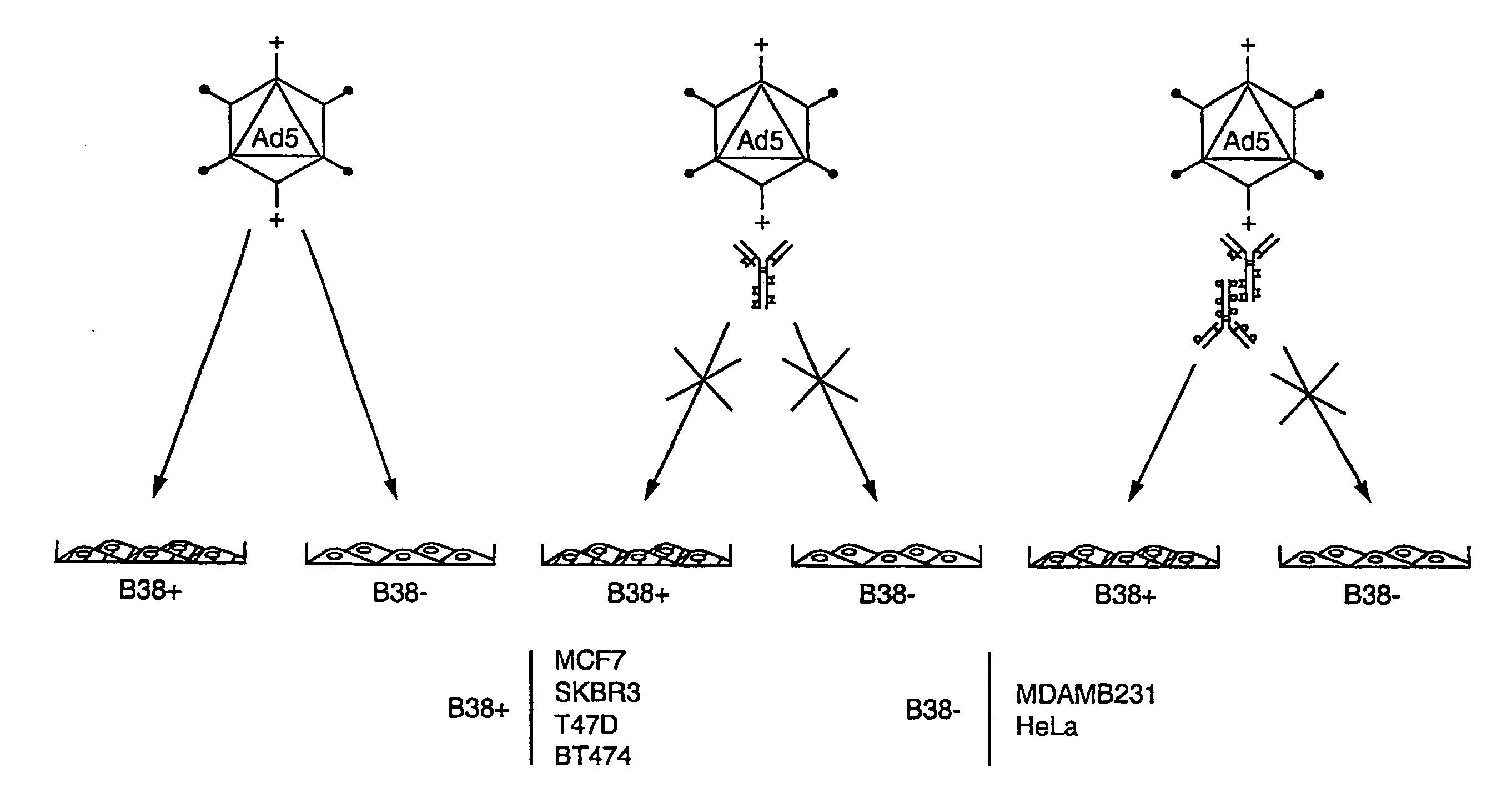
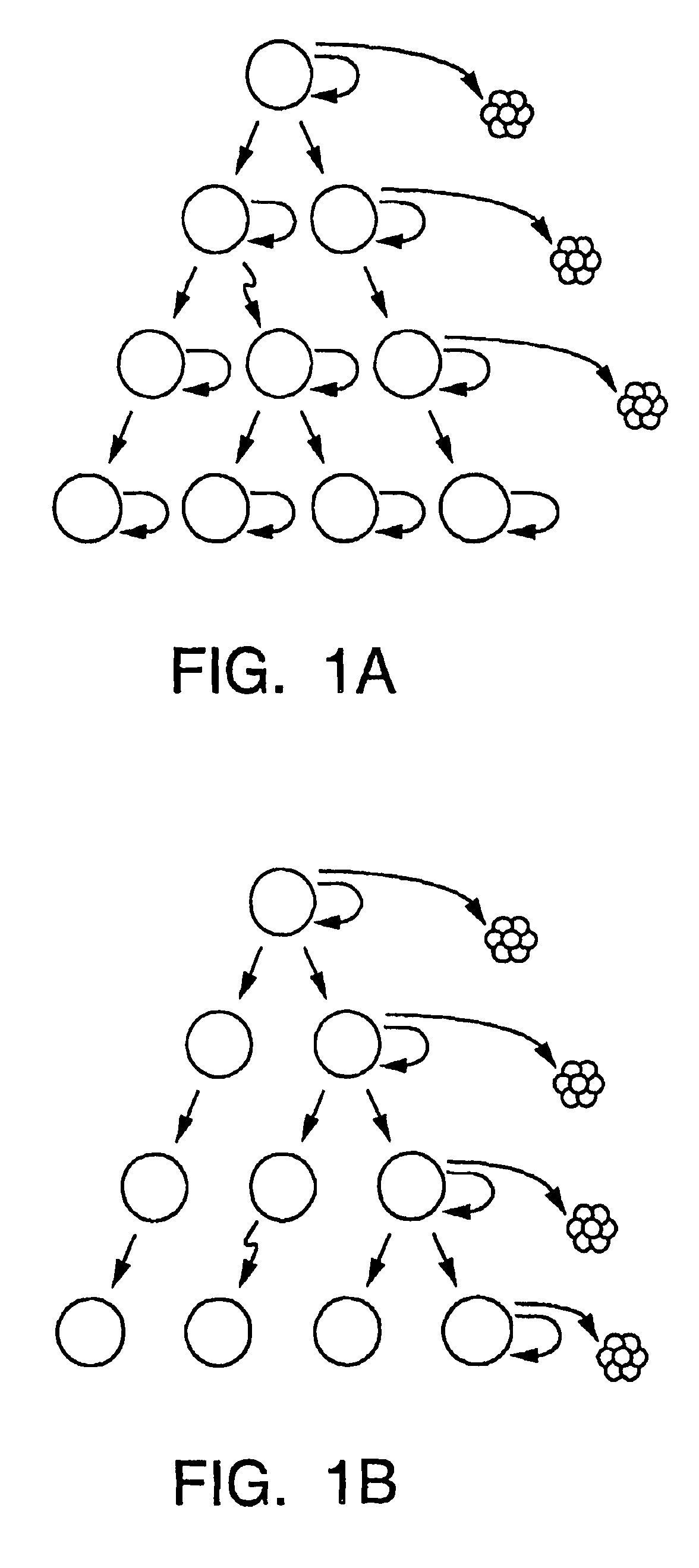
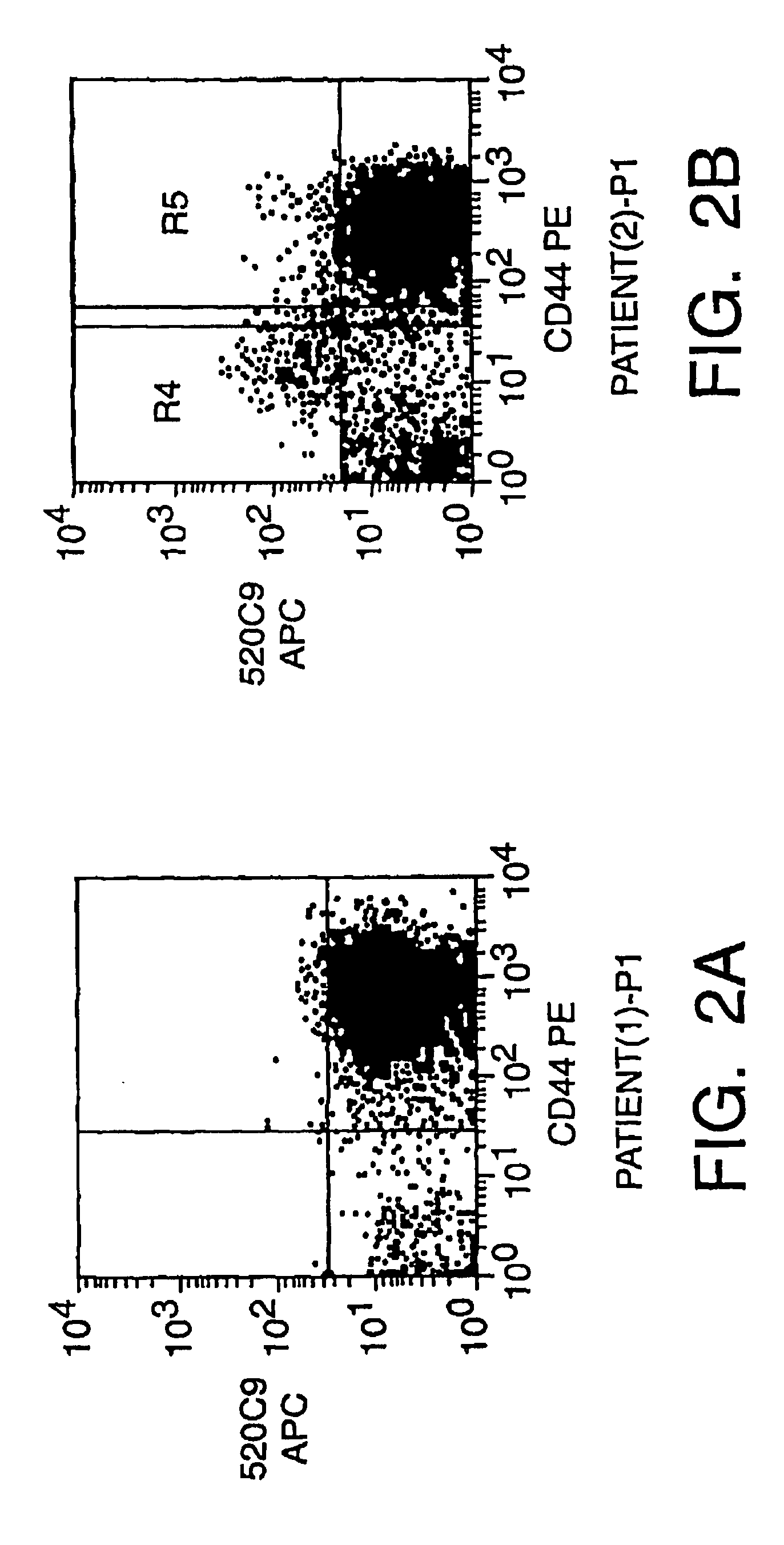
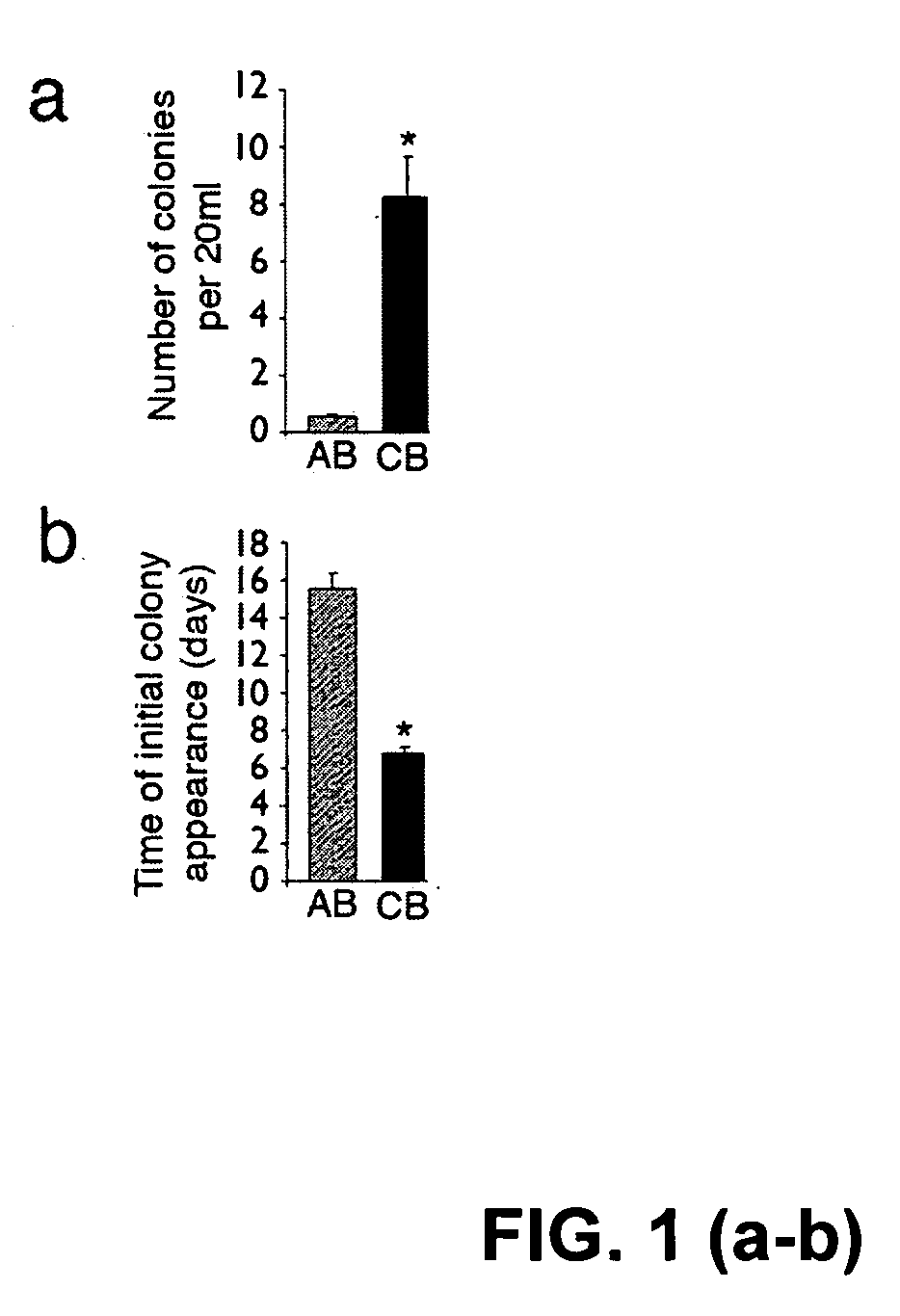
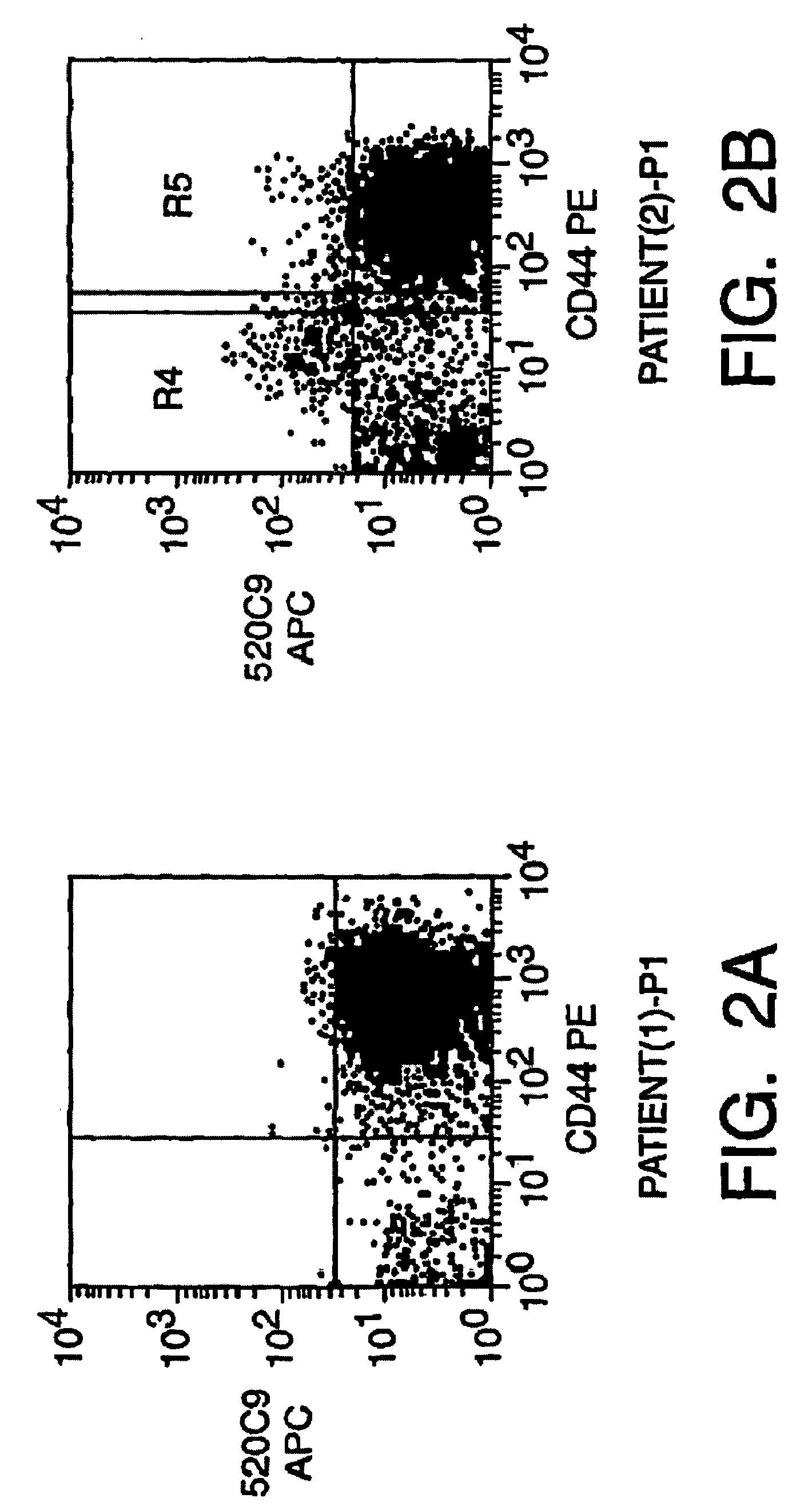
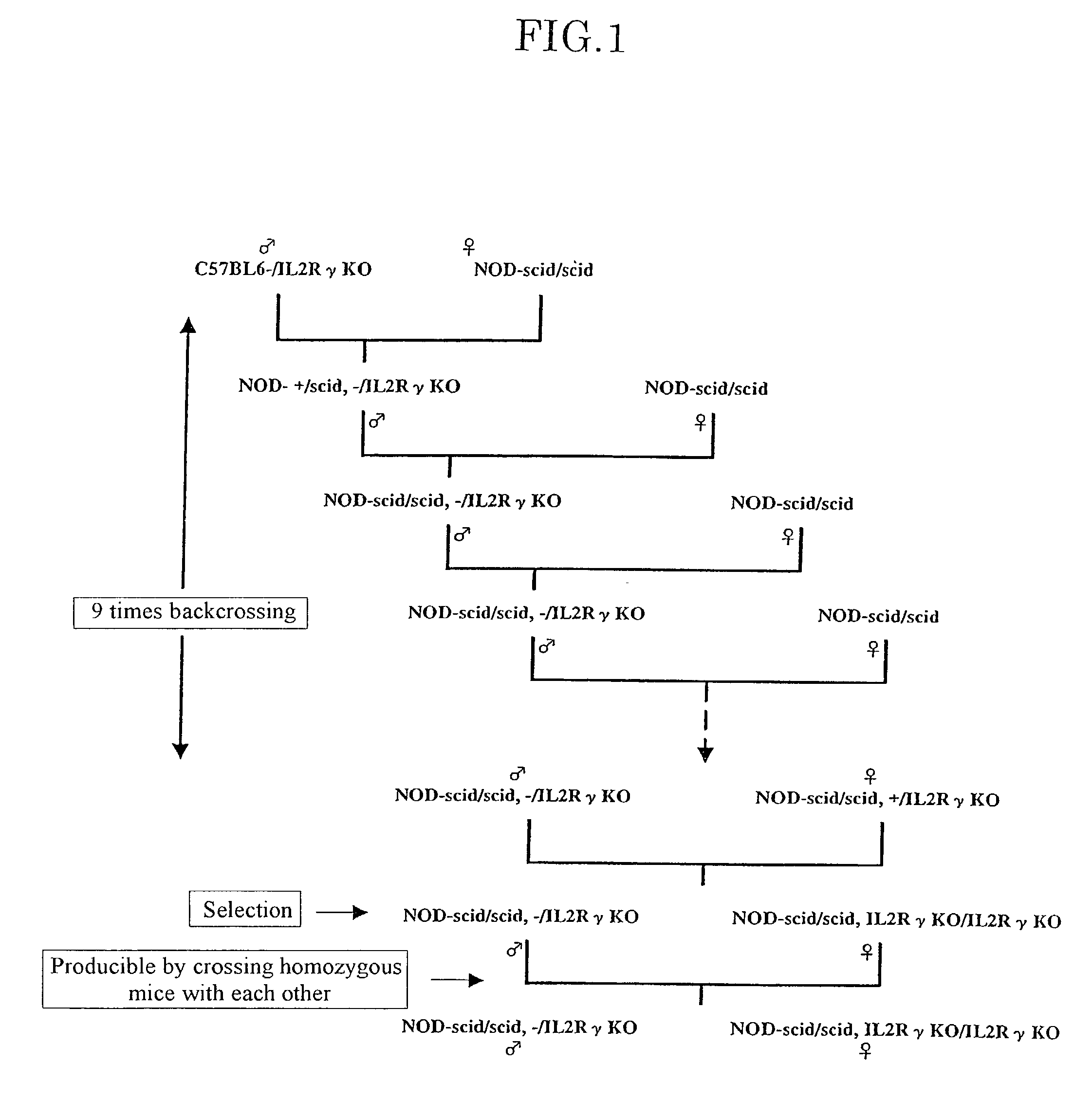
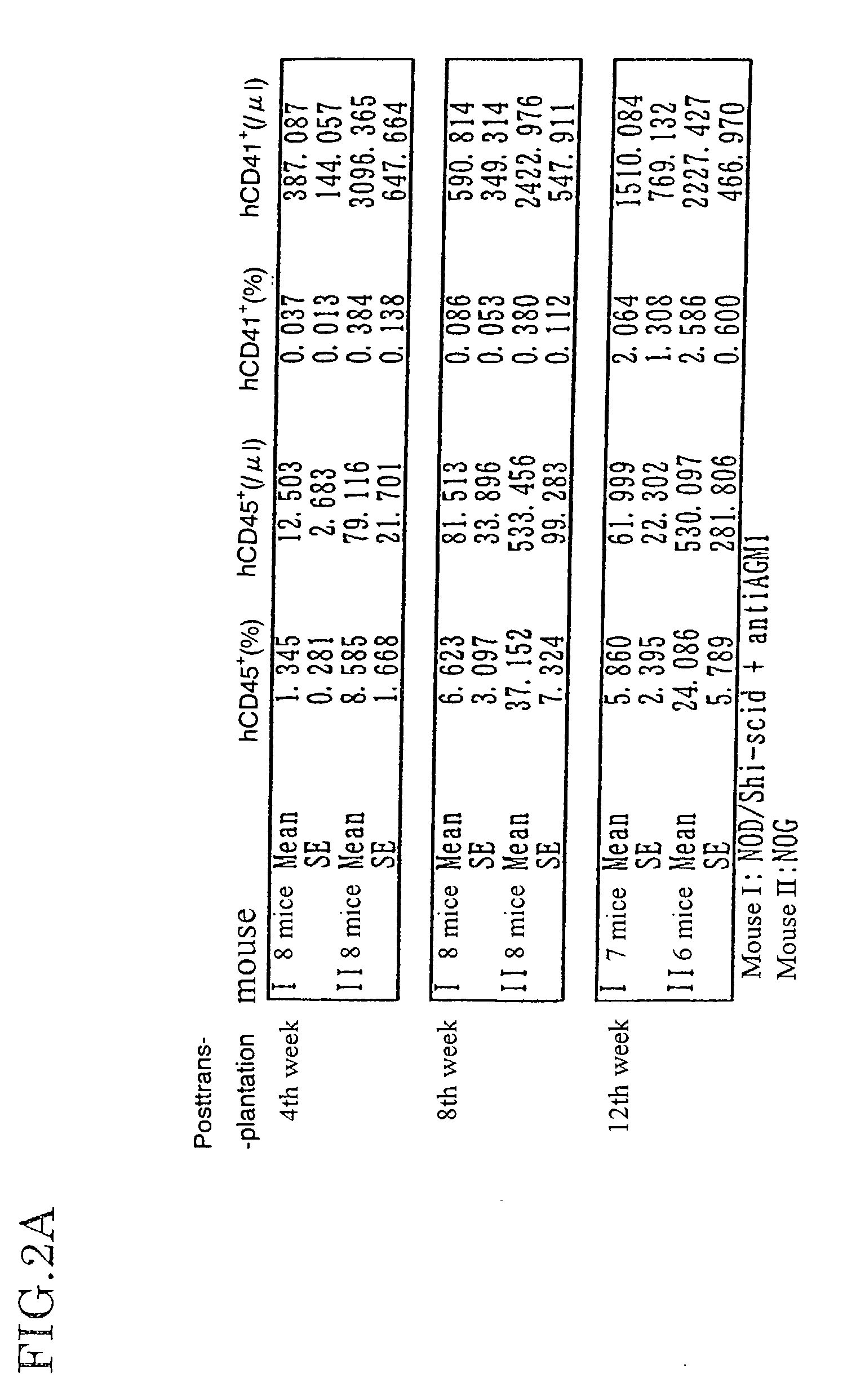
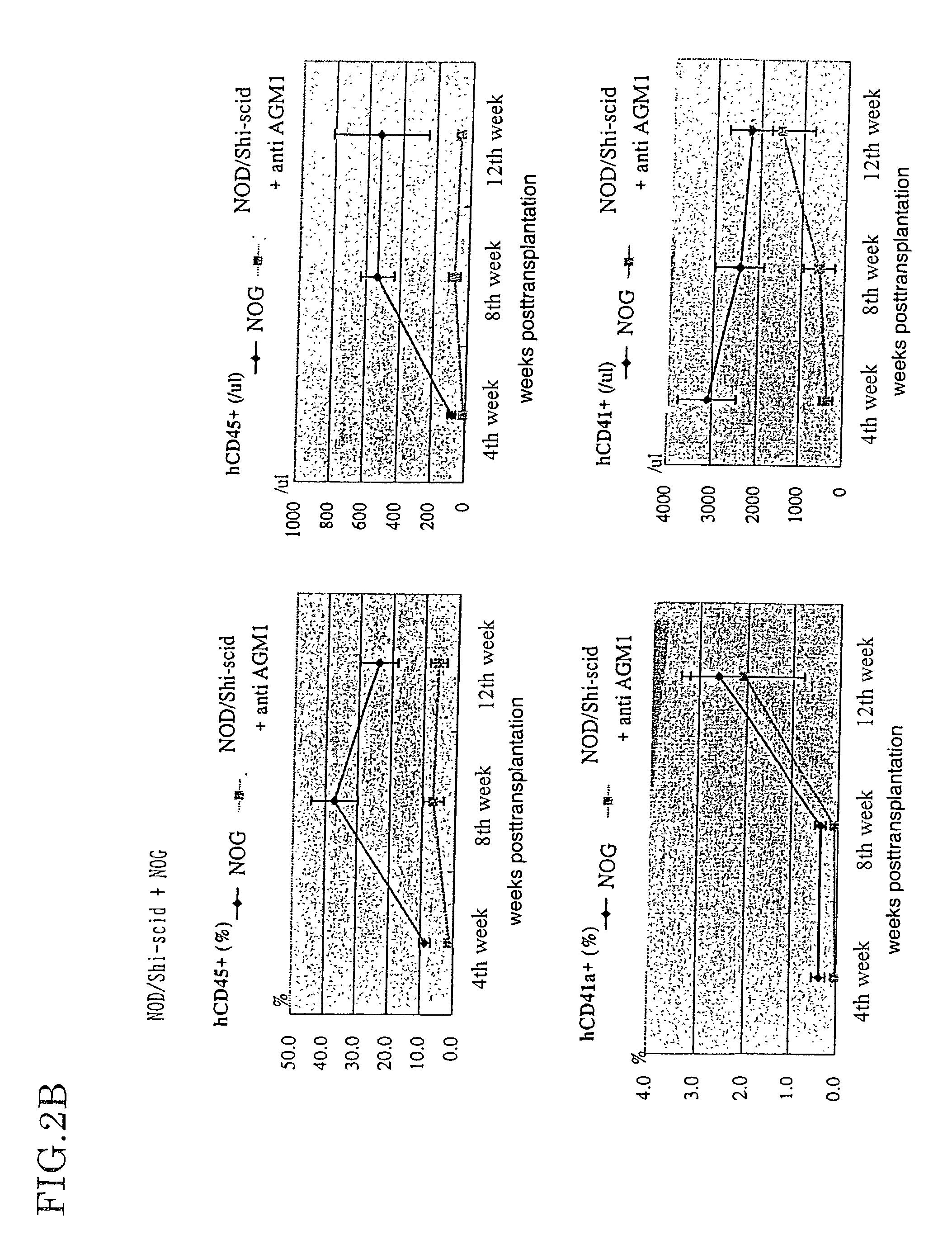
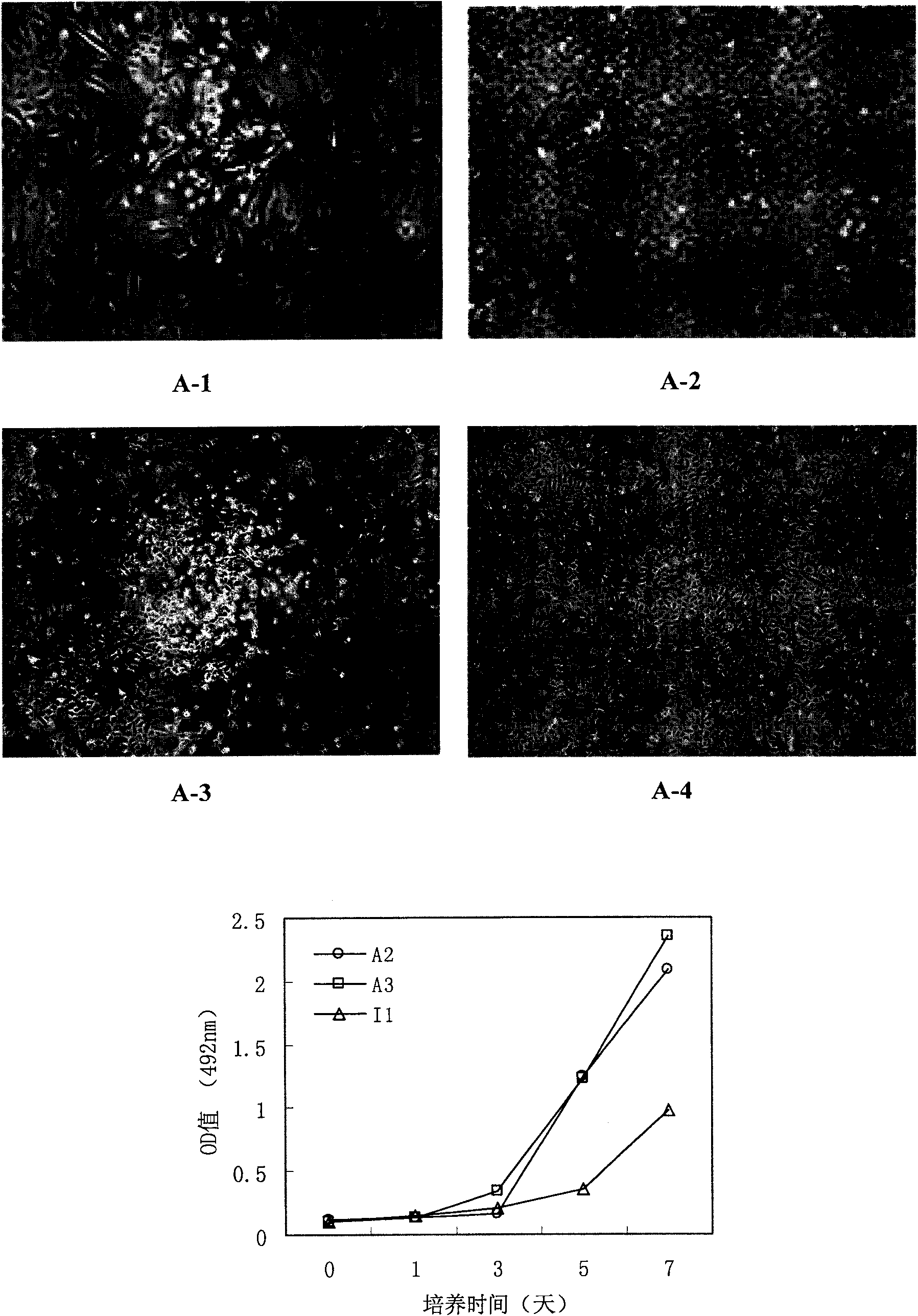
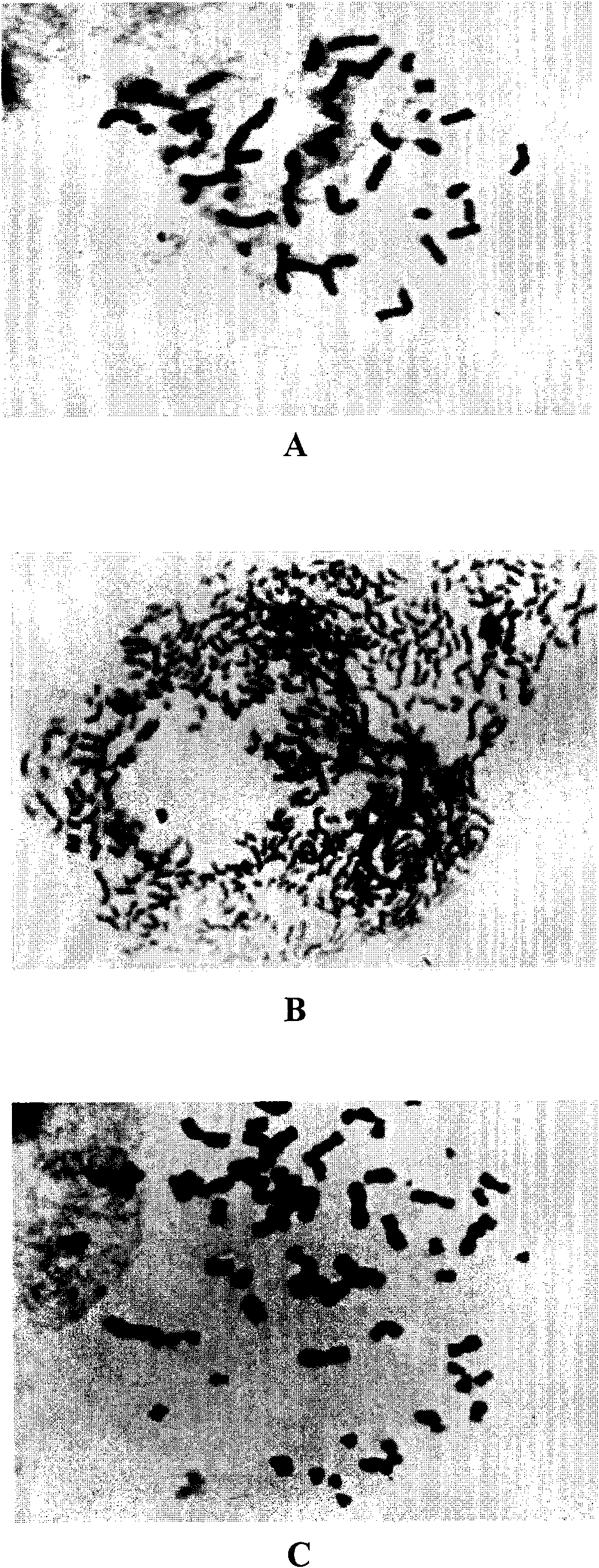
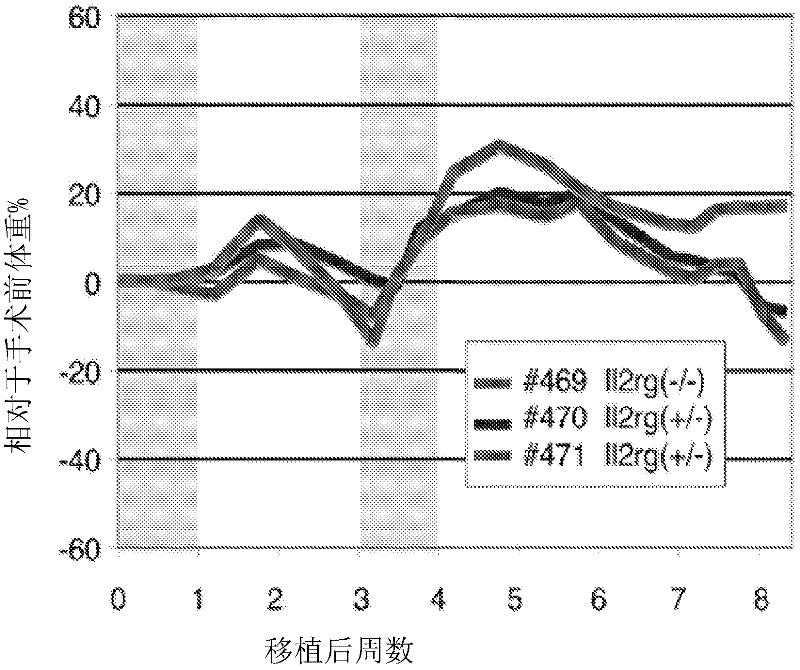
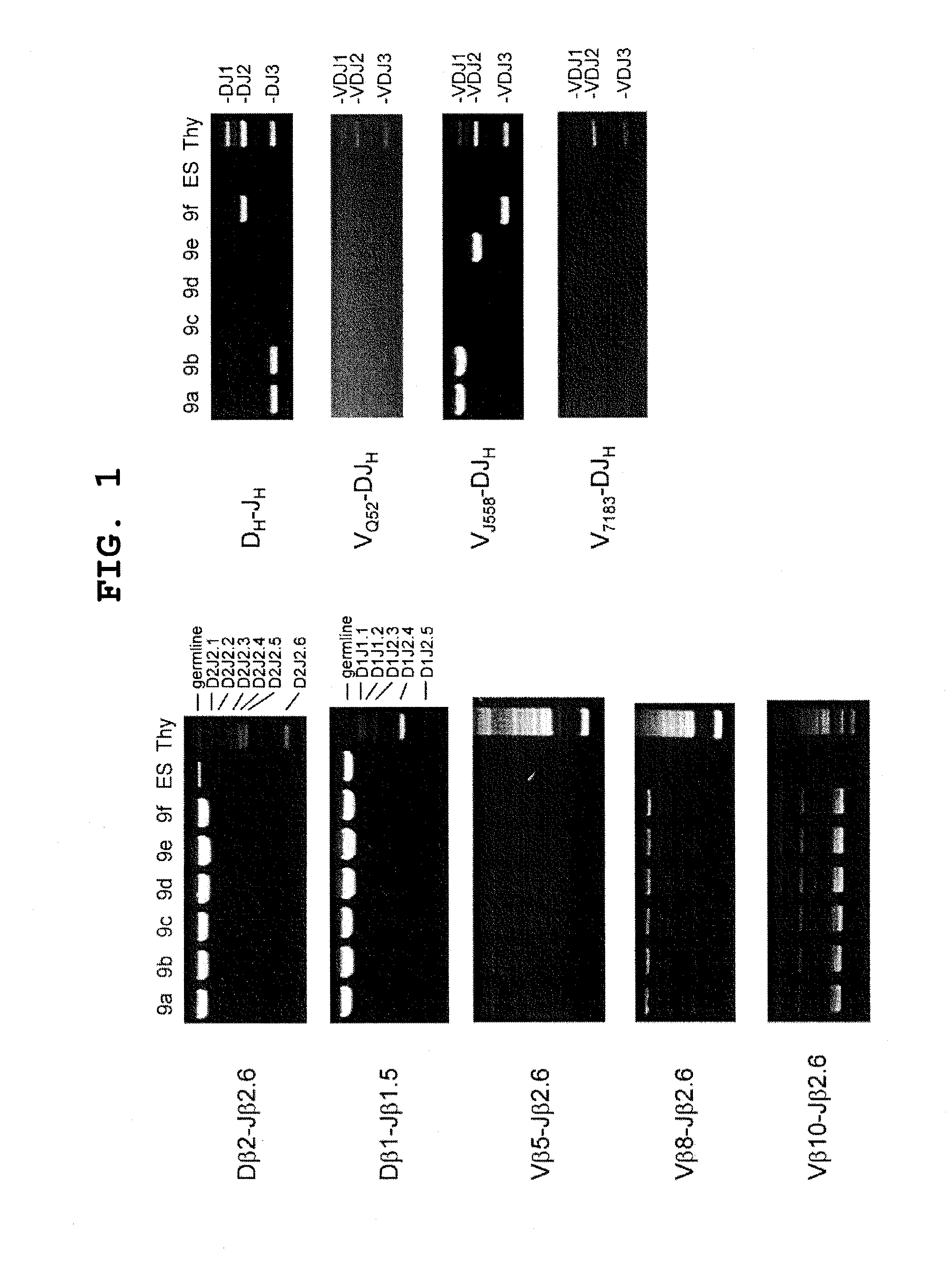
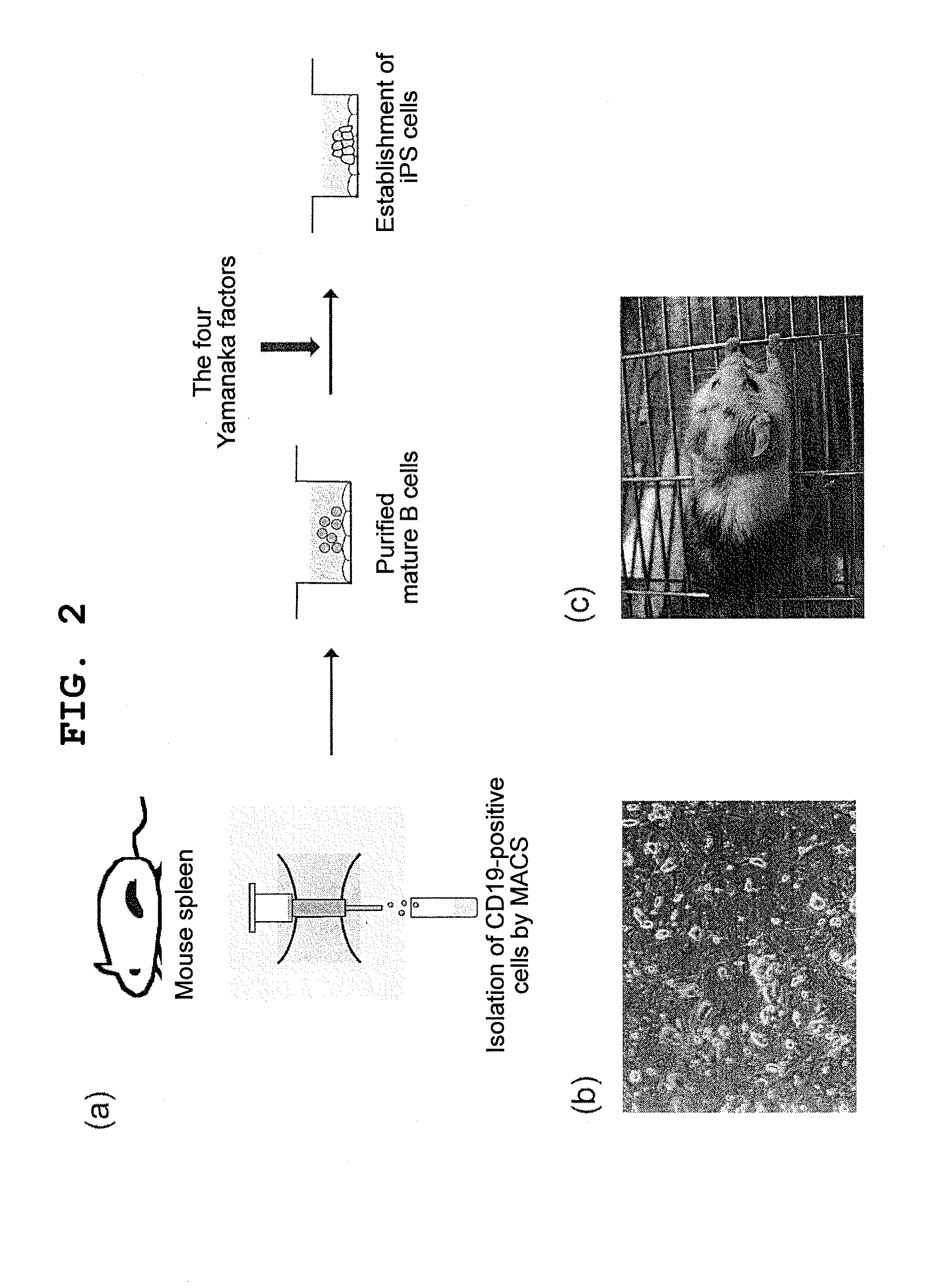
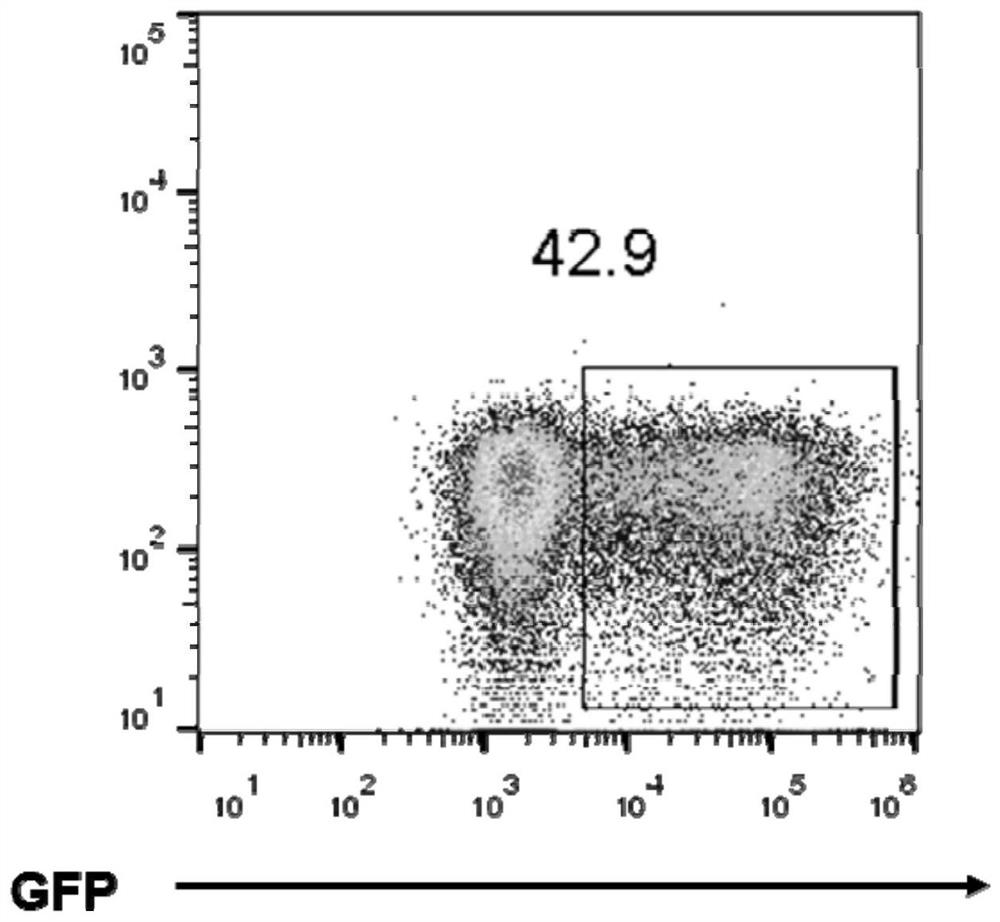
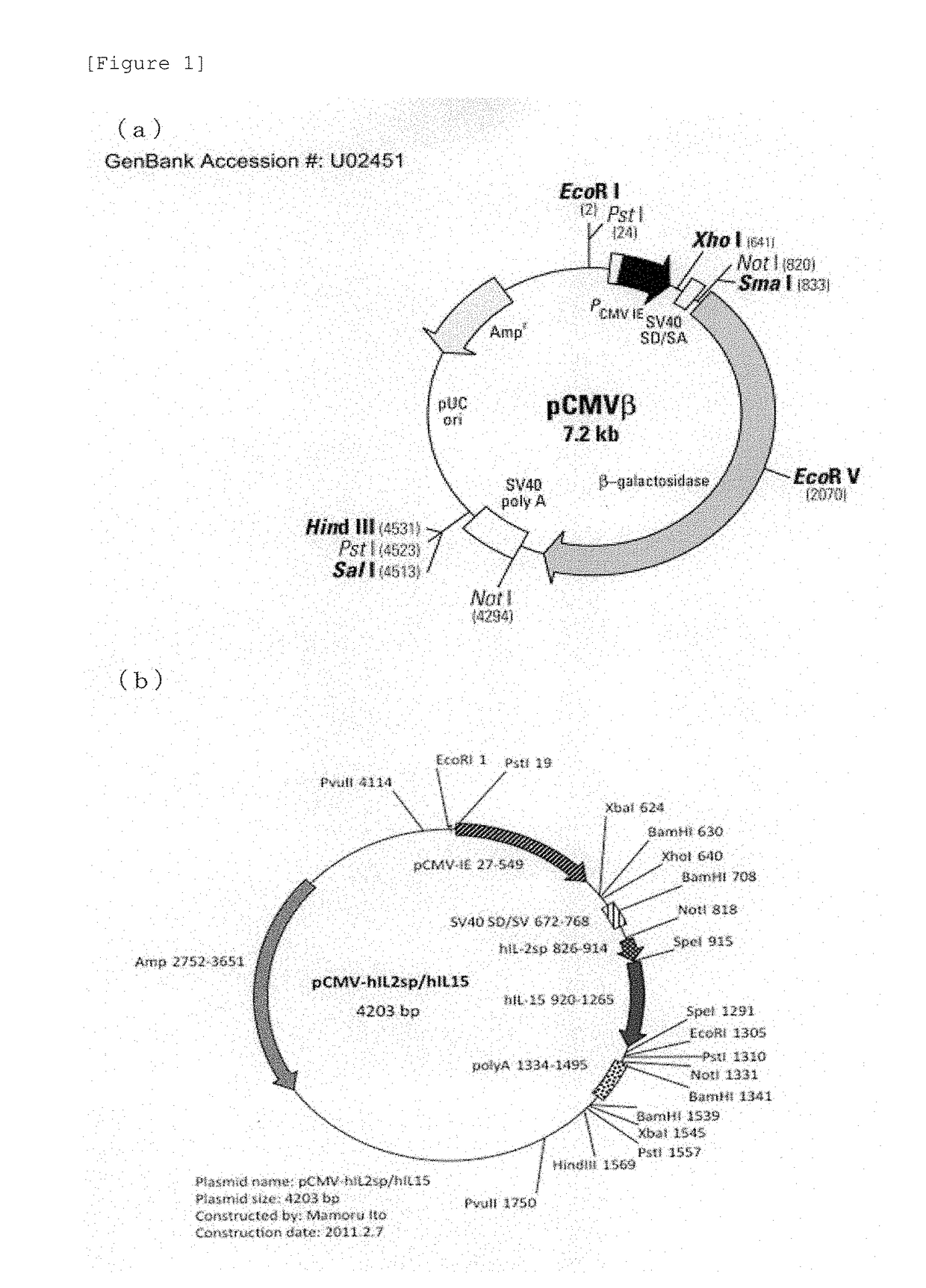
Patents
Literature
108 results about "Immunodeficient Mouse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any mouse strain with a faulty immune system such that its ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or ablated. Immunodeficient mice may be derived by inbreeding or genetic engineering. Immunodeficiency may also be induced by some chemicals, heavy metals, alkylating agents, radiation, and thymectomy.
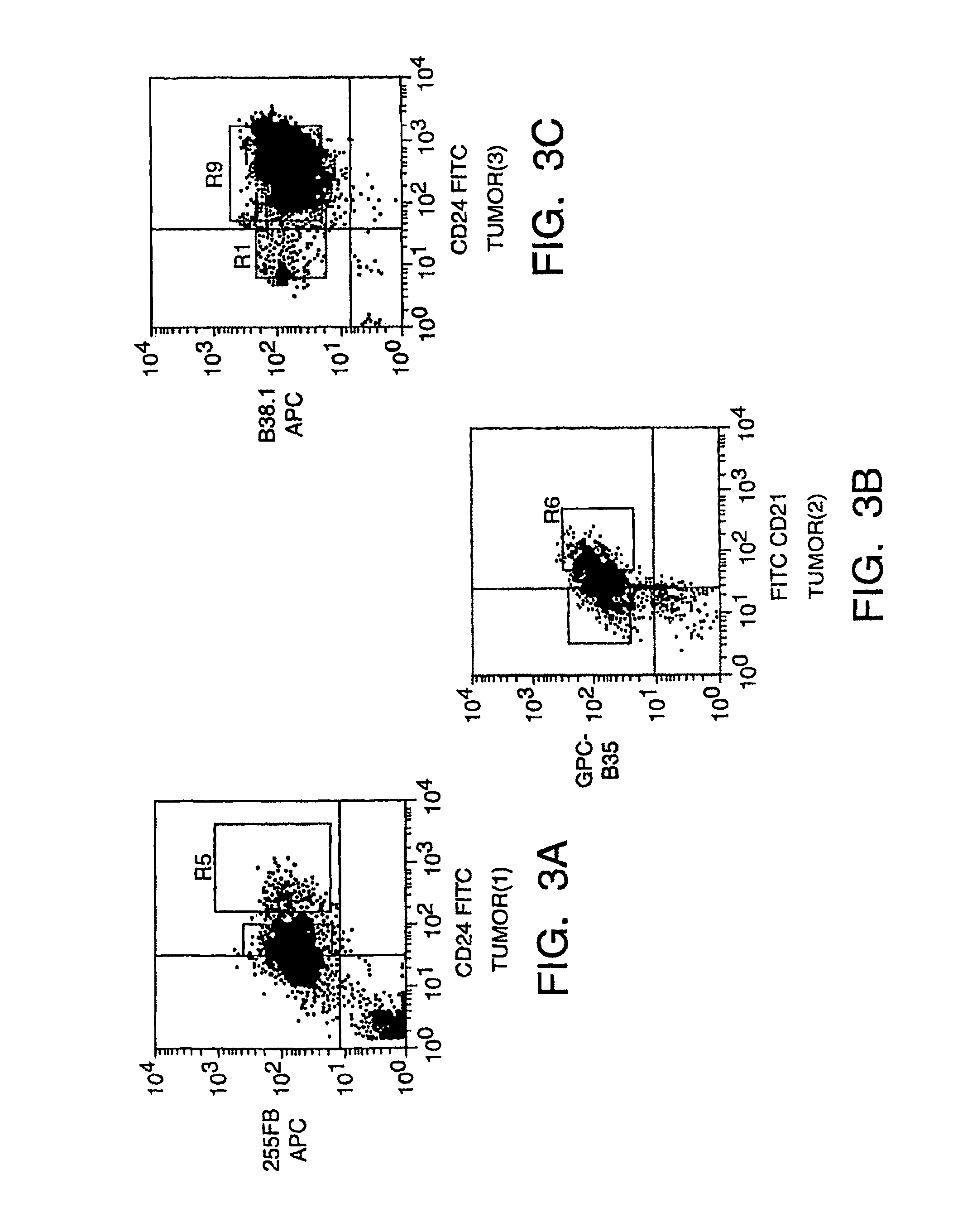
Isolation And Use Of Solid Tumor Stem Cells
InactiveUS20080178305A1Reduce spreadIncreased proliferationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthMammary gland structure
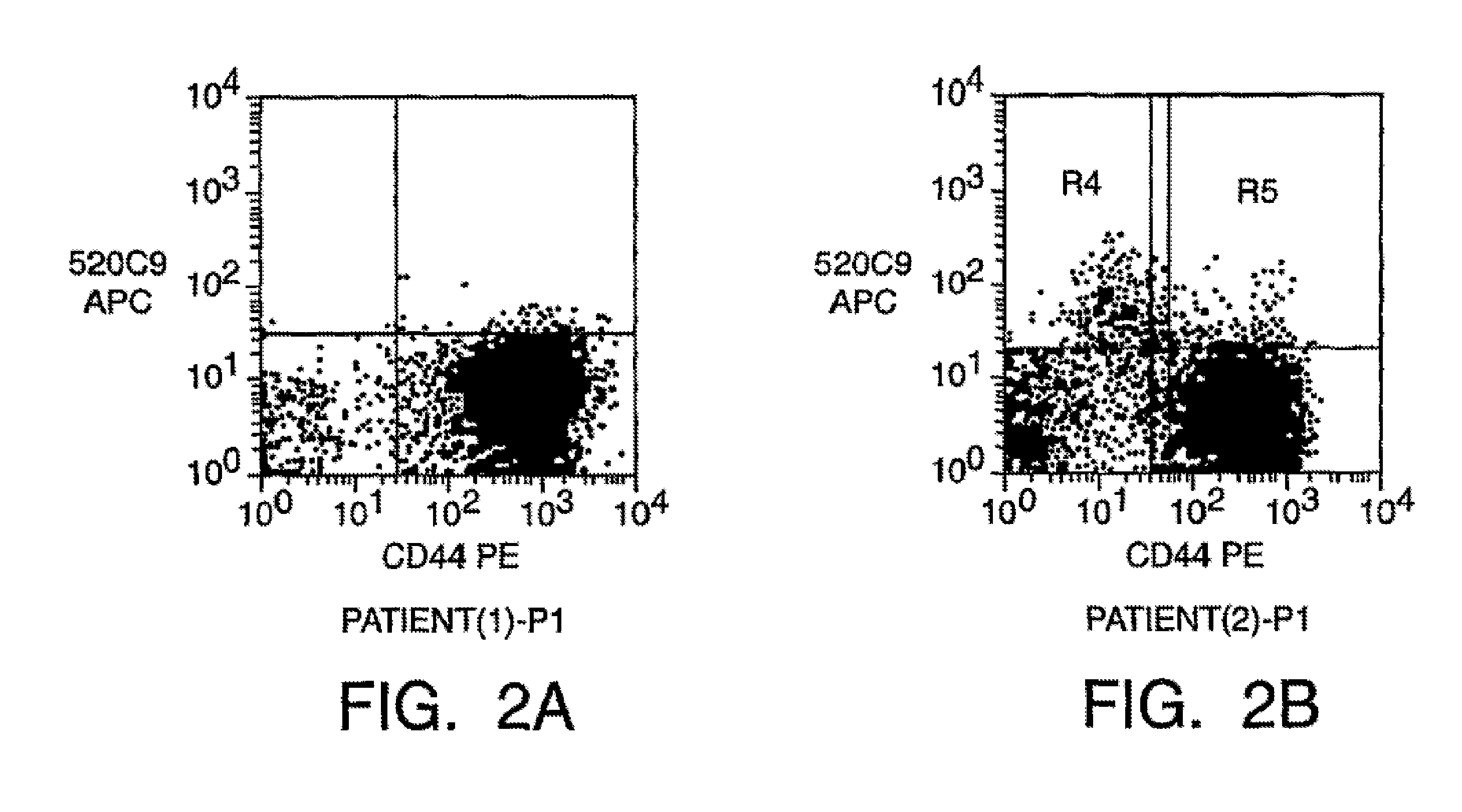
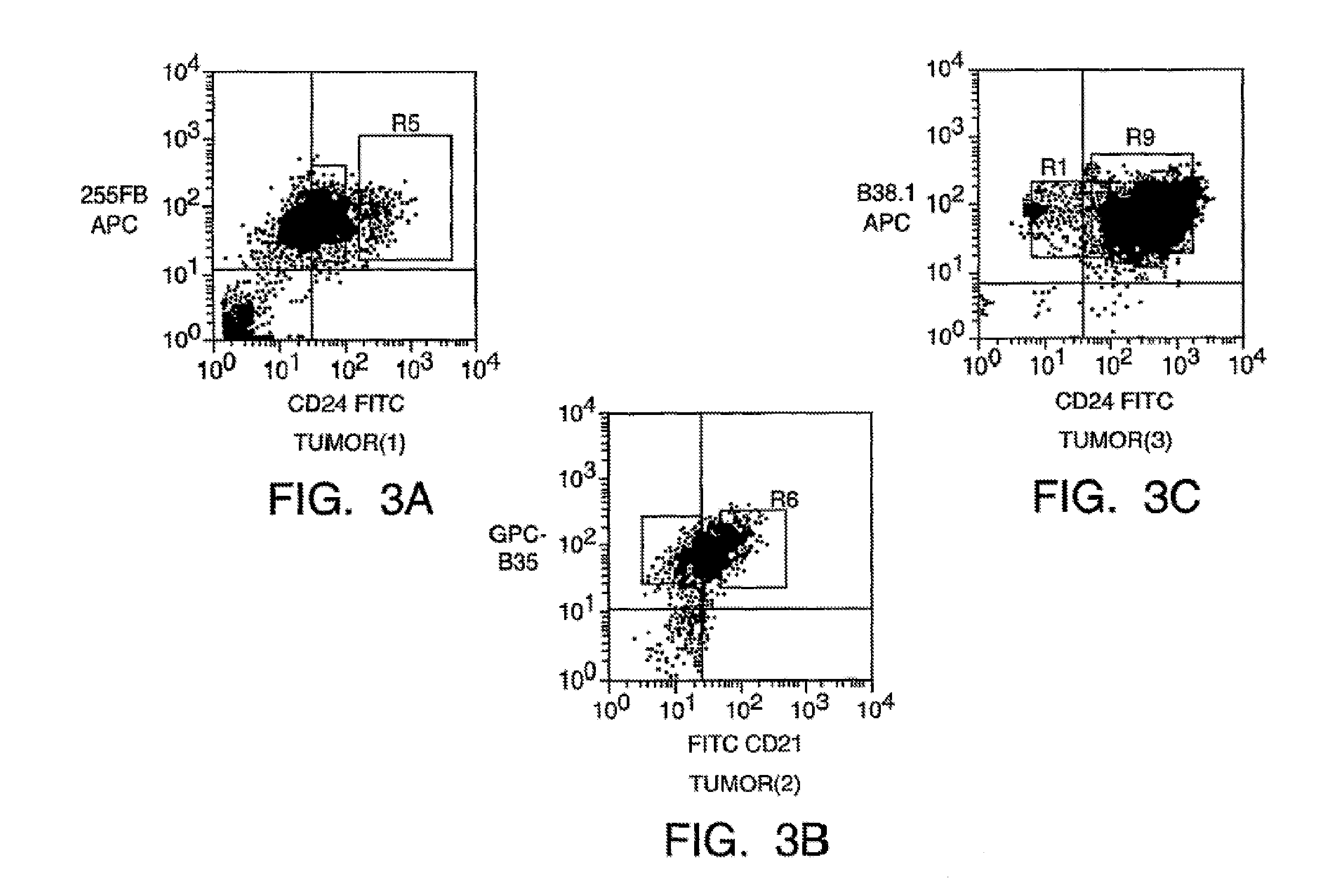
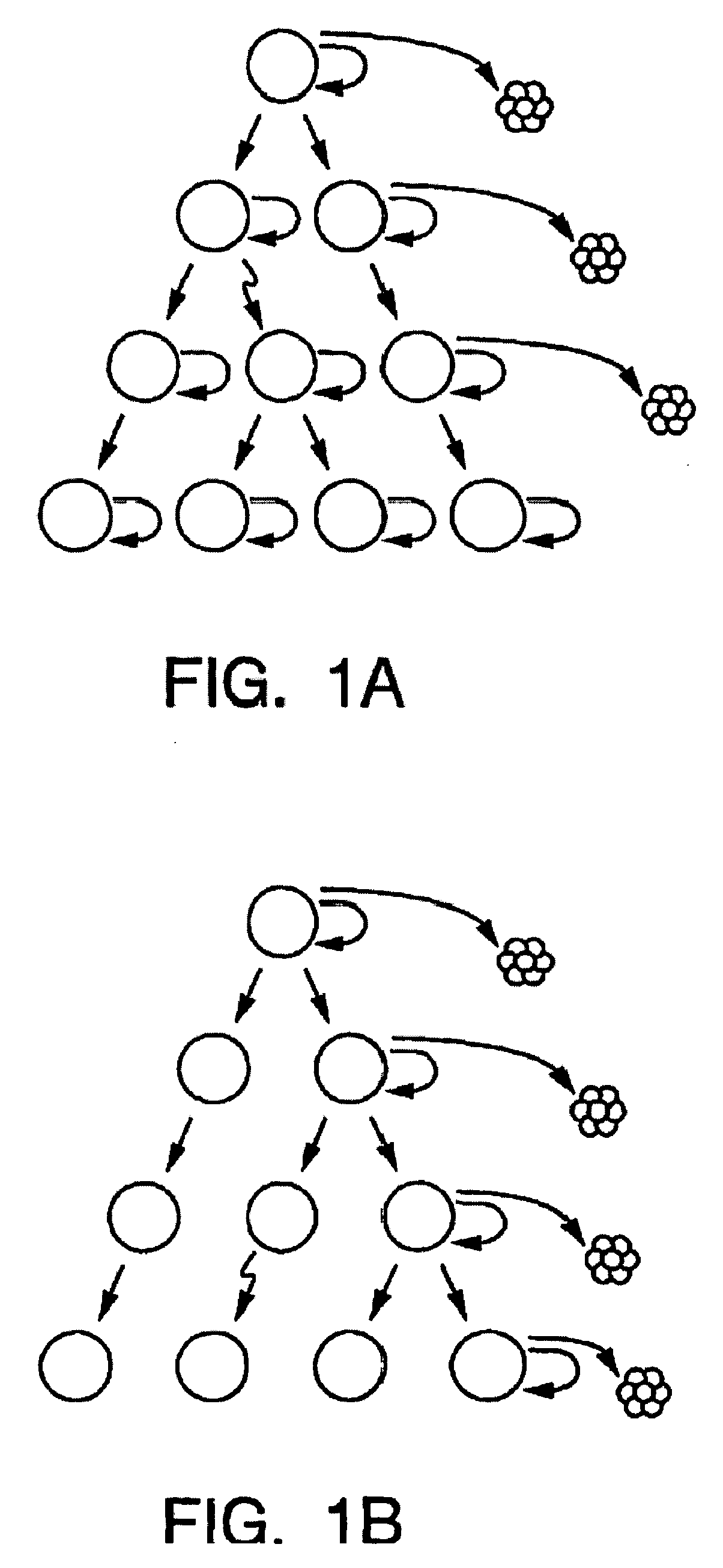
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell. We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumor cells in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells. We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA +1
Isolation, expansion and use of clonogenic endothelial progenitor cells
InactiveUS20050266556A1Increase in HSCHigh activityBiological material analysisMammal material medical ingredientsCord blood stem cellFeeder Layer
A hierarchy of endothelial colony forming cells (EPCs) was identified from mammalian cord blood, umbilical vein and aorta. A newly isolated cell named high proliferative potential—endothelial colony forming cell (HPP-ECFC) was isolated and characterized. Single cell assays were developed that test the proliferative and clonogenic potential of endothelial cells derived from cord blood, or from HUVECs and HAECs. EPCs were found to reside in vessel walls. Use of a feeder layer of cells derived from high proliferative potential-endothelial colony forming cells (HPP-ECPCS) from human umbilical cord blood, stimulates growth and survival of repopulating hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Stimulation of growth and survival was determined by increased numbers of progenitor cells in in vitro cultures and increased levels of human cell engraftment in the NOD / SCID immunodeficient mouse transplant system.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Hemangioblast progenitor cells
InactiveUS20040052771A1Reduce bleedingAvoid adjustmentBiocideArtificial cell constructsP-selectinProgenitor
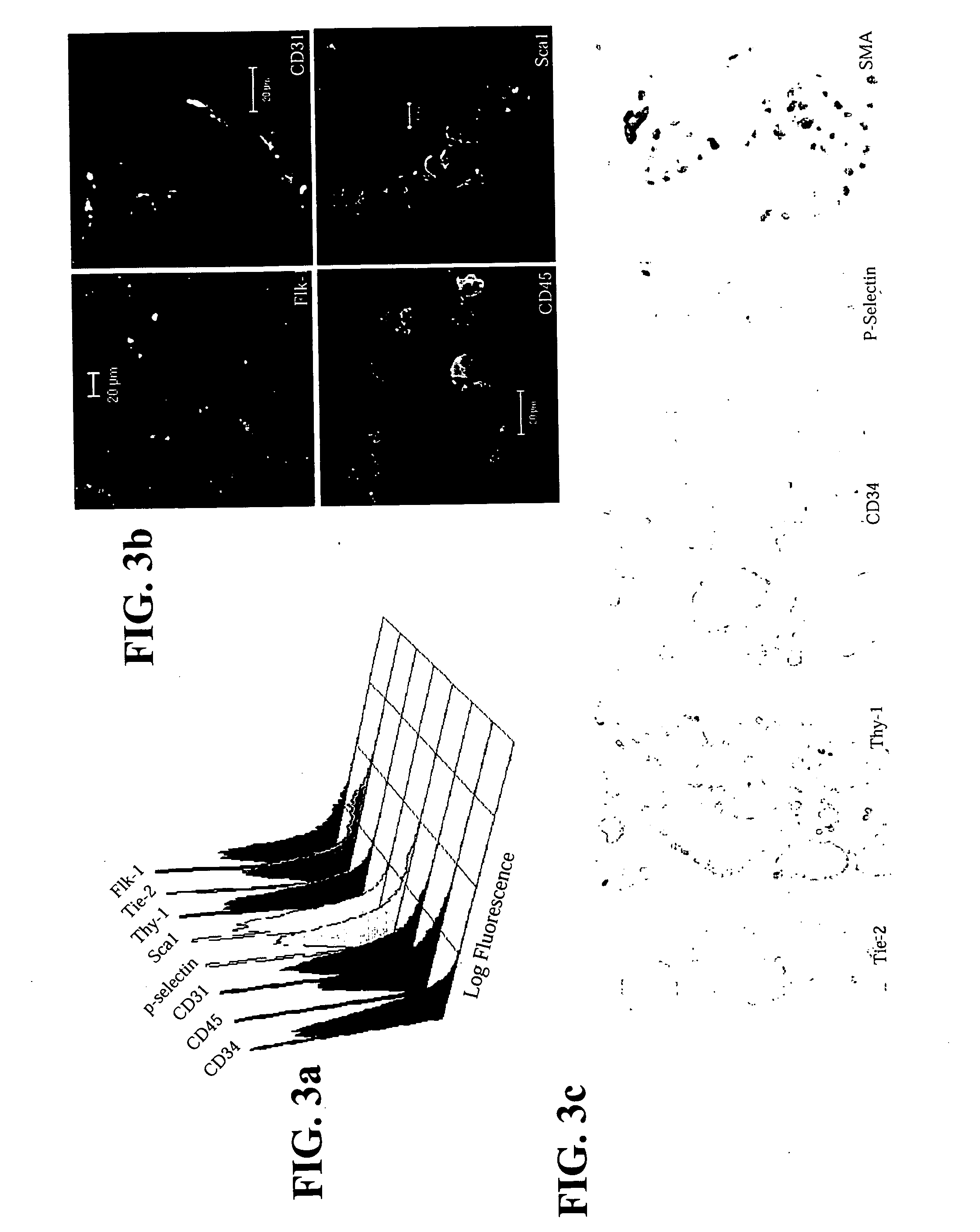
The invention relates to isolated hemangioblast cells. Hematopoietic and endothelial cells are postulated to be derived from a common progenitor, hemangioblast. While hemangioblast has been isolated retrospectively during embryonic stem cell differentiation, it has not been isolated from embryos or from bone marrow. Prospectively stable clonal cell lines have been isolated from mammalian embryos, from embryonic stem cells and from mammalian bone marrow that can differentiate in vitro into tubular structures with both endothelial and hematopoietic markers such as CD34, CD31, Flk-1, TIE2, P-selectin, Sca-1, thy-1, CD45, and smooth muscle actin. Gene expression profiles in the undifferentiated and differentiated cells were consistent with endothelial and hematopoietic differentiation potential. Transplantation studies in isogenic or immunodeficient mice demonstrated that these cells were not tumorigenic. In an appropriate microenvironment, the cells incorporate into the vasculature and participate in hematopoiesis.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Construction method and application of immunodeficient mouse animal model
InactiveCN107460196AImprove the level ofPromote basic researchCompounds screening/testingGenetically modified cellsKnockout animalWilms' tumor
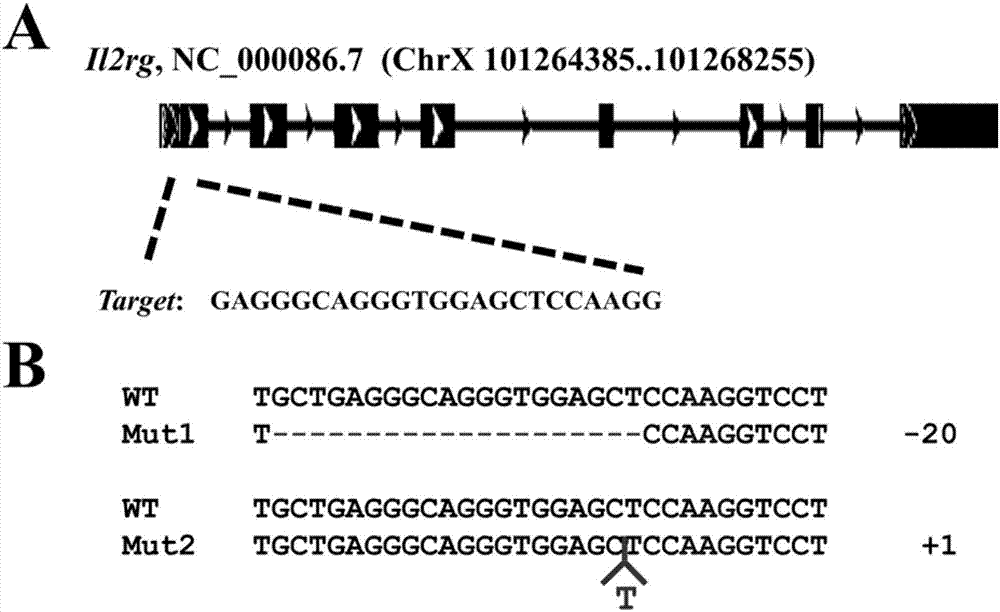
The invention relates to a construction method and application of an immunodeficient mouse animal model, belonging to the field of animal gene engineering and genetic modification. Il2rg gene knockout mice can be obtained by using a CRISPR / Cas9 technology; the Il2rg gene knockout mice have an immunodeficient phenotype. The construction method can be widely applied to multiple fields such as humanized animal models as well as stem cell and tumor research.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
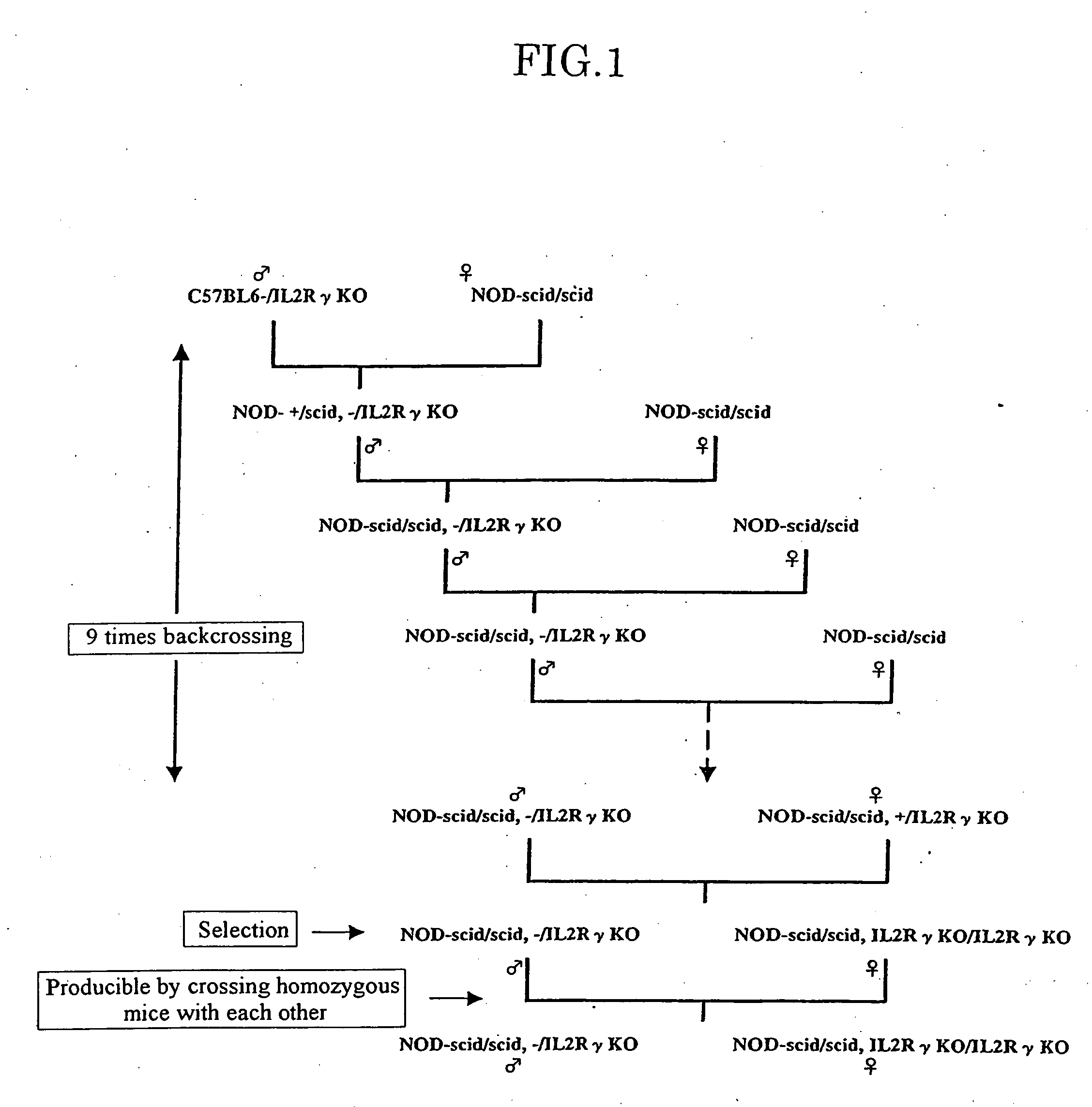
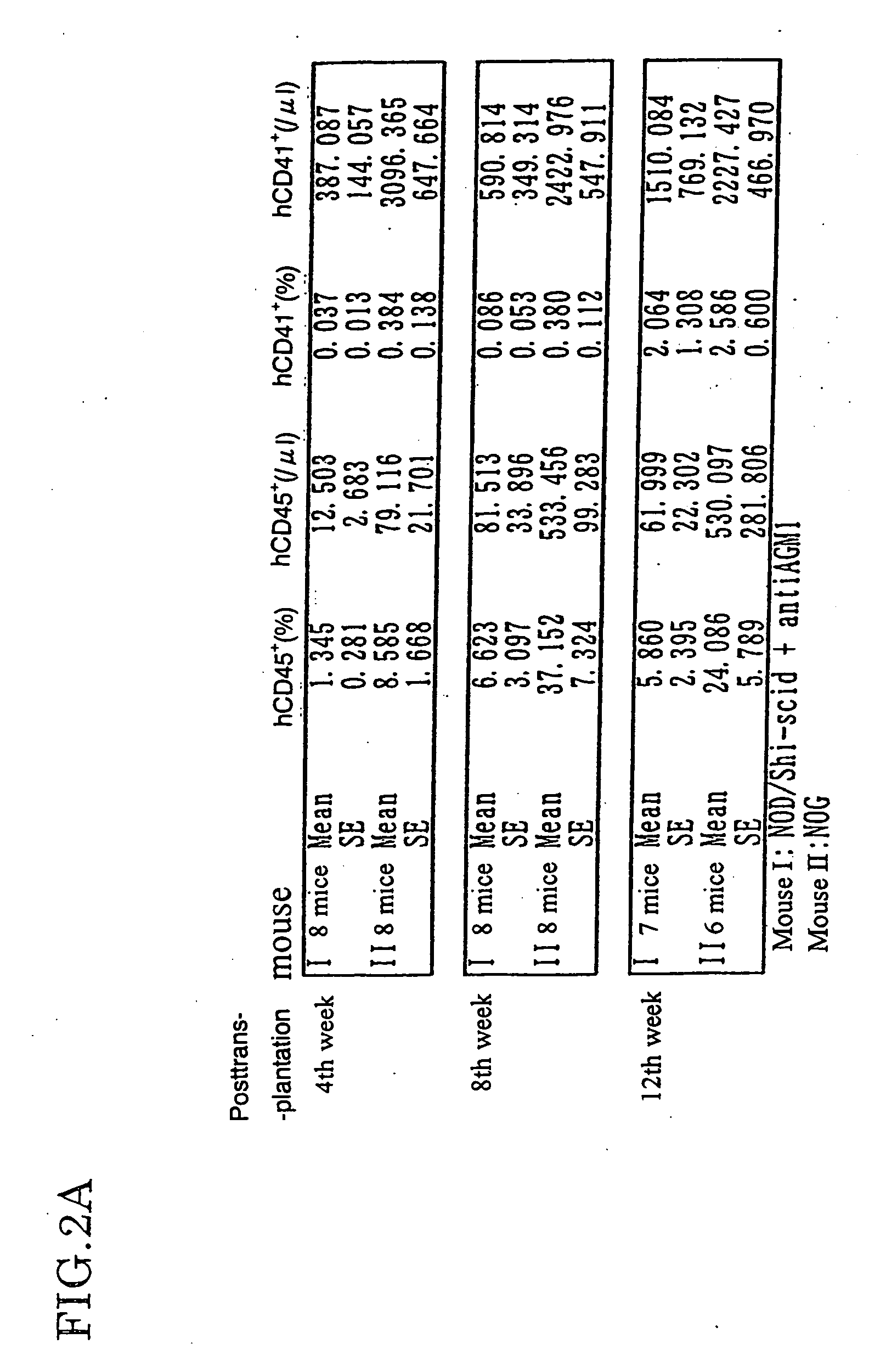
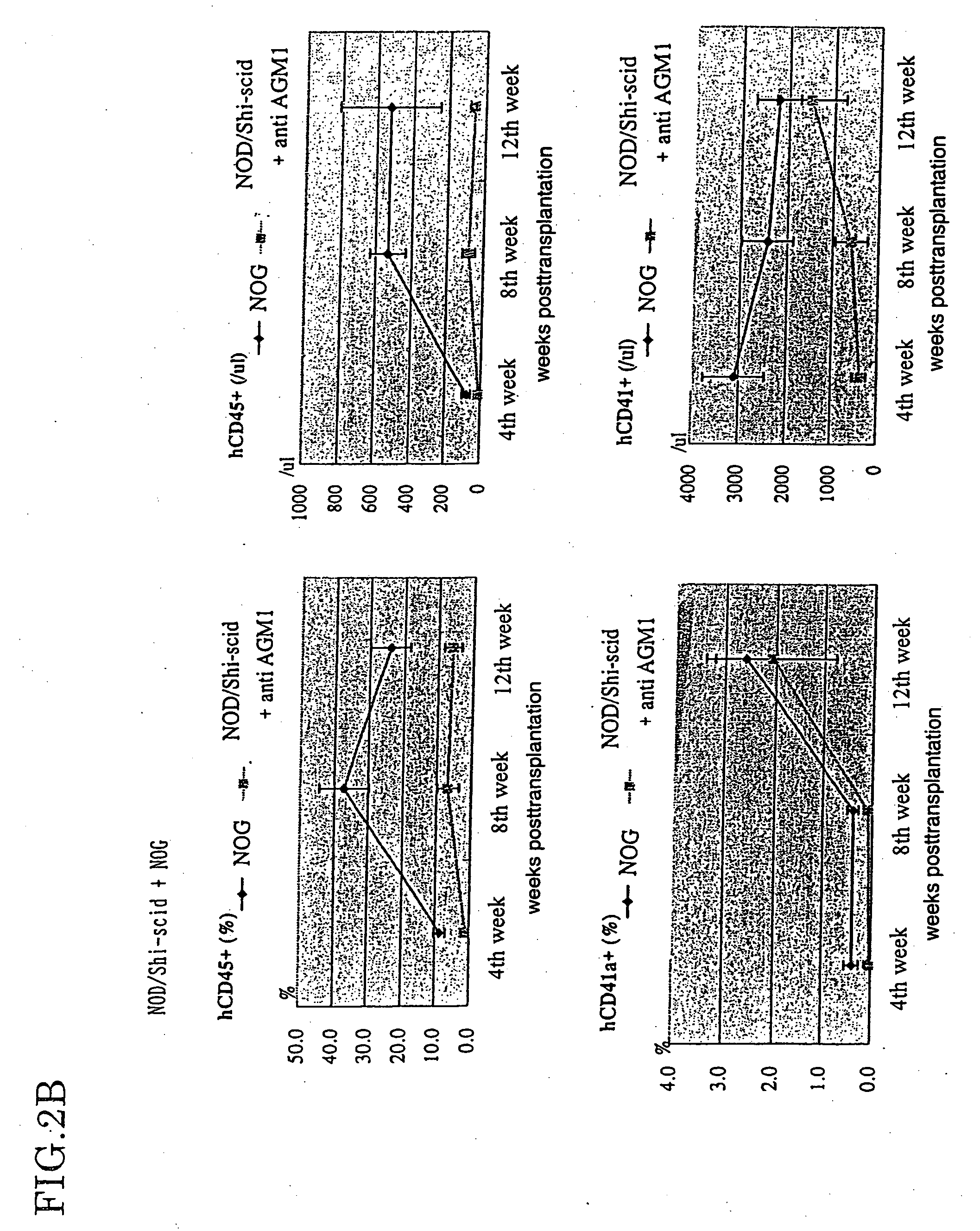
Method of producing a mouse suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS20070011753A1Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:ITO MAMORU +9
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20110092378A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise to both more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Isolation and use of solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS20080194022A1Promote resultsPromotes significant proliferationDiagnosticsBiological testingPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell.We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumors in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells.We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of producing a mouse suitable for the engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS7145055B2Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMutant preparationAbnormal tissue growthHeterologous
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
Human tumor stem cell line and application thereof
ActiveCN101659940AImprove transfer abilitySelf-renewingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAbnormal tissue growthHuman tumor
The invention provides a human tumor stem cell line T3A-A3, which is obtained by separation of liver cancer tissue excised in an operation of a primary hepatic carcinoma patient. The separated cells can be in long-term passage culture in vitro, can grow rapidly and retain stem cell property after more than 100 times of passage. The cell can express markers of multiple stem cells, has self-updatingcapability of stem cells and directional differentiation potentials for different tumor cells, and also has tumor property, tumorigenicity ability and metastatic ability. The invention is a powerfultool for preparing stem cell drugs for targeting tumor, due to the facts that the cells can be in long-term passage culture in vitro and retain unchanged stem cell property, and the tumorigenicity ability and metastatic ability thereof are strong in immunodeficient mice.
Owner:SUZHOU BOJUHUA BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo
Described herein is a method of expanding human hepatocytes in vivo using an immunodeficient mouse which is further deficient in fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (Fah). The method comprises transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fan-deficient mice, administering an IL-IR antagonist to the mouse and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. Alternatively, the method includes transplanting human hepatocytes into the immunodeficient and Fah-deficient mice, wherein the mouse is further deficient for IL-IR and allowing the hepatocytes to expand. The method also allows serial transplantation of the human hepatocytes into secondary, tertiary, quaternary or additional mice.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Immunodeficient mice, manufacturing method thereof and application
PendingCN106661593AEasy to observeEasy to observe growthMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryAnimal GeneticsImmunodeficiency
The invention belongs to technical field of animal genetic engineering, and specifically relates to immunodeficient mice, a manufacturing method thereof and applications. The manufacturing method comprises using NOD-Scid IL2rg- / - immunodeficient mice (NSI mice), and deleting Foxnl gene or Fah gene. Through deleting the Fah gene on the NSI mice, NSIF mice are obtained. The NSIF mice can be used to efficiently establish a novel humanized mouse model, used for liver physiological and pathological research. Through deleting the Foxnl gene on the NSI mice, the NSIF mice are obtained. The NSIF mice have no body hair, and immune system is further defected. The NSIF mice provide convenience for establishment, monitoring, and measurement of solid tumor.
Owner:湖南昭泰生物医药有限公司
Circulating tumor cell mouse model and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107137425AConsistent biological backgroundEasy to carry outCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsPrimary tumorLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to a circulating tumor cell mouse model and a construction method and application thereof. The method includes the following steps of 1, subcutaneous transplantation, wherein a primary tumor tissue sample is transplanted into the body of an immunodeficient mouse to construct a primary cancer heterotransplantation model PDX; 2, collection of circulating tumor cells, wherein the circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood in the primary cancer heterotransplantation model obtained in the step 1 are collected; 3, renal sac membrane transplantation, wherein the circulating tumor cells collected in the step 2 are transplanted into the renal sac membrane of the immunodeficient mouse, and then the circulating tumor cell mouse model is successfully constructed. According to the method, the mode of transplantation with two or more times of passages is adopted, the CTCs in the primary cancer heterotransplantation model are transplanted into the body of the immunodeficient mouse through renal sac membrane, and the circulating tumor cell mouse model is obtained; the circulating tumor cell mouse model can be applied to research on the in-vivo metastasis mechanism and proliferation condition of CTCs.
Owner:湖南昭泰生物医药有限公司
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
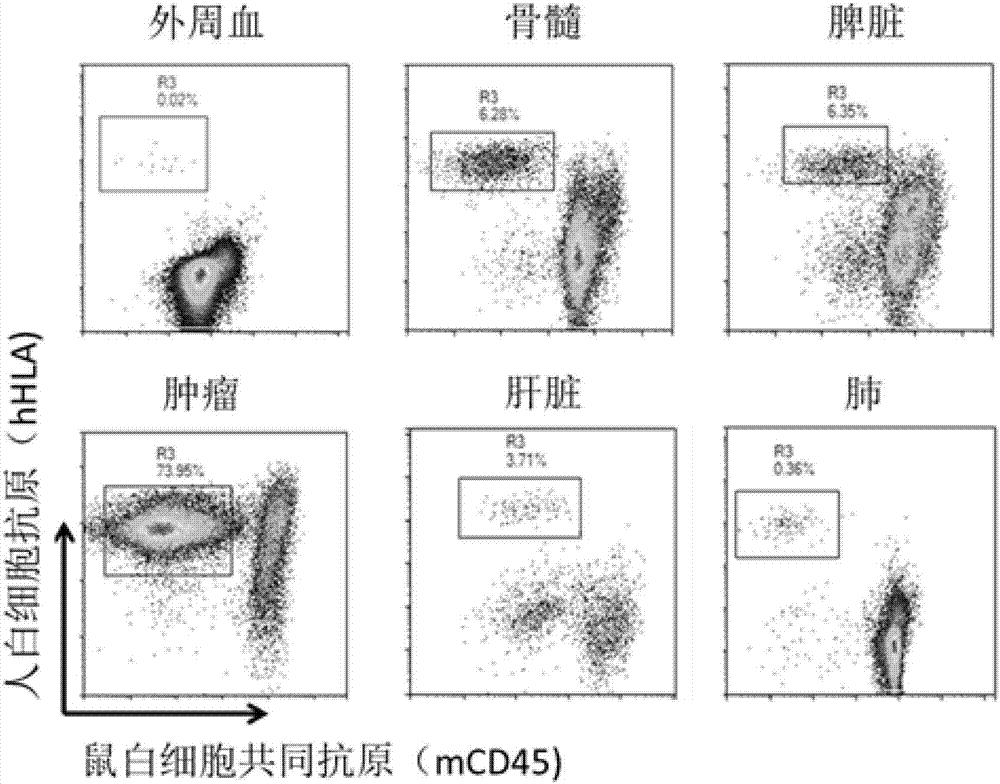
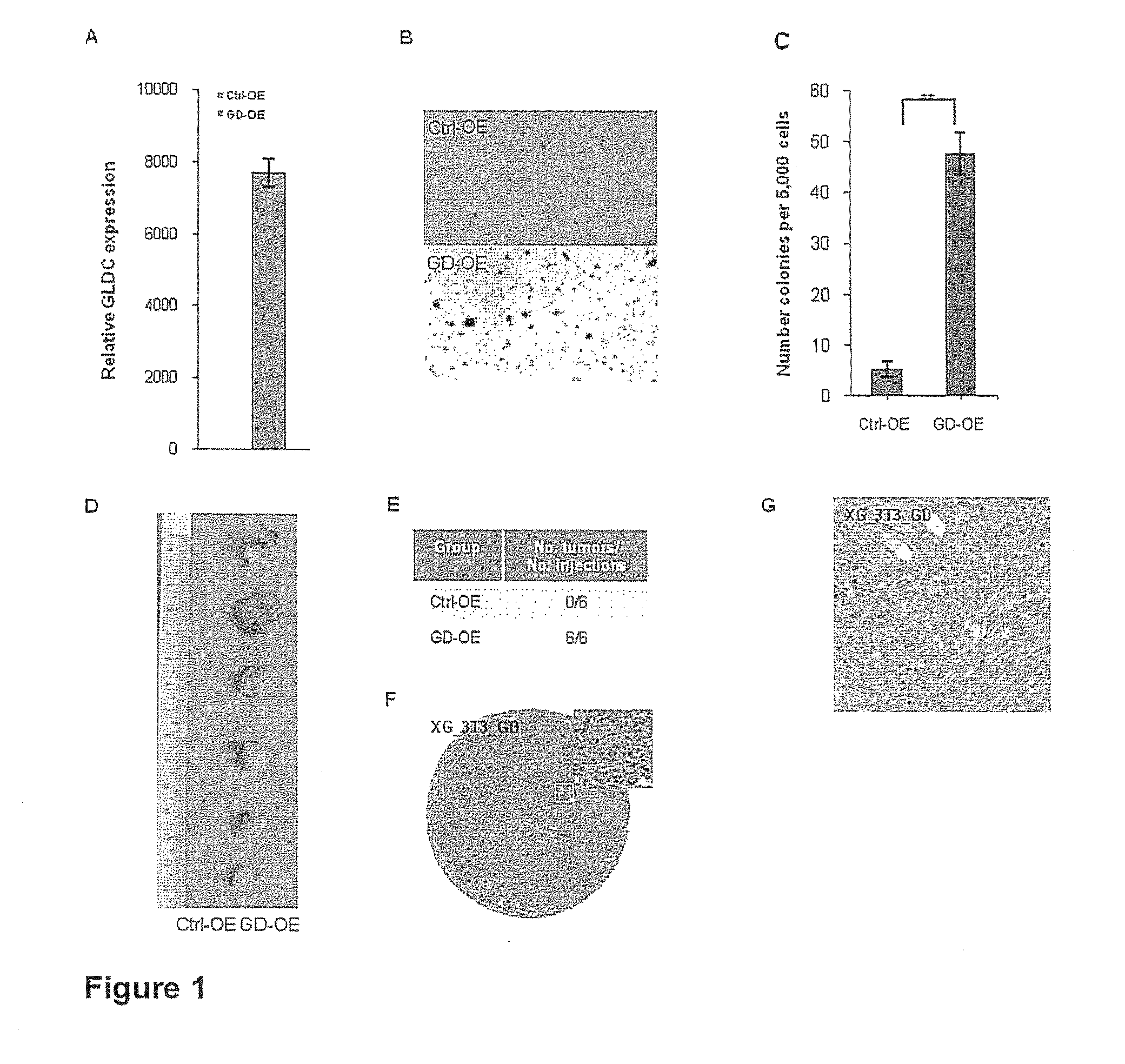
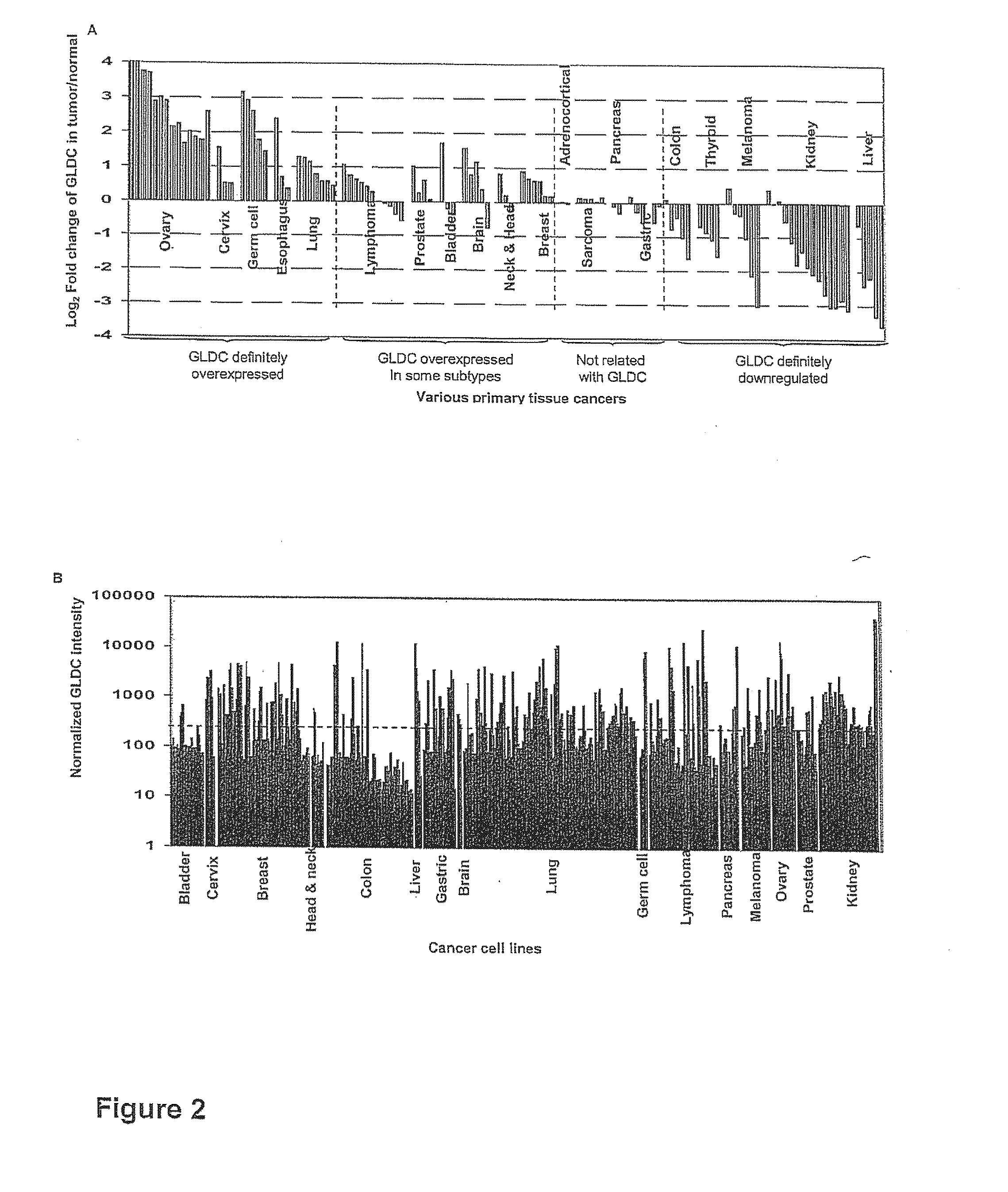
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
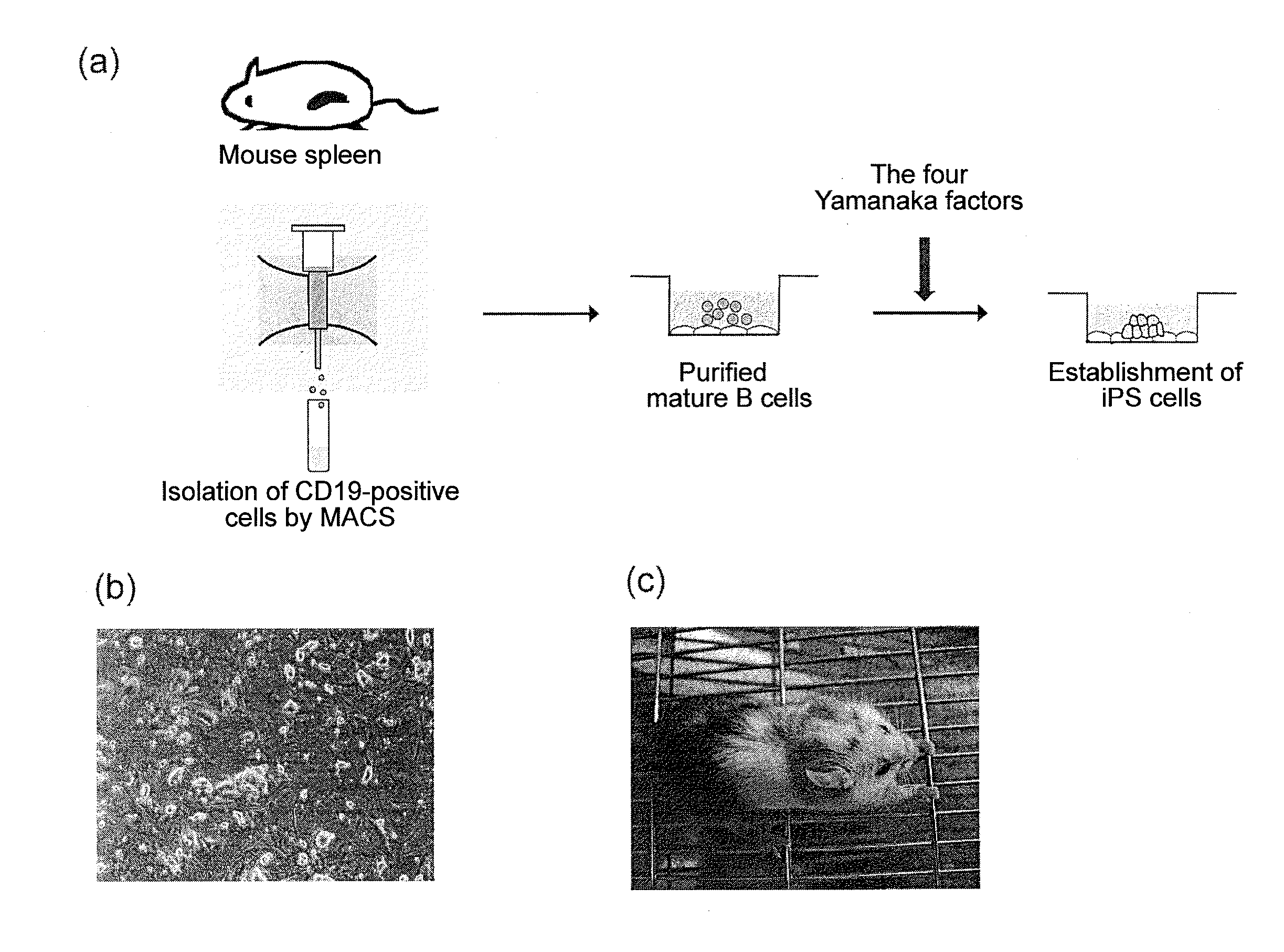
B cell-derived ips cells and application thereof
InactiveUS20110231944A1Low costLow cost productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsMonoclonal antibodyImmunodeficient Mouse
Provided are a B cell-derived iPS cell generated using a convenient technique, a technology for providing a human antibody at low cost using the iPS cell, an immunologically humanized mouse prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell, and the like. Also provided are a cloned cell obtained by contacting a B cell with nuclear reprogramming factors excluding C / EBPα and Pax5 expression inhibiting substances, particularly nucleic acids that encode Oct3 / 4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc, wherein the cloned cell has an immunoglobulin gene rearranged therein and possesses pluripotency and replication competence (B-iPS cell). Still also provided are a method of producing a monoclonal antibody against a specified antigen, comprising recovering an antibody from a culture of B cells obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell derived from a B cell immunized with the specified antigen, and a method of generating an immunologically humanized mouse, comprising transplanting to an immunodeficient mouse a human immunohematological system cell obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell.
Owner:RIKEN
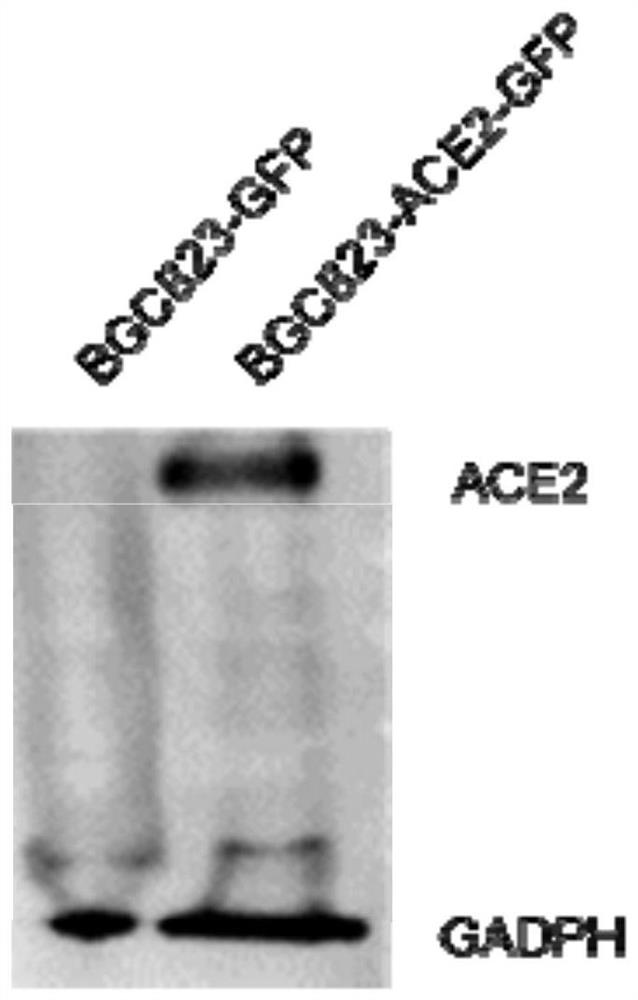
ACE2 cell humanized mouse model as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN111621523AHigh infection efficiencyAvoid xenograft rejectionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionReceptorHuman cell
The invention provides an ACE2 cell humanized mouse model as well as a construction method and application thereof. The mouse model adopts an immunodeficient mouse as a parent and the body of the mouse contains humanized cells for overexpressing an ACE2 receptor. The mouse model can overexpress the ACE2 receptor in human cells in the body of the immunodeficient mouse, the infection efficiency of acoronavirus taking the ACE2 receptor as an infection medium is improved, meanwhile, xenograft rejection can be avoided, and background pollution is reduced. In addition, the mouse model can also be used for transplantation and immune reconstruction of human immune cells, and is of great significance for further research on the killing effect of the human immune system on the virus, screening of vaccines and evaluation of immune treatment means.
Owner:湖南昭泰生物医药有限公司
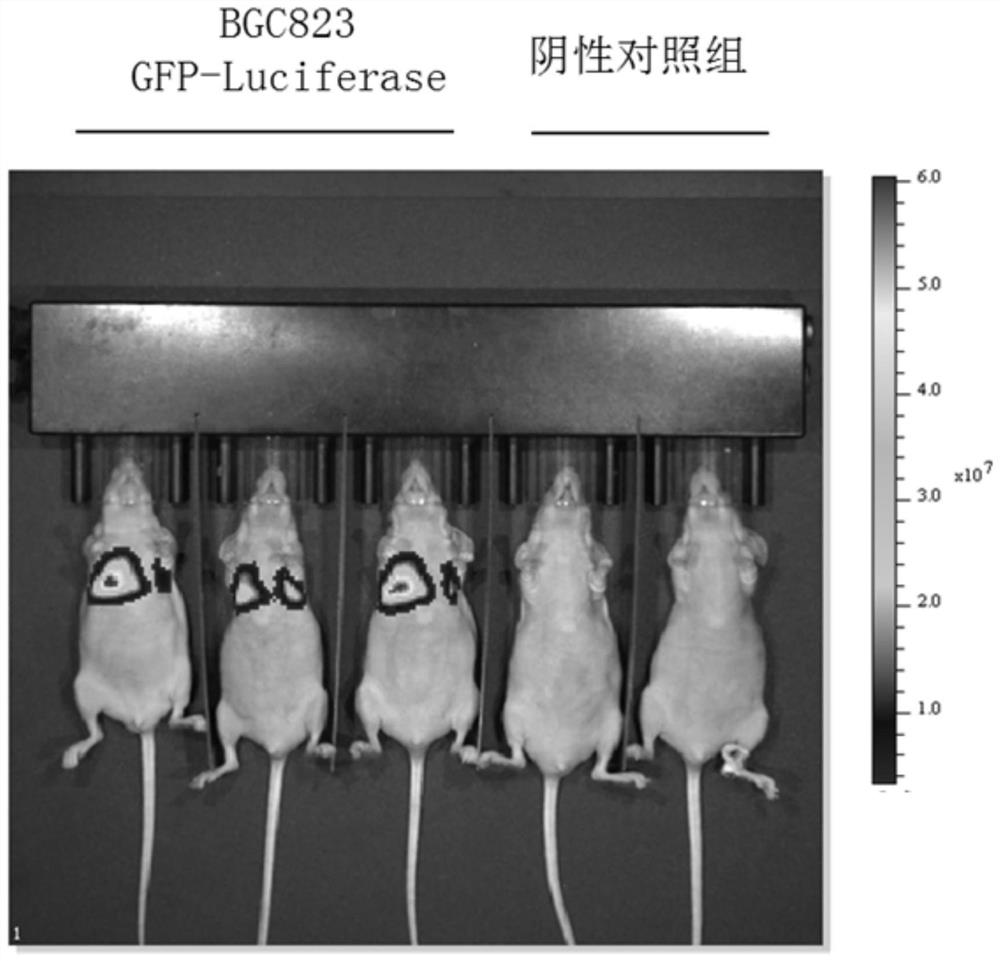
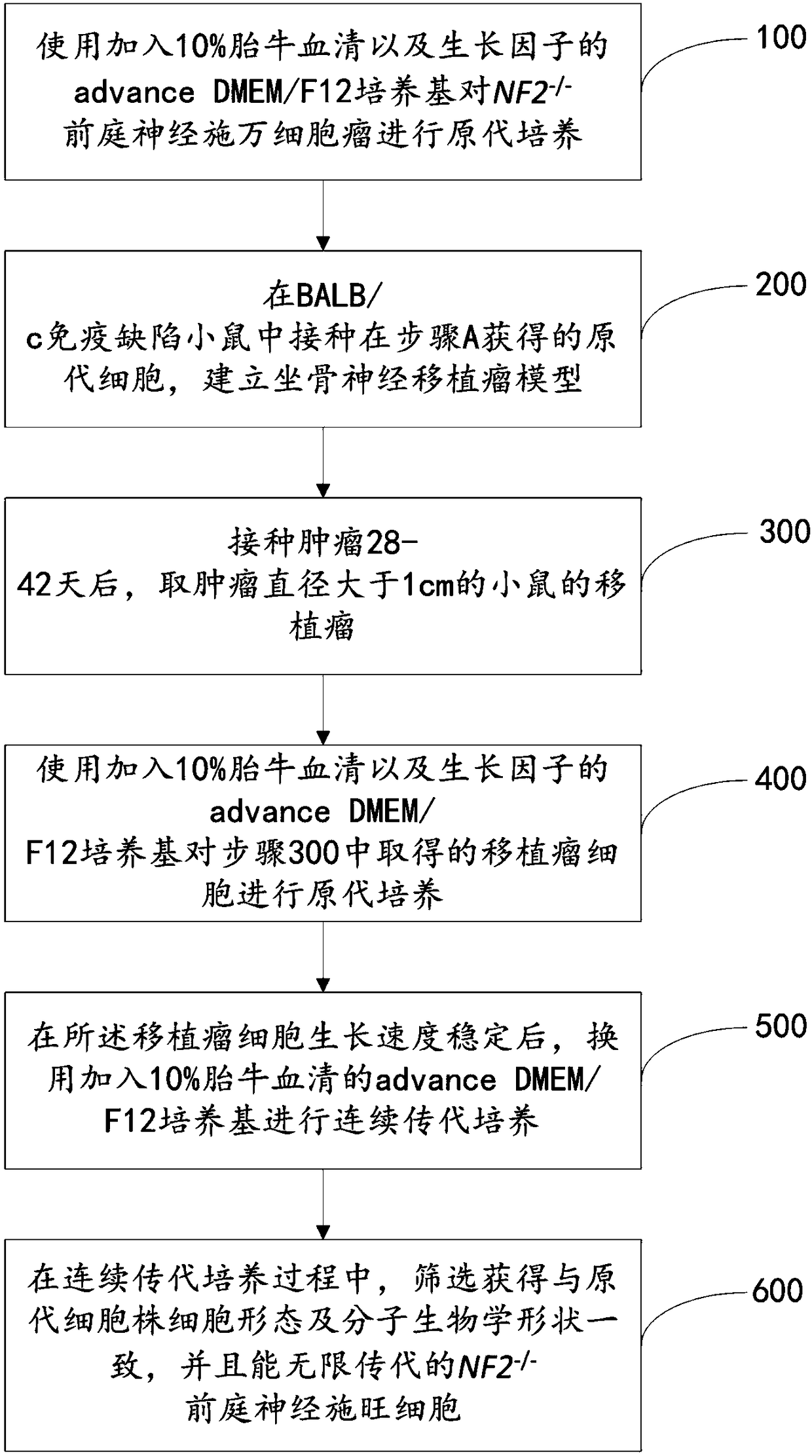
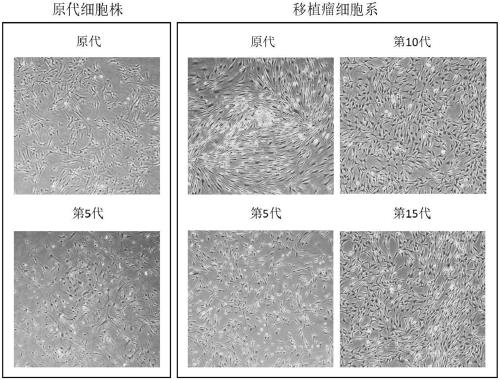
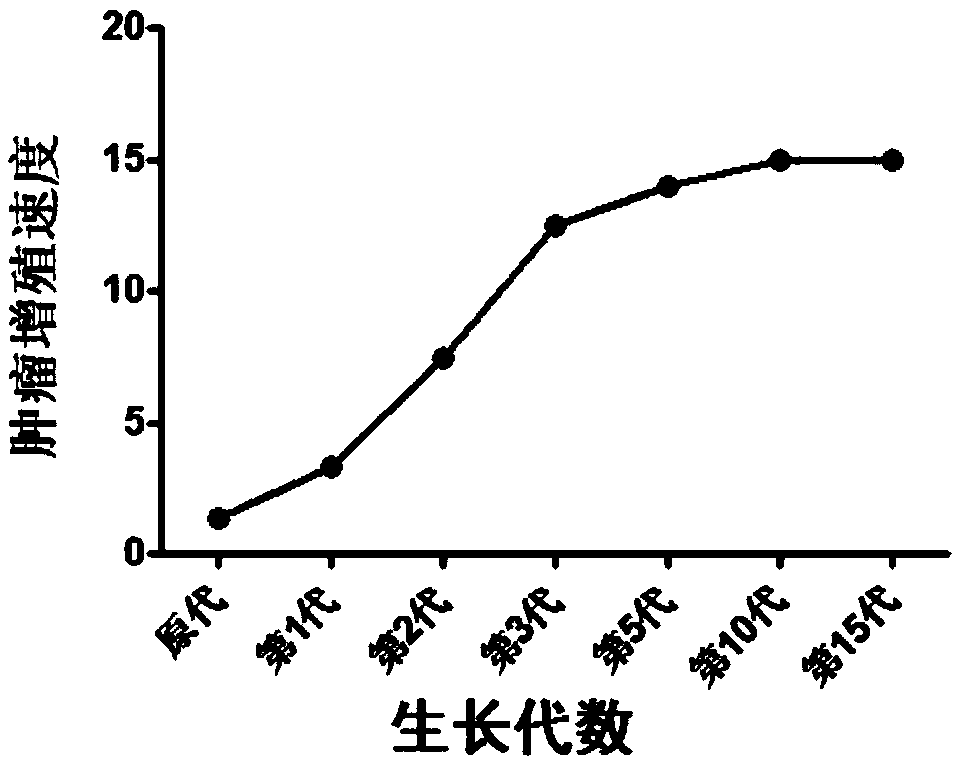
NF2-/- vestibular schwannoma Schwann cell line and establishment method thereof
ActiveCN109486765AConsistent growth rateOptimizing Primary Culture MethodsNervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingPrimary cellVestibular Schwannomas
The invention discloses a human NF2- / - vestibular schwannoma Schwann cell line and an establishment method thereof. The establishment method includes: A, separating Schwan cells in tumors to obtain human NF2- / - primary Schwann cells (human NF2- / - Schwann cells), and carrying out primary culture; B, establishing immunodeficient mouse sciatic nerve human NF2- / - primary Schwann cell transplanted tumor model; C, collecting transplanted tumors greater than 1 cm in diameter from mouse sciatic nerves by screening; D, separating Schwann cells, and carrying out primary cell culture; E, carrying out five successive generations and more of passage culture; F, performing screening to obtain NF2- / - vestibular Schwann cells which are consistent to human NF2- / - primary Schwann cells and transplanted tumor primary cell strains in cellular form and main biological characteristic and which are capable of infinite passage. The NF2- / - vestibular schwannoma Schwann cell line herein has the success rate of95% and above to grow transplanted tumors.
Owner:BEIJING NEUROSURGICAL INST
Cervices intraepithelial neoplasia model and model establishing method
InactiveCN101125102ARich sourcesExplore the mechanism of carcinogenesisDiagnosticsSurgeryHuman tumorImmunodeficiency
The present invention relates to a cervical intraepithelial neoplasia model and the method of establishing model, which is characterized in that the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue is embedded in the immunodeficiency mice to establish cervical intraepithelial neoplasia model. The method of establishing model is characterized in that the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue is respectively taken from the biopsy under the vaginoscope and the tissues which are confirmed by the department of pathology and is inoculated subcutaneously in the back of the mice; the immunodeficiency mice of the present invention can overcome the xenoislet immune rejection reaction and receive the transplantation of the human tumor tissues, the tissue model after the transplantation has significant and stable character, short observation period and greater clinical reference significance of the experimental results. The present invention can explore the mechanism of the carcinogenesis of cervical carcinoma by outcome of the pathological process of CIN I, CIN II and CIN III animal models. Furthermore, by observing the period of the outcome of the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue of the animal model, the present invention provides the feasible clinical animal experimental model for reversing the malignant transformation of the CIN I and CIN II lesion tissues.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Method for reconstitution of hair follicle in vivo
InactiveCN107164310AEasy to operateTraumaEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsDiseaseCuticle
Relating to the technical field of aesthetic and plastic surgery, the invention discloses a method for reconstitution of hair follicle in vivo. The method includes the steps of: firstly performing cell separation, culturing and amplifying freshly isolated cells, and using cell spheres or cell lumps for culture, conducting cell preparation before transplantation, directly taking freshly isolated skin single cells, or cultured and amplified epidermal and dermal cells mixed in proportion, or cell spheres or cell lumps, and resuspending them in a culture solution, narcotizing an immunodeficient mouse, using a syringe needle or cutisector to pierce a hole on the skin of the naked mouse, using a pipette gun head to transfer the well prepared cell suspension into the pierced hole, after transferring all the cells, performing covering with a silica gel membrane and conducting suturing, then laying a layer of vaseline gauze, conducting bandaging and timely observation and treatment, thus finding hair growth 3 weeks later. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, small trauma, high hair follicle formation efficiency, and large injectable cell number range, is suitable for injection of clump cells and a large number of cells, and is suitable for development and application in clinical practice or cosmetic medicine for treatment of hair loss diseases.
Owner:山东省口腔医院
Humanized mouse
The present invention provides embryonic stem cells obtainable from an embryo of an immunodeficient mouse which is deficient in both Rag2 and Jak3 genes by culture in the presence of a GSK3 inhibitor and an MEK inhibitor, as well as a transgenic mouse, which is created with the use of these embryonic stem cells.
Owner:TRANSGENIC +1
Feed applied to immunodeficient mice and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses feed applied to immunodeficient mice. The feed is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 10-20 parts of wheat middlings, 2-10 parts of bran, 35-45 parts of expended maize, 17-25 parts of soybean meal, 5-11 parts of fish meal, 1-4 parts of maize protein powder, 0.5-1.5 parts of beer yeast, 1-4 parts of vegetable oil, 0.3-0.6 part of choline chloride, 0.1-0.5 part of methionine, 0.1-0.5 part of lysine, 3-5 parts of mineral salt premix and 0.1-0.2 part of vitamin premix. Through frequent adjustment of the formula and the process, a formula and a preparation process of the feed which is balanced in nutrition and high in palatability, and is applicable to the immunodeficient mice are determined; through the optimization of the raw materials and the adoption of the special ratio and the production process, complex feed capable of meeting requirements on growth, gestation and lactation of the immunodeficient mice is provided.
Owner:北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司 +1
Method for constructing ovarian cancer transplantation tumor model based on organoid method and application of method
InactiveCN109392843AConvenient researchNormal food intakeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrocarriersDrug allergyImmunodeficiency
The invention discloses a method for constructing an ovarian cancer transplantation tumor model based on an organoid method, and belongs to the field of medicines. According to the invention, an "organoid" culture technology is adopted, and a micro-carrier is used as a support material for culturing a patient-derived ovarian cancer cell-3D material complex; then the cell-3D material complex is directly inoculated under the skin of a normal immune mouse, and a patient-derived ovarian cancer transplantation tumor model is constructed, so that a problem that immune-deficiency mice such as severecombined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice, nude mice and the like are adopted in existing human ovarian cancer transplantation tumor models, the price is high, breeding is difficult, the tumor forming rate is low and the like can be solved, especially a problem that the existing immune-deficiency mouse human ovarian cancer transplantation tumor model cannot reflect impotent effects of an organism immune system in occurrence and development processes of tumors is solved, and a problem that an immune-deficiency mouse human transplantation tumor model is long in tumor forming period and cannot meet drug allergy requirements of patients urgently needing clinic drug therapy is solved. The method is applied to the field of mouse model construction.
Owner:上海美峰生物技术有限公司
Preparation method and application of transgenic mouse with severe immunodeficiency
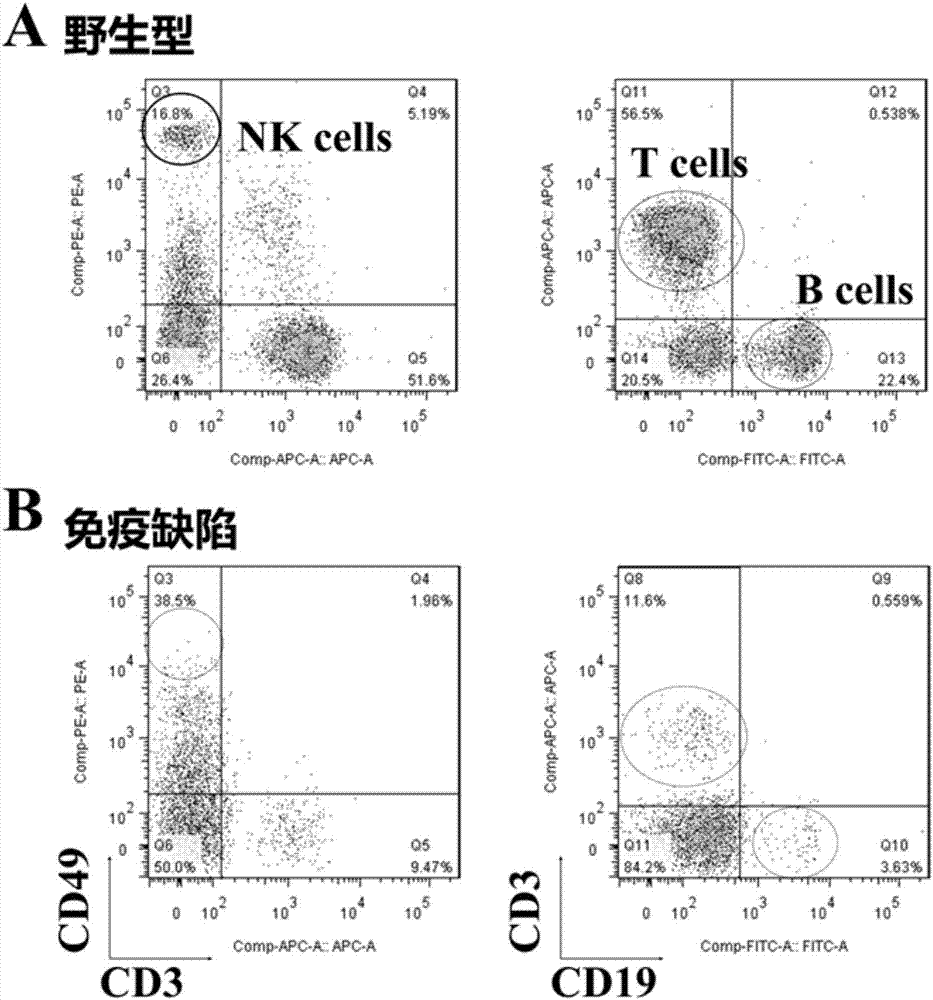
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a transgenic mouse with severe immunodeficiency. The method comprises the step of knocking out a gene for encoding a gamma chain of an interleukin-2 receptor in a mouse chromosome through a CRISPR / CAS9 technology, exons 1 and 2 of a gene of a gamma chain of an interleukin-2 receptor are selected as knockout sites, and Cas9 messenger RNA and guide RNA are jointly injected into fertilized eggs of a mouse through microinjection. The mouse with severe immunodeficiency cannot generate T, B and NK immune cells, so that the greatest convenient condition is created for transplantation of human hematopoietic stem cells.
Owner:澎立生物医药技术(上海)股份有限公司
Determining the capability of a test compound to affect solid tumor stem cells
InactiveUS8044259B2Reduce spreadIncreased proliferationMaterial nanotechnologyDrug screeningPrimary tumorImmunodeficient Mouse
A small percentage of cells within an established solid tumor have the properties of stem cells. These solid tumor stem cells give rise both to more tumor stem cells and to the majority of cells in the tumor that have lost the capacity for extensive proliferation and the ability to give rise to new tumors. Thus, solid tumor heterogeneity reflects the presence of tumor cell progeny arising from a solid tumor stem cell. We have developed a xenograft model in which we have been able to establish tumors from primary tumors via injection of tumor cells in the mammary gland of severely immunodeficient mice. These xenograft assay have allowed us to do biological and molecular assays to characterize clonogenic solid tumor stem cells. We have also developed evidence that strongly implicates the Notch pathway, especially Notch 4, as playing a central pathway in carcinogenesis.
Owner:ONCOMED PHARMA INC +1
Method for constructing tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with gastric cancer based on organ-like method, and application thereof
InactiveCN109182271AConvenient researchNormal food intakeTumor/cancer cellsGeneral culture methodsWilms' tumorStomach cancer
The invention discloses a method for constructing a tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with gastric cancer based on an organ-like method, and an application thereof. The invention relates to a medical tumor animal model, based on an organ-like method. For the first time, the present invention employs a quasi-organ technique, that is, using a microcarrier as substrate. The composite human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 / MKN-45 is transplanted subcutaneously into C57BL / 6 mice to establish a tumor model of human gastric cancer with normal immune function. The tumor model constructed by this method has good tumorigenicity, and the tumorigenicity rate is up to 75%. The HE staining and the immunohistochemistry of the transplanted tumor accord with the characteristics of human gastric cancer. Compared with the existing immunodeficient mice transplanted tumor model, the model can better study and further clarify the mechanism of tumor occurrence and development in the normal immune system, and also provides a more valuable new animal model for the research and development of anticancer drugs. The invention is applied to the tumor model field.
Owner:上海美峰生物技术有限公司
Expression plasmid adjuvant for enhancing chemotherapeutic effect of tumor chemotherapeutics and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101954077AIncreased sensitivityImprove the effect of chemotherapyOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMitochondrial pathwayApoptosis
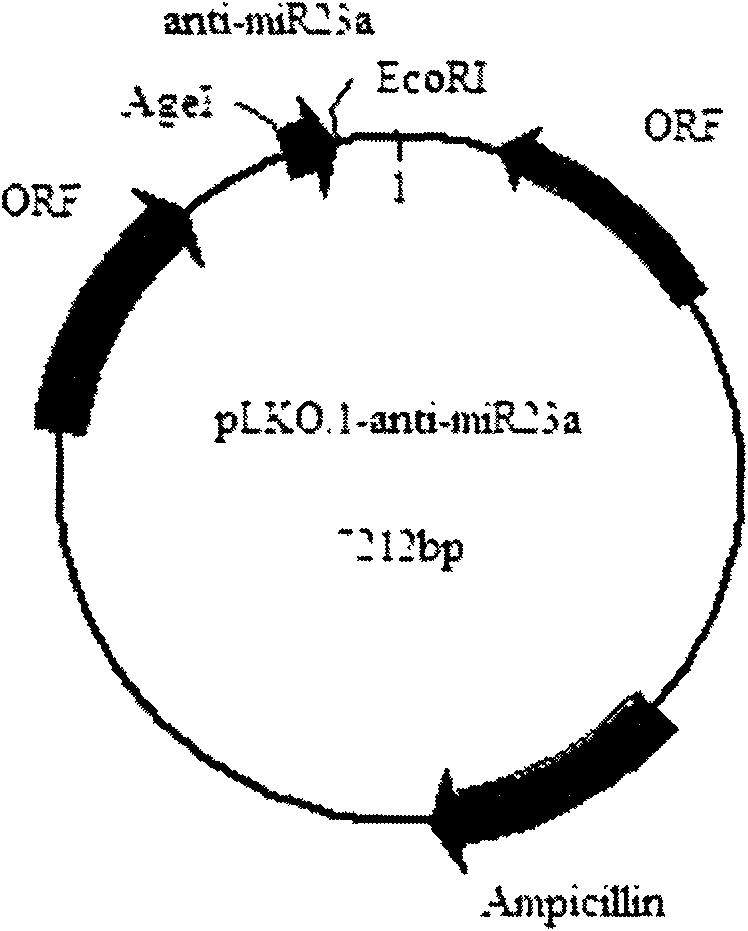
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine. 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is widely applied to the chemotherapy of gastral malignant tumors, but primary and acquired medicament resistant phenomena in the chemotherapy of colon cancer are universal; cell apoptosis is an important approach that chemotherapeutics play a role, and APAF-1 serving as regulatory protein is mainly involved in signal transduction of a mitochondrion approach of apoptosis; miR-23a can be combined with APAF1 serving as a target gene thereof so as to reduce the expression of the APAF1, and the apoptosis caused by the mitochondrion approach due to the chemotherapy is reduced so as to enhance the tolerance of the tumors to the chemotherapeutics; and the number of apoptotic cells is increased by reducing the expression amount of the in-vivo miR-23a so as to enhance the sensibility of the chemotherapeutics. The invention provides a PLKO-anti-miR-23a vaccine adjuvant for enhancing the chemotherapeutic effect of the chemotherapeutics, particularly the 5-FU. In-vitro experiments prove that the vaccine adjuvant can enhance the apoptosis level of colon cancer cells caused by the 5-FU serving as the chemotherapeutics obviously, and in-vivo experiments show that the vaccine adjuvant can enhance the chemotherapeutic effect of the 5-FU obviously, inhibit tumor growth and prolong the survival period of immunodeficient mice.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
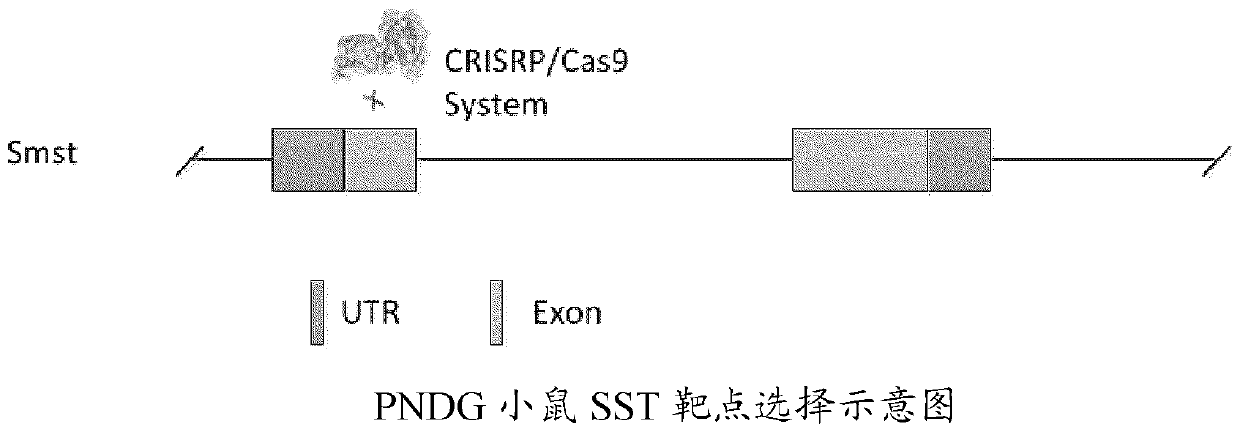
Somatostatin gene defective immunodeficient mice, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to somatostatin gene defective immunodeficient mice, a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a method for building somatostatin gene knocked-out SST-PNDG somatostatin combined immunodeficient mice on NOD-Prkdc and IL2rg- / -immunodeficient mice (PNDG mice), SST-PNDG somatostatin immunodeficient mice obtained thereby and application thereof. The mice can be used for biomedicine, pharmacy and clinical researches like heterograft, tumor growth and drug screening.
Owner:南京普恩瑞生物科技有限公司
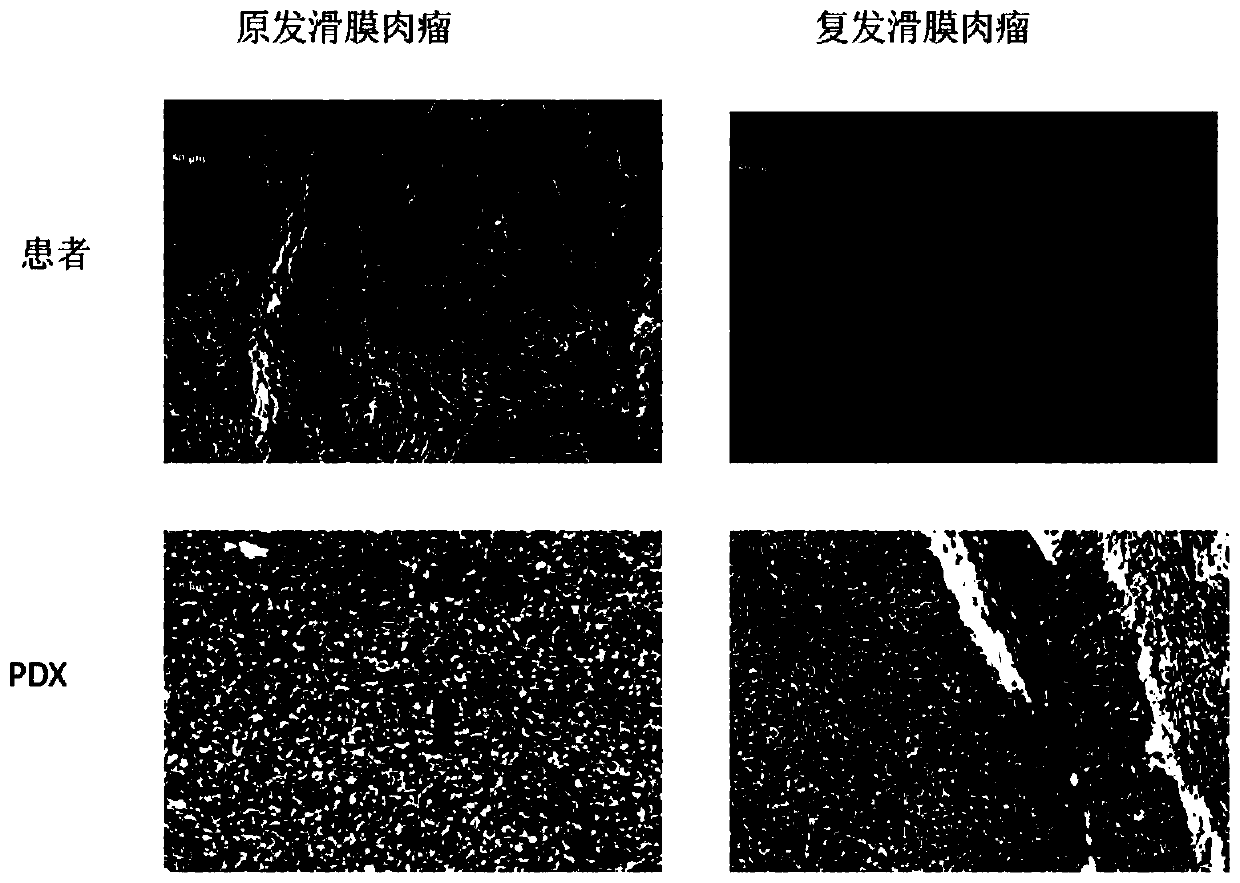
Construction method and application of synovial sarcoma heterogenous transplanting mouse model
ActiveCN110476891AMaintain a stable relationshipConsistencyCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandrySynovial sarcomaAbnormal tissue growth
The invention provides a construction method and application of a synovial sarcoma heterogenous transplanting mouse model. The method comprises the steps of firstly, collecting a synovial sarcoma patient tumor tissue block, and performing heterogenous in-situ transplanting of the fresh patient tumor tissue block into an immune deficiency mouse body under the sterile condition, wherein heterogenousin-situ planting includes the steps of selecting a 2-6-week old immune deficiency mouse, the mouse is consistent with the patient in gender, the collected fresh patient tumor tissue block is soaked with a sterile incubation solution containing fetal calf serum, the mouse is fixed after anesthesia, the patient tumor tissue block is planted into the joint capsule of the mouse, an incision is sewn,and the mouse is bred so that a tumor in the joint capsule can grow. Compared with subcutaneous modeling, the in-situ modeling condition is more real, the screened medicine scheme can be better used for the patient, and on the basis of the in-situ modeling theory, tumor metastasis is more likely to happen compared with subcutaneous modeling.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for improving success rate of colon cancer PDX model
InactiveCN108685946AHigh tumor formation rateOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthBALB/c
The invention relates to the field of medicines, relates to a method for establishing an animal model, and particularly relates to a method for establishing a human colon cancer transplanted carcinomamouse model. A preclinical tumor model is made through preprocessing mice with prostaglandin E2 and inoculating immunodeficient mice (Balb / c or NOD / SCID) with the in-vitro in-situ tumors of a patientagainst the defects of low establishing success rate and instability of existing colon cancer models. The invention provides a method for improving the success rate of a colon cancer PDX model, and especially provides the method for preparing the high-infiltration and high-metastasis stable human colon cancer transplanted carcinoma mouse model. The model has great values for preclinical evaluation, treatment and prognosis of the colon cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
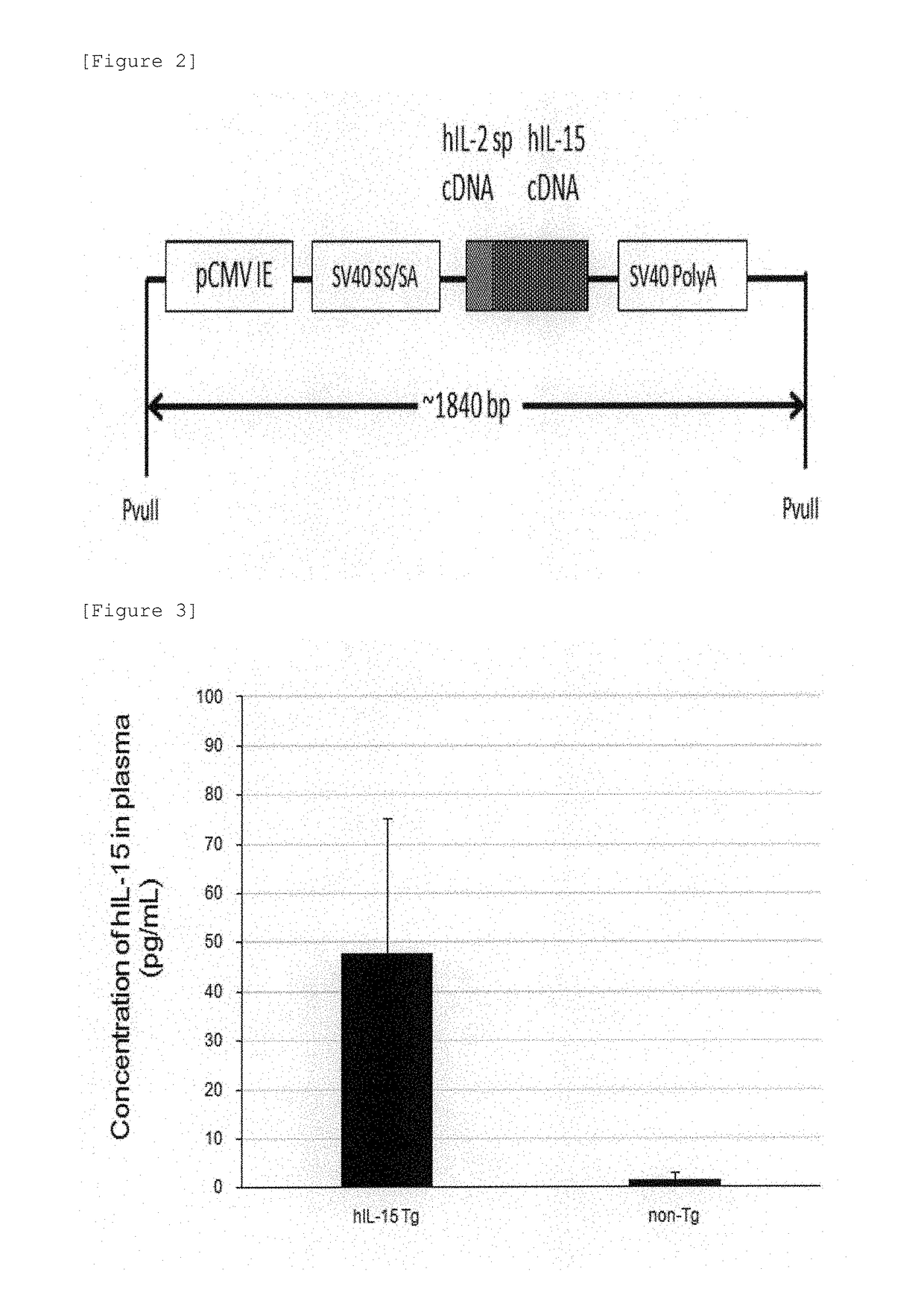
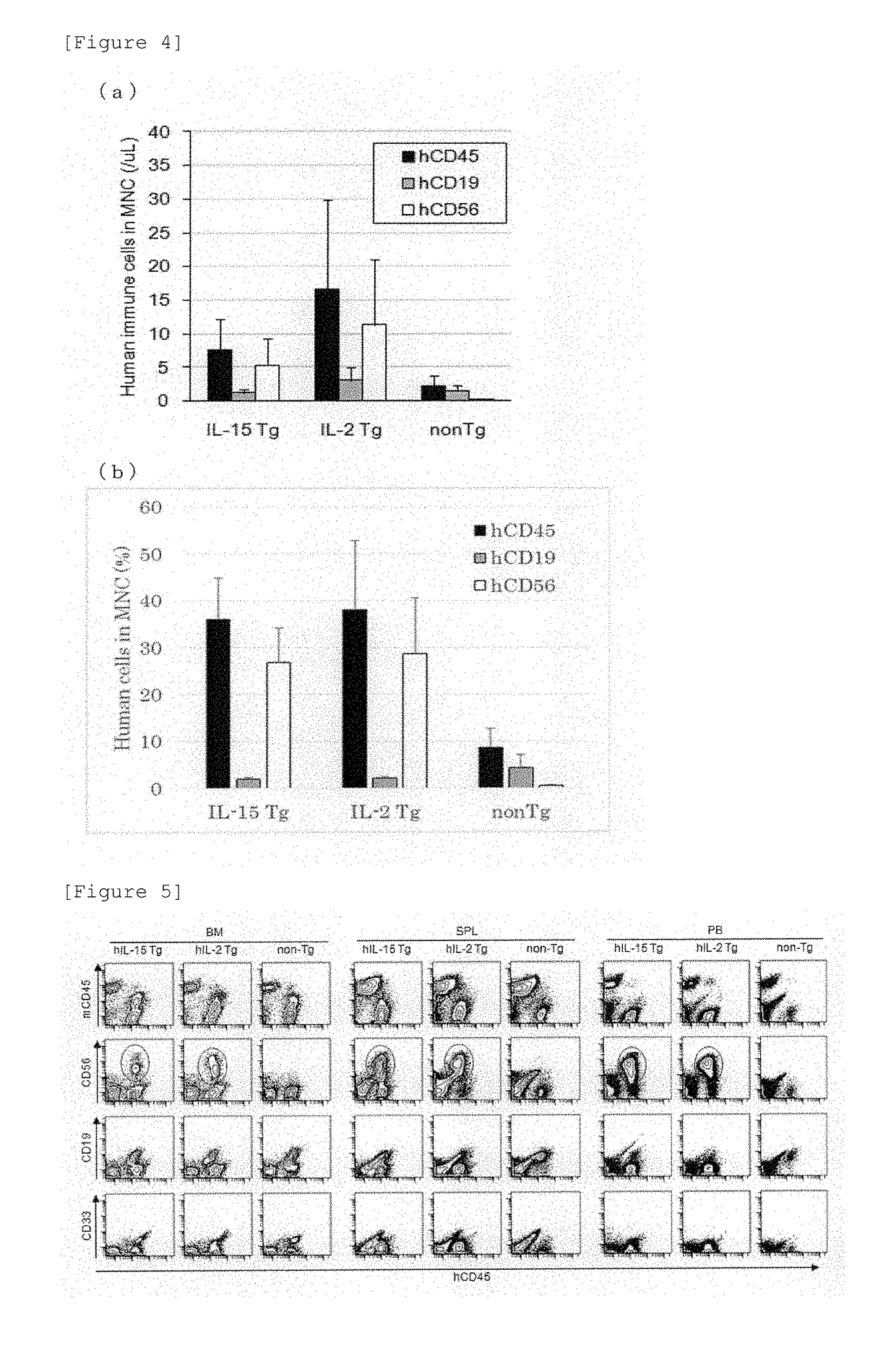
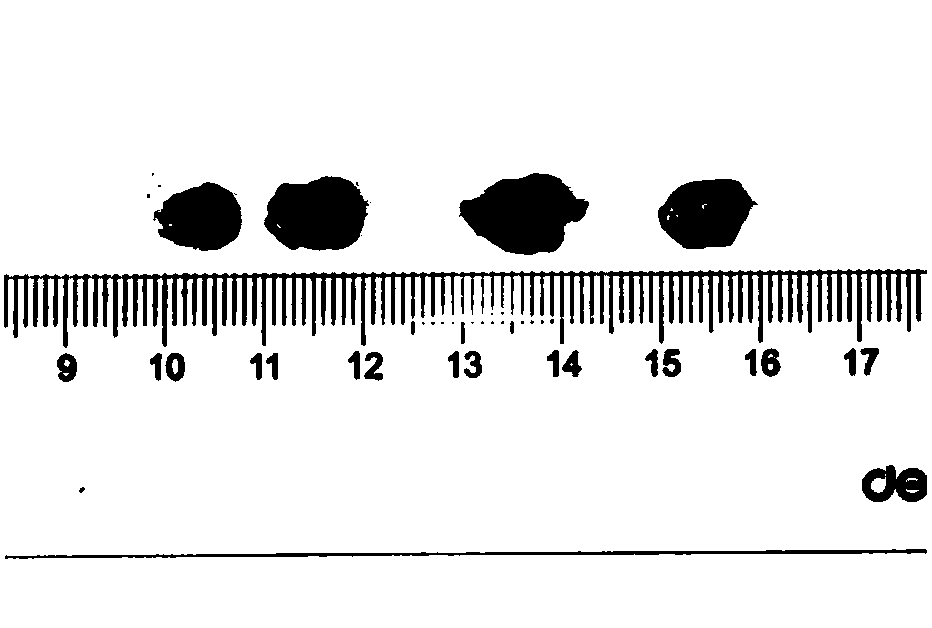
Human il-15-secreting immunodeficient mouse
ActiveUS20180213755A1PeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
An object of the present invention is to provide a mouse that enables the functions of human NK cell to be studied. A DNA consisting of a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, which is a gene region comprising a DNA in which a cDNA sequence encoding interleukin 15 (IL-15) is operably ligated to a cDNA sequence encoding the signal peptide of human interleukin (IL-2), is inserted to immunodeficient mouse cDNA. In NOD-scid, IL-2rγnull-hIL-15 Tg mice thus generated, hCD56+ cell having a concentration sufficient for conducting in vivo study on human mature NK cell are detected for at least 6 months after transplantation.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
Method for constructing a patient-derived tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with hepatocellular carcinoma based on organ-like method, and application thereof
InactiveCN109182272AConvenient researchNormal food intakeTumor/cancer cellsGeneral culture methodsAbnormal tissue growthHuman tumor
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a method for constructing a patient-derived tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with hepatocellular carcinoma based on an organ-likemethod, and an application thereof. The aim of the invention is to use the organ-like culture technology, adopts microcarrier as scaffold material, and combines the liver cancer cells from patient toculture the cells. The invention also discloses an organ-like method for preparing the liver cancer cells-3D material complex, and then directly into that cell-3D material complex is inoculated subcutaneously into normal immunized mice to construct liver cancer transplanted tumor model from patients in vivo, which solved the problems of using nude mice, SCID mice and other immunodeficient mice, which are difficult to feed, expensive and lower tumor formation rate. Especially, it can solve the problem that human hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor model in immunodeficiency mice can notreflect the important role of immune system in tumor occurrence and development, and human tumor transplanted tumor model in immunodeficiency mice has a long tumor formation cycle, which urgently needs the drug-sensitive demand of patients with clinical urgent need. The invention is applied to the field of mouse model construction.
Owner:上海美峰生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com