Patents
Literature
34415 results about "Combustion chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
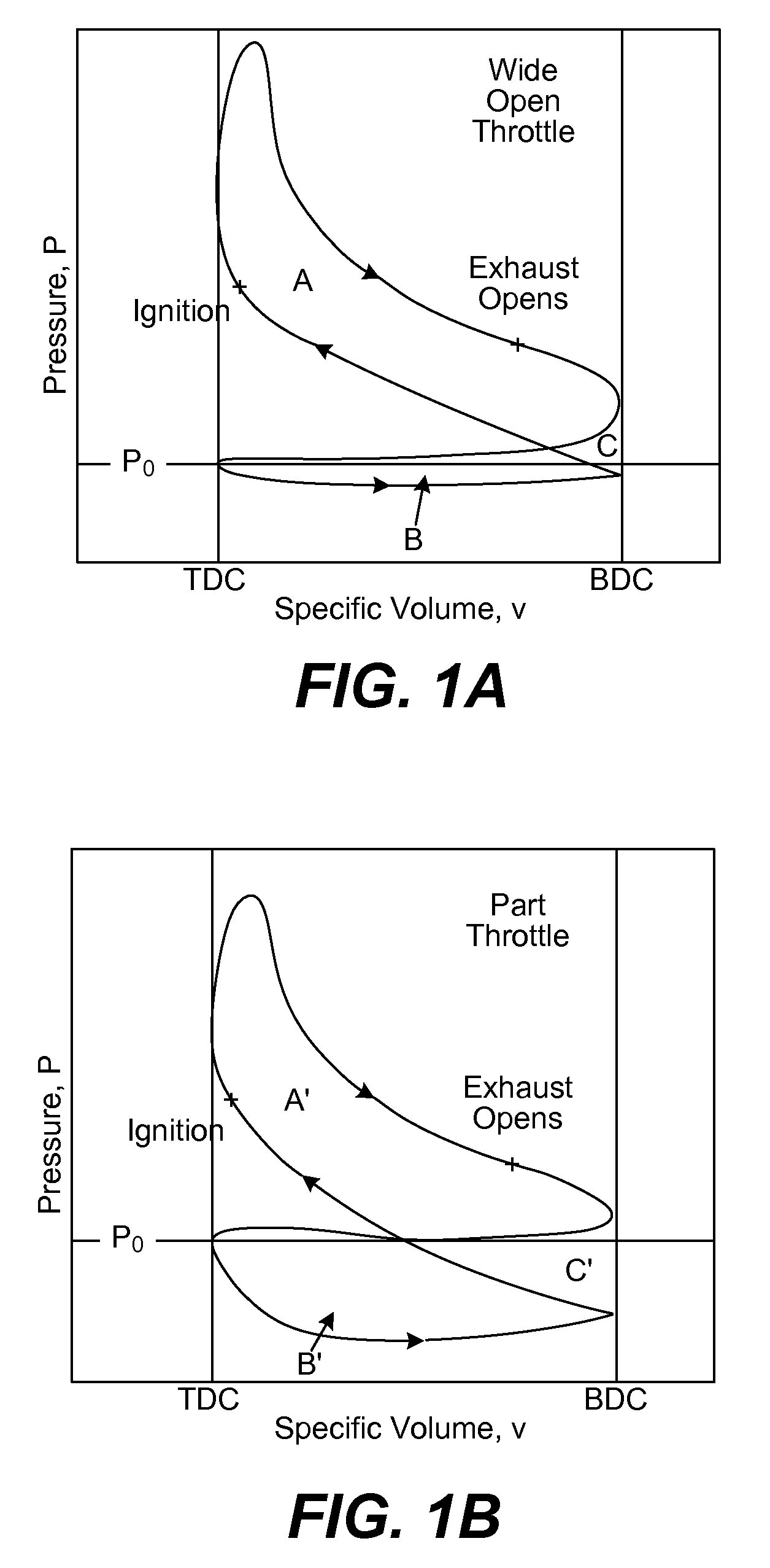
A combustion chamber is that part of an internal combustion engine (ICE) or a reaction engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned.
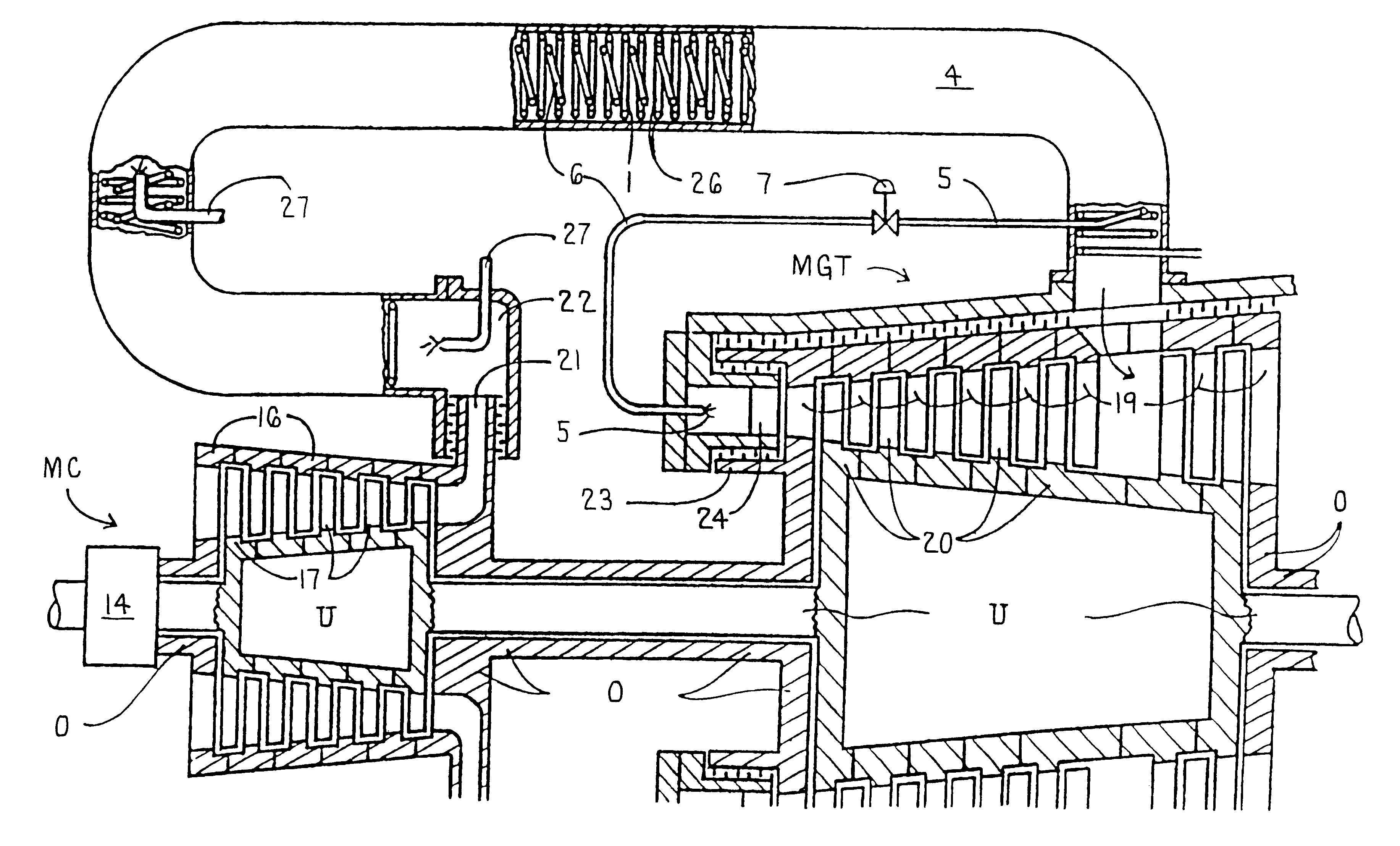
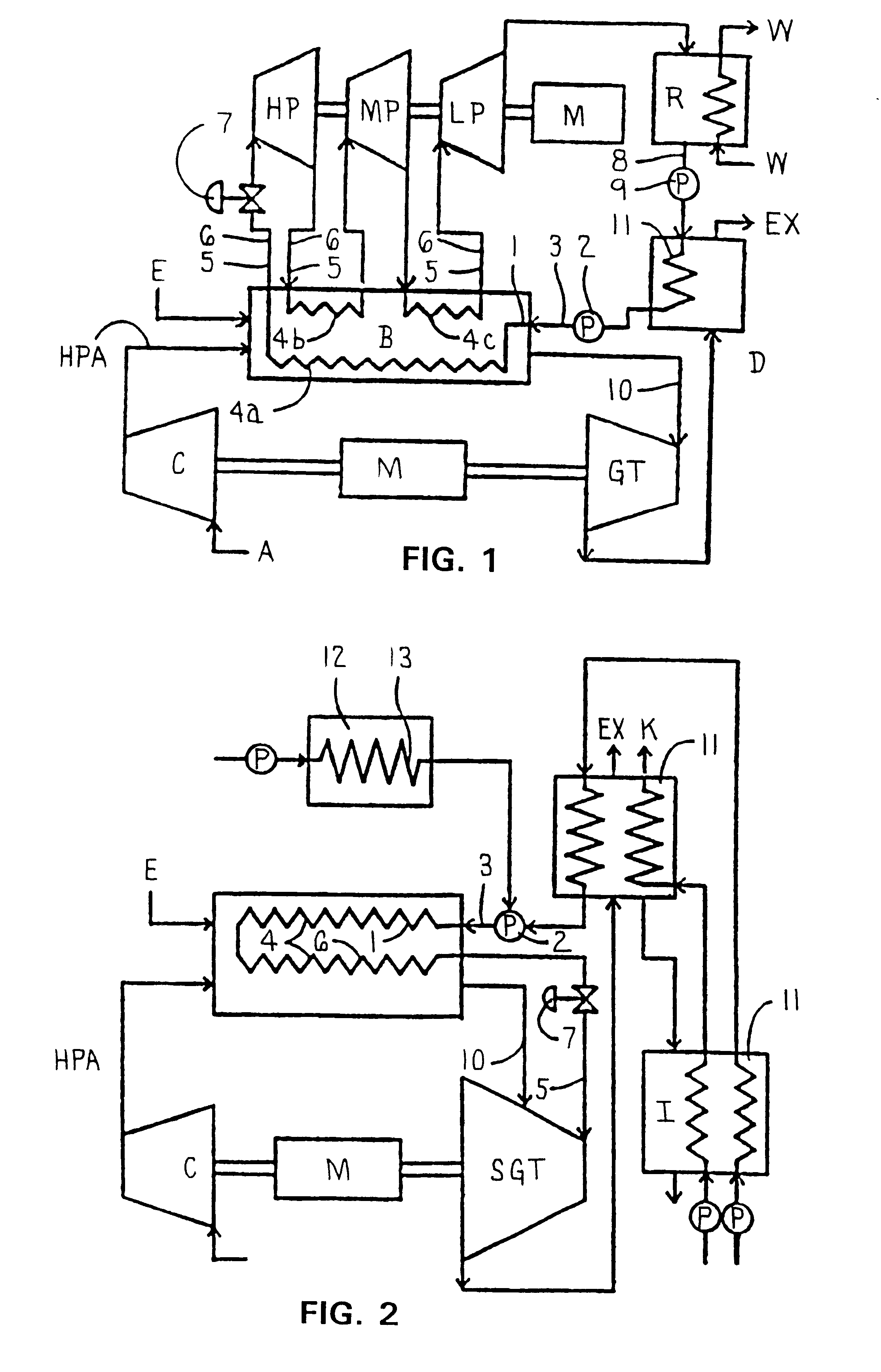
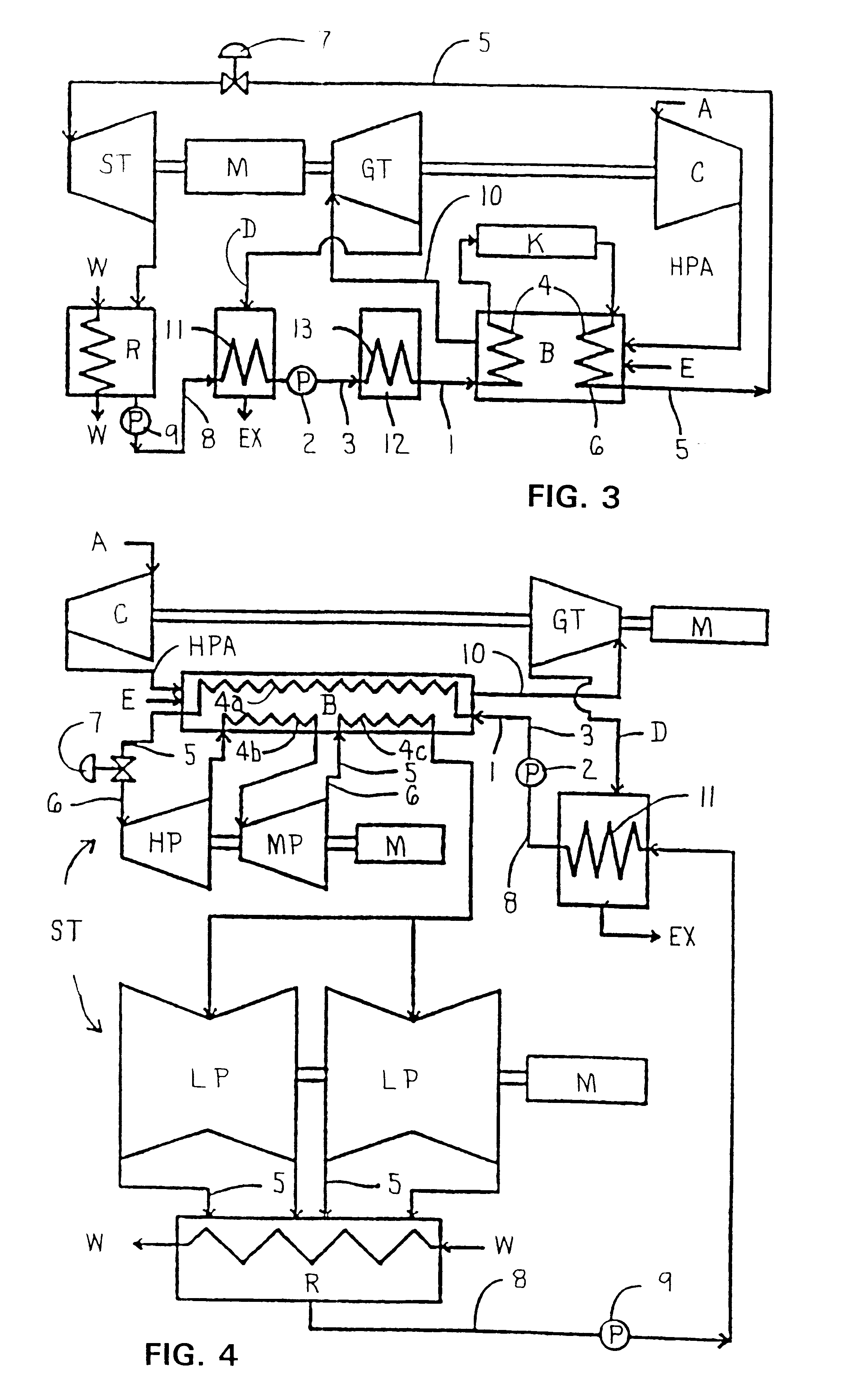
Combined steam and gas turbine engine with magnetic transmission
InactiveUS6263664B1Wide areaImprove system efficiencyContinuous combustion chamberGearingThermal energyCombustion chamber
In a combined steam and gas turbine engine cycle, a combustion chamber is made durable against high pressure and enlarged in length to increase the operation pressure ratio, without exceeding the heat durability temperature of the system while increasing the fuel combustion gas mass flow four times as much as the conventional turbine system and simultaneously for greatly raising the thermal efficiency of the system and specific power of the combined steam and gas turbine engine.Water pipes and steam pipes are arranged inside the combustion chamber so that the combustion chamber can function as a heat exchanger and thereby convert most of the combustion thermal energy into super-critical steam energy for driving a steam turbine and subsequently raising the operation pressure ratio and the thermal efficiencies of the steam turbine cycle and gas turbine cycle. The combustion gas mass flow can be also increased by four times as much as the conventional turbine system (up to the theoretical air to fuel ratio) and the thermal efficiency and the specific power of the gas turbine cycle are considerably increased.Further, the thermal efficiency of the combined system is improved by installing a magnetic friction power transmission system to transmit the power of the system to outer loads.
Owner:TANIGAWA HIROYASU +1
Flameless combustor
InactiveUS6019172AEasy to igniteImprove the level ofApparel holdersInsulationCombustorCombustion chamber
A combustor method and apparatus is provided. The method utilizes flameless combustion with one or more of three improvements to enhance ignition of the flameless combustor. A catalytic surface can be provided within a combustion chamber to provide flameless combustion at least in the vicinity of the catalytic surface at a temperature that is much lower than the autoignition temperature of fuel in air without the presence of the catalytic surface. Nitrous oxide or supplemental oxygen may also be used as an oxidant either instead of air or with air to reduce ignition temperatures. Further, electrical energy can be passed through the fuel conduit, raising the temperature of the conduit to a temperature above which the fuel will ignite when combined with the oxidant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Inhalation device and heating unit therefor
The invention relates to a heating unit for an inhalation device for the inhalation administration of an inhalation mixture of air and at least one additive material, having a fuel storage (252) which is filled or can be filled with a thermally combustible solid or liquid fuel (258), and with a combustion chamber (256) for the combustion of the fuel (258), which is essentially sealed from the surroundings by a combustion chamber wall (222). The invention further relates to an inhalation device (210) with such a heating unit.According to the invention, the combustion chamber (256) is designed for forming a flame, and the combustion chamber wall (222) has at least some micro openings (224). The micro openings are designed in such a way that the sum of the outer side lengths of all micro openings (224) is at least 140 mm, and the sum of the outer side lengths of the micro openings (224) per surface in the area of the combustion chamber wall (222) averages at least 80 mm / cm2.Application as cigarette substitute or as aid for nicotine withdrawal.
Owner:SILLER FRIEDRICH
Dry 3-way catalytic reduction of gas turbine NOx
ActiveUS20090284013A1Reduction in amount of NOxIncrease carbon dioxide concentrationInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustion chamberGas compressor
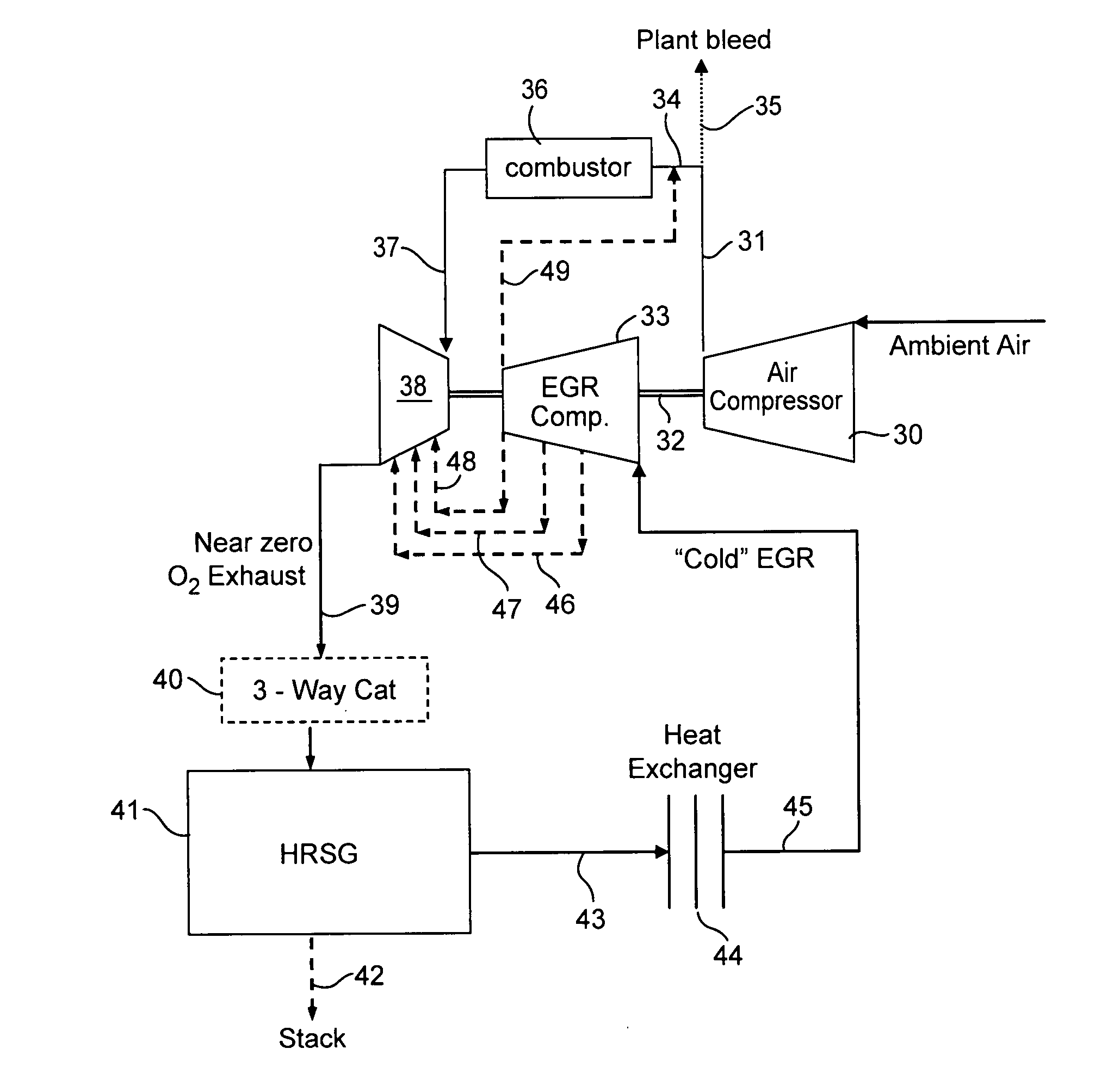
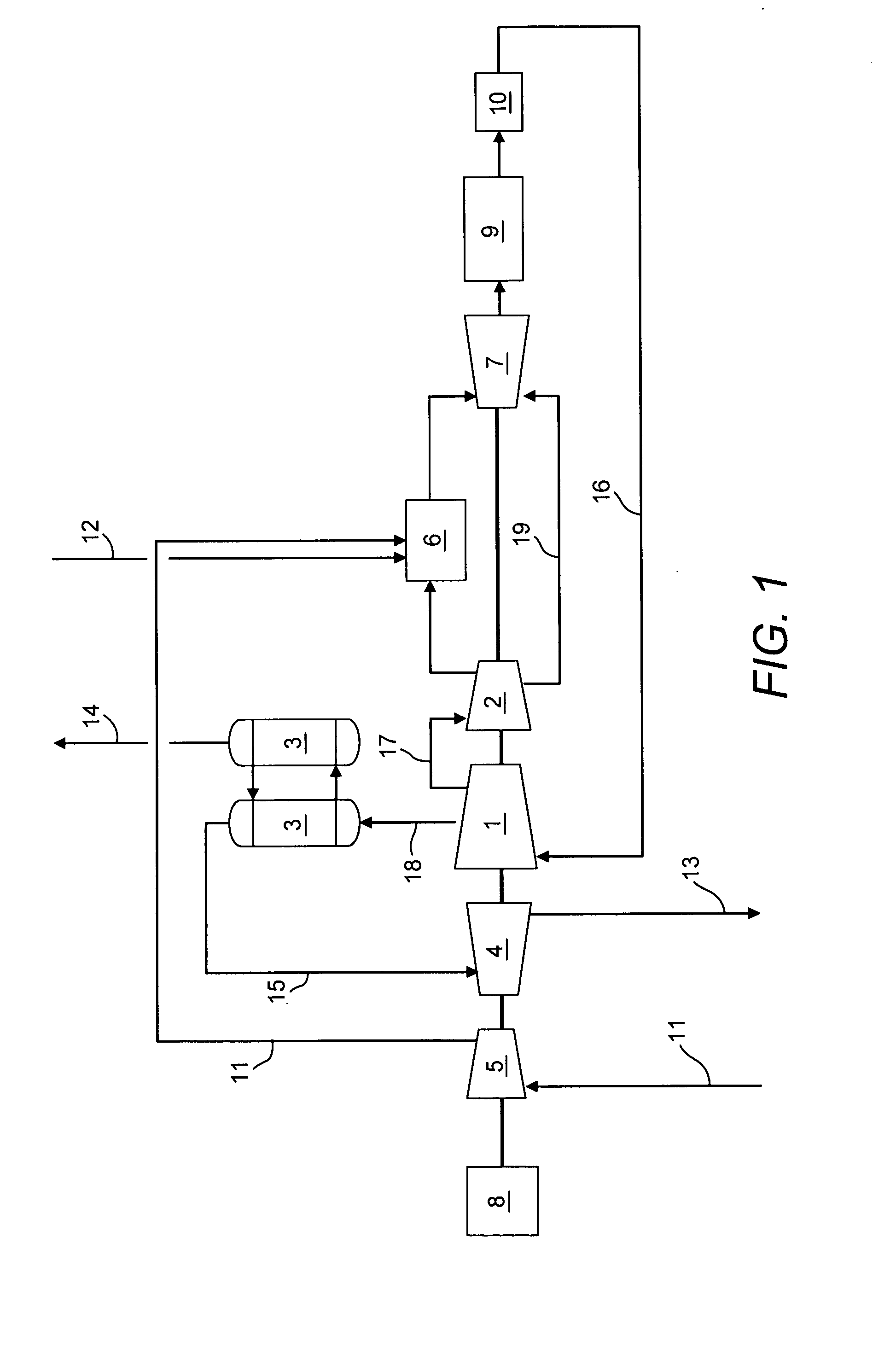
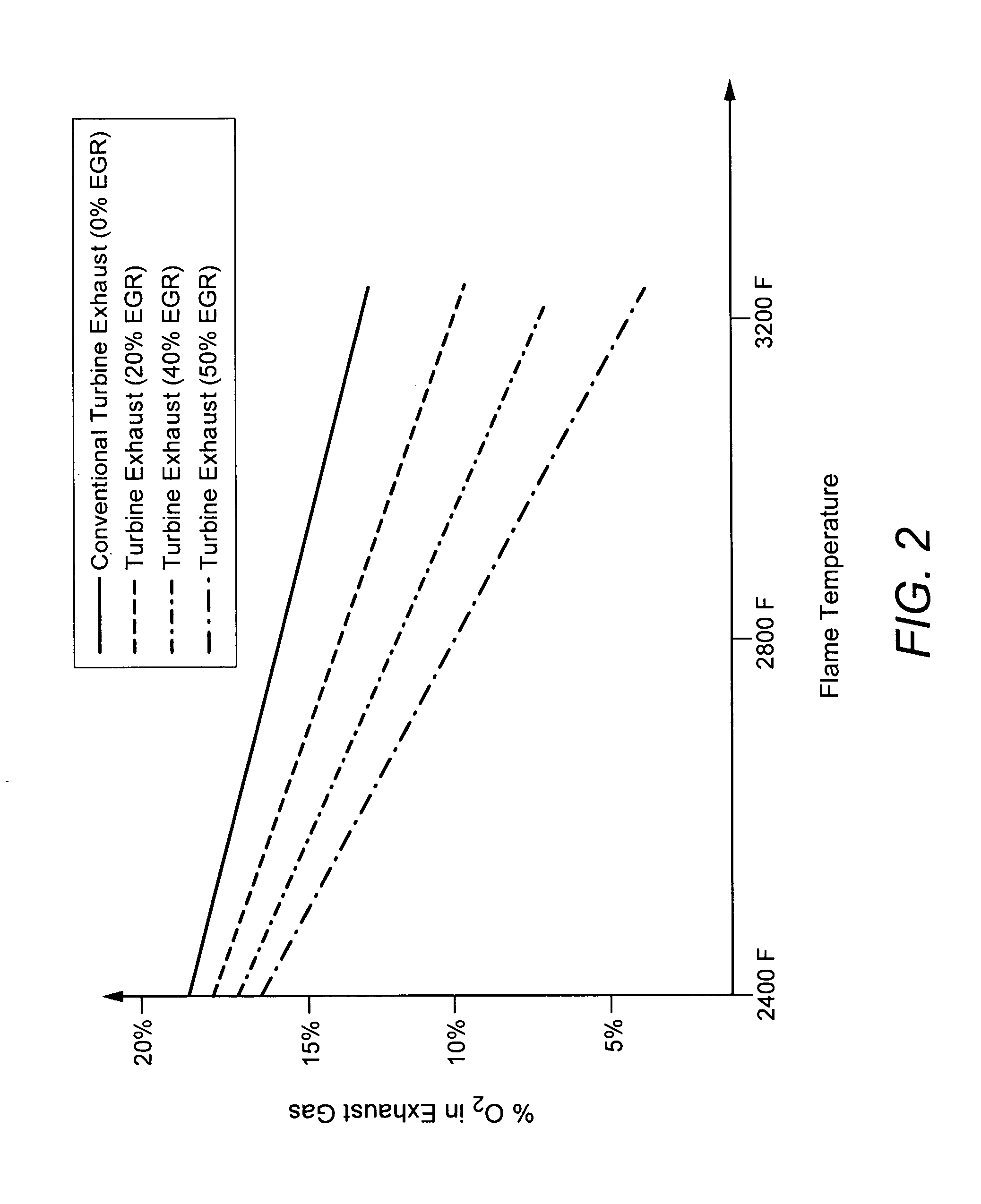
A power generation system capable of eliminating NO, components in the exhaust gas by using a 3-way catalyst, comprising a gas compressor to increase the pressure of ambient air fed to the system; a combustor capable of oxidizing a mixture of fuel and compressed air to generate an expanded, high temperature exhaust gas; a gas turbine engine that uses the force of the high temperature gas; an exhaust gas recycle (EGR) stream back to the combustor; a 3-way catalytic reactor downstream of the gas turbine engine outlet which treats the exhaust gas stream to remove substantially all of the NOx components; a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG); an EGR compressor; and an electrical generator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
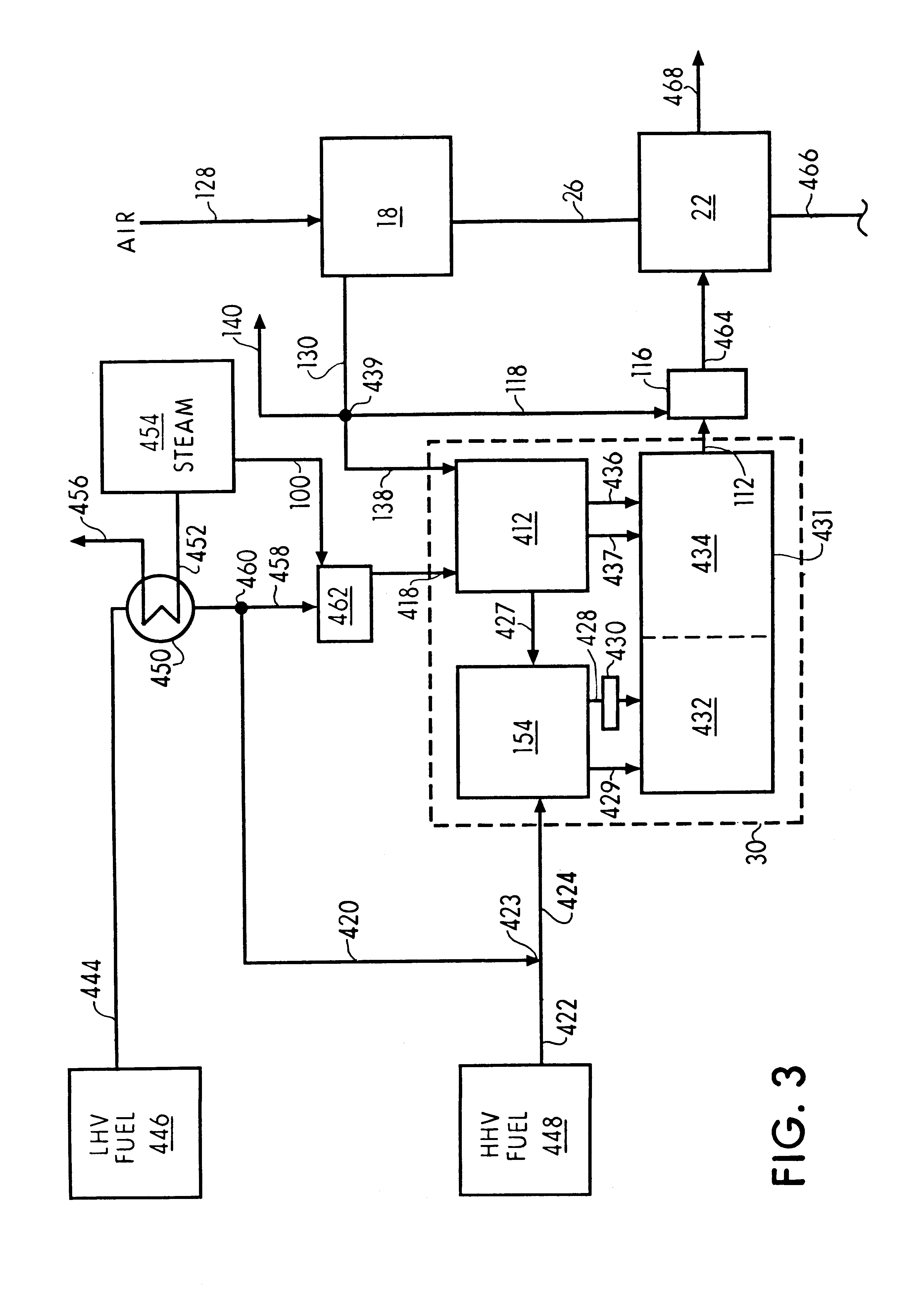
Staged combustion of a low heating value fuel gas for driving a gas turbine
A process is provided for combusting a low heating value fuel gas in a combustor to drive an associated gas turbine. A low heating value fuel gas feed is divided into a burner portion and a combustion chamber portion. The combustion chamber portion and a combustion air are conveyed into a mixing zone of the combustor to form an air / fuel mixture. The burner portion is conveyed into a flame zone of the combustor through a burner nozzle while a first portion of the air / fuel mixture is conveyed into the flame zone through a burner port adjacent to the burner nozzle. The burner portion and first portion of the air / fuel mixture are contacted in the flame zone to combust the portions and produce flame zone products. The flame zone products are conveyed into an oxidation zone of the combustor downstream of the flame zone while a second portion of the air / fuel mixture is also conveyed into the oxidation zone. The second portion is combusted in the oxidation zone in the presence of the flame zone products to produce combustion products. The combustion products are conveyed into the associated gas turbine and drive the gas turbine.
Owner:MARATHON OIL CO +1
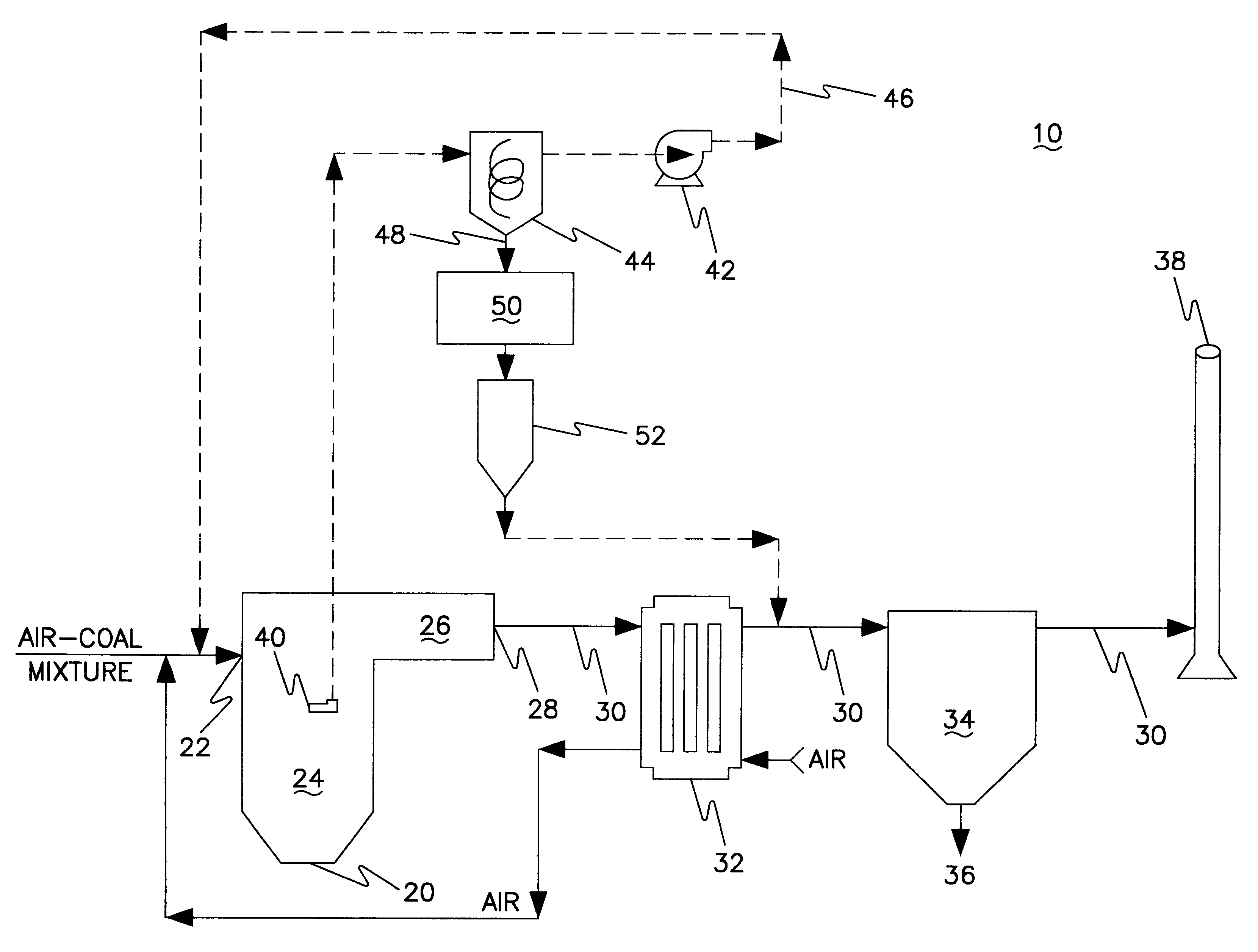
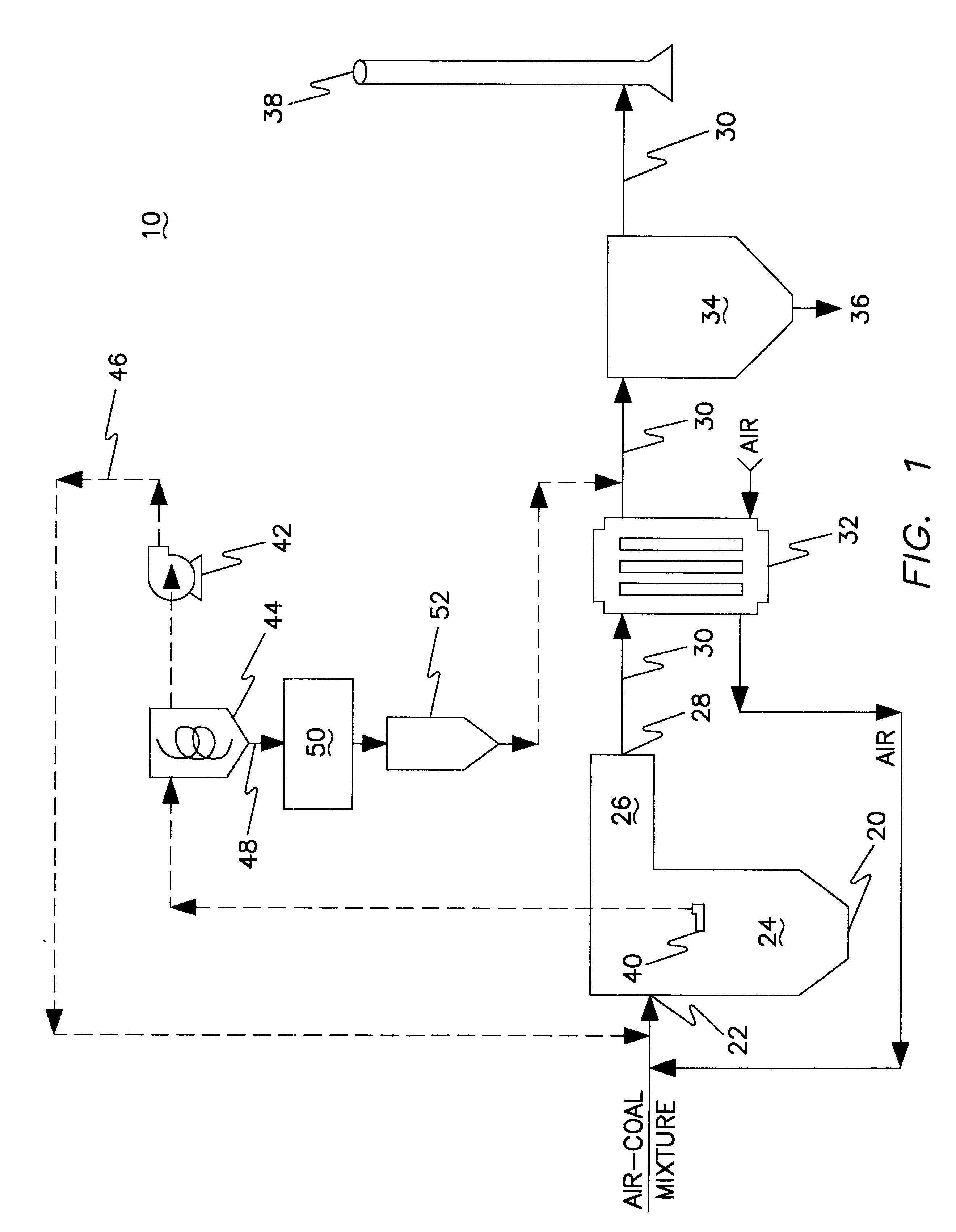
Thief process for the removal of mercury from flue gas
InactiveUS6521021B1Low costQuench oxidationGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentParticulatesCombustion chamber
A system and method for removing mercury from the flue gas of a coal-fired power plant is described. Mercury removal is by adsorption onto a thermally activated sorbent produced in-situ at the power plant. To obtain the thermally activated sorbent, a lance (thief) is inserted into a location within the combustion zone of the combustion chamber and extracts a mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas. The semi-combusted coal has adsorptive properties suitable for the removal of elemental and oxidized mercury. The mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas is separated into a stream of gas and semi-combusted coal that has been converted to a stream of thermally activated sorbent. The separated stream of gas is recycled to the combustion chamber. The thermally activated sorbent is injected into the duct work of the power plant at a location downstream from the exit port of the combustion chamber. Mercury within the flue gas contacts and adsorbs onto the thermally activated sorbent. The sorbent-mercury combination is removed from the plant by a particulate collection system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Apparatus and method for generating nitrogen oxides
InactiveUS20080176335A1Possible to useIncrease productionChemical analysis using combustionNitrogen compoundsCombustion chamberWorking temperature
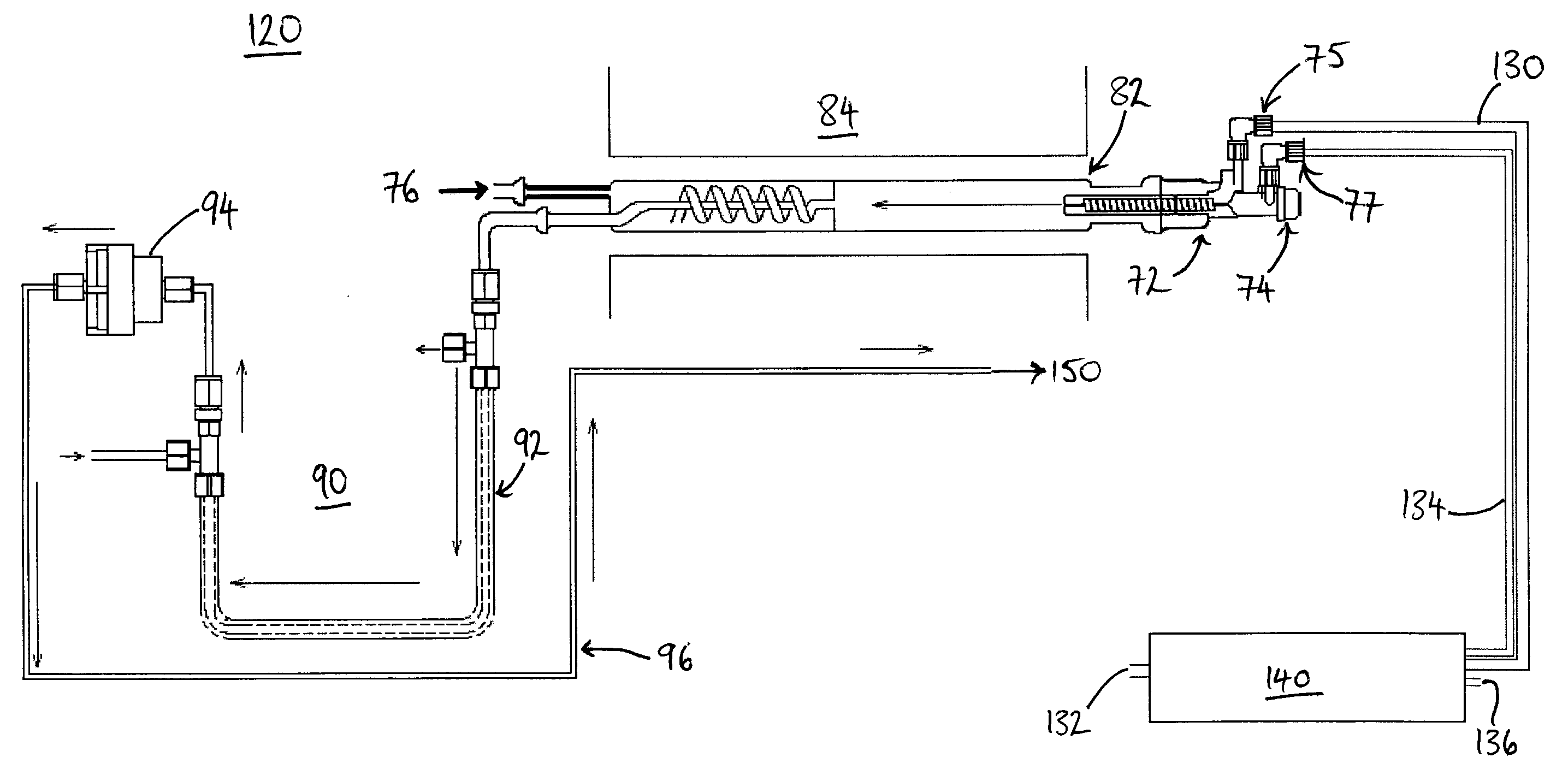
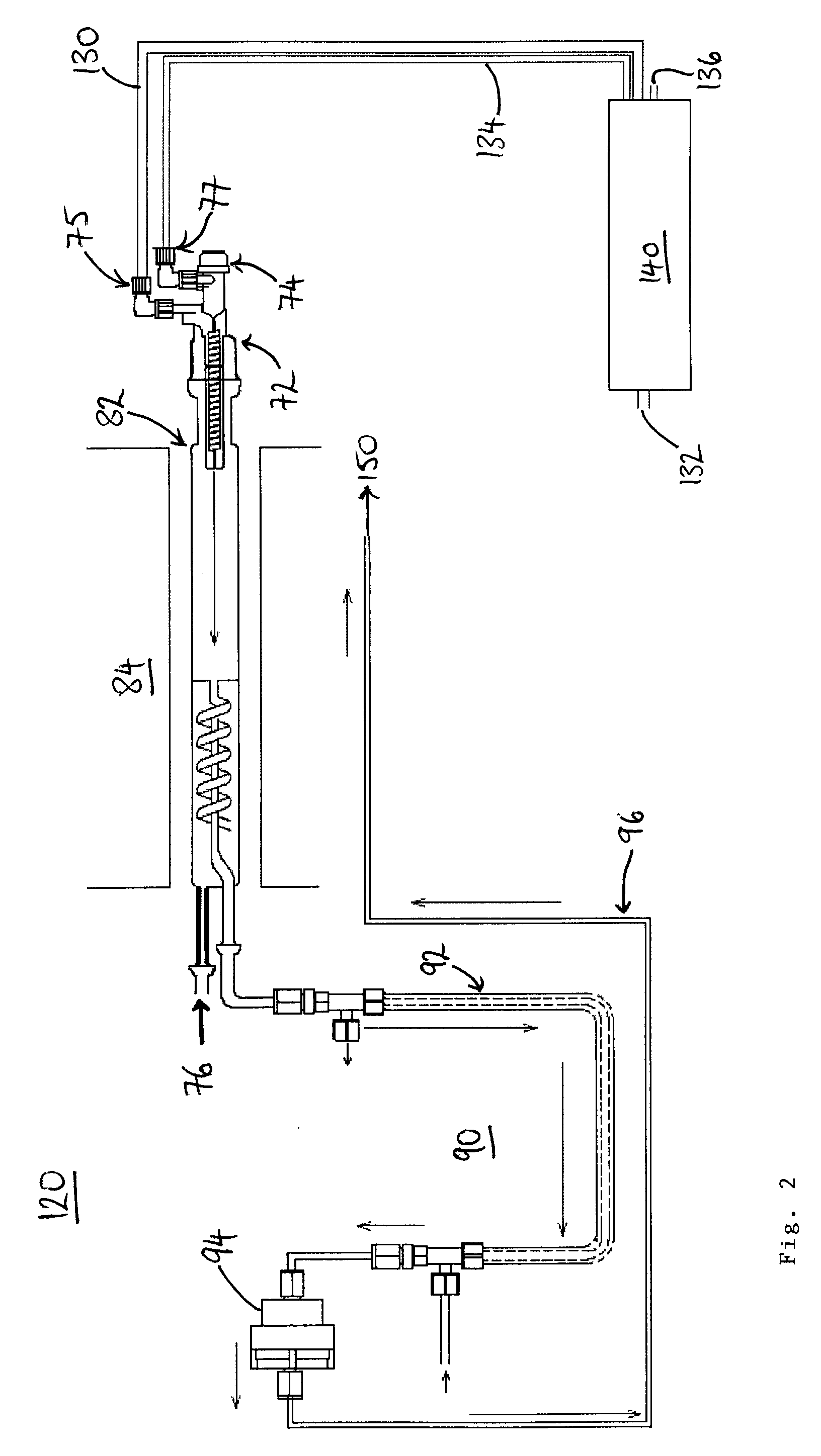
A combustion analyzer apparatus and method for combustion analysing a sample, the analyzer comprising a combustion chamber (82) for receiving a sample for combustion therein to form combustion products, and a fluid supply apparatus for supplying fluid(s) into the chamber. The fluid supply apparatus (130-140) comprises a nitrogen oxides (NOx) generating apparatus (140,190,210,240) and is arranged to supply NOx into the combustion chamber. A yield of sulphur dioxide in the combustion products may thereby be improved. The NOx generating apparatus may be operated at a raised working temperature. The NOx generating apparatus may be provided by an ozonator with a supply of nitrogen and oxygen. A Venturi tube arrangement (246) may draw the generated NOx into a (carrier or oxygen) gas line to the combustion chamber. Ozone may be supplied to the combustion products to convert nitrogen monoxide therein to nitrogen dioxide. The NOx and ozone may be supplied by a single device (210,240).
Owner:THERMO ELECTRON MFG
Method for Generating Energy in an Energy Generating Installation Having a Gas Turbine, and Energy Generating Installation Useful for Carrying Out the Method
InactiveUS20080010967A1Efficient removalImprove efficiencyDispersed particle separationGas turbine plantsCyclic processCombustion chamber
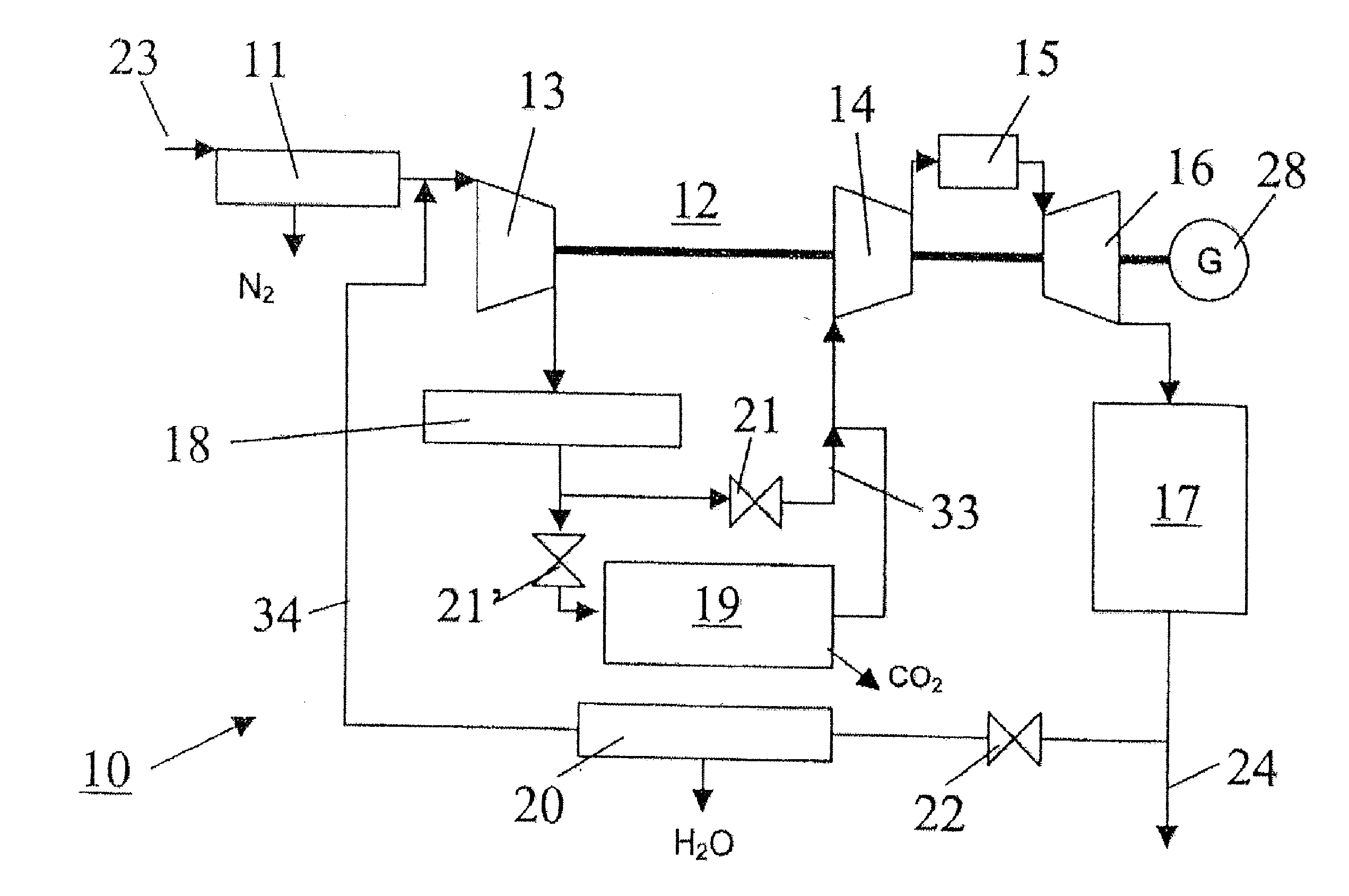
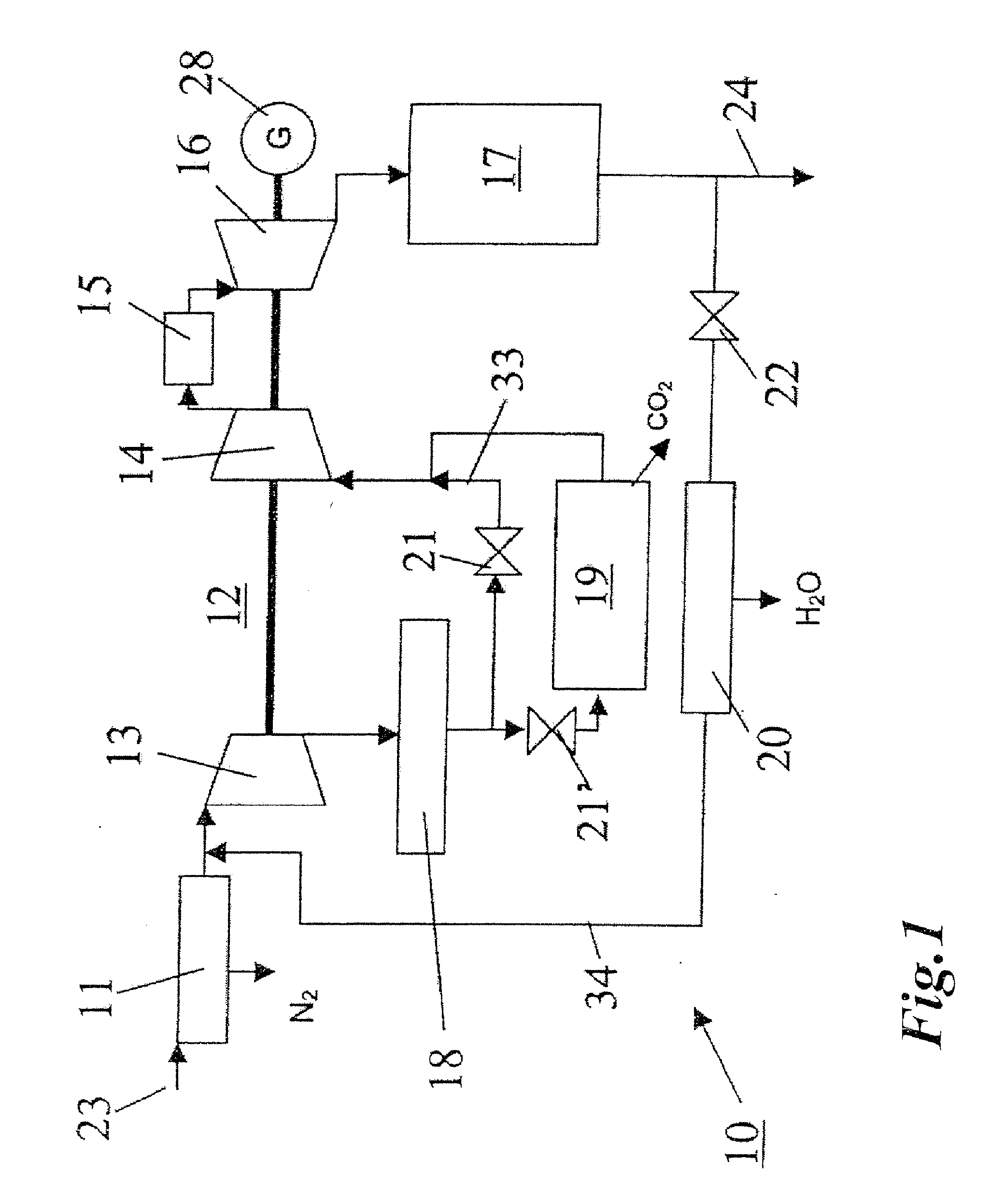
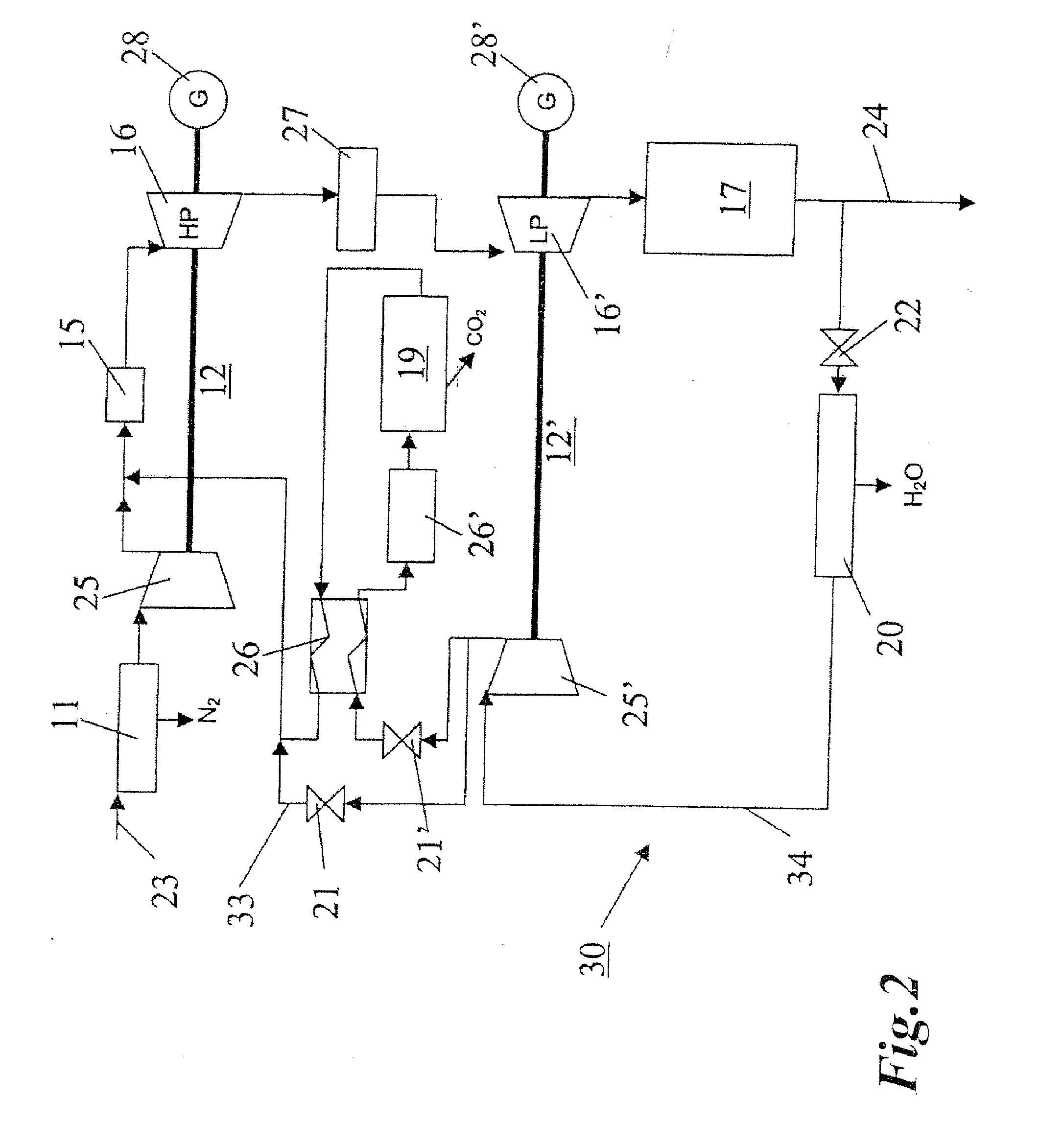
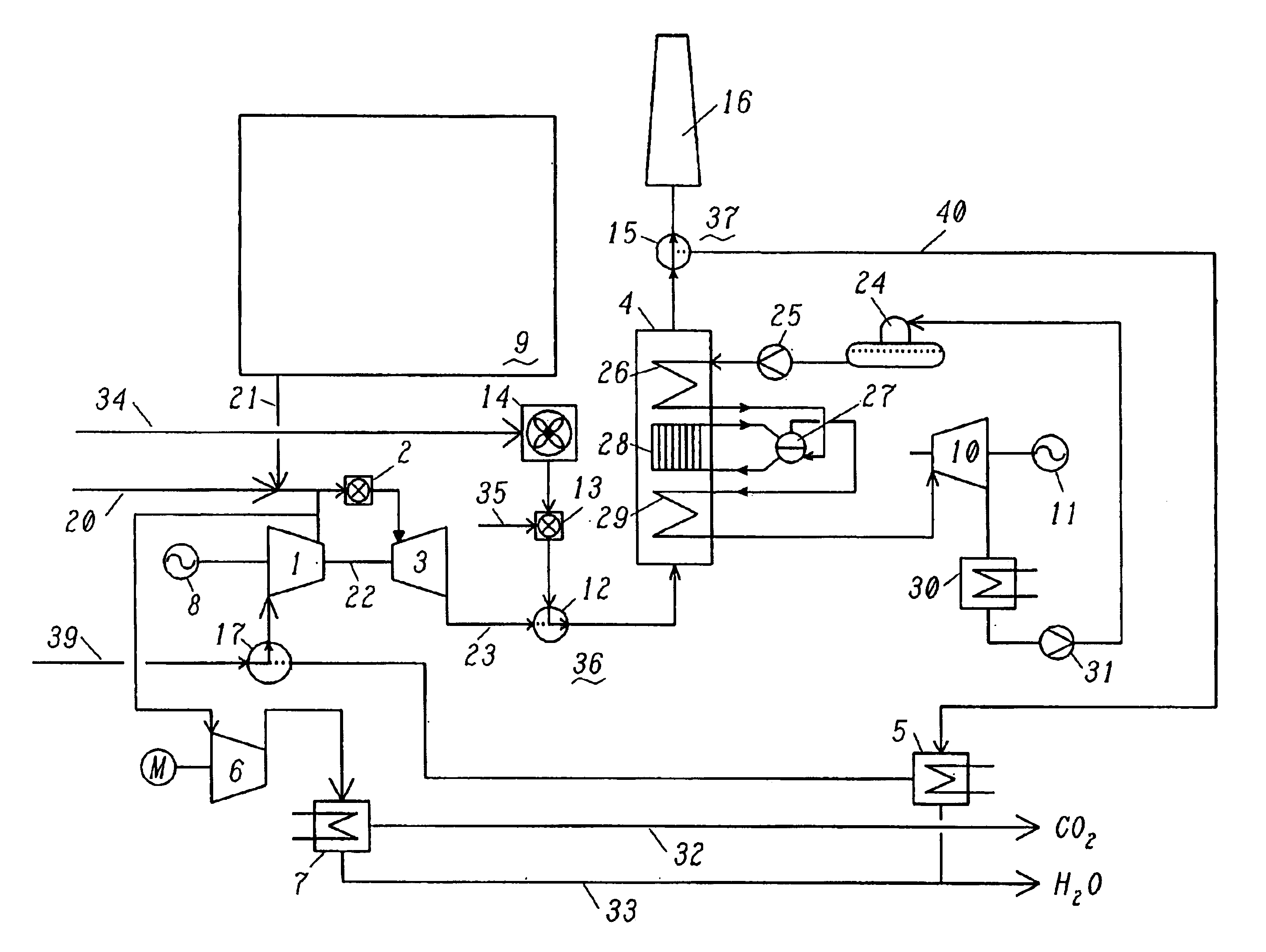
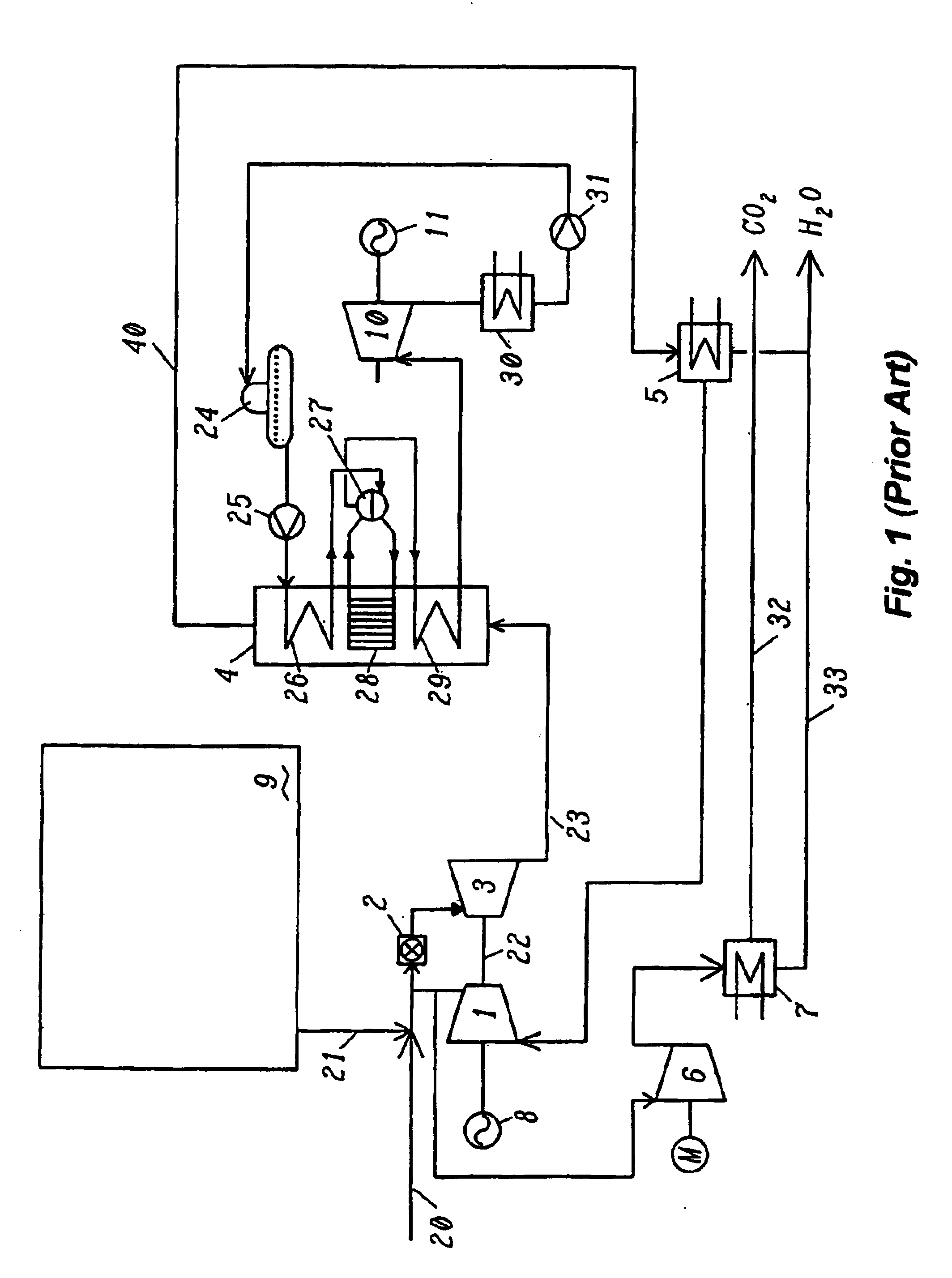
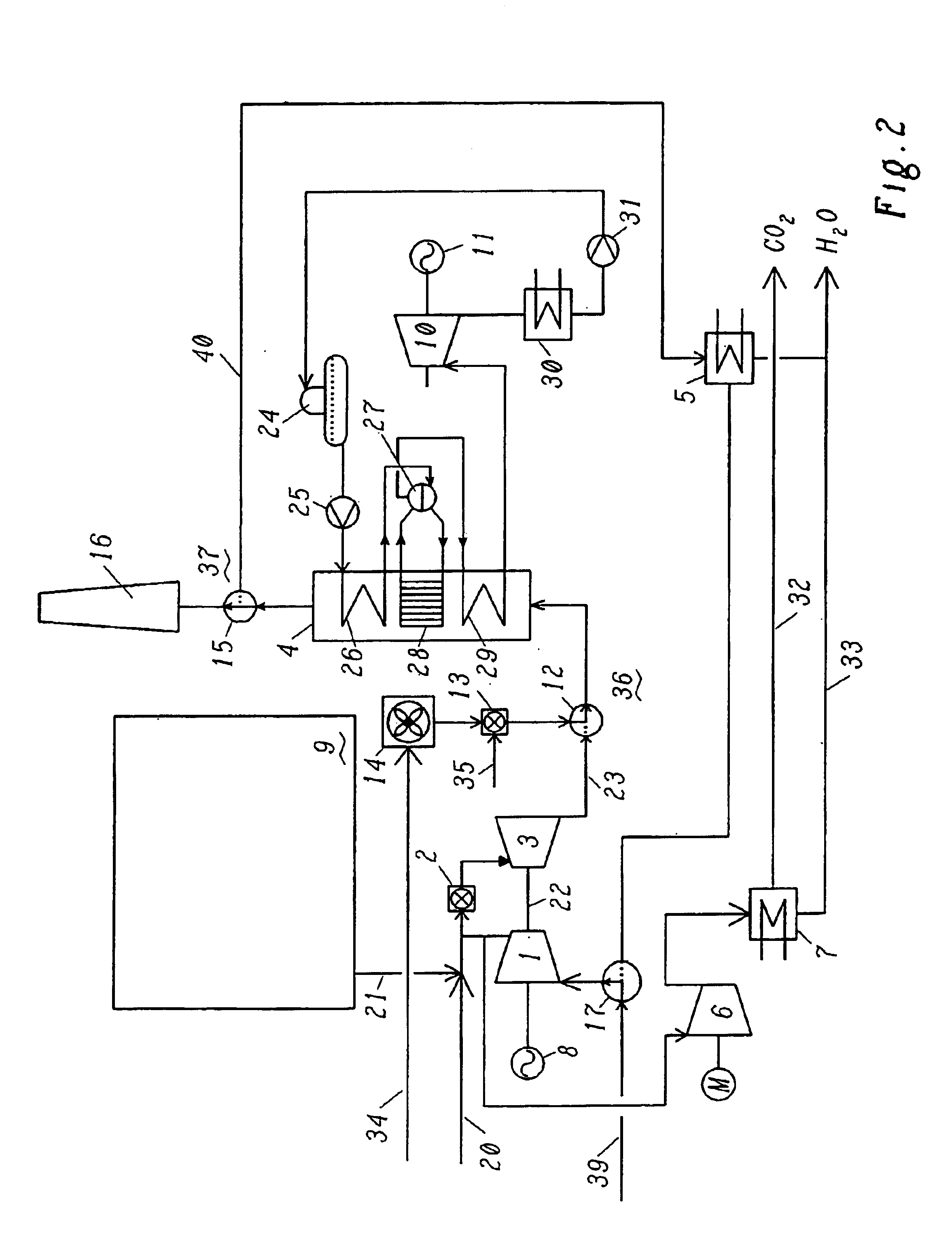
In a method for generating energy in an energy generating installation (10) having a gas turbine (12), in a first step, an oxygen-containing gas is compressed in a compressor (13, 14) of the gas turbine (12), in a second step the compressed gas is supplied, with the addition of fuel, for combustion in a combustion chamber (15), in a third step the hot flue gas from the combustion chamber (15) is expanded in a turbine (16) of the gas turbine (12) so as to perform work, and, in a fourth step, a branched-off part stream of the expanded flue gas is recirculated into a part of the gas turbine (12) lying upstream of the combustion chamber (15) and is compressed. A reduction in the CO2 emission, along with minimal losses of efficiency, is achieved in that carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the circulating gas in a CO2 separator (19), and in that measures are taken to compensate for the efficiency losses in the gas turbine cyclic process which are associated with the CO2 separation.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
System and method for generating and sustaining a corona electric discharge for igniting a combustible gaseous mixture
InactiveUS6883507B2Sufficient energySparking plugsCombustion enginesCombustion chamberElectric discharge
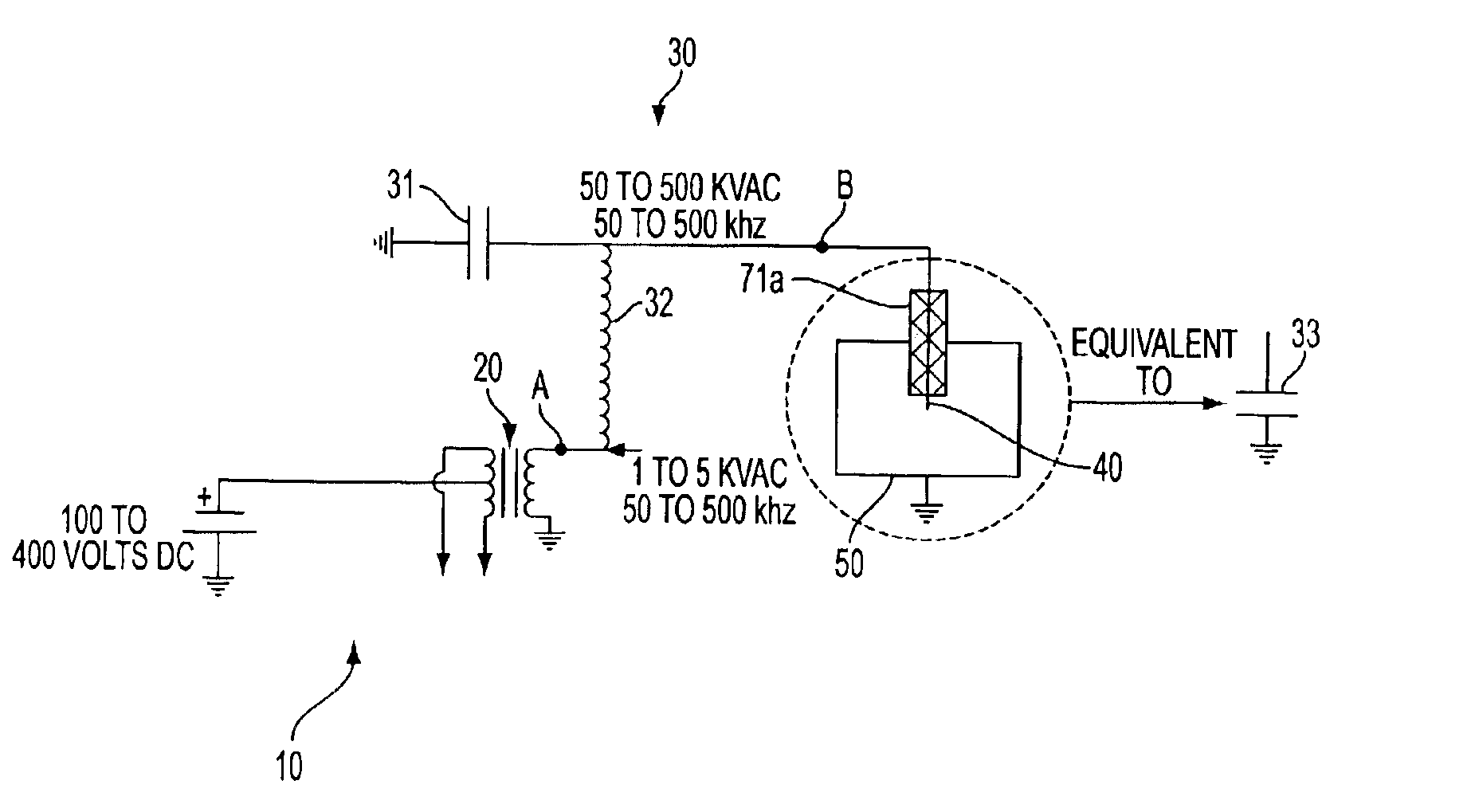
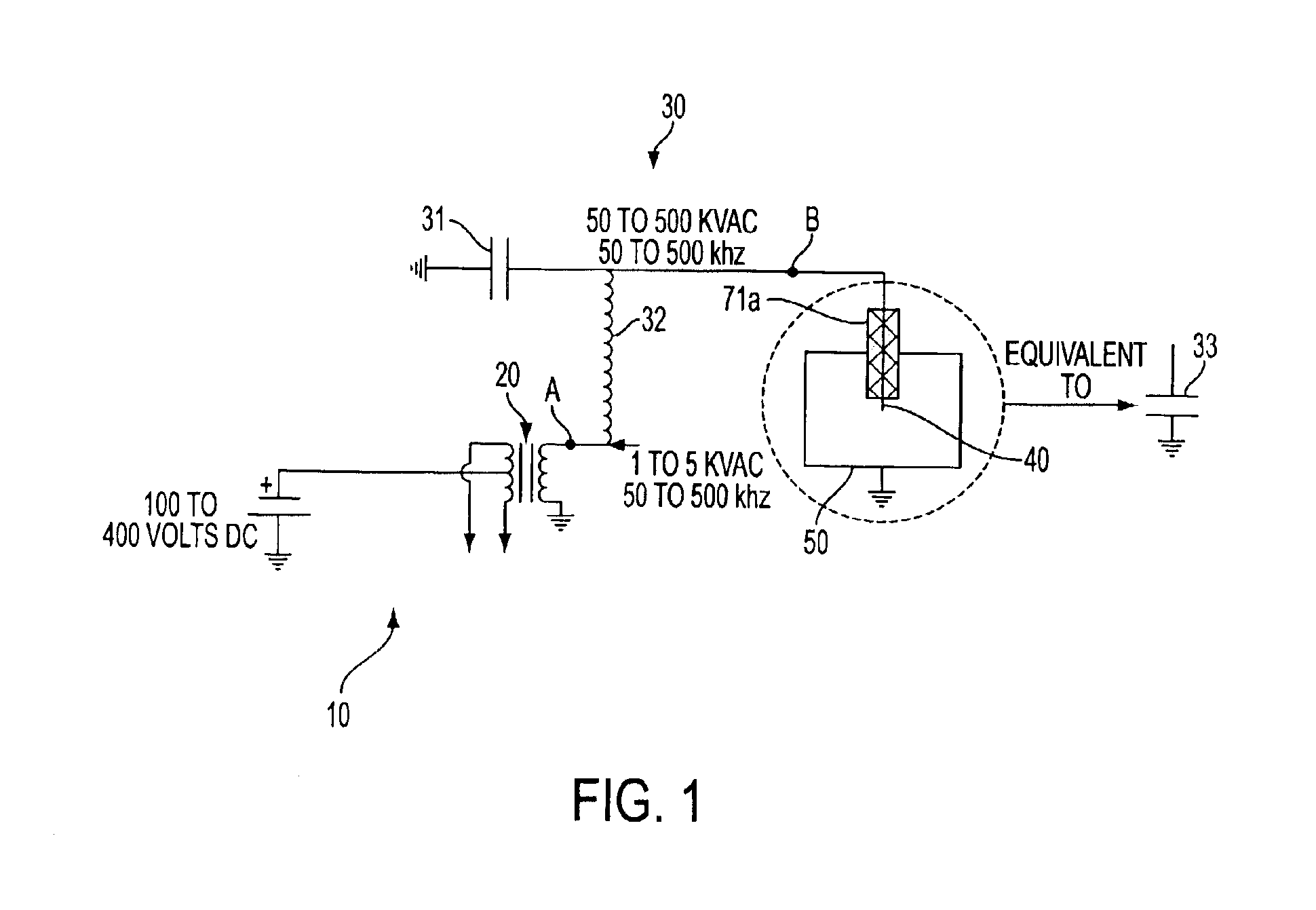
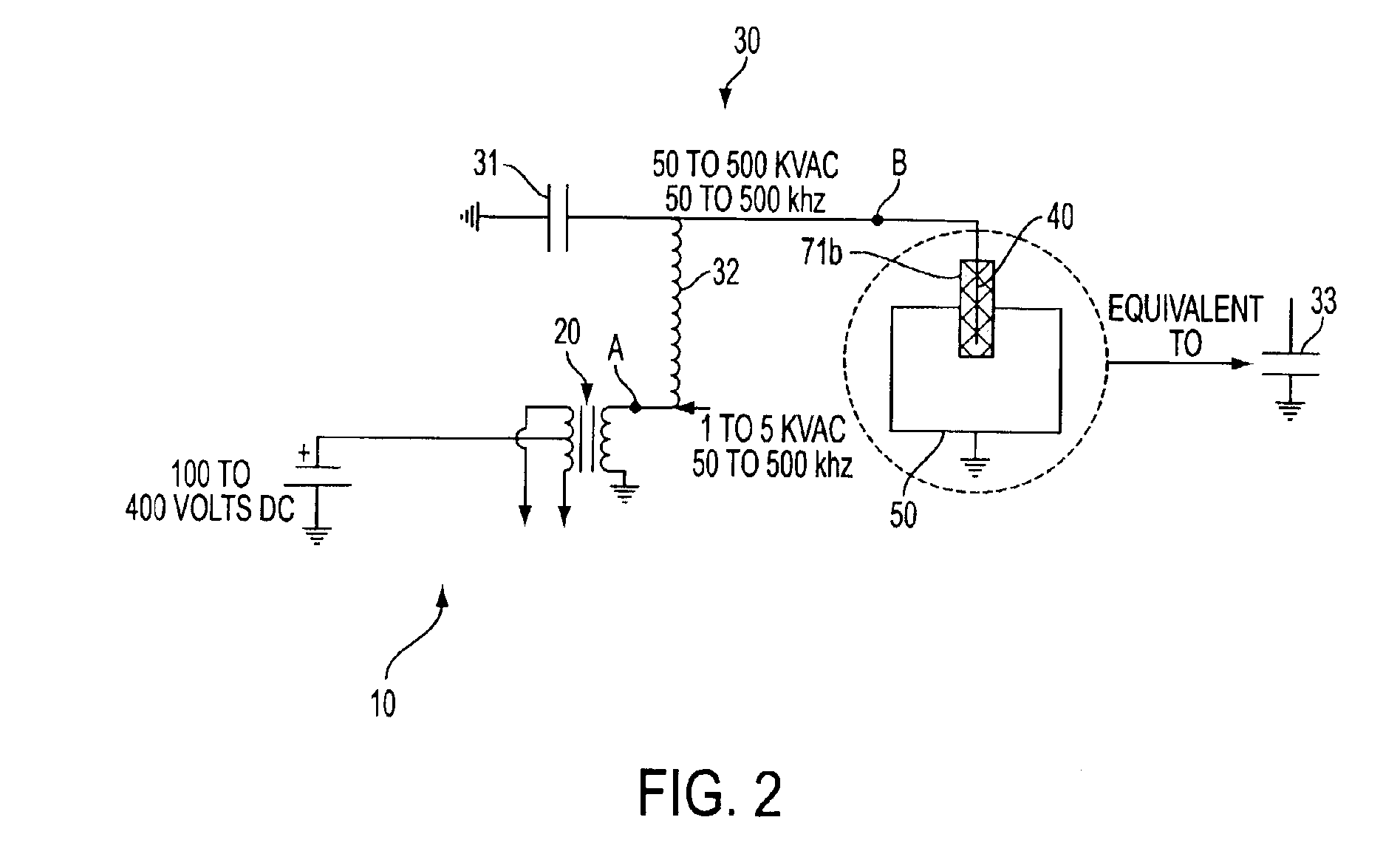
The invention relates to a system for igniting a fuel-air mixture in a combustion chamber with a corona discharge. The system comprises an electrode inside of the combustion chamber, an electric circuit which provides radio frequency electric power to the electrode, and a ground formed by the combustion chamber walls. A radio frequency voltage differential formed between the electrode and the ground produces a radio frequency electric field therebetween which causes a fuel-air mixture to ionize resulting in combustion of the fuel-air mixture. The system can be utilized in engines such as internal combustion engines or gas turbine engines, for example.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
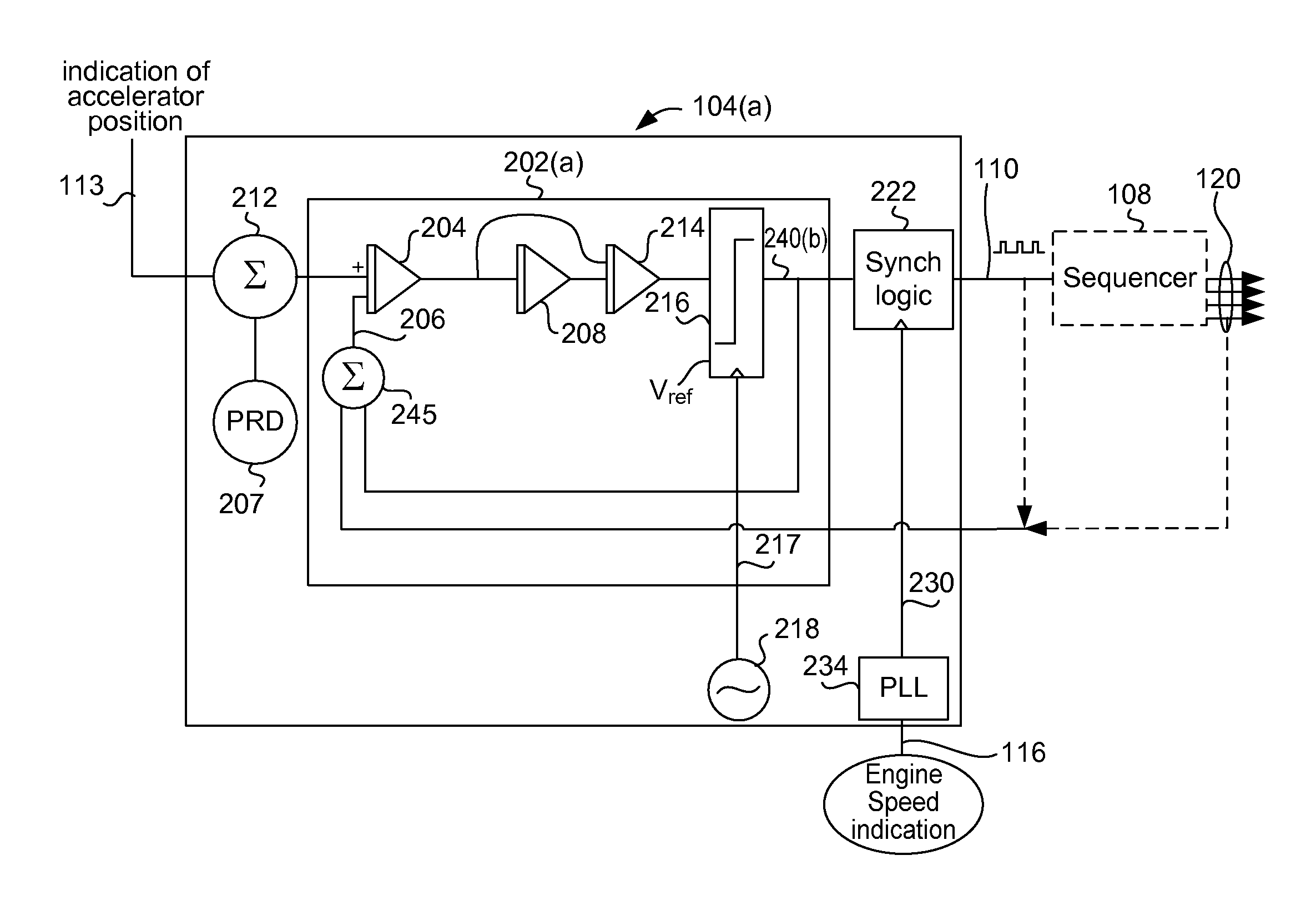
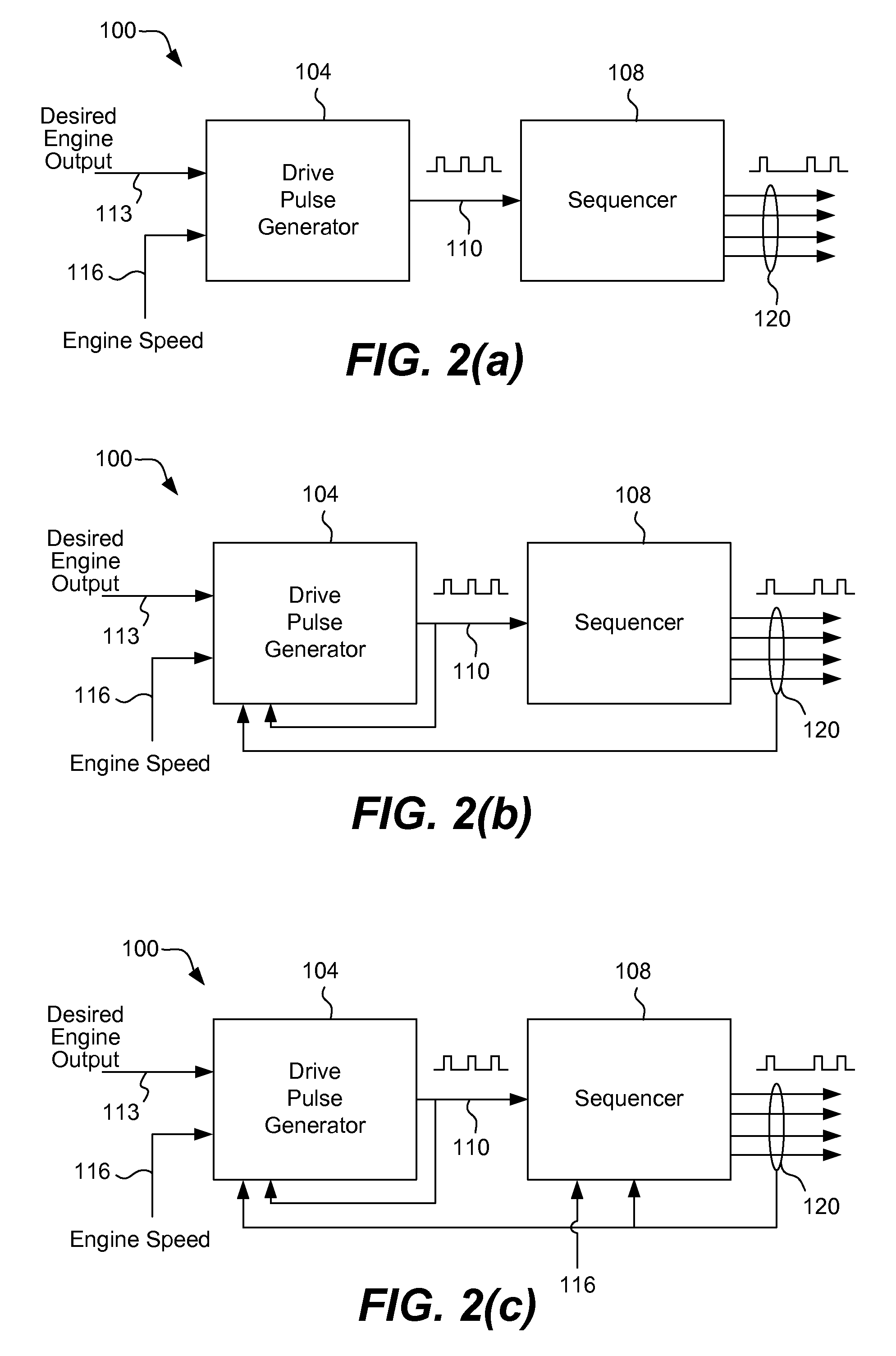
Internal combustion engine control for improved fuel efficiency
ActiveUS8131447B2Undesirable vibration reductionConvenient amountElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberWork cycle
A variety of methods and arrangements for improving the fuel efficiency of internal combustion engines are described. Generally, selected combustion events are skipped during operation of the internal combustion engine so that other working cycles can operate at a better thermodynamic efficiency. In one aspect of the invention, an engine is controlled to operate in a variable displacement mode. In the variable displacement mode, fuel is not delivered to the working chambers (e.g. cylinders) during selected “skipped” working cycles. During active (“non-skipped”) working cycles, a maximum (e.g., unthrottled) amount of air and an optimized amount of fuel is delivered to the relevant working chambers so that the fired working chambers can operate at efficiencies closer to their optimal efficiency. A controller is used to dynamically determine the chamber firings required to provide the engine torque based on the engine's current operational state and conditions. The chamber firings may be sequenced in real time or in near real time in a manner that helps reduce undesirable vibrations of the engine.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
Method and apparatus for operating a dual fuel internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7627416B2Reduce modificationShorten the timeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberElectronic controller
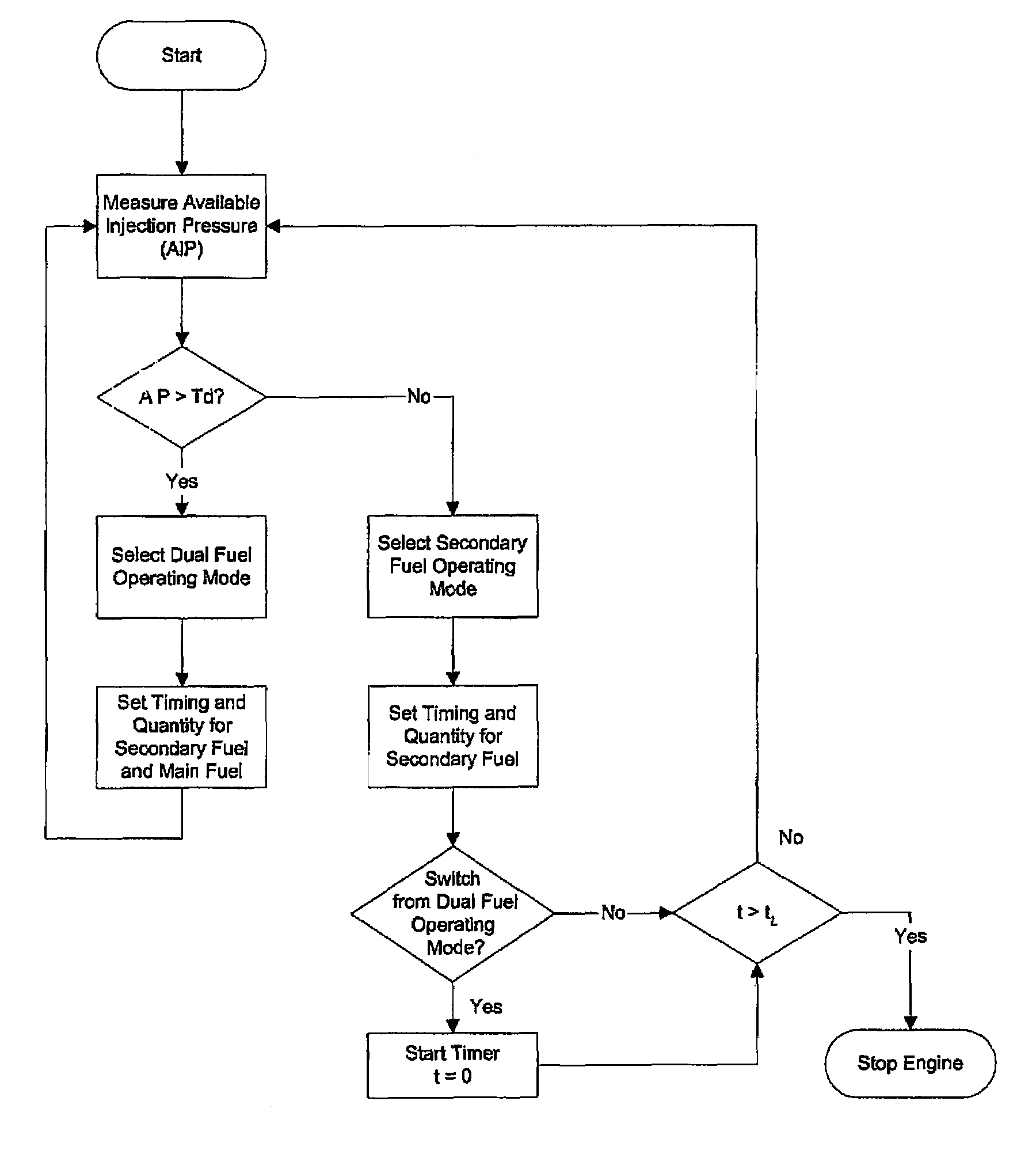
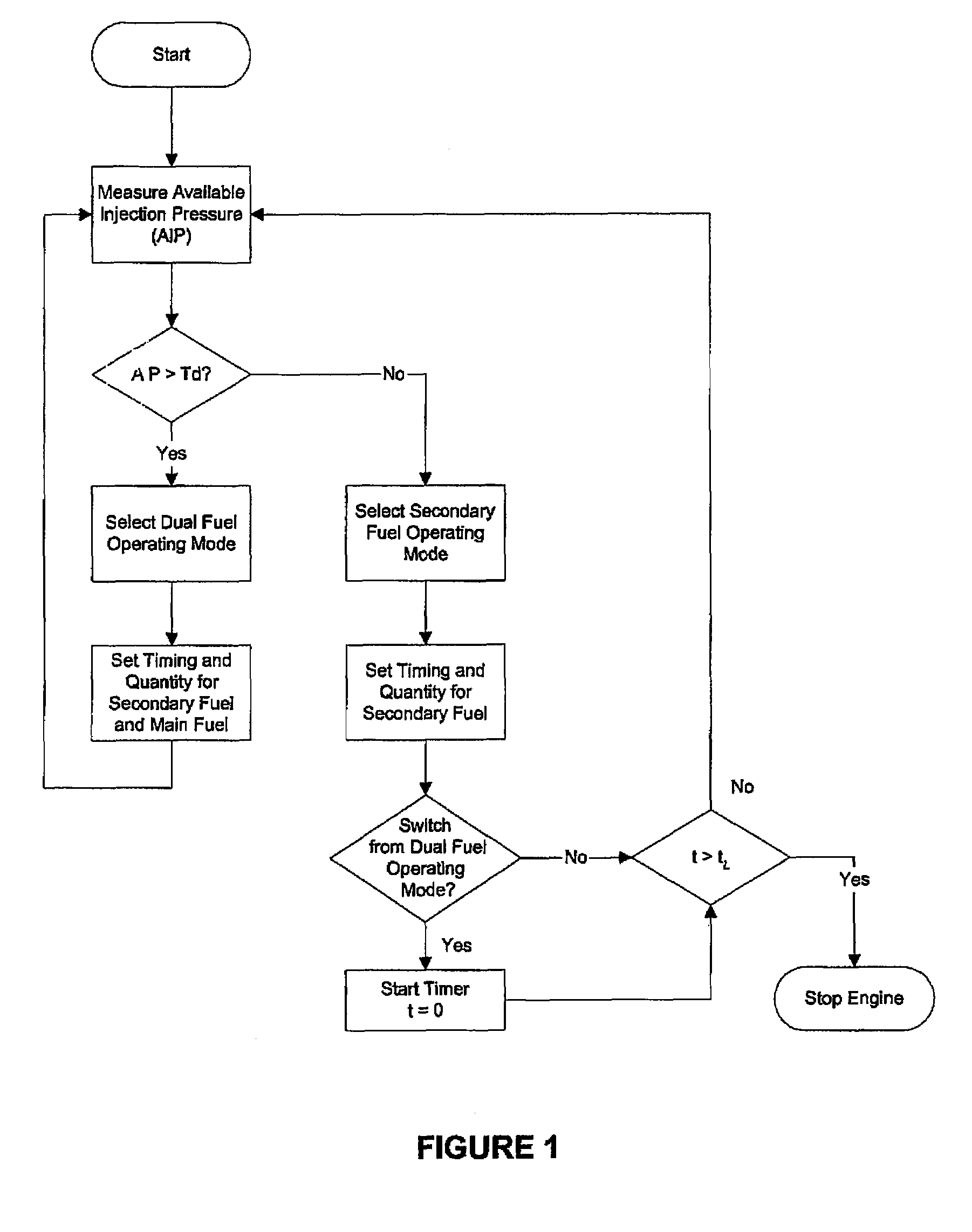
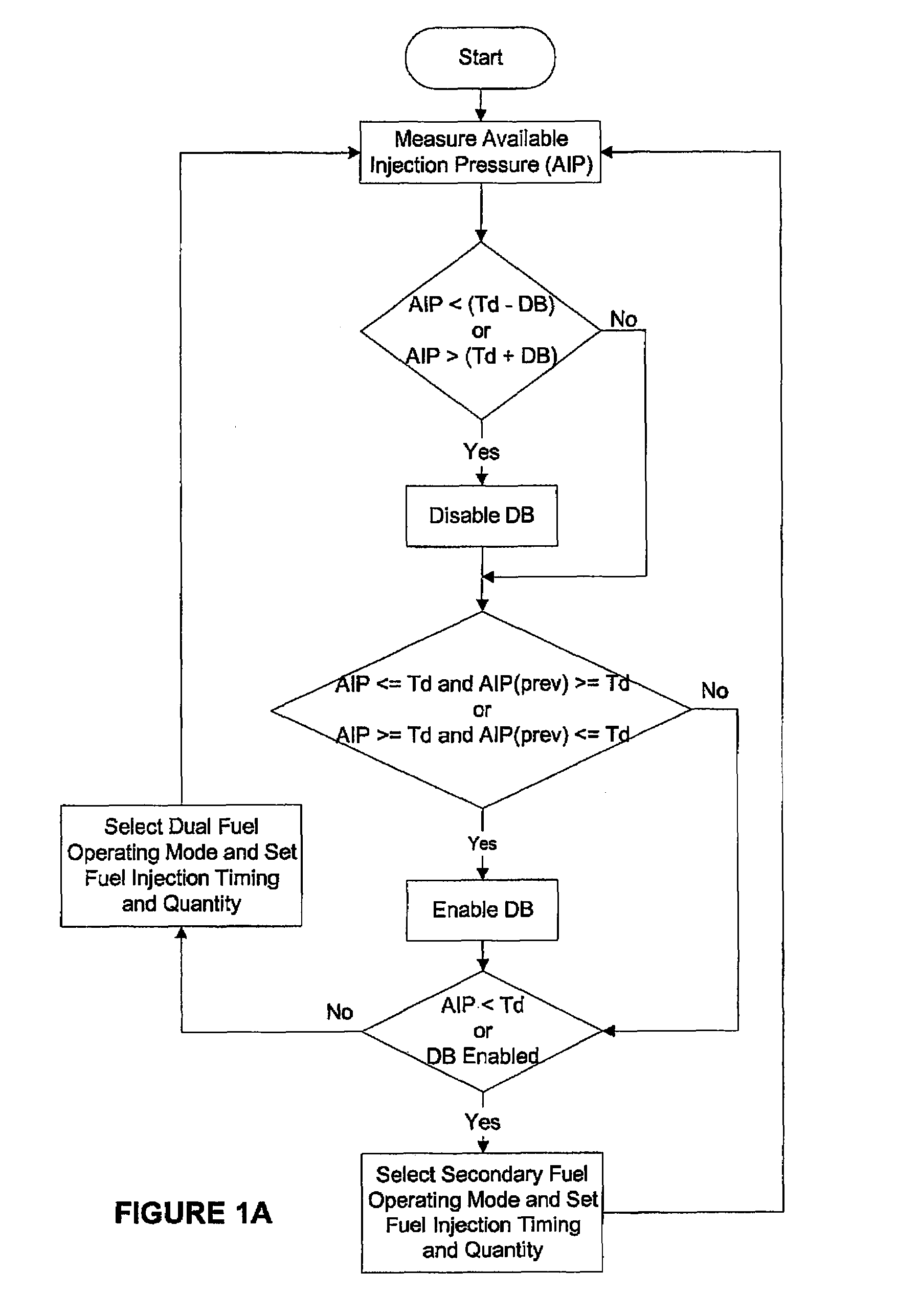
In an internal combustion engine that can burn two fuels, the main fuel may become unavailable, either temporarily or until the main fuel is replenished. The present apparatus determines when to fuel an engine with main fuel and secondary fuel, or secondary fuel alone. The apparatus includes a main-fuel supply system comprising a main-fuel injection valve that introduces main fuel into an engine combustion chamber; a secondary-fuel injection system comprising a secondary-fuel injection valve that introduces secondary fuel directly into the combustion chamber; a pressure sensor associated with the main-fuel supply system for determining injection pressure inside the main-fuel injection valve; and an electronic controller in communication with the pressure sensor and programmable to separately command actuation of the secondary-fuel and the main-fuel injection valve when injection pressure is greater than a predetermined threshold, and to otherwise command actuation of the secondary-fuel injection valve and not the main-fuel injection valve.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Reheat combustion system for a gas turbine
ActiveUS6981358B2Good cooling propertiesDamp pulsationBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustion systemCombustion chamber
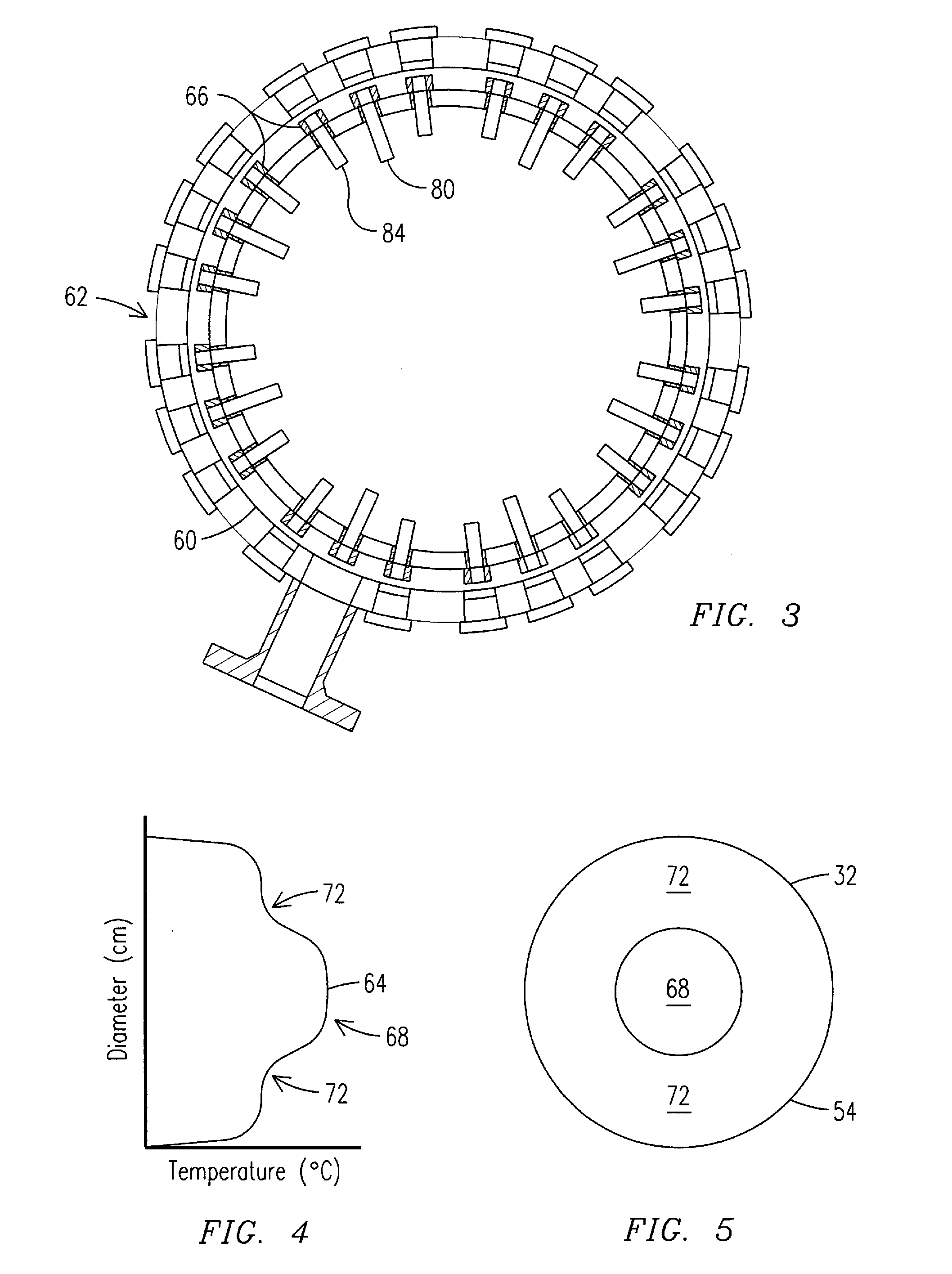
A reheat combustion system for a gas turbine comprises a mixing tube adapted to be fed by products of a primary combustion zone of the gas turbine and by fuel injected by a lance; a combustion chamber fed by the said mixing tube; and at least one perforated acoustic screen. The or each said acoustic screen is provided inside the mixing tube or the combustion chamber, at a position where it faces, but is spaced from, a perforated wall thereof. In use, the perforated wall experiences impingement cooling as it admits air into the combustion system for onward passage through the perforations of the said acoustic screen, and the acoustic screen damps acoustic pulsations in the mixing tube and combustion chamber.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Turbulent jet ignition pre-chamber combustion system for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS20120103302A1Promote flame quenchingHigh-drive cycle (part load) fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemCombustion chamber
An ignition system for an internal combustion engine having at least one combustion chamber where the ignition system includes a housing, an ignition device, an injector, and a pre-chamber having a nozzle disposed spaced from the proximal portion of the pre-chamber. The igniter portion of the ignition device and the nozzle of the injector are operatively supported in the proximal portion of the pre-chamber and disposed flush therewith. The igniter portion ignites the fuel in pre-chamber such that partially combusted pre-chamber products are forced through orifices in the pre-chamber nozzle and extinguish, but dispersed through the combustion chamber so as to ignite the main fuel charge therein.
Owner:MAHLE POWERTRAIN
Reciprocating machine & other devices
InactiveUS20120227389A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyLiquid coolingCasingsCombustionReciprocating motion
The disclosure relates to reciprocating fluid working devices including internal combustion engines, compressors and pumps. A number of arrangements for pistons and cylinders of unconventional configuration are described, mostly intended for use in IC engines operating without cooling. Included are toroidal combustion or working chambers, some with fluid flow through the core of the toroid, a single piston reciprocating between a pair of working chambers, tensile valve actuation, tensile links between piston and crankshaft, energy absorbing piston-crank links, crankshafts supported on gas bearings, cylinders rotating in housings, injectors having components which reciprocate or rotate during fuel delivery. In some embodiments pistons mare rotate while reciprocating. High temperature exhaust emissions systems are described, including those containing filamentary material, as are procedures for reducing emissions during cold start by means of valves at reaction volume exit. Also disclosed are improved vehicles, aircraft, marine craft, transmissions and exhaust emission systems suited to the engines of the invention.
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
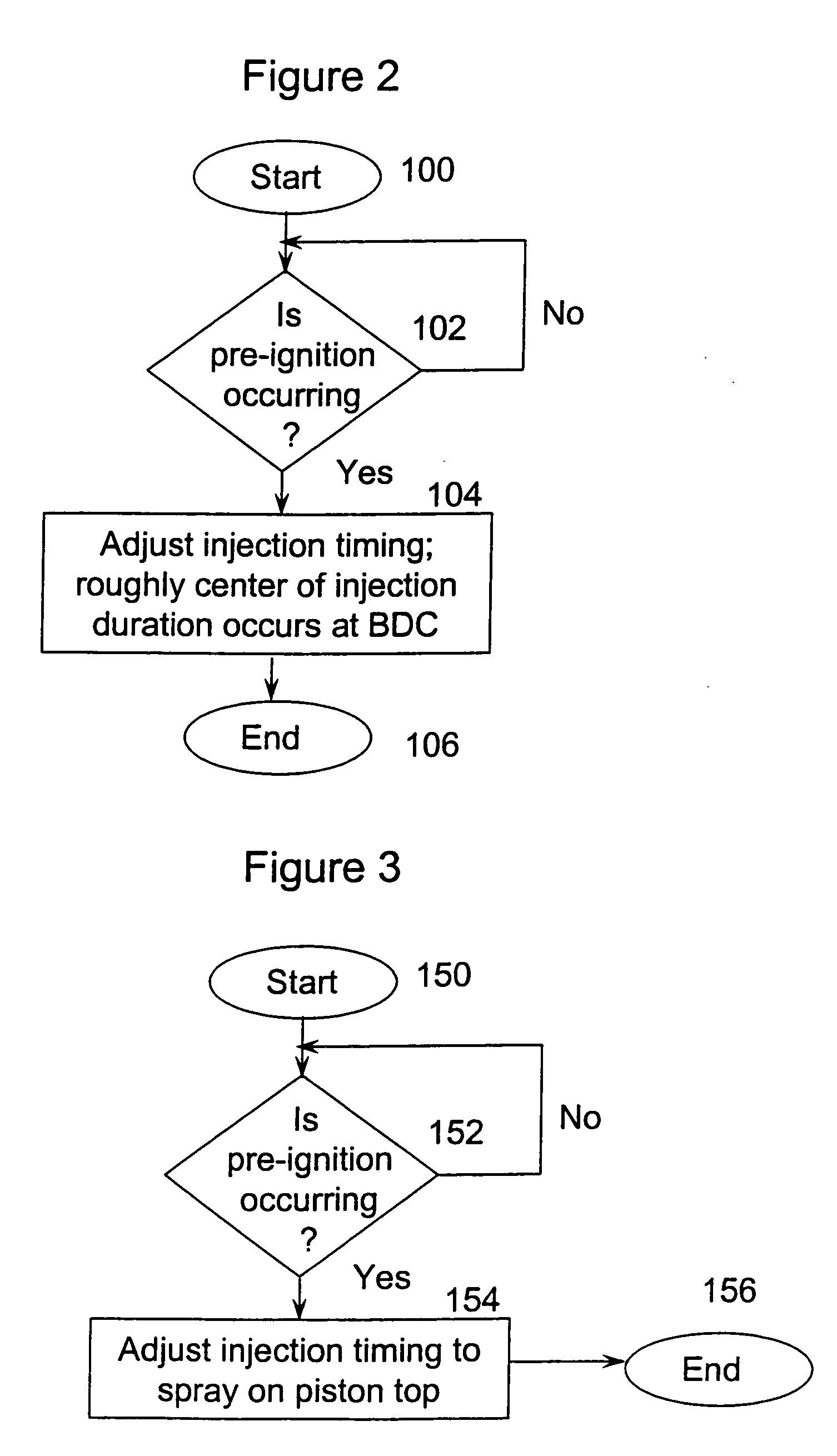
System and method to pre-ignition in an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS7178503B1Mitigate pre-ignitionReduce air densityAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlCombustion chamberAlcohol fuel
An engine system and method are disclosed for controlling pre-ignition of an alcohol fuel. In one embodiment, the fuel injection timing is adjusted to cause the fuel to avoid combustion chamber surfaces. In another embodiment, the fuel injection timing is adjusted to spray the fuel directly onto the piston surface to cool the piston. Also disclosed is a cylinder cleaning cycle in which engine knock is purposely caused for one to hundreds of engine cycles by adjusting the fuel content away from alcohol toward gasoline. Further measures to cause knock which are disclosed: adjusting spark timing, intake boost, exhaust gas fraction in the cylinder, cam timing, and transmission gear ratio.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
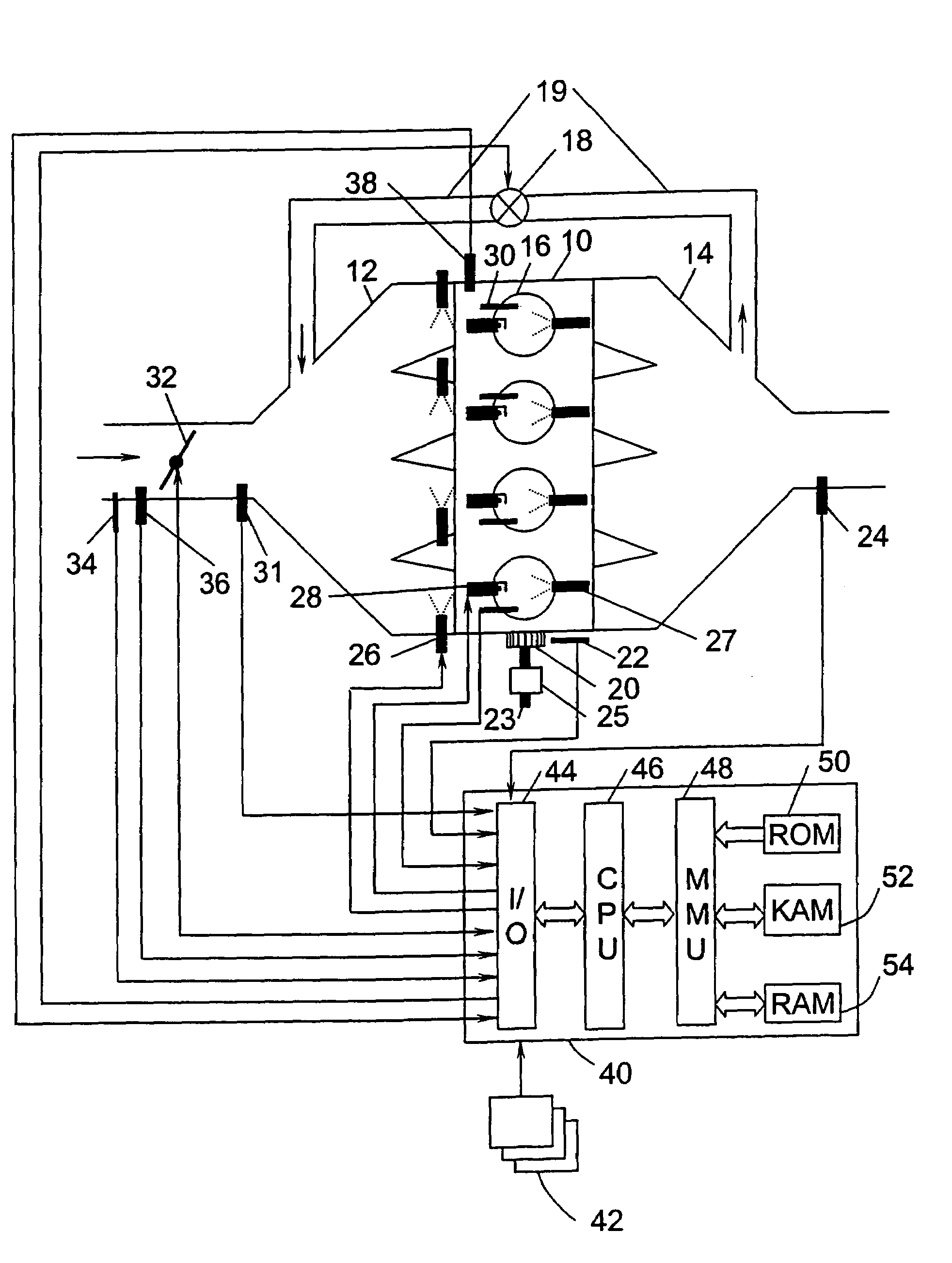
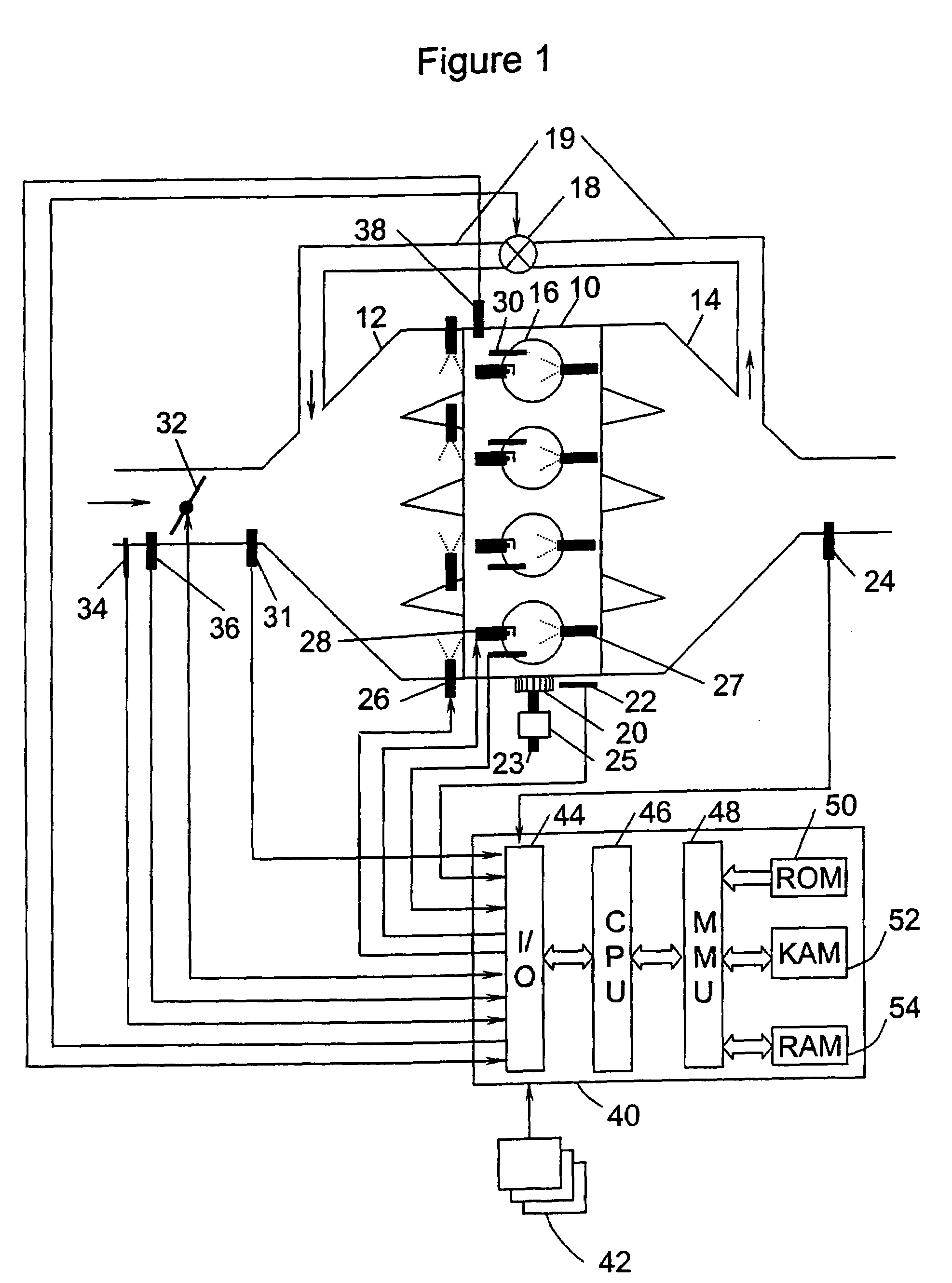
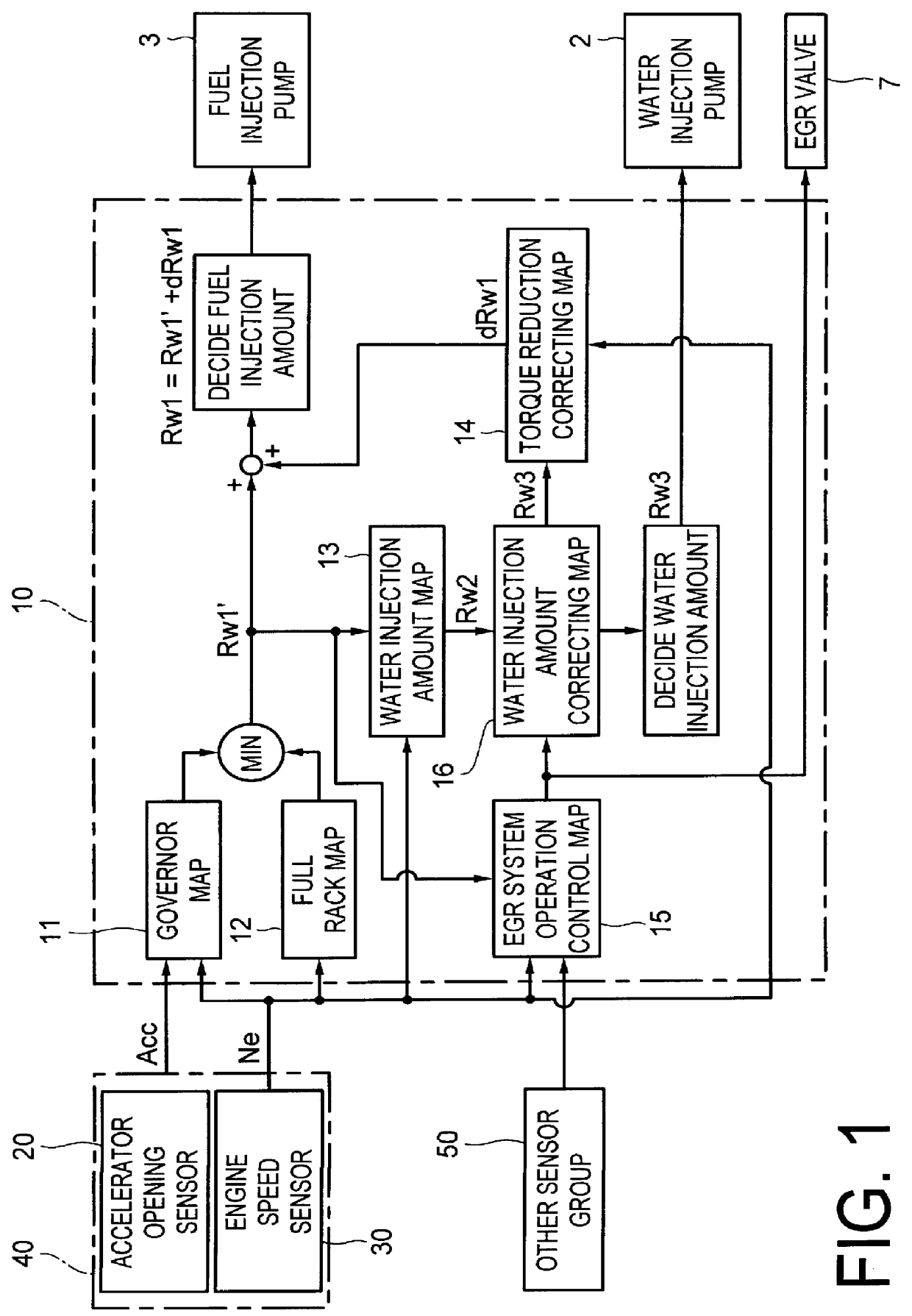
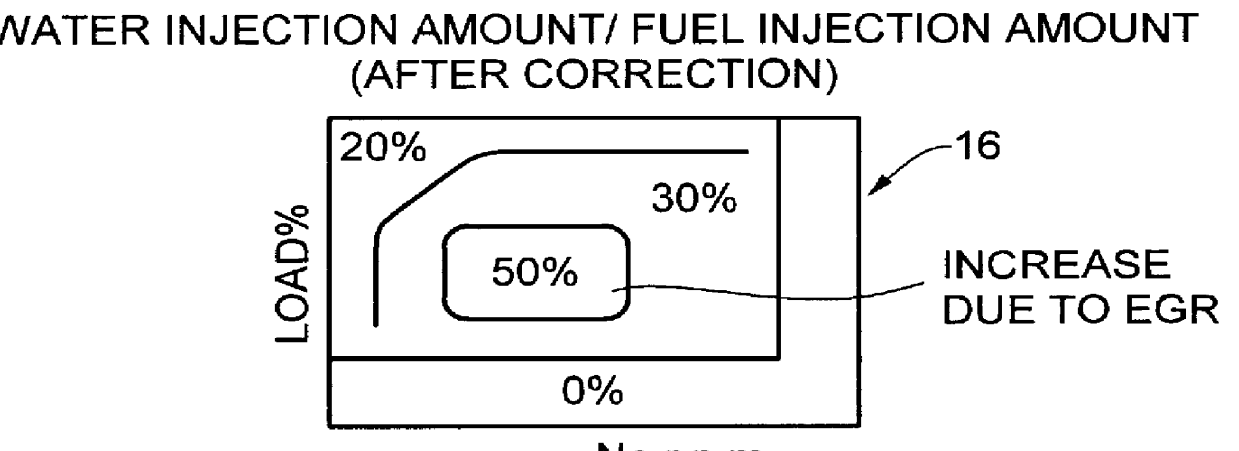
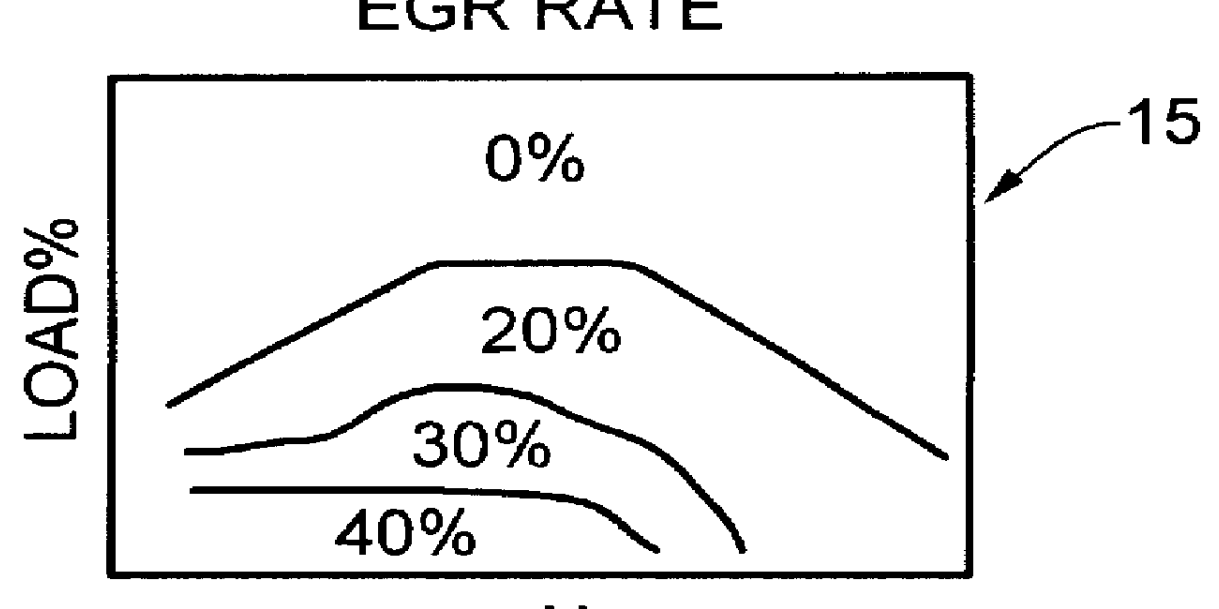
Water injection amount control system for fuel and water injection engine
InactiveUS6112705AEnhance NOx reducing effectImprove reducibilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberControl system
A water injection amount control system for a fuel and water injection engine, comprises running state detecting unit for detecting the running state of the engine; an EGR system for recirculating part of exhaust gas of the engine to a combustion chamber of the engine; EGR system operating state detecting unit for detecting or estimating the operating state of the EGR system; water injection amount regulating unit for regulating an amount of water to be injected to the combustion chamber of the engine; and control unit for controlling the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit: wherein the system is arranged to have water injection amount setting unit for deciding a water injection amount based on information from the running state detecting unit and on the operating state of the EGR system detected by the EGR system operating state detecting unit, so that the control unit controls the operation of the water injection amount regulating unit based on the water injection amount decided by the water injection amount setting unit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
Method for ignition of flameless combustor
InactiveUS6269882B1Easy to igniteImprove the level ofApparel holdersIncandescent ignitionCombustorCombustion chamber
A combustor method and apparatus is provided. The method utilizes flameless combustion with one or more of three improvements to enhance ignition of the flameless combustor. A catalytic surface can be provided within a combustion chamber to provide flameless combustion at least in the vicinity of the catalytic surface at a temperature that is much lower than the autoignition temperature of fuel in air without the presence of the catalytic surface. Nitrous oxide or supplemental oxygen may also be used as an oxidant either instead of air or with air to reduce ignition temperatures. Further, electrical energy can be passed through the fuel conduit, raising the temperature of the conduit to a temperature above which the fuel will ignite when combined with the oxidant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
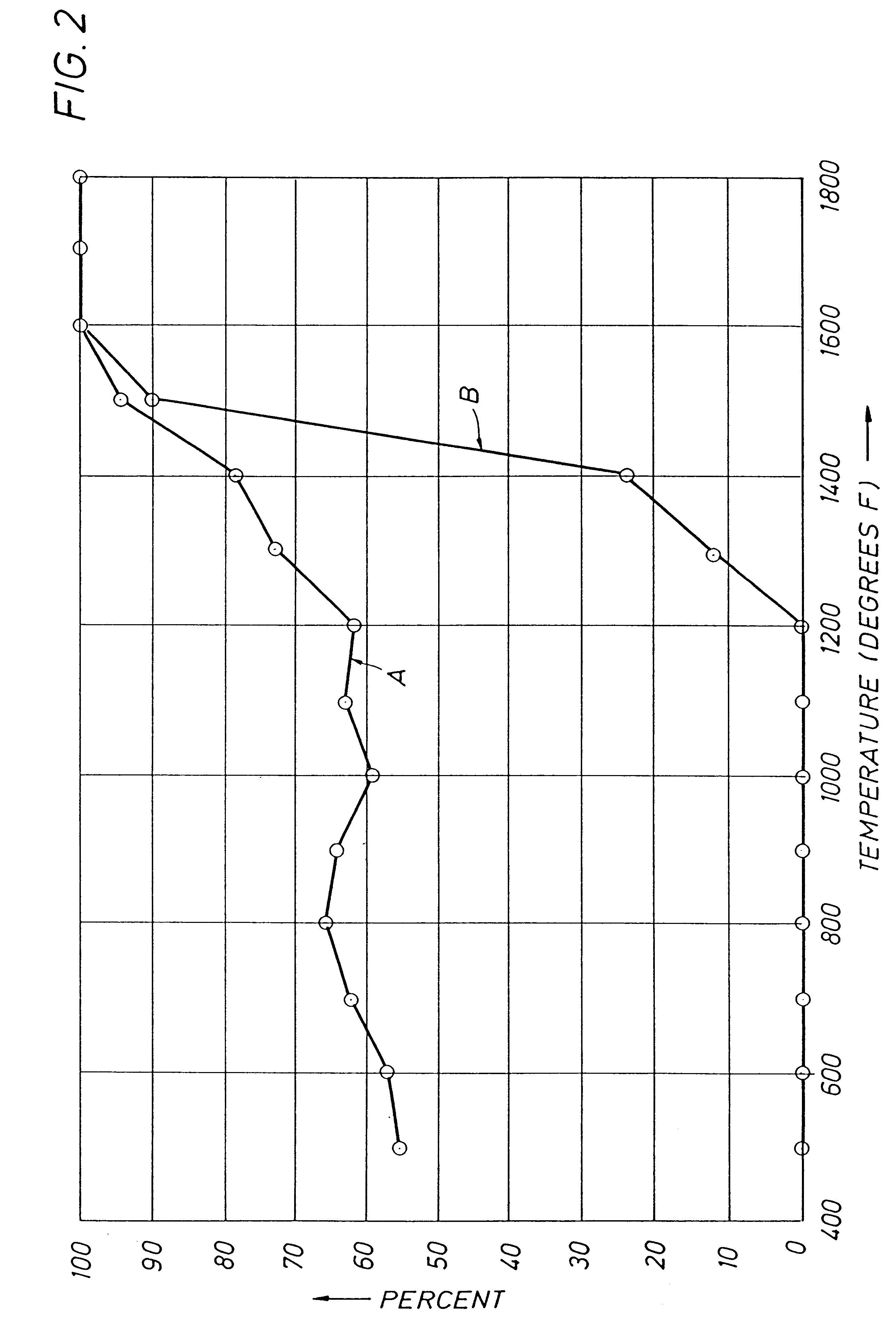
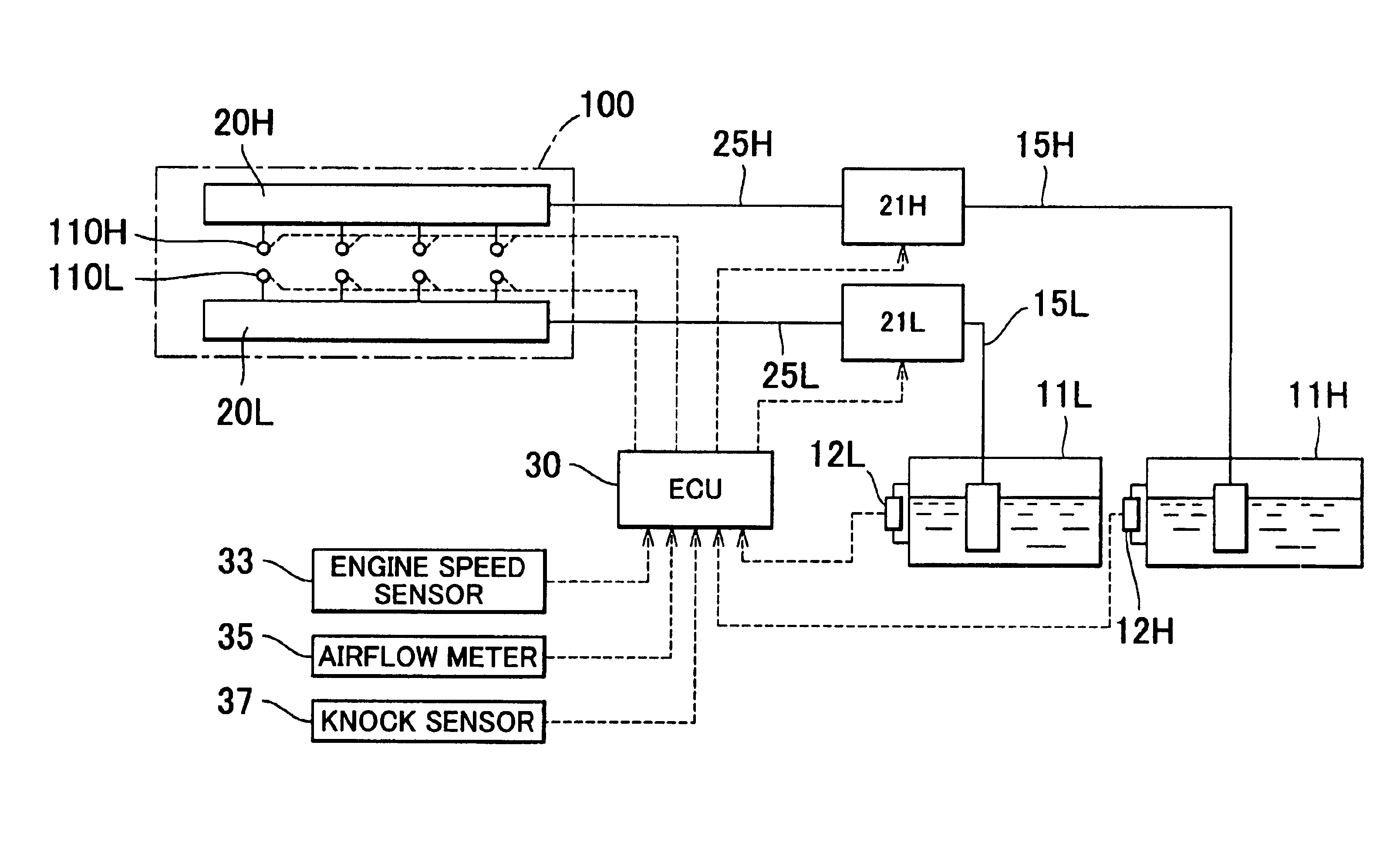
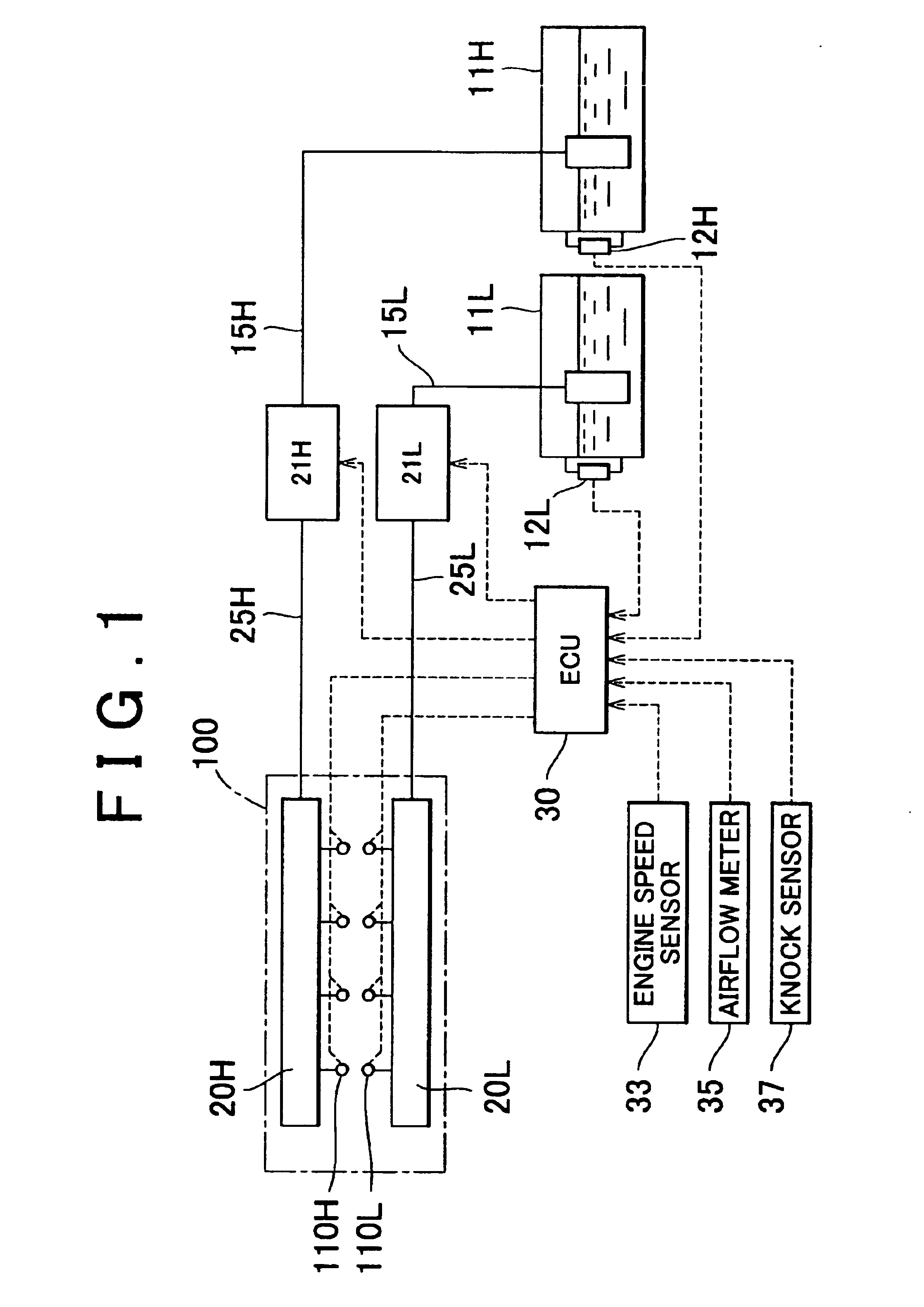
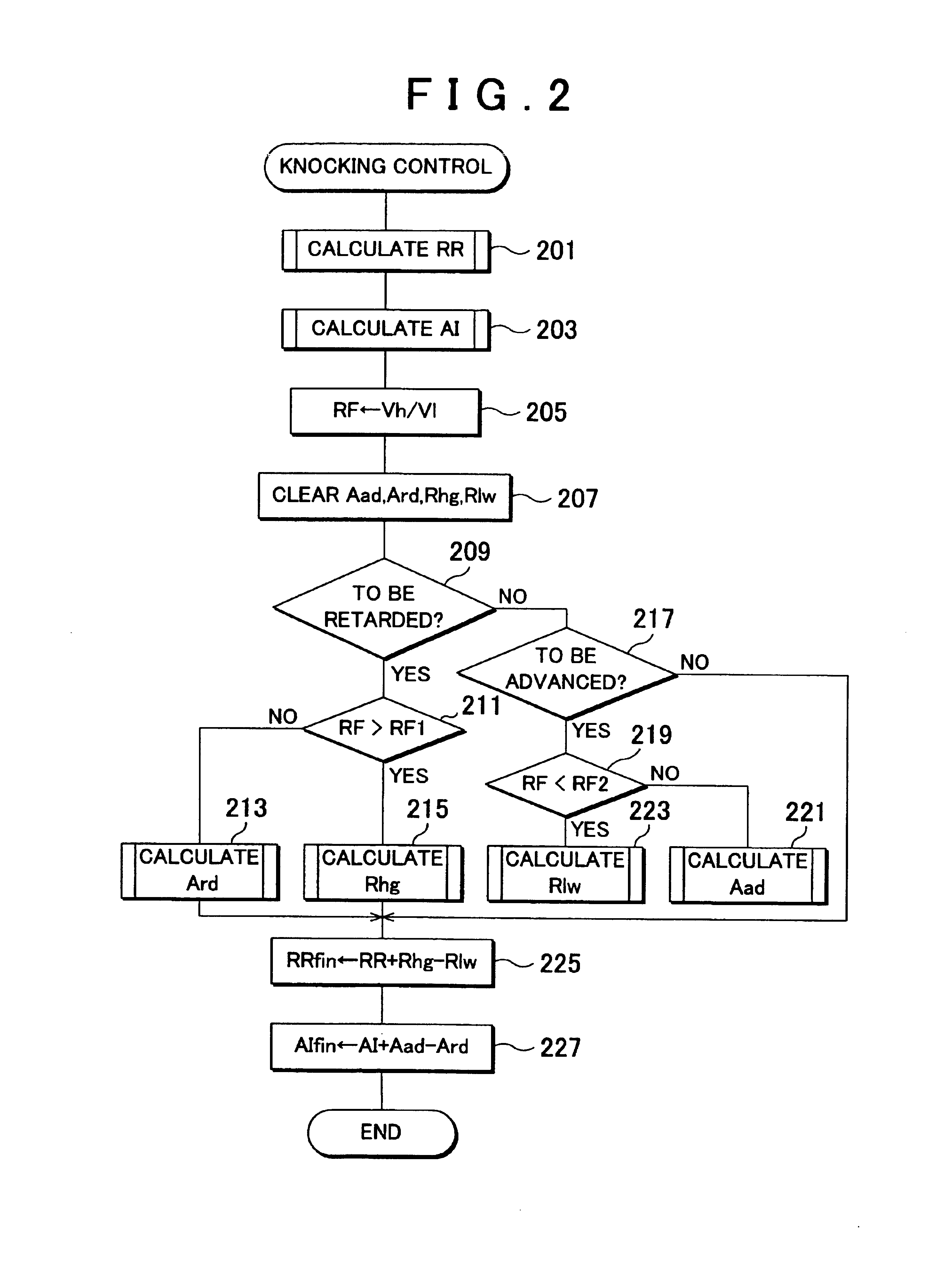
Knocking control system and method for internal combustion engine using multiple fuels
InactiveUS6951202B2Maintain balanceImprove balanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMultifuelCombustion chamber
High octane fuel and low octane fuel are supplied into the combustion chamber of an engine from high-octane fuel tank and low octane fuel tank via a high octane fuel injector and a low octane fuel injector. During a knocking control, if the quantity of high and low octane fuels in the respective tanks has been unbalanced, the supply ratio between high octane fuel and low octane fuel is changed 1 to control a knocking occurring in the engine without changing the ignition timing.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for reducing vibration in a vehicle and a device for accomplishment of the method
A method and an arrangement for reducing vibrations in an internal combustion engine (2) which has a plurality of drive units (3-8) connected to a common output shaft (9). These are equipped with a combustion chamber and inlets (34-39) for fuel from organs for fuel supply. Any one of the driving units (7) can be switched from a normal operating condition to an alternative operating condition, in which the supply of fuel to the drive unit is blocked, which causes an alteration in the torque of the driving unit which has been thus switched. The amount of fuel supplied to the drive units which are in a normal operating condition is distributed according to a chosen pattern in order to create torques in these which cause a chosen suppresion of vibrations.
Owner:AB VOLVO
Liquified natural gas (LNG) fueled combined cycle power plant and a (LNG) fueled gas turbine plant
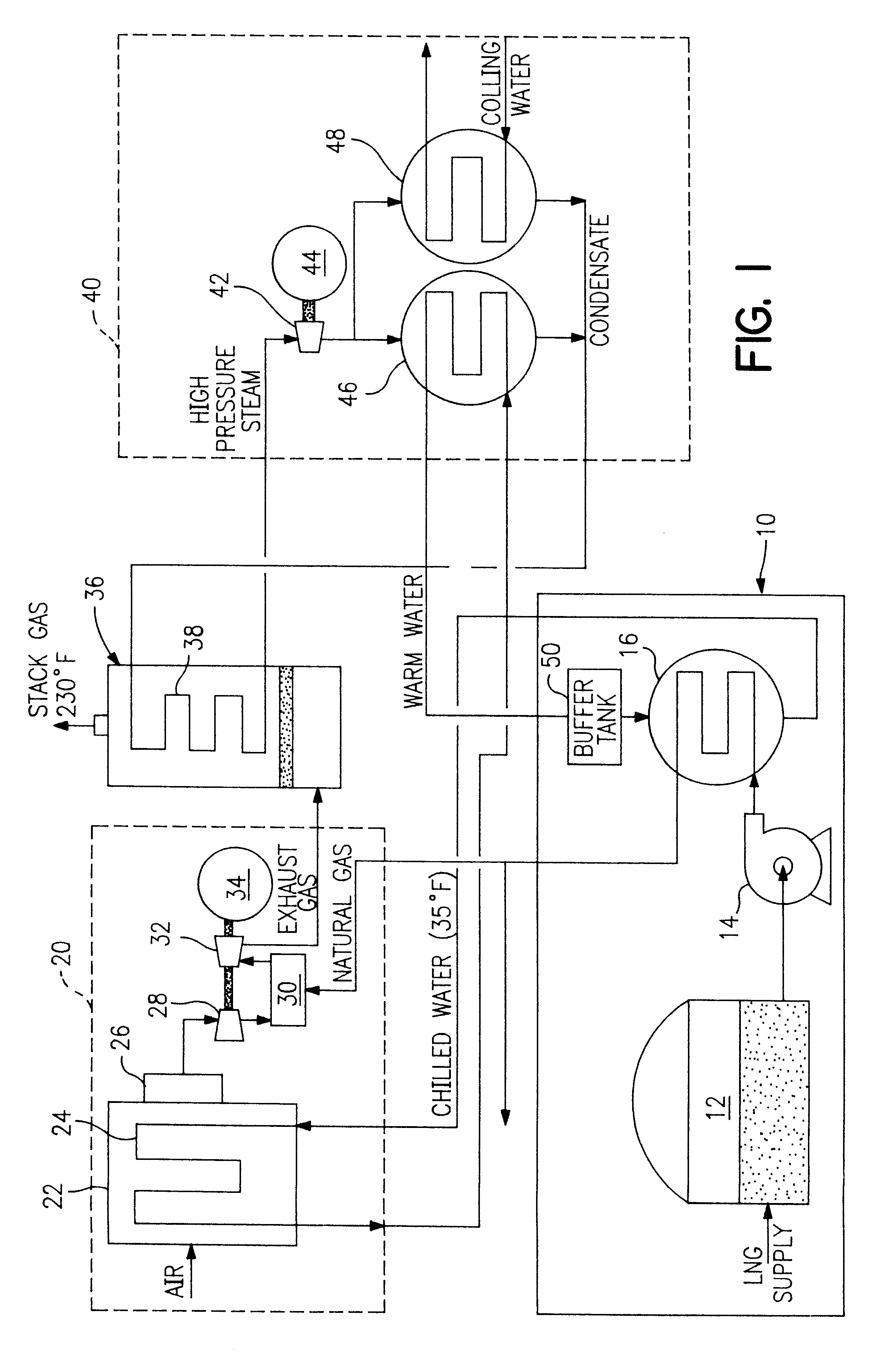
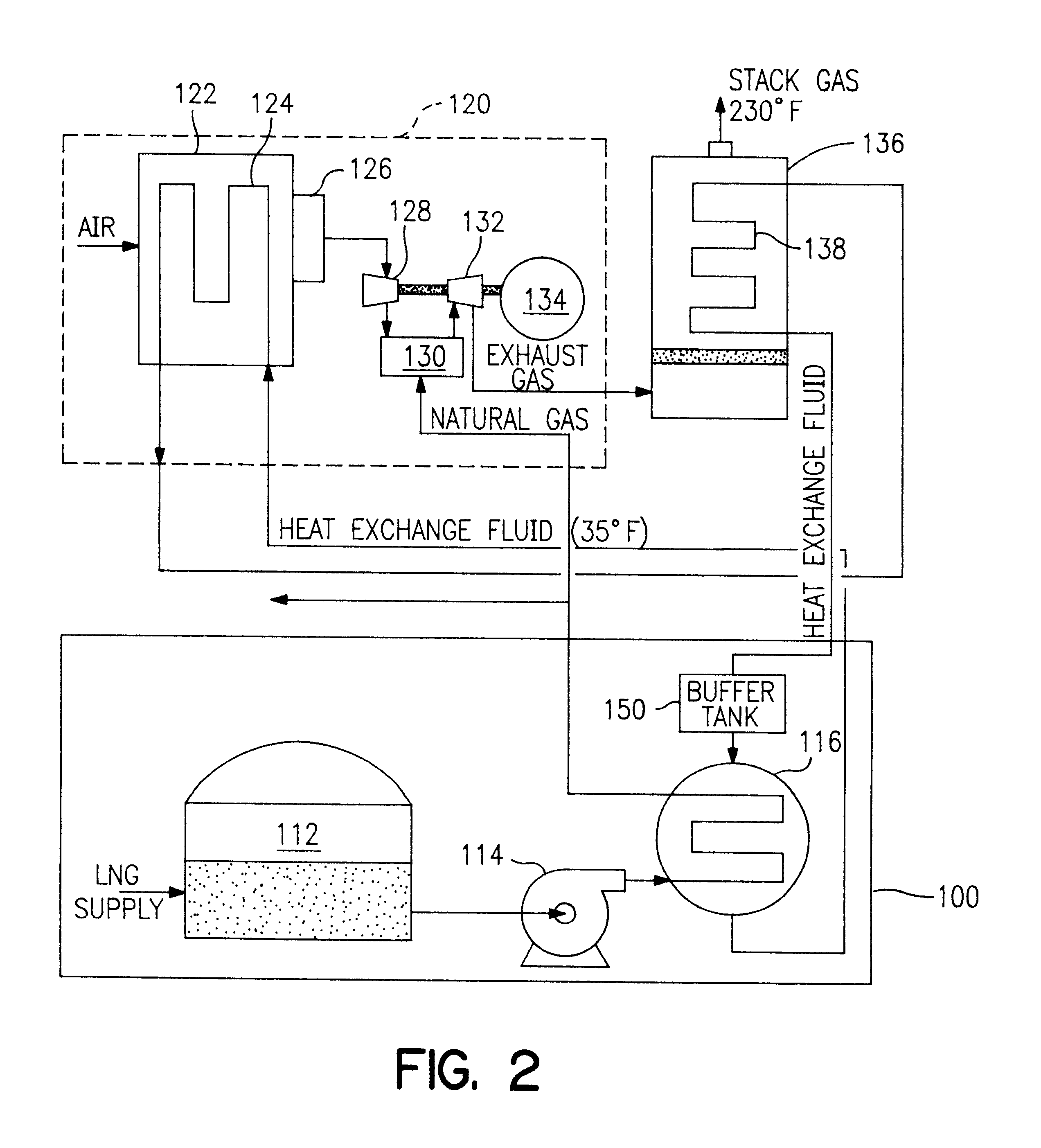
InactiveUS6374591B1Improve efficiencyParts are smallGas handling applicationsGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberPower station
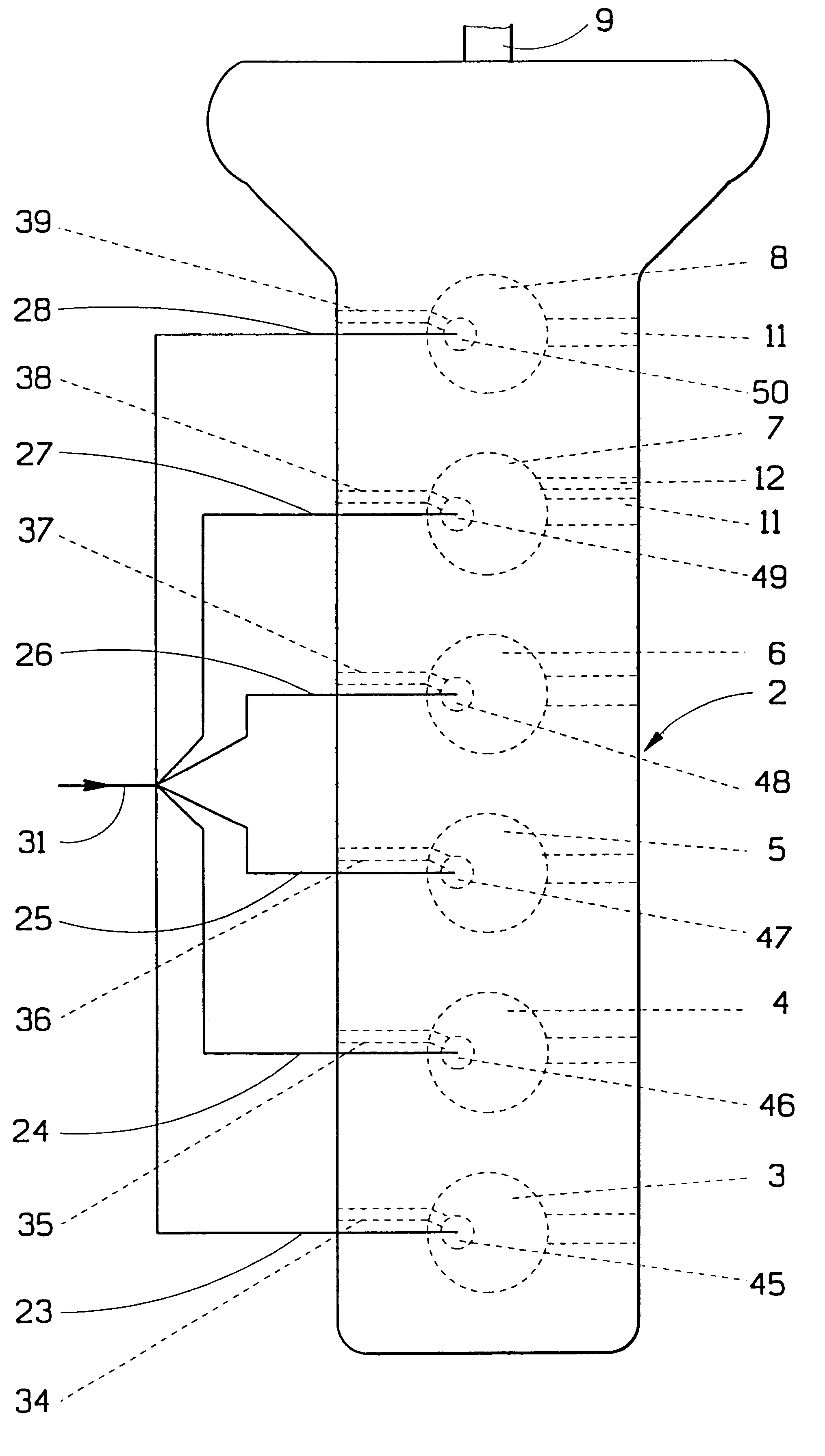
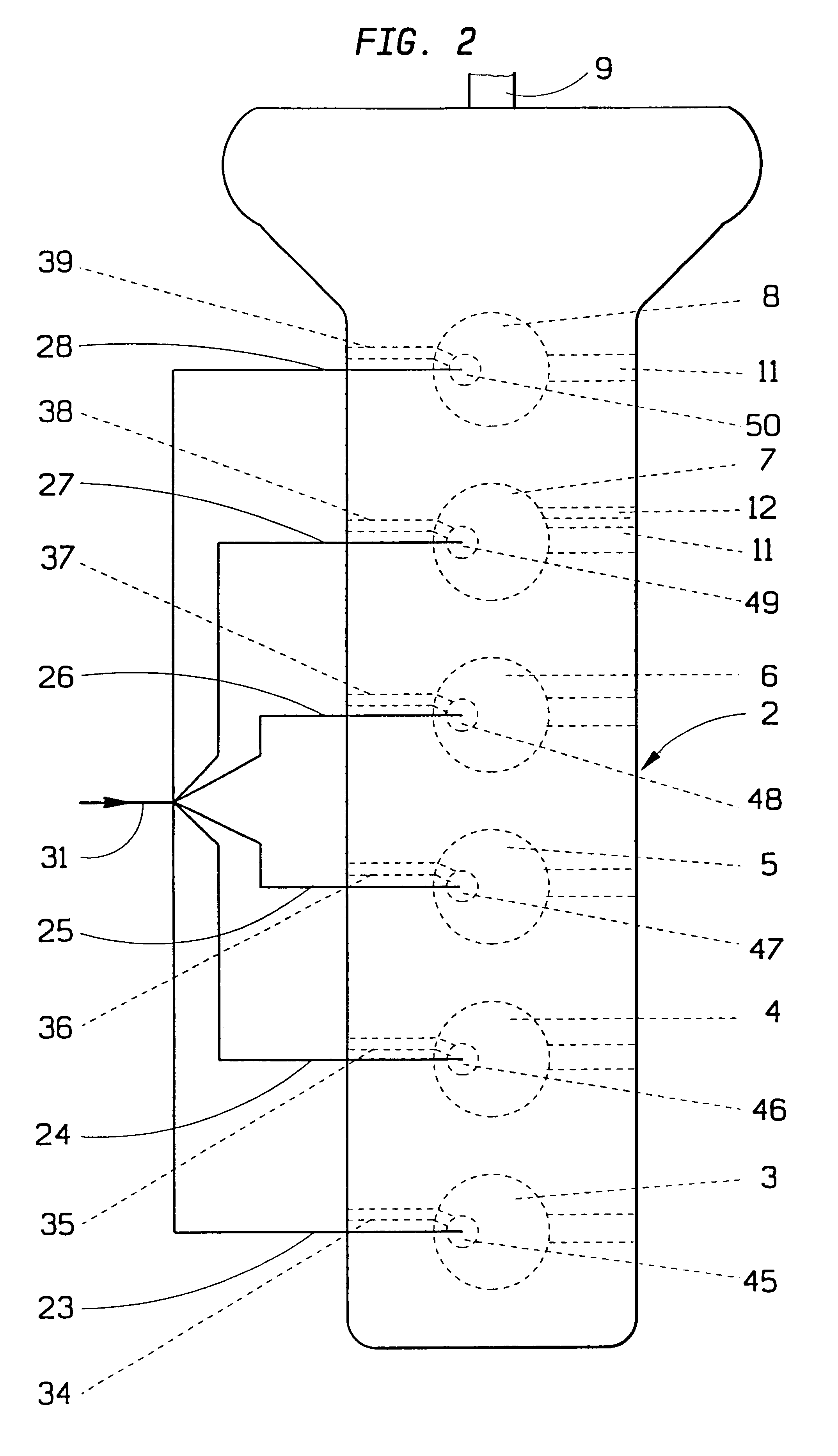
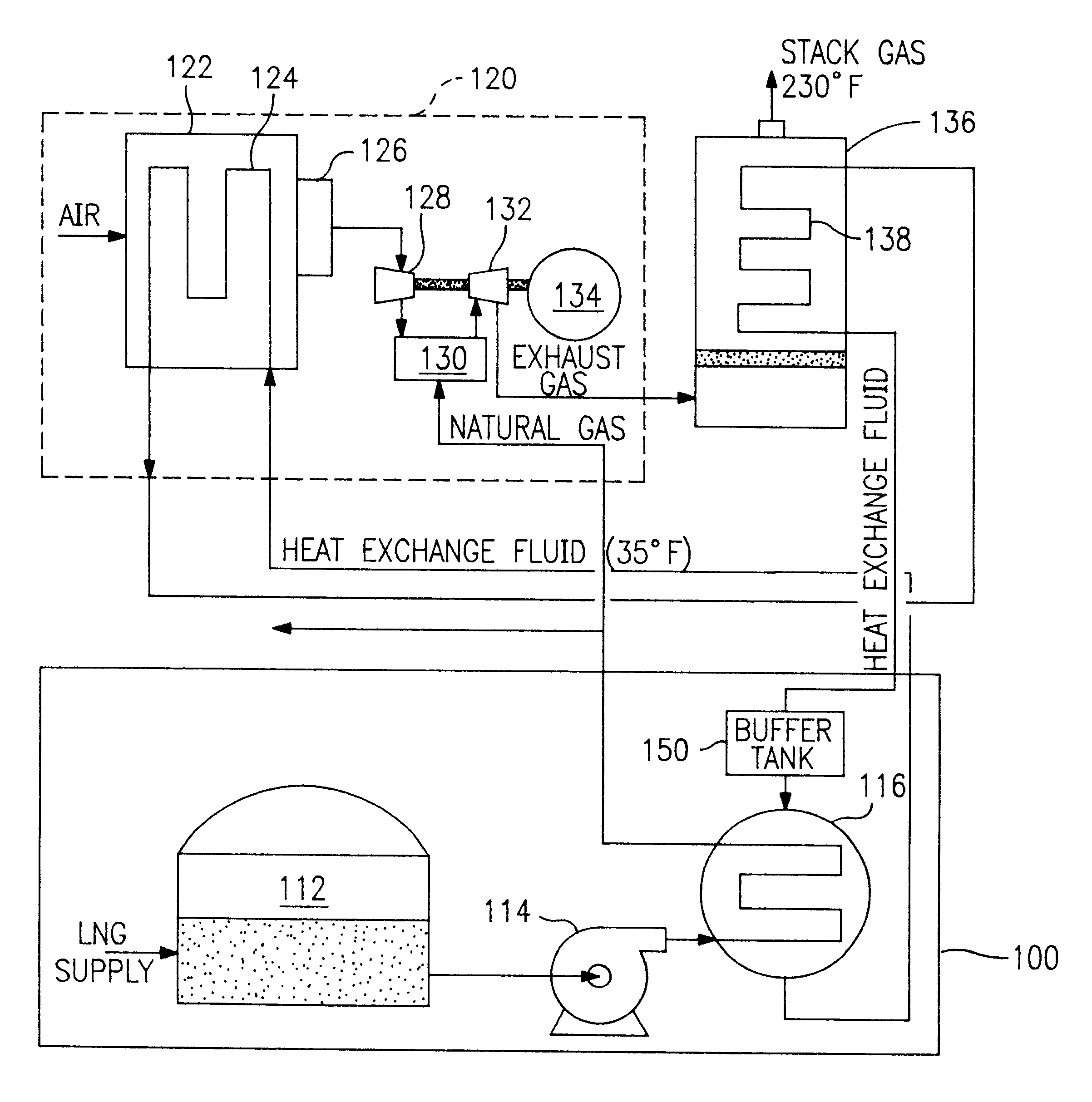
A process and system which improves the capacity and efficiency of a power plant. A LNG supply system fuels the plant. Gasified LNG in a combustor mixes with the air from an air compressor to provide the hot combustion gas for a gas turbine. The expanding LNG is used to chill a heat exchange fluid, e.g. water, which heat exchange fluid cools and densifies the intake air for the air compressor. Subsequently, the heat exchange fluid is used in another heat exchange step and is then re-chilled and recycled to cool and densify the intake air.
Owner:SUEZ LNG NA
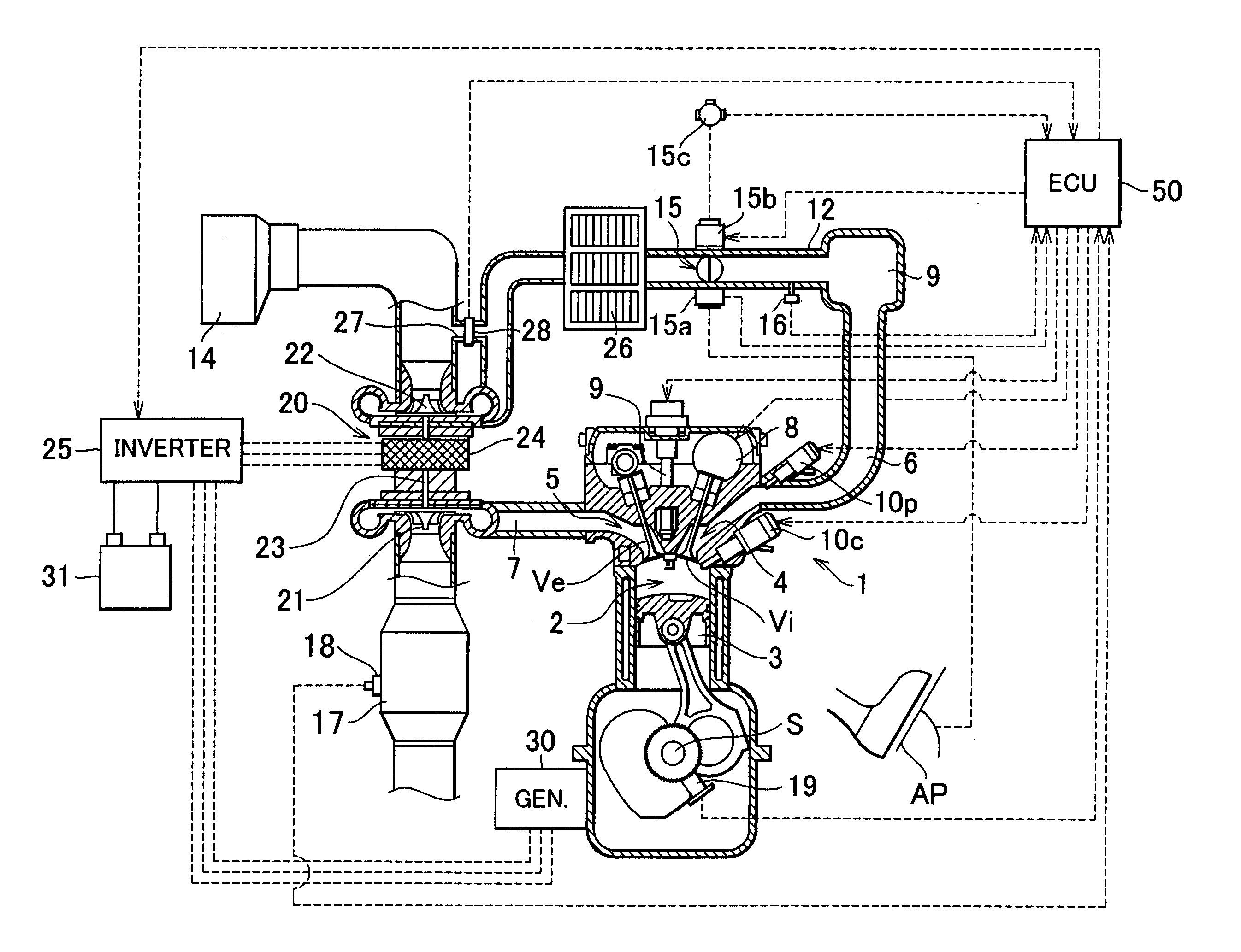
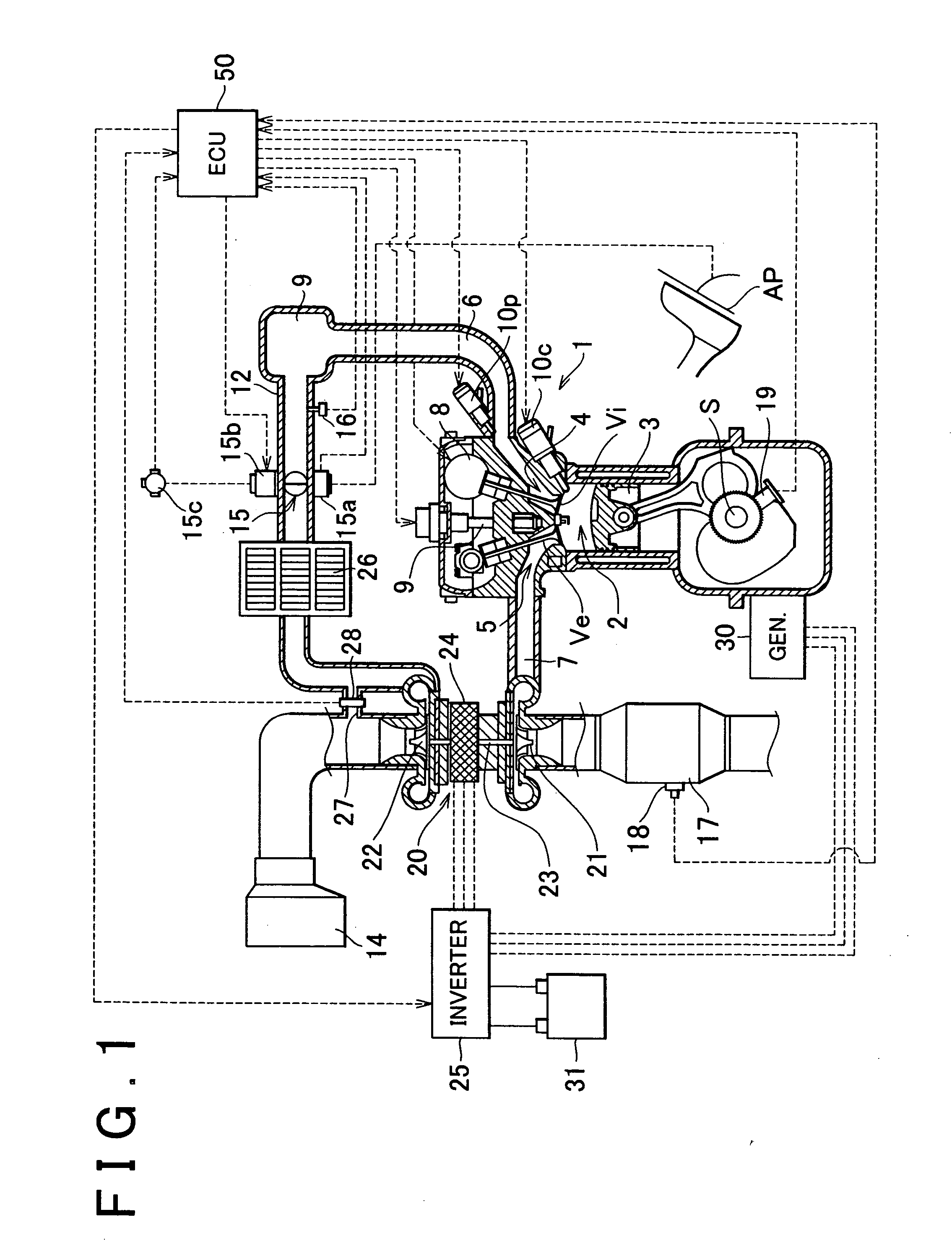
Internal combustion engine and control method thereof
InactiveUS20050097888A1Reliably activatedReduce exhaust emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
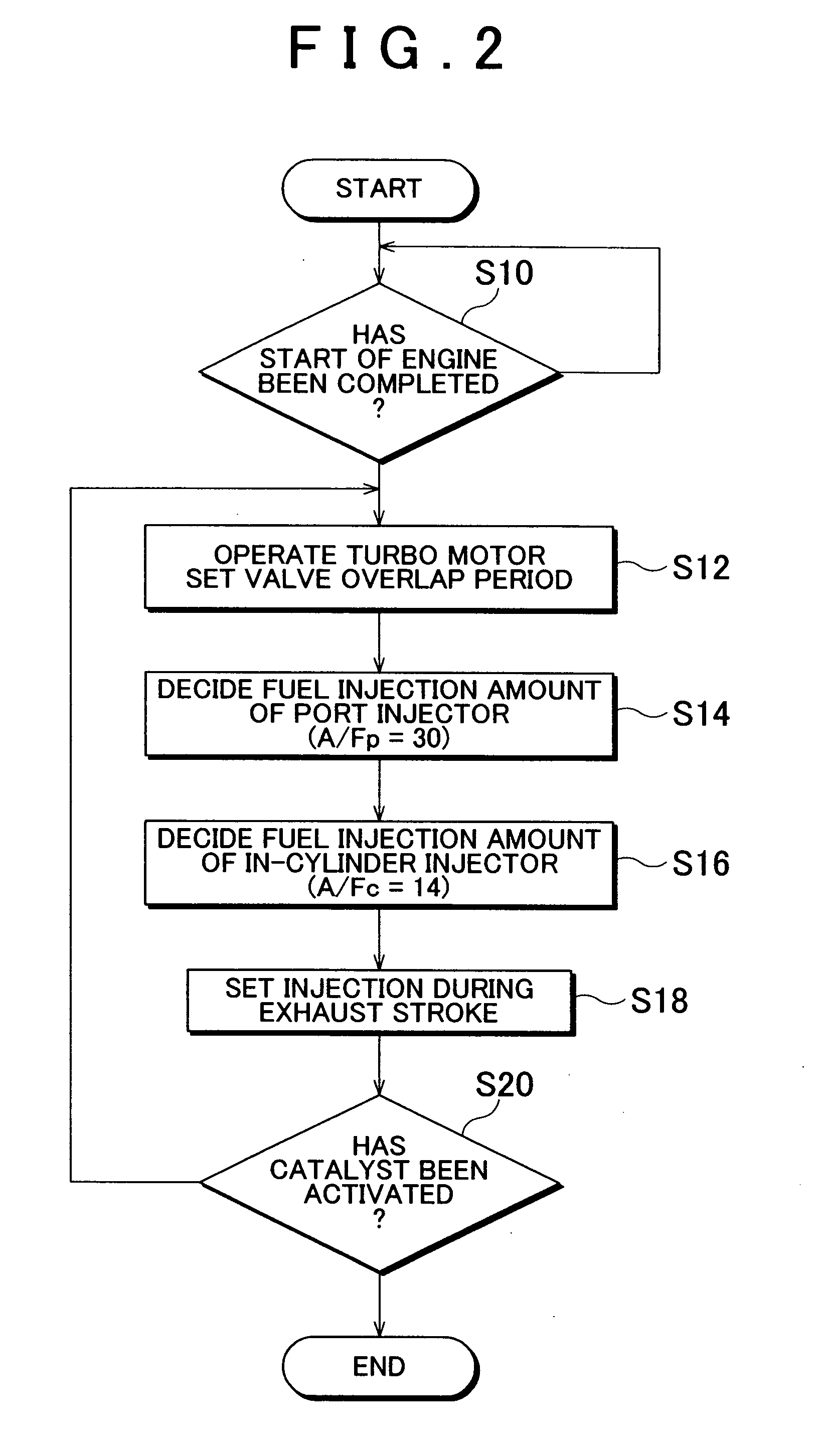
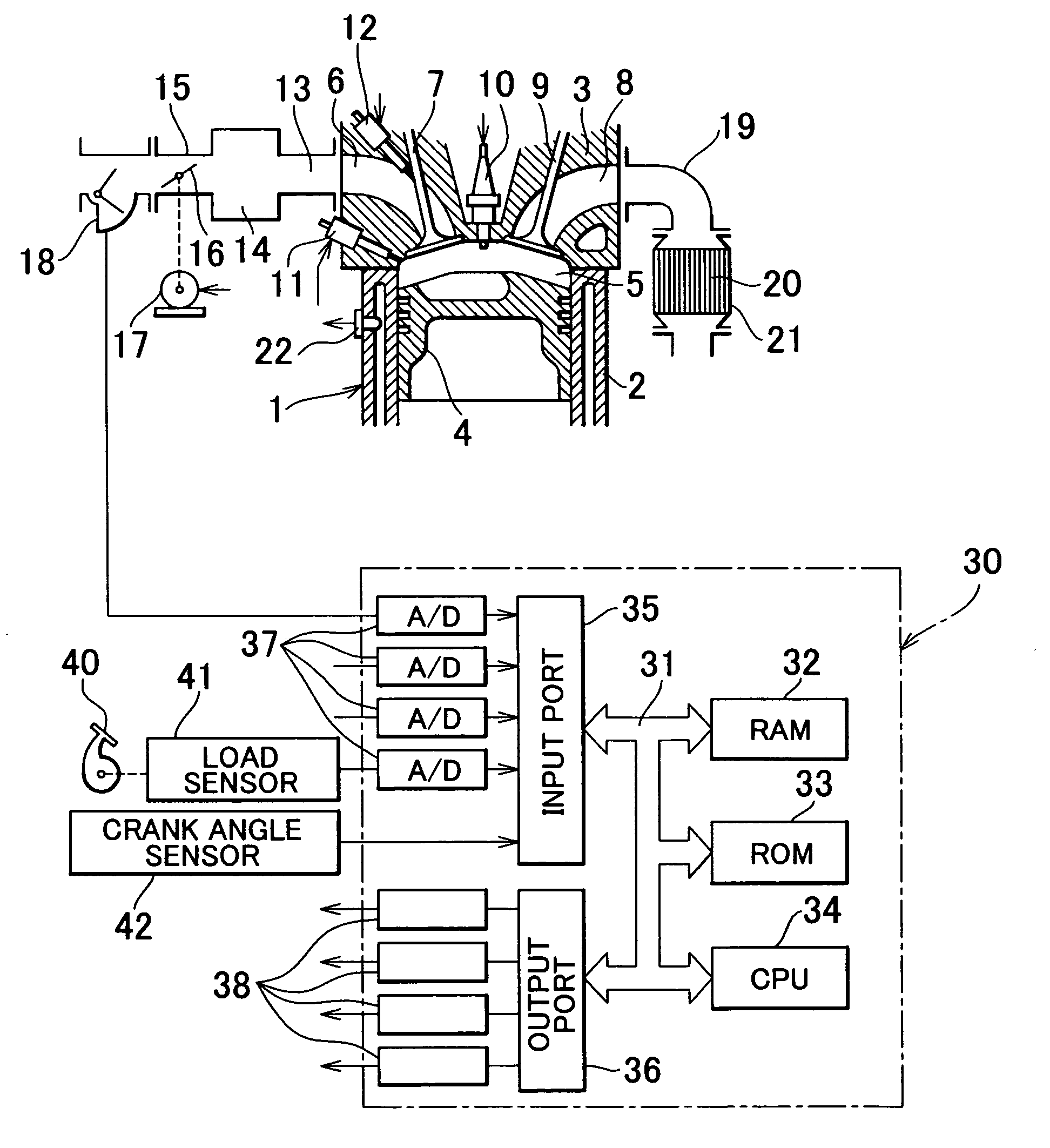
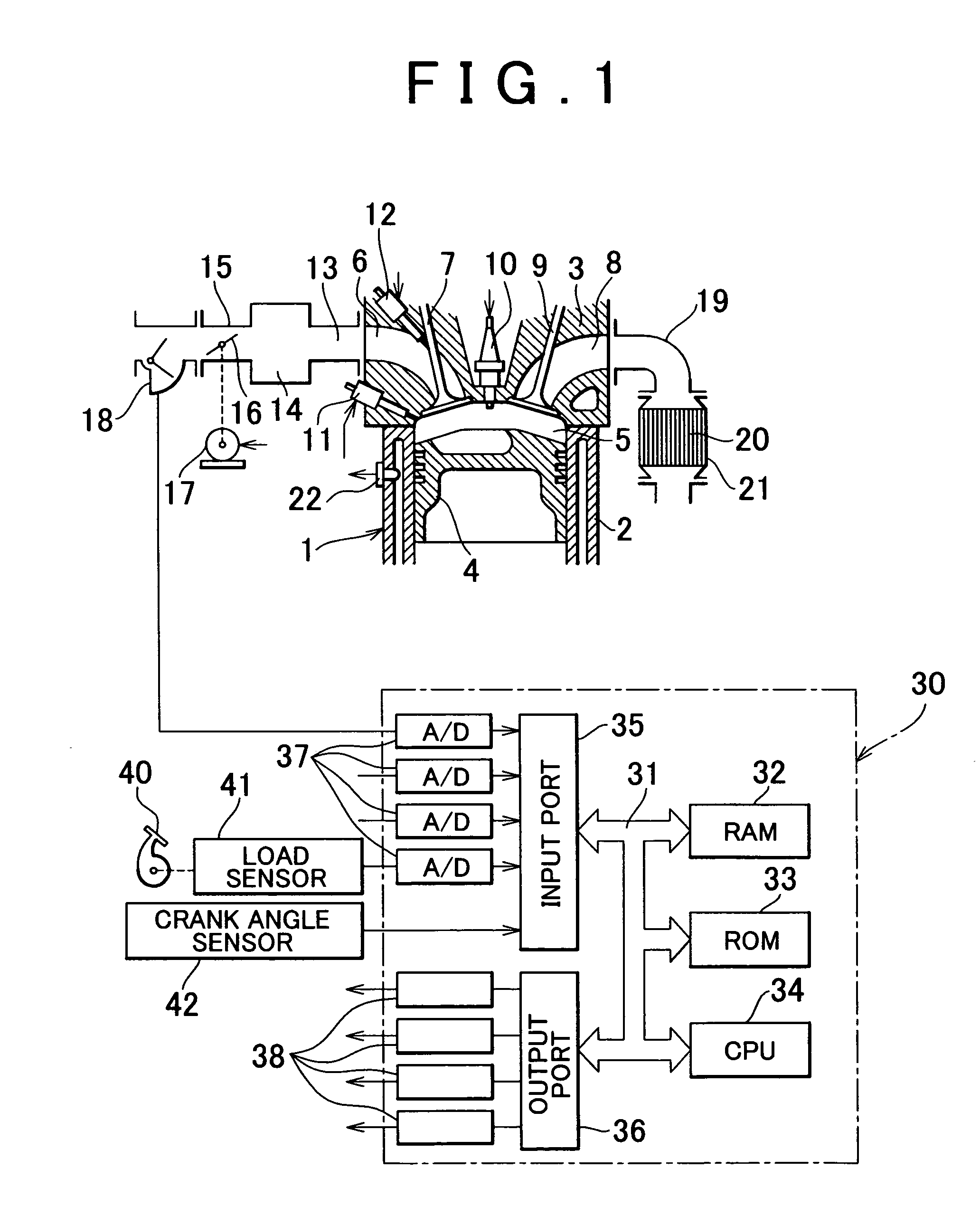
An internal combustion engine in which power is generated by burning a mixture of fuel supplied from a port injector and / or an in-cylinder injector and air in a combustion chamber, includes a valve drive mechanism which can change a valve opening characteristic of at least one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve; a turbocharger which supercharges air taken into the combustion chamber; a turbo motor which changes supercharging pressure generated by the turbocharger; a catalyst device including a catalyst which purifies exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber; and an ECU which controls the turbo motor such that pressure of the air taken into the combustion chamber becomes larger than back pressure until it is determined that the catalyst has been activated, and which sets a valve overlap period during which both of the intake valve and the exhaust valve are opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel injection system and method
InactiveUS6959693B2Electrical controlCoolant flow controlCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
A fuel injection system includes a first fuel injector that injects a lower-octane fuel into a combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, and a second fuel injector that injects a higher-octane fuel into an intake passage of the engine. When the engine temperature is equal to or lower than a predetermined temperature during a start-up period of the internal combustion engine, fuel having the lower octane is injected via the first injector while prohibiting injection of the higher octane fuel via the second fuel injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Methods and apparatus for starting up emission-free gas-turbine power stations
InactiveUS6945052B2Large capacityGas turbine plantsIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationPower stationCombustion chamber
In a power generation plant having at least one gas turbine cycle with heat-recovery boiler (4) and at least one steam turbine cycle operated via the heat-recovery boiler (4), the gas turbine cycle being designed to be semi-closed and essentially free of emissions and essentially comprising a compressor (1), a combustion chamber (2) arranged downstream of the compressor (1), a gas turbine (3) arranged downstream of the combustion chamber (2), a heat-recovery boiler (4) arranged downstream of the gas turbine (3), and at least one generator (8) coupled to the gas turbine (3), modes of operation with the gas turbine cycle stopped and start-up using fresh air are made possible by first means (12) being arranged which alternatively or additionally allow hot gas to be fed into the hot-gas path (23) between gas turbine (3) and heat-recovery boiler (4), and by second means (15) being arranged which alternatively or additionally allow exhaust gas to be expelled from the exhaust-gas path (40) downstream of the heat-recovery boiler (4).
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Engine fuel injection control system
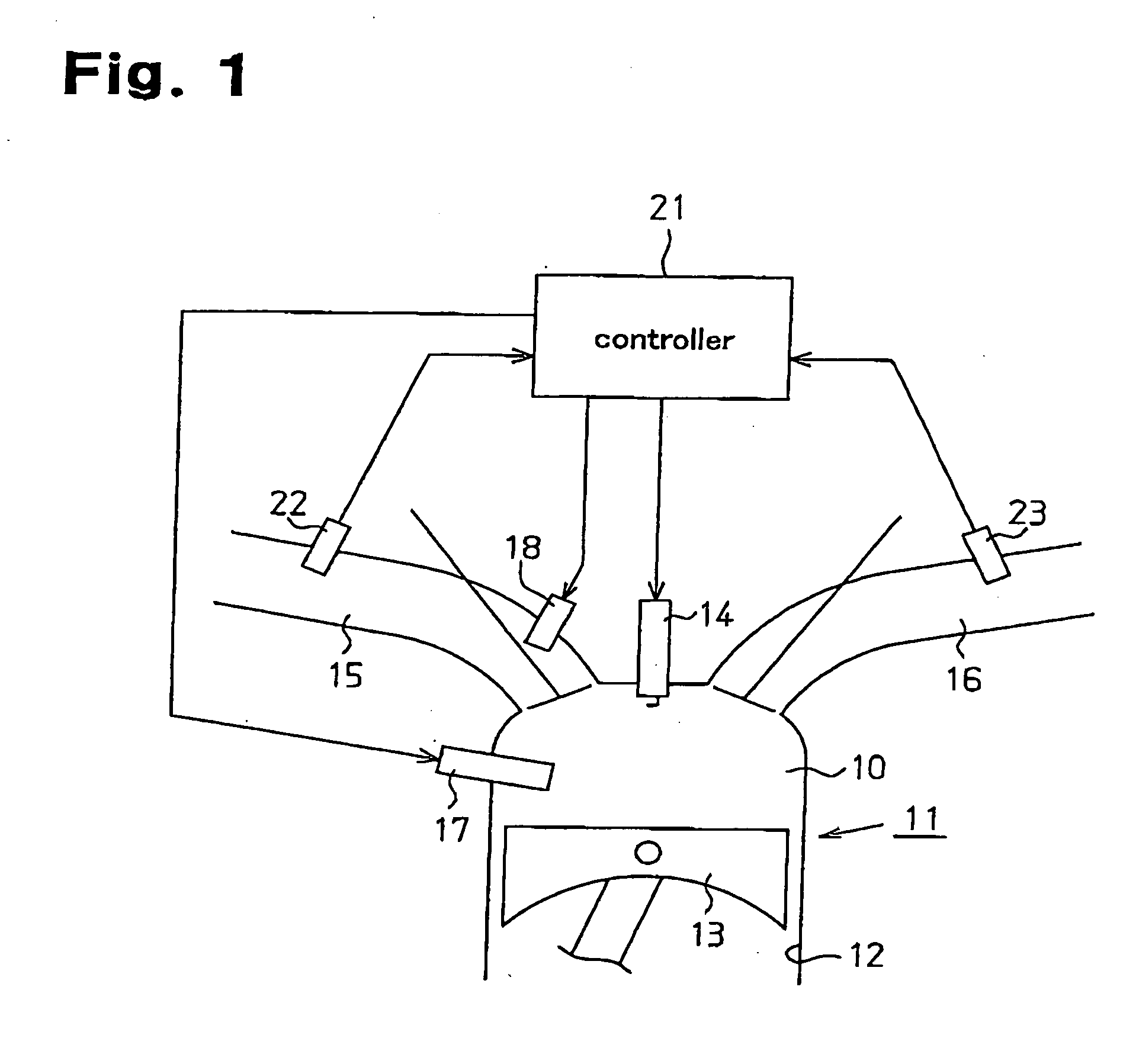
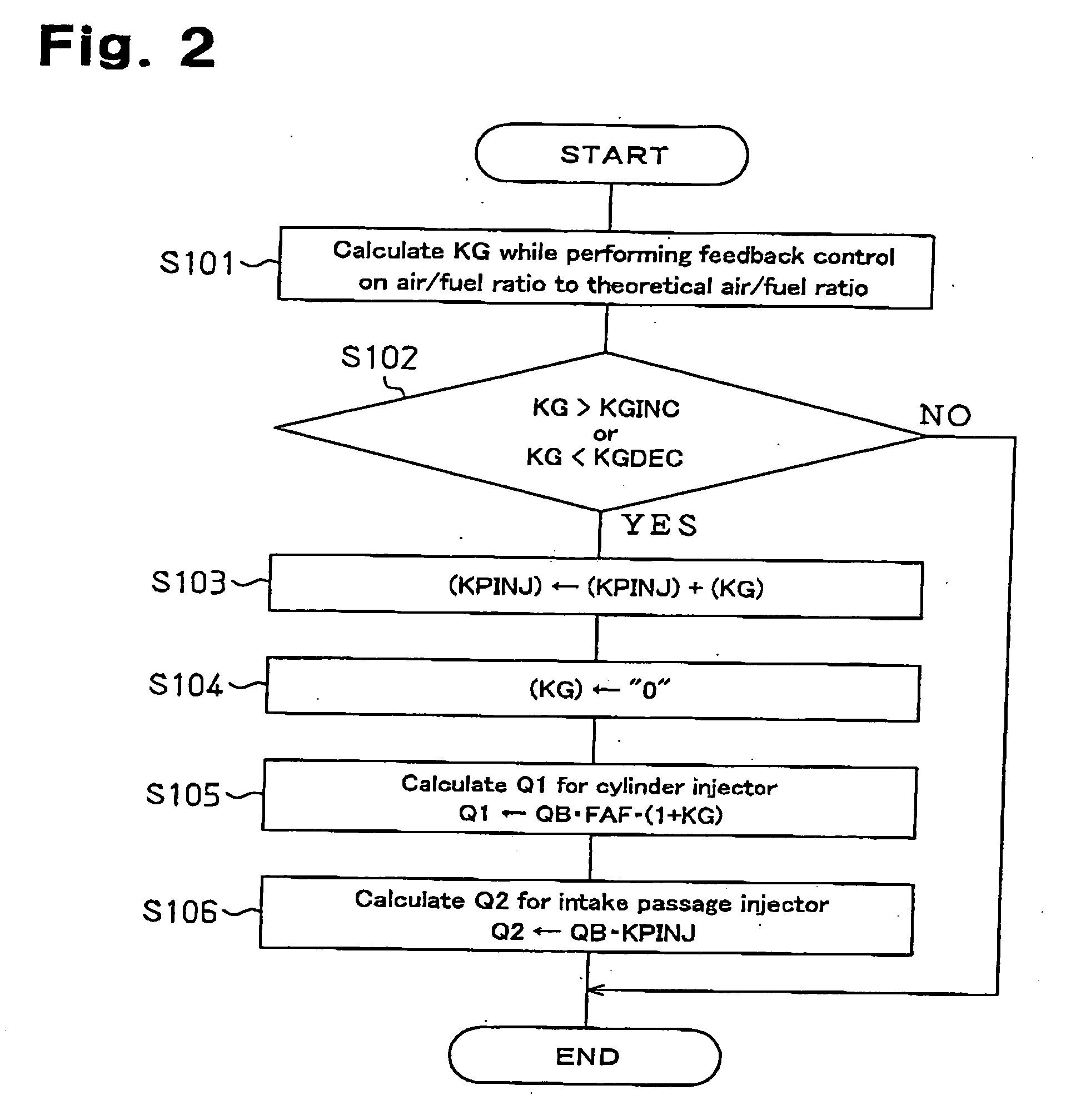
InactiveUS20050178360A1Inhibit deteriorationImprove suction efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
A system for controlling fuel injection in an engine. The engine includes an intake passage, an intake passage injector, a cylinder having a combustion chamber, and a cylinder injector for injecting a target amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. The system includes a controller for controlling the intake passage and cylinder injectors to permit fuel injection, each with an injection ratio, while said engine operates in a condition in which said engine permits fuel injection from said cylinder injector, a sensor for sensing the amount of fuel injected from the cylinder injector, a detector for detecting the difference between the target injection amount and the amount of fuel injected and an adjustor for adjusting the injection ratio based on the result of the detection by the detector so that the intake passage injector performs fuel injection together with the fuel injection performed by the cylinder injector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Apparatus and Method for Controlling the Secondary Injection of Fuel
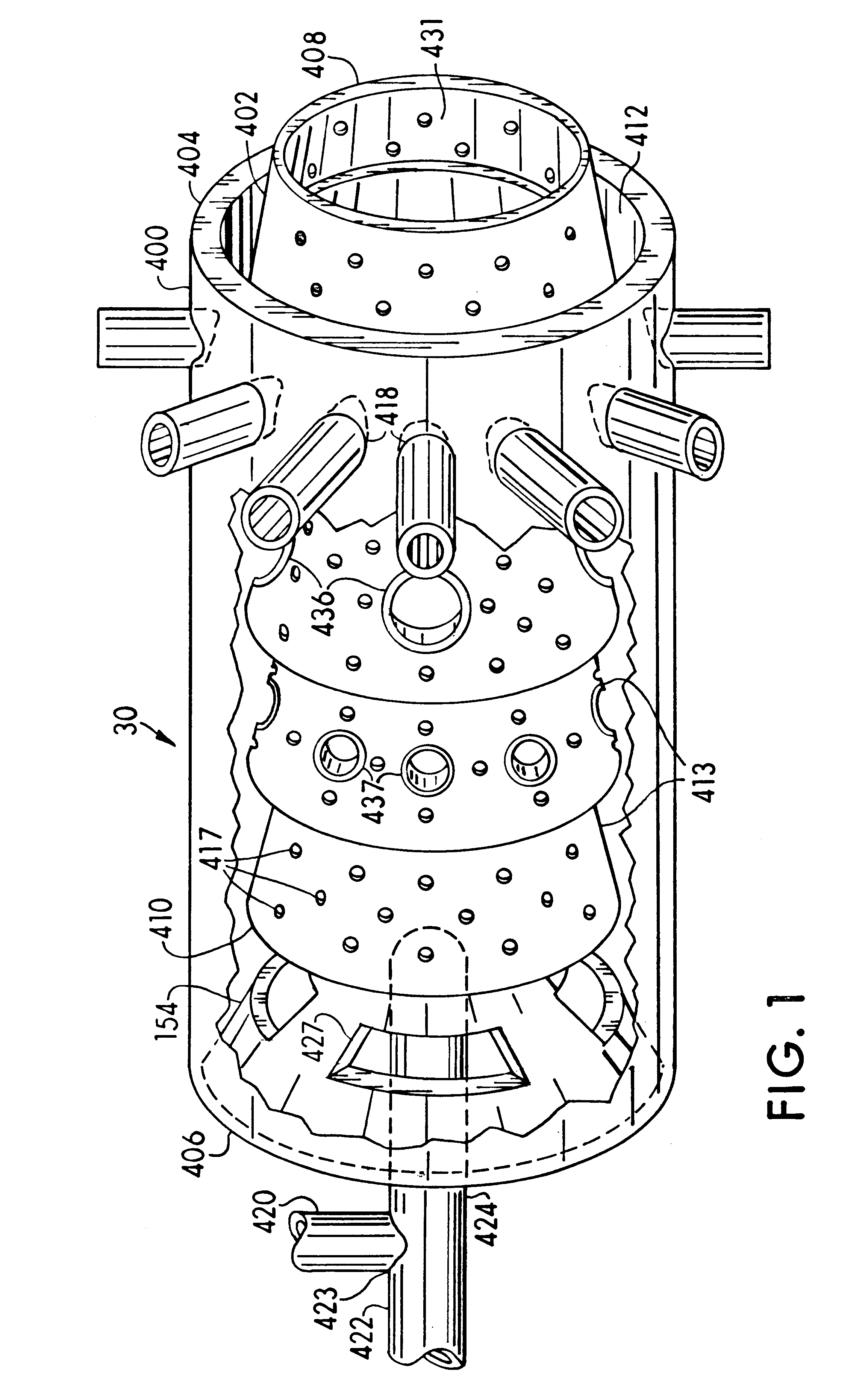
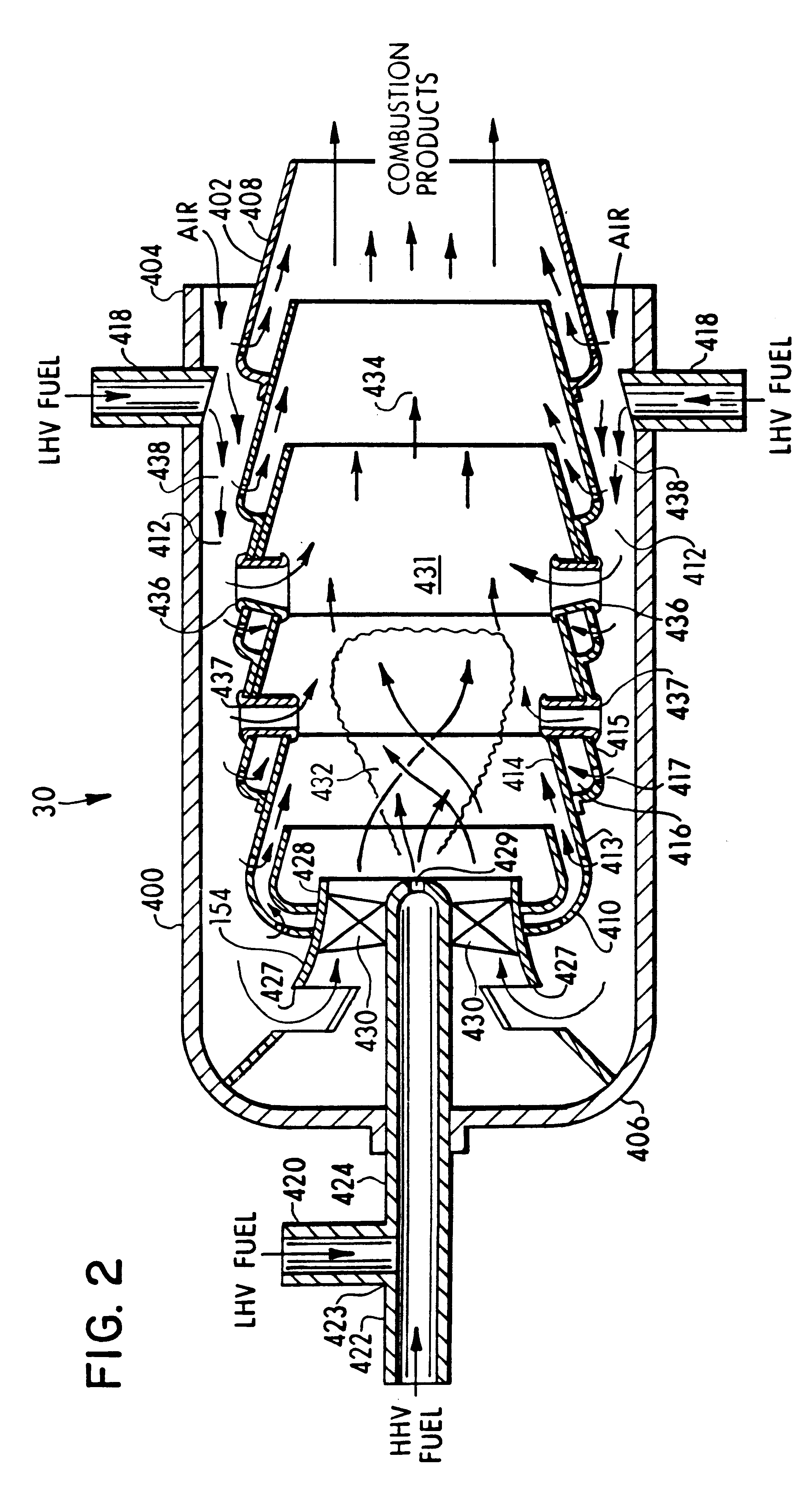
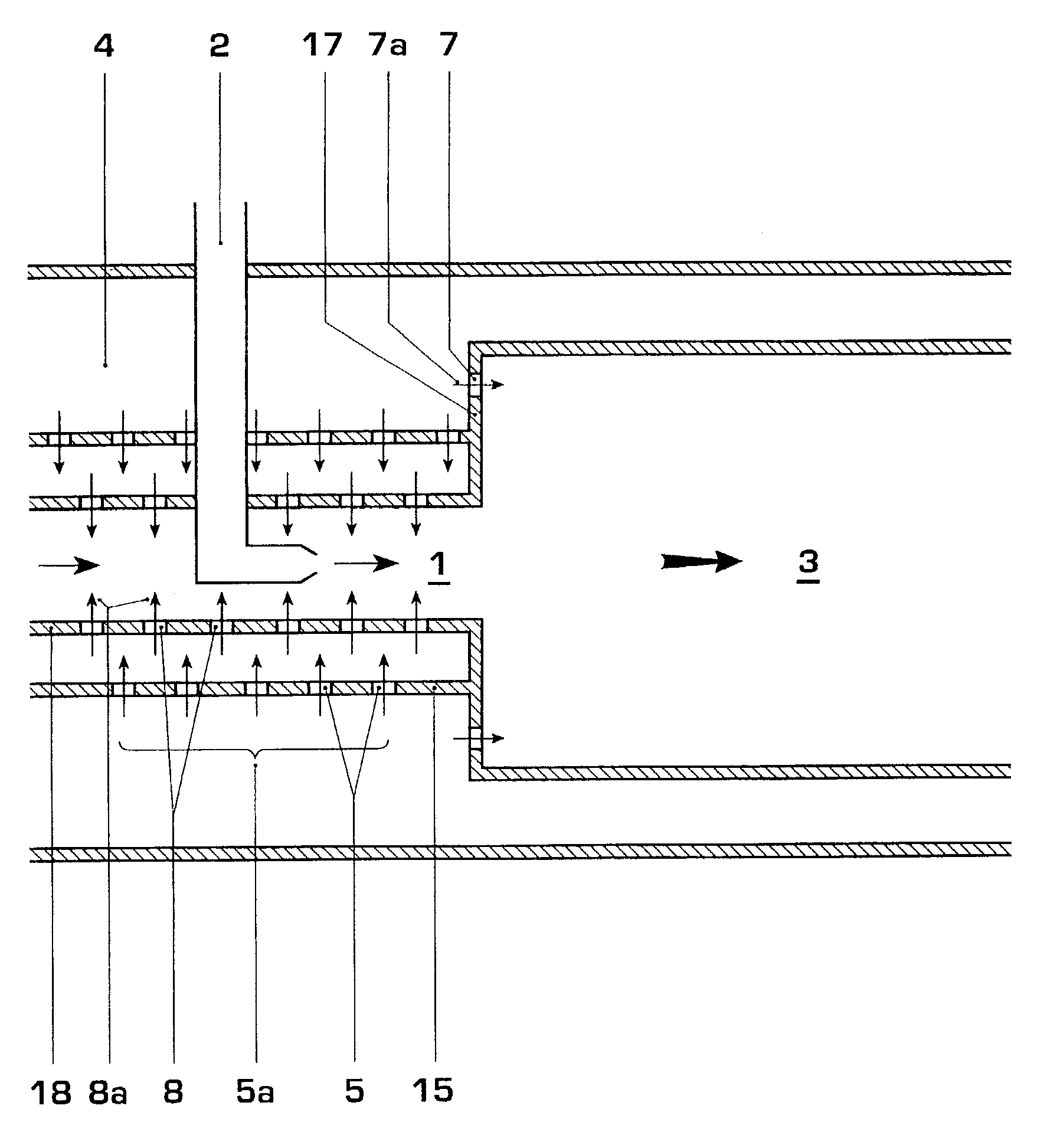
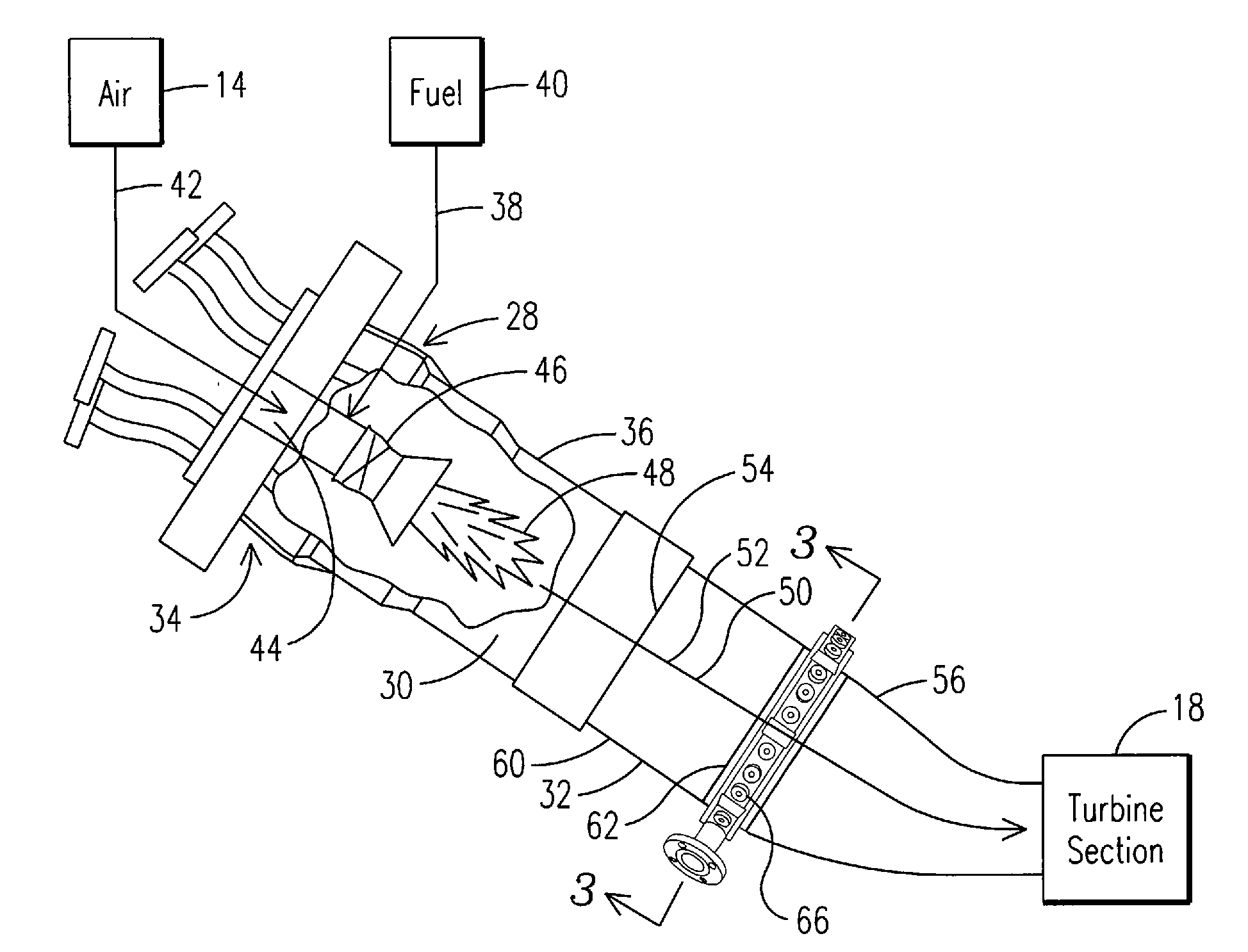
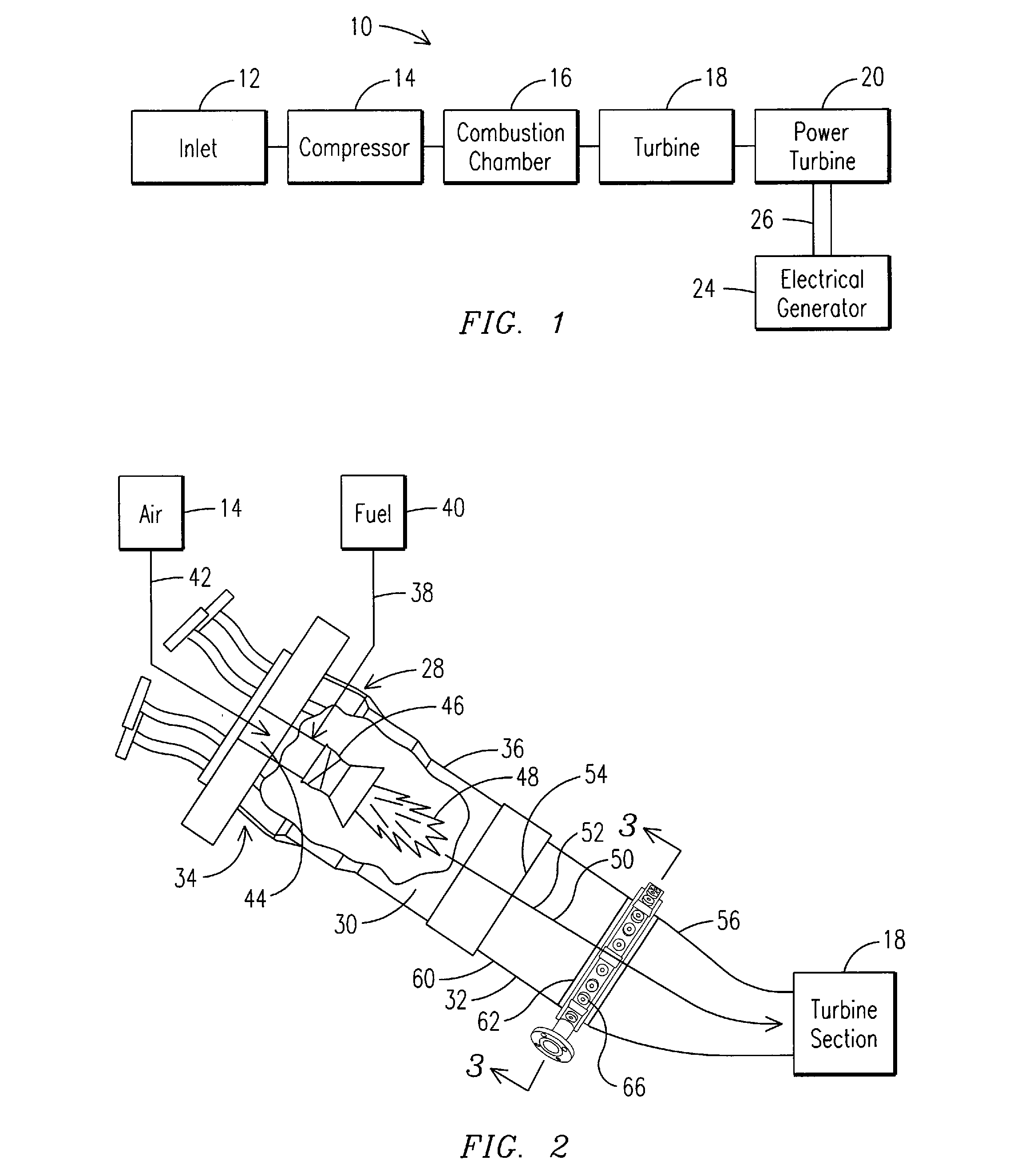
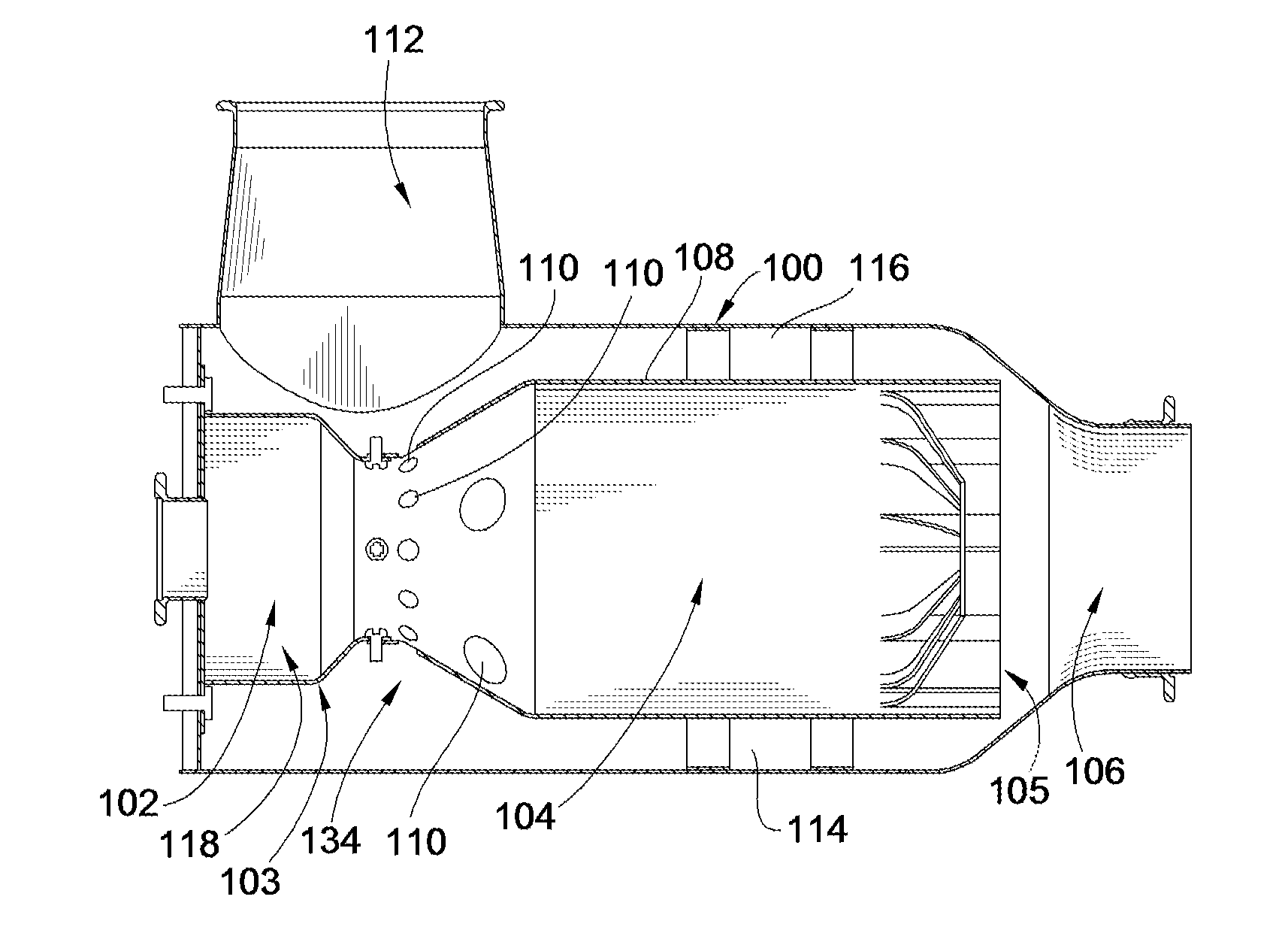
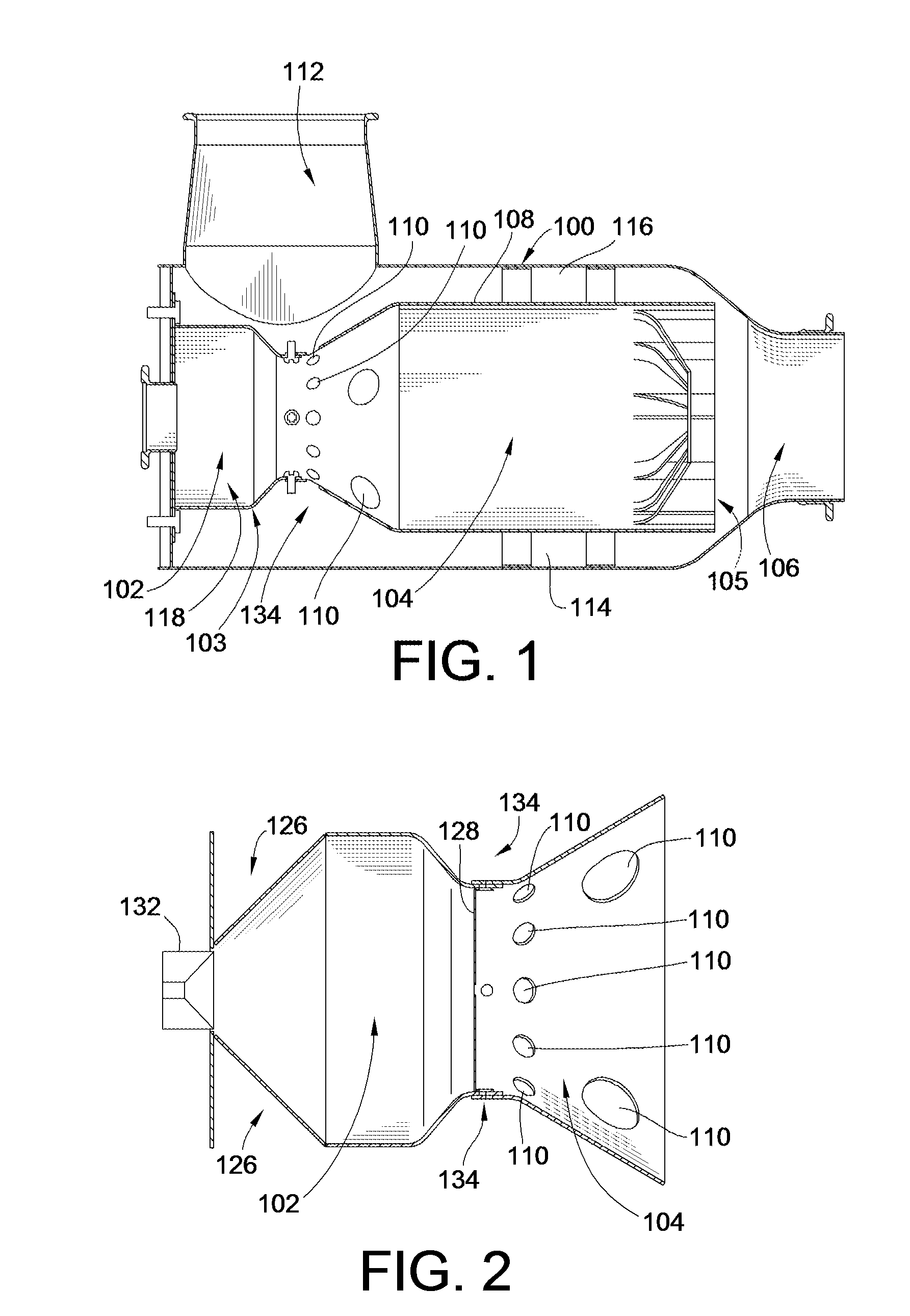
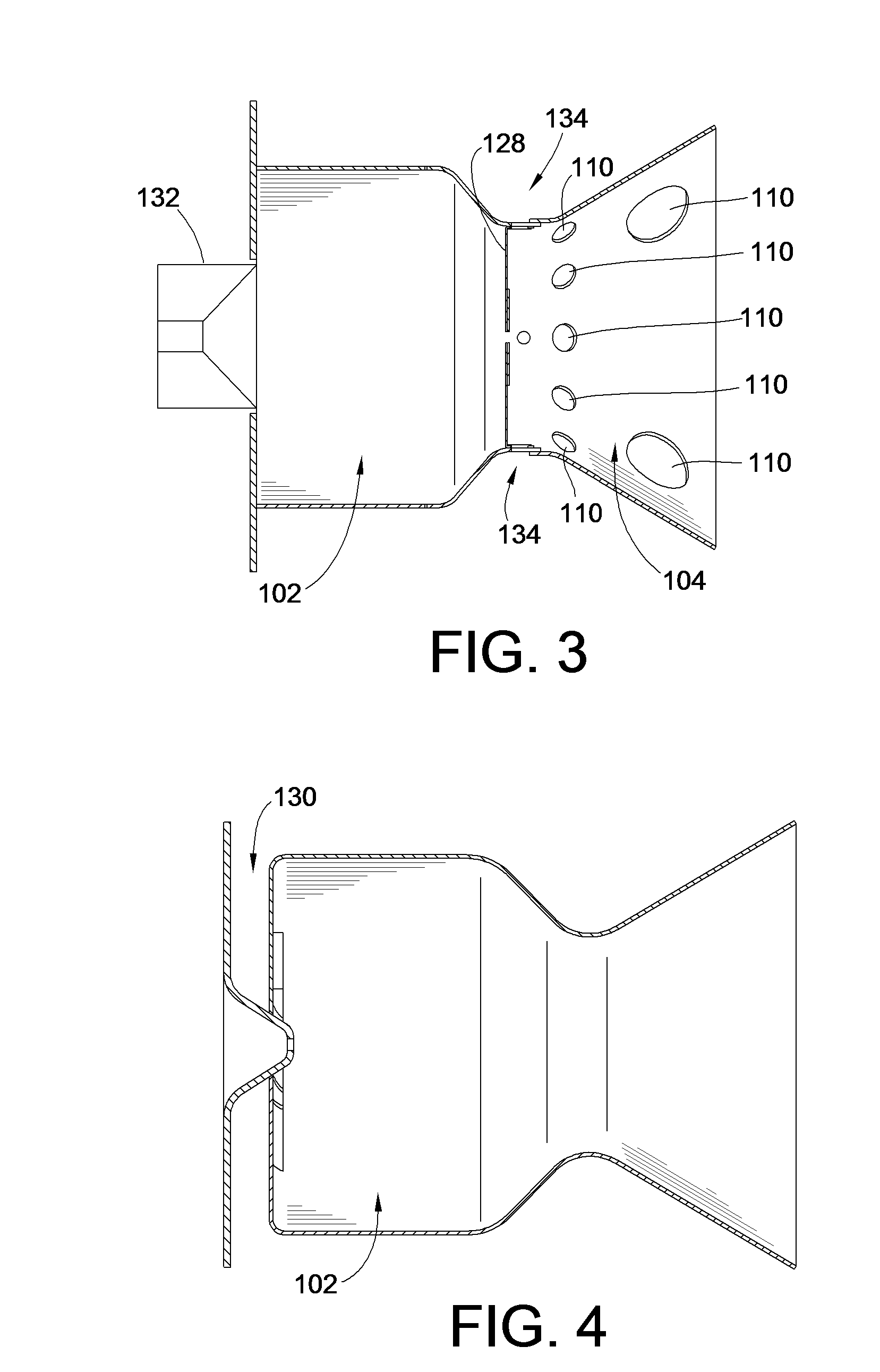
In one embodiment, a combustor (28) for a gas turbine engine is provided comprising a primary combustion chamber (30) for combusting a first fuel to form a combustion flow stream (50) and a transition piece (32) located downstream from the primary combustion chamber (30). The transition piece (32) comprises a plurality of injectors (66) located around a circumference of the transition piece (32) for injecting a second fuel into the combustion flow stream (50). The injectors (66) are effective to create a radial temperature profile (74) at an exit (58) of the transition piece (32) having a reduced coefficient of variation relative to a radial temperature profile (64) at an inlet (54) of the transition piece (32). Methods for controlling the temperature profile of a secondary injection are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Low Pressure Drop Mixer for Radial Mixing of Internal Combustion Engine Exhaust Flows, Combustor Incorporating Same, and Methods of Mixing
ActiveUS20090255242A1Increase surface areaEnhanced interactionInternal combustion piston enginesFlow mixersCombustion chamberCombustor
An exhaust aftertreatment system is provided. The exhaust aftertreatment system includes a mixing arrangement for mixing flows of exhaust along a flow path. The mixing arrangement radially and angularly rearranges segments of two different portions of flow to mix the different portions of flow. The mixing arrangement initially converts a generally radially stratified temperature profile into an angularly stratified temperature profile to increase surface area between cool segments of exhaust gas and hot segments of exhaust gas. The aftertreatment system may also include a combustion chamber, a combustor housing and a combustor liner. The mixing arrangement is downstream from the combustion chamber to direct radially outward hot gas passing through the combustor liner and to direct radially outer cool gas passing between the liner and the combustor housing radially inward in an interleaving fashion.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
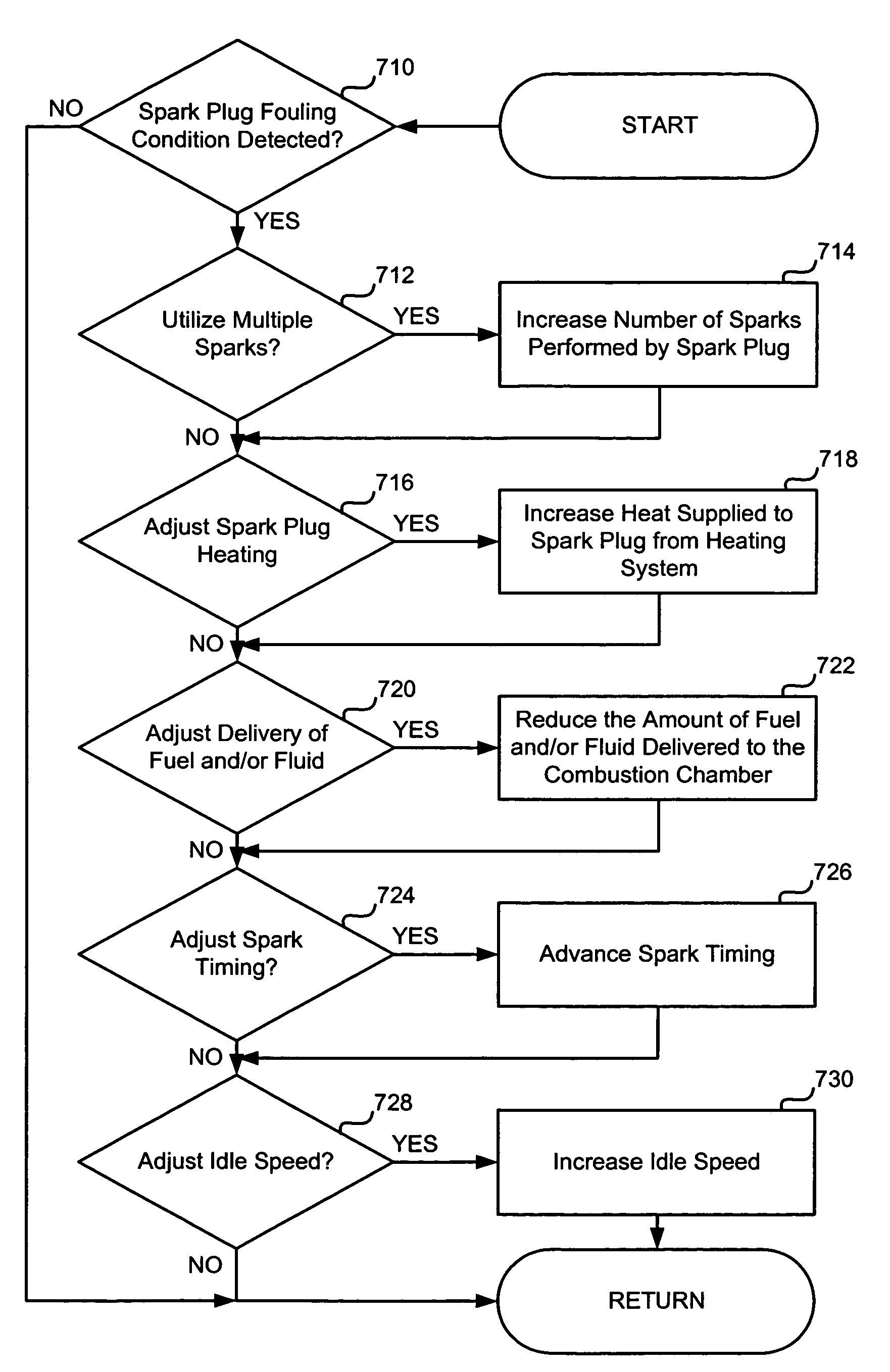
Spark plug heating for a spark ignited engine
A system for an engine of a vehicle, comprising of at least one combustion chamber located in the engine, a delivery system configured to deliver a fuel and a fluid to the combustion chamber, an ignition system including a spark plug configured to ignite the fuel within the combustion chamber, a spark plug heating system configured to supply heat to the spark plug, and a control system configured to vary an amount of heat supplied to the spark plug by the spark plug heating system responsive to a condition of the ignition system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Integrated solid oxide fuel cell and reformer
A disclosed apparatus for generating electrical power has, according to one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells contained in a reaction chamber. The fuel cells are secured at one end thereof in a manifold block, the other ends thereof passing freely through apertures in a baffle plate to reside in a combustion chamber. Reaction gases are supplied to the insides of the tubular fuel cells from a plenum chamber below the manifold block and to the reaction chamber surrounding the outsides of the fuel cells through an annular inlet path, which may include a reformation catalyst. The gases inlet path to the plenum chamber, and the annular inlet path surround the reaction chamber, are both in heat conductive relation with the reaction chamber and the combustion chamber, and raise the gases to formation and reaction temperatures as appropriate.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
Apparatus and process for production of high purity hydrogen
InactiveUS20060248800A1High purityEnhanced overall recoveryCarbon compoundsIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationSteam reformingCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a new and improved process and apparatus for the production of high purity hydrogen by steam reforming. The apparatus is an integrated flameless distributed combustion-membrane steam reforming (FDC-MSR) or reactor for steam reforming of a vaporizable hydrocarbon to produce H2 and CO2, with minimal CO, and minimal CO in the H2 stream. The flameless distributed combustion drives the steam reforming reaction which pro-vides great improvements in heat exchange efficiency and load following capabilities. The reactor may contain multiple flameless distributed combustion chambers and multiple hydrogen-selective, hydrogen-permeable, membrane tubes. The feed and reaction gases may flow through the reactor either radially or axially. A further embodiment of the invention involves producing high purity hydrogen by dehydrogenation using an integrated FDC-membrane de-hydrogenation reactor. A still further embodiment of the invention involves a zero emission hybrid power system wherein the produced hydrogen is used to power a high-pressure internally manifolded molten carbonate fuel cell. In addition, the design of the FDC-SMR powered fuel cell makes it possible to capture good concentrations of CO2 for sequestration or use in other processes.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Spark control for improved engine operation
InactiveUS20070215130A1Low costImprove charge cooling effectElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberControl system
A system for an engine of a vehicle, comprising of at least one combustion chamber located in the engine, a delivery system configured to deliver a fuel and a substance to the combustion chamber, an ignition system including a spark plug configured to ignite the fuel within the combustion chamber, and a control system configured to vary a number of sparks performed by the spark plug in relation to a combustion event of the combustion chamber responsive to a condition of the ignition system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com