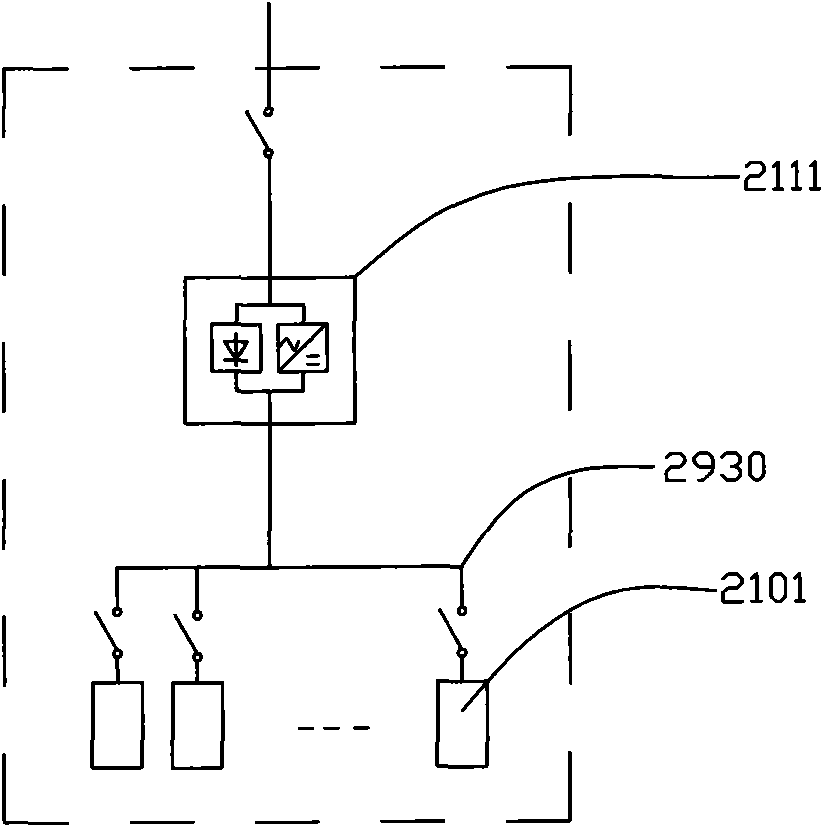
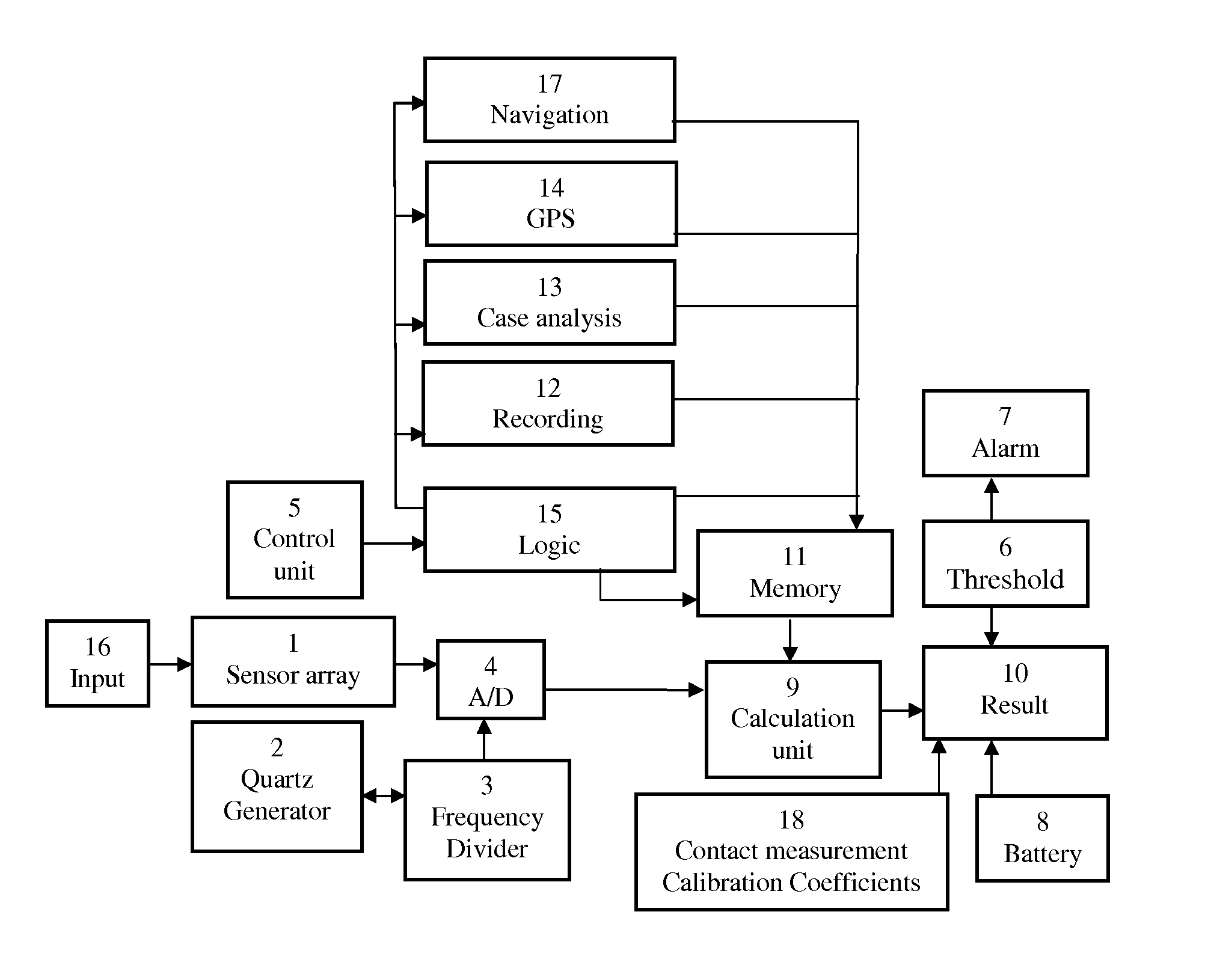
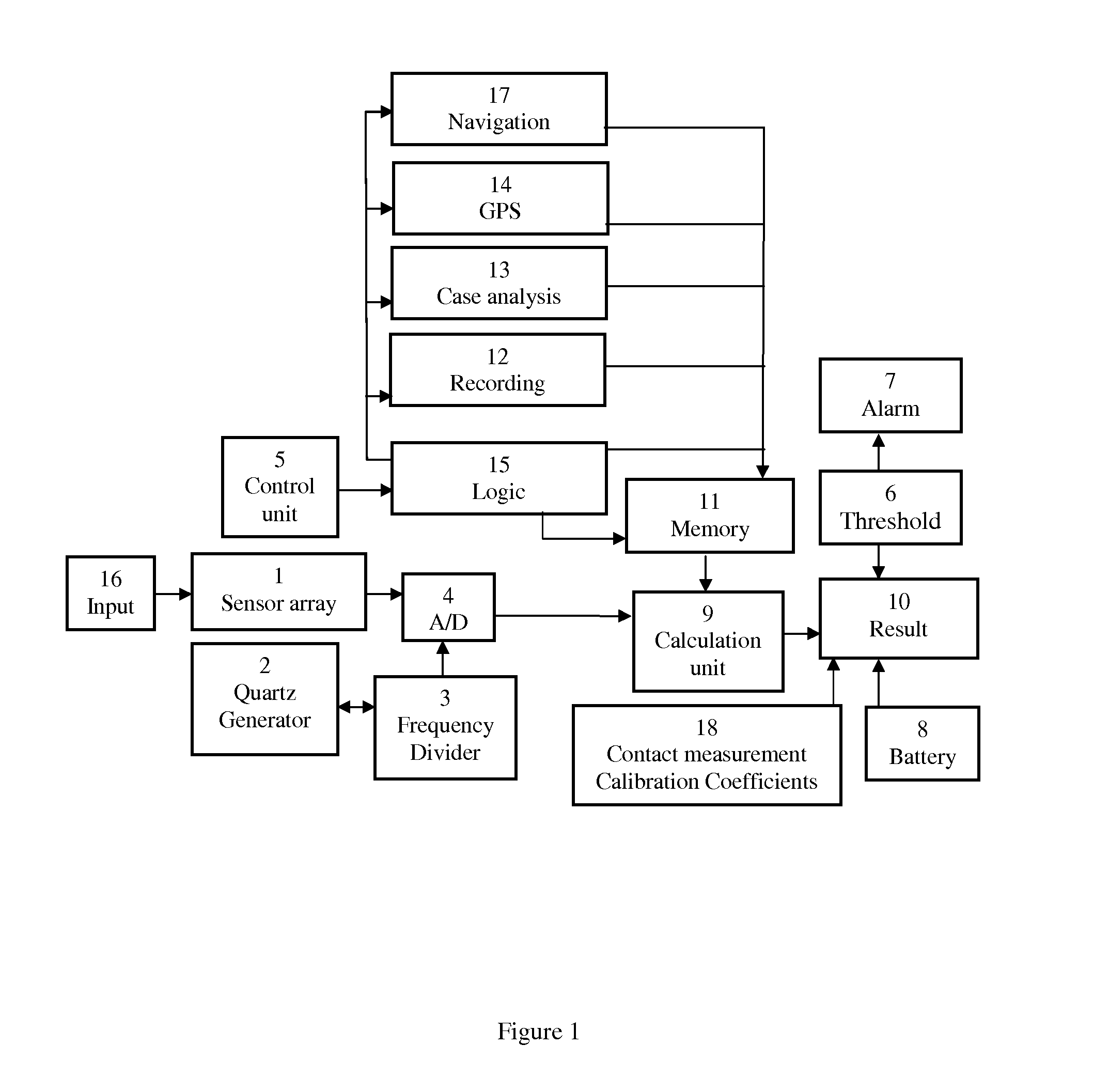
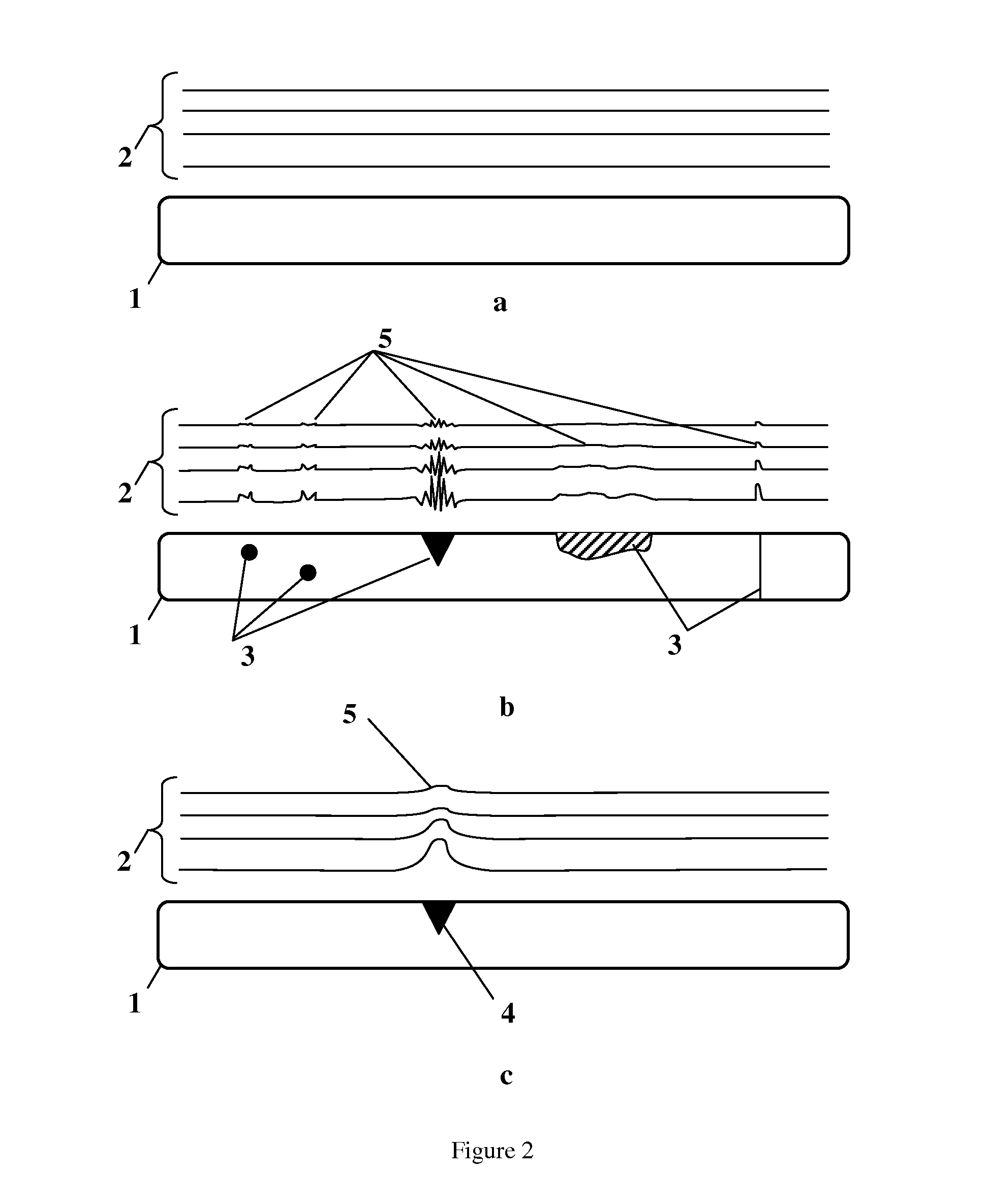
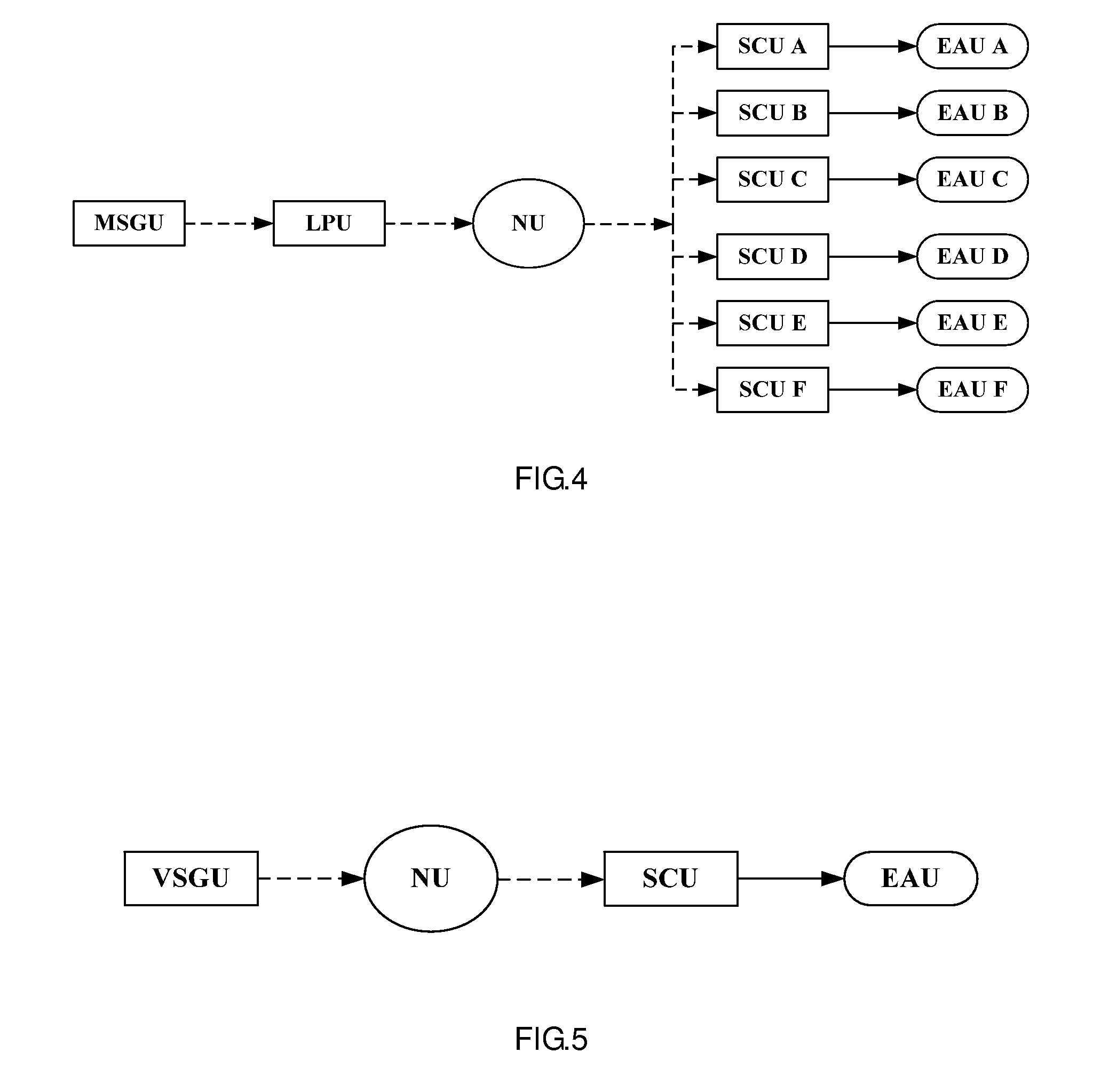
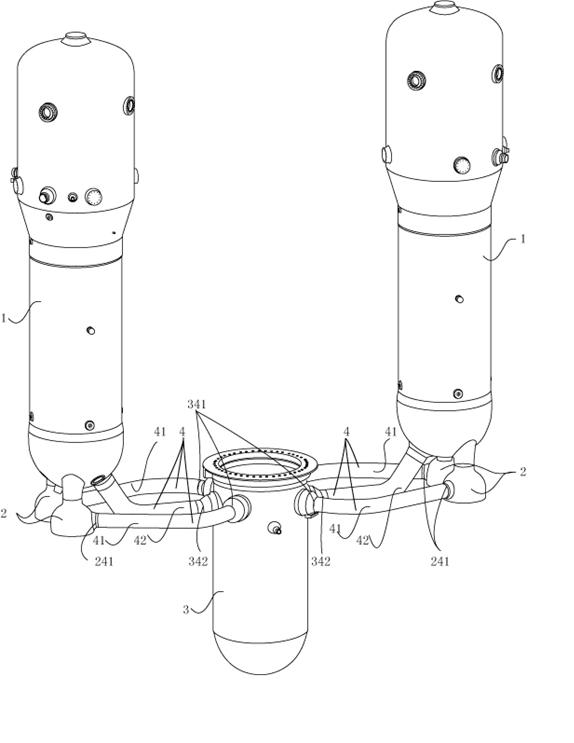
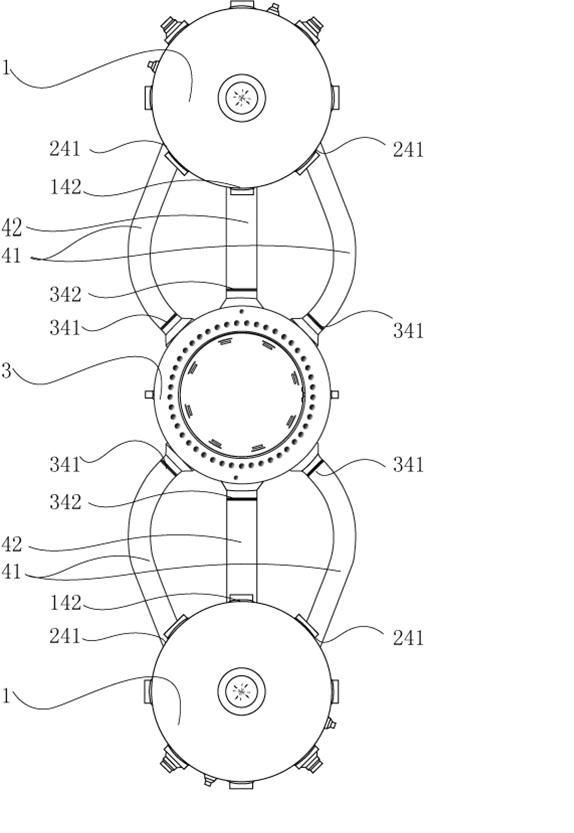
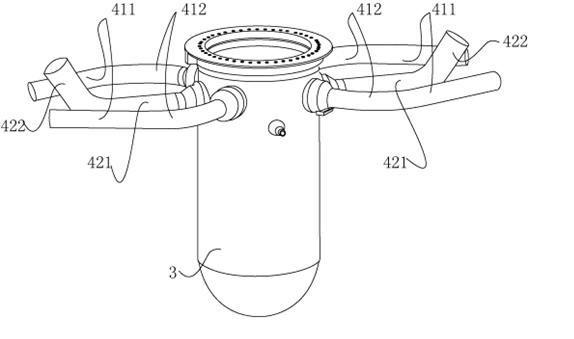
Patents
Literature
8690 results about "Nuclear power plant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
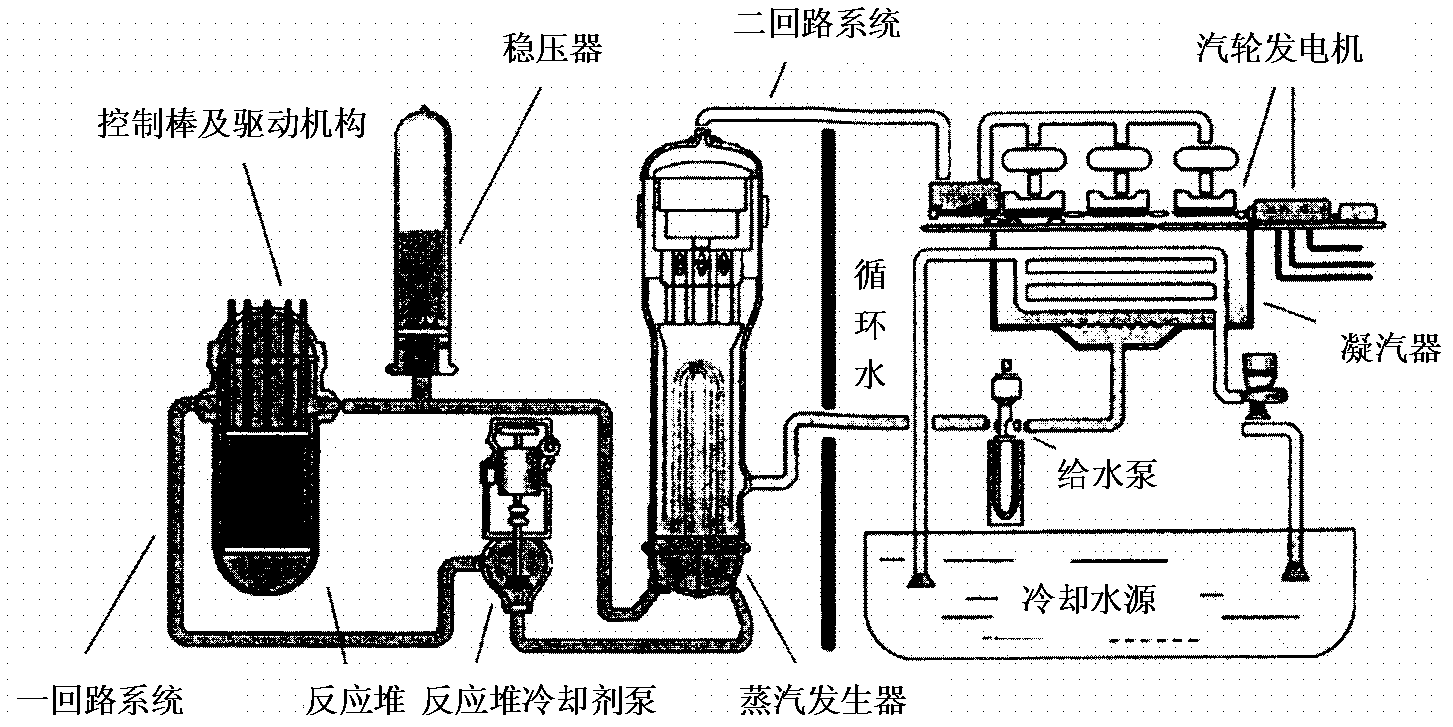
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity. As of 2014, the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 450 nuclear power reactors in operation in 31 countries.
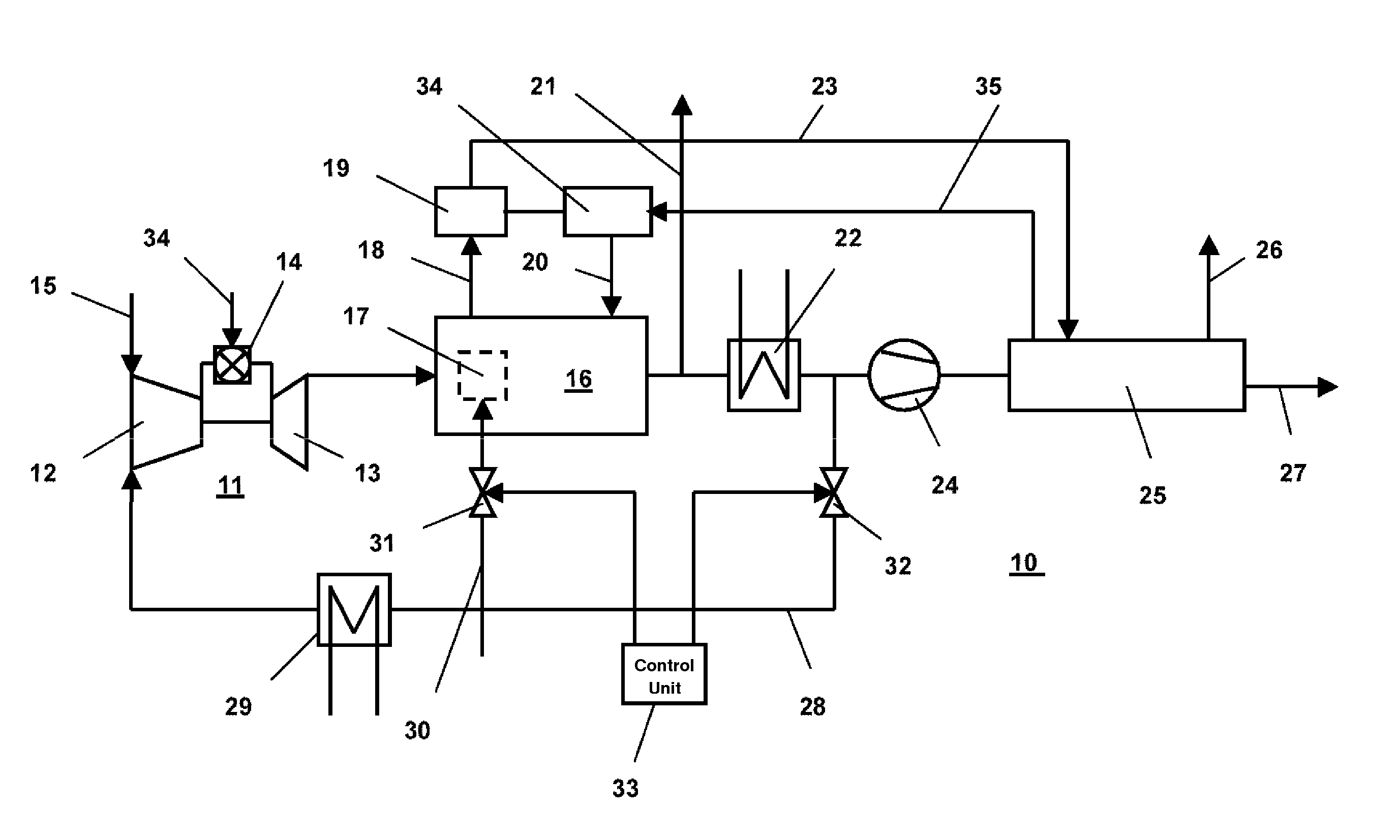
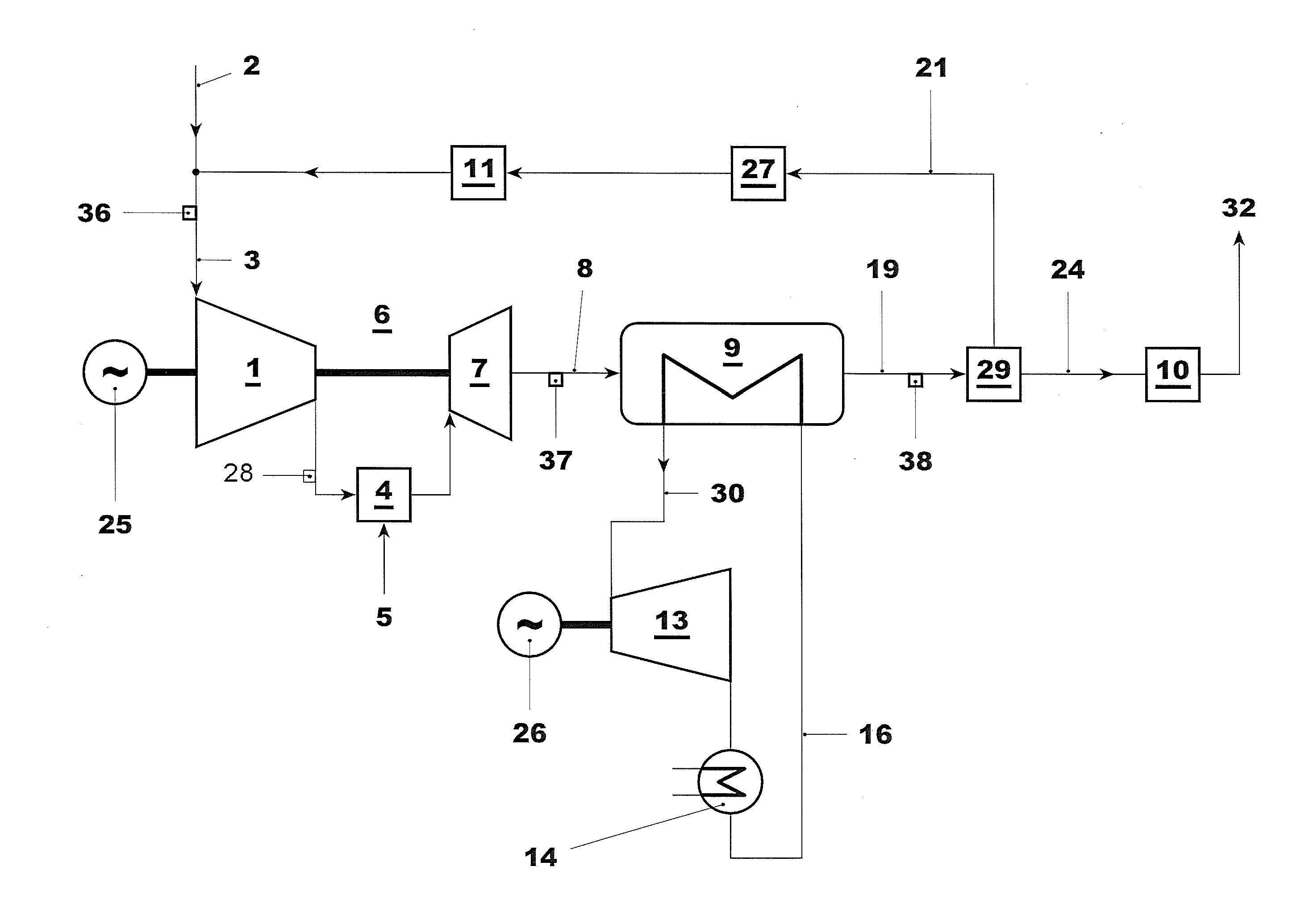
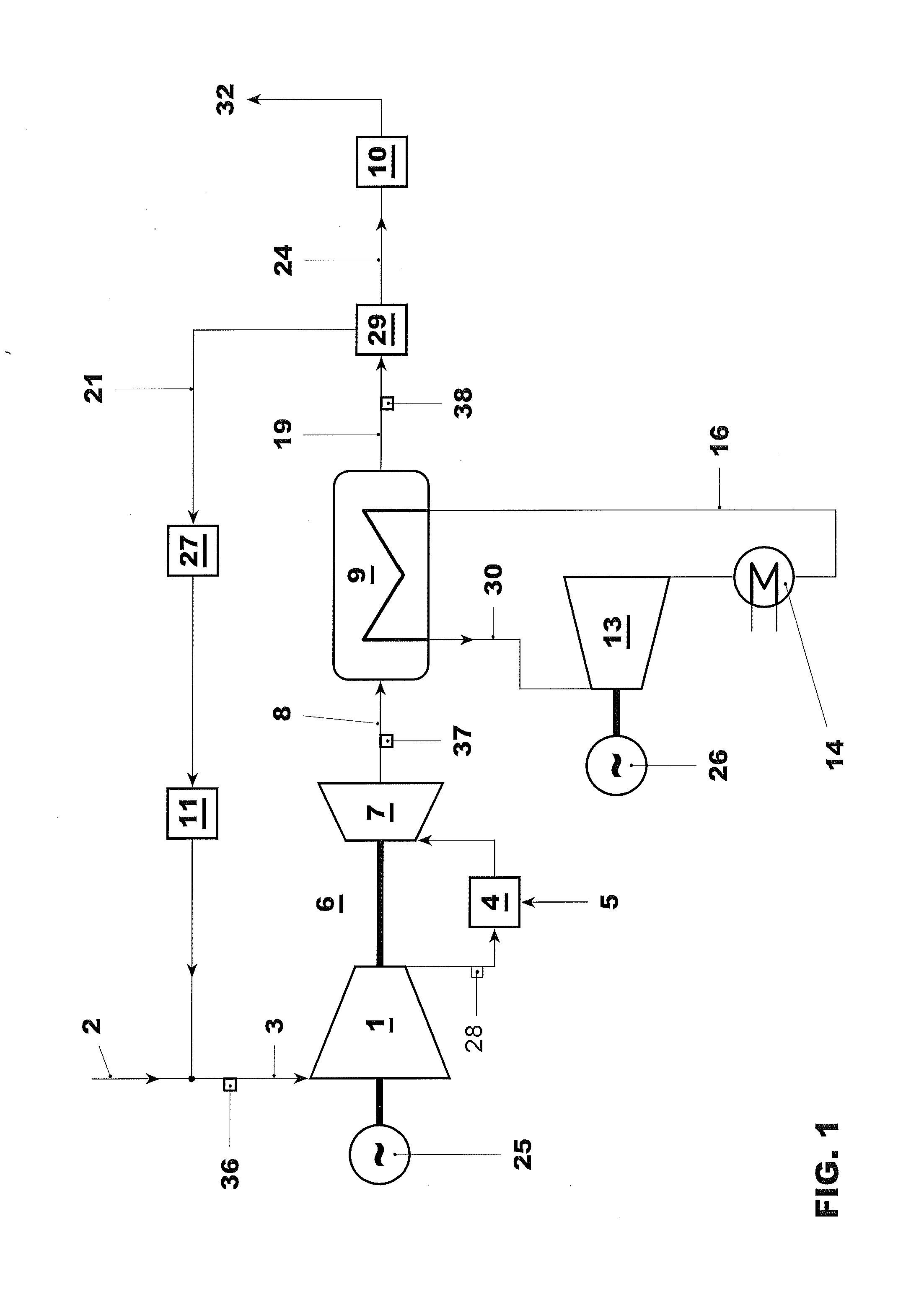
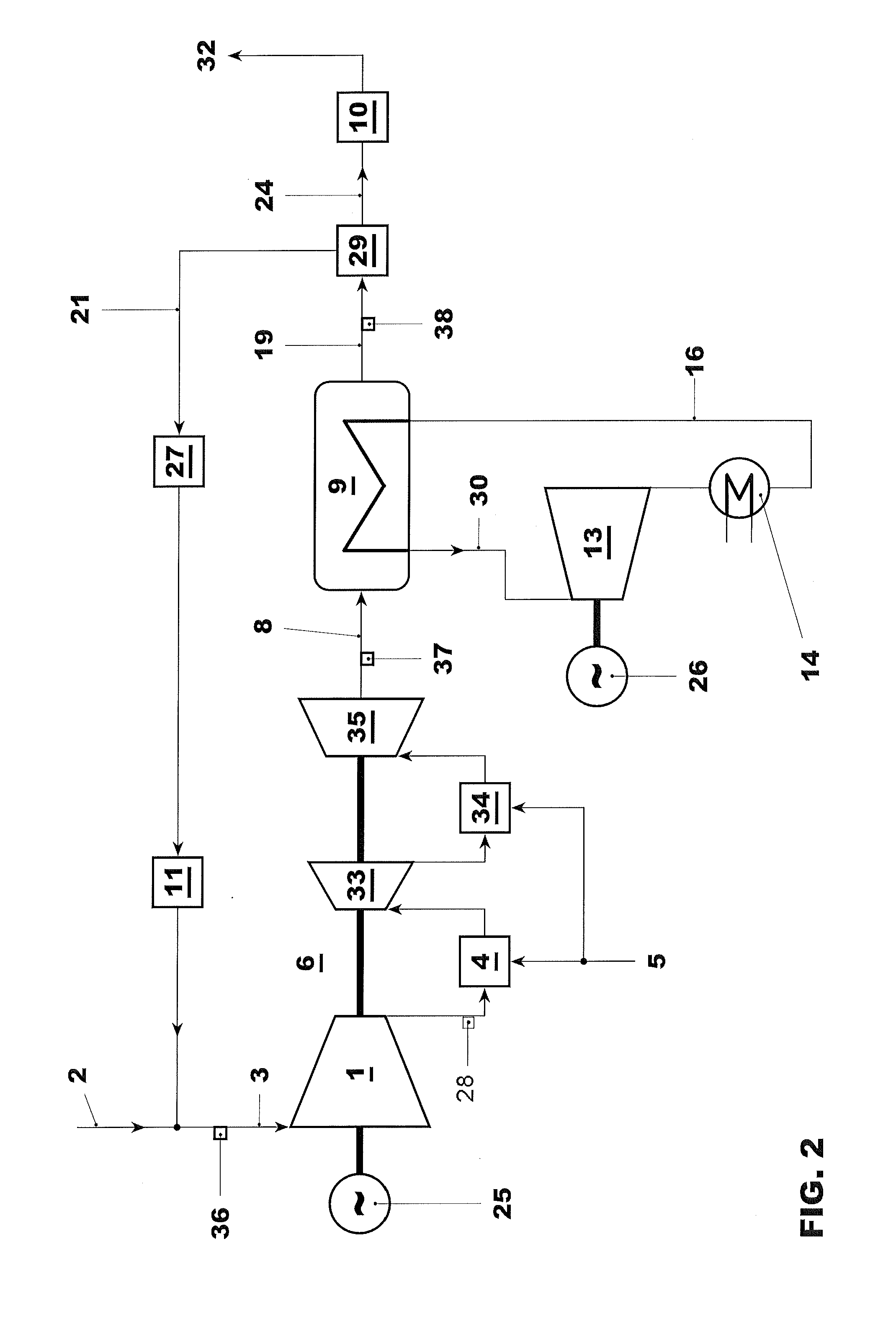
High power density combined cycle power plant
InactiveUS6230480B1Reduce installation costsService degradationEnergy industryGas turbine plantsPower stationCogeneration
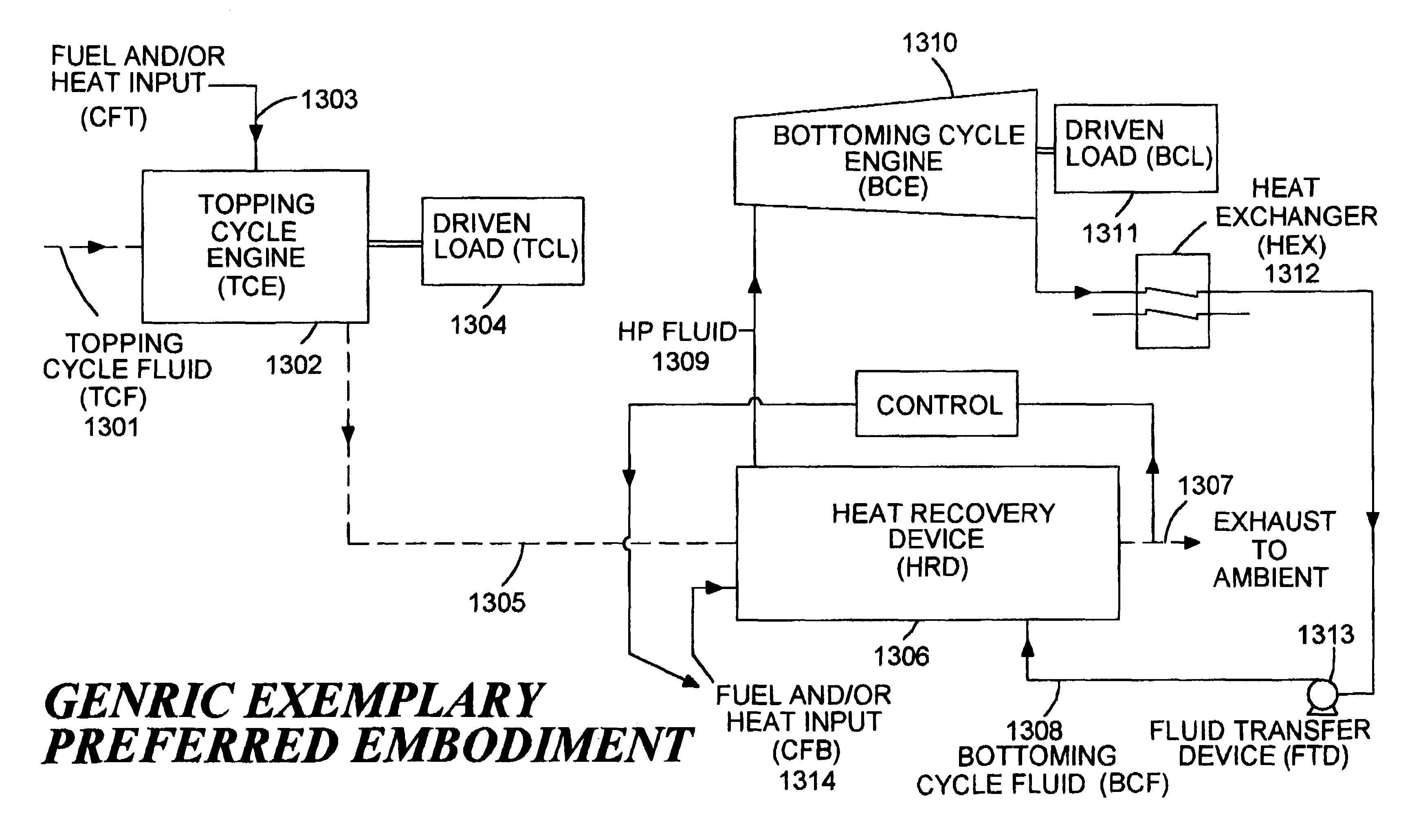
A system and method for increasing the specific output of a combined cycle power plant and providing flexibility in the power plant rating, both without a commensurate increase in the plant heat rate, is disclosed. The present invention demonstrates that the process of upgrading thermal efficiencies of combined cycles can often be accomplished through the strategic use of additional fuel and / or heat input. In particular, gas turbines that exhaust into HRSGs, can be supplemental fired to obtain much higher steam turbine outputs and greater overall plant ratings, but without a penalty on efficiency. This system and method by in large defines a high efficiency combined cycle power plant that is predominantly a Rankine (bottoming) cycle. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention include a load driven by a topping cycle engine (TCE), powered by a topping cycle fluid (TCF) which exhausts into a heat recovery device (HRD). The HRD is fired with a supplementary fuel or provided an additional heat source to produce more energetic and / or a larger quantity of the bottoming cycle fluid (BCF) which is used to power a bottoming cycle engine, (BCE) which drives a load (potentially the same load as the topping cycle engine). Energy contained in either the TCF or BCF is used to power the TCE and BCE respectively, but these fluids, and / or their respective engine exhausts, may also be used to support a wide variety of cogeneration applications.
Owner:ROLLINS III WILLIAM SCOTT
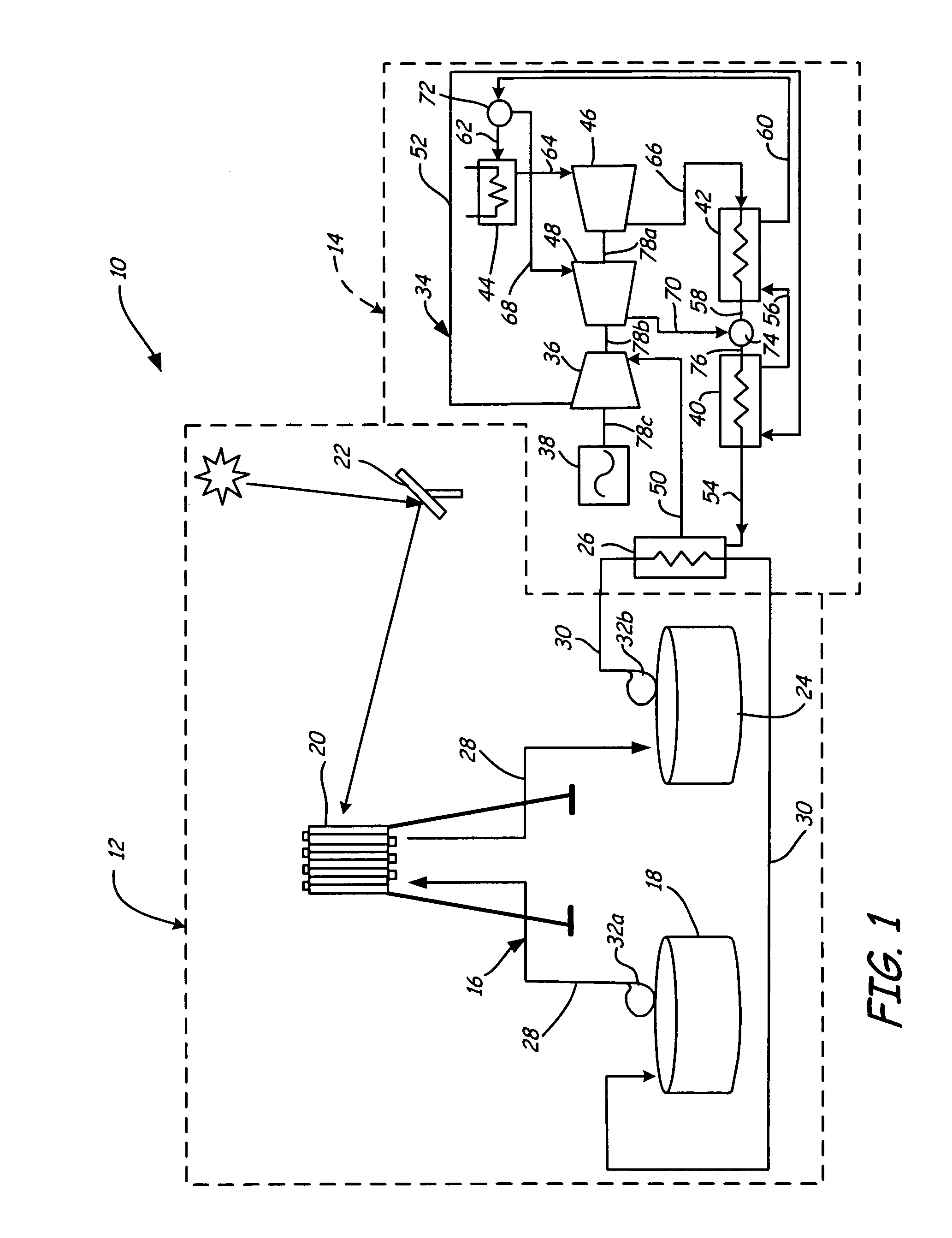
Supercritical CO2 turbine for use in solar power plants
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH
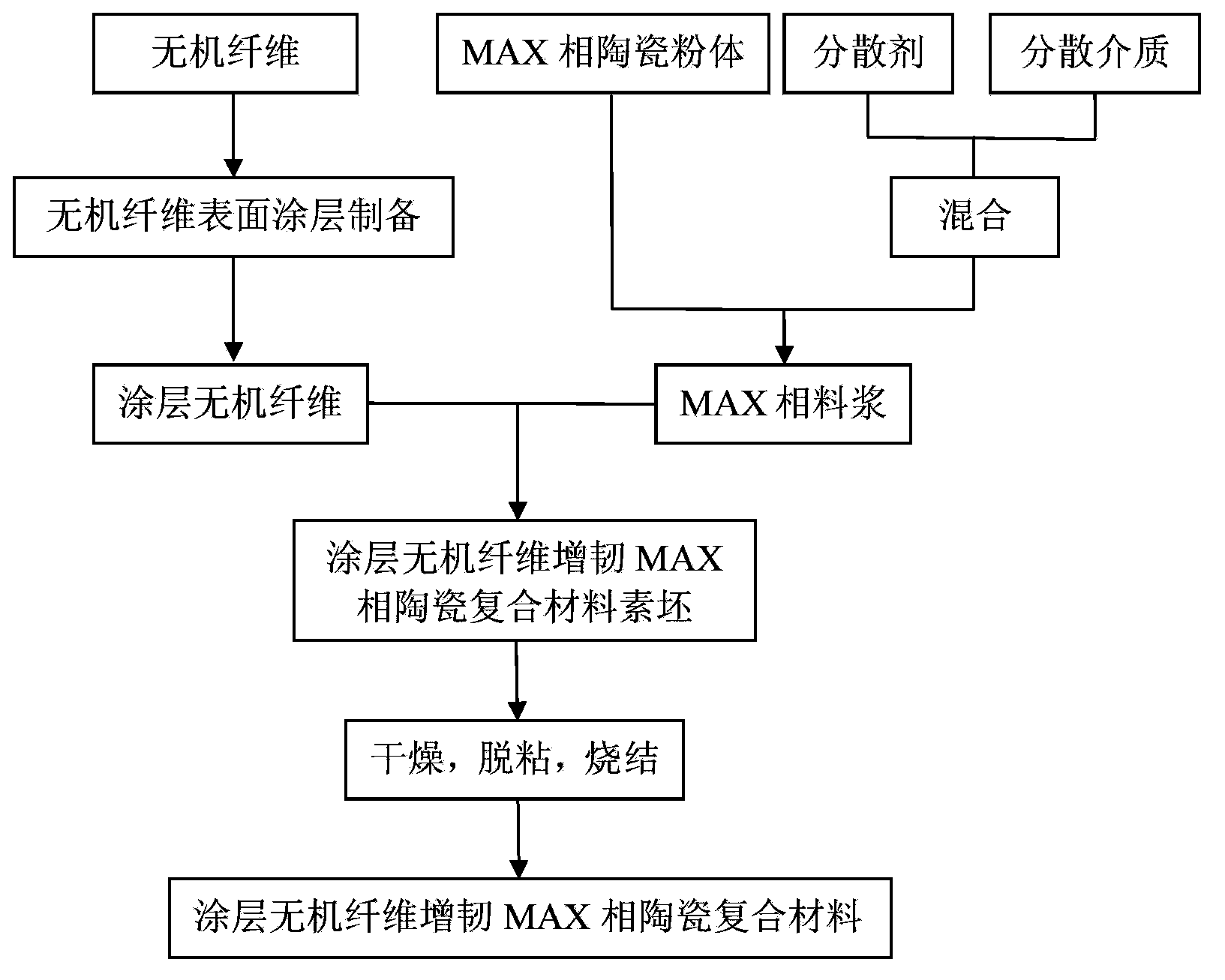
Coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN103910532AAppropriate bonding interface strengthFree control of interface strengthNuclear energy generationContainmentAviationFiber
The present invention provides a coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material adopts a MAX phase ceramic material as a matrix and adopts coating inorganic fibers as a toughening phase, wherein the coating inorganic fiber content is 0.5-90% (by volume), and the coating inorganic fibers are completely dispersed in the matrix and are inorganic fibers with the surface coated with the coating. Compared with the composite material in the prior art, the composite material of the present invention has the following characteristics that: the interface reaction between the inorganic fibers and the MAX phase ceramic can be effectively inhibited, the thermal expansion coefficient and elasticity modulus matching degree between the inorganic fibers and the MAX phase ceramic can be effective regulated, the effective improvement of the fracture toughness and the high temperature resistance of the MAX phase ceramic composite material can be achieved, the problems of high brittleness and insufficient use reliability of the MAX phase ceramic can be fundamentally solved, and the coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material has potential application prospects in the high technology fields of civil use, aviation, aerospace, nuclear industry and the like, and is especially for the fission and fusion reactor nuclear power plant inner wall structure material.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
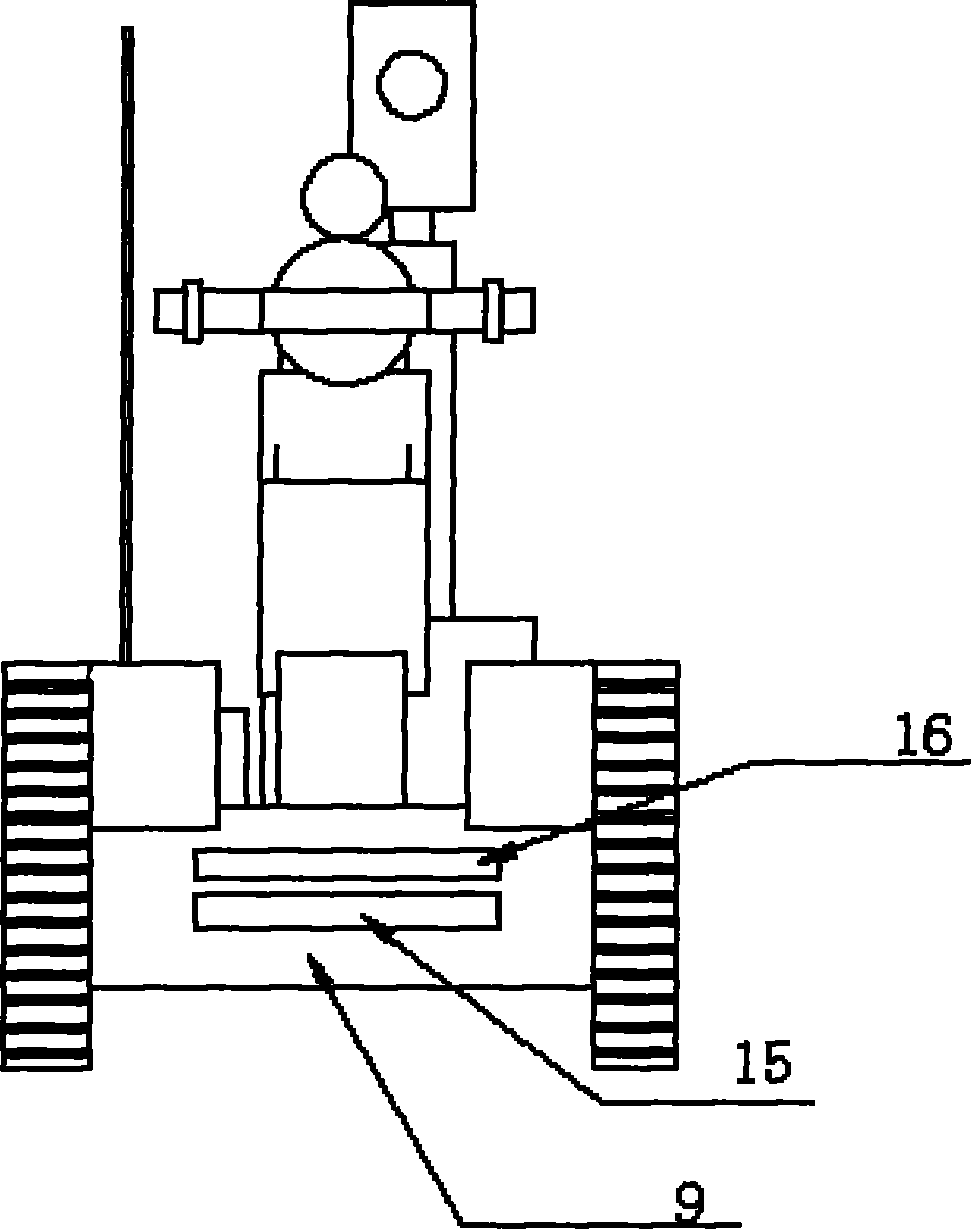
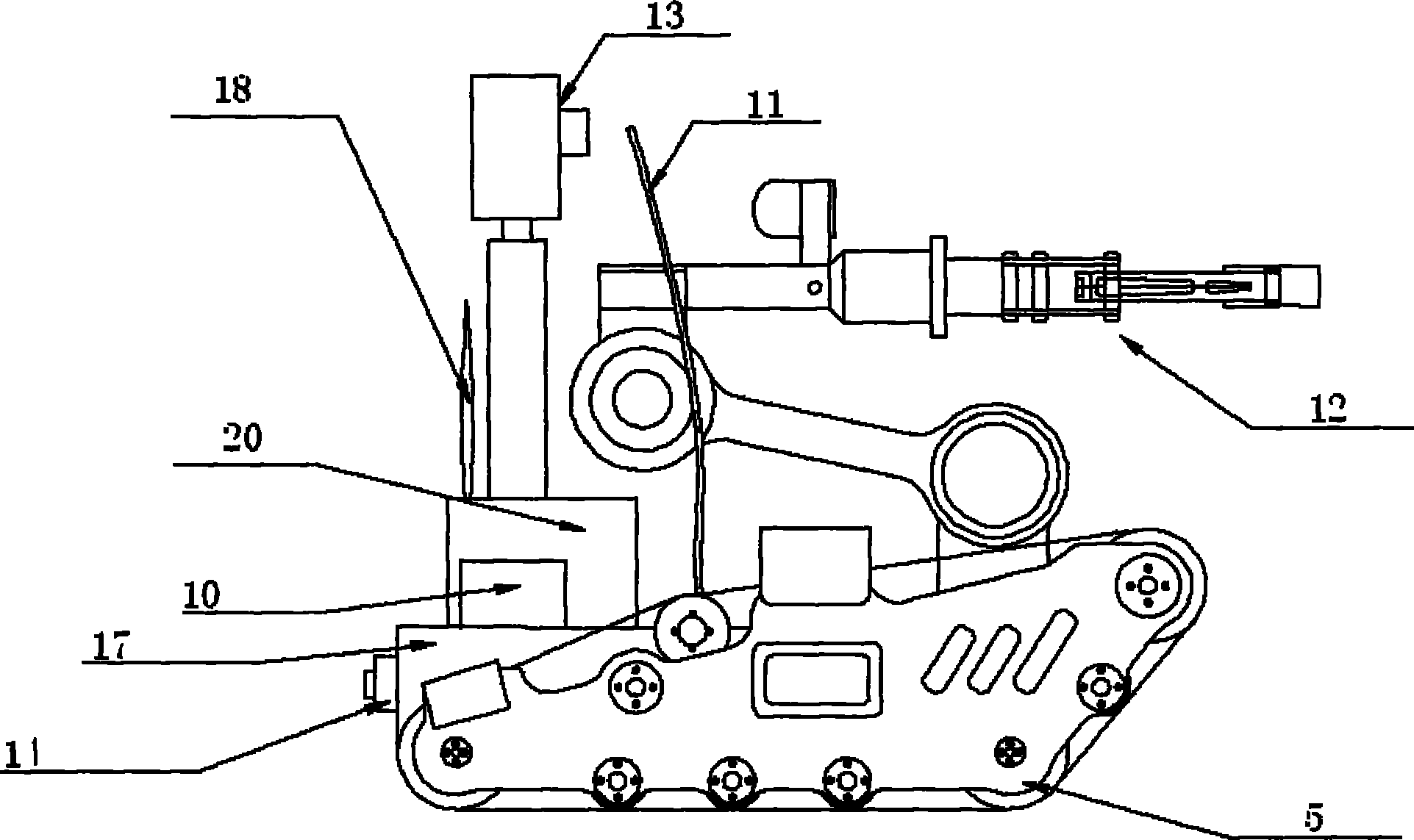
Nuclear power plant working robot and control system thereof
InactiveCN101774170ACapable of autonomous navigationRealize online monitoringEndless track vehiclesManipulatorTerrainOperational costs
The invention relates to a nuclear power plant working robot and a control system thereof, which belong to the fields of robots and automation equipment. The nuclear power plant working robot is a crawler-type mobile manipulator and is composed of a mobile platform driven by double crawlers and a four freedom degree manipulator carried on the mobile platform. The nuclear power plant working robot can move inside a nuclear power plant, has two control modes of manual remote control and autonomous control, and is remotely controlled by a wireless or wired mode. The control system of the nuclear power plant working robot includes a host monitoring and planning control system and a robot control system which are matched to control the operation of the robot. The robot operates autonomously, is safe and reliable, can complete certain dangerous tasks in high radioactivity environment; the robot has small size, stable performance, great maneuverability and low operation cost; a crawler-type chassis has strong gripping force as well as certain climbing and obstacle clearing ability, and is suitable to walking over complex terrains; and the robot has high intelligence degree and can realize autonomous control and manual remote control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
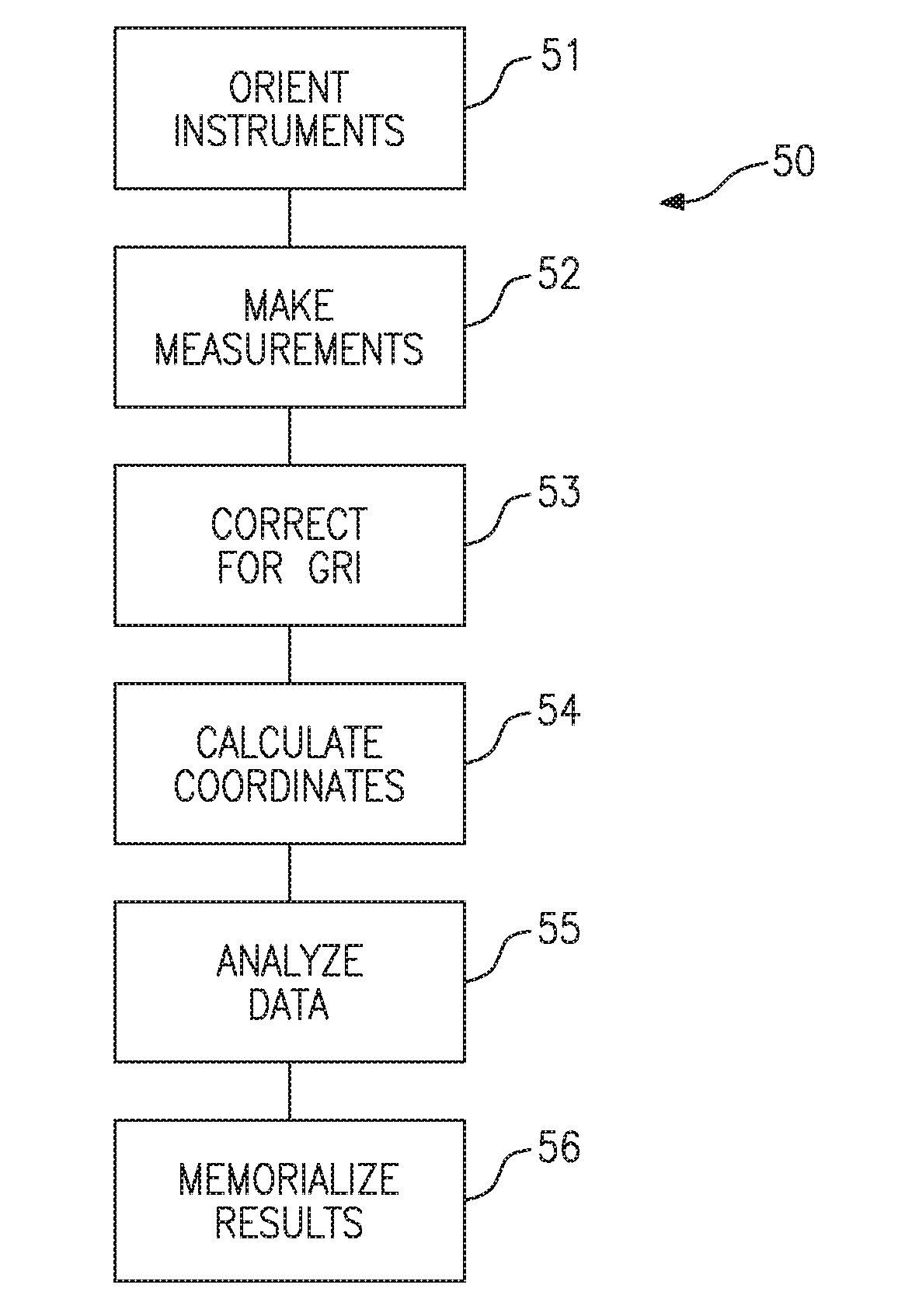
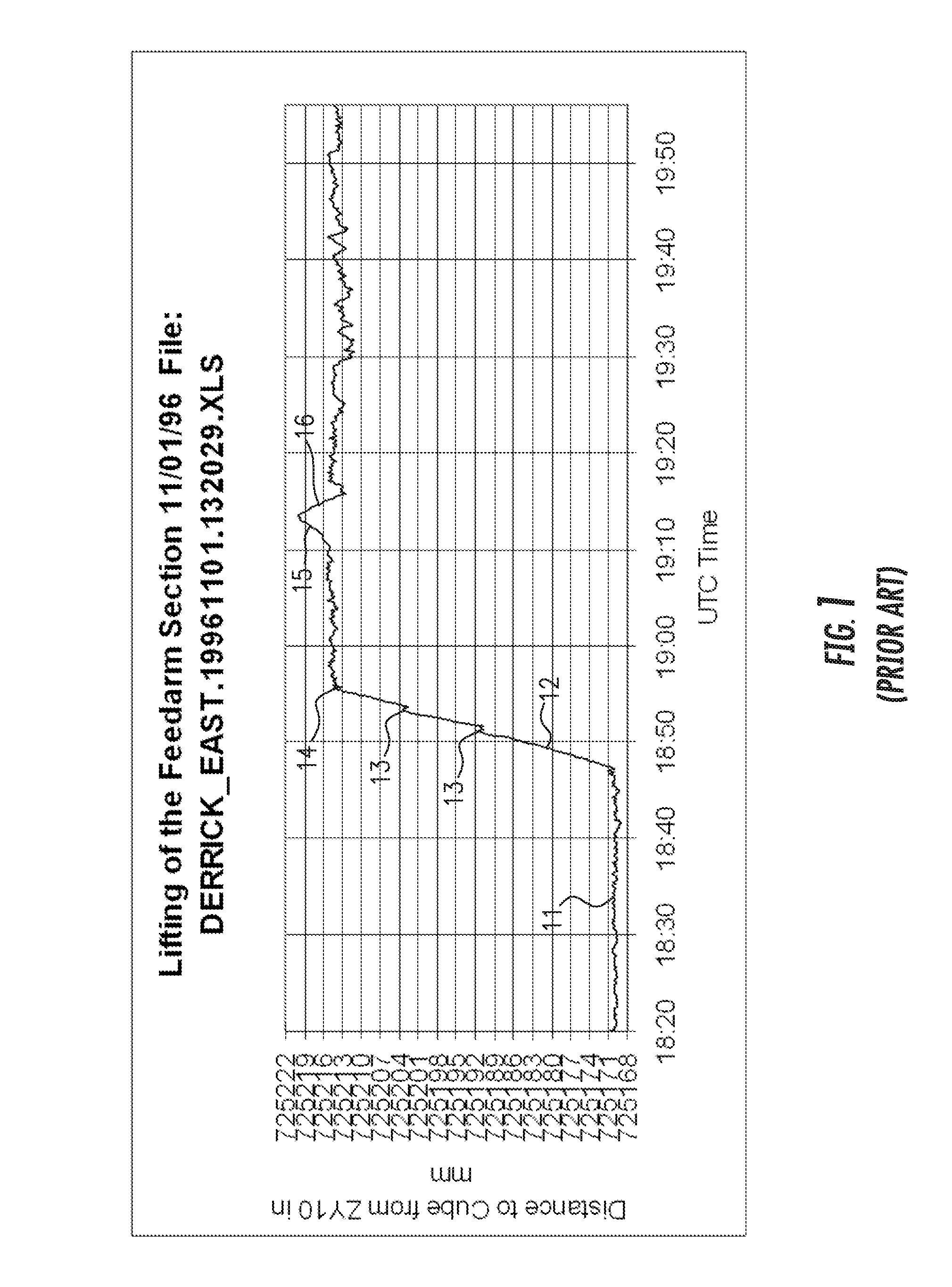
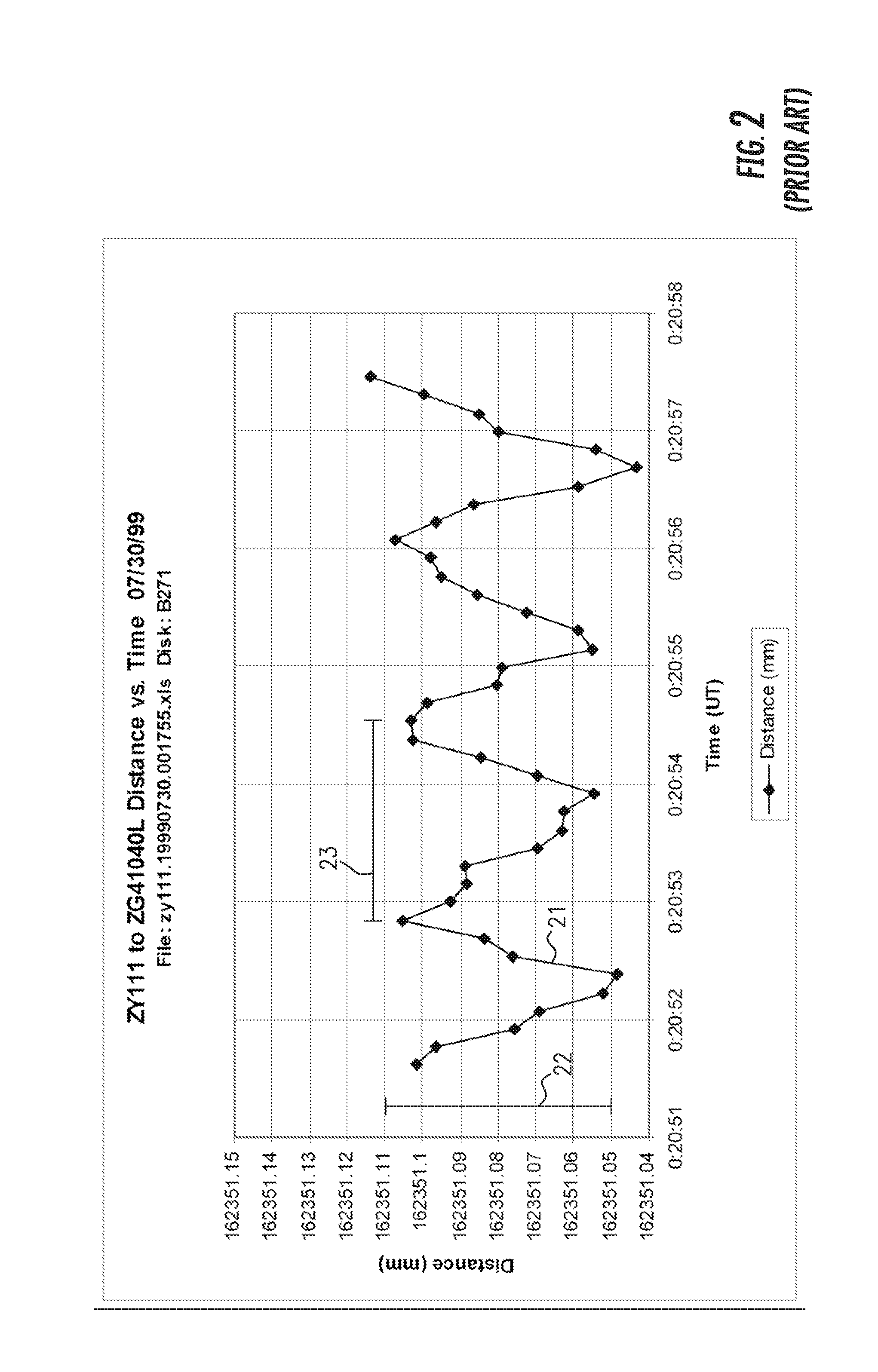
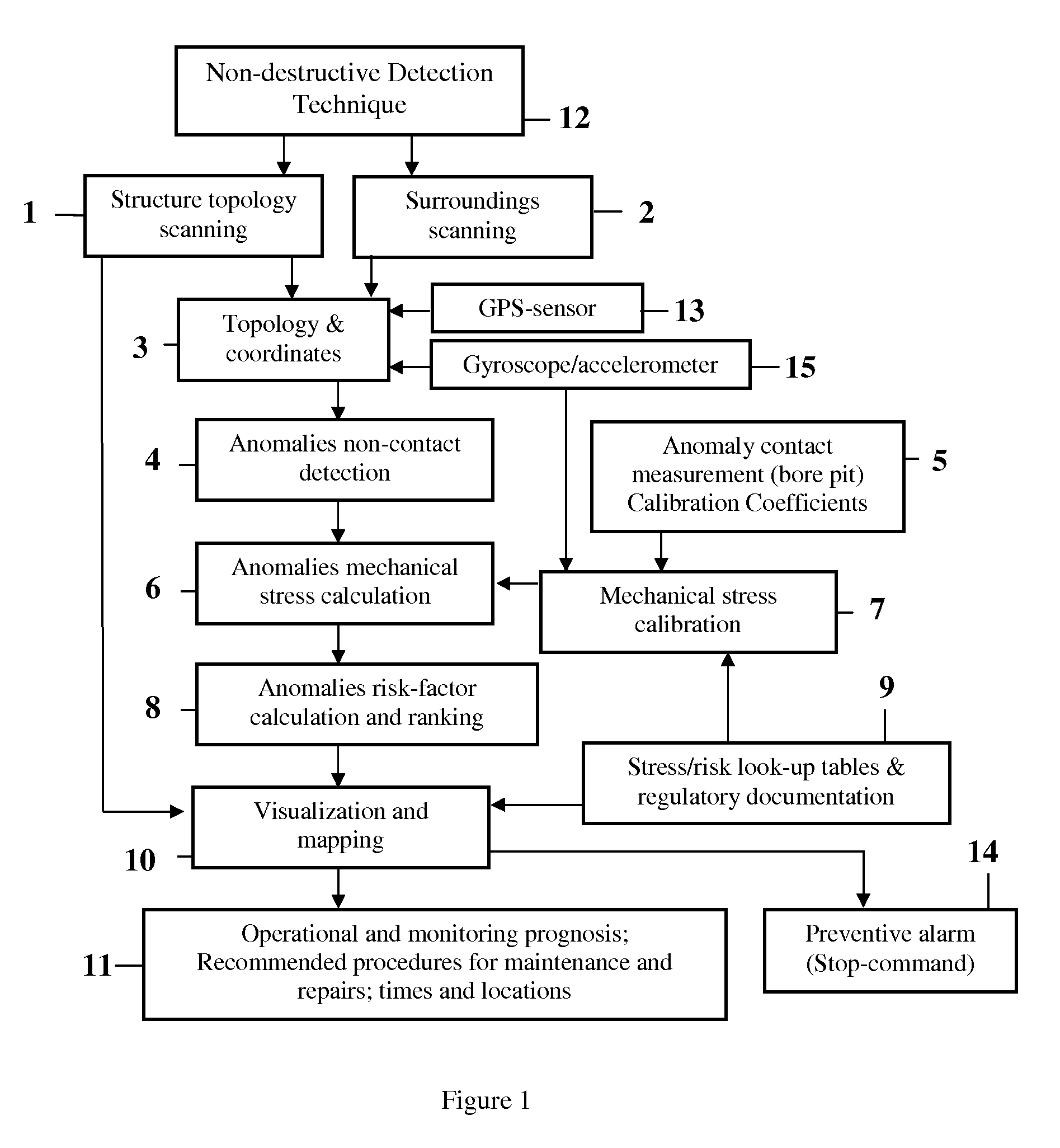
Methods for measuring and modeling the process of prestressing concrete during tensioning/detensioning based on electronic distance measurements
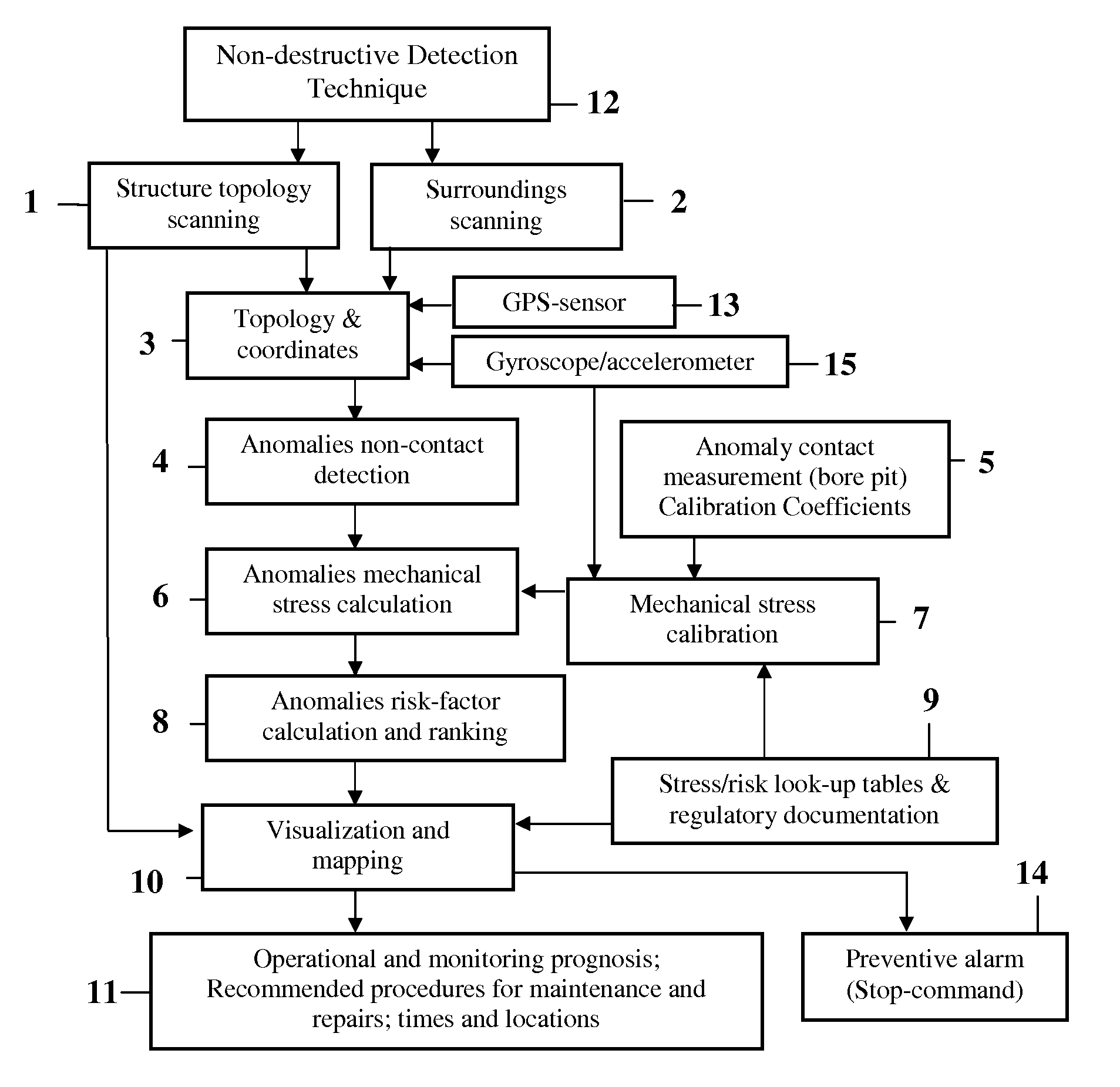
Methods are disclosed for nondestructive testing and measuring the structural health of prestressed concrete structures, such as slabs, columns, girders, bridges, towers, elevated storage tanks, silos, cooling towers, wind power generation towers, liquefied gas storage tanks, nuclear power containment buildings, and the like. Measurements are made as the structure undergoes tensioning and detensioning operations. By measuring actual movements of cardinal points on the structure, in an absolute three-dimensional coordinate system, and comparing the measurements to a model—as tension on a tendon is changed—a margin of safety is assured. High accuracy measurements are made by electronic distance measurement (EDM) instruments over hundreds of meters, which yield coordinates of cardinal points with an uncertainty of the order of one part per million. The methods are proposed as possible alternatives to prior failures of post-tensioned concrete, including the Las Lomas Bridge, the Kapiolani Interchange On-Ramp, Turkey Point Unit 3 Nuclear Power Plant, and Crystal River Unit 3 Nuclear Power Plant. An extensive review of the most closely related prior arts is included.
Owner:SOPHIE LIN TRUSTEE OF THE JOHN MICHAEL PAYNE FAMILY TRUST +1
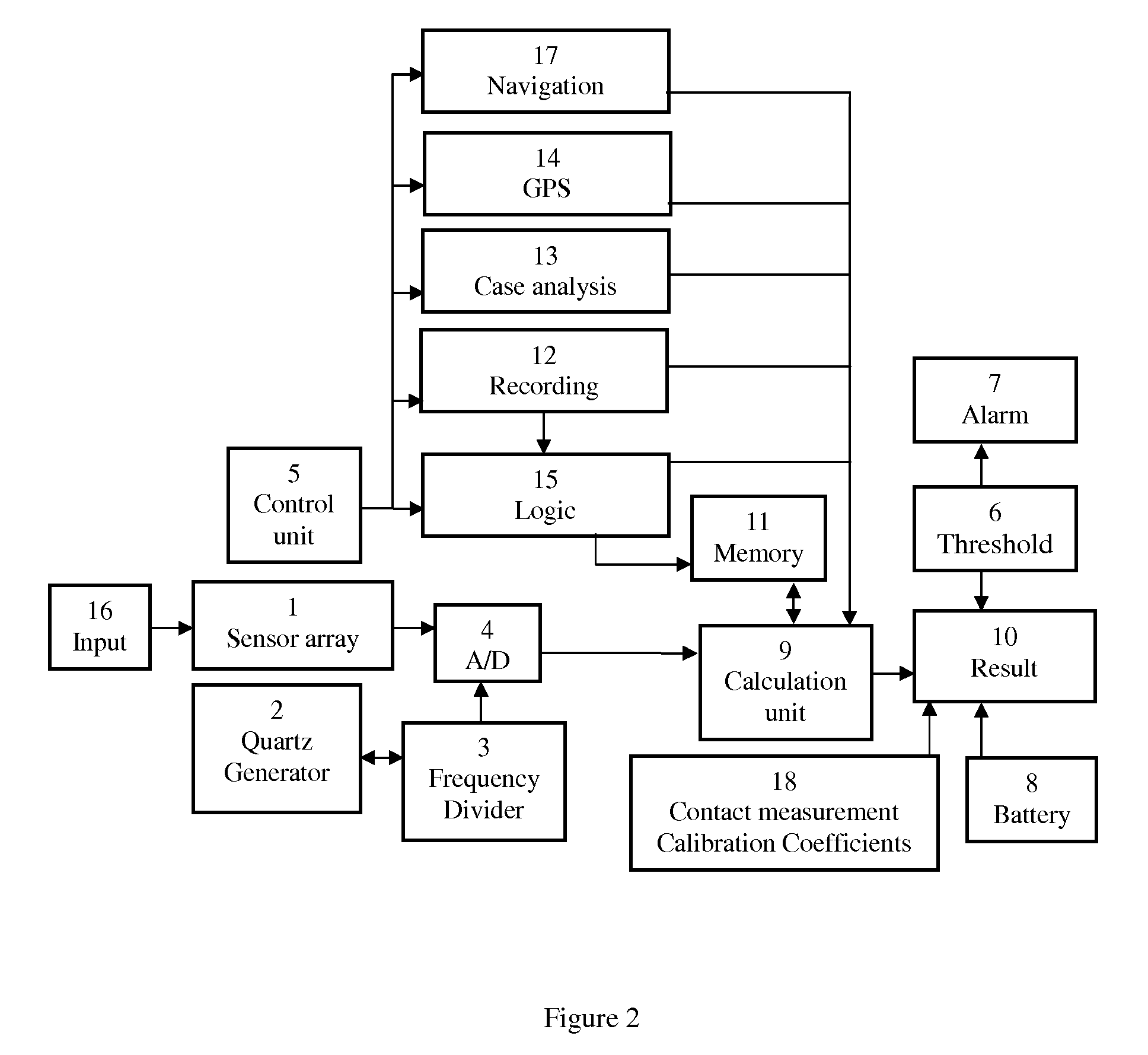
Apparatus and method for metallic constructions assessment
ActiveUS20140368191A1Improve accuracyEnsure qualitySusceptibility measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesEngineeringHeavy duty
A device for discovering, identification and monitoring, of mechanical flaws in metallic structures is disclosed, based on magneto-graphic / magnetic tomography technique to identify stress-related defects. The device includes registration means that optimized for use with metallic structures of various types, shapes and sizes. Applications include a real-time quality control, monitoring and emergency alarms, as well structural repairs and maintenance work recommendations and planning. Examples of the device implementation include pipes for oil and gas industry monitoring, detection of flaws in rolled products in metallurgical industry, welding quality of heavy duty equipment such as ships, reservoirs. etc. It is especially important for loaded constructions, such as pressured pipes, infrastructure maintenance, nuclear power plant monitoring, bridges, corrosion prevention and environment protection.
Owner:GOROSHEVSKIY VALERIAN +2
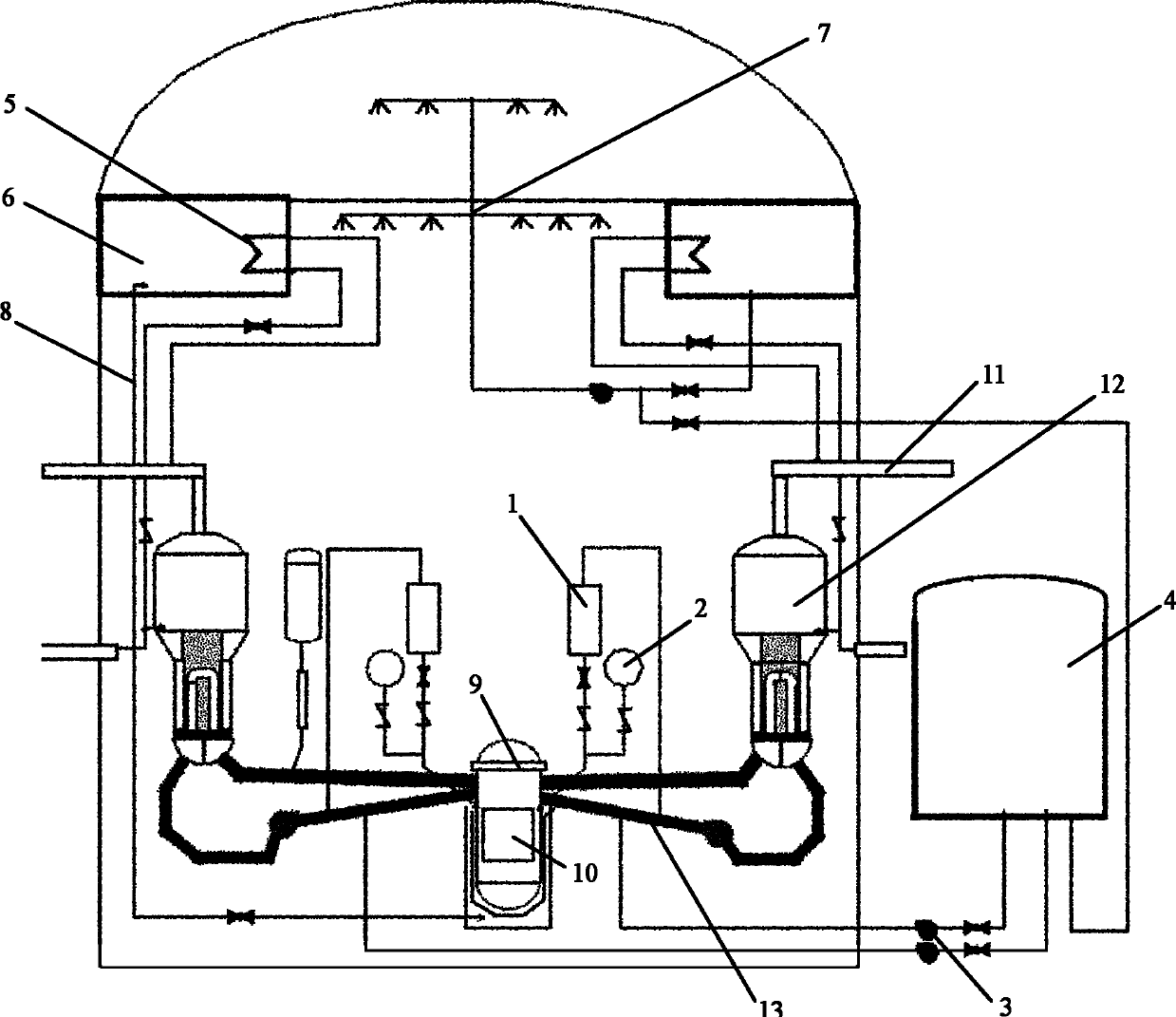
Passive and active combined special safety system for nuclear power plant
InactiveCN102169733AImprove securityReduced risk of serious accidentsNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementActive safetyNuclear power
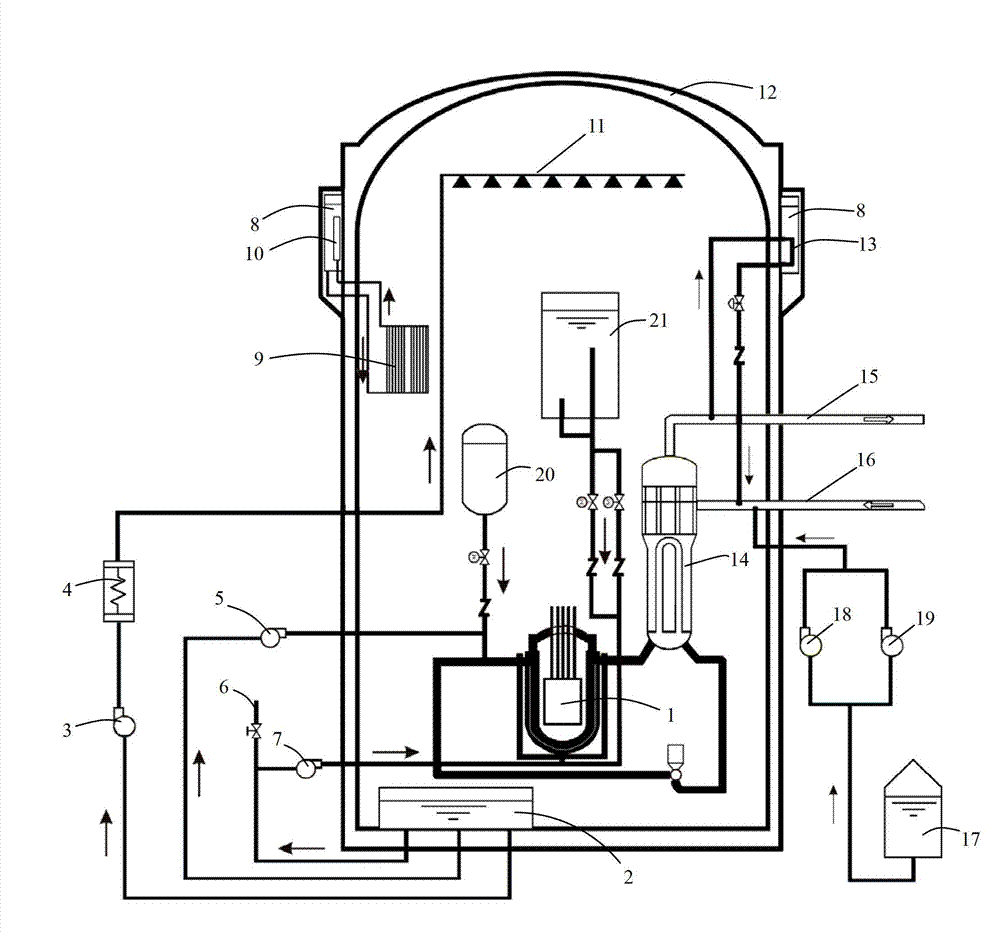
The invention belongs to safety equipment for a nuclear power plant, in particular to a passive and active combined special safety system for the nuclear power plant. The system comprises a passive high-pressure core water supply tank, an accumulator, a low-pressure safety injection pump, a refueling water tank, a secondary-side passive residual heat removal heat exchanger, a vapor condensation water tank, a containment spray system, a passive reactor cavity water injection system, related valves and related pipes. When the nuclear power plant has a design basis accident or beyond design basis accident, through a series of passive and active safety facilities used in all steps, the circuit of a reactor and the core can be cooled effectively, so that the nuclear power plant can enter a safe cold shutdown condition smoothly; and thus, the serious accident consequence of the reactor is inhibited or relieved, damage caused by accidents is relieved, and the safety of the nuclear power plant is improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
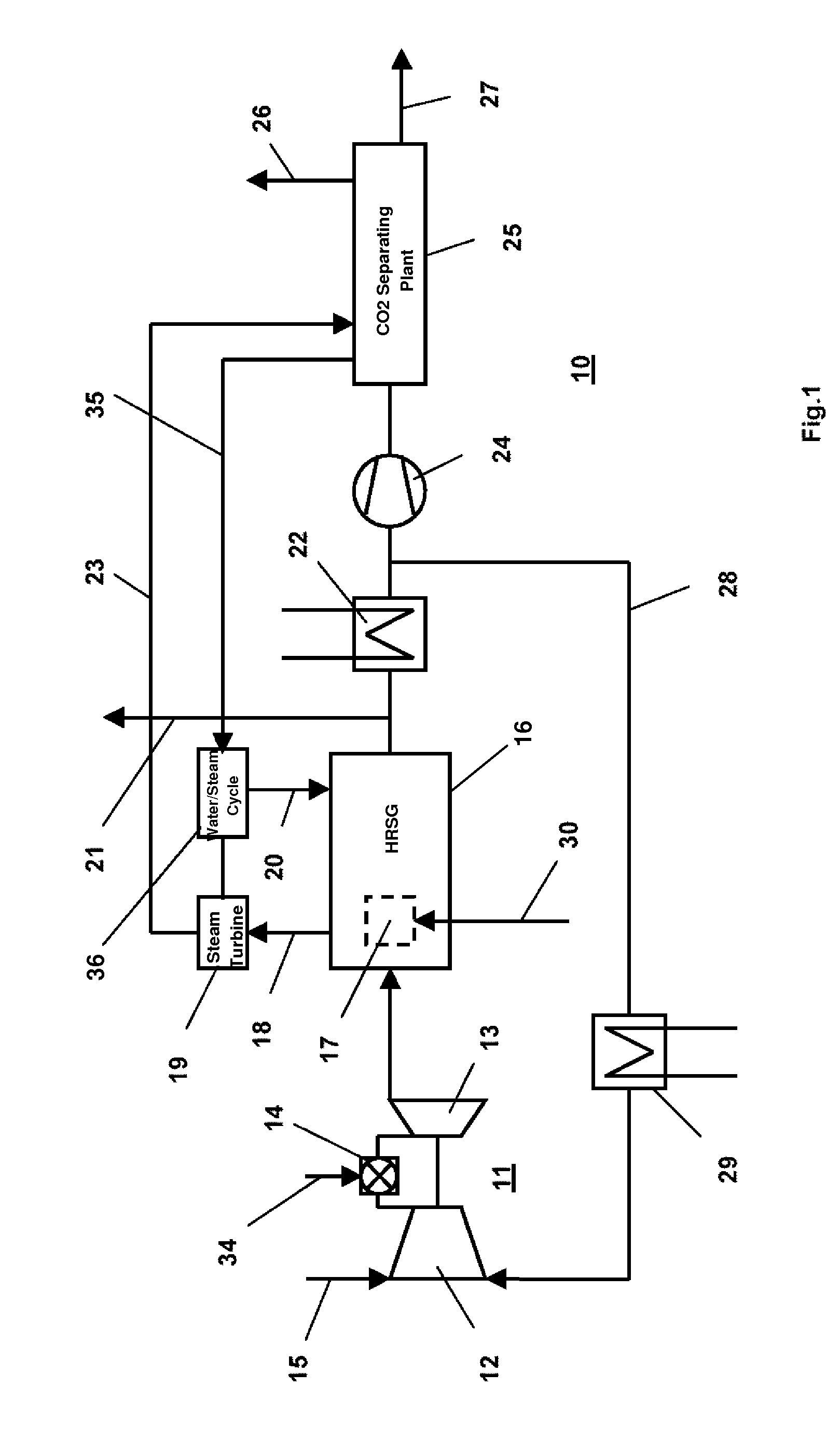
Combined-cycle power plant with exhaust gas recycling and CO2 separation, and method for operating a combined cycle power plant
InactiveUS8424282B2High outputReduce probabilityGas turbine plantsDirect carbon-dioxide mitigationPower stationExhaust fumes
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
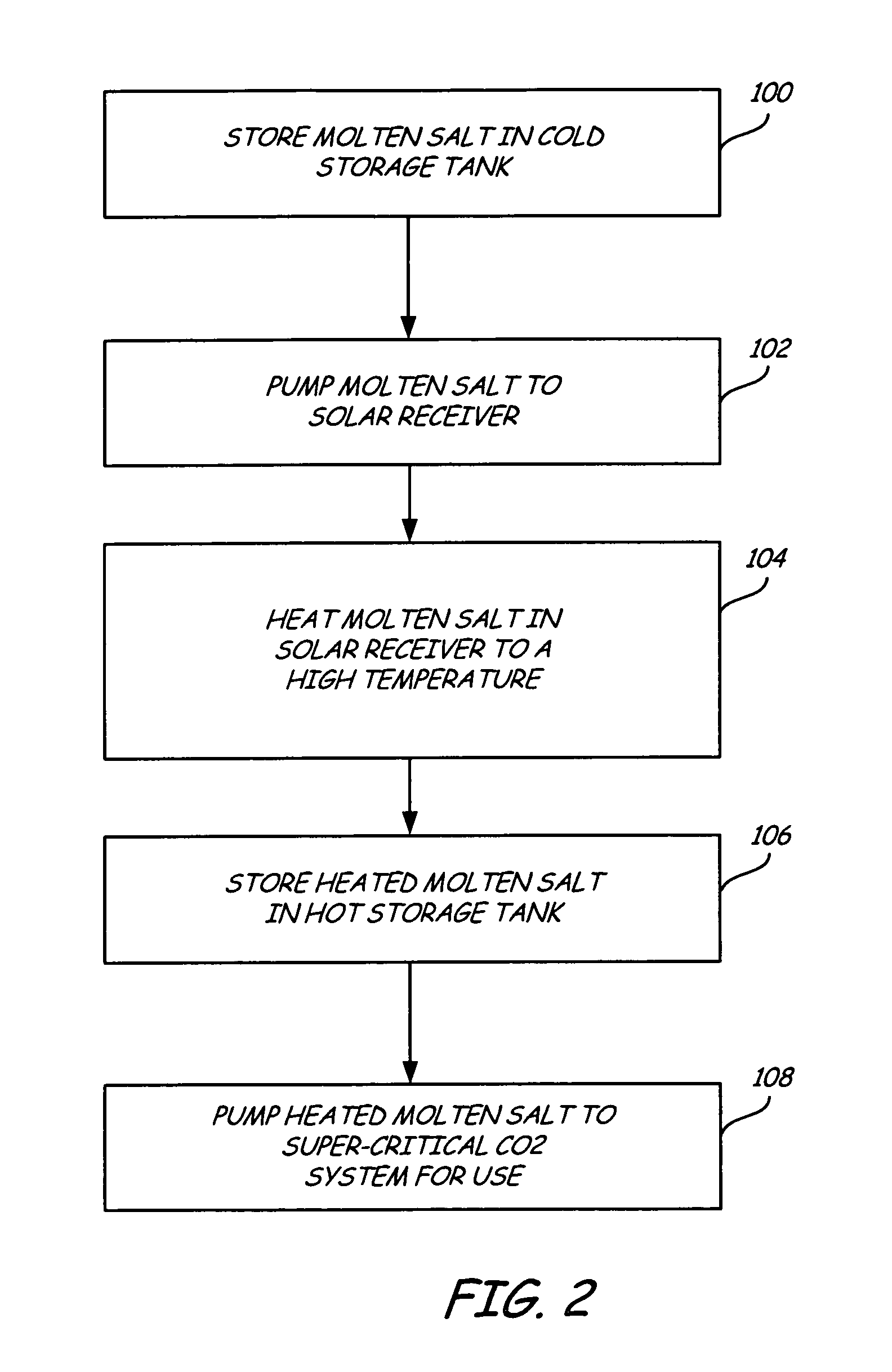
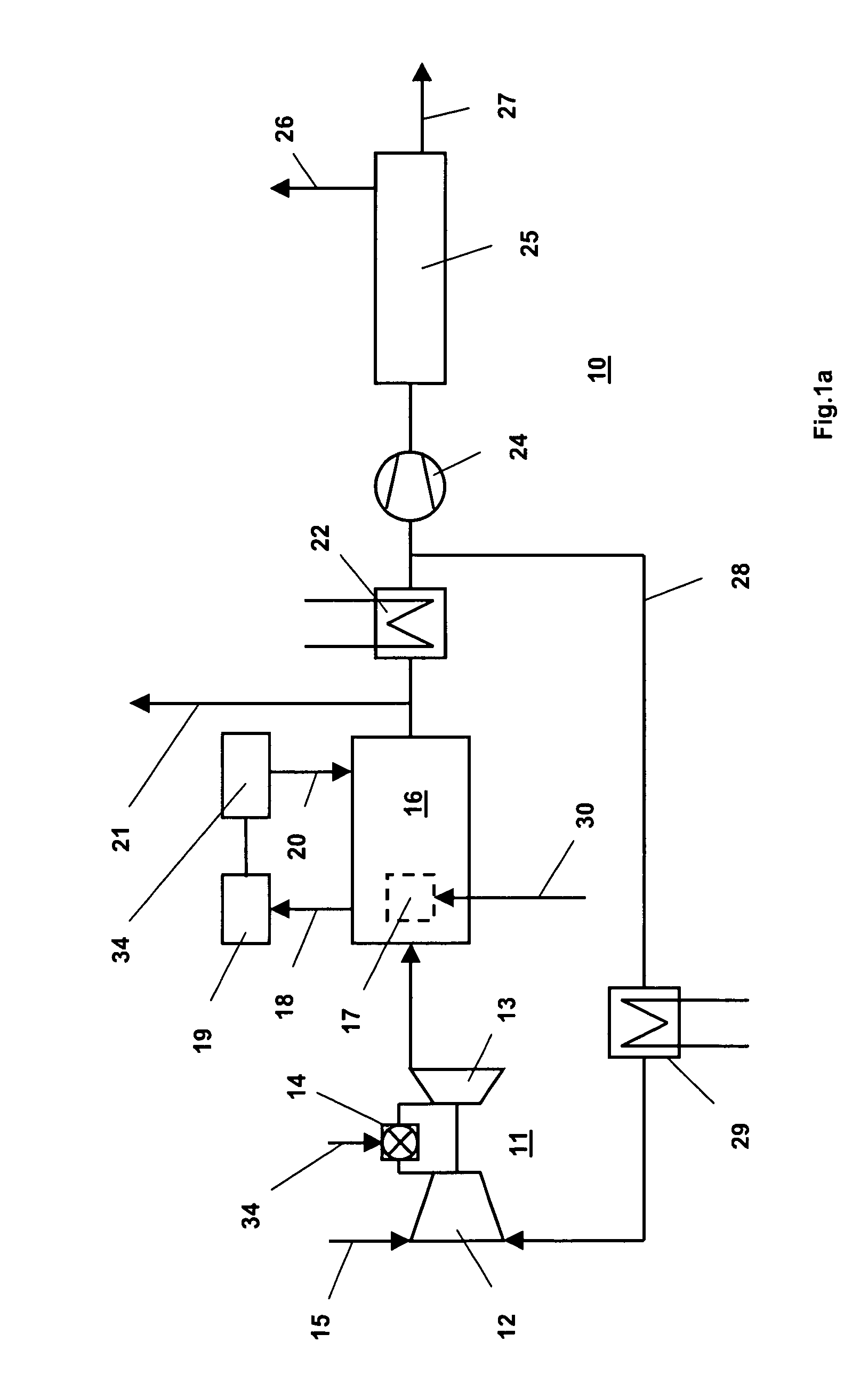
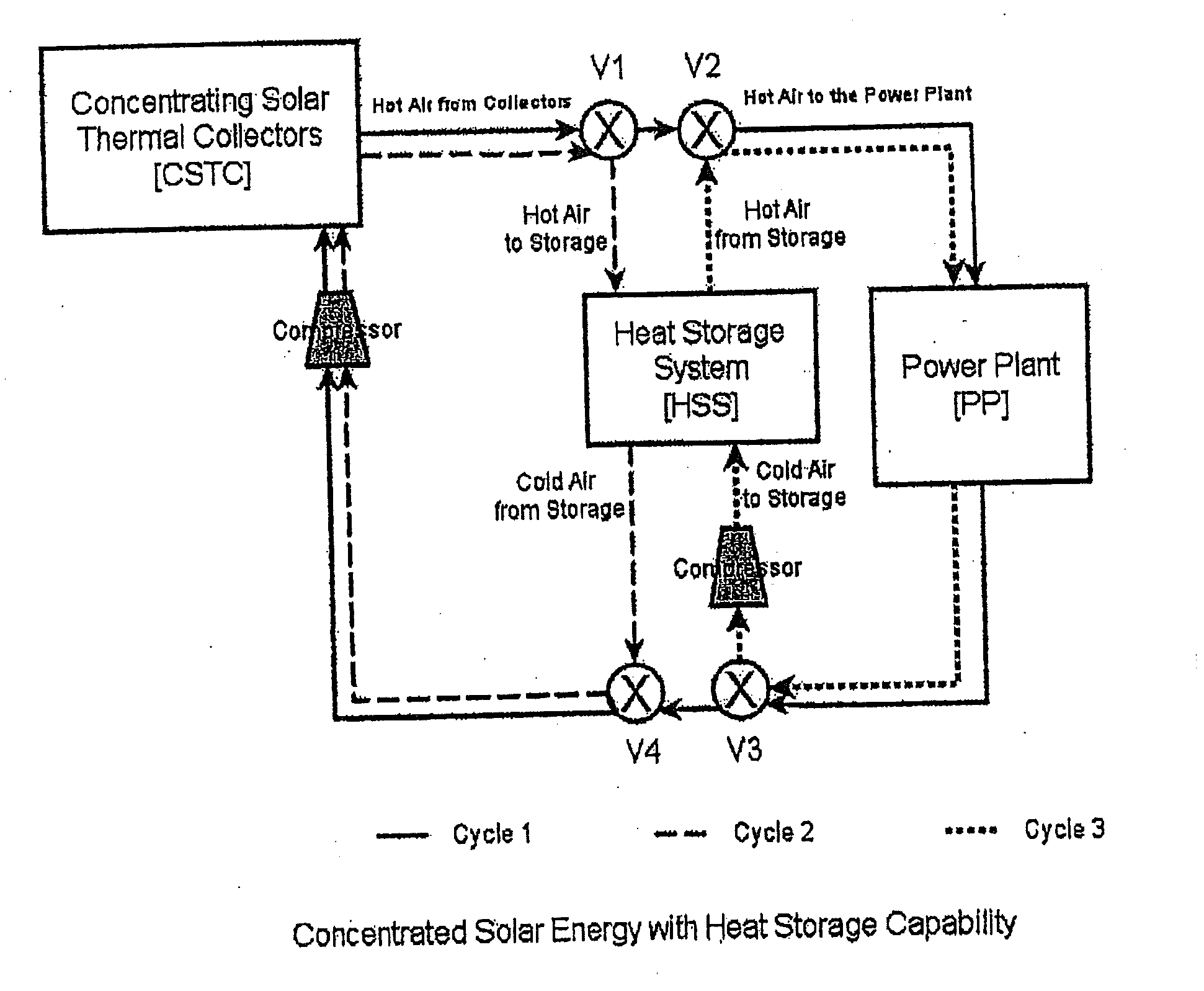
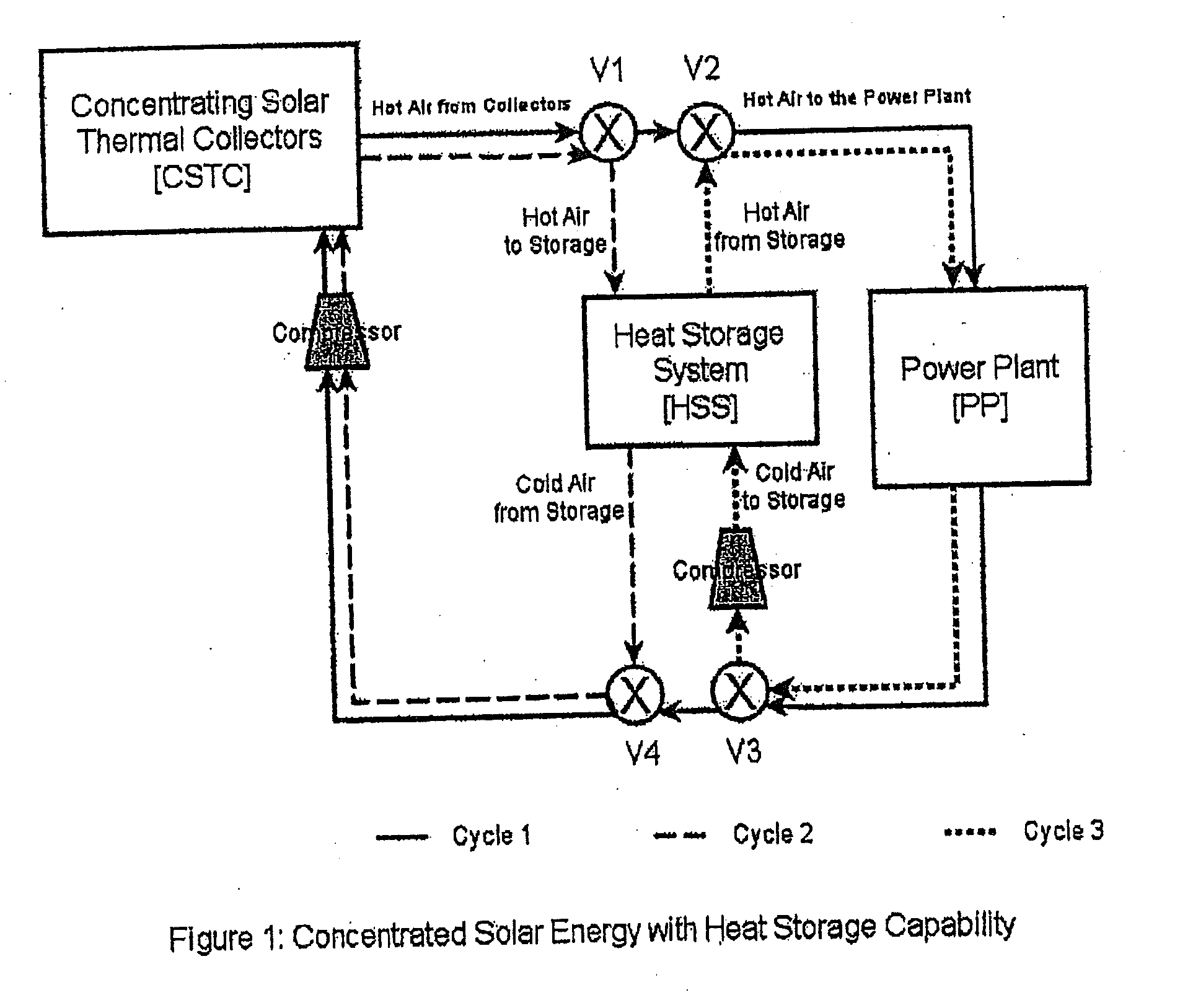
Solar power plant and method and/or system of storing energy in a concentrated solar power plant
ActiveUS20110277471A1Big advantageLower energy requirementsSolar heating energyFrom solar energyPower stationEngineering
A method for storing heat from a solar collector CSTC in Concentrating Solar Power plants and delivering the heat to the power plant PP when needed. The method uses a compressed gas such as carbon dioxide or air as a heat transfer medium in the collectors CSTC and transferring the heat by depositing it on a bed of heat-resistant solids and later, recovering the heat by a second circuit of the same compressed gas. The storage system HSS is designed to allow the heat to be recovered at a high efficiency with practically no reduction in temperature. Unlike liquid heat transfer media, our storage method itself can operate at very high temperatures, up to 3000° F., a capability which can lead to greater efficiency.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Combined cycle power plant with flue gas recirculation
ActiveUS20110289898A1Continuous combustion chamberNon-fuel substance addition to fuelPower stationFlue gas
An exemplary system method for the operation of a CCP P with flue gas recirculation to reduce NOx emissions and / or to increase the CO2 concentration in the flue gases to facilitate CO2 capture from the flue gases is disclosed. The flue gas recirculation rate (rFRG) is controlled as function of the combustion pressure and / or the hot gas temperature. Operability is enhanced by admixing of oxygen or oxygen enriched air to the gas turbine inlet gases or to the combustion.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
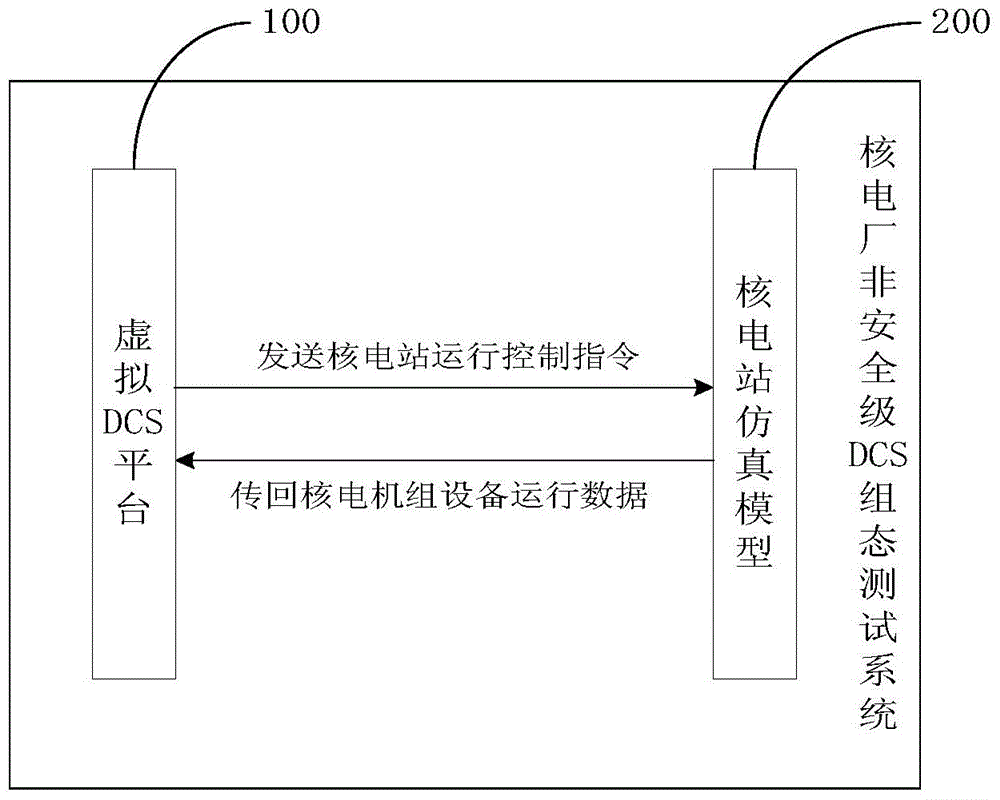
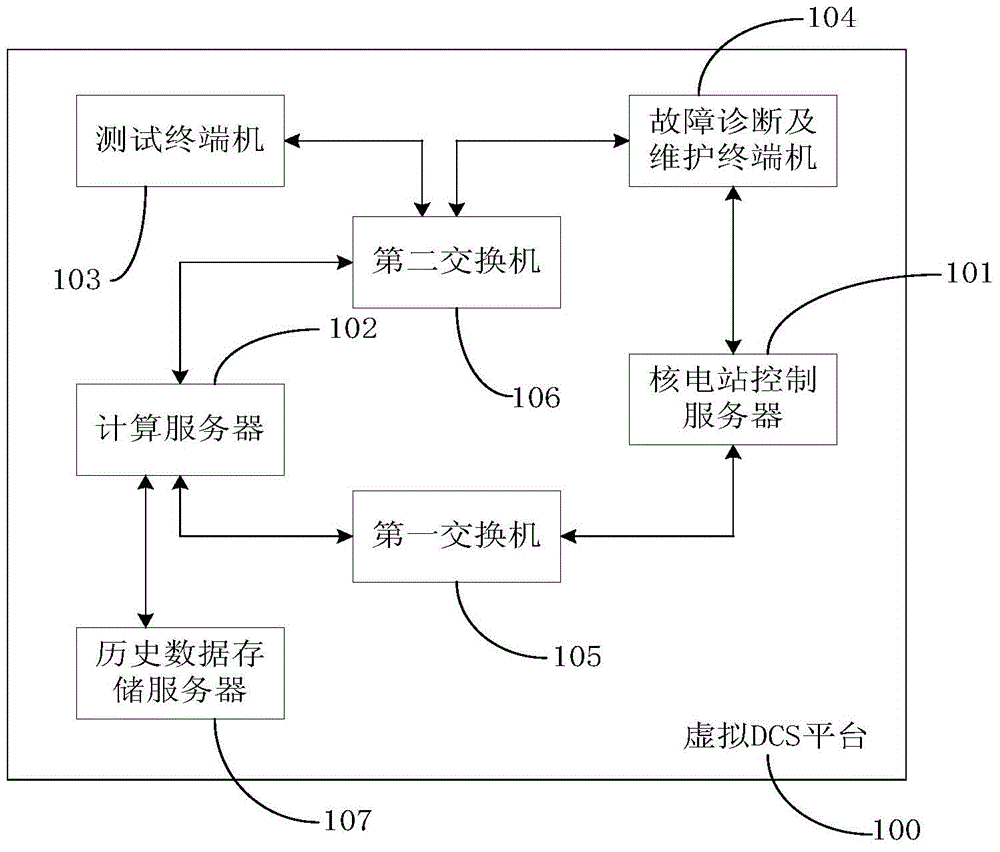
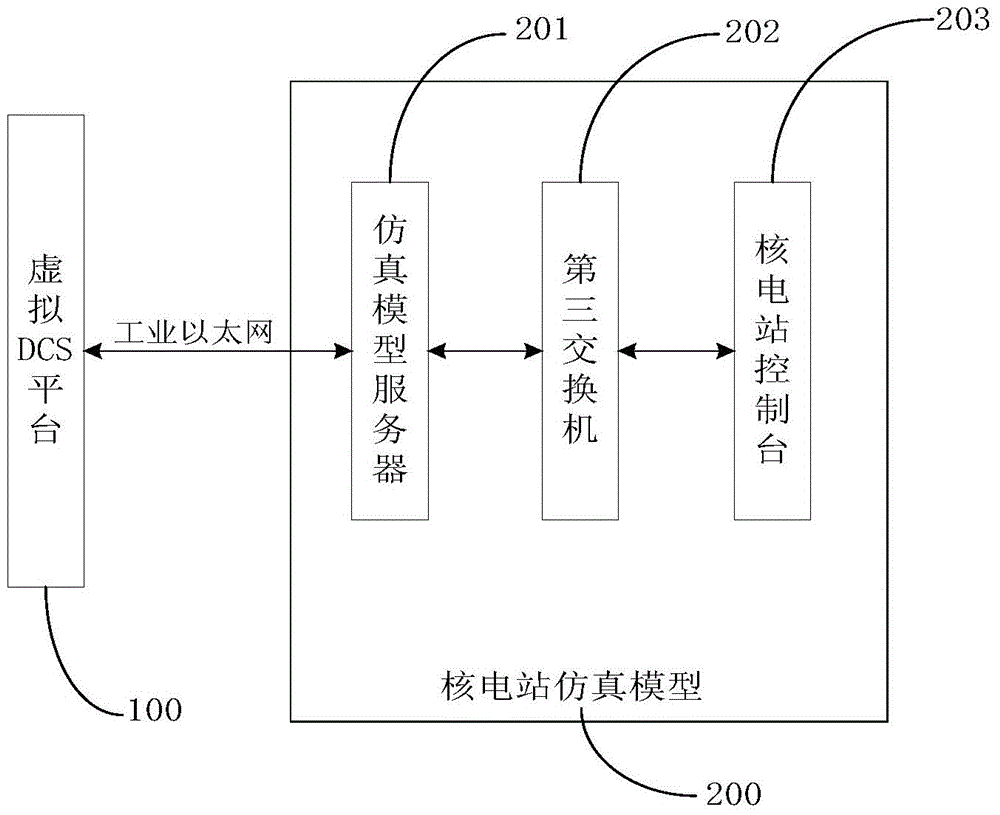
Nuclear power plant non-security-level DCS configuration testing method and system
ActiveCN104898633ALow input costSimple network structureTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a nuclear power plant non-security-level DCS configuration testing method and system comprising a virtual DCS platform and a nuclear power station simulating model coupled to the virtual DCS platform. The nuclear power station simulating model is used for, according to a nuclear power unit operation control instruction given by the virtual DCS platform, simulating the operation of a real nuclear power station, acquiring the operating data of the nuclear power unit, and returning the acquired data to the virtual DCS platform. The virtual DCS platform is used for, according to the operating data of the nuclear power unit, computing and analyzing the operating condition of the nuclear power unit in real time, evaluating a difference between an analyzed result and a designed operating condition, determining the correctness and the rationality of DCS configuration logic and parameters, giving corresponding logic modification and parameter optimization, and transplanting and applying a tested and modified result to the DCS configuration of a real nuclear power unit. The nuclear power plant non-security-level DCS configuration testing method and system may reduce the investment cost of the nuclear power station, shorten the construction period of nuclear power engineering, and decrease equipment loss.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
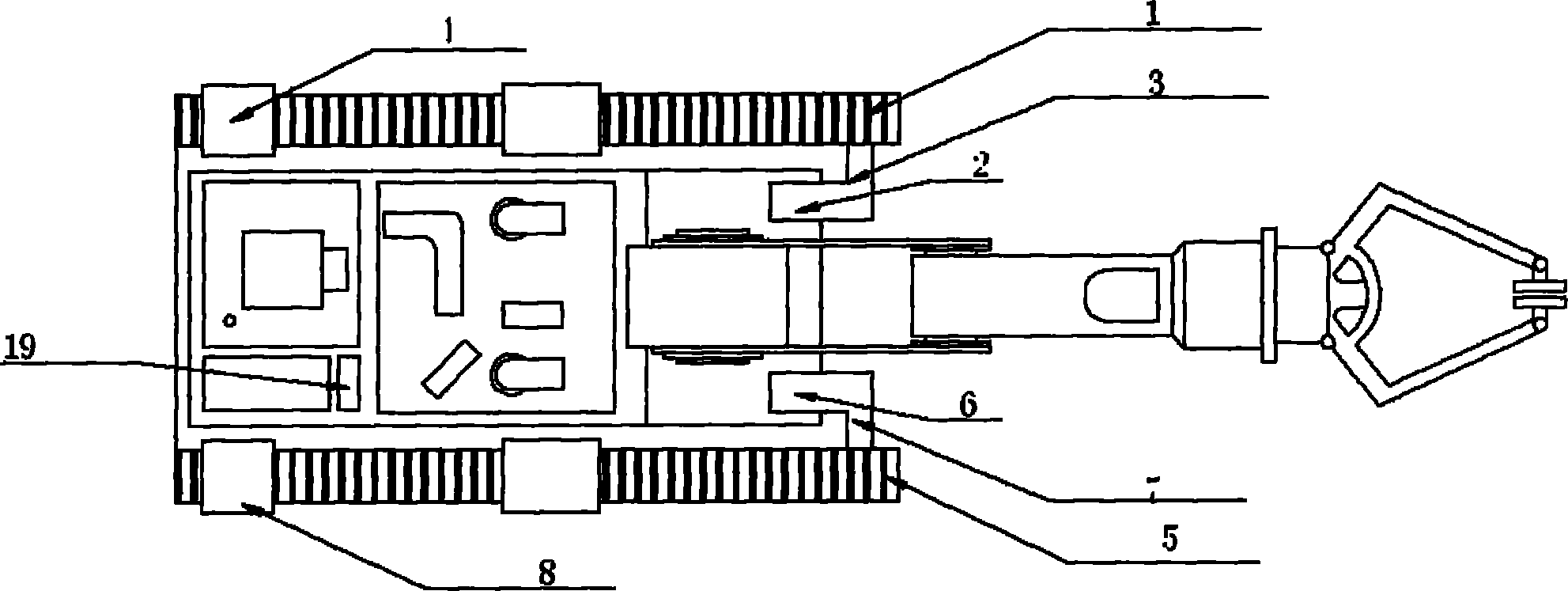
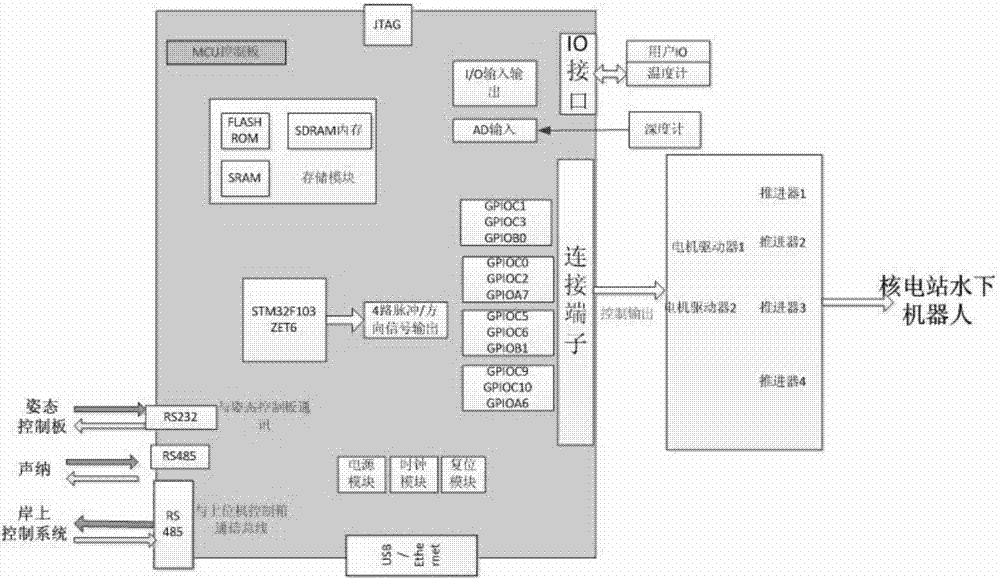
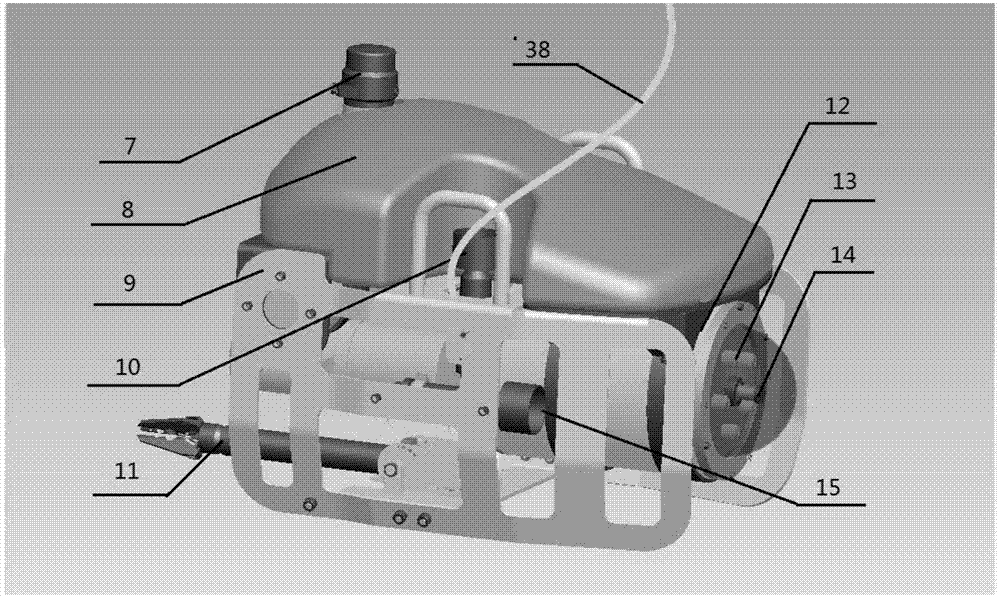
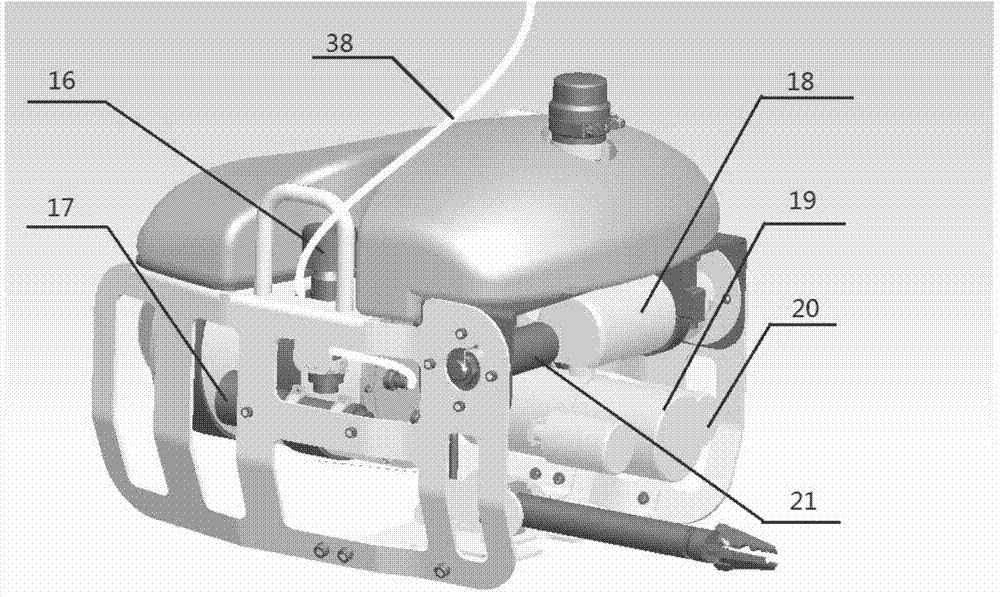
Microminiature operation underwater robot of nuclear power plant
The invention relates to a microminiature operation underwater robot of a nuclear power plant, and the robot comprises an underwater robot body and an onshore control system, wherein two propellers are respectively arranged in the horizontal and vertical directions of the robot body, a depth gauge is arranged on the right side of the front part of the robot body, a manipulator is arranged at the bottom in front of the robot body, and a sonar is arranged on the top of the robot body; a control cabin is arranged in the middle rear part of the robot body; an outer cabin is sealed by a transparent glass cover, and is provided with a rearview camera and an auxiliary lighting light-emitting diode (LED) lamp; a front-view camera system is arranged at the front part of the robot body, and comprises a zooming radiation resistant camera tube, a tripod head and a lighting lamp; a video image and control signal is transmitted to the onshore control system through a shield cable; and the control system comprises a movement control rod, a manipulator control button, a keyboard, a main display screen and a speed governing knob. The microminiature operation underwater robot of the nuclear power plant is used for the monitoring and the simple foreign body fishing of a core pool, a spent fuel pool and a component pool of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
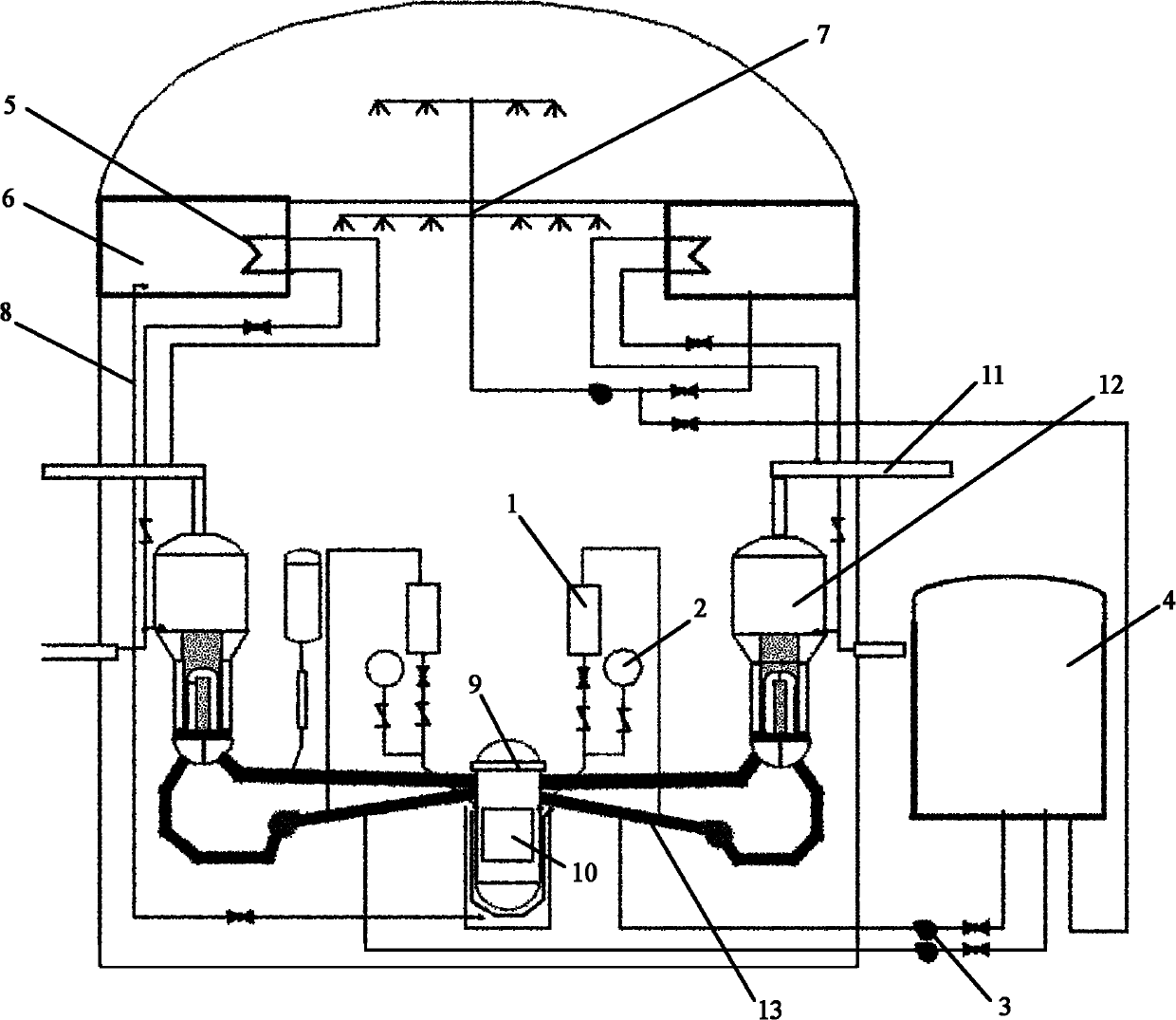
Active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system for nuclear power station
ActiveCN102903404AReduced risk of serious accidentsGuaranteed completeness of security functionsNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention relates to an active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system for a nuclear power station. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system comprises a safety injection system, a containment spraying system, an auxiliary water supply system, a reactor cavity water injection system, a secondary side passive residual heat removal system, a passive containment heat leading-out system and related valves and pipelines. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system provided by the invention realizes three safety functions of controlling reactivity, discharging reactor core heat and containing radioactive substance when an accident occurs in an active-passive combined multi-redundancy diversity manner. The active-passive combined reactor core residual heat removal system provided by the invention can completely realize the safety functions of safety injection and safety spraying under the condition that the accident occurs in a nuclear power plant, reactor cavity water injection under the serious accident working condition and the like, effectively improve reliability of a safety system, enhance coping capability of the safety system under the working condition that the accident occurs in the nuclear power station, can effectively prevent and relieve the serious accident, reduce the reactor core melting probability and risk probability of large-scale radioactivity release and greatly improve safety performance of the nuclear power station.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Method and system for improving reliability of emergency power supplies of nuclear power plant
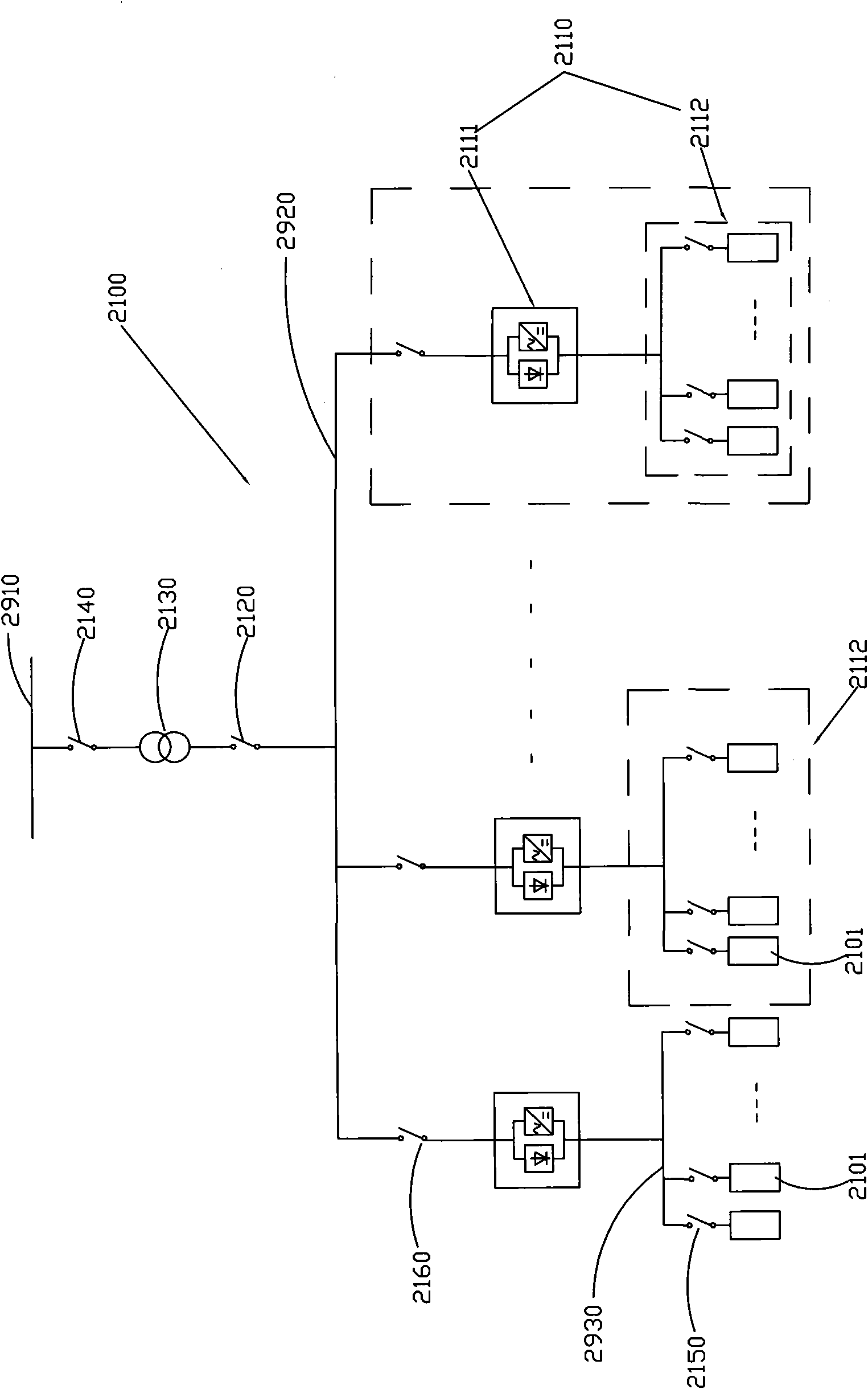
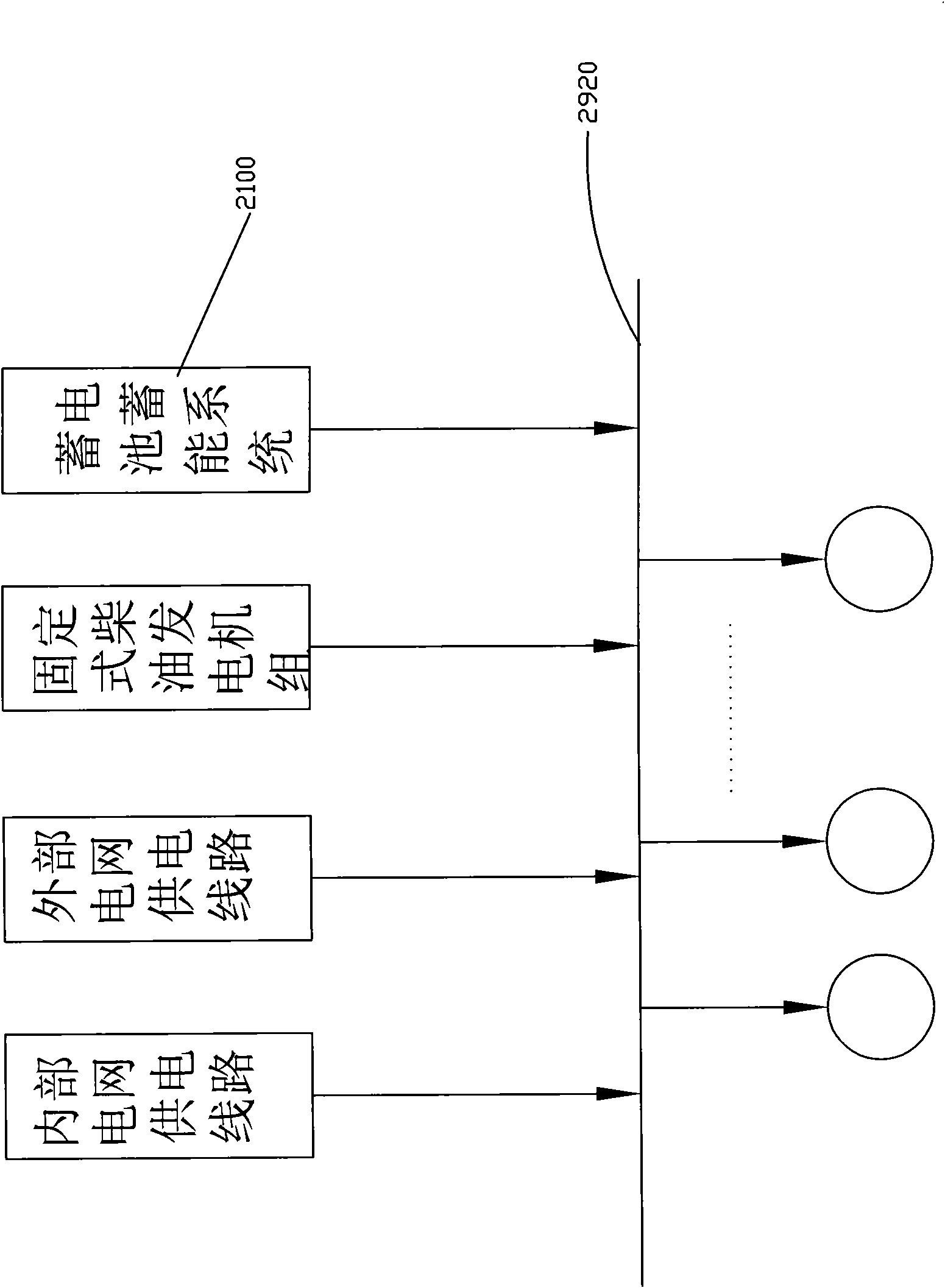
ActiveCN102195334AImprove reliabilityImprove securityBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerExtreme weatherNatural disaster
The invention relates to a method and system for improving reliability of emergency power supplies of a nuclear power plant. At least one path of high-capacity battery energy storage system (fixed energy storage system and / or movable energy storage system) is used to supplement or replace final emergency power supplies of a nuclear power plant. When all existing emergency power supplies of the nuclear power plant fail, the system is started to supply power for equipment in an emergency plant of the nuclear power plant so as to keep discharging waste heat of reactor cores and cooling spent fuel pools of the nuclear power plant, thus ensuring the safety of the nuclear power station. The method and system provided by the invention can be used for resisting against extreme weathers and avoiding common mode failure of the emergency power supplies in the extreme weathers, can strength the reliability of the emergency power supplies of the nuclear power plant and can at least reduce the melting probability of reactor cores by 21.6%, thereby improving the integral nuclear safety level of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:GUANGDONG NUCLEAR POWER JOINT VENTURE +1
Apparatus for the non-contact metallic constructions assessment
ActiveUS8542127B1The result is accurate and reliableAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectrical measurementsHeavy equipmentHeavy duty
A device and method for discovering, identification and monitoring of mechanical flaws in metallic structures is disclosed, based on magneto-graphic / magnetic tomography technique to identify stress-related defects. The technique is specifically optimized for extended, not-accessible underground and underwater metallic structures quality control, emergency alarms as well as timeline planning for structural repairs and maintenance work. Examples of the technique implementation include pipes for oil and gas industry, detection of flaws in rolled products in metallurgical industry, welding quality of heavy duty equipment such as ships, reservoirs, etc. It is especially important for loaded constructions, such as pressured pipes, infrastructure maintenance, nuclear power plant monitoring, bridges, corrosion prevention and environment protection.
Owner:GOROSHEVSKIY VALERIAN +2
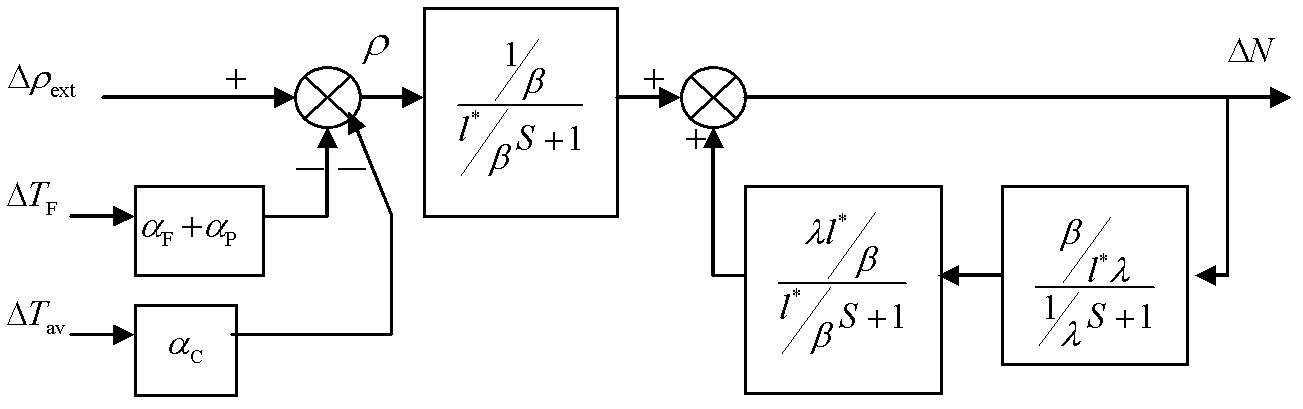
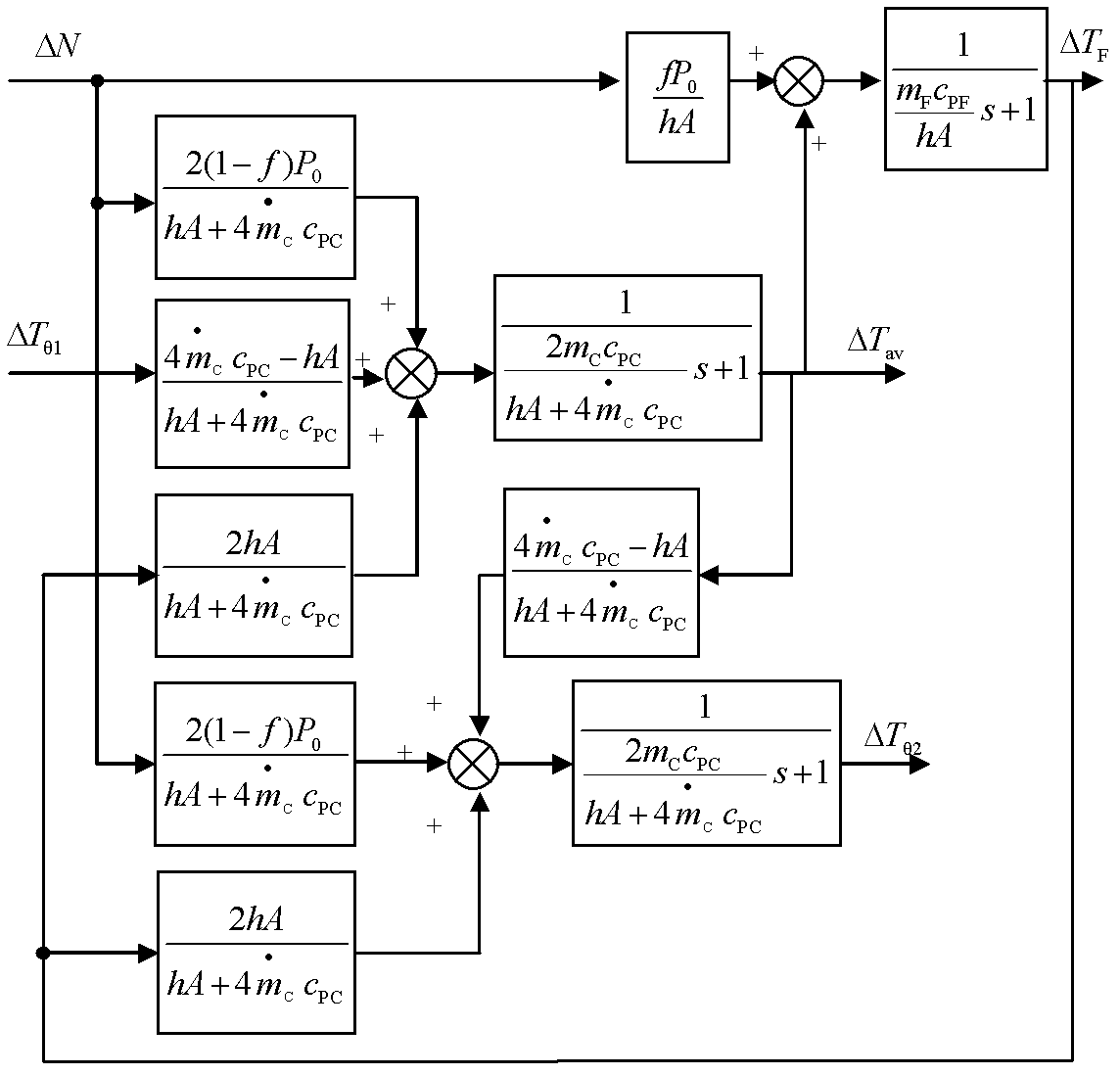
A Modeling Method for the Third Generation Pressurized Water Reactor Nuclear Power Unit
ActiveCN102279901ASolving Co-SimulationHas engineering application valueSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a modeling method for a third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating unit. The modeling method comprises the following steps of: 1, decomposing a nuclear power generating unit system into a plurality of subsystem models; 2, establishing the subsystem models in the step 1 according to heat engineering and energy transfer and conversion rules; 3, combining the subsystem models obtained in the step 2 into a nuclear power generating unit full system model, and connecting the nuclear power generating unit full system model with a power system model toobtain a combined model of a nuclear power generating unit and the power system; and 4, establishing a customized model of the third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating uniton the basis of the combined model of the nuclear power generating unit and the power system, and simulating the performance of the nuclear power generating unit and machine-grid interaction according to the customized model. The method effectively solves combined emulation of the nuclear power generating unit and a power unit, can be applied to machine-grid coordination analysis of a nuclear power plant and a power grid, and has high practicability.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
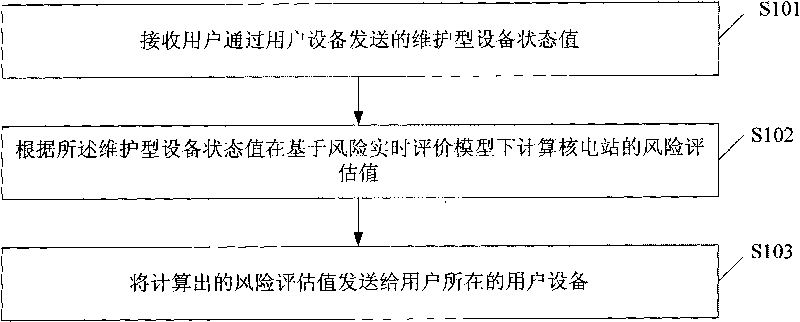
Method and device for evaluating risk of nuclear power station
ActiveCN101710400AGuaranteed correctnessGuaranteed accuracyForecastingInformation technology support systemNuclear engineeringNuclear power
The invention discloses a method for evaluating risk of nuclear power station, comprising the following steps: receiving the maintenance device state value transmitted by the user device, wherein the maintenance device is a power plant device to be regularly maintained by the user or regularly tested or a power plant device for evaluating risk value when something is wrong with the device, computing the risk evaluation value of the nuclear power station based on the risk real-time evaluation model according to the maintenance device state value, and transmitting the computed risk evaluation value to the user device where the user is. The invention further discloses a device for evaluating risk in real time. The embodiment of the invention is convenient for the operator to realize the riskcondition of the nuclear power station in real time.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
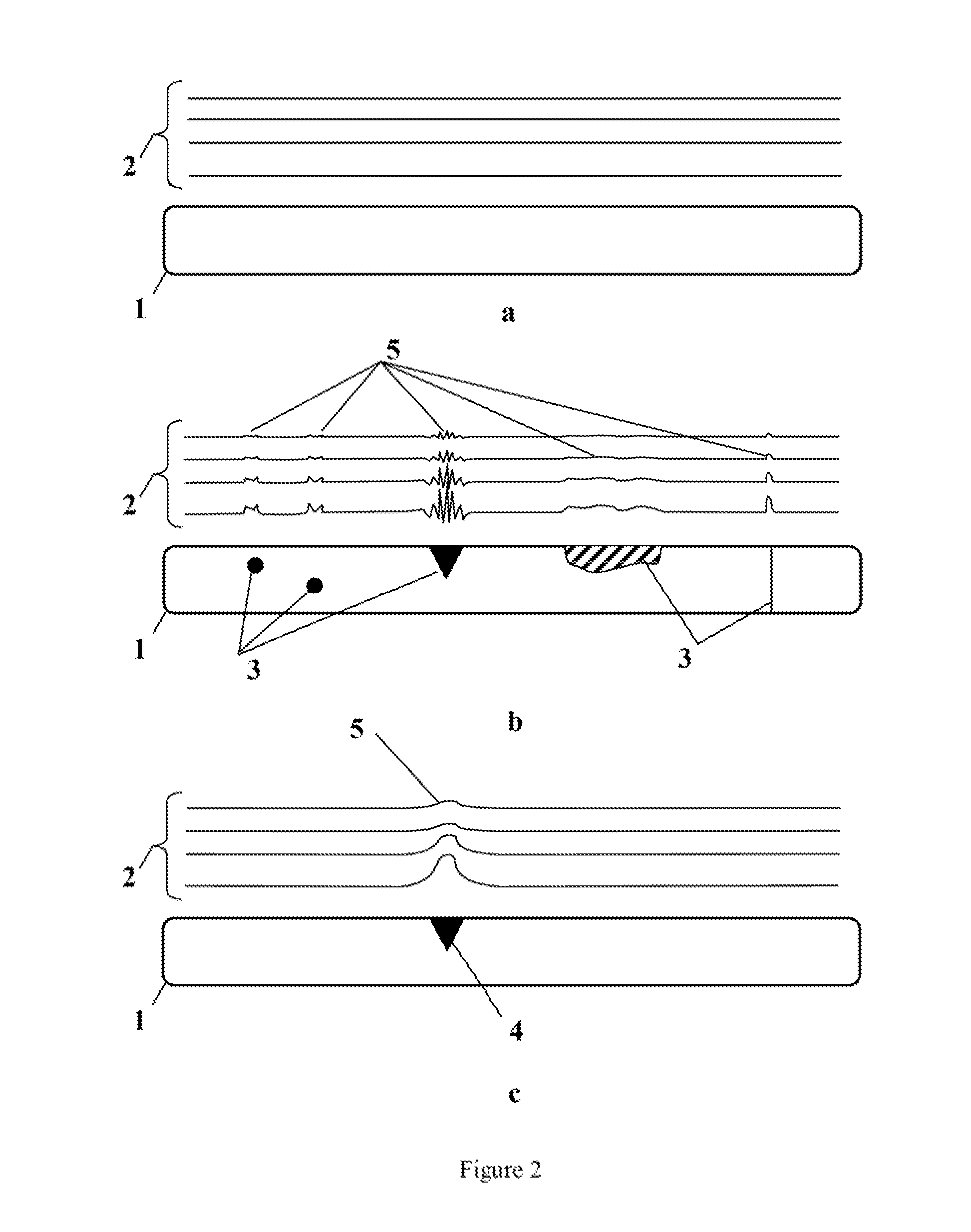
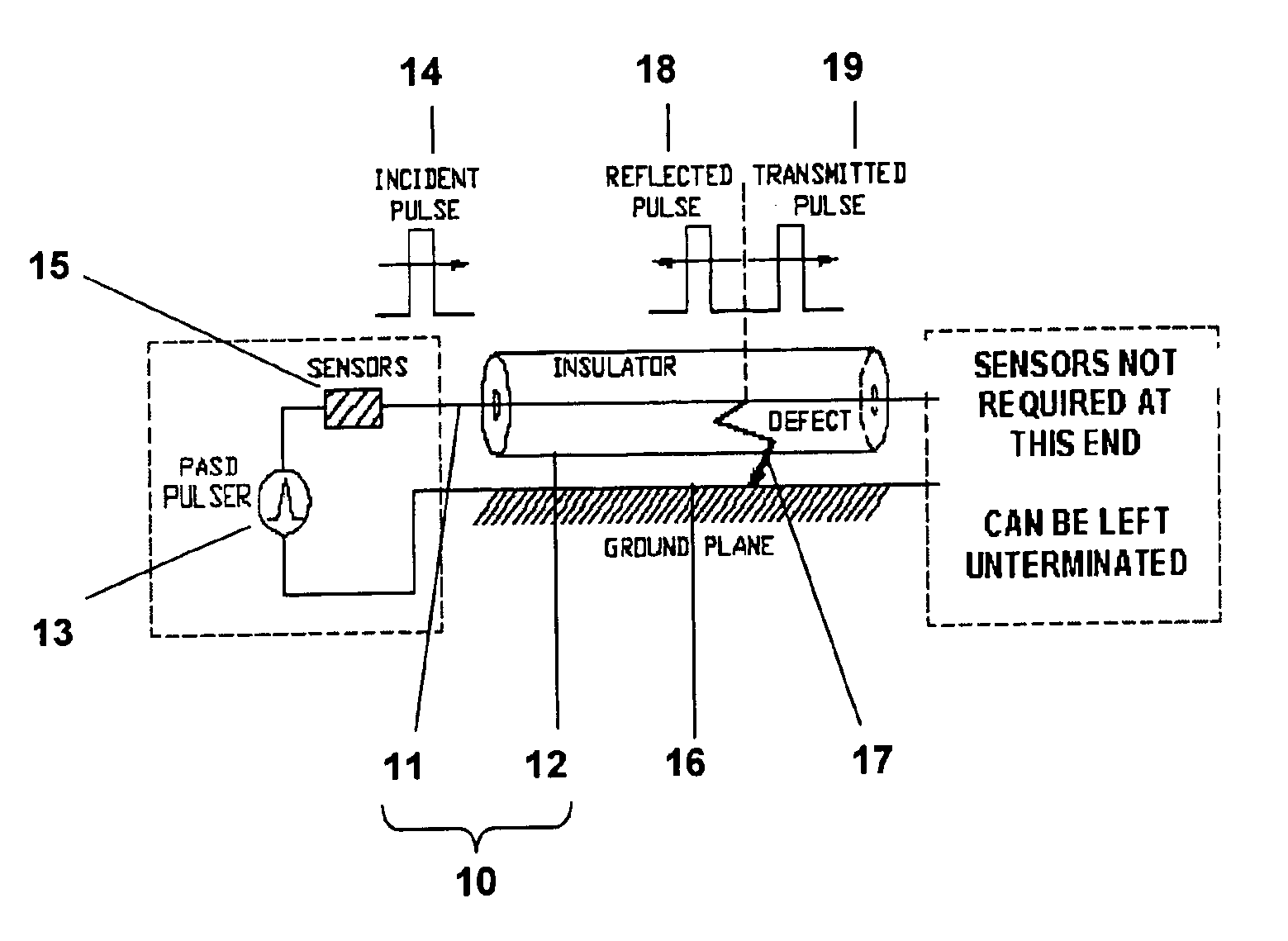
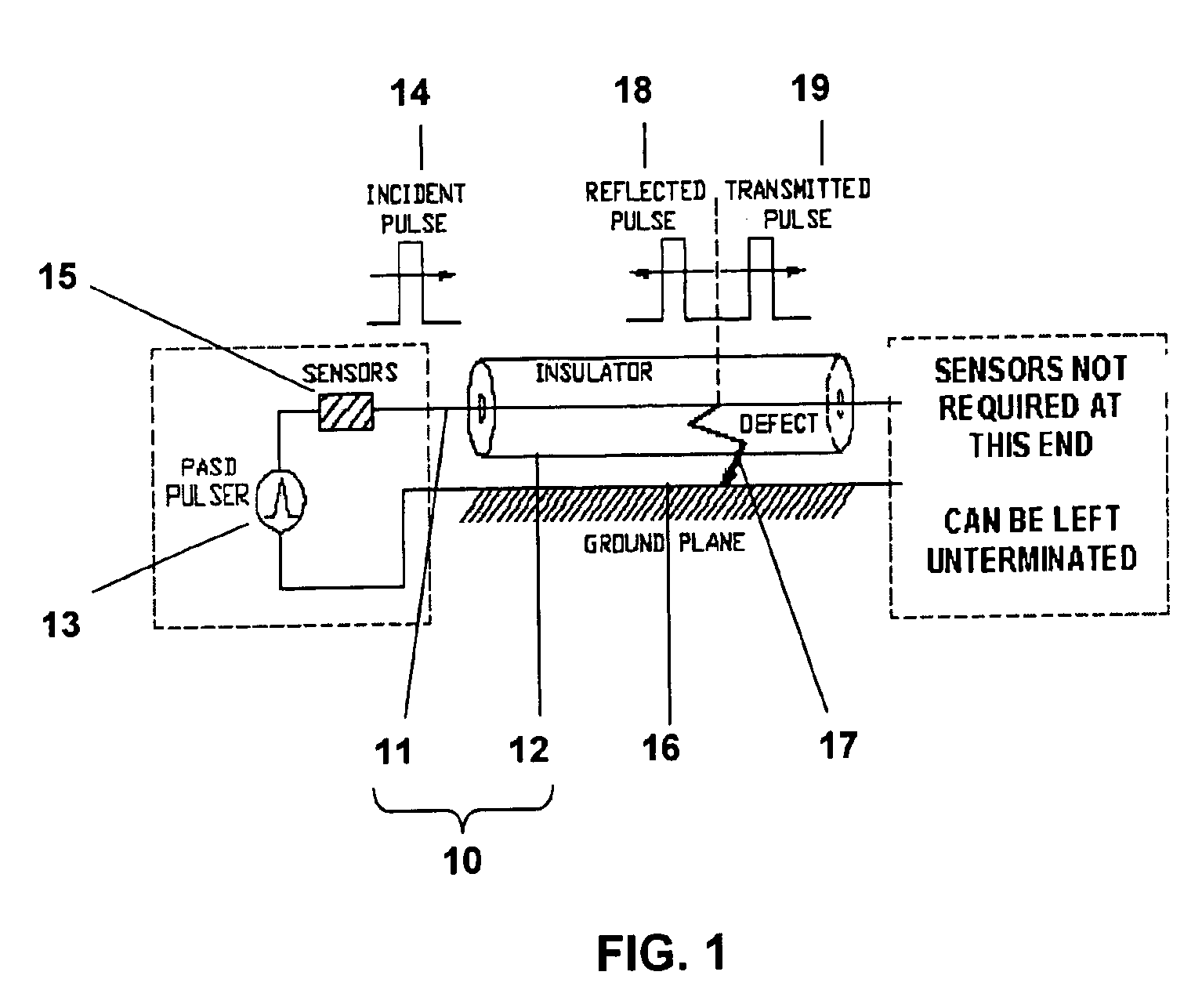
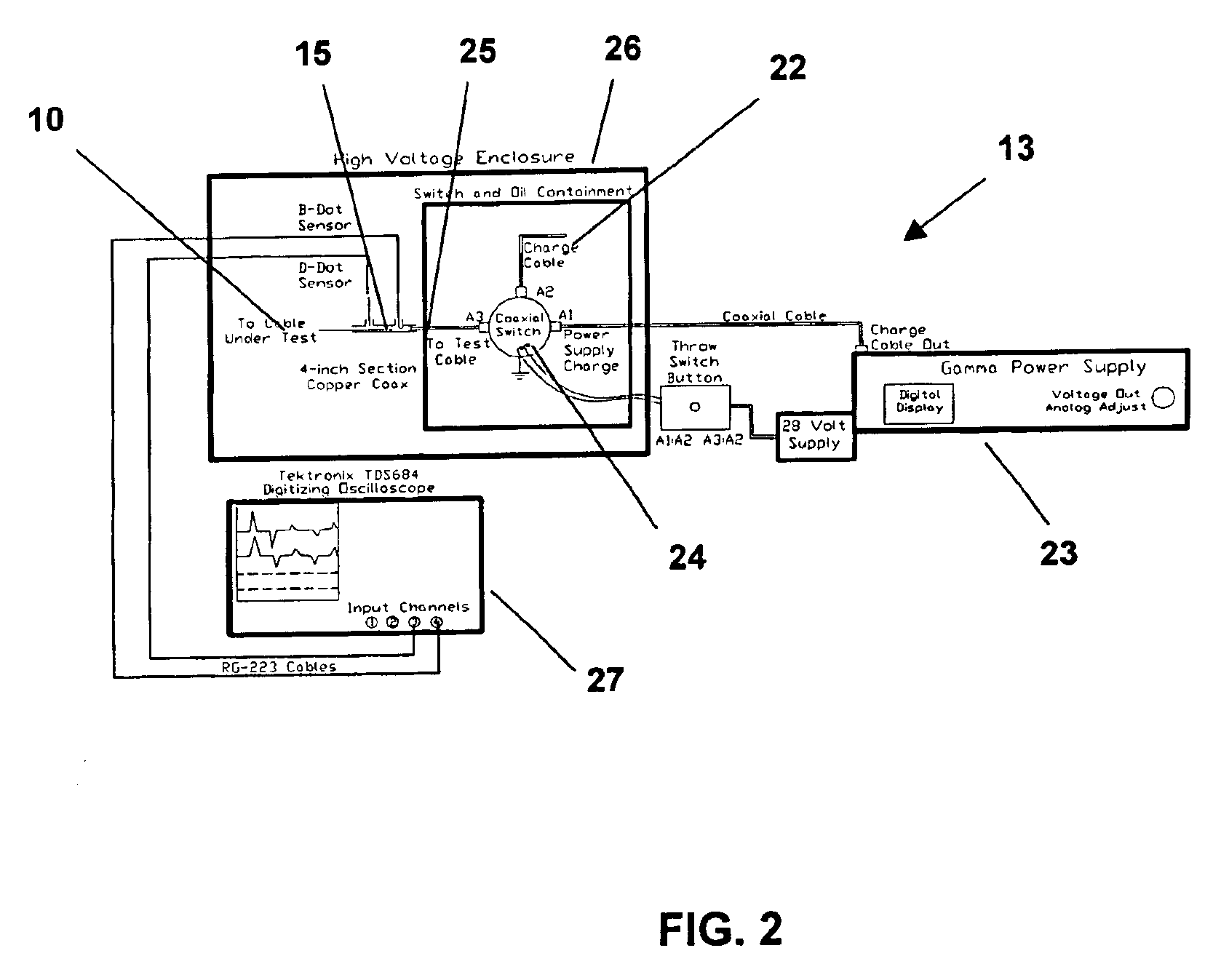
Method and apparatus for electrical cable testing by pulse-arrested spark discharge
InactiveUS6853196B1Enhance and inhibit onsetLower breakdown voltageResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsElectricityNuclear power
A method for electrical cable testing by Pulse-Arrested Spark Discharge (PASD) uses the cable response to a short-duration high-voltage incident pulse to determine the location of an electrical breakdown that occurs at a defect site in the cable. The apparatus for cable testing by PASD includes a pulser for generating the short-duration high-voltage incident pulse, at least one diagnostic sensor to detect the incident pulse and the breakdown-induced reflected and / or transmitted pulses propagating from the electrical breakdown at the defect site, and a transient recorder to record the cable response. The method and apparatus are particularly useful to determine the location of defect sites in critical but inaccessible electrical cabling systems in aging aircraft, ships, nuclear power plants, and industrial complexes.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Integrated low-temperature nuclear heat supplying pile
ActiveCN101154472ASmall sizeCompact layoutIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationReactor pressure vesselPressurized water reactor
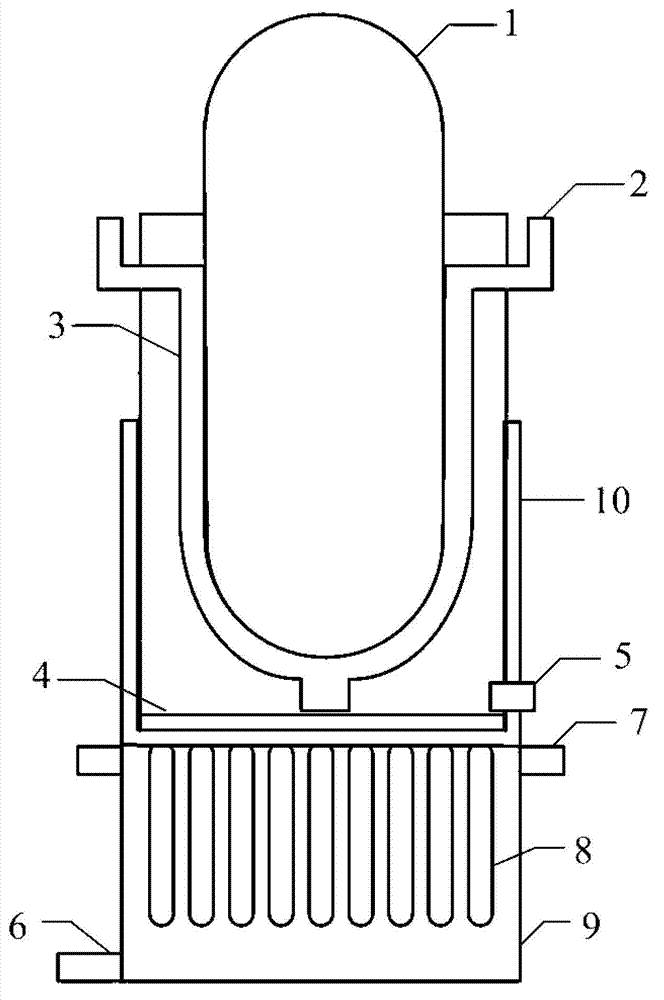
The invention discloses an integral low-temperature nuclear heat reactor with the circuit equipment adopting integral arrangement and belonging to the low- and medium-parameter pressurized-water reactor, wherein, a reactor core adopts the mature nuclear power plant fuel component and control rod component; a main heat exchanger is of integral coil type; a voltage stabilizer is a built-in nitrogen partial pressure control voltage stabilizer; coolant circulation is completed by a built-in jet apparatus and the equipment of an external drive circuit; the drive circuit and the equipment and a main circuit auxiliary system are arranged at the circumference of a reactor pressure vessel; a containment vessel consists of a reactor body containment vessel and a reactor top containment vessel; the reactor body containment vessel which is a structure combined by a reactor vault of reinforced concrete structure and a casing of steel structure is connected with a sealed refueling water storage pool through a pipe and a valve. The thermal power of the reactor can be selected between 50MW and 500MW at will and the outlet temperature of the reactor can be selected between 100 DEG C to 200 DEG C according to application, requirement and power.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
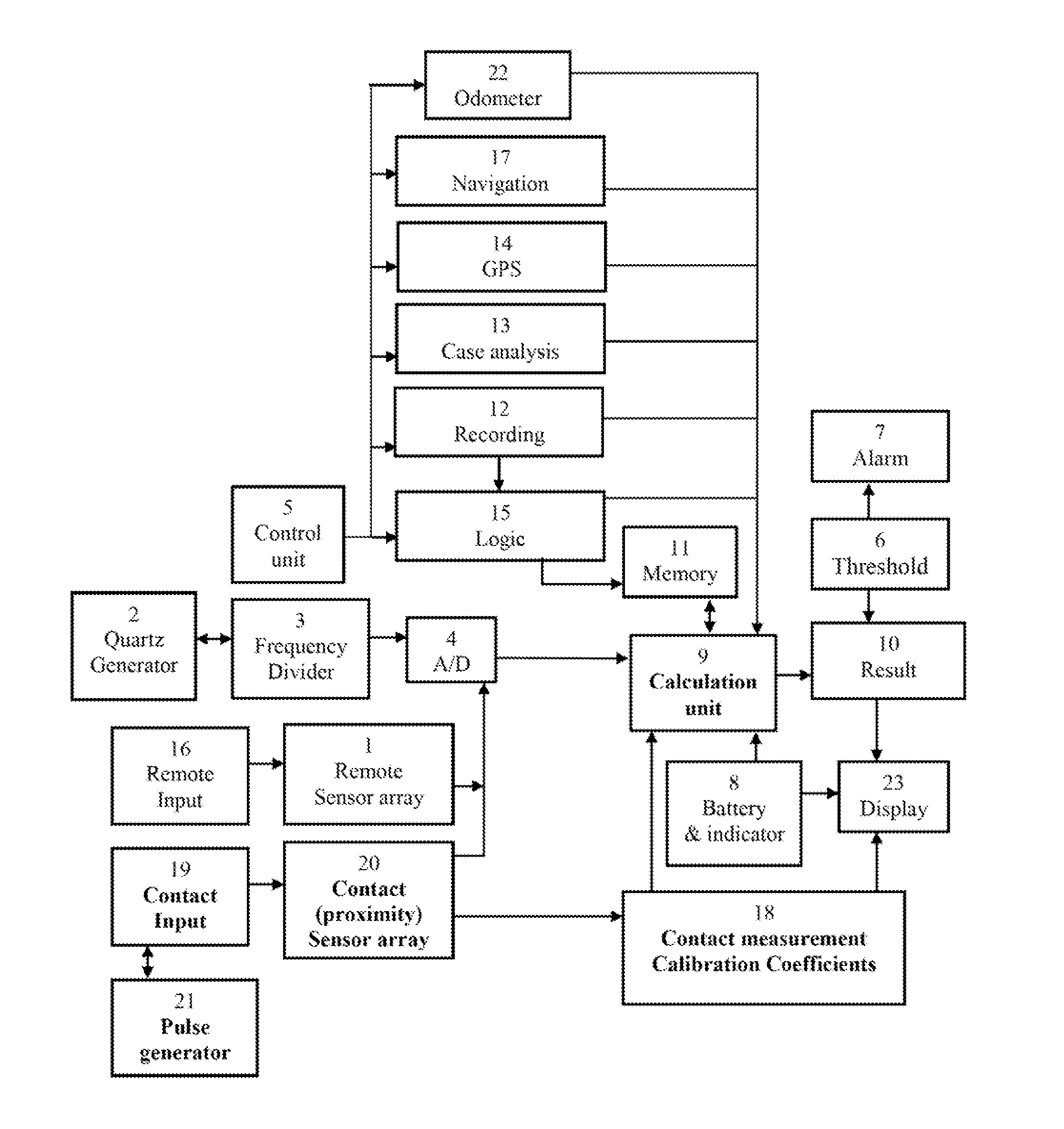
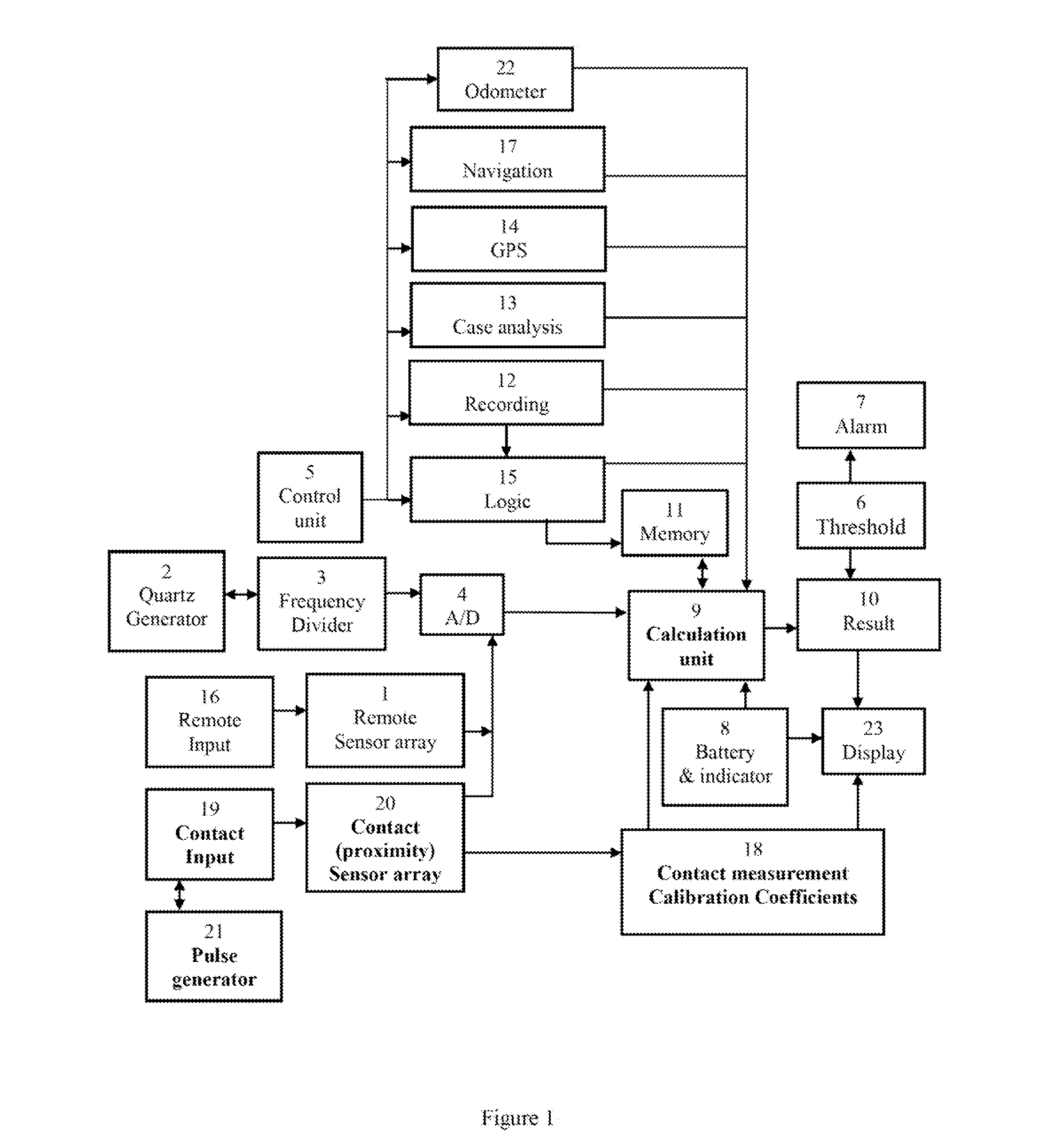
Transmission frame structure for control communication network of distributed control system for nuclear power plant
InactiveUS20060007927A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl communicationsData field
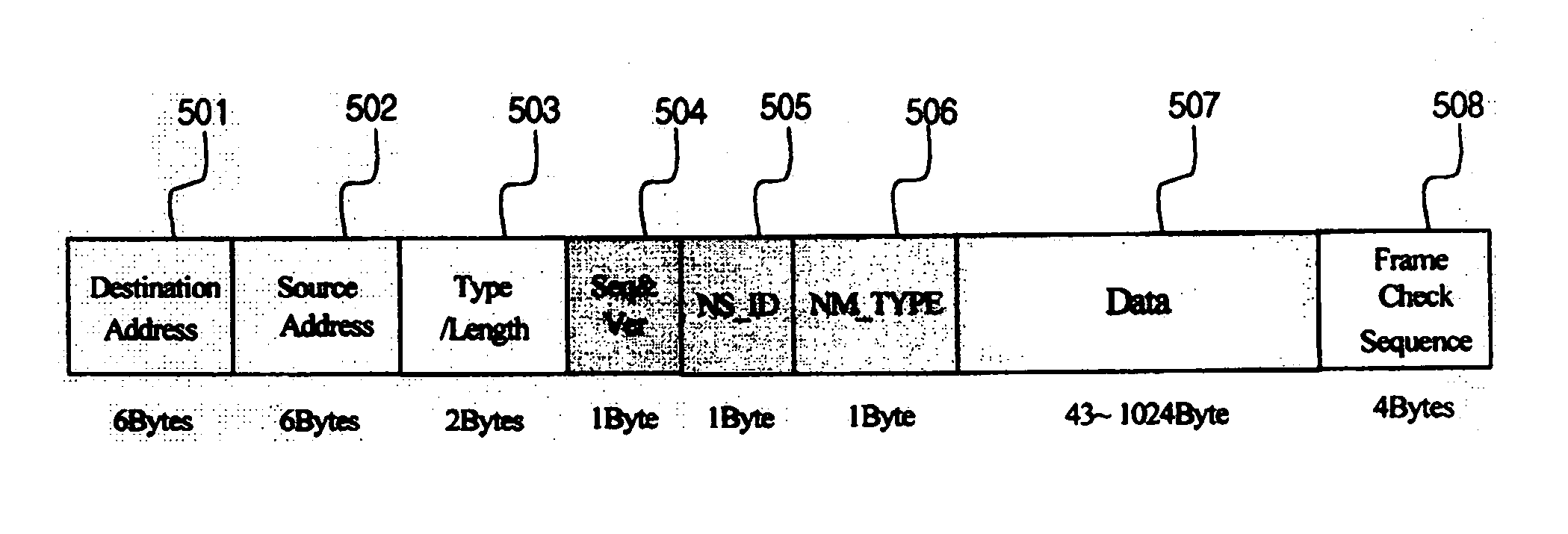
A transmission frame structure for use in a control communication network allows all process control stations contained in the control communication network to share monitoring / control information received from a field communication network or an information communication network, and properly copes with faulty operations of channels (i.e., ring-shaped lines) or process control stations for use in the control communication network. The transmission frame structure of a control communication network for use in a nuclear-power-plant distributed control system which broadcasts data received from a node having transmission authority to all nodes via a bypass line, and allows a ring accelerator to detour the data and to isolate an erroneous station from normal stations, includes a transmission frame. The transmission frame includes: a destination address for performing the broadcasting operation; a source address for recording a source node address (ID) therein; a type / length field for classifying frames into a control data frame and a network management event frame; a network management (NM_TYPE) field which is valid only when it is designated by type / length field, and performs different roles according to network management event frame types; a Seq&Ver field for including the number of transmissions of a data frame and frame upgrade version information; a NS_ID field for recording number information of a node equal to the next token reception node, and being used when one station transmits a token to the next station; a data field having a predetermined maximum size of 1 kbyte, for including not only general control information according to a value of the type / length field, but also 7 event frames such as a token frame; and a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Code) field for inspecting the presence or absence of a CRC error, whereby the transmission frame operates the communication network, solves a malfunction or error of the communication network, and recovers the communication network.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
Metallic constructions integrity assessment and maintenance planning method
ActiveUS8447532B1Easy maintenancePromote repairPlug gaugesForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMaintenance planningHeavy duty
A method for metallic structure maintenance is disclosed. The method includes a magneto-graphic / Magnetic Tomography technique to identify stress-related defects. The method is specifically optimized for extended, non-accessible underground and underwater metallic structures in providing quality control, emergency alarms as well as timeline planning for structural repairs and maintenance work. Examples of the method implementation include pipes for oil and gas industry, detection of flaws in rolled products in metallurgical industry, welding quality of heavy duty equipment such as ships reservoirs, etc. It is especially important for loaded constructions, such as pressured pipes, infrastructure maintenance, nuclear power plant monitoring, bridges, corrosion prevention and environment protection.
Owner:GOROSHEVSKIY VALERIAN +2
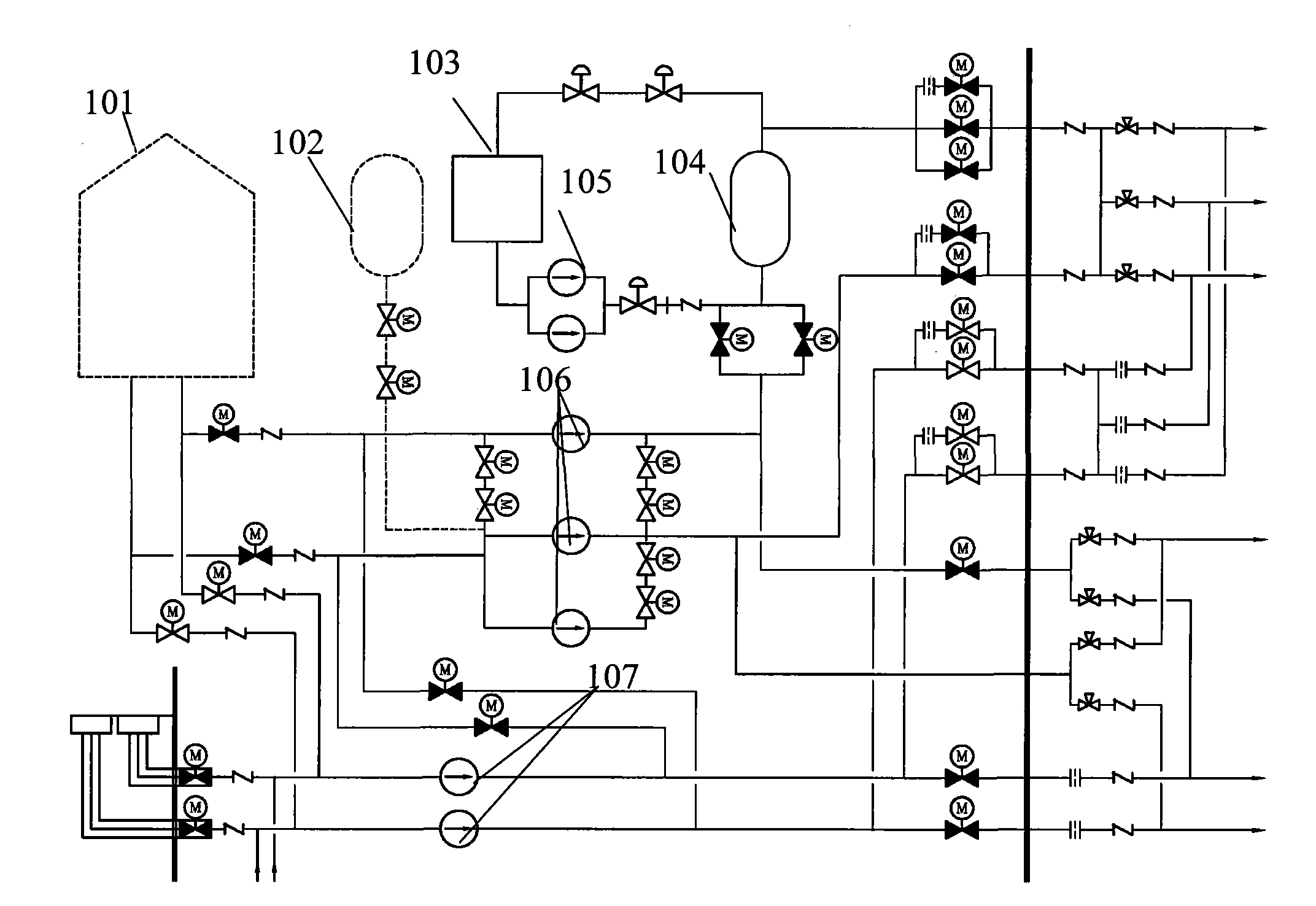
Safety injection system
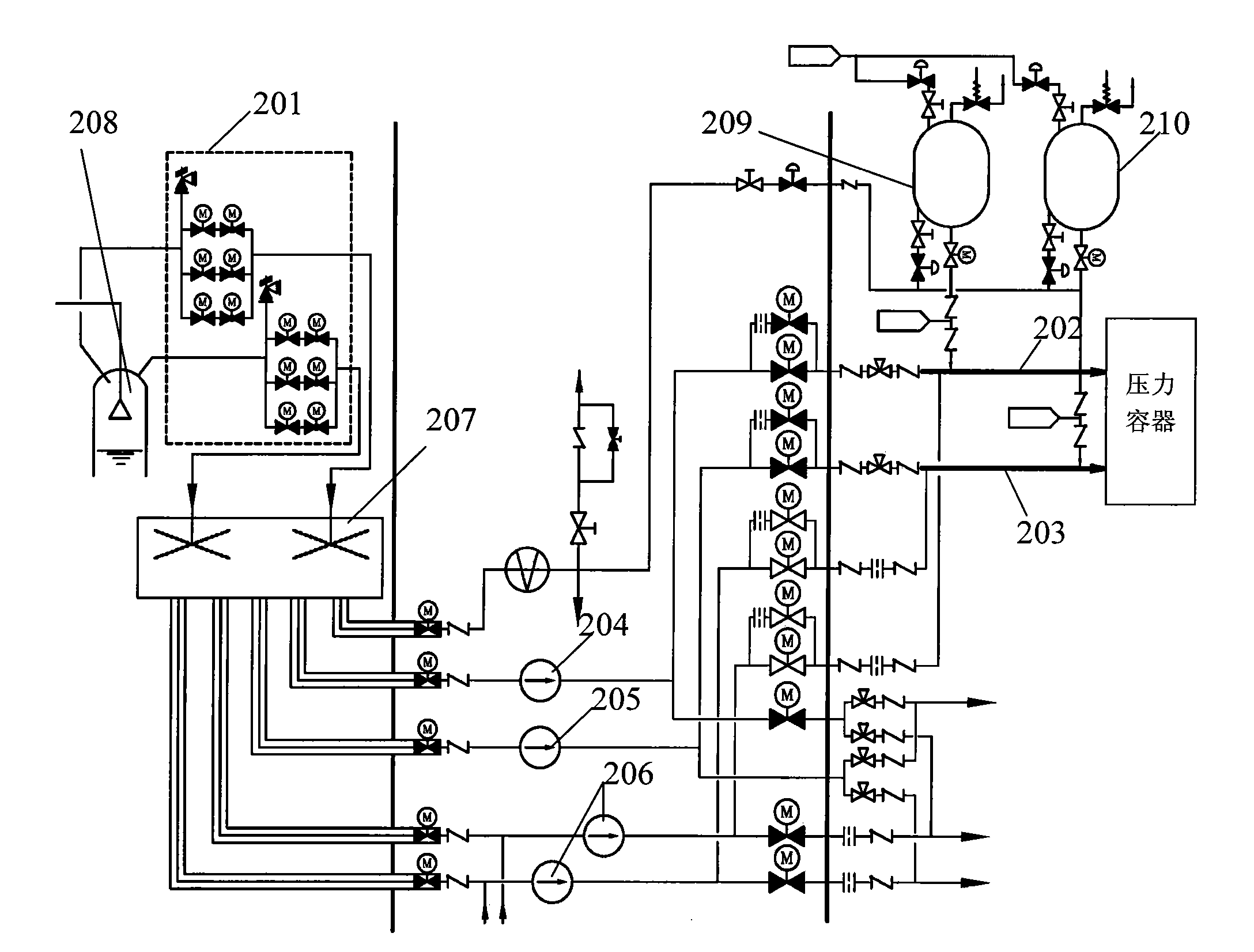
ActiveCN101847451AReduce headReduce cross pipeNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear engineeringControl valves
The invention relates to a safety injection system, which is used for mitigating an accident and protecting the safety of a reactor core of a nuclear power plant and comprises a high-pressure safety injection pump, a low-pressure safety injection pump, a safety injection tank and a refueling water tank for containing safety injection water, wherein the refueling water tank is positioned in a safety shell of the nuclear power plant; the safety injection tank is connected on a direct pressure vessel injection pipeline by a pipeline provided with a control valve; the high-pressure safety injection pump is connected between the refueling water tank and the direct pressure vessel injection pipeline by a pipeline provided with a control valve; and the low-pressure safety injection pump is connected between the refueling water tank and the direct pressure vessel injection pipeline by a pipeline provided with a control valve. The safety injection system has the advantages of reducing cross pipelines of the system, realizing continuous operation, simplifying the system operation, also strengthening mitigating capability of the system for the serious accident and improving safety of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
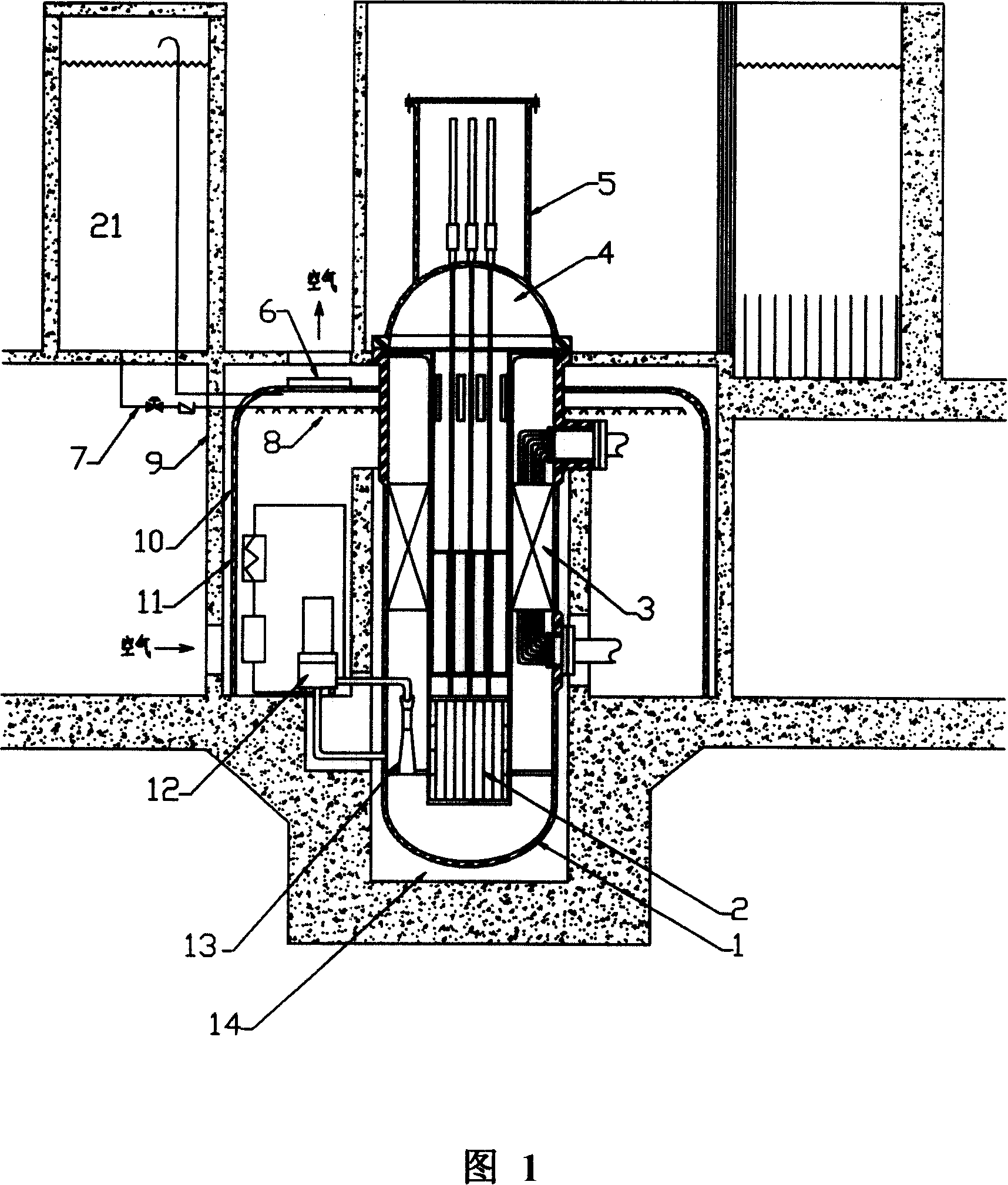
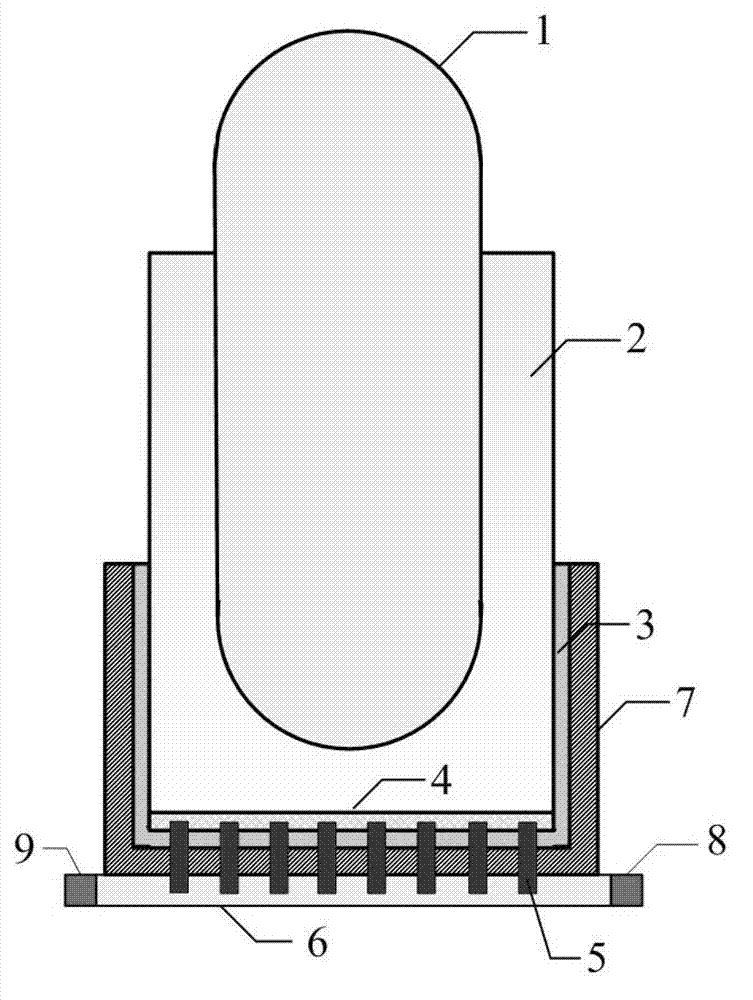
Large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling
InactiveCN103177778AImplement off-heap retentionImprove securityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention provides a large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling. The catcher comprises a reactor cavity coating the lower middle part of a reactor pressure vessel, and a reactor cavity concrete soleplate is formed at the bottom of the reactor cavity; a refractory layer is formed on the side surface of the reactor cavity and the bottom of the reactor cavity concrete soleplate; a steel cylinder is sleeved outside the refractory layer; an external cooling passage is formed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and a cooling passage inlet and a cooling passage outlet are respectively formed at the two outward-extending ends of the external cooling passage; and dozens of nozzles are fixed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and the upper ends of the nozzles extend into the reactor cavity concrete soleplate while the lower ends of the nozzles extend into the external cooling passage. According to the invention, the dilution and the temperature reduction of a melt are implemented through the melting of concrete by adopting the reactor cavity concrete soleplate as a sacrificial material. A reactor core melt is collected in the refractory layer after the reactor cavity concrete soleplate is molten through, so that the security and the reliability of a nuclear plant are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
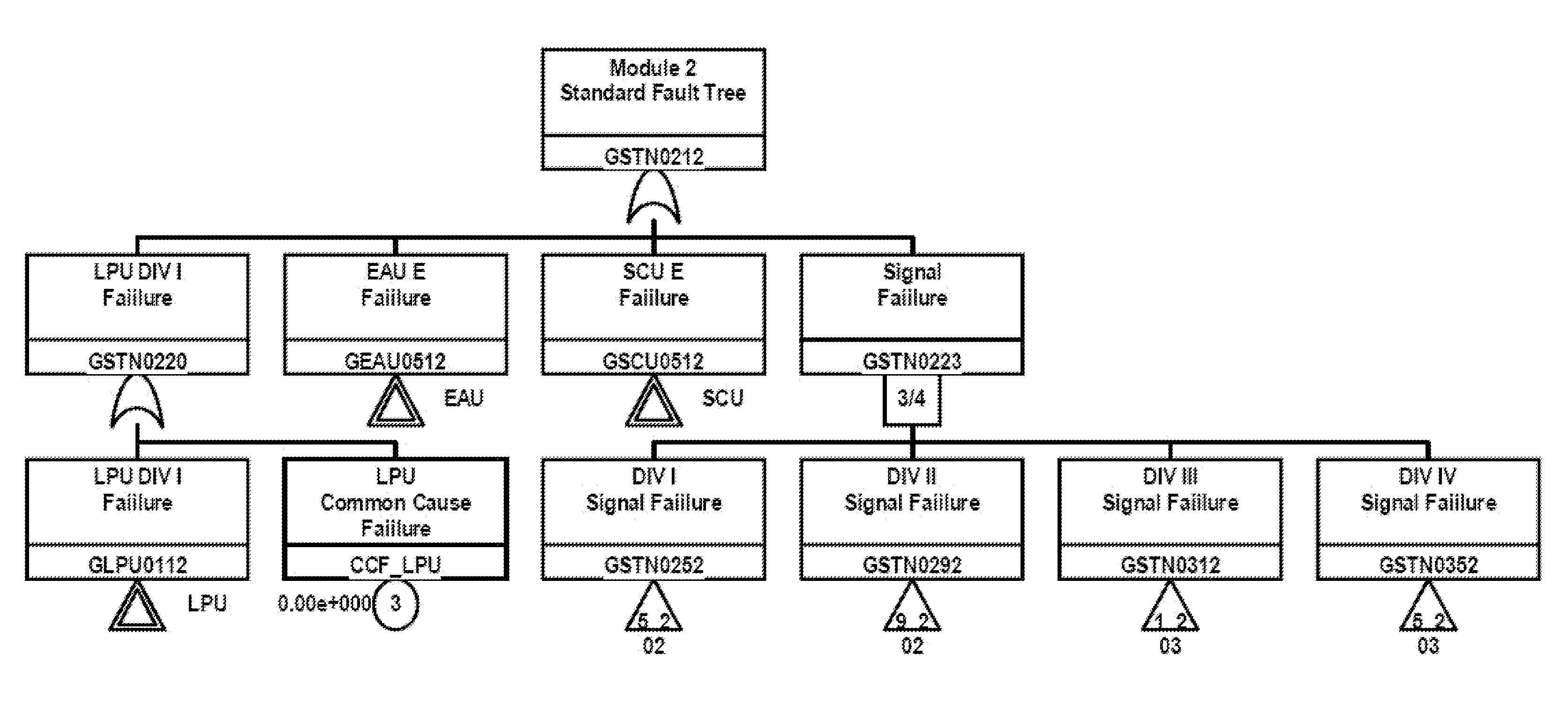
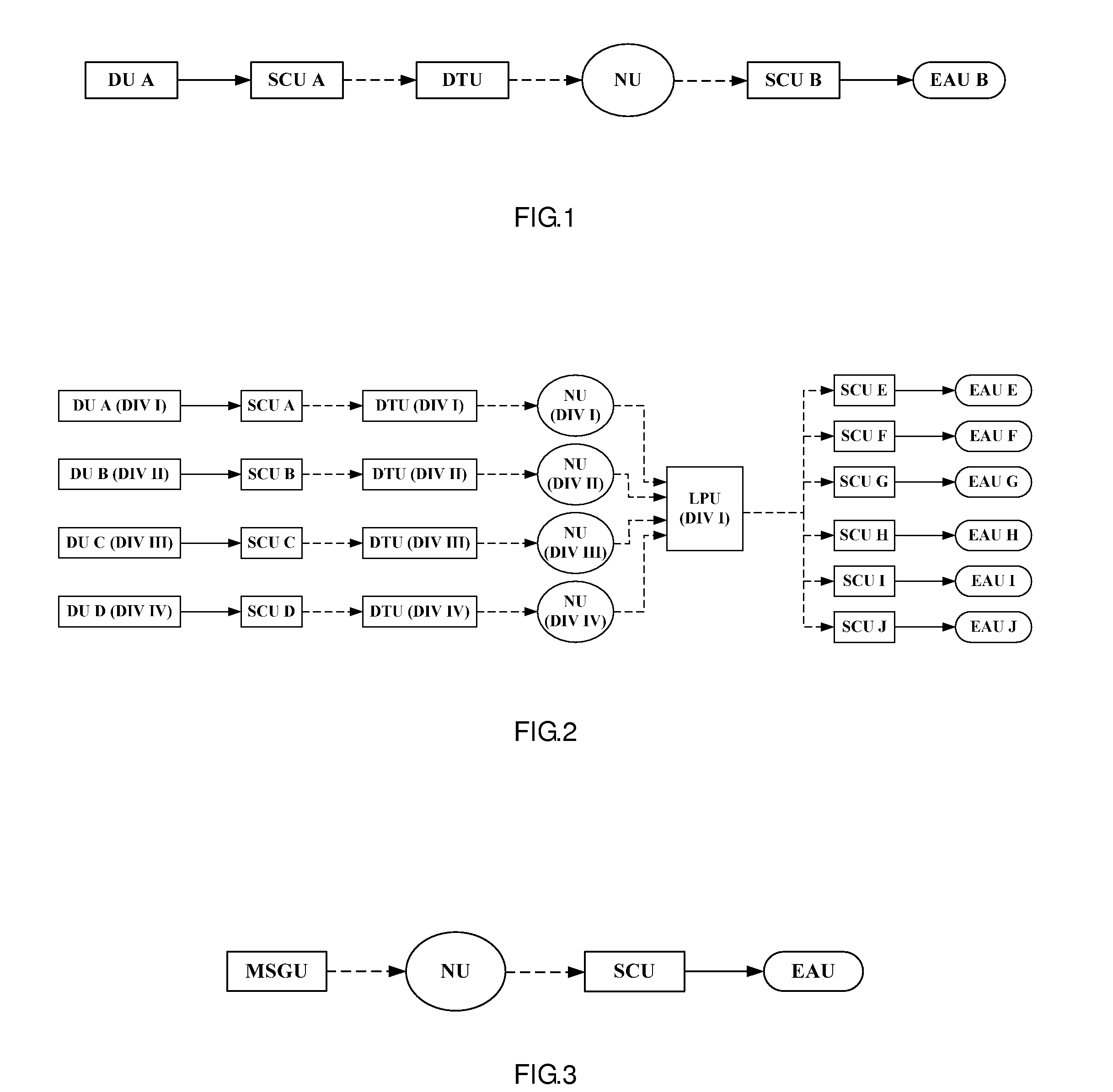
Fault Tree Analysis System for the Instrument Control Process for Nuclear Power Plant with Advanced Boiling Water Reactor Background
InactiveUS20100100251A1Fast and accurate to establishLevel controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsProbabilistic risk assessmentBiology
The invention relates to the fault tree analysis system for a nuclear power plant with advanced boiling water reactor. The full digital instrument control system uses six different modes to simulate the transmission of the digital signals and the analog signals from the detection units. It is to develop the fault tree for various signal transmission modes to support the nuclear power plant in probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) and meet requirements for simulated signal detection, transmission, logic operation and equipment actuation. Thus, the digital instrument control flow process can fit into PRA model and properly reflect its importance in risk assessment.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Installing method for main pipeline of coolant system of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102169736ASimple structureReduce elbowNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNumerical controlPressurized water reactor
The invention relates to an installing method for a main pipeline of a coolant system of a nuclear power station, which is characterized in that the main pipeline of the coolant system of a reactor of the pressurized water reactor nuclear power station comprises a cool section (41) and a hot section (42), and a steam generator is directly connected with a main pump. According to the invention, the problem that the main pipeline is installed and welded by only a pressure container or steam generator in place by adopting the installing method of the main pipeline without a transition section issolved, and technical limit that the main pipeline is installed after the pressure container is in place and the steam generator or main pump is in place in the traditional main pipeline constructiontechnology is eliminated. A main pipeline groove is processed by adopting a site numerical control machining technology, the main pipeline and equipment connected with the main pipeline are subjectedto measurement, modeling and process monitoring by adopting a laser tracking measuring and 3D modeling technology, the main pipeline is regulated to meet the assembly welding requirement and is installed by using a narrow TIG (argon tungsten-arc welding) automatic welding technology, thus a feasible method is provided for shortening the construction period of the nuclear power station.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR IND FIFTH CONSTR CO LTD
Method for monitoring pressure pipeline leakage acoustic emission in nuclear power plant and monitoring system thereof
ActiveCN101706039AImprove real-time performanceHigh sensitivityPipeline systemsNuclear engineeringNuclear power
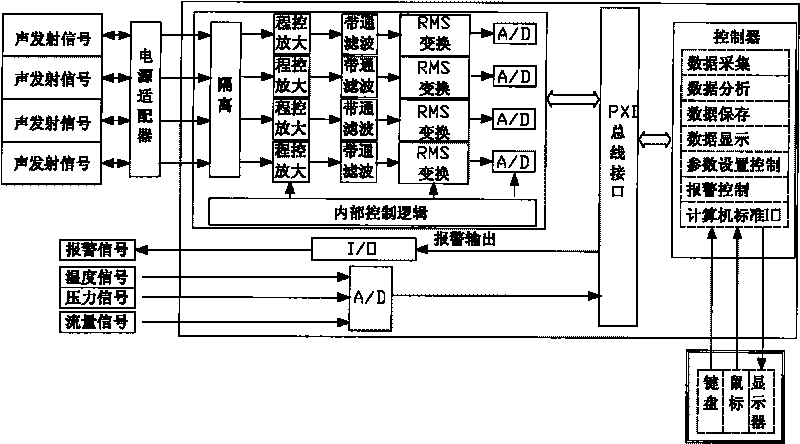
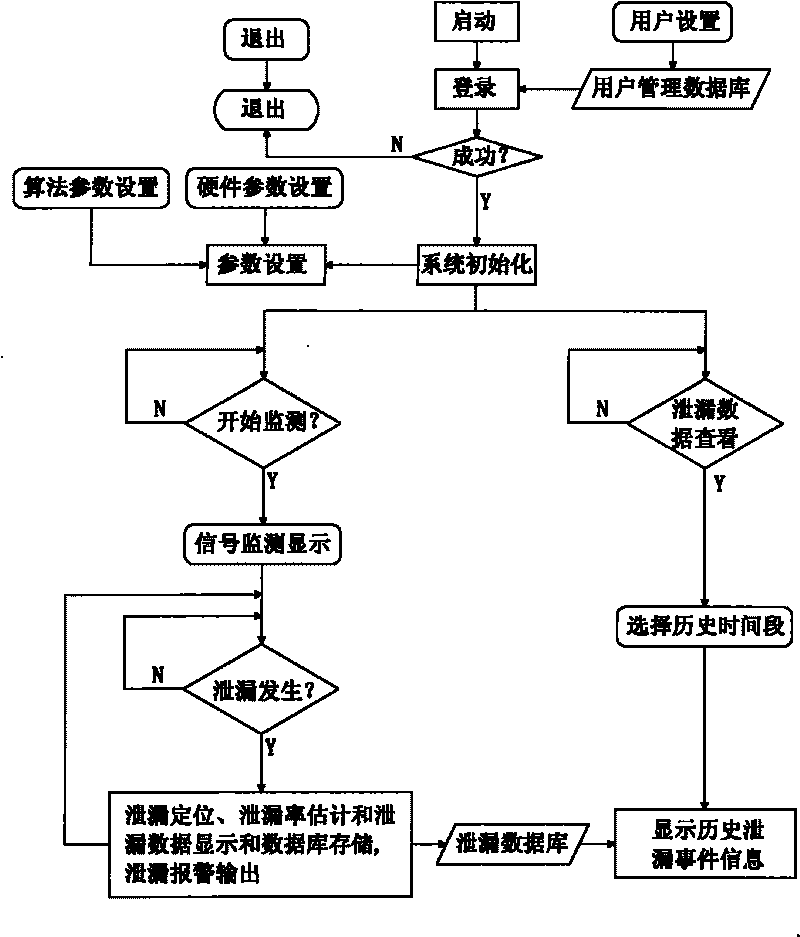
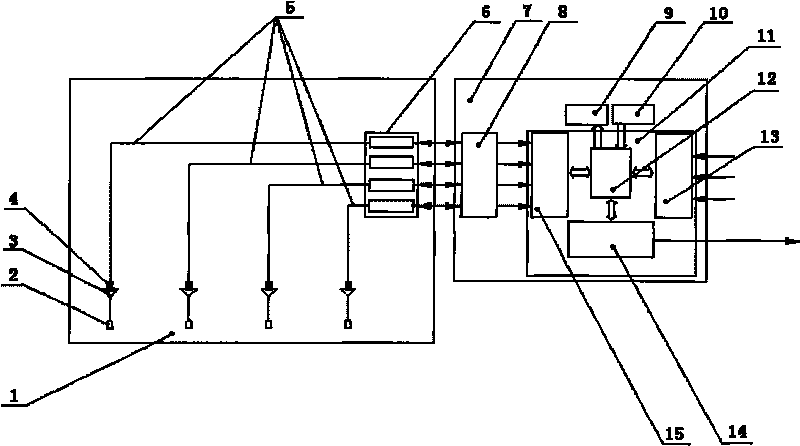
The invention relates to a method for monitoring pressure pipe leakage acoustic emission in a nuclear power plant and a monitoring system thereof. The monitoring method adopts the technical scheme that a pressure pipe leakage test piece is prepared; the initiation, crack, expansion and through leakage of the pipeline of the nuclear power plant are imitated, a leakage acoustic emission calibration test is performed, and the through crack leakage of the pipeline under high temperature and high pressure environment in nuclear power plant is imitated. The monitoring system adopts a standardized and modularized design which is based on PXI bus and convenient for system maintenance and part replacement. Through adopting the monitoring method and the monitoring system, the data record of leakage event and the database management of monitoring result can be achieved; moreover, the leak position and the dynamic change of leak rate are completely reflected.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
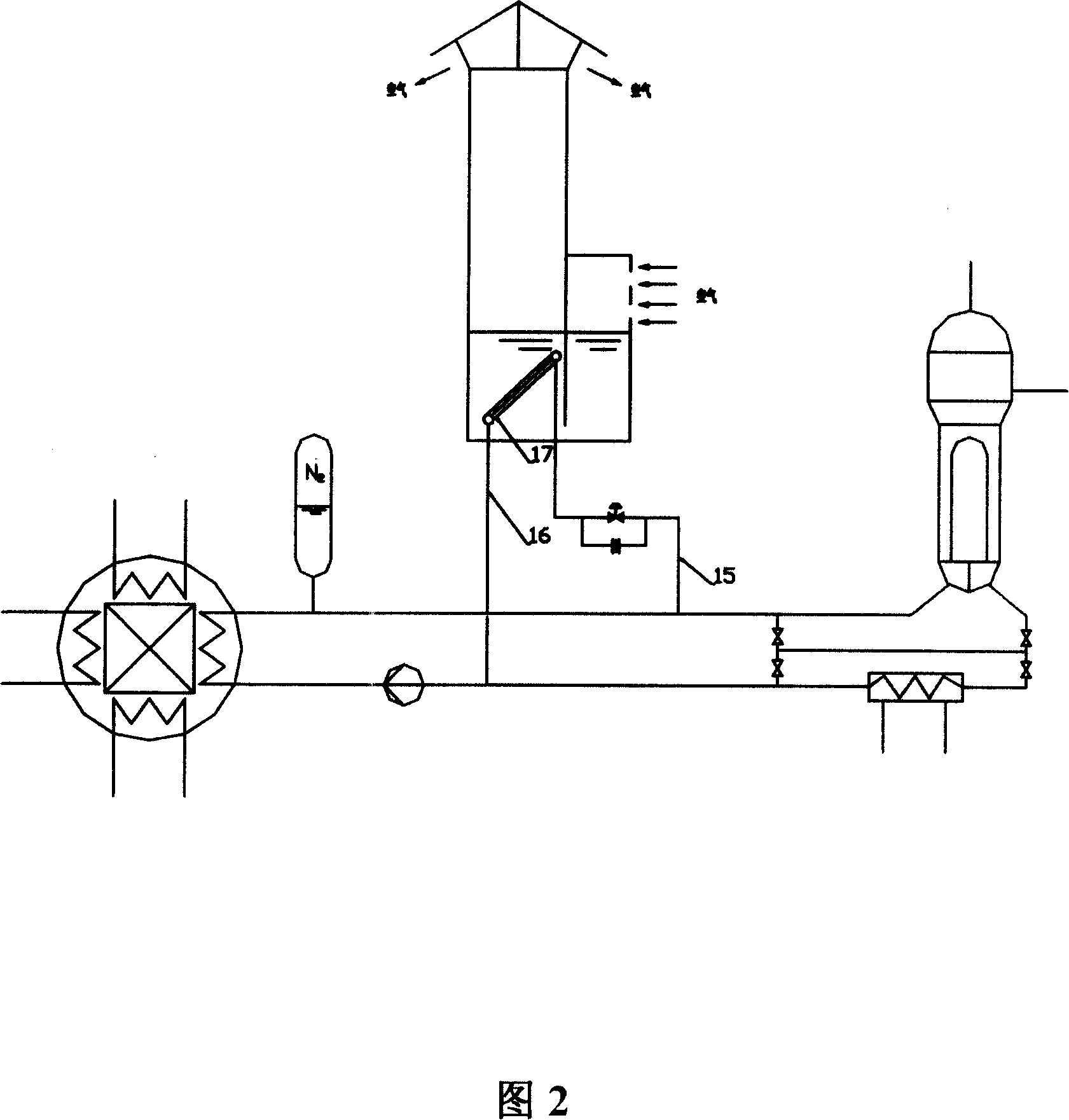
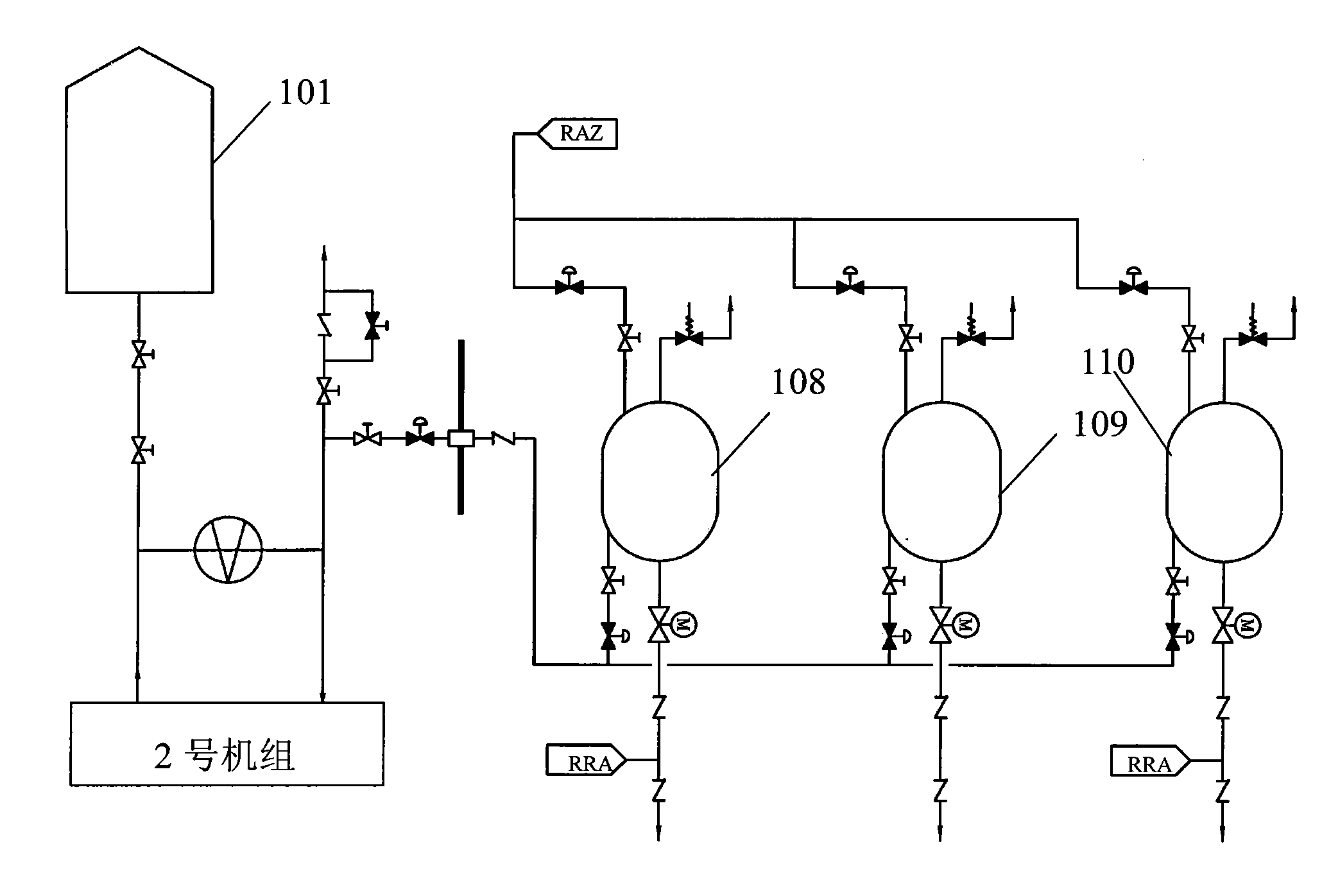
Large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher
InactiveCN103177779AImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention discloses a large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher which comprises a reactor cavity concrete bottom plate (4), a crucible cooling system water filling nozzle (6), a crucible cooling system water vapor outlet (7), a crucible component (8), a crucible cooling system cavity (9) and a melt collector (10). The reactor core catcher is organically combined with an interactive voice response (IVR) system, the safety of the nuclear power plant can be further improved, and the reliability of the system is higher due to the crucible design.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Nickel-based welding wire for main equipment of nuclear island of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102581513AProcess stabilityReduce defectsArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsChemical compositionNuclear power
The invention belongs to the technical field of welding materials, and particularly discloses a nickel-based welding wire for main equipment of a nuclear island of an AP1000 nuclear power station. The method is applicable to welding pressure containers of reactors (including welding of driving tube seats, safe seats of connecting tubes and supporting blocks of reactor cores) and welding of steam generators (including build-up welding of tube plates and welding of tubes and the tube plates), and solves problems that welding wires of the kind in the prior art are always imported, cost is high and the like. Basic chemical components of the nickel-based welding wire include, by weight ratio, from 28.0 to 31.5% of Cr, from 7.0 to 11.0% of Fe, from 0.4 to 1.0% of Ti, from 0.25 to 1.10% of Al, from 0.90 to 1.5% of Al+Ti, lower than or equal to 1.0% of Mn, lower than or equal to 0.02% of Nb, lower than 0.04% of C, lower than or equal to 0.15% of Si, lower than 0.005% of P, lower than 0.005% of S, lower than 0.001% of B, lower than 0.02% of Zr, lower than 0.005% of Ca, lower than 0.005% of Mg, lower than 0.02% of Ta, lower than 0.02% of Cu, lower than 0.05% of Co, lower than 0.5% of Mo and the balance Ni. By the aid of the welding wire, microalloying of weld joints can be realized, the weld joints meet standard requirements, and the welding wire can replace imported welding wires.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with melt expansion room
InactiveCN103165198AIncrease heat transfer areaImprove cooling effectNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsCore catcherPressurized water reactor
The invention provides a large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with a melt expansion room. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room comprises a reactor cavity which coats the middle lower portion of a reactor pressure vessel, a reactor cavity concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity, and a reactor cavity refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the reactor cavity concrete base plate. The upper end of a melt release passage is communicated with the reactor cavity refractory layer, and the lower end of the melt release passage is communicated with the melt expansion room. The inner wall of the melt release passage surrounds the refractory layer. An expansion room concrete base plate is arranged on the lower portion of the melt expansion room, an expansion room refractory layer is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room concrete base plate, and an expansion room outside cooling passage is arranged on the lower portion of the expansion room refractory layer. Two ends of the expansion room outside cooling passage extend outwards and are respectively an outside cooling passage entrance and an outside cooling passage exit. The large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant reactor core catcher with the melt expansion room is used for successively implementing expansion, retention and cooling of the melt when the a pressure container loses efficacy and can strengthen capacity of relieving severe accidents of the large-scale passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
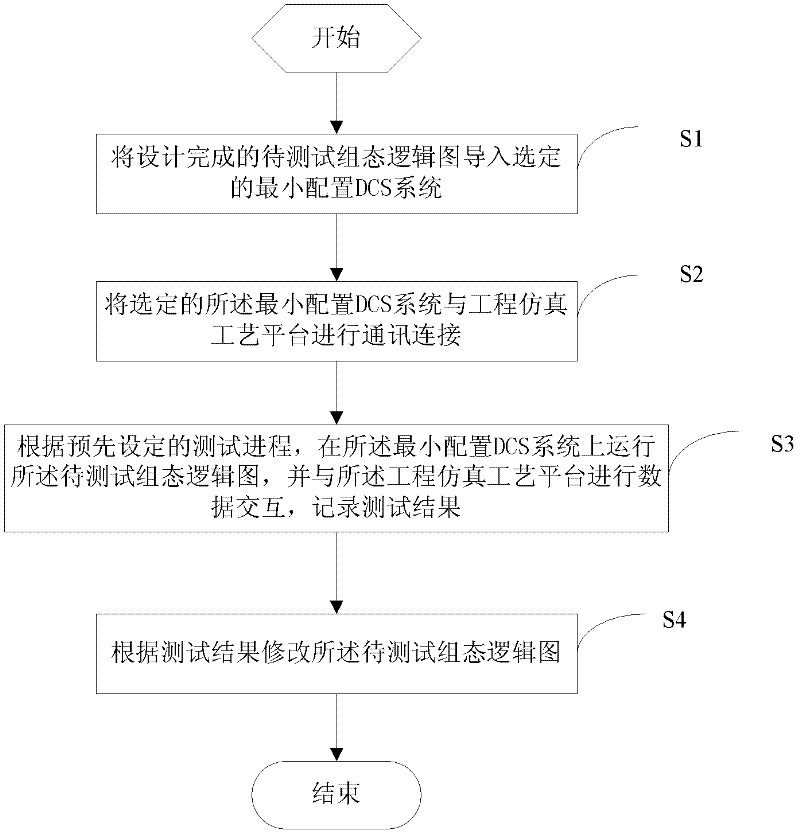
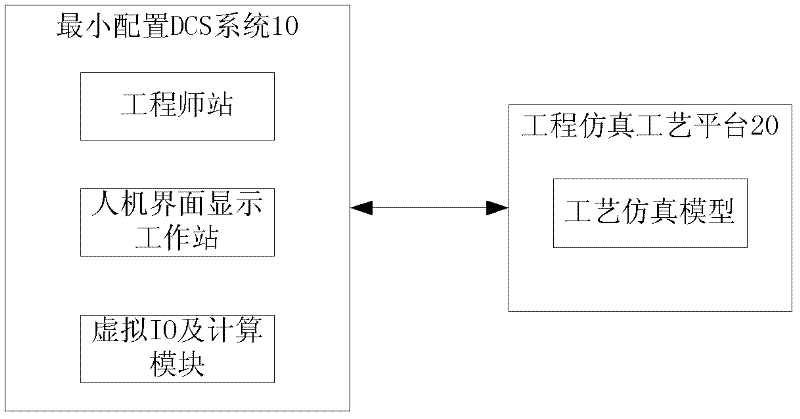
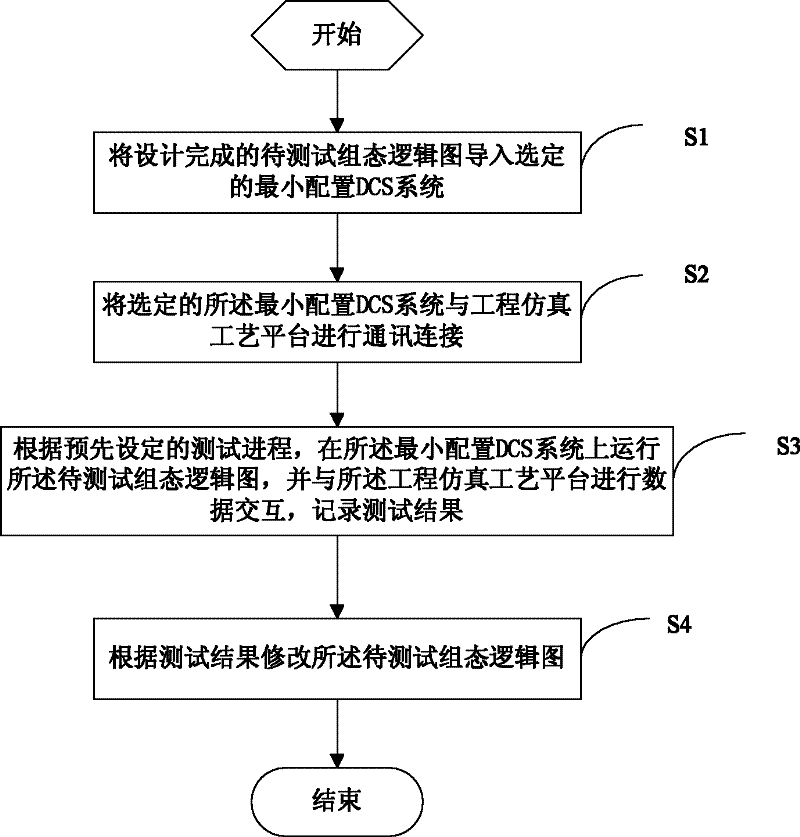
Method and system for testing configuration logic design of DCS (Distributed Control System) of nuclear power station
ActiveCN102522128AShorten the commissioning periodGuaranteed safety and reliabilityNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringWork periodNuclear power
The invention discloses a method and system for testing a configuration logic design of a DCS (Distributed Control System) of a nuclear power station. The method comprises the following steps of: importing a designed configuration logic diagram to be tested into a selected minimal configuration DCS; communicatively connecting the selected minimal configuration DCS with an engineering simulation process platform; according to the preset test progress, running the configuration logic diagram to be tested on the minimal configuration DCS, and interacting data with the engineering simulation process platform, then recording a test result; and according to the test result, modifying the configuration logic diagram to be tested. According to the method and system disclosed by the invention, the configuration logic diagram is tested by using the minimal configuration DCS and the engineering simulation process platform, the correctness and completeness of the result can be virtually verified without depending on real field equipment, the debugging work period is shortened, and the safety and reliability of the design process is guaranteed.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com