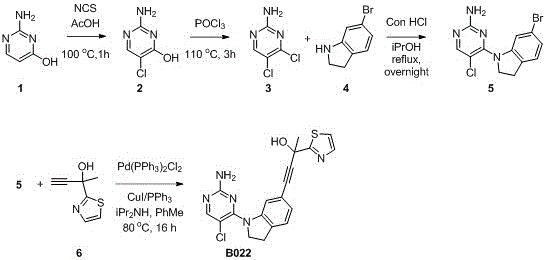
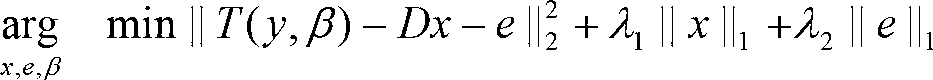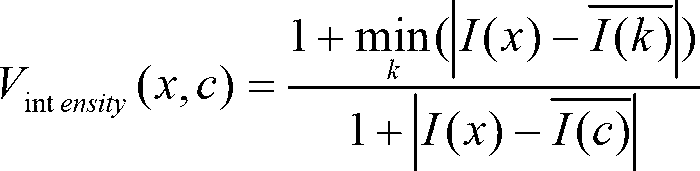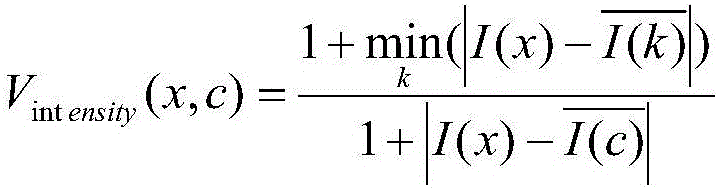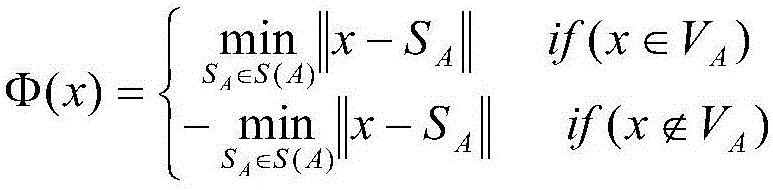Patents
Literature
53 results about "Liver parenchyma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The liver parenchyma is the functional component of the liver, made up of the hepatocytes that filter blood to remove toxins. This contrasts with the stroma, the connective tissue that supports the liver and creates a framework for the hepatocytes to grow on.
Hepatic portal vein tree modeling method and system thereof
InactiveCN101393644AEnhancement effect is goodEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisLiver parenchymaFiltration
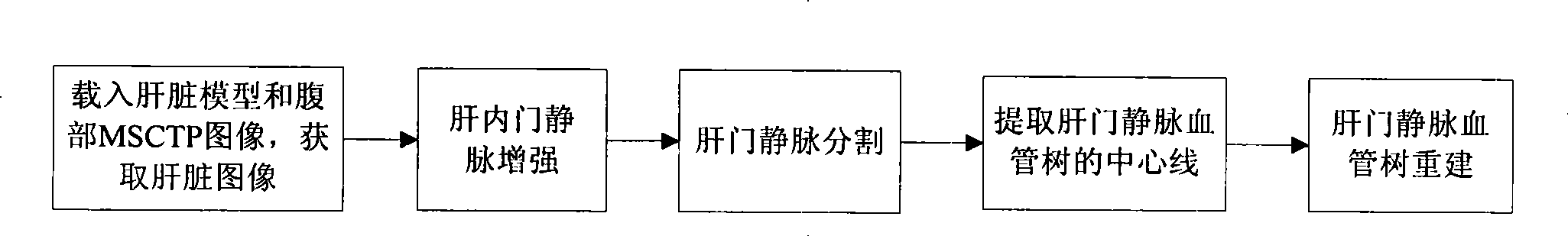
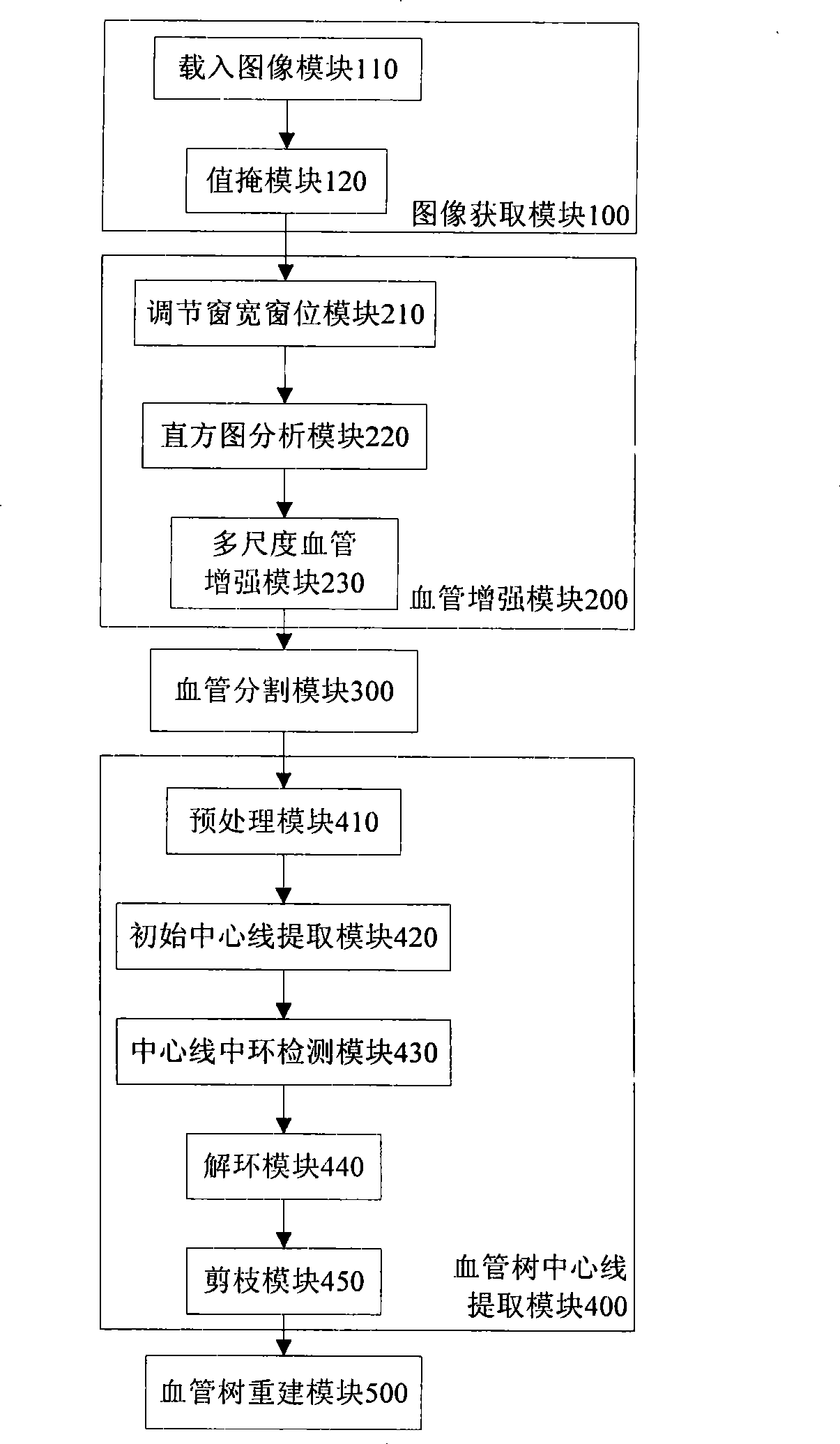
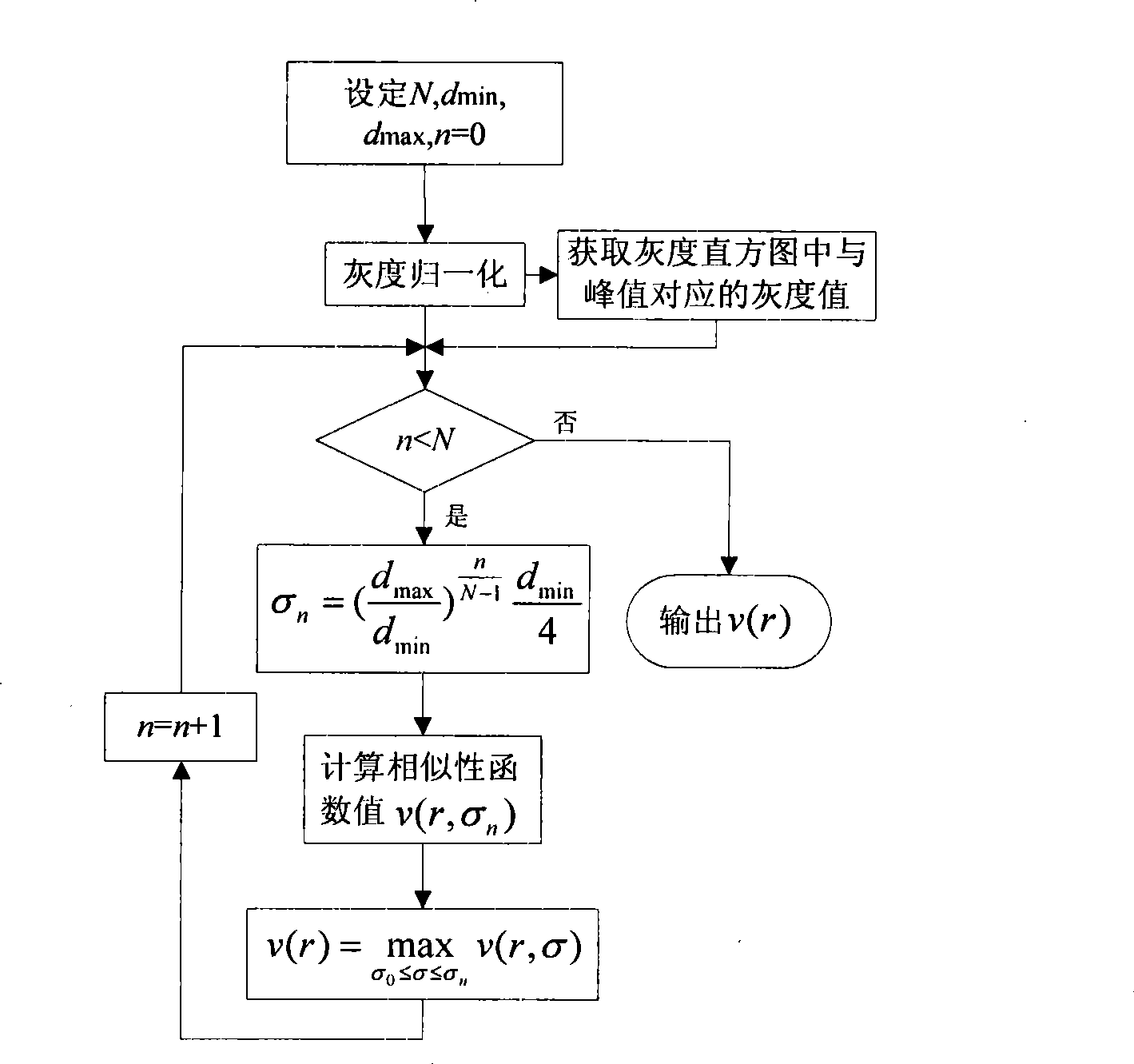
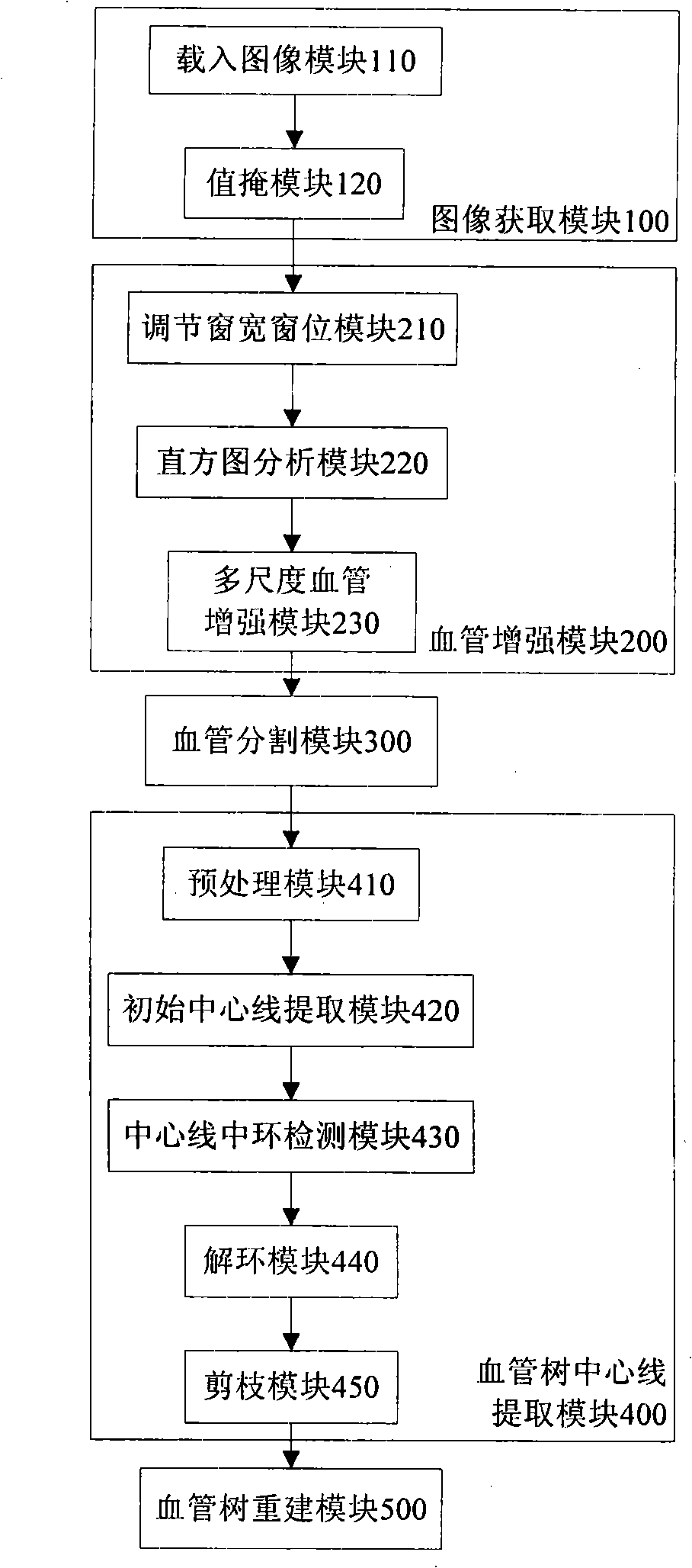
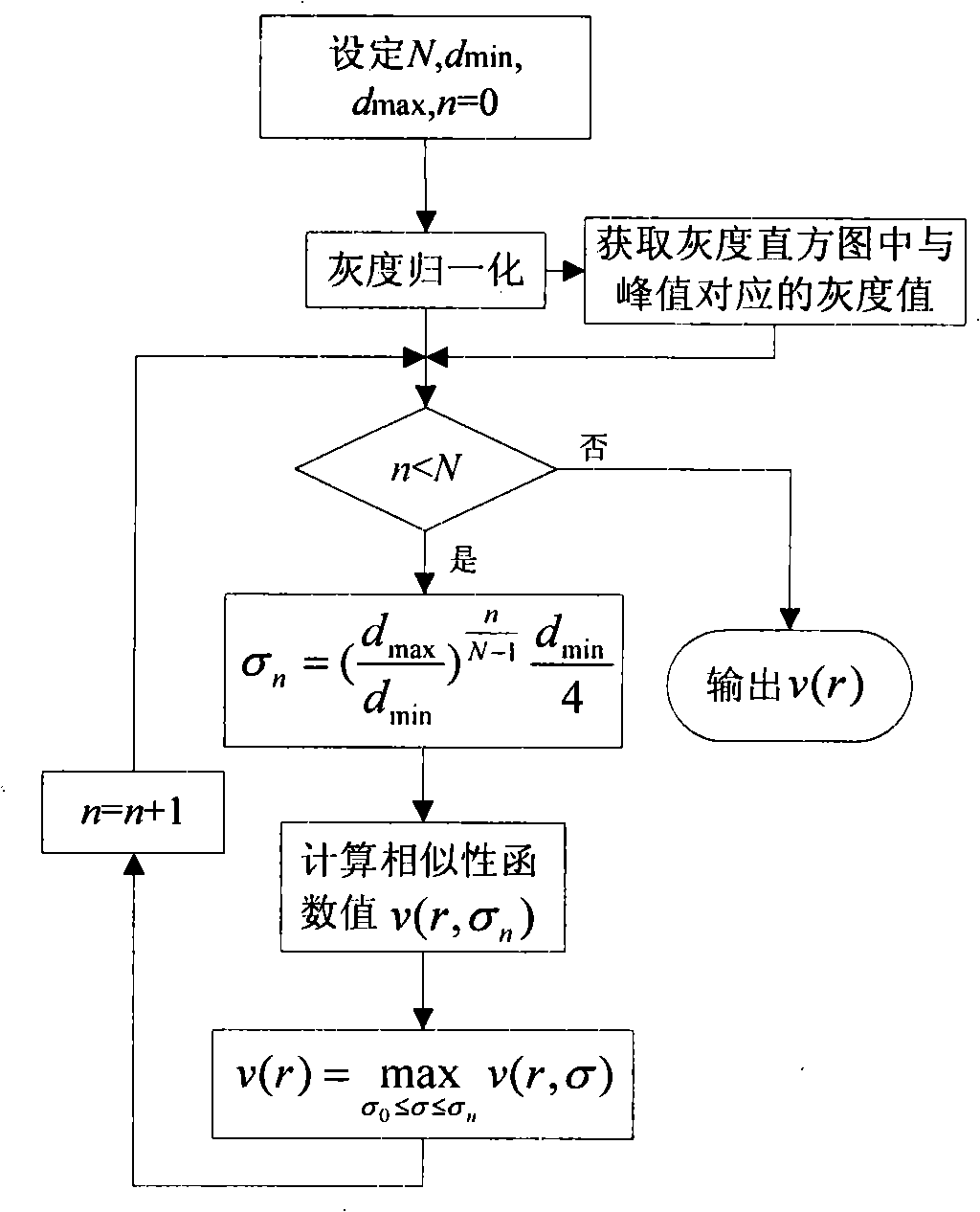
The invention discloses a hepatic vein vascular tree modeling method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a liver model to obtain a liver image, and utilizing the multi-scale filtration method to strengthen a blood vessel; cutting a hepatic vein; extracting a central line of the hepatic vein; detecting and removing a link in the central line; and utilizing OSG / VTK to rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree after pruning. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a blood vessel strengthening module, a blood vessel cutting module, a vascular tree central line extracting module and a vascular tree rebuilding module. The invention improves similarity functions in the filtering process, analyzes the characteristics of the ring and adopts corresponding unlinking methods for different links; and utilizes the relation of radius of blood vessel and the branch length when pruning. The invention effectively enhances the hepatic vein, improves the contrast between the blood vessel and liver parenchyma, and can extract more than five class branches, effectively unlink and prune the central line of the hepatic vein, rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree and directly display the branches of the heptatic vein.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
In vivo, animal model for expression of hepatitis C virus
Disclosed is a method for expressing hepatitis C virus in an in vivo, animal model. Viable, hepatitis C virus-infected, human hepatocytes are transplanted into a liver parenchyma of a scid / scid mouse host. The scid / scid mouse host is then maintained in a viable state, for up to five days or greater, whereby viable, morphologically intact human hepatocytes persist in the donor tissue and hepatitis C virus is replicated in the persisting human hepatocytes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
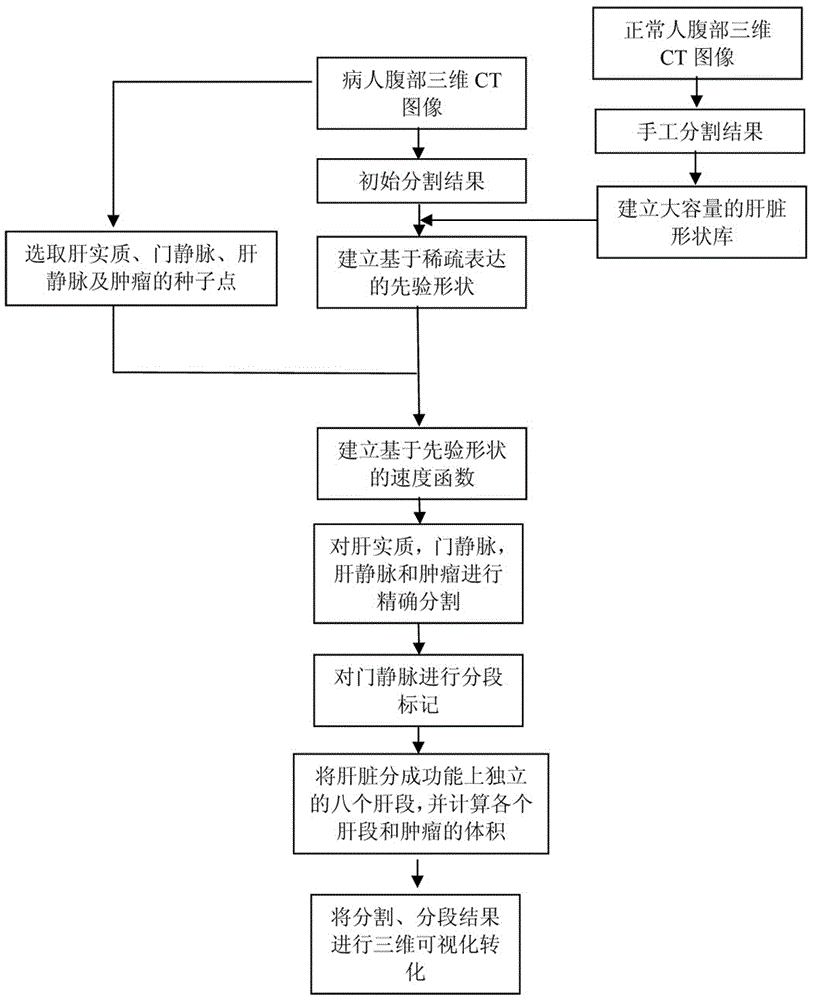
Realization method of computer-assisted liver transplantation operation planning system
InactiveCN102938027AStable and efficient shape priorsEffective adaptabilityImage enhancementImage analysisVeinLiver parenchyma
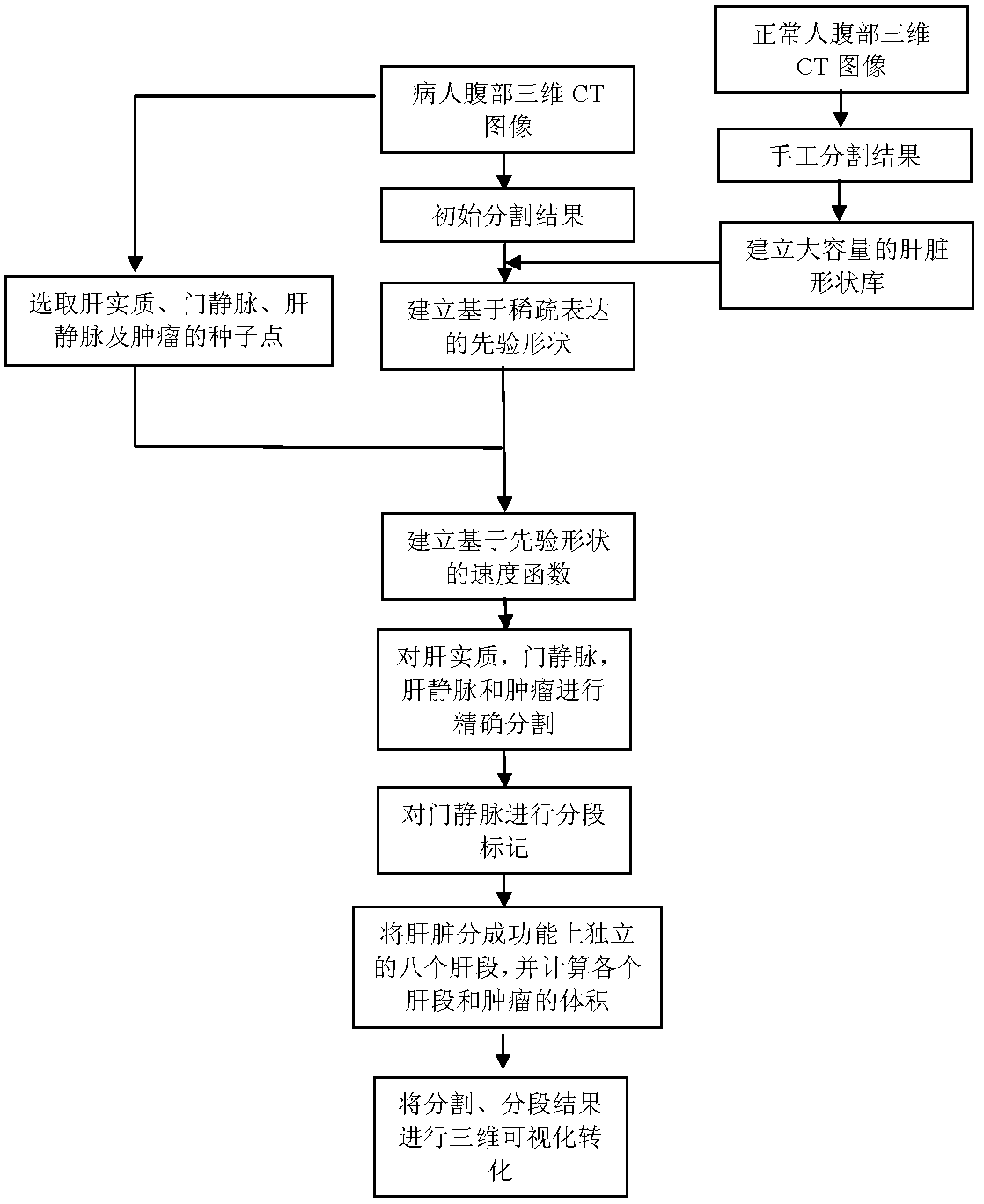
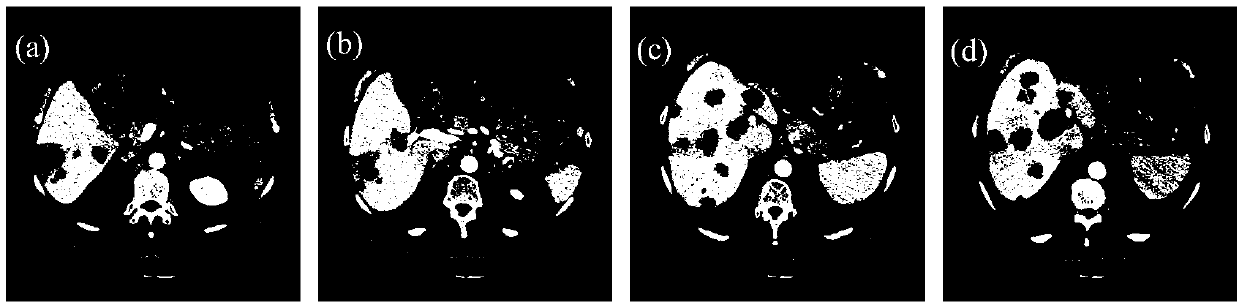
The invention relates to a realization method of a computer-assisted liver transplantation operation planning system, comprising the following steps: step 1, establishing a normal person liver shape library; step 2, for the liver to be operated, modeling the initial partition result of the liver area by using a method based on sparse representation, and eliminating disturbance of singular point and noise data, so as to obtain a prior shape having a liver area with patient adaptability; steps 3, precisely partitioning the liver by utilizing the prior shape, and simultaneously separating out liver parenchyma, portal vein, liver vein and tumour; step 4, dividing the liver into eight liver segments independent in functions by utilizing the liver vein partition result, and calculating the volume of each liver segment and the tumour; and step 5, carrying out 3D visualization on the partitioning and segmenting result. Compared with the prior art, the realization method has the advantages of high precision and robustness, convenience in realization and capability of treating complicated liver shapes.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Method for automatically segmenting liver tumors in abdominal CT sequence images
ActiveCN108596887ASolve the problem of inaccurate automatic segmentationHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a method for automatically segmenting liver tumors in abdominal CT sequence images. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing: preprocessing an abdominal CT sequence image so as to obtain a liver area in the image; liver enhancement: improving a contrast ratio of normal liver parenchyma to tumor tissue by adoption of a segmented nonlinear enhancement operation and an iterative convolution operation according to a grey level distribution characteristic of the liver area; automatic segmentation: constructing an image segmentation energy function for multi-target segmentation by utilizing the enhancement result and combining image boundary information, minimizing the energy function by adoption of an optimal algorithm and obtaining a liver tumor preliminary automatic segmentation result; and post-processing: optimizing the preliminary segmentation result by adoption of a three-dimensional mathematic morphological open operation, and removing mis-segmented areas to improve the segmentation precision. The method is beneficial for helping radiological experts and surgeons to timely and effectively obtaining overall information and three-dimensional display of liver tumors and providing technical support for computer-aided diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in surgical planning system
ActiveCN102663416AOvercoming the deficiency of error accumulationImprove robustnessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional ctPattern recognition
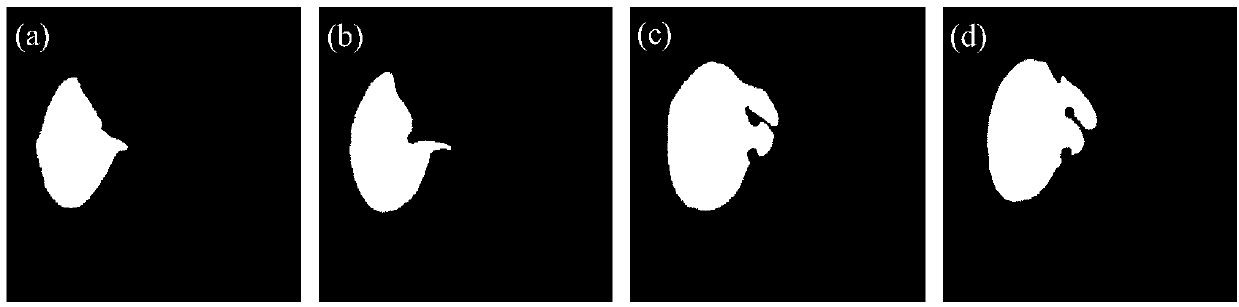
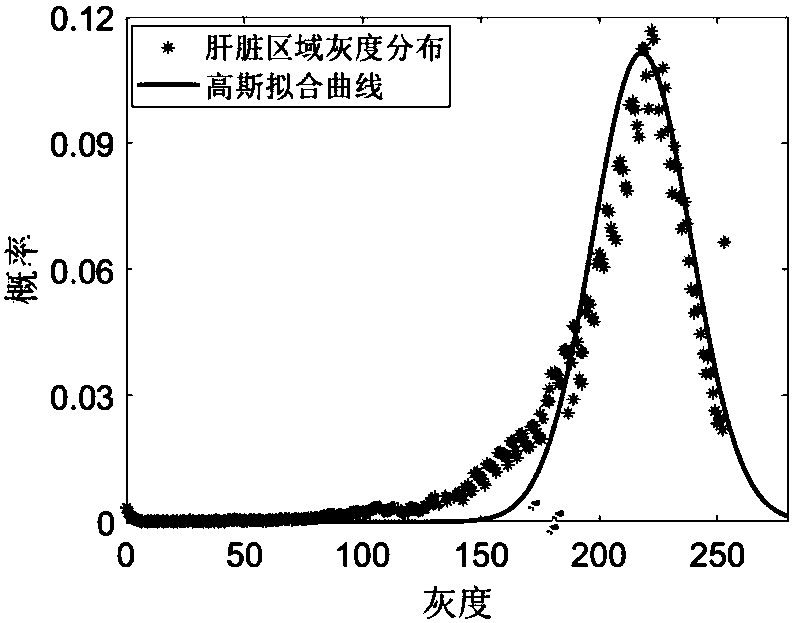
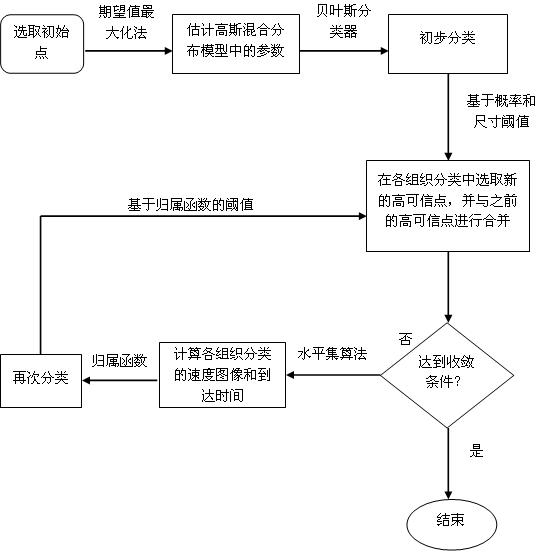
The invention relates to a segmentation method of medical images, and specifically relates to a segmentation method of viscera and internal blood vessels thereof in a surgical planning system. The method designs a segmentation method of images of liver parenchyma, portal veins and hepatic veins based on minimal supervised classification of the three-dimensional CT images of the viscera and internal tubular tissues thereof. The method applies methods of statistics and spatial information, introduces high credible points, and obtains segmentation results based on arrival time of fast march of grey level. The method assumes that spatially adjacent points belong to a same organ, and performs segmentation calculation on the images by using a classification algorithm based on the above assumption, wherein the segmentation calculation comprises the steps of: acquiring estimated values of parameters of a Gaussian mixture distribution model; selecting the high credible points; and calculating the mean value of the grey level of the images and calculating the arrival time by using a fast marching algorithm to obtain arrival time images of three tissue classifications. According to the invention, good robustness and good anti-noise interference capability are obtained, accumulated errors are eliminated effectively, classification accuracy is improved, and great application value in clinical treatment is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU DIKAIER MEDICAL TECH
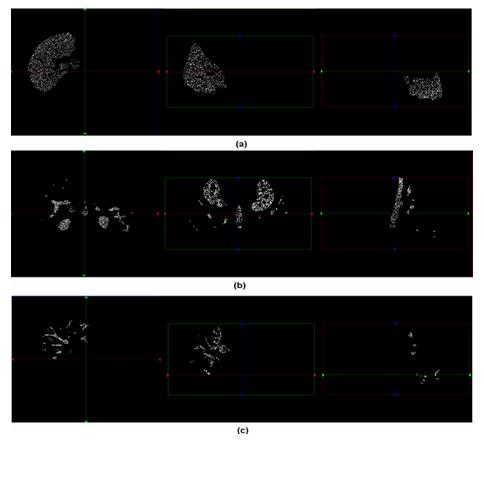
Systems, methods and apparatus automatic segmentation of liver in multiphase contrast-enhanced medical images
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
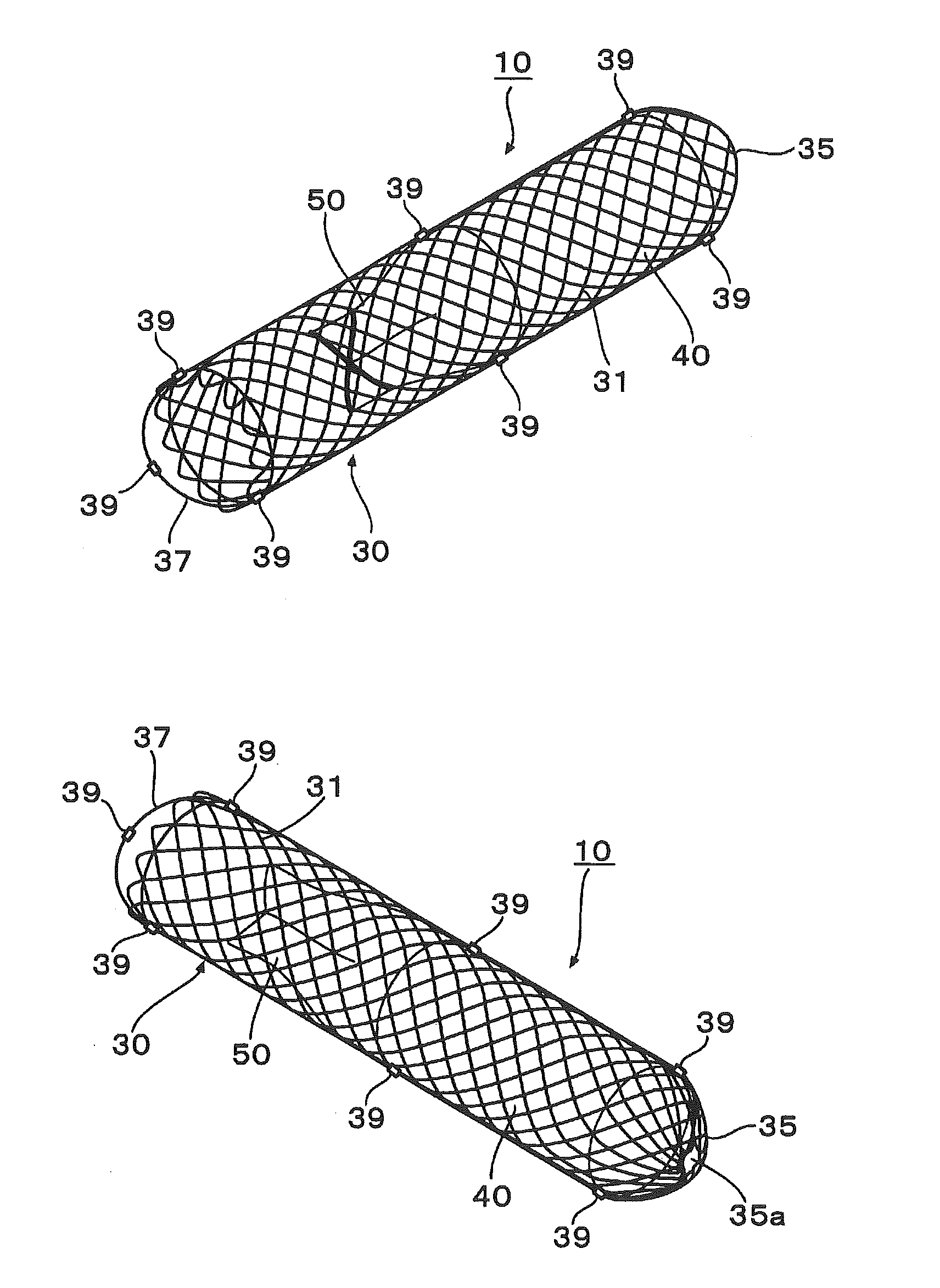
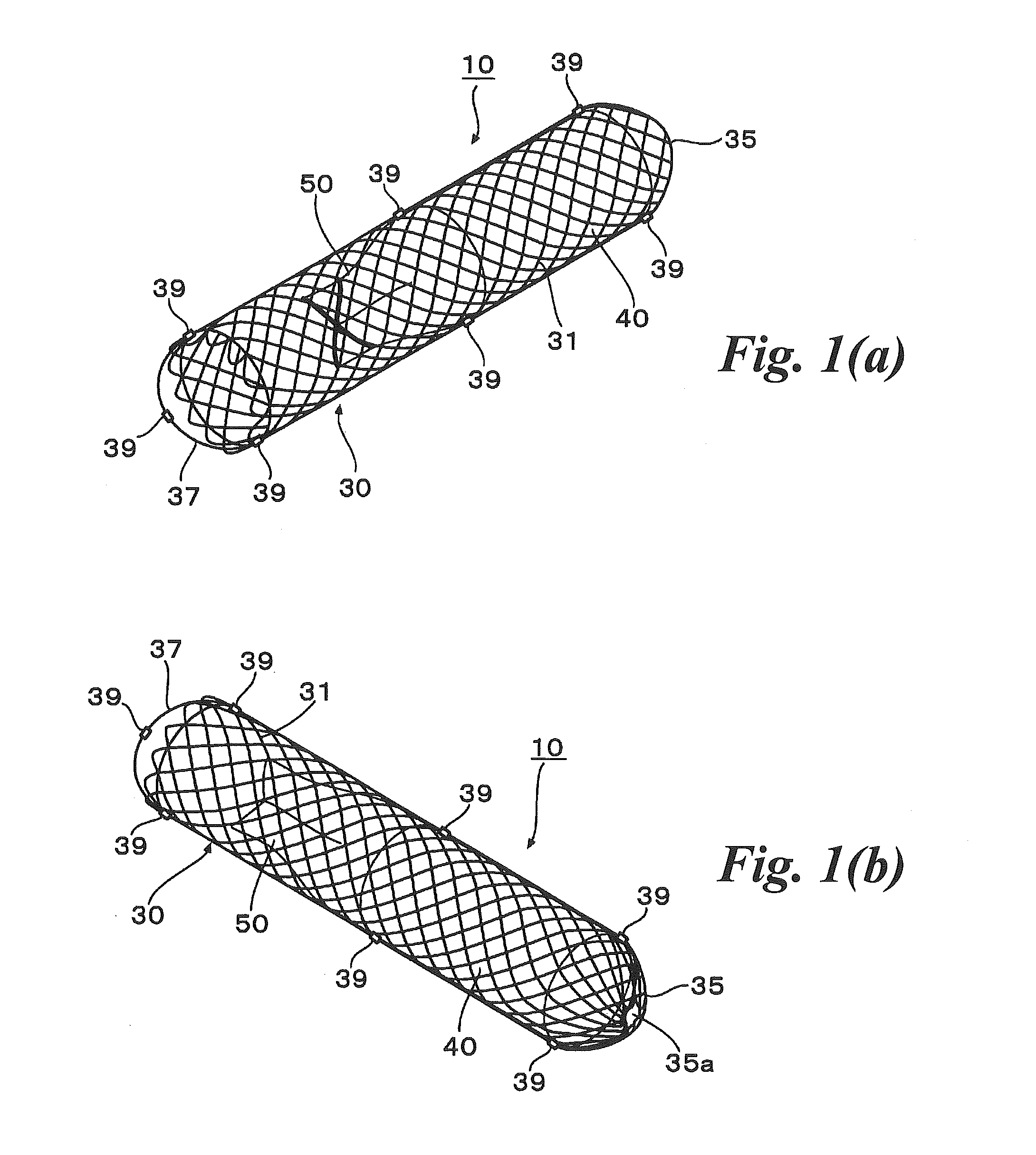
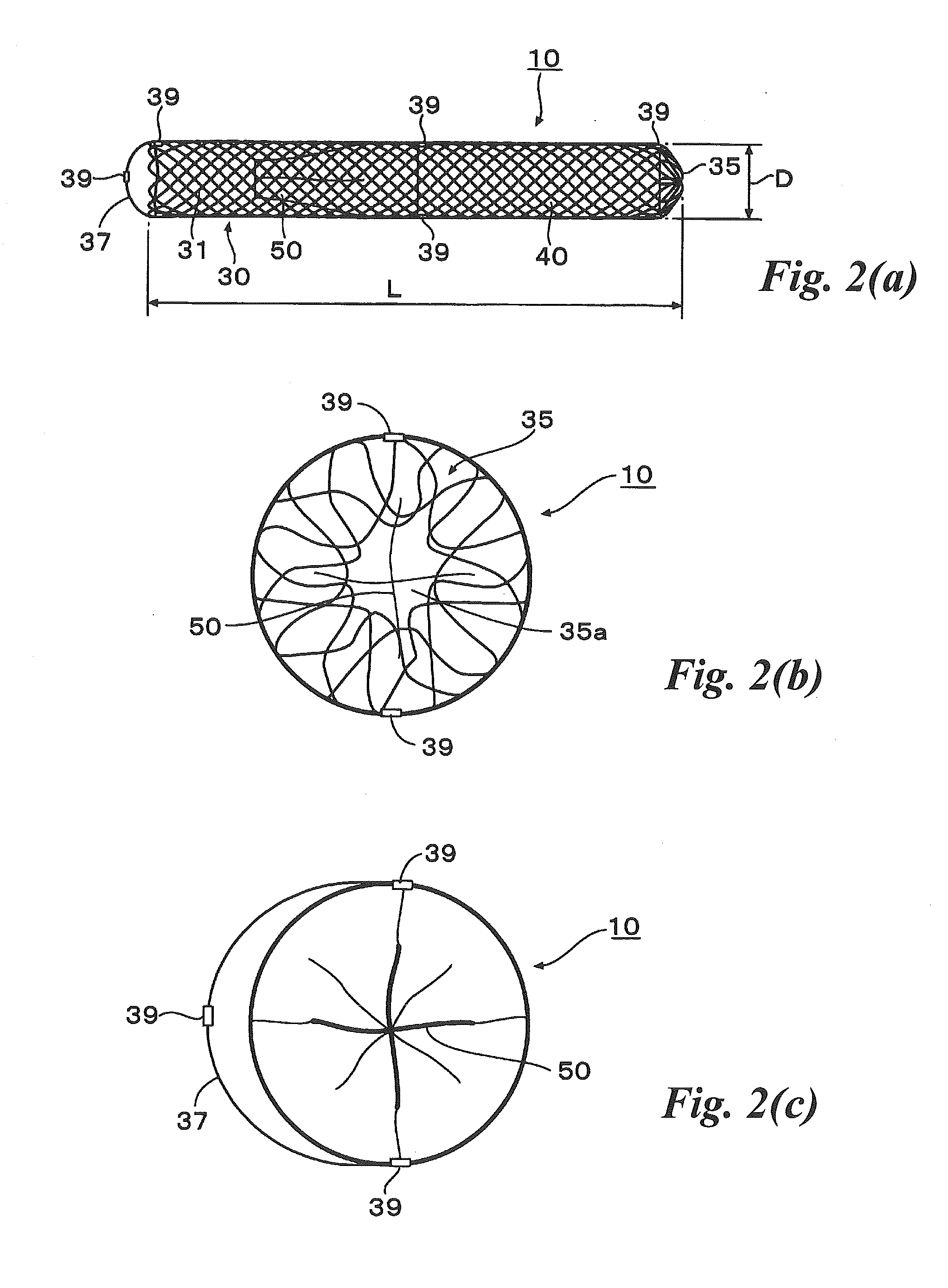
Abdominal cavity-vein shunt stent
An abdominal cavity-vein shunt stent provided for transporting ascites accumulated in the abdominal cavity of a patient to a vascular system, includes: a stent body which extends cylindrically long and which has one end disposed in the intrahepatic vein, and the other end piercing the liver parenchyma and disposed in the abdominal cavity; and a one-way valve which is disposed in the stent body, which is opened to drain ascites into the intrahepatic vein when a differential pressure obtained by subtracting the pressure of the intrahepatic vein from the pressure in the abdominal cavity is not lower than a predetermined value, and which is closed when the differential pressure is lower than the predetermined value.
Owner:PIOLAX MEDICAL DEVICES +1
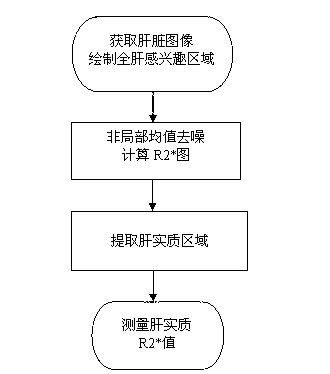
Method for measuring liver magnetic resonance crosswise relaxation rate R2* parameter
A method for measuring a liver magnetic resonance crosswise relaxation rate R2* parameter includes the steps: (1) obtaining a magnetic resonance liver image, and drawing a full-liver region-of-interest; (2) obtaining a magnetic resonance liver image which is denoised, re-obtaining a gray level of each pixel within the full-liver region-of-interest of the magnetic resonance liver image which is denoised, enabling the gray level of each pixel and echo time to be matched on a first moment model formula (I) of a single-index model under the influences of non-central Chi noise, and then obtaining a full-liver R2* image; (3) dividing a R2* value of the full-liver region-of-interest into two types, enabling the two types to respectively correspond to liver parenchyma and blood vessels, and re-obtaining a liver parenchyma region-of-interest; and (4) a calculating gray level average value and echo time of the liver parenchyma region-of-interest of each echo image and enabling the gray level average values and the echo time to be matched on the formula (1), and then obtaining a final liver parenchyma R2* value. The method can improve precision of the crosswise relaxation rate R2* parameter and is good in repeatability.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
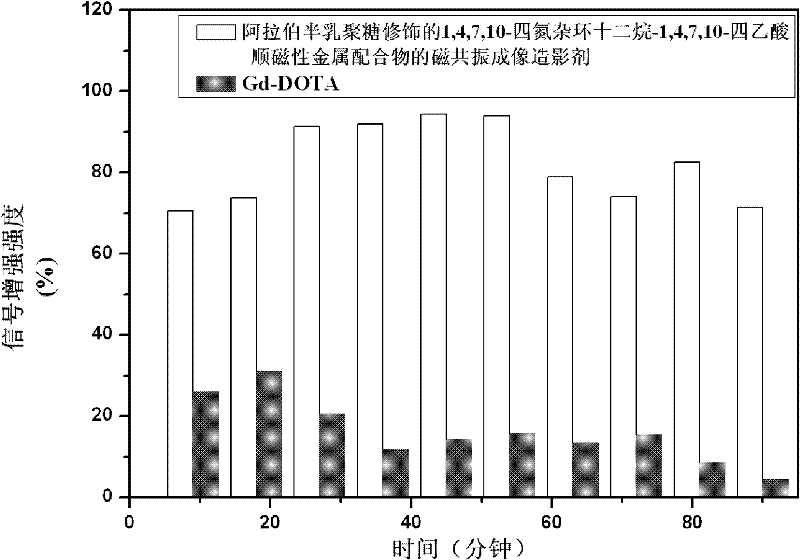
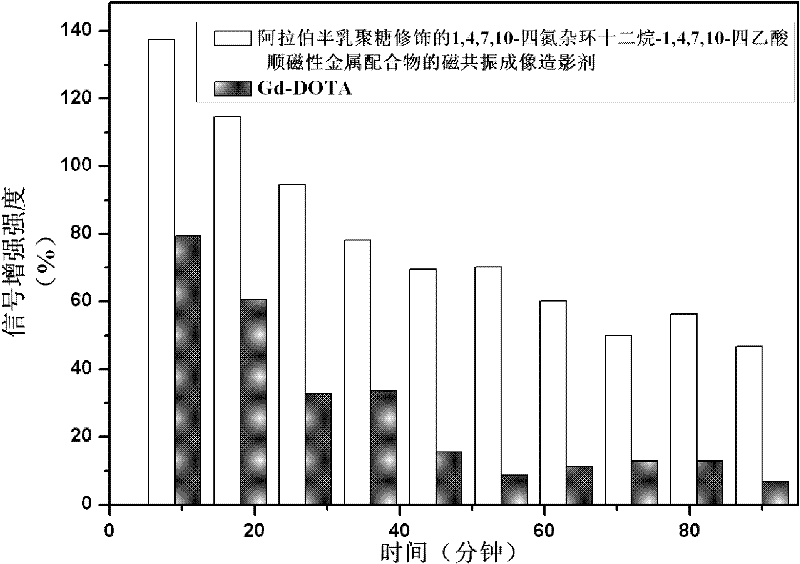
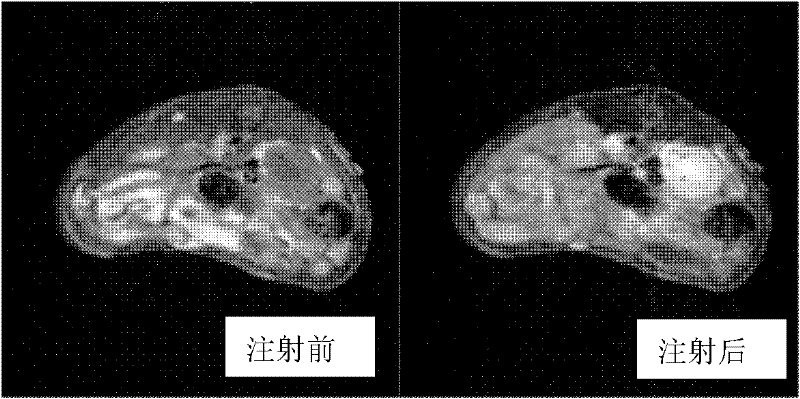
Paramagnetic metal complex and synthetic method and application thereof
ActiveCN102336838AIncreased toxicityShort retention timeNMR/MRI constrast preparationsDiseaseSolubility
The invention provides a paramagnetic metal complex and a synthetic method and application thereof. The paramagnetic metal complex is an arabinogalactan-modified 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacethyl paramagnetic metal complex. A magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent prepared from the paramagnetic metal complex has high stability, water solubility and relaxation rate and is targeted to liver and kidney, so that targeted imaging is realized, and the imaging contrast and definition are improved. The paramagnetic metal complex has a good effect on raising the early diagnosis levels of diseases of liver and kidney organs, is about 2 times the relaxation rate of dotarem, has very long targeted radiography imaging time, can be easily prepared into a solution with required concentration for intravenous injection, is suitable for sterilizing and disinfecting with a hot pressing method, can be selectively identified by an asialoglycoprotein receptor on a liver parenchyma surface, and has high selectivity on livers of human beings or other mammals.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
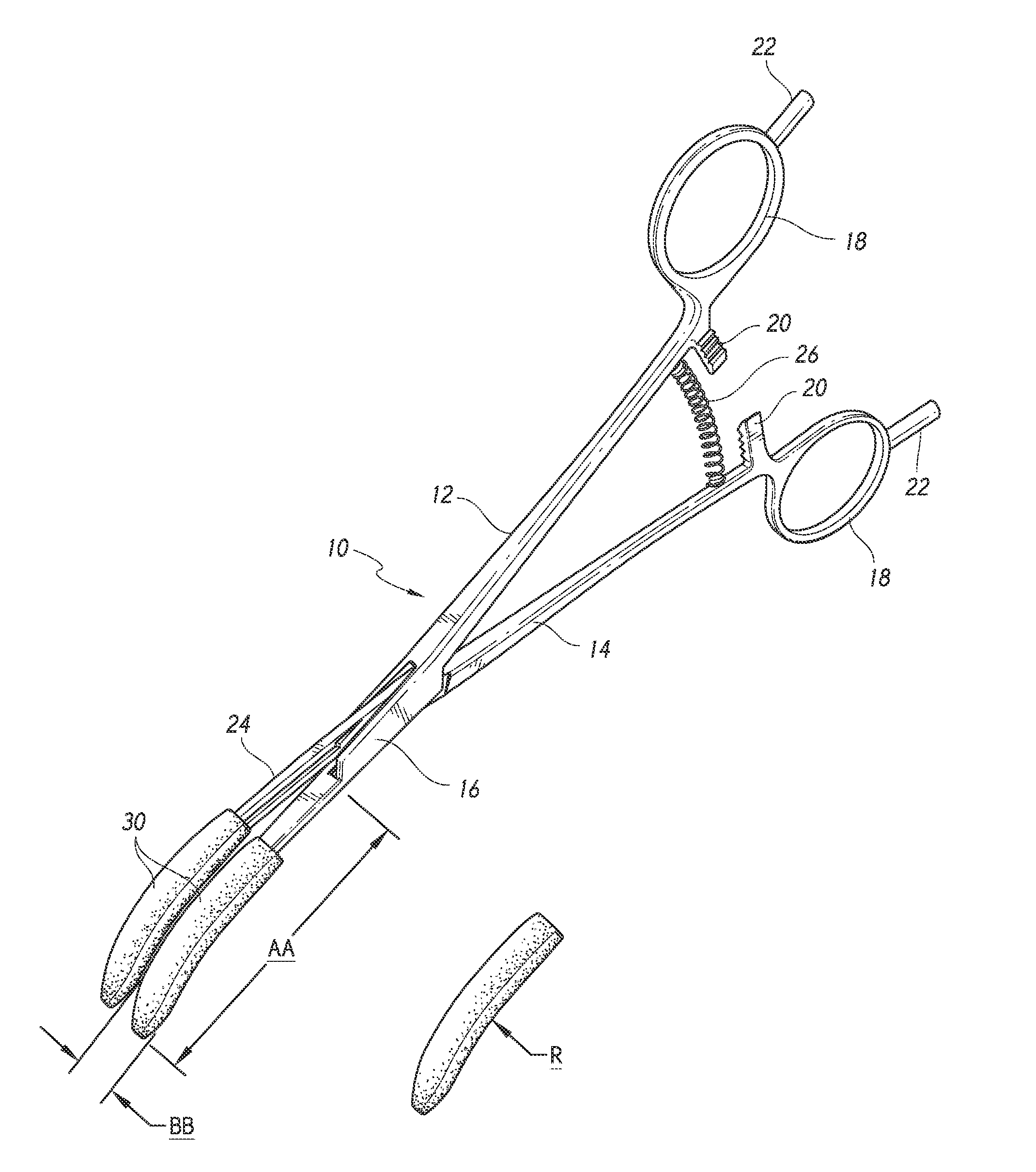
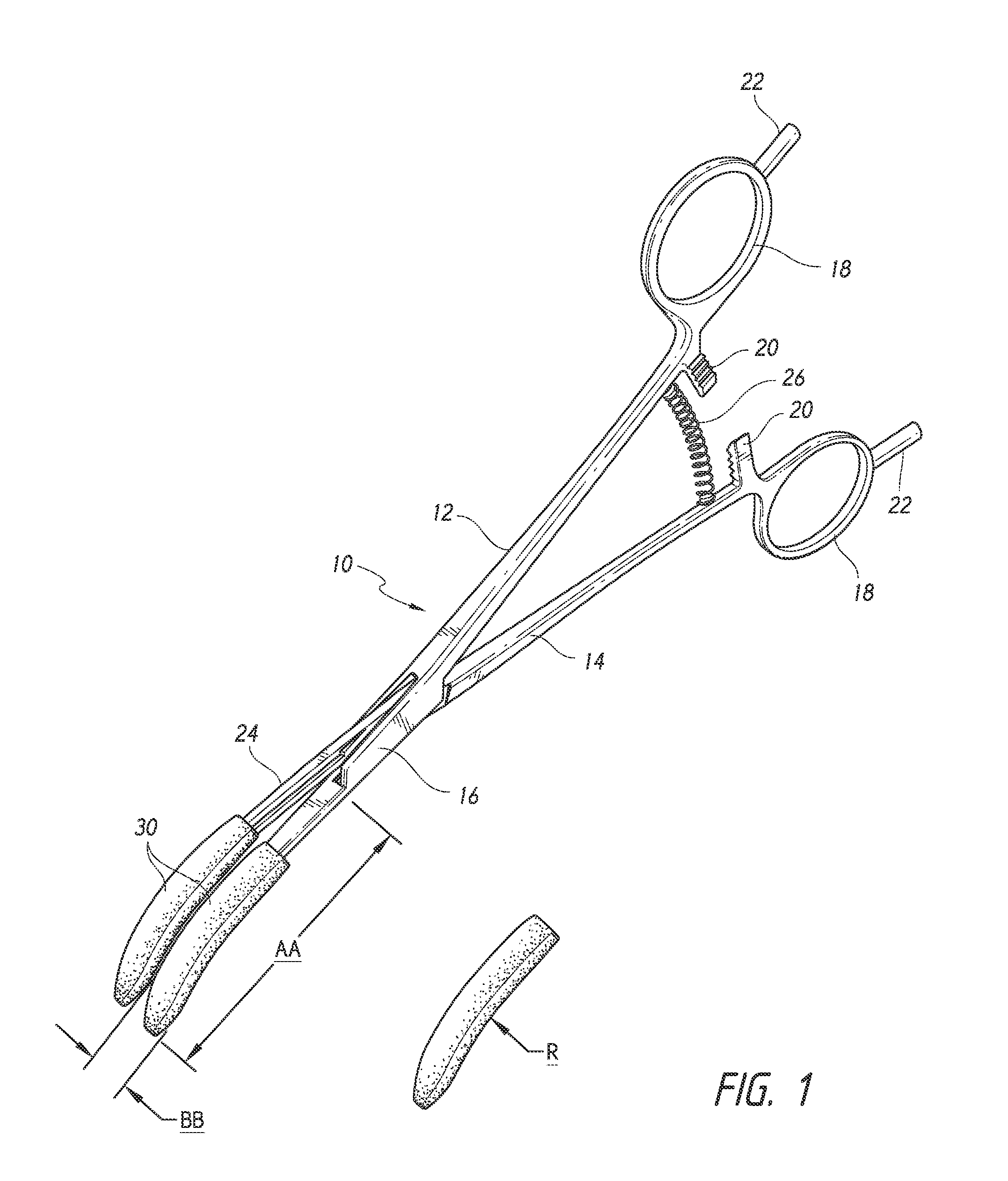
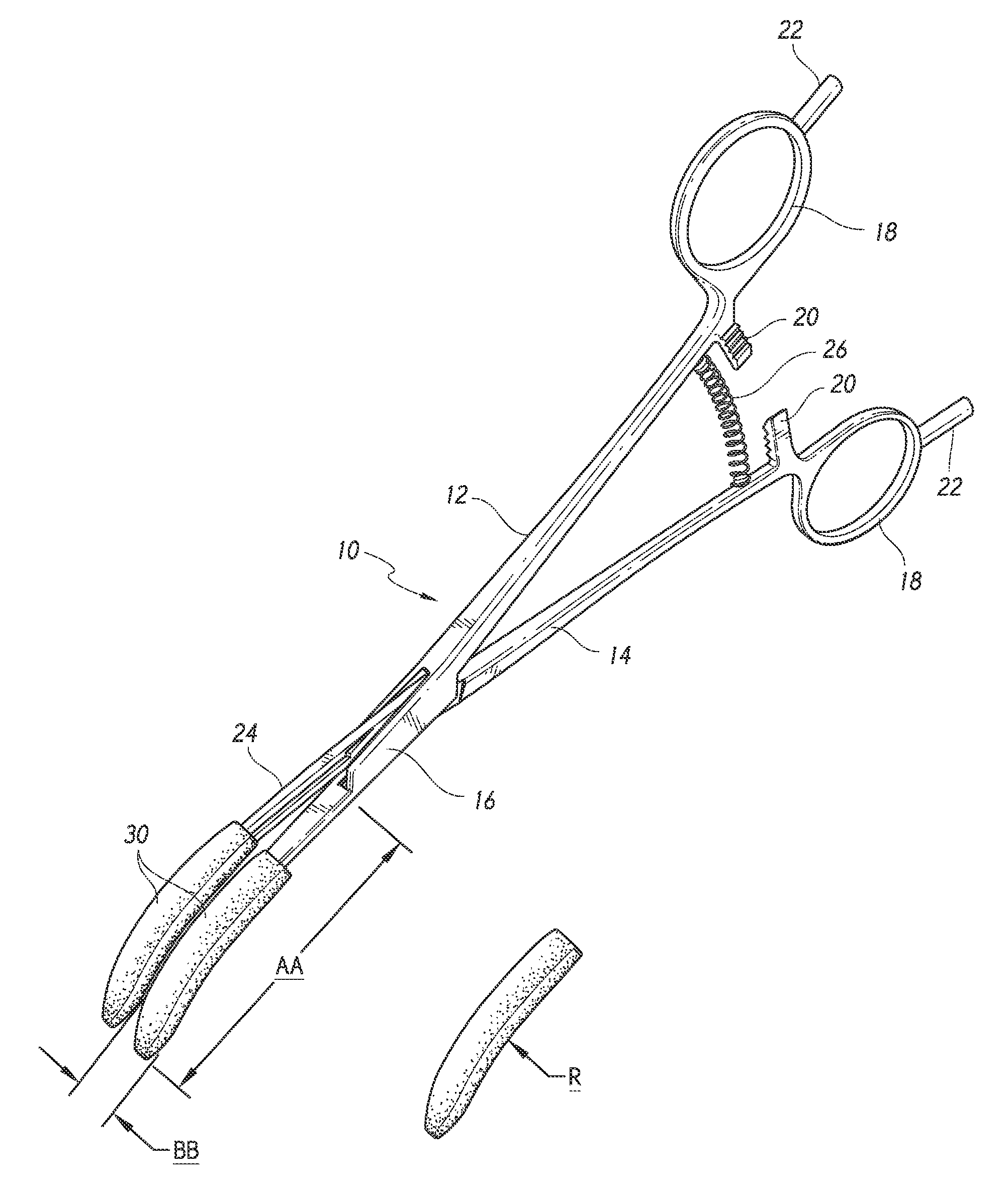
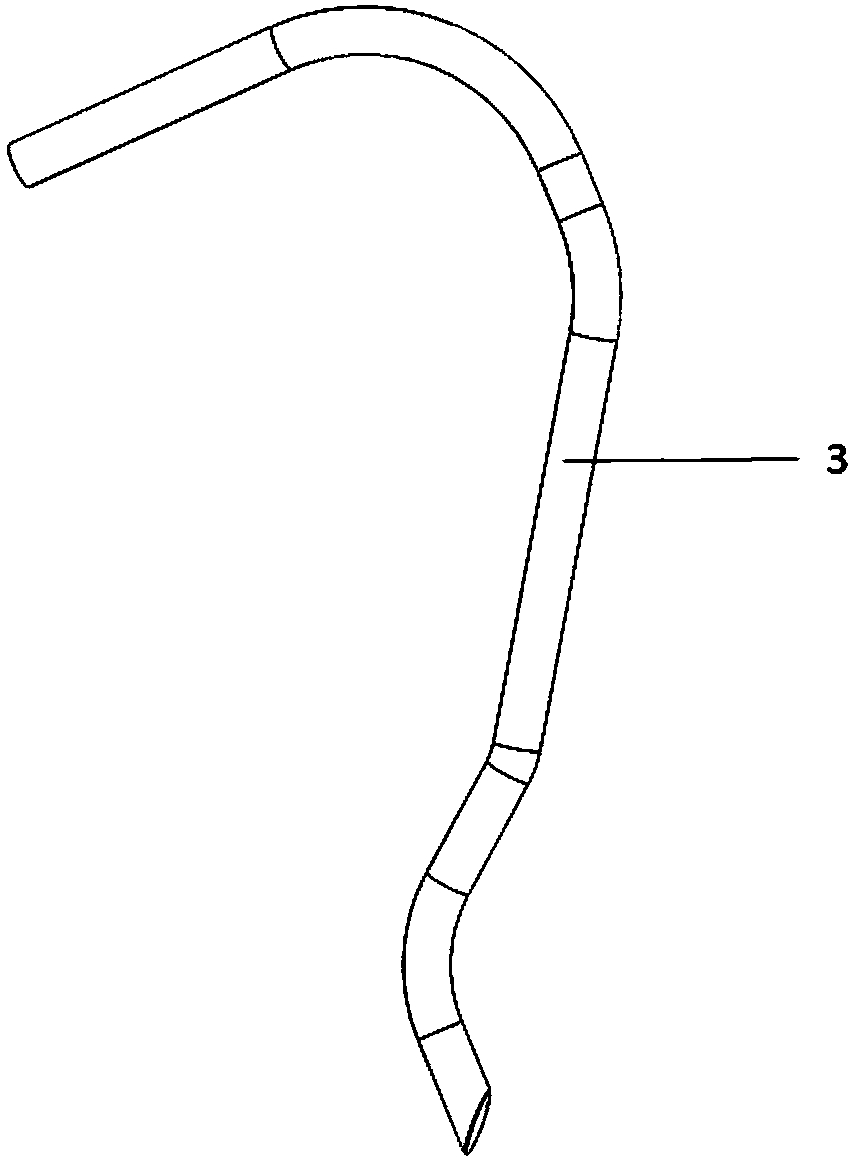
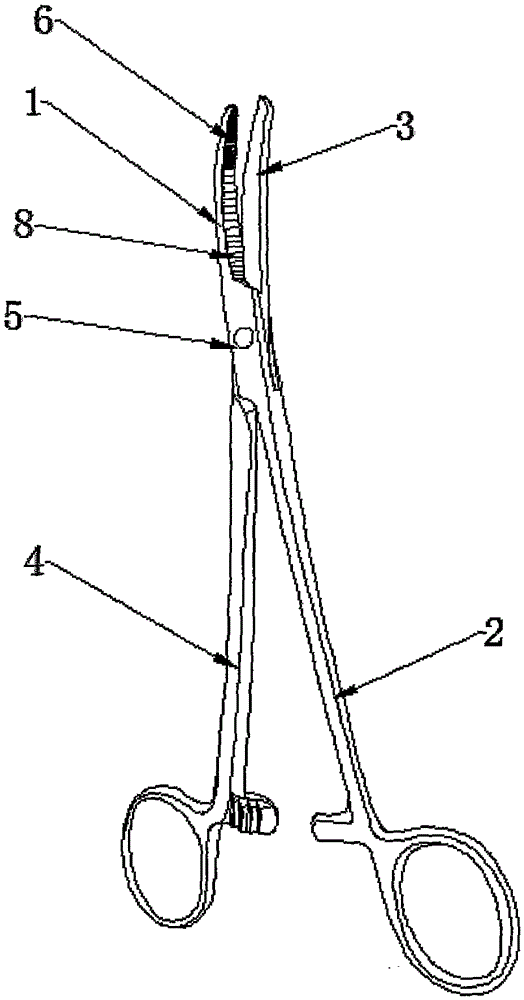
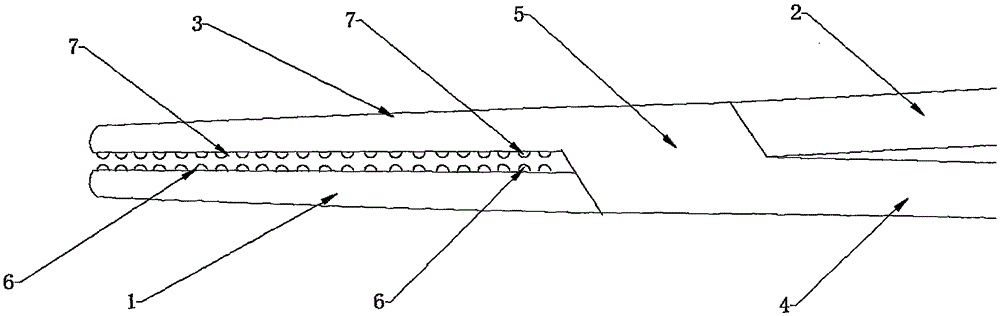
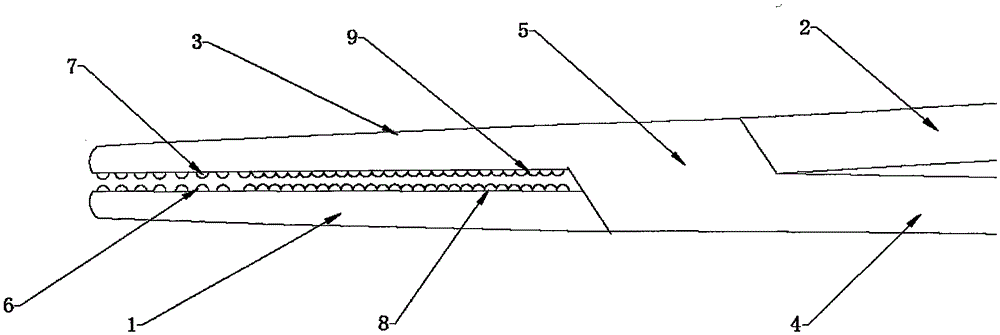
Coaptive surgical sealing tool
ActiveUS20140088582A1Uniform compressionAvoid closing too quicklySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsLiver parenchymaEngineering
A coaptive surgical sealing tool may be similar to an ordinary hemostat with long (50, 60, 70 or 80 mm) thin jaws for sliding into the liver parenchyma, without tearing the larger blood vessels. The jaws are spring loaded and are designed for uniform compression, and to avoid closing too quickly. The jaws are capable of sealing a 50, 60, 70 or 80 mm sealing length, in a single bite, although it can also seal shorter lengths as well. The tool can be used with existing RF / bi-polar cautery generators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
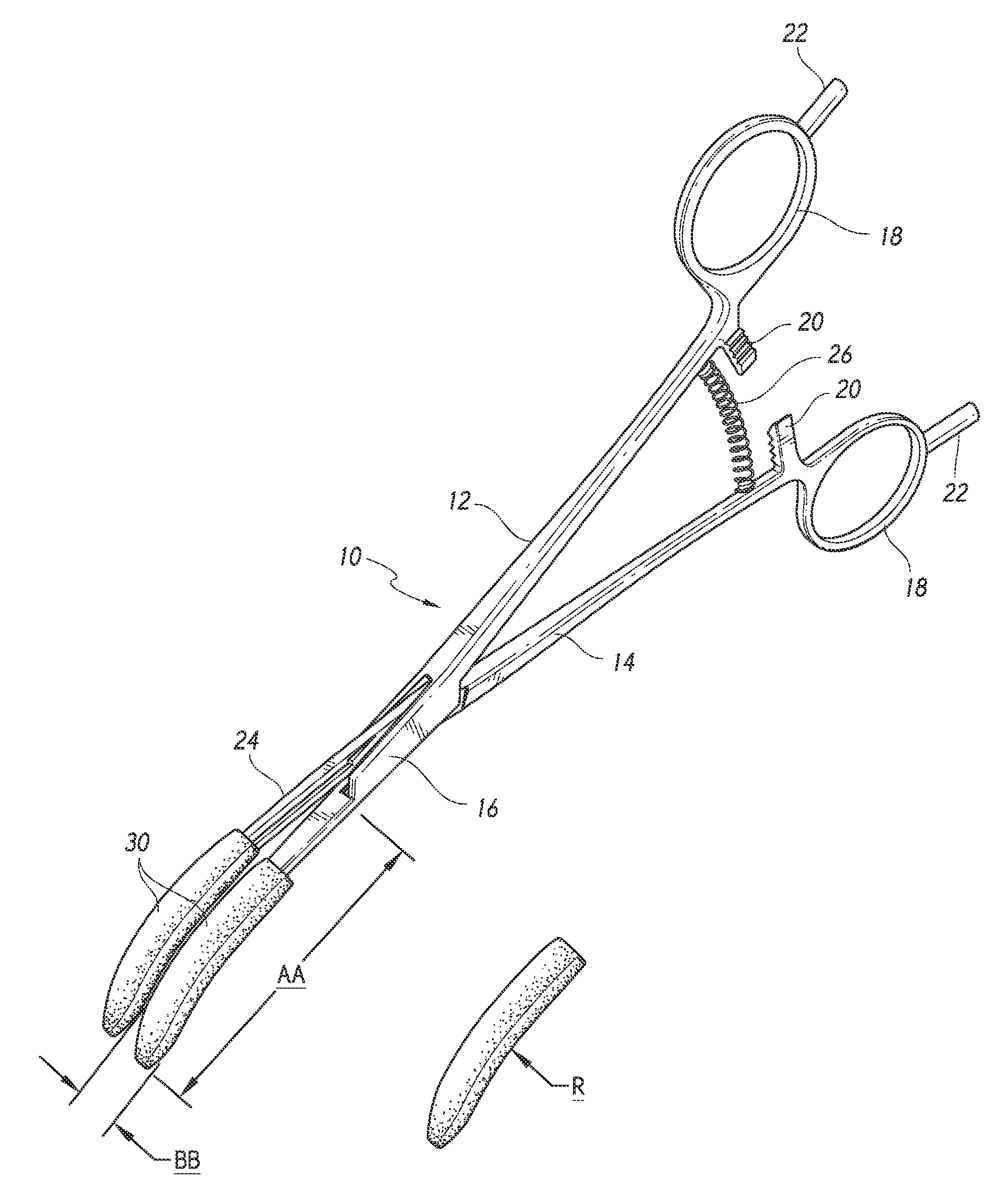
Coaptive surgical sealing tool
ActiveUS9186214B2Uniform compressionAvoid closing too quicklySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsLiver parenchymaEngineering
A coaptive surgical sealing tool may be similar to an ordinary hemostat with long (50, 60, 70 or 80 mm) thin jaws for sliding into the liver parenchyma, without tearing the larger blood vessels. The jaws are spring loaded and are designed for uniform compression, and to avoid closing too quickly. The jaws are capable of sealing a 50, 60, 70 or 80 mm sealing length, in a single bite, although it can also seal shorter lengths as well. The tool can be used with existing RF / bi-polar cautery generators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Liver tumor automatic accurate robust segmentation method in CT image
The invention discloses a liver tumor automatic accurate robust segmentation method in a CT image, and the method comprises the steps: (1) carrying out the preprocessing of the CT image, and extracting a liver region in the CT image; (2) applying an LIB-based application The SLIC image super-pixel segmentation method comprises the following steps: carrying out multi-level iterative segmentation ona liver region, dividing a region with relatively consistent gray scale and texture in the liver into the same super-pixel, and obtaining a boundary between a normal liver parenchyma and a liver tumor; (3) performing normal hepatic parenchyma / hepatic tumor binary classification on each pixel point of the liver region according to the local gray scale and the texture characteristics of the image;and (4) classifying the superpixels generated in the step (2) according to a liver region pixel point classification result to obtain a final liver tumor segmentation result. The method can effectively solve the segmentation difficulty caused by CT imaging noise, fuzzy liver tumor boundaries in CT images, complex structure, various gray levels and the like, and improves the efficiency and precision of computer-aided diagnosis of liver diseases.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
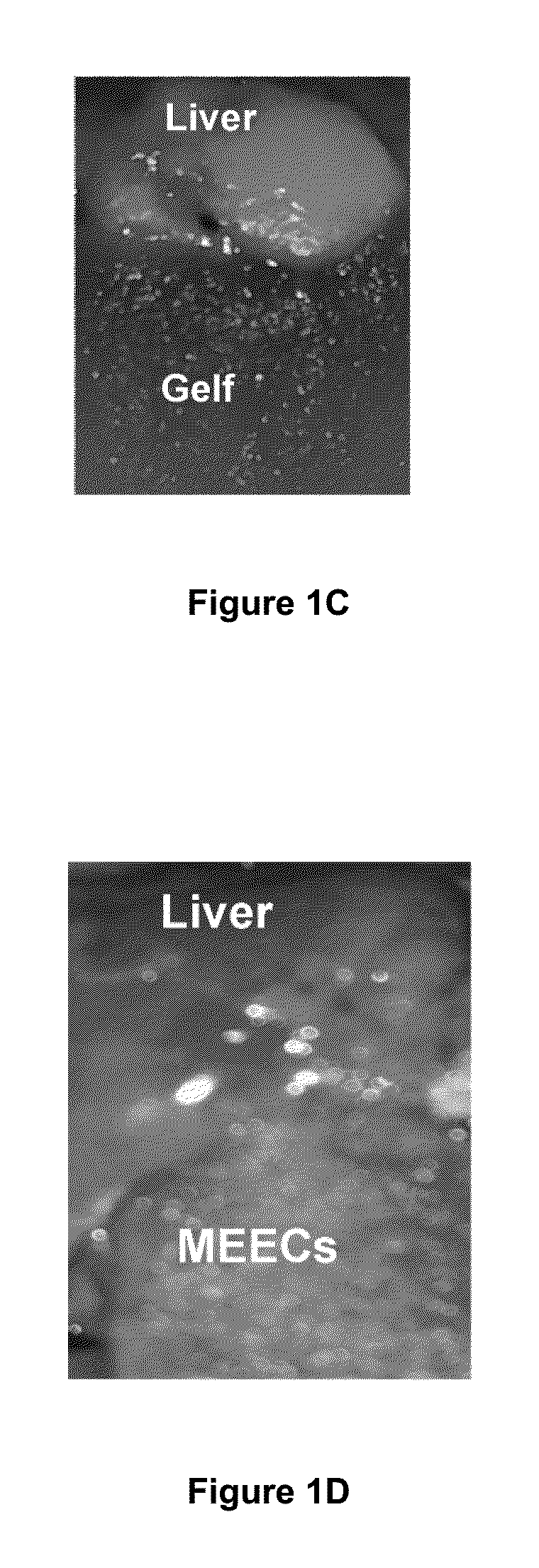
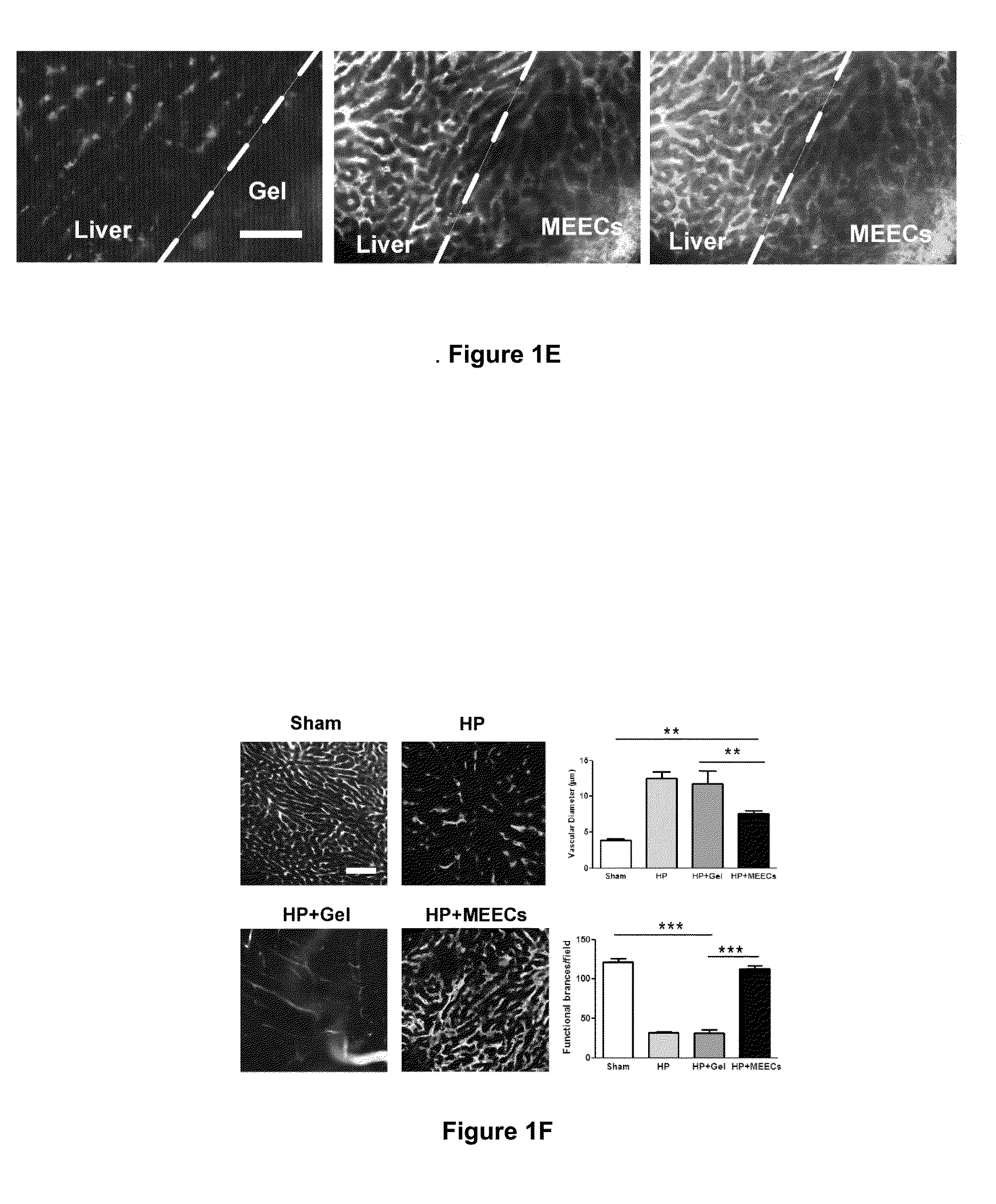
Materials and Methods for Rescue of Ischemic Tissue and Regeneration of Tissue Integrity During Resection, Engraftment and Transplantation
InactiveUS20160121023A1Improve liver functionIncrease ratingsBiocideDigestive systemParenchymaIschemic injury
Cell-containing implants populated with endothelial cells rescue liver donor and recipient endothelium and parenchyma from ischemic injury after major hepatectomy and engraftment. The inventions disclosed herein highlight the discovery that endothelial-hepatocyte physiologically communicate and cooperate during hepatic repair. The present inventions provide materials and methods for a new approach to improve transplant and regenerative medicine outcomes, for example, liver transplantation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
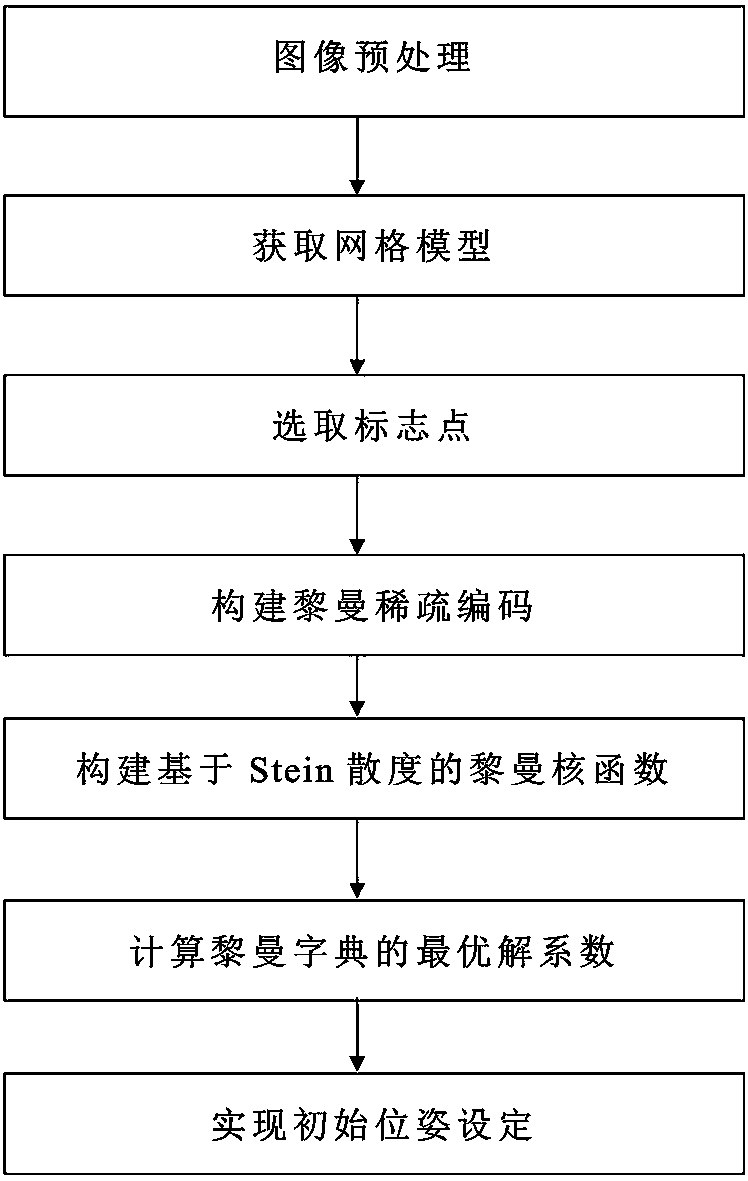
Method for setting initial position and posture of liver statistical shape model
The invention discloses a method for setting the initial position and posture of a liver statistical shape model, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of a to-be-segmented image, obtaining a binary image, obtaining a shape grid model of liver, selecting mark points, carrying out the manual segmentation of a plurality of groups of other liver CT images at the same time, carrying out the surface meshing, obtaining a prior shape model, and selecting mark points; taking the mark points on the prior shape model as a training set, and constructing Riemann sparse coding;further constructing a Riemann kernel function based on Stein divergence, and calculating an optimal solution coefficient of a Riemann dictionary; obtaining a deformation field of the mark points relative to the positions of the original mark points through the spatial position relation of the mark points in the updated to-be-segmented image, and mapping the deformation field to each top point inthe shape model of the to-be-segmented image, and achieving the setting of the initial position and posture. The method can achieve the quick construction of the statistical shape model of liver andthe precise determining of the initial position and posture, improves the segmentation efficiency and precision, and is suitable for the segmentation and recognition of liver parenchyma and a focus ofinfection.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
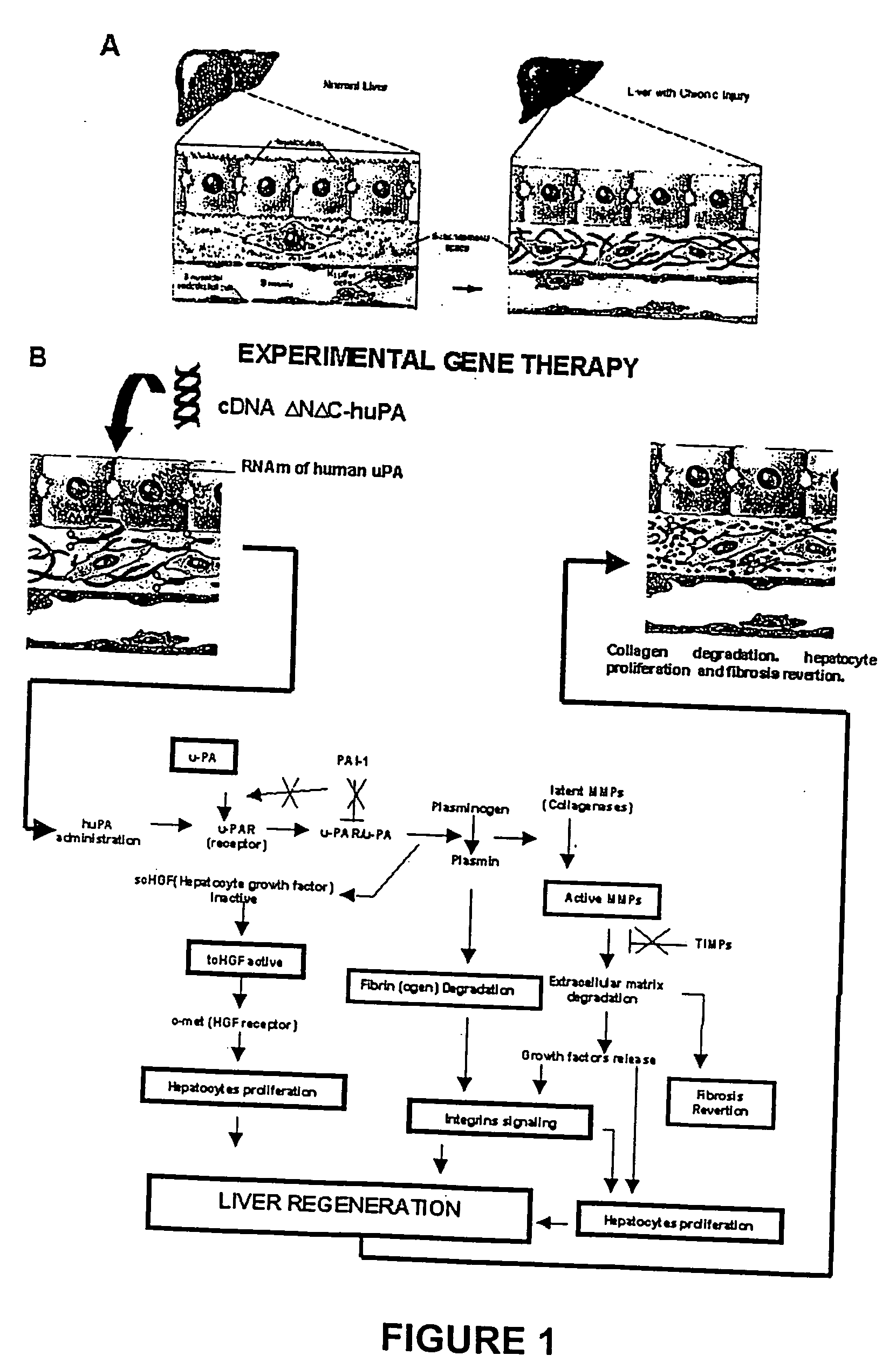
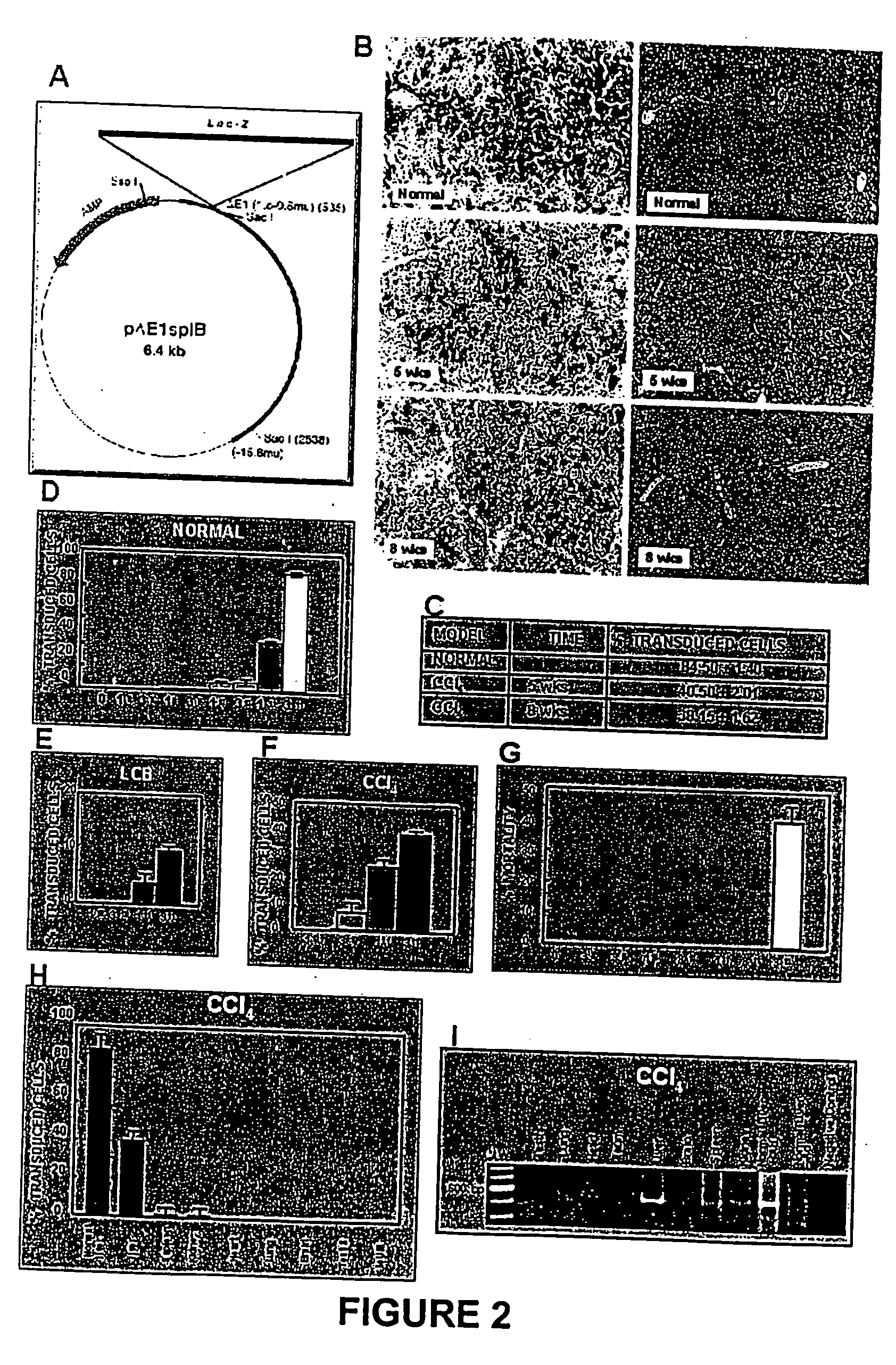
Recombinant viral and non-viral vectors containing the human urokinase plasminogen activator gene and its utilization in the treatment of various types of hepatic, pulmonary, pancreatic and cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophic scars
InactiveUS20040097455A1Reestablishment of liver functionFacilitated DiffusionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCardiac fibrosisCause of death
Hepatic cirrhosis is considered a severe health problem in Mexico, since it is the third mortality cause in working-age people and there is no 100% effective treatment. Cirrhosis is characterized by an exacerbated increase of collagen in liver parenchyma, replacing the hepatocytes and thus provoking liver failure. This is one of the reasons why we have used a gene therapy through specific delivery to cirrhotic livers of the gene of human urokinase plasminogen activator (huPA), which activates mechanisms that induce the degradation of excess cellular matrix and stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, obtaining thus a fast re-establishment of the liver function. In the instant invention, the modified human uPA gene was inserted in the adenoviral vector (pAd-DeltahuPA), because it is not secreted and does not provoke hypercoagulation or spontaneous internal bleedings. Moreover, data from the bio-distribution essay with an adenoviral vector with reporter gene beta-gal have shown liver specificity as the target organ of the vector. Using ELISA, huPa protein was detected in liver homogenates (4500 pg / ml) in animals treated with pAd-DeltahuPA and was also intracellularly detected through immunochemistry in liver cuts (80% positive cells). huPa induced a dramatic fibrosis reduction (85%) on day 10 of vector administration, compared to control cirrhotic rats and 55% hepatocyte proliferation increase. Liver function tests (ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin) dropped to nearly normal levels and hepatocyte proliferation was observed. Because of the two beneficial event cascades, gene therapy with modified huPA can be developed as a definite potential treatment for patients with liver cirrhosis.
Owner:TGT LAB DE C V
Application of activin receptor-interacting protein 2 (ARIP2) gene to preparation of medicament
InactiveCN102343102AHas preventive effectPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides application of an activin receptor-interacting protein 2 (ARIP2) gene to preparation of a medicament, relating to the field of liver disease gene therapy medicaments. The application of the ARIP2 gene as a gene therapy medicament for treating liver diseases is characterized in that: a eukaryotic cell expression vector of a recombinant ARIP2 gene is transfected with liver cells, and ARIP2 proteins expressed by the ARIP2 gene in the liver cells can be used for maintaining liver cell survival and reducing inflammatory mediators and extracellular matrixes, so that the regeneration of liver parenchyma cells is facilitated, and liver inflammation and fibration are suppressed. The ARIP2 gene can be used for treating acute liver diseases and chronic liver diseases, including liver diseases such as hepatofibrosis, hepatocirrhosis and the like.
Owner:柳忠辉
Separating and extracting method for primary liver parenchyma cells and application of primary liver parenchyma cells
ActiveCN112251398APromote growthImprove survival rateCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsCellular DebrisLiver parenchyma
The invention relates to the technical field of cell separation and particularly discloses a separating and extracting method for primary liver parenchyma cells and application of the primary liver parenchyma cells. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps: injecting perfusate I and perfusate II into a hepatic tissue mass to digest and separate the liver parenchyma cells so as toobtain a cell suspension, then, subjecting filter liquor, obtained after filtering the cell suspension, to normal-temperature centrifugation for 5 times sequentially, wherein centrifugation conditionssequentially are 1000-1580rpm / min*3-5min, 500-650rpm / min*3-5min, 200-300rpm / min*4min, 200-300rpm / min*4min and 200-300rpm / min*4min. According to the method, the operation is simple, consumed time is short, low-temperature centrifugation equipment is not required, red blood cells and cell debris can be efficiently removed, and obtained liver parenchyma cells are relatively high in survival rate andpurity.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
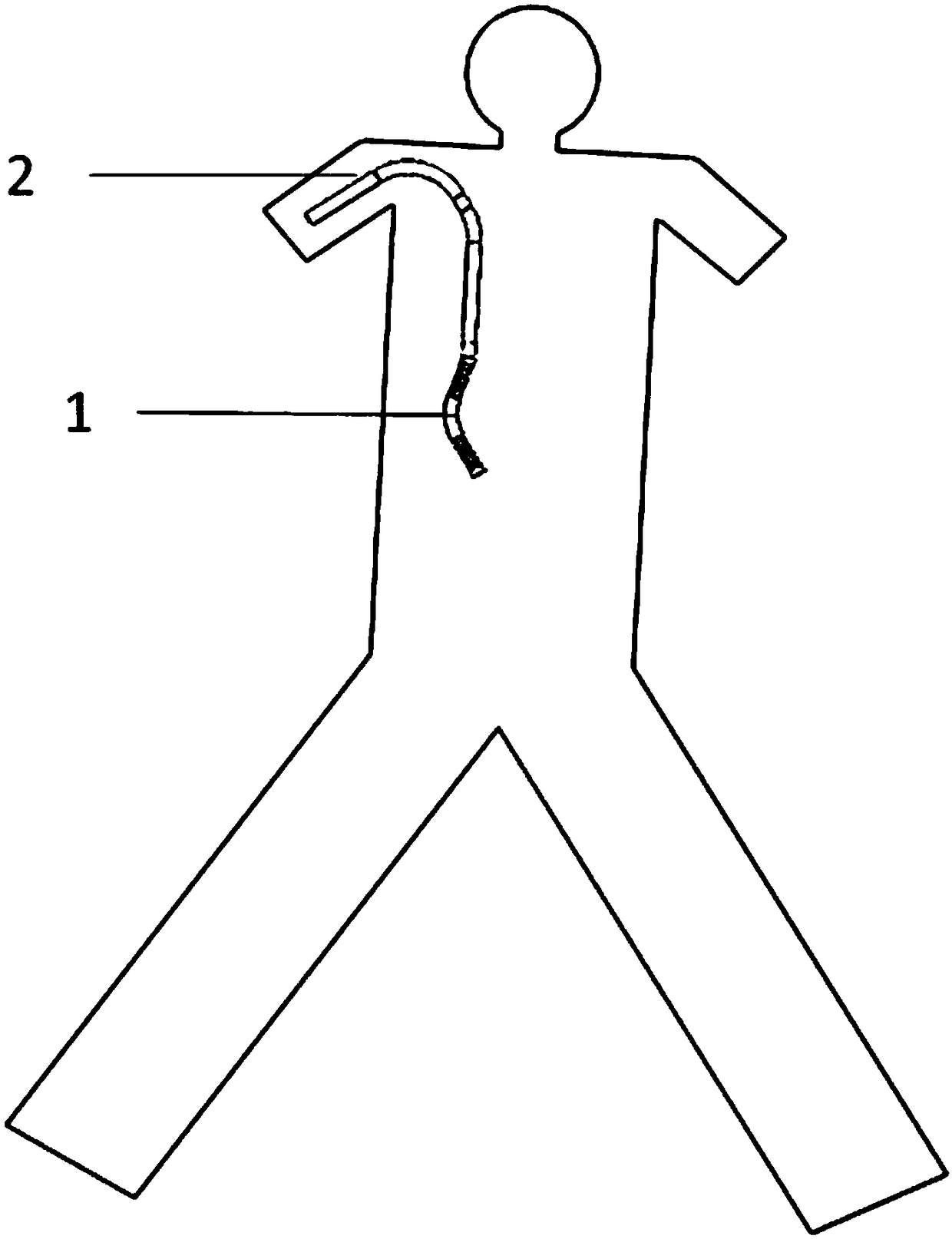
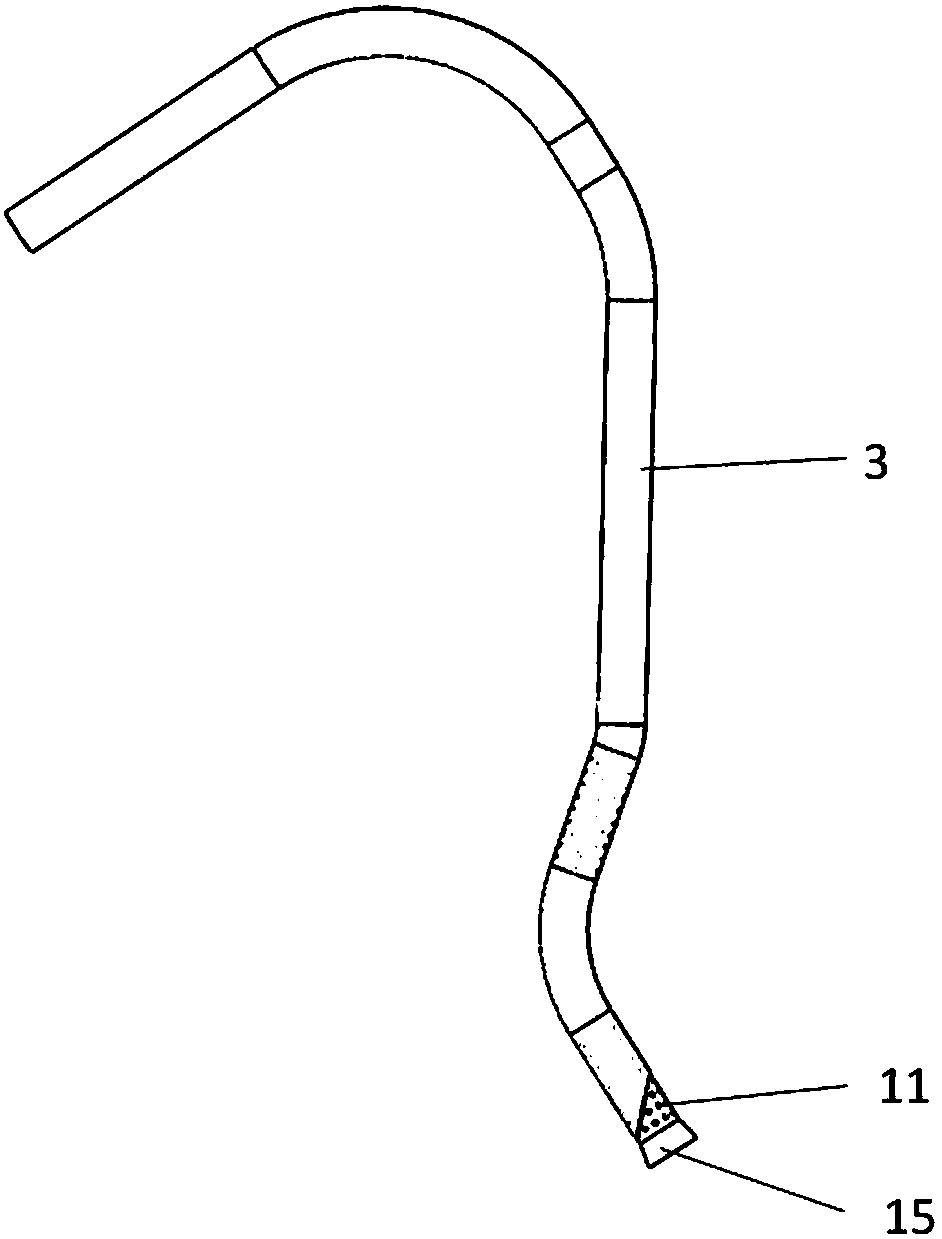
Recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter
A recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter is provided. The recoverable transjugular portosystemic shunt thrombolysis catheter comprises a conduit segment and a draw segment;it is characterized in that the conduit segment comprises a portal vein part, a connecting part and a liver vein part; the connecting part connects the portal vein part and the liver vein part; the draw segment is connected with the liver vein part; the draw segment is a solid segment; during usage, the draw segment is fixed after extending out from the portal vein to the jugular vein and then extending to the outside or extending to a subclavian vein or an upper arm vein to be fixed in an infraclavicular region or the upper arm vein; during usage, the portal vein part is arranged in the portal vein; the liver vein part is arranged in the liver vein; besides, the portal vein part and the liver vein part are arranged as mesh structures; the connecting part is a structure does not include meshes. After the conduit is imbedded and thrombus in portal vein is removed, the thrombus can be taken out by the draw segment; the purpose of the setting of the draw segment solid is to ensure that blood flow through the portal vein into the inferior vena cava after passing through the hepatic vein, but not into the liver parenchyma or in vitro through the draw segment.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
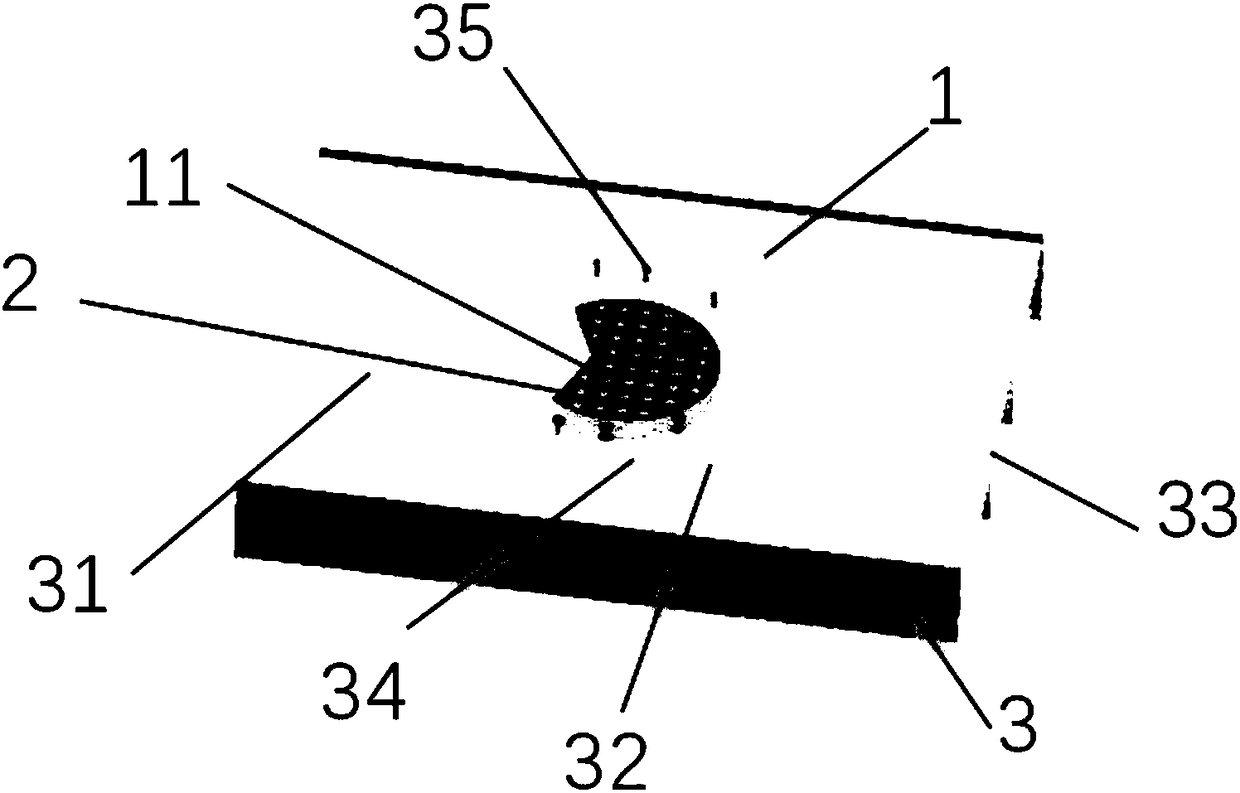
Vessel forceps
ActiveCN105395233AAccurate and quick crushingAccurate and quick disconnectionSurgical forcepsLiver tissueLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses vessel forceps. The vessel forceps comprise a first forceps body and a second forceps body which are hinged together, wherein the first forceps body comprises a first forceps mouth and a first forceps arm, the second forceps body comprises a second forceps mouth and a second forceps arm, the first forceps arm and the second forceps arm can be closed or opened by taking the hinging part as the moving center, and the first forceps mouth and the second forceps mouth are closed or opened under the driving of the first forceps arm and the second forceps arm; a plurality of first bulges are arranged on the closed face of the first forceps mouth, when the first forceps mouth and the second forceps mouth are closed, the plurality of first bulges contact the closed face of the second forceps mouth, when the structure is used for clamping the liver parenchymal tissue to be broken, the plurality of bulges can extrude blood vessels or biliary ducts distributed in the liver tissue to be positioned in the gaps among the bulges, so that the risk that a sharp multi-rack structure easily damages the biliary ducts or the blood vessels is reduced, and a doctor can carry out accurate clamping and dividing operations on the liver parenchyma.
Owner:蔡建强
Indocyanine green fluorescence combined multimodal image-guided liver portal vein watershed developing method
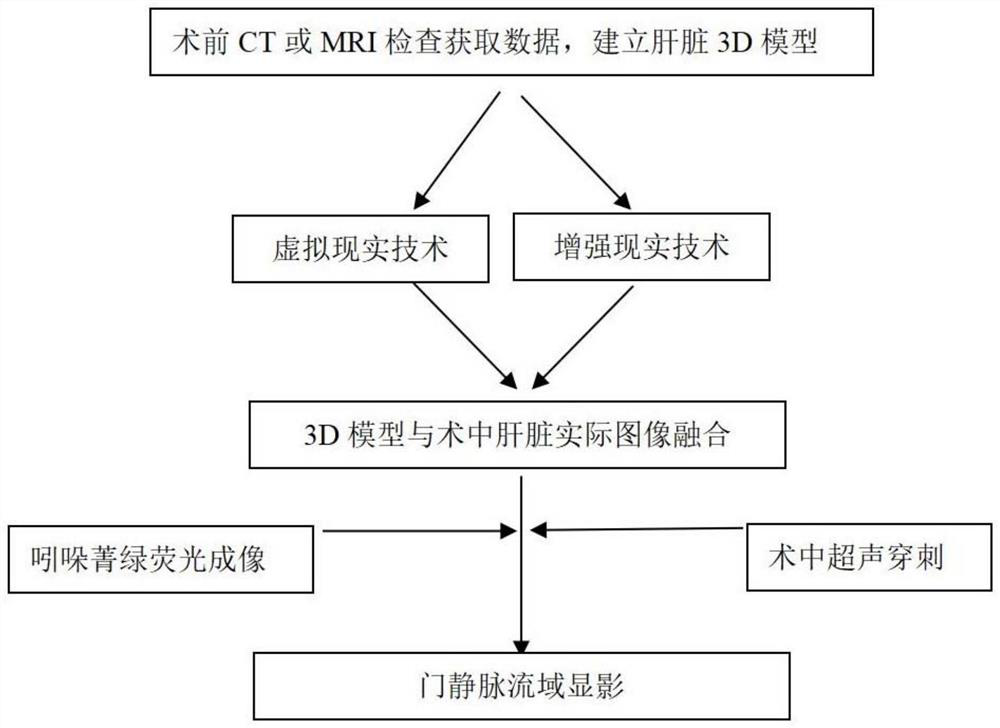
PendingCN111887817AAccurate timingPrecise positioningSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical structuresLiver parenchyma
The invention relates to an indocyanine green fluorescence combined multimodal image-guided liver portal vein watershed developing method, and belongs to the technical field of medical images. According to the method, artificial intelligence technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality and the like are integrated with traditional intraoperative ultrasound and indocyanine green fluorescent staining technologies, so that a surgeon can visualize three-dimensionally complex liver anatomical structures, accurately locate tumors in an operation, plan an operation scheme, accurately achieve developing of a target portal vein watershed, monitor and correct a liver parenchyma disconnection plane in real time, and perform accurate anatomical liver resection. In a liver operation, the method can display a portal vein branch blood flow supply area for supplying tumors in real time, accurately guide a liver resection range, can not only remove micrometastatic tumors that may exist in theportal vein, but also can ensure blood supply of the remaining liver, improve accuracy and safety of the operation, reduce operative complications, and improve efficacy of tumor operation.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
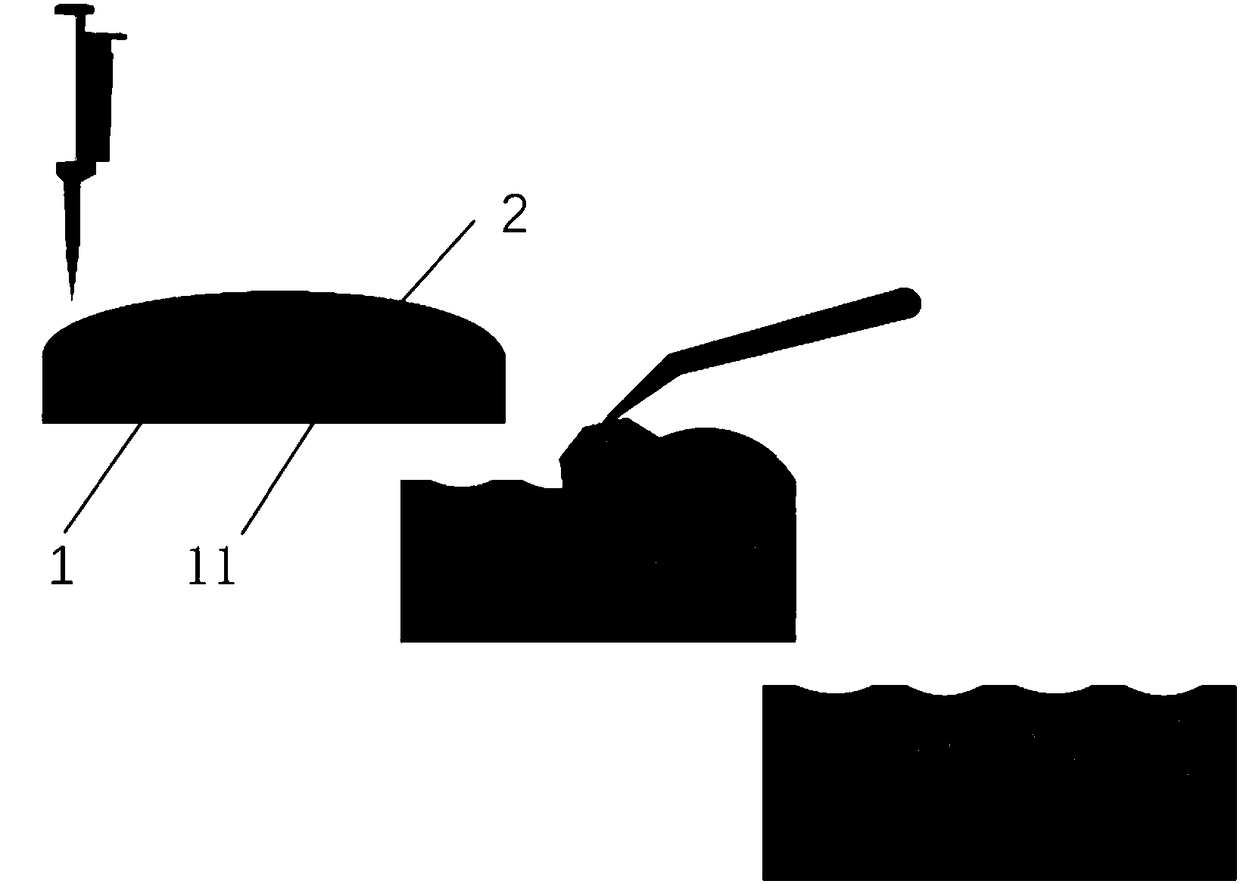
Constructing device and constructing method of artificial liver lobule functional unit
InactiveCN108504571AGood biocompatibilityThe result is accurateHepatocytesArtificial cell constructsArtificial liverLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a constructing device and a constructing method of an artificial liver lobule functional unit. The constructing device comprises a liver plate basal layer, a liver parenchyma cell zone and a fluid passageway layer, wherein a liver plate patterning groove is formed in the liver plate basal layer through processing; the fluid passageway layer comprises a fluid inlet passageway, an endothelial cell oriented growth zone and a fluid outlet passageway. The constructing method corresponding to the constructing device comprises the following steps: paving collagen containing liver parenchyma cells to the inner part of the liver plate patterning groove, bonding the liver plate basal layer with the fluid passageway layer after solidifying the collagen, pouring an endothelialcell suspension solution to the endothelial cell oriented growth zone, and enabling a cell culture medium solution to unidirectionally flow in the fluid inlet passageway, the endothelial cell orientedgrowth zone and the fluid outlet passageway after increasing endothelial cells to a certain amount. According to the constructing device and the constructing method, disclosed by the invention, reallayer-to-layer position relationship between endodermis and liver parenchyma cells is realized under dynamic culturing, the response of the liver parenchyma cells to physicochemical and biochemical irritation under the protection of the endodermis of blood vessels more tends to reality, and a more accurate result can be obtained when the artificial liver lobule functional unit is applied to drug screening, case research and therapy detection.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride and preparation method thereof
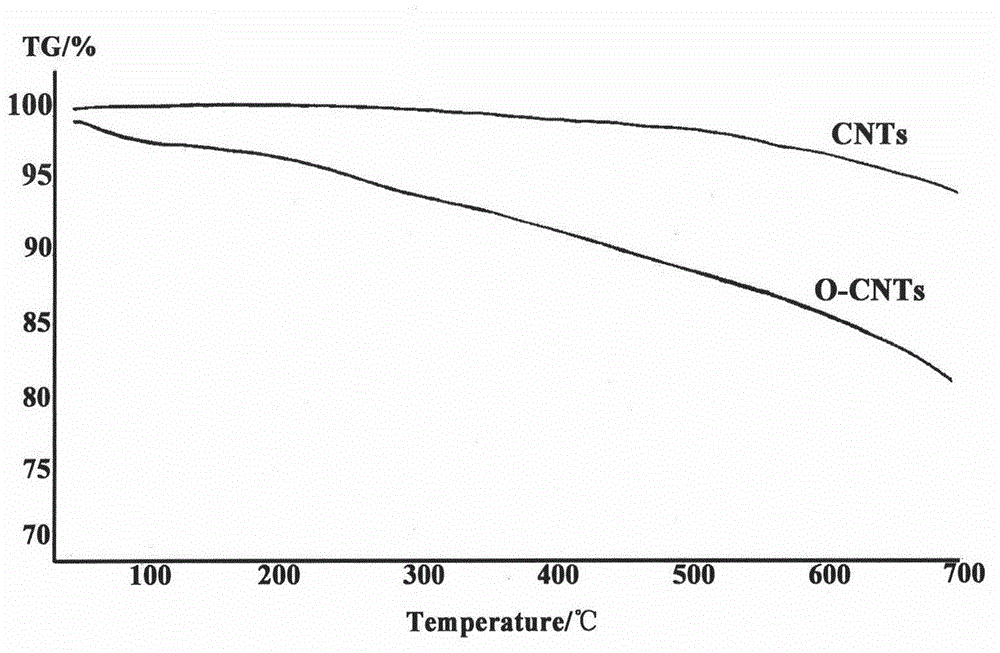
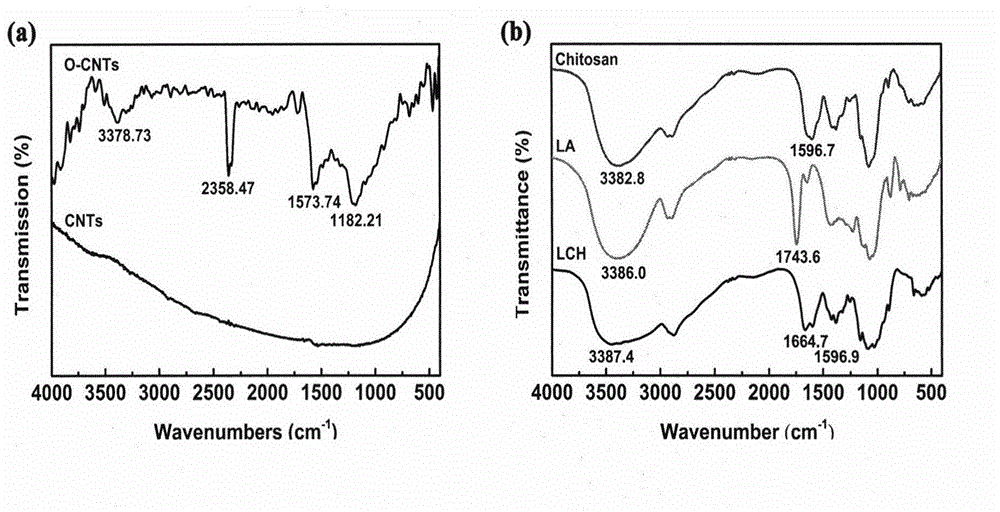
InactiveCN104689334AGood biocompatibilitySmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride and a preparation method thereof. Amidation reaction of amino in a chitosan structure and carboxyl in lactobionic acid is carried out; galactosyl is coupled to chitosan so as to obtain galactosylated chitosan; the galactosylated chitosan is modified onto the carbon nano tube; therefore, the water solubility and the biocompatibility of the carbon nano tube are increased; simultaneously, the specificity of non-reductive galactose or N-acetyl-galactose is identified and taken by utilizing an asialoglycoprotein acceptor on a liver parenchyma cell membrane, so that the active hepatoma targeting effect is realized; simultaneously, doxorubicin hydrochloride is combined with a vector in a non-covalent manner through phi-phi accumulation acting force; and therefore, the hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride is prepared. The hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process, moderate in experimental condition and easy to operate; release of the medicine loaded targeting carbon nano tube has pH dependency, good biocompatibility and obvious in-vivo tumour inhibition effect; and thus, the hepatoma targeting carbon nano tube has good practical value.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Animal experiment substitution method for toxicological evaluation of exogenous compounds
InactiveCN101735974AIncreased sensitivityHigh simulationMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureLiver parenchymaMetabolic enzymes
The invention relates to a cell separation culture method of biological tissues and use thereof, in particular to a method for separating and culturing hepatic cells of a newborn rat (or mouse) and using the hepatic cells as a substitutional animal experiment model for toxicological evaluation of exogenous compounds. The method for separating and culturing the hepatic cells of the newborn rat (or mouse) of the invention has simple operation, does not need a liver perfusion process and expensive instruments, equipment and reagents, and can obtain more than 90% of liver parenchyma cells which have good uniformity and stability and high sensitivity and are easy for manual control. The hepatic cells separated and cultured by the invention are very sensitive to the toxicity of the exogenous compounds, have some functions and activity of in vivo hepatic cells, especially reserve the activity of drug metabolic enzyme, can well simulate the physiological environment of the in vivo liver, have the advantage of combining in vitro and integral animal toxicity tests, and can be expected to be used in high flux rapid detection of the toxicity of the exogenous compounds.
Owner:伍义行
Functional liver parenchyma cells and preparation method therefor
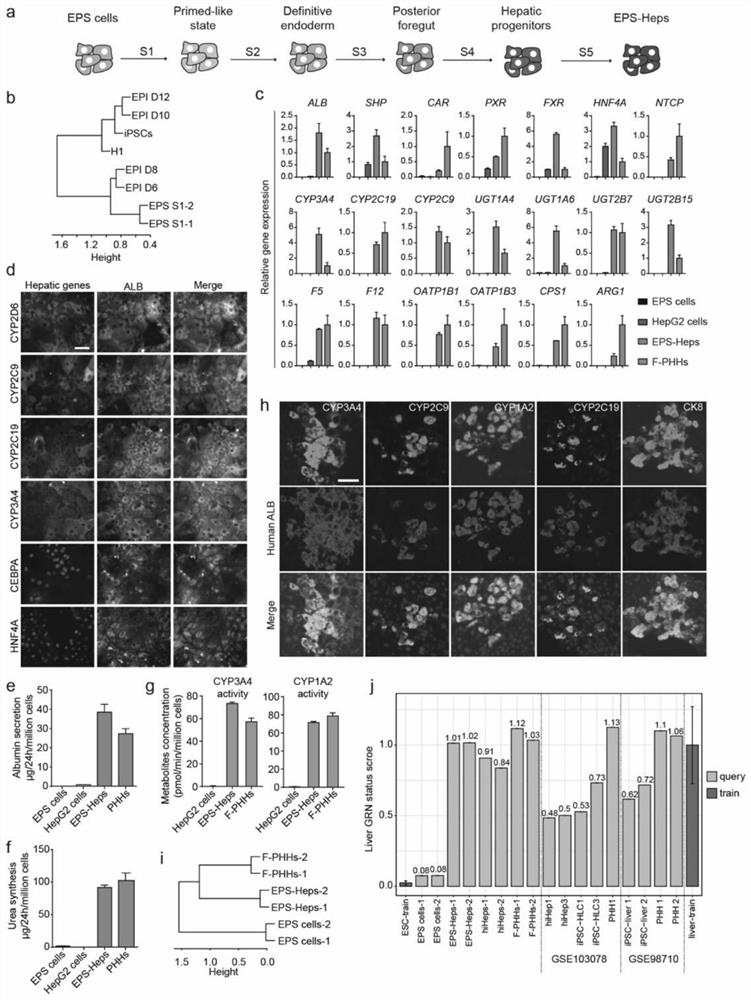
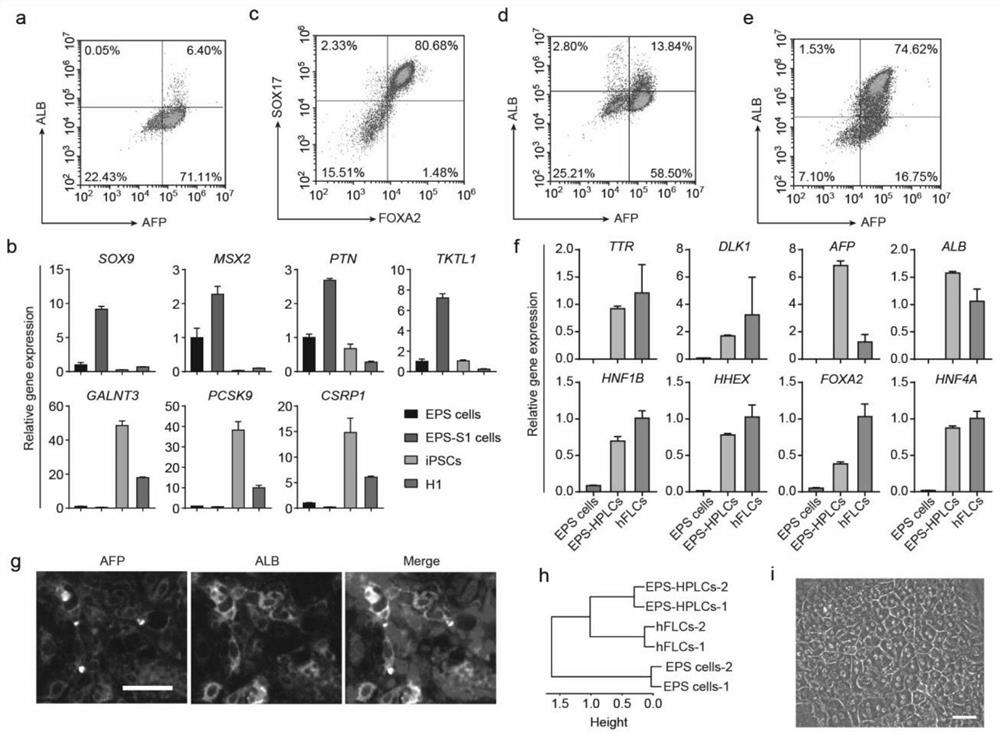
PendingCN113151147AStrong chimerismHigh proliferation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processLiver parenchymaDirected differentiation
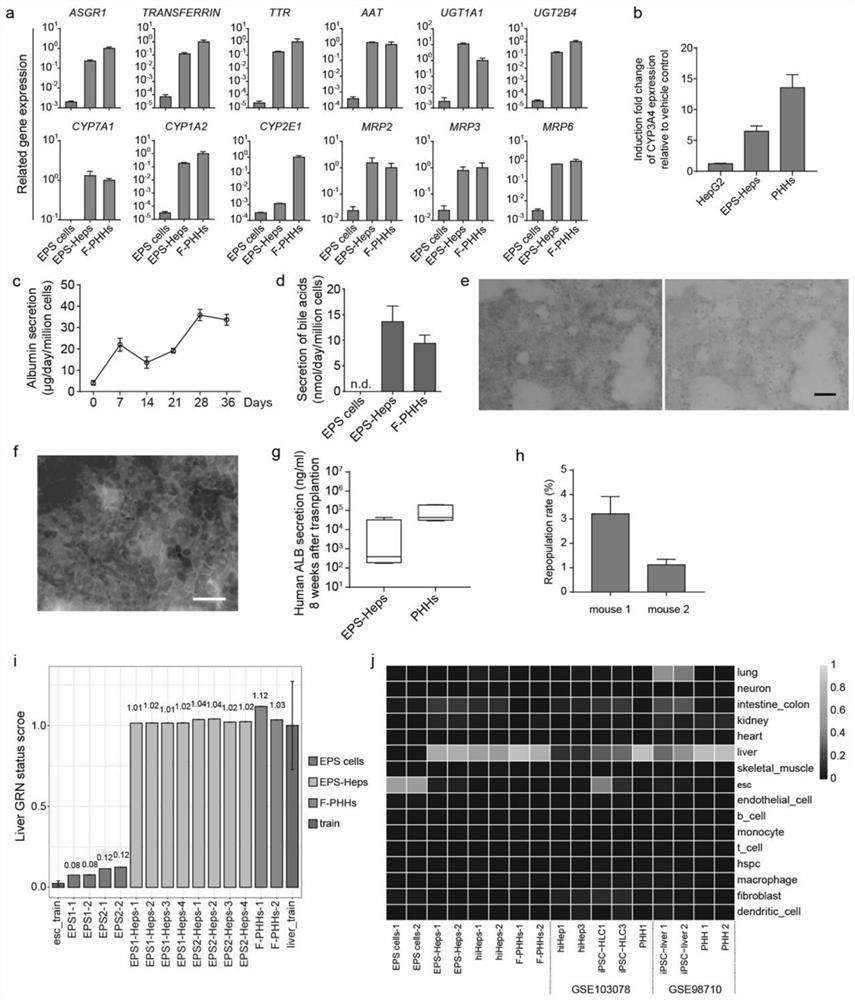
The invention discloses functional liver parenchyma cells and a preparation method therefor. According to the preparation method, potential-extended multipotential stem cells, i.e., EPS cells are subjected to directed differentiation, so as to prepare the functional liver parenchyma cells (or called liver cells). Furthermore, before directed differentiation of the EPS cells, the EPS cells is firstly pretreated in an iPSCs / ESCs culture medium. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, human EPS cells can be more efficiently differentiated into the functional liver parenchyma cells, and the functional liver parenchyma cells EPS-Heps obtained through EPS differentiation are more similar to fresh-separated primary liver cells in a full-gene transcription level.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
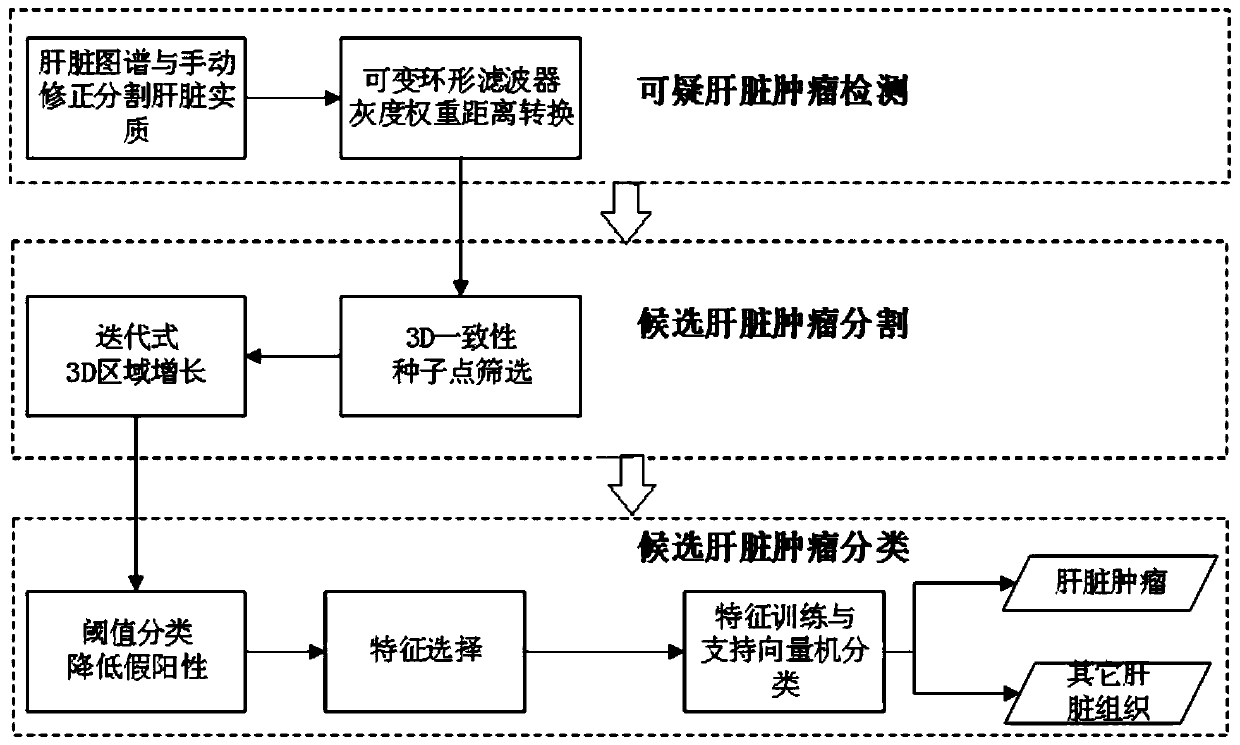
Liver CT tumor classification system and classification method
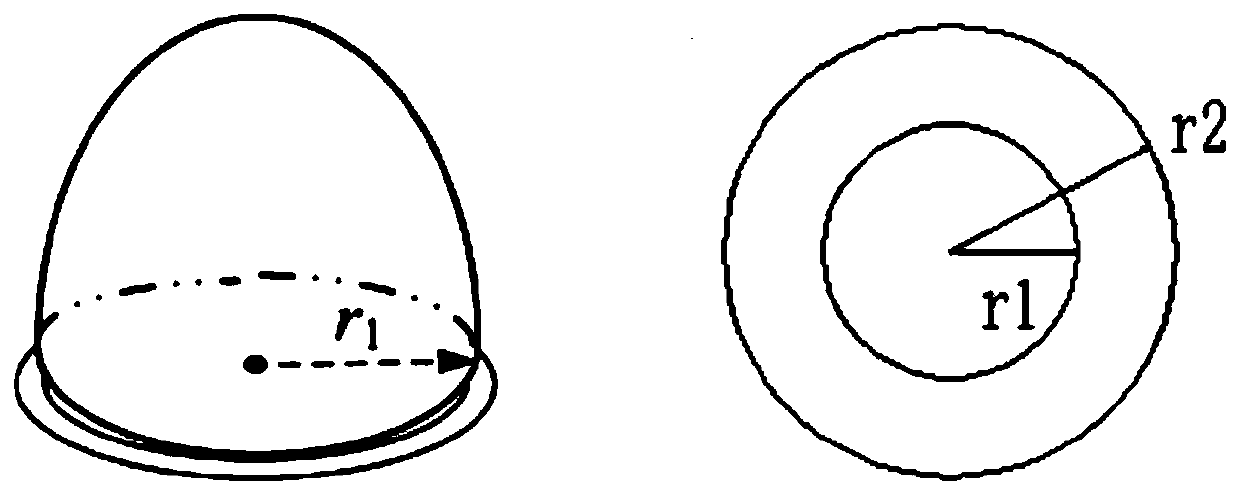
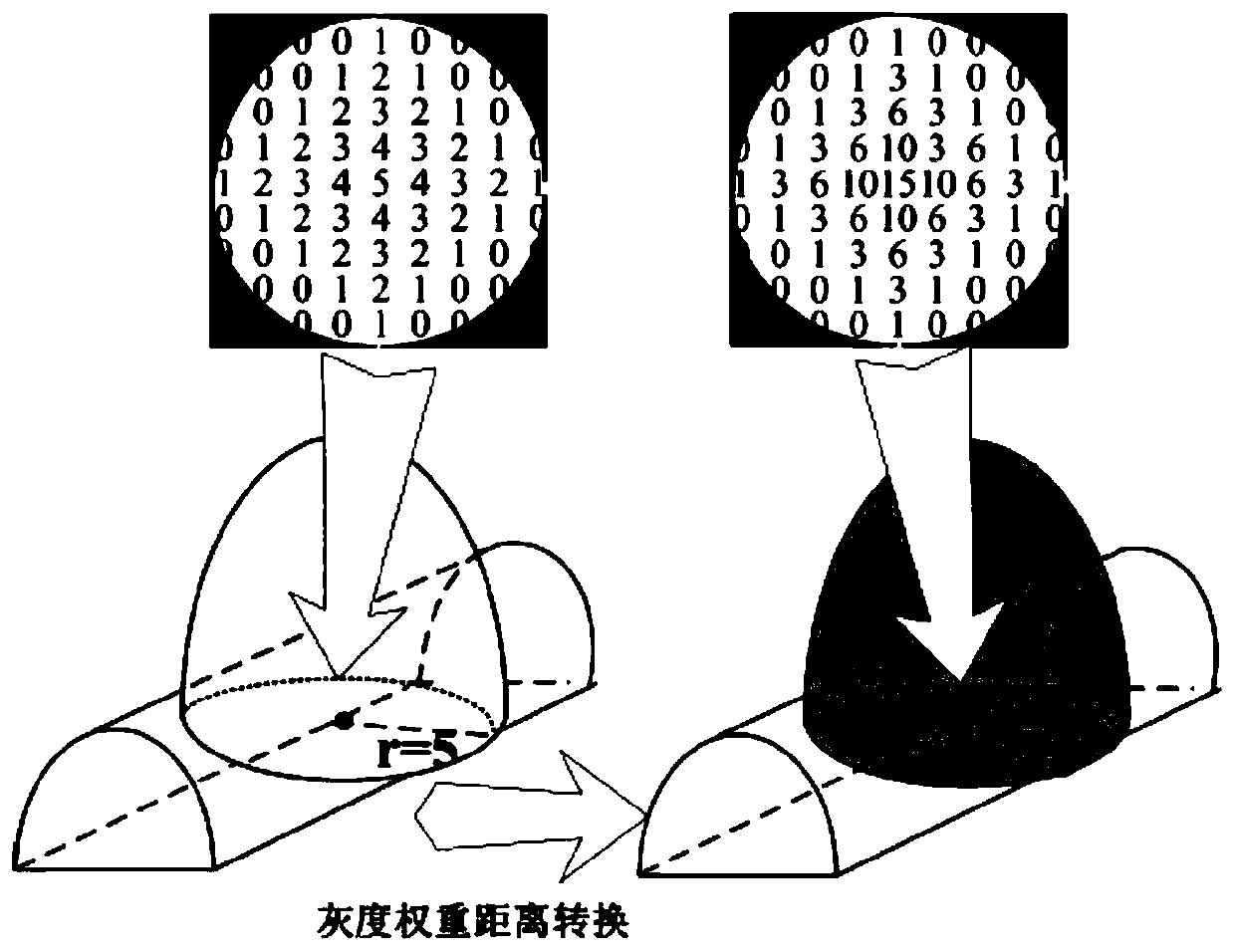
InactiveCN110276407AHigh detection sensitivityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisLiver tissueLiver parenchyma
The invention discloses a liver CT tumor classification system and classification method. The liver CT tumor classification system comprises a suspicious liver tumor detection module, a candidate liver tumor segmentation module and a candidate liver tumor classification module. The suspicious liver tumor detection module adopts a liver spectrum and manual correction combined method to segment out liver parenchyma, then a variable annular filter is adopted to carry out suspicious liver tumor detection to obtain candidate liver tumors, and the center of the variable annular filter is determined through gray scale weight distance conversion to serve as a candidate liver tumor seed point; the candidate liver tumor segmentation module completes candidate liver tumor segmentation by using a 3D region growing algorithm; the candidate liver tumor classification module is used for carrying out rough false positive reduction on candidate liver tumors by adopting an empirical threshold method, and dividing the candidate liver tumors into tumors and other liver tissues by taking an SVM algorithm as a classifier. The liver CT tumor detection sensitivity is high, and the classification accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
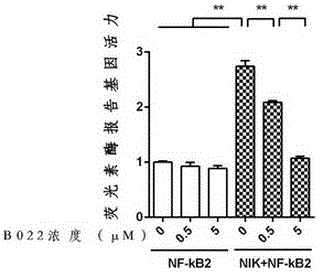
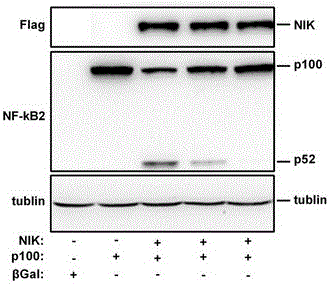
Application of NIK protein kinase inhibitor in serving as medicine for treating liver diseases
InactiveCN105769871ARelieve inflammationMitigating treatment damageOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticLiver parenchymaLiver fibrosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical medicine and particularly relates to an NIK protein kinase inhibitor serving as medicine for treating liver inflammation, acute liver damage, liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis.Experiment results show that the NIK inhibiter can inhibit activation of NIK-induced NF-kappaB2 in liver parenchyma cells, wherein the activation indicates that an inactive precursor p100 is converted into active p52.The activity of an NIK-induced NF-kappaB promoter can be inhibited.Expression of genes related to NIK-induced inflammation in liver parenchyma cells can be inhibited.CCL4-induced liver damage, inflammation and fibrosis can be inhibited.The medicine prepared from the NIK protein kinase inhibitor is achieved and has a remarkable effect on relieving and treating liver inflammation, damage, fibrosis and liver cirrhosis.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for segmenting liver medical images on basis of shape prior
ActiveCN106355582AStable and efficient shape priorsAdaptableImage enhancementImage analysisVeinLiver parenchyma
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Hepatic portal vein tree modeling method and system thereof
InactiveCN101393644BEnhancement effect is goodEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisLiver parenchymaFiltration
The invention discloses a hepatic vein vascular tree modeling method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a liver model to obtain a liver image, and utilizing the multi-scale filtration method to strengthen a blood vessel; cutting a hepatic vein; extracting a central line of the hepatic vein; detecting and removing a link in the central line; and utilizing OSG / VTKto rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree after pruning. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a blood vessel strengthening module, a blood vessel cutting module, a vascular tree central line extracting module and a vascular tree rebuilding module. The invention improves similarity functions in the filtering process, analyzes the characteristics of the ring and adopts corresponding unlinking methods for different links; and utilizes the relation of radius of blood vessel and the branch length when pruning. The invention effectively enhances the hepatic vein, improves the contrast between the blood vessel and liver parenchyma, and can extract more than five class branches, effectively unlink and prune the central line of the hepatic vein, rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree and directly display the branches of the heptatic vein.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lung function state classification method based on quantitative report template
PendingCN114711749AAccurate pulmonary function diagnosis resultsMedical data miningDiagnostic recording/measuringAlgorithmLiver parenchyma
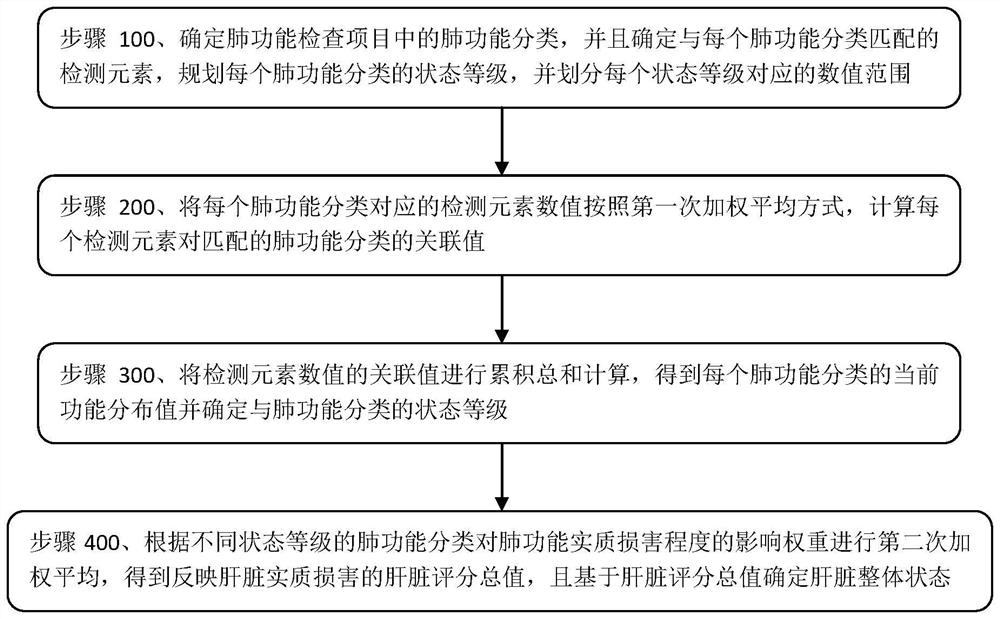
The invention discloses a lung function state classification method based on a quantitative report template, and the method comprises the steps: determining lung function classifications in a lung function examination item, determining a detection element matched with each lung function classification, planning the state grade of each lung function classification, and dividing a numerical range corresponding to each state grade; calculating a correlation value of each detection element pair matched with the lung function classification according to the detection element value corresponding to each lung function classification in a first weighted average mode; performing cumulative sum calculation on the correlation values of the detection element numerical values to obtain a current function distribution value of each lung function classification and determine a state level of the lung function classification; and according to the influence weight of the lung function classification of different state levels on the lung function parenchyma damage degree, carrying out second weighted averaging to obtain a liver score total value reflecting liver parenchyma damage, and determining the overall state of the liver based on the liver score total value. According to the invention, medical personnel can be helped to quickly obtain an accurate lung function diagnosis result.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
A Fusion Method of Hepatic Multiphase CT Images
InactiveCN104835112BHigh precisionEfficient extractionImage enhancementImage analysisSource imageMutual information
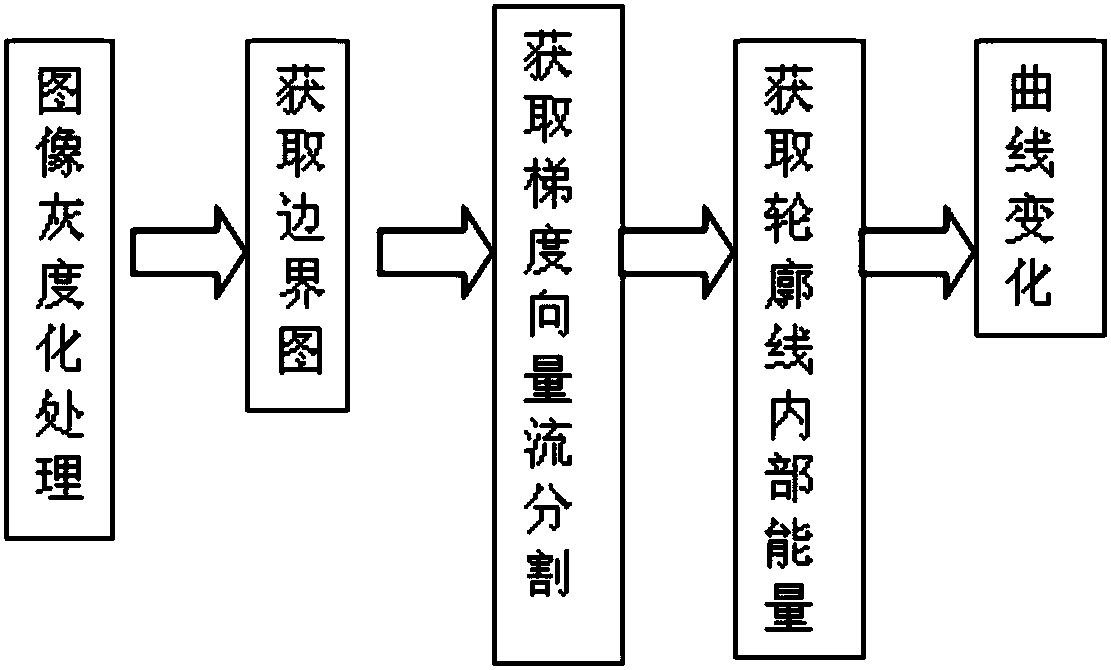
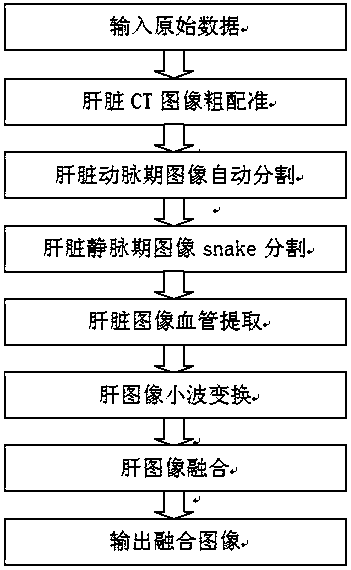
The invention discloses a liver multi-phase CT image fusion method. First, a multi-resolution CT image registration method based on joint histograms is used to roughly register the source image sequence, and then combined with a region growing algorithm of confidence connection to realize liver The automatic image segmentation and the liver image segmentation based on the gradient vector flow snake model effectively extract the edge information of the liver; then the liver image is subjected to blood vessel extraction based on the directional region growing algorithm, and then the liver parenchyma image is subjected to free deformation based on B-spline Transformation and liver non-rigid registration based on spatial weighted mutual information to accurately find image pairs at the same location in space; finally, image fusion is performed based on wavelet transform. In view of the characteristics of liver CT images, the present invention combines the image segmentation and image registration processes into the image fusion process, thereby greatly improving the fusion accuracy.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com