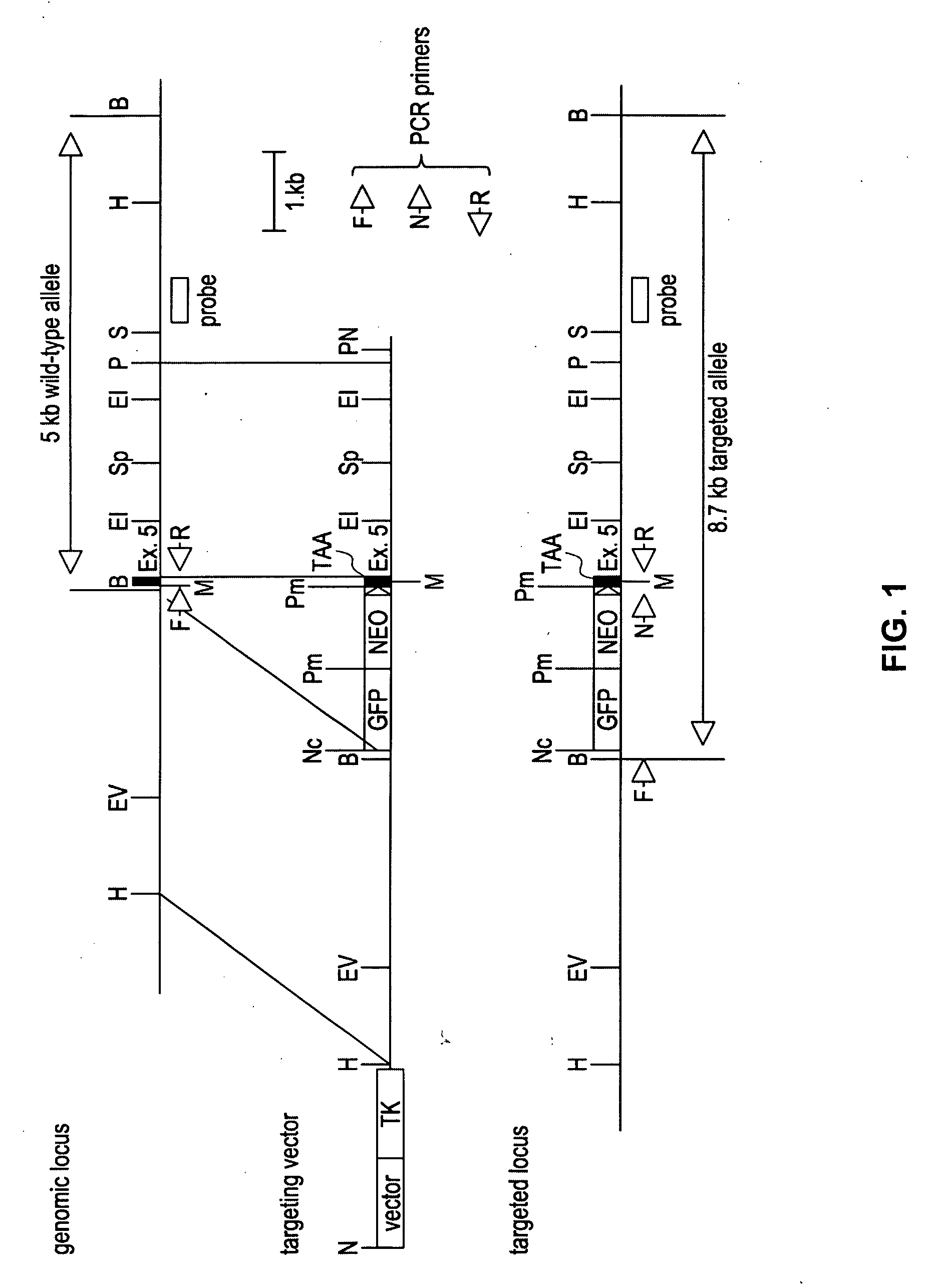
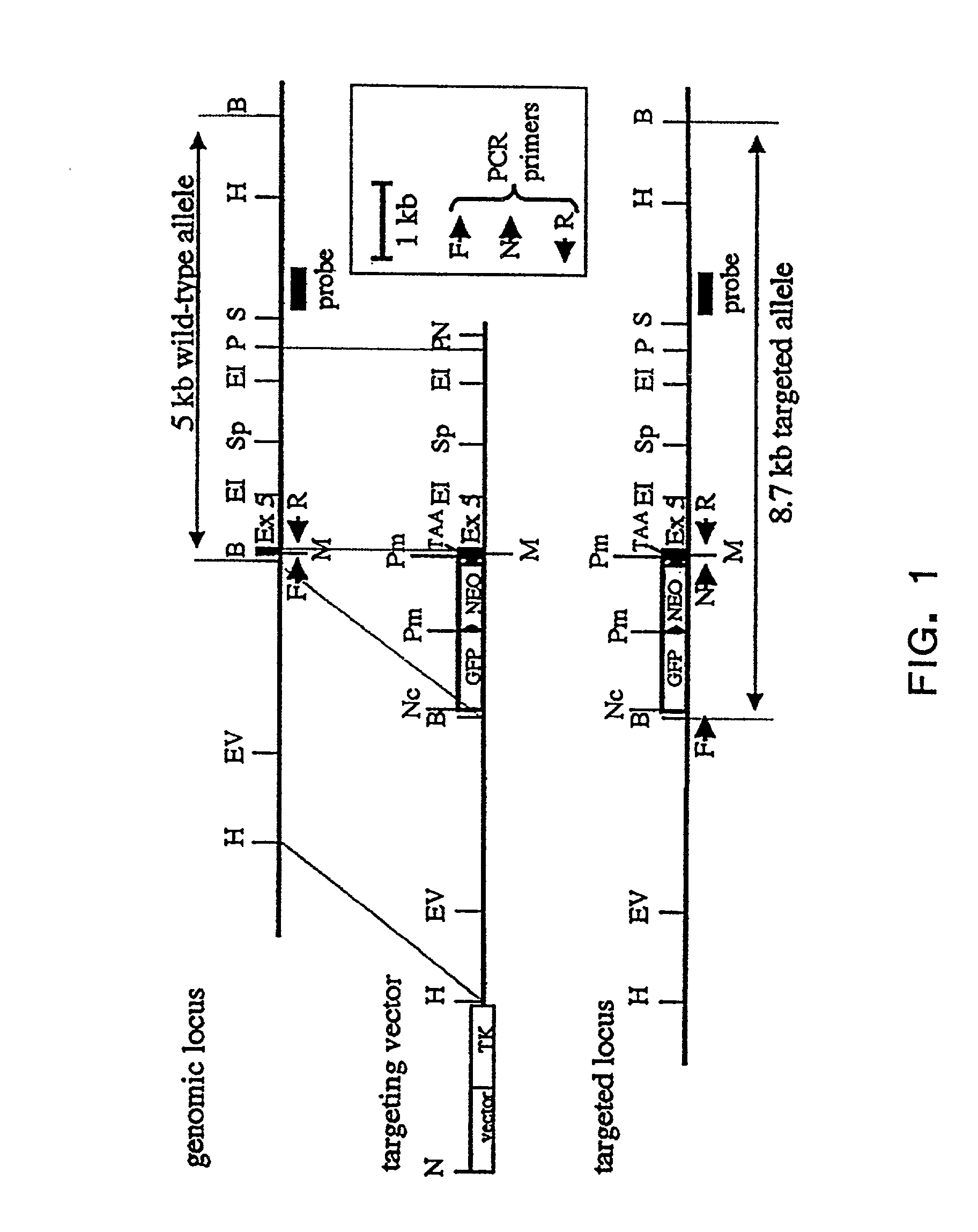
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Deficient mouse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The colitis in IL-10 deficient mice is characterized by immune system dysregulation, in that regulatory T cells either fail to develop or are functionally impaired in the absence of IL-10.
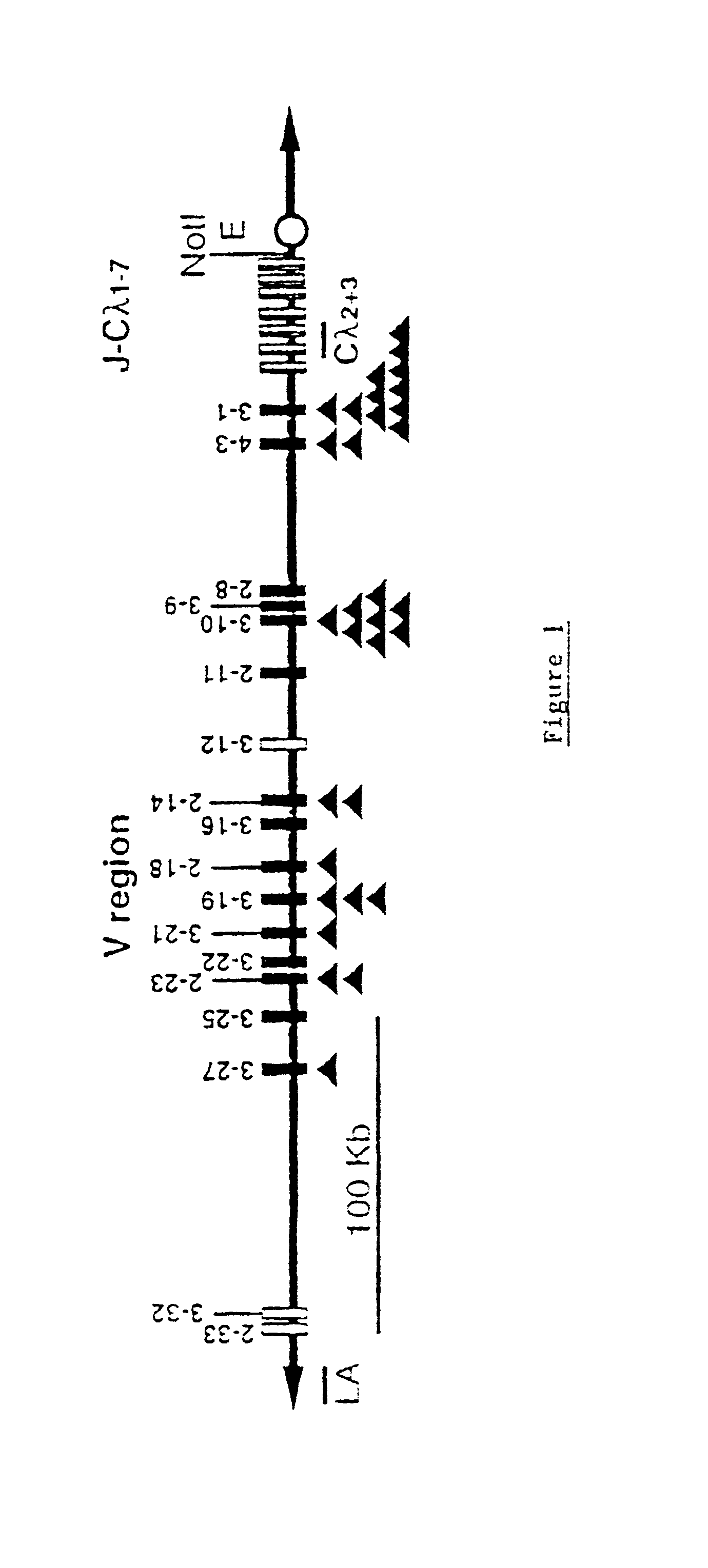
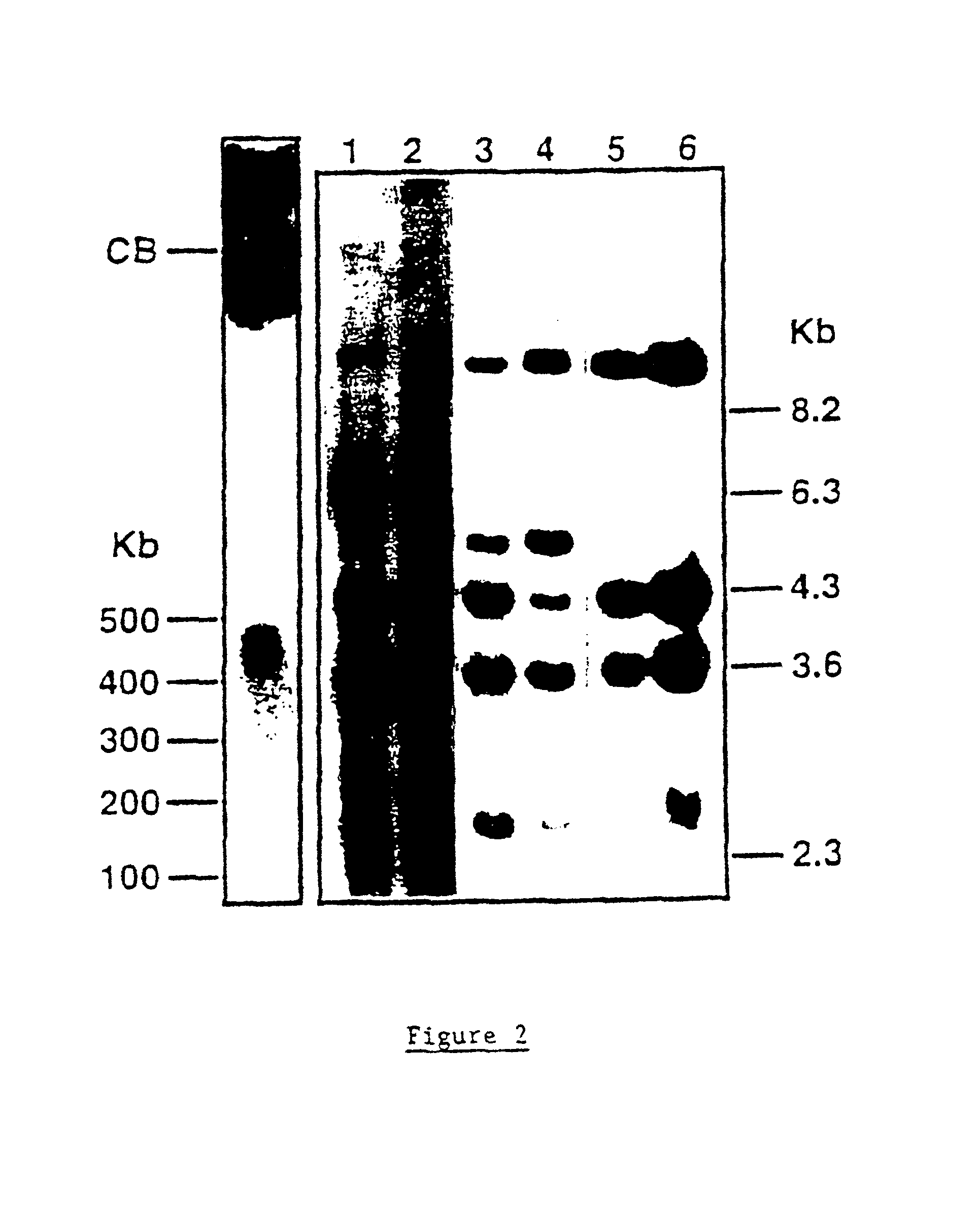
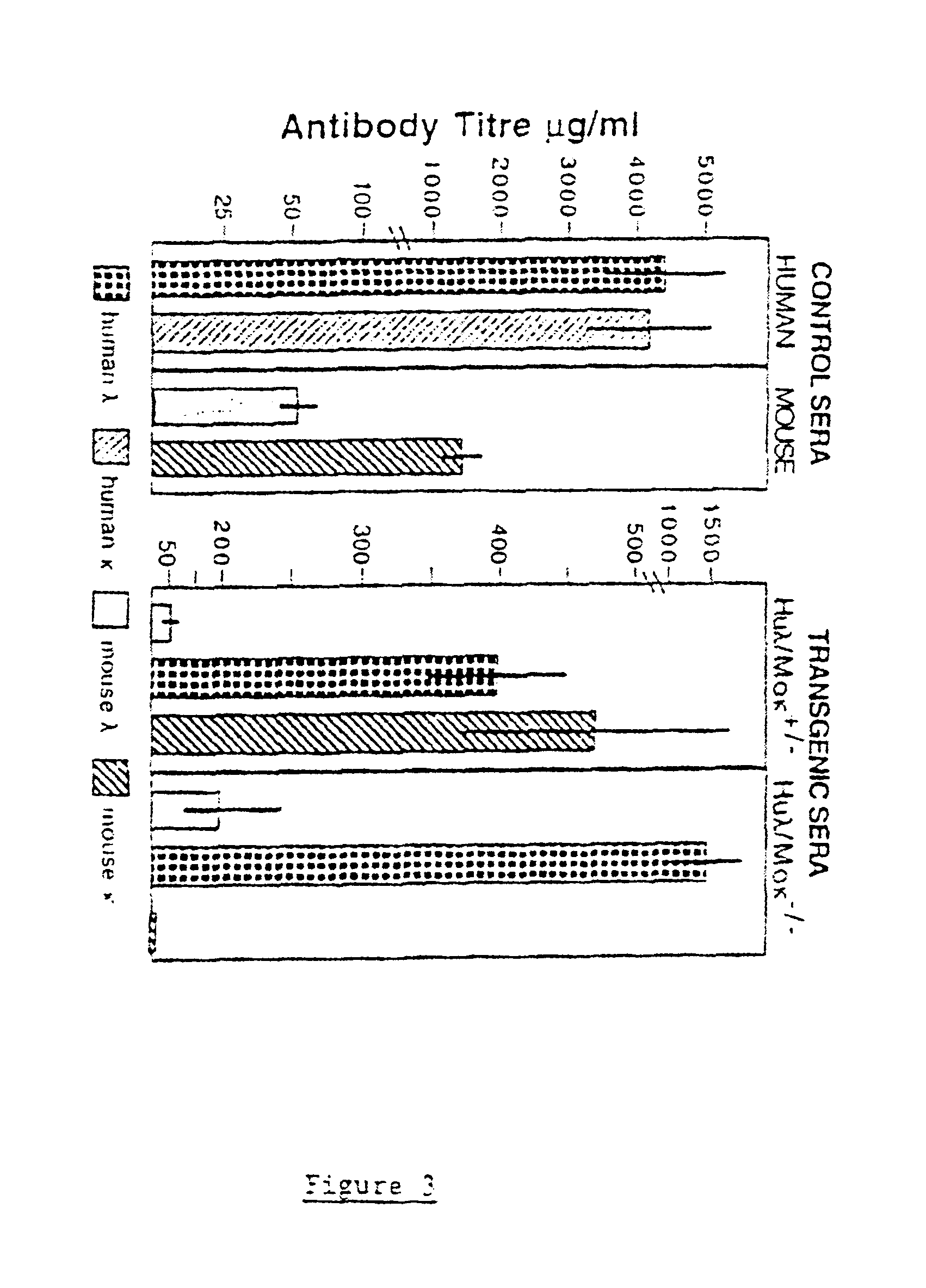
Murine expression of a human IgA lambda locus
InactiveUS6998514B2High expressionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin light chainMonoclonal antibody
In humans, approximately 60% of expressed immunoglobulin light chains are of the Kappa type and 40% of the Lambda type. In mice, there is almost no expression from the Lambda locus and over 95% of light chains are of Kappa type. The present invention discloses, among other things, transgenic mice carrying most of the human Ig Lambda light chain locus in their genome. The resulting mice express light chains with Kappa / Lambda ratio similar to the human ratio. Breeding of HuIg Lamda mice to Kappa-deficient mice also is described, as well as the generation of human monoclonal antibodies from transgenic mice with human Ig Lambda locus.
Owner:BABRAHAM INST
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176258A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesImmunodominant EpitopesMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein among other MN / CA IX-related inventions are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Subsets of the new antibodies are to either the proteoglycan-like (PG) domain or to the carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain of MN / CA IX, and methods are provided by which antibodies can be prepared to the other MN / CA IX domains. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176310A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesOxidoreductasesFermentationKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with Her-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080177046A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The Predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (S-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX'S coexpression with HER-2/NEU/C-ERBB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7816493B2Good curative effectSugar derivativesBiological material analysisKilodaltonC erbb 2
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) found in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Soluble CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer / cancer that detect or detect and quantitate s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 that provides potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer / cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer / precancer. Preferred are new antibodies, specific for non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, useful to detect soluble CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, preferably in combination with antibodies specific to immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Muir-Torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
InactiveUS20060075511A1Drug screeningNucleic acid vectorParanasal Sinus CarcinomaGastrointestinal cancer
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:CROCE CARLO +1
Muir-torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
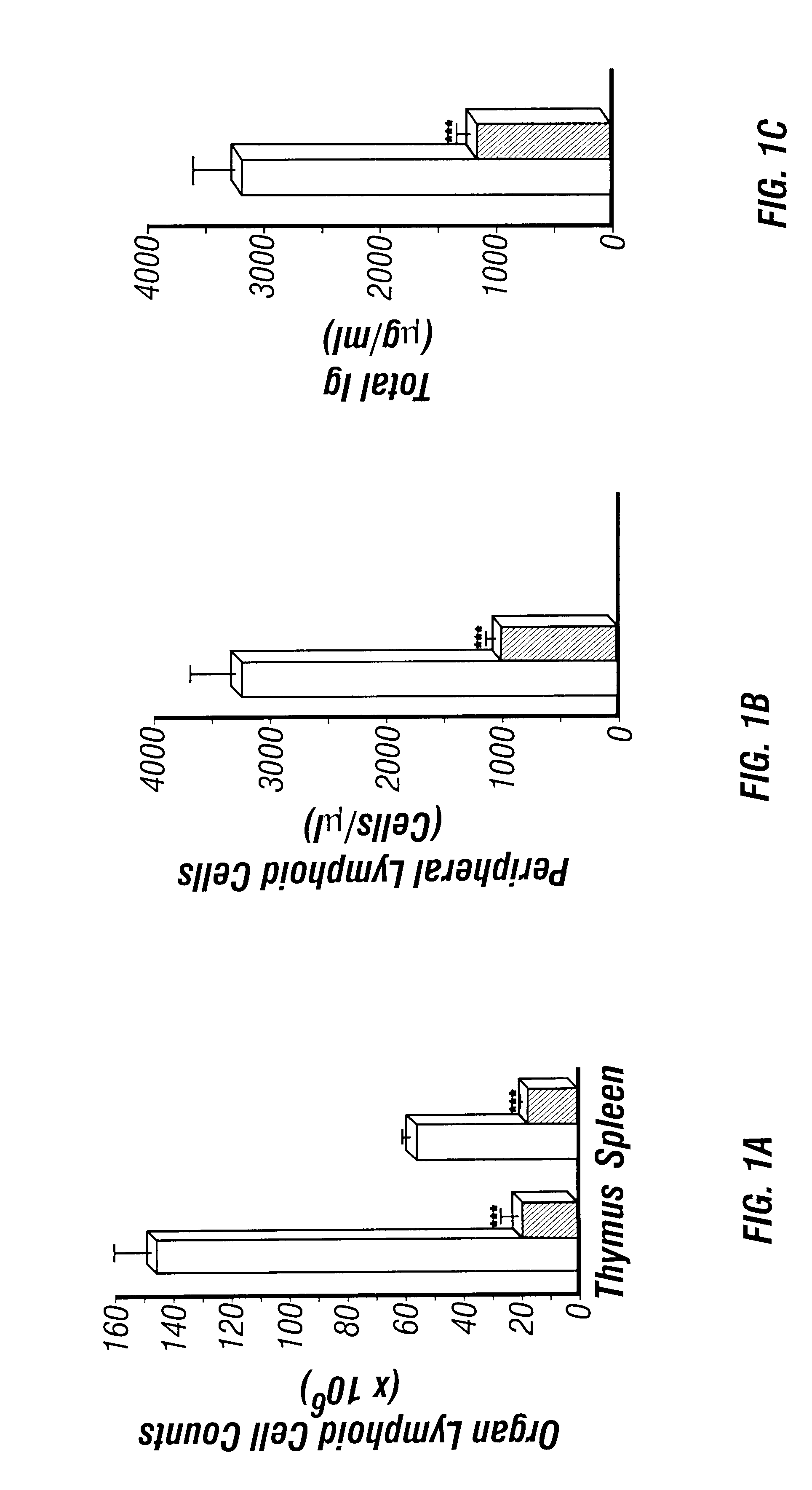
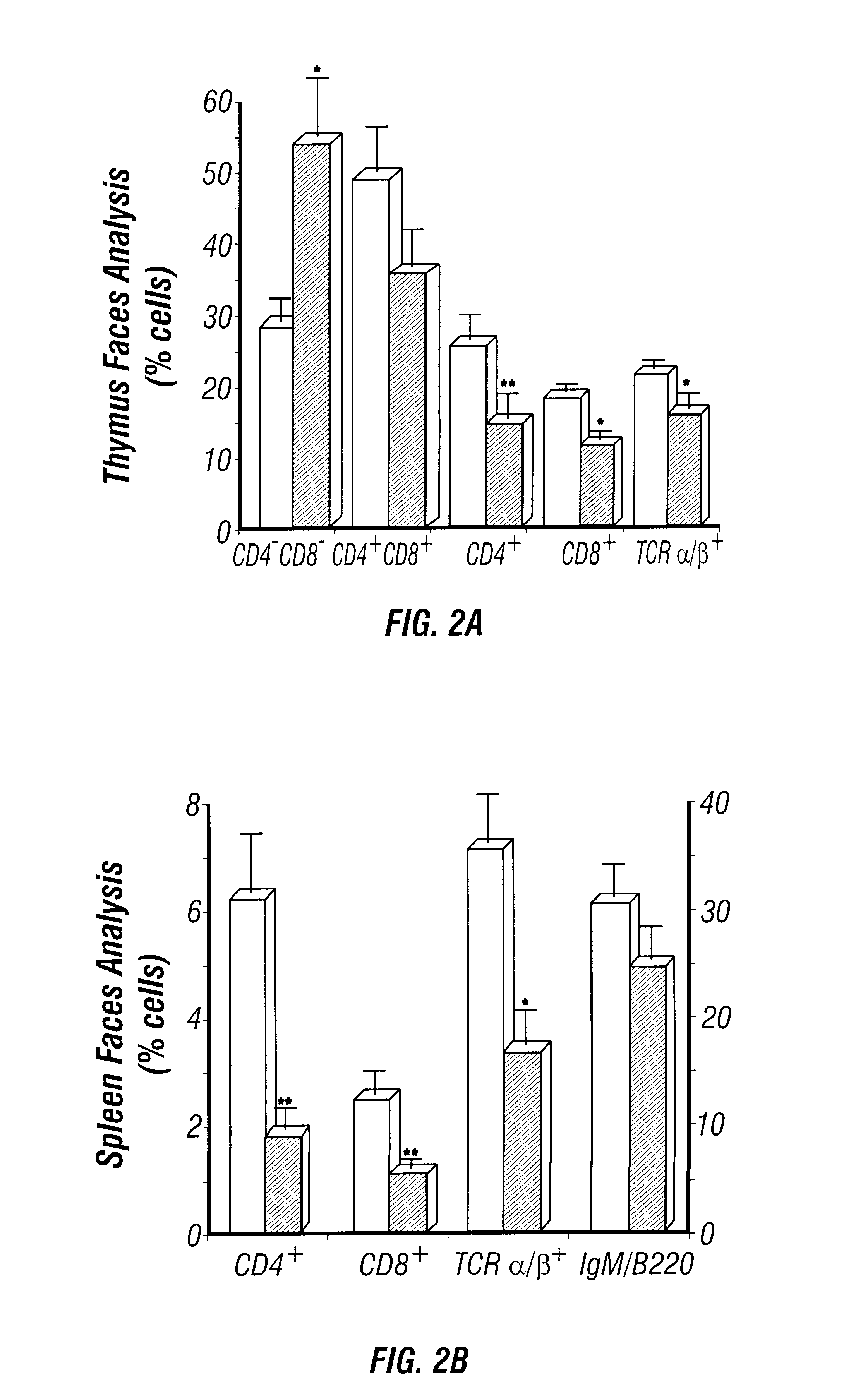
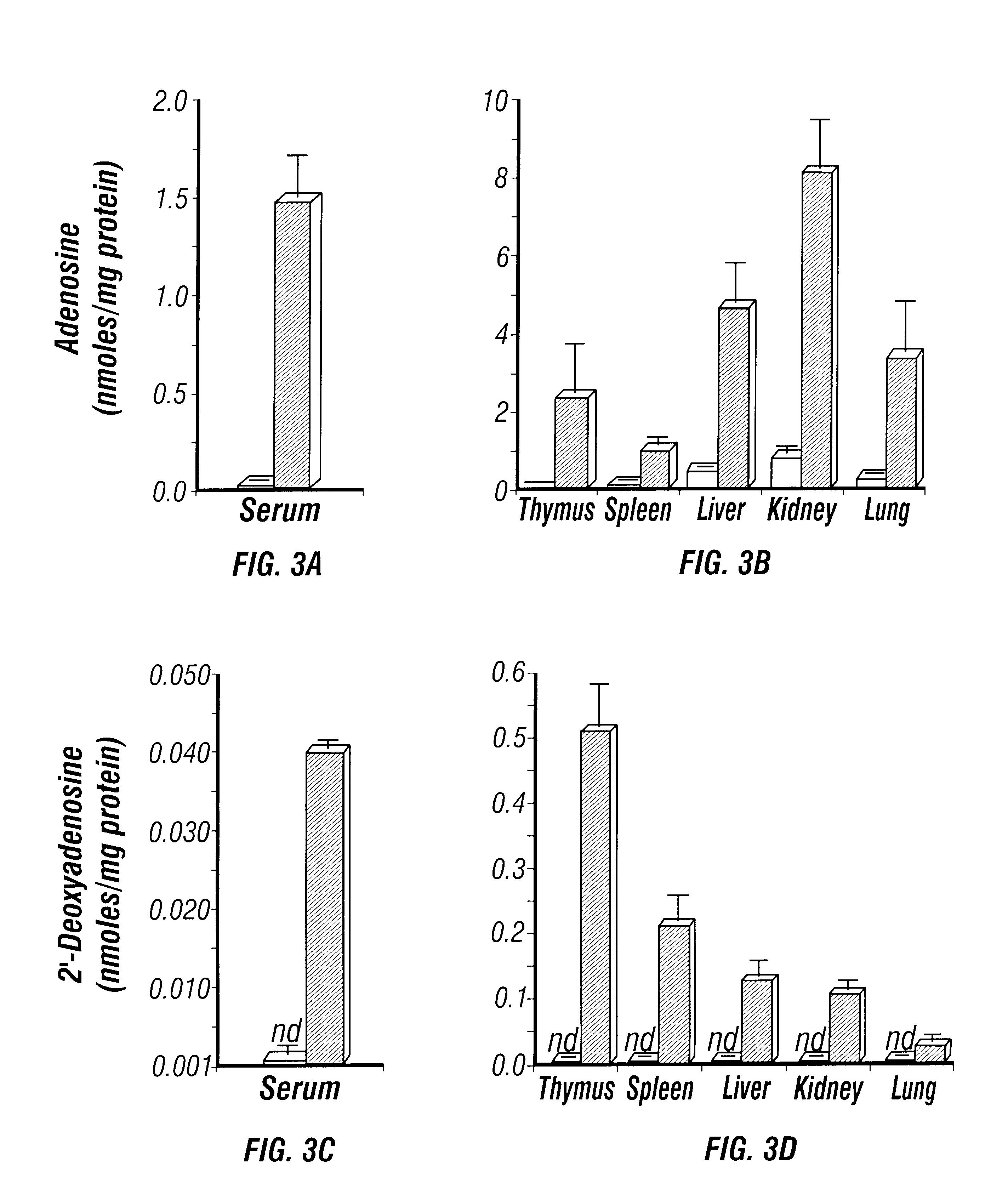
Adenosine deaminase deficient transgenic mice and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS6207876B1Determining effectGuaranteed flatnessVectorsTissue cultureMedicineDeficient mouse
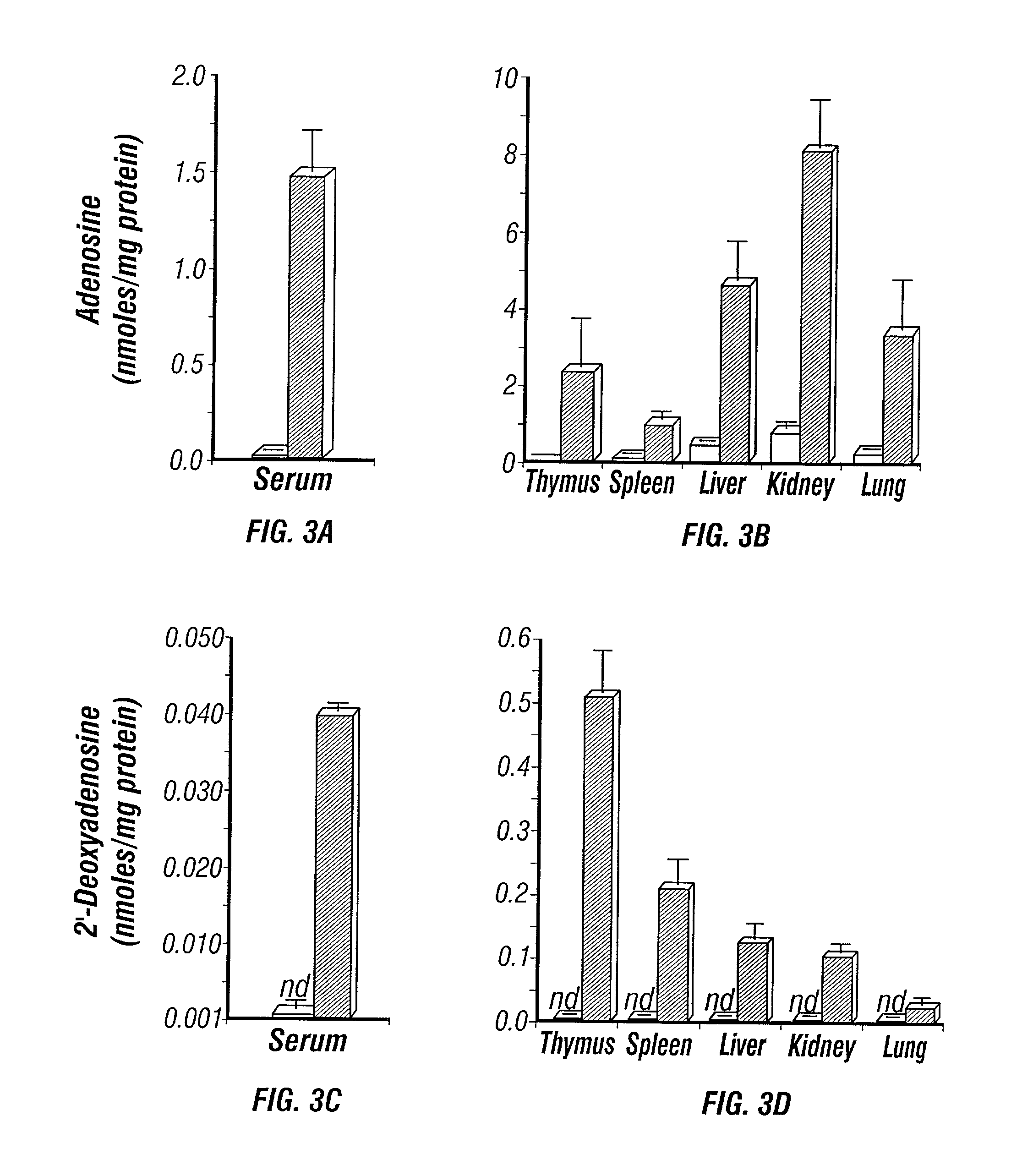
The present invention relates to the production of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficient mice and the use of such mice as an animal model for dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels. Also, provided by the present invention are methods of treating dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels and methods of screening compounds for pharmaceutical activity in the treatment of dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Muir-torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Method of resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1g protein
InactiveUS20060025397A1Suppressing functionResisting epilepsyOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsKnockout animalSuppressor
The disclosure concerns a method for resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1 G protein of T-type calcium channels, use of suppressor of alpha 1 G protein for prevention or treatment for epilepsy, knockout mice resisting epilepsy by disrupting alpha 1 G subunit of T-type calcium channel, and preparation method thereof. In addition, suppressing alpha 1 G protein of T-type calcium channels does not occur epilepsy, and alpha 1 G-deficient mice are useful to study of mechanism related to epilepsy.
Owner:POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for establishing immunodeficiency mouse model
ActiveCN103409468AShorten the timeStrain background pureMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryReverse transcriptaseImmunodeficient mouse model
The invention discloses a method for establishing an immunodeficiency mouse model. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which enables functions of an immune related gene in a mouse cell to be lost; (2) purifying mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid), and cryopreserving in a super-purified water of RNAase free; (4) feeding a pregnant female mouse and a pseudopregnant female mouse under an SPF (specific pathogen free) level feeding condition; (5) taking a fallopian tube from the abdominal cavity of the pregnant female mouse in the step (4), and collecting fertilized ovum; (6) injecting the mRNA obtained in the step (3) into the pronucleus of the fertilized ovum in the step (5) by using a microinjection method; (7) transplanting the fertilized ovum obtained in the step (6) into the body of the pseudopregnant female mouse obtained in the step (4), and enabling the pseudopregnant female mouse to culture the second generation; (8) establishing a stable deficient mouse strain. The method has the advantages that a mouse model which completely does not have immunological rejection to allotransplantation can be obtained for testing.
Owner:湖南昭泰生物医药有限公司
Nonhuman model animal suffering from Guillain-Barré syndrome and/or fisher syndrome
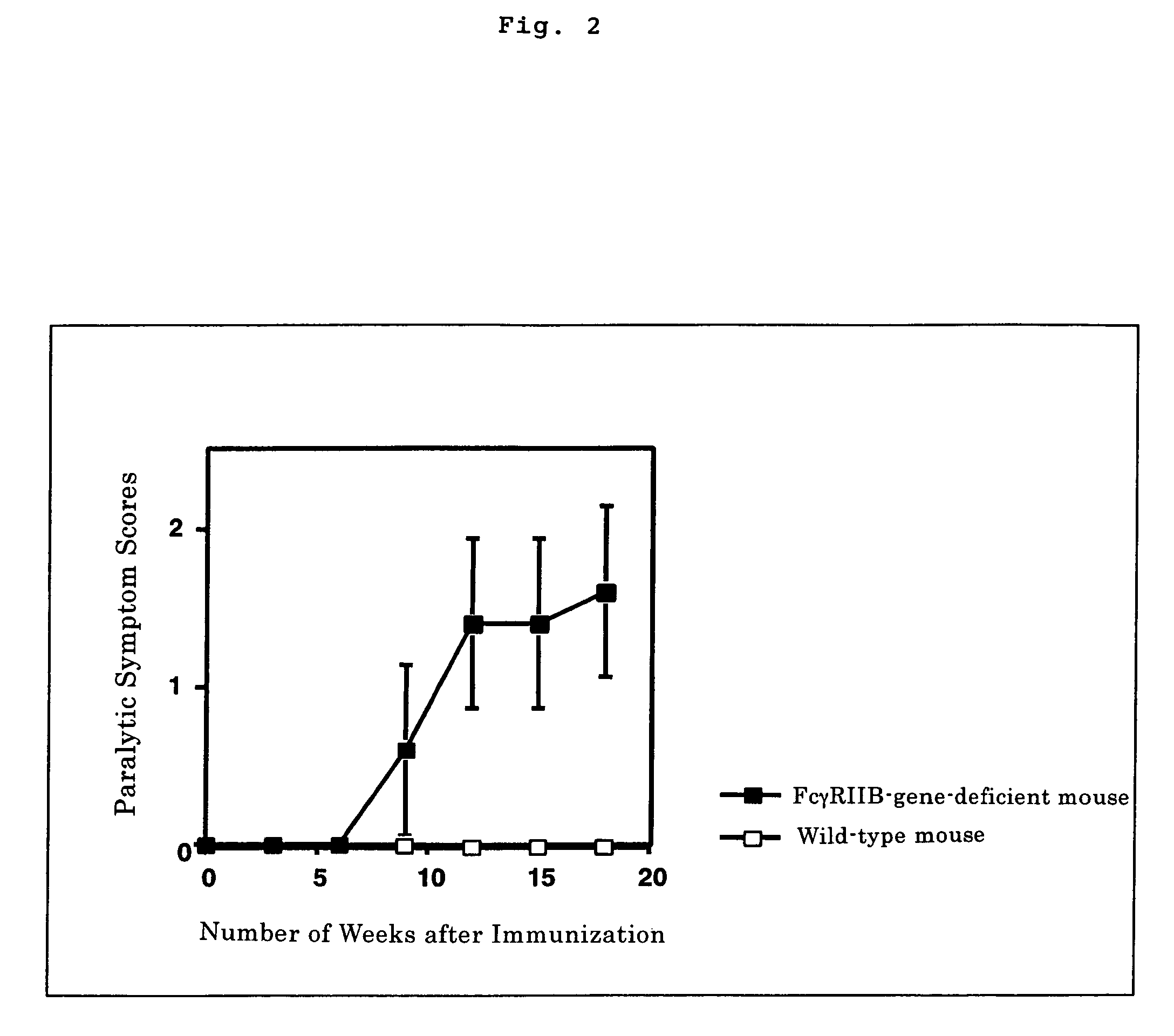
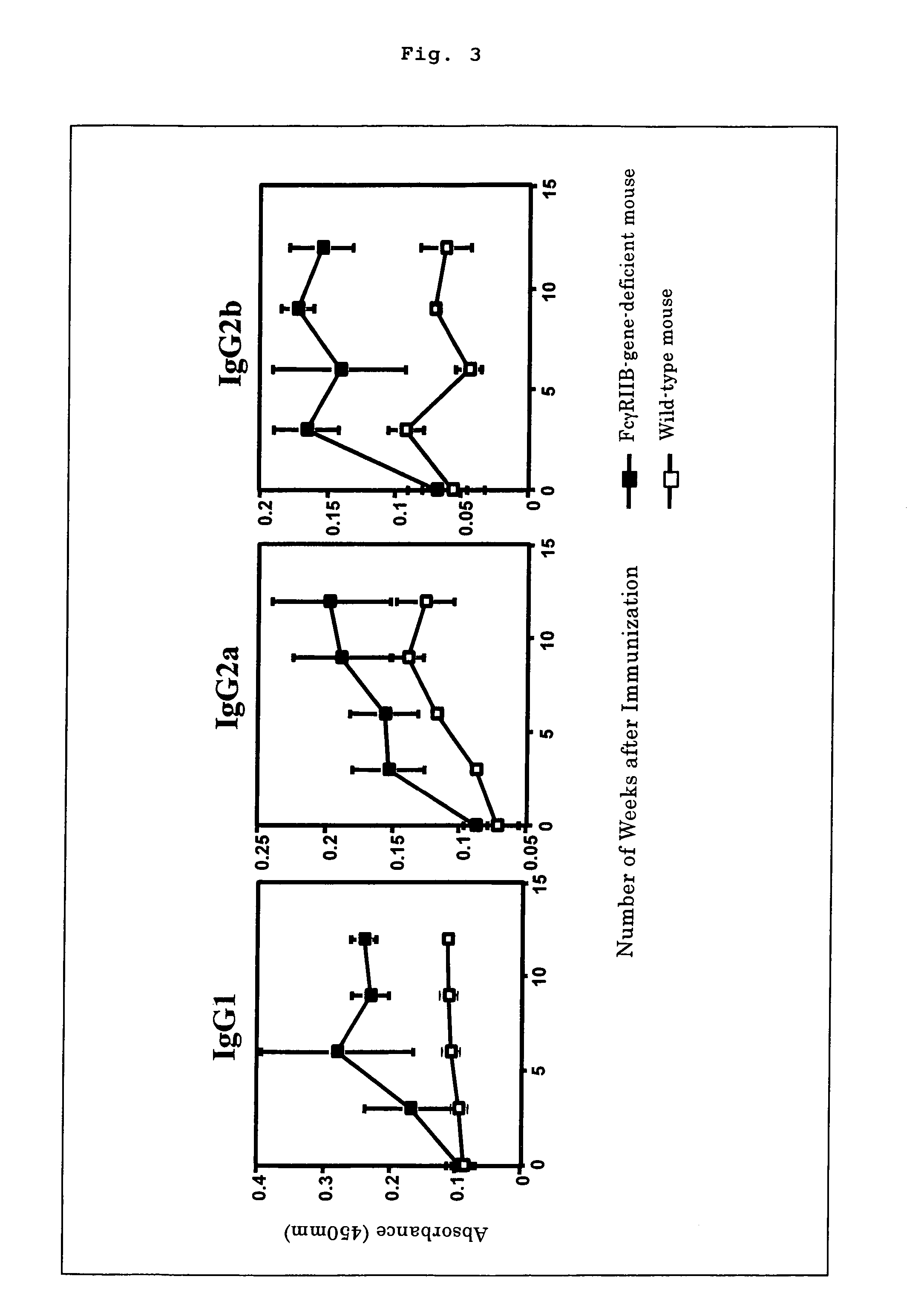
The present invention intends to provide a non-human animal model of Guillain-Barré syndrome, which can be obtained by immunizing FcγRIIB-gene-deficient non-human animal with ganglioside GQ1b, and a screening method of a therapeutic agent for Guillain-Barré syndrome using the non-human animal model. A mouse model of Guillain-Barré syndrome is generated by immunizing FcγRIIB-gene-deficient mice with gangliosides GM1, GM2, GD1a, and GQ1b together with Freund's adjuvant every three weeks four times in total.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Non-human animal model of systemic lupus erythematosus
InactiveUS7265261B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansScreening methodAnti-dsDNA antibodies
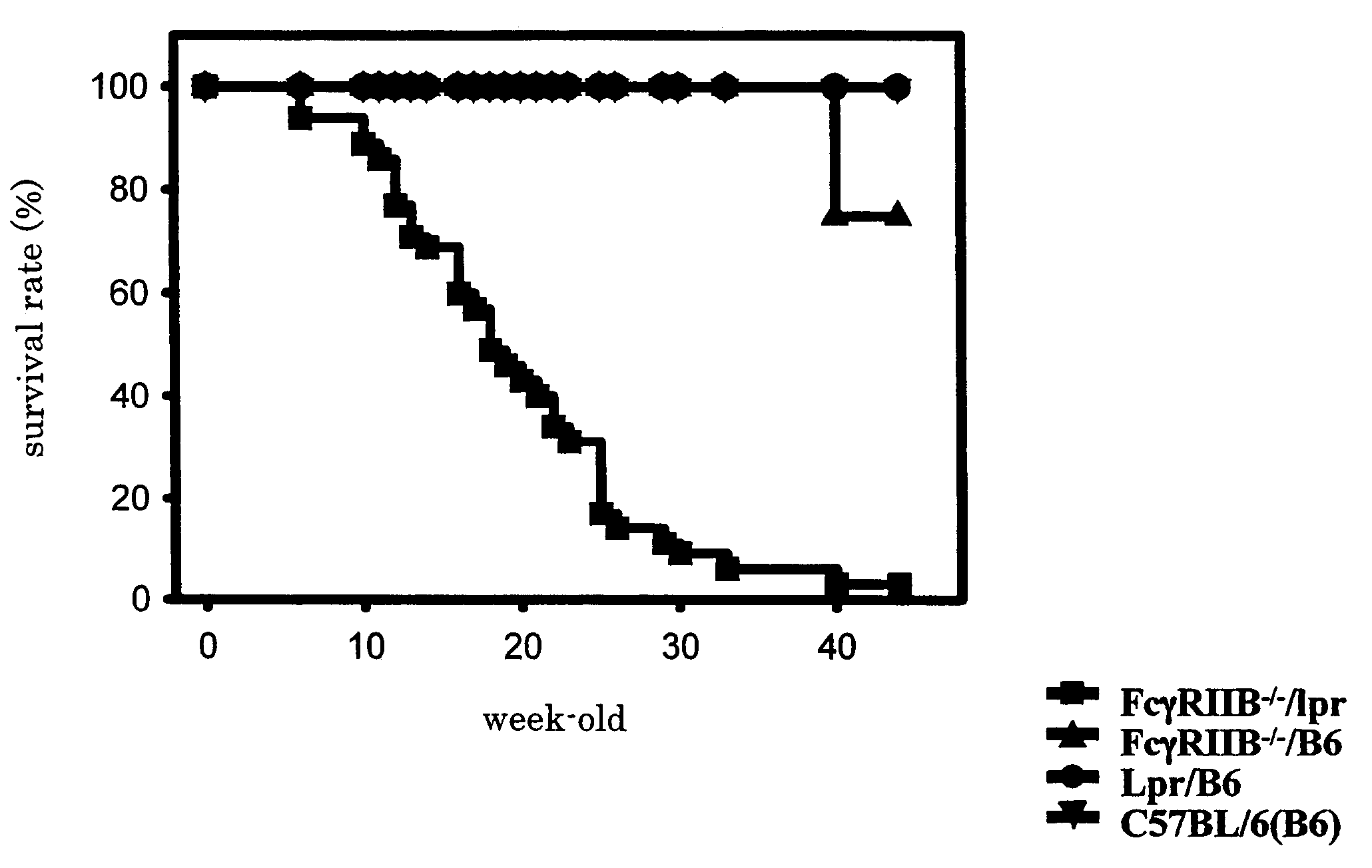
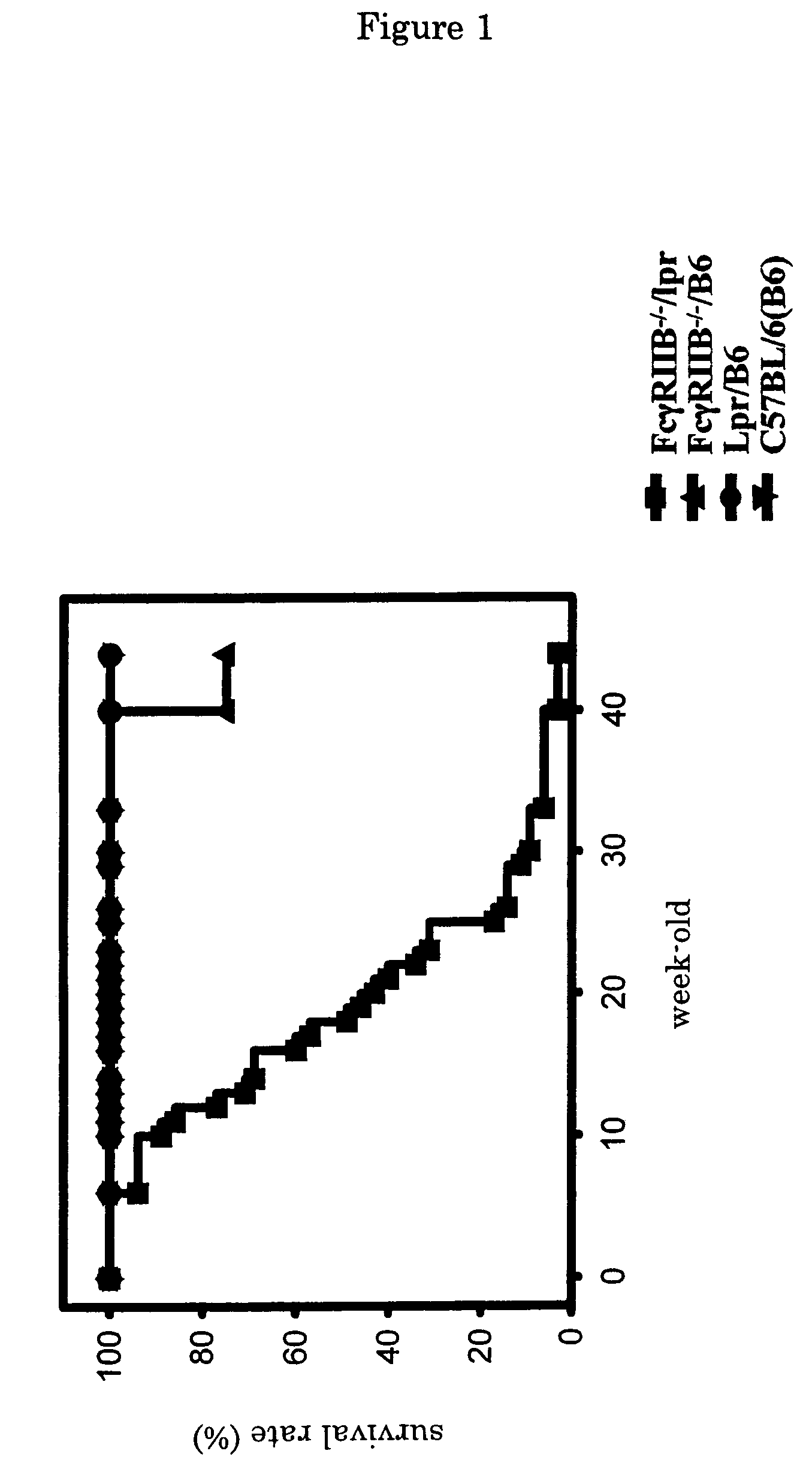
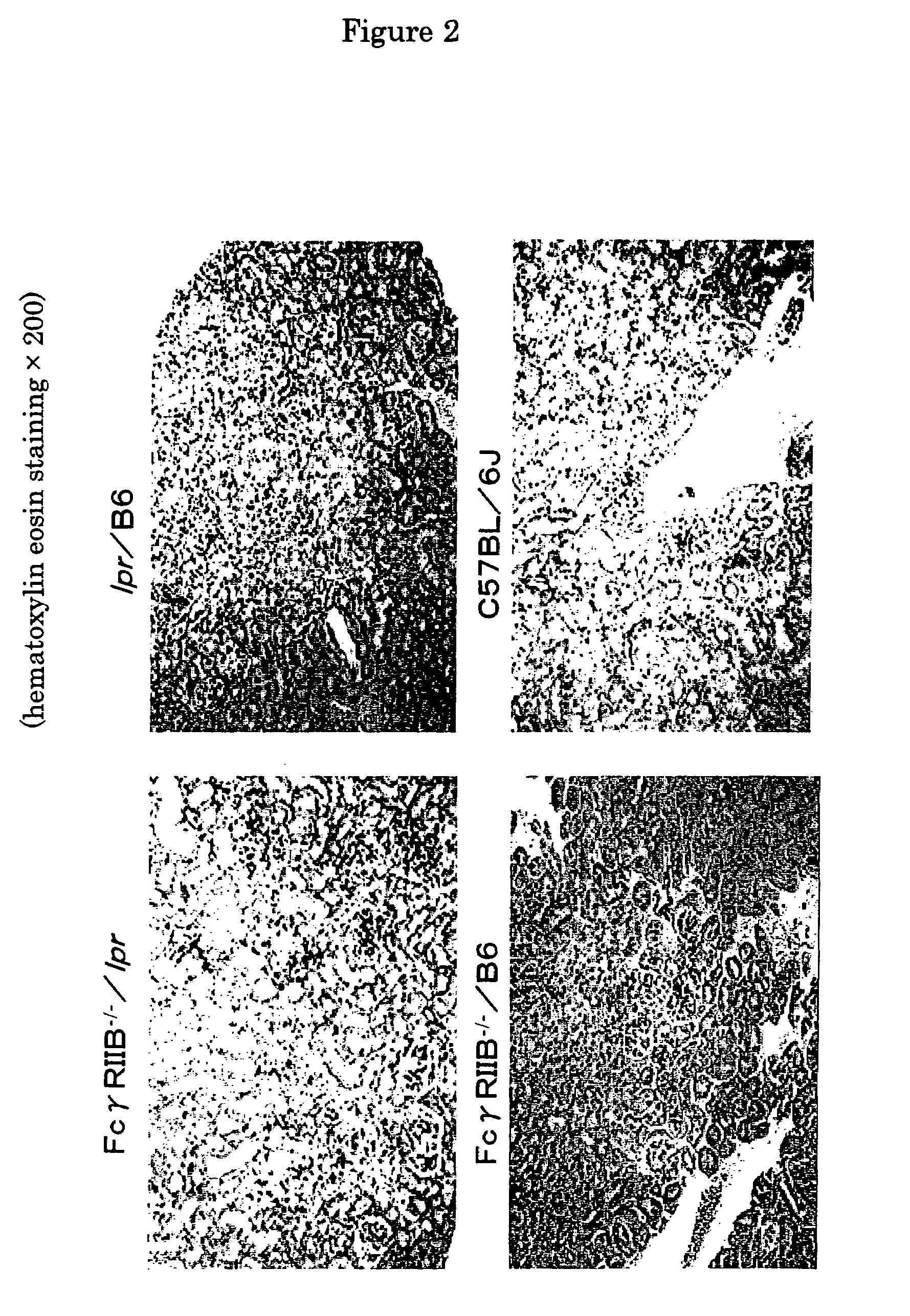
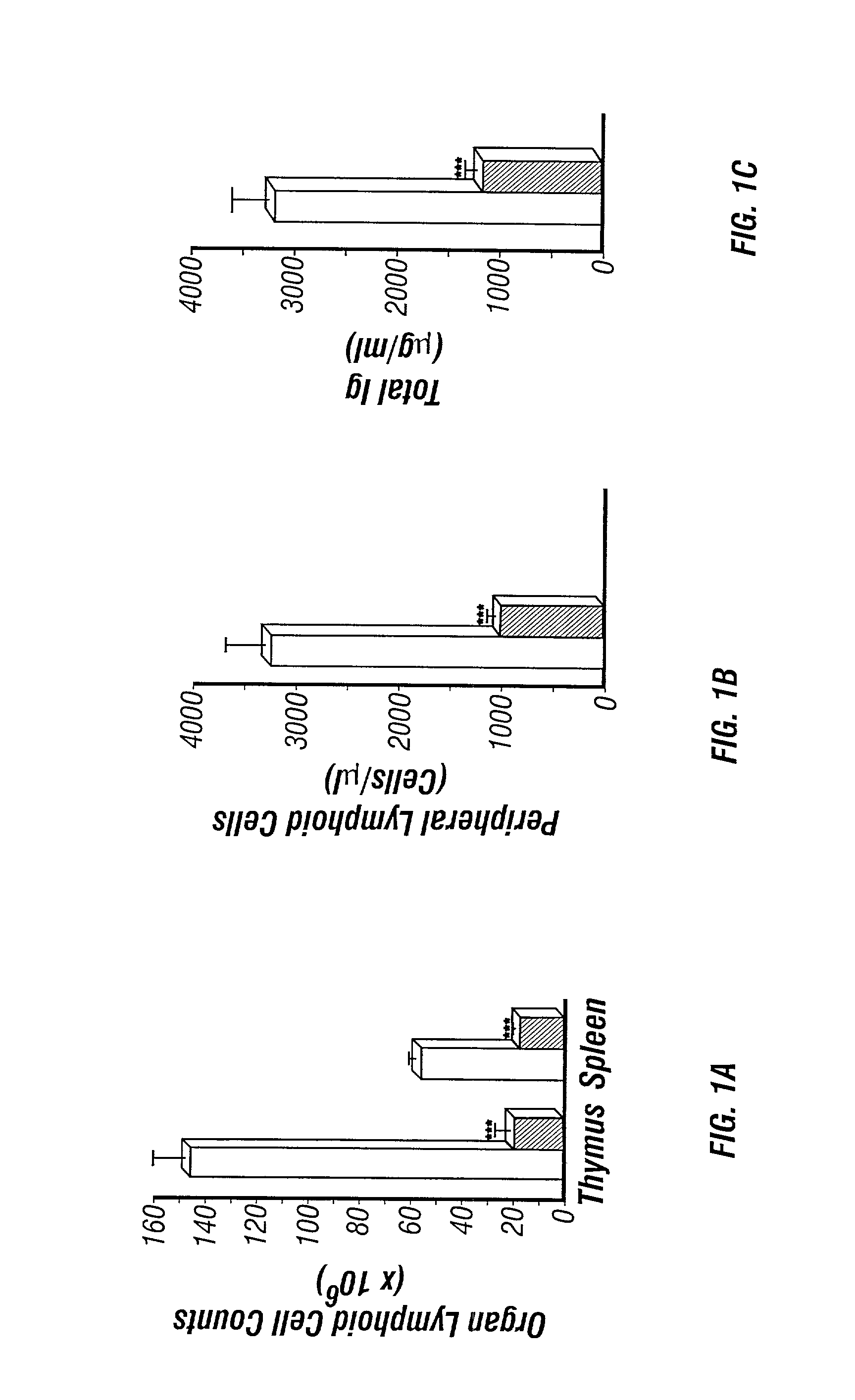
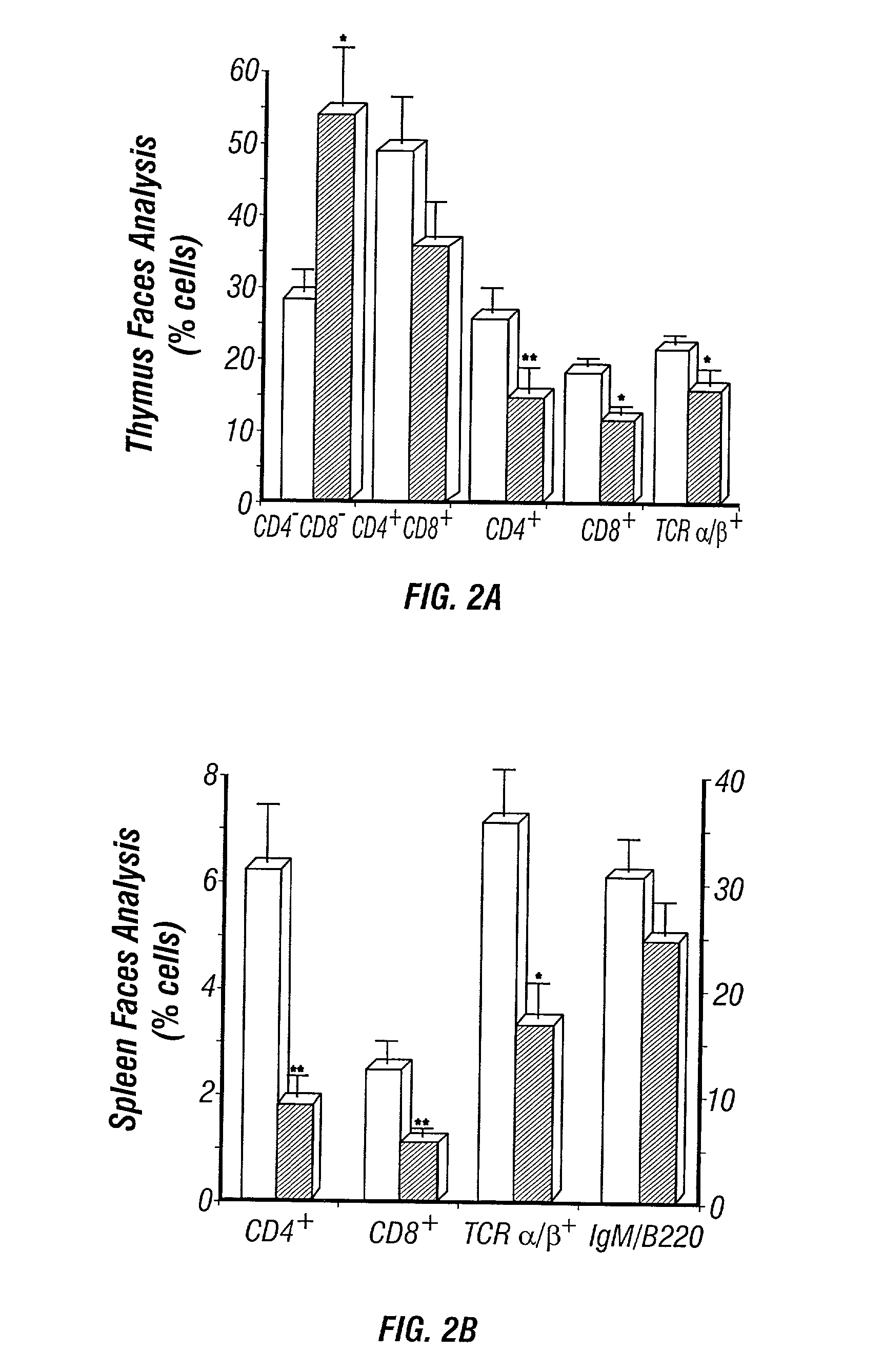
The present invention is to provide a non-human animal model of systemic lupus erythematosus wherein generation of anti-double stranded DNA antibody and anti-single stranded antibody is induced, and that is made to spontaneously develop glomerulonephritis and arthritis, and a screening method for a therapeutic agent for systemic lupus erythematosus wherein the non-human animal model is used. FcγRIIB deficient mouse that is not made to spontaneously develop autoimmune pathology although its autoantibody response is enhanced is backcrossed into C57BL / 6J (B6) mouse for 12 generations to generate FcγRIIB deficient B6 mouse, the FcγRIIB deficient B6 male mouse is intercrossed with lpr / B6 female mouse, and thus obtained FcγRIIB+ / − / lpr+ / − mice were further crossed to generate a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Adenosine deaminase deficient transgenic mice and methods for the use thereof
The present invention relates to the production of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficient mice and the use of such mice as an animal model for dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels. Also, provided by the present invention are methods of treating dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels and methods of screening compounds for pharmaceutical activity in the treatment of dysfunctions associated with elevated adenosine levels.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Lipocalin-type prostaglandin d2 synthase as a biomarker for lung cancer progression and prognosis
InactiveUS20110318308A1Small toxicityEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTube formationLipocalin-type PGDS
A PGD(2) receptor (DP) deficiency enhances tumor progression accompanied by abnormal vascular expansion. In tumors, angiogenic endothelial cells highly express DP receptor, and its deficiency accelerates vascular leakage and angiogenesis. Administration of a synthetic DP agonist, BW245C, markedly suppresses tumor growth as well as tumor hyperpermeability in WT mice, but not in DP-deficient mice. In a corneal angiogenesis assay and a modified Miles assay, host DP deficiency potentiates angiogenesis and vascular hyperpermeability under COX-2-active situation, whereas exogenous administration of BW245C strongly inhibits both angiogenic properties in WT mice. In an in vitro assay, BW245C does not affect endothelial migration and tube formation, processes that are necessary for angiogenesis; however, it strongly improves endothelial barrier function via an increase in intracellular cAMP production. PGD(2) / DP receptor is a newly identified regulator of tumor vascular permeability, indicating DP agonism can be exploited as a therapy for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:WINTHROP UNIV HOSPITAL
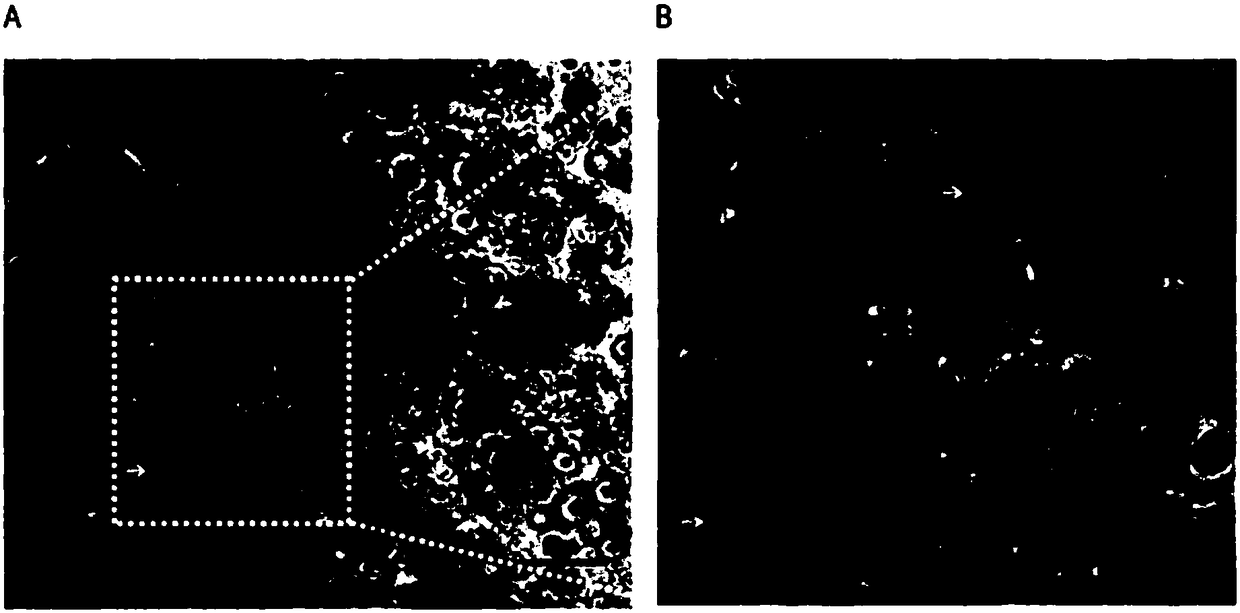
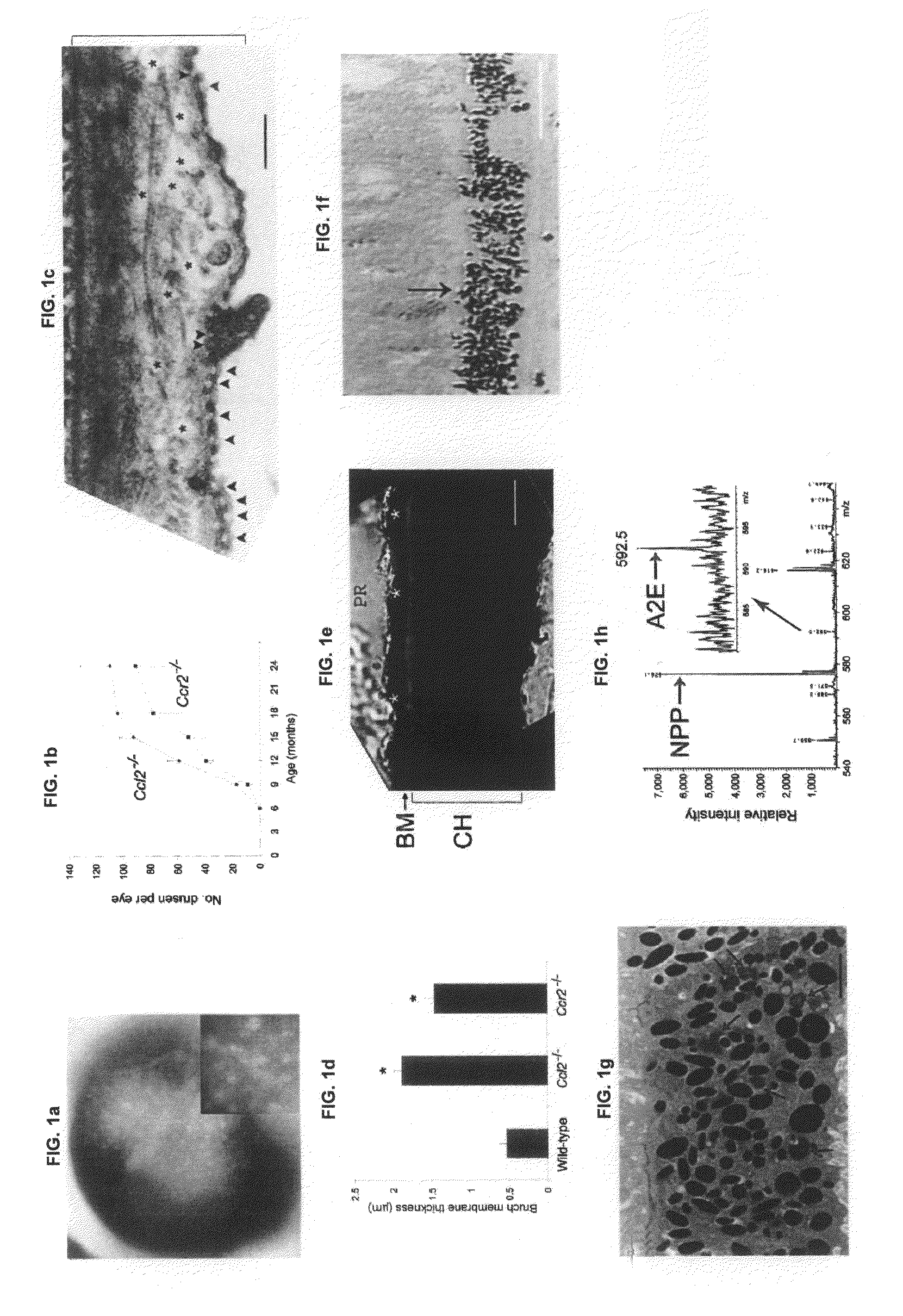
Methods and animal model for analyzing age-related macular degeneration
InactiveUS7595430B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementCCL2Knockout animal
Methods for testing candidate drugs for treatment of age-related macular degeneration are provided. Ccl2-deficient, and Ccr2-deficient mice are used to determine the effect of candidate drugs and treatments on development of age-related macular degeneration. Also provided is a Ccl2-deficient, Ccr2-deficient dual knockout mouse, which is a useful animal model for age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Methods for increasing HSC graft efficiency
InactiveUS20060018885A1Minimize and eliminate needBiocideGenetic material ingredientsMechanism of actionHsc transplantation
This invention demonstrates that FC function via TNF-α to affect function of HSC. FC from TNF-α deficient mice are impaired in facilitating HSC engraftment in both the syngeneic and allogeneic models. Co-incubation of FC with HSC results in significant increase in TNF-α at the mRNA and protein level, and increase in transcript for Bcl-3 in HSC. Furthermore, neutralization of TNF-α results in the loss of FC ability to increase HSC clonogenicity and survival, as well as to upregulate Bcl-2 transcript in HSC, demonstrating a critical role for TNF-α in FC function. These results offer a mechanism of action for HSC regulation by accessory cells in the bone marrow and confirm the advantage of their co-transplantation with HSC to improve graft efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Method for establishing colorectal cancer patient-derived xenograft model through three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel
ActiveCN108148811AEnhance tumorigenic abilityGood subcutaneous tumor formation abilityCell culture supports/coating3D cultureMature technologyStem cell culture
The invention relates to a three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel. The three-dimensional culture system is prepared by combining the following reagents: thermo-sensitive biogel, digestive fluid required for separating and culturing tumor cells, a basal culture medium and a human intestinal stem cell culture medium. The invention also provides a method for establishing acolorectal cancer patient-derived xenograft model through the three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel. The three-dimensional culture system has the advantages that colorectalcancer cells can be further amplified and grown in the three-dimensional culture system based on thermo-sensitive biogel, and the tumor formation capability of the colorectal cancer cells in the immune deficient mice can be enhanced. Polyclonal tumor cells cultured in the system have high subcutaneous tumor formation capability in nude mice. The three-dimensional culture system has the advantagesof simple preparation method and mature technology, and is capable of greatly reducing the time and the cost for establishing the human-derived colorectal cancer xenograft model.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo
Described herein is a method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo using an immunodeficient mouse which is further deficient in fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah). The method comprises transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fan-deficient mice, administering an IL-IR antagonist to the mouse and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. Alternatively, the method includes transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fah-deficient mice, wherein the mouse is further deficient for IL-IR and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. The method also allows serial transplantation of the human hepatocytes into secondary, tertiary, quaternary or additional mice.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Methods and animal model for analyzing age-related macular degeneration
ActiveUS20090260091A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementCCL2Knockout animal
Methods for testing candidate drugs for treatment of age-related macular degeneration are provided. Ccl2-deficient, and Ccr2-deficient mice are used to determine the effect of candidate drugs and treatments on development of age-related macular degeneration. Also provided is a Ccl2-deficient, Ccr2-deficient dual knockout mouse, which is a useful animal model for age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
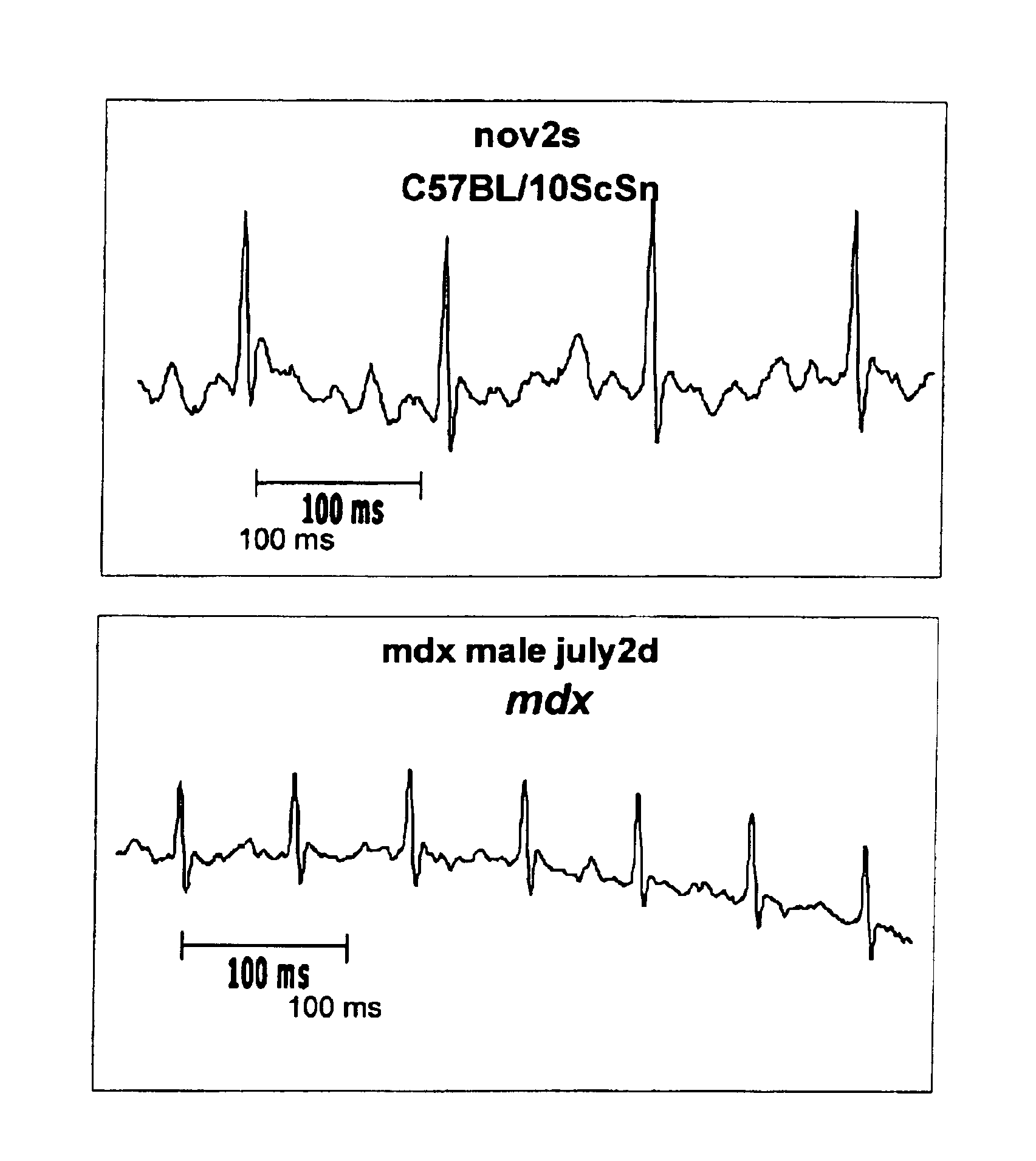
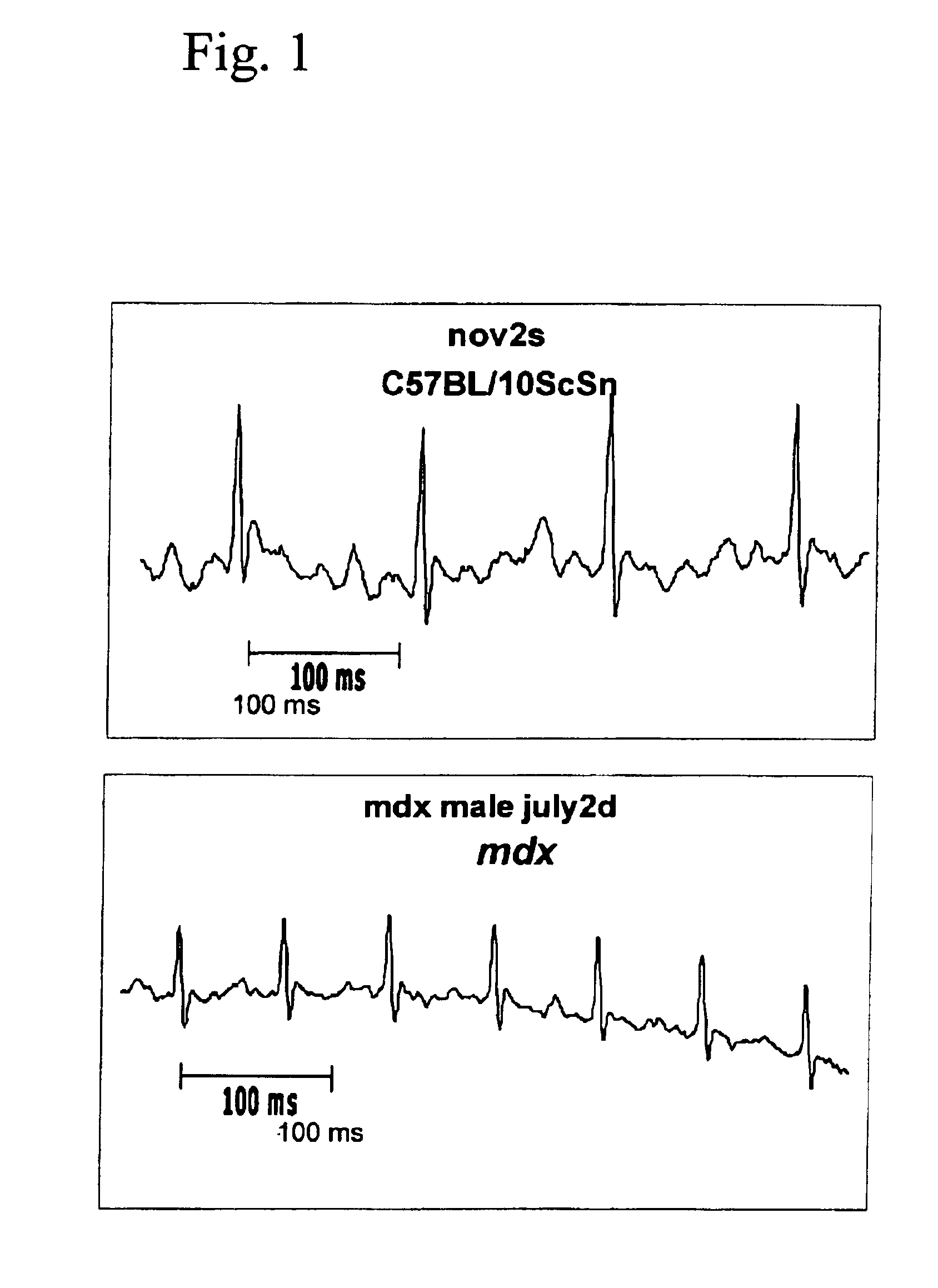
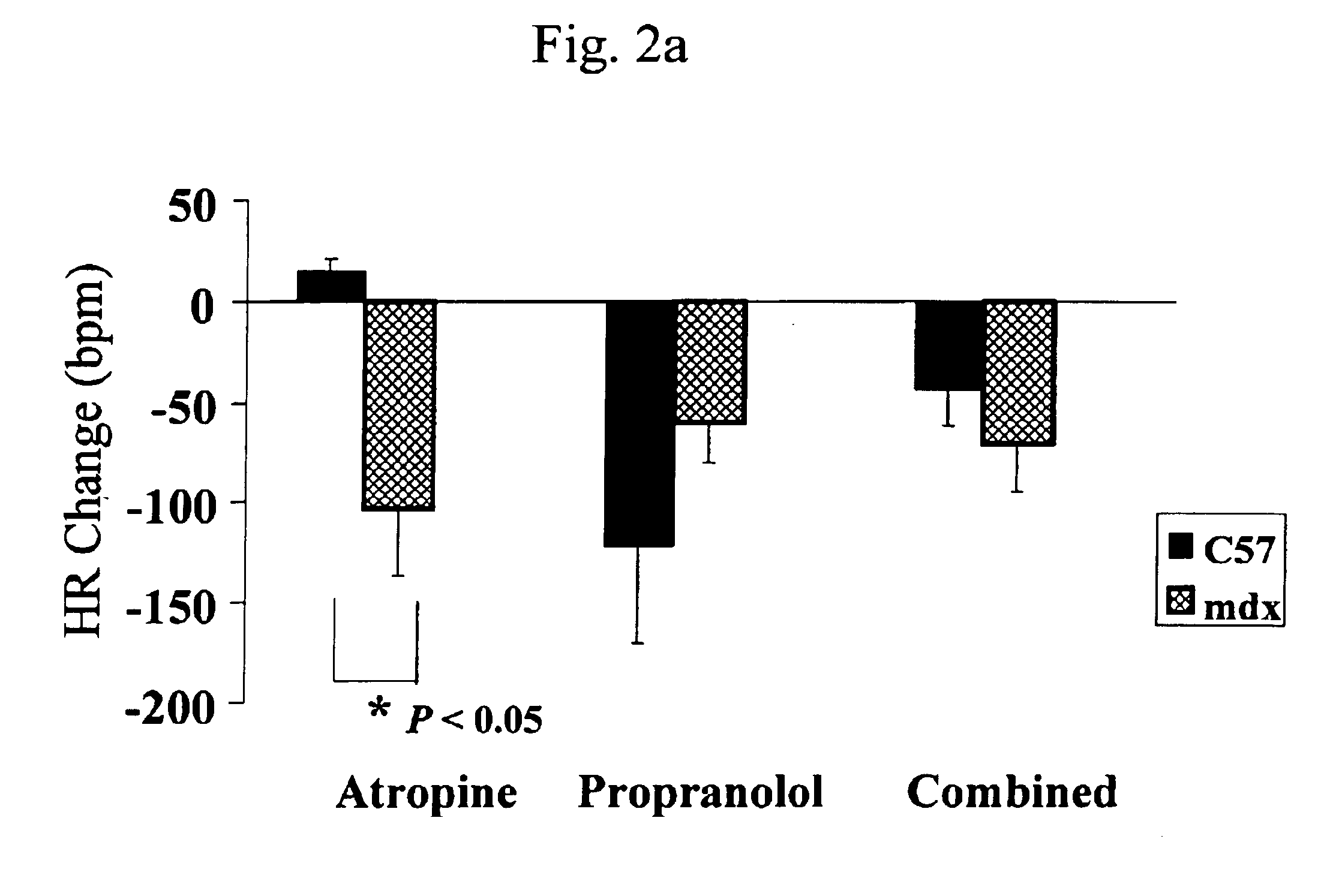
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Application of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in cancer inhibition
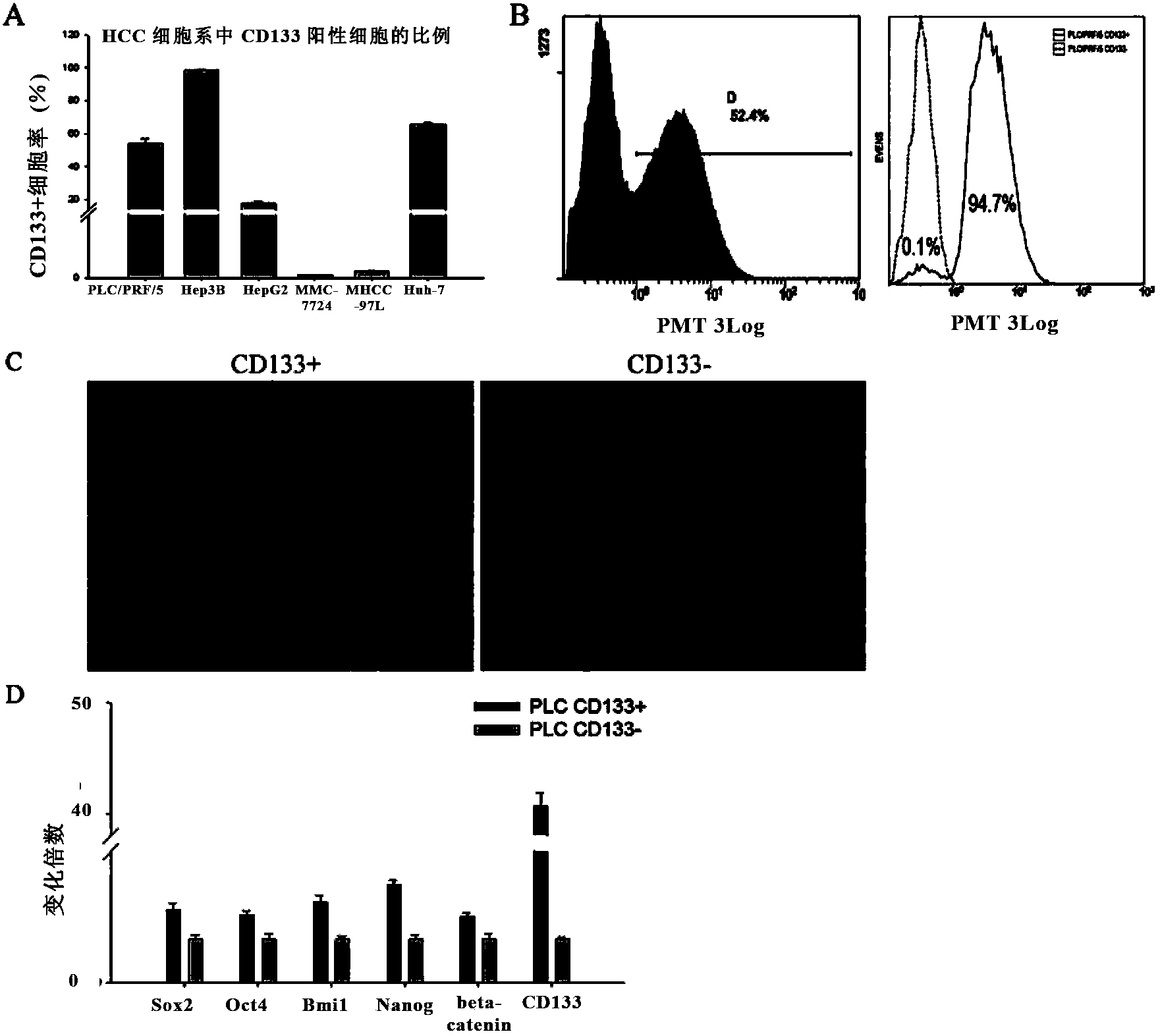
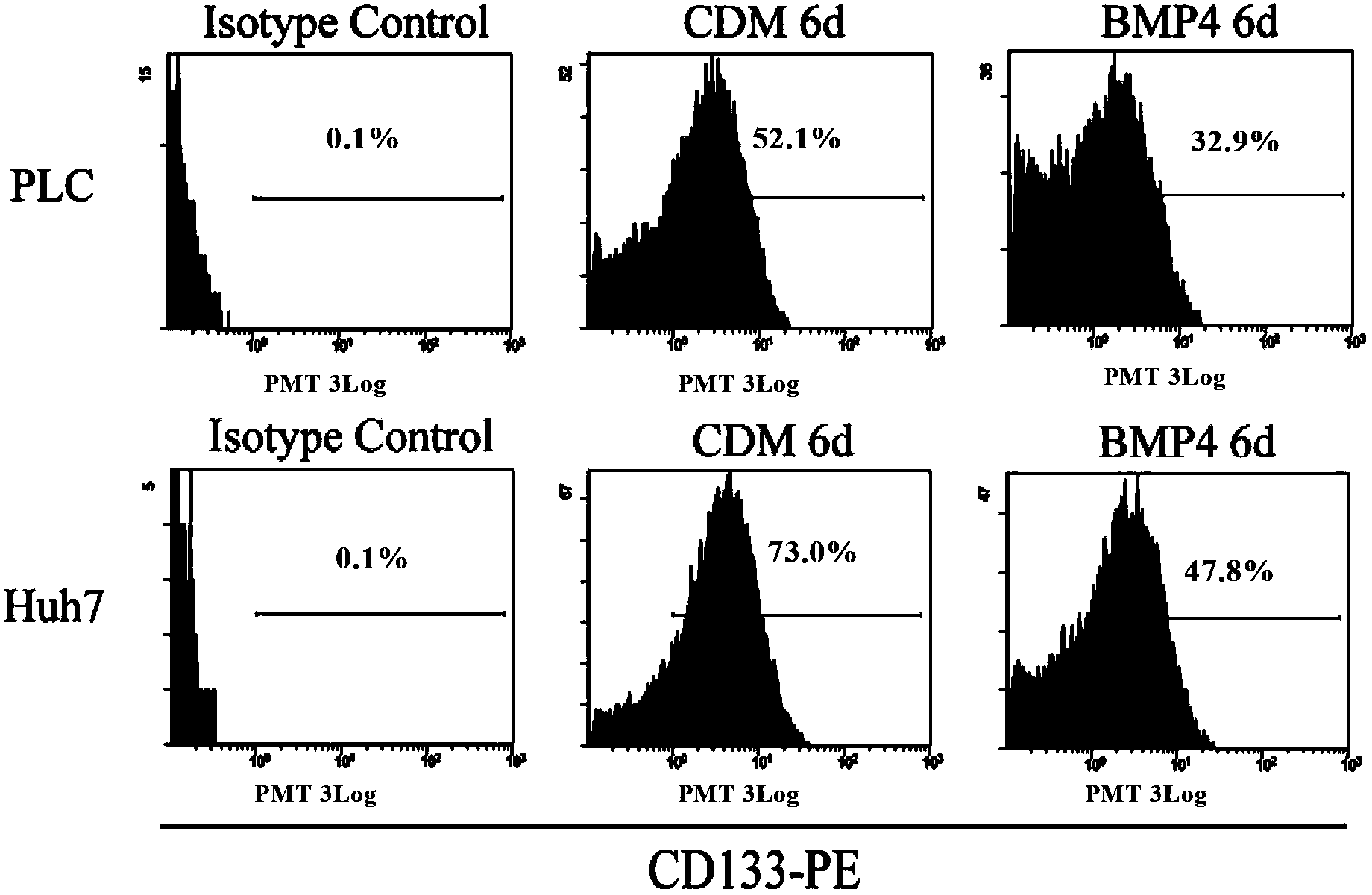
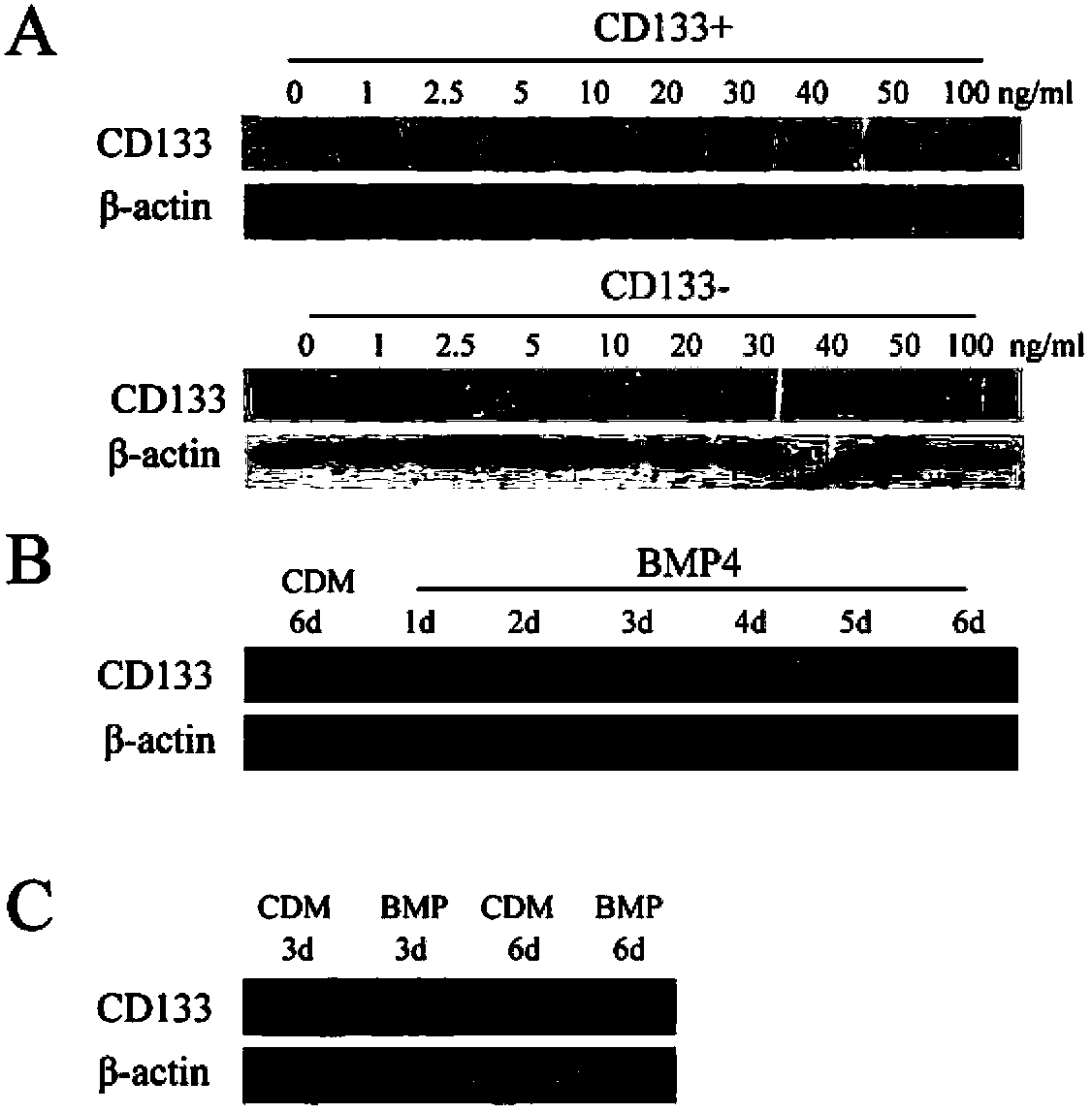
The present invention relates to an application of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in cancer inhibition. Specifically bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) has a liver cancer stem cell differentiation induction effect, wherein CD133 protein expression of liver cancer cell lines can be down-regulated and liver cancer cell line CD133+ liver cancer stem cell differentiation can be promoted with BMP4, and BMP4 can further be provided for inhibiting in vitro proliferation and self-renewal of liver cancer cell lines and inhibiting tumorigenicity of immune-deficient mice. The present invention further provides BMP4-induced liver cancer stem cell differentiation action mechanism.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
CARD-4 molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050287612A1Septic shock can be prevented or treatedReduce and inhibit symptomBiological material analysisApoptosis related proteinsCell signaling pathwaysDeficient mouse
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
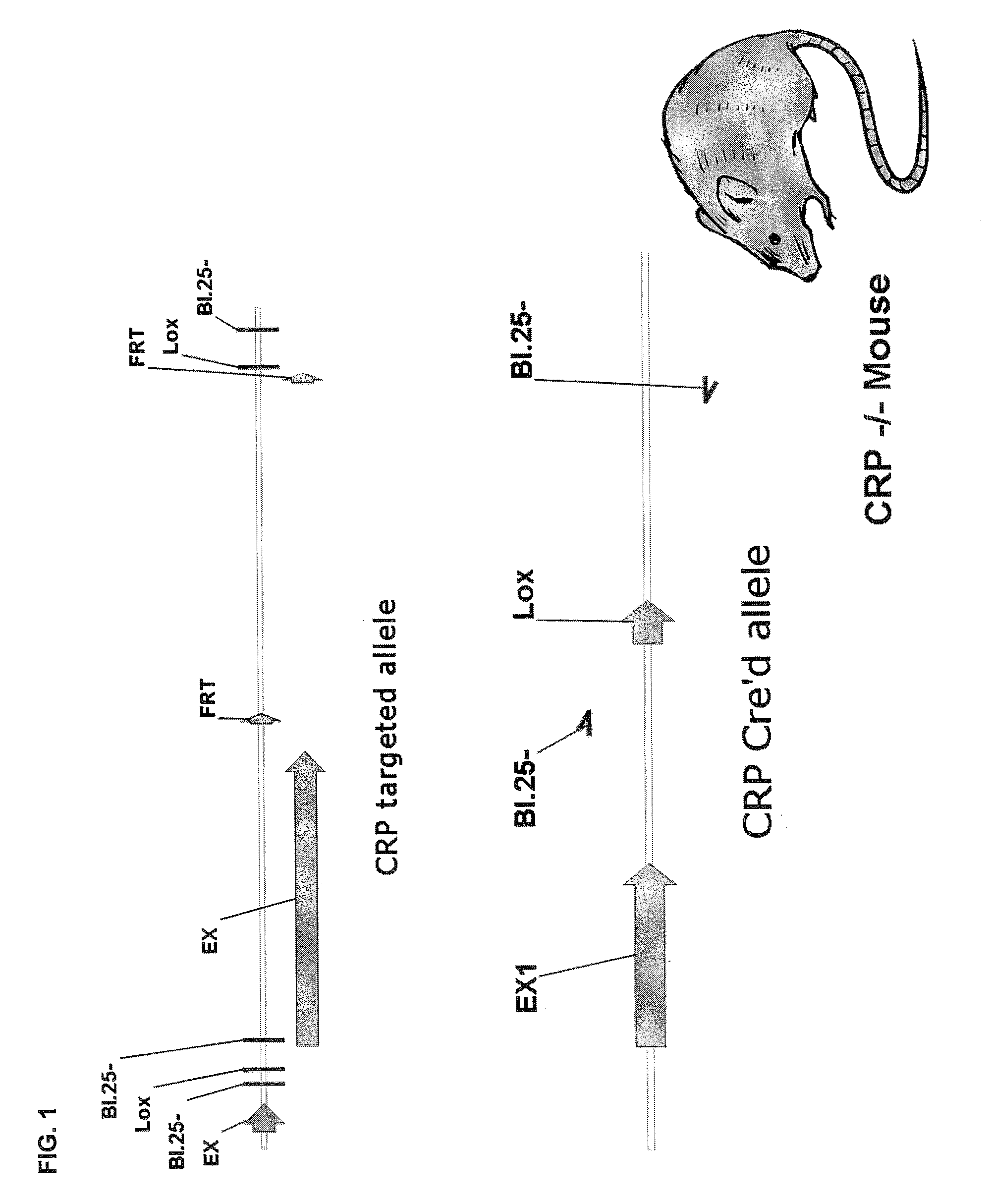
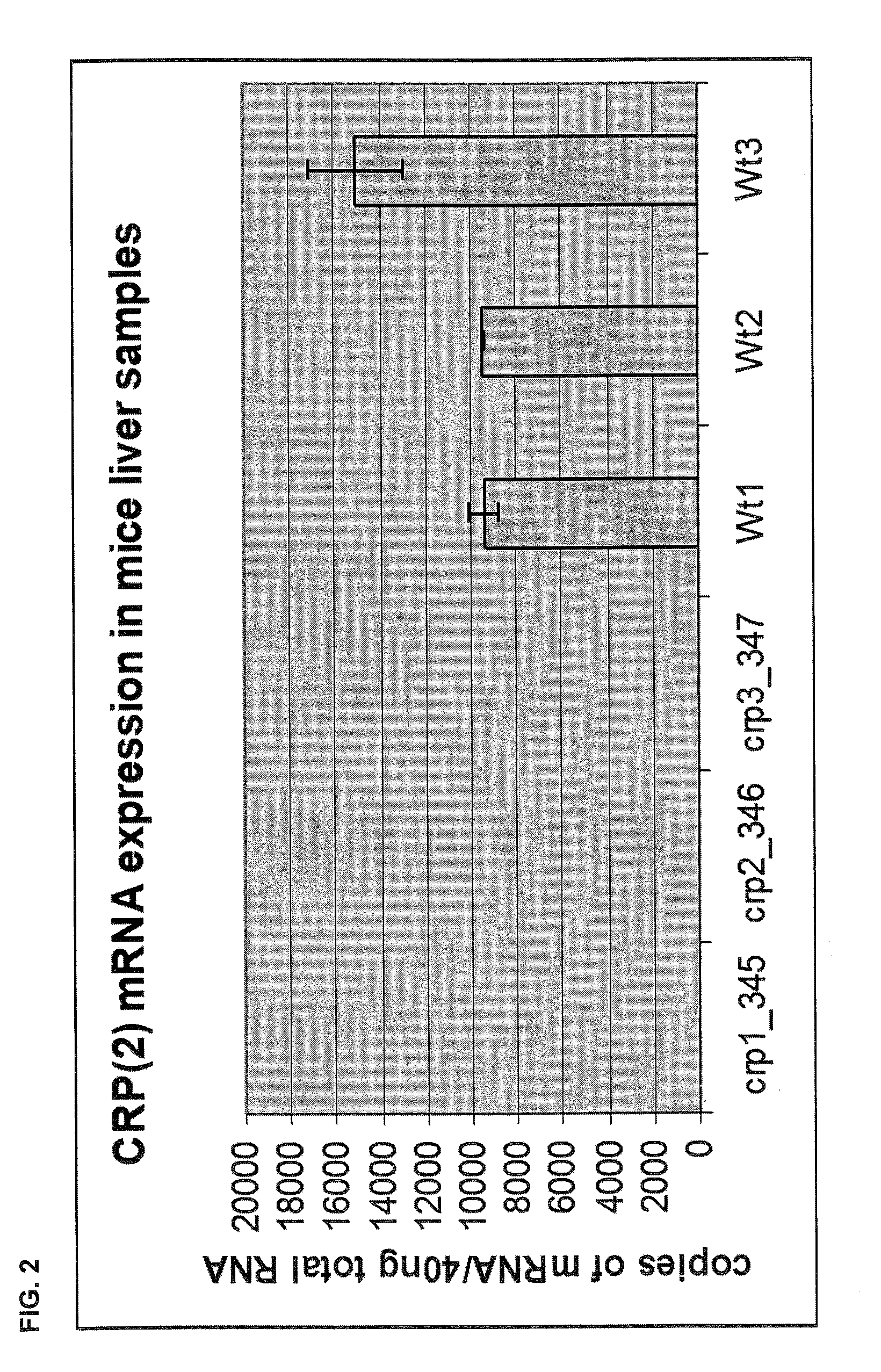
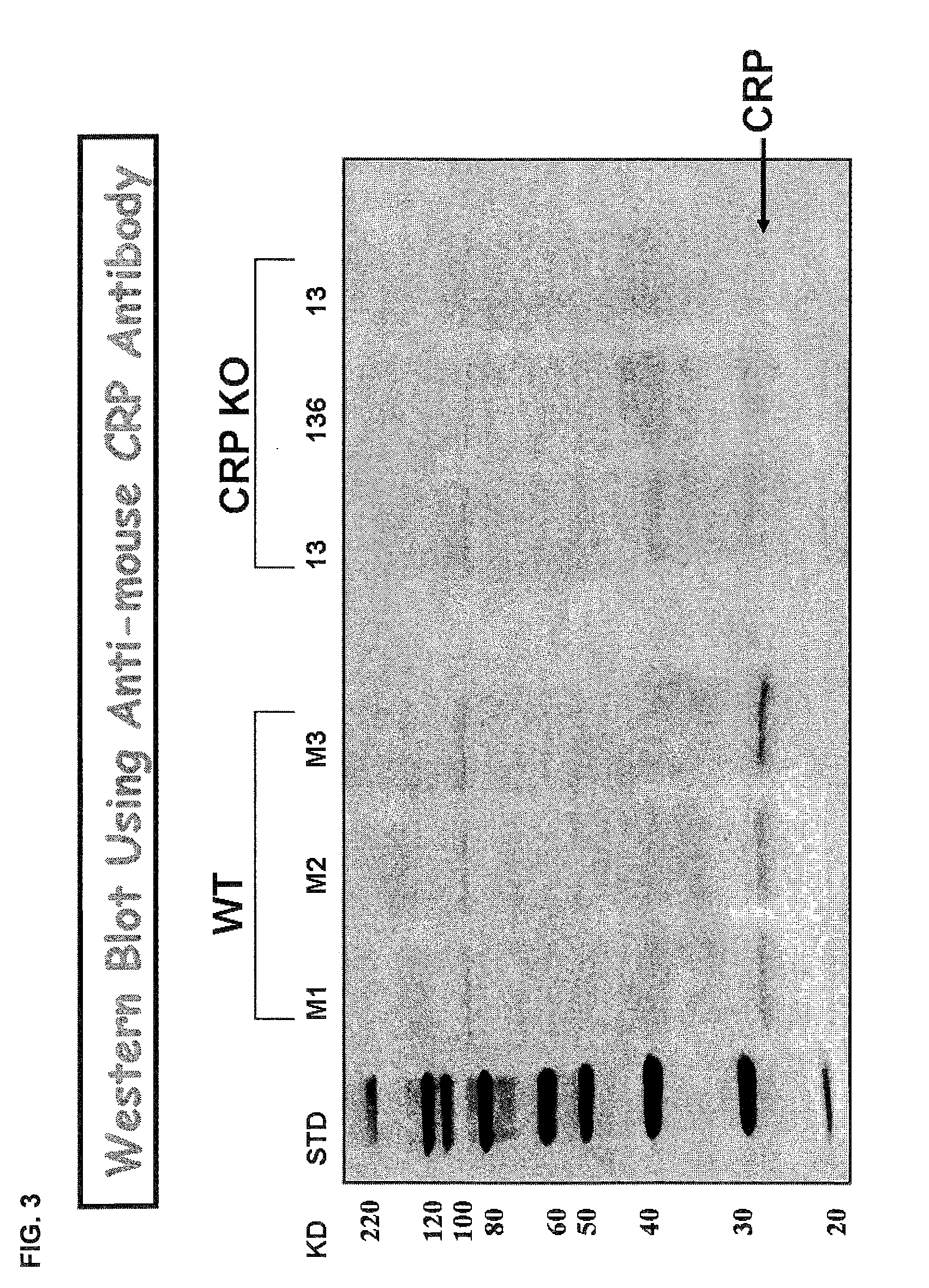
C-reactive protein (CRP) knockout mouse
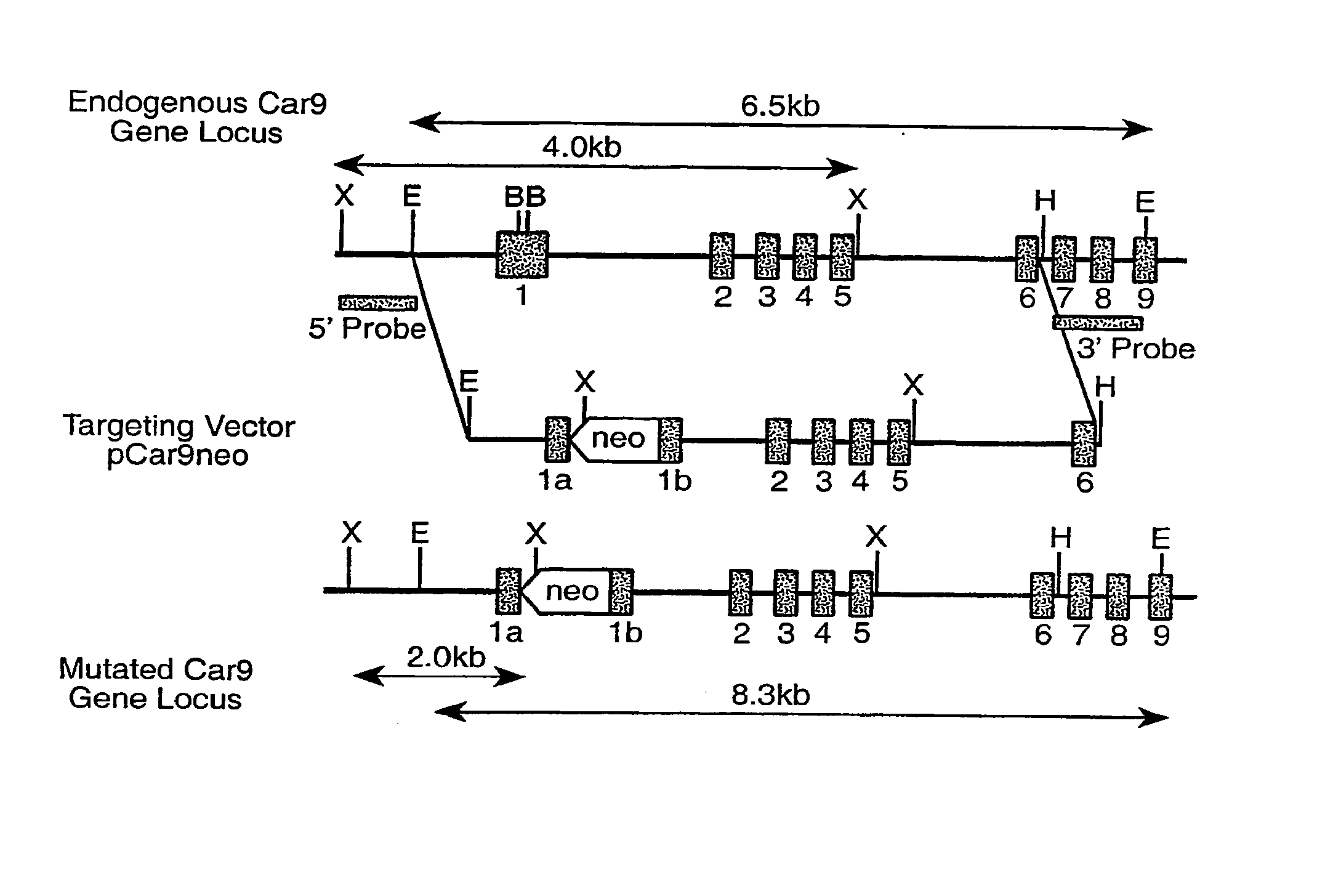
InactiveUS20100107263A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationKnockout animalDeficient mouse
The instant invention relates to a transgenic, non-human animal that carries a mutation in the gene encoding C-reactive protein (CRP). Preferably, the invention relates to an animal comprising a homozygous CRP-deficient mouse and techniques for producing such animals. The invention also relates to organs, tissues, cells, cell lines and sub-cellular fractions derived from such animals. Techniques for generating total or tissue-specific CRP knockout animals are also described. The invention further relates to the use of such knockout animals for the study of the role of CRP proteins in vivo or ex vivo, particularly in relation to its role in inflammatory pathway and in the etiology human diseases.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Method for in-vitro screening of PXR activation characteristics
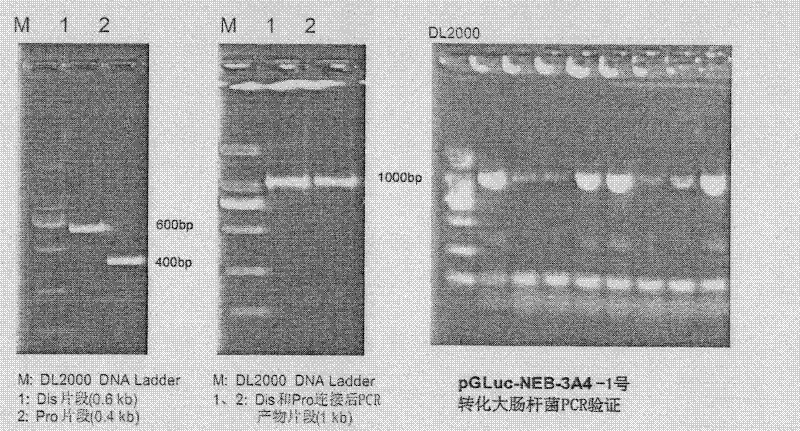
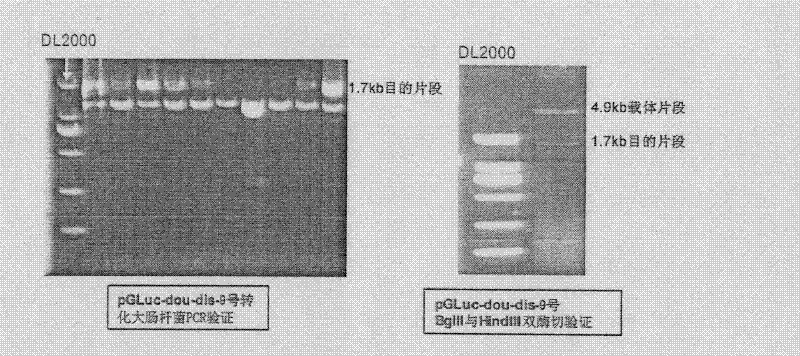
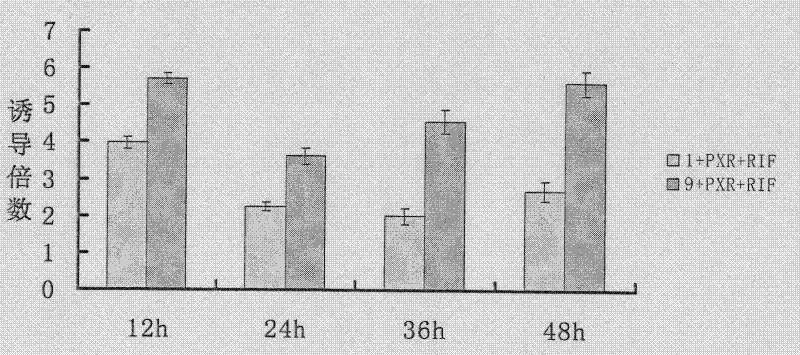
InactiveCN102533925AGuide developmentGuide its clinical applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionCYP3AHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a method for in-vitro screening inducers, particularly to a method for in-vitro screening of PXR (pregnane X receptor) activation characteristics, which comprises the following steps: constructing a reporter gene vector; culturing cells, and screening G418 working concentration; carrying out transient transfection of cells; screening stably transfected cell clones; inducing and identifying stably transfected cell strain with a tested drug (ligand drug); and screening the PXR activation characteristics. When the PXR is activated by the ligand drug, the PXR can regulate the expression CYP3A gene. PXR gene-deficient mice lose drug inductivity of CYP3A. Contrarily, hPXR (human pregnane X receptor) receptor in activation state expressed in liver of a transgenic mouse can lead to continuous high expression of CYP3A enzyme. The method of the invention establishes critical technology for high-throughput screening based on the passway and carries out screening of PXR activation characteristics from mass compounds in a compound library at the early stage of drug development, and can reduce the risk of adverse drug interactions after the new drug comes into the market, and greatly reduce development cost.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
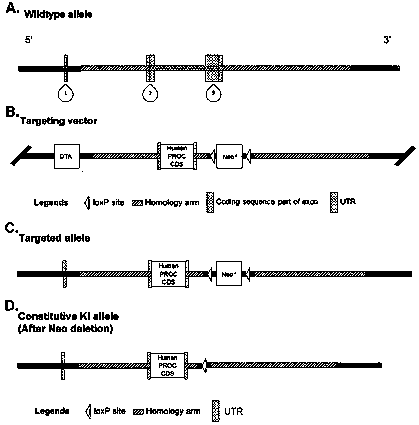
Genetically-modified non-human animal and application thereof
The invention relates to a genetically-modified non-human animal and application thereof, in particular to a transgenic mouse model and application thereof in the aspect of screening of a targeted medicine. According to the transgenic mouse model and application thereof in the aspect of screening of the targeted medicine, by targetedly knocking out and replacing a mouse protein C gene by means ofa human protein C gene expression cassette, a humanized protein C knock-in mouse is generated. The mouse has fertility, and can hybridize with another mouse disease model (such as a mouse in the deficiency of a blood coagulation factor VIII or a blood coagulation factor IX) to produce a humanized protein C mouse disease model (such as a humanized protein C factor VIII-deficient mouse model or a humanized protein C factor IX-deficient mouse model). The mouse model can be used for studying functions in vivo of human protein C and human activated protein C (APC). The mouse model is the first mouse model used for testing a therapeutic candidate medicine, which targets the human protein C or the APC, in vivo, and has very high economic value and scientific research value.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAAS BLOOD PRODUCTS CO LTD
Method for constructing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected mouse model
ActiveCN104212835ADoes not induce an immune responseSimplify the build processIn-vivo testing preparationsVector-based foreign material introductionSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseImmunodeficiency
Owner:张欣欣 +6
Detection model for mouse intestinal mucosa epithelial barrier function and intestinal mucosa immune tolerance cell
InactiveCN107385008AHas immunomodulatory functionUnraveling the intrinsic mechanism of induction of immune tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIntestinal structureIntraperitoneal route
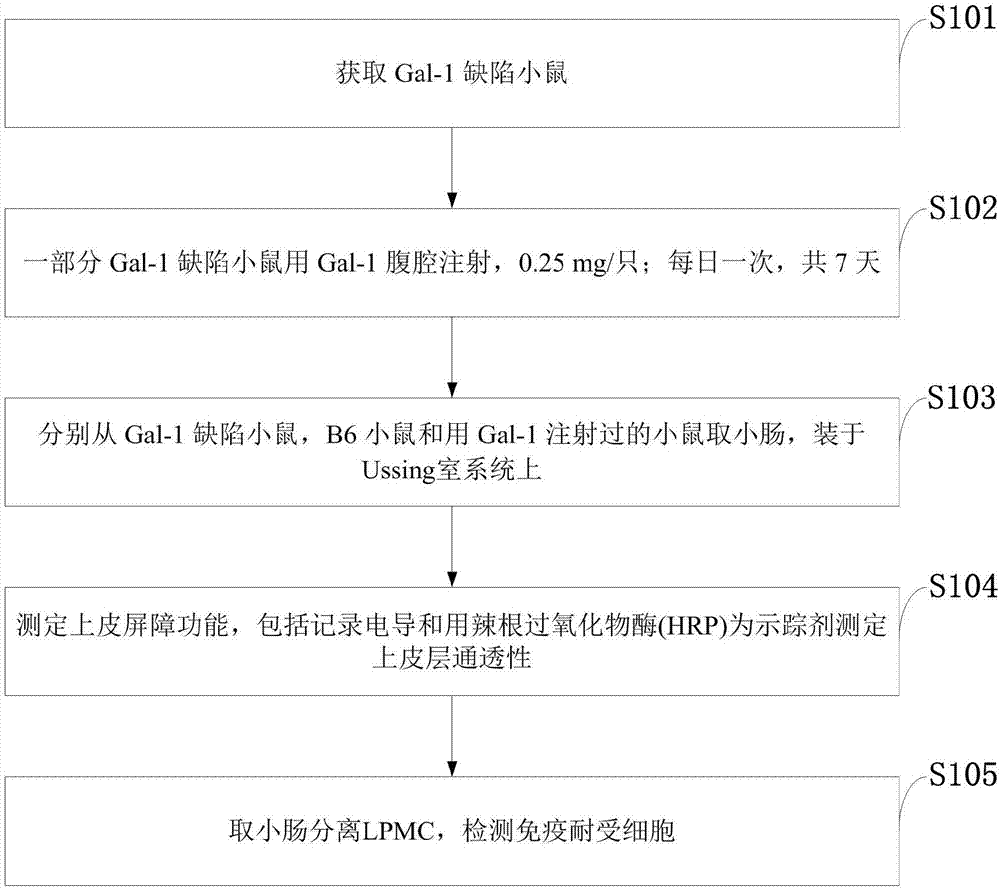
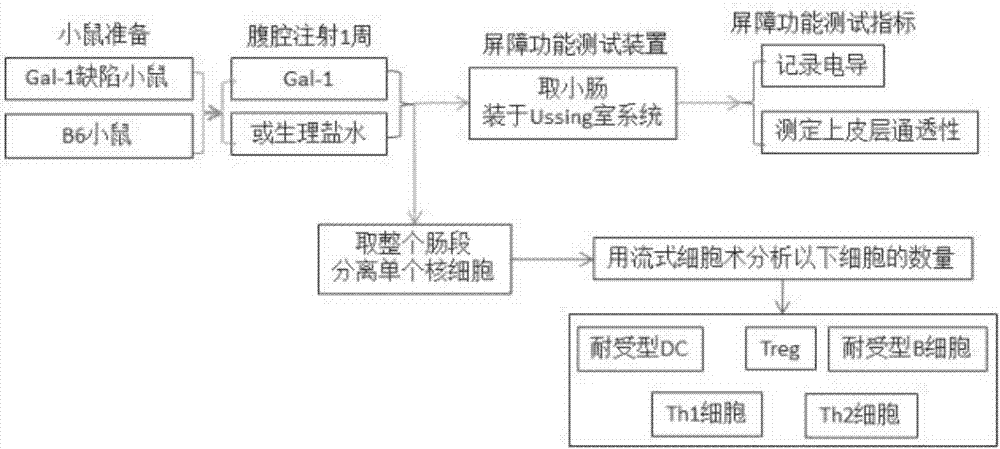
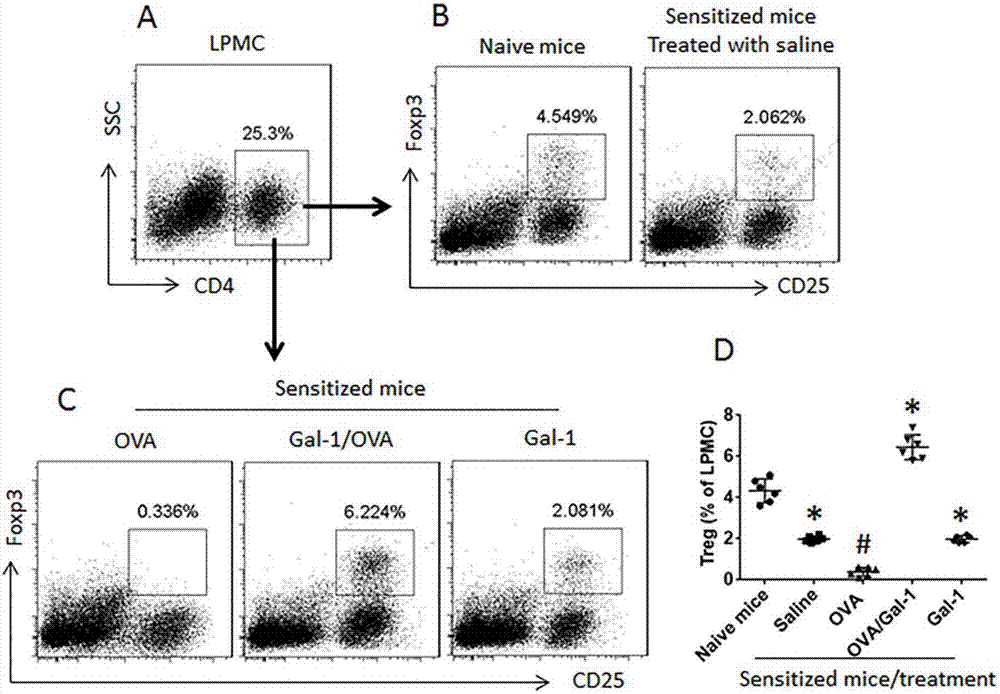
The invention belongs to the technical field of body immunity, and discloses a detection model for a mouse intestinal mucosa epithelial barrier function and an intestinal mucosa immune tolerance cell. The model is characterized in that one part of Gal-1 deficient mice is subjected to Gal-1 intraperitoneal injection, and each mouse is injected with 0.25mg each time per day, and injection is carried out for 7 days; small intestines are respectively taken from the Gal-1 deficient mice, B6 mice and mice injected with Gal-1. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the Gal-1 deficient mice, wherein the Gal-1 deficient mice are subjected to the Gal-1 intraperitoneal injection; respectively taking the intestines from the Gal-1 deficient mice, the B6 mice and the mice injected with Gal-1, and installing in a Ussing chamber system; measuring an epithelial barrier function; taking the small intestines to separate LPMC (Lamina Propria Mononuclear Cells), and detecting immune tolerance cells. The Gal-1 has an immunoregulation function, the intestinal mucosa is an important organ for forming oral tolerance, and the IEC (Intestinal Epithelial cCells) has an immune tolerance function.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
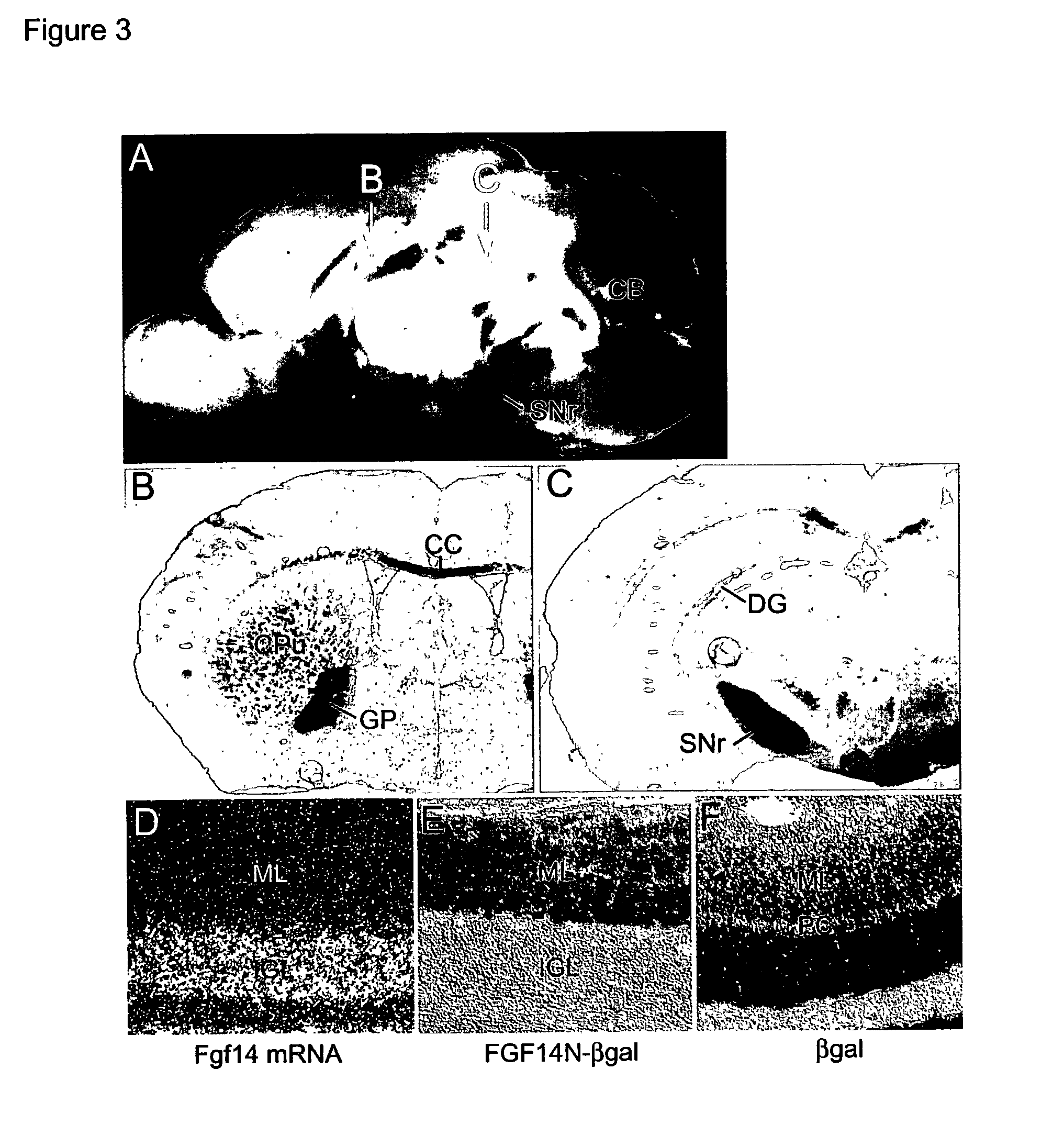
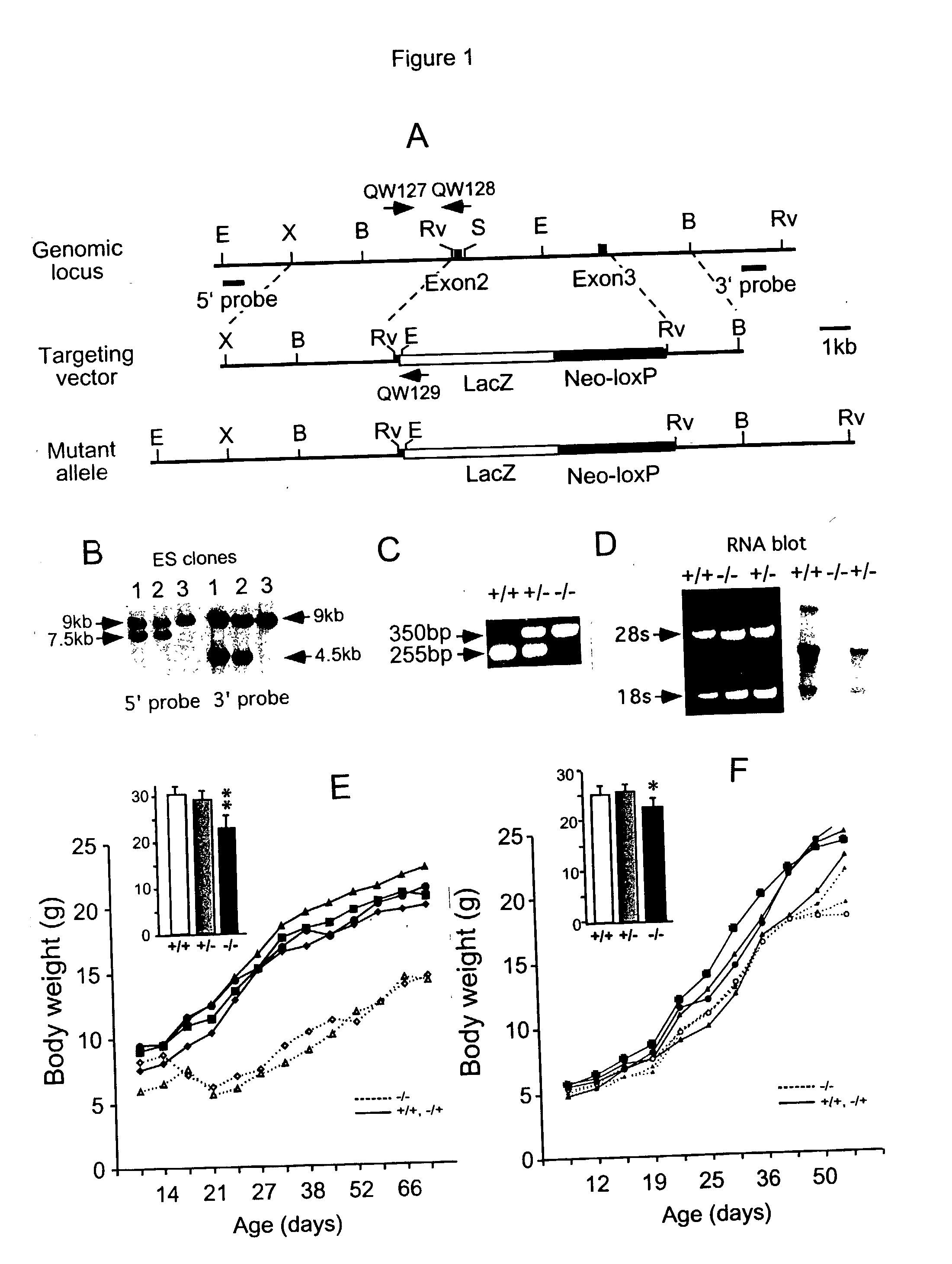
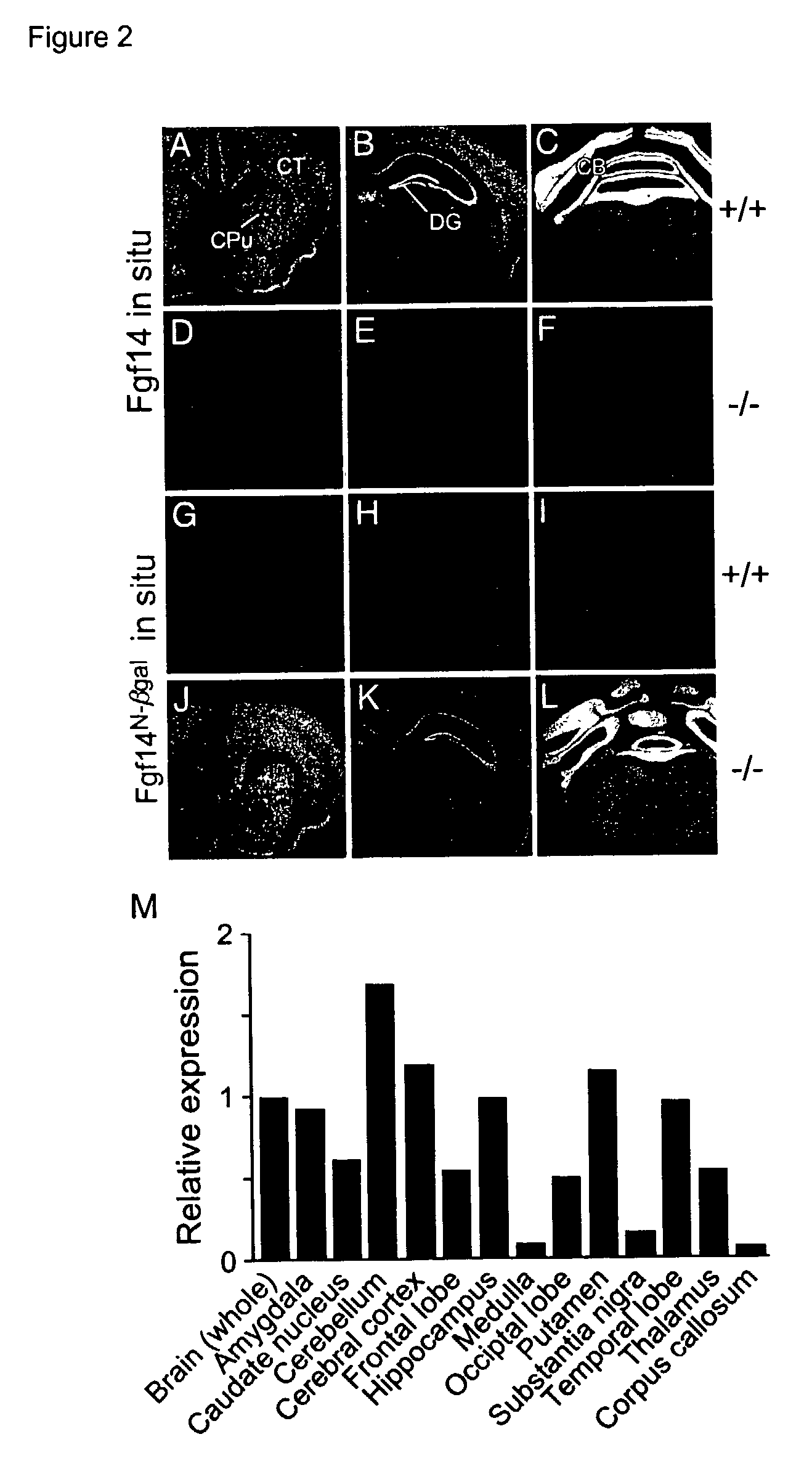
Animal model with disrupted Fgf14 gene
InactiveUS20030037354A1Effective trafficMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorExonNeuropharmacology
The disclosure describes a unique animal model which is useful for studying the role of FGF14 in the central nervous system (CNS) and testing of potential drugs for treatment of CNS diseases. To provide this animal model, the Fgf14 gene is disrupted in mice by replacing the second and third exons with beta-galactosidase. Neuropharmacological studies are disclosed which show that the Fgf14 deficient mice have disrupted striatal-nigra and striatal-pallidal pathways resulting in increased excitatory input to the cortex. The paroxysmal hyperkinetic disorder in Fgf14 deficient mice phenocopies a form of dystonia, a disease often associated with dysfunction of the putamen.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX's coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7833728B2Good curative effectBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com