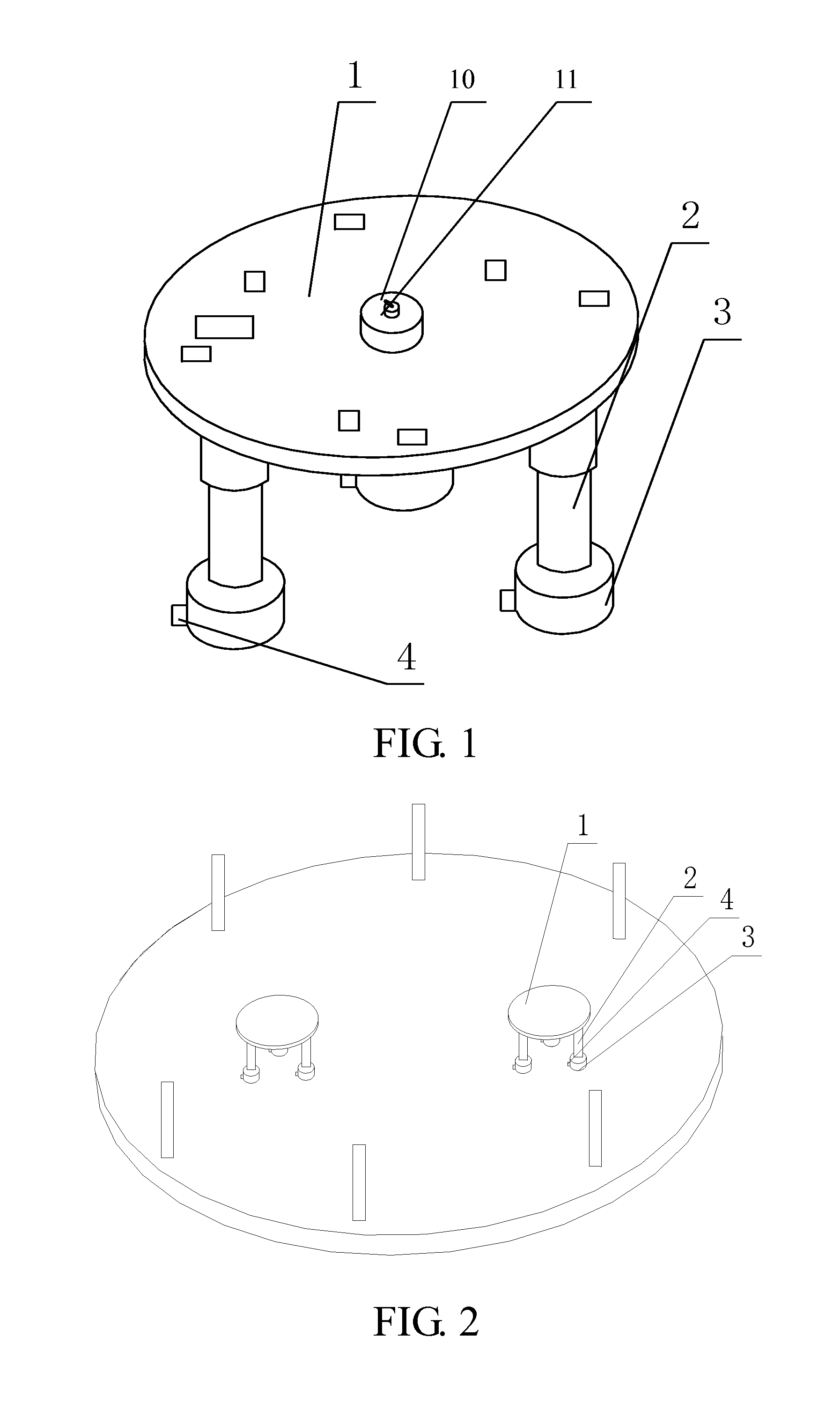
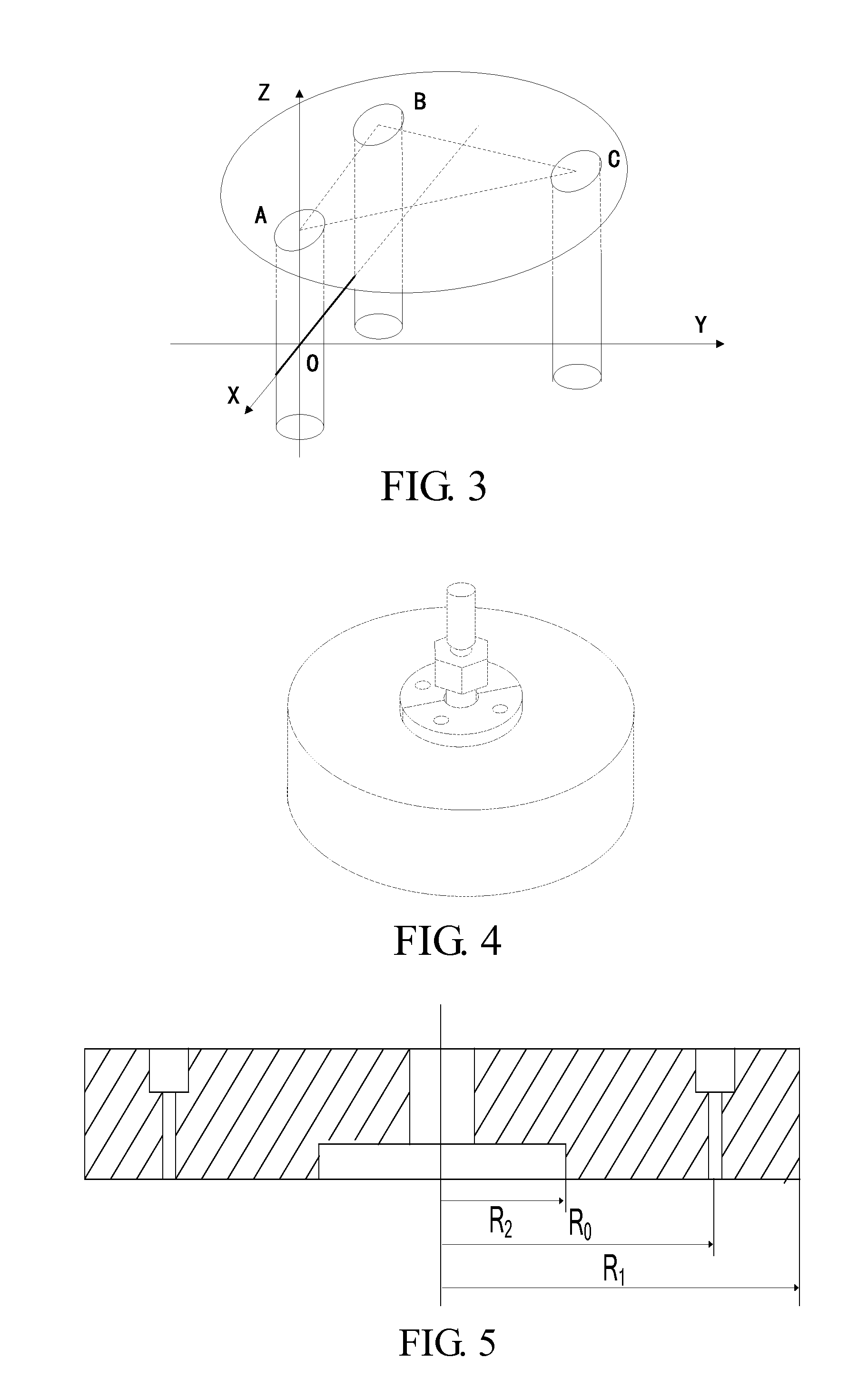
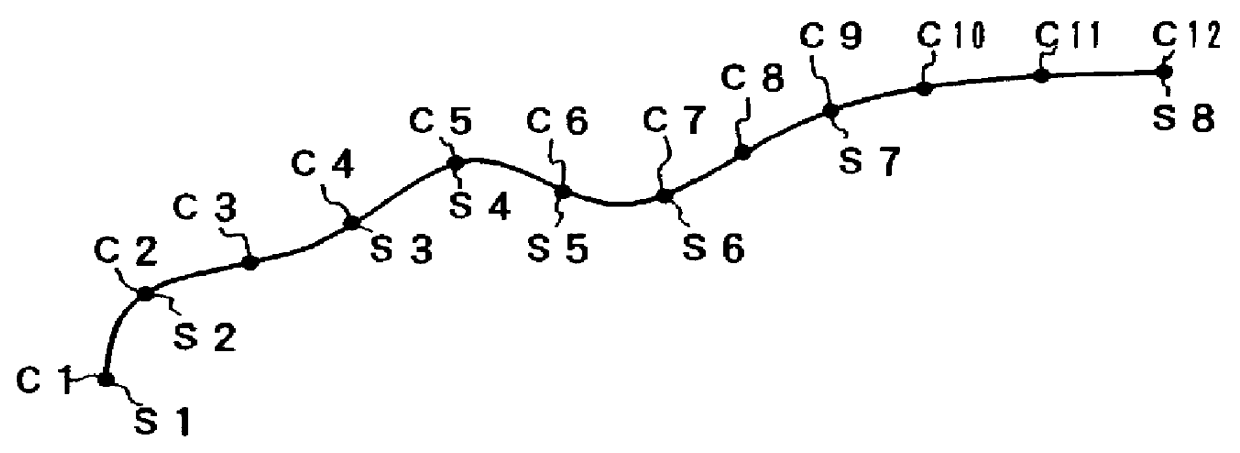
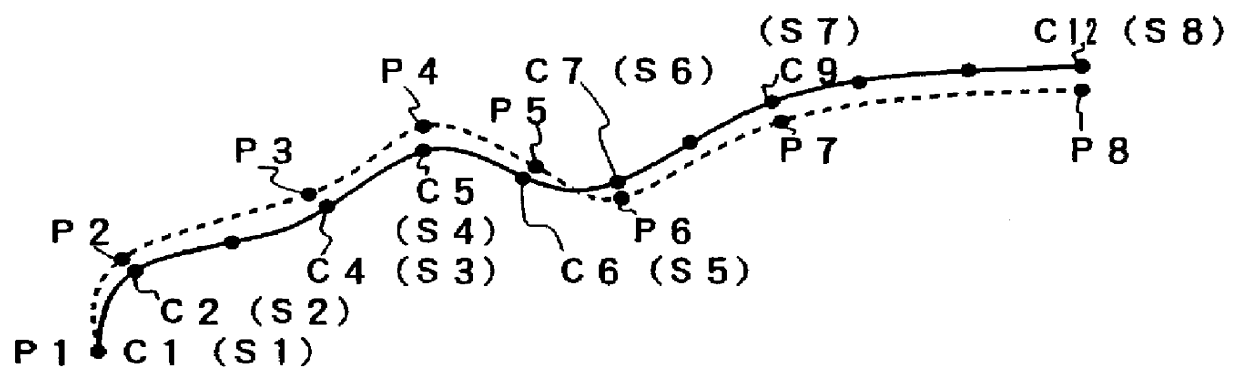
Patents
Literature
14116 results about "Servo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Servos (also RC servos) are small, cheap, mass-produced servomotors or other actuators used for radio control and small-scale robotics. Most servos are rotary actuators although other types are available. Linear actuators are sometimes used, although it is more common to use a rotary actuator with a bellcrank and pushrod. Some types, originally used as sail winches for model yachting, can rotate continuously.
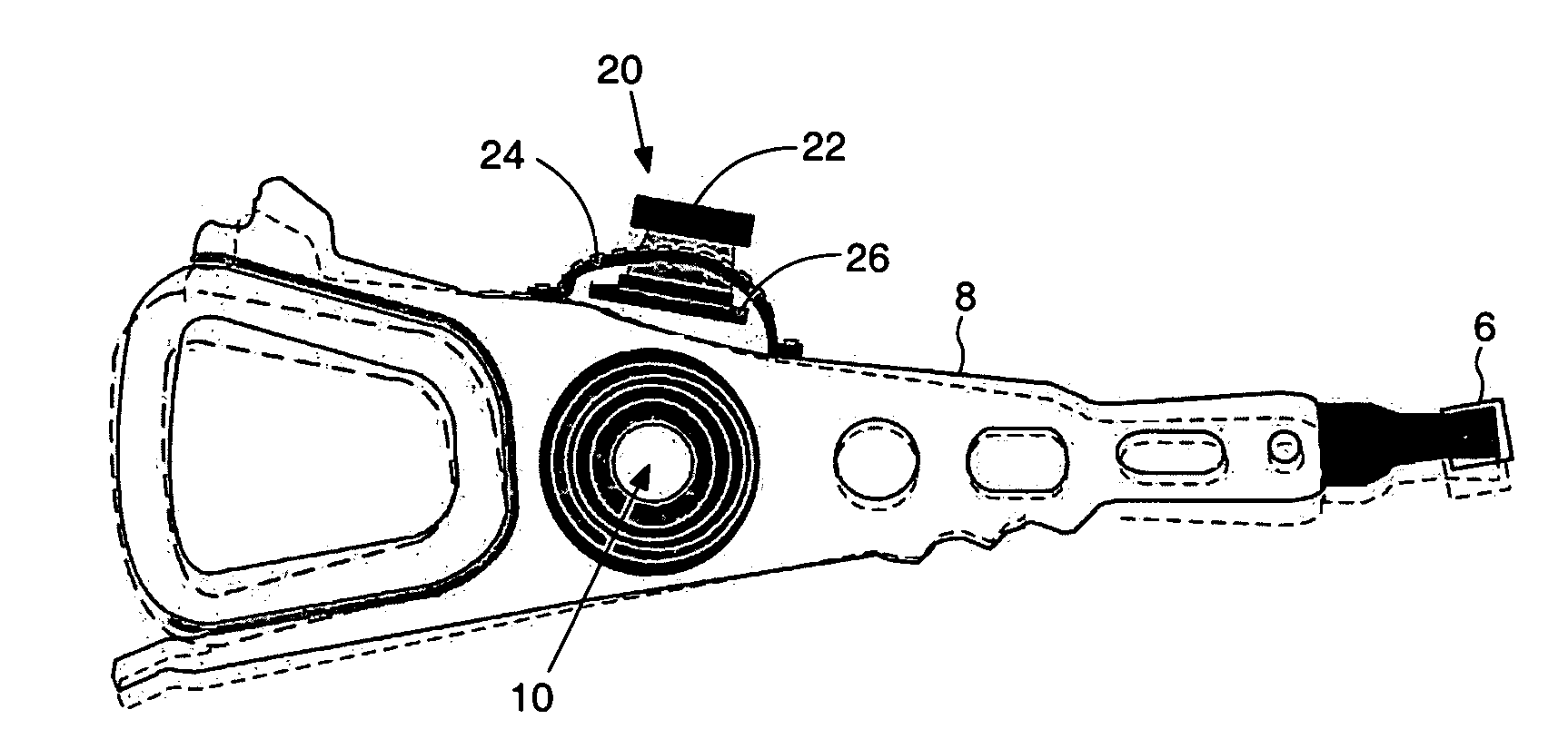
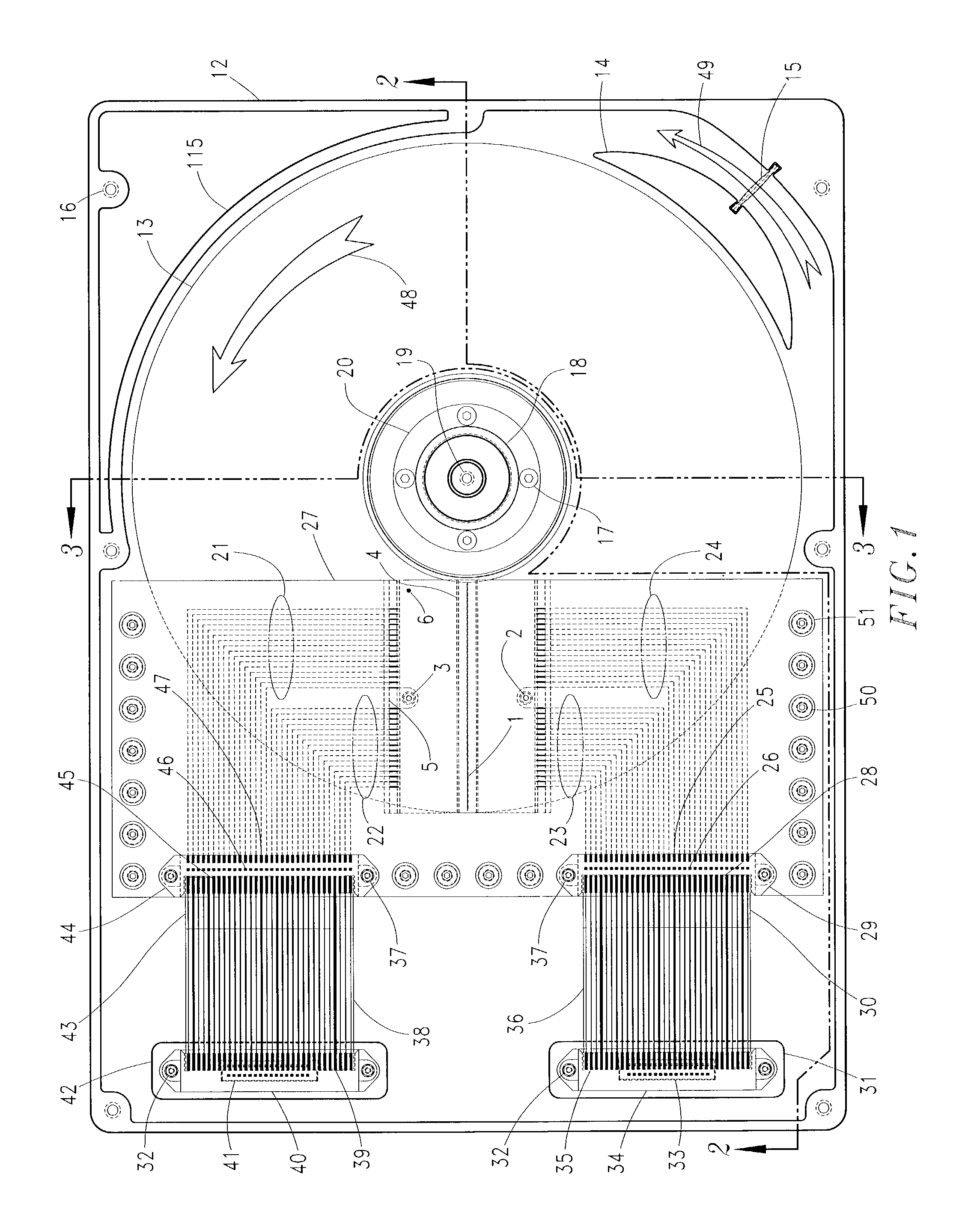
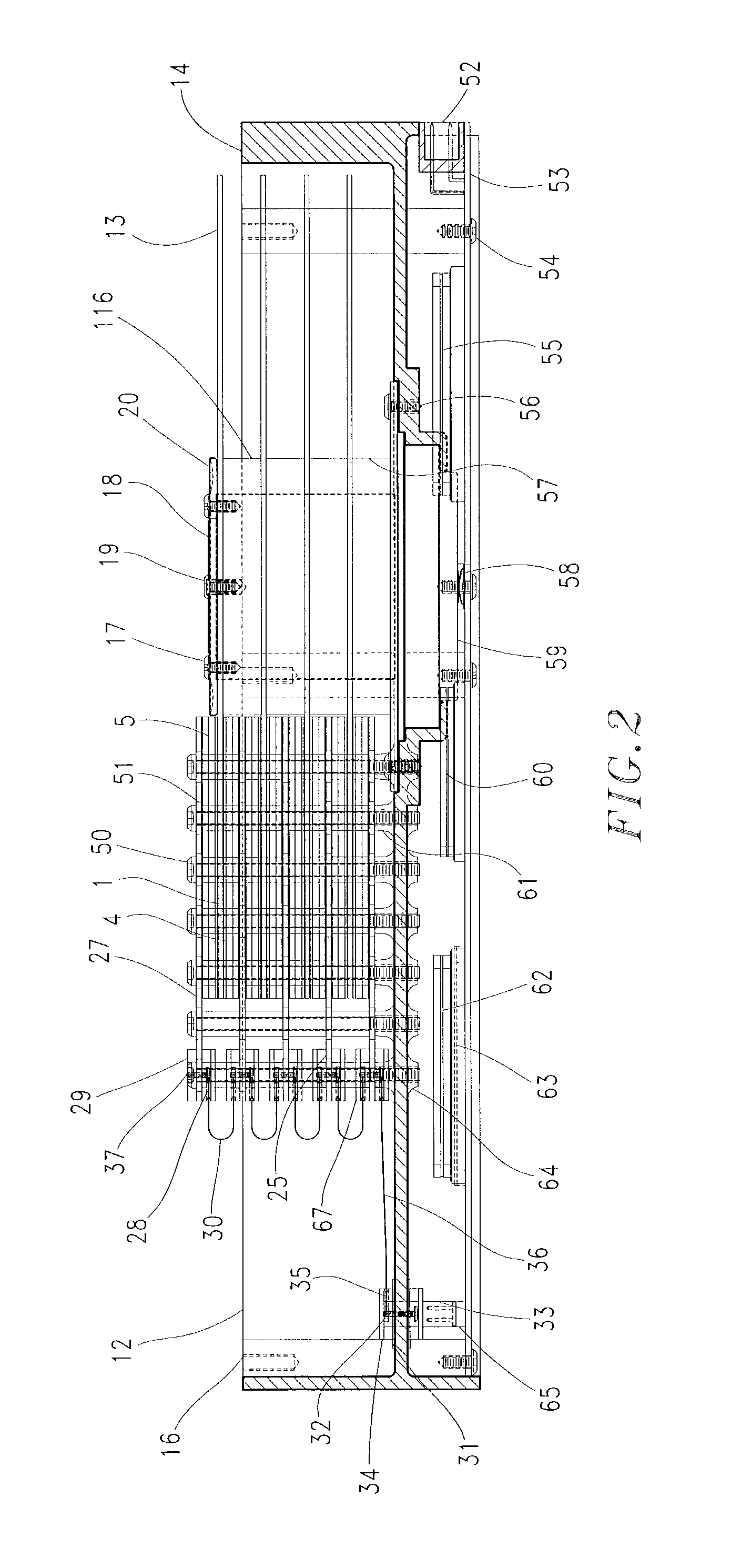
Disk drive comprising an optical sensor for vibration mode compensation
InactiveUS7365932B1Large componentUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionFilamentary/web record carriersControl signalControl theory
A disk drive is disclosed comprising an actuator arm, a head attached to a distal end of the actuator arm, a voice coil motor for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot, and an optical sensor operable to generate a first position signal representing a position of the actuator arm with respect to the disk, wherein the first position signal is substantially unaffected by a vibration mode of the actuator arm. Servo sectors recorded on the disk are processed to generate a second position signal representing a position of the head with respect to the disk, wherein the second position signal comprises a significant component due to the vibration mode of the actuator arm. A control signal is applied to the voice coil motor in response to the first and second position signals.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Three-degree-of-freedom flexible manipulator control device and method
InactiveCN102501242AAchieve precise positioning controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric machineryManipulator
The invention discloses a three-degree-of-freedom flexible manipulator control device and method. The device comprises flexible manipulator body parts, a servo motor driving part and a control part. The three-degree-of-freedom distribution is characterized in that two rotating flexible manipulators connected in series are respectively driven by a connected motor and speed reducer and are connected on a moving sliding block driven by a screw; a screw substrate and a fixed base are connected; three alternating servo motors are all provided with photoelectric encoders for detecting a rotation angle. A plurality of piezoelectric ceramic sheets are stuck to the part near a fixing end, on each flexible manipulator to respectively serve as a photoelectric sheet sensor and a photoelectric driver; and acceleration sensors are respectively installed at the parts near a free end, on each flexible manipulator. The photoelectric sheet sensor or the acceleration sensor can respectively detect the vibration of flexible beams. The detected signal is fed back, and three motors are respectively controlled by a motion control card to move after a control algorithm is operated. A control part is used for processing the detected flexible beam rotation and a vibration signal and carries out corresponding processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Hybrid servopositioning systems
InactiveUS6873487B2Driving/moving recording headsHeads using thin filmsData recordingComputer science
Servopositioning systems, methods, formats, and data recording media used in association with the same, employing both time-based and amplitude-based transverse tracking servo bands in the same or different locations on the medium.
Owner:SONY CORP
Rail car door opener
A servo that is attachabley secured to the rail car frame at each door lock that is connected to the latch via a draw bar with sufficient modulus to withstand the repeated force required to move the latch thus opening the door. The servo provides a pulling action with the motive force being pneumatic pressure but not limited to pneumatic whereas hydraulic or electric energy can be supplied to the servo providing the motive force to pull the draw bar attached to the latch, that when said servo provides a pulling force sufficient to over come the friction ot the latch to the striker plate the latch moves in a upward direction thus releasing the door to open. A second element of the servo is to provide a pushing action via the draw bar to the door latch to drive it all the way into the closed position.
Owner:MARCHIORI DAVID +1
In-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of material in multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition
ActiveUS20160216182A1Innovative structureEffective testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTesting equipmentTest material
An in-situ testing equipment for testing micromechanical properties of a material in a multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition is disclosed. The equipment comprises a frame supporting module, a tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module, a torsioning module (21), a three-point bending module (6), an impressing module (33), a thermal field and magnetic field application module (34), an in-situ observation module (32) and a clamp body module (22). The frame supporting module provides a structural support for the whole testing equipment, the tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module is arranged at upper and lower ends of the testing equipment, the torsioning module (21) is directly arranged at a front end of the tension / compression-low cycle fatigue module, the three-point bending module (6), the impressing module (33) and the thermal field and magnetic field application module (34) are disposed on a support post at one side of the whole testing equipment through a common replacing component, and the in-situ observation module is disposed on another support post at the other side of the testing equipment. The clamp body module is connected to a front segment of the torsioning module, so as to clamp a test piece. An overall structure of the testing equipment is configured in a vertically symmetrical arrangement achieved by using four support posts. Two identical servo hydraulic cylinders (10) and two torsioning modules (21) are located at the upper and the lower ends of the testing equipment respectively and are used to perform a symmetrical tension / compression test and a symmetrical torsion test on the test piece (23) positioned centrally. The testing equipment is capable of realizing applications of five different types of loads including tension / compression, low cycle fatigue, torsion, bending and impressing, performing an intensive study on micromechanical properties of the material in the multi-load and multi-physical field coupled condition by using built-in electric, thermal and magnetic application modules and the in-situ observation module, and acquiring relations between deformation behavior, mechanism of damage, performance weakening of the material, applied loads and material properties.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Kalman filter prediction-based robot obstacle avoidance method
InactiveCN101943916AEasy to implementImprove real-time performanceControl using feedbackKaiman filterObservation data
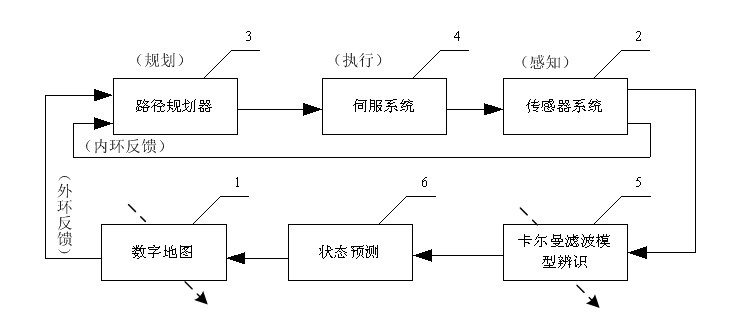
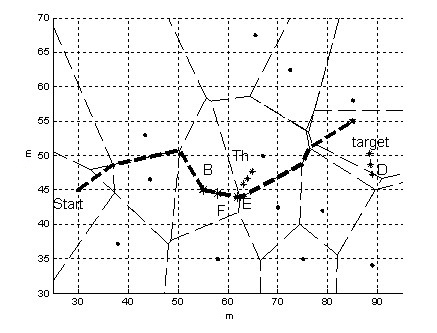
The invention relates to a Kalman filter prediction-based robot obstacle avoidance method. In a complex environment, the robot travelling environment changes dynamically; and when an environment of a preplanned mission is determined to have a significant change, the target objective is modified, the target is planned in real time, and the path is modified. In the obstacle avoidance method, a path scheduler sorts a target set according to a digital map, the target set and the state of the robot acquired by a sensor system so as to generate a robot travelling point sequence; the robot travelling point sequence is executed by a servo system; when the sensor system detects a new obstacle, a Kalman filter model is established according to observation data; and parameters are identified and modified by using the observation data and an expectation maximization model identification algorithm of a classical linear dynamic system; and the digital map is updated for the next turn of local re-planning of the path scheduler. The method can realize obstacle avoidance path planning of the robot generated locally and dynamically in an undetermined environment, and has the advantages of simple implementation and good real-time performance.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
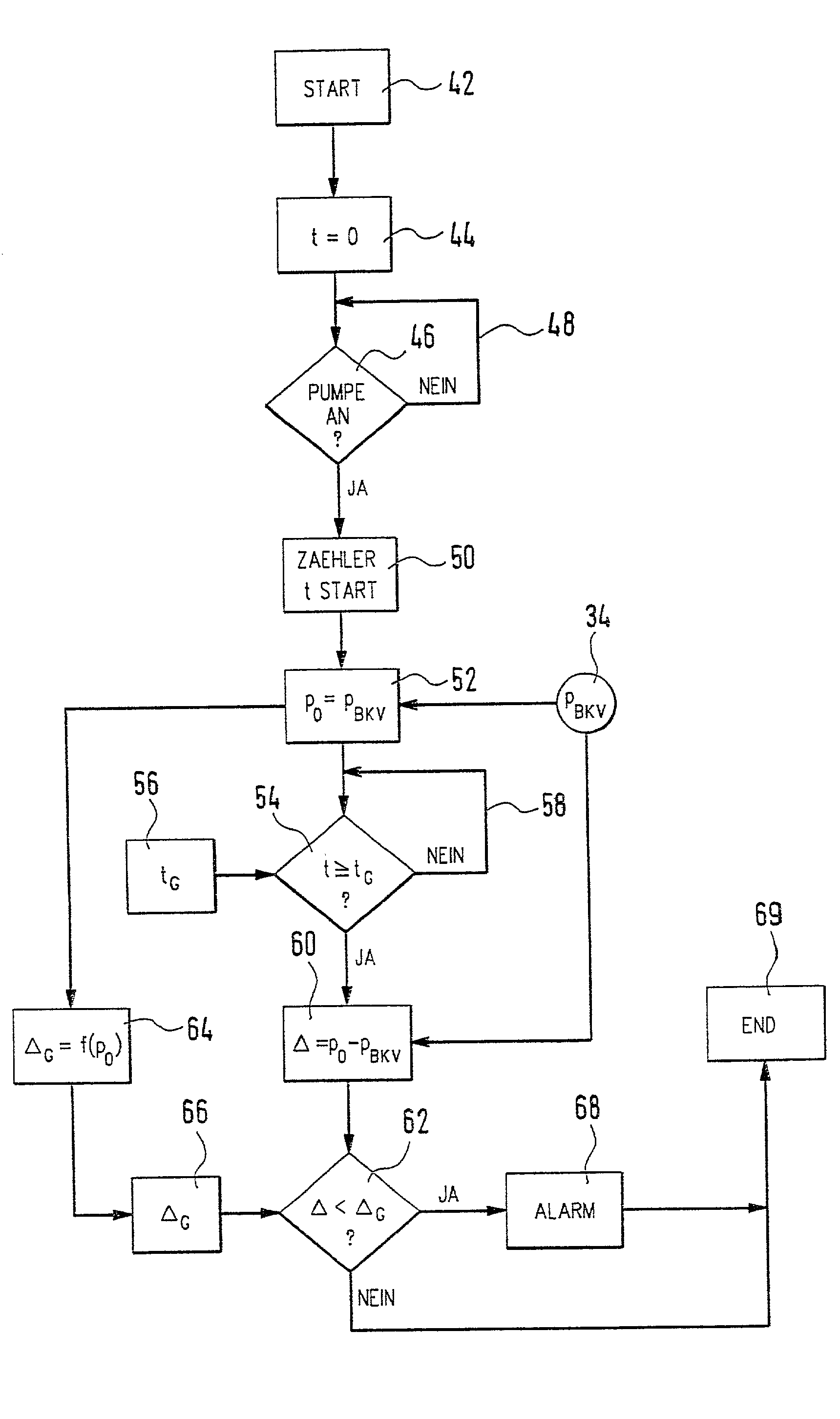
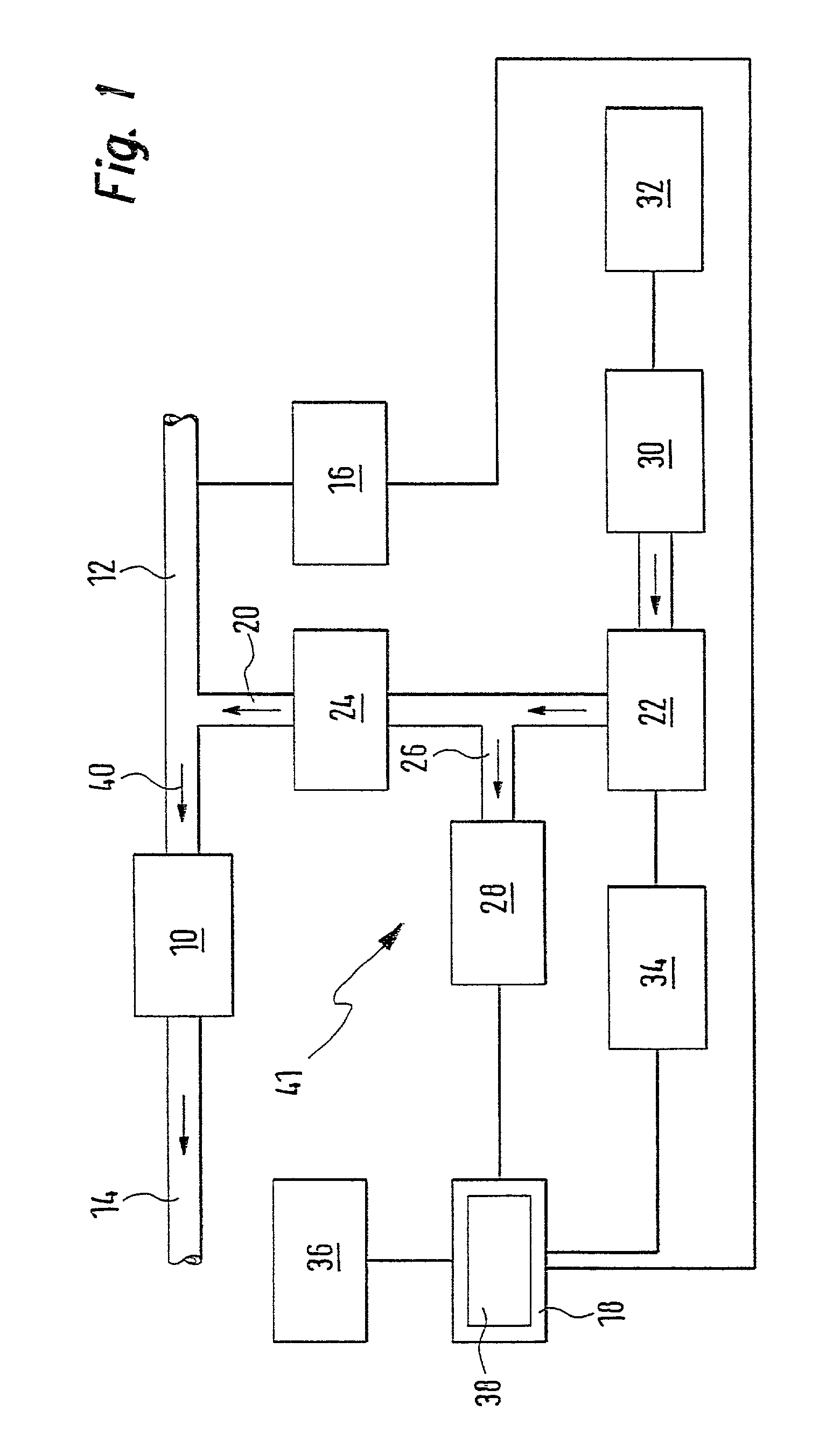
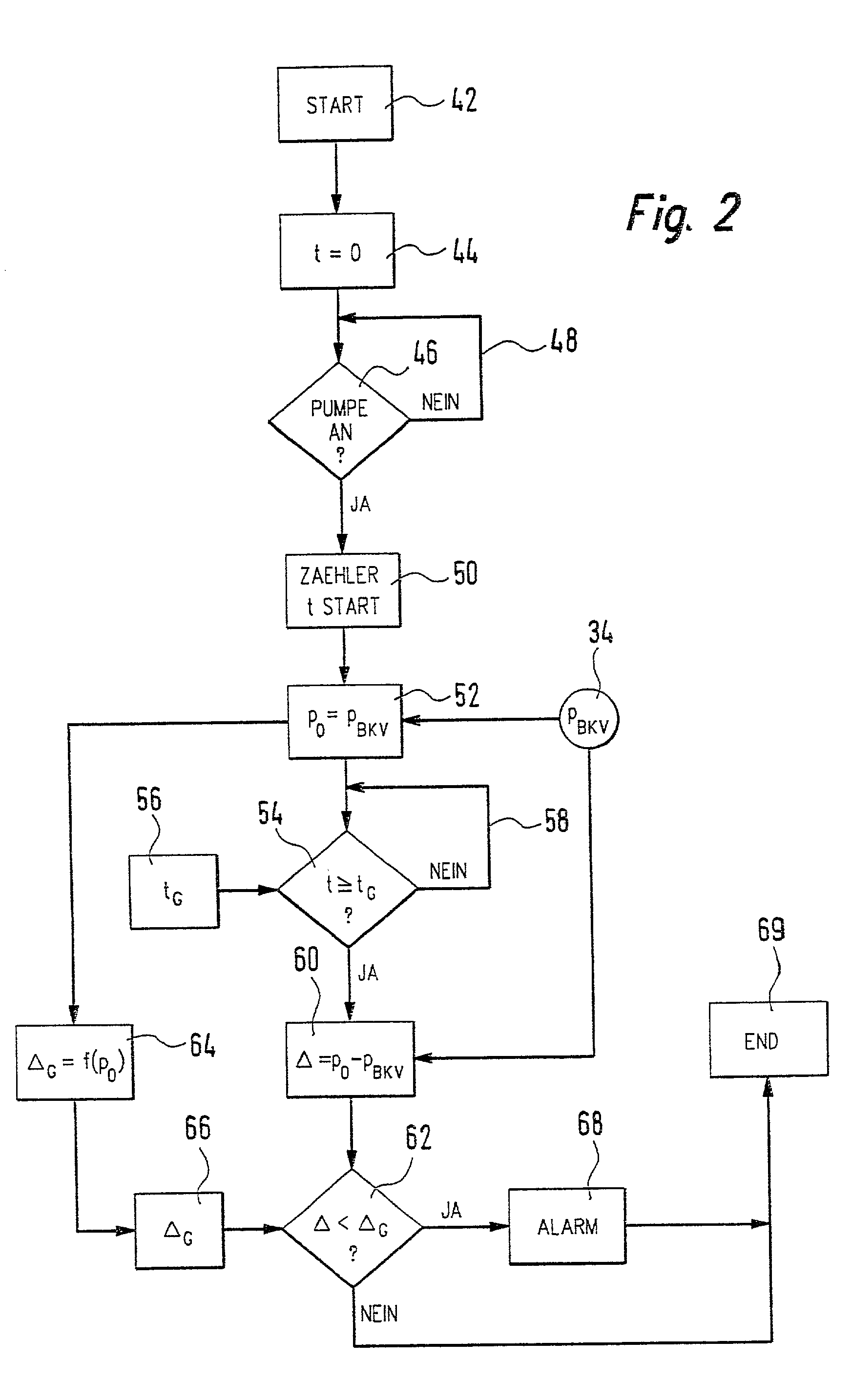
Method, computer program and device for monitoring a vacuum device
A vacuum chamber (22) of a pneumatically operated servo unit (30) of a motor vehicle is subjected to vacuum by an electric suction pump (28). In order to monitor the vacuum chamber (22) and the electric suction pump (28), the invention proposes that a starting pressure in the vacuum chamber (22) be determined. In addition, after a certain time interval, an ending pressure in the vacuum chamber (22) is determined. Furthermore, the difference between the ending pressure and the starting pressure is calculated and compared to a limit value. If this difference falls below the limit value, a signal is generated, in particular a warning and / or alarm signal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and apparatus for controlling numerically controlled machine tool
InactiveUS6291959B1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic control devicesNumerical controlProcess engineering
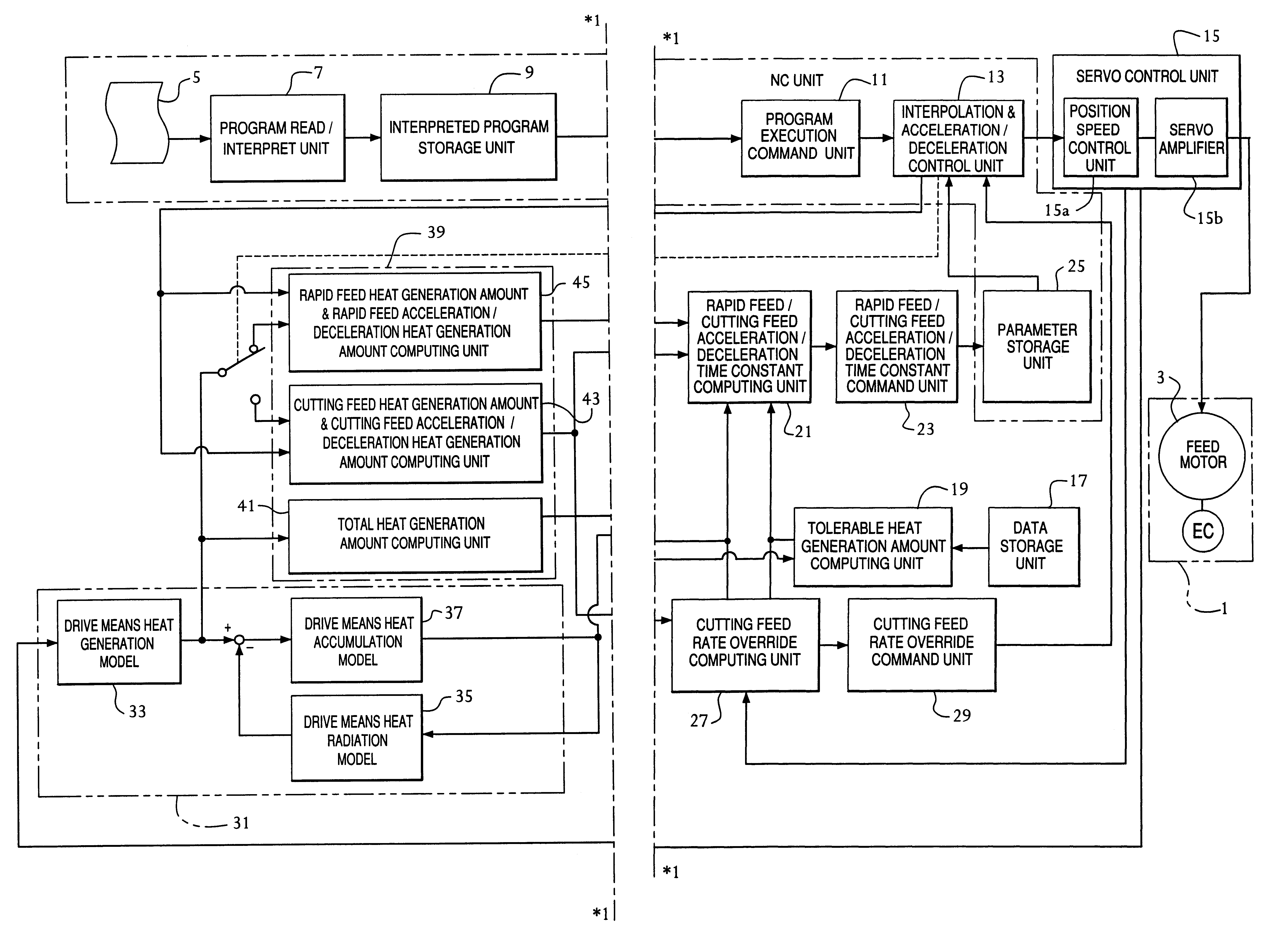
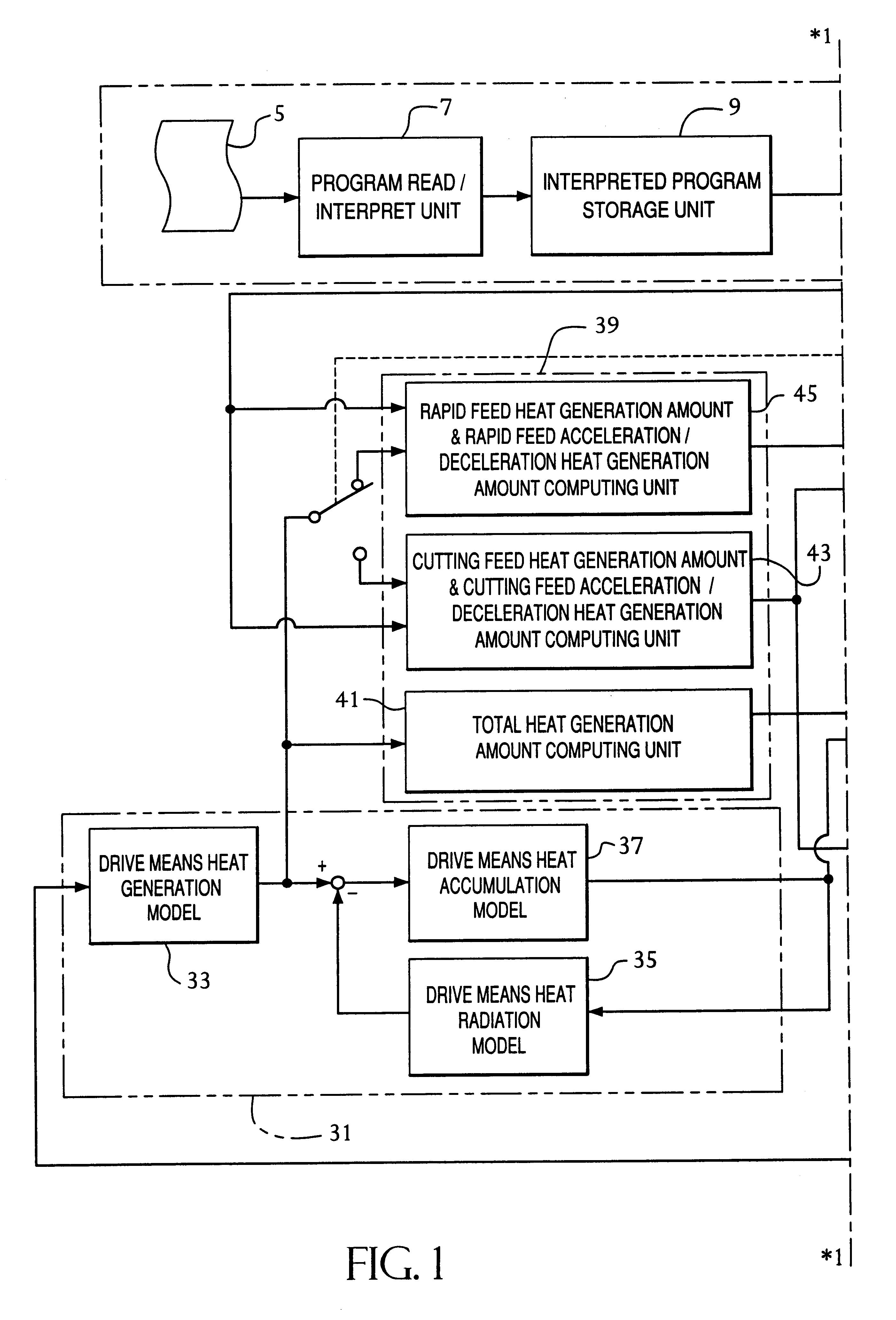
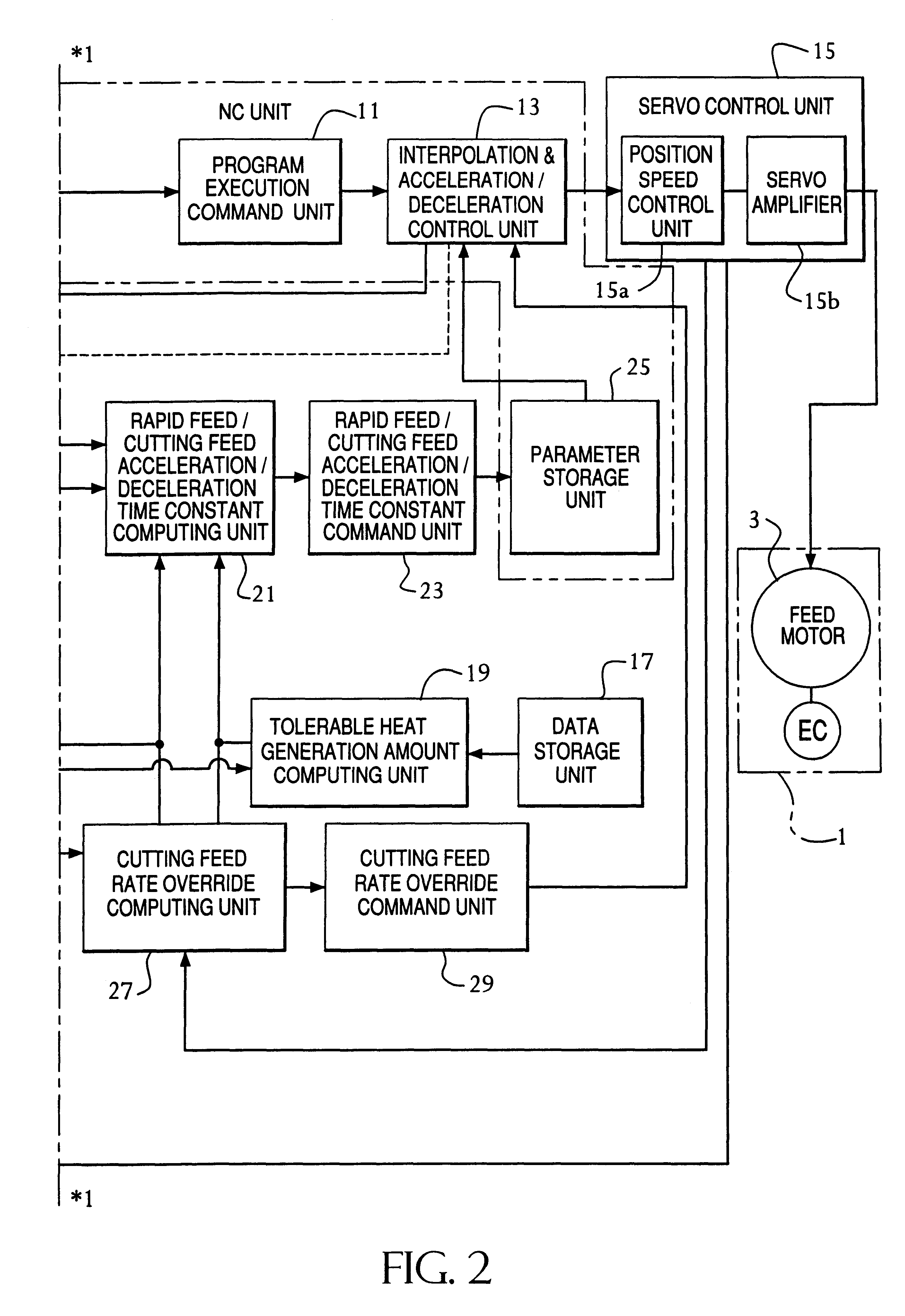
A method and an apparatus for controlling a numerically controlled machine tool, wherein the heat generation amount and the temperature of a drive unit including a servo amplifier 15b and a feed shaft motor 3 are computed by a drive unit heat generation amount computing unit 31 by simulation, and from the computed heat generation amount and the computed temperature, the total heat generation amount of the drive unit, the cutting feed heat generation amount, the cutting load heat generation amount, etc. are computed by a feed heat generation amount computing unit 39, so that the cutting feed rate override value of the numerically controlled machine tool 1 is computed by a cutting feed rate override computing unit 27 and effectuated by being output to a NC unit. Further, based on the temperature of the drive unit computed by a computing unit 31 or the temperature computed by a temperature data computing unit 47 or the temperature detected by a temperature detection sensor 49, etc., the proper values of the feed acceleration / deceleration time constants τ<SMALLCAPS>r < / SMALLCAPS>and τ<SMALLCAPS>c < / SMALLCAPS>are computed and output as a ratio with respect to the set and stored initial values τ<SMALLCAPS>r0 < / SMALLCAPS>and τ<SMALLCAPS>C0 < / SMALLCAPS>thereby to control the NC commanded rate. The overheating of the feed axis drive unit is prevented while at the same time improving the machining efficiency.
Owner:MAKINO MILLING MASCH CO LTD
Phase-change microhead array chip hard disk drive
InactiveUS20030161245A1Electron beam carrier recordingOptical beam sourcesStationary phaseEngineering
An optical data-storage hard disk drive that uses stationary Phase-Change Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional flying-heads, rotary voice-coil actuators, or other similar types of servo-tracking mechanisms to simultaneously record and / or reproduce data to and / or from a multitude of data-tracks located across the data-surfaces of a multitude of phase-change based disc media using a multitude of microheads.
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Inclination-angle-constraint-based kinematic calibration method for Stewart parallel robot
InactiveCN102152307AAvoid difficultiesHigh degree of automationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlLeast squaresKinematic calibration
The invention discloses an inclination-angle-constraint-based kinematic calibration method for a Stewart parallel robot. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, theoretically establishing a novel kinematic constraint, which is an inclination angle constant constraint, namely keeping two inclination angles of a motion platform of the Stewart parallel robot relative to a horizontal plane constant group by group; secondly, using a servo regulating way to physically realize the established kinematic constraint in a high-precision way; thirdly, establishing a calibration model on the basis of a principle of least square according to the kinematic constraint; and finally, identifying a model parameter by solving a nonlinear least square optimizing problem and compensating for the model parameter in a robot control software. By making full use of a characteristic that a repeating precision of a measuring instrument is superior to a position measuring precision of the measuring instrument, the method has the advantages of good calibration effect, simple measurement, high automatism in the calibrating process and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatus and method for controlling a force-activated controller
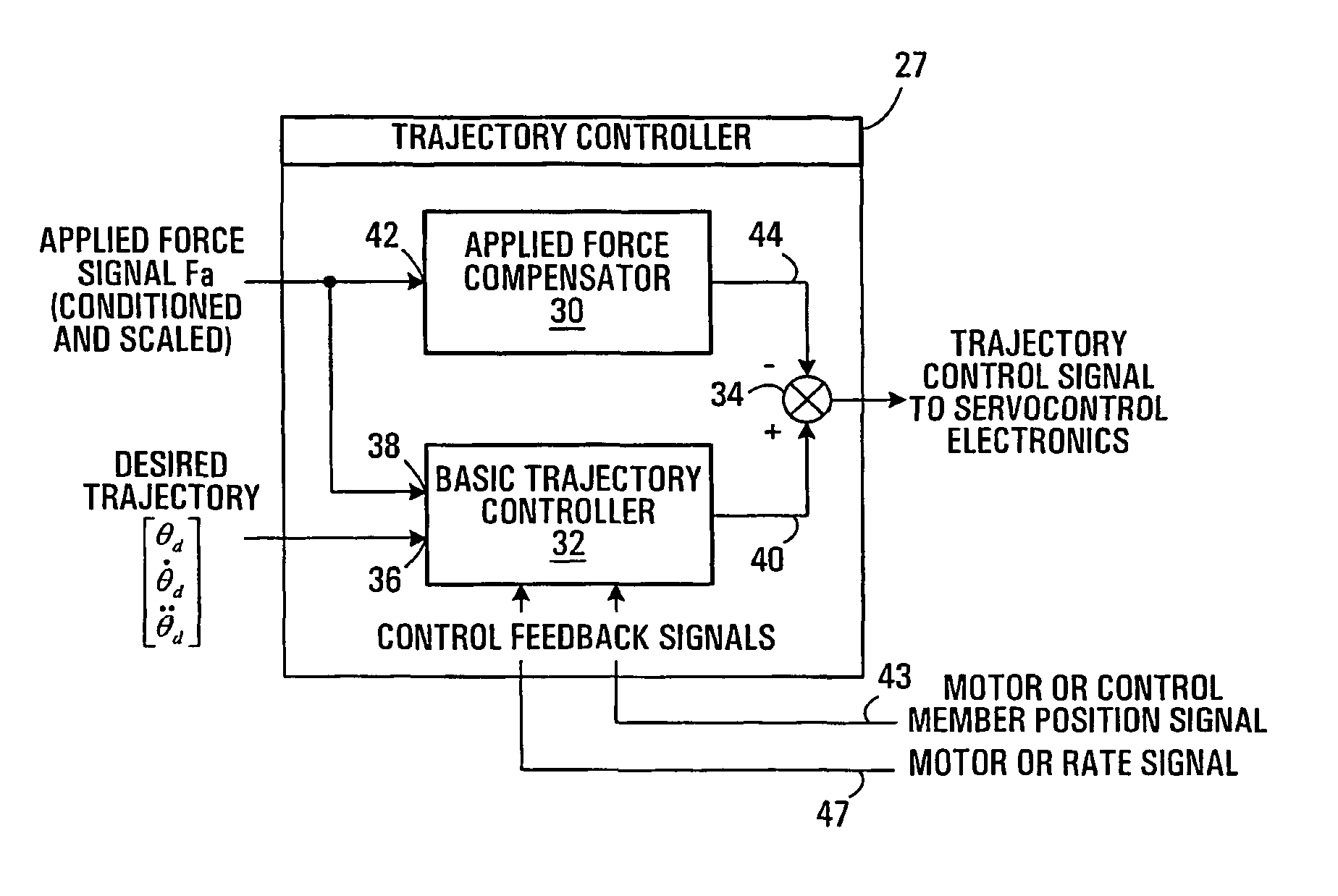
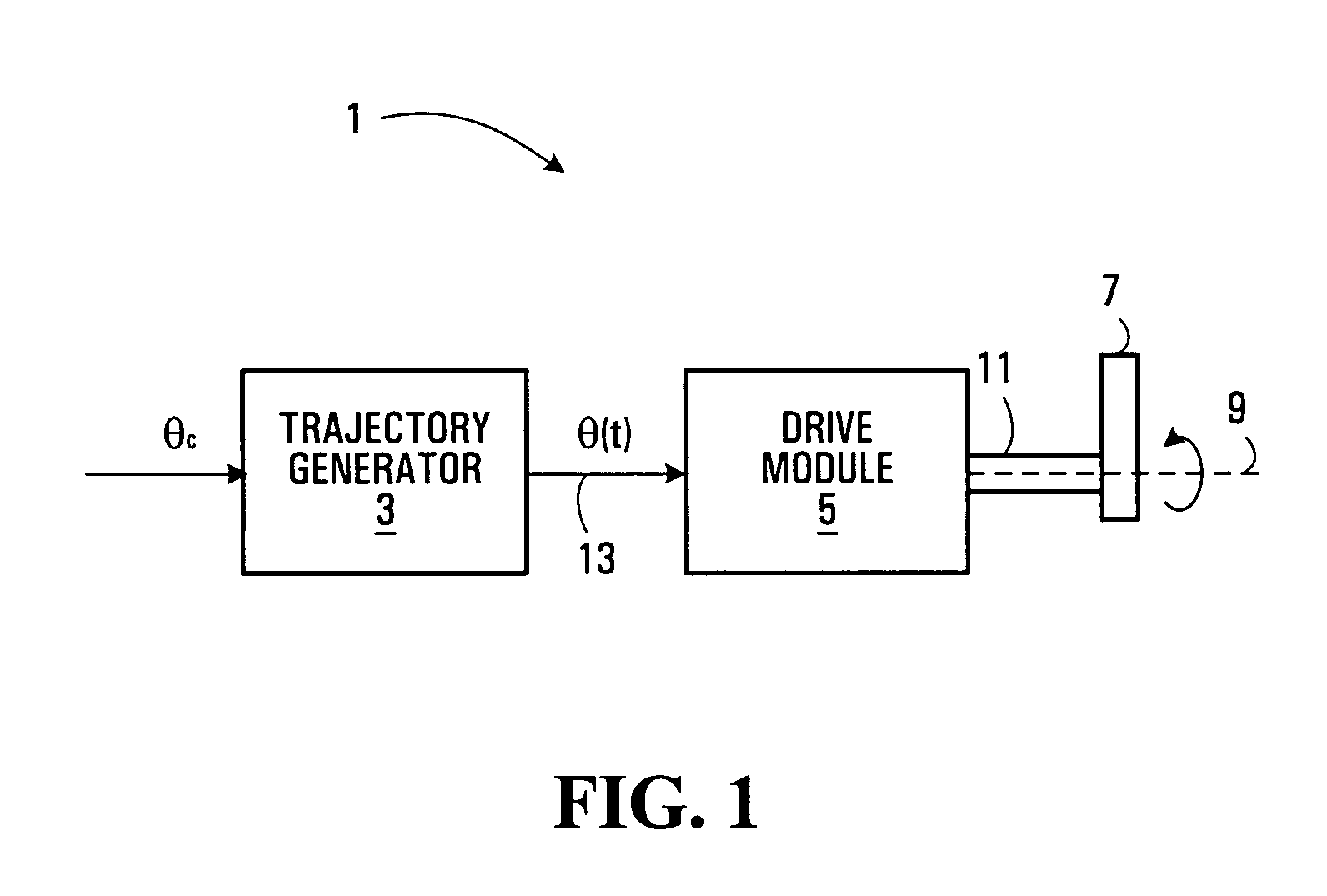
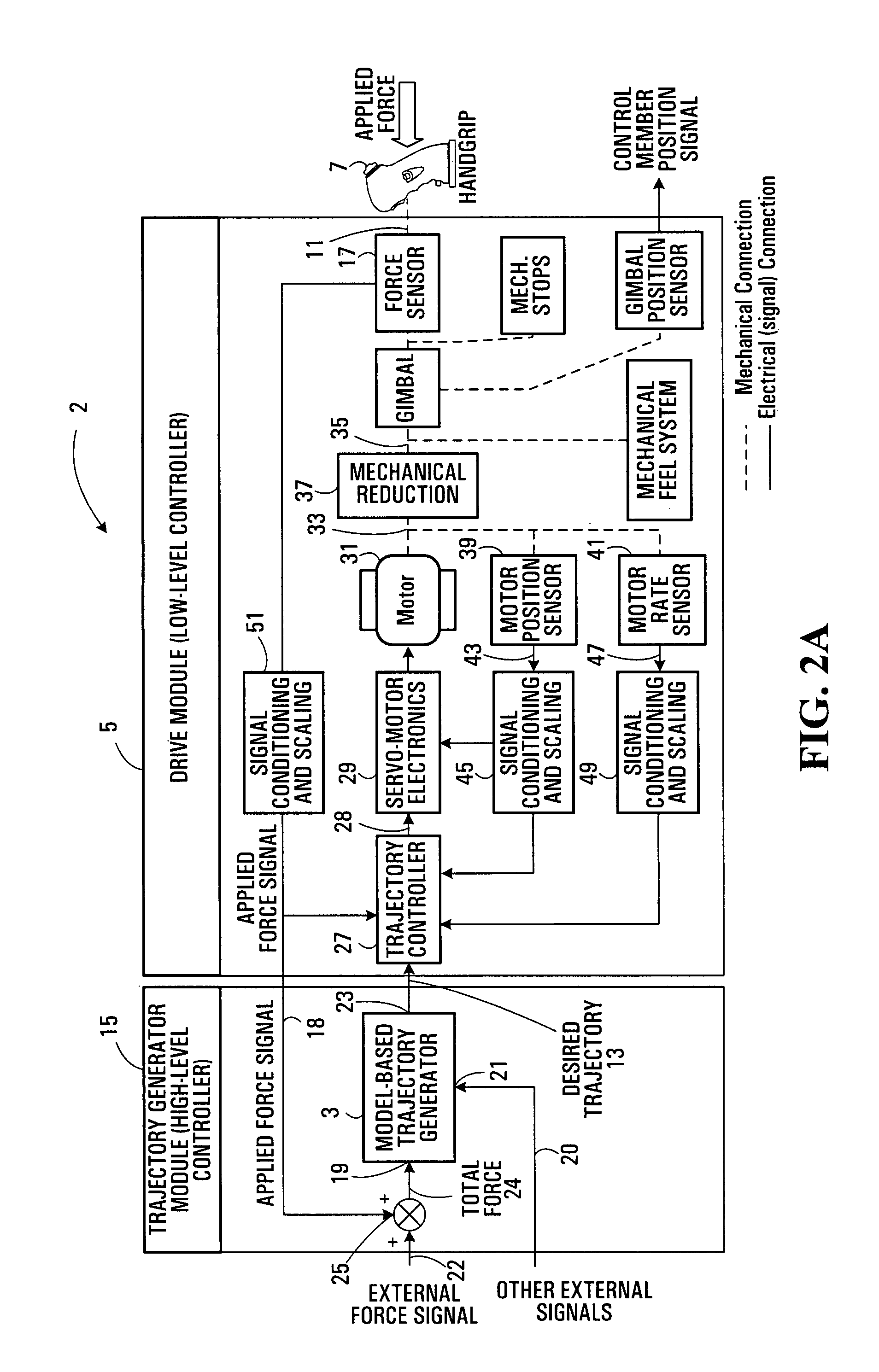
A servo-controlled system is disclosed for providing simulated feel equivalent to that of traditional mechanical hand controllers. Processed position and force sensor signals are used in a feedback loop that controls the motor mechanically connected to the stick. The feedback loop comprises a low-level motor feedback loop, and high-level force feel loop. The latter comprises static and dynamic performance components. The system allows variable and additional force cues to be specified externally to the system and felt by the operator, and / or external signal to backdrive the stick to follow a specified motion. The control framework permits the electronic coupling of the motion and applied forces by pilots in a dual arrangement while retaining the above-mentioned features. It simulates cross-coupling mechanical compliance due to force fight between pilots, detents and asymmetric force feel gradients. Parameters associated with loops and performance components can be specified independently.
Owner:BOMBARDIER INC
Three-dimensional (3D) rapid forming printing system and method
The invention relates to the field of rapid prototyping and discloses a three-dimensional (3D) rapid forming printing system. The system comprises a personal computer (PC) end with a control unit, an extruder, a printing base plate with a heating function, a servo motor which controls motion of the printing base plate, and a motion control unit, wherein the extruder is positioned above the printing base plate on the top of a body operating area; the servo motor and the printing base plate are positioned below the extruder at the bottom of the body operating area; the motion control unit is an embedded chip group; each chip comprises a task module for executing a control task; the motion control unit is positioned in a chip group slot below the body operating area; the extruder, the servo motor and the printing base plate are respectively and electrically connected with the motion control unit; the motion control unit is electrically connected with the PC end. By virtue of an incremental manufacturing method, namely models are established on the printing base plate layer by layer, rapid manufacturing is realized, processing of any model can be finished, and the system has certain application value and application prospects and can be applied to household and industrial production.
Owner:林岚 +1
An online monitoring method for turning stability of CNC machine tools
InactiveCN102284888ARealize online monitoringReal-time online monitoringMeasurement/indication equipmentsMetal working apparatusNumerical controlMathematical model
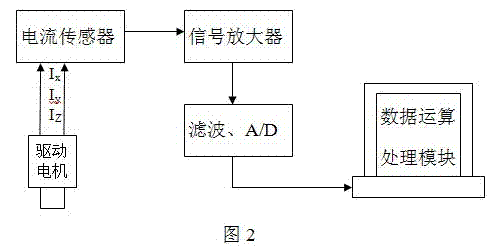
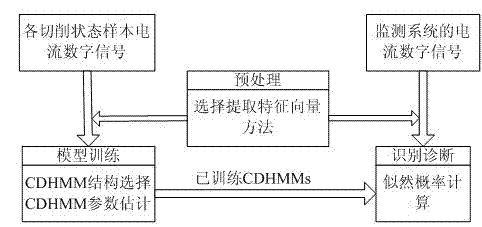
The invention provides a monitoring method for the turning stability of a digital control machine tool, relating to the monitoring technical field. As the performance of a servo system is continuously improved, a response speed, the sensibility and the like of the servo system are also continuously improved, thus, states of the machine tool can be reflected on a current of a driving motor during a cutting process. In the invention, through various signal processing methods, a plurality of characteristic values of current signals are extracted, a characteristic status vector is established as an input of a mathematical model, and a cutting status of the machine tool is output through analysis and calculation of the mathematical model. As the invention has the characteristics that the current signal has high anti-interference performance and is easy to be acquired, assistant tools are fewer, and the like, compared with a plurality of existing monitoring methods, the invention has the advantages of simple and feasible operation, good monitoring effects and the like; thereby, the invention can more easily realize the online monitoring for the processing states, and can effectively guarantee the processing security and the product quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
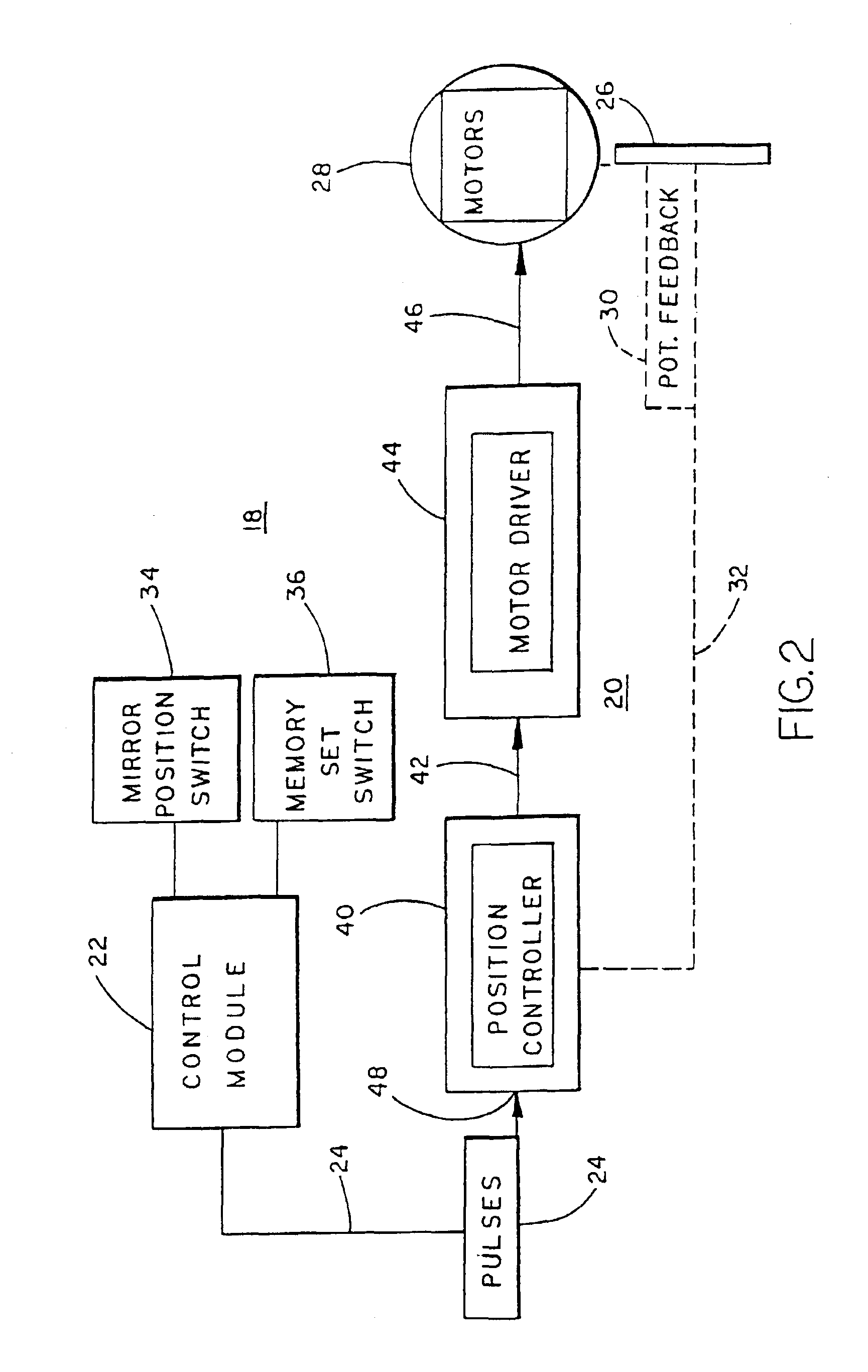
Memory mirror system for vehicles
InactiveUS6867510B2Low cost mass productionPrecise positioningElectric devicesElectrical apparatusSignal onAnalog signal
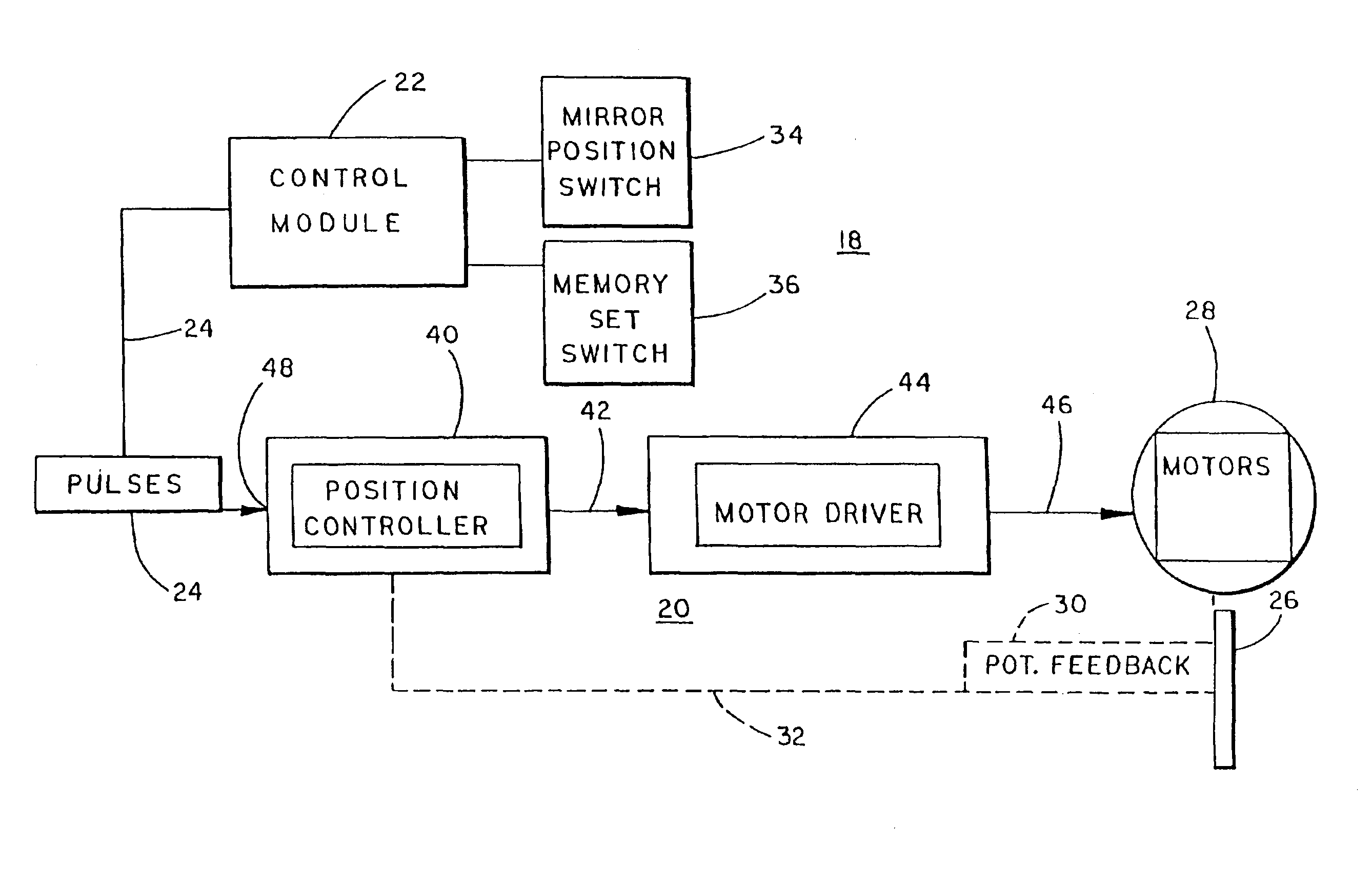
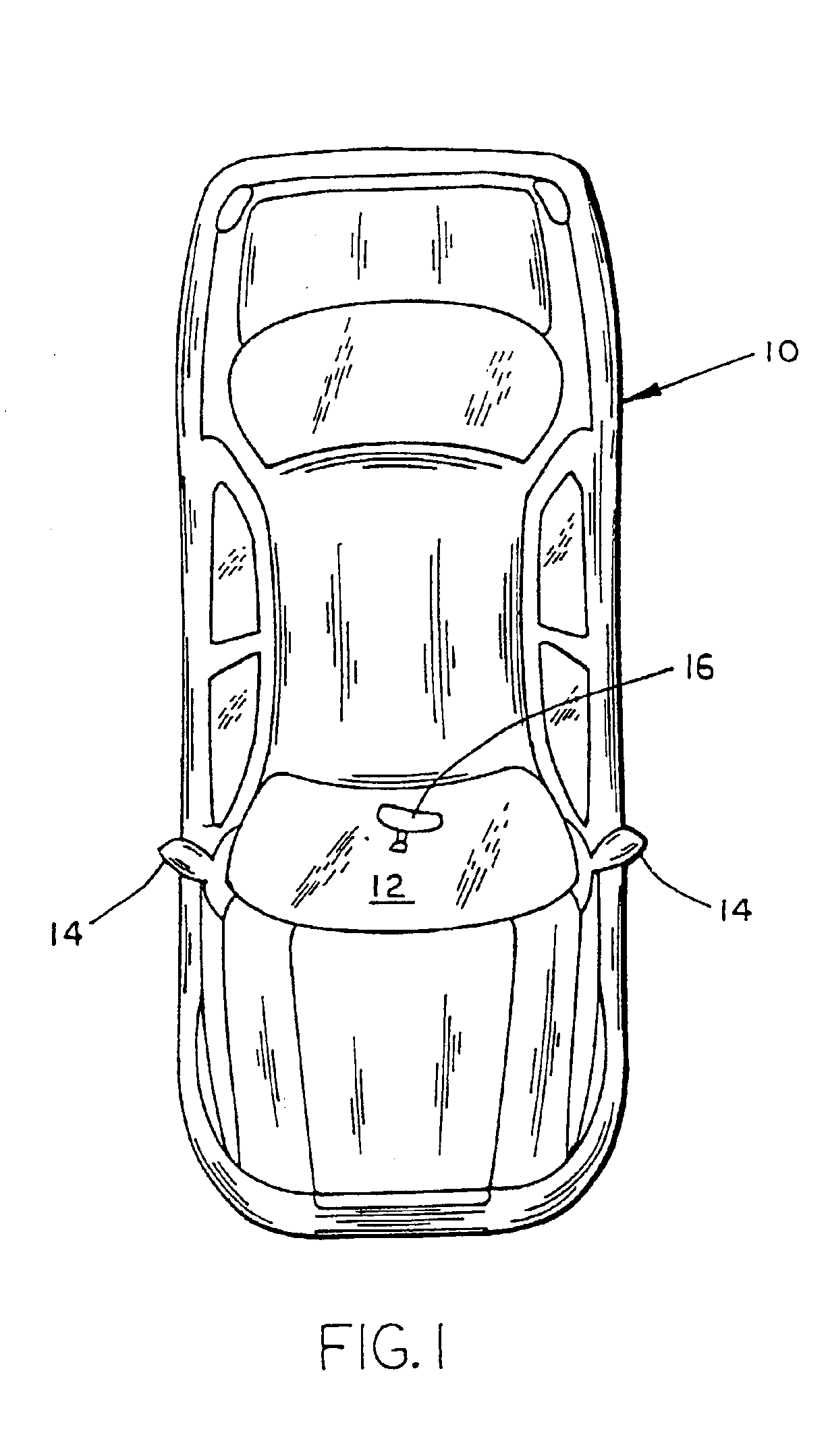
A vehicle memory mirror system includes a vehicle mirror assembly and a control module. The vehicle mirror assembly includes a reflective element, a motor for positioning the reflective element about an axis, a monitor for monitoring the position of the reflective element with respect to the axis, and a mirror-based control including a position control which is operatively connected with the motor and the monitor in order to position the reflective element at a particular position. The control module is interconnected with the mirror-based control by an analog interface and includes a processor for providing analog signals on the analog interface indicative of a desired position of the reflective element with respect to the axis. The mirror-based control preferably includes a servo-amplifier circuit. The control module can control the speed of movement by formatting a series of sequential signals on the interface, each representing an incremental movement of the reflective element.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
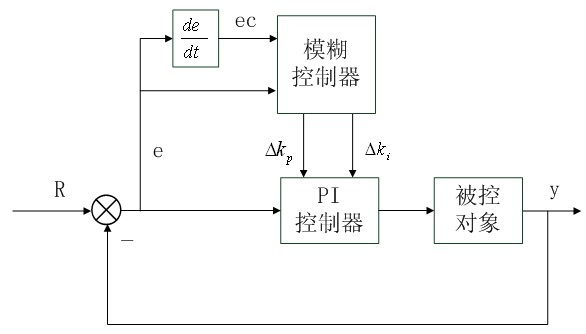
Control method of speed regulator of servo system of flat knitting machine
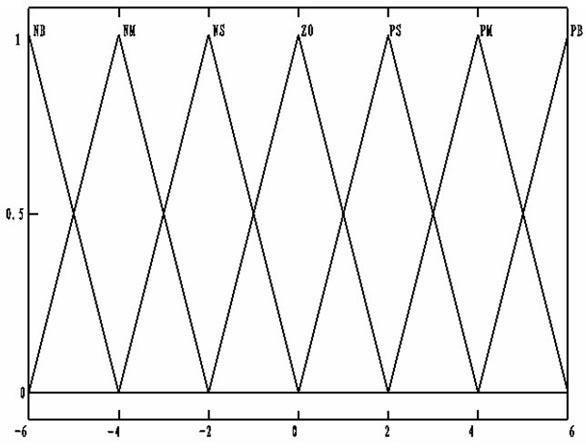
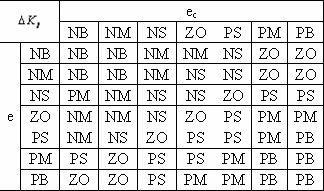
InactiveCN102621892AGuaranteed parametersGuaranteed reliabilityWeft knittingAdaptive controlDefuzzificationFuzzy rule
Aiming at the defects in the prior art, the invention discloses a control method of a speed regulator of a servo system of a flat knitting machine. A system in the prior art has low adaptability and low stability. According to a fuzzy proportional-integral (PI) control algorithm of the control method, the running speed of a transmission mechanism of the computerized flat knitting machine is used as a control object; the difference value between the practical reference speed and the feedback speed and the change rate of the difference value are served as input of a fuzzy controller; the input quantity is fuzzified through selecting an appropriate universe of discourse and an appropriate membership function; appropriate fuzzy rule tables are set by utilizing the practical tuning strategies of PI parameters; and after a Mamdani fuzzy reasoning algorithm and defuzzification processing are adopted, the variable quantities of parameter values of the PI controller are output, thereby realizing on-line correction of the PI parameters. By adopting the control method, the disadvantages of a traditional manual correction method for the PI parameters are overcome, and on-line real time correction of the PI parameters is realized, thereby improving the adaptability and the stability of the system.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
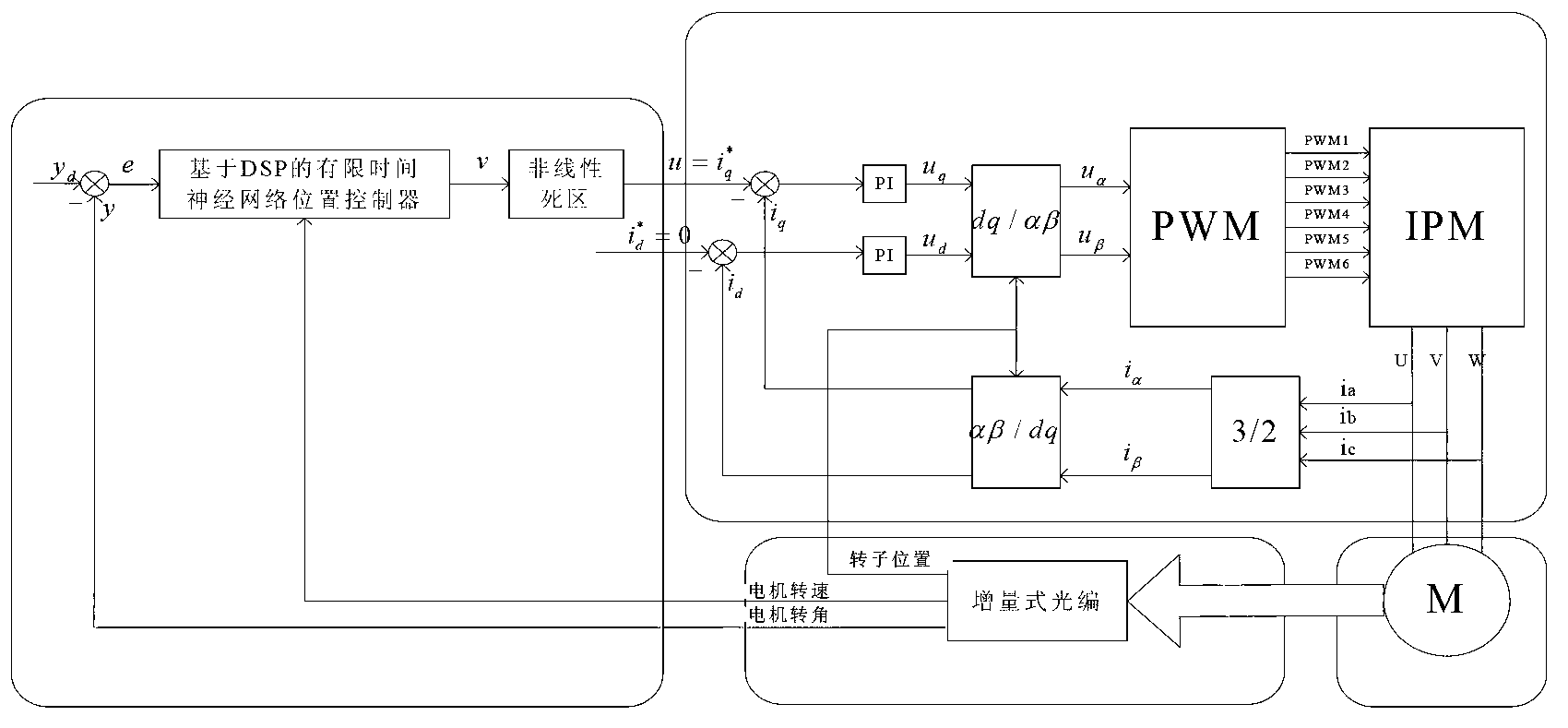
Limit time cooperative control method of mechanical arm servo system
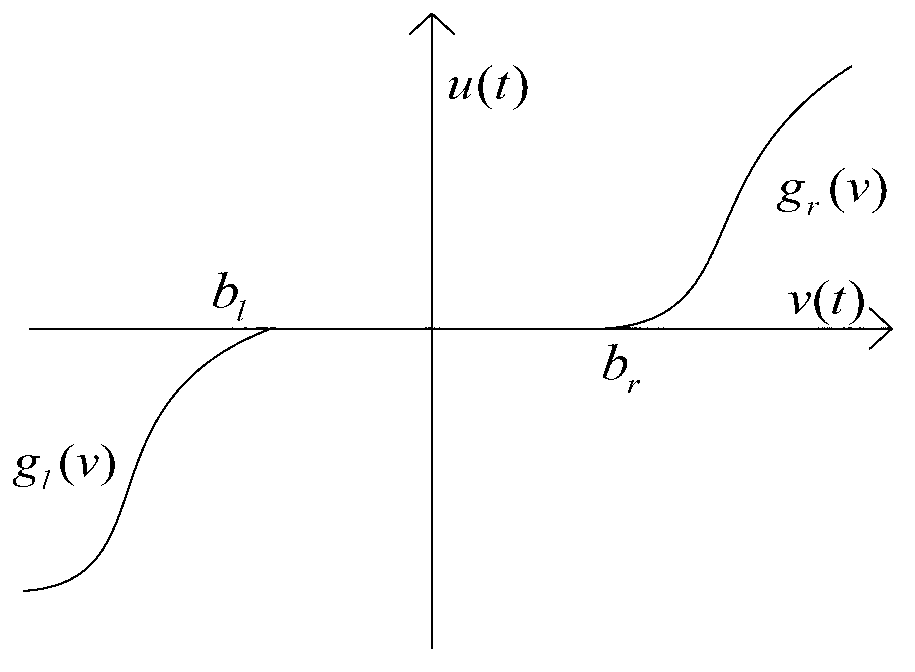
InactiveCN104216284AAvoid Dead Zone Additional Inverse CompensationAvoid High Frequency ChatteringAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime-variant system
A limit time cooperative control method of a mechanical arm servo system includes: building the dynamic model of the mechanical arm servo system, and initiating the system state, sampling time and related control parameters; approximating the nonlinear input dead zone linearity in the system into a simple time-varying system according to the differential mean value theorem, and deriving a mechanical arm servo system model with an unknown dead zone; calculating the tracking error, the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface and the first derivative of a control system; selecting a neural network approximation unknown function on the basis of the mechanical arm servo system model with the unknown dead zone, designing a neural network limit time cooperative controller according to the system tracking error and the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface, and updating a neural network weight matrix. By the method, additional inverted compensation of a nonlinear dead zone can be avoided, sliding model high-frequency buffeting is reduced, and limit time fast tracking of the mechanical arm servo system is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rotary machine with axial stop incorporating a current generator
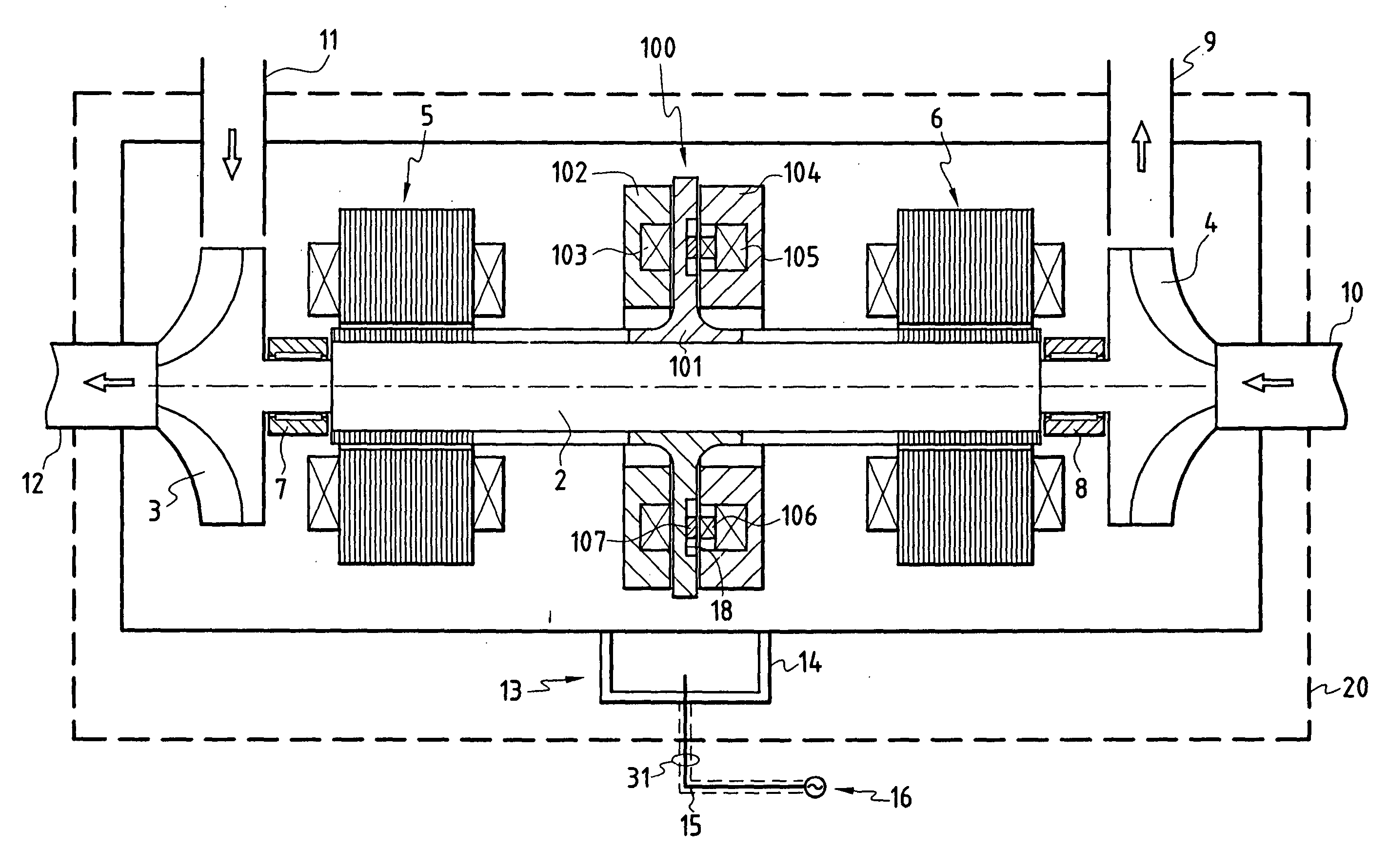
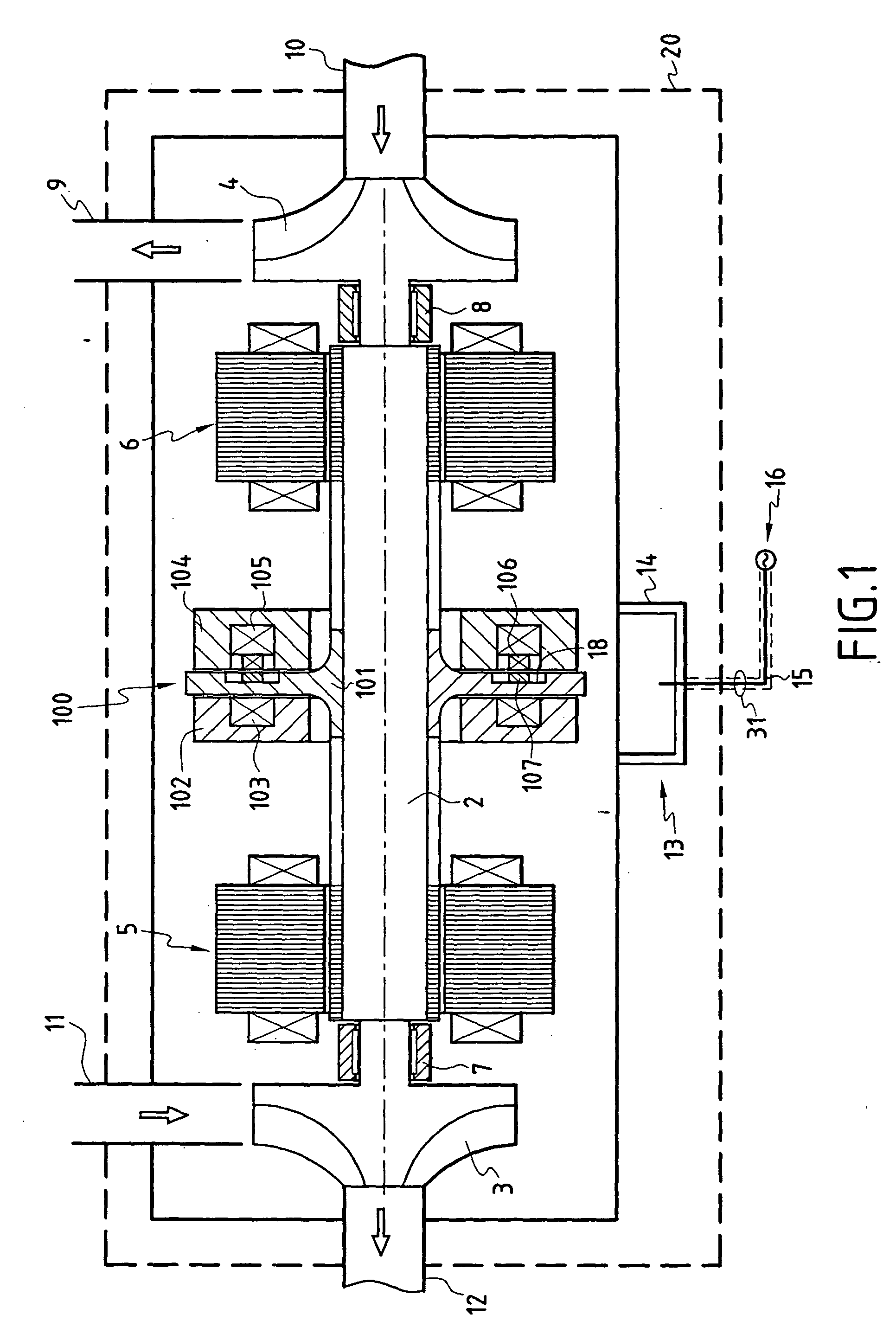
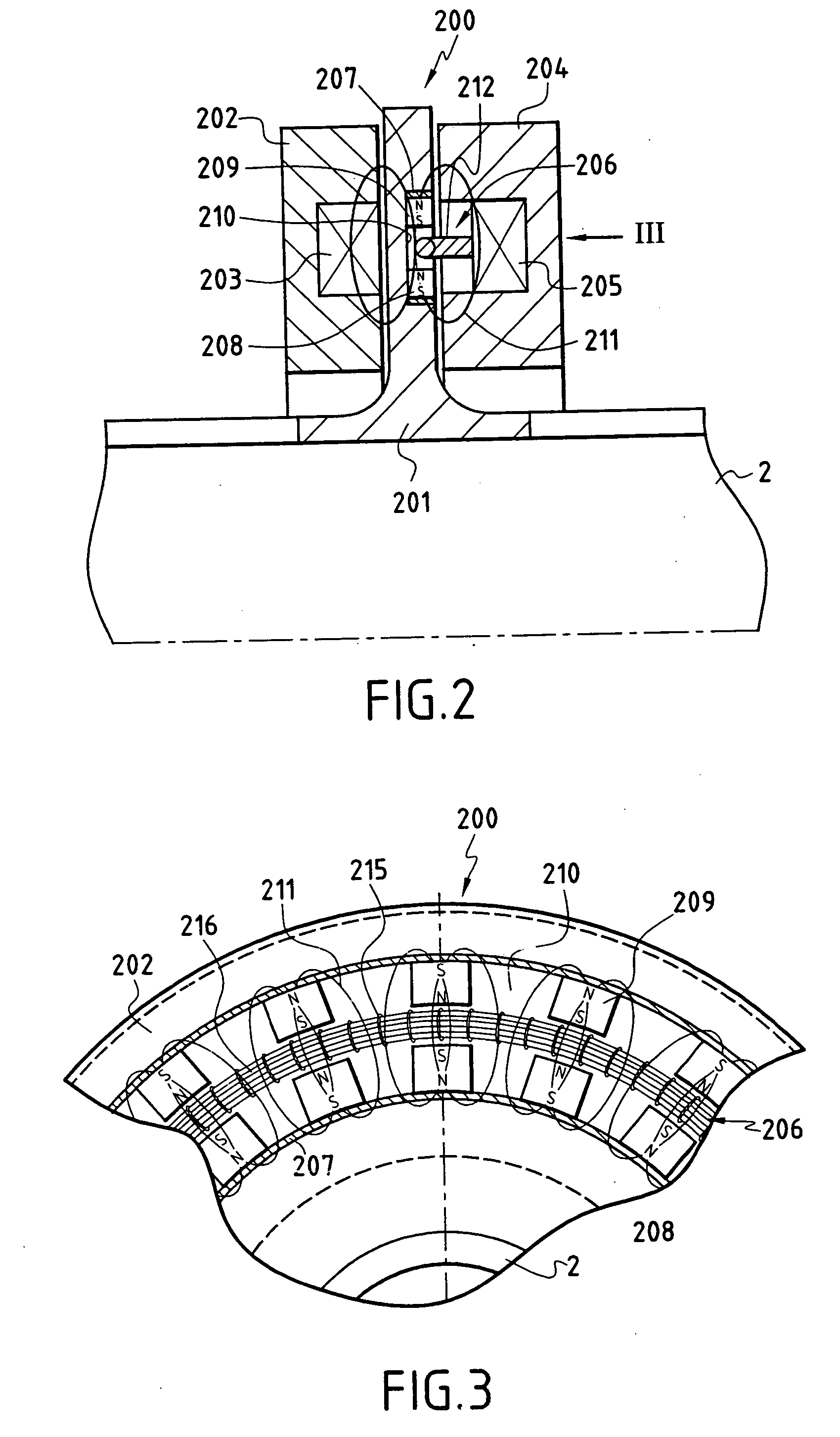
The rotary machine comprises a rotary shaft (2) supported by first and second radial magnetic bearings (5, 6) that are electrically controlled by a control device (13), said rotary shaft being fitted with an axial abutment device (100) comprising a rotor formed by a disk (101) secured to the rotary shaft (2) and interposed between first and second stators (102, 104) formed annularly around the rotary shaft and each including at least one annular coil (103; 105) controlled electrically by a system for servo-controlling the axial position of the rotary shaft. The stator (104) of the axial abutment device (100) further comprises a secondary induction circuit (106), and the disk (101) secured to the rotary shaft comprises a primary induction circuit (107) so that during rotation of the shaft, electricity is excited in the secondary induction circuit in order to supply energy to the radial magnetic bearings.
Owner:SOCIETE DE MECHANIQUE MAGNETIQUE
Biped robot capable of walking rapidly
ActiveCN104228993ASimplify the control problemSimplified Motion AlgorithmVehiclesRatchetControl engineering
The invention discloses a biped robot capable of walking rapidly. The biped robot is composed of a servo motor, a motor support, a driving bevel gear, driven bevel gears, check pawls, ratchet wheel cam sets, ratchet wheel connecting pins, a driving pawl, oscillating bars, roller connecting pins, rollers, shanks, compression springs, screws, thighs and feet. The servo motor drives the driving bevel gear to rotate so as to drive the symmetrically-arranged driven bevel gears to rotate oppositely and the thighs to swing forwards and backwards; the shanks always make contact with cams in the ratchet wheel cam sets through the compression springs and supporting legs are longer than swinging legs through telescopic motion of the shanks. Compared with the prior art, the biped robot has the advantages that the robot can be driven by one servo motor, so that the robot is convenient to control and high in control accuracy; except for the servo motor, other structures of the robot are all mechanical structures, so that motion cooperation is convenient; the structure is simple, machining and installation are convenient, and the robot can walk rapidly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Synergetic control method of aircraft part pose alignment based on four locater
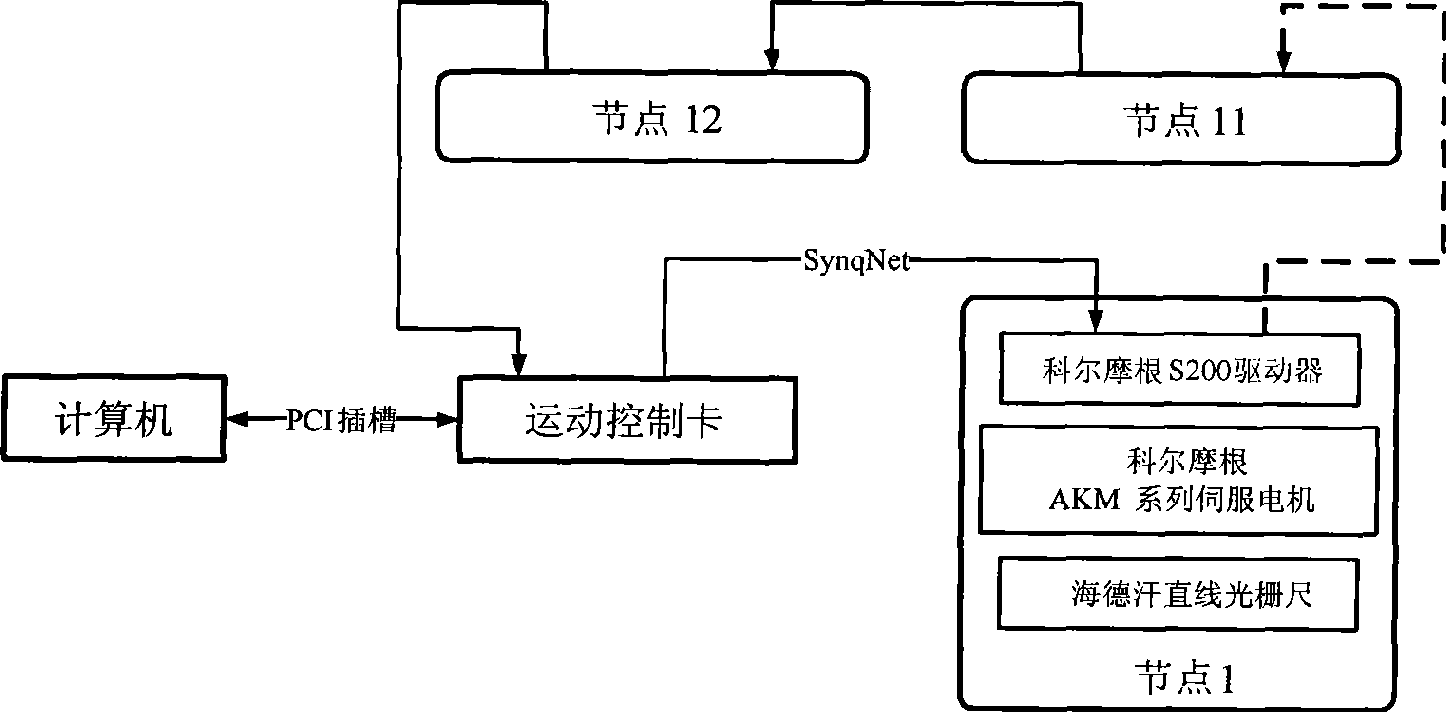
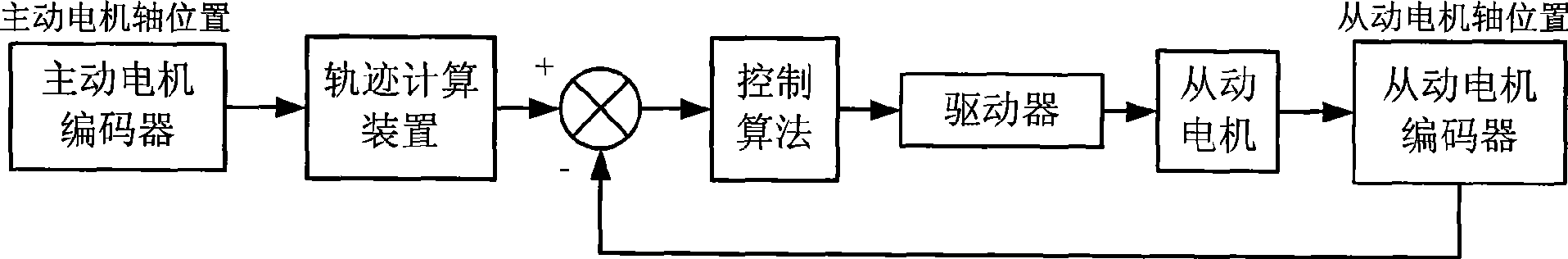
The invention discloses a method for adjusting and synergetically controlling the position and pose of an aircraft component based on four locators. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a global coordinate system OXYZ is established, and the current position and pose and the target position and pose of the aircraft component are calculated under the global coordinate system; secondly, the automatic adjusting path and the inch adjusting path of the aircraft component are formed; thirdly, the track of the sphere pivot wiring point between the locator and the aircraft component is planed according to the automatic adjusting path and the inch adjusting path; fourthly, the track of the sphere pivot wiring point is inverted into the driving parameter of a 12 motor axle synchronous control network; fifthly, the 12 motor axle synchronous control network is built based on a SynqNet bus, and the position servo of single motor axle adopts the full-closed loop digit controlling; and sixthly, two locators are selected, and the collocated relation between the locators is the master-slave motion mode. The method has the following advantages: firstly, the path for adjusting the position and pose of the aircraft component can be planed; secondly, the full-closed loop controlling of the single axle motion of the locator can be realized; and thirdly, the 12 axle synchronous motion of the position and pose adjusting system can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Industrial robot visual servo system and servo method and device
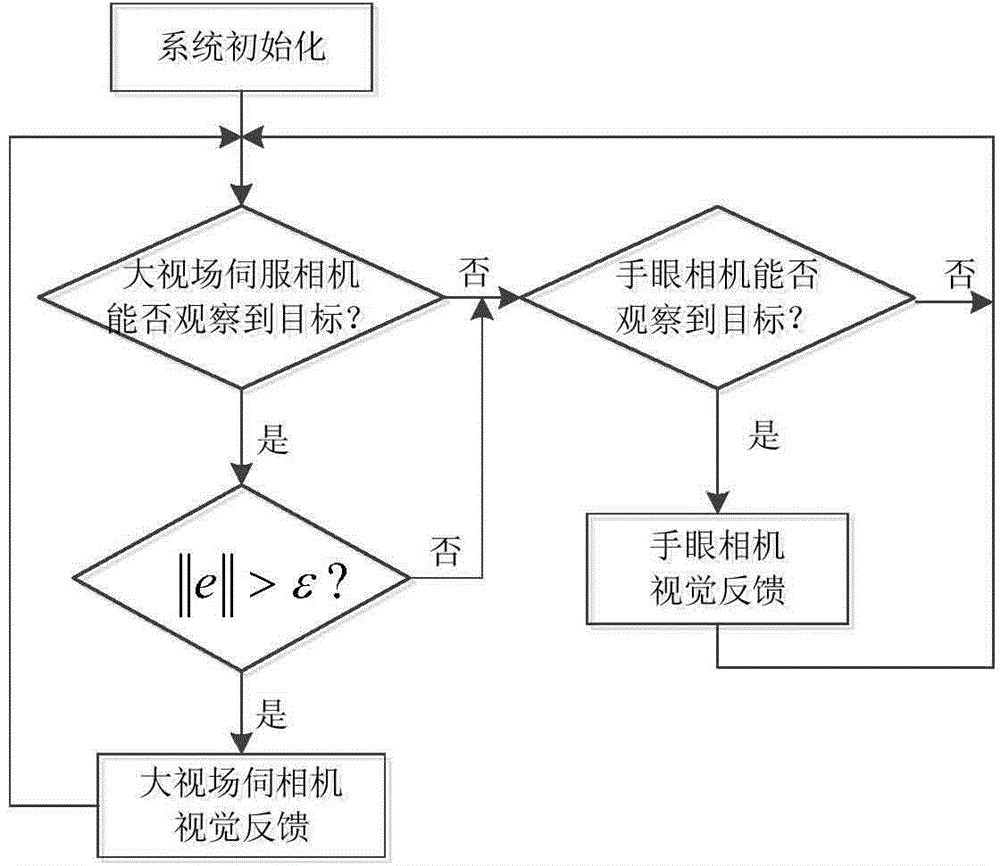
InactiveCN110039523ARealize real-time trackingOptimize workflowProgramme-controlled manipulatorWelding/cutting auxillary devicesRobot controlReal time tracking
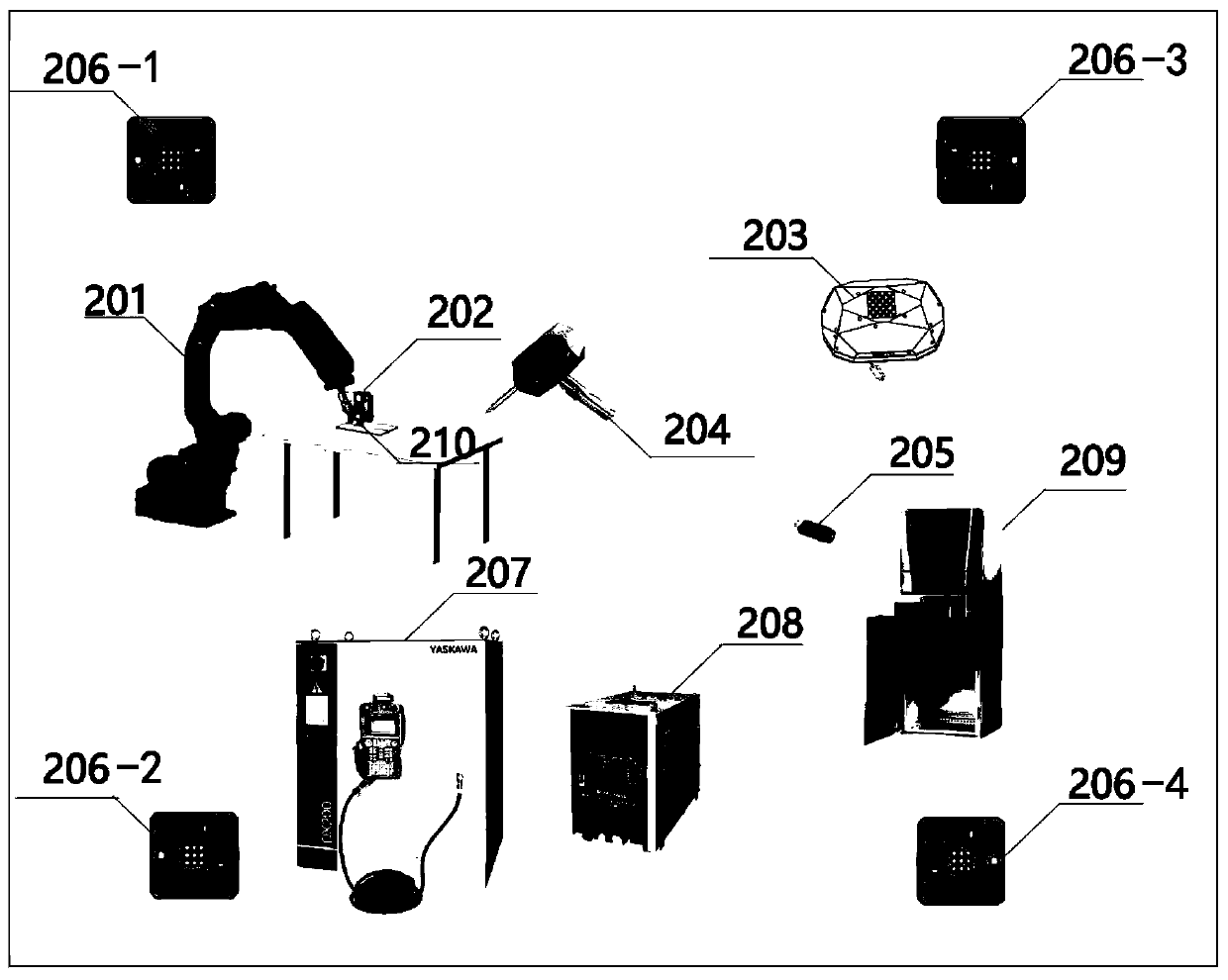
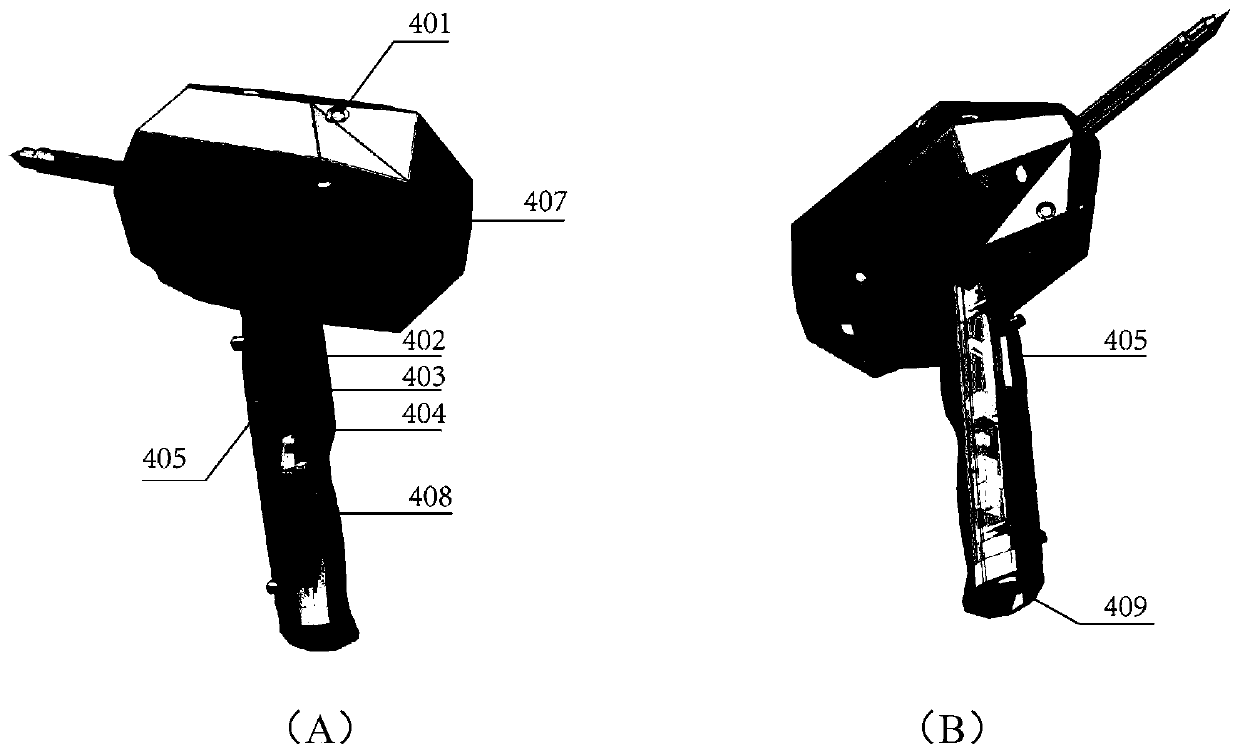
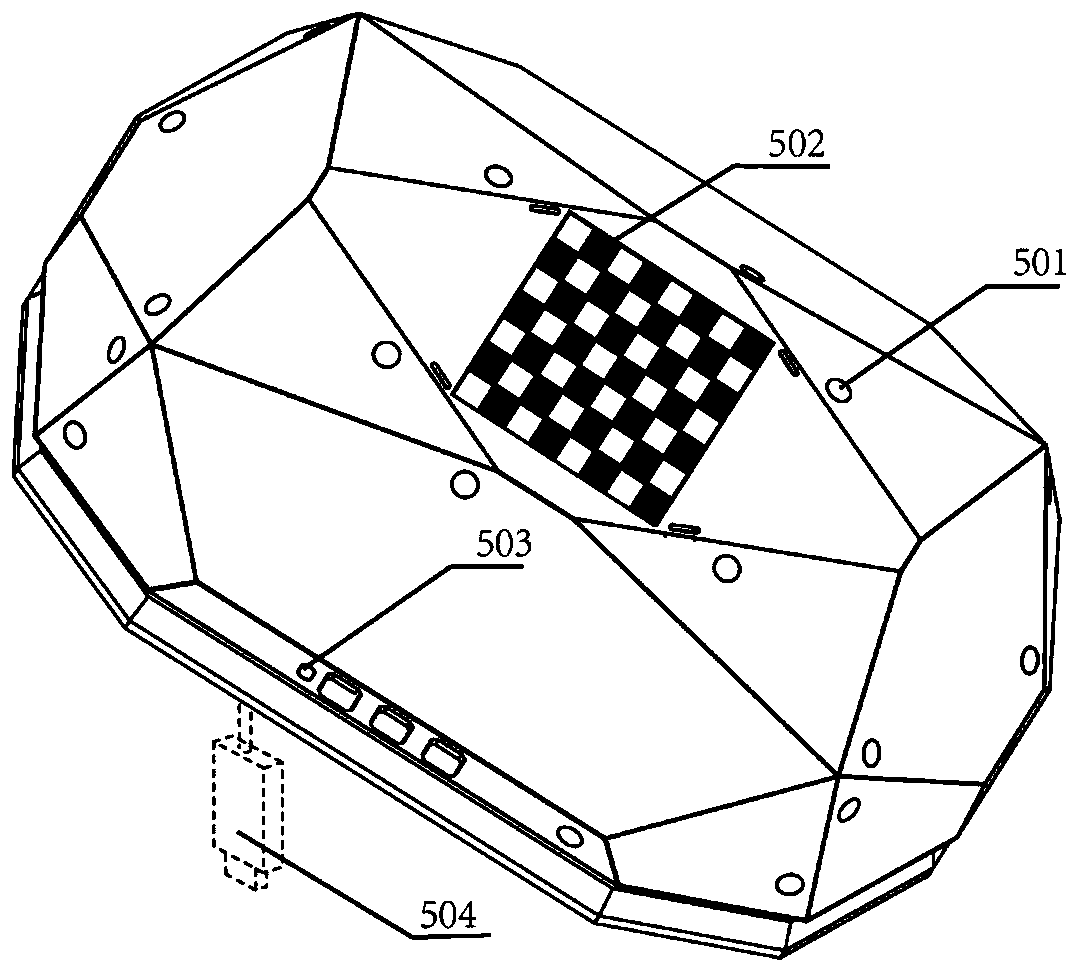
The embodiment of the invention discloses an industrial robot visual servo system and a servo method and device. The industrial robot visual servo system comprises a six-axis robot, a weld joint tacker, a calibration object, a wireless handheld demonstrator, a USB wireless receiver, an infrared laser positioning base station, a robot control cabinet, a welding machine power supply control cabinet,an upper computer control cabinet and an automatic wire feeding system. Rapid demonstration without programming is achieved, non-uniform workpiece incoming is avoided, and real-time tracking of welding thermal deformation is achieved; the working process of a traditional welding automatic system is improved, and an operator does not need to use the demonstrator to carry out complex demonstrationprogramming; as the recognition technology based on deep learning is adopted for weld joint tracking, the universality of welding automation is greatly improved; and in addition, welding path planning, demonstration, system calibration and welding real-time tracking are completely integrated in the same upper computer interface, and therefore the process operation and management can be conveniently carried out by the operator.
Owner:北京无远弗届科技有限公司
All-hydraulic autonomous moving manipulator and moving method thereof
InactiveCN104476550ACapable of force controlRealize flexible assembly functionProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual field lossControl system
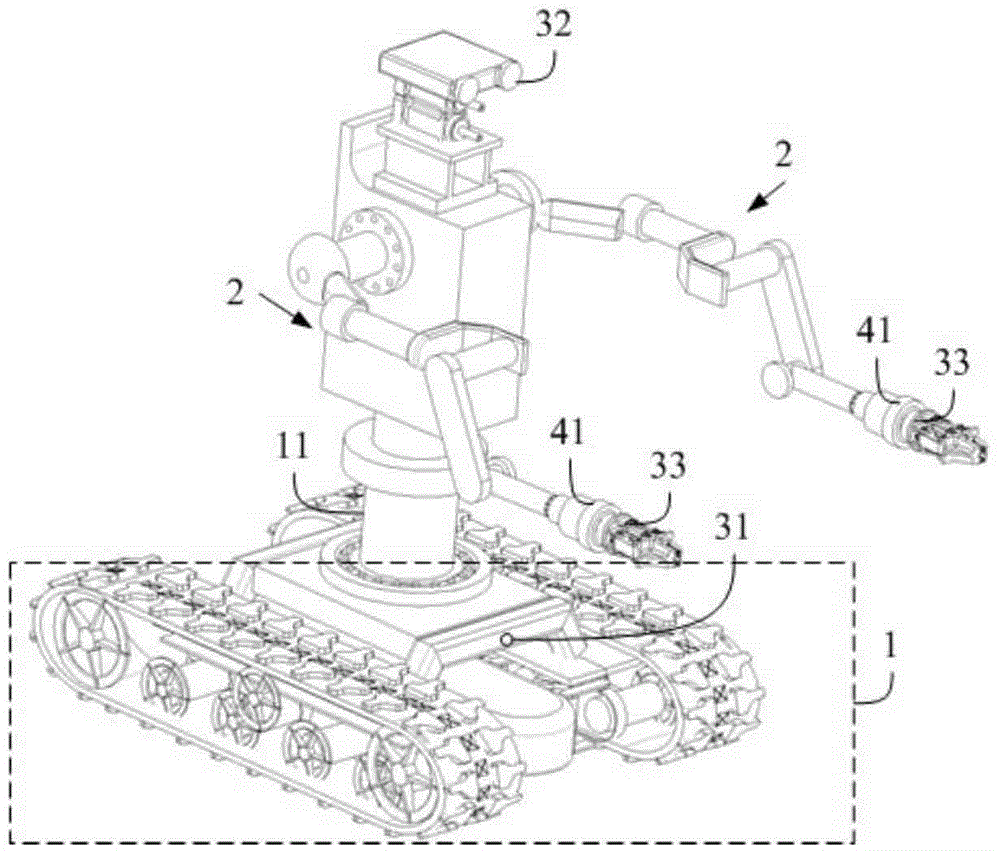
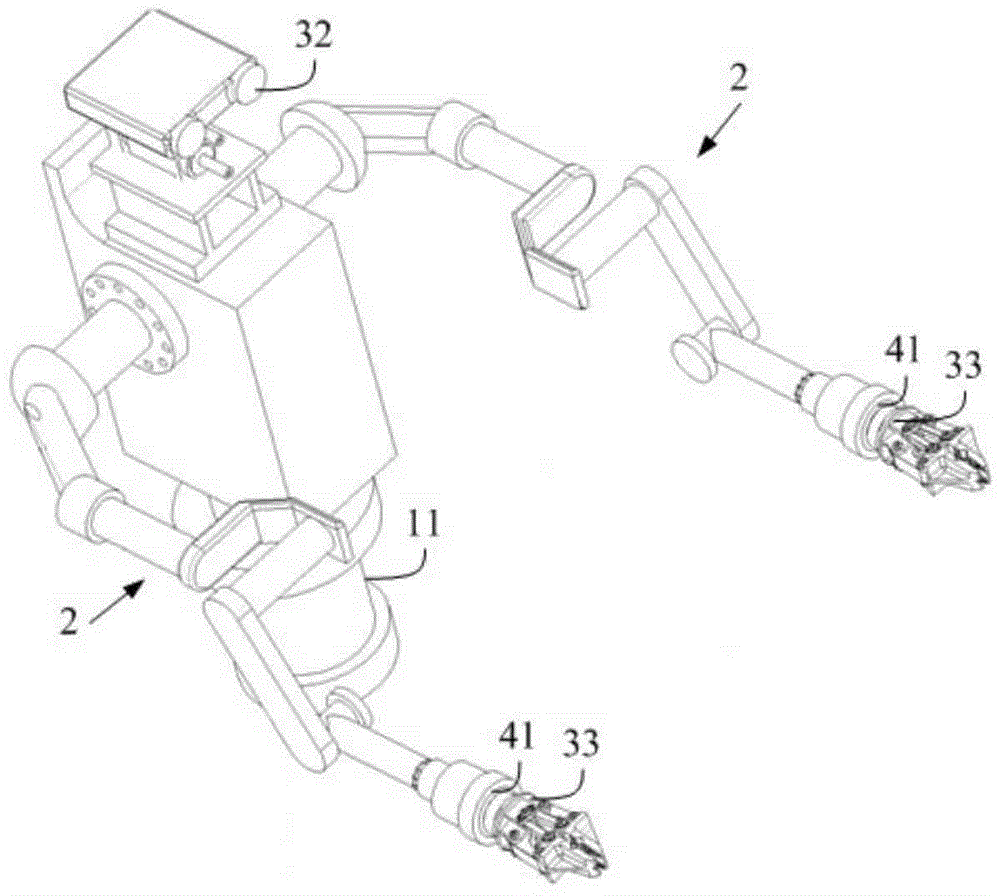
The invention discloses an all-hydraulic autonomous moving manipulator and a moving method thereof and belongs to the technical field of manipulators. The all-hydraulic autonomous moving manipulator comprises an omnidirectional moving platform, a double manipulator, a power system, a visual system and a sensing and control system are arranged on the omnidirectional moving platform, a rotary waist device is arranged on the omnidirectional moving platform, the double manipulator is arranged on the omnidirectional moving platform through the rotary waist device and is of a human-simulated double arm structure with multiple degrees of freedom, the power system is in an engine-hydraulic driving mode, the visual system comprises a navigation camera, a large-visual-field servo camera and a hand-eye camera, and the sensing and control system comprises a joint force sensor, a joint position sensor and a six-dimensional sensor. The all-hydraulic autonomous moving manipulator can meet needs on wide-range moving of large-mass workpieces.
Owner:济南鲁智电子科技有限公司
Rotary-table servo system neural network control method
ActiveCN103197562AAvoid complex calculationsImprove algorithm efficiencyAdaptive controlDynamic modelsNetwork approach
A rotary-table servo system neural network control method comprises (1) building a mechanical dynamic model of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotary-table servo system, and initializing the system state, sampling time and relative control parameters; (2) according to the differential mean value theorem, enabling a non-linear input dead zone in the system to linearly approximate to a simple time-varying system, avoiding complex calculation of dead-zone inverse compensation, and finally inferring a rotary-table servo system model provided with an unknown dead zone; (3) at each sampling moment, calculating and controlling a system tracking error, a fast terminal sliding mode surface and a first-order derivative of the system; (4) based on the rotary-table servo system model provided with the unknown dead zone, selecting a neural network approaching unknown trend, designing an adaptive robust finite-time neural network controller according to the system tracking error, the fast terminal sliding mode surface and the first-order derivative of the system, and updating a neural network weight matrix; and (5) entering the next sampling moment, and repetitively executing the steps from (3) to (5).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
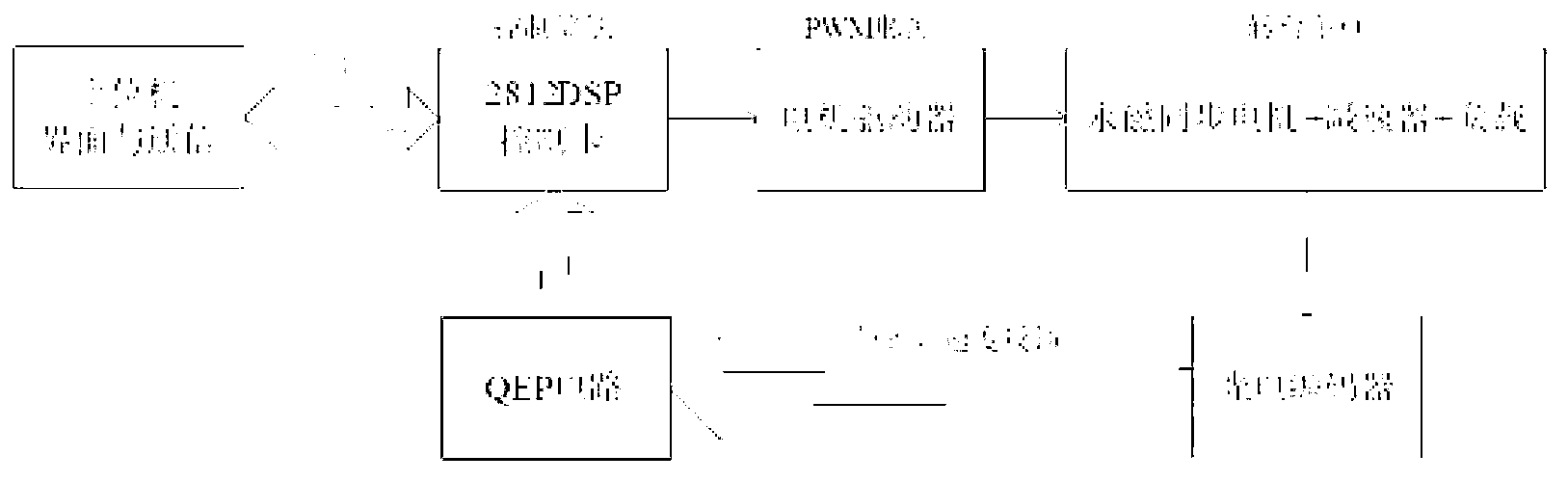
Servo motor control system of all-electric injection molding machine and control method thereof
The invention discloses a servo motor control system of an all-electric injection molding machine, comprising an injection molding machine computer controller, a servo motor controller and a PLC controller; the computer controller is connected with the servo motor controller through a CAN bus, the servo motor controller is connected with a servo motor, and the computer controller is connected with PLC controller; the servo motor controller can be a mould opening / closing servo motor controller, a plastic injection servo motor controller, a plasticizing pressure holding servo motor controller and an ejection servo motor controller; and the servo motor can be a mould opening / closing servo motor, a plastic injection servo motor, a plasticizing pressure holding servo motor and an ejection servo motor. The invention also discloses a control method for the control system; and technological procedures capable of being performed simultaneously are synchronously controlled through performing mould opening / closing control, plasticizing control, plastic injection control, pressure holding control, ejection control, mobile control of an injection platform and mould adjustment control on the motor of the electric injection molding machine, thereby saving one third of the production time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cross-scale micro-nano-scale in-situ composite load mechanical performance testing platform
ActiveCN102262016ARealize acquisitionEasy to controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNanotechnologyMicro nanoElectromechanics
The invention relates to a cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform, belonging to electromechanics. The cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform is composed of a precision drive and transmission unit, a signal detection and control unit and a clamping, connecting and supporting unit, wherein,in the precision drive and transmission unit, a DC servo motor provides power output, and a two-stage worm and gear mechanism with large reduction ratio and a precision ball screw mechanism transmit power; the signal detection and control unit is composed of a precision displacement sensor, a precision pull pressure sensor and a coder in coaxial rigid connection with the DC servo motor; and the clamping, connecting and supporting unit comprises a clamper component for locating and mounting a standard test specimen, and the like. The cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform can be compatible with imaging instruments, and performs a cross-scale in-situ micro nanometer composite load test on a macroscopic test specimen through observation via the imaging instruments, so as to perform in-situ monitoring on processes of microscopic deformation, injury and fracture of materials, so that a new testing method for revealing the mechanical properties and the injury mechanism of the materials at the micro nanometer grade is provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Measurement Control System for Multi-Shaft Supported Air Floatation Platform
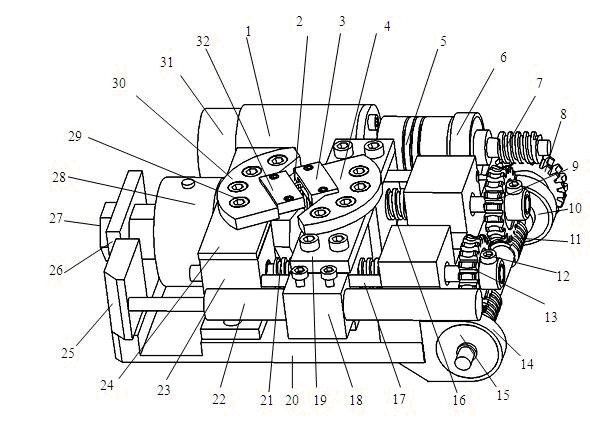
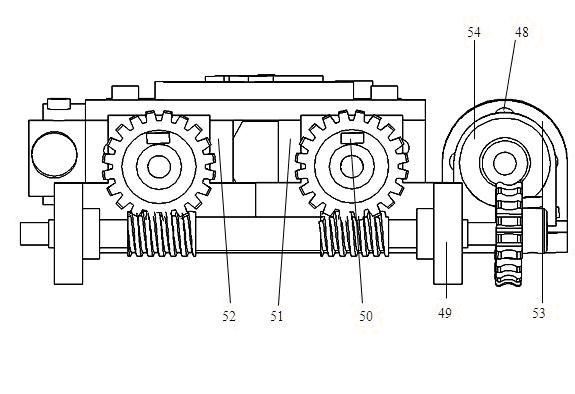
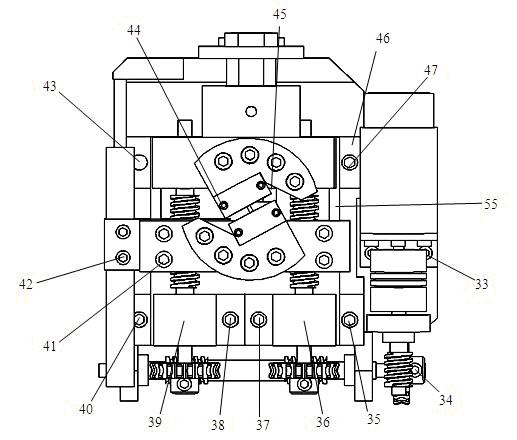
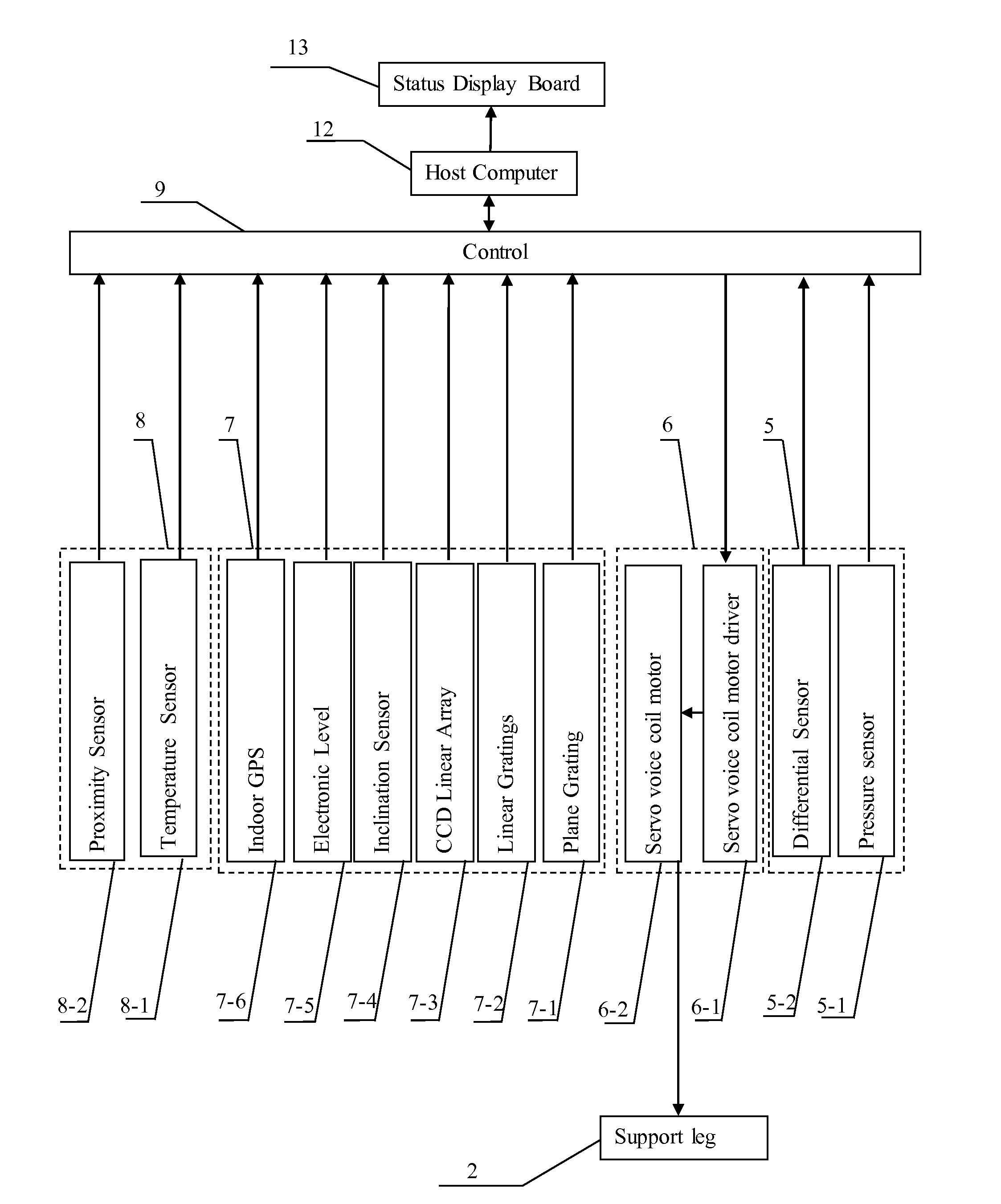
ActiveUS20160124437A1Increased load-bearing capacityIncreased accuracy levelComputer controlStands/trestlesGratingProximity sensor
A measurement control system for a multi-shaft supported air floatation platform, the system comprising a load feedback unit (5), an execution unit (6), a position measurement unit (7), a safety protection unit (8), a controller (9), a rotating motor (10), and a linear light source 11; the load feedback unit comprises M pressure sensors (5-1) and four differential sensors (5-2); the execution unit comprises M servo voice coil motors (6-1) and M servo voice coil motor drivers (6-2); the position measurement unit comprises a plane grating (7-1), M linear gratings (7-2) a linear array CCD (7-3), a tilt sensor (7-4), M electronic levels (7-5), and an indoor GPS (7-6); the safety protection unit comprises 2M proximity sensors (8-1) and M temperature sensors (8-2); and the linear array CCD consists of no few then six CCDs. The system solves the problems of leveling limitations and narrow application range of existing supporting platforms.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
CNC data correction method
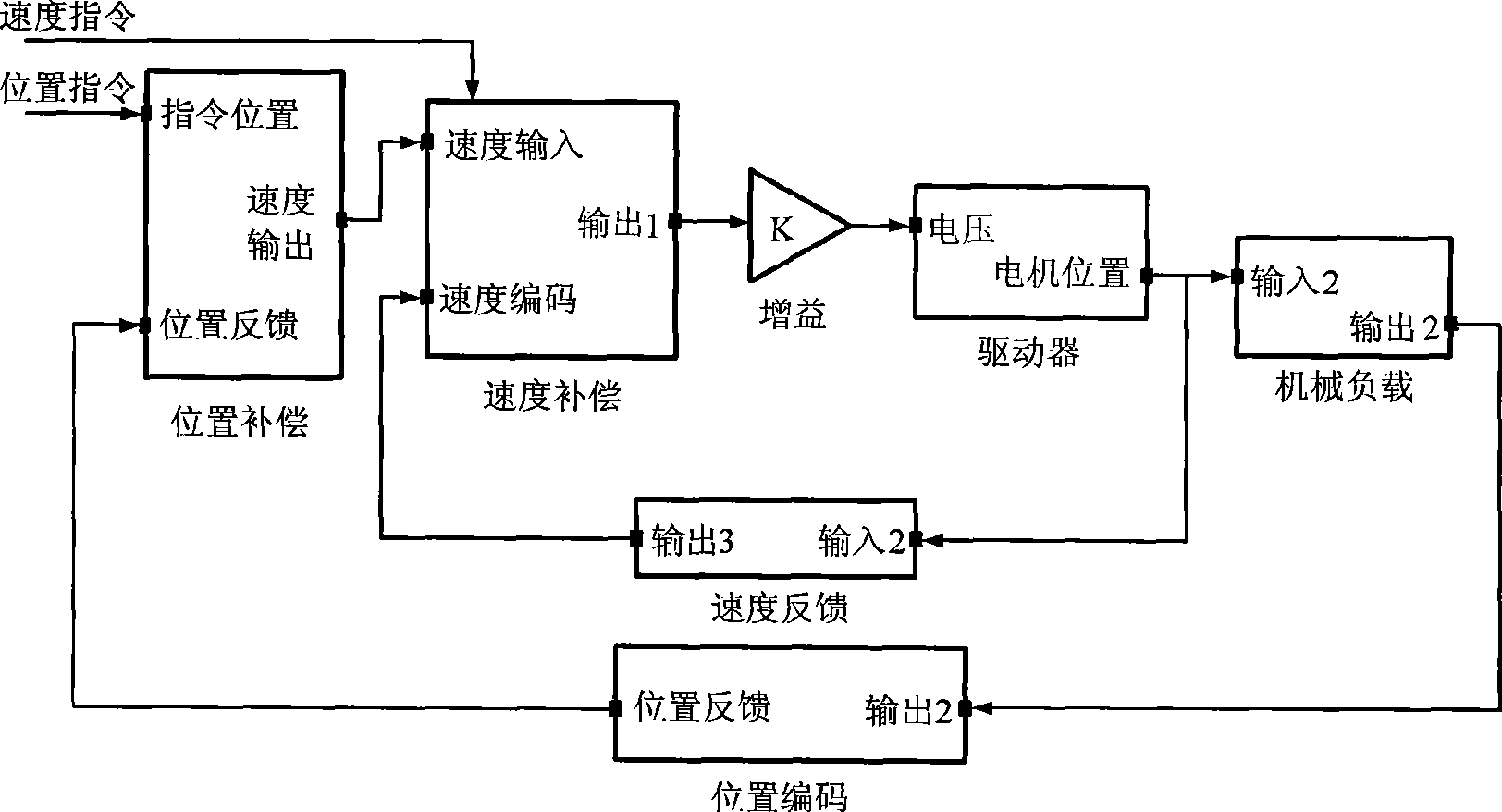
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 01089 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 26, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 26, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 28, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 37291 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 9, 1997Actual machining positions P1, P2, . . . corresponding to command positions S1, S2, S3 . . . of each block of NC data are obtained by trial machining. Positions that correspond symmetrically to the actual machining positions P1, P2, . . . with respect to the command positions S1, S2, S3 . . . of each block are obtained. Modified NC data are created with use of the symmetrical positions as modified command positions for each block. The modified NC data include correction values for modifying positional differences attributable to a delay in a servo system. Therefore, if machining is carried out in accordance with the modified NC data, the correction values and a follow-up delay attributable to the actual delay in the servo system cancel one another, so that a high-accuracy work shape can be obtained.
Owner:FANUC LTD
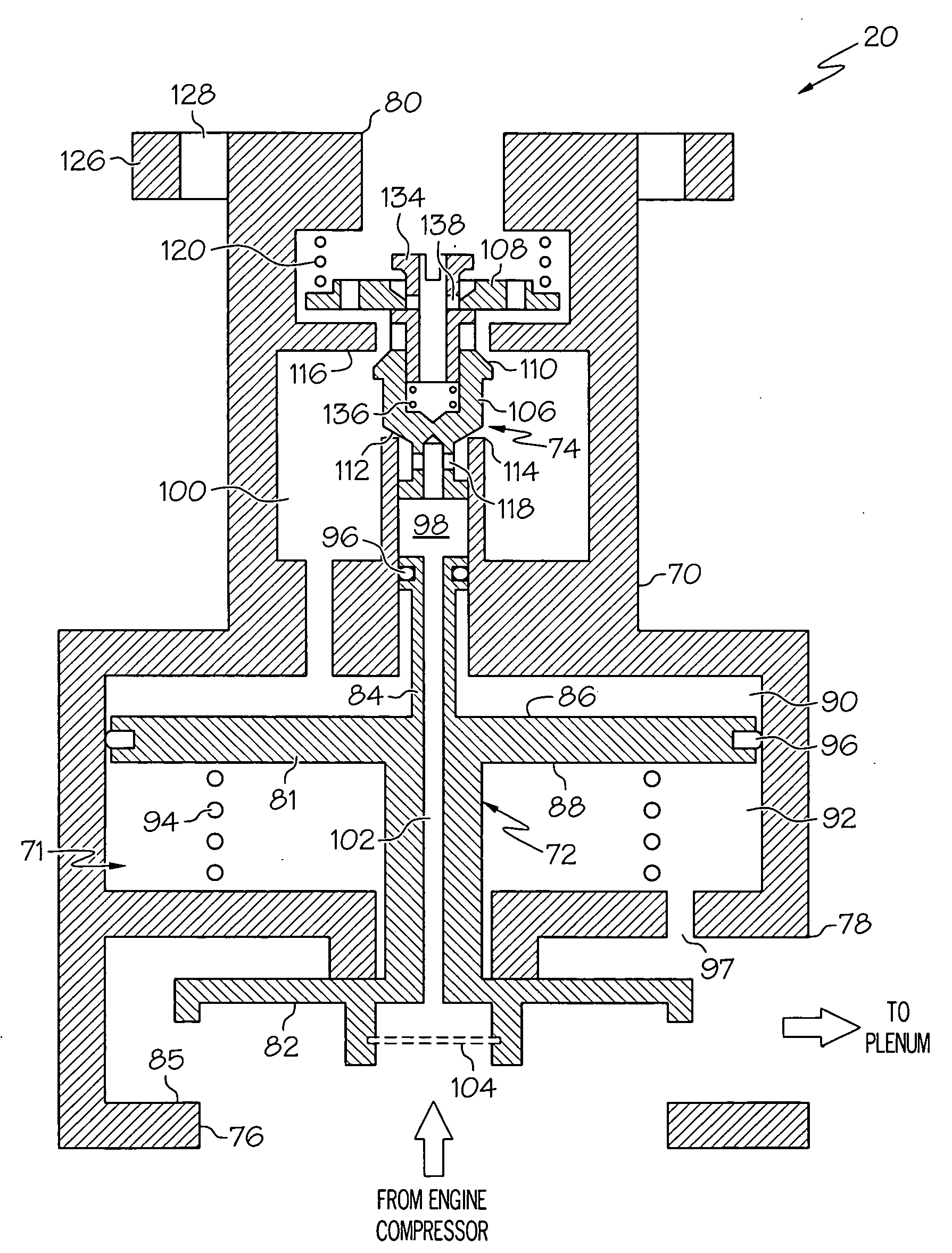
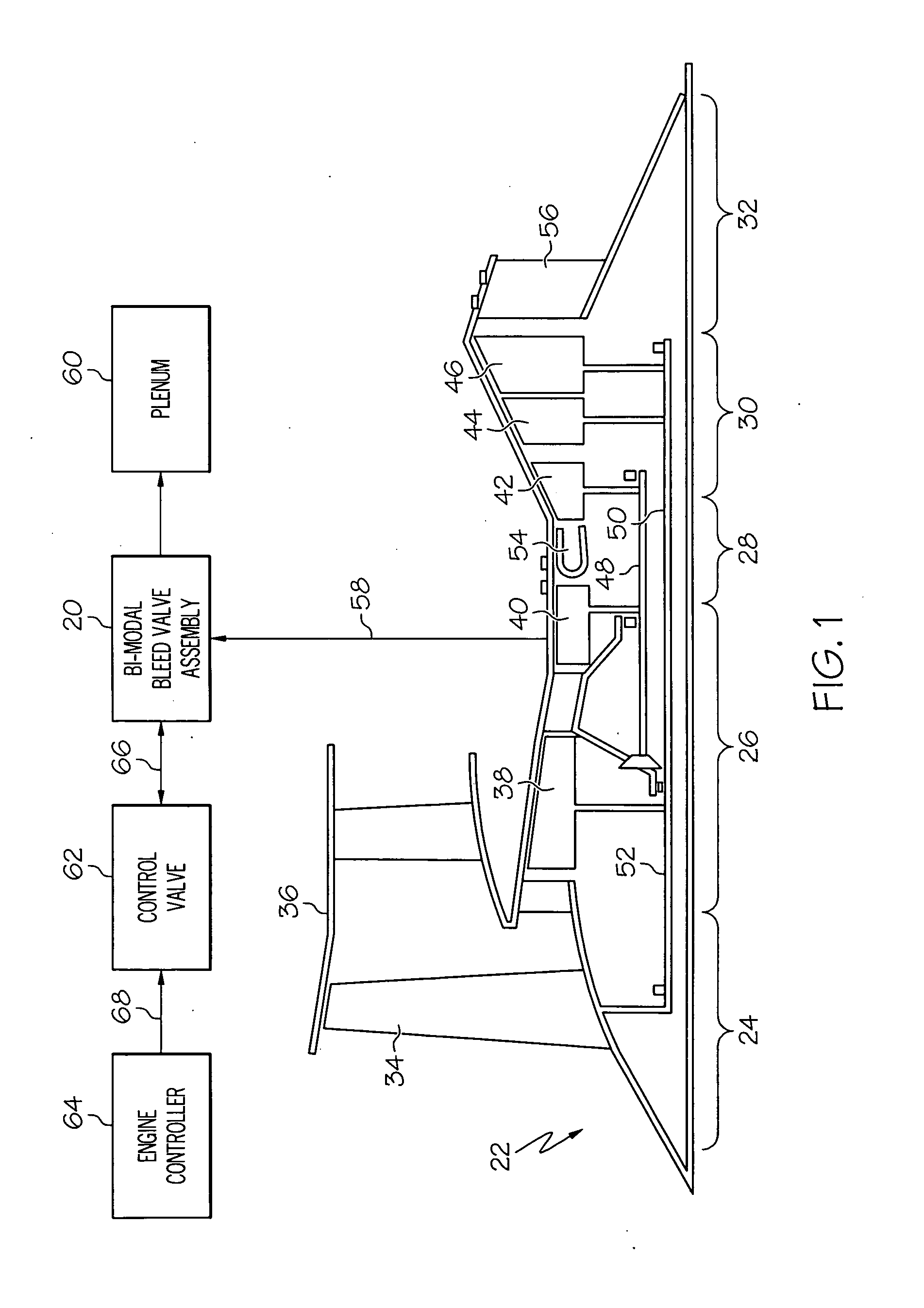
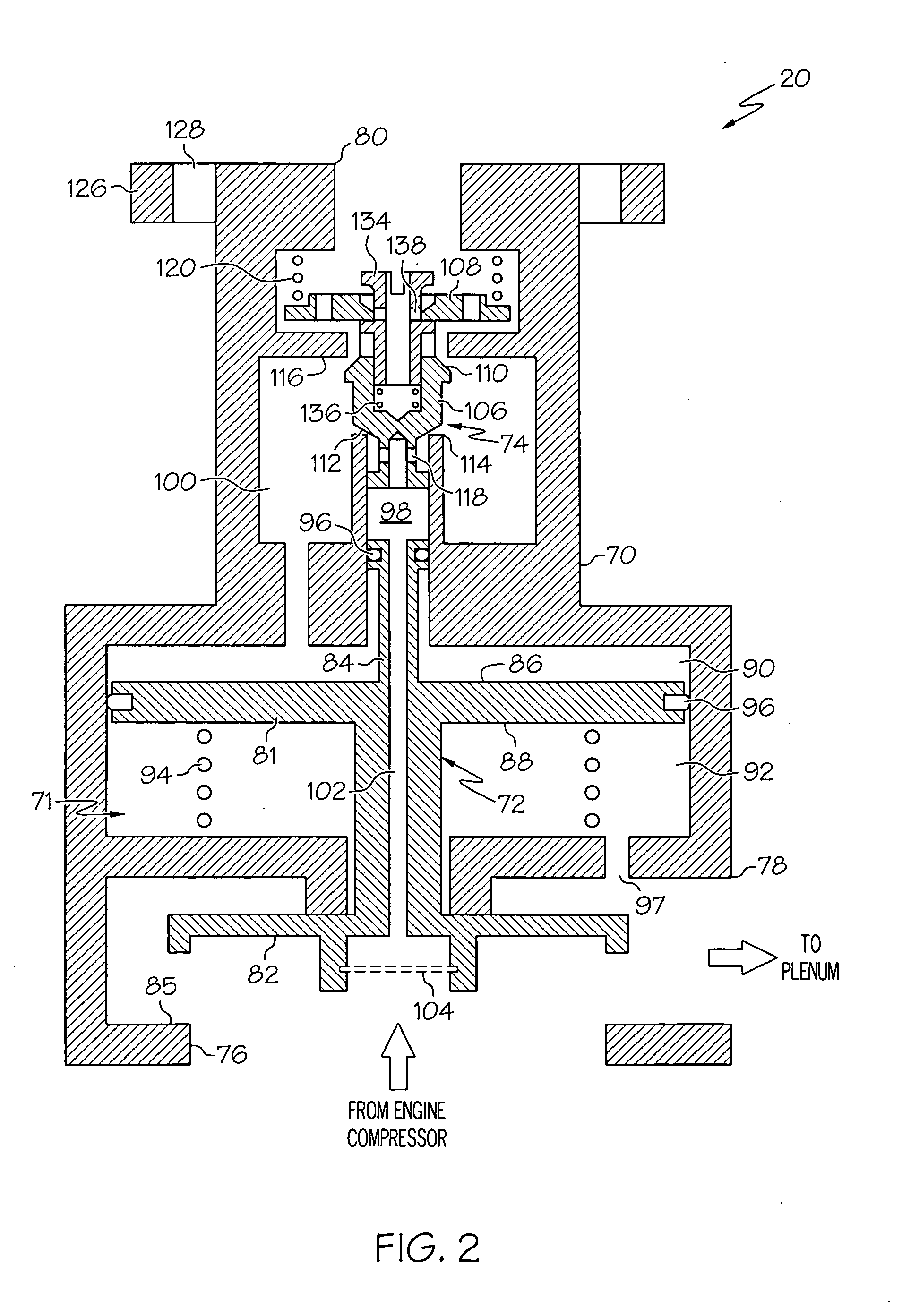
Bi-modal bleed valve assembly for gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20100083667A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesGas turbine plantsControl roomControl valves
A bi-modal bleed valve assembly is provided. In one embodiment, the bi-modal bleed valve assembly includes a housing assembly having a bleed inlet, a bleed outlet, a control servo port, and a control chamber therein. A main flow control valve is fluidly coupled to the control chamber and configured to move between an open position and a closed position to regulate fluid flow from the bleed inlet to the bleed outlet. The main flow control valve is configured to move from an open position to a closed position when the pressure within the control chamber surpasses a predetermined threshold. A switching valve is fluidly coupled between the bleed inlet, the servo control port, and the control chamber. The switching valve is configured to route fluid flow into the control chamber from: (i) the bleed inlet in an autonomous mode, and (ii) the servo control port in a servo-controlled mode.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Automatic polishing system for cylindrical workpiece
ActiveCN105619213ARealize automatic deliveryIncrease the level of automationGrinding drivesBelt grinding machinesDrive wheelElectric machinery
The invention provides an automatic polishing system for a cylindrical workpiece. The automatic polishing system comprises a feeding mechanism, a feed mechanism and an outer circle polishing mechanism. The feeding mechanism comprises a feeding rack, a conveying table unit and a pressing unit, and the conveying table unit and the pressing unit are mounted on the feeding rack. The feed mechanism is mounted on a support face plate of the feeding mechanism and comprises a feed rack and a motion control unit mounted on the feed rack. The outer circle polishing mechanism comprises a polishing rack, a motion unit and a polishing unit, and the motion unit and the polishing unit are mounted on the polishing rack. The polishing unit comprises linear guide rails, a sliding base, a stepping motor support, a driving wheel, a lead screw, a servo motor, a sanding belt, a tensioning wheel, a driven wheel and a stepping motor. The automatic polishing system can completely replace manual operation, work efficiency is remarkably improved, manpower cost is reduced, and the automation level of an enterprise is improved; and all polishing parameters are precisely controlled, and the more stable and better polishing quality can be achieved.
Owner:LYNCWELL INNOVATION INTELLIGENT SYST ZHEJIANG CO LTD
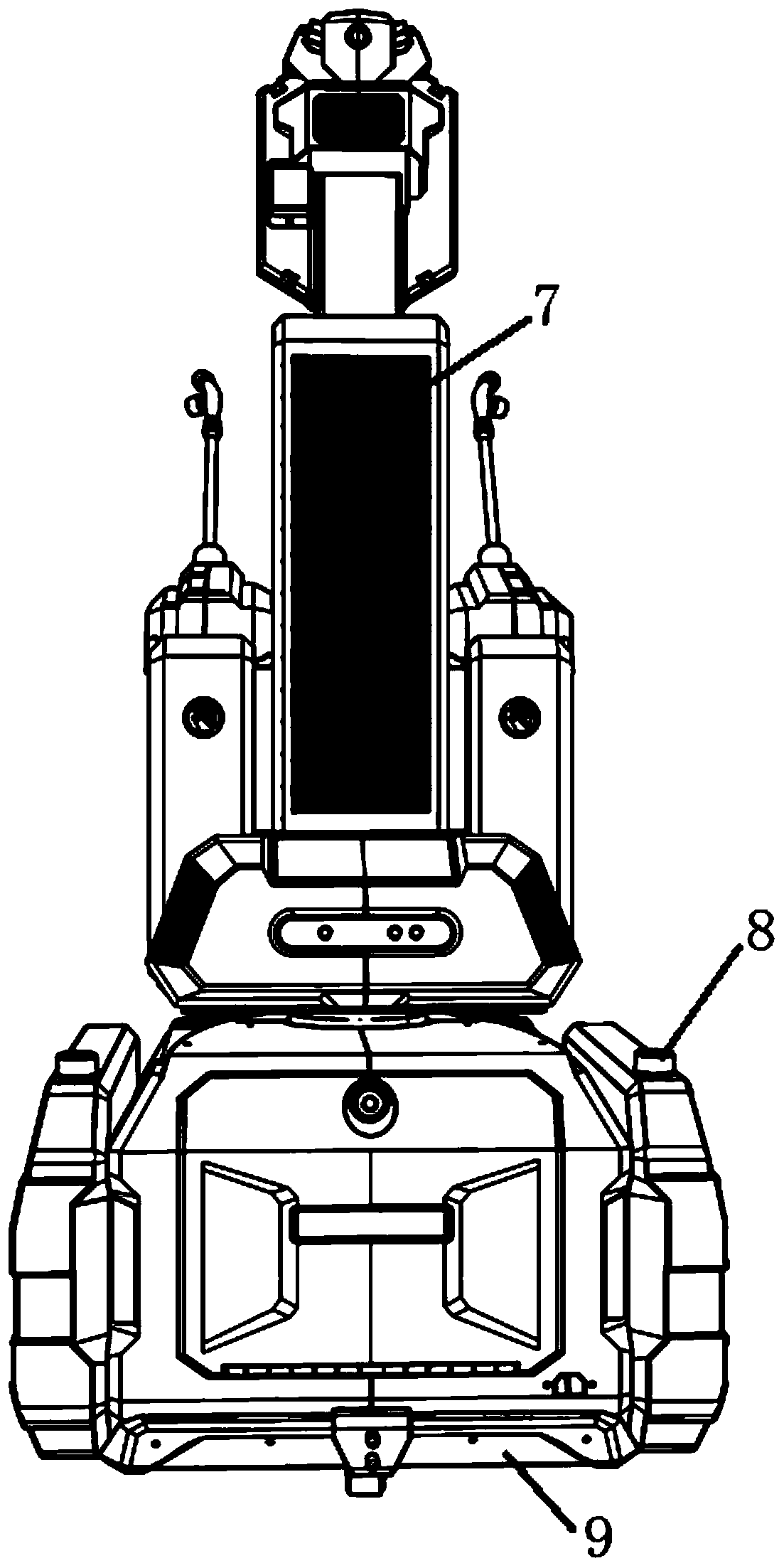
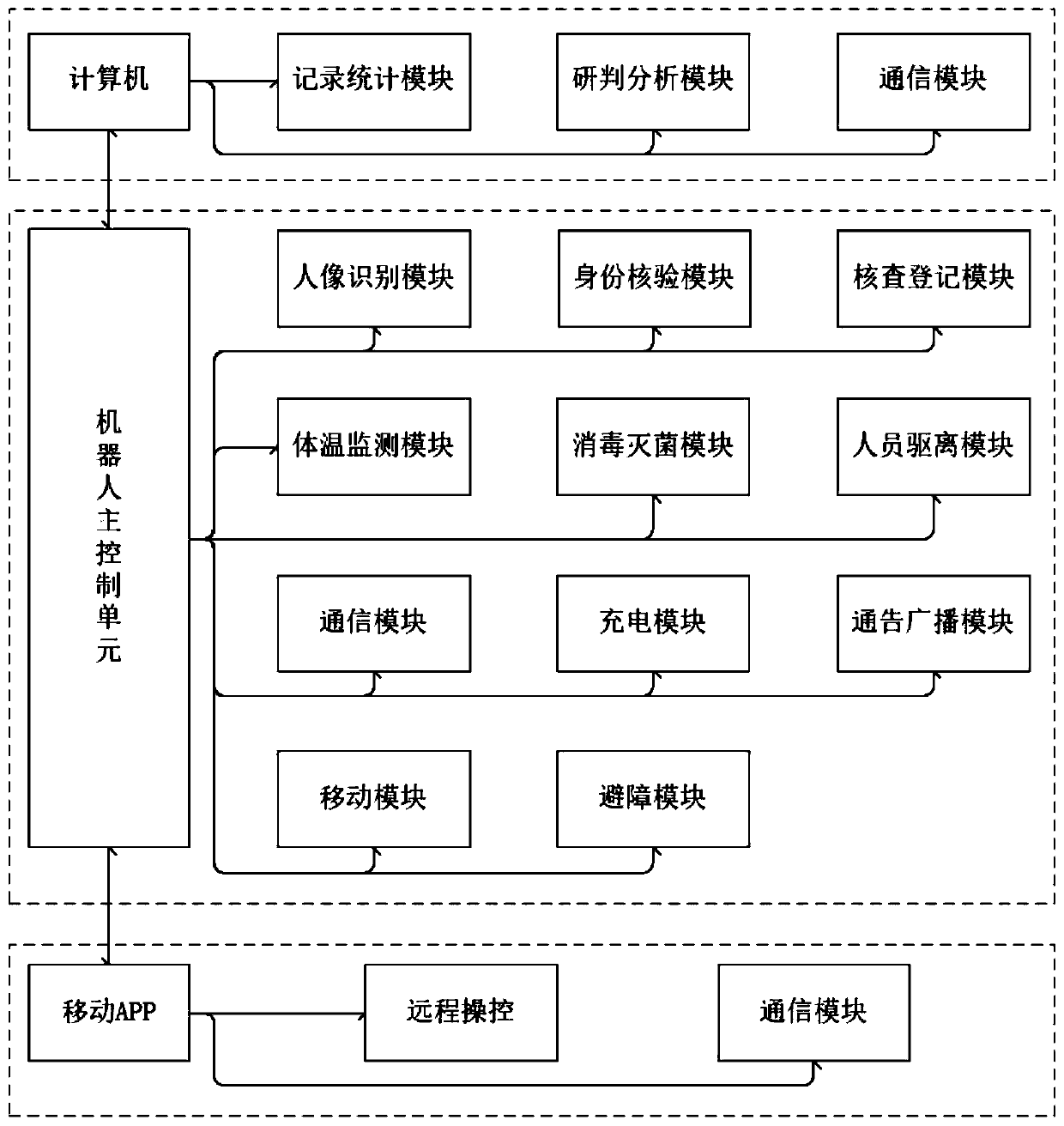
Epidemic prevention robot and control system thereof
PendingCN111347439AAvoid direct contactStop the spreadLavatory sanitoryAtomized substancesRotary stageSprayer
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent robots and discloses an epidemic prevention robot and a control system thereof. The epidemic prevention robot comprises a robot body, a mechanical part and an electric appliance part, wherein the mechanical part comprises a moving chassis, a disinfectant storage box, a rotating table, an ultraviolet lamp box, a disinfection sprayer, and an intelligent recognition head; the electric appliance part comprises a laser radar, a servo motor outline, a control mainboard, a thermal imager, a portrait recognition module, a voice system and thelaser radar; a disinfection mode comprises an ultraviolet disinfection mode and a disinfectant spraying mode, and double disinfection sterilization is carried out through disinfectant spraying and ultraviolet irradiation. The epidemic prevention robot replaces manual work and is mainly used for safety epidemic prevention work; the functions of intelligent cruising, face recognition, remote shouting, autonomous charging, body temperature monitoring, voice alarm, disinfection sterilization and the like are provided, the robot can be greatly popularized in medical places, public places with large personnel flow and the like, and the probability that personnel are infected is greatly reduced.
Owner:山东西部智能科技有限公司
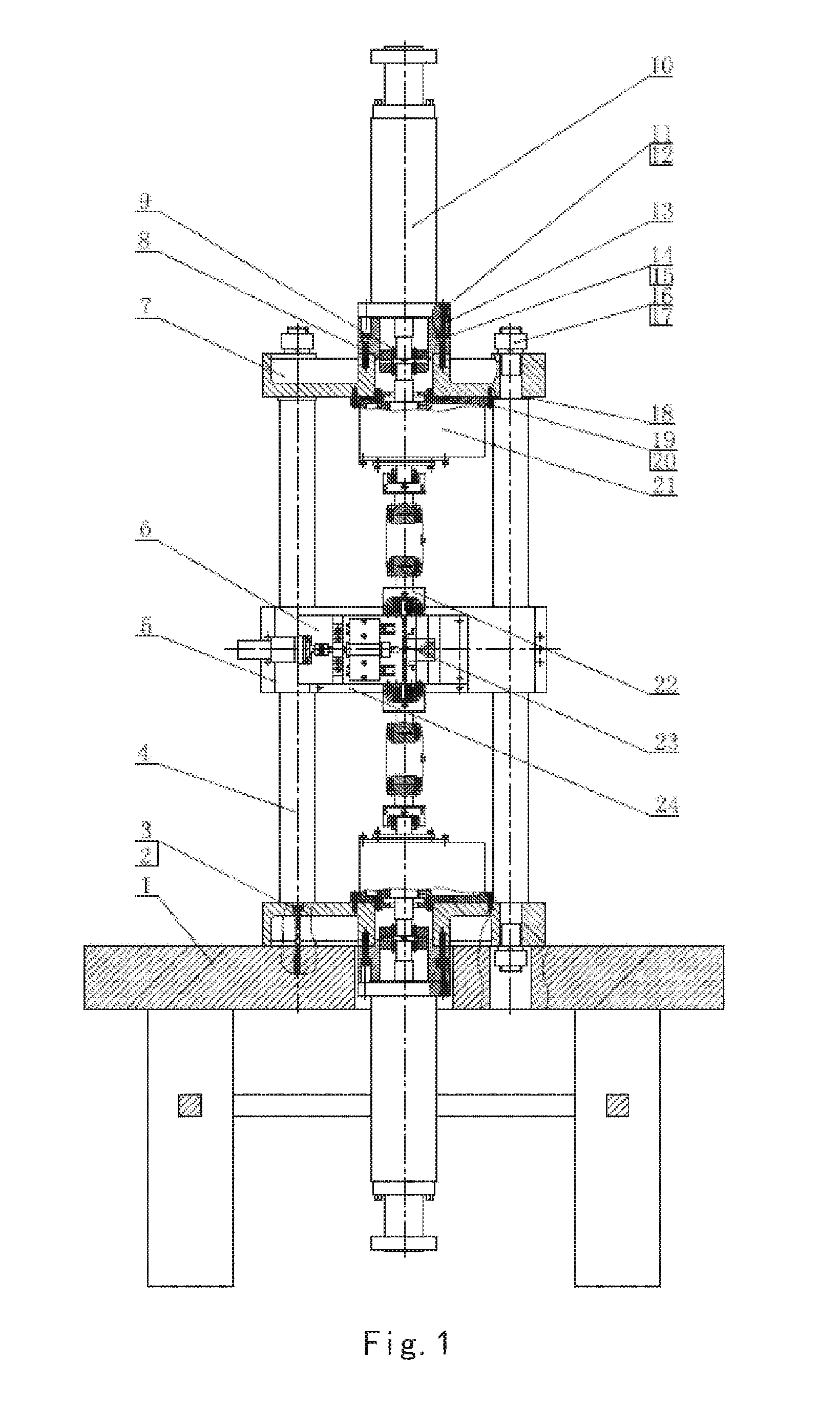
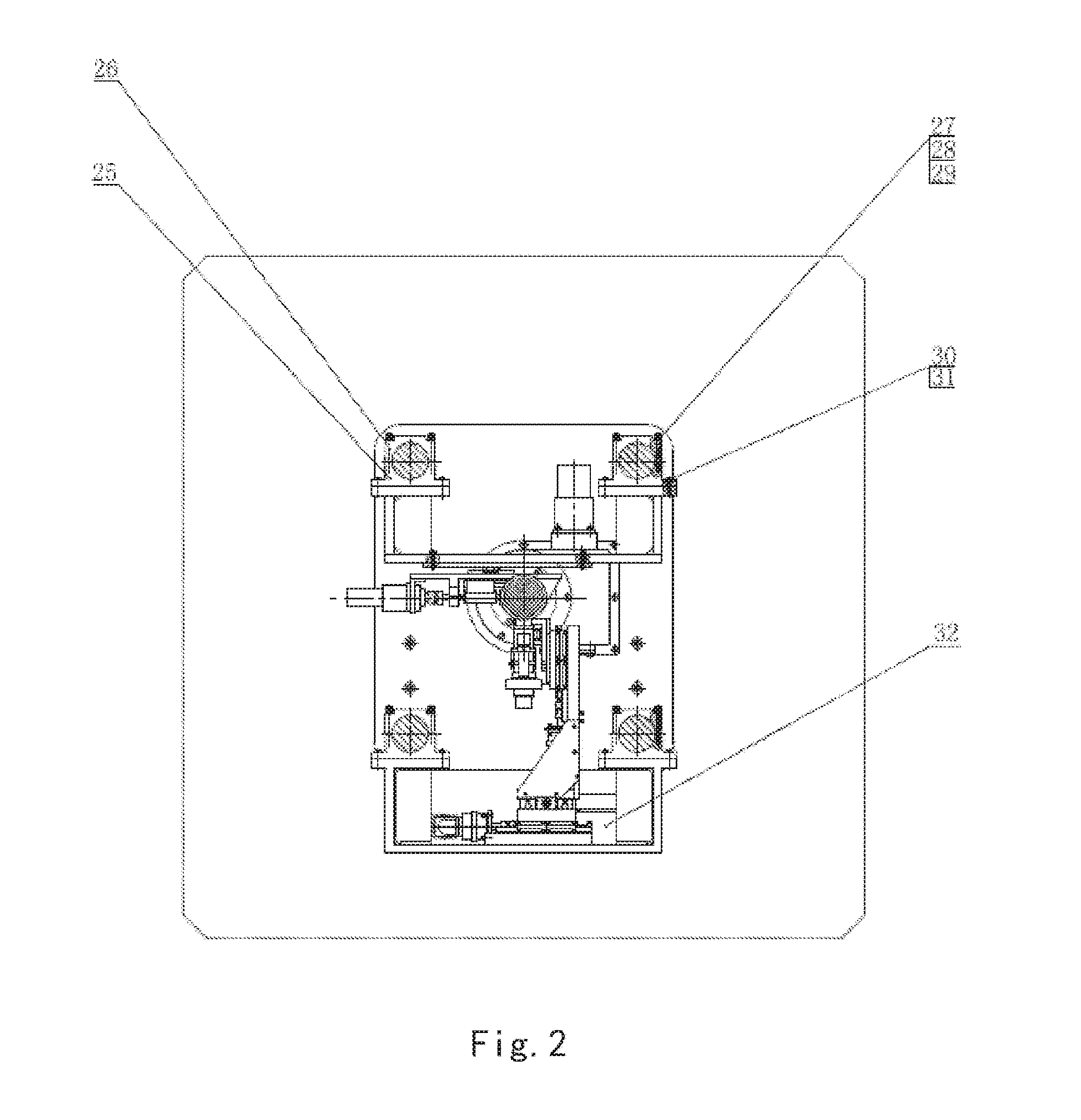
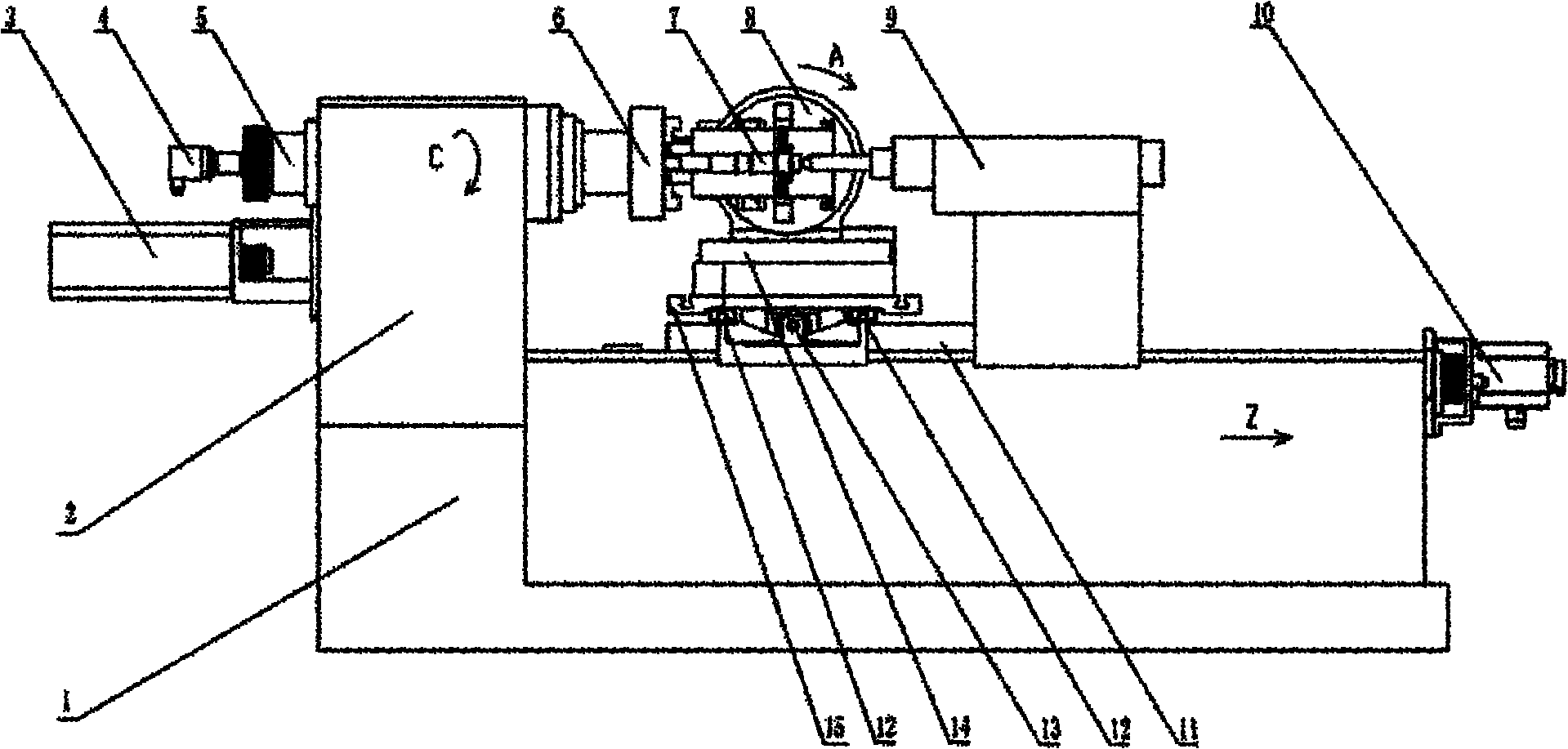
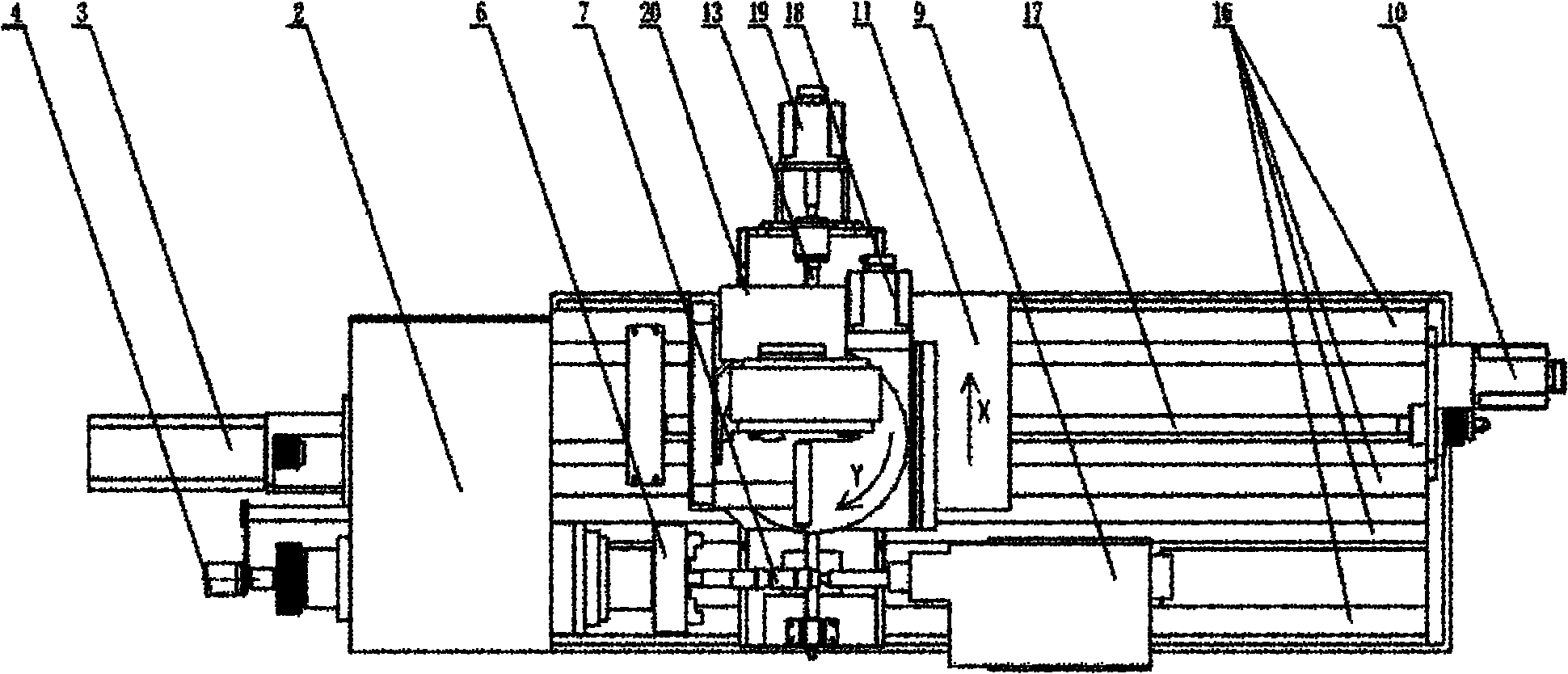
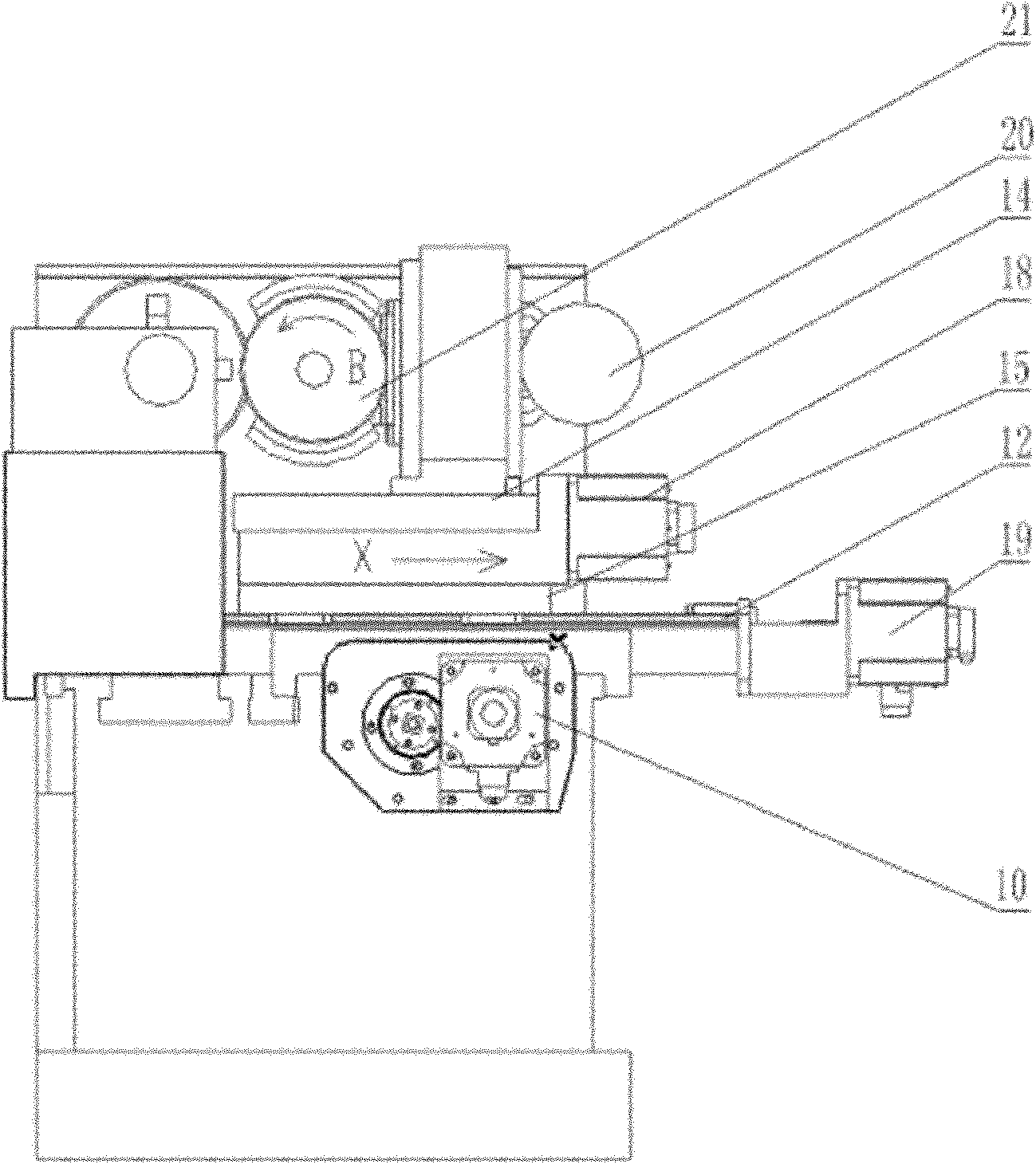
CNC (computerized numerical control) combined turning and grinding machine tool for four-linkage enveloping worms and processing method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of machinery, specifically relates to a CNC (computerized numerical control) combined turning and grinding machine tool for four-linkage enveloping worms and a processing method thereof. The machine tool and processing method thereof provided by the invention are characterized in that a main shaft motor 3 drives a main shaft 5 and an enveloping worm 7 to rotate around a C-axis by a synchronous belt, a Z-axis servo motor 10 drives a ball screw 17 to lead a large support plate 11 to move along a Z-direction guide rail 16 by the synchronous belt, an X-axis servo motor 19 drives a ball screw 13 to lead a small support plate 15 to move along an X-direction guide rail 12 by a coupler, a Y-axis servo motor 18 drives a CNC rotary table 14 to rotate around a Y axis by gears, a CNC tool rest or grinding head is fixedly connected to the CNC rotary table, a grinding head motor 20 drives a grinding wheel 21 to rotate around a B-axis by the synchronous belt, and the grinding wheel and the motor synchronously rotate around an A-axis by turning a hand wheel. Compared with the prior art, the machine tool disclosed by the invention is simple and novel instructure, convenient and safe in operation, high in processing efficiency and wide in application range; and in addition, the machine tool can rotate at a high speed, and the operations of turning and grinding are completed on a same machine tool, therefore, the machine tool is complete in function, high in reliability, strong in environment adaptivity, and more accurate in transmission precision and machining precision.
Owner:上海合纵重工机械有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com