Patents
Literature
3114 results about "Air separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An air separation plant separates atmospheric air into its primary components, typically nitrogen and oxygen, and sometimes also argon and other rare inert gases. The most common method for air separation is fractional distillation. Cryogenic air separation units (ASUs) are built to provide nitrogen or oxygen and often co-produce argon. Other methods such as membrane, pressure swing adsorption (PSA) and vacuum pressure swing adsorption (VPSA) are commercially used to separate a single component from ordinary air. High purity oxygen, nitrogen, and argon used for semiconductor device fabrication requires cryogenic distillation. Similarly, the only viable source of the rare gases neon, krypton, and xenon is the distillation of air using at least two distillation columns.
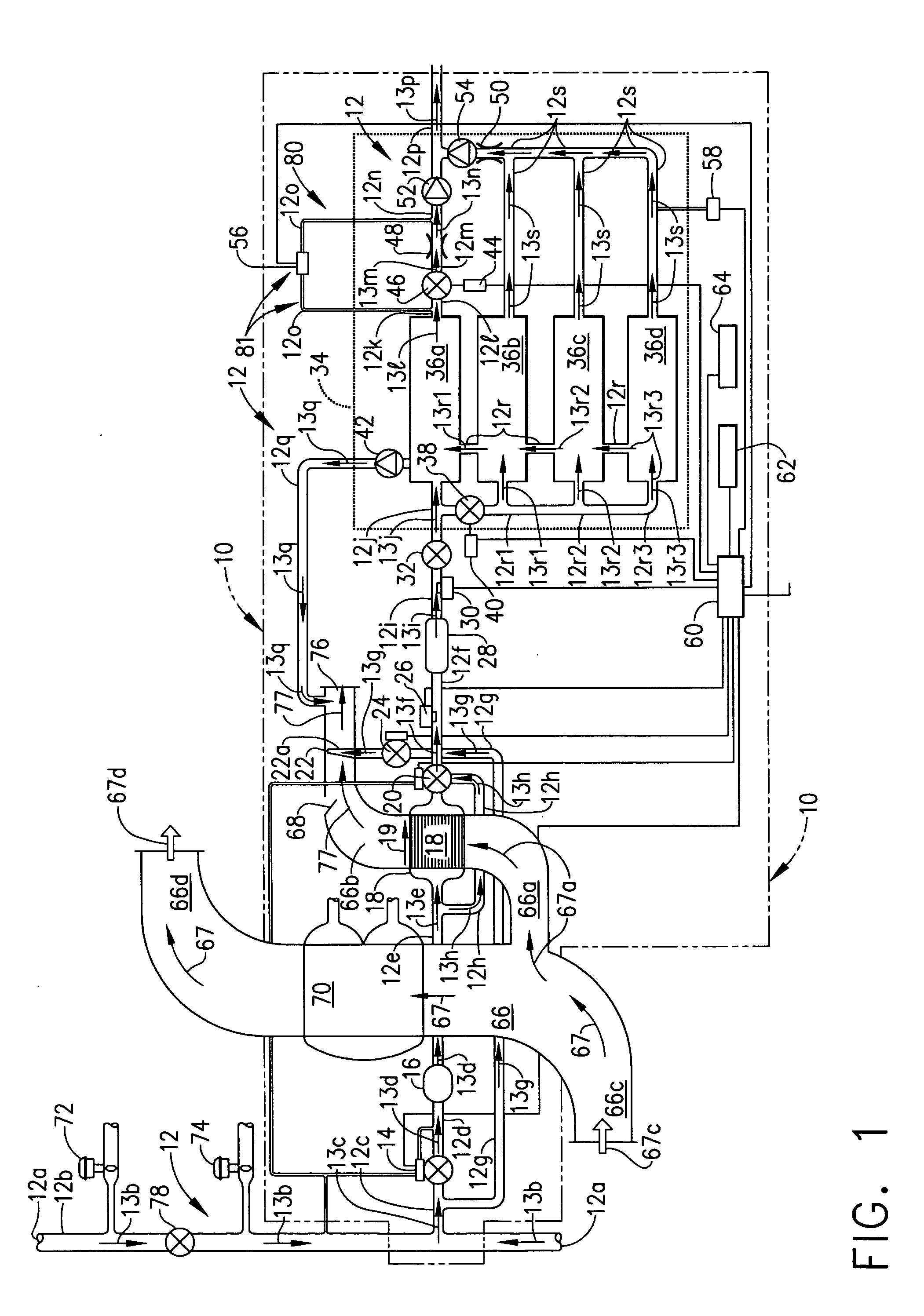
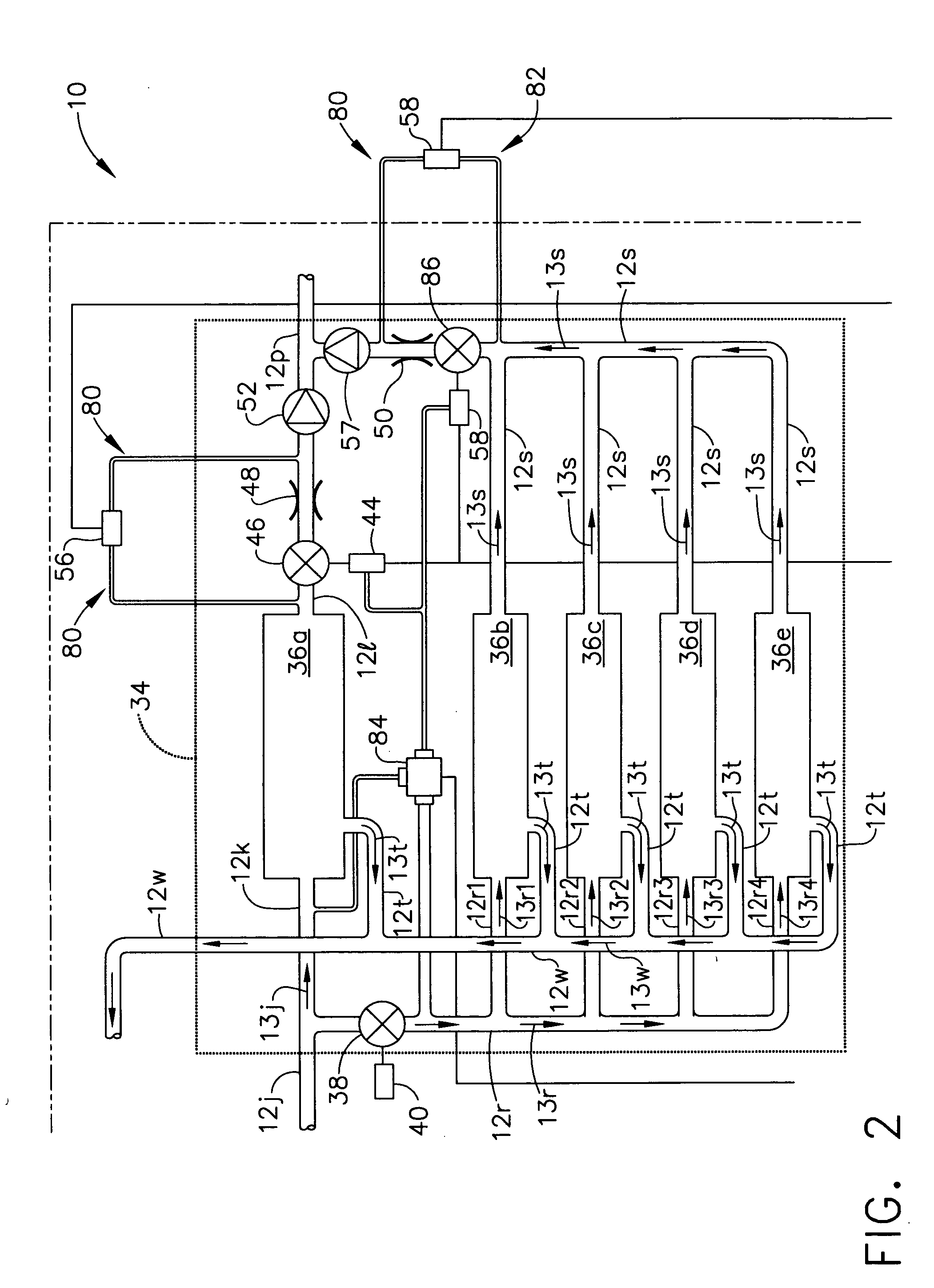
Systems, methods and apparatuses for pumping cassette-based therapies
InactiveUS7238164B2Simple materialSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionMultiplexingAir separation
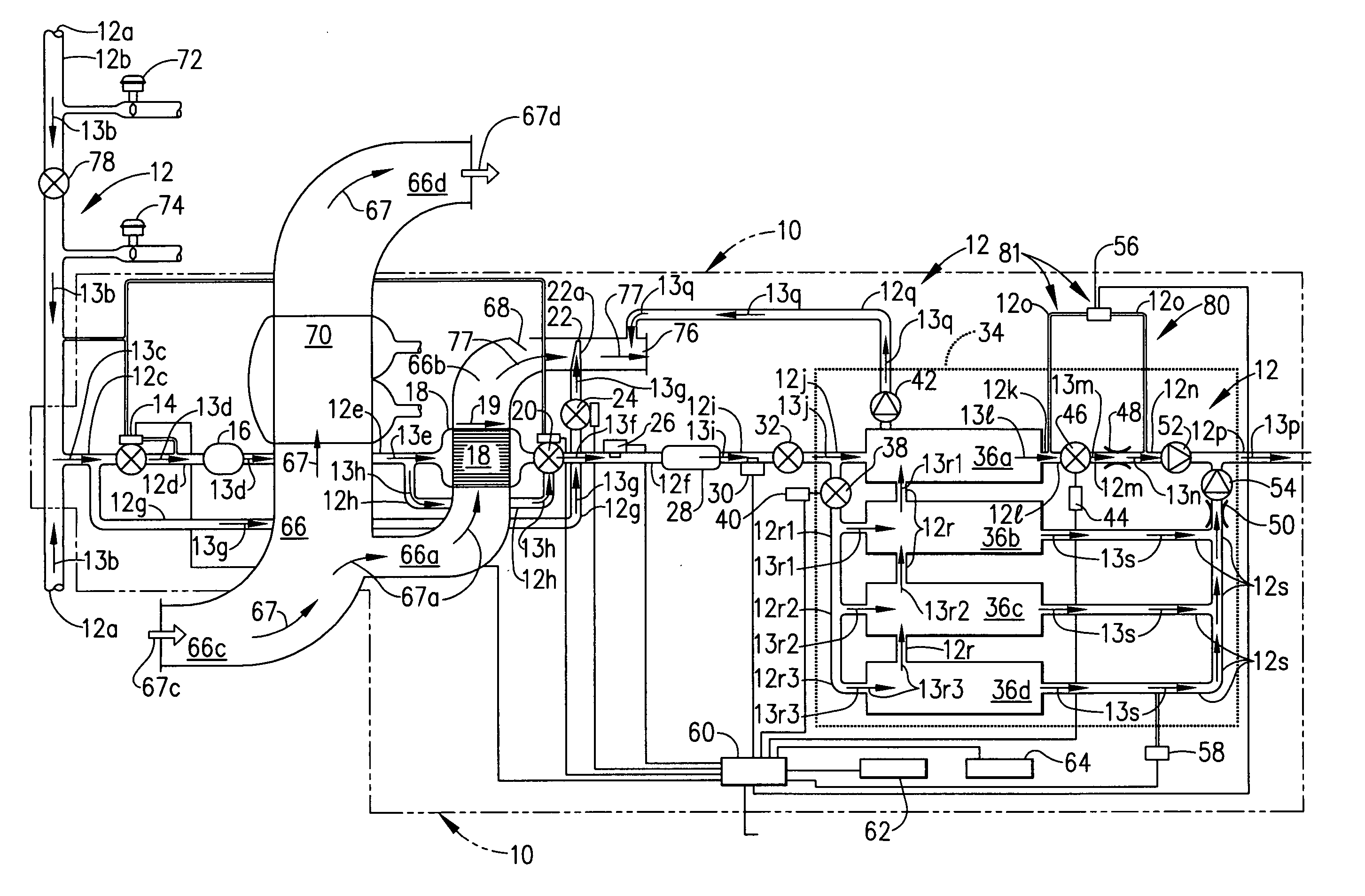
The present invention provides systems, methods and apparatuses for medical fluid delivery systems that employ a pumping cassette. In particular, the present invention provides systems, methods and apparatuses for cassette-based dialysis therapies including hemodialysis, hemofiltration, APD (including tidal modalities) and CFPD. The embodiments described include a combined pump / valve housing, a fail safe pump / valve arrangement, a cassette auto-alignment feature, a pumping membrane material, a multiplexing valve arrangement, an expert fluid pumping management system, an integral port vent and an in-line air separation chamber and combinations of each of these.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
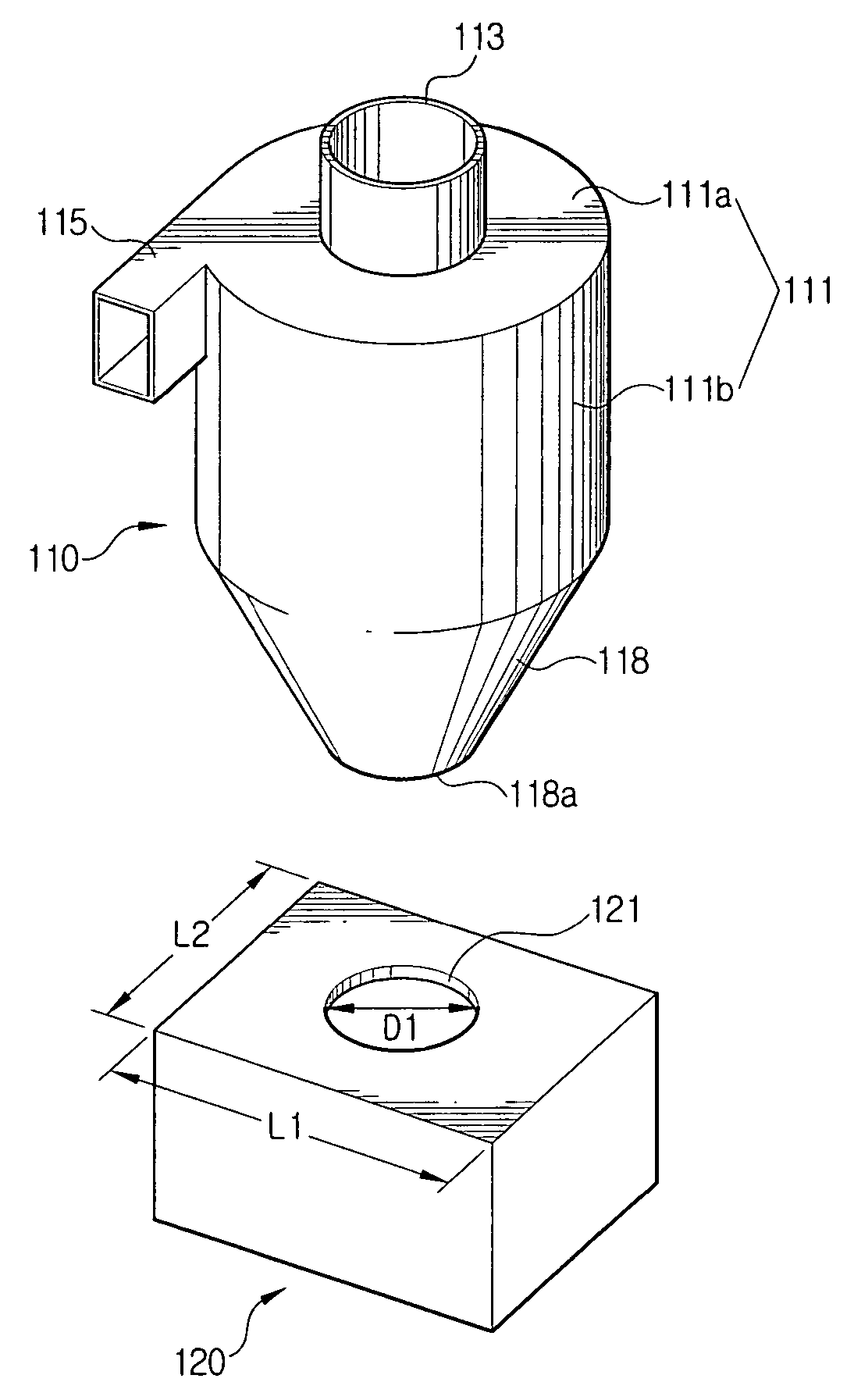
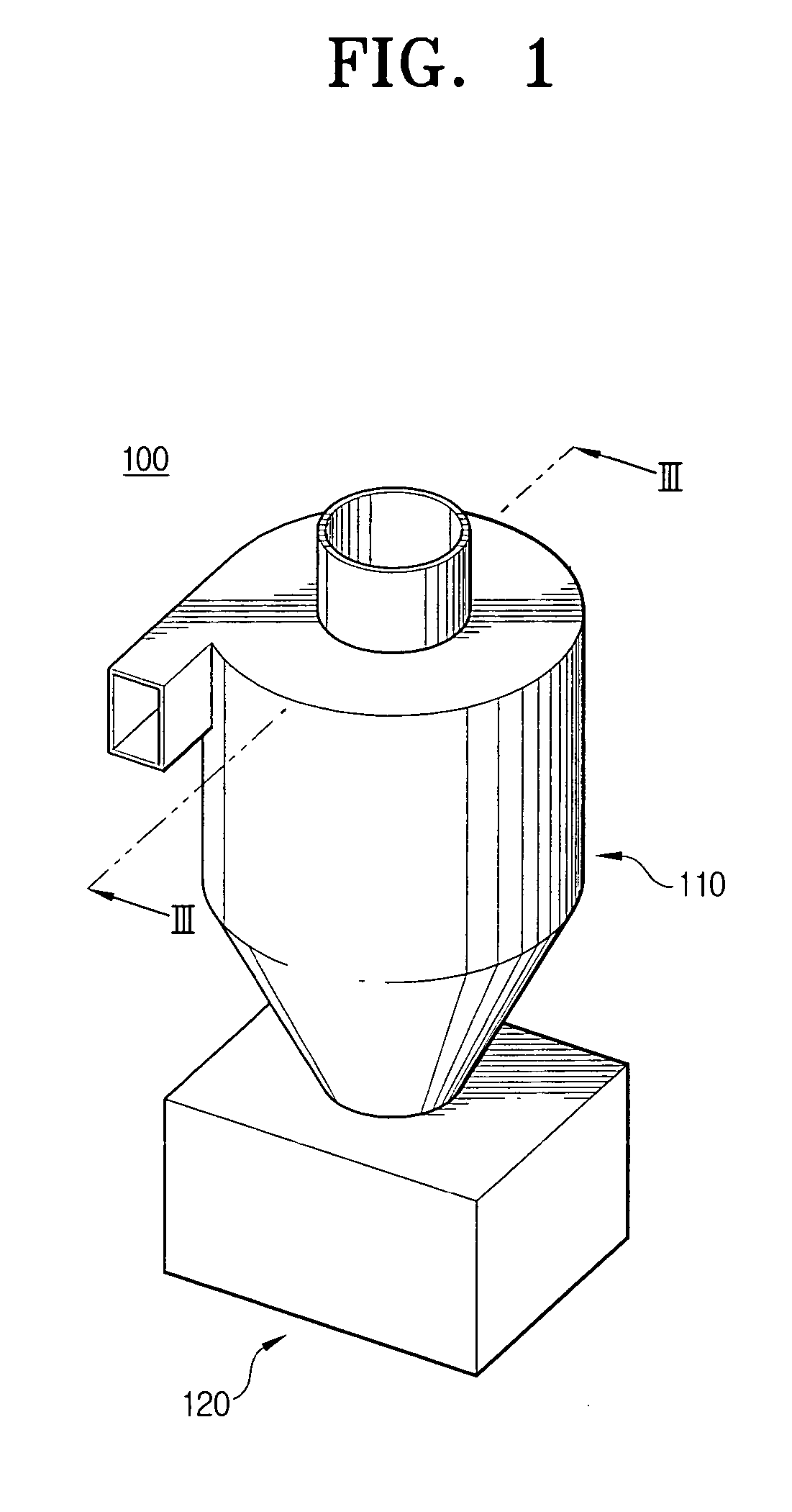
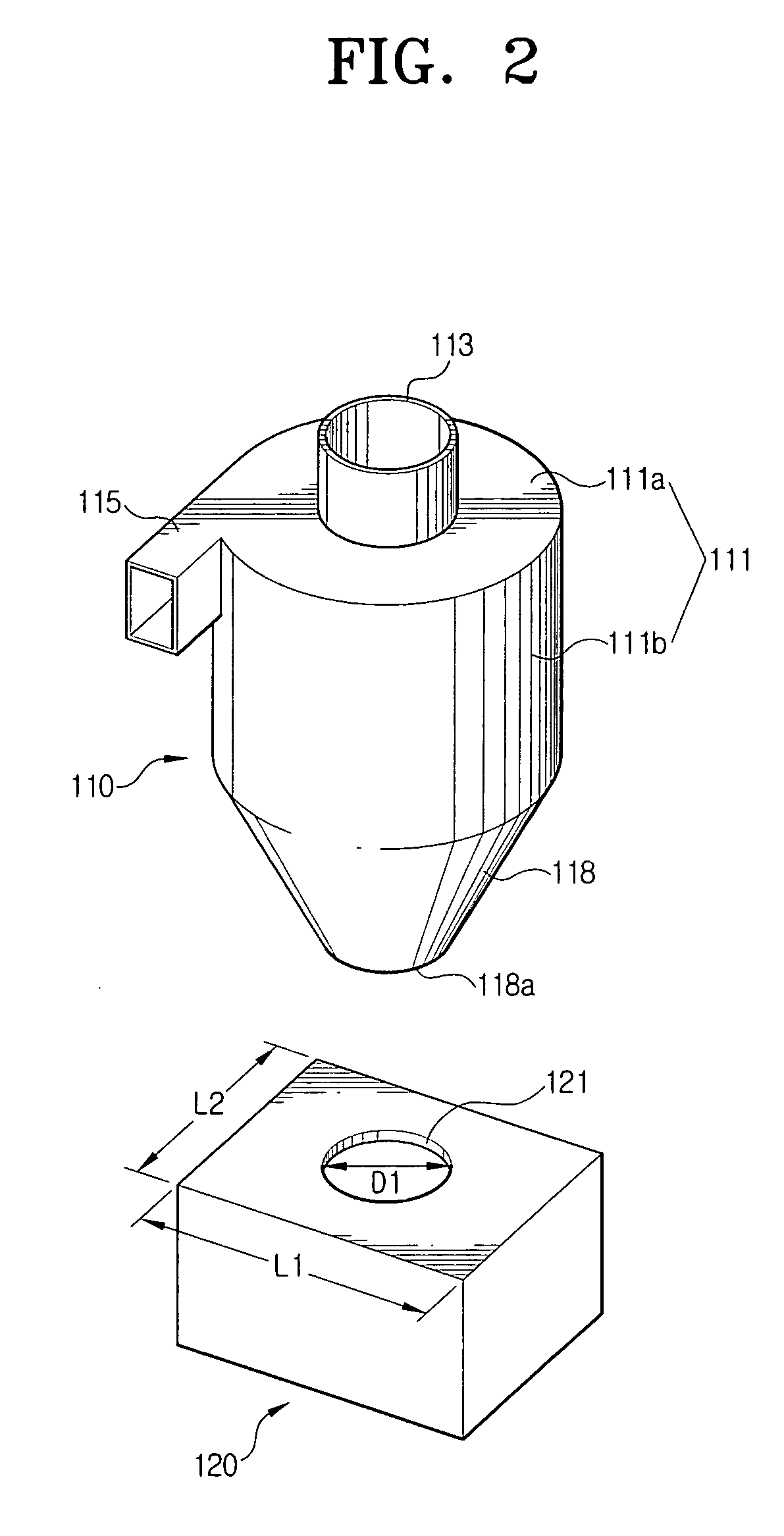
Multi-cyclone dust separating apparatus
A multi-cyclone dust separating apparatus includes: a multi-cyclone unit including a first cyclone chamber body having a first cyclone chamber and at least one protection chamber formed around at least a portion of an outer circumference of the first cyclone chamber, and at least one secondary cyclone chamber body disposed in the protection chamber, each secondary cyclone chamber body having at least one secondary cyclone chamber; a cover unit connecting an upper end of the multi-cyclone unit and guiding air discharged from the first cyclone chamber to the at least one secondary cyclone chamber; a dirt collecting unit adapted to connect to a lower end of the multi-cyclone unit and configured to collect dirt separated from the air in the first and secondary cyclone chambers; and an air discharge duct configured to discharge air that has passed through the multi-cyclone unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
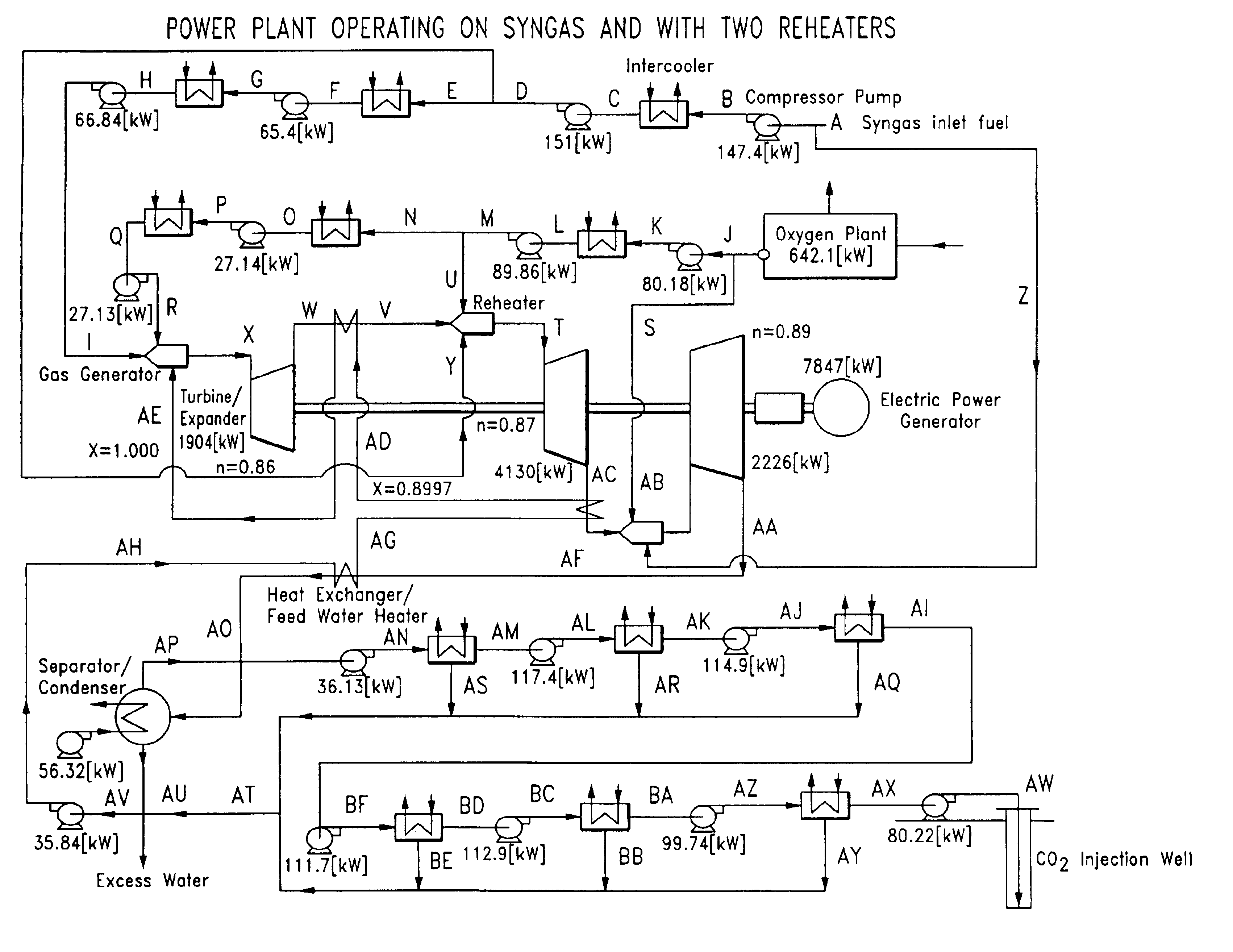
Low pollution power generation system with ion transfer membrane air separation
InactiveUS6945029B2Nitrogen oxideReduce electricity demandSolidificationLiquefactionPollutionCombustion products
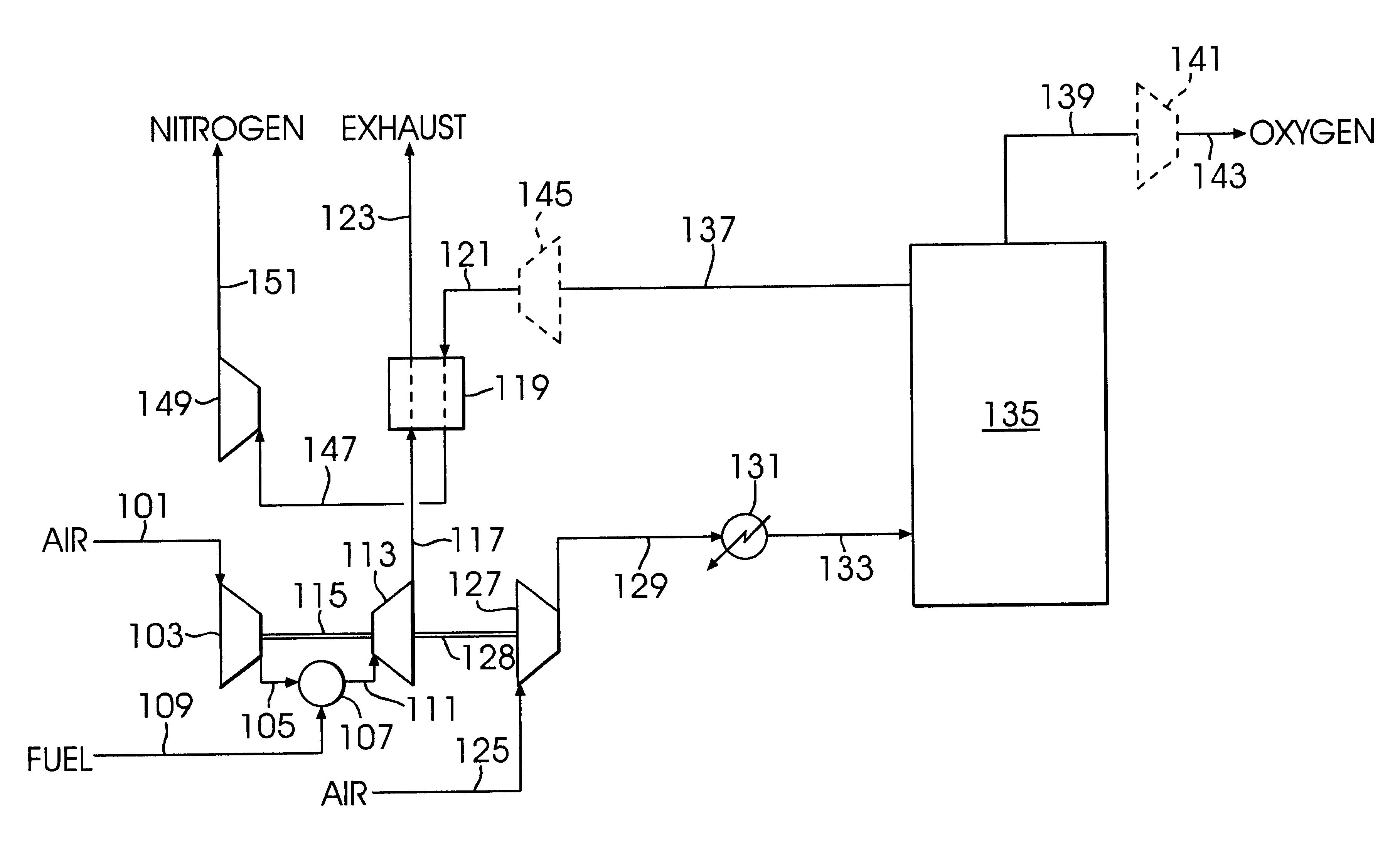
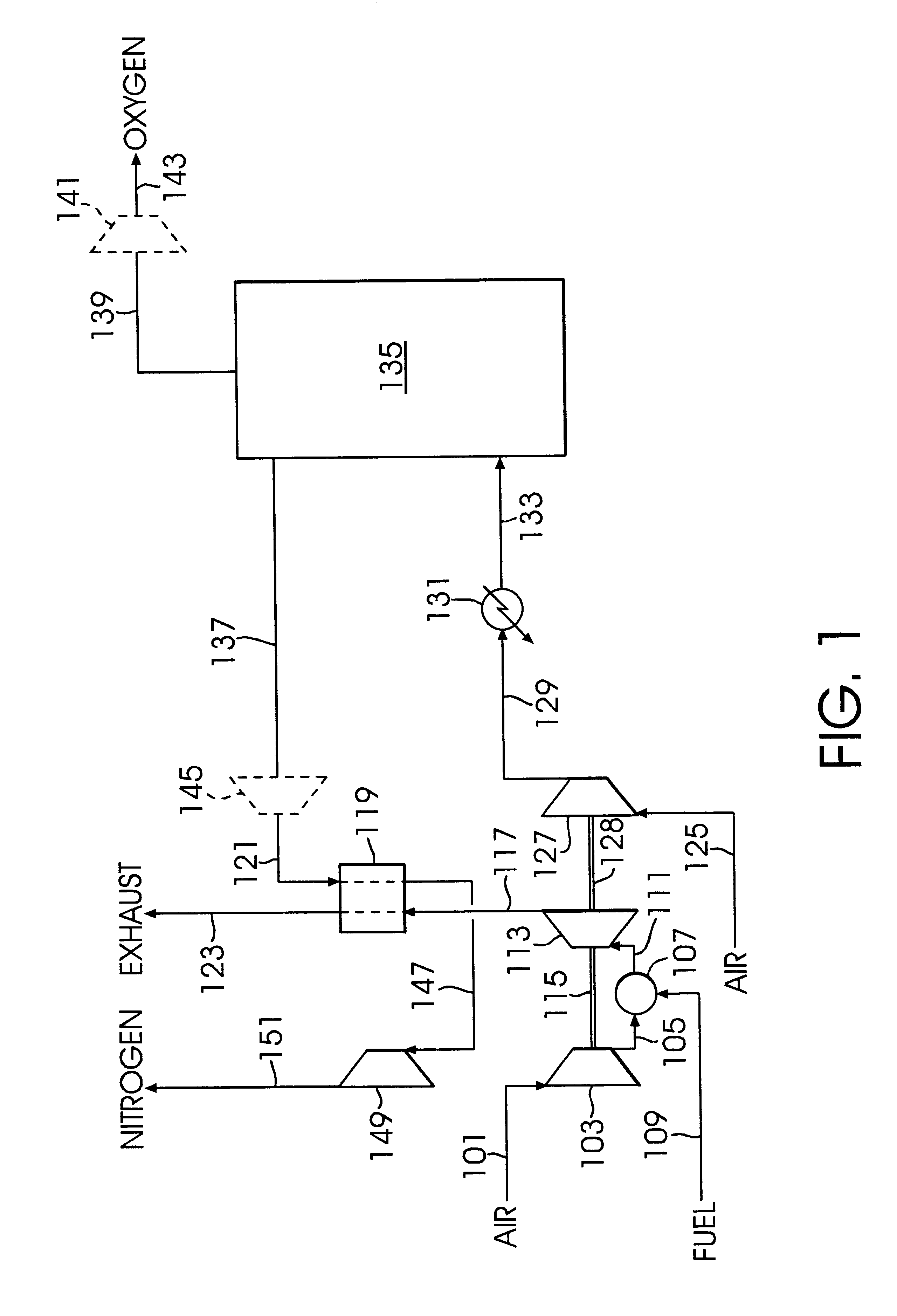
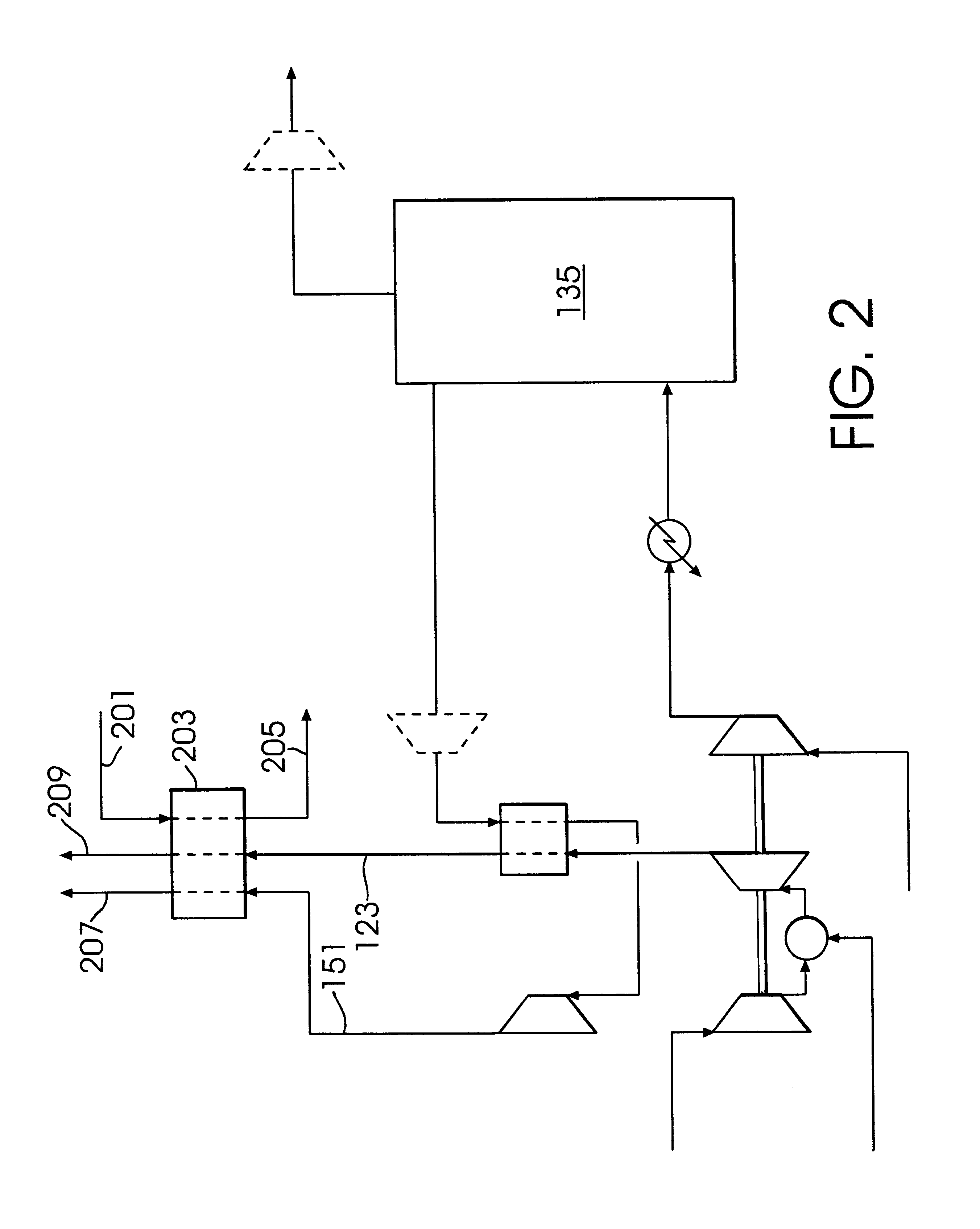
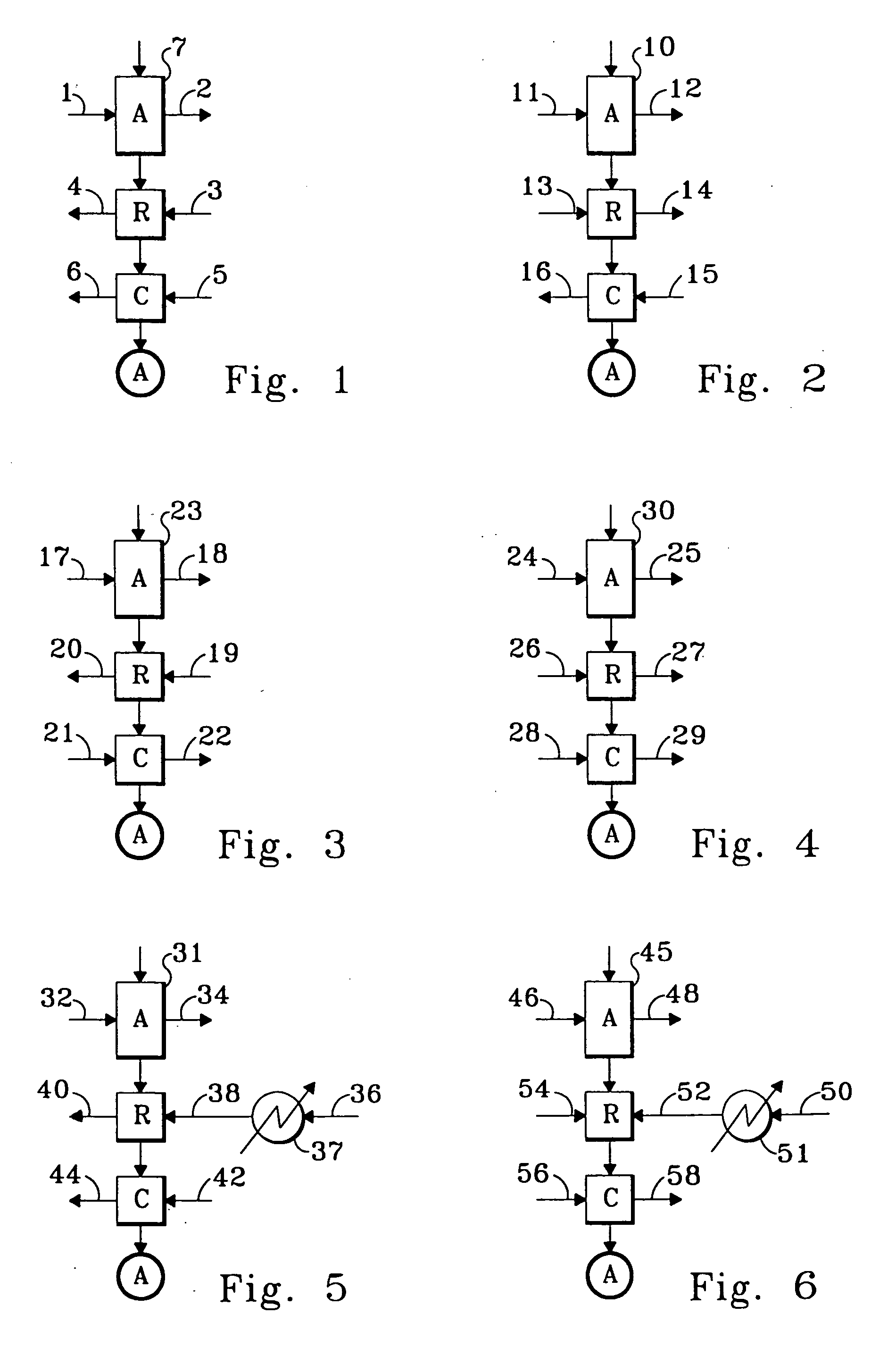
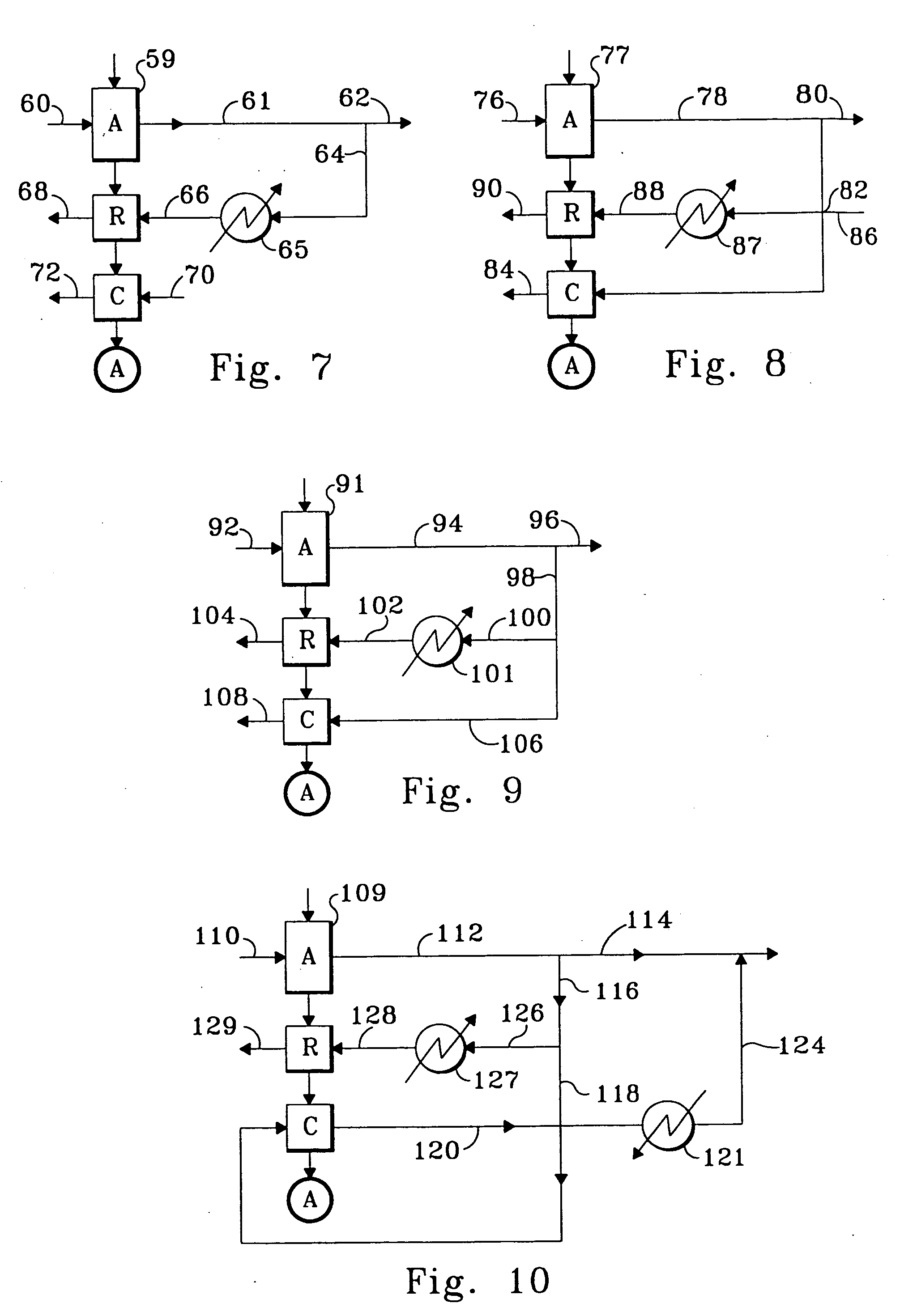
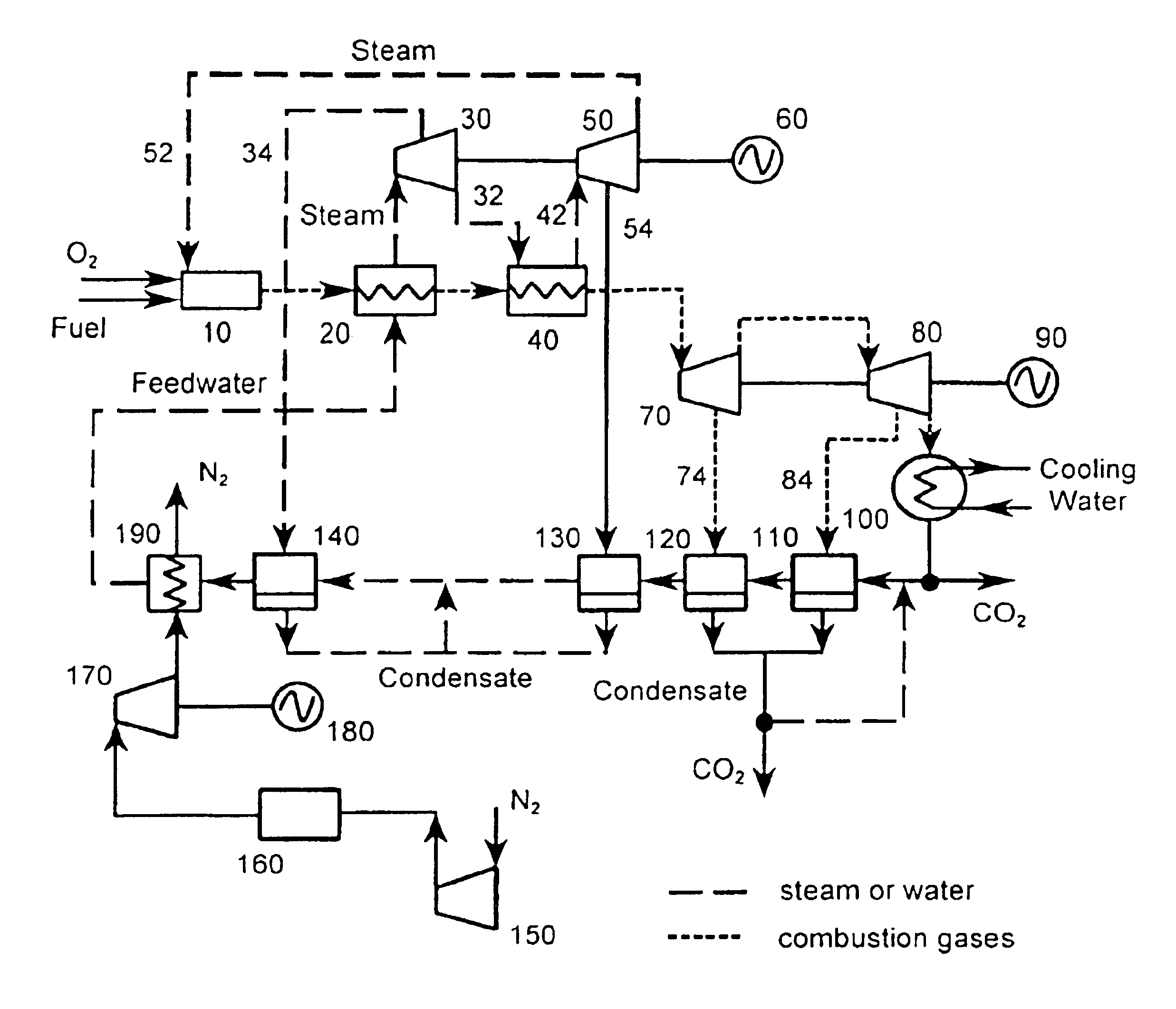
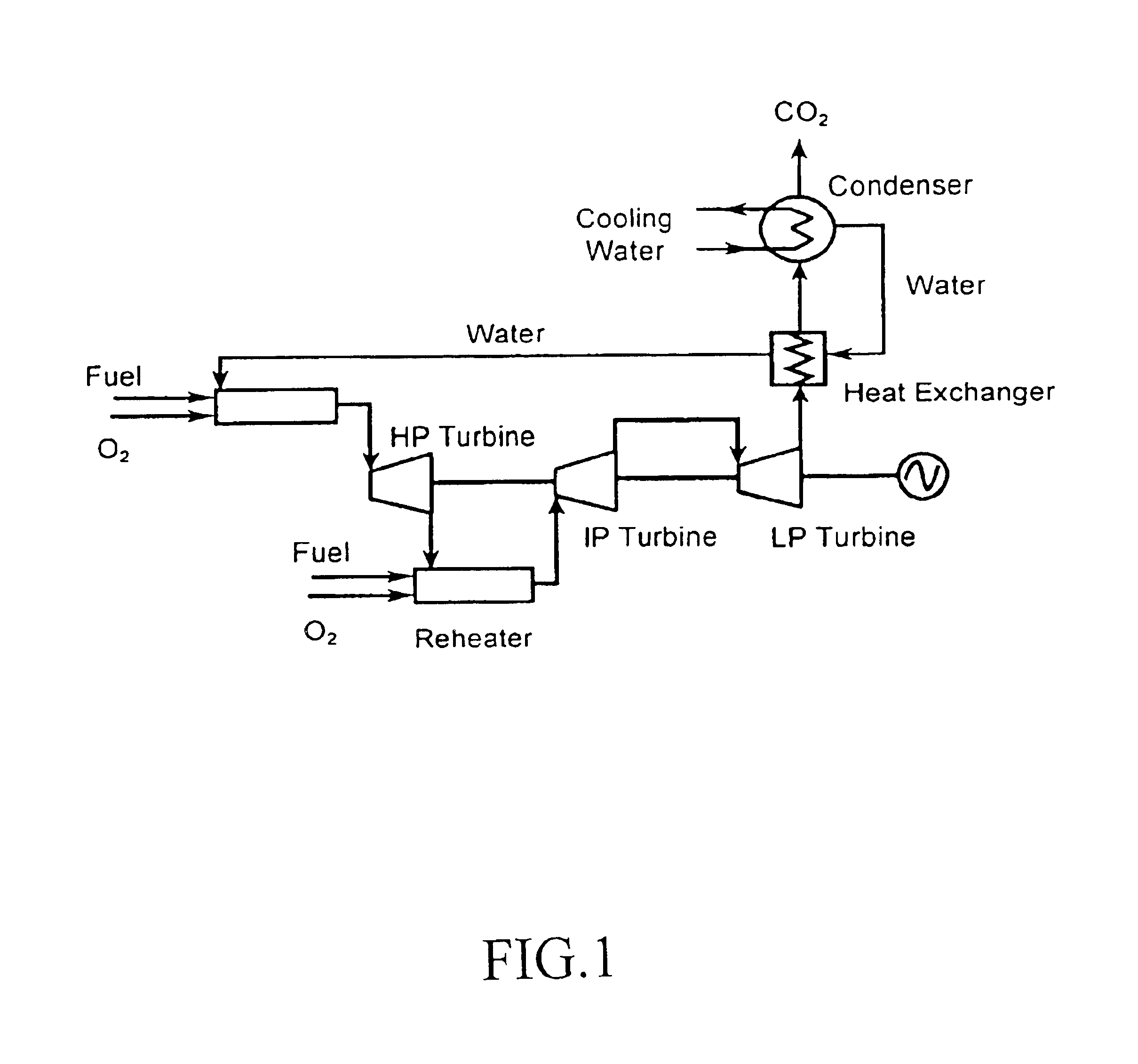
A low or no pollution power generation system is provided. The system has an air separator to collect oxygen. A gas generator is provided with inputs for the oxygen and a hydrocarbon fuel. The fuel and oxygen are combusted within the gas generator, forming water and carbon dioxide. Water or other diluents are also delivered into the gas generator to control temperature of the combustion products. The combustion products are then expanded through at least one turbine or other expander to deliver output power. The combustion products are then passed through a separator where the steam is condensed. A portion of the water is discharged and the remainder is routed back to the gas generator as diluent. The carbon dioxide can be conditioned for sequestration. The system can be optimized by adding multiple expanders, reheaters and water diluent preheaters, and by preheating air for an ion transfer membrane oxygen separation.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
Cyclonic separating apparatus for vacuum cleaner which is capable of separately collecting water from dust
InactiveUS20060162298A1Easy to separatePreventing dispersion and subsequent backflowCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentInterior spaceCyclonic separation
A cyclonic separating apparatus for a vacuum cleaner that can separately collect dust and water. The cyclonic separating apparatus includes: a cyclone body having an air inlet passage and an air discharge passage; a dust receptacle connected to a lower end of the cyclone body; and a screen dividing the cyclone body and interior space of the dust receptacle into a first chamber and a second chamber, the screen having a plurality of passing holes, wherein drawn air rotates in the first chamber and water separated from the air moves to the second chamber through the passing holes.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Power plant with emissions recovery
InactiveUS20100018218A1Reduce deliveryEnvironment safetySolidificationLiquefactionParticulatesNitrogen gas
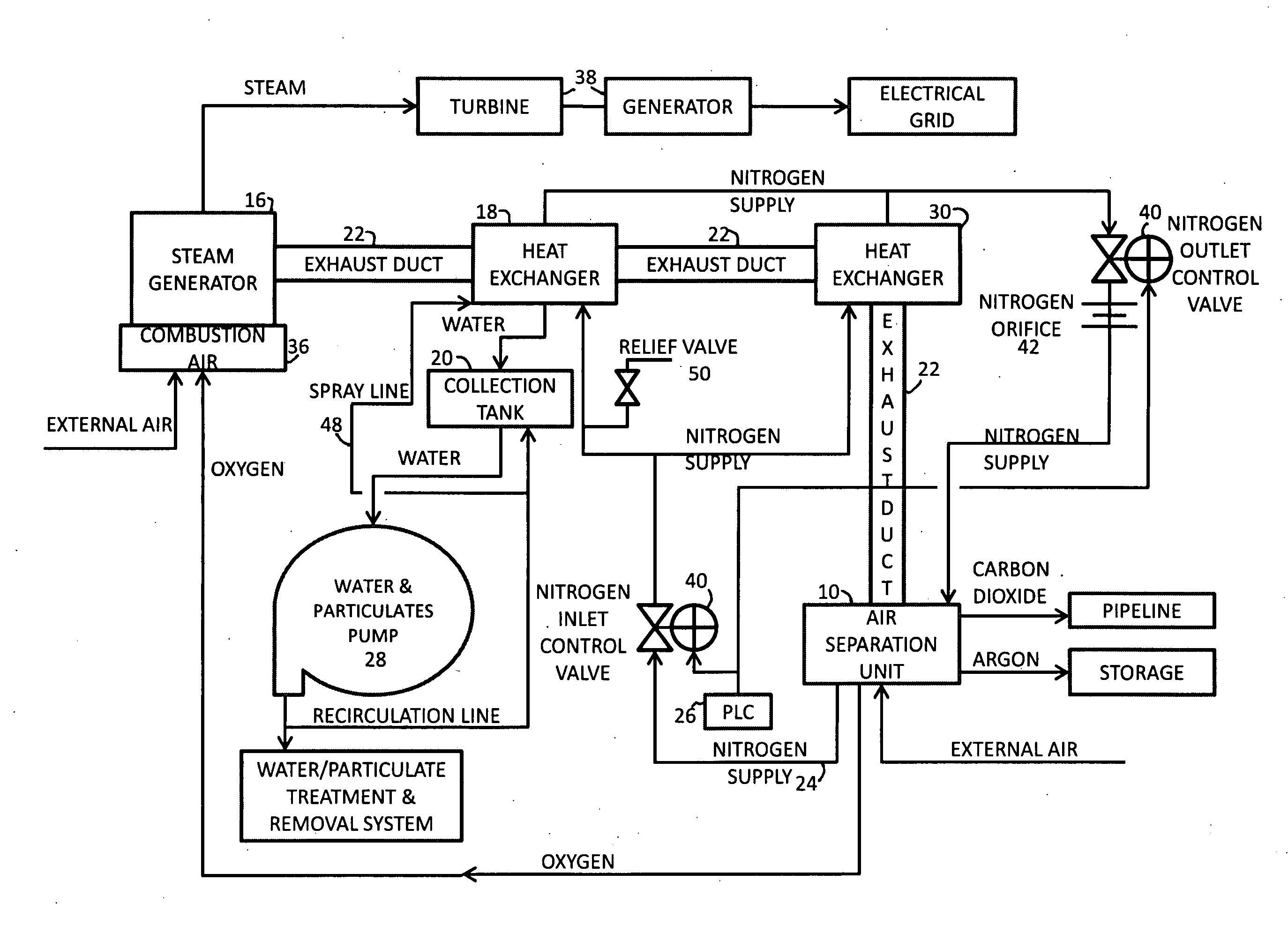
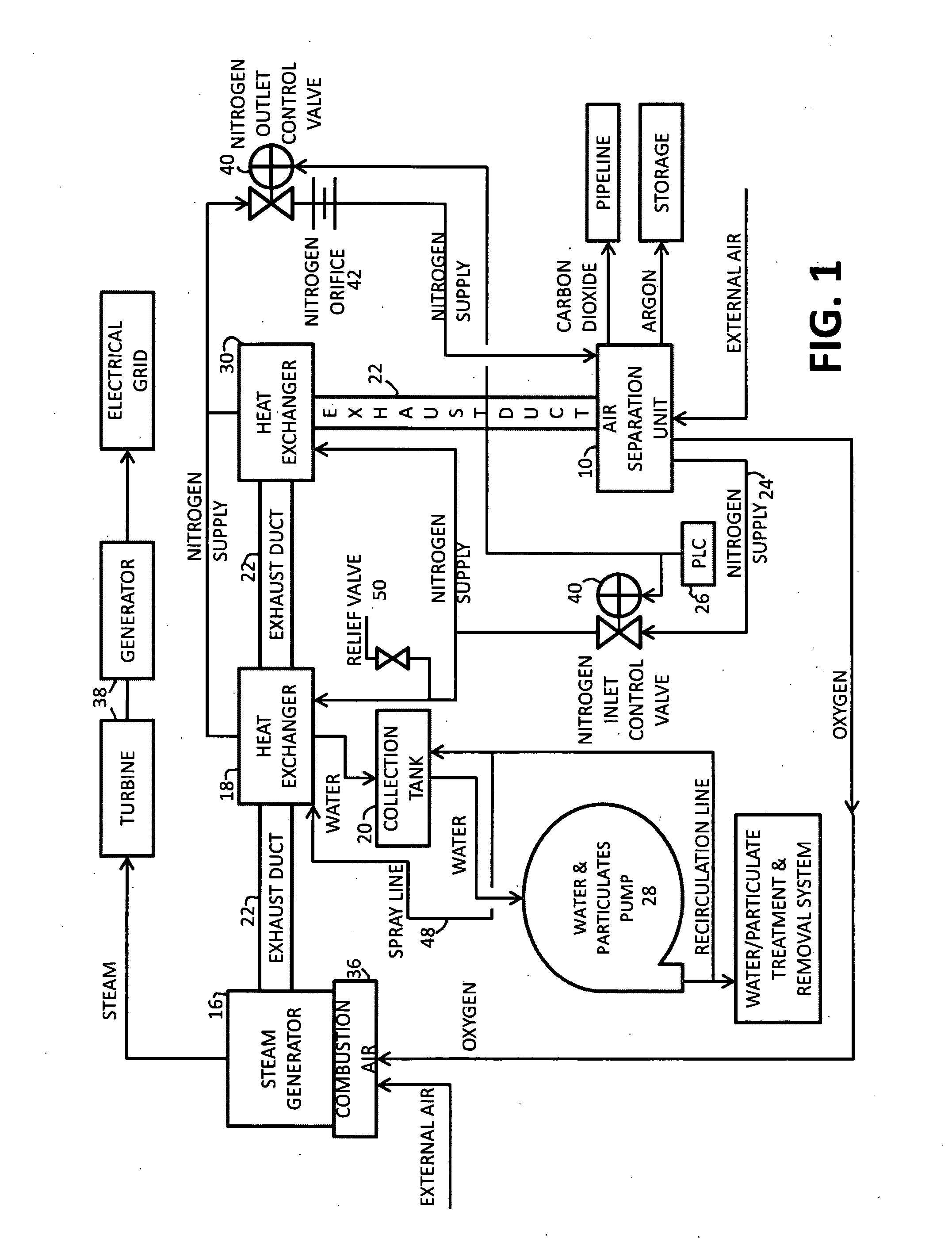
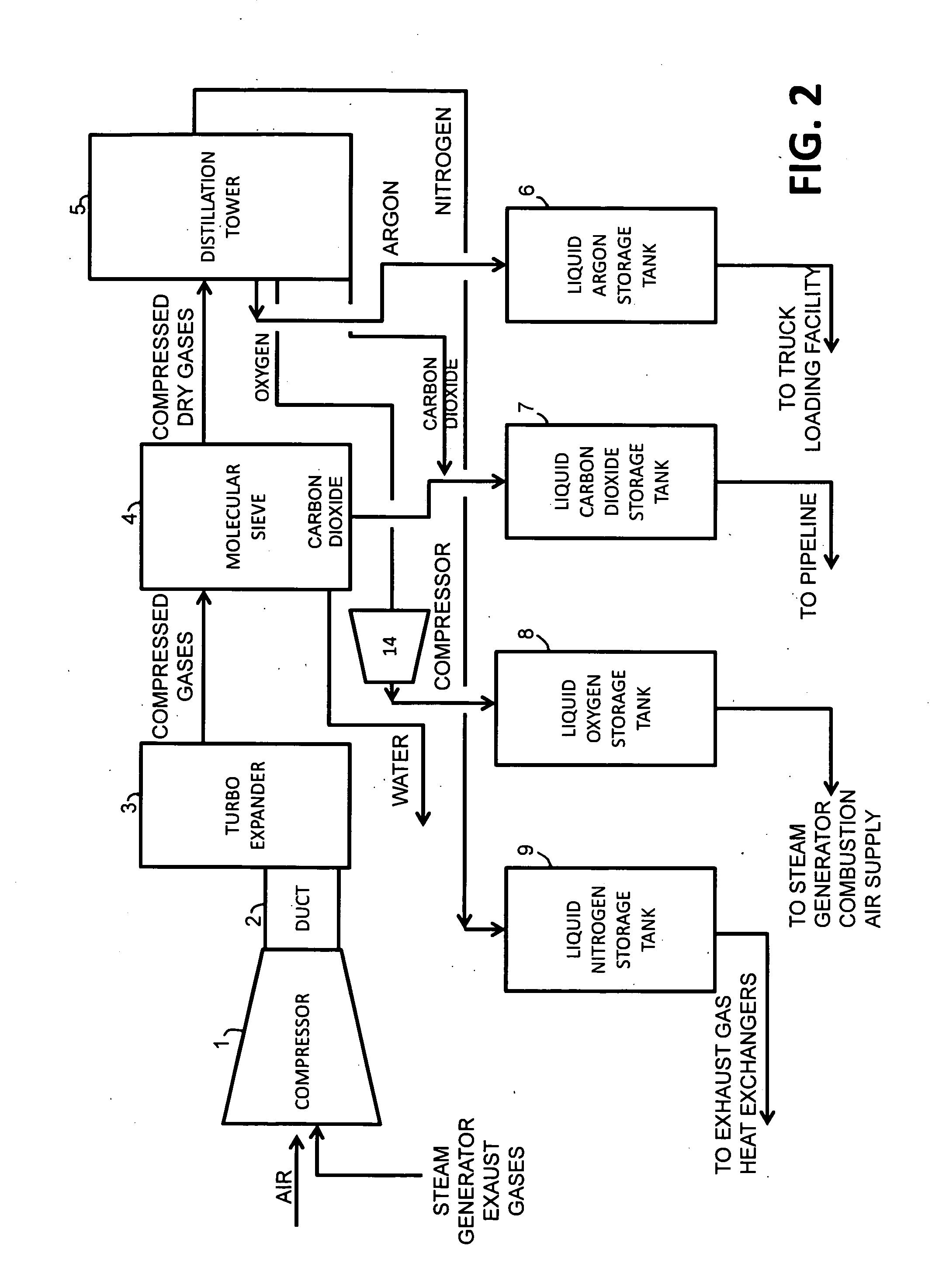
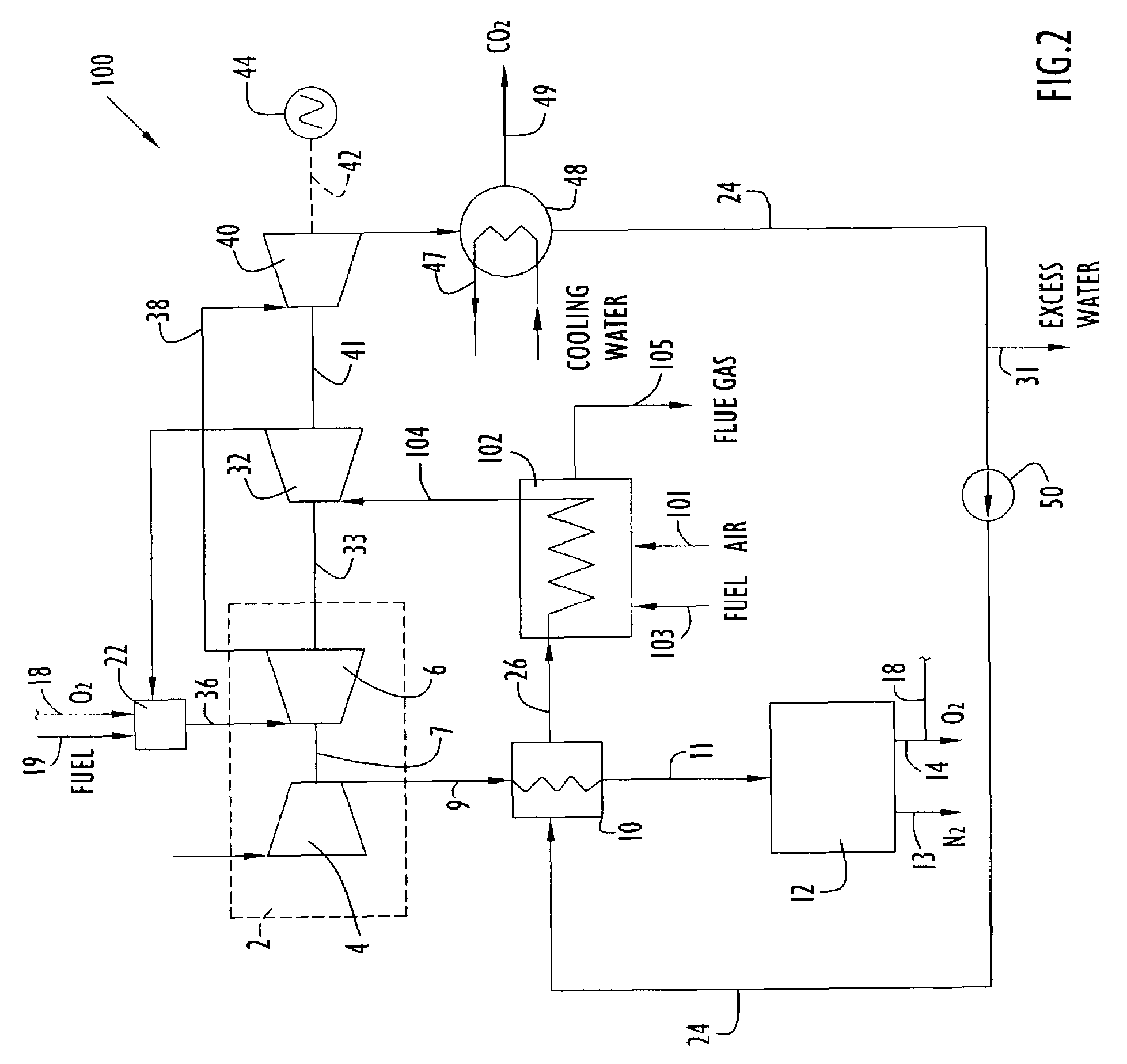
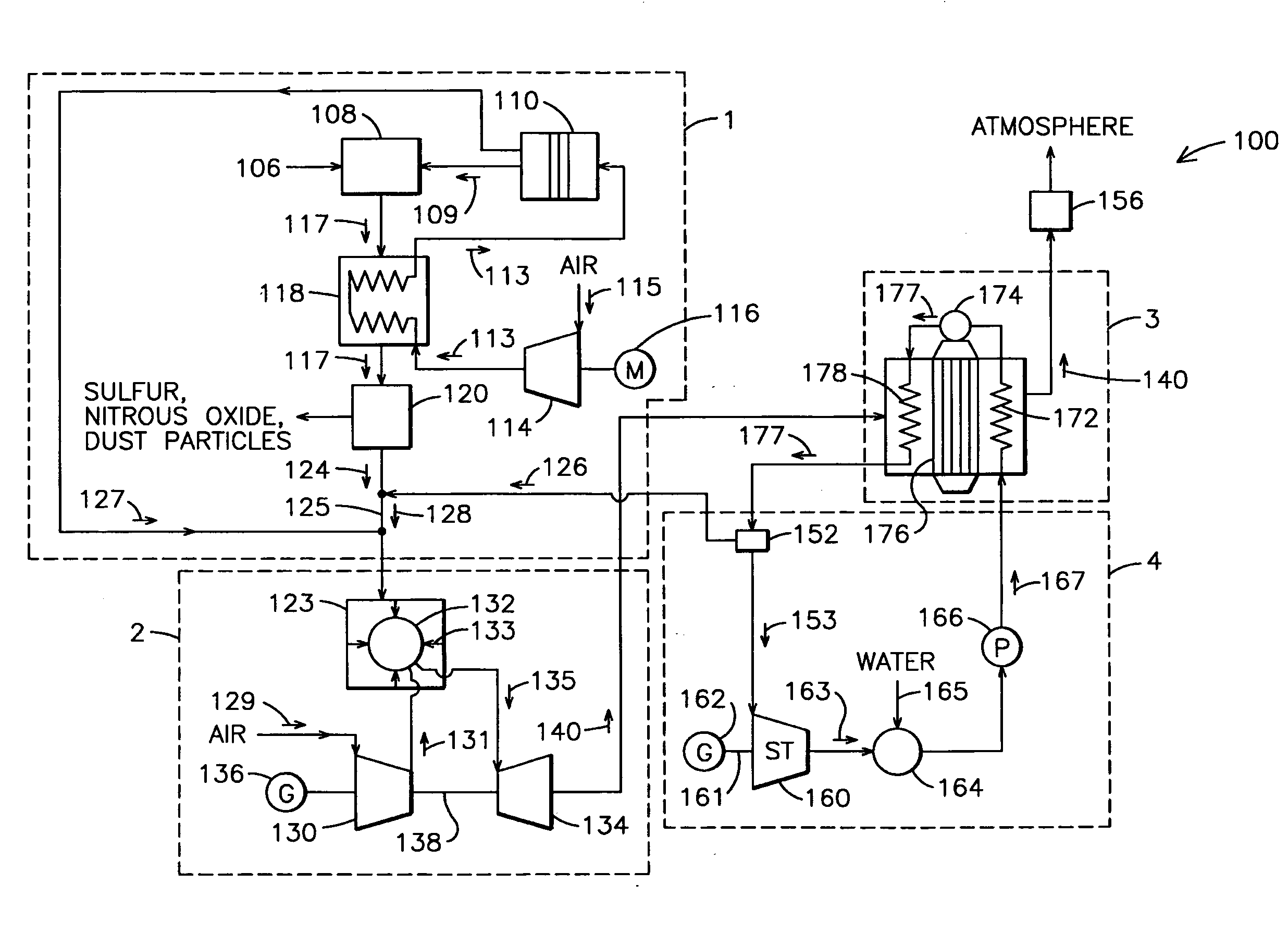
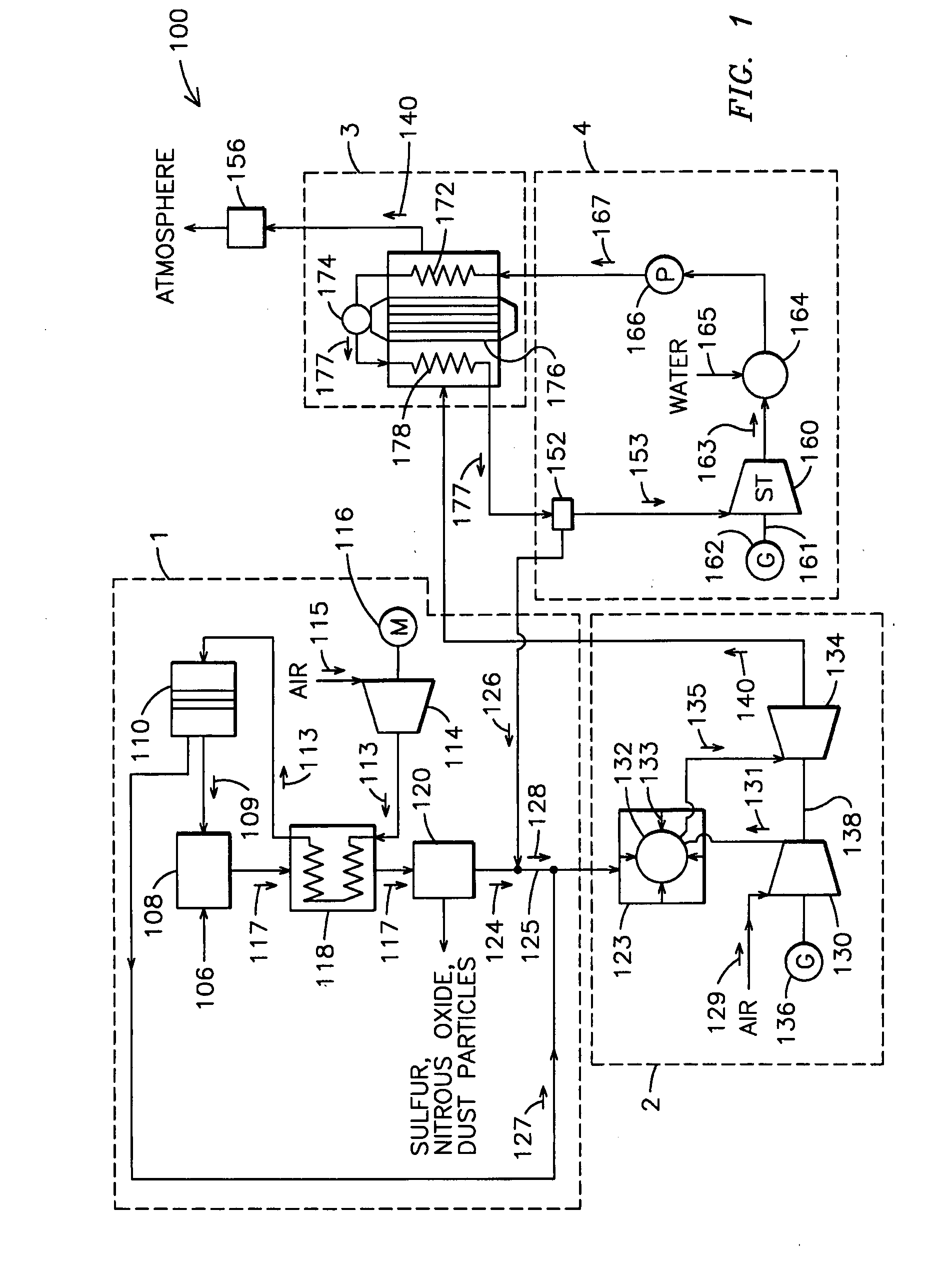
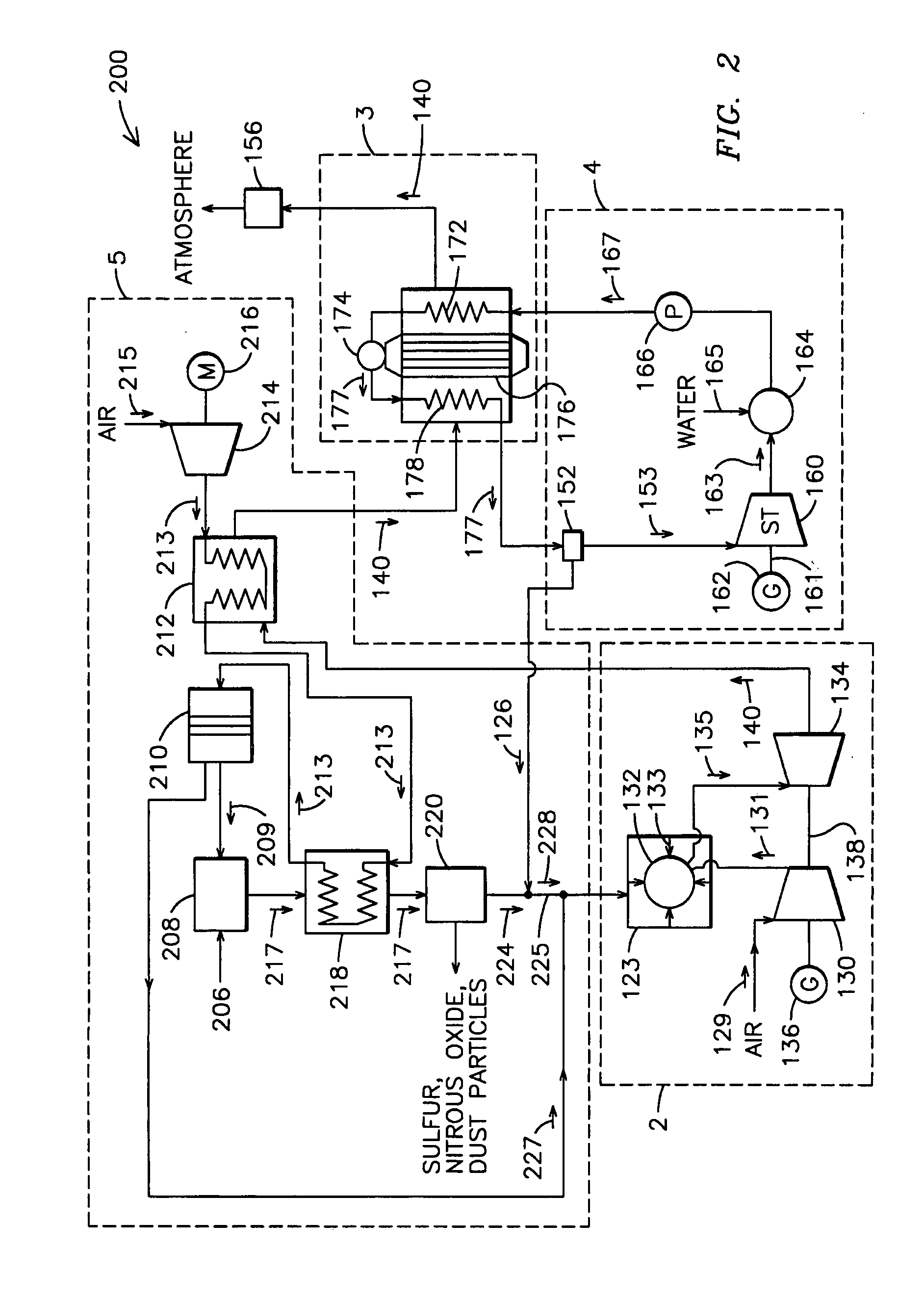
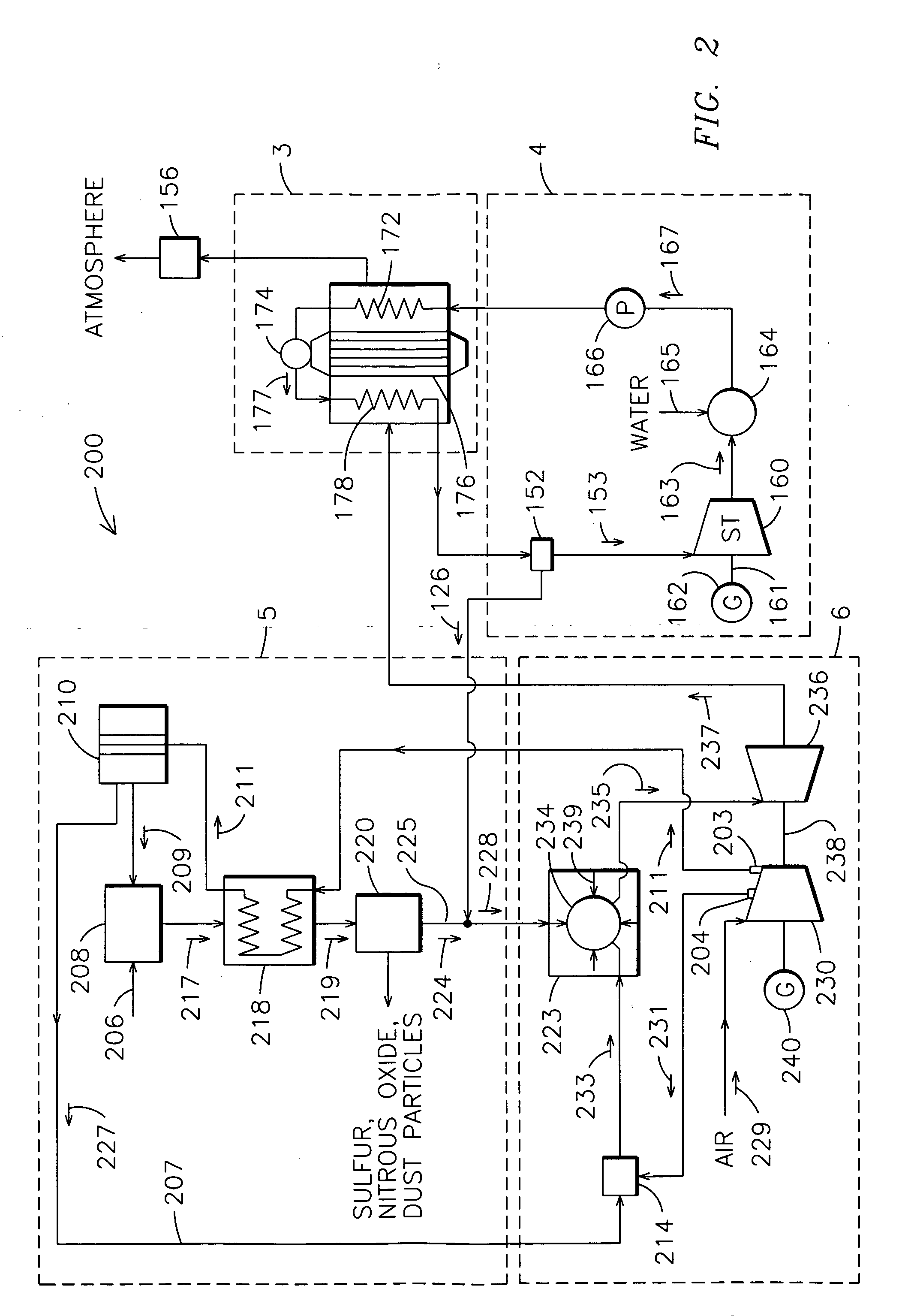
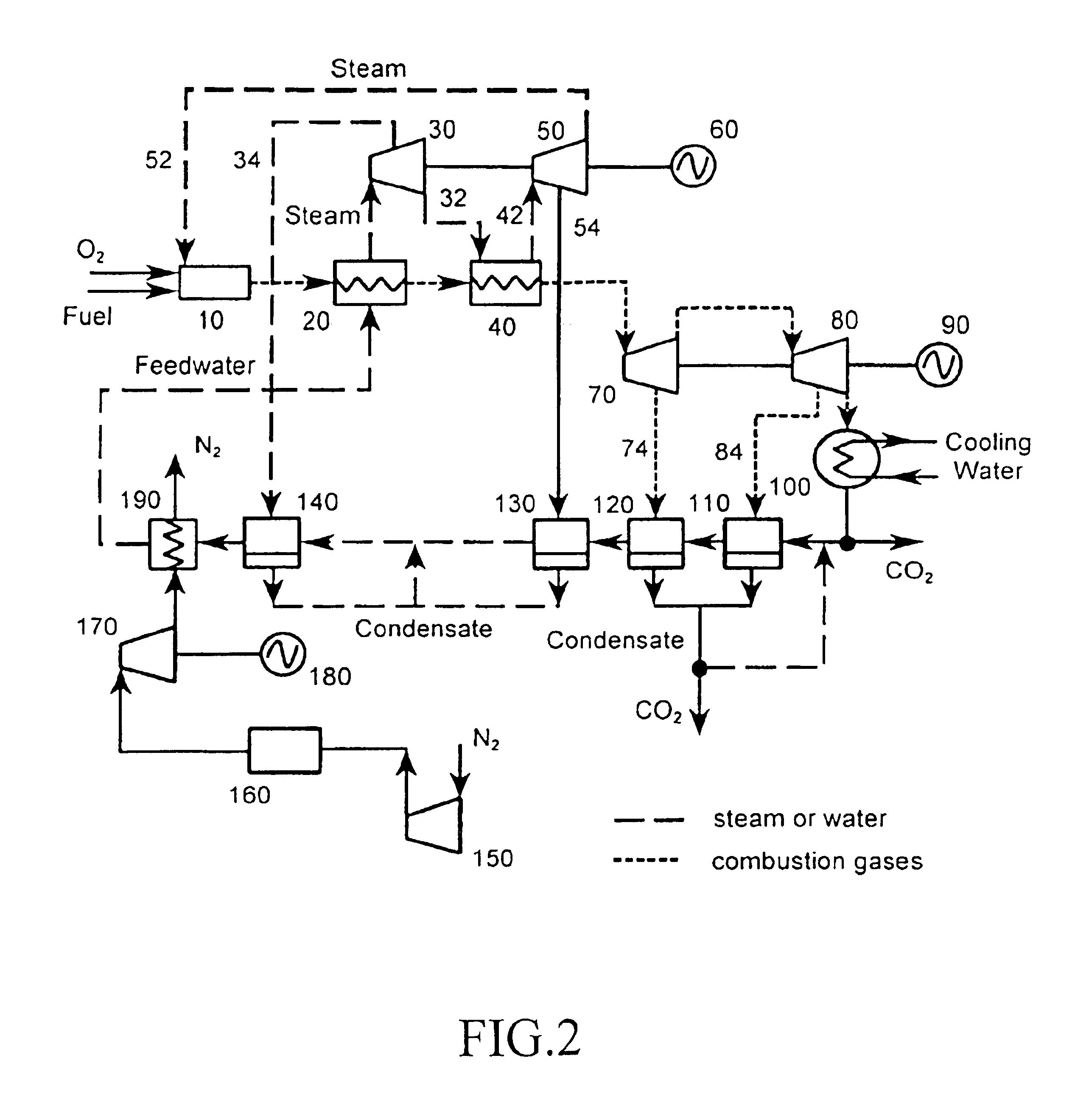
A power plant including an air separation unit (ASU) arranged to separate nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon from air and produce a stream of substantially pure liquid oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and argon; a steam generator, fired or unfired, arranged to combust a fuel, e.g., natural gas, liquefied natural gas, synthesis gas, coal, petroleum coke, biomass, municipal solid waste or any other gaseous, liquid or solid fuel in the presence of air and a quantity of substantially pure oxygen gas to produce an exhaust gas comprising water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides and other trace gases, and a steam-turbine-generator to produce electricity, a primary gas heat exchanger unit for particulate / acid gas / moisture removal and a secondary heat exchanger arranged to cool the remainder of the exhaust gases from the steam generator. Exhaust gases are liquefied in the ASU thereby recovering carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides, oxygen, and all other trace gases from the steam generator exhaust gas stream. The cooled gases are liquefied in the ASU and separated for sale or re-use in the power plant. Carbon dioxide liquid is transported from the plant for use in enhanced oil recovery or for other commercial use. Carbon dioxide removal is accomplished in the ASU by cryogenic separation of the gases, after directing the stream of liquid nitrogen from the air separation unit to the exhaust gas heat exchanger units to cool all of the exhaust gases including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur oxides, and other trace gases.
Owner:TRIENCON SERVICES
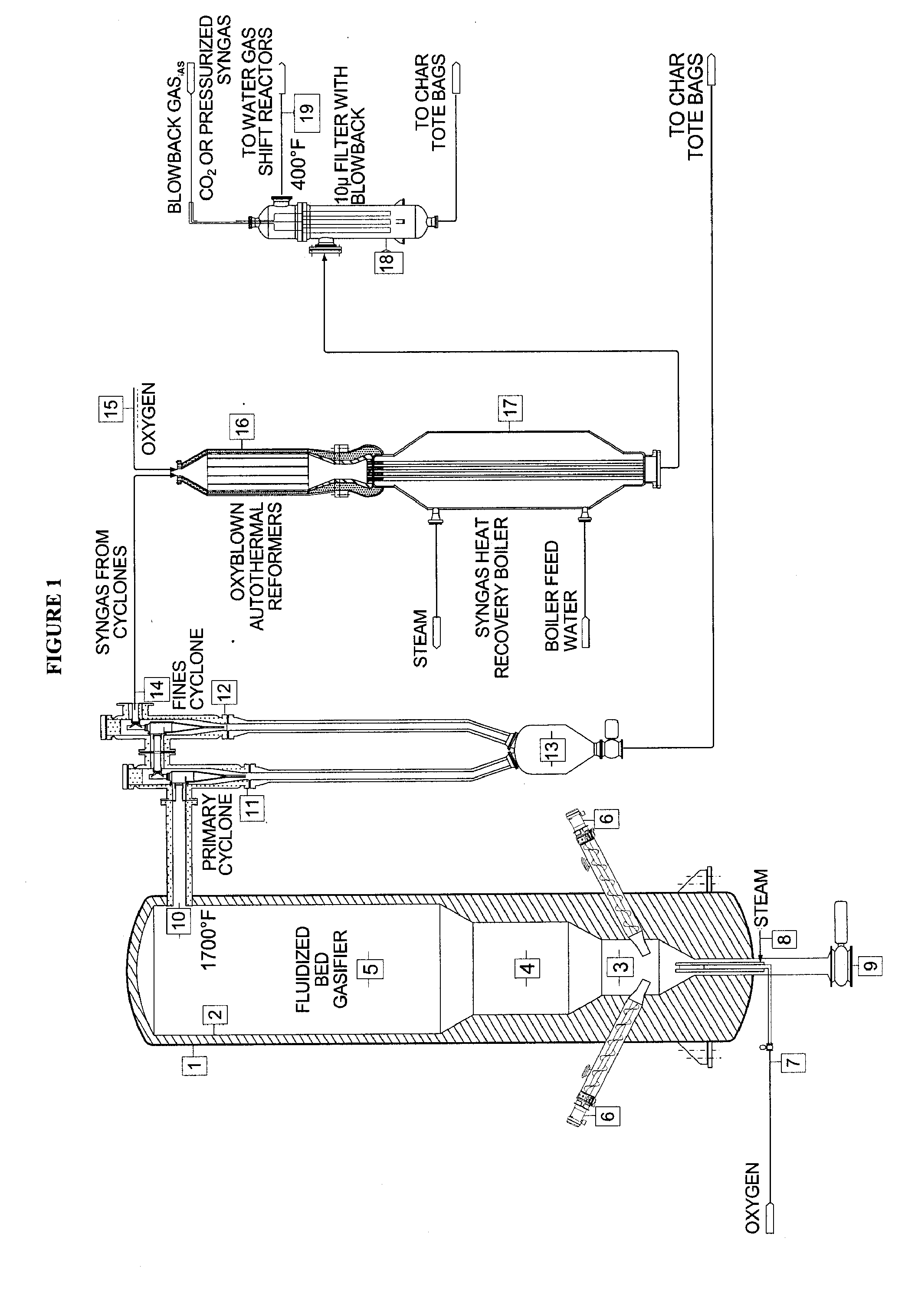
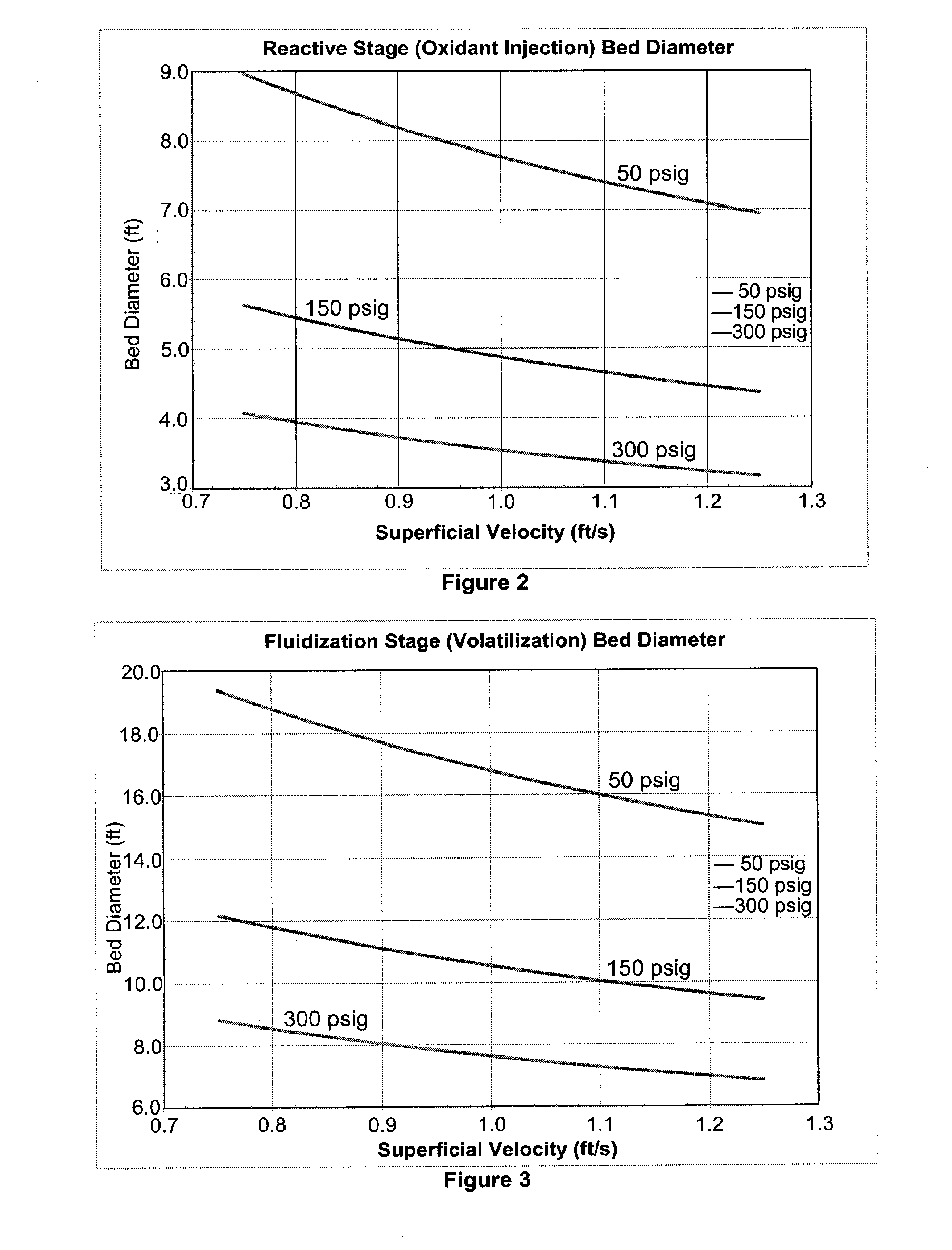
Method for converting biomass into synthesis gas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier followed by an oxyblown autothermal reformer to reduce methane and tars
InactiveUS20100040510A1Lower Level RequirementsGasifier mechanical detailsCombustible gas catalytic treatmentSyngasFluidized bed gasifier
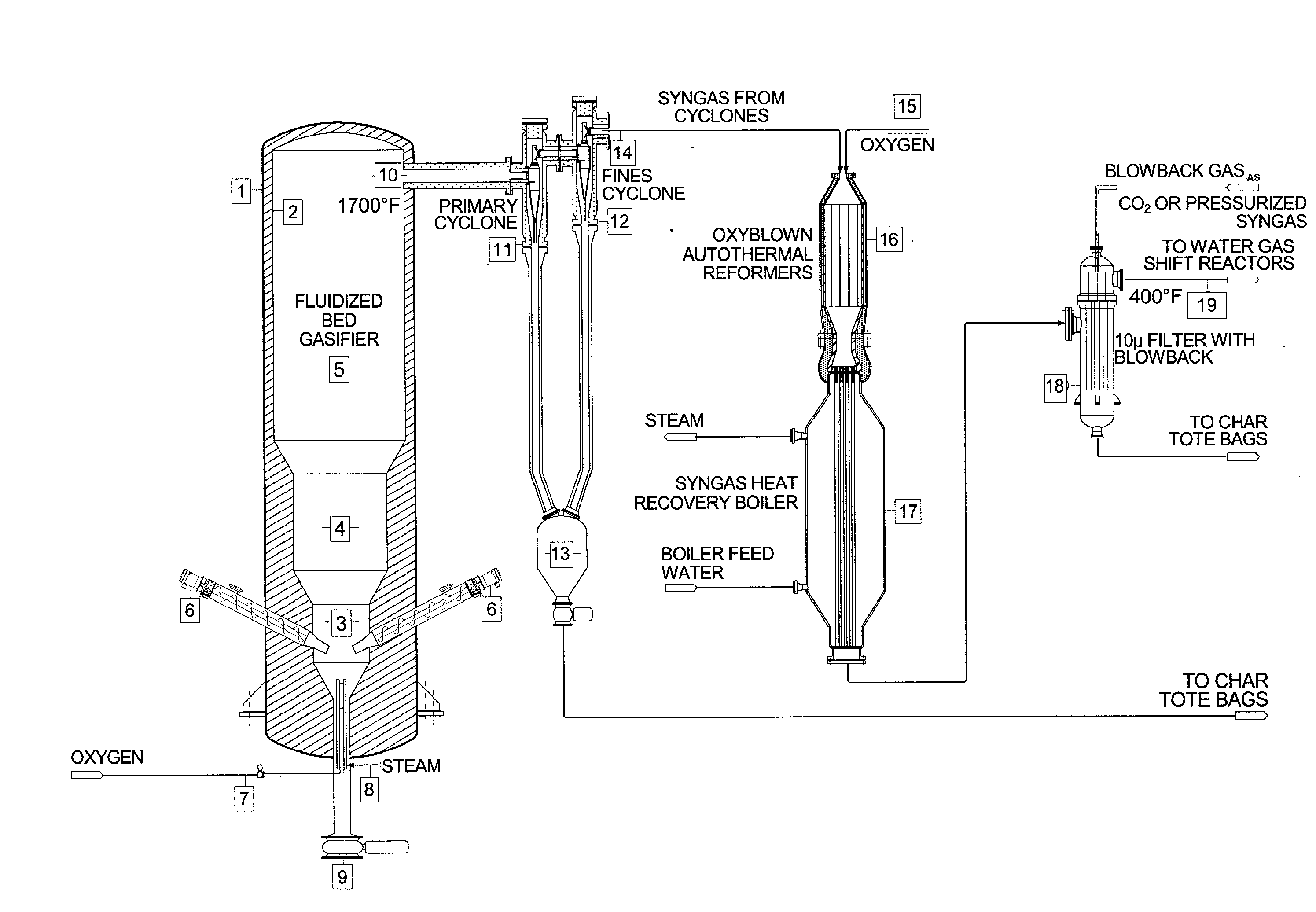
The invention provides systems and methods for converting biomass into syngas using a pressurized multi-stage progressively expanding fluidized bed gasifier to eliminate or reduce the formation of methane, volatiles such as BTX, and tars. The gasifier may include a reactive stage that may receive a biomass feed through a feed line and oxygen through an oxygen feed line. The gasifier may also include a fluidized bed section that may be configured to receive the reaction products from the first stage, mix them and perform fluidized bed activity. A gasifier may also have a disengagement section that may be configured to separate fluidized media and particulate matter from syngas product. A gasification system may also include oxyblown catalytic autothermal reactor and a cryogenic air separation unit.
Owner:SYNT
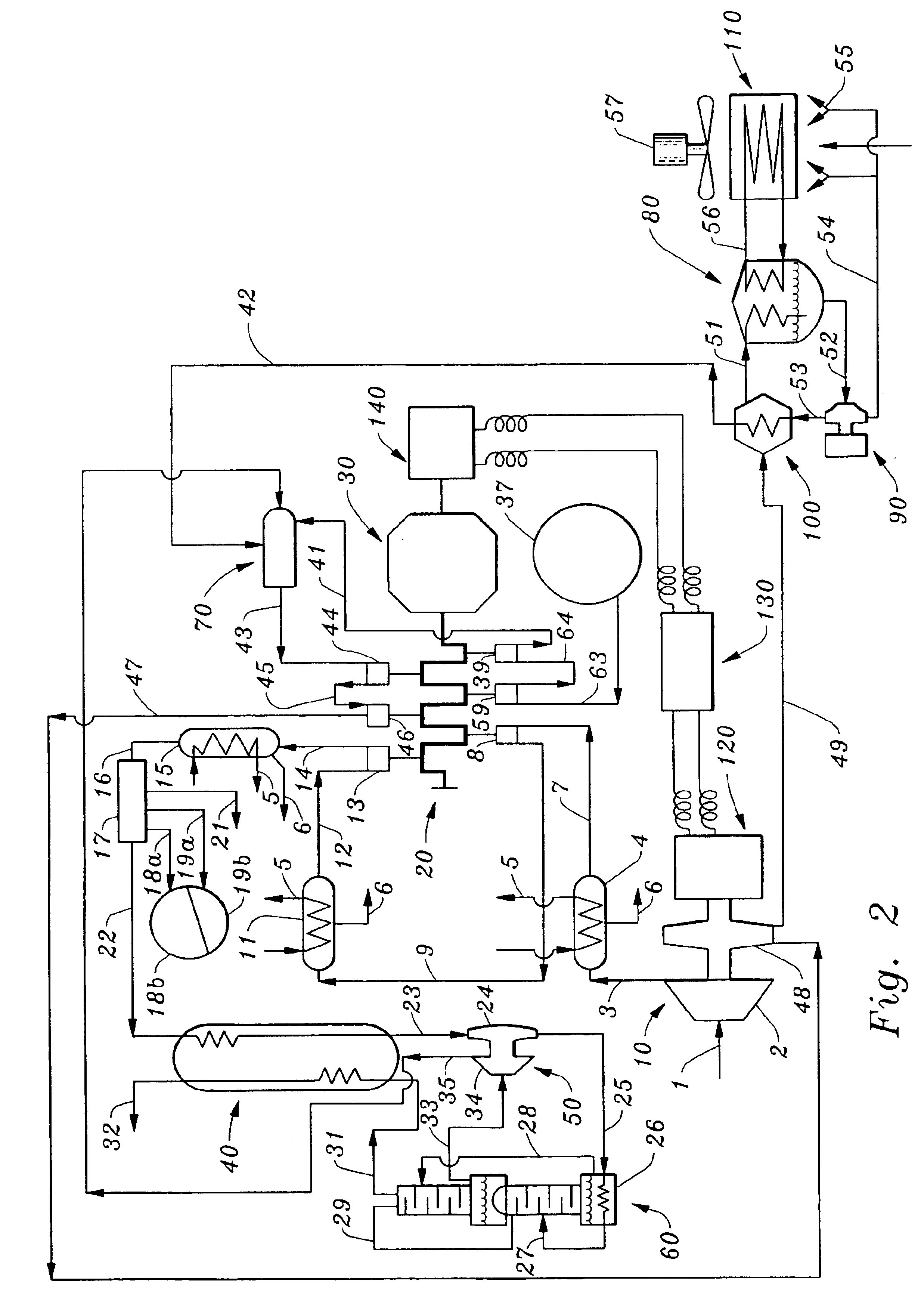
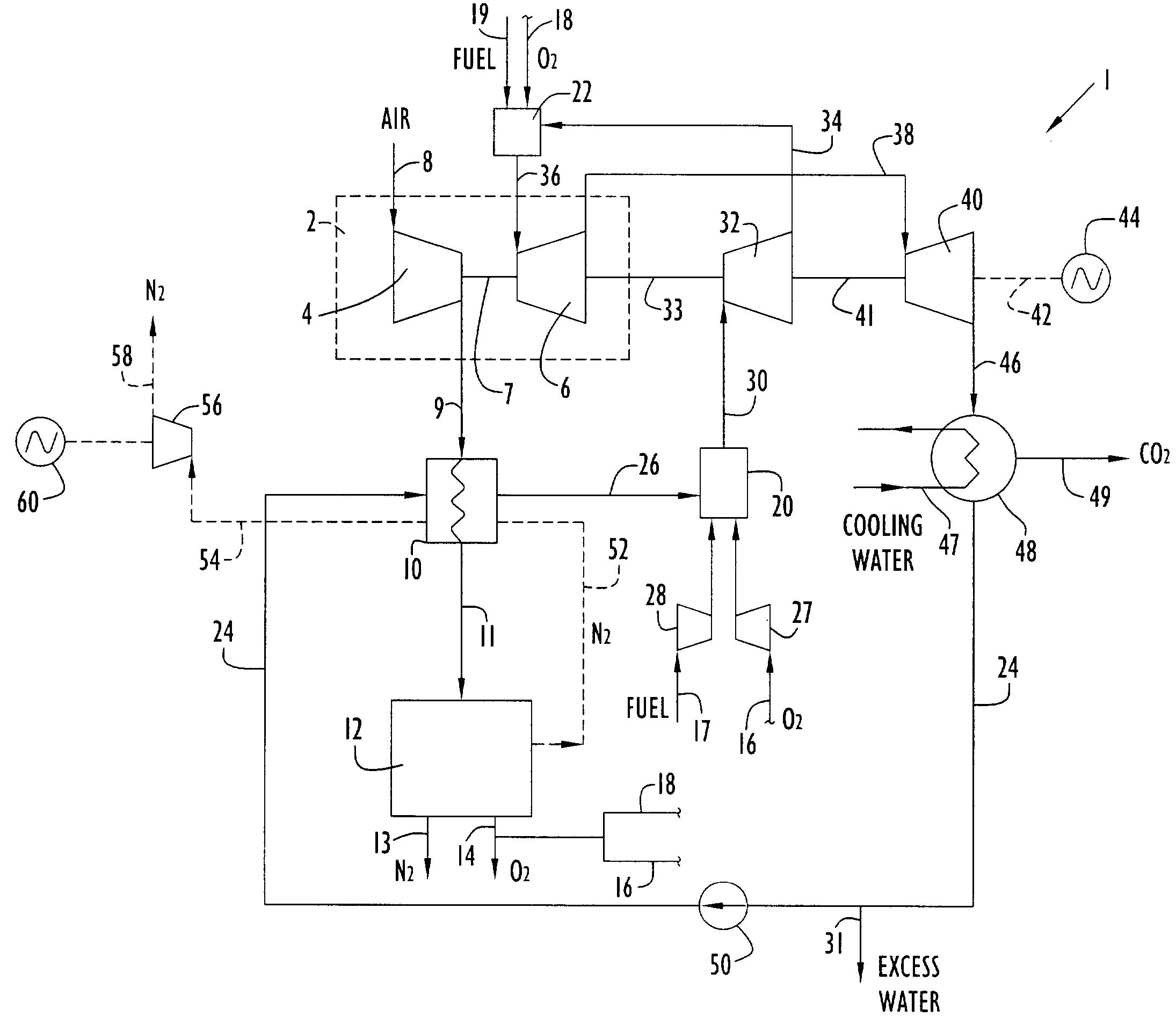
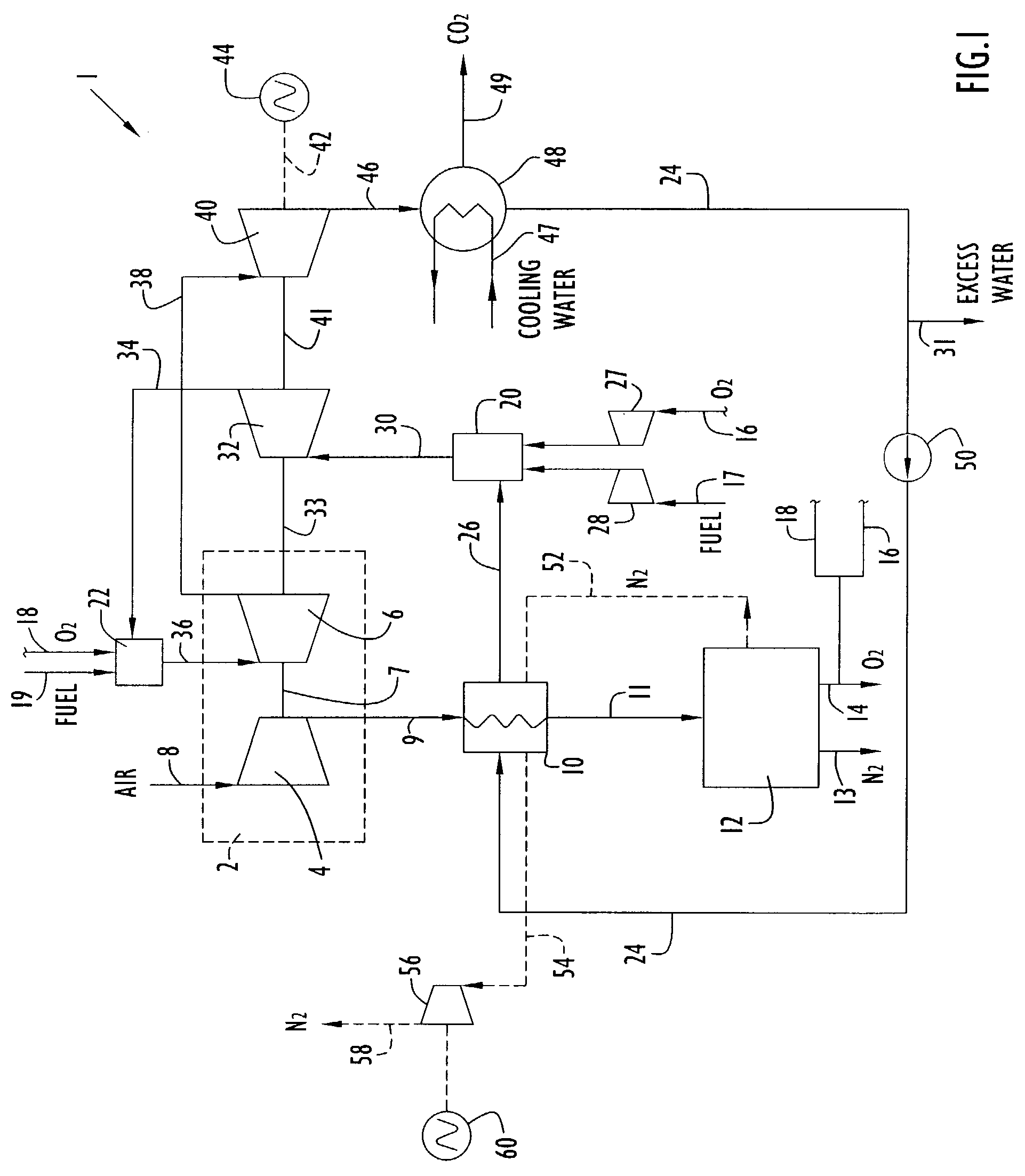
Integrated air separation and oxygen fired power generation system
An integrated air separation and oxygen fired power generation system includes an air separation unit and a gas turbine including an air compressor to provide compressed air for the air separation unit. The system further includes a gas turbine expander and at least one additional turbine to drive the air compressor, as well as at least one combustion unit to provide drive gas for expander and additional turbine(s). A portion of oxygen produced by the air separation unit is delivered to the combustor(s) to facilitate production of drive gas for use by the expander and additional turbine(s). Turbine inlet temperatures are controlled by recycling water or steam to the combustor(s).
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Method and plant or increasing oil recovery by gas injection
A method and a plant for simultaneous production of a gas for injection into an oil field and production of methanol, dimethyl ether and / or other oxygenated hydrocarbons or production of higher hydrocarbons from natural gas is disclosed. An air separation unit (ATR) for production of pure nitrogen for injection and pure oxygen for production of synthesis gas (“syngas”) by authermal reformation of a natural gas is an essential part of the method and plant.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
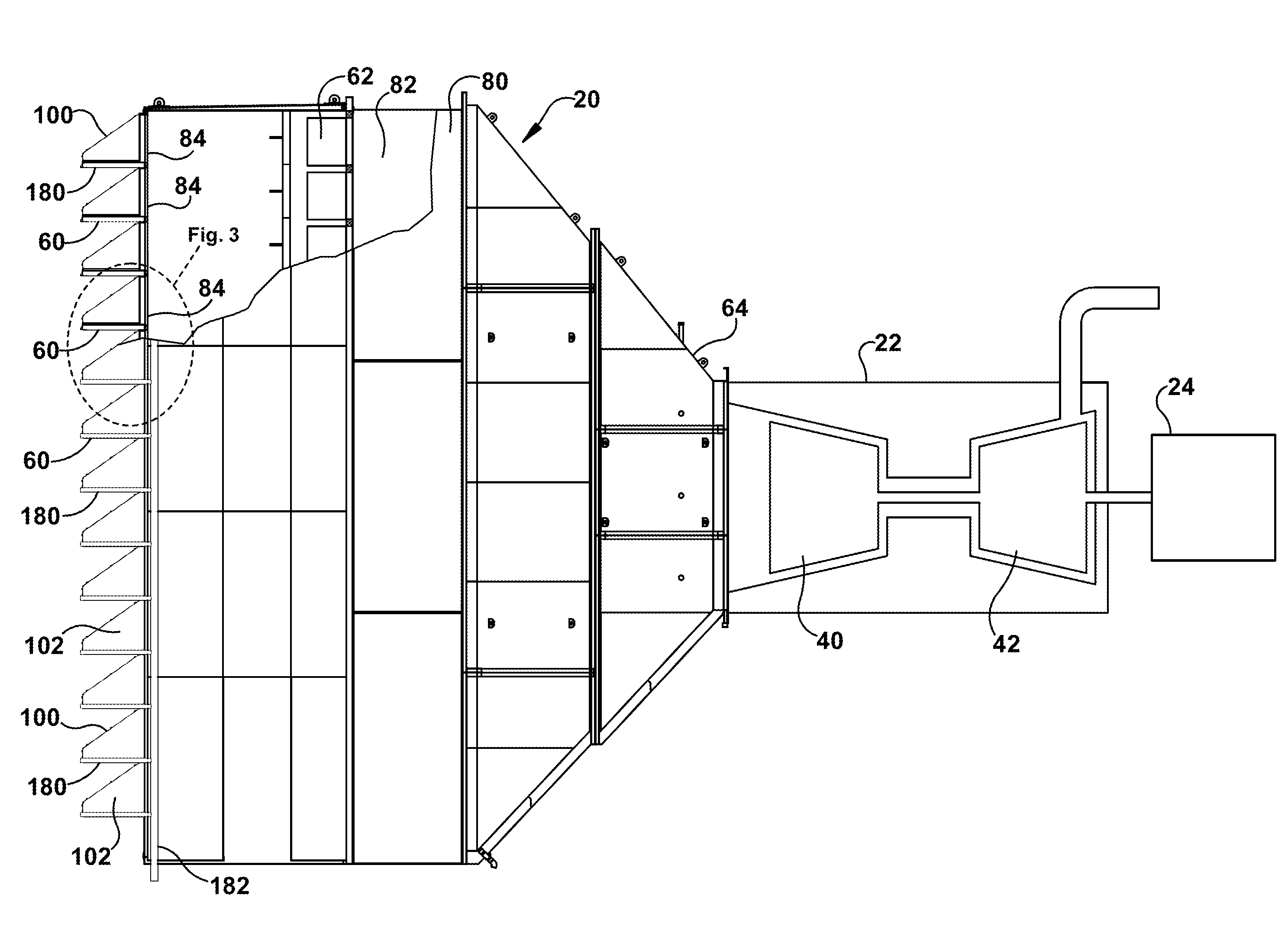
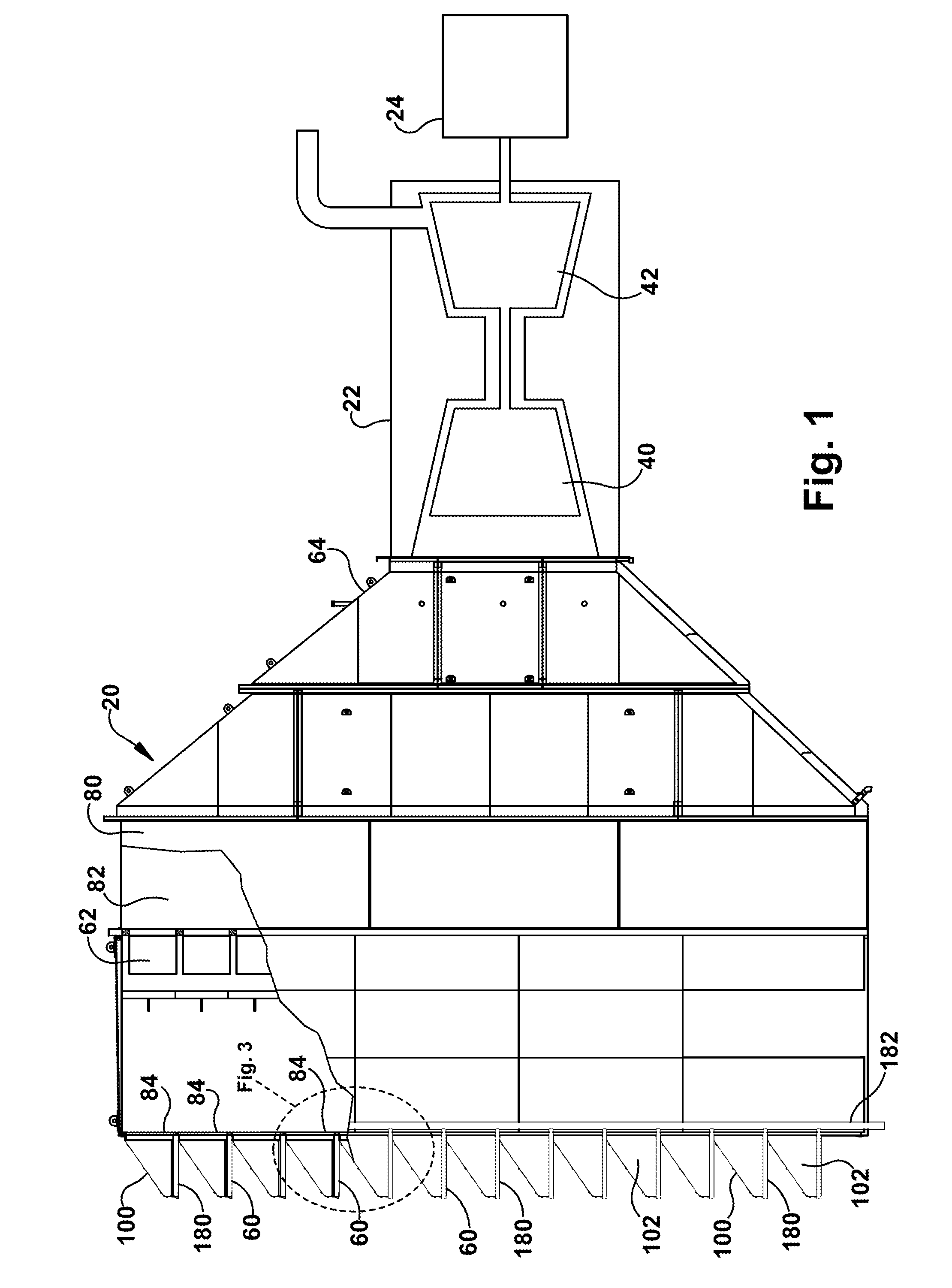
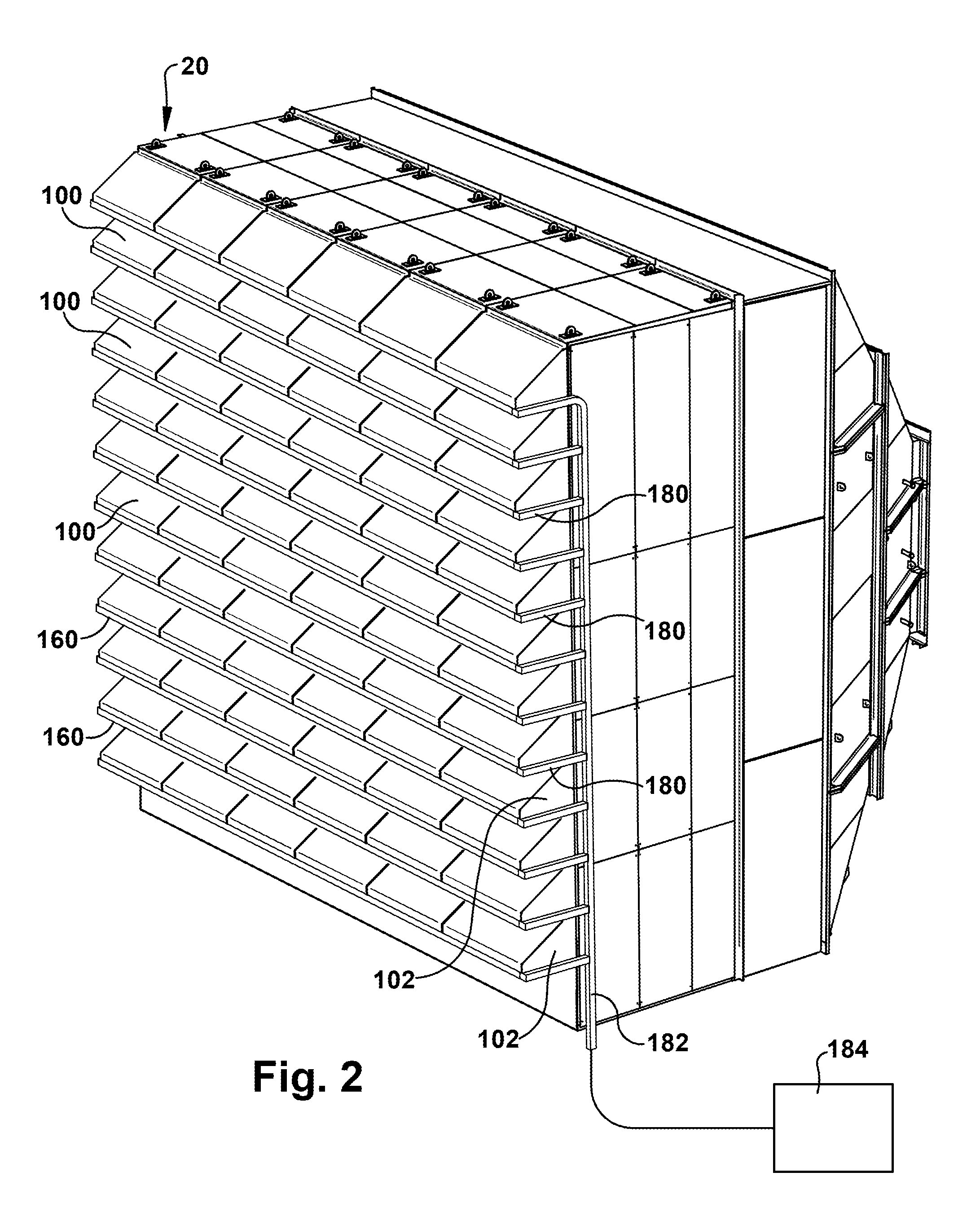
Moisture diversion apparatus for air inlet system and method
InactiveUS20120199001A1Avoid flowCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationAcute angleAir separation
A moisture diversion system for a gas turbine inlet. The moisture diversion system comprises a housing that is operably connected with a gas turbine and defines an opening through which air flows to the gas turbine. A hood is attached to the housing adjacent the opening. The hood has a surface disposed at an acute angle relative to horizontal. A device is disposed relative to the hood to separate moisture from air flowing through the device. Separated moisture is directed onto the hood. A gutter is disposed adjacent an edge of the hood to collect moisture from the hood. A conduit is fluidly connected with the gutter to conduct water away from the gutter and the opening in the housing to inhibit separated moisture from re-entering the air flow through the opening to the gas turbine.
Owner:BHA ALTAIR
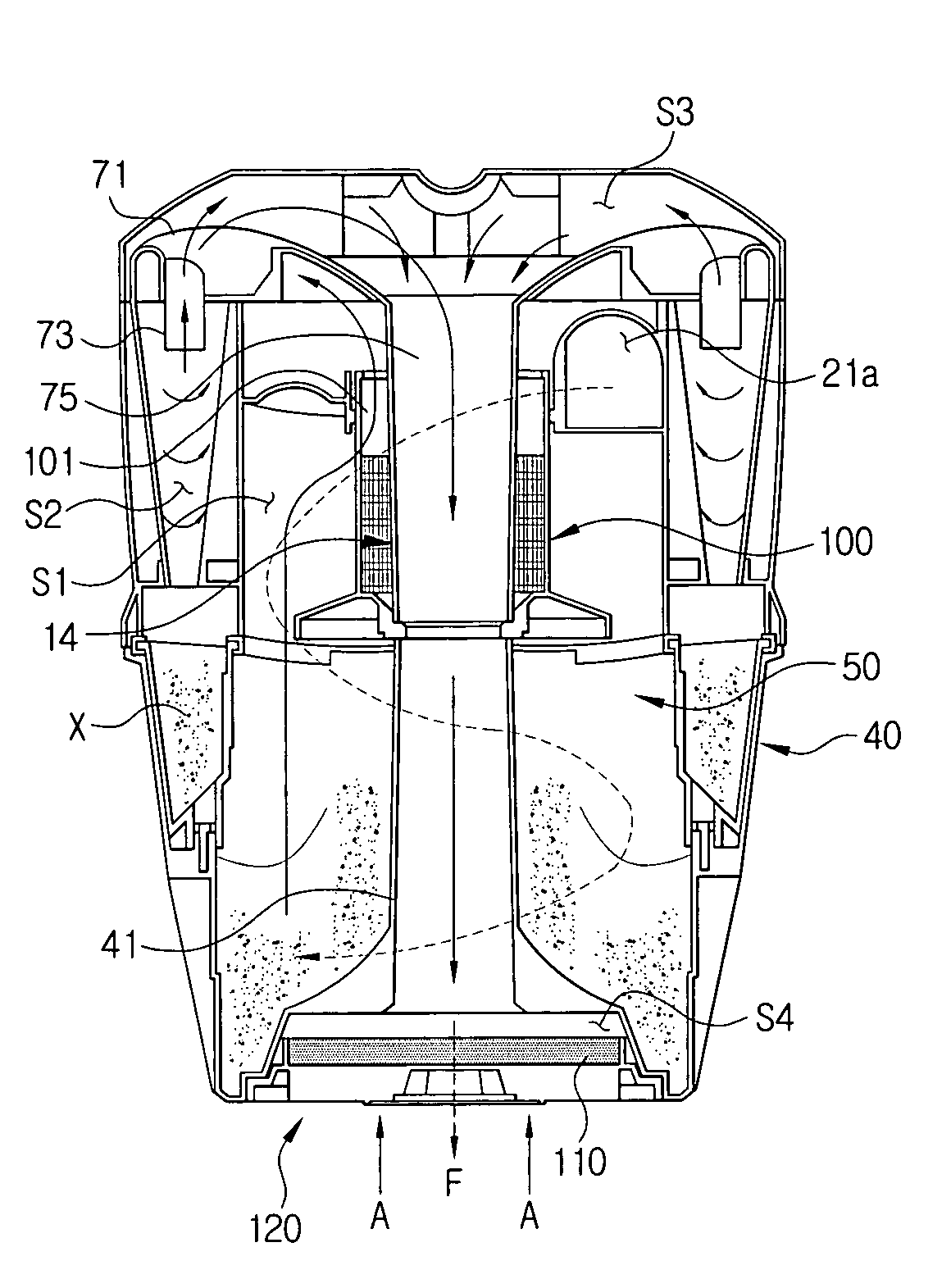
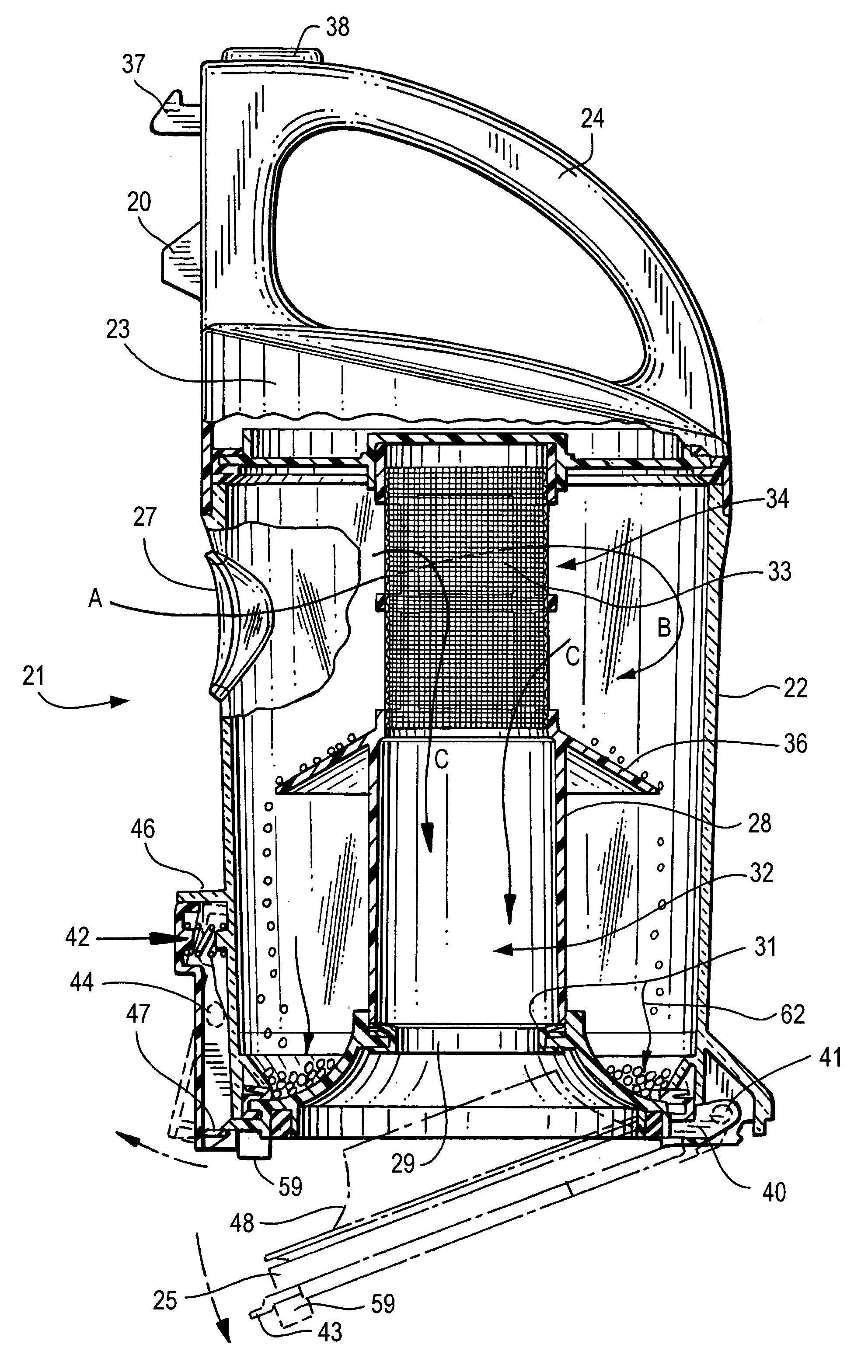
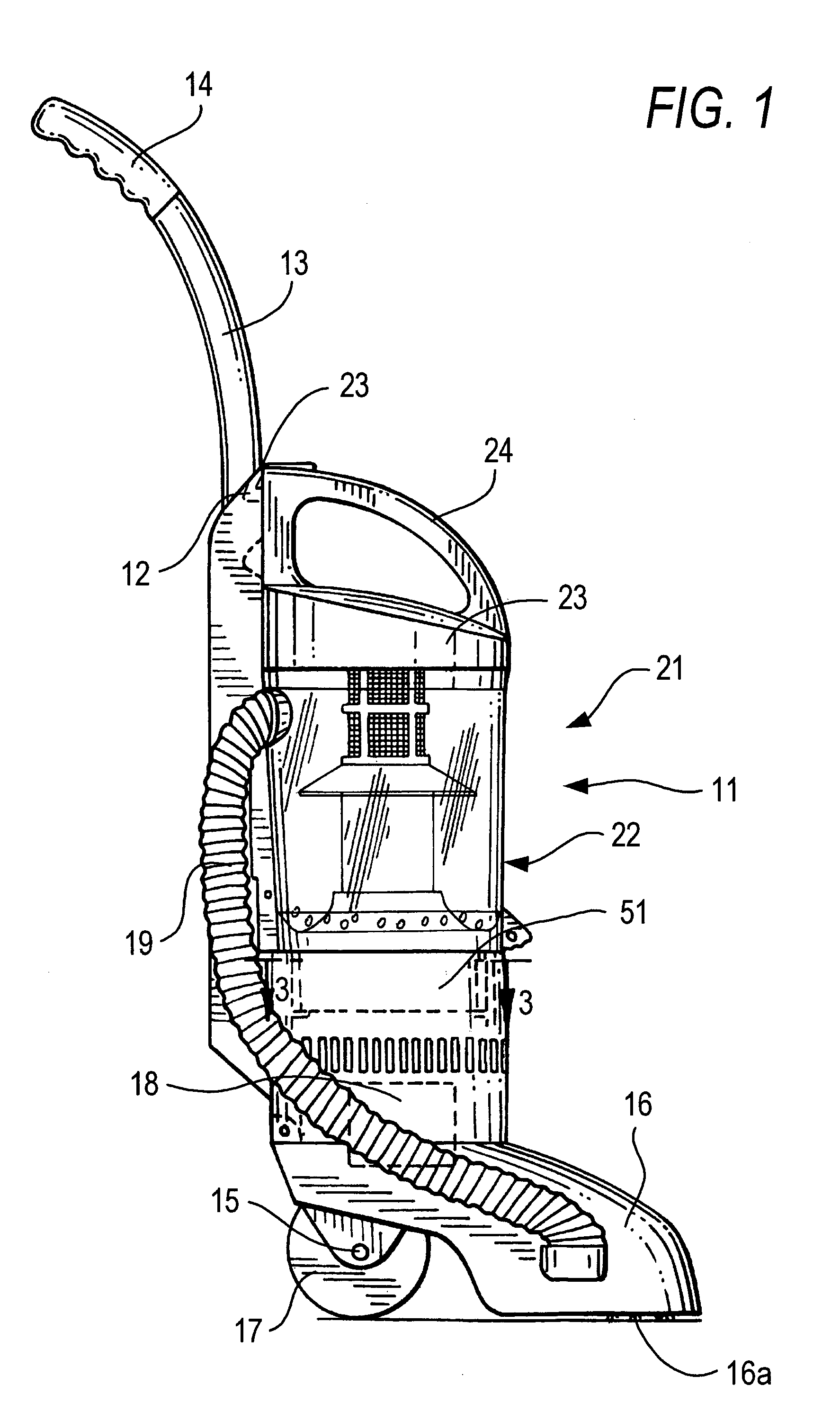
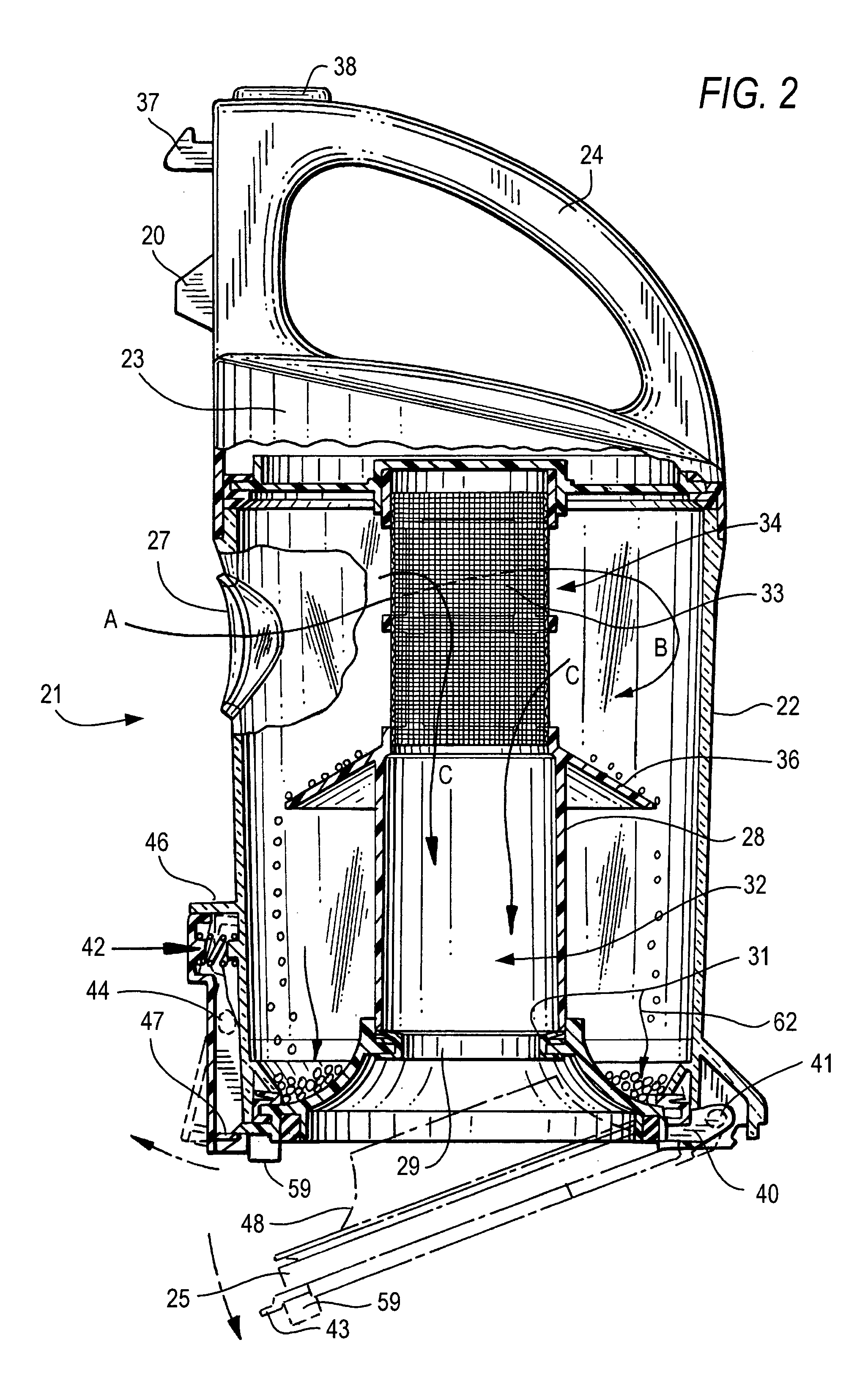
Compact cyclonic bagless vacuum cleaner
ActiveUS7341611B2Prevent reentrainmentEasy to separateCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentAir separationEngineering
A compact vacuum container includes a tangential air inlet at the upper portion, a closed top and a central outlet at the bottom having an improved air separation and dirt collection container is provided. A hollow central column with a skirt formed with a downwardly extending flange having an outer diameter is less than the inner diameter of the container, extends from the closed to the bottom outlet opening the upper position above the skirt is open and the lower portion of the column is solid. Dirt particles that separate from the air flow above the skirt drop to the lower portion below the skirt. Clean air then exits an open upper portion of the column to the suction source below the container. The air exiting the bottom of the column may pass through an radially pleated filter before being drawn into the vacuum source.
Owner:SHARKNINJA OPERATING LLC
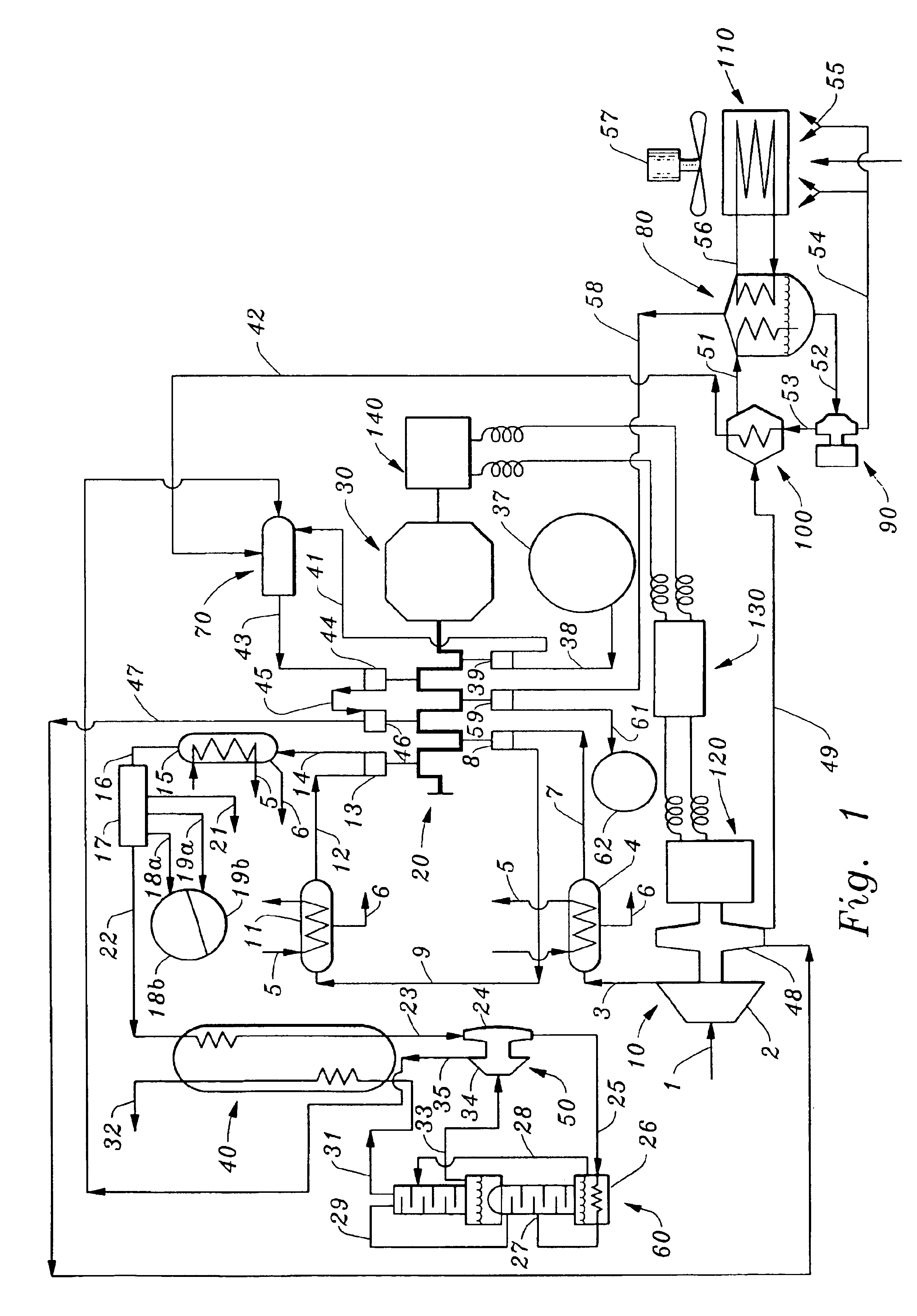
Compression stripping of flue gas with energy recovery
InactiveUS6898936B1Low costReduced Power RequirementsLiquid degasificationSteam regenerationWorking fluidWater vapor
A method of remediating and recovering energy from combustion products from a fossil fuel power plant having at least one fossil fuel combustion chamber, at least one compressor, at least one turbine, at least one heat exchanger and a source of oxygen. Combustion products including non-condensable gases such as oxygen and nitrogen and condensable vapors such as water vapor and acid gases such as SOX and NOX and CO2 and pollutants are produced and energy is recovered during the remediation which recycles combustion products and adds oxygen to support combustion. The temperature and / or pressure of the combustion products are changed by cooling through heat exchange with thermodynamic working fluids in the power generation cycle and / or compressing and / or heating and / or expanding the combustion products to a temperature / pressure combination below the dew point of at least some of the condensable vapors to condense liquid having some acid gases dissolved and / or entrained and / or directly condense acid gas vapors from the combustion products and to entrain and / or dissolve some of the pollutants while recovering sensible and / or latent heat from the combustion products through heat exchange between the combustion products and thermodynamic working fluids and / or cooling fluids used in the power generating cycle. Then the CO2, SO2, and H2O poor and oxygen enriched remediation stream is sent to an exhaust and / or an air separation unit and / or a turbine.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Air separation process integrated with gas turbine combustion engine driver
A method for the separation of a feed gas mixture comprising oxygen and nitrogen in which an oxidant gas and fuel are combusted in a combustion engine to generate shaft work and a hot exhaust gas, the feed gas mixture comprising oxygen and nitrogen is compressed, and the resulting compressed feed gas mixture is separated into two or more product gas streams with differing compositions. The shaft work of the combustion engine is utilized to provide at least a portion of the work required for compressing the feed gas mixture, one of the product gas streams by is heated by indirect heat exchange with the hot exhaust gas from the combustion engine, and the resulting heated product gas is work expanded to generate shaft work and yield an expanded product gas stream. The combustion engine may be a gas turbine combustion engine.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
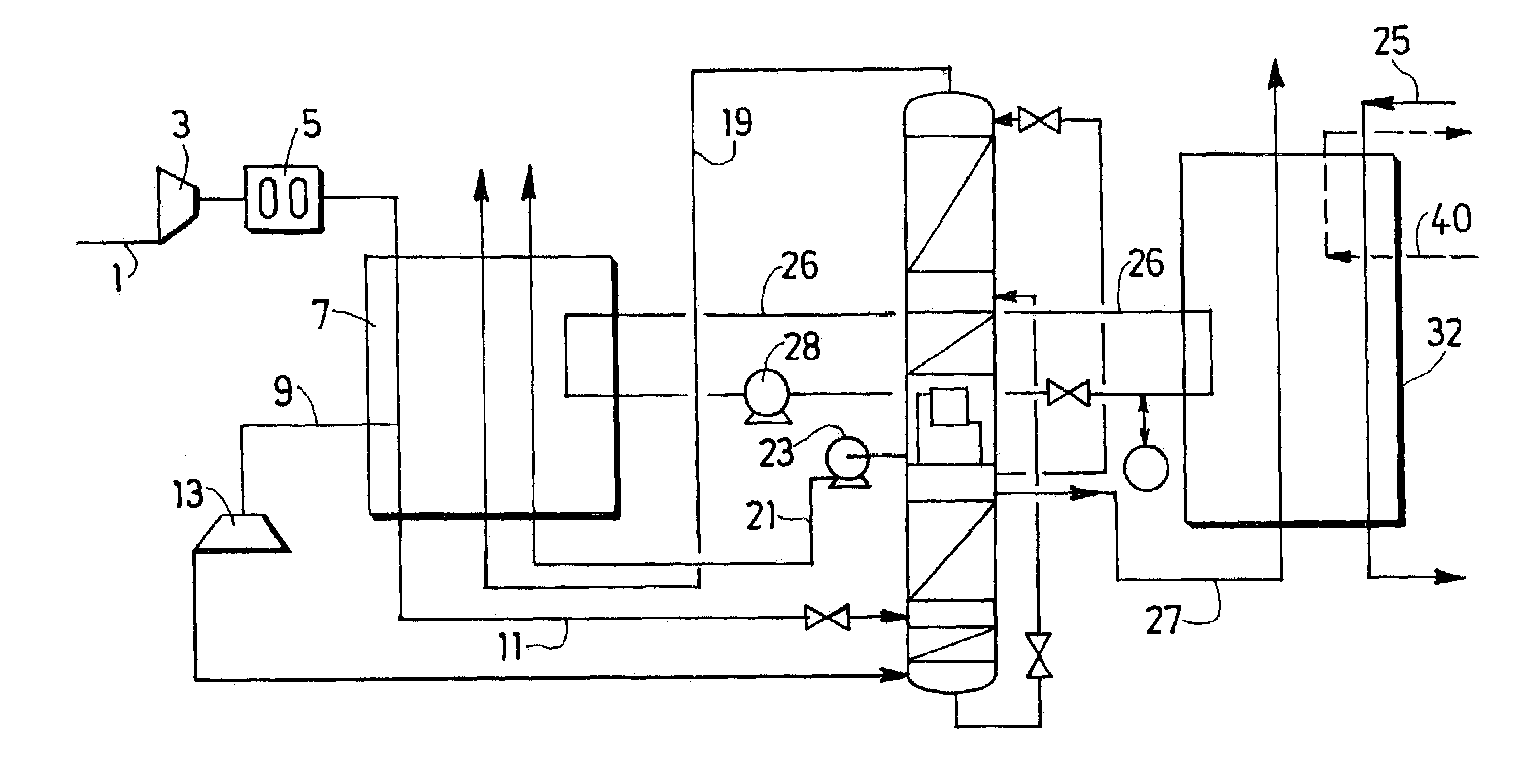
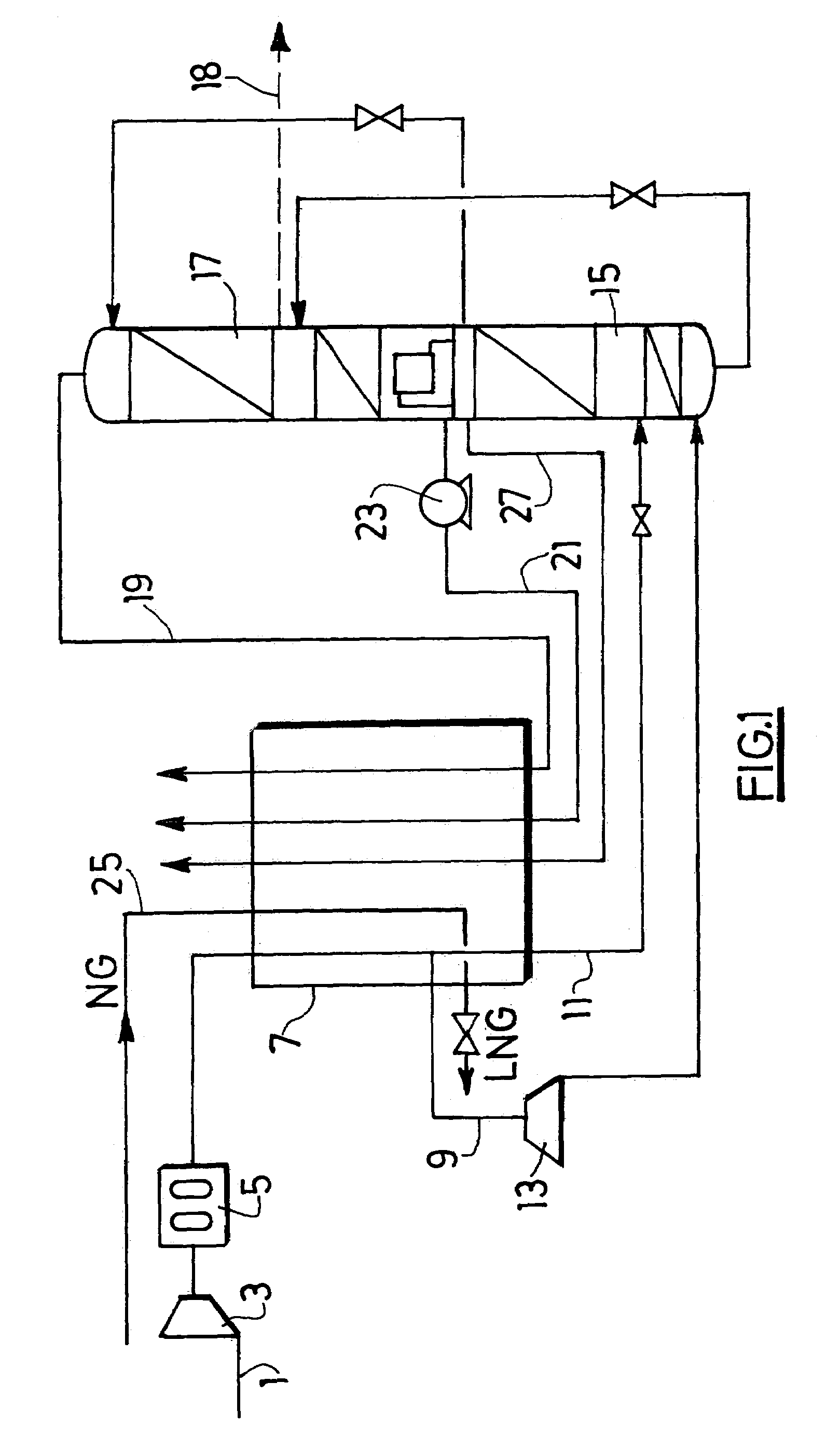
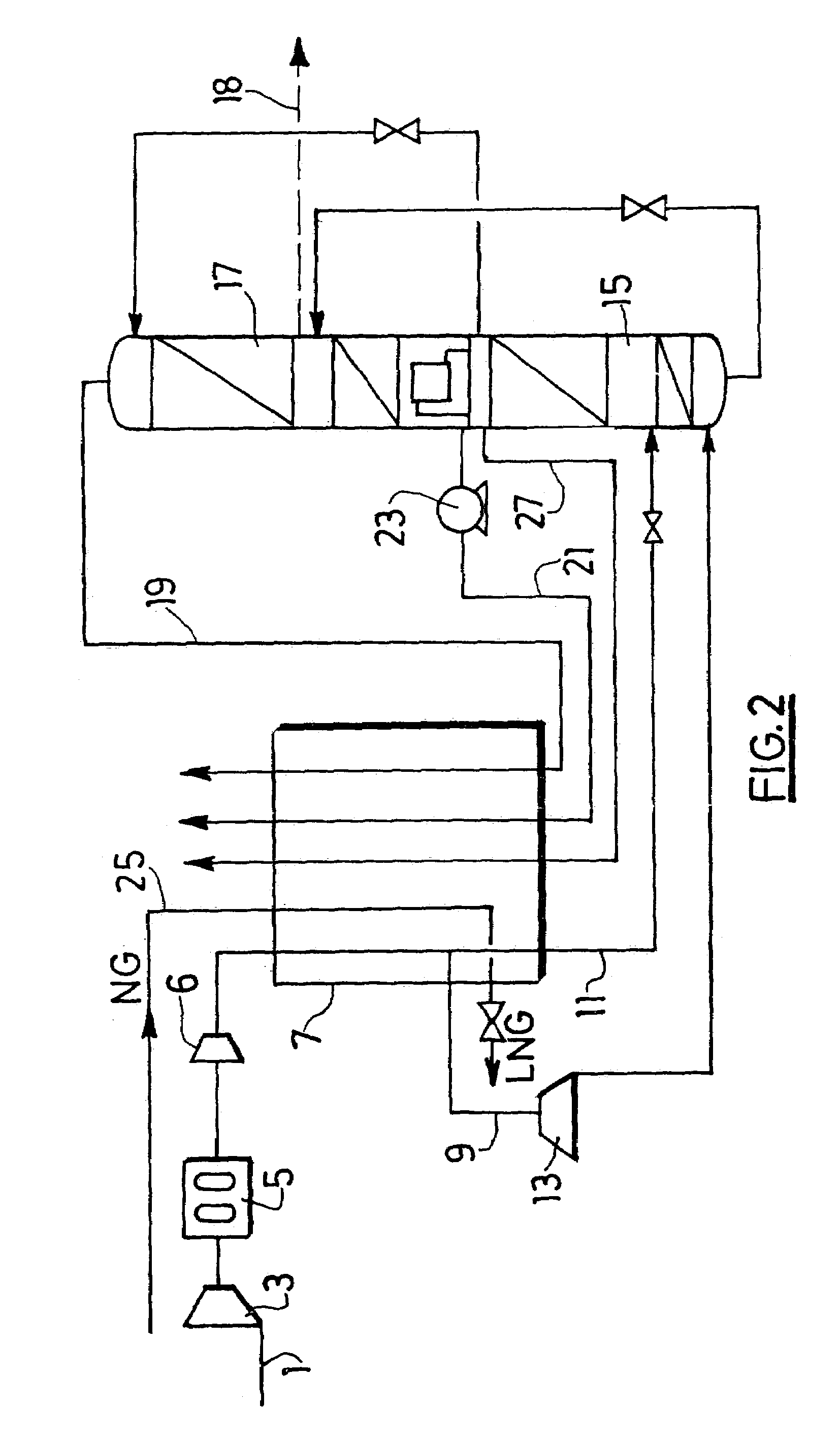
Combined air separation natural gas liquefaction plant
ActiveUS7143606B2Increase power consumptionIncrease the number ofSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnProcess engineering
In an integrated process and apparatus for the separation of air by cryogenic distillation and liquefaction of natural gas in which at least part of the refrigeration required to liquefy the natural gas is derived from at least one cryogenic air distillation plant comprising a main heat exchanger (7) and distillation columns (15, 17), wherein the natural gas (25) liquefies by indirect heat exchange in a heat exchanger (7, 32, 34) with a cold fluid (21, 26), the cold fluid being sent to the heat exchanger at least partially in liquid form and undergoing at least a partial vaporisation in the heat exchanger.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
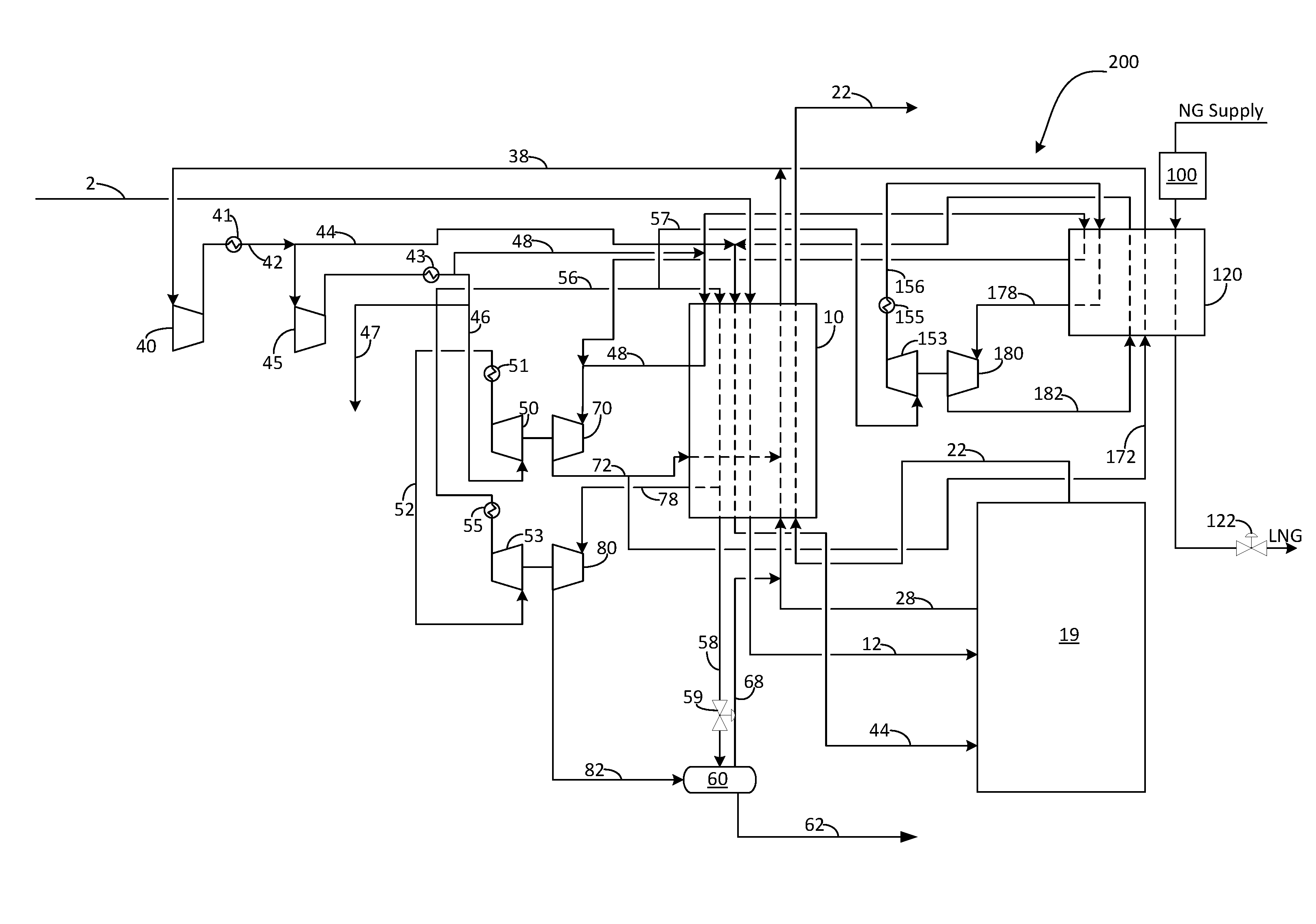
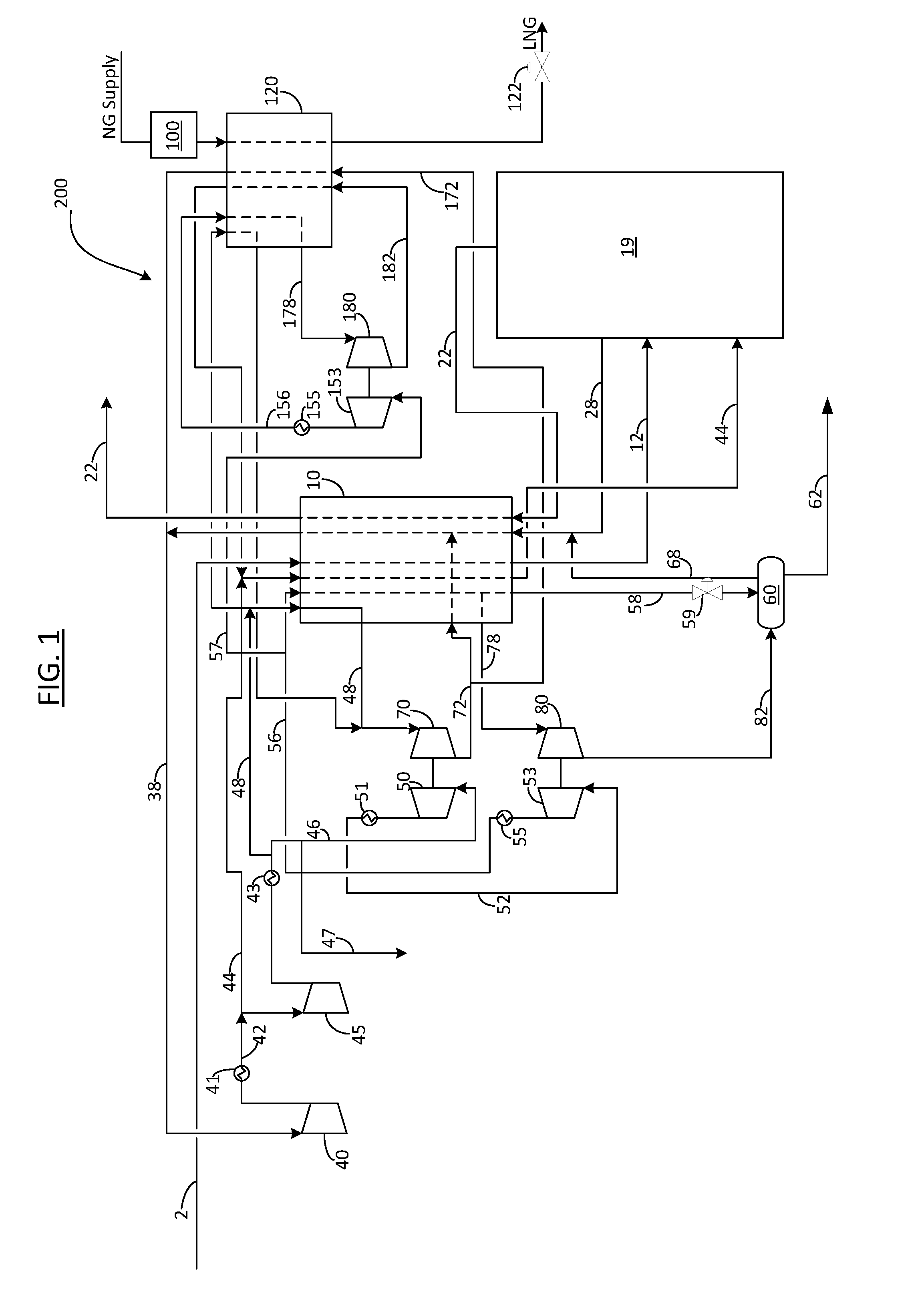
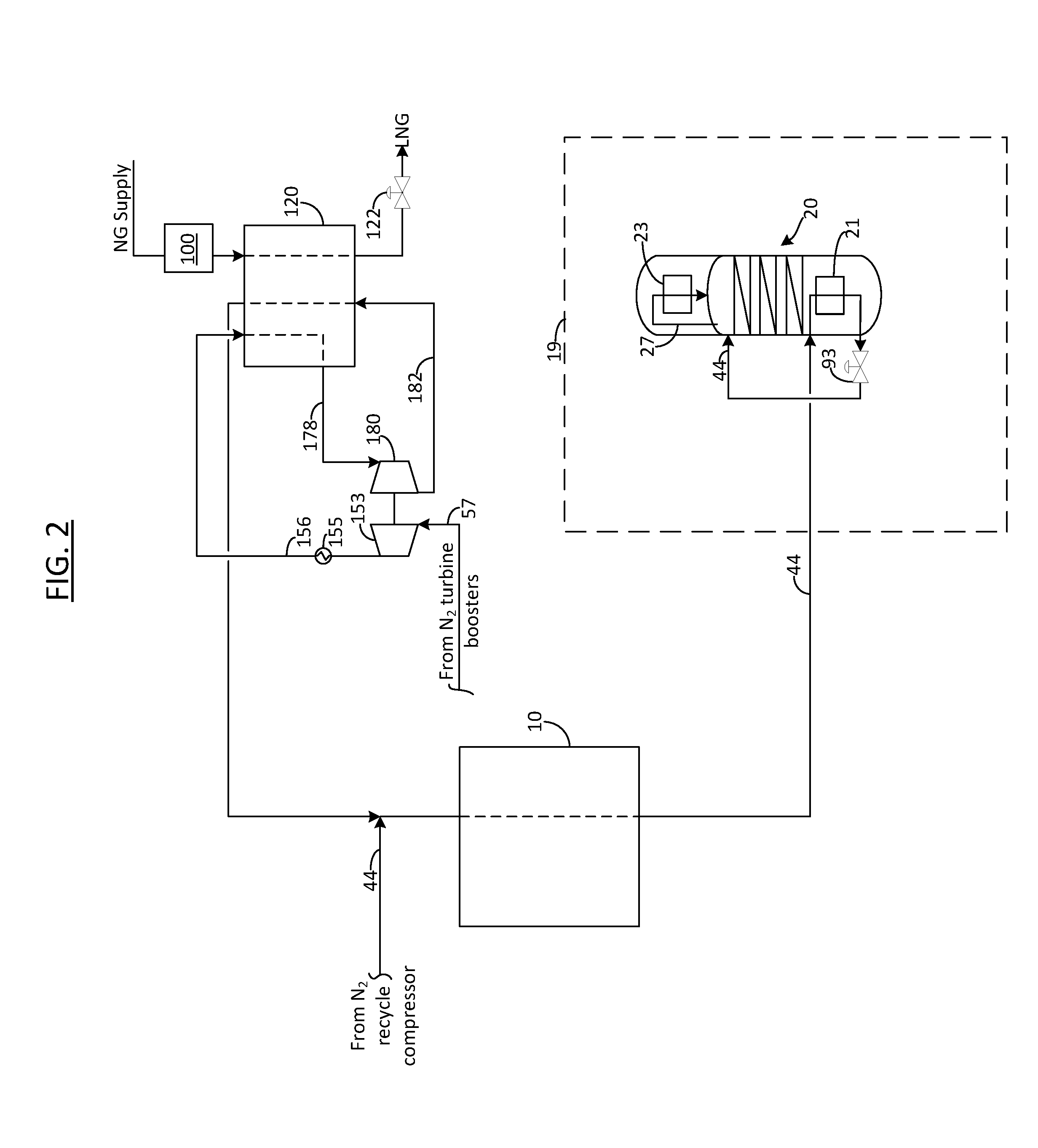
Method for the production of liquefied natural gas and nitrogen
InactiveUS20170038137A1Low costEfficient and flexible to produceSolidificationLiquefactionNitrogenProcess engineering
A method for the production of liquefied natural gas (“LNG”) and nitrogen is provided. The method may include the steps of: a) providing a nitrogen production facility, wherein nitrogen production facility comprises: a main heat exchanger, an air separation unit, a nitrogen recycle compressor, a first nitrogen refrigeration supply configured to provide refrigeration to the main heat exchanger for cooling a main air feed, b) providing a secondary refrigeration supply; c) liquefying a natural gas stream using refrigeration from the secondary refrigeration supply to form an LNG product stream; wherein the secondary refrigeration supply is configured to compress and expand a refrigerant to produce refrigeration, wherein the refrigerant of the secondary refrigeration supply is shared with refrigerant of the first nitrogen refrigeration supply
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Integrated enhanced oil recovery process
InactiveUS20110146978A1Enhanced overall recoveryIncrease productionSolidificationLiquefactionGeneration processSyngas
The present invention relates to an enhanced oil recovery process that is integrated with a synthesis gas generation process, such as gasification or reforming, and an air separation process for generating (i) an oxygen stream for use, for example, in the syngas process or a combustion process, and (ii) a nitrogen stream for EOR use.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
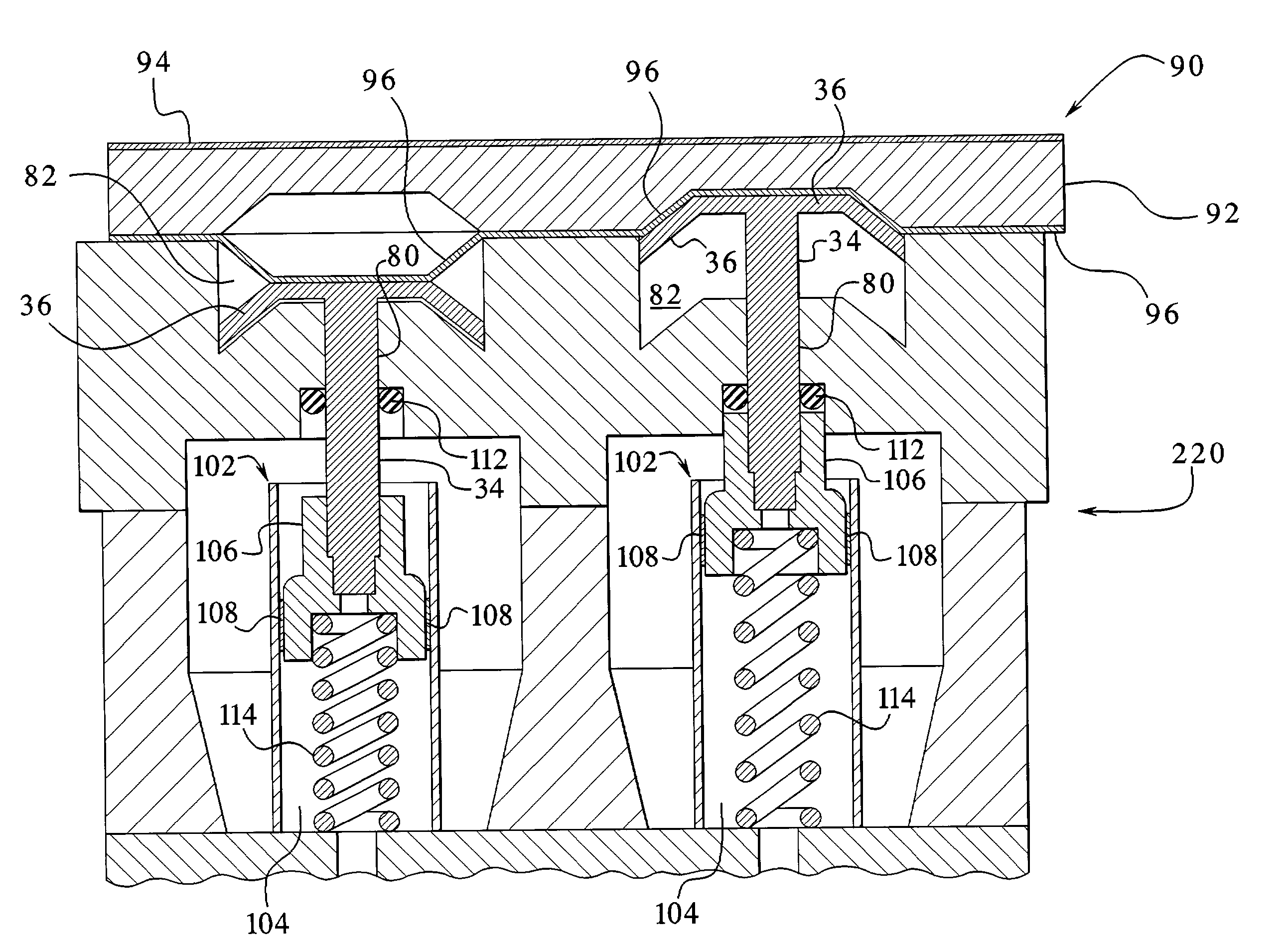
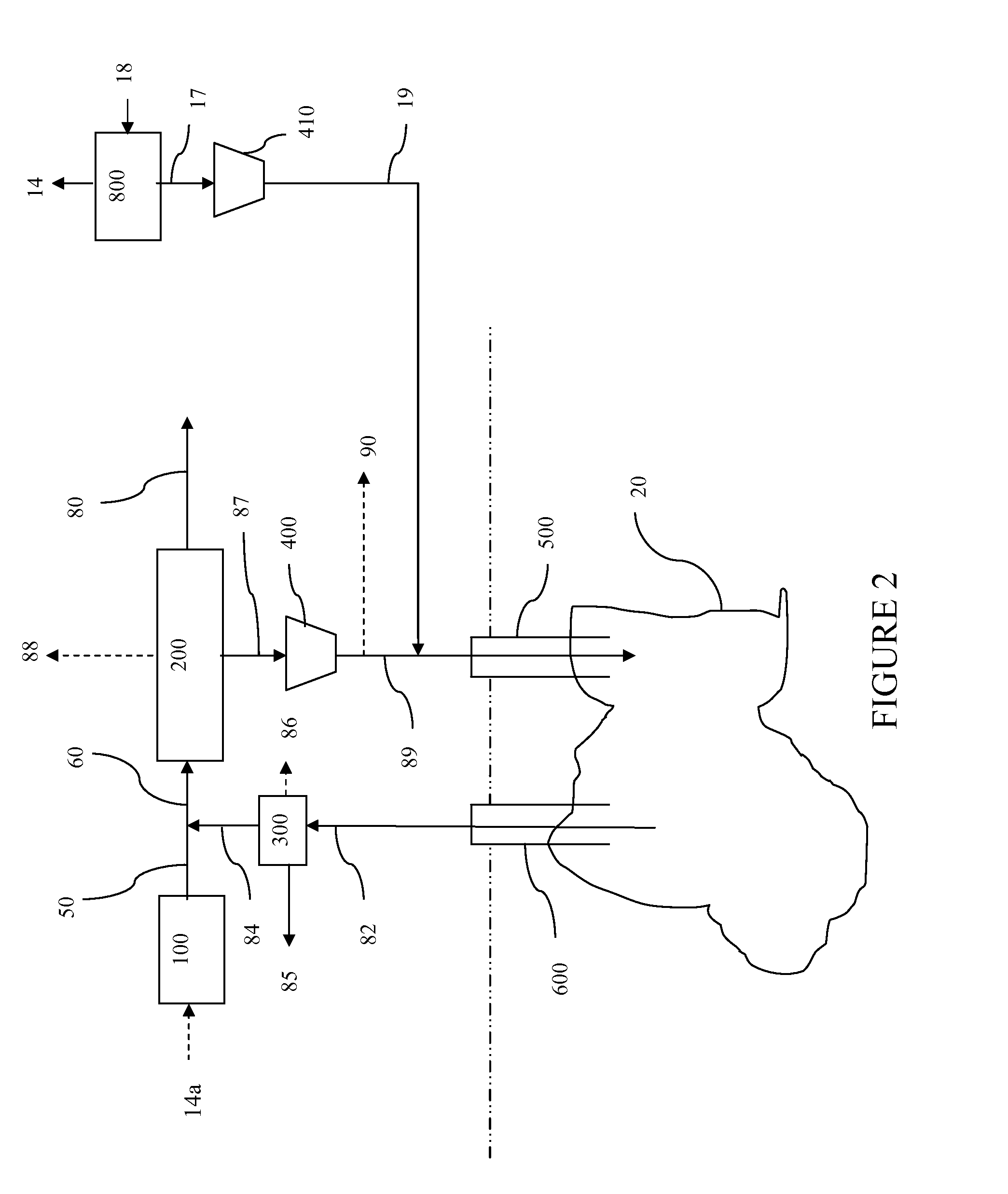
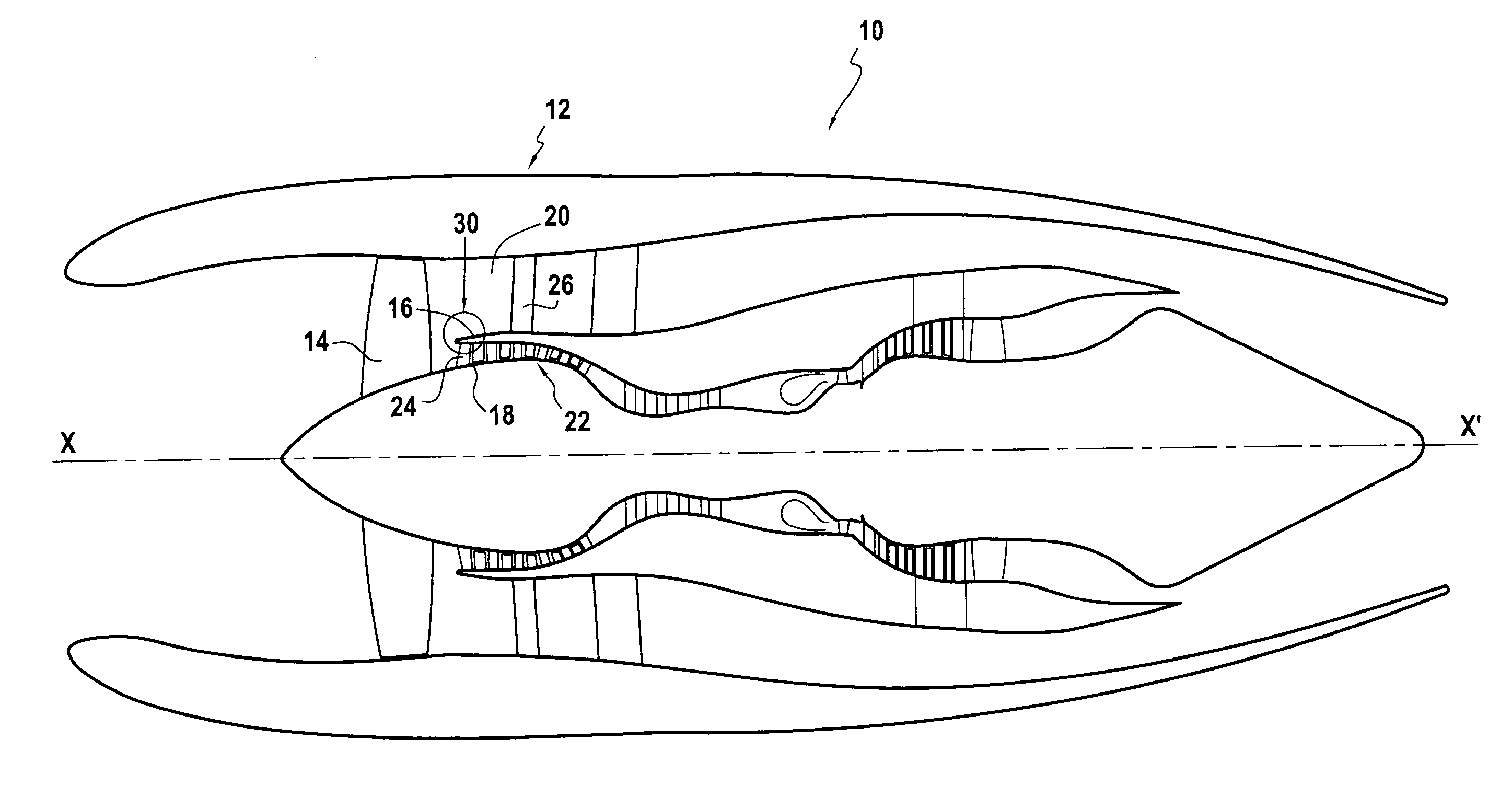
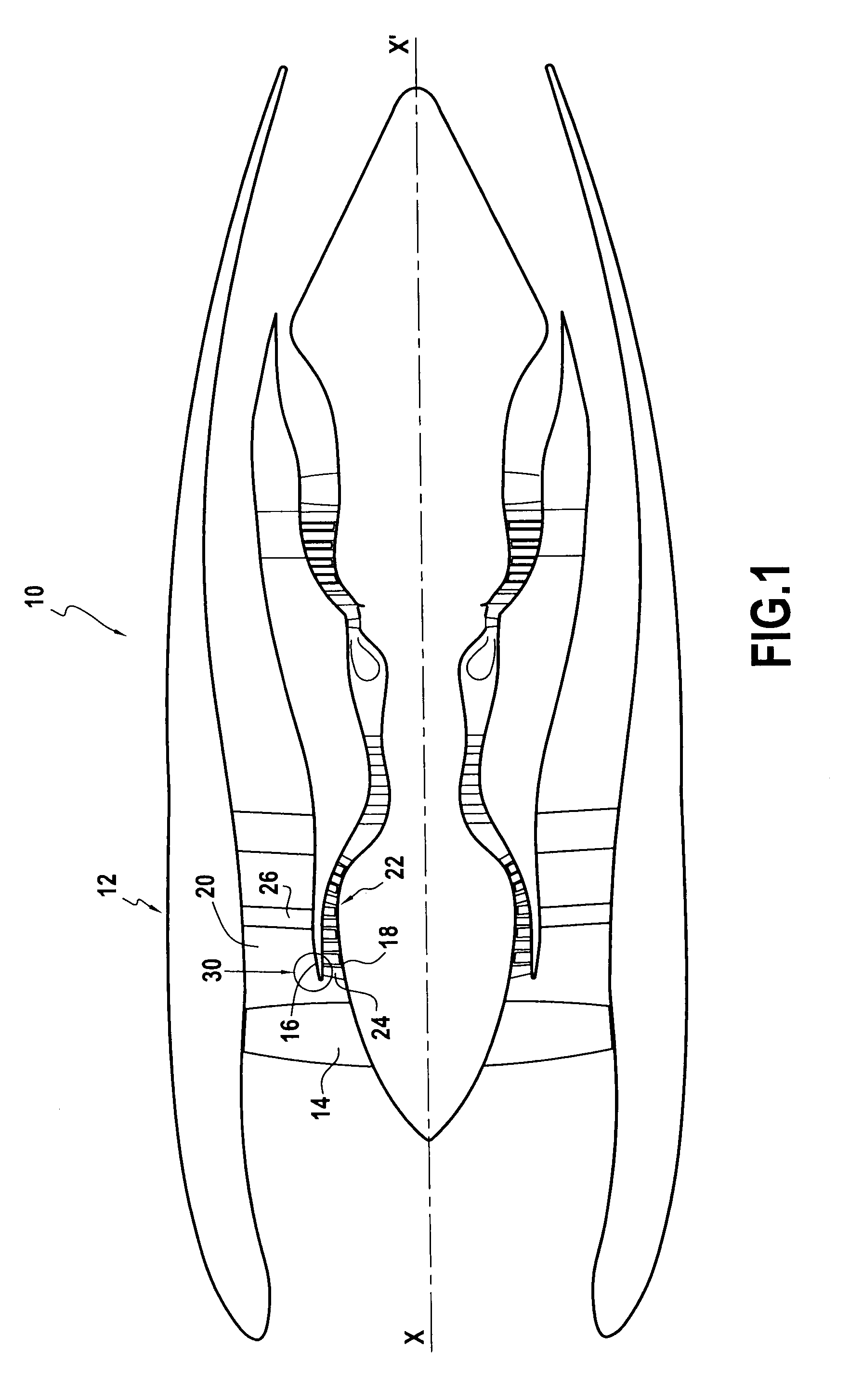
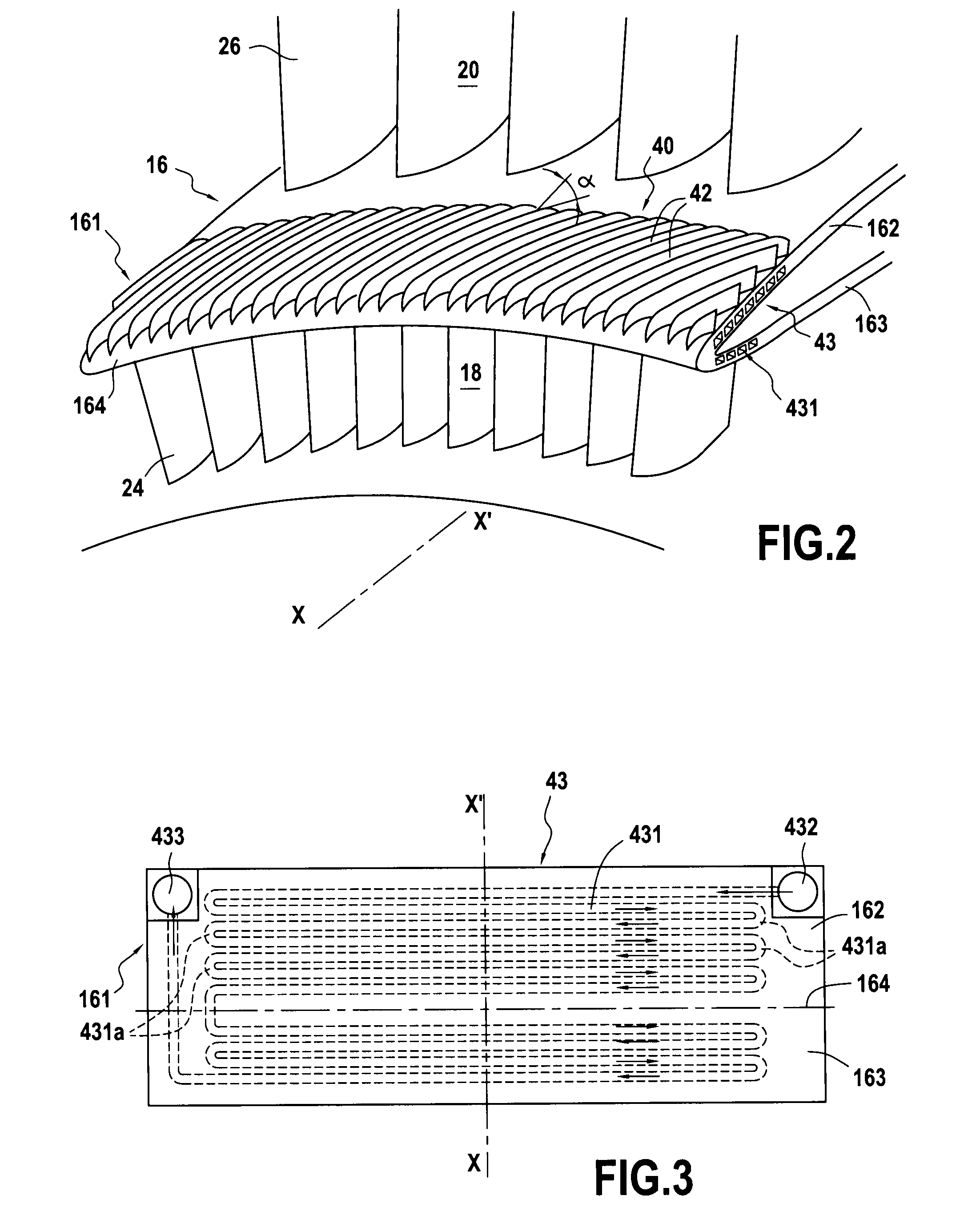
Air-oil heat exchanger placed at the location of the air separator nose of a turbojet, and a turbojet including such an air-oil heat exchanger
InactiveUS20090165995A1Prevent freezingWithout significantly disturbing the air streamExhaust apparatusTurbine/propulsion engine coolingLeading edgeJet engine
The invention relates to an air-oil heat exchanger located at the inner shroud of the secondary duct of a turbojet. In characteristic manner, it comprises an oil circuit placed inside the separator nose and fins placed outside the top wall of the separator nose, between the leading edge of the separator nose and the outlet guide vanes.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
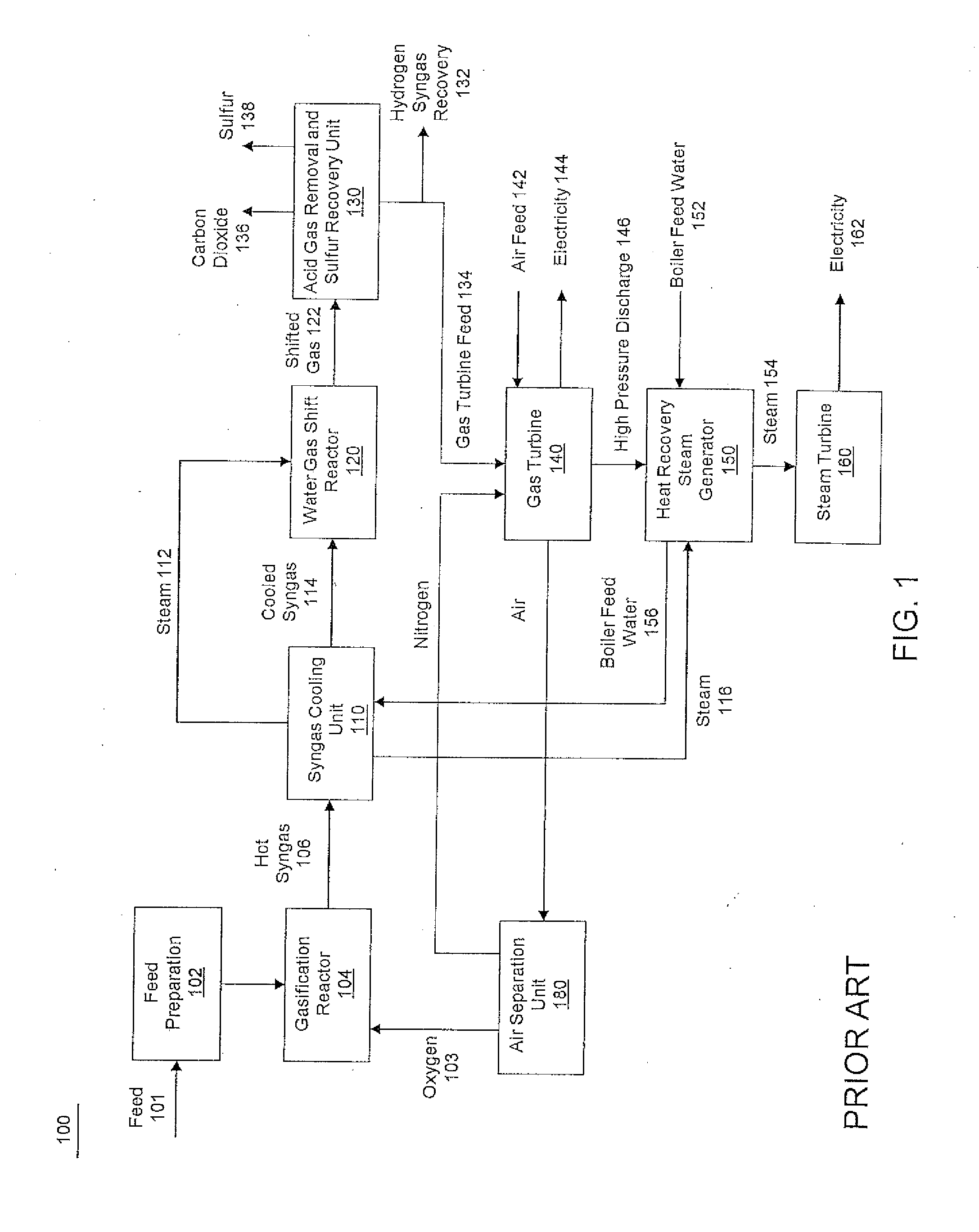
System and method for oxygen separation in an integrated gasification combined cycle system
An integrated gasification combined cycle power generation system (100). In one embodiment, shown in FIG. 1, a gasifier (108) is configured to generate synthetic gas (117) from a carbonaceous material (106) and an oxygen supply (109) with a cleaning stage (120) positioned to receive synthetic gas (117) from the gasifier (108) and remove impurities therefrom. A gas turbine combustion system (2) including a turbine (123) is configured to receive fuel (128) from the gasifier (108) and a first air supply (131) from a first air compressor (130). A steam turbine system (4) is configured to generate power with heat recovered from exhaust (140) generated by the gas turbine system (2) and an ion transport membrane air separation unit (110) includes a second air compressor (114) for generating a second air supply (113). A first heat exchanger (118) is configured to cool the synthetic gas (117) prior to removal of impurities in the cleaning stage (120) by flowing the second air supply (113) through the first heat exchanger (118) so that the second air supply (113) receives heat from the synthetic gas (117).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
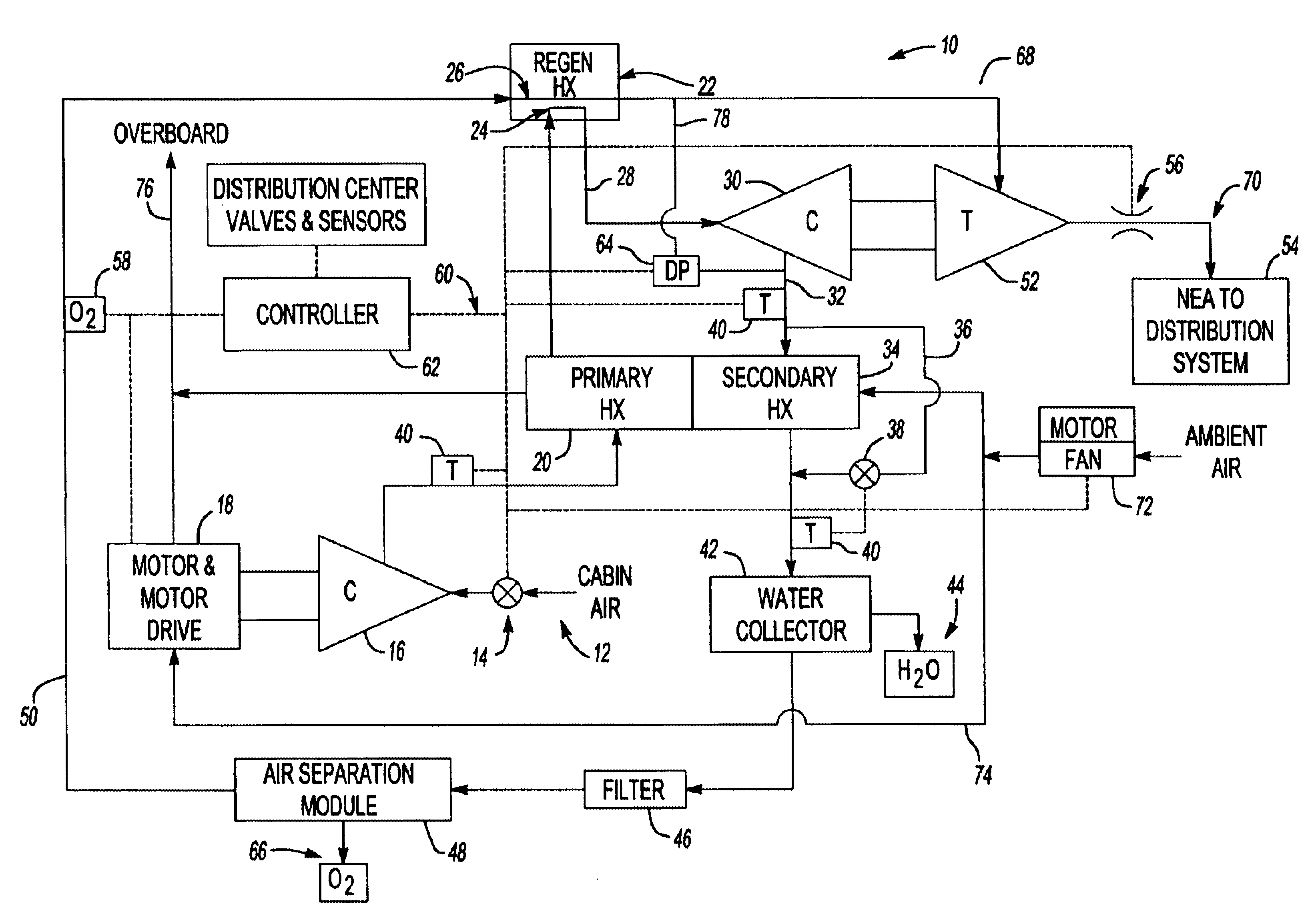
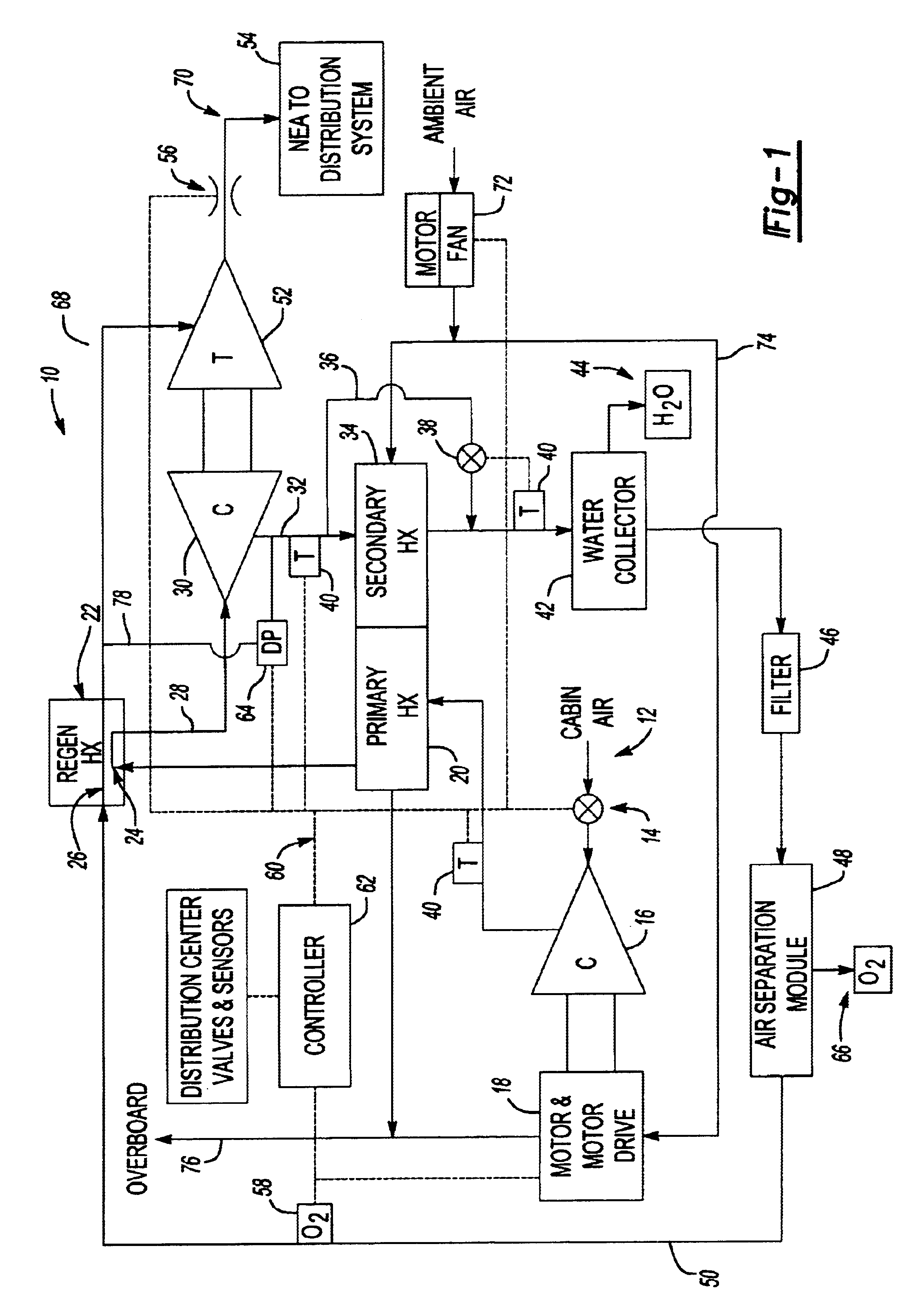
Gas generating system and method for inerting aircraft fuel tanks
ActiveUS20050115404A1Avoid flowPrevent contamination from enteringGas treatmentDispersed particle filtrationOperational costsFuel tank
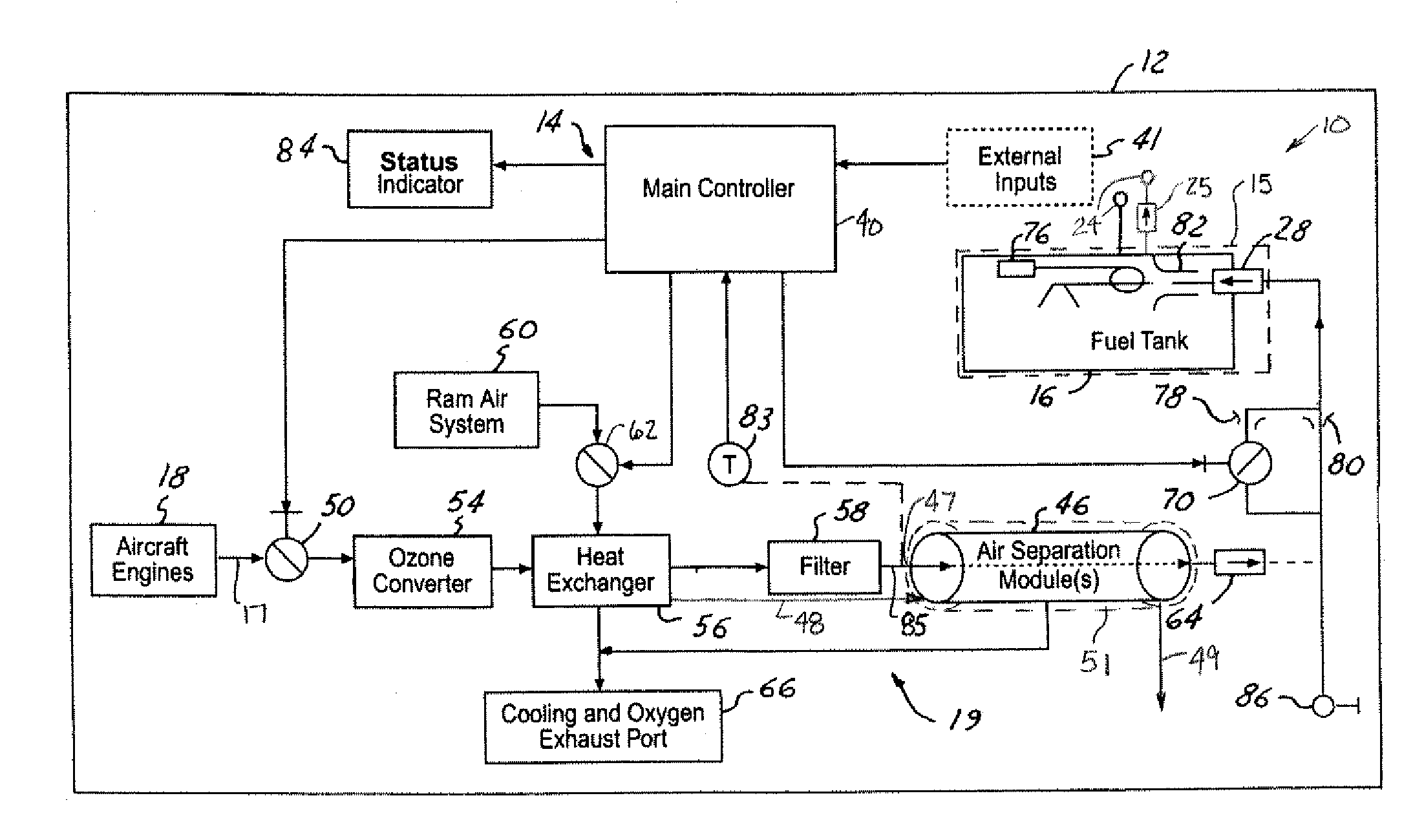
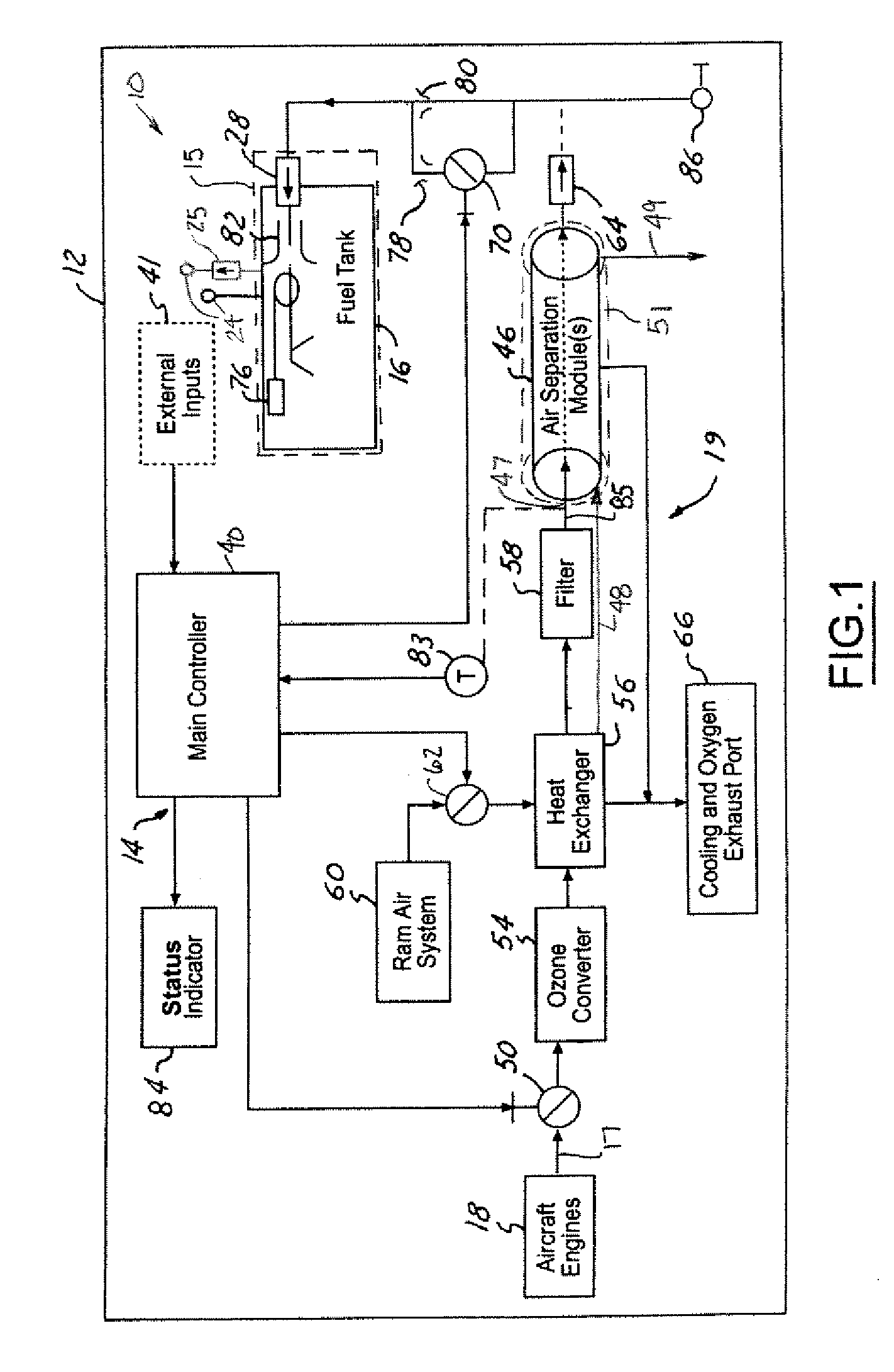
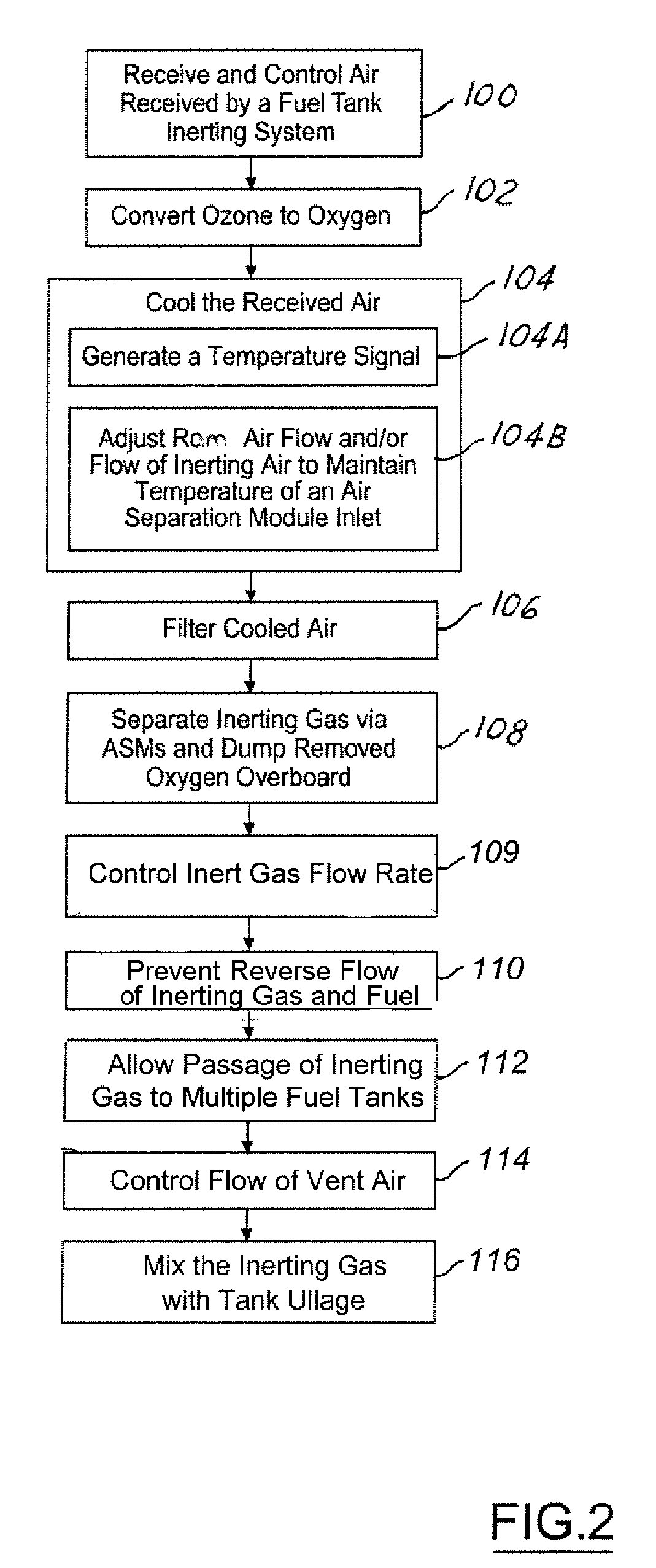
The present invention provides a system and method for generation of nitrogen enriched air for inerting aircraft fuels tanks. One embodiment of the present invention includes a duct assembly; a primary heat exchanger; a gas generating system heat exchanger; a first temperature sensor; a second temperature sensor; a controller monitor; a valve; an air separation module assembly having a primary module and a secondary module; at least one flow control orifice; and a pressure sensor. The present invention utilizes a minimal complement of components and streamlined processes, thus minimizing structural and operational costs while optimizing performance and safety features.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for generation of high pressure air in an integrated gasification combined cycle system
InactiveUS20080115478A1Reduces capital equipment cost and operational costEasy temperature controlMuffle furnacesCombustion enginesAir separationProcess engineering
An integrated gasification combined cycle system. In one embodiment (FIG. 2) a system (200) includes an ion transport membrane air separation unit (210) for producing oxygen-enriched gas (209) and oxygen-depleted air (227), a gasification system (5) for generating syngas with the oxygen-enriched gas (209), a gas combustor (234) for reacting the syngas (224), and a subsystem configured to provide a first stream of air to the combustor (234) at a first pressure and to provide a second stream of air to the air separation unit (210) at a second pressure greater than the first pressure. The subsystem includes a compressor (230) having multi-pressure outlets (203, 204).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Commercial aircraft on-board inerting system
ActiveUS7152635B2Reduce flammabilityImprove flammabilityLiquid fillingPower plant fuel tanksInerting systemOn board
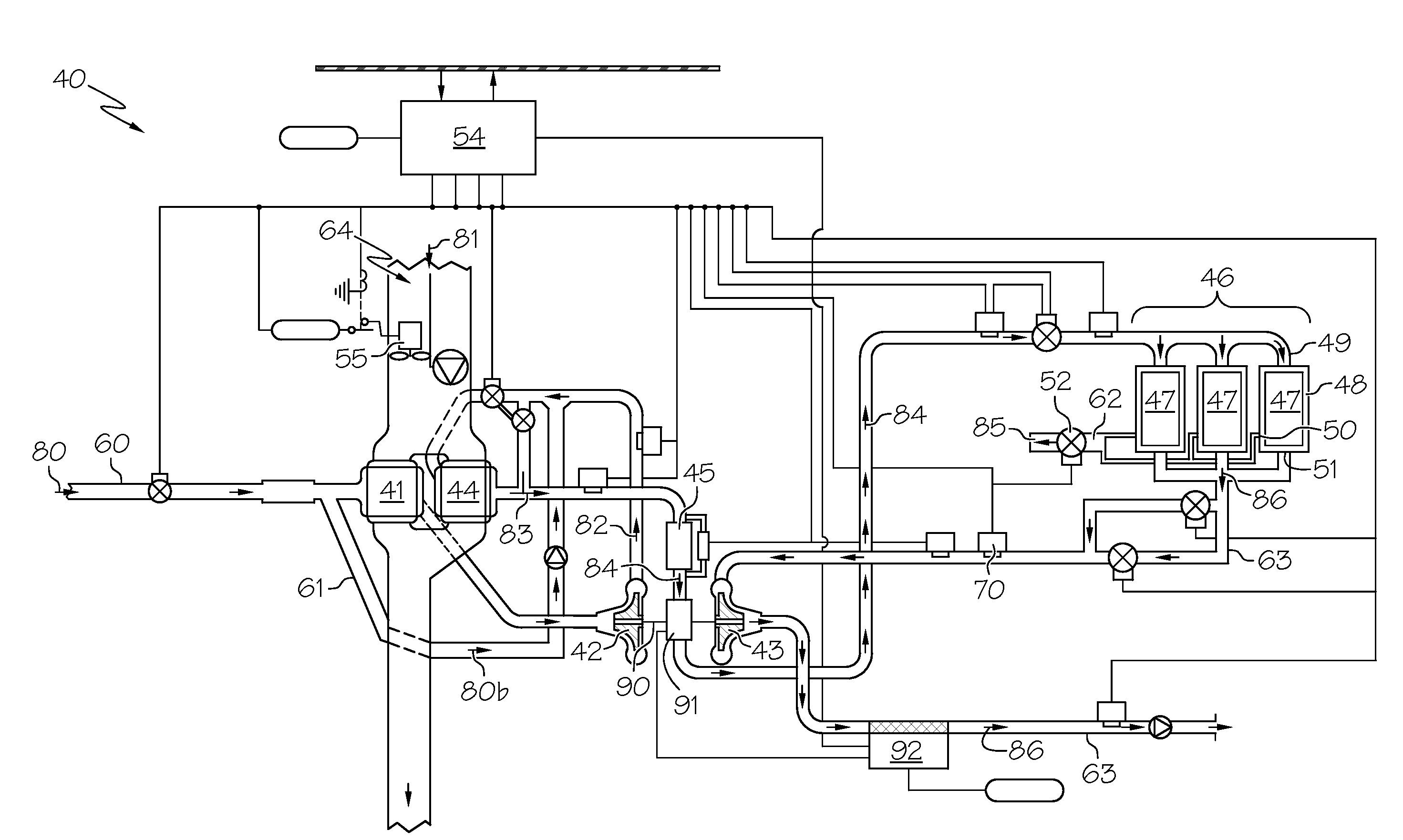
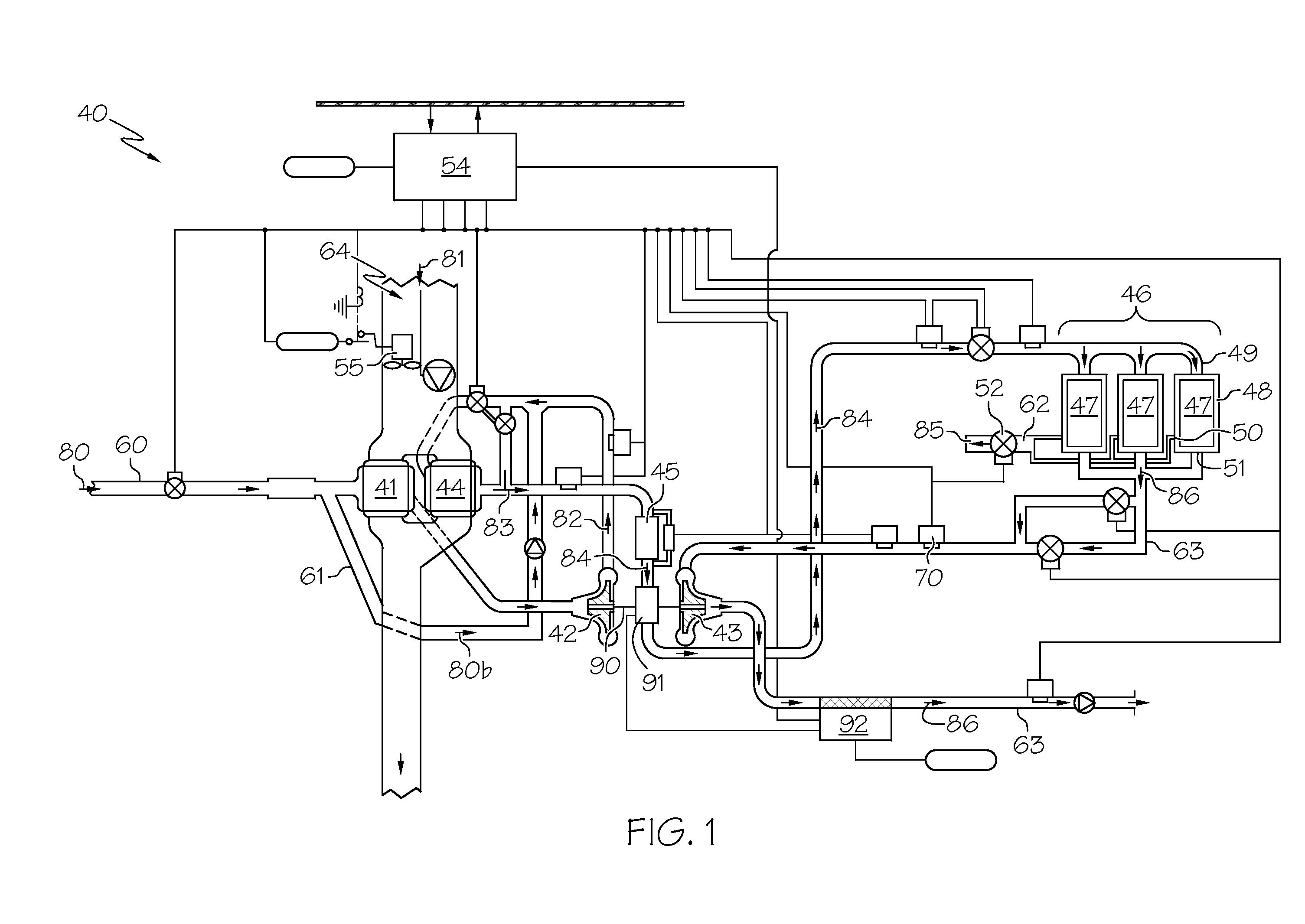
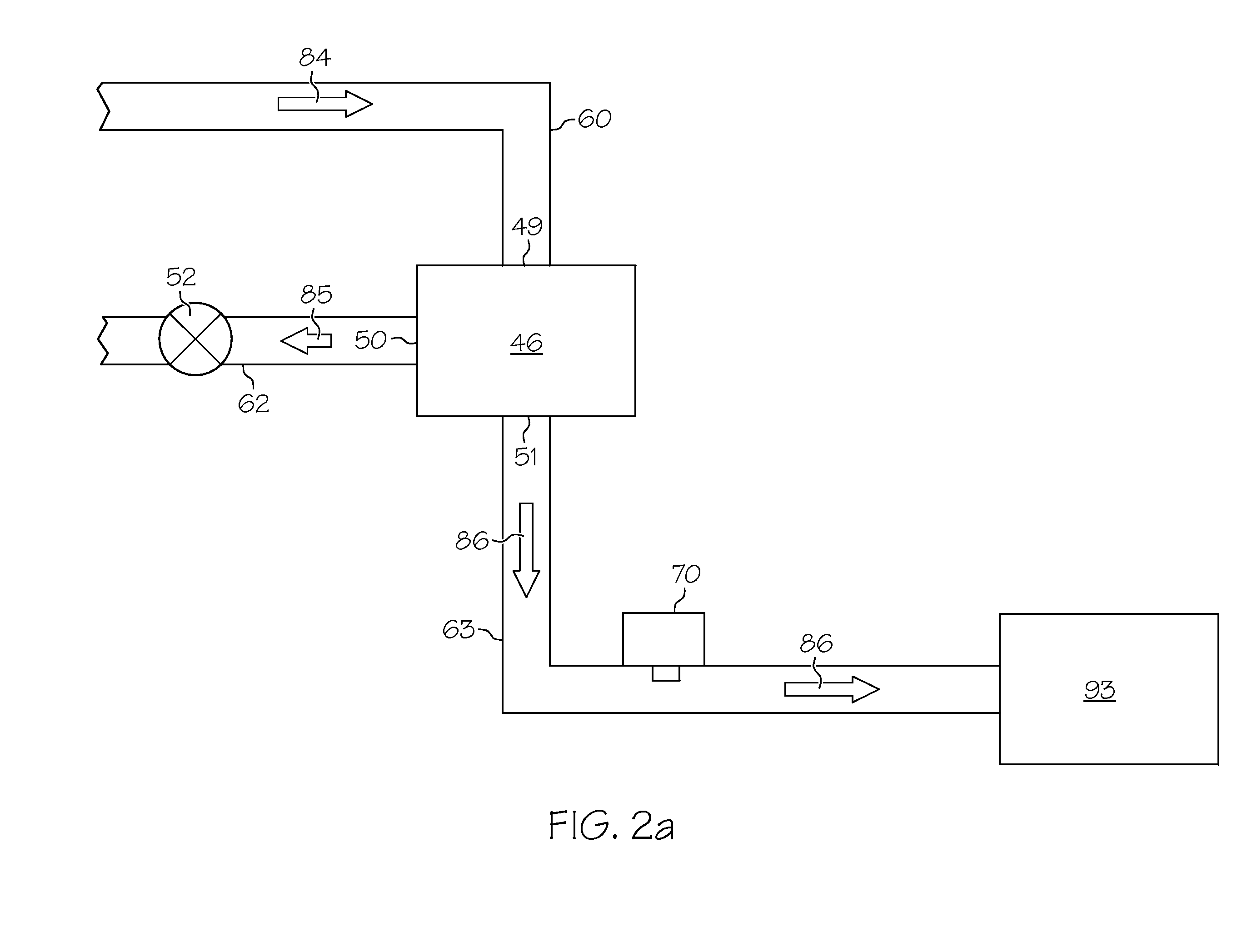
An inerting system (10) for an aircraft (12) includes one or more fuel tank circuits (15) associated with fuel tanks (16). An air source (17) supplies pressurized air. A heat exchanger (56) cools the pressurized air. An air separation module (46) is in fluid communication with the heat exchanger (56) and separates inerting gas from the pressurized air. A controller (40) controls flow of the inerting gas from the air separation module (46) to the fuel tanks (16).
Owner:THE BOEING CO
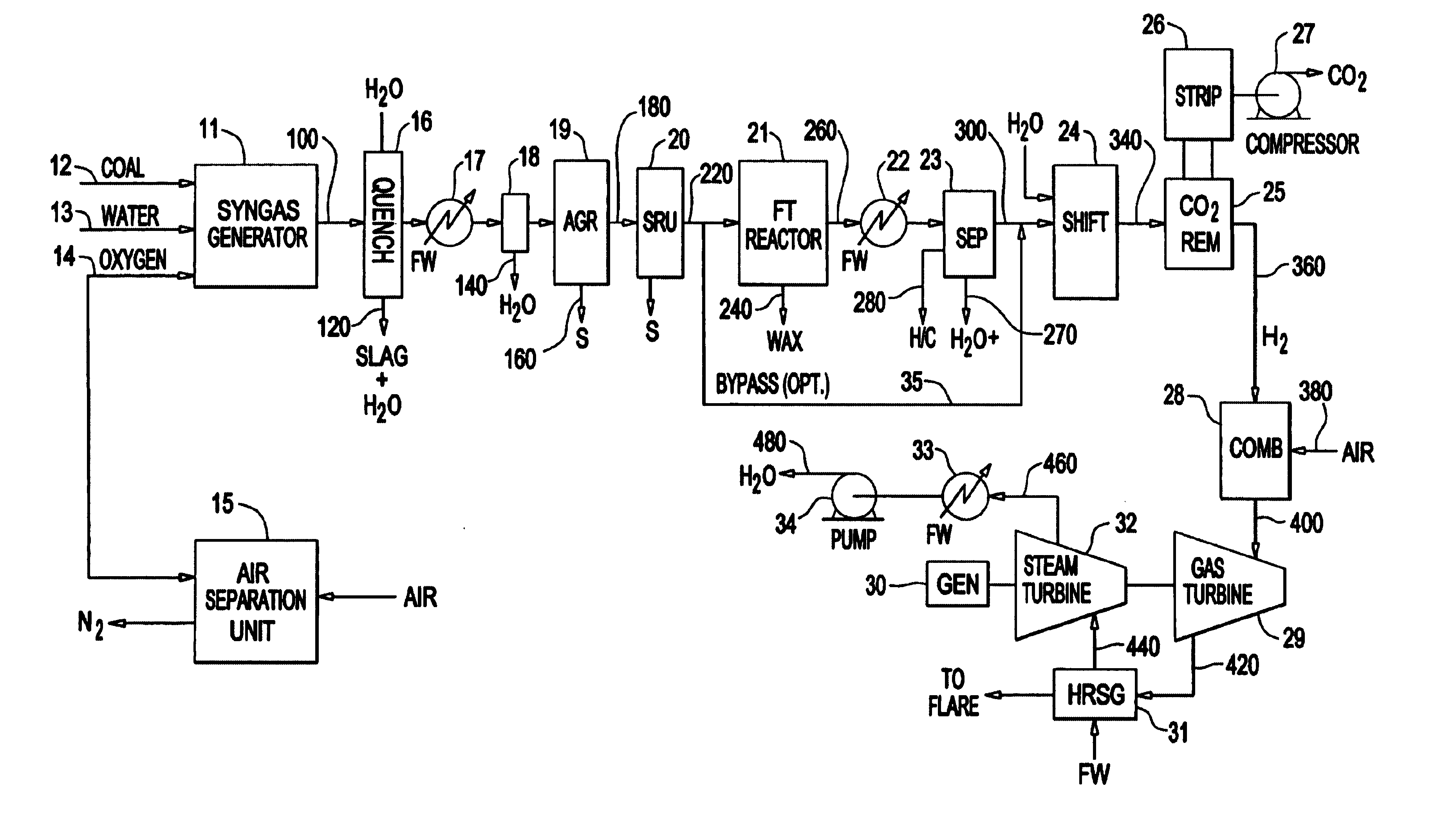
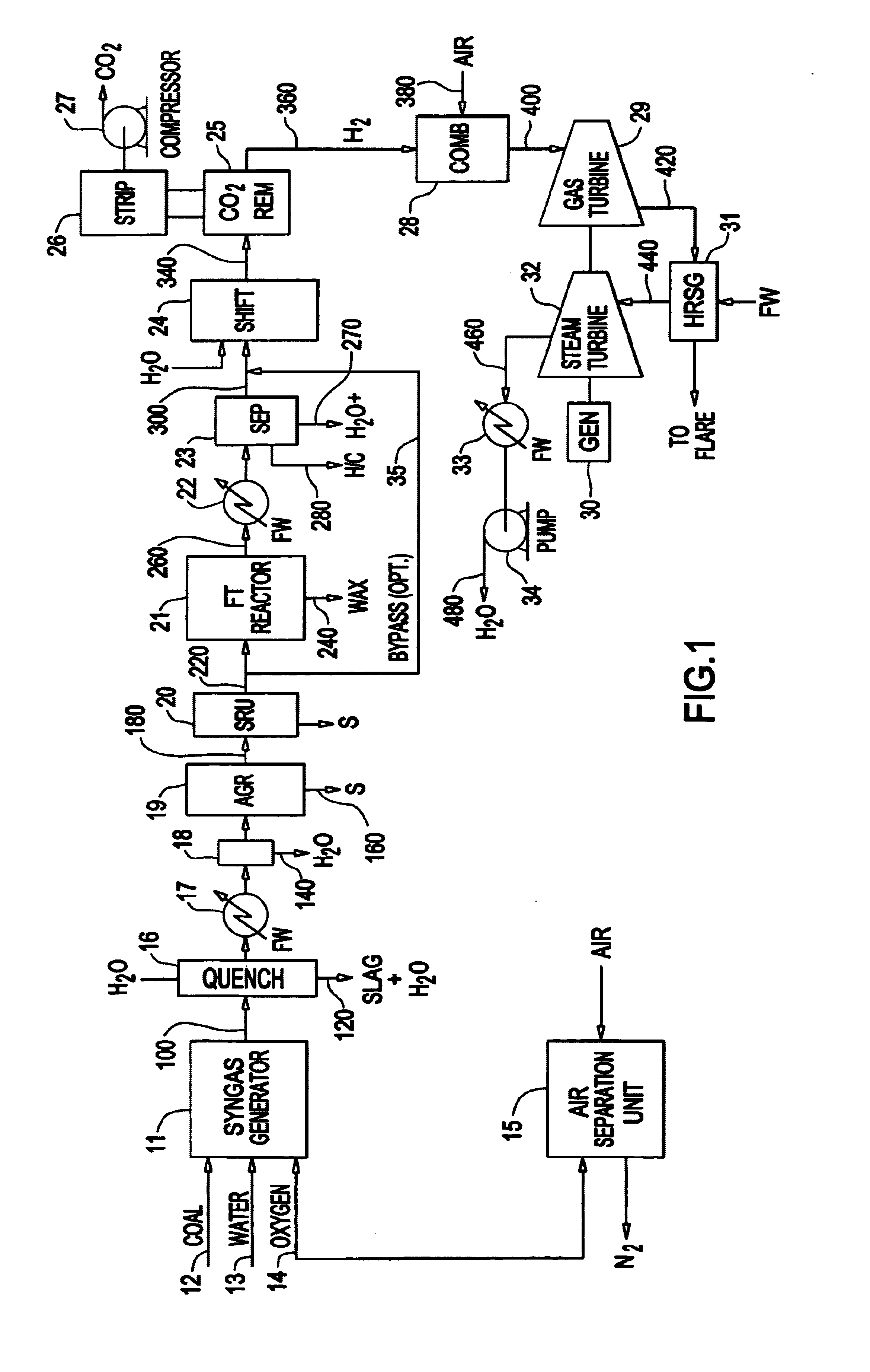
Integrated Fischer-Tropsch and power production plant with low CO2 emissions
A plant for producing Fischer-Tropsch liquids and electrical power with greatly reduced emissions of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere is made up of a syngas generator unit, an air separation unit, a Fischer-Tropsch unit, a CO2 removal unit, and a combined cycle electricity generation unit. Each of Fischer-Tropsch liquids, carbon dioxide, and electrical power can be recoverable under proper economic conditions. Electrical power is recoverable by the use of a gas turbine fueled by predominantly hydrogen and a steam turbine powered by steam generated by cooling exhaust gases from the gas turbine. Sequestration of CO2 and fueling the gas turbine with hydrogen reduces the amount of greenhouse gases emitted to the atmosphere.
Owner:RES USA LLC
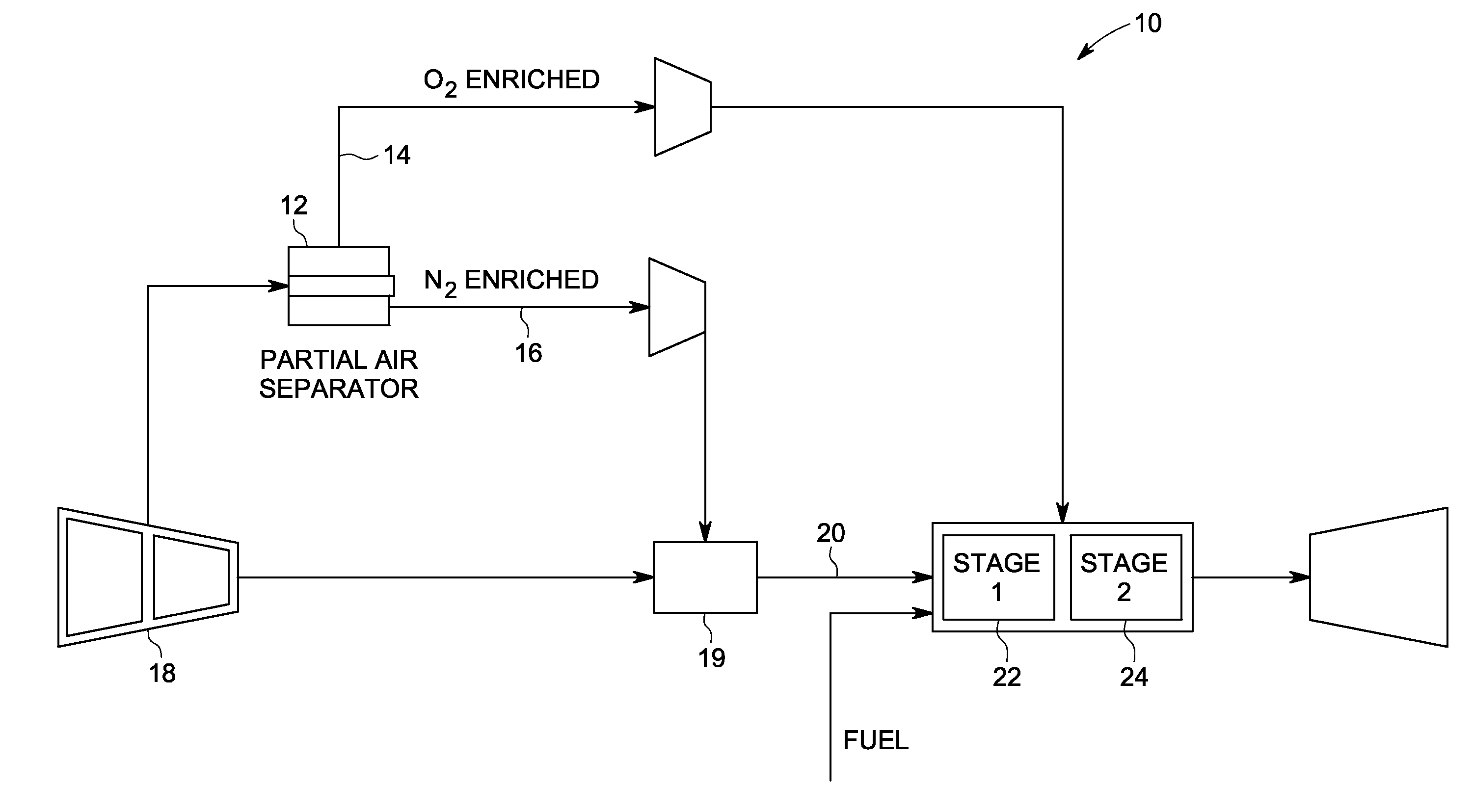
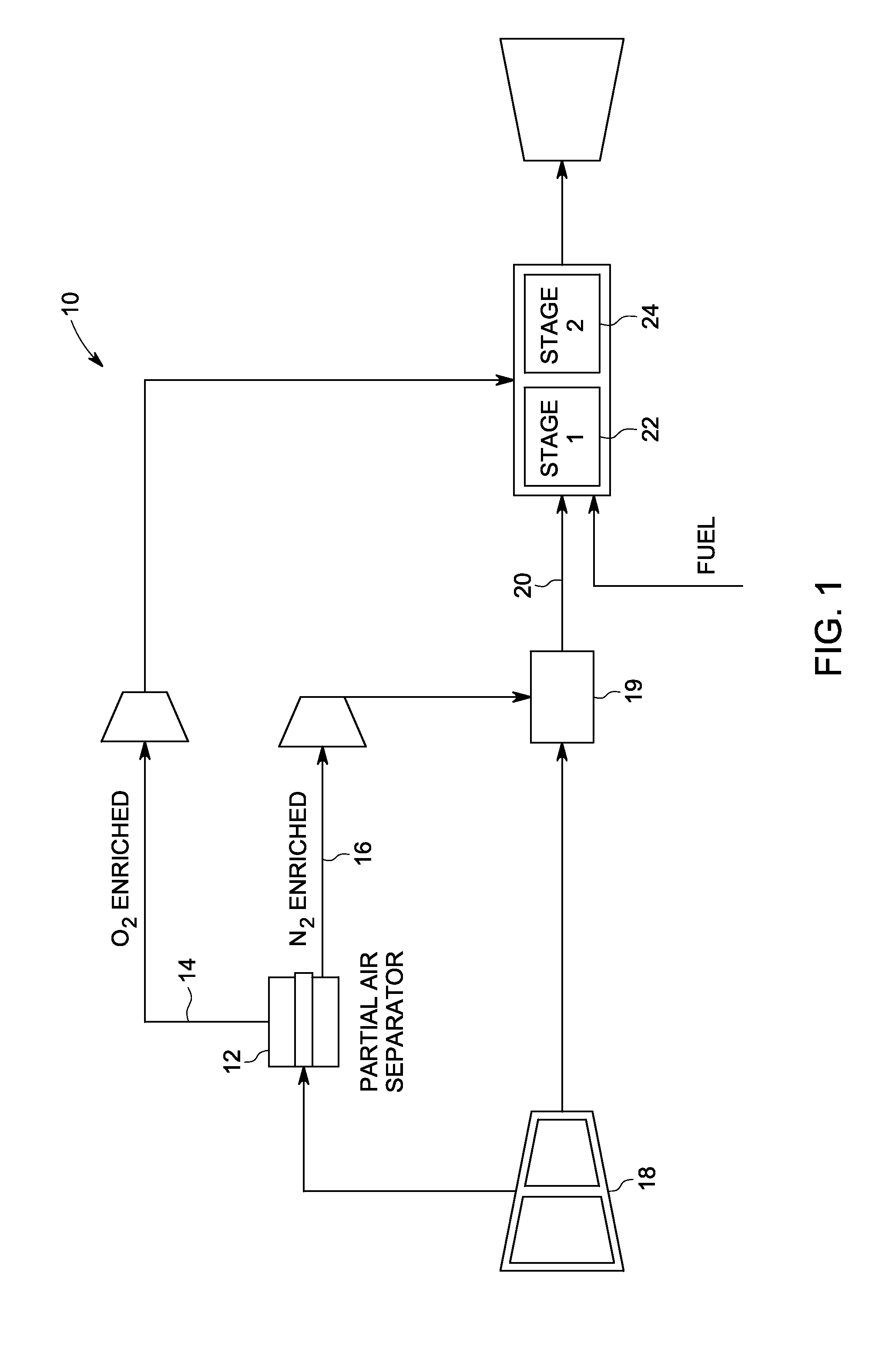
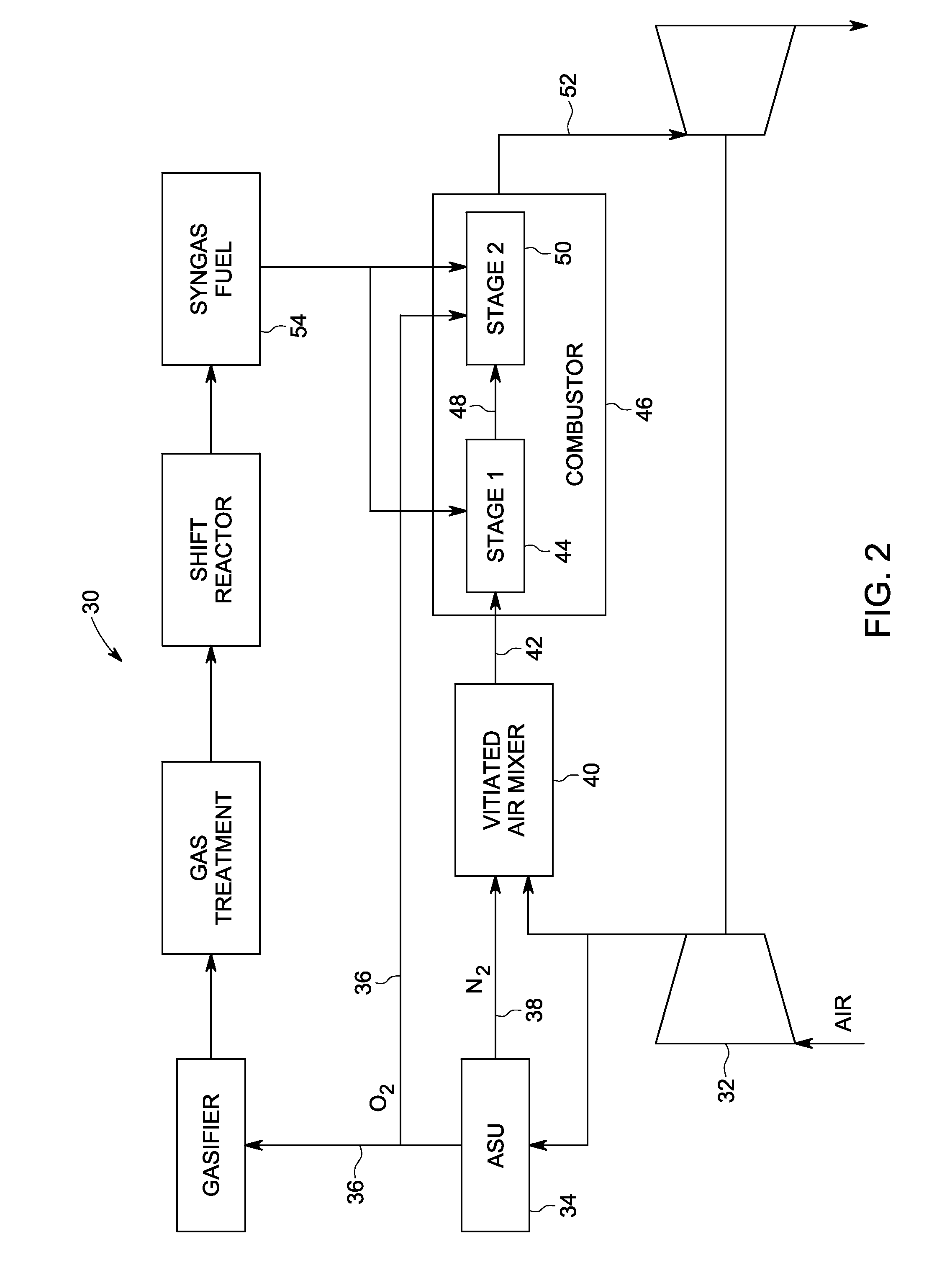
System and method using low emissions gas turbine cycle with partial air separation
A system and method of reducing gas turbine nitric oxide emissions includes a first combustion stage configured to burn air vitiated with diluents to generate first combustion stage products. A second combustion stage is configured to burn the first combustion stage products in combination with enriched oxygen to generate second combustion stage products having a lower level of nitric oxide emissions than that achievable through combustion with vitiated air alone or through combustion staging alone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
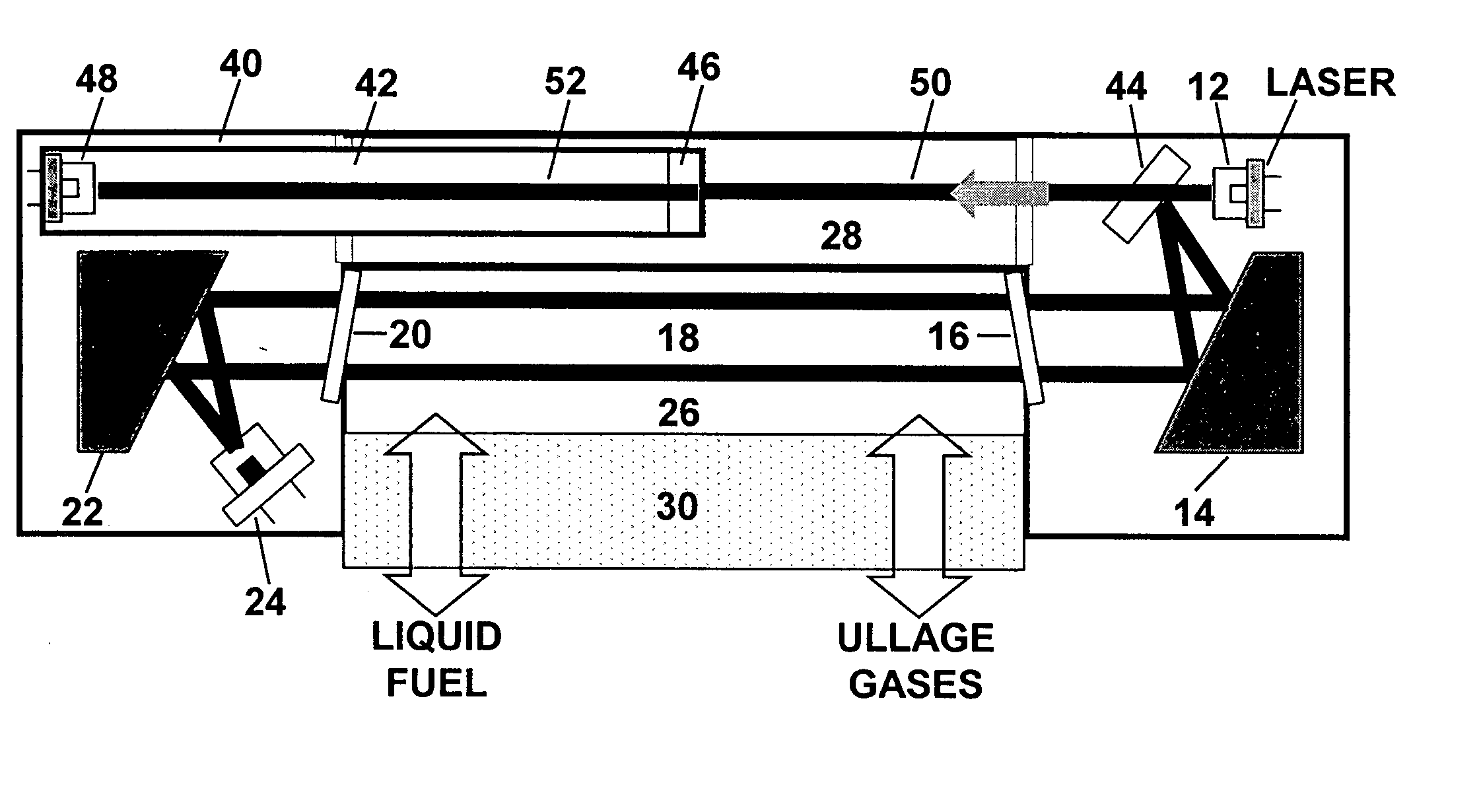
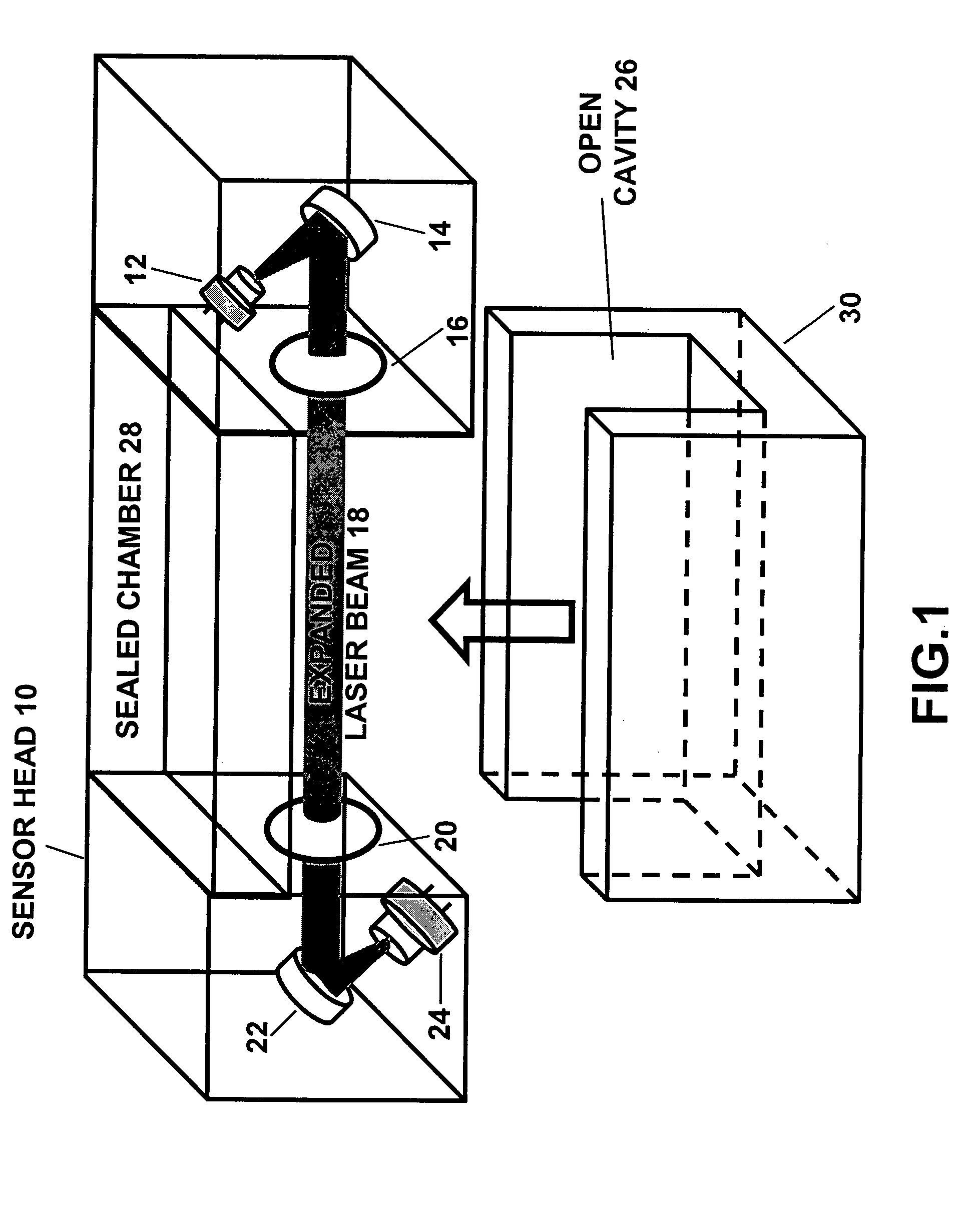
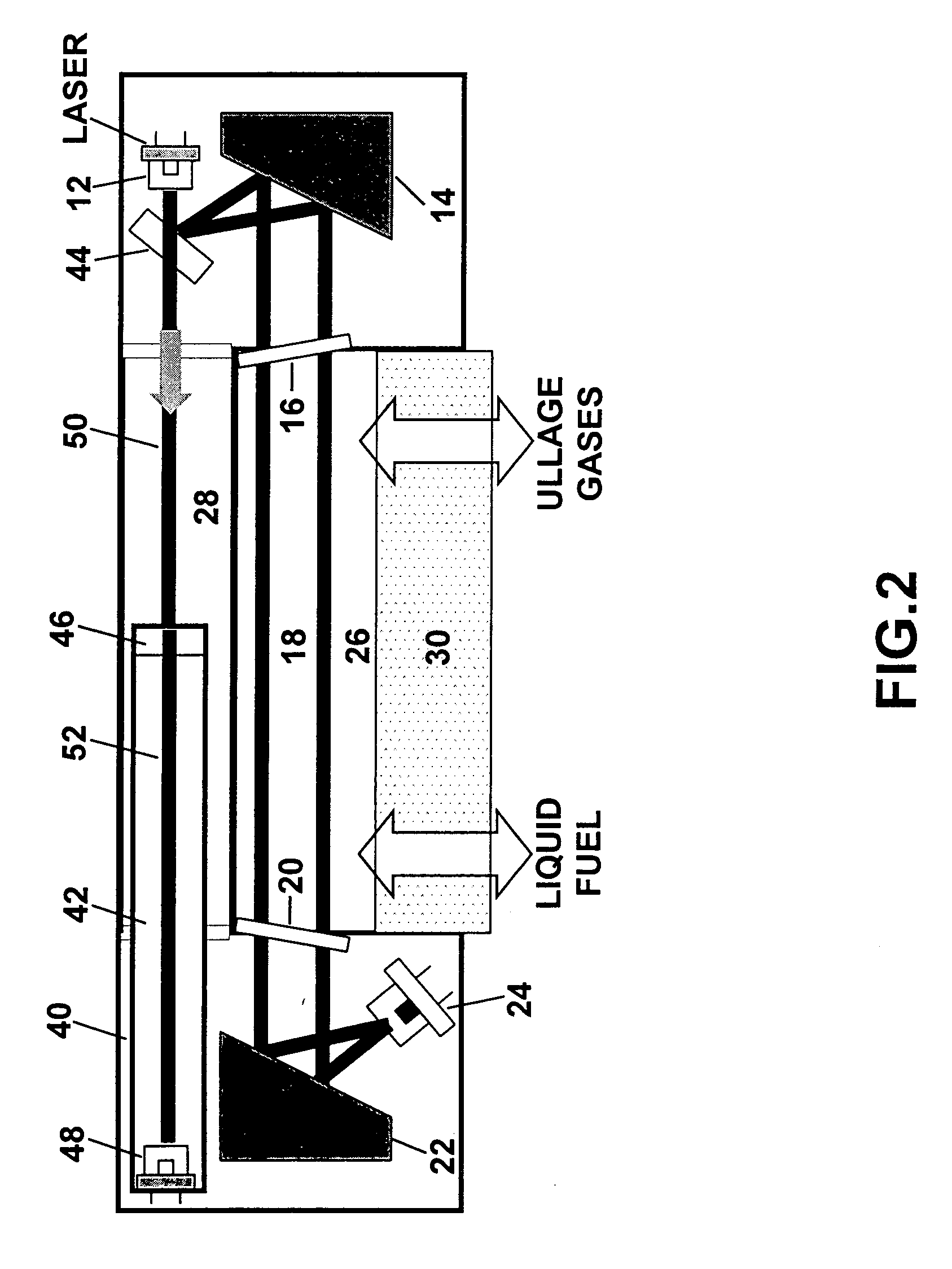
Oxygen sensor for aircraft fuel inerting systems
ActiveUS20050286054A1Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFuel tankEngineering
An apparatus and method for monitoring oxygen concentrations in fuel tank ullage comprising providing a sensor head comprising an optical cavity, exposing the optical cavity to an ambient gaseous environment of a fuel tank or air separation module, via a laser light source emitting wavelength modulated light through the cavity, and receiving the wavelength modulated light with a detector.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
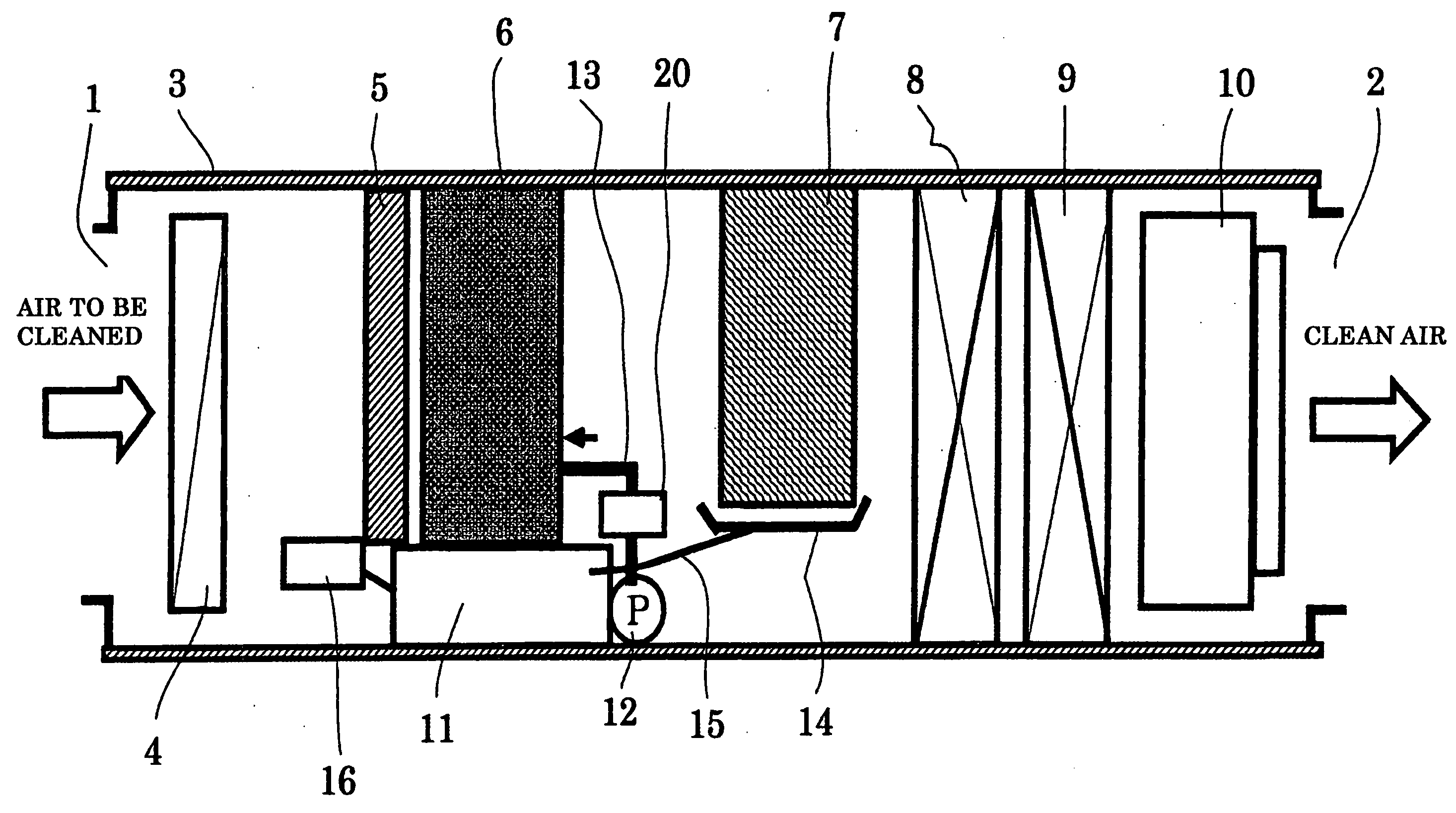
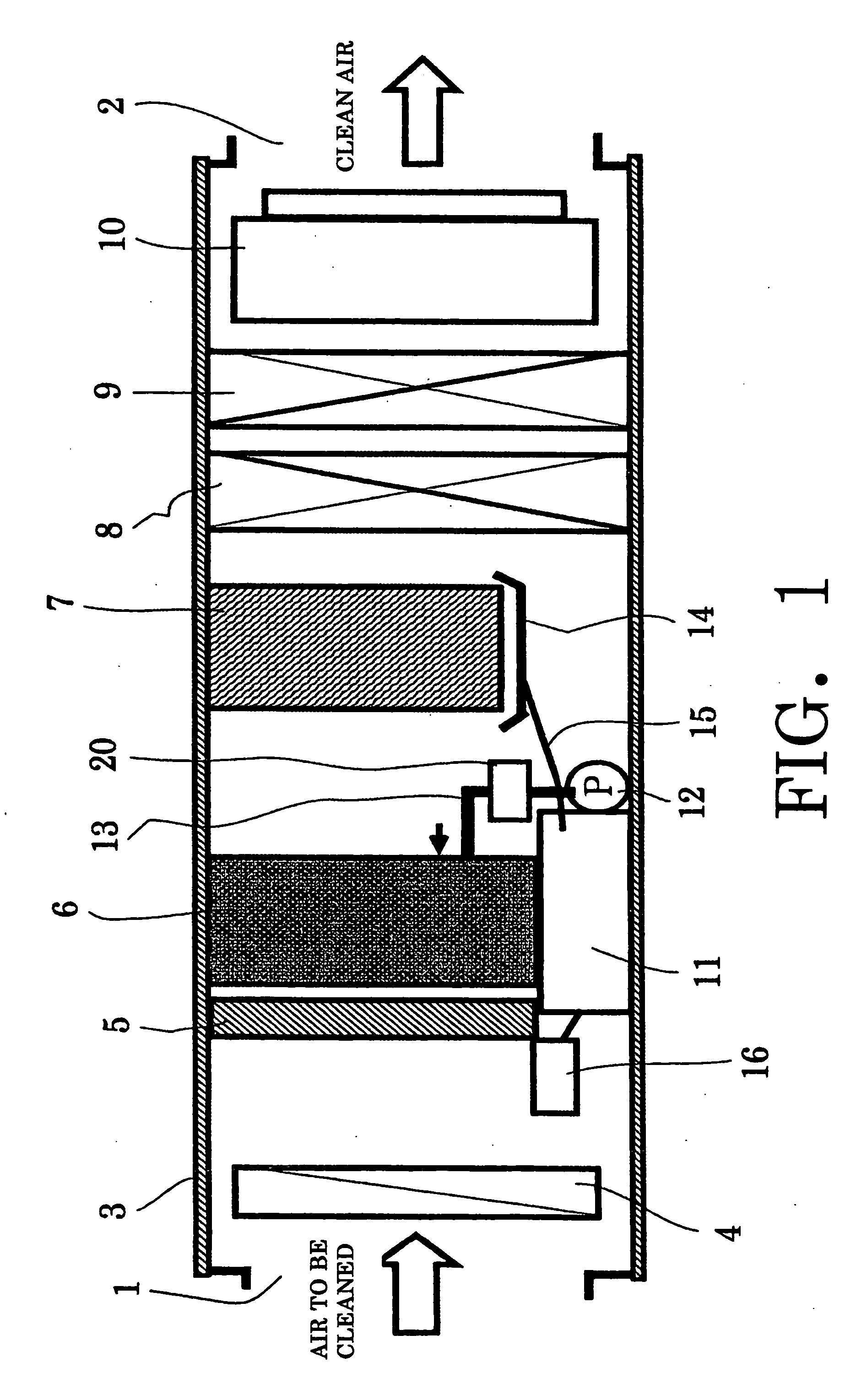
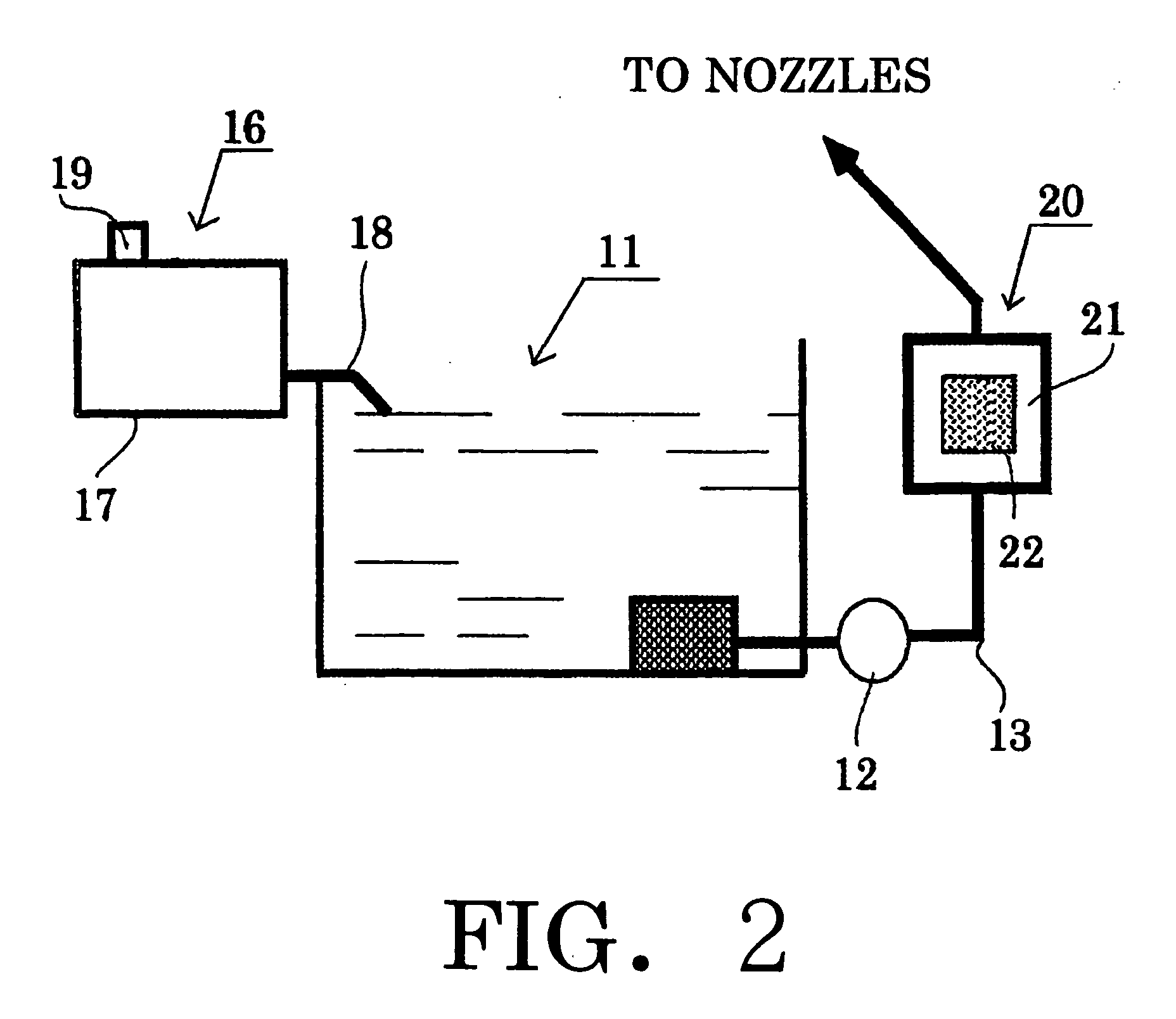
Air cleaner
ActiveUS20050072308A1Improve contact efficiencyEasy to handleCombination devicesMechanical apparatusForeign matterChlorine dioxide
An air cleaner for cleaning air and for providing sterilization and deodorization effects, includes an air-liquid contact part, for bringing the air into contact with a water screen formed by spraying, using nozzles, pressurized circulating water, and for removing foreign materials from the air; a liquid separating part for separating from the air, tiny water droplets that are included in the air passing through the air-liquid contact part; a cylindrical body into which air to be cleaned is guided, and in which the air-liquid contact part and the liquid separating part are arranged in order; a chlorine dioxide addition unit, for adding a stabilized chlorine dioxide solution to a water tank for the water that is circulated; and a chlorine dioxide activation unit, for activating chlorine dioxide added to the circulating water, that is arranged in a circulating water pipe that extends from the water tank to the spray nozzles.
Owner:FM IWATE
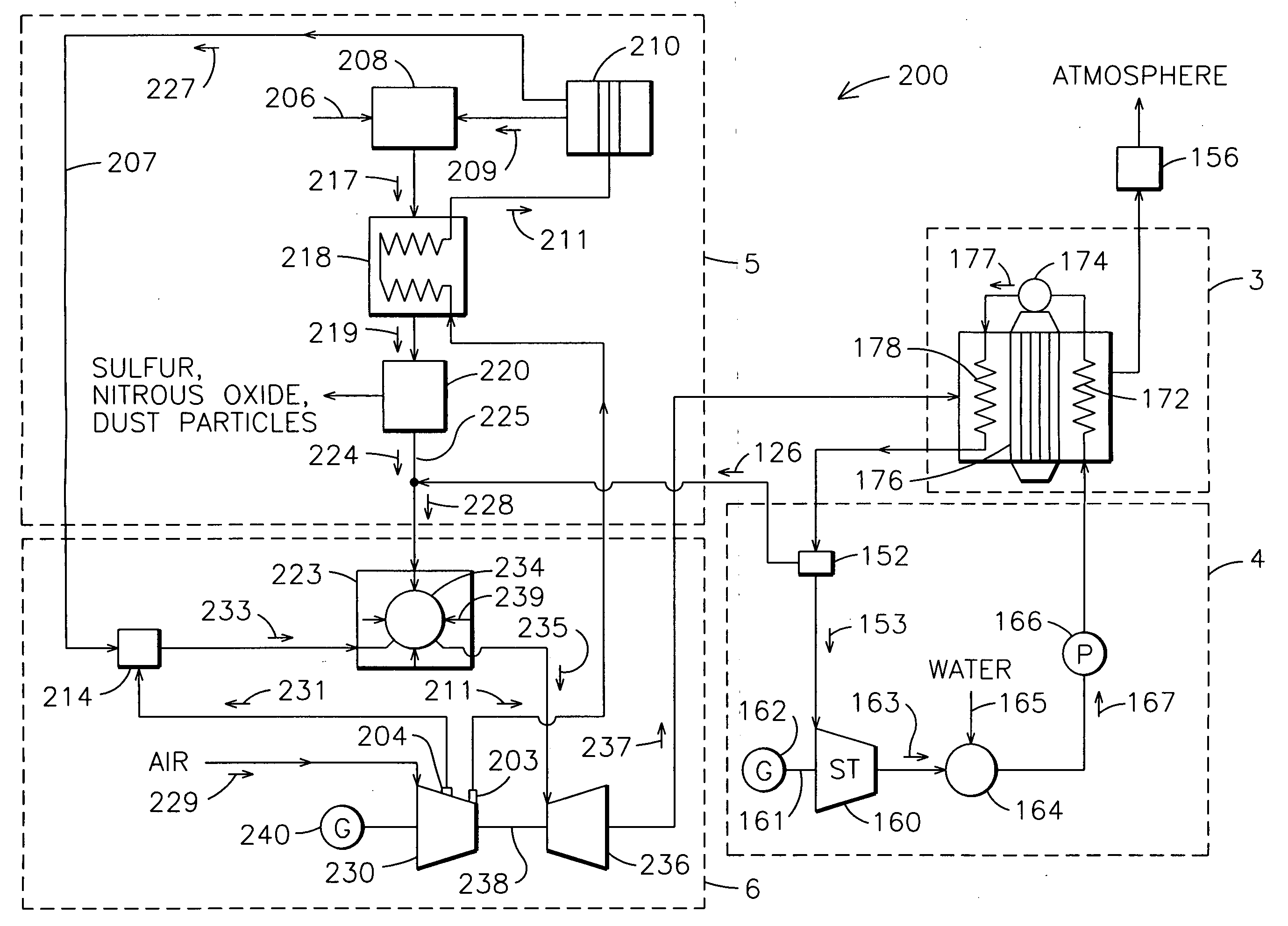
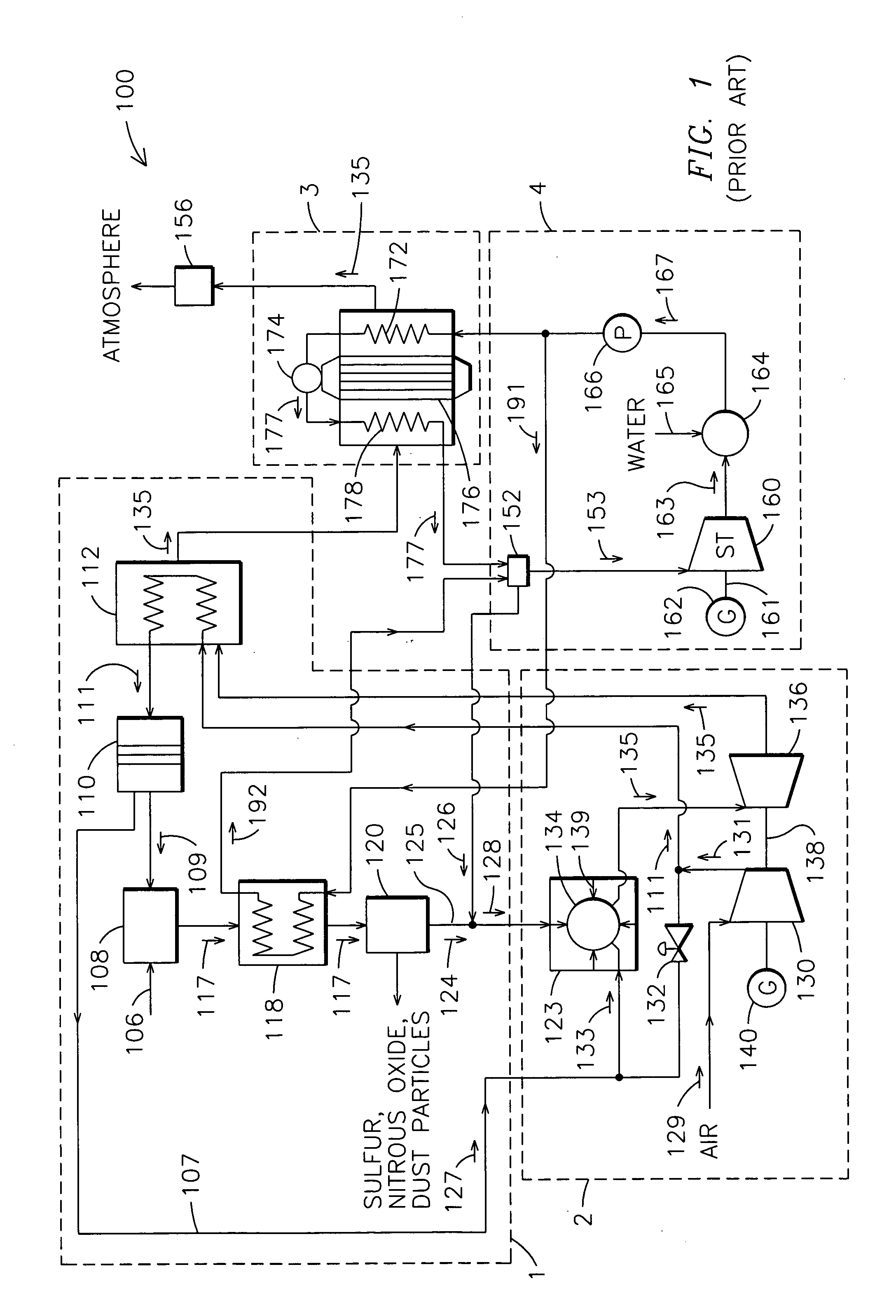
Optimized power generation system comprising an oxygen-fired combustor integrated with an air separation unit
InactiveUS6871502B2Maximize efficiencyImprove efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionHigh pressureCycle efficiency
A novel power generation system, more specifically an integrated power generation and air separation system and an integrated power generation and air separation process is provided. A key component of the system and process is an oxygen-fired combustor designed for gas turbine operating pressures. The combustor produces a high-temperature gas stream that enters one or more heat exchangers to generate / heat steam, and then enters one or more turbines to generate power. The steam from the heat exchanger drives one or more steam turbines to generate power, and the discharged steam is admitted to the combustor. To maximize cycle efficiency, steam extraction and reheat is incorporated in the process. Additional power is generated from a high-pressure nitrogen stream produced by an air separation unit (ASU). This process has the potential to attain high cycle efficiencies with zero emissions, while utilizing existing or near-term steam turbines, and moderate-pressure combustion systems.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Enhanced obiggs
A gas generating system comprises an air separation module (ASM) in fluid communication with a nitrogen enriched air (NEA) line and an oxygen enriched air (OEA) line. A valve is positioned in the OEA line and an oxygen sensor is positioned in the NEA line. The valve can be modulated in response to the oxygen sensor to create a backpressure forcing more airflow into the NEA line. The OEA line can be backpressured until a predetermined NEA oxygen concentration is reached.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
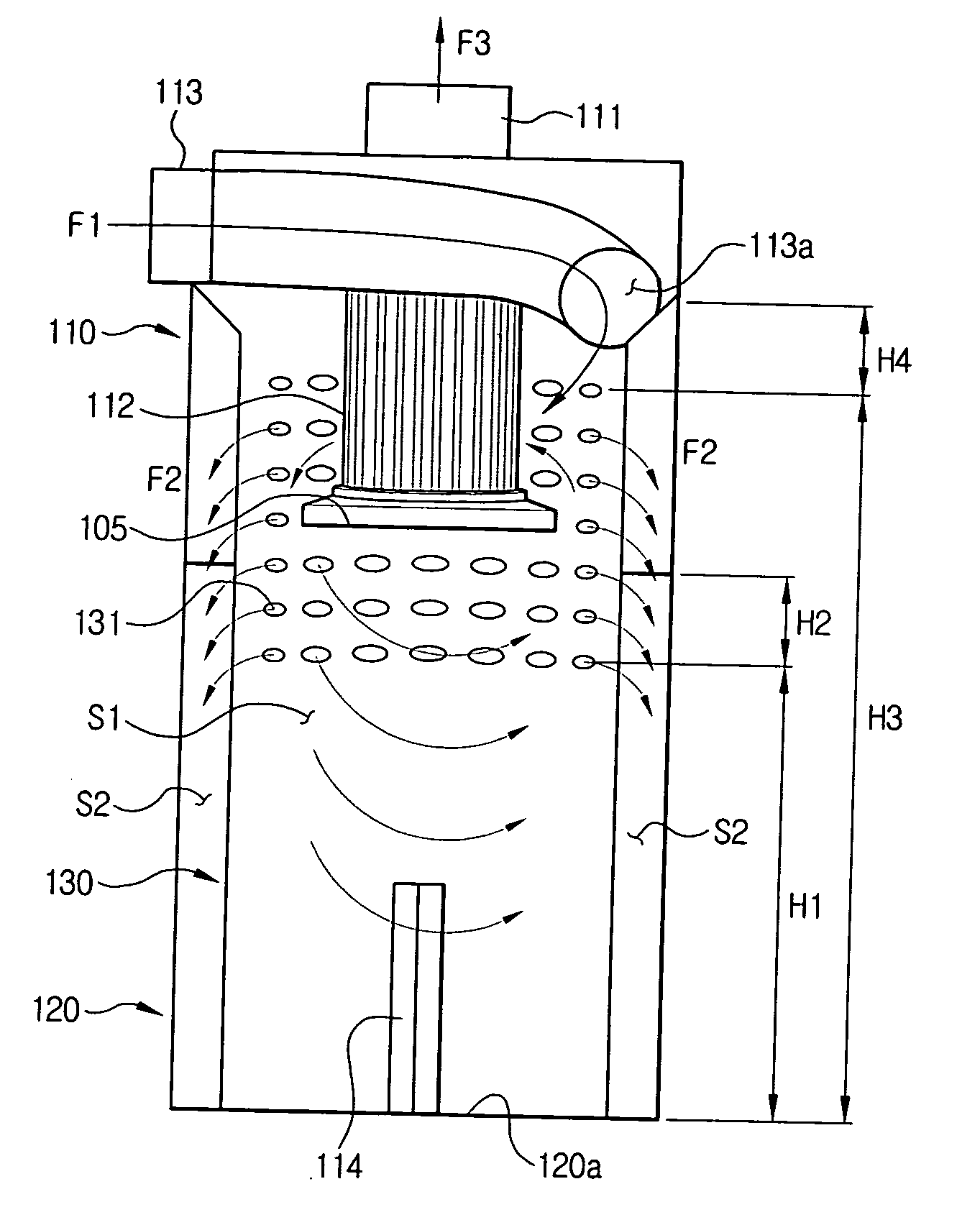
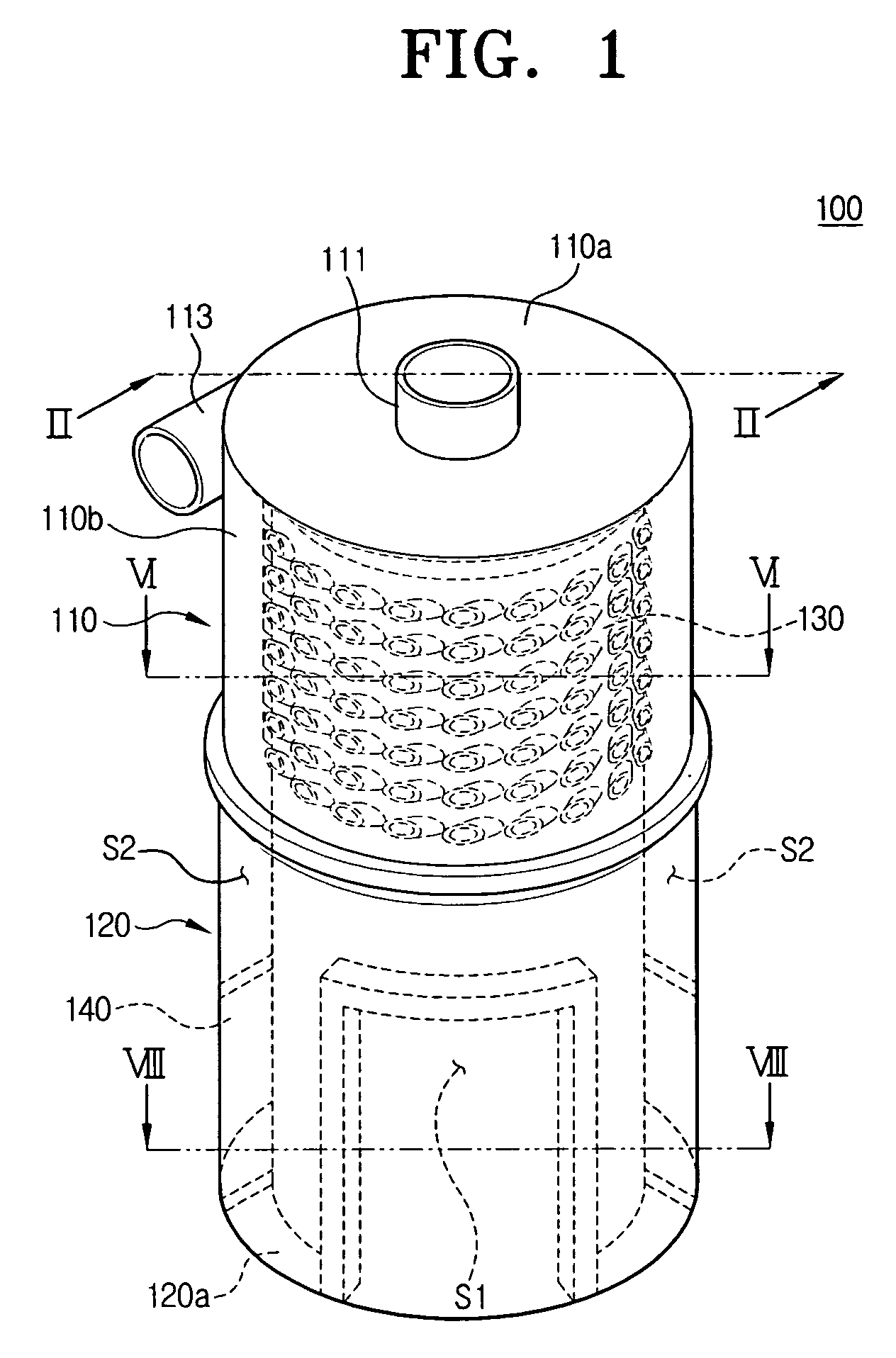
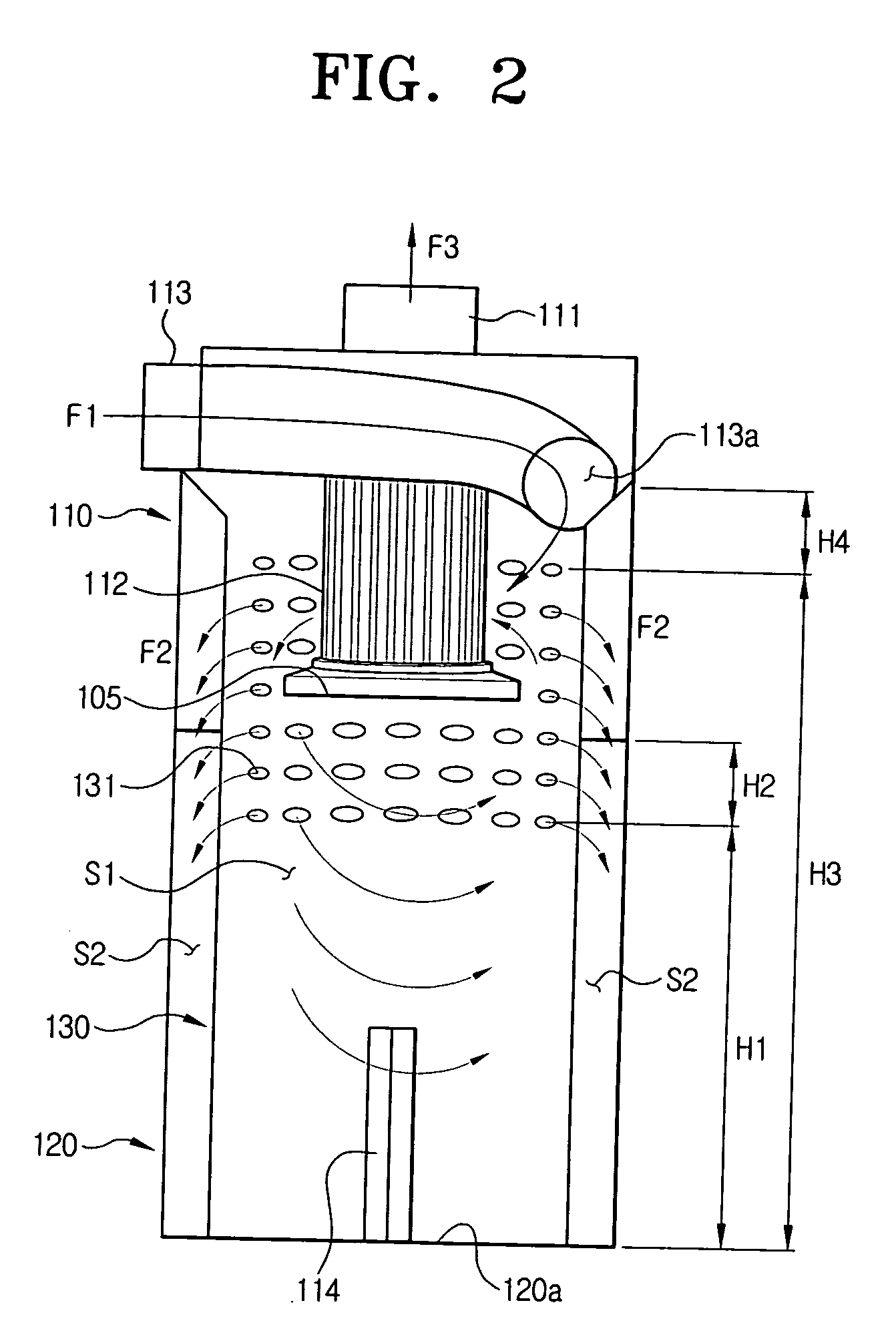
Dust collecting apparatus for a vacuum cleaner
InactiveUS20060130448A1Improved in capability of collecting moistureReversed direction vortexSuction cleanersAir separationMoisture
A dust collecting apparatus for a vacuum cleaner, for separating dust and moisture from external air, comprises a cyclone body having an air inlet and an air outlet, a screen mounted in the cyclone body and having a plurality of moisture passing holes, and a dust receptacle engaging the cyclone body to collect therein the dust and moisture separated from the air.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low power nitrogen enriched air generation system
InactiveUS6913636B2Reduce capacityReduce weightDispersed particle filtrationAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsNacelleInerting system
An inerting system provides air with reduced oxygen content by flowing and directing air through an air separation module. Optimal working pressure for the air separation module is obtained with two compressors. A first compressor elevates air from the aircraft cabin to a second pressure. The second pressure is at an intermediate level below the working pressure of the air separation module. A second compressor elevates air from the second pressure to the working pressure. The second compressor is driven by air that is exhausted through a turbine. The pressure difference between air at the working pressure and air required by the fuel distribution system is used to power the turbine and drive the second compressor.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
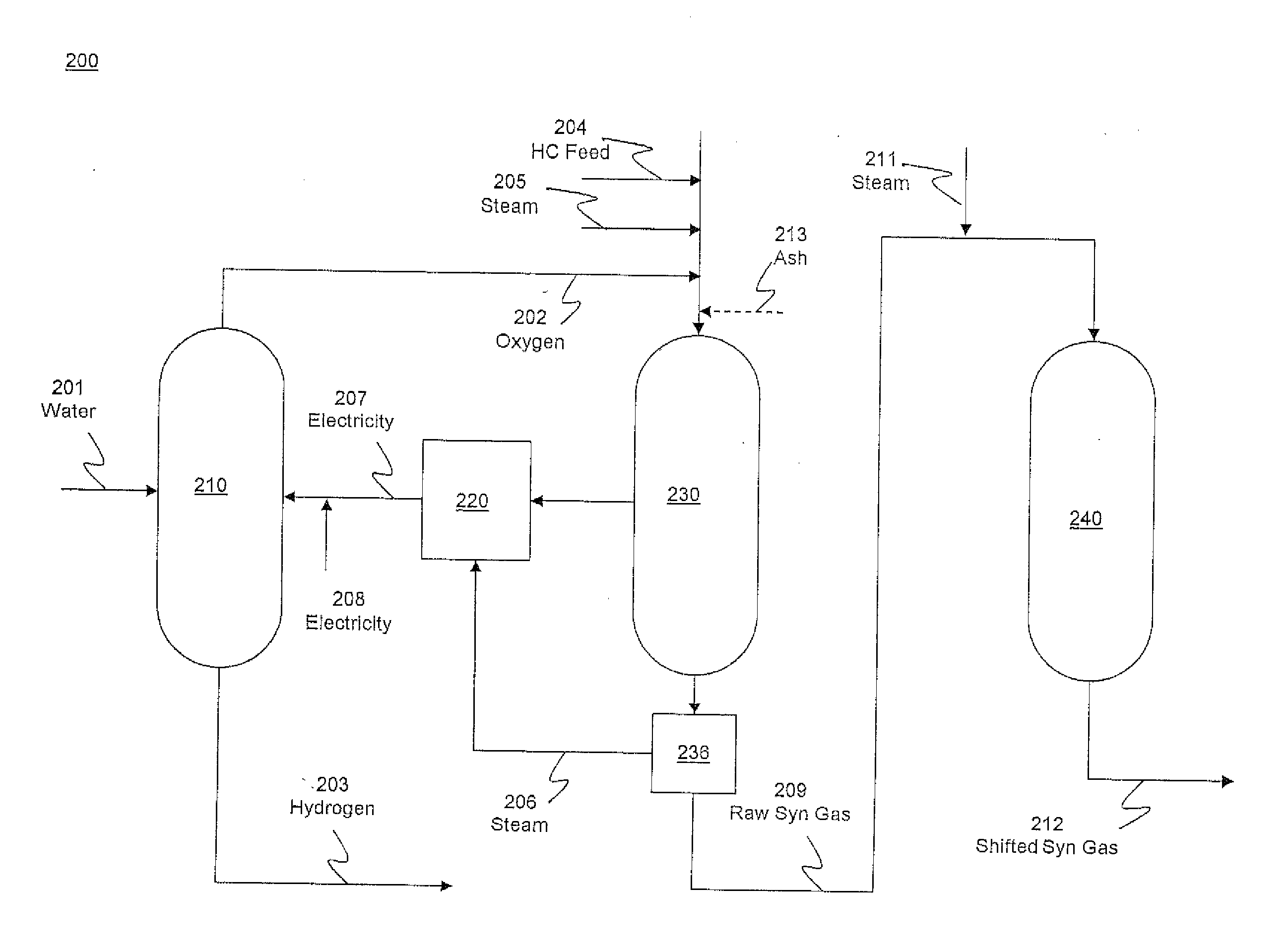
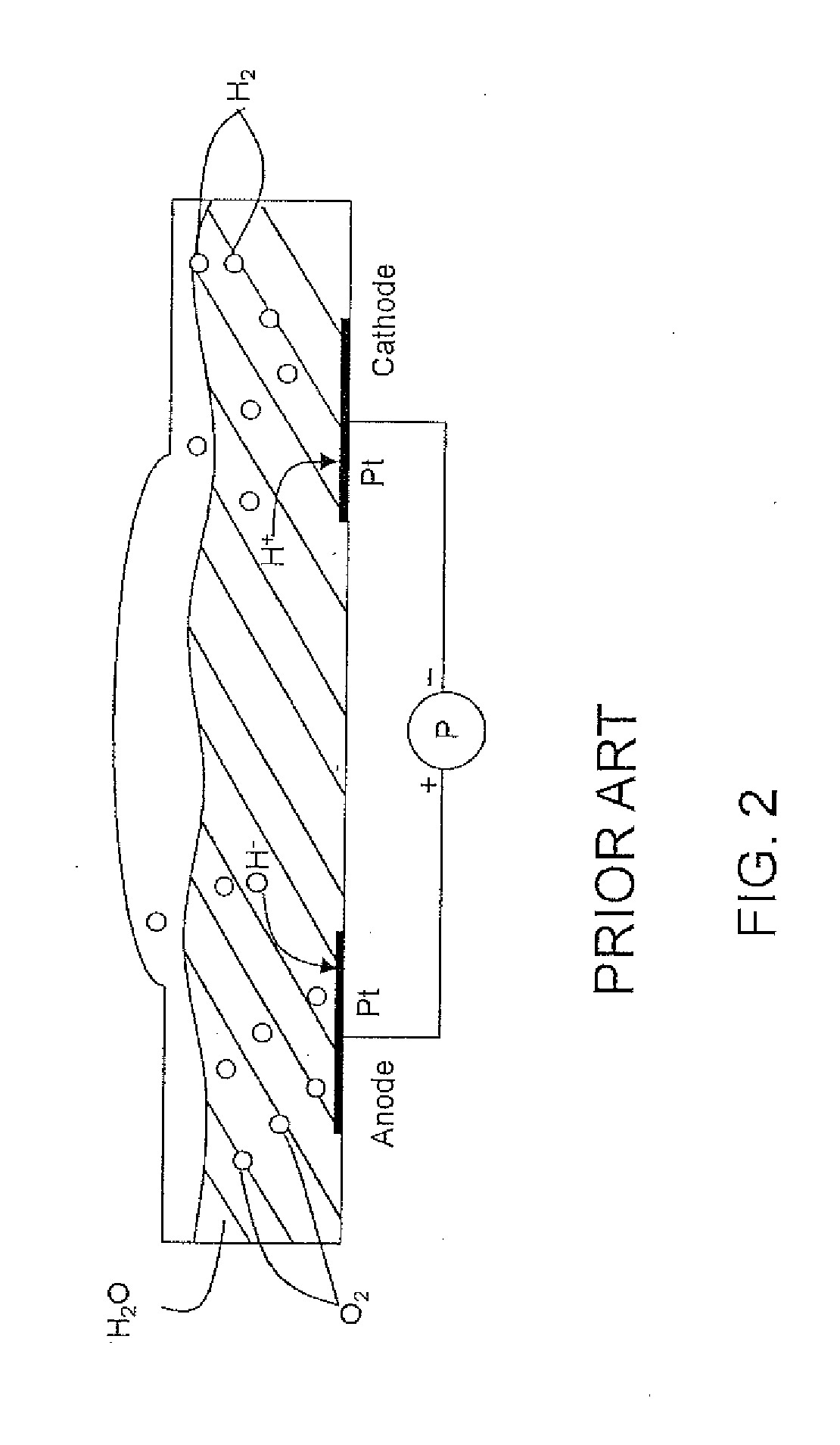
Hydrogen production from an integrated electrolysis cell and hydrocarbon gasification reactor
An integrated process for hydrogen gas production includes:a. operating a water electrolysis cell with an external source of electricity to produce oxygen and hydrogen;b. optionally operating an air separation unit to produce additional oxygen for the process;c. introducing a hydrocarbon feedstock into a membrane wall gasification reactor with an ash-forming material and steam, and oxygen from the electrolysis cell and, optionally, oxygen from the air separation unit to produce hot raw synthesis gas;d. passing the hot raw synthesis gas from the gasification reactor to a steam-generating heat exchanger to produce steam and a cooled raw synthesis gas;e. introducing the steam generated in the heat exchanger into a turbine to produce electricity to operate the electrolysis cell; andf. recovering the hydrogen gas from the water electrolysis cell and, optionally, subjecting the synthesis gas to a water-gas shift reaction to increase the hydrogen content and recovering the hydrogen.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com