Patents
Literature
3563 results about "Energy absorbing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absorption of energy: An atom absorbs energy in the form of heat, light, or electricity. Electrons may move from a lower-energy orbit to a higher-energy orbit.
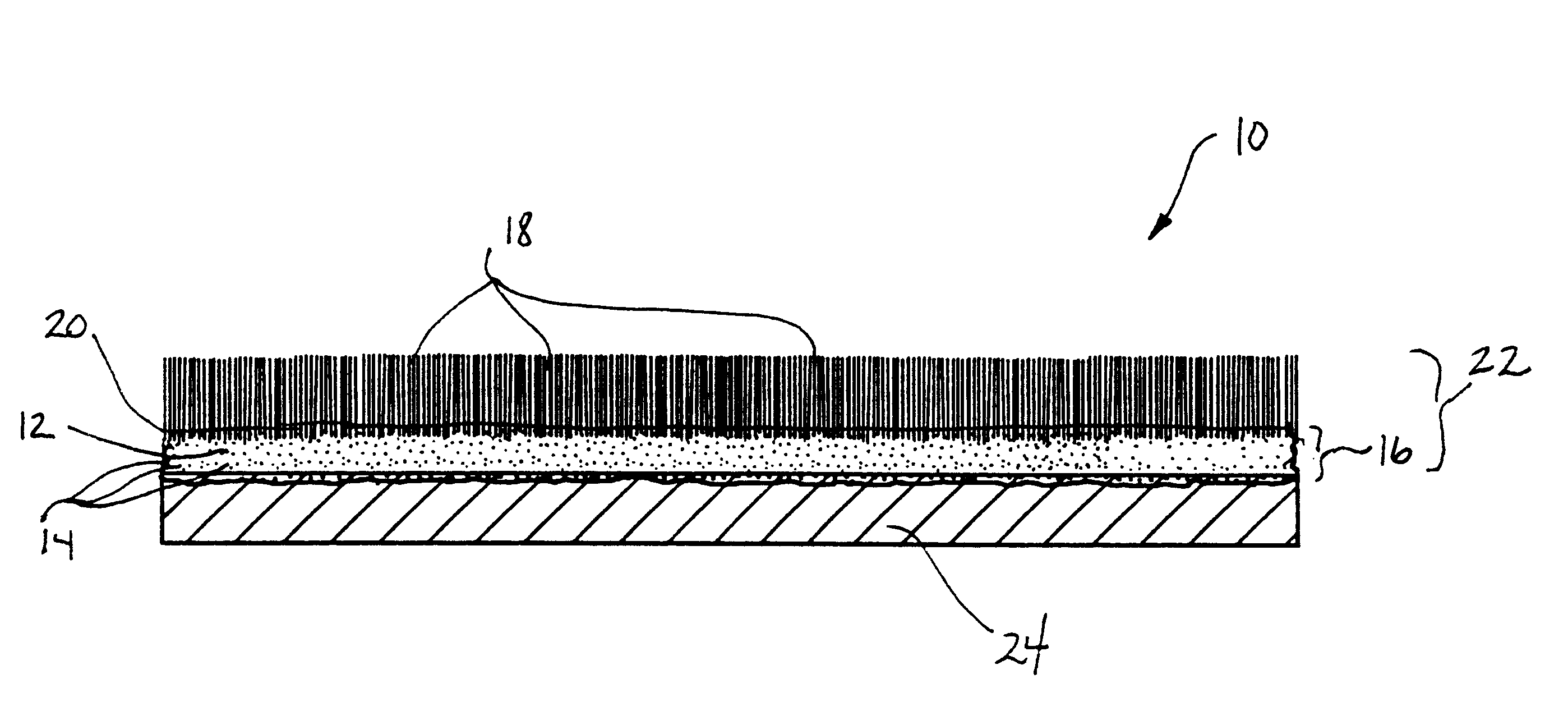
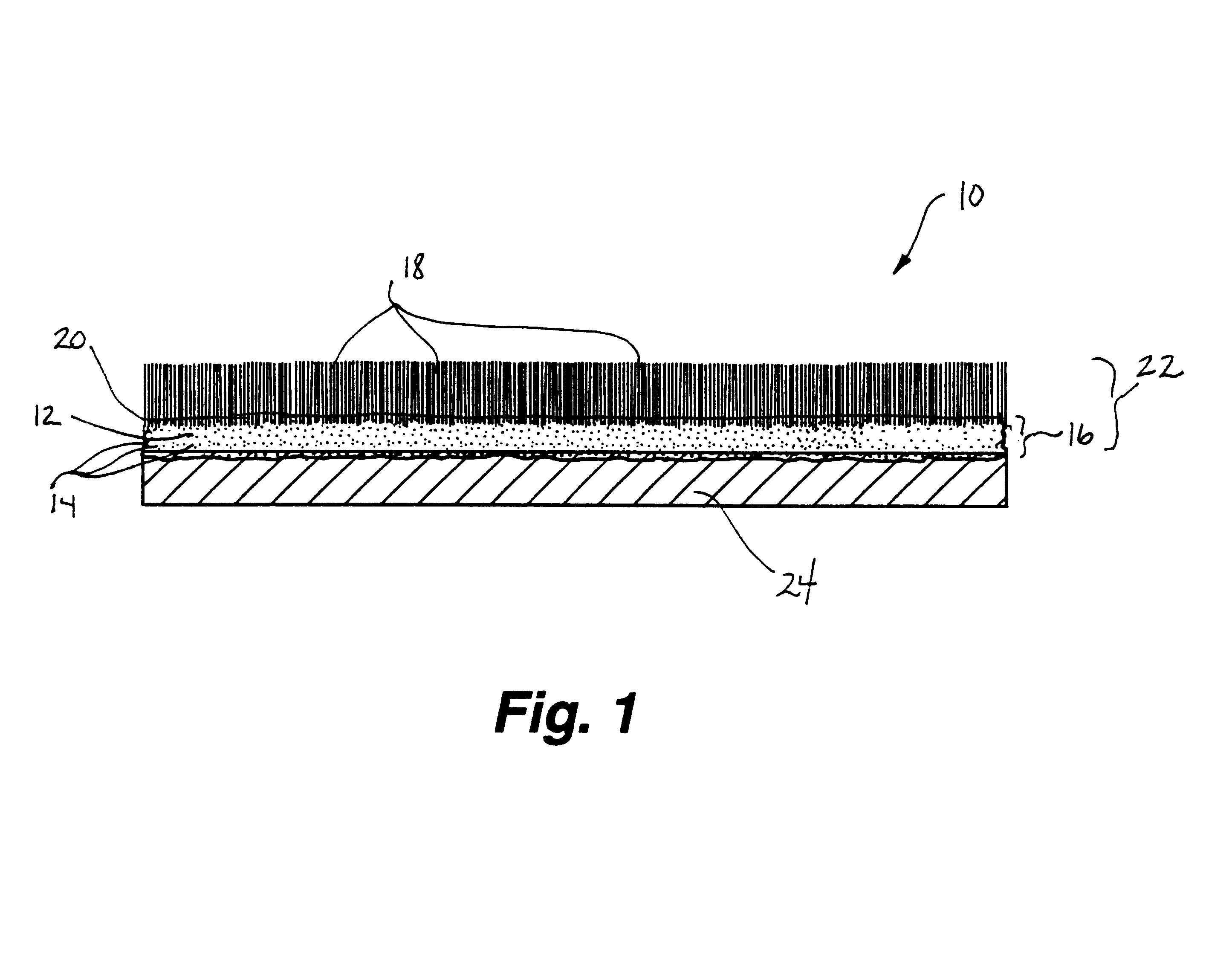
Fabric coating composition containing energy absorbing phase change material
InactiveUS6207738B1Solve the lack of densityReduce and eliminate heat transferHeat storage plantsFibre treatmentMicrosphereEnergy absorption
A coating composition for fabrics includes wetted microspheres containing a phase change material dispersed throughout a polymer binder, a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a thickener. Preferred phase change materials include paraffinic hydrocarbons. The microspheres may be microencapsulated. To prepare the coating composition, microspheres containing phase change material are wetted and dispersed in a dispersion in a water solution containing a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a polymer mixture. The coating is then applied to a fabric.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
Fabric coating containing energy absorbing phase change material and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6514362B1Evenly dispersedEqually distributedDecorative surface effectsHeat storage plantsMicrosphereEnergy absorption
A coating composition for fabrics includes wetted microspheres containing a phase change material dispersed throughout a polymer binder, a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a thickener. Preferred phase change materials include paraffinic hydrocarbons. The microspheres may be microencapsulated. To prepare the coating composition, microspheres containing phase change material are wetted and dispersed in a dispersion in a water solution containing a surfactant, a dispersant, an antifoam agent and a polymer mixture. The coating is then applied to a fabric. In an alternative embodiment, an extensible fabric is coated with an extensible binder containing microencapsulated phase change material to form an extensible, coated fabric. The coated fabric is optionally flocked. The coated fabrics are manufactured using transfer techniques.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
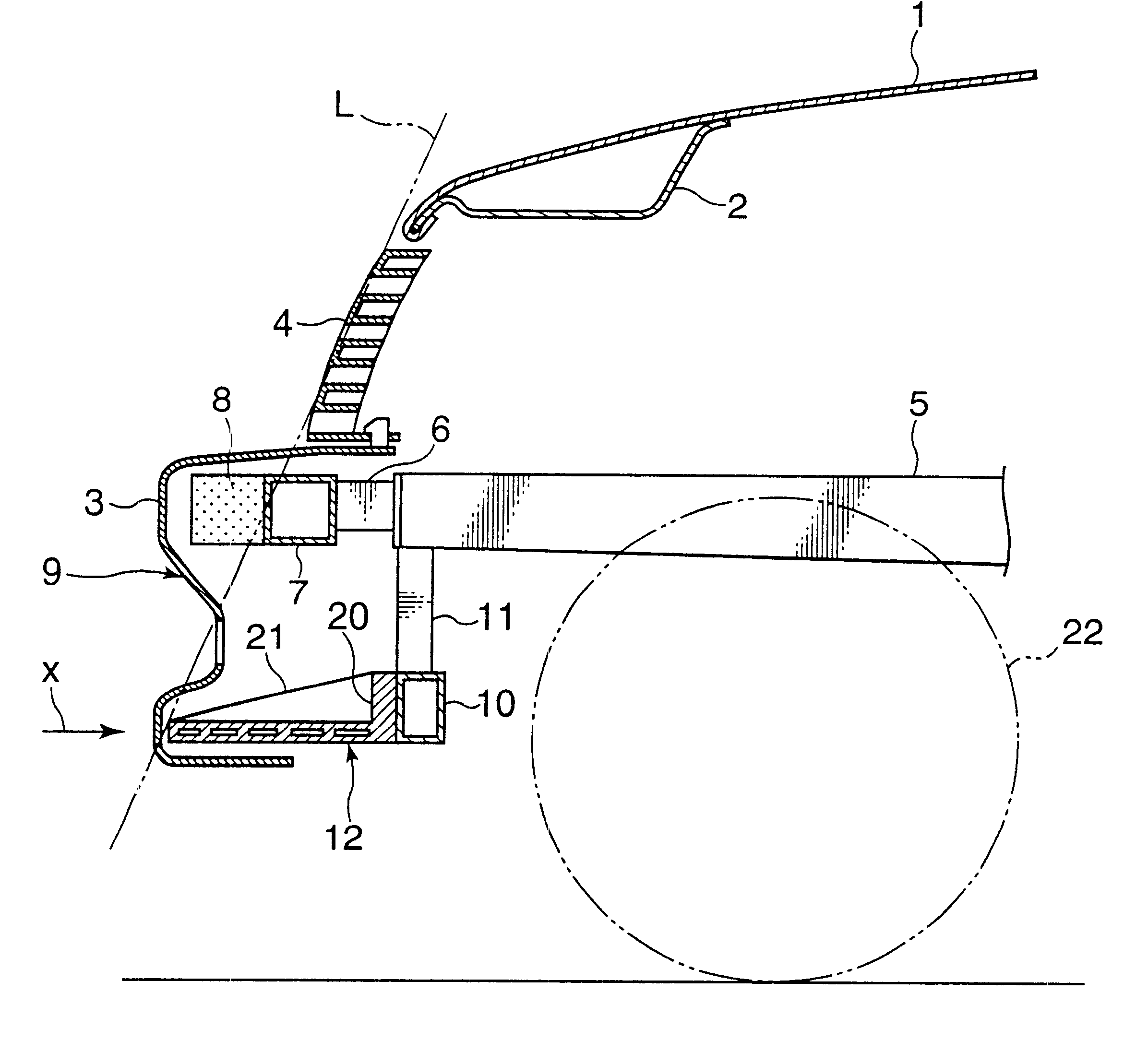
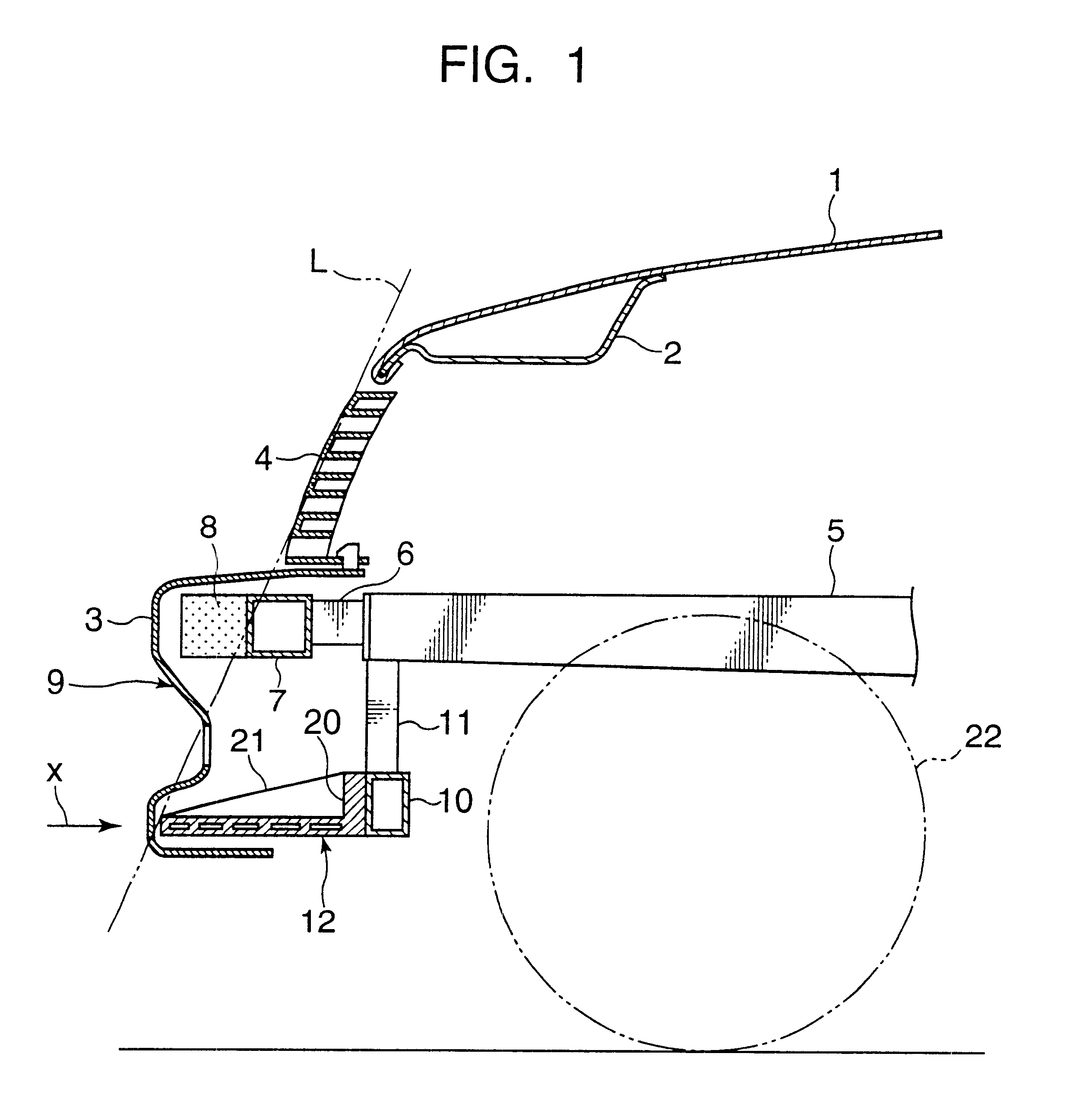
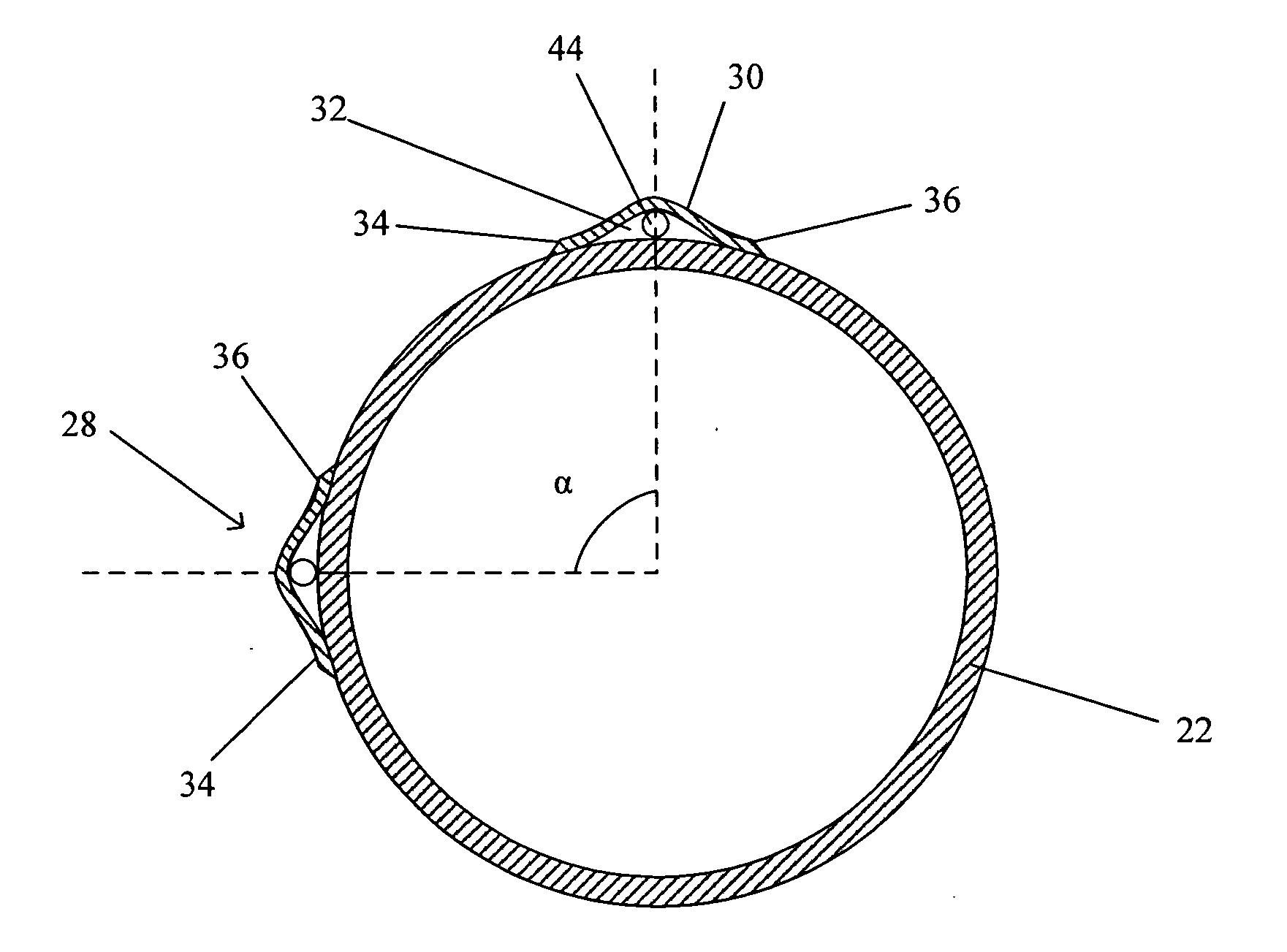
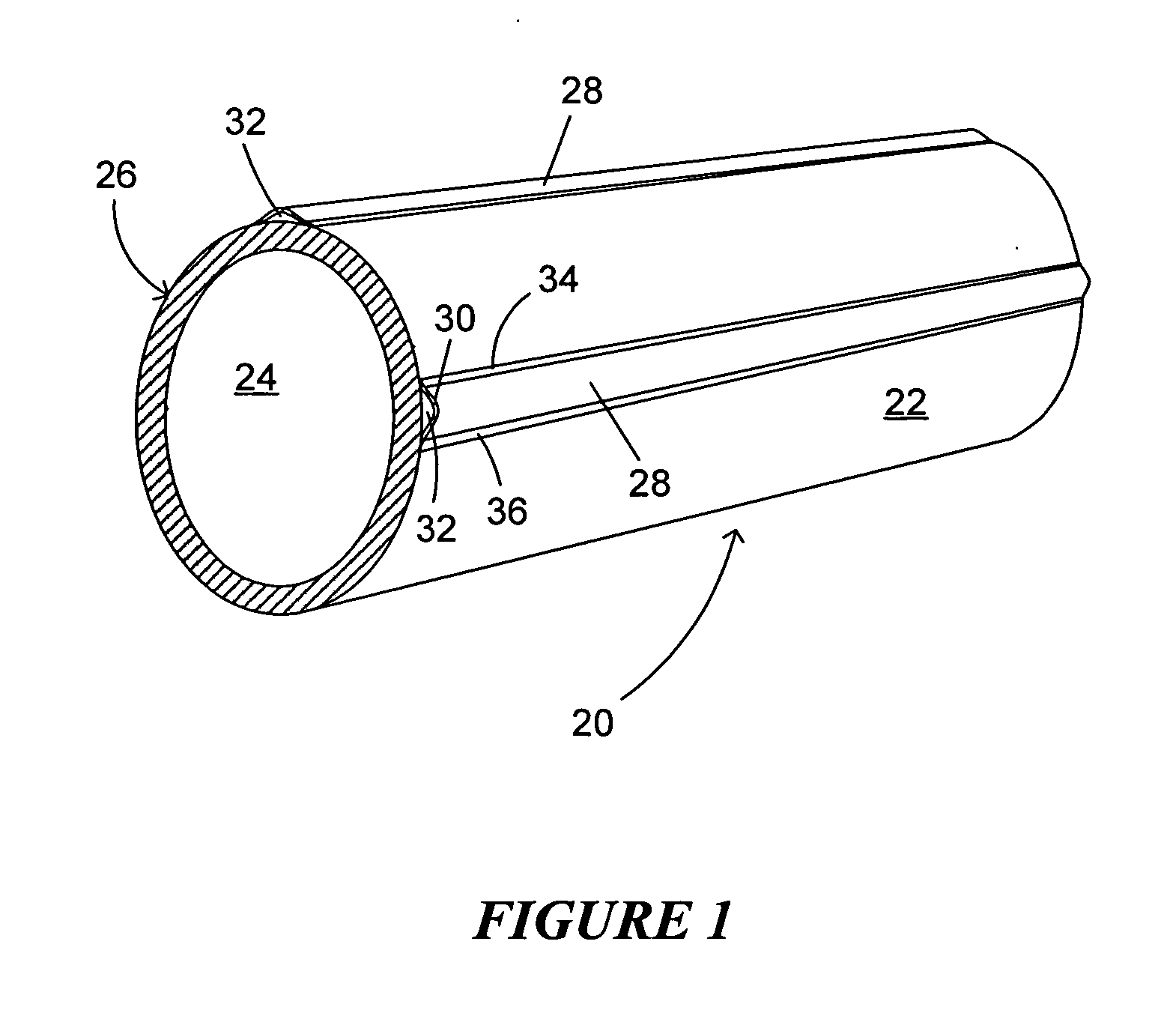
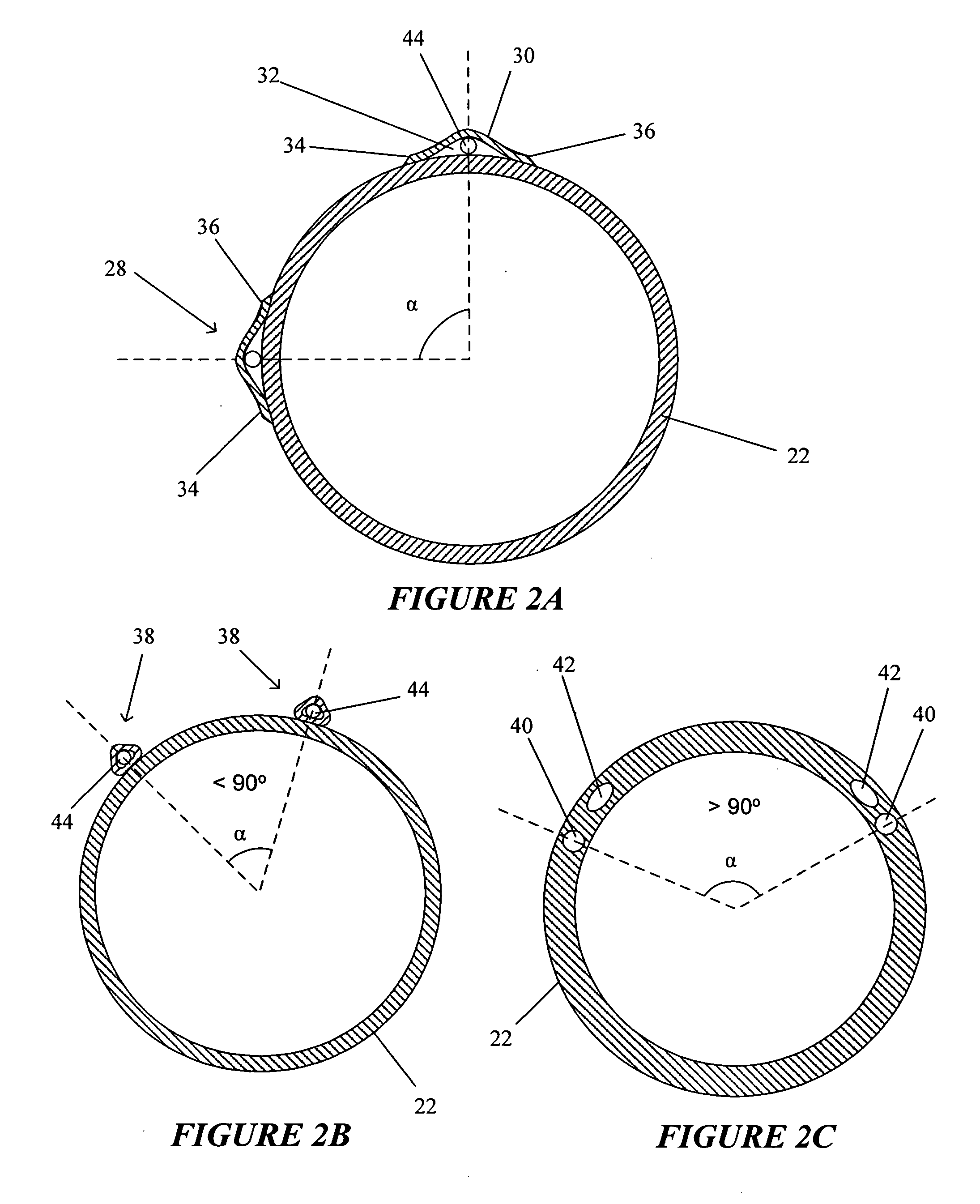
Structure of the front of a vehicle body
InactiveUS6540275B1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRailway wheel guards/bumpersEnergy absorptionEngineering
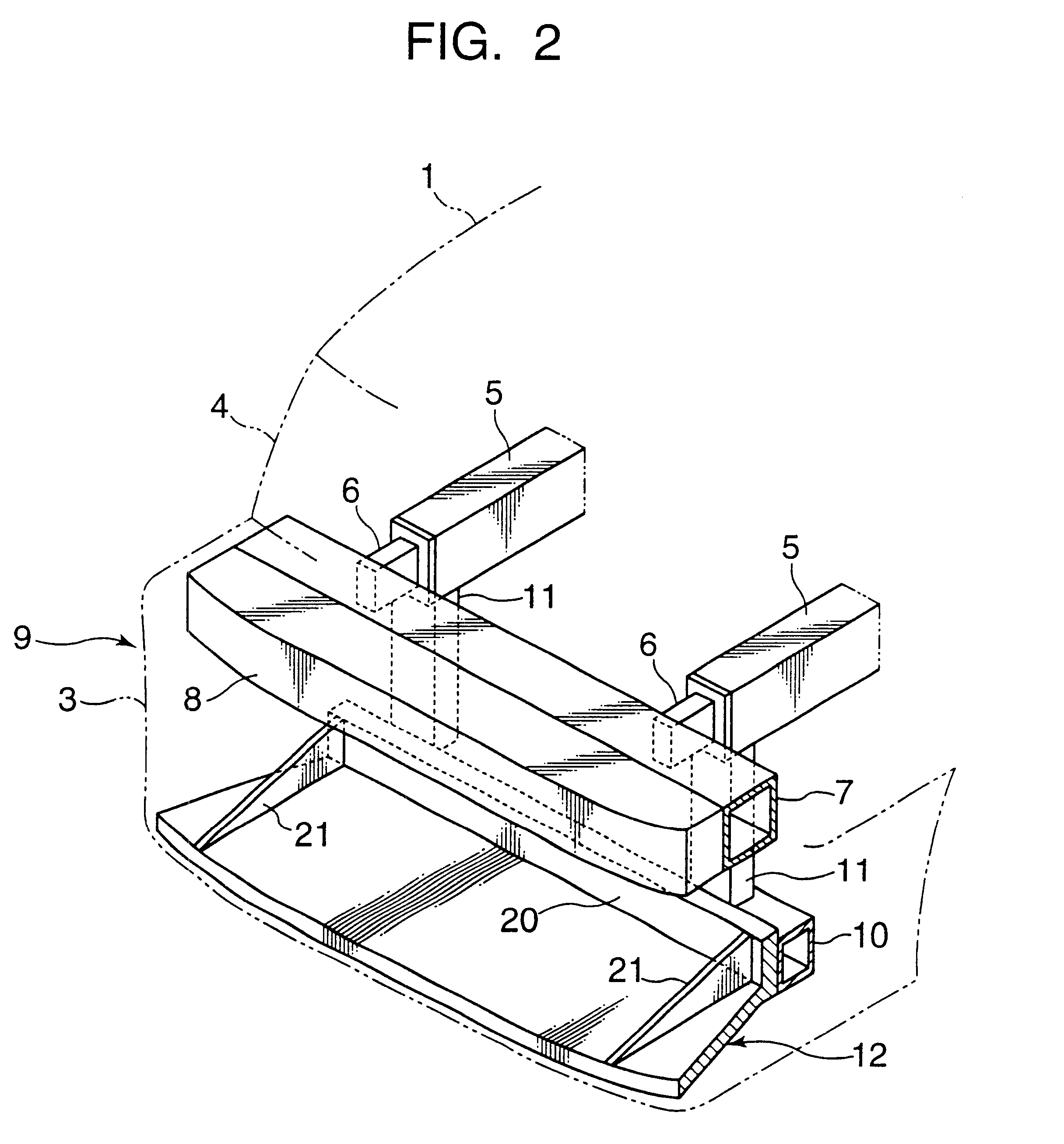
The invention provides a structure of a front part of a vehicle body that is simple and free from the risk of maloperation. In the event of a collision between the vehicle and a pedestrian, a projecting part sweeps the pedestrian by parts of his or her legs lower than the knees in the event of a collision between the vehicle and the pedestrian, causing the pedestrian to be thrown over toward the vehicle, and after an energy-absorbing member has absorbed impact energy exerted on the legs, the pedestrian is caused to drop onto the top of a hood and protected from secondary damage. In one specific example, a structure of a front part of a vehicle body in which a bumper (9) is provided at a lower front position of a hood (1) of the vehicle comprises a lateral supporting member (7) provided in the front part of the vehicle body and extending in the direction of vehicle width, an energy-absorbing member (8) provided ahead of the lateral supporting member (7), and a projecting part (12) provided at a lower part of the bumper 9 in such a manner that a forward end of the projecting part (12) juts out more frontward than the lateral supporting member (7).
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Reciprocating machine & other devices
InactiveUS20120227389A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyLiquid coolingCasingsCombustionReciprocating motion
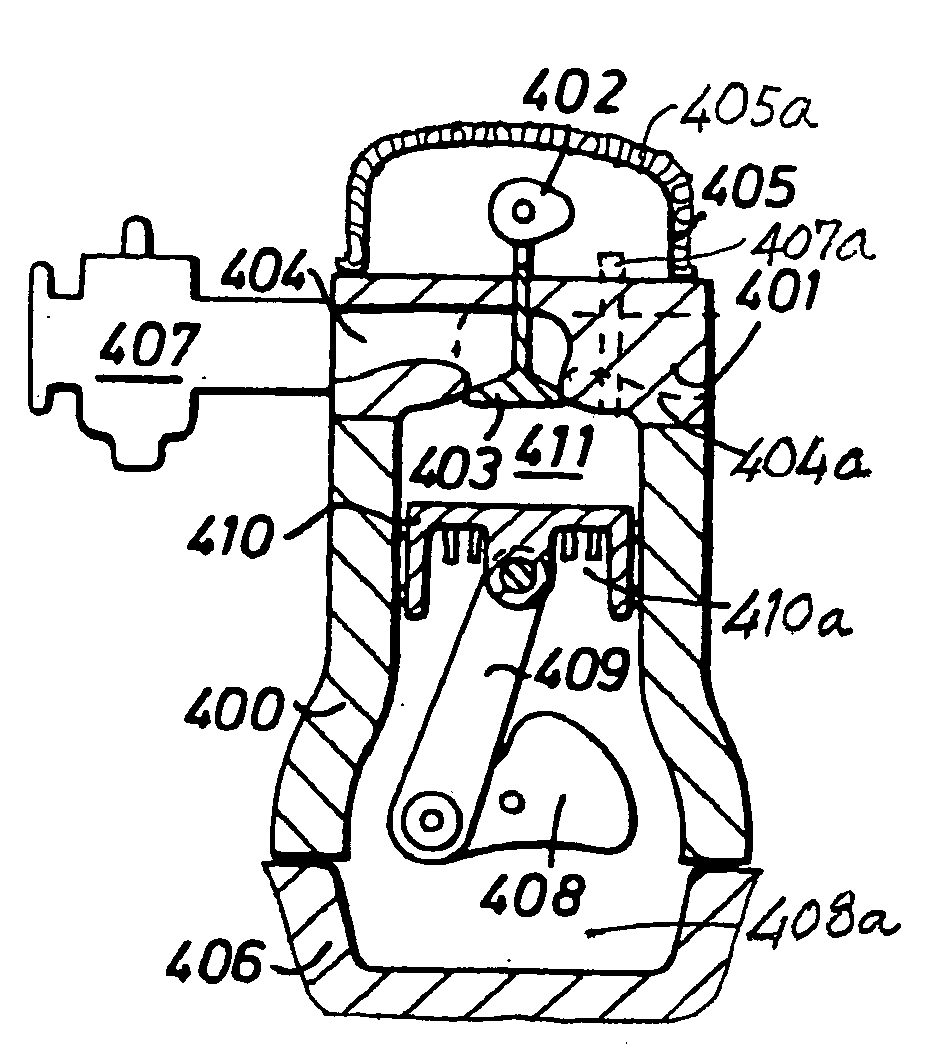
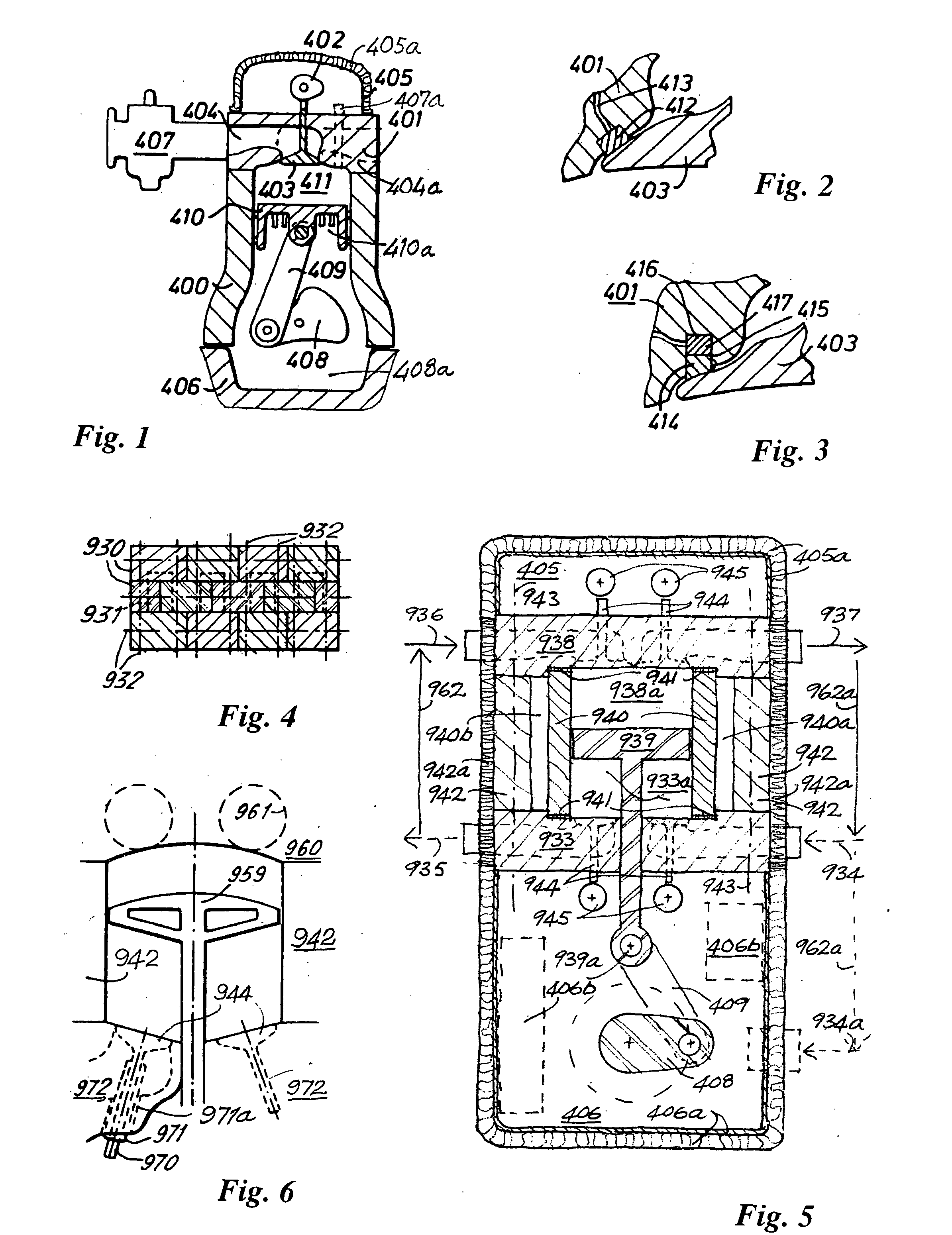
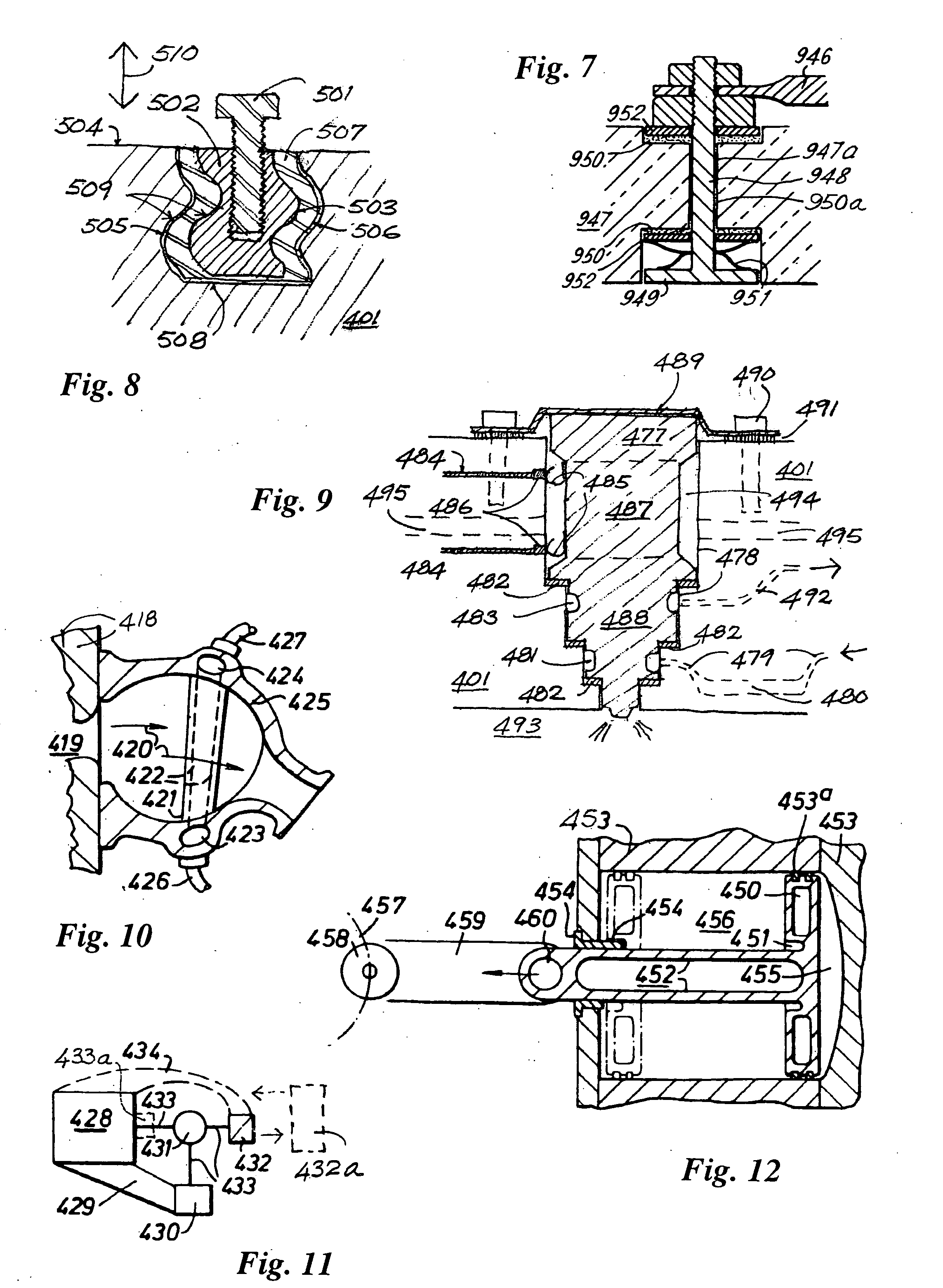
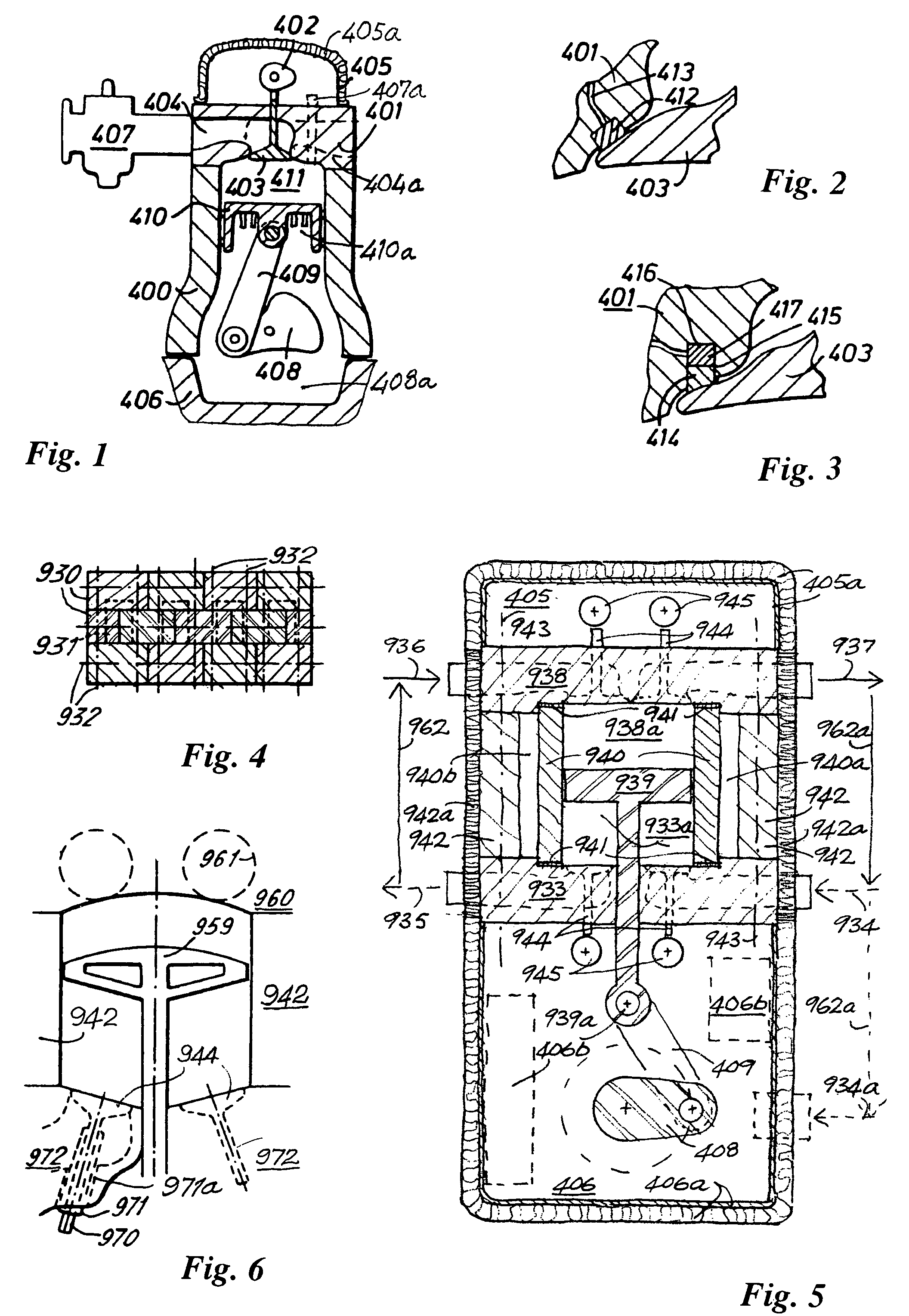
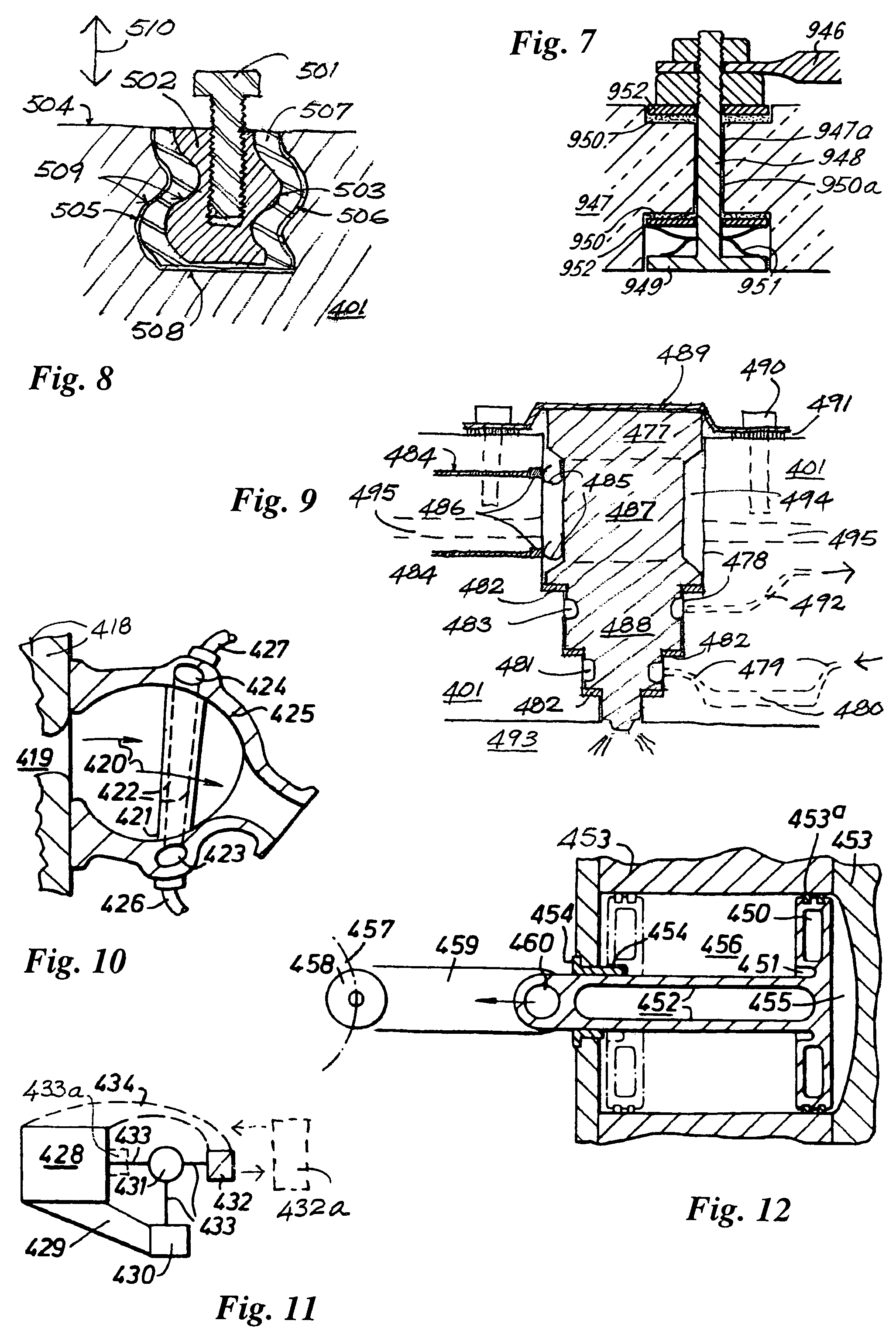
The disclosure relates to reciprocating fluid working devices including internal combustion engines, compressors and pumps. A number of arrangements for pistons and cylinders of unconventional configuration are described, mostly intended for use in IC engines operating without cooling. Included are toroidal combustion or working chambers, some with fluid flow through the core of the toroid, a single piston reciprocating between a pair of working chambers, tensile valve actuation, tensile links between piston and crankshaft, energy absorbing piston-crank links, crankshafts supported on gas bearings, cylinders rotating in housings, injectors having components which reciprocate or rotate during fuel delivery. In some embodiments pistons mare rotate while reciprocating. High temperature exhaust emissions systems are described, including those containing filamentary material, as are procedures for reducing emissions during cold start by means of valves at reaction volume exit. Also disclosed are improved vehicles, aircraft, marine craft, transmissions and exhaust emission systems suited to the engines of the invention.
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
Reciprocating devices
ActiveUS20080141921A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEnergy absorption
The disclosure relates to fluid working devices including reciprocating internal combustion engines, compressors and pumps. A number of arrangements for pistons and cylinders of unconventional configuration are described, mostly intended for use in reciprocating internal combustion IC engines operating without cooling. Included are toroidal combustion or working chambers, some with fluid flow through the core of the toroid, pistons reciprocating between pairs of working chambers, tensile valve actuation, tensile links between piston and crankshaft, energy absorbing piston-crank links, crankshafts supported on gas bearings, cylinders rotating in housings, injectors having components reciprocate or rotate during fuel delivery. In some embodiments pistons mare rotate while reciprocating. High temperature exhaust emissions systems are described, including those containing filamentary material, as are procedures for reducing emissions during cold start by means of valves at reaction volume exit. Compound engines having the new engines as a reciprocating stage are described. Improved vehicles, aircraft, marine craft and transmissions adapted to receive or be linked to the improved IV engines are also disclosed.
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
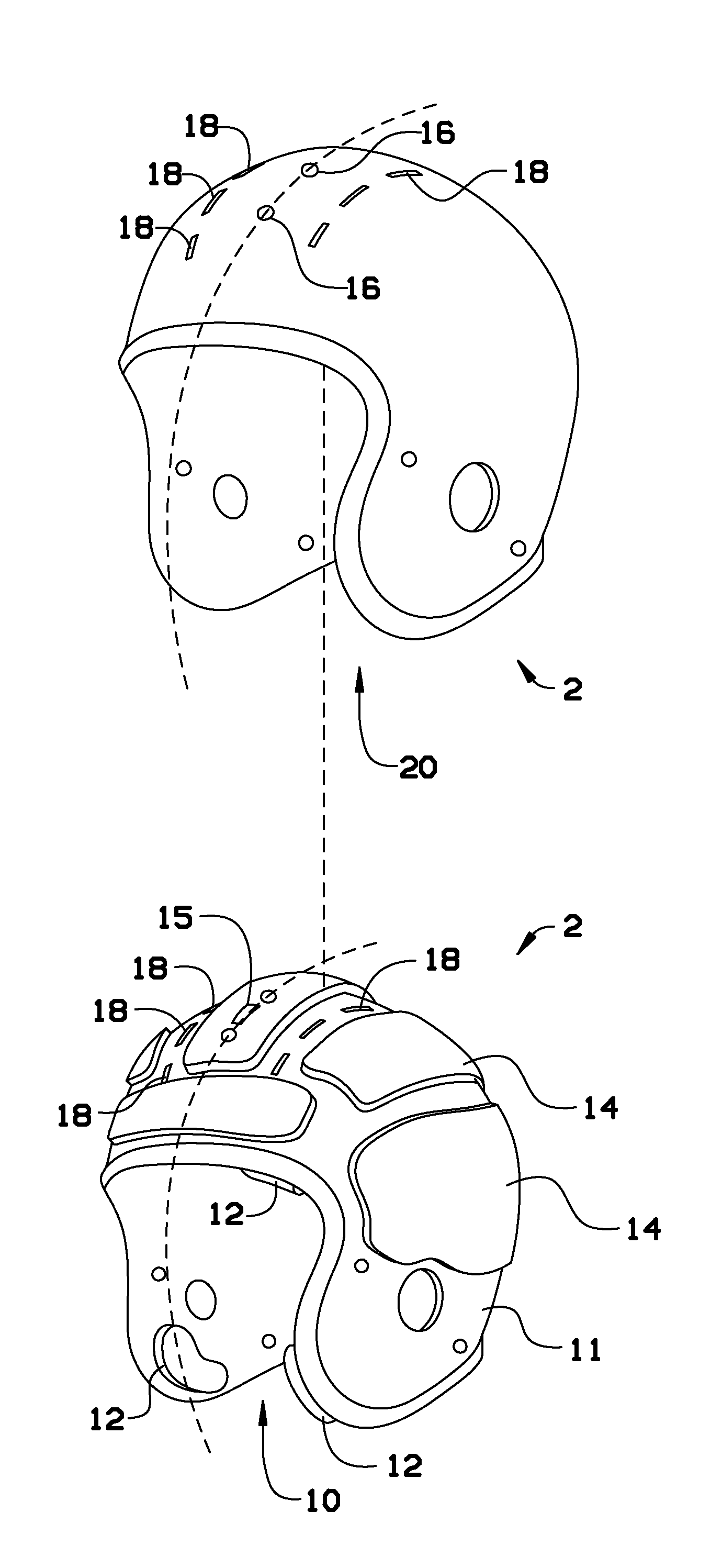
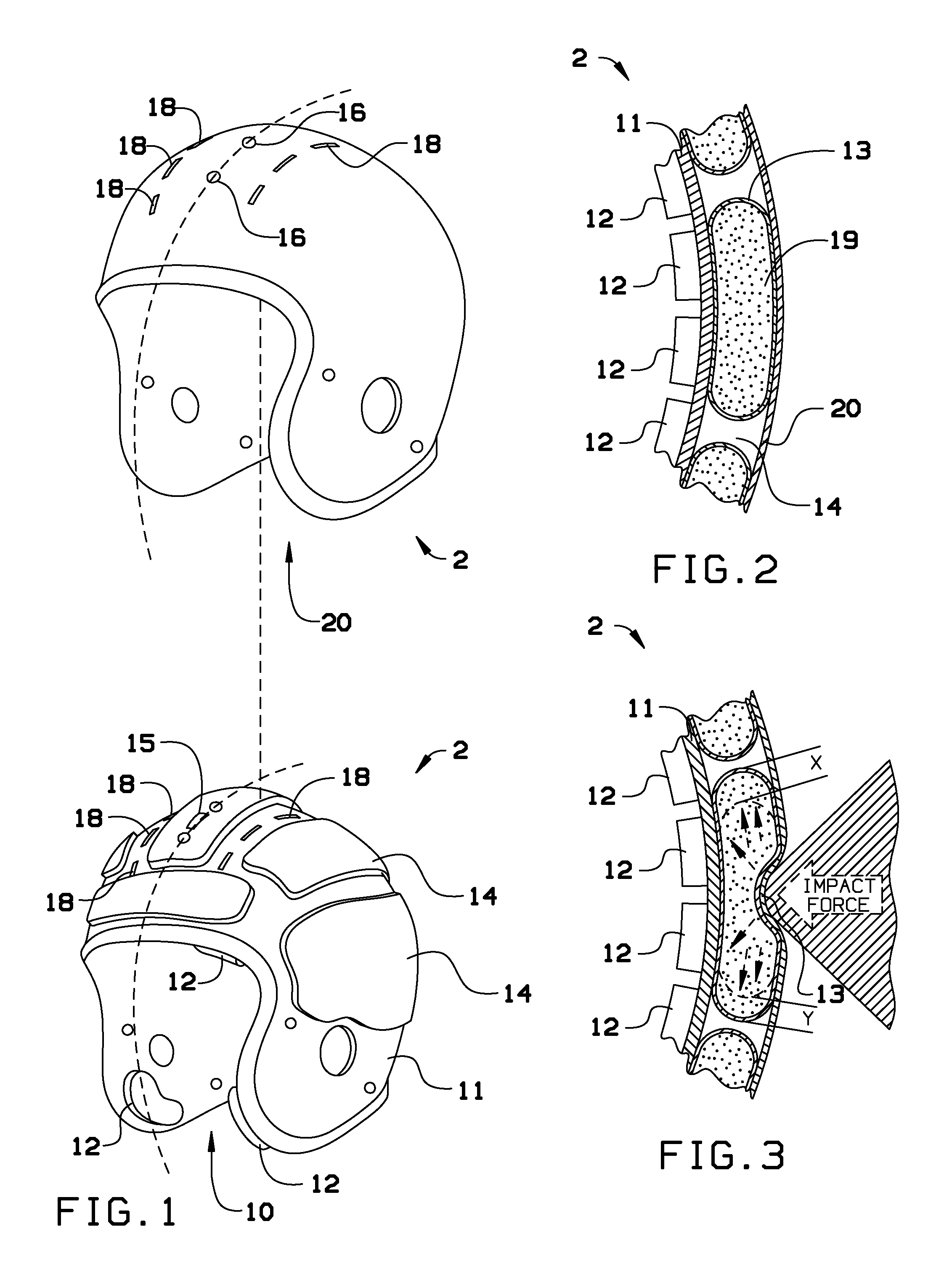
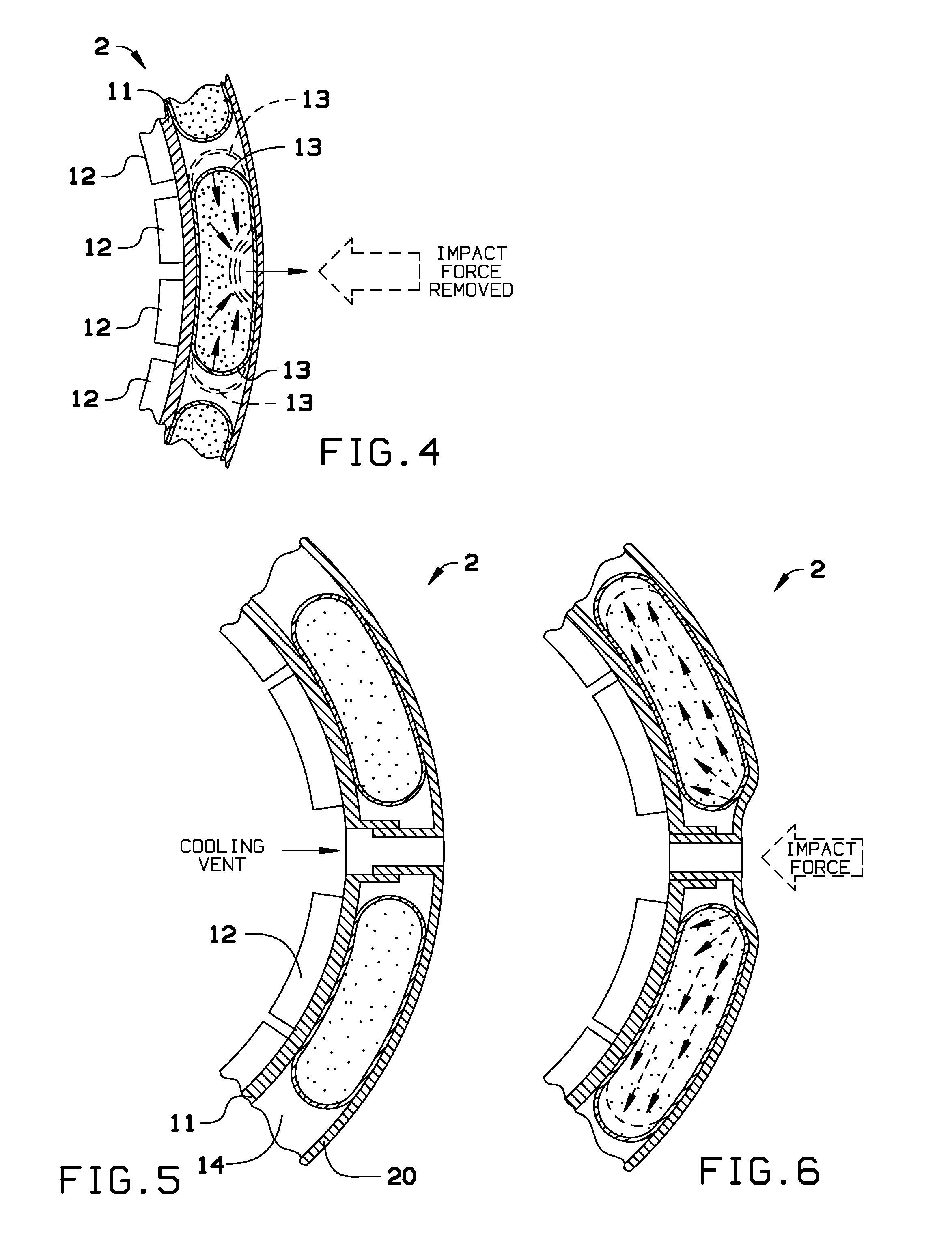
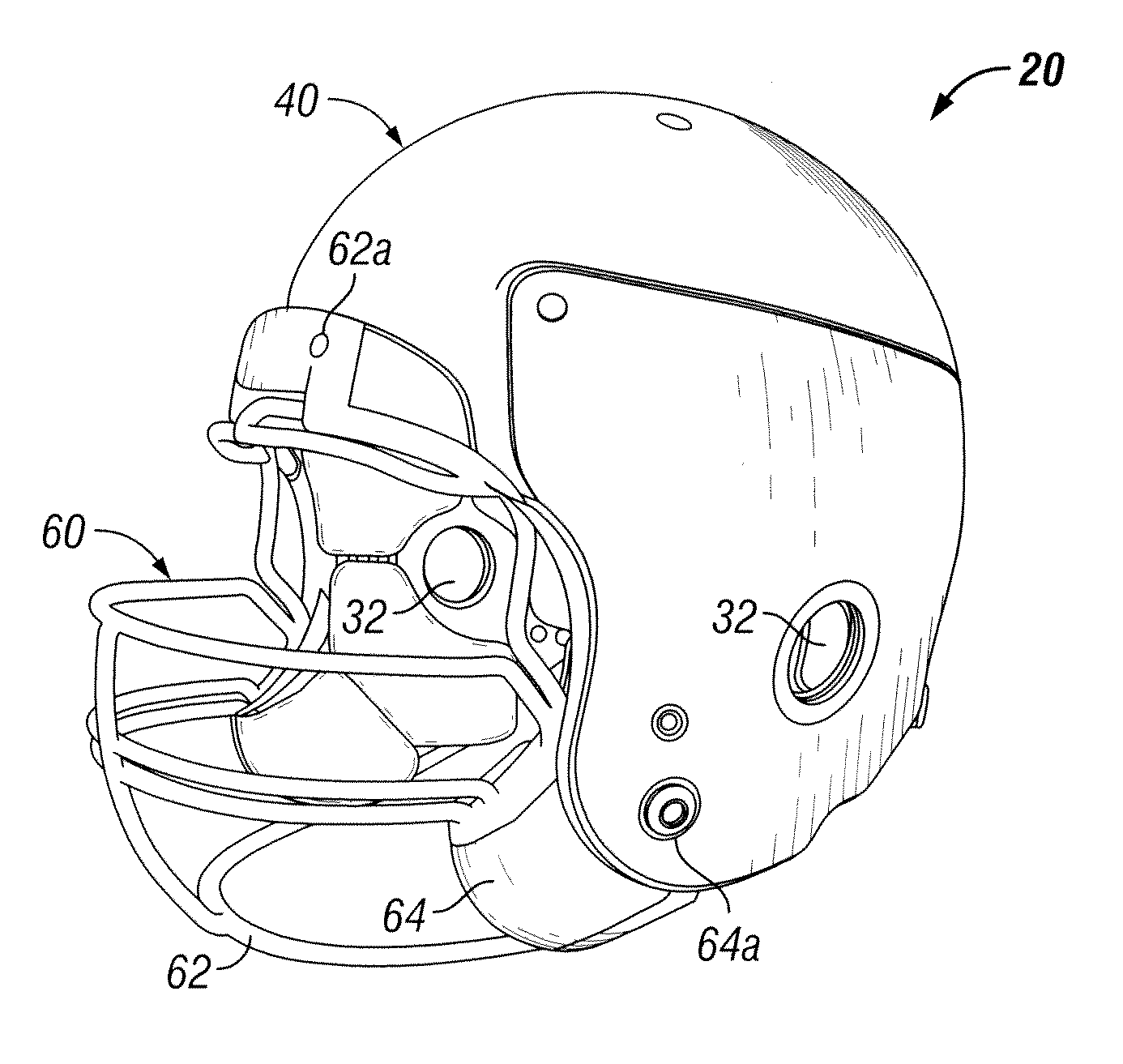
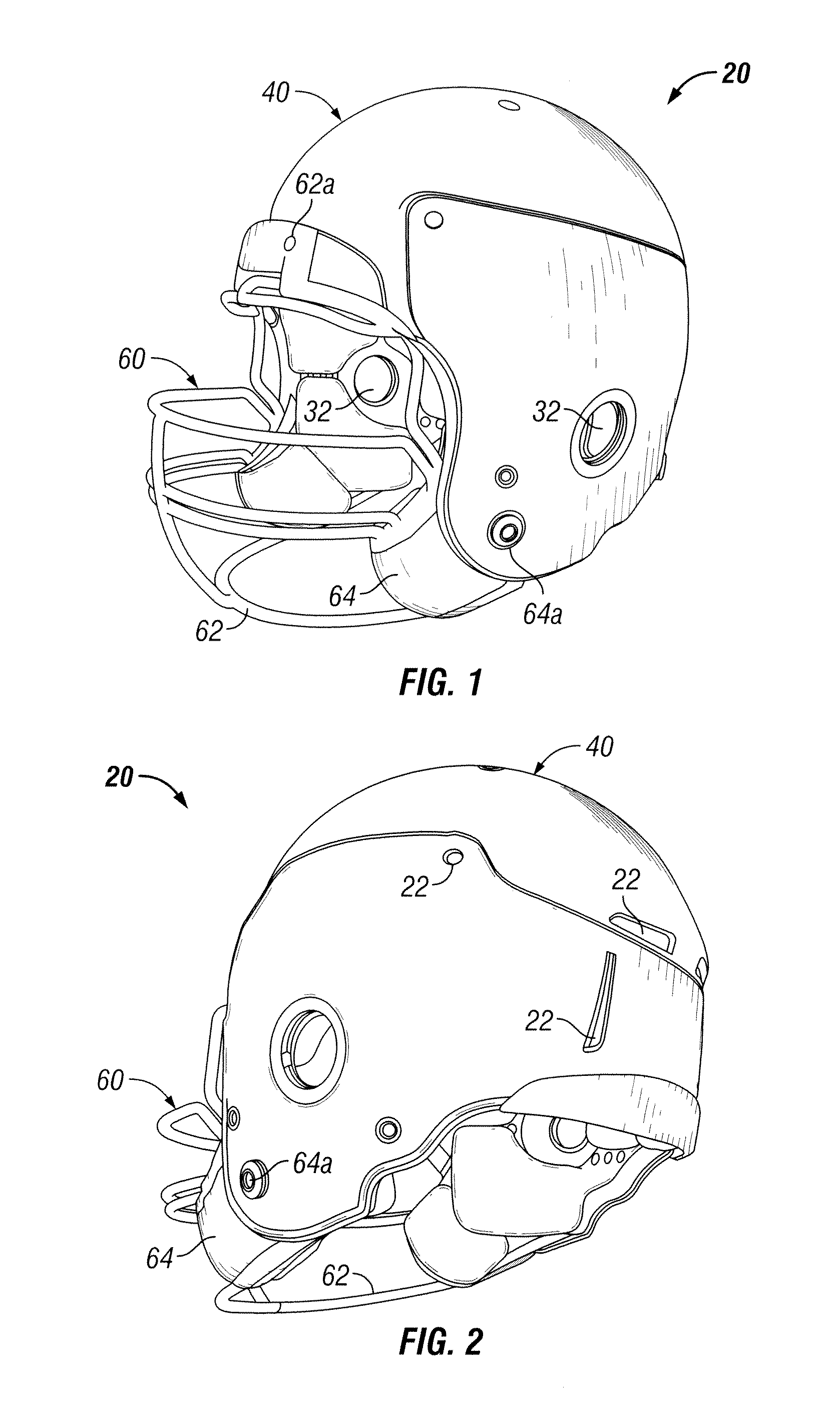
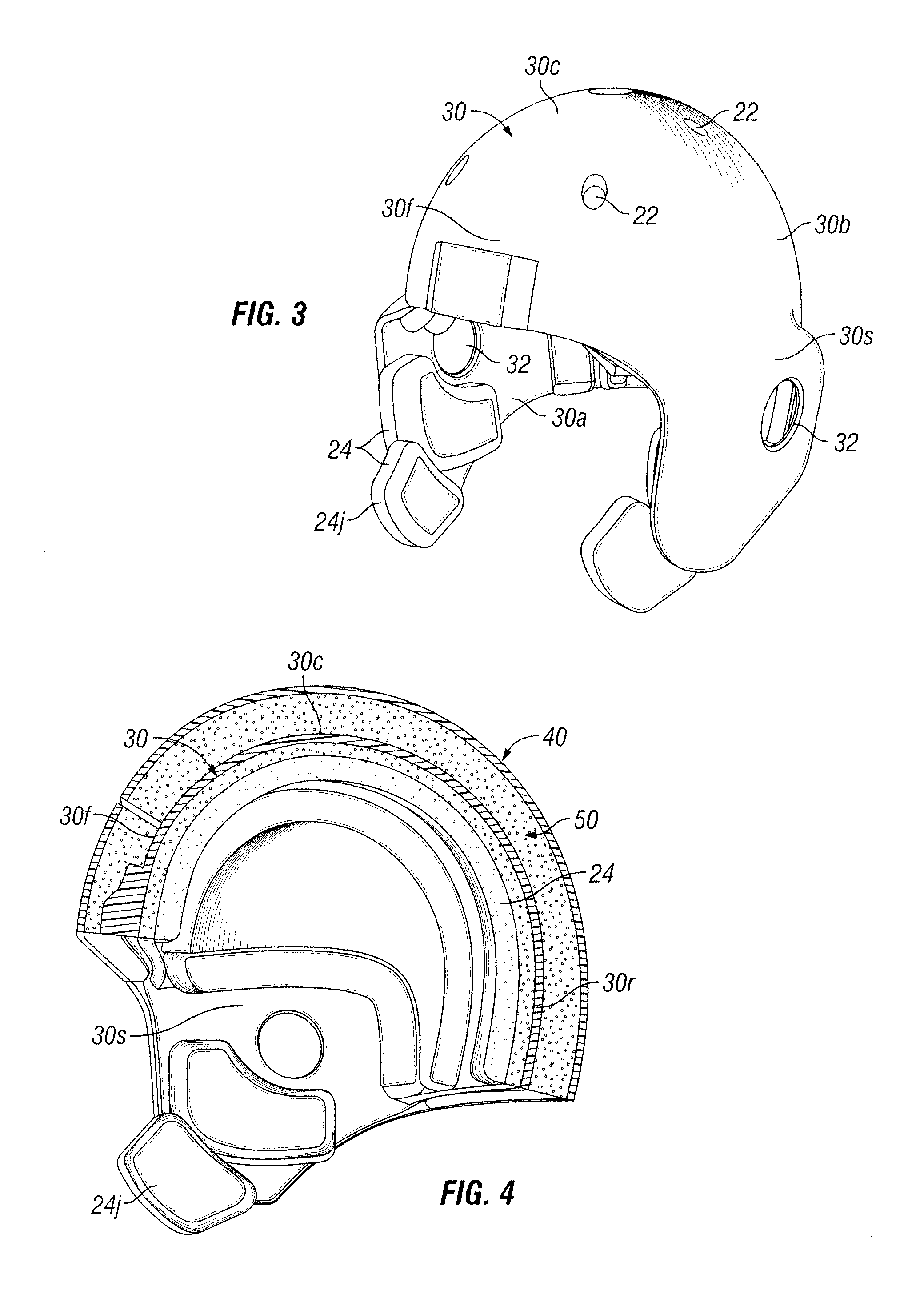
Method and apparatus for an adaptive impact absorbing helmet system
A method and apparatus for construction of a protective head covering (helmet) to be worn by individuals engaged in activity that may, without the apparatus, cause concussive brain injury. The helmet, which is comparable in weight and envelope to conventional helmets, can be constructed from commercially available materials. The design features a dual shell concept where outer shell deflection under load triggers the primary attenuation mechanism. A second more rigid inner shell defines a space where one or more compartmentalized sealed elastomer energy absorbing cells are located. These cells contain either a gas or liquid agent designed to adaptively convert potentially injurious normal impact force energy to energy that is channeled between the shells and therefore harmless to the wearer. A portion of this converted energy will be stored and then utilized to automatically re-set the apparatus for the next impact event.
Owner:VEAZIE WALDEMAR
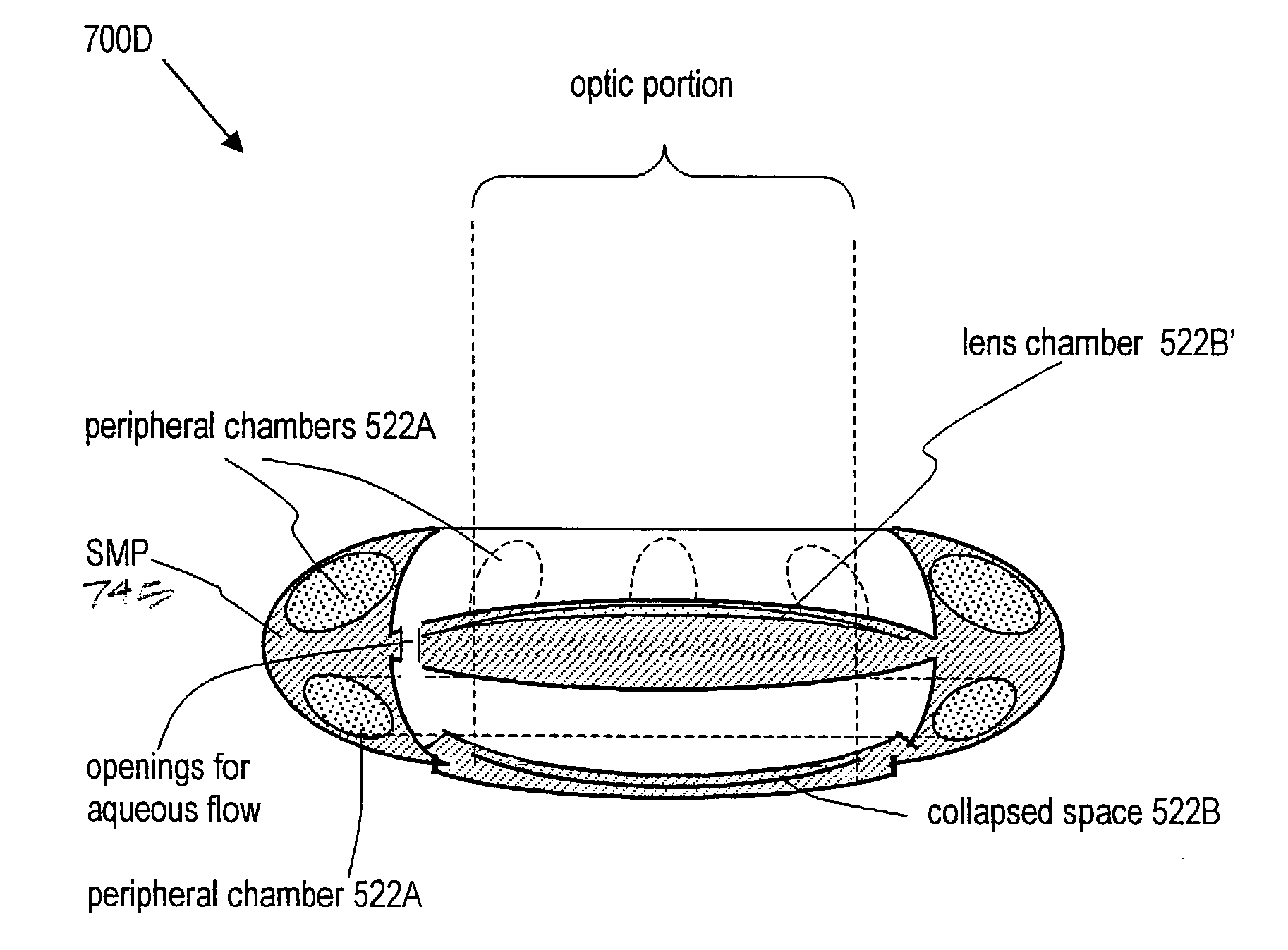
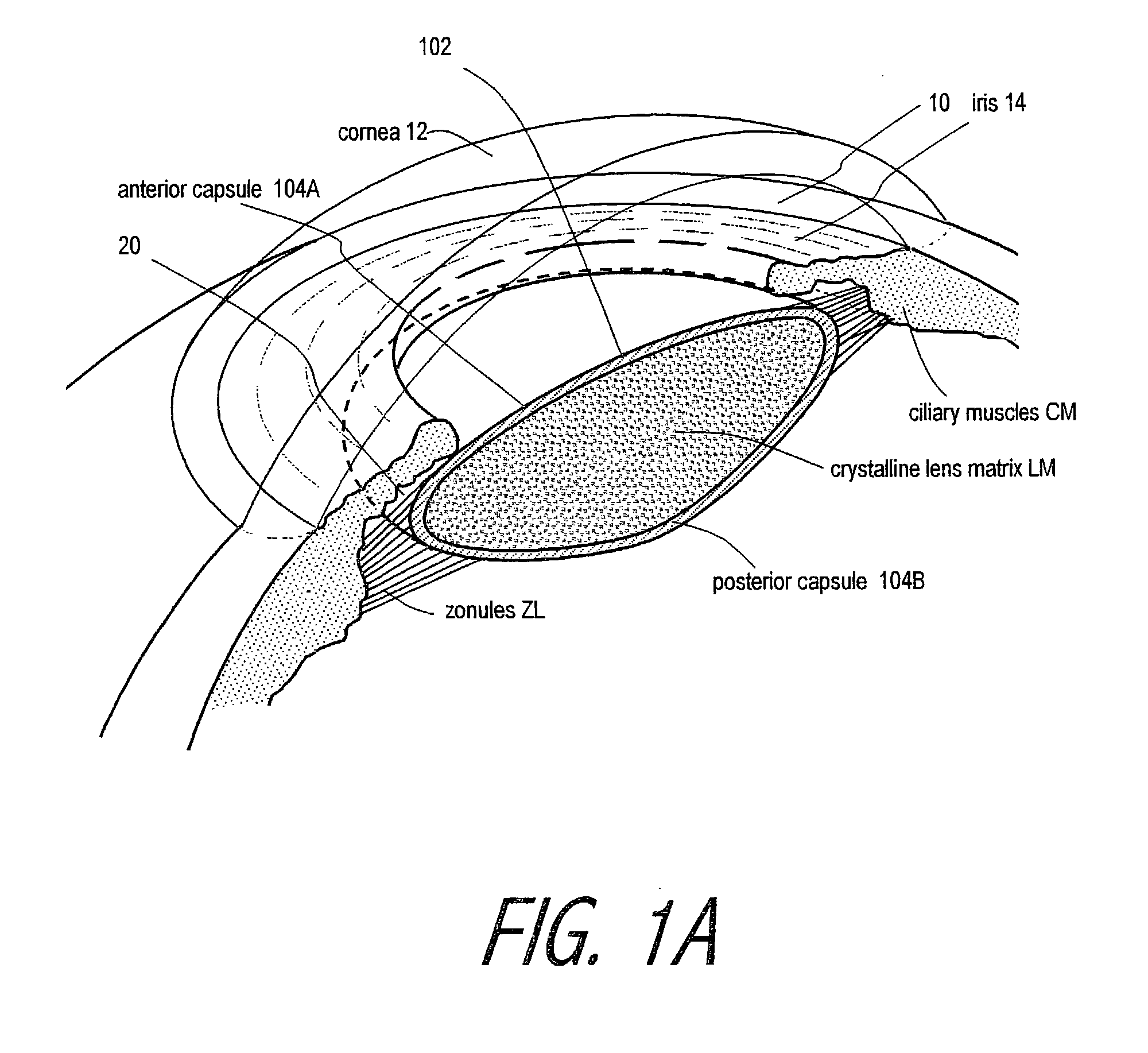
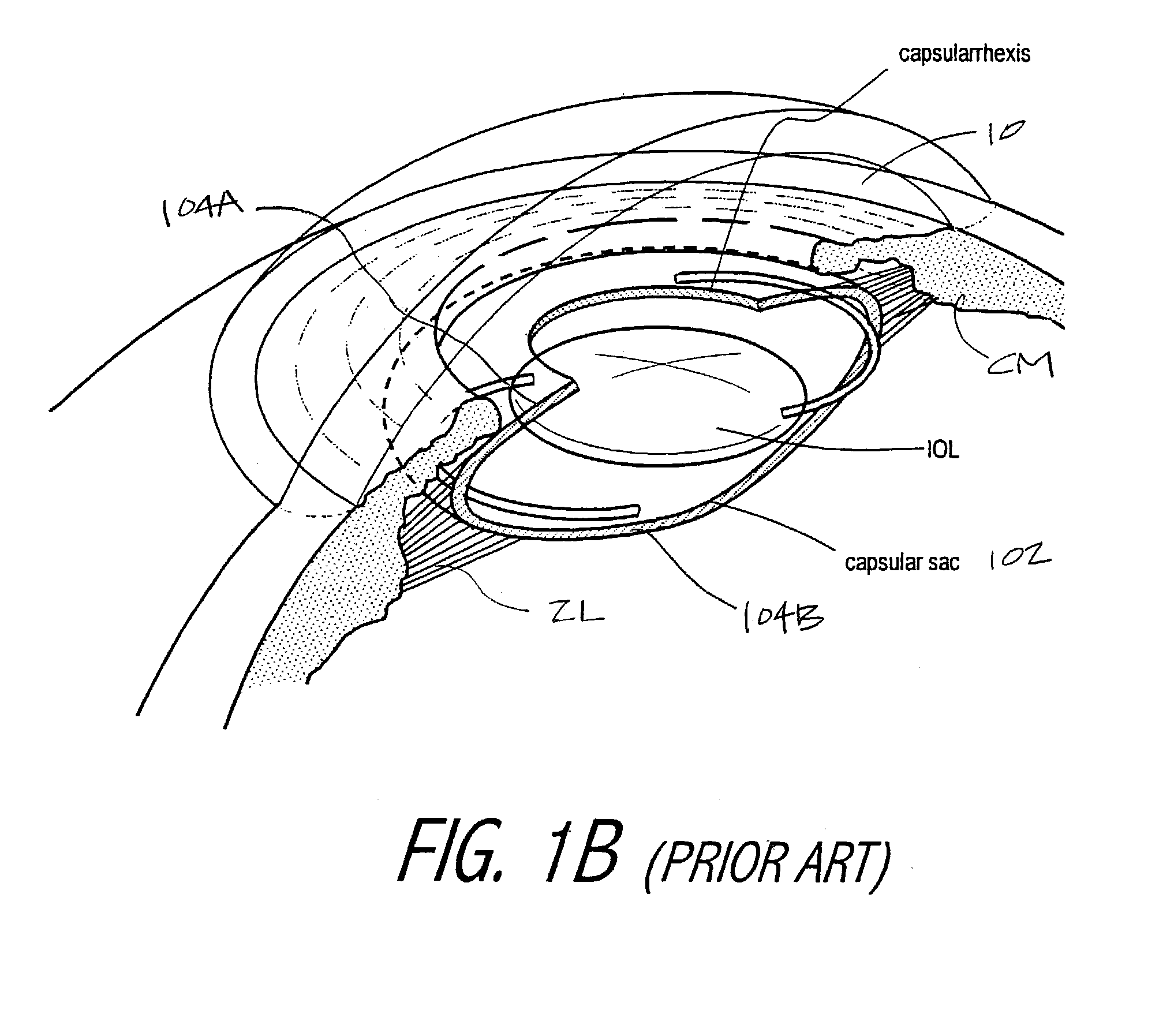
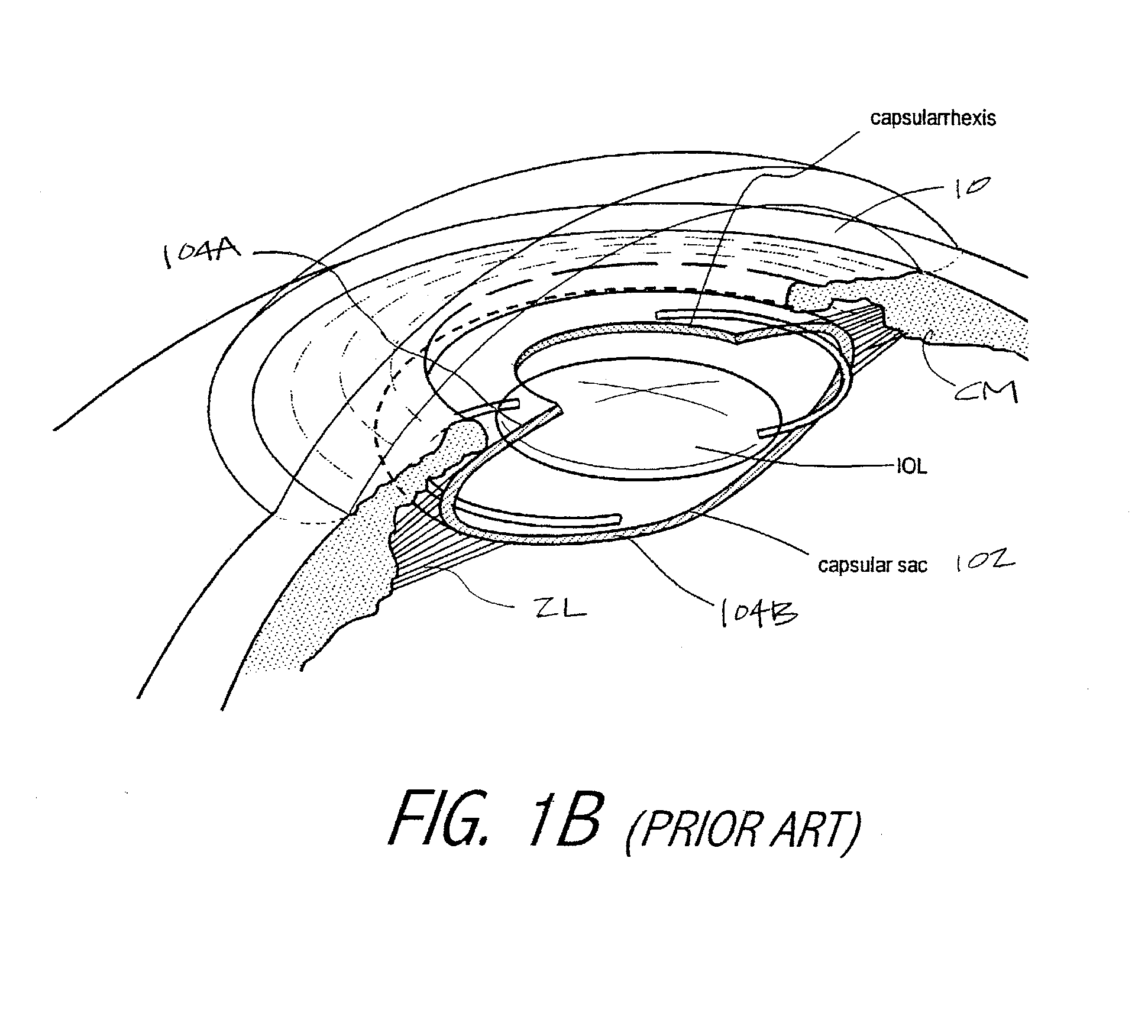
Intraocular implant devices
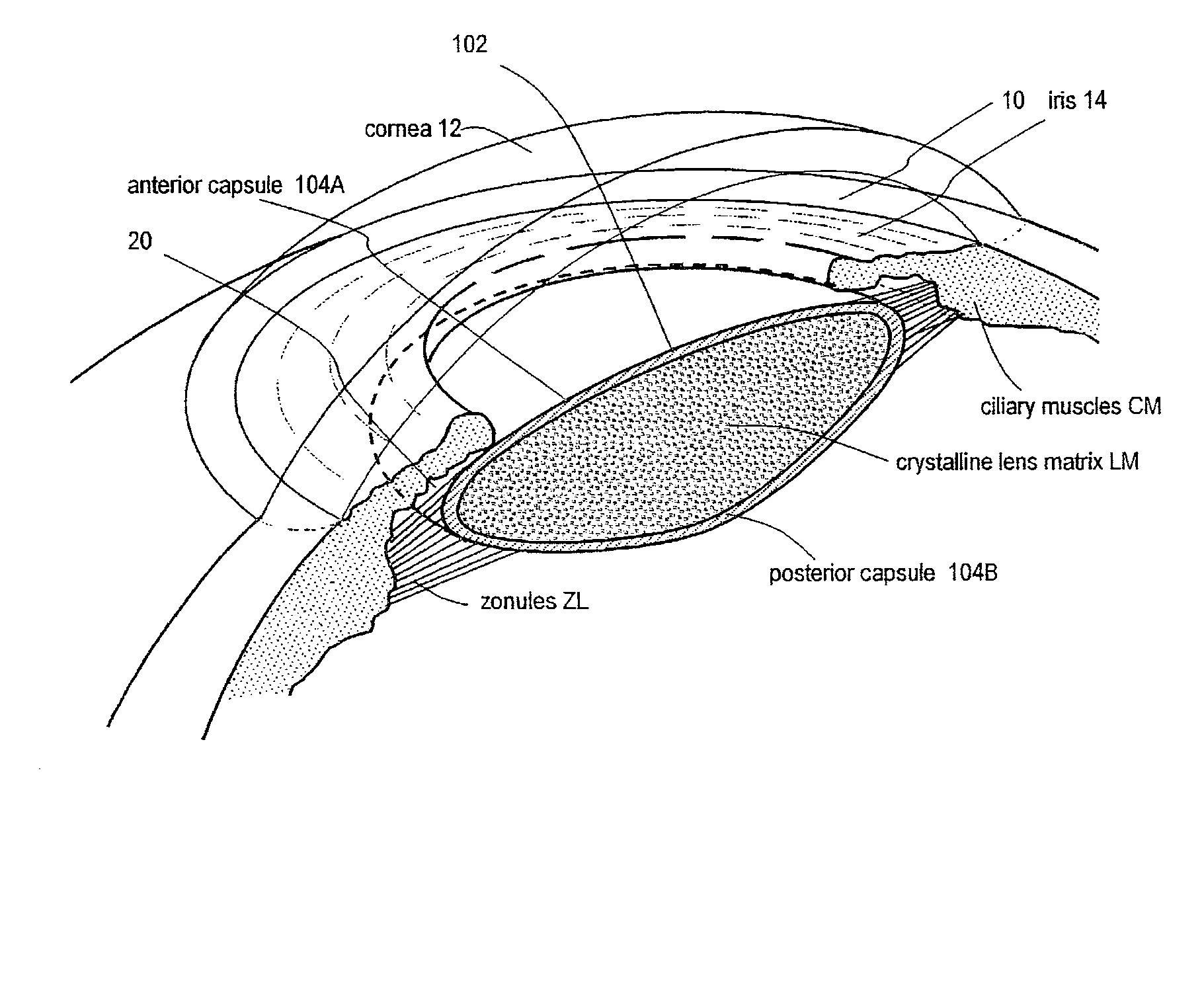
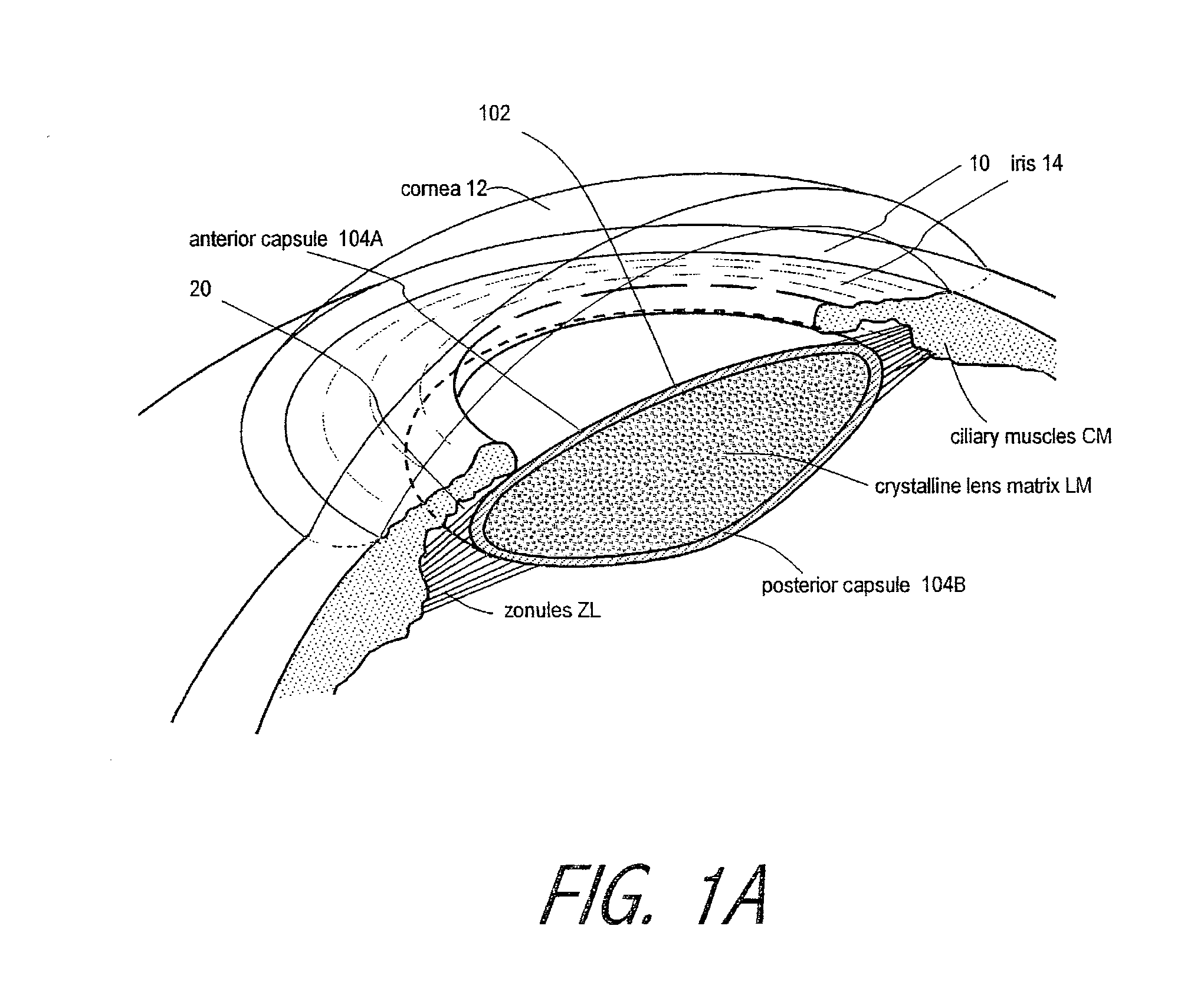
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
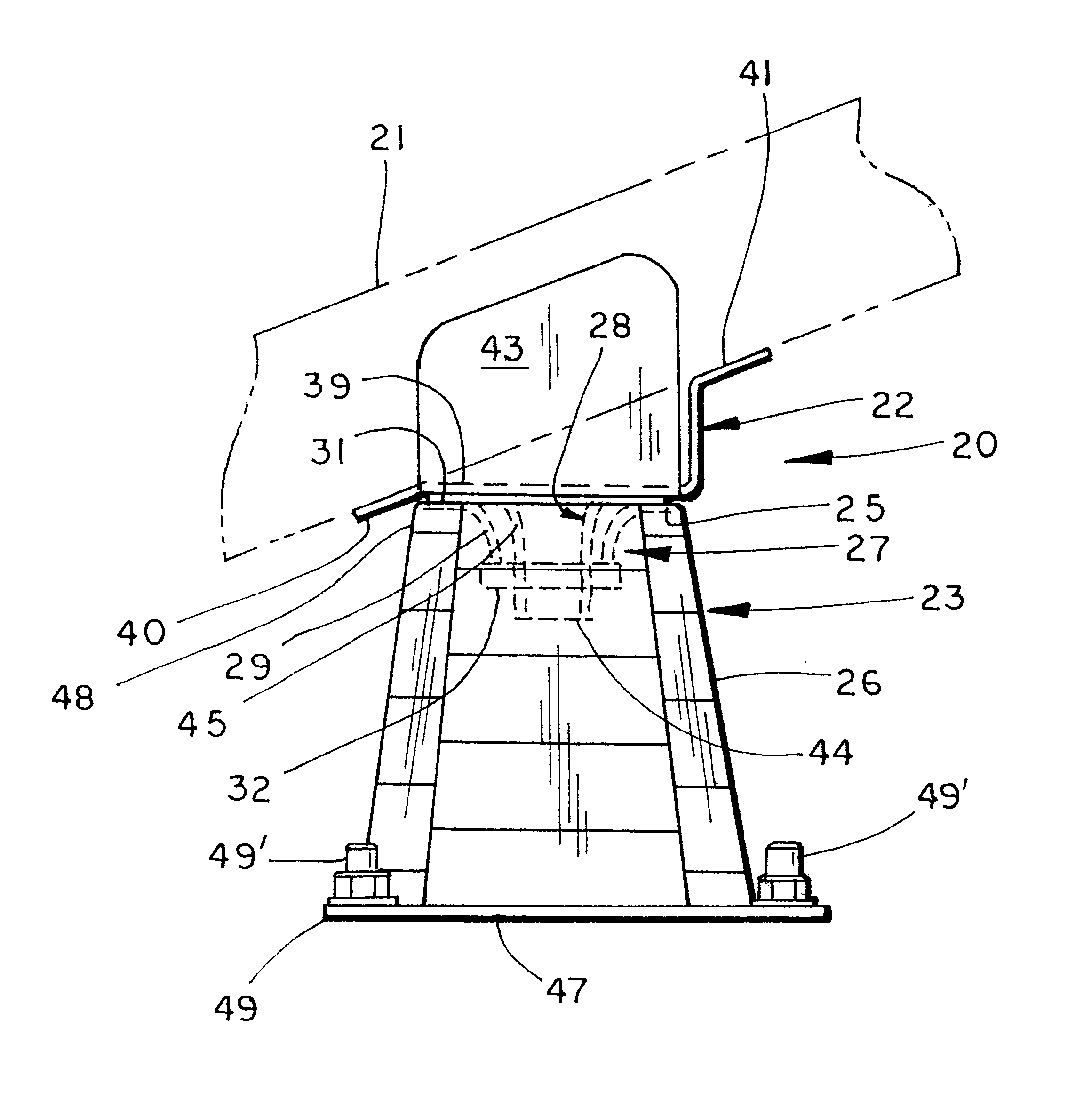
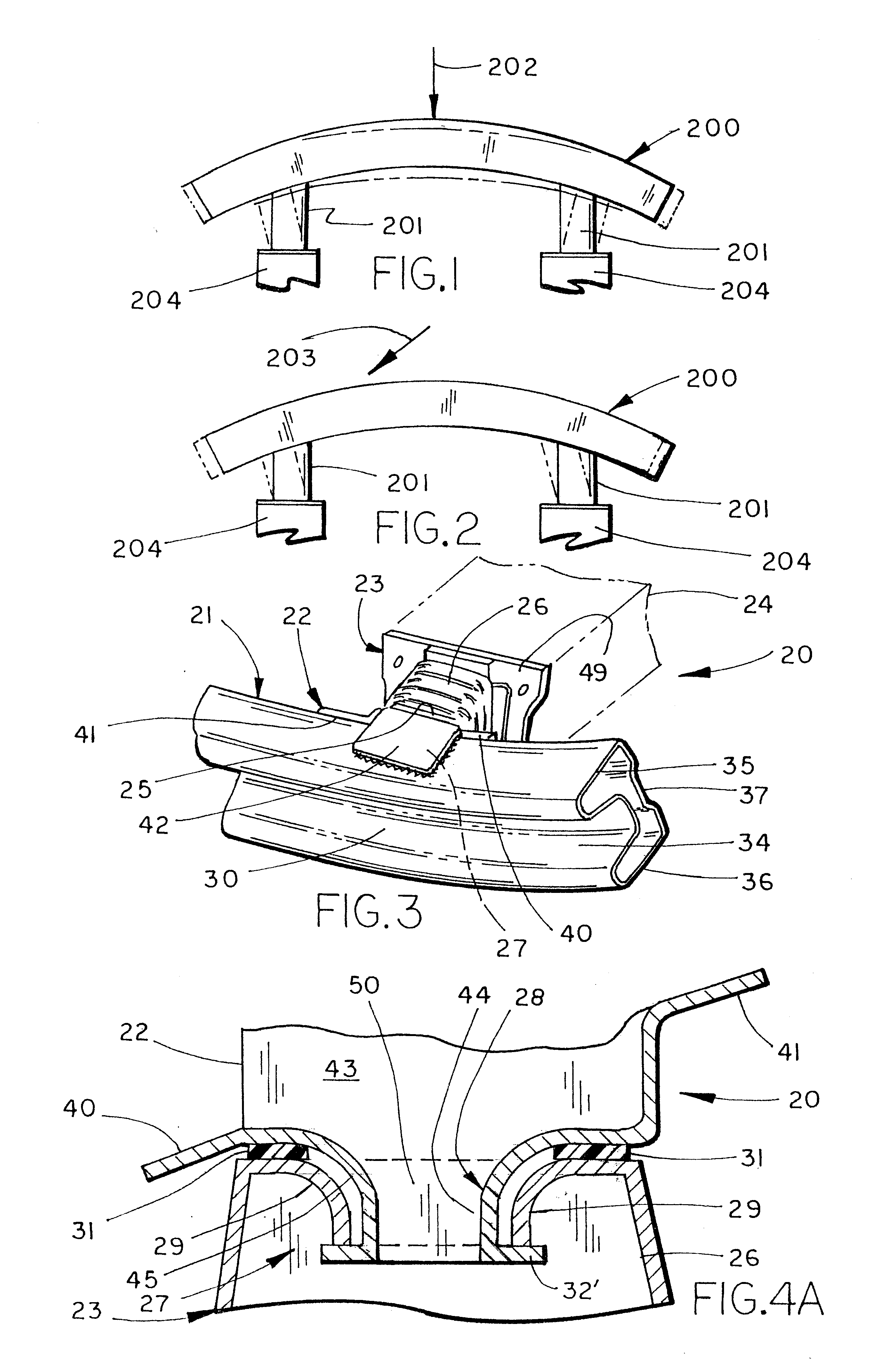
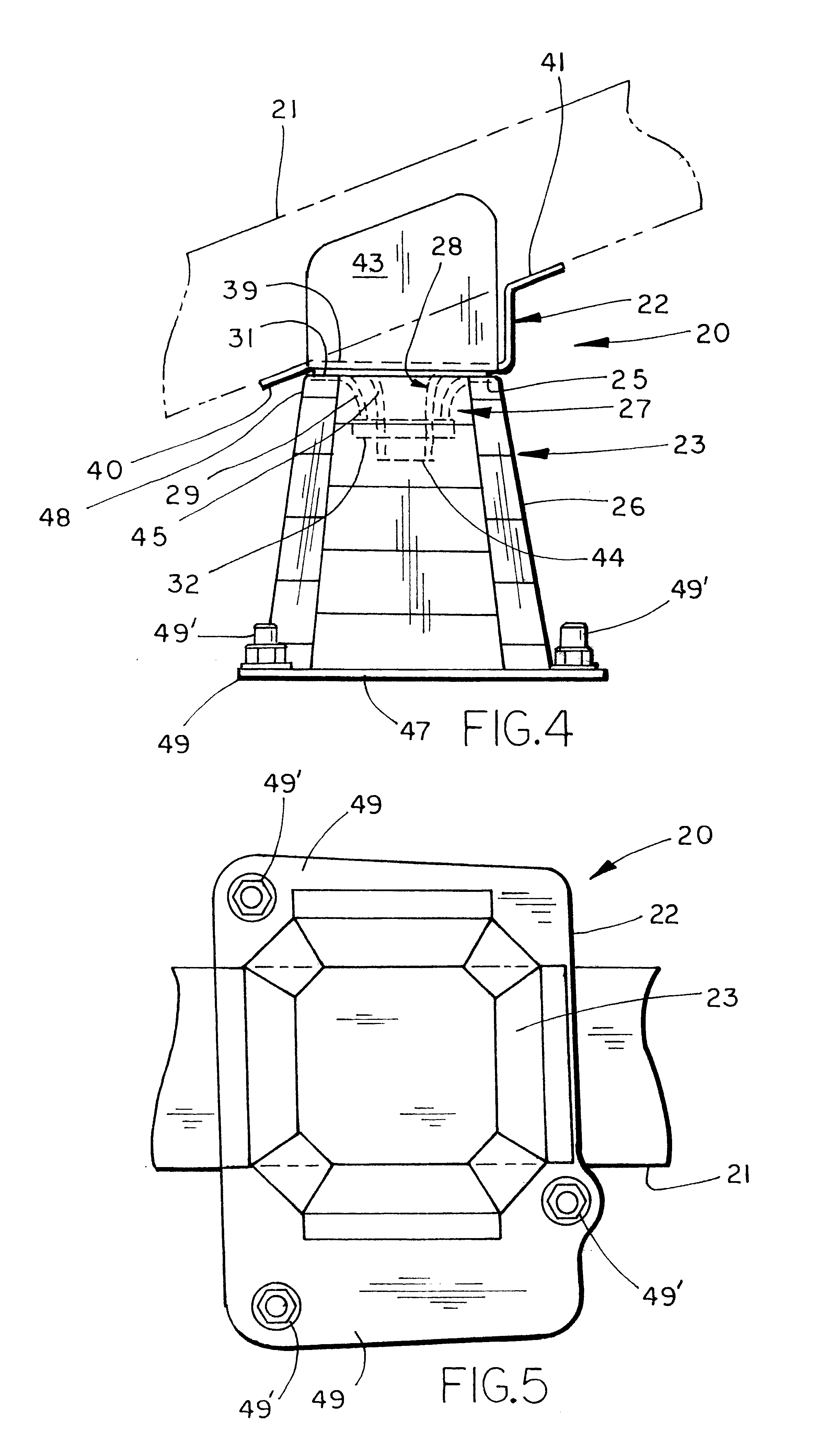
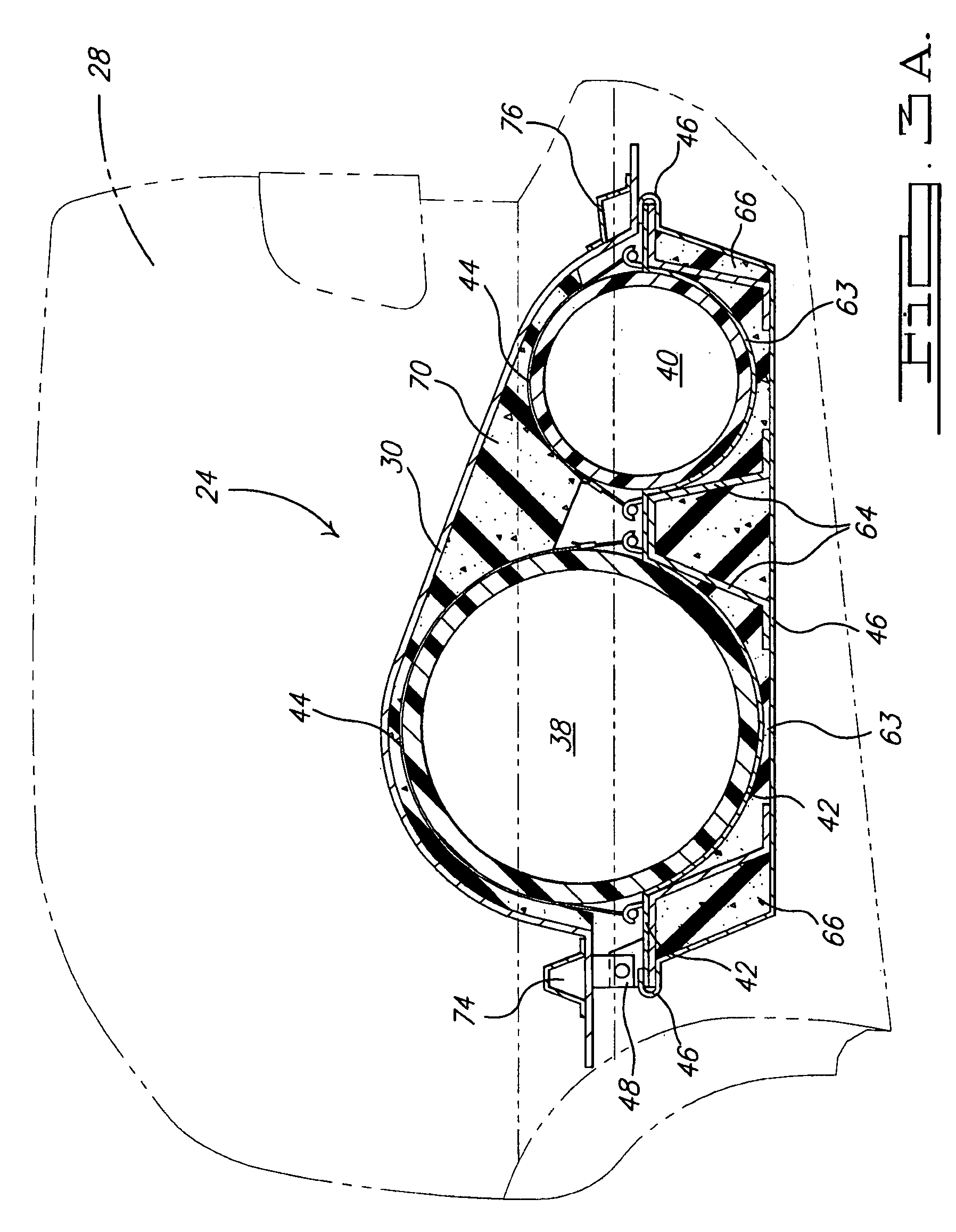
Bumper construction including self-orienting support towers providing consistent energy absorption on impact
InactiveUS6174009B1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementElastic dampersEnergy absorptionHigh energy
A bumper construction for a vehicle includes a swept tubular bumper beam having a pair of spaced-apart brackets and a pair of towers configured to attach to the brackets and support the bumper beam on a vehicle. The towers each include a platform configured for attachment to one of the brackets, and further include an elongated portion configured for connection to the vehicle. A swivel connection connects the tower to the bumper beam. The connection includes a protruding section on one of the bracket and the tower, and a socket receiving the protruding section on the other of the bracket and the tower. The protruding section and the socket are configured to draw the tower toward an impacting force during a catastrophic impact, such that the tower is more likely to crush with a high-energy absorbing, accordion-like collapse (as opposed to a low-energy absorbing parallelogram-like collapse).
Owner:SHAPE CORP
Catheters having stiffening mechanisms
InactiveUS20060264907A1Solve the lack of flexibilitySufficient pushabilityCatheterVariable stiffnessShape change
Catheters having selectively insertable or selectively activatable and releasable stiffening mechanisms are provided. In general, the catheter is inserted, navigated and withdrawn from a subject in a relaxed, flexible condition and stiffening mechanisms are deployed to prevent the catheter from shifting during placement or operation of an accessory device or tool through the catheter. Stiffening members(s) may be inserted into and removed from one or more longitudinal channel(s) provided in proximity to the catheter wall and generally coaxial with the primary catheter lumen to change the stiffness properties of the catheter. The properties, configuration and size of the stiffening members and channels may be varied to vary the stiffness properties of the catheter and stiffening members may be constructed from materials having shape change properties or materials that change conformation or stiffness with application of heat, current or electrical field. Stiffening mechanisms may also employ energy absorbing and viscoelastic polymer materials having variable stiffness properties depending on ambient conditions.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Wave energy conversion device for desalination, ETC
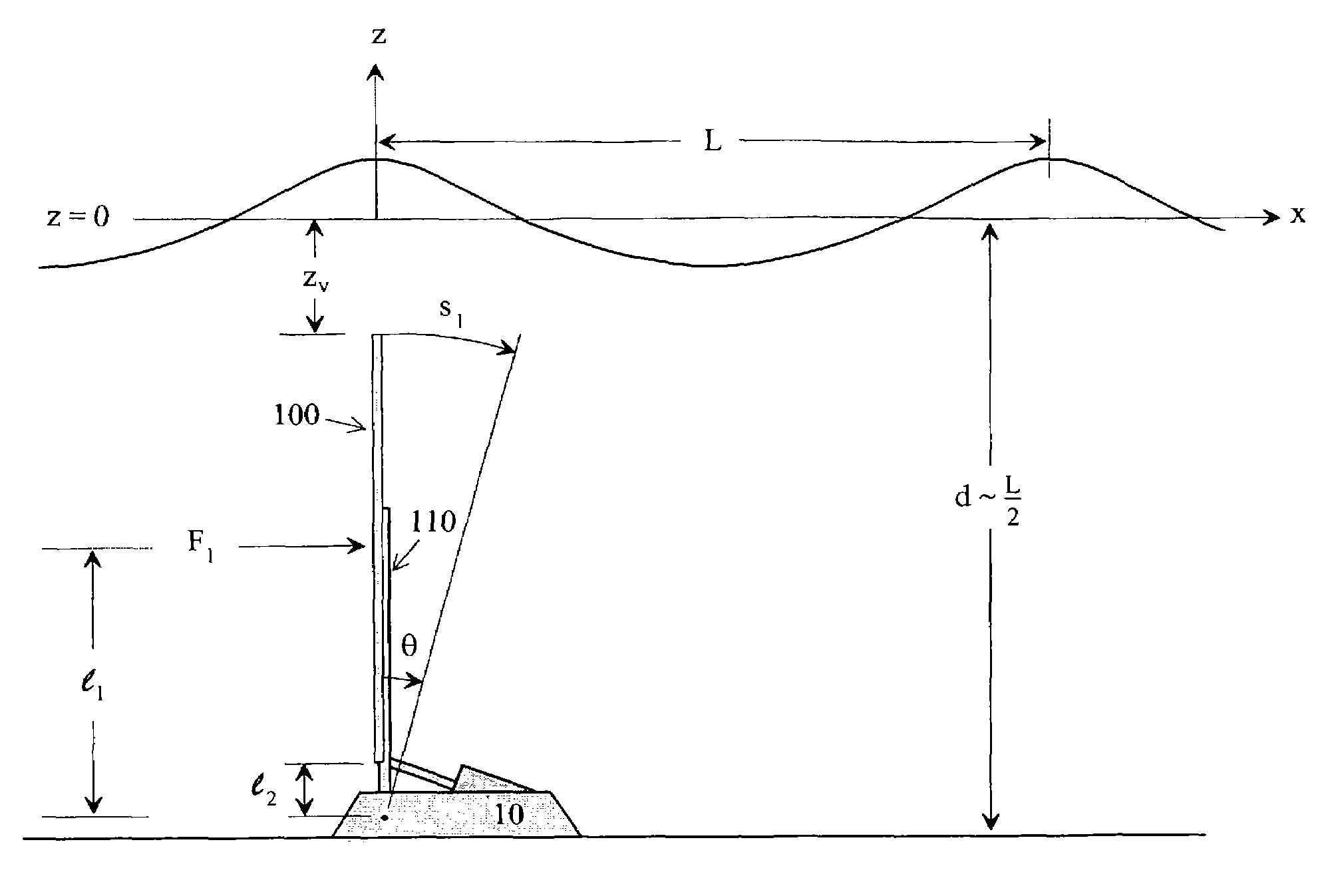
InactiveUS7023104B2Improve efficiencyEasy to operateWind motor controlGeneral water supply conservationWater qualityEngineering
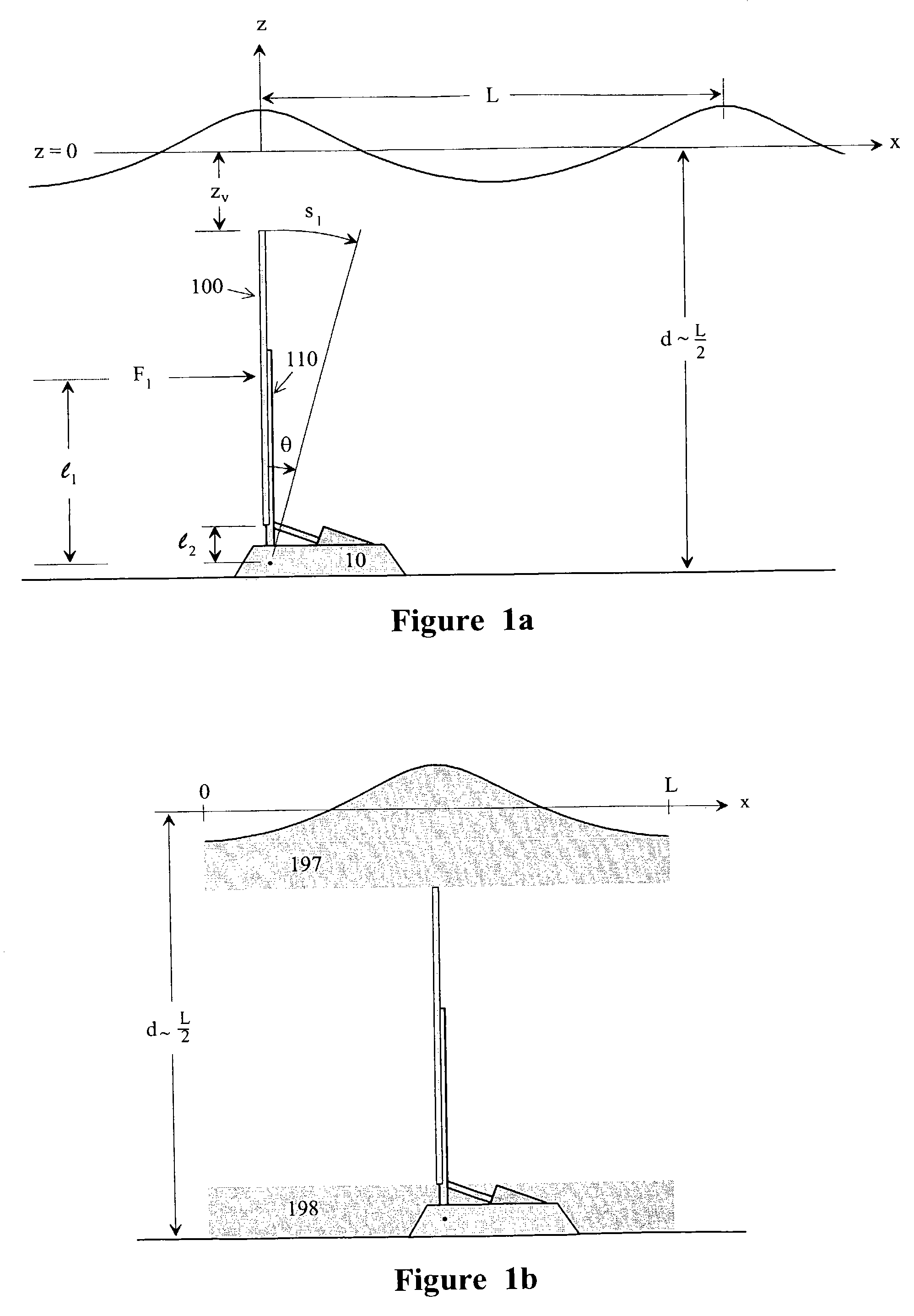
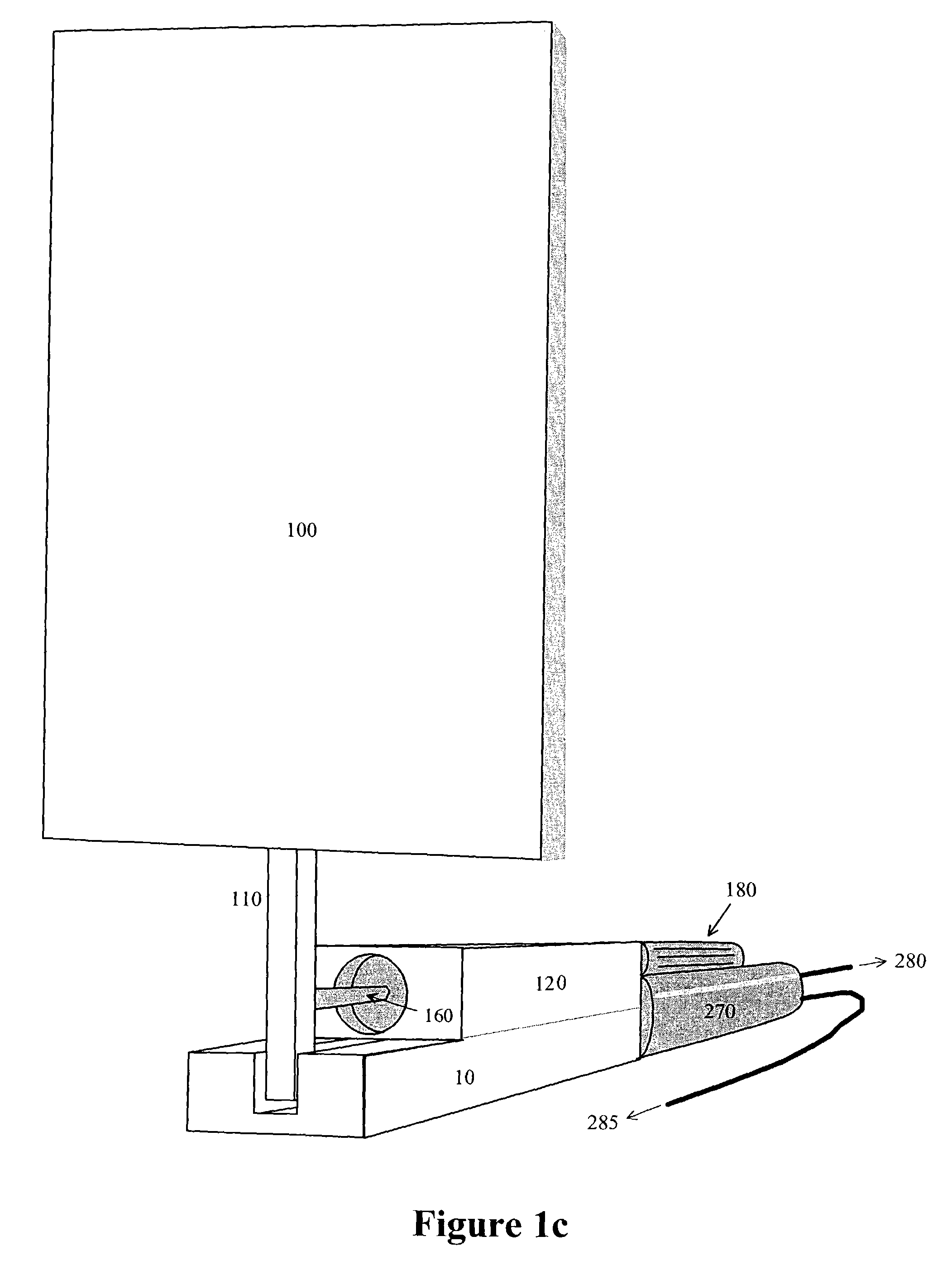
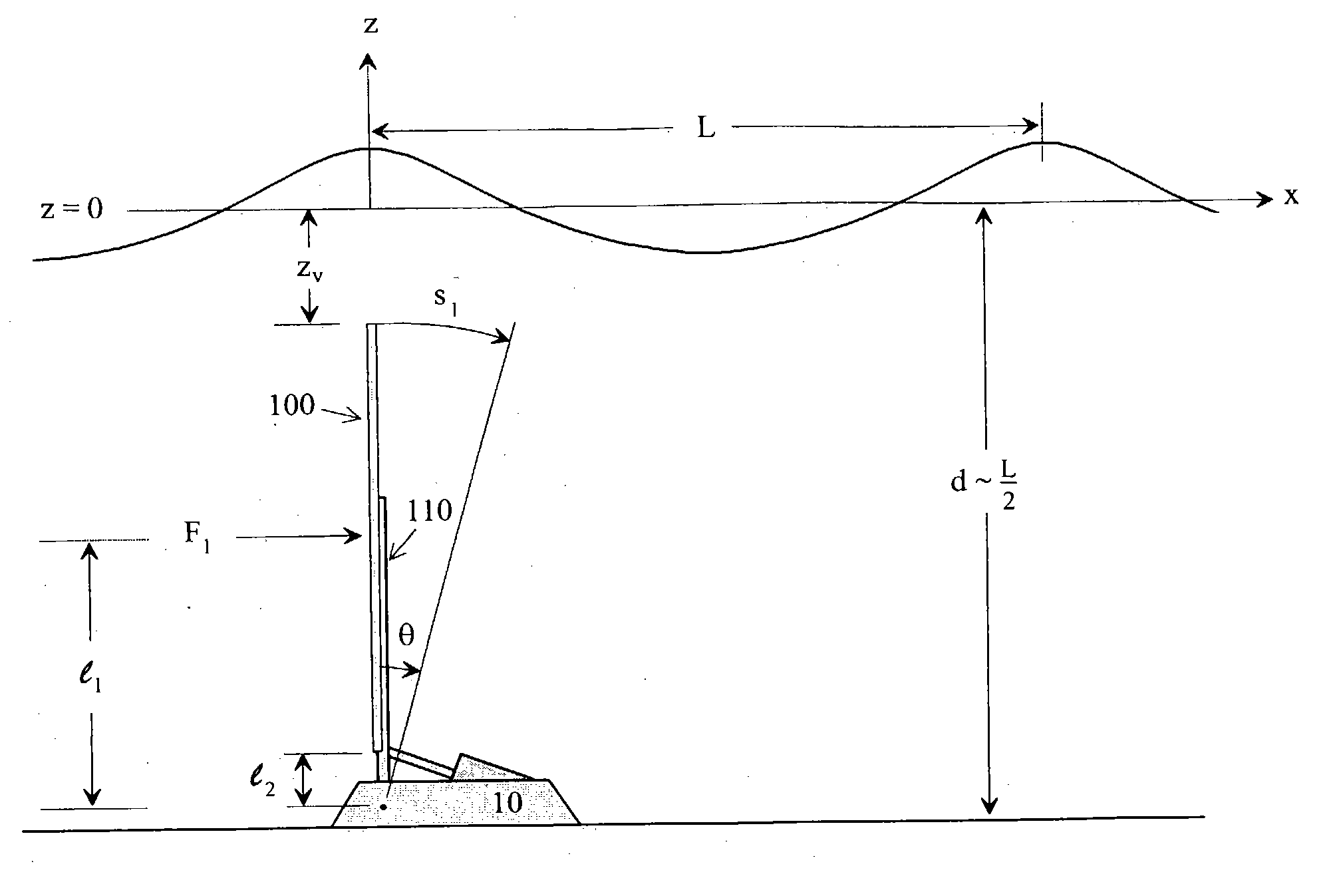
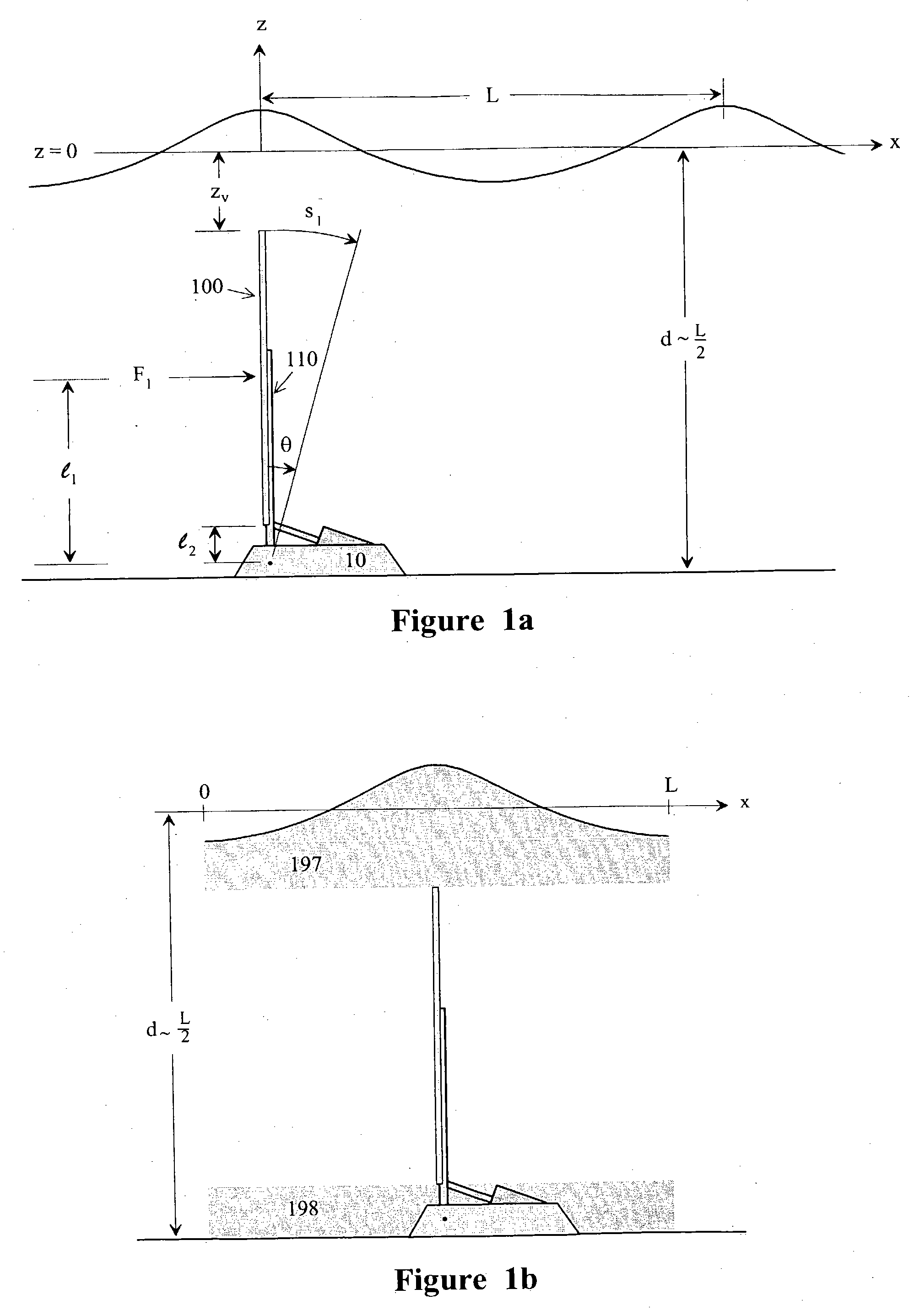
An impulse-type “wave motor” employs a seabed-mounted or supported structure mounting a wave energy absorbing panel on a hinged lever arm for reciprocation motion to obtain optimal absorption of wave energy from wave motion in the sea. For deepwater wavelengths of L, the panel is optimally positioned in a region within L / 2 depth from the sea surface. The panel motion is coupled by a connecting rod to a fluid pump which generates a high-pressure fluid output that may be used to drive a reverse osmosis desalination unit or to produce other useful work. Seawater or brackish water may be desalinated through reverse osmosis membranes to produce water quality for consumption, agricultural, or other uses. The submerged operating environment of the device in a region of one-half the design wavelength provides the maximum available energy flux and forced oscillations. The pump may be of the positive-displacement piston type, plunger type, or multi-staging driver type, or a variable volume pump.
Owner:KOBASHIKAWA ALVIN +1
Accommodating Intraocular Lens
InactiveUS20100228344A1Minimal incisionSimplified lens exchangeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method of producing fused biomaterials and tissue
InactiveUS6087552AReduce the possibilityGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsUrinary bladderVeinTissue repair
It is a general object of the invention to provide a method of effecting tissue repair or replacement using a biomaterial. It is a specific object of the invention to provide a biomaterial suitable for use as a stent, for example, a vascular stent, or as a conduit replacement, as an artery, vein or a ureter replacement. The biomaterial can also be used as a stent or conduit covering or lining. The present invention relates to a method of repairing, replacing or supporting a section of a body tissue. The method comprises positioning a biomaterial at the site of the section and bonding the biomaterial to the site or to the tissue surrounding the site. The bonding is effected by contacting the biomaterial and the site, or tissue surrounding the site, at the point at which said bonding is to be effected, with an energy absorbing agent. The agent is then exposed to an amount of energy absorbable by the agent sufficient to bond the biomaterial to the site or to the tissue surrounding the site.
Owner:GREGORY KENTON W +1
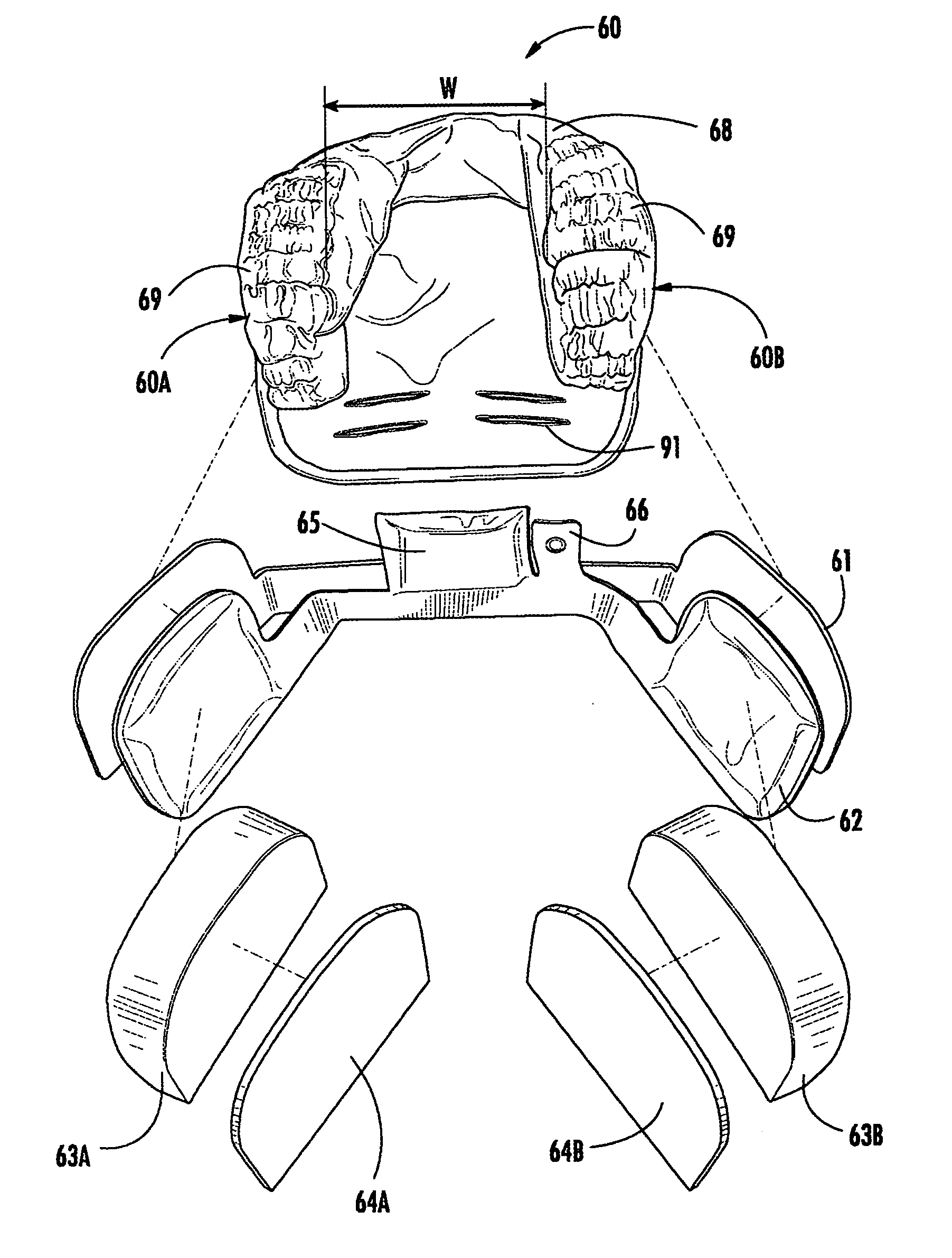
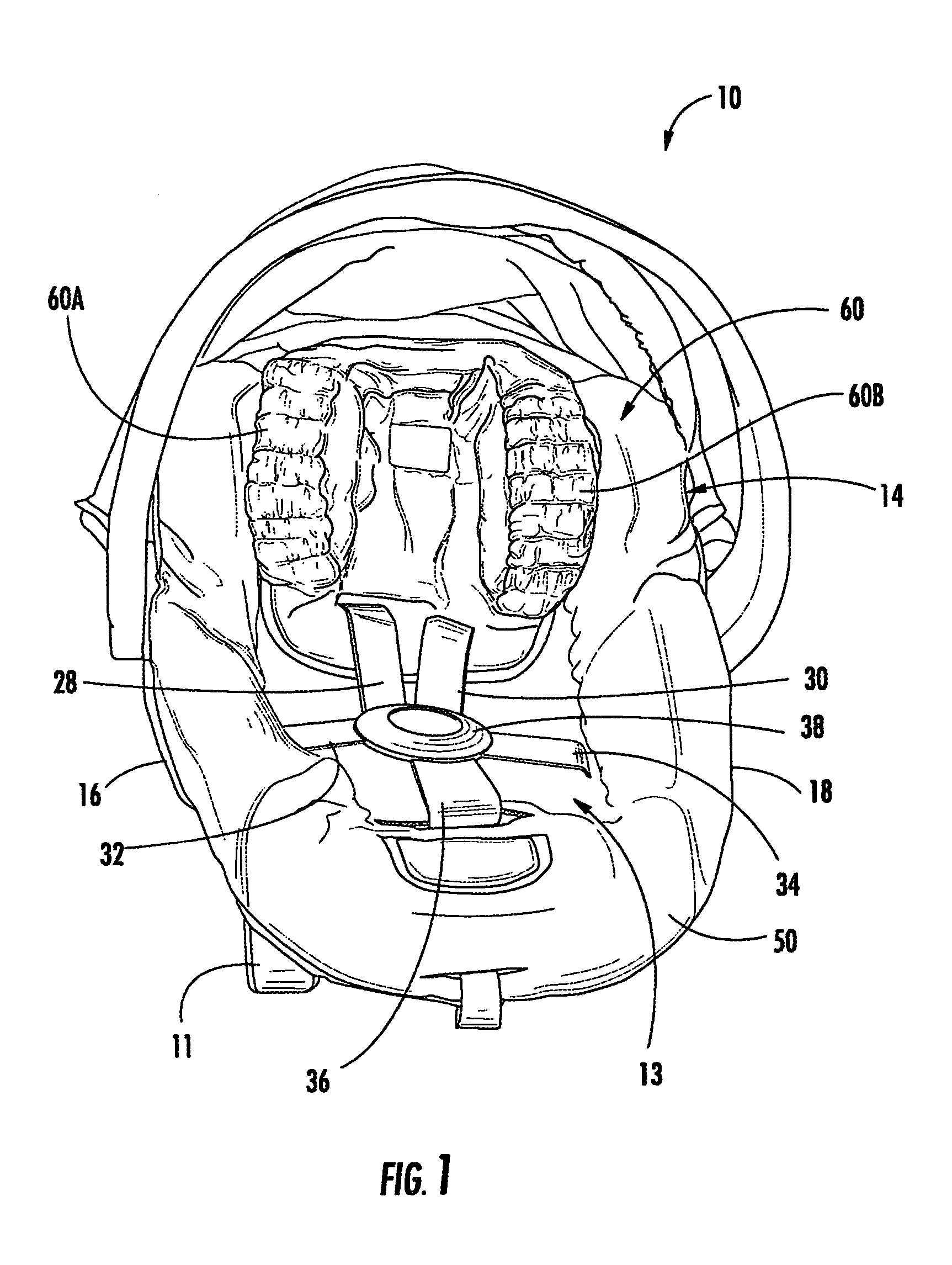
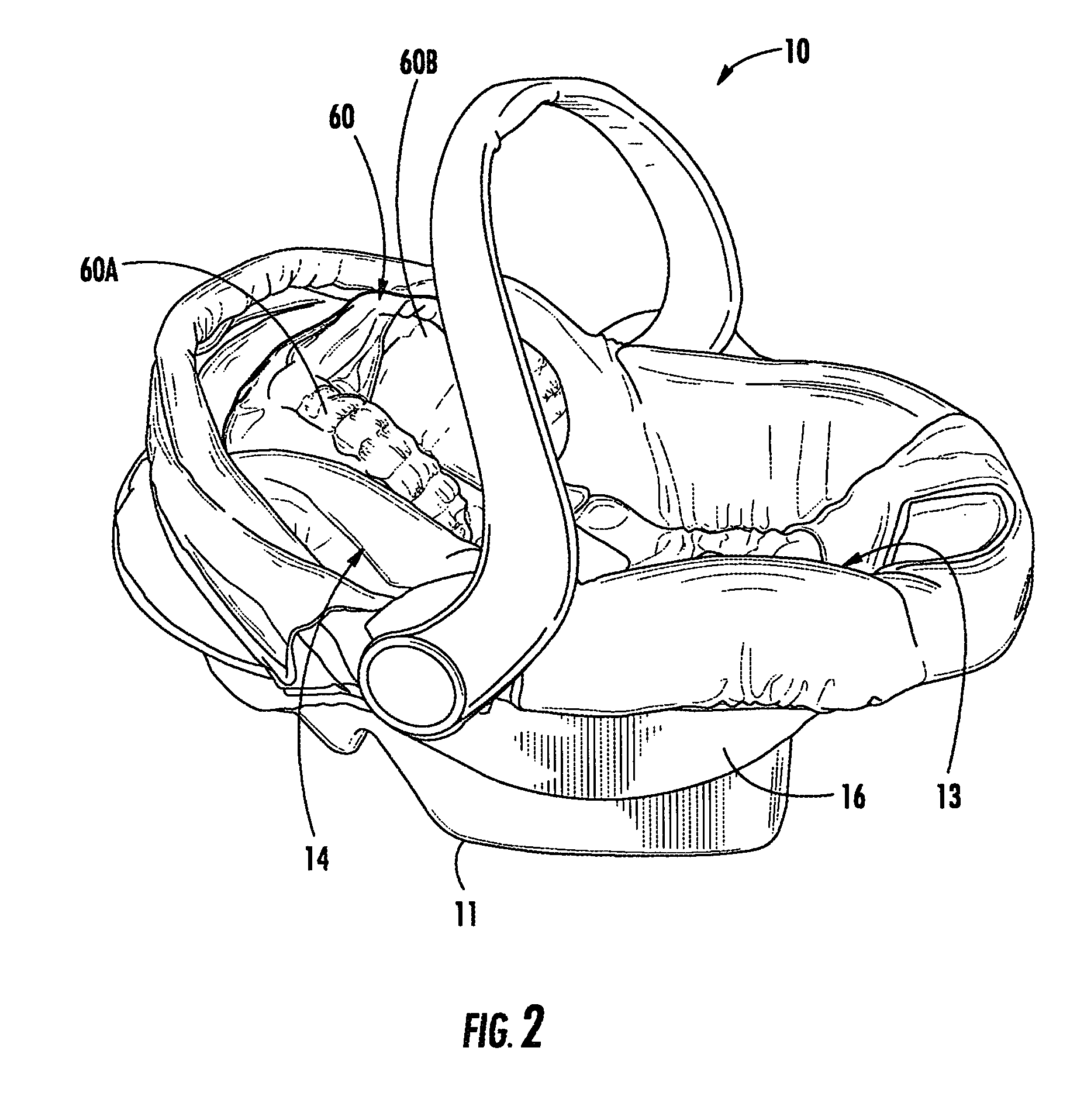
Child safety seat with adjustable head restraint
ActiveUS7234771B2Improve protectionIncrease or decrease thicknessOperating chairsSofasEnergy absorptionEngineering
A side-protective head restraint pad, pad assembly and safety seat. The restraint pad includes an air bladder with a pump for selectively inflating the air bladder and a release valve for selectively deflating the air bladder, an energy-absorbing component and a comfort component. A flexible enclosure is provided within which the air bladder, energy-absorbing component and comfort component are positioned in overlaid configuration to define a unit. The head restraint pad is adapted for being placed in a seat in lateral alignment with one side of the head of an occupant and inflatable or deflatable as appropriate to restrain the head against injurious lateral movement caused by a side impact relative to the seat.
Owner:BRITAX CHILD SAFETY
Power generation devices and methods
ActiveUS20060046907A1Reduce “locomotion energyVarying levelSwimming detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEnergy absorbingAutomotive engineering
A method for generating power from an exerted energy associated with muscles acting across a joint is provided. The method including: absorbing energy during one or more periods of a periodic motion of the joint in which energy is absorbed by the muscles; and at least partially returning the absorbed energy to one of an energy storage device or power consuming device.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC
Modular fuel storage system for a vehicle
A gaseous fuel storage system for a vehicle is disclosed. The fuel storage system can be installed as a modular unit in the vehicle. The fuel storage system is pivotable relative to the vehicle to allow easy accessibility to the storage tanks without requiring the storage tanks to be unmounted from the vehicle. The fuel storage system also provides protection for the storage tanks through the use of shielding and energy absorbing material.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
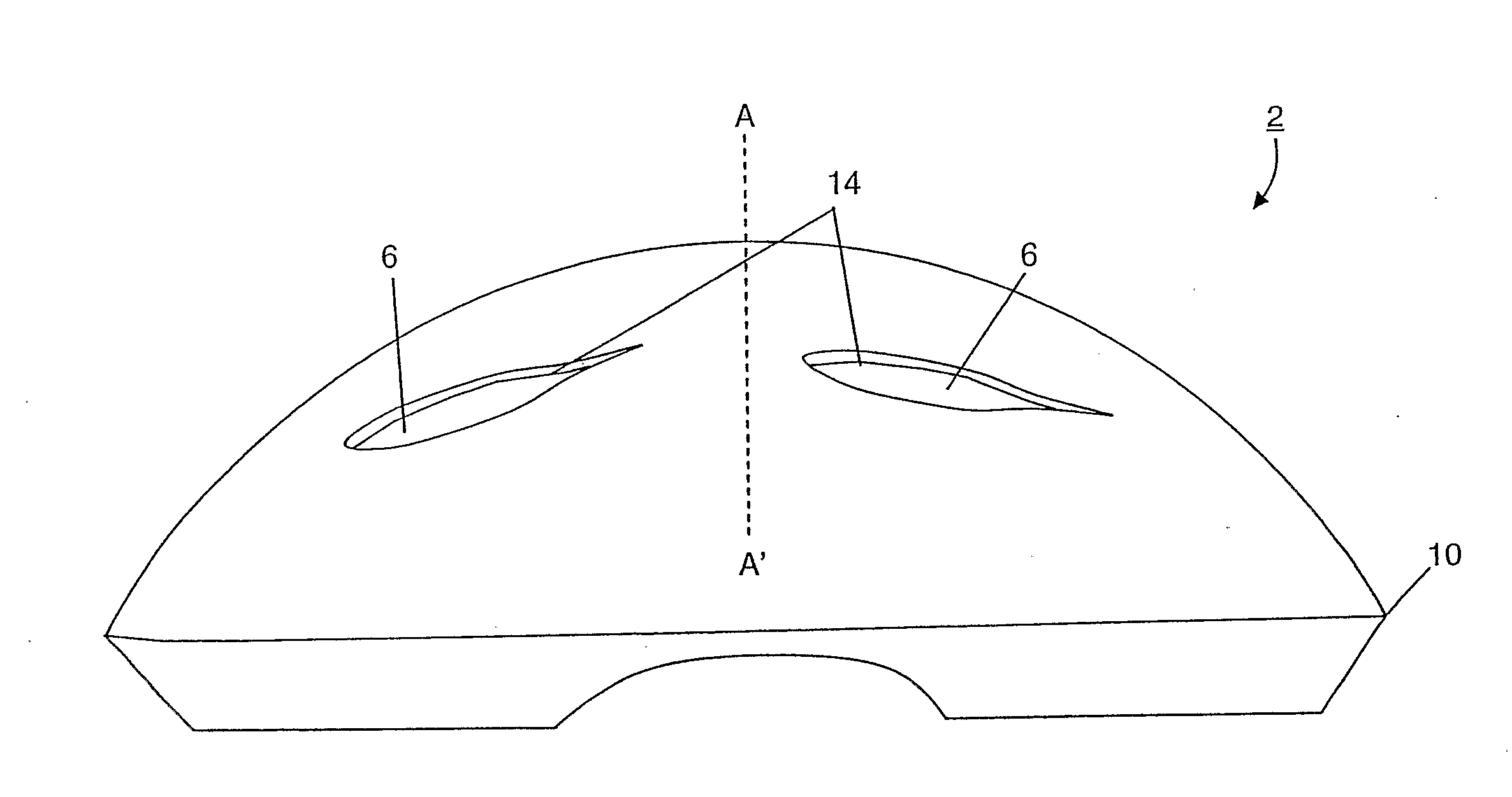
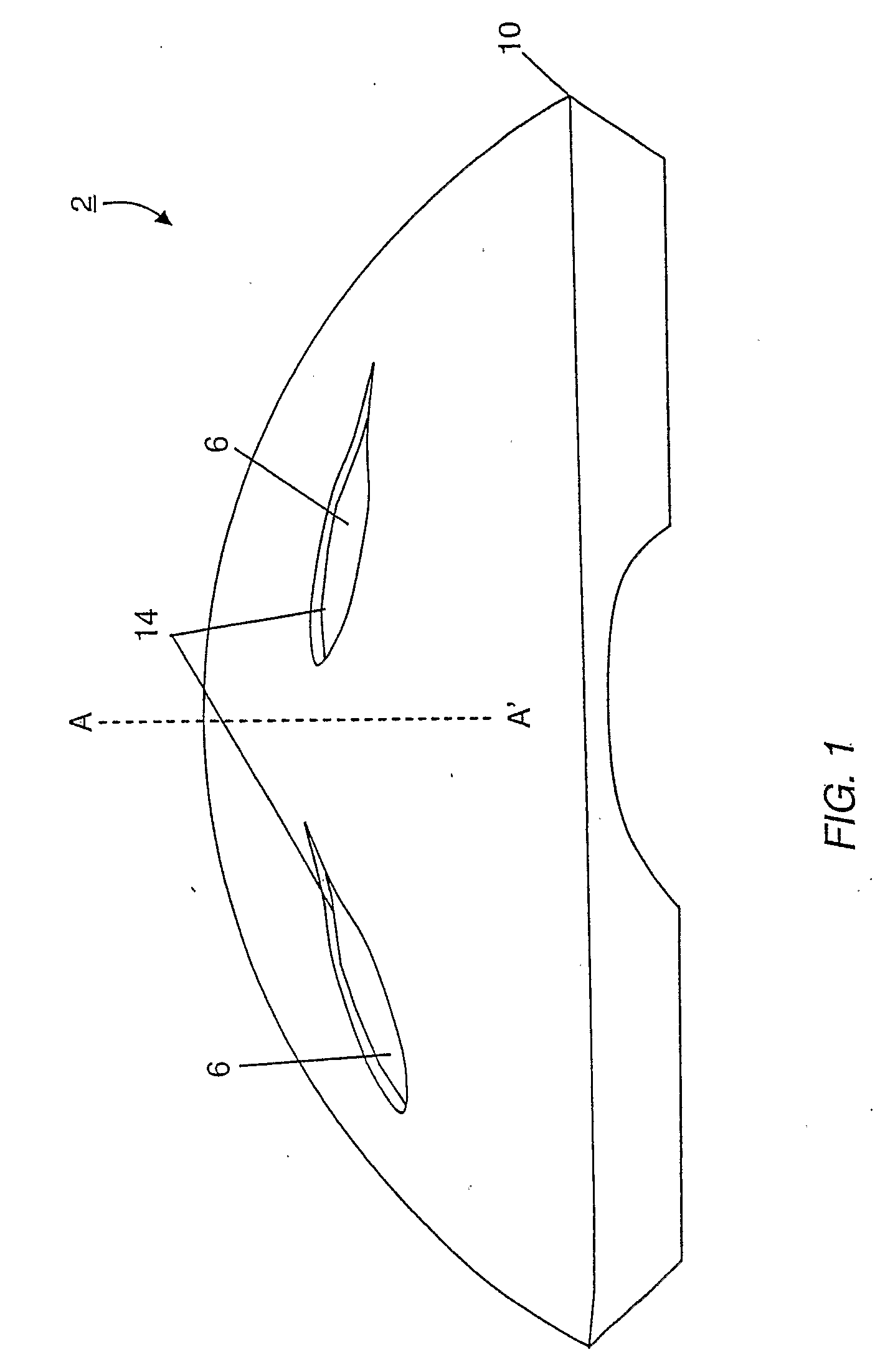
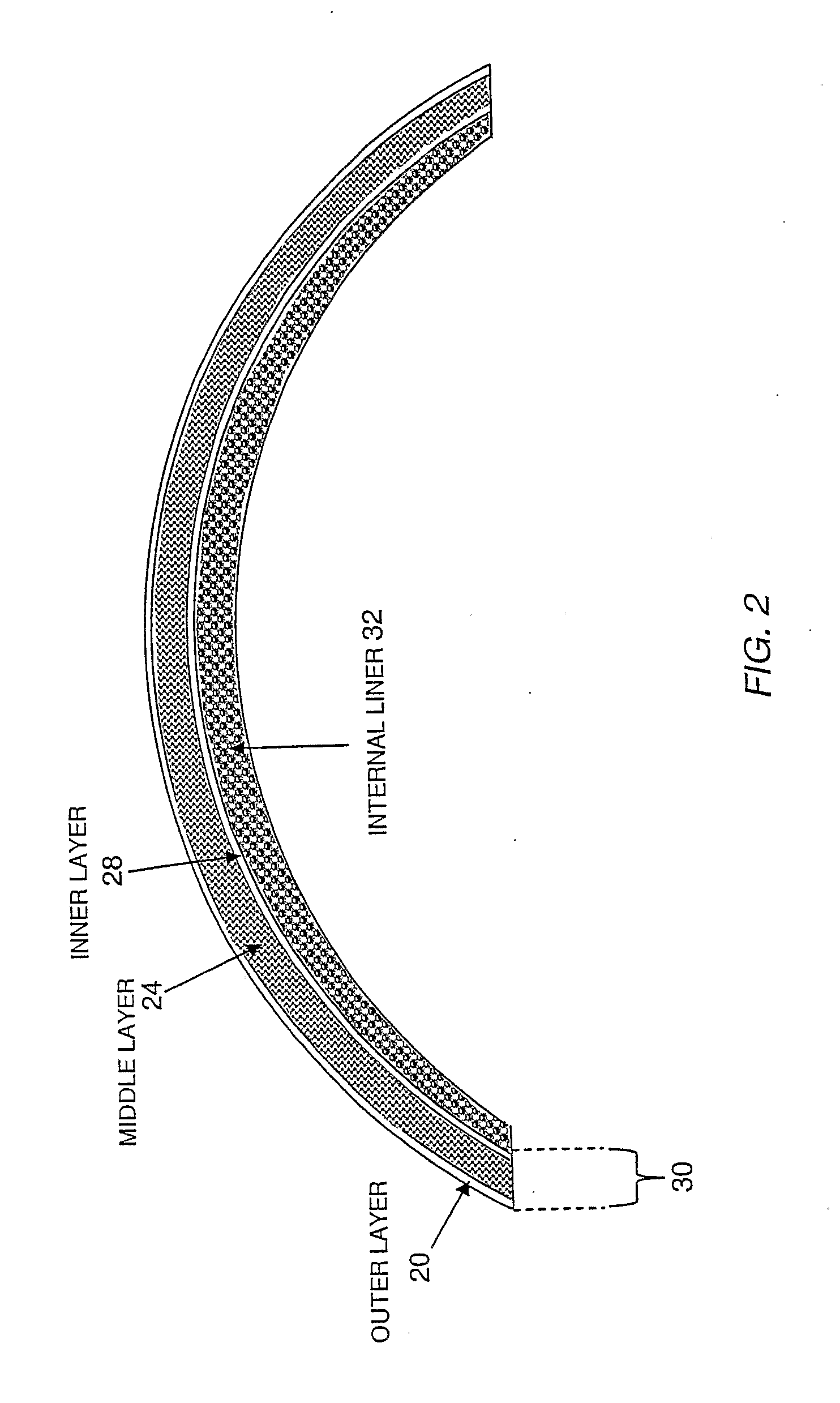
Energy-Absorbing Liners and Shape Conforming Layers for Use with Pro-Tective Headgear
InactiveUS20080155735A1Weight increaseEnhance user fit and comfortBiocideAnimal repellantsProtective headgearEnergy absorption
A multilayer shell for use in the construction of protective headgear, the shell including an outer layer, an inner layer, a middle layer disposed between the outer and inner layer which resiliently compresses in response to an impact to the outer layer, and an internal liner disposed inwardly of the inner layer. The middle layer includes a plurality of compressible members, which resiliently compress to absorb the energy of a direct impact to the outer layer and resiliently shear with respect to the inner layer in response to a tangential impact to the outer layer. The inner layer includes an open configuration, which reduces the weight of the shell, provides for greater heat ventilation from the head of the user, and permits for visualization of the compressible elements. The internal liner is formed from contourable materials which enhance user fit and comfort and reduce the weight of the protective headgear without compromising user safety.
Owner:XENITH
Energy absorbing articles
InactiveUS7160621B2Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringEnergy analysis
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Marine hulls and drives
InactiveUS7984684B2Improve power densityNo coolingHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesTravel modeCombustion
Owner:HINDERKS MITJA VICTOR
Wave energy conversion device for desalination, ETC
InactiveUS20040007881A1Minimize exposureLow profileWind motor controlGeneral water supply conservationWater qualityWave motor
An impulse-type "wave motor" employs a seabed-mounted or supported structure mounting a wave energy absorbing panel on a hinged lever arm for reciprocation motion to obtain optimal absorption of wave energy from wave motion in the sea. For deepwater wavelengths of L, the panel is optimally positioned in a region within L / 2 depth from the sea surface. The panel motion is coupled by a connecting rod to a fluid pump which generates a high-pressure fluid output that may be used to drive a reverse osmosis desalination unit or to produce other useful work. Seawater or brackish water may be desalinated through reverse osmosis membranes to produce water quality for consumption, agricultural, or other uses. The submerged operating environment of the device in a region of one-half the design wavelength provides the maximum available energy flux and forced oscillations. The pump may be of the positive-displacement piston type, plunger type, or multi-staging driver type, or a variable volume pump.
Owner:KOBASHIKAWA ALVIN +1
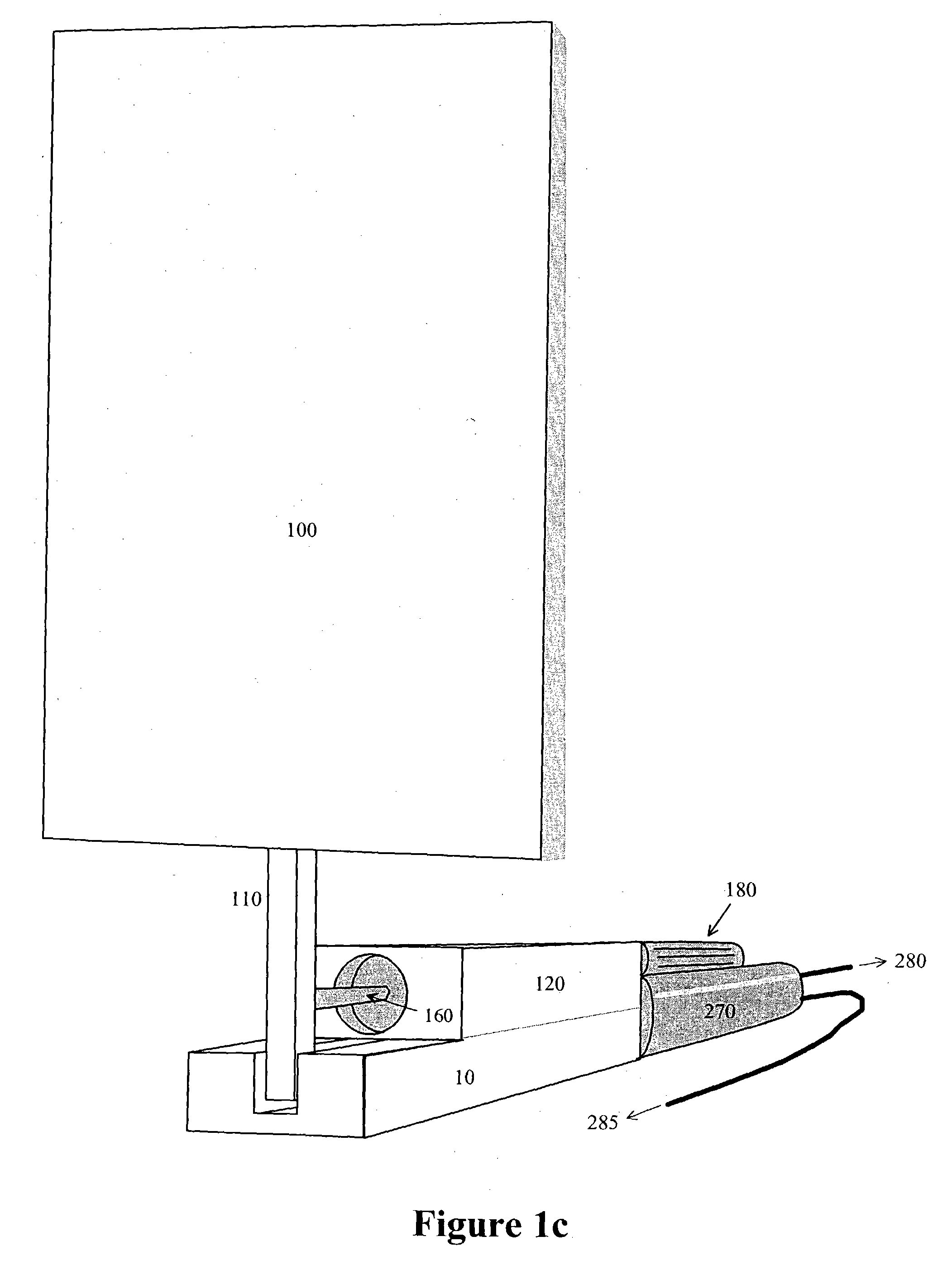
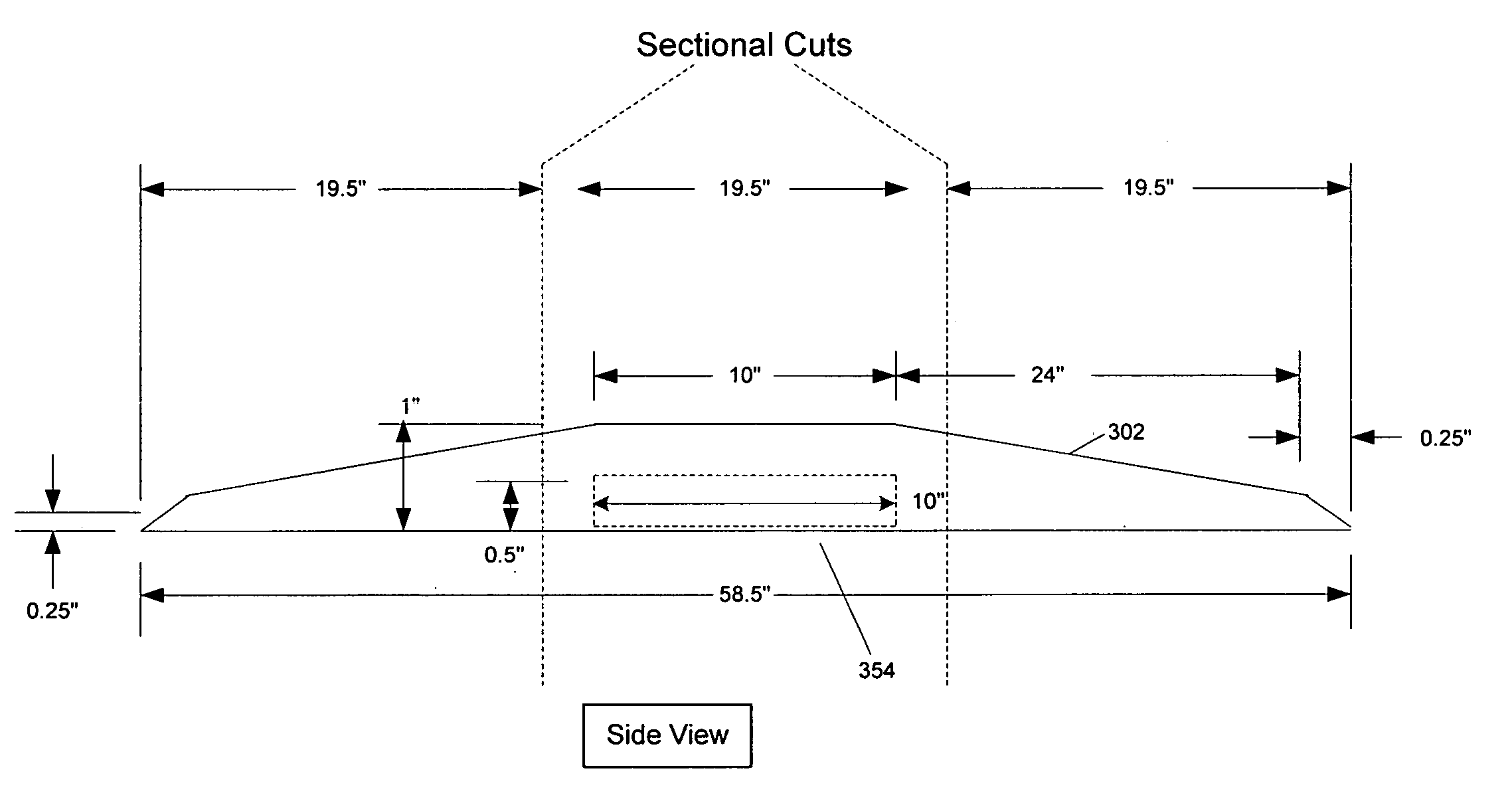
Radio frequency identification for advanced security screening and sortation of baggage
ActiveUS6967579B1Avoid readingMemory record carrier reading problemsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalEnergy absorbingConveyor system
An RFID conveyor system comprises one or more wedges designed to allow an RFID scanner to detect and uniquely identify RFID-tagged baggage as they are conveyed through an antenna array. The RFID conveyor system can also be designed to prevent the reading of previous or subsequent bags by using antennas with highly focused RF read fields in conjunction with RF energy absorbing materials, such as RF curtains, designed to eliminate the identification of any baggage located outside of the “read” area.
Owner:SMARTRAC TECH FLETCHER INC
Protective helmet
InactiveUS20120017358A1Reduce gravityImprove protectionSport apparatusHelmetsExternal energyEngineering
A protective helmet having an inner shell and an outer shell assembly. Internal padding contacts an inner surface of the inner shell and an energy absorbing layer is positioned between the inner shell and the outer shell assembly. The outer shell assembly includes a plurality of rigid, outer shell segments with at least one of the outer shell segments designed and arranged to move relative to the other outer shell segments upon receiving an impact force. The external energy absorbing layer and the outer shell assembly dampens impact energy before it reaches the inner shell.
Owner:KRANOS IP CORP
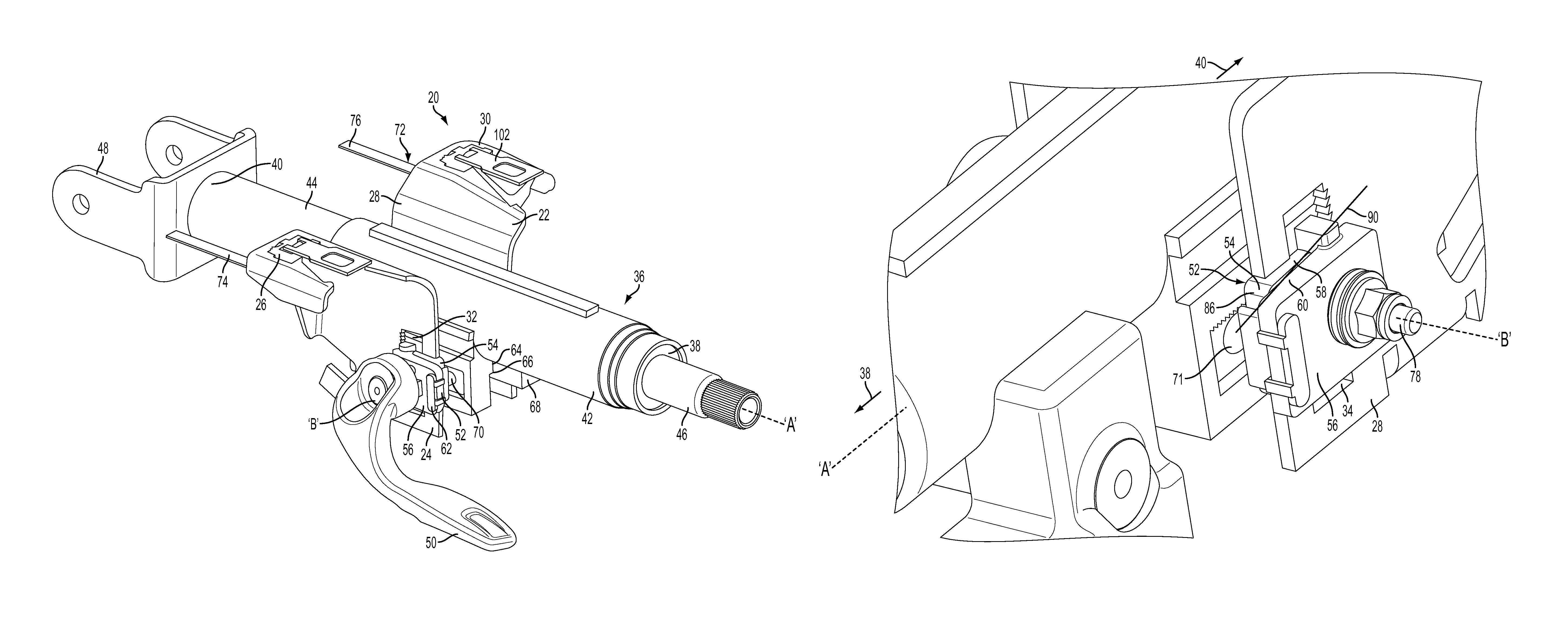
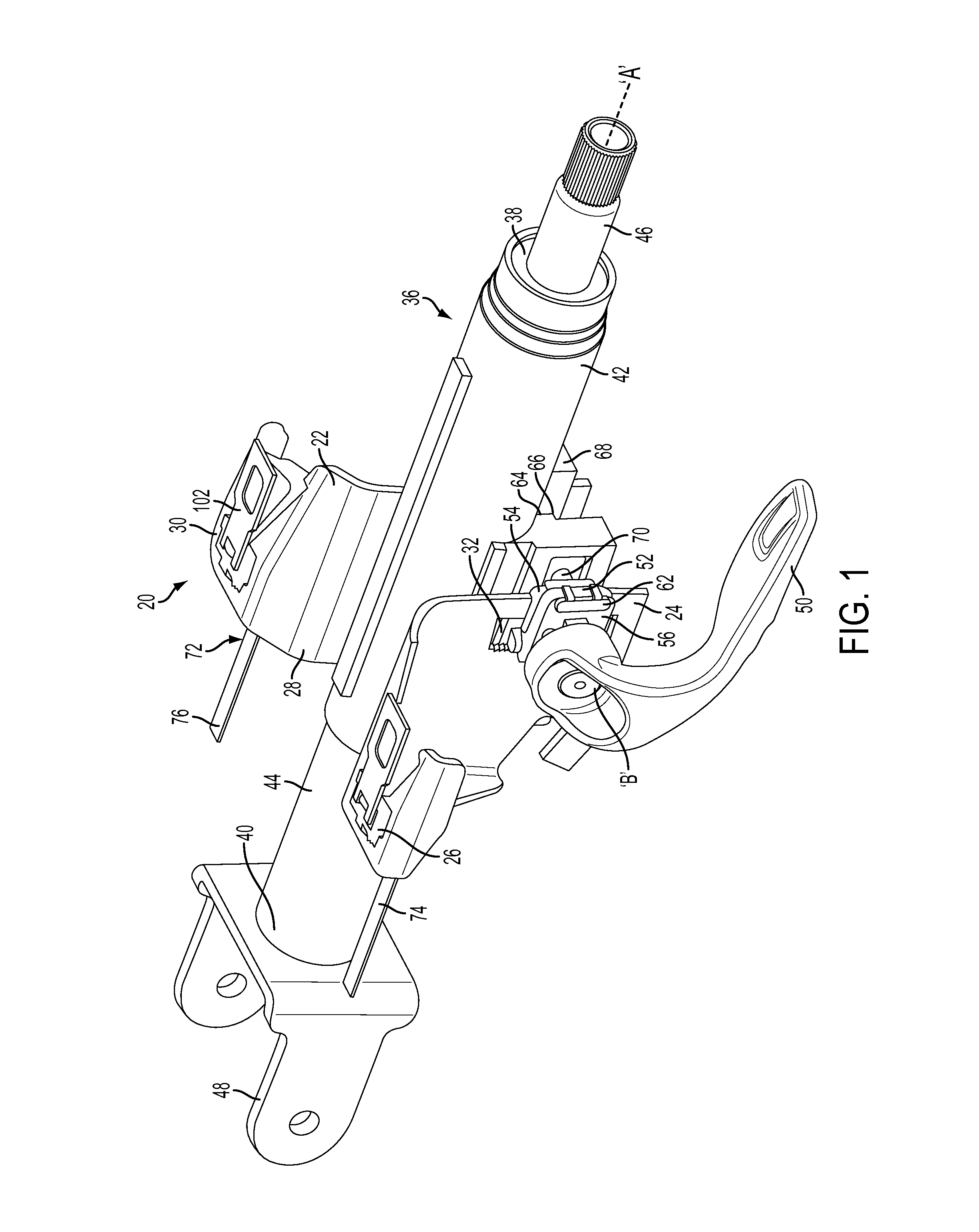
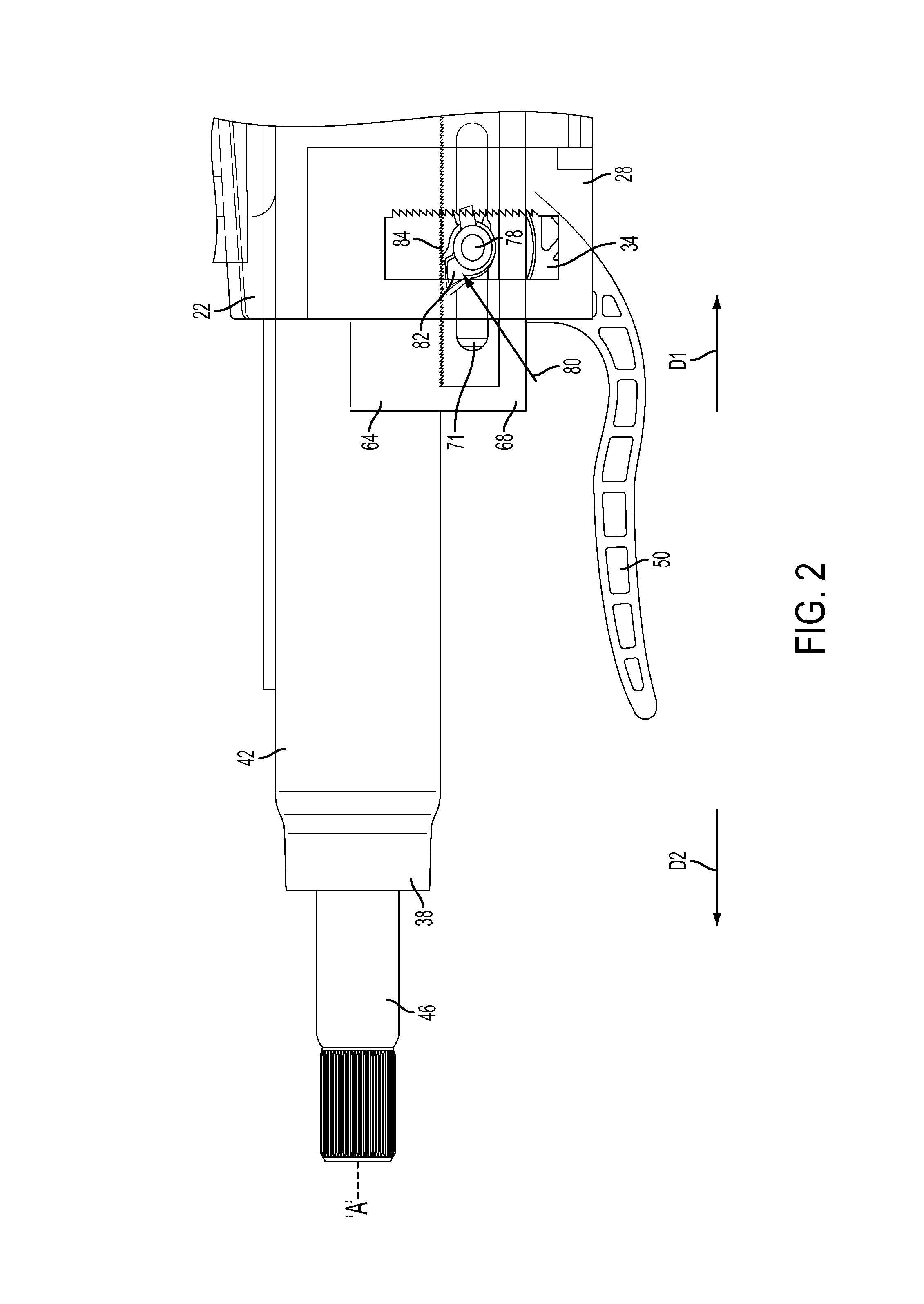
Crash release mechanism for automotive steering column
An adjustable steering column for a vehicle is provided. The adjustable steering column includes a mounting bracket configured to be secured to an adjacent vehicle component, a compression bracket movably positioned relative to the mounting bracket, and a column jacket extending along a first axis and having an upper jacket and a lower jacket telescopically coupled to one another. The adjustable steering column further includes a locking mechanism movable between a locked position and an unlocked position configured to selectively restrict adjustment of the upper jacket in a telescope direction, and at least one release mechanism configured to allow telescoping movement of the upper jacket with the locking mechanism in the locked position in response to an excessive axial force applied to the column jacket. At least one energy absorbing mechanism is configured to absorb energy during telescoping movement of the upper jacket with the locking mechanism in the locked position.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG
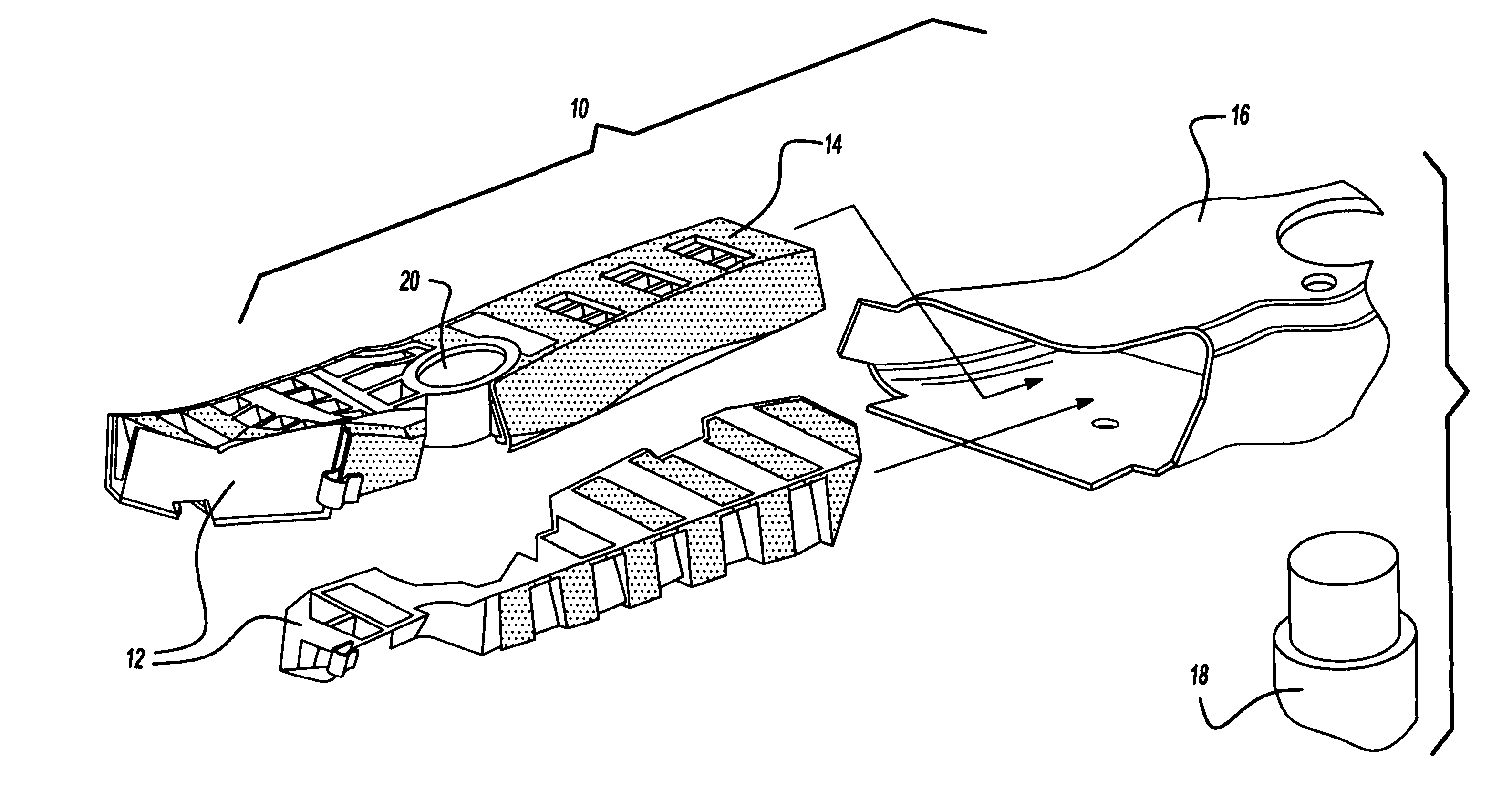
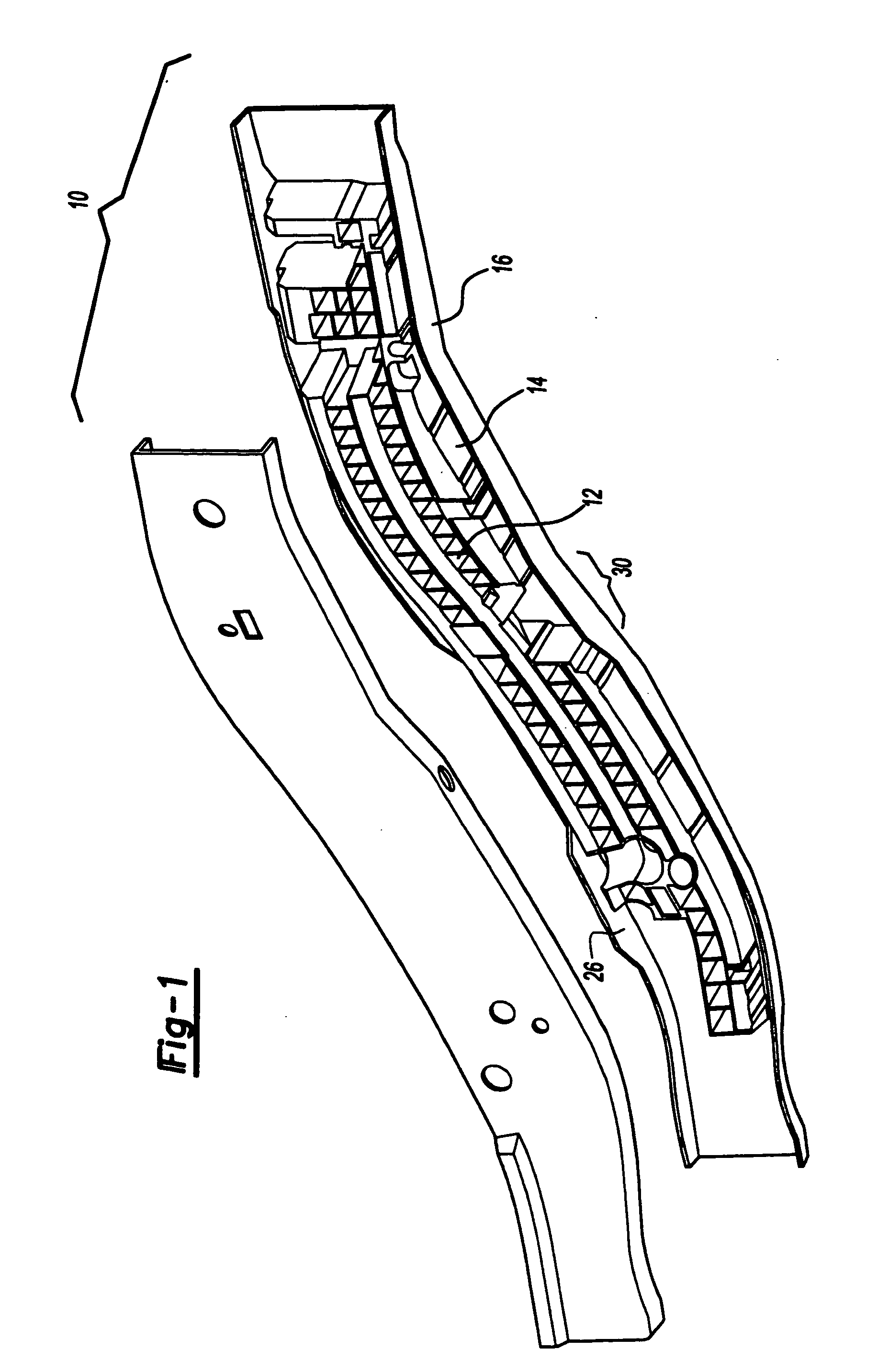
Automotive rail/frame energy management system
InactiveUS20050017543A1Reduce laborReduced capitol expenseVehicle seatsUnderstructuresVehicle frameAbsorbed energy
An energy management system and device for use in an automotive frame, rail, or other structural component of an automotive vehicle. The frame or rail having a cavity or exposed surface capable of supporting at least one member. The member having an interior portion and an exterior portion with the interior portion being defined by at least one trigger or step change to the geometry of the inner portion to target and direct axial bending of the system. A reinforcing material, such as a polymer-based expandable material, is disposed along the exterior portion of a member prior to final assembly of the vehicle by the vehicle manufacturer. The system is activated as the vehicle undergoes the final vehicle assembly process and paint operation which activates and transforms the reinforcing material to expand, bond and structurally adhere the frame rail to mange, direct, and / or absorb energy in the event of an impact to the vehicle from an applied load or an external force.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC +1
Systems and methods for the treatment of eye conditions
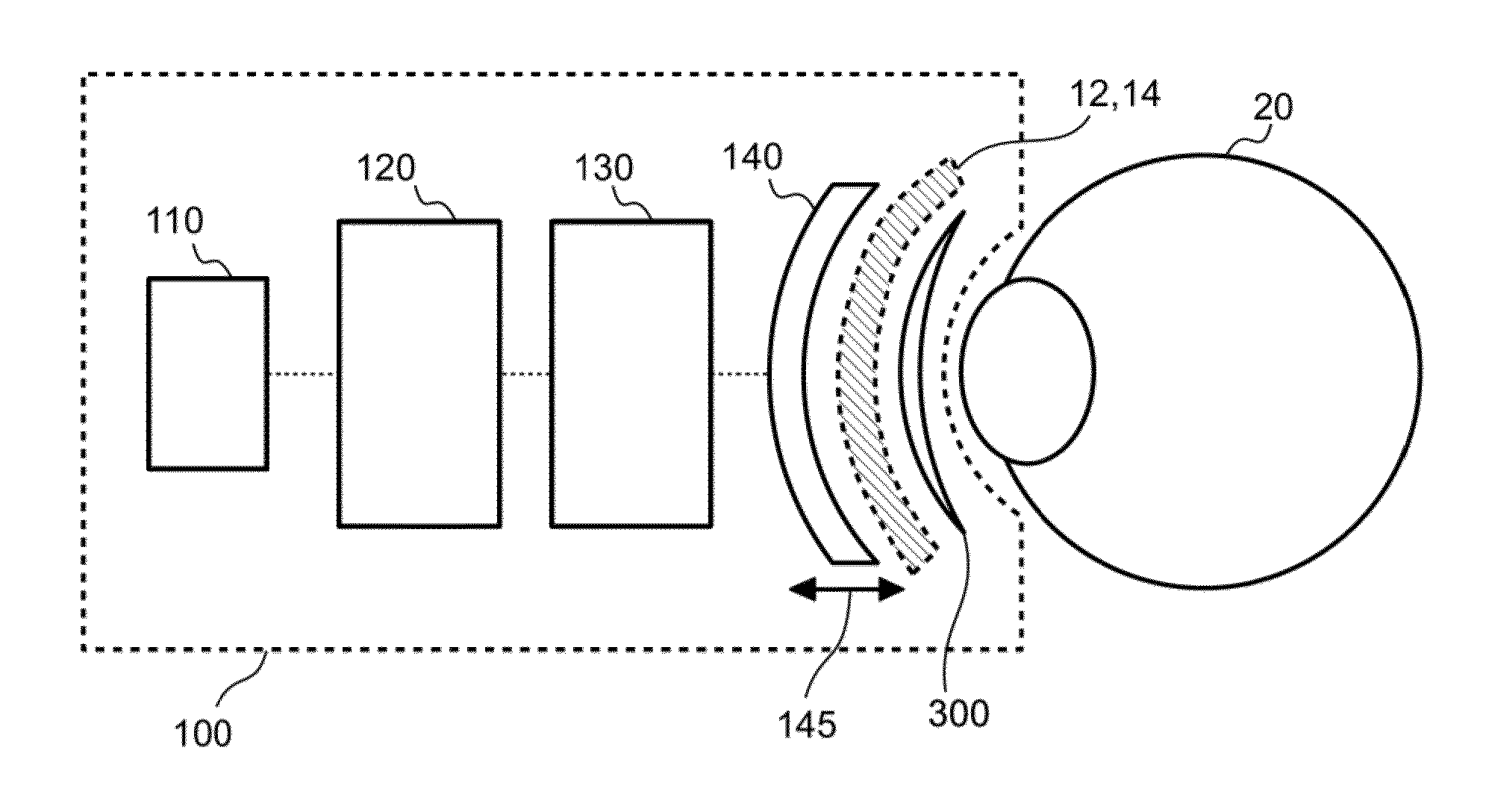
ActiveUS20150057701A1Minimizing amount of energyUltrasound therapyEye surgeryMeibomian glandLight energy
Systems, methods, and devices used to treat eyelids, meibomian glands, ducts, and surrounding tissue are described herein. In some embodiments, an eye treatment device is disclosed, which includes a scleral shield positionable proximate an inner surface of an eyelid, the scleral shield being made of, or coated with, an energy-absorbing material activated by a light energy, and an energy transducer positionable outside of the eyelid, the energy transducer configured to provide light energy at one or more wavelengths, including a first wavelength selected to heat the energy-absorbing material.
Owner:ALCON INC
Energy absorbing assembly and methods for operating the same
An energy absorbing assembly includes a covering; and a shape memory material in operative communication with the covering, wherein the shape memory material has a first shape attached to an underside of the covering and is operative to change to a second shape in response to an activation signal. The second shape of the shape memory material can cause the covering to expand or expand and detach from a surrounding surface medium. The energy absorbing assembly is used to absorb kinetic energy of an object impacting the assembly. Methods of operating the assembly are also disclosed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
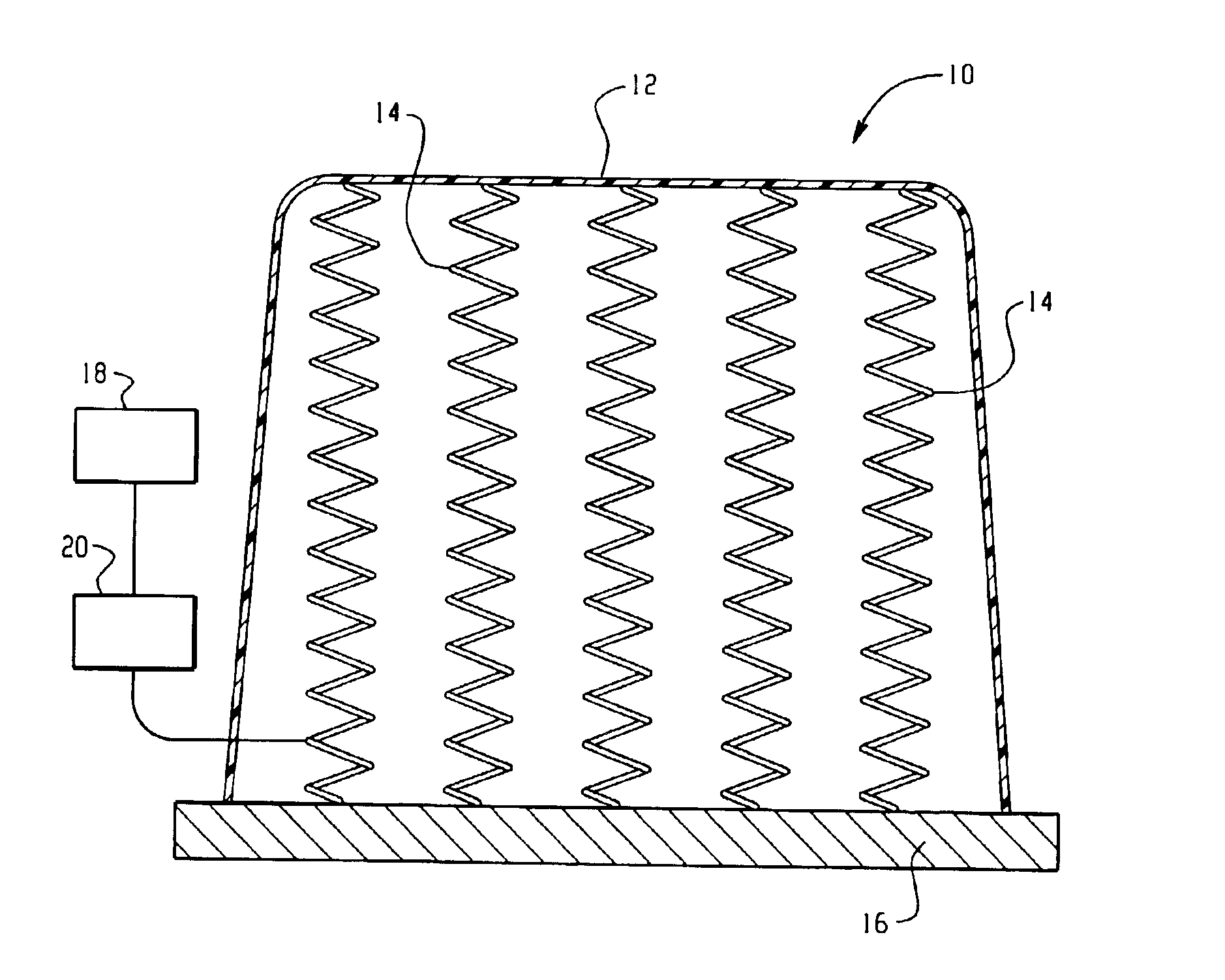
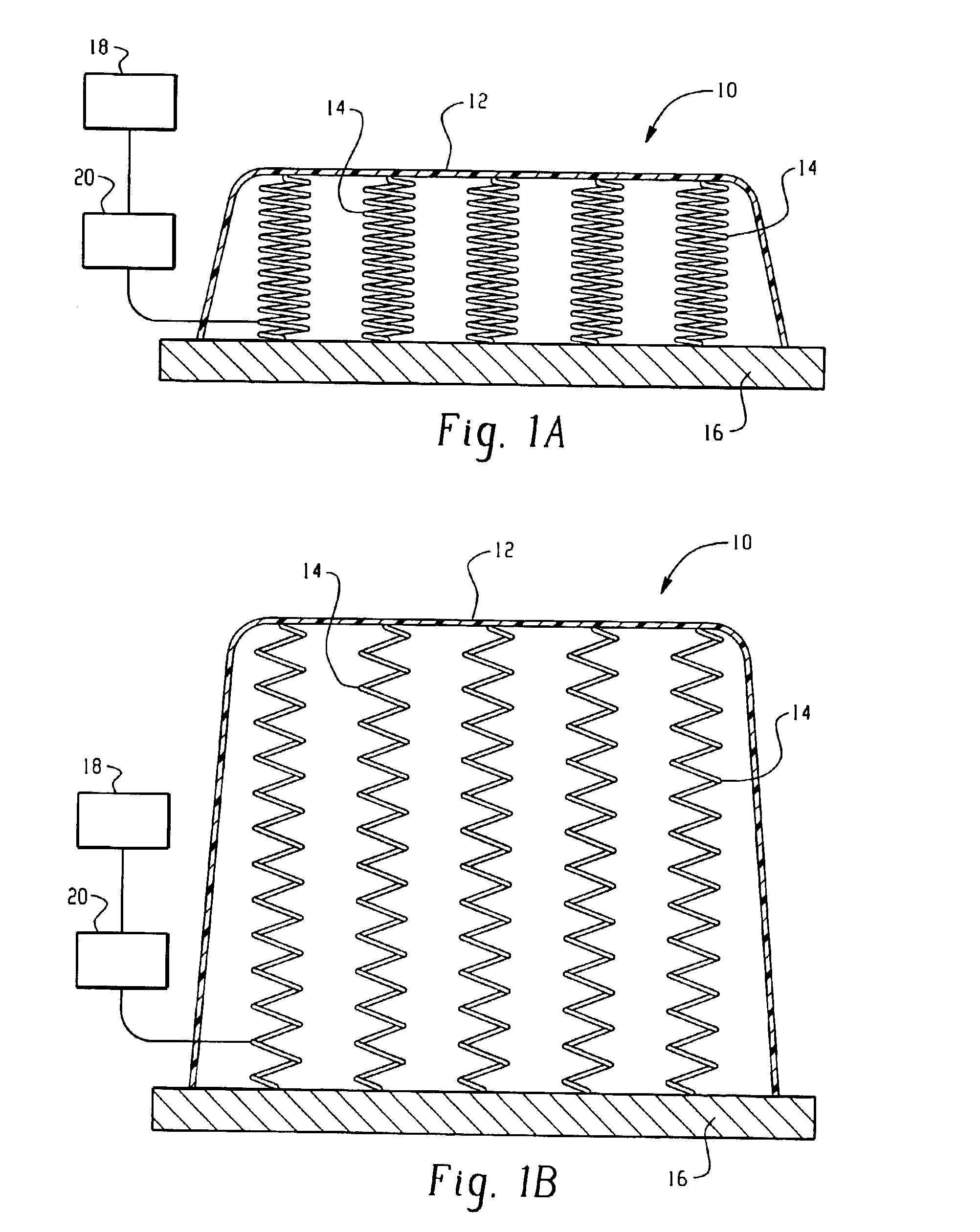
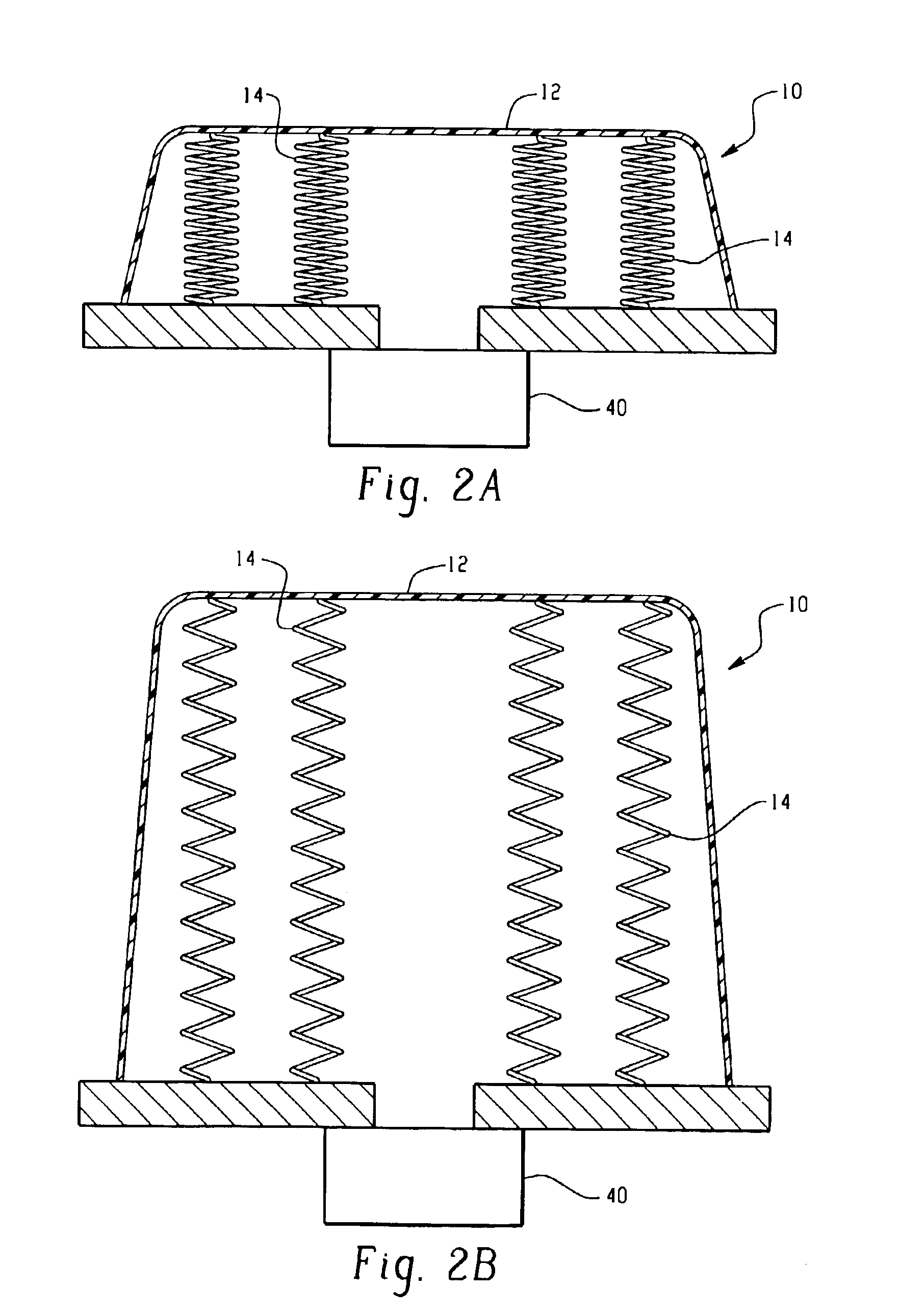
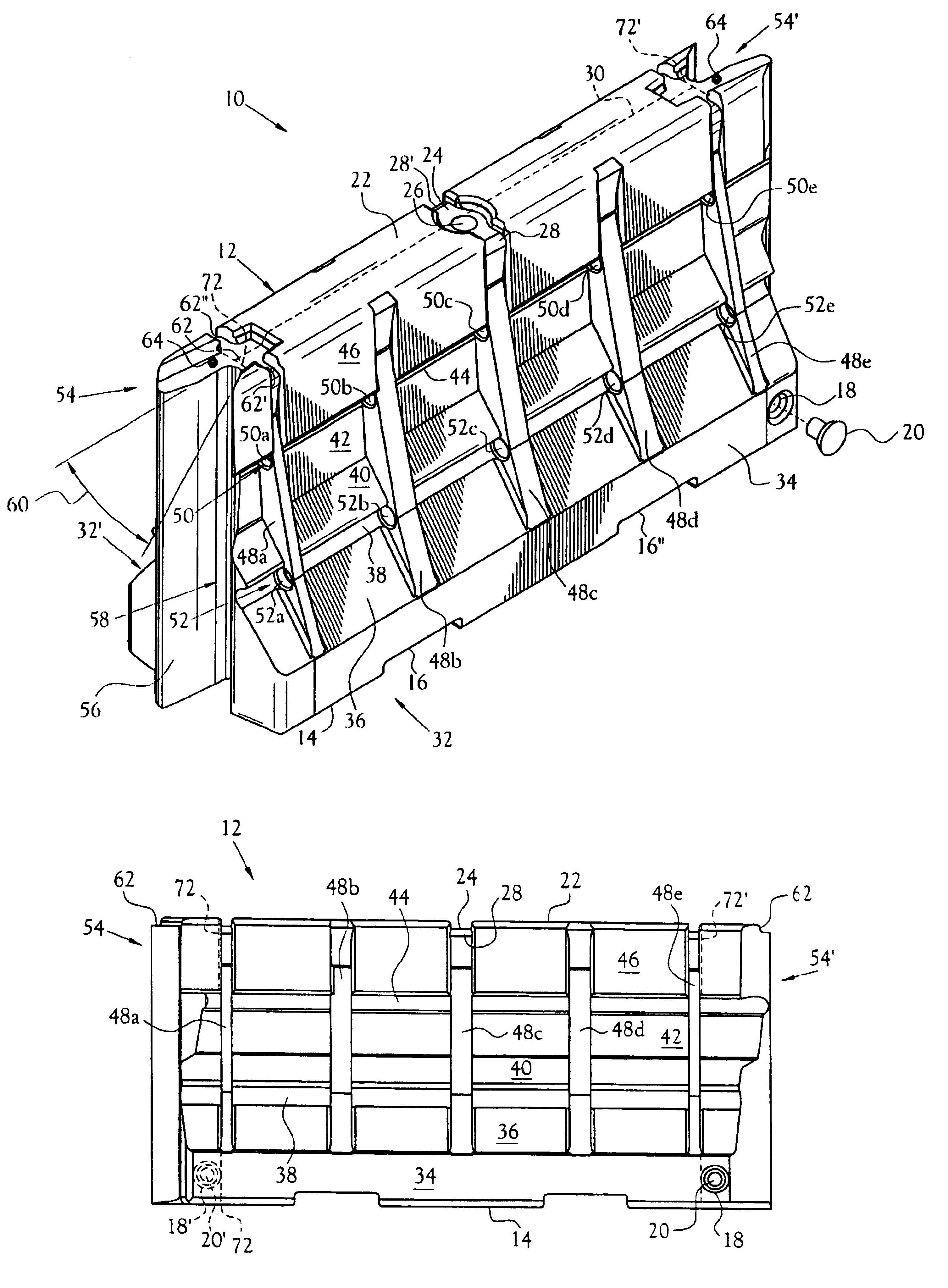
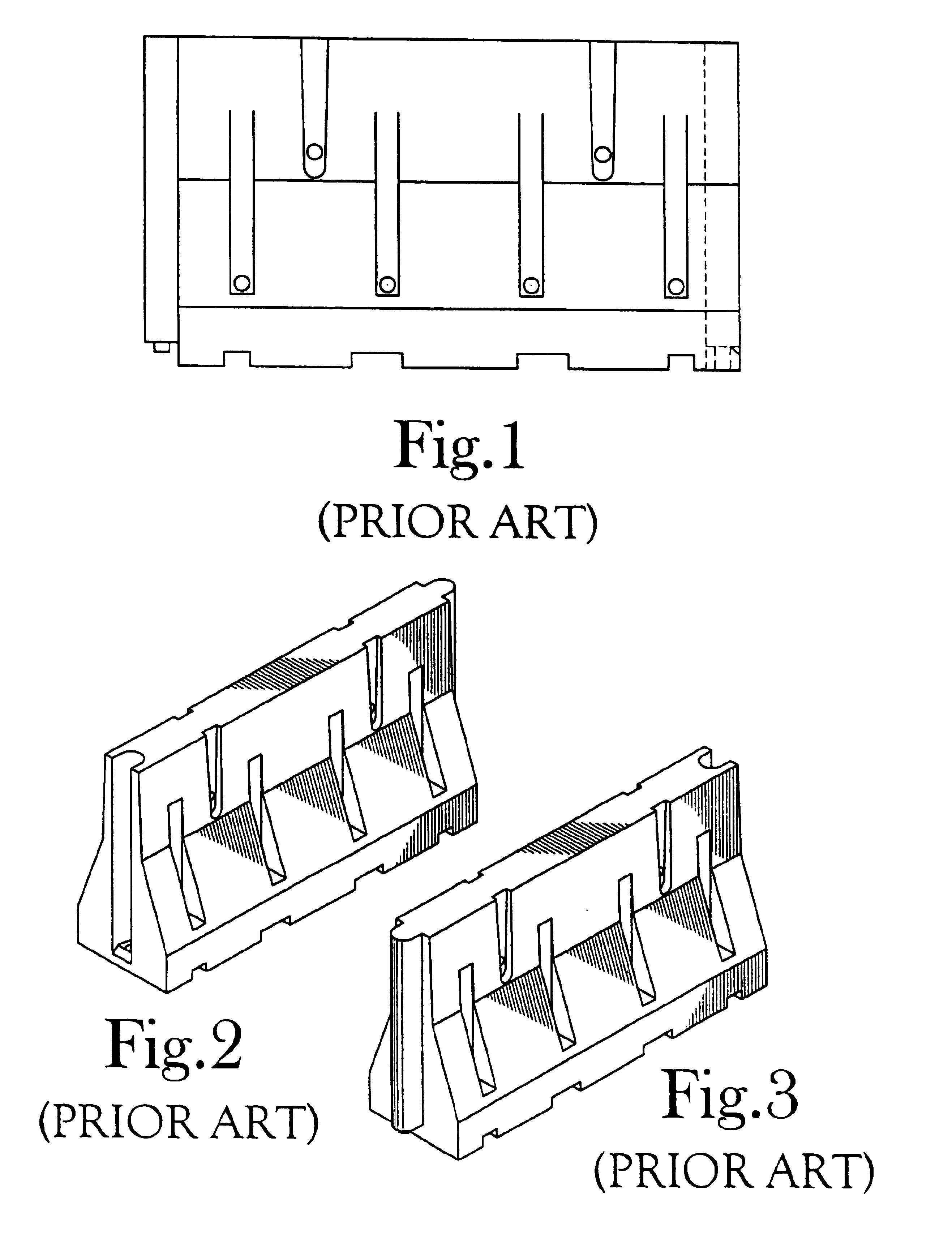
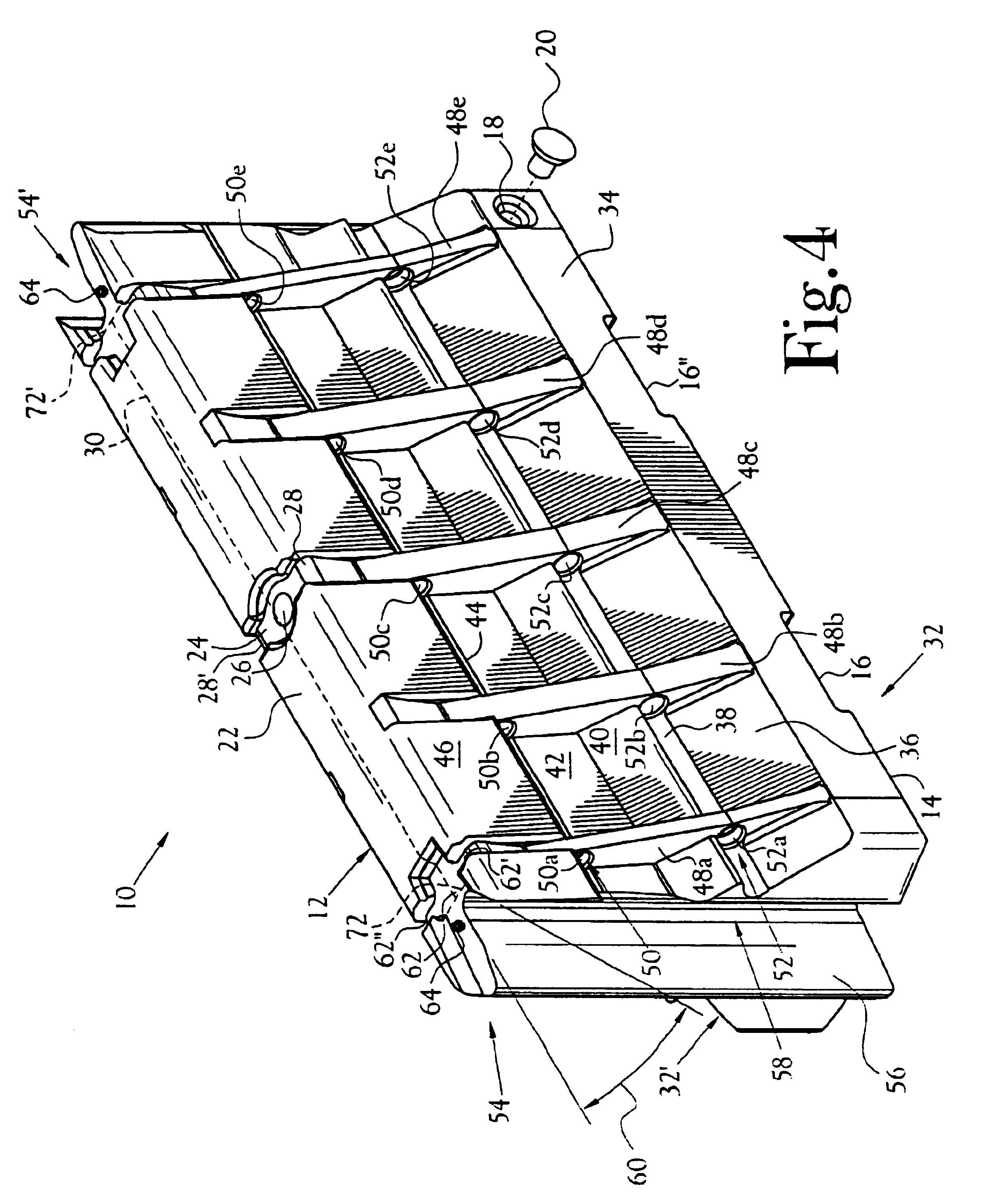
Protection barrier system
A protection barrier system for energy-absorption of impacts includes an elongated barrier defining a chamber therein. The barrier includes side walls having a plurality of connected non-vertical wall segments and a plurality of buttresses positioned vertically at spaced apart locations along each side wall. One or more guide channels are positioned on each side wall in horizontal alignment with similar guide channels on like-configured barriers. A coupling is disposed on each opposed end of the barrier for coupling of either barrier end juxtaposed in end-to-end nested arrangement with like barriers. A supplemental energy-absorbing system is connectable between opposed ends of end-to-end coupled barriers, providing energy-absorbing tubes removably inserted through each guide channel of each barrier. Cables are extendable through the tubes in the guide channels of the nested barriers, providing additional energy-absorption and deterrence from breaching of the barriers. A method of manufacture for the protection barrier is also disclosed.
Owner:SAFETY BARRIERS
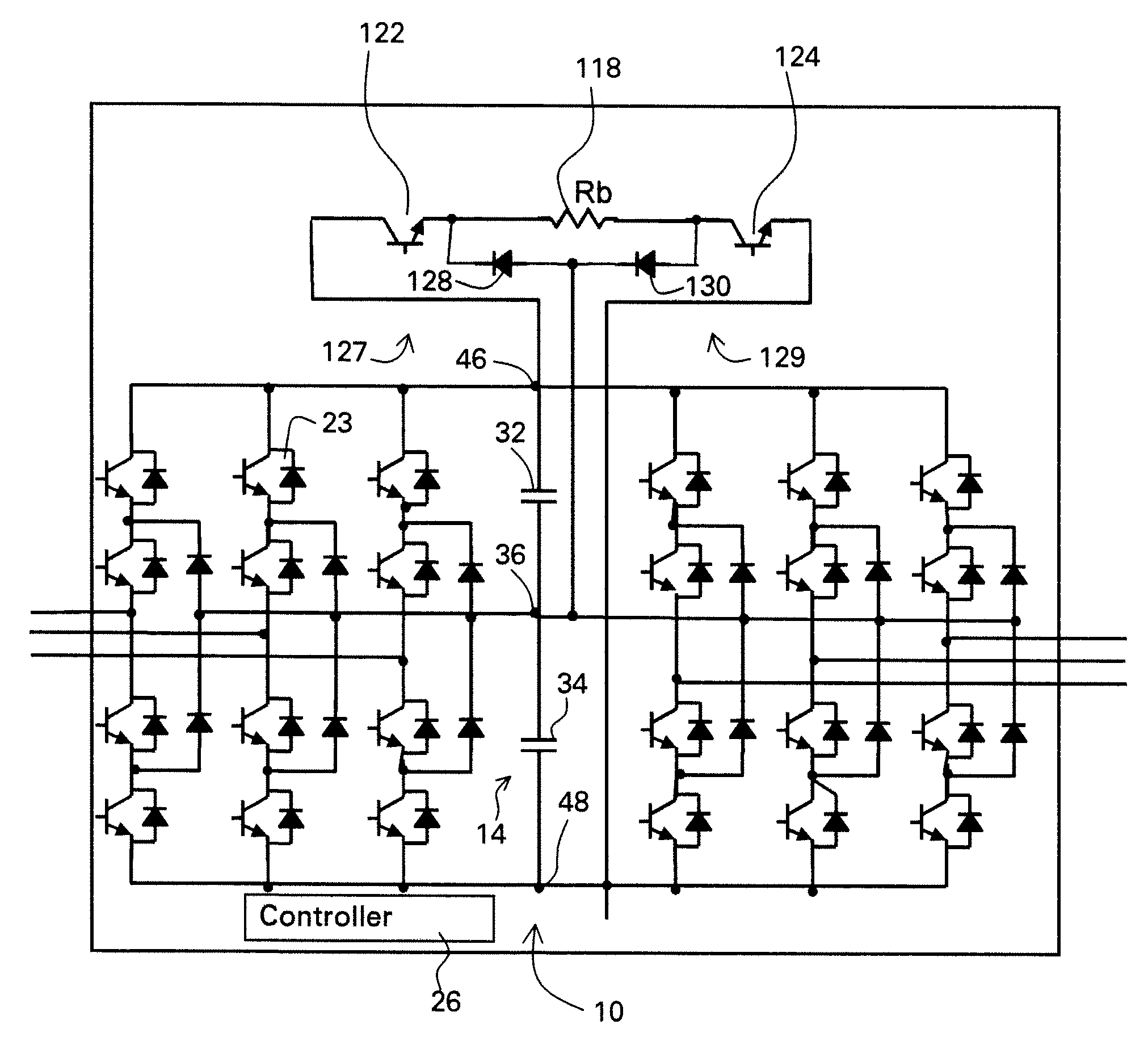
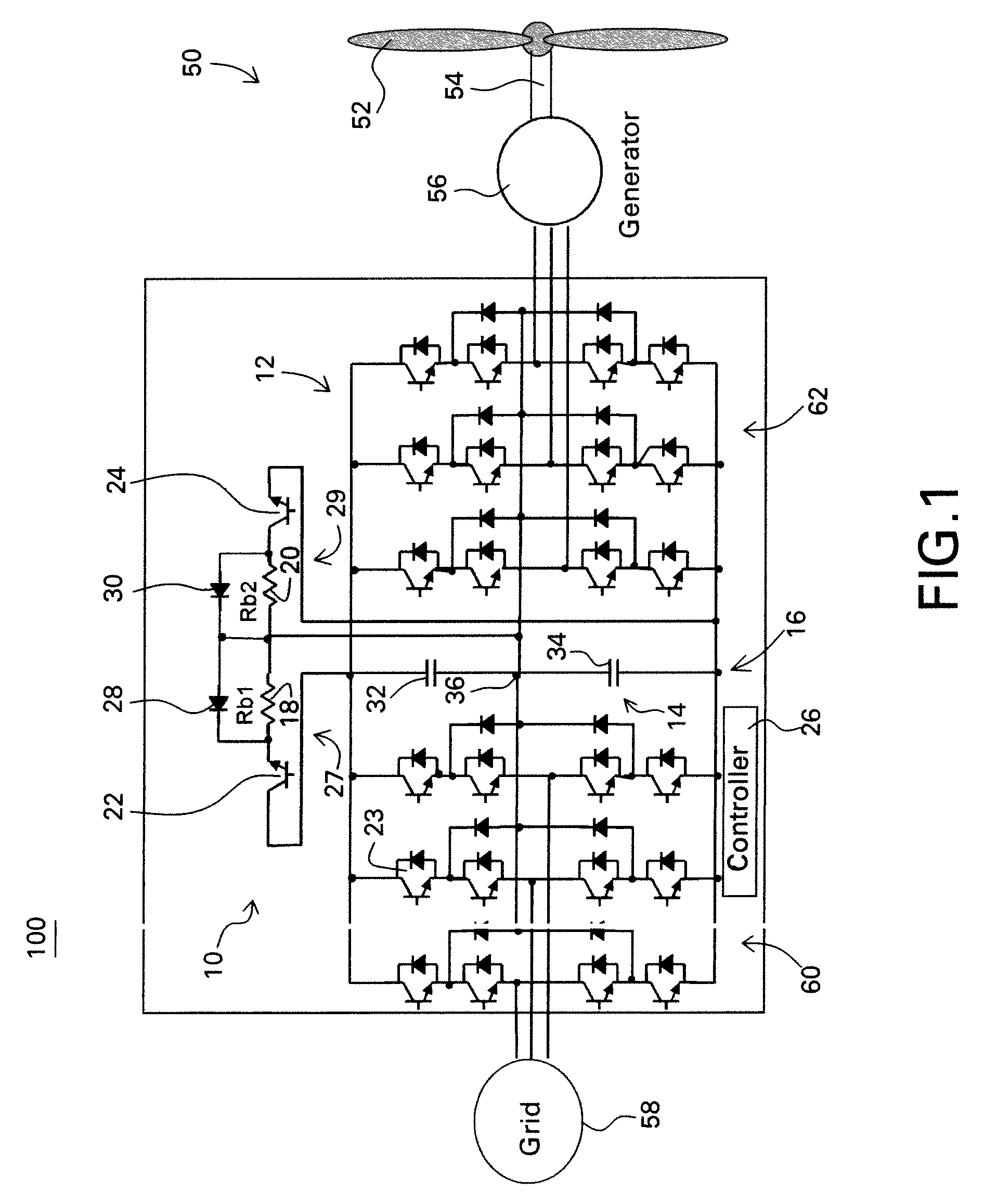
Protective circuit and method for multi-level converter
ActiveUS7573732B2Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalEngineering
A protective circuit for a multi-level converter including a DC link capacitor bank includes: an energy absorbing element; switches, wherein at least two of the switches each couple the energy absorbing element to the capacitor bank; and a controller configured to provide control signals to the switches to selectively actuate the switches to enable control of energy dissipation and to enable control of voltage balance on the capacitor bank of the multi-level converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Modular sports helmet
InactiveUS20120317705A1Improve performanceStage increaseHelmetsHelmet coversModularityEnergy absorbing
The present disclosure provides a modular helmet comprising a shell, an energy-absorbing layer, and at least one energy-absorbing panel or other modular element, which is removably attached to the helmet. For example, in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, an improved football helmet comprises an outer shell with six apertures, an inner, energy-absorbing layer, a face mask, and six modular panels, each of which sits inside an aperture and is releasably attached to the outer shell.
Owner:VYATEK SPORTS
Stabilizer for switch-mode powered RF plasma
InactiveUS6046546AAvoid instabilityEffect can be causedElectric discharge tubesAc-dc conversionHarmonicInstability
Circuitry and techniques designed to allow stable and continuous delivery of alternating power to a plasma with switch-mode power supply (16) include a variety of embodiments. Parallel, series, and other circuit elements connected across switching element (7) are tuned so that energy at other than the fundamental frequency is absorbed and dissipated. This energy may be only at the second harmonic or it may be across broad frequency ranges through selecting high impedance at the fundamental frequency and relatively low impedance at other frequencies. In overcoming instabilities, oscillations, and even changing class of operation of the switch-mode power supply, the stabilizing element absorbs the energy to avoid allowing it to affect switch (7) of power supply (16).
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Method and apparatus for vibrational damping of implantable hearing aid components
A method and apparatus for minimizing or eliminating the transmission of vibration away from, as well as induction of vibration into, a middle ear driving or sensing structure of an at least partially implantable hearing aid system. A vibration damping intermediary layer may be positioned between an originating structure and its housing, and / or between a housing and its mounting to the surrounding. The intermediary layer may be formed of a structure having elastic and damping characteristics. The intermediary layer may also have a number of fluid flow paths for absorbing energy and damping vibration.
Owner:ST CROIX MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com