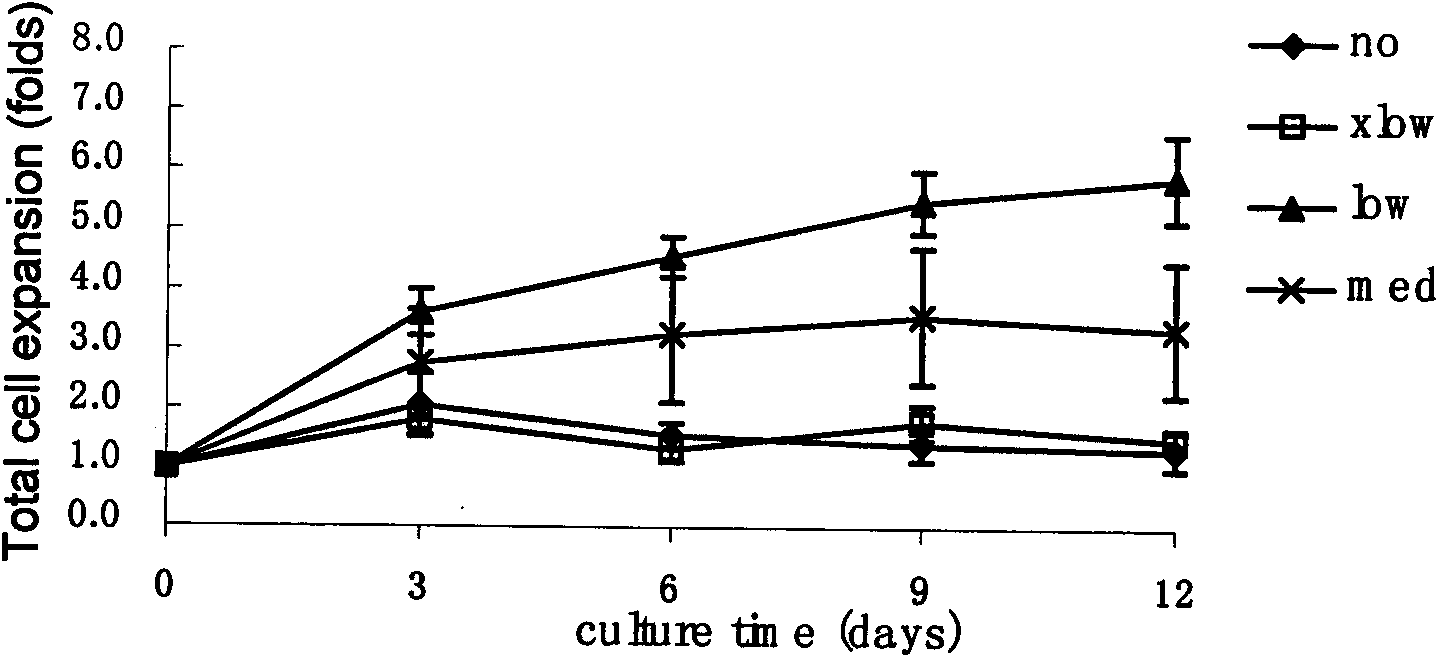
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Scid mice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
SCID mouse (severe combined immunodeficiency) a strain of mice lacking in T and B lymphocytes and immunoglobulins, either from inbreeding with an autosomal recessive trait or from genetic engineering, used as a model for studies of the immune system. SCID mouse.
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
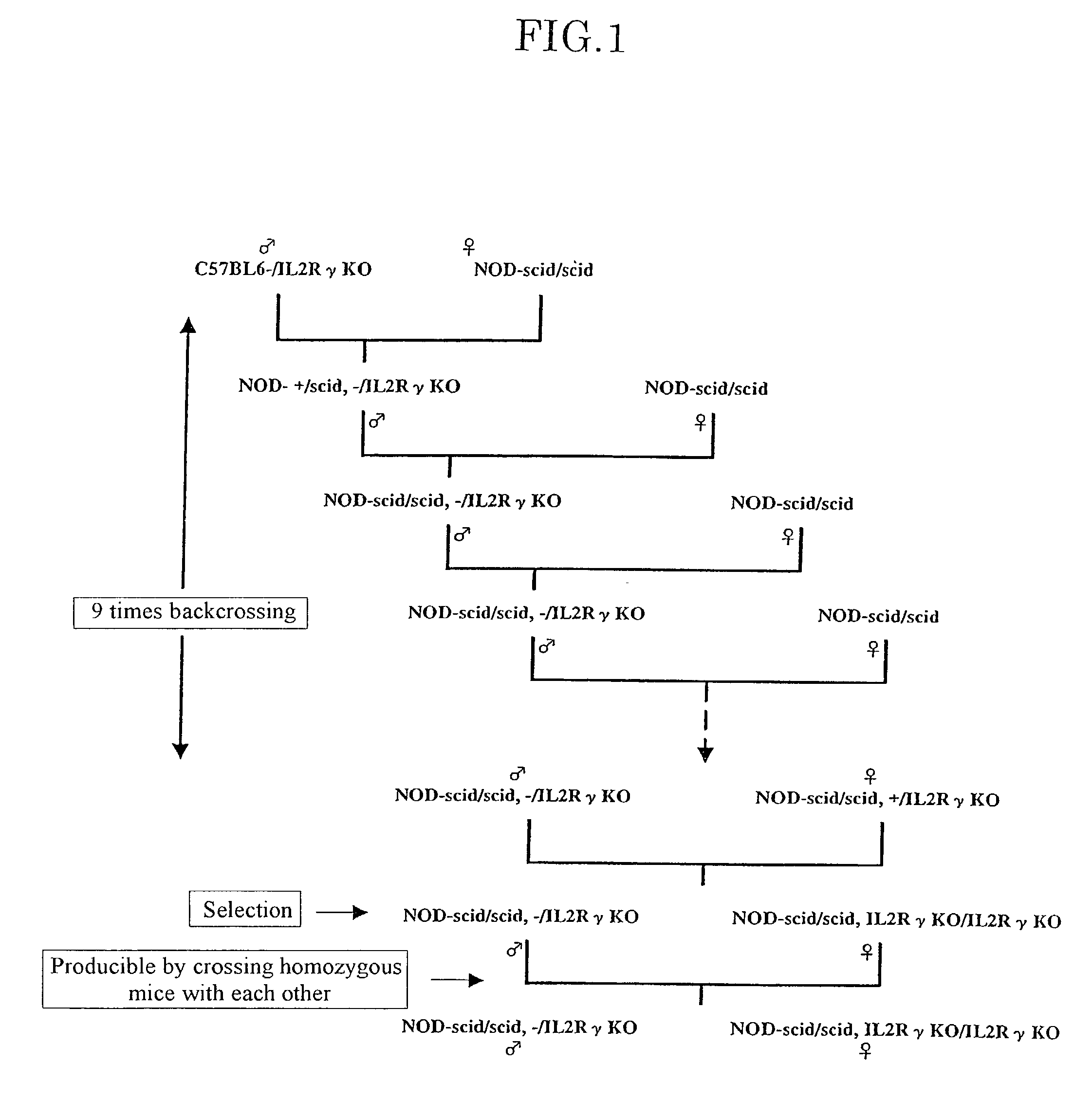
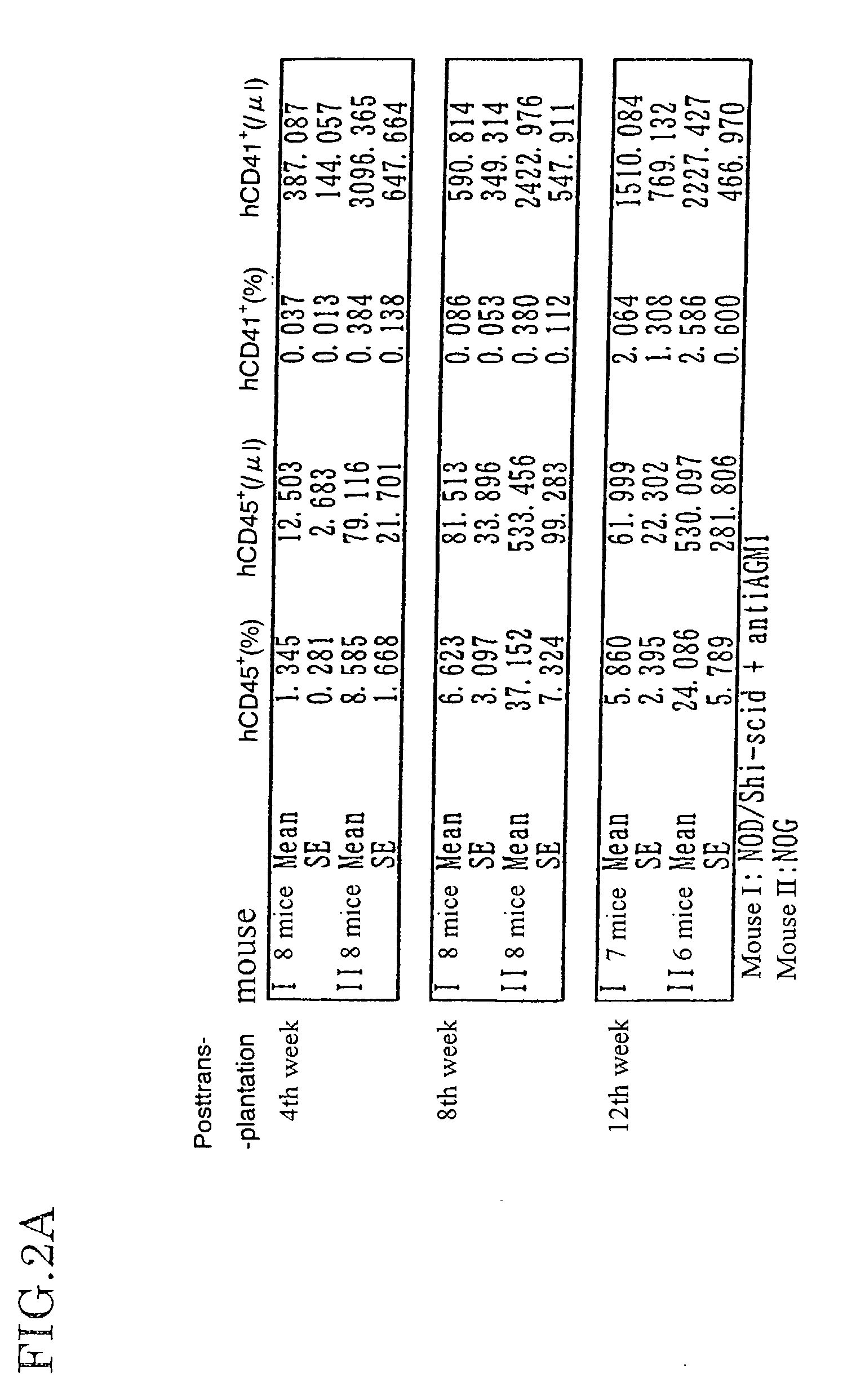
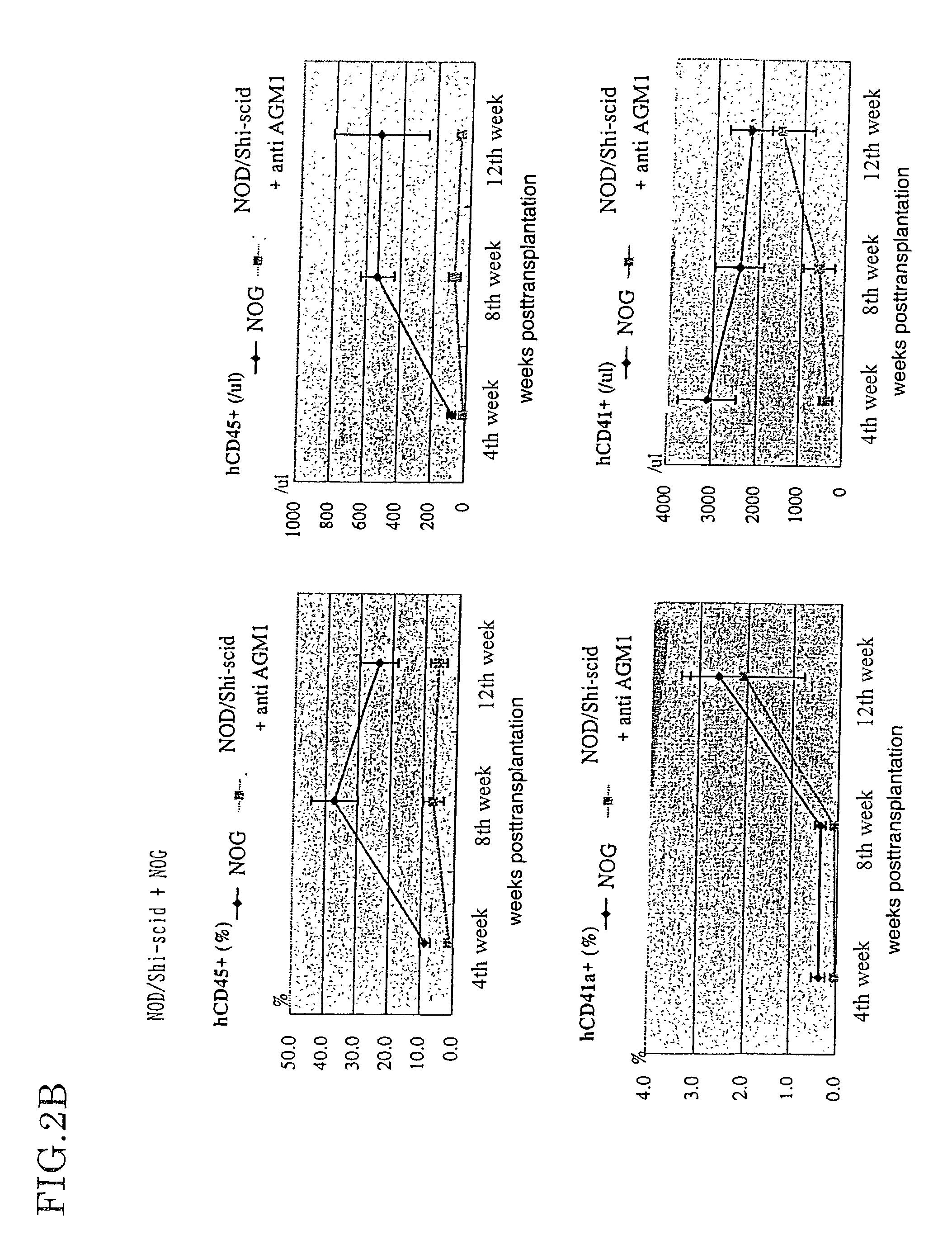
Method of producing a mouse suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS20070011753A1Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousAbnormal tissue growth
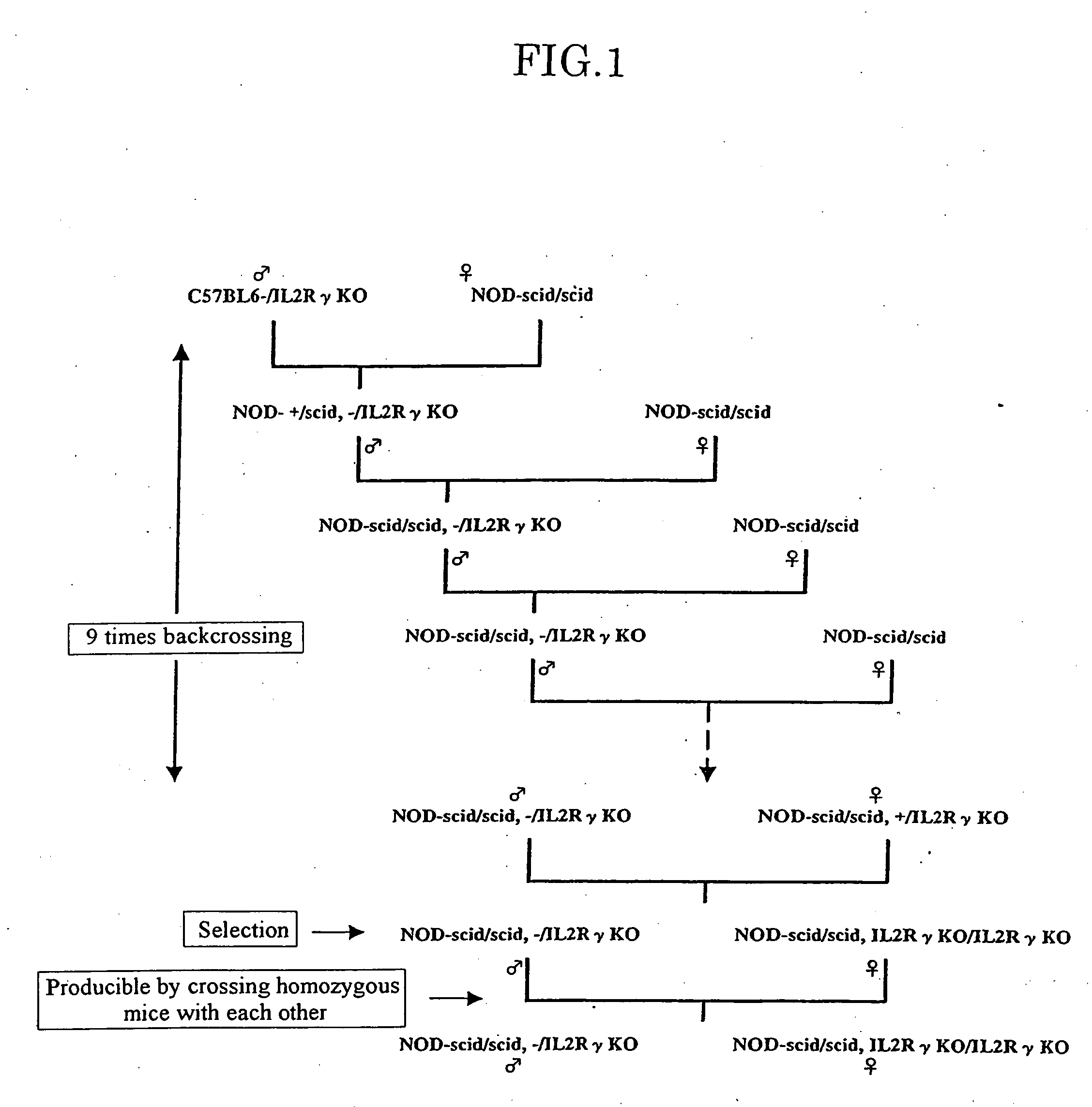
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:ITO MAMORU +9
Chimeric mouse having an immune system constructed with human CD34+ cells and use thereof
InactiveUS20070067854A1Maintaining immunityReduced activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntigenScid mice
Owner:HABU SONOKO
In vivo, animal model for expression of hepatitis C virus
Disclosed is a method for expressing hepatitis C virus in an in vivo, animal model. Viable, hepatitis C virus-infected, human hepatocytes are transplanted into a liver parenchyma of a scid / scid mouse host. The scid / scid mouse host is then maintained in a viable state, for up to five days or greater, whereby viable, morphologically intact human hepatocytes persist in the donor tissue and hepatitis C virus is replicated in the persisting human hepatocytes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
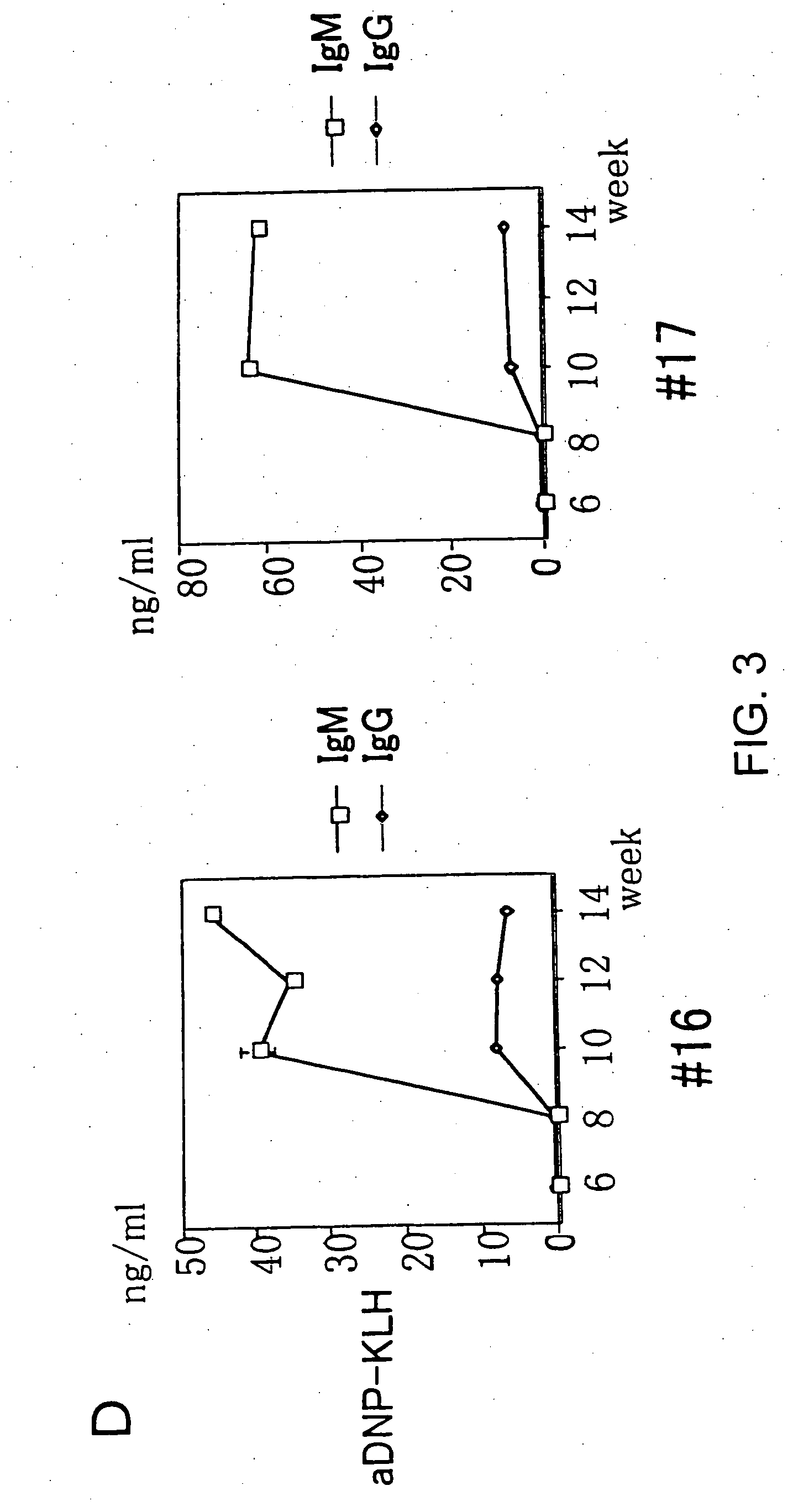
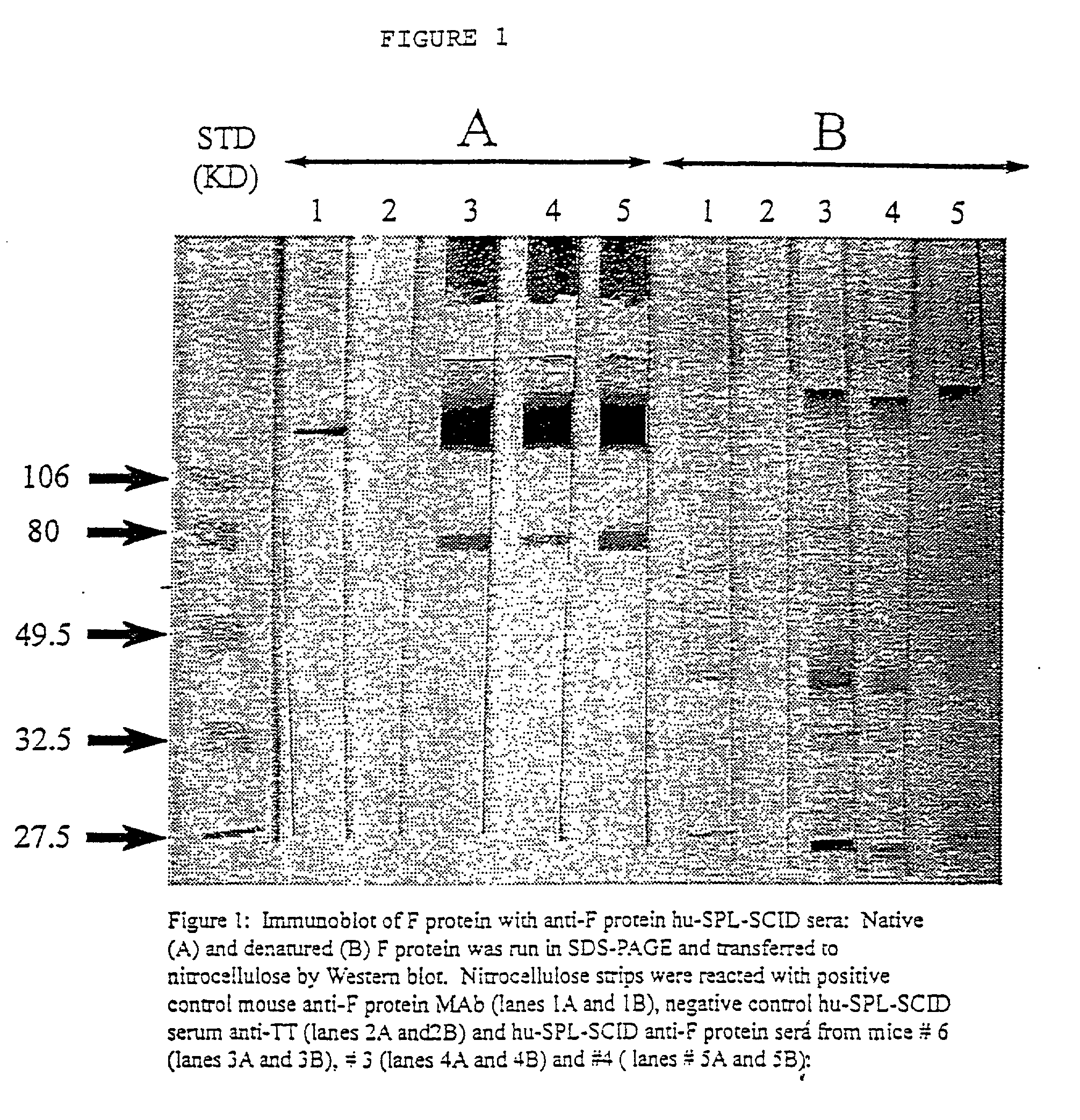
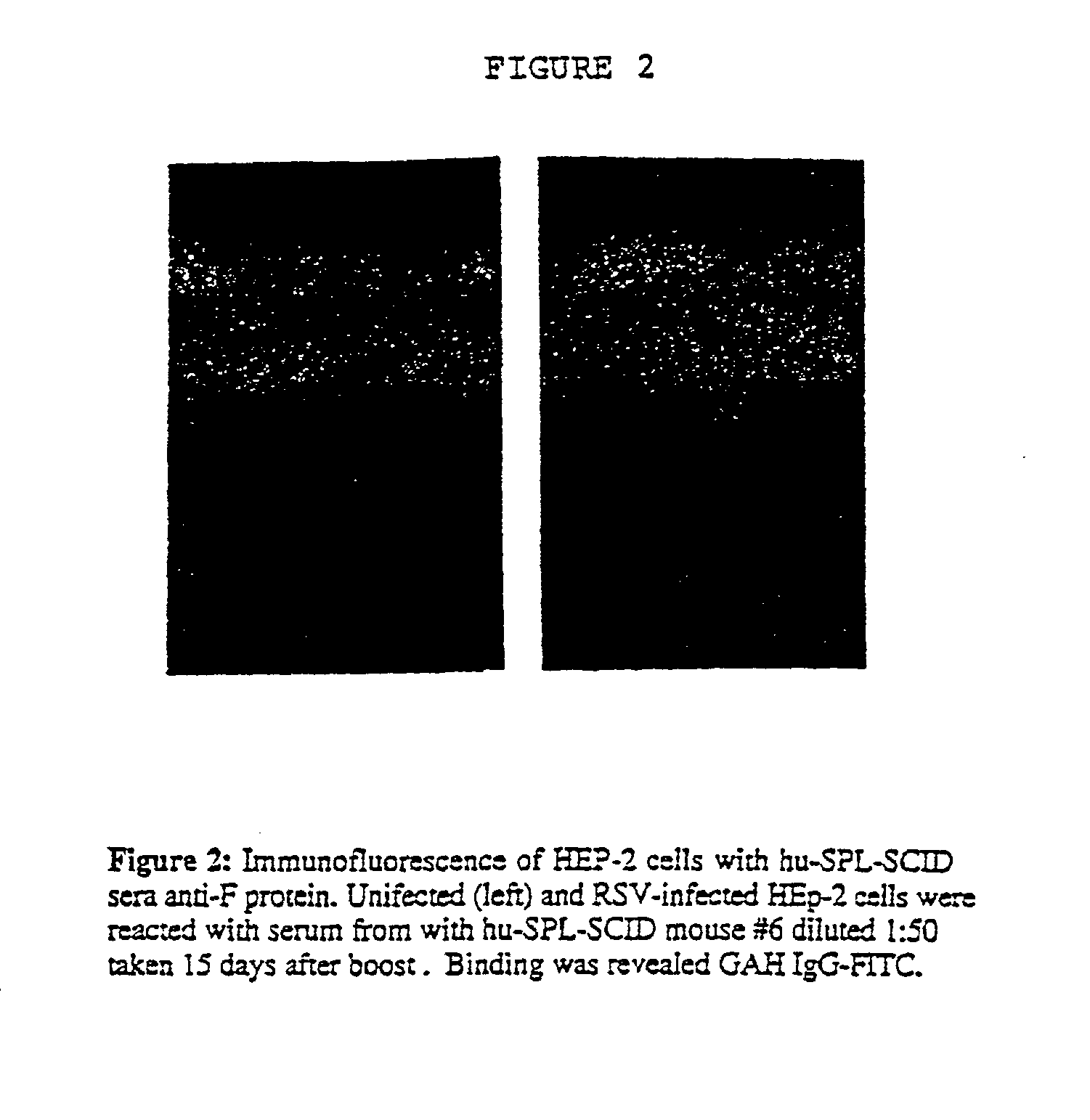
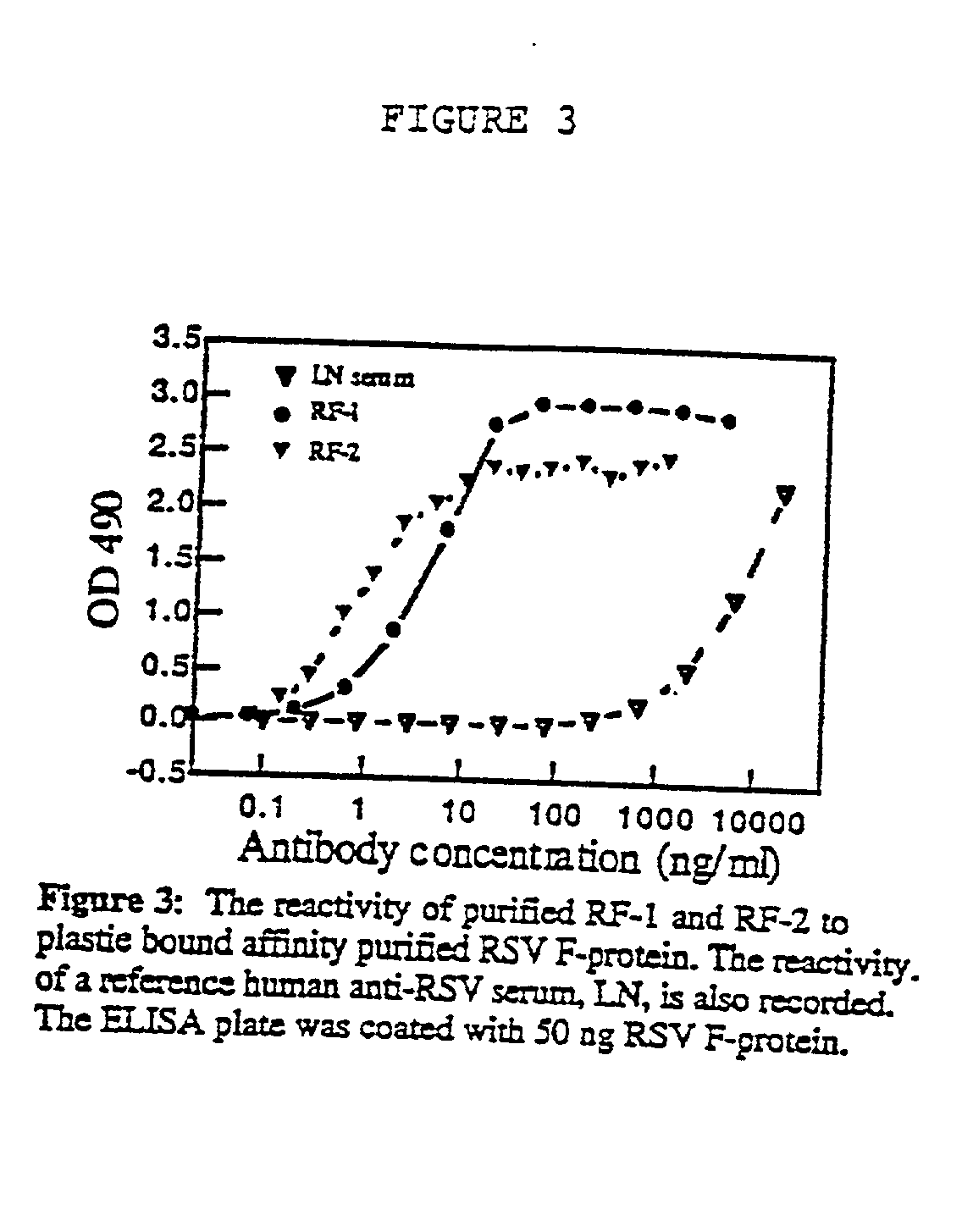
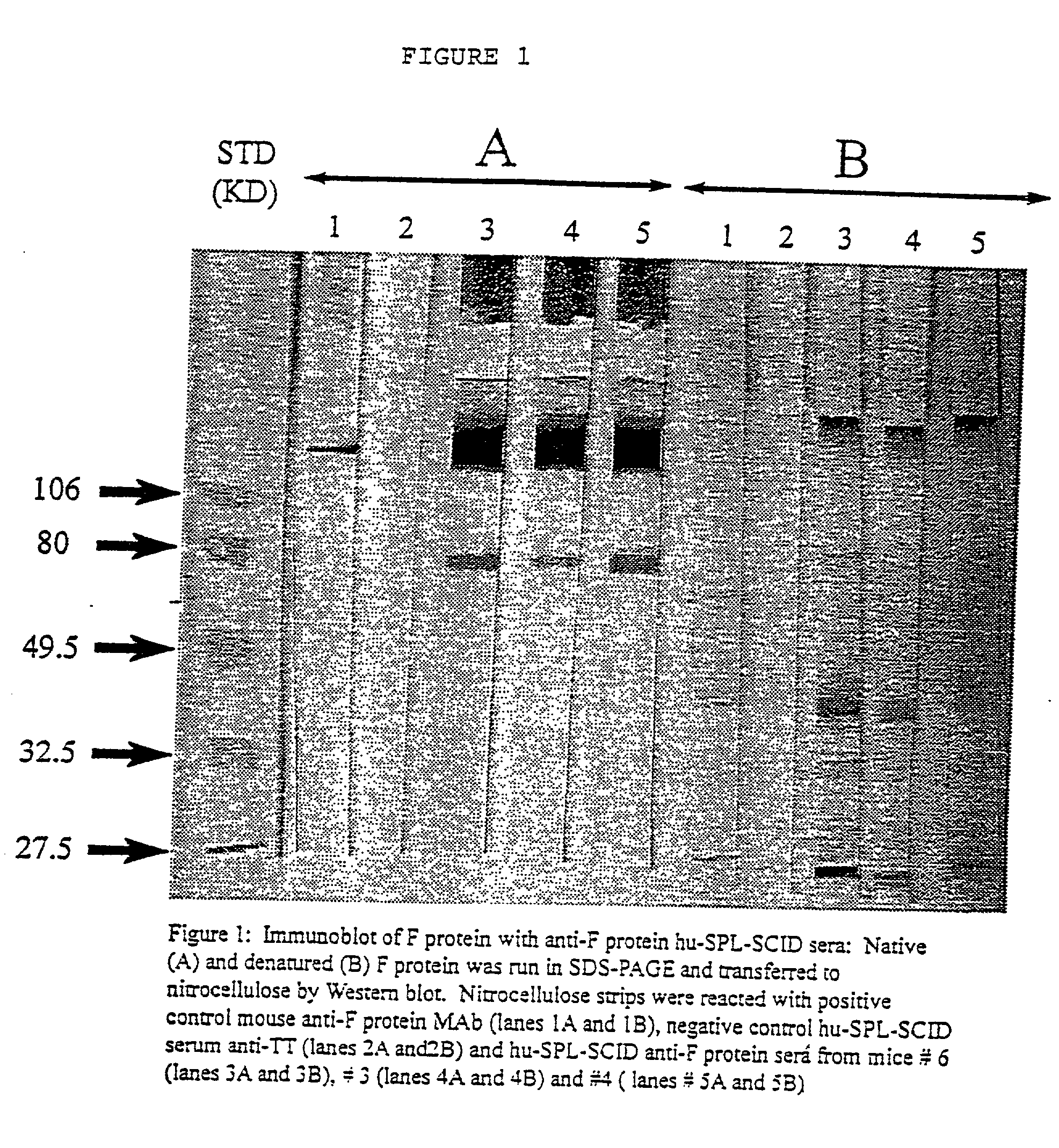
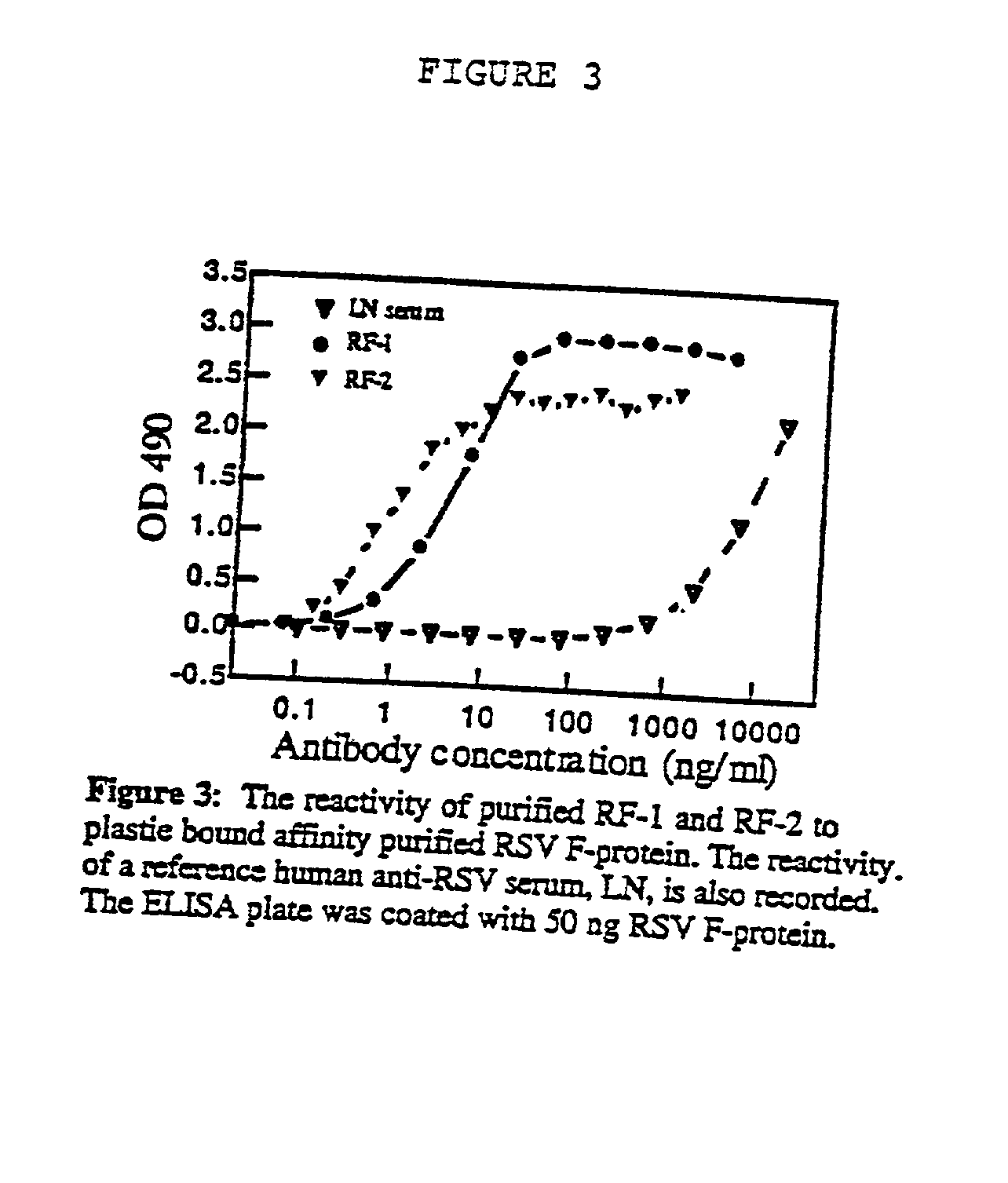
Neutralizing high affinity human monoclonal antibodies specific to RSV F-protein and methods for their manufacture and therapeutic use thereof
InactiveUS20020001798A1Simple methodPromote formationSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsF proteinRSV Infections
A highly efficient method for generating human antibodies in particular which are specific to be RSV fusion protein which combines in vitro primary of human spleen cells and antigen boosting in SCID mice is taught. This method provides for very high human antibody titers which are predominantly of the IgG isotype which contain antibodies of high specificity and affinity to desired antigens. This method is well suited for generating human monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic applications as well as for rescue of human cells for generation of combinational human antibody gene libraries. Two human monoclonal antibodies, RF-1 and RF-2 which each possess an affinity for RSV F-protein <=2x10--9 Molar are taught as well as their corresponding amino acid and DNA sequences. These antibodies are to be used therapeutically and prophylactically for treating or preventing RSV infection, as well as for diagnosis of RSV in analytes.
Owner:XENEREX BIOSCI +1
Method of producing a mouse suitable for the engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS7145055B2Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMutant preparationAbnormal tissue growthHeterologous
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
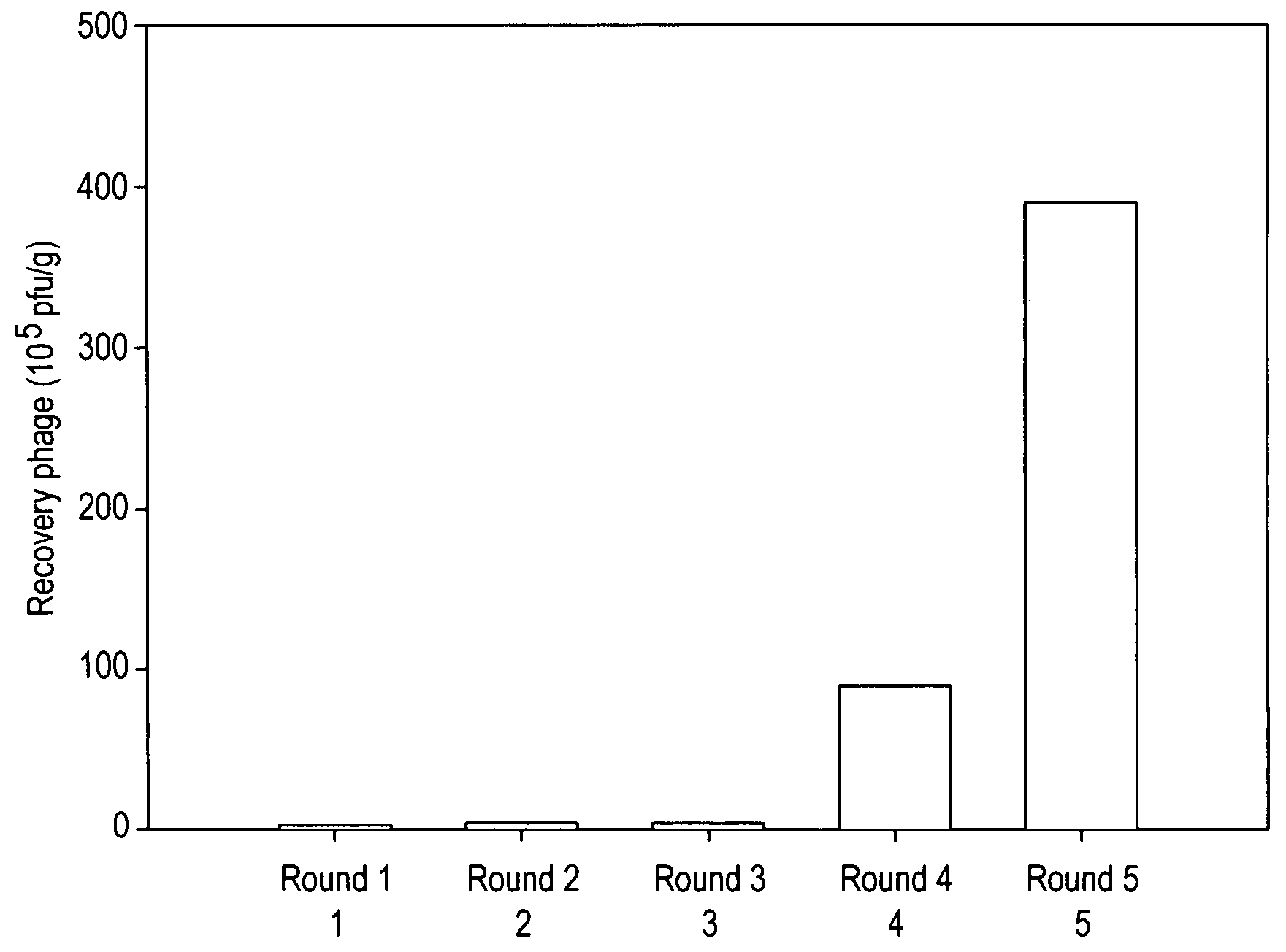
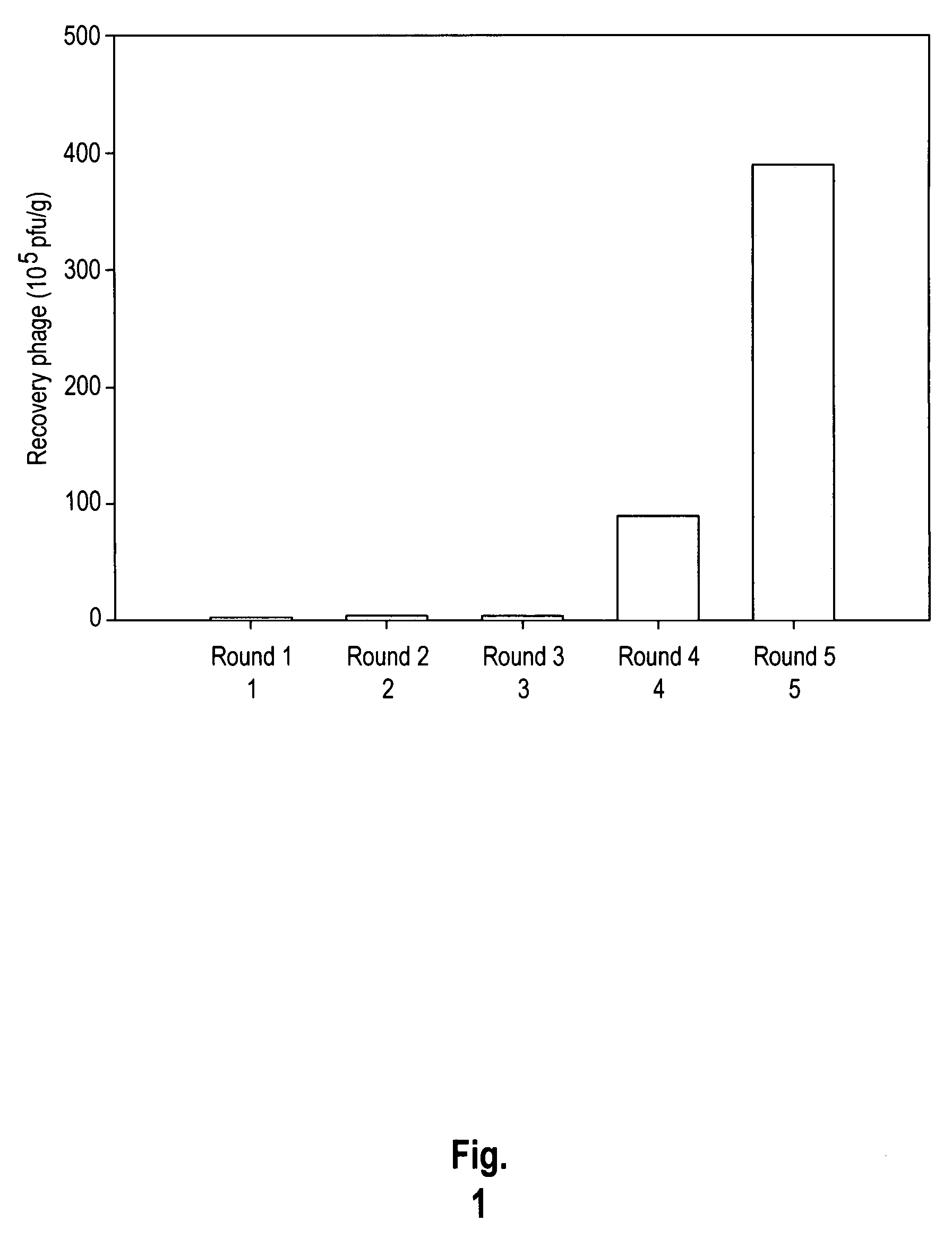
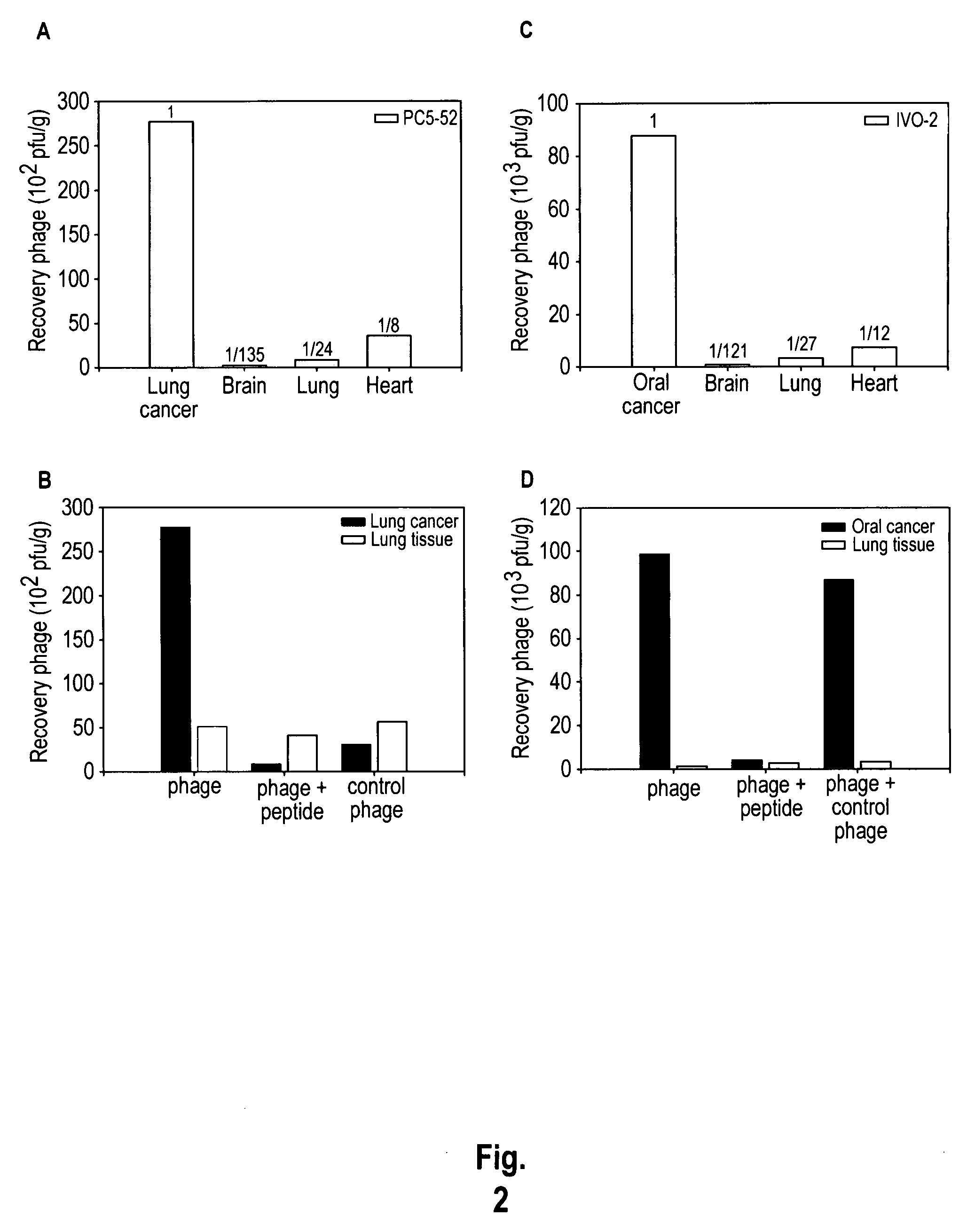
Peptides that target to tumor blood vessels of lung cancer and applications thereof
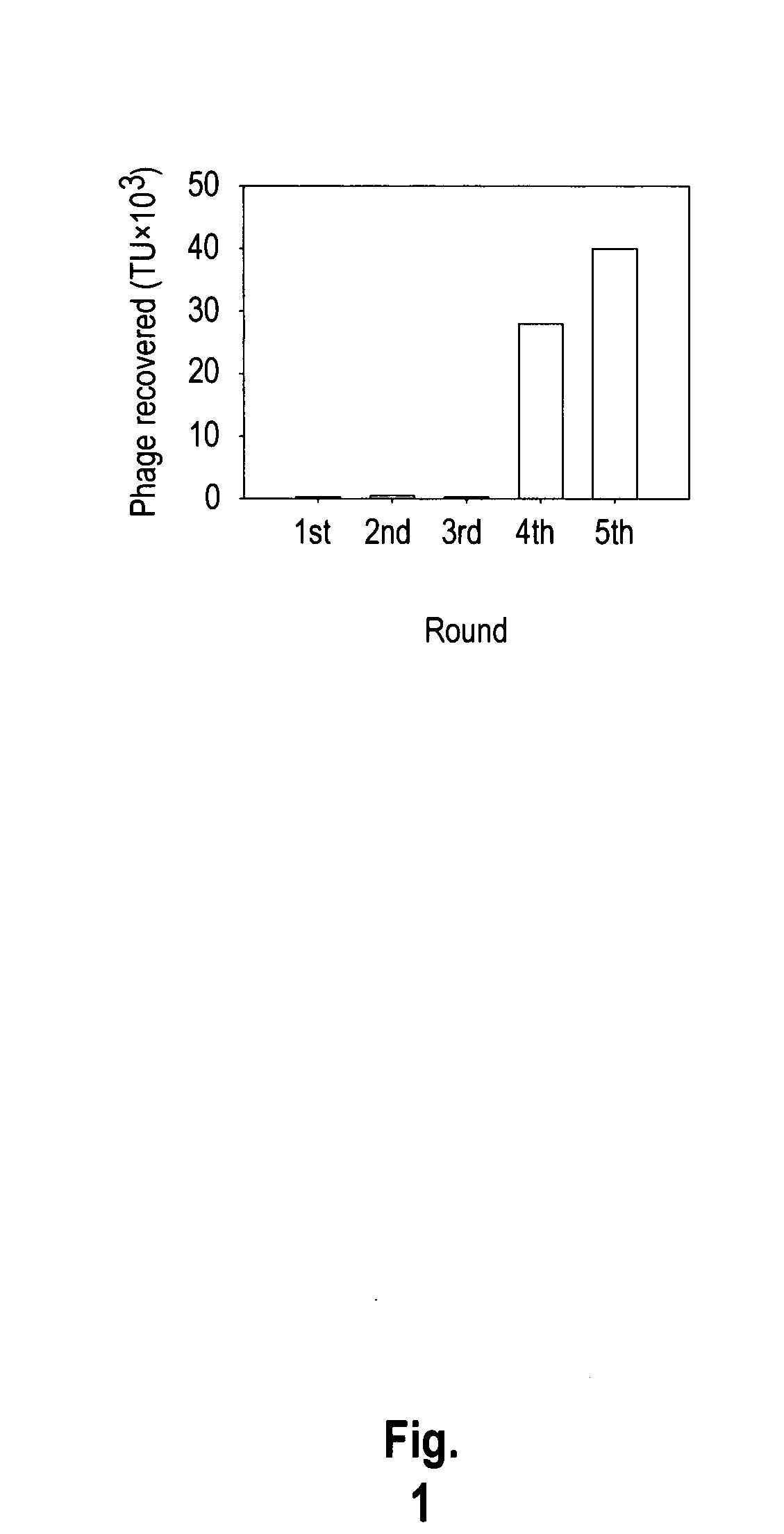
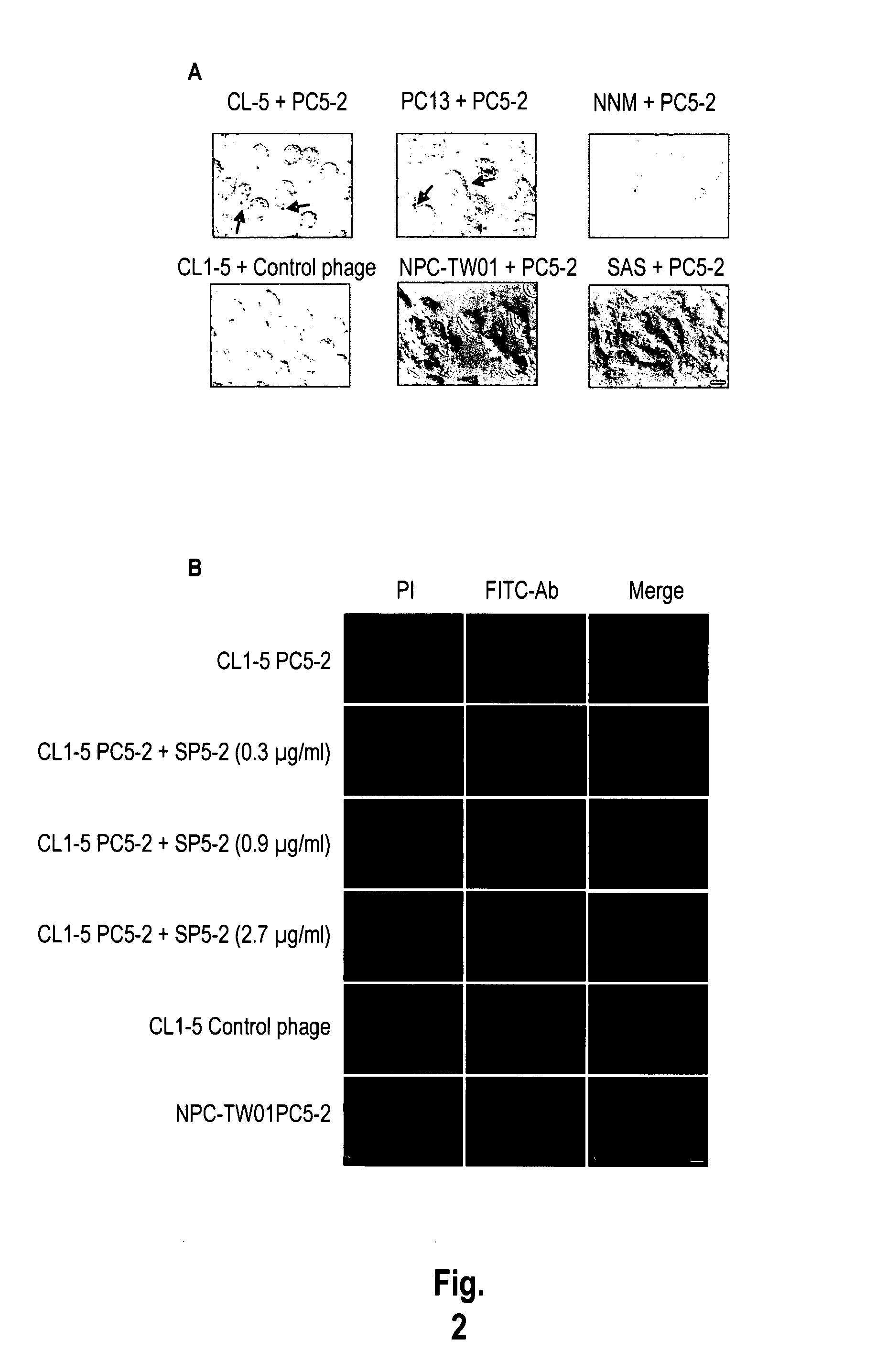
The invention provides nucleic acids, peptides, and antibodies for use in applications including diagnosis and therapy. The peptides target neovasculature and were identified by in vivo phage display. One such peptide, SP5-52, recognized the neovasculature of multiple tumors in SCID mice, but did not target normal blood vessels. This peptide also binds to blood vessels of human lung cancer biopsy specimens. Liposomes comprising SP5-52 and doxorubicin enhanced the efficacy of the drug against multiple human cancer xenografts in SCID mice.
Owner:SINICA ACAD +1
Application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor strain CH-H-1
The invention relates to an application of an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor strain CH-H-1 in a mammal for producing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. The primary tumor strain CH-H-1 disclosed by the invention can realize multiple passages through NOD / SCID mice, has significance for solving the bottleneck that the current treatment of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma can not avoid distant metastasis, and is an ideal object for fundamental research on the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and clinical early application.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Methods and uses of leptin in immune modulation and hepatocellular carcinoma
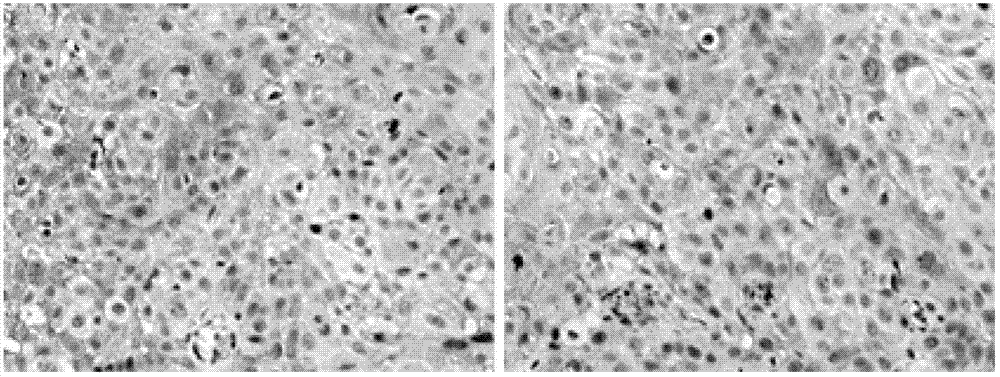
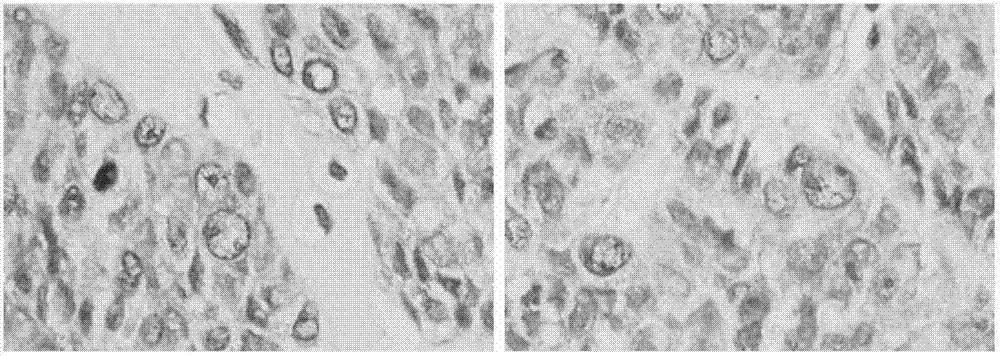
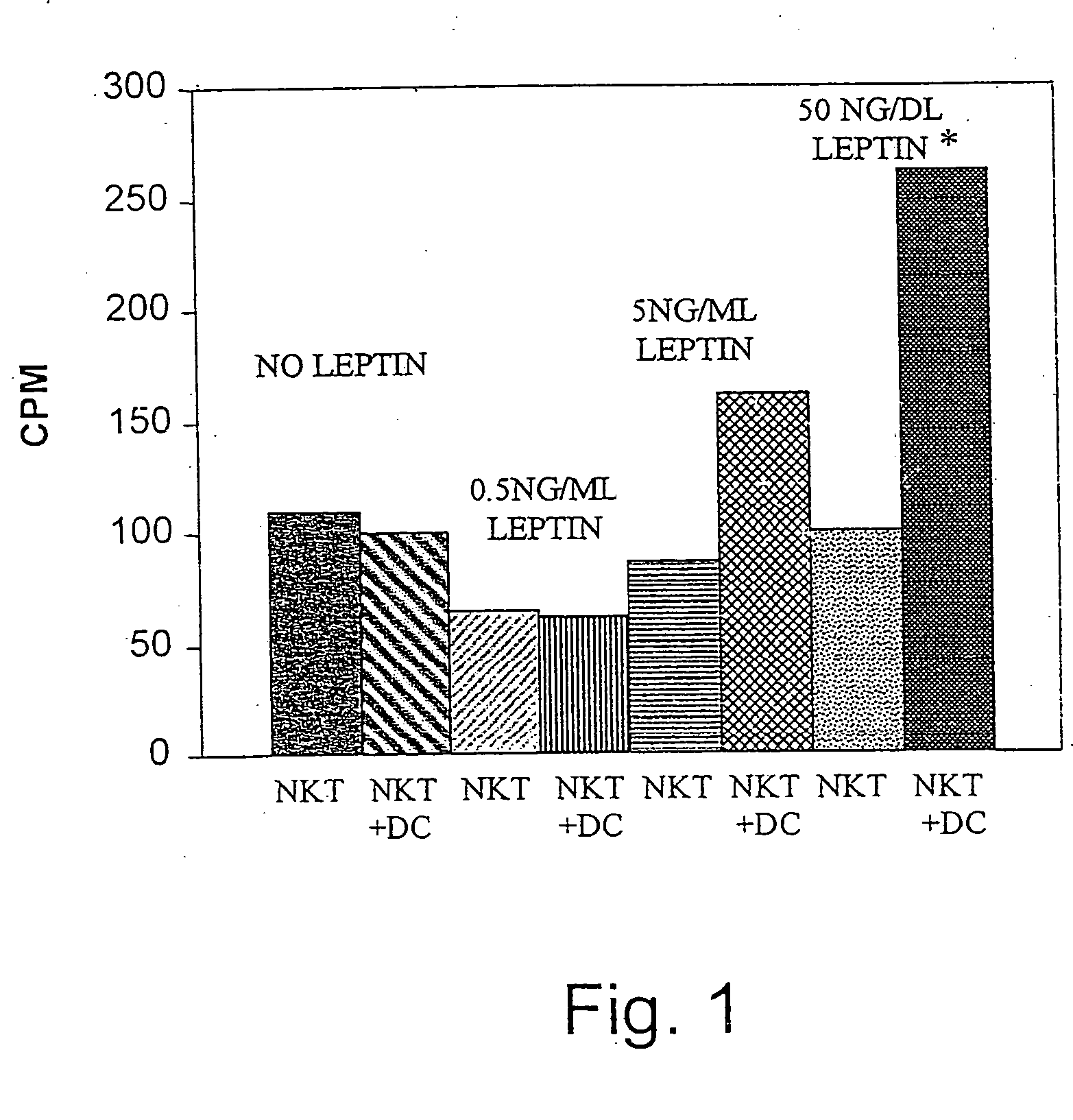
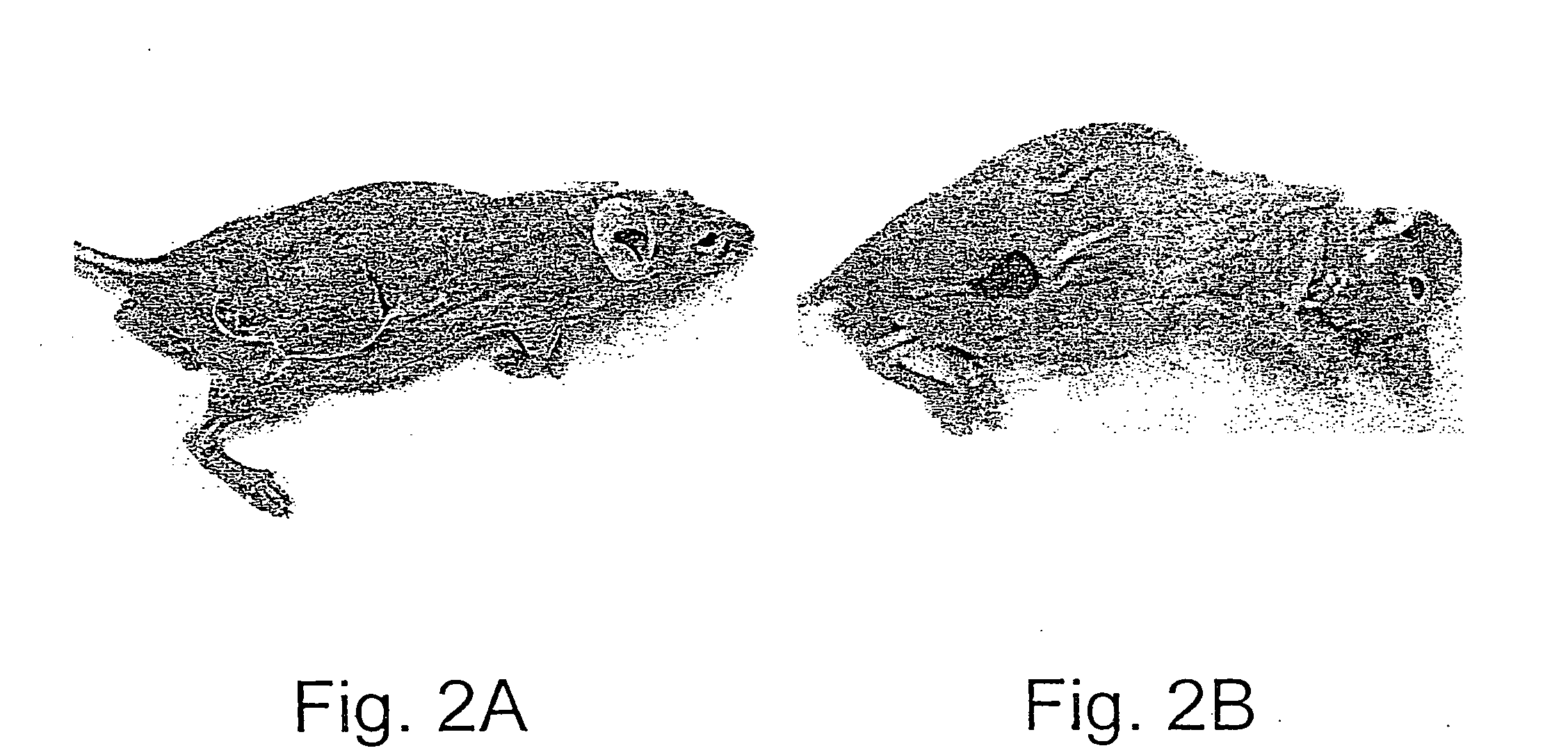
Leptin was previously demonstrated to exert potent immune modulatory properties in several immune mediated disorders. The aim of the study was to determine leptin's anti-tumor effect in a murine model of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In vivo, Athymic T cell deficient (nude) mice transplanted with 1×106 human Hep3B cells, followed by administration of two daily intraperitoneal doses of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. Leptin administration induced a significant reduction in tumor size and improved survival in nude mice. Histologically, tumors of leptin-administered mice featured increased inflammatory exudate in interphase areas. Leptin-induced tumor suppression was associated with a significant increase in peripheral natural killer (NK) cell number. Splenocytes from leptin-treated mice featured decreased expression of CIS mRNA. To determine which lymphocyte subset is a prerequisite for the anti tumor effect of leptin, T&B cell deficient (Scid) mice and T,B& NK deficient (Scid-Beige) mice were subcutaneously implanted with Hep3B tumor cells, with and without the daily intraperitoneal administration of 0.5 mg / gram leptin for 6 weeks. SCID mice featured leptin-associated tumor suppression similar to those of nude mice. In contrast, NK-deficient SCID-Beige mice developed larger tumors. To further establish natural killer cell's central role in mediation of leptin's anti-tumor effect, NK cells were incubated in vitro with increasing doses of leptin, demonstrating a dose-dependent increase in cytotoxic activity. Incubation of leptin with hepatoma cell line was found to induce a dose-dependent reduction in hepatoma cell proliferation, suggesting an additive direct anti-tumor effect. Further synergism in inhibition of hepatoma cell proliferation in vitro was achieved following addition of natural killer cells. HCC cells expressed leptin receptor mRNA, while addition of leptin induced increased mRMA expression of STAT2 and SOCS1 on tumor cell lines. Leptin administration induces a significant suppression of human HCC. This effect is mediated by induction of natural killer cell proliferation and activation, and by direct inhibition of tumor growth. Decreased natural killer cell expression of inhibitory CIS protein and over expression of the anti-proliferative STAT2 and SOCS1 proteins in HCC lines may underline both anti cancerous effects of leptin.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS
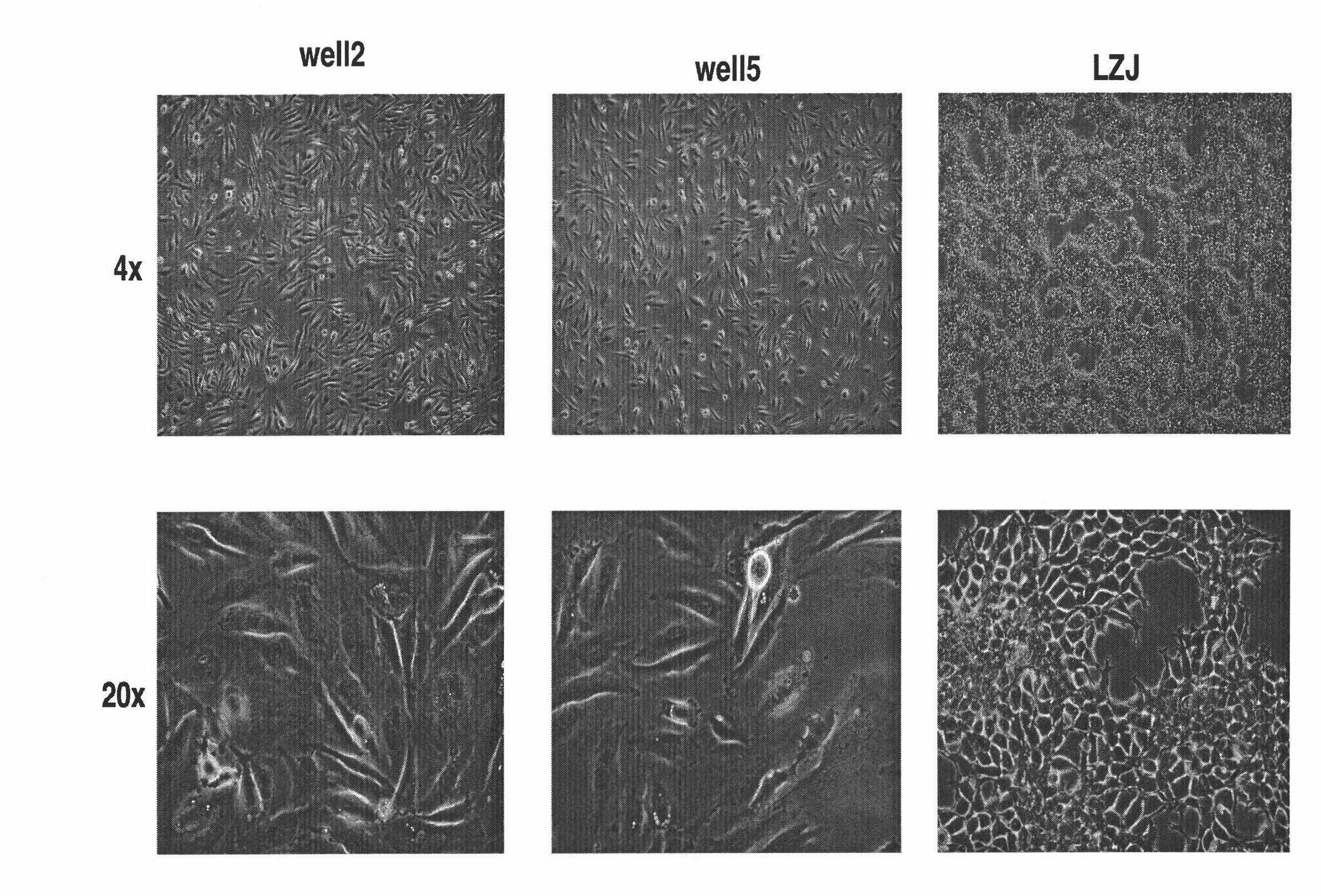
Human osteosarcoma cell line group and mouse in-vivo transplantation model
ActiveCN102051344AKeep activeStable traitsMicroorganism based processesTumor/cancer cellsCombined immunodeficiency diseaseSevere combined immunodeficiency disease
The invention discloses three human osteosarcoma cell lines well2, well 5 and LZJ, the collection numbers of the three human osteosarcoma cell lines are CCTCC C200961, CCTCC C200962 and CCTCC C200963 respectively, and the invention further discloses establishment of a corresponding NOD / SCID (nonobese diabetic / severe combined immunodeficiency disease) mouse in-vivo transplantation model, thereby providing a good and stable experimental subject and a model platform for clinical and fundamental research work of osteosarcoma. The established osteosarcoma cell lines can enable the in-vitro stable passage to be more than two years, have stable characters and enable morphology, have immuno-phenotype, chromosome genetics and other characteristics similar to the common osteosarcoma cell lines. The tumorigenesis of NOD / SCID mice is stable, the pathomorphism of tumor bodies is similar to primary tumor tissues of patients, and the animal model is simultaneously sensitive to common chemotherapeutic drugs for the osteosarcoma and can well simulate clinical retracking for clinical patients with the osteosarcoma.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for culturing hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells
InactiveCN101597594AA large amountGood ability to rebuild bloodTissue cultureProgenitorBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a method for expanding the hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood in vitro by an alginate three-dimensional culture system. The method combines SCF, TPO and FL cytokines to support the expansion of the hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells in a single karyocyte of human umbilical cord blood, does not need adding other cytokines, and cultures the single karyocyte of human umbilical cord blood packaged in an alginate microsphere in a three-dimensional stationary culture system and a three-dimensional rotary culture system to observe the expansion effect of the single karyocyte of human umbilical cord blood packaged in the alginate microsphere in the rotary culture system. Compared with the conventional two-dimensional system, the three-dimensional culture system improves the total cells and obviously increases CD34+ cells under the condition of culturing low-concentration cytokines; and colony forming unit-granulocytes and macrophages of cells expanded in the three-dimensional culture system are cloned to form obviously increased cells, and the single karyocyte of human umbilical cord blood in a transplanted NOD / SCID mouse has better engraftment and reconstructs hemopoiesis.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Highly metastatic model of human melanoma, cell subline, creation methods, and dynamic detection of metastasis
InactiveCN102067828AMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsMetastatic melanomaLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a highly metastatic model of human melanoma, a highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma, creation methods for the highly metastatic model and the highly metastatic cell subline, and the dynamic detection of metastasis. The subcutaneously-transplanted mouse highly metastatic model and the corresponding cell subline are established in an in-vivo screening way in a mouse with severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) by using mouse lung metastasis, namely human malignant melanoma cell strain A375 pulmonary metastasis, wherein the highly metastatic cell subline of the human melanoma is A375sci, and has a human tumor cell karyotype; and 60 to 75 hypo-triploid-dominated chromosomes are acrocentric and have a heteroploid karyotype. The cell subline has the two routes of metastasis of blood trails and lymph. The in-vivo screening of the highly-metastatic model is performed by using animals with severe immune deficiency, and is expressed and applied in nude mice. A method for detecting Alu genes by using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is simple, highly sensitive and highly specific, and can be used for detecting organ metastasis, particularly micrometastasis, in a human tumor animal-xenotransplantation model.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor line CH-H-2
InactiveCN102766600AStable traitsHigh metastatic potentialTumor/cancer cellsPrimary tumorBasic research
The invention relates to an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma primary tumor line CH-H-2 which is used in mammals to produce esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. The primary tumor line CH-H-2 can be passed by NOD / SCID mice for multiple times, is significant in solving the inevitable bottleneck problem of distant metastasis in the current esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treatment, and is an ideal object for the basic research and clinical early application of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Lung cancer-targeted peptides and applications thereof
The invention provides nucleic acids, peptides, and antibodies for use in applications including diagnosis and therapy. The peptides target lung cancer and were identified by phage display. Targeting phage PC5-2 and synthetic peptide SP5-2 were both able to recognize human pulmonary tumor specimens from lung cancer patients. In SCID mice bearing NSCLC xenografts, the targeting phage was able to target tumor masses specifically. When the peptide was coupled to liposomes containing the anti-cancer drugs vinorelbine or doxorubicin, the efficacy of these drugs against human lung cancer xenografts was improved, the survival rate increased, and the drug toxicity was reduced.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
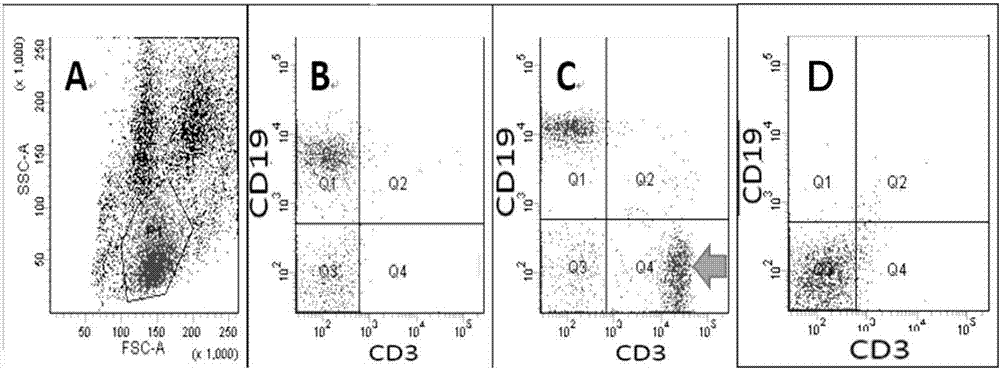
Method for establishing xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease model for NOD/SCID (non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient) mice
InactiveCN102550486AImprove efficiencyGood repeatabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansAnimal husbandryPeripheral blood mononuclear cellWhite blood cell
The invention provides a method for establishing a xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease model for NOD / SCID (non-obese diabetic / severe combined immunodeficient) mice, which includes: preparing active human PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells), establishing a model of NOD / SCID mice, detecting number and content of mouse-to-human white blood cells in implantation, and establishing pathologicalmanifestations of a mouse GVHD (graft-versus-host disease) target organ. Application of cyclophosphamide with anti-mouse CD122 (IL-2R beta chain) monoclonal antibody to pretreatment is used to substitute the sublethal dose irradiation process to establish the humanized GVHD model for NOD / SCID mice. The model is capable of simulating characteristics of graft-versus-host diseases after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in clinical chemotherapeutic pretreatment, and is high in establishing efficiency and high in repeatability. The model establishment process is simple and easy. The shortage that domestic research centers lacking relevant irradiation equipment fail to carry out relevant researches is overcome, and an experimental platform for human immune system GVHD researchon live animals can be provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Non-Human mammalian Arthritis Model Featuring Human Antibodies Against Citrul-Linated Proteins
Use of a non-human mammalian disease model, wherein the non-human mammal has been implanted with human synovial tissue or other human inflamed tissue containing anti-CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide) antibody producing cells for (i) analyzing cellular processes in a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies in such human synovial tissue or other human inflamed tissue, (ii) studying the role of anti-CCP antibodies in the induction and progression of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies, (iii) testing the efficacy of a therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies, and (iv) identifying a therapeutic agent useful for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies. In one embodiment the non-human mammalian disease model is a mouse, such as a SCID mouse, and the disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies is arthritis, such as RA (rheumatoid arthritis).
Owner:GENMAB AS
Phenylbutyryl curcumin derivate and application thereof in anti-tumor drug preparation
InactiveCN101830819AImprove anti-tumor effectNo deathOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationProstate cancerChronic granulocytic leukemia
The invention relates to phenylbutyryl curcumin derivate and application thereof in anti-tumor drug preparation, in particular to 4-(di(2-chloroethyl) amino) phenylbutyryl curcumin, 4,4'-(di(2-chloroethyl)amino) diphenylbutyryl curcumin, pharmaceutically acceptable salts and a preparation method thereof, and applications of 4-(di(2-chloroethyl) amino) phenylbutyryl curcumin, and 4,4'-(di(2-chloroethyl)amino) di phenylbutyryl curcumin in anti-tumor drug preparation. The phenylbutyryl curcumin derivate can be used for (but not limited to) preparing drugs for treating leukemia, skin cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer or prostatic cancer. The derivate has obvious inhibition on a plurality of animal tumor cell transplanting modules, especially for the human chronic granulocytic leukemia model constructed by NOD-SCID mice inoculated with the human chronic granulocytic leukemia K562 cell stain, the life prolonging rate is obviously enhanced, and the serious toxicity to mice does not exist.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
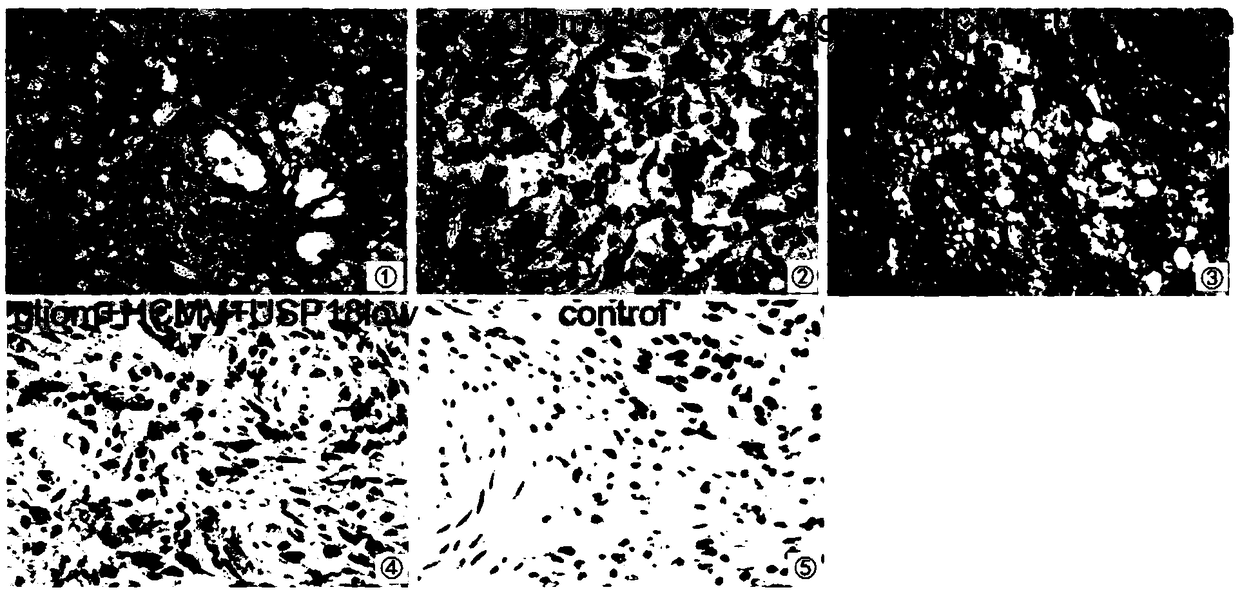
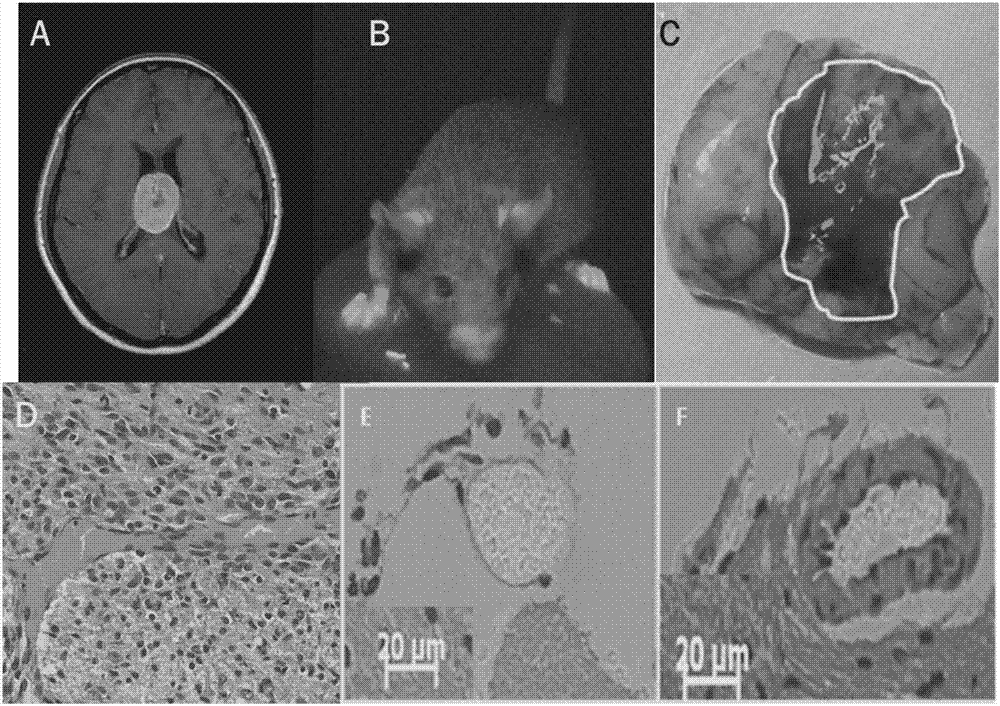
Building method of human spongioblastoma cell SCID mouse brain transplantation tumor model
InactiveCN108186681AReflect the actual infection statusGrowth toleranceMammal material medical ingredientsVeterinary instrumentsSingle cell suspensionHCMV Infection
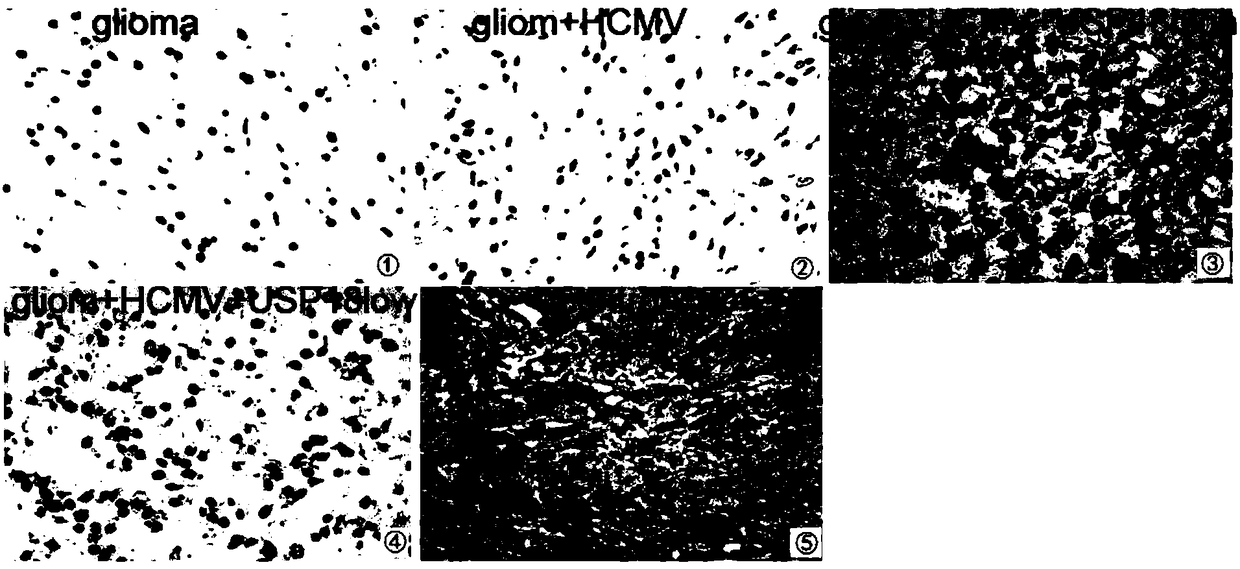
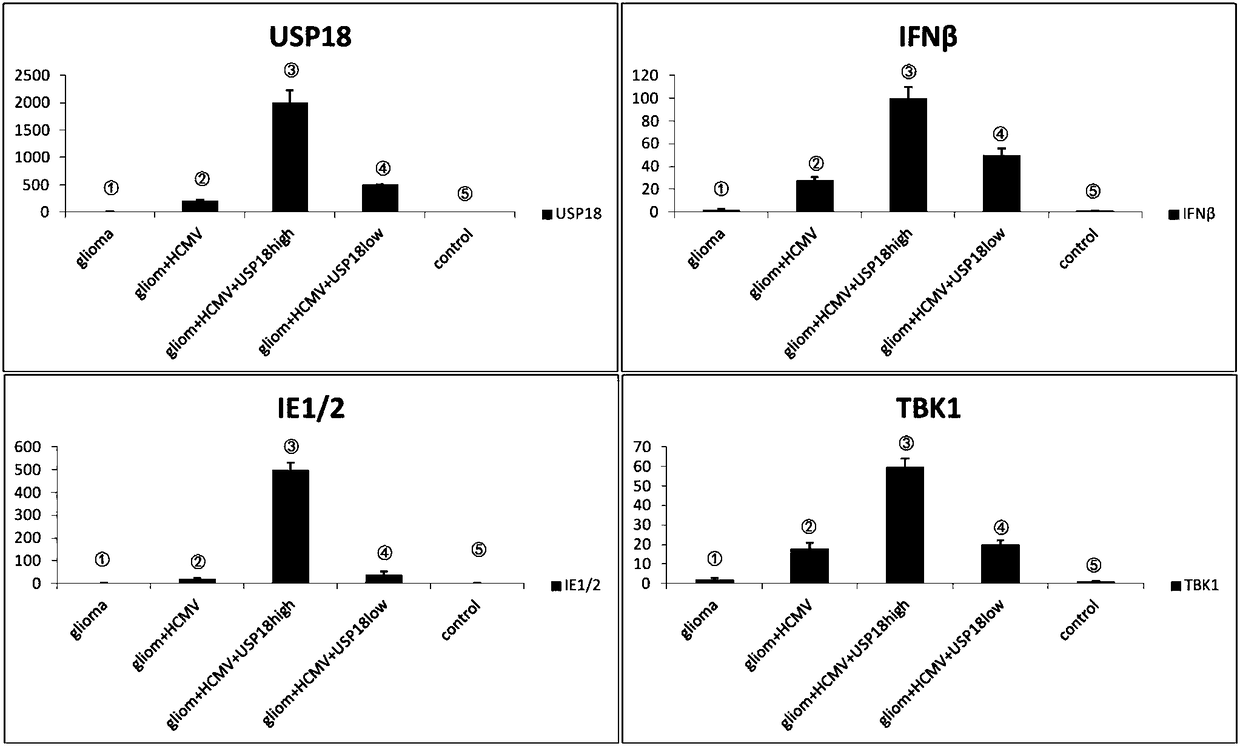
The invention discloses a building method of a human spongioblastoma cell SCID mouse brain transplantation tumor model. The method comprises the following steps of preparing primary spongioblastoma cells; selecting male SCID mice; dividing the mice into five groups (the first group of mice are inoculated with primary generation spongioblastoma cells in the brain; the second group of mice are inoculated with primary generation spongioblastoma cells in the brain and are infected with HCMV; the third group of mice are inoculated with primary spongioblastoma cells, and are infected with HCMV, andUSP18 high expression adenovirus carriers are used for processing the group; the fourth group of mice are inoculated with primary generation spongioblastoma cells in the brain and are infected with HCMV, interference adenovirus carrier USP18 small interference adenovirus carriers USP18 are used for treating the group of mice; the fifth group of mice is a normal control group); determining a targeted point; performing aseptic inoculation of single-cell suspension; during experiment termination, cutting the head; taking the brain; identifying whether the building of the human spongioblastoma cell SCID mouse brain transplantation tumor model is successful or not. The tumor model can better embody the practical infection state of the HCMV infected human spongioblastoma.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD/SCID mice and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101548909AIncrease success rateProlong survival timeDiagnosticsSurgeryMolecular Targeted TherapiesScid mice
The present invention relates to a method for preparing model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a single karyocyte of marrow of leukemia patient, 2. preprocessing the NOD / SCID mice, 3. establishing a model, and 4. identifying the model. The invention firstly adopts a mode of injecting single karyocyte of marrow of leukemia patient through tail-vein injection for establishing the model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice. Furthermore the prepared model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice has the advantages of high success rate and long survival time. The invention can provide new animal model for researching the outer marrow infiltration mechanism of leukemia, sieving the leukemia medicine, and the targeted therapy of gene and molecule.
Owner:天津中医药大学第一附属医院
High metastasis human breast cancer cell system and its establishing method
The present invention relates to cancer cell system. The establishment of tumor metastasis animal model is essential for the deep research of tumor invasion and metastasis mechanism. SCID mouse is used as experiment target, and the establishment includes subcutaneously inoculating breast cancer parent MCF-7 cell suspension in shoulder of SCID mouse, killing SCID mouse 68 days after inoculation to take out lung for primary culture, cell passage after cells fill the bottom of the culture bottle with the cell being named as LM-MCF-7, subcutaneously re-injecting tumor cell to SCID mouse after 20 generation culture in vivo of LM-MCF-7 and repeating the said steps. The process has tumor forming rate of 100 % and wide metastasis in lung, kidney, spleen, marrow, lymph node, heart, etc. of SCIDmouse is found.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
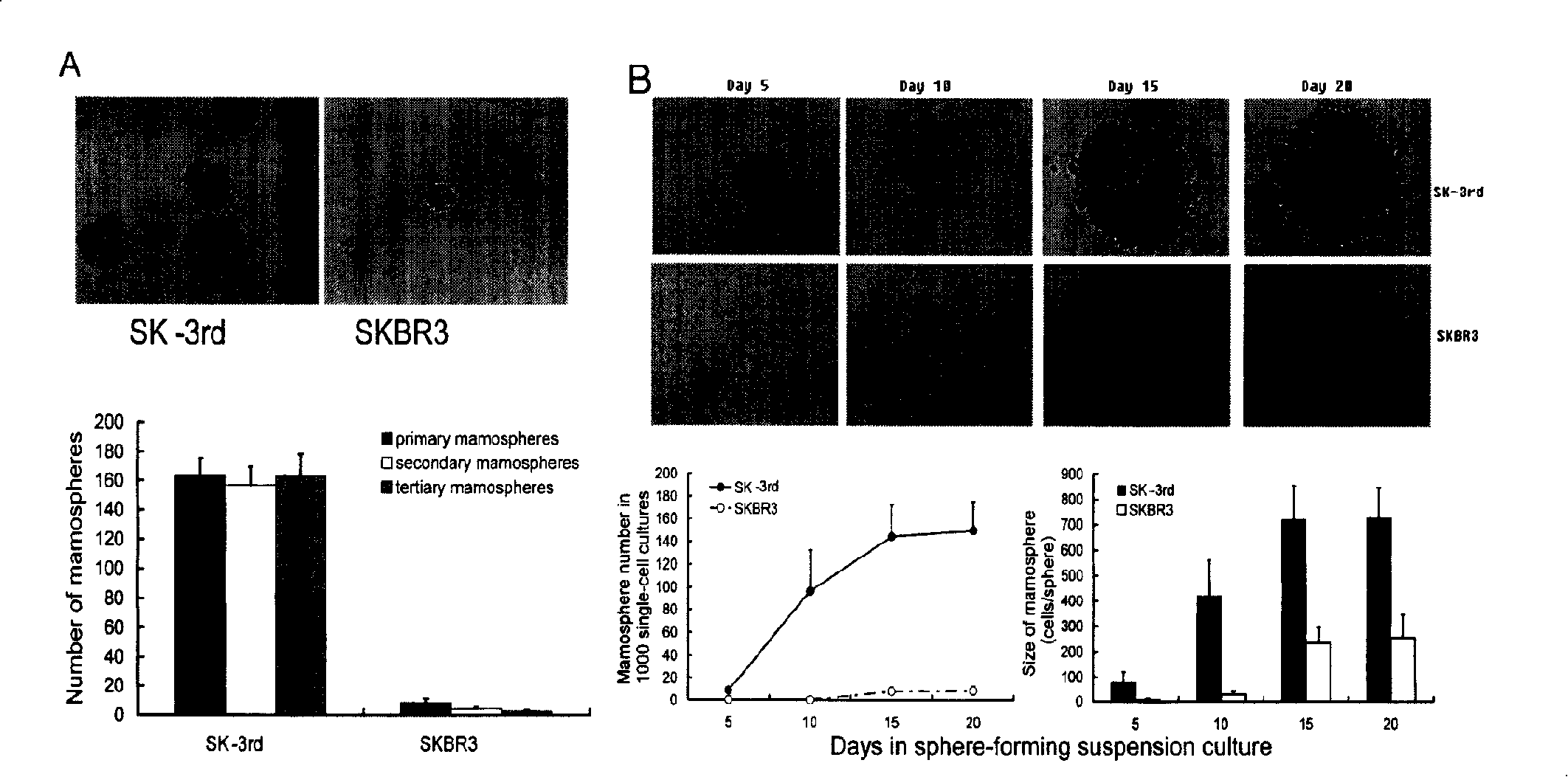
Human breast cancer cell line SK-3rd and construction method thereof
Human breast carcinoma SK-BR-3 cell strain as source cell for building train adapted by the invention is continuously inoculated on female NOD / SCID mouse mammary gland fat pad and filtered in pressure of low dose chemotherapy drug tail intravenous injection to build human breast carcinoma cell line SK-3rd rich in tumour breast carcinoma stem cell. The proper of knub stem cell in the cell is increased greatly comparing with non NOD / SCID vivo passage source cell. The formation rate of saccule and the number of cell in the saccule are increased greatly in case of cell suspension culture. The ratio of undifferentiation cancer cell is reduced but is higher evidently than source cell in process of SK-3rd saccule cell inducing differentiation. The saccule cell formed from SK-3rd cell has carcinoma stem cell phenotype which gradually dies out in process of differentiation. NOD / SCID mouse orthotopic transplantation has high tumour-forming rate, high long-distance transferring rate, short tumour-forming periodic time and less number of cells needed by tumour-forming. The invention is an ideal mould for studying breast carcinoma stem cell and has wide applications foreground for disclosing generation mechanism of breast carcinoma and neoplastic treat.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
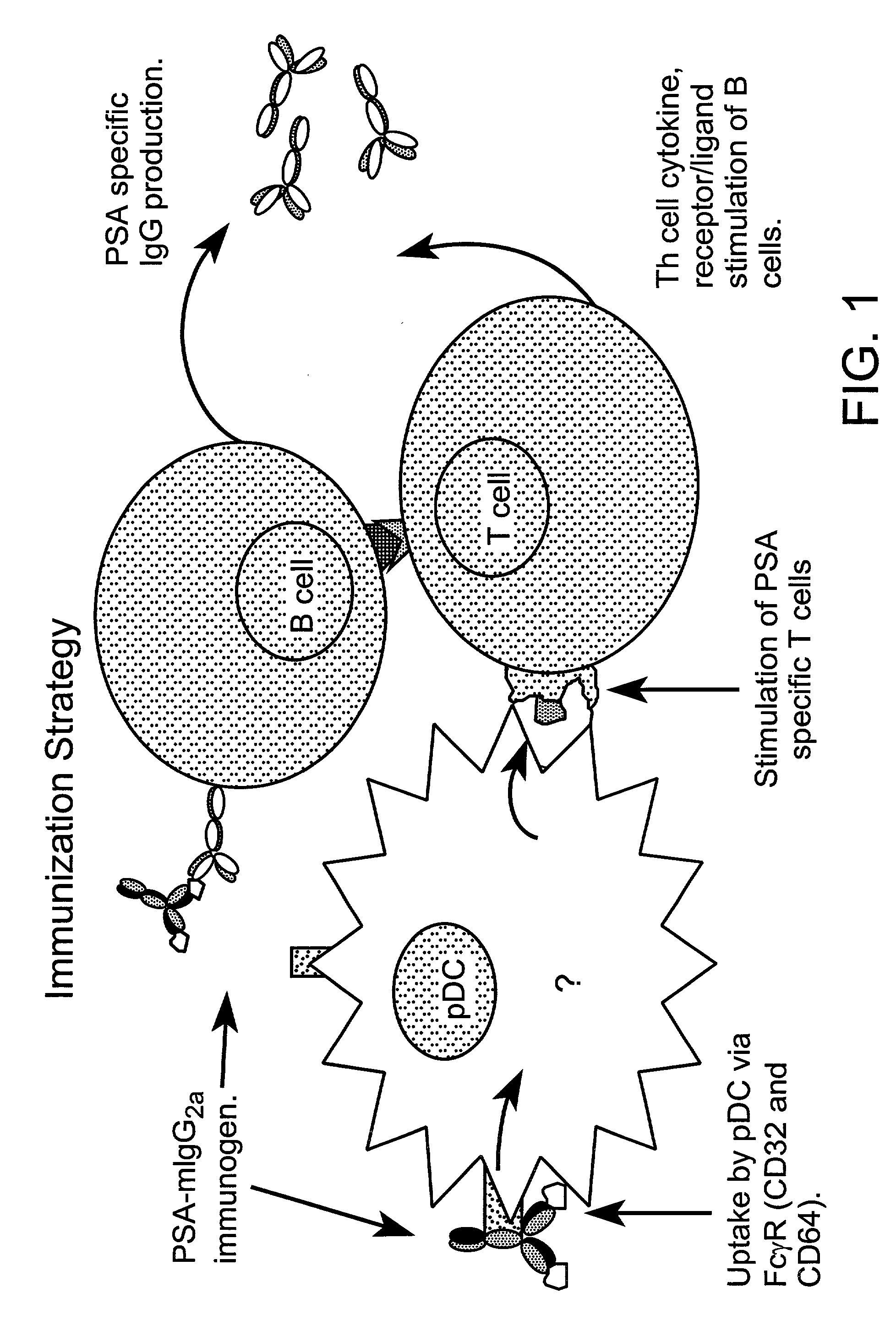
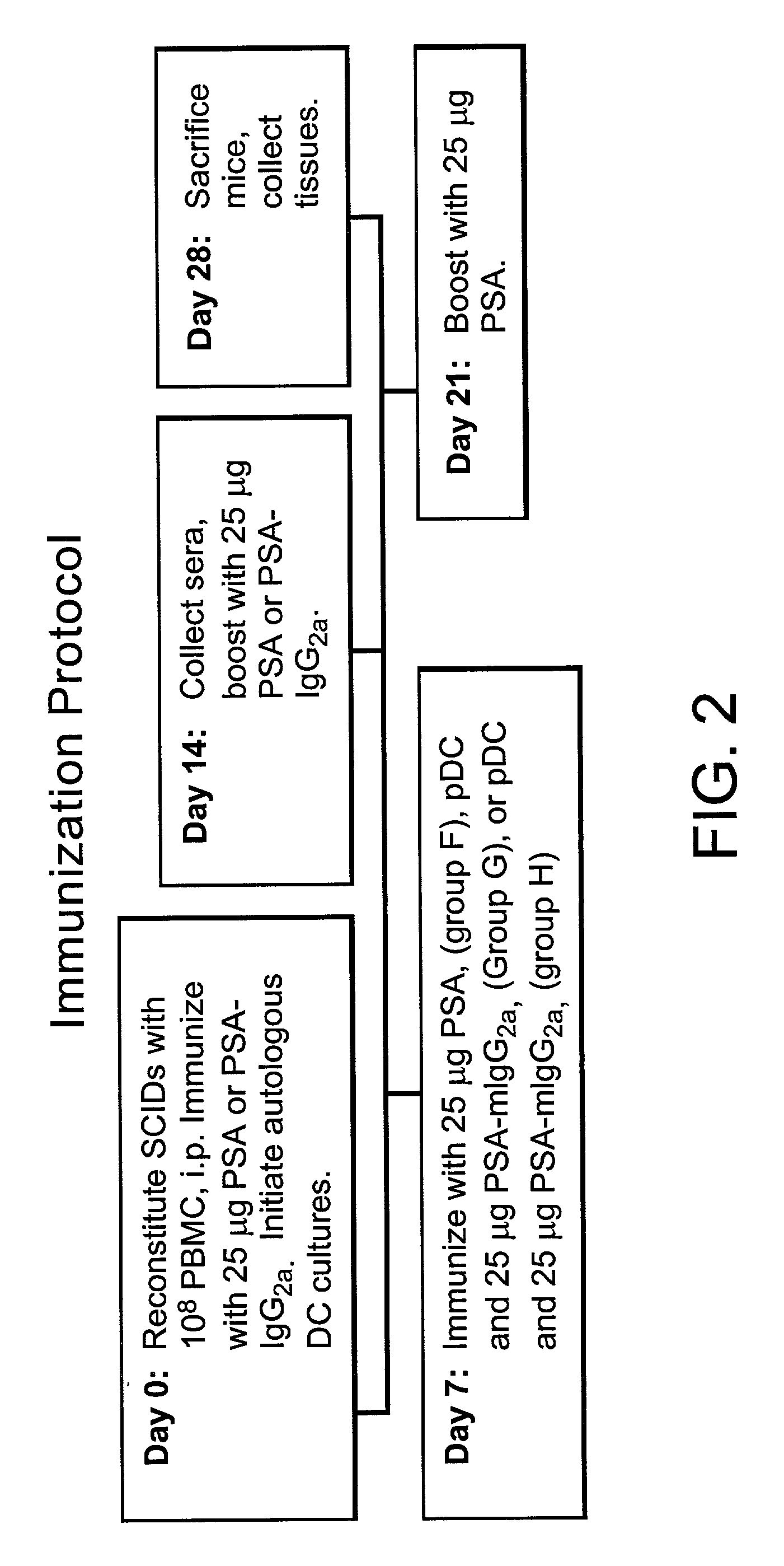
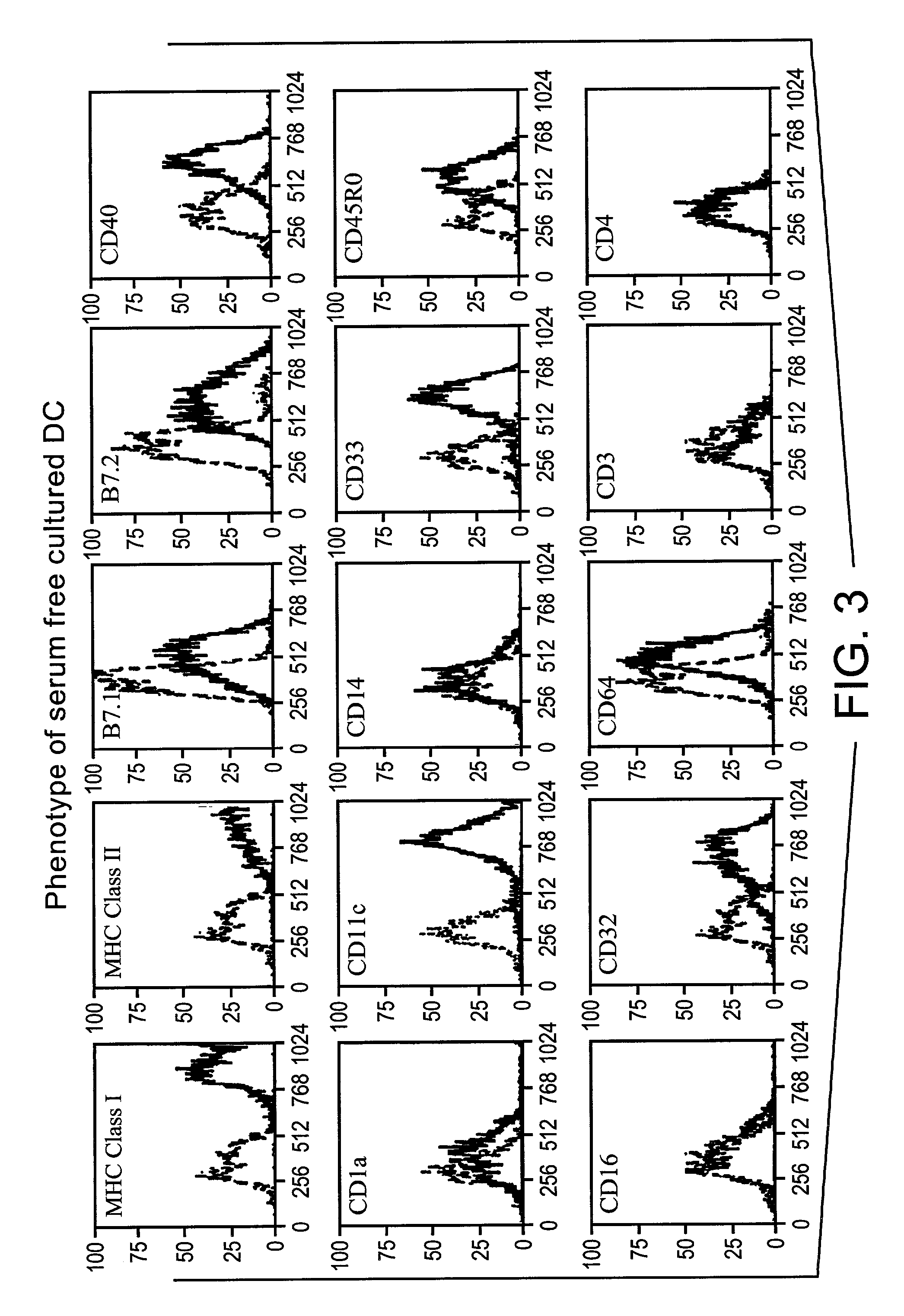
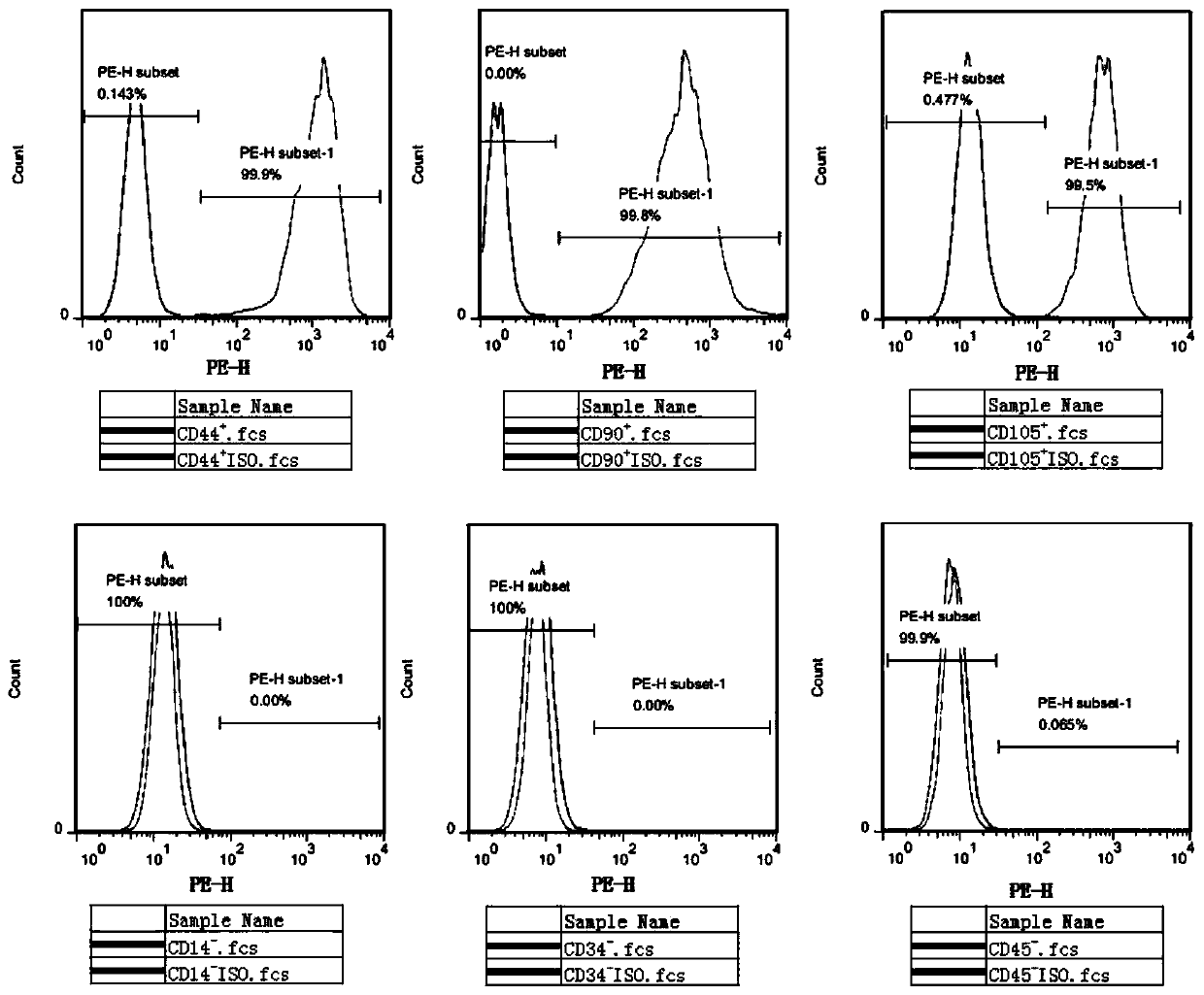
Method for producing human antibodies in SCID mice which uses dendritic cells pulsed with antigen-antibody complexes and antigen-antibody complexes as immunizing agents
InactiveUS20020044930A1Promote resultsHigh serum antibody titersBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEpidermal Dendritic CellsImproved method
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Experimental method for preventing generation and growth of liver cancer by using umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
PendingCN110358726AReduce serum residualImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsExperimental methodsMesenchymal stem cell
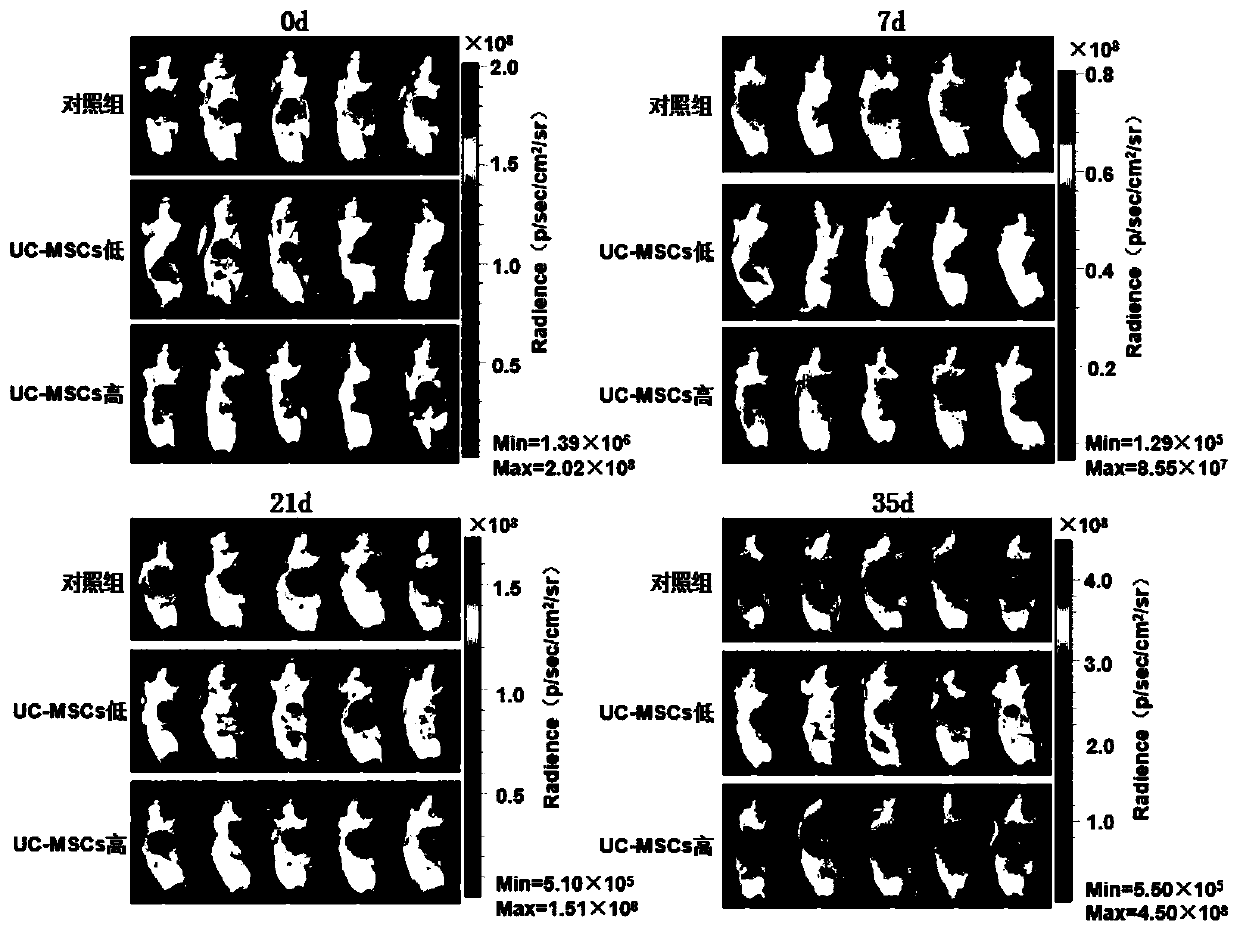
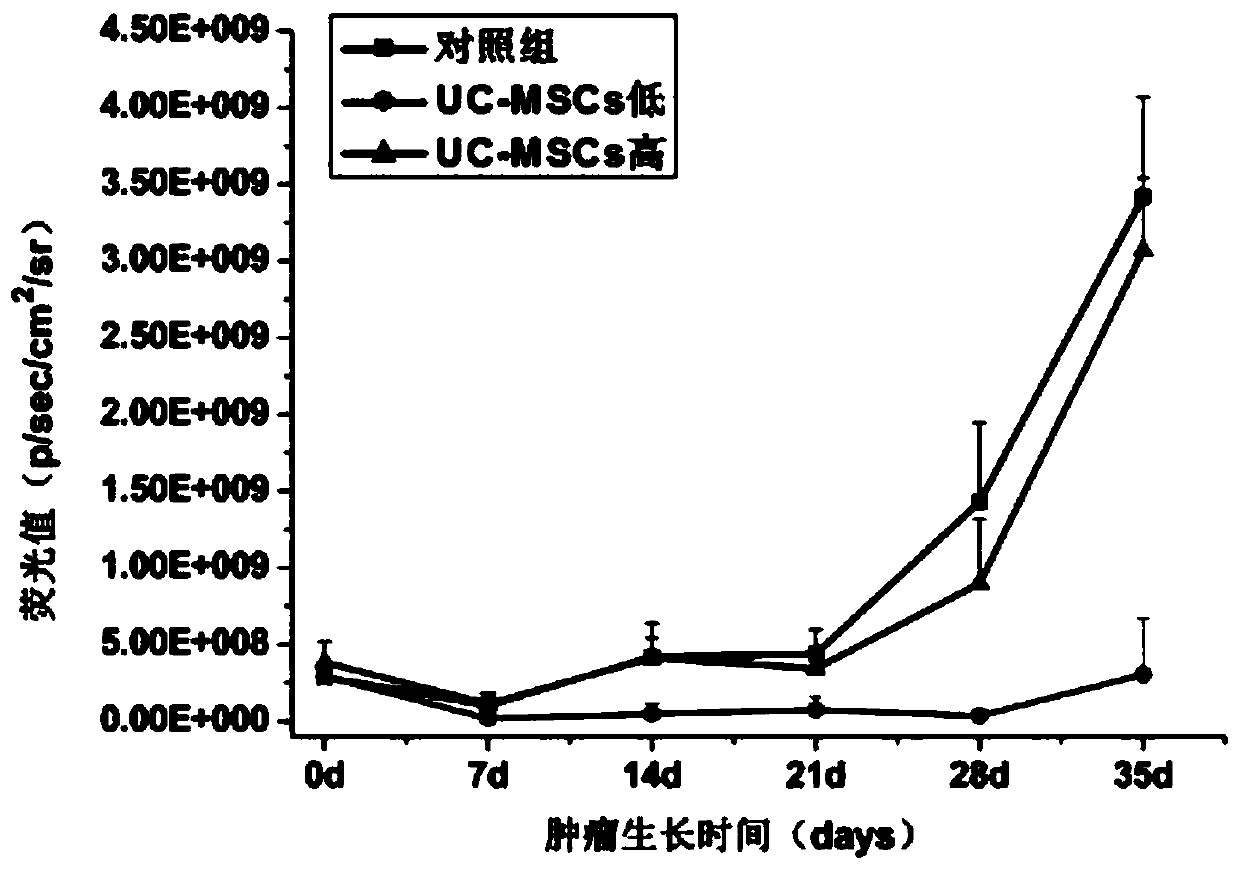
The invention relates to an experimental method for preventing generation and growth of liver cancer by using umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. For the first time, an application of the umbilicalcord mesenchymal stem cells to prevent the generation and growth of liver cancer is provided. The UC-MSCs cell preparation method is provided, and the experimental data of the dose of 1*104 cells / treatment course and administration method of the UC-MSCs cells for preventing liver cancer are provided. A UC-MSCs preparation is transplanted firstly, then the liver cancer cells are implanted, and thetumor growth of NOD / SCID mice is observed and compared, the method proves that the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can prevent the generation and development of liver cancer and the dosage of UC-MSCs is provided, the self-renewal and damage repair functions of UC-MSCs in the body's adult organ tissue can be maximized, the body's immunity is improved, and the generation of liver cancer can be prevented, which is beneficial to play a more significant and stable role in later research and clinical applications.
Owner:TIANJIN KANGTING BIOLOGICAL ENG GRP CO LTD
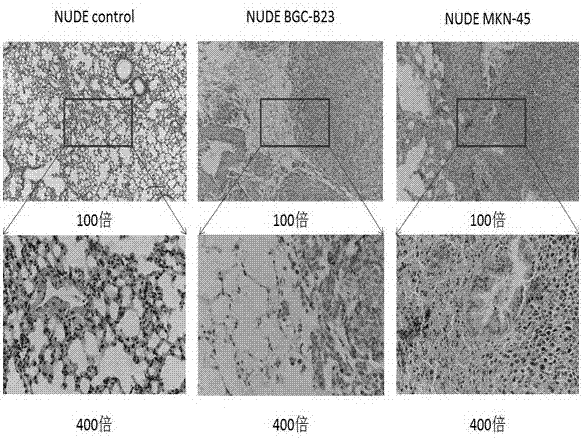
Mouse model with lung metastasis of gastric cancer and establishment method thereof
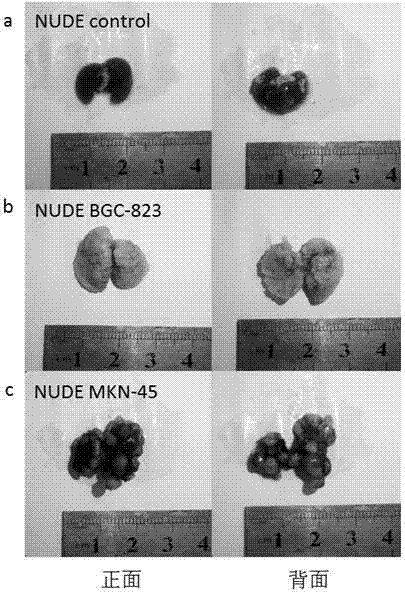
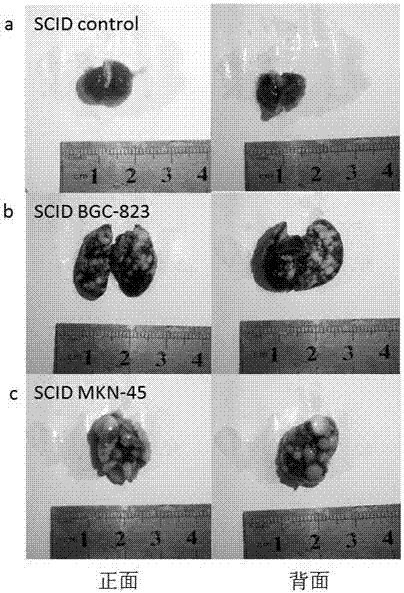
InactiveCN107006429AImprove transfer efficiencyAssessing the science of transfer methodsMammal material medical ingredientsMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to a mouse model with lung metastasis of gastric cancer and an establishment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of experimental animals. According to the mouse model and the establishment method thereof, BGC-823 and MKN-45 gastric cancer cells are cultured in vitro, and resuspended to a proper concentration with sterile PBS when the cell viability is strong. After the cells are cultured inside the body of immunodeficient NUDE and SCID mice inoculated in immunodeficience through the caudal vein, the mouse model with lung metastasis of gastric cancer is successfully obtained by the identifications including the statistics of surface lung nodules, HE staining and IHC staining. According to the mouse model establishment, needed experimental conditions and operation are simple and convenient, lung metastasis lesions after the experiment are obvious, metastasis efficiency is high, and mice with metastatic lesions have moderate survival cycles. In the evaluation and statistics of the metastasis results, the macroscopic counting of the lung nodules is improved into the microscopic counting of the IHC staining positive cells, thereby obtaining more objective and accurate results. The animal model of tumor metastasis may be widely used in scientific research and teaching.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
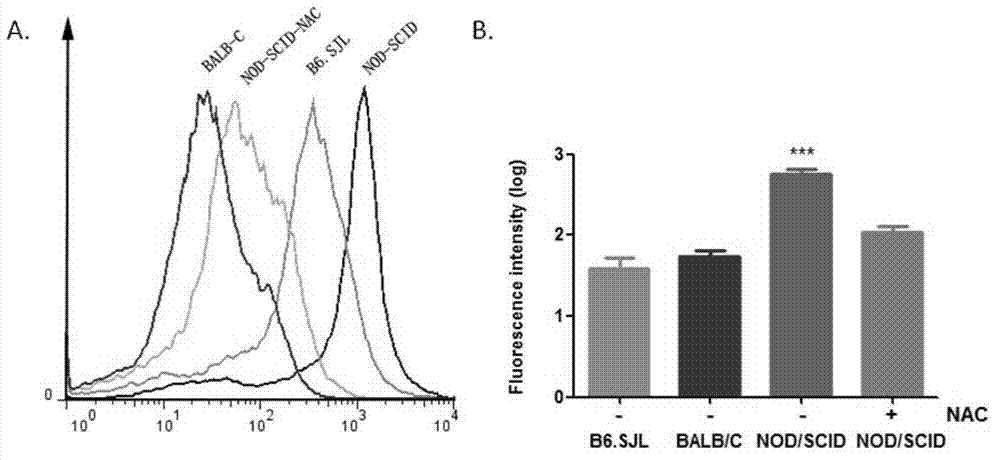
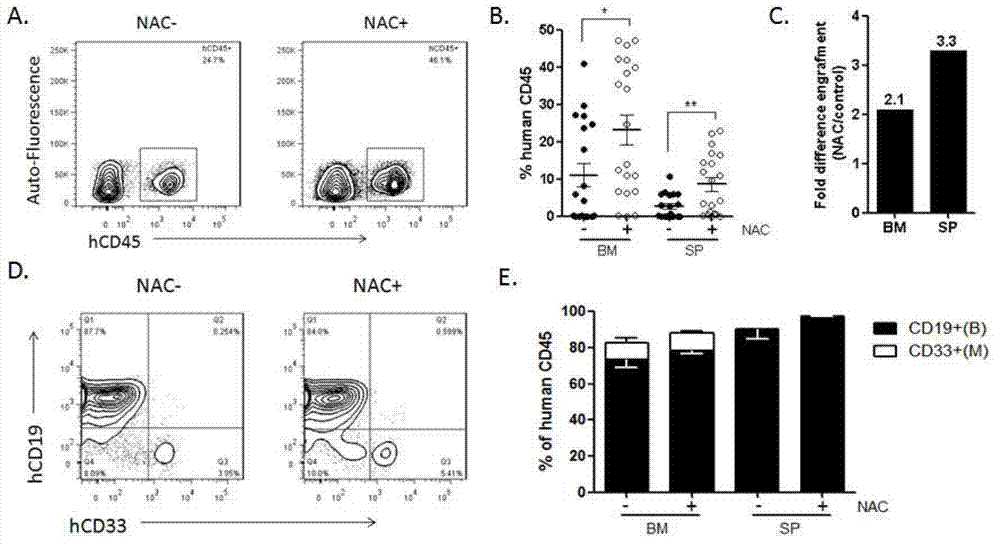
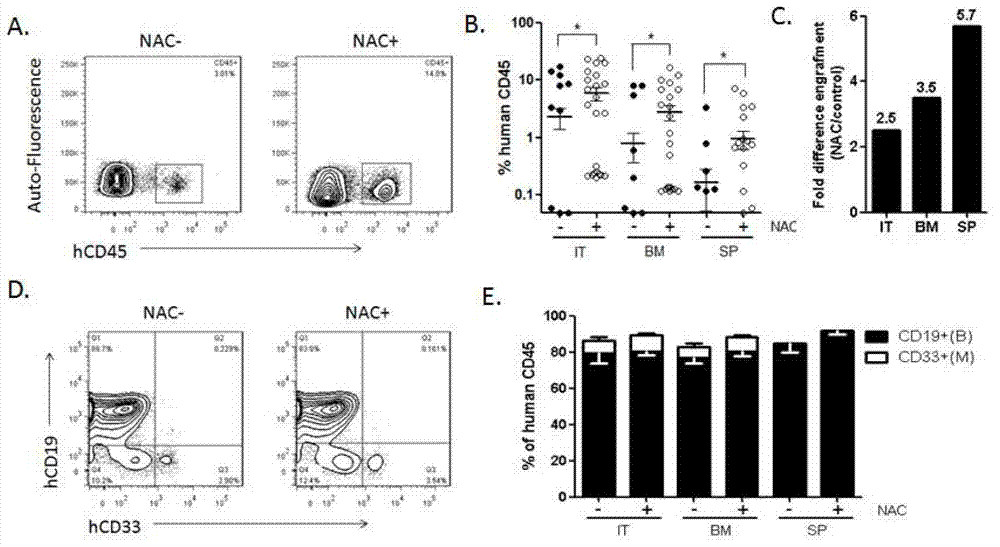
Method for constructing immunodeficiency mouse transplant model of human stem cells
ActiveCN102920522AReducing ROS levelsNovel methodSurgical veterinaryIntraperitoneal routeAntioxidant
The invention discloses a method for constructing an immunodeficiency mouse transplant model of human stem cells. The method comprises the following steps of: performing intraperitoneal injection on a receptor mouse (NOD / SCID) by adopting an N-acetylcysteine (NAC) antioxidant before transplanting, supplying drinking water containing NAC to the receptor mouse, continuously supplying the drinking water containing the NAC to the receptor mouse after the human stem cells are transplanted, and thus obtaining the immunodeficiency mouse transplant model of the human stem cells. The optimal model of NOD / SCID mouse transplant is successful established; and by the method, no matter in caudal vein or medullary cavity transplant, the implantation rate of the human stem cells is effectively improved, and the mouse is low in death rate and good in status in the transplant process and can survive for a long term. The method is simple, novel, easy to implement and low in wound to the mouse; and the NAC antioxidant used by the method is low in price.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for constructing a patient-derived tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with hepatocellular carcinoma based on organ-like method, and application thereof
InactiveCN109182272AConvenient researchNormal food intakeTumor/cancer cellsGeneral culture methodsAbnormal tissue growthHuman tumor
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a method for constructing a patient-derived tumor xenograft model in mice immunized with hepatocellular carcinoma based on an organ-likemethod, and an application thereof. The aim of the invention is to use the organ-like culture technology, adopts microcarrier as scaffold material, and combines the liver cancer cells from patient toculture the cells. The invention also discloses an organ-like method for preparing the liver cancer cells-3D material complex, and then directly into that cell-3D material complex is inoculated subcutaneously into normal immunized mice to construct liver cancer transplanted tumor model from patients in vivo, which solved the problems of using nude mice, SCID mice and other immunodeficient mice, which are difficult to feed, expensive and lower tumor formation rate. Especially, it can solve the problem that human hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumor model in immunodeficiency mice can notreflect the important role of immune system in tumor occurrence and development, and human tumor transplanted tumor model in immunodeficiency mice has a long tumor formation cycle, which urgently needs the drug-sensitive demand of patients with clinical urgent need. The invention is applied to the field of mouse model construction.
Owner:上海美峰生物技术有限公司
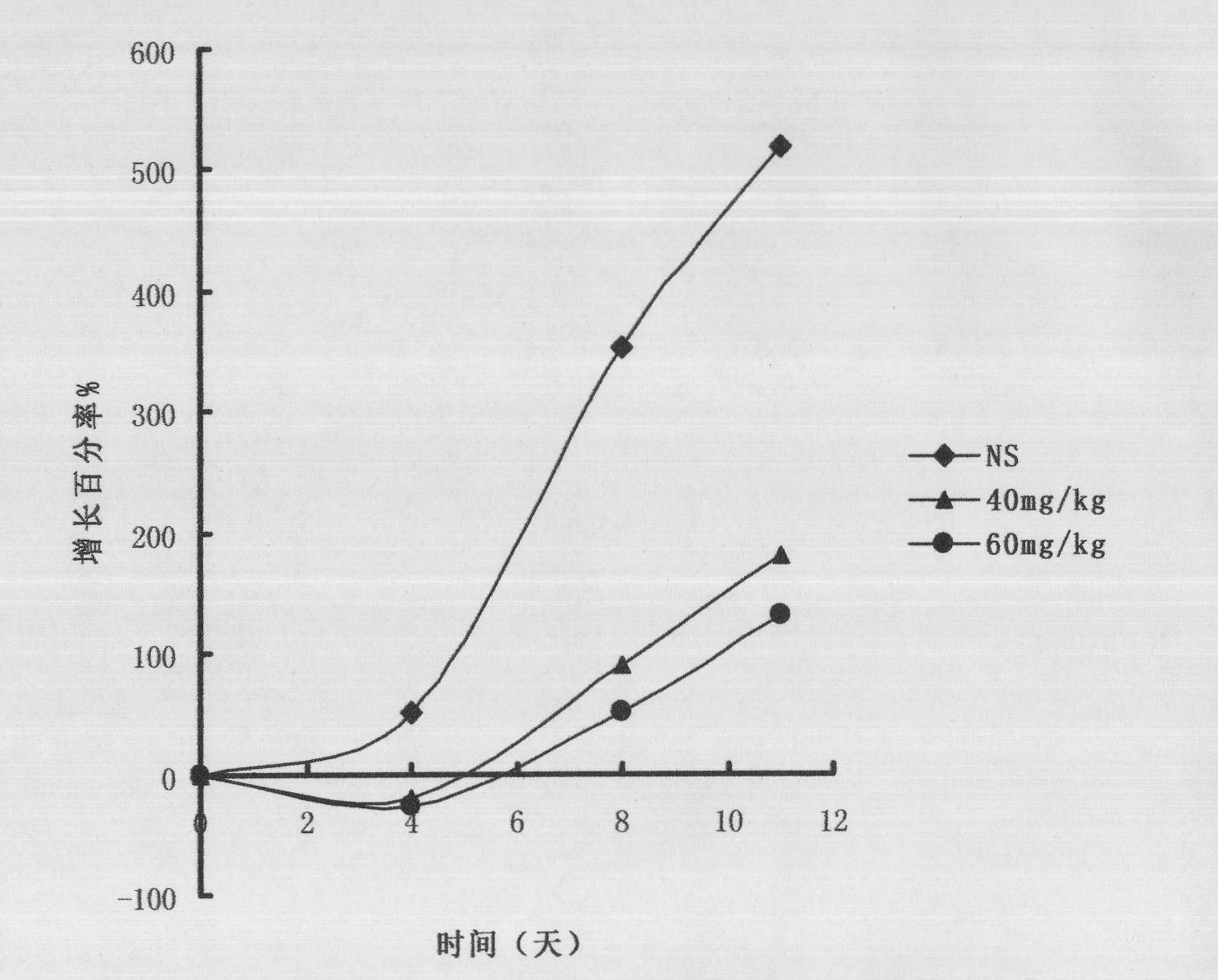
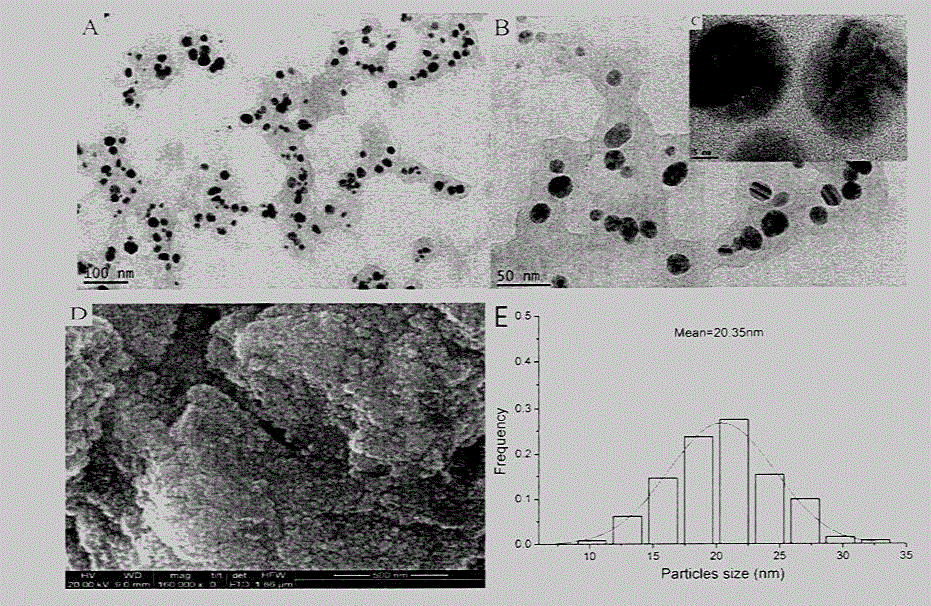
Silver nanoparticle composition for control of lung cancer and prostate cancer
InactiveCN105640986AProven anti-lung cancer effectPrevent proliferationInorganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsProstate cancerBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
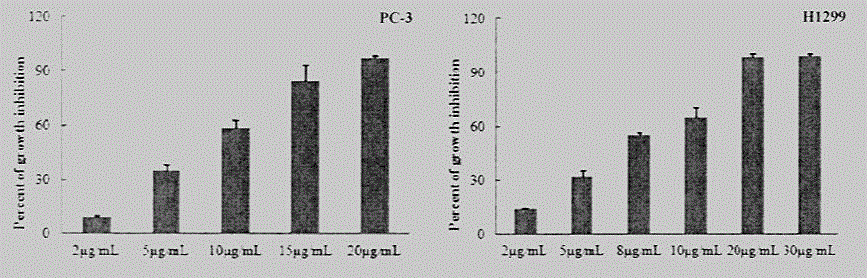
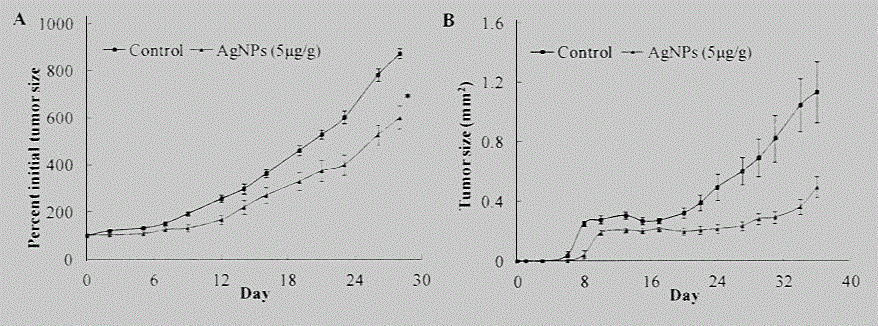
The invention provides a silver nanoparticle composition with lung cancer and prostate cancer resistant activity. The composition contains 20-500mg / kg nano-silver and pharmaceutically acceptable injection excipients (a suspending aid, a dispersing agent, a surfactant, an analgesic, a pH adjustment buffer agent, an osmotic pressure regulator, and water). In the spherical silver nanoparticle powder, the purity of silver is greater than or equal to 99%, and the particle size of silver nanoparticles is 8-75. The experimental result shows that the silver nanoparticle involved in the invention has very strong inhibitory activity on lung cancer H1299 cells and prostate cancer PC-3 cells, and can significantly inhibit H1299 tumor cell transplanted SCID mouse tumor growth in vivo. Therefore, the silver nanoparticle anticancer composition can be used as an antitumor active ingredient individually or in combination for prevention of lung cancer and prevention and treatment of prostate cancer.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model and model application
InactiveCN107361012AHigh xenotransplantation efficiencyGood effectAnimal husbandryFluorescenceT lymphocyte
The invention discloses a preparation method of an enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model. The method comprises the following steps: adopting the mode of crossing and backcrossing among multiple generations of C57BL / 6-Tg (CAG-EGFP) mice and NOD / SCID mice and screening the multiple generations to establish steadily hereditary NOD / SCID / EGFP mice systemically expressing green fluorescence, namely, an enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model sheet. The preparation method employs the breeding method featuring crossing and backcrossing among multiple generations to raise NOD / SCID mice expressing enhanced green-florescent protein genes. Compared with nude mice, the SCID mice have more severe immune deficiency including combined T and B cell deficiencies. The invention further discloses an application of the enhanced green fluorescence SCID mice model. In terms of xenotransplantation study, the SCID mice are more efficient in xenotransplantation than the nude mice with deficient t lymphocytes. The method of the model is an excellent model for fluorescent animals with immune deficiencies.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SUZHOU UNIV
Sub-clone cell line mestastatic-human liver cancer and establishing method
This invention disclose a human cancinoma of liver transfer subclone cell system and its set-up method in the following way: a human cancinoma of liver cell HT402 unicell suspension is inoculated into a SCID mouse and the transferred position it determined at lung part and by primary culture and secondary culture, the fetal calf serum concentration in the solution reduces to 10%, cell grows very well thus a cancinoma of liver transfer subclone cell system from parent human cancinoma of liver cell HT402 is set up matched with the parent cell, providing a new experiment material for its study.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Neutralizing high affinity human monoclonal antibodies specific to rsv f-protein and methods for their manufacture and theraputic use thereof
InactiveUS20020081723A1Promote formationHigh affinitySsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsF proteinRSV Infections
A highly efficient method for generating human antibodies in particular which are specific to be RSV fusion protein which combines in vitro primary of human spleen cells and antigen boosting in SCID mice is taught. This method provides for very high human antibody titers which are predominantly of the IgG isotype which contain antibodies of high specificity and affinity to desired antigens. This method is well suited for generating human monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic applications as well as for rescue of human cells for generation of combinational human antibody gene libraries. Two human monoclonal antibodies, RF-1 and RF-2 which each possess an affinity for RSV F-protein <=2x10-9 Molar are taught as well as their corresponding amino acid and DNA sequences. These antibodies are to be used therapeutically and prophylactically for treating or preventing RSV infection, as well as for diagnosis of RSV in analytes.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com