Patents
Literature
2690 results about "Operational costs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition - In information technology, operational costs document the price of running of IT services on a day-to-day basis. Operational costs may include expenditures for staffing, hardware maintenance, electricity, software procurement, storage rental and security.
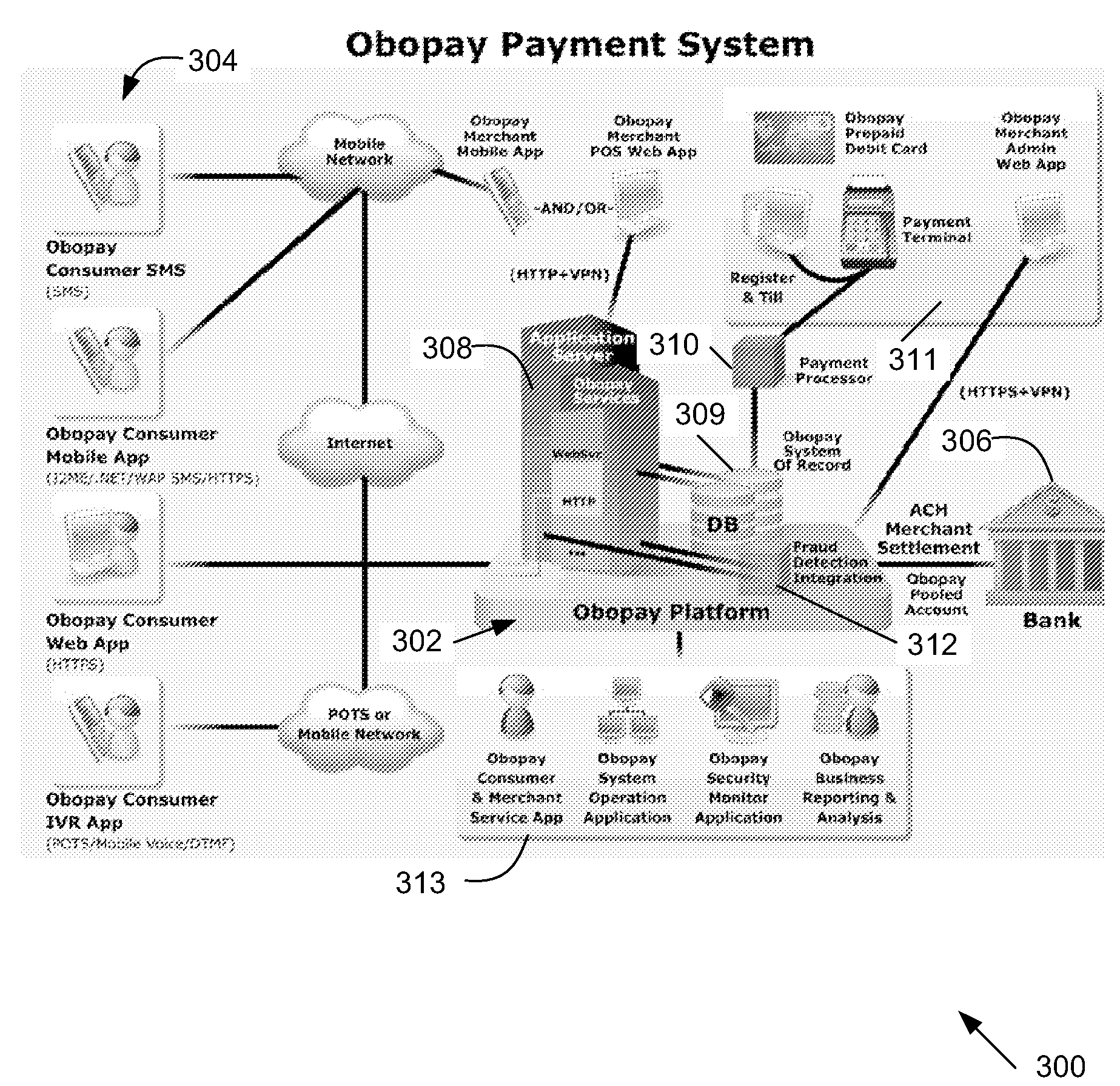
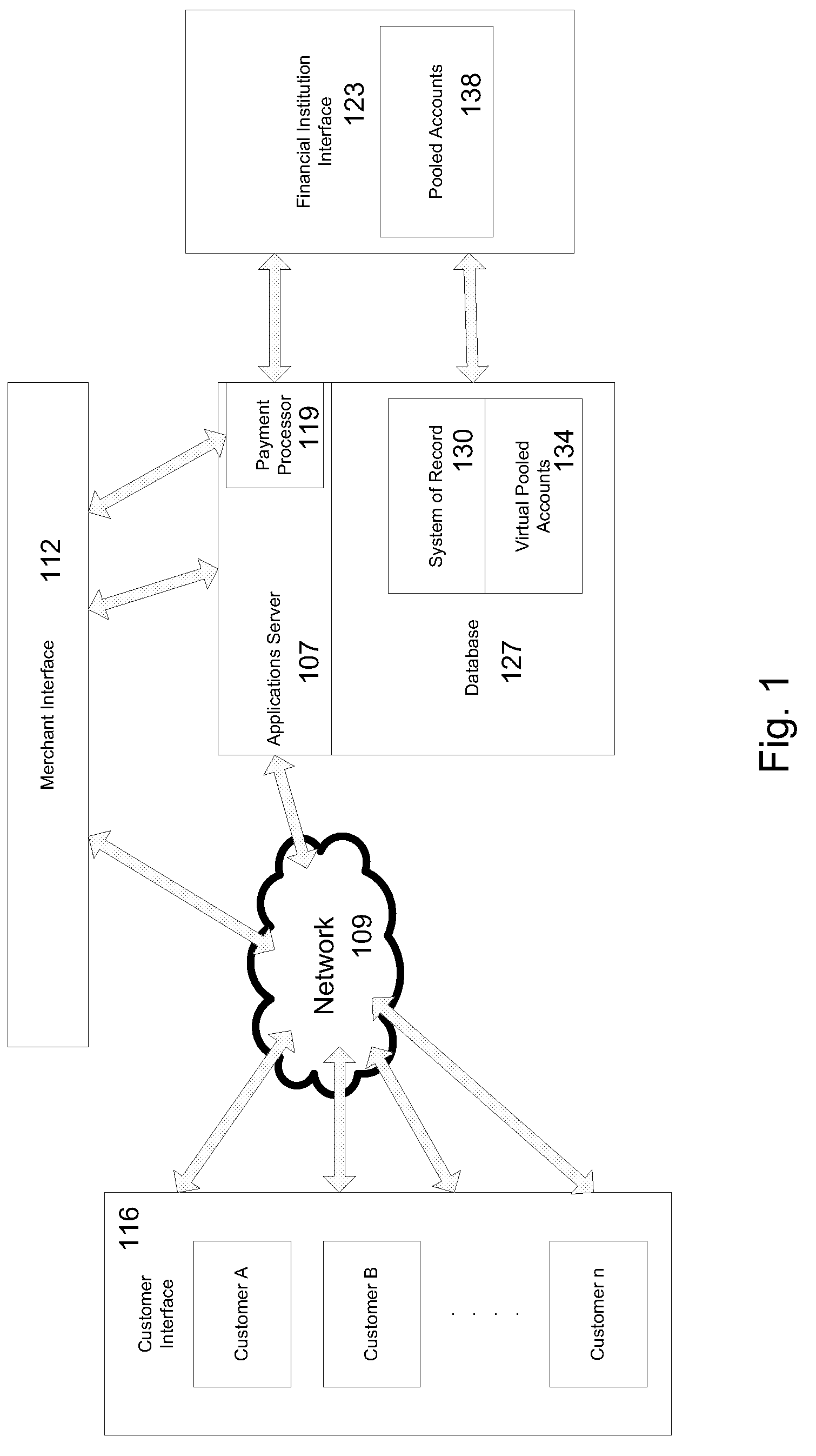
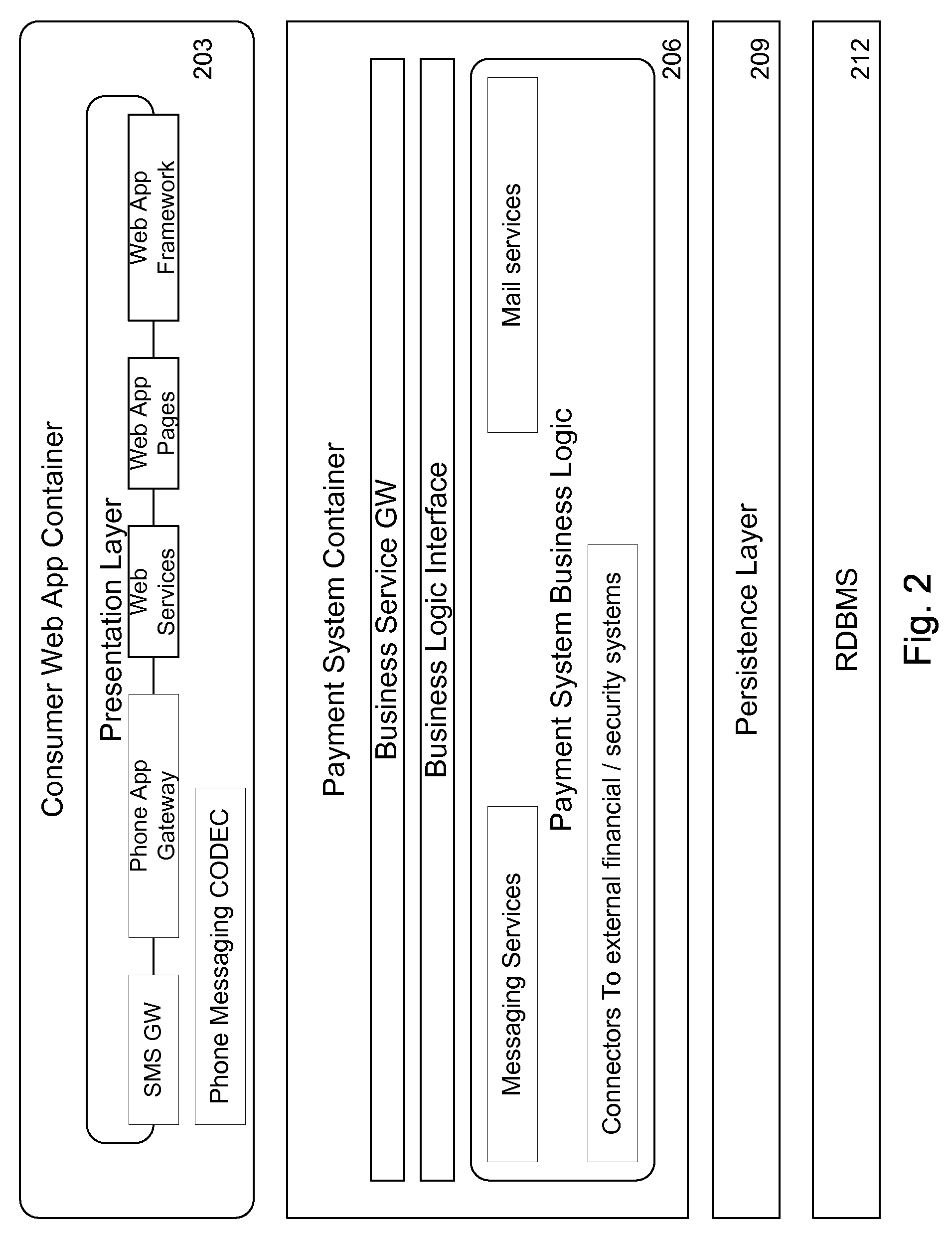
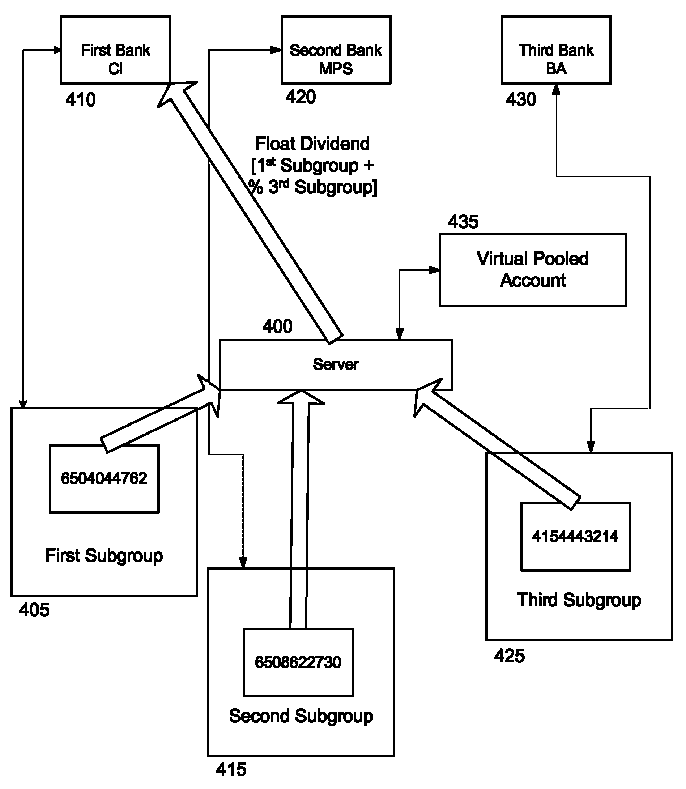
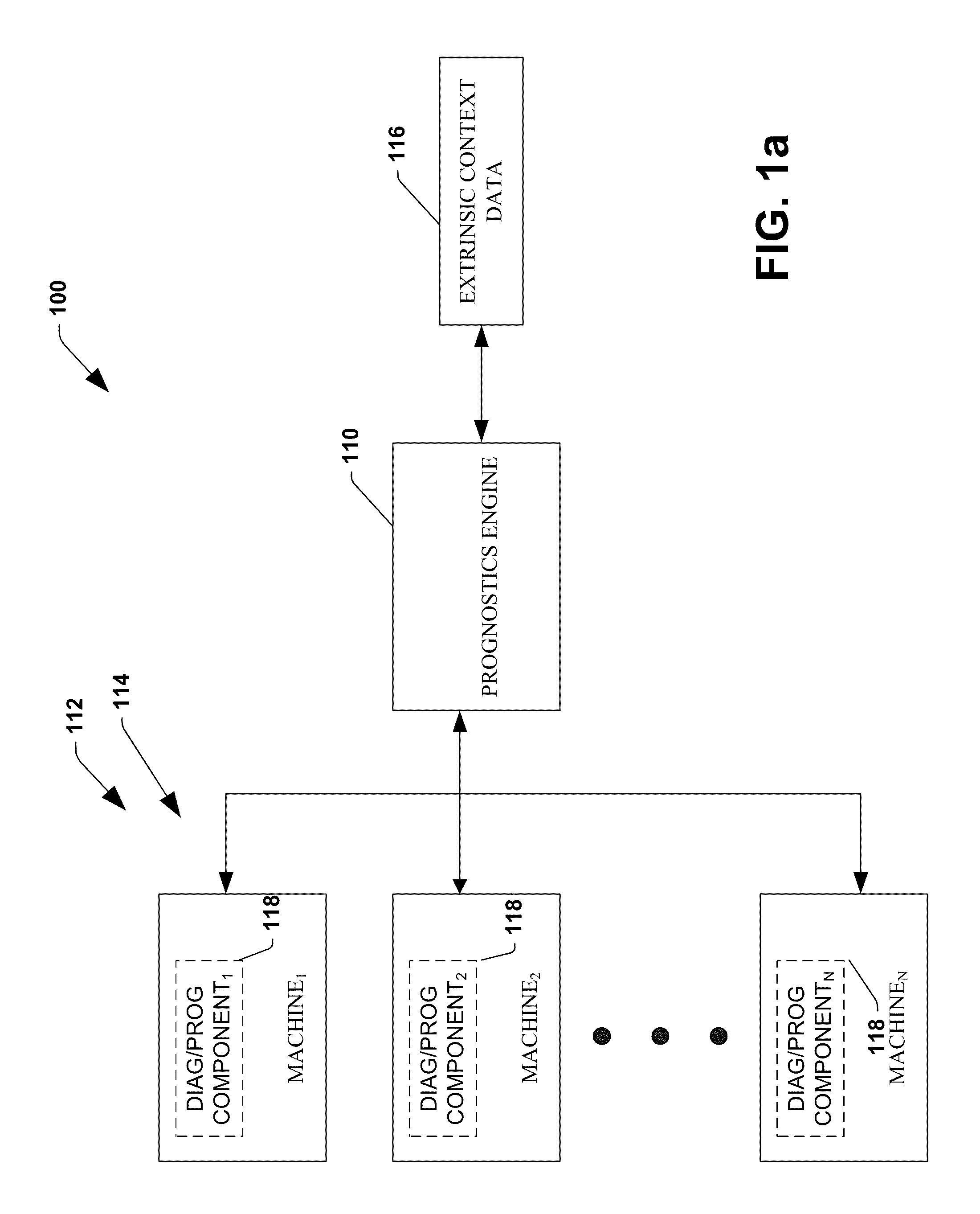
Virtual Pooled Account for Mobile Banking
InactiveUS20090119190A1Reduce settlementReduce operating costsComplete banking machinesFinanceOperational costsSimulation
A virtual pooled account is used in operating a system having multiple financial partners. In a specific implementation, the system is a mobile banking system. Instead of maintaining separate general ledgers for each financial institution, the system will keep one general virtual pooled account. This will reduce the settlement and operational costs of the system. The owner of the virtual pooled account will receive the float on the virtual pooled account, and this float will be distributed to the multiple financial partners according to a formula.
Owner:OBOPAY MOBILE TECH INDIA PTE LTD
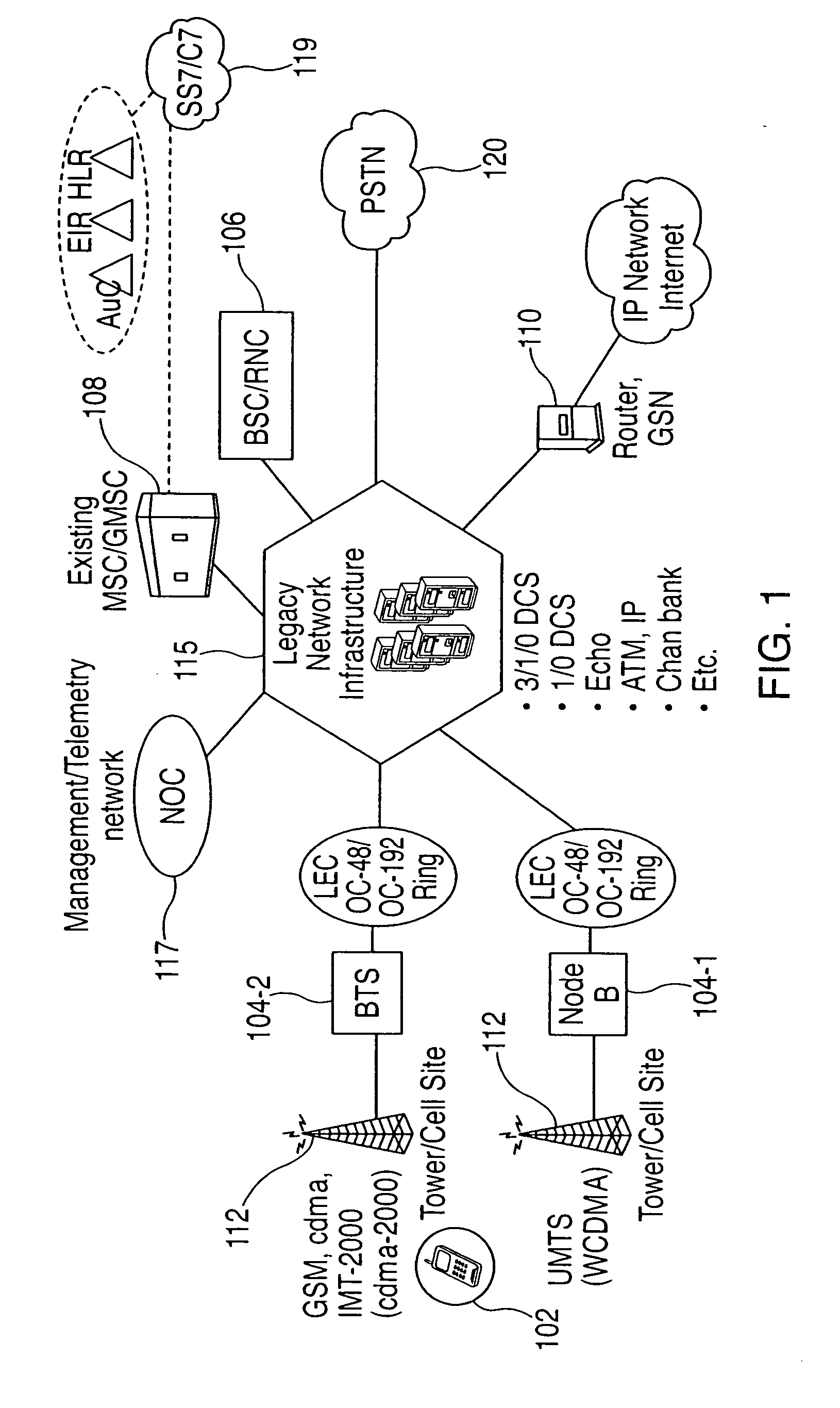
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS20050007993A1Easy to adaptNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
Method of cleaning CVD equipment processing chamber
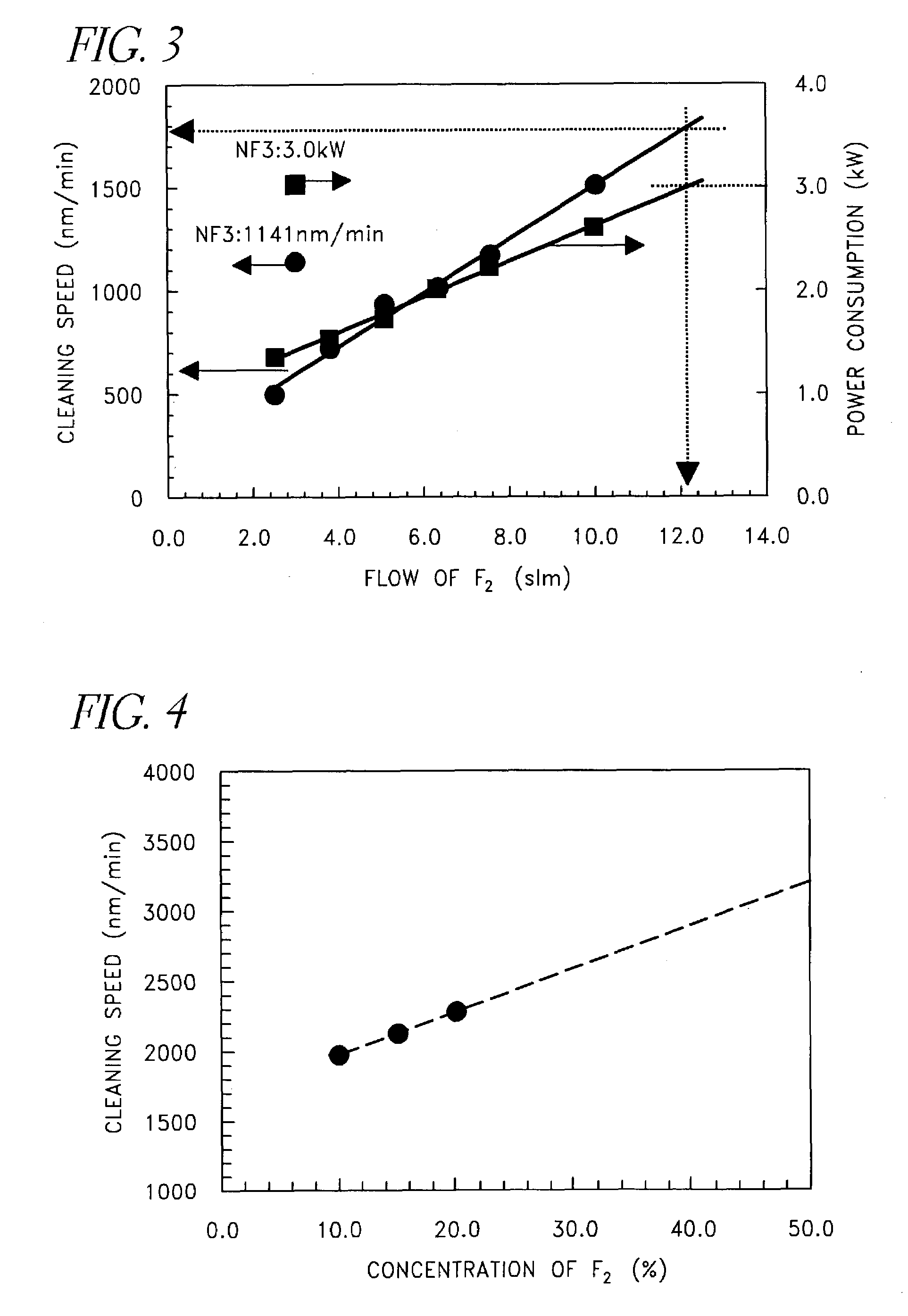
ActiveUS7234476B2Reduce operating costsImprove efficiencyElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningRemote plasmaOperational costs
A method of remote plasma cleaning a processing chamber of CVD equipment, which has high cleaning rates, low cleaning operational cost and high efficiency, is provided. The method comprises supplying cleaning gas to the remote plasma-discharge device; activating the cleaning gas inside the remote plasma-discharge device; and bringing the activated cleaning gas into the processing chamber and which is characterized in that a mixed gas of F2 gas and an inert gas are used as the cleaning gas. A concentration of the F2 gas is 10% or higher. The F2 gas, which is a cleaning gas, is supplied to the remote plasma-discharge device from an F2 gas cylinder by diluting F2 gas at a given concentration by an inert gas.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
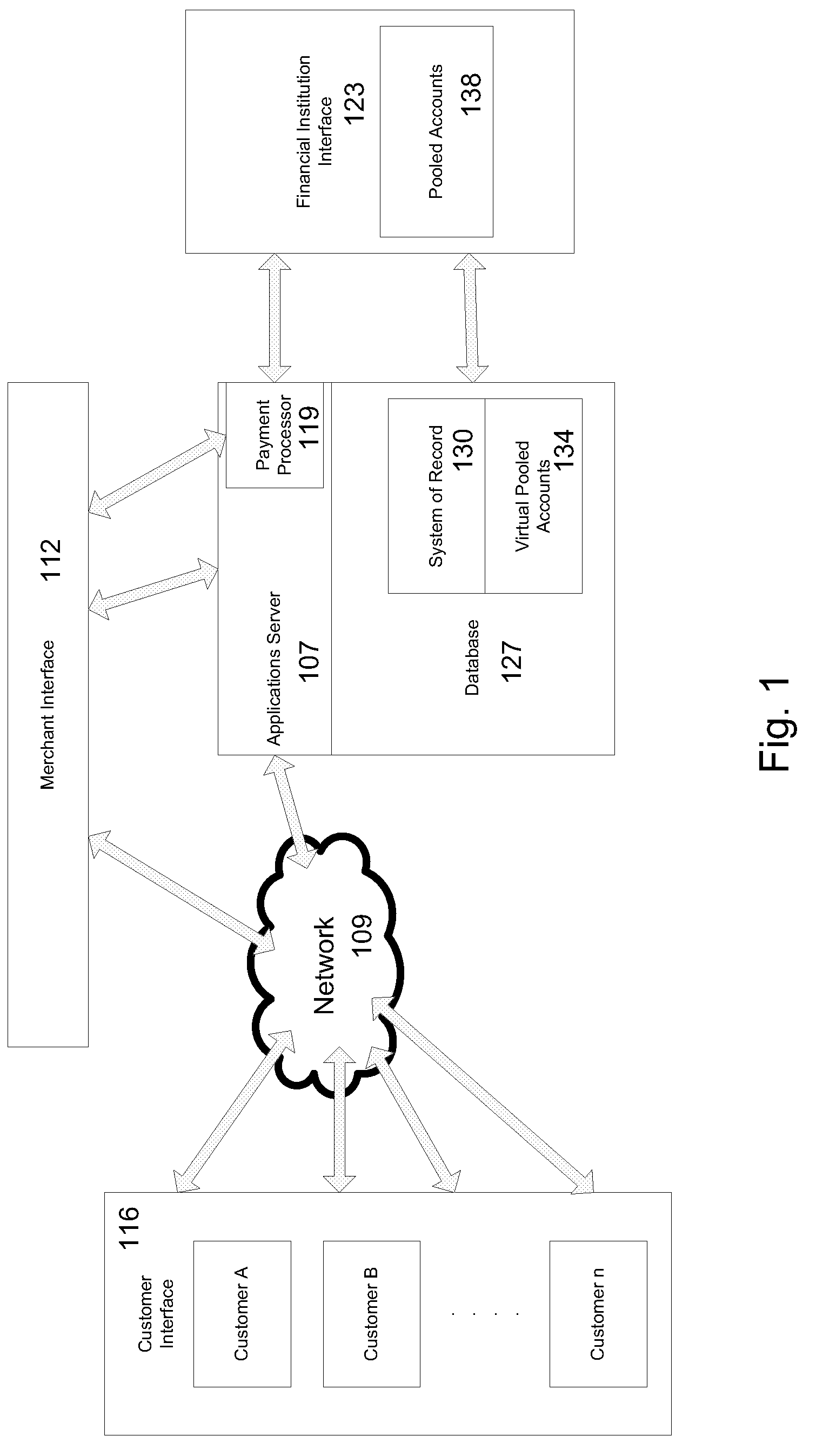
Virtual pooled account for mobile banking
ActiveUS7873573B2Reduce settlement and operational cost of systemThe process is simple and fastComplete banking machinesFinanceOperational costsSimulation
A virtual pooled account is used in operating a system having multiple financial partners. In a specific implementation, the system is a mobile banking system. Instead of maintaining separate general ledgers for each financial institution, the system will keep one general virtual pooled account. This will reduce the settlement and operational costs of the system. The owner of the virtual pooled account will receive the float on the virtual pooled account, and this float will be distributed to the multiple financial partners according to a formula.
Owner:OBOPAY MOBILE TECH INDIA PTE LTD
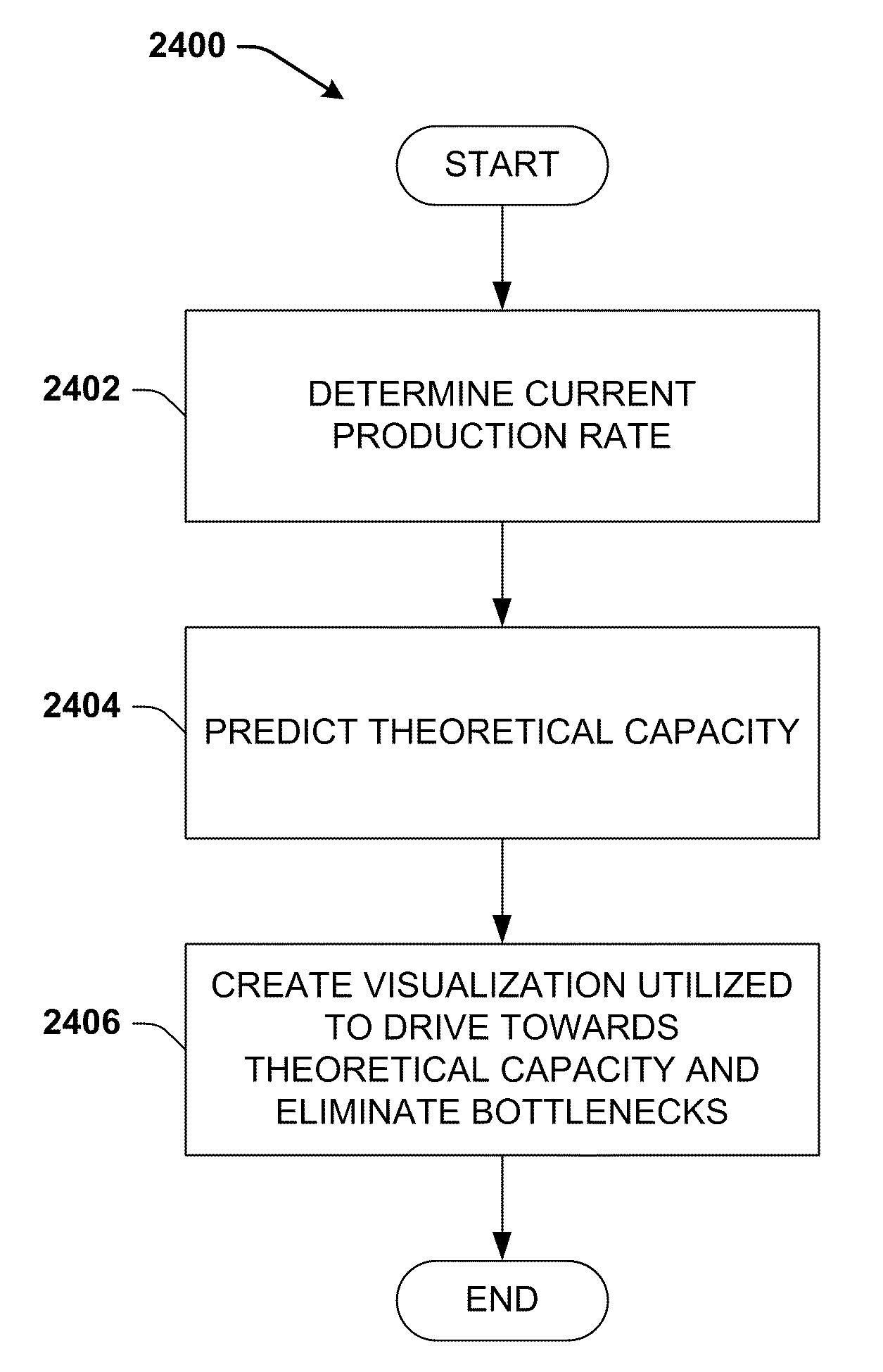
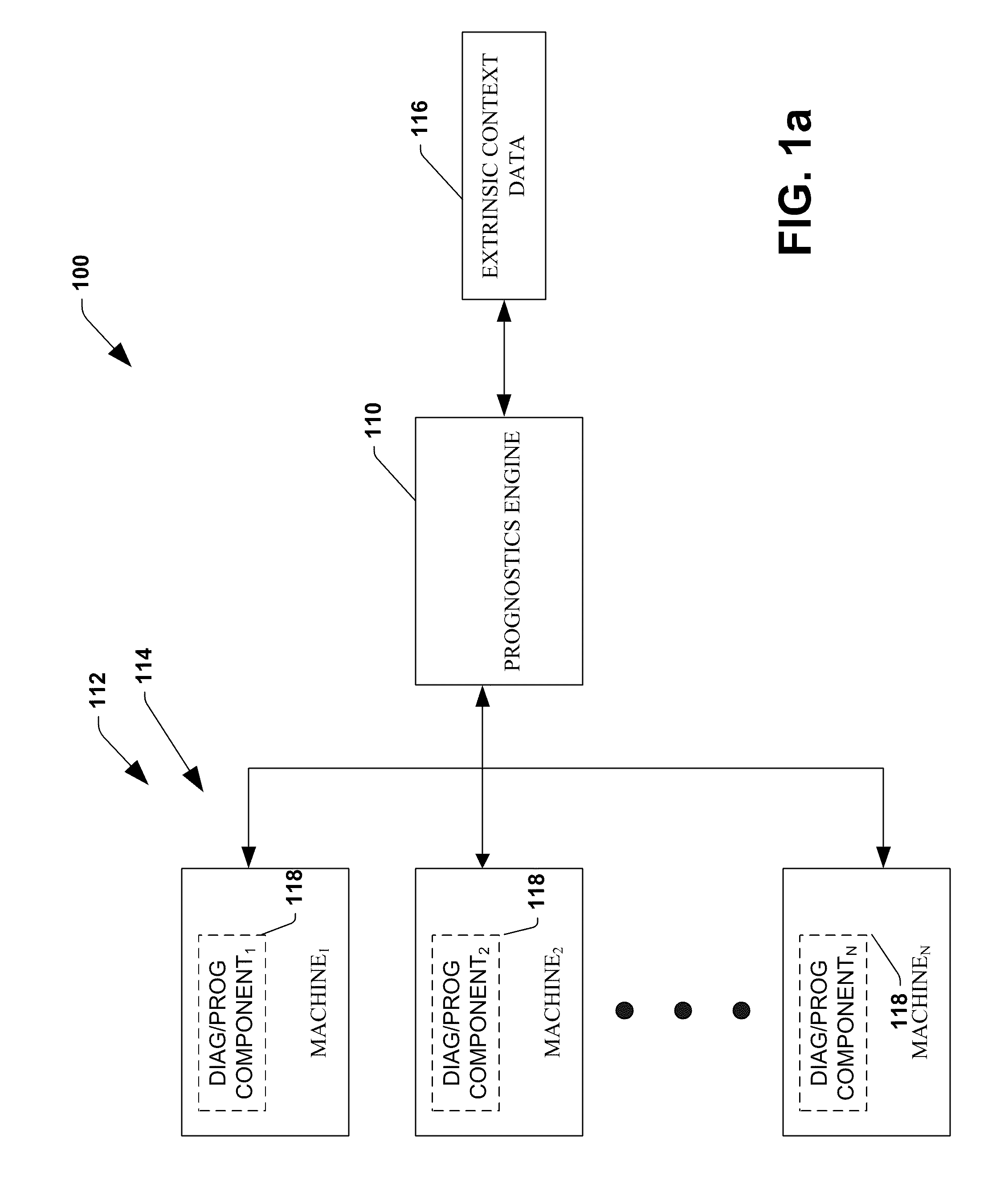
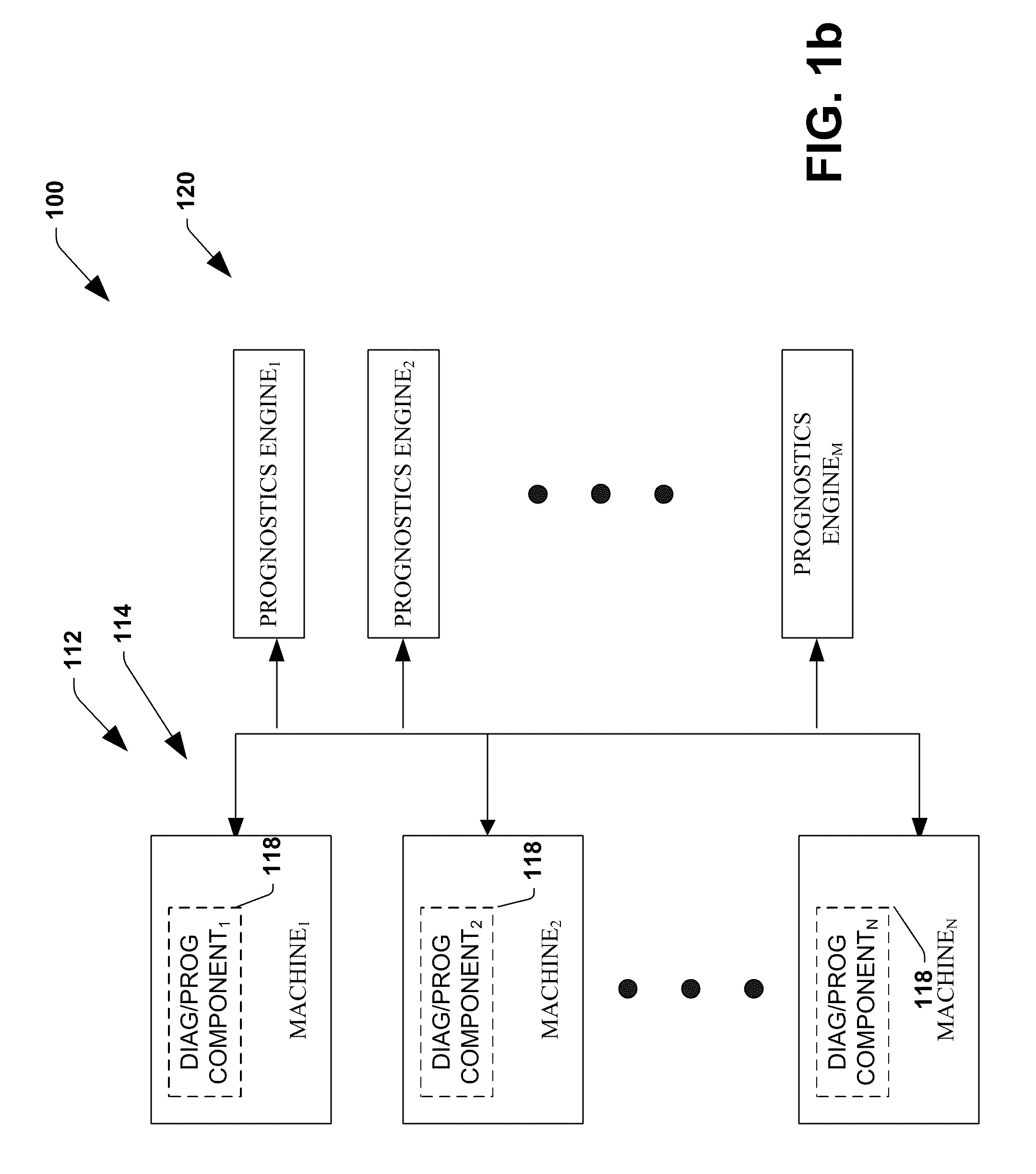
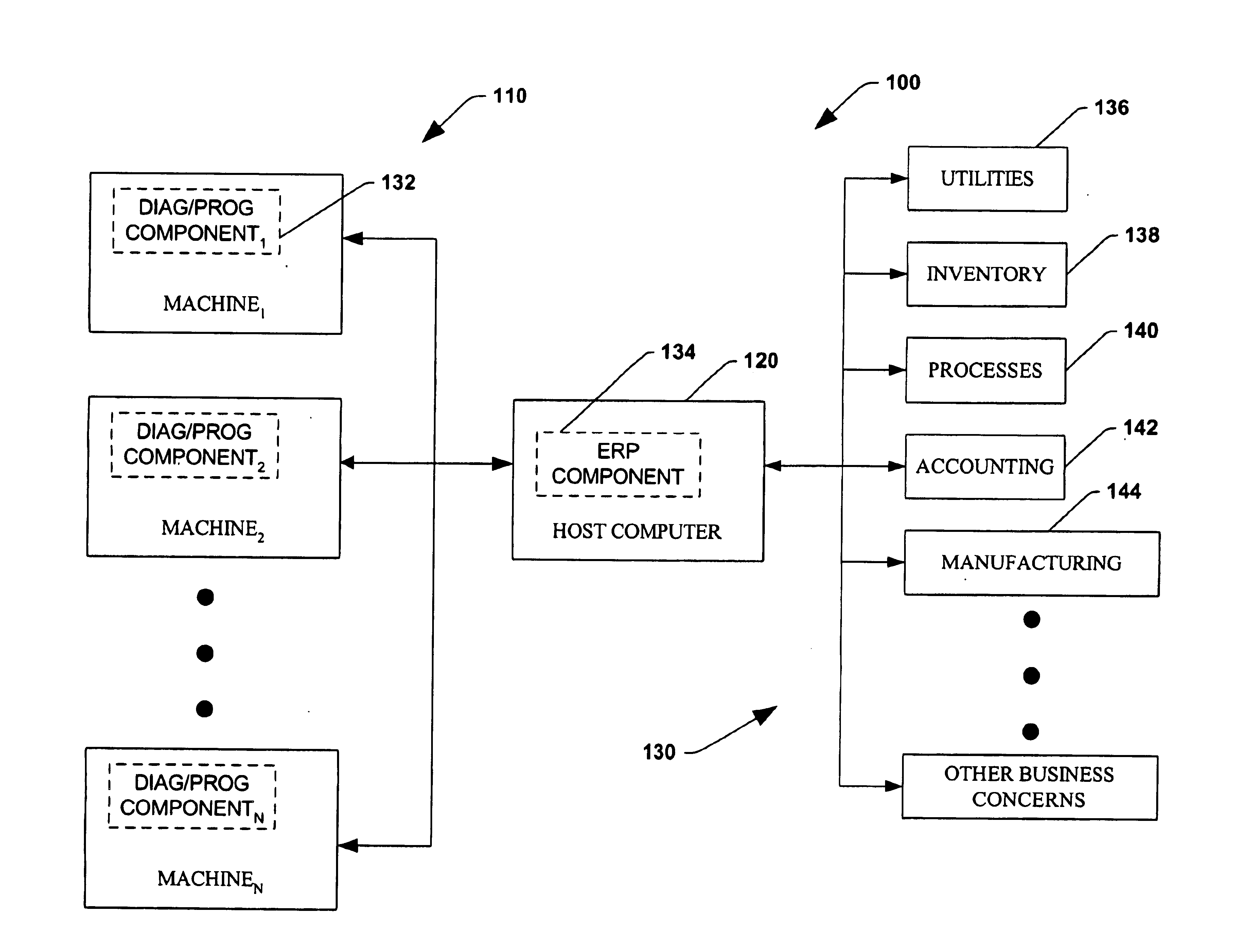
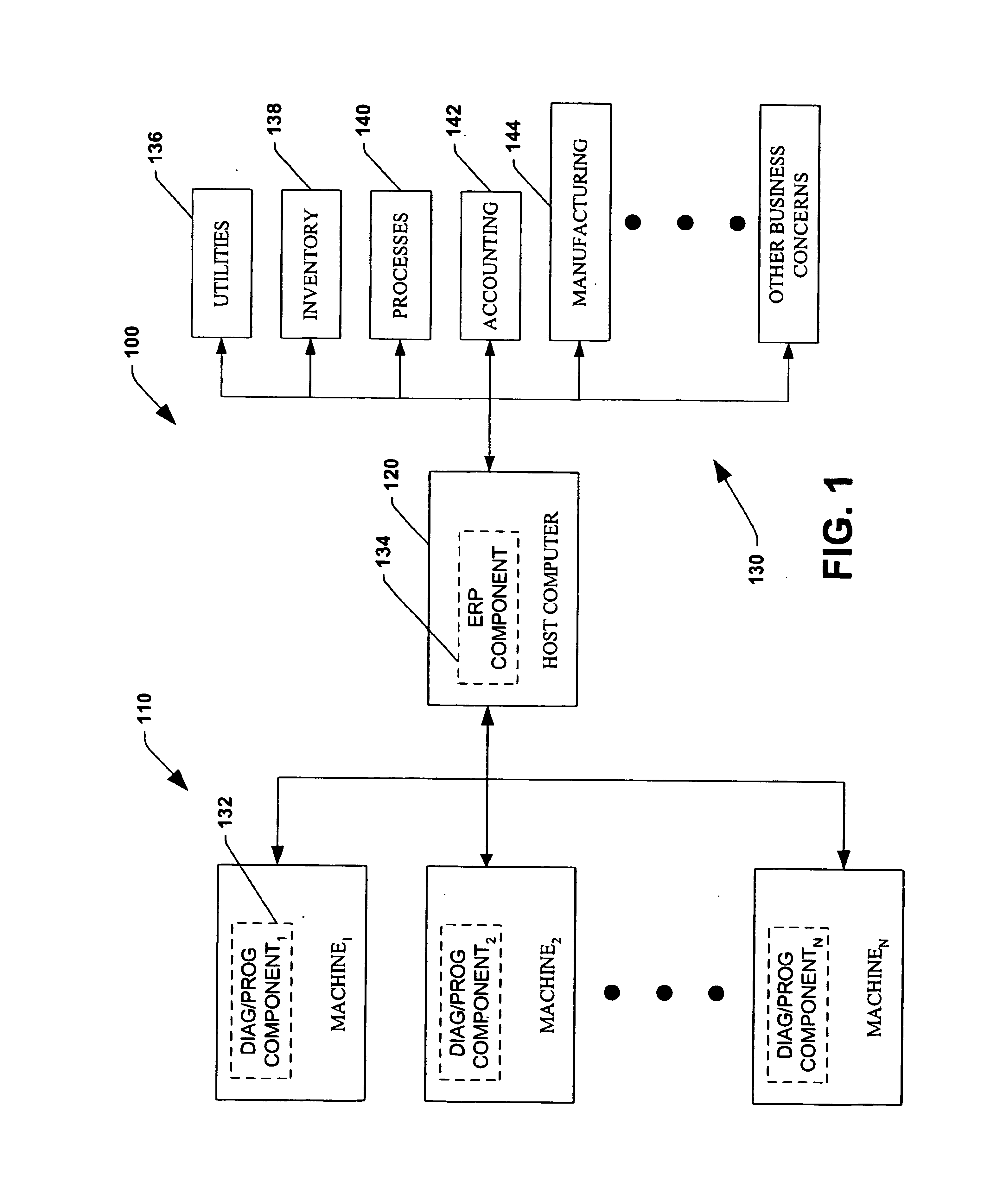
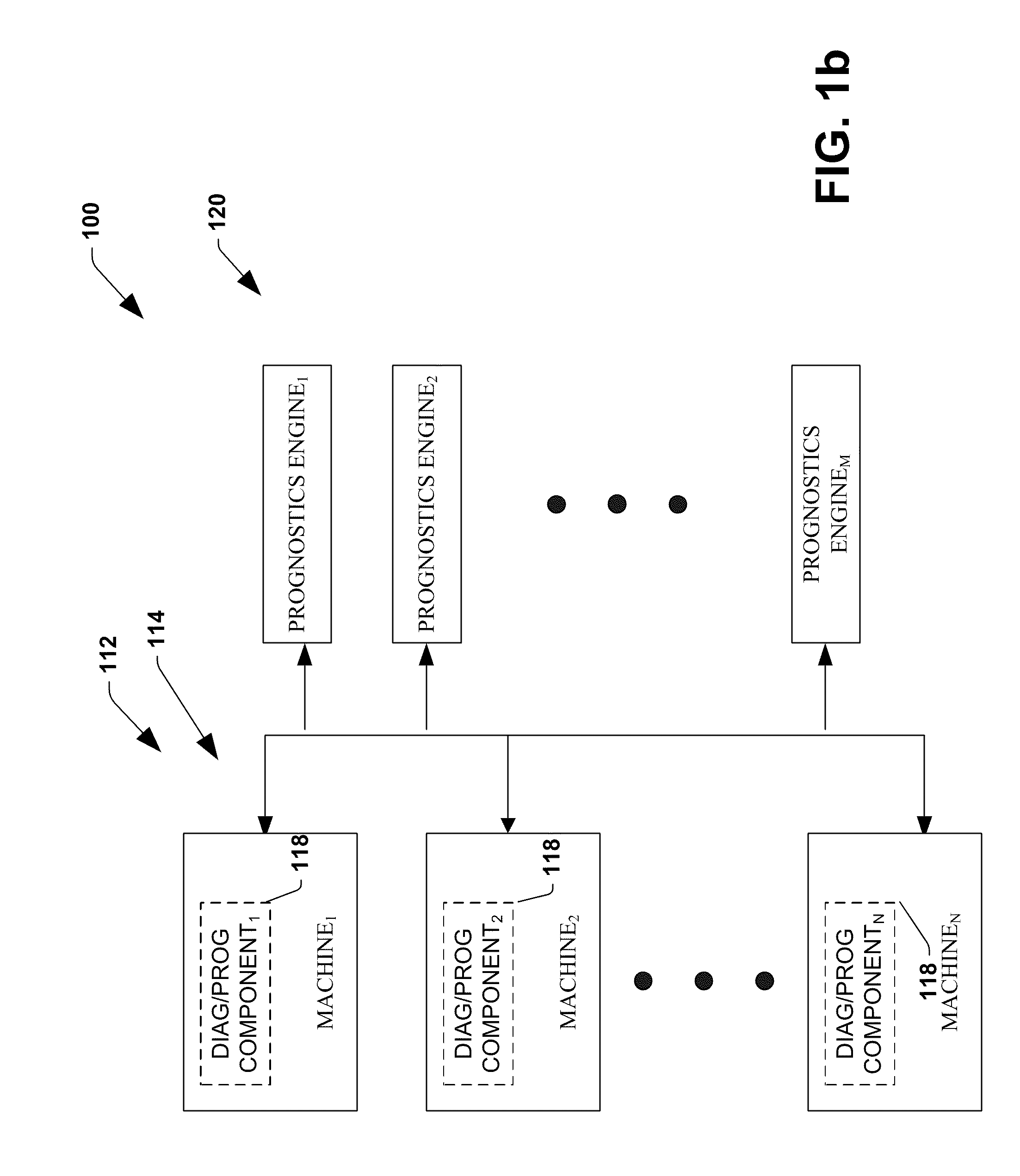
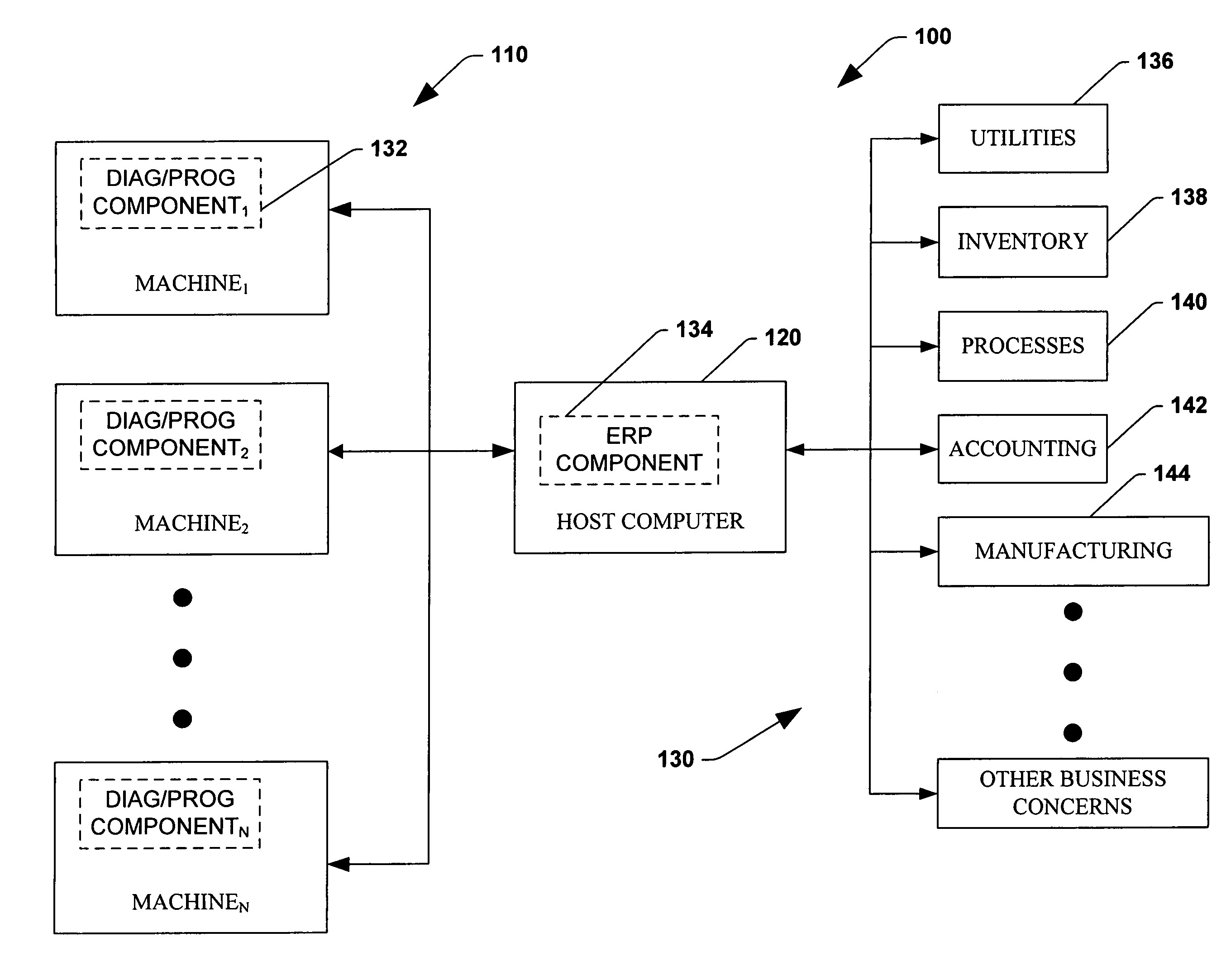
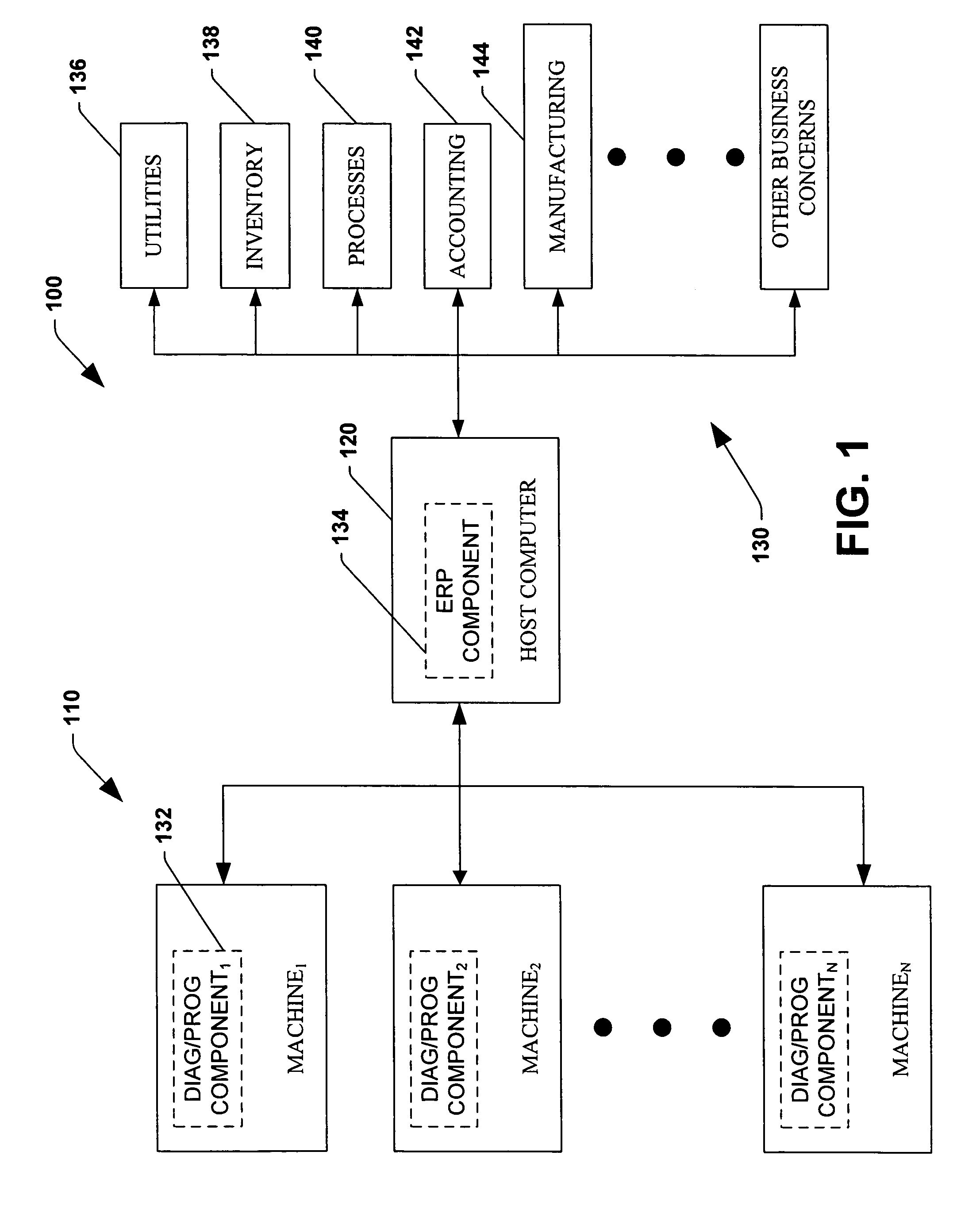
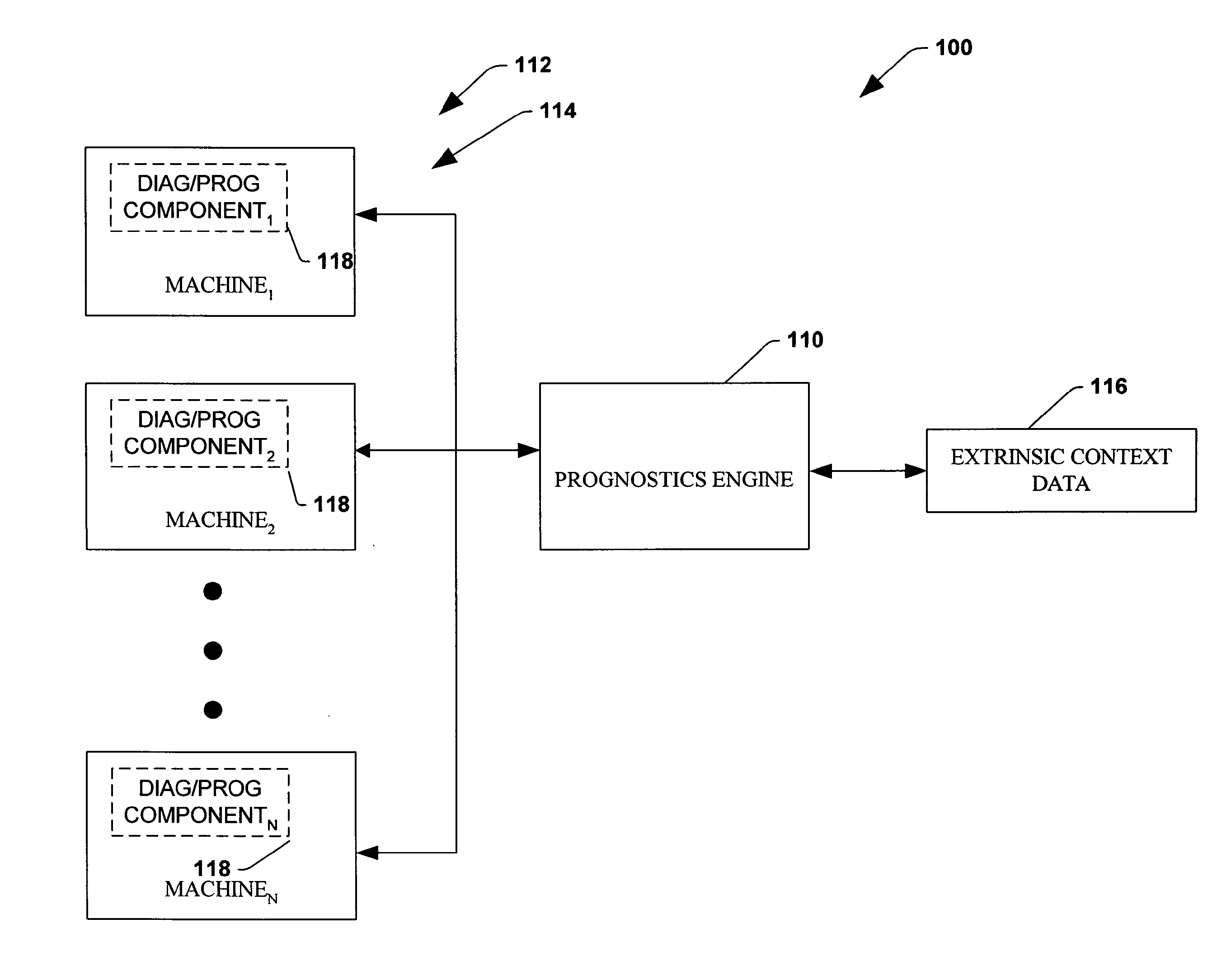
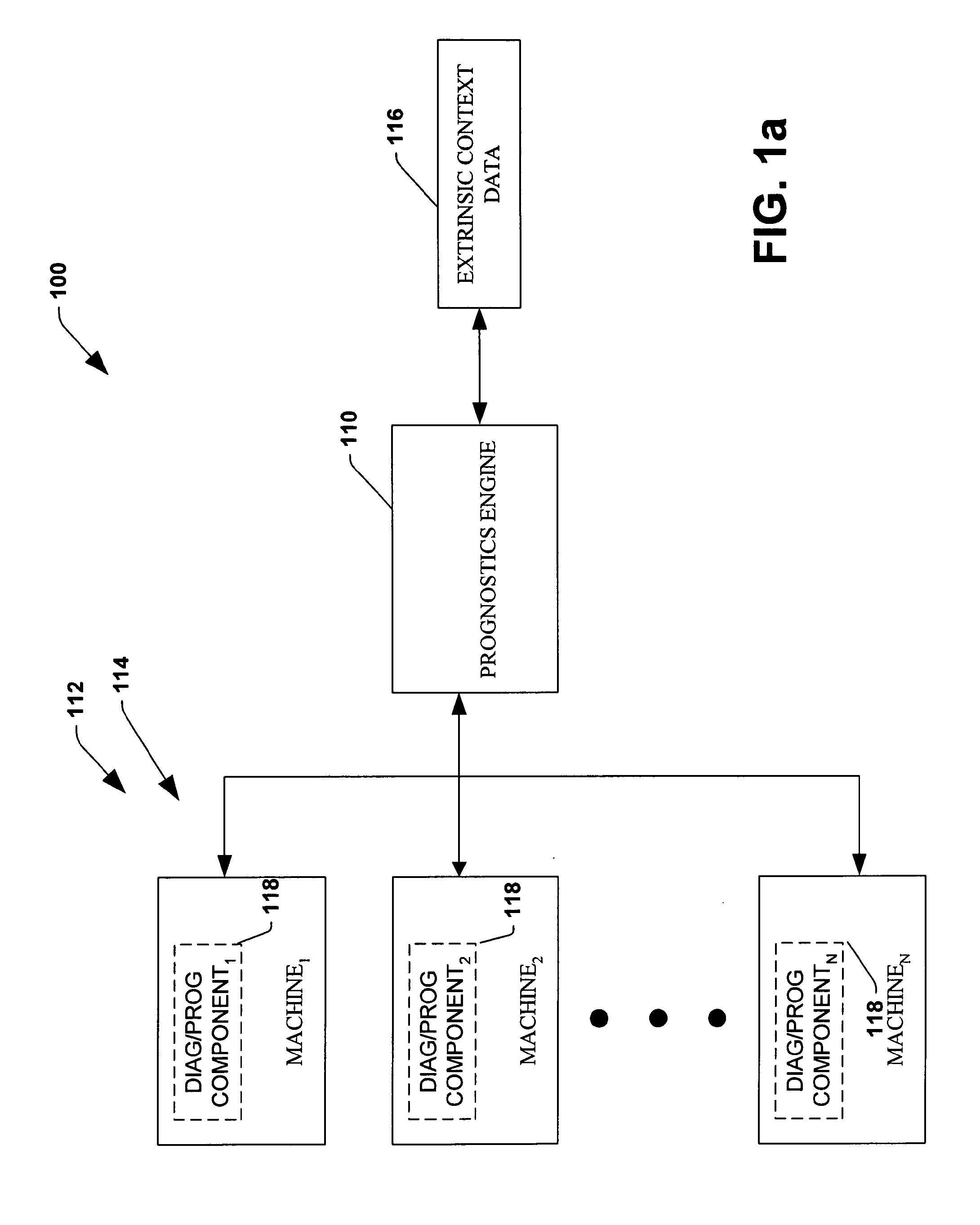
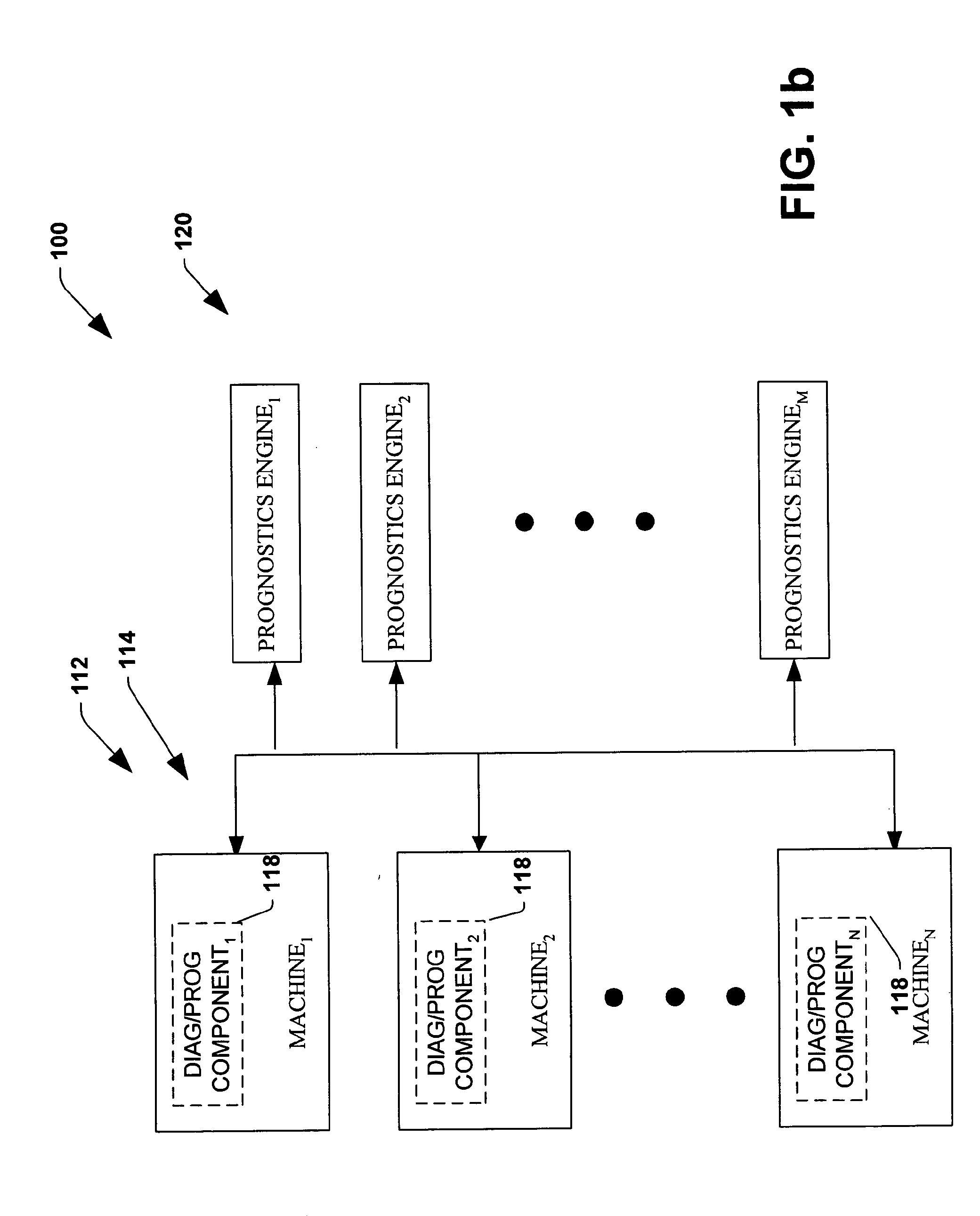
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS20090210081A1Improve overall utilizationImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionForecastingMachine selectionOperational costs
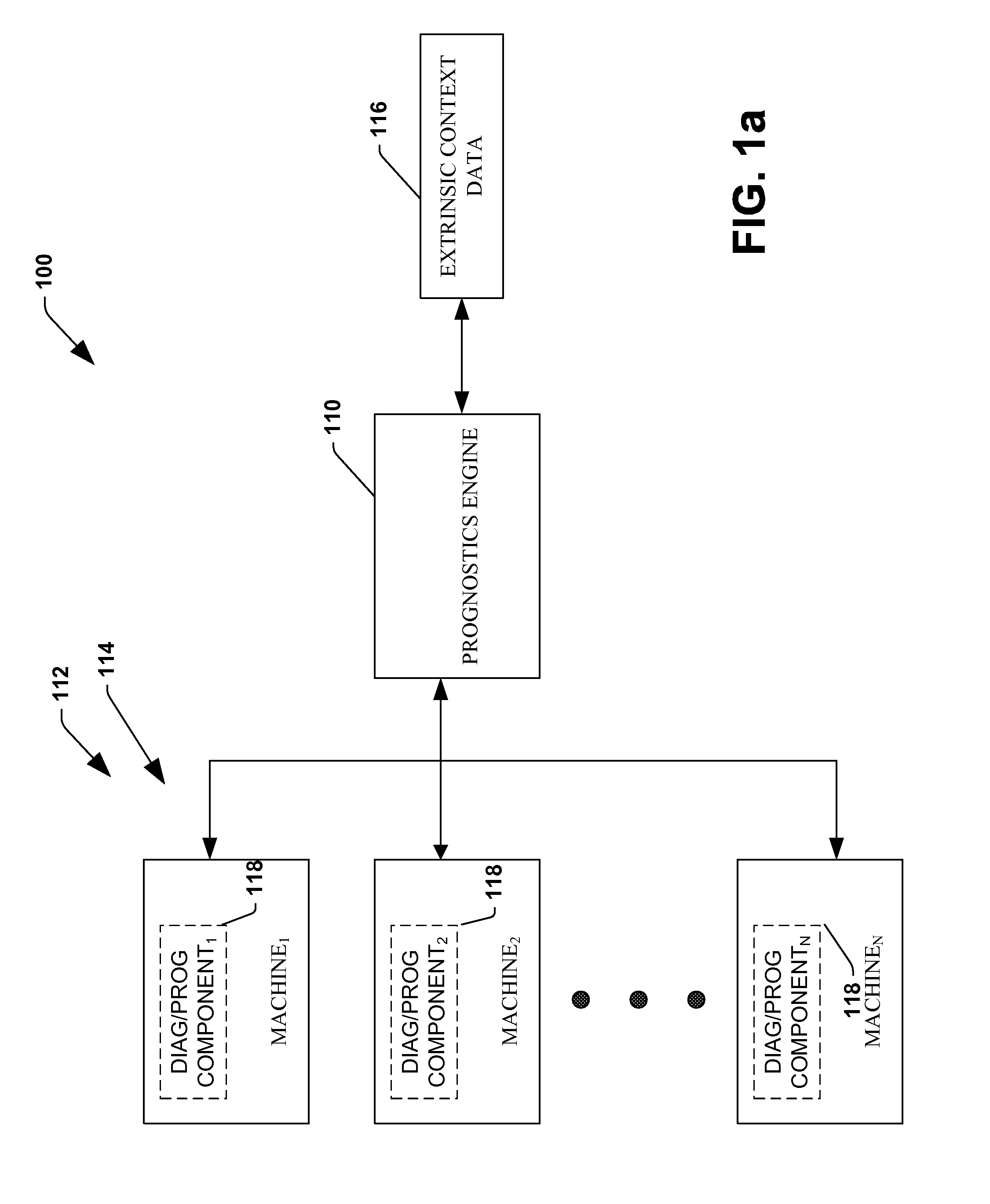
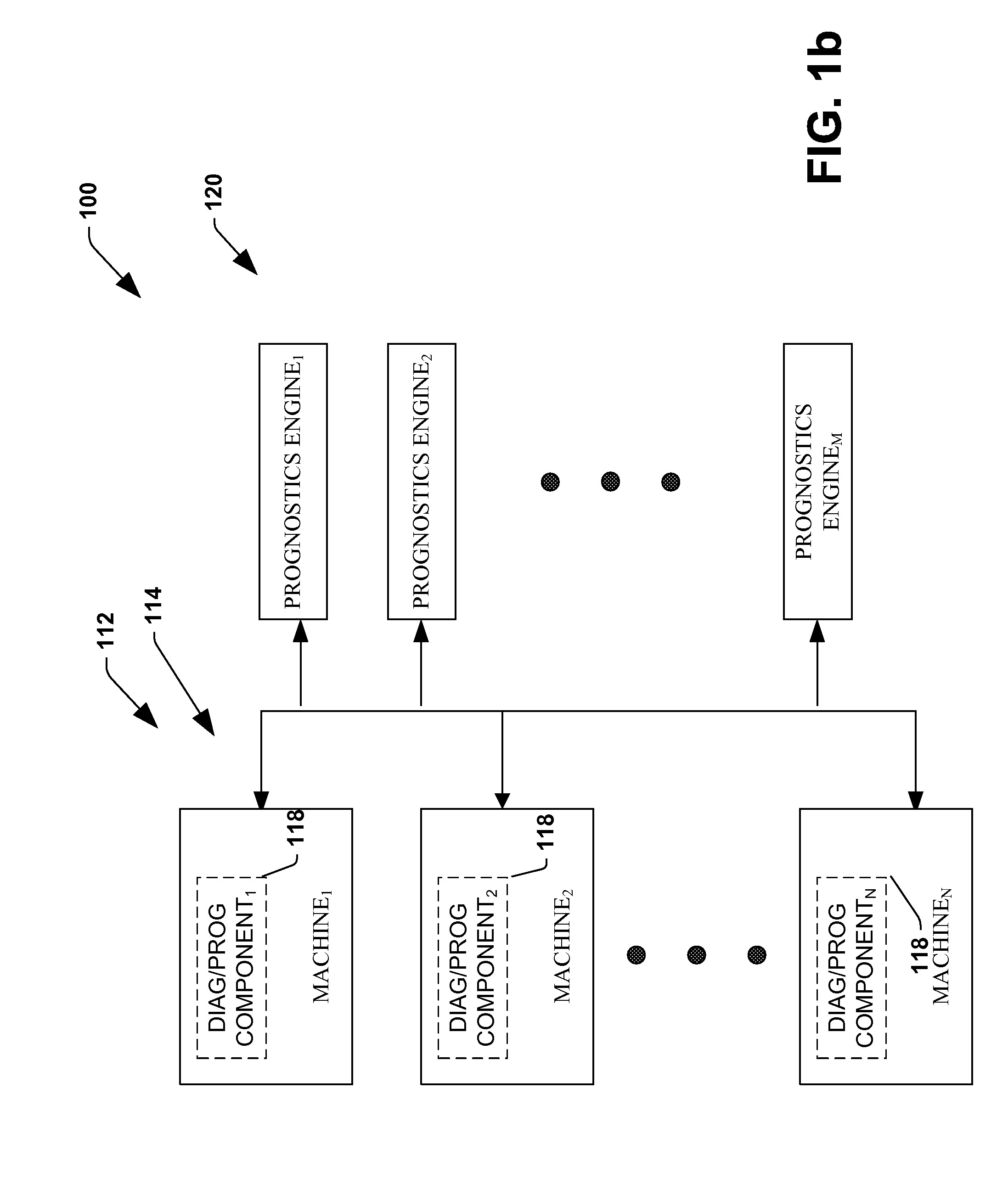
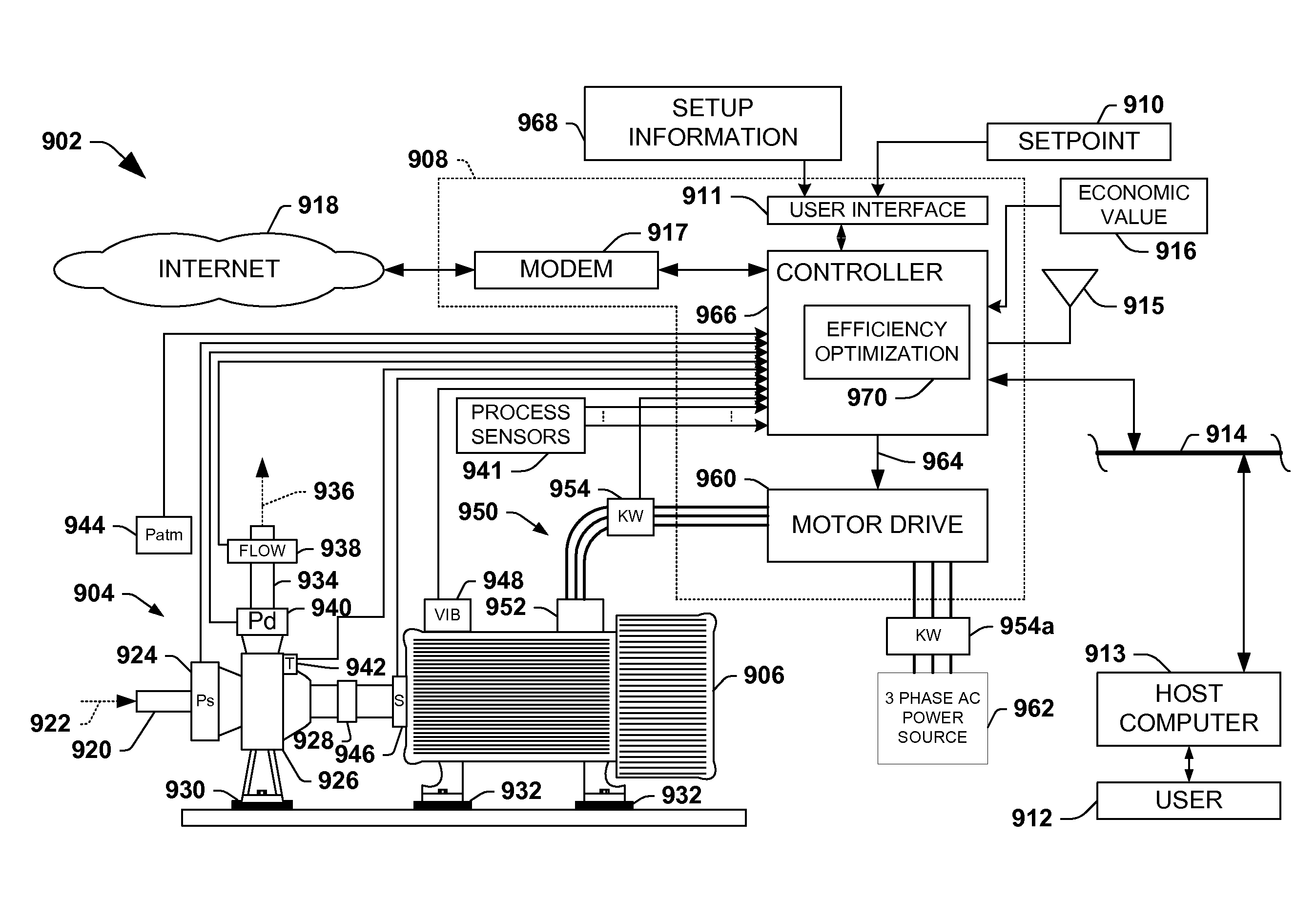
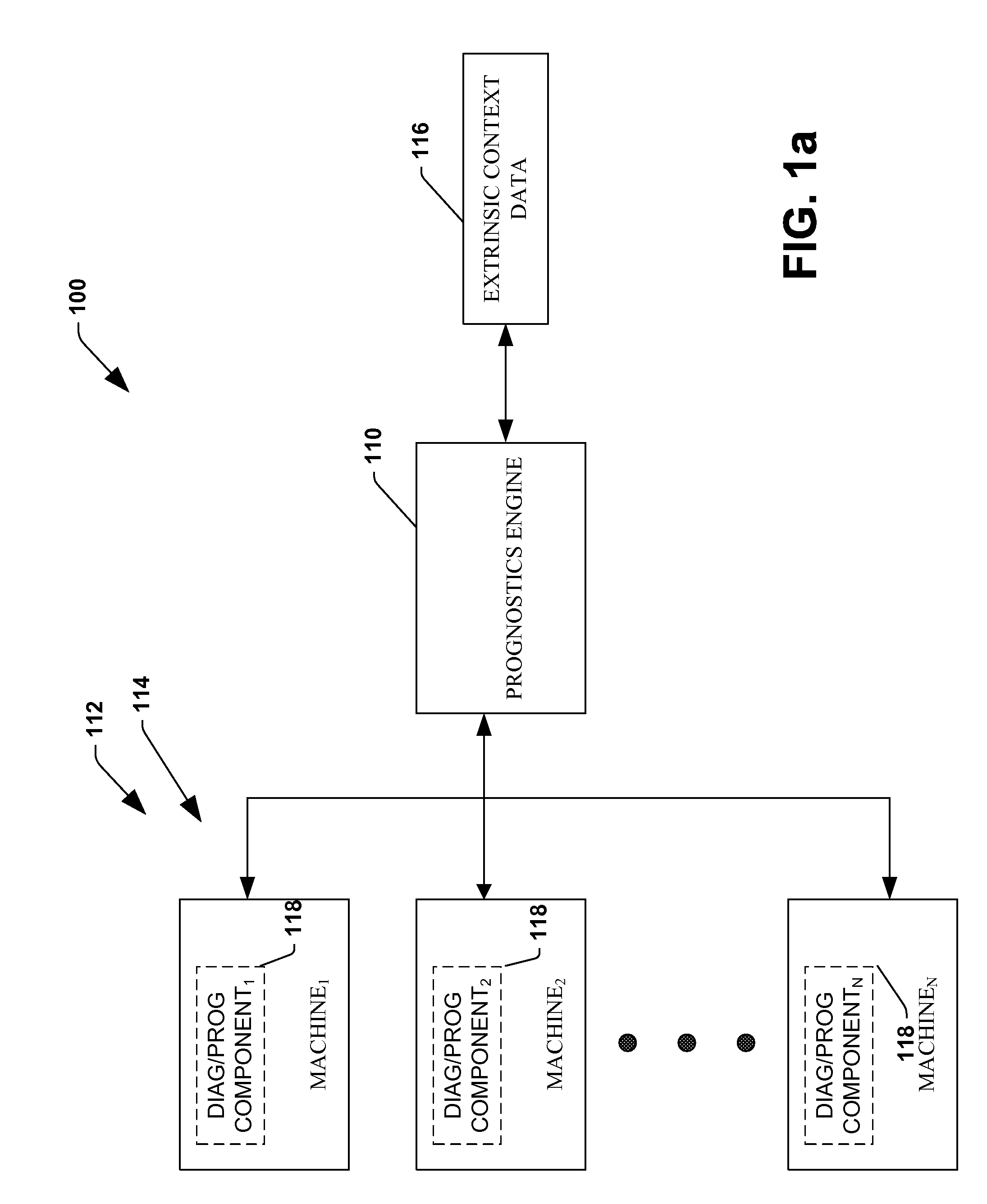
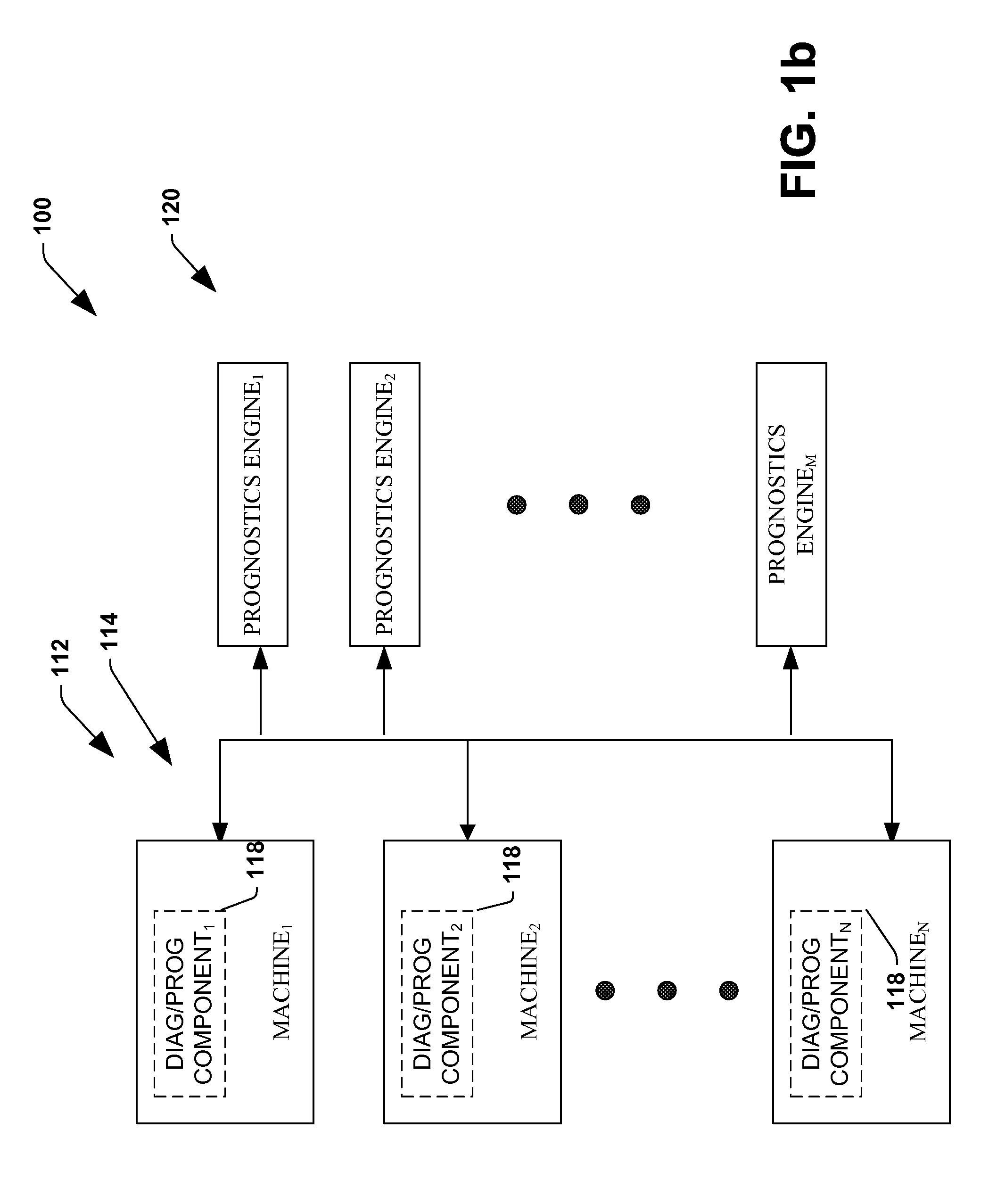
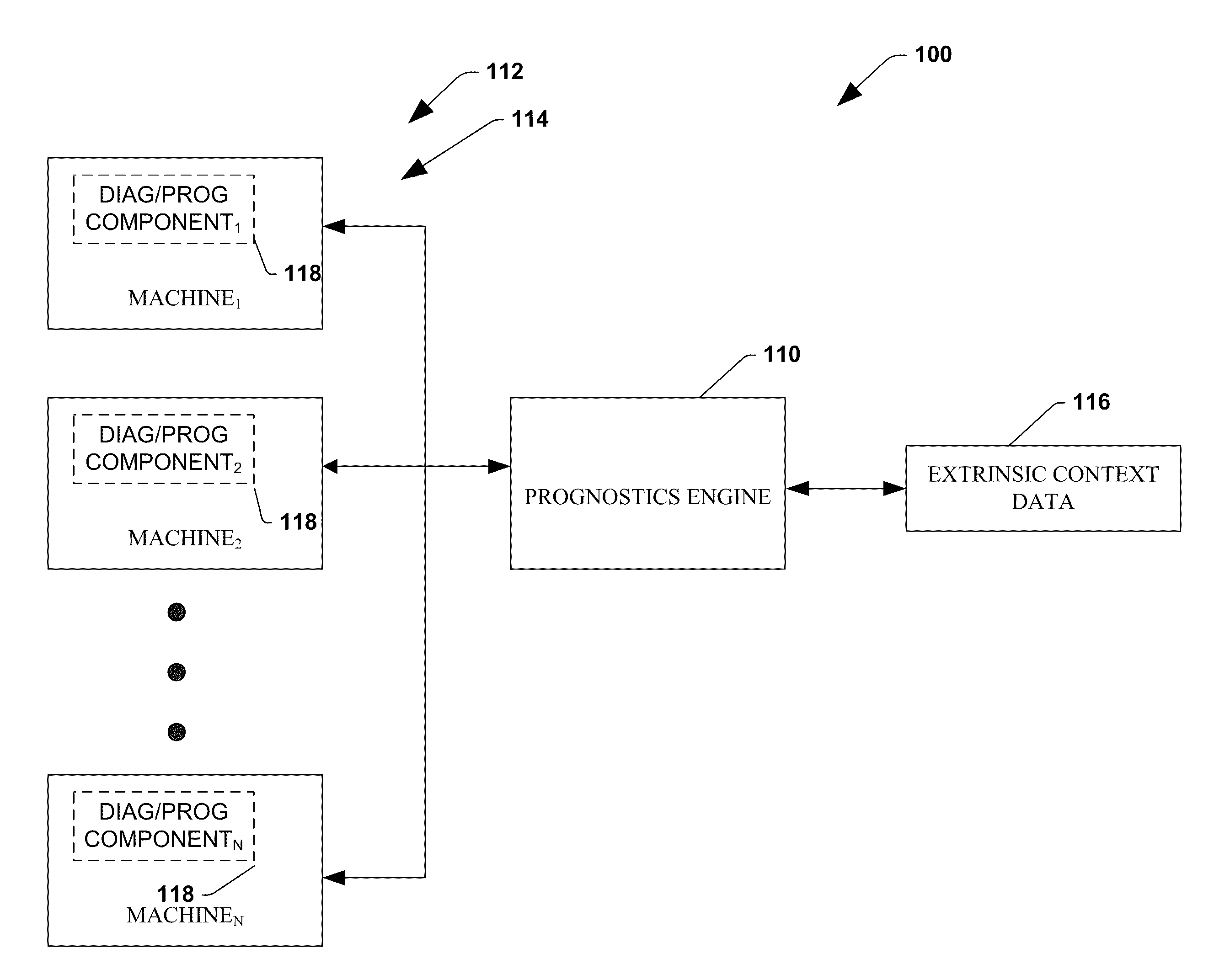
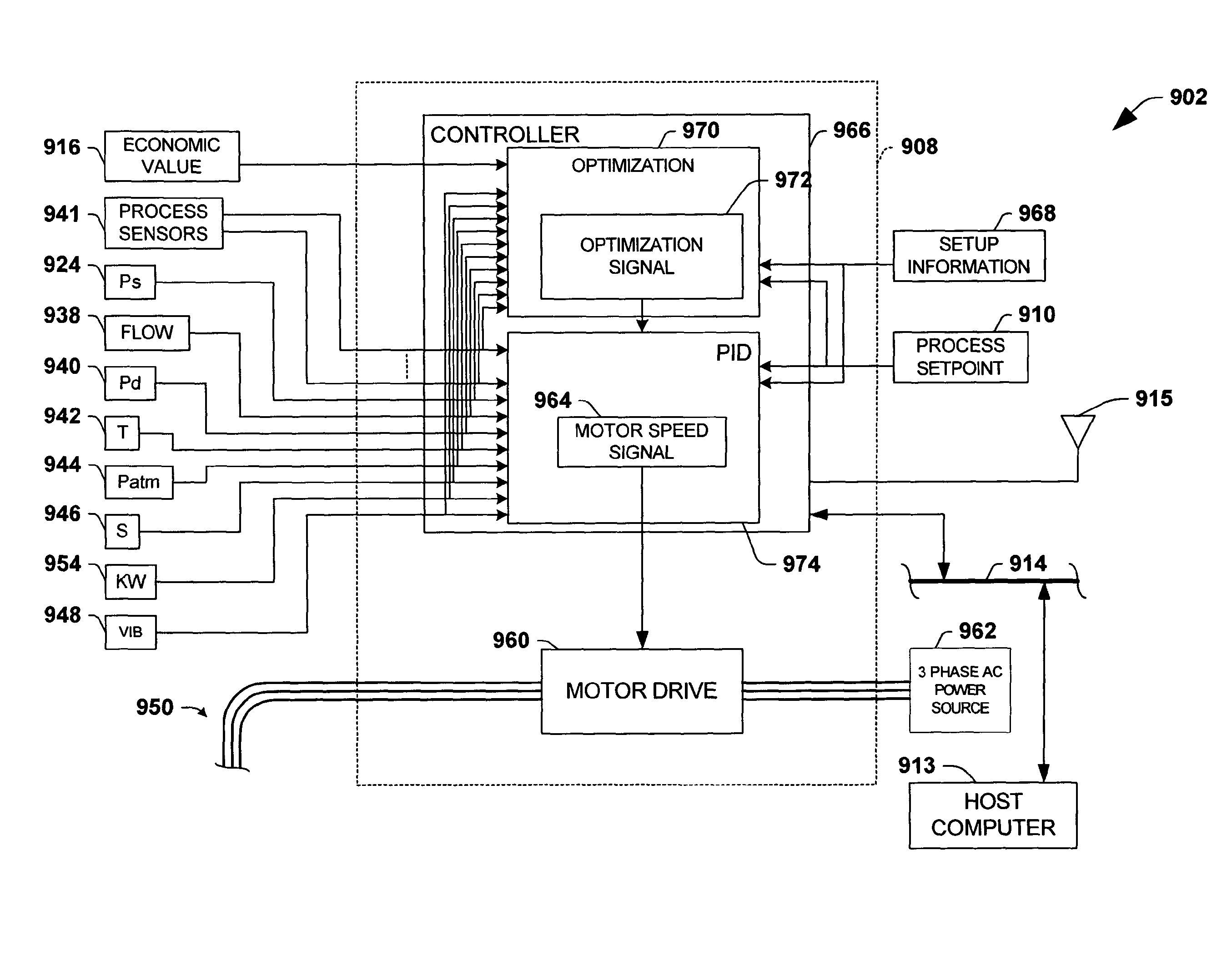
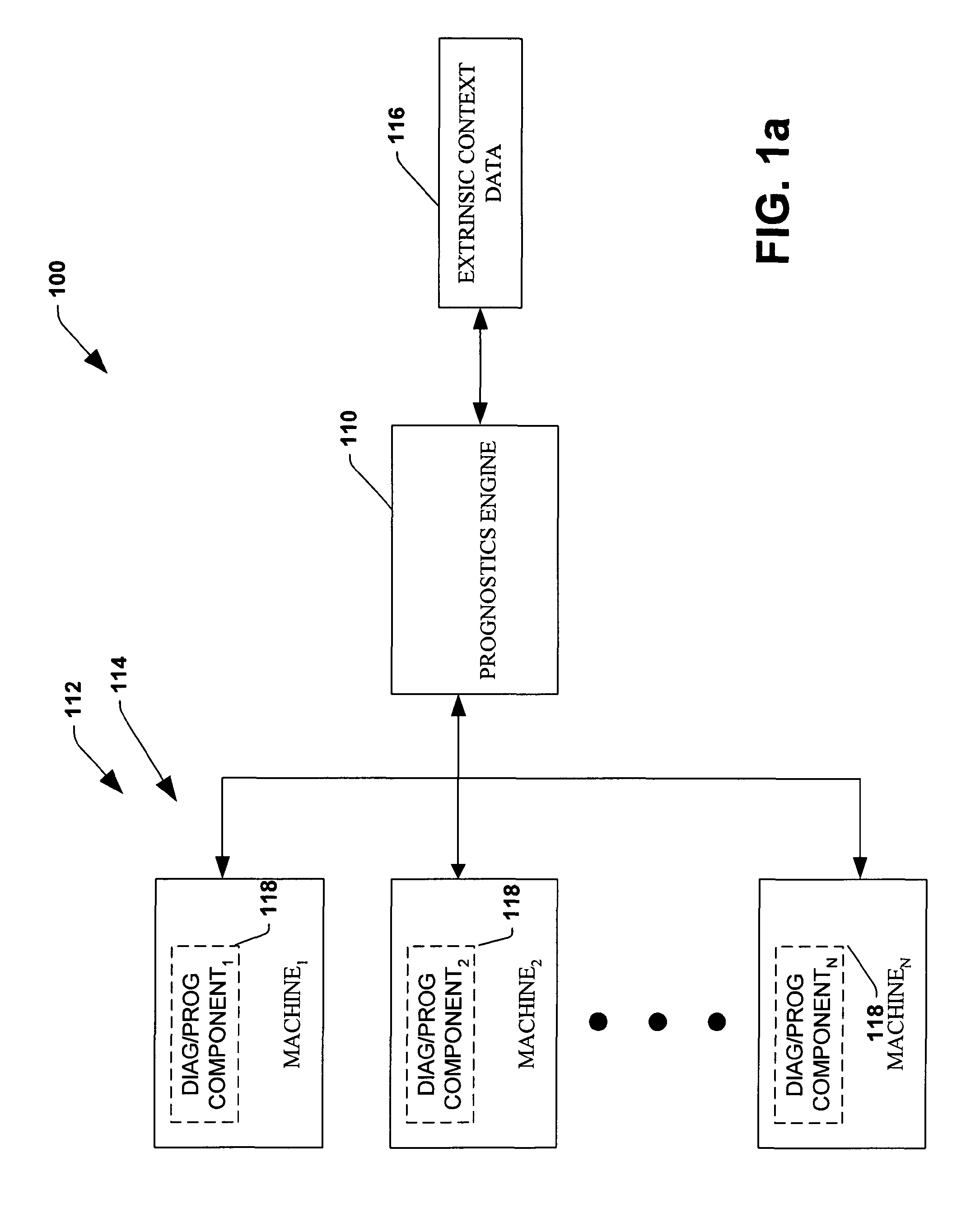
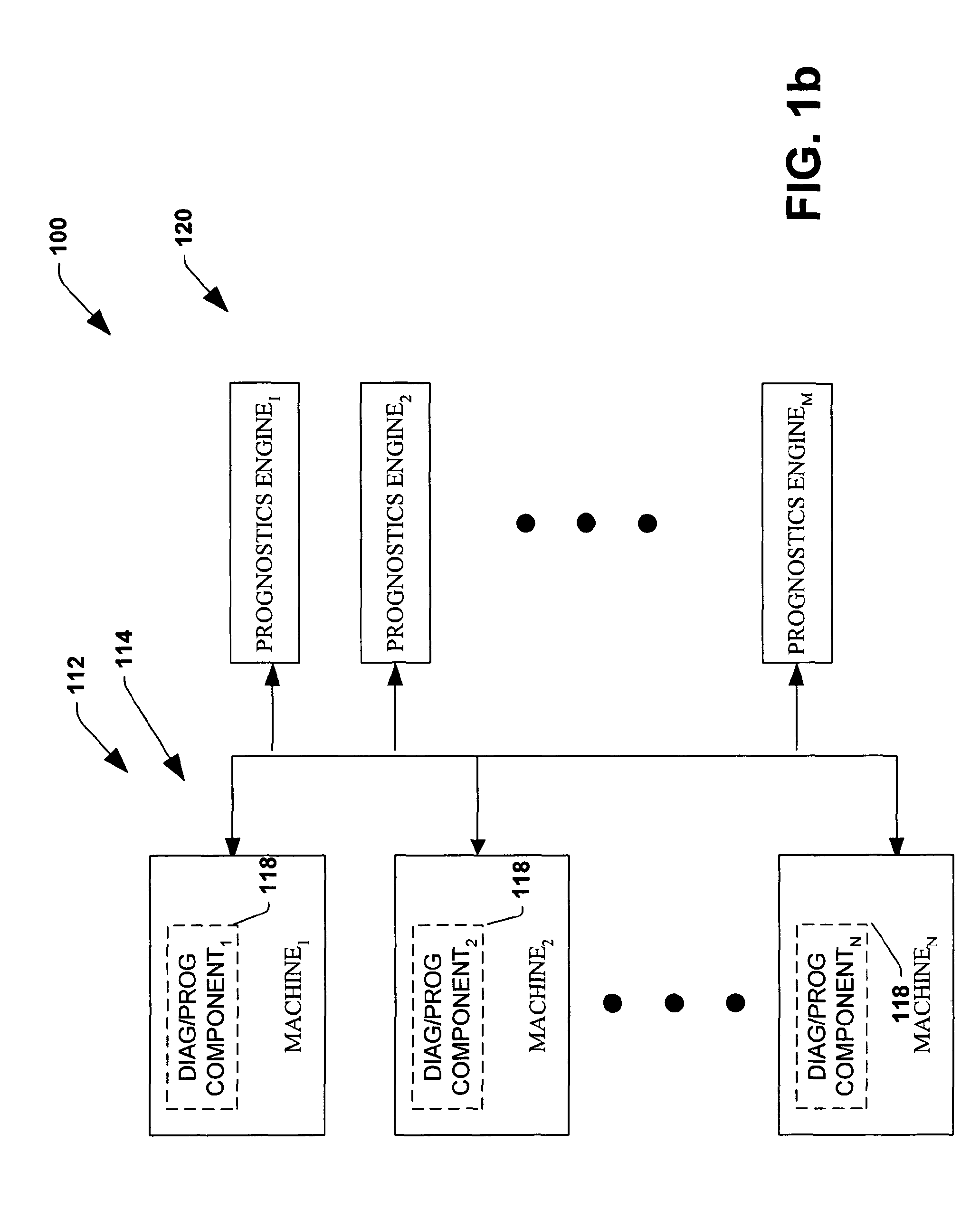
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS6847854B2Improve efficiencyEasy to operateProgramme controlComputer controlMachine selectionOperational costs
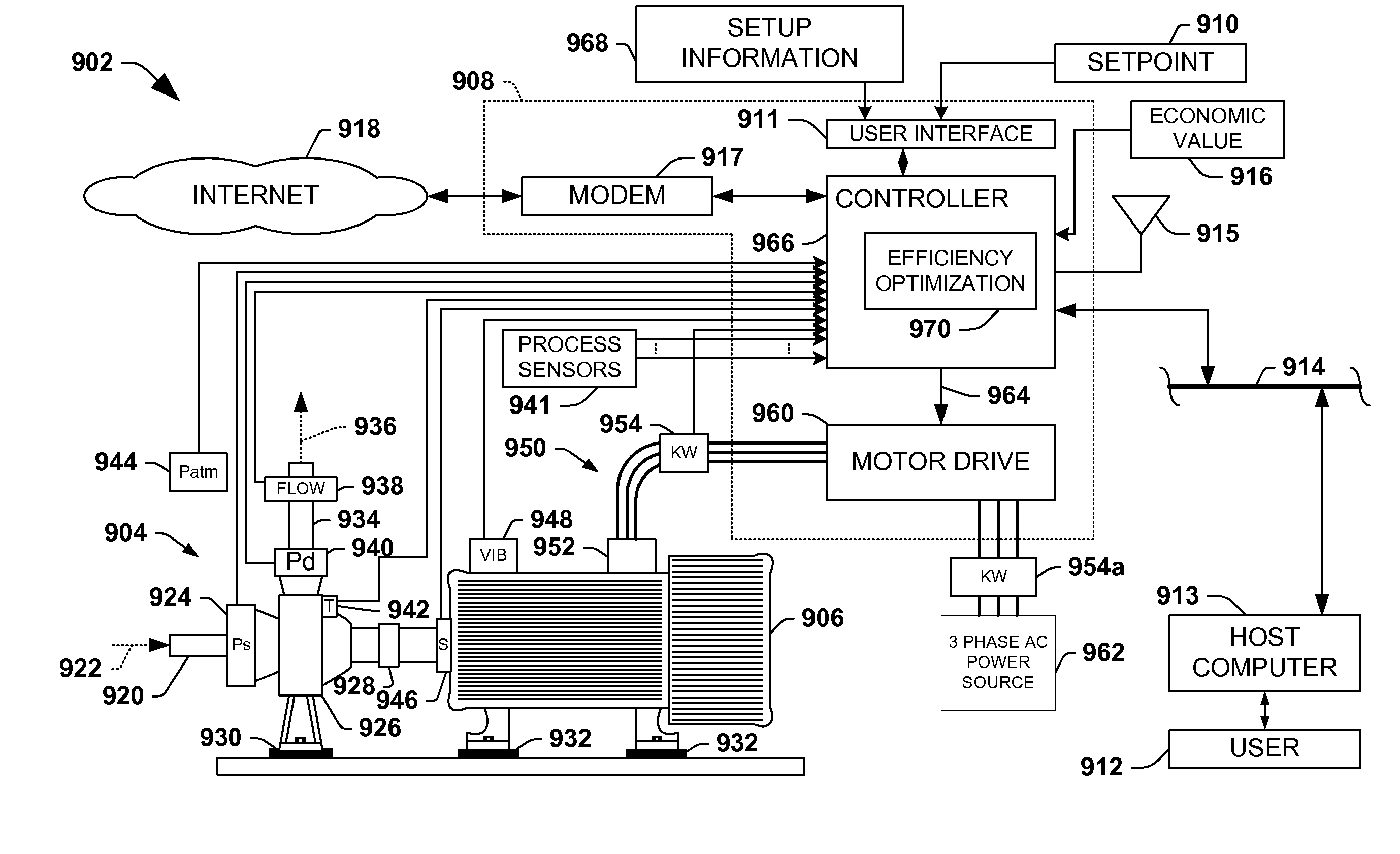
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having one or more motorized pumps and associated motor drives, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS20090204234A1Minimize power consumptionLow costSimulator controlForecastingMachine selectionOperational costs
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS20090204245A1Minimize power consumptionLow costForecastingTechnology managementOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS20090204237A1Minimize power consumptionLow costForecastingTechnology managementOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS7050873B1Improve efficiencyEasy to modifyProgramme controlComputer controlOperational costsMotor drive
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having one or more motorized pumps and associated motor drives, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Long range hybrid electric airplane
InactiveUS20080184906A1Long range of flightLow system efficiencyPropellersAircraft stabilisationOperational costsCombustion
An advanced internal combustion-electric hybrid airplane, having at least double the flight range and flight duration than a conventional equivalent airplane, while using the same amount of any desirable fuel. This is achieved by using 2-3× smaller and ultra-lightweight engine for cruising, and ultra-lightweight electric motor powered by lithium batteries during take-off and climbing. The electric motor becomes a generator during cruising and descent, recharging said batteries. The airplane has also temporary silent electric stealth capability and added safety by the electric back-up power. Due to its high efficiency, the operational cost is substantially reduced. Additional features include highly advanced, minimum drag and weight airframe.
Owner:KEJHA JOSEPH B
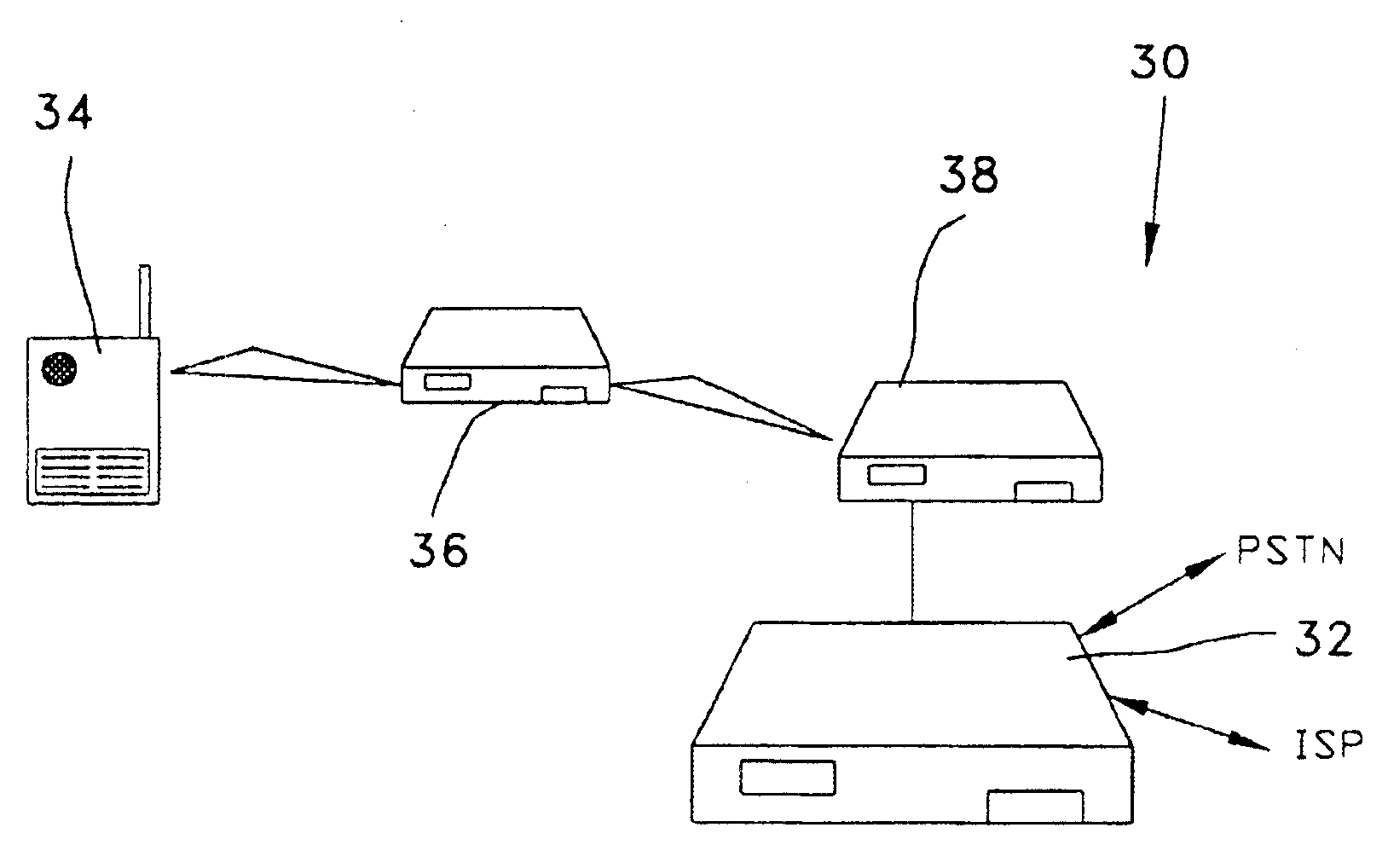
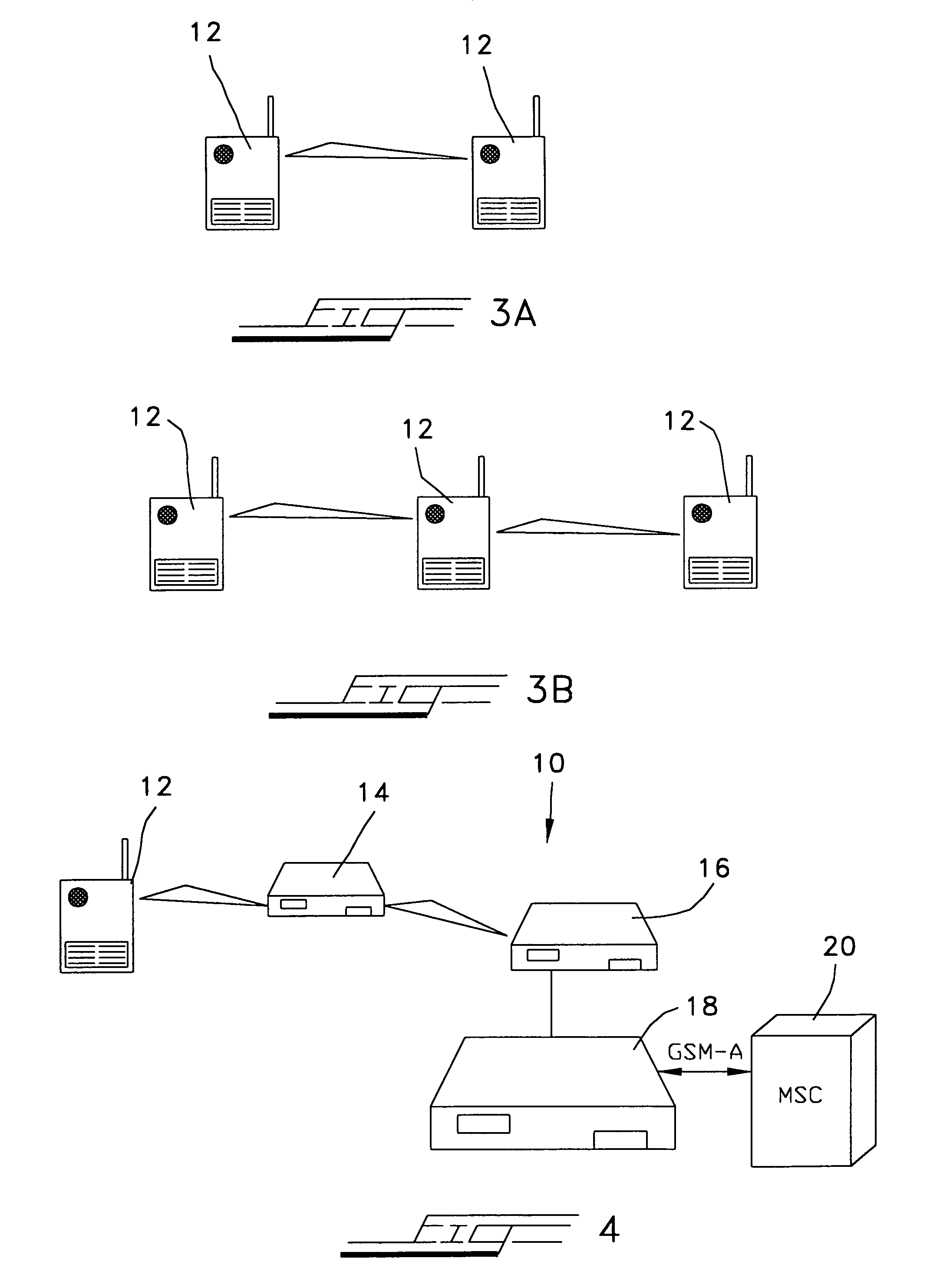
Ad Hoc peer-to-peer mobile radio access system interfaced to the PSTN and cellular networks
InactiveUS6961575B2Complete transparencyHigh transparencyNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationFrequency spectrumOperational costs
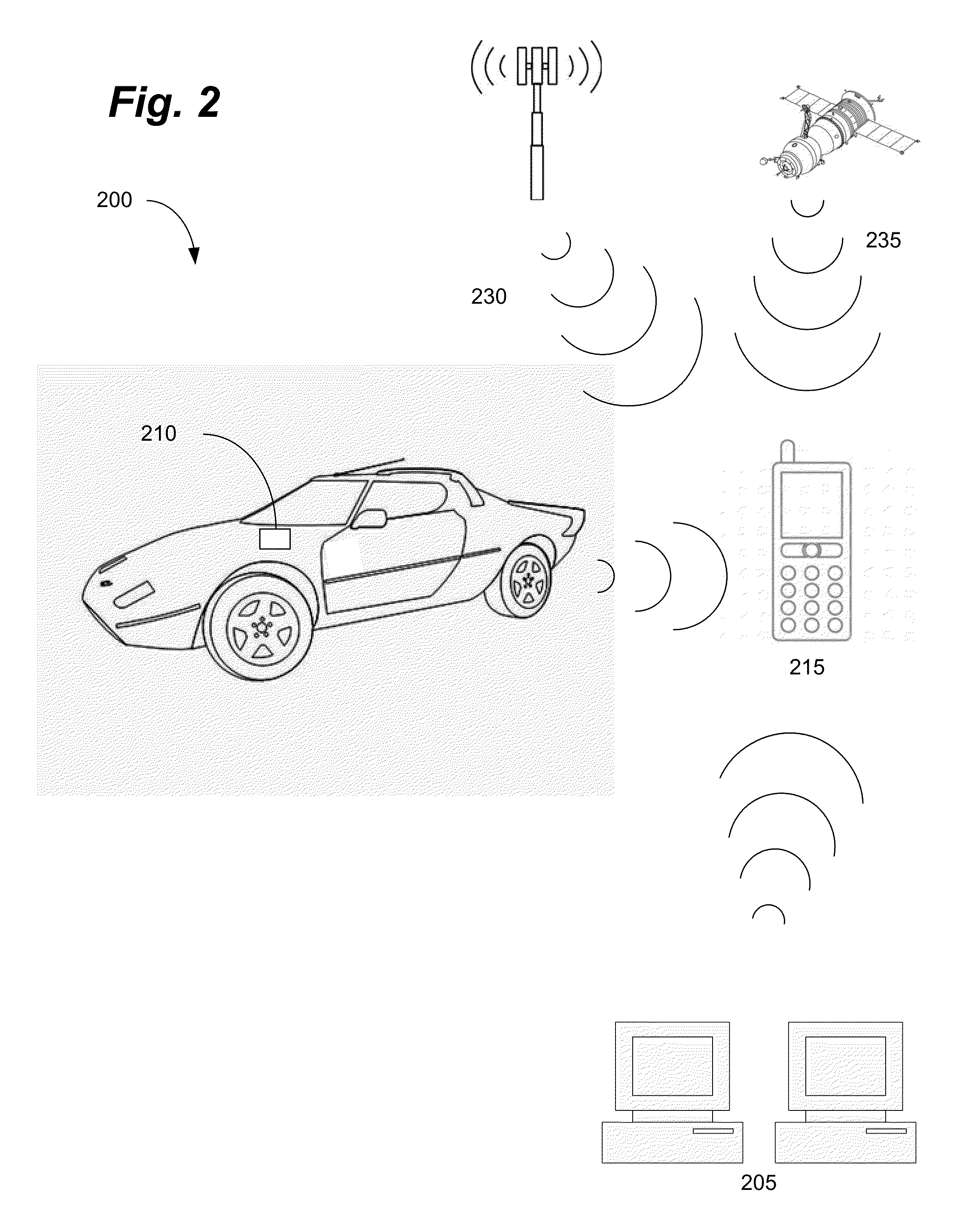
An ad-hoc, peer-to-peer radio access system for cellular communications systems using time division duplex as a way of maximizing the bits / hz / km2 for cellular systems. The network architecture of the ad-hoc system allows the radio access to be integrated with the fixed components of a conventional cellular system, PSTN or ISP. The objective is to make the system of the invention transparent to the features and services provided by the external network. The advantages of such a system to a cellular operator are that significantly less infrastructure is required, and that the RF spectrum is more efficiently utilized resulting in much lower building and operating costs. The system architecture is comprised of remote terminals, routers, gateways, and at least one gateway controller that interfaces the ad-hoc system to a cellular network system. The ad-hoc system of the invention allows for both voice and data transmissions and receptions.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
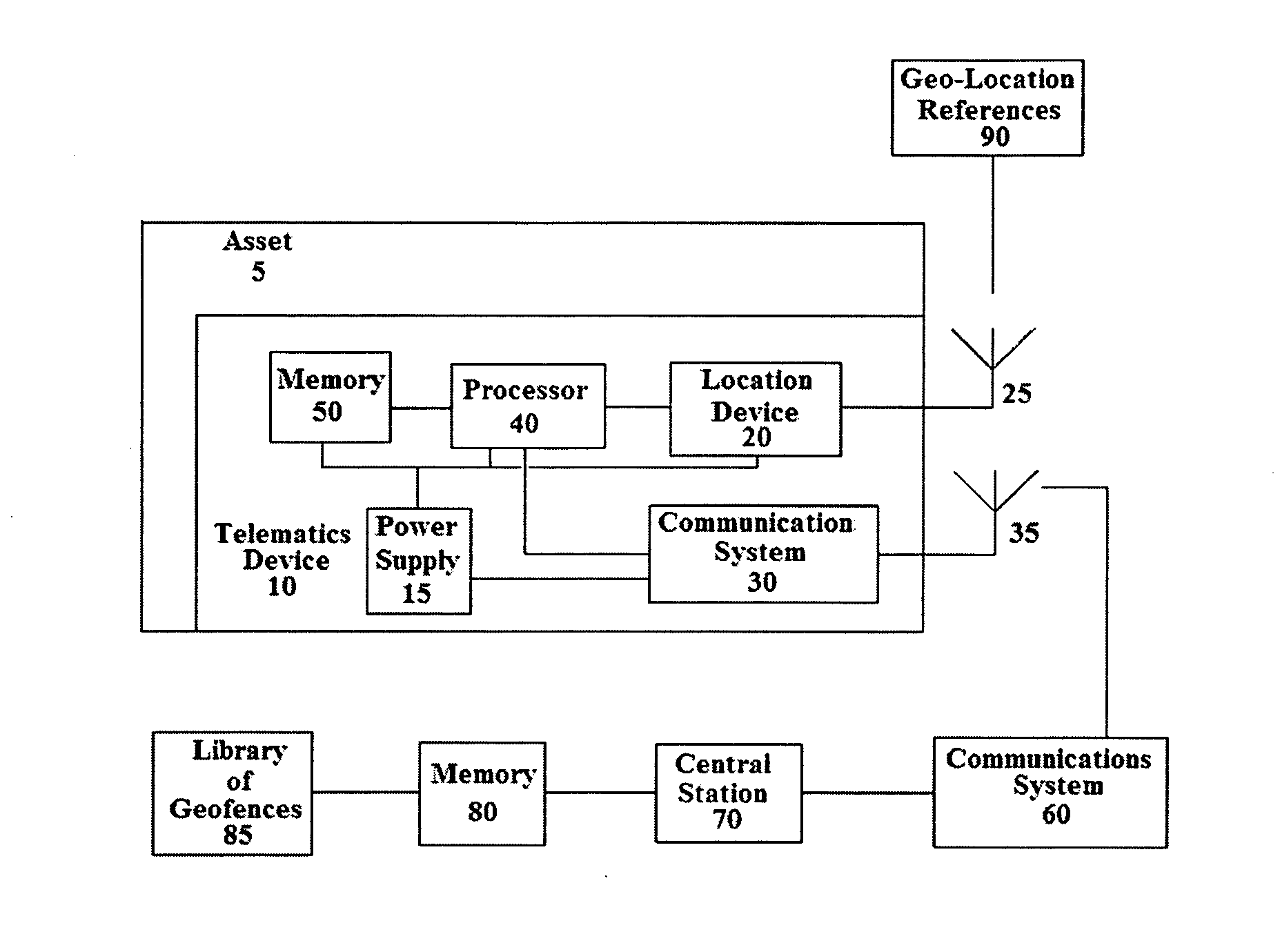
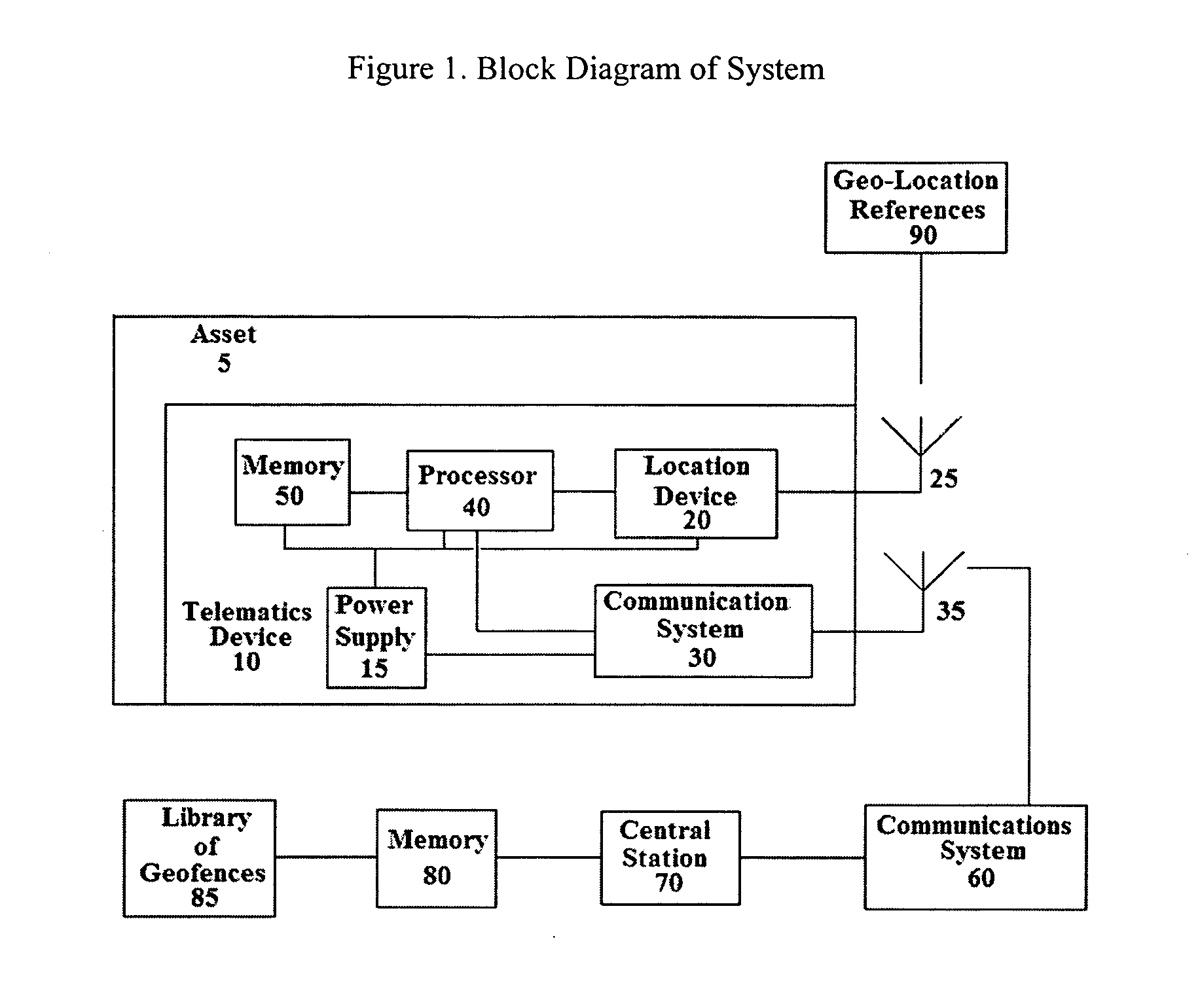
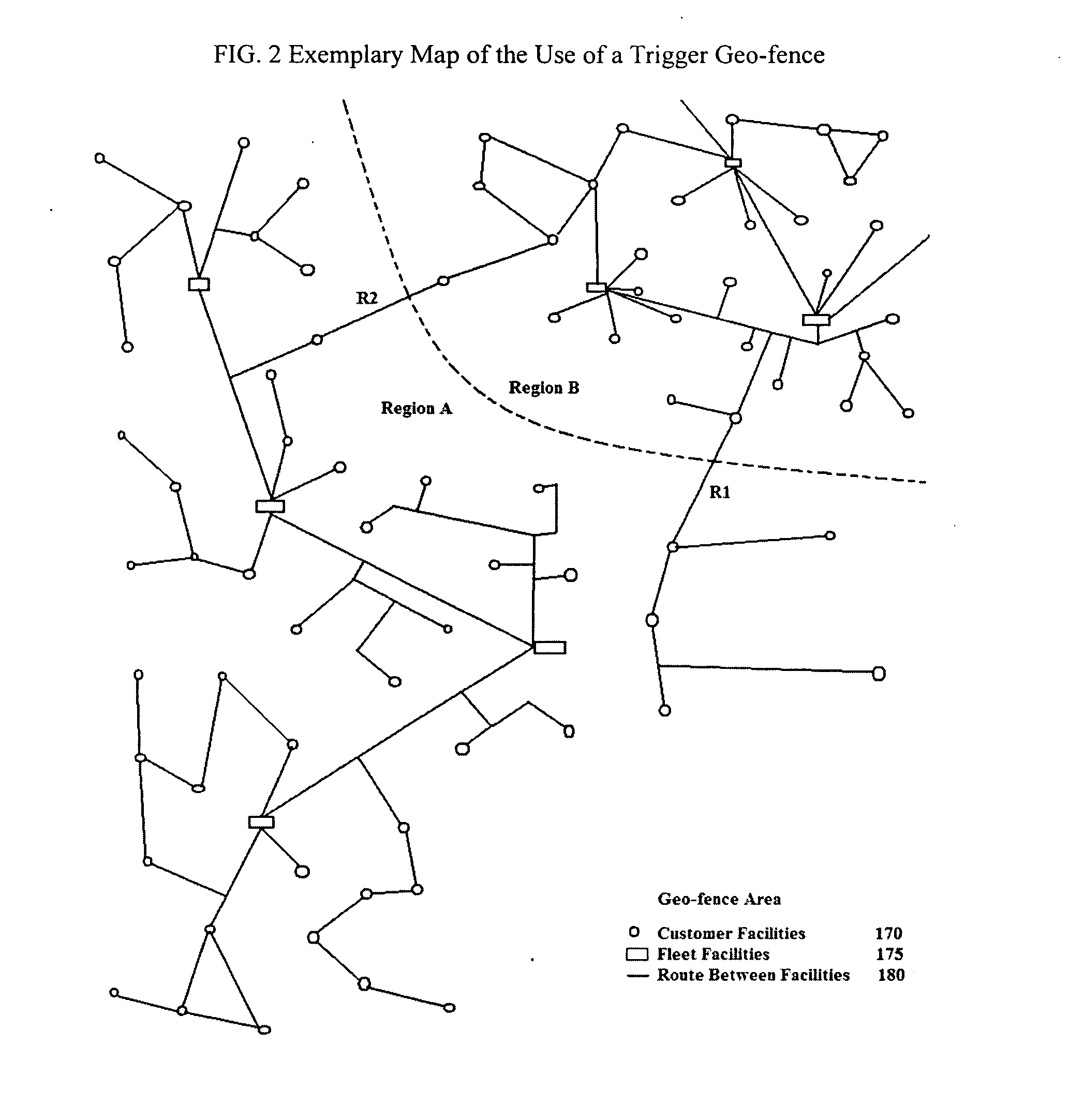
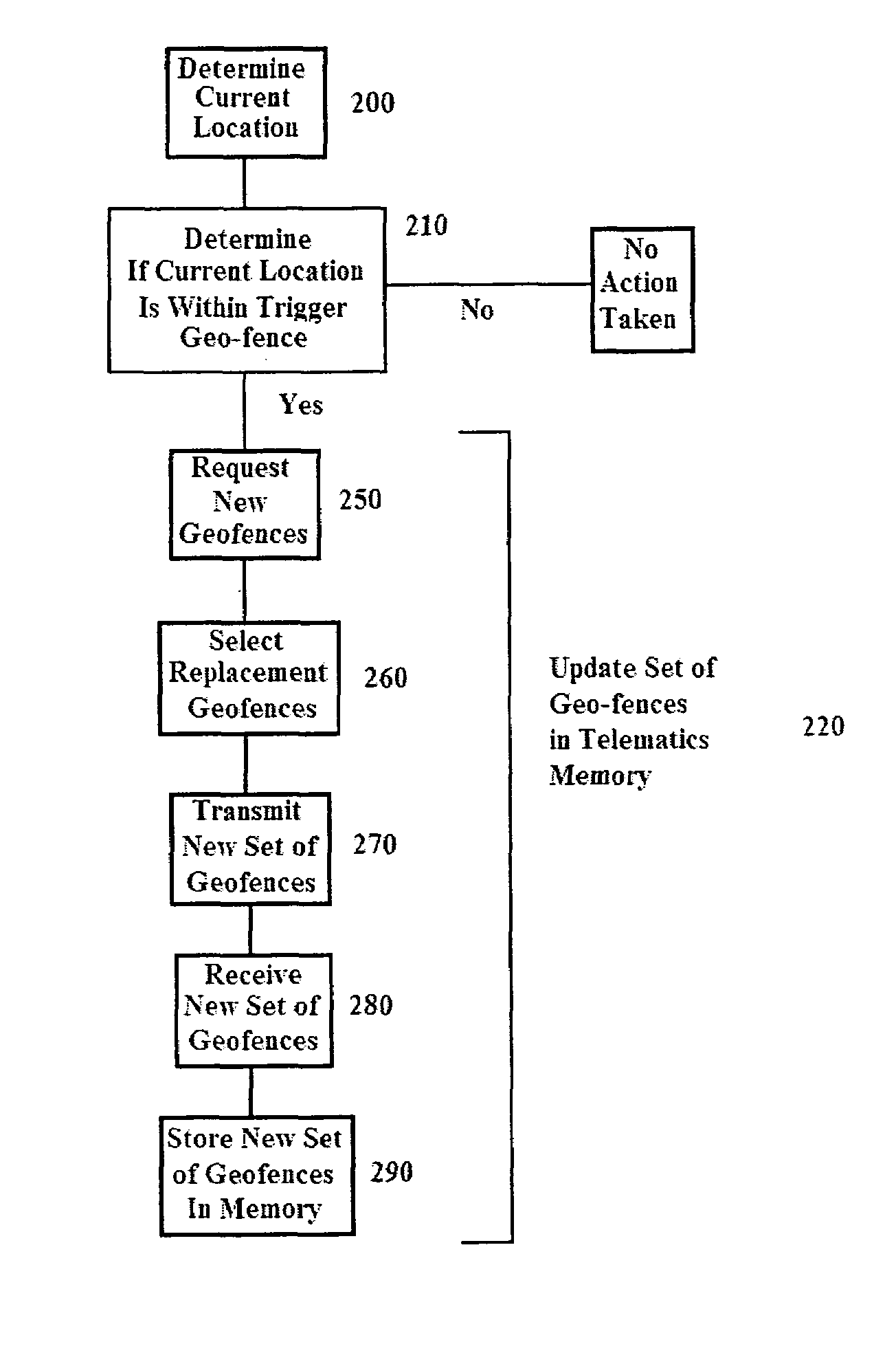
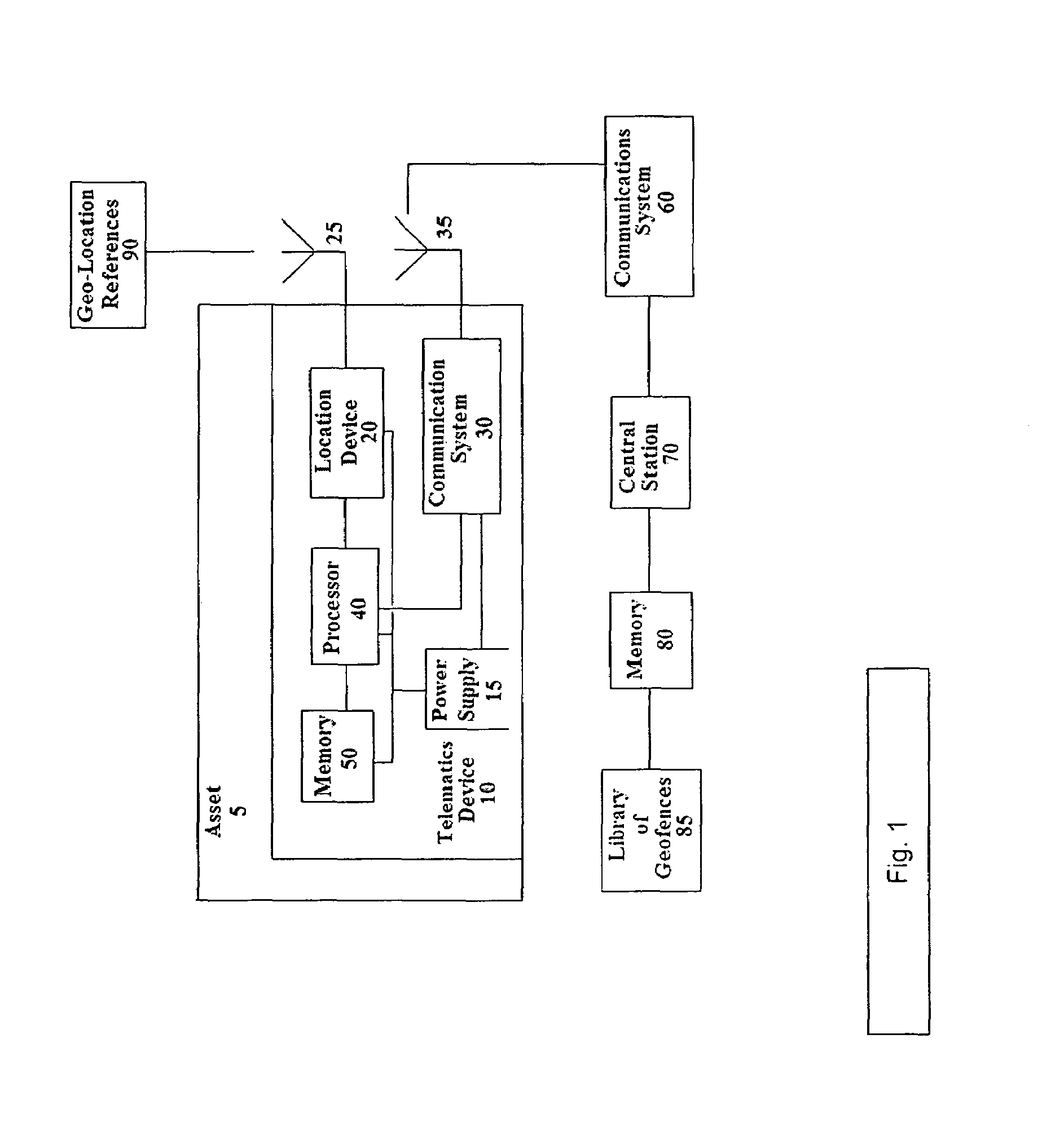
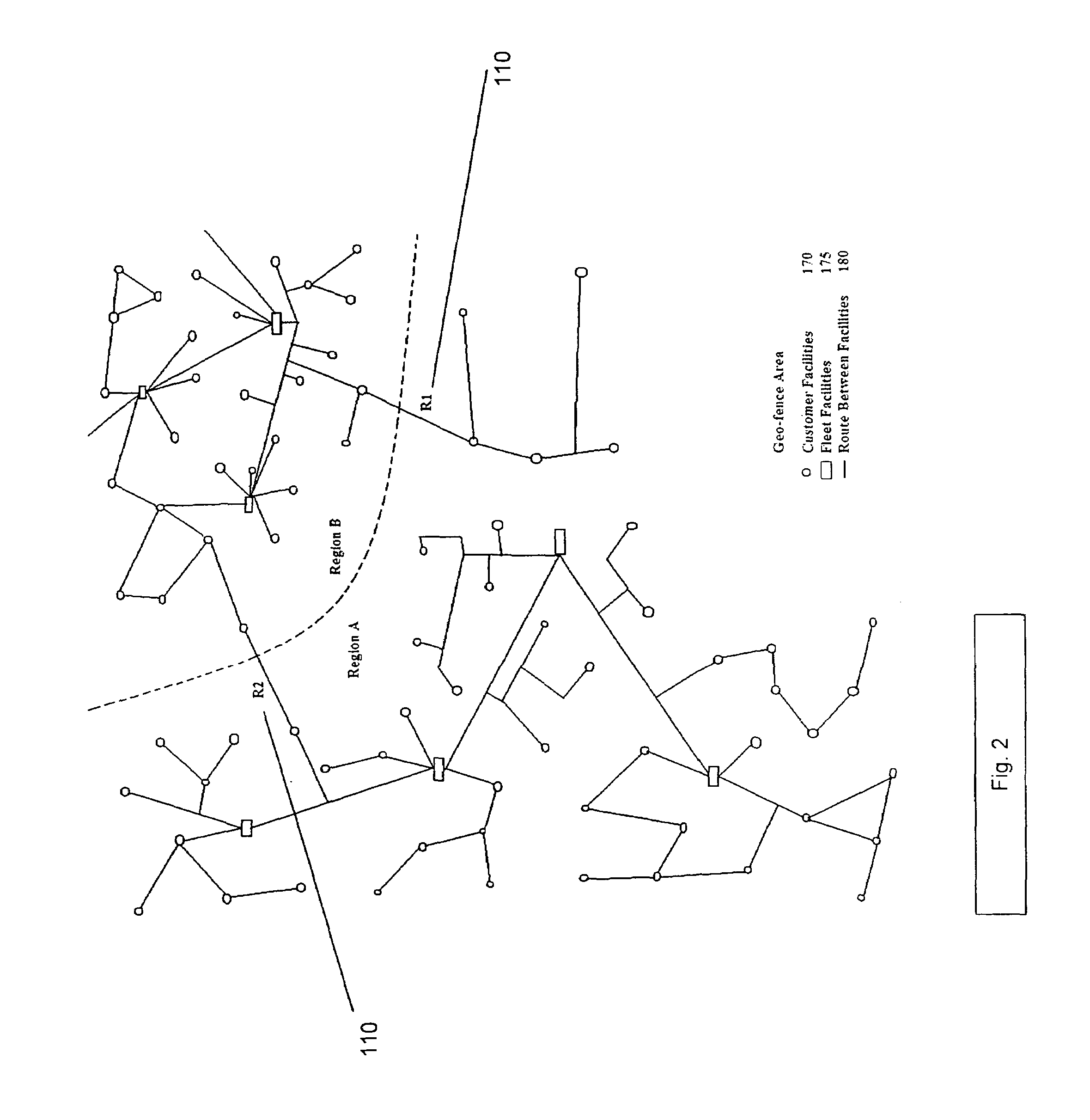
System and method for updating geo-fencing information on mobile devices
ActiveUS20070143013A1Reduce operating costsVehicle testingInstruments for road network navigationOperational costsOn board
A system and method of automatically replacing the geographic location of geo-fences stored in memory of a telematics system is described. The location of an asset is determined using an on-board telematics device with a location device. The location of the asset is compared with the location of predefined geo-fences stored in memory on the asset. When the asset is located within a geo-fence which triggers the replacement of geo-fences, the telematics system causes the asset to receive a new set of geo-fences, which replace the existing set of geo-fences in the telematics system memory. The operational cost of the system is reduced by minimizing communications charges when a reduced number of transmissions is needed to replace geo-fences stored in memory on the asset.
Owner:ASSET INTELLIGENCE
Ad hoc peer-to-peer mobile radio access system interfaced to the PSTN and cellular networks
InactiveUS7072650B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsFrequency spectrumOperational costs
An ad-hoc, peer-to-peer radio access system for cellular communications systems using time division duplex as a way of maximizing the bits / hz / km2 for cellular systems. The network architecture of the ad-hoc system allows the radio access to be integrated with the fixed components of a conventional cellular system, PSTN or ISP. The objective is to make the system of the invention transparent to the features and services provided by the external network. The advantages of such a system to a cellular operator are that significantly less infrastructure is required, and that the RF spectrum is more efficiently utilized resulting in much lower building and operating costs. The system architecture is comprised of remote terminals, routers, gateways, and at least one gateway controller that interfaces the ad-hoc system to a cellular network system. The ad-hoc system of the invention allows for both voice and data transmissions and receptions.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS9729639B2Improve overall utilizationImprove efficiencyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS8126574B2Improve overall utilizationImprove efficiencyLevel controlTechnology managementOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having one or more motorized pumps and associated motor drives, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
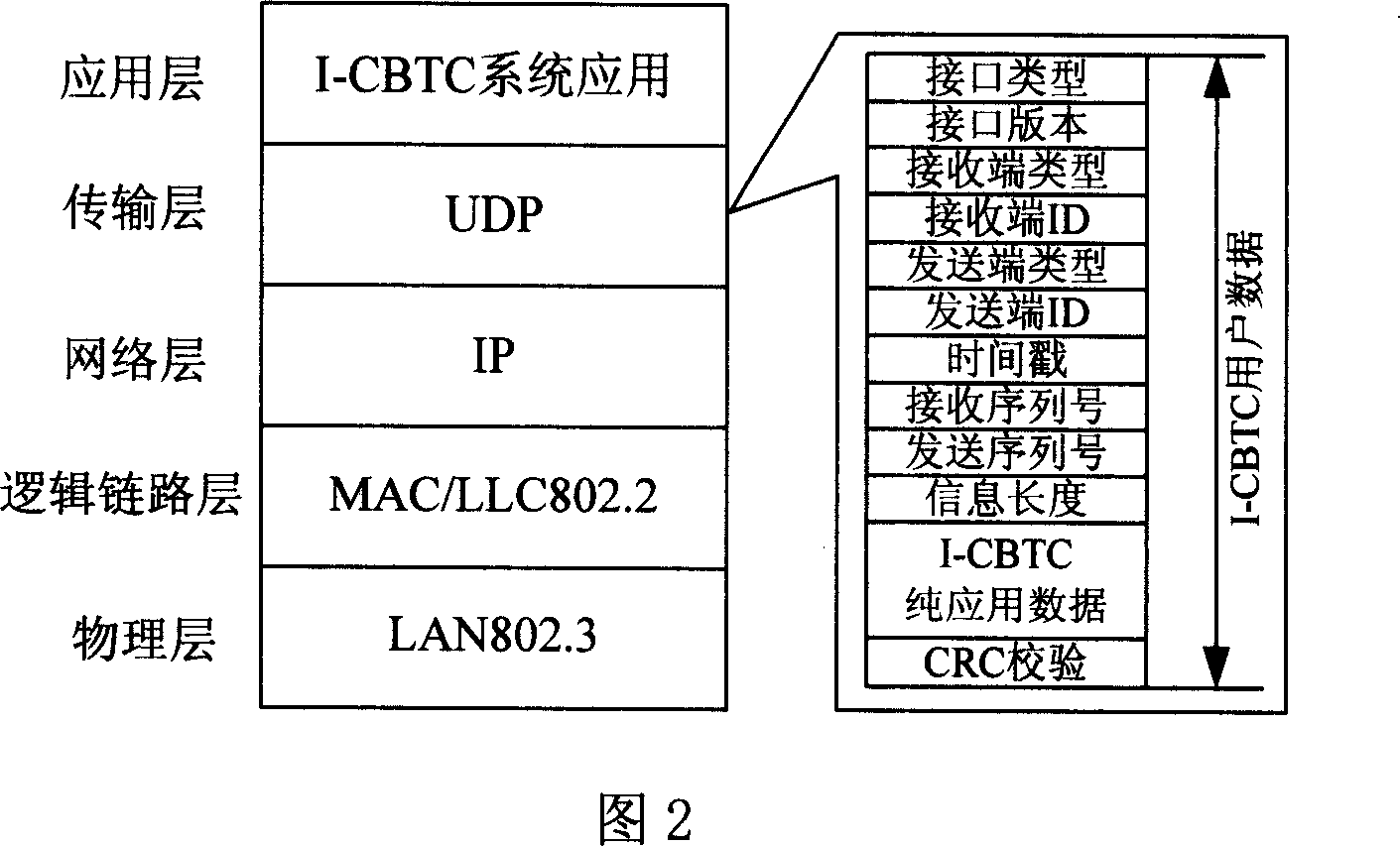
Communication-based interconnected and intercommunicated I-CBIT train operation control system
ActiveCN101009679AFacilitate resource sharingMaintain "transparencyVehicle route interaction devicesTransmissionOperational costsControl system
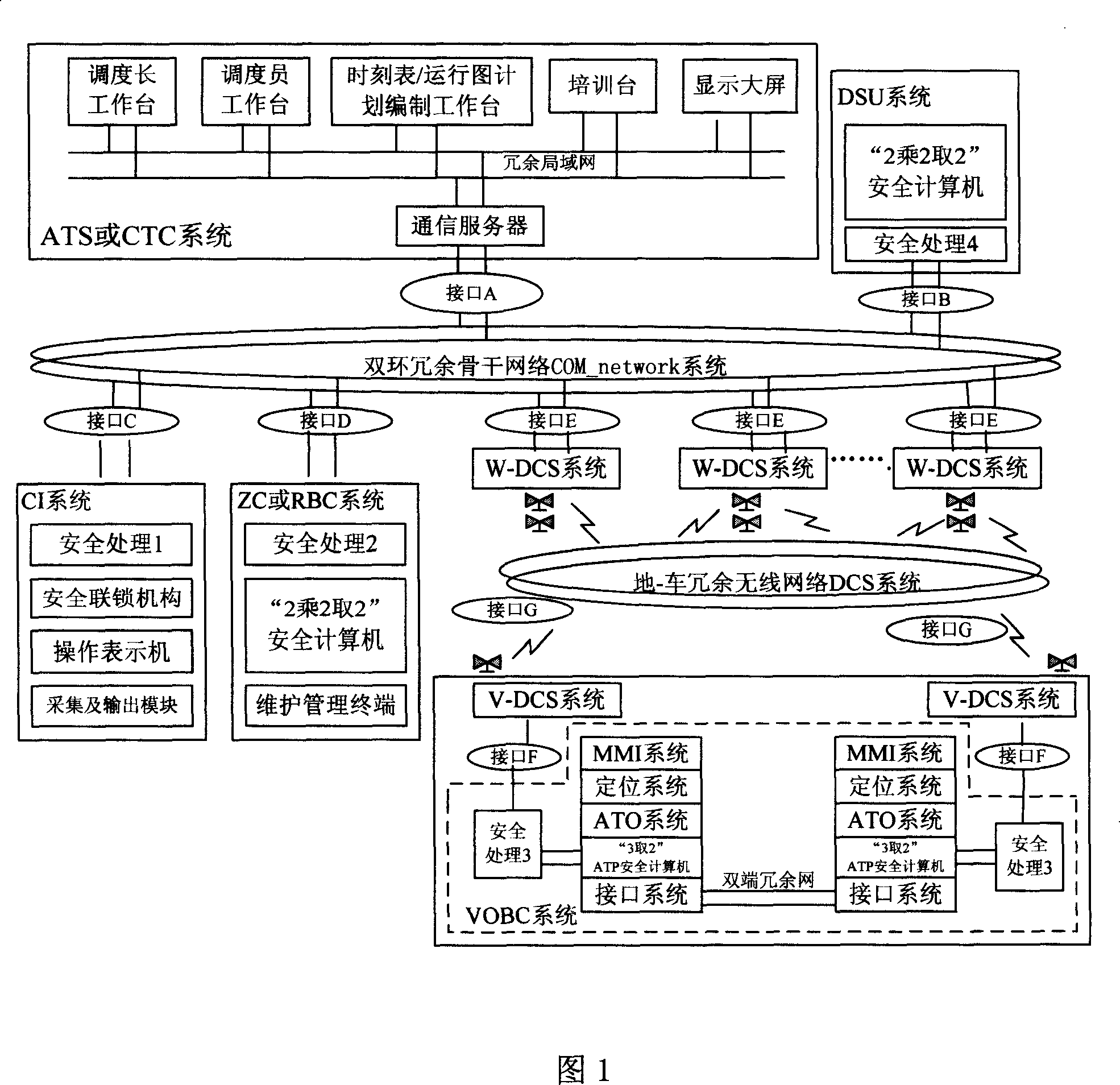
The disclosed I-CBTC mobile closed train operation control system applies wireless communication way to transmit information between ground control center and train, and comprises an ATS or CTC system, a DSU system, a CI system, a ZC or RBC system, a VOBC system, a dual-ring redundant backbone network COM_network system, a ground-train redundant wireless network DCS system, and interfaces among nodes. This invention normalizes and standardizes former function, performance index and interfaces, and reduces cost greatly.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
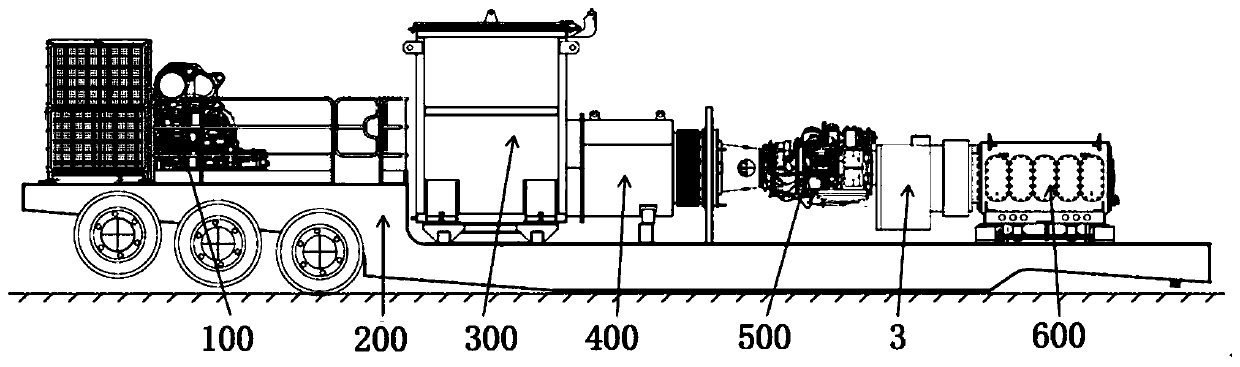
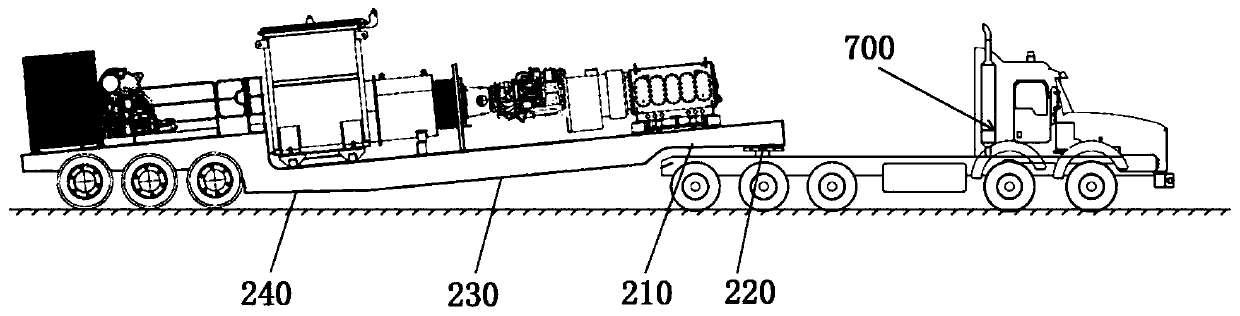
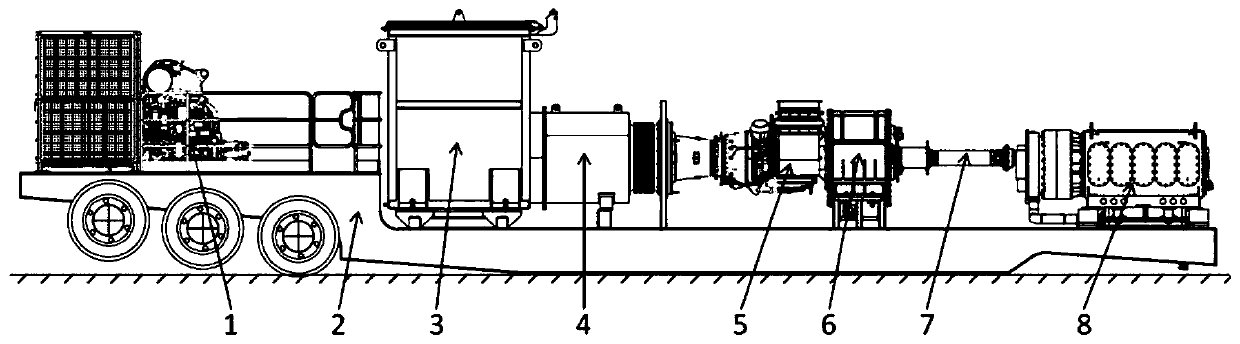
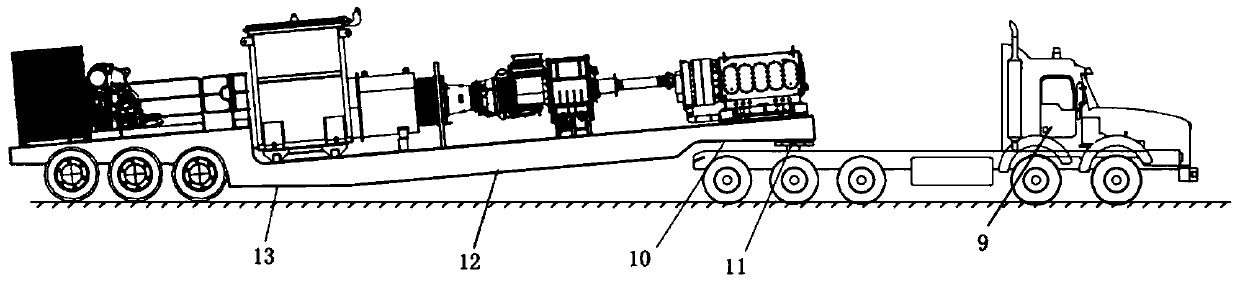
Semitrailer-mounted turbine fracturing equipment
PendingCN110485984AReduce weightLower center of gravityPositive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsOperational costsGravity center
The invention discloses semitrailer-mounted turbine fracturing equipment. Straight-line connection and special chassis design of the whole equipment can double reduce center of gravity of the equipment, stability and safety are better ensured, the structure is simpler, the investment cost and the operation cost are lowered, risks of the whole breakdown of fracturing sites are reduced, transmissionis better, and the semitrailer-mounted turbine fracturing equipment is suitable for continuous operation working conditions with long time and large load. By improving a plunger pump, optimization ofrotating center distances of a crank throw and a crankshaft makes rated power input of the crank throw and the crankshaft increase to 5000-7000 hp, optimization of the transmission ratio of an integrated reduction gearbox on the plunger pump makes the maximum input speed of the integrated reduction gearbox reach 16000 rpm, and ultra-high speed enables reduction gearboxes to be directly connectedwith a turbine engine so as to the solve the problems that turbine fracturing equipment slows down depending on the two reduction gearboxes, and weight of the whole semitrailer is reduced, and boundary dimension of the semitrailer-mounted turbine fracturing equipment is reduced.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS20100306001A1Improve overall utilizationImprove efficiencyTesting/monitoring control systemsForecastingOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having one or more motorized pumps and associated motor drives, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
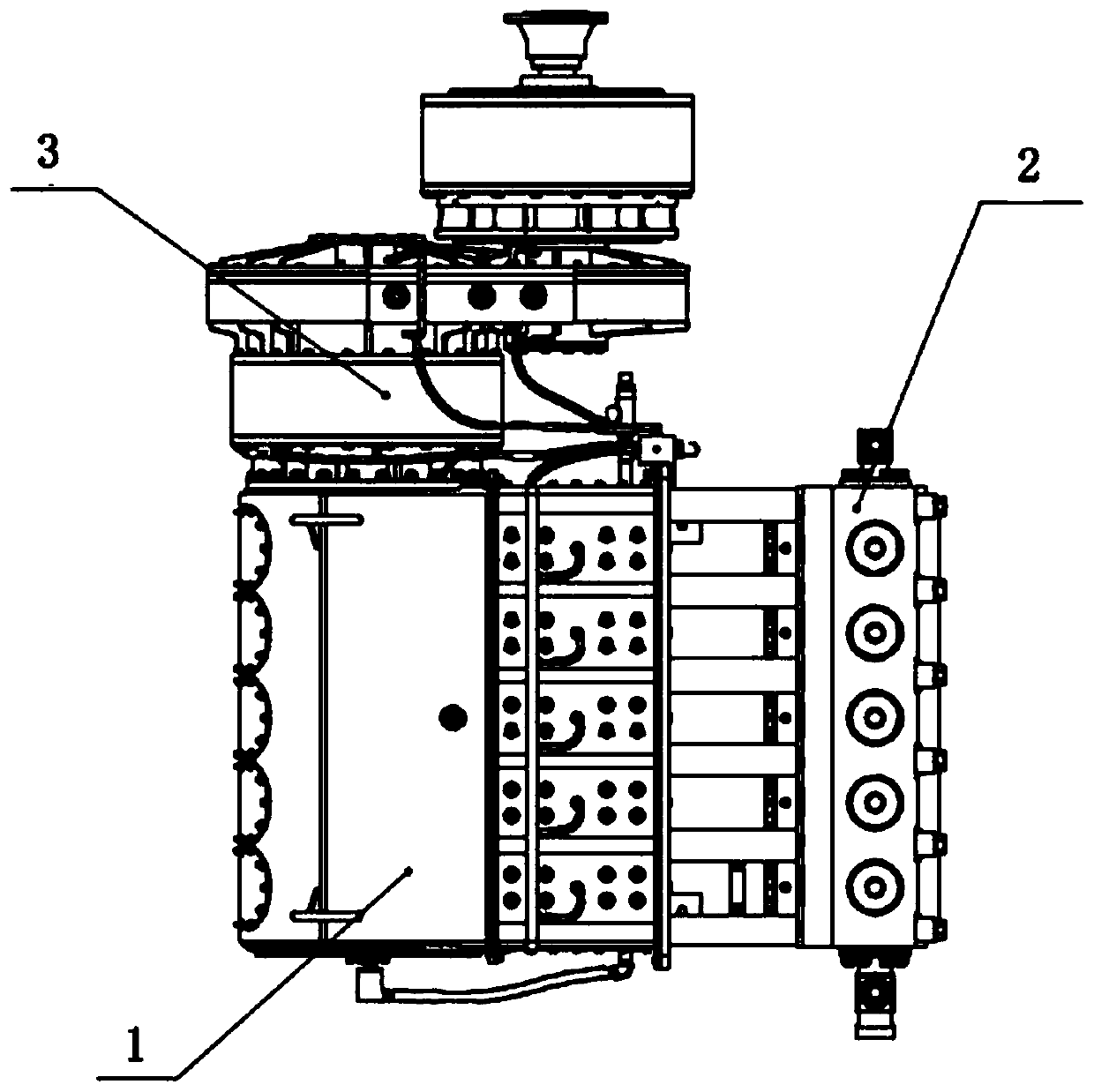
Turbine fracturing equipment
PendingCN110485982AReduce volumeReduce weightPositive displacement pump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingOperational costsGravity center
The invention discloses turbine fracturing equipment. The turbine fracturing equipment comprises a transporting device, a turbine engine, a reduction gearbox, a transmission mechanism and a fracturingpump, wherein the output end of the turbine engine is connected with one end of the reduction gearbox; the other end of the reduction gearbox is in transmission connection with the fracturing pump; the transportation device is used for bearing the turbine engine, the reduction gearbox, the transmission mechanism and the fracturing pump and comprises a chassis; the chassis is provided with a transporting section, a bearing section and a lapping section which are connected in sequence; when the turbine fracturing equipment is in a working state, the bearing section can be contacted with the ground; and when the turbine fracturing equipment is in a transporting state, the bearing section does not make contact with the ground. The turbine fracturing equipment has the beneficial effects that the equipment adopts the design of linear connection and a special chassis, so that the gravity center of the turbine fracturing equipment is doubly reduced, and the stability and the safety are well ensured; the structure is simpler, and the investment cost and the operation cost are reduced; the collapse risk of the whole fracturing site is reduced; and the turbine fracturing equipment is good intransmission property and is suitable for long-time and bulky load continuous operation conditions.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
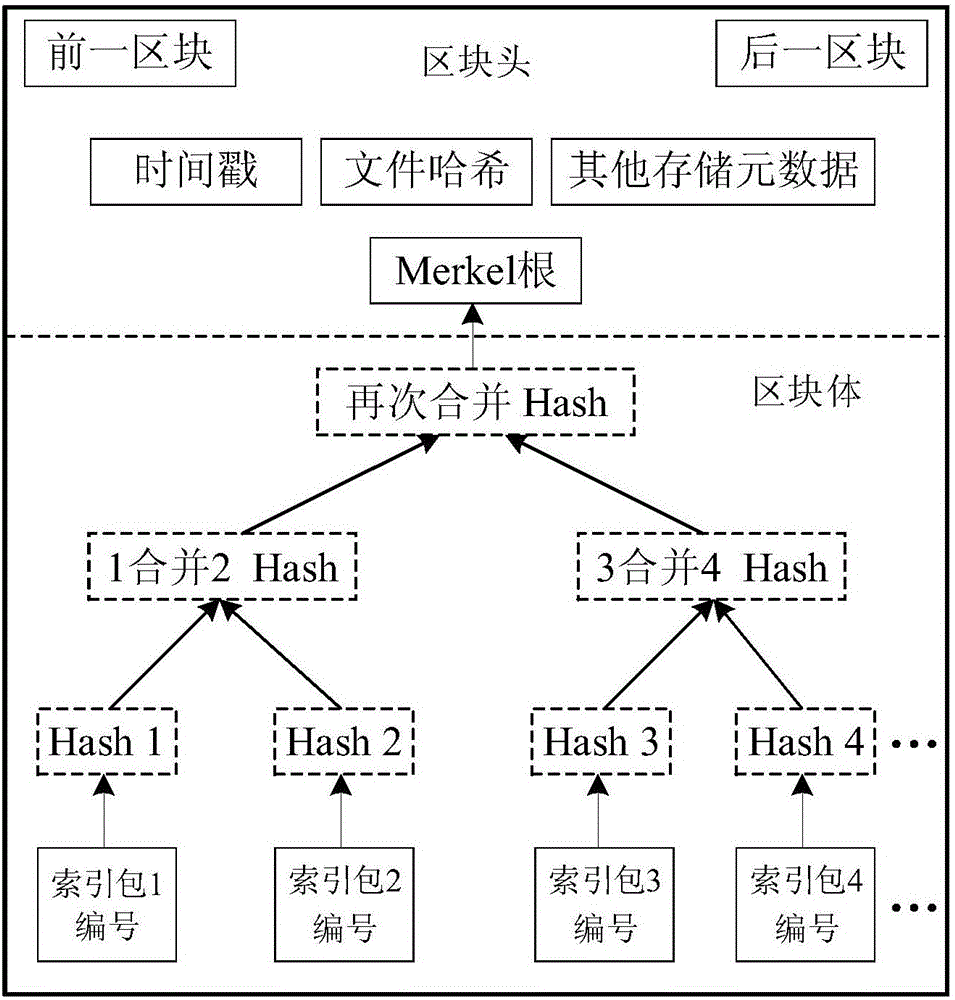
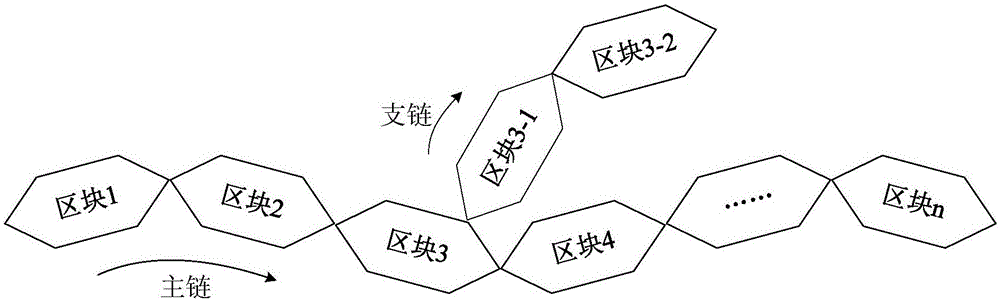
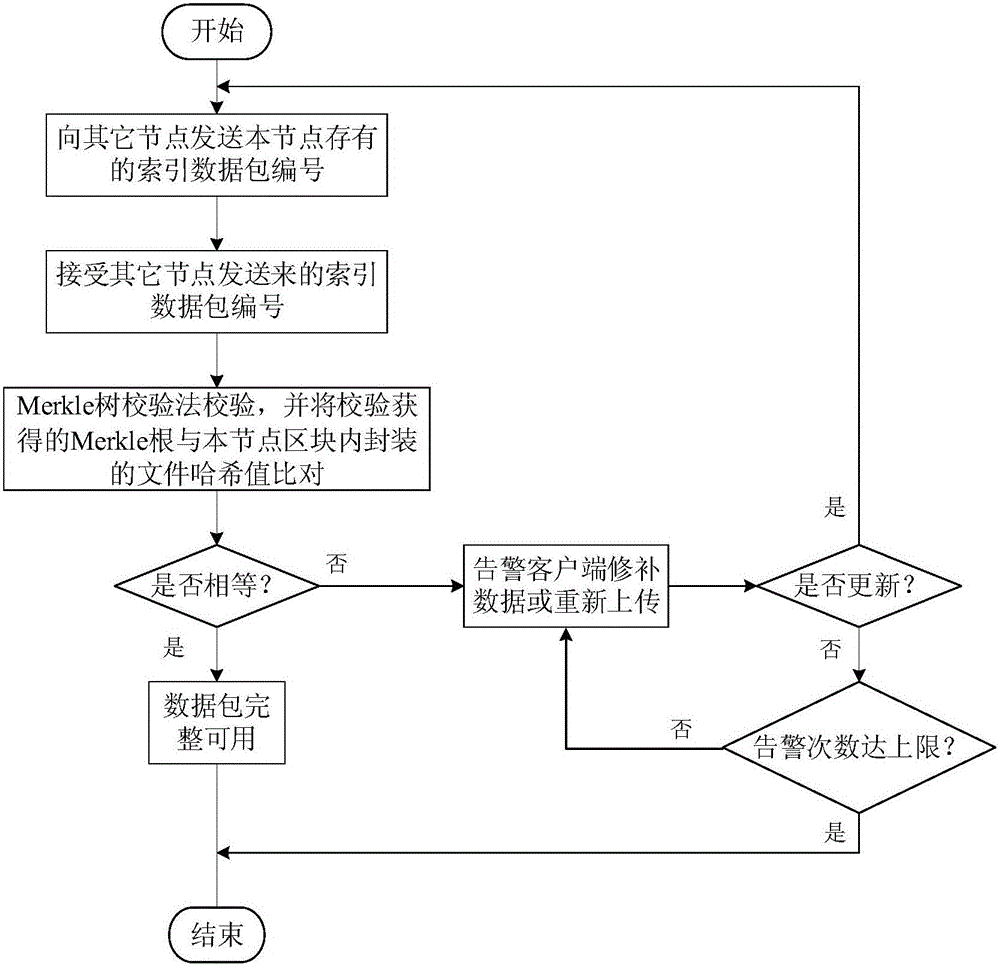
Disaster recovery cloud storage system construction method based on block chain technology
ActiveCN106534317AReduce storage costsImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesOperational costsData cloud
The invention discloses a disaster recovery cloud storage system construction method based on a block chain technology. The block chain technology is introduced in a cloud storage system construction process. The characteristics of decentration and de-trust of the block chain technology are used to realize the distribution autonomy of storage nodes in a cloud storage system and data exchange and data sharing between the storage nodes based on a consensus algorithm. Compared with the current mainstream centralized cloud service system, the method has the advantages that network nodes can establish many-to-many rather than one-to-many contact relationship, which can greatly improve the transmission efficiency of data; and in the processes of data storage, exchange, upload and download, data block packaging and anonymous exchange and an asymmetric encryption algorithm are used, which greatly guarantees the safety and reliability of the entire ecological chain of data cloud storage. Compared with the current mainstream centralized cloud service system, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that on the basis of improved data safety, the operation efficiency of the system is greatly improved, and the operating cost of a cloud storage service is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNXIANG NETWORK TECH
System and method for updating geo-fencing information on mobile devices
ActiveUS7493211B2Reduce operating costsVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesOperational costsOn board
A system and method of automatically replacing the geographic location of geo-fences stored in memory of a telematics system is described. The location of an asset is determined using an on-board telematics device with a location device. The location of the asset is compared with the location of predefined geo-fences stored in memory on the asset. When the asset is located within a geo-fence which triggers the replacement of geo-fences, the telematics system causes the asset to receive a new set of geo-fences, which replace the existing set of geo-fences in the telematics system memory. The operational cost of the system is reduced by minimizing communications charges when a reduced number of transmissions is needed to replace geo-fences stored in memory on the asset.
Owner:ASSET INTELLIGENCE
Gas generating system and method for inerting aircraft fuel tanks
ActiveUS20050115404A1Avoid flowPrevent contamination from enteringGas treatmentDispersed particle filtrationOperational costsFuel tank
The present invention provides a system and method for generation of nitrogen enriched air for inerting aircraft fuels tanks. One embodiment of the present invention includes a duct assembly; a primary heat exchanger; a gas generating system heat exchanger; a first temperature sensor; a second temperature sensor; a controller monitor; a valve; an air separation module assembly having a primary module and a secondary module; at least one flow control orifice; and a pressure sensor. The present invention utilizes a minimal complement of components and streamlined processes, thus minimizing structural and operational costs while optimizing performance and safety features.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
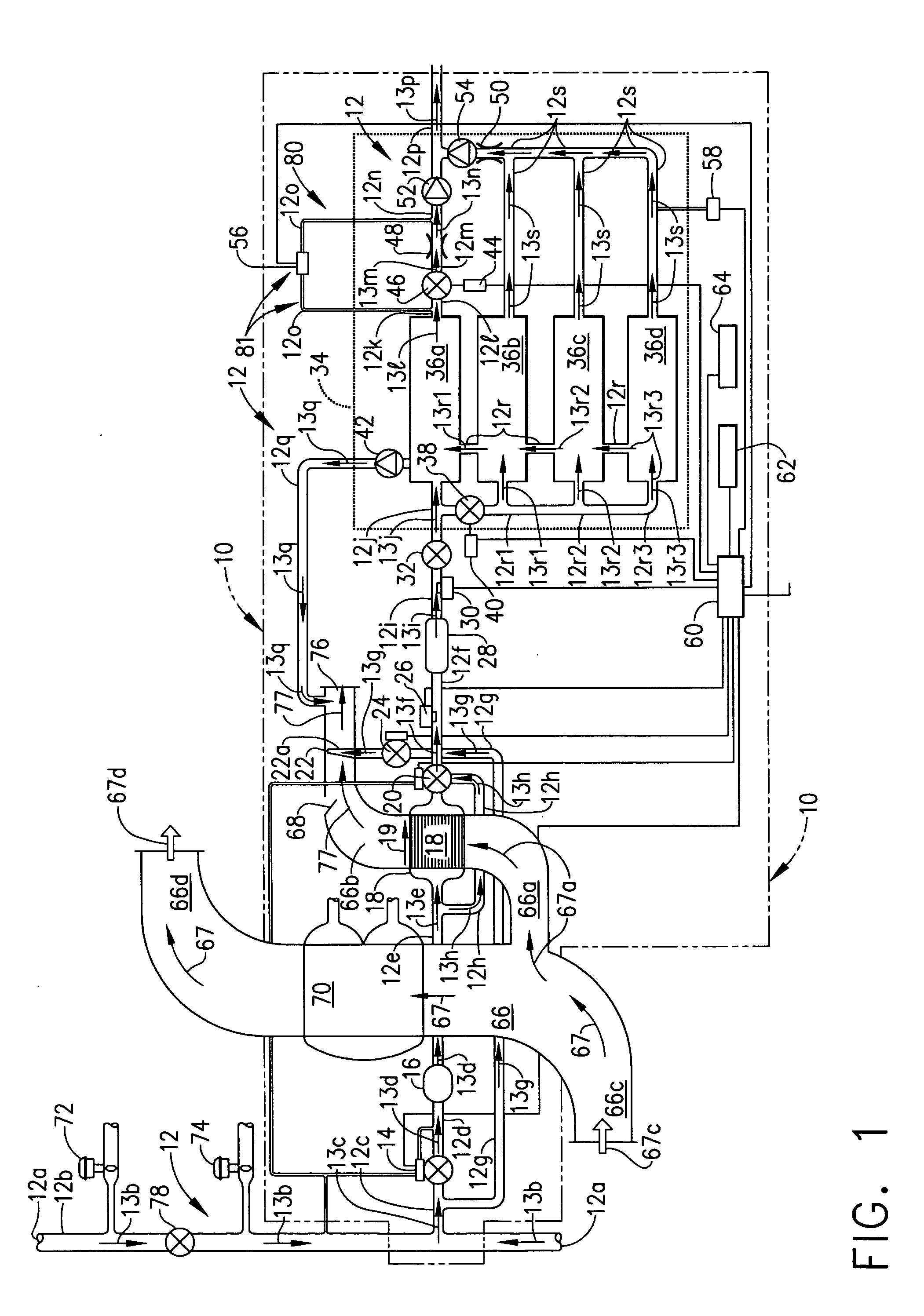
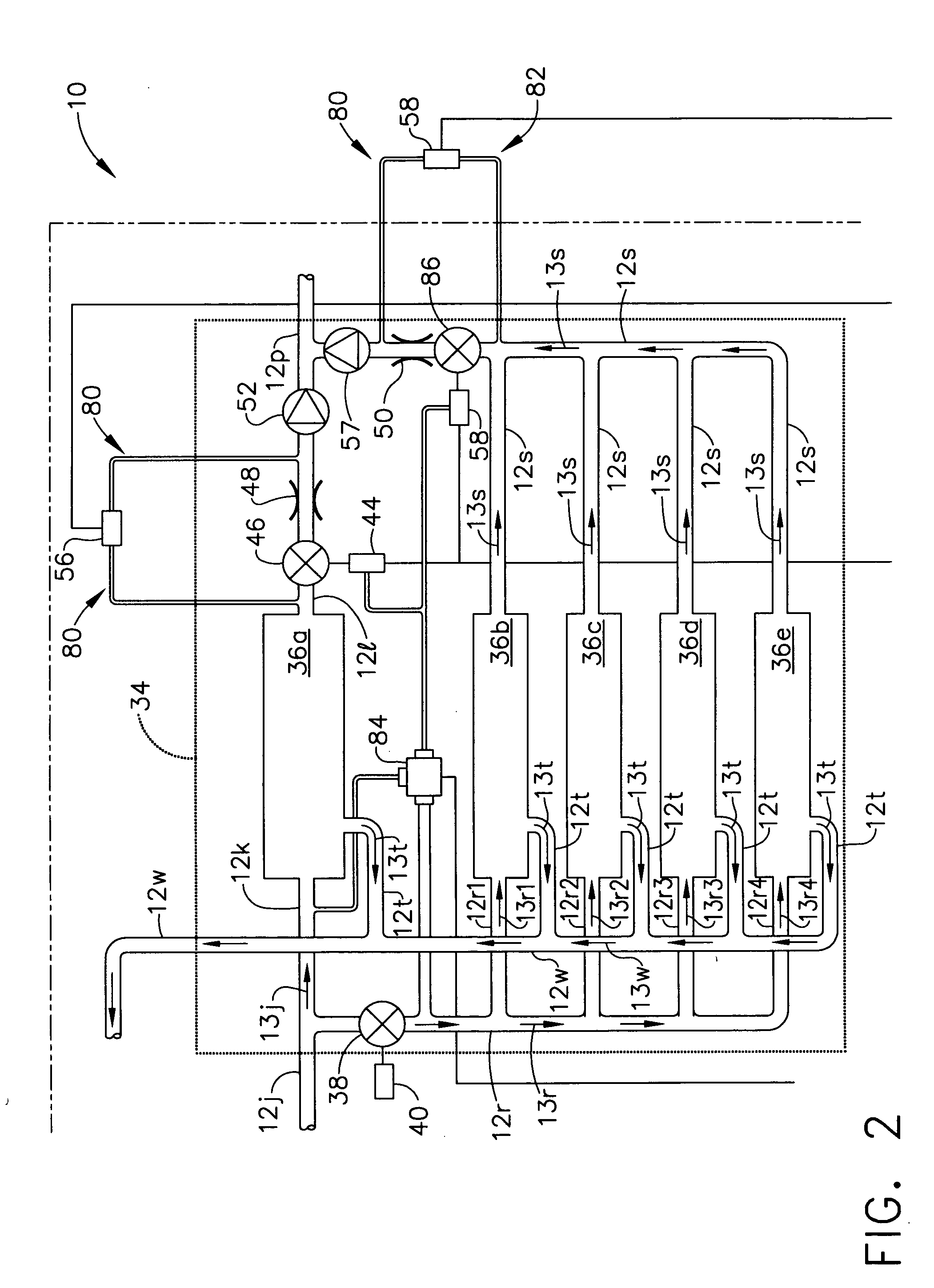
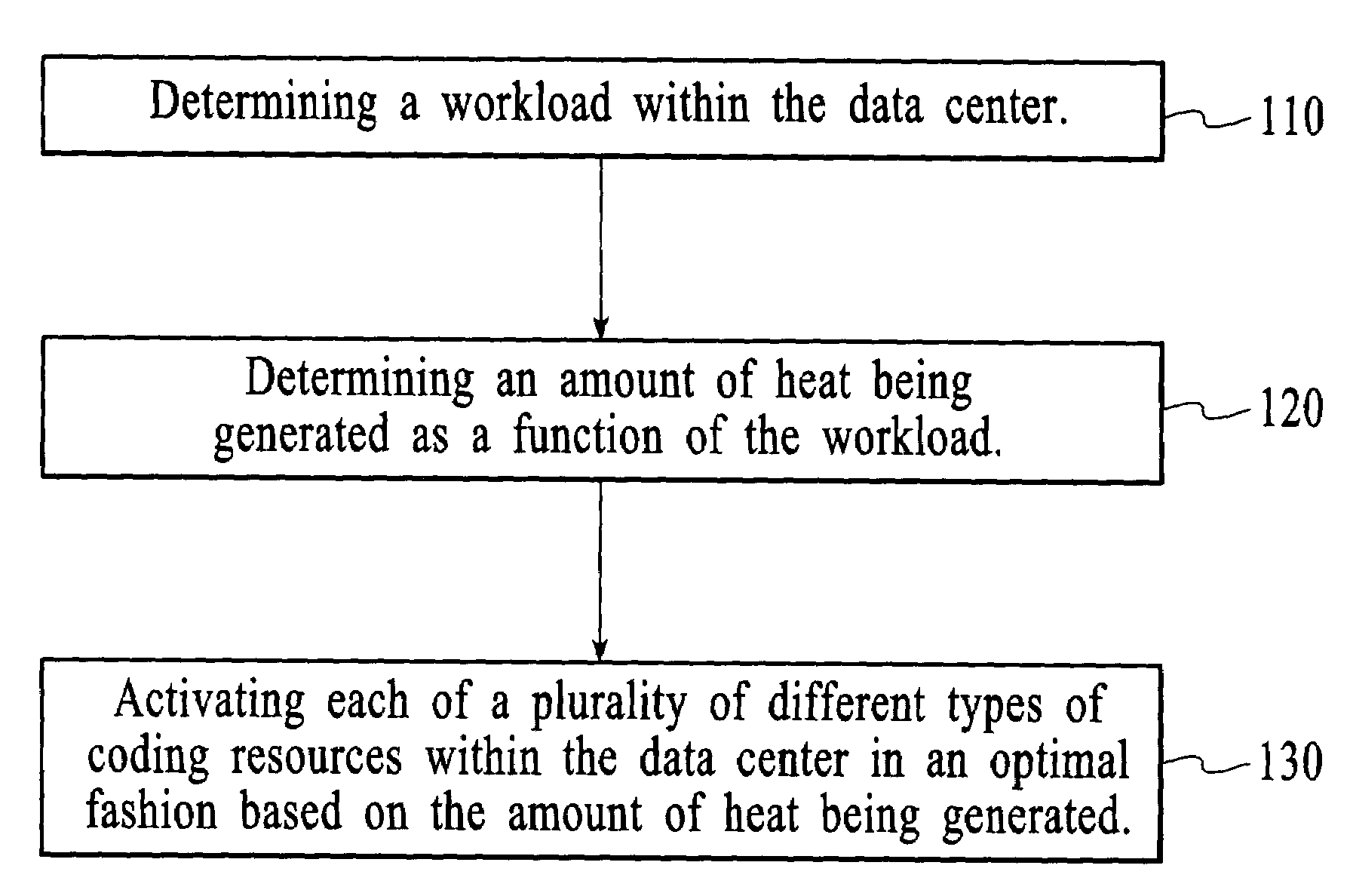
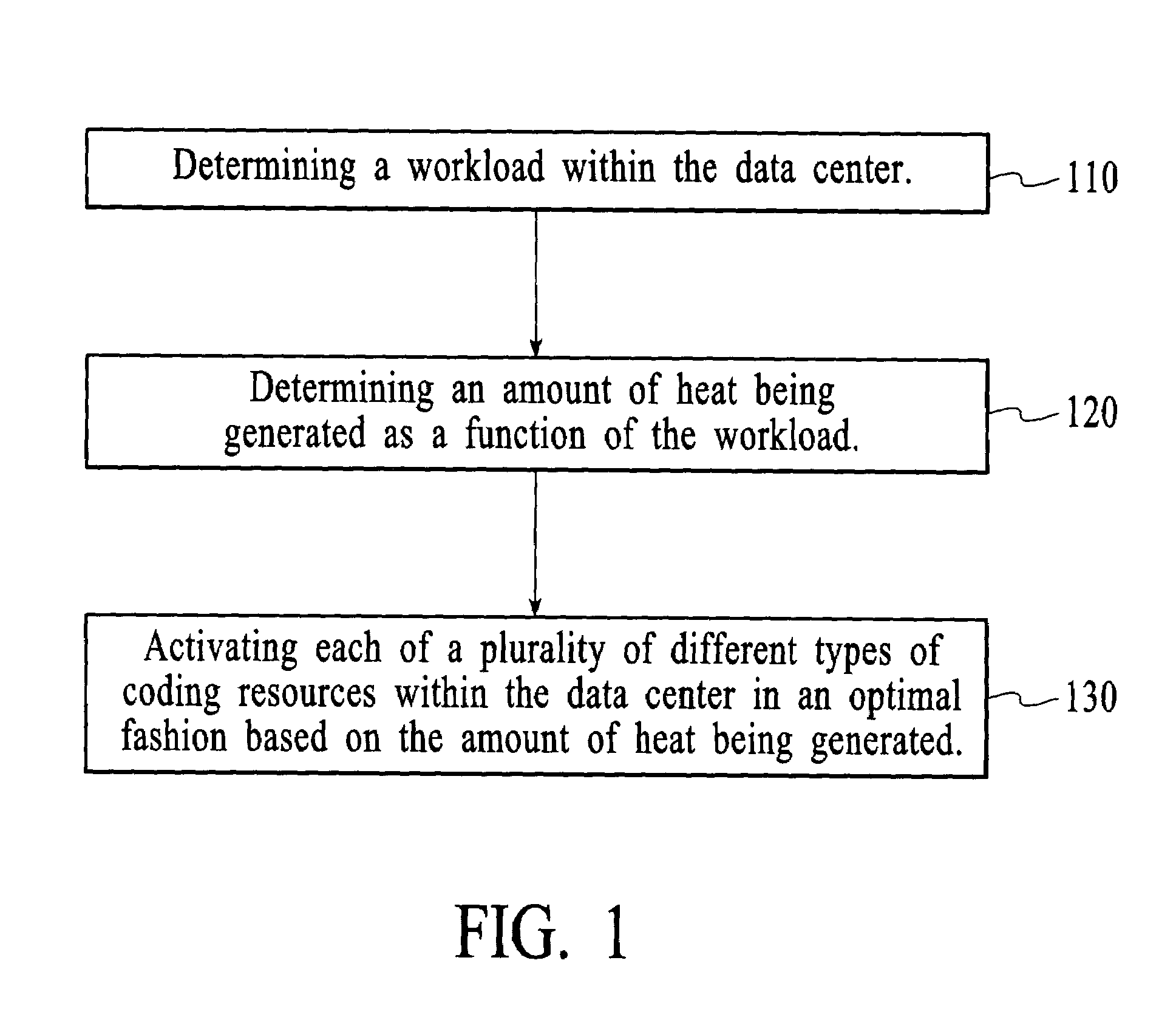
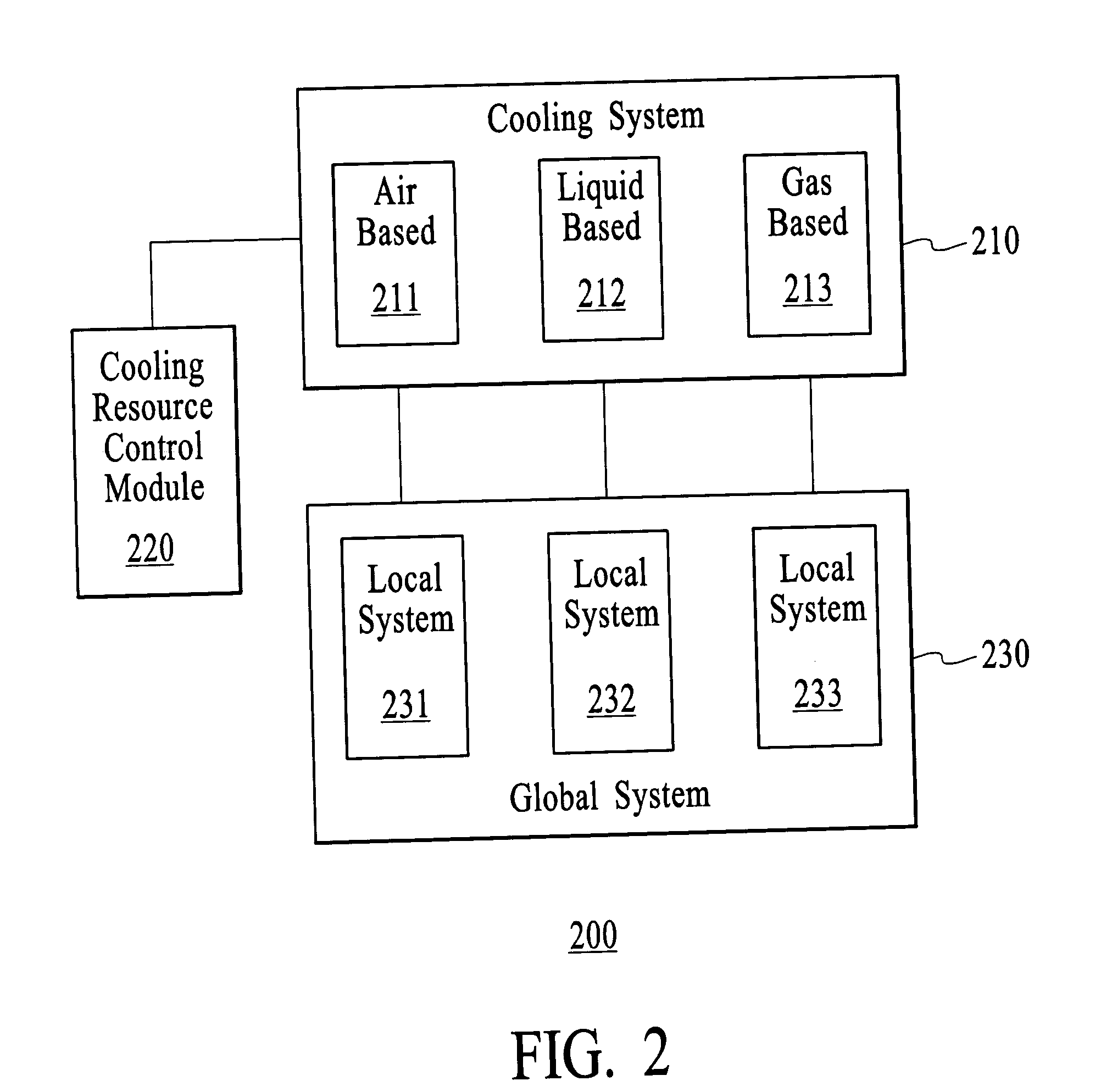
Method and system for dynamically controlling cooling resources in a data center
ActiveUS7373268B1Reduce operating costsHuge savingsThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTOperational costsWorkload
The present invention includes a method and system for dynamically controlling cooling resources in a data center based on the workload of the data center. Accordingly, based on the workload constraints (power consumed, latency, etc.) of the data center, each of a plurality of different types of cooling resources is activated in an optimal fashion. Consequently, a substantial savings in operational costs related to cooling resources is achieved. A first aspect of the present invention is a method for dynamically controlling cooling resources in a data center. The method comprises determining a workload within the data center, determining an amount of heat being generated as a function of the workload and activating each of a plurality of different types of cooling resources within the data center in an optimal fashion based on the amount of heat being generated.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Information detection bionic spiral robot in grain bin
ActiveCN105235771AImproved detection techniquesReduce manpowerMeasurement devicesVehiclesTime informationOperational costs
The invention discloses an information detection bionic spiral robot in a grain bin; the robot comprises the following structures: a housing; at least three spiral propellers, each propeller comprises a grain inlet and a grain outlet, can rotate to suck in the grains from the grain inlet and discharge the grains through the grain outlet, so the spiral propeller can advance in the grain bin; a sensor unit arranged outside the housing and used for detecting ecology information of the grains in the grain bin. The spiral propeller comprises the following elements: a hollow transmission shaft with two opening ends, and the transmission shaft can rotate relative to the housing; a spiral body arranged in the transmission shaft; a drive motor driving the transmission shaft to rotate through a pair of meshing gear wheels. The robot can obtain real time information of the grain condition in a remote mode, so no temperature measuring cable is needed in the grain bin, thus reducing grain bin labor and material operation cost, and fundamentally solving the problems that wiring in the grain bin is hard, and the temperature measuring cable can disturb grain incoming and outgoing works.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method, Apparatus and System for Transmitting User Plane Data
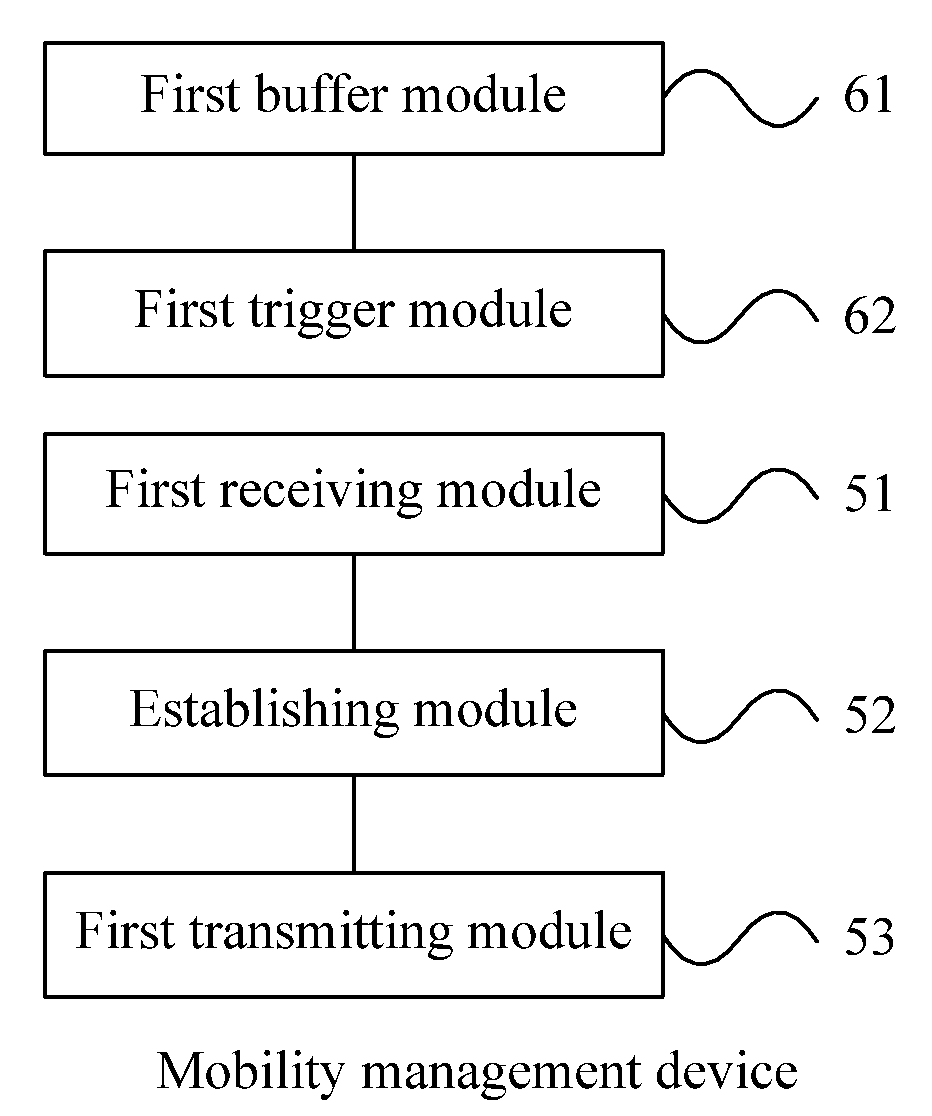
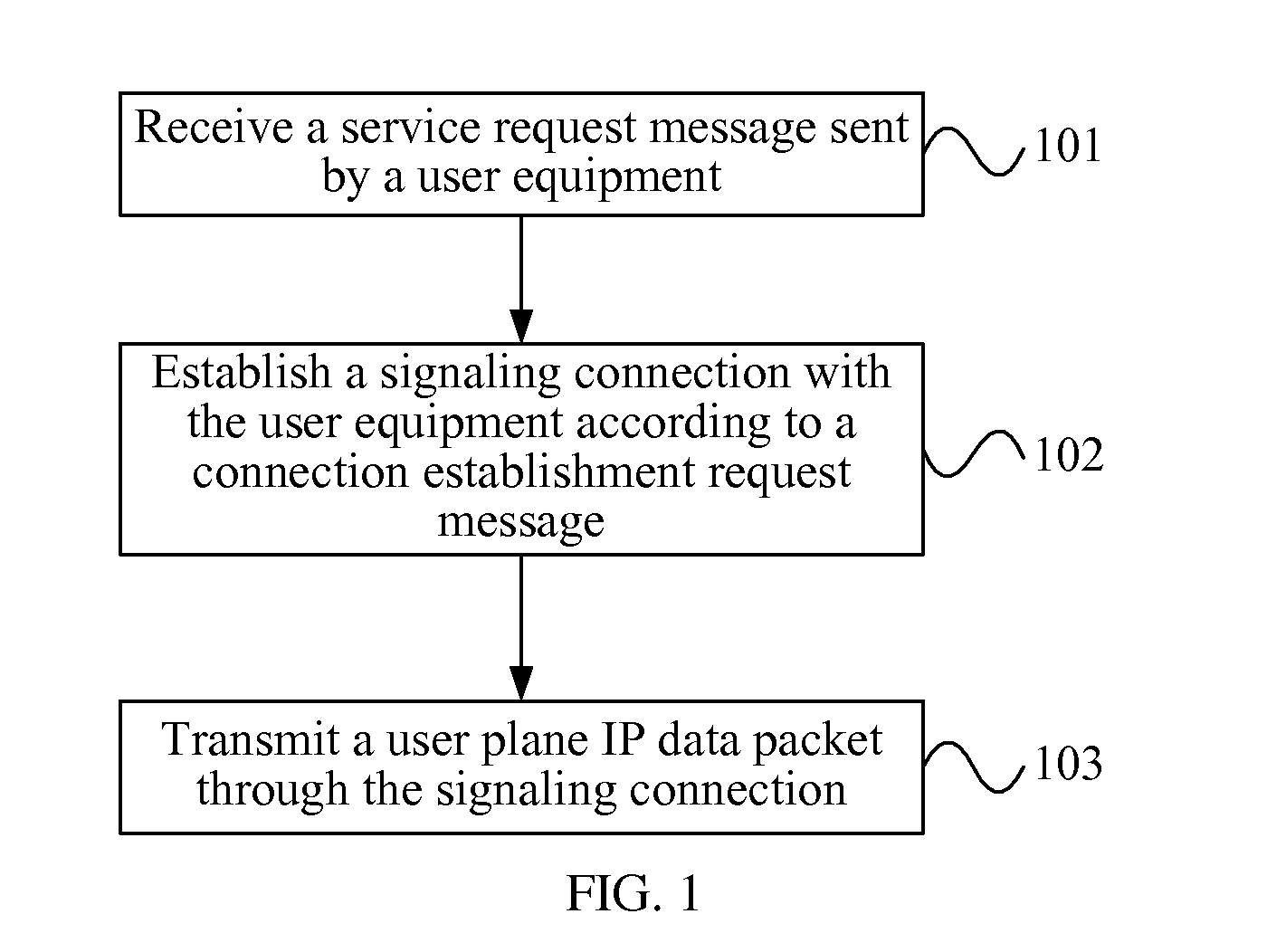
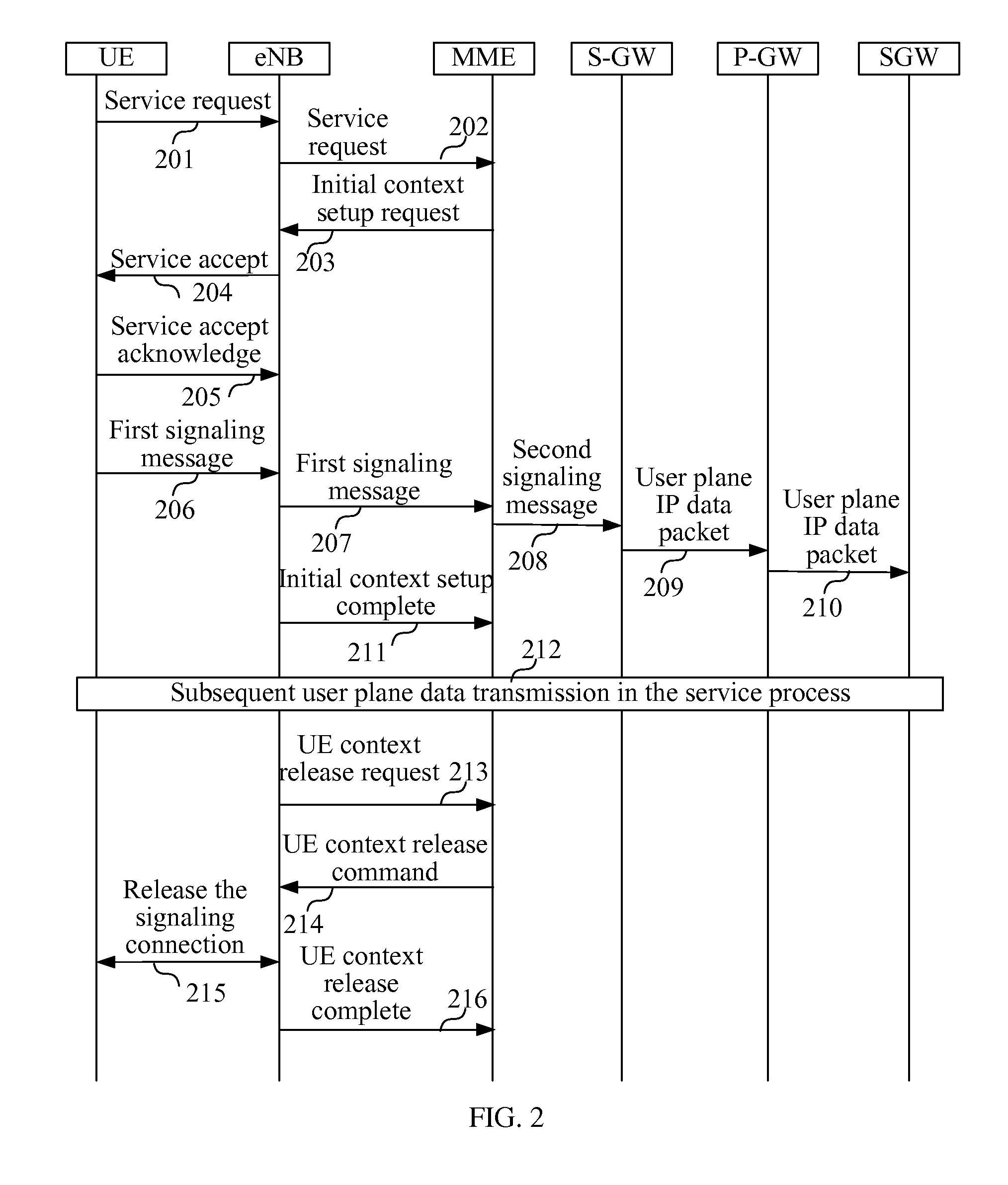
ActiveUS20120093086A1Save signaling overheadReduce network loadConnection managementWireless commuication servicesOperational costsNetwork packet
Receiving a connection establishment request message sent by a user equipment; establishing a signaling connection with the user equipment according to the connection establishment request message; and transmitting a user plane IP data packet through the signaling connection. After a signaling connection is established between a UE in an idle state and a mobility management device, an uplink user plane IP data packet or a downlink user plane IP data packet, is directly transmitted between the UE and the network side through the signaling connection, with no need to specifically establish (recover) an RAB between the UE and an S-GW, which can save the signaling overhead, thus reducing the network load and lowering the operating cost of an operator.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Nuclear power plant working robot and control system thereof
InactiveCN101774170ACapable of autonomous navigationRealize online monitoringEndless track vehiclesManipulatorTerrainOperational costs
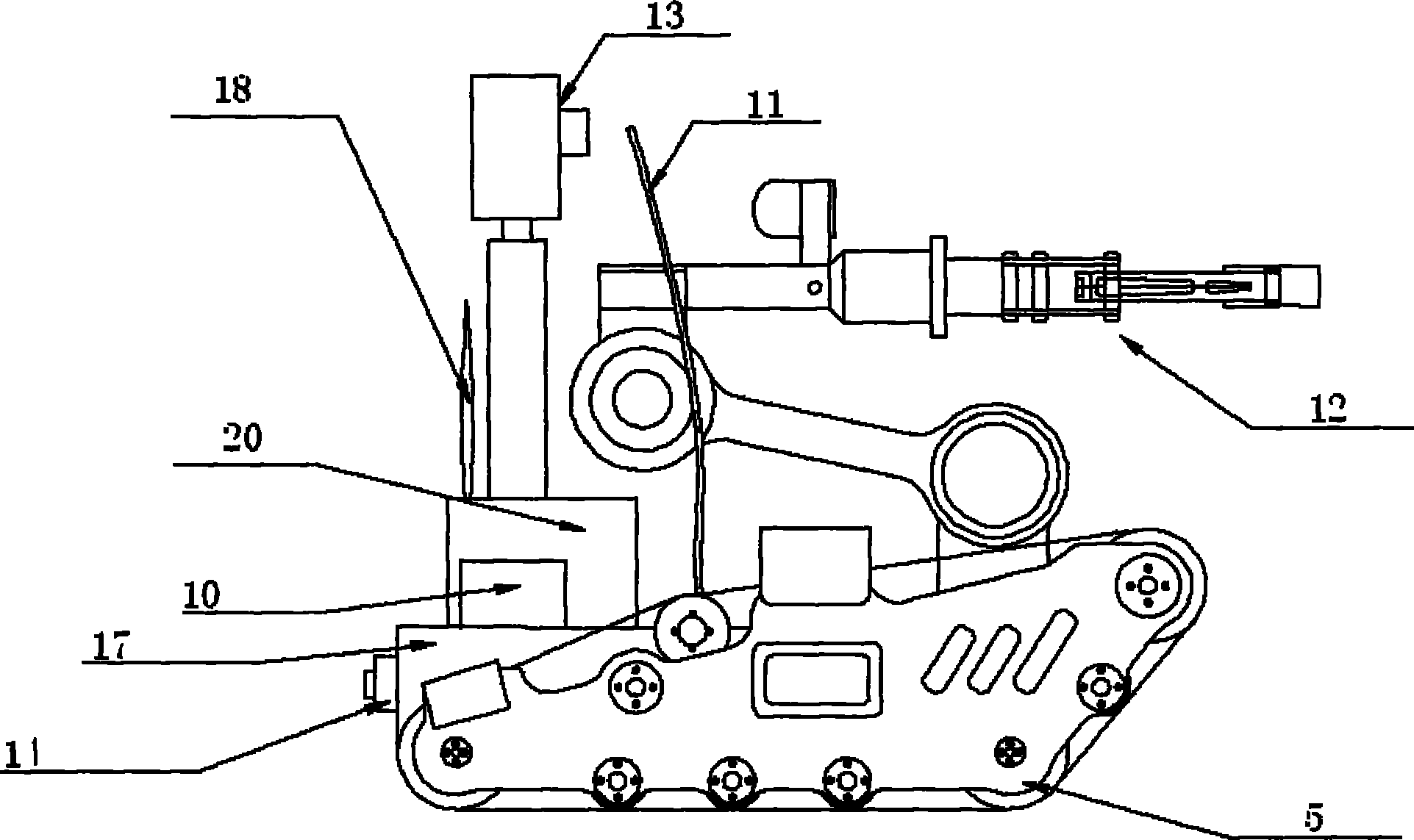
The invention relates to a nuclear power plant working robot and a control system thereof, which belong to the fields of robots and automation equipment. The nuclear power plant working robot is a crawler-type mobile manipulator and is composed of a mobile platform driven by double crawlers and a four freedom degree manipulator carried on the mobile platform. The nuclear power plant working robot can move inside a nuclear power plant, has two control modes of manual remote control and autonomous control, and is remotely controlled by a wireless or wired mode. The control system of the nuclear power plant working robot includes a host monitoring and planning control system and a robot control system which are matched to control the operation of the robot. The robot operates autonomously, is safe and reliable, can complete certain dangerous tasks in high radioactivity environment; the robot has small size, stable performance, great maneuverability and low operation cost; a crawler-type chassis has strong gripping force as well as certain climbing and obstacle clearing ability, and is suitable to walking over complex terrains; and the robot has high intelligence degree and can realize autonomous control and manual remote control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
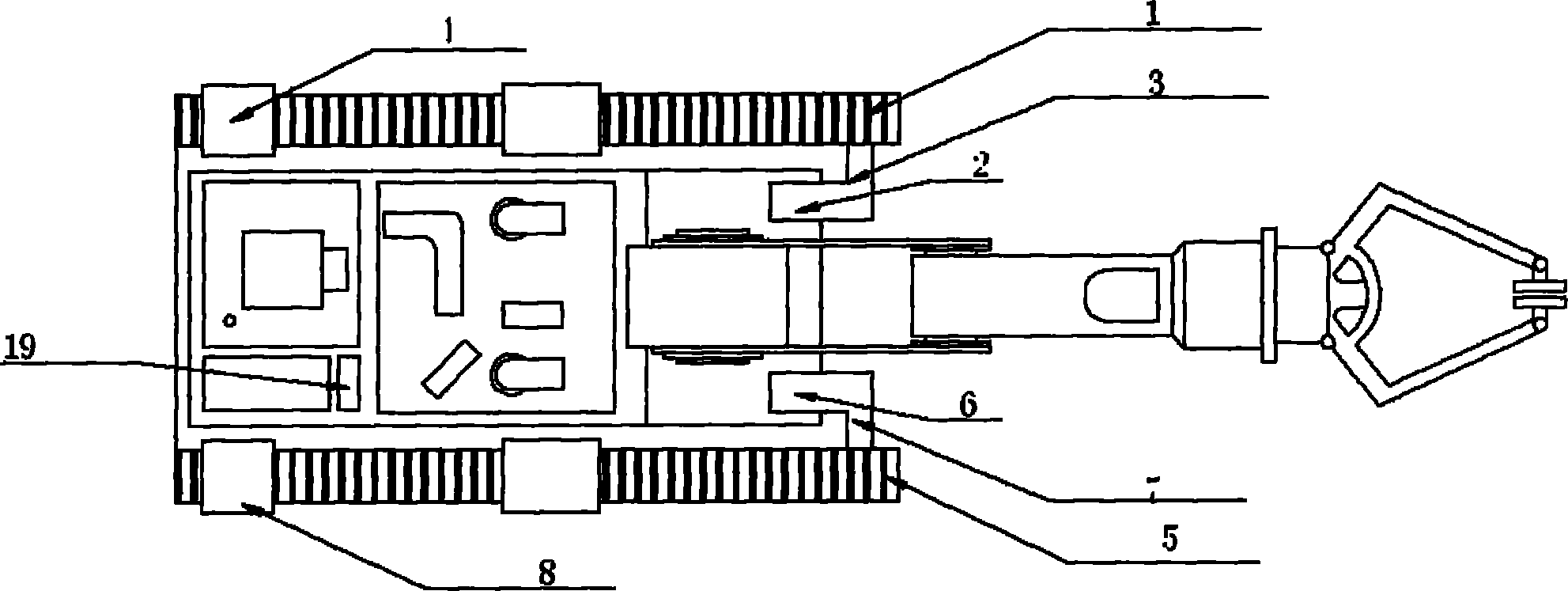
Remote vehicle rental systems and methods
ActiveUS20140156111A1Reduce infrastructure complexityLow costTicket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsOperational costsOdometer
A system for renting vehicles is disclosed. The system can comprise a vehicle access communicator (“VAC”) capable of interfacing with one or more functions of a rental vehicle and a user provided portable electronic device. The VAC can control various functions of the vehicle including, but not limited to, the door locks and / or enabling / disabling the vehicle. The VAC can also monitor various functions of the vehicle including, but not limited to, the fuel level and / or the odometer readings. The VAC can connect to the portable electronic device using a suitable connection method to access additional functionality such as, for example and not limitation, locations services, cellular, and / or internet access. The VAC and the portable electronic device can be used to provide a rental system with reduced infrastructure and operating costs. The system can enable the use of “Green Zones” to provide permanent or temporary vehicle rental areas.
Owner:I D SYST
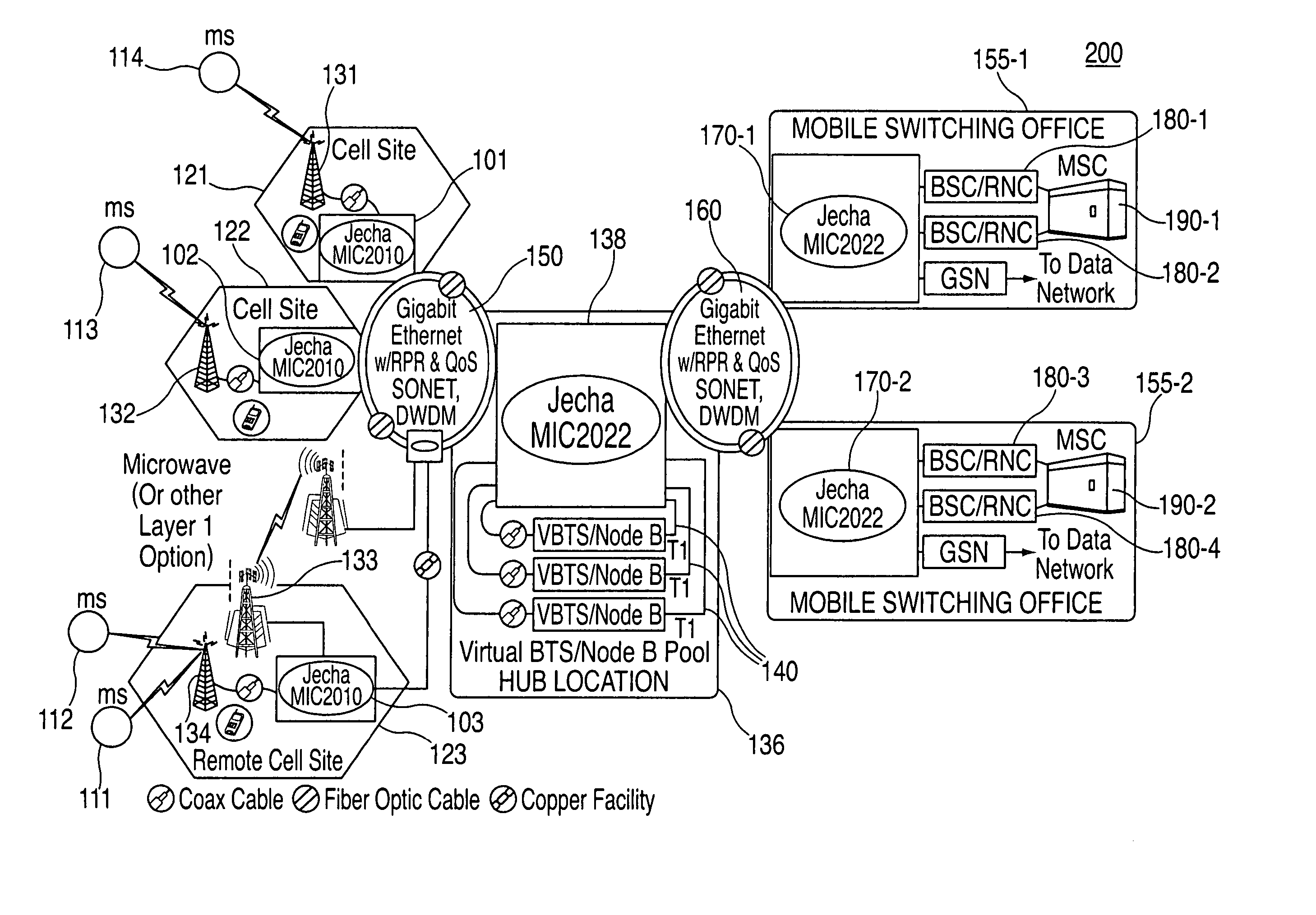
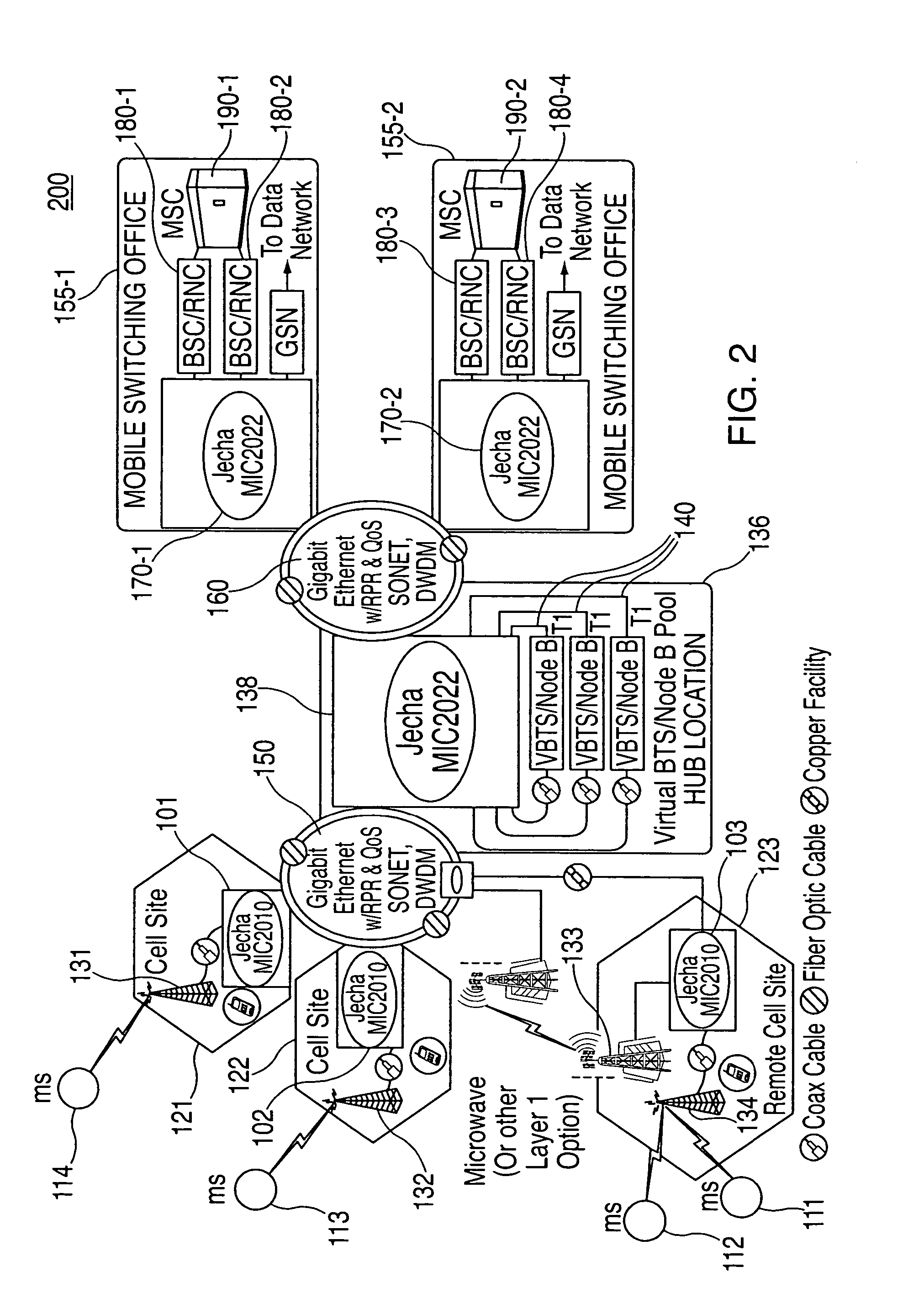
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS7573862B2Improve efficiencyReduce operating costsNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
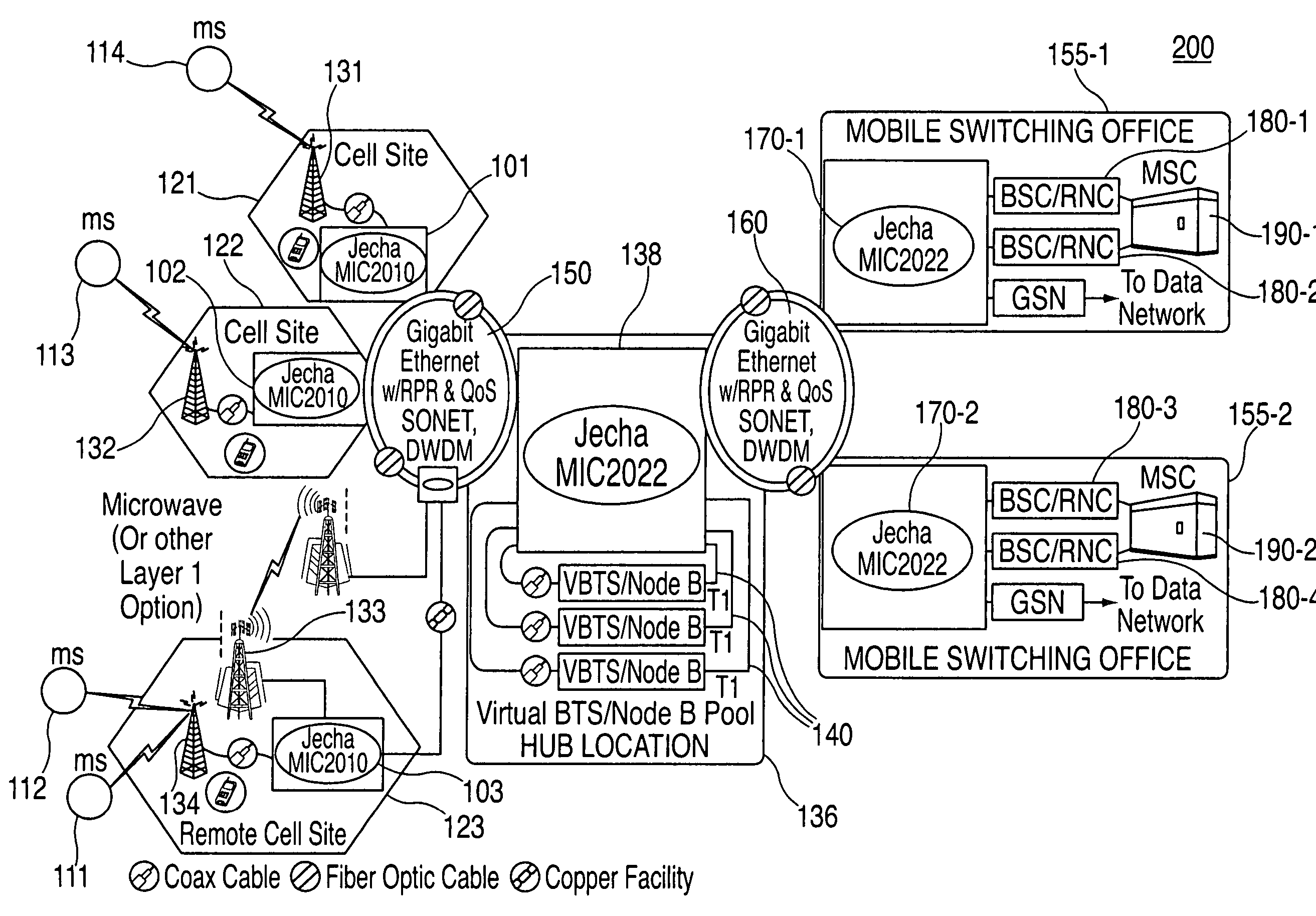
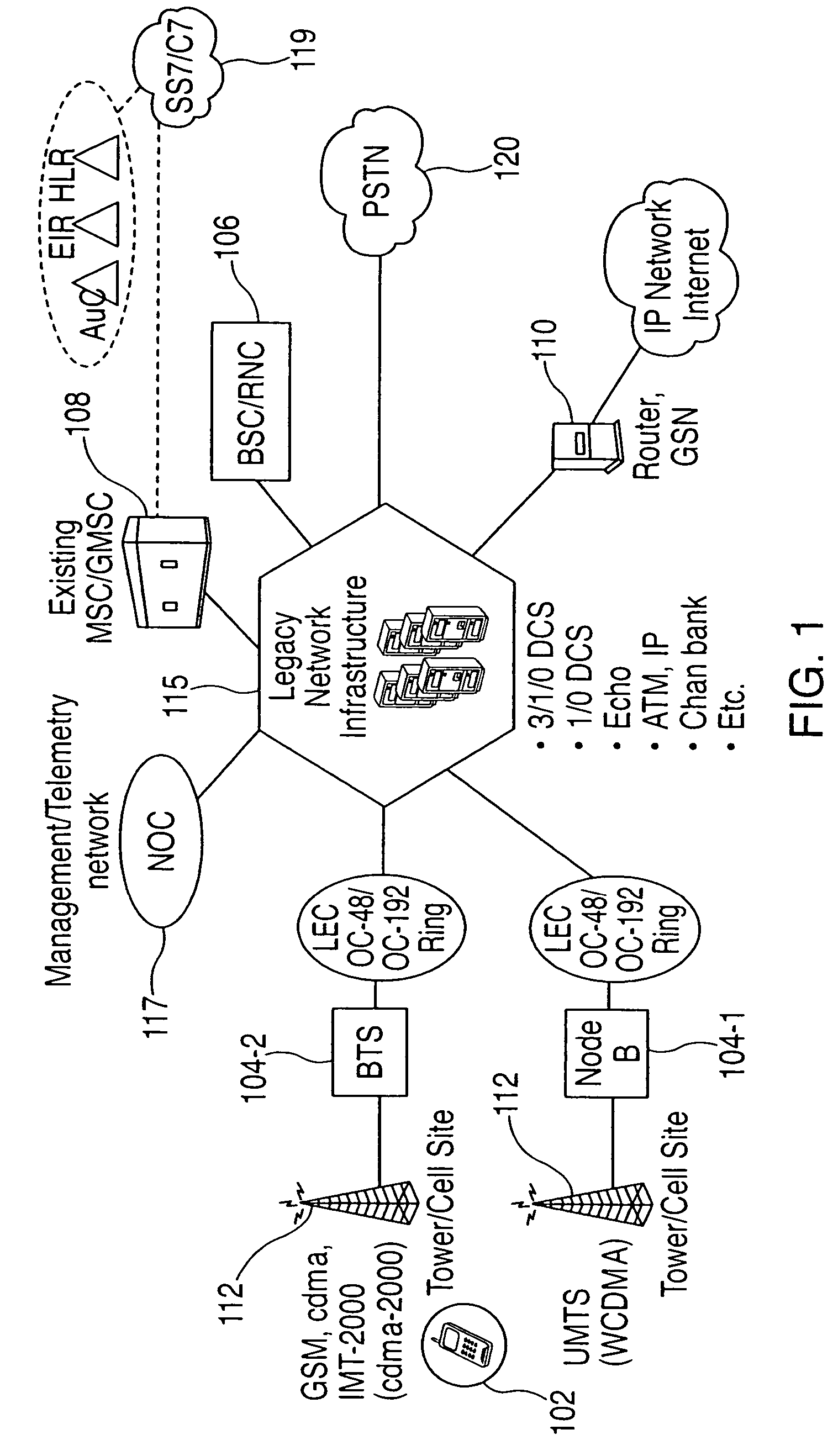
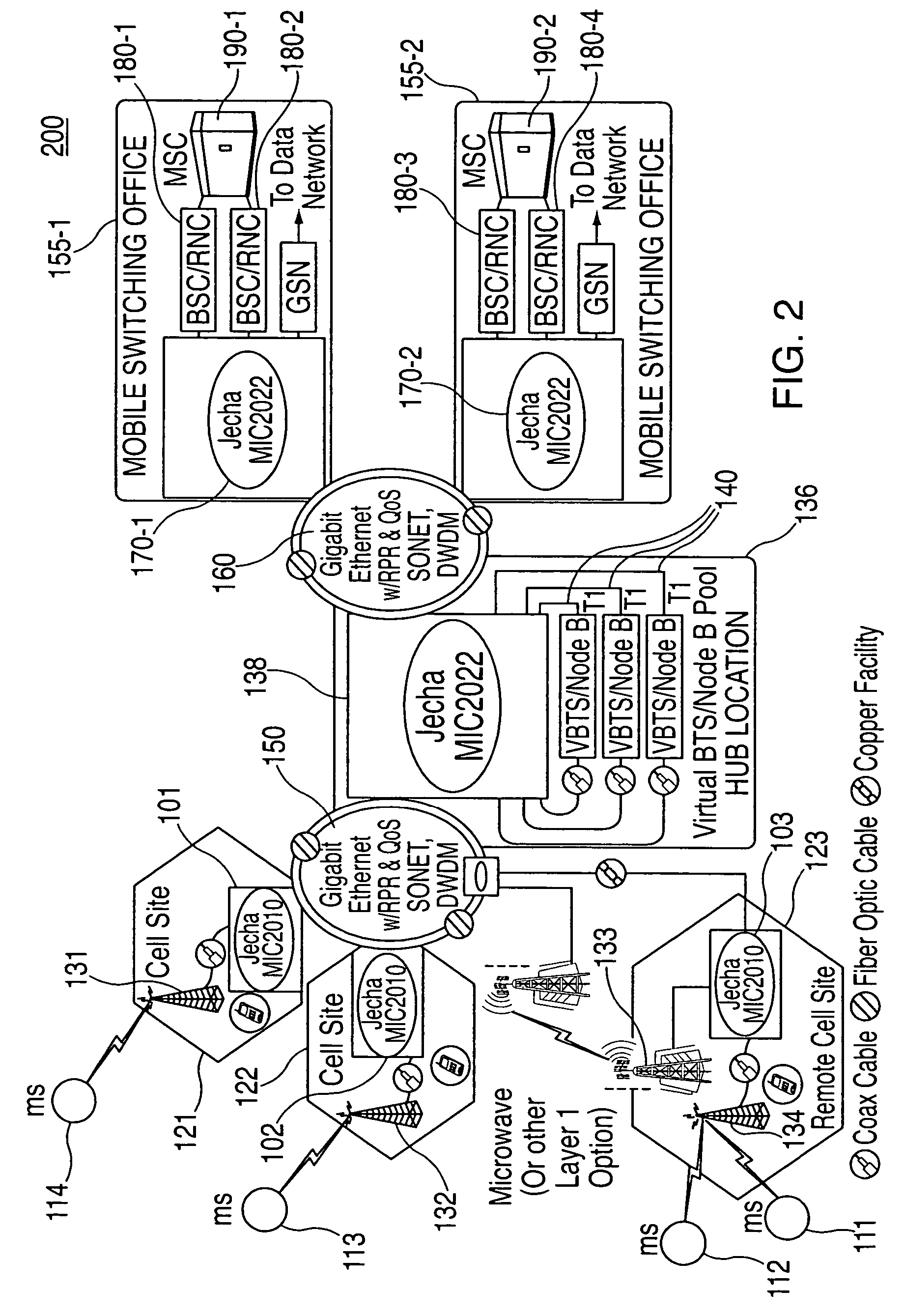
A system and method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network, reduce ongoing operating costs and increase revenue. According to one aspect, a method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network whereby network capacity in the radio access network (RAN) and baseband processing for wireless connections are dynamically adjusted to automatically provision sufficient bandwidth and baseband processing capacity in response to changes in the network. The method is further extended by implementing policy management which allows wireless carriers to develop and implement network based policies to automatically increase or decrease the amount of processing resources and network bandwidth required from any cell site, hub or mobile switching office. According to another aspect, network efficiency is enhanced by utilizing a novel cellular network infrastructure. RF signals from cell site antennas of various technology types are demodulated, digital bit information is extracted from the RF signals, processed, and groomed into Gigabit Ethernet / Resilient Packet Ring (GigE / RPR) or Ethernet over copper traffic flows using specific Quality of Service (QoS) priorities. The GigE / RPR traffic flows are routed to hub sites or mobile switching offices, at which point the packetized information is extracted and converted to RF signals that are equivalent to the signals that were received at the antenna. The RF signals are sent over coaxial cable to a network hub including a pool of Base Transceiver Stations (BTSs) (or Node Bs). The hub is coupled to one or more mobile switching offices via a second fiber optic ring.
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
Energy-saving method and apparatus for base station
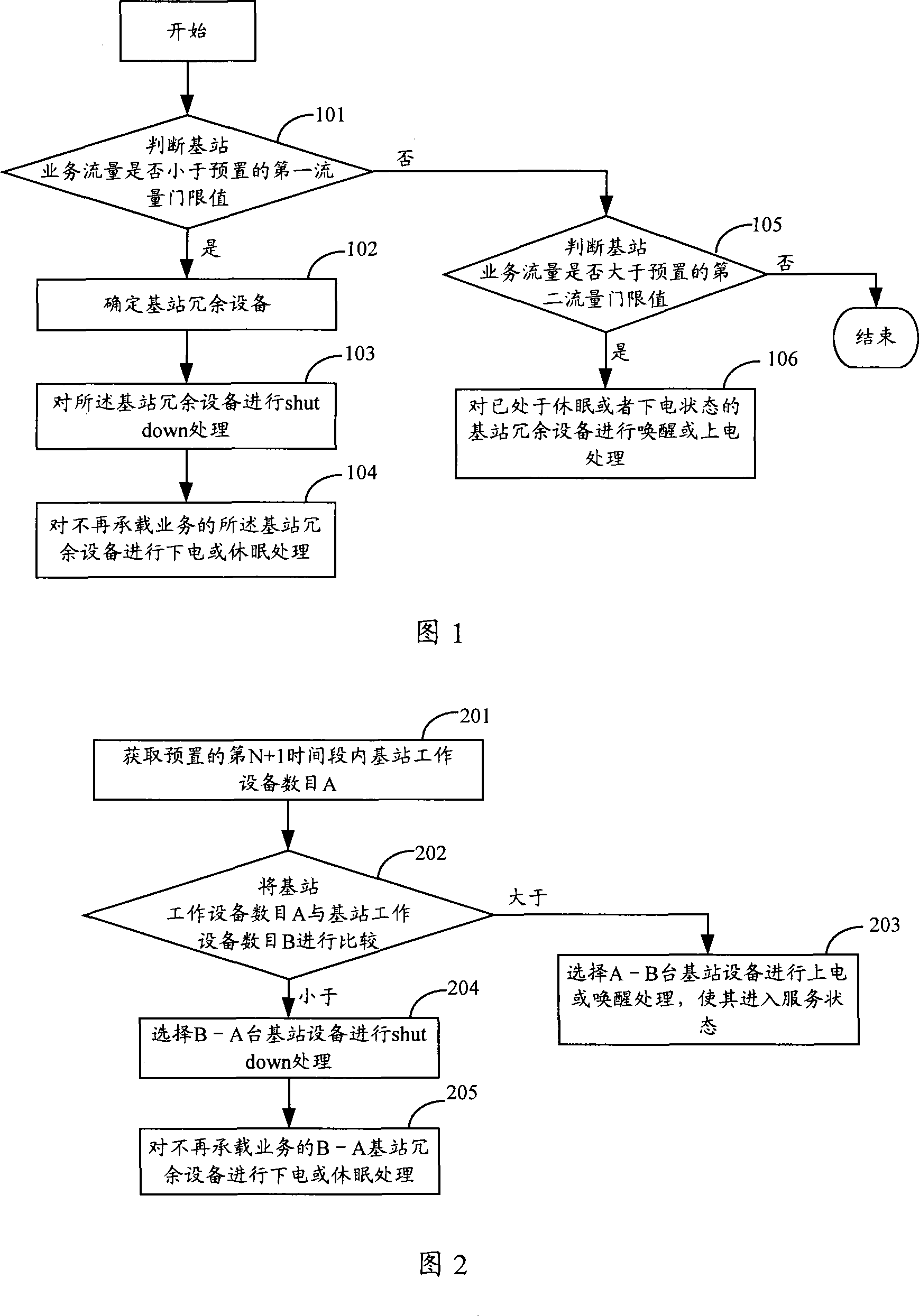
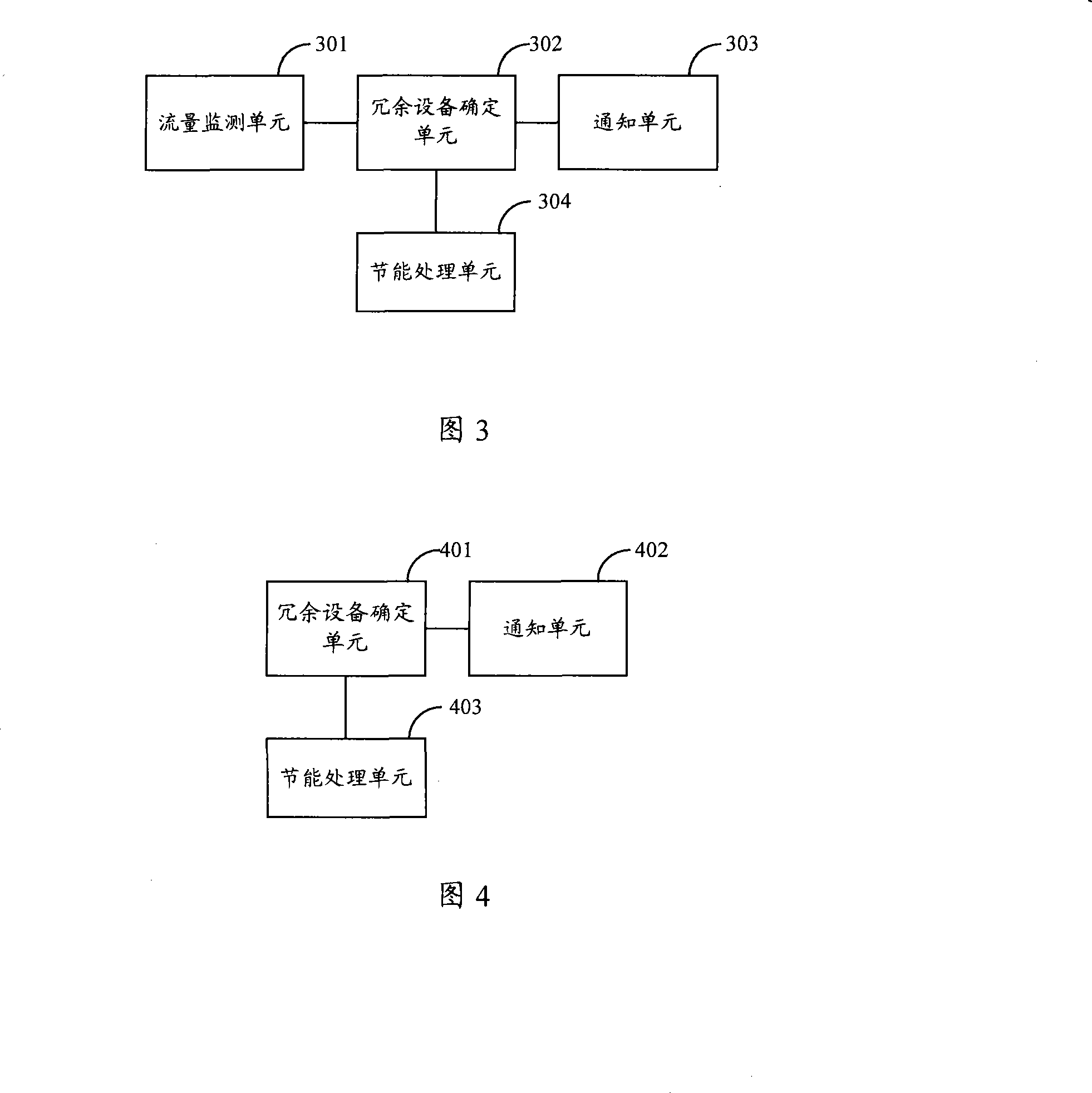
InactiveCN101179814AReduce manufacturing costTo achieve the purpose of energy savingEnergy efficient ICTPower managementElectricityOperational costs
An energy-saving method for the base station includes: determining a base station redundancy device; stopping allocating new service to the base station redundancy device; performing the discharging or dormancy process to the base station redundancy device when it does not carry any service any more. And, accordingly, the embodiments of the present invention also disclose an energy-saving apparatus for the base station. The Energy-saving method and apparatus for the base station provided by the invention launch on from the root of energy consumption for the base station, reduce the power energy waste of the base station by performing the discharging or dormancy process to the base station redundancy device without increasing the cost of the base station manufacture, achieve the aim of saving energy for the base station, and save on the operation cost. The invention also provides an energy-saving apparatus for the base station.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com