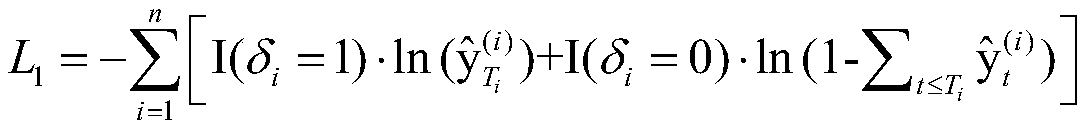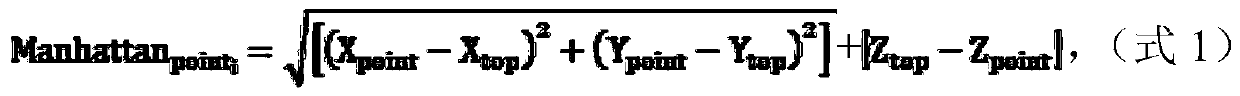Patents
Literature
65 results about "Tree modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Robust vessel tree modeling
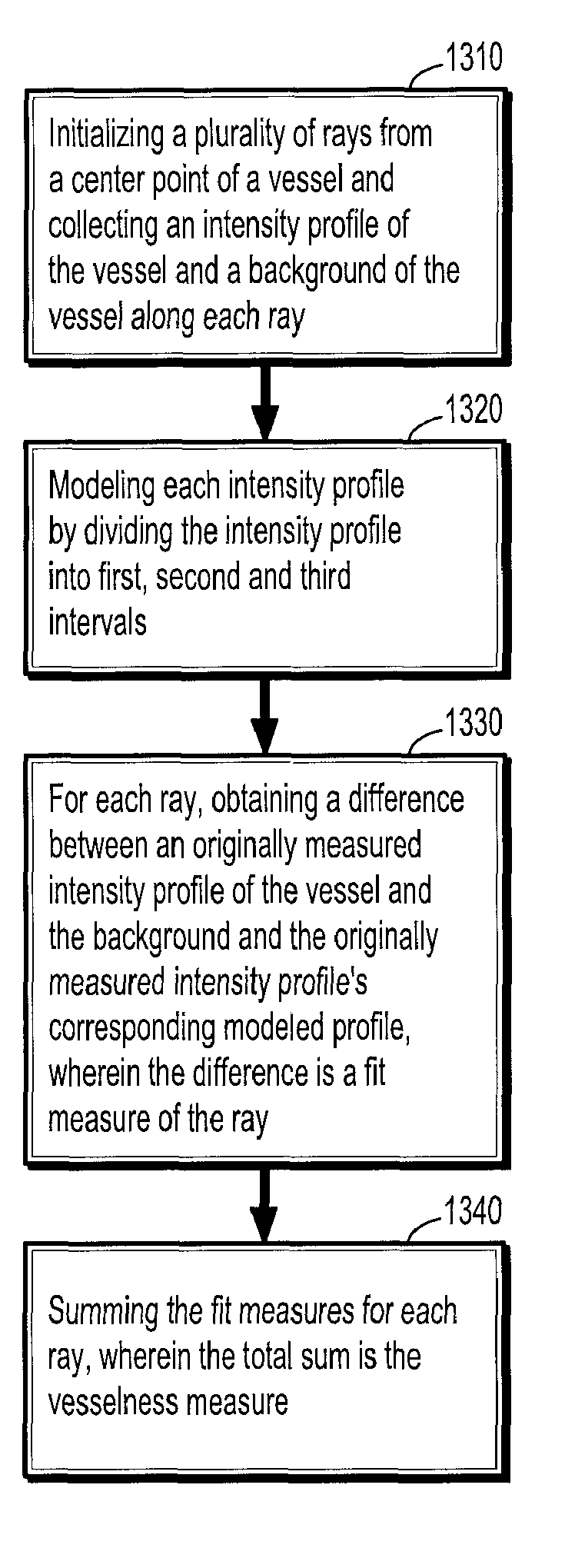
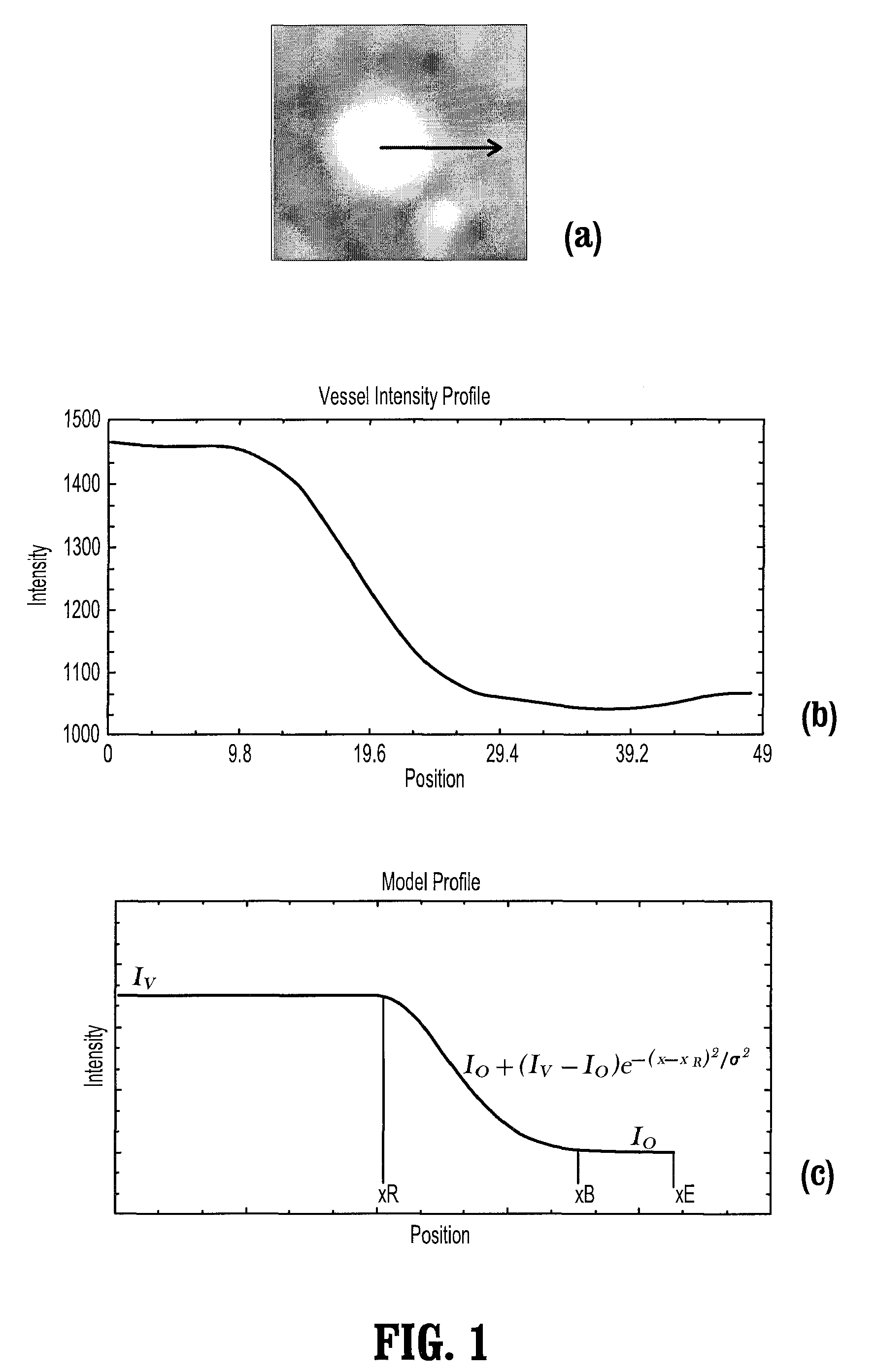
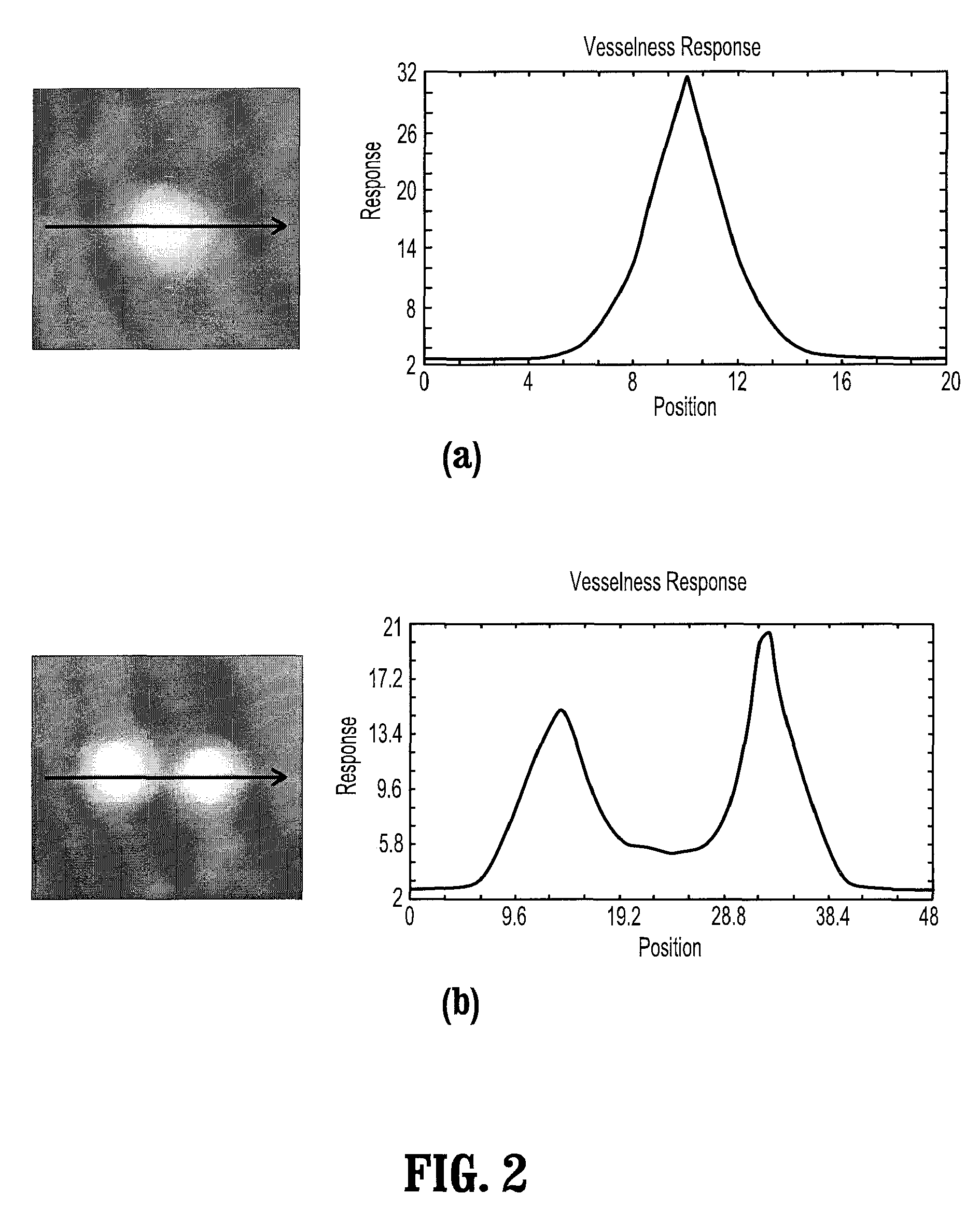
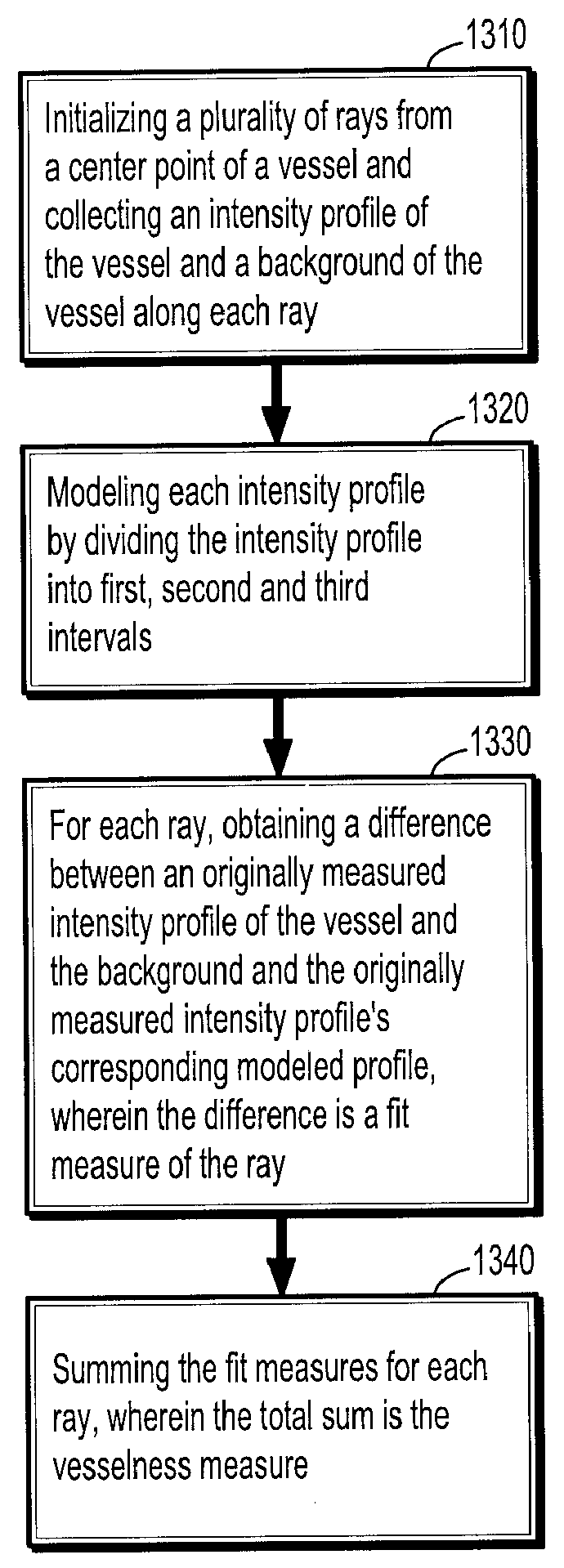
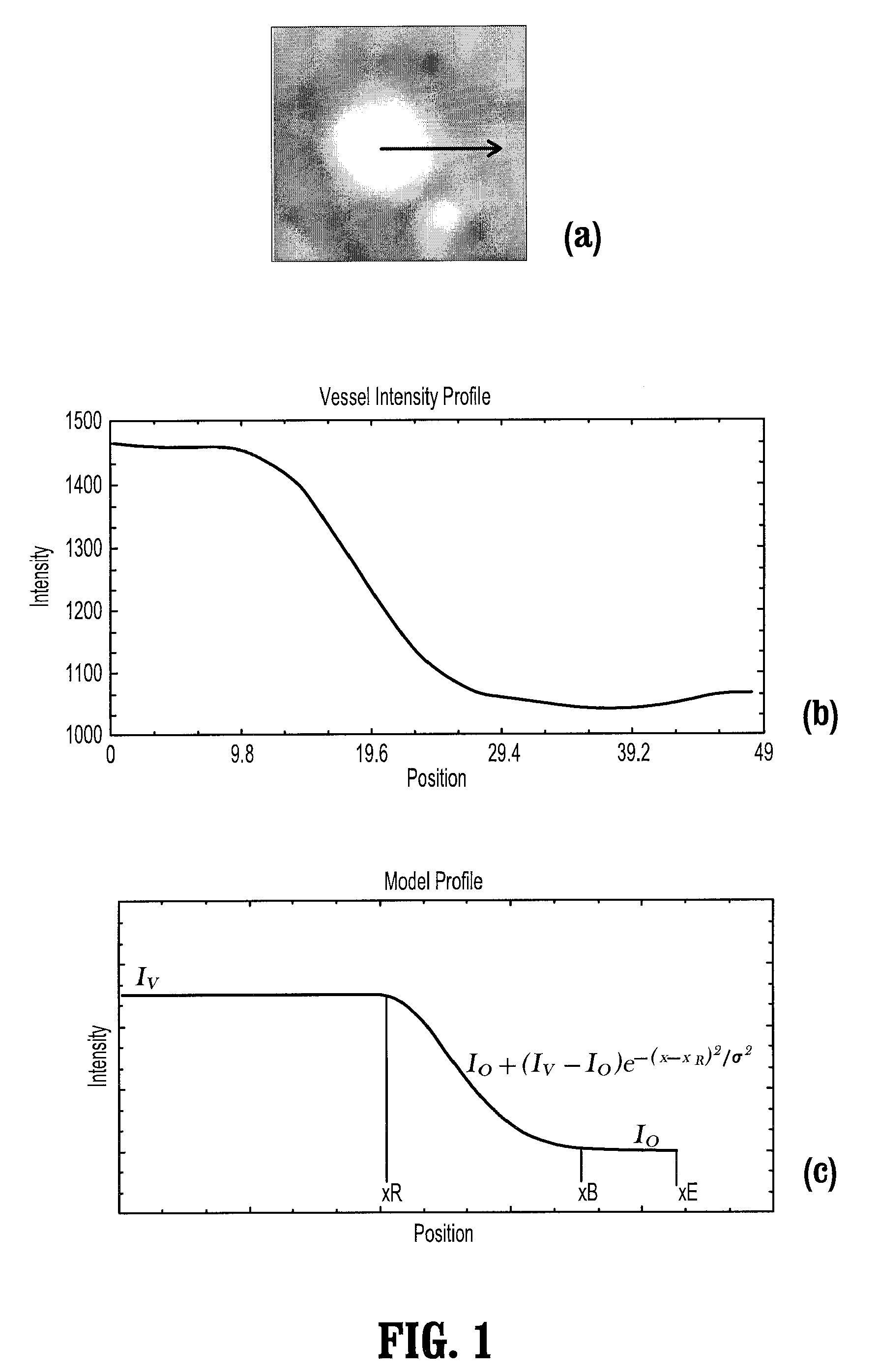
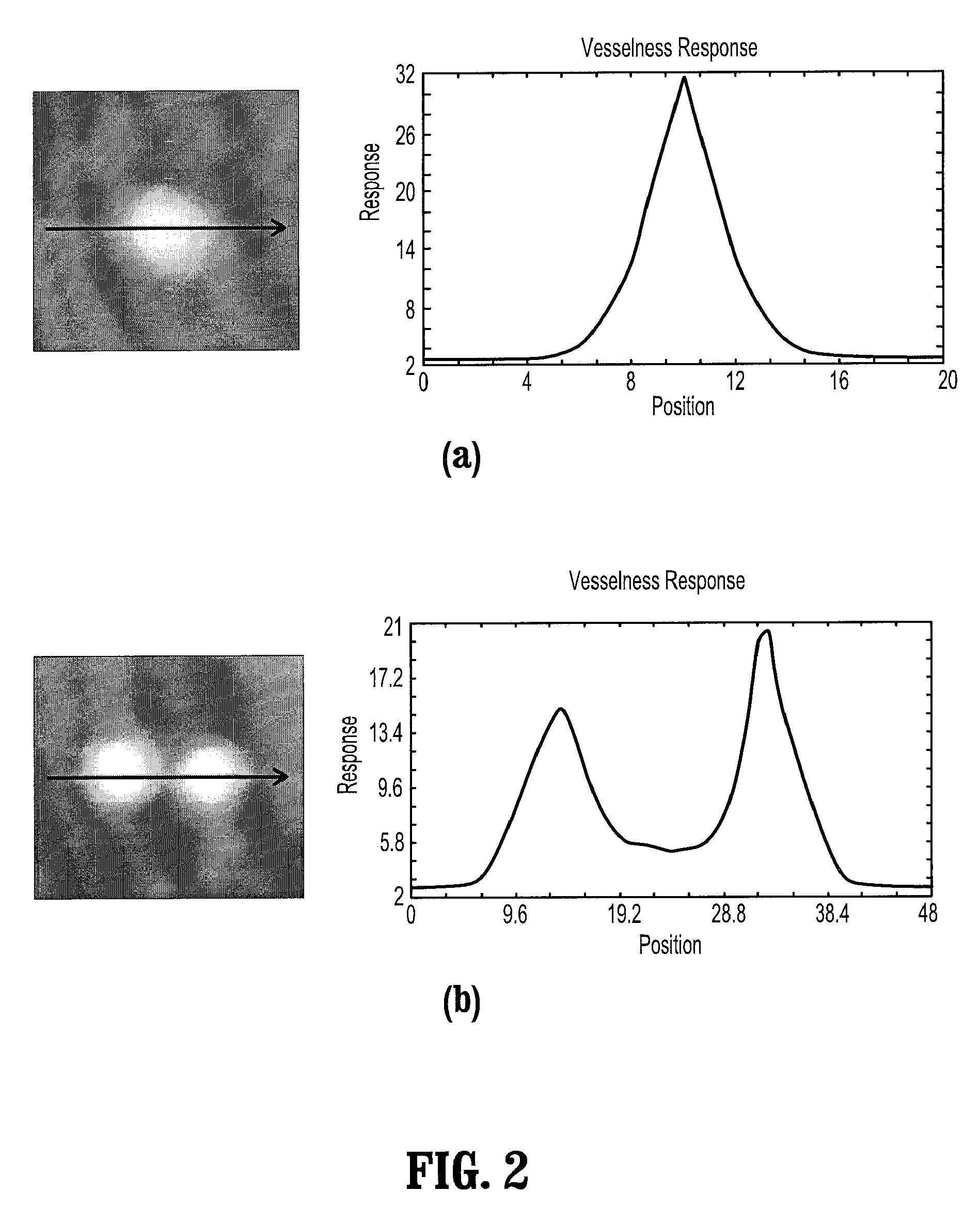
A method for extracting a local center-axis representation of a vessel, includes: placing first and second seed points in an image that includes the vessel, wherein the first and second seed points are placed near a beginning and an end of a centerline of the vessel; representing the image as a discrete graph having nodes and edges, wherein the first seed point is a source node and the second seed point is a goal node; and finding a minimum-cost path between the first and second seed points by computing a cost of edges between the first and second seed points, wherein the cost of each edge is reciprocal to a vesselness measure of the edge.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
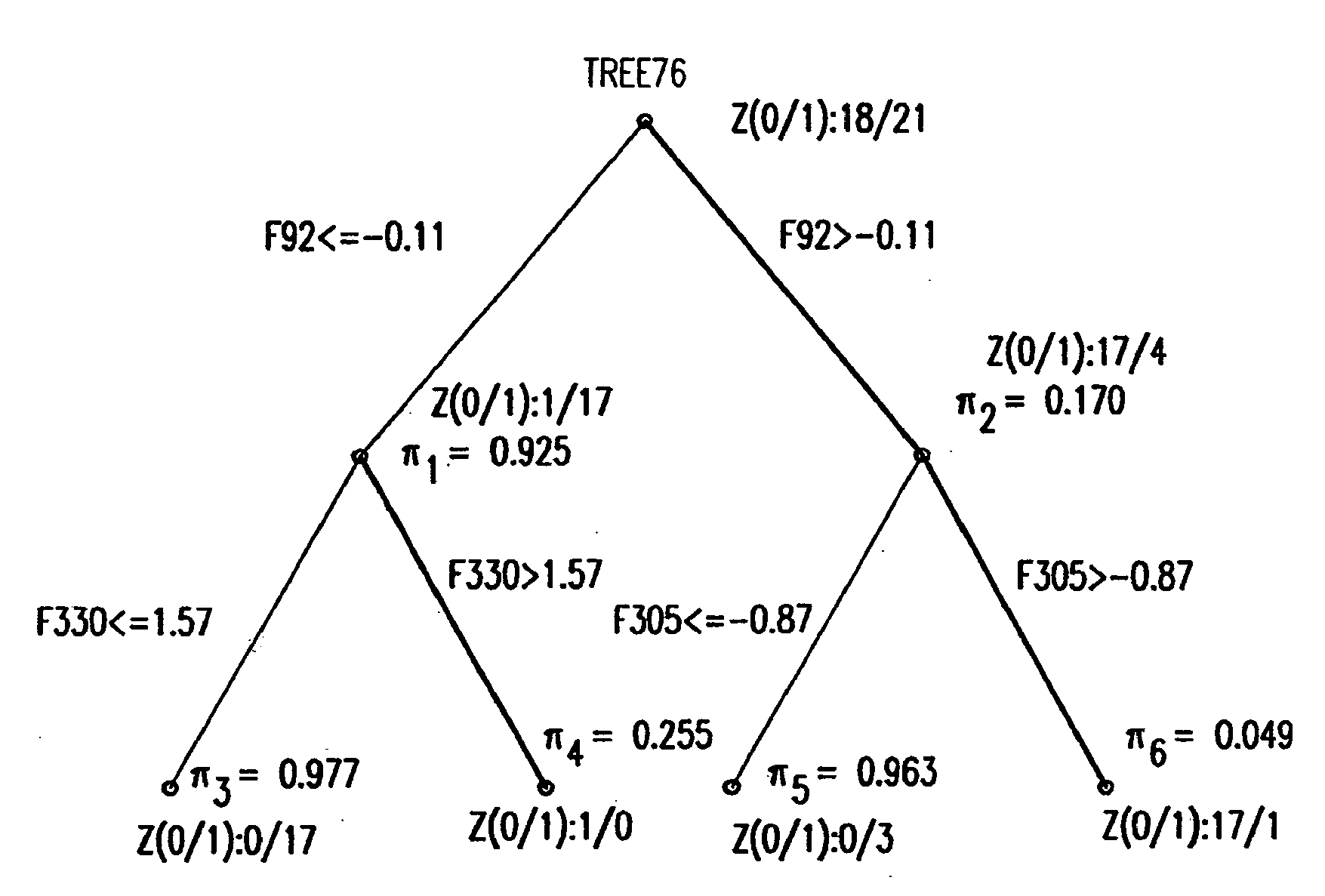
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
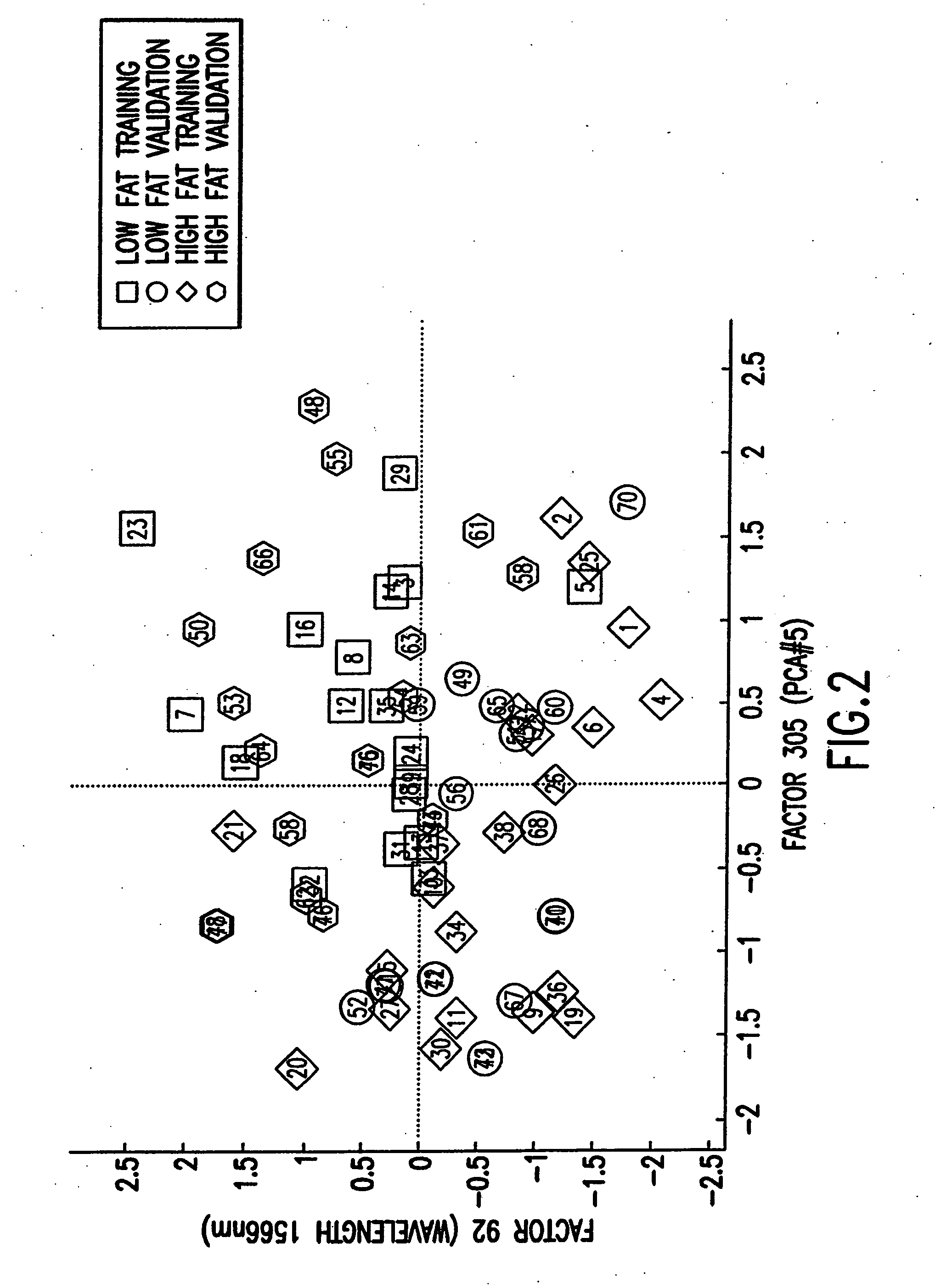
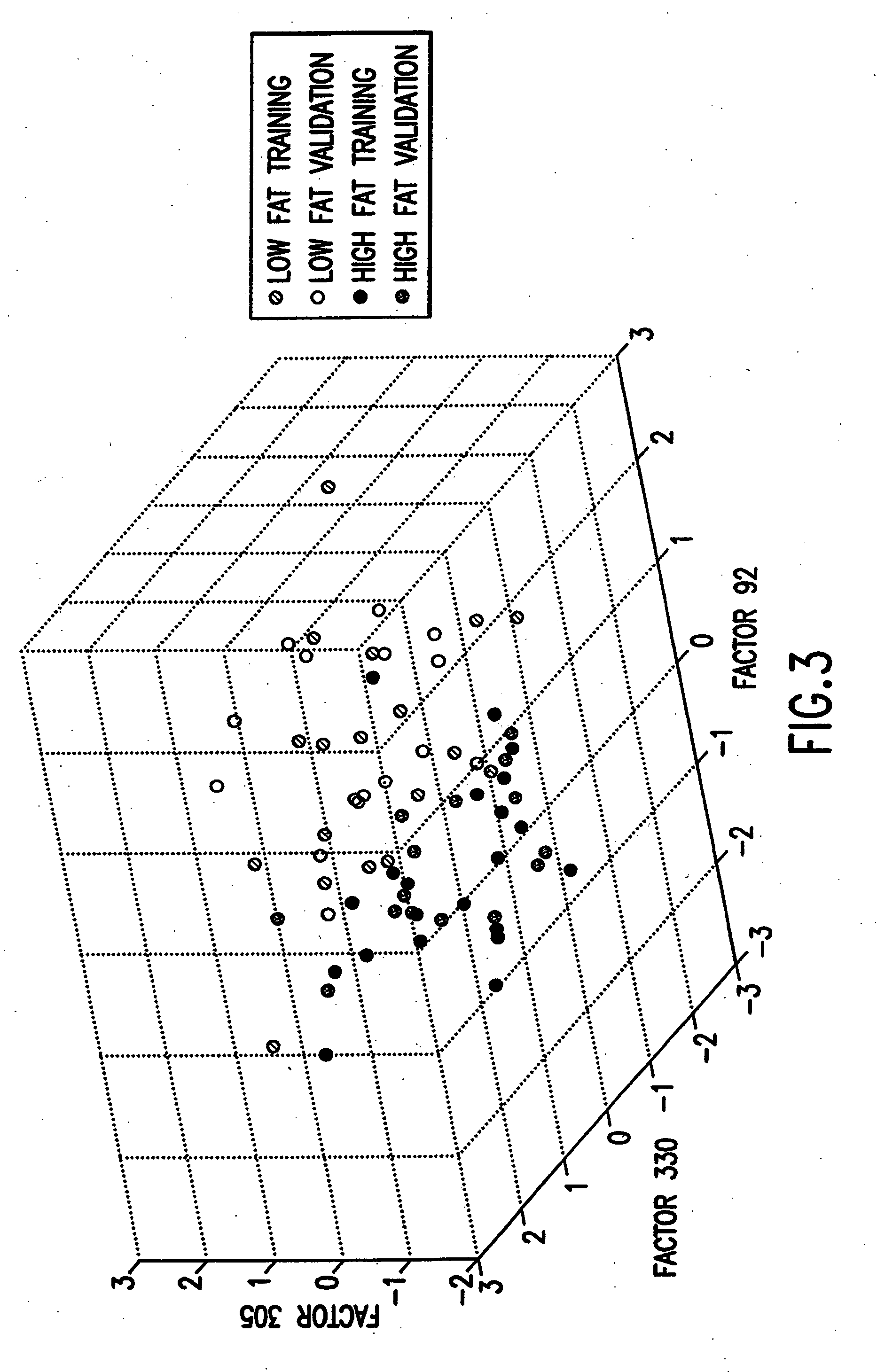
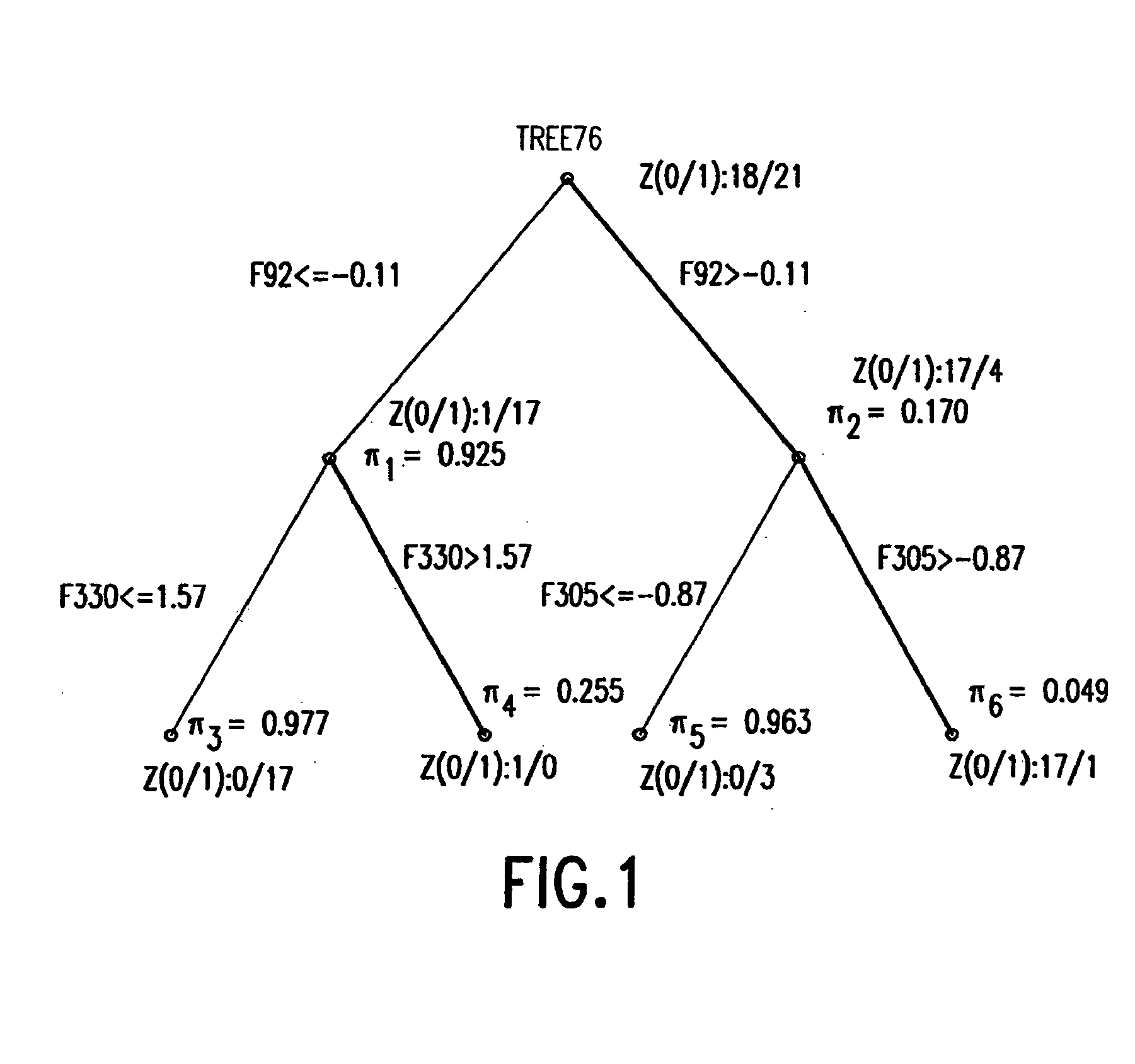
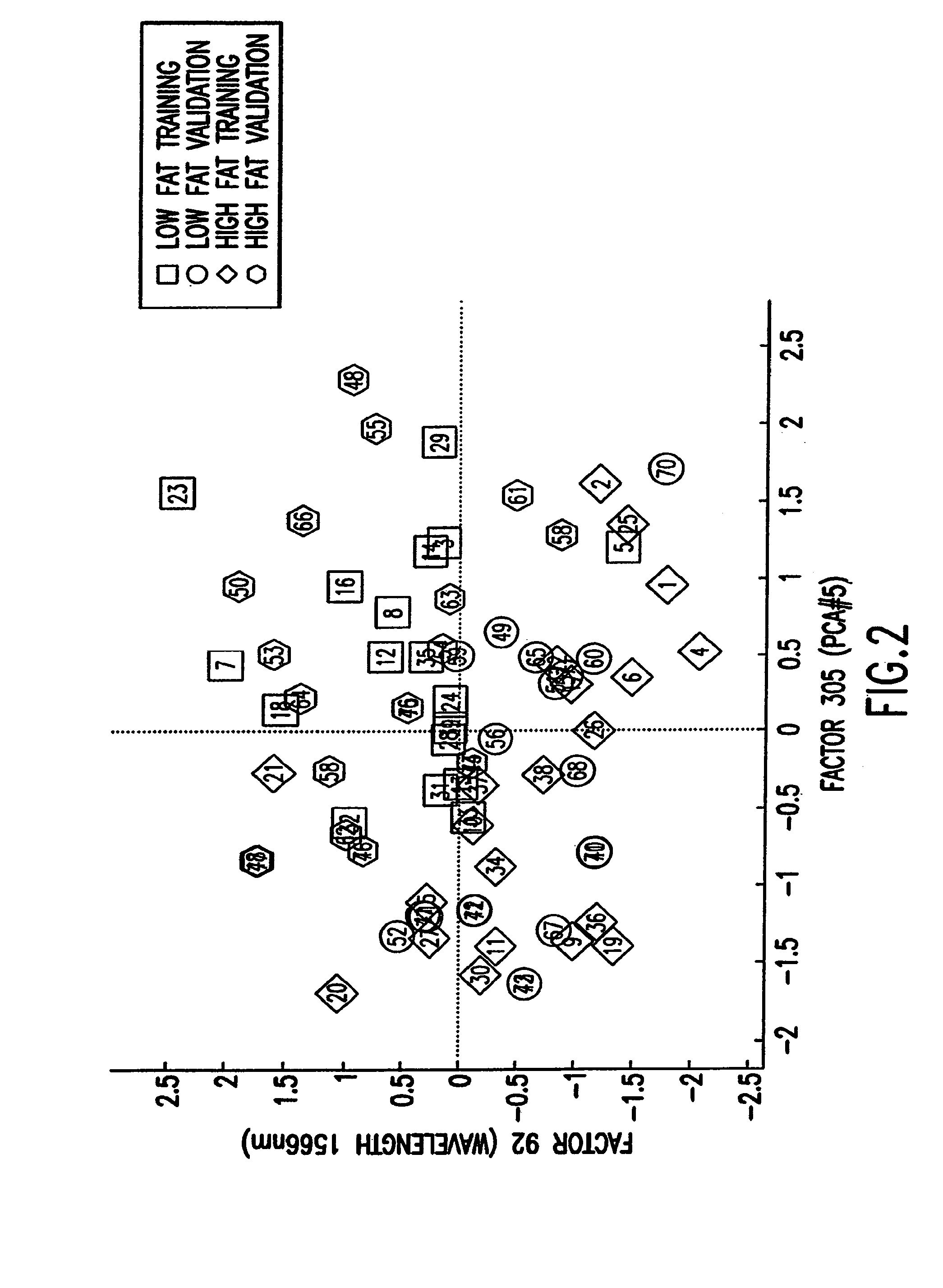
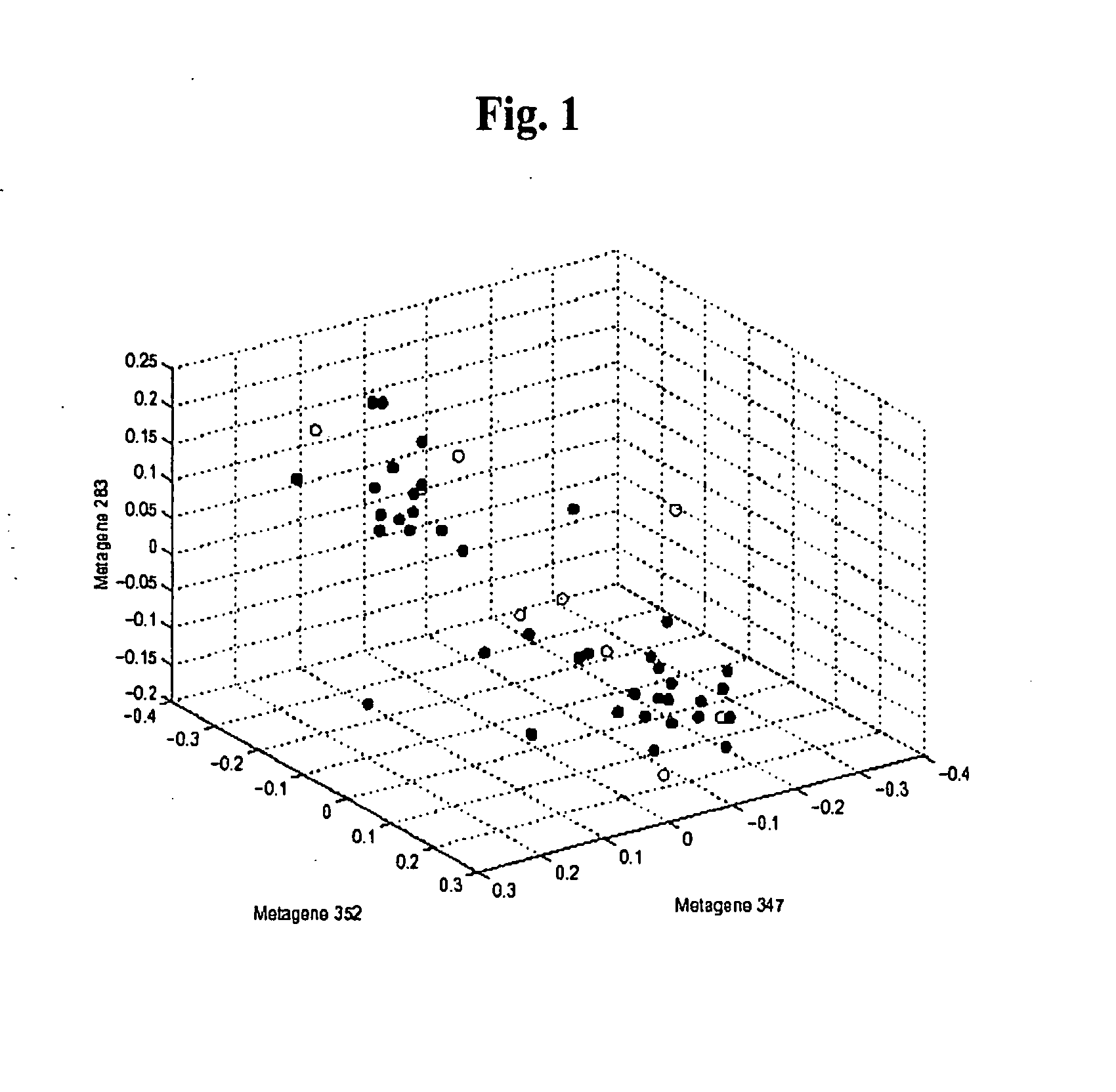
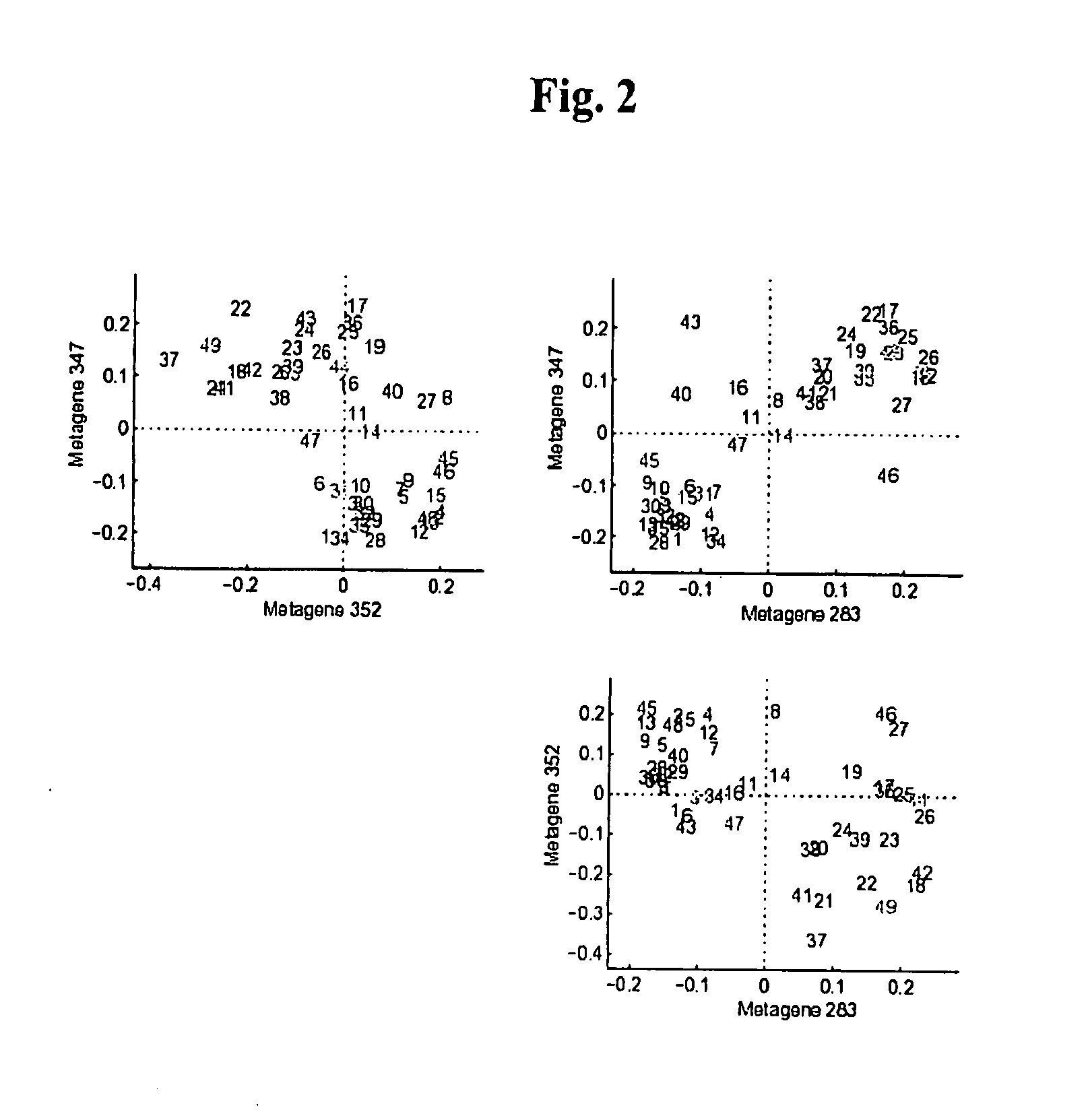
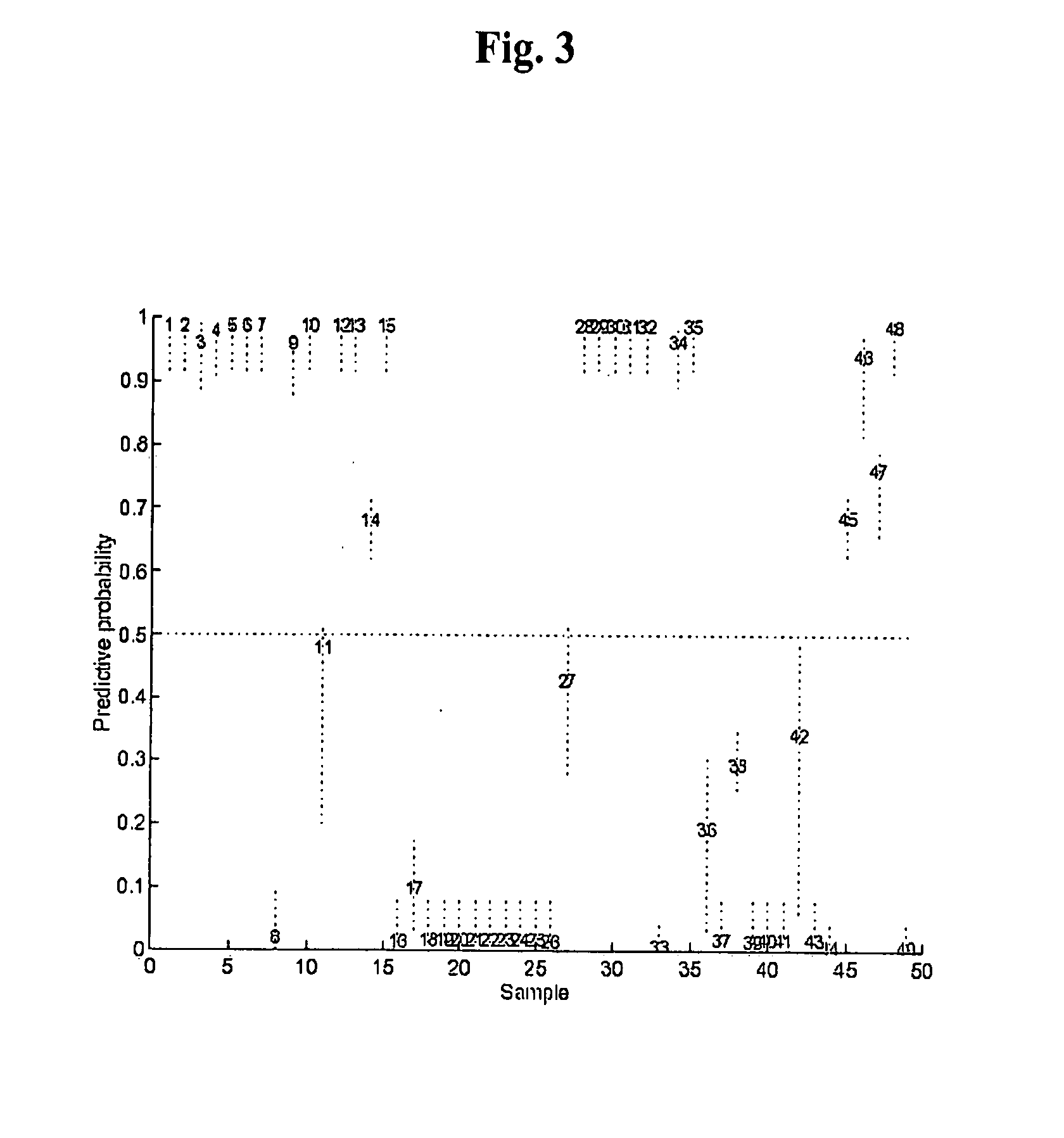
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Hepatic portal vein tree modeling method and system thereof
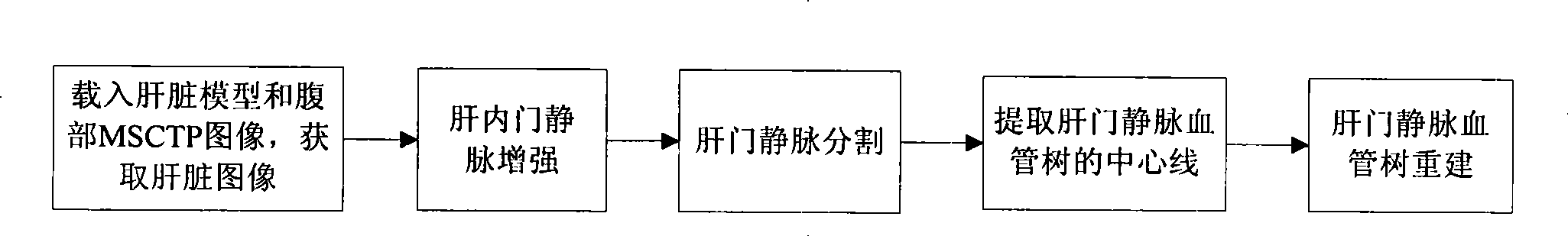
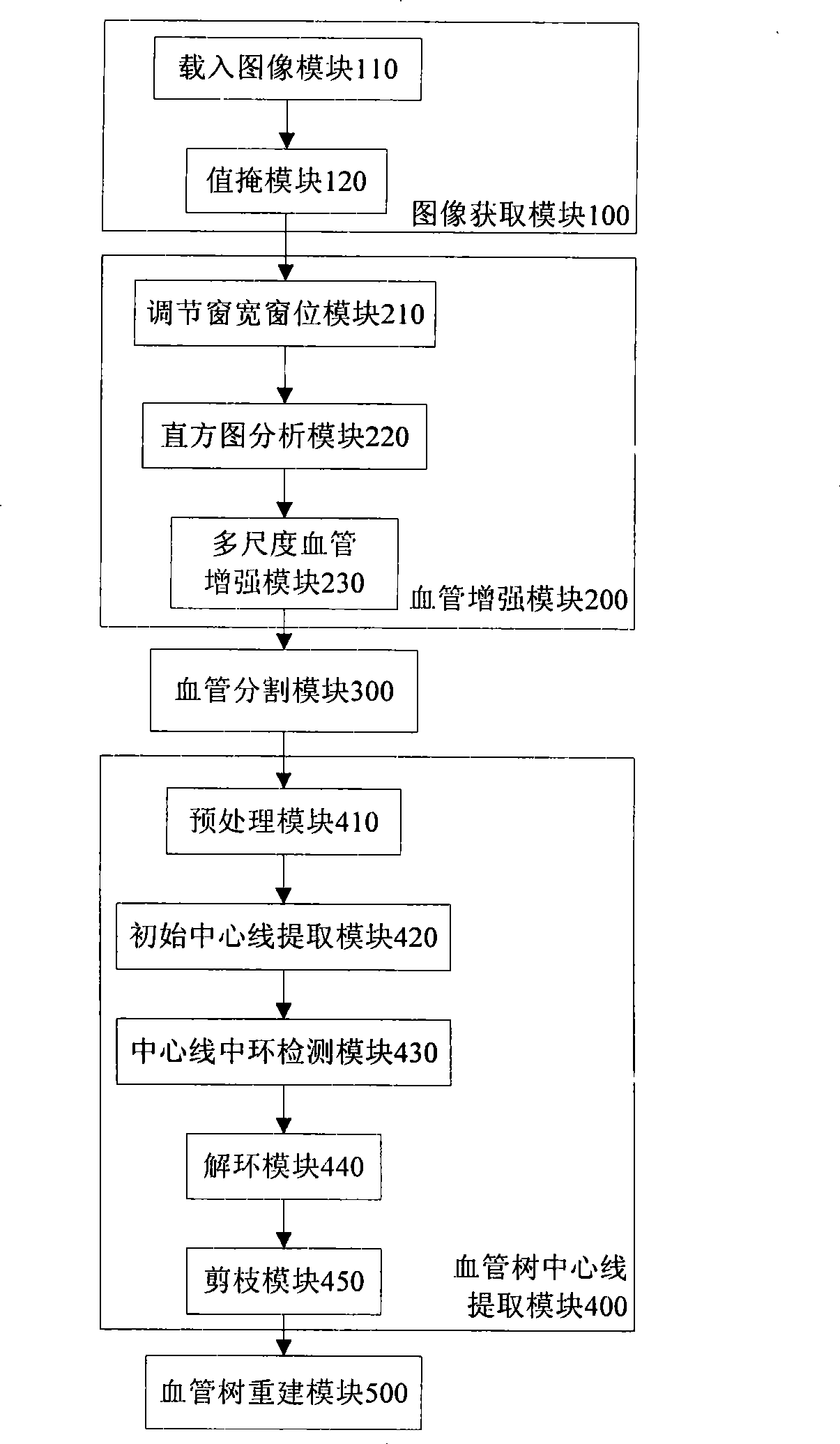
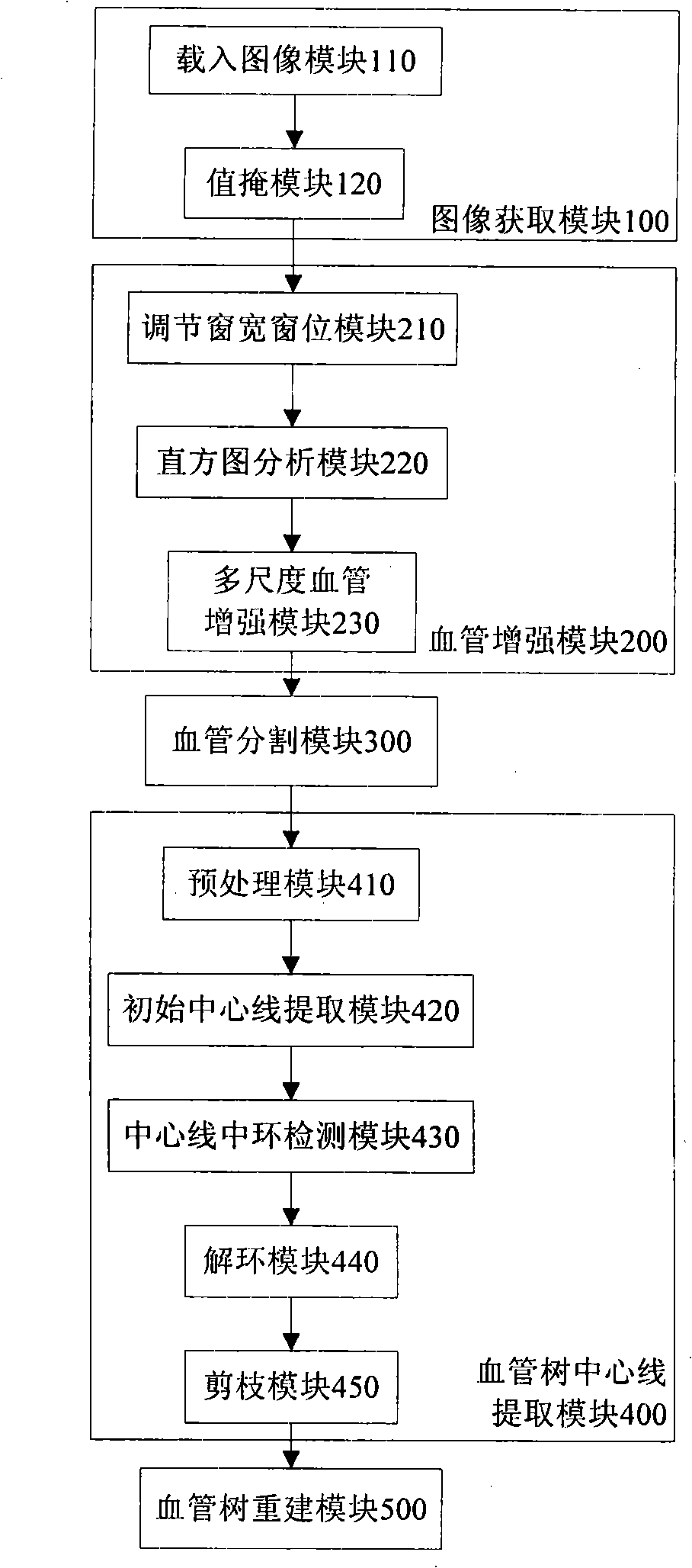
InactiveCN101393644AEnhancement effect is goodEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisLiver parenchymaFiltration
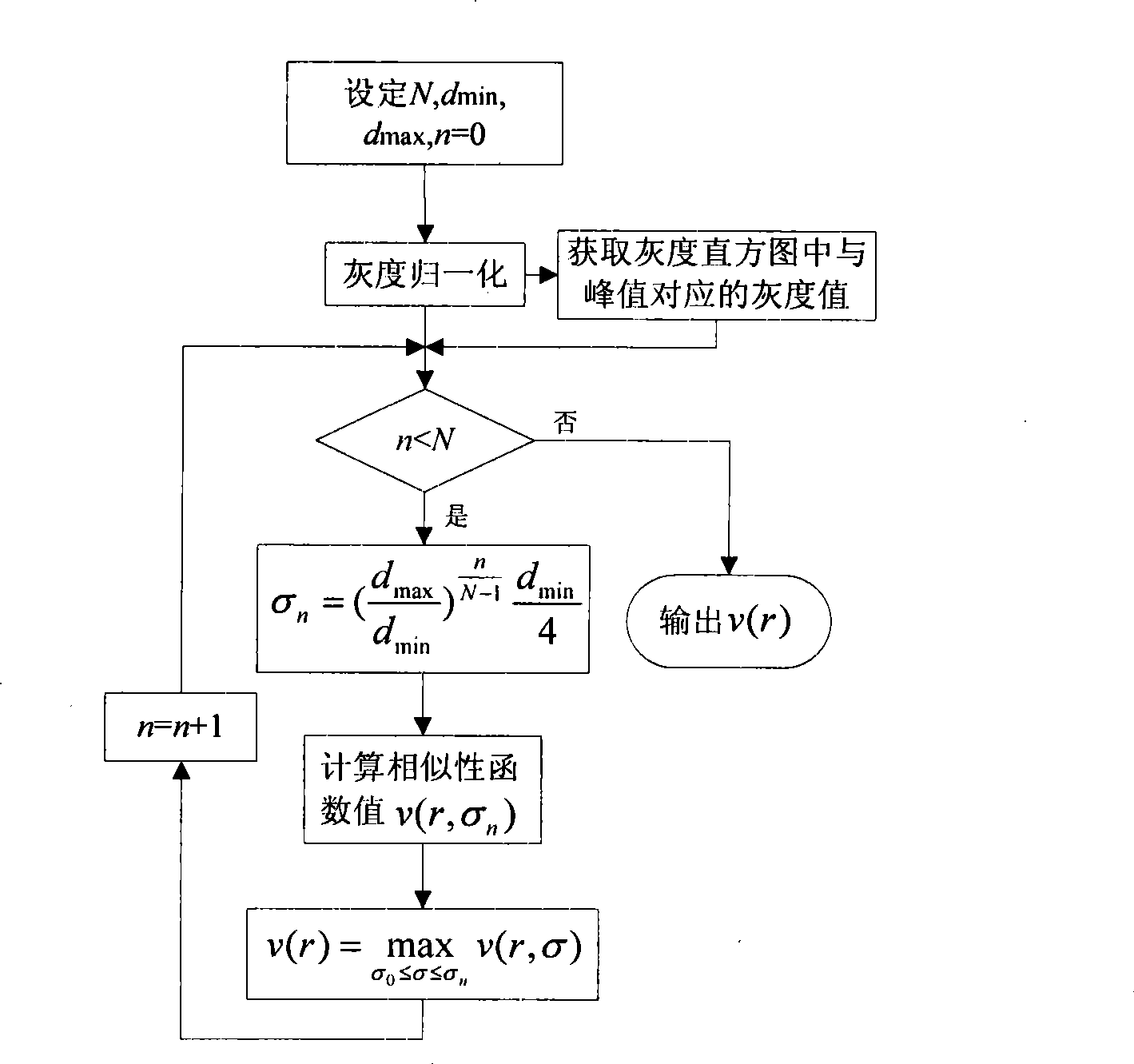
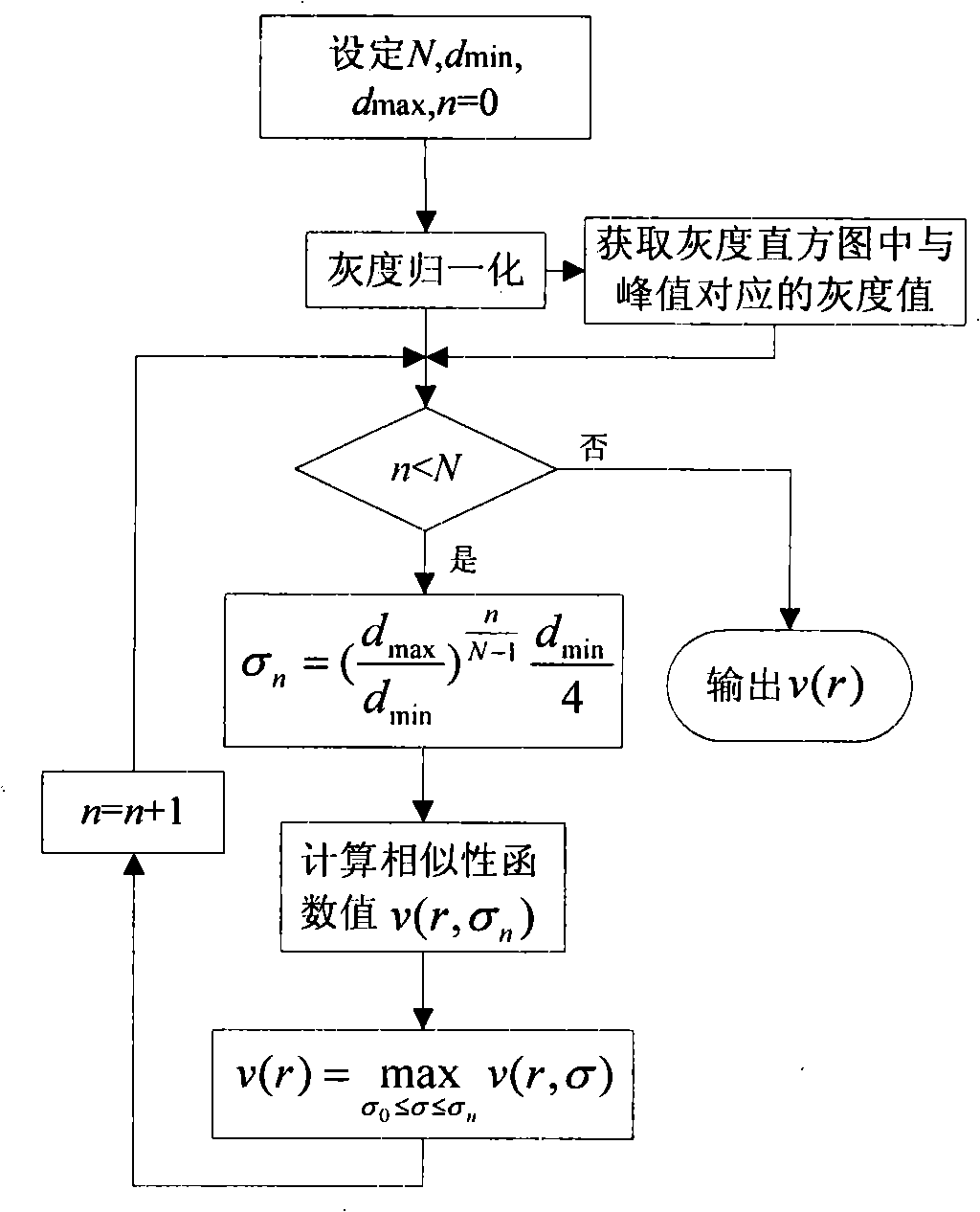
The invention discloses a hepatic vein vascular tree modeling method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a liver model to obtain a liver image, and utilizing the multi-scale filtration method to strengthen a blood vessel; cutting a hepatic vein; extracting a central line of the hepatic vein; detecting and removing a link in the central line; and utilizing OSG / VTK to rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree after pruning. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a blood vessel strengthening module, a blood vessel cutting module, a vascular tree central line extracting module and a vascular tree rebuilding module. The invention improves similarity functions in the filtering process, analyzes the characteristics of the ring and adopts corresponding unlinking methods for different links; and utilizes the relation of radius of blood vessel and the branch length when pruning. The invention effectively enhances the hepatic vein, improves the contrast between the blood vessel and liver parenchyma, and can extract more than five class branches, effectively unlink and prune the central line of the hepatic vein, rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree and directly display the branches of the heptatic vein.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Robust Vessel Tree Modeling
A method for extracting a local center-axis representation of a vessel, includes: placing first and second seed points in an image that includes the vessel, wherein the first and second seed points are placed near a beginning and an end of a centerline of the vessel; representing the image as a discrete graph having nodes and edges, wherein the first seed point is a source node and the second seed point is a goal node; and finding a minimum-cost path between the first and second seed points by computing a cost of edges between the first and second seed points, wherein the cost of each edge is reciprocal to a vesselness measure of the edge.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH +1
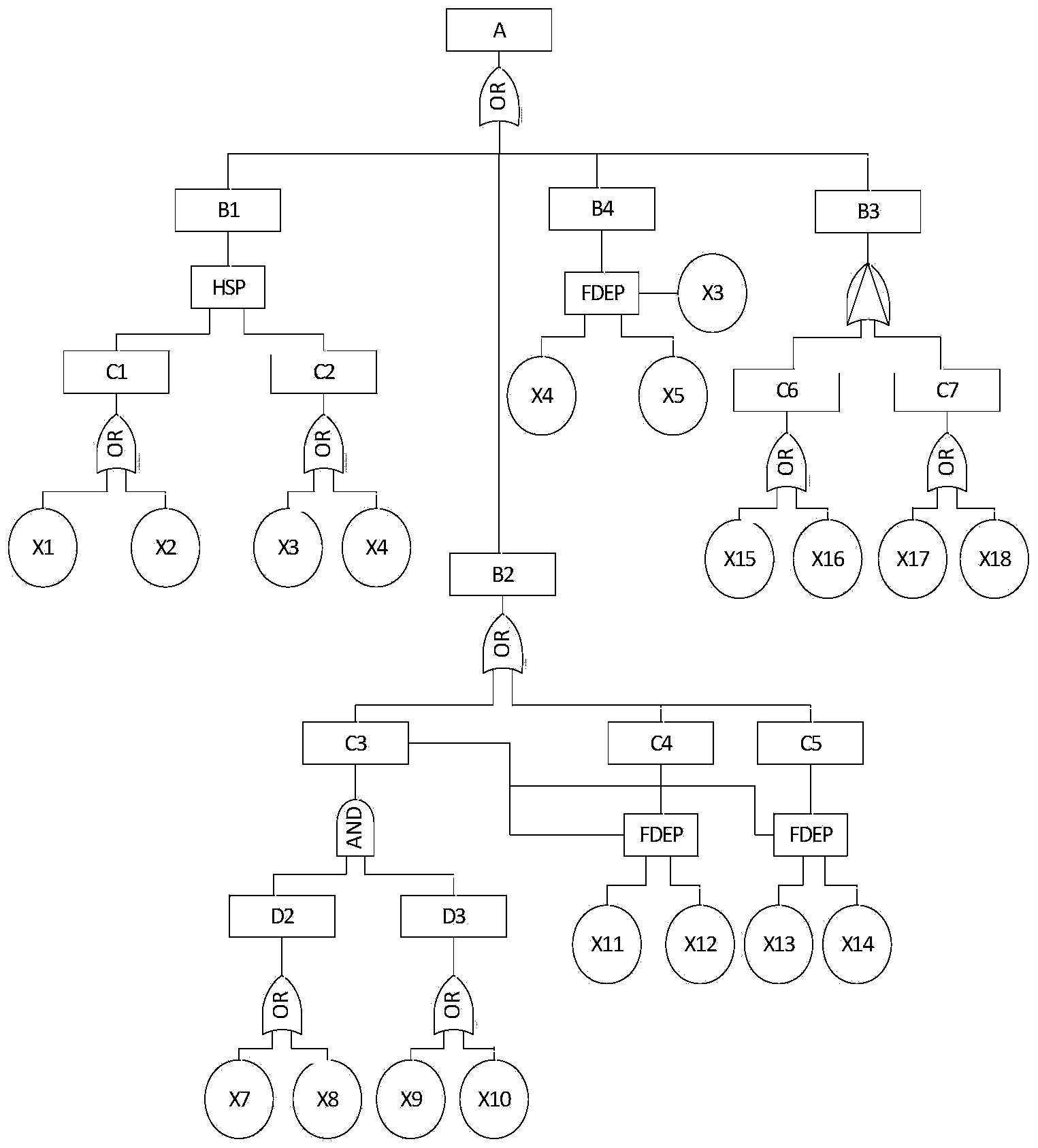
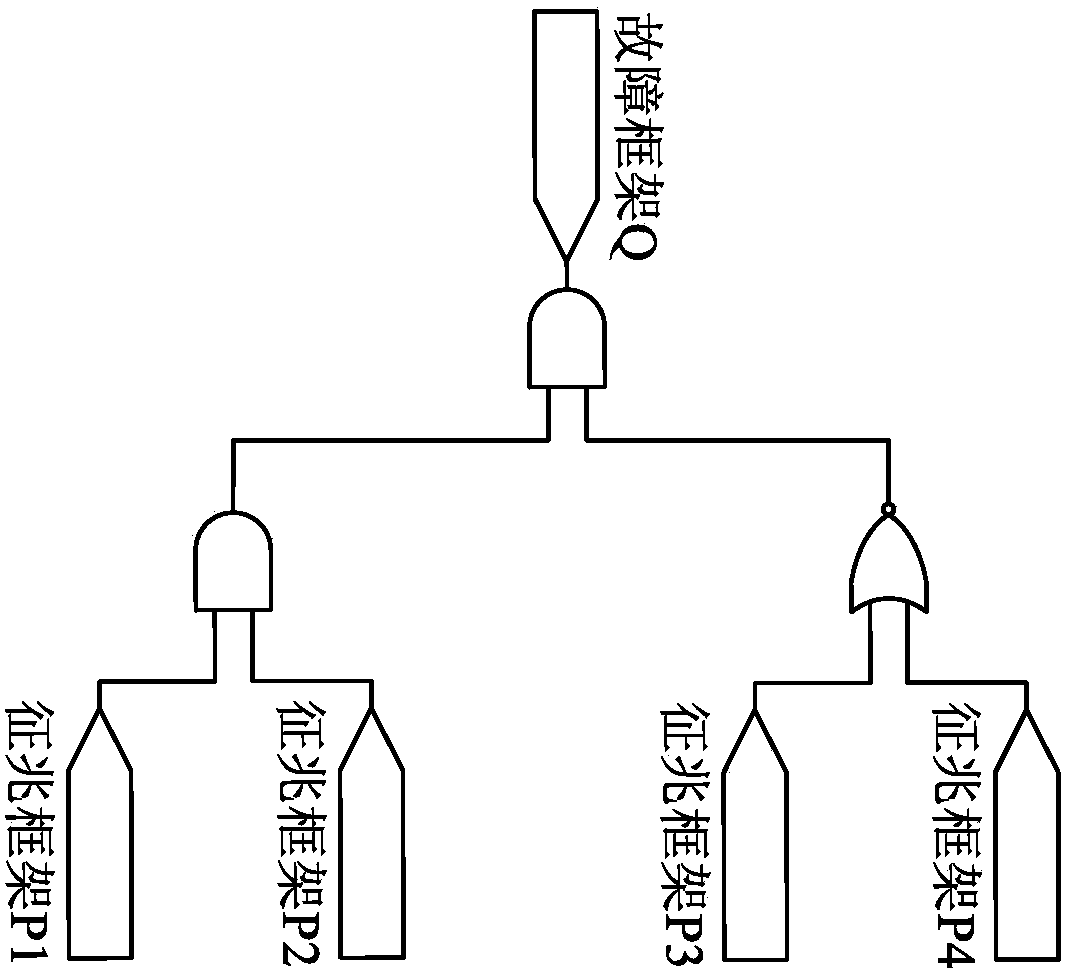
Equipment integration system reliability analysis method based on dynamic fault tree
InactiveCN104392072AImprove efficiencyImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMarkov chainStructure function
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Binary prediction tree modeling with many predictors and its uses in clinical and genomic applications
InactiveUS20090319244A1Mathematical modelsAnalogue computers for chemical processesSingular value decompositionData set
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of a disease in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. This model first screens genes to reduce noise, applies k-means correlation-based clustering targeting a large number of clusters, and then uses singular value decompositions (SVD) to extract the single dominant factor (principal component) from each cluster. This generates a statistically significant number of cluster-derived singular factors, that we refer to as metagenes, that characterize multiple patterns of expression of the genes across samples. The strategy aims to extract multiple such patterns while reducing dimension and smoothing out gene-specific noise through the aggregation within clusters. Formal predictive analysis then uses these metagenes in a Bayesian classification tree analysis. This generates multiple recursive partitions of the sample into subgroups (the “leaves” of the classification tree), and associates Bayesian predictive probabilities of outcomes with each subgroup. Overall predictions for an individual sample are then generated by averaging predictions, with appropriate weights, across many such tree models. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case. This rigorously tests the predictive value of a model and mirrors the real-world prognostic context where prediction of new cases as they arise is the major goal.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
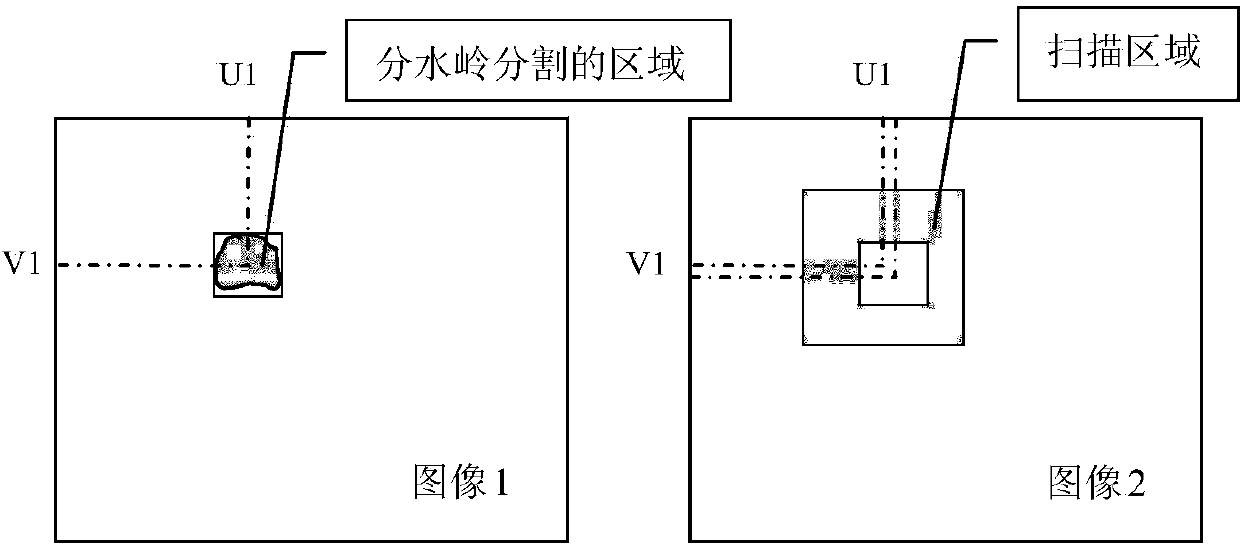
Tree three-dimensional reconstruction method based on unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photo sequence image
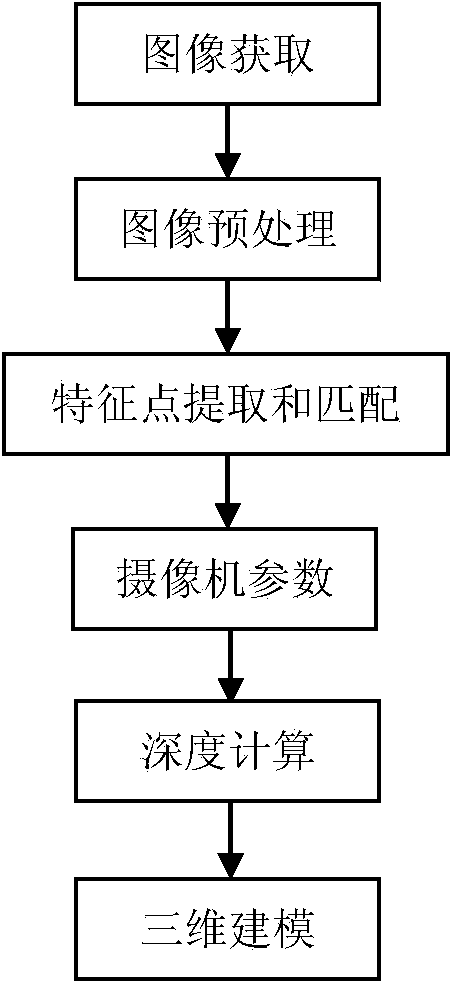
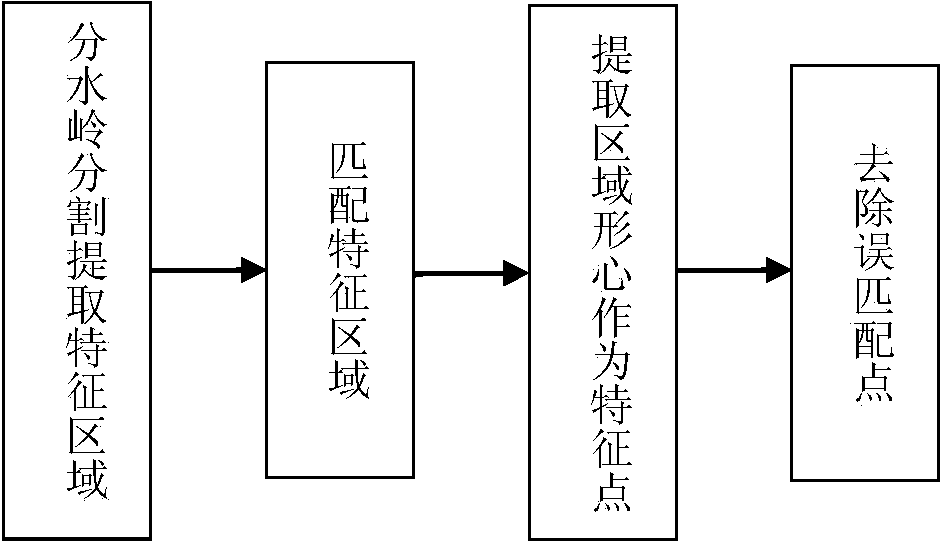
The invention discloses a tree three-dimensional reconstruction method based on unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photo sequence images. According to the tree three-dimensional reconstruction method, firstly, characteristic regions of a crown are extracted in a watershed partition method, then, the characteristic regions are matched by calculating region correlation coefficients in an RGB color space, matched characteristic dot pairs are extracted, depth information is calculated through the binocular stereo vision principle combined with imaging models of an aerial photo camera, and finally a three-dimensional model of a tree is constructed based on L system laws. Compared with the prior art, the tree three-dimensional reconstruction method has the advantages that grain, color and outline information of the crown are considered, and the characteristic spot set which can show the crown complicated structure is fully extracted; in addition, the depth information of the characteristic spot set is calculated according to complicated imaging models of the aerial photo camera with shake, transverse moving and the like of the camera in the aerial photo process of an unmanned aerial vehicle considered, a reasonable tree modeling approach is adopted, and therefore reasonable approximate three-dimensional models of the tree are constructed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Lodgepole pine landscape tree modeling method
InactiveCN102318920AHigh artistic valueImprove product valueArtificial flowers and garlandsHorticulture methodsGreeningLodge-pole pine
The invention relates to the technical field of tree modeling, in particular to a lodgepole pine landscape tree modeling method, which comprises the following steps of 1) material selection; 2) modeling design; 3) curling and tying modeling; and 4) formation. In the modeling method, auxiliary modeling tools and curling and tying material aluminum wires are adopted for being matched with trimming, hanging and tying, so lodgepole pines are modeled and grown into an artistic modeling, the ancient and magical tree verve is shown, and the artistic ornamental value and the commodity value of the lodgepole pines are improved. The modeling method is mainly used for important scenery spots or flower stands of outdoor gardens and can meet the continuously improved requirements on greening and garden construction trees along the urban development.
Owner:FLOWER KING ECO ENG CO LTD
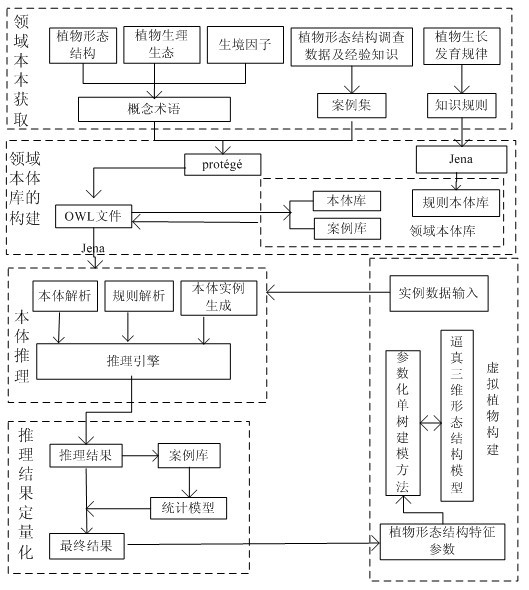
Individual plant wood modeling method driven by domain ontology
The invention discloses an individual plant wood modeling method driven by domain ontology, belonging to the intersection filed of an ontology method and plant modeling. The individual plant wood modeling method is characterized by including the steps as follows: firstly obtaining the morphological structure characteristics, the habitat domain concept terms and the growth rhythm of a plant, and creating a plant domain concept ontology base by utilizing an ontology tool protege and a plant growth rhythm ontology base by utilizing a semantic network developing tool Jena; then creating a three-dimensional morphological structure model base of the plant in different growth stages by utilizing a parameterization individual-tree modeling method; and later obtaining the morphological characteristic parameters of the plant by utilizing ontology reasoning according to the morphological structure characteristics or the habitat, the growth stages and the phenological period description of the plant, and creating a vivid three-dimensional morphological structure model by utilizing the parameterization individual-tree modelling method. By utilizing the individual plant wood modeling method, a user with less botany knowledge can create a model confirming to the characteristics of botany, or a botanist creates a vivid three-dimensional model in a short time.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fault tree collaborative analysis system based on authority management and model decomposition
InactiveCN104298825AIncrease workloadAvoid duplication of workSpecial data processing applicationsAviationNuclear power
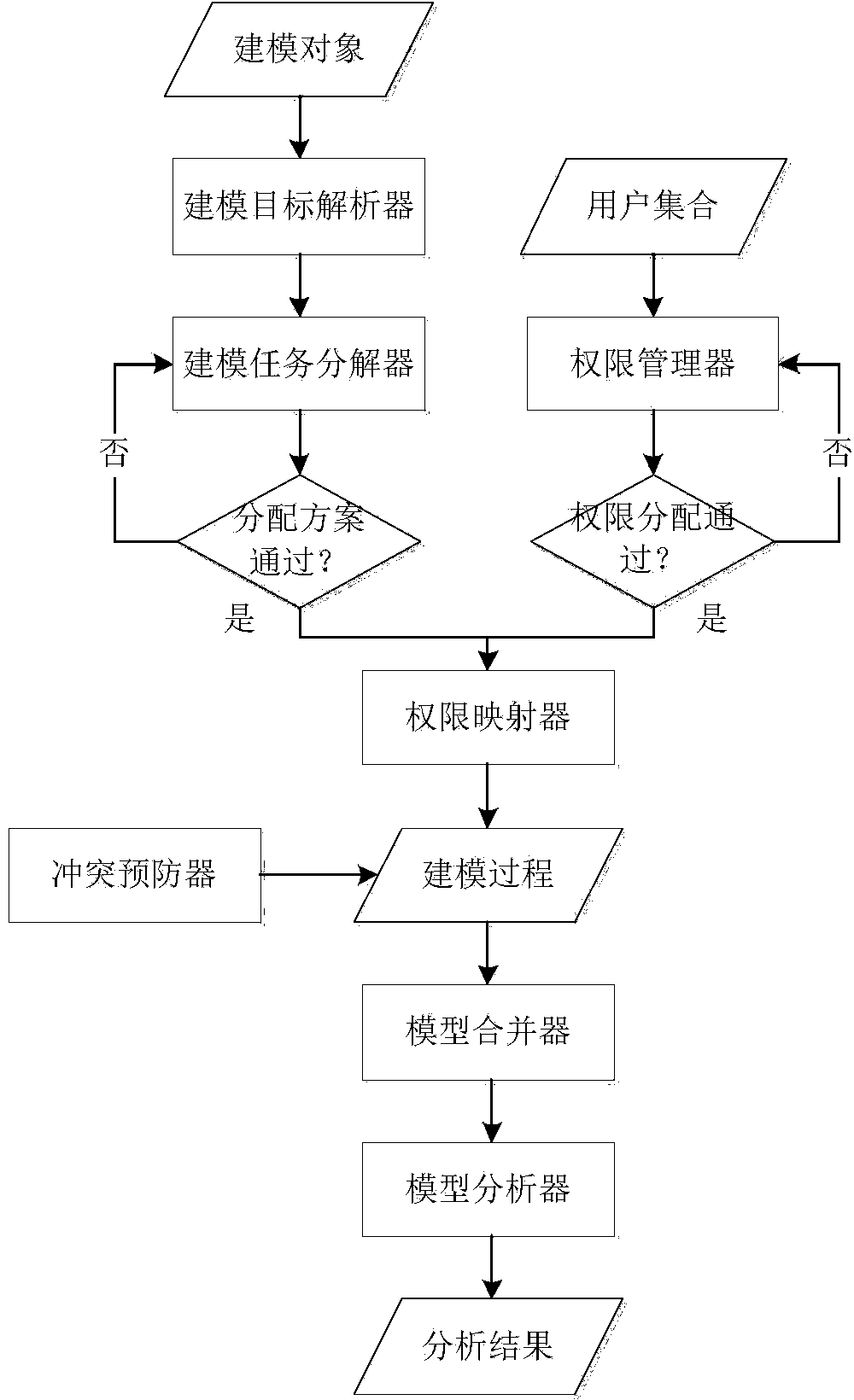
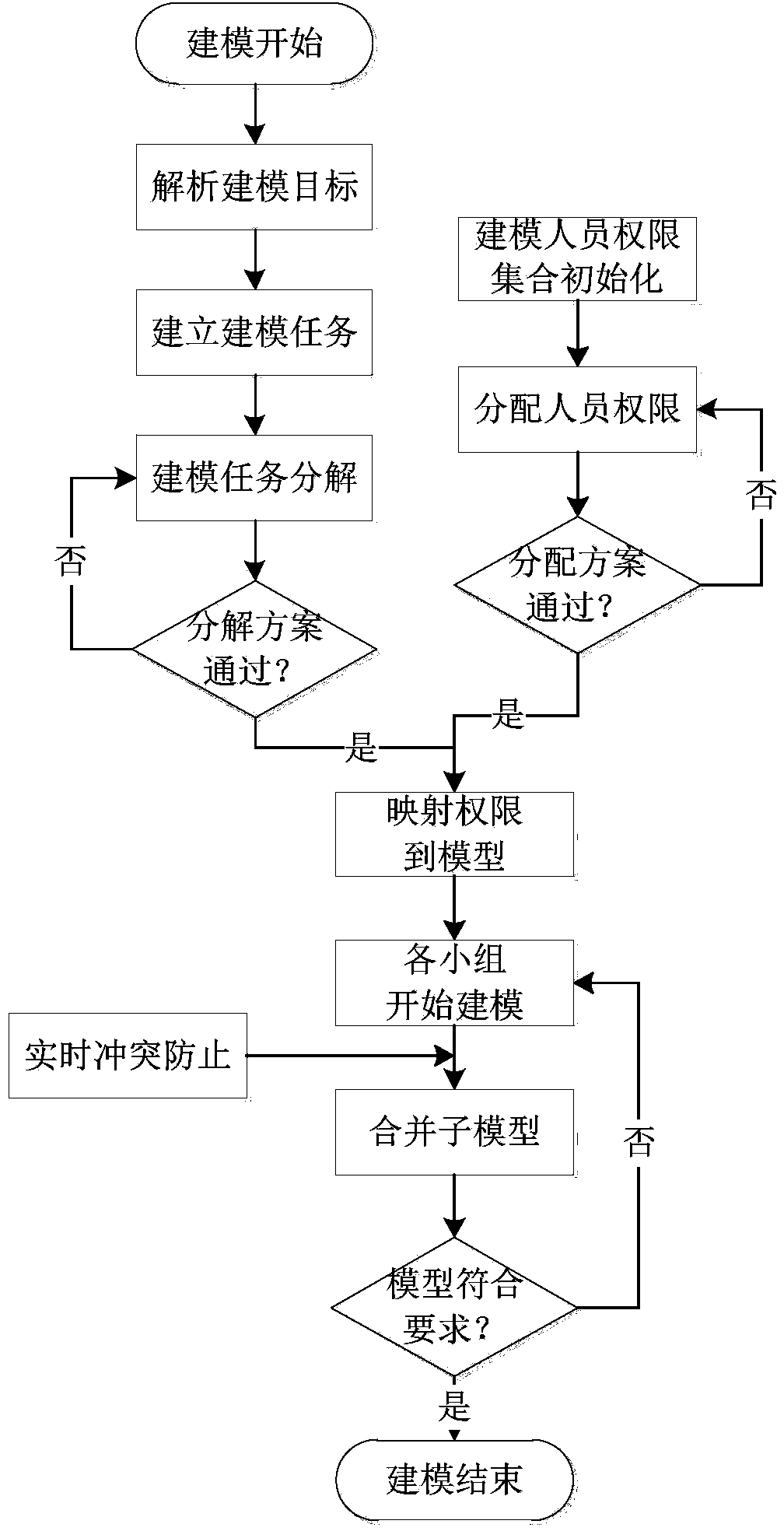
The invention discloses a fault tree collaborative analysis system based on authority management and model decomposition. The system mainly comprises the following seven modules which include a modeling target resolver, a modeling task decomposer, an authority manager, an authority mapper, a conflict inhibitor, a model combiner and a model analyzer. According to the system, a collaborative technology is applied from modeling target analysis and task definition to specific modeling processes, and fault tree modeling analysis can be achieved by cooperation of multiple persons and multiple roles under the action of authority management and mapping mechanism; a collaboration platform is provided for fault tree modeling staff, and fault tree modeling tasks of large complicated systems in fields of navigation, aerospace, nuclear power energy and the like can be achieved; requirements in terms of model scale and multidisciplinary approach in fault tree modeling of current large complicated systems can be met, and the task of fault tree modeling analysis can be efficiently finished by cooperation of modeling staff with different knowledge backgrounds and professional skills.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tree modeling method based on skeleton point cloud
InactiveCN101866495AOptimize calculation timeImprove model performance3D modellingModel methodPoint cloud
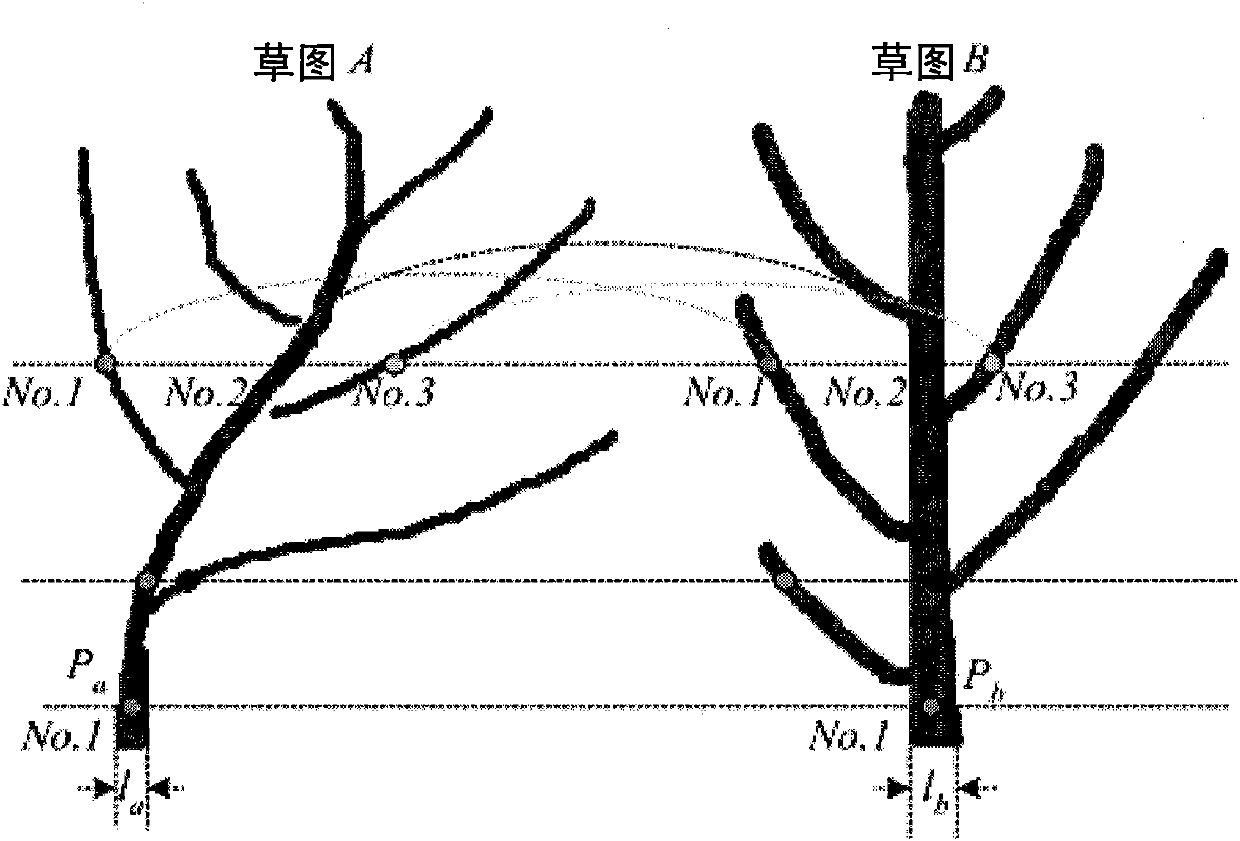
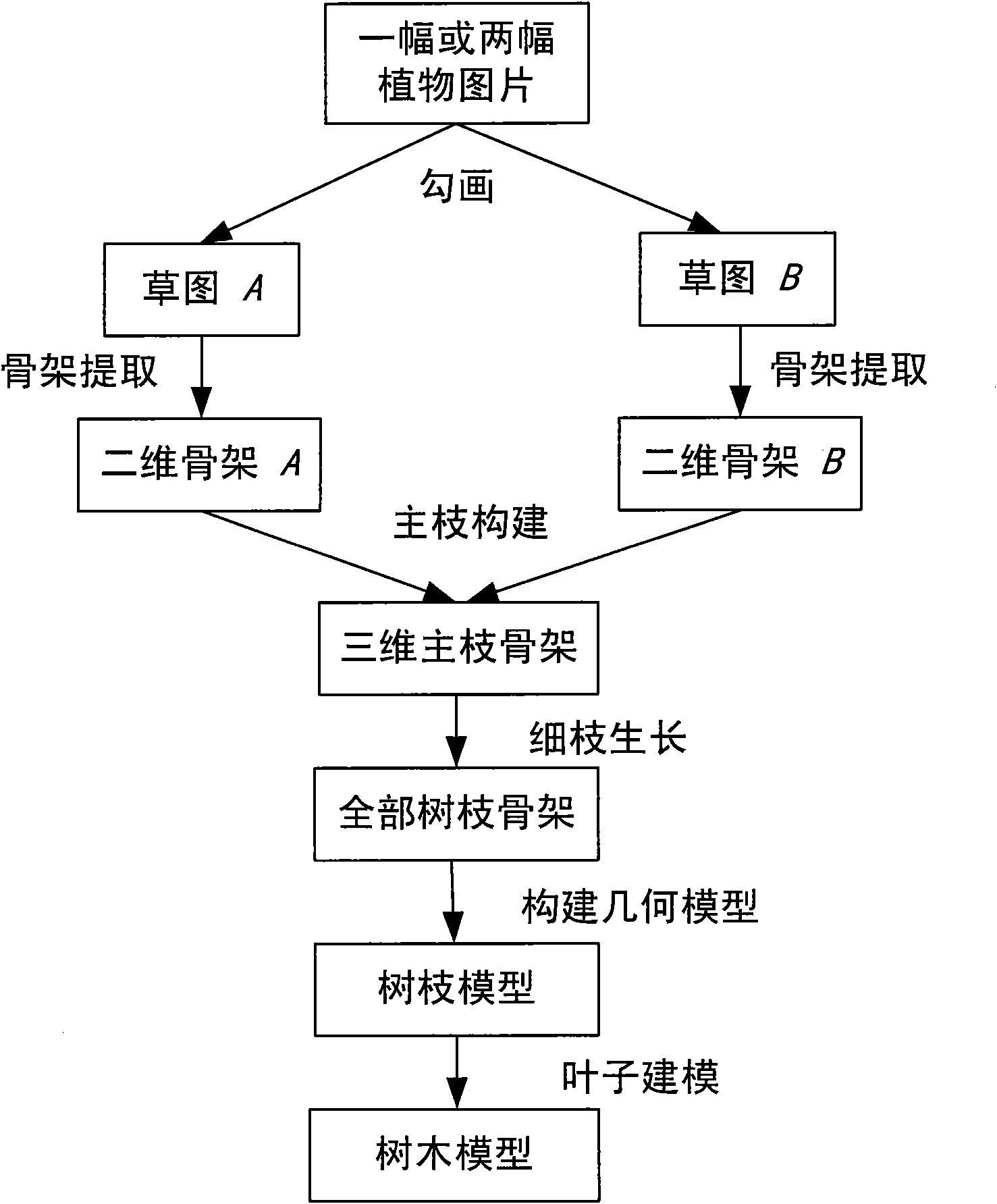
The invention relates to a tree modeling method based on skeleton point cloud. In the method, scaffold branches of the tree and outline of the crown which are sketched manually are taken as input automatic constructed tree model, comprising the following steps: extracting two-dimensional skeleton from the sketched strokes through pixel analysis; constructing a three-dimensional skeleton point cloud with two two-dimensional skeletons; expanding the two-dimensional skeleton into a three-dimensional scaffold branches skeleton under the guidance of the three-dimensional point cloud information; and constructing twigs and leaves based on the outline of the crown. The invention has easy application, simple algorithm and high modeling efficiency, and can create tree models with sense of reality. The modeling results of the invention have significant application values in fields of computer games, three-dimensional films, network roaming, urban landscape design and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tree modeling method based on depth search
InactiveCN101847267AOptimize calculation timeImprove model performance2D-image generation3D modellingModel methodMain branch
The invention relates to a tree modeling method based on the depth search, and the method is to automatically build a tree model by taking a tree main branch and a tree crown outline drawn by hands as input. The method comprises the following main steps of: extracting two-dimension frameworks from drawn strokes through pixel analysis; directly converting the two two-dimension frameworks into a three-dimension main branch framework through the depth search; and building withes and leaves on the basis of restriction of the tree crown outline. The method can efficiently build the tree model which has the reality sense and accords with input restriction by simple algorithm. The modeling result obtained by the tree modeling method has the significant application value in fields of computer games, three-dimension movies, network roaming, city view design and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tree lightweight 3D reconstruction method based on enhanced PyrLK optical flow method
The invention discloses a tree lightweight 3D reconstruction method based on an enhanced PyrLK optical flow method. Firstly, for solving problems that a traditional pyramid LK optical flow method does not support rotation of characteristic points and does not have bidirectional coupling performance, enhancement of support affine transformation and reverse direction tracking on the PyrLK optical flow method is carried out, and an instance is given to explain robustness after enhancement; secondly, a complete tree framework is extracted through a three dimensional voxel flooding and linearity fitting method; lightweight at a designated degree on the tree framework is carried out based on combination of vertical and transverse limbs to meet Web lightweight application requirements; then an objective tree modeling reduction degree evaluation method is further provided; lastly, a model improvement method based on user interaction is further provided for acquiring a tree model which can completely meet user demands. Through the method, the 3D tree model having properties of better lightweight and higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:JILIN ANIMATION INST +1
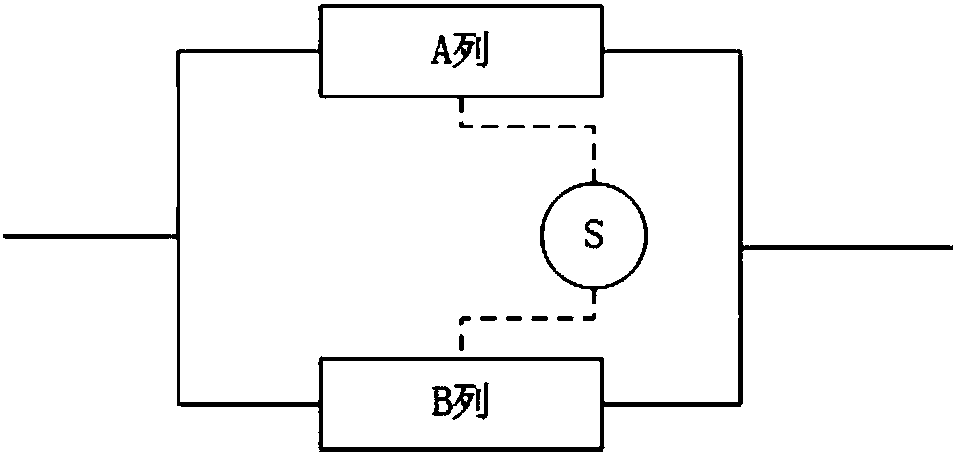
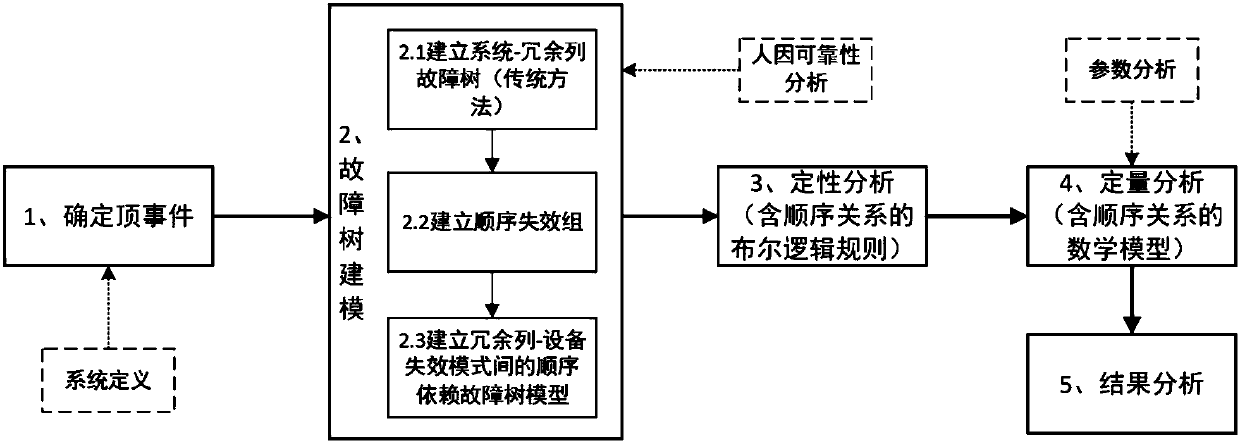
Method for analyzing reliability of standby redundant system on basis of fault tree
ActiveCN108388740ATrue failure pathAccurate quantitative evaluationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystem failureAccurate estimation
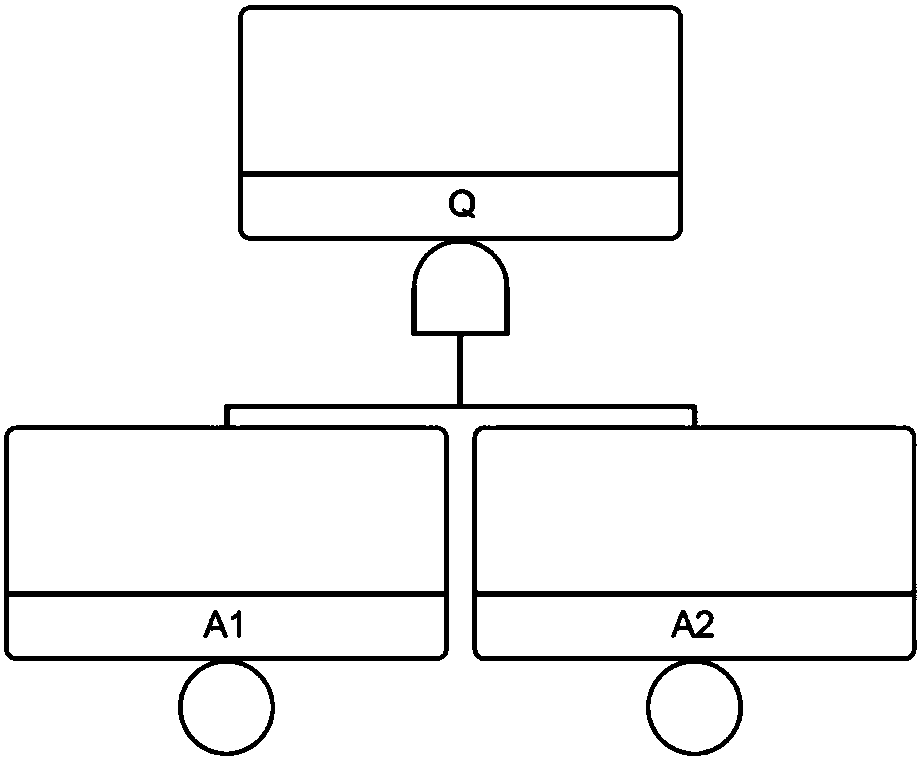
The invention discloses a method for analyzing reliability of a standby redundant system on the basis of a fault tree. The method comprises: establishing a fault tree model of the standby redundant system; carrying out qualitative analysis on the established fault tree; on the basis of a qualitative analysis result, carrying out quantitative analysis on the fault tree. When the fault tree model ofthe standby redundant system is established, according to a system-subsystem-equipment-equipment failure mode sequence, a system-redundant row model, a sequence failure group and a model of a sequence dependence relationship among redundant rows, equipment and equipment failure modes are sequentially established, and each equipment failure mode is completely analyzed and used as a lowermost layerevent. According to the fault tree modeling and analysis method disclosed by the invention, a more real system failure path is described, a system failure probability is subjected to more accurate quantitative evaluation, the unnecessary conservative property possibly introduced in an original fault tree method is eliminated, and more accurate estimation on the reliability level of the system isimplemented.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Prediction of estrogen receptor status of breast tumors using binary prediction tree modeling
InactiveUS20070294067A1Effectively self-pruningRaise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesEstrogen Receptor StatusData set
The statistical analysis described and claimed is a predictive statistical tree model that overcomes several problems observed in prior statistical models and regression analyses, while ensuring greater accuracy and predictive capabilities. Although the claimed use of the predictive statistical tree model described herein is directed to the prediction of estrogen receptor status in individuals, the claimed model can be used for a variety of applications including the prediction of disease states, susceptibility of disease states or any other biological state of interest, as well as other applicable non-biological states of interest. The model includes the use of iterative out-of-sample, cross-validation predictions leaving each sample out of the data set one at a time, refitting the model from the remaining samples and using it to predict the hold-out case.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Modelling method for tree potted landscape
InactiveCN1457998AEasy to operateThree-dimensional effectsSpecial ornamental structuresModel methodYoung tree
The present invention relates to the technology of making potted landscape, and is especially tree modeling method for potted landscape. Tough young trees are tied and trimmed through cooperating with circular molding articles to constitute certain mold. The young trees may be also new branch growing from the root. Making young trees grow along the circular articles can form beautiful shape. The said method is simple and makes it possible to produce great amount of potted landscape in the same shape or in complicated shape.
Owner:胡泽林
Rapid individual tree modeling method by close shot ordinary digital camera
InactiveCN102750729AEasy to take picturesFlexible to take picturesSpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingGeometric primitiveTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a rapid individual tree modeling method by a close shot ordinary digital camera and belongs to a real three-dimensional visualization expression method for forest resource information. The method is characterized in that the ordinary digital camera is used as a tool, an individual tree is photographed around, artificial marks are arranged around the tree to be tested to establish relative control, and then the space coordinate of a tree morphological structure is obtained through a self-checking analysis method; a structural geometric primitive function is used for modeling, and then a three-dimensional model of an individual tree morphological structure is obtained; and finally tree texture information obtained through photographing is combined with the individual tree three-dimensional morphological structure model by texture mapping to obtain an individual tree three-dimensional model with reality. According to the rapid individual tree modeling method by the close shot ordinary digital camera, the characteristics of portability and flexibility of the digital camera are adequately used, the operating mode is easy to learn, the cost of modeling is reduced, and the modeling period is shortened; and the highly reductive tree morphological structure model is combined with the real texture information, so that the precision and the sense of reality of the individual tree model are greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
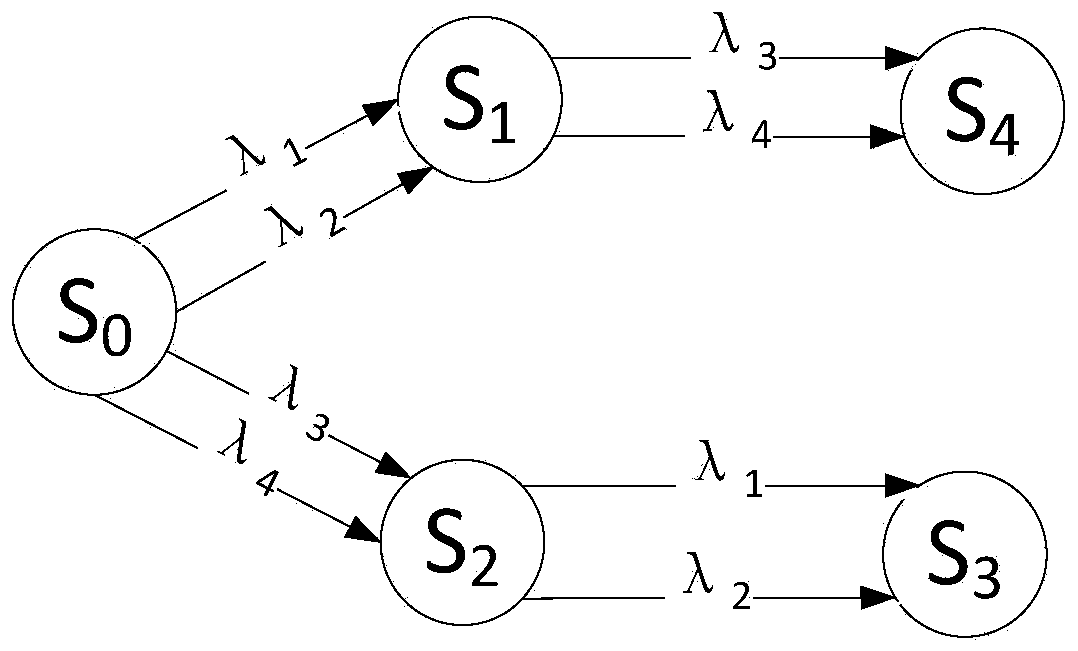
Fault-tree-based nuclear power plant valve body failure reliability monitor method
ActiveCN106226055AReduce development costsSmall scaleMachine part testingDesign optimisation/simulationModularityReliability model
The invention belongs to the field of nuclear power plant risk monitor, particularly relates to a fault-tree-based nuclear power plant valve body failure reliability monitor method which is based on a fault tree modeling technology and suitable for valve equipment body failure in nuclear power plant online risk monitor. The method comprises the steps that (1) state monitor information of a nuclear power plant valve is acquired online; (2) the initial state of the valve is identified online and an initial state transition diagram is established; (3) a modular fault tree reliability model for valve equipment body failure is established and updated online; and (4) the fault-tree-based valve equipment body failure reliability is calculated online. The framework and the steps of the reliability monitor method for nuclear power plant valve equipment body failure are given based on the fault tree method and the state monitor technology so that the defects of the conventional fault tree method in the aspects of valve equipment state modeling and online updating can be overcome.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
An enterprise informatization series product version control method
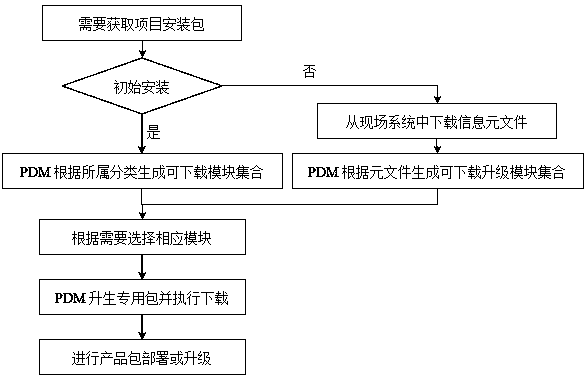
ActiveCN109901872AReduce version control costsCollaborate efficientlyVersion controlInformatizationSoftware engineering
The invention discloses an enterprise informatization series product version management and control method, which comprises the following steps: tree modeling is performed on enterprise informatization series products, and a dependency relationship is defined to uniformly store product data in a database; Demand import is associated with a sign-in sign-out action of a software configuration management tool, and unified and complete enterprise informatization series product version control is realized in combination with an effective database script control mechanism. Unified source code management of enterprise informatization series products is achieved, and unified coordinated management of source codes of different levels and strong correlation of product package sending updating are ensured; Unified version control is provided for obtaining and updating a product package in practical application of a project, and product version updating and upgrading can be smoothly carried out. And a unified enterprise informatization series product version management and control mechanism from development to application is completed on the whole.
Owner:江苏睿孜星智控科技有限公司
Improved availability evaluation method for nuclear power design phase
InactiveCN109407507AOvercome limitationsCalculation results are accurate and reliableAdaptive controlFailure rateDesign phase
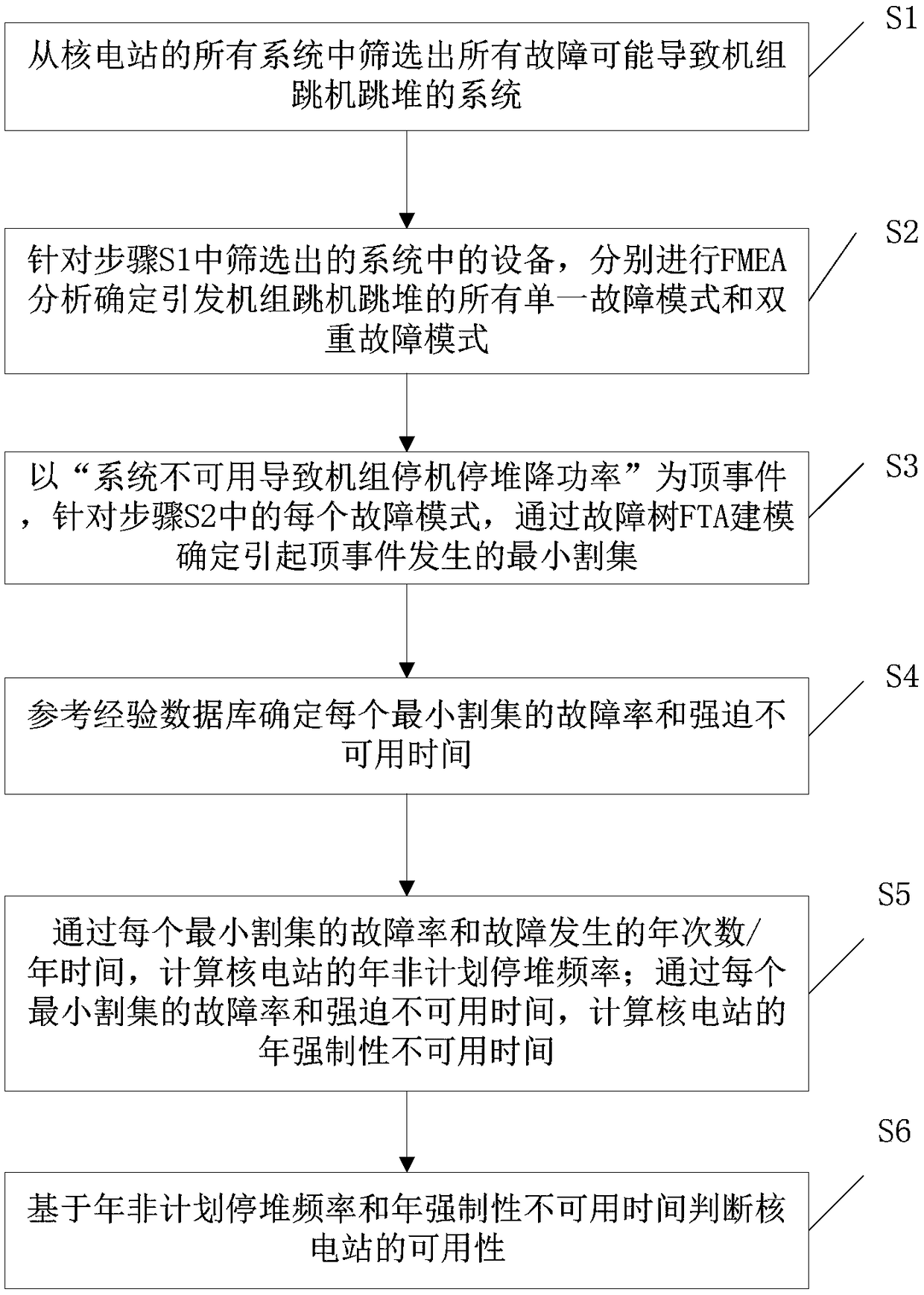
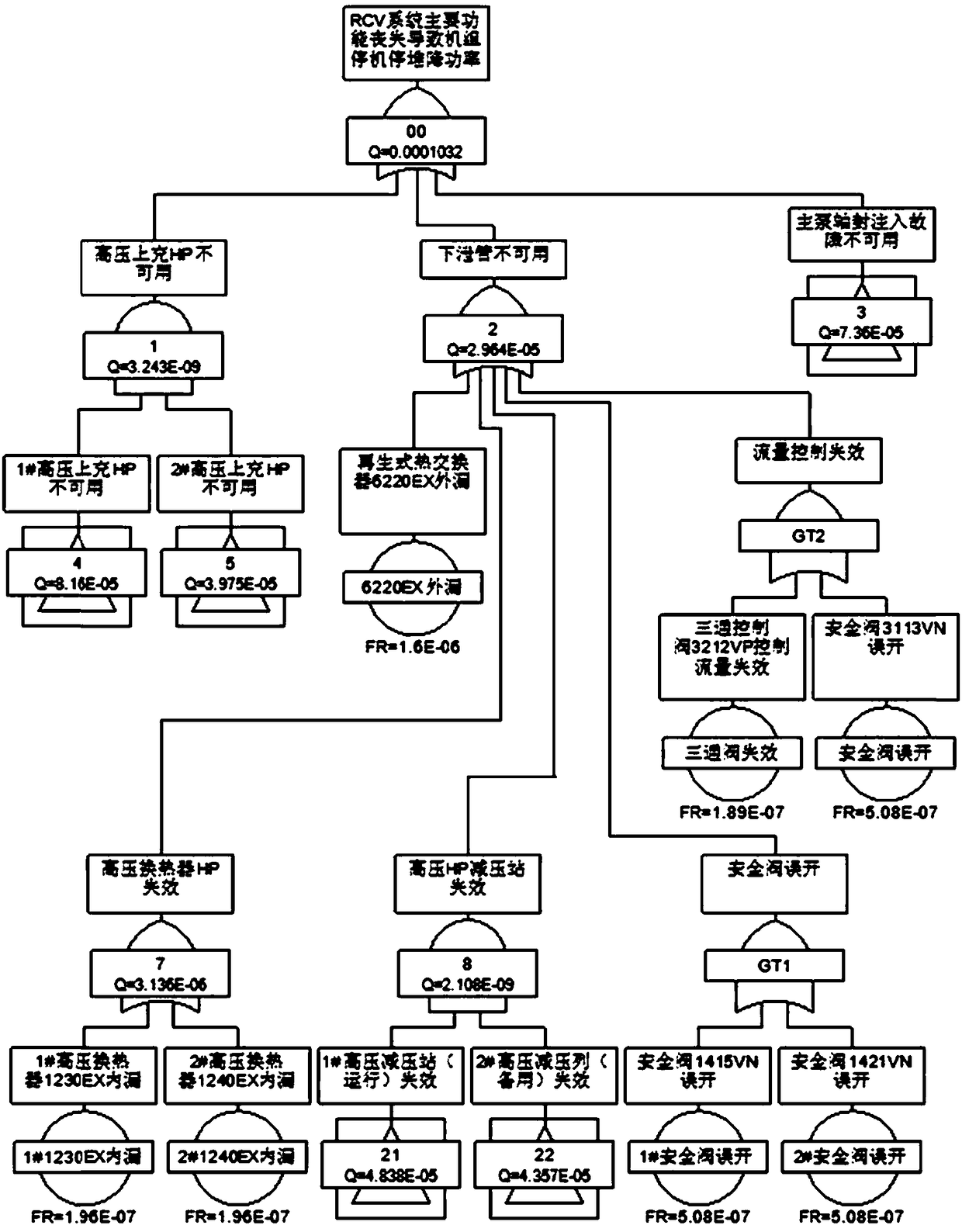
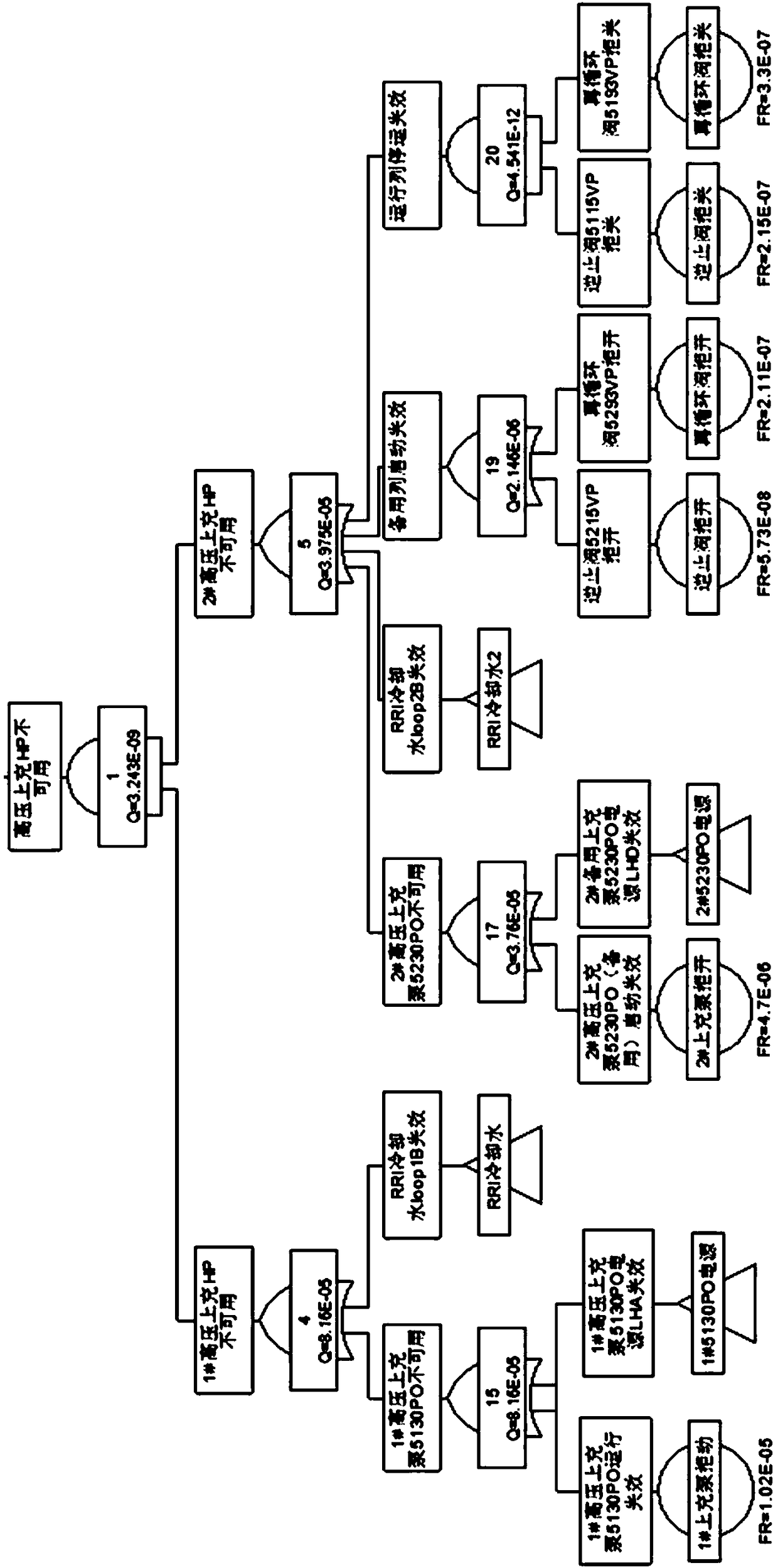
An improved availability evaluation method for a nuclear power design phase comprises S1, screening out a system in which a fault may cause the reactor tripping and the turbine tripping of a unit; S2,performing FMEA analysis on the equipment in the system screened out in the step S1 to determine all single and dual failure modes that cause the reactor tripping and the turbine tripping of the unit; S3, taking an event that the system is unavailable and causes the unit to stop and reduce the power as a top event, and for each failure mode, determining the minimum cut set by fault tree modeling;S4, determining a failure rate and a mandatory unavailable time of each minimum cut set; S5, calculating an annual unplanned shutdown frequency of a nuclear power plant by using the failure rate of each minimum cut set and the annual number of times / annular time of the fault; and calculating the annual mandatory unavailable time of the nuclear power plant based on the failure rate and the mandatory unavailable time of each minimum cut set; and S6, determining the availability of the nuclear power plant based on the annual unplanned shutdown frequency and the annual mandatory unavailable time.The method can quantitatively predict the availability of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +2
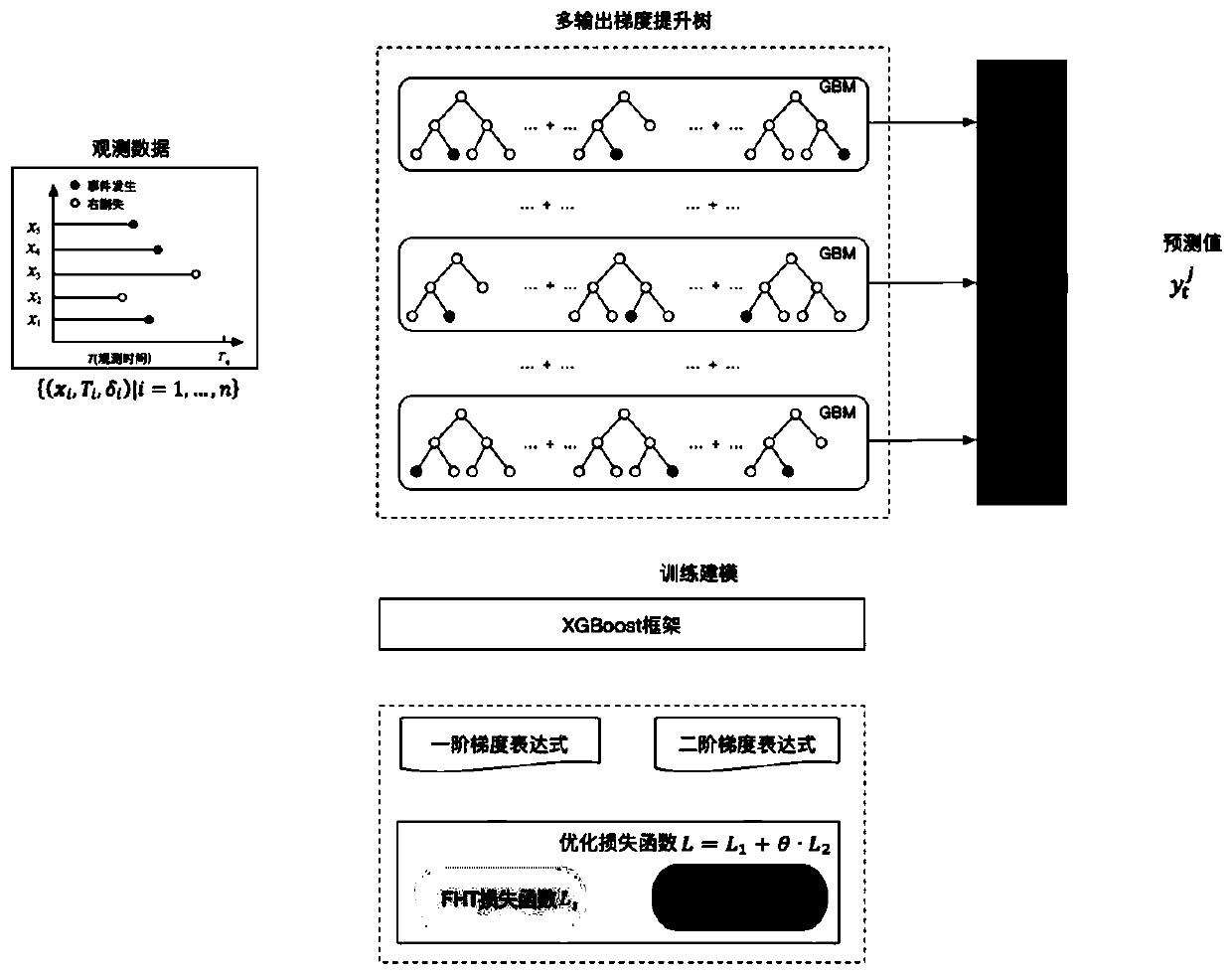
Multi-output gradient lifting tree modeling method for survival risk analysis
ActiveCN110119540AImprove accuracySolve the problem of insufficient explanationForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationRisk profilingSurvival analysis
The invention provides a multi-output gradient lifting tree modeling method for survival risk analysis, which comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing an expression of survival data for establishing a survival prediction model of financial, insurance, medical, traffic or industrial target industries under a model algorithm framework of an optimal gradient lifting tree (XGBoost); then defining and calculating a loss function corresponding to the survival data; then, defining and calculating a first step degree and a second step degree corresponding to the loss function; and finally,inputting the calculated loss function value and the first-order gradient value and the second-order gradient value of the loss function into an XGBoos model algorithm framework at the same time, andperforming automatic training to generate a survival prediction model of the target industry. The modeling method provided by the invention can better represent the relationship between the model covariable and the risk prediction value. The prediction performance and the generalization capability of the model are improved. The prediction performance and the risk distinguishing degree are better,and the application scene is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Complex system dynamic fault tress modeling method based on service path
InactiveCN106027285AMeet reliability analysis needsAvoiding Reliability Modeling ChallengesData switching networksModel methodNetworked system
The invention discloses a complex system dynamic fault tree modeling method based on a service path, and belongs to the technical field of reliability and security. The method comprises the steps of analyzing a complex system, abstracting out the service path, determining a fault treetop event according to a service object, and establishing a function sequential dependency graph; and establishing a fault tree according to a conversion rule of the function sequential dependency graph to the dynamic fault tree. According to the method, the complex logic relation of the networked system can be effectively modeled, and the reliable analysis requirement on different devices in the engineering can be flexibly met; and meanwhile the flow-type reliable modeling method is provided, thus being convenient to be applied to engineering practice.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Fault diagnosis method for flight control system based on rules
InactiveCN108519769AEnhance expressive abilityBuild fastElectric testing/monitoringControl systemSystem failure
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircraft fault diagnosis, and specifically relates to a fault diagnosis method for a flight control system based on rules. A knowledge representation method of a production rule tree + a frame is employed for representing the fault diagnosis knowledge, and a graphical rule tree modeling tool and a text inputting tool are combined as a knowledge learner. The method provided by the invention improves the representation capability of a fault diagnosis method based rules for the complex knowledge, speeds up the construction of a knowledge base, and improves the fault diagnosis performances.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
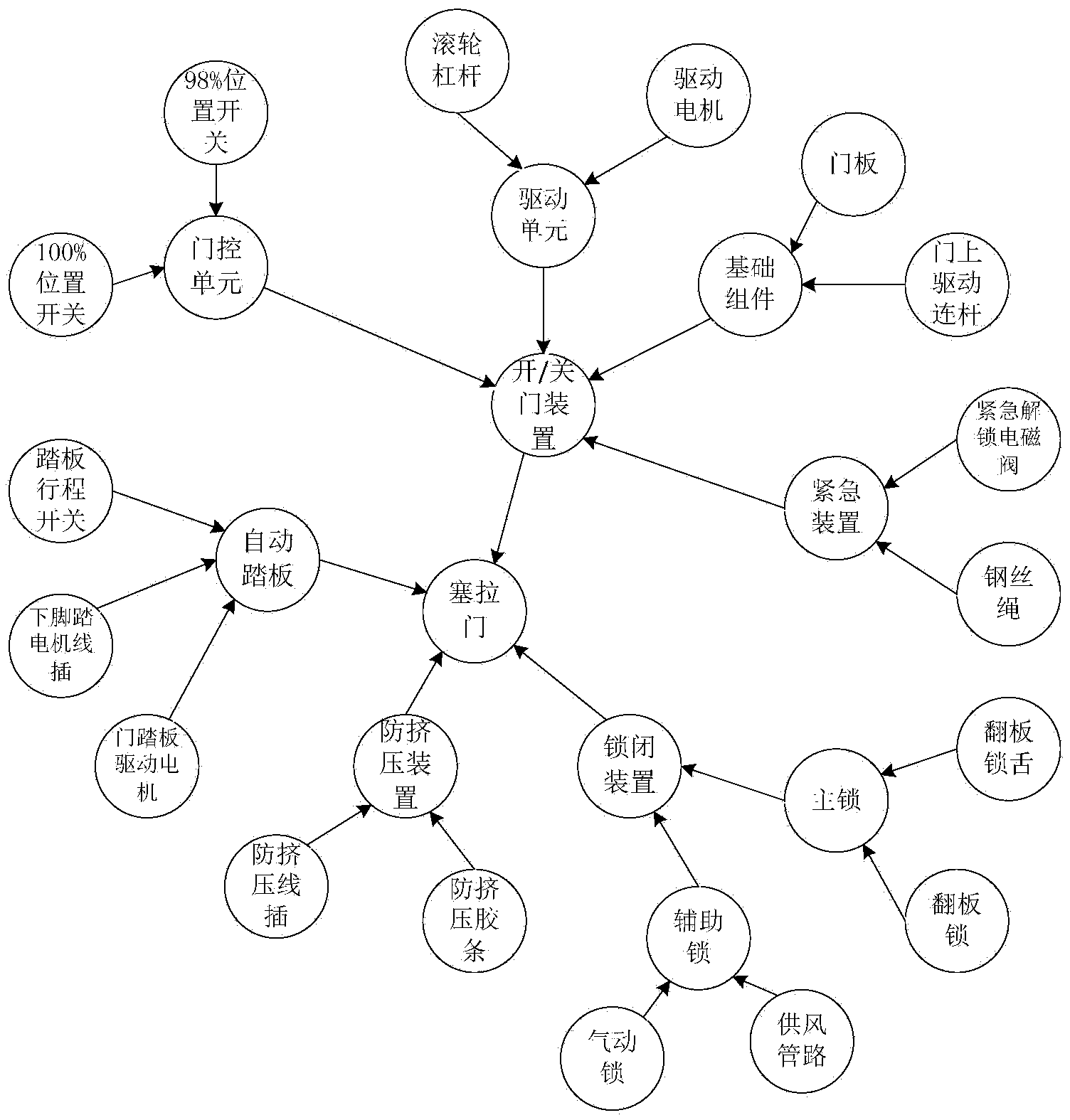
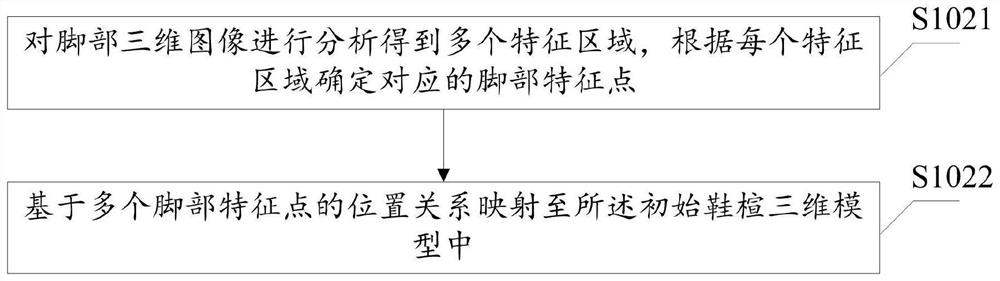
Shoe tree modeling adjustment method, device and equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114445555AImprove modeling efficiencyReduce computation3D modellingAlgorithmDimensional modeling
The embodiment of the invention discloses a shoe tree modeling adjustment method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out shoe tree three-dimensional modeling initialization, and generating an initial shoe tree three-dimensional model; determining a plurality of foot feature points based on foot big data analysis, and mapping the plurality of foot feature points to the initial shoe tree three-dimensional model to obtain a first shoe tree model containing model feature points; receiving an adjustment operation on the first shoe tree model, adjusting the first shoe tree model according to the adjustment operation to generate a second shoe tree model, and displaying the second shoe tree model. According to the scheme, the calculation amount of shoe tree modeling adjustment is remarkably reduced, the shoe tree modeling efficiency is improved, and the intelligent degree is high.
Owner:广东时谛智能科技有限公司
Urban tree three-dimensional visualization method based on vehicle-mounted laser point cloud data
The invention belongs to the technical field of vehicle-mounted laser radar point cloud data processing, and particularly relates to an urban tree three-dimensional visualization method based on vehicle-mounted laser point cloud data. Based on original point cloud data, after tree segmentation and crown and trunk separation, tree trunks and crowns are modeled independently, and finally a tree three-dimensional model in an urban scene is constructed. Compared with a traditional tree three-dimensional modeling method, independent modeling can be carried out according to different morphological characteristics of trunks and crowns, the defect that morphological characteristic expression of single-tree modeling is not accurate is avoided, the urban tree three-dimensional model can be simply, rapidly and accurately constructed, and the method can be applied to forestry resource investigation and 3D urban modeling and has a wide application prospect. Tree parameter extraction and the like.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINE HUZHOU
Domain feature tree modeling method based on i* framework
InactiveCN103885774AResolve dependenciesSpecial data processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsModel methodAlgorithm
The invention discloses a domain feature tree modeling method based on an i* framework. The domain feature tree modeling method includes the steps of firstly, reading a tel file or a q7 file or an XML file of the i* framework, obtaining participant information, and sequentially placing participants into a participant queue in the access sequence; secondly, mapping an i* element in each participant into a feature tree model, and building repulsion relations between the features in the feature tree models; thirdly, building dependence relations between the features according to different dependence chains, and automatically associating the multiple feature tree models generated by the different participants; finally, improving a domain feature tree model, and outputting information of the final domain feature tree model. According to the domain feature tree modeling method, it is guaranteed that the mapped i* elements are more comprehensive than mapped i* elements in original methods, and the domain feature tree model is constructed in a semi-automation mode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TOPCHEER INFORMATION TECH +1
Gradient boosting tree modeling method and device and terminal
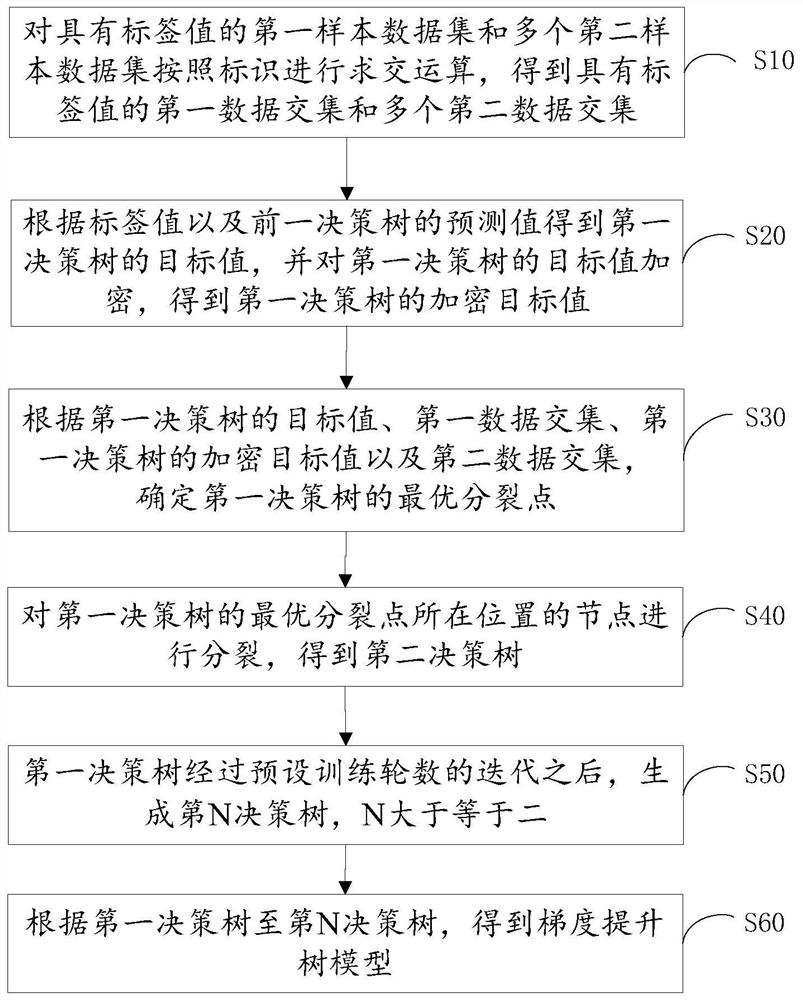
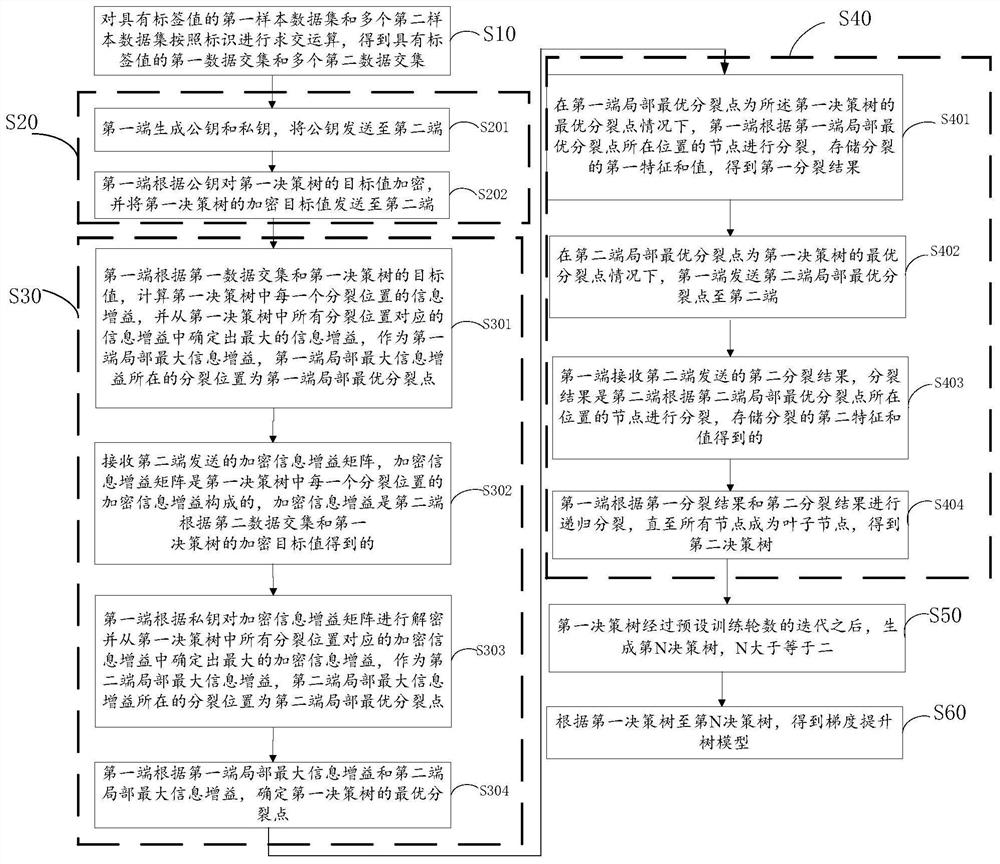
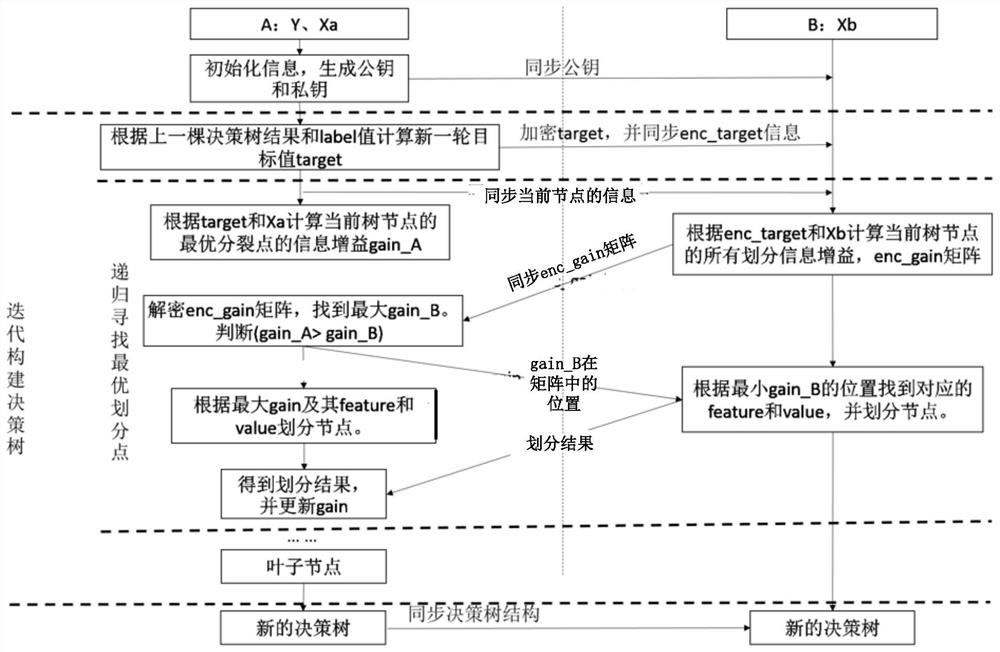
PendingCN112052954ASpeed up circulationEffective Privacy ProtectionMachine learningData setAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a gradient boosting tree modeling method and device and a terminal, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the intersection operation of a first sample data set with a label value and a plurality of second sample data sets according to an identification, and obtaining a first data intersection set with a label value and a plurality of second dataintersection sets; obtaining a target value of the first decision tree according to the label value, and encrypting the target value of the first decision tree to obtain an encrypted target value of the first decision tree; determining an optimal splitting point of the first decision tree according to the target value of the first decision tree, the first data intersection, the encryption target value of the first decision tree and the second data intersection; splitting the node at the position of the optimal splitting point of the first decision tree to obtain a second decision tree; after the first decision tree is subjected to iteration of a preset training round number, an Nth decision tree is generated, and N is larger than or equal to 2; and obtaining a gradient boosting tree modelaccording to the first decision tree to the Nth decision tree. Multi-party joint gradient boosting tree modeling is adopted, and respective private data cannot be leaked.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
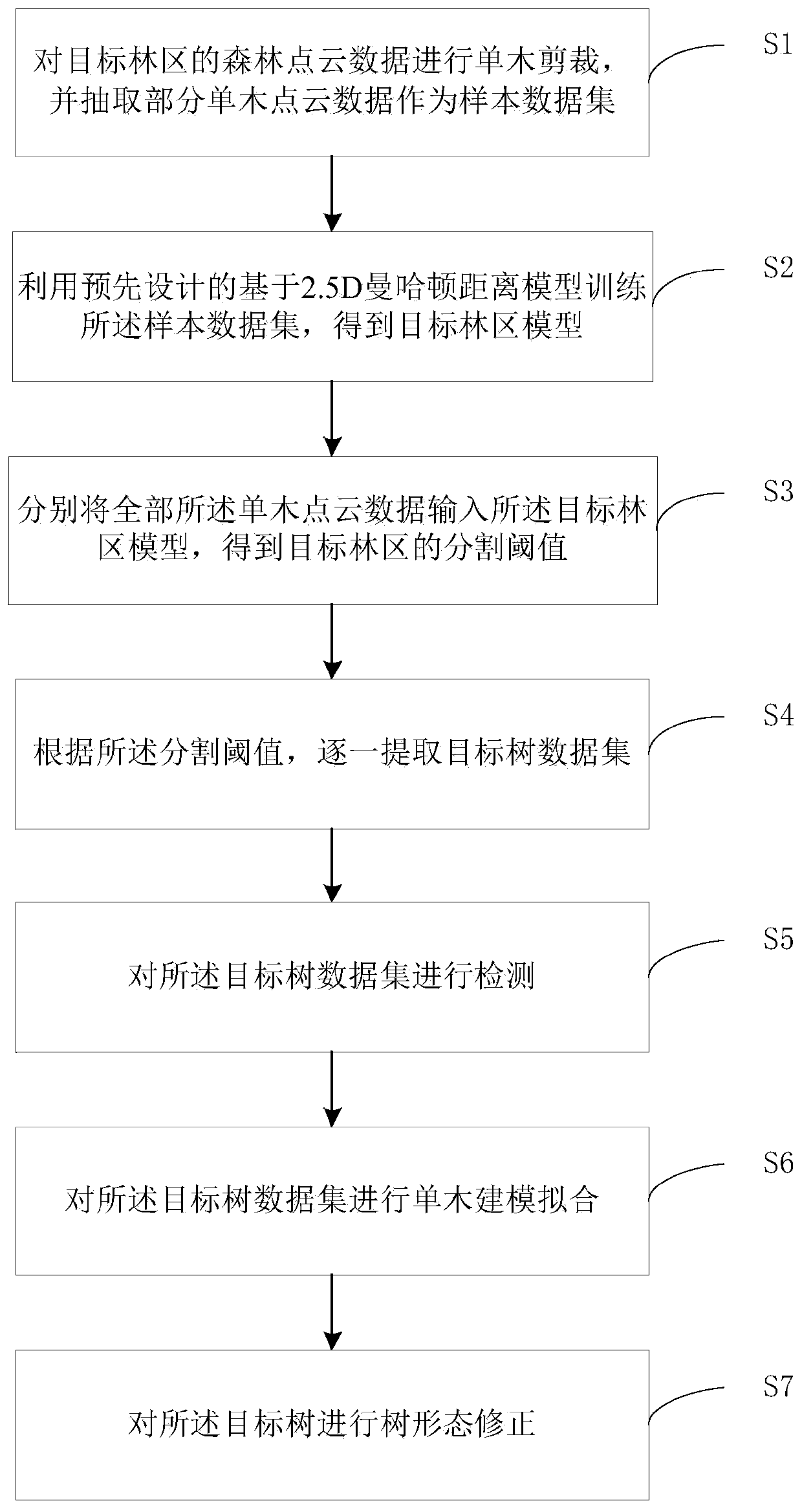
Single tree modeling method and device and storage medium
The invention discloses a single tree modeling method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out individual tree clipping on forest point cloud data of a target forest region, and extracting part of individual tree point cloud data as a sample data set; training the sample data set by utilizing a pre-designed 2.5 D Manhattan distance model to obtain a target forest region model; inputting all the single tree point cloud data into the target forest region model to obtain a segmentation threshold of a target forest region; and extracting target tree data sets one by one according to the segmentation threshold. By utilizing the single tree model constructed by the method, the reference form of the tree species can be obtained by inputting all realsingle tree sample point clouds into the single tree model, the parameter threshold required by the algorithm is extracted from the form, and the de-empirical thresholding is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QILIANG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Multifunctional intelligent tree modeling equipment
InactiveCN107047090APromote repairAchieve rotationCuttersMotor driven pruning sawsBaseboardArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses multifunctional intelligent tree modeling equipment. The equipment comprises a baseboard, a supporting column is arranged at the center of the upper surface of the baseboard, the upper end of the supporting column is provided with a first cylinder telescopic rod, an L-shaped connecting plate is arranged at the telescopic end of the first cylinder telescopic rod, a first electric telescopic rod is connected with the upper surface of the fold of the L-shaped connecting plate through a hinging base, an electric saw is arranged at one end, far away from connection with the first cylinder telescopic rod, of the L-shaped connecting plate, the first cylinder telescopic rod is welded with a supporting base, one side of the supporting base is connected with a third cylinder telescopic rod through a bolt. Trimming on trees by the modeling machine in the advancing process is achieved through the arrangement of the first cylinder telescopic rod, the L-shaped connecting plate, the first electric telescopic rod and the electric saw, the L-shaped connecting plate can be driven to rotate through extension and retraction of the first electric telescopic rod to adjust the angle of the electric saw, and trees are trimmed through the electric saw so as to make tree trimming more convenient.
Owner:吴海锋
Hepatic portal vein tree modeling method and system thereof
InactiveCN101393644BEnhancement effect is goodEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisLiver parenchymaFiltration
The invention discloses a hepatic vein vascular tree modeling method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a liver model to obtain a liver image, and utilizing the multi-scale filtration method to strengthen a blood vessel; cutting a hepatic vein; extracting a central line of the hepatic vein; detecting and removing a link in the central line; and utilizing OSG / VTKto rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree after pruning. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a blood vessel strengthening module, a blood vessel cutting module, a vascular tree central line extracting module and a vascular tree rebuilding module. The invention improves similarity functions in the filtering process, analyzes the characteristics of the ring and adopts corresponding unlinking methods for different links; and utilizes the relation of radius of blood vessel and the branch length when pruning. The invention effectively enhances the hepatic vein, improves the contrast between the blood vessel and liver parenchyma, and can extract more than five class branches, effectively unlink and prune the central line of the hepatic vein, rebuild the hepatic vein vascular tree and directly display the branches of the heptatic vein.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com