Patents
Literature
4170 results about "Lambda" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lambda (uppercase Λ, lowercase λ; Greek: λάμ(β)δα lám(b)da) is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the sound /l/. In the system of Greek numerals lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as [laːbdaː] (λάβδα) in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced [lamða].
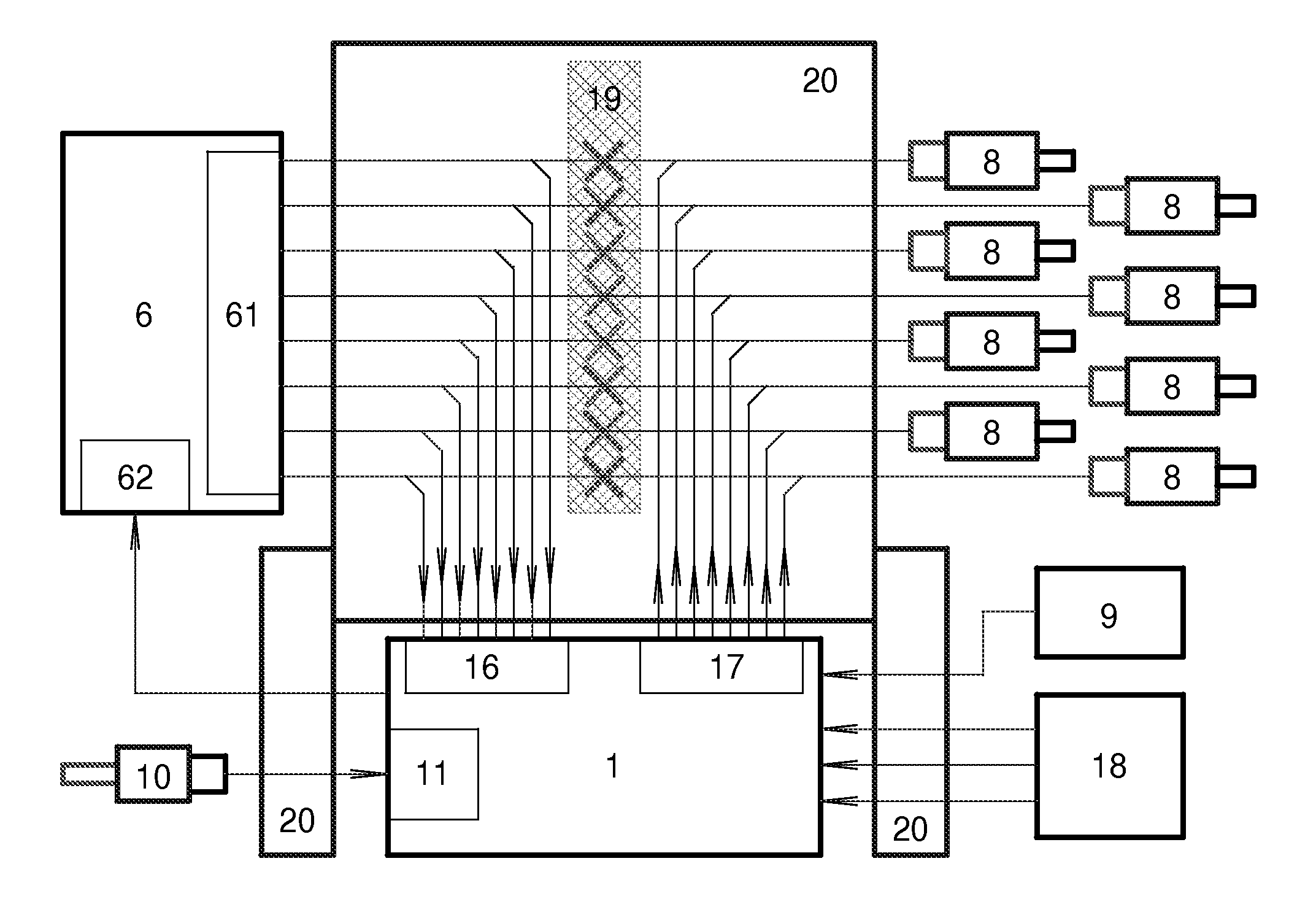
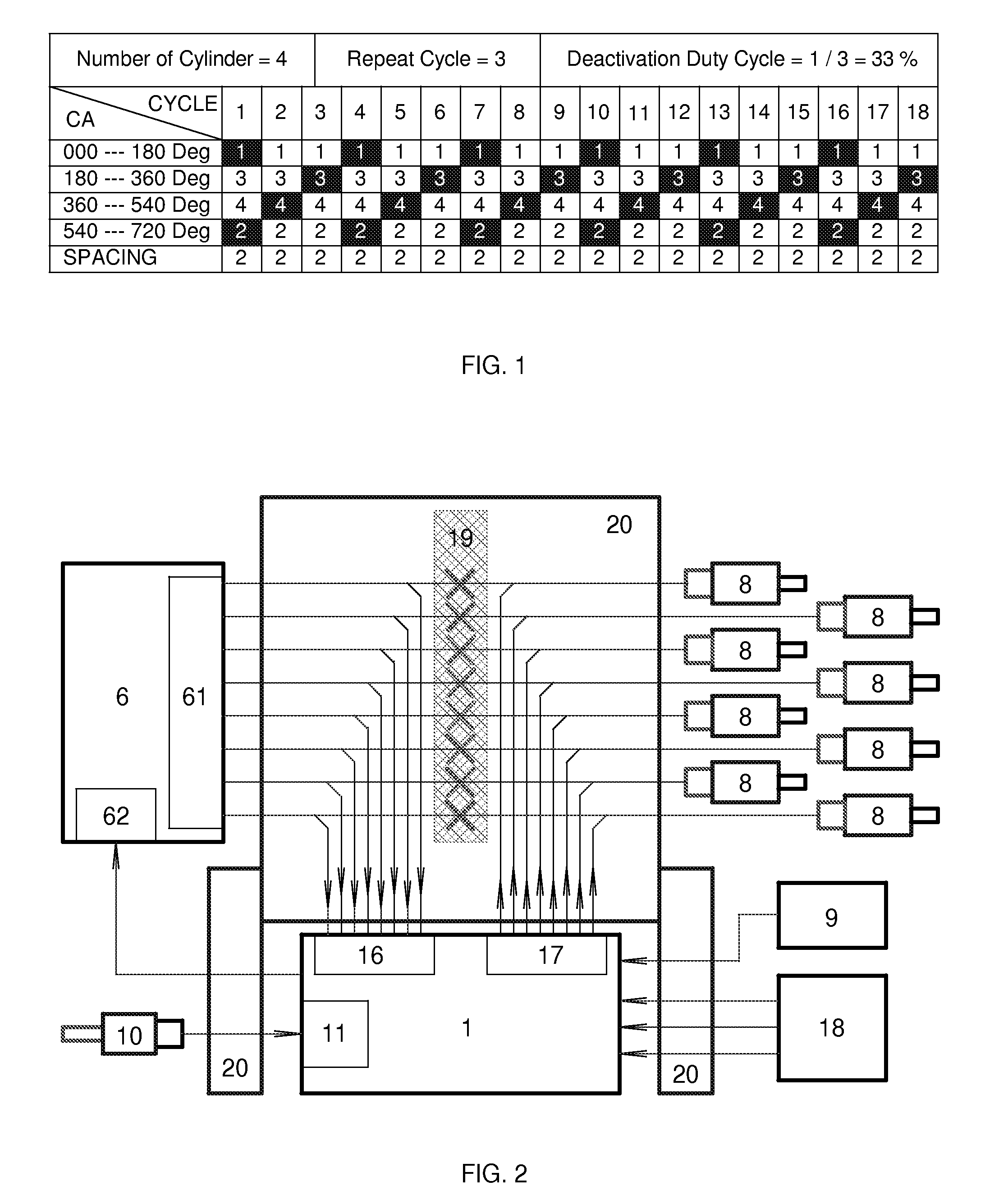
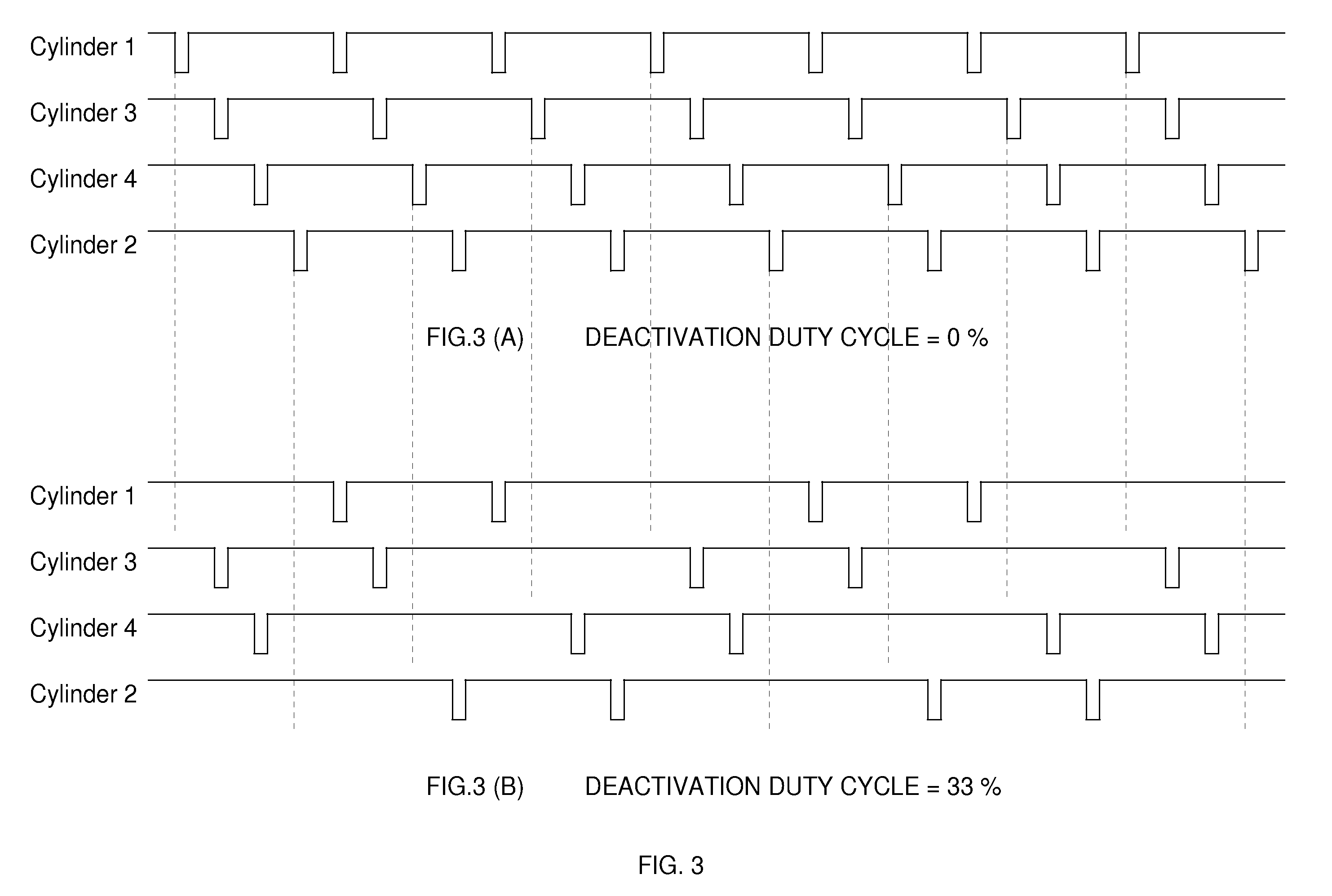
Dynamic Cylinder Deactivation with Residual Heat Recovery
InactiveUS20100050993A1Improve conversion efficiencyElectrical controlMachines/enginesEngine efficiencyFuel efficiency
Cylinder deactivation is a proven solution to improve engine fuel efficiency. The present invention is related to Dynamic Cylinder Deactivation (DCD) solution to conventional internal combustion engine. DCD is an energy saving method based on engine thermodynamics and residual heat recovery. It deactivates all the cylinders within the engine alternatively and dynamically, totally different from traditional sealed-valves cylinder deactivation solutions. DCD has many advantages over traditional sealed-valves cylinder deactivation. Thermodynamic efficiency gain, residual heat recovery, high Lambda and “Air-Hybrid” are the most attractive features of DCD. DCD also makes engine displacement variable.
Owner:ZHAO YUANPING +1
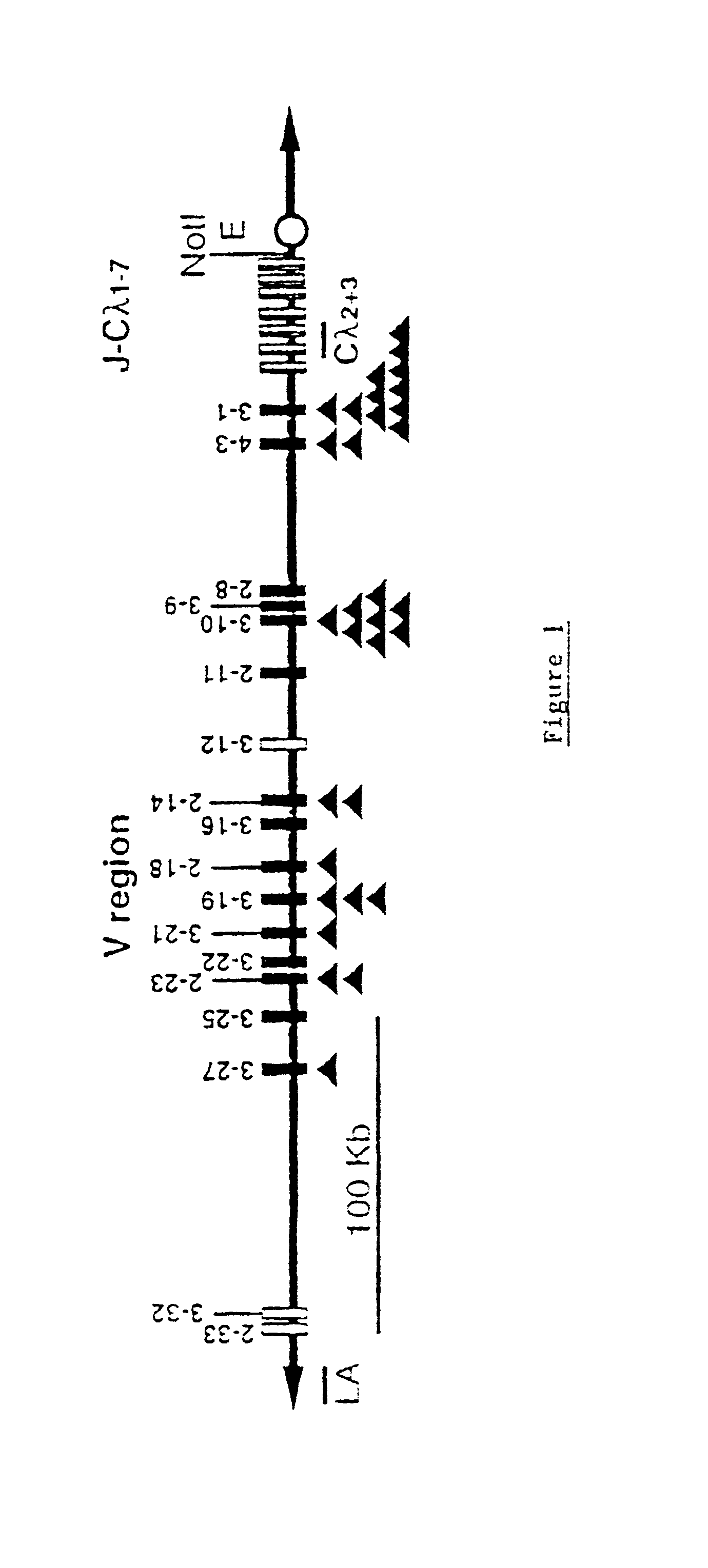
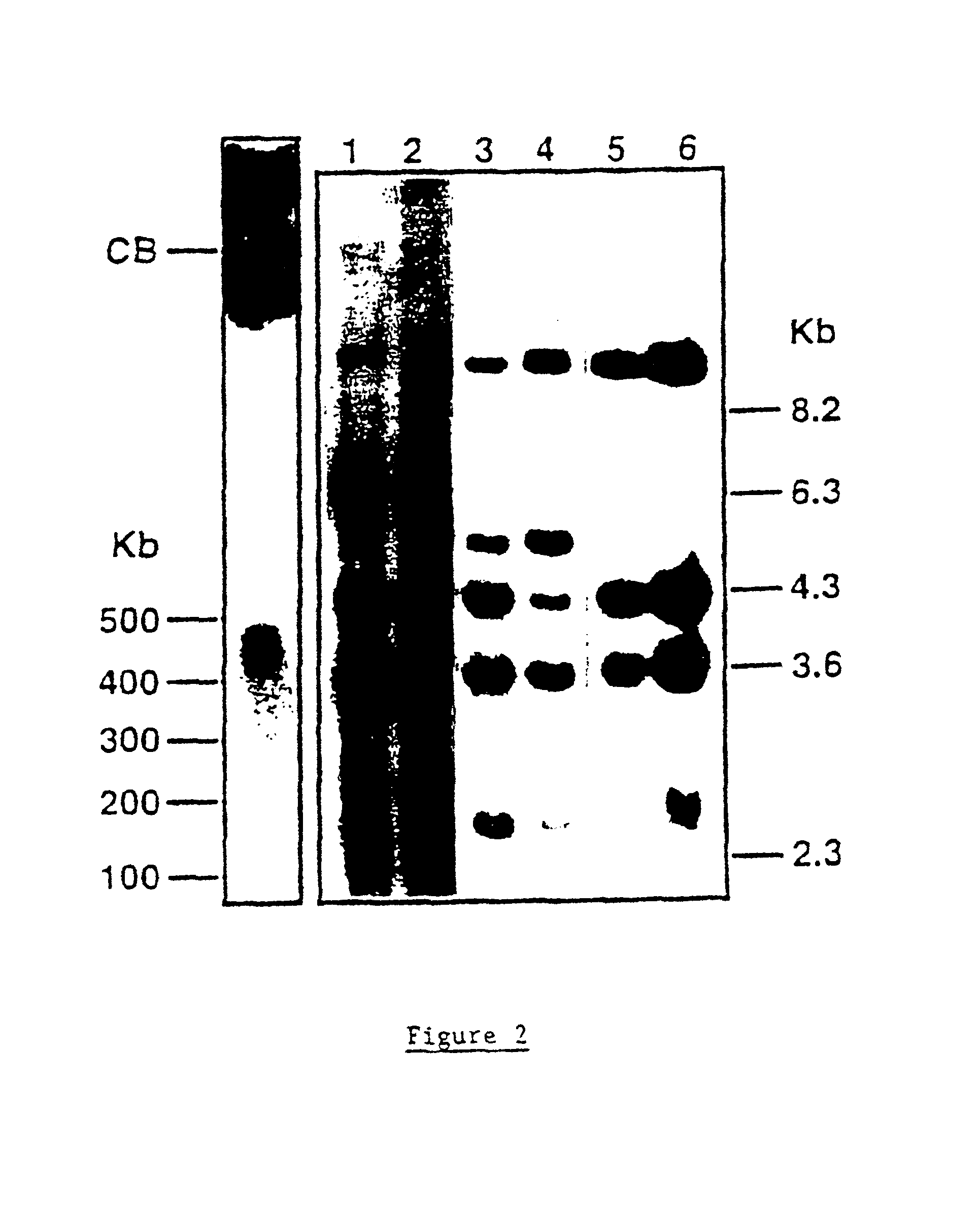
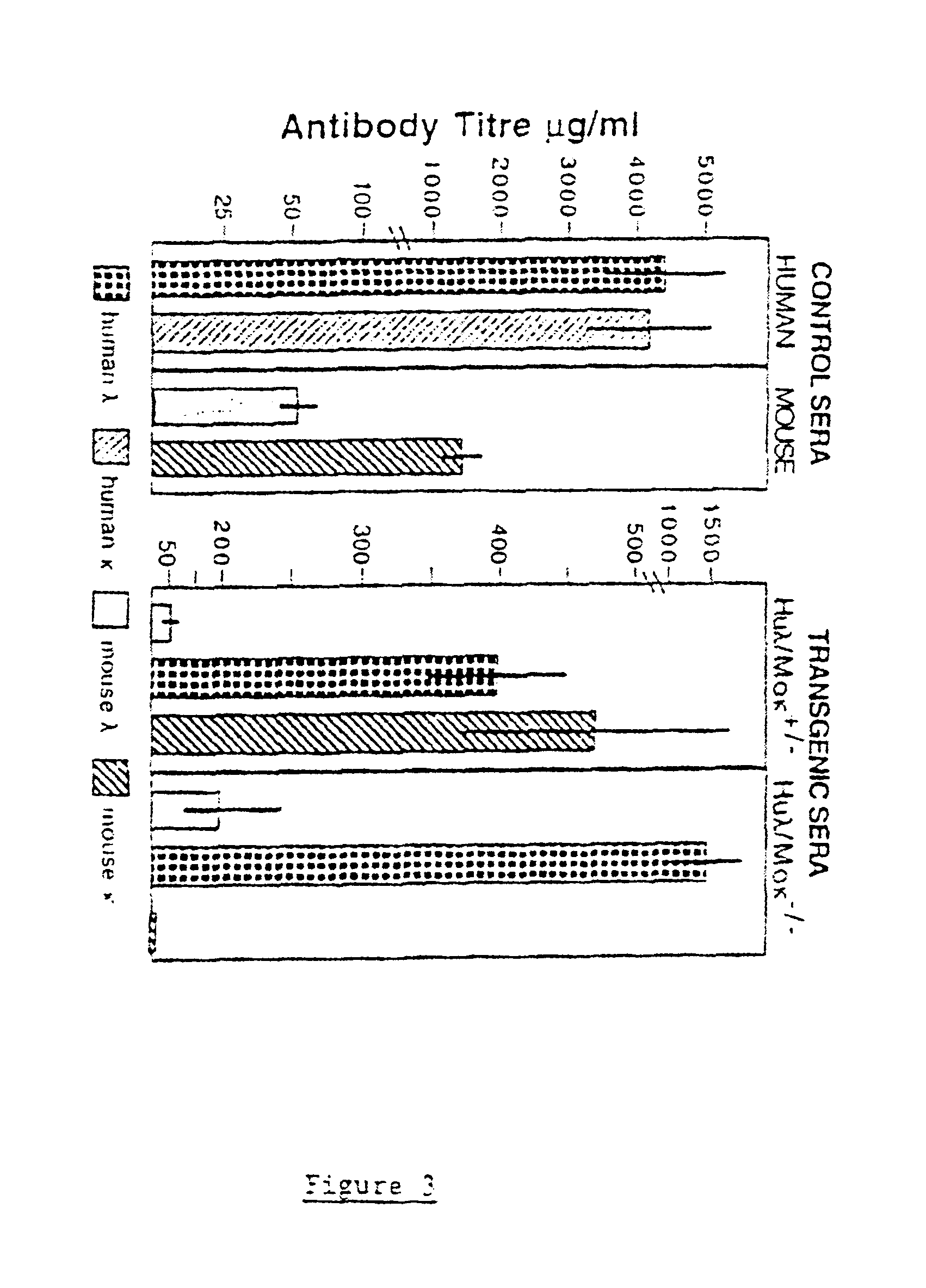
Murine expression of a human IgA lambda locus
InactiveUS6998514B2High expressionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin light chainMonoclonal antibody
In humans, approximately 60% of expressed immunoglobulin light chains are of the Kappa type and 40% of the Lambda type. In mice, there is almost no expression from the Lambda locus and over 95% of light chains are of Kappa type. The present invention discloses, among other things, transgenic mice carrying most of the human Ig Lambda light chain locus in their genome. The resulting mice express light chains with Kappa / Lambda ratio similar to the human ratio. Breeding of HuIg Lamda mice to Kappa-deficient mice also is described, as well as the generation of human monoclonal antibodies from transgenic mice with human Ig Lambda locus.
Owner:BABRAHAM INST
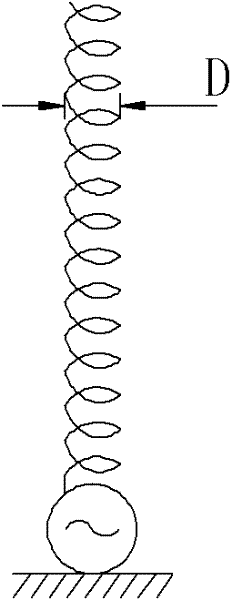
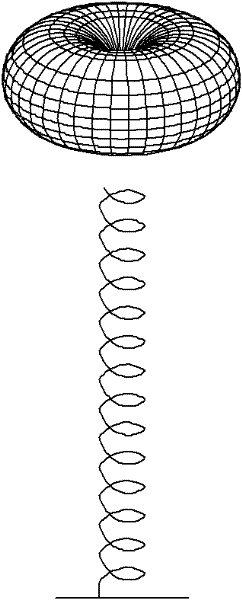
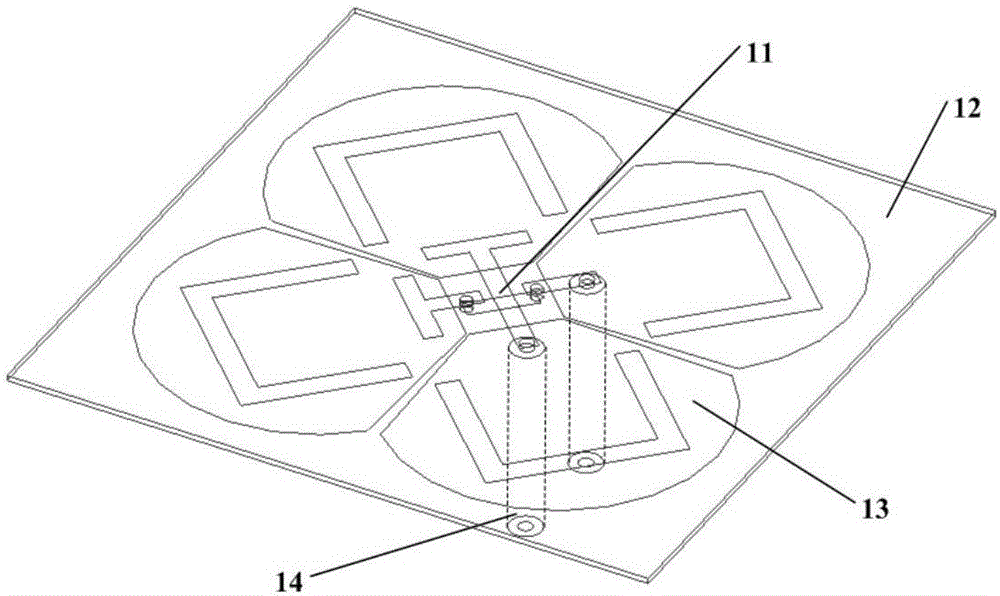
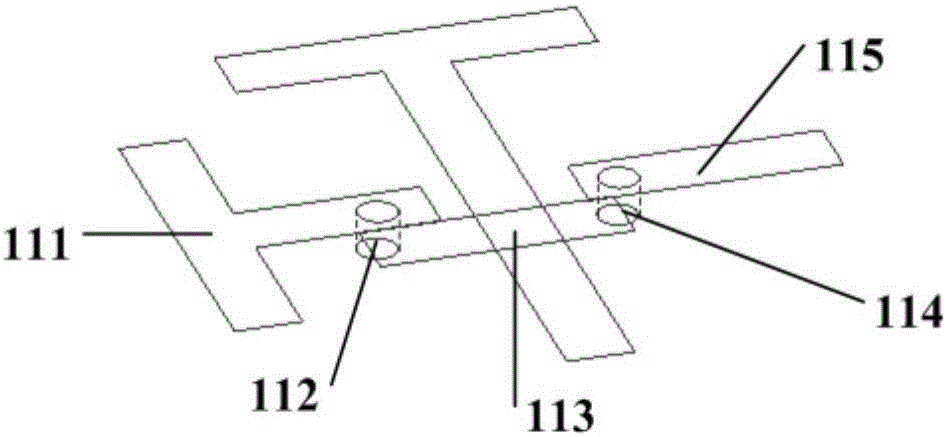
Helical antenna with small reflection surface
InactiveCN102544736AHigh gainIncreased launch coverageLogperiodic antennasHelical antennasNormal modeLength wave
The invention discloses a helical antenna with a small reflection surface, aiming at improving the helical antenna gain, enlarging the launching coverage range of a launcher and meeting the long-distance communication requirement of a tire pressure monitor system (TPMS). The helical antenna comprises a body and the reflection surface, wherein the body has a spiral structure formed by winding a metal wire or a metal tube, and is a normal mode helical antenna; and the reflection surface is arranged under the body and is connected with a negative pole or a ground wire of a feeding point of the body. The reflection surface meets the condition that (D0-D) / 2 is more than or equal to A-x and less than or equal to A, wherein D is the screw diameter of the body, D0 is the diameter of the reflection surface, A and x are constants, x is more than 0 and less than A, A is more than x and less than or equal to 0.01 lambda, and lambda is the wavelength of a signal transmitted by the launcher within the free space.
Owner:BAOLONG HUF SHANGHAI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
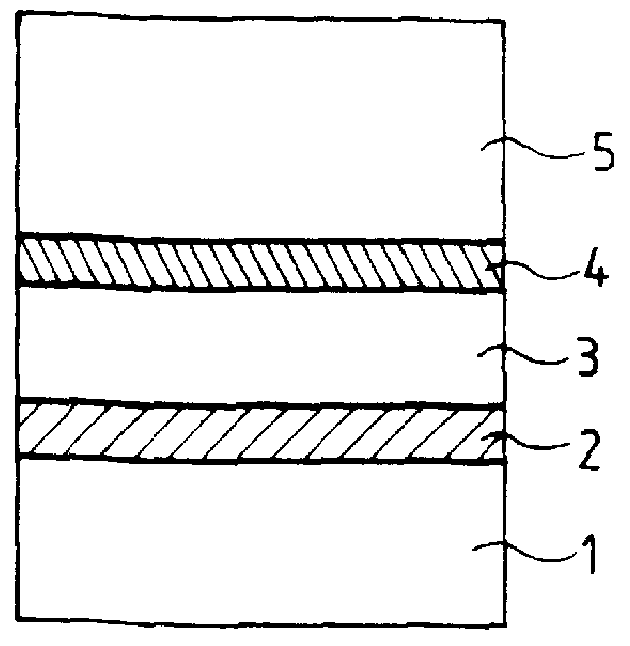
Laminated retardation optical element, process of producing the same, and liquid crystal display
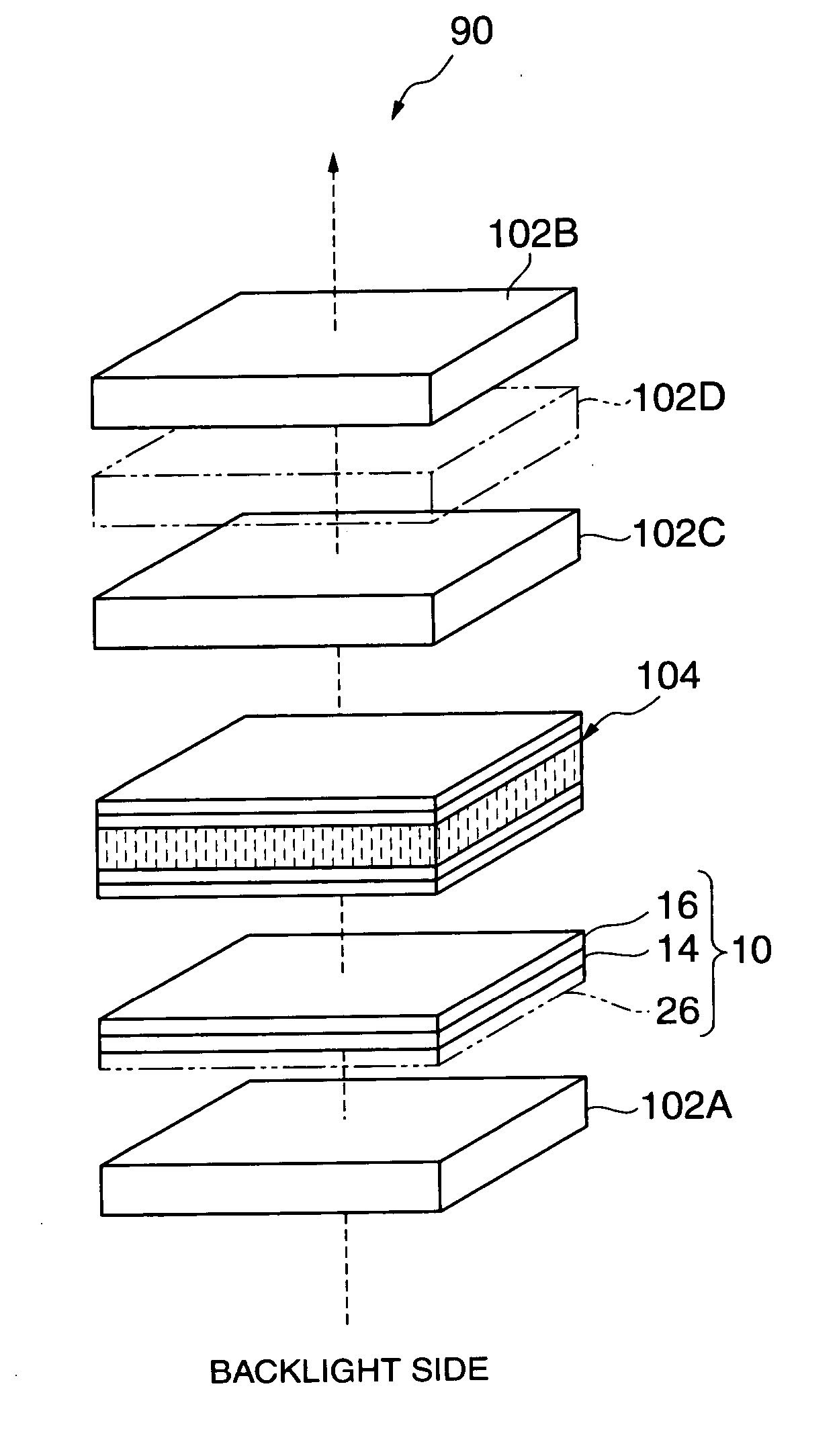
The present invention provides a laminated retardation optical element that never lowers contrast and thus never degrades display performance even when placed between a liquid crystal cell and a lambda / 4 retardation film. In a liquid crystal display 90, a laminated retardation optical element 10 is placed between a polarizer 102A on the incident side and a liquid crystal cell 104, and a lambda / 4 retardation film 102C is placed between a polarizer 102B on the emergent side and the liquid crystal cell 104. The laminated retardation optical element 10 comprises: a lambda / 4 retardation layer 14 having the function of bringing, to light that passes through this retardation layer, a phase difference corresponding to a quarter of the wavelength of the light; and a C plate-type retardation layer 16 that acts as a negative C plate. The lambda / 4 retardation layer 14 and the C plate-type retardation layer 16 are laminated to a transparent substrate 12 in the order mentioned, and are optically bonded to each other. The lambda / 4 retardation layer 14 comprises as its main component a horizontally-aligned, cross-linked nematic liquid crystal, while the C plate-type retardation layer 16 comprises as its main component a cross-linked chiral nematic liquid crystal (a cross-linked nematic liquid crystal and a cross-linked chiral agent) or cross-linked discotic liquid crystal.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Methods for producing an antireflection surface on an optical element, optical element and associated optical arrangement
InactiveUS20100149510A1Reduce reflectionGood reflection-reducing effectMirrorsOptical filtersMetallic materialsLength wave
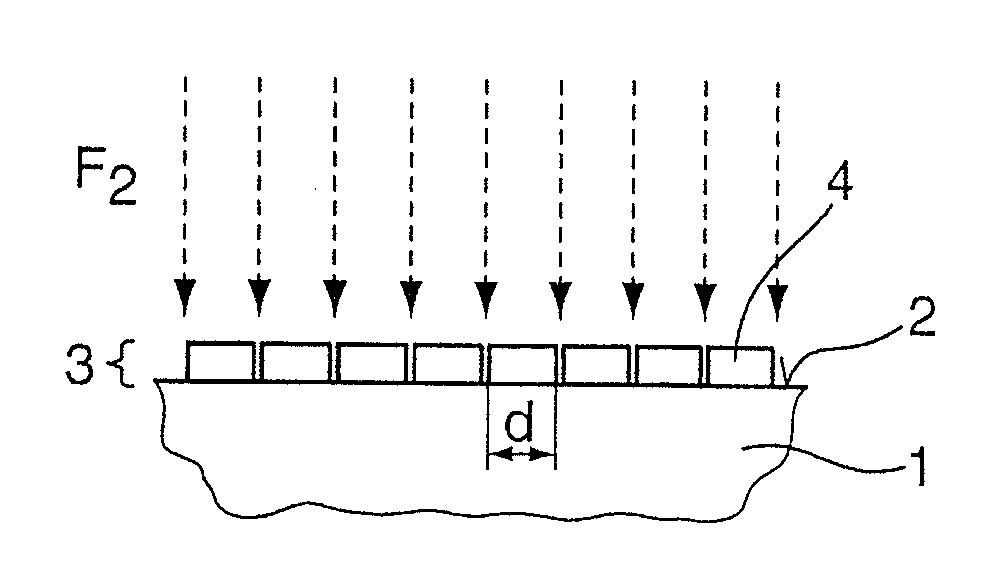
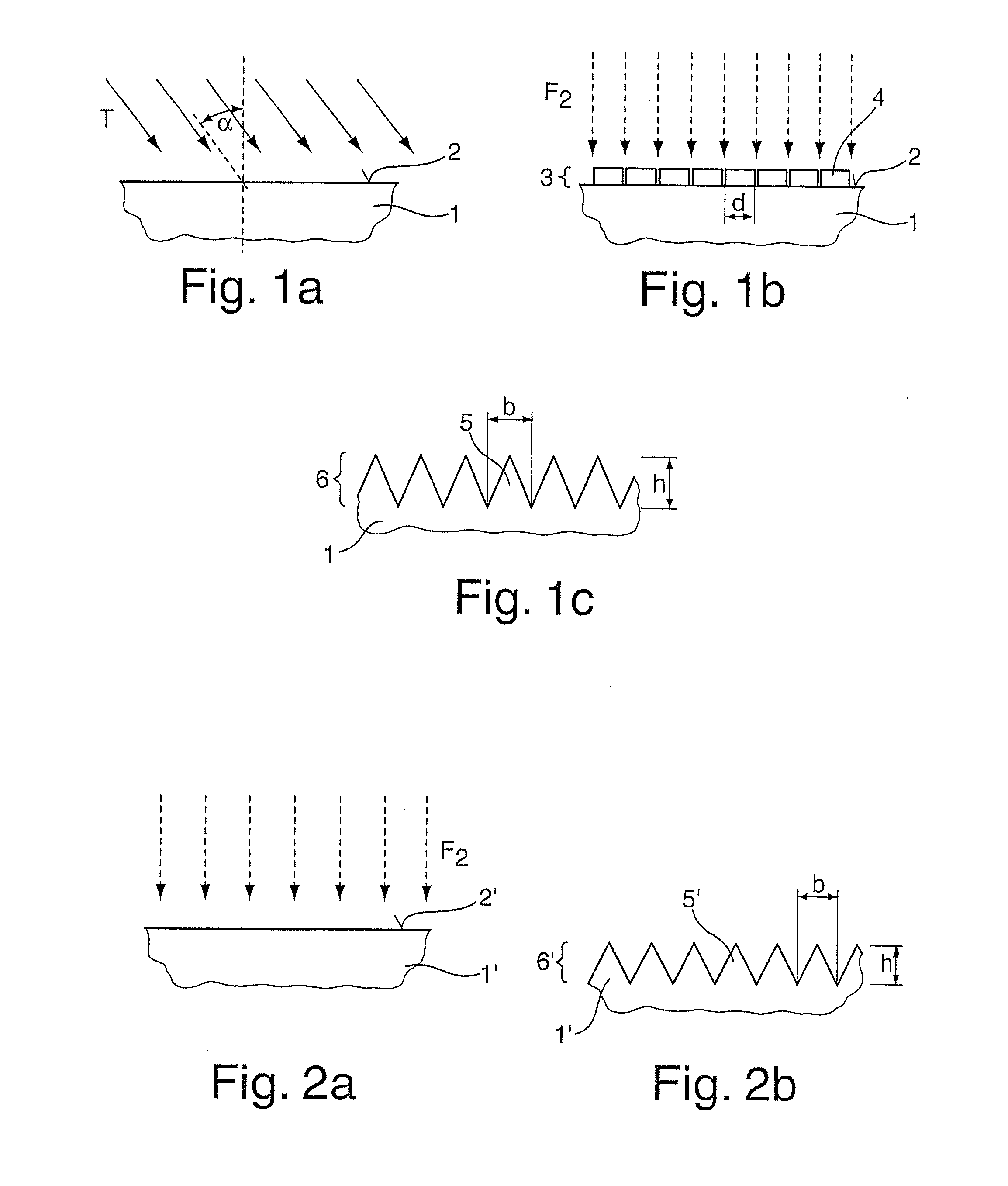
Methods for producing an antireflection surface (6) on an optical element (1) made of a material that is transparent at a useful-light wavelength λ in the UV region, preferably at 193 nm. A first method includes: applying a layer (3) of an inorganic, non-metallic material, which forms nanostructures (4) and is transparent to the useful-light wavelength λ, onto a surface (2) of the optical element (1); and etching the surface (2) while using the nanostructures (4) of the layer (3) as an etching mask for forming preferably pyramid-shaped or conical sub-lambda structures (5) in the surface (2). In a second method, the sub-lambda structures are produced without using an etching mask. An associated optical element (1) includes such an antireflection surface (6), and an associated optical arrangement includes such an optical element (1).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Procedure to recognize the diffusion gas composition in a wideband lambda sensor
InactiveUS7744740B2High sensitivityDiffusion coefficientWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementMobile vehicleDiffusion
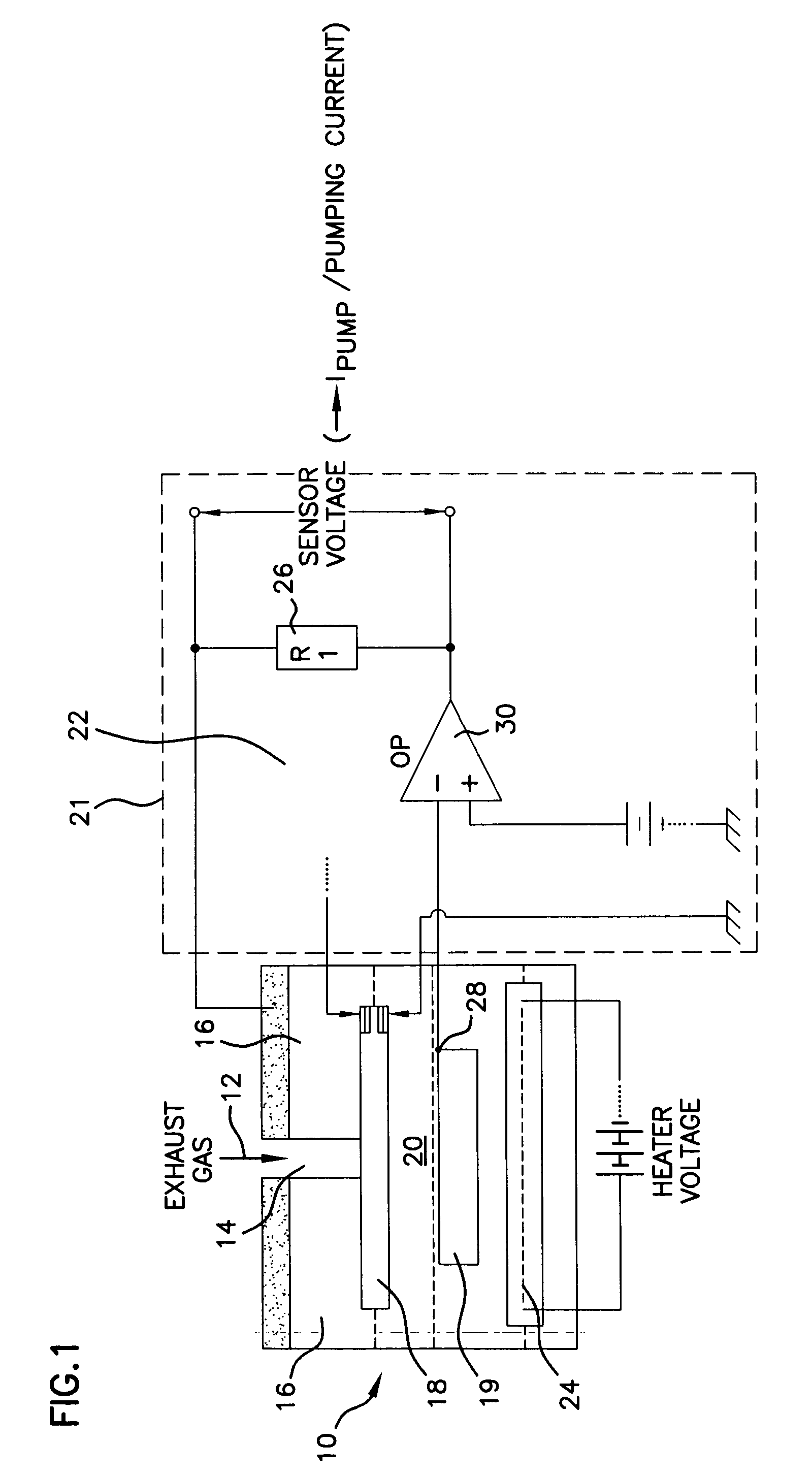
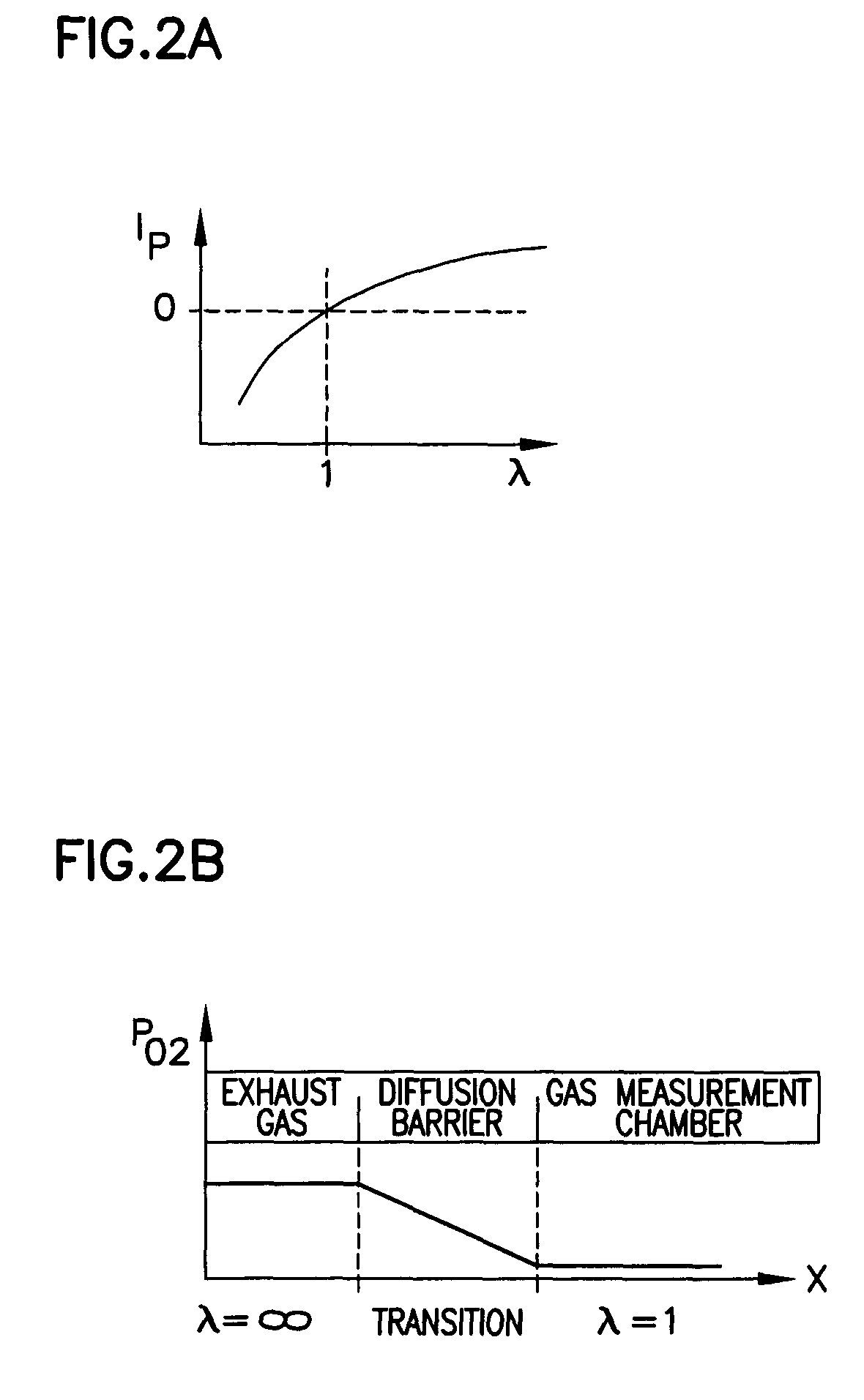
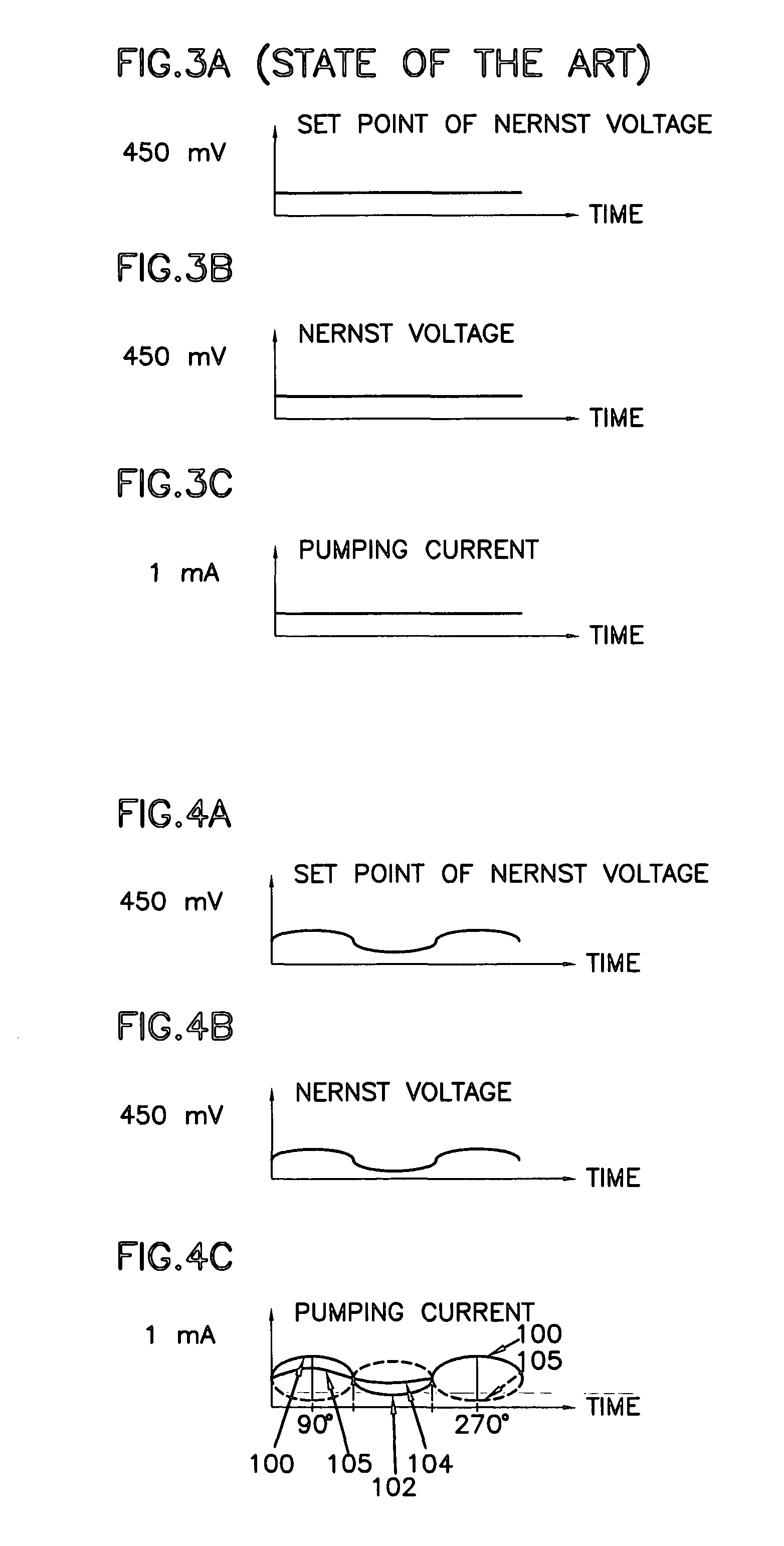
In a procedure to recognize the gas composition of a gas mixture, which consists of at least two gases of preferably different diffusion properties, delivered to a wideband lambda sensor, especially a gas mixture of an exhaust gas of an internal combustion engine of a motor vehicle, whereby the lambda sensor has a pumping cell with at least one gas measurement chamber, provision is made for the recognition of the gas composition of the gas mixture to result by means of modulation of the gas in the gas measurement chamber. Preferably the air number in the gas measurement chamber of the pumping cell is periodically altered, whereby the sensitivity of the lambda sensor to the gases, of which there are at least two, likewise periodically changes.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101788605ARealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower combinerPhase difference
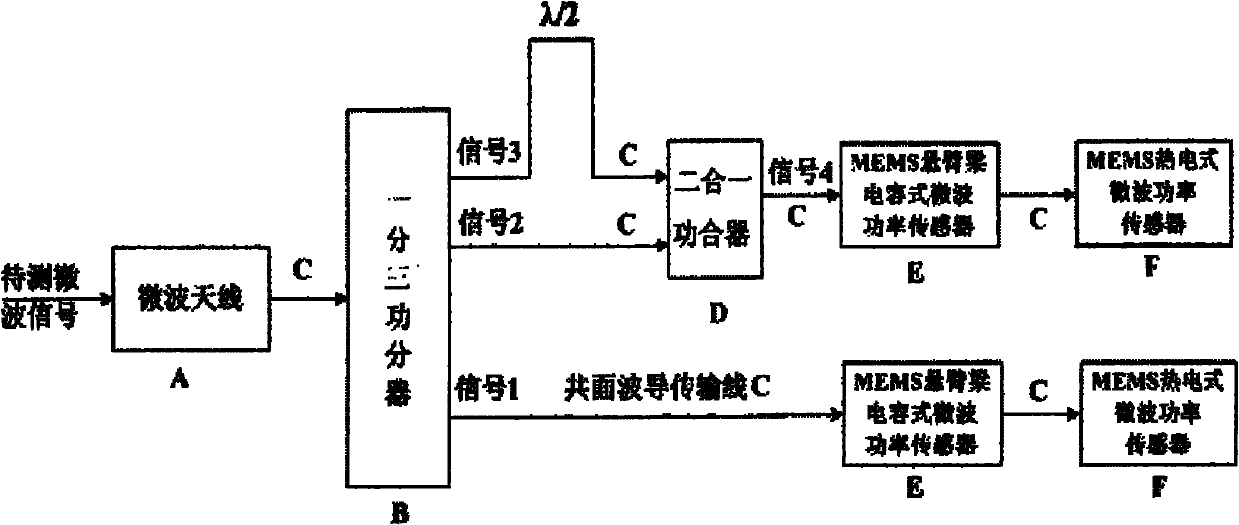
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Radiating member,illuminating device, electro-optical device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20040004424A1Reduce the temperatureIncrease brightnessMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLight guideRoom temperature
A radiating member, an illuminating device, an electro-optical device, and an electronic device are provided which are capable of absorbing the heat generated from an LED, thereby increasing the amount of electric current flowable through the LED. More particularly, there are provided a point light source, a light guide plate for receiving the light radiated from the point light source, and a radiating plate including an adhesive layer formed to contact the point light source, and a metal layer formed over the adhesive layer and made of the material having a thermal conductivity (lambda) equal to or greater than 90 W / mK at room temperature.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
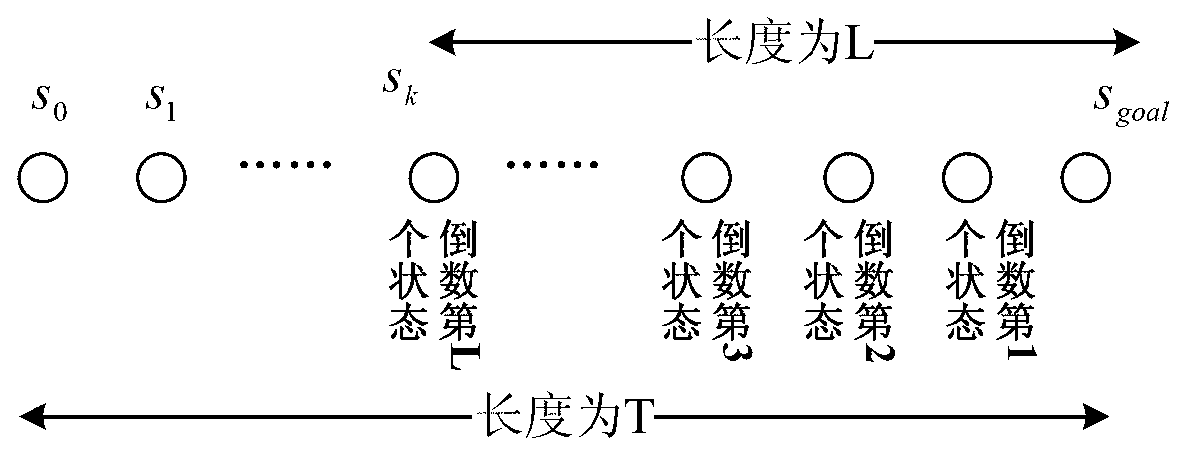
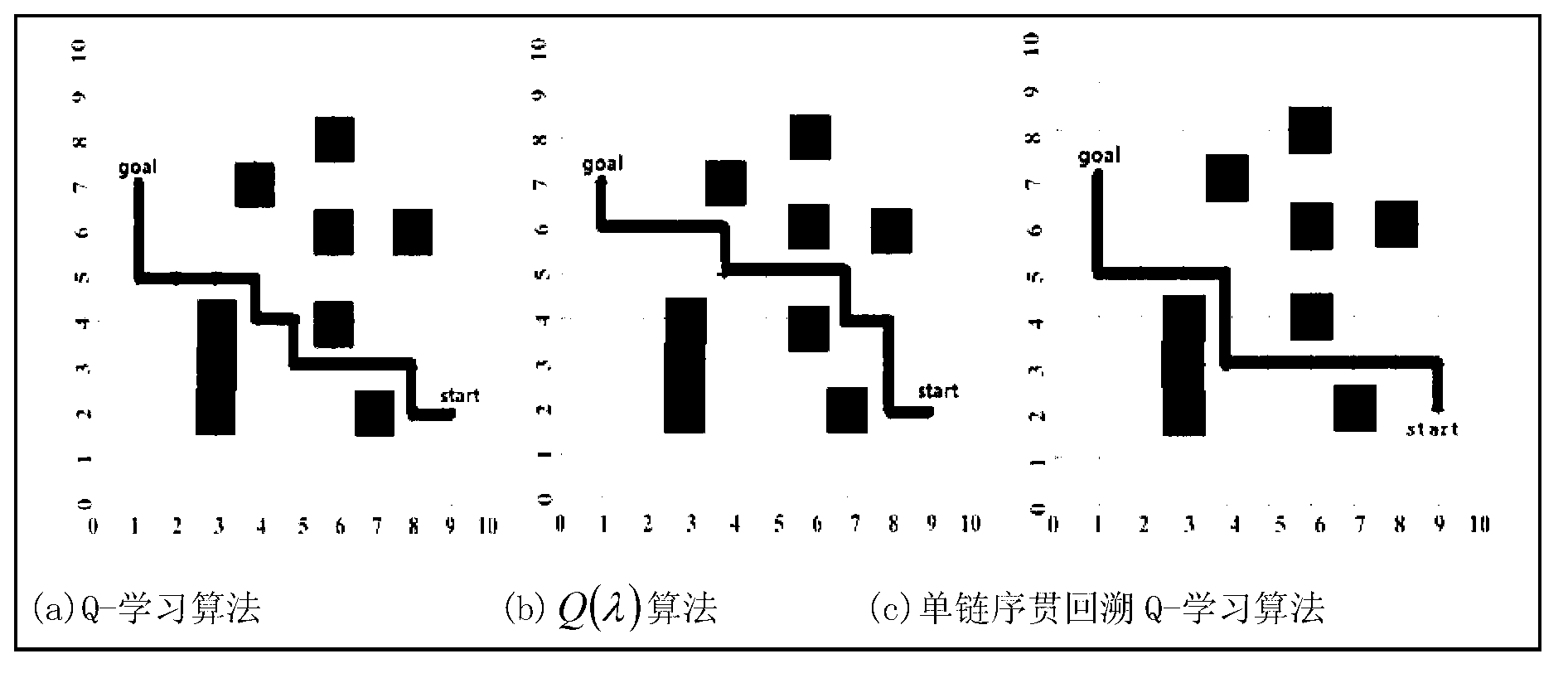
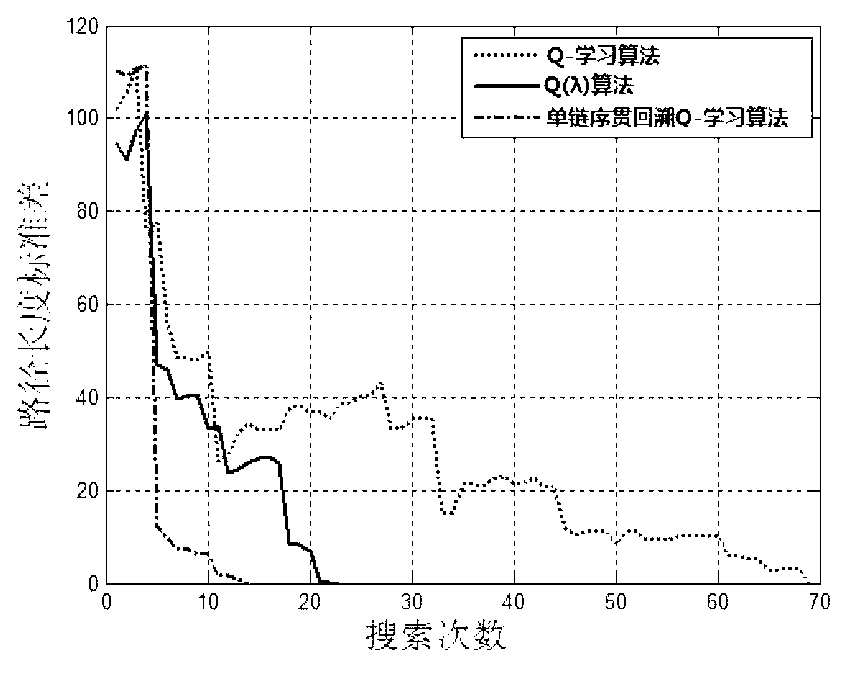
Mobile robot path planning algorithm based on single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning
InactiveCN102799179AImprove learning efficiencyShort learning timePosition/course control in two dimensionsMobile robots path planningPath plan
The invention provides a mobile robot path planning algorithm based on single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning. According to the mobile robot path planning algorithm based on the single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning, a two-dimensional environment is expressed by using a grid method, each environment area block corresponds to a discrete location, the state of a mobile robot at some moment is expressed by an environment location where the robot is located, the search of each step of the mobile robot is based on a Q-learning iterative formula of a non-deterministic Markov decision process, progressively sequential backtracking is carried out from the Q value of the tail end of a single chain, namely the current state, to the Q value of the head end of the single chain until a target state is reached, the mobile robot cyclically and repeatedly finds out paths to the target state from an original state, the search of each step is carried out according to the steps, and Q values of states are continuously iterated and optimized until the Q values are converged. The mobile robot path planning algorithm based on the single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning has the advantages that the number of steps required for optimal path searching is far less than that of a classic Q-learning algorithm and a Q(lambda) algorithm, the learning time is shorter, and the learning efficiency is higher; and particularly for large environments, the mobile robot path planning algorithm based on the single-chain sequential backtracking Q-learning has more obvious advantages.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS6124024ADischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesRefractive indexWavelength
An organic electroluminescence device in which the following total optical thickness is set at a value which enhances the intensity of the central wave length lambda ( lambda being selected in the ranges of 440 to 490 nm, 500 to 550 nm, and 600 to 650 nm) of the electroluminescence light emitted from the organic multi-layer part having a refractive index of 1.6 to 1.8: (1) in the construction of a substrate / a transparent electrode of a high refractivity / an organic multi-layer part / a cathode, the total optical thickness of the transparent electrode of a high refractivity and the organic multi-layer part; (2) in the construction of a substrate / an underlayer of a high refractivity / a transparent electrode / an organic multi-layer part / a cathode, the total optical thickness of the underlayer of a high refractivity, the transparent electrode, and the organic multi-layer part or the total optical thickness of the transparent electrode and the organic multi-layer part; and (3) in the construction of a substrate / a underlayer of a low refractivity / a transparent electrode / an organic multi-layer part / a cathode, the total optical thickness of the transparent electrode and the organic multi-layer part. The device has a simple construction and the color purity of the blue light emission is particularly increased.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Defining biological states and related genes, proteins and patterns
InactiveUS20020169562A1Reduce the valueSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseProtein insertion
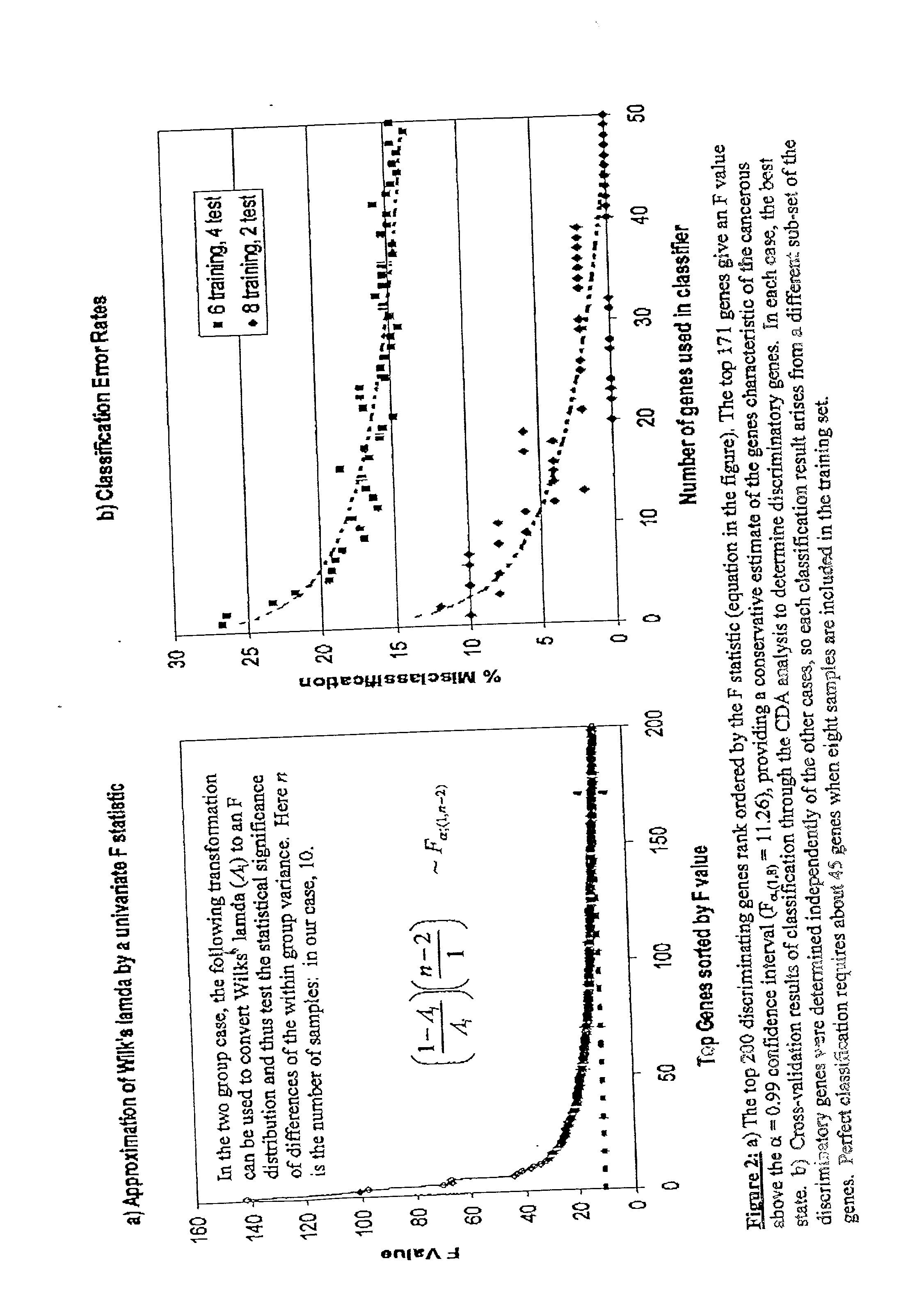
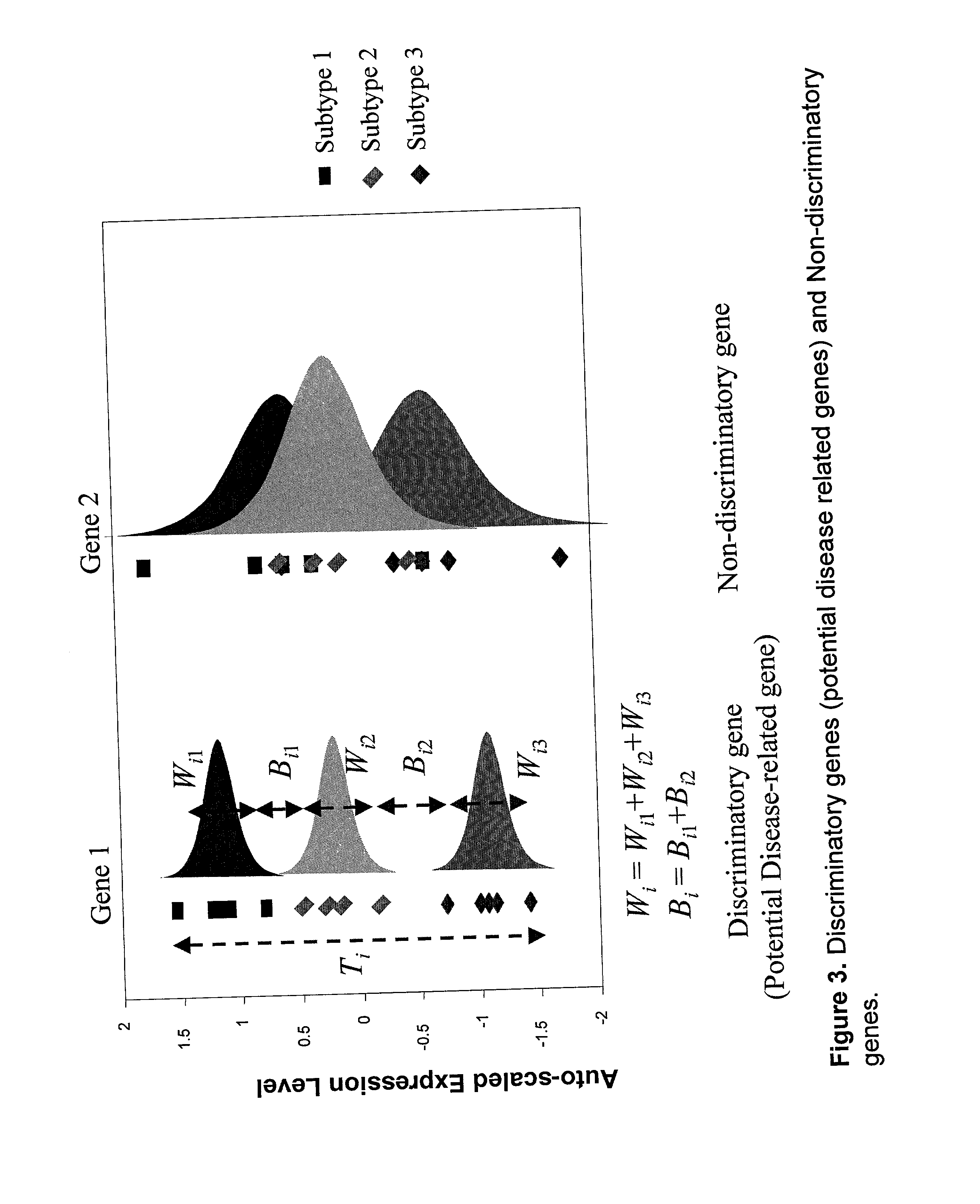
Disclosed are a variety of methods and computer systems for use in the analysis of gene and protein expression data. Also disclosed are methods for the definition of the cellular state of cells and tissues from multidimensional physiological data such as those obtained from gene expression measurements with DNA microarrays. A variety of classification methods can be applied to expression data to achieve this goal. Demonstrated is the application of several statistical tools including Wilks' lambda ratio of within-group to total variance, Fisher Discriminant Analysis, and the misclassification error rate to the identification of discriminating genes and the overall classification of expression data. Examples from several different cases demonstrate the ability of the method to produce well-separated groups in the projection space representing distinct physiological states. The method can be augmented and is useful in disease diagnosis, drug screening and bioprocessing applications.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Stable antibody compositions and methods of stabilizing same
InactiveUS20100172862A1Improve propertiesMaintain stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderFractionationAntigen binding
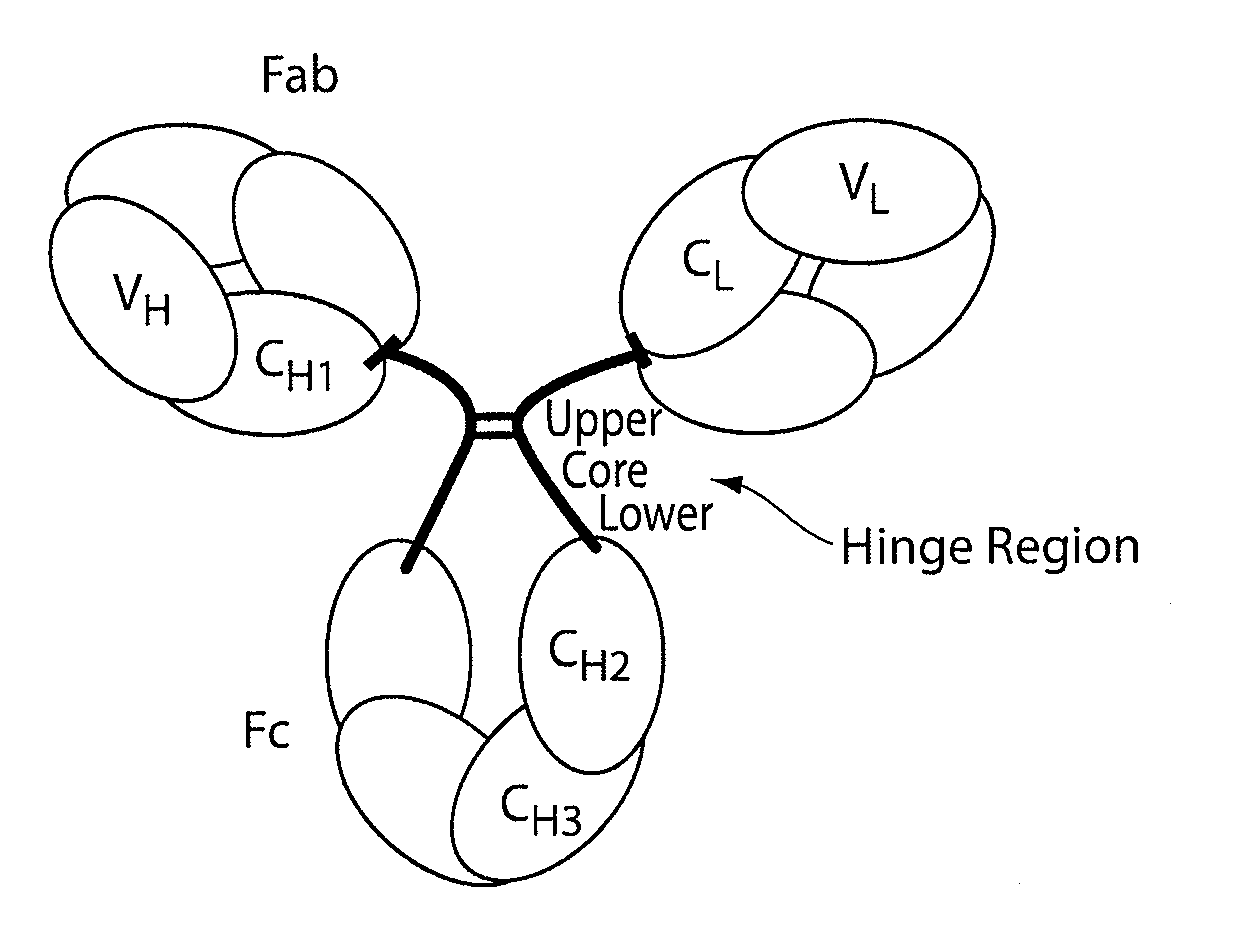
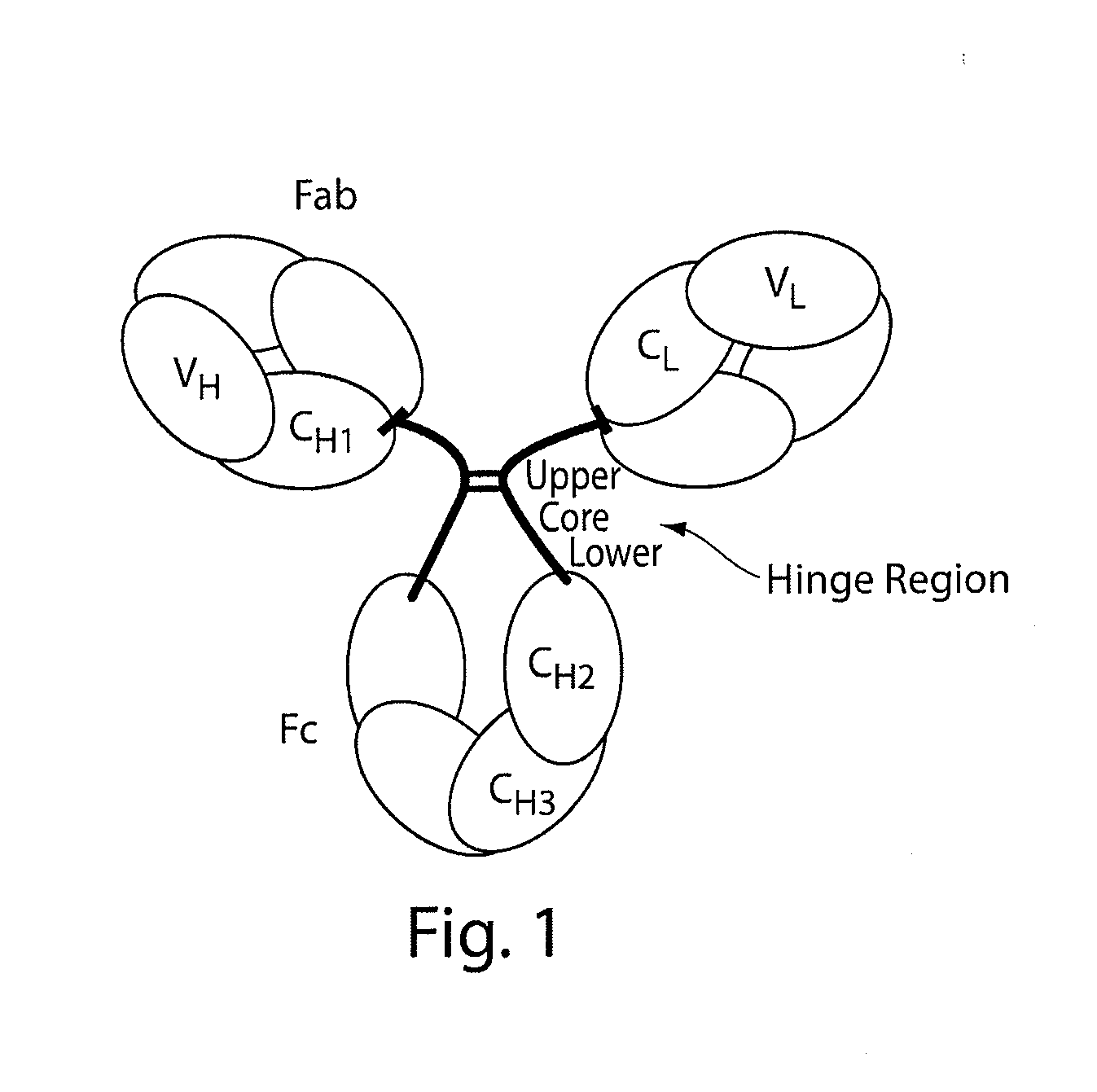
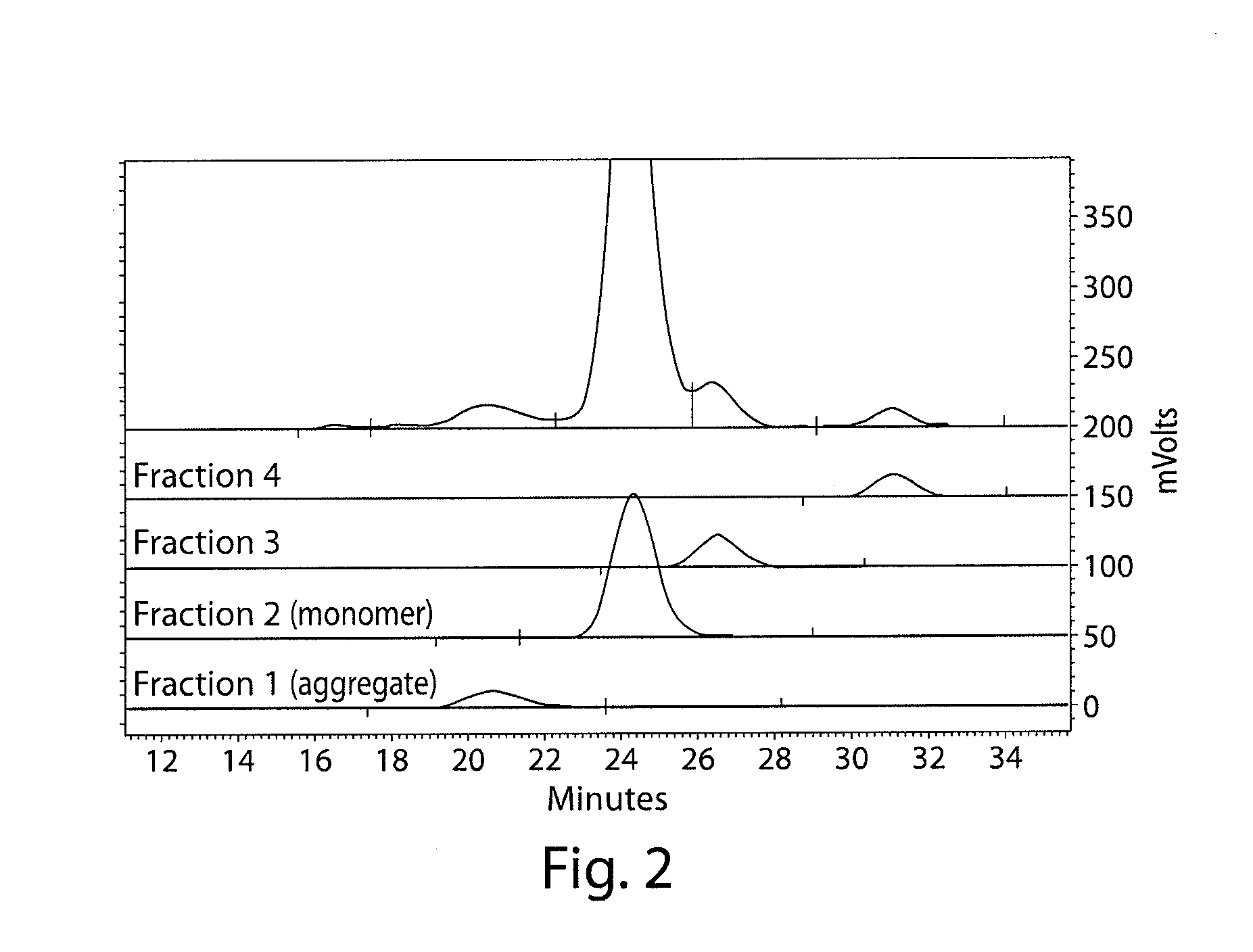
The invention provides compositions and methods for inhibiting fractionation of immunoglobulins comprising a lambda light chain based on the observation that iron, in the presence of histidine, results in increased fragmentation of a recombinant fully human IgG molecule containing a lambda light chain due to cleavage in the hinge region. The invention further provides an aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising an antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, that binds the p40 subunit of IL-12 / IL-23 and a buffer system comprising histidine, wherein the formulation has enhanced stability, including enhanced resistance to fragmentation.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
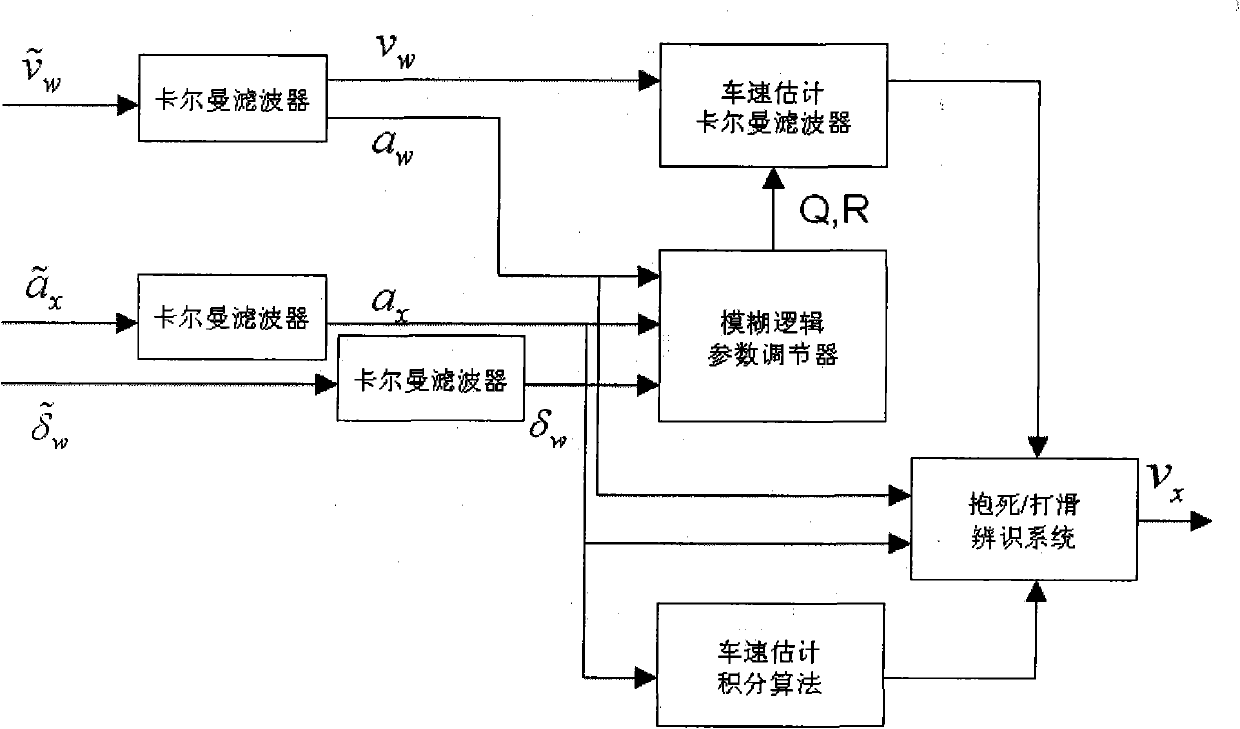
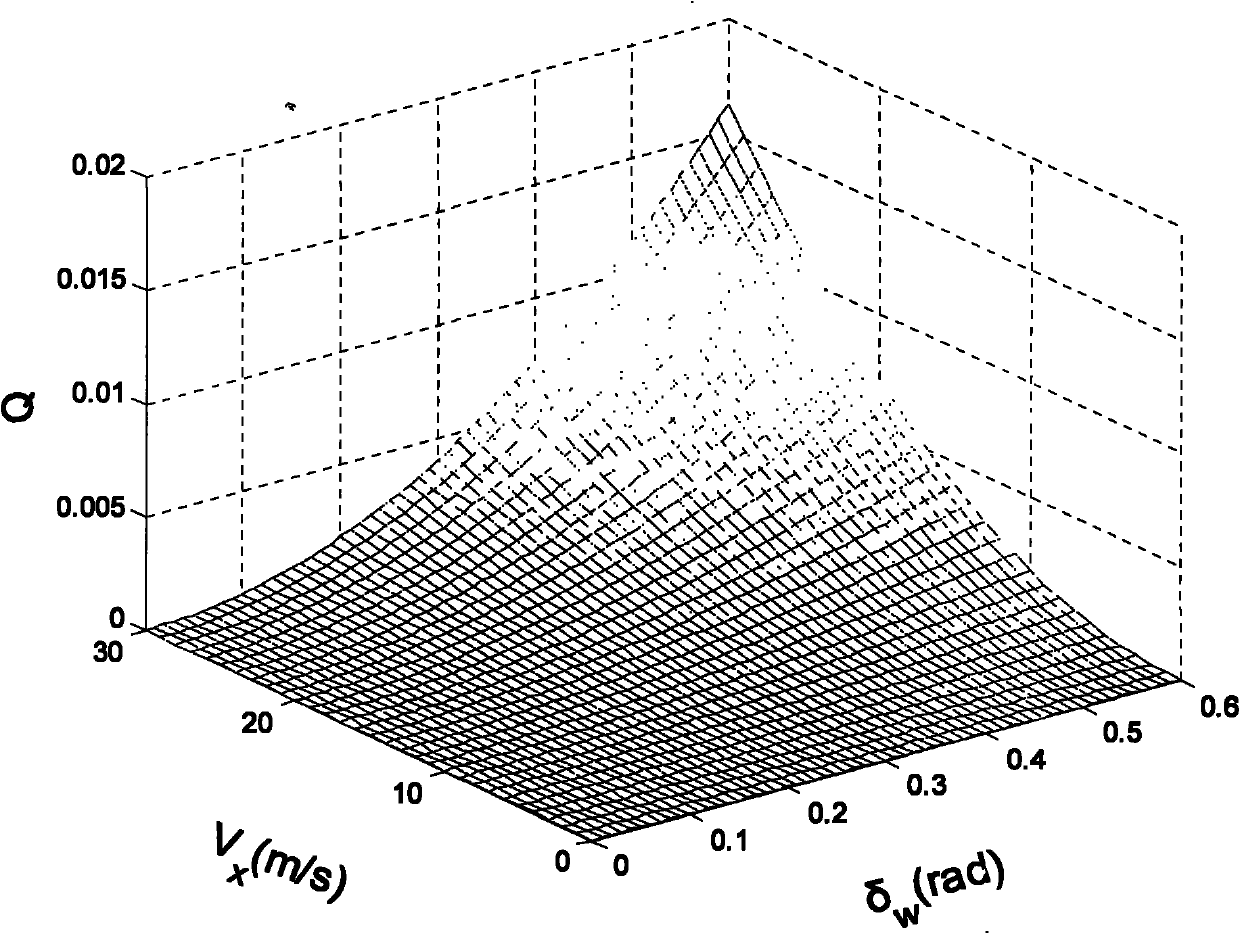
Longitudinal speed evaluation method of full-wheel electrically-driven vehicle
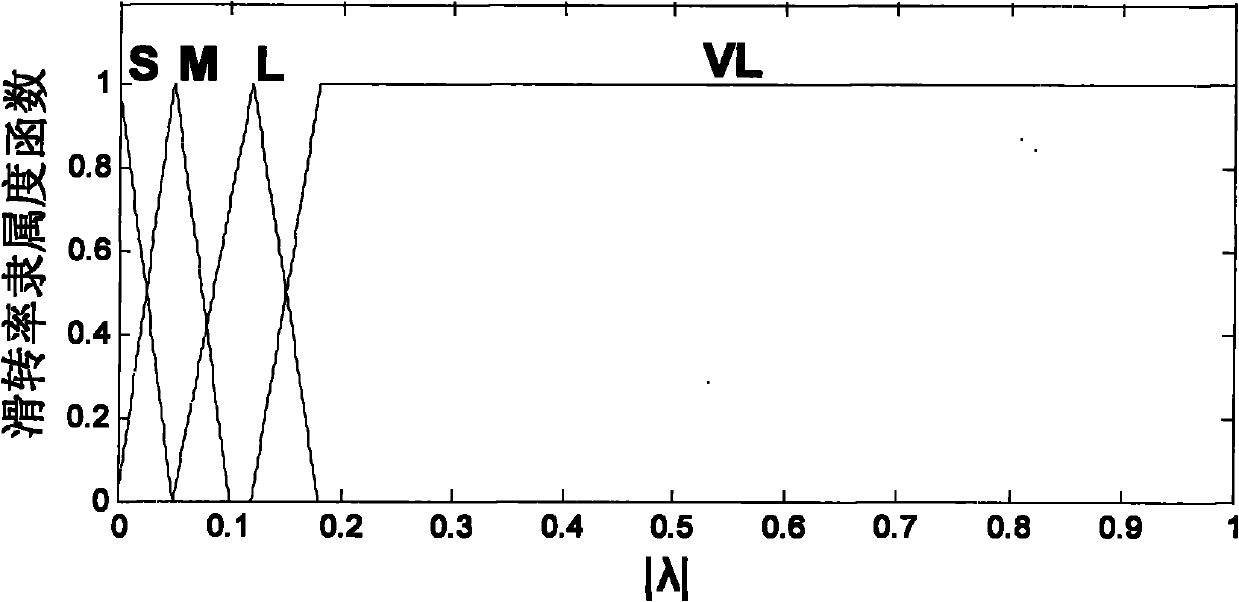
The invention relates to a longitudinal speed evaluation method of a full-wheel electrically-driven vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: 1) configuring a speed measuring system; 2) collecting signals shown in the specification in real time; 3) carrying out filtering treatment on the collected signals in a Kalman filtering mode; 4) establishing a speed evaluation formula based on a Kalman filter space equation structure and a speed evaluation formula based on integrated acceleration; and 5) switching discretion by using a speed evaluation algorithm: setting a threshold value for the absolute value of the trackslip / slip rate lambda as epsilon, when the absolute value of lambda is less than the epsilon, adopting the speed evaluation formula based on the Kalman filtering, and when the absolute value of lambda is more than or equal to the epsilon, adopting the speed evaluation formula based on the integrated acceleration. The method provided by the invention is suitable for online speed evaluation of the full-wheel electrically-driven vehicle, comprising exact observation for the longitudinal speed when the wheel is subject to excessive trackslip / slippage and even locking.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Characterization of highly scattering media by measurement of diffusely backscattered polarized light
InactiveUS6011626APolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsBiological cellOptical property
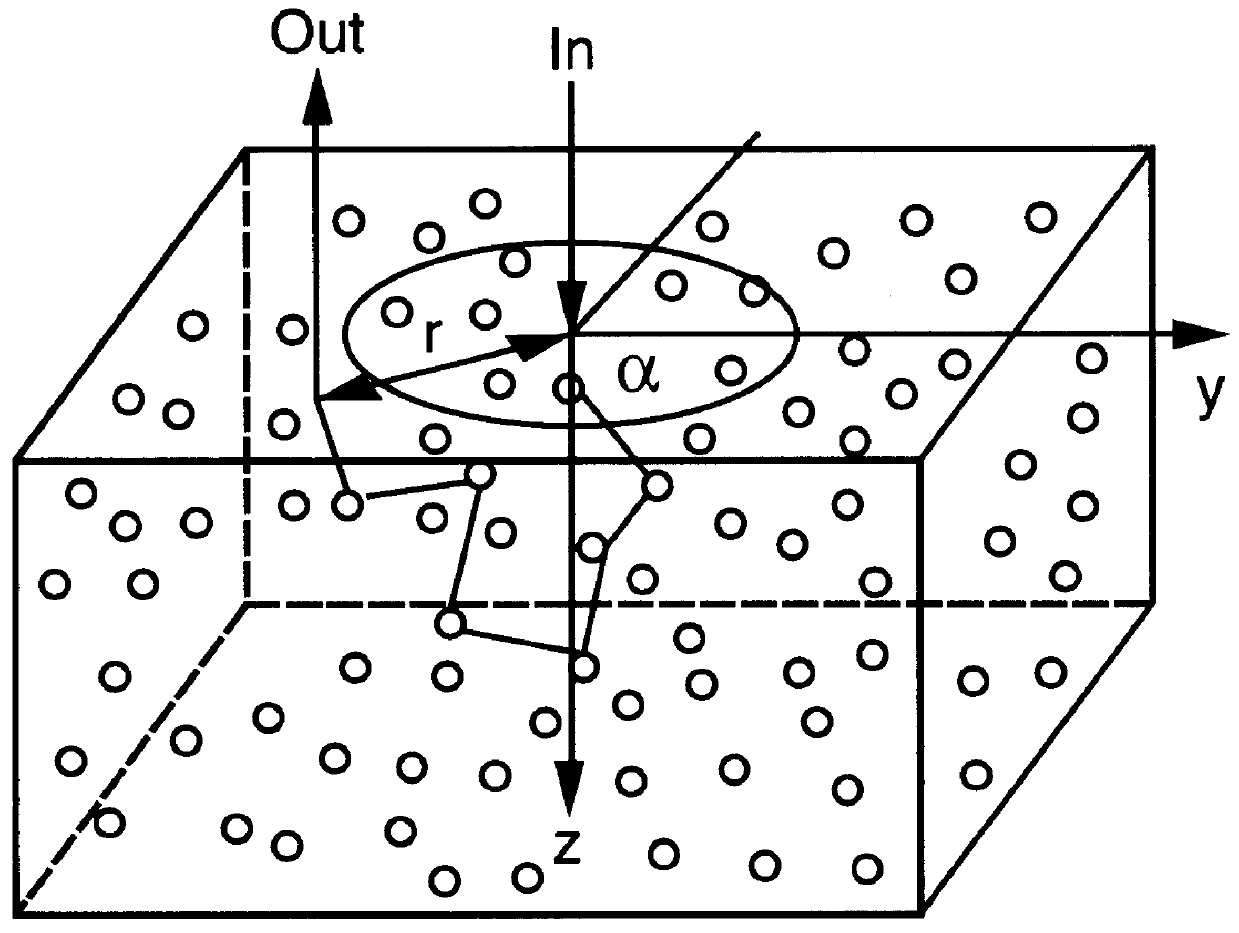
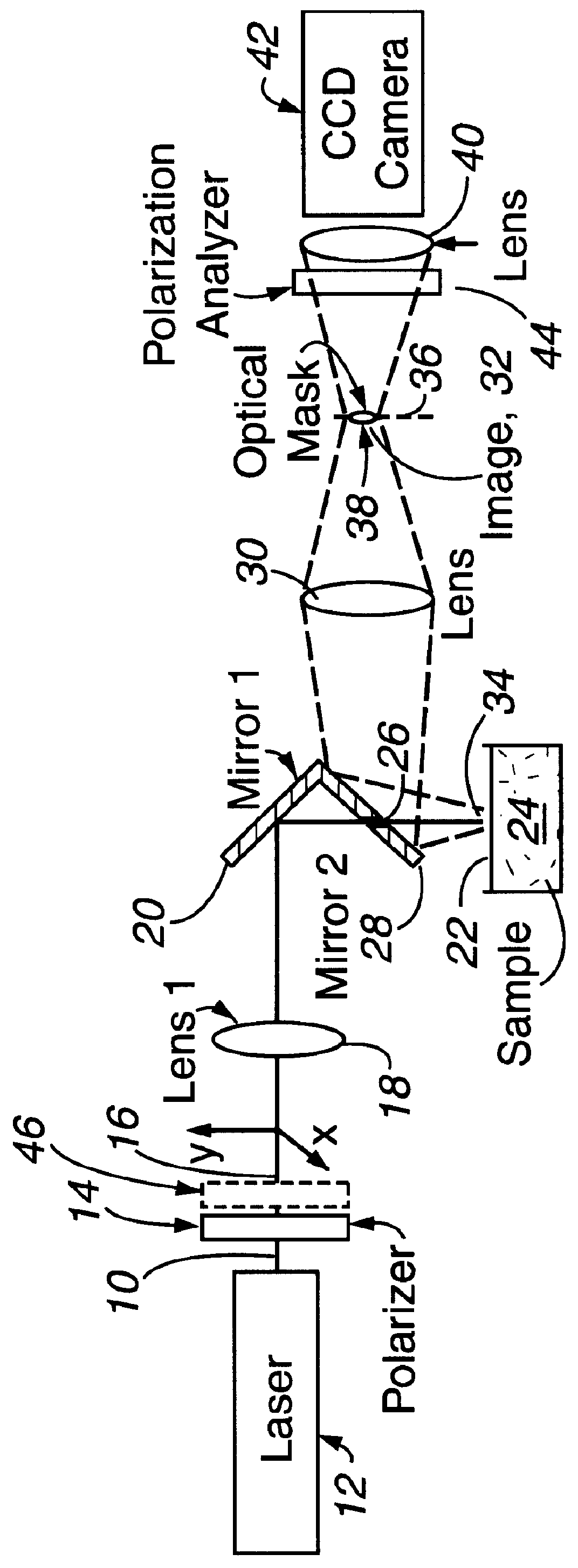
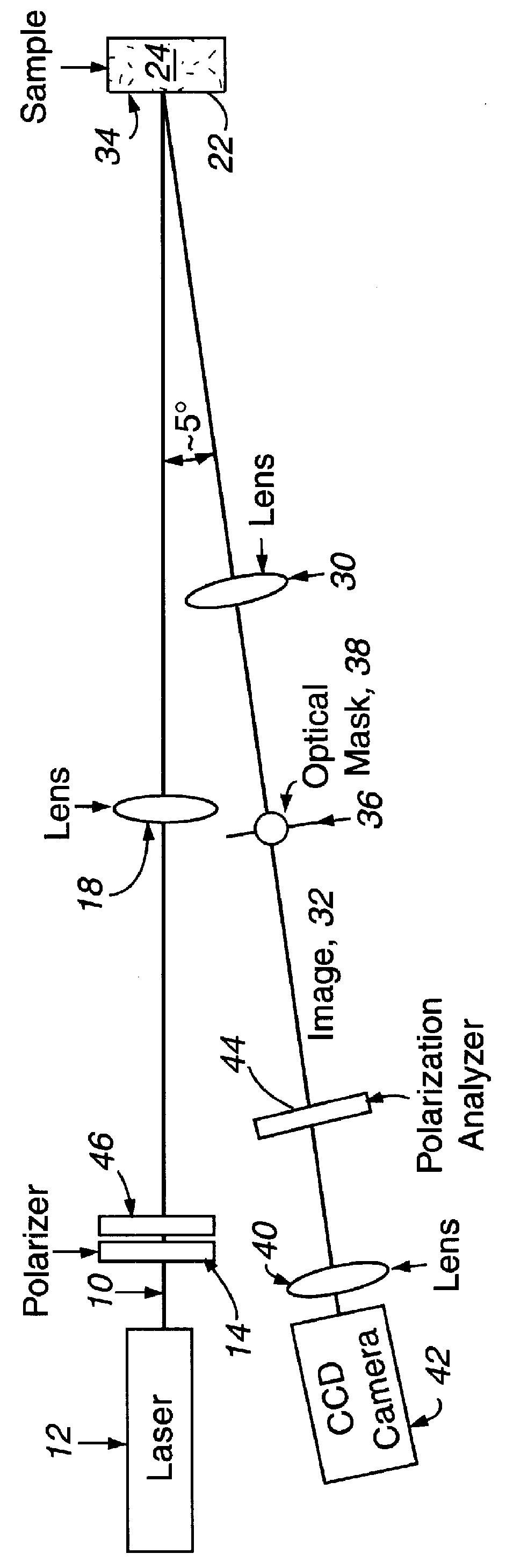
An apparatus and method for recording spatially dependent intensity patterns of polarized light that is diffusely backscattered from highly scattering media are described. These intensity patterns can be used to differentiate different turbid media, such as polystyrene-sphere and biological-cell suspensions. Polarized light from a He-Ne laser ( lambda =543 nm) is focused onto the surface of the scattering medium, and a surface area of approximately 4x4 cm centered on the light input point is imaged through polarization analysis optics onto a CCD camera. A variety of intensity patterns may be observed by varying the polarization state of the incident laser light and changing the analyzer configuration to detect different polarization components of the backscattered light. Experimental results for polystyrene-sphere and Intralipid suspensions demonstrate that the radial and azimuthal variations of the observed pattern depend on the concentration, size, and anisotropy factor, g, of the particles constituting the scattering medium. Measurements performed on biological cell suspensions show that intensity patterns can be used to differentiate between suspensions of cancerous and non-cancerous cells. Introduction of the Mueller-matrix for diffusely backscattered light, permits the selection of a subset of measurements which comprehensively describes the optical properties of backscattering media.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
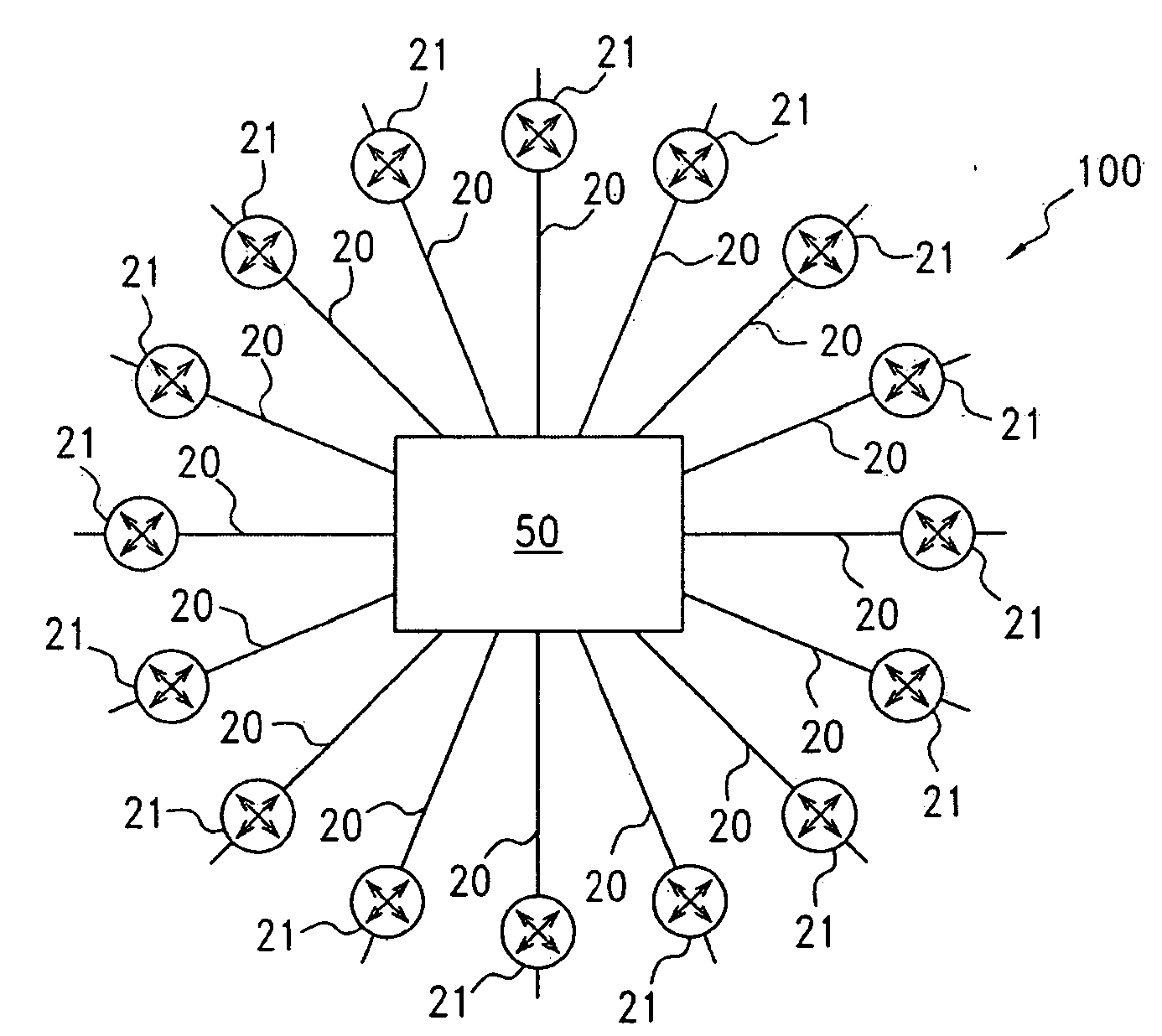
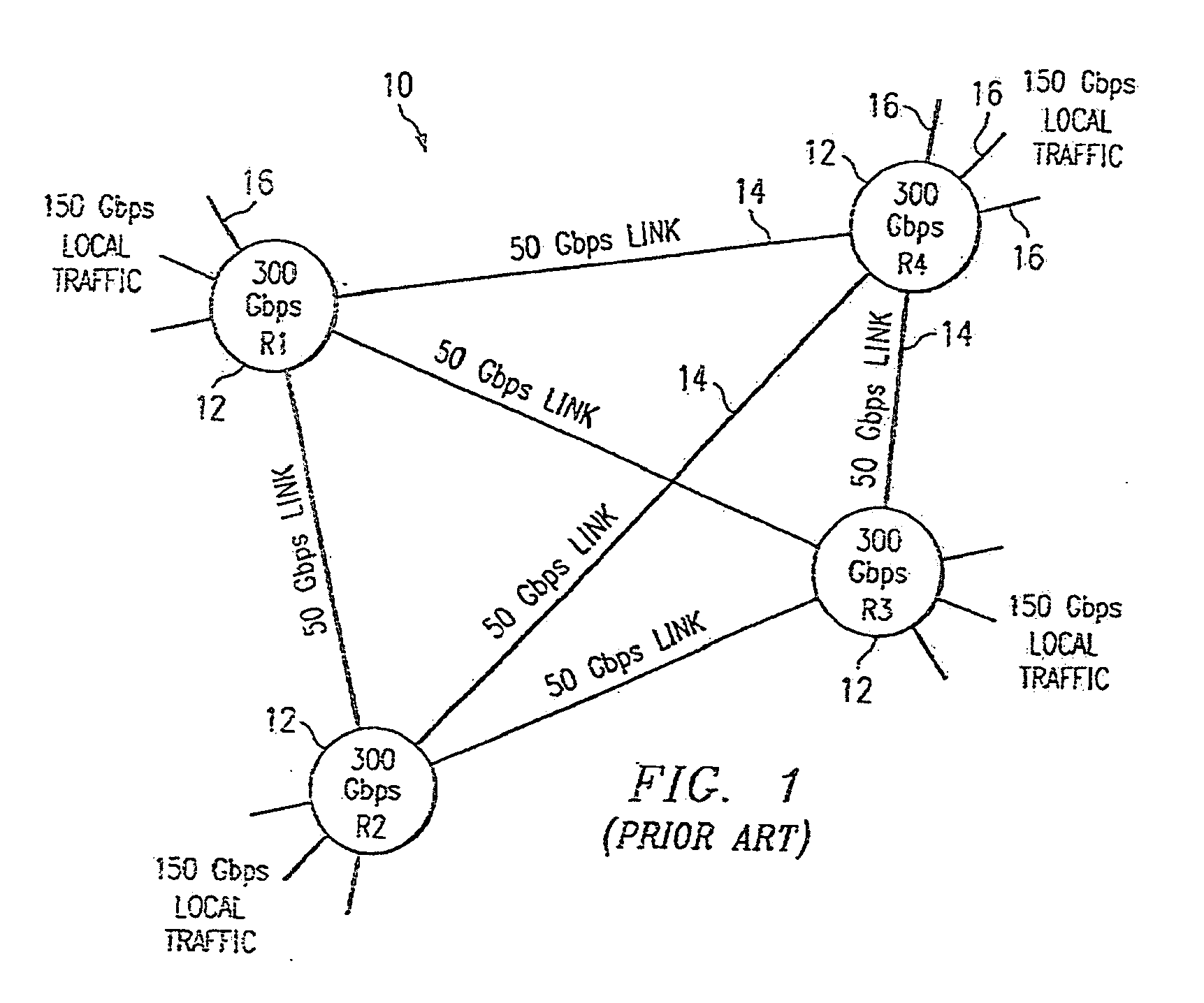
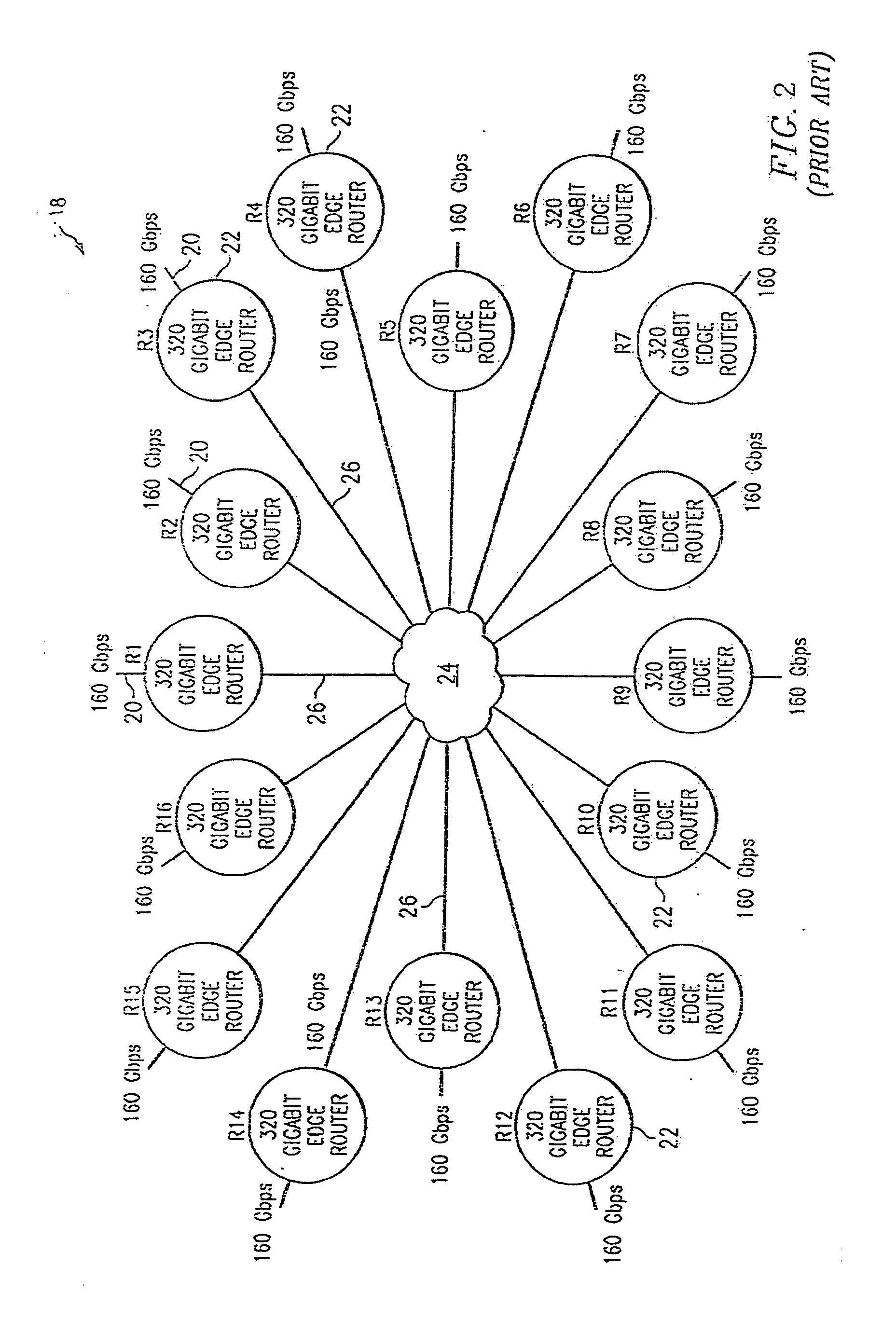
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
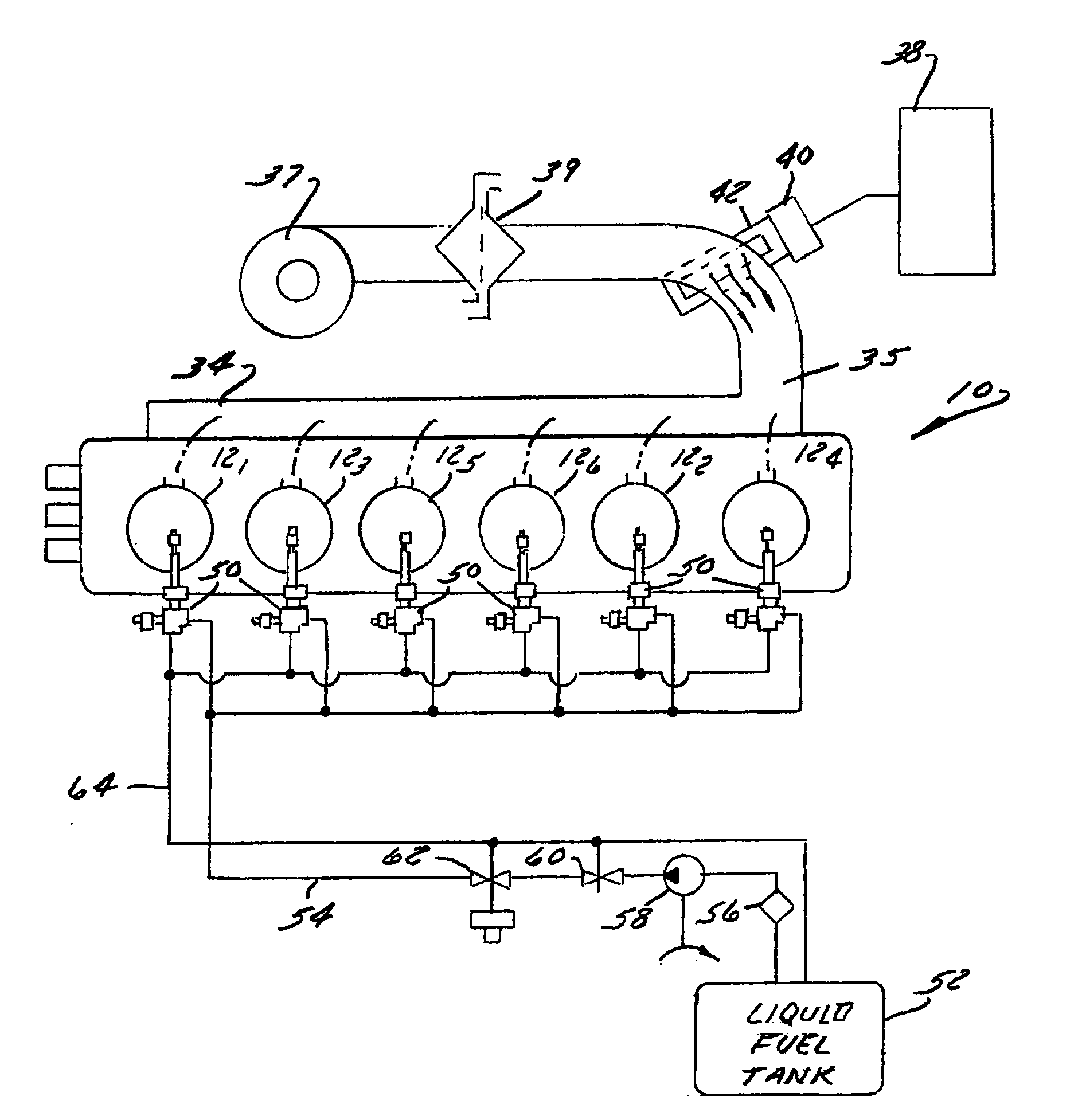
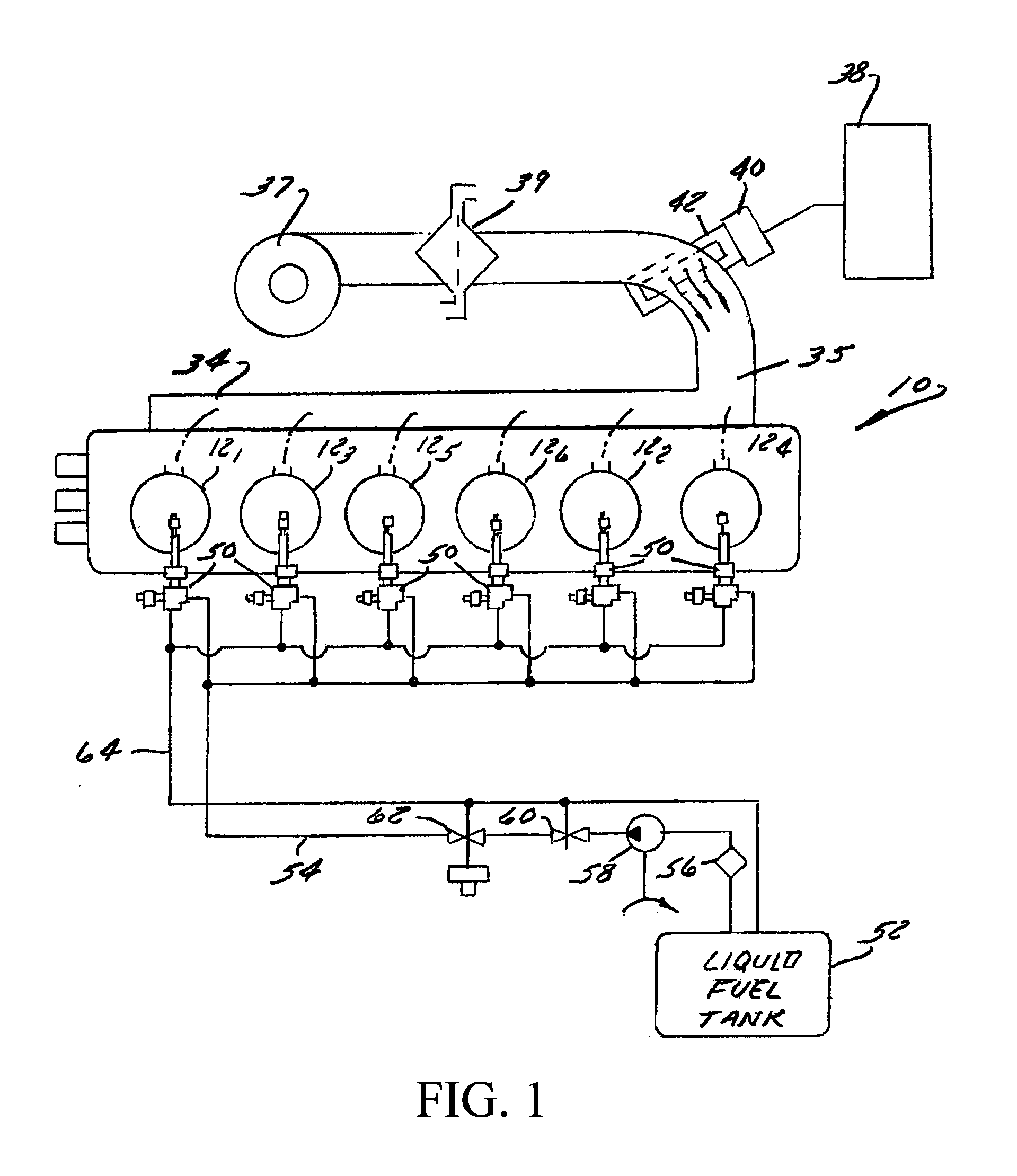
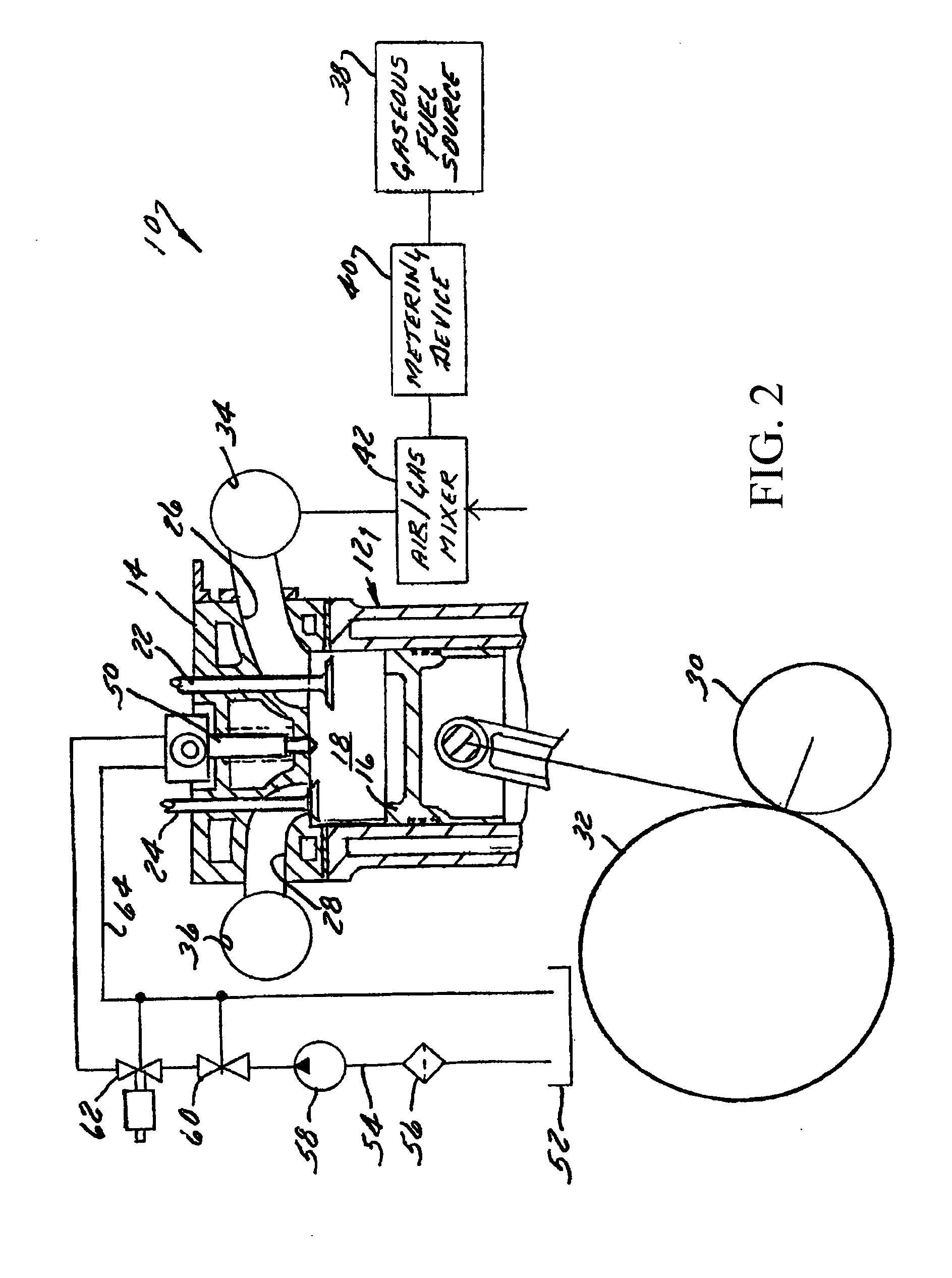
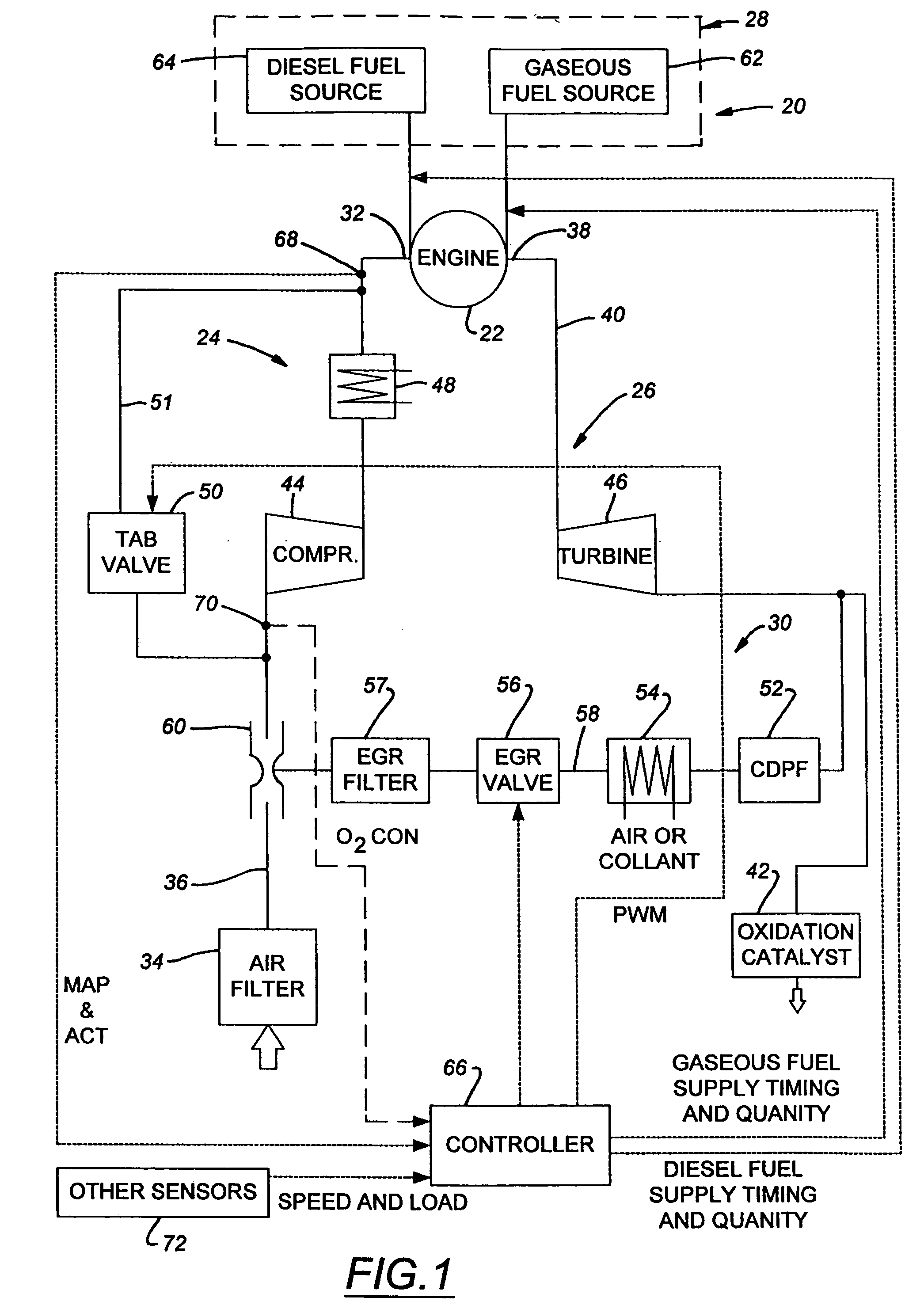
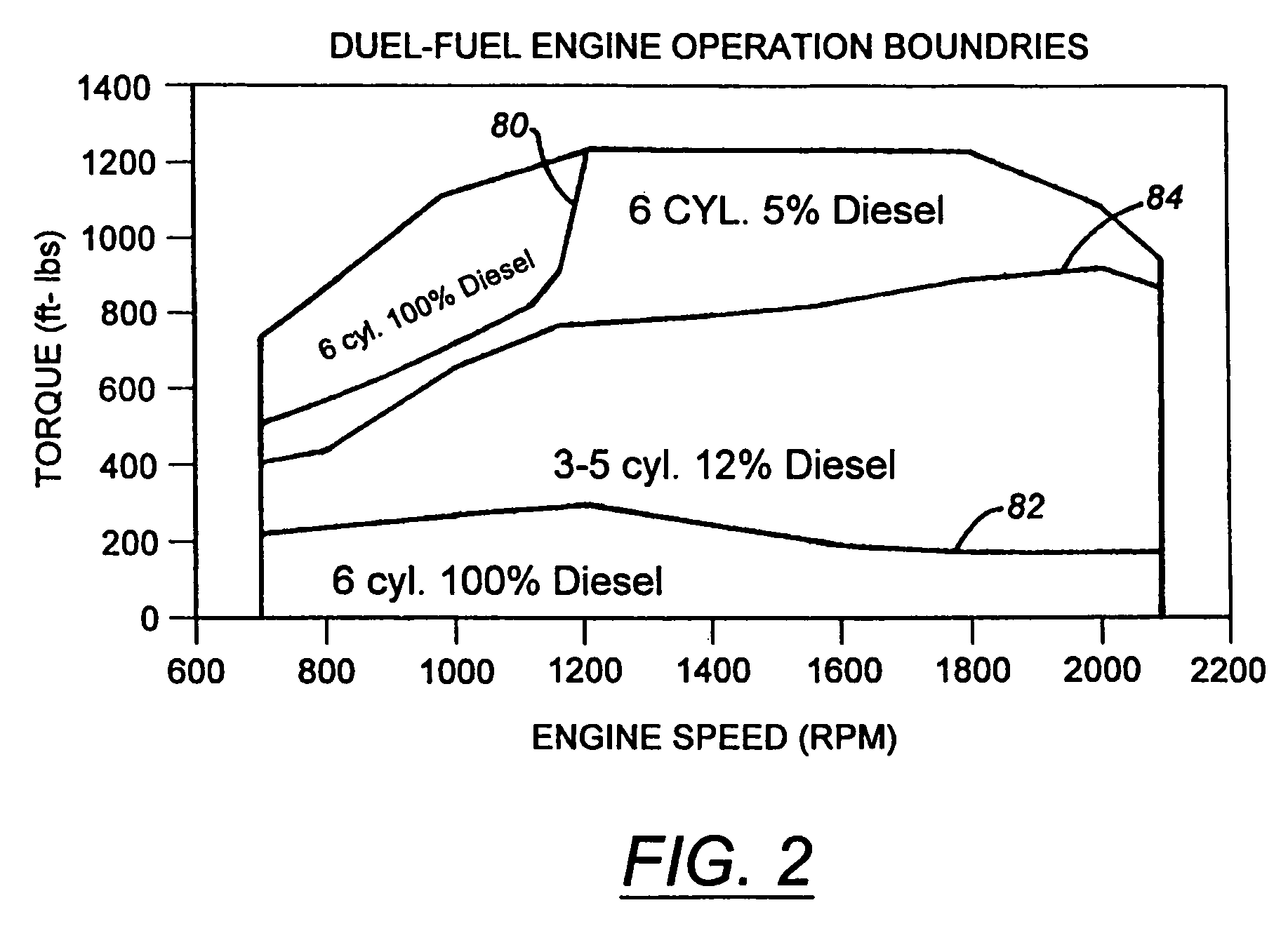
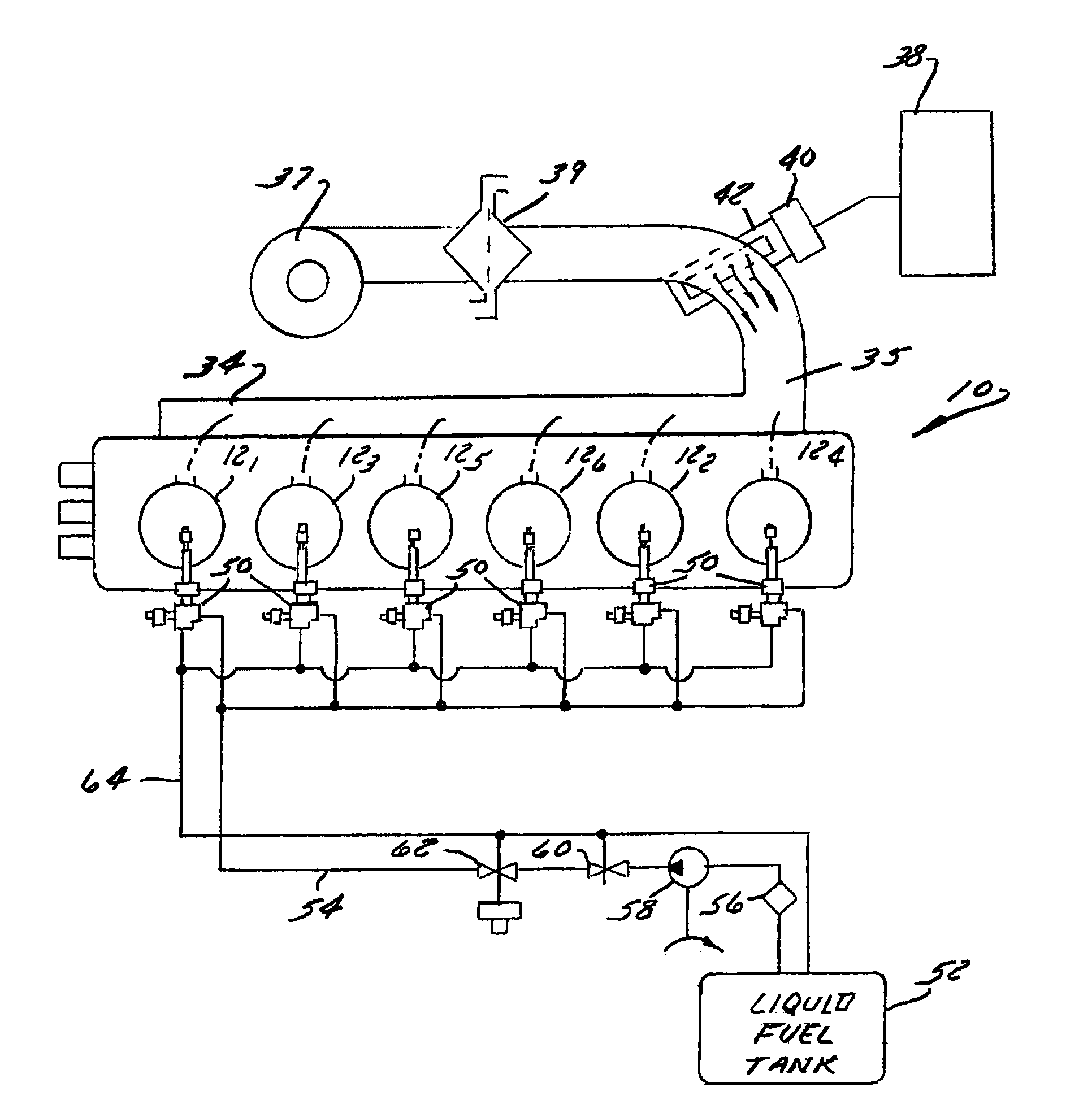
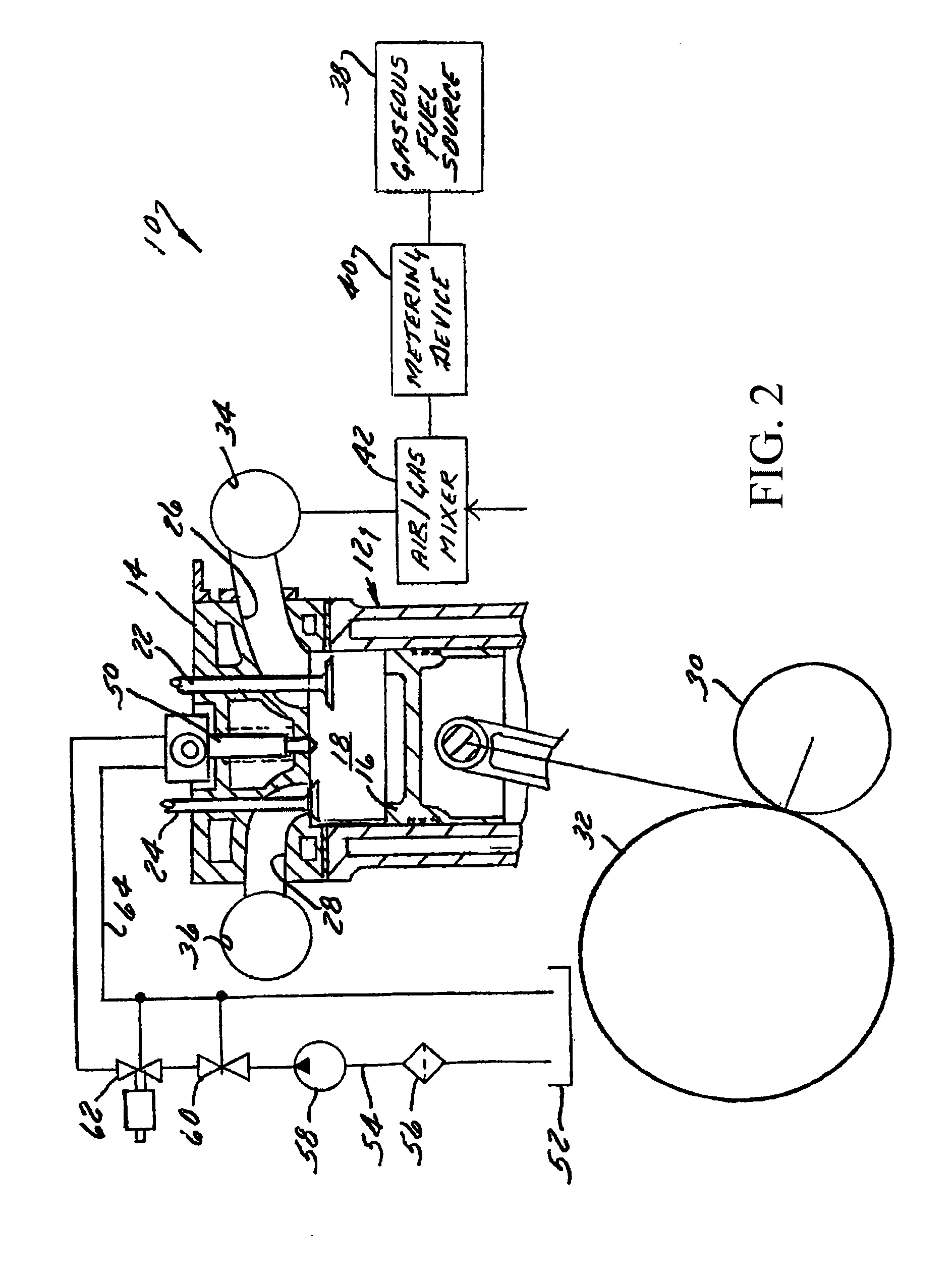
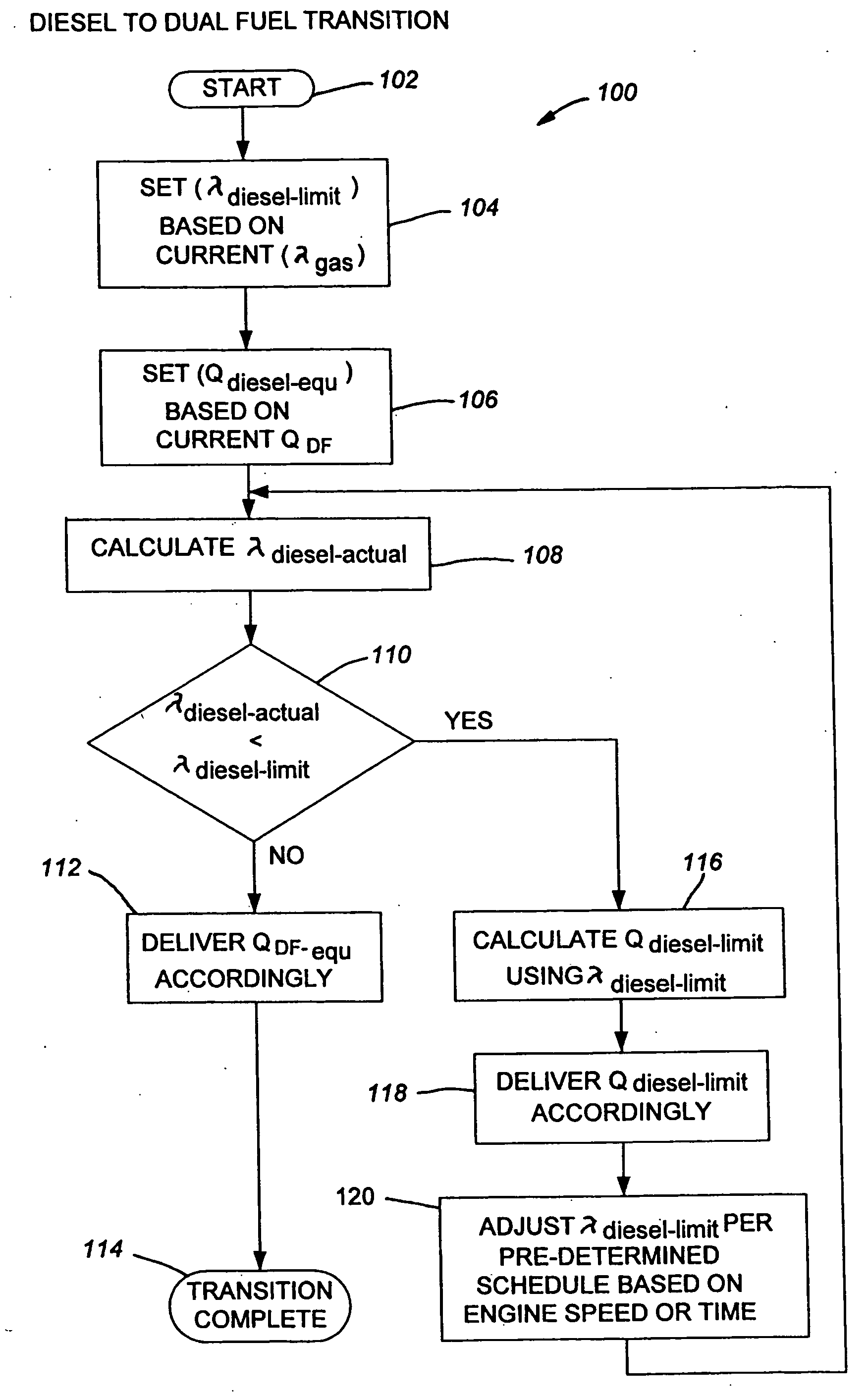
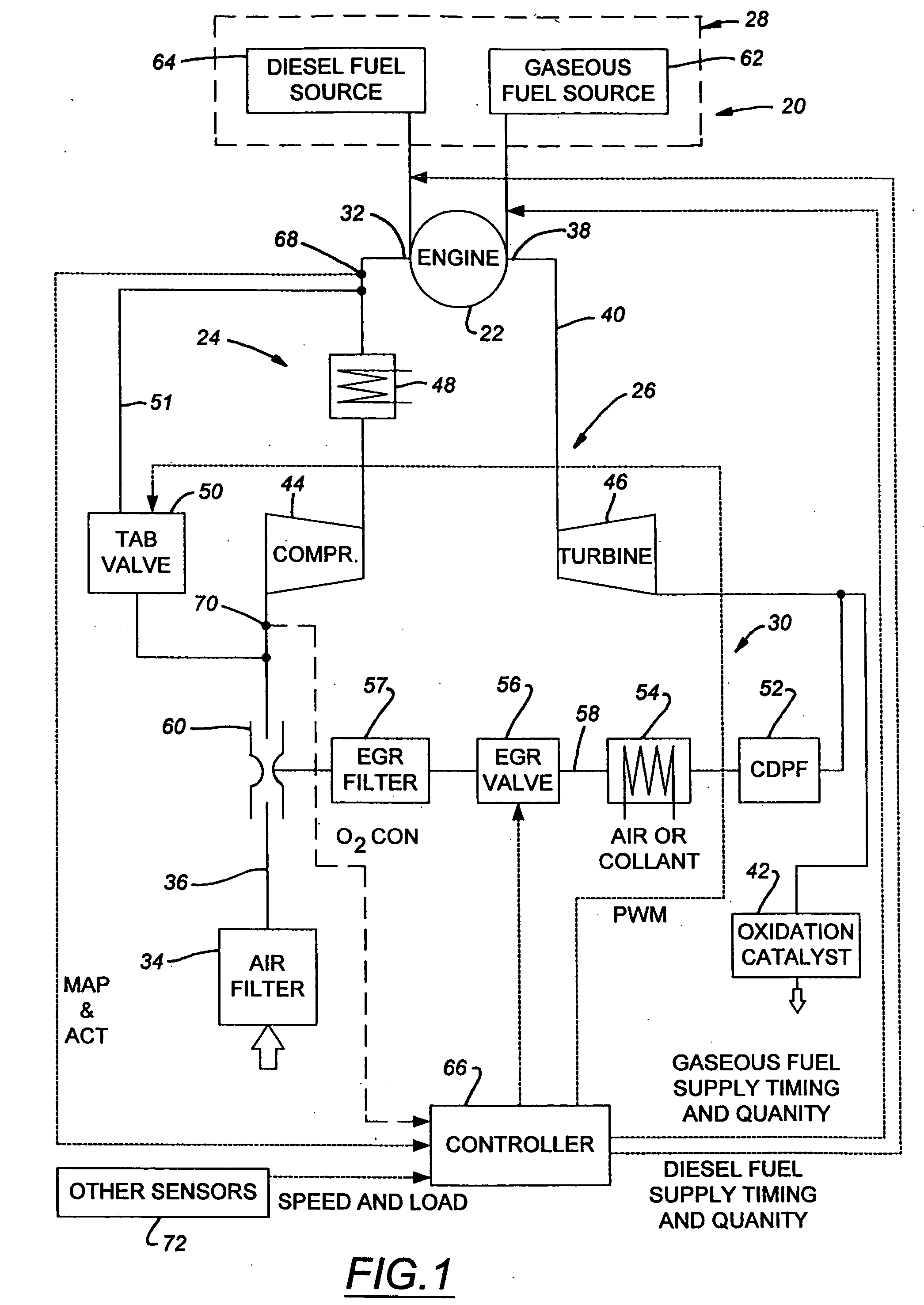
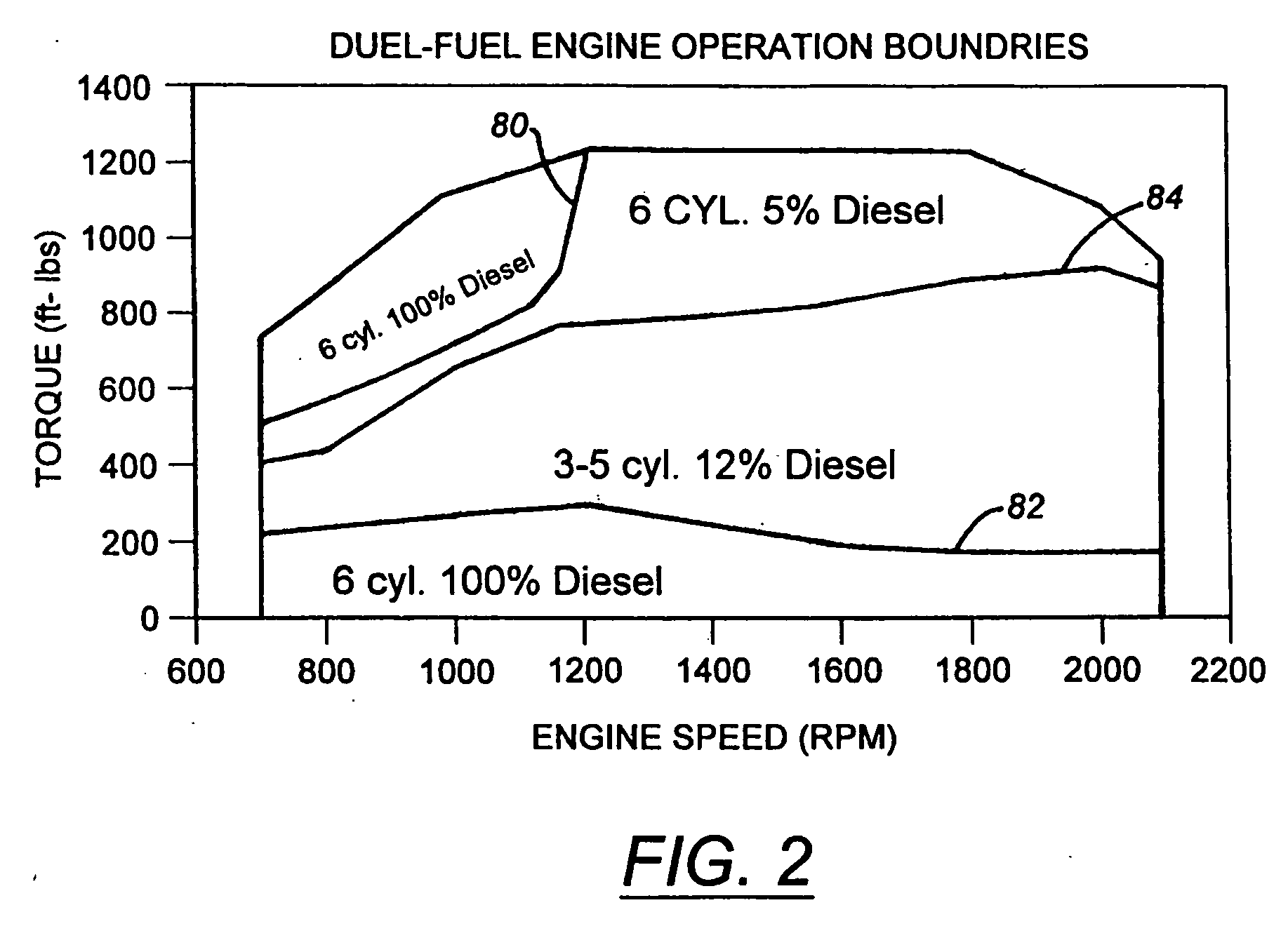
Method and apparatus for controlling liquid fuel delivery during transition between modes in a multimode engine
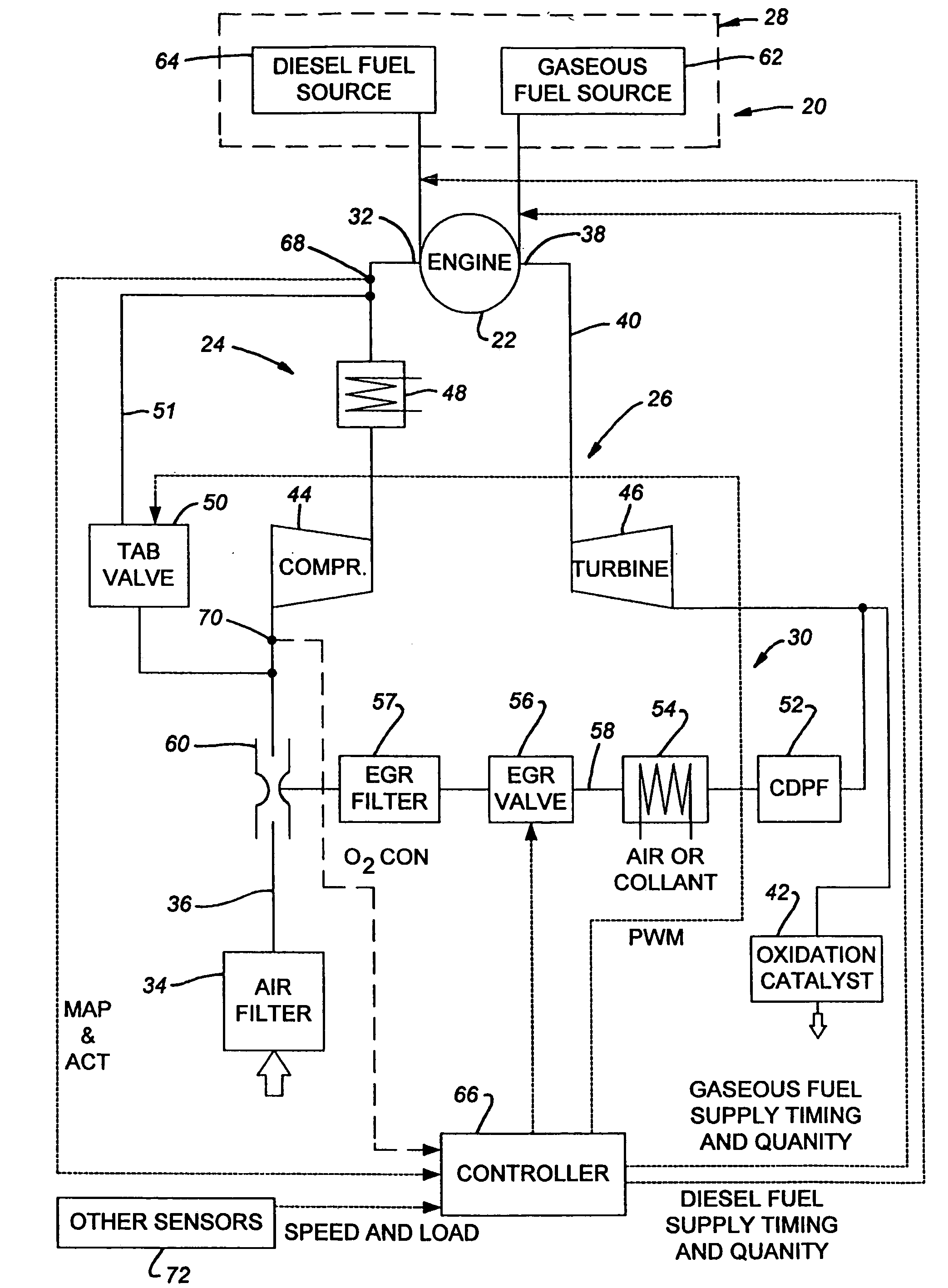
ActiveUS20100332106A1Decreasing and increasing liquid fuel supply quantityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesOperation modeLiquid fuel
A method of transitioning between operating modes in a multimode engine including a diesel-only mode and a diesel pilot, gas mode includes first terminating or initiating the supply of a gaseous fuel, depending on whether the system is transitioning to or from the pilot mode, and thereafter decreasing or increasing the diesel fuel supply quantity. Liquid fuel supply quantity is preferably altered in steps rather than discretely in order to avoid exceeding the lean limit of gas lambda. The number of steps and the percentage decrease or increase in each step preferably varies based at least in part on prevailing speed and load conditions.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER GT LTD
Light amount adjusting device, and optical device using the light amount adjusting device
To provide an ND filter and a light amount adjusting device, in which a deterioration of optical performance of an optical system is small, and in addition, an optical system having the light amount adjusting device, and an optical device having the optical system. More specifically, an ND filter according to the present invention includes: a base that transmits light having a predetermined wavelength lambda; and a filter member selectively formed on the base, in which: a transmittance of the filter member gradually changes in a region in a predetermined direction; and a phase difference which is produced between light transmitting through the filter member and light transmitting through a region on the base in which the filter member is not formed is lambda / 5 or less in a boundary of the filter member.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for regularizing measured HRTF for smooth 3D digital audio
InactiveUS7085393B1Quality improvementTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsTrade offsComputer science
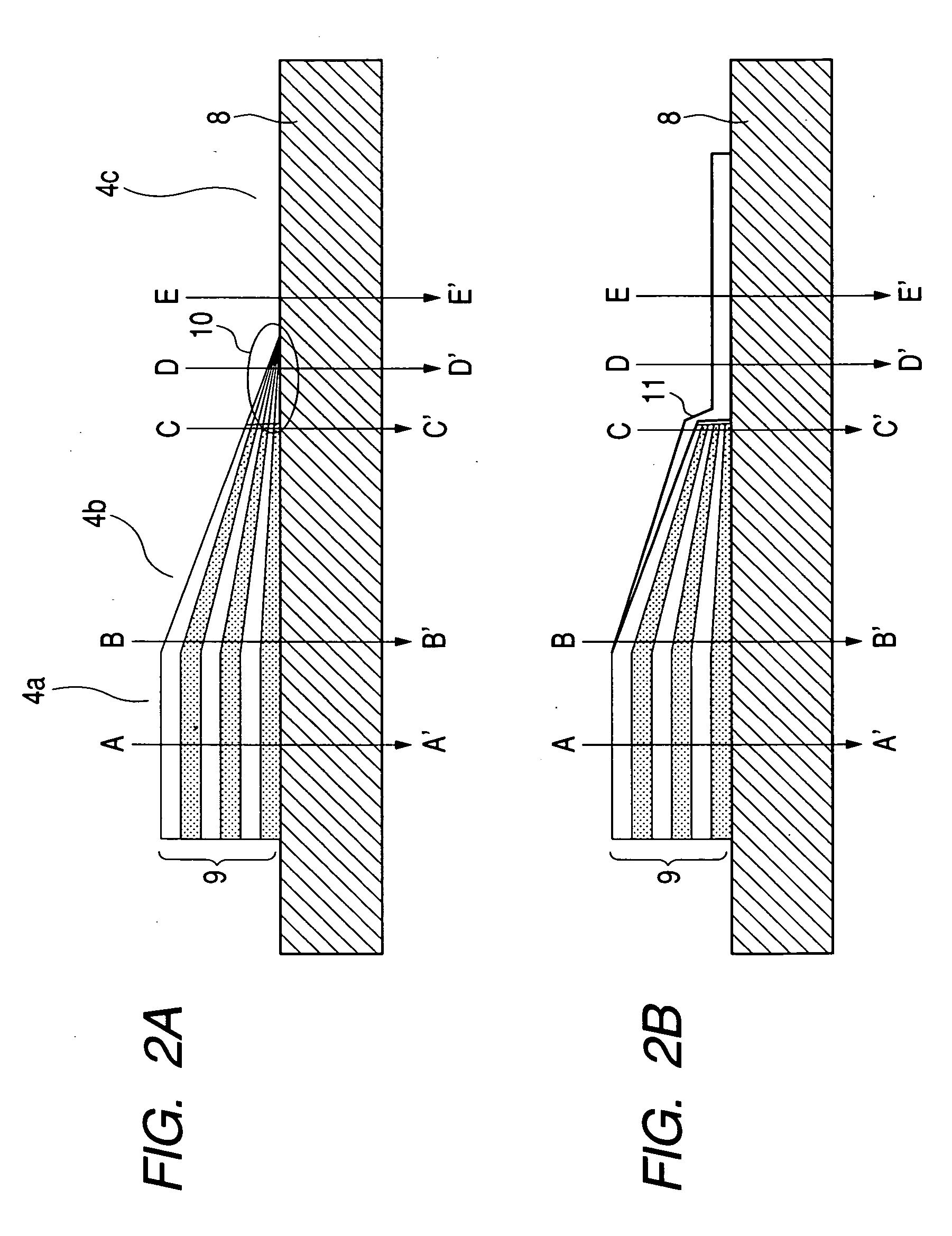
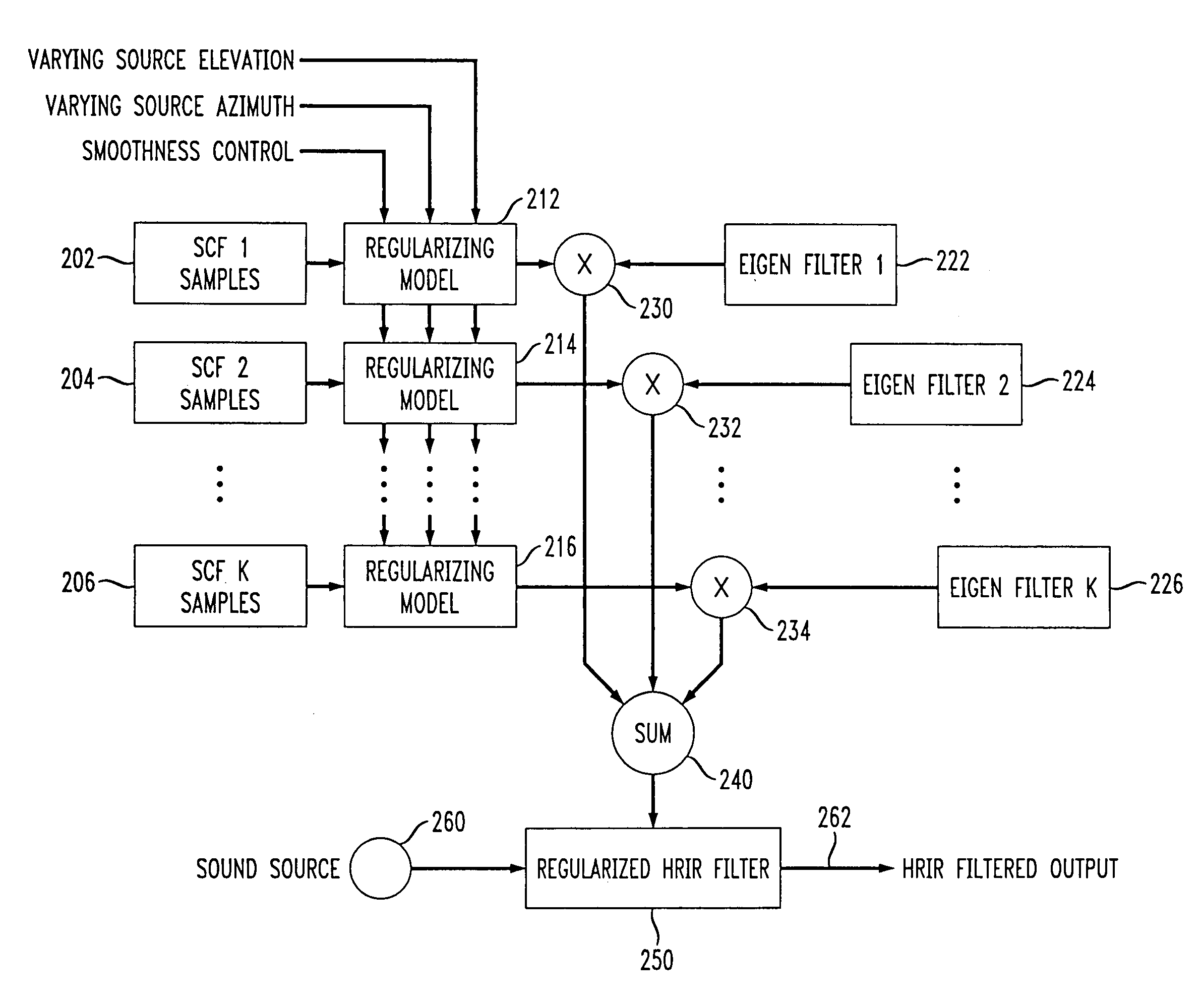
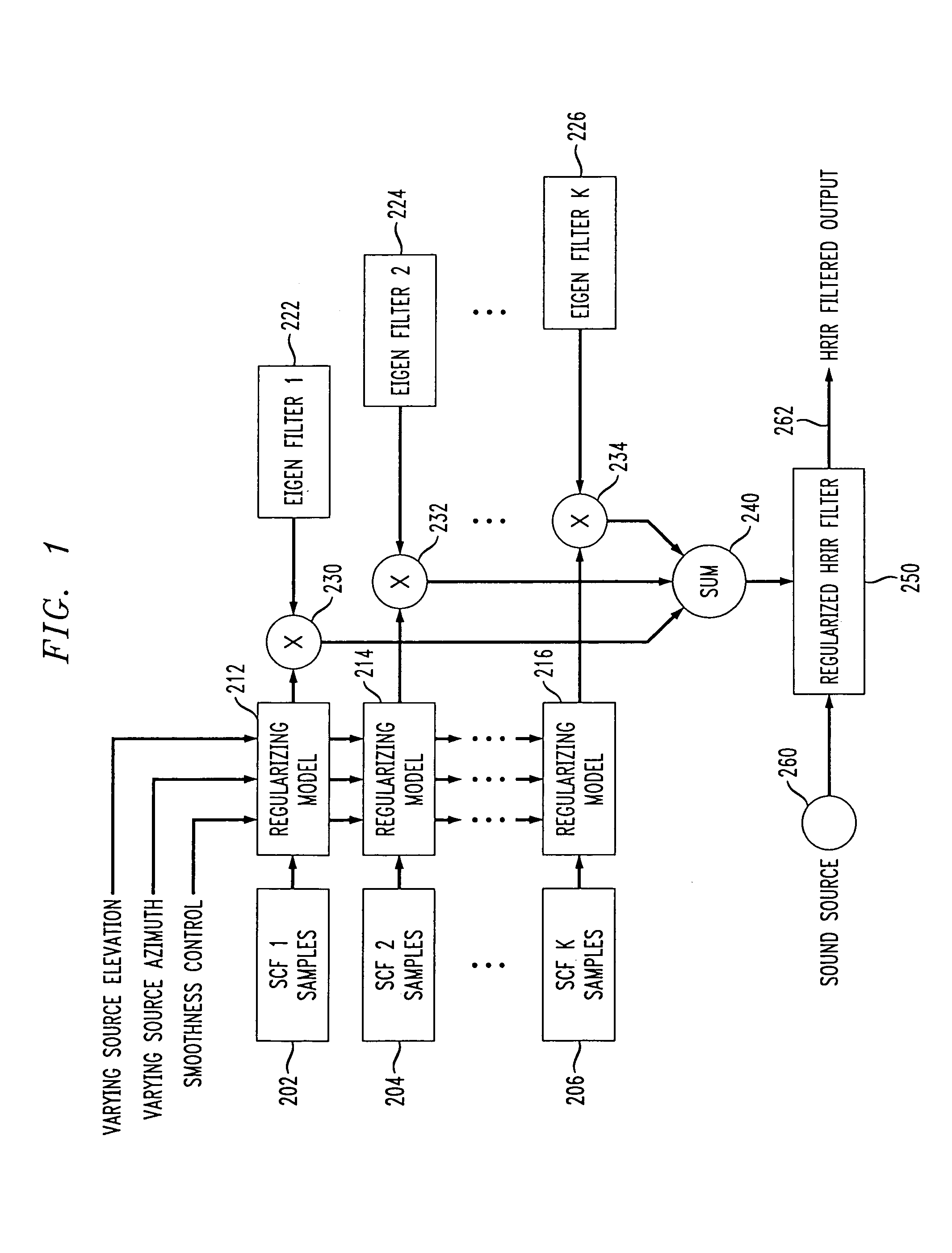
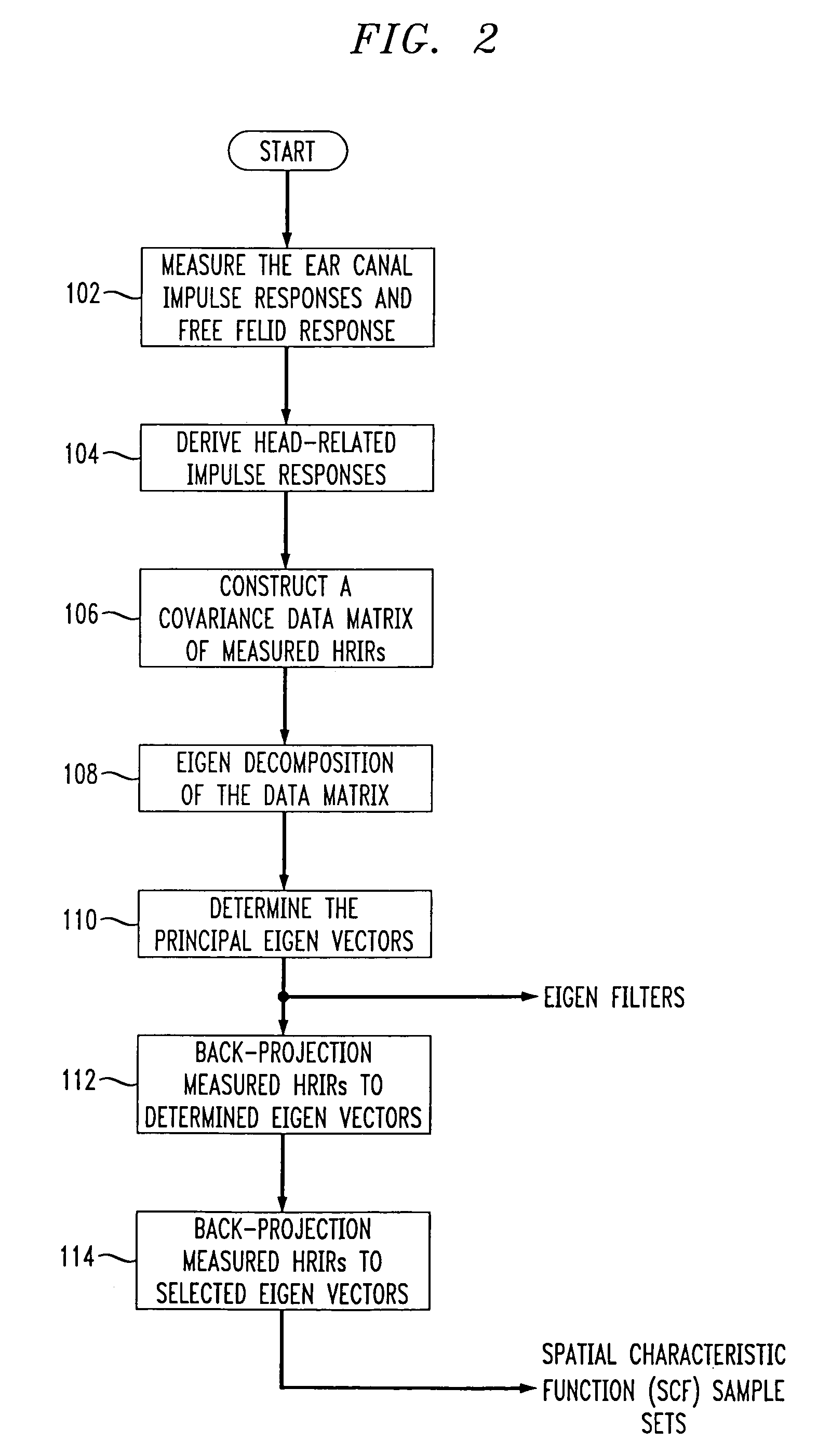
The present invention provides an improved HRTF modeling technique for synthesizing HRTFs with varying degrees of smoothness and generalization. A plurality N of spatial characteristic function sets are regularized or smoothed before combination with corresponding Eigen filter functions, and summed to provide an HRTF (or HRIR) filter having improved smoothness in a continuous auditory space. A trade-off is allowed between accuracy in localization and smoothness by controlling the smoothness level of the regularizing models with a lambda factor. Improved smoothness in the HRTF filter allows the perception by the listener of a smoothly moving sound rendering free of annoying discontinuities creating clicks in the 3D sound.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS7426210B1Reduce complexityImprove data throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTime domainMicrowave
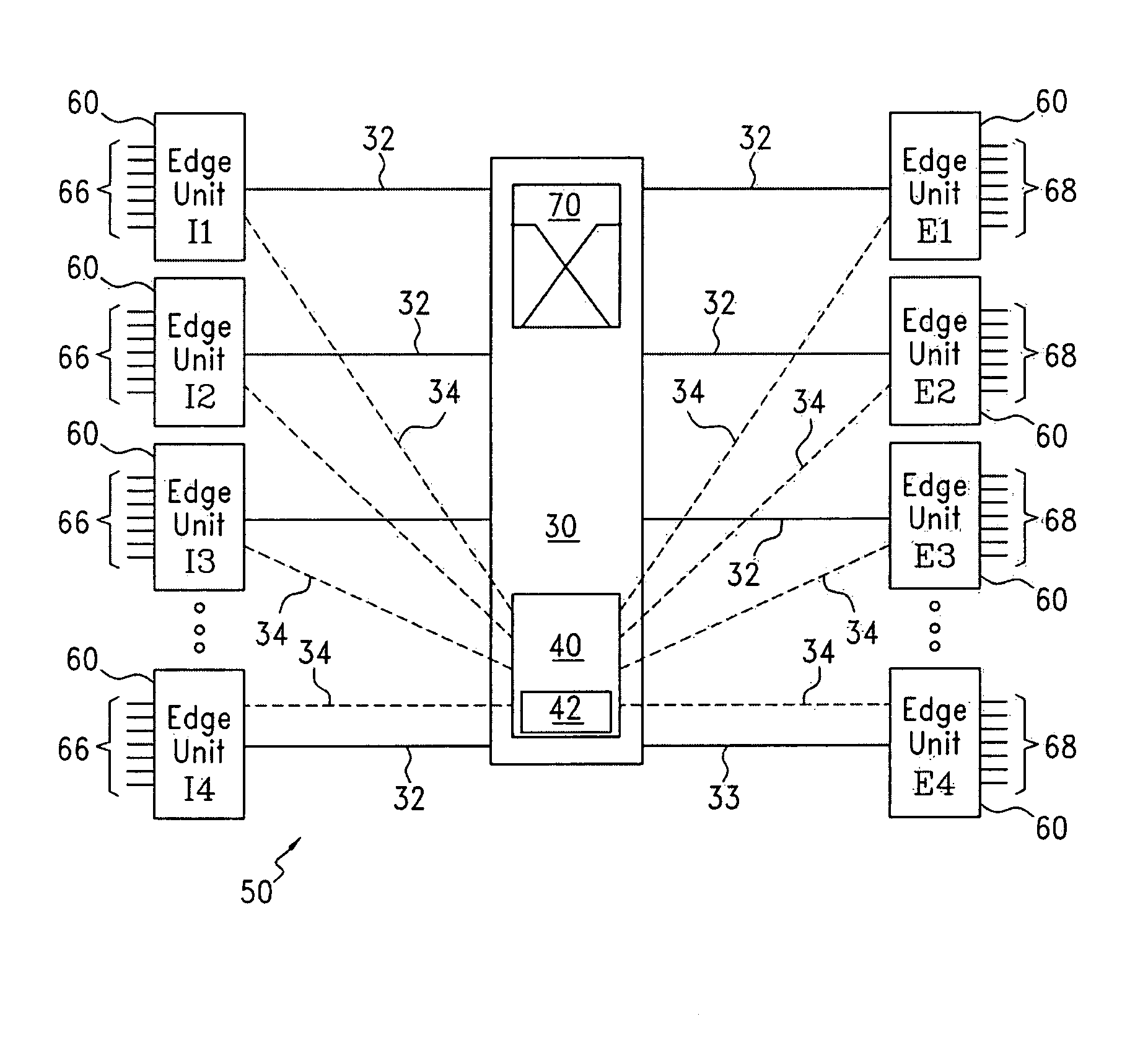
One embodiment of the present invention includes a router comprising an ingress edge unit with one or more ports and an egress edge unit with one or more ports connected by a switch fabric. The ingress edge unit can receive optical data and convert the optical data into a plurality of micro lambdas. The ingress edge unit can convert the incoming data to micro lambdas by generating a series of short-term parallel data bursts across multiple wavelengths. The ingress edge unit can also wavelength division multiplex and time domain multiplex each micro lambda for transmission to the switch fabric in a particular order. The switch fabric can receive the plurality of micro lambdas and route the plurality of micro lambdas to the plurality of egress edge units in a non-blocking manner.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
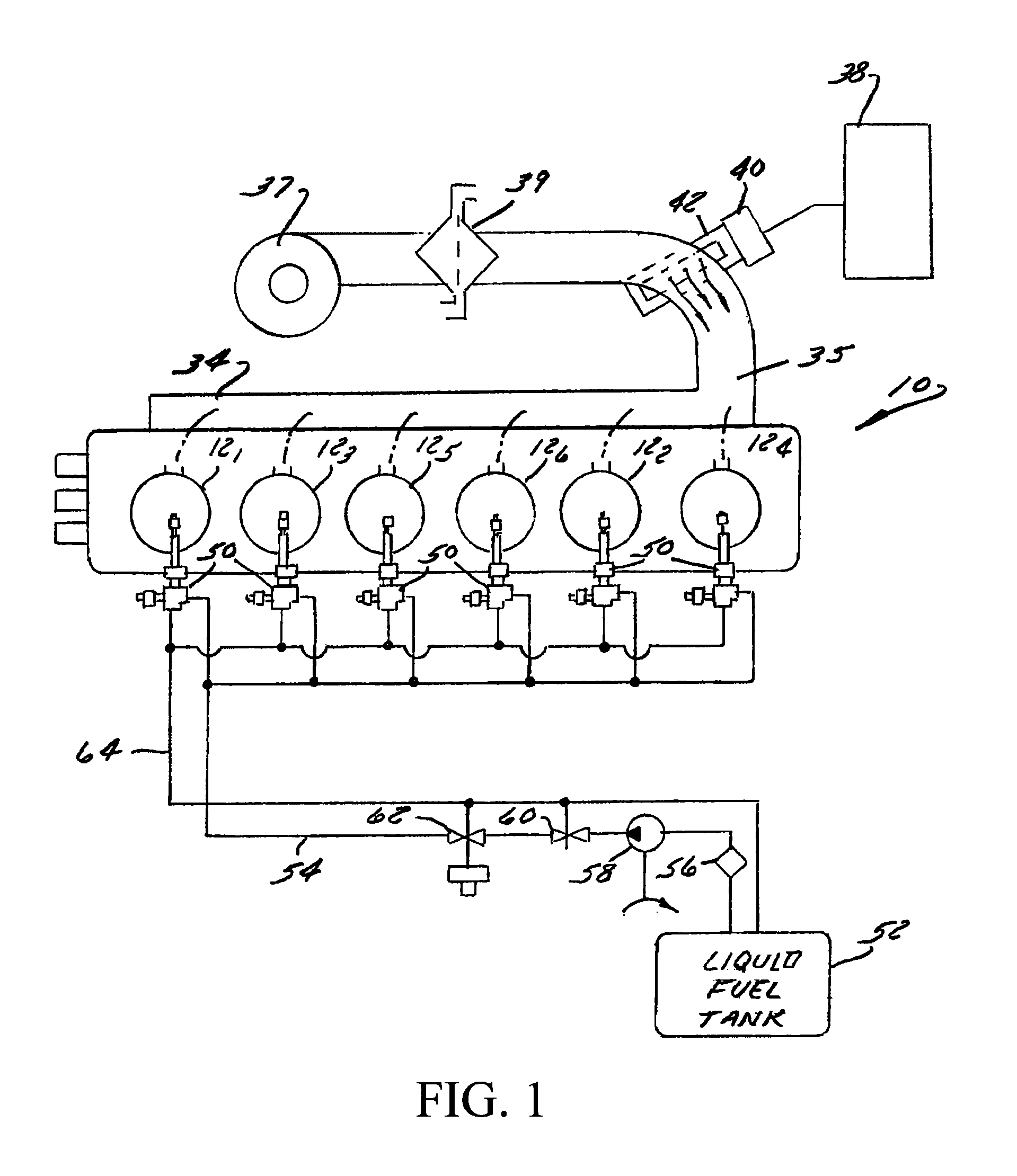
Method and apparatus for controlling transition between operating modes in a multimode engine
InactiveUS7270089B2Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
At least one engine operating parameter other than total fuel energy content is taken into account when transitioning between operating modes in a dual fuel or other multimode engine (20) in order to maintain a smooth transition between modes. The parameter preferably comprises at least one of primary fuel excess air ratio (lambda) and ignition timing and preferably is controlled in addition to total fuel energy content control. Lambda control is especially beneficial because it permits the control system to compensate for the engine's inability to substantially alter the instantaneous air mass in the combustion chamber during the transition period. For instance, during a transition from pilot ignited gaseous fuel mode to diesel mode, the controlled parameter preferably comprises diesel lambda, and the controlling step comprises setting diesel lambda at a relatively high value at the beginning of the transition period and thereafter reducing diesel lambda during the transition period.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
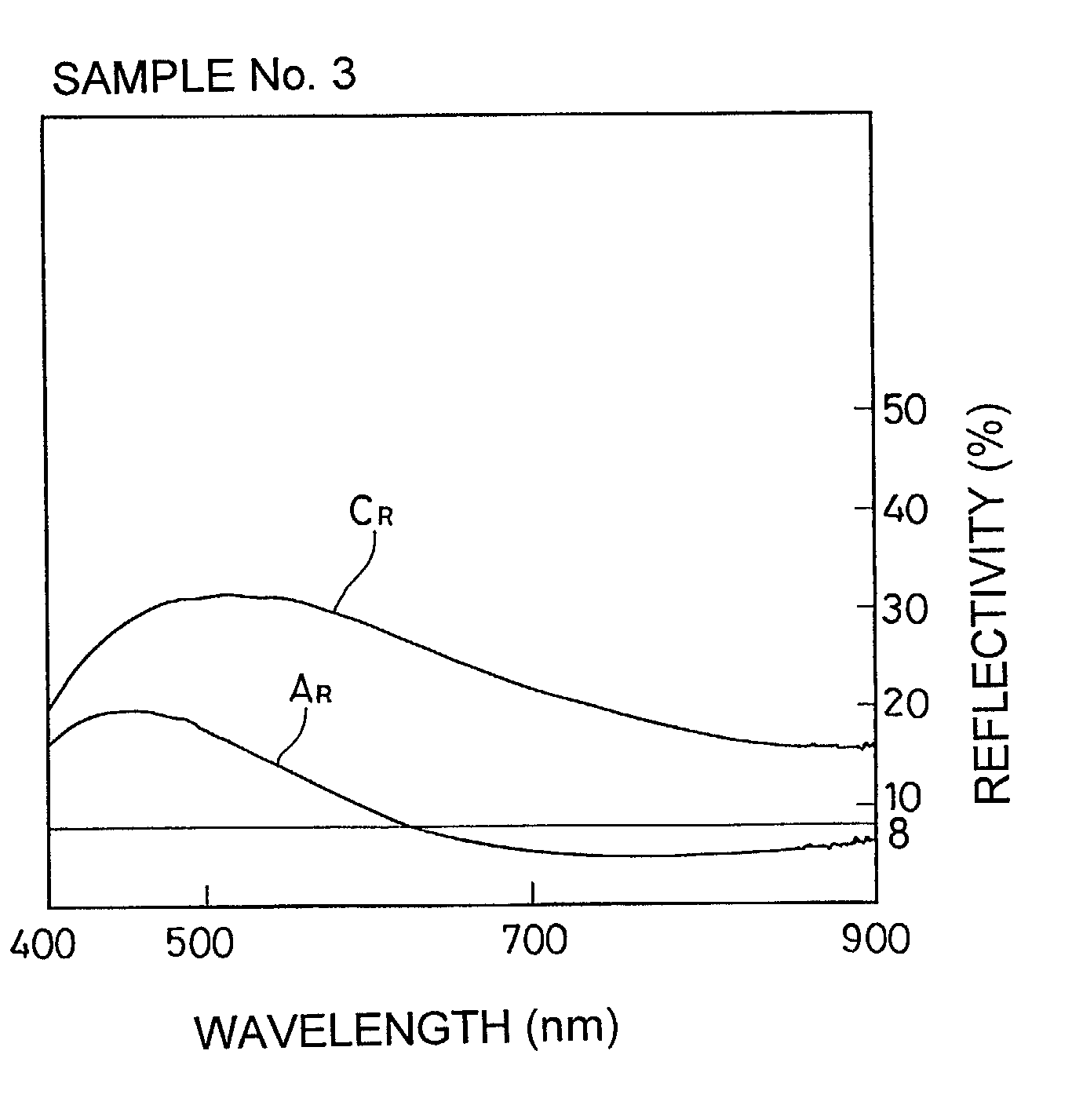
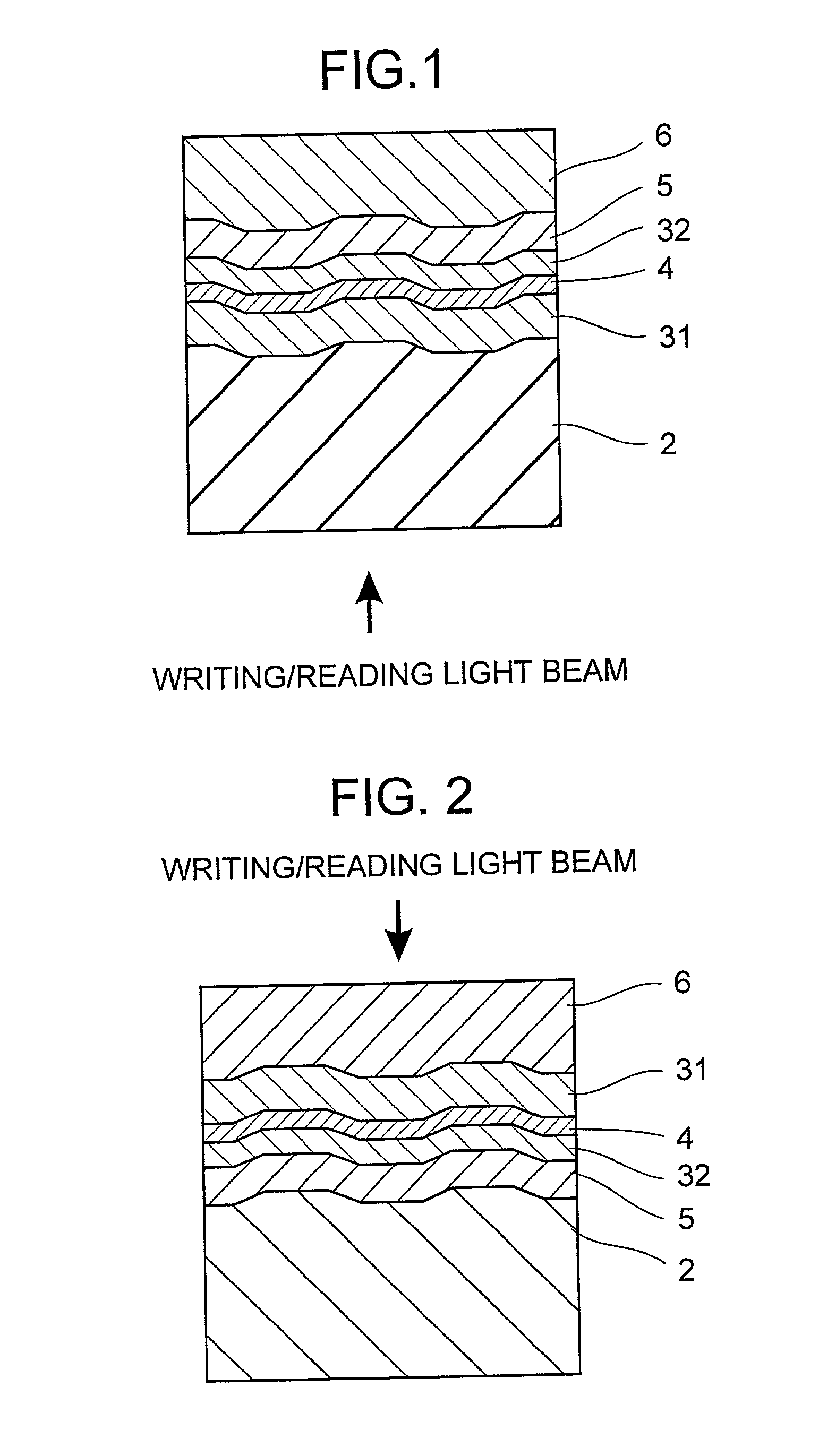
Optical recording medium and method for its initialization
InactiveUS20030008235A1Reduce laser powerRadiation applicationsLayered productsLight beamRecording layer
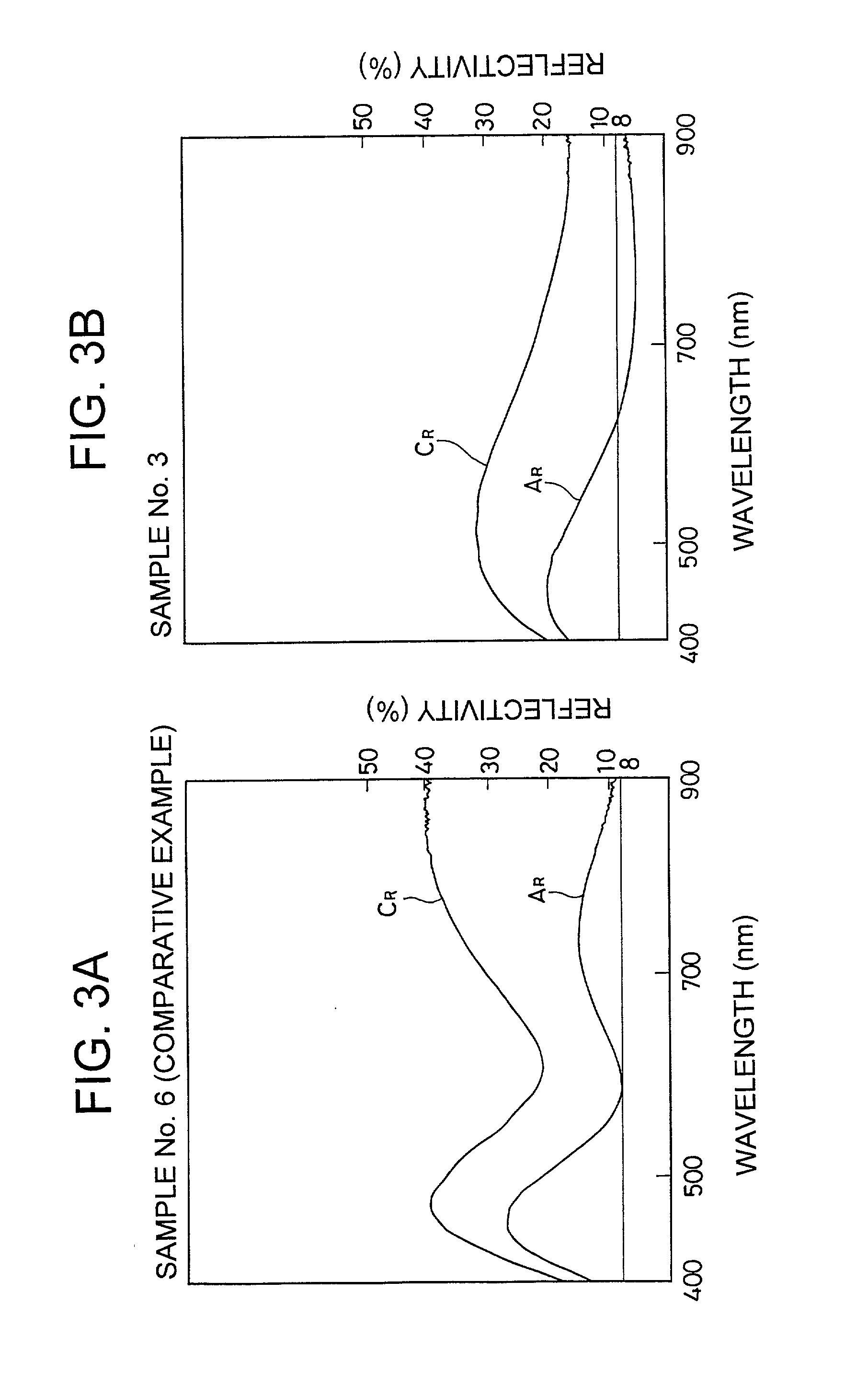
A phase change optical recording medium is provided wherein the power of the laser beam per unit area required in the initialization is reduced. The optical recording medium has a phase change recording layer satisfying the relations: A.sub.I.ltoreq.8.0%, and C.sub.I / A.sub.I.gtoreq.3.0 when the medium is initialized with a light beam having a wavelength .lambda..sub.I, and said recording layer exhibits a reflectivity A.sub.I in amorphous region and a reflectivity C.sub.I in crystalline region at said wavelength .lambda..sub.I.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Antireflective member, optical element, display device, method of making stamper and method of making antireflective member using the stamper
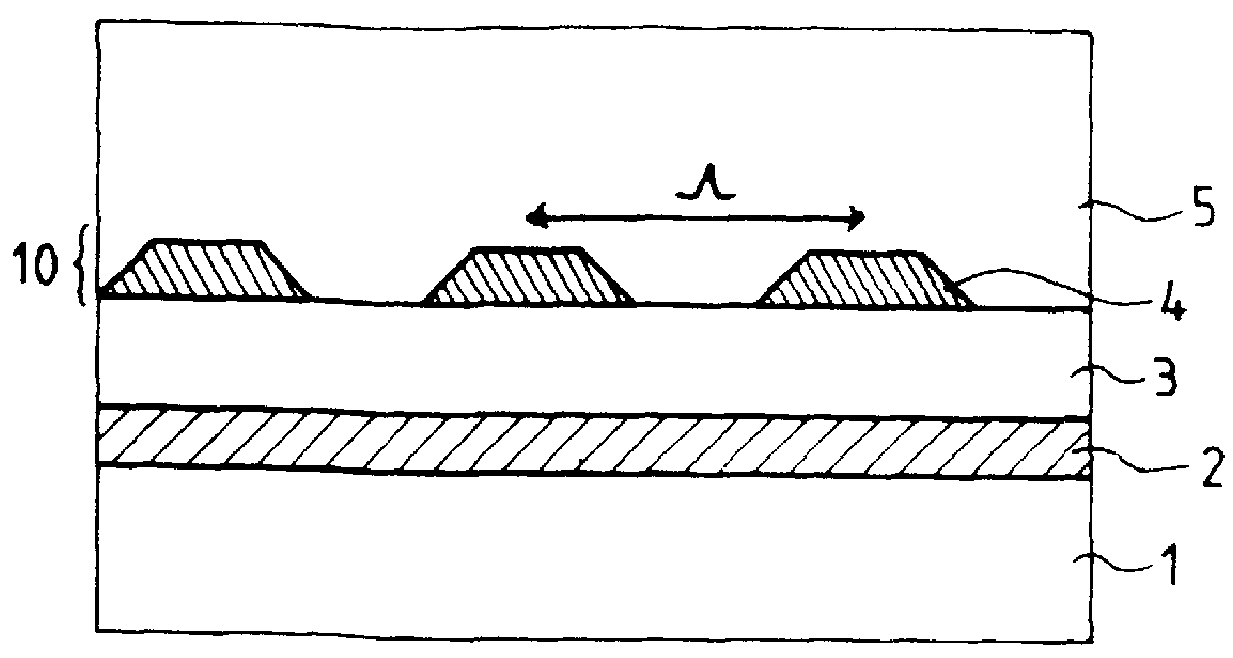
ActiveCN101088030ASuppression of regular reflectionImprove anti-reflection effectLayered productsCoatingsSurface patternAngle of incidence
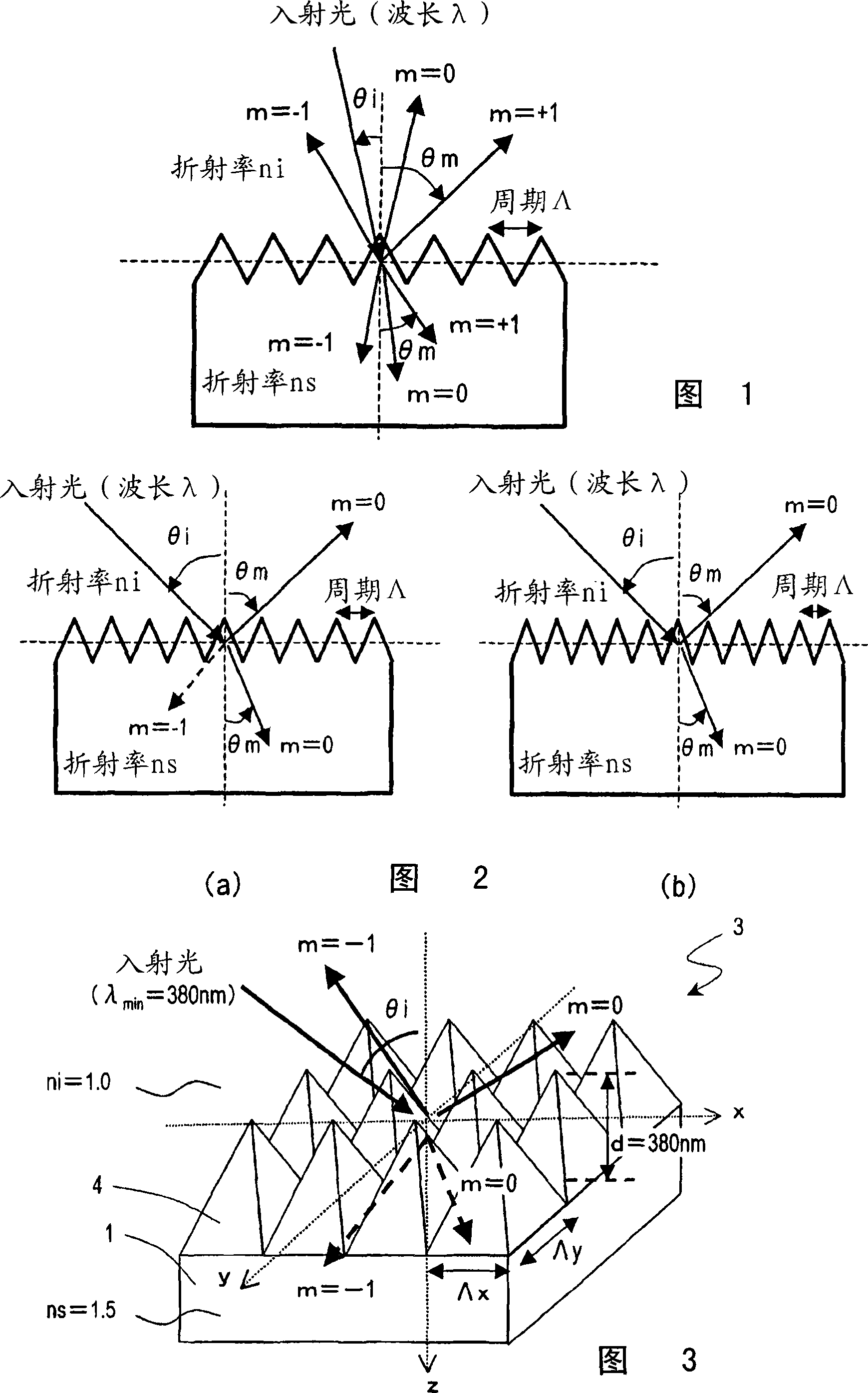
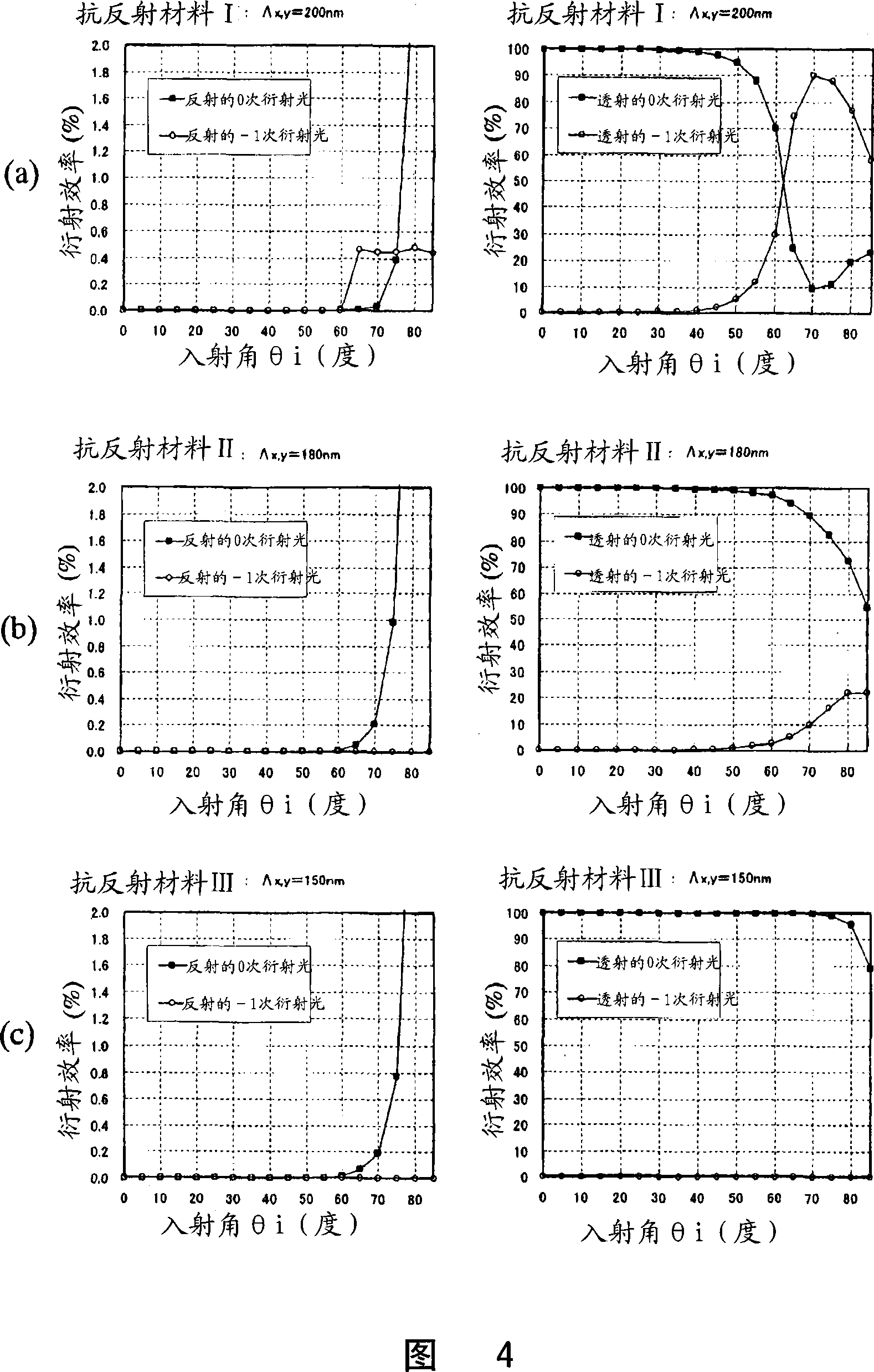
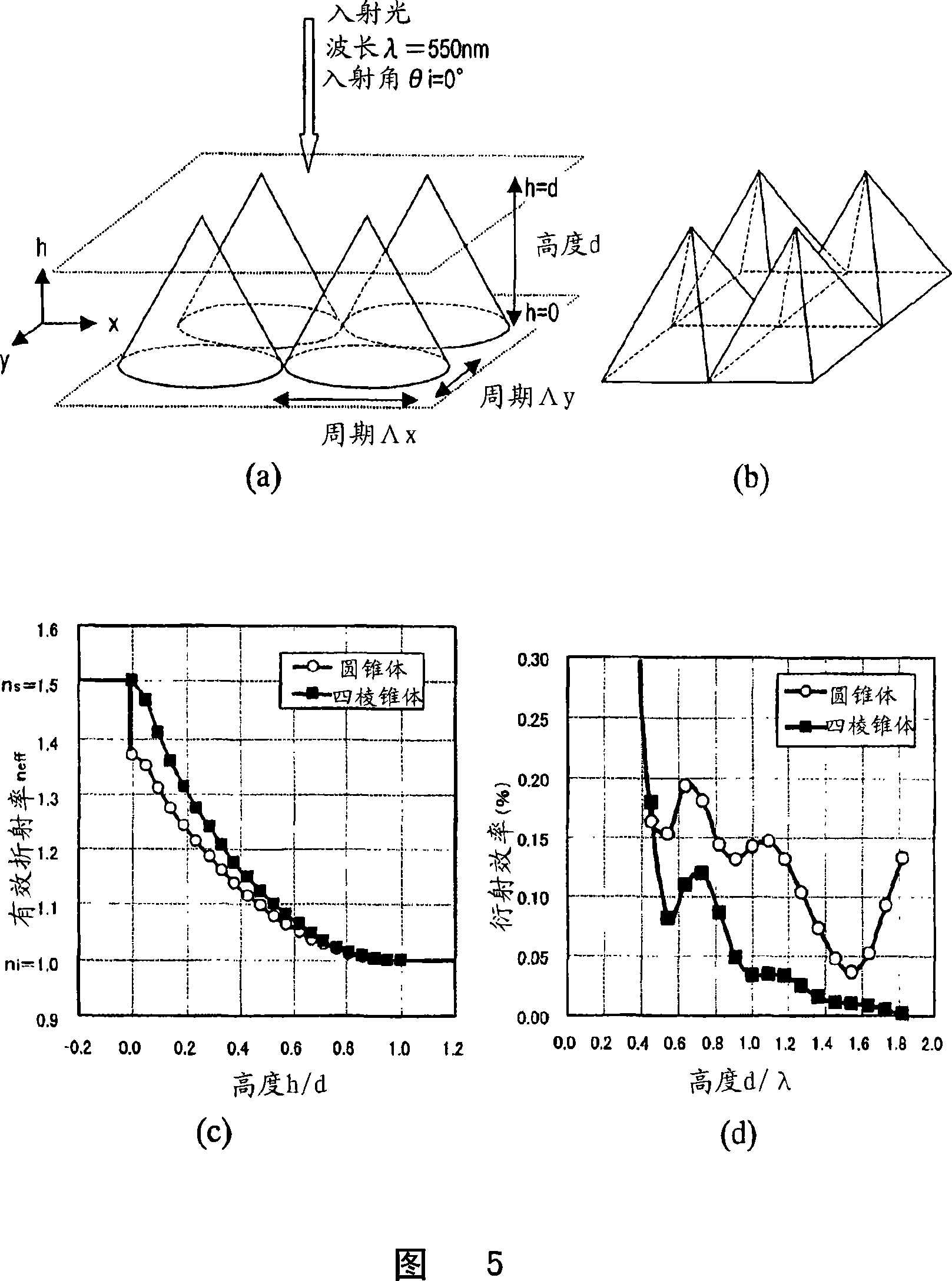
An antireflective member according to the present invention has an uneven surface pattern, in which unit structures are arranged in x and y directions at respective periods that are both shorter than the shortest wavelength of an incoming light ray, on the surface of a substrate and satisfies the following inequality (1): lambda, / lambda ) . . ., where lambda is the shortest wavelength of the incoming light ray, theta i is the largest angle of incidence of the incoming light ray, ni is the refractive index of an incidence medium, lambda is the period of the uneven surface pattern in the x direction, and lambda is the period of the pattern in the y direction. As a result, diffraction of short-wave light components can be reduced in a broad wavelength range.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for controlling liquid fuel delivery during transition between modes in a multimode engine
A method of transitioning between operating modes in a multimode engine including a diesel-only mode and a diesel pilot, gas mode includes first terminating or initiating the supply of a gaseous fuel, depending on whether the system is transitioning to or from the pilot mode, and thereafter decreasing or increasing the diesel fuel supply quantity. Liquid fuel supply quantity is preferably altered in steps rather than discretely in order to avoid exceeding the lean limit of gas lambda. The number of steps and the percentage decrease or increase in each step preferably varies based at least in part on prevailing speed and load conditions.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER GT LTD
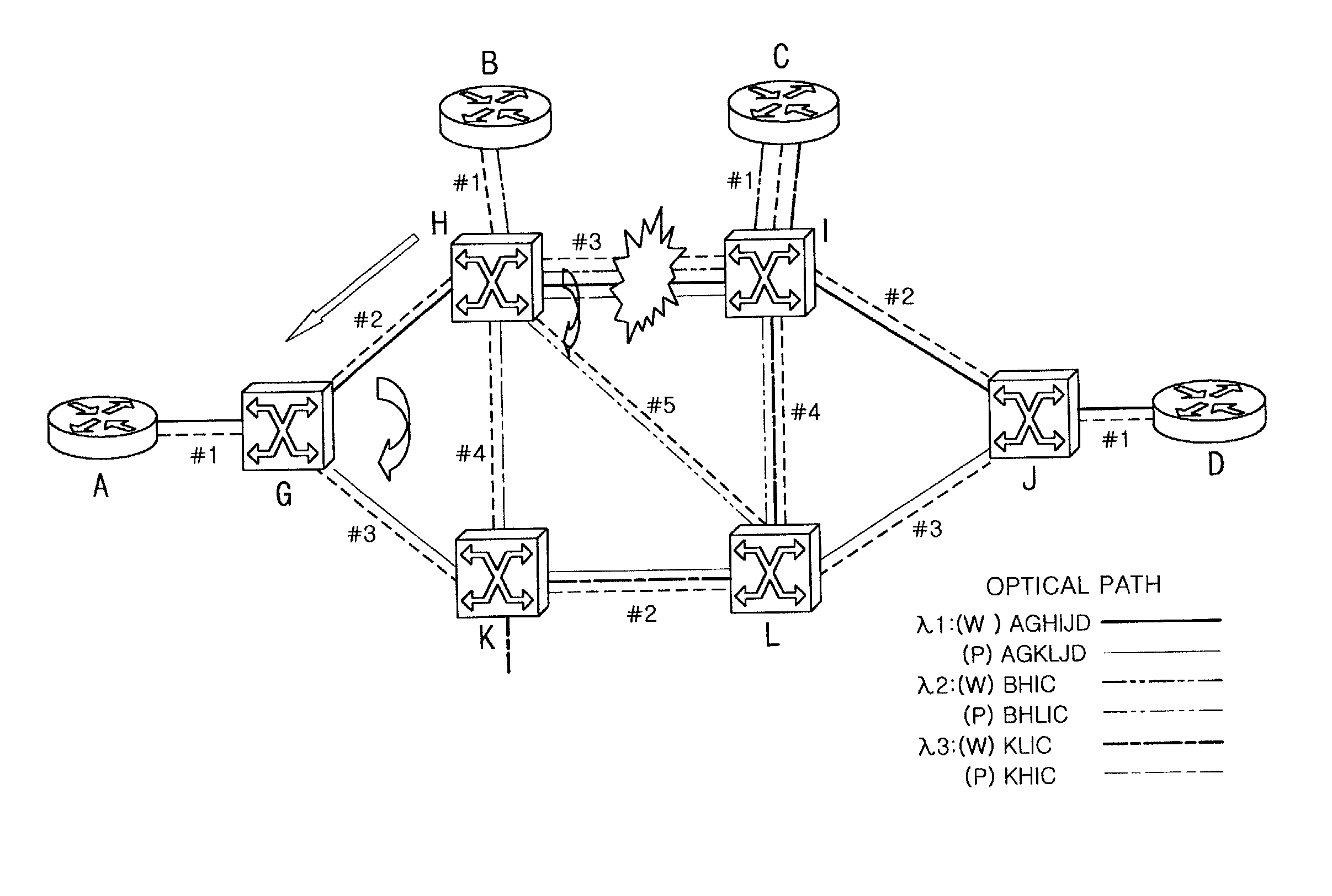
Routing table configuration for MPlambdaS (multi-protocol lambda switching) protection and restoration in optical mesh networks
InactiveUS20020089712A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsOptical mesh networkRouting table
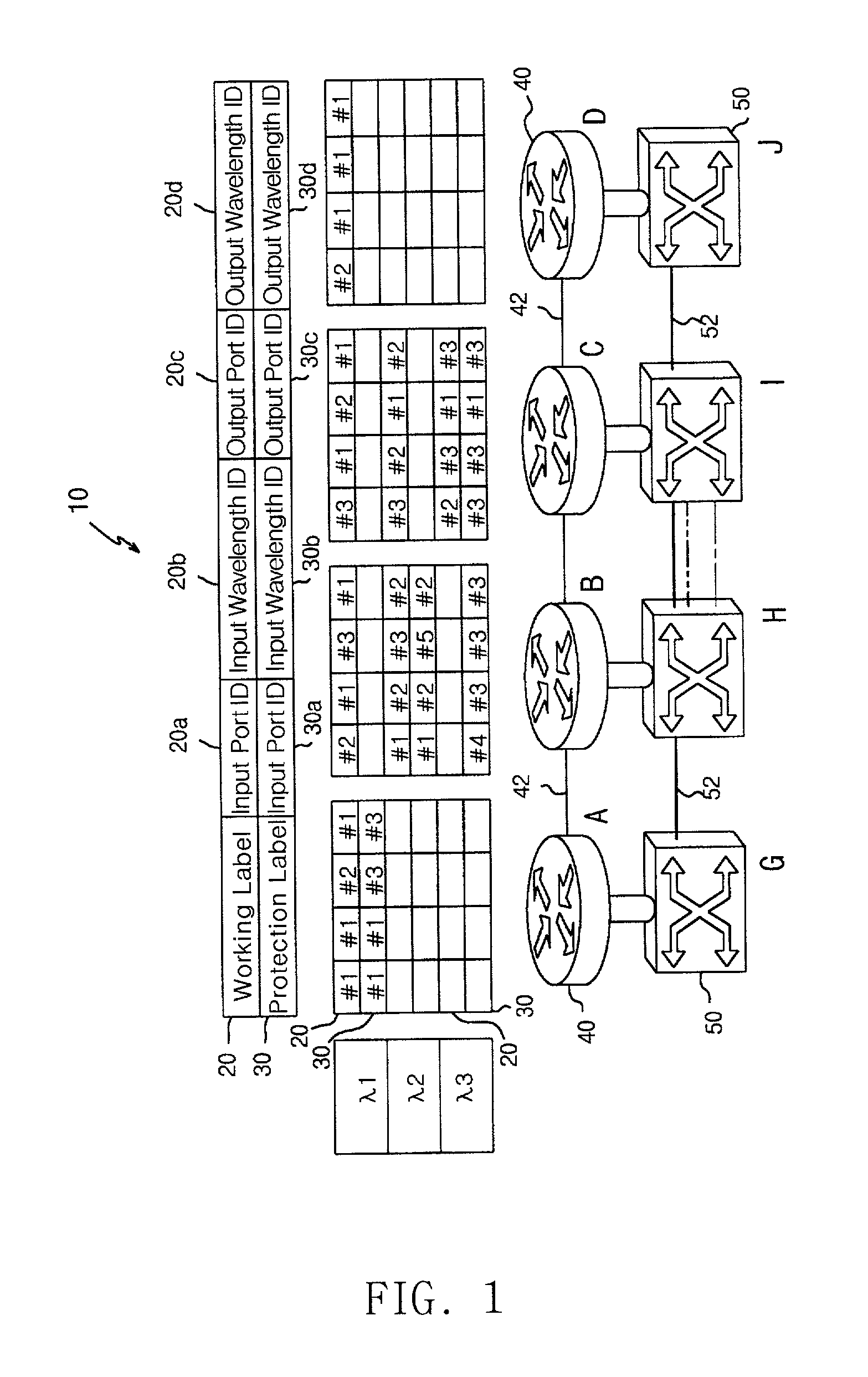
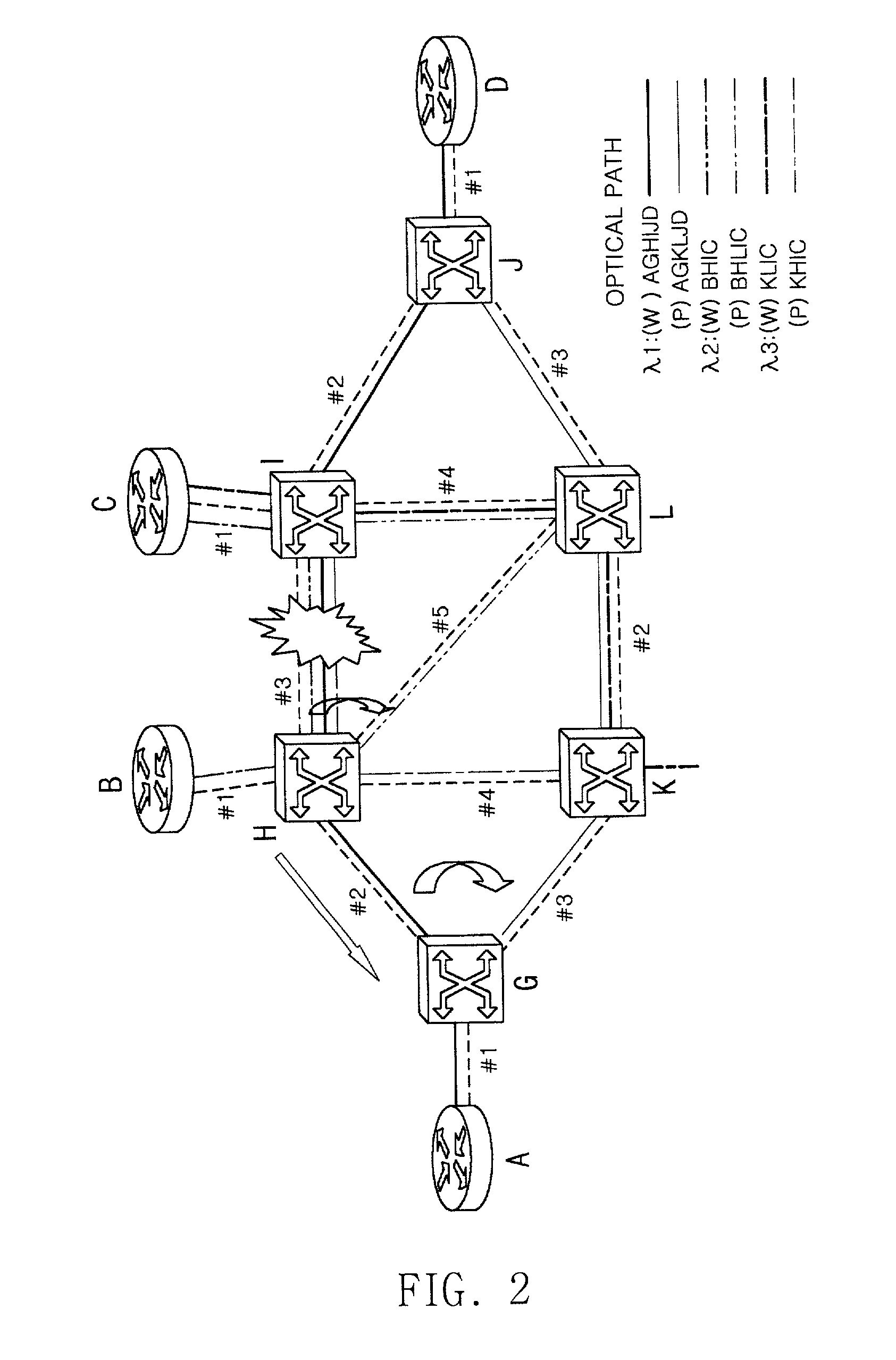
The present invention relates to protection and restoration method for MPXS in optical mesh networks, particularly to protection and restoration method which can find and restore fast failures by configuring routing table with working label and protection label when failures occur at links or nodes. According to the present invention, by configuring a routing table consisted of working label and protection label and by setting an optical path as working path and protection path, data is transferred through the working path, and when a failure occurs in a optical path, data is transferred through a protection path by using a preliminarily configured protection label and by switching to. According to the present invention, by configuring routing table with working label and protection label, failures can be restored fast when failures occur at links or nodes, and whole network resources can be applicable.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Semiconductor optical reflector and a method of manufacturing the same
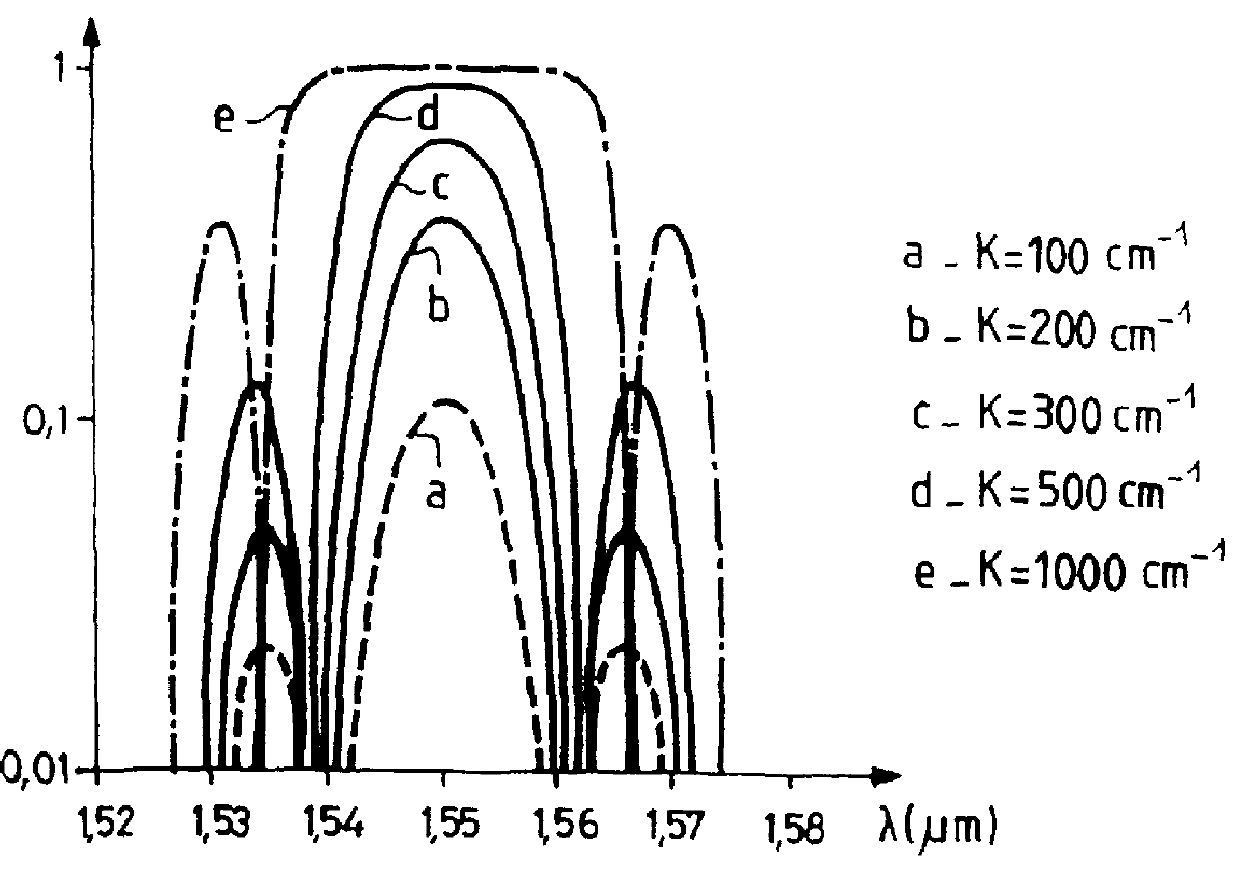
InactiveUS6064685AImprovement factorIncrease the difficultyLaser optical resonator constructionMirrorsFrequency spectrumCoupling
The invention relates to a semiconductor optical reflector serving in particular for being disposed facing an integrated laser cavity so as to feed light back into said cavity, and enable it to oscillate continuously. The reflector is made up of a plurality of cascaded Bragg reflector sections. More particularly, said sections are of the same length L and have the same coupling coefficient, and the length L of each pair of sections is given by the following relationship:L= lambda 2 / [(ni+1+ni)x1.7(ni+1 LAMBDA i+1-ni LAMBDA i)]where lambda is the mean value of the Bragg wavelengths reflected by the reflector; ni+1 and ni are the respective effective refractive indices of said adjacent sections; and LAMBDA i+1 and LAMBDA i are the respective periods of said adjacent sections. The reflector of the invention has a wide spectrum band independent of the value of the coupling coefficient.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
Phase difference plate comprising polymer film containing compound having rod- shaped molecular structure
InactiveUS20040096594A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsUv spectrumPhase difference
A phase difference plate which comprises one sheet of polymer film containing a compound having a rod-shaped molecular structure and exhibiting a maximum absorption wavelength (lambdamax) of less than 250 nm in an ultraviolet spectrum of its solution and which exhibits a retardation value as measured at a wavelength of 450 nm (Re450) of 60 to 135 nm and a retardation value as measured at a wave-length of 590 nm (Re590) of 100 to 170 nm, where the relationship: Re590-Re450>=2 nm is satisfied. The phase difference plate functions as a lambda / 4 plate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning method
InactiveCN101825717AHigh precisionOvercoming the disadvantages of decreased success rateSatellite radio beaconingAlgorithmAmbiguity
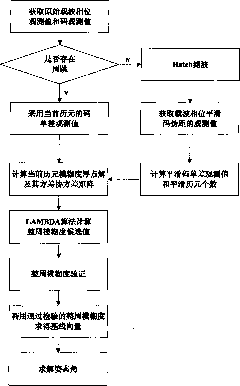
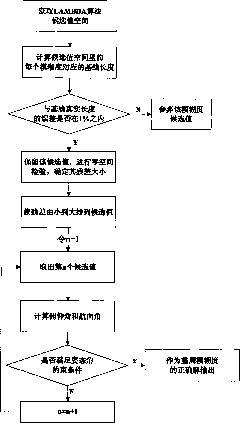
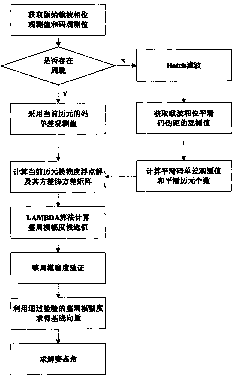
The invention discloses a carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning algorithm method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) detecting whether cycle slip occurs in the current epoch by using a three-difference method, if so, using the code observation of the current epoch, otherwise, acquiring the smoothed code observation by using Hatch filtering and recording the smoothing window length k; (2) solving the floating solution of the integer ambiguity and the variance-covariance matrix of the floating solution by utilizing the code observation and the code observation of the current epoch; (3) taking the floating solution of the integer ambiguity and the variance-covariance matrix of the floating solution as initial parameters, substituting the initial parameters into an LAMBDA algorithm for solving the fixed solution of the ambiguity, and acquiring former N ambiguity candidate values; and (4) performing the ambiguity test on the former N ambiguity candidate values in turn, until the ambiguity candidate solution meeting the constraint condition is found, and solving the obtained attitude angle. The carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning algorithm method does not have the problem of initialization time, can be effectively used for real-time dynamic attitude measurement, and can self-adaptively regulate the smoothing window length and the ambiguity candidate solution space aiming at the occurrence of the cycle slip. Therefore, the success rate and the overall efficiency of the algorithm are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Heat insulating layer based on la2zr2o7 for high temperatures
InactiveUS20040101699A1Improve the overall coefficientLow thermal conductivityMolten spray coatingEfficient propulsion technologiesThermal coefficientLanthanum
The invention relates to a heat insulating layer on a metallic substrate for using for high temperatures, especially for temperatures above 1300° C. Starting with a base of La2Zr2O7, the properties of the heat insulating substance to be used as the heat insulating layer are regularly improved, by substituting lanthanum cations with ions of elements Nd, Eu, Dy, Sm and / or Gd. An additional, at least partial substitution of the zirconium cations by Ce, Hf or Ta is advantageous. Improving the properties results especially in a high thermal coefficient of dilation alpha and low heat conductivity lambda.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Low-profile dual-polarization dipole base station antenna loaded with AMC reflecting plate
InactiveCN106785405AEasy to expandImprove isolationRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial lineHigh isolation
The invention discloses a low-profile dual-polarization dipole base station antenna loaded with an AMC reflecting plate. The antenna comprises a dual-polarization planar dipole antenna, four plastic support columns and the AMC reflecting plate. The dual-polarization planar dipole antenna comprises coupling microstrip lines, an upper dielectric plate, a radiating structure and coaxial lines from top to bottom in sequence; the AMC reflecting plate comprises a rectangular patch, a lower dielectric plate, an air dielectric, metal support columns and a metal plate which are periodically arranged from top to bottom in sequence, the coupling microstrip lines and the radiating structure are located on the upper side and the lower side of the upper dielectric plate in the same placing direction, and + / -45-degree dual-polarization is achieved in a coaxial line feeding mode. The dual-polarization planar dipole antenna is fixed to the AMC reflecting plate through the plastic support columns. Accordingly, the AMC reflecting plate is adopted for replacing an original metal reflecting plate, the antenna profile height is lowered to 0.132 lambda 2.2 GHz from 0.264 lambda 2.2 GHz, and meanwhile the advantages of being wide in frequency band, high in isolation, low in cross polarization, low in cost and the like are reserved. The application requirement of the current communication industry is met, and the low-profile dual-polarization dipole base station antenna conforms to the development trend of miniaturization of current base station antennae and has practical reference value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for controlling transition between operating modes in a multimode engine
InactiveUS20070000456A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
At least one engine operating parameter other than total fuel energy content is taken into account when transitioning between operating modes in a dual fuel or other multimode engine (20) in order to maintain a smooth transition between modes. The parameter preferably comprises at least one of primary fuel excess air ratio (lambda) and ignition timing and preferably is controlled in addition to total fuel energy content control. Lambda control is especially beneficial because it permits the control system to compensate for the engine's inability to substantially alter the instantaneous air mass in the combustion chamber during the transition period. For instance, during a transition from pilot ignited gaseous fuel mode to diesel mode, the controlled parameter preferably comprises diesel lambda, and the controlling step comprises setting diesel lambda at a relatively high value at the beginning of the transition period and thereafter reducing diesel lambda during the transition period.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com