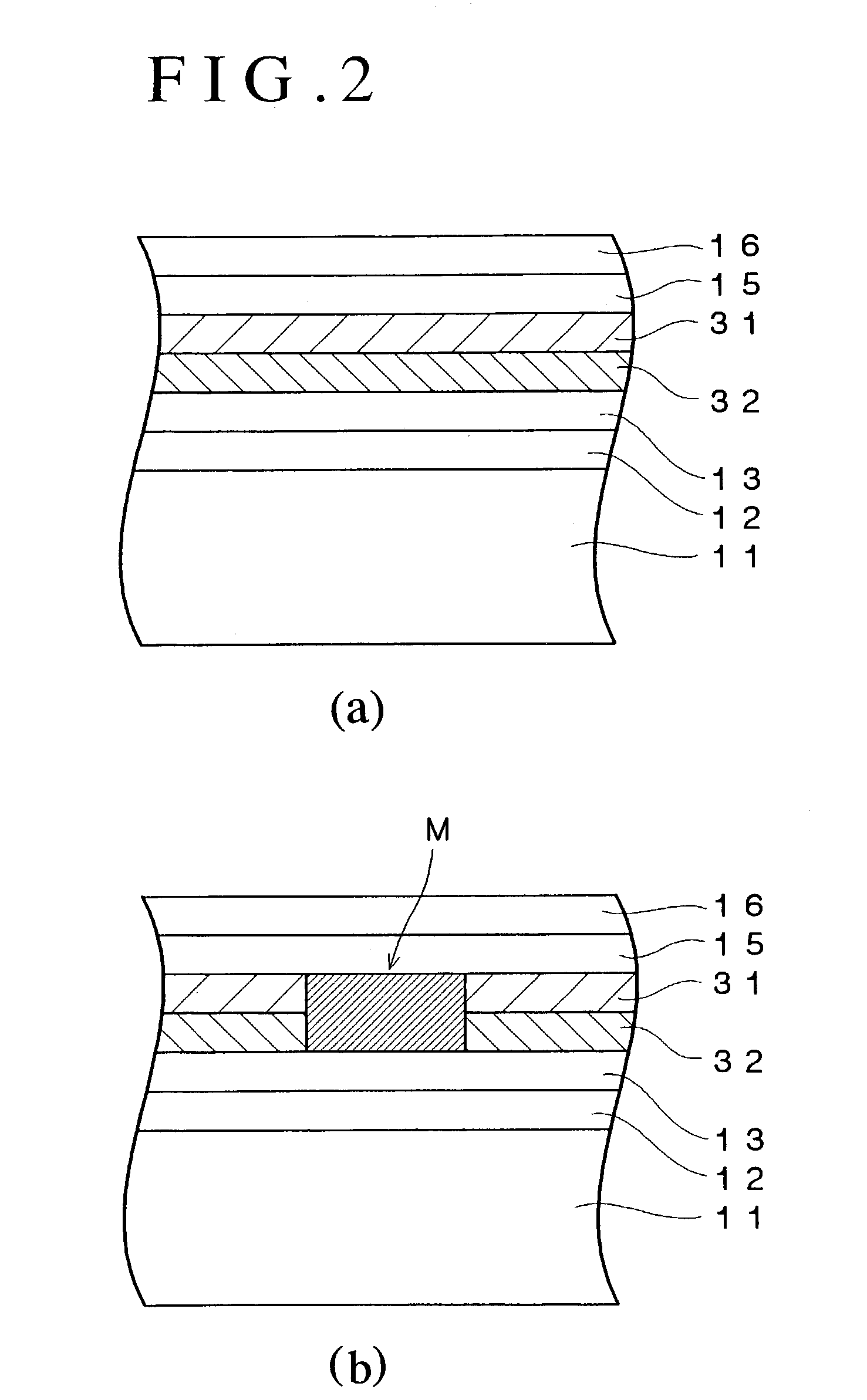
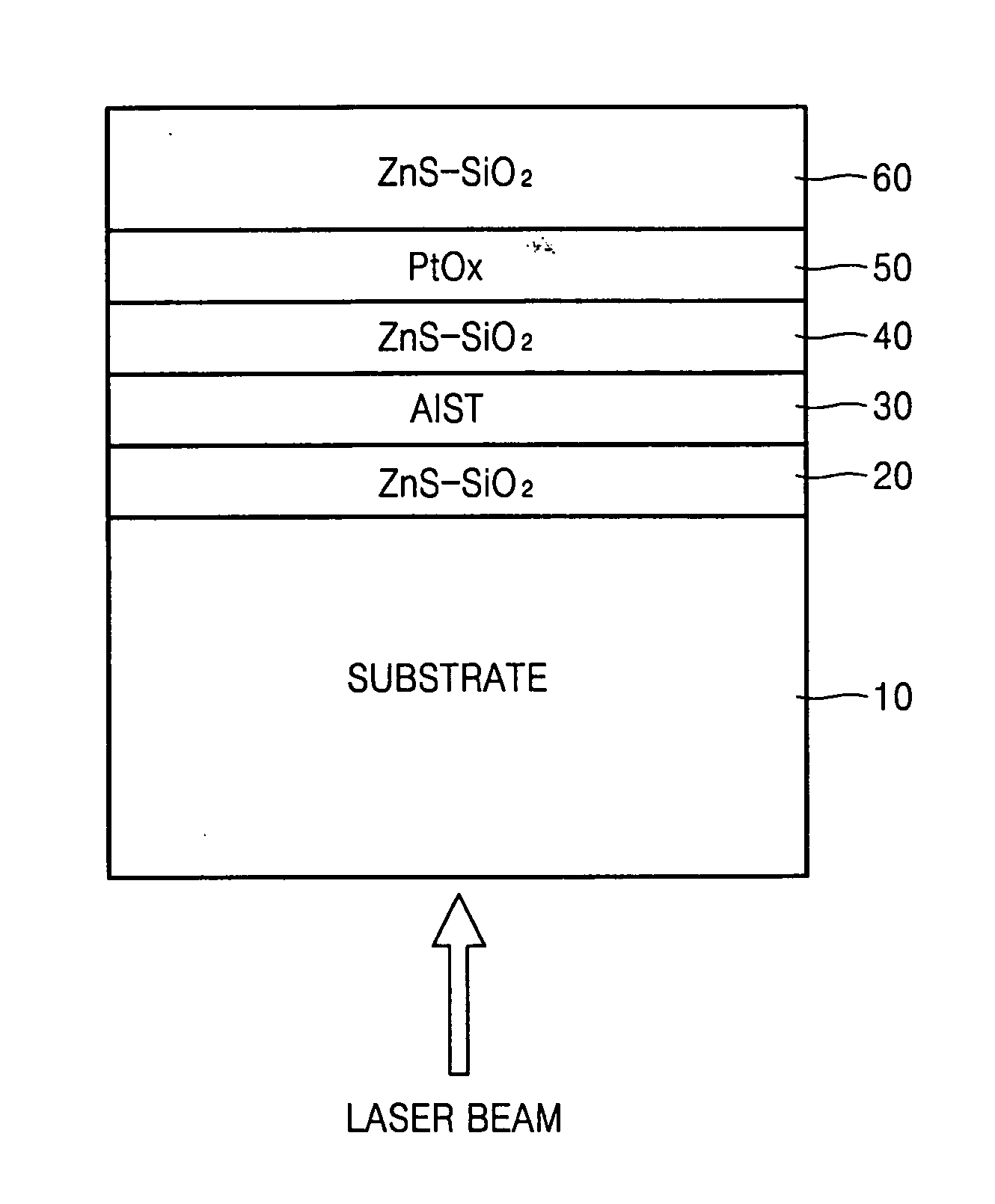
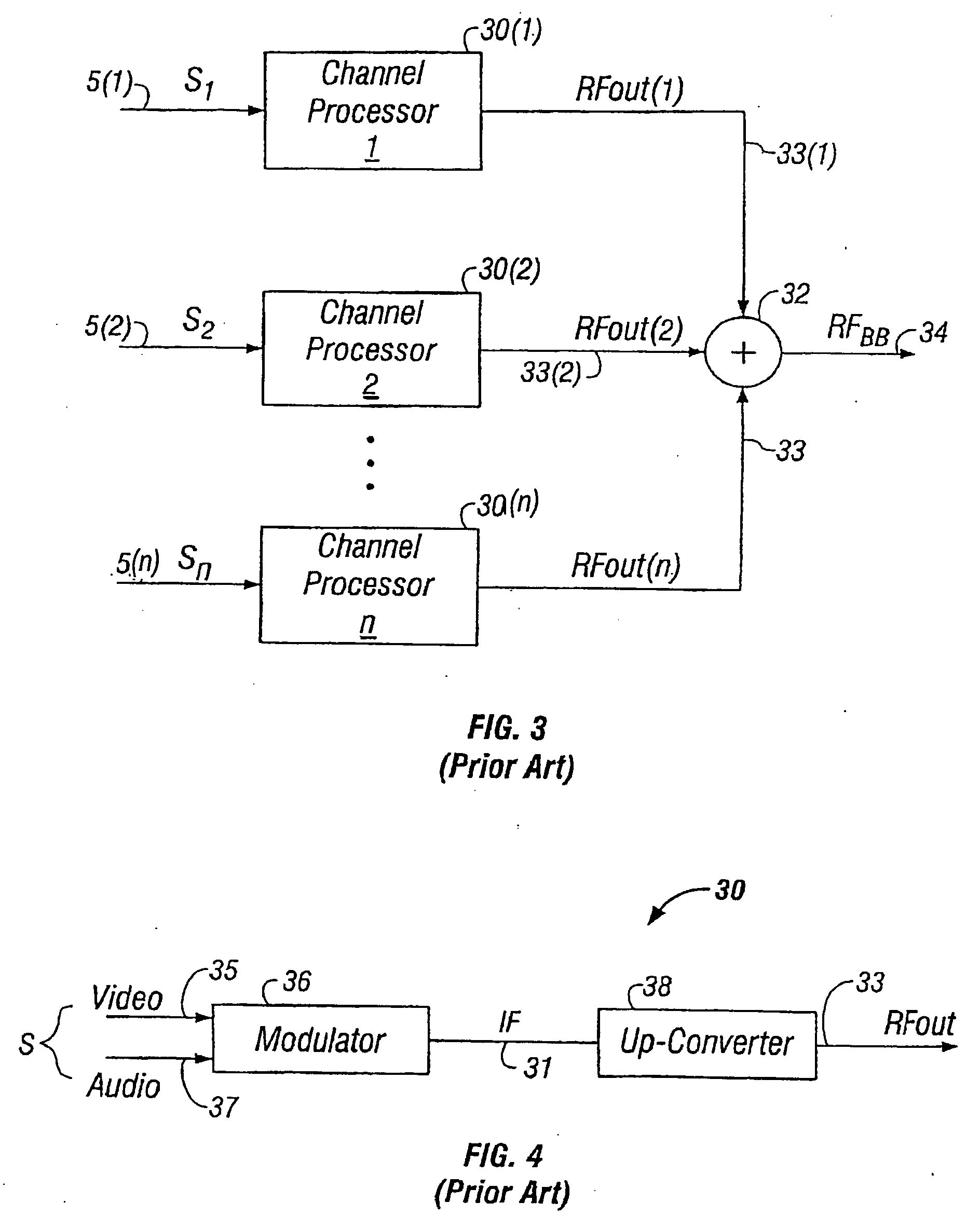
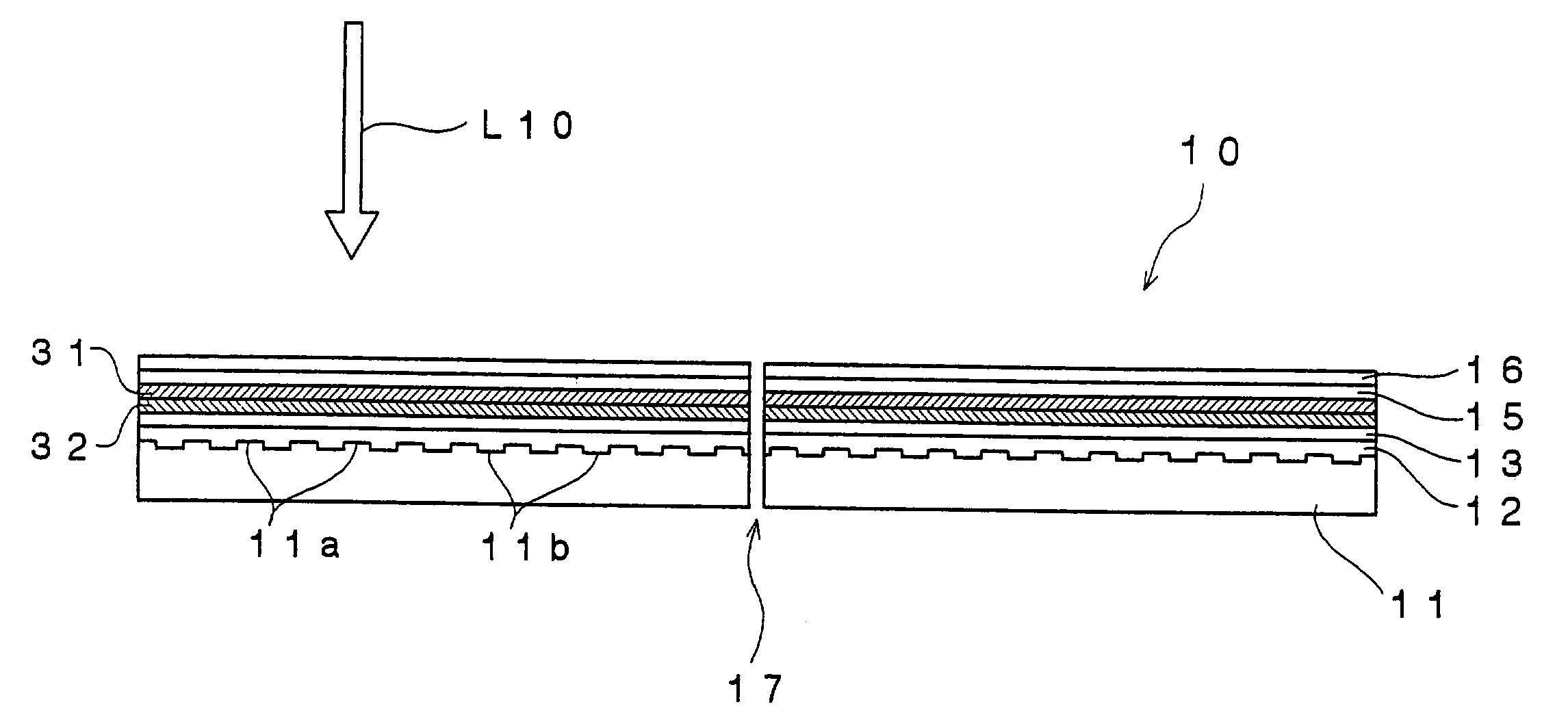
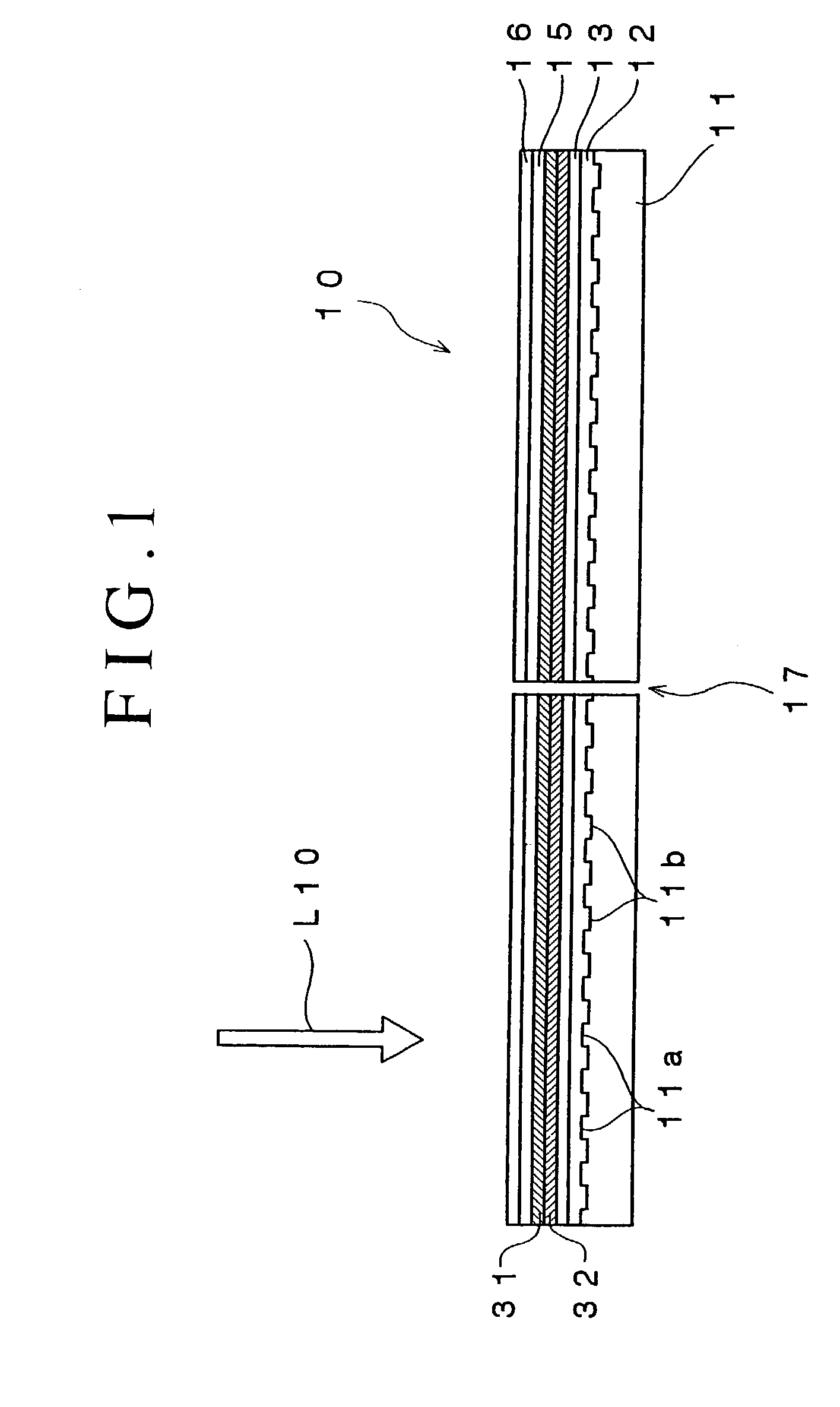
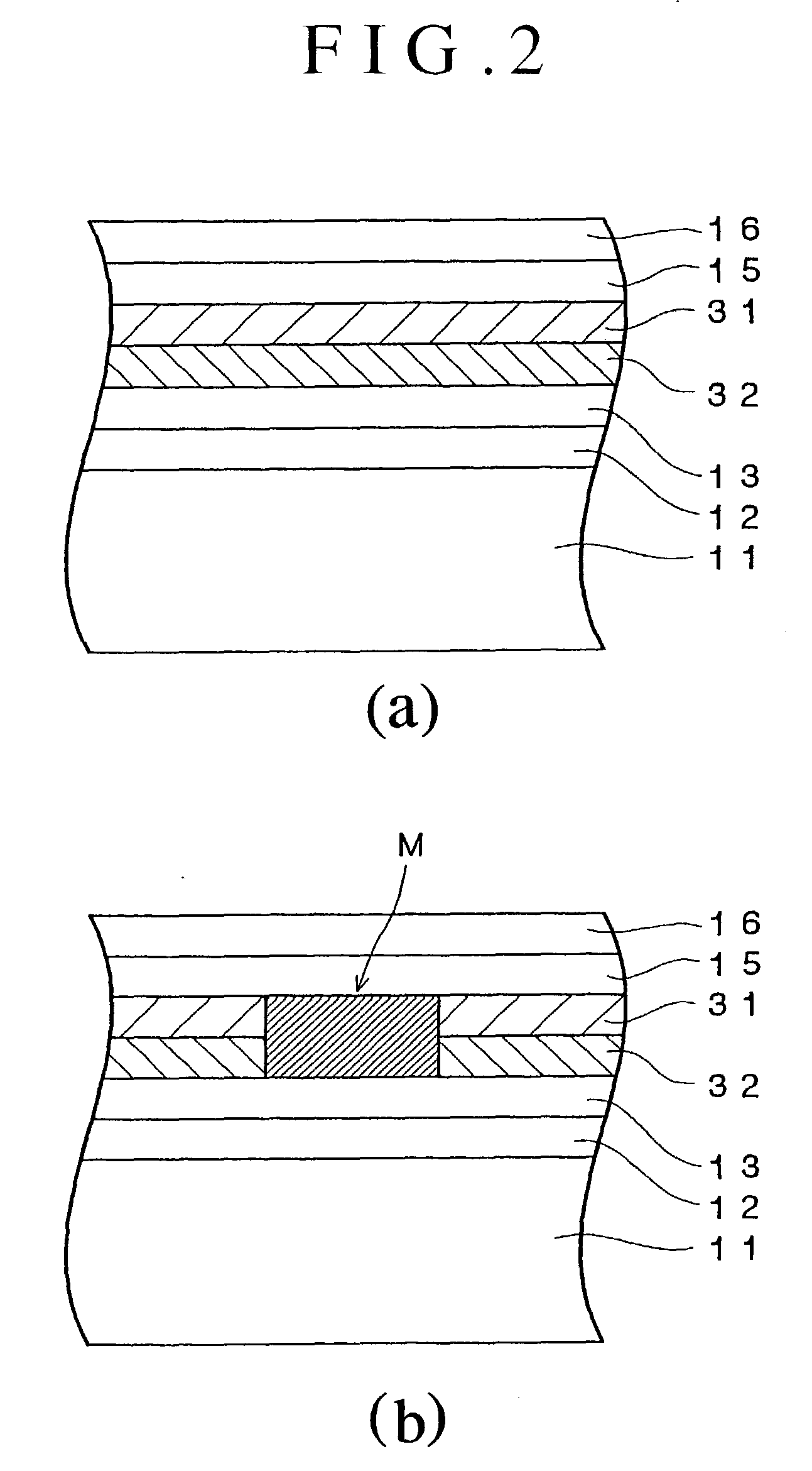
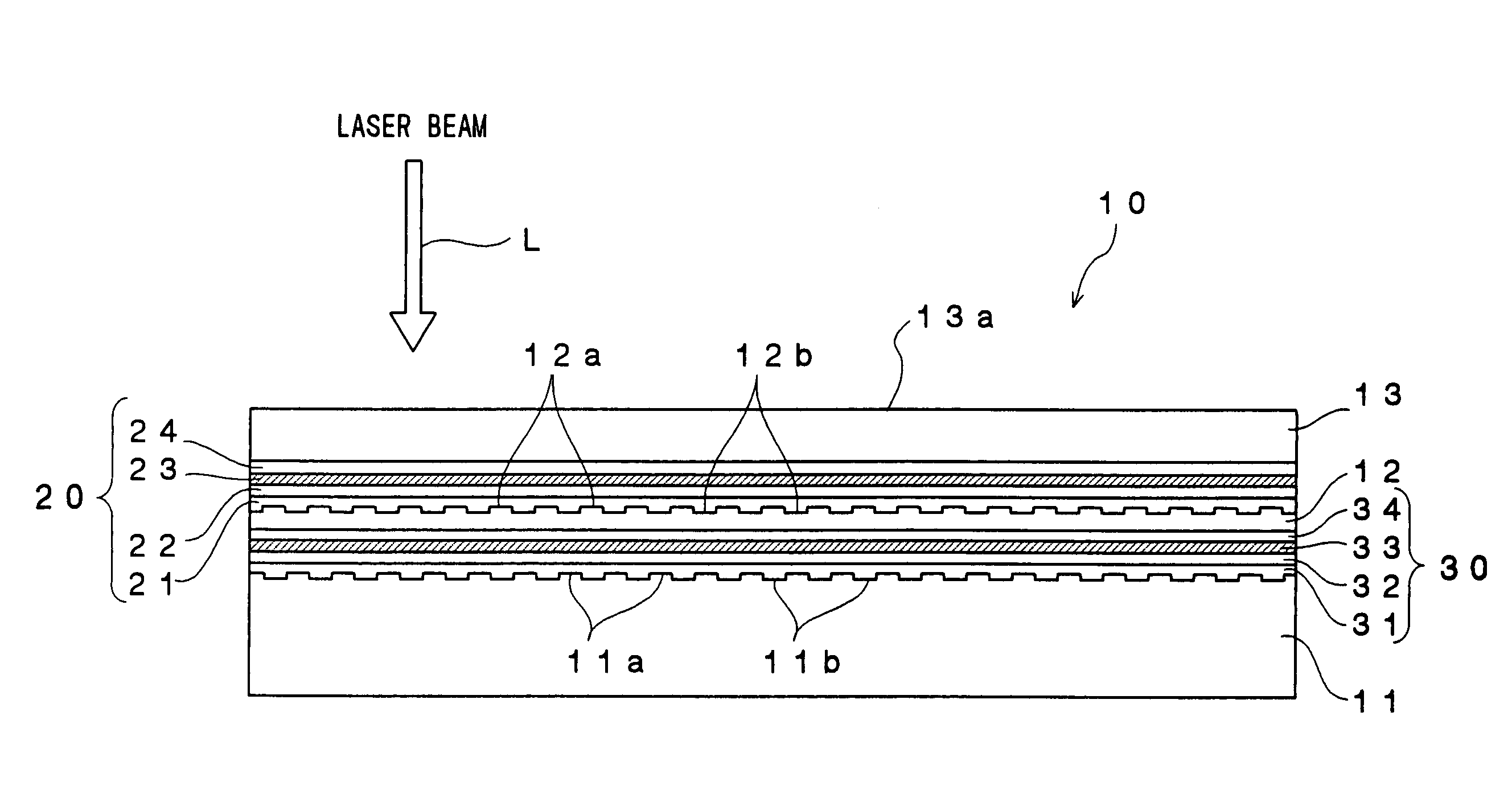
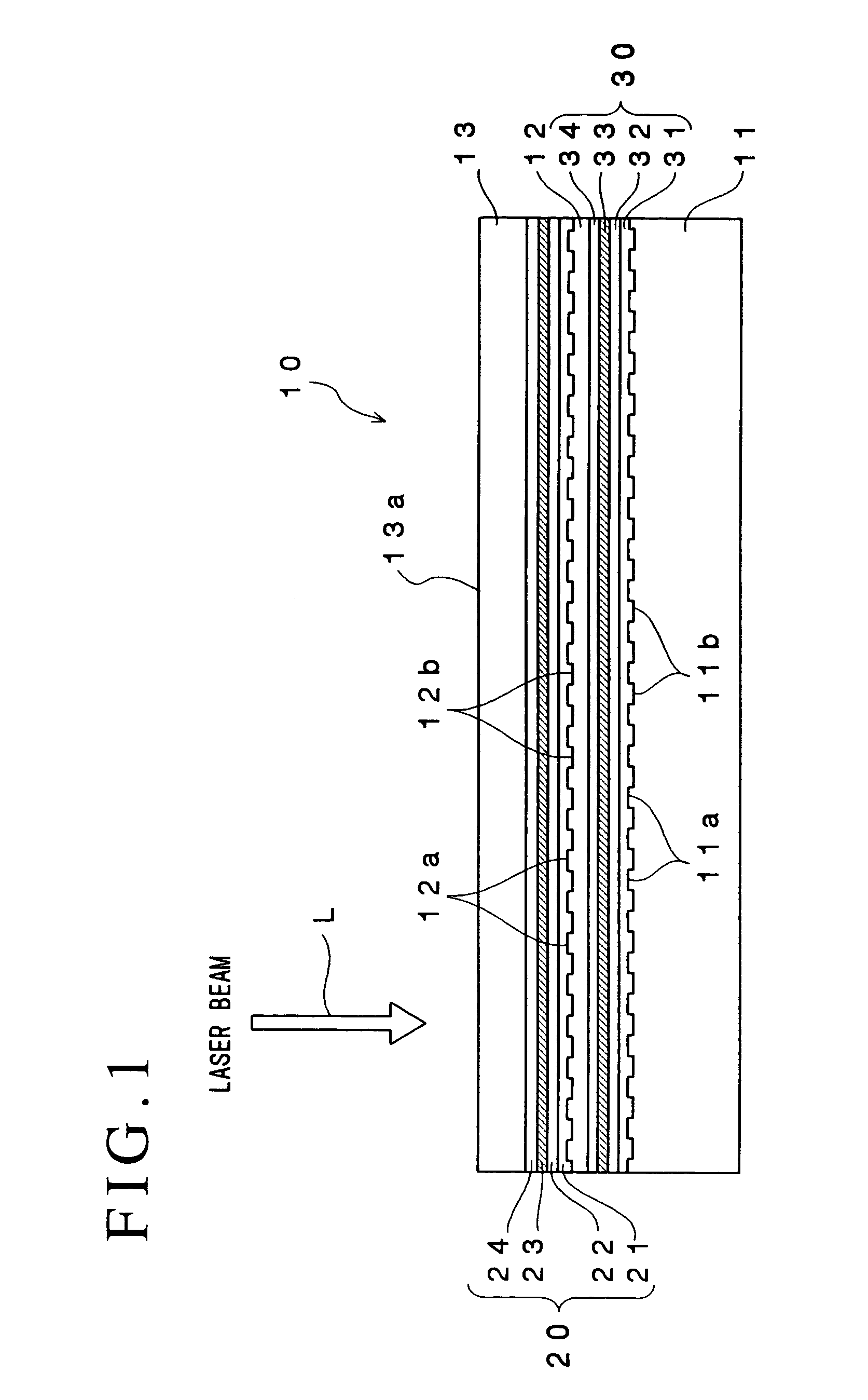
An optical recording device 10 of the present invention has a support substrate 11; an optical transmitting layer 12; and a first dielectric layer 31, a noble metal oxide layer 23, a second dielectric layer 32, a light absorption layer 22, a third dielectric layer 33, and a reflection layer 21, all of which are interposed, in this sequence from the optical transmitting layer, between the optical transmitting layer and the support substrate. The thickness of the support substrate 11 ranges from 0.6 mm to 2.0 mm; the thickness of the optical transmitting layer ranges from 10 μm to 200 μm; the thickness of the noble metal oxide layer ranges from 2 nm to 50 nm; the thickness of the second dielectric layer ranges from 5 nm to 100 nm; the thickness of the light absorption layer 22 ranges from 5 nm to 100 nm; and the thickness of the third dielectric layer 33 ranges from 10 nm to 140 nm. A superior characteristic can be acquired through super-resolution recording and super-resolution reproduction using an optical system for use with an optically recording medium of the next generation type.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS7182990B2Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioCombination recordingLayered productsNoise levelRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which makes it possible to reduce the noise level and improve the C / N ratio. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproducing record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as a main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Zn as a main component and having Al added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film. The laser beam is irradiated to the recording layer via a light transmitting layer formed in a manner covering the recording layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium and method for recording and reproducing data
InactiveUS20040052194A1Improve carrier-to-noise ratioSmall reliabilityLayered productsMechanical record carriersLight beamOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a light transmission layer and a plurality of recording layers between the substrate and the light transmission layer and capable of recording data in the plurality of recording layers and reproducing data recorded in the plurality of recording layers by projecting a laser beam via the light transmission layer onto the plurality of recording layers, at least one recording layer other than a farthest recording layer from the light transmission layer among the plurality of recording layers including a first recording film containing Si as a primary component and a second recording film located in the vicinity of the first recording film and containing Cu as a primary component. In the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to record data in a farthest recording layer from the light transmission layer and reproduce data from the farthest recording layer in a desired manner.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Variable directivity antenna and variable directivity antenna system using such antennas
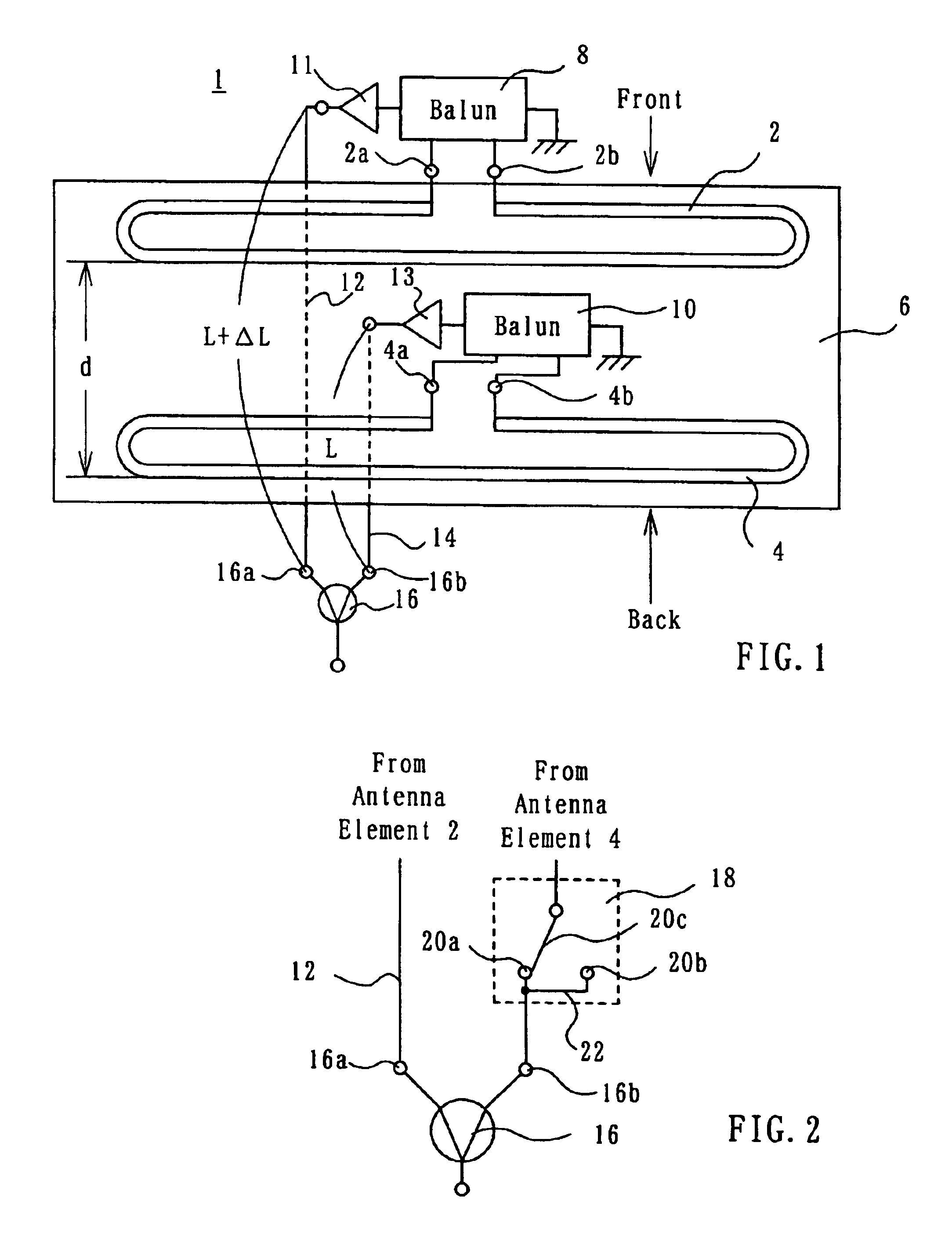
InactiveUS6933907B2Improved F/B ratioSmall sizeAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringLength wave
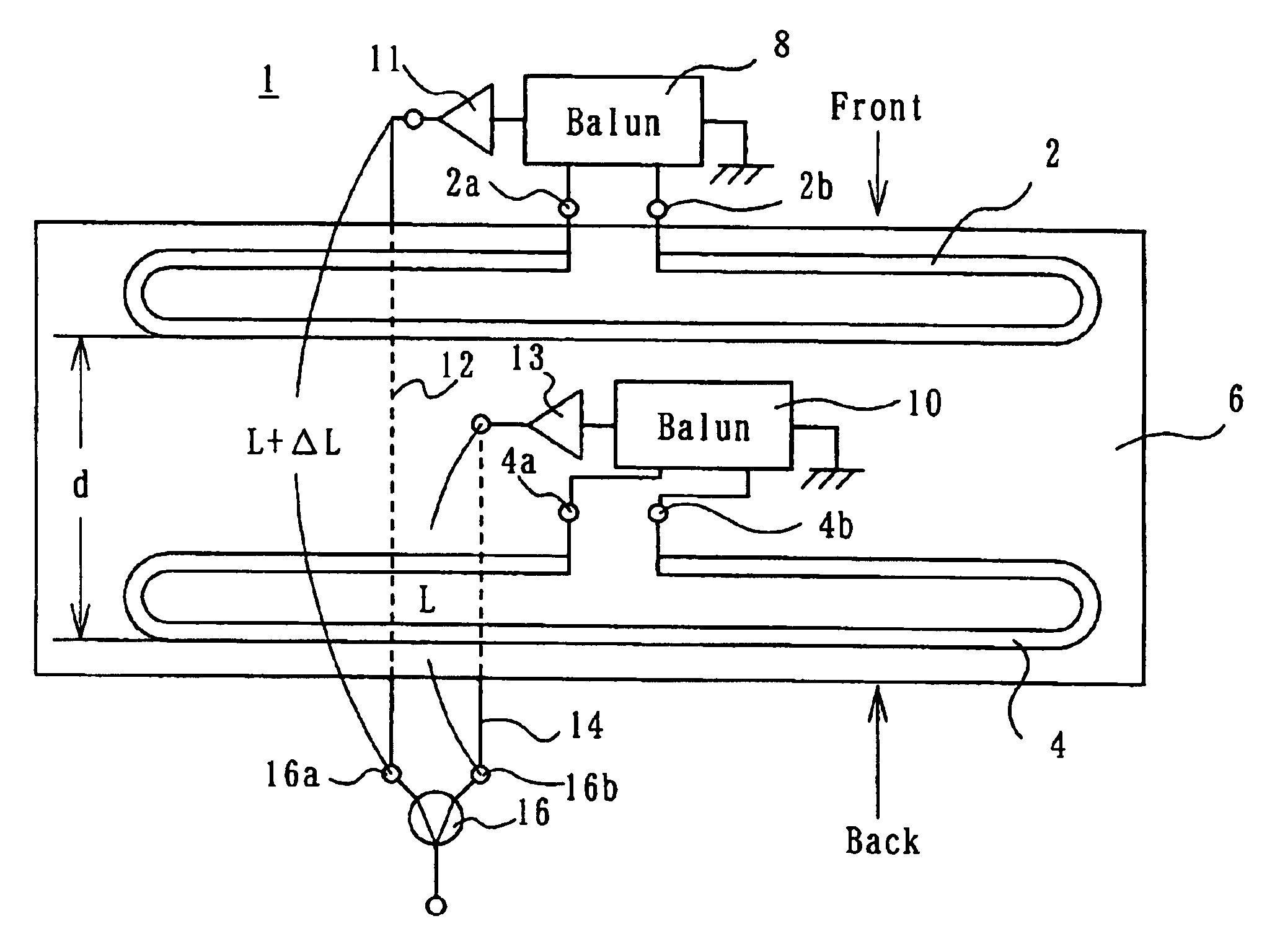
Folded dipole antenna elements (2, 4) are disposed generally in parallel, being spaced by a distance smaller than a quarter of the wavelength employed. The antenna elements (2, 4) are connected to a combiner (16) via feeders (12, 14) having different lengths. The difference in length between the feeders (12, 14) is such that received signals resulting from a radio wave coming to the antenna elements (2, 4) from the front and received by the antenna elements (12, 14) are in phase with each other at the inputs (16a, 16b) of the combiner (16), whereas received signals resulting from a radio wave coming to the antenna elements (2, 4) from the back and received by the antenna elements (12, 14) are 180° out of phase with each other at the inputs (16a, 16b) of the combiner (16). A variable phase device (18) is connected between one of the antenna elements (2, 4) and the combiner (16) to selectively couple the in-phase or 180° out of phase version of the received signal from that one antenna element to the combiner (16).
Owner:DX ANTENNA CO LTD
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
InactiveUS20040027973A1Reduce noise levelImprove carrier-to-noise ratioMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusNoise levelRecording layer
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of C, Si, Ge and Sn as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing an element selected from the group consisting of C, Si, Ge and Sn and different from the element contained as a primary component in the first recording layer as a primary component. According to thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to optically record data therein and reproduce data therefrom by projecting a laser beam having a wavelength of 350 nm to 450 nm thereonto, which includes two or more recording layers and is capable of decreasing noise level and improving C / N ratio of a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
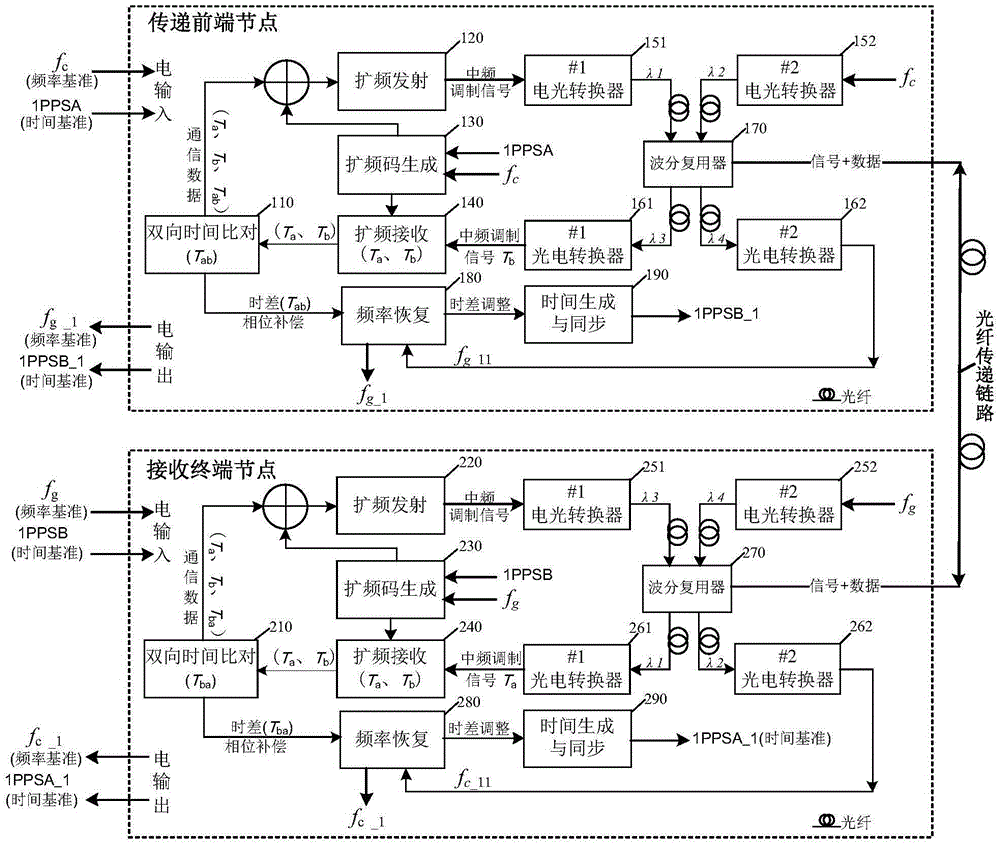
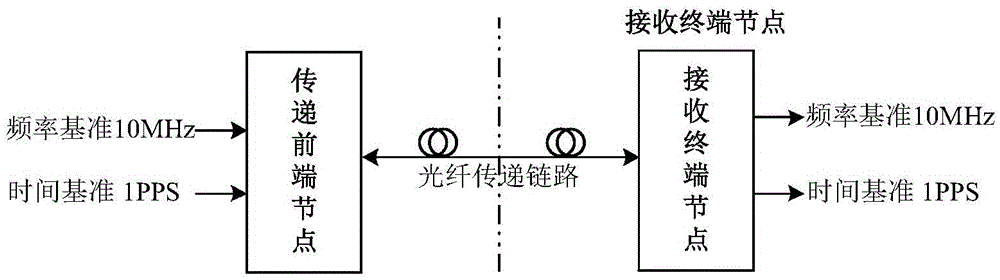
Fiber time and frequency transfer method, device and system based on bidirectional spread spectrum ranging
ActiveCN105634643ALow code phase jitterImprove remote time synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsTime and frequency transfer
The invention provides a fiber time and frequency transfer method, device and system based on bidirectional spread spectrum ranging for solving the problems of time and frequency signal transfer and synchronization in a remote fiber system of a large ground station. The system comprises a transfer front-end node, a receiving terminal node and a fiber transfer link connected between the transfer front-end node and the receiving terminal node; the transfer front-end node and the receiving terminal node have the same composition structure, and each of the transfer front-end node and the receiving terminal node comprises a bidirectional time comparison module, a spread spectrum transmitting module, a spread spectrum code generation module, a spread spectrum receiving module, two analog electrical to optical converters, two analog photoelectric transducers, a wavelength division multiplexer, a frequency recovery module and a time generation and synchronization module. Fiber cable transfer and spread spectrum pseudo code measurement technologies are adopted, and the carrier-to-noise ratio is higher when the fiber transfers a signal, so that the ranging accuracy is improved while the additional comparison of the data transfer link is avoided.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
InactiveUS6996055B2Improve carrier-to-noise ratioReduce noise levelMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusNoise levelOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Ge, C and Al as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing Zn as a primary component, the optical recording medium being constituted to be irradiated by a laser beam projected onto the side opposite from the substrate and the total thickness of the first recording layer and the second recording layer being equal to or thinner than 30 nm. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to decrease a noise level and improve a C / N ratio in a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Recording medium having super-resolution near-field structure and method and apparatus for reproducing the same
InactiveUS20050009260A1Improve carrier-to-noise ratioMaterial nanotechnologyInformation arrangementNanoparticleOptoelectronics
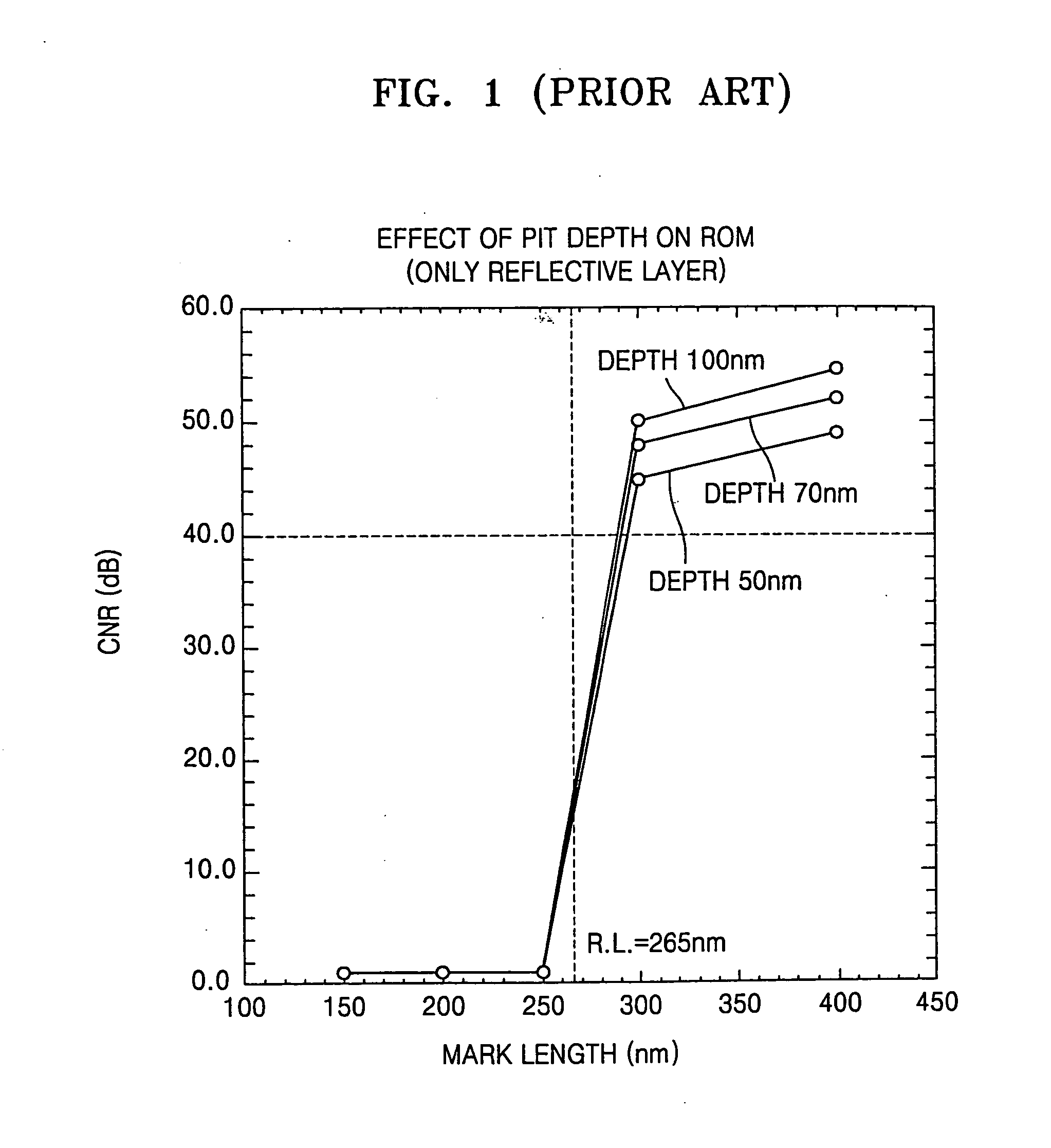
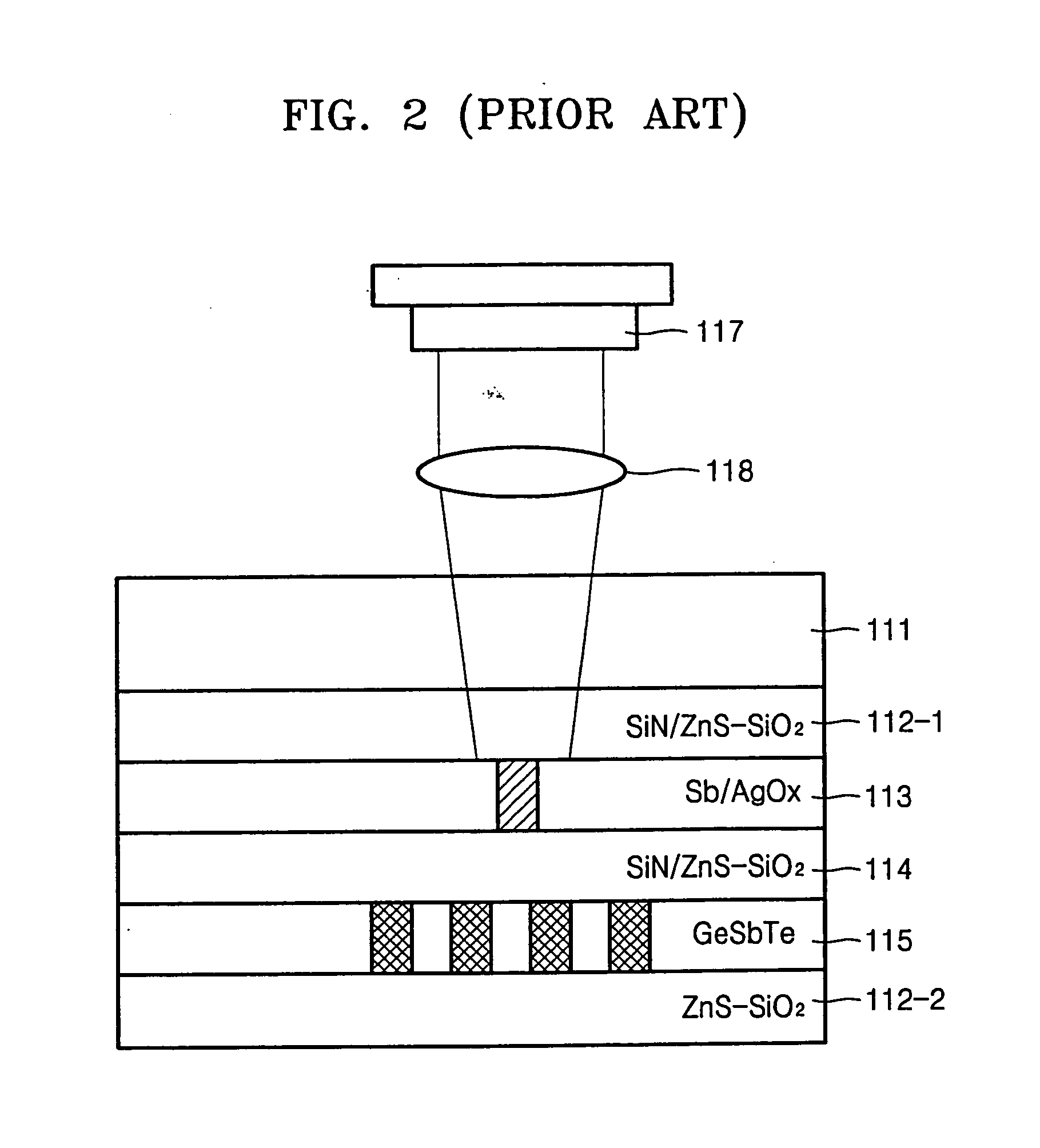
A read-only recording medium for achieving a carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR) using a super-resolution near-field structure (Super-RENS) on which information has been prerecorded includes a substrate having the information recorded on its surface, a reflective layer formed from a phase change material on the substrate, a first dielectric layer formed on the reflective layer, and a mask layer formed from metal oxide or nanoparticles on the first dielectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Varactor tunable RF filters having low distortion and high signal level capability
InactiveUS20060128339A1Improve performanceReduce system noiseMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsLow distortionFrequency conversion
An agile frequency converter provides IF-RF level exchange and notch filtering. System noise and spurious levels generated by channel frequency conversion is reduced in applications requiring broadband combining of frequency converters to form multichannel composite signal. A pair of varactor banks is connected in an arrangement whereby varactor pairs are connected in parallel and capacitor pairs are connected in anti-parallel. Tuning is achieved by circuitry for tuning first and second varactors.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
InactiveUS20030231577A1Minimal loadingHigh long-term storage reliabilityMechanical record carriersPhotomechanical apparatusNoise levelRecording layer
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Ge, C and Al as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing Zn as a primary component, the optical recording medium being constituted to be irradiated by a laser beam projected onto the side opposite from the substrate and the total thickness of the first recording layer and the second recording layer being equal to or thinner than 30 nm. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to decrease a noise level and improve a C / N ratio in a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Opto-magnetic recording medium with a garnet ferrite recording layer, and opto-magnetic information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS6759137B1Raise the ratioReduce the required powerRecord information storageMagnetic materialsFerrite layerRecording layer
This invention relates to magneto-optical recording media such as magneto-optical disks and cards, manufacturing methods of the medium and a magneto-optical recording and playback device to record and play back data using the magneto-optical recording media. The magneto-optical recording medium of the present invention has a recording layer and a reflective layer on a substrate, and the recording layer has a layered structure in which at least one spinel ferrite (or rutile-type oxide or hematite) layer and at least one garnet ferrite layer are piled together. It is preferable that the layered structure is formed on tracks where data are recorded. The manufacturing method of the present invention comprises the steps of heat treatment in the range of 500-700° C., preferably 600-630° C., after the formation of the recording layer. In the magneto-optical recording and playback device to record and play back data of the present invention, the wavelength of light for recording data is different from that for reading data, which is preferable for a magneto-optical recording medium comprising a garnet ferrite layer.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Optical recording medium and method for optically recording data in the same
ActiveUS20030223351A1Minimal loadingHigh long-term storage reliabilityMechanical record carriersRecord information storageNoise levelRecording layer
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a first recording layer formed on the substrate and containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Sn and Ge as a primary component, and a second recording layer located in the vicinity of the first recording layer and containing Ag as a primary component, the optical recording medium being constituted to be irradiated by a laser beam projected onto the side opposite from the substrate. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to decrease a noise level and improve a C / N ratio in a reproduced signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium and method for recording and reproducing data
InactiveUS7276274B2Improve carrier-to-noise ratioSmall reliabilityLayered productsMechanical record carriersRecording layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, a light transmission layer and a plurality of recording layers between the substrate and the light transmission layer and capable of recording data in the plurality of recording layers and reproducing data recorded in the plurality of recording layers by projecting a laser beam via the light transmission layer onto the plurality of recording layers, at least one recording layer other than a farthest recording layer from the light transmission layer among the plurality of recording layers including a first recording film containing Si as a primary component and a second recording film located in the vicinity of the first recording film and containing Cu as a primary component. In the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to record data in a farthest recording layer from the light transmission layer and reproduce data from the farthest recording layer in a desired manner.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical recording medium and method for recording data in the same
InactiveUS20060078825A1Good signalImprove carrier-to-noise ratioRecording strategiesLayered productsRecording layerOptical recording
An optical recording medium includes a substrate, two recording layers provided on the substrate and two dielectric layers each provided adjacent to one of the recording layers, the optical recording medium being constituted so that when it is irradiated with a laser beam having a wavelength λ via an objective lens having a numerical aperture NA satisfying λ / NA≦640 nm from the side opposite from the substrate, a record mark whose reflection coefficient is different from those of other regions of the recording layers is formed in the recording layers and at least a part of a region(s) of the dielectric layers adjacent to the record mark is crystallized to form a crystallized region. According to the thus constituted optical recording medium, it is possible to reproduce a signal having excellent signal characteristics.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Double replacement rate carrier tracking loop circuit
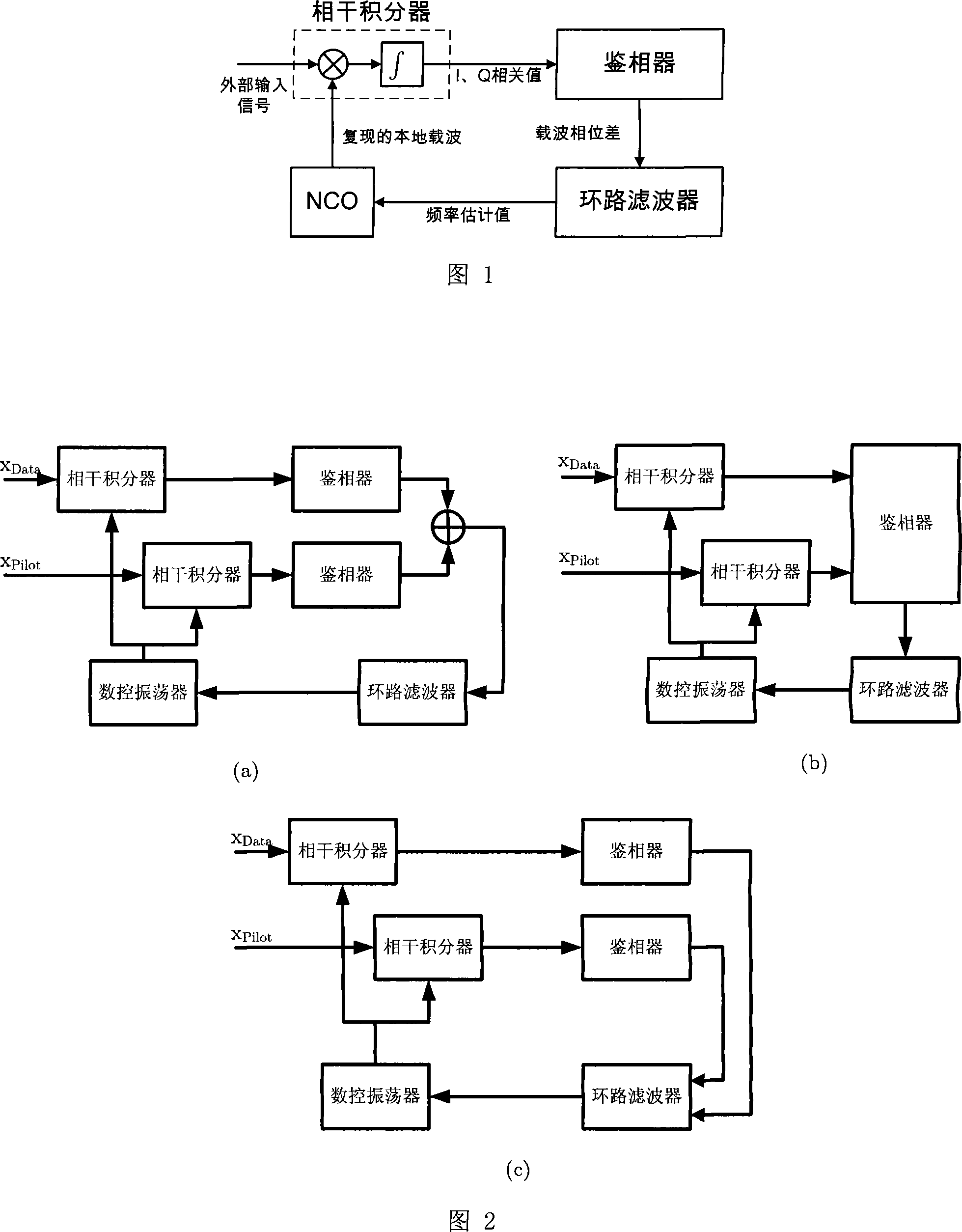
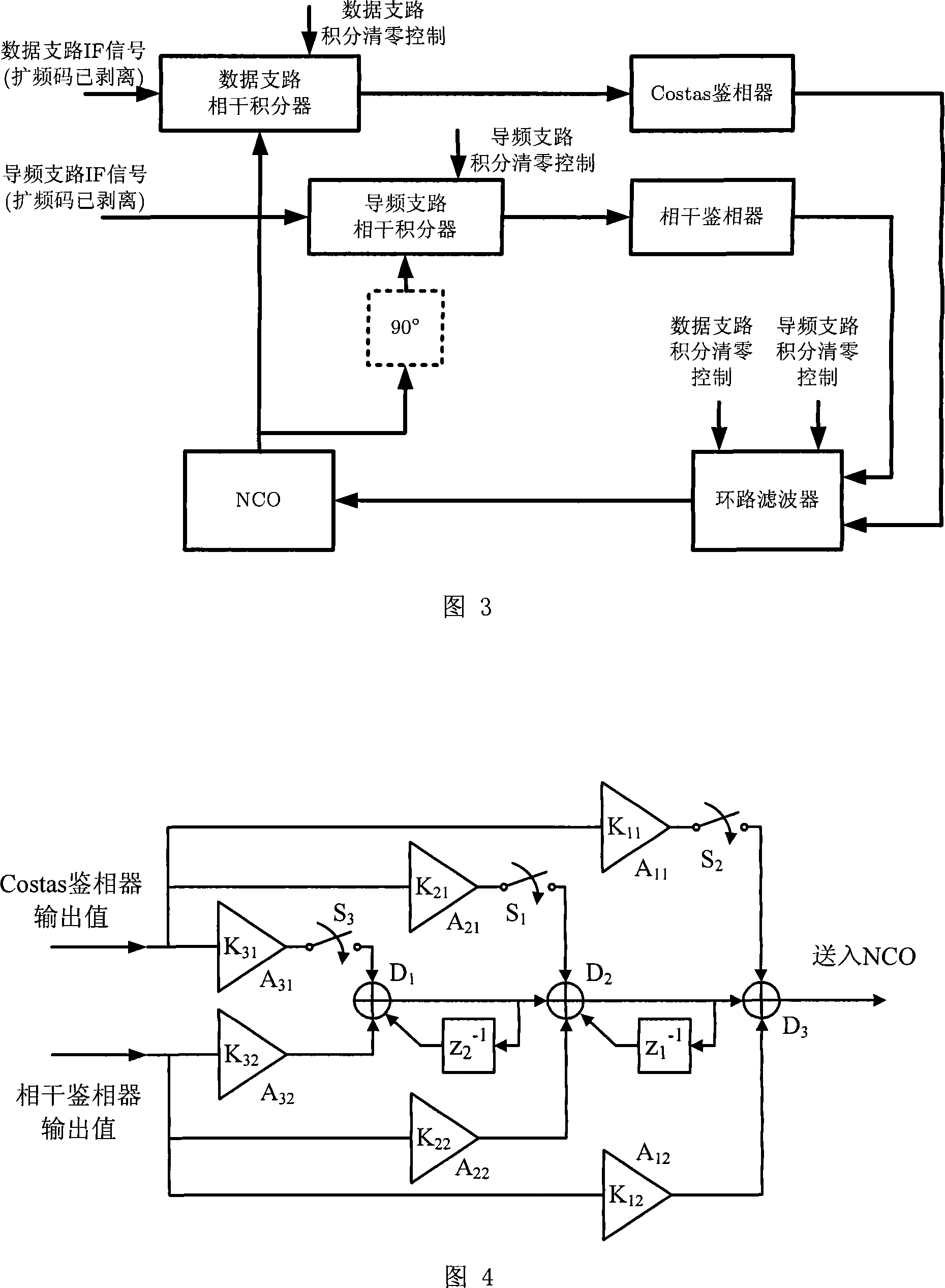
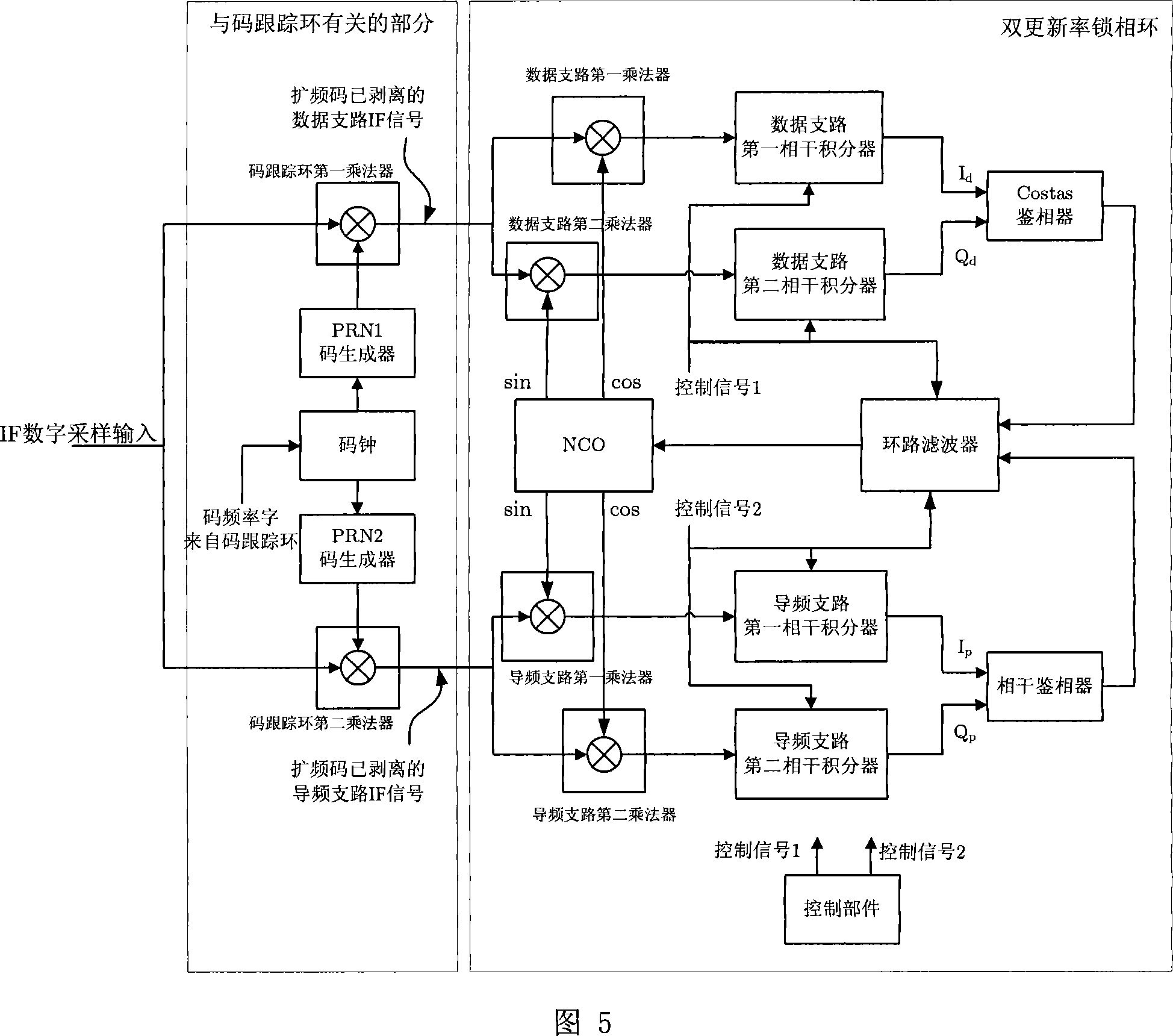
ActiveCN101183149ALow carrier-to-noise ratioImprove carrier-to-noise ratioPulse automatic controlBeacon systems using radio wavesDigitally controlled oscillatorPhase detector
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ferromagnetic powder, and coating material and magnetic recording medium using same
InactiveUS20070059557A1Reduce noiseImprove carrier-to-noise ratioMaterials with cobaltSynthetic resin layered productsVolumetric Mass DensityMaterials science
A magnetic powder is provided composed of particles having a balanced shape and distribution, the particles having a small, uniform volume, making it possible to achieve improved density and reliability of a coating type magnetic recording medium. The magnetic powder has Fe as a main component, and is comprised of particles having a cross-section perpendicular to the particle major axis that is substantially round or elliptical, wherein a standard geometrical deviation indicating the variation in cross-sectional area thereof is within the range of 1.01 to 3.0. The invention is also directed to a magnetic powder in which the standard geometrical deviation indicating the variation in the particle volume is within the range of 1.01 to 4.0, and the standard geometrical deviation indicating variation in the flat acicularity is within 1.01 to 2.0.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
Magnetic recording medium comprising a backcoat layer having specific protrusions
InactiveUS6645648B2Improve featuresIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersHigh densityMetallurgy
Provided is a magnetic recording medium having good electromagnetic characteristics, particularly both improved high-density recording characteristics and good durability, and particularly a C / N ratio that is markedly improved in the high-density recording region. A magnetic recording medium comprising a nonmagnetic lower layer and a magnetic layer provided in this order on a support wherein said magnetic layer comprises a ferromagnetic metal powder or a ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder and a binder and has a coercive force equal to or higher than 143 kA / m. Said magnetic recording medium is a medium for recording signals having a surface recording density ranging from 0.2 to 2 Gbit / inch<2>; said support has a thickness equal to or less than 5.5 mum and a Young's modulus in the MD direction equal to or higher than 11,000 Mpa; and said support has on the reverse surface from said magnetic layer a backcoat layer, said backcoat layer having not fewer than 200 and not more than 1,000 protrusions having a height equal to or higher than 50 nm per 10,000 mum<2>.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
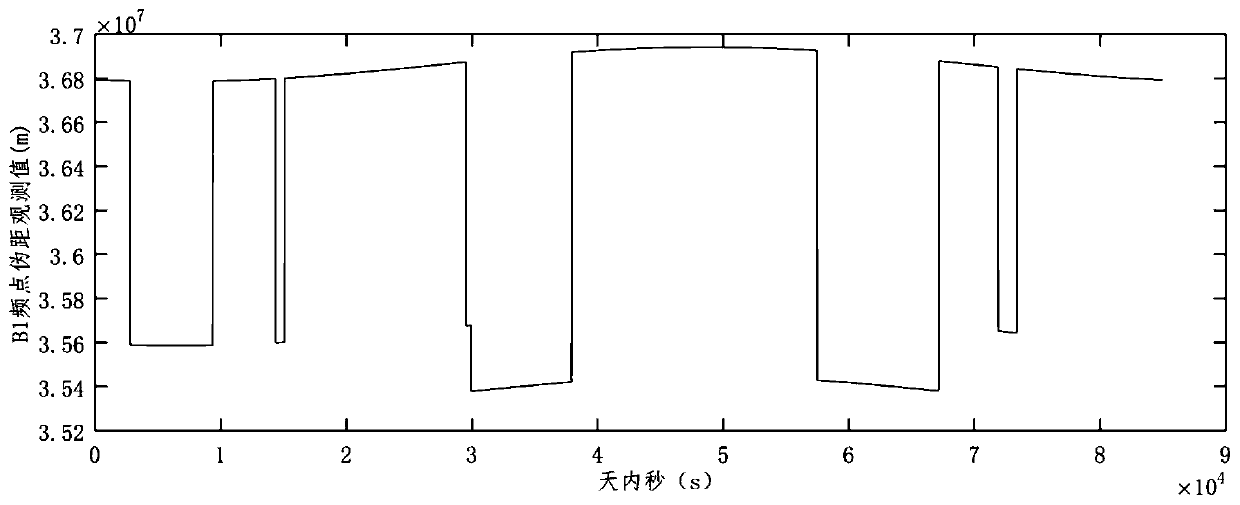
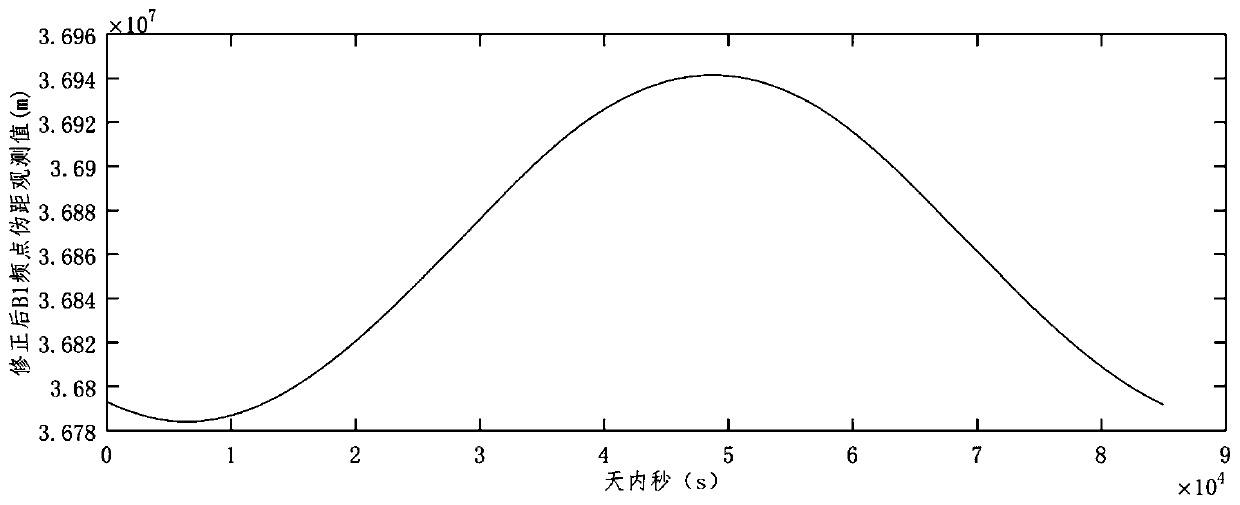
Method for measuring Beidou inter-frequency deviation based on parabolic antenna observation
ActiveCN110221320AEffective Anti-MultipathImprove the accuracy of inter-frequency deviation calculationSatellite radio beaconingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention provides a method for measuring Beidou inter-frequency deviation based on parabolic antenna observation, and the method comprises the following steps of arranging at least three stationsin the area covered by a Beidou satellite signal, wherein each station is equipped with a parabolic antenna; observing local visible Beidou satellites by polling to obtain prediction orbits during the observation period or estimate the orbits during the observation period by the number of two-row orbits; designing an observation plan by using the orbit data and the coordinates of the stations, wherein the observation plan ensures that each visible satellite has an observation time; and separating the ionospheric delay by using a model to solve the inter-frequency deviation. The method provided by the invention can effectively resist multipath and improve signal to noise ratio, thereby improving the ranging accuracy of the observation of the Beidou satellites, and further improving the accuracy of solving the inter-frequency deviation of the Beidou satellites.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Near-field optical recording medium and near-field optical recording method
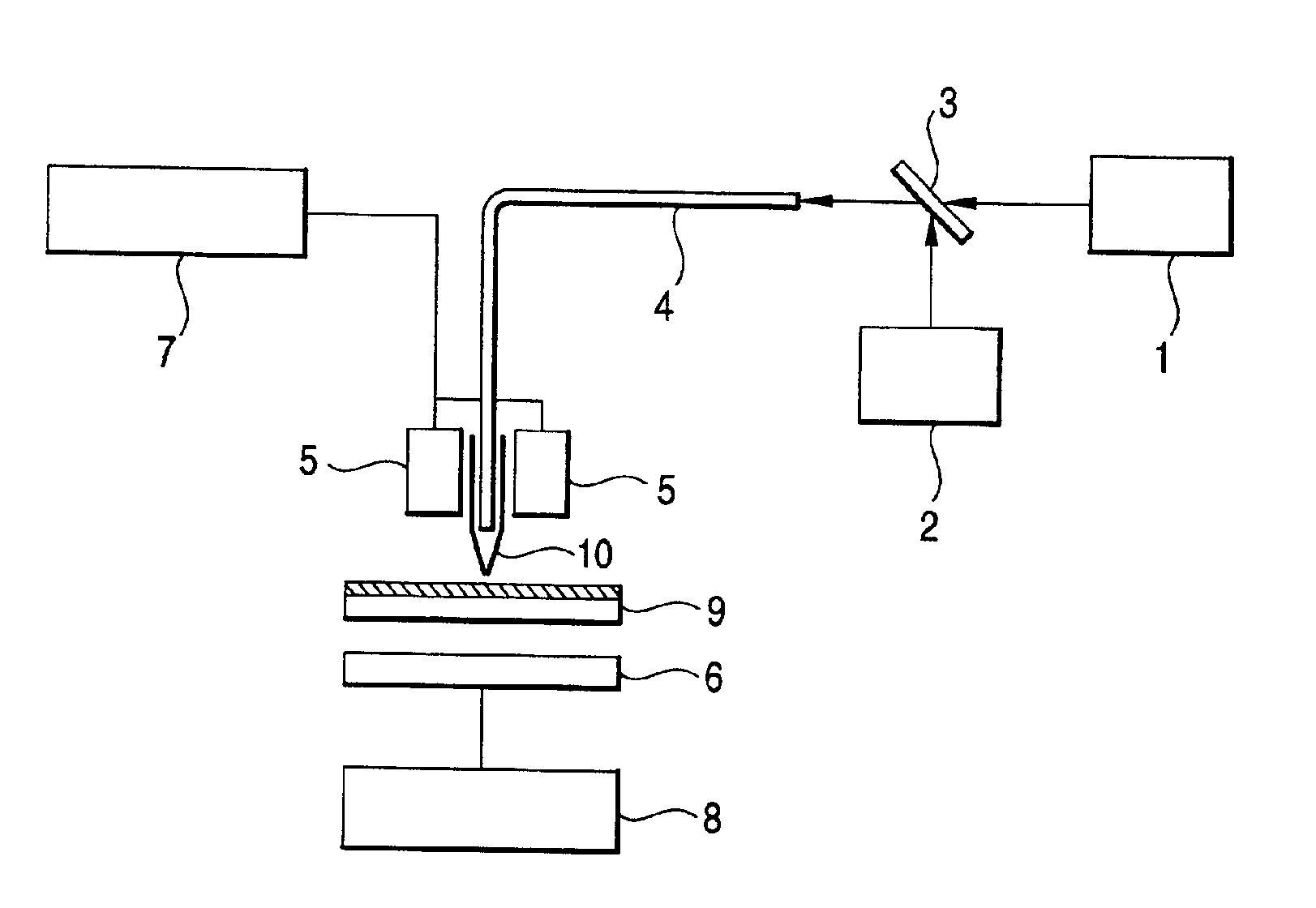
InactiveUS6884553B2Improve recording densitySolve the lack of durabilityPhotography auxillary processesRadiation applicationsConfocalGlass transition point
A near-field optical recording medium comprises a recording layer capable of writing, reading and erasing information using an evanescent light, the evanescent light having a beam spot size smaller than the wavelength of a source light, wherein the recording layer is a stable amorphous layer mainly comprising a photochromic compound having a glass transition point of 55° C. or higher and a molecular weight of 3000 or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com