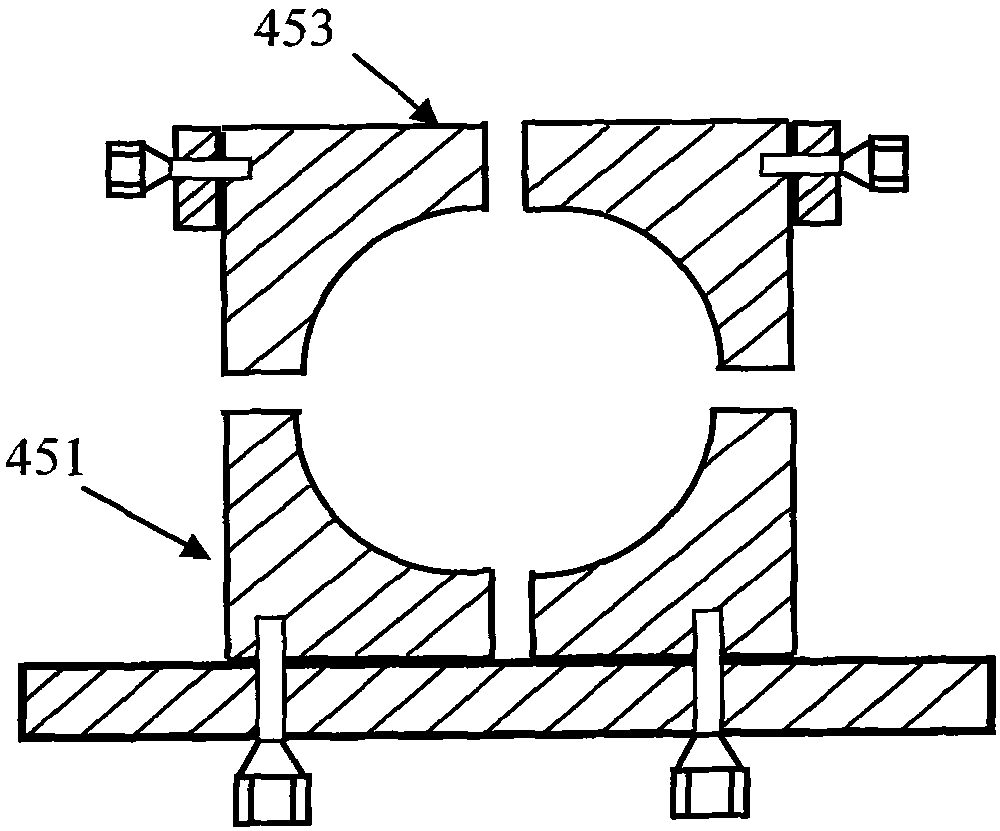
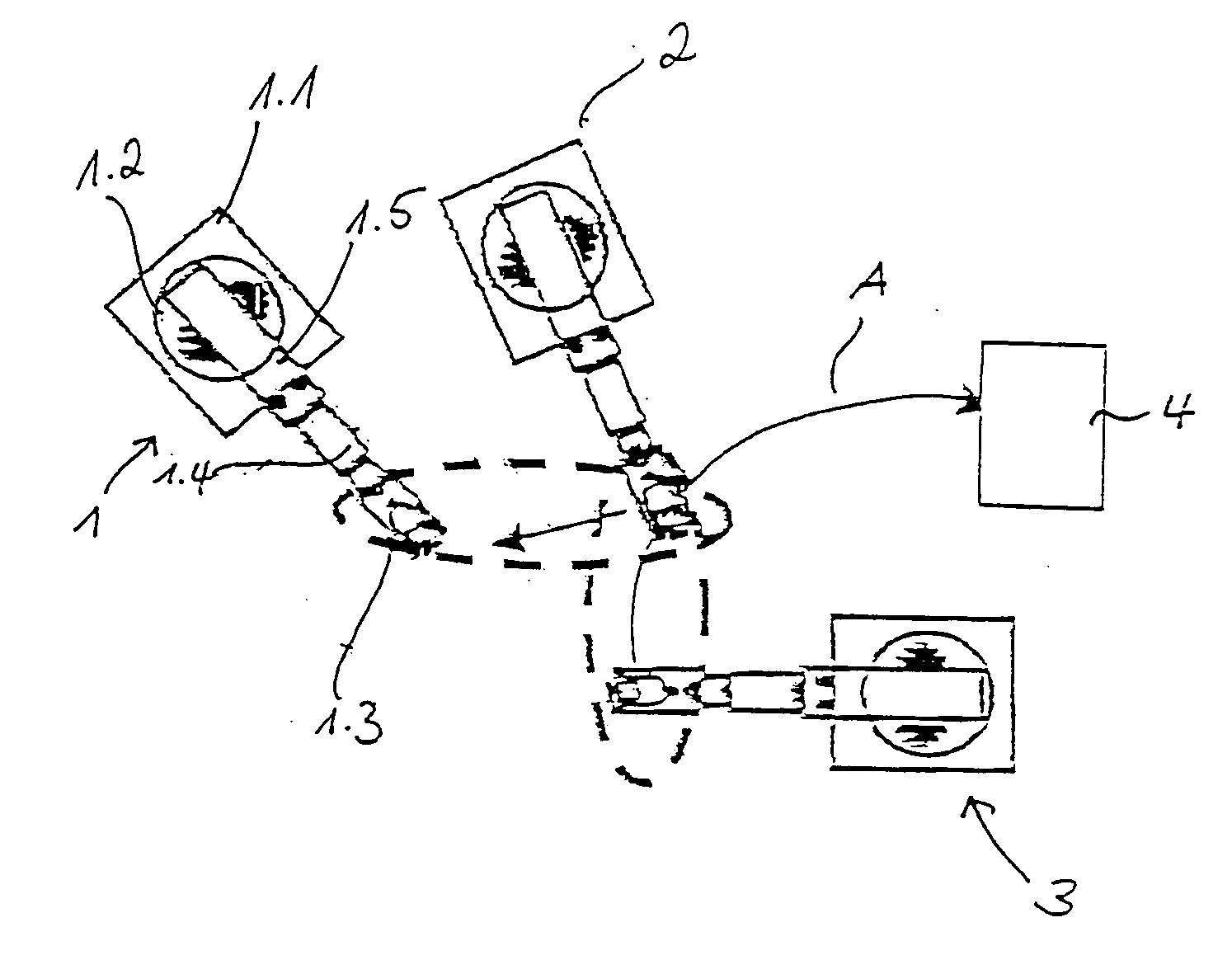
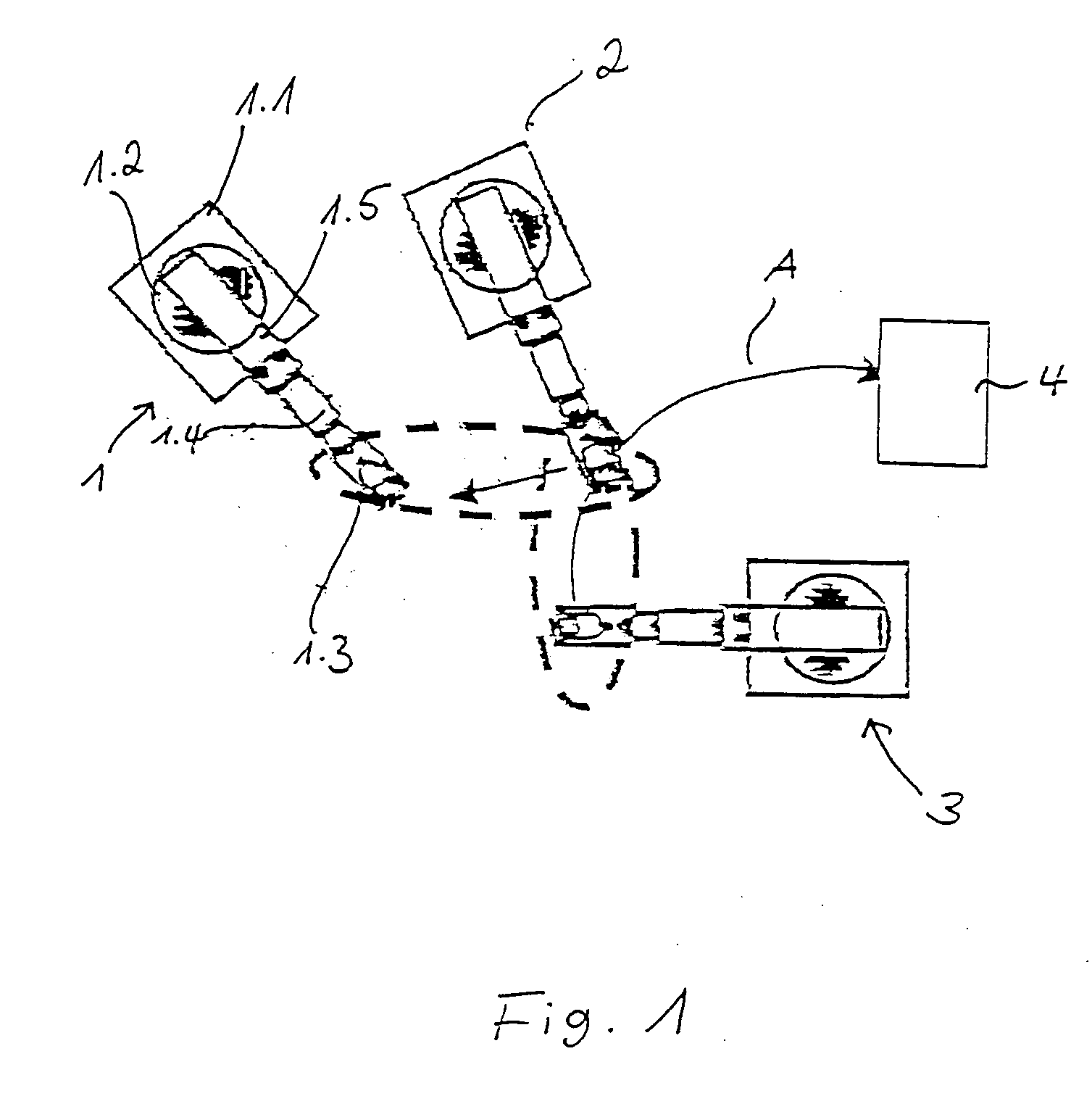
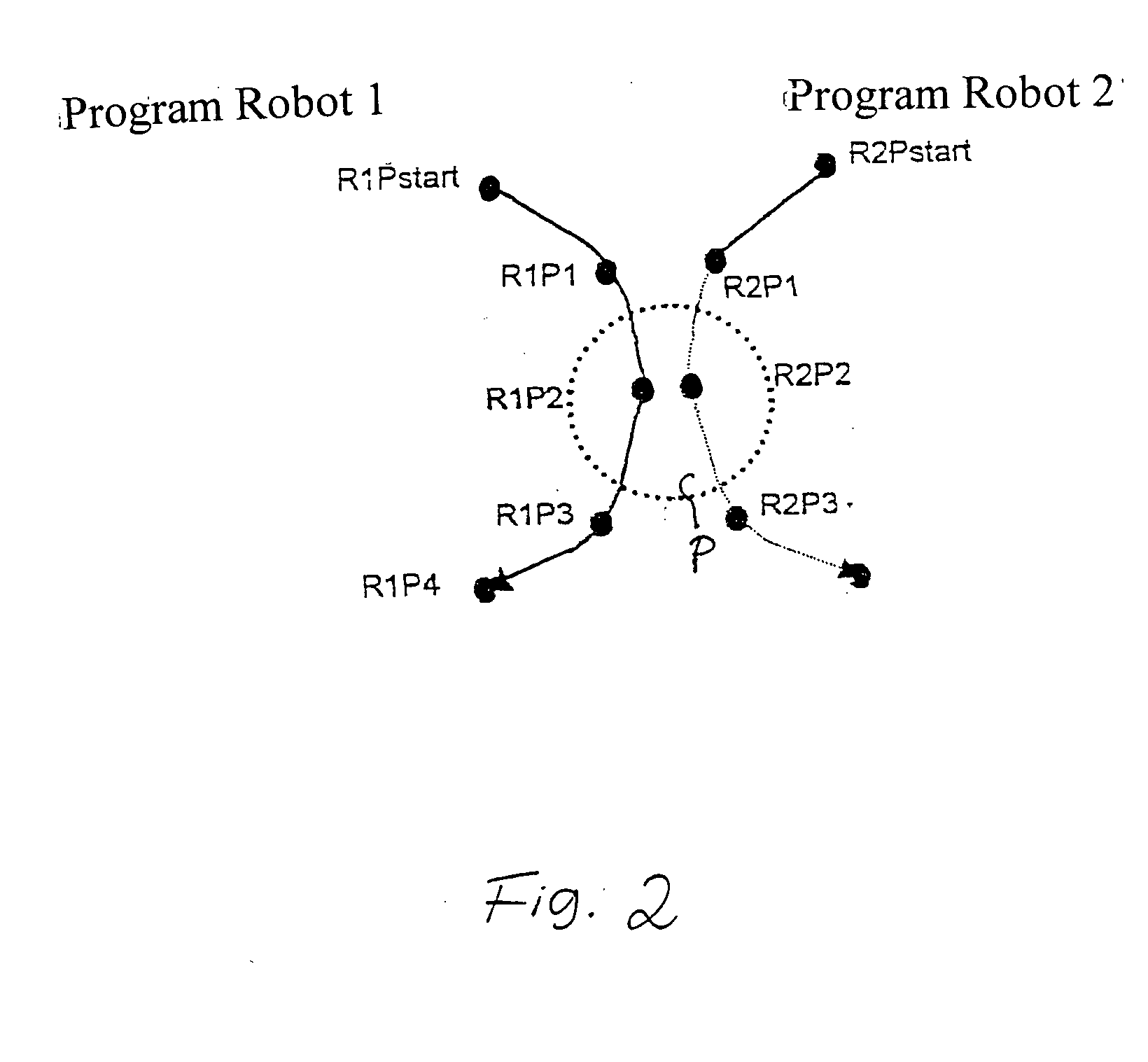
Patents
Literature
4735 results about "Industrial robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
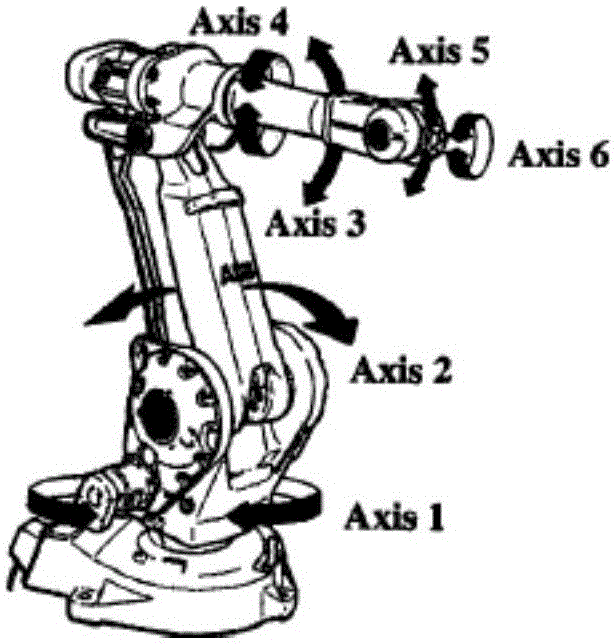
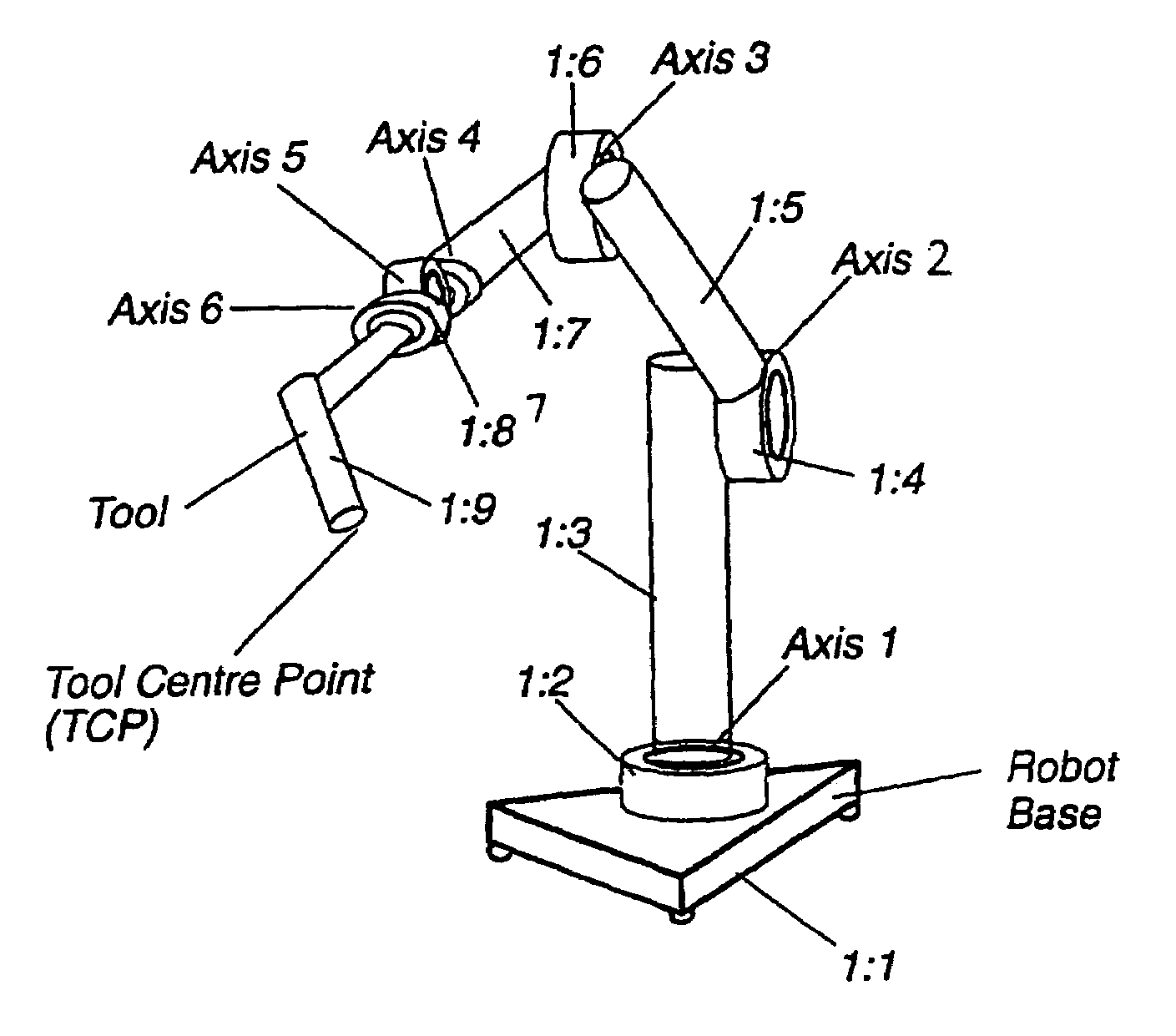
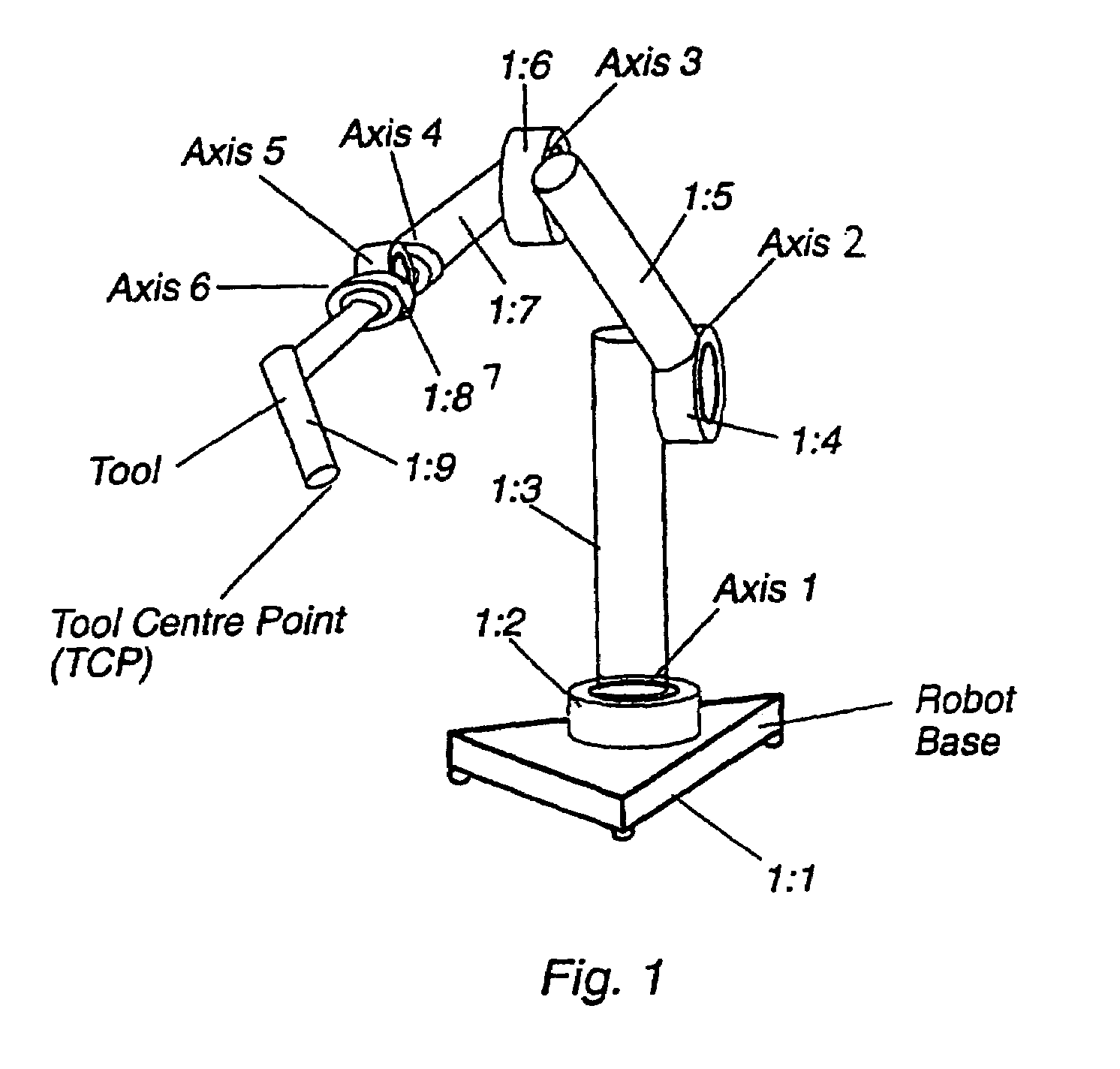
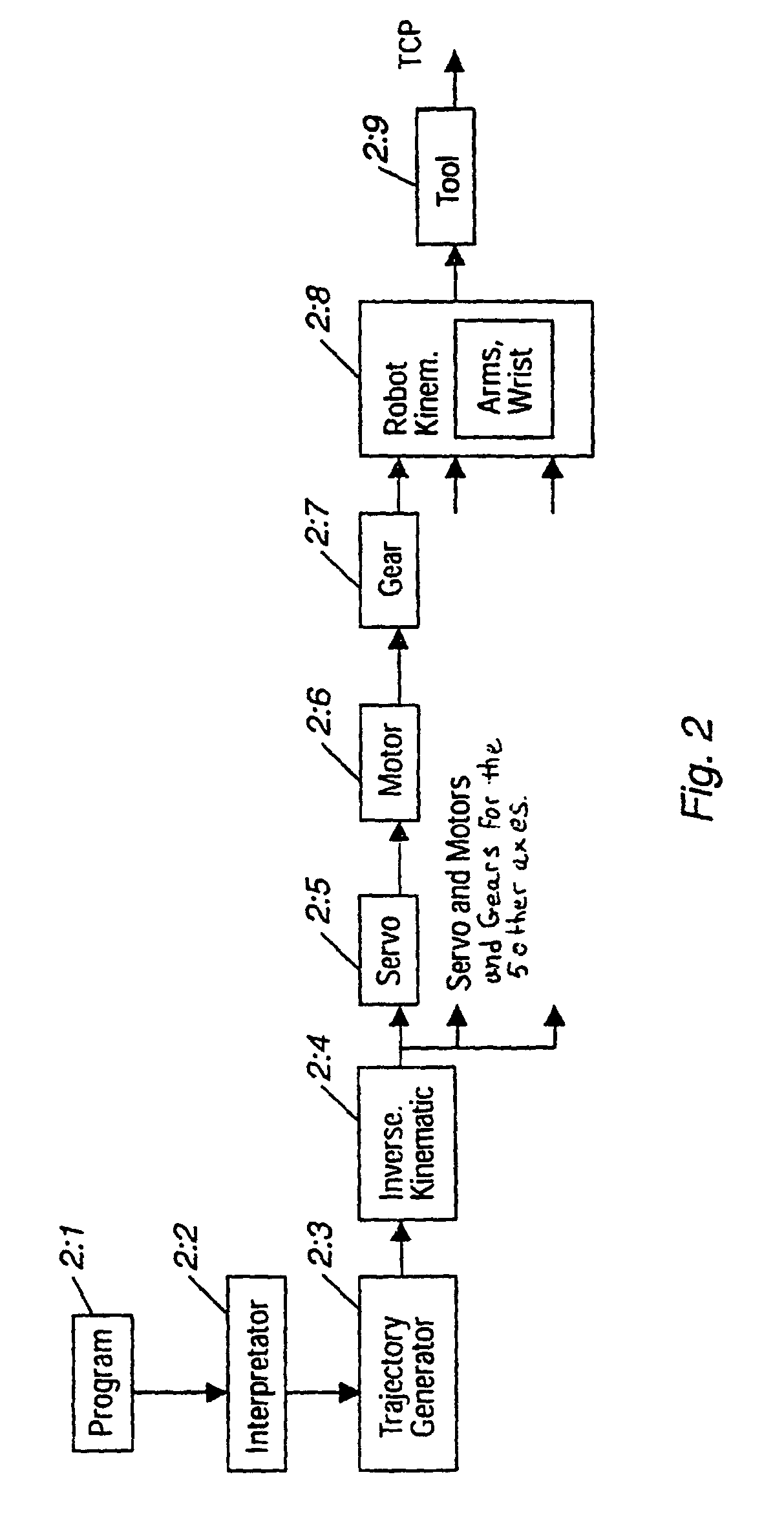
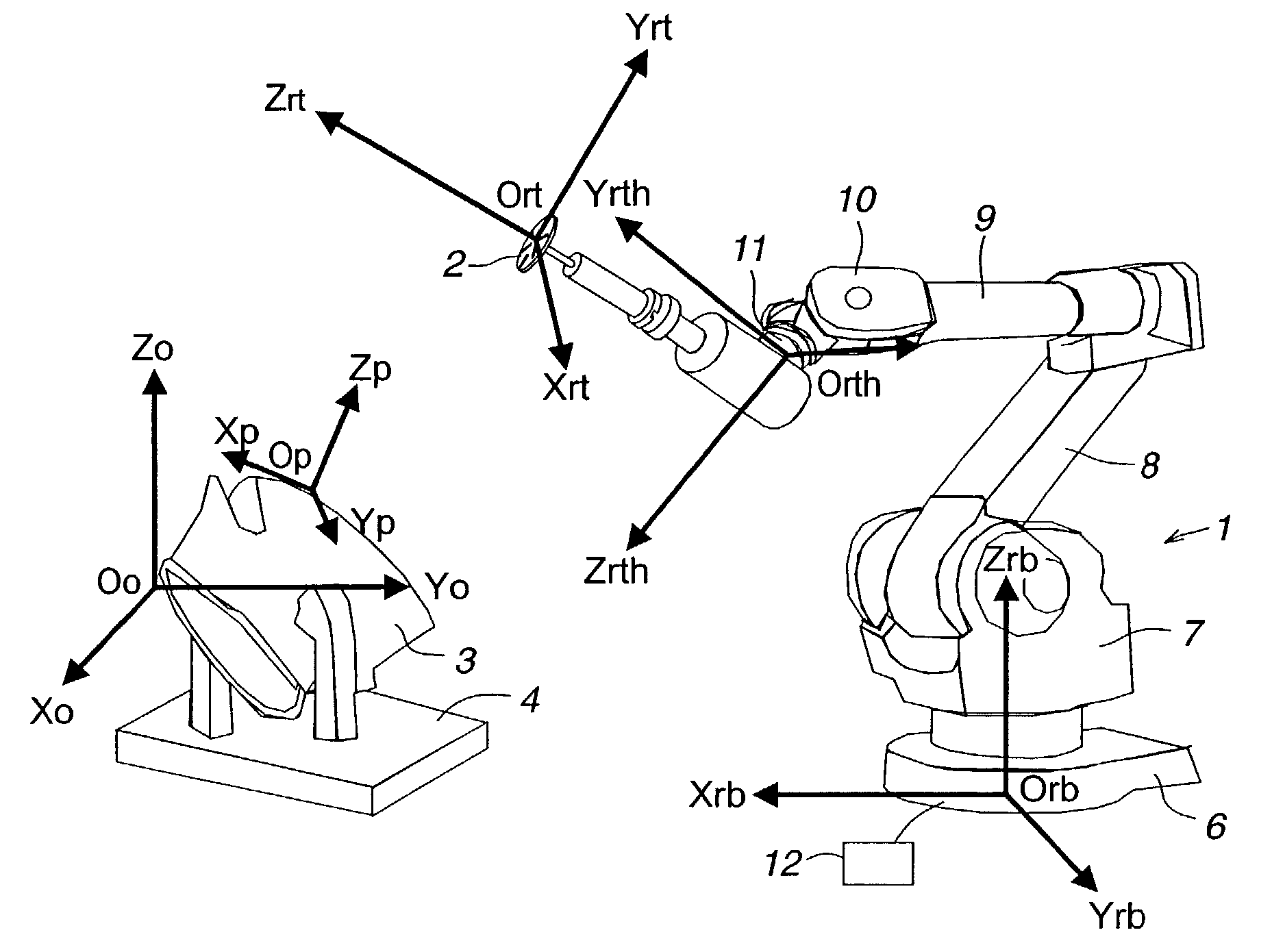
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axis. Typical applications of robots include welding, painting, assembly, disassembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision. They can assist in material handling.
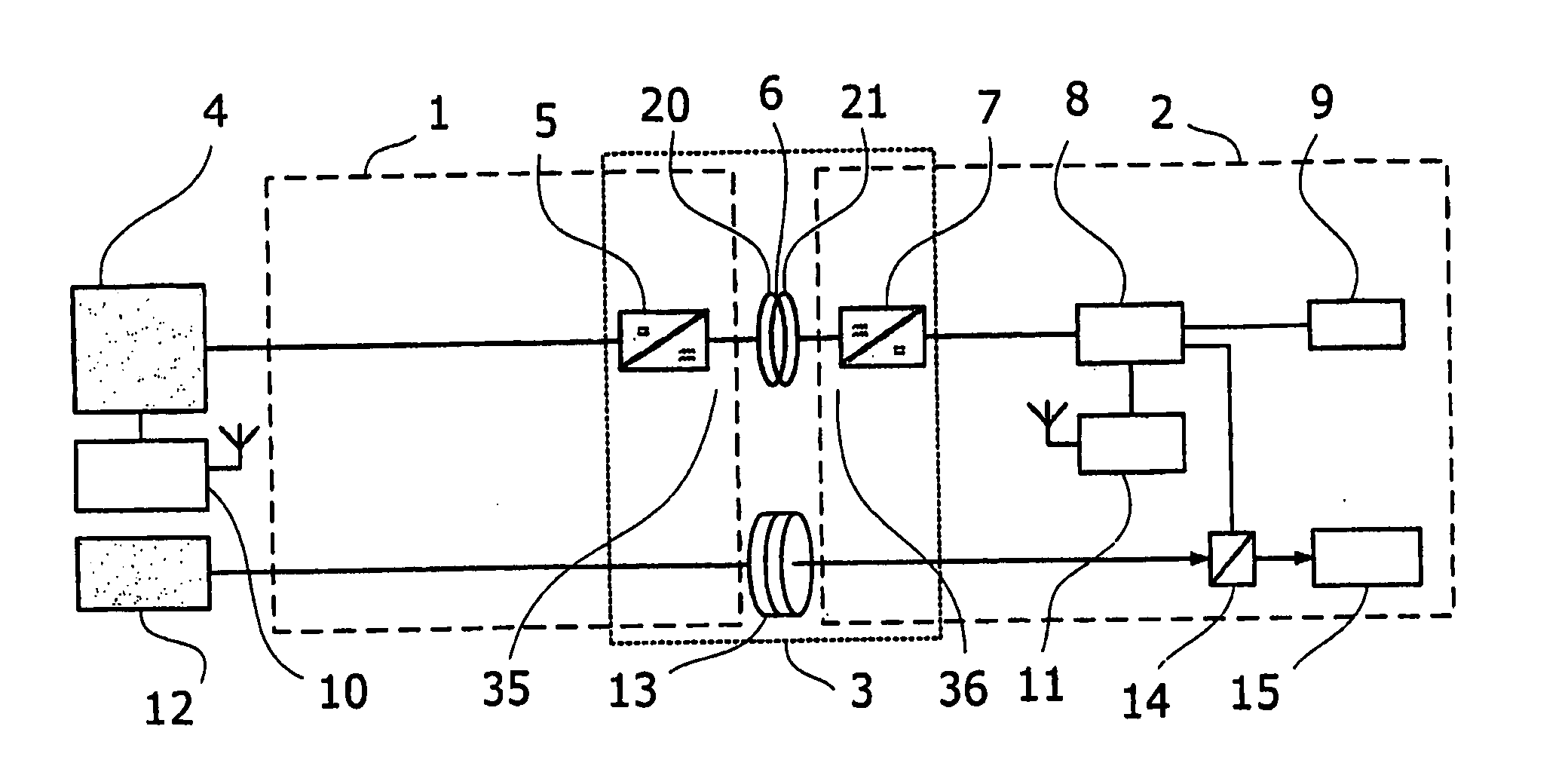
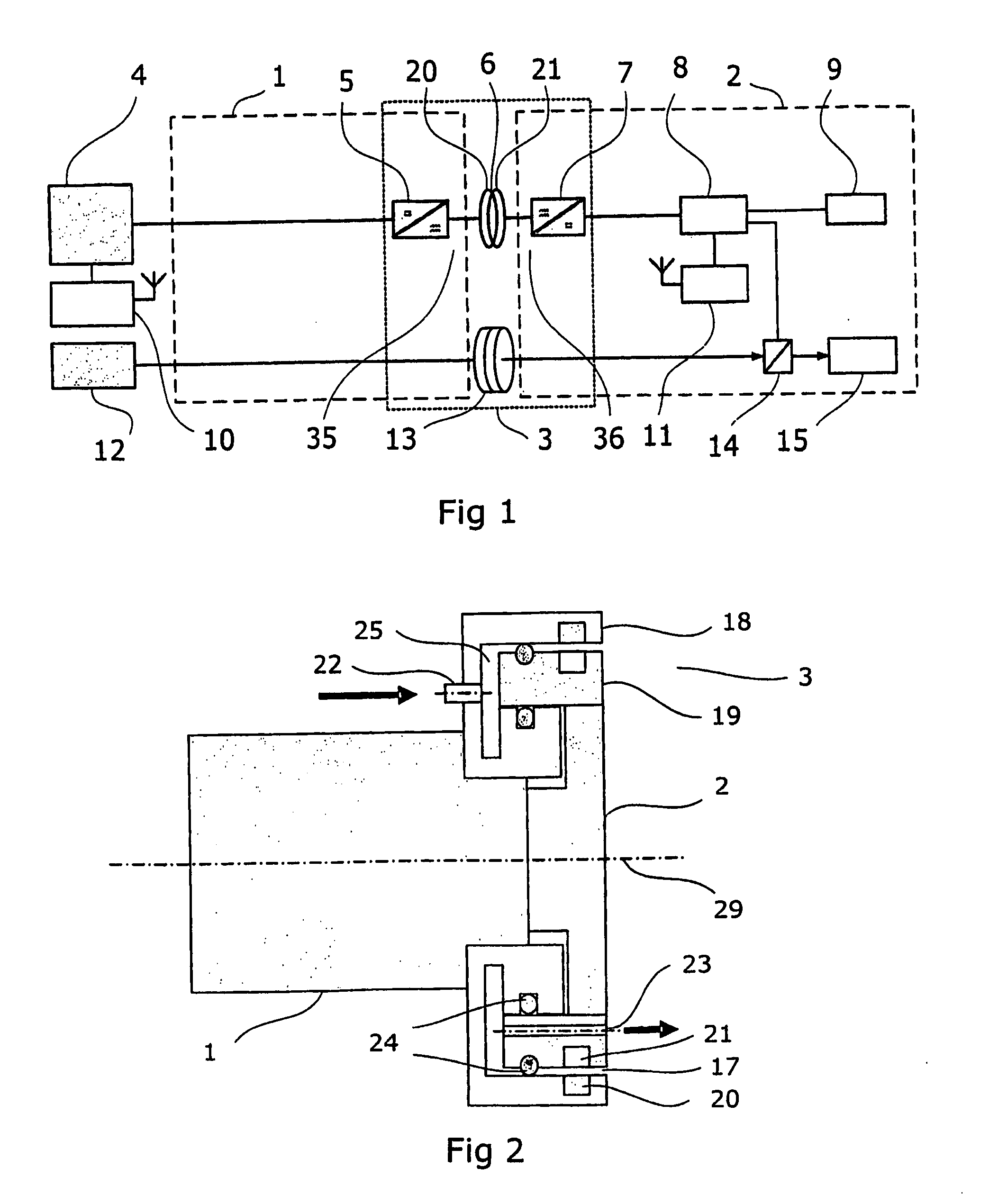
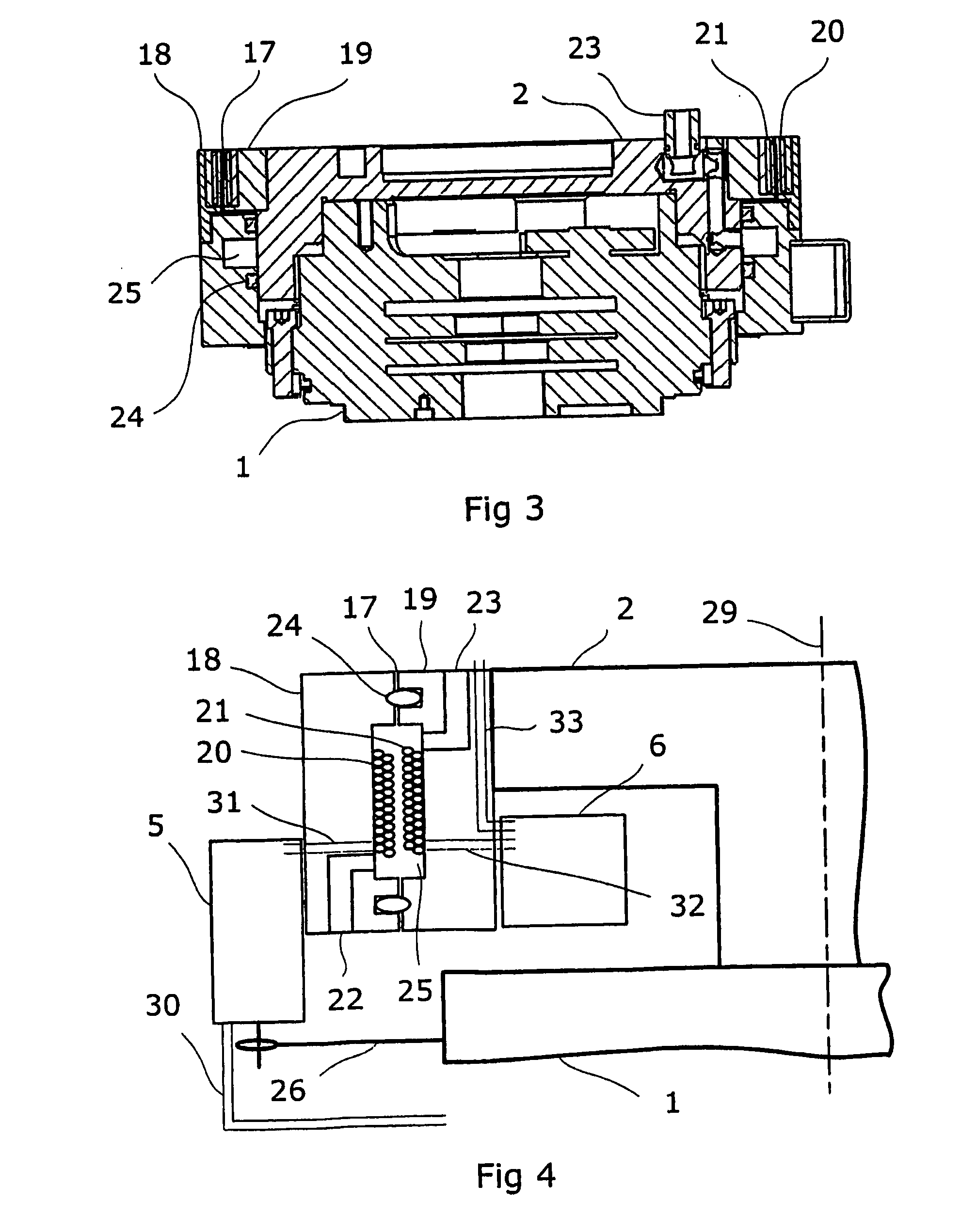
Transmission Of Power Supply For Robot Applications Between A First Member And A Second Member Arranged Rotatable Relative To One Another
InactiveUS20080197710A1Strengthen the magnetic fluxTransformersCircuit arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A process media transfer unit for an industrial robot including a first part for attachment to a first robot part, and a second part for attachment to a second robot part. The first and second parts being coaxially arranged about a common axis and separated by an airgap to provide an endless rotation relative to each other.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
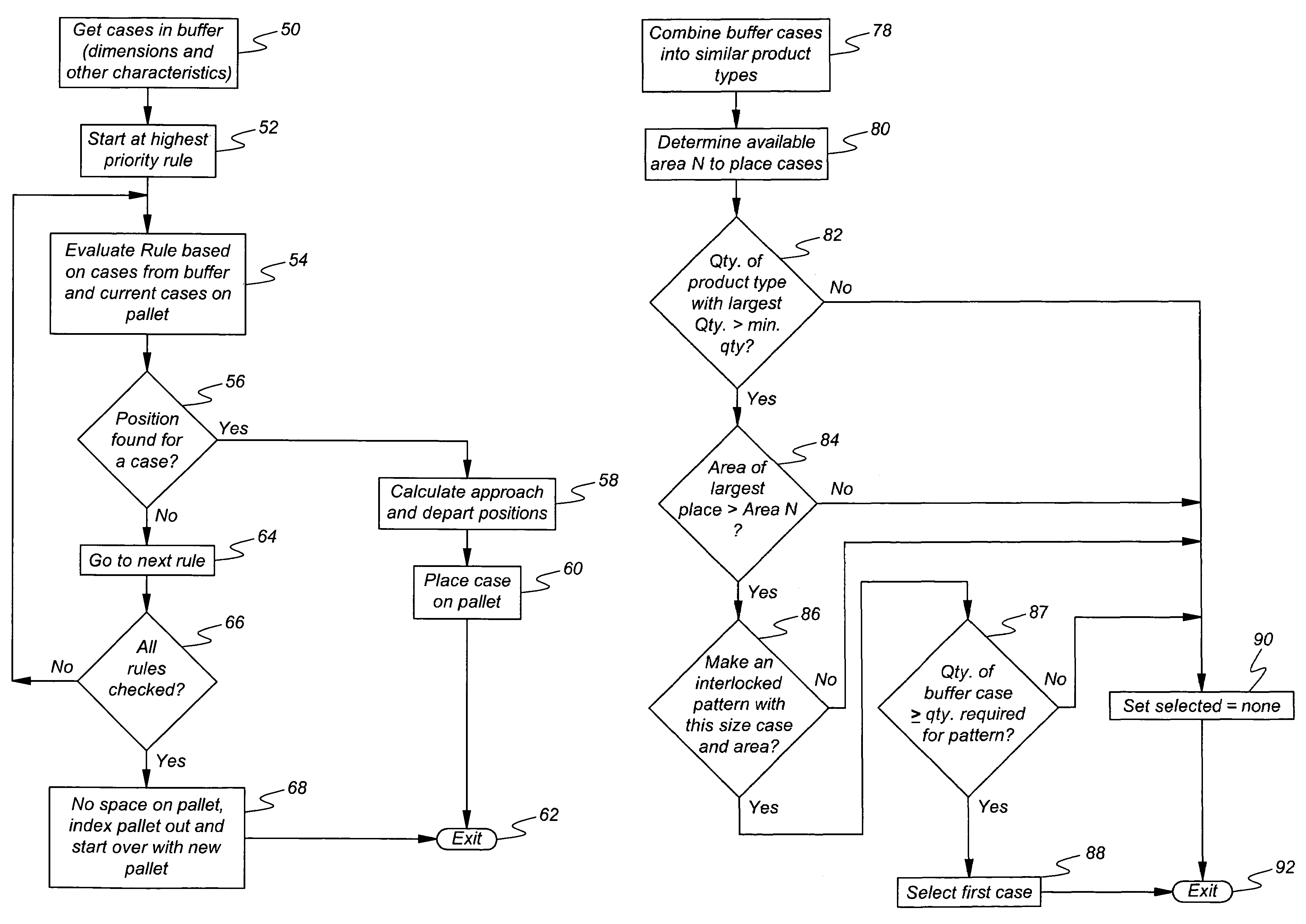
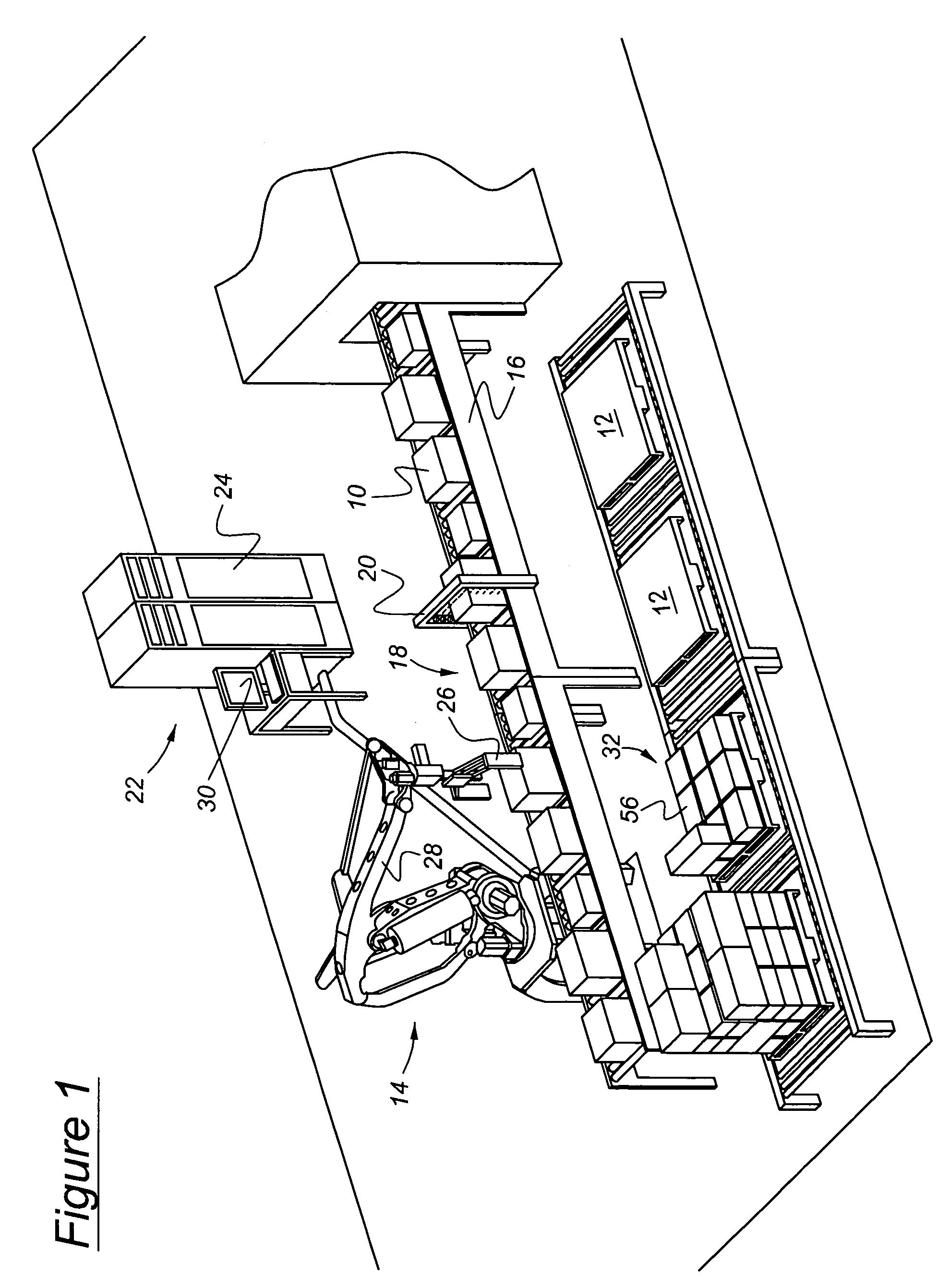
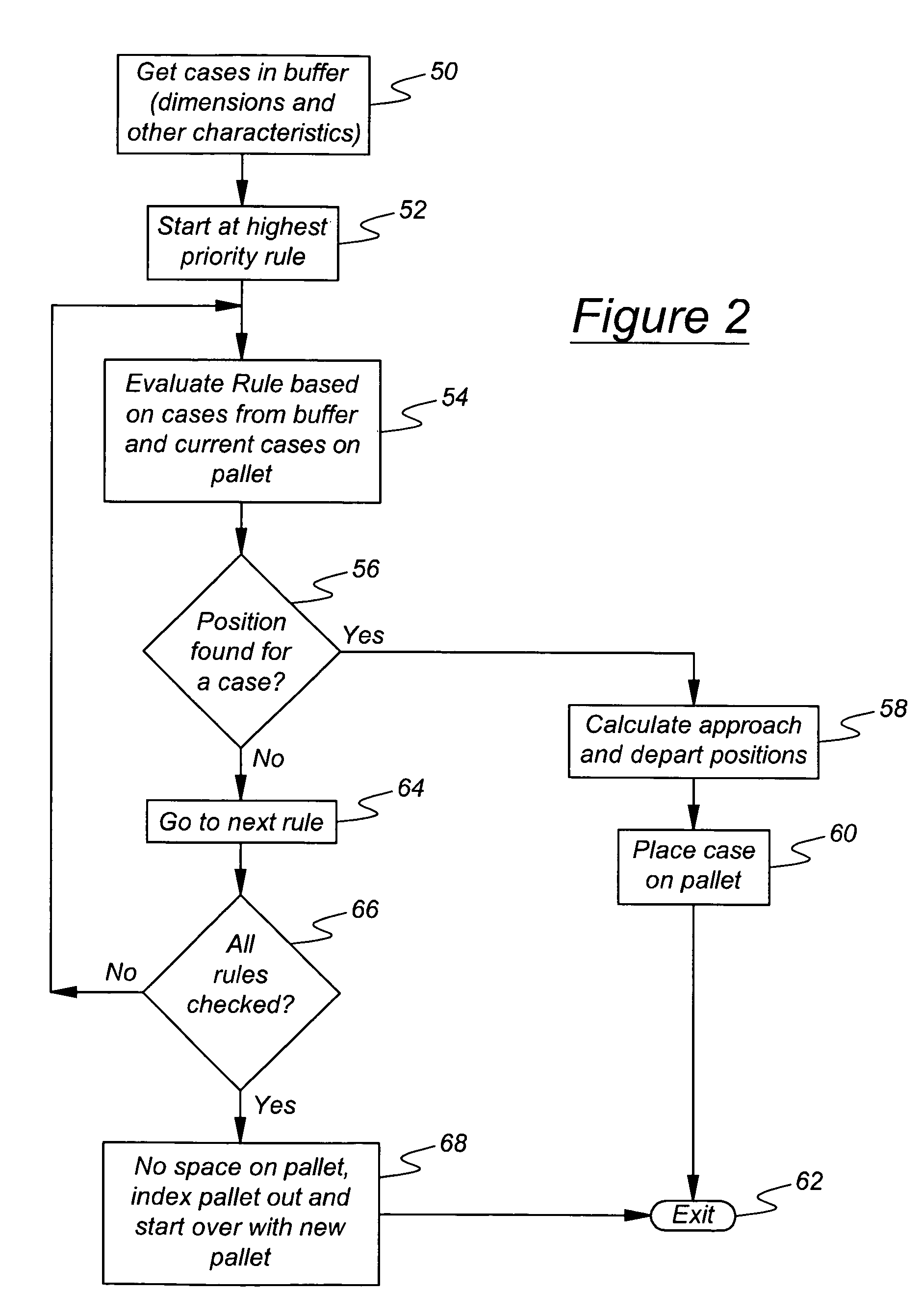
Automated palletizing cases having mixed sizes and shapes
InactiveUS7266422B1Increase the use of spaceGuaranteed smooth progressProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringPallet
A method for stacking cases on a pallet includes supplying cases to a buffer, determining physical characteristics of buffer cases including dimensions of a case base and case height, and determining available positions on the pallet where a buffer case can be placed. Rules for selecting a case from the buffer for placement on the pallet are applied to at least a portion of the buffer cases to identify a selected buffer case that satisfies at least one of the rules and a corresponding place on the pallet for the selected case. Then the selected case is removed from the buffer and placed on the pallet in the corresponding place by an industrial robot.
Owner:FANUC ROBOTICS AMERCA
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS20050256611A1Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlBody areaVisual perception
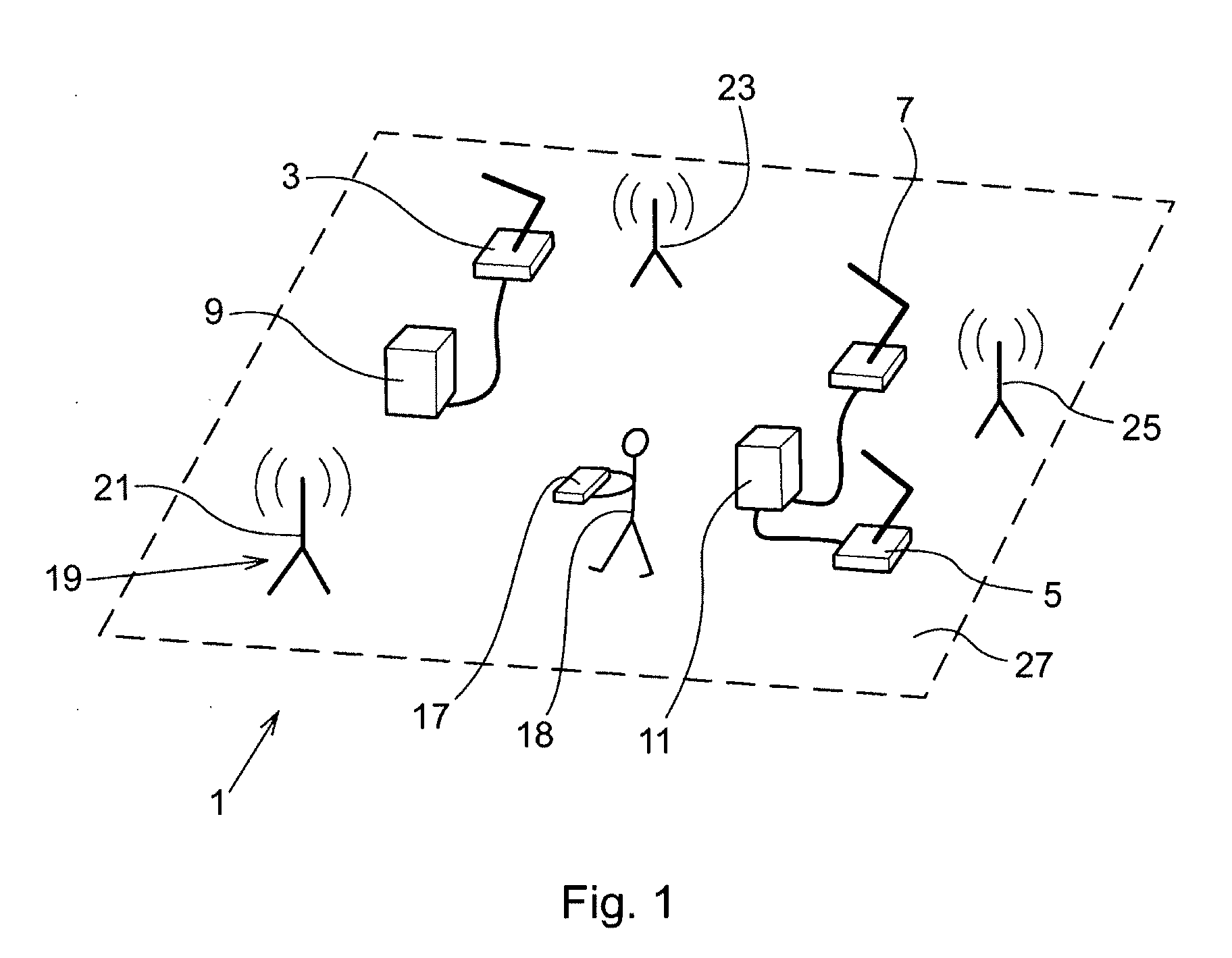
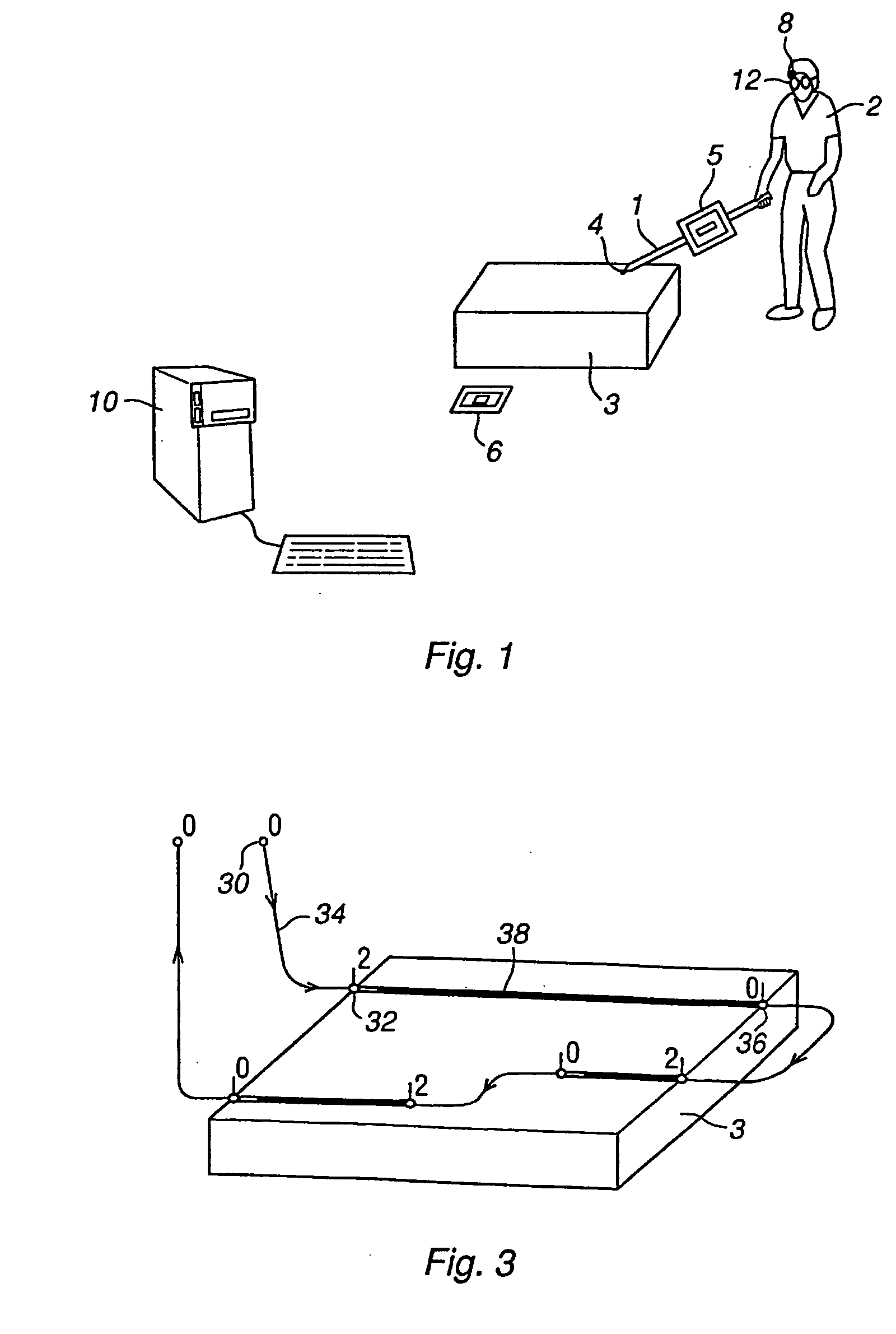
A method and a system for use in connection with off-line programming of an industrial robot. The robot is taught a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of at least one object to be processed by the robot. The system includes a tracking system unit adapted to provide information about the position of a part of the body of an operator pointing by the part at points on or in the vicinity of the object, a visual feed-back unit generating a visual feed-back to the operator of the position of the point being presently pointed at by the part of the body, in relation to the object, and a storage unit adapted for storing the position of the part of the body as a waypoint upon receiving a recording command.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot to move relative to defined positions on an object, including generation of a surface scanning program
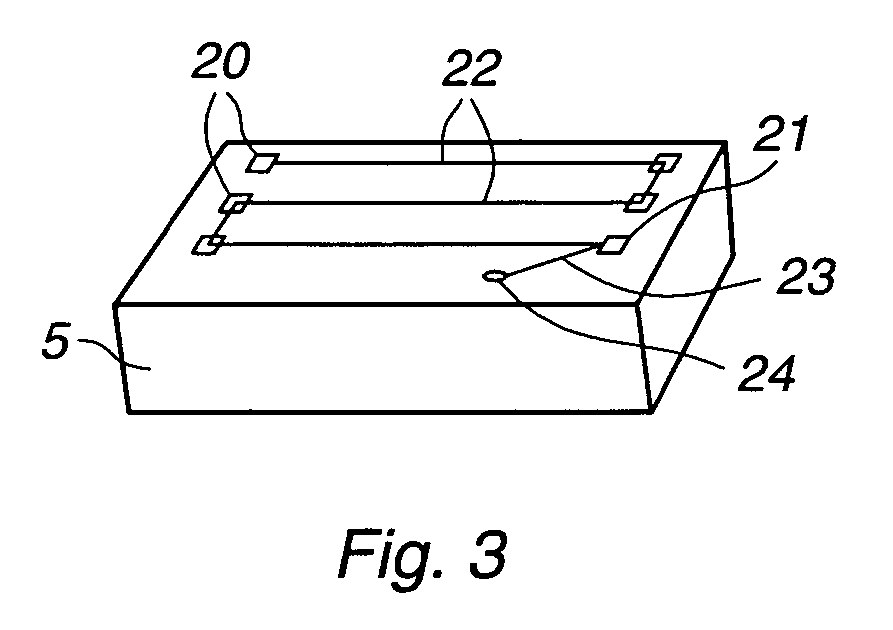
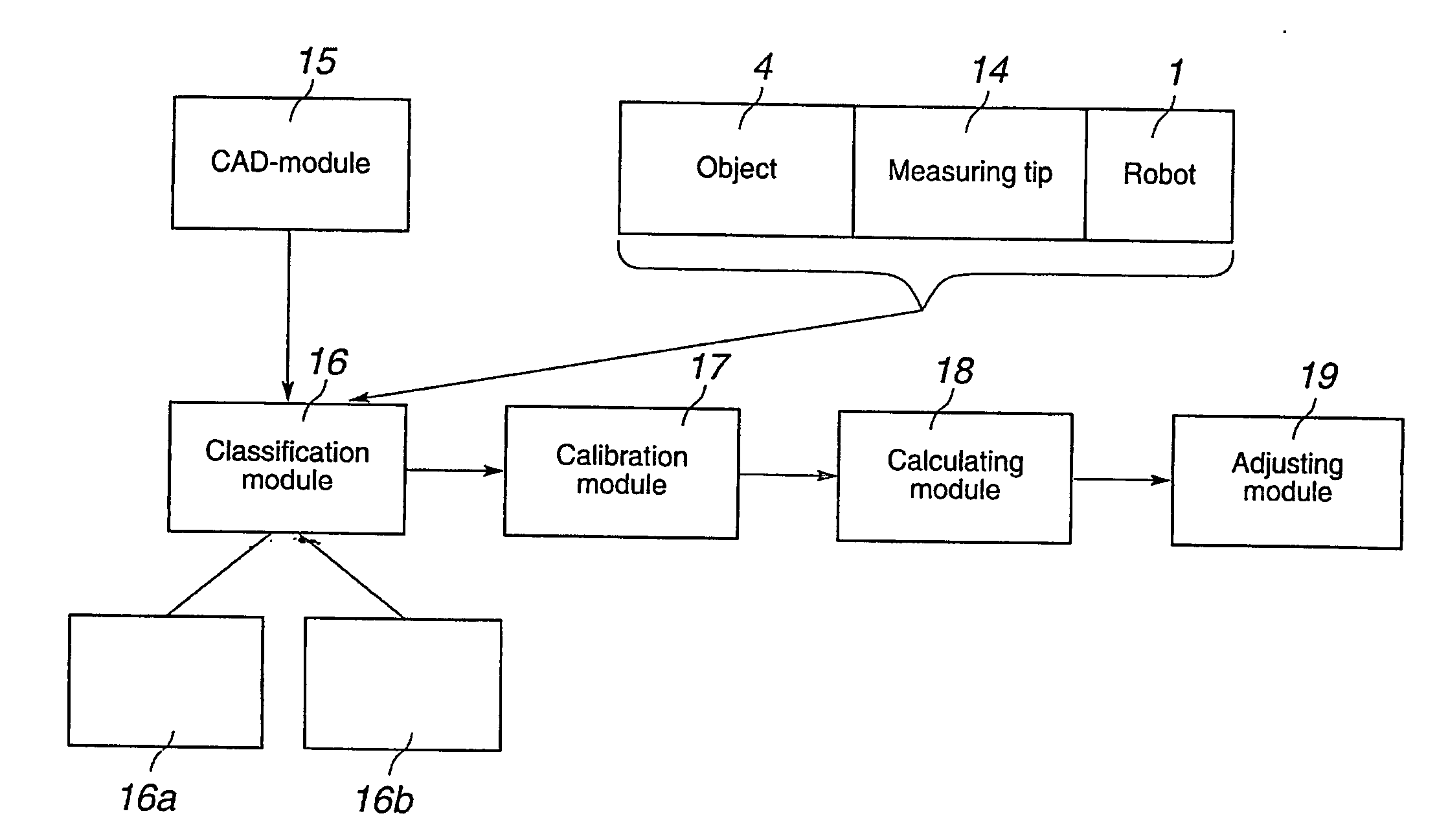
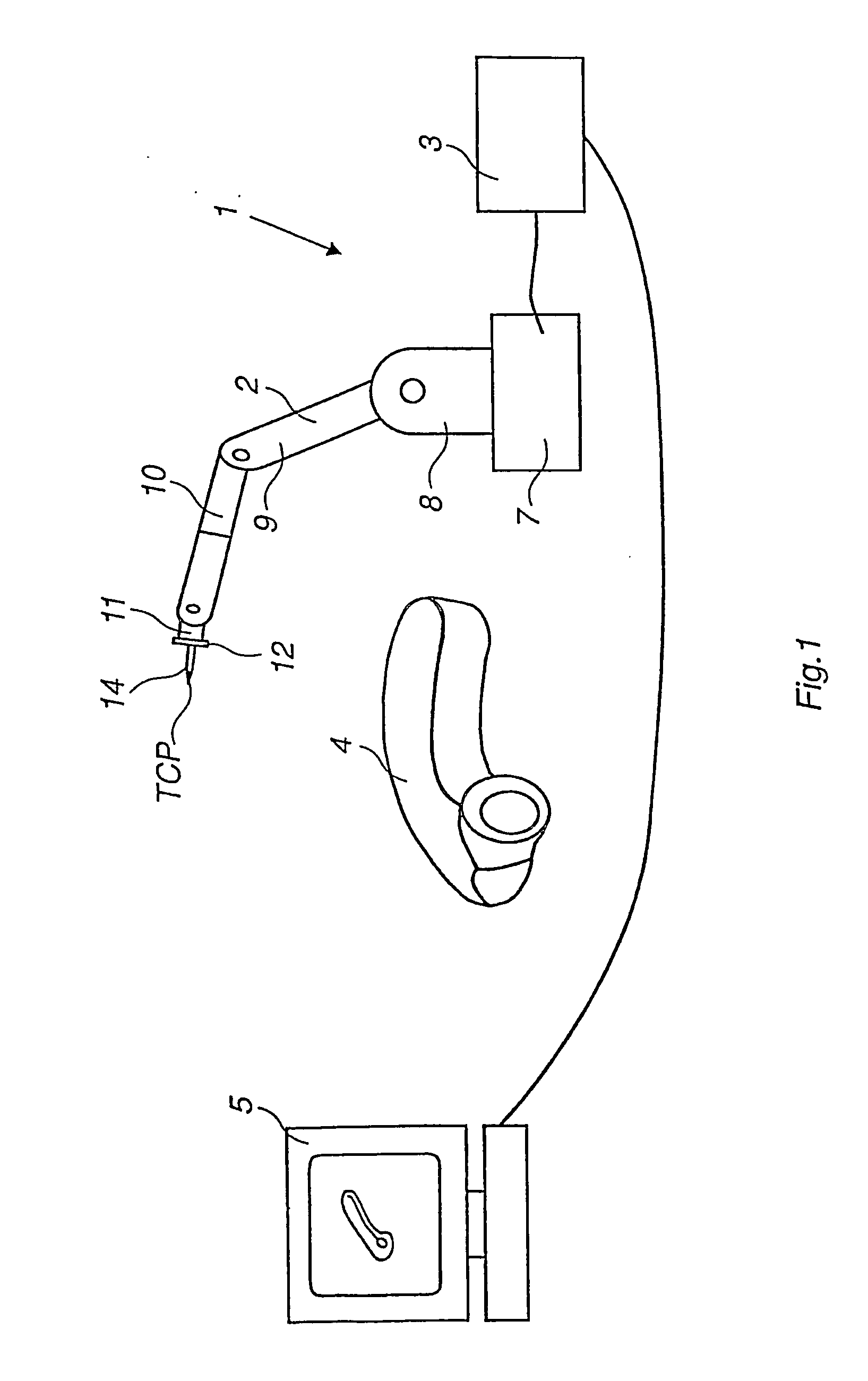
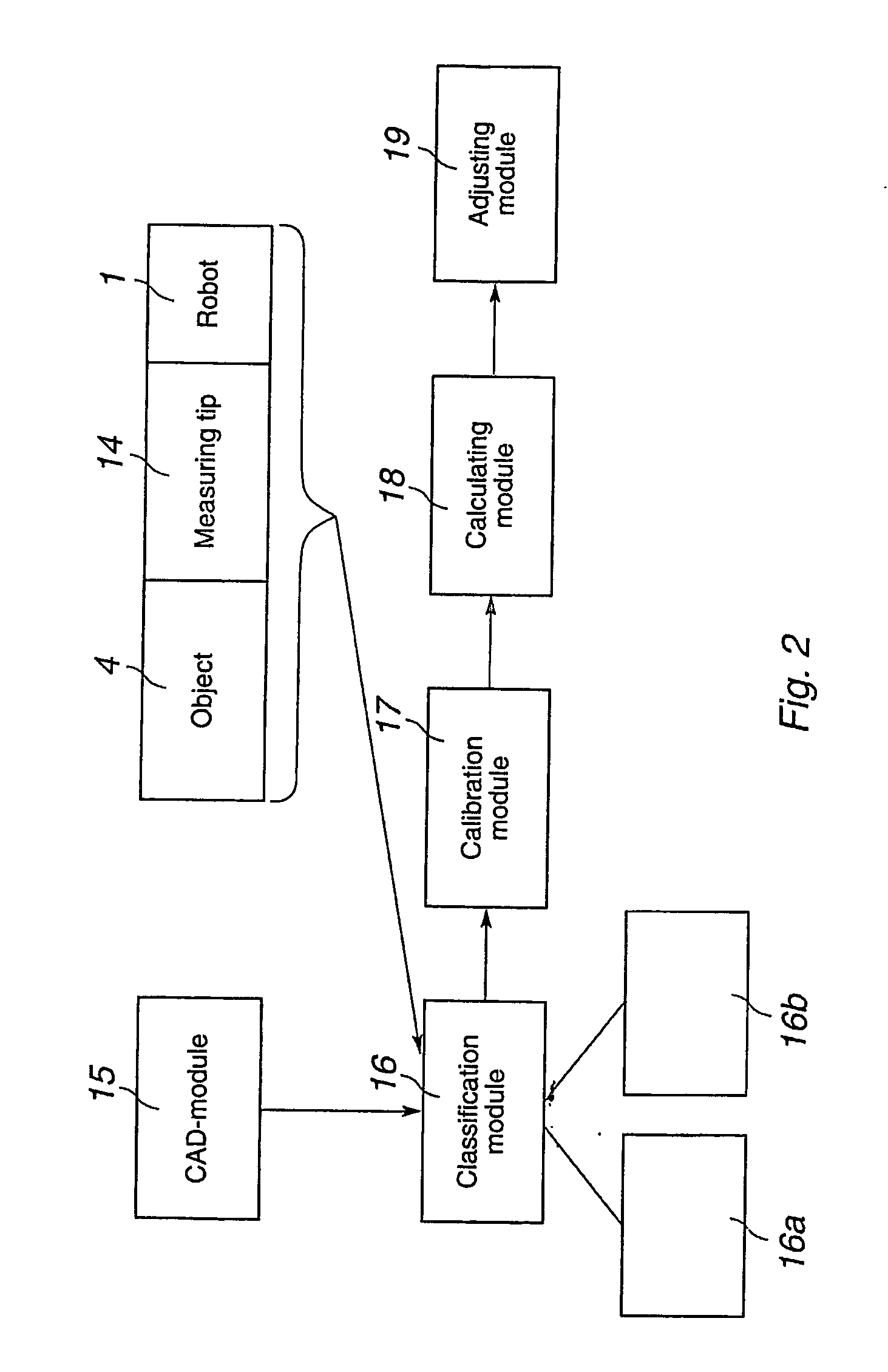
ActiveUS20060181236A1Easy CalibrationSimple programmingProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMeasurement pointSimulation
A method and a system for programming an industrial robot to move relative to defined positions on an object. The system includes a geometrical model of the object, the real object, and an industrial robot. A plurality of measuring points are generated corresponding to different points on the surface of the real object expressed in a coordinate system associated with the robot. The system further includes a calibration module arranged to determine orientation and position of the geometrical model of the object relative to the coordinate system associated with the robot, a calculating module arranged to calculate the deviation between the measuring points and corresponding points on the geometrical model, and an adjusting module arranged to adjust the defined positions based on the calculated deviations.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Industrial robot system
InactiveUS20090204261A1Simple processReduce movement speedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorManipulatorEmbedded system
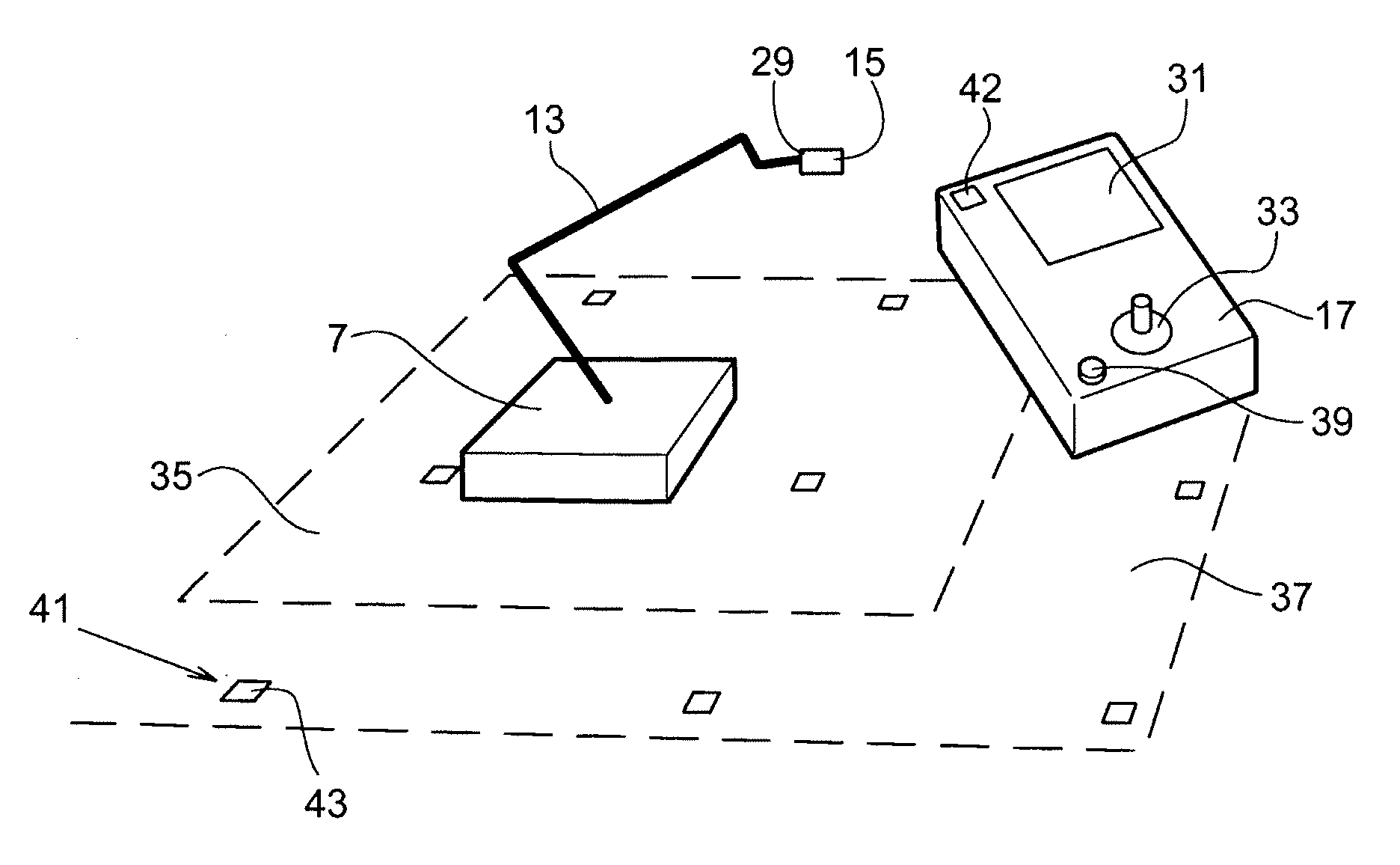
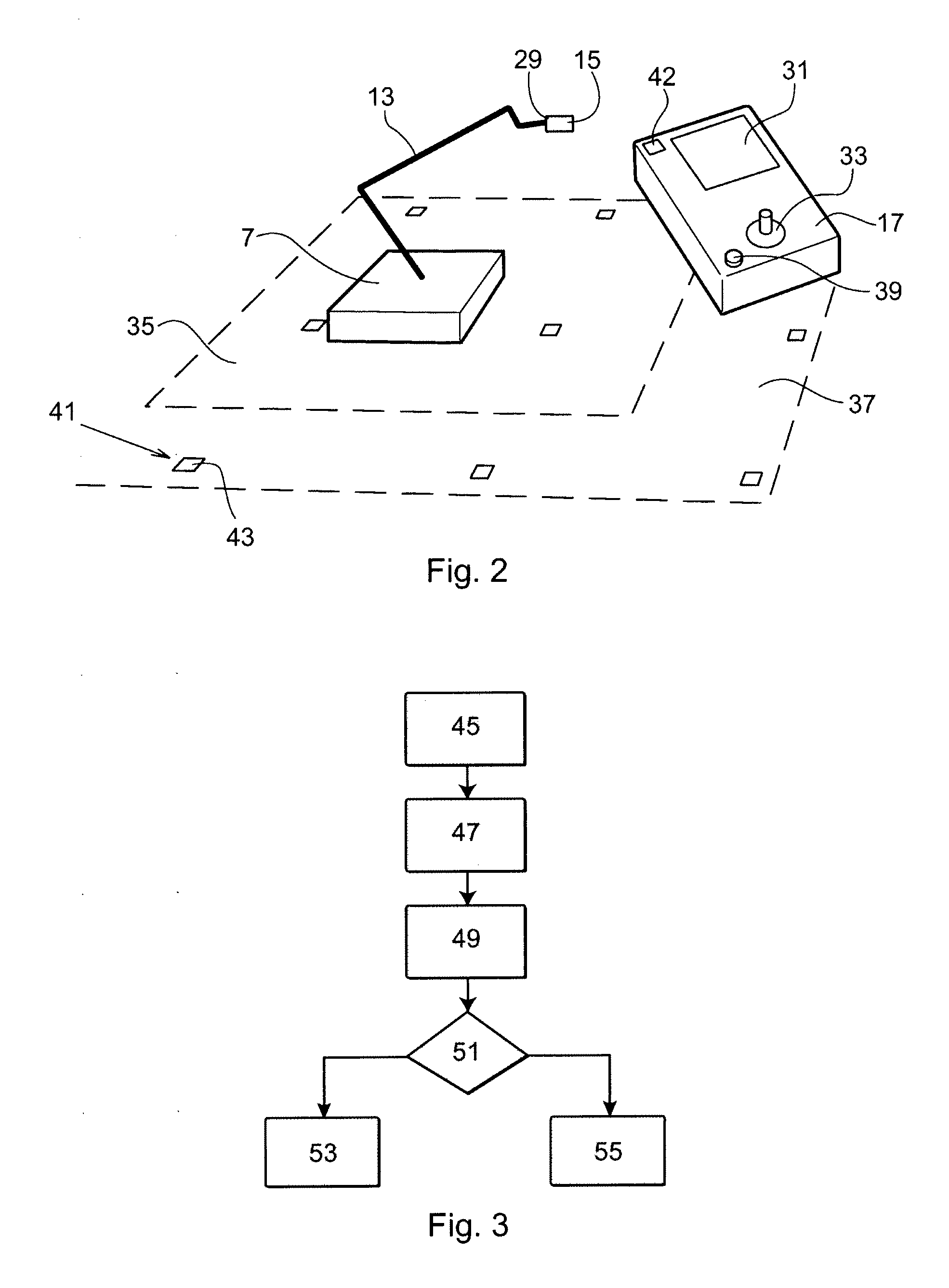
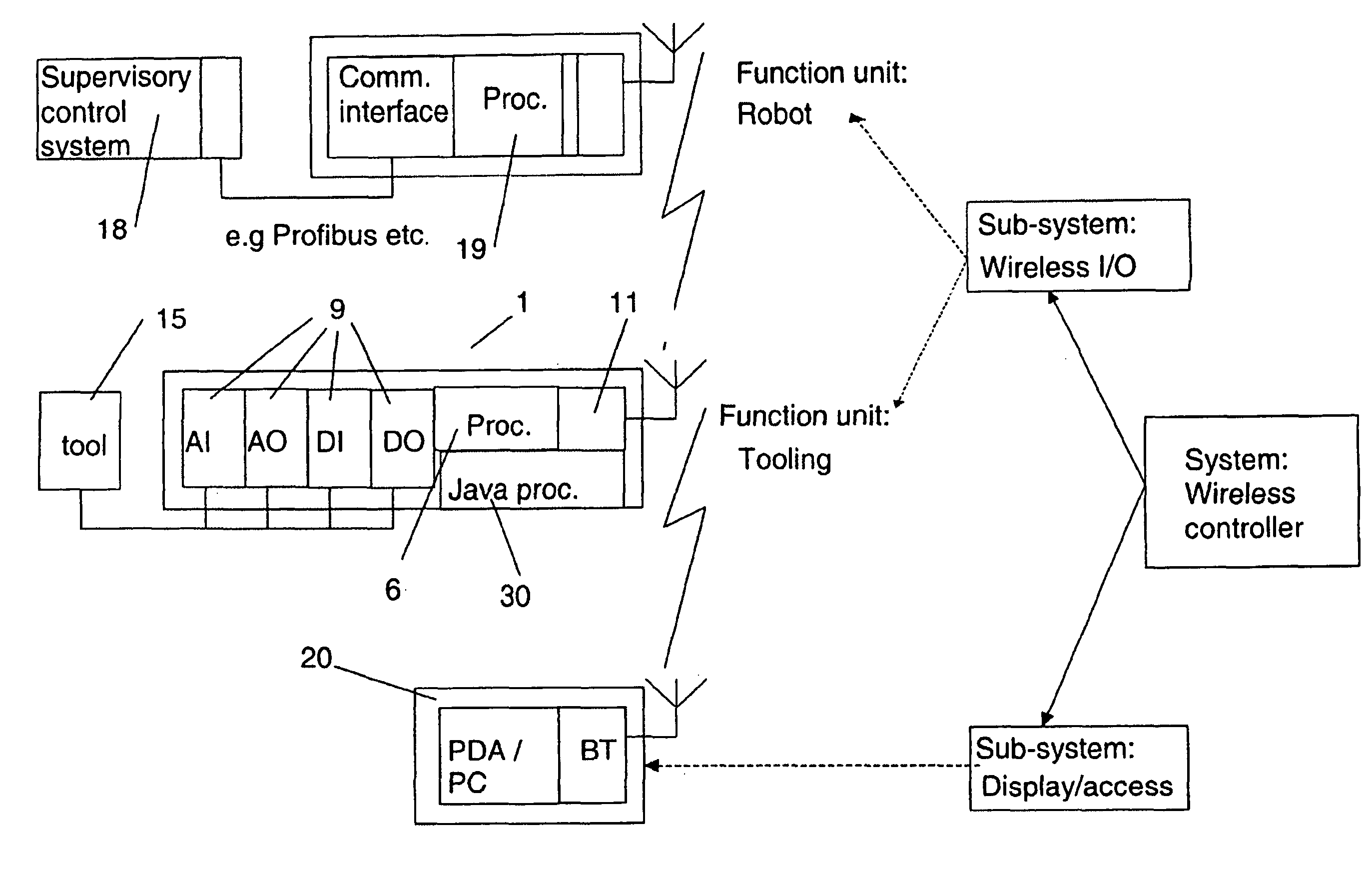
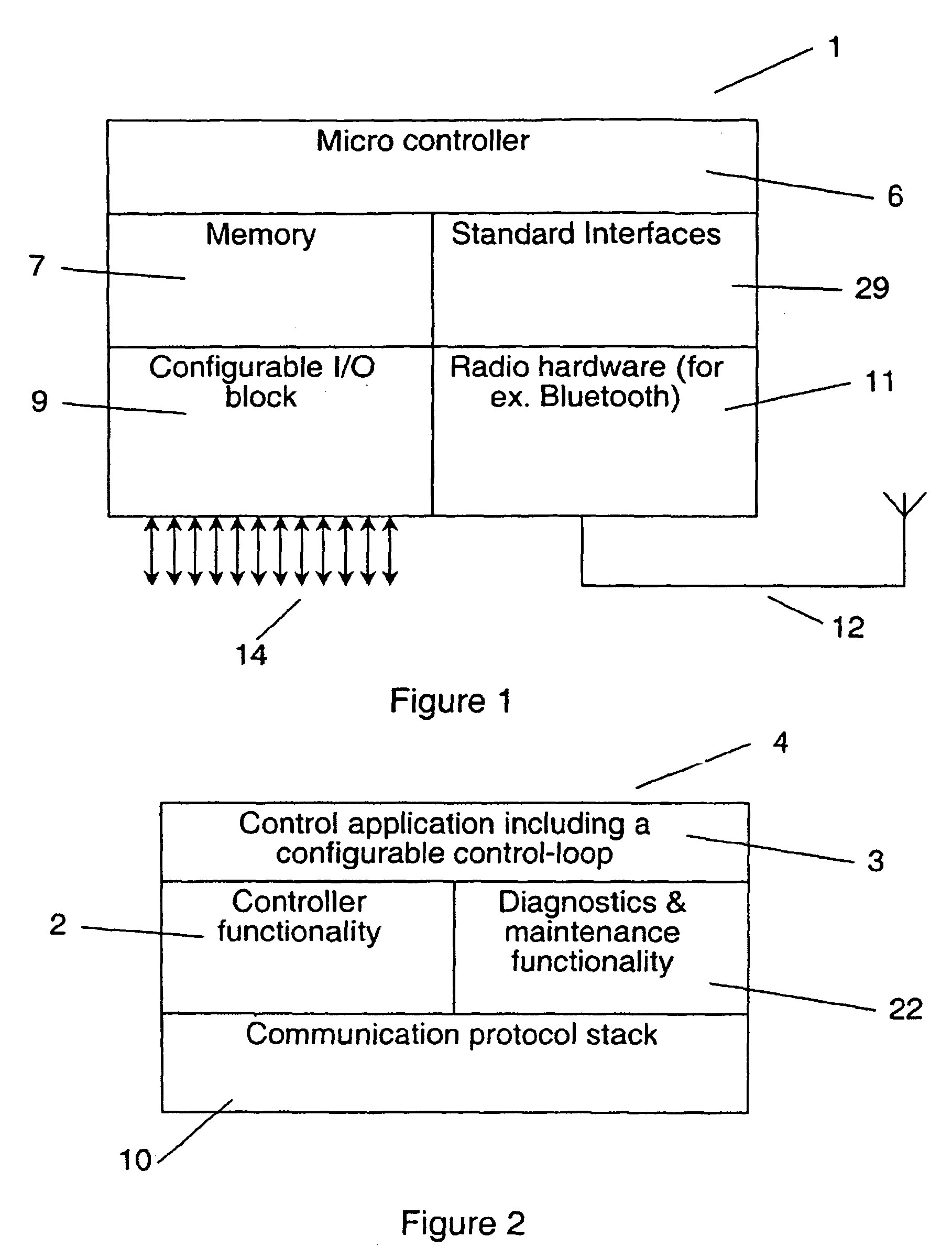
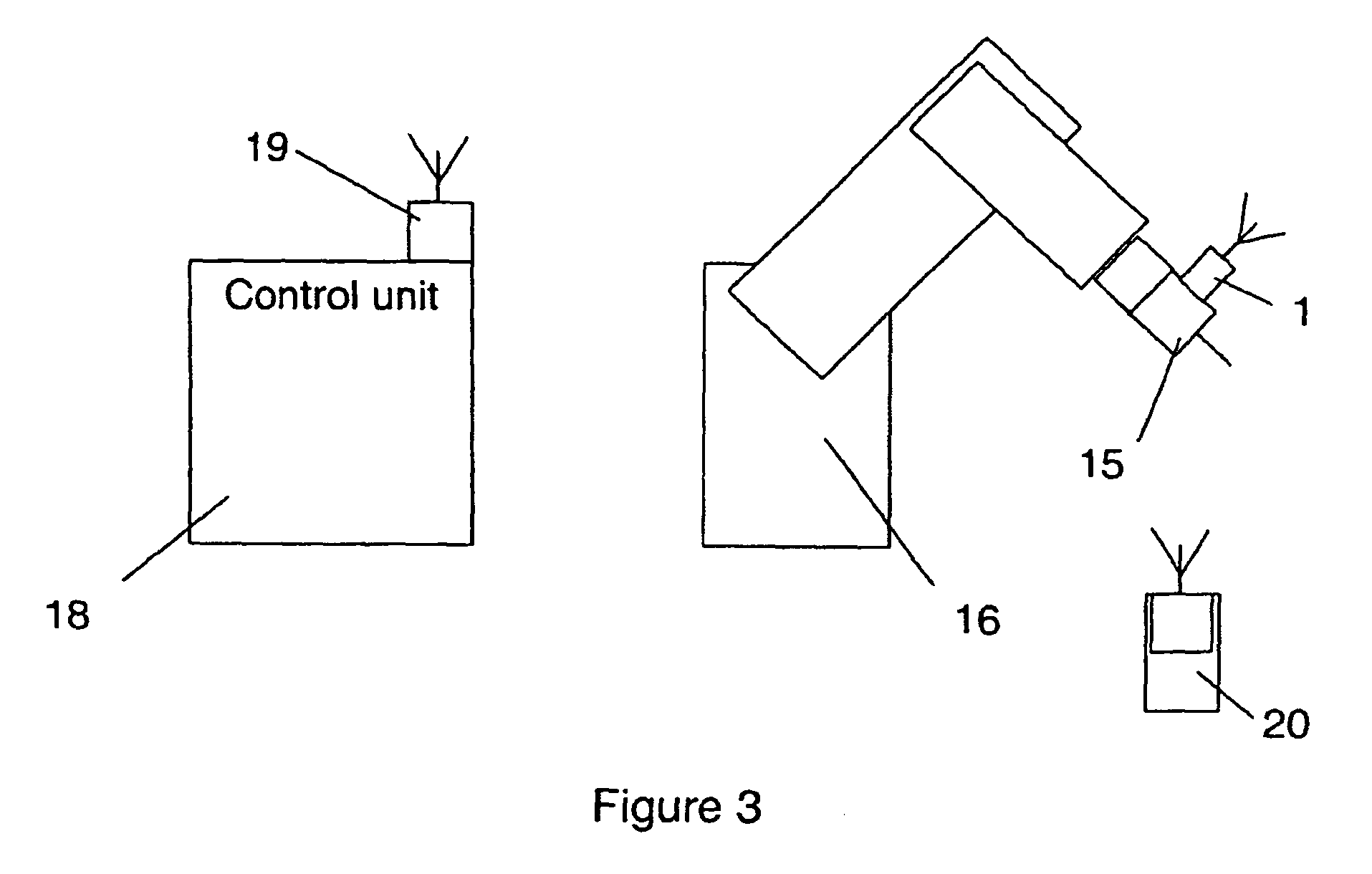
An industrial robot system including at least one manipulator, at least one control device adapted to control the operation of the at least one manipulator and at least one wireless, portable interface device adapted for communication with a user and for communication with at least one control device. The industrial robot system is adapted to sense the position of the portable interface device. Also a wireless, portable, interface device and to a control device.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Industrial robot base coordinate system calibration method based on laser tracker
InactiveCN105058387AReduce calibration timeHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer visionLaser tracker
The invention discloses an industrial robot base coordinate system calibration method based on a laser tracker. The method includes the steps that target bases needed for measurement are installed, a calibration system is preprocessed, coordinate systems needed for calibration are established, the relational expression of posture relation matrixes of the coordinate systems is acquired, data are collected through a control robot and the laser tracker, the corresponding posture matrixes are acquired, and finally the posture relation between a robot base coordinate system and a measurable coordinate system is acquired so as to determine the specific posture of the robot base coordinate system. The robot base coordinate system can be calibrated only through the laser tracker, no repetition is needed after calibration, repeated calibration time is shortened, meanwhile, the accuracy of the laser tracker is high, and the accuracy of acquired data of the base coordinate system is high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
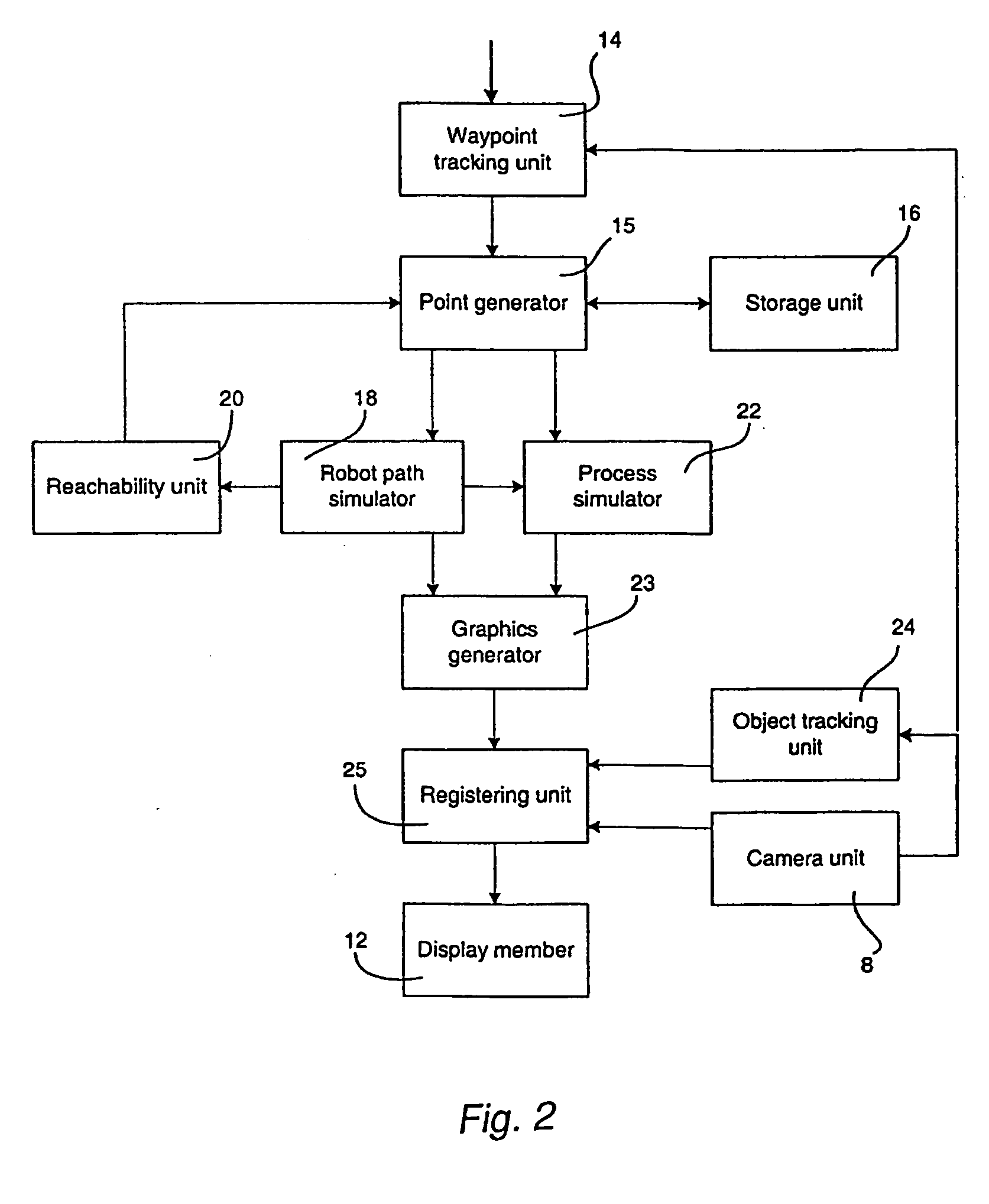
Method and a system for programming an industrial robot
ActiveUS20050149231A1Shorten teaching timeQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsAnalog robot
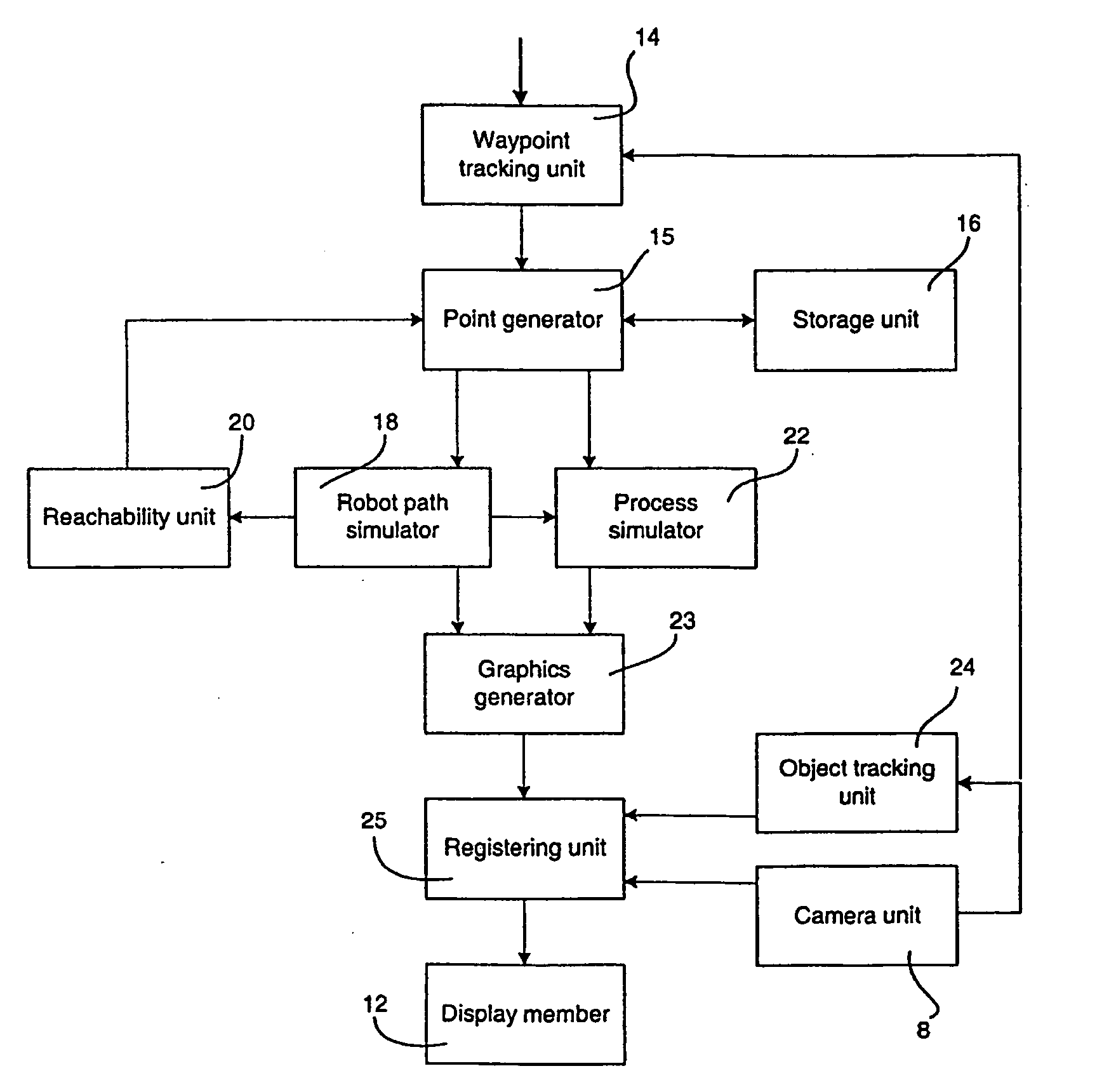
A method and a system for use in connection with programming of an industrial robot, the programming comprises teaching the robot a path having a number of waypoints located on or in the vicinity of an object to be processed by the robot. The system comprises: means for obtaining information about the waypoints of the path in relation to the object, a storage unit (16), for storing the obtained information, a simulation unit (18), simulating the robot path based on the obtained information about the waypoints and a model of the robot, a graphics generator (23), generating a graphical representation of the simulated robot path, and a display member (12) displaying a view comprising the object and said graphical representation of the robot path projected on the object.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
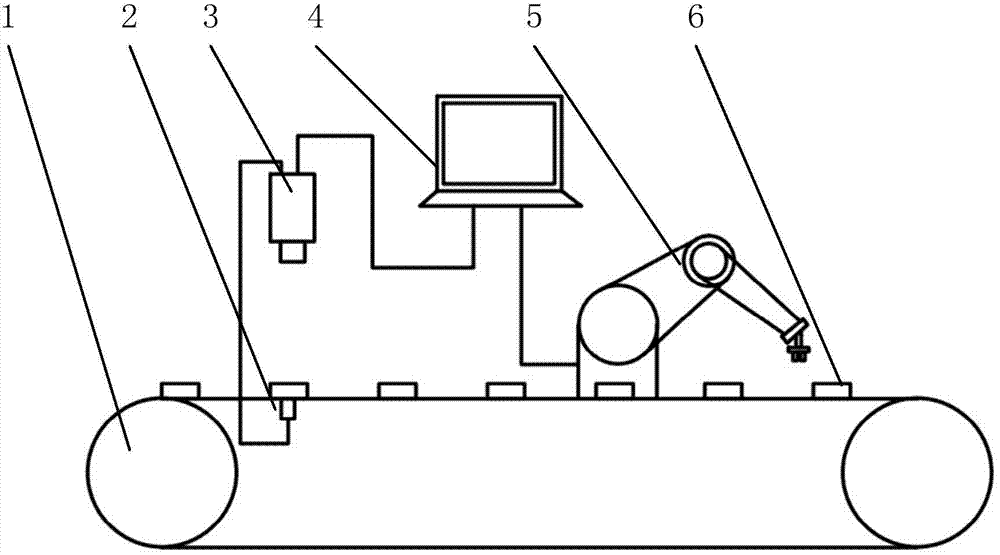
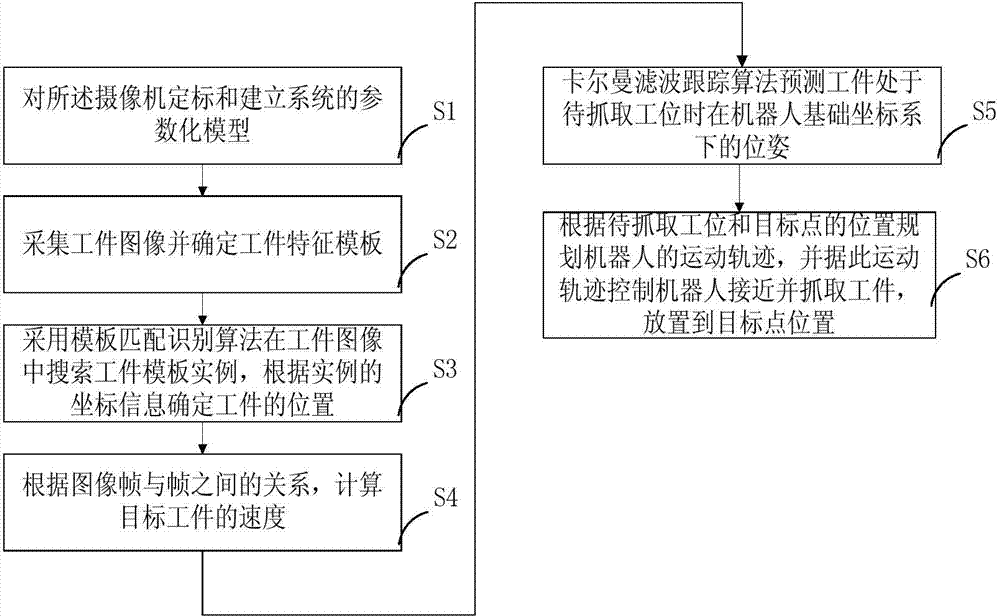
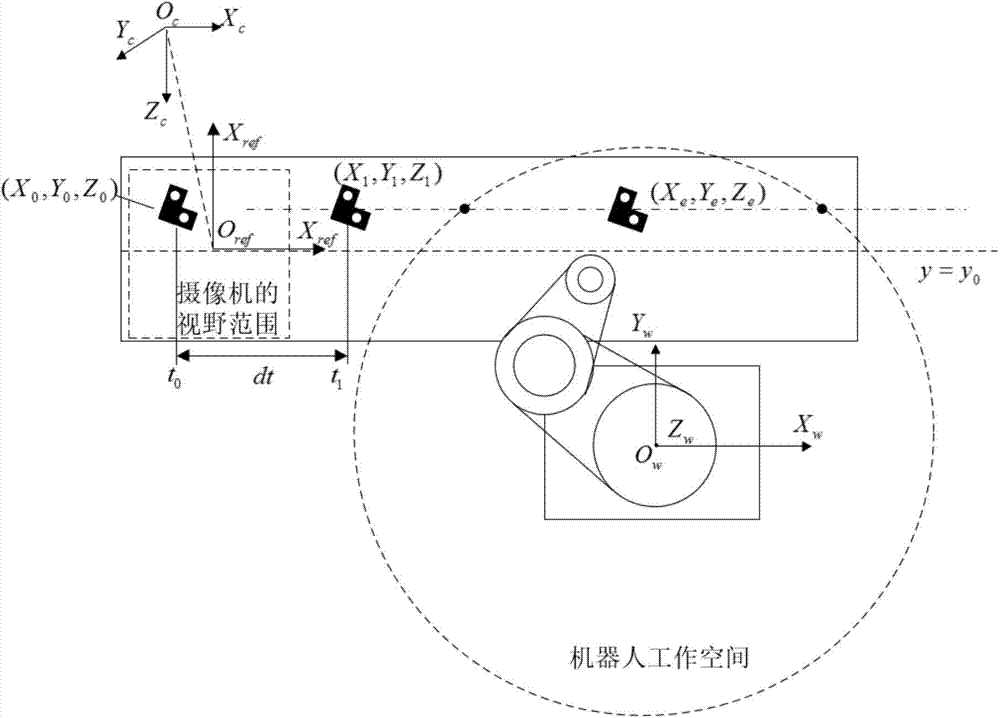
Industrial robot workpiece positioning grabbing method and system based on visual guidance
InactiveCN103895042AAccurate calculationHigh positioning accuracyManipulatorVisual perceptionComputer science
The invention discloses an industrial robot workpiece positioning grabbing method based on visual guidance. The method includes the following steps that 1, a system parametric model is established, and calibration of a camera is conducted; 2, a workpiece feature template is determined; 3, workpiece template living examples are sought for, and the positions of workpieces are determined according to coordinate information of the living examples; 4, the speed of a target workpiece is calculated; 5, the pose, in a robot basic coordinate system, of the workpiece is predicted when the workpiece is located at a station to be grabbed; 6, a robot moves according to a planned path to approach and grab the workpiece and place the workpiece at the position of a target point. The invention further discloses a system for implementing the industrial robot workpiece positioning grabbing method based on visual guidance in the patent claim 1. The system comprises a conveying belt, an optoelectronic switch, a camera, an industrial control computer, the robot and the target workpiece. The system has the advantages of being high in positioning accuracy, high in working efficiency, high in automation degree and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Wireless controller and a method for wireless control of a device mounted on a robot
InactiveUS7979162B2Reduce weightLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlWireless controlGraphical user interface
A wireless controller for controlling and / or monitoring a device arranged mounted on or relative to an industrial robot. A wireless communicator including a processor arranged with software means handles wireless communication to and from the device. A control carries out at least one control function for one or more actuators of the device. Also, a method, a computer program and a graphic user interface.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
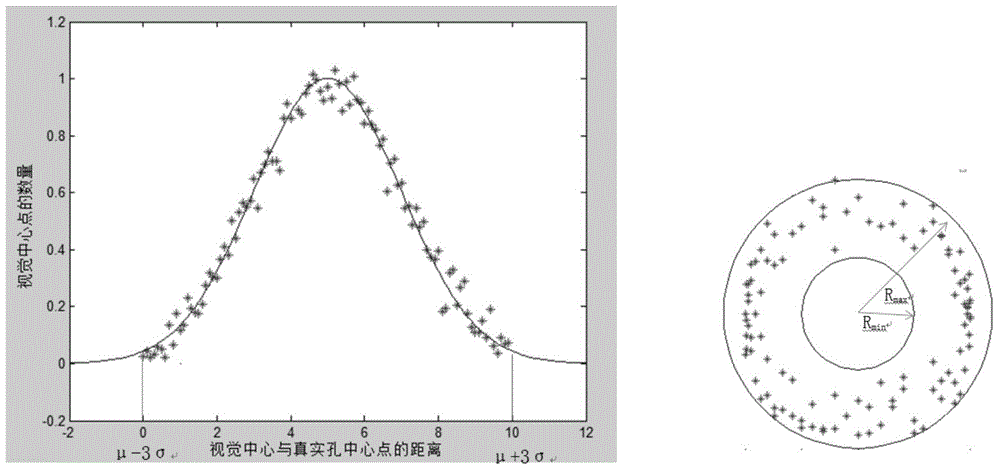
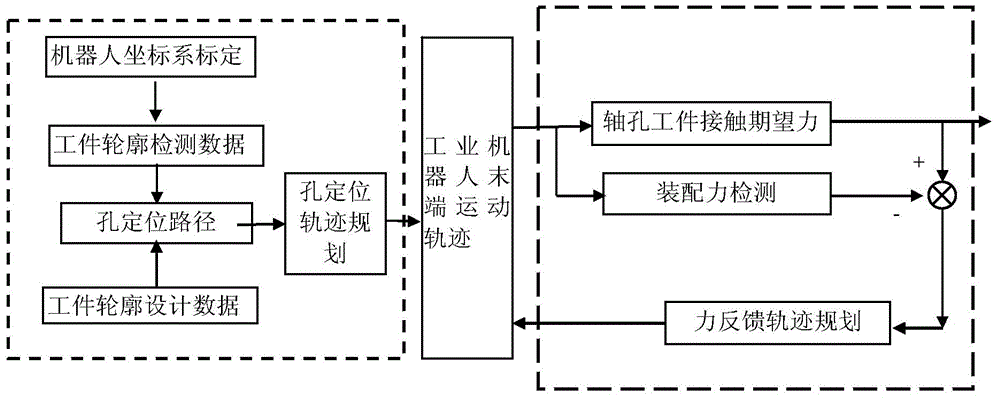
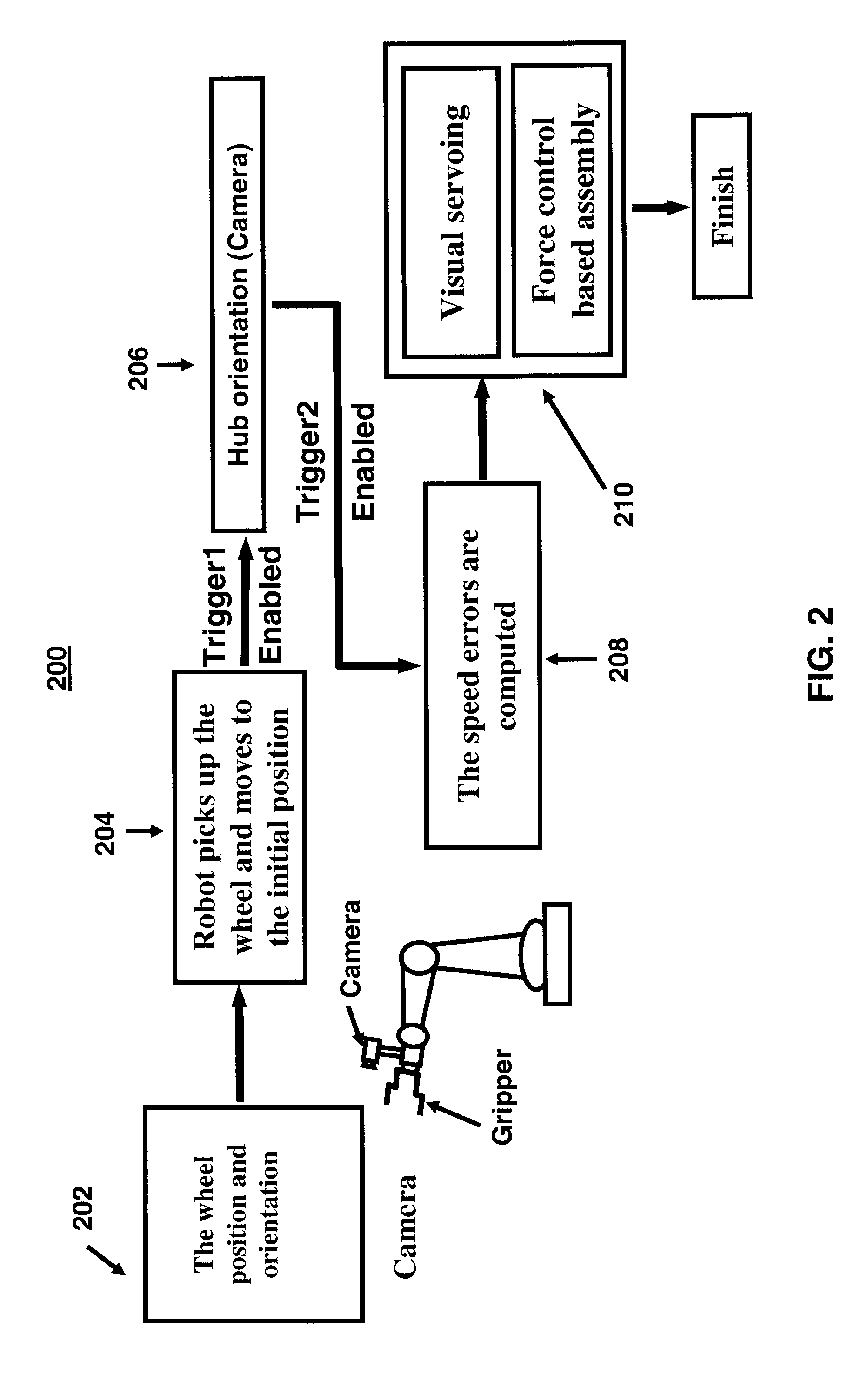
Method and system for assembling robot based on visual sense and force feedback control
ActiveCN104057290AQuick assemblyEffective positioningProgramme-controlled manipulatorMetal working apparatusSimulationVision based
The invention discloses a system for assembling a robot based on visual sense and force feedback control. The system comprises an industrial robot, a workpiece contour detection unit, an assembling force detection unit, a clamping unit and a system control host machine, wherein the industrial robot is used for driving the tail end to move according to a control command of the system control host machine; the assembling force detection unit is used for acquiring the contact force between a shaft workpiece and a hole during the assembling process; the clamping unit is used for clamping the shaft workpiece; the workpiece contour detection unit is used for acquiring the measured data of workpiece contour; the system control host machine is used for receiving the position and the force data and positioning the assembled workpiece according to received data so as to generate the control command to be sent to the industrial robot. The invention further discloses a method for assembling the robot based on visual sense and force feedback control. Rapid hole positioning is carried out and the optimal path of assembling is planned according to the three-dimensional data of hole contour and the force feedback data when the axle hole is assembled, and thus high-precision self-assembling of the axle hole is realized.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
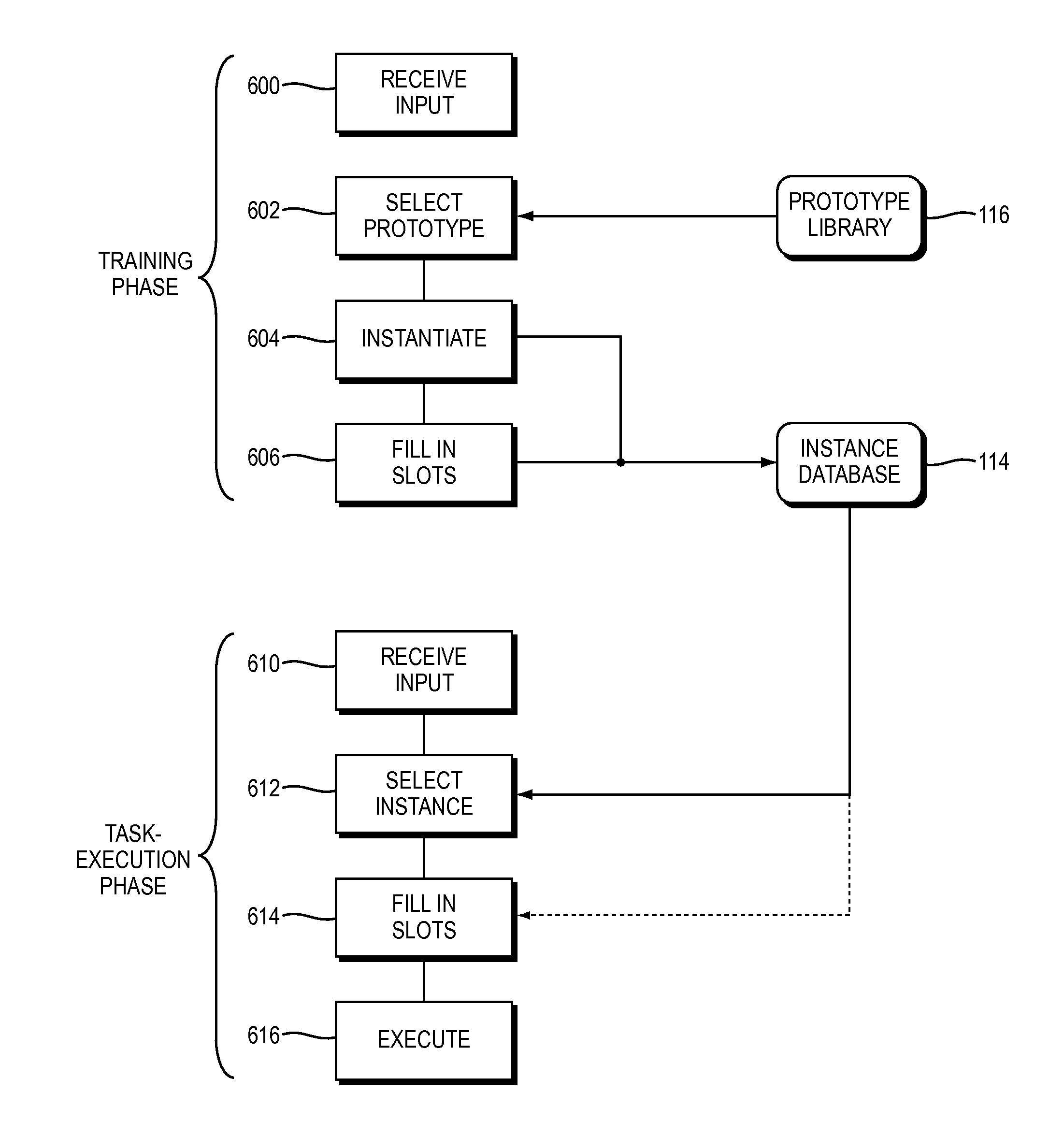
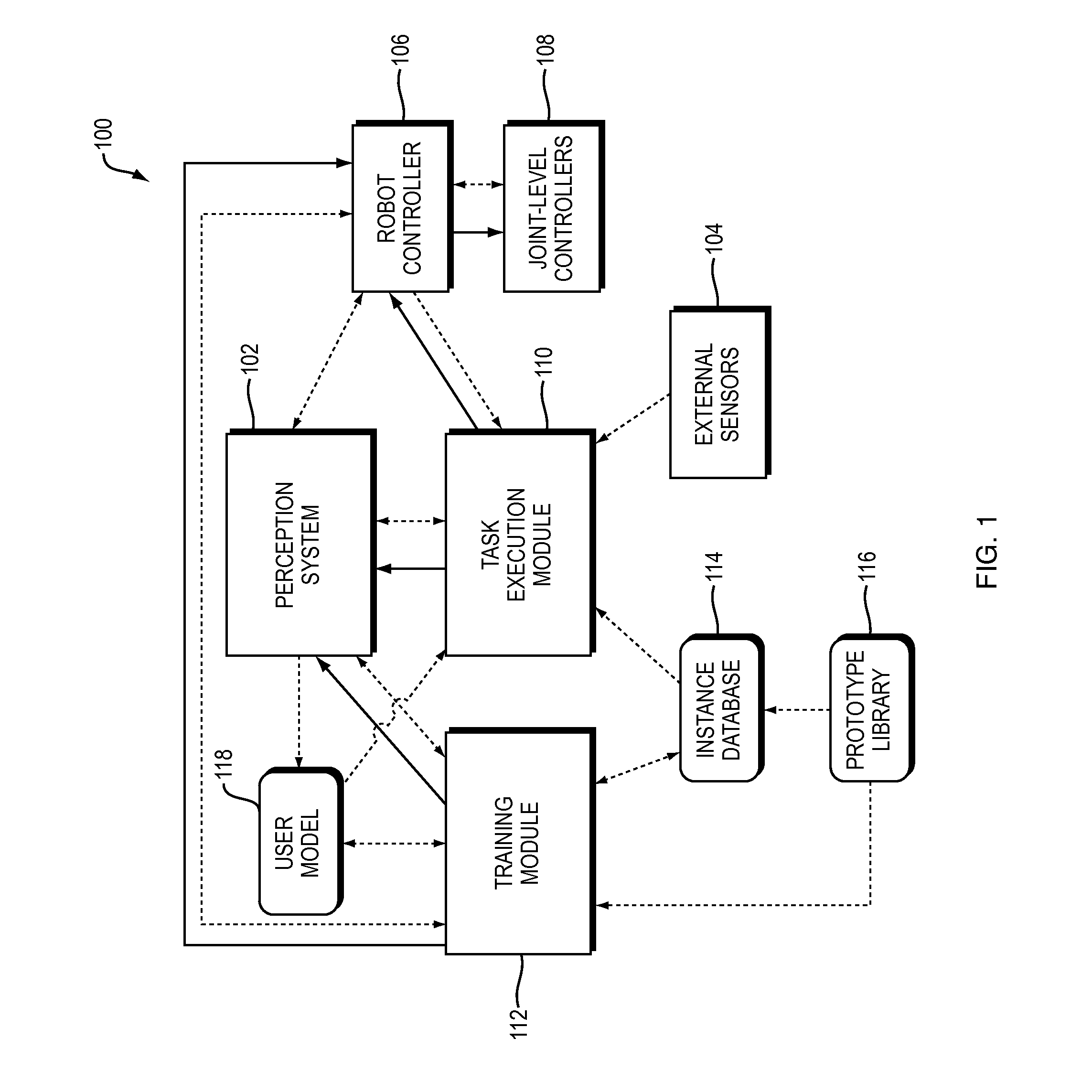
Training and operating industrial robots
ActiveUS8958912B2MorePrototypes—facilitates tuning the degreeProgramme-controlled manipulatorMathematical modelsObject basedSoftware engineering
Owner:RETHINK ROBOTICS
External system for robotic accuracy enhancement
InactiveUS20090240372A1Low priceTighter poseProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMetrologyEngineering
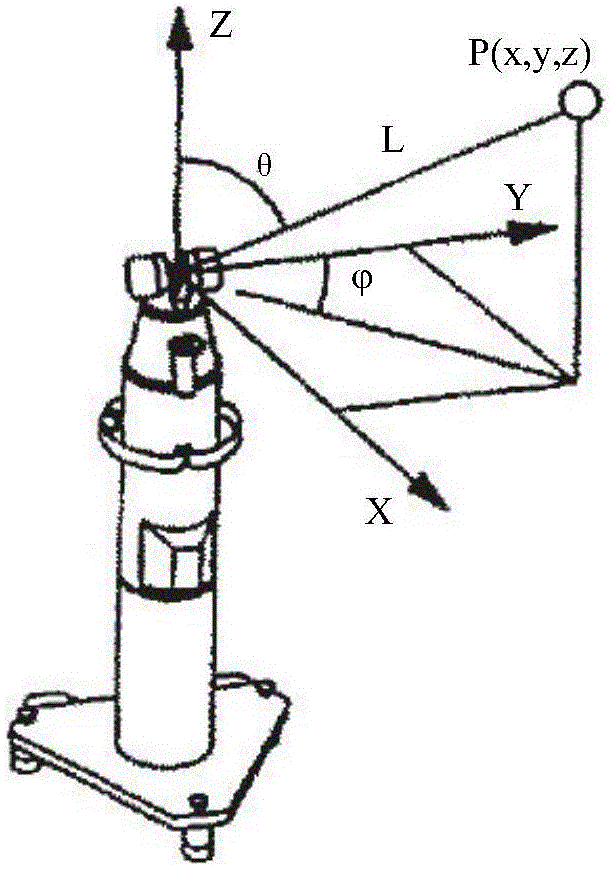
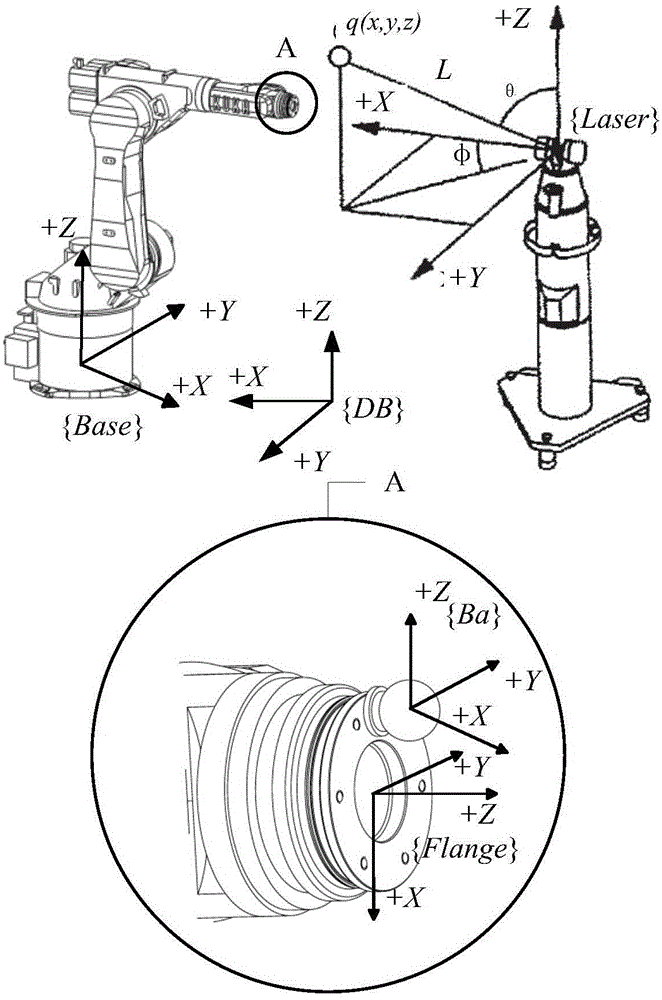
The inventive concept of the metrology system (the system) actively determines the 6 Degree of Freedom (6-DOF) pose of a motion device such as, but not limited to, an industrial robot employing an end of arm tool (EOAT). A concept of the system includes using laser pointing devices without any inherent ranging capability in conjunction with the EOAT-mounted targets to actively determine the pose of the EOAT at distinct work positions of at least one motion device.
Owner:VARIATION REDUCTION SOLUTIONS
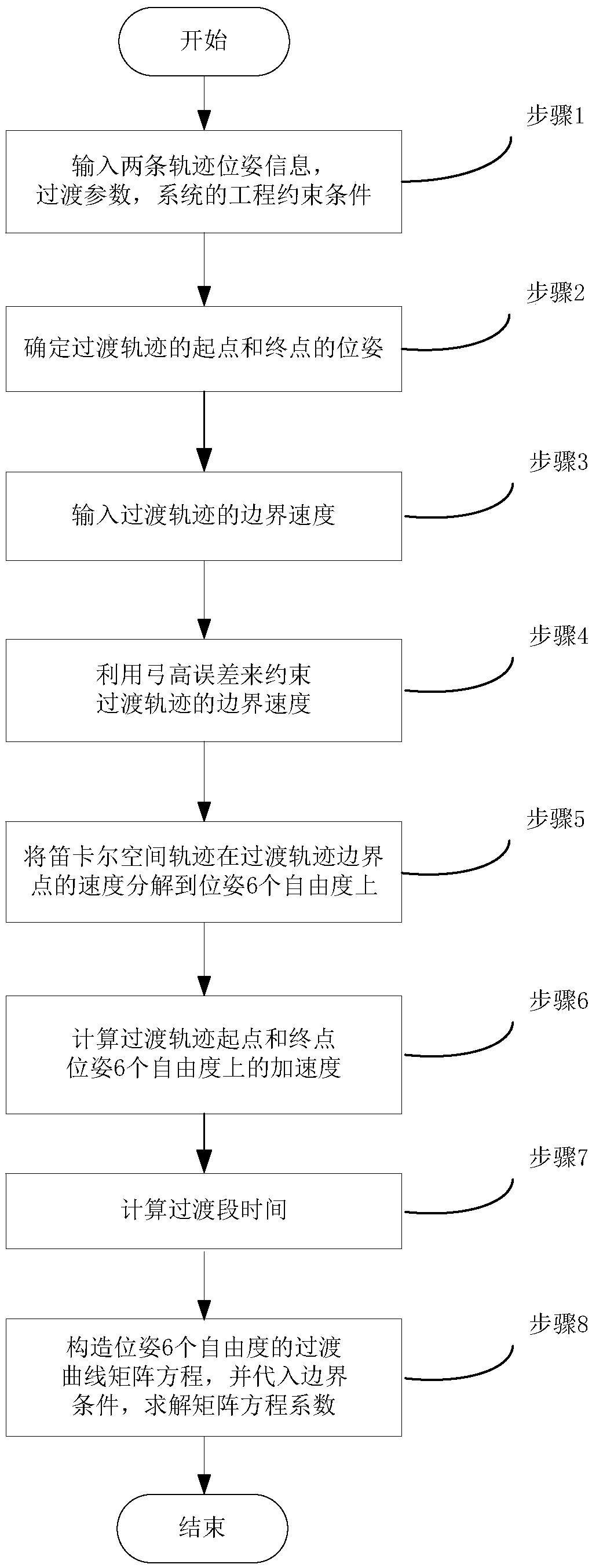
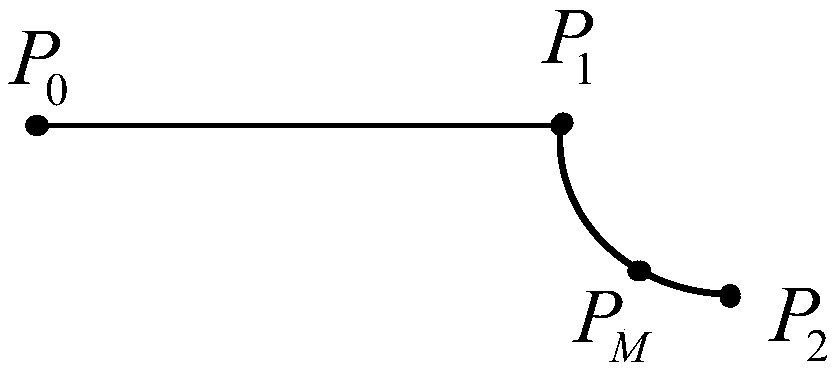
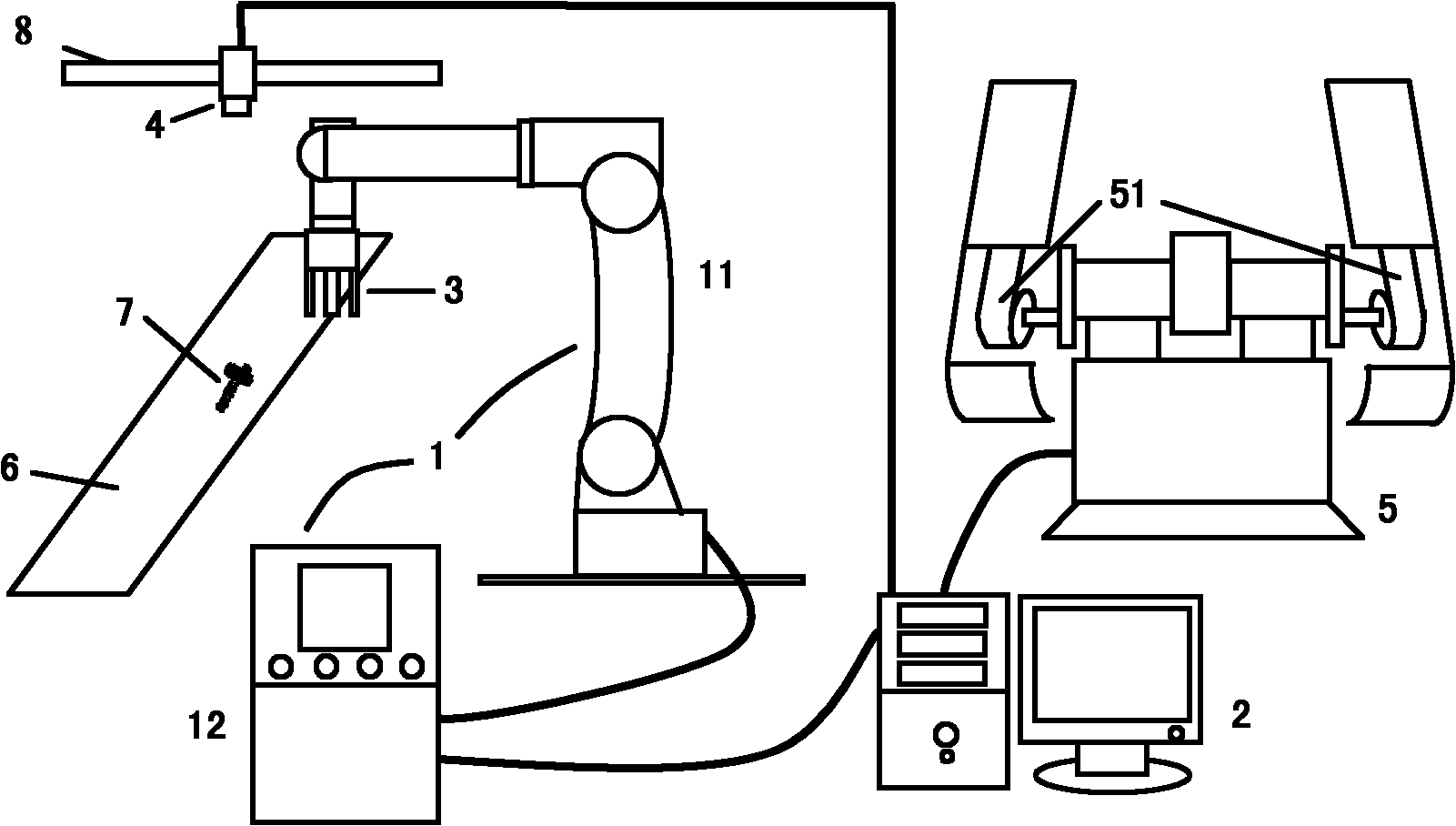
Transitional track planning method applied by industrial robot
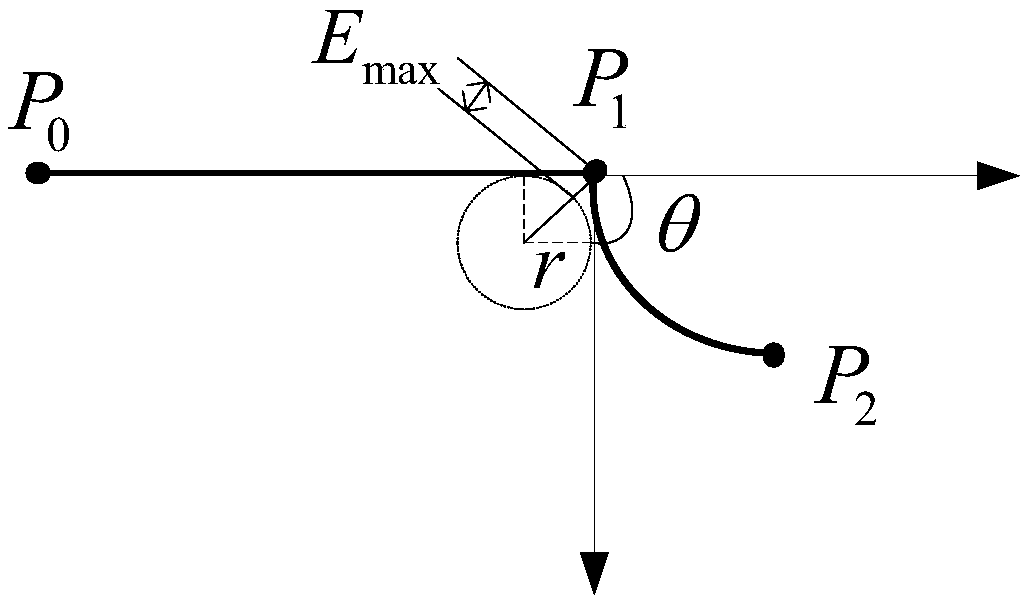
ActiveCN105500354AAvoid multiple solutionsIntuitive curveProgramme-controlled manipulatorCurve shapeRotation velocity
The invention discloses a transitional tracking planning method applied by an industrial robot, which can realize the transition between a joint space track and a cartesian space track, and the transition between two tracks of the cartesian space, the transitional track between different movement tracks are planned under the cartesian space, and has an intuitive shape; by adopting the algorithm that two parabolas are fused into one transitional curve, the smoothness of the track, speed and acceleration can be ensured, and the curve shape is controllable; the transitional track is formed by six independent curves, and the transition can be realized on the track with only posture change without position change; from the engineering application angle, the path velocity of transitional track boundary is restrained by utilizing the included angle between the tracks and the system allowable chord error, the boundary posture rotation speed is restrained by the similar mode, so that the large impact on a mechanical system caused by overhigh engagement speed can be prevented.
Owner:埃斯顿(广东)机器人有限公司
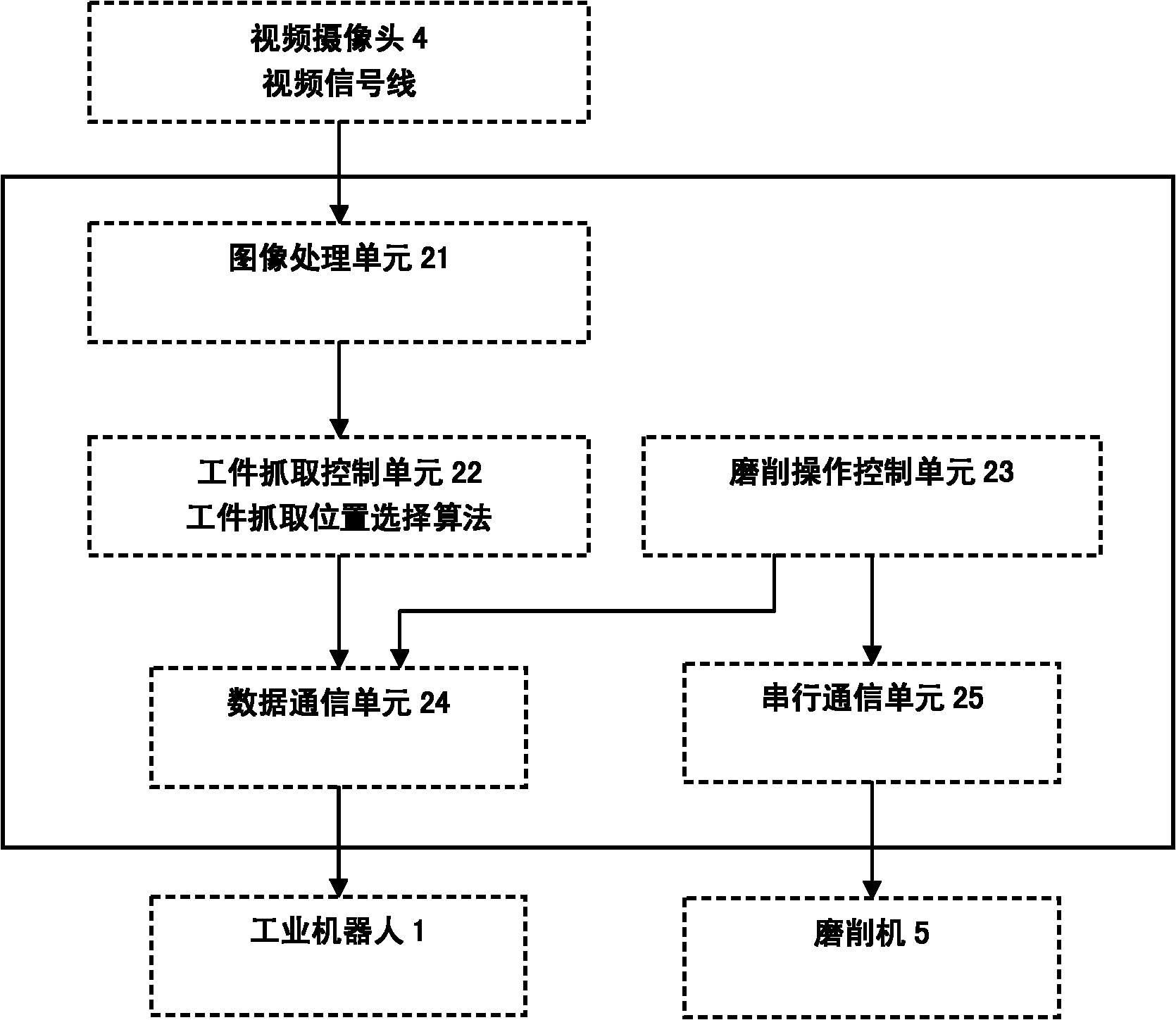
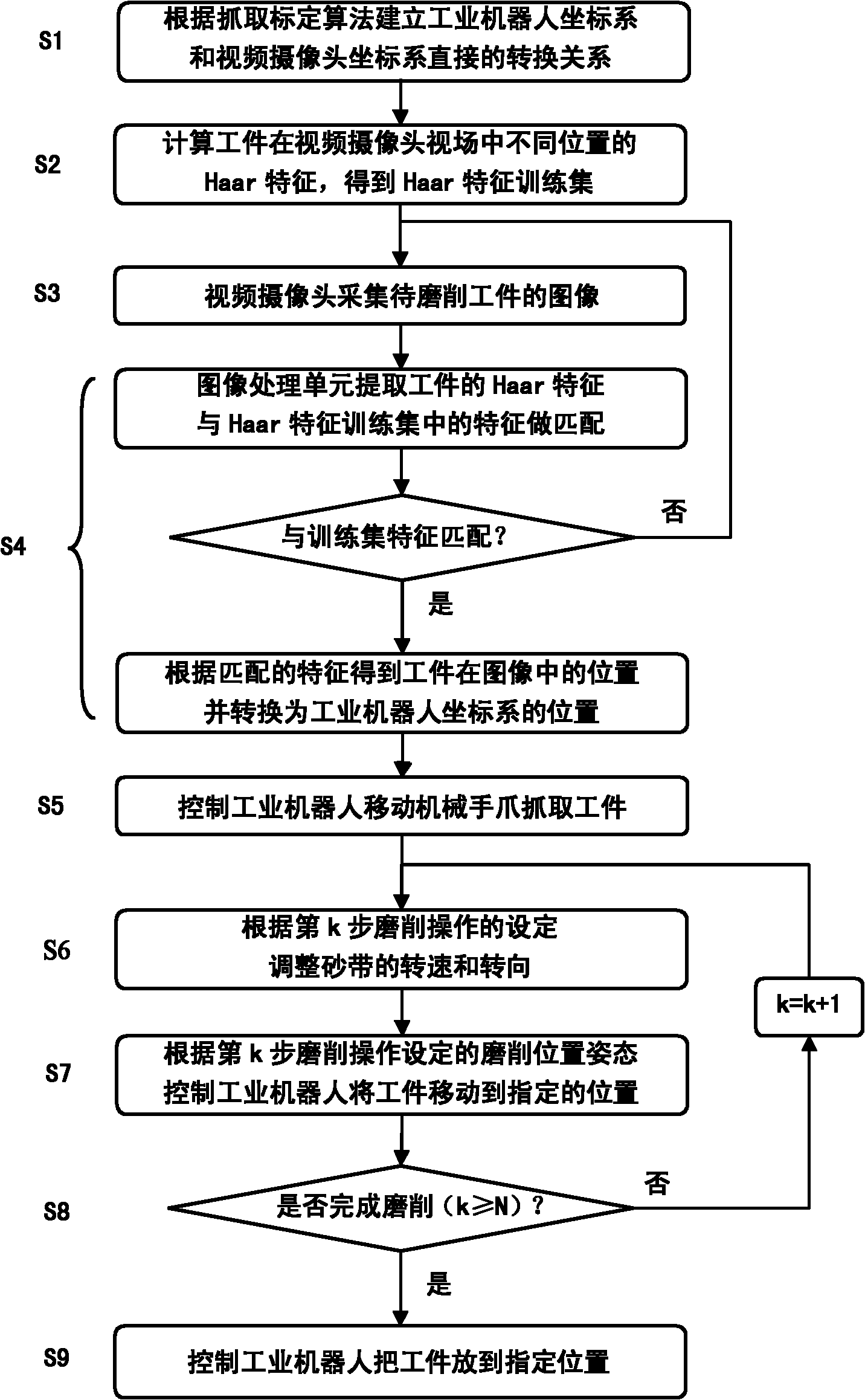
System and method for grinding industrial robot on basis of visual information
InactiveCN102120307AIncrease flexibilityImprove intelligenceGrinding feed controlAutomatic grinding controlVision basedIndustrial engineering
The invention relates to a system and a method for grinding an industrial robot on the basis of visual information. In the system, the image of a workpiece is collected by a video camera; the workpiece is positioned by computer recognition; the movement locus points of a mechanical arm from the current position to a fetching position are planned on line to control the mechanical arm to fetch the workpiece; and then, the revolving speed and the revolving direction of an abrasive belt are controlled by a preset operation step of grinding so as to control the industrial robot to move the workpiece to an appointed position and gesture for grinding and polishing the workpiece. In the system, the video camera collects the image of the workpiece in real time; the workpiece is identified and positioned by the computer to control the mechanical arm to fetch the workpiece; the movement of the industrial robot and the running state of a grinder in the workpiece grinding operation are controlled; the data end of a computer is connected with the data end of the control cabinet of the industrial robot; output locus points controls the industrial robot to move; and the data end of the computer is connected with the data end of the grinder to control the grinder to start and stop and control the revolving speed and the revolving direction of the abrasive belt.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
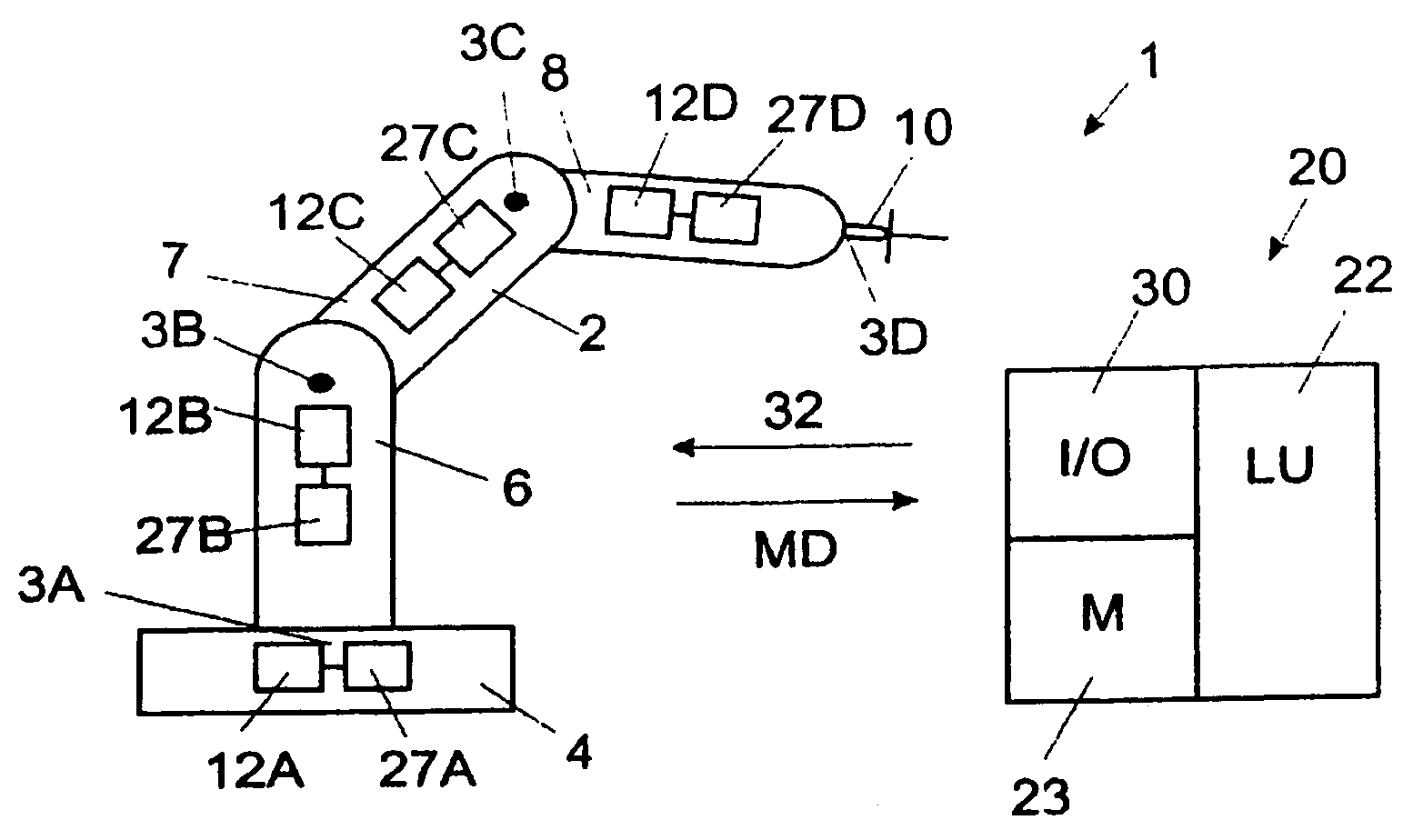
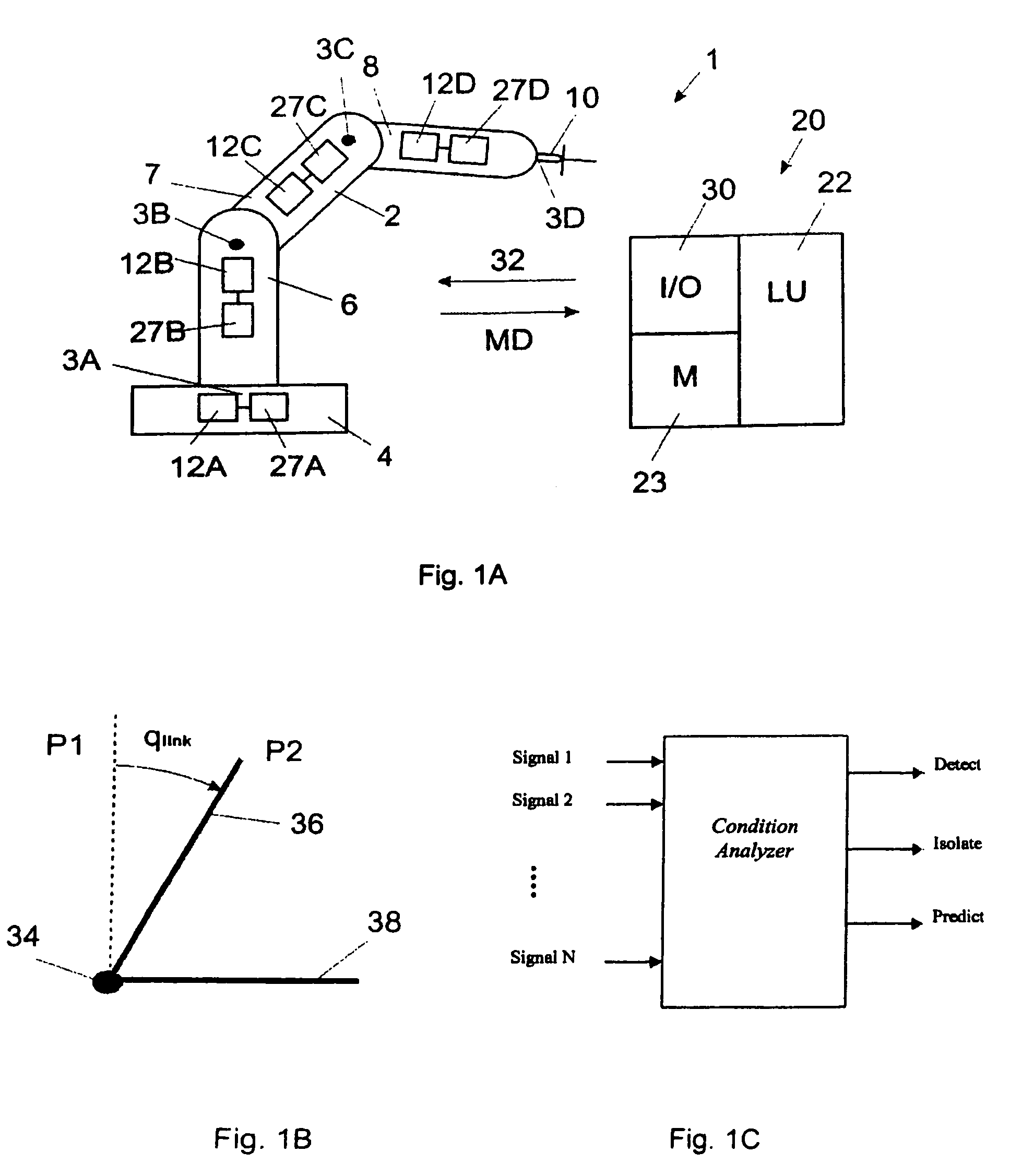
Method and a control system for monitoring the condition of an industrial robot
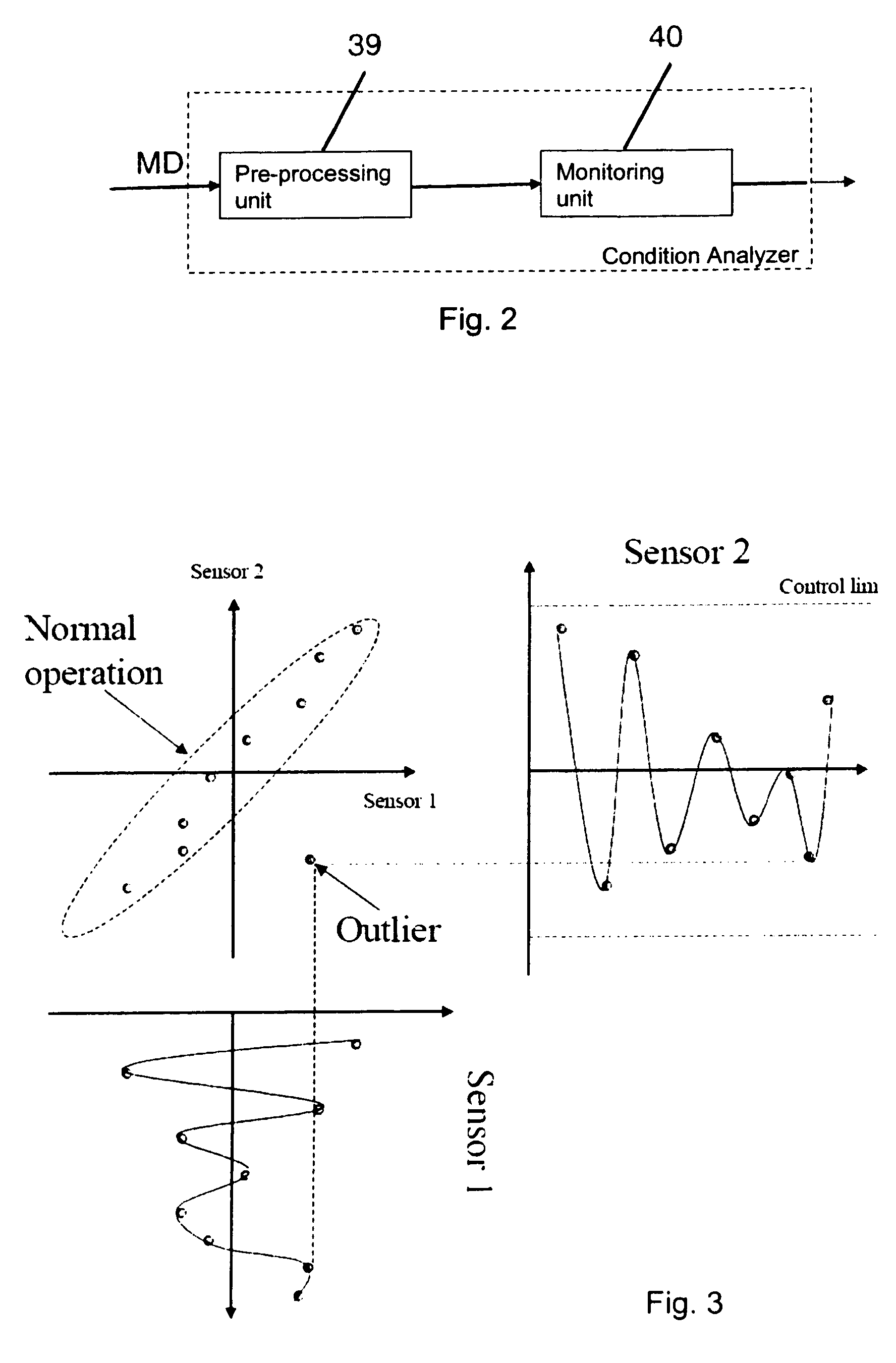
ActiveUS7826984B2Overcomes drawbackAutomatically conditionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsControl system
An industrial robot diagnostic method including performing a condition analysis utilizing at least two selected input signals, wherein each selected input signal indicates a condition related to a property of the industrial robot, performing an analysis of any combination of the selected input signals utilizing a signal modeling of the signals and outputting from the condition analyzer a result being at least one of: a detection of a malfunction of the robot system, an identification of a root cause failure in the robot system and prediction of a potential malfunction in the robot system. Also an industrial robot system utilizing the method.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG +1
Device and a method for calibration of an industrial robot
InactiveUS6418774B1Reduce in quantityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPlane of referenceEngineering
A device for calibration of an industrial robot, which calibration device is adapted for being in contact during the calibration with at least one plane of reference arranged on the robot, the calibration device includes an angle measuring member arranged for measuring an angle relative to the vertical line. The device further comprises two contact elements each having a curved surface, and the contact elements are arranged for being in contact with the plane of reference.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Robot parts assembly on a workpiece moving on an assembly line
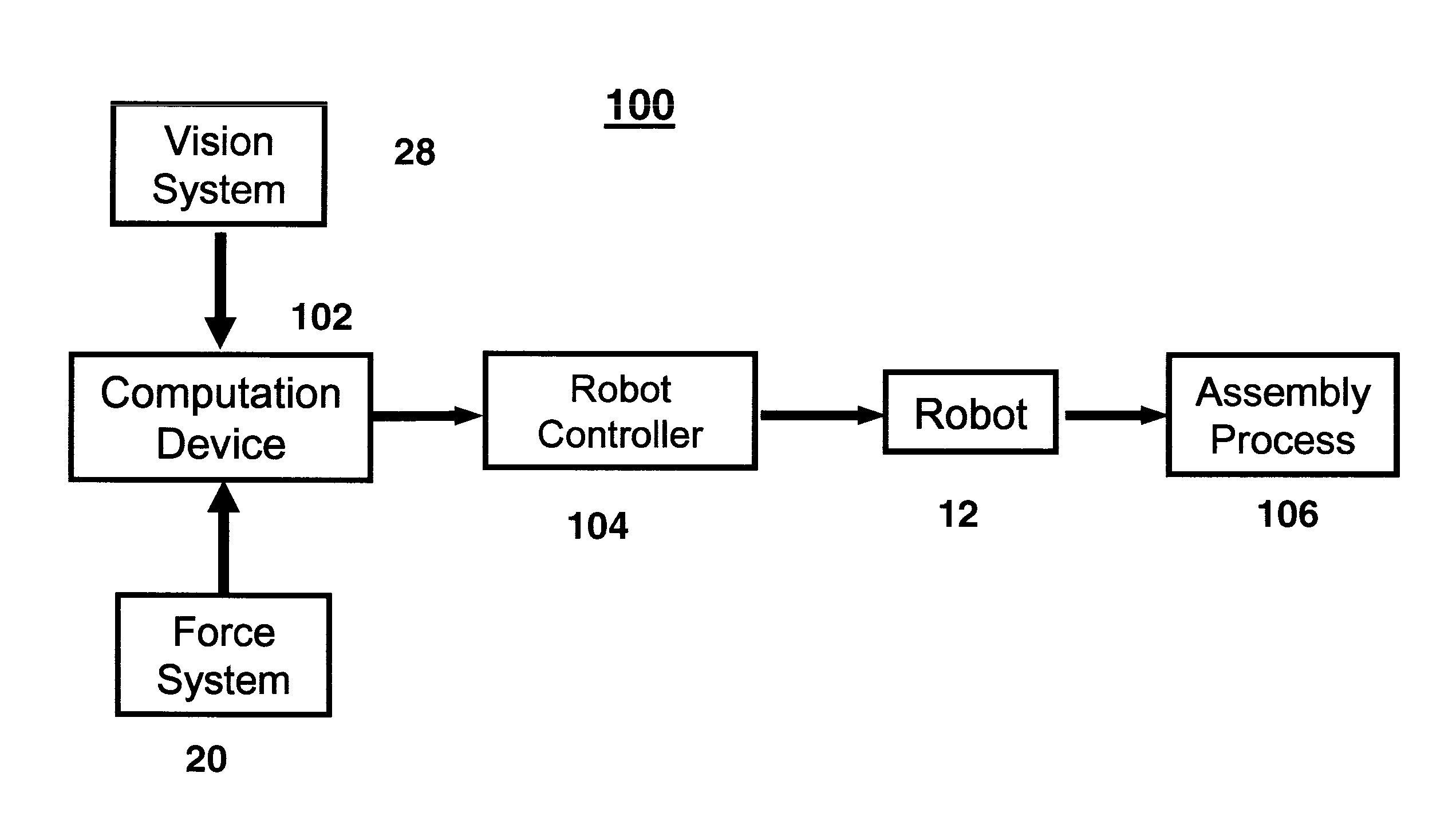
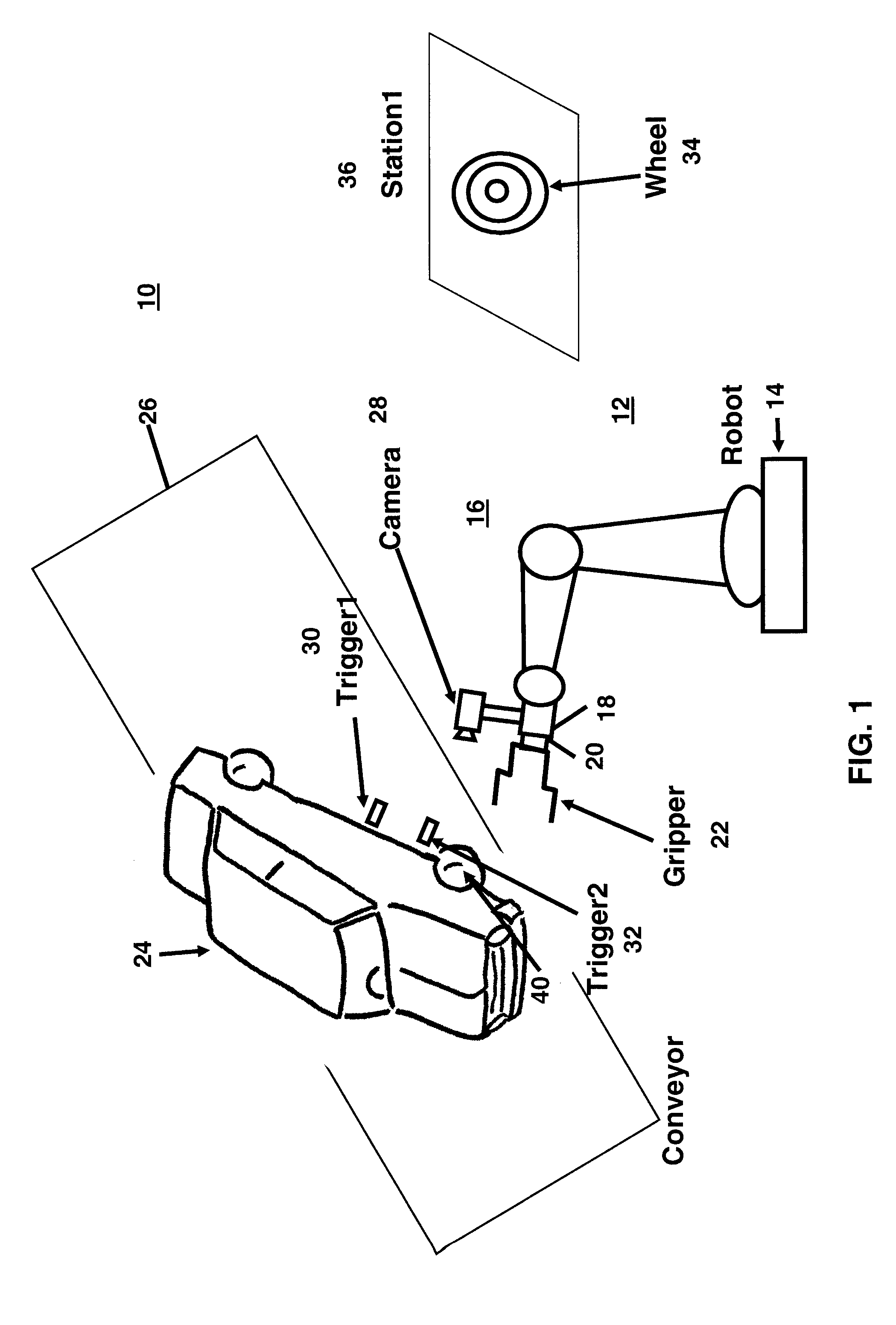
An industrial robot is used to assemble a part to a predetermined location on a randomly moving workpiece. The workpiece may be an automobile on an assembly line and the part may be a wheel (a tire mounted on a rim) to be assembled on one of the wheel hubs of the automobile. The robot has mounted on it a camera, a force sensor and a gripper to grip the part. After the robot grips the part, signals from both the force sensor and vision are used by a computing device to move the robot to a position where the robot can assemble the part to the predetermined location on the workpiece. The computing device can be the robot controller or a separate device such as a PC that is connected to the controller.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
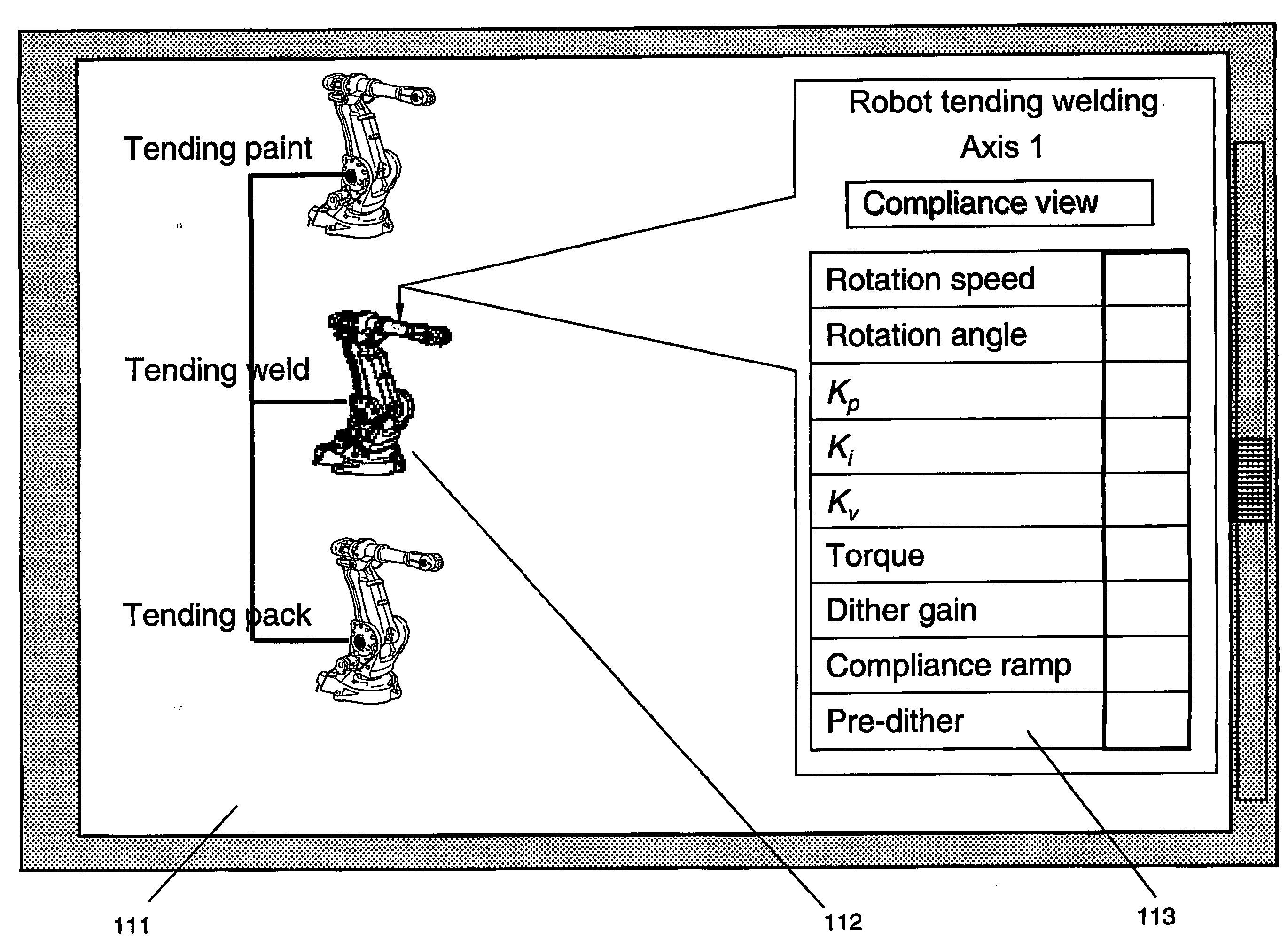
Control Method for a Robot
ActiveUS20070260356A1Reduce the effects of frictionFaster and accurate responseProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
An apparatus, a method and a control system for controlling an industrial robot with at least one axis of rotation and / or translation. The robot includes at least one actuator or motor at each of the axes for driving a movement of an arm of the robot and at least one sensor at each of the rotatable shafts. A dither-signal generator for generation of a periodic signal is used to provide a varying dither signal to a servo of the actuator. Automatic adaption of the dither signal is provided. A computer program for carrying out the method and a graphical user interface.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Industrial robot-based assembly method and device of piston, piston pin and connecting rod
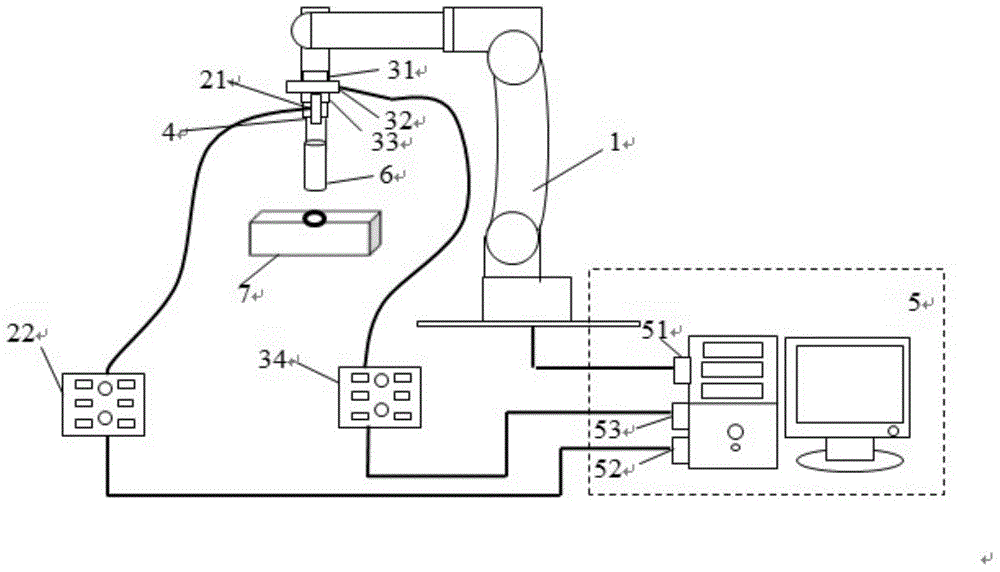
ActiveCN101913076AImplement automatic assemblyImprove assembly efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorAssembly machinesData terminalControl circuit
The invention relates to an industrial robot-based assembly method and device of a piston, a piston pin and a connecting rod. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: a vision camera is used to identify the positions and directions of the piston, piston pin and connecting rod, the grabing positions are calculated by a computer, a mechanical paw grabs the piston, the piston pin and the connecting rod to place on an intelligent assembly table; the connecting rod is inserted in the piston under the control of the intelligent assembly table; an industrial robot places the piston pin in a piston assembly hole; the vision camera in the device identifies and positions the piston, piston pin and connecting rod on a work platform; the data terminal of the industrial robot is connected with the data terminal of the computer; the vision camera is connected with the computer; the industrial robot controls the mechanical paw to grab the piston, piston pin and connecting rod and place on the intelligent assembly table; the serial signal line of the intelligent assembly table is connected with the computer, the control circuit board of the intelligent assembly table controls a connecting rod jig to insert the connecting rod in the piston; and the industrial robot assembles the piston pin in the piston assembly hole according to the sensorless assembly method.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for protecting a robot from collisions
InactiveUS20050273200A1Improve protectionHigh degreeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringIndustrial robot
A process for protecting at least two robots is provided, especially multiaxial industrial robots, from collisions, in which movements of a robot are automatically checked for possible collisions. Interlocks are automatically inserted in the movement process.
Owner:KUKA ROBOTER
Industrial robot with controlled flexibility and simulated force for automated assembly
ActiveUS20050113971A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringRobot end effector
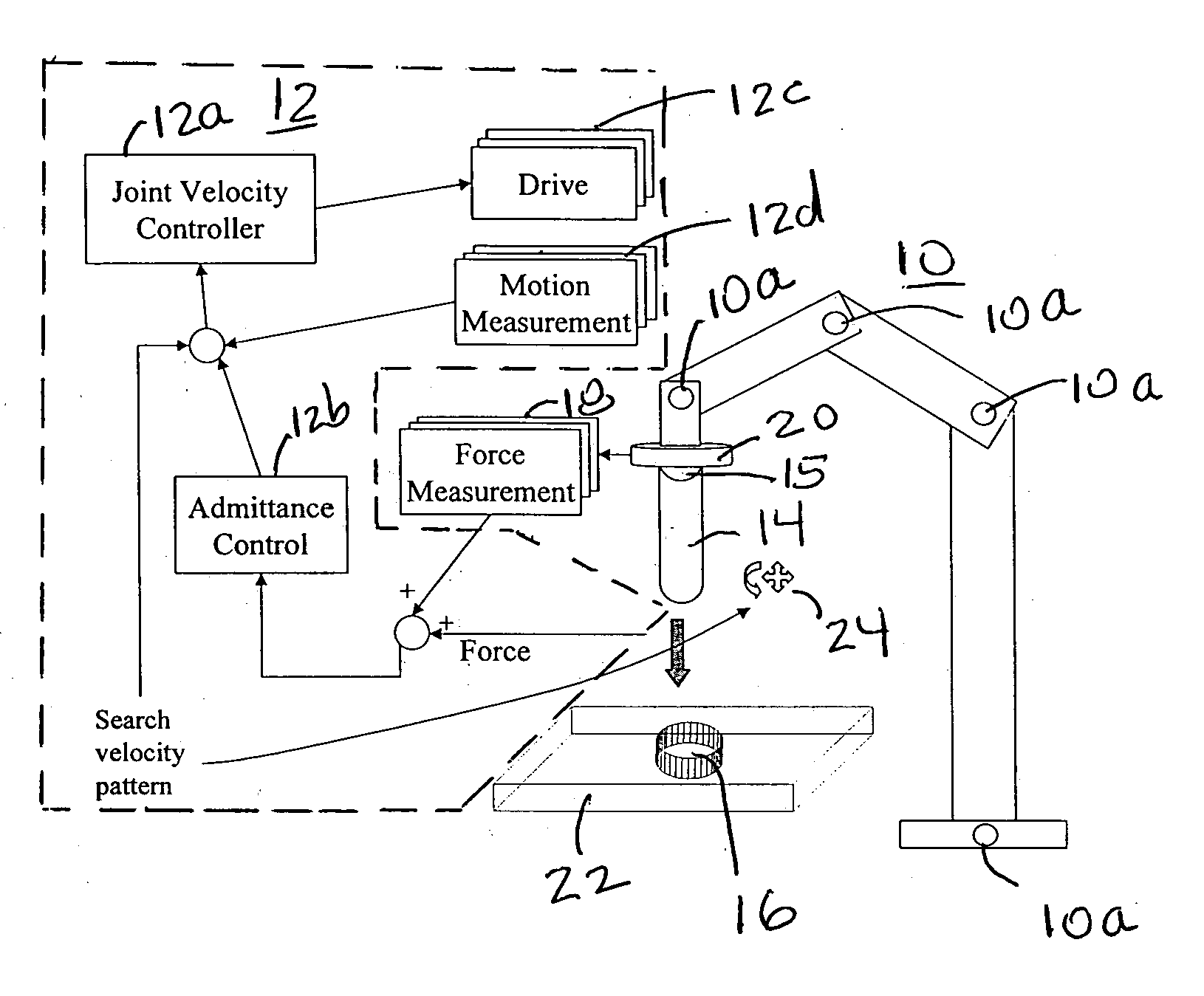
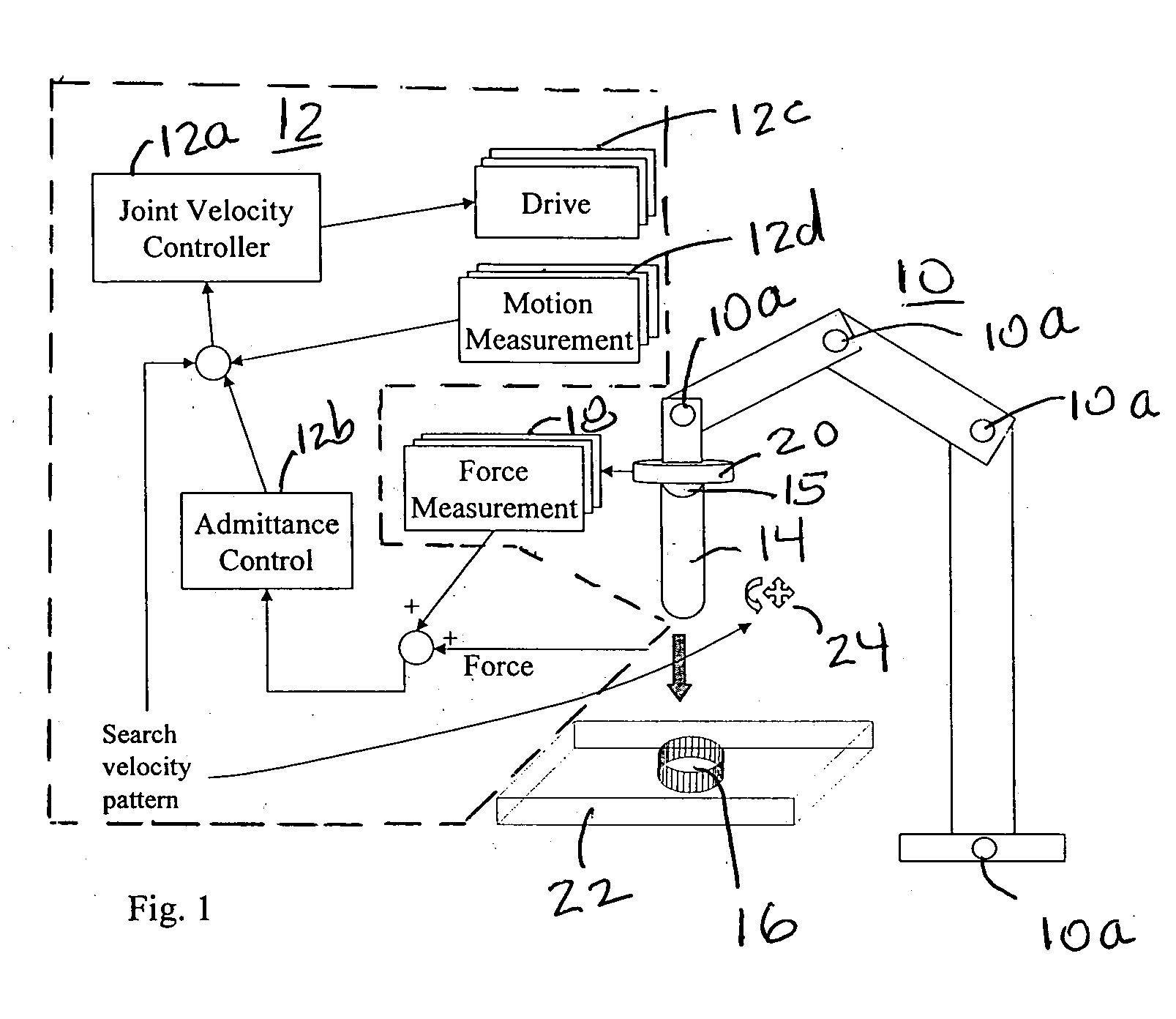
An industrial robot that has uses a simulated force vector to allow a work piece held by the robot end effector to be mated with a work piece whose location and orientation is not precisely known to the robot. When the end effector makes contact with the location and orientation in which the other work piece is held the robot provides a velocity command to minimize the force of the contact and also provides a search pattern in all directions and orientations to cause the end effector to bring the work piece it is holding in contact with the other work piece. The search pattern and the velocity command are continued until the two work pieces mate.
Owner:ABB RES LTD +1
Industrial robot collision detection method
ActiveCN104985598AWorking conditions without any restrictionsWorking condition limitProgramme-controlled manipulatorProgramme controlCollision detectionEngineering
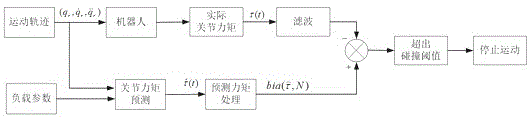
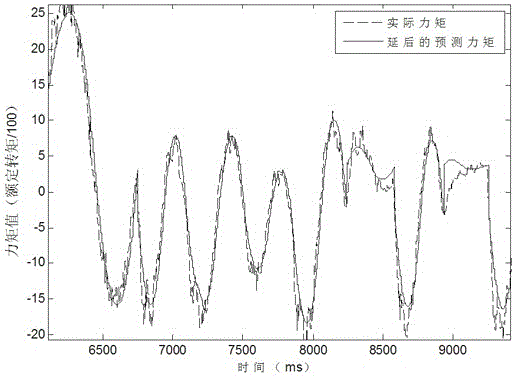
The invention discloses an industrial robot collision detection method. By the adoption of a collision detection method based on torque difference, in a robot operation process, theoretical torque values of joints are predicted in real time according to a movement track, and differences between the theoretical torque values of the joints and actual sampled torque values of the joints are calculated in real time. When the torque differences exceed a collision threshold, it is regarded that collision happens, a motor stops running immediately, and a robot stops moving. According to the method, a sensor does not need to be additionally arranged, the structure of the robot does not need to be changed, the method is suitable for any operation working condition of the robot, and there is no limit on the working conditions. The whole process is carried out off-line, people only need to use prediction results in online programs of collision detection, the programs are simple, and the execution efficiency is high. According to the method, the predicted torque of the joints is delayed by N cycles and processed, the actual torque is filtered through an average value, and then the torque differences are solved so that the collision threshold can be reduced, and sensitivity of the collision detection is improved.
Owner:NANJING ESTUN ROBOTICS CO LTD
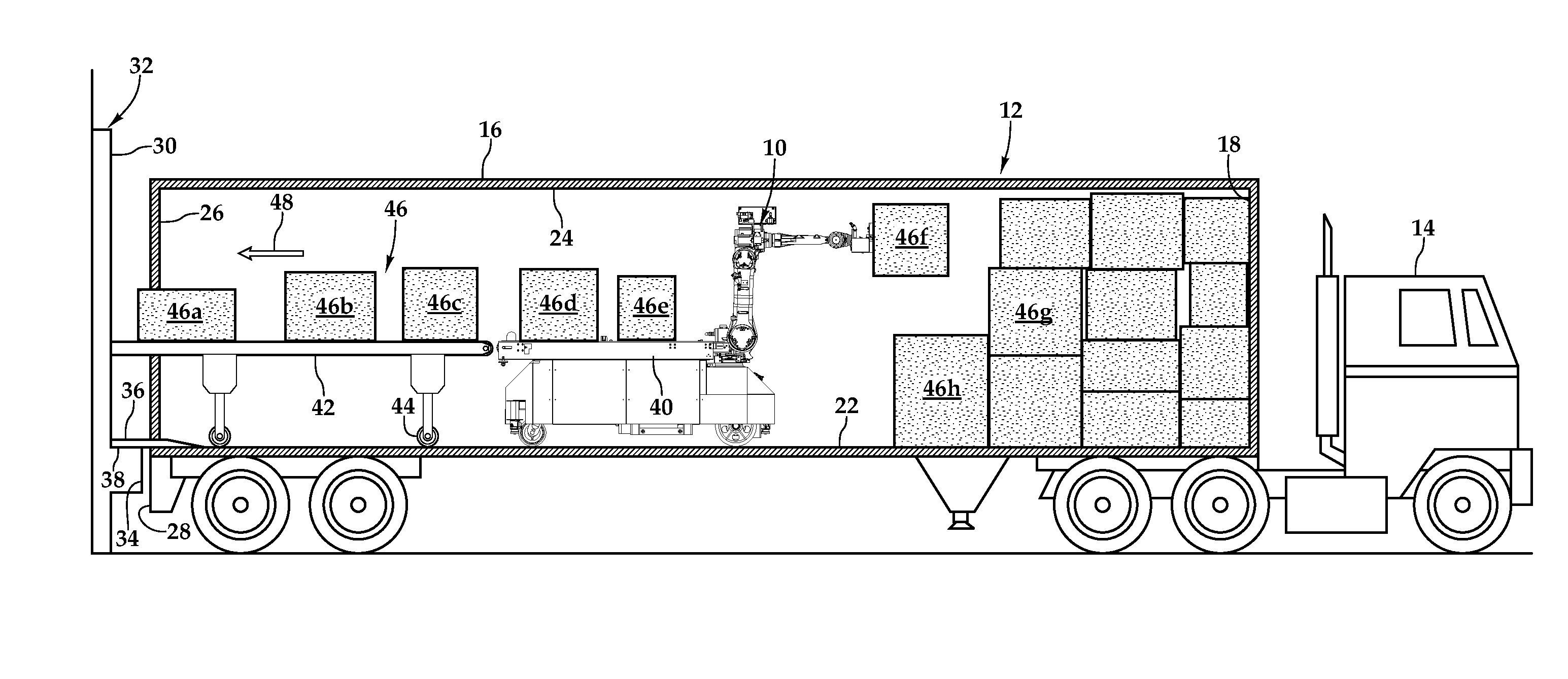
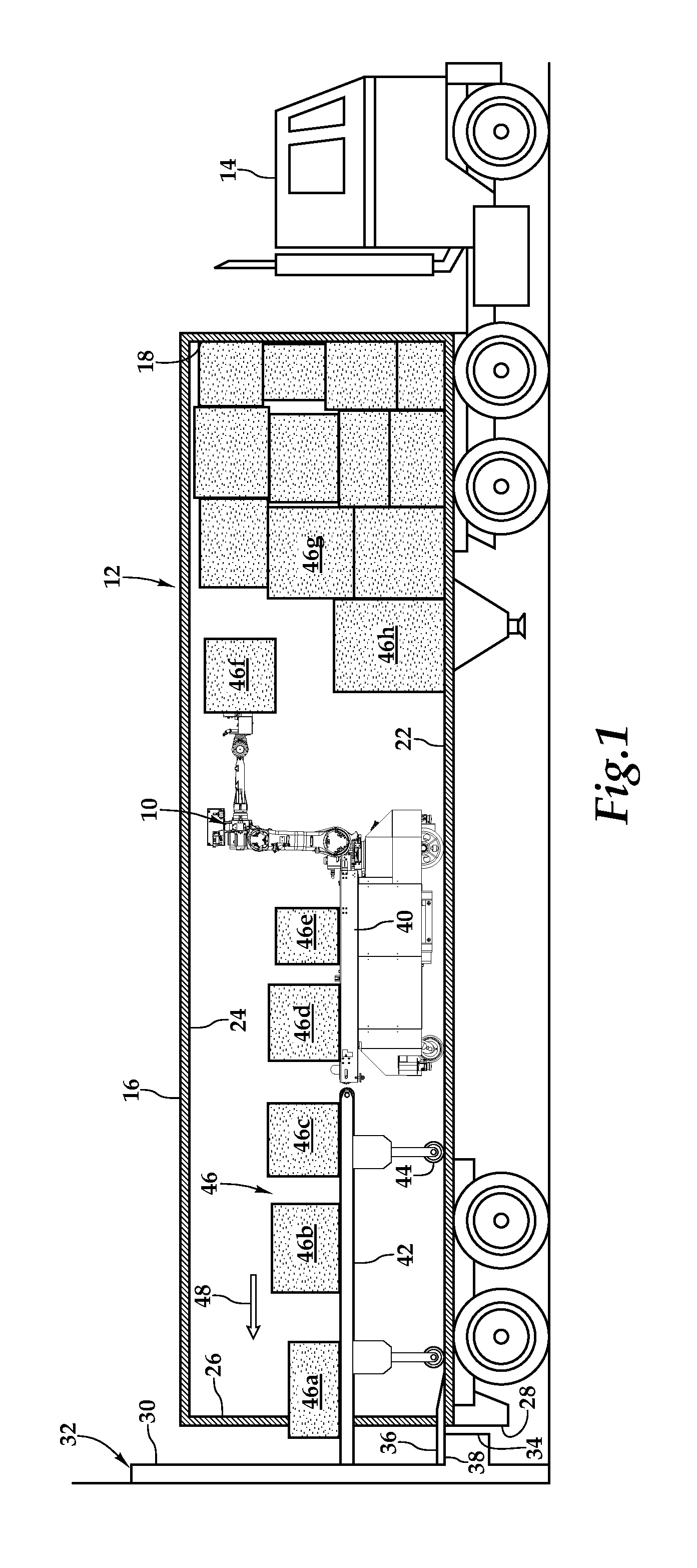
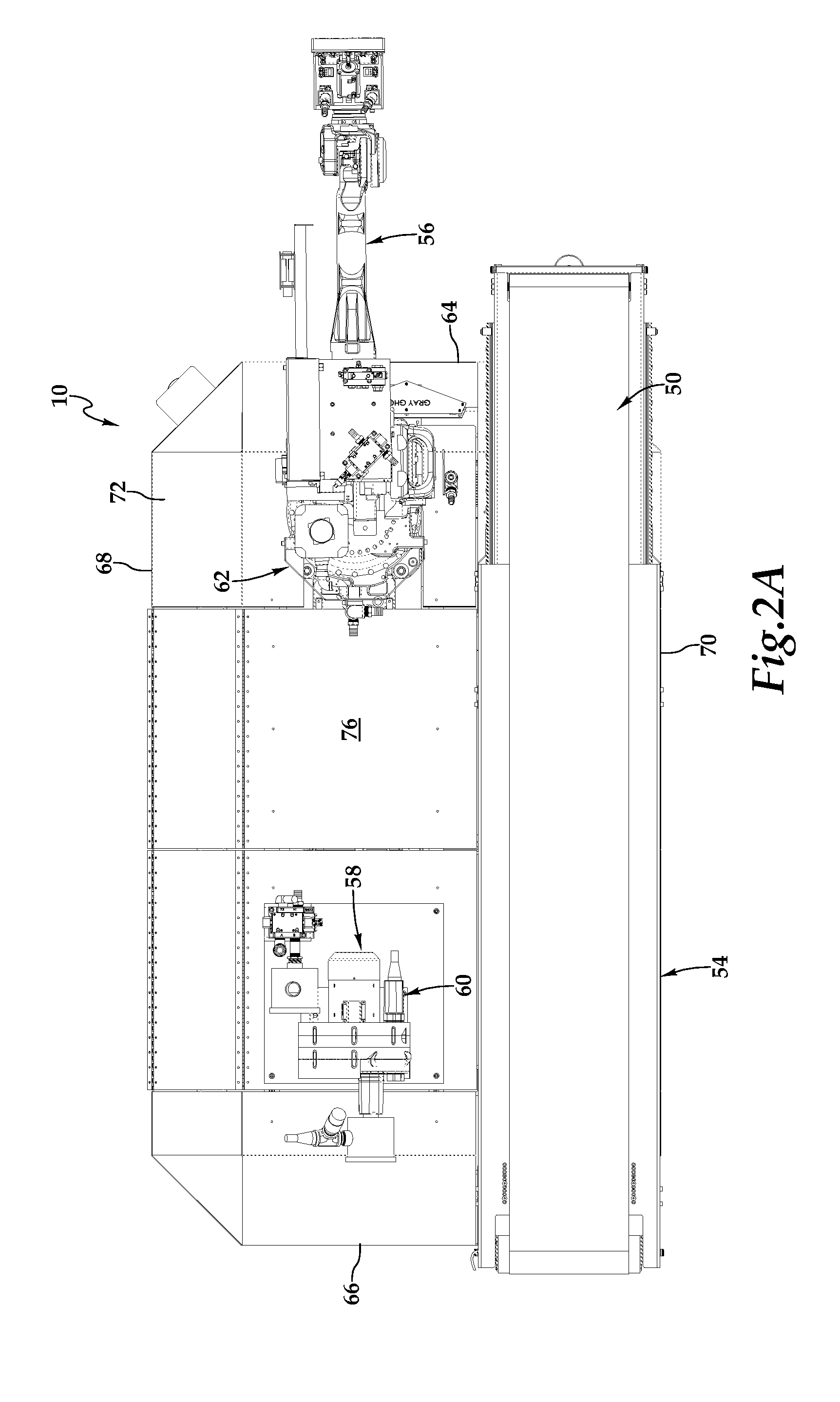
Automated Truck Unloader for Unloading/Unpacking Product from Trailers and Containers
ActiveUS20140205403A1Quantity maximizationProtect and extend lifeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringBiological activation
An automatic truck unloader for unloading / unpacking product, such as boxes or cases, from trailers and containers is disclosed. In one embodiment, a mobile base structure provides a support framework for a drive subassembly, conveyance subassembly, an industrial robot, a distance measurement subassembly, and a control subassembly. Under the operation of the control subassembly, an industrial robot having a suction cup-based gripper arm selectively removes boxes from the trailer and places the boxes on a powered transportation path. The control subassembly coordinates the selective articulated movement of the industrial robot and the activation of the drive subassembly based upon the distance measurement subassembly detecting objects, including boxes, within a detection space, and dimensions of the trailer provided to the control subassembly.
Owner:WYNRIGHT CORP
Pathcorrection for an industrial robot
InactiveUS7130718B2Improve accuracyHigh movement precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlControl theoryPath deviation
A method for an industrial robot to increase accuracy in movements of the robot. A first path is formed by bringing a tool supported by the robot to adopt a plurality of generated positions. A plurality of observed positions of the tool moving along the first path are determined. A second path is formed of the determined tool positions. A correction is determined by a path deviation between geometrically determined positions in the first path and the second path.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method for calibrating and programming of a robot application
InactiveUS20040251866A1Fast and easy programmingImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlMathematical modelApplication software
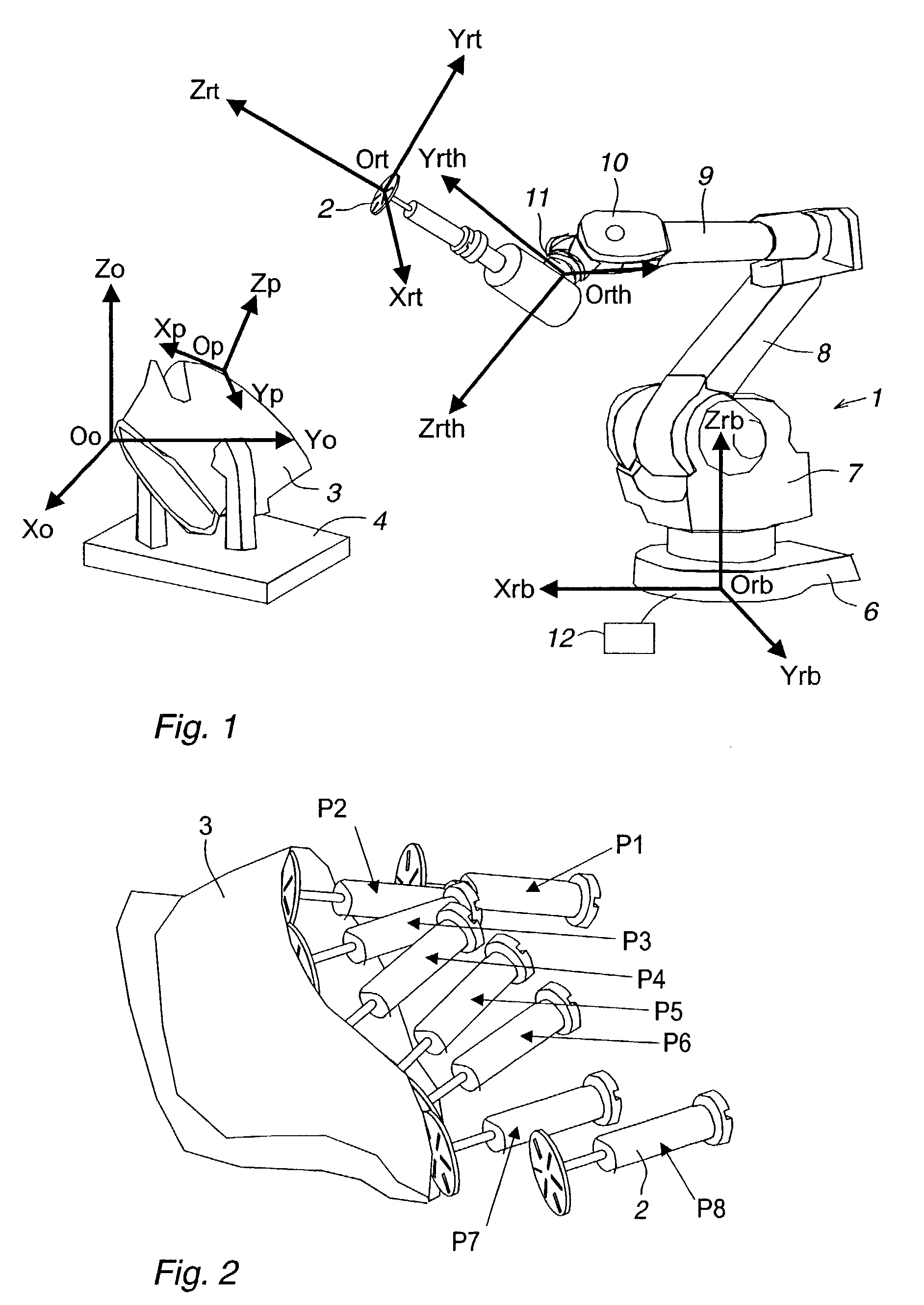
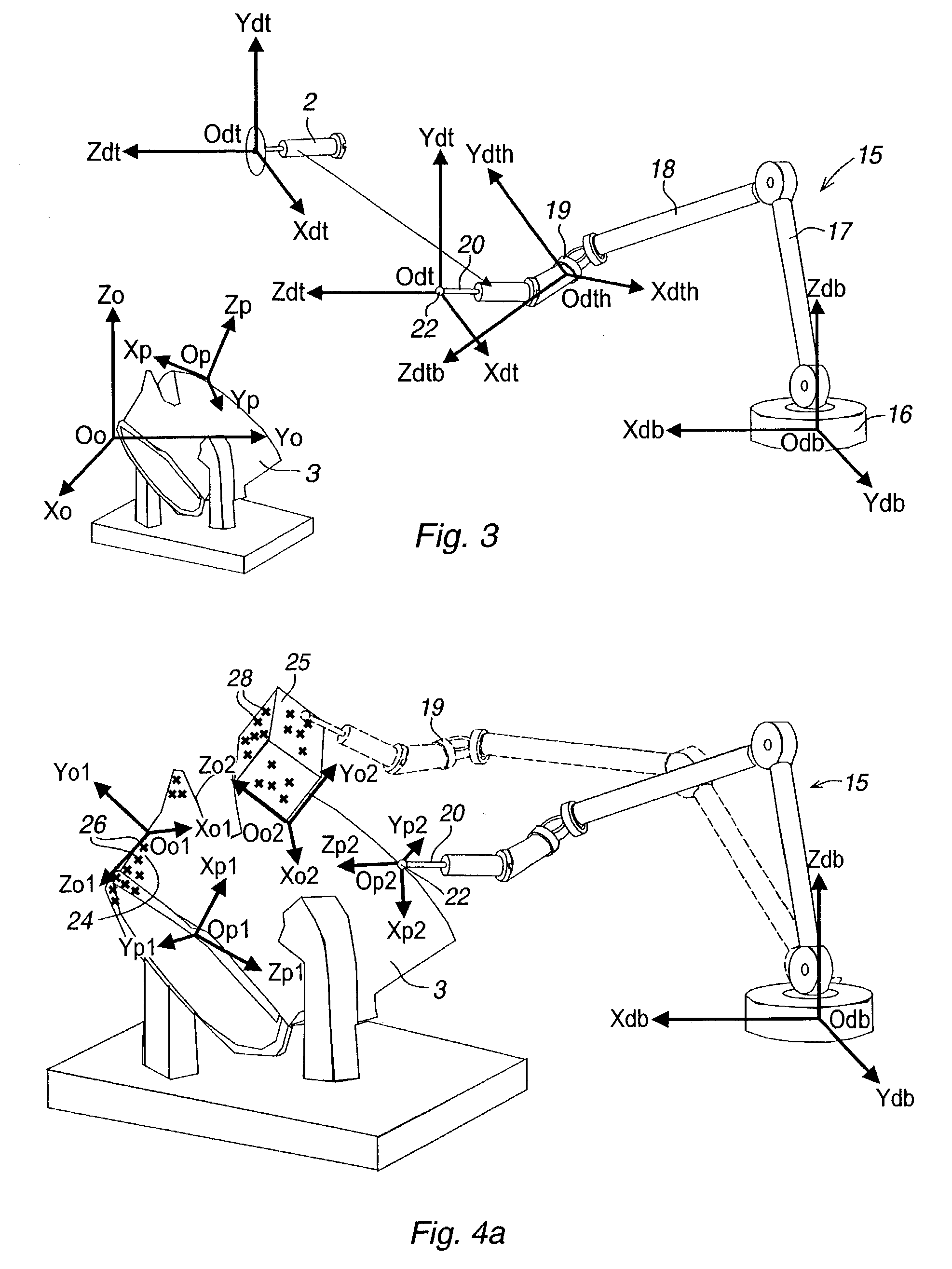
A method for programming of a robot application comprising an industrial robot having a robot coordinate system, a tool having a tool coordinate system and a work object (3) to be processed by the tool. The application is programmed by means of a position-measuring unit (15) adapted for measuring positions relative a measuring coordinate system (db). The programming method comprises: selecting an object reference structure (25) on the object, defining a mathematical model for the object reference structure, defining an object coordinate system (o2), providing measurements by the position-measuring unit on the surface of the object reference structure, determining the object coordinate system in relation to the measuring coordinate system (db) by best fit between said measurements and said mathematical model of the object reference structure.
Owner:GAN ZHONGXUE +6
Physical coordinate positioning method based on binocular vision
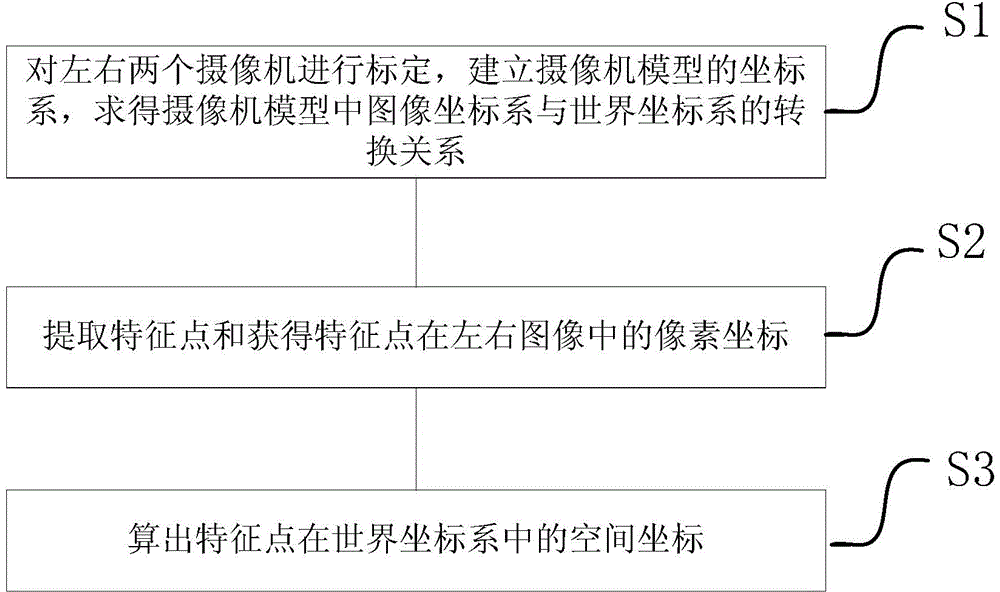
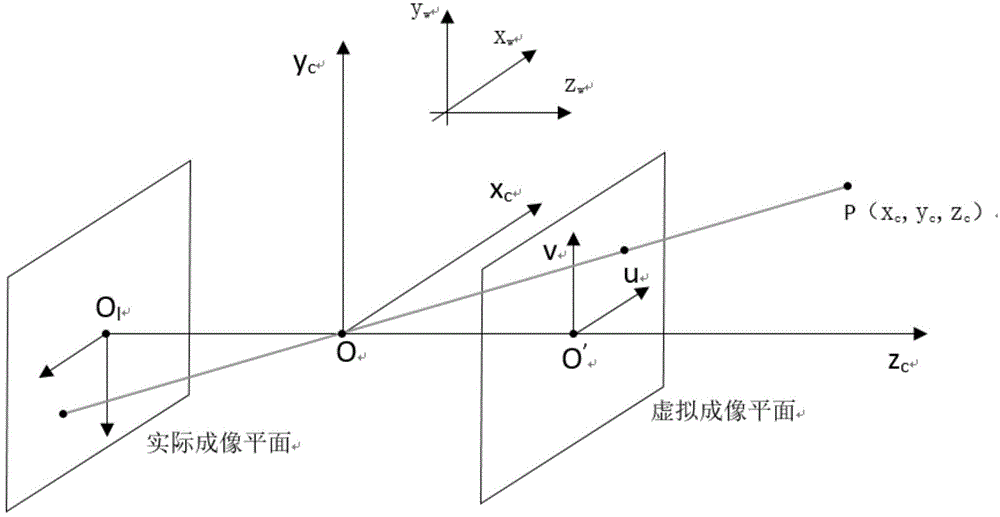
ActiveCN104933718AHigh measurement accuracyImprove measurement efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVisual perceptionBinocular distance
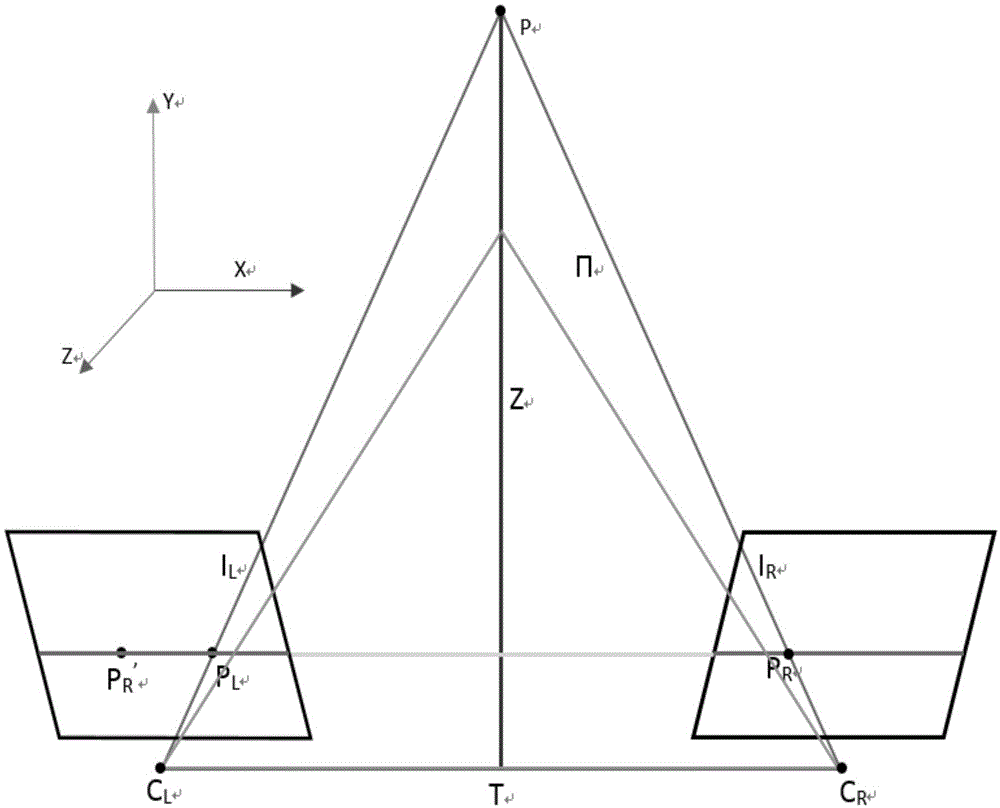
The invention discloses a physical coordinate positioning method based on binocular vision. The physical coordinate positioning method comprises the following steps: S1) setting a left camera and a right camera, establishing a coordinate system of a camera model, and obtaining a conversion relationship between the coordinate system of the camera model and a world coordinate system; S2) extracting a feature point, and obtaining a pixel coordinate of the feature point in a left image and a right image; and S3) calculating a space coordinate of the feature point in the world coordinate system. The left camera and the right camera are used for simulating two eyes, the coordinate system conversion model is established, then, each image shot by the two cameras is subjected to feature point extraction and pixel coordinate calculation, the pixel coordinate is converted into a theoretical coordinate of the camera model, and finally, the space coordinate of a target point is calculated. Measurement accuracy and efficiency is improved, and binocular coordinate positioning can have a better application prospect in the fields including an eye-in-hand system of an industrial robot, industrial cutting, logistics transportation business, packaging business, optical detection and processing and the like.
Owner:INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Industrial robot safety protection intelligent control method and system
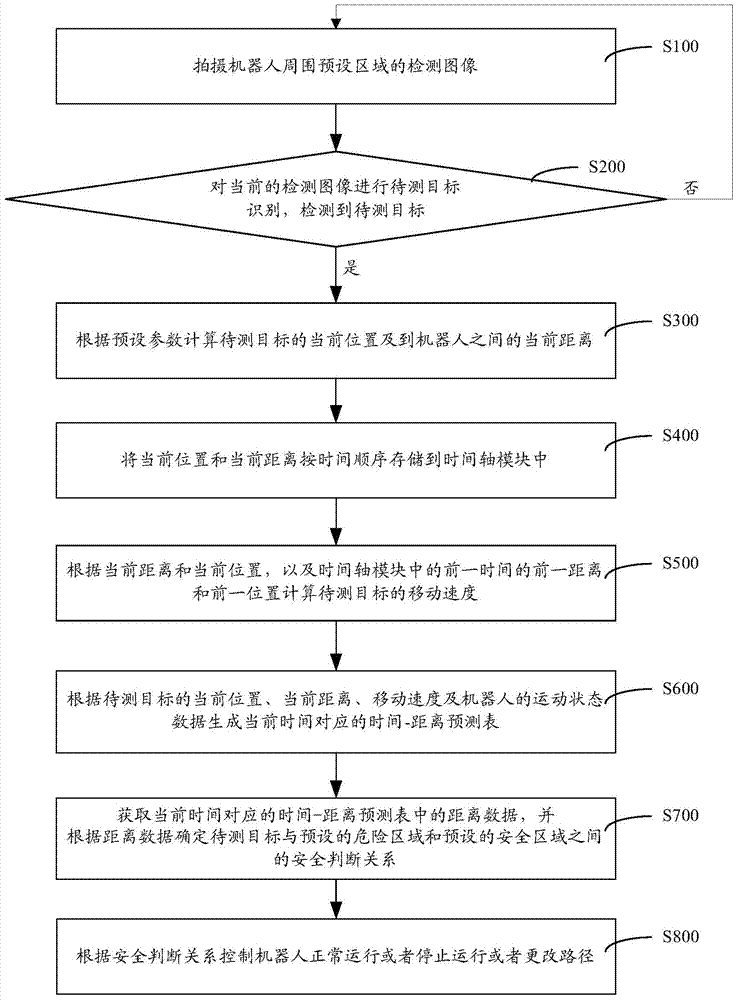
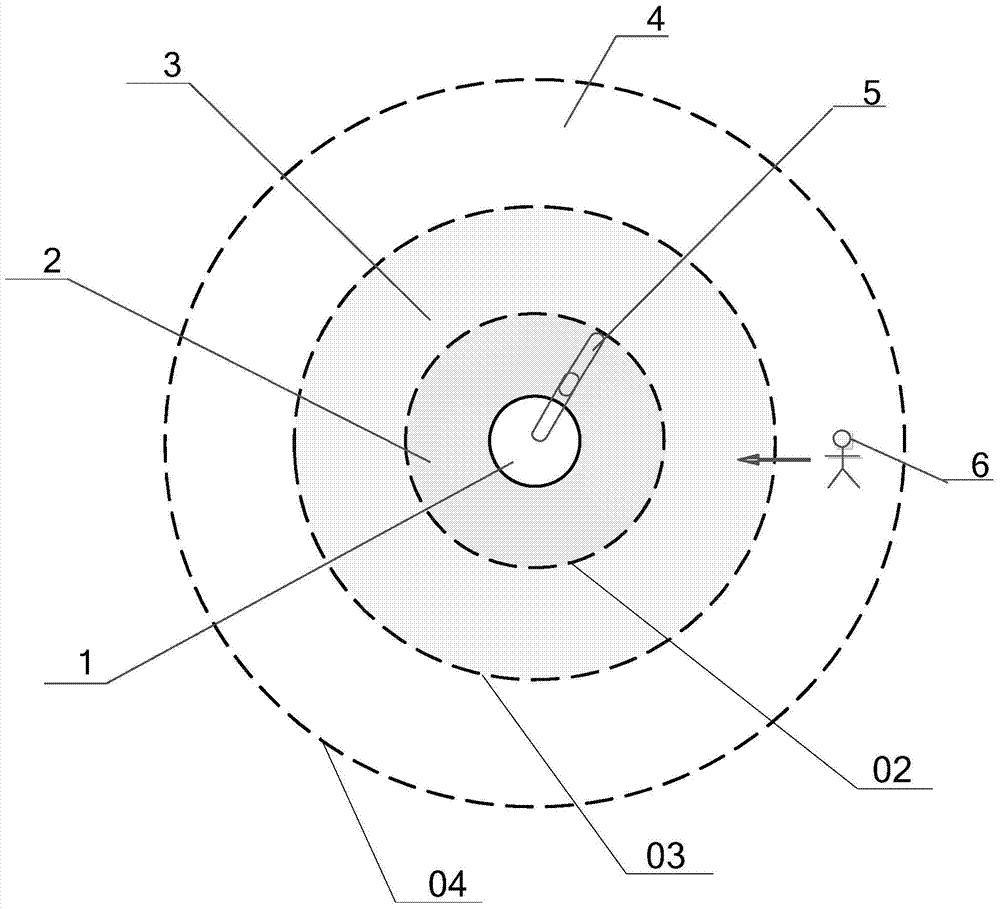
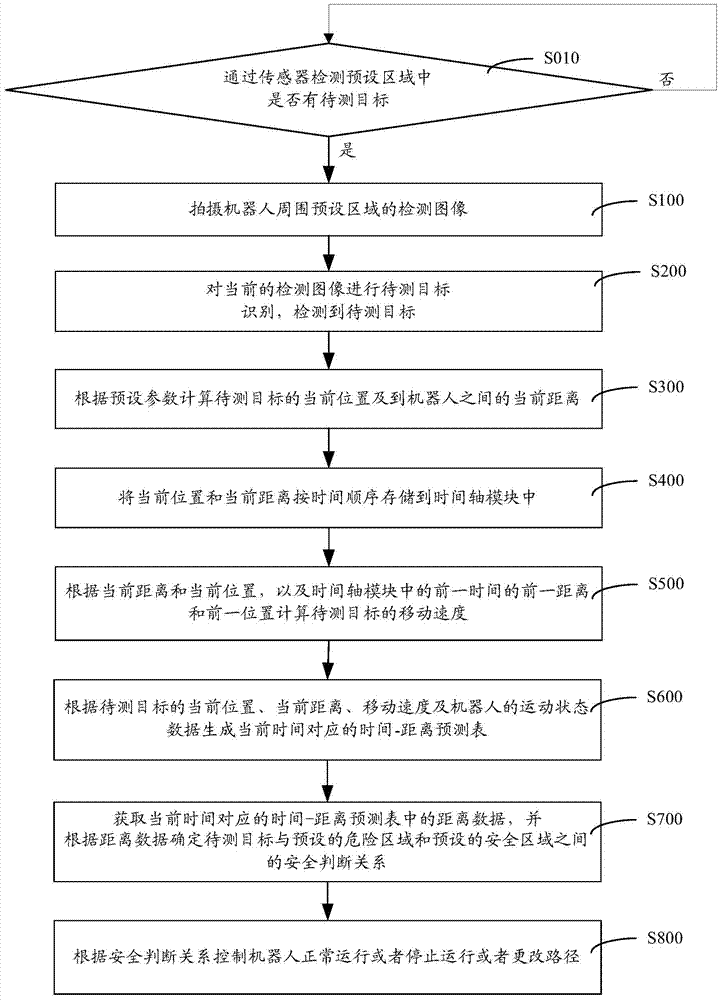
The invention discloses an industrial robot safety protection intelligent control method and system. The method comprises the following steps that a detection image of a preset area around a robot is taken; to-be-detected target recognition is carried out on the current detection image; if a target to be detected is recognized in the current detection image, the current position and the current distance between the target to be detected and the robot are computed according to preset parameters; the current position and the current distance are stored in a time shaft module according to the time sequence; according to the current distance, the current position and the former distance and former position of the former time in the time shaft module, the moving speed of the target to be detected is computed; according to the current position, current distance and the moving speed of the target to be detected and the moving state data of the robot, the safe judgment relation between the target to be detected and the preset dangerous area as well as between the target to be detected and the preset safe area is determined; the robot is controlled to normally operate or stop operating or change a path according to the safe judgment relation. The safety of staff can be effectively ensured.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE INTELLIGENT EQUIP TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Automatic storage system of industrial robot
InactiveCN105292892AFree laborReasonable assemblyStorage devicesAcquired characteristicIdentification device
The invention discloses an automatic storage system of an industrial robot. The automatic storage system comprises a robot sorting area, a speed-fold chain, an AGV trolley, an intelligent three-dimensional warehouse and a central controller. The robot sorting area comprises a flat belt conveyor, a robot and a vision identification device. The flat belt conveyor receives a signal sent by the central controller and controls trays to move in the conveying direction of the flat belt conveyor. The vision identification device is installed on any side of the flat belt conveyor and located above the trays. A camera of the vision identification device is used for photographing the tray area below the camera, and the photographing area of the camera at least includes one tray. The vision identification device detects and identifies photos photographed by the camera, sends feature data obtained through identification to the central controller and sends a signal to the robot, and the robot receives the signal to transfer and put specified articles on the storage trays of the speed-fold chain to achieve sorting. According to the automatic storage system of the industrial robot, labor force of workers is liberated, and product detecting, sorting and storing efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUIBO ROBOTICS TECH CO LTD +1
Simulation method and device of digital twin system of industrial robot
InactiveCN108724190AAvoid exceptionImprove adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual technologyWork task
The invention provides a simulation method and device of a digital twin system of an industrial robot. The simulation device comprises the industrial robot, a vision perception unit and a computer, wherein the vision perception unit is arranged at the tail end of the robot and is composed of a camera and a wire structure light emitter; an industrial robot simulation system is established, the robot is modeled, and three instructions are analyzed and run; a target three-dimensional measurement model of a robot visual system is acquired by using a wire structure optical geometric triangular method; a motion instruction is determined for the working task of the robot, virtual simulation is carried out through the computer, and reachable points and collision point detection are carried out; and the robot is actually used for identifying a target object through the visual perception unit, and the actual movement of the robot is driven. The simulation device is safe and reliable in virtual simulation, abnormal operation possibly in actual operation is avoided, the visual perception unit is used for identifying the target object through three-dimensional visual technology, the self-adaptive capacity of the robot to the field environment is improved, and flexibility and intelligence are enhanced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Mobile Robot For A Harsh, Corrosive Outdoor Environment
InactiveUS20130011234A1Shorten the timePrevent and minimize and eliminate degradationProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusSimulationOil and natural gas
An industrial robot including a plurality of arms movable relative each other about a plurality of joints, and electrical motors moving the arms. The robot is also arranged and designed to resist corrosion in a harsh environment. The robot is also mobile and arranged for movement or travel and suitable for maintenance and inspection tasks in an installation for oil and gas.
Owner:ABB AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com