Patents
Literature
25978 results about "Combustor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A combustor is a component or area of a gas turbine, ramjet, or scramjet engine where combustion takes place. It is also known as a burner, combustion chamber or flame holder. In a gas turbine engine, the combustor or combustion chamber is fed high pressure air by the compression system. The combustor then heats this air at constant pressure. After heating, air passes from the combustor through the nozzle guide vanes to the turbine. In the case of a ramjet or scramjet engines, the air is directly fed to the nozzle.
Flameless combustor
InactiveUS6019172AEasy to igniteImprove the level ofApparel holdersInsulationCombustorCombustion chamber
A combustor method and apparatus is provided. The method utilizes flameless combustion with one or more of three improvements to enhance ignition of the flameless combustor. A catalytic surface can be provided within a combustion chamber to provide flameless combustion at least in the vicinity of the catalytic surface at a temperature that is much lower than the autoignition temperature of fuel in air without the presence of the catalytic surface. Nitrous oxide or supplemental oxygen may also be used as an oxidant either instead of air or with air to reduce ignition temperatures. Further, electrical energy can be passed through the fuel conduit, raising the temperature of the conduit to a temperature above which the fuel will ignite when combined with the oxidant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method and system for supplying hydrogen for use in fuel cells
InactiveUS6348278B1Reduce hydrogen concentrationImprove concentrationElectricity cogenerationRegenerative fuel cellsHydrogenCombustor
The present invention provides a method and system for efficiently producing hydrogen that can be supplied to a fuel cell. The method and system of the present invention produces hydrogen in a reforming reactor using a hydrocarbon stream and water vapor stream as reactants. The hydrogen produced is purified in a hydrogen separating membrane to form a retentate stream and purified hydrogen stream. The purified hydrogen can then be fed to a fuel cell where electrical energy is produced and a fuel cell exhaust stream containing water vapor and oxygen depleted air is emitted. In one embodiment of the present invention, a means and method is provided for recycling a portion of the retentate stream to the reforming reactor for increased hydrogen yields. In another embodiment, a combustor is provided for combusting a second portion of the retentate stream to provide heat to the reforming reaction or other reactants. In a preferred embodiment, the combustion is carried out in the presence of at least a portion of the oxygen depleted air stream from the fuel cell. Thus, the system and method of the present invention advantageously uses products generated from the system to enhance the overall efficiency of the system.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Dry 3-way catalytic reduction of gas turbine NOx
ActiveUS20090284013A1Reduction in amount of NOxIncrease carbon dioxide concentrationInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustion chamberGas compressor
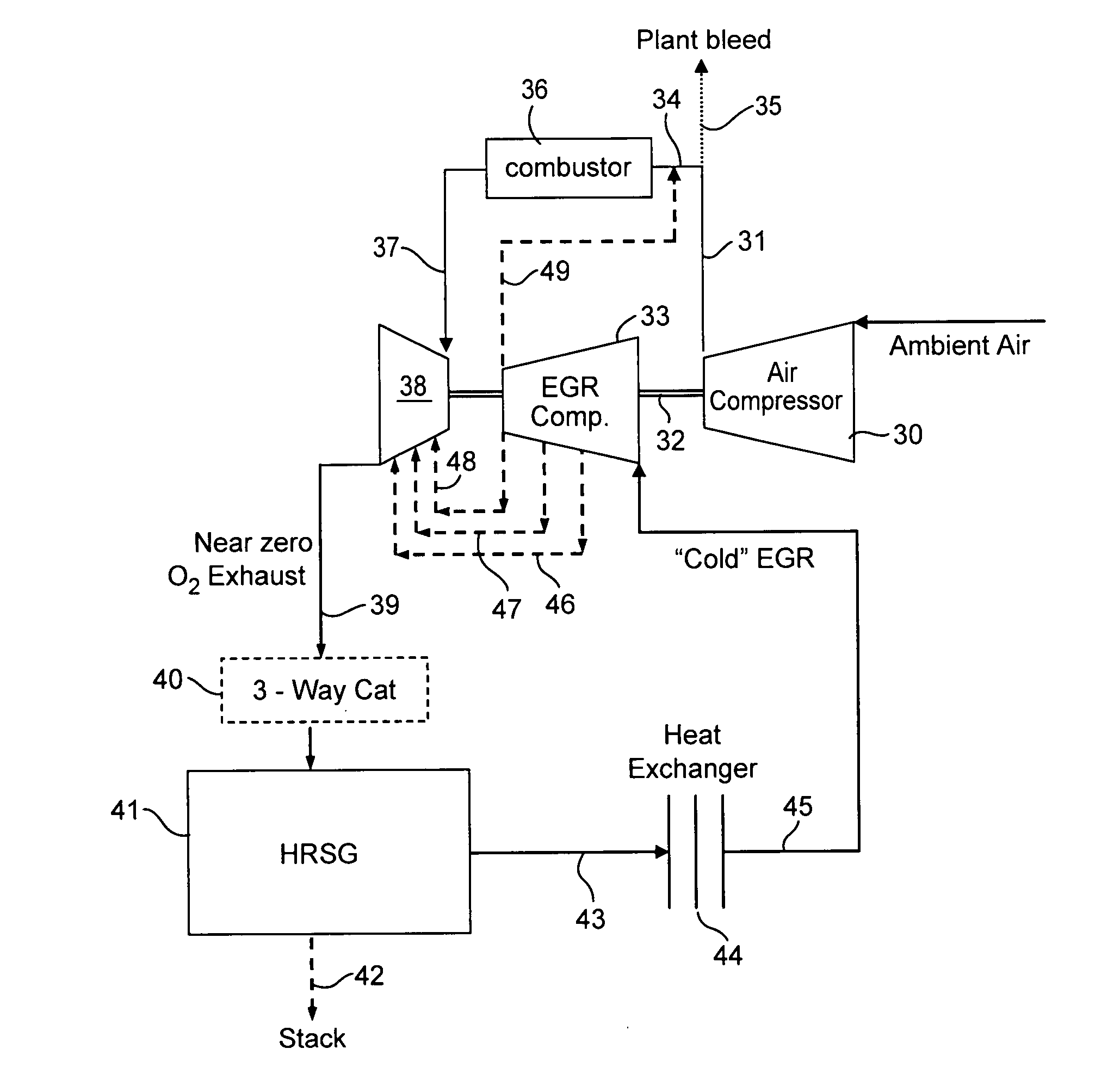
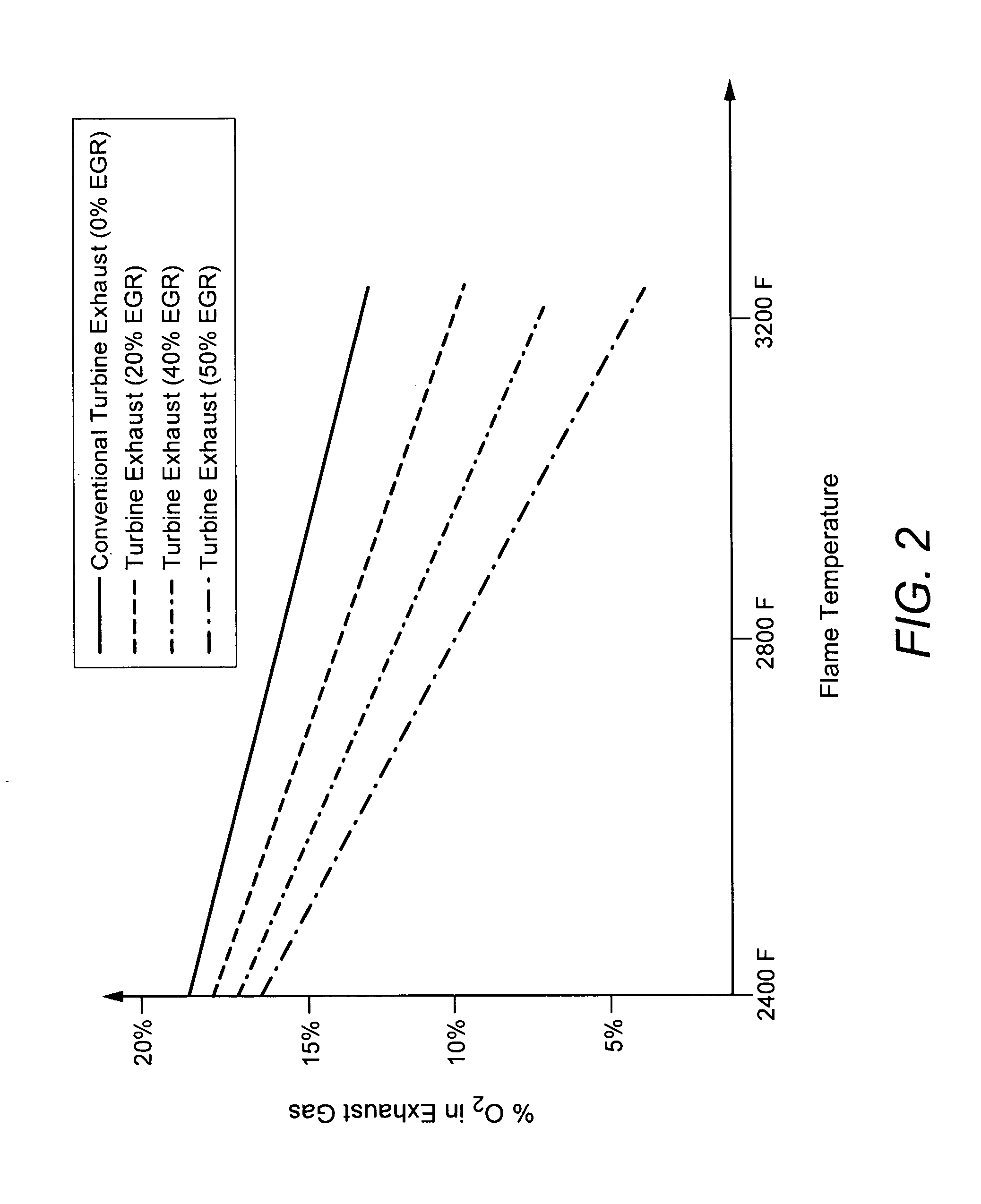
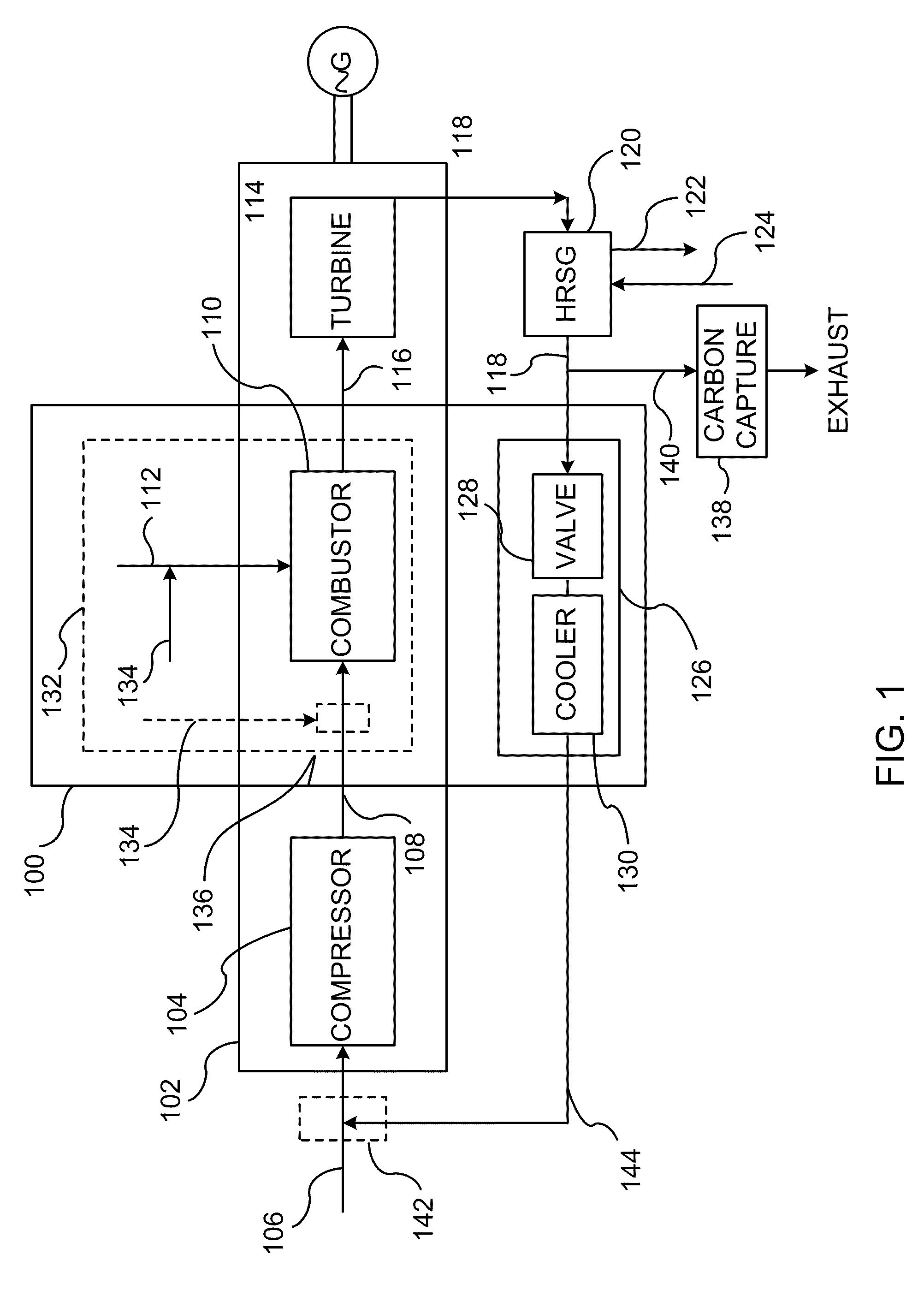
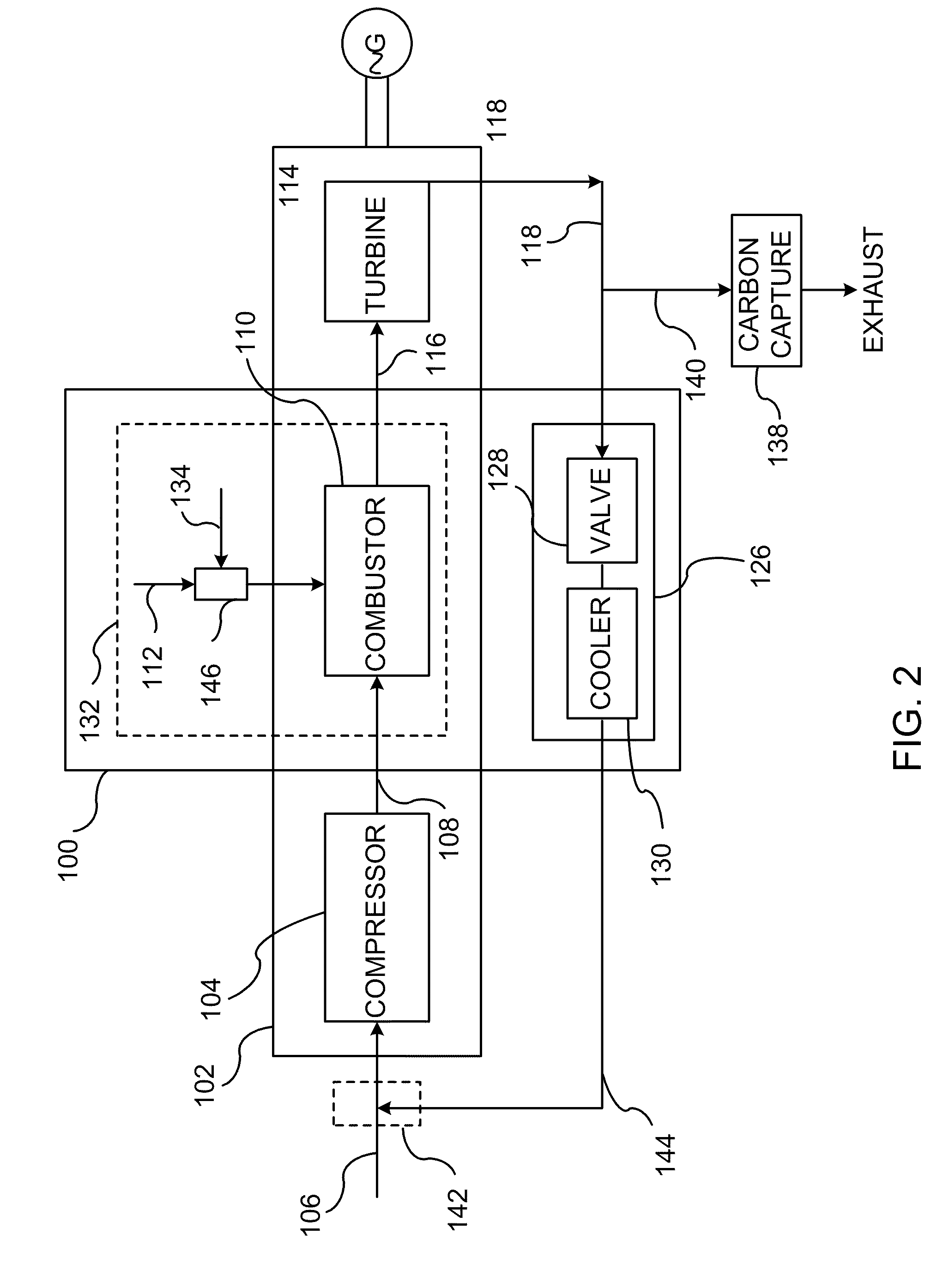
A power generation system capable of eliminating NO, components in the exhaust gas by using a 3-way catalyst, comprising a gas compressor to increase the pressure of ambient air fed to the system; a combustor capable of oxidizing a mixture of fuel and compressed air to generate an expanded, high temperature exhaust gas; a gas turbine engine that uses the force of the high temperature gas; an exhaust gas recycle (EGR) stream back to the combustor; a 3-way catalytic reactor downstream of the gas turbine engine outlet which treats the exhaust gas stream to remove substantially all of the NOx components; a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG); an EGR compressor; and an electrical generator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Staged combustion of a low heating value fuel gas for driving a gas turbine
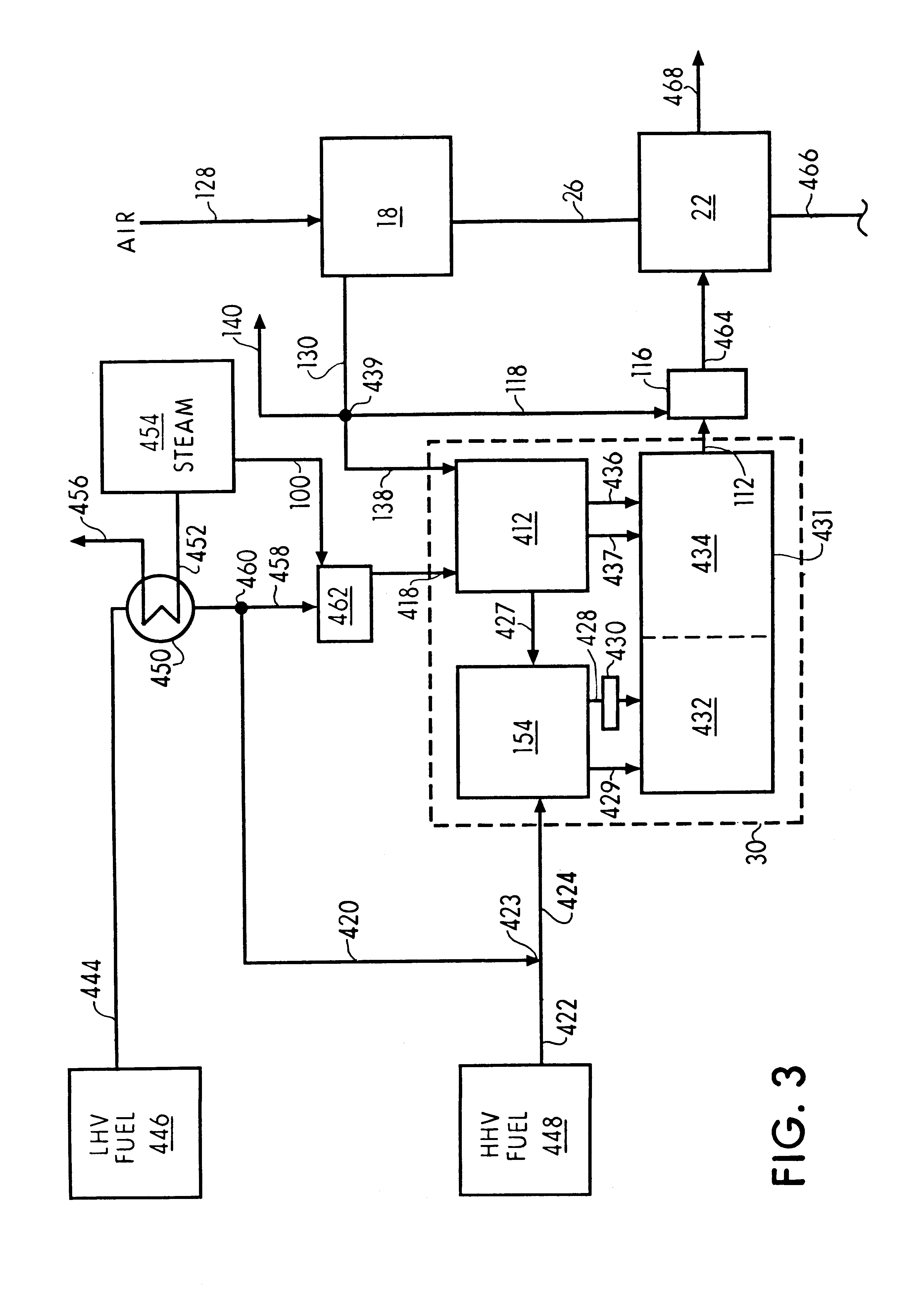
A process is provided for combusting a low heating value fuel gas in a combustor to drive an associated gas turbine. A low heating value fuel gas feed is divided into a burner portion and a combustion chamber portion. The combustion chamber portion and a combustion air are conveyed into a mixing zone of the combustor to form an air / fuel mixture. The burner portion is conveyed into a flame zone of the combustor through a burner nozzle while a first portion of the air / fuel mixture is conveyed into the flame zone through a burner port adjacent to the burner nozzle. The burner portion and first portion of the air / fuel mixture are contacted in the flame zone to combust the portions and produce flame zone products. The flame zone products are conveyed into an oxidation zone of the combustor downstream of the flame zone while a second portion of the air / fuel mixture is also conveyed into the oxidation zone. The second portion is combusted in the oxidation zone in the presence of the flame zone products to produce combustion products. The combustion products are conveyed into the associated gas turbine and drive the gas turbine.
Owner:MARATHON OIL CO +1
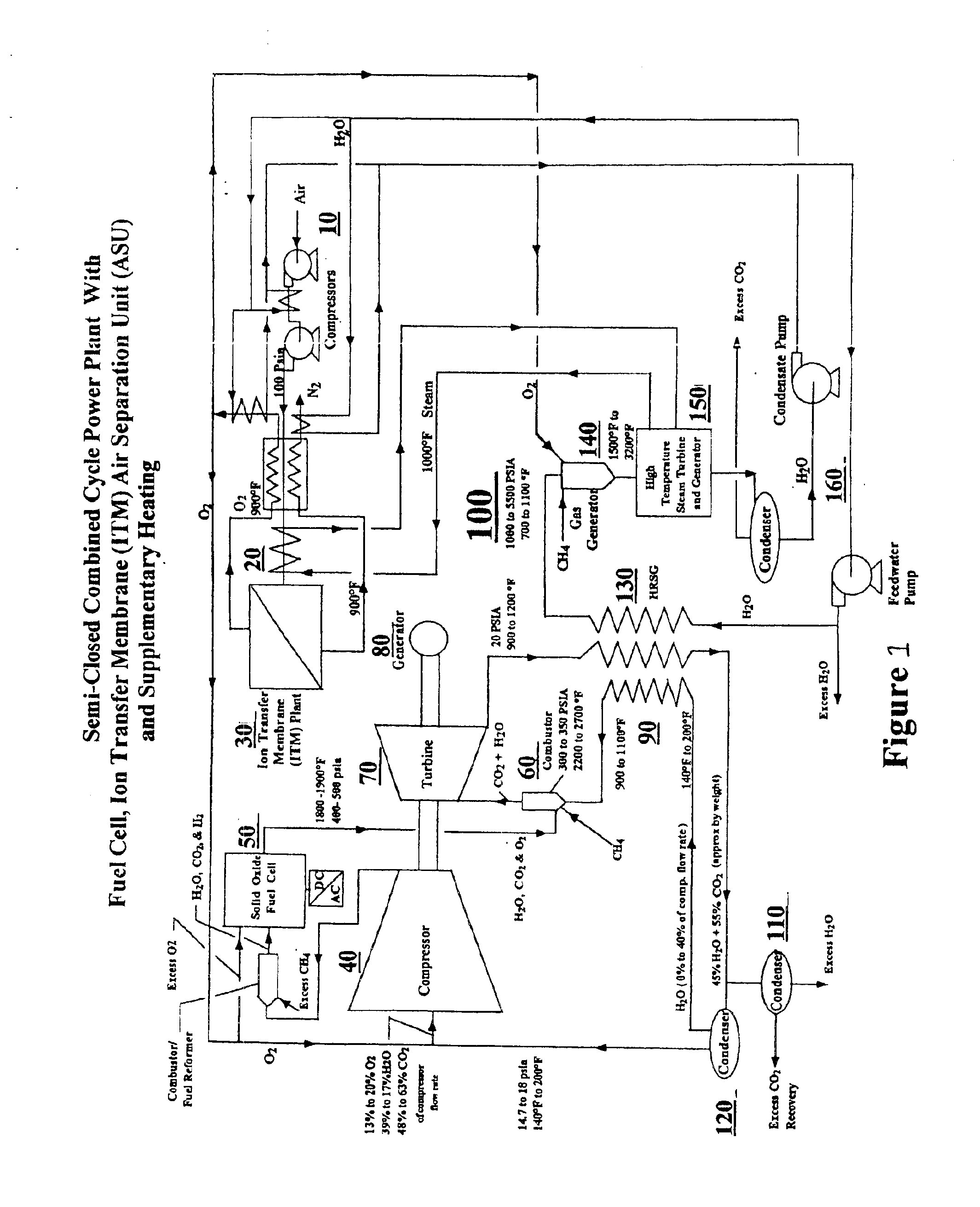
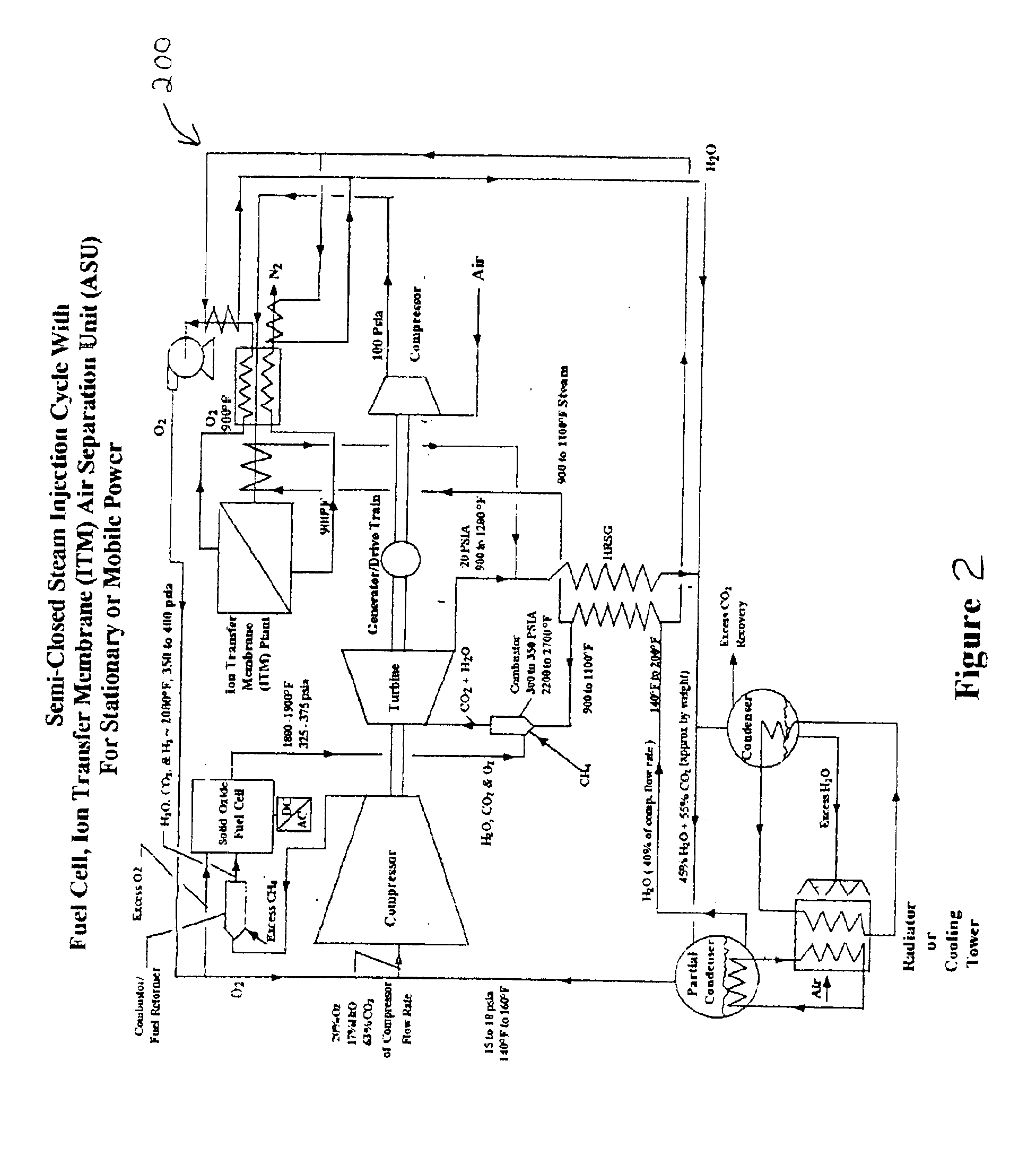
System and method for high efficiency power generation using a carbon dioxide circulating working fluid
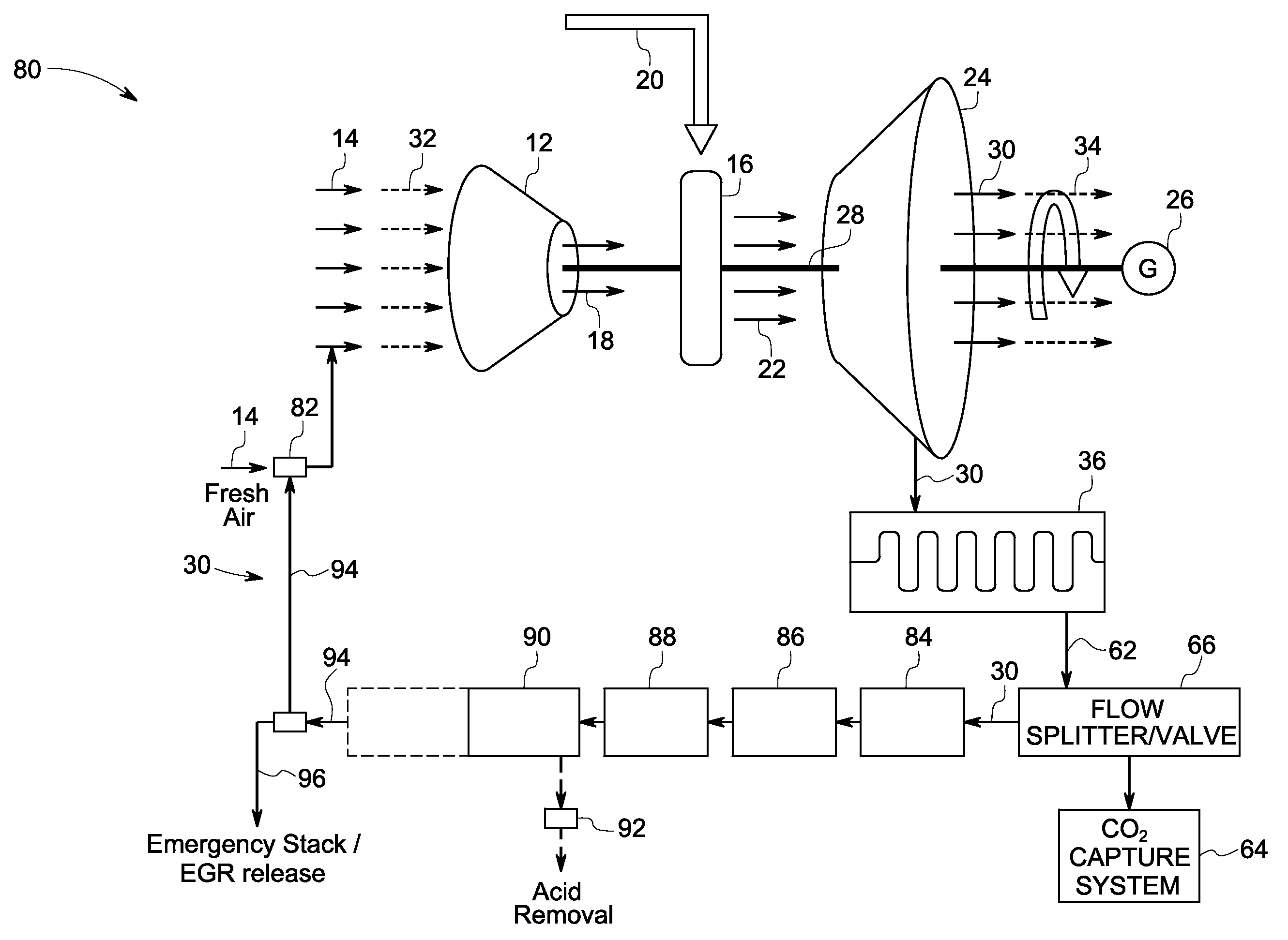
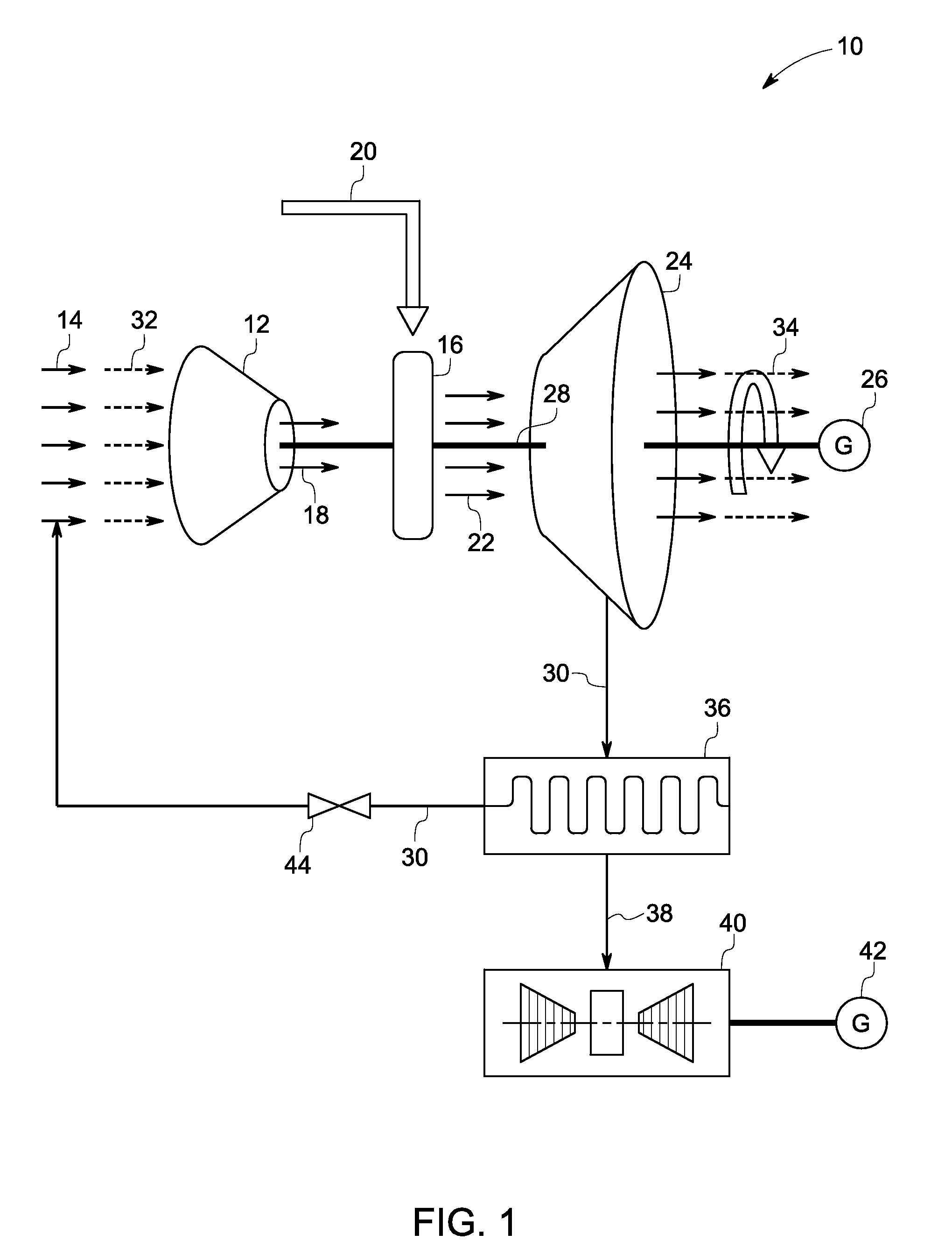
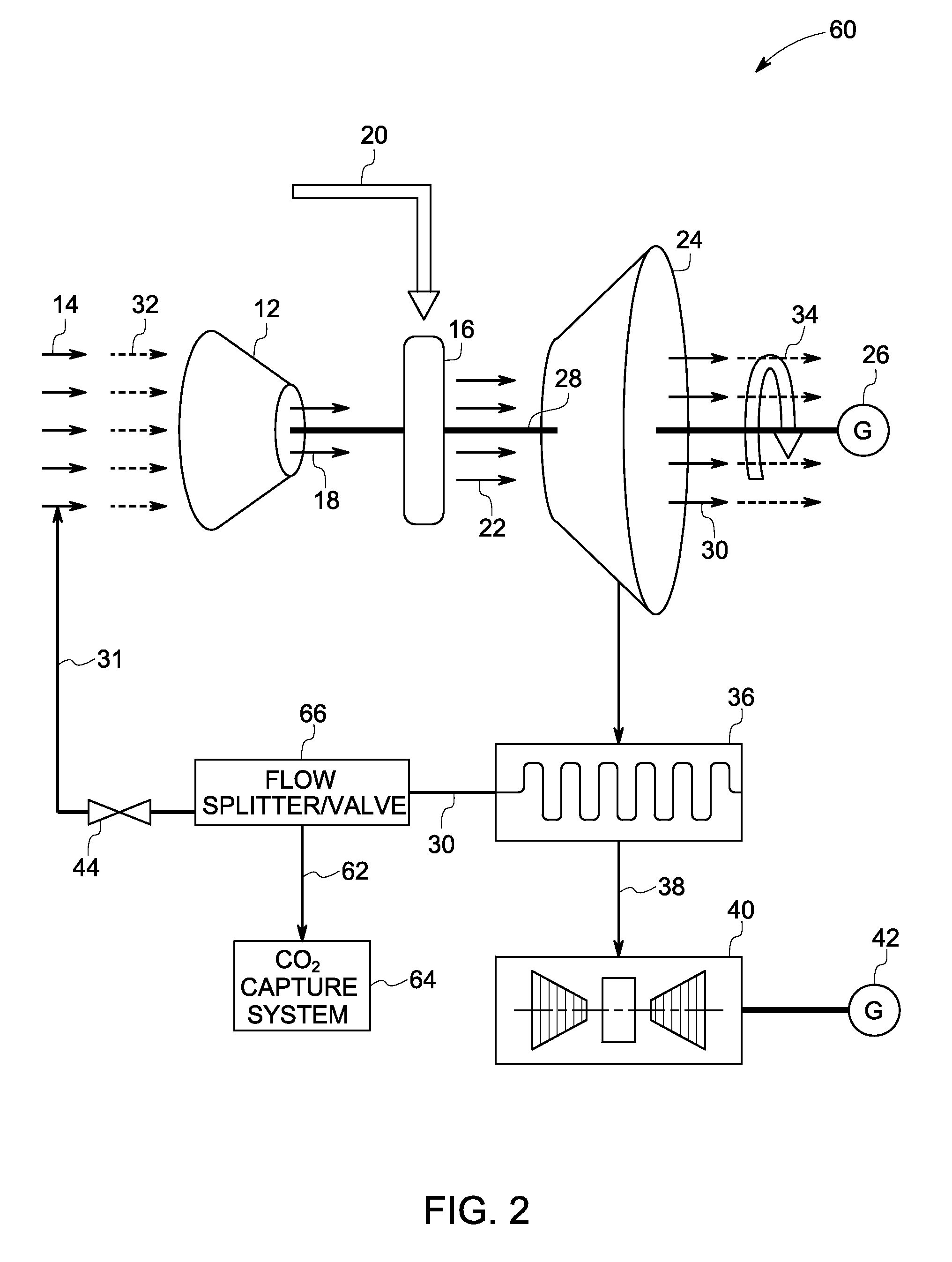
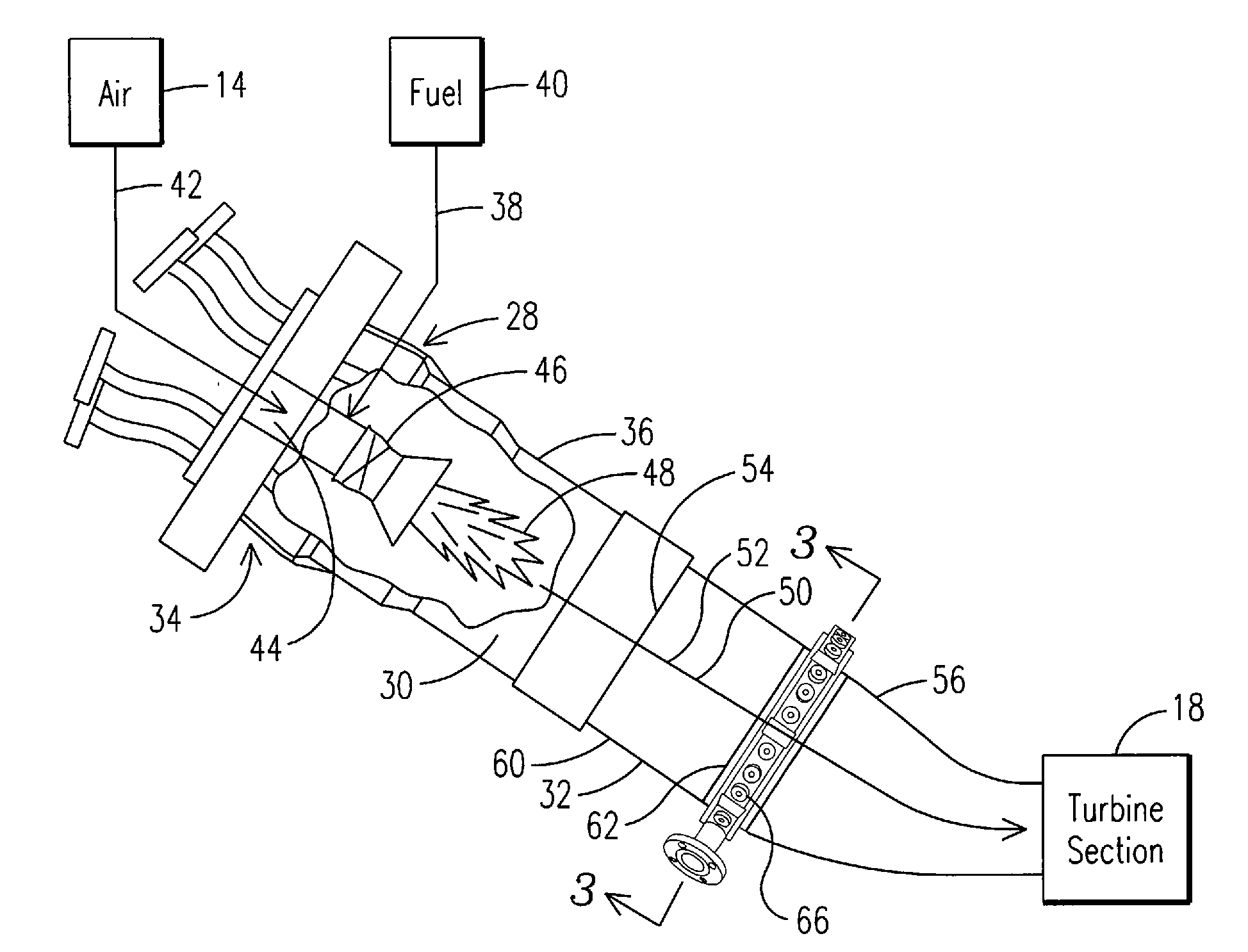
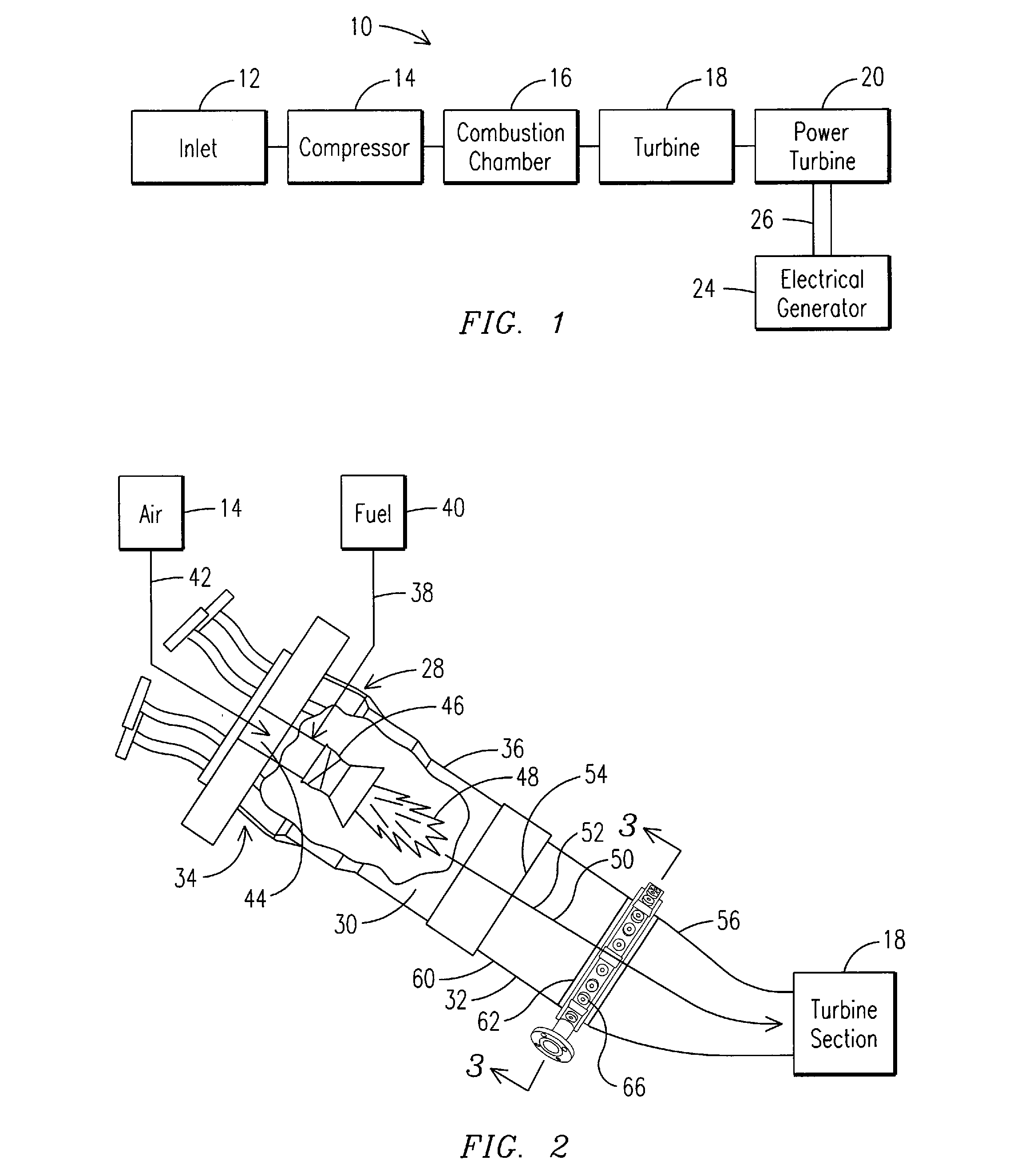
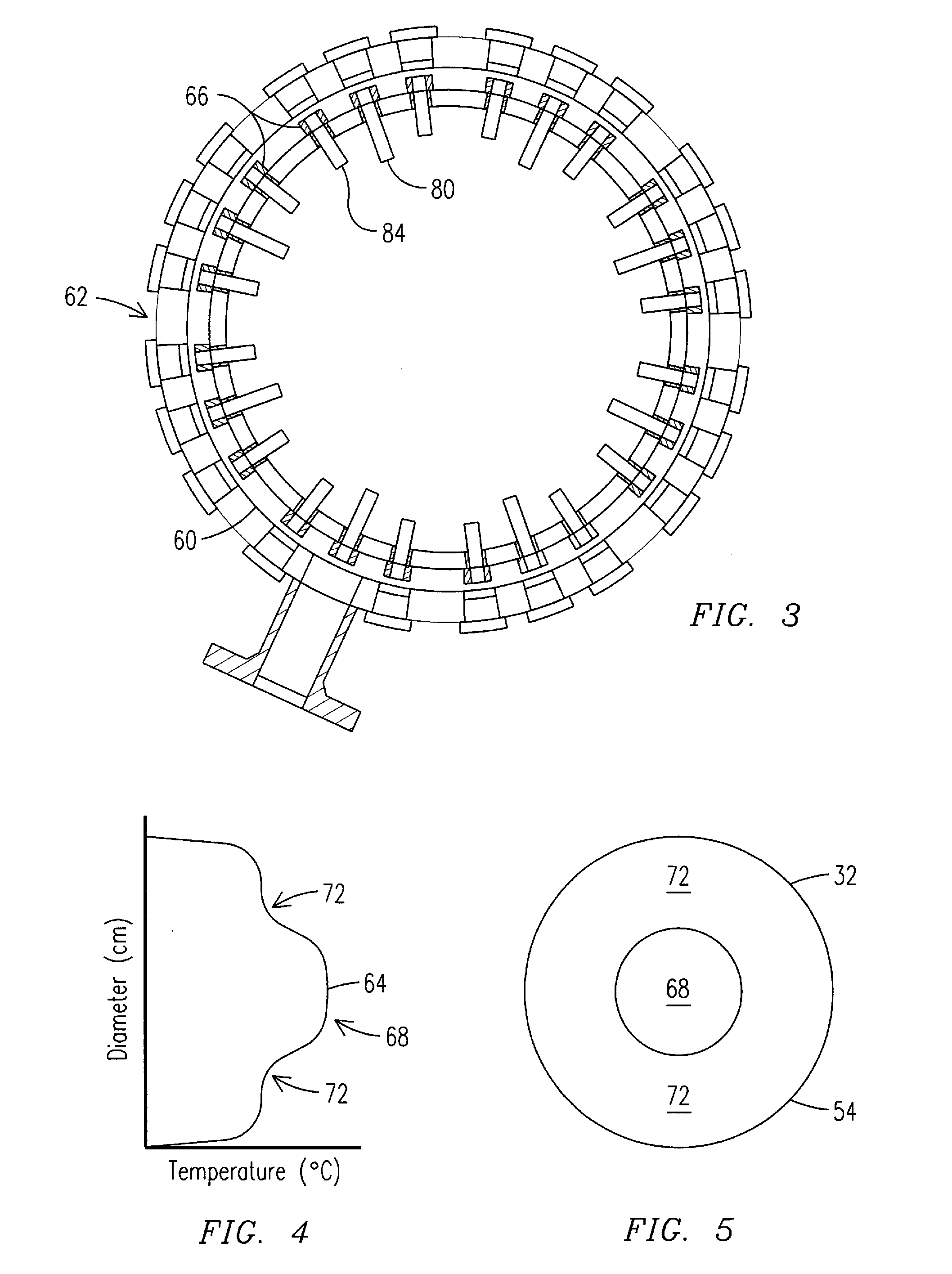
ActiveUS20110179799A1Improve efficiencyIncrease pressure ratioSolidificationLiquefactionWorking fluidCombustor
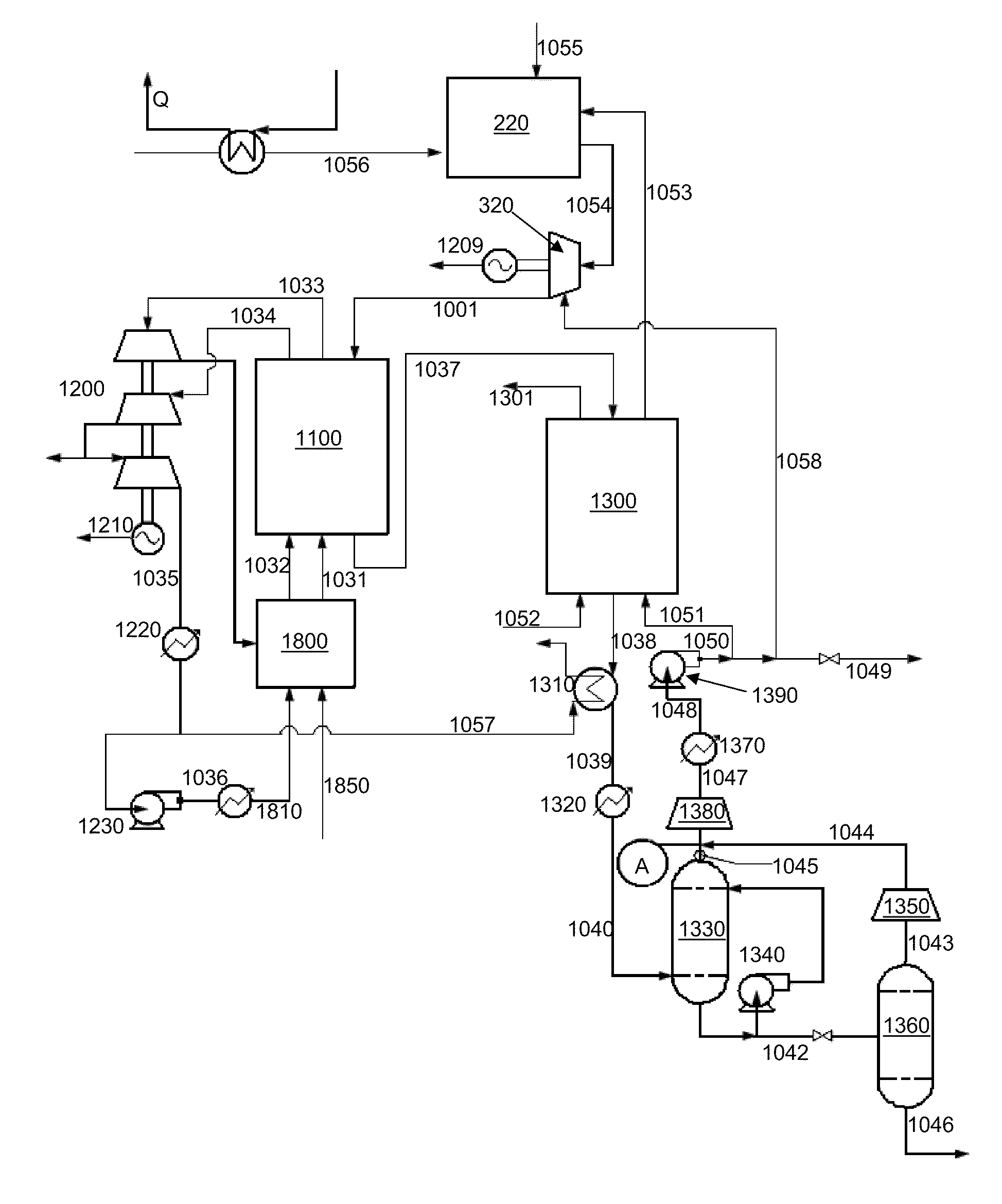
The present invention provides methods and system for power generation using a high efficiency combustor in combination with a CO2 circulating fluid. The methods and systems advantageously can make use of a low pressure ratio power turbine and an economizer heat exchanger in specific embodiments. Additional low grade heat from an external source can be used to provide part of an amount of heat needed for heating the recycle CO2 circulating fluid. Fuel derived CO2 can be captured and delivered at pipeline pressure. Other impurities can be captured.
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
Gas turbine engine assembly and method of assembling same
A method of assembling a gas turbine assembly includes providing a core gas turbine engine including a high-pressure compressor, a combustor, and a turbine, coupling a low-pressure turbine axially aft from the core gas turbine engine, coupling a fan assembly axially forward from the core gas turbine engine, and coupling a booster compressor to the low-pressure turbine such that the booster compressor and the low-pressure turbine rotate at a first rotational speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Burner tube and method for mixing air and gas in a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS6993916B2Good mixing propertiesImprove flame stabilityContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustorGas turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transportable pumping unit and method of fracturing formations
InactiveUS20060260331A1Increase chanceReduced operating requirementsNon-pressured vesselsPumpsCombustorControl system
A high capacity pumper for liquefied gas incorporates multiple pumping systems distributed in a parallel arrangement and in opposing orientation on a transportable platform such as a trailer. Vaporizers incorporate a burner control system utilizing a primary set of burners operating a baseline and a secondary set of burners providing fine regulating control. A system for fracturing formations is now possible using a minimum number of components including the high capacity pumper, a coiled tubing rig and a source of liquefied gas. An improved manifold for a cryogenic plunger pump includes unions and angled connectors between a supply conduit and each of a plurality of pump heads.
Owner:CENTURY OILFIELD SERVICES
Supercharging system for gas turbines
InactiveUS7065953B1Increase turbine capacityReduce installation costsEfficient propulsion technologiesGas turbine plantsCombustorPower station
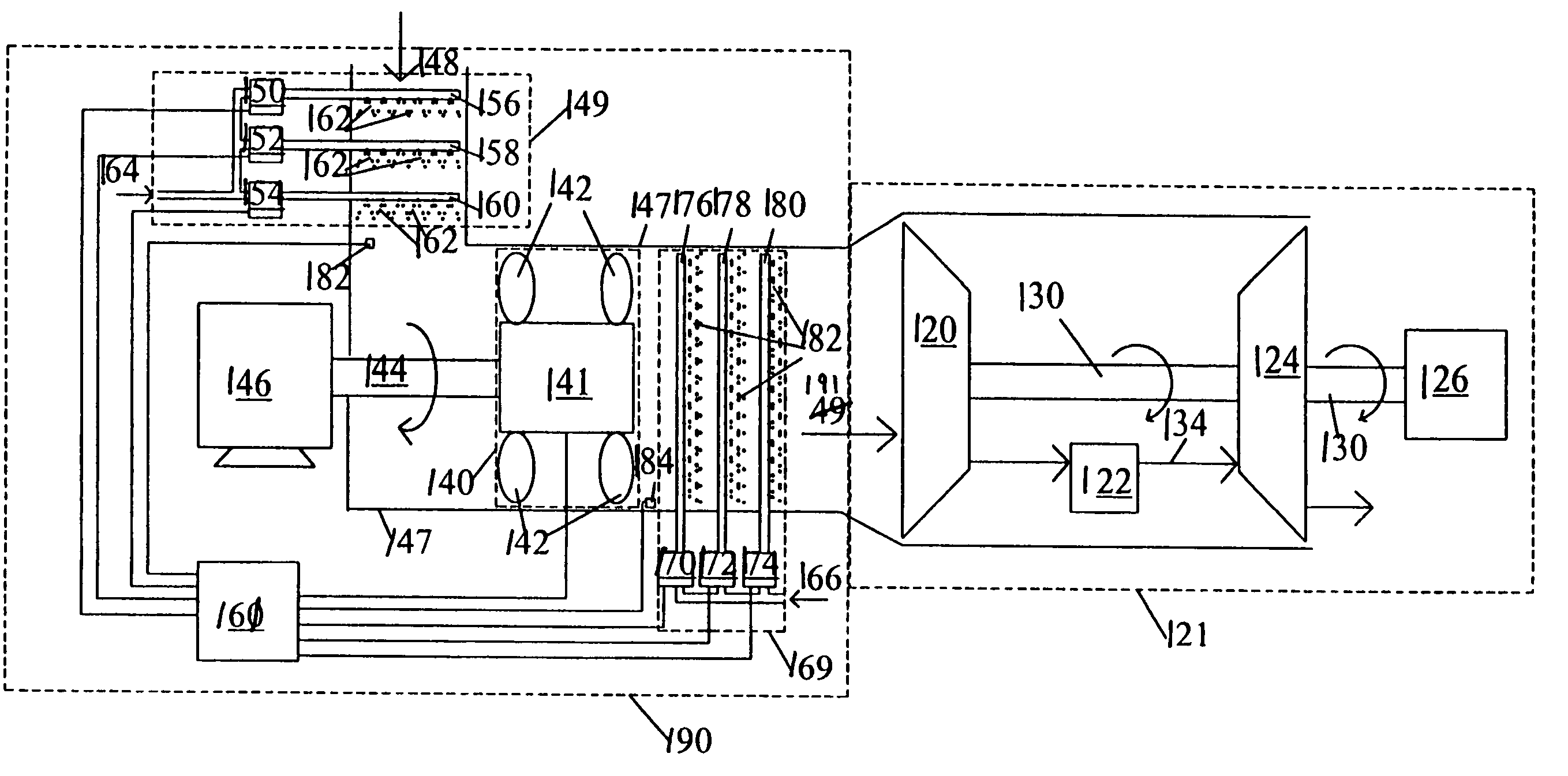
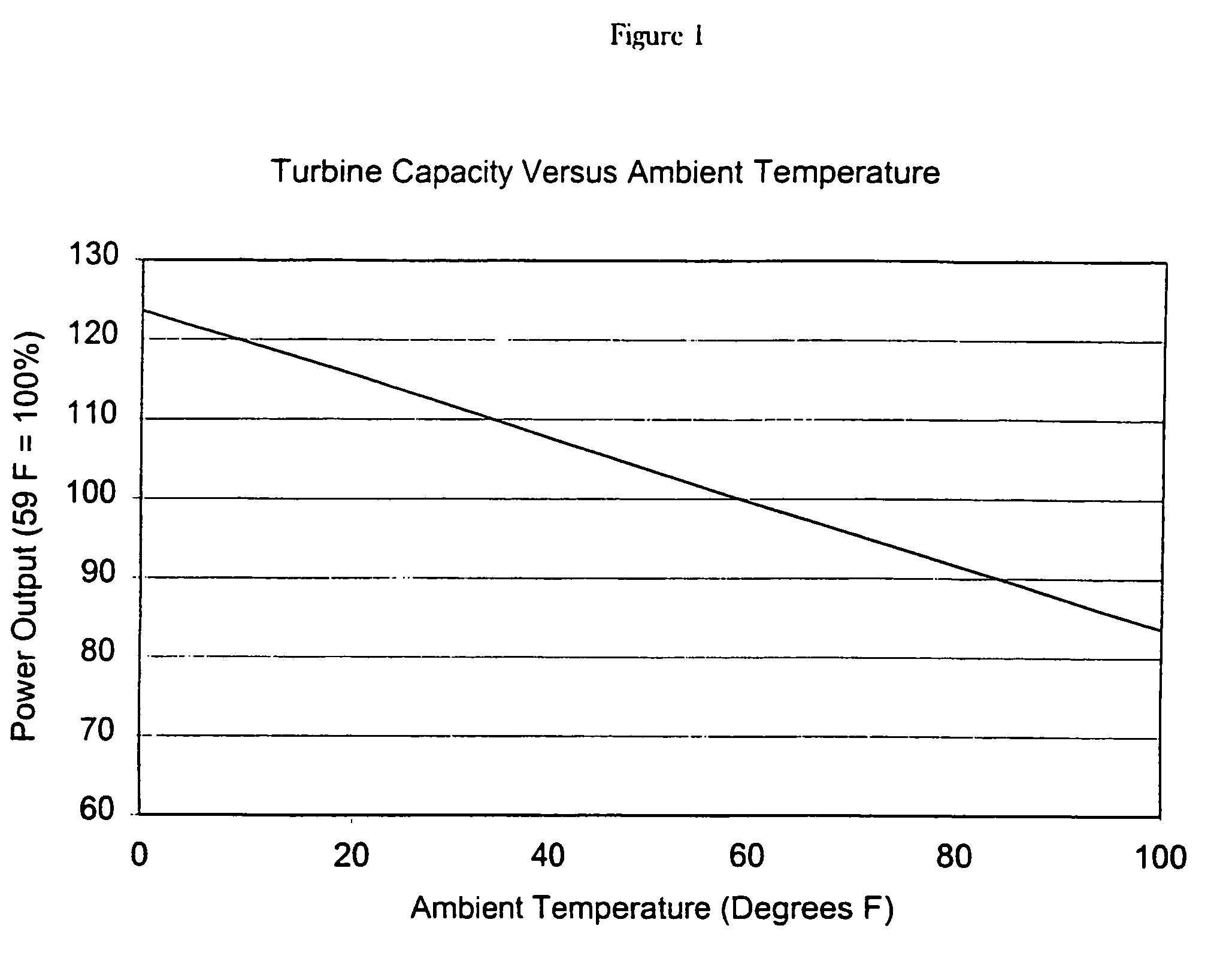
A supercharging system for gas turbine power plants (11). The system includes a supercharging fan (30, 32) and controller (50) for limiting turbine power output to prevent overload of the generator (28) at lower ambient temperatures. The controller can limit power output by burner control, inlet temperature control, control of supercharging fan pressure and other options. The system can be retrofit on an existing turbine without replacing the generator and associated parts.
Owner:ENHANCED TURBINE OUTPUT HLDG
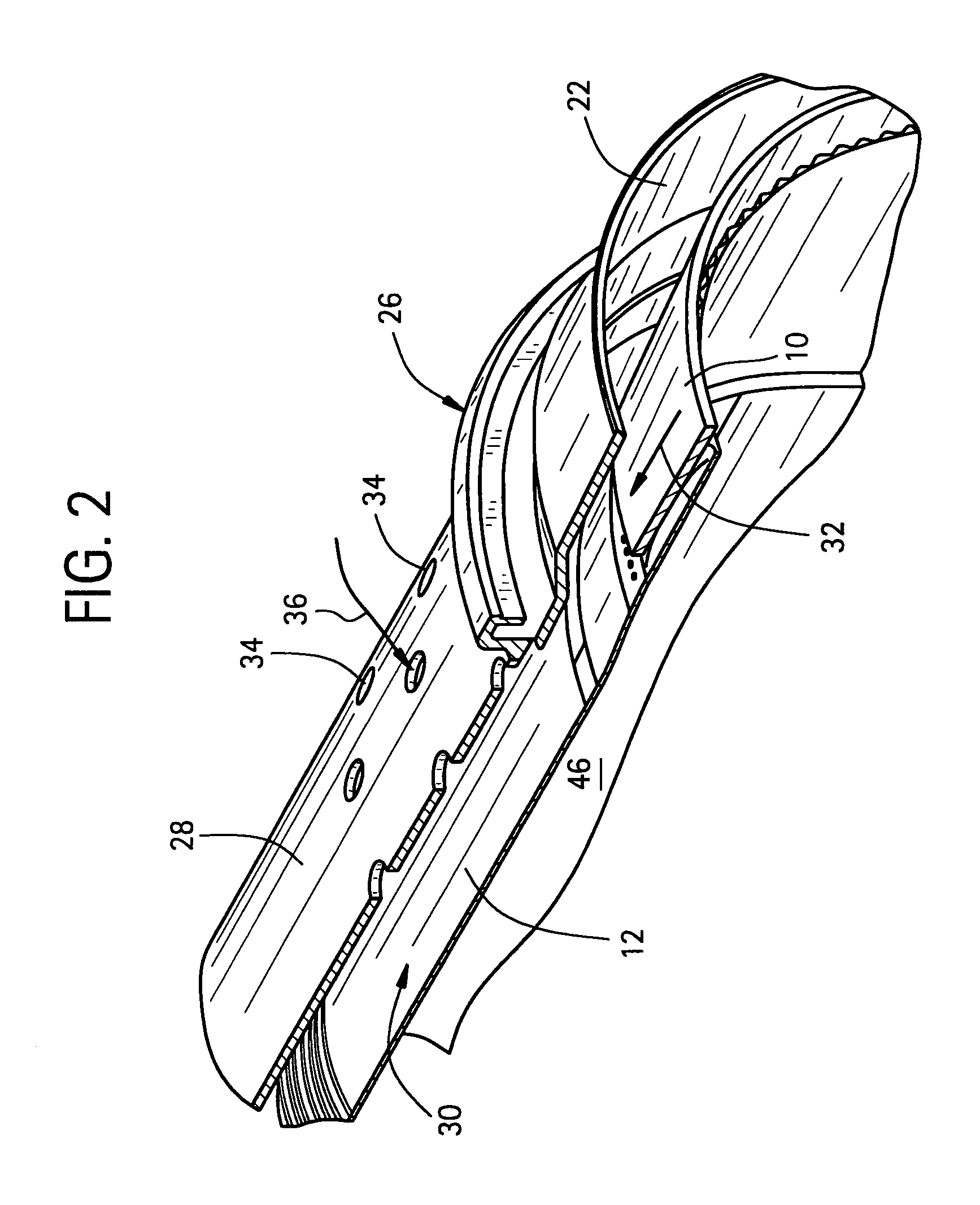
Method and apparatus for cooling combustor liner and transition piece of a gas turbine
ActiveUS7010921B2Easy to installContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustorTurbine
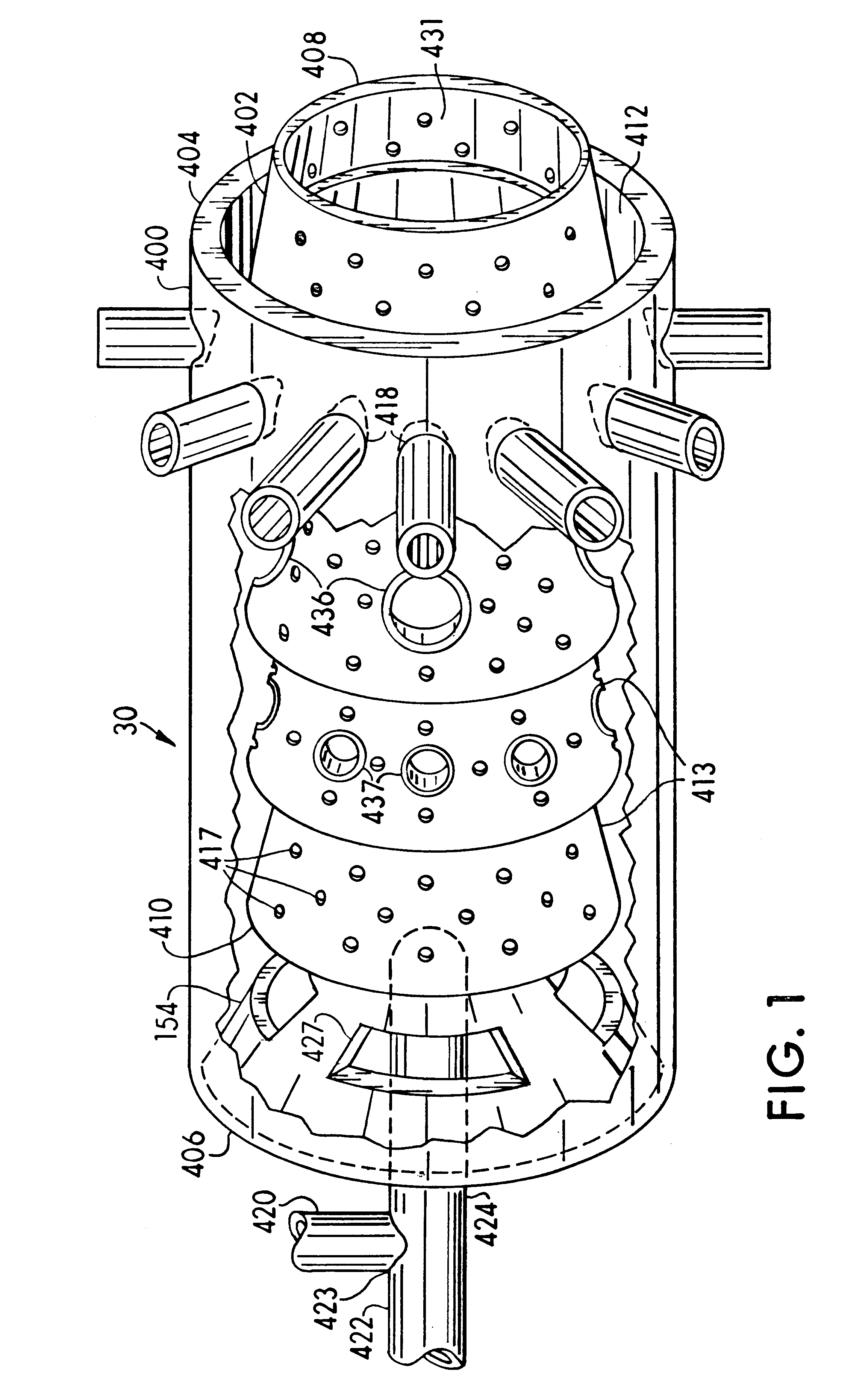
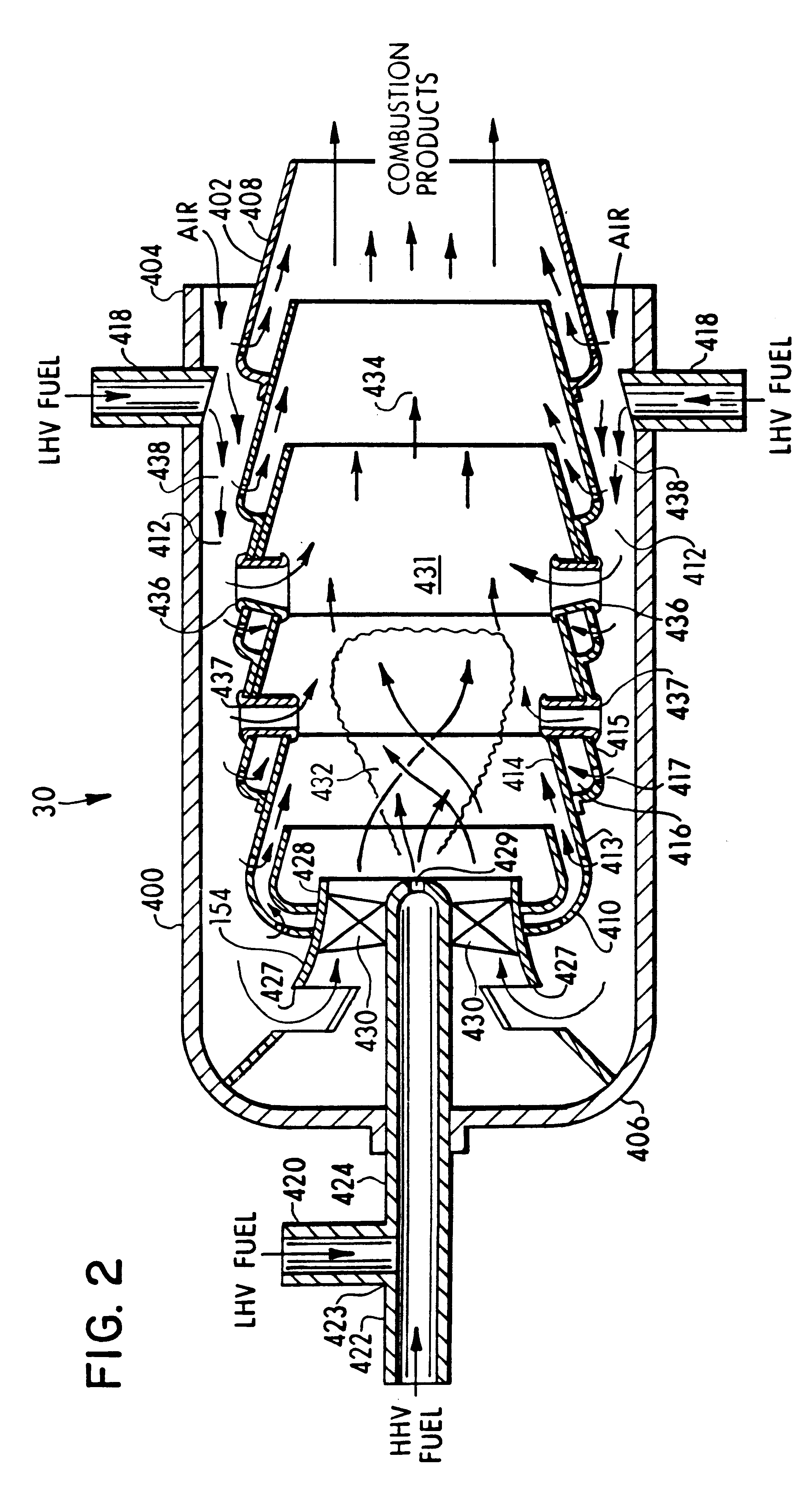
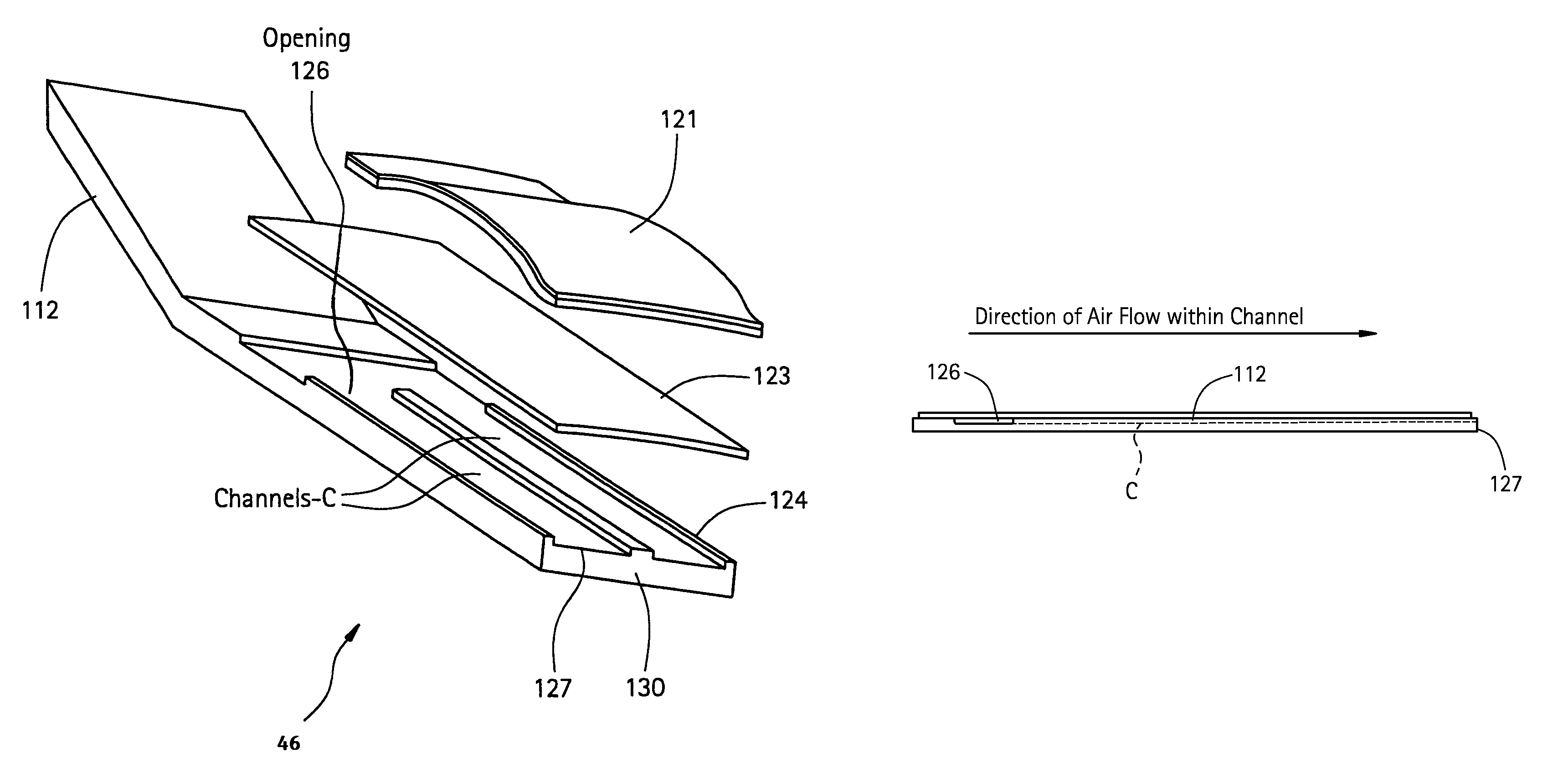
A method and apparatus for cooling a combustor liner and transitions piece of a gas turbine include a combustor liner with a plurality of circular ring turbulators arranged in an array axially along a length defining a length of the combustor liner and located on an outer surface thereof; a first flow sleeve surrounding the combustor liner with a first flow annulus therebetween including a plurality of axial channels (C) extending over a portion of an aft end portion of the liner parallel to each other, the cross-sectional area of each channel either constant or varying along the length of the channel, the first flow sleeve having a plurality of rows of cooling holes formed about a circumference of the first flow sleeve for directing cooling air from the compressor discharge into the first flow annulus; a transition piece connected to the combustor liner and adapted to carry hot combustion gases to a stage of the turbine; a second flow sleeve surrounding the transition piece a second plurality of rows of cooling apertures for directing cooling air into a second flow annulus between the second flow sleeve and the transition piece; wherein the first plurality of cooling holes and second plurality of cooling apertures are each configured with an effective area to distribute less than 50% of compressor discharge air to the first flow sleeve and mix with cooling air from the second flow annulus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
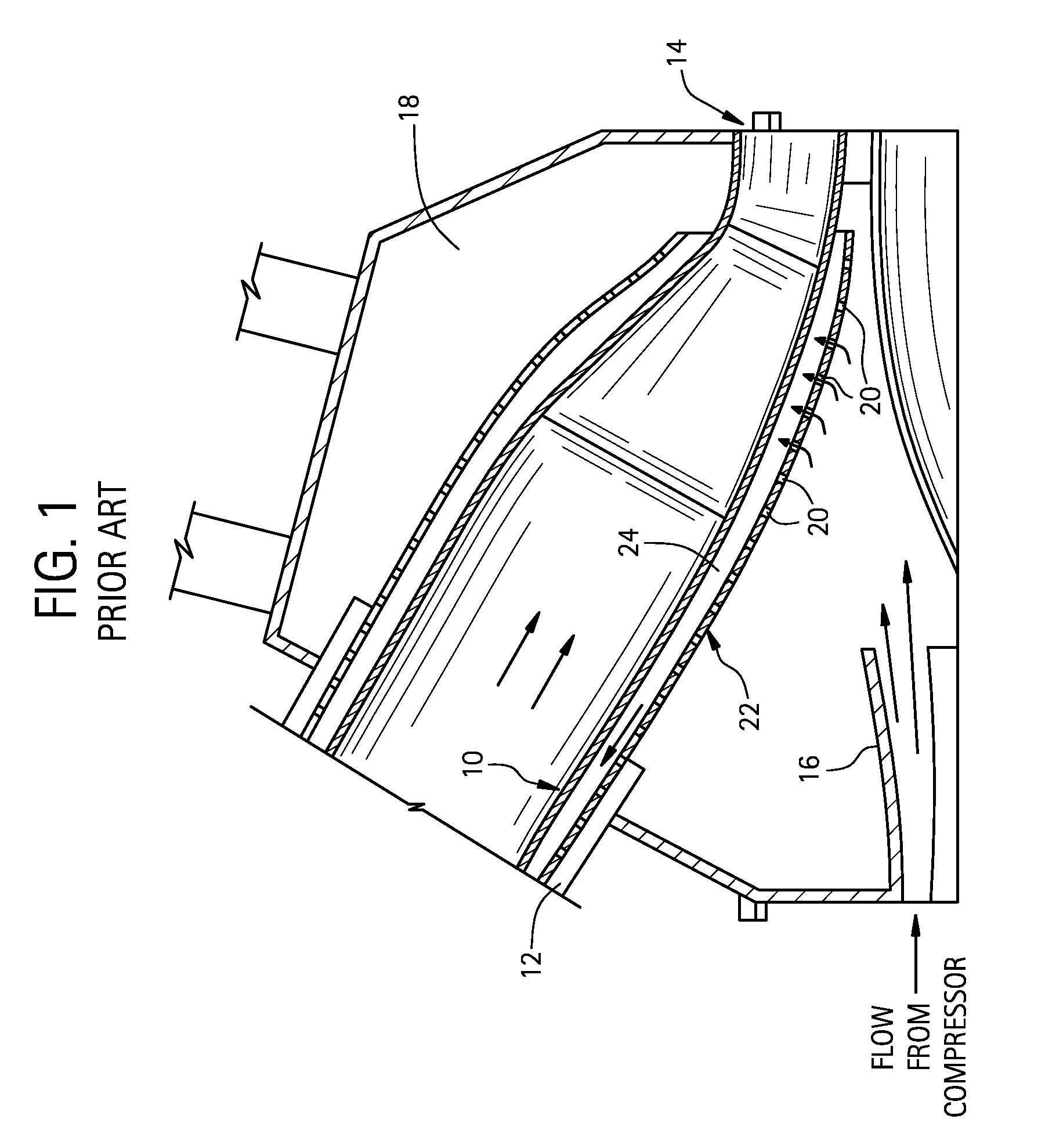
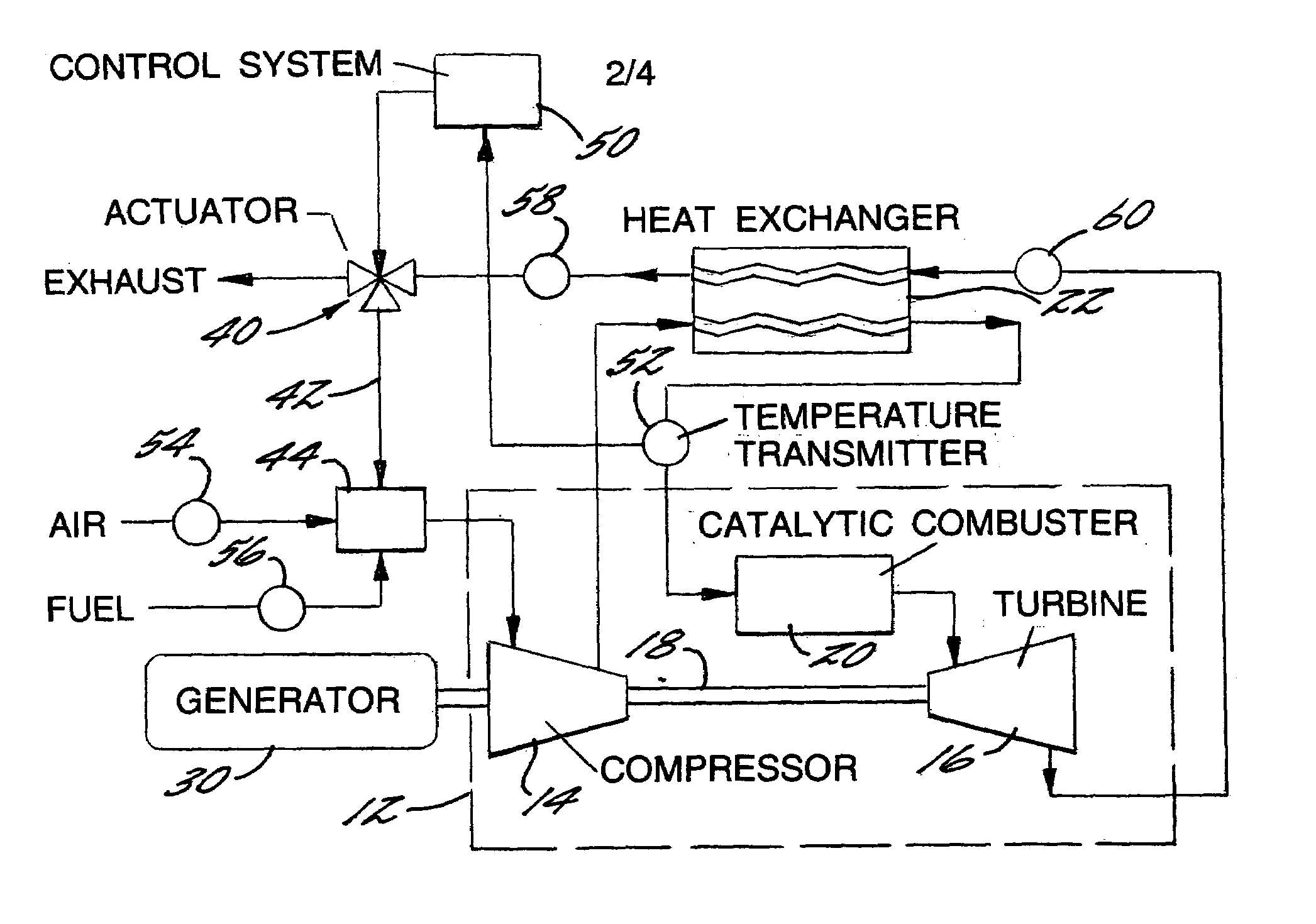
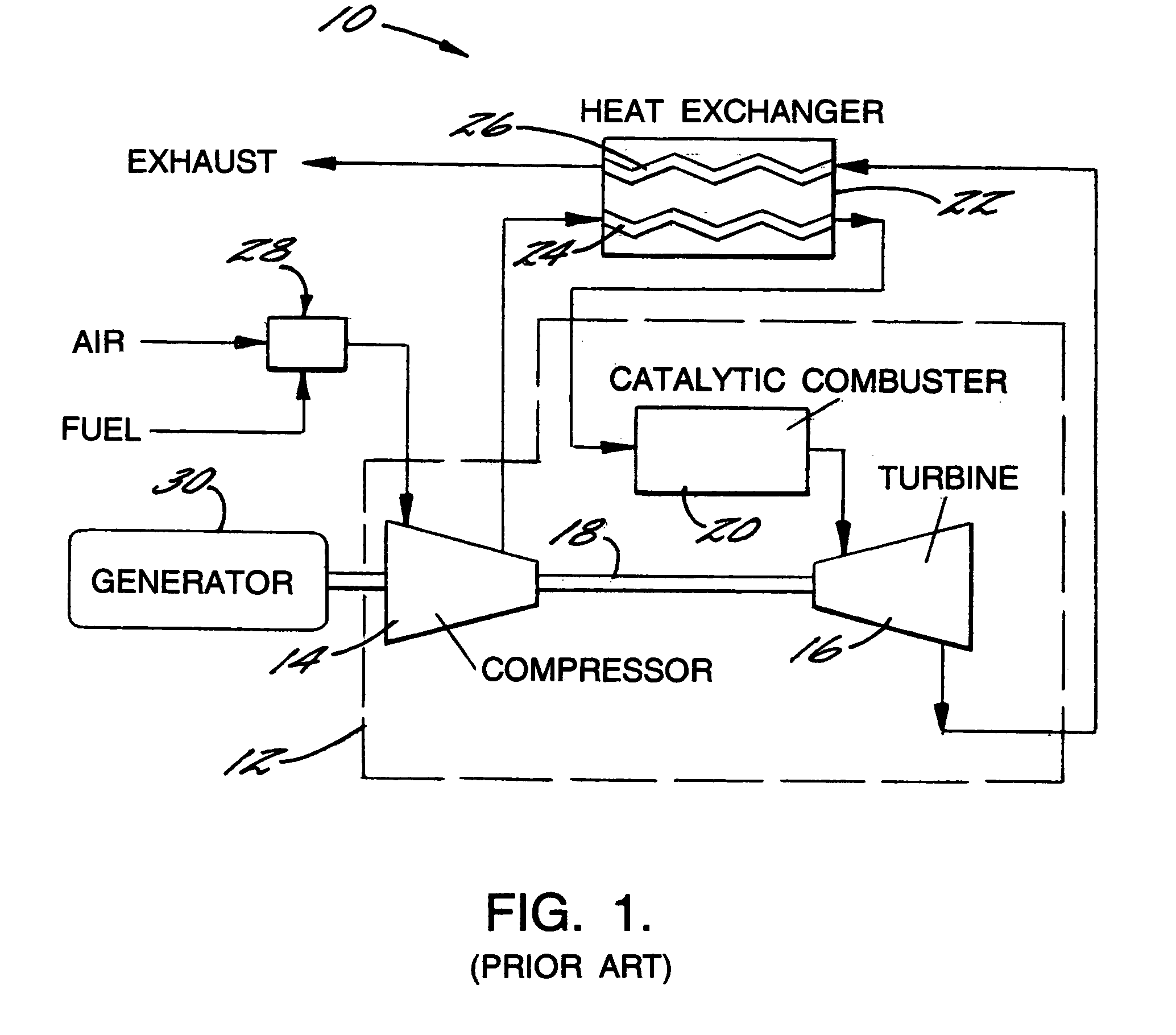
Recuperated gas turbine engine system and method employing catalytic combustion
InactiveUS7007487B2Maximize efficiencyReduce air pollutionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCold weather
A recuperated gas turbine engine system and associated method employing catalytic combustion, wherein the combustor inlet temperature can be controlled to remain above the minimum required catalyst operating temperature at a wide range of operating conditions from full-load to part-load and from hot-day to cold-day conditions. The fuel is passed through the compressor along with the air and a portion of the exhaust gases from the turbine. The recirculated exhaust gas flow rate is controlled to control combustor inlet temperature.
Owner:MES INT INC
Method of generating energy in a power plant comprising a gas turbine, and power plant for carrying out the method
InactiveUS20050028529A1Small sizeLow costContinuous combustion chamberDispersed particle separationPower stationCombustor
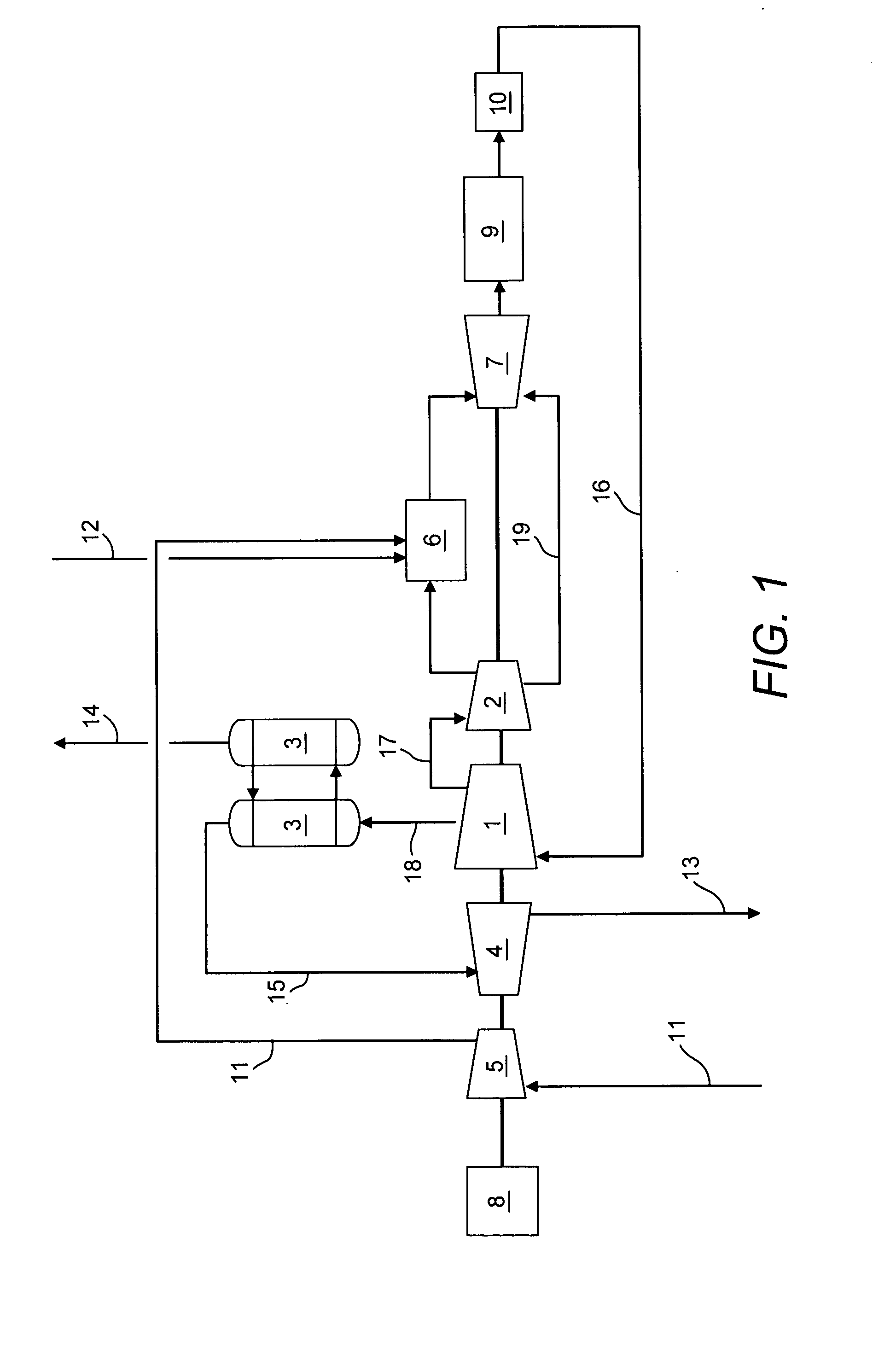
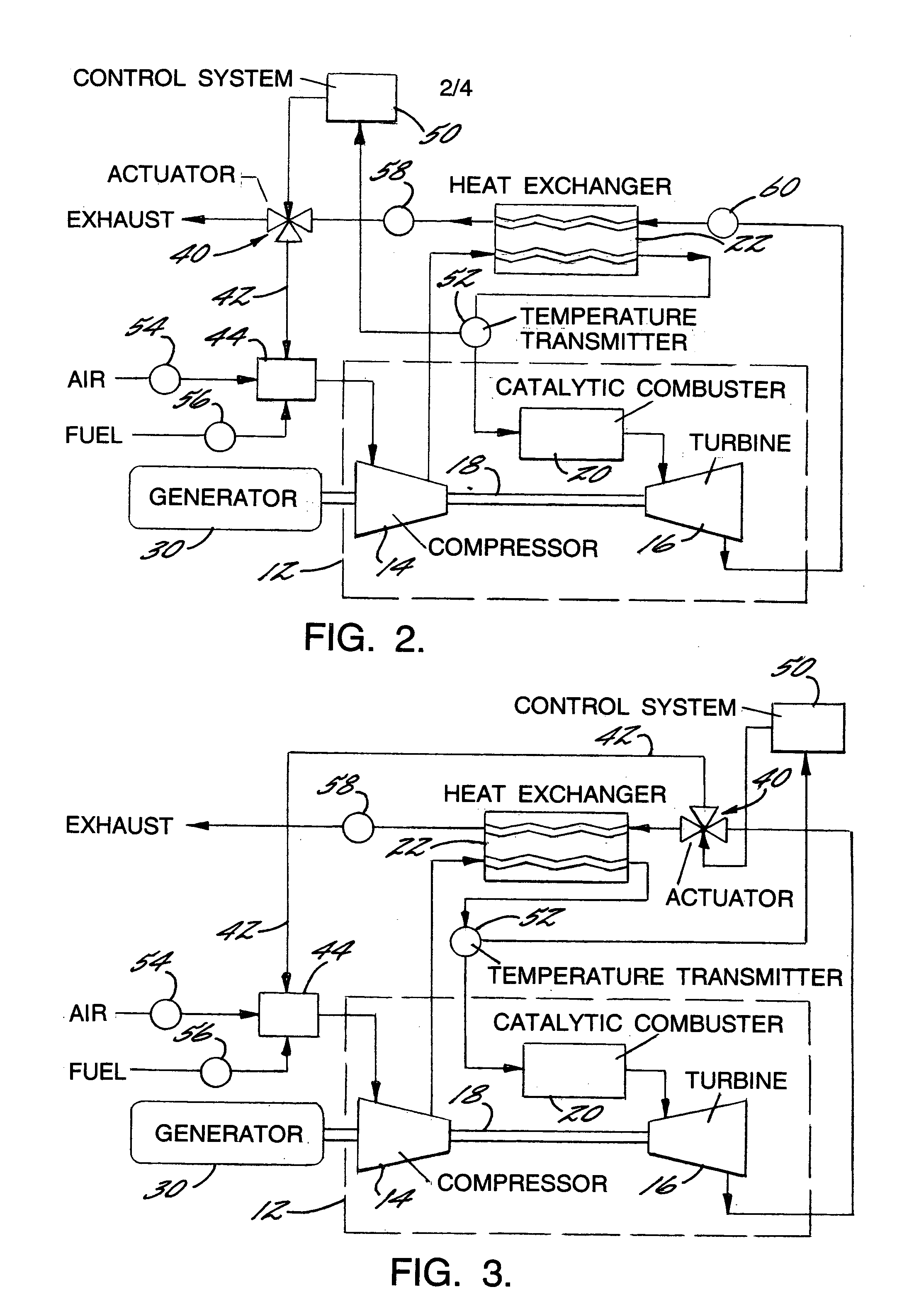
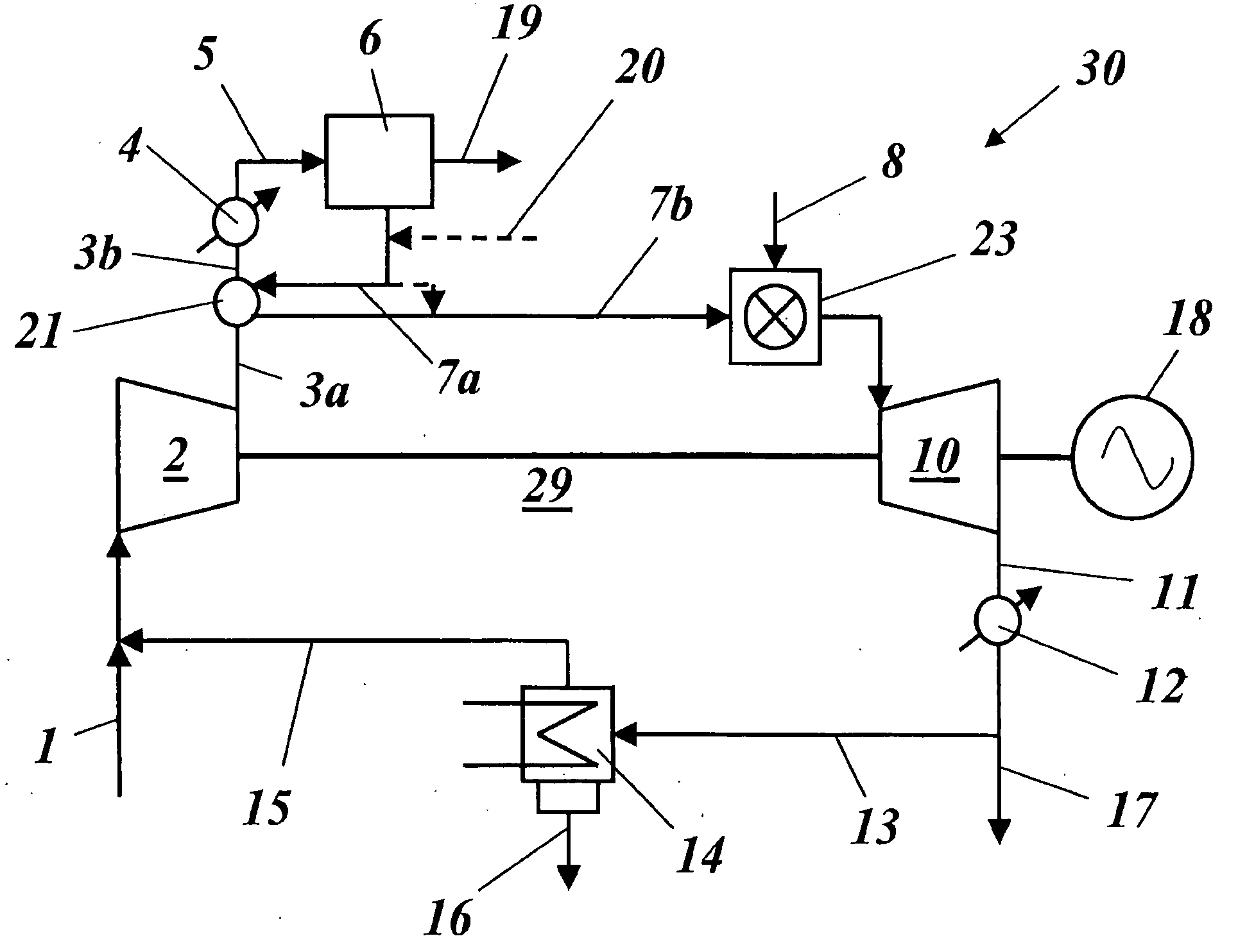
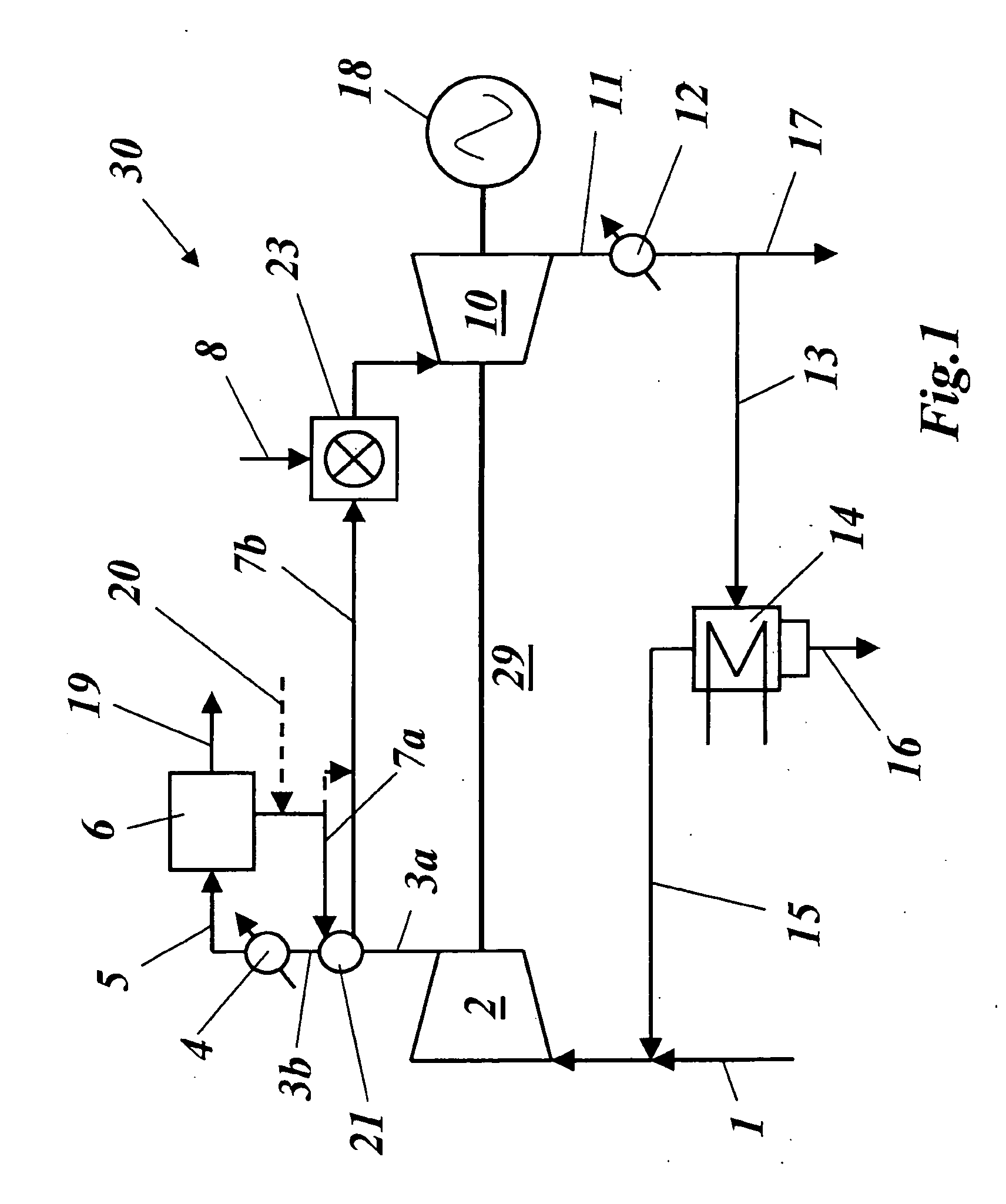
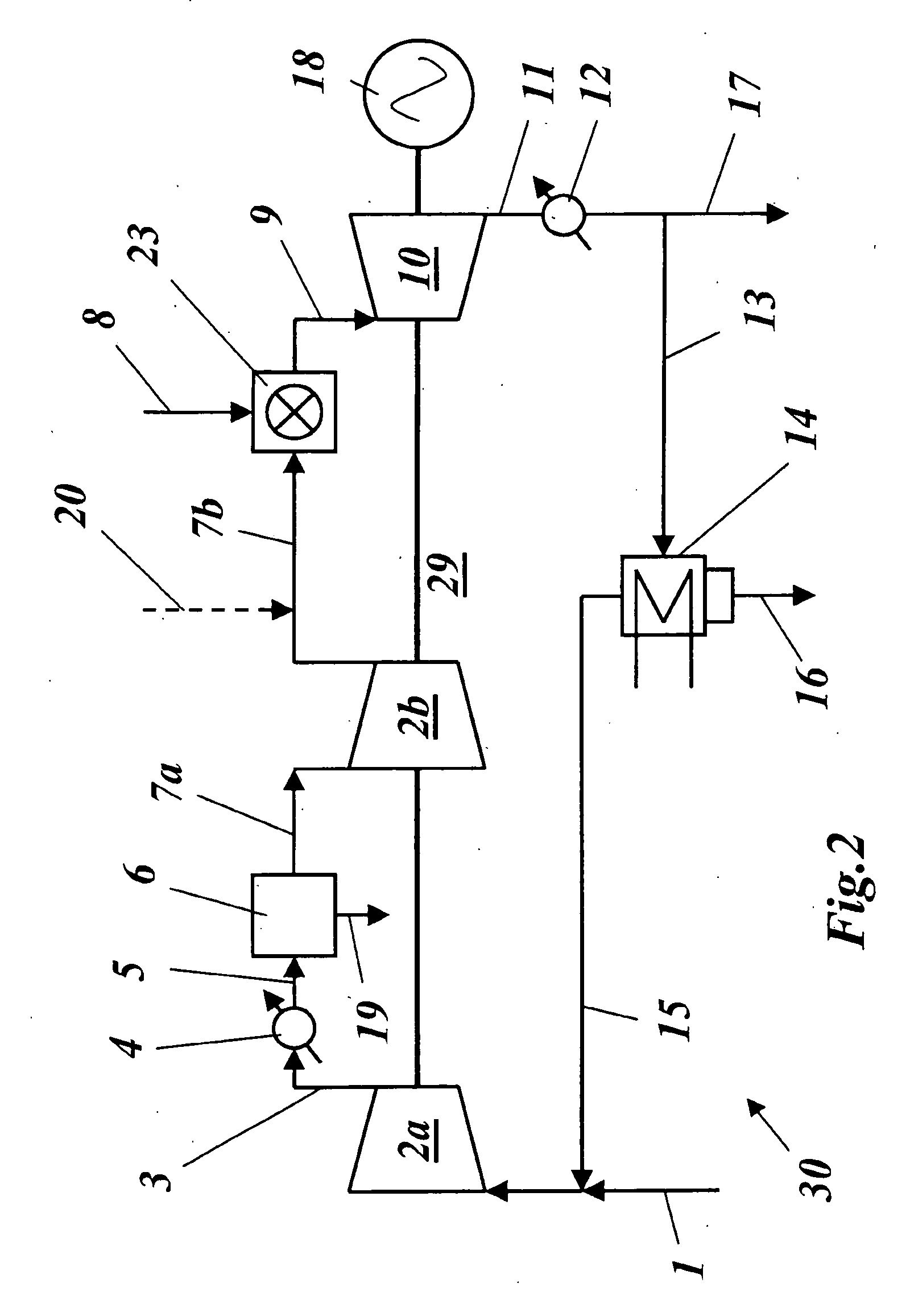
A method of generating energy in a power plant (30) having a gas turbine (29), includes a first step a gas containing air (1) is compressed in a first compressor (2) of the gas turbine (29), a second step the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) is fed to a combustion process with the addition of fuel (8) in a combustor (23), a third step the hot flue gas (9) from the combustor (23) is expanded in an expander or a turbine (10), driving a generator (18), of the gas turbine (29) while performing work, and a fourth step a partial flow of the expanded flue gas (11) is recirculated to the inlet of the first compressor (2) and admixed with the gas containing air (1). Carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) in a CO2 separator (6) before the third step. In such a method, the overall size and energy costs are reduced by virtue of the fact that, to permit increased CO2 concentrations in the CO2 separator (6), not more than about 70% of the carbon dioxide contained in the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b) is removed from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b).
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
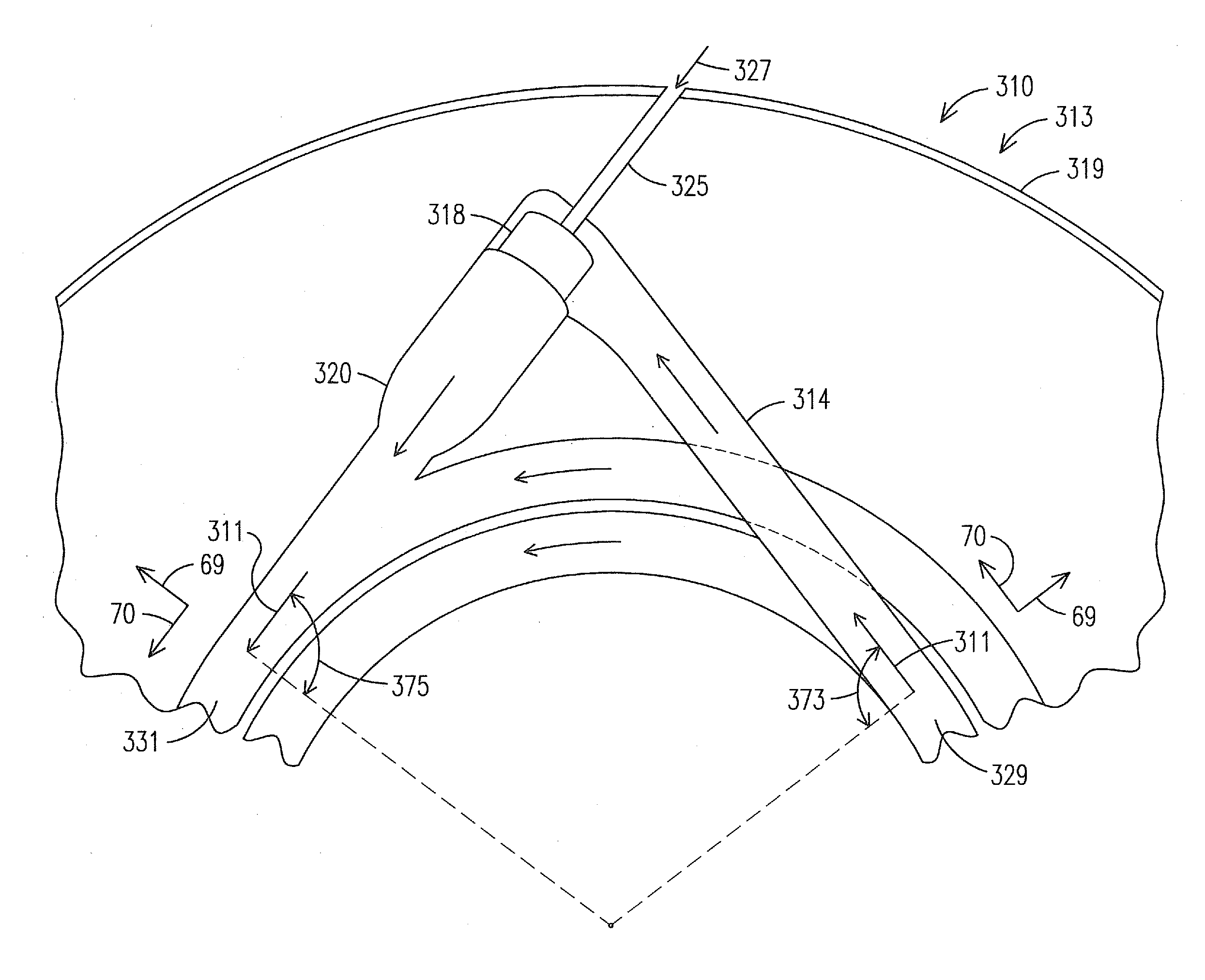
Mid-section of a can-annular gas turbine engine with an improved rotation of air flow from the compressor to the turbine
InactiveUS20130219853A1Easy to operateReduce lossesContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustorTurbine
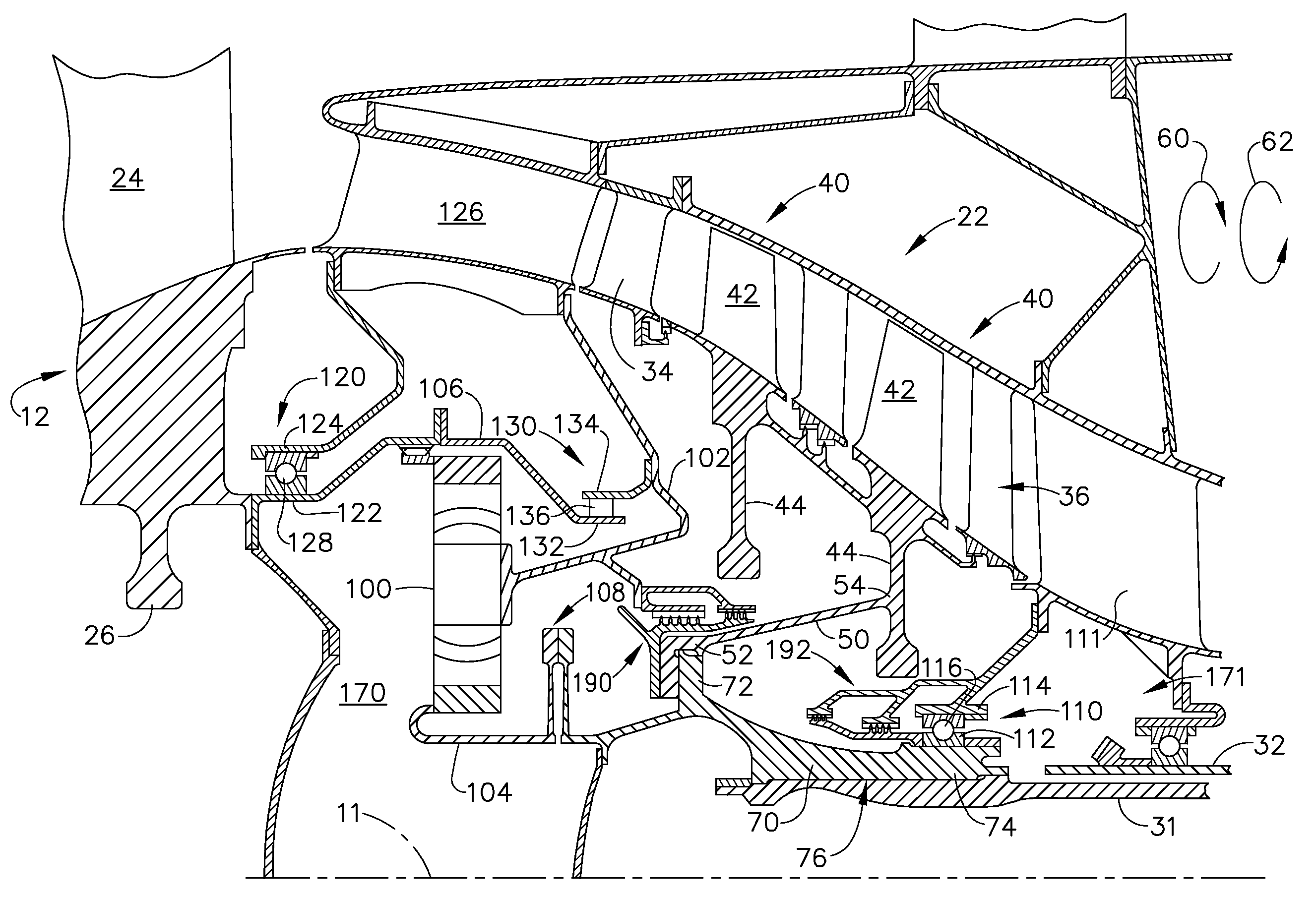
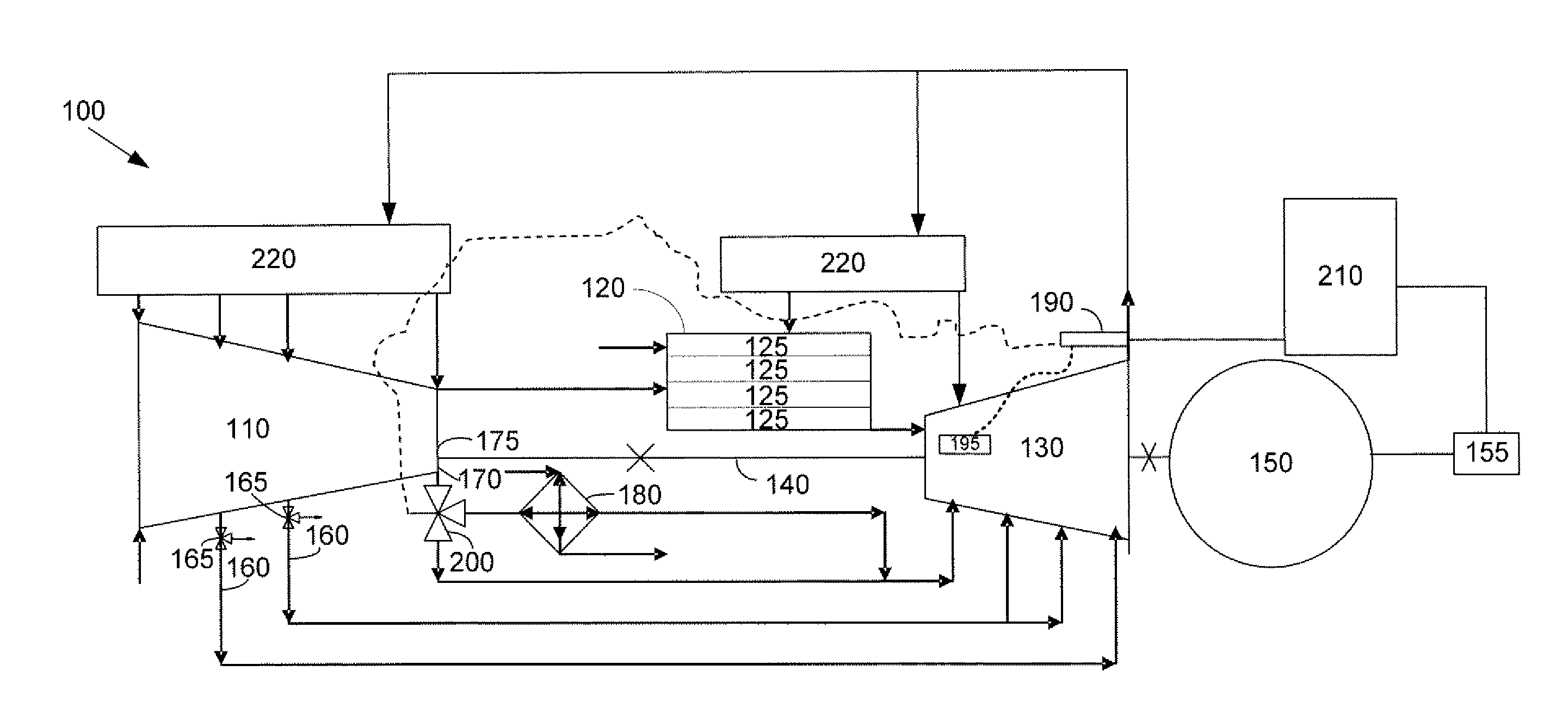
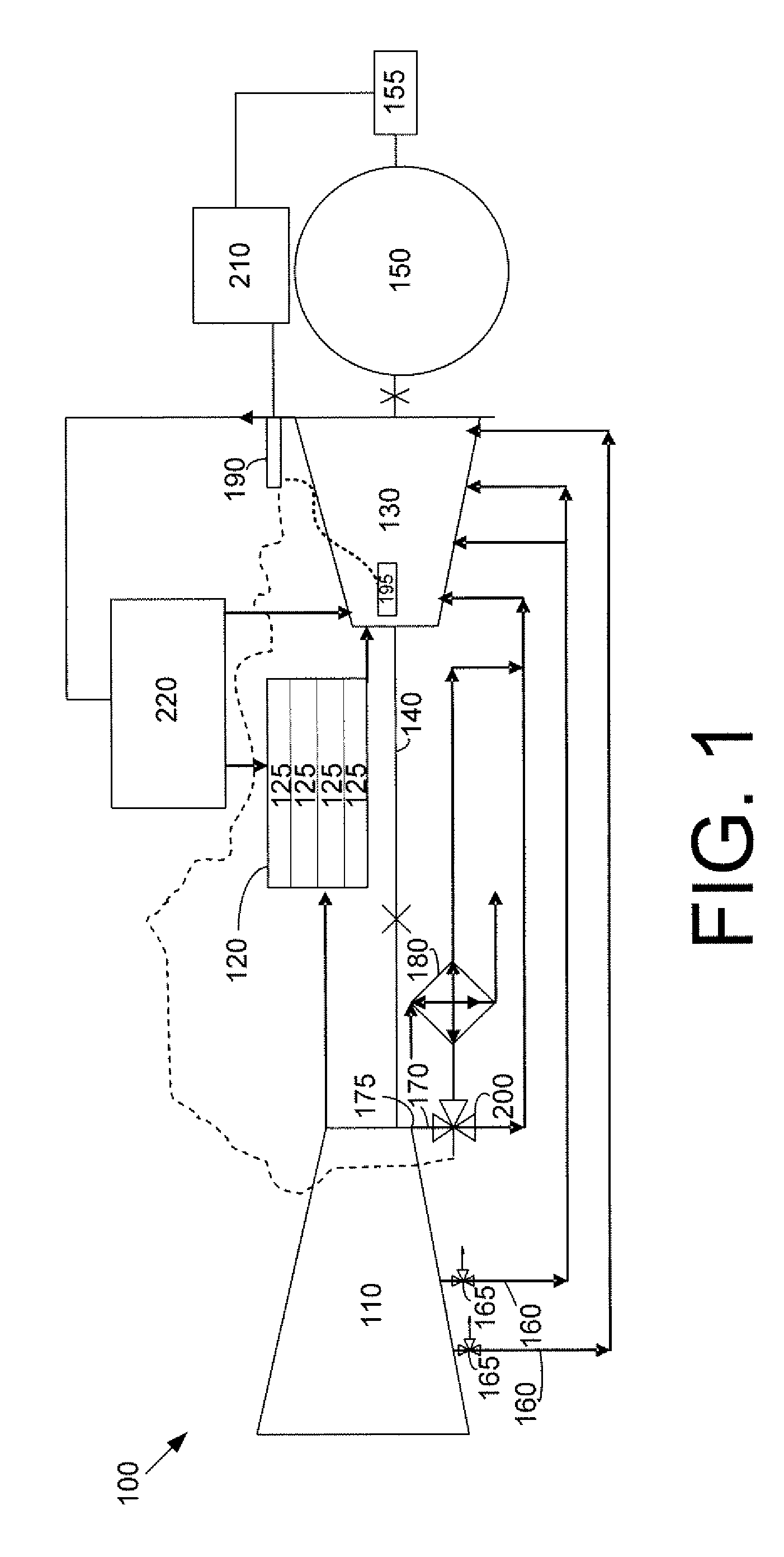
A midframe portion (313) of a gas turbine engine (310) is presented and includes a compressor section with a last stage blade to orient an air flow (311) at a first angle (372). The midframe portion (313) further includes a turbine section with a first stage blade to receive the air flow (311) oriented at a second angle (374). The midframe portion (313) further includes a manifold (314) to directly couple the air flow (311) from the compressor section to a combustor head (318) upstream of the turbine section. The combustor head (318) introduces an offset angle in the air flow (311) from the first angle (372) to the second angle (374) to discharge the air flow (311) from the combustor head (318) at the second angle (374). While introducing the offset angle, the combustor head (318) at least maintains or augments the first angle (372).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method and apparatus to increase combustion efficiency and to reduce exhaust gas pollutants from combustion of a fuel
InactiveUS6851413B1Improve combustion efficiencyFacilitate fuel combustionBurnersLiquid fuel feeder/distributionCombustorExhaust fumes
A method and apparatus is disclosed for increasing combustion efficiency in internal combustion engines and external combustors resulting in increased fuel economy and reduced exhaust pollutants. The same principles and apparatus of the invention are used in the exhaust stream to further reduce pollutants.
Owner:RONNELL
High temperature erosion resistant, abradable thermal barrier composite coating
InactiveUS6235370B1Improve wear resistanceImprove adhesionMolten spray coatingPump componentsCombustorHoneycomb
A composite thermal barrier coating system includes a honeycomb metallic structure filled with high thermal expansion ceramic hollow spheres in a phosphate bonded matrix. The composite thermal barrier coating system may be manufactured to thicknesses in excess of current thermal barrier coating systems, thereby imparting greater thermal protection. Superior erosion resistance and abrasion properties are also achieved. The composite thermal barrier coating is useful on combustion turbine components such as ring seal segments, vane segment shrouds, transitions and combustors.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
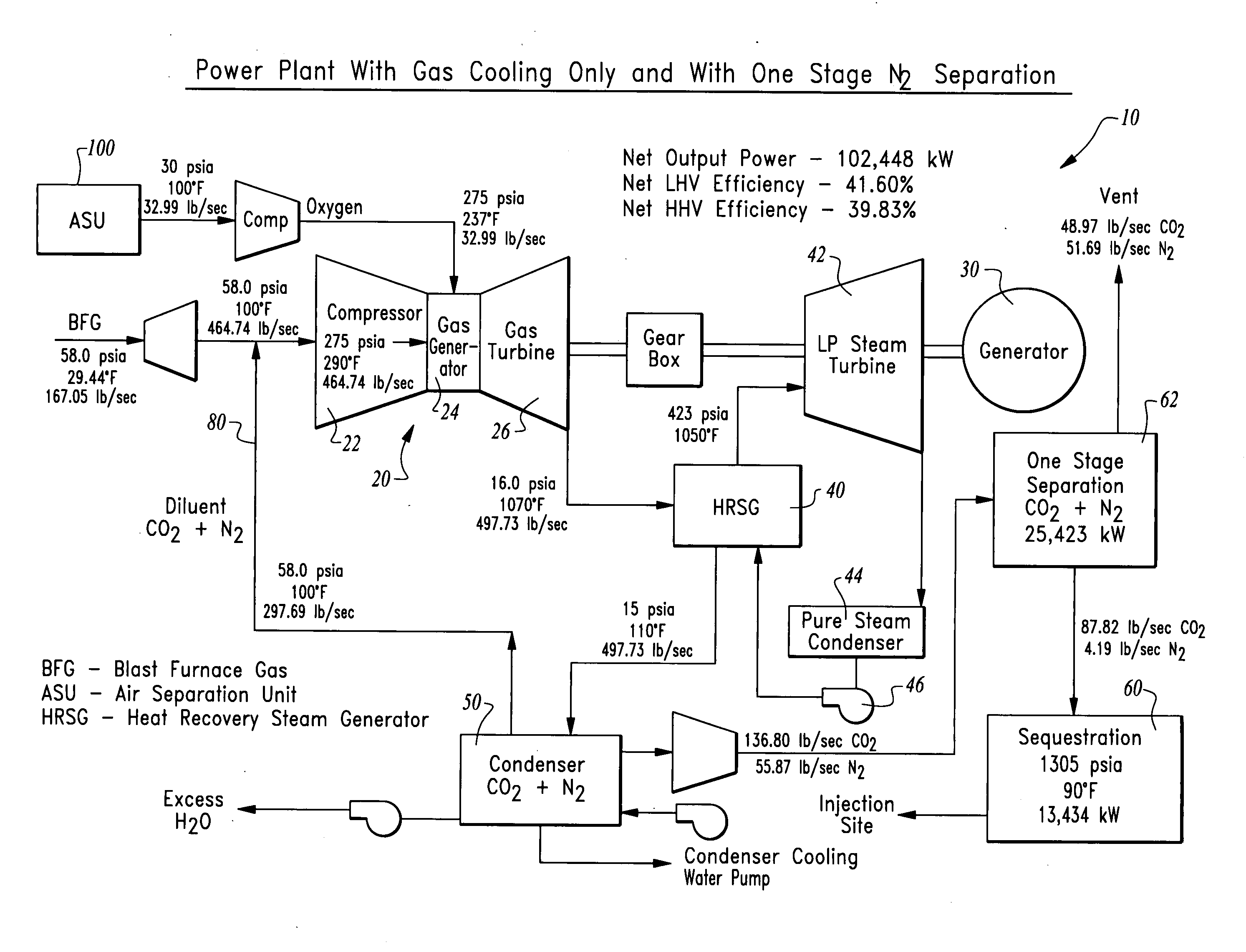
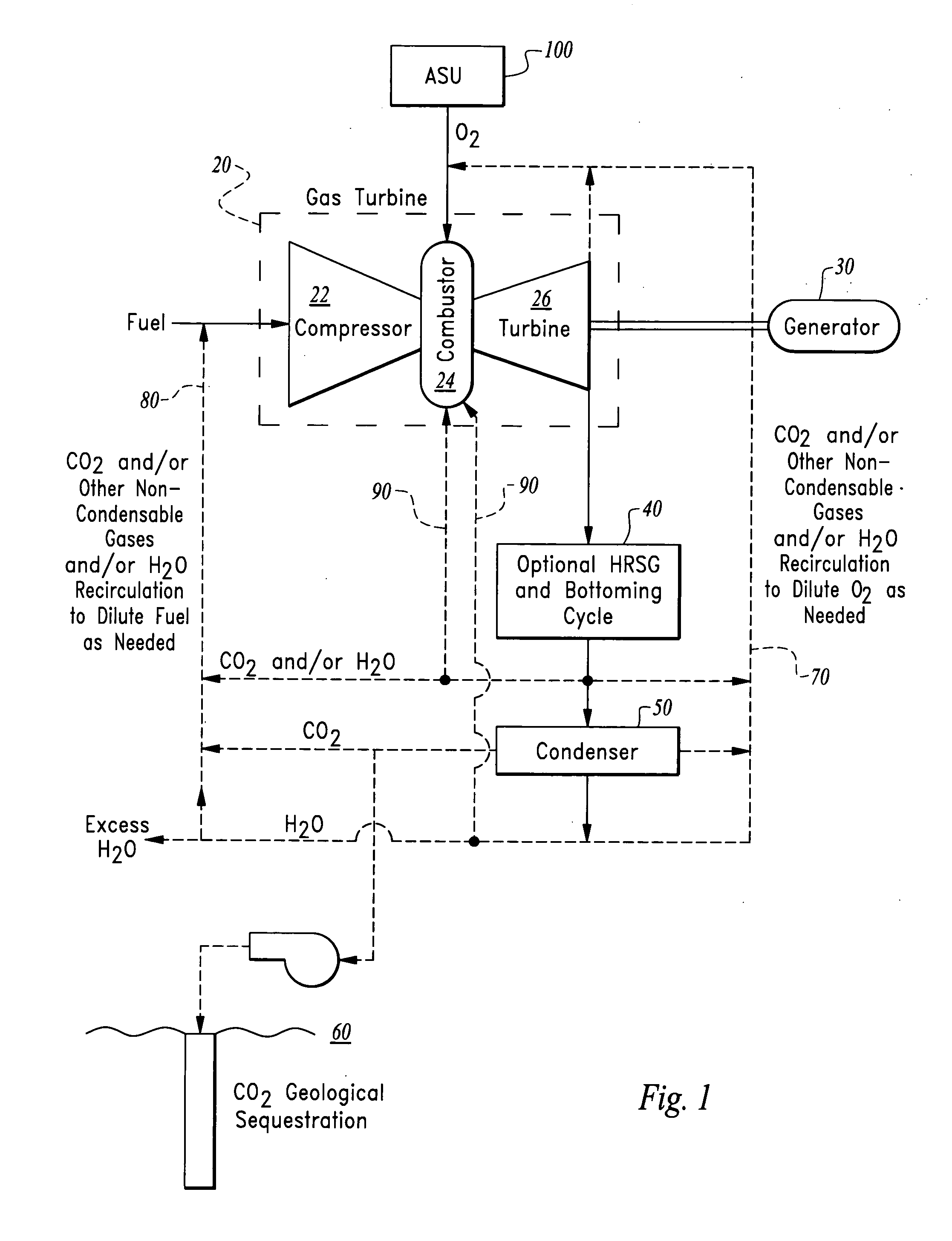
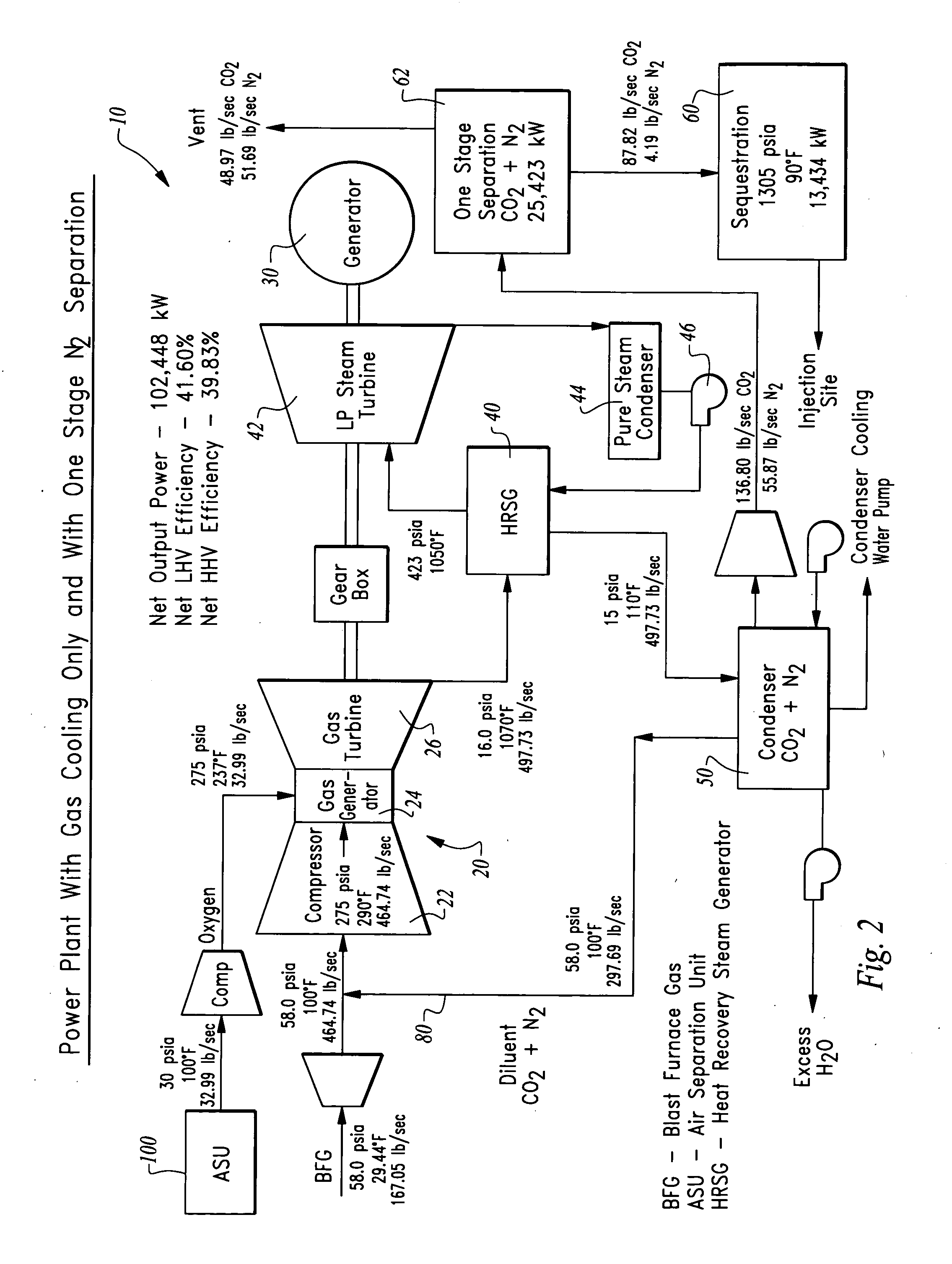
Methods of oxy-combustion power generation using low heating value fuel
An oxy-combustor is provided to combust oxygen with gaseous low heating value fuel. A compressor upstream of the combustor compresses the fuel. The combustor produces a drive gas including steam and carbon dioxide as well as other non-condensable gases in many cases, which pass through a turbine to output power. The drive gas can be recirculated to the combustor, either through the compressor, the oxygen inlet or directly to the combustor. Recirculation can occur before or after a condenser for separation of a portion of the water from the carbon dioxide. Excess carbon dioxide and steam is collected from the system. The turbine, combustor and compressor can be derived from an existing gas turbine with fuel and air / oxidizer lines swapped.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
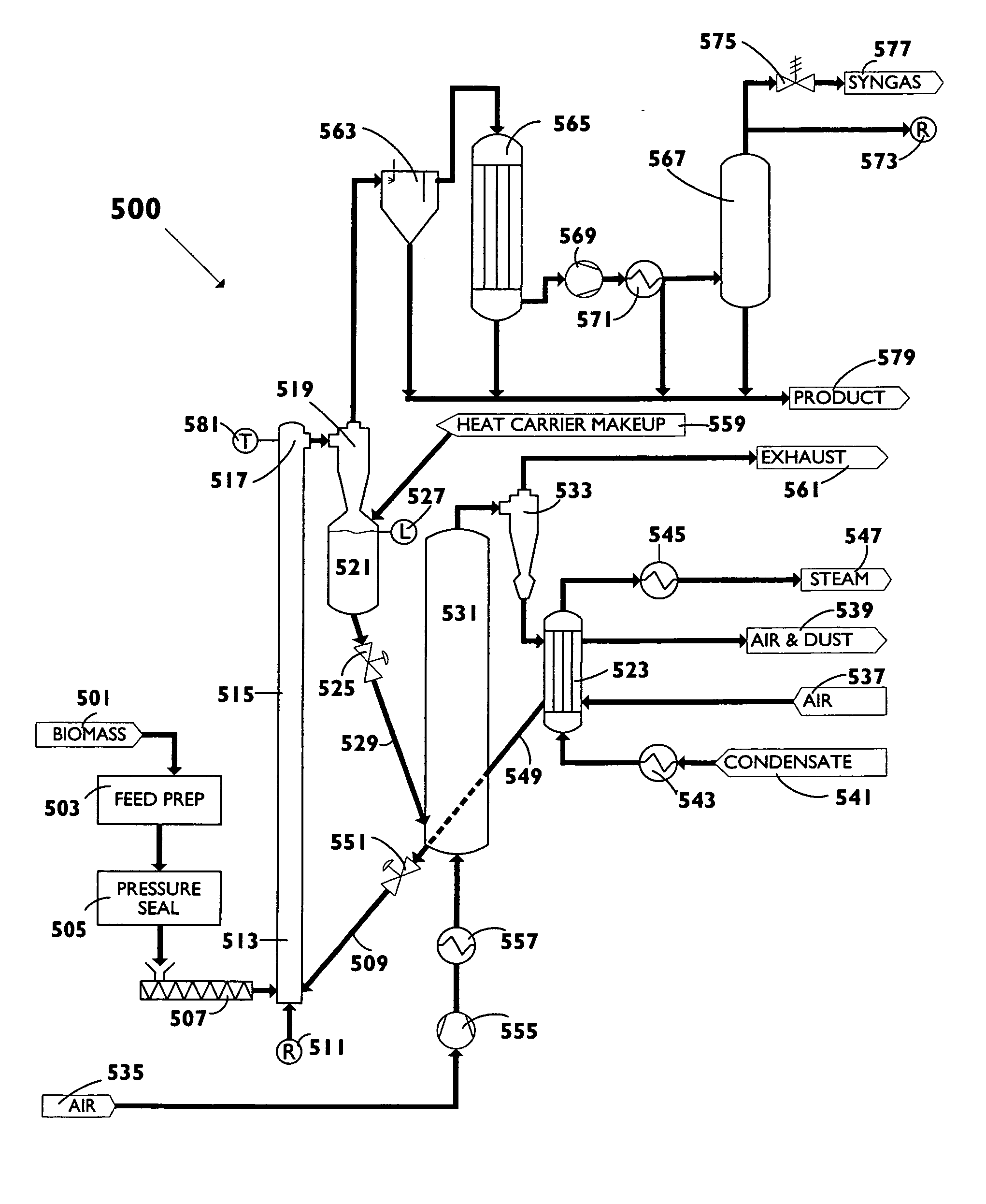
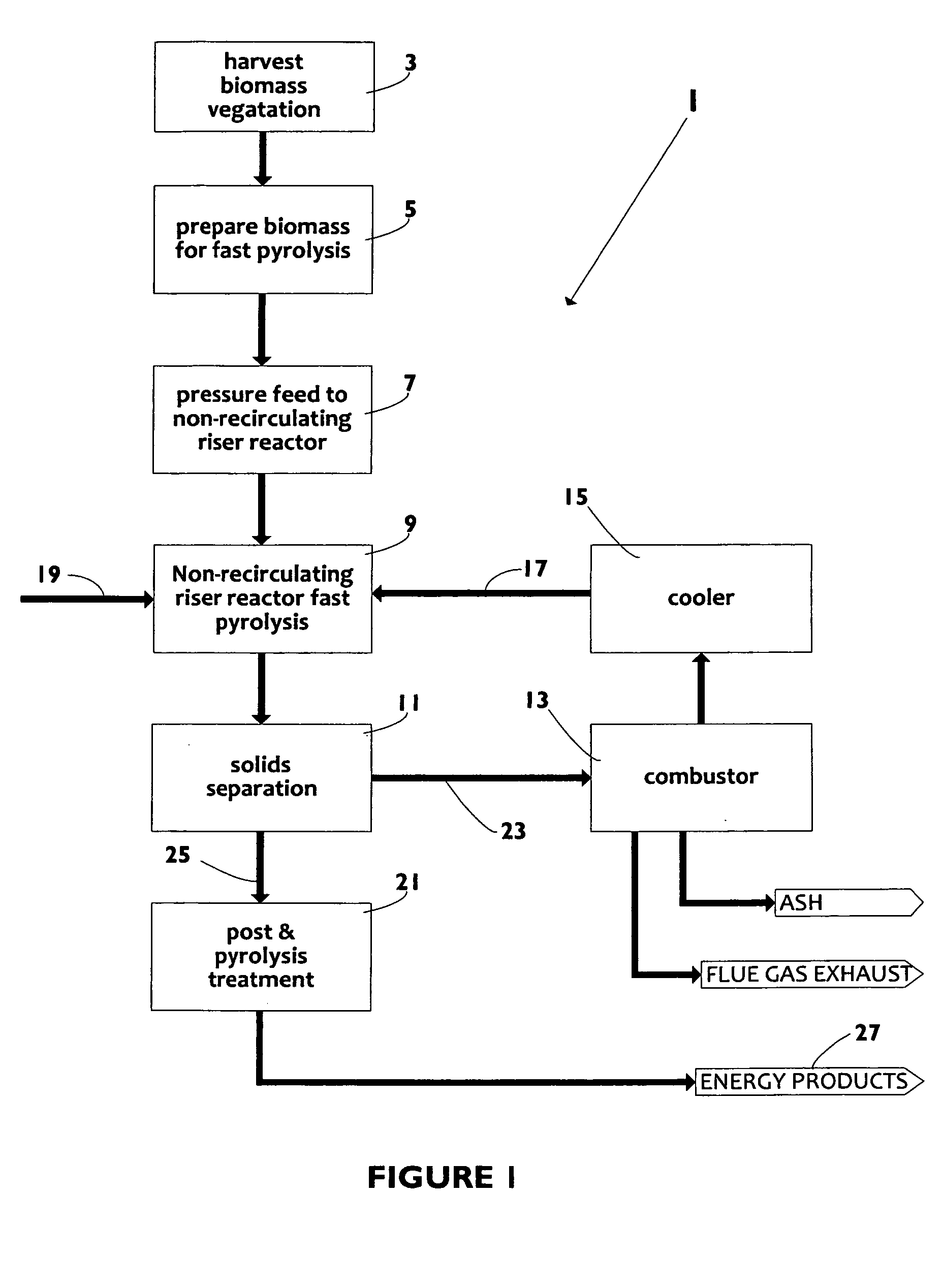
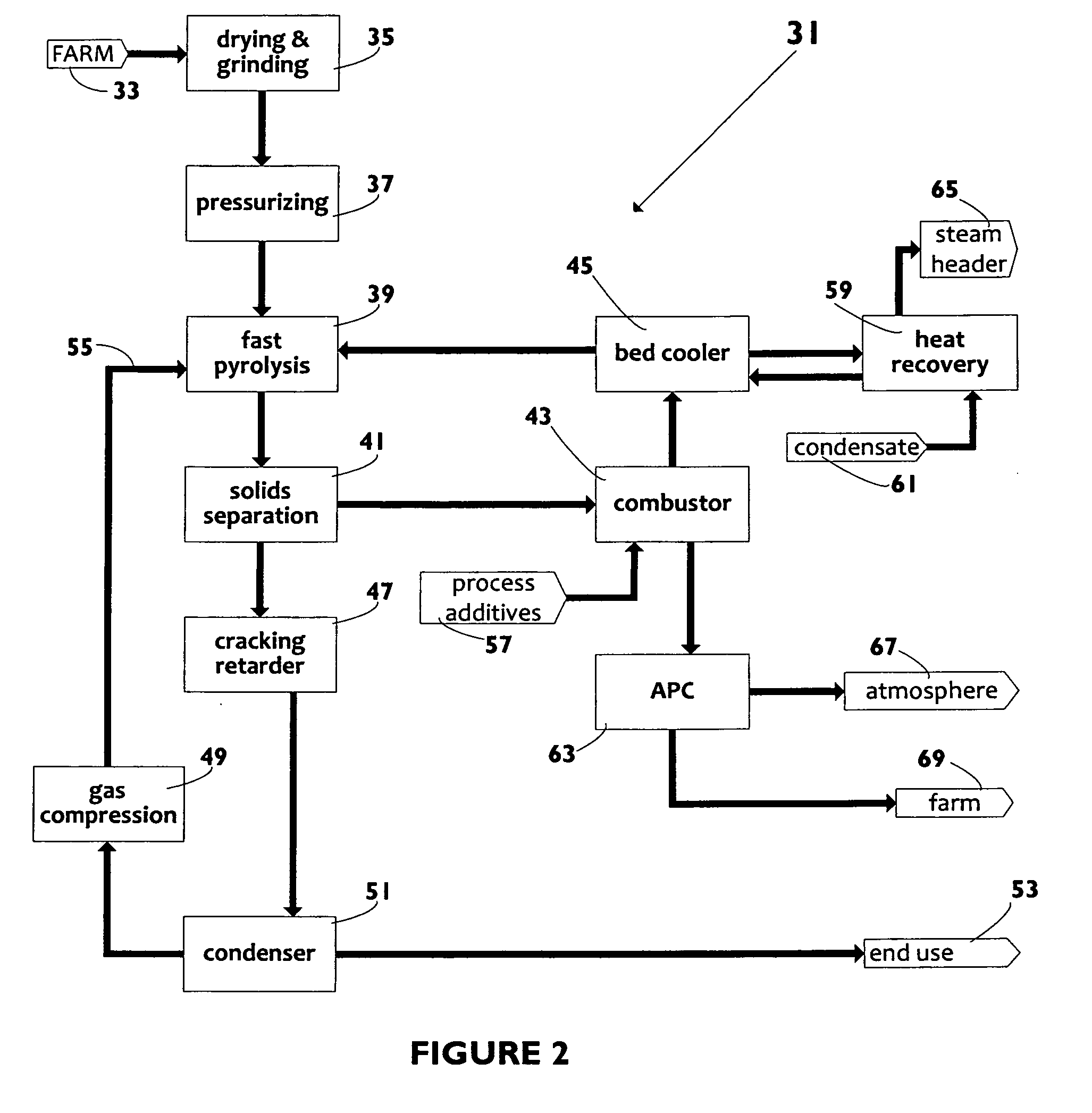
Biomass fast pyrolysis system utilizing non-circulating riser reactor
A biomass fast pyrolysis system for conversion of biomass vegetation to synthetic gas and liquid fuels includes: a) a non-circulating riser reactor for pyrolysis of biomass vegetation feedstock utilizing a heat carrier, the non-circulating riser reactor being physically structured and adapted to have a rate of reaction of at least 8,000 biomass vegetation feedstock lbs / hr / ft2, utilizing a ratio of heat carrier to biomass vegetation feedstock of about 7:1 to about 11.5:1, the riser reactor having a base input region at its bottom, a central reaction region and an output region at its top, the riser reactor including a cyclone disengager at its output region for separation of pyrolysis resulting char and heat carrier from the pyrolysis product gases, the cyclone disengager having an output downcomer and an output upcomer, the cyclone disengager output downcomer being connected to and feeding into a side combustor unit, the riser reactor being a non-circulating riser reactor in that the heat carrier is not returned directly to the riser reactor from the cyclone disengager and travels first down the cyclone disengager output downcomer to the side combustor unit; and, b) the side combustor unit for combusting pyrolysis resultant char and reheating the heat carrier the side combustor having a heat carrier downcomer connected to the base input region of the riser reactor.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENERGY GLOBAL
Oxidant control in co-generation installations
InactiveUS6247315B1Steam regenerationIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationControl system designCogeneration
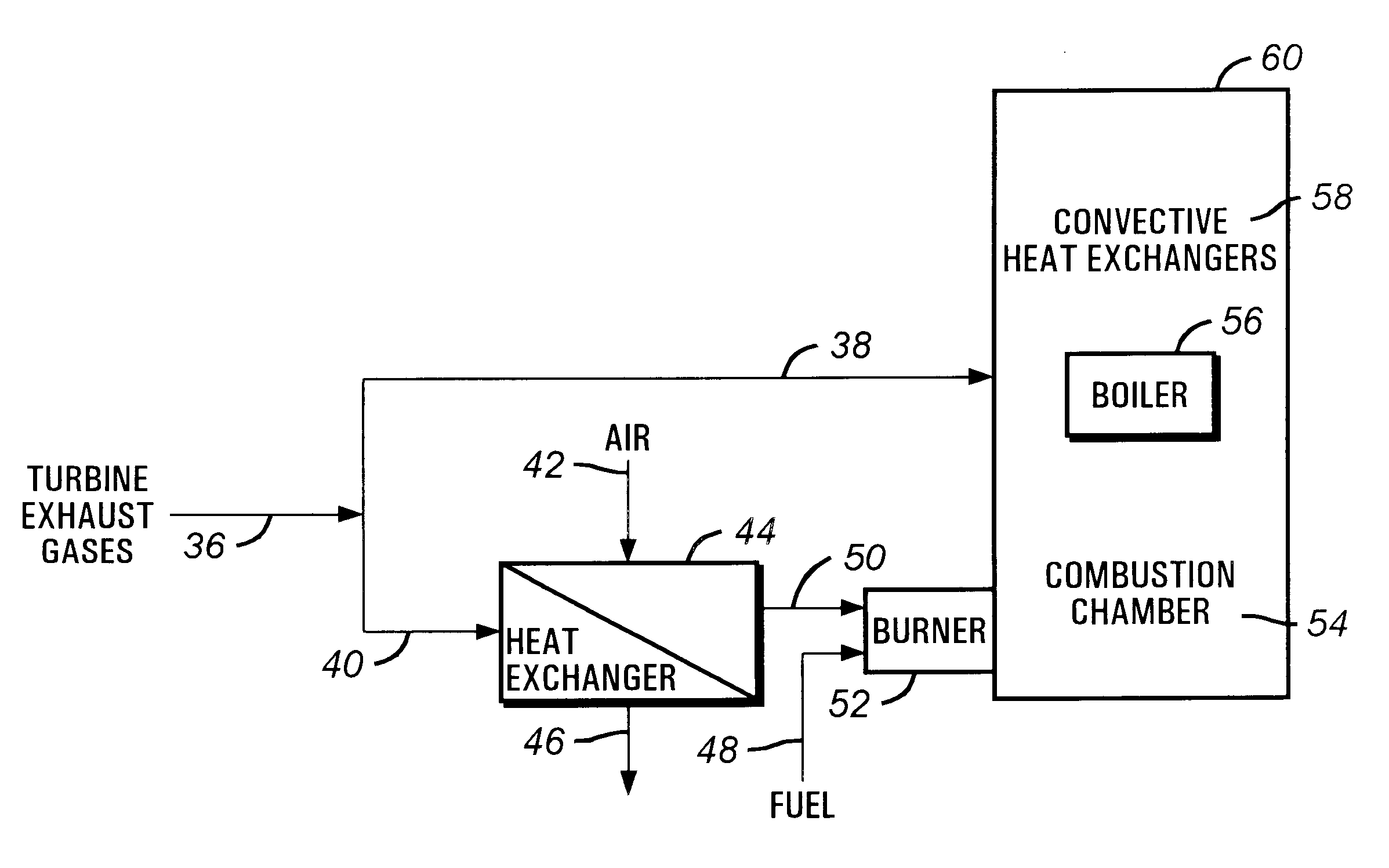
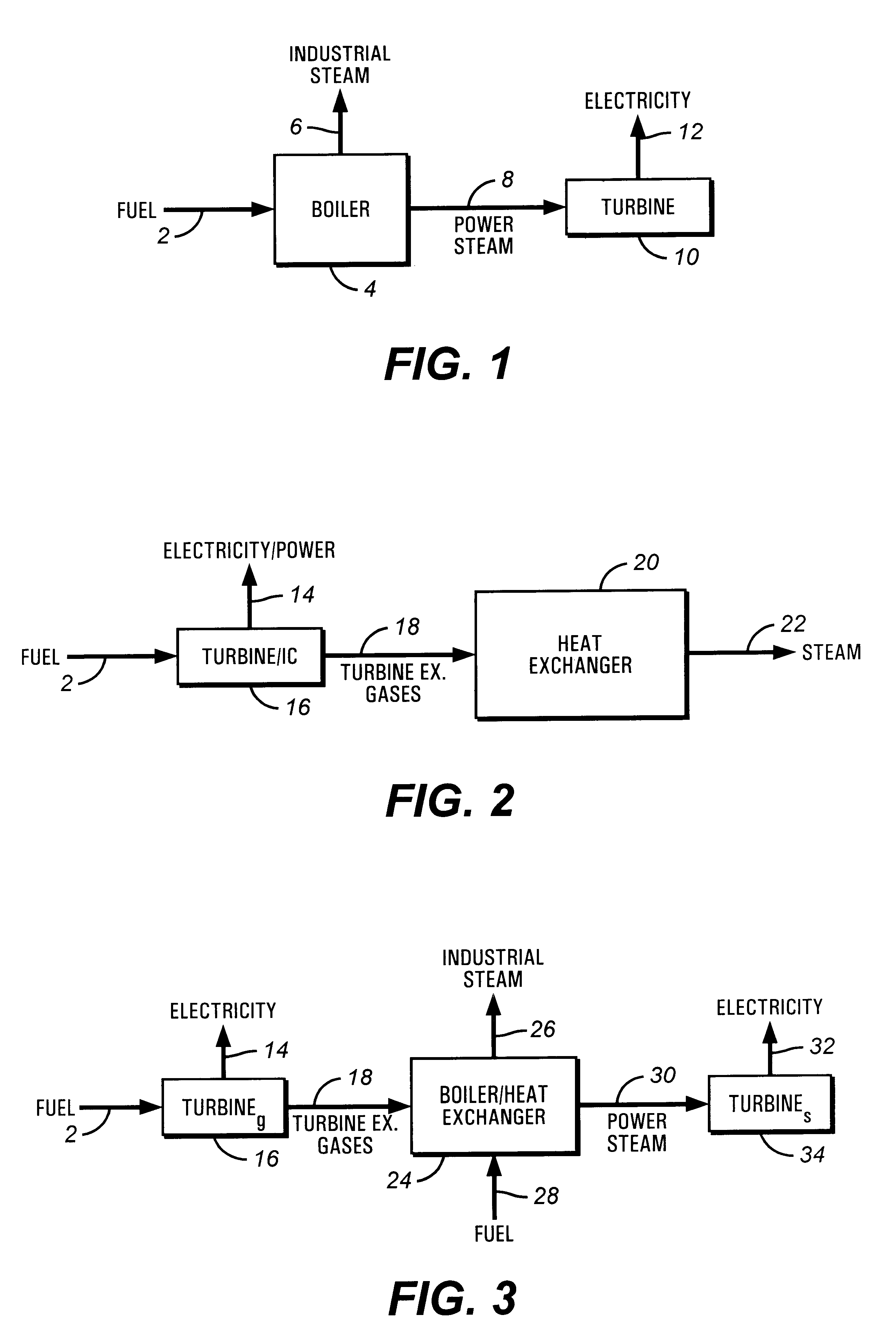
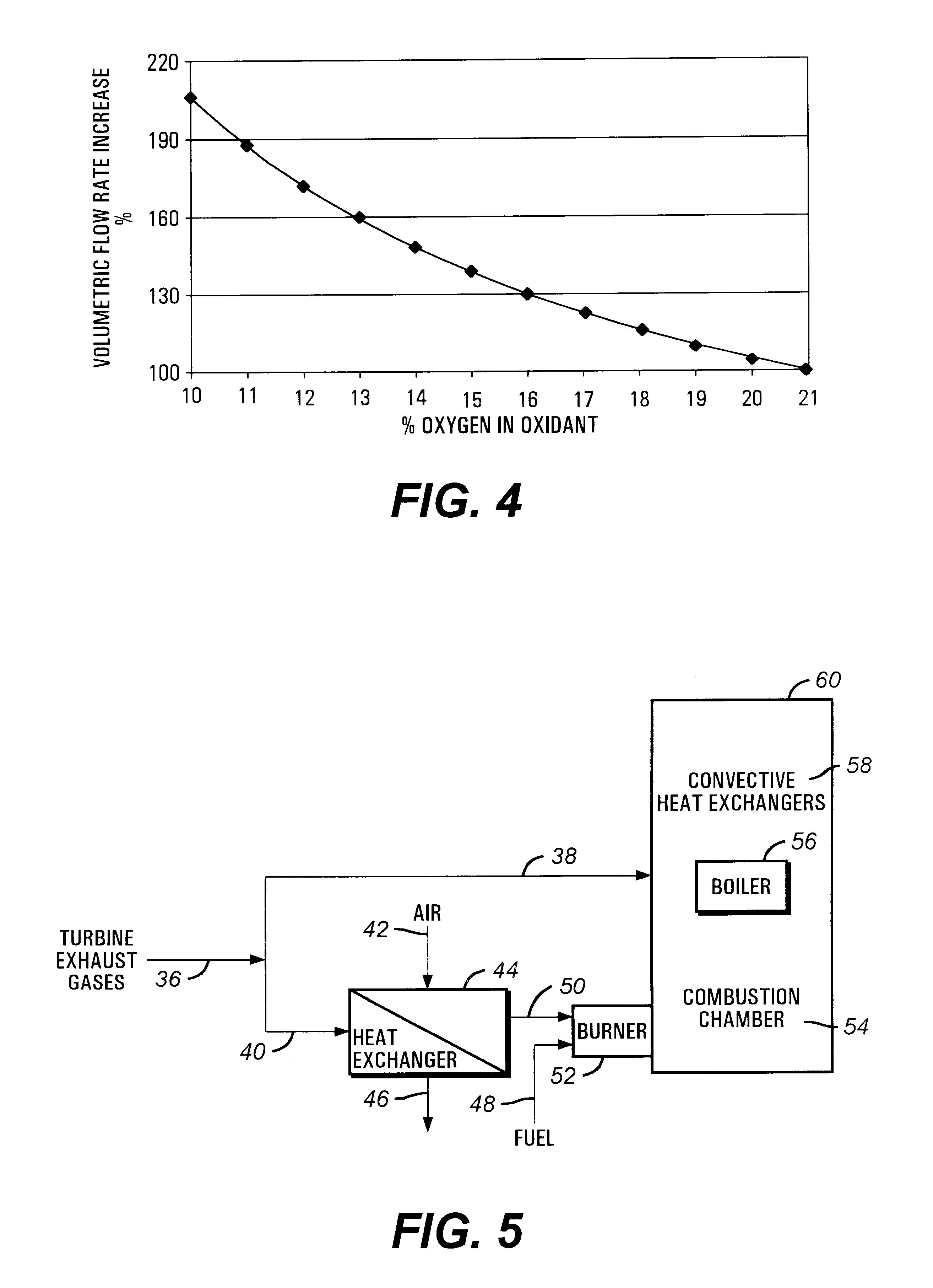
This invention is related to so-called combined cycle co-generation installations, and it addresses present concerns of the industry. Among these, combustion stability, corrosion (due to large water content in the flue gases), large heat transfer areas, and the like. In some embodiments, an additional heat exchanger is added to heat combustion air with a portion of the exhaust gases resulting from an engine, preferably a gas turbine. As a result, the efficiency of the cycle will improve, the oxidant will be enriched by above 50% oxygen, the combustion process will be enhanced, and the dimensions of the boiler may be reduced. It is considered that the combustion air will require between 10% and 80% of the total flue gas volume, more preferably between 20% and 40%. This is the portion of the flue gases sent through the heat exchanger. A control system designed to optimize the flow of the different streams is also presented. Other inventive embodiments forego heat exchanges in lieu of precise control of two flows of exhaust gas, with preferred addition of additional oxidant to the boiler bumers.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Heat shield panels for use in a combustor for a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS7093439B2Extended service lifeContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCold sideCombustor
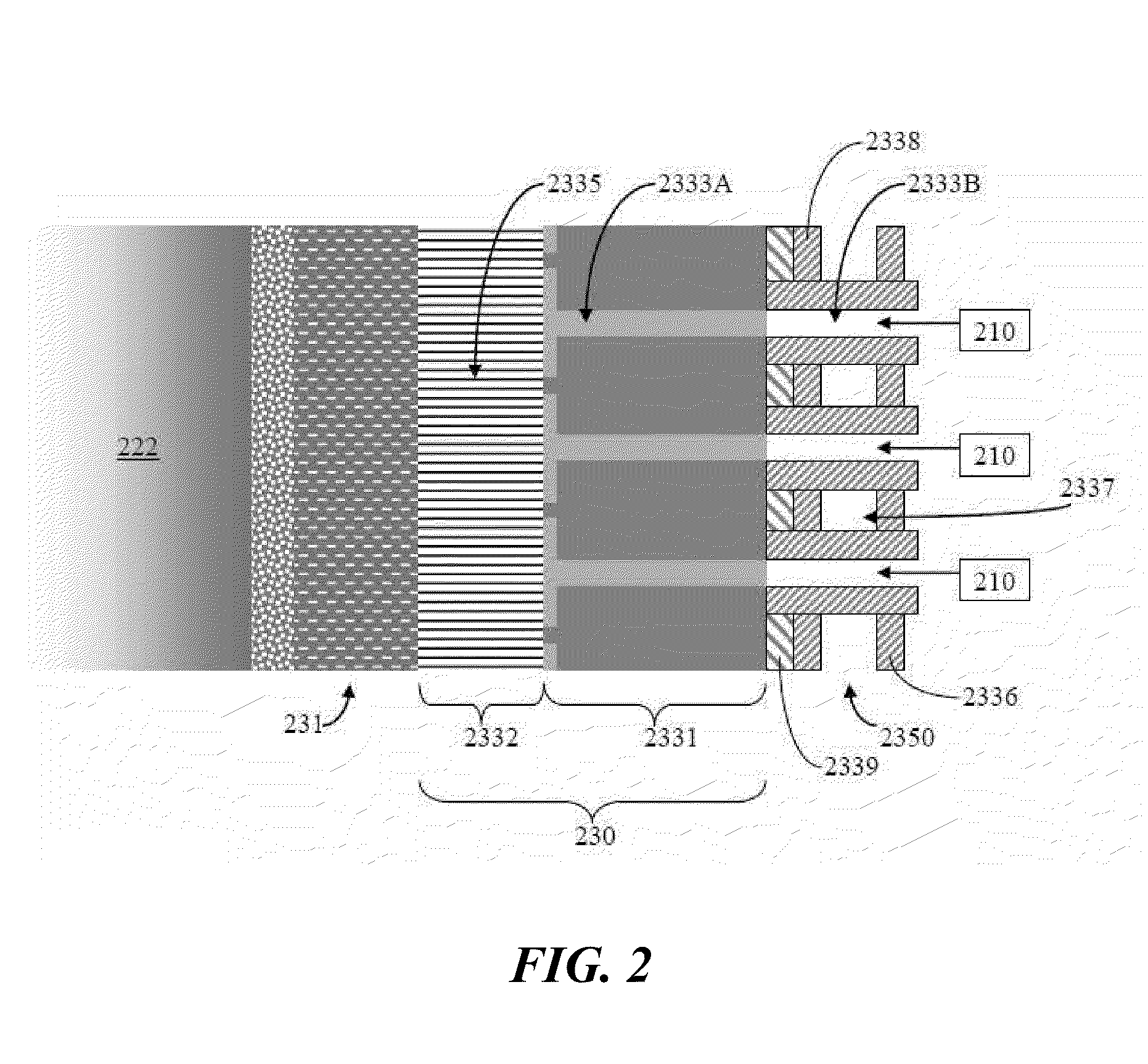
The present invention relates to heat shield panels or liners to be used in combustors for gas turbine engines. The heat shield panels each comprise a hot side and a cold side and at least one isolated cooling chamber on the cold side. Each cooling chamber has a plurality of cooling film holes for allowing a coolant, such as air, to flow from the cold side to the hot side. A combustor having an arrangement of heat shield panels or liners is also described.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Dual orifice bypass system for dual-fuel gas turbine
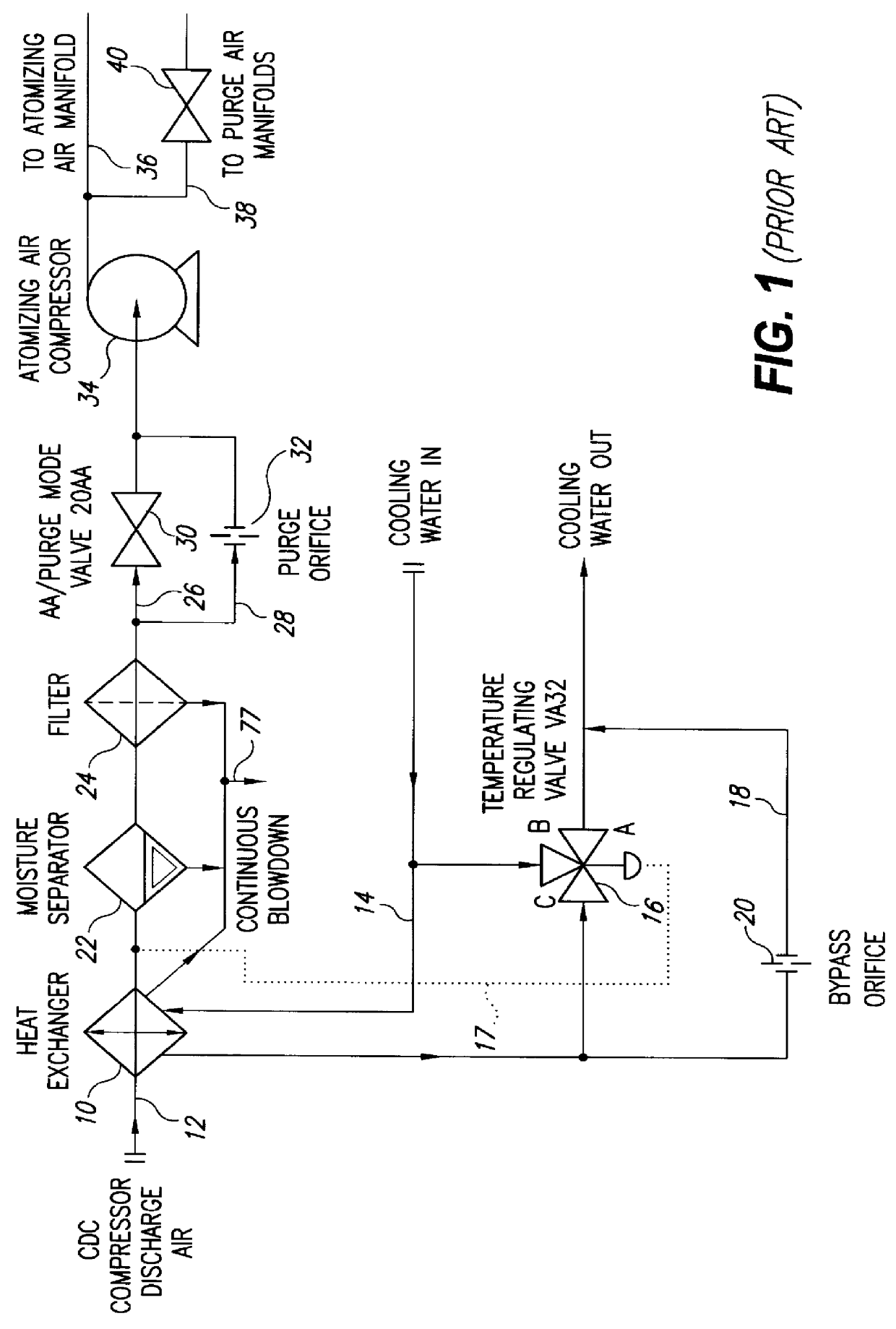
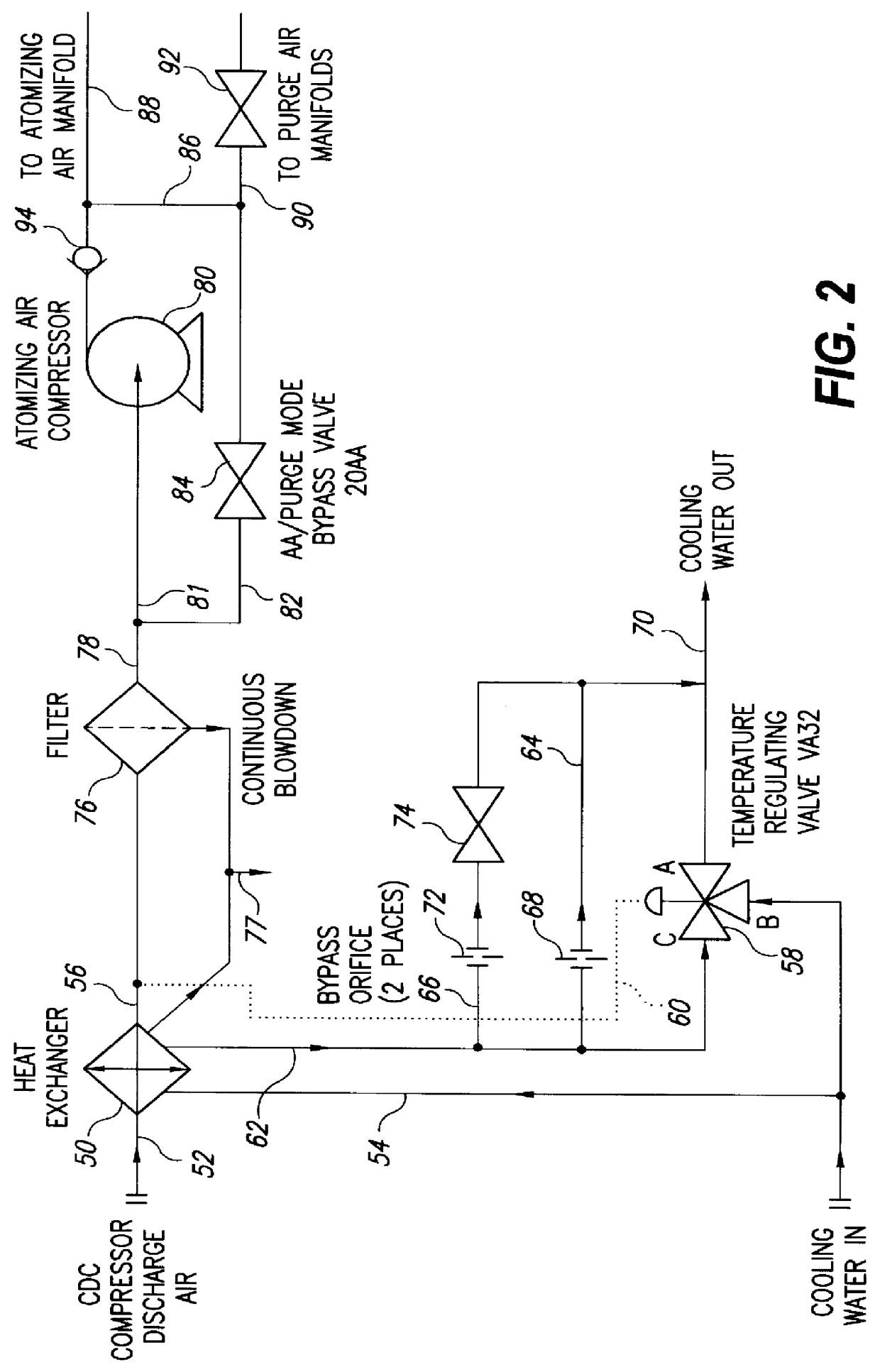
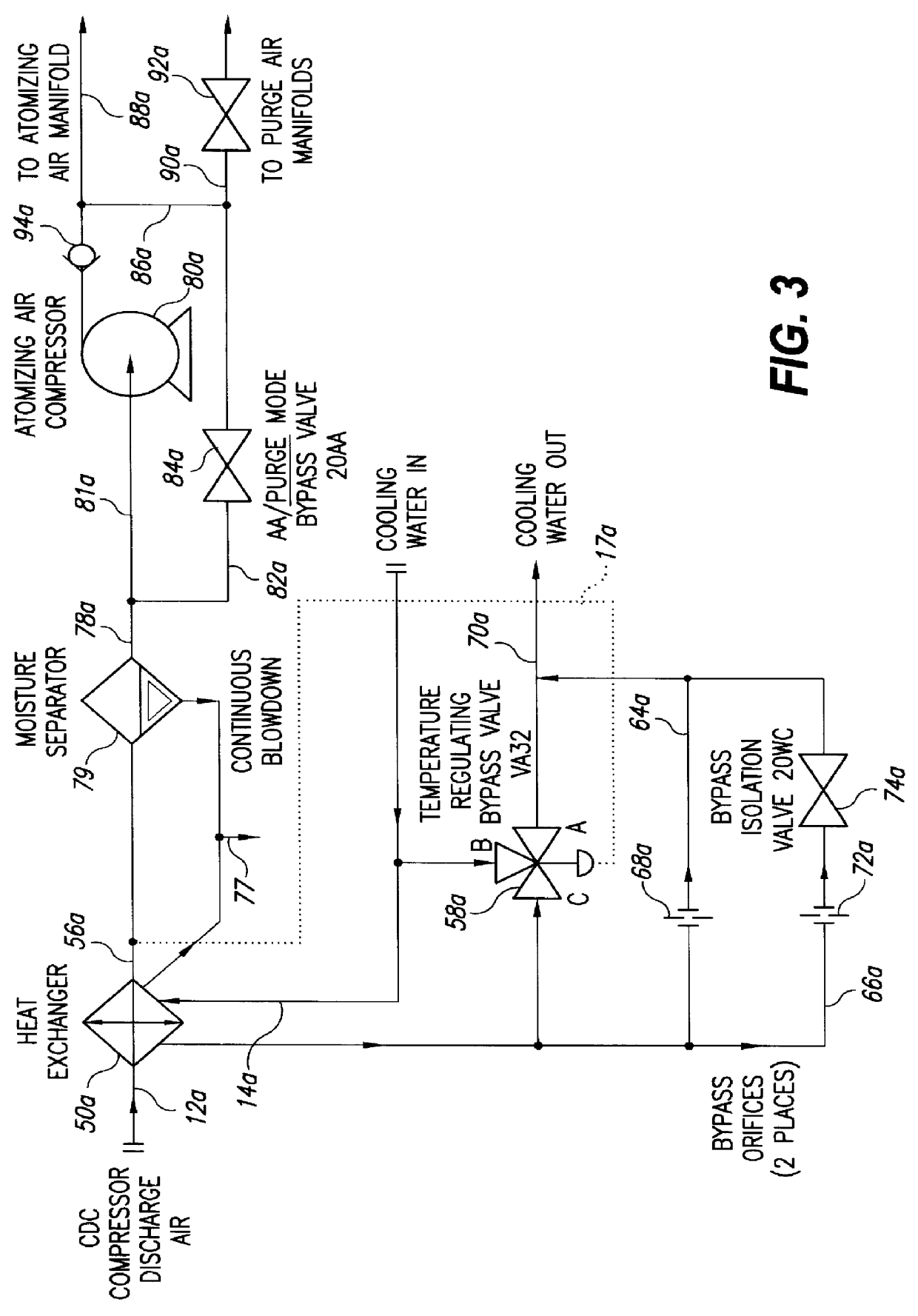
InactiveUS6145318AReduce trafficAvoid heat buildupBurner safety arrangementsBurnersCombustorHeat rejection
Compressor discharge air flows through a heat exchanger in heat exchange relation with cooling water and is supplied at reduced temperature in atomizing air and purge modes to combustors in a dual-fuel gas turbine. The heat exchanger has a pair of bypass passages in parallel with a temperature regulating valve controlling flow of water through the heat exchanger in response to the temperature of the compressor discharge air exiting the heat exchanger. Should the flow control valve close in response to low temperature of the compressor discharge air, in the air atomizing mode, the bypass passages with orifices therein provide a minimum protective flow of cooling water to the heat exchanger. In the purge mode where only half the air flow and heat rejection is required in the heat exchanger and the flow control valve closes, a bypass valve in one of the bypass passages closes to enable reduced flow of cooling water through the heat exchanger.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for ignition of flameless combustor
InactiveUS6269882B1Easy to igniteImprove the level ofApparel holdersIncandescent ignitionCombustorCombustion chamber
A combustor method and apparatus is provided. The method utilizes flameless combustion with one or more of three improvements to enhance ignition of the flameless combustor. A catalytic surface can be provided within a combustion chamber to provide flameless combustion at least in the vicinity of the catalytic surface at a temperature that is much lower than the autoignition temperature of fuel in air without the presence of the catalytic surface. Nitrous oxide or supplemental oxygen may also be used as an oxidant either instead of air or with air to reduce ignition temperatures. Further, electrical energy can be passed through the fuel conduit, raising the temperature of the conduit to a temperature above which the fuel will ignite when combined with the oxidant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
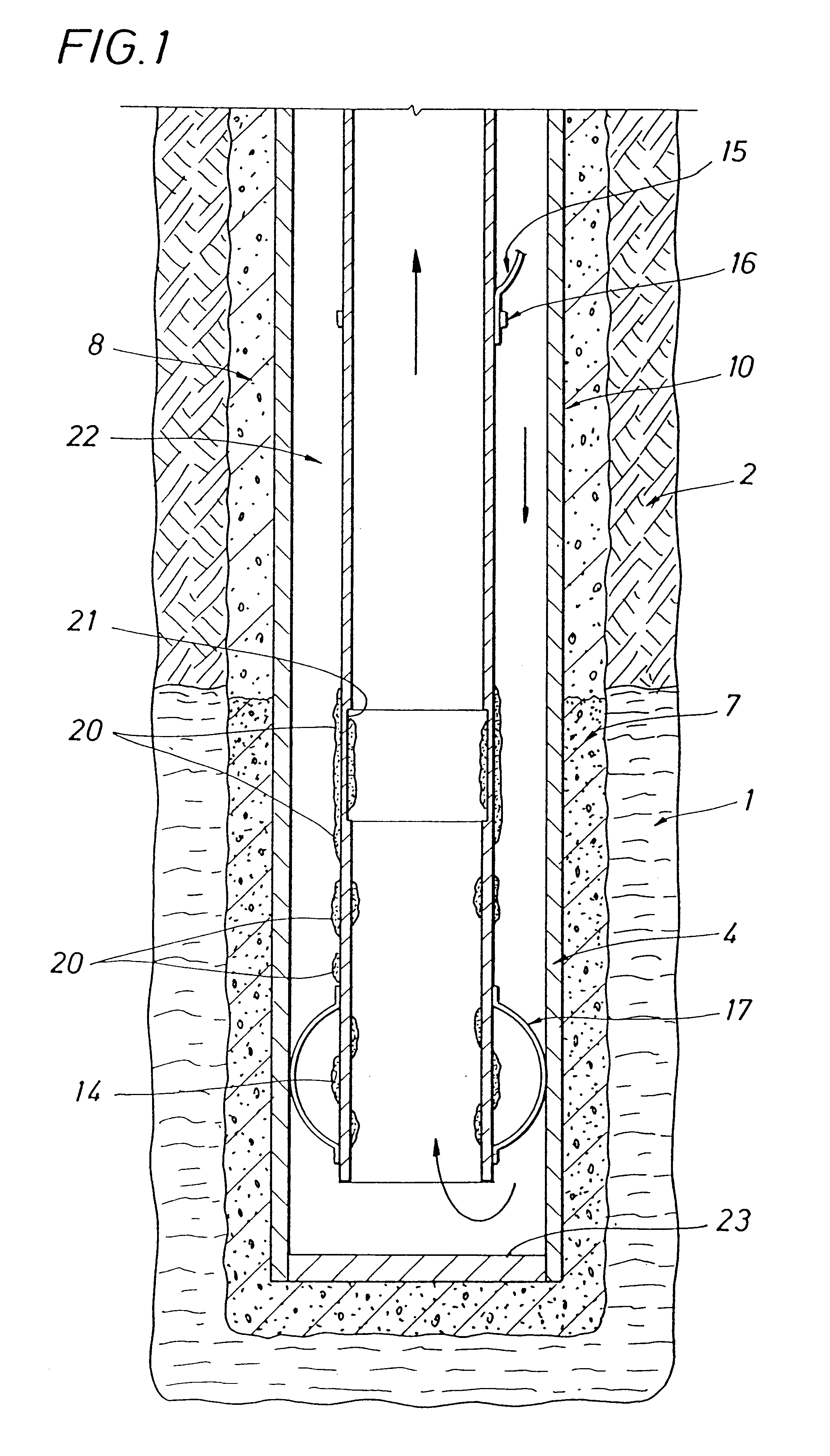
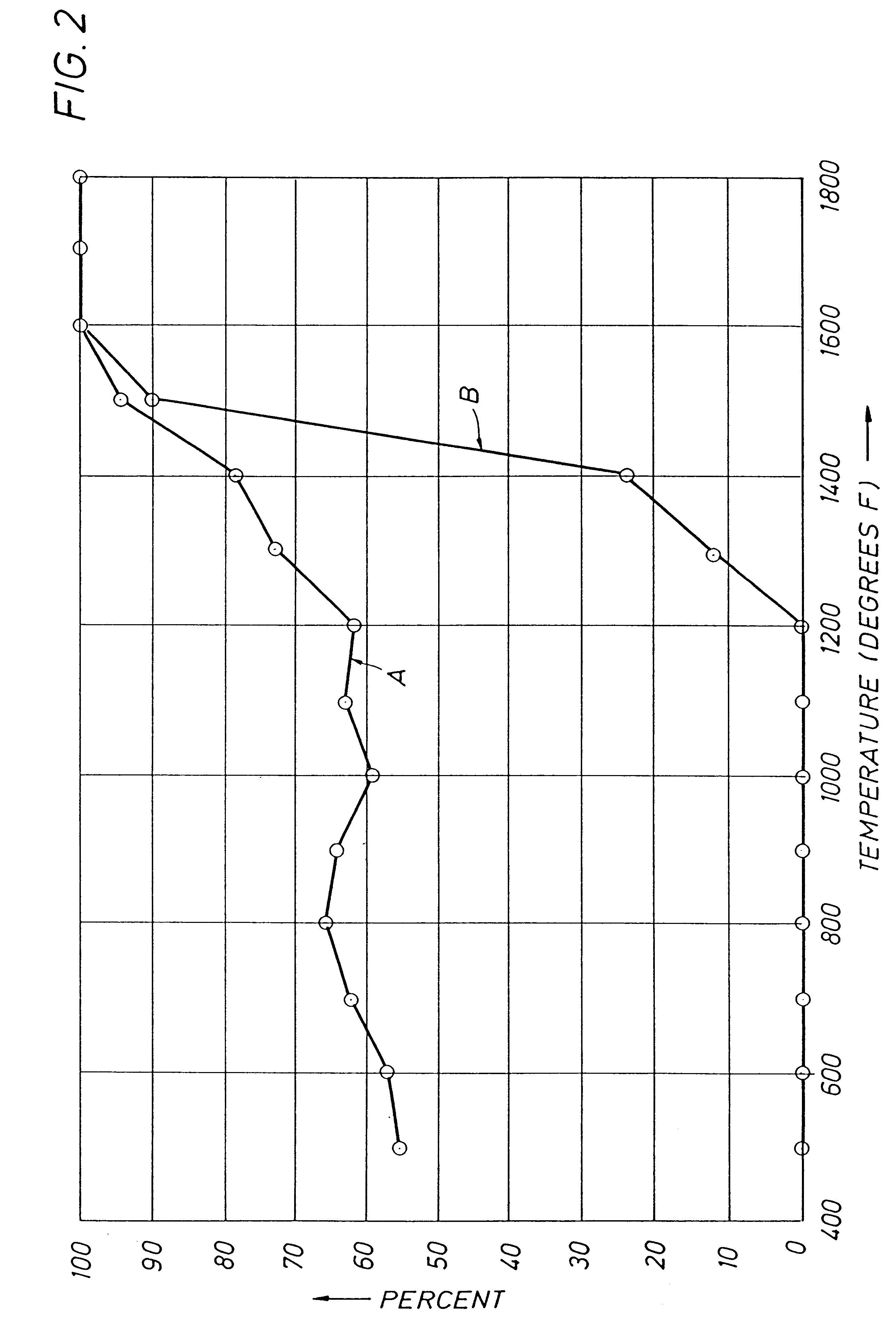
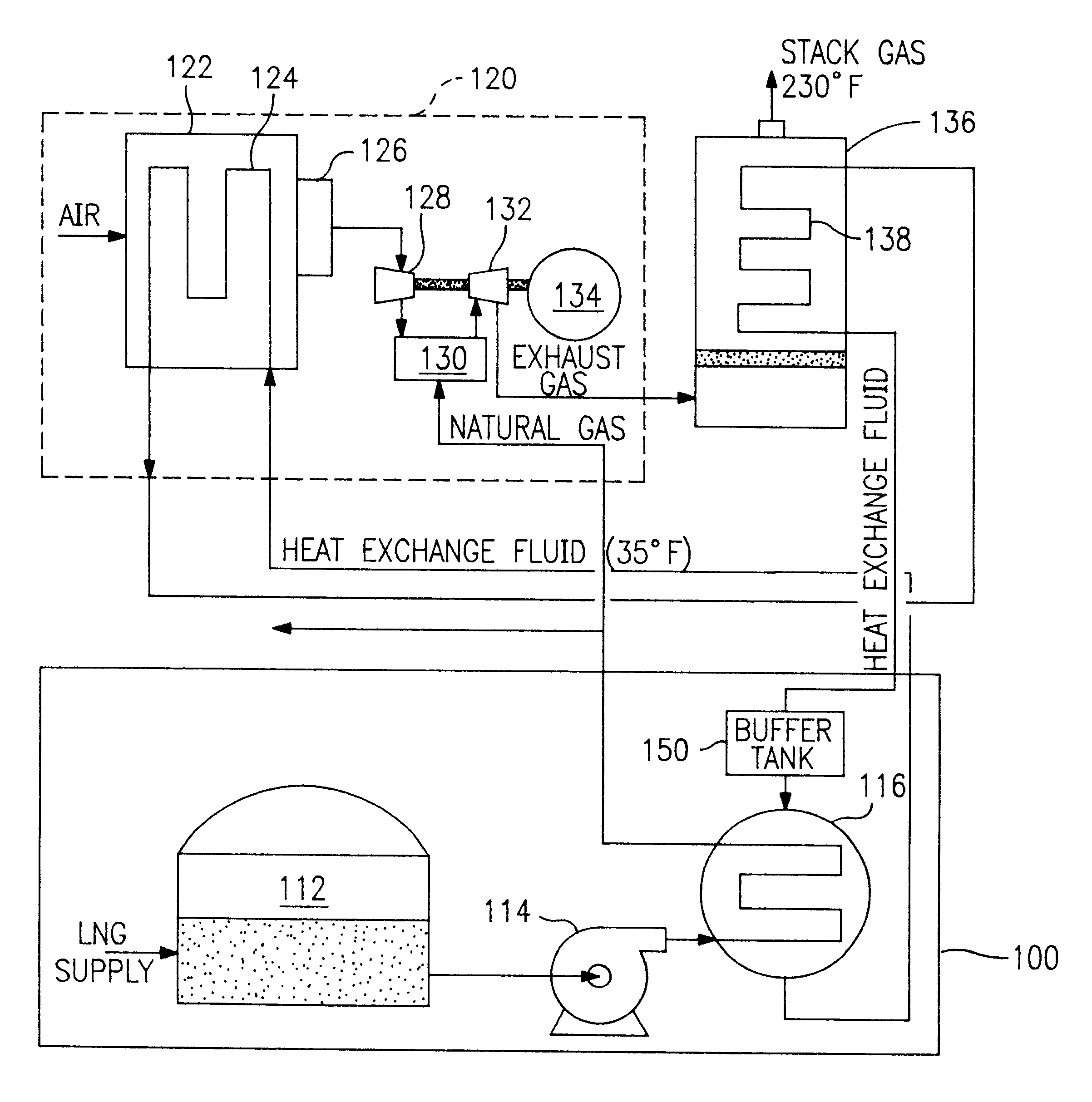
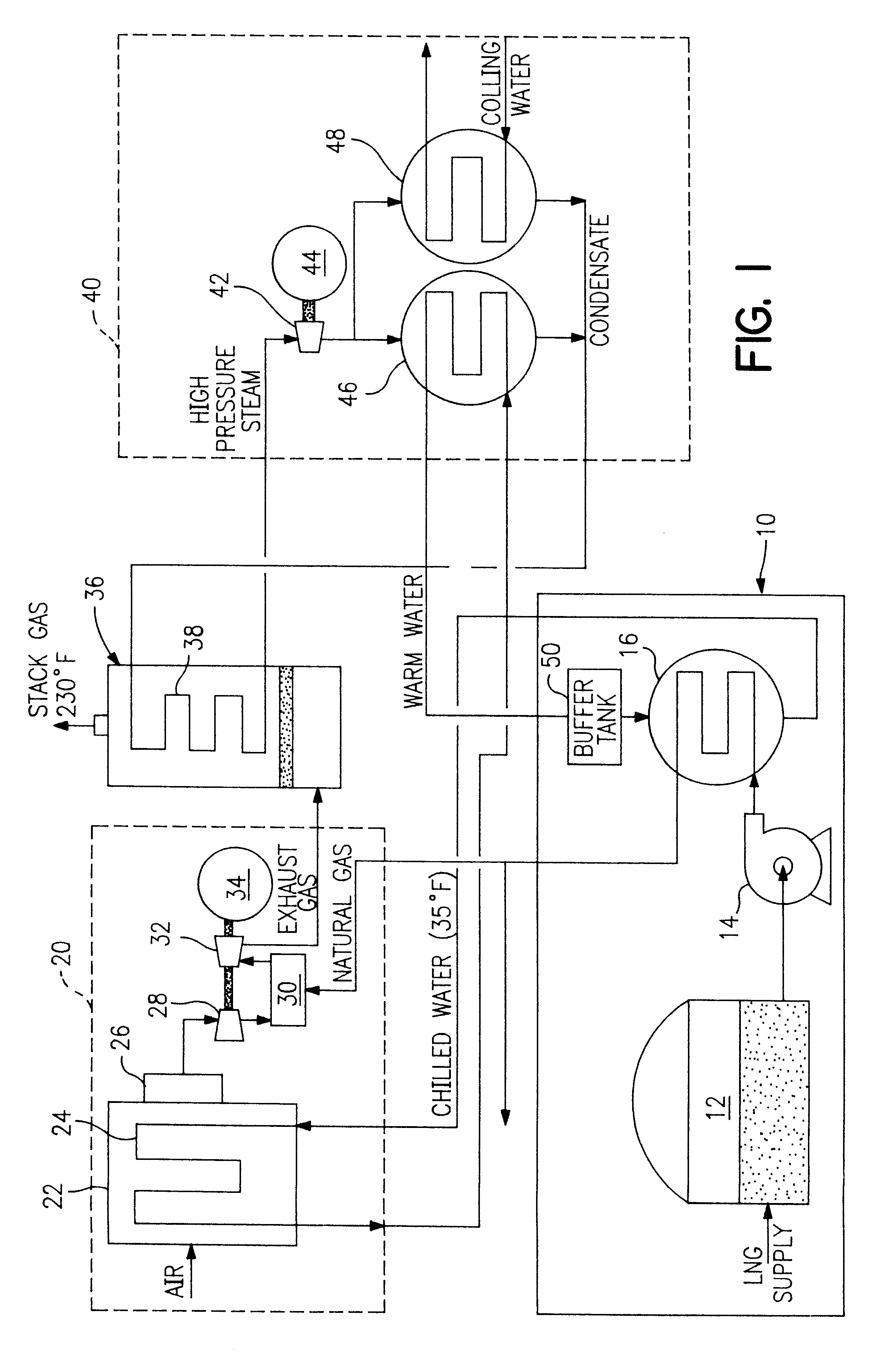
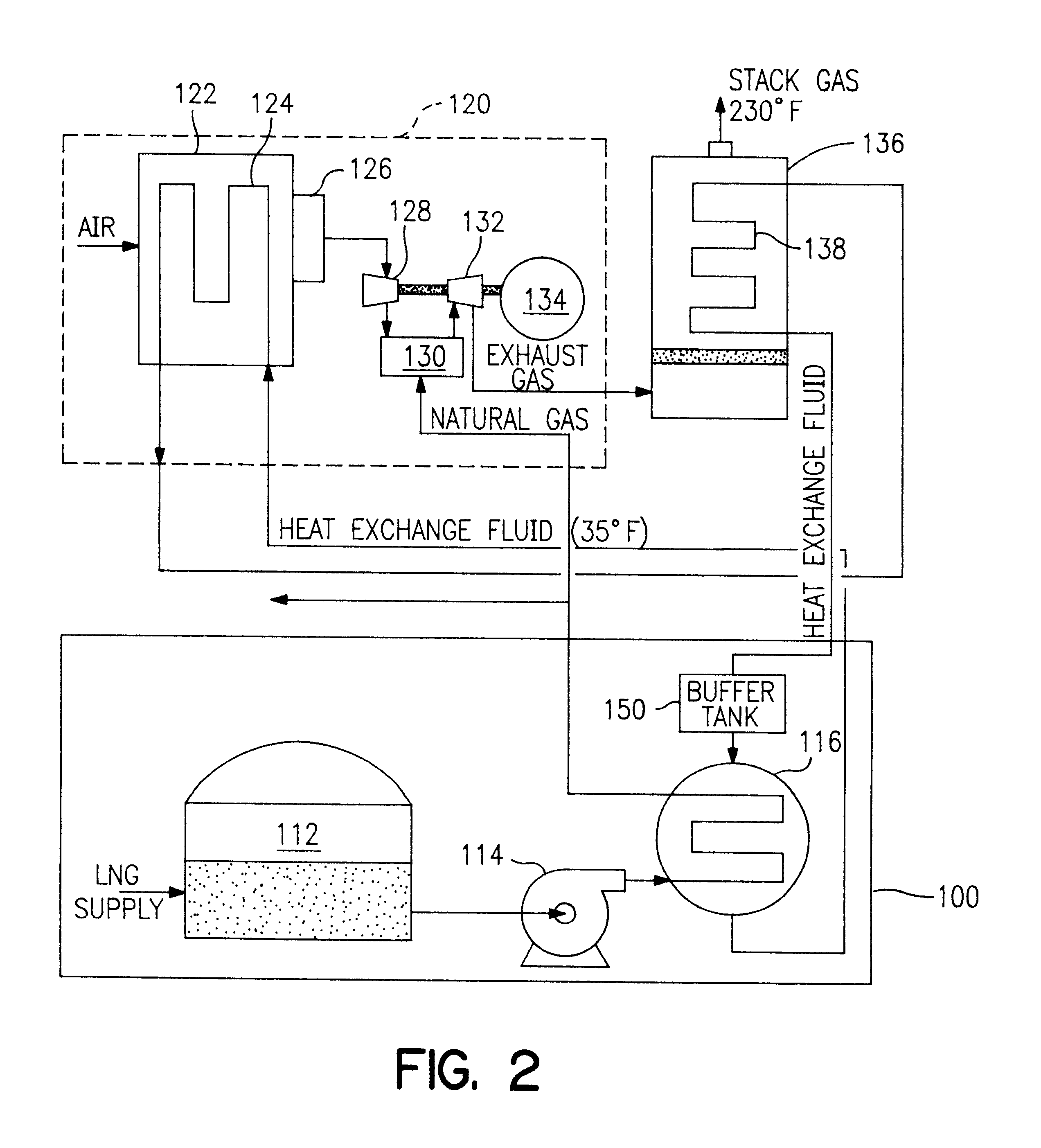
Liquified natural gas (LNG) fueled combined cycle power plant and a (LNG) fueled gas turbine plant
InactiveUS6374591B1Improve efficiencyParts are smallGas handling applicationsGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberPower station
A process and system which improves the capacity and efficiency of a power plant. A LNG supply system fuels the plant. Gasified LNG in a combustor mixes with the air from an air compressor to provide the hot combustion gas for a gas turbine. The expanding LNG is used to chill a heat exchange fluid, e.g. water, which heat exchange fluid cools and densifies the intake air for the air compressor. Subsequently, the heat exchange fluid is used in another heat exchange step and is then re-chilled and recycled to cool and densify the intake air.
Owner:SUEZ LNG NA
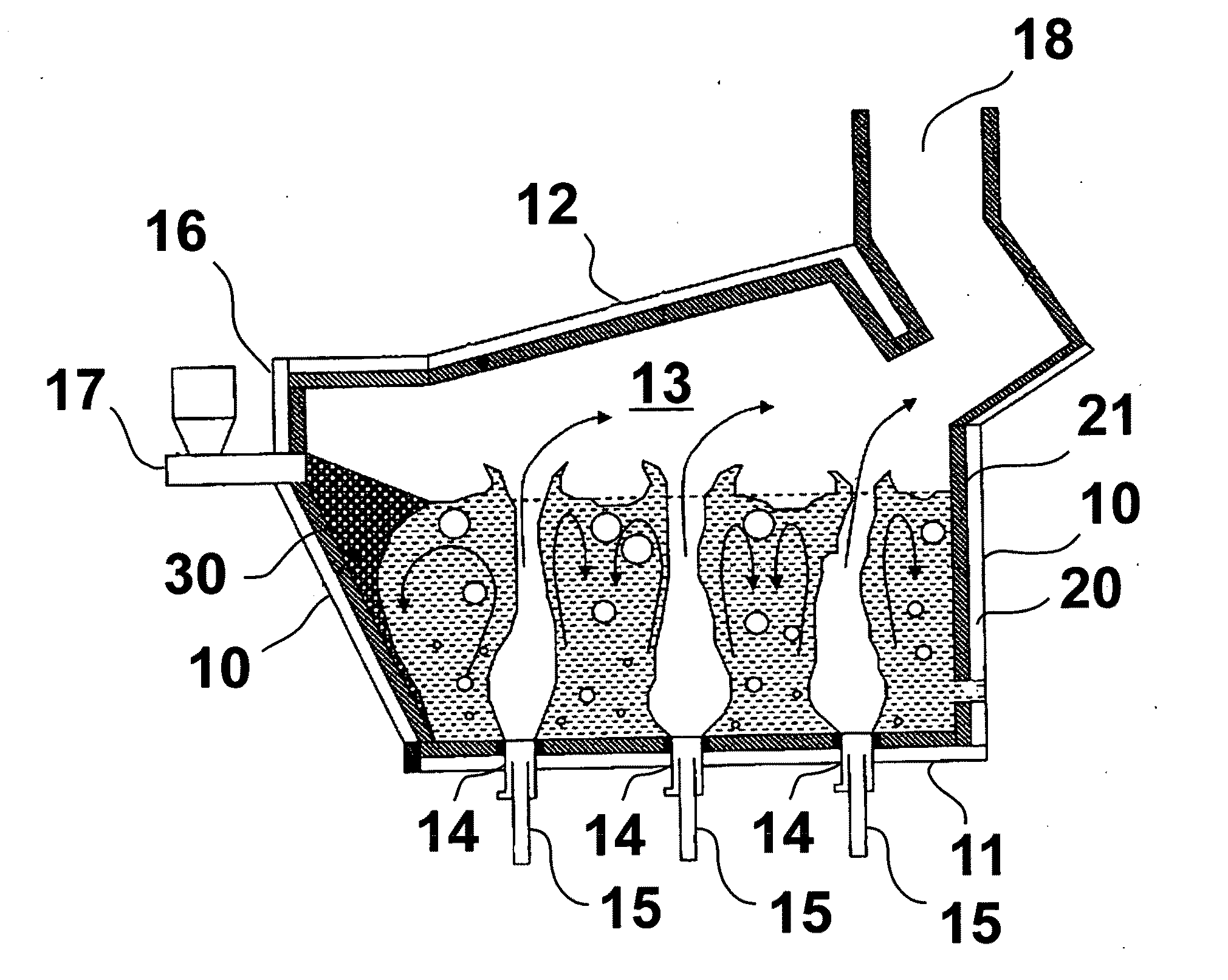
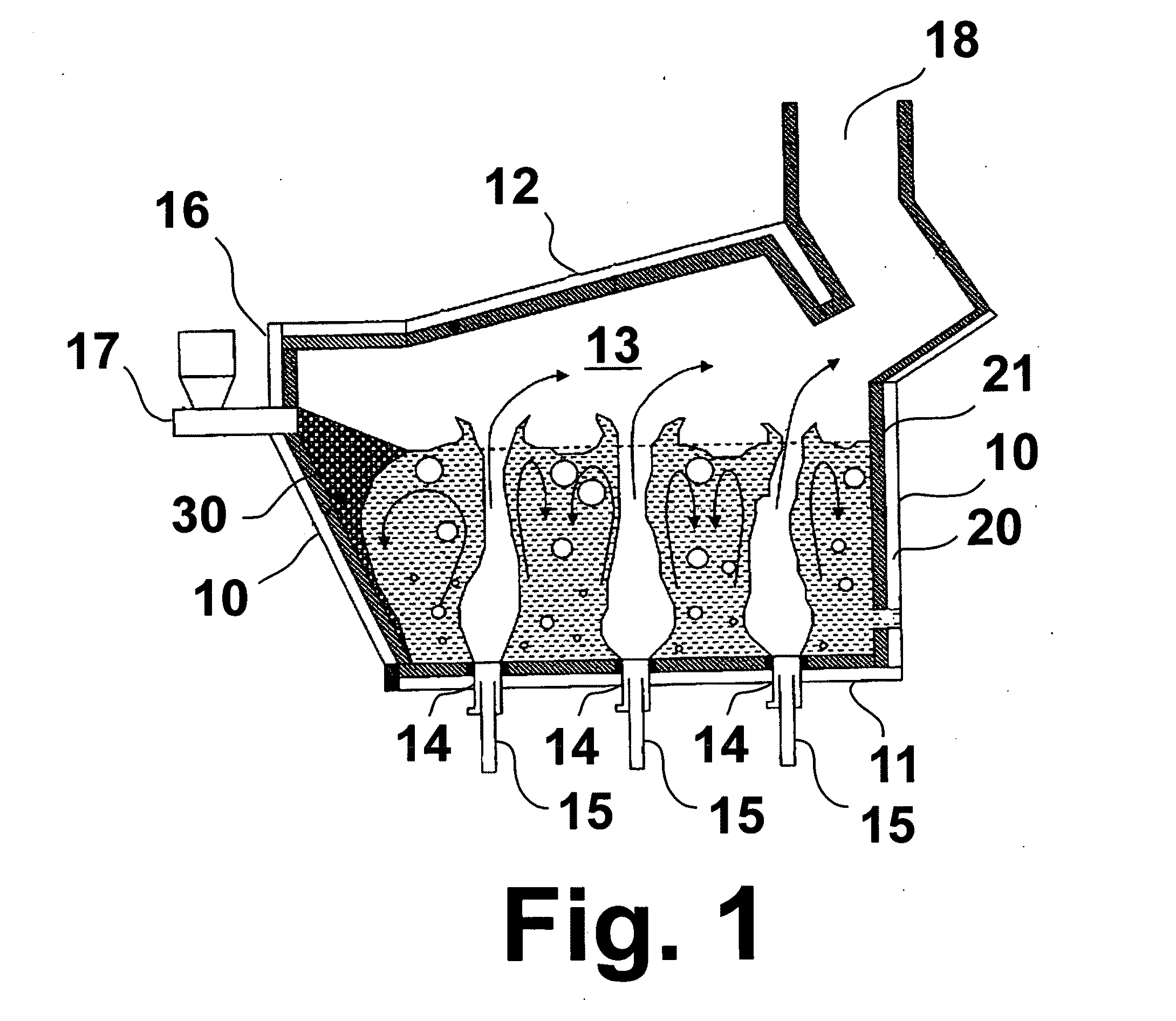
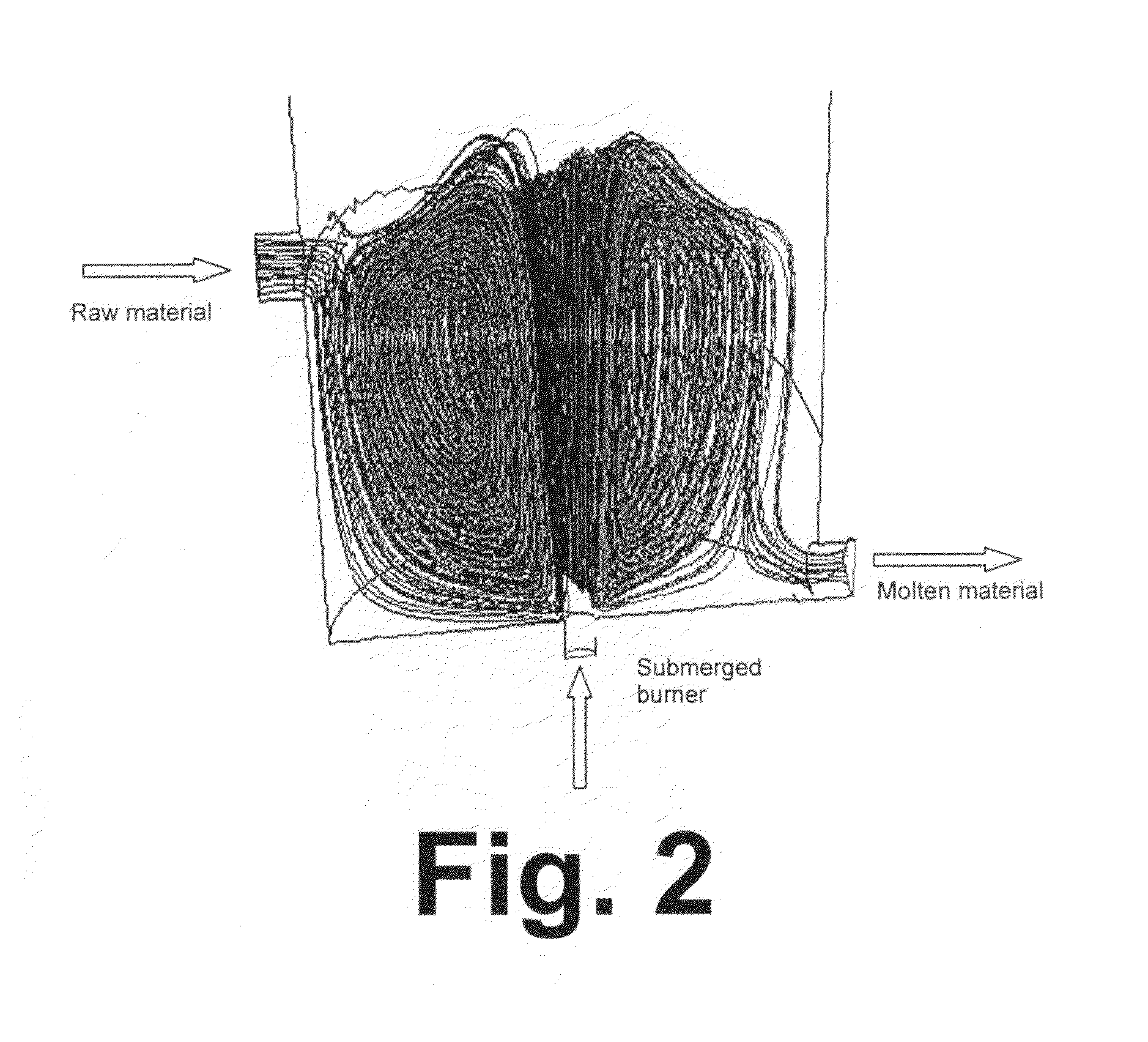
Submerged combustion melter
InactiveUS20110236846A1Increase melter efficiencyReduce bypassCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusCombustorEngineering
A submerged combustion melter having a plurality of side walls, a bottom wall adjacent the side walls, and a top wall adjacent the side walls, the walls collectively enclosing a melting chamber, and the bottom wall forming a plurality of openings, each of which is adapted to receive a submerged combustion burner. Each of the submerged combustion burners is positioned at least 4 inches from the side walls, at least twice as far apart from each other as the distance between the submerged combustion burners and the side walls, and less than or equal to about 20 inches apart.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Low emission turbine system and method
InactiveUS20090218821A1Emission reductionGas turbine plantsMechanical energy handlingElectricityCombustor
A turbine system is provided. The turbine system includes a compressor configured to compress ambient air and a combustor configured to receive compressed air from the compressor, and to combust a fuel stream to generate an exhaust gas. The turbine system also includes a turbine for receiving the exhaust gas from the combustor to generate electricity; wherein a first portion of the exhaust gas is mixed with the ambient air to form a low-oxygen air stream, and wherein the low-oxygen air stream is compressed using the compressor, and is directed to the combustor for combusting the fuel stream to generate a low-NOx exhaust gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
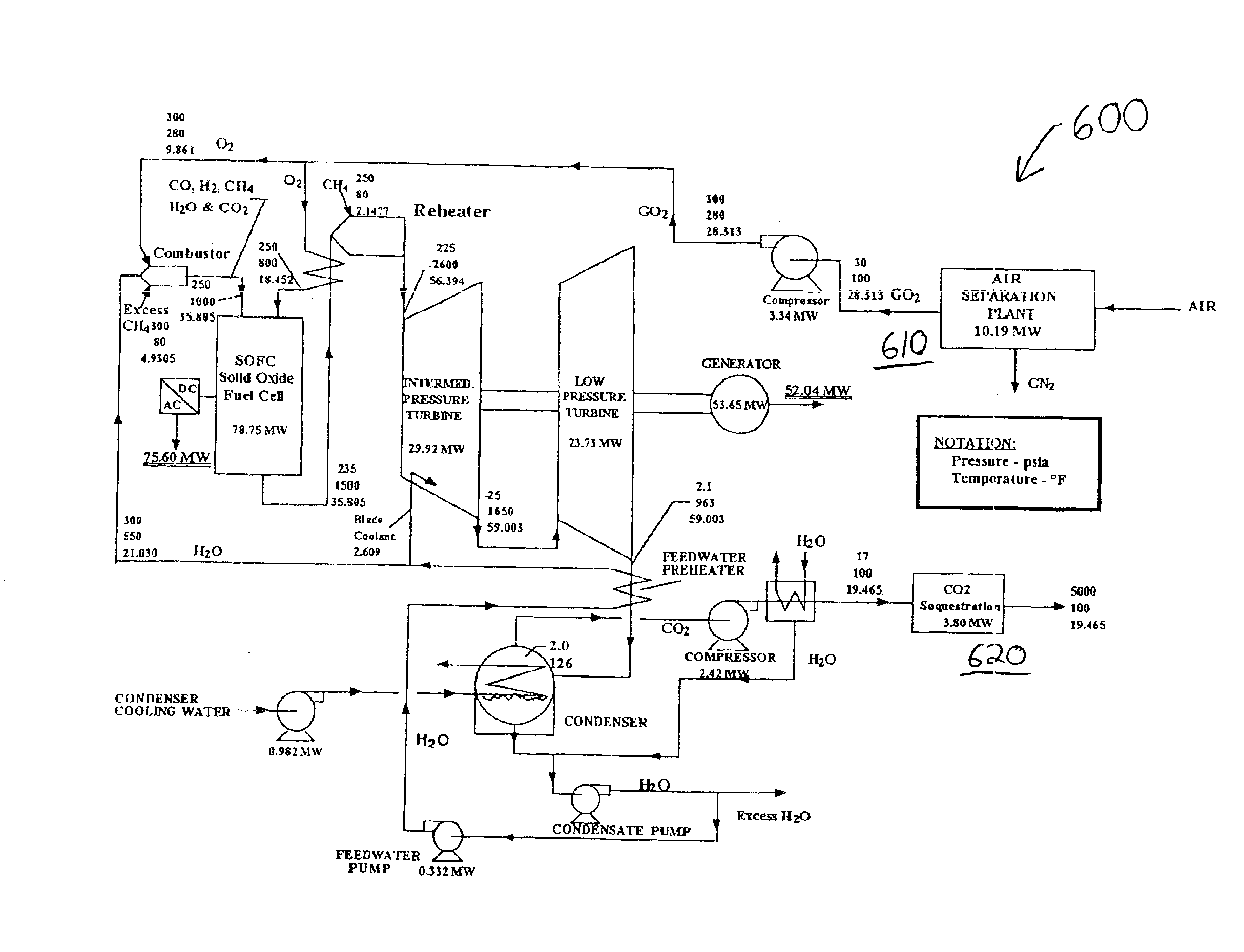
Combined fuel cell and fuel combustion power generation systems
A power generation system is provided which converts chemical energy in one or more fuels into electrical and / or mechanical power. The system includes both fuel cells to directly convert electrical energy in a fuel into electrical power and at lest one combustor and expander to generate mechanical power, optionally than converted to electrical power in a generator. Fuel cell products disclosed from the fuel cell are entered into the combustor to be heated along with products of combustion created in the combustor and expanded in the expander along with the products of combustion.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
Control system for a water heater
InactiveUSRE37745E1Detect presenceHarmful and dangerousMachines/enginesFuel injecting pumpsCombustorControl system
A multi-function controller for a water heater is advanced comprising a control panel and a plurality of sensors that monitor a variety of functions that impact the operation of a water heater. A flammable gas sensor, placed in proximity to the air intake, detects the presence of an unsafe concentration of gas and issues a signal to the control panel, which subsequently discontinues the operation of the burners. Detection of a blocked vent pipe is achieved by a carbon monoxide sensor placed near the draft hood. The control panel is equipped with circuitry which monitors usage of the heater for a specified time period to develop a pattern of use. Subsequent to the monitoring period, the controller will activate the burners a predetermined time prior to an anticipated period of high use. During periods of low use, the controller will decrease the temperature to which the water is to be heated, thereby resulting in a more efficient heater. Non-volatile memory records data from the sensors so that the operation status of the heater may be ascertained subsequent to a power outage. The control panel contains a plurality of visual alarms, each of which corresponds to a sensor. Consequently, repair and maintenance are simplified because the cause of a malfunction is quickly recognized.
Owner:AOS HLDG CO
Turbofan engine assembly and method of assembling same
InactiveUS20080120839A1Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCombustorHigh pressure
A turbofan engine assembly includes a core gas turbine engine including a high-pressure compressor, a combustor, and a high-pressure turbine, a first fan assembly disposed upstream from the core gas turbine engine, a first gearbox coupled to the first fan assembly, and a second gearbox coupled to a booster compressor such that the booster compressor rotates in a rotational direction that is opposite to the rotational direction of the first fan assembly. A method of assembling the above turbofan engine assembly is also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and Method for Controlling the Secondary Injection of Fuel
In one embodiment, a combustor (28) for a gas turbine engine is provided comprising a primary combustion chamber (30) for combusting a first fuel to form a combustion flow stream (50) and a transition piece (32) located downstream from the primary combustion chamber (30). The transition piece (32) comprises a plurality of injectors (66) located around a circumference of the transition piece (32) for injecting a second fuel into the combustion flow stream (50). The injectors (66) are effective to create a radial temperature profile (74) at an exit (58) of the transition piece (32) having a reduced coefficient of variation relative to a radial temperature profile (64) at an inlet (54) of the transition piece (32). Methods for controlling the temperature profile of a secondary injection are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
System and method of improving emission performance of a gas turbine
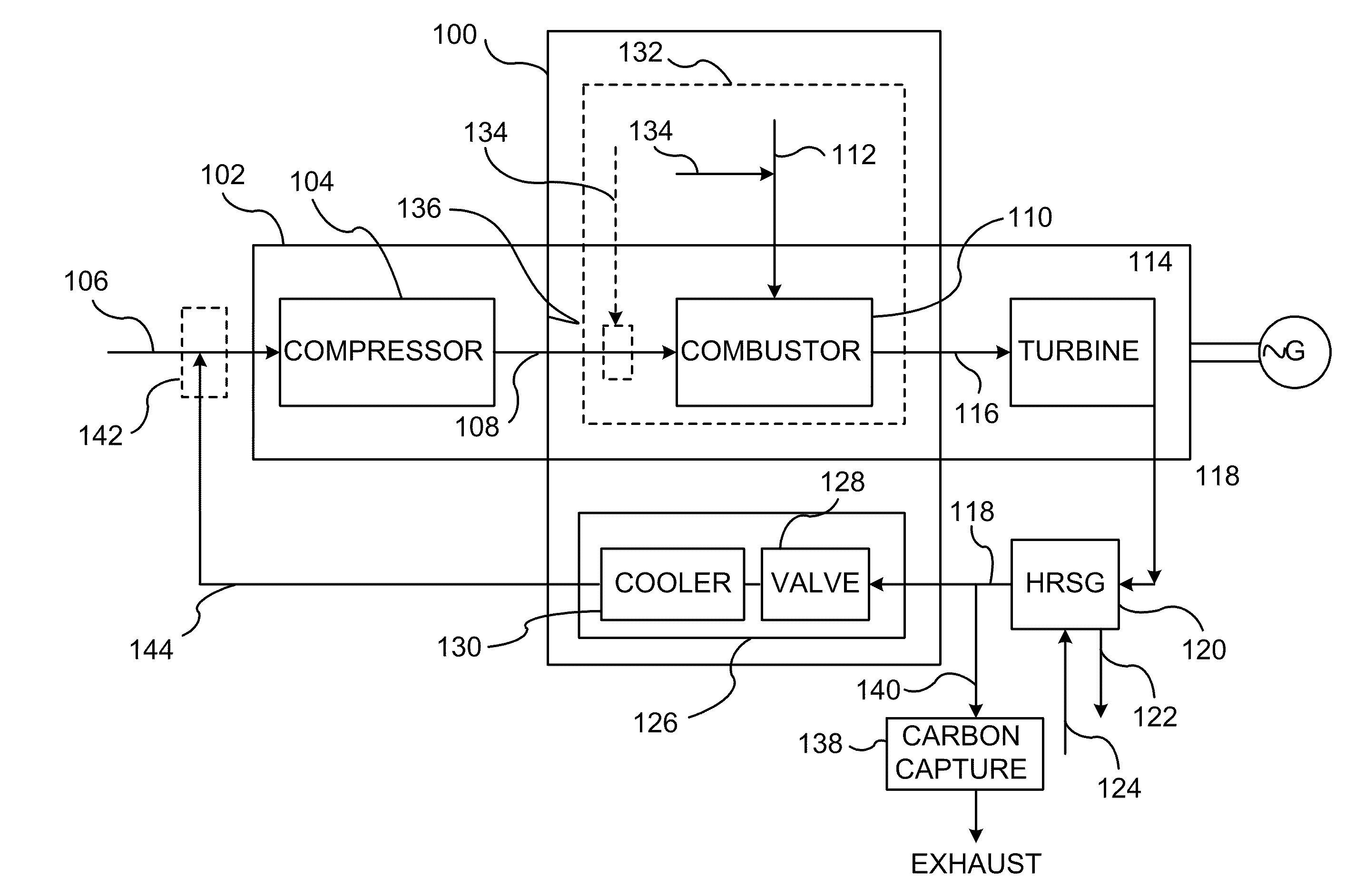
InactiveUS20110138766A1Improve emission effectReduce oxygen concentrationEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsHigh pressureOxygen
A method of improving emission performance of a gas turbine is provided. The method includes recirculating a portion of an exhaust gas stream to a compressor of the gas turbine via an exhaust gas recirculating system, to reduce concentration of oxygen in a high pressure feed oxidant stream into a combustor of the gas turbine. The method further includes adding diluent to at least one of a fuel stream directed to the combustor or a low pressure feed oxidant stream directed to the compressor, to reduce concentration of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and increase concentration of carbon dioxide in a resultant exhaust gas stream.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and Systems for Gas Turbine Part-Load Operating Conditions
A method and system for operating at partial load a gas turbine system having a compressor, a combustor, and a turbine. The method and system may include the steps of lowering a flow of fuel to the combustor, extracting air from the compressor so as to lower a flow of air to the compressor, and returning the extracted air to the turbine or a component of the gas turbine system other than the combustor. Extracting air from the compressor raises a combustion temperature within the combustor. Raising the combustion temperature maintains a combustion exhaust below a predetermined level, maintains stable combustion, and extends turbine turndown values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com