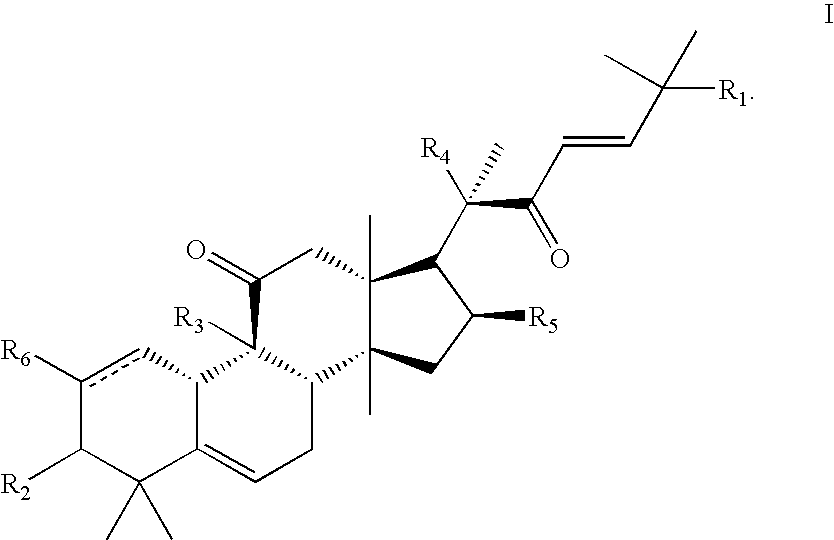
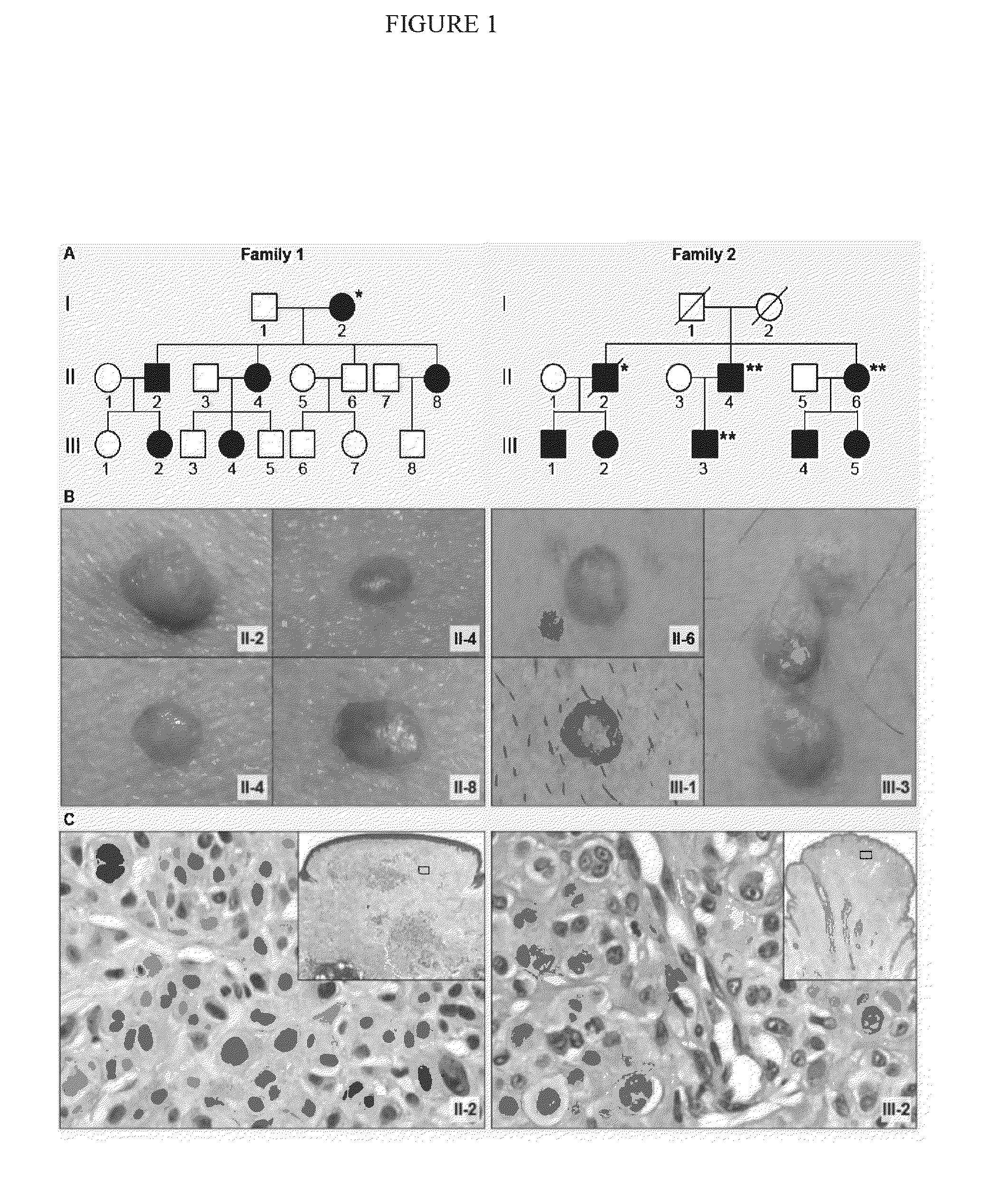
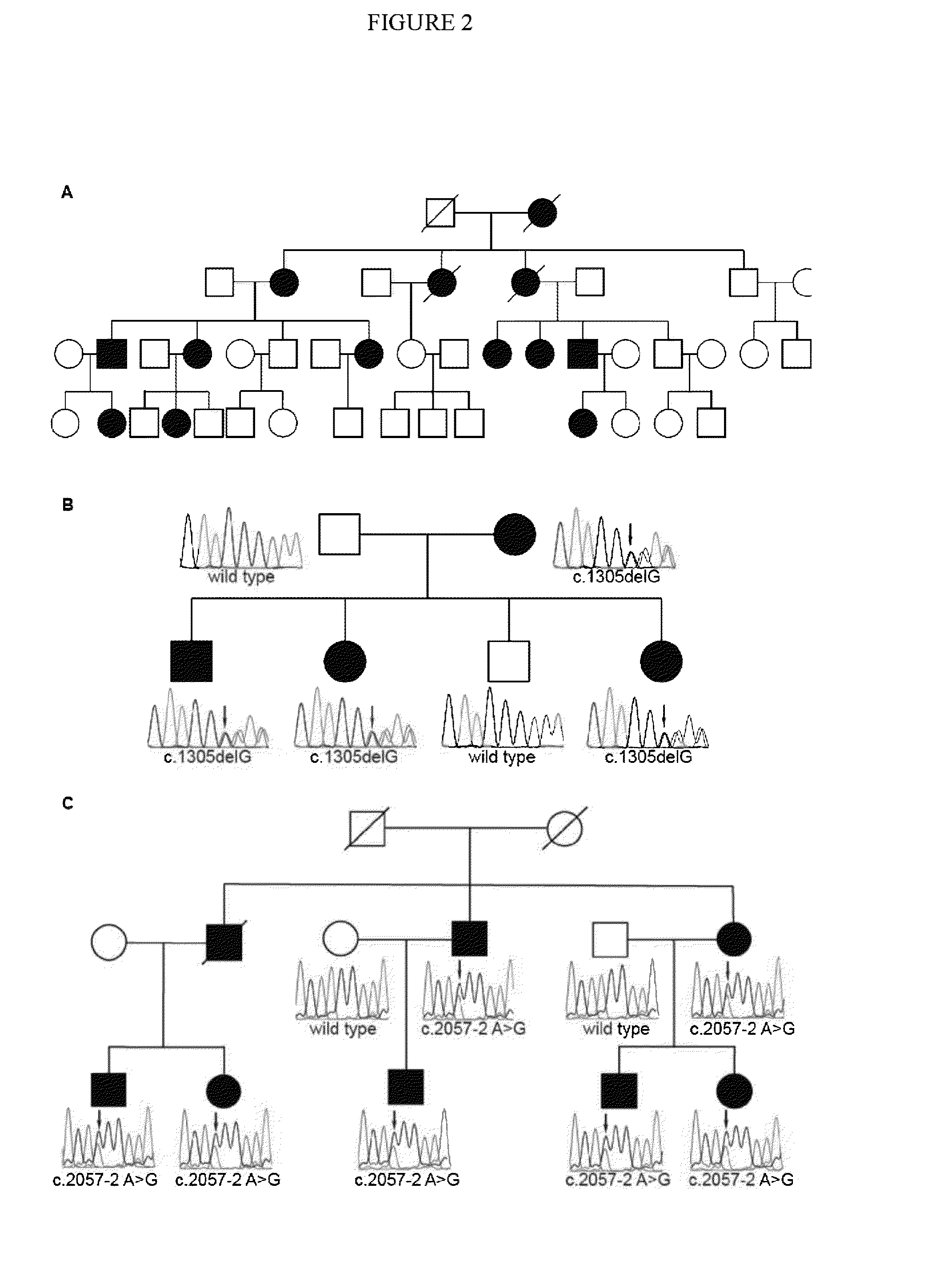
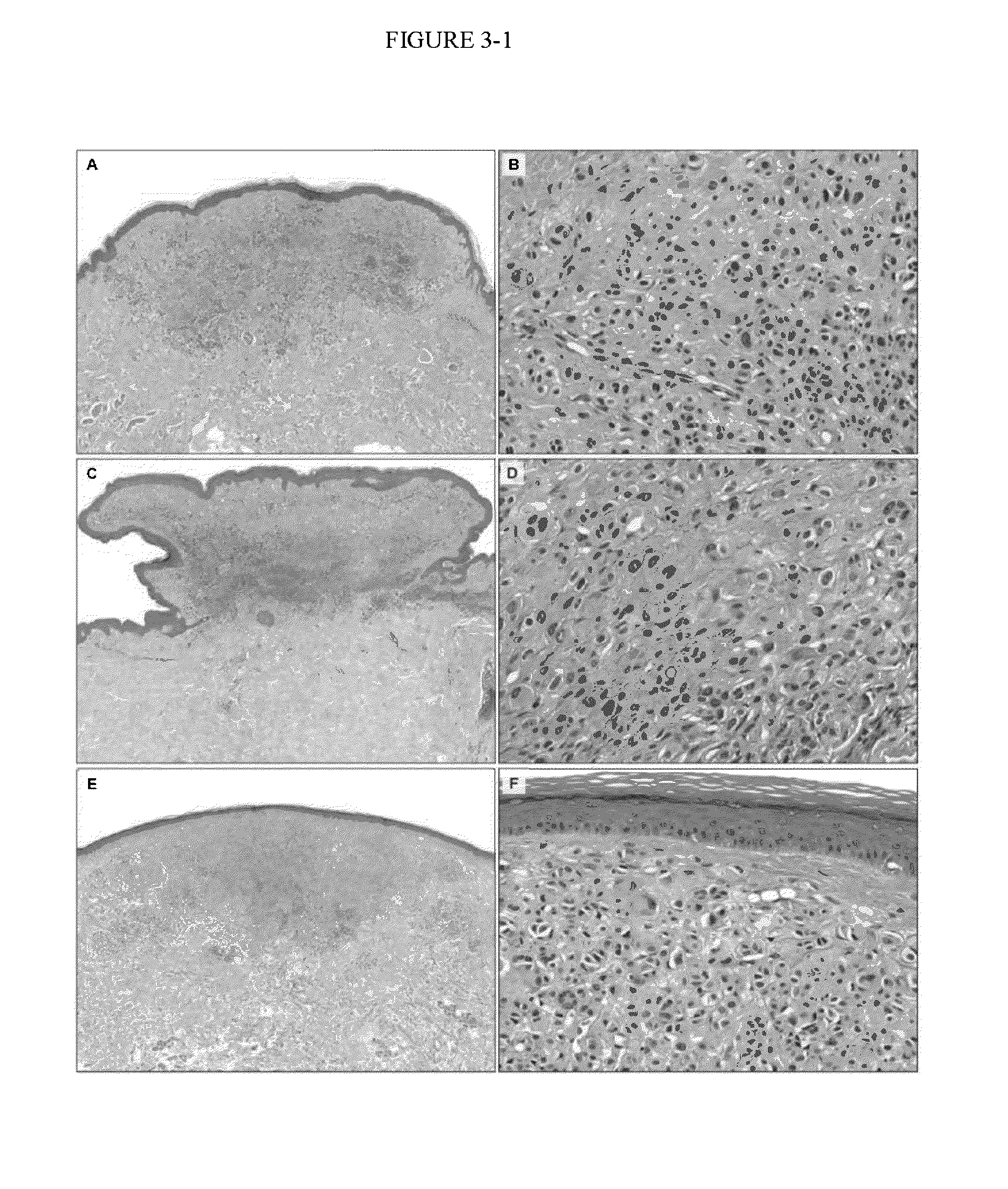
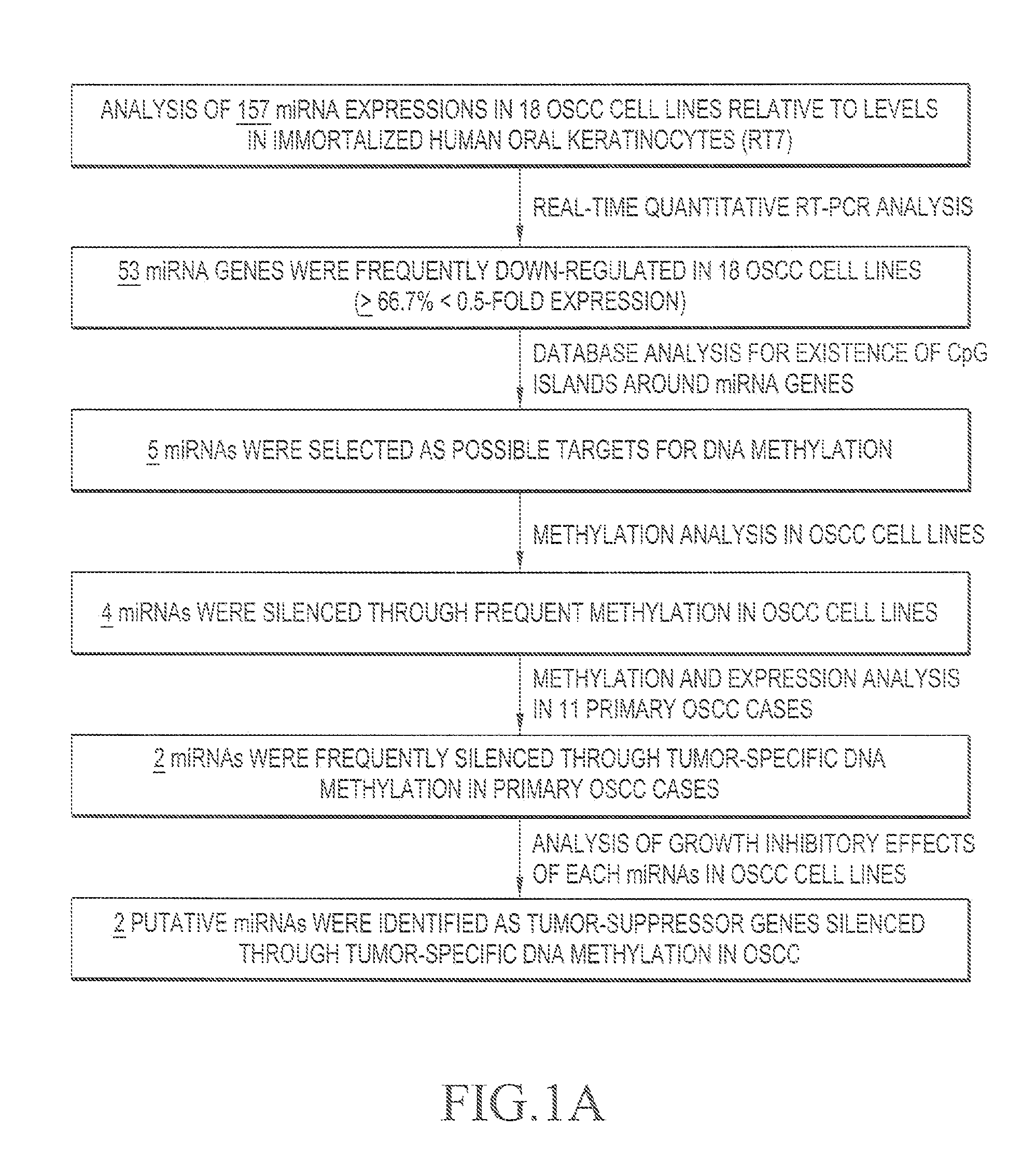
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Malignant transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as malignant degeneration of a previously existing benign tumor.
Materials and methods for treatment of cancer and identification of anti-cancer compounds
The subject invention pertains to the treatment of tumors and cancerous tissues and the prevention of tumorigenesis and malignant transformation through the modulation of JAK / STAT3 intracellular signaling. The subject invention concerns pharmaceutical compositions containing cucurbitacin I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or analog thereof, to a patient, wherein the tumor is characterized by the constitutive activation of the JAK / STAT3 intracellular signaling pathway. The present invention further pertains to methods of moderating the JAK and / or STAT3 signaling pathwaysin vitro or in vivo using cucurbitacin I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or analog therof. Another aspect of the present invention concerns a method for screening candidate compoudns for JAK AND / or STAT3 inhibition and anti-tumor activity.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
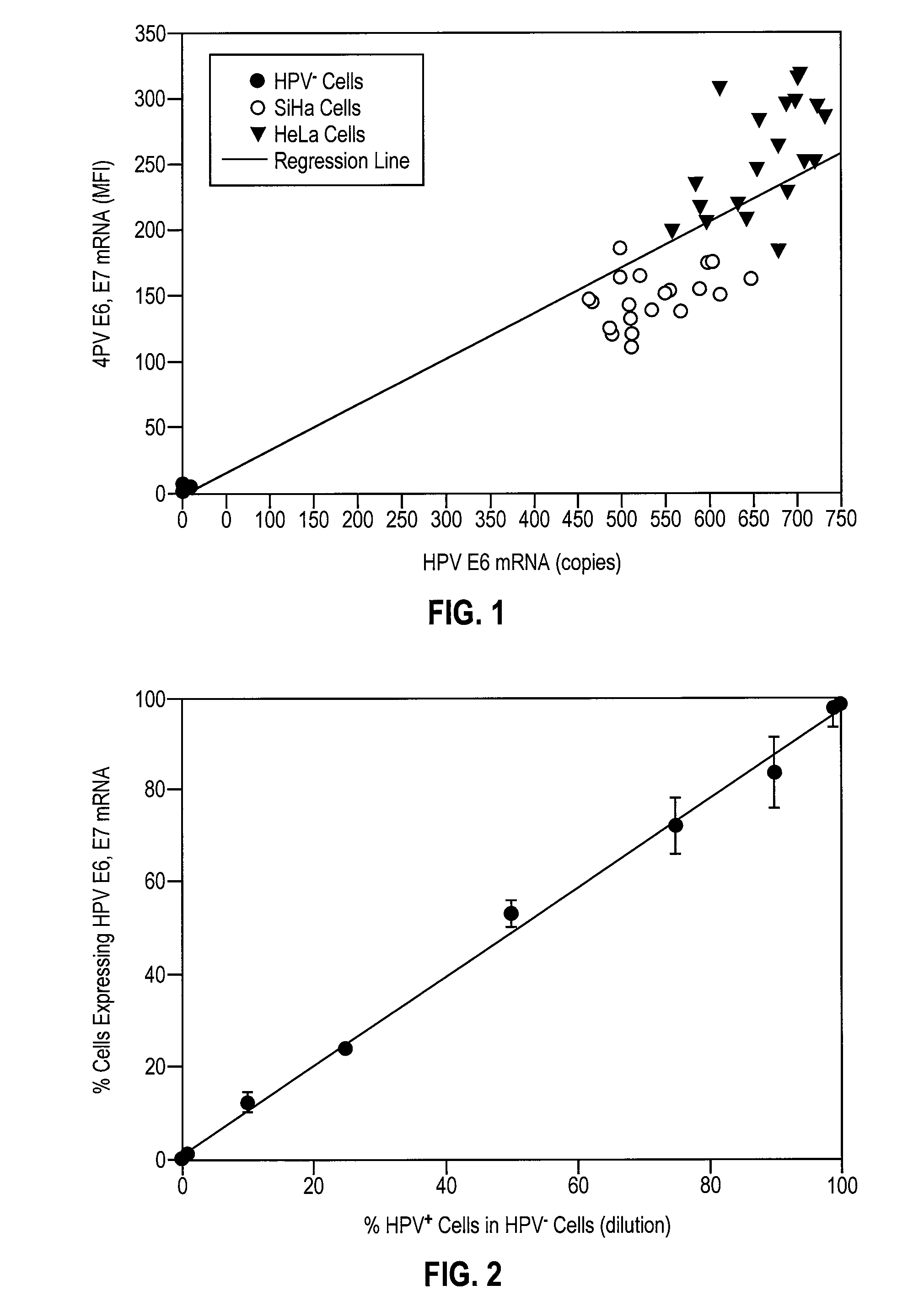
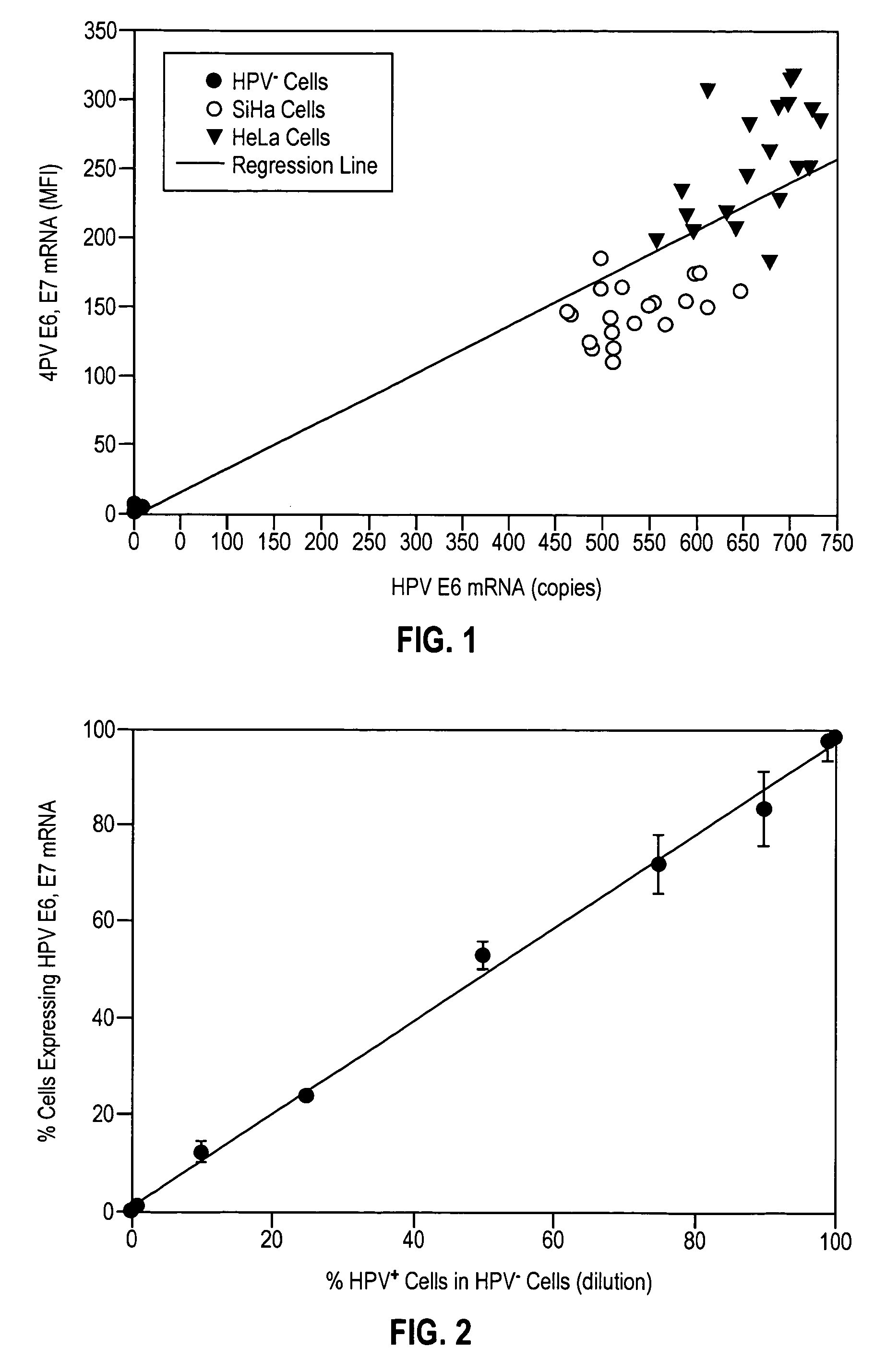
HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay and methods of use thereof
Provided is an HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay, referenced herein as the “In Cell HPV Assay,” that is capable of sensitive and specific detection of normal cervical cells undergoing malignant transformation as well as abnormal cervical cells with pre-malignant or malignant lesions. The In Cell HPV Assay identifies HPV E6, E7 mRNA via in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for HPV E6, E7 mRNA and quantitates the HPV E6, E7 mRNA via flow cytometry. The In Cell HPV Assay can be carried out in less than three hours directly from liquid-based cervical (“LBC”) cytology specimens. The In Cell HPV Assay provides an efficient and highly sensitive alternative to the Pap smear for determining abnormal cervical cytology.
Owner:INCELLDX
HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay and methods of use thereof
Provided is an HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay, referenced herein as the “In Cell HPV Assay,” that is capable of sensitive and specific detection of normal cervical cells undergoing malignant transformation as well as abnormal cervical cells with pre-malignant or malignant lesions. The In Cell HPV Assay identifies HPV E6, E7 mRNA via in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for HPV E6, E7 mRNA and quantitates the HPV E6, E7 mRNA via flow cytometry. The In Cell HPV Assay can be carried out in less than three hours directly from liquid-based cervical (“LBC”) cytology specimens. The In Cell HPV Assay provides an efficient and highly sensitive alternative to the Pap smear for determining abnormal cervical cytology.
Owner:INCELLDX
Construction method for sialidase gene knockout mouse model and application thereof
InactiveCN108486154AShort experiment cycleReduce experiment costVector-based foreign material introductionGlycosylasesCancer cellWilms' tumor
The invention relates to the field of biotechnologies, and provides a construction method for a sialidase gene knockout mouse model and application thereof. An in vitro and vivo targeted mouse genomeNPL is used for genetically recombining a CRISPR knockout plasmid vector, and a diploid double-knockout NPL mouse knockout model is successfully constructed through an oosperm microinjection technology. The NPL has the important function in a pathophysiological process of a body. Vicious transformation of a cancer cell is always along with overexpression of sialic acid. Now, the overexpression ofthe sialic acid has become one of important markers of the malignant transformation and transferring of a tumor. The model is capable of constructing a new research platform for researching a processof cell canceration, beneficial to a key step of researching generation and transferring of the tumor, and providing a foundation for the research and development of a novel anti-tumor drug.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Adipose tissue source exosome gel, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106676065AAvoid time consumingAvoid potential malignant cancer and other disadvantagesArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsNude mouseExosome
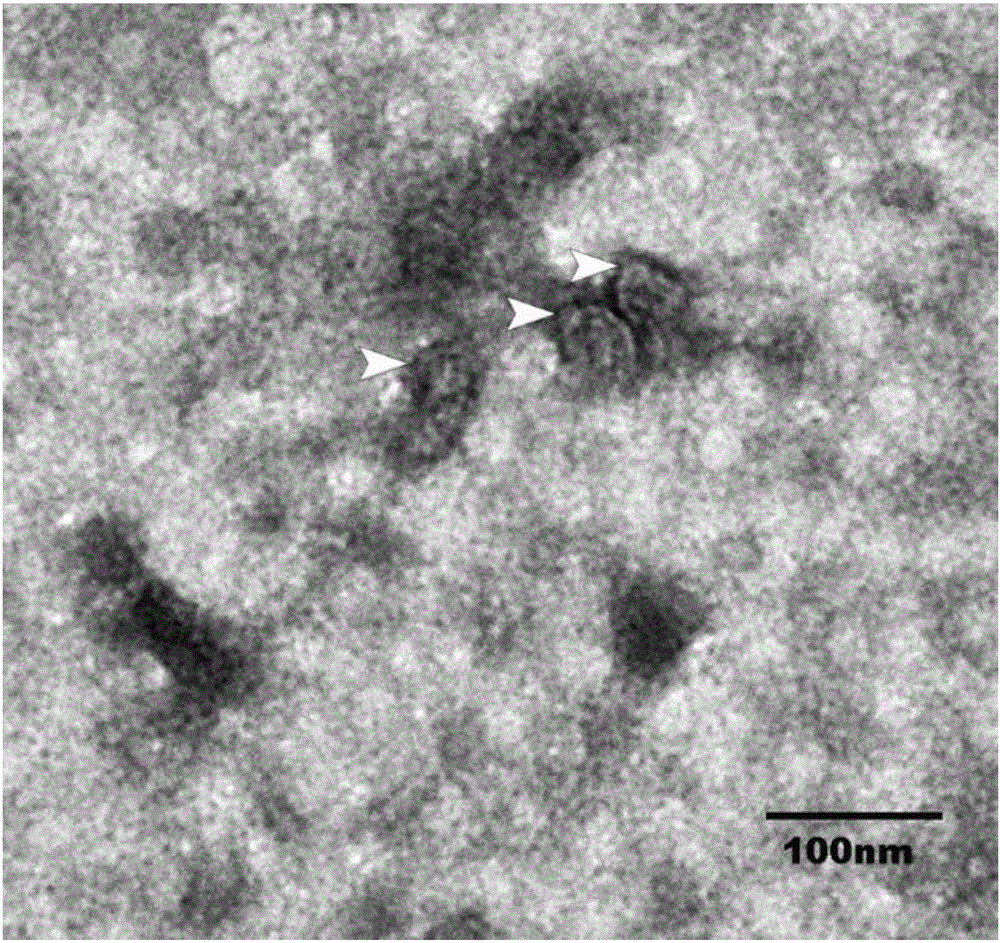
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue engineering and particularly relates to adipose tissue source exosome gel, a preparation method and application. The adipose tissue source exosome gel is characterized by comprising an adipose tissue exosome and a solvent in a mass-volume ratio of (1-3):1, wherein an aquogel is served as the solvent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: treating an adipose tissue, acquiring an adipose tissue extract, acquiring the adipose tissue source exosome and preparing the adipose tissue source exosome gel. The adipose tissue source exosome gel is mainly used for promoting the fat regeneration. The invention particularly relates to the exosome extracted from the adipose tissue. When the exosome is applied to the nude mouse body, a new mature adipose tissue can be generated. The defects of insufficient seed cell resource, potential malignant transformation and tumor formation of the traditional tissue engineering can be overcome; the exosome has the advantage of easiness in storage and transportation; a new thought is supplied for acquiring the fat for the tissue engineering.
Owner:成都世联康健生物科技有限公司
Spleen polypeptide extract, its preparing process and use
ActiveCN1634987AThe preparation process is stable and matureImprove malignant transformationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryImmunomodulatory drugSecondary immune deficiency
The invention discloses a spleen polypeptide extract extracted from the spleen tissue of mammals other than humans. The mammalian tissue is subjected to fat removal, homogenization, acid adjustment, freezing and thawing, pH adjustment, precipitation, heating, and centrifugation. Filtration, ultrafiltration and other steps to obtain the spleen polypeptide extract; the drug is an immunomodulatory drug that can improve and improve the immune function of the body, and can be used for primary and secondary cellular immune deficiency diseases (such as eczema, thrombocytopenia, multiple Infection syndrome, etc.), respiratory tract and lung infection, habitual cold, chronic hepatitis B, mumps, recurrent aphtha and other diseases, can be used in the treatment of leukopenia, leukemia, aplastic anemia caused by radiotherapy and chemotherapy , Lymphoma and other malignant tumors, to improve the malignant transformation of tumor patients, to improve postoperative or critically ill patients when they are weak.
Owner:融致丰生制药有限公司
DNA methylation markers based on epigenetic stem cell signatures in cancer
ActiveUS20100172880A1Guaranteed maximum utilizationPoor outcomeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationNon targeted
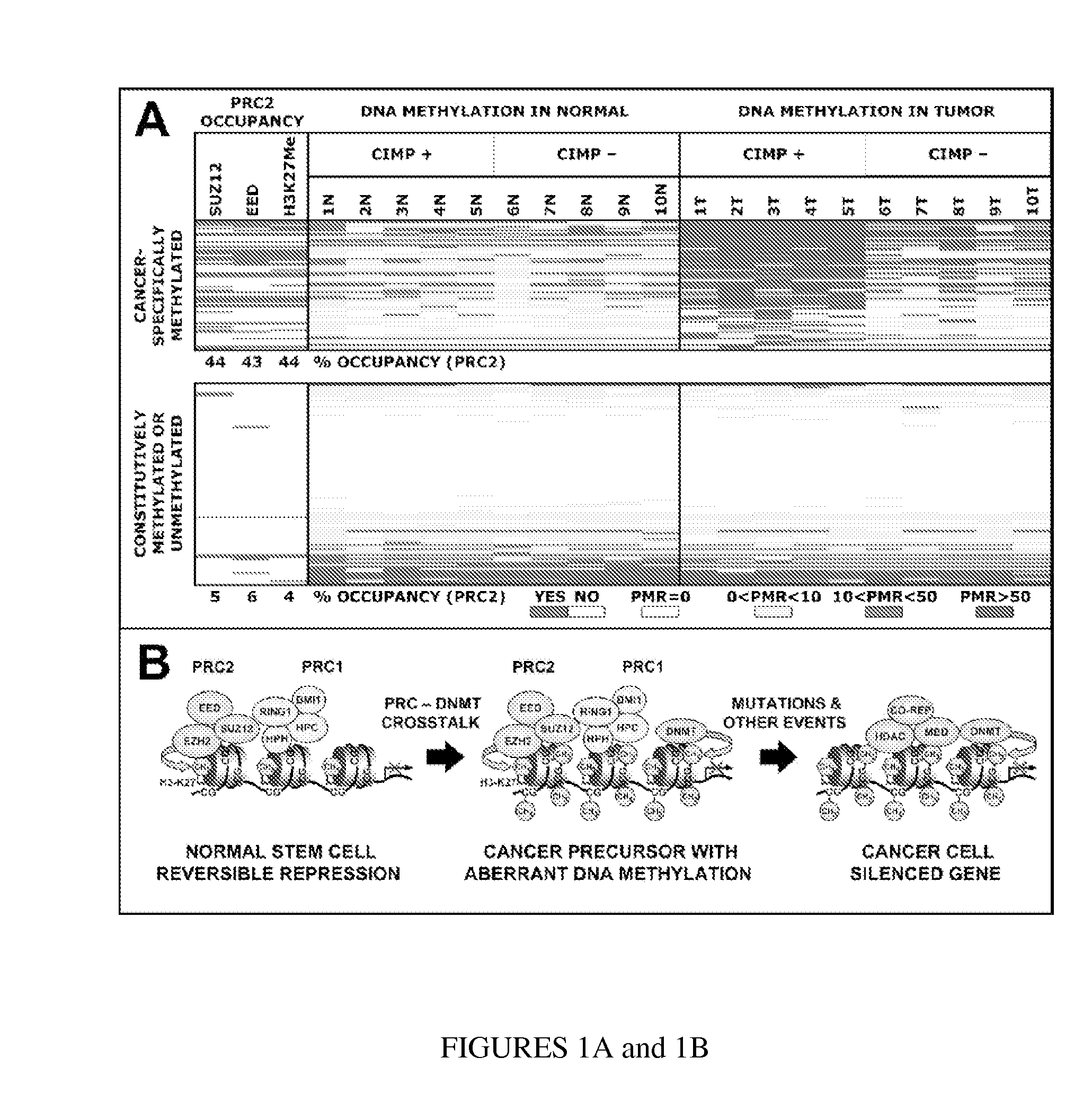
In particular aspects, stem-cell polycomb group (PcG) targets are more likely to have cancer-specific promoter DNA methylation than non-targets, indicating a stem-cell origin of cancer, where reversible gene repression is replaced by permanent silencing, locking the cell into a perpetual state of self-renewal and predisposition to subsequent malignant transformation. Exemplary aspects provide methods for identifying preferred DNA methylation markers for a cellular proliferative disorder and / or cancer and markers for developmental lineages and / or stages, based on identifying PcG protein or PcG repressive complex genomic target loci within a precursor cell (e.g., stem or progenitor cell) population, and determining, in cells of the proliferative disorder and / or cancer or cell of the particular developmental lineages and / or stages, a characteristic methylation status of the PcG target loci. Additional aspects provide methods for validating and / or monitoring a precursor cell (e.g., stem cell) population. Diagnostic and prognostic methods for ovarian and breast cancer are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
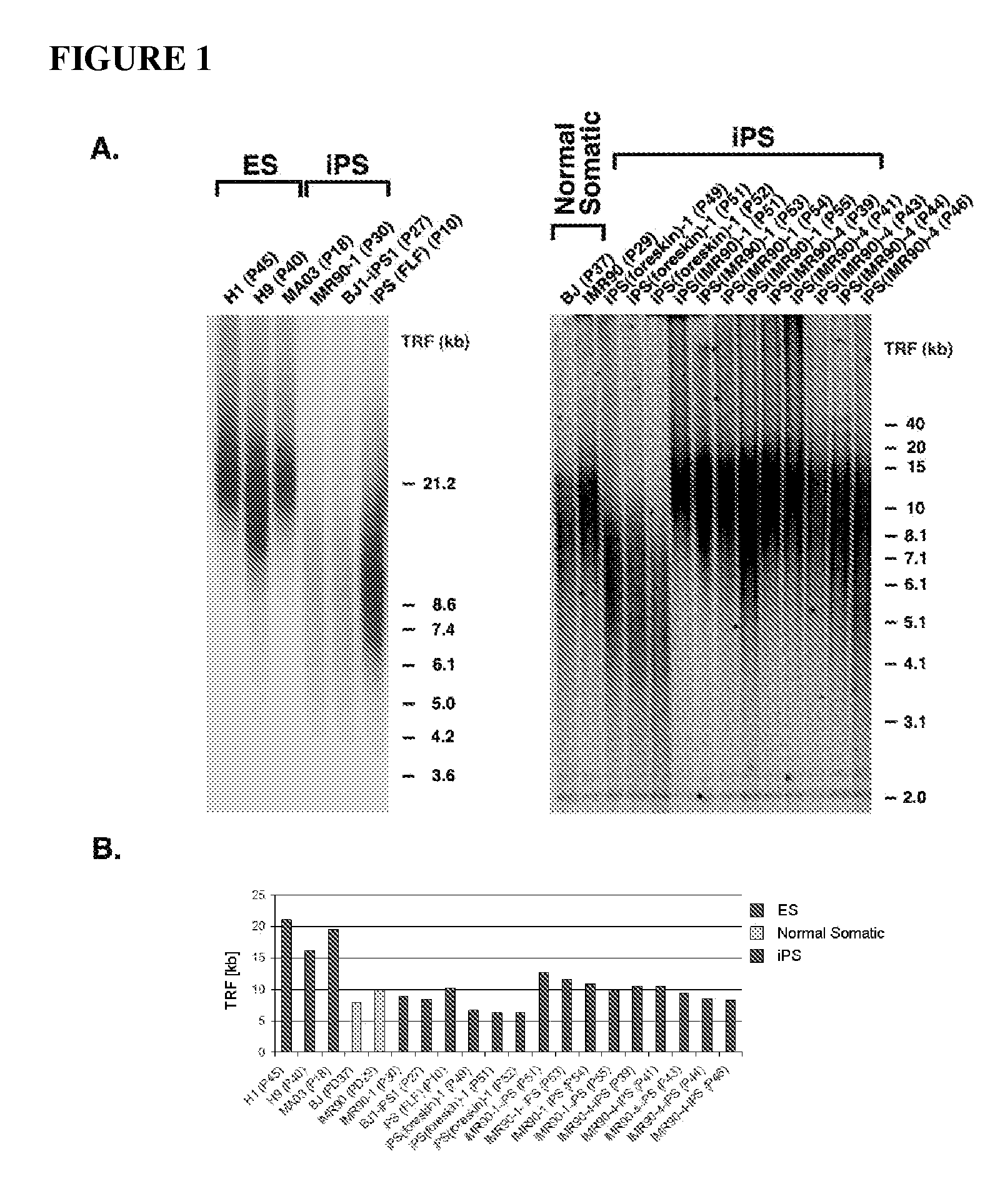
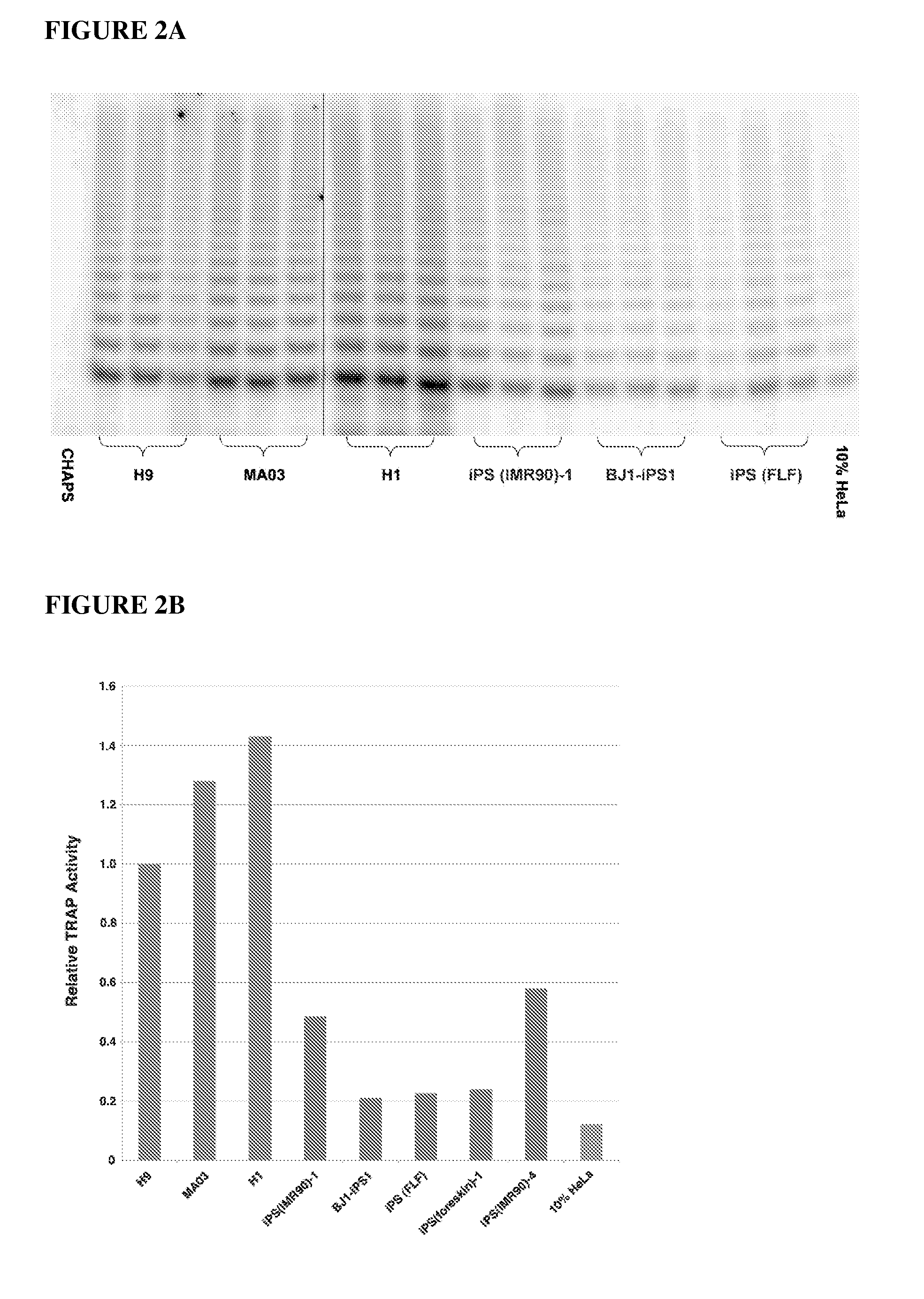
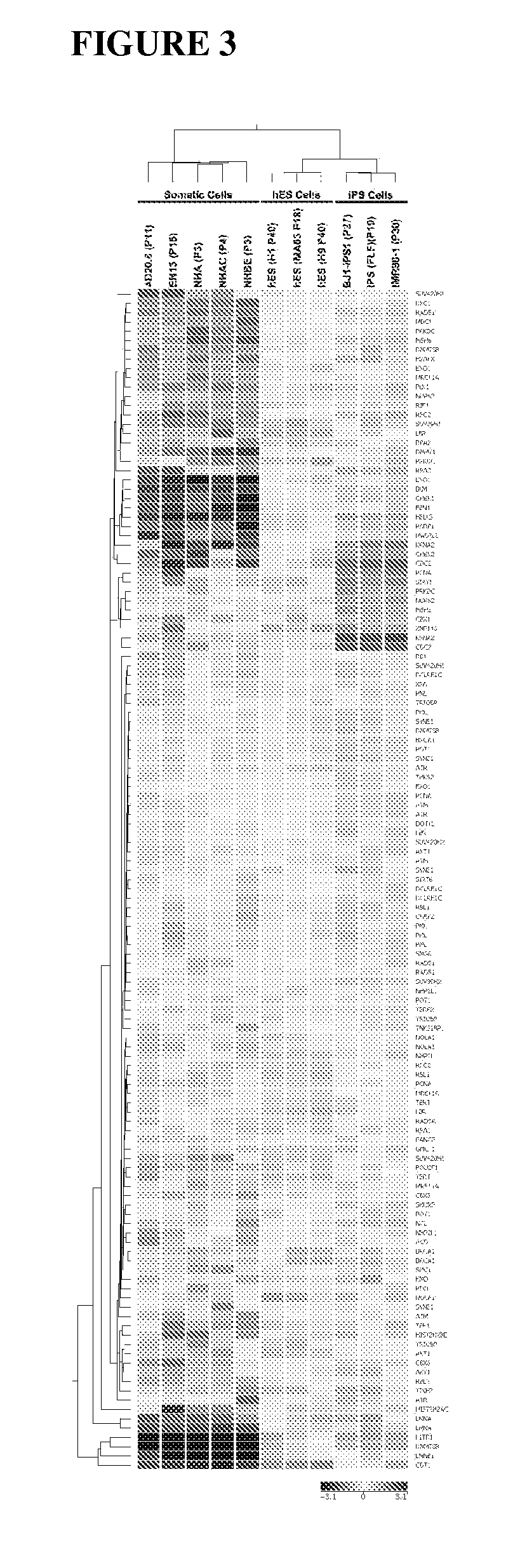
Methods for telomere length and genomic DNA quality control and analysis in pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20130011918A1Reduce riskDesired phenotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPluripotential stem cellClinical grade
The generation of clinical-grade cell-based therapies from human embryonic stem cells or cells reprogrammed to pluripotency from somatic cells, requires stringent quality controls to insure that the cells have long enough telomeres and resulting cellular lifespan to be clinically useful, and normal gene expression and genomic integrity so as to insure cells with a desired and reproducible phenotype and to reduce the risk of the malignant transformation of cells. Assays useful in identifying human embryonic stem cell lines and pluripotent cells resulting from the transcriptional reprogramming of somatic cells that have embryonic telomere length are described as well as quality control assays for screening genomic integrity in cells expanded and banked for therapeutic use, as well as assays to identify cells capable of abnormal immortalization,
Owner:LINEAGE CELL THERAPEUTICS INC
miRNA marker related to malignant transformation of colitis and proctitis and kit
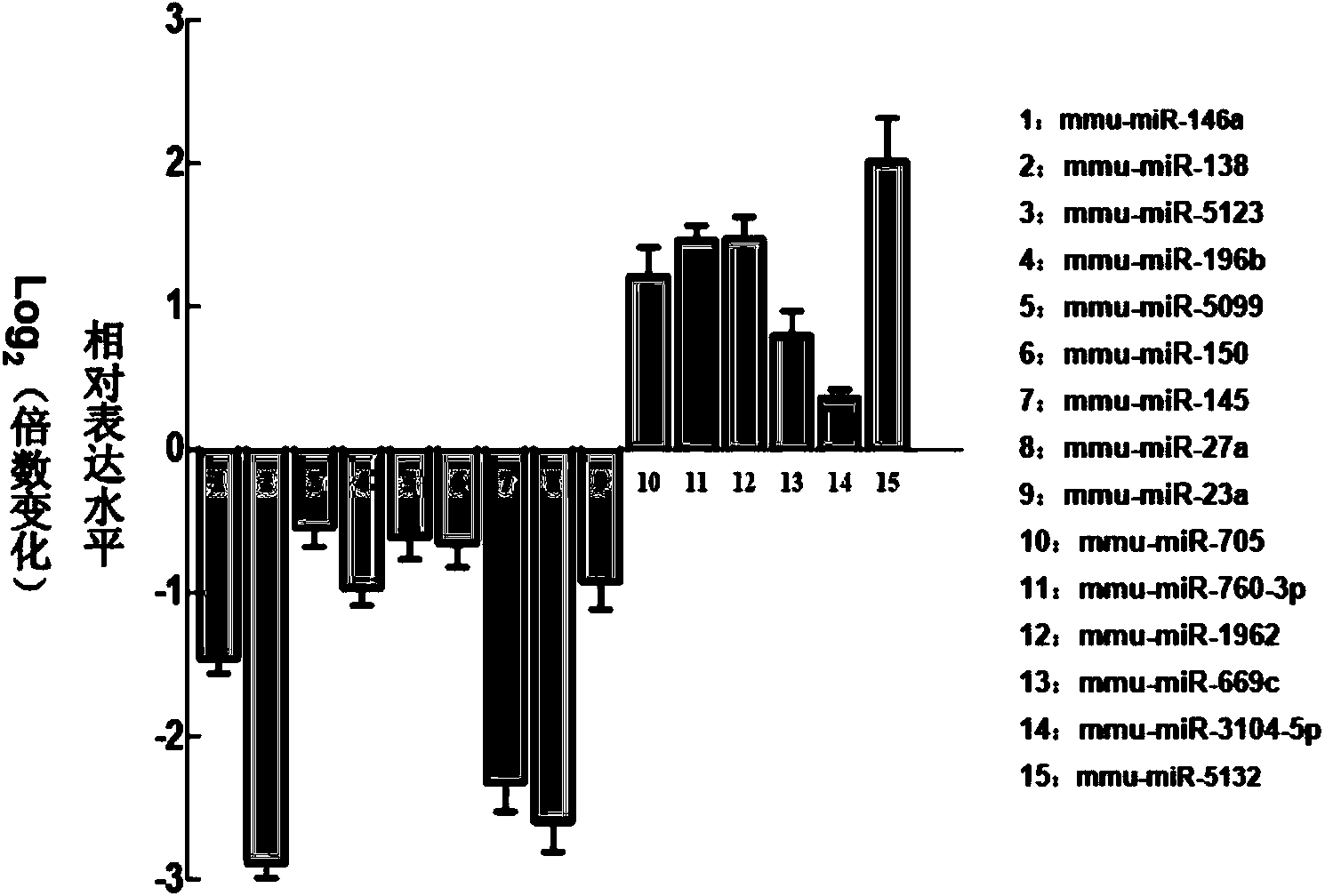
ActiveCN103966328AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMir 145 5pCancer Early Diagnosis
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and medical technology and provides a miRNA marker related to malignant transformation of colitis and proctitis. The marker is a composition of miR-138-5p, miR-145-5p, miR-146a-5p and miR-150-5p. The invention further provides a primer of the miRNA marker, application of the miRNA marker in preparation of a rectal cancer early-diagnosis kit, and the rectal cancer early-diagnosis kit. The provided miRNA marker, including miR-138-5p, miR-145-5p, miR-146a-5p and miR-150-5p and related to malignant transformation of colitis and proctitis is used for early screening of the colon cancer and the rectal cancer and has the characteristics of easiness in operation, high specificity and high sensitivity.
Owner:江西佰延生物技术有限公司
Cancer-associated epitope
The present invention provides a cancer-associated epitope consisting of two polypeptides, wherein the first polypeptide is derived from cytokeratin K8, and the second polypeptide is derived from cytokeratin K18. The cancer-associated epitopes become exposed during malignant transformation, especially in colon, breast, ovarian, kidney, lung and testicular tissues. Exposure of the cancer-associated epitopes occurs by cleavage and removal of the N-terminal peptides of cytokeratins K8 and K18. The invention also provides a cancer-associated epitope up to 10M-1 in cancer tissue, which is 100 times higher than that of cytokeratin K8 / K18 complex in normal tissue. The present invention provides cancer-associated epitopes, binding entities, antibodies and methods for detecting and treating cancer using the epitopes, binding entities and antibodies.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Bap1 mutational analysis in determining susceptibility to, prognosis of, and treatment of melanocytic neoplasia
InactiveUS20140011696A1Increased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMelanocytomaNeoplasm
Methods and compositions for diagnosing and prognosing neoplasms, particularly malignant melanomas, and for identifying patients at high risk for melanocytic nevi and / or melanomas or other cancers are provided. Methods for distinguishing between nevi at high and low risk for malignant transformation and for characterizing or classifying lesions or nevi are also disclosed. Assays and kits for prognosis of melanoma in a human subject comprising assessment of BAP1 protein and / or BAP1 nucleic acid are provided.
Owner:MEDICAL UNIV OF GRAZ +1
Preparation method of dendrobium officinale caulis wine
InactiveCN106190694AImprove stabilityCan inhibit growthSugar food ingredientsYeast food ingredientsOxygenFood flavor
The invention discloses a preparation method of dendrobium officinale caulis wine. Bacillus coagulans and saccharomycetes are mixed and fermented, wherein the bacillus coagulans is an aerobic bacterium; in a fermentation process, the mildewing of dendrobium officinale caulis and the malignant transformation of flavor substances can be inhibited by consuming oxygen; an experiment verifies that an anti-oxidization substance has good stability in the fermentation process and a storage process; the reservation of original nutrient components is facilitated, and a sufficient C source and N source exist in a fermentation system; the alcohol content of the prepared dendrobium officinale caulis wine is 6 volume percent to 8 volume percent; the prepared dendrobium officinale caulis wine has a coordinated taste, good color and luster and an excellent flavor, and has the characteristics of abundant nutrients, health-care function and the like; an operation process is relatively simple and the wine is not easily infected by infectious microbes; only one time of fermentation is performed and a fermentation period is short; a fermentation byproduct can be used as a raw material of stuffing or is dried by mist spraying to obtain dendrobium officinale caulis powder; the loss of the nutrient components of the obtained product is less and the product does not easily go moldy in a processing process; the product has good quality and an excellent mouth feel, good comprehensive utilization is realized, and the dendrobium officinale caulis wine is suitable for being produced in a factory in a large batch.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting carcinoma and agent for suppressing carcinoma
ActiveUS20110076768A1Suppressing carcinomaConveniently and rapidly analyzingMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemSquamous cancerSquamous Carcinomas
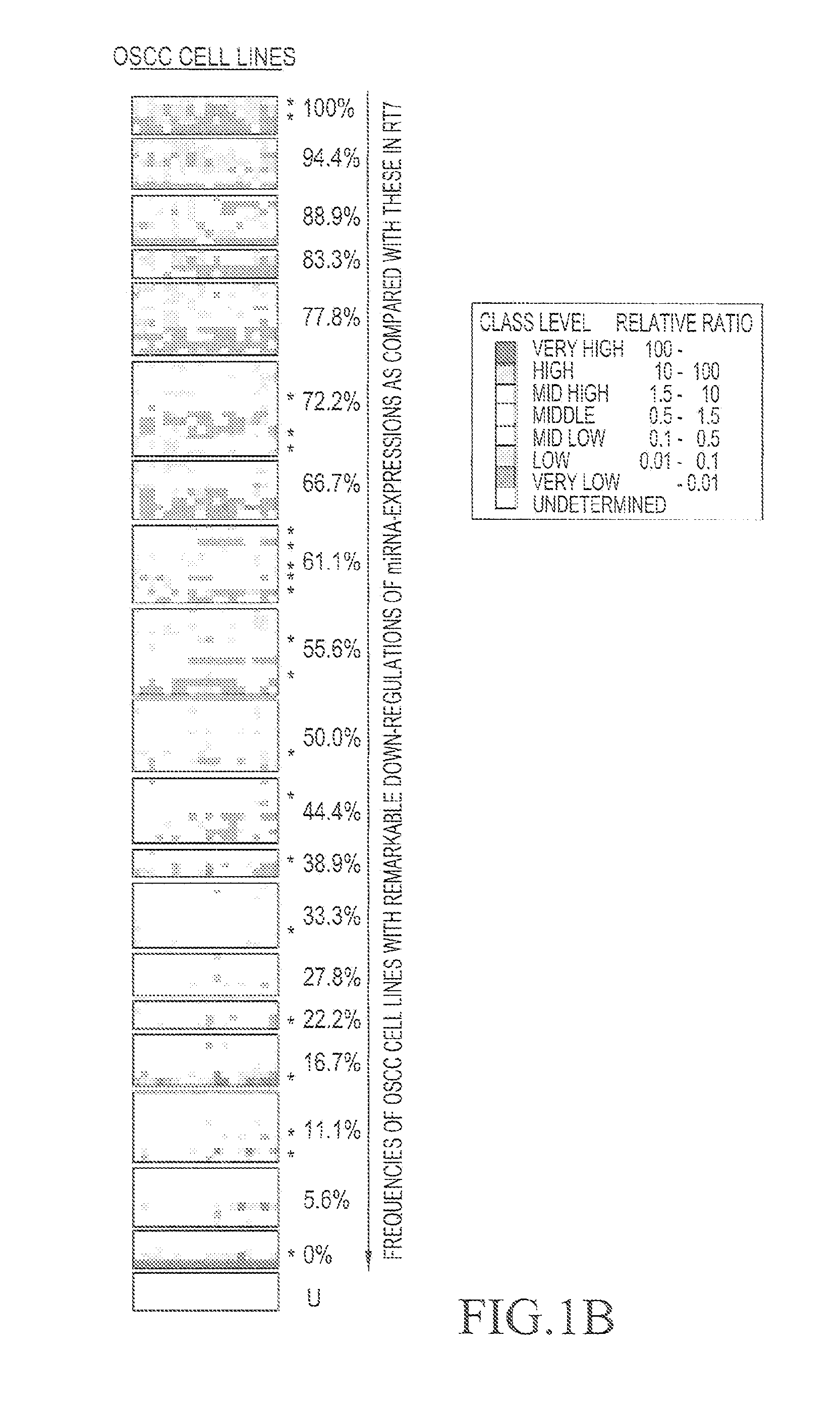
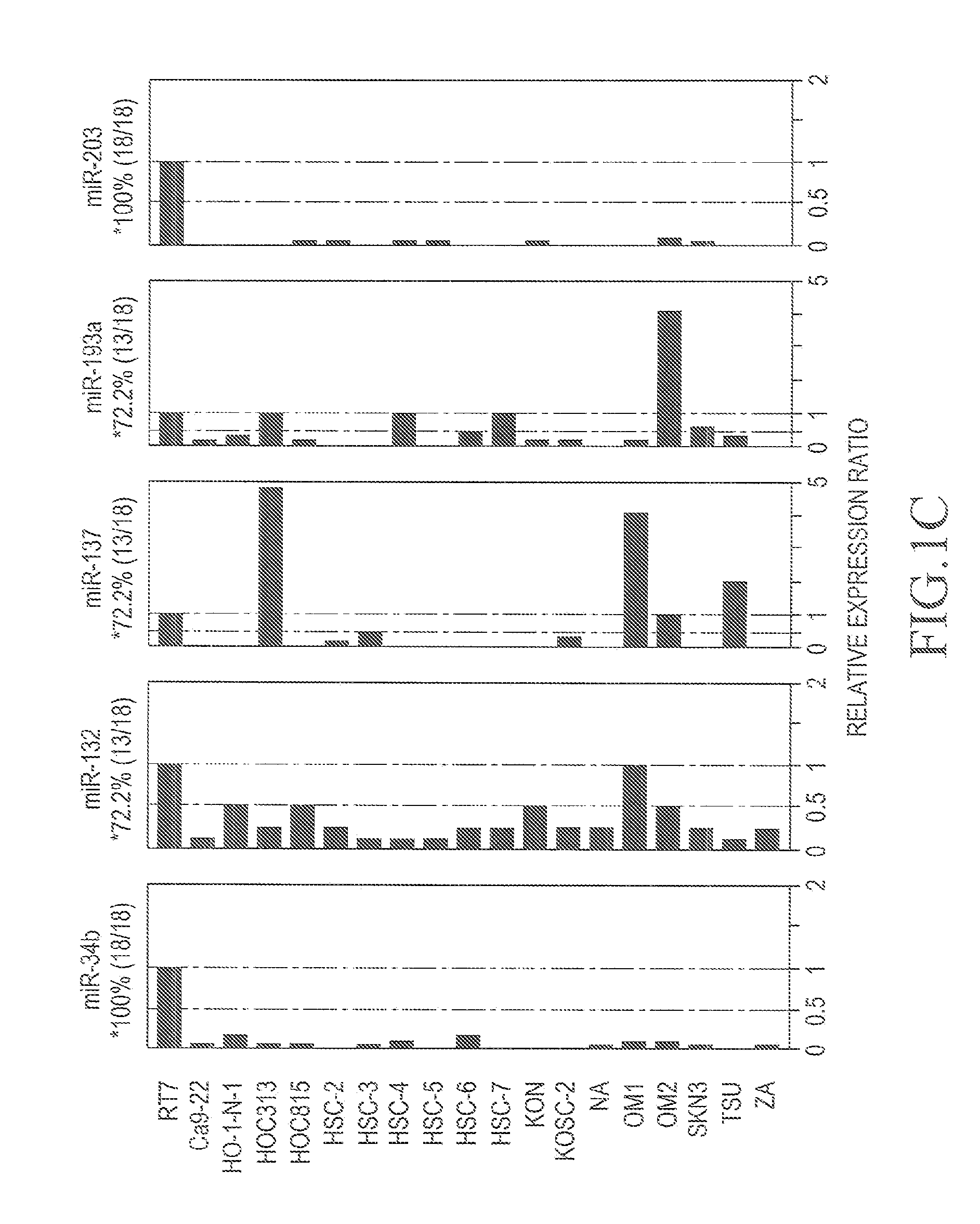
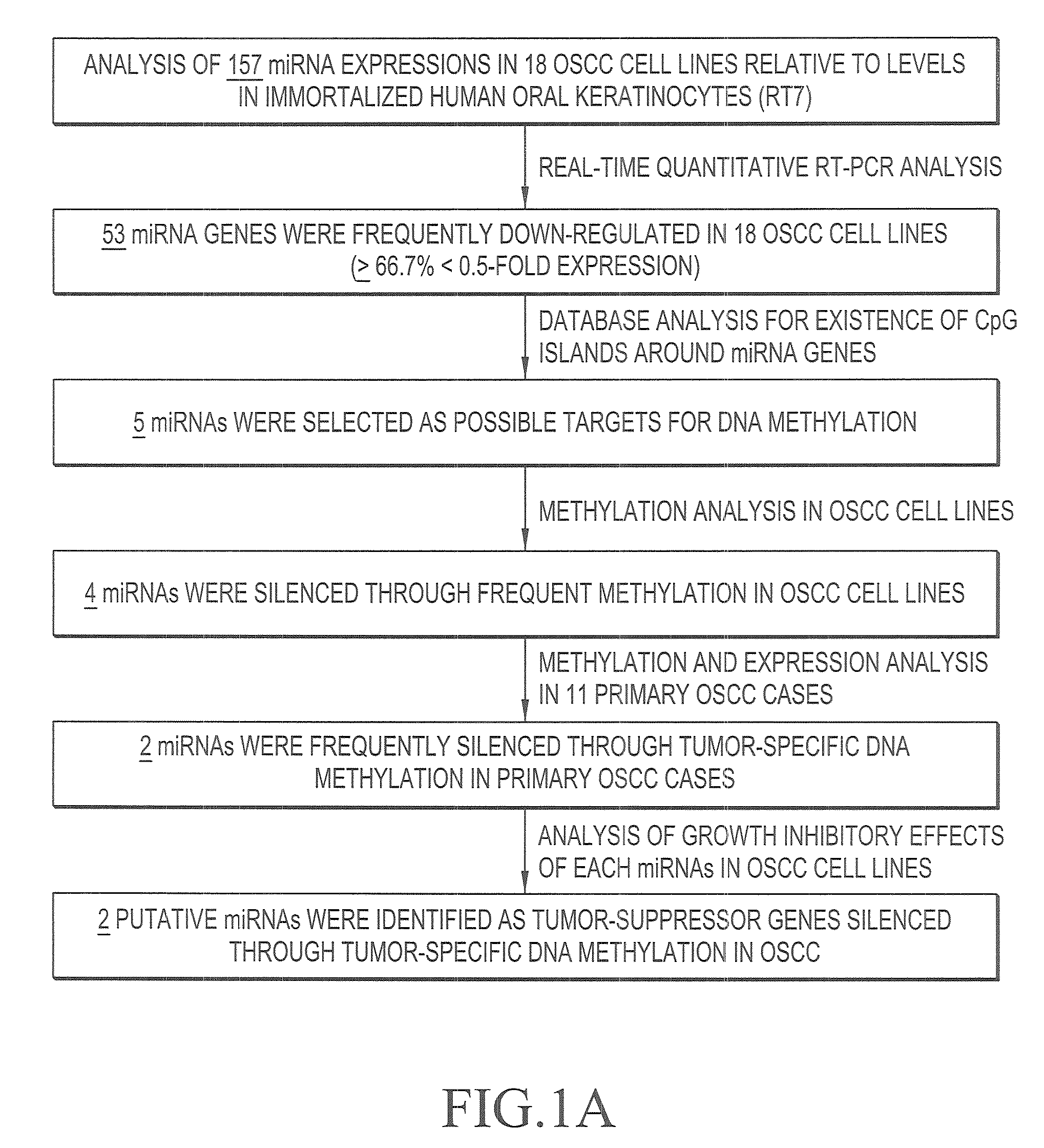
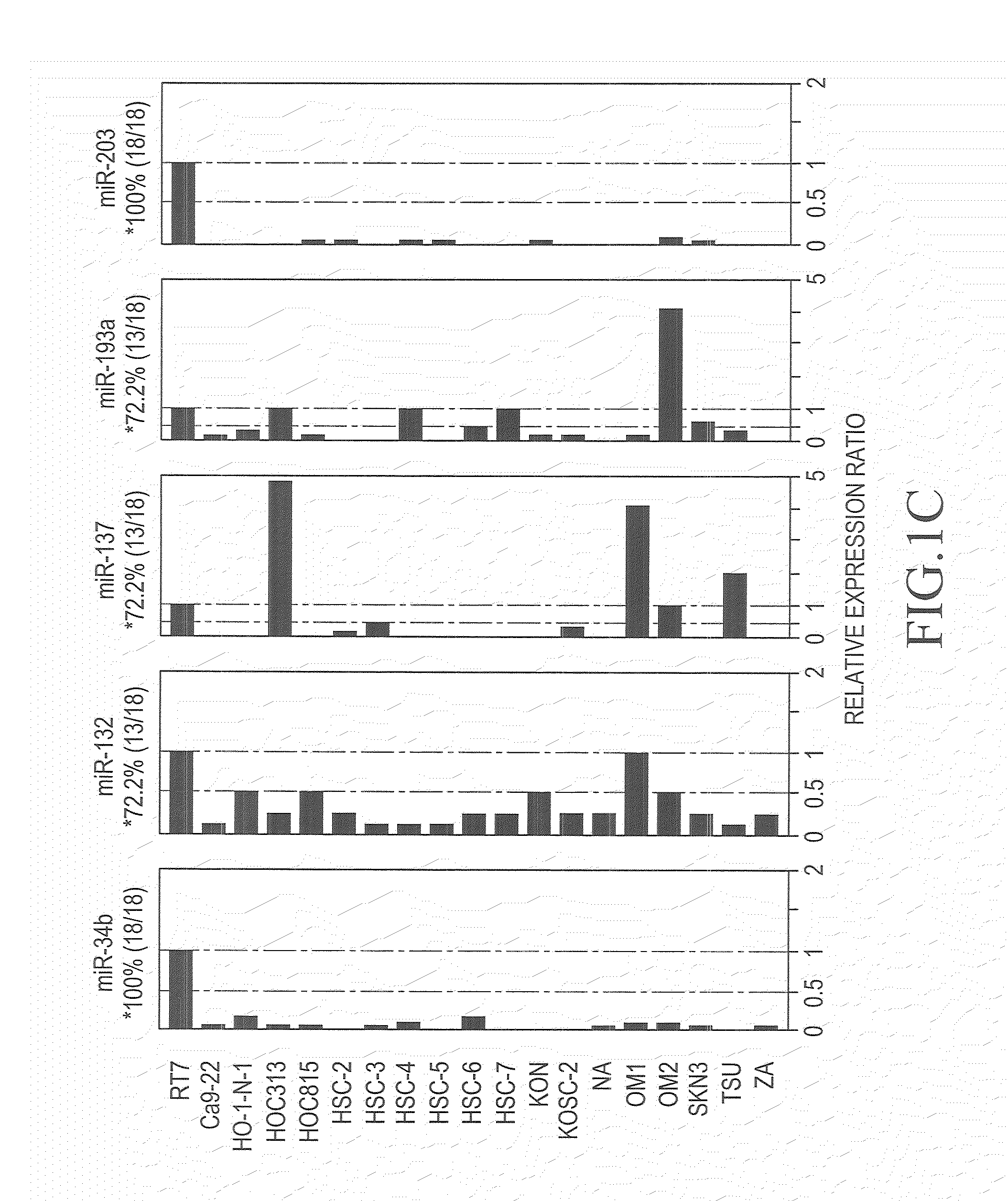
An object of the present invention is to identify genes exhibiting characteristic behavior in the cases of carcinoma such as oral squamous-cell carcinoma using a change of expression level of micro RNA in oral squamous-cell carcinoma as an indicator, so as to provide a method for detecting carcinoma and an agent for suppressing carcinoma. The present invention A method for detecting oral squamous-cell carcinoma, which comprises detecting malignant transformation of specimens by employing a change of expression level of micro RNA as an indicator, and an agent for suppressing oral squamous-cell carcinoma using micro RNA.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Application of Astragalus polysaccharide in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105349486AAvoid damageOrganic active ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAstragalus polysaccharideMalignant transformation
The invention provides application of Astragalus polysaccharide in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The application refers to effect, on protecting proliferative and genetic stability of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, of Astragalus polysaccharide. Researches show that Astragalus polysaccharide has protective effect on damage to the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells caused by various factors, and the Astragalus polysaccharide can serve as drug for preventing malignant transformation of damage.
Owner:GANSU UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Dual inhibitors of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I
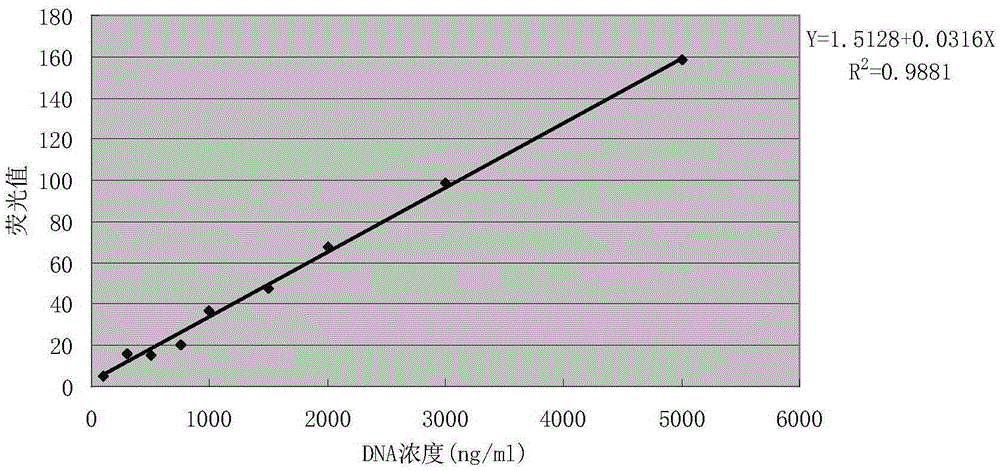
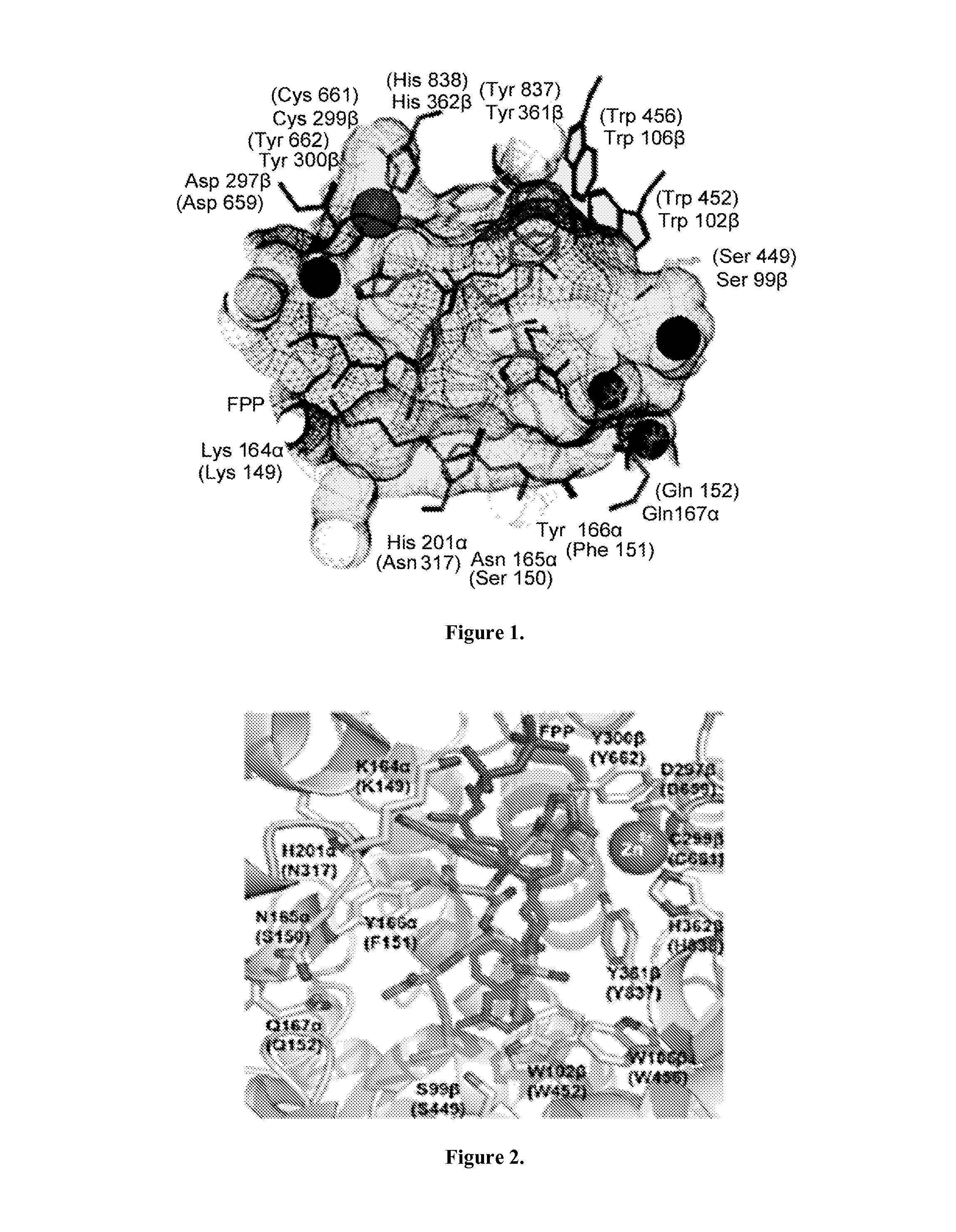
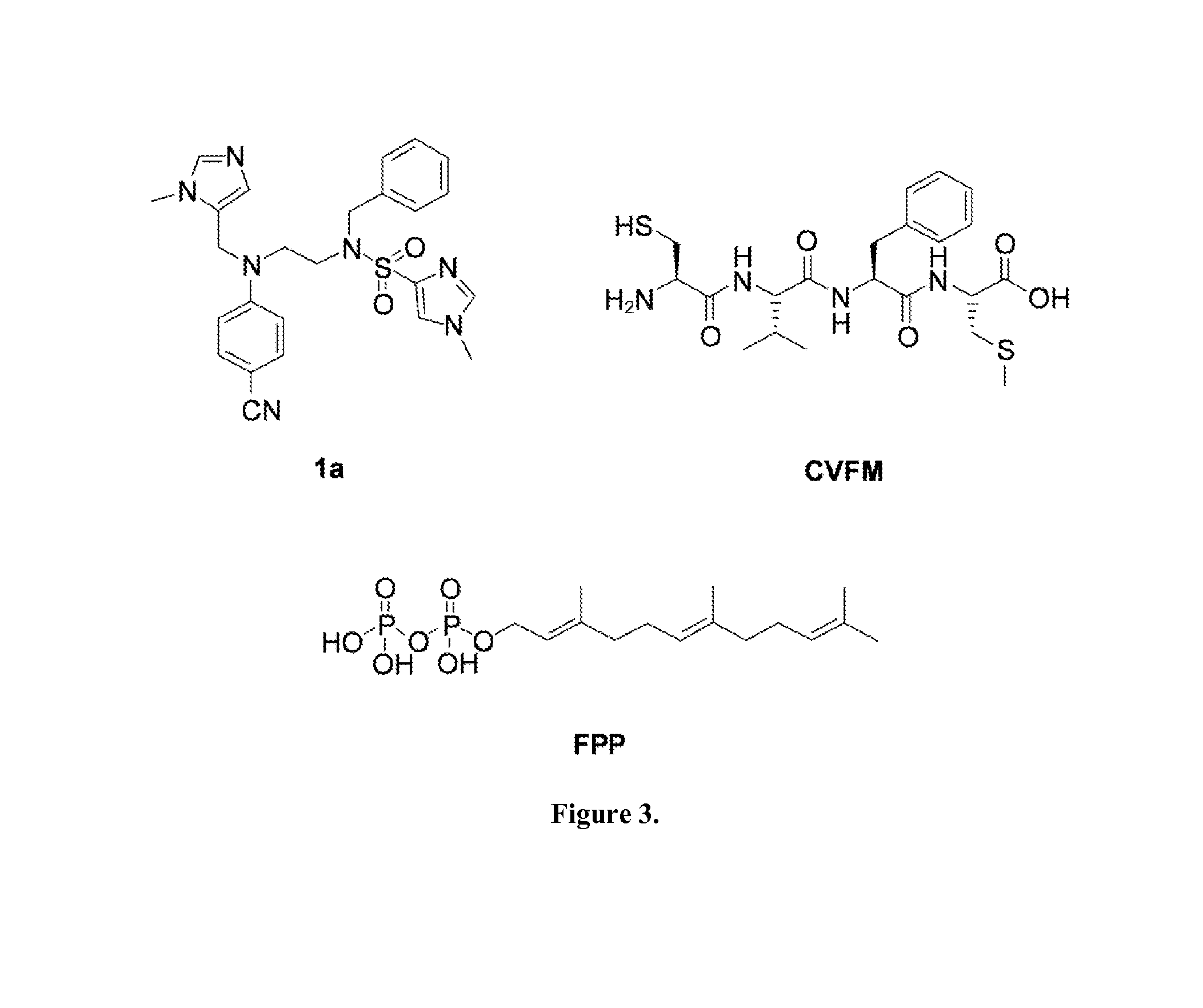
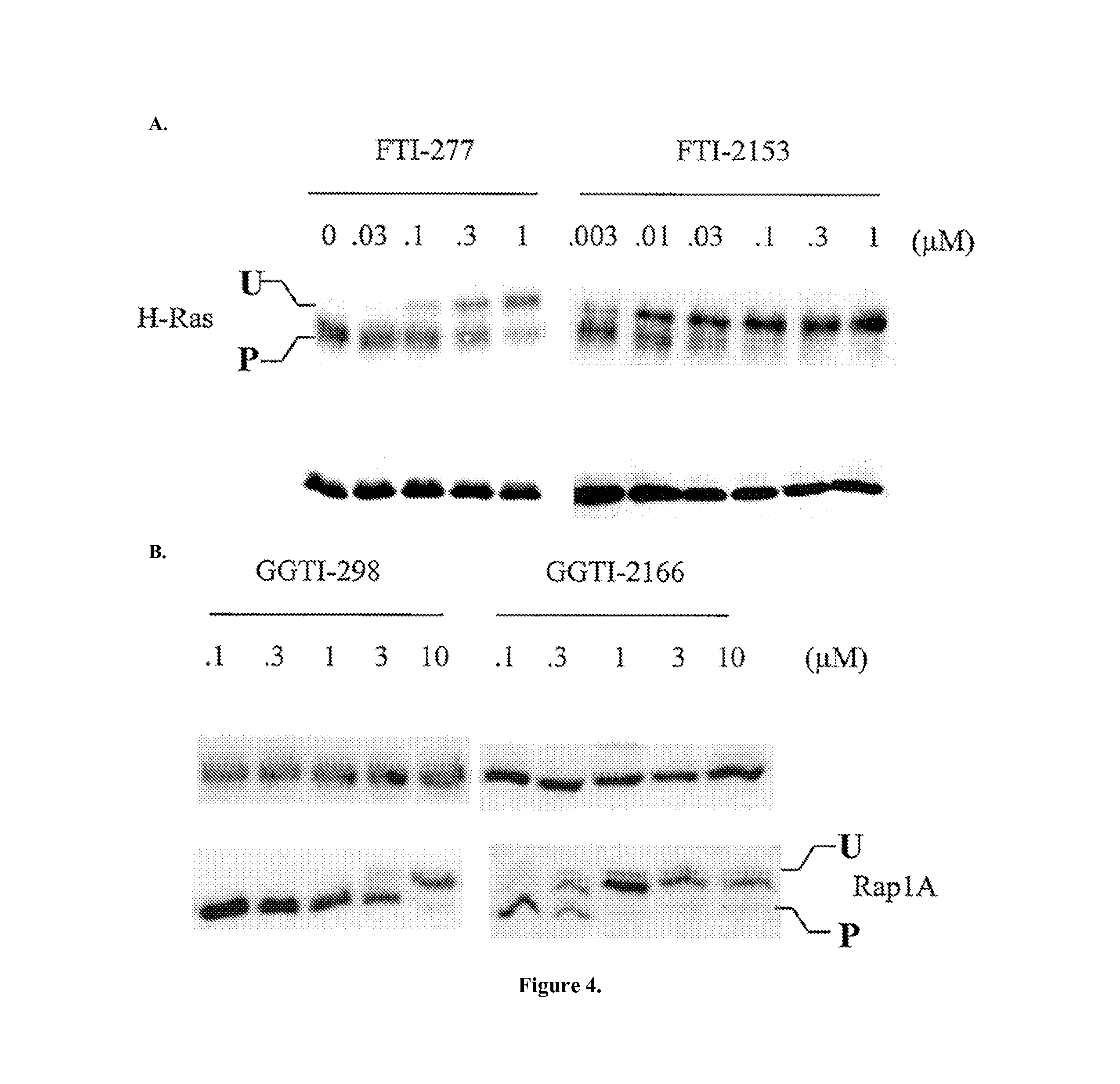
ActiveUS9040563B2Easy to derivatizeExtensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) studyBiocideOrganic chemistryEthylenediamineAnticarcinogen
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Monoclonal antibody hybrid tumor cell strain KGH-R1 of broad spectrum anti-human p21Ras protein and monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN102796707AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTissue cultureAnticarcinogenic EffectAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody hybrid tumor cell strain KGH-R1 of broad spectrum anti-human p21Ras protein and a monoclonal antibody, belongs to the field of medical biology, and in particular relates to the monoclonal antibody hybrid tumor cell strain KGH-R1 of broad spectrum anti-human p21Ras protein and the monoclonal antibody. The hybrid tumor is preserved in a China center for type culture collection in September 23rd 2011, and has the preservation number of CCTCCNO: C201197. A mouse monoclonal antibody which has synchronous antagonism to three types of active Ras protein is finally obtained; and the monoclonal antibody which aims at a p21Ras protein target can be used for protein clinical test, can also construct an intracellular antibody, has an active tumor prevention function by inhibiting tissue vicious transformation through resisting overexpressed Ras protein, and has an active target antitumous effect on the tumor which corresponds to the overexpressed Ras protein.
Owner:杨举伦
Cervices intraepithelial neoplasia model and model establishing method
InactiveCN101125102ARich sourcesExplore the mechanism of carcinogenesisDiagnosticsSurgeryHuman tumorImmunodeficiency
The present invention relates to a cervical intraepithelial neoplasia model and the method of establishing model, which is characterized in that the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue is embedded in the immunodeficiency mice to establish cervical intraepithelial neoplasia model. The method of establishing model is characterized in that the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue is respectively taken from the biopsy under the vaginoscope and the tissues which are confirmed by the department of pathology and is inoculated subcutaneously in the back of the mice; the immunodeficiency mice of the present invention can overcome the xenoislet immune rejection reaction and receive the transplantation of the human tumor tissues, the tissue model after the transplantation has significant and stable character, short observation period and greater clinical reference significance of the experimental results. The present invention can explore the mechanism of the carcinogenesis of cervical carcinoma by outcome of the pathological process of CIN I, CIN II and CIN III animal models. Furthermore, by observing the period of the outcome of the cervical intraepithelial neoplasia tissue of the animal model, the present invention provides the feasible clinical animal experimental model for reversing the malignant transformation of the CIN I and CIN II lesion tissues.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
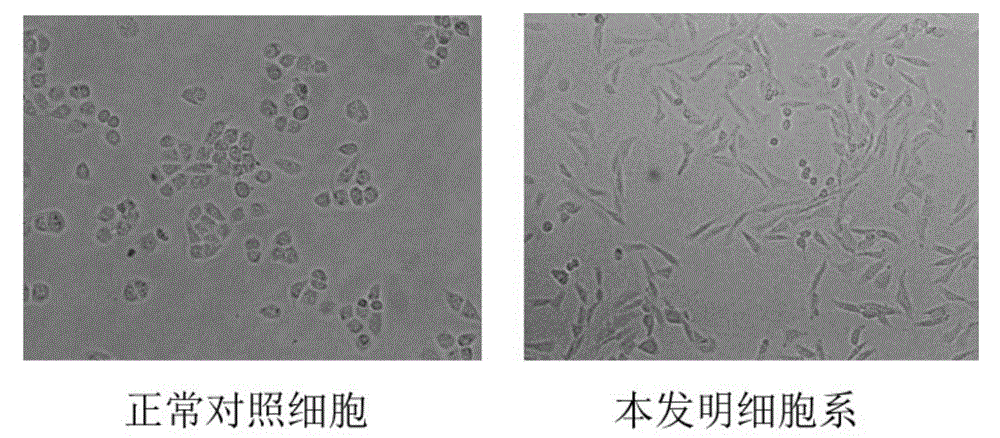
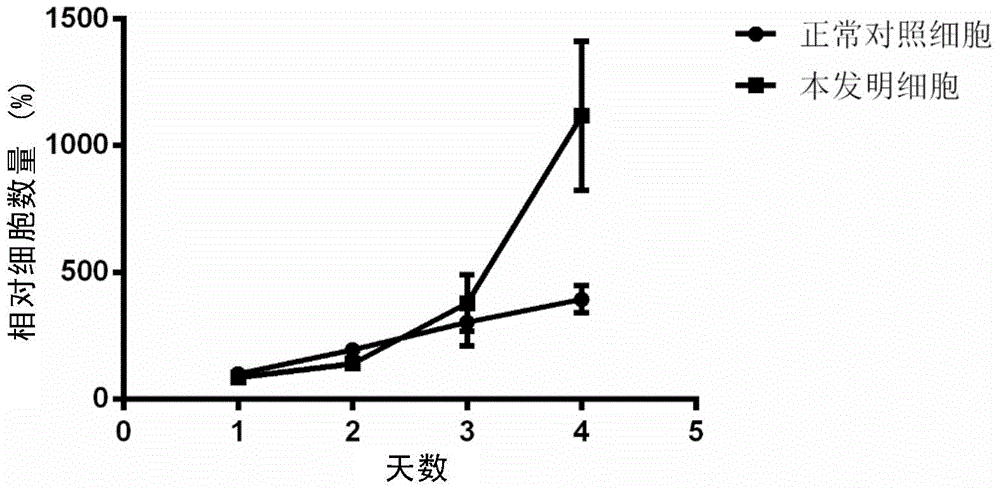
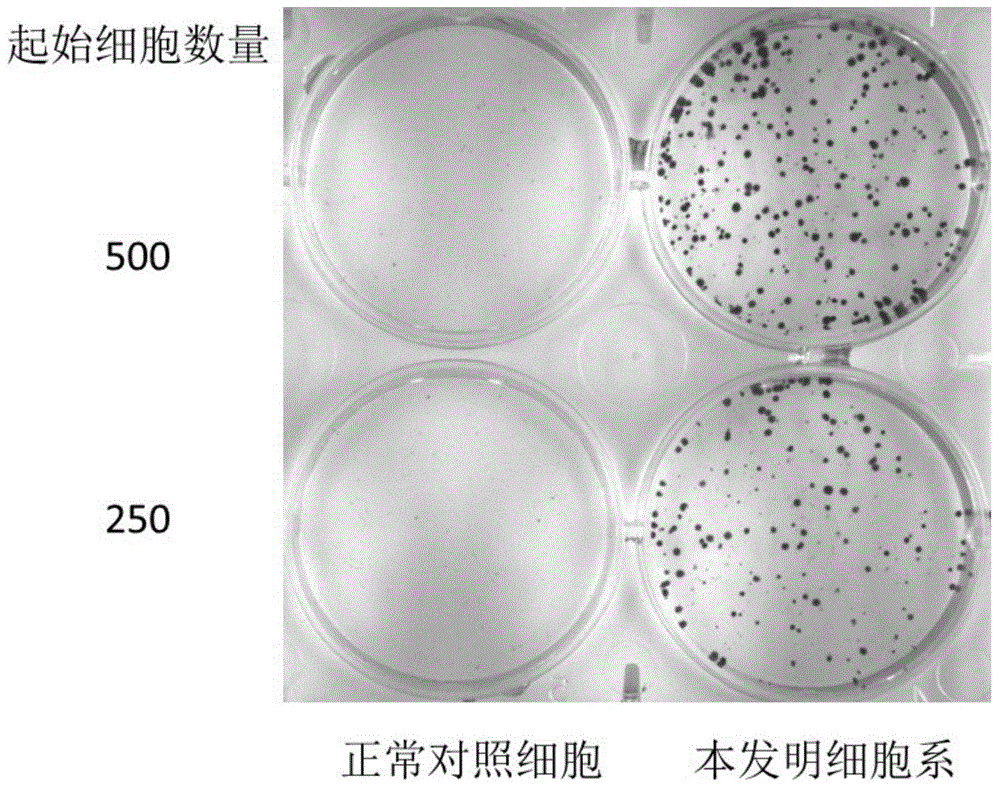
Cell model having undergone vicious transformation
ActiveCN105802915AMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsNormal cellBiochemistry
The invention relates to a cell model having undergone vicious transformation. A novel cell line having undergone vicious transformation is developed on the basis of human-derived normal cell for the first time in the invention. The cell line is screened out after long-term stimulation by low-concentration benzopyrene; and identification results show that the cell model has undergone vicious transformation. The cell line can be used as a cell model for research on pathogenic effect of benzopyrene or screening of drugs capable of inhibiting vicious transformation of cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
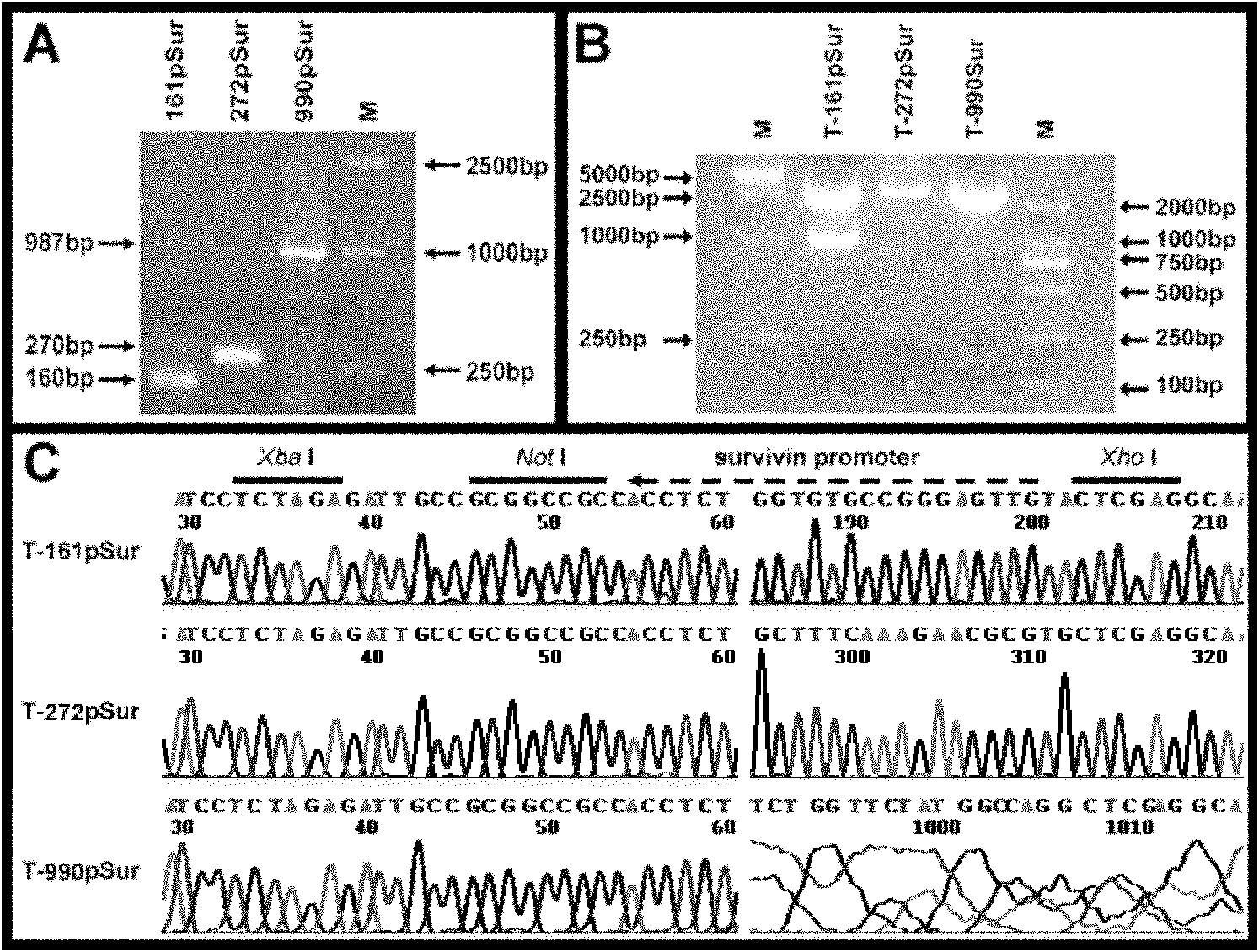
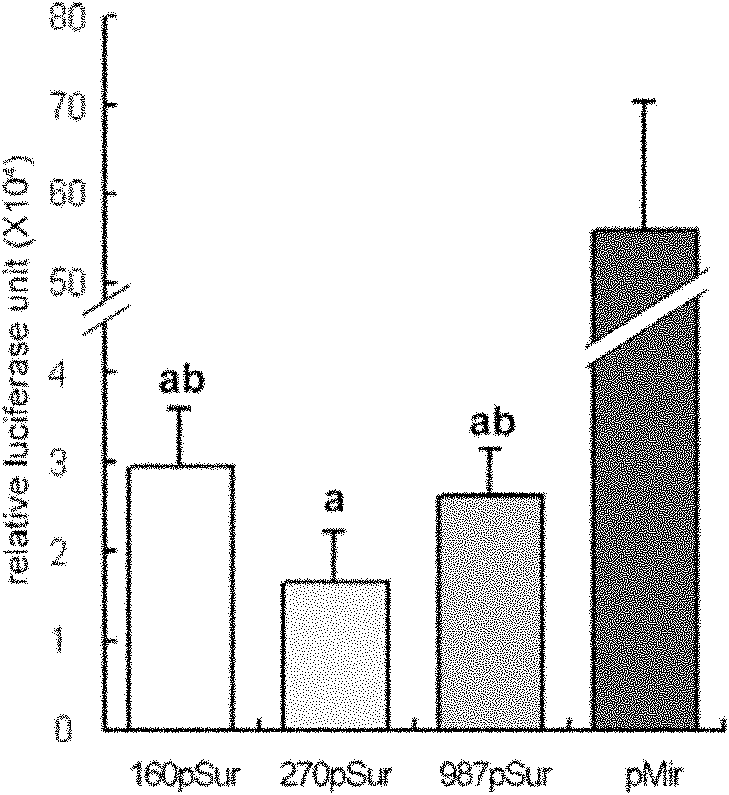
Recombinant slow virus vector, recombinant slow virus and stem cell containing recombinant slow virus
The invention discloses a recombinant slow virus vector, a recombinant slow virus and a stem cell containing recombinant slow virus, belonging to the field of medical molecular biology. The recombinant slow virus vector is characterized in that: a Survivin prompter, an Apoptin gene and a SV40Poly A sequence are sequentially inserted into a plurality of cloning sites of the slow virus vector; and the slow virus vector is FG-12. Due to the application of the recombinant slow virus, such as transfection applied to a transplanted stem cell, the stem cell transplanted into the body of a patient is under the monitoring of the promoter of the recombinant slow virus vector. Once the transplanted stem cell is transformed severely, the expression of a suicide gene Apoptin in the recombinant slow virus is started immediately, so that the severely-transformed cell is dead by apoptosis. During clinical application, the recombinant slow virus plays a role in specifically pre-warning, reacting, tracing and clearing the transformed stem cell.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Chrysotile-induced human pleural mesothelial cell malignant transformation strain and application thereof
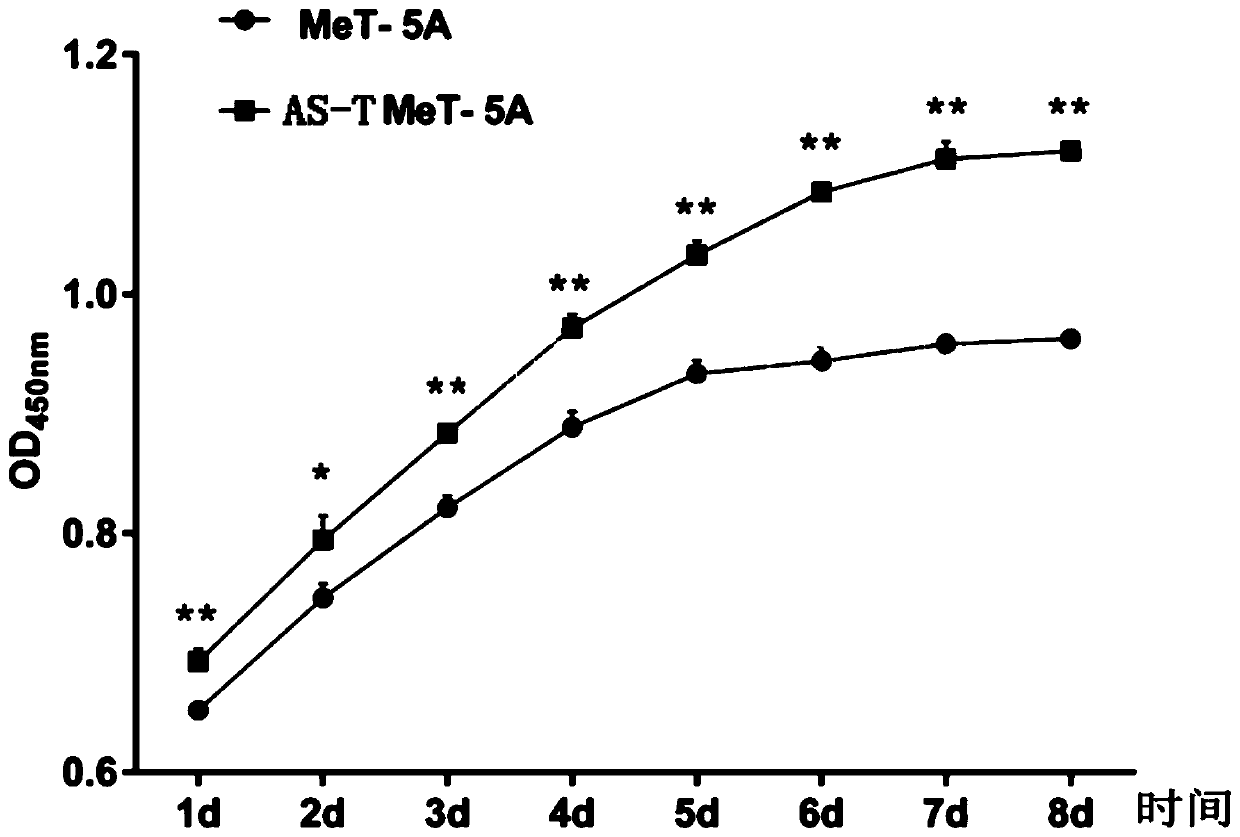
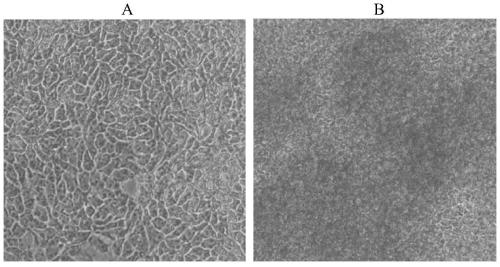
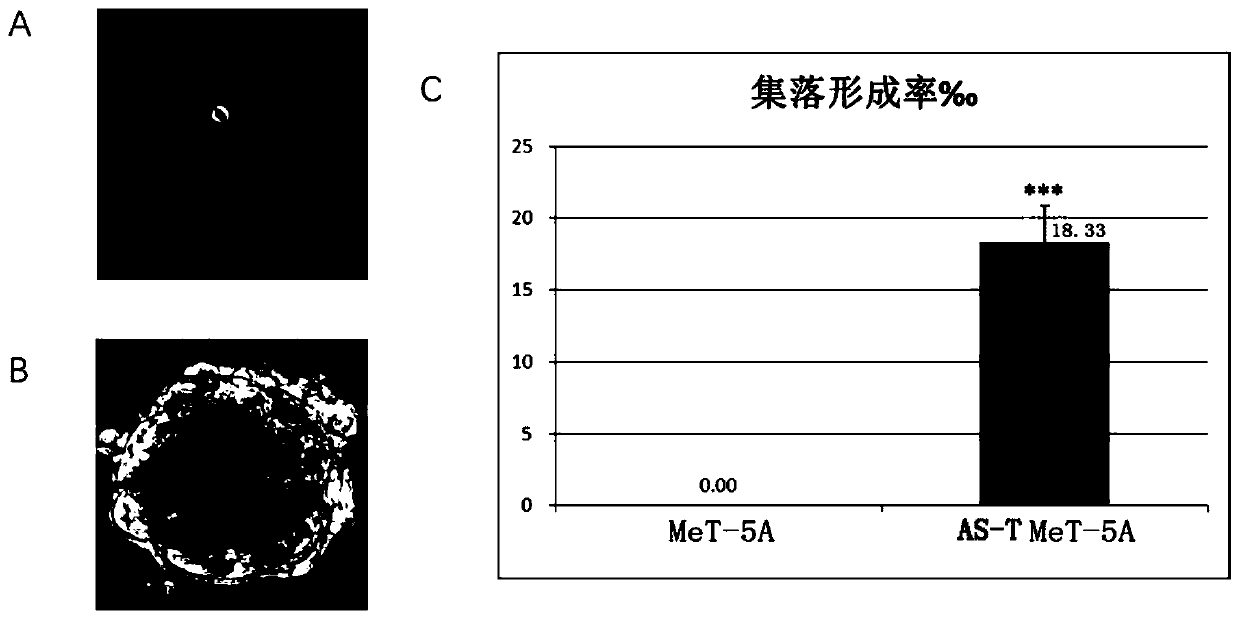
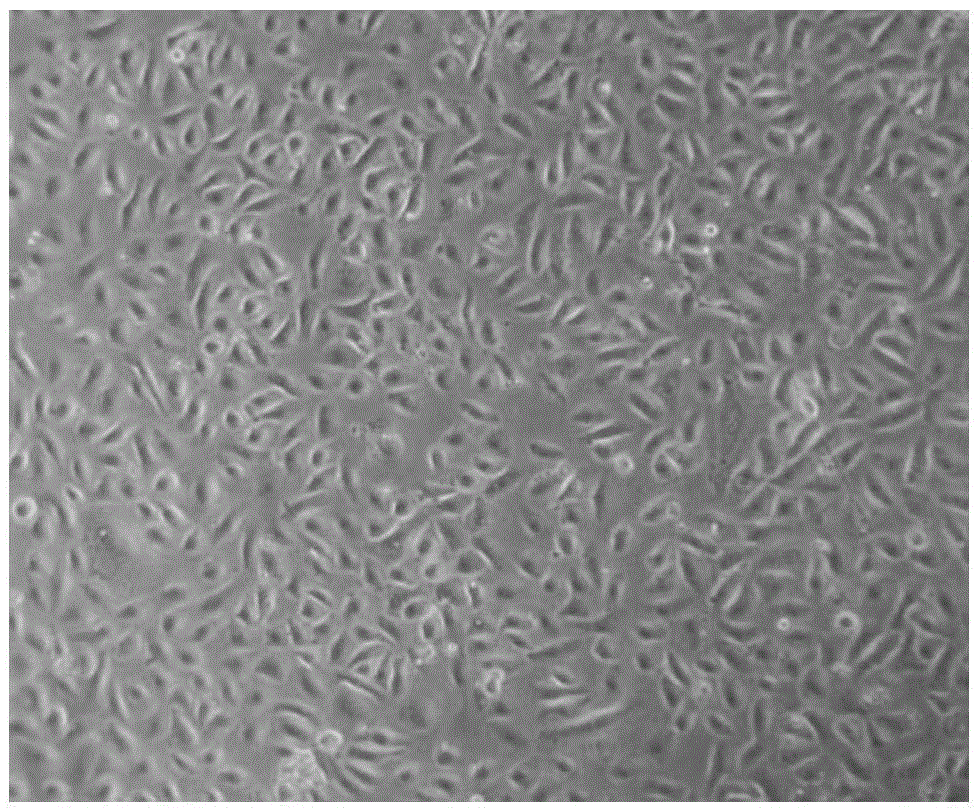
The invention discloses a chrysotile-induced human pleural mesothelial cell malignant transformation strain and an application thereof. The human pleural mesothelial cell malignant transformation strain is classified and named as human pleural mesothelial cells, the strain number is AS-T, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO.C201923. The human pleural mesothelial cell malignant transformation strain is obtained by carrying out malignant transformation on human pleural mesothelial cells (MeT-5A) after being subjected to chrysotile multi-stage multi-time contamination treatment, and has a good application prospect in multiple aspects such as a cell model for researching a carcinogenic mechanism of carcinogenic substances and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Human bronchial epithelial cell strain HBE-TT
ActiveCN105483087AMaintain normal featuresNo features of malignant transformationForeign genetic material cellsMycoplasma contaminationPulmonary disease
The invention a novel human bronchial epithelial cell strain HBE-TT, collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan) under CCTCC NO: C201560. The cell strain HBE-TT is verified to be good in purity, free of sundry cell contamination and differed from all existing other cell strains. In addition, the immortalized cells retain typical features of primary bronchial epithelial cells and are free of mycoplasma contamination and vicious transformation features, and it is suggested that cells HBE-TT can retain trait stability during in-vitro subculture. The cells HBE-TT are expected to be a forcible tool for the deep discussion on occurrence and development molecular mechanism of lung diseases caused by environmental toxic factor exposure and for pharmacological study, and the cells are significant to the study on health damage effect of toxic factors on human lung as well as risk estimation and new drug development.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
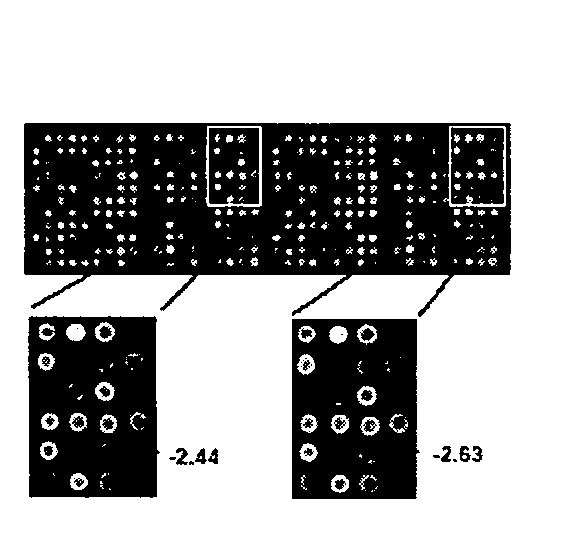
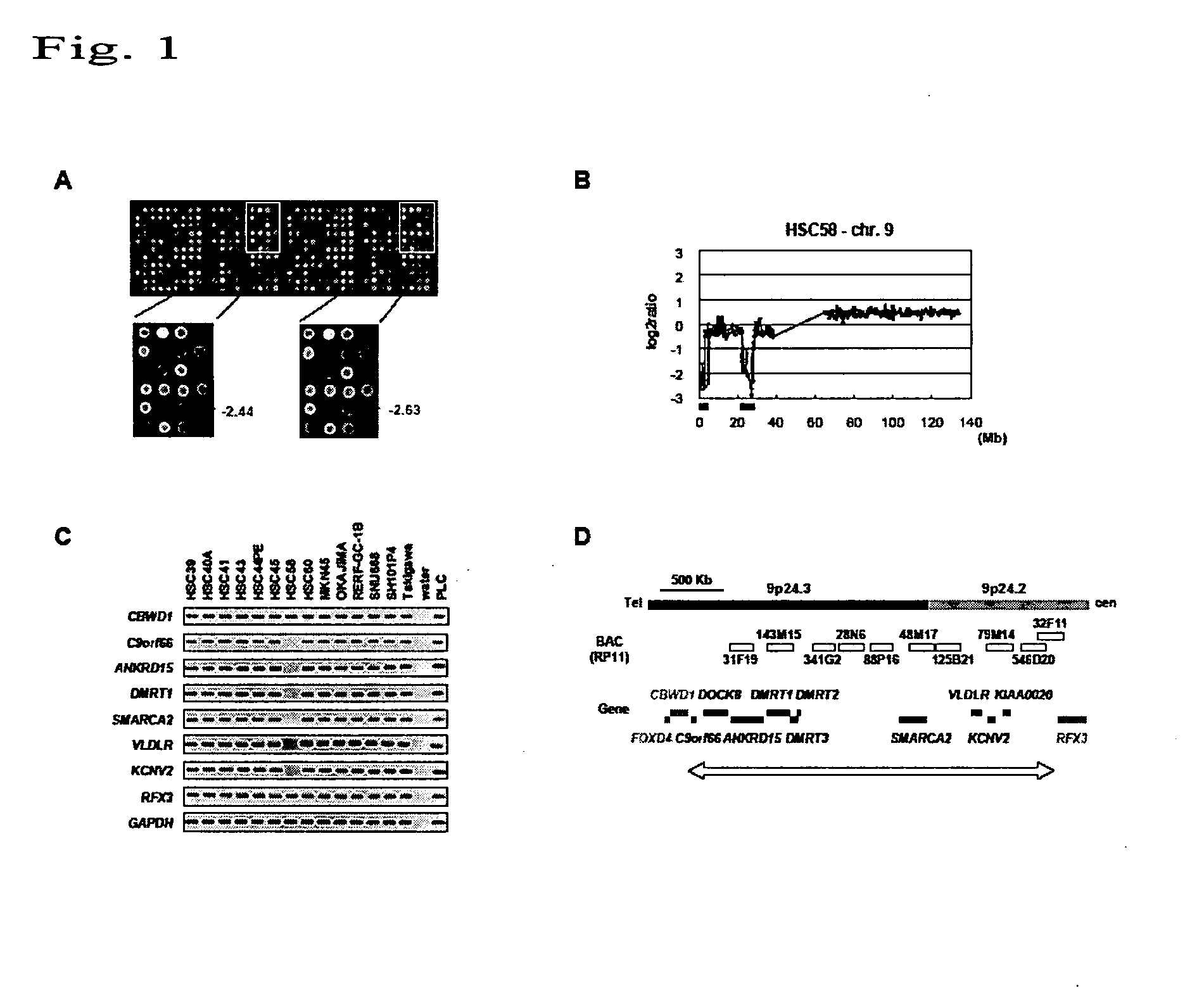
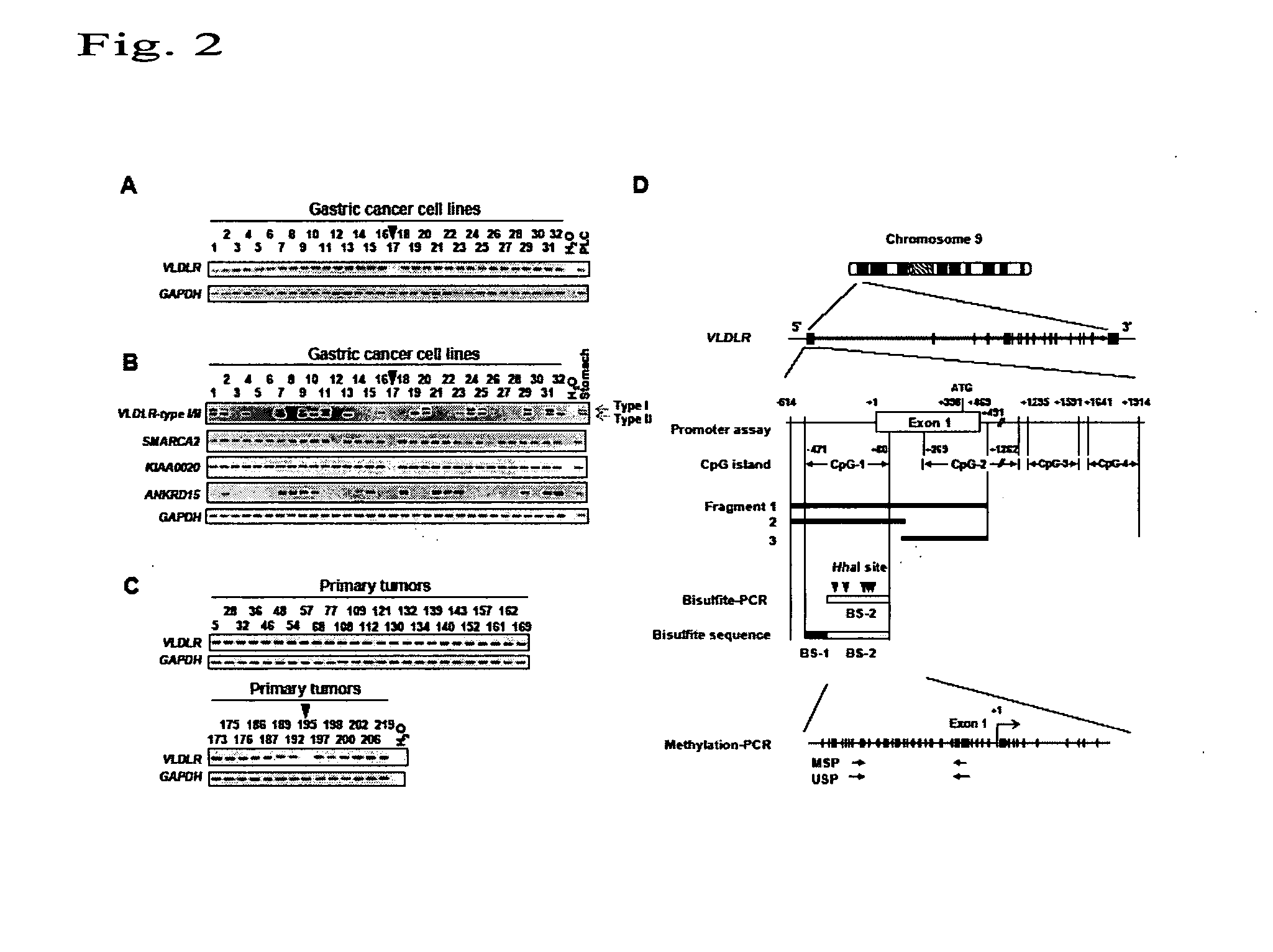
Method for detecting gastric cancer by detecting VLDLR gene
InactiveUS20090054245A1Highly stable and reproducible methodMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGastric carcinomaHistiocyte
It is an objective of the present invention to provide a highly stable and reproducible method for detecting gastric cancer, by finding a novel gastric cancer-related gene and detecting the inactivation of such cancer-related gene. The present invention provides a method for detecting gastric cancer, comprising detecting malignant transformation of a gastric tissue cell by detecting the inactivation of the human VLDLR gene in the gastric tissue cell.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
gRNA sequence of targeted editing bcr-abl fusion gene and application thereof
PendingCN109957570AInhibition of feasibilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorBCR-ABL Fusion GeneDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a gRNA sequence of a targeted editing bcr-abl fusion gene and an application thereof. By location of three specific target sequence site DNA fragments in a bcr-abl gene, a gRNAexpression plasmid is constructed for a specific site, the plasmid and a FokI-dCas9 expression plasmid and a donor nuclear are transfected into a K562 cell, so that the bcr-abl gene is subjected to fixed-point fracture, homologous repair is performed by using a donor DNA as a template, and 8 basic groups are inserted to ultimately lead to disruption of the bcr-abl gene. Significant advantages of the sequence and the application thereof are that RFNs constructed for the pecific target sequence site in a bcr-abl sequence can efficiently target the bcr-abl gene to cause occurrence of DNA double-strand break, repair is performed in a HDR manner to enable bcr-abl to undergo mutation such as frame shift and to be destroyed, thereby losing potential for malignant transformation such as proliferation and apoptosis suppression.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
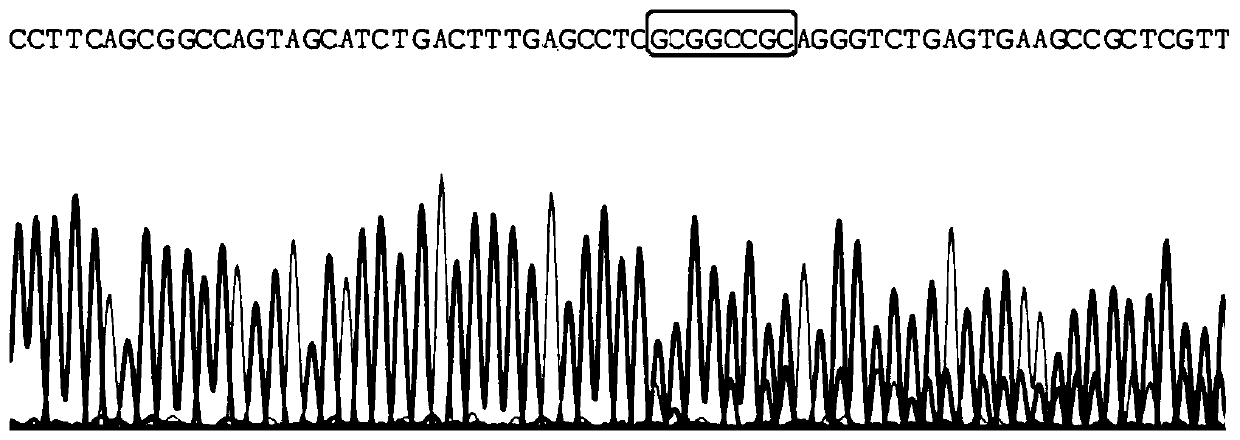
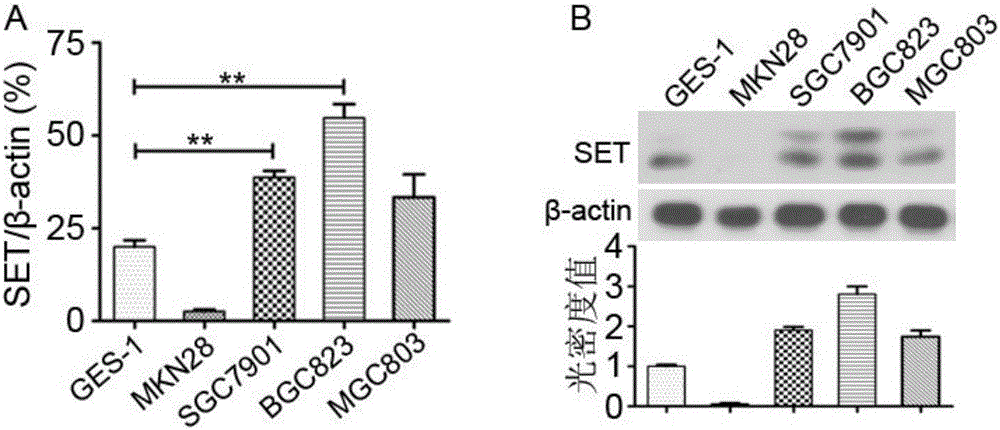
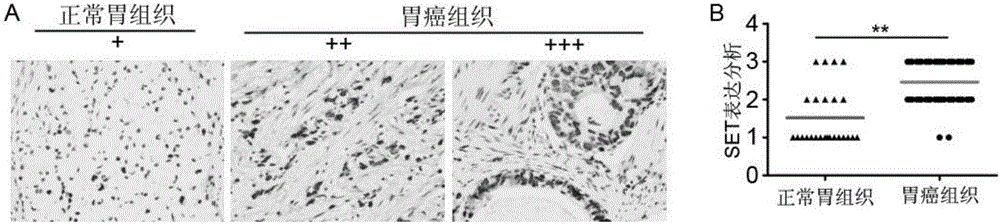
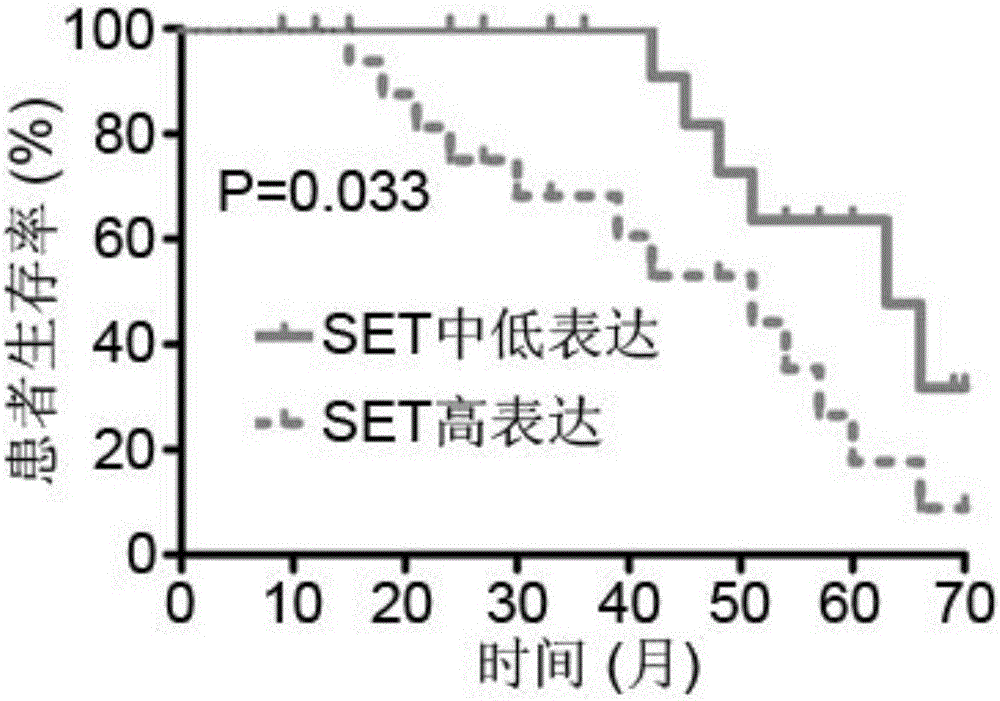
Application of SET gene in preparing product for diagnosing and/or treating gastric cancer
InactiveCN106521022AIncrease protein levelsInhibit migrationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAkt signallingGastric carcinoma
The invention belongs to the fields of biotechnology and medicine, and in particular relates to an application of an SET gene in preparing a product for diagnosing and / or treating gastric cancer. It is provided that the SET achieves frequent high expression (80%) in gastric cancer tissues, and the increase in SET expression is significantly correlated to aggressive phenotype and worse prognosis of a patient with the gastric cancer (P is less than 0.05). The low expression of the SET can obviously inhibit the migration and the invasion of gastric cancer cells. In addition, the SET, by virtue of a PP2A / Akt signaling pathway, can promote tumor malignant transformation. Furthermore, the gastric cancer tissues are obviously higher than para-carcinoma tissues in SET protein level. Therefore, the SET gene can serve as a specific marker gene for diagnosing the gastric cancer, so that it is more accurate and rapid to diagnose the gastric cancer. The SET gene provided by the invention provides a novel therapeutic target for the prevention and the treatment of the gastric cancer.
Owner:HUBEI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE
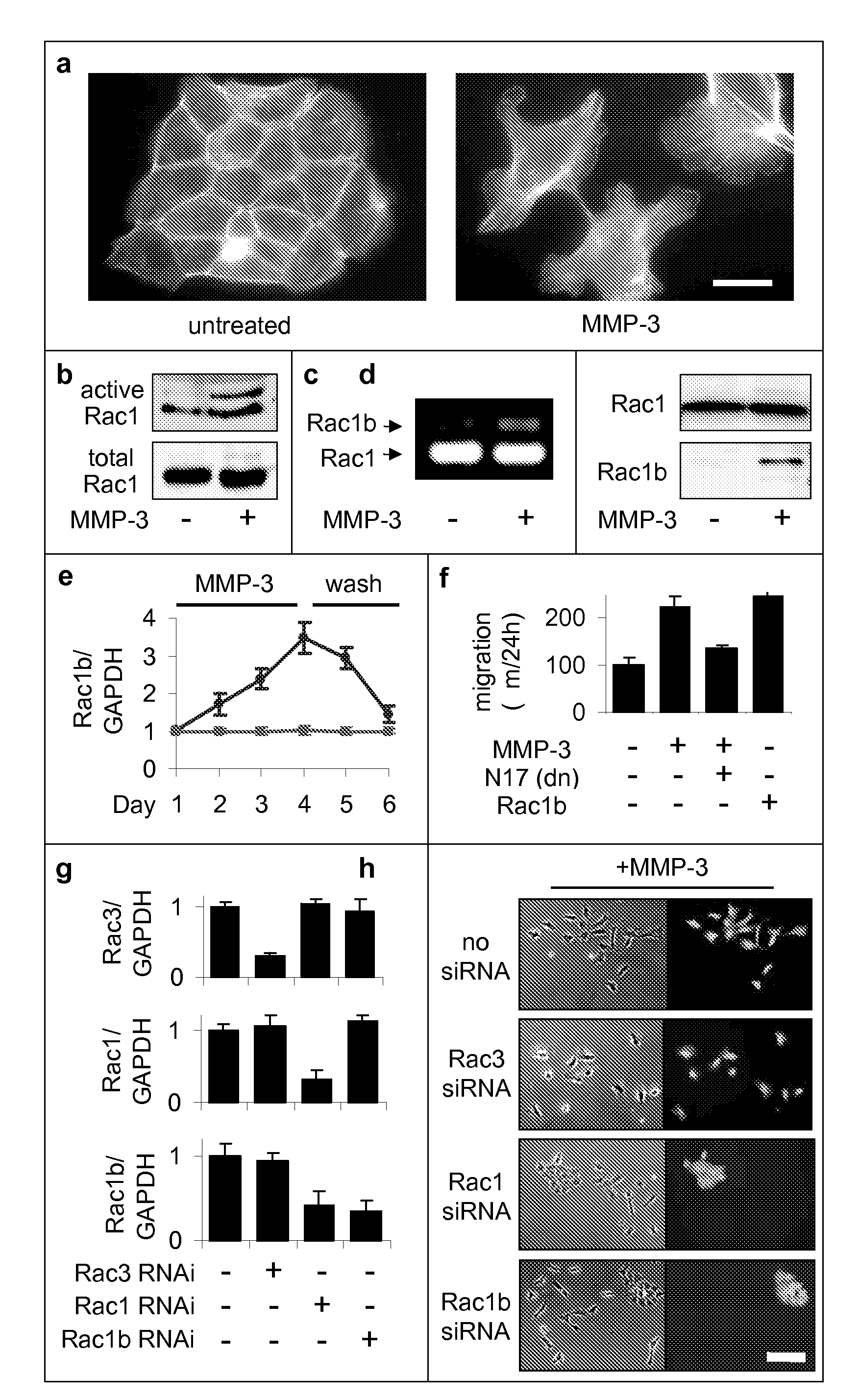
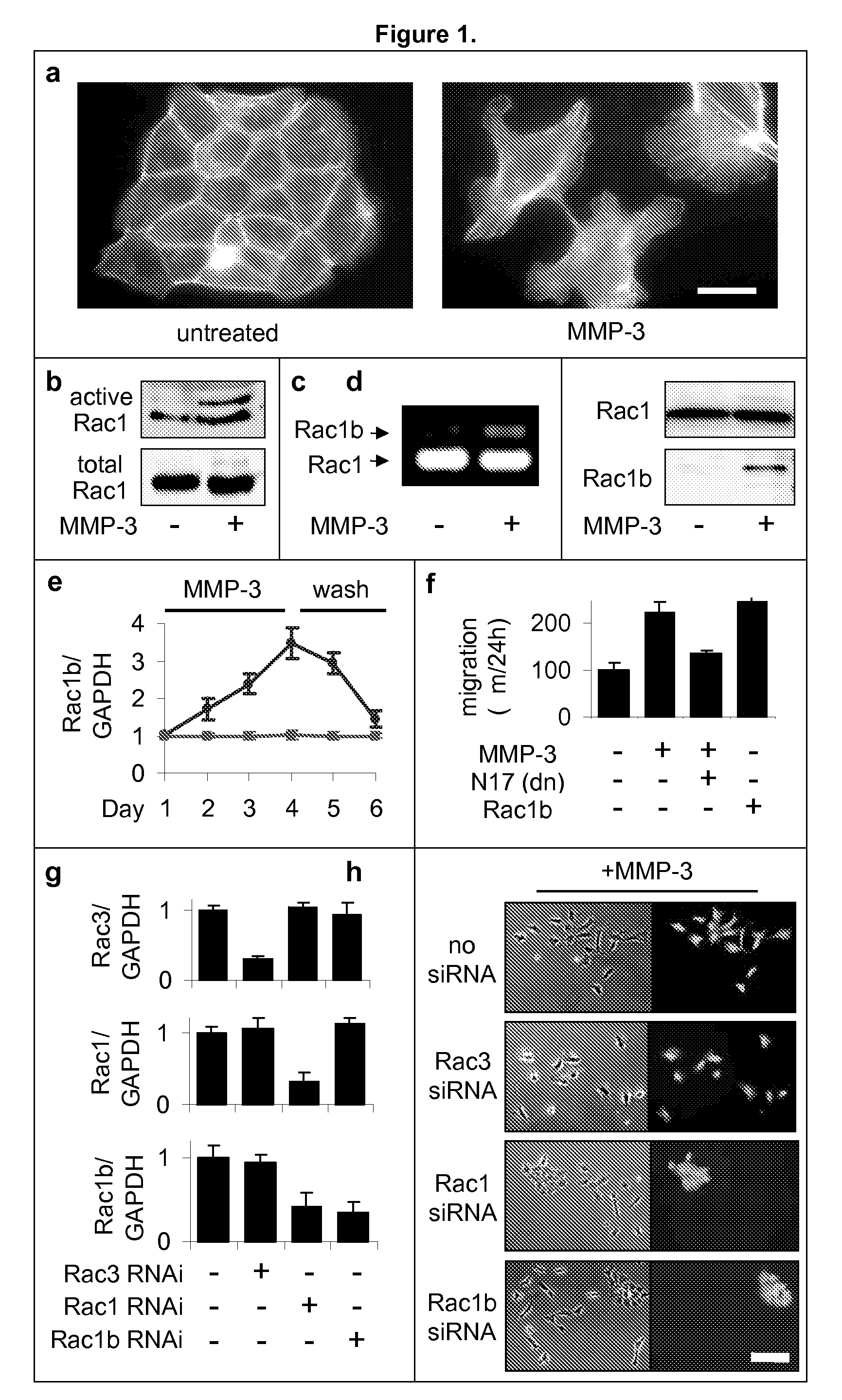
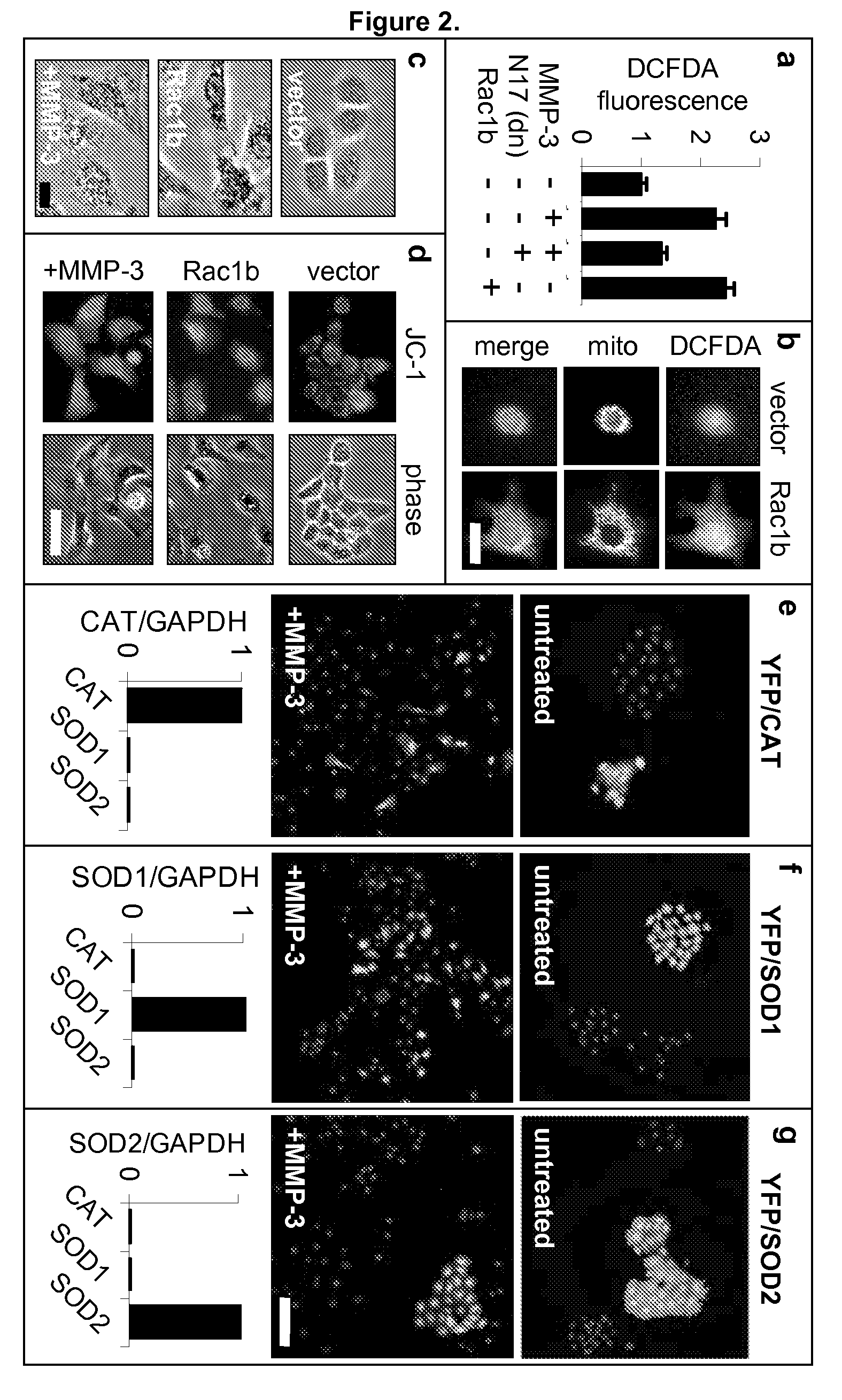
Identification of rac1b as a marker and mediator of metalloproteinase-induced malignancy
The present invention provides compositions and methods for detecting MMP-induced malignancies by detecting Rac1b expression. The invention further provides compositions and in vitro and in vivo methods for inhibiting MMP-induced malignant transformation by modulating Rac1b expression and / or function.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Scid mouse model of electromagnetic radiation carcinogenesis and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN101838633AGood effectSimple stepsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentEmbryonic cellsAbnormal tissue growthElectromagnetic radiation
The invention relates to a Scid mouse model of electromagnetic radiation carcinogenesis and a constructing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing an NIH / 3T3 cell and carrying out passage; exposing the cell in the presence of the electromagnetic radiation of 30-90W / m<2> and culturing for 4-6 weeks; and carrying out a soft agarose culturing experiment and inoculating the cultured soft agaroes into a Scid mouse for carrying out an oncogeen experiment. The result shows that a cell colony is formed in the soft agarose experiment and Scid mice in the oncogeen experiments all generate tumors. By using the method, the Scid mouse model with tumors induced by using the electromagnetic radiation can be established; and the method has the advantages of remarkable effect, simple steps and favorable repeatability. An in vitro cell transformation experimental model established by the method can be used for simulating the vicious transformation of an in vivo cell and provides a favorable experimental model and a powerful technical means for the research on a pathogenesis and prevention and treatment measures of the tumor induced by the electromagnetic radiation. The method can be applied to the carcinogenic risk pre-evaluation on the electromagnetic radiation in the industry, science, medical treatment and daily life and has an important value of preventing the long-term harm of the electromagnetic radiation on the human health.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Establishing method and applications of cell model capable of simulating lung cancer occurrence mechanism
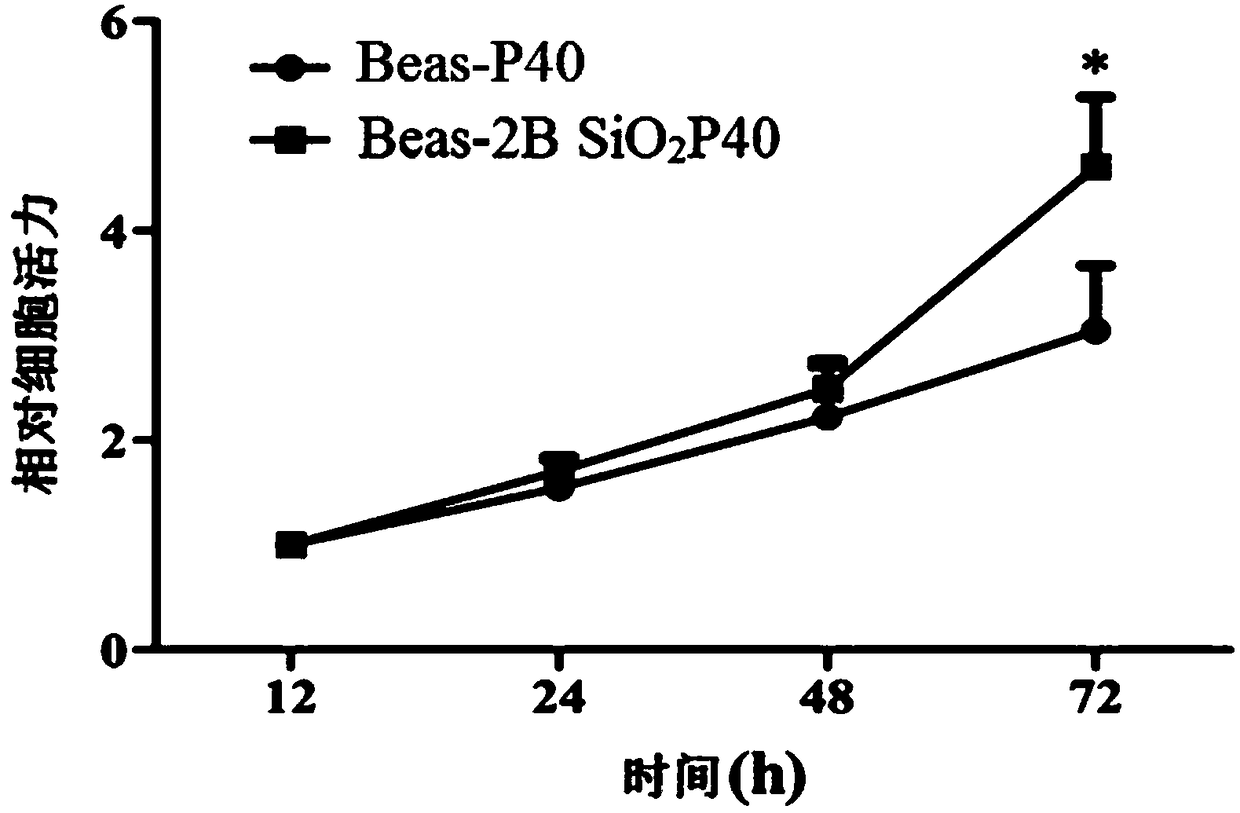
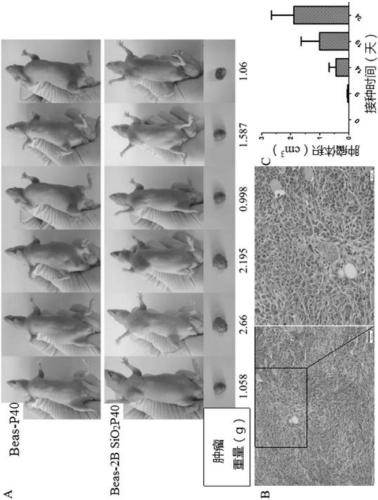
InactiveCN109294990AIncrease contentPromote malignant transformationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processLung Cancer PreventionBiology
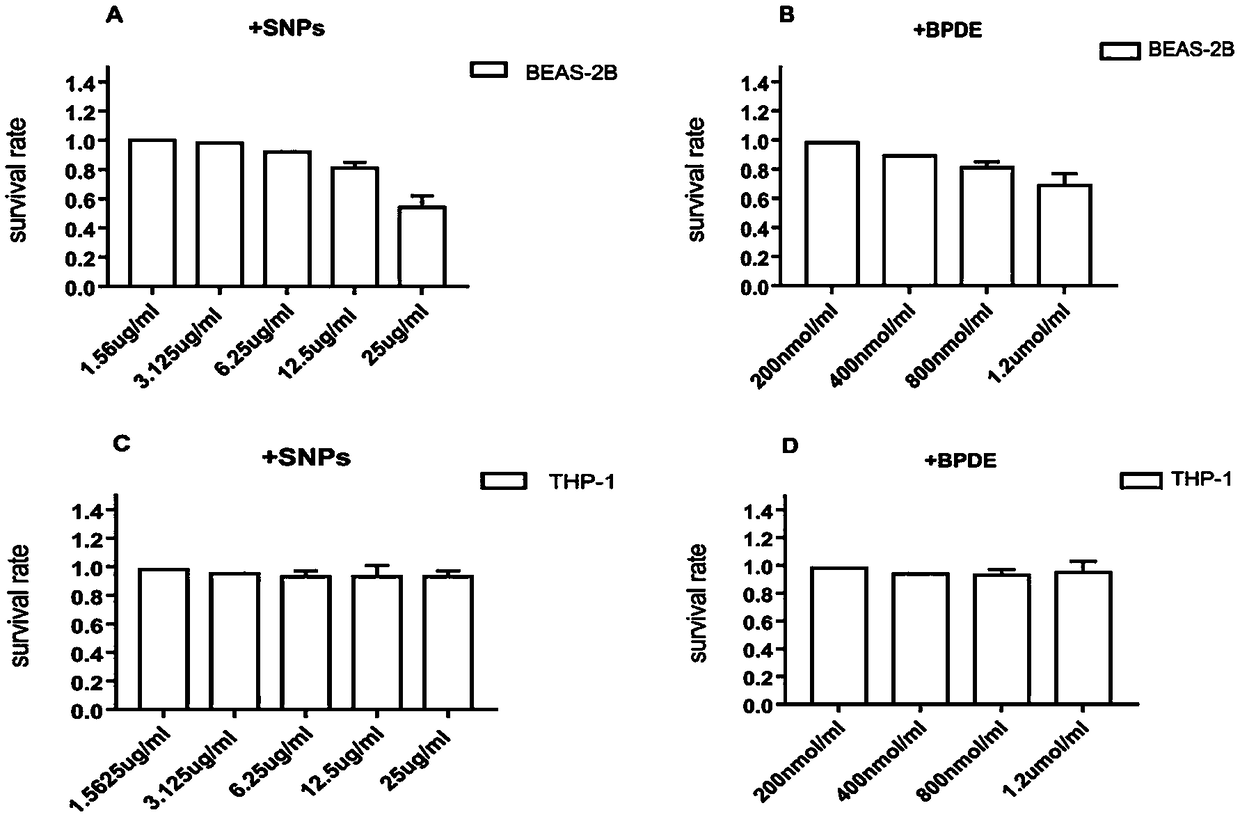
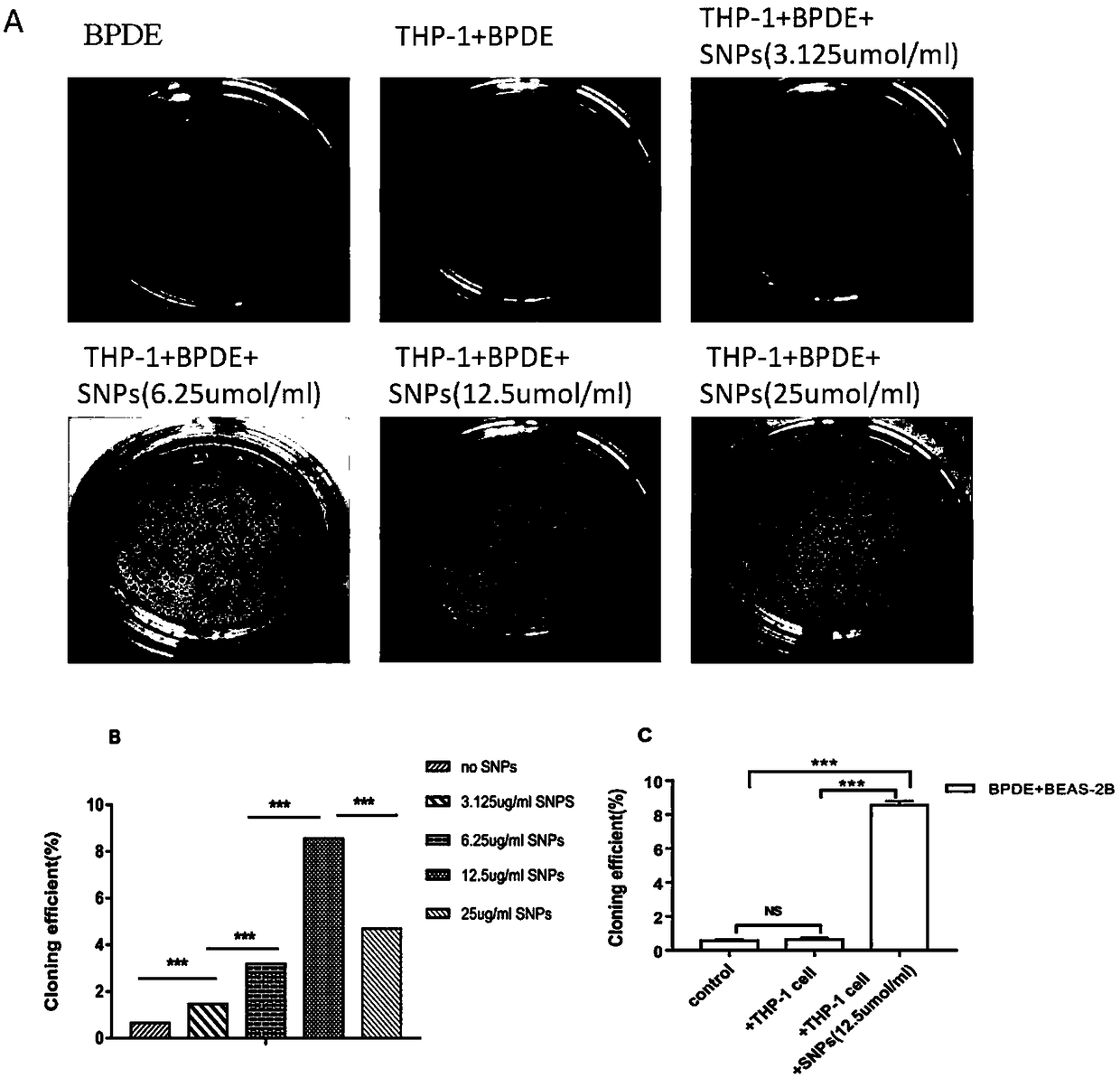
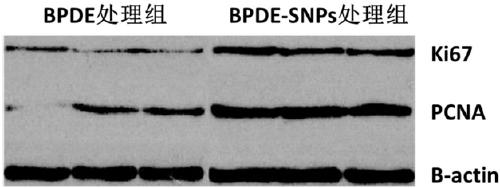
The invention relates to the field of cell medicine, particularly to an establishing method and applications of a cell model capable of simulating lung cancer occurrence mechanism, and provides an establishing method of a cell model capable of simulating lung cancer occurrence mechanism. The establishing method comprises: inducing the malignant transformation of BEAS-2B cells in a BEAS-2B cell andTHP-9 cell co-culture system by using BPDE and spherical SNPs as inducing agents. According to the present invention, the established cell model can highly simulate the lung cancer induction processhaving the same pathogenesis as Xuanwei lung cancer, and has application value in the study of lung cancer occurrence and the screening of lung cancer prevention and treatment drugs.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for detecting carcinoma and agent for suppressing carcinoma
InactiveUS20090202624A1Accurate understandingGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSquamous CarcinomasMalignant transformation
An object of the present invention is to identify genes exhibiting characteristic behavior in the cases of carcinoma such as oral squamous-cell carcinoma using a change of expression level of micro RNA in oral squamous-cell carcinoma as an indicator, so as to provide a method for detecting carcinoma and an agent for suppressing carcinoma. The present invention A method for detecting oral squamous-cell carcinoma, which comprises detecting malignant transformation of specimens by employing a change of expression level of micro RNA as an indicator, and an agent for suppressing oral squamous-cell carcinoma using micro RNA.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
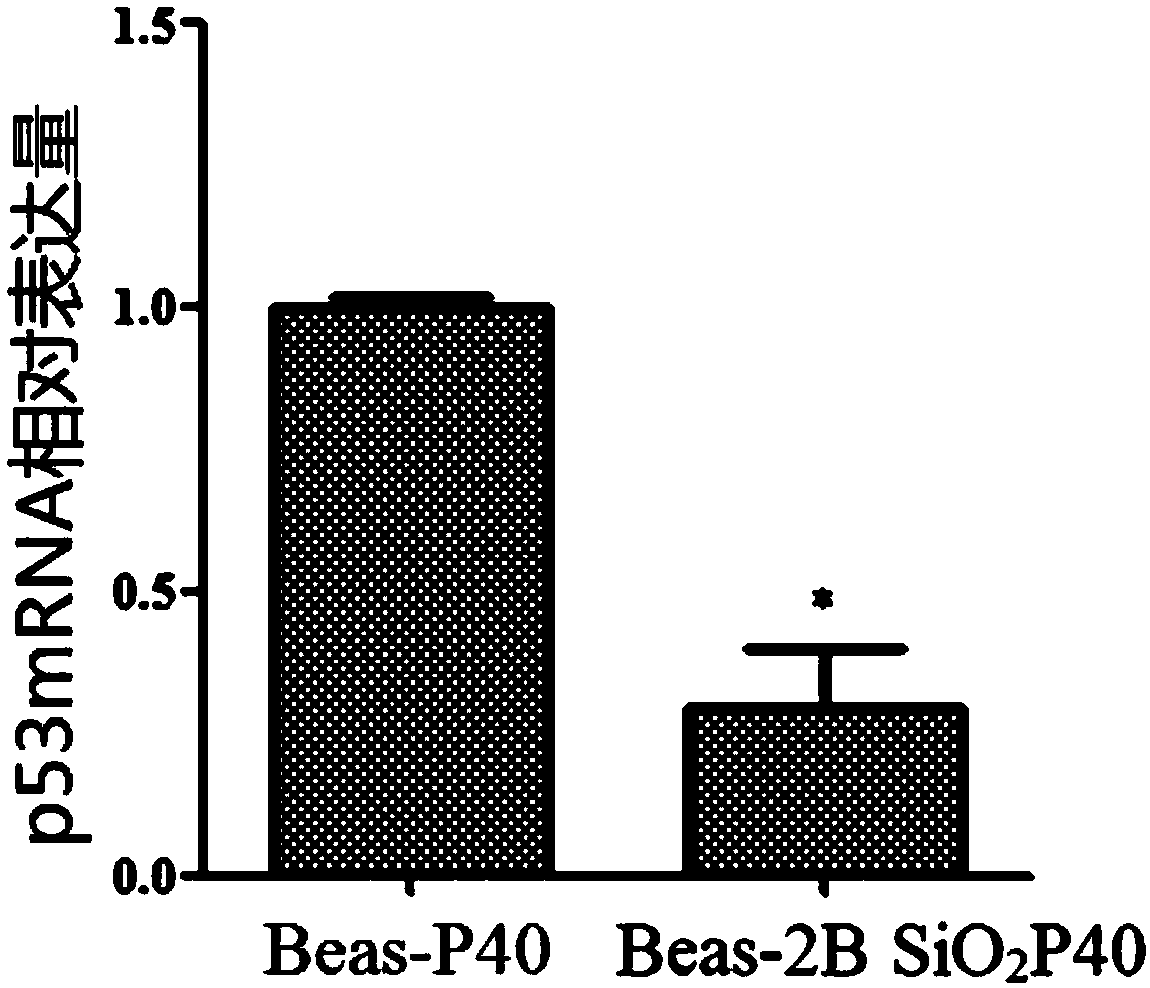
Model cell strain for malignant transformation of lung cell induced by nano-silica dioxide and application thereof
The invention provides a model cell strain for malignant transformation of a lung cell induced by nano-silica dioxide and an application thereof. The accession number of the model cell strain is CGMCCNO. 12676. The model cell strain and a daughter cell strain thereof can provide a basis for carcinogenicity research by utilizing in vitro experiments, can be used to study a mechanism of revealing carcinogenicity of the nano-silica dioxide, and can also be used for screening early biomarkers of carcinogenesis of the nano-silica dioxide and developing corresponding detection kits and drugs related to lung cancer treatment.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
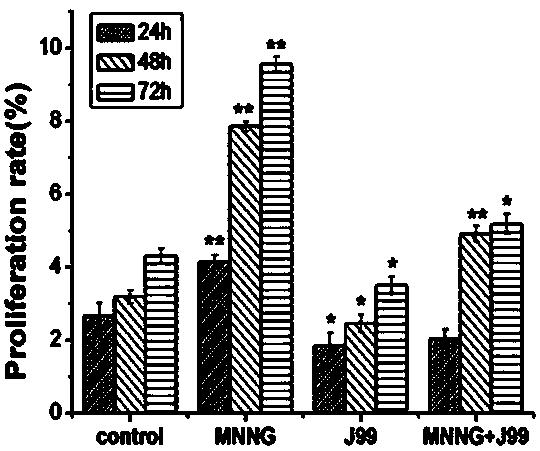
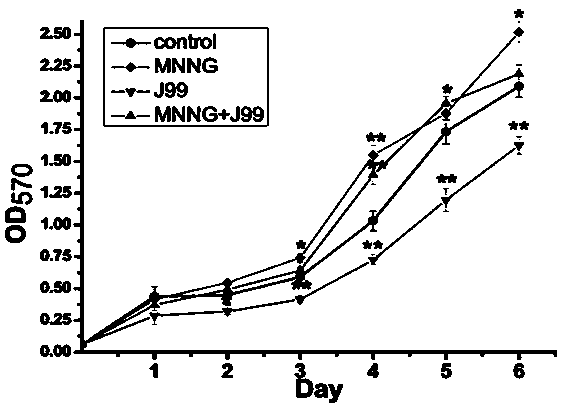
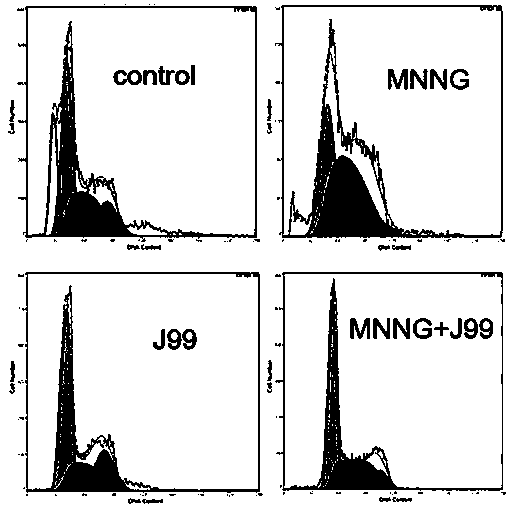
Method for inducing cell malignant transformation culture model
The invention relates to a method for inducing a cell malignant transformation culture model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing immortalized human gastric mucosal epithelial GES-1 in a DMEM culture solution containing 10% fetal bovine serum to obtain cultured cells; (2) culturing Cag A-positive helicobacter pylori J99 in a brain heart infusion medium containing 10% of newborncalf serum and centrifuging to remove a supernatant to obtain cultured bacteria; (3) diluting the cultured bacteria with DMEM, adding the bacteria into the cultured cells for induction by inoculationevery other day, adding an MNNG solution daily, and obtaining an induced helicobacter pylori infection model 48 weeks later. The method is simple and convenient, not only various indexes of malignanttransformation of the cells can be observed, but also the cell model in which the helicobacter pylori and MNNG work together for long-term for malignant transformation of gastric mucosa can be established, and a good experiment foundation is laid for study of the subsequent gastric cancer formation mechanism and the development of cancer treatment drugs.
Owner:蔺莉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com