Patents
Literature
6139results about "Roadway safety arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
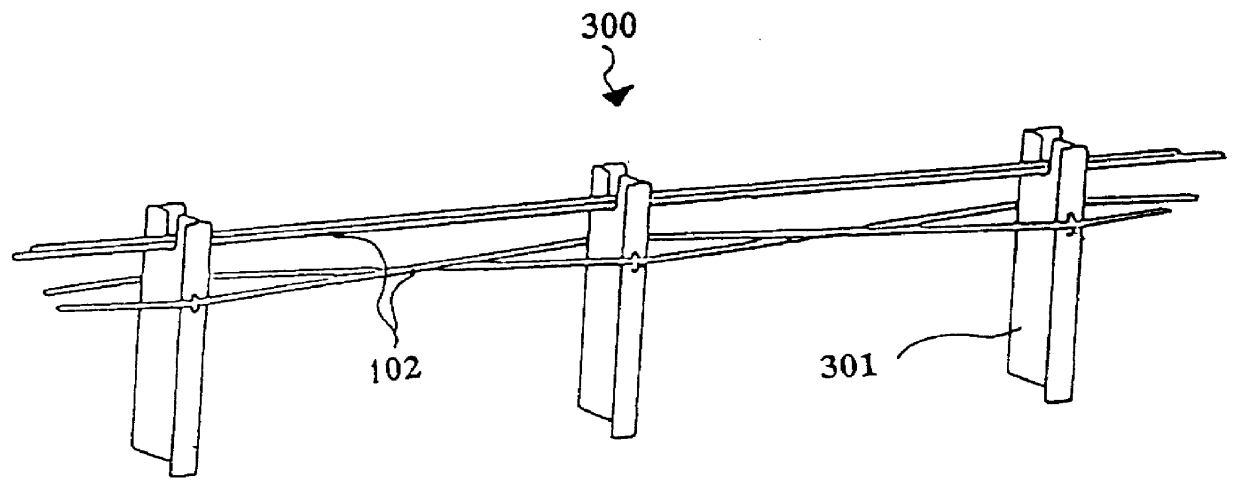
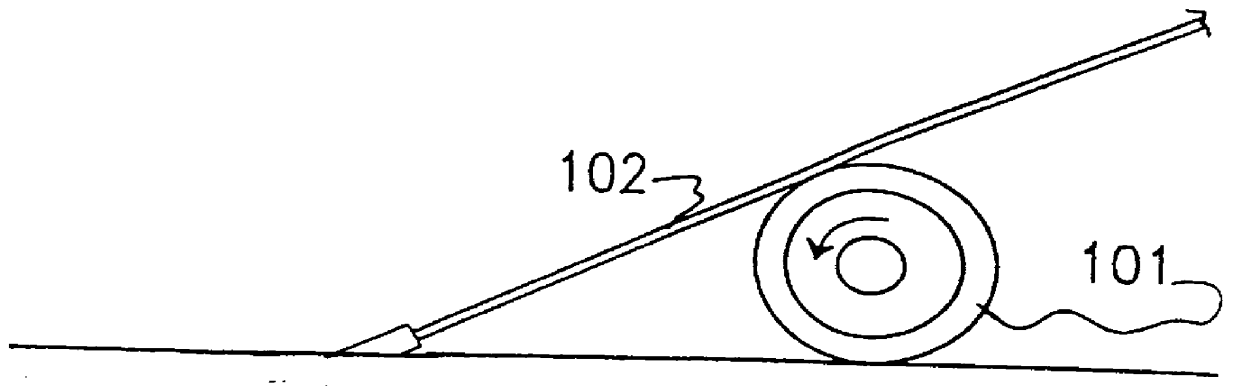
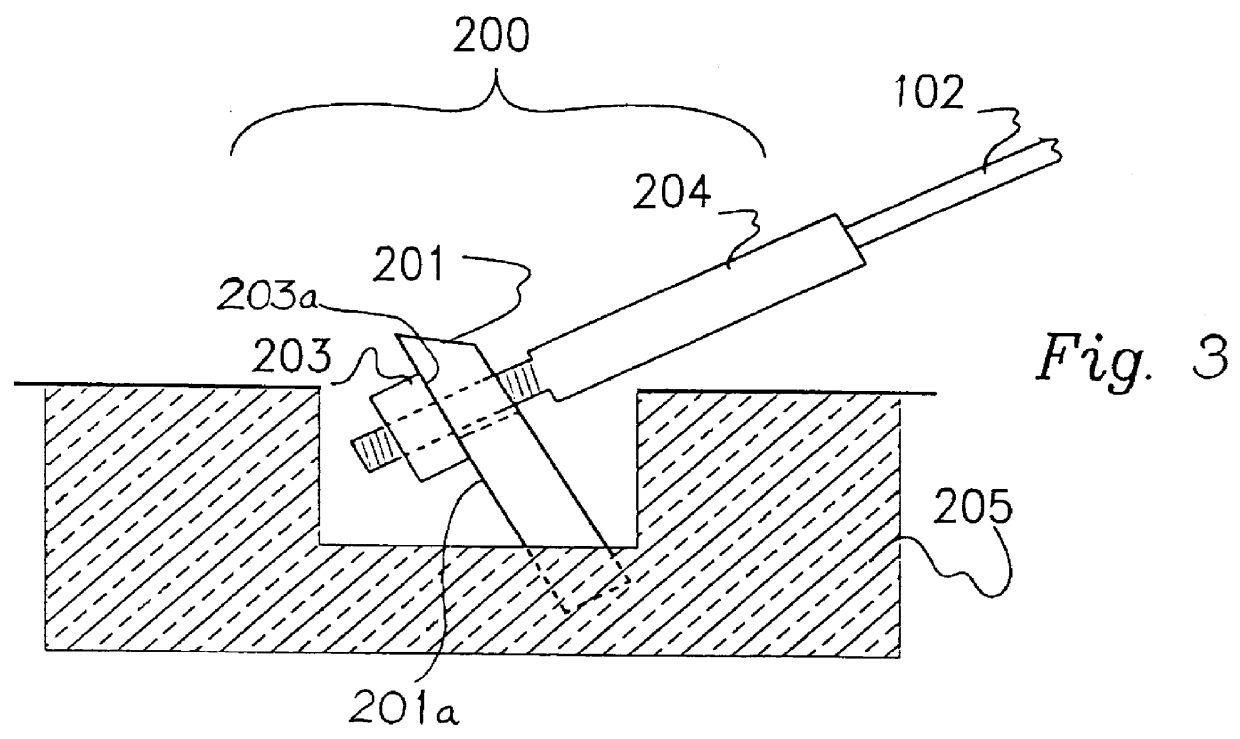
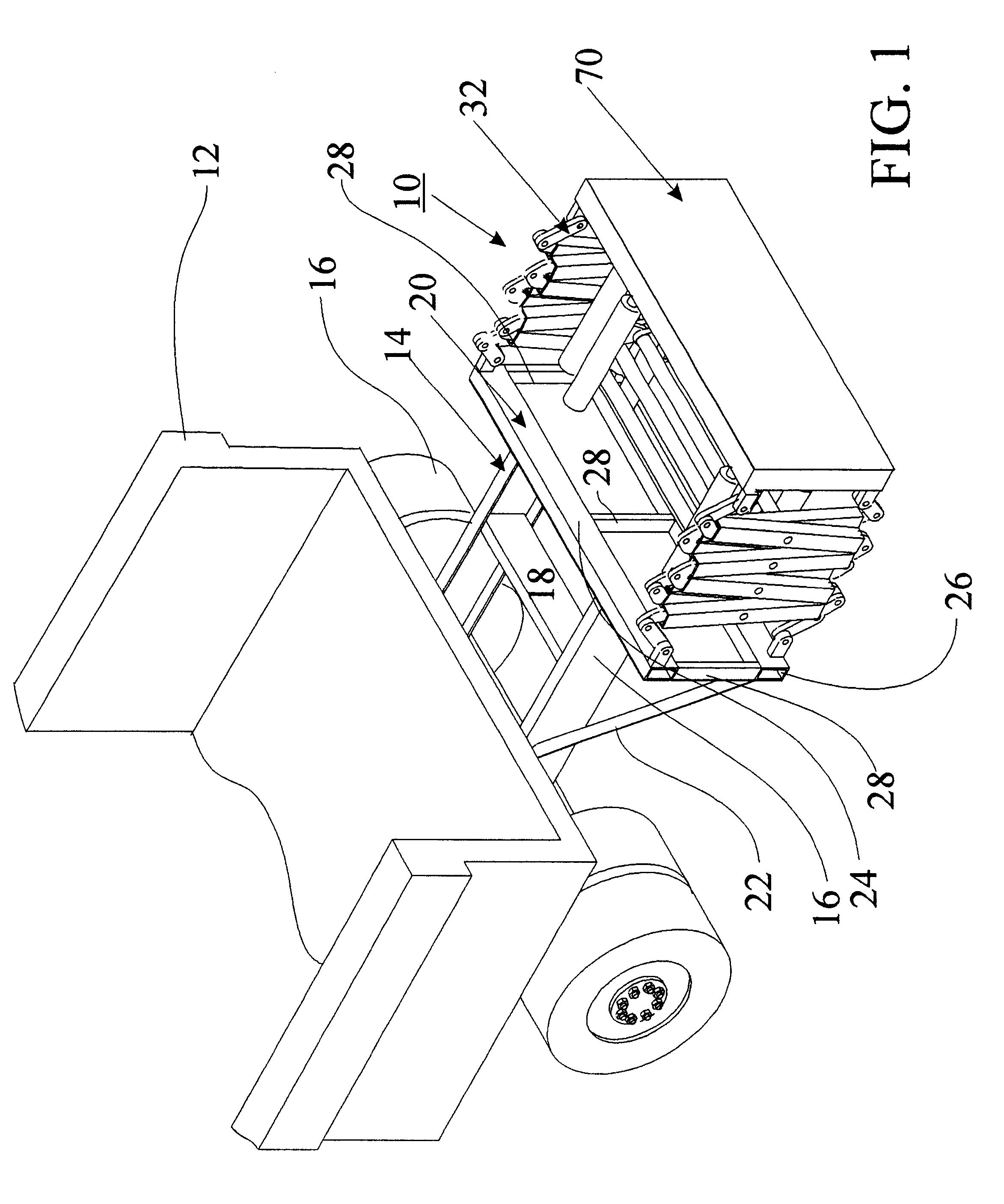
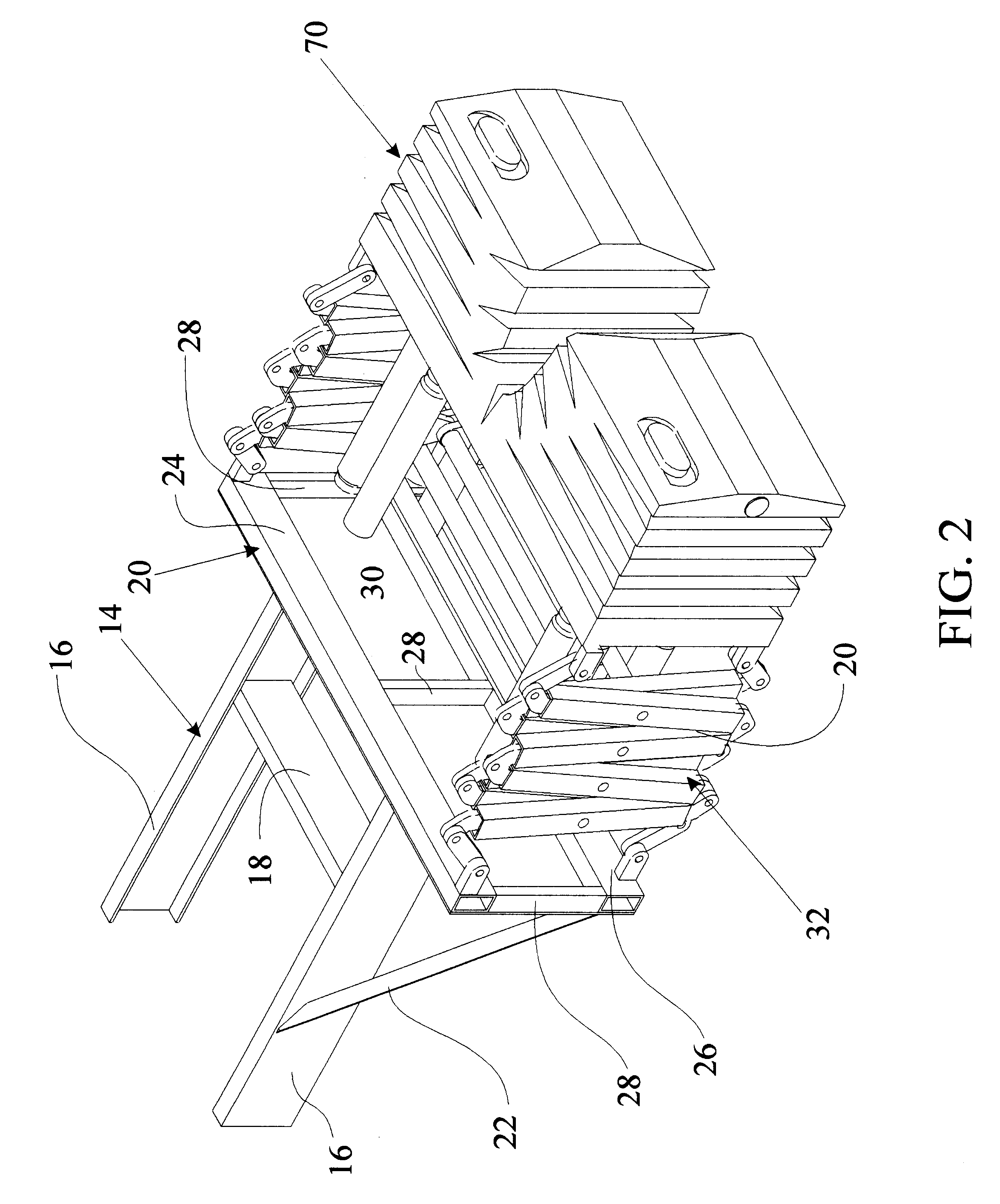
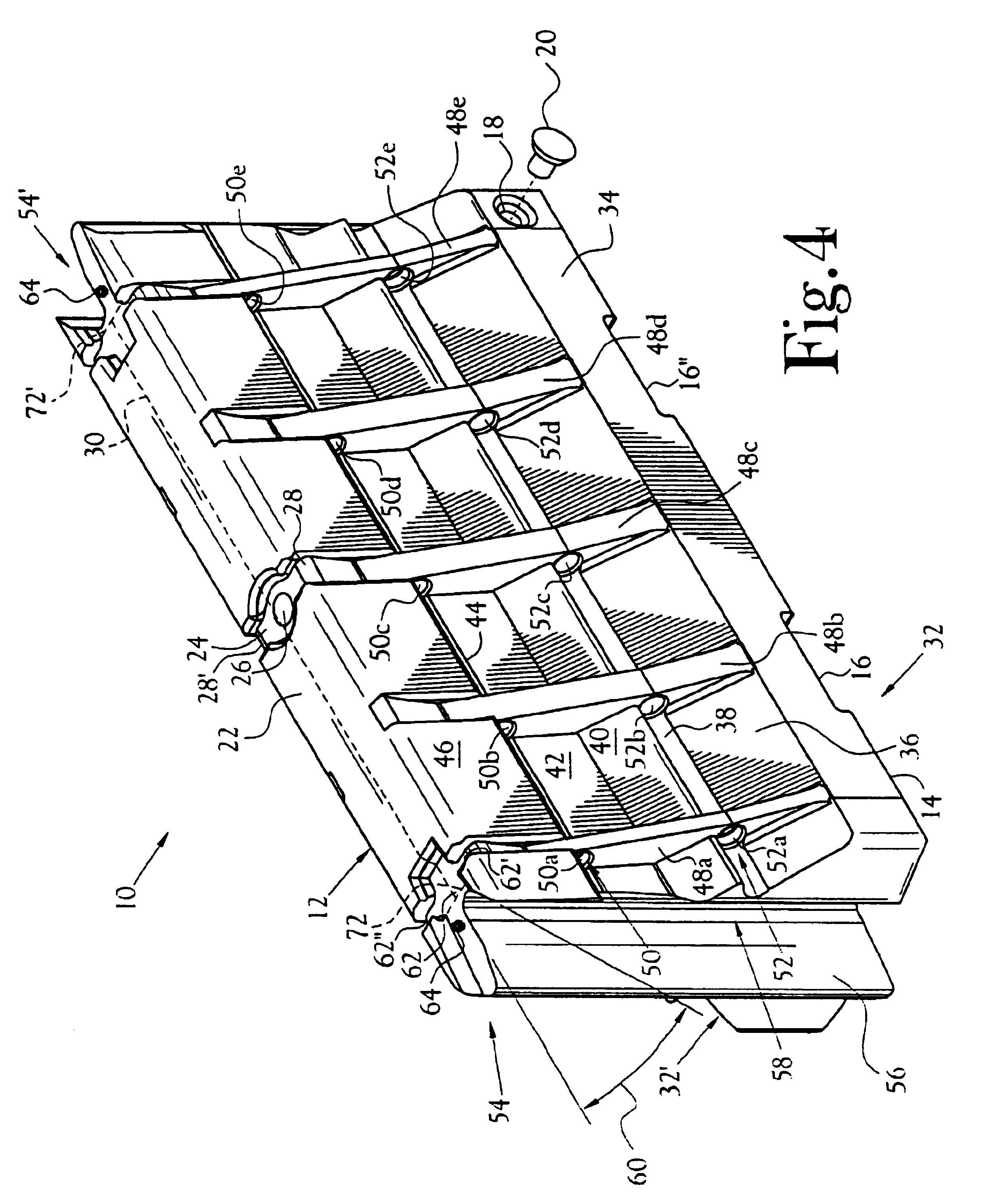
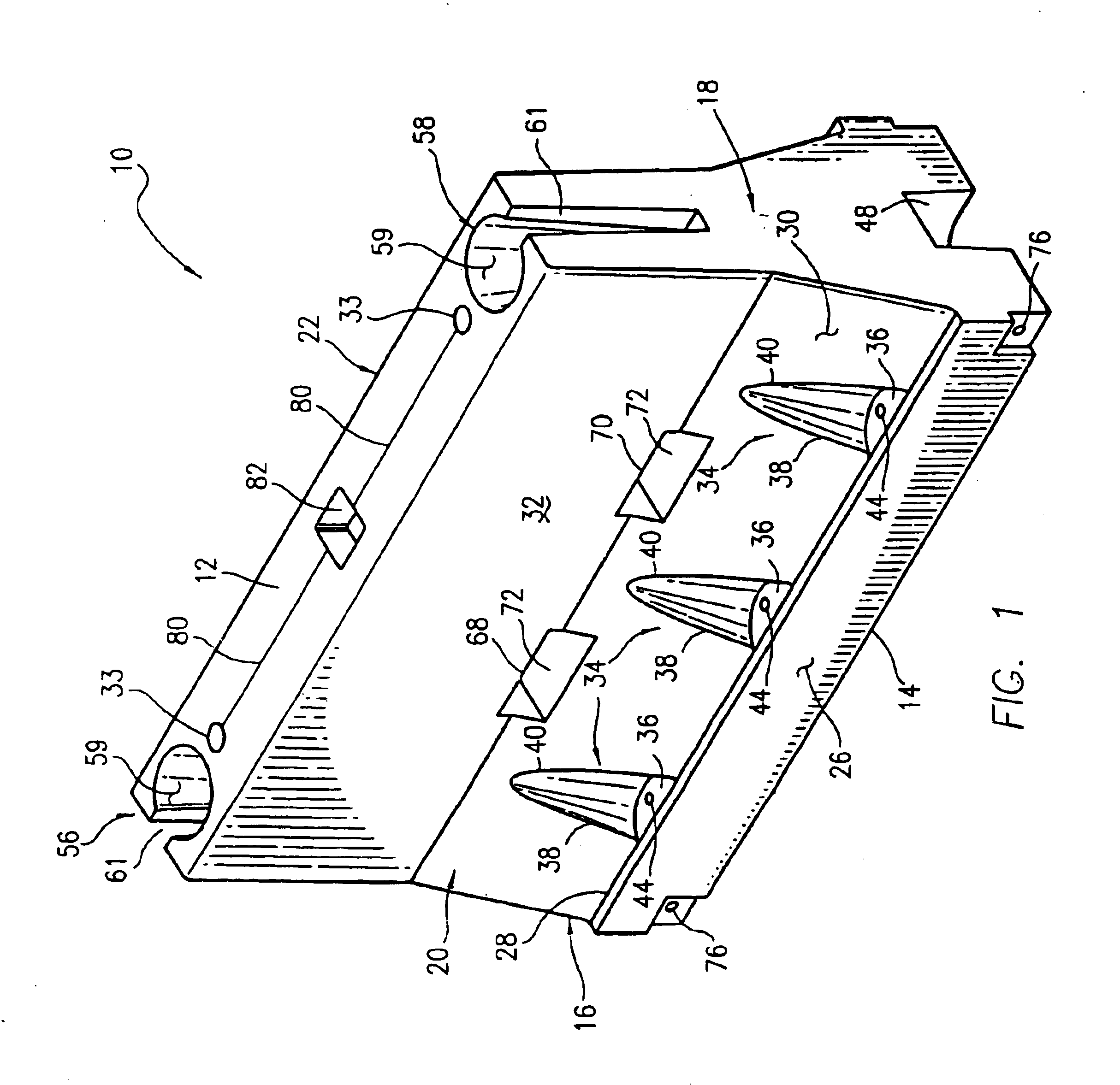
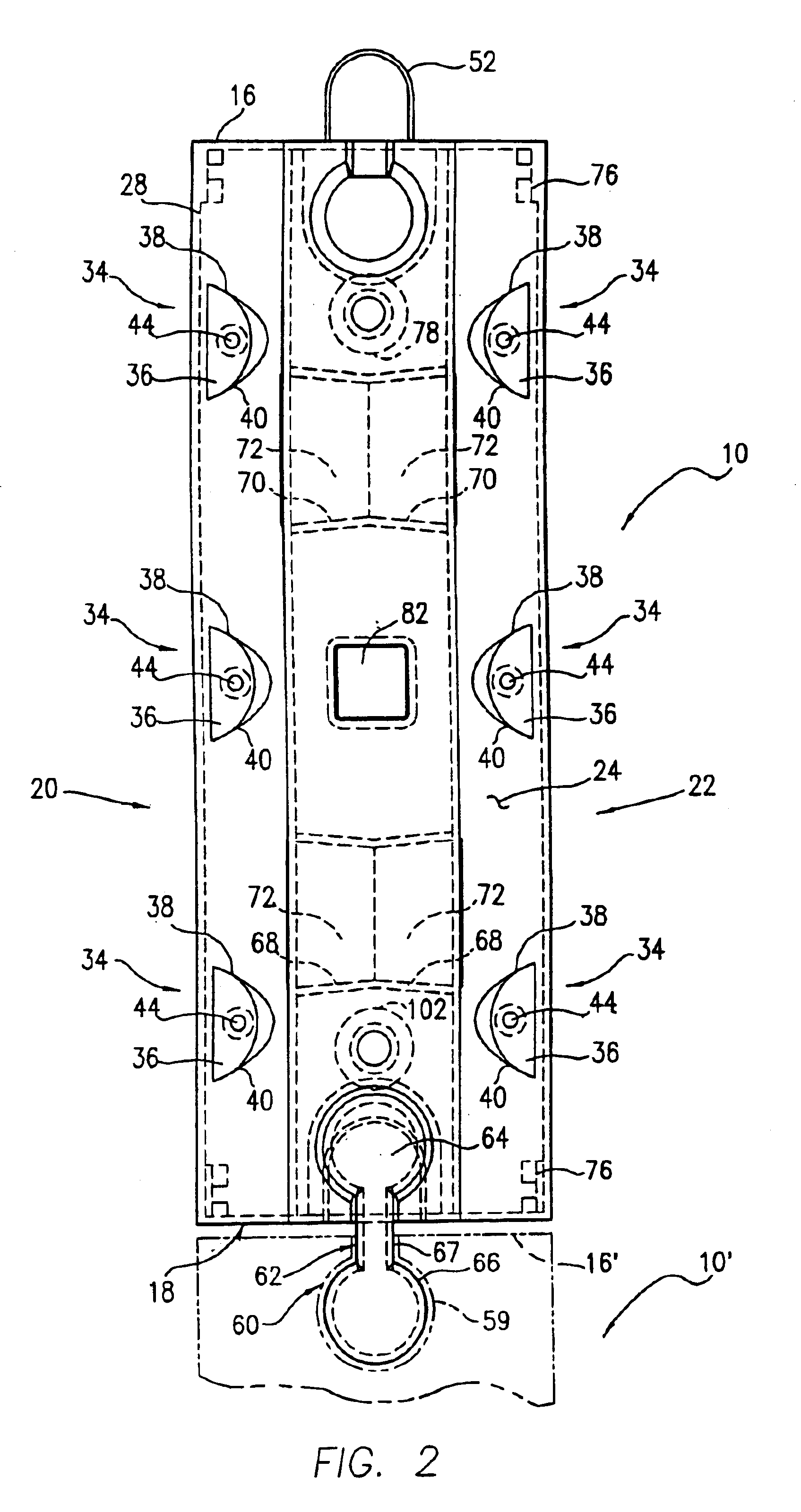
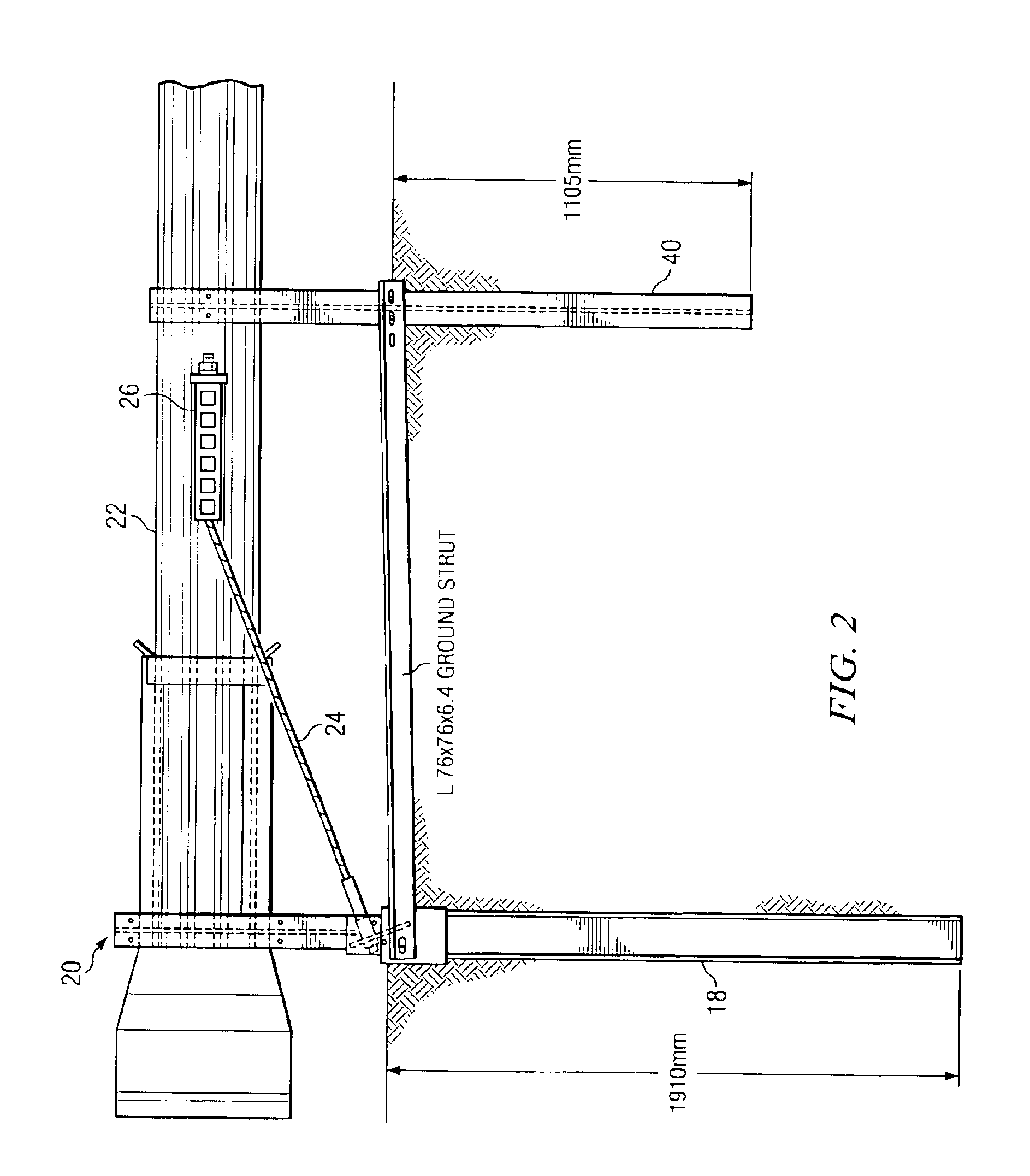
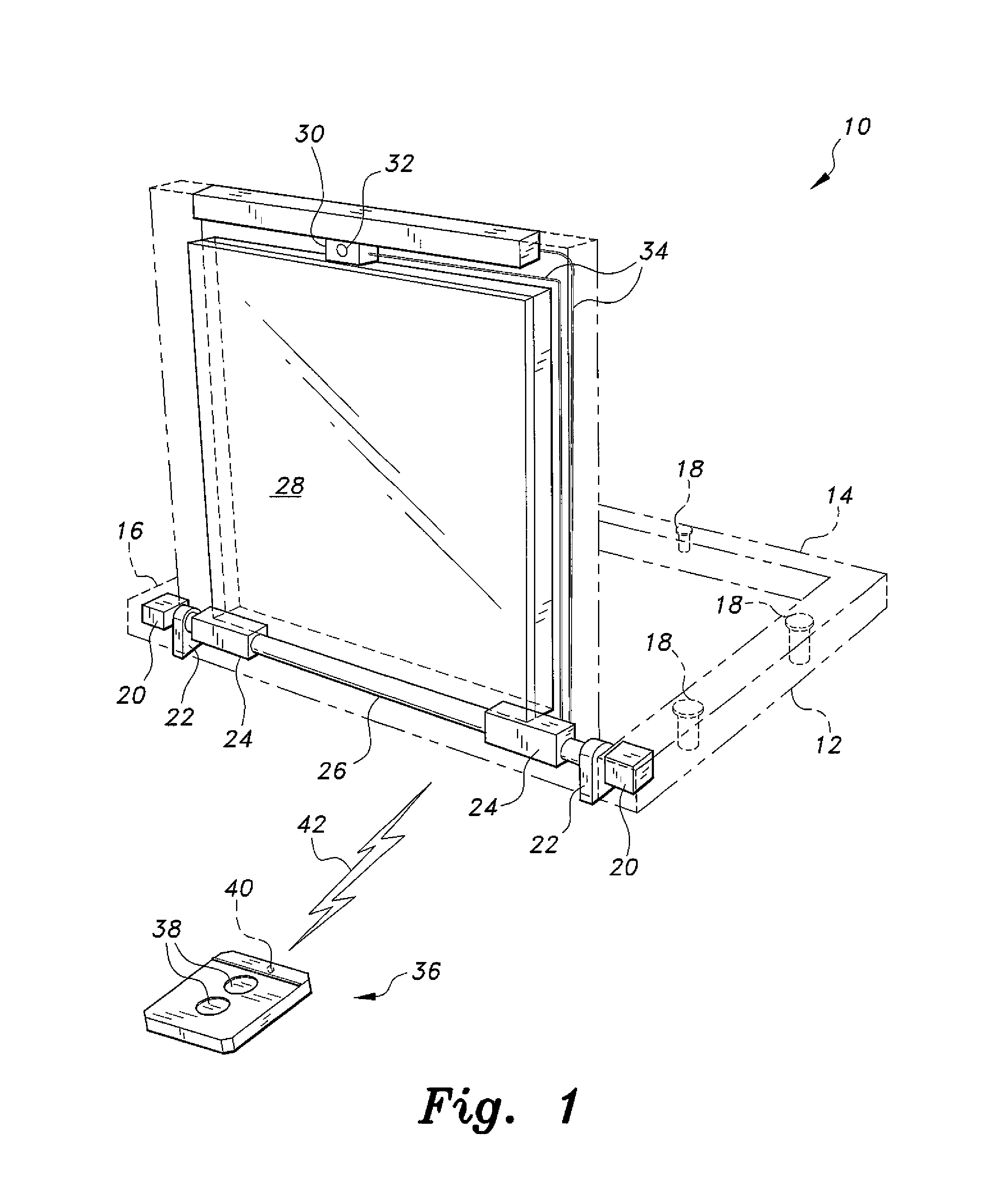
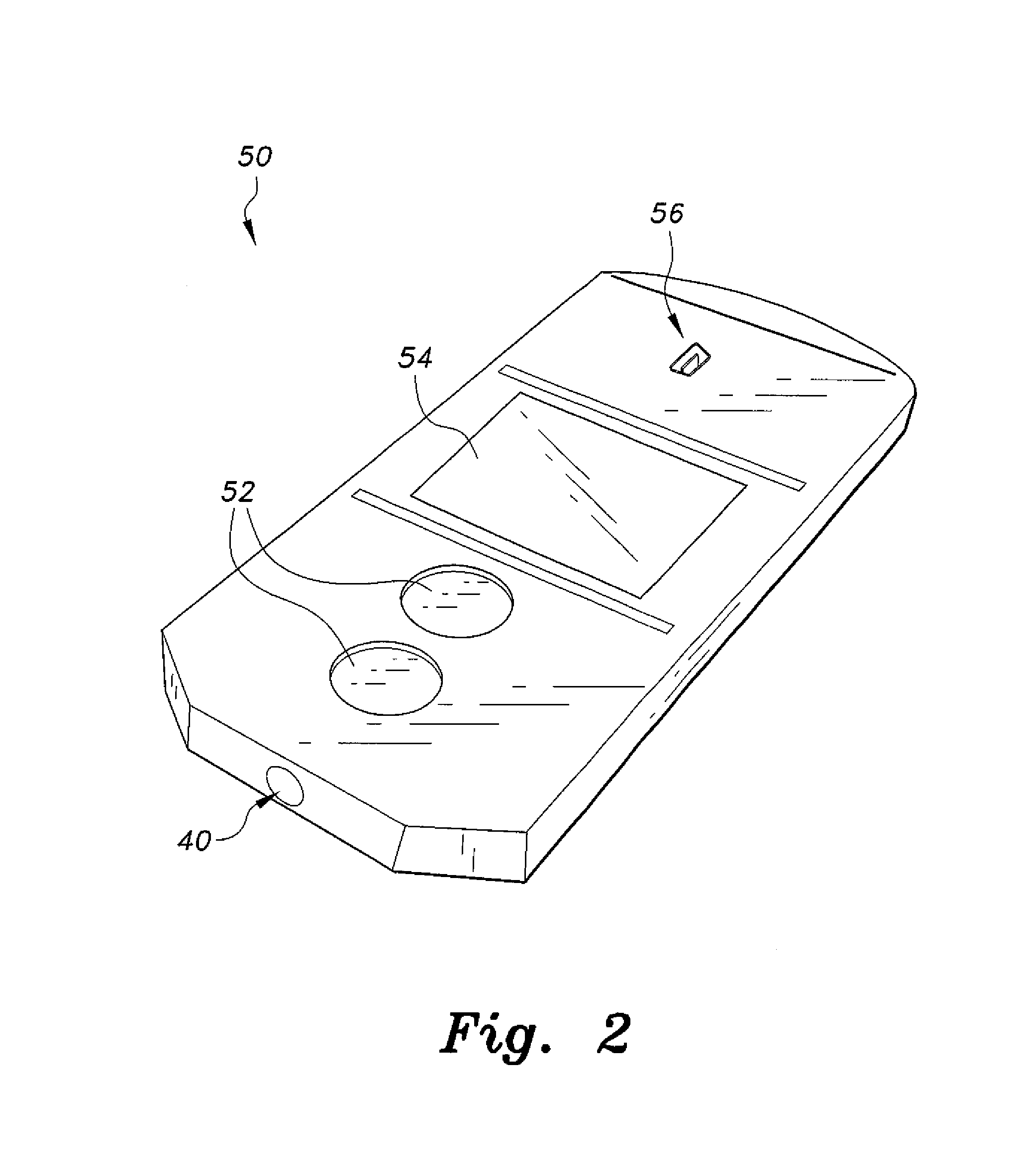
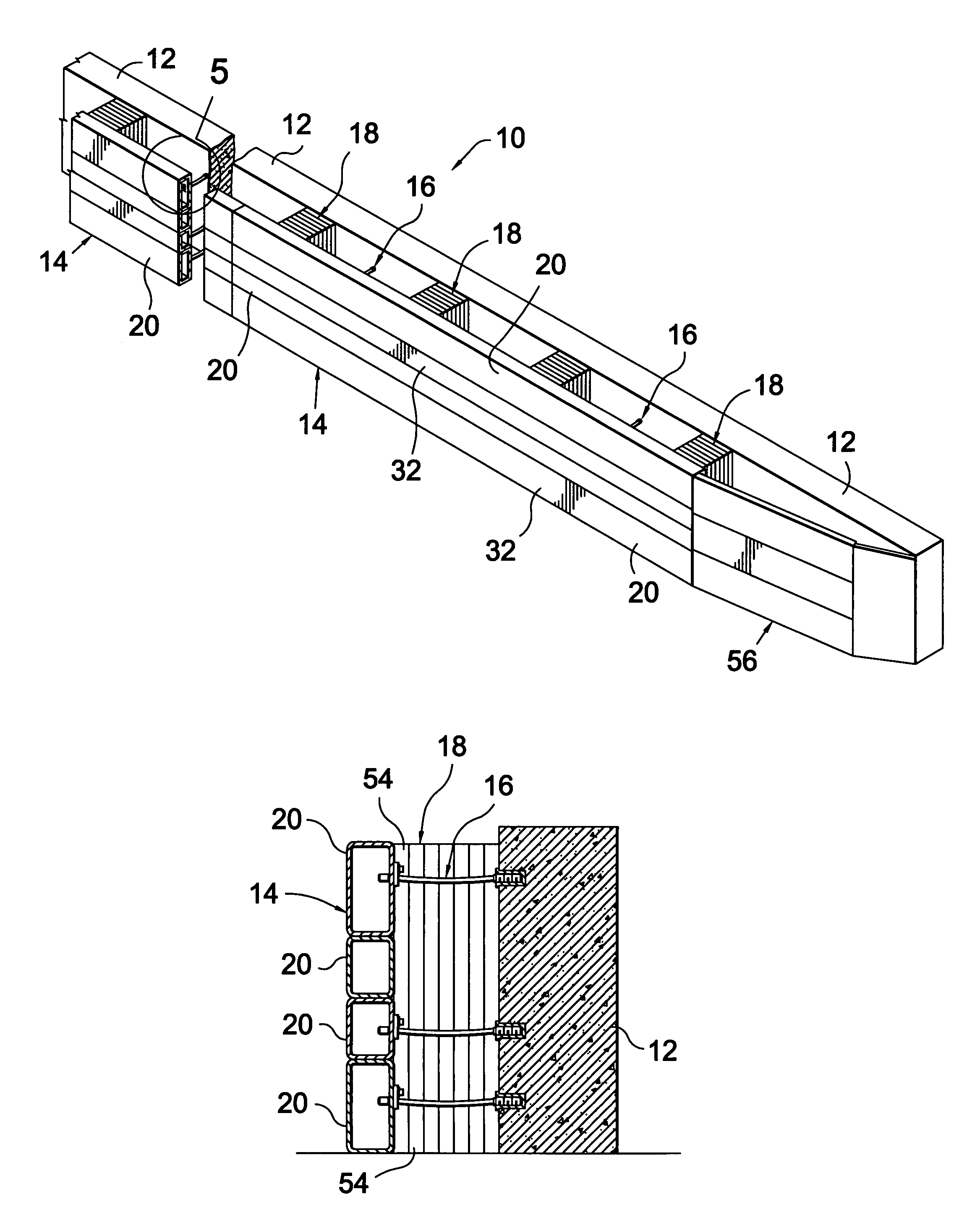
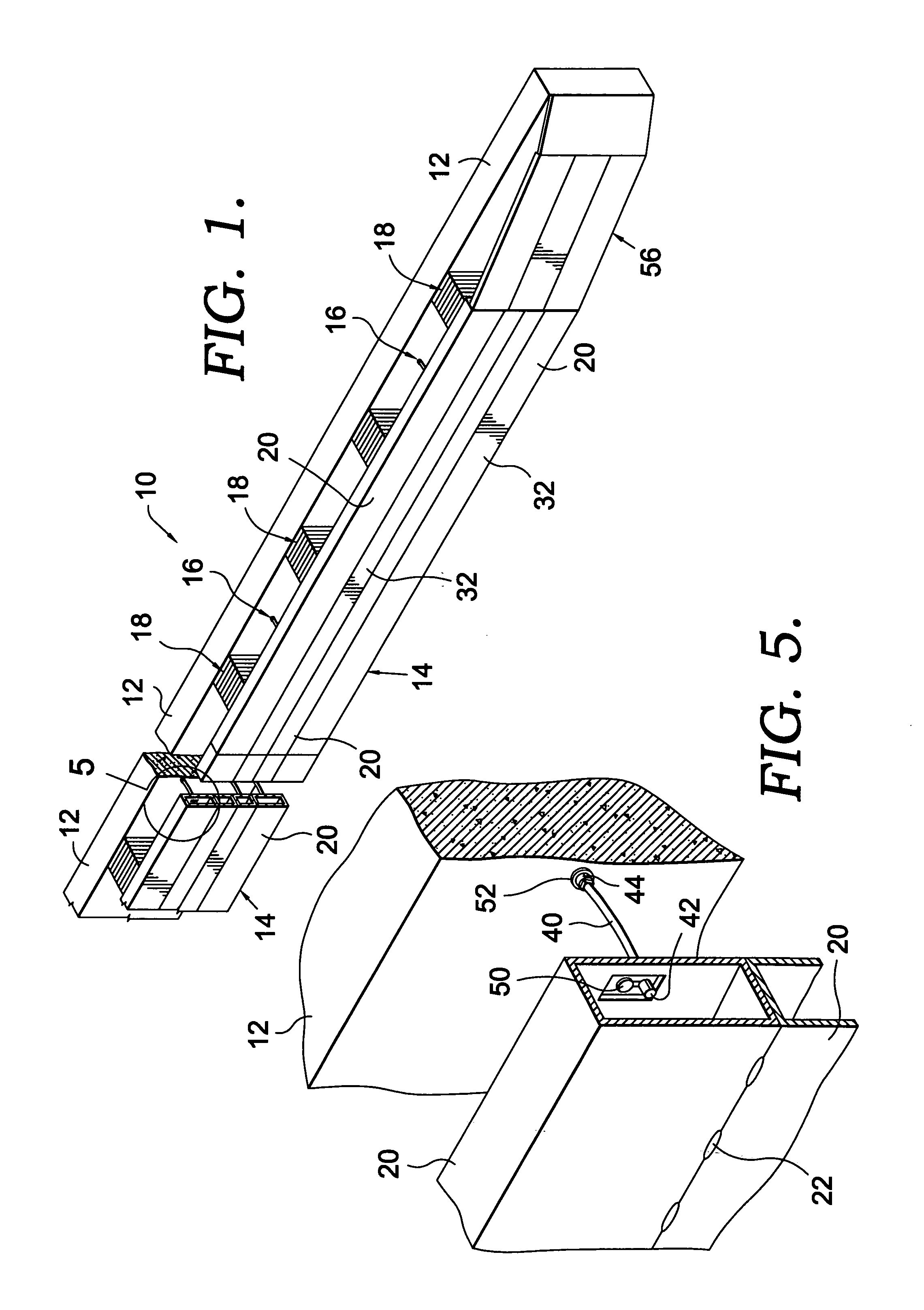
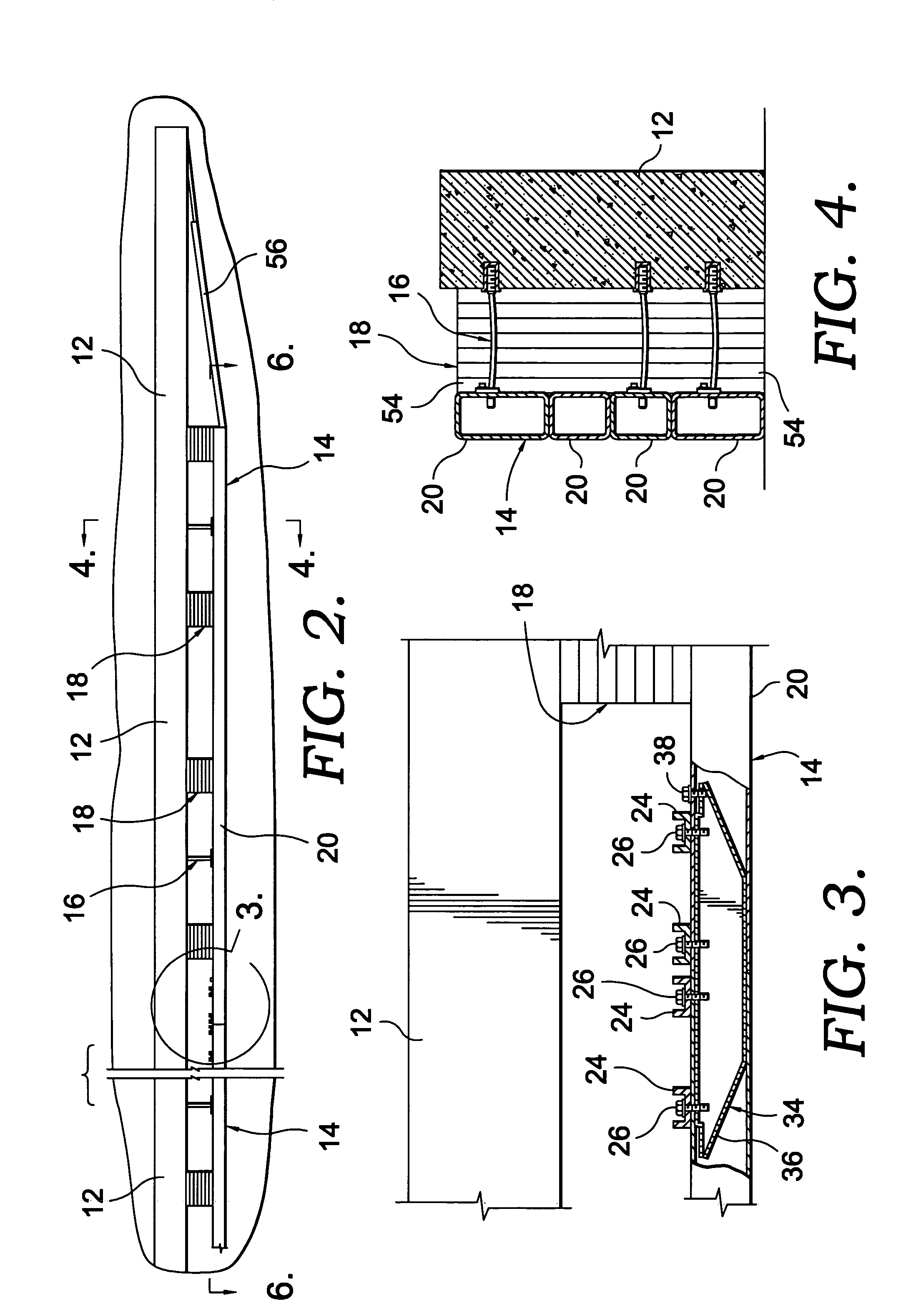
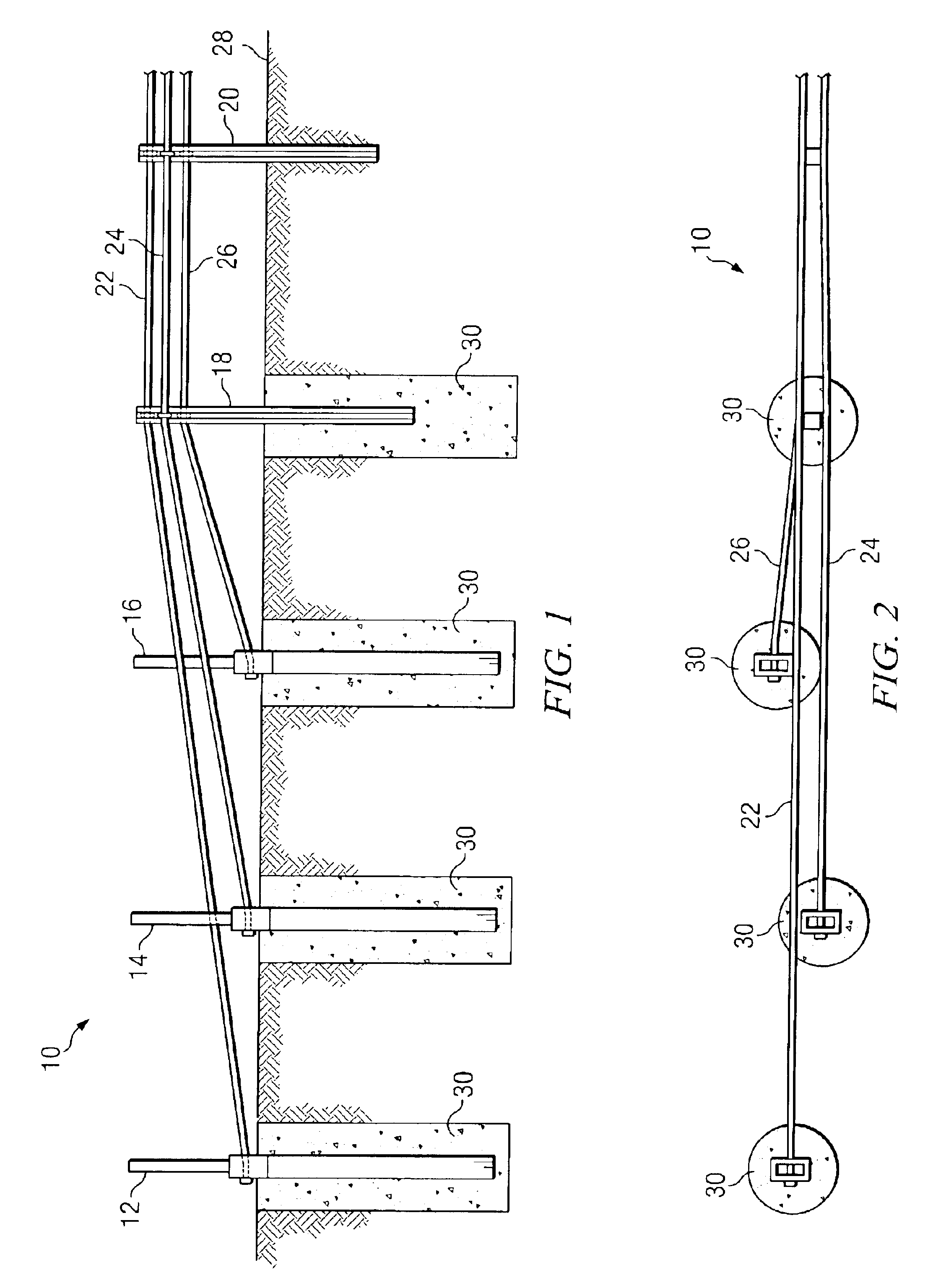
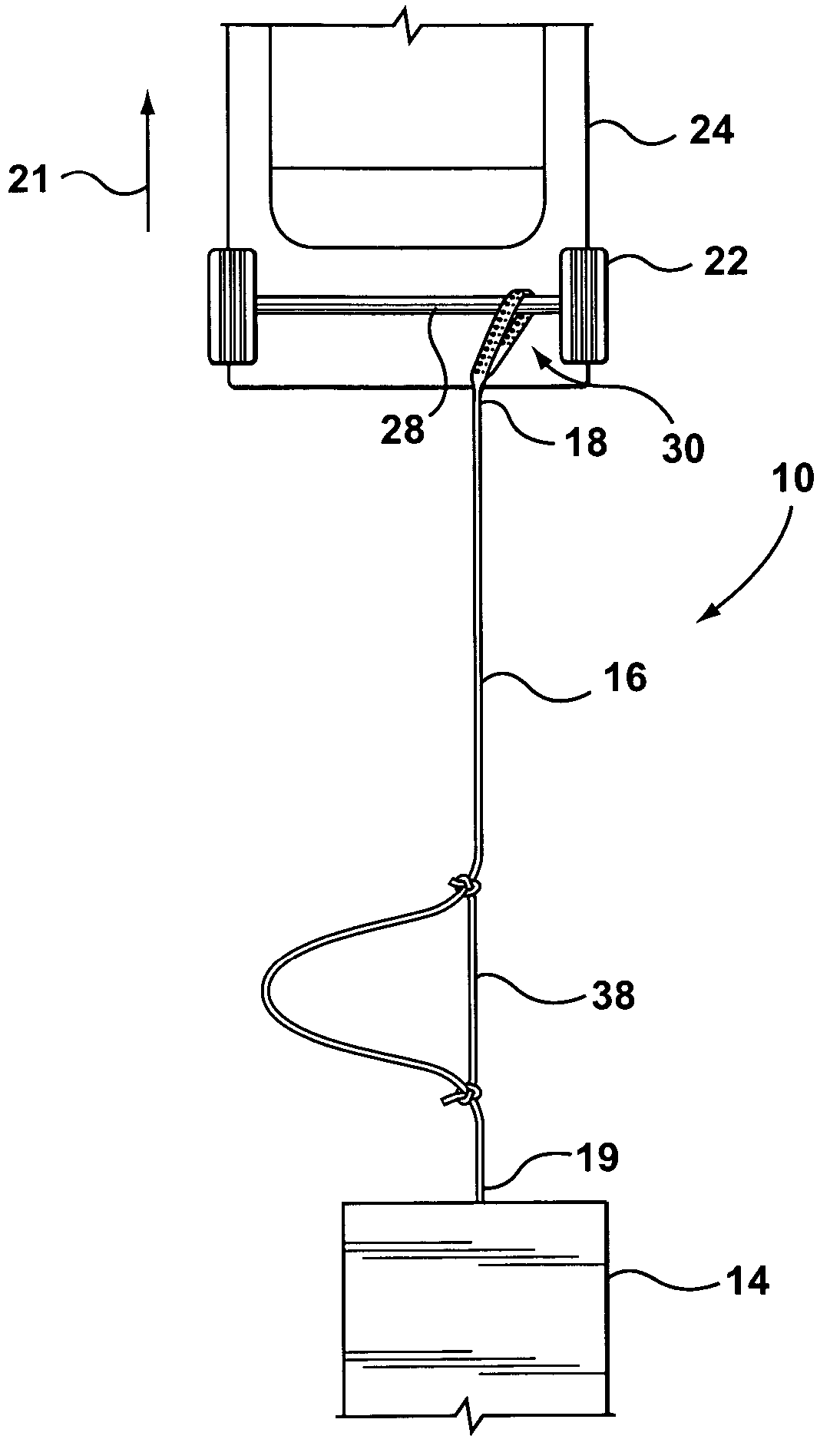
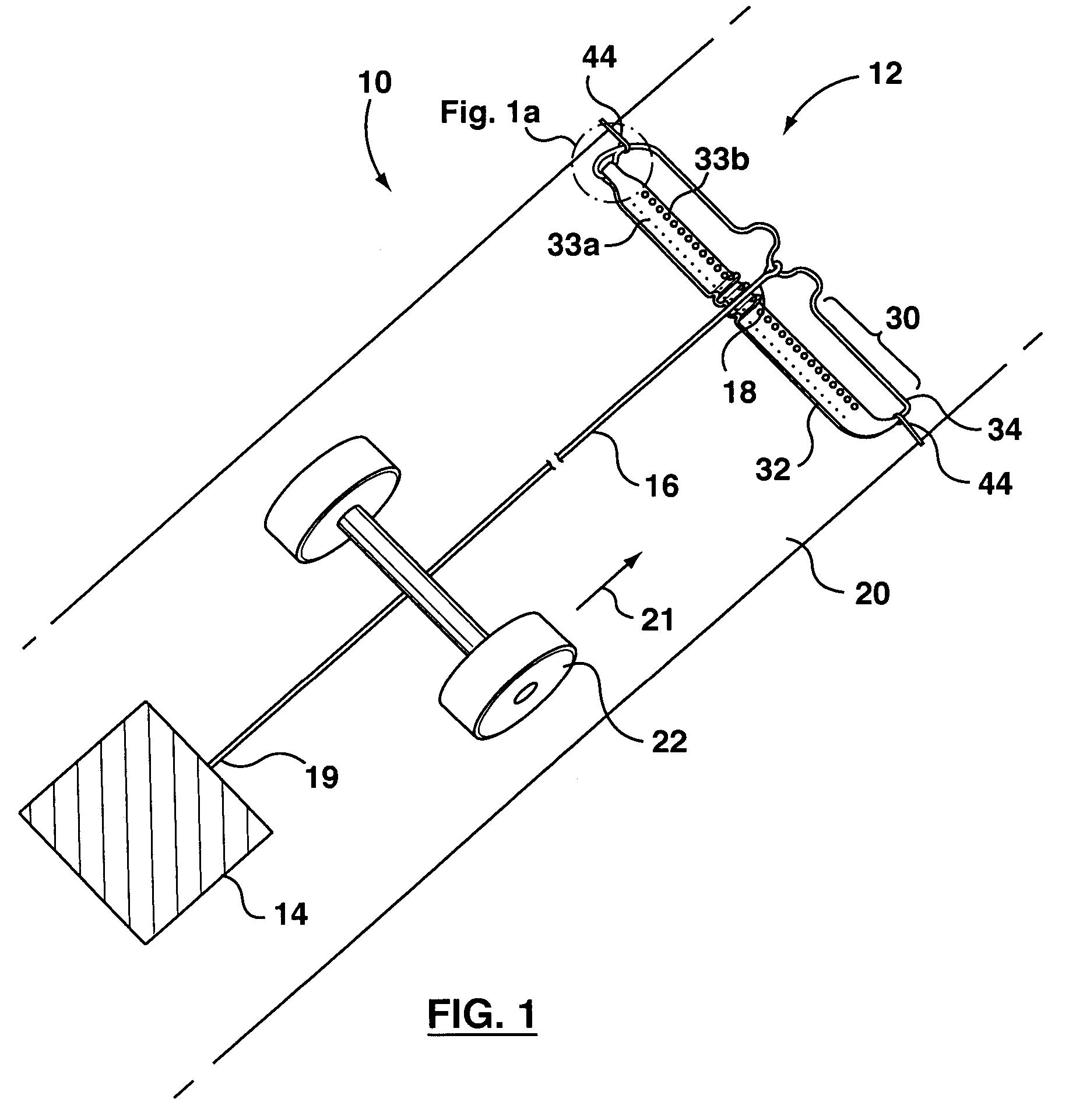
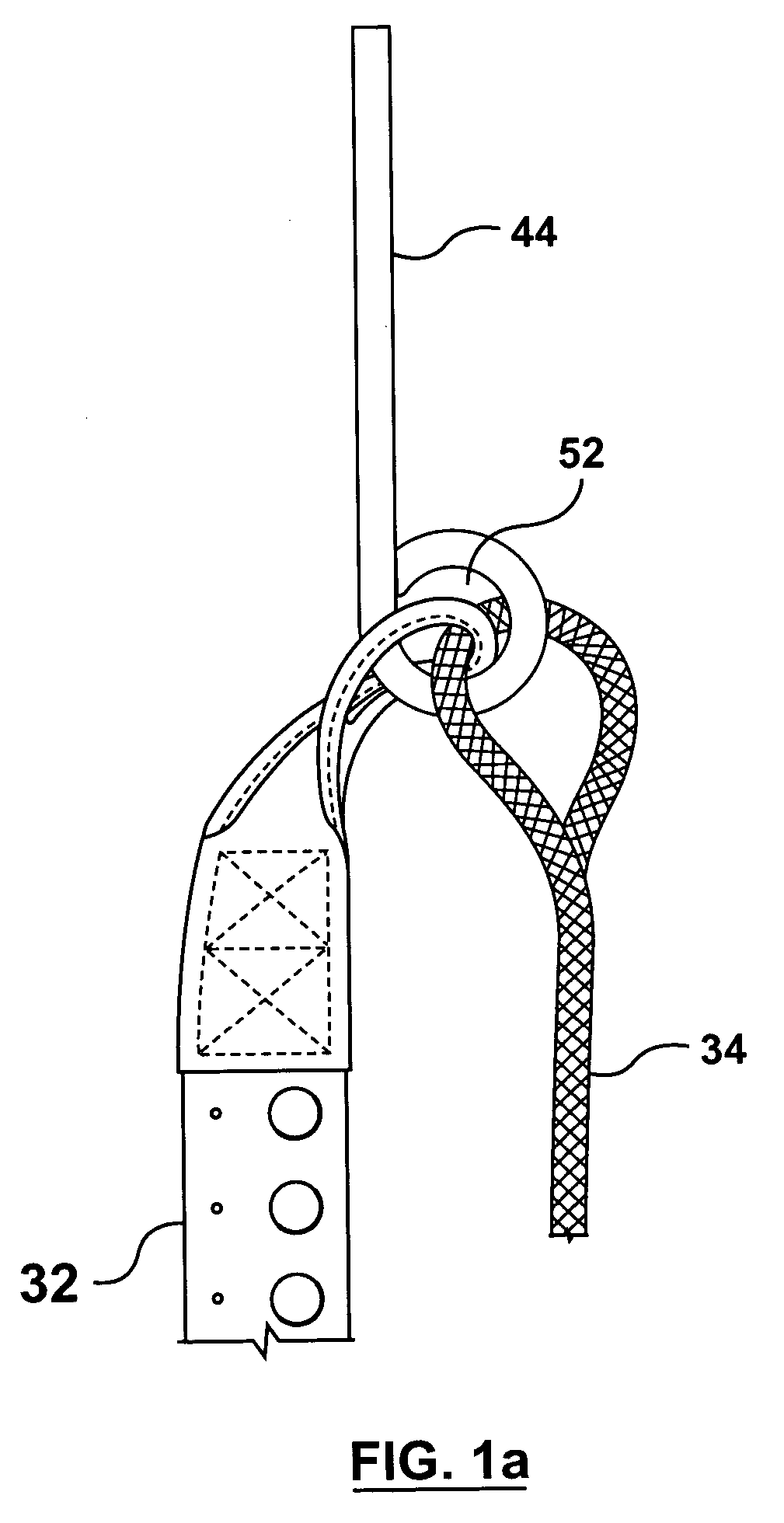
Anchor for cables
A cable safety barrier has means for disengagement of the cable from an anchor portion of the cable safety barrier when certain vehicle impact conditions are met. Disengaging of the cable may involve allowing a cable end fitting to escape from an open ended slot, when the cable is deflected upwards, or causing the cable fitting to fail.
Owner:HILL & SMITH LTD
Damped crash attenuator
Crash attenuator for protecting a truck or stationary structure from damage resulting from impact of an object including a frame mountable to the structure, a bumper having an impact-receiving face adapted to receive an impact from the object, a movable displacement structure interposed between the frame and bumper and having a first position in which the bumper is relatively distant from the frame and a second position in which the bumper is relatively proximate to the frame, and an energy dissipation system coupled to the displacement structure for dissipating impact energy of the object received by the bumper which causes the displacement structure to be moved from the first position toward the second position. The energy dissipation system includes one or more deformable members which deform upon movement of the displacement structure from the first position toward the second position with such deformation causing dissipation of impact energy.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
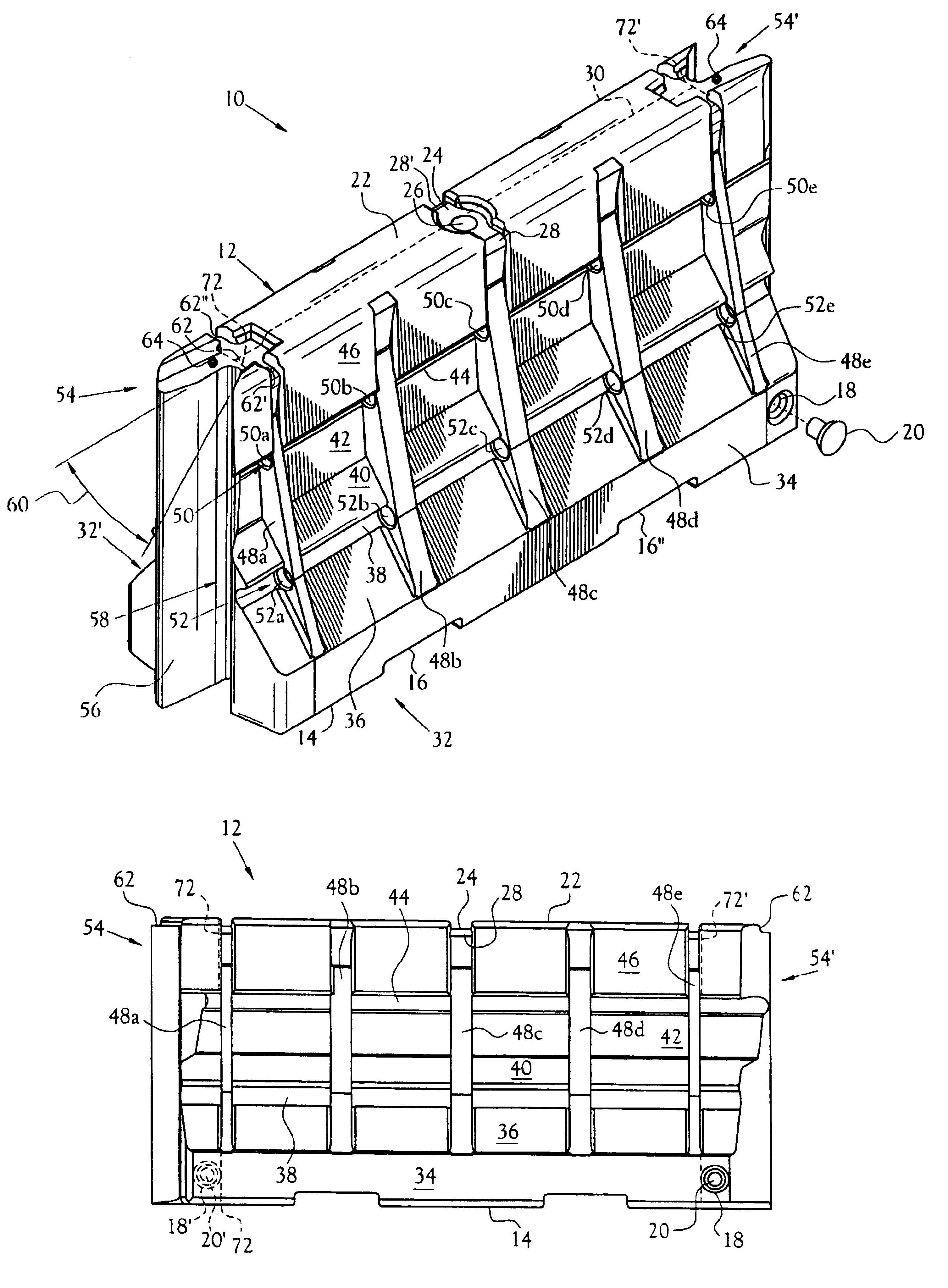
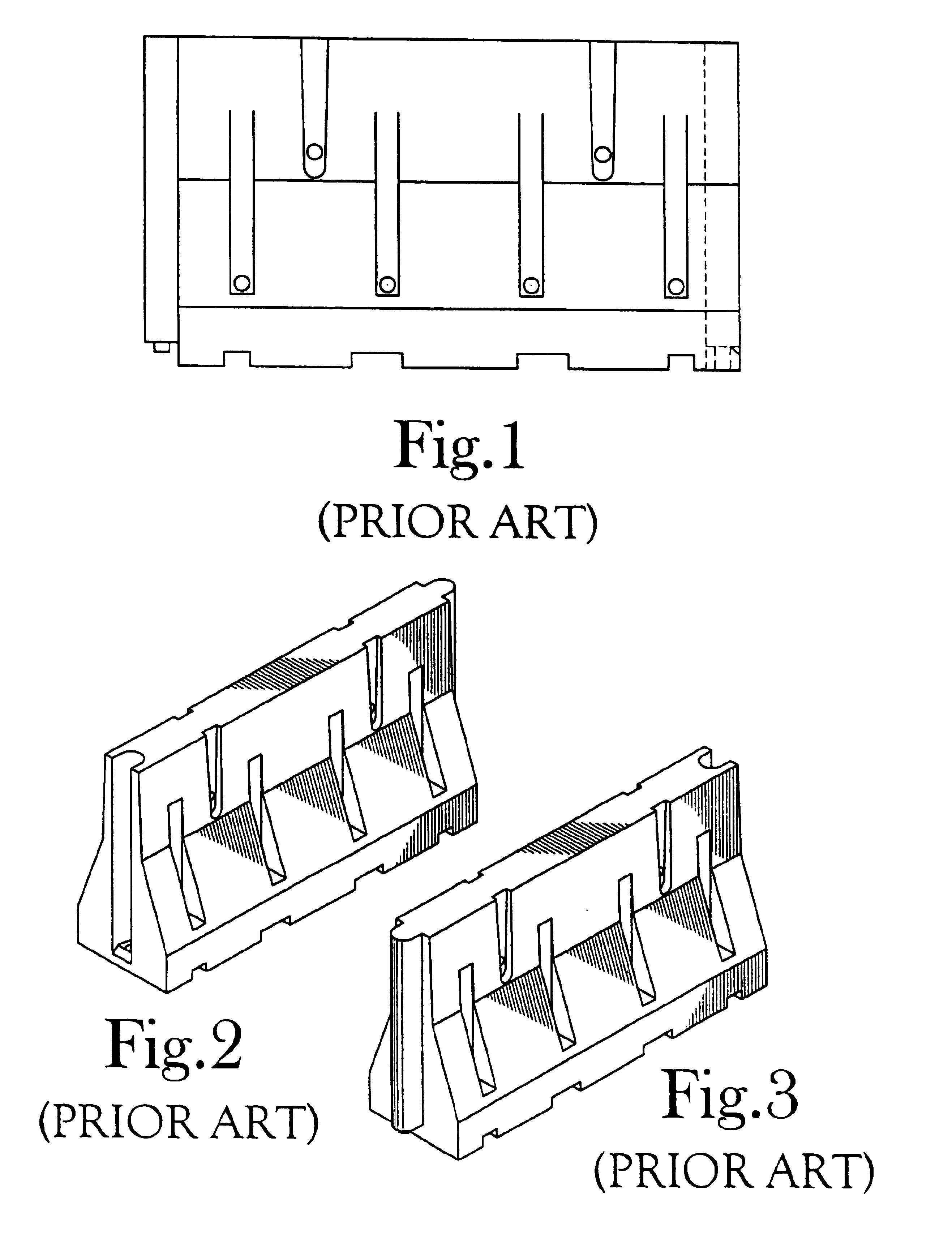
Protection barrier system
A protection barrier system for energy-absorption of impacts includes an elongated barrier defining a chamber therein. The barrier includes side walls having a plurality of connected non-vertical wall segments and a plurality of buttresses positioned vertically at spaced apart locations along each side wall. One or more guide channels are positioned on each side wall in horizontal alignment with similar guide channels on like-configured barriers. A coupling is disposed on each opposed end of the barrier for coupling of either barrier end juxtaposed in end-to-end nested arrangement with like barriers. A supplemental energy-absorbing system is connectable between opposed ends of end-to-end coupled barriers, providing energy-absorbing tubes removably inserted through each guide channel of each barrier. Cables are extendable through the tubes in the guide channels of the nested barriers, providing additional energy-absorption and deterrence from breaching of the barriers. A method of manufacture for the protection barrier is also disclosed.
Owner:SAFETY BARRIERS
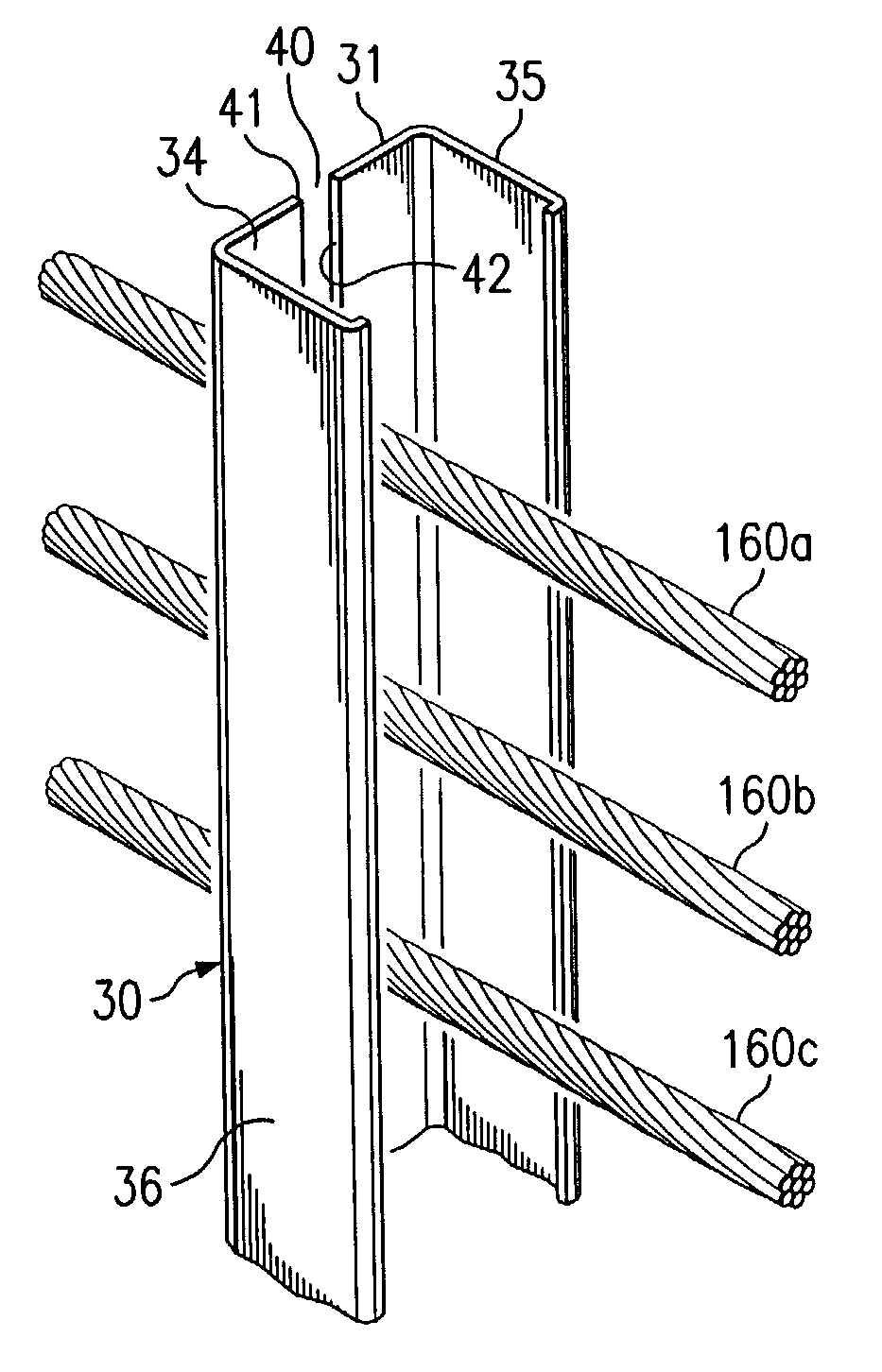
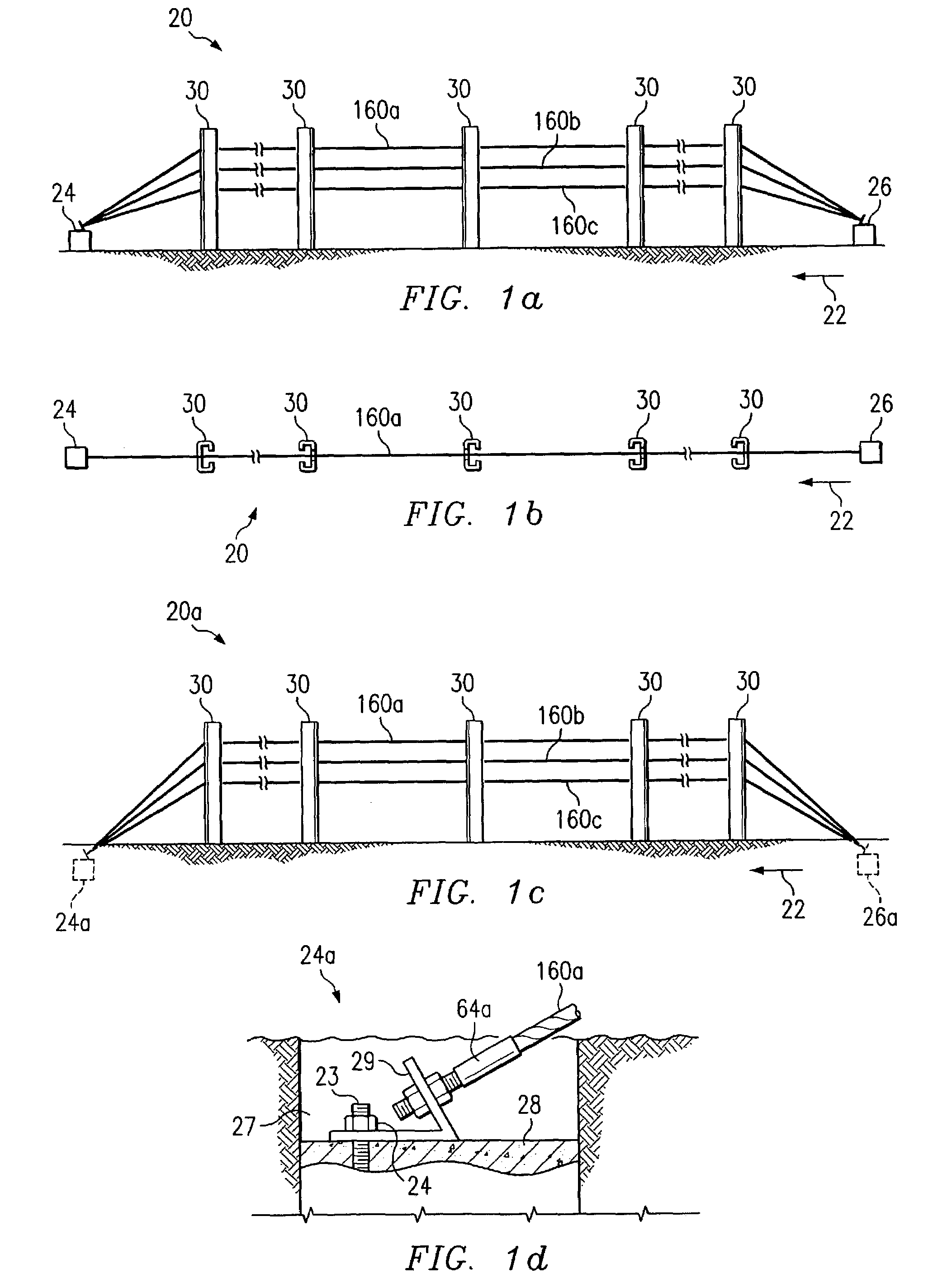
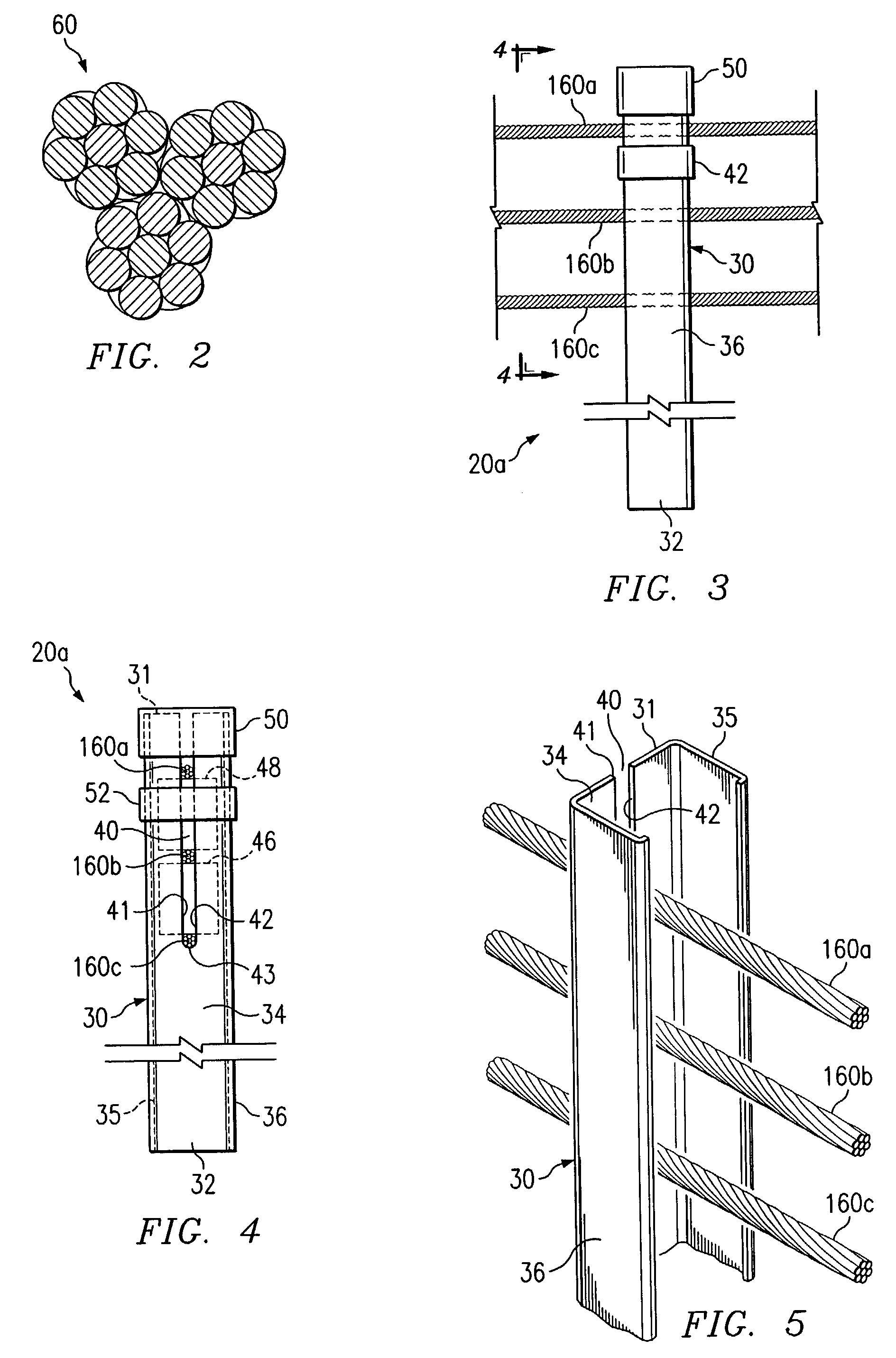
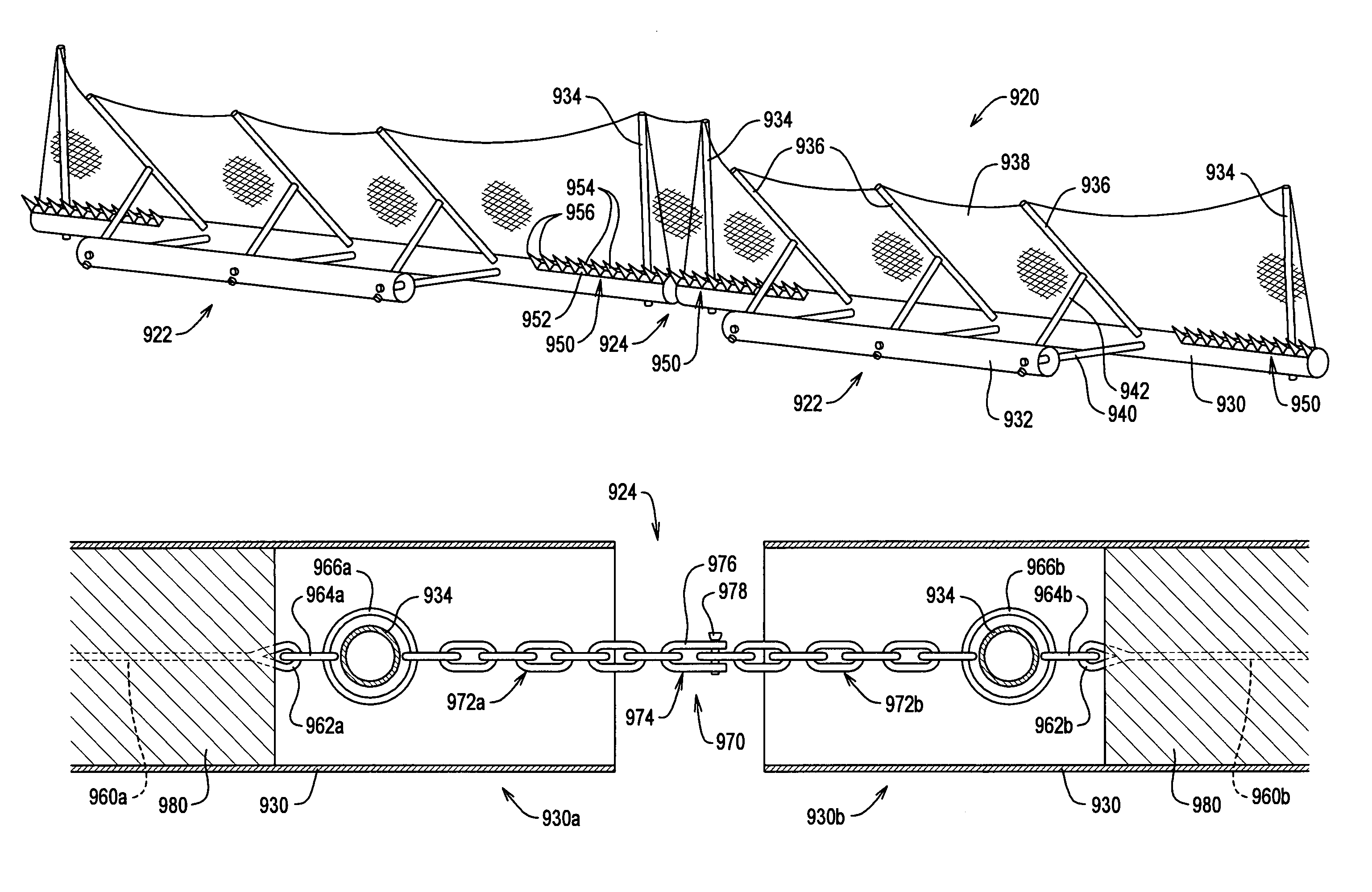
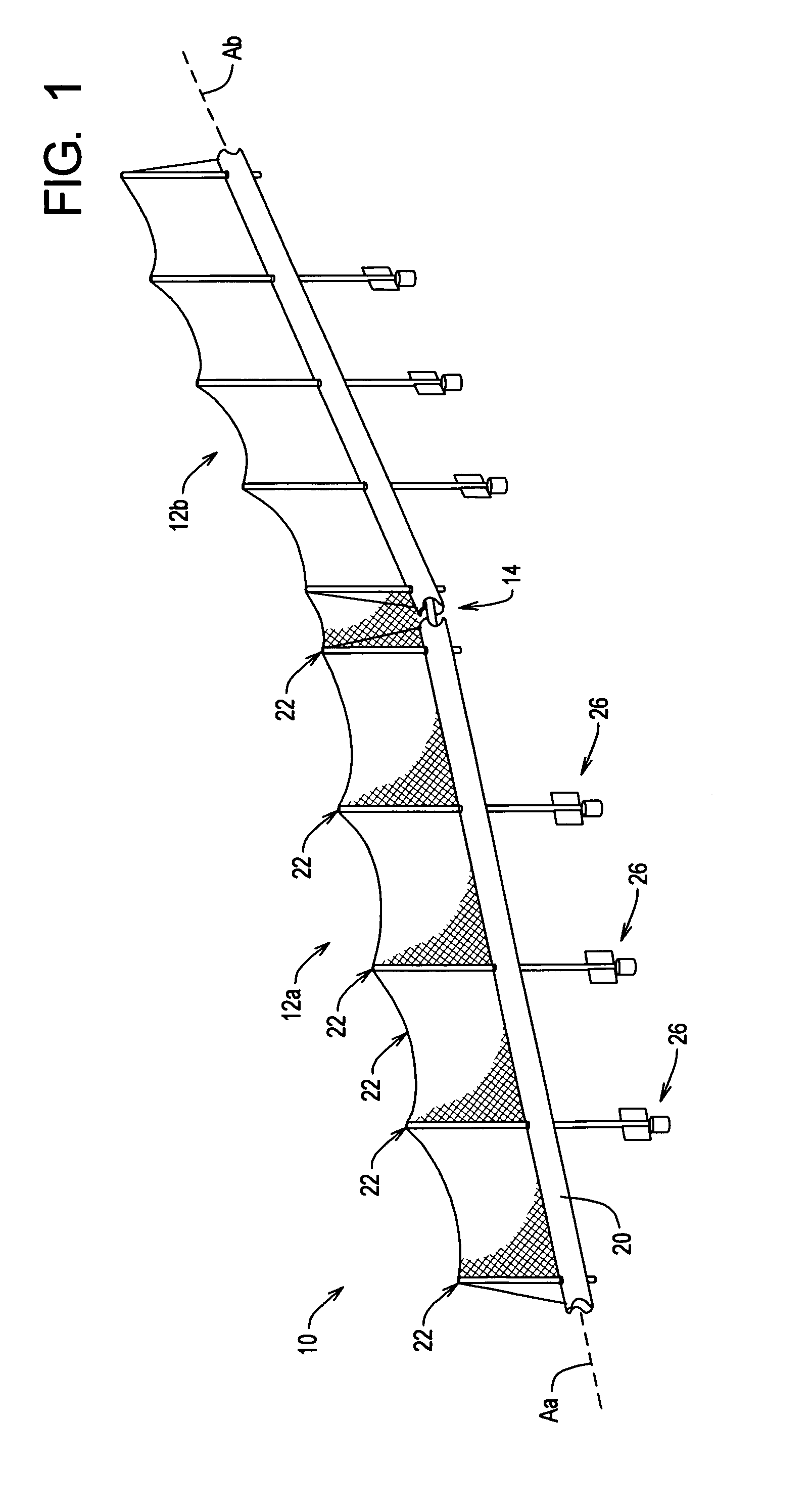
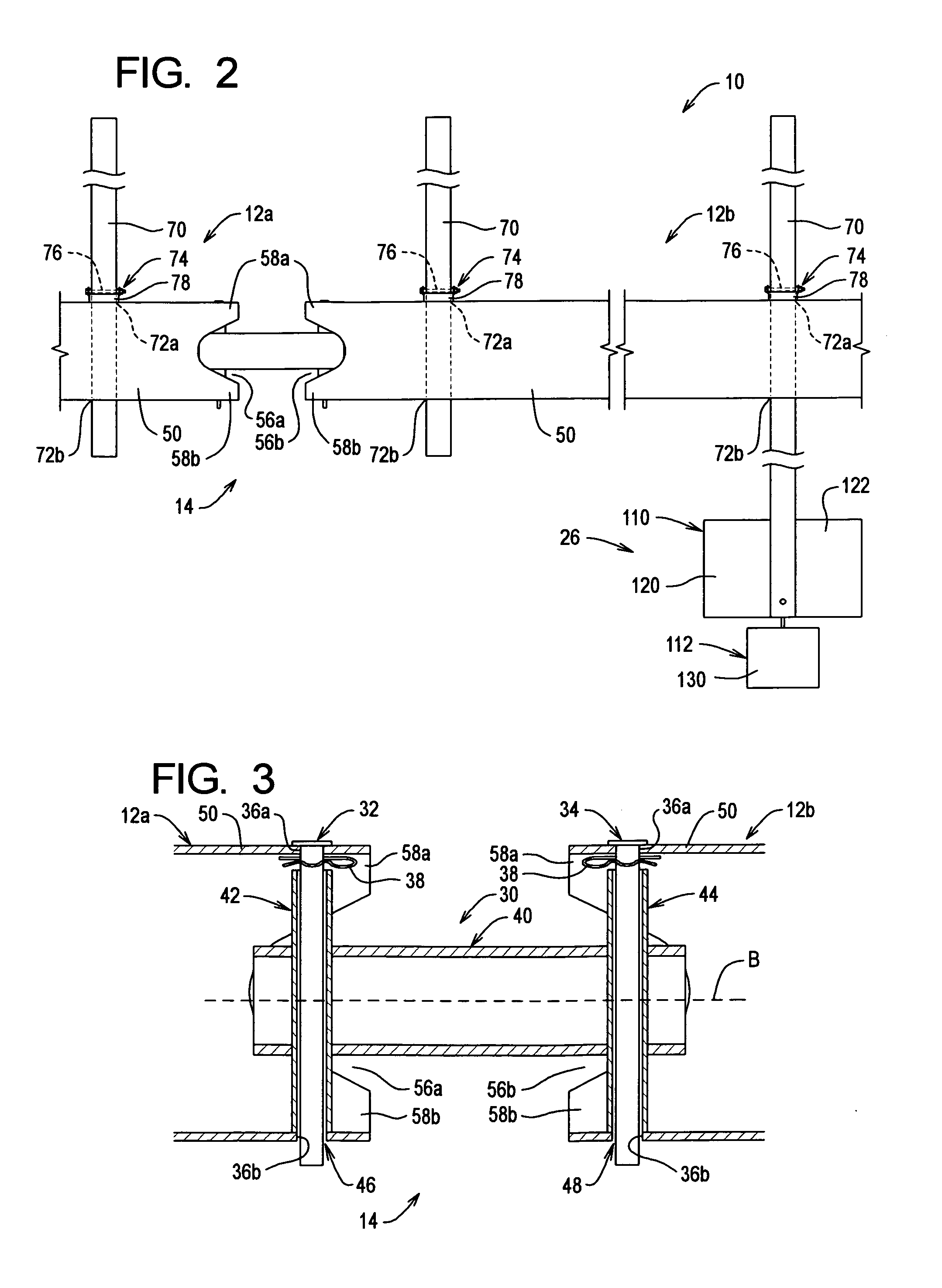
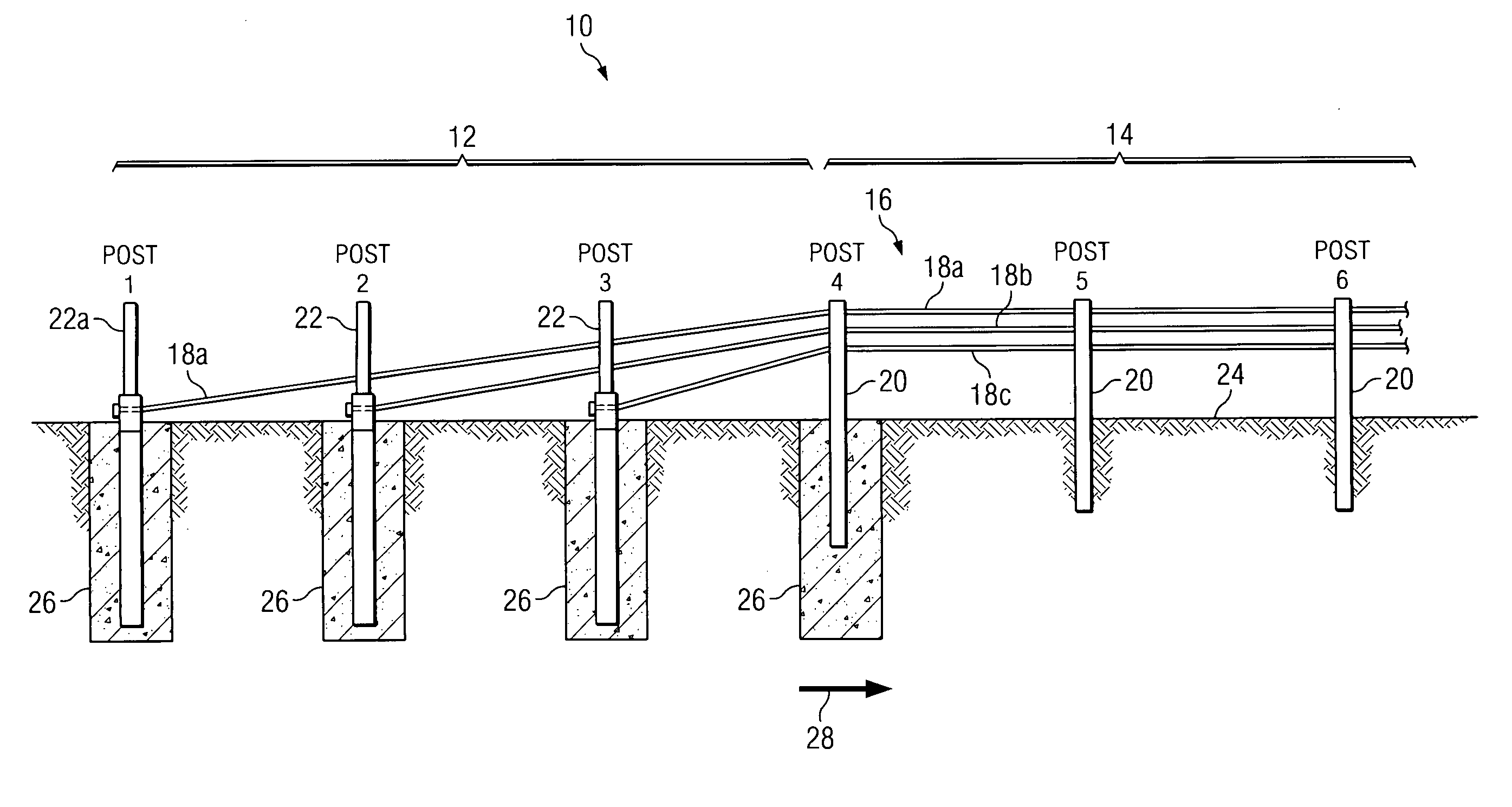
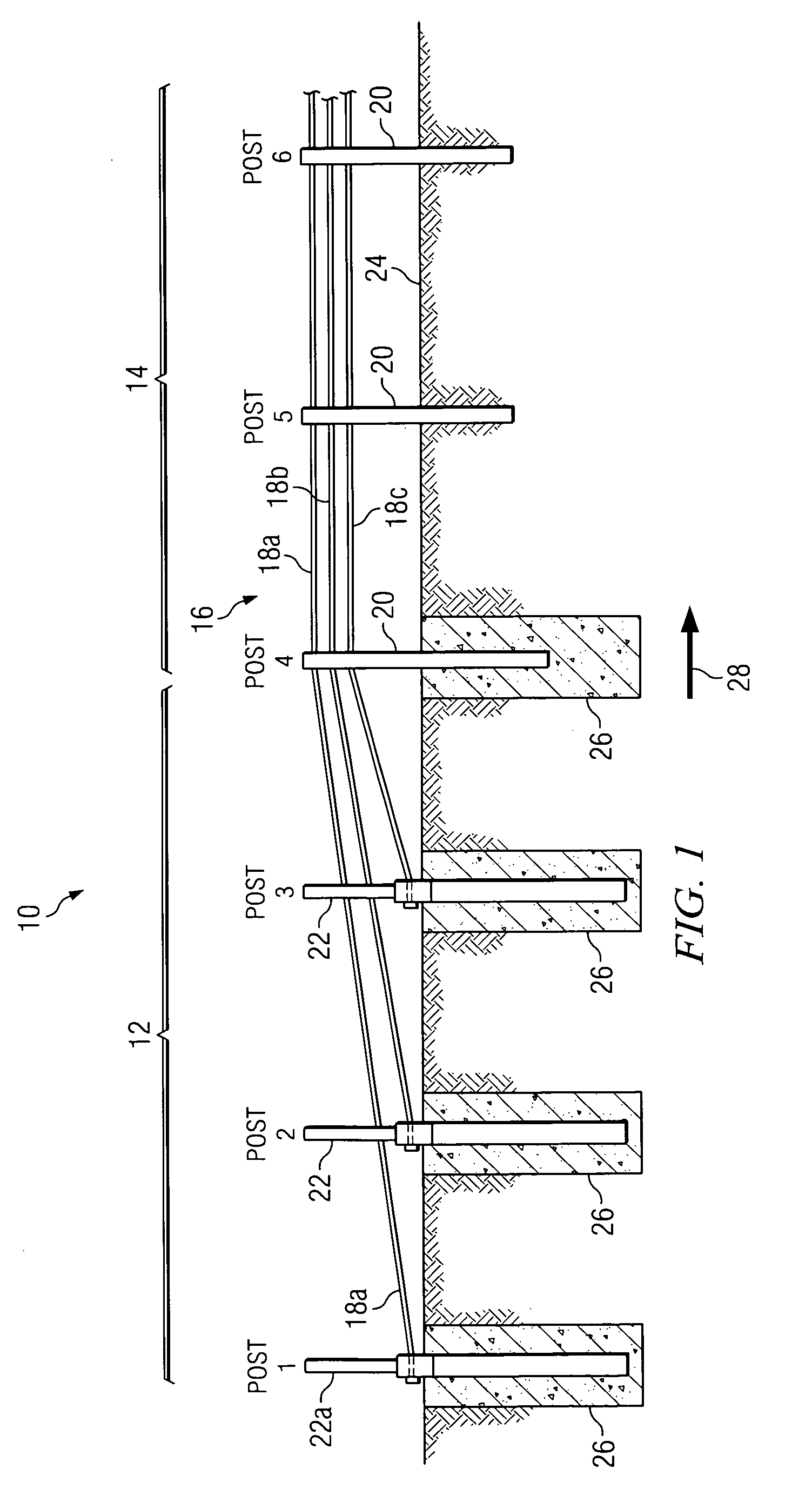
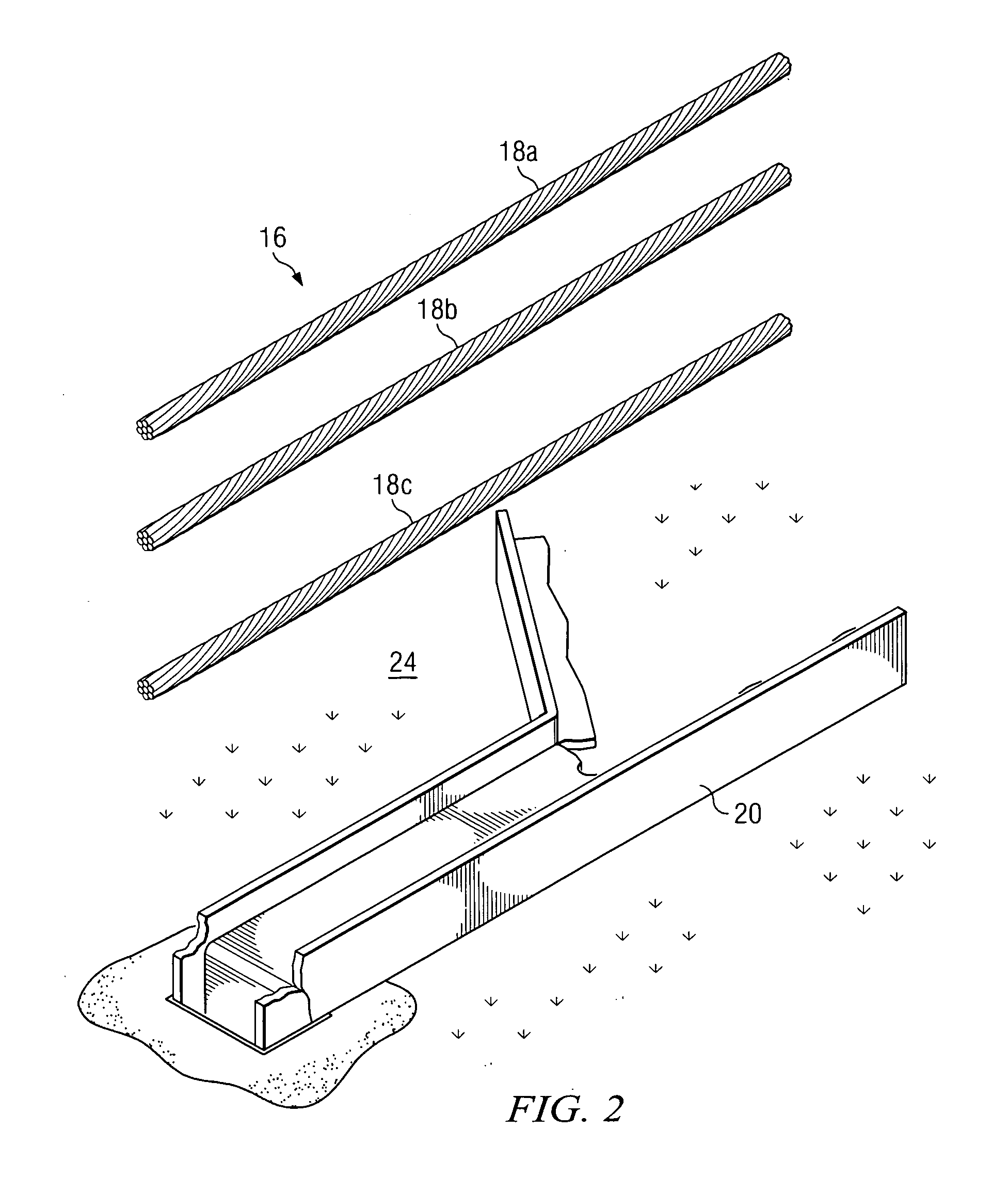
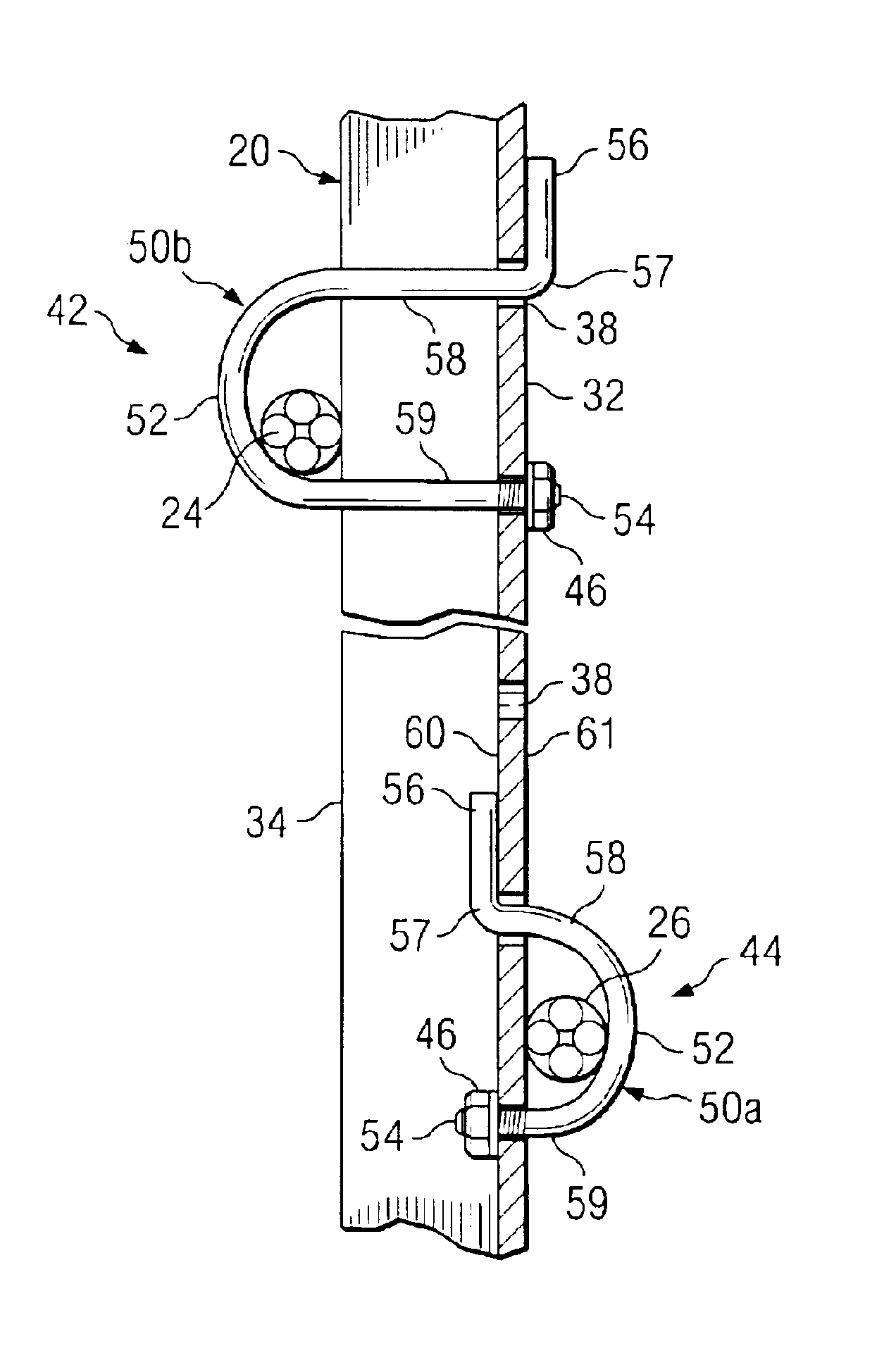
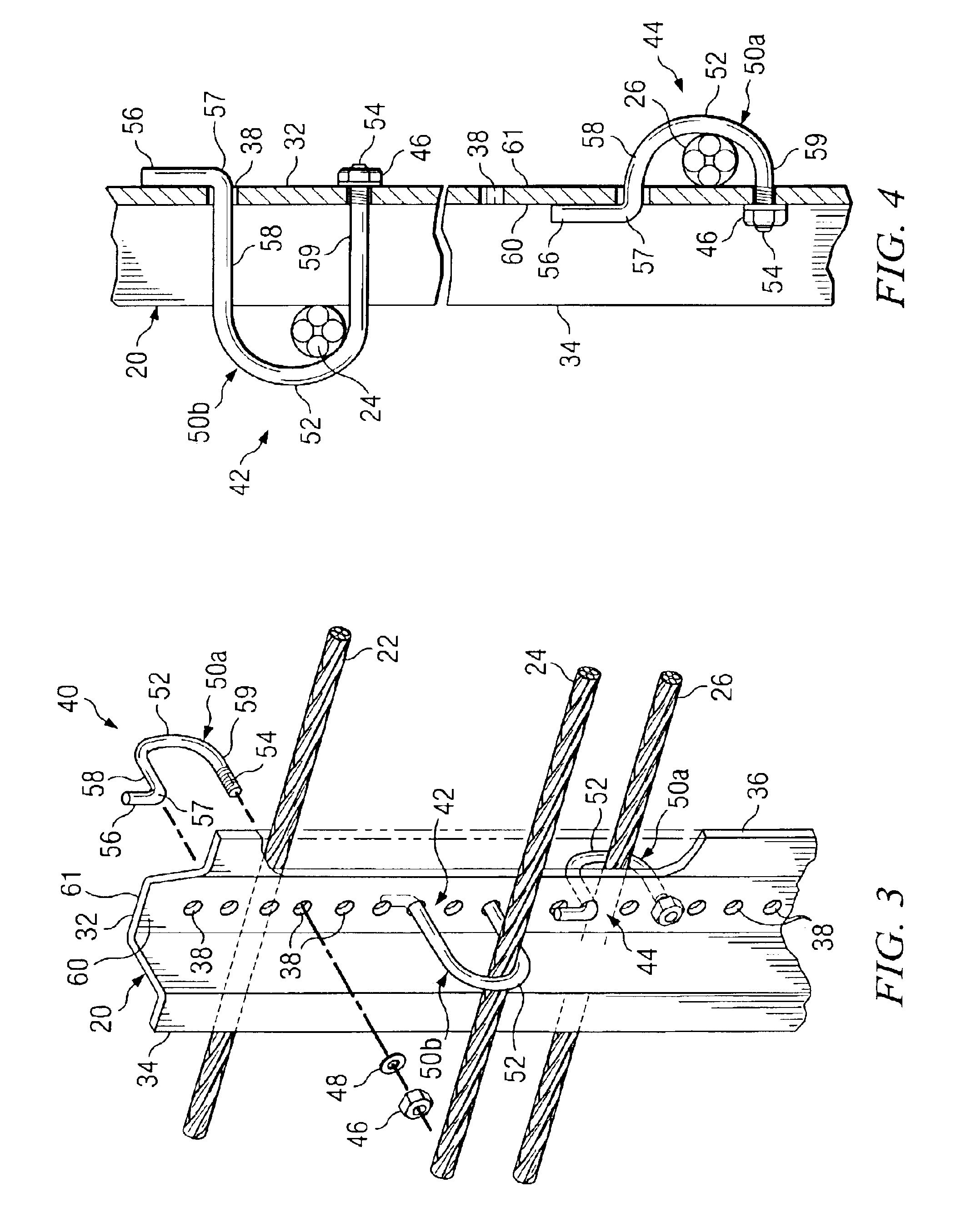
Cable safety system
InactiveUS6962328B2Low costShorten the timeFencingPasturing equipmentReliability engineeringSafe system
A safety system including cables and support posts is provided. The safety system may be used to prevent vehicles from impacting with an associated roadside hazard. The safety system will typically maintain engagement between associated cables and support posts for a longer period of time as the posts are bent during a vehicle impact.
Owner:TRINITY HIGHWAY PROD LLC
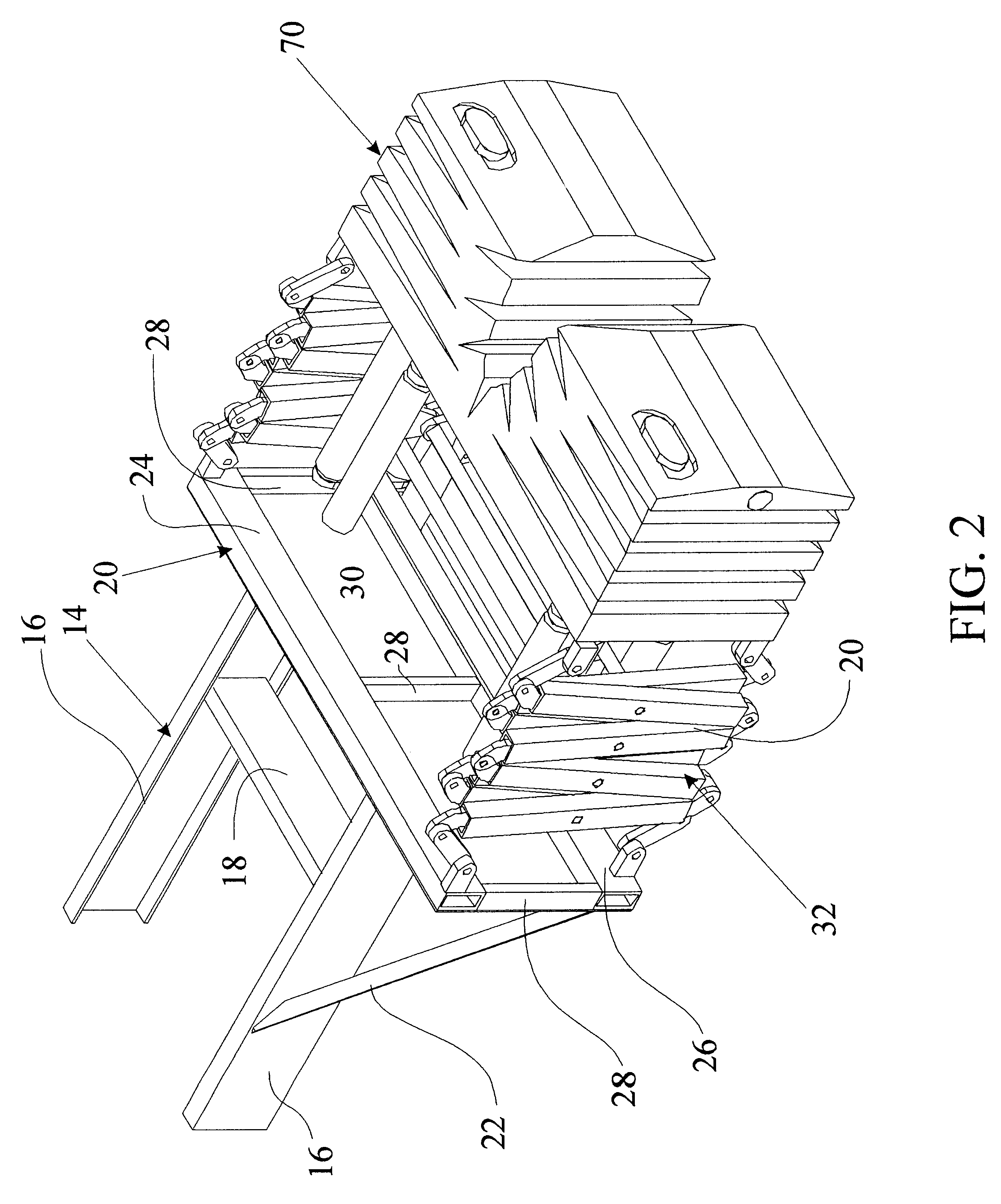
Energy absorbing system
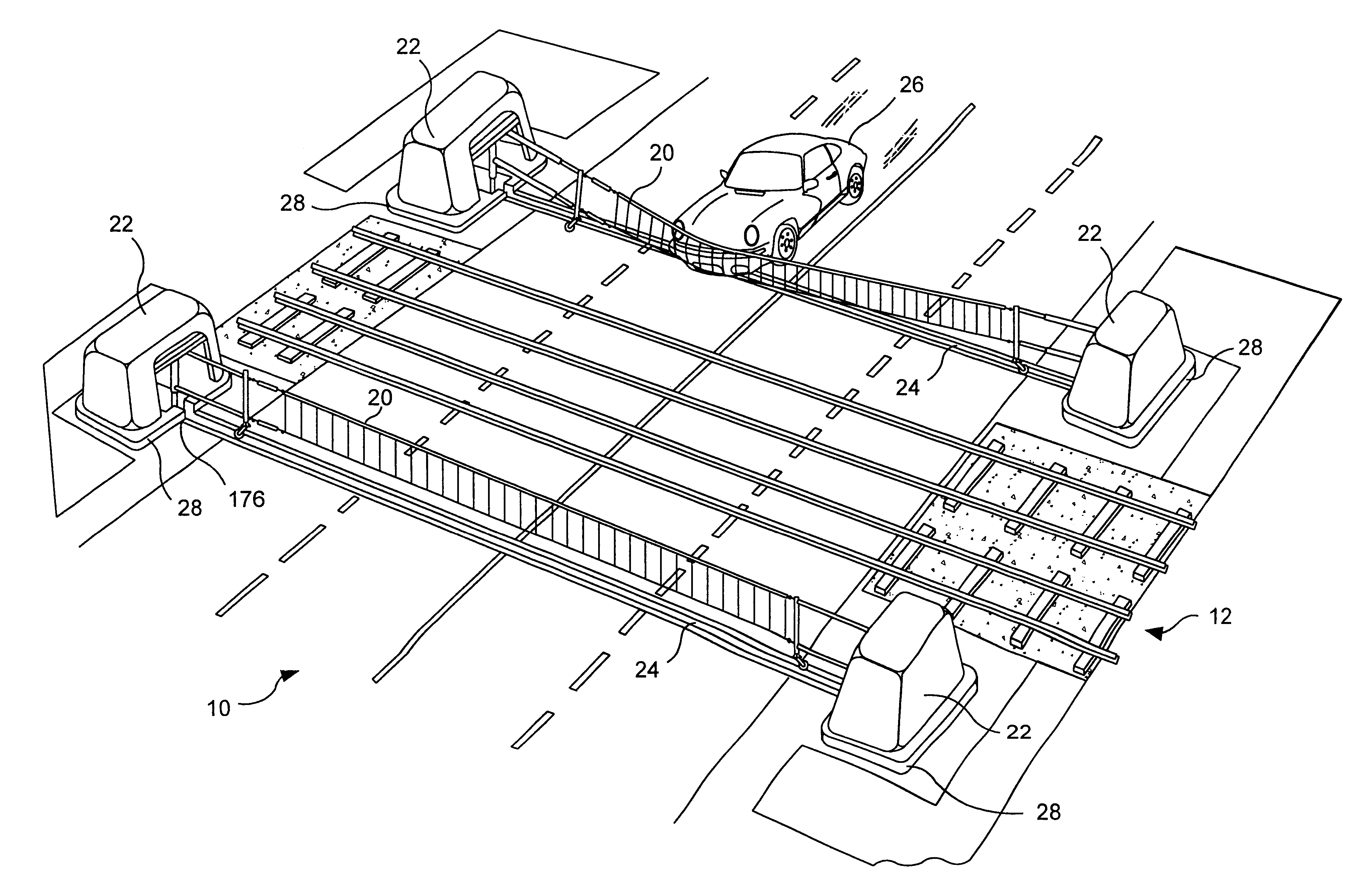
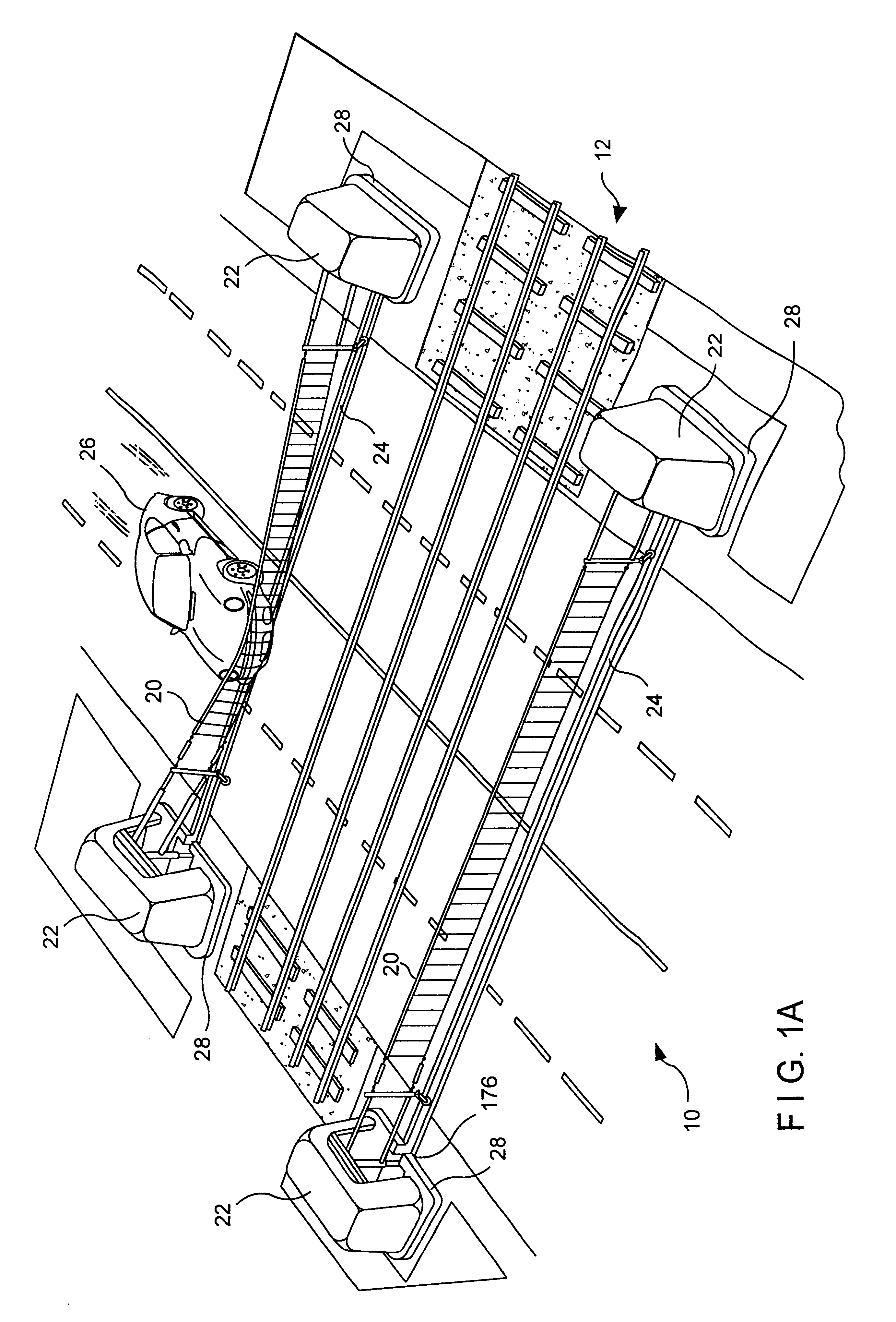
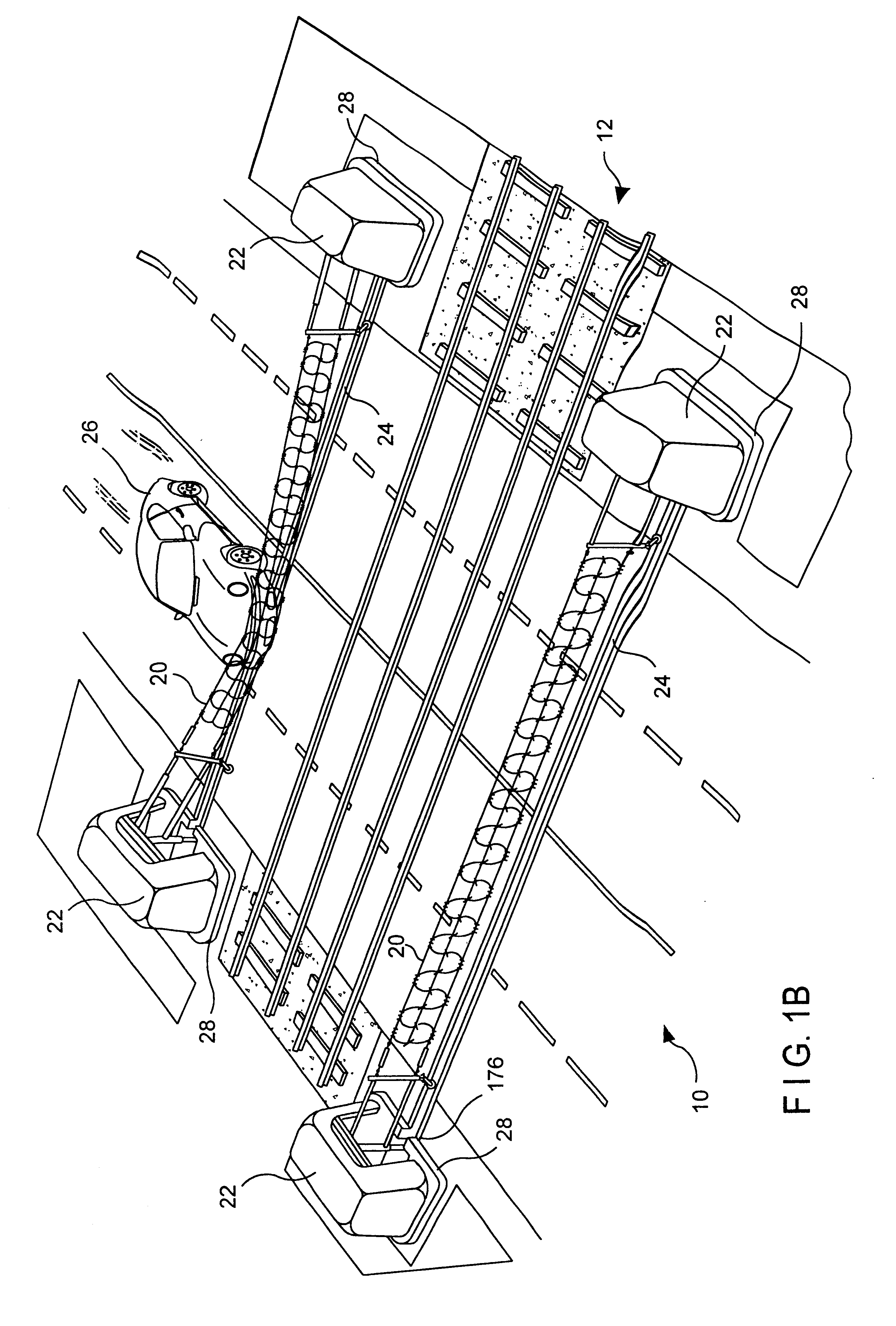
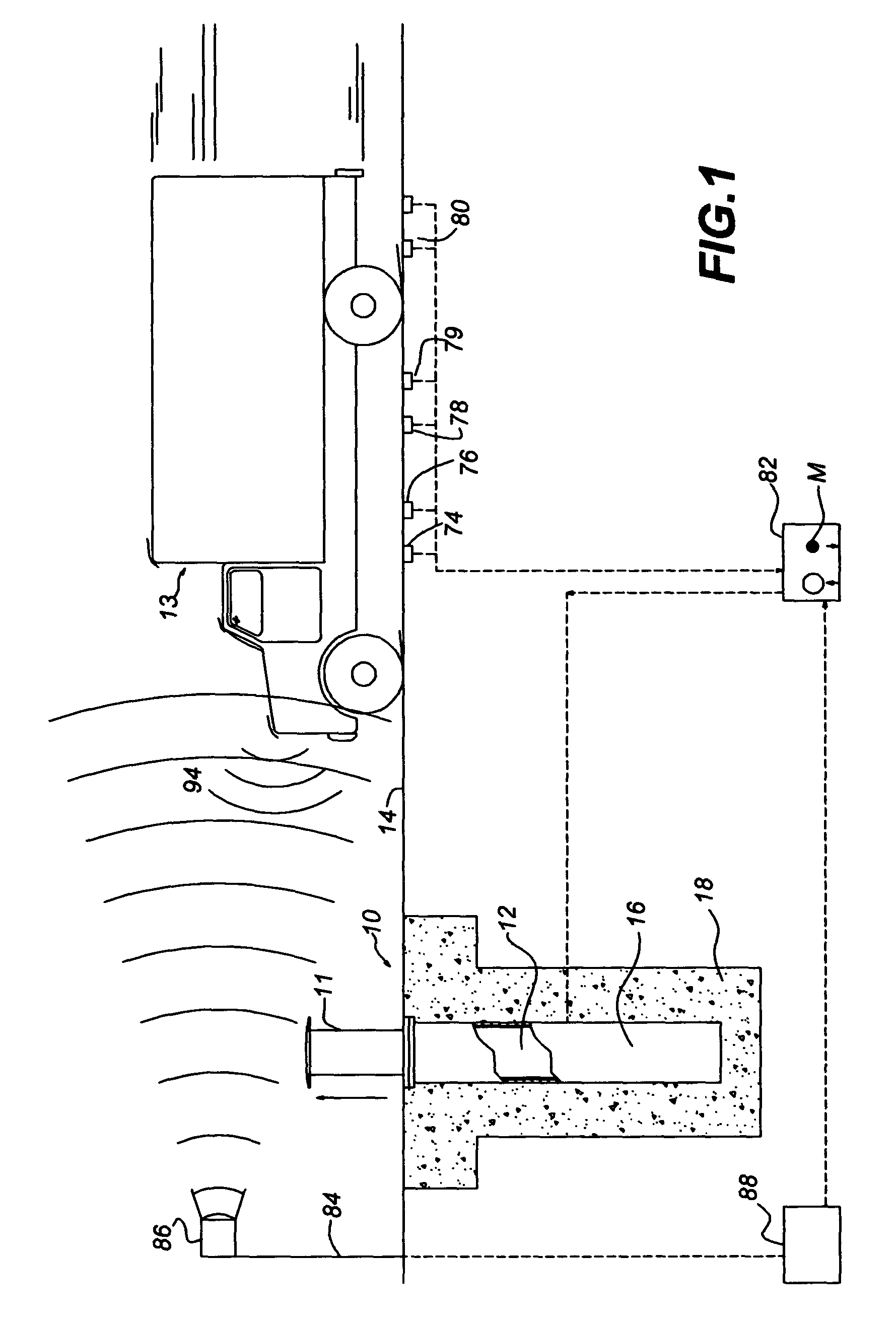
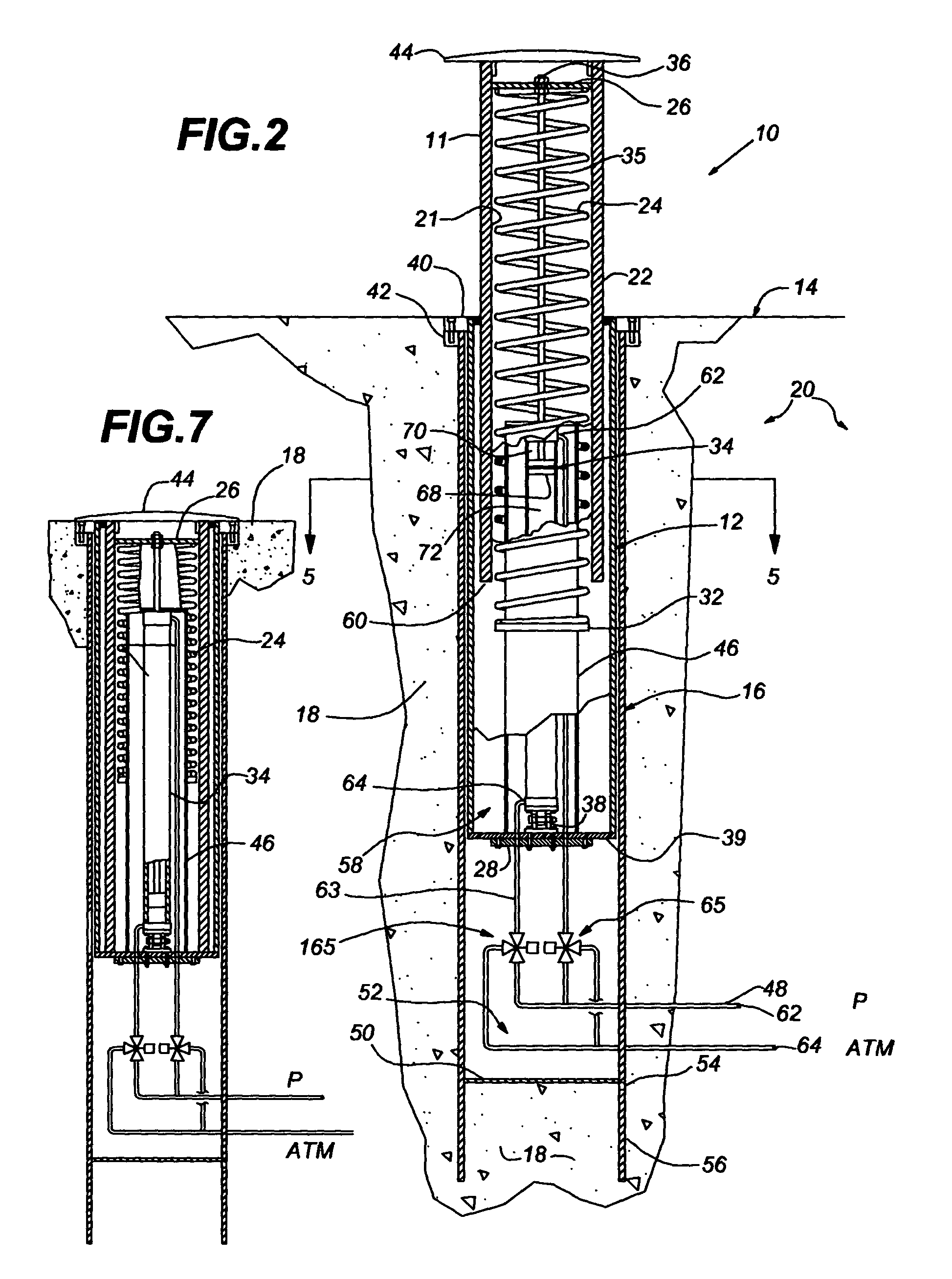
A heavy duty ground retractable automobile barrier for a railroad crossing. Concrete bunkers are placed at each side of a roadway. An upstanding concrete-filled steel pipe fixed in each bunker has a sleeve for rotational and axial movement. Shock absorbers are mounted on each sleeve. A net extends across the road and is attached to the opposite ends of the shock absorbers. Collision of an automobile with the net creates tensile forces in the net. The shock absorbers expand while rotating about the pipe's axis in response to tensile forces from the net that meet or exceed a minimum threshold. Forces from the net pass through the axis of the steel pipe. The net is stored in a pit transverse the roadway parallel to the railroad tracks and is raised and lowered as appropriate. The net includes a cable that extends across the road in a wave pattern, having peaks, valleys and midpoints, wherein tangents of the wave midpoints are at least 90 degrees from tangents of the peaks and valleys.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAB TECH INC
Vehicle barrier system
A barrier vehicle system for an amusement race track is formed from a chain of pivotally coupled barrier modules. Each barrier module has a top and a bottom link separated by a spacer structurally joined with the top and bottom links to create a rigid structure when assembled. A pin extends through the top and bottom links, to one side of the spacer. An resilient, deformable barrel is journalled on the pin. To assist in attenuating high energy impacts, an extendable, energy-absorbing mechanism is attached to one end of the barrier, and the other end of the barrier is anchored to the ground.
Owner:FESTIVAL FUN PARKS +1
Damped crash attenuator
InactiveUS6203079B1Low level of energy absorptionImprove energy consumptionPortable framesPasturing equipmentEngineeringTruck
A crash attenuator for protecting a truck or stationary structure from damage resulting from impact of an object such as a vehicle including a frame mountable to a truck or stationary structure, a bumper having an impact-receiving face adapted to receive an impact from an object in a crash, a movable displacement structure coupled to the frame and interposed between the frame and the bumper and having a first position in which the bumper is relatively distant from the frame and a second position in which the bumper is relatively proximate to the frame, and an energy dissipation system coupled to the displacement structure for dissipating the impact energy of the object into the bumper which causes said displacement structure to be moved from the first position toward the second position.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Coupling systems and methods for marine barriers
A marine barrier system comprising first and second barrier sections and a coupler system. The first and second barrier sections comprise first and second main flotation members, respectively, and each main flotation member contains buoyant material. The coupler system is arranged at the juncture of the first and second barrier sections. The coupler system is arranged such that the first and second main flotation members may be placed in a storage configuration and in a deployed configuration. In the storage configuration, the first and second main flotation members are arranged in a parallel, side by side arrangement. In the deployed configuration, the first and second main flotation members are arranged end to end to define a barrier line in a body of water across which movement is limited.
Owner:SPINK RICHARD
Mobile work zone protection device
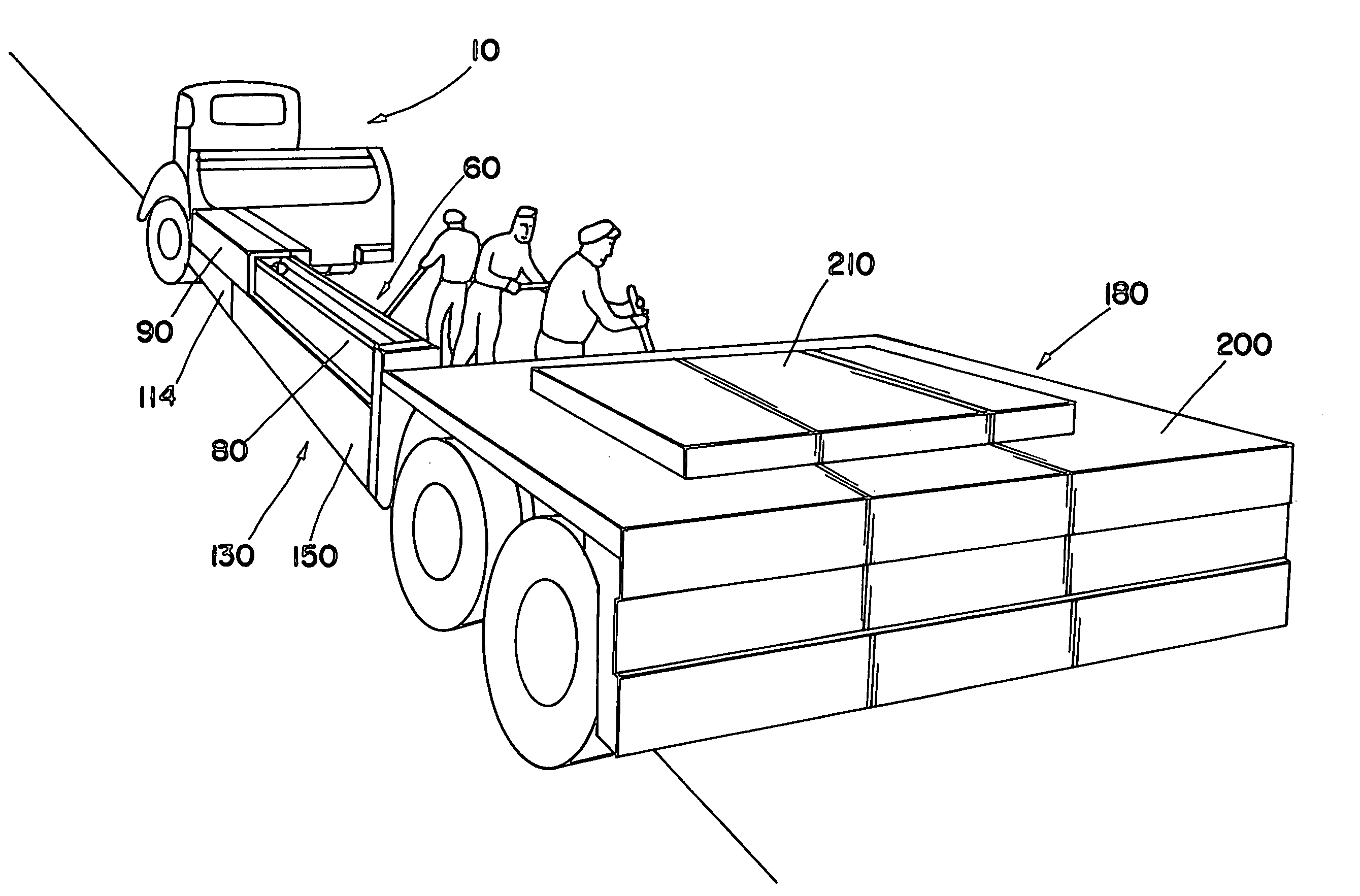
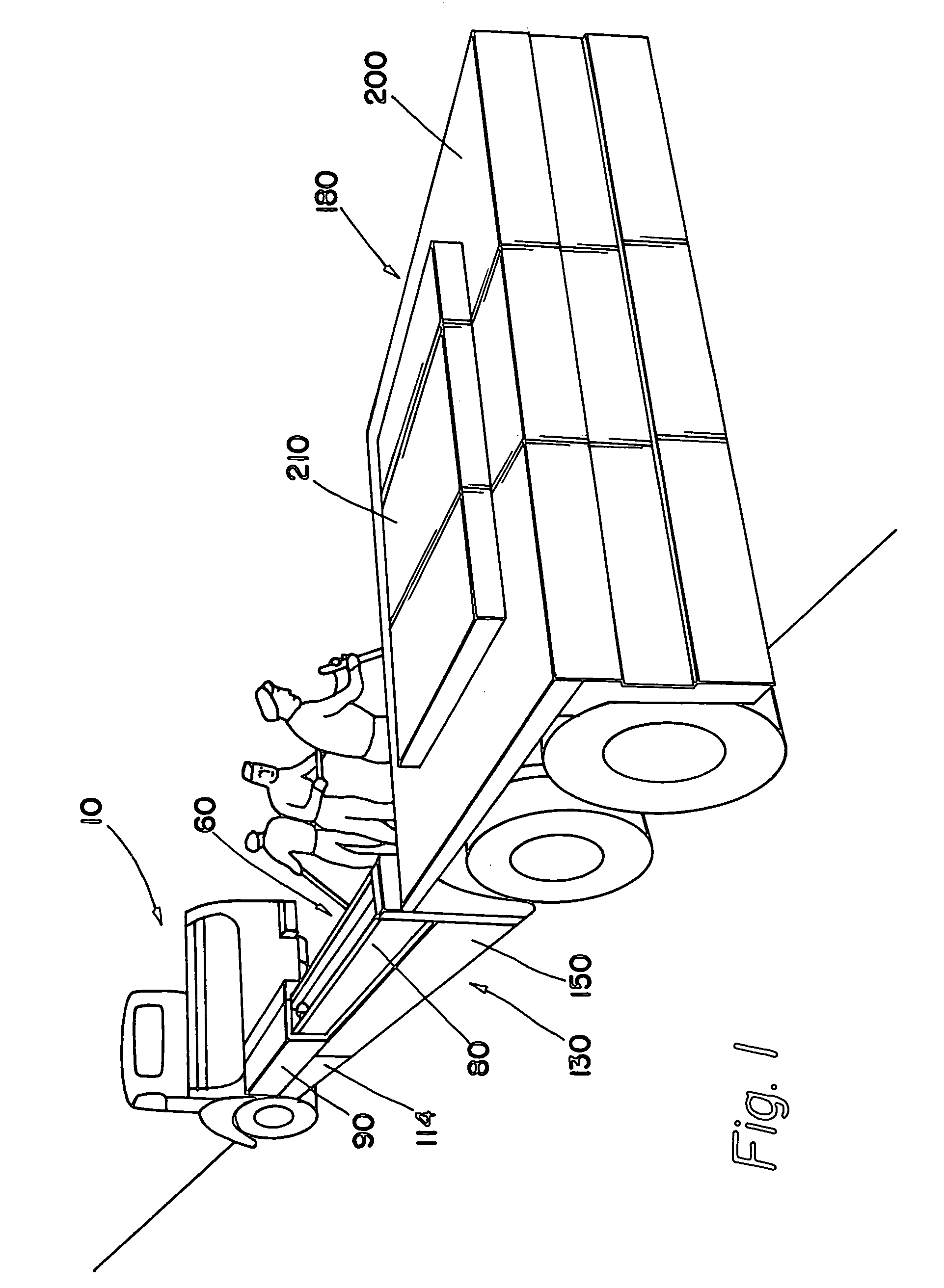
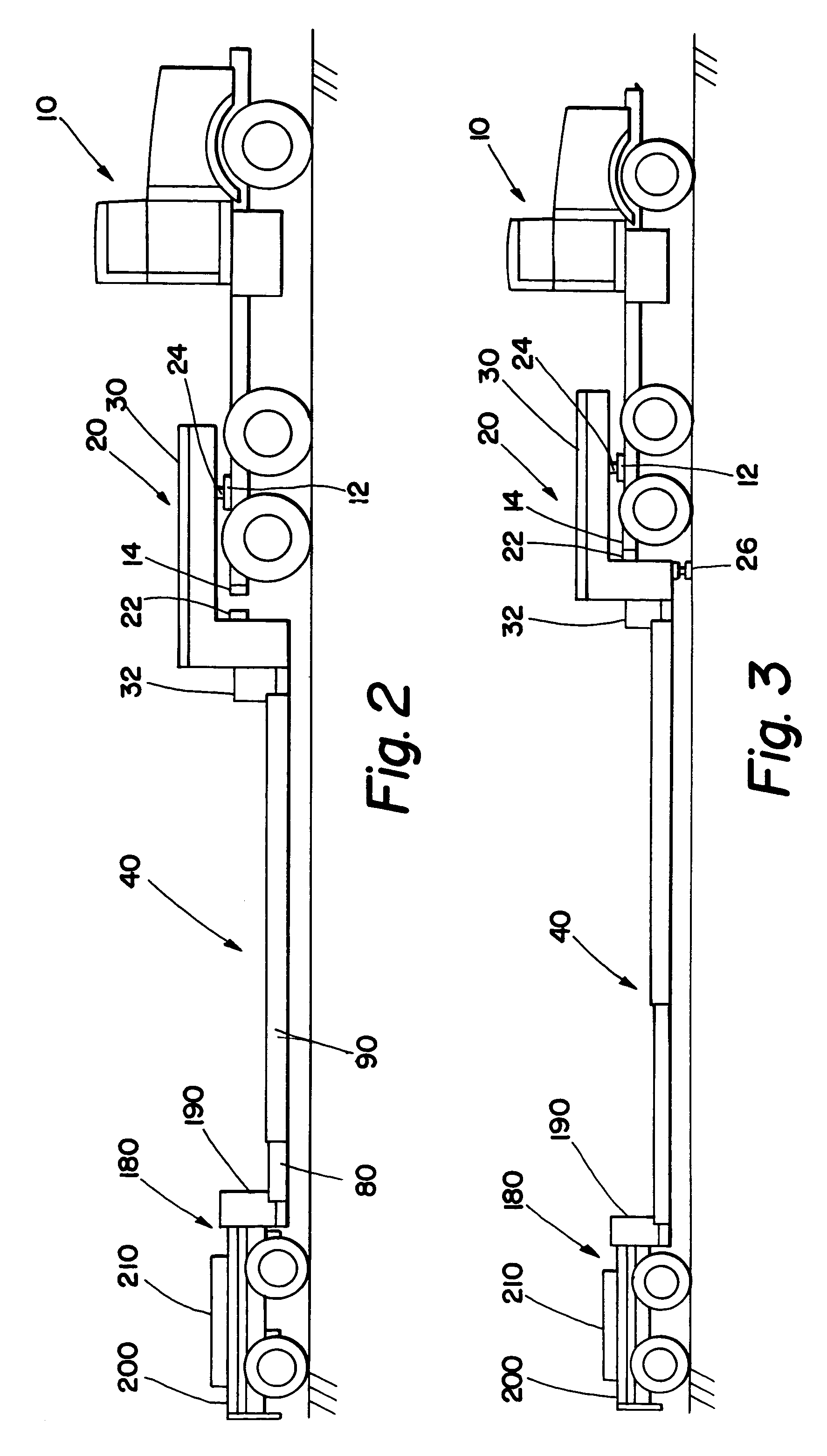
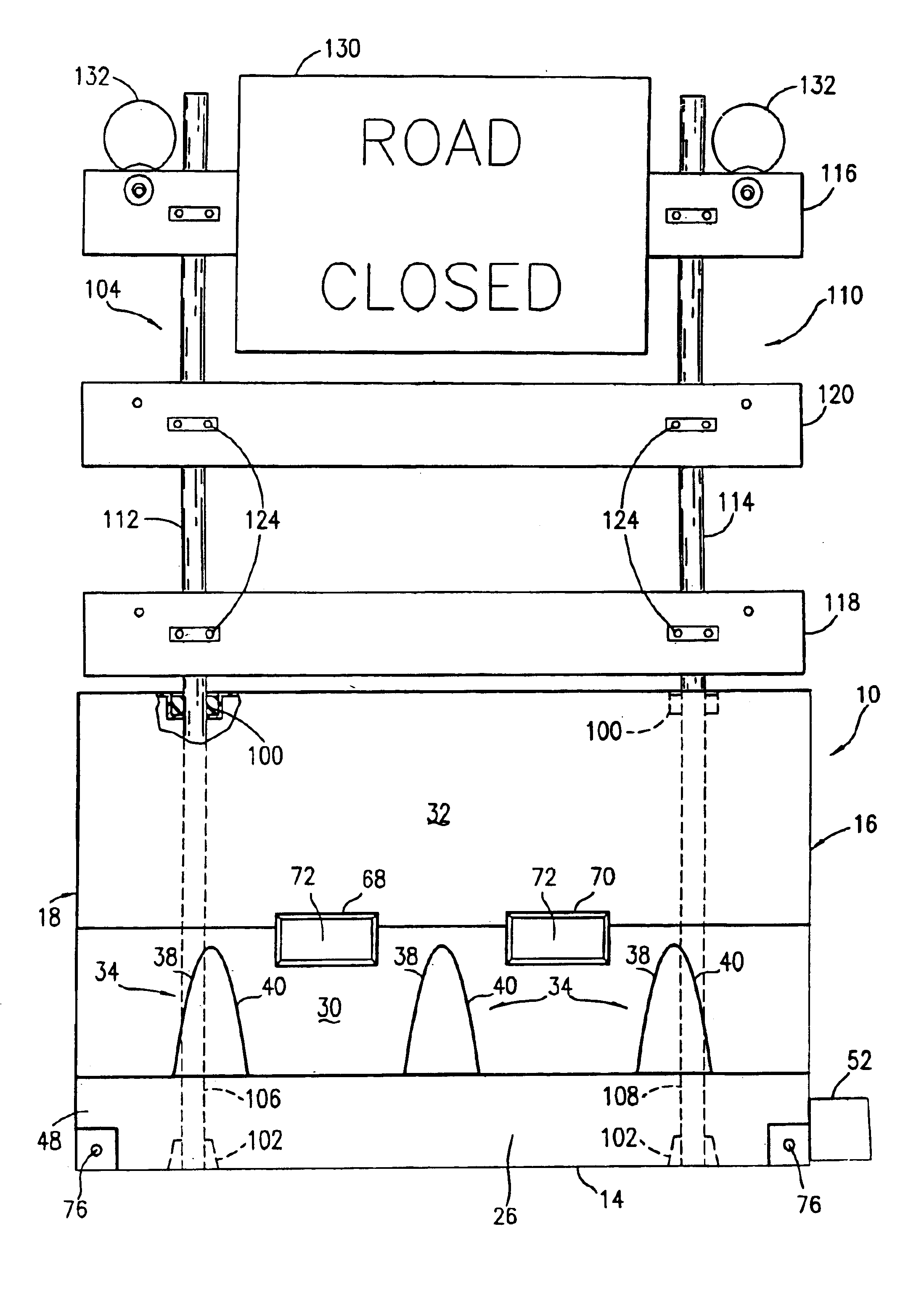
A mobile work zone protection device includes a front carrier, a barrier beam assembly, and a rear carrier. In one embodiment, the barrier beam assembly includes two sets of telescoping beam structures. Each of these structures can rotate from one side of the device to the other, and thus can be deployed to create a safe work zone for roadway workers on either side of the device. The structure can also be left in the transit position to provide an enclosed safe work zone.
Owner:STATE OF CALIFORNIA DEPT OF TRANSPORTATION
Traffic control device
Owner:TRINITY HIGHWAY PROD LLC
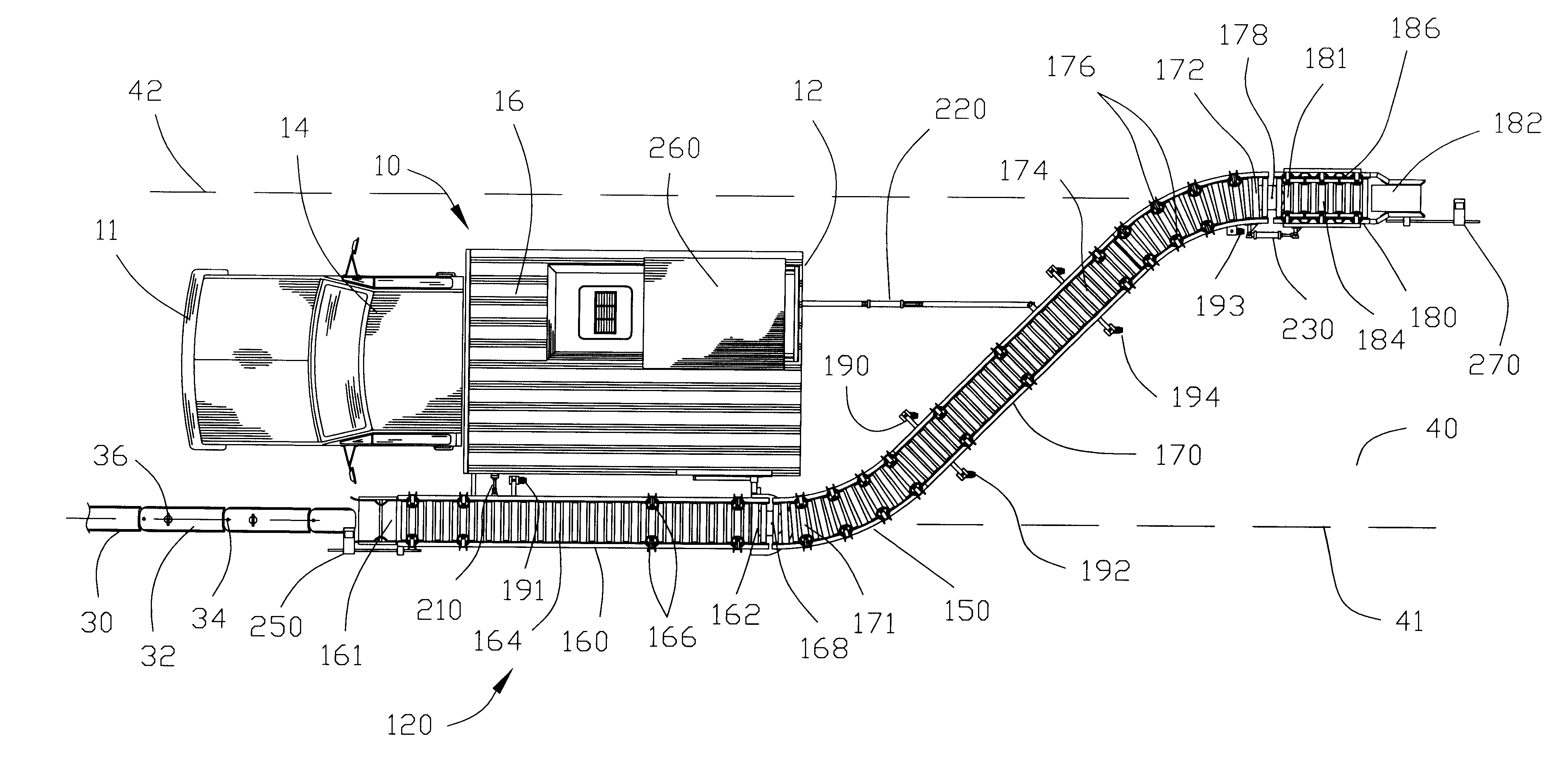
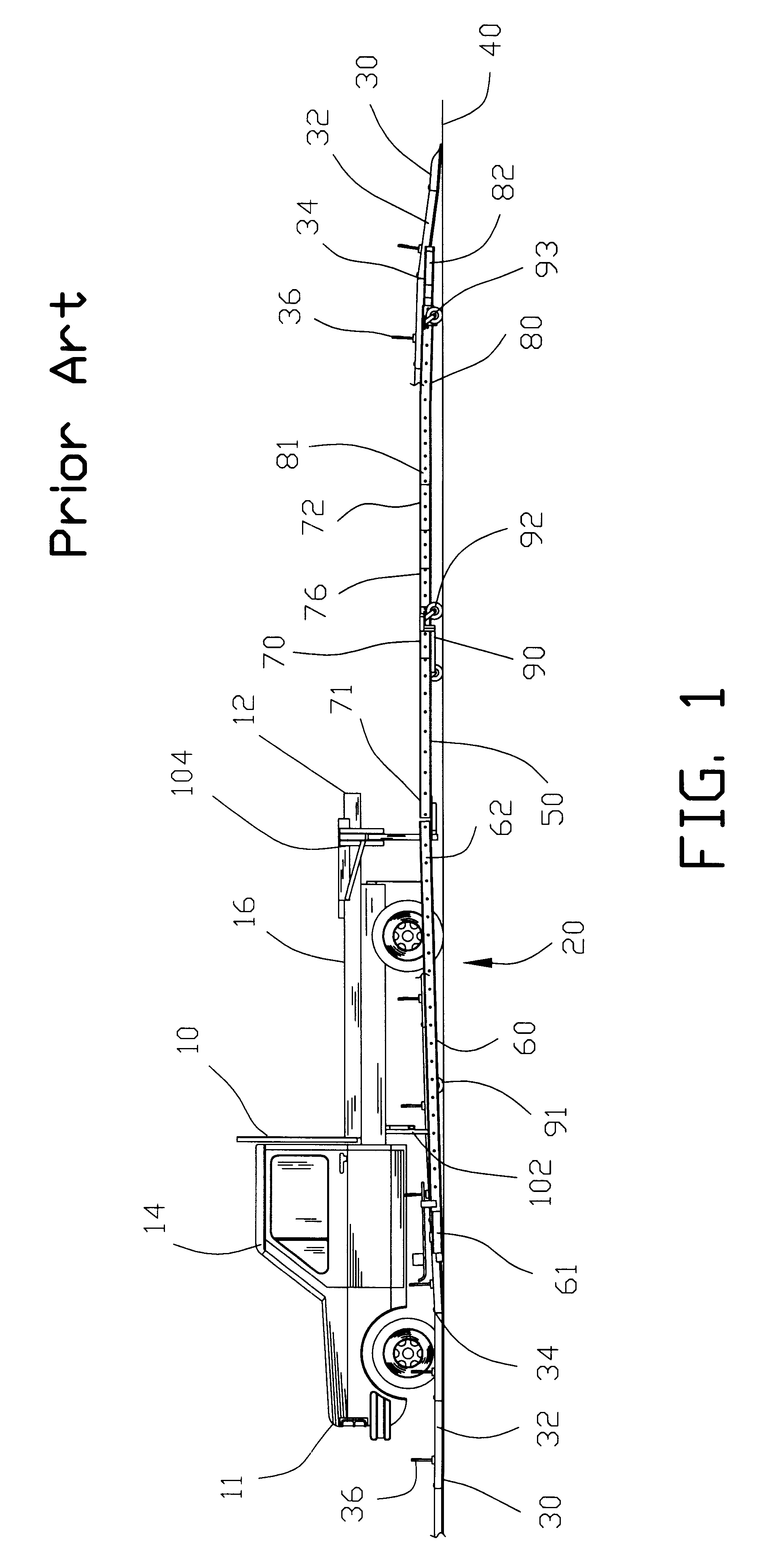
Apparatus for translocating lane divider
An apparatus and method is described for translocating a lane divider from an initial position to a final position on a roadway. The apparatus comprises a conveyor connected to a vehicle. The conveyor includes a receiving segment for receiving the lane divider from the initial position on the roadway and a discharging segment for discharging the lane divider to the final position on the roadway. The receiving segment and the discharging segment are pivotally connected relative to one another. The receiving segment may be pivoted to enable the lateral movement of the receiving segment to accommodate for variation in the initial position of the lane divider on the roadway. The discharging segment may be pivoted for discharging the lane divider to a final position aligned on the roadway. A translocating segment may be interposed between the receiving segment and the discharging segment for moving the lane divider from one lane to another lane on the roadway.
Owner:QWICK KURB
System and method for operating multiple moveable barrier operators
ActiveUS7332999B2Easy to useImprove user convenienceElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsTelecommunicationsWireless signal
A first moveable barrier is actuated by using a first moveable barrier operator. Responsive to the receipt of a signal initiating actuation of the first moveable barrier, a wireless signal is transmitted from the first moveable barrier to a second moveable barrier operator. The signal is received at the second moveable barrier operator and the second moveable barrier operator is controlled in response to receiving the signal.
Owner:THE CHAMBERLAIN GRP INC
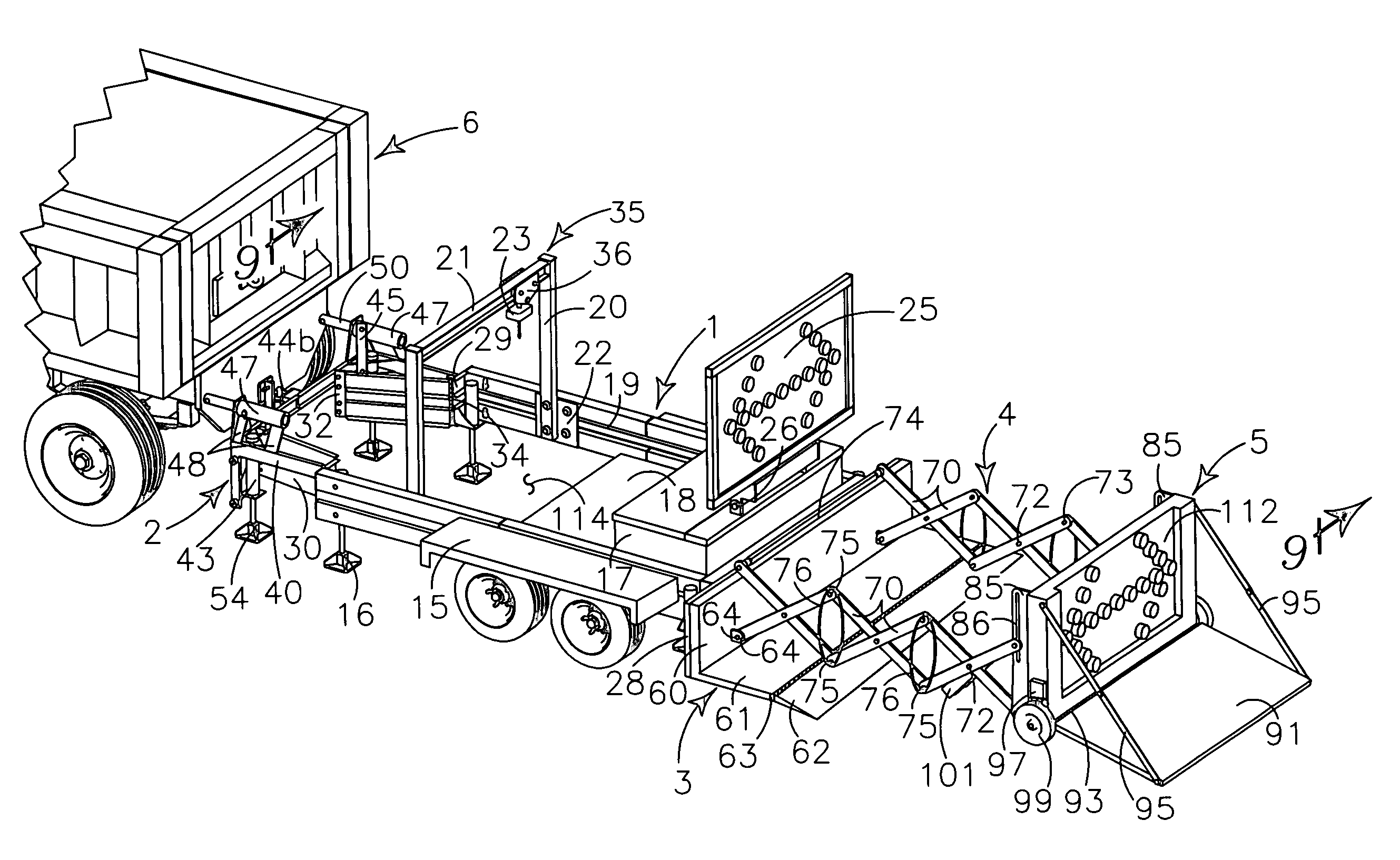
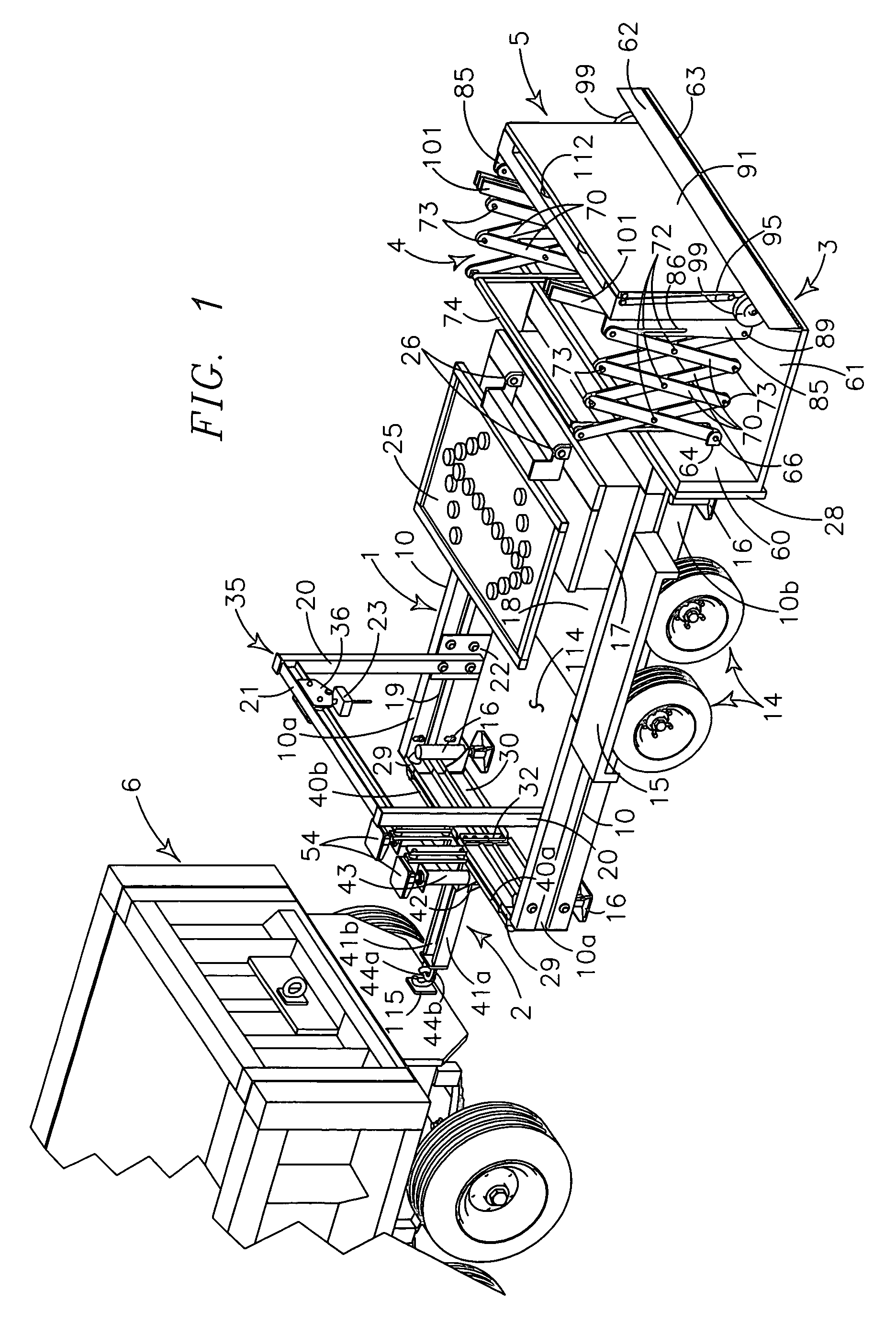
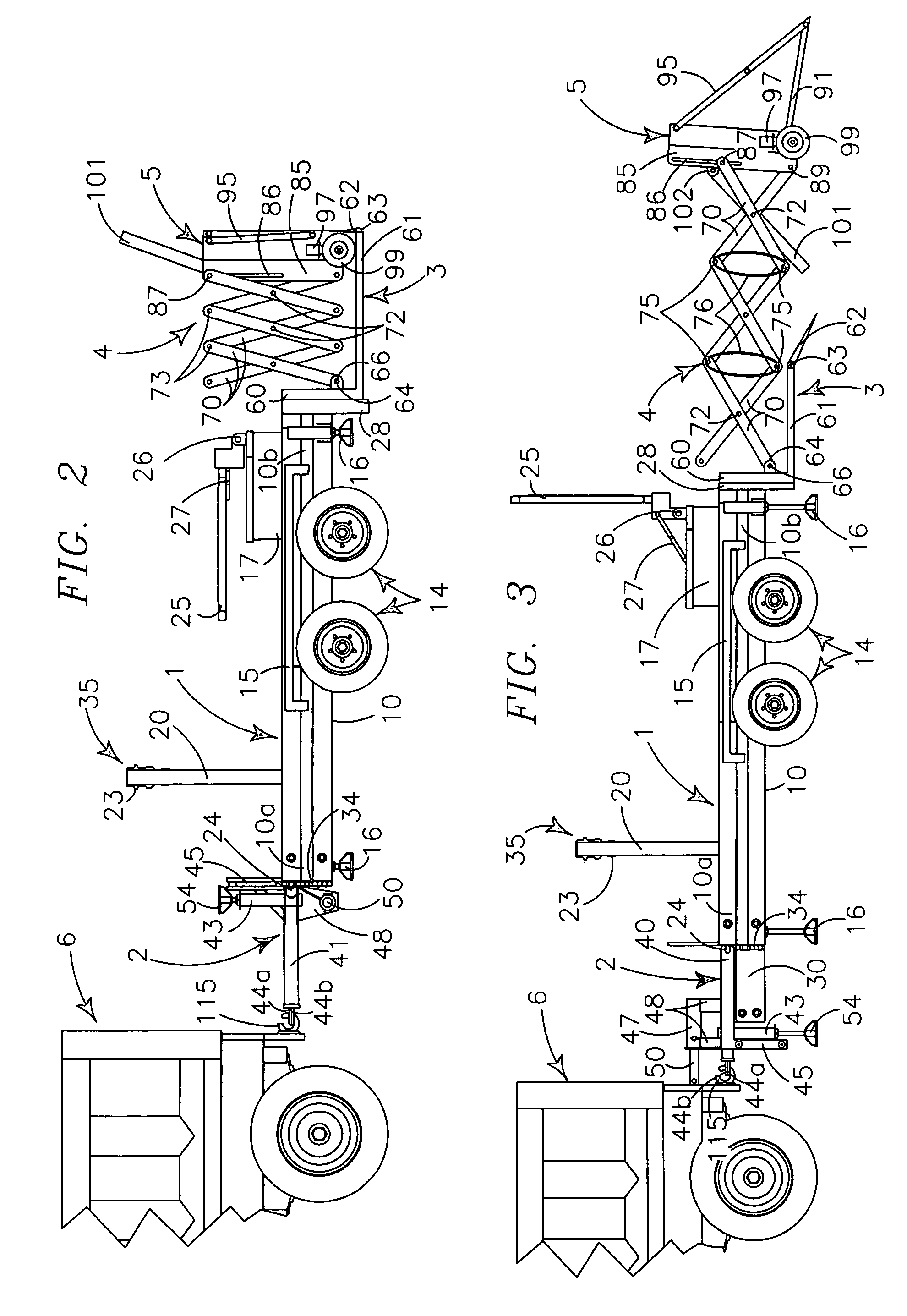
Utility trailer and safety barrier for street repair
A utility trailer provides a frame defining a forward open bottom work space, a medially rearward deck and a rearwardmost extendable impact attenuator. Hitch structure encloses the forward portion of the work space. The impact attenuator is deployable spacedly rearwardly of the utility trailer in work site mode and provides frictional, mechanical and inertial devices to attenuate a forwardly directed impact. Additional impact attenuators extend between the hitch structure and a vehicle in towing motion. Plural jacks provide work site leveling and positional stability. The utility trailer provides an arch supported hoist to service the workspace and carries signs to provide traffic information and direction.
Owner:MURPHY WILLIAM T
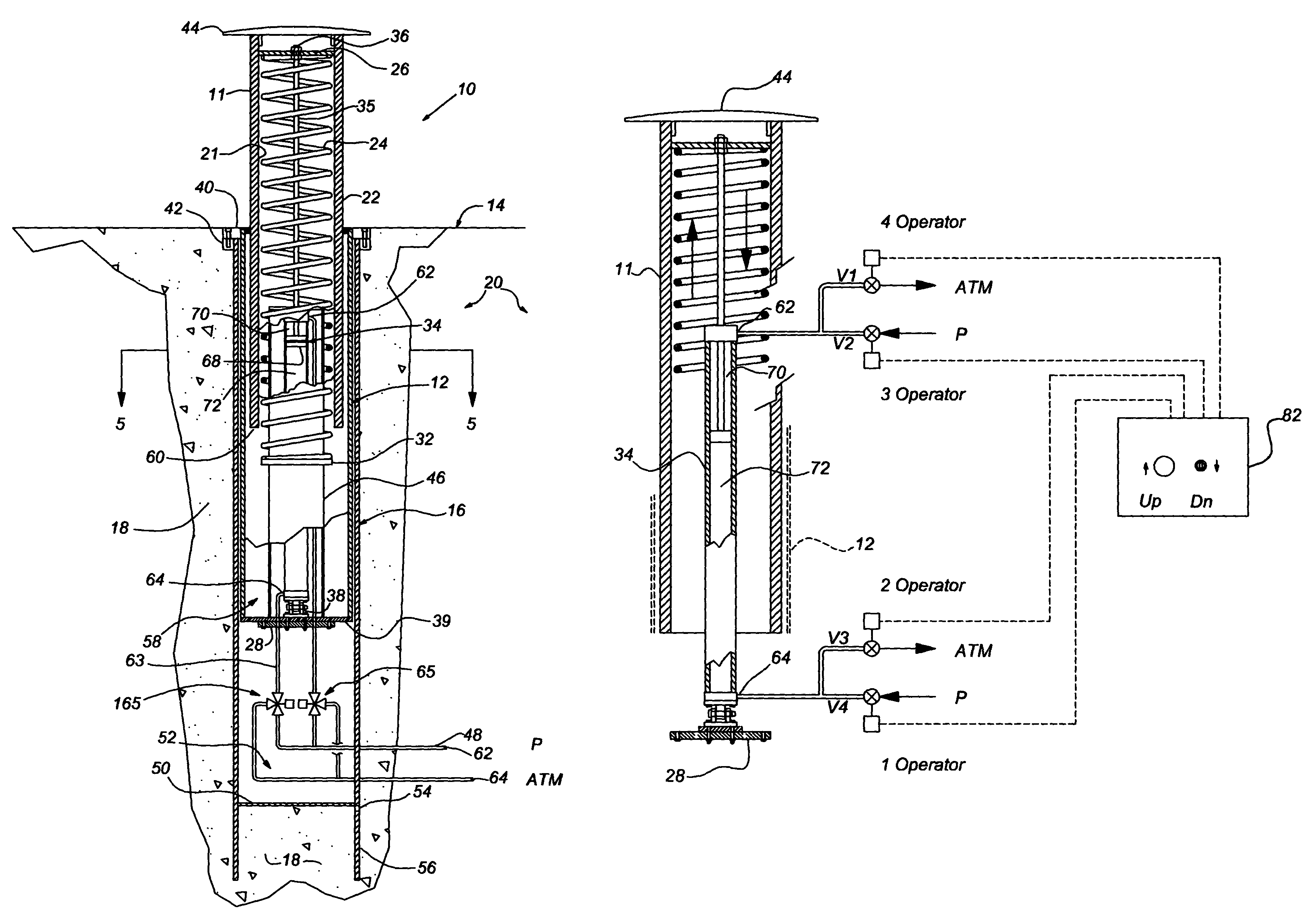
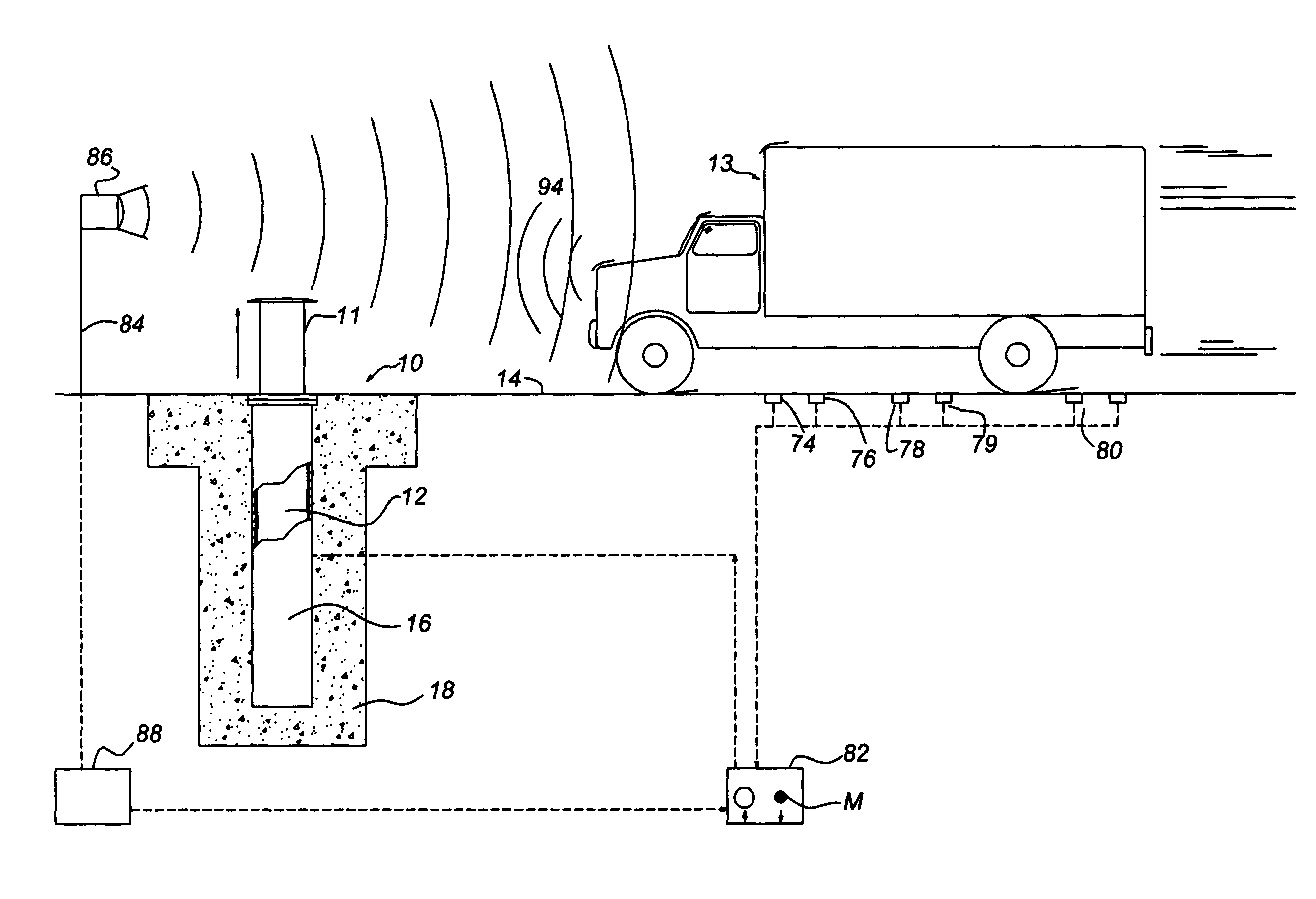
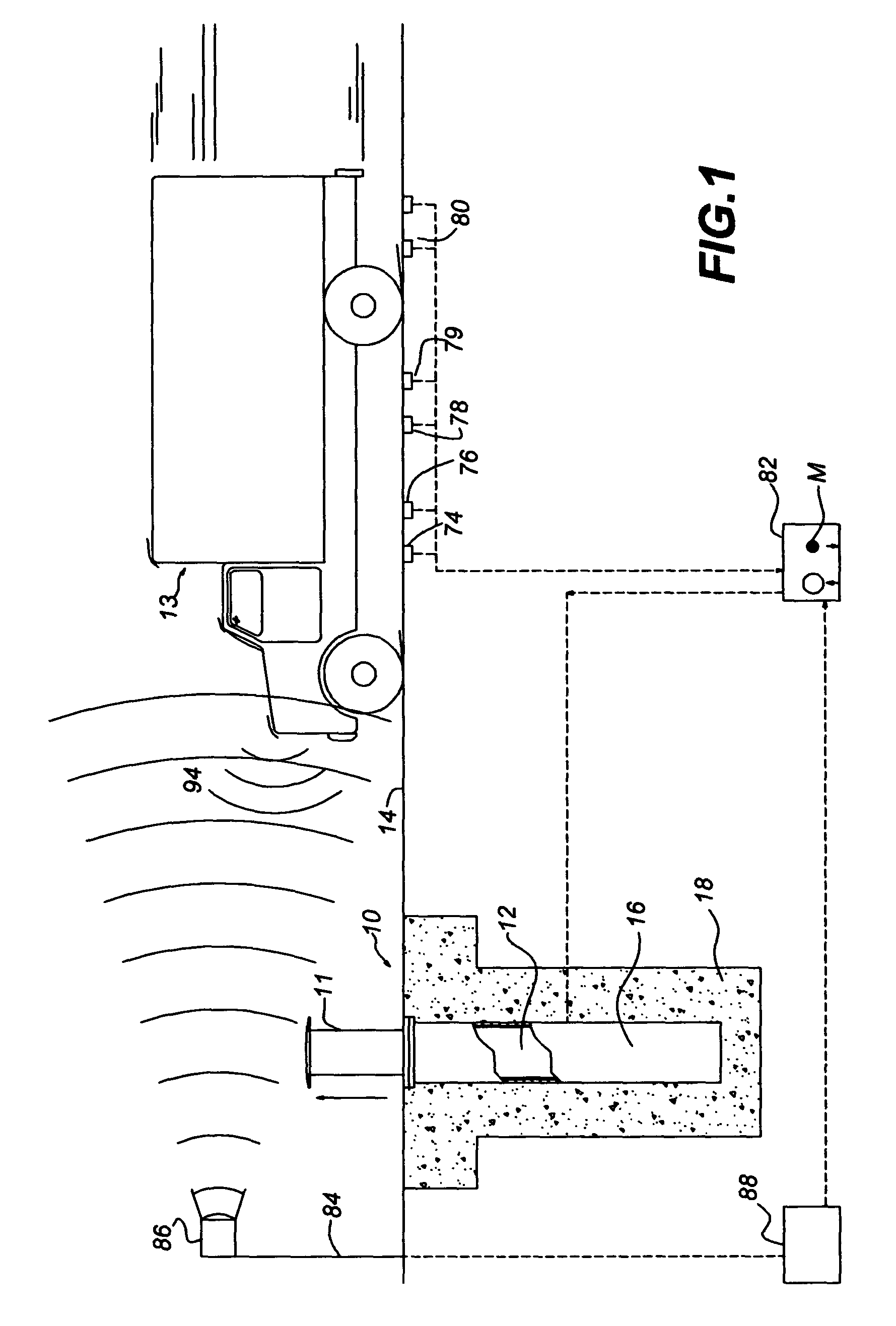
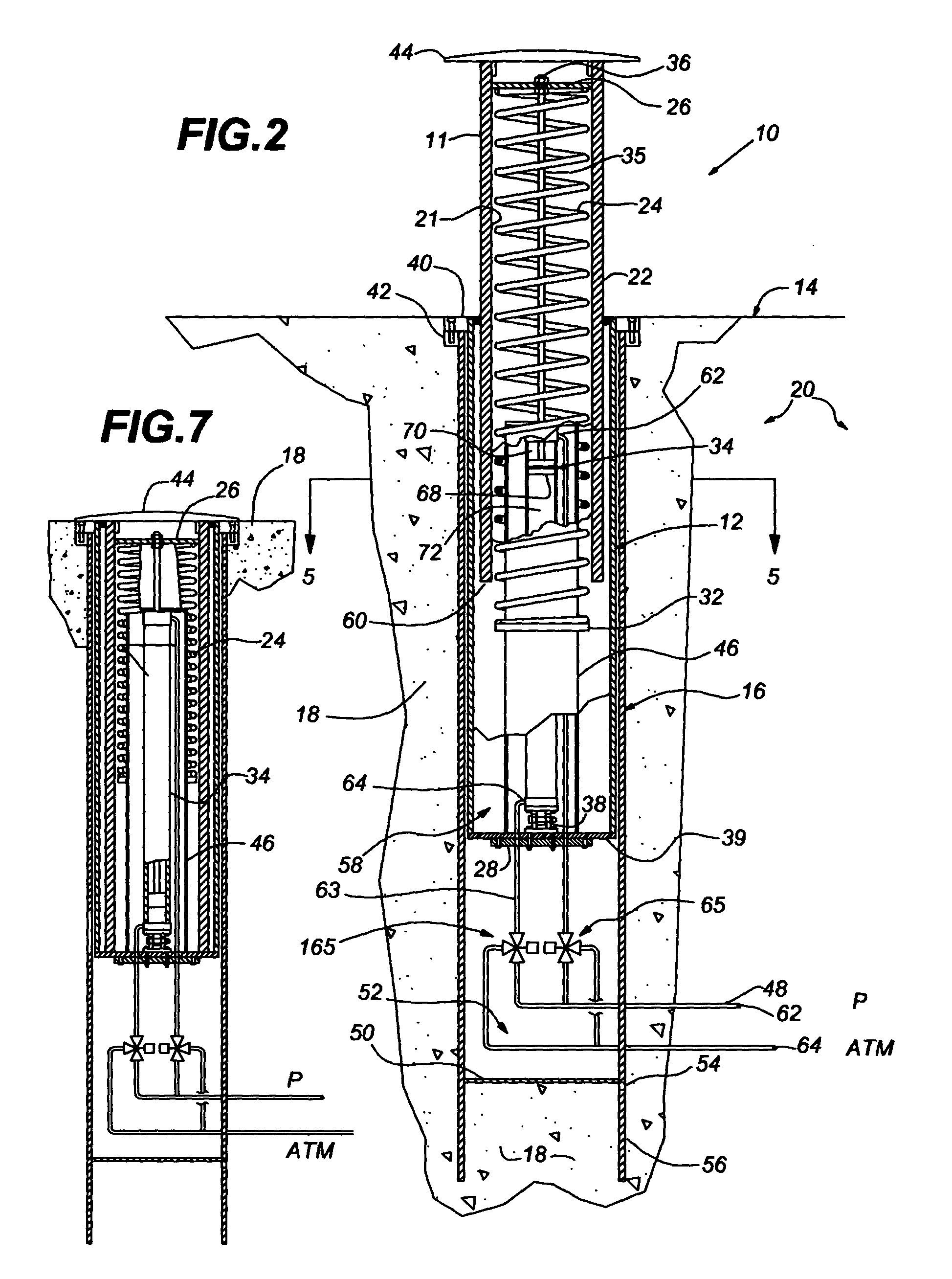
Anti-terrorist road block
A road block having an extensible bollard that is manually or electronically actuated by a powerful spring force for slow extension, and by both the spring and a power lift for rapid extension.
Owner:PERIMETER DEFENSE TECH
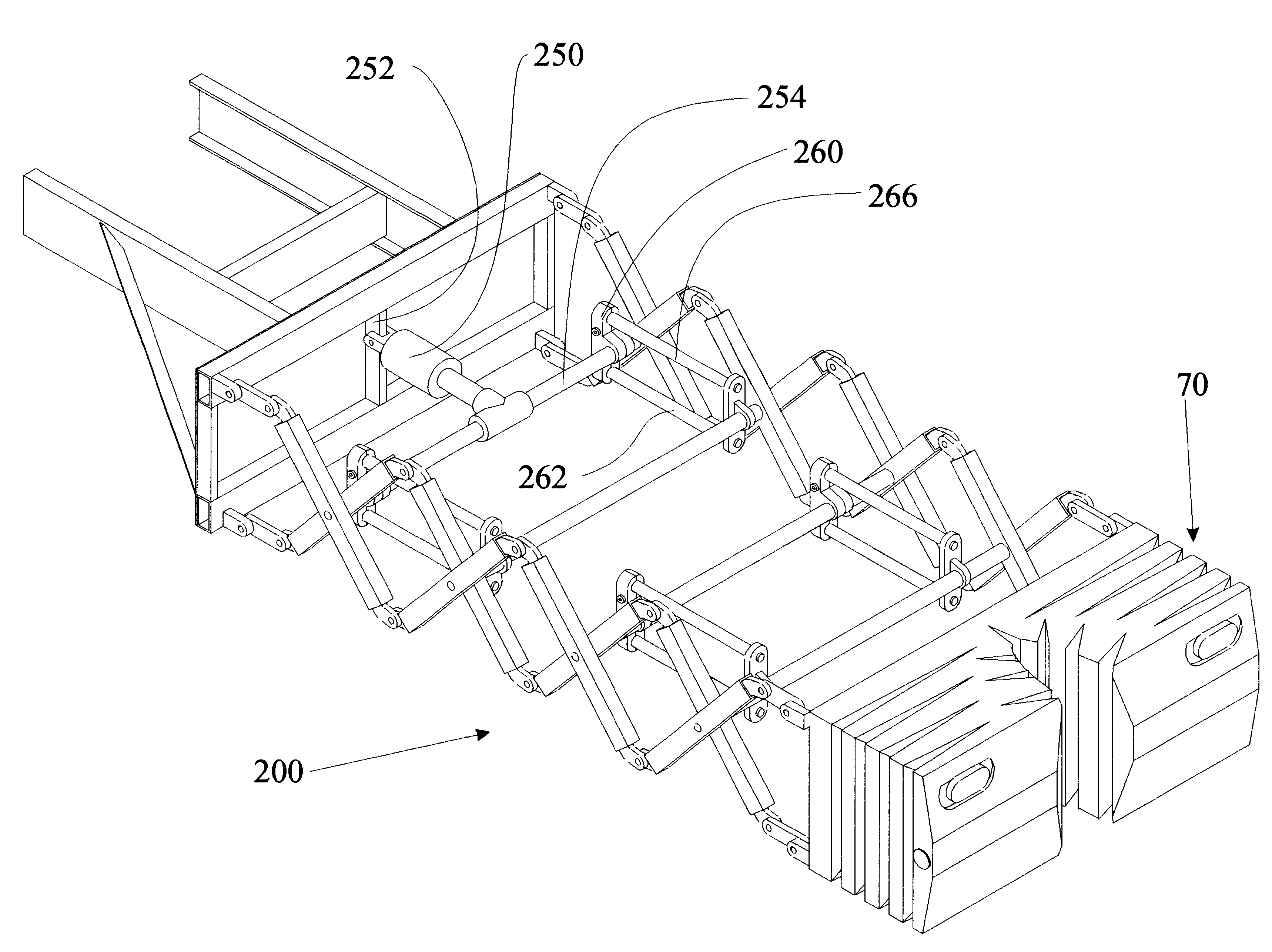
Steel yielding guardrail support post
A guardrail support post includes a continuous structural member having a top edge, a bottom edge, and a generally uniform cross section from the top edge to the bottom edge. The structural member includes first and second generally parallel flanges, and a web forming a coupling between, and extending generally perpendicular to the first and second flanges. The structural member includes a lower portion for installing below grade adjacent a roadway, and an upper portion configured to be coupled with a guardrail beam. A mid portion of the structural member is disposed between the upper portion and the lower portion. In accordance with a particular embodiment of the present invention, the first and second flanges include first and second cutouts, respectively, that occur within the mid portion. The cutouts are operable to weaken the structural member about an axis generally perpendicular to the flanges without substantially weakening the structural member about an axis generally parallel to the flanges.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Cable barrier guardrail system with steel yielding support posts
InactiveUS20070102689A1Improve lateral strengthDecreases longitudinal strengthPasturing equipmentRoadway safety arrangementsEngineeringStrip steel
In accordance with a particular embodiment of the present invention, a guardrail system includes at least one cable operable to contain and redirect an errant vehicle. The guardrail system also includes a plurality of guardrail support posts spaced apart in relation to one another. Each support post includes a lower portion, a mid portion, and an upper portion. The lower portion is for installing below grade adjacent the roadway. The mid portion lies substantially adjacent the grade and includes a weakened section operable to weaken the support post about a longitudinal axis. The upper portion is releasably coupled to the at least one cable such that the upper portion is uncoupled from the at least one cable when the support post is displaced.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
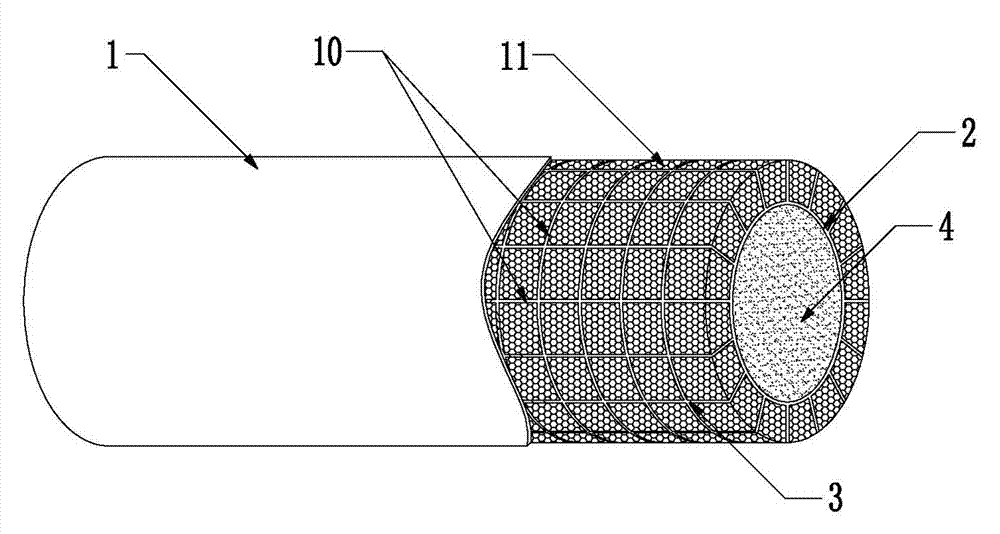
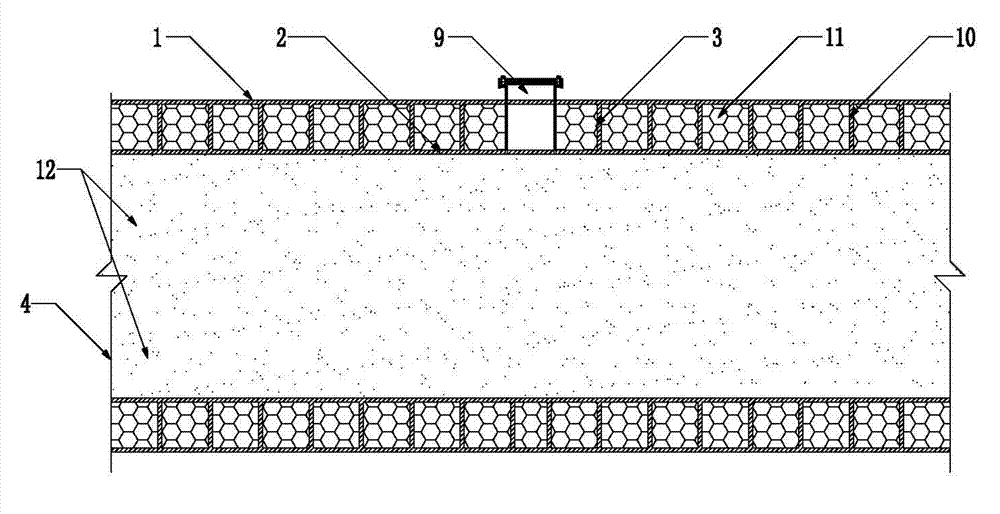
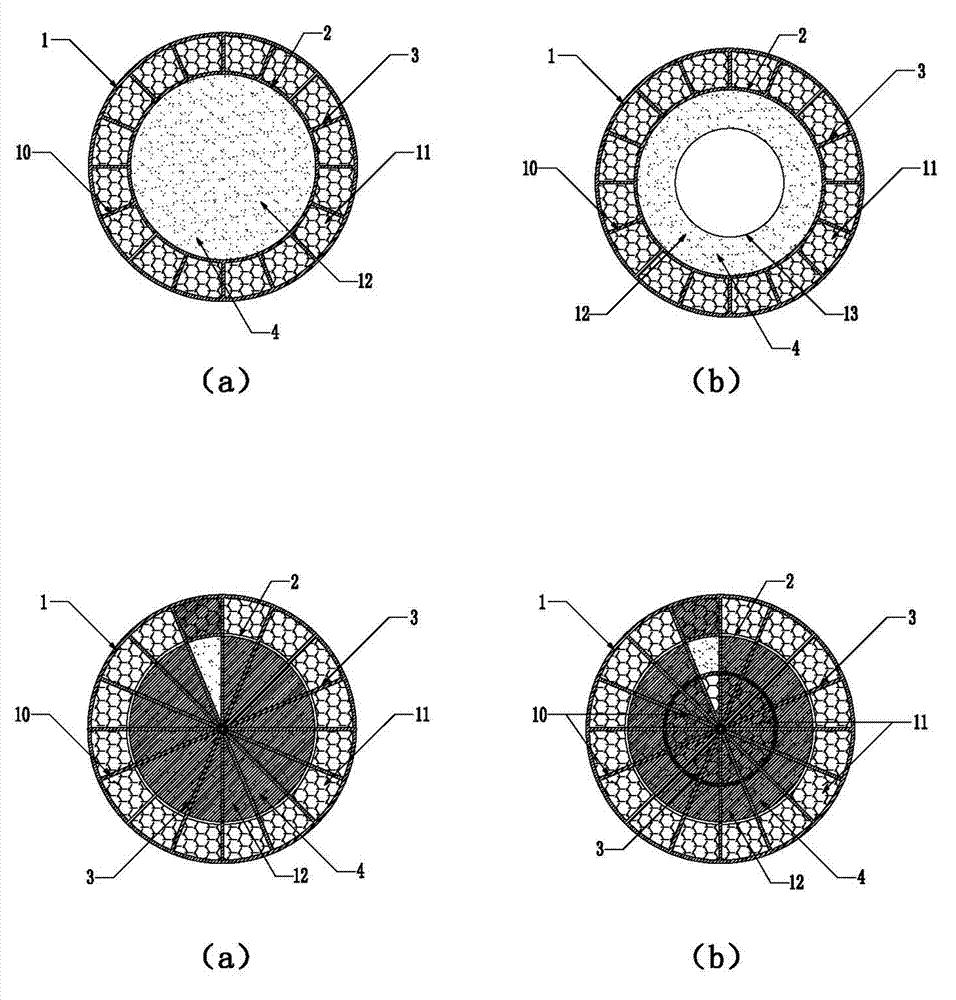
Honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure and anti-collision system using same
InactiveCN103031817AEffectively distributes impact loadsWithstand multiple impactsClimate change adaptationShipping equipmentMortise and tenonFilling materials
The invention discloses a honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure and an anti-collision system using the same. The double-cylinder structure comprises an outer cylinder (1) and an inner cylinder (2), wherein a honeycomb lattice enhanced body (3) is arranged between the outer cylinder (1) and the inner cylinder (2); and a filling material body (4) is filled into the inner cylinder (2). The anti-collision system comprises the honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure, wherein the double-cylinder structure comprises straight cylinder units (5) and bent cylinder units (6); adjacent and mutually connected straight cylinder units (5), the straight cylinder units (5) and the bent cylinder units (6), or the bent cylinder units (6) are connected together through mortise and tenon joints (7) and bolts bars (16) so as to form a strip-shaped or annual anti-collision system; and a moving device (8) is arranged on the inner side of the anti-collision system. The double-cylinder structure is integrally formed in a weaving mode, and the filling material body has higher rigidity, so that the deformation degree can be limited without crack, and the double-cylinder structure is long in service life, low in cost and easy to maintain.
Owner:JIANGSU BOHONG NEW MATERIAL TECH +1
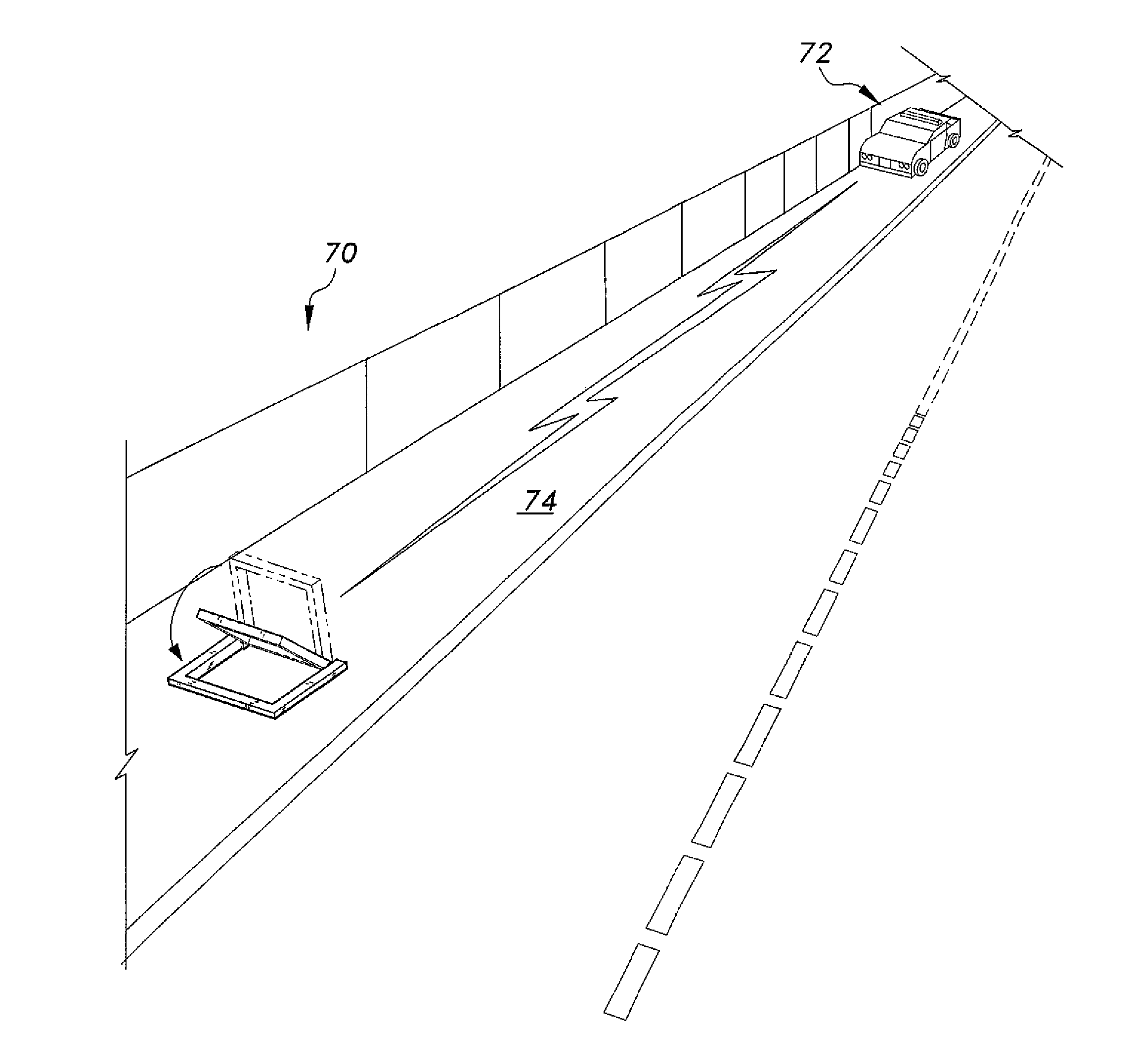
System for remote control of retractable, ground-based vehicle barriers
InactiveUS8678701B1Easily and quickly approachLower the thresholdPasturing equipmentPaving detailsRemote controlGround vehicles
The system for remote control of retractable, ground-based vehicle barriers increases control of the emergency lane of the road by mounting ground signboards in the emergency lane to prevent any vehicle to pass through this lane and so the police vehicle or the ambulance can easily and quickly approach the site of accident through the emergency lane. The signboards include a U-shaped frame permanently mounted in the emergency lane and a panel pivotally attached to the frame. Servo motors are provided to rotate the panels between a vertical position providing a barrier to traffic and a horizontal position permitting an emergency response vehicle to travel through the emergency lane. The emergency response vehicle is provided with a remote control unit having a short-range transmitter that transmits a trigger signal that is received by a unit at the barrier sign to activate a motor controller to lower the sign.
Owner:ALDASEM FARRAJ J A
High-impact, energy-absorbing vehicle barrier system
InactiveUS6926461B1Reduces the potentially harmful deceleration forces experiencedReduces eliminates potentialTraffic signalsRoad signsEnergy absorptionHigh energy
A high-impact, energy-absorbing vehicle barrier system generally includes a substantially rigid outer containment wall coupled via cable restraint assemblies with an energy-absorbing inner impact wall, and energy-absorbing cartridges strategically positioned between the impact wall and containment wall. The impact wall is constructed of a number of rectangular tubes coupled with one another to presents a substantially smooth, uniform surface to passing vehicles. The energy-absorbing cartridges generally consist of a number of foam sheets which compress and crush between the containment wall and impact wall to absorb energy from an errant vehicle striking the face of the impact wall, while the deflection and deformation of the impact wall tubes dissipates additional energy to reduce peak decelerations and mitigate the severity of high-energy vehicular impacts. The splice units and quick-disconnect cable restraint system provide for relatively easy and quick replacement of damaged impact wall sections and energy-absorbing cartridges.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Anti-terrorist road block
A road block having an extensible bollard that is manually or electronically actuated by a powerful spring force for slow extension, and by both the spring and a power lift for rapid extension.
Owner:PERIMETER DEFENSE TECH
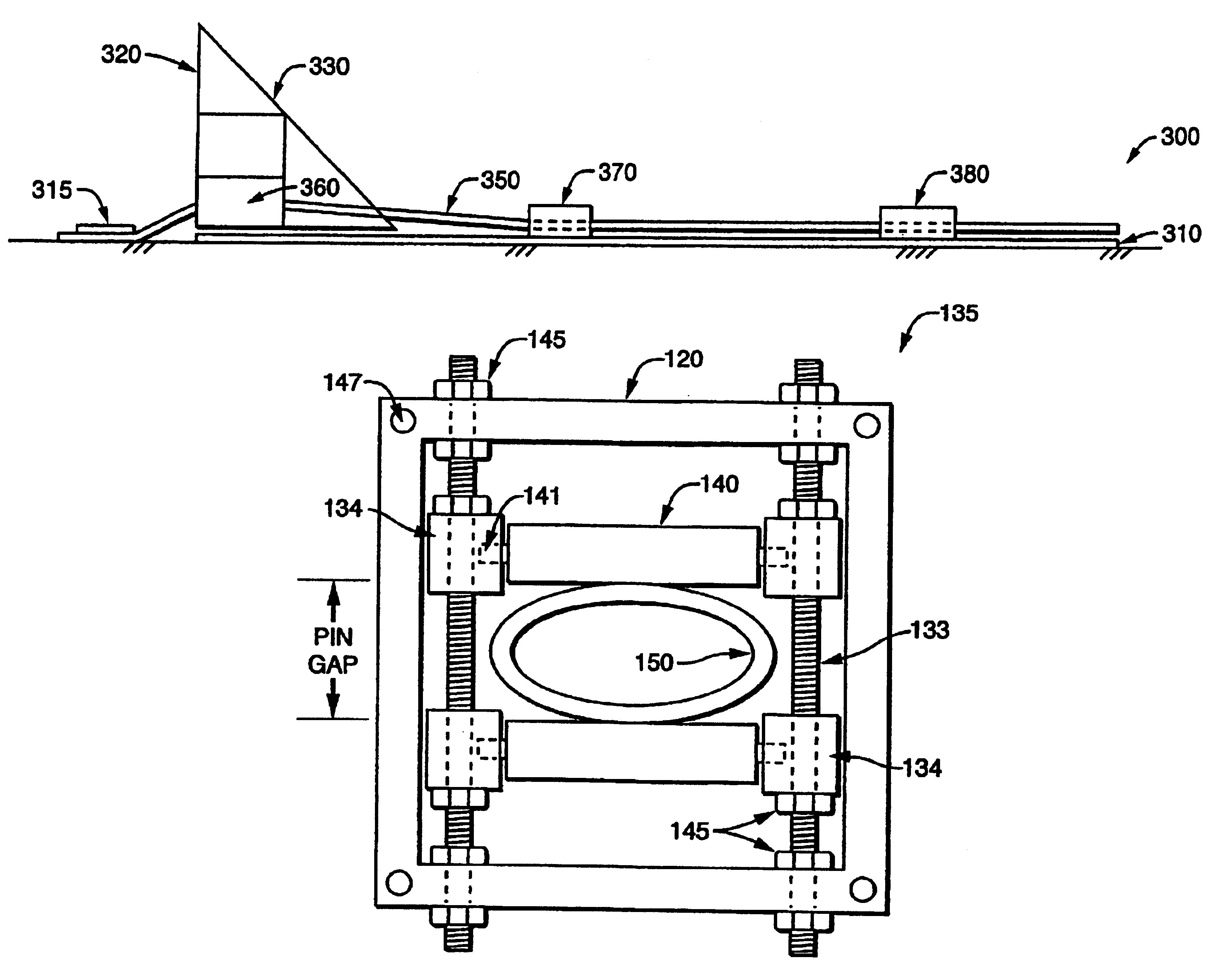
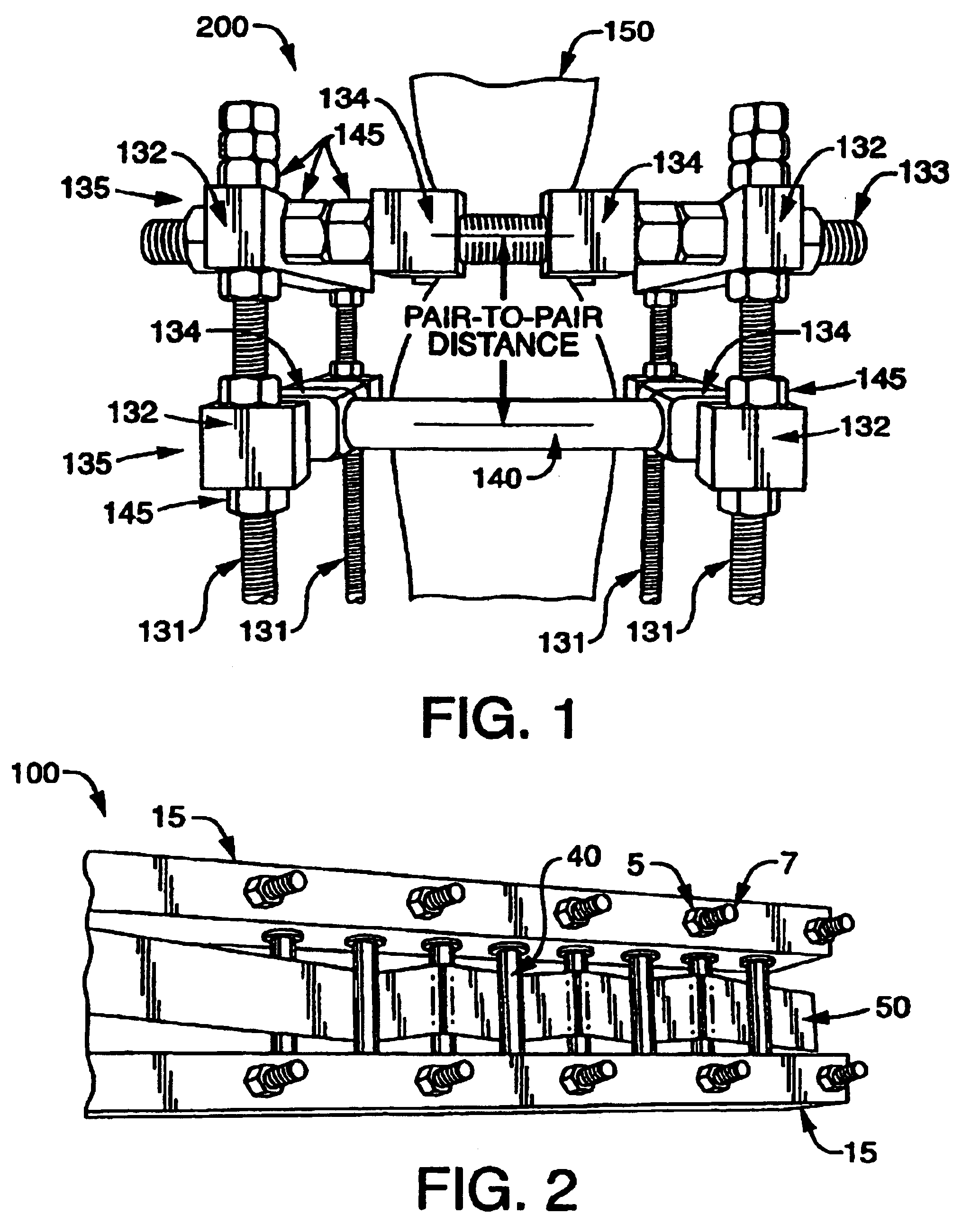
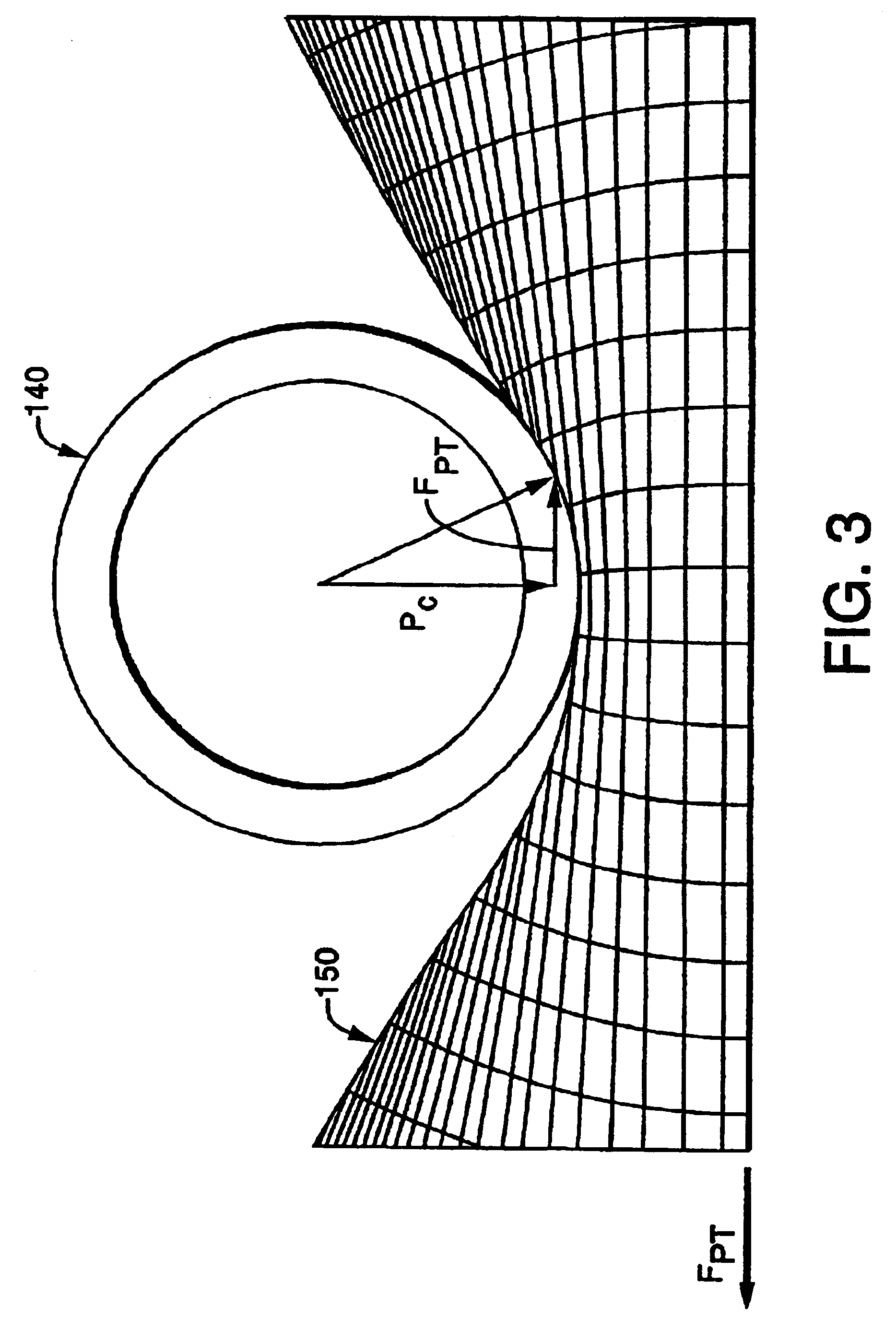
Variable force energy dissipater and decelerator
InactiveUS6962245B2Efficient and cost-effective managementMore kinetic energyTraffic signalsElastic dampersUltrasound attenuationSteering column
Tunable pull-through energy attenuator and decelerator devices is disclosed which provide for variable force-time profiles, deceleration and kinetic energy attenuation of moving objects so as to prevent damage or injury to impacting objects, vehicles or persons. The device employs either consumable inelastic or reusable, viscoelastic deforming elements, such as tubes, rods, plates or strips, which absorb substantial amounts of energy through repeated inelastic or viscoelastic deformation when the deforming element is pulled-through a tunable array of rigid pins having a variety of configurations and settings. The disclosed devices provide for variable force-time profiles which control the cumulative deformation and thereby the amount of energy absorbed and rate of deceleration of impacting objects. The device may be readily adapted and deployed as highway vehicle guardrails, road barriers or crash cushions for frontal and side impacts and as load attenuators for crash-resistant aircraft seats, spacecraft landing pods, crash-resistant aircraft landing gear, aircraft and vehicle passenger restraint harnesses, cargo tie-downs, vehicle bumpers and collapsible vehicle steering columns.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
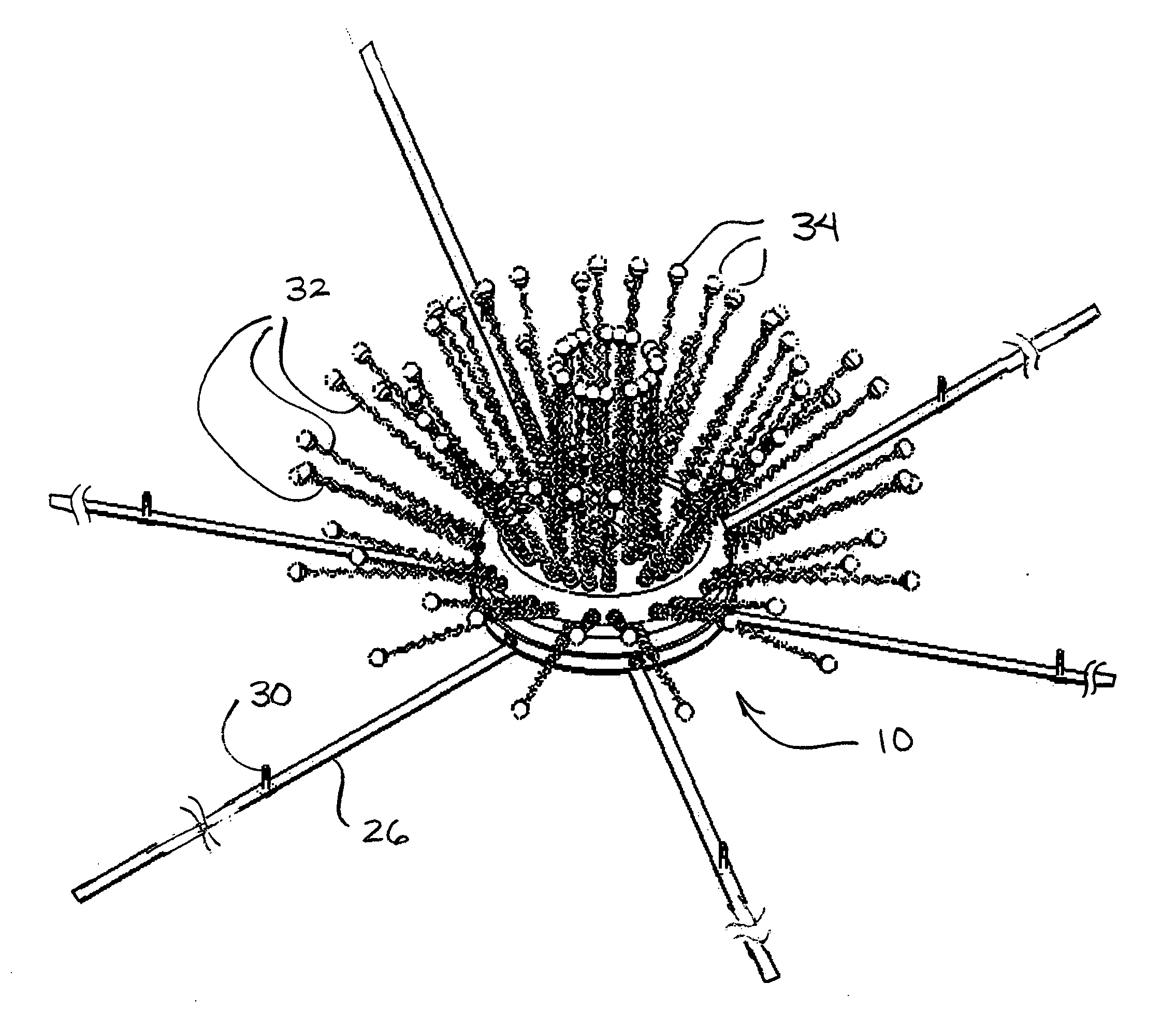
System and method for non-lethal vehicle restraint
An undercarriage immobilization device and method of restraining a vehicle uses tendrils and straps to engage the vehicle. The tendrils and straps will wrap around moving parts of the vehicle and restrain the moving parts to eventually incapacitate the vehicle. The undercarriage immobilization device includes a housing that contains tendrils that are launched from the housing by a propellant or compressed gas. The tendrils may be attached to the straps carried by the undercarriage immobilization device. Straps may be pulled off the housing leaving the housing near the point of deployment.
Owner:ENG SCI ANALYSIS
Portable Vehicle Barrier
InactiveUS20120177439A1Easy to assembleEasy to deployTraffic restrictionsRoadway safety arrangementsEngineeringCantilever
Owner:SECURITY SOLUTIONS INT
Releasable highway safety structures
InactiveUS20060011900A1Maximized strengthStable and predictable responsePasturing equipmentTraffic signalsEngineeringFastener
Consistent and reliable releasing of a guardrail during a vehicle impact is enabled by a releasable fastener for safety structures along a highway. The release of secured components such as guardrail is controlled, and precise positional cooperation is provided between securing members and the guardrail. Forces may be attenuated to further optimize response.
Owner:OCHOA CARLOS M
Lane maker
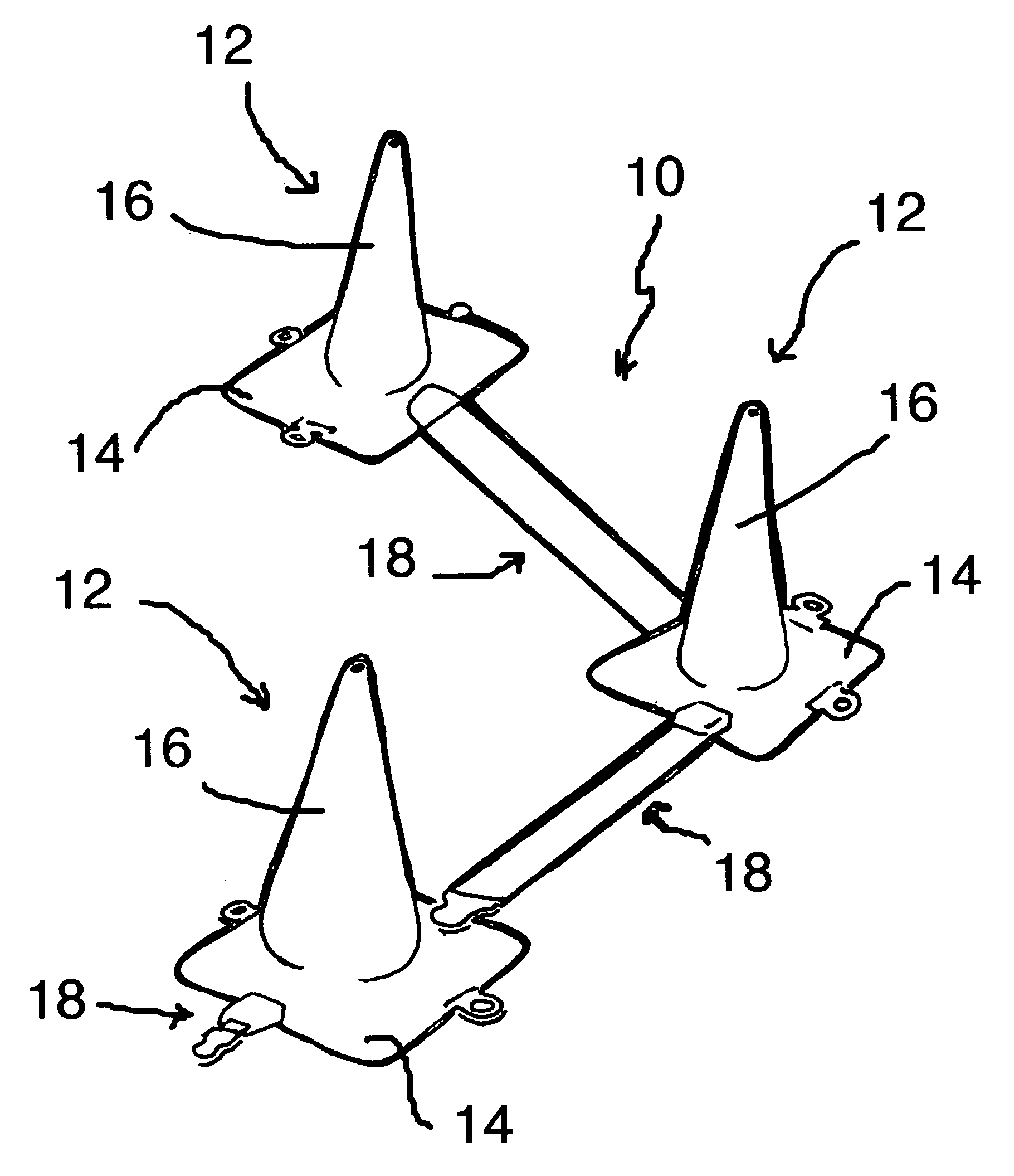
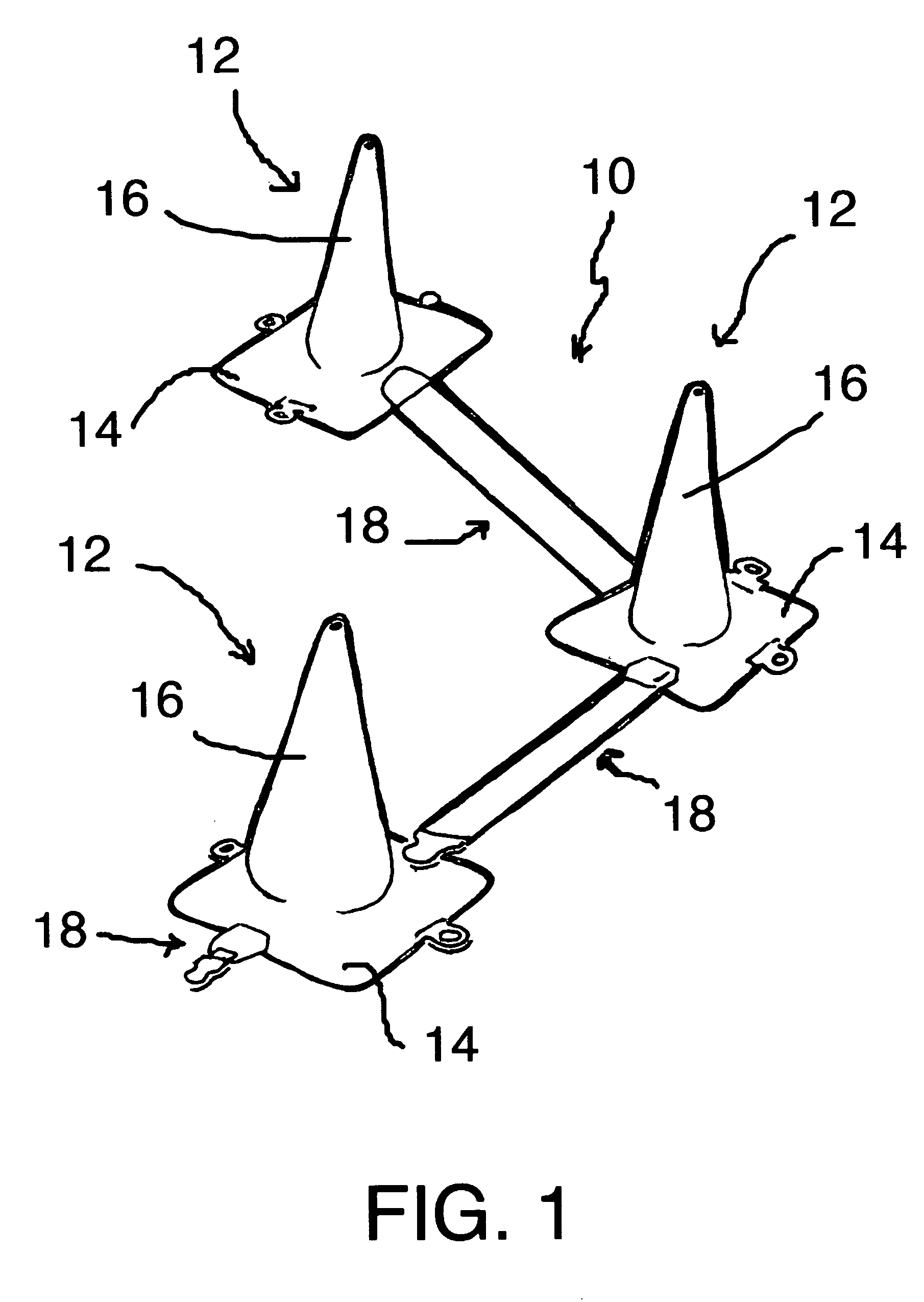
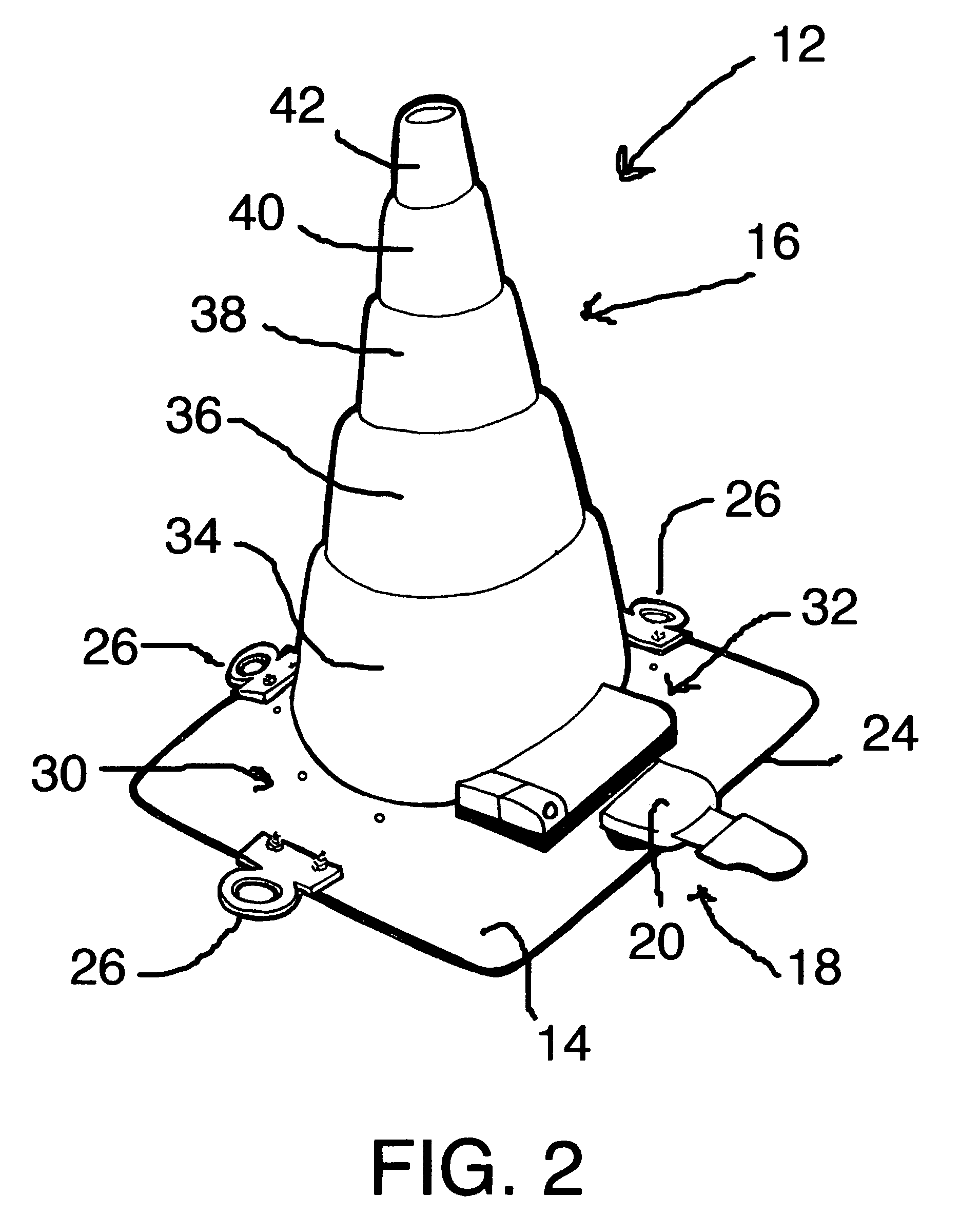
A collapsible traffic control cone includes a lane marker for delineating lines of demarcation between lanes approved for traffic flow and areas where traffic is prohibited. When in use, the lane marker extends from a rotatable housing mounted on one of the cones and is releasably attached to an anchor on an adjacent cone. The lane marker is a flat, highly reflective web which lies flat on the roadway between the cones. In the event of a cone being tipped over from its base or when not in use, the lane marker retracts into its housing. A light responsive to oncoming traffic is also provided.
Owner:STEWART ROBIN HARDIE
Composite railway crosstie, shaped like an I beam
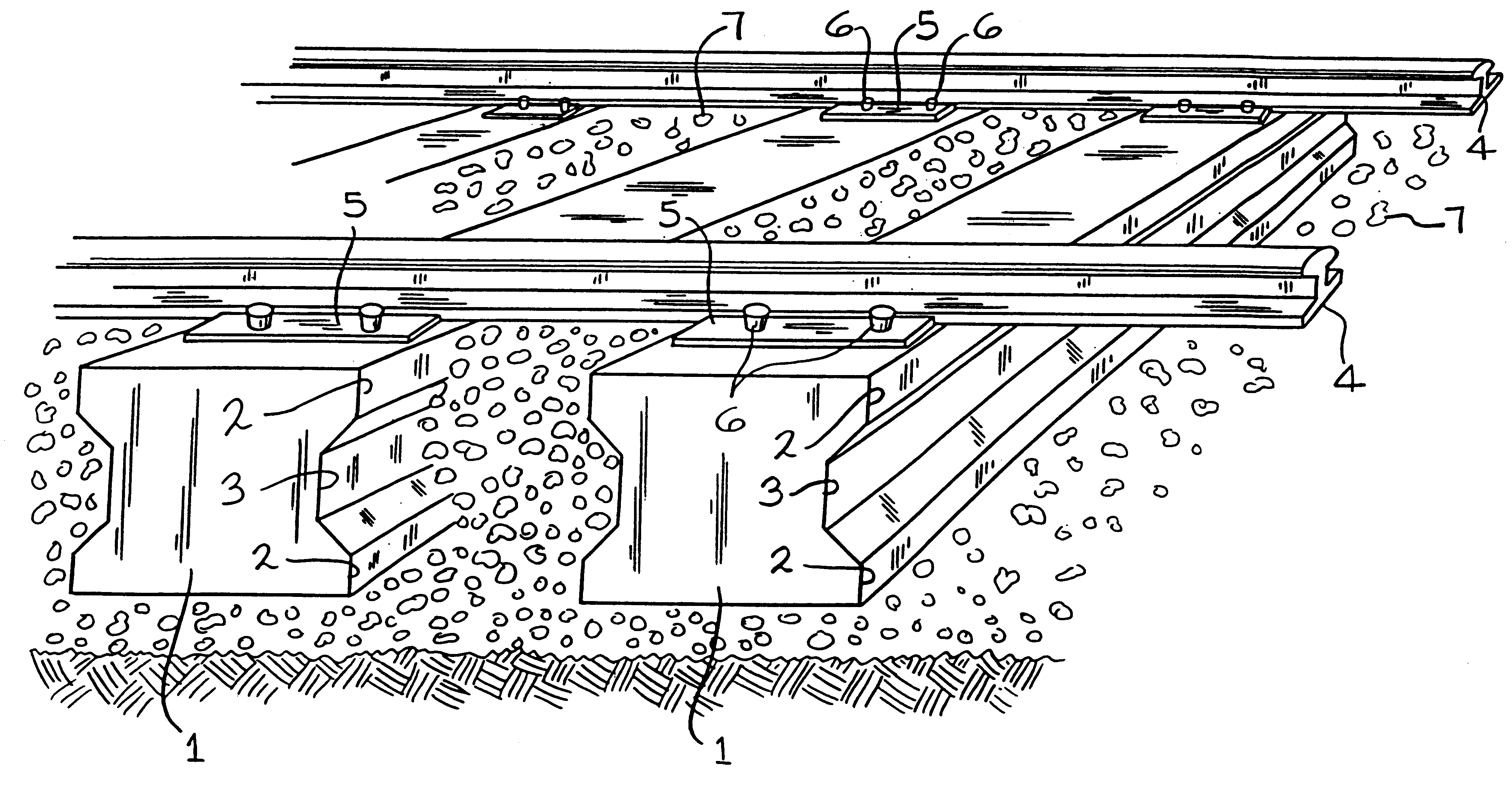
InactiveUS6247651B1The implementation process is simpleBallastwayPlastic recyclingElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
A railway crosstie is adapted for use in a track system having a pair of rails supported on longitudinally spaced crossties. The railway crosstie includes an I-beam member made of a combination of recycled materials.
Owner:FLANNER JR GEORGE C
Jet blast resistant vehicle arresting blocks, beds and methods
InactiveUS6971817B2Reduce transmission of effectIn situ pavingsArresting gearCompressive failureCompressible material
Aircraft arresting beds constructed of cellular concrete at ends of runways may be subject to damaging effects of jet blast phenomena. Arresting units resistant to such effects are described. A block of compressible material, such as cellular concrete, provides compressive failure characteristics suitable for arresting travel of an aircraft overrunning a runway. Relatively thin frangible material positioned above the block provides a stronger, more damage resistant surface, while still readily fracturing in an arresting incident. Intermediate material, such as a foam layer, positioned under the frangible material may be included to provide a protective cushioning effect by mitigating transmission of external phenomena forces to the block. A fastening configuration at least partially enclosing other portions of the arresting unit provides a stable unified composite, without destroying desired compressive failure characteristics of the unit. Arresting units may also include a bottom layer of material stronger than the block of compressible material and a sealant coating with water resistant properties.
Owner:RUNWAY SAFE IPR AB
Locking hook bolt and method for using same
InactiveUS6948703B2Firmly connectedFull strengthFencingWire networkEngineeringMechanical engineering
A locking hook bolt, which may be used for securing cable to support posts in guardrail assemblies, and a method for using the same are provided. The locking hook bolt includes a first leg, a second leg, and an arcuate portion coupling the first and second legs such that the second leg extends generally parallel with, and spaced apart from, the first leg. A locking portion configured to engage a support post extends from, and forms an angle of approximately 90 degrees with, the second leg. The first leg of the locking hook bolt includes a threaded portion opposite the arcuate portion.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Vehicle stopping method and apparatus
Owner:BOLTEK CORP
Method for optimally setting expressway traffic safety facilities
InactiveCN101818470AMaximize safetyOptimize applicable conditionsClimate change adaptationTraffic signalsRoad surfaceTransport engineering
The invention discloses a method for optimally setting expressway traffic safety facilities, which comprises the following steps of: determining key sections of the optimally-set expressway traffic safety facilities; optimally setting the safety facilities of sharp bend, inflection and continuous curve road sections; optimally setting the safety facilities of a bridge head combined with a sharp curve section; optimally setting the safety facilities of a long and steep longitudinal slope section; optimally setting an emergency lane; optimally setting the safety facilities of a long straight line section; optimally setting the safety facilities of a poor sight distance section; optimally setting the safety facilities of roads and bridges, and roads and tunnels transition sections; and optimally setting the safety facilities of a vertical crossing section. In the method, requirements of a driver on safety, quickness, high efficiency and comfortableness are fully met according to the influence of road conditions such as a plane and vertical section line, a pavement structure, roadbed and side slopes, bridges and tunnels, an overhead crossing project of the expressway on driving safety.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com