Patents
Literature
10448 results about "Distance measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
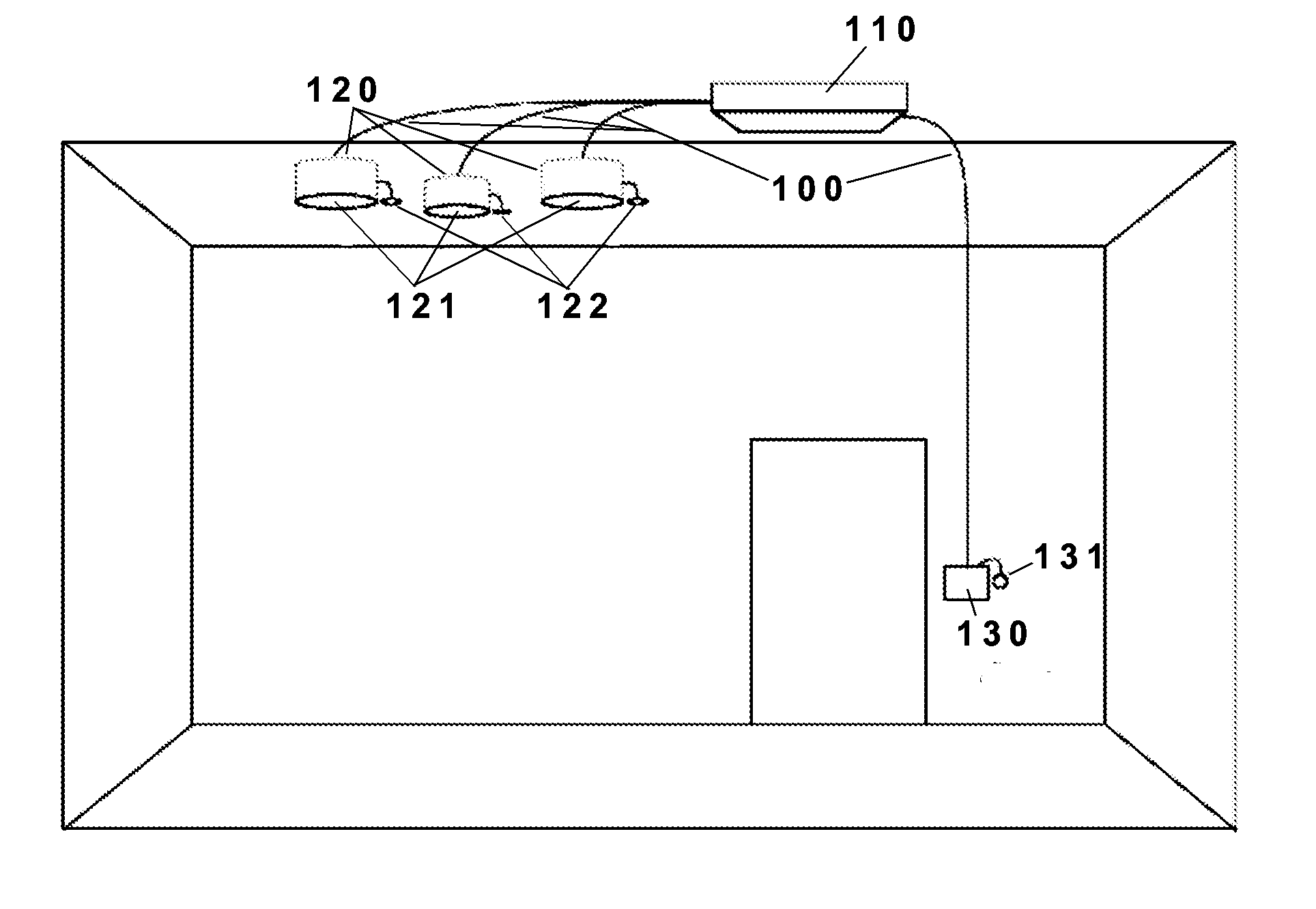
Lighting systems and methods of auto-commissioning
ActiveUS20110031897A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectrical apparatusMicrocontrollerEngineering
A lighting system for areal illumination is disclosed which includes a remote driver and a plurality of fixtures including luminaires, control devices, and / or standalone sensors. The luminaires include a light source whose output light level can be adjusted, a light sensor co-located therewith adapted to measure light received from adjacent fixtures, and a microcontroller capable of transmitting the output of the light sensor over wires to the remote driver. The remote driver is capable of bidirectional communication with the luminaires and provides independently controllable power for the light sources of the luminaires. A method of commissioning a lighting system is also disclosed which includes installing a plurality of luminaires above the area to be illuminated, causing a light source co-located with each luminaire to emit a signal, detecting the signal at light sensors co-located with each luminaire, converting the signals obtained by the light sensors into distance measurements between luminaires, creating a map recording the relative location of luminaires, and assigning luminaires to groups based on their relative locations in the map. A movable orb region large enough to containing a plurality of luminaires can also be defined and the light levels of individual luminaires can be set according to a defined mathematical function of their location within the orb region, where the defined mathematical function sets light levels which vary from the center to the periphery of said orb region.
Owner:WTEC GMBH
Method and apparatus for enhancing security in a wireless network using distance measurement techniques
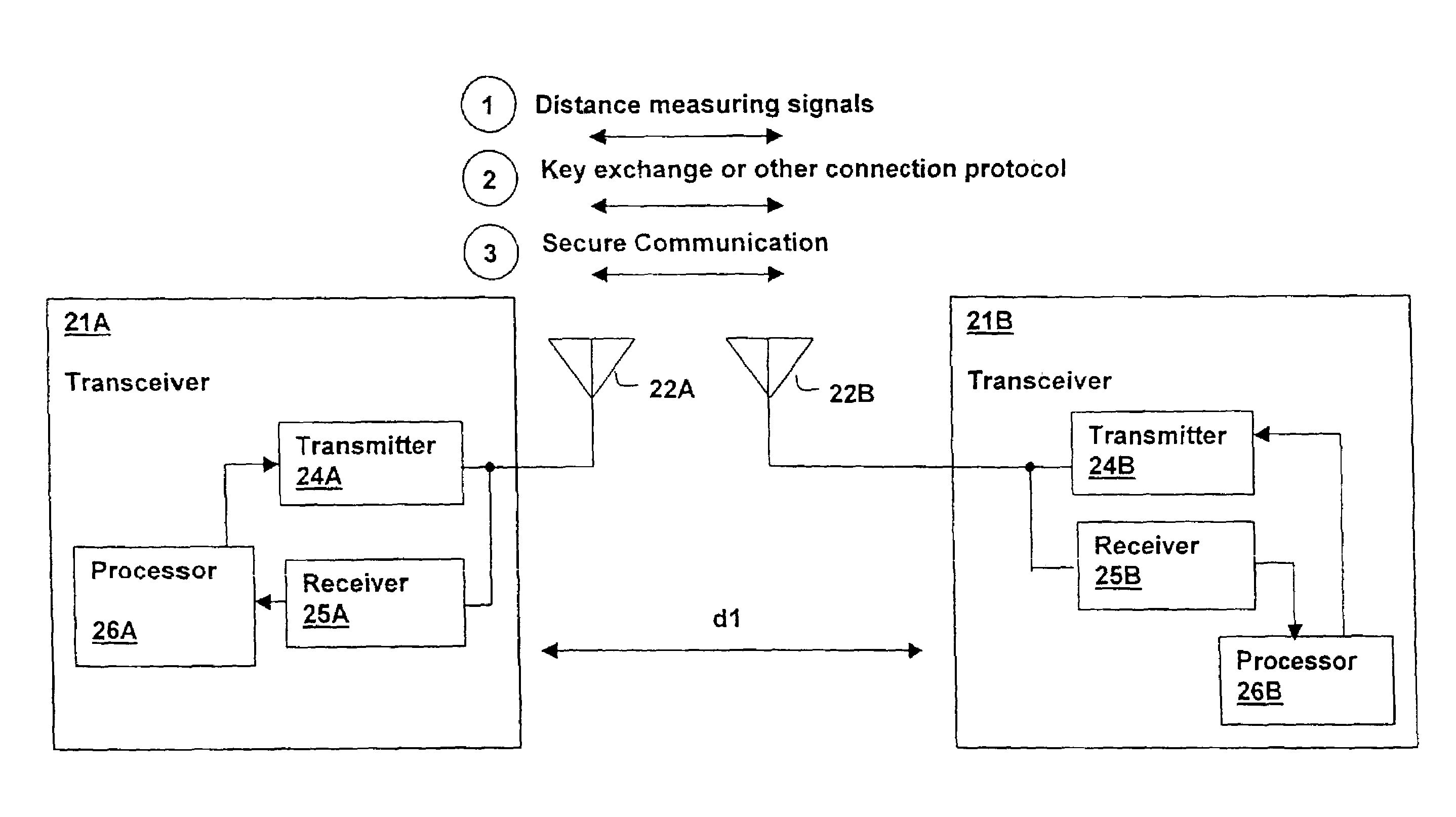
InactiveUS6961541B2Improve securityNear-field transmissionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionShortest distanceCombined use
A method and apparatus for enhancing security in a wireless network using distance measurement techniques provides an additional layer of security and privacy in wireless communications. A distance measurement or location-finding is performed between two devices by transmitting and receiving one or more signals and computing a distance between the two devices or a location of a connecting device. The resulting computed distance or location is used to determine whether or not to permit pairing, secure connection or secure transactions between the two devices. The computed distance or location can be further used in combination with a signal strength measurement to link to locate and measure nearby devices first, reducing the time required to initialize network communications. Management software may be enhanced to facilitate connecting to desired devices by providing an indication of computed distance or location of each device, and a list may be generated in order of proximity, further facilitating connection to the desired devices. Set-up of wireless networks may automated by using a short distance to facilitate connection between nodes.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
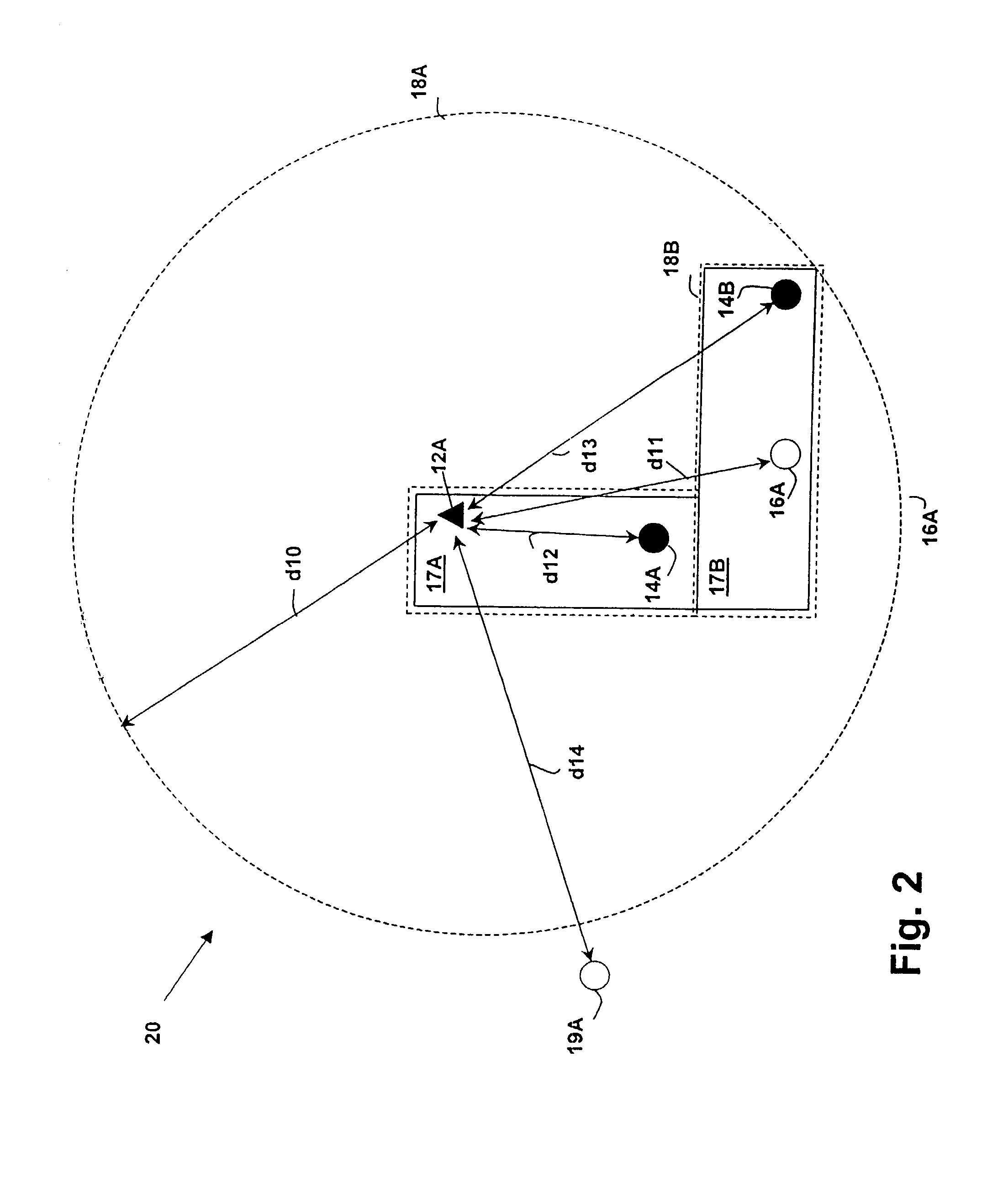
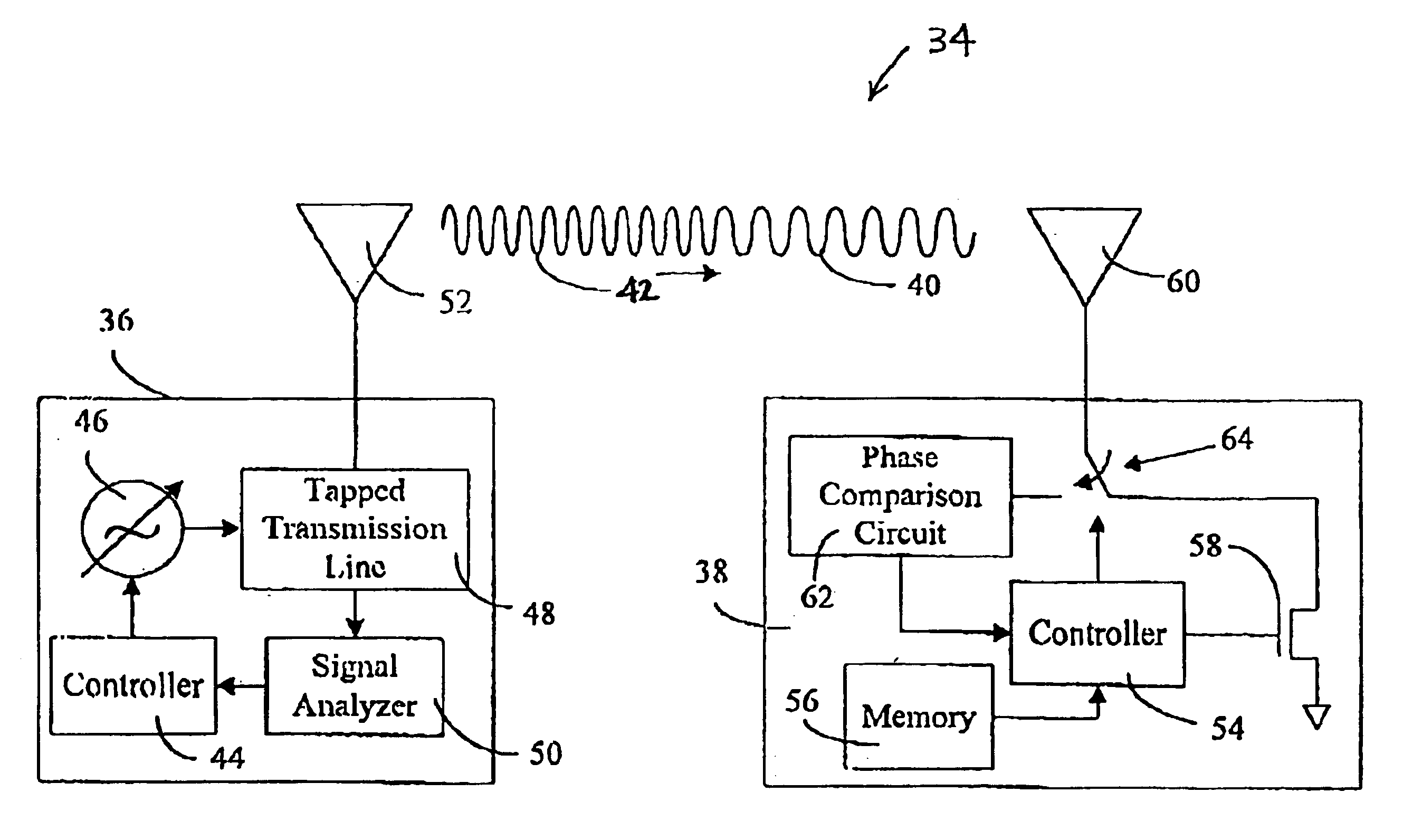
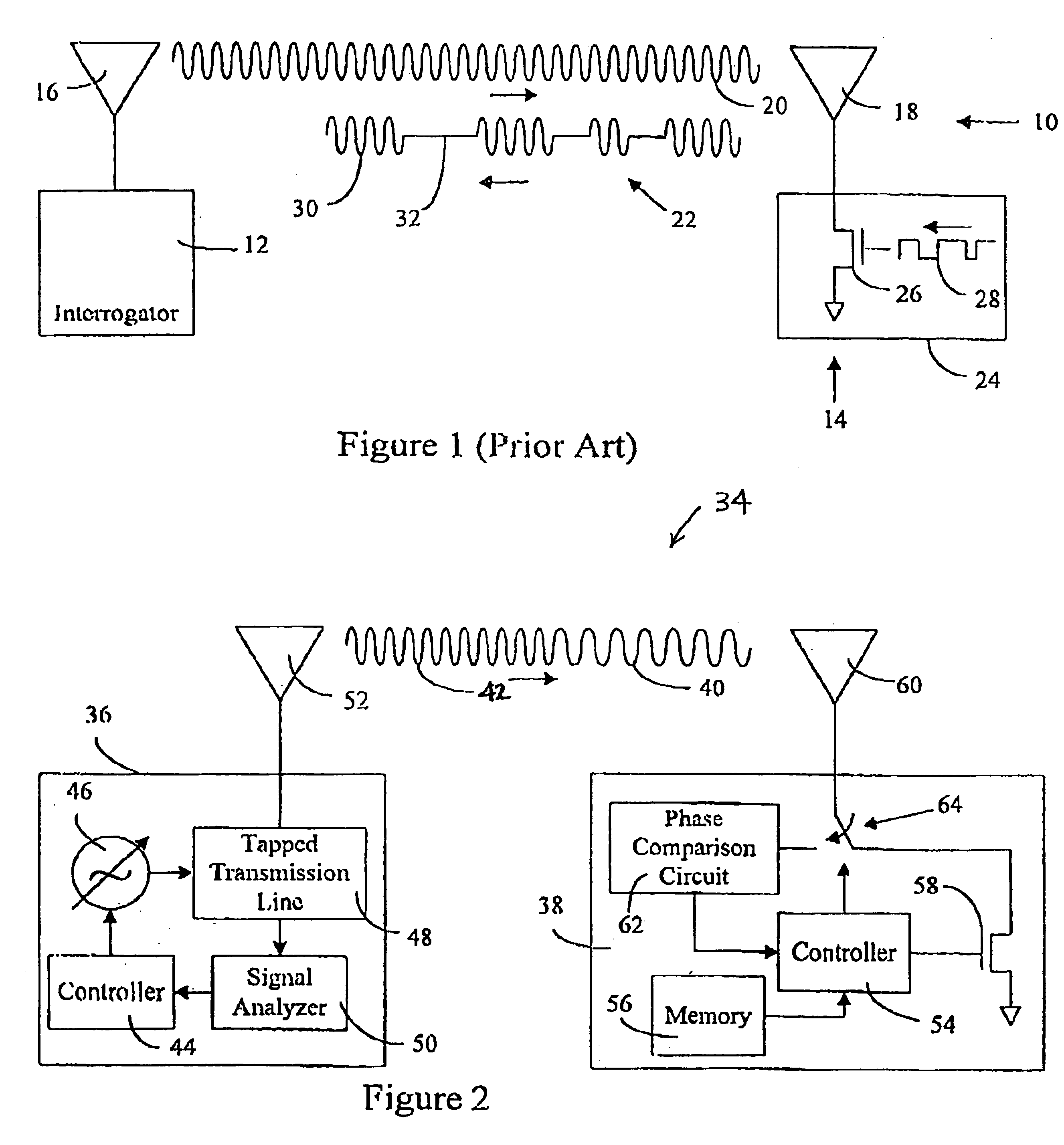
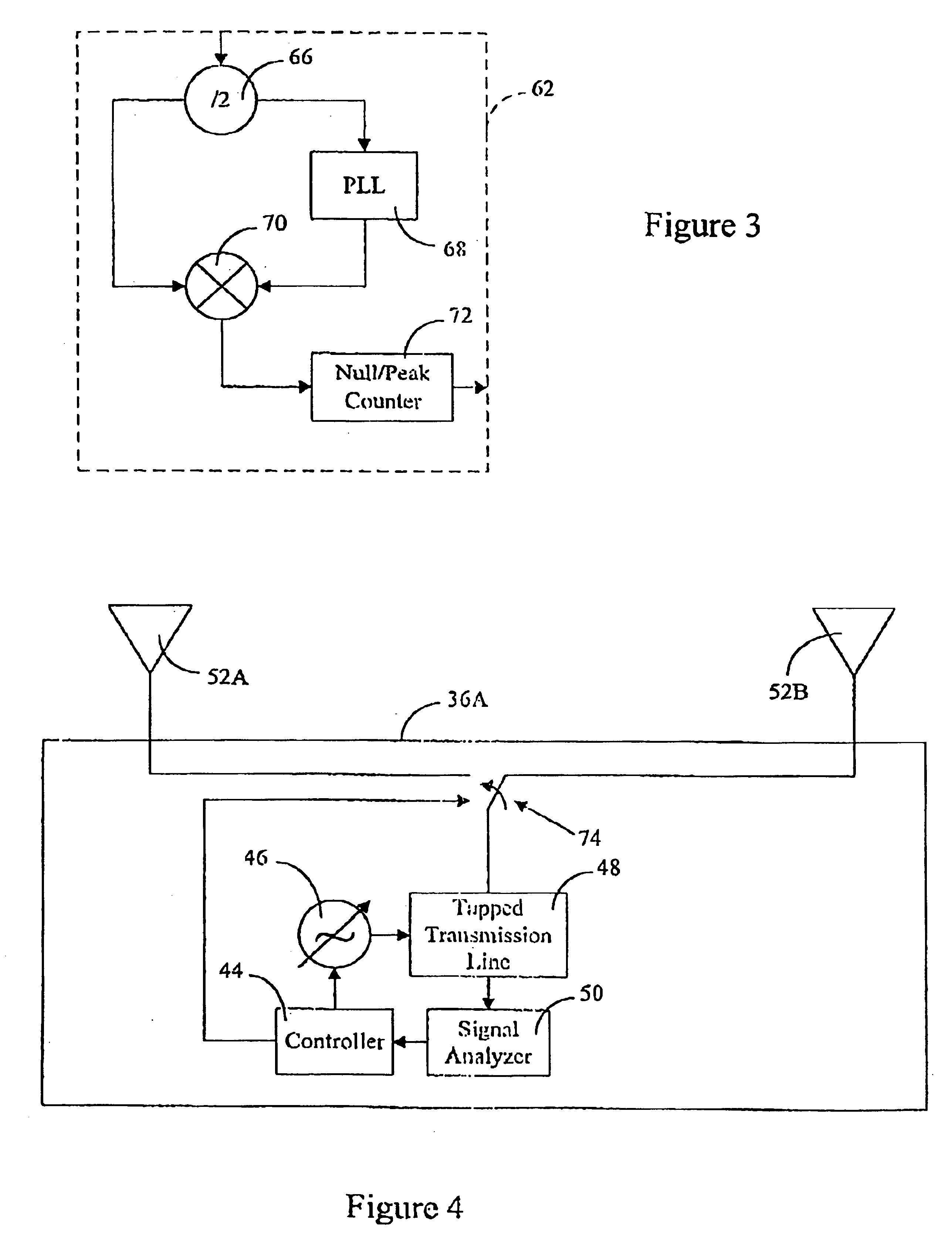
Distance/ranging by determination of RF phase delta
A method and system can locate an RF transponder based on phase differences between signals transmitted to the RF transponder. The method transmits from a first transponder to a second transponder first and second signals at first and second frequencies, respectively. The second signal is compared with the first signal and a distance between the first and second transponders is determined based on the phase difference between the first and second signals. In one embodiment, the first transponder is an interrogator, the second transponder is an RF tag, and the RF tag determines the phase difference between the two signals. In another embodiment, the first and second transponders are the interrogator and RF tag, respectively, but the interrogator determines the phase difference between the two signals after the two signal are reflected back to the interrogator. The method can also determine a position (distance and direction) of the RF tag by measuring the distances from two different locations of the interrogator to the RF tag. In one embodiment, the two distances are measured from two spaced-apart antennas of the interrogator. In another embodiment, the interrogator is moved from one known location to another known location. With distance measurements from both known locations, the location of the RF tag can be determined by simple geometry.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
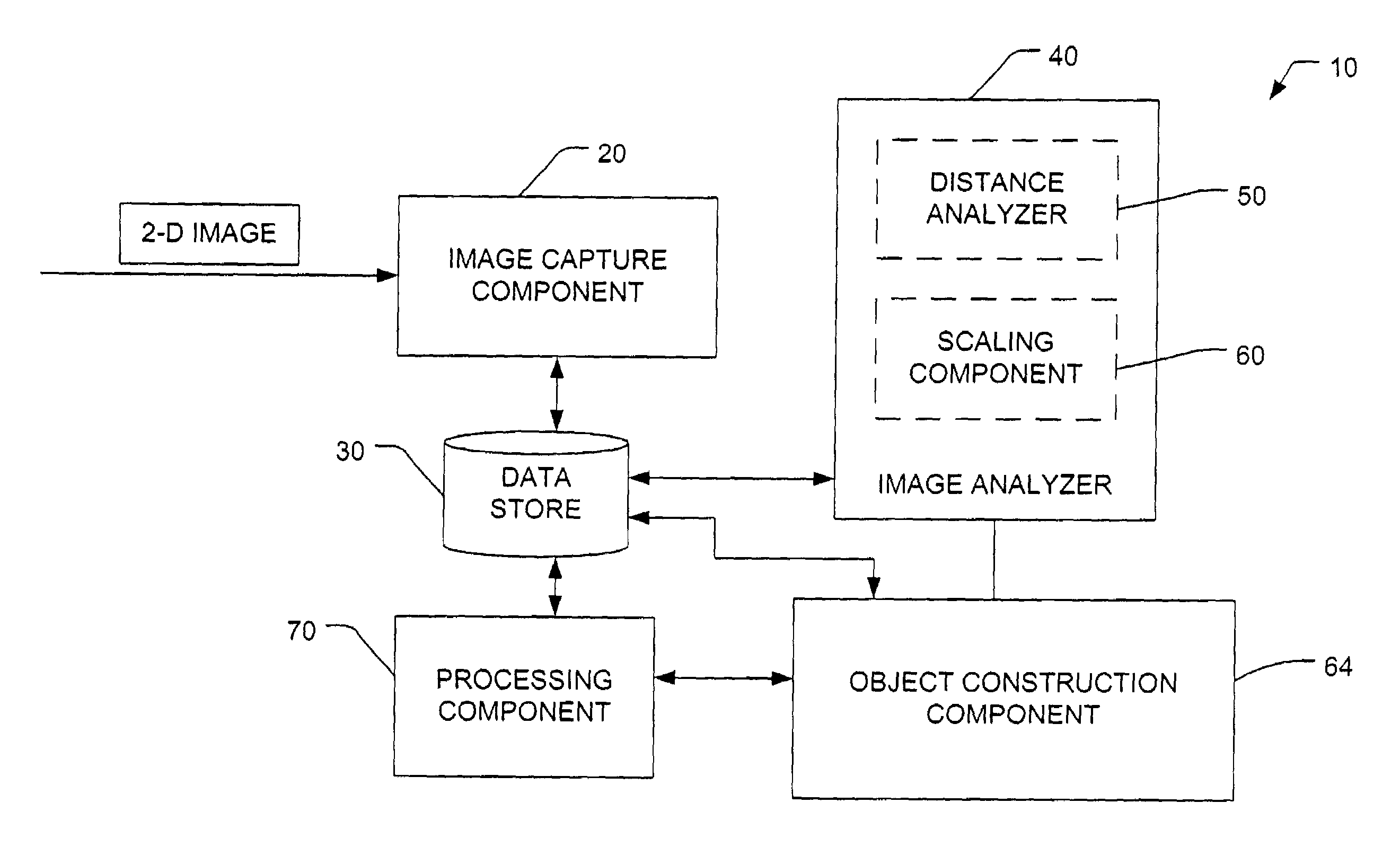
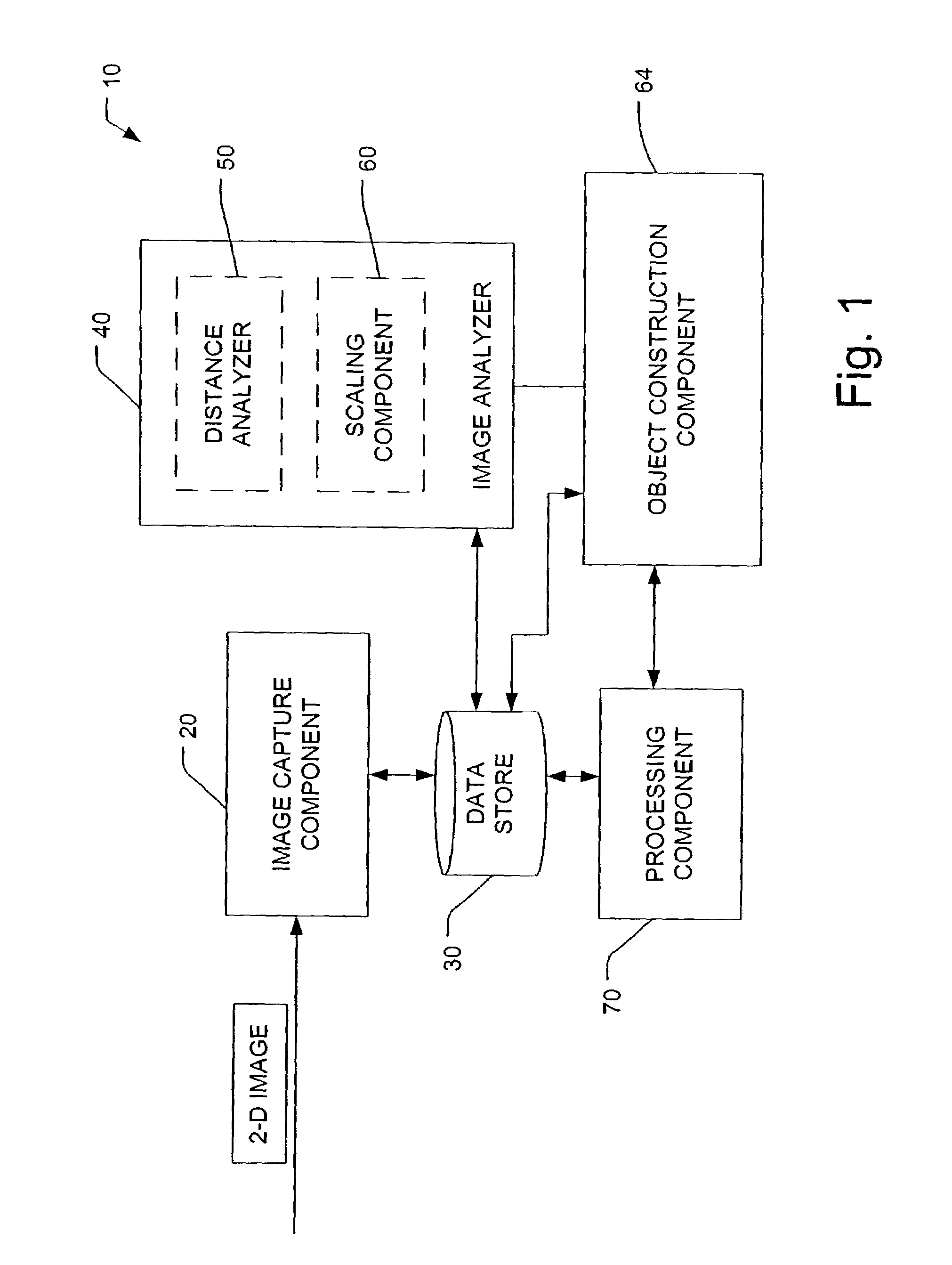
Measurement of dimensions of solid objects from two-dimensional image(s)
The present invention facilitates solid object reconstruction from a two-dimensional image. If an object is of known and regular shape, information about the object can be extracted from at least one view by utilizing appropriate constraints and measuring a distance between a camera and the object and / or by estimating a scale factor between a camera image and a real world image. The same device can perform both the image capture and the distance measurement or the scaling factor estimation. The following processes can be performed for object identification: parameter estimation; image enhancement; detection of line segments; aggregation of short line segments into segments; detection of proximity clusters of segments; estimation of a convex hull of at least one cluster; derivation of an object outline from the convex hull; combination of the object outline, shape constraints, and distance value.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
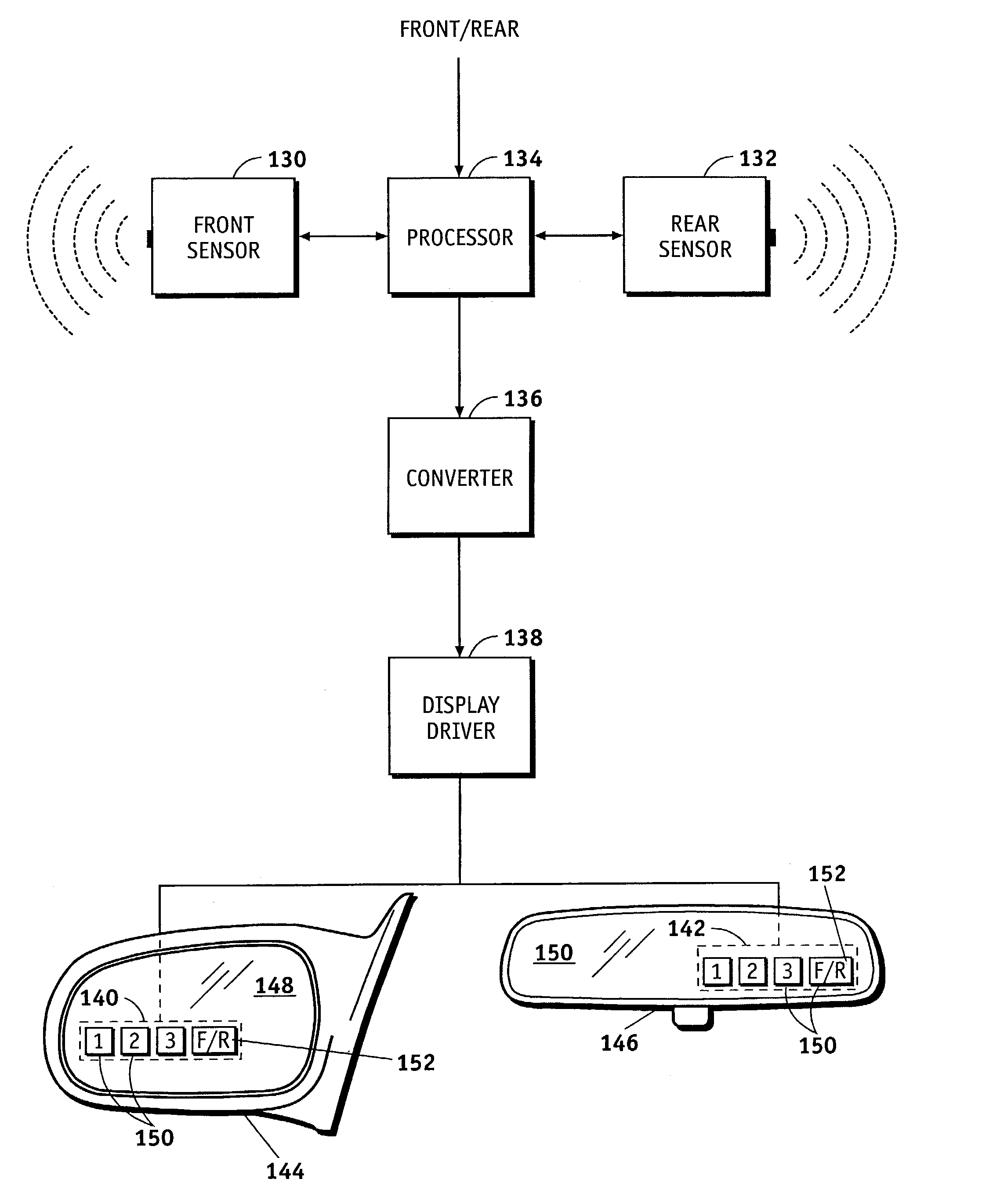
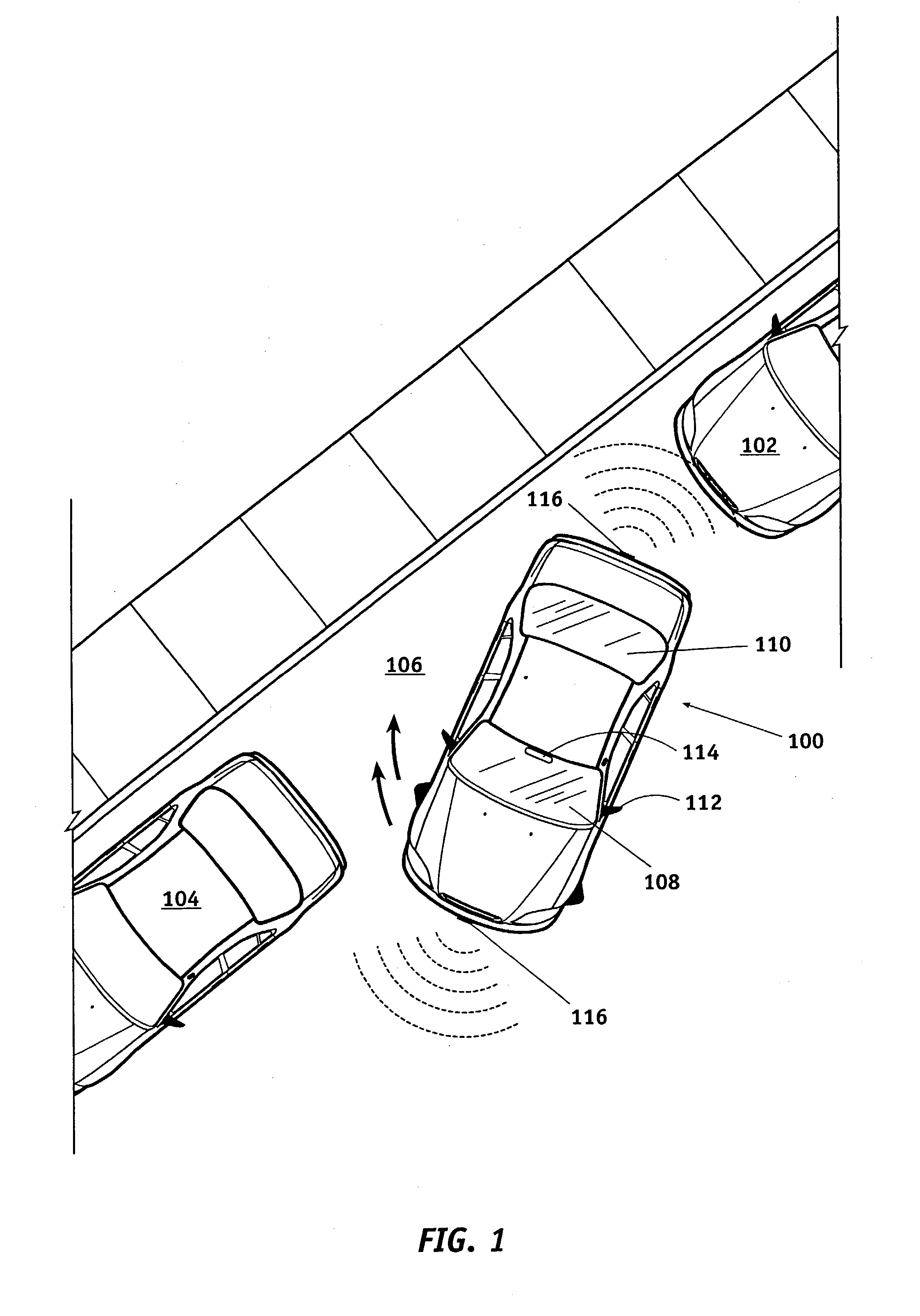
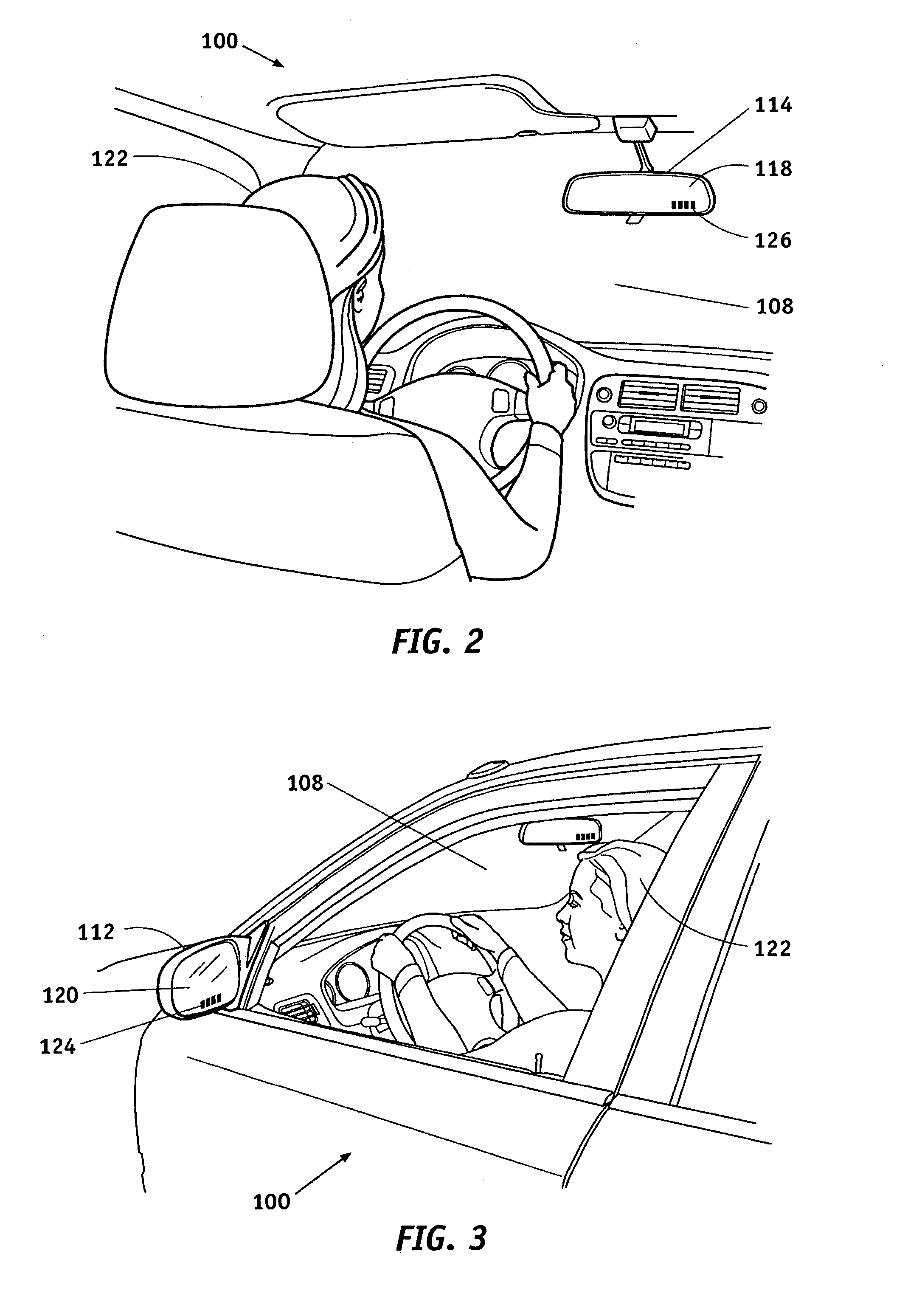
Distance detection and display system for use in a vehicle
A distance measuring and display system for use on a vehicle having a mirror assembly thereon comprises at least one front distance measuring sensor for measuring the distance to an obstacle in front of the vehicle, at least one rear distance measuring sensor for measuring the distance to an obstacle to the rear of the vehicle, and a display coupled to the front distance measuring sensor and to the rear distance measuring sensor for displaying a distance and an indication of whether it is a front distance or a rear distance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
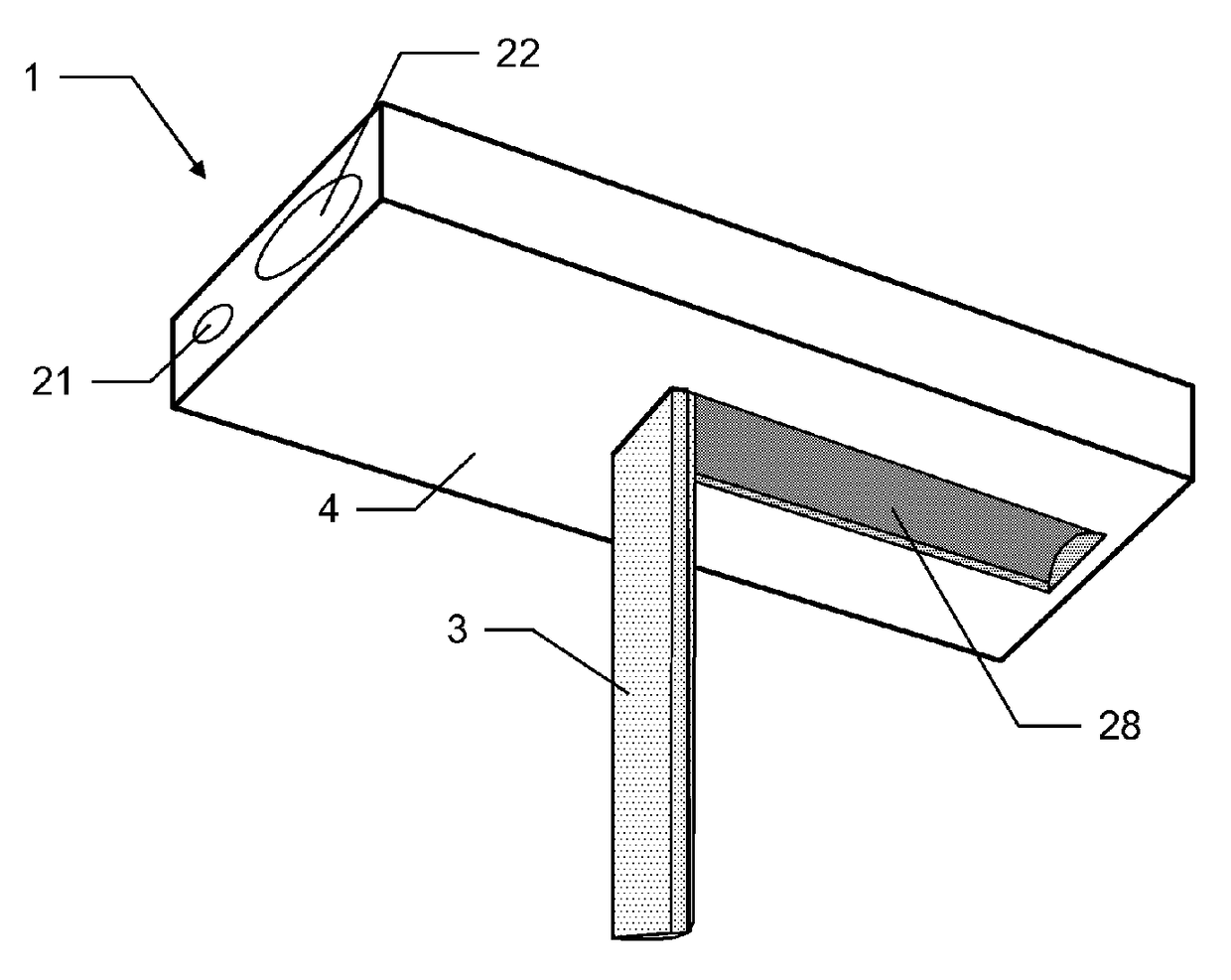
Hand-held distance-measuring device having an angle-determining unit
ActiveUS9753135B2Small designEasy to fixOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansMeasurement deviceHand held
Some embodiments of the invention relate to a hand-held distance-measuring device, comprising a housing, a distance-measuring unit for measuring distances to spatial points along an emission direction in a space, an evaluating component, a dimensionally stable referencing support, and an angle-determining unit for determining an angle of rotation (a, between the housing and the referencing support. In some embodiments, the housing and the referencing support are designed in such a way and coordinated with each other in such a way that the referencing support can assume a passive position, in which the referencing support is inserted into an recess of the housing or is fastened such as to lie flatly against the housing. In some embodiments, the referencing support can assume a referencing position in which the referencing support is connected to the housing at a first end of the referencing support by means of a joint.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Implantable medical device for measuring mechanical heart function
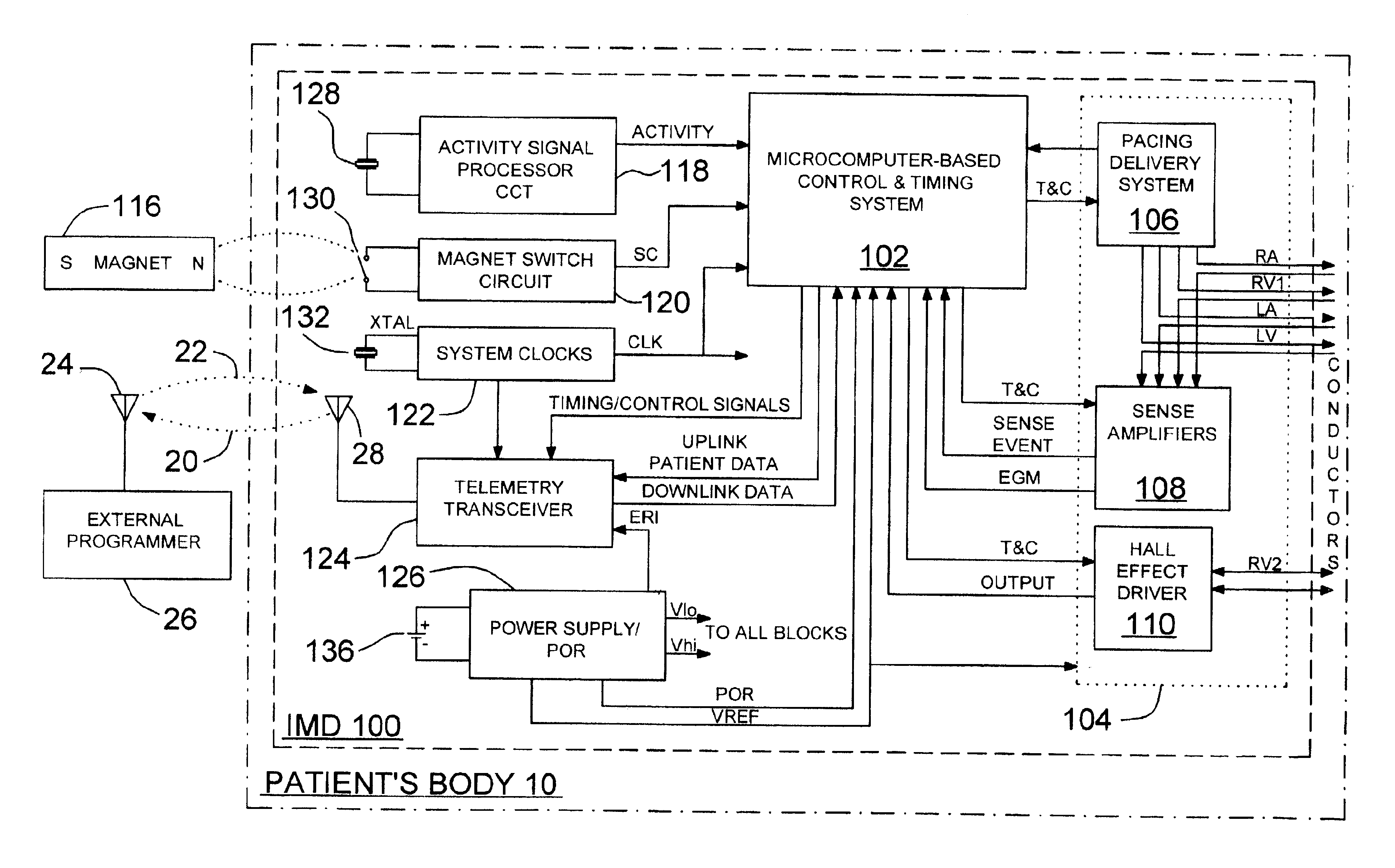
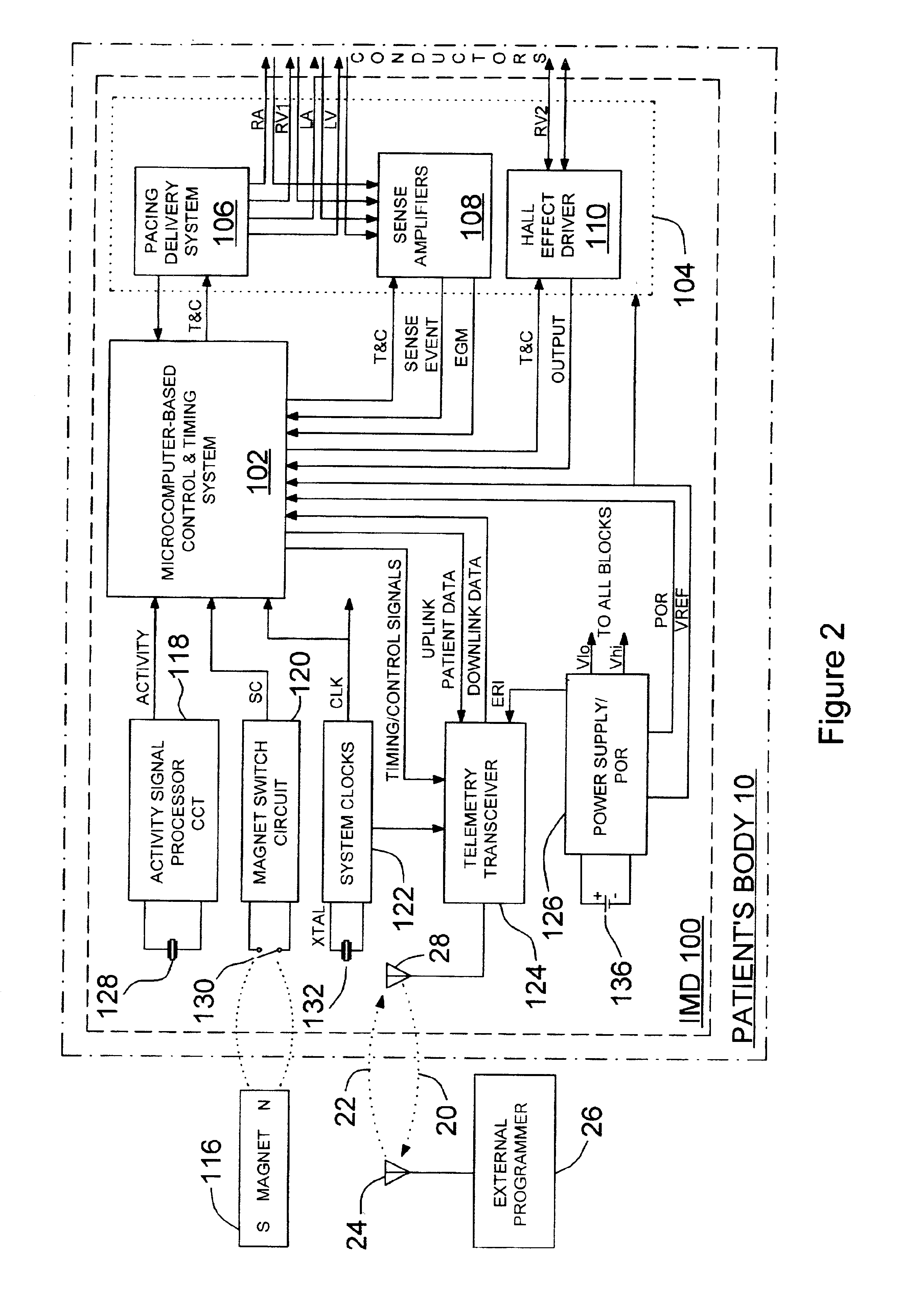
InactiveUS6959214B2Output maximizationPrecise positioningHeart stimulatorsProper treatmentHeart chamber
An implantable device for measuring mechanical heart function of selected heart chambers using a heart contraction detection system that includes a magnetic field sensor. The system may be used for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure, to enable diagnosis of the condition of the heart, to prescribe appropriate therapies, and to assess delivered pacing therapies. Distance measurements within the heart are made using the magnetic field sensor which is implanted at a sensor site in or on one of the right or left ventricle. A magnet implanted at a site relative to the other of the left or right heart ventricle is sufficiently spaced at a distance that fluctuates with expansion and contraction of the ventricles. The magnetic field sensor provides a sensor output signal having a signal magnitude proportional to the magnetic field strength of the magnet, and which is indicative of changing cardiac dimensions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
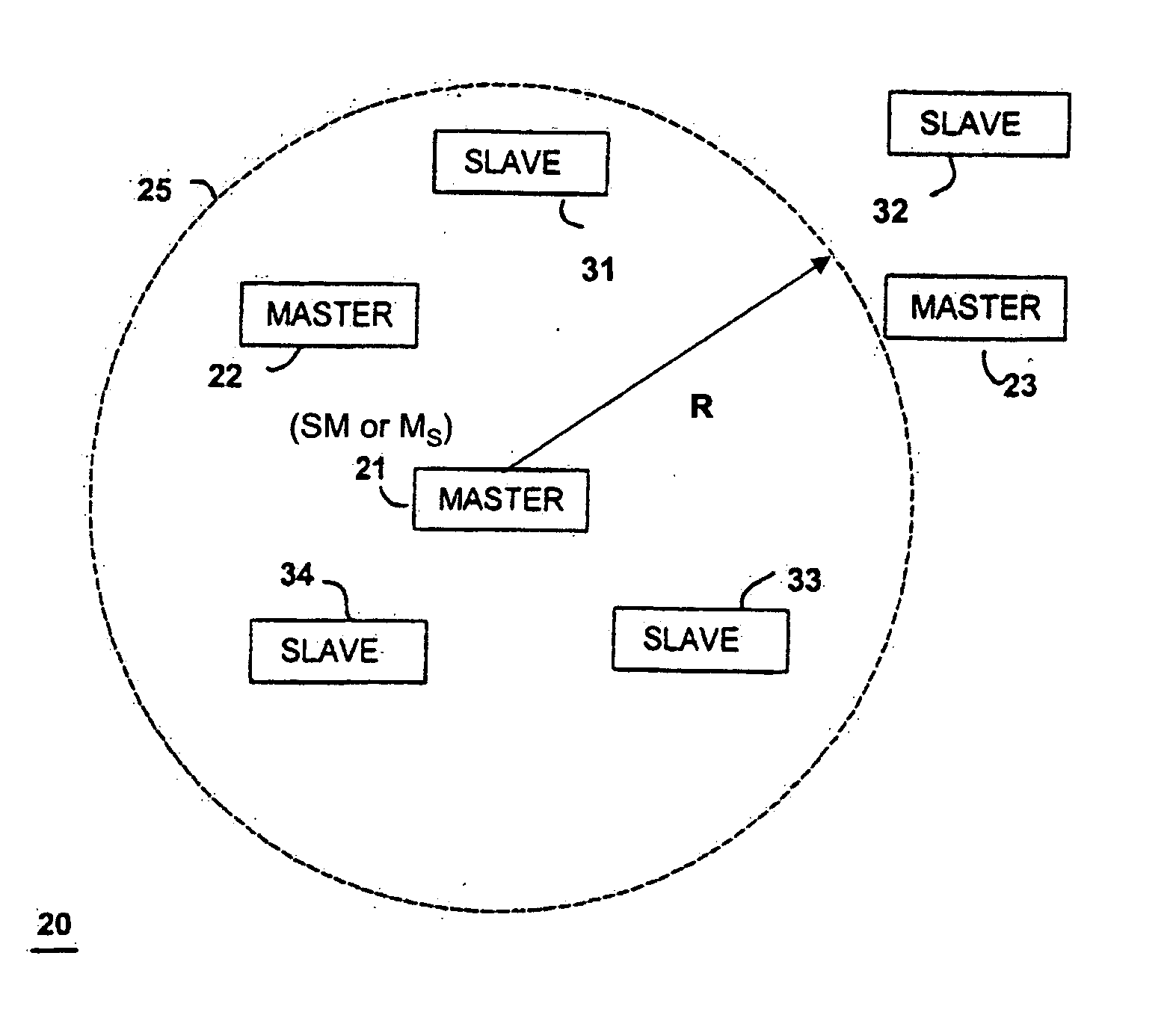
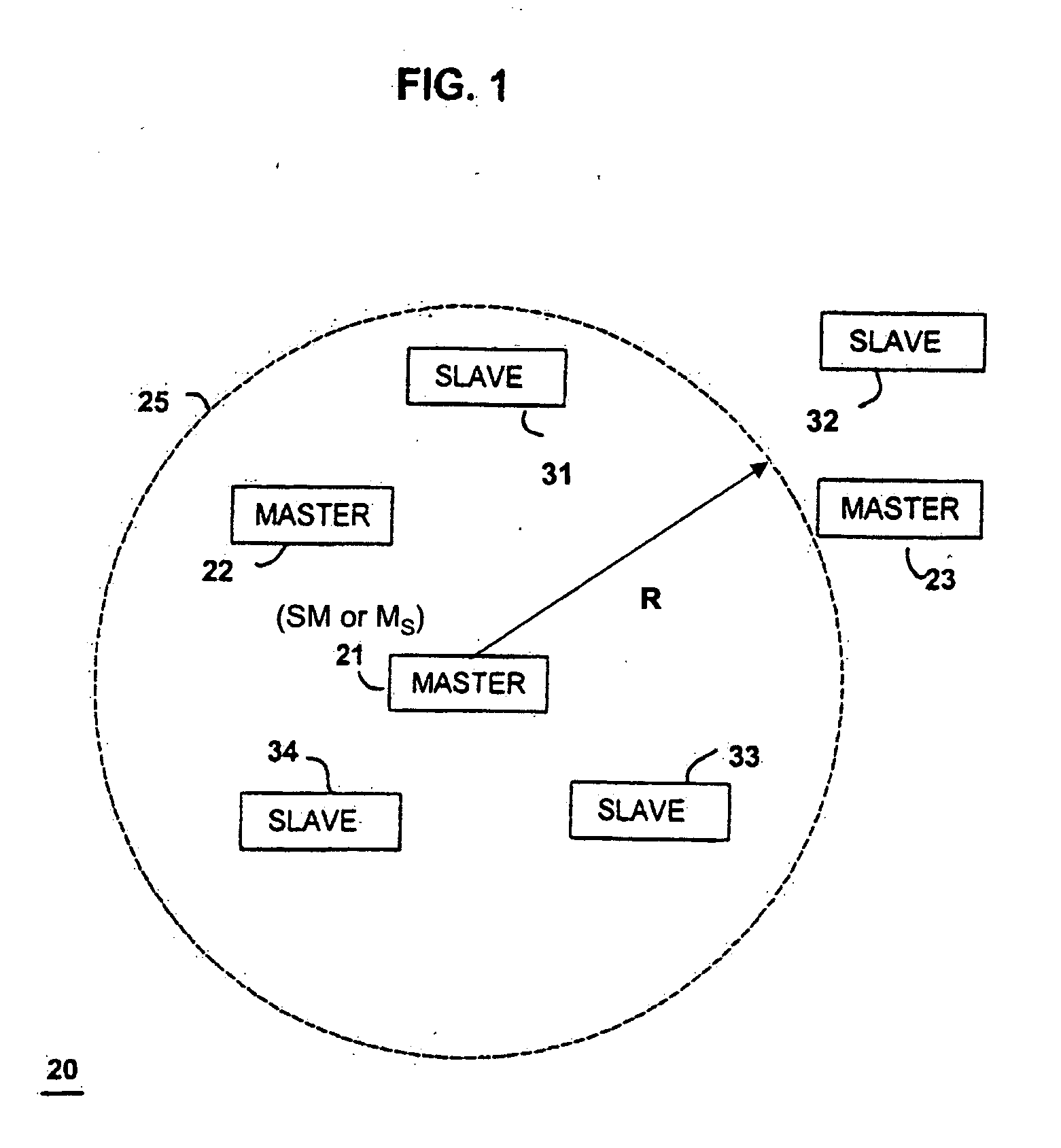
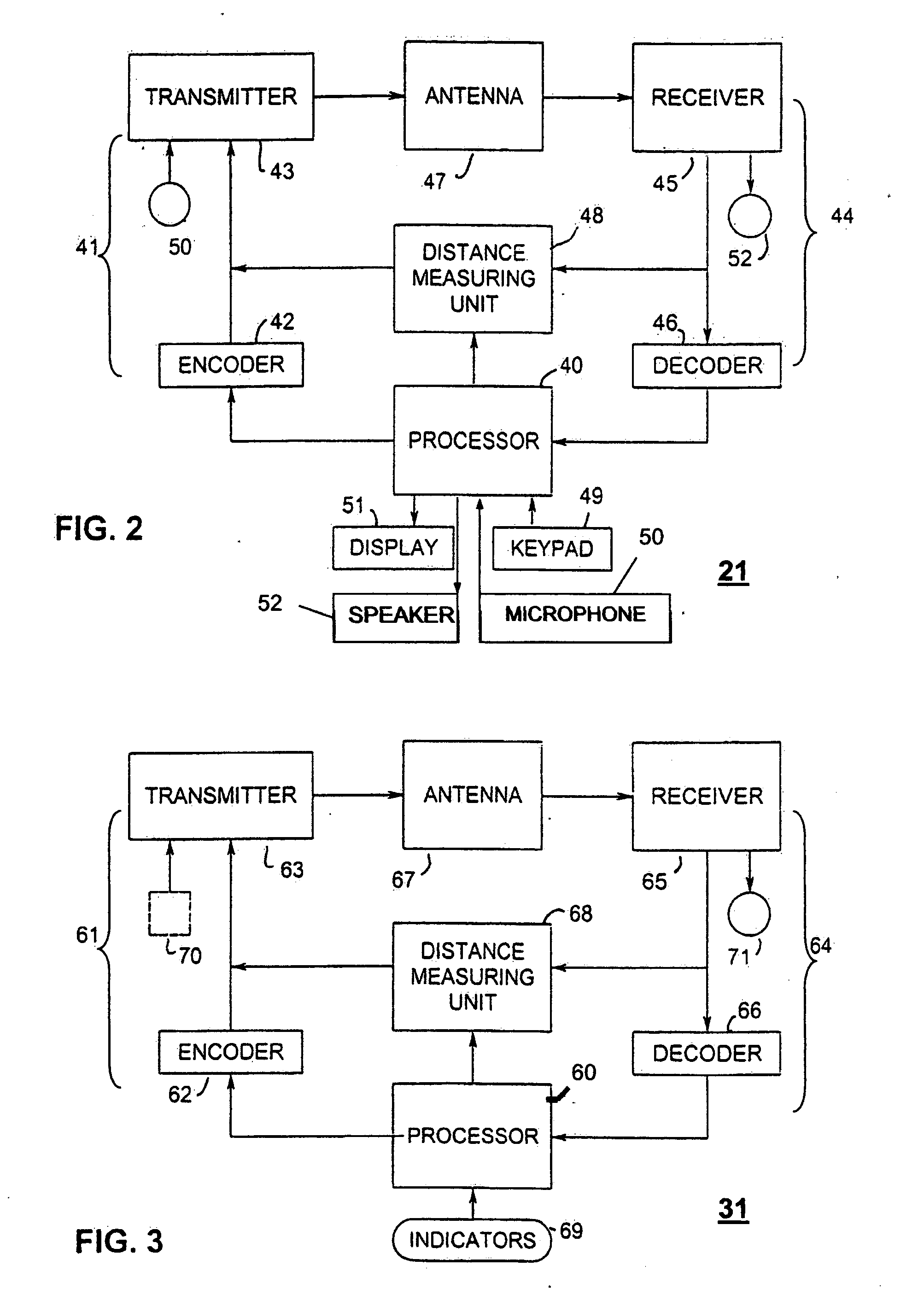
Method and system for finding
ActiveUS20060012476A1Simplified triangulationUser-device interaction is minimized—eliminatingElectric signalling detailsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalUser deviceTransceiver
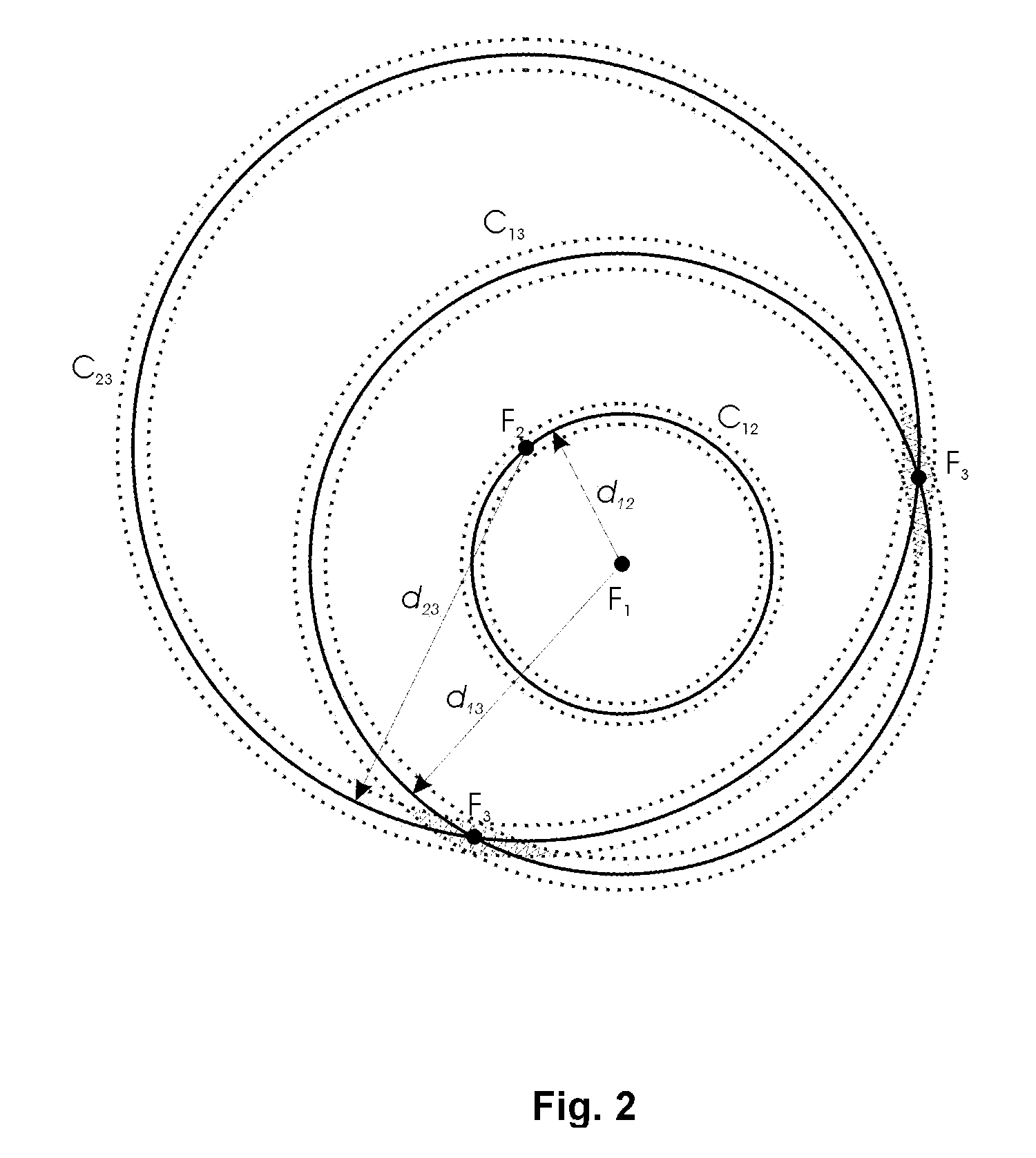
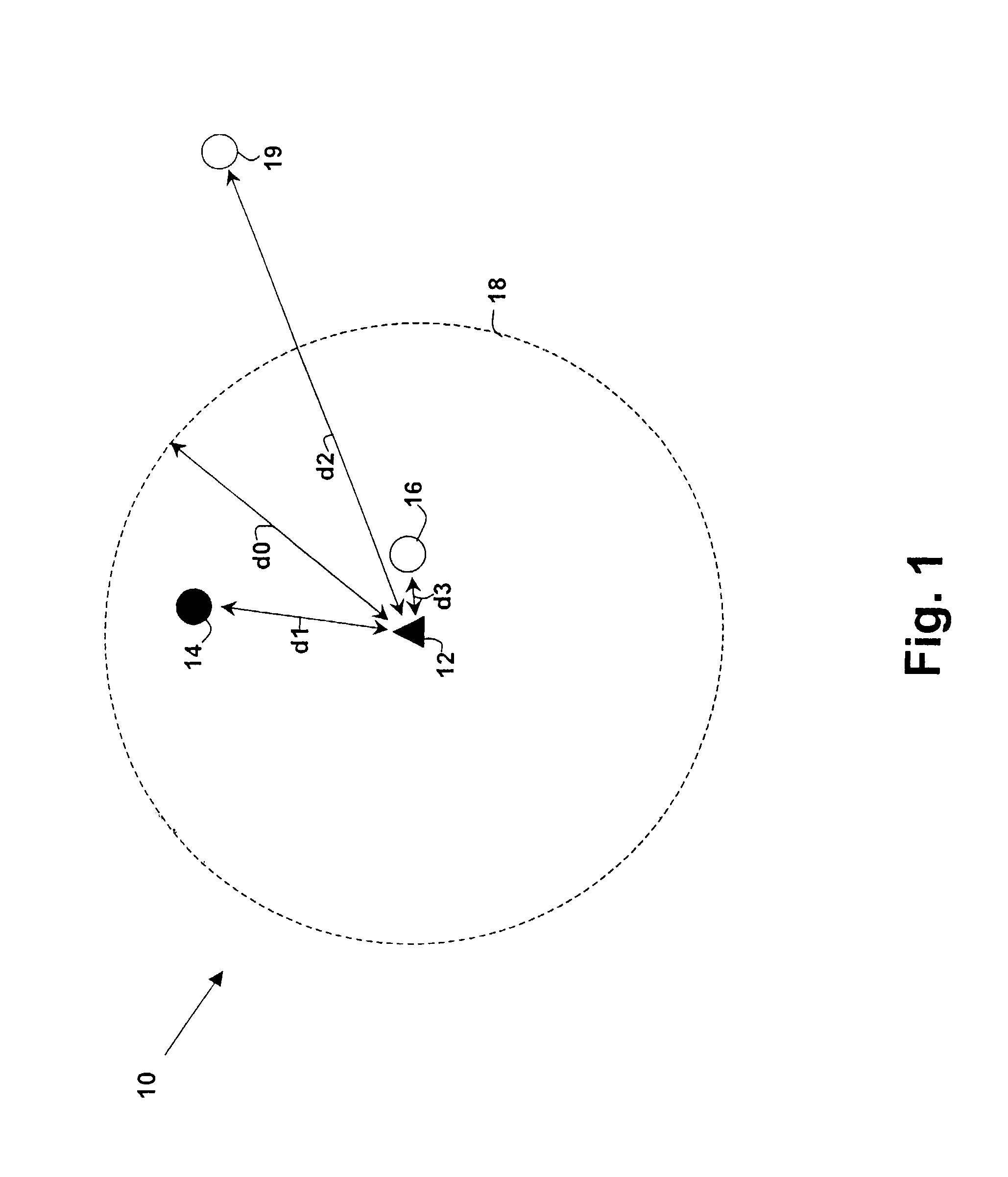
A wireless system and method for determining the location of a fixed or mobile subject or object includes a transponder disposed on the target, a transceiver for monitoring the location of the target, a wireless communication system operating on at least one Radio Frequency (RF) band configured to allow communication between the transponder and the transceiver, and a processor configured to find the target by virtual triangulation based on values of position information received from the transponder and the transceiver. The processor is configured to determine virtual triangulation based on successive values of the position information using at least three points P1, P2 and P3 of the transponder respective of the transceiver. The processor can include a means for position ambiguity reduction (PAR) configured to find the target by correcting the direction to the location of the target T based on the values of the position information. The processor can also determine the position of the target based on the average speed of the motion of the user of the transponder respective of the transceiver. Furthermore, the processor can determine virtual triangulation based on successive values of the position information from user input on the transceiver. The method finding the target T (“finder” techniques) based on one or more position determination principles including determining the position of the target using virtual triangulation between the master or monitoring unit and at least one target T, whereby the monitoring device Ms measures the distance between it and the slave unit and, alternatively, in addition to measuring the distance between itself and the slave unit, between itself and another monitoring unit, or the monitoring device Ms measures the distance between its own successive locations. The present invention also discloses methods for finding with virtual triangulation by: (1) finding with virtual triangulation by generating position information in real-time, in the case of (i) stationary and moving target, and or (ii) in the case of the presence of obstacles; (2) finding with virtual triangulation relating to the average speed of the motion of operator; and or (3) finding with simplified virtual triangulation, whereby the user-device interaction is minimized—eliminating the need for monitoring device Ms to measure the distance between its own successive locations as well as the user's signaling to the monitoring or master unit when in motion or during stops.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
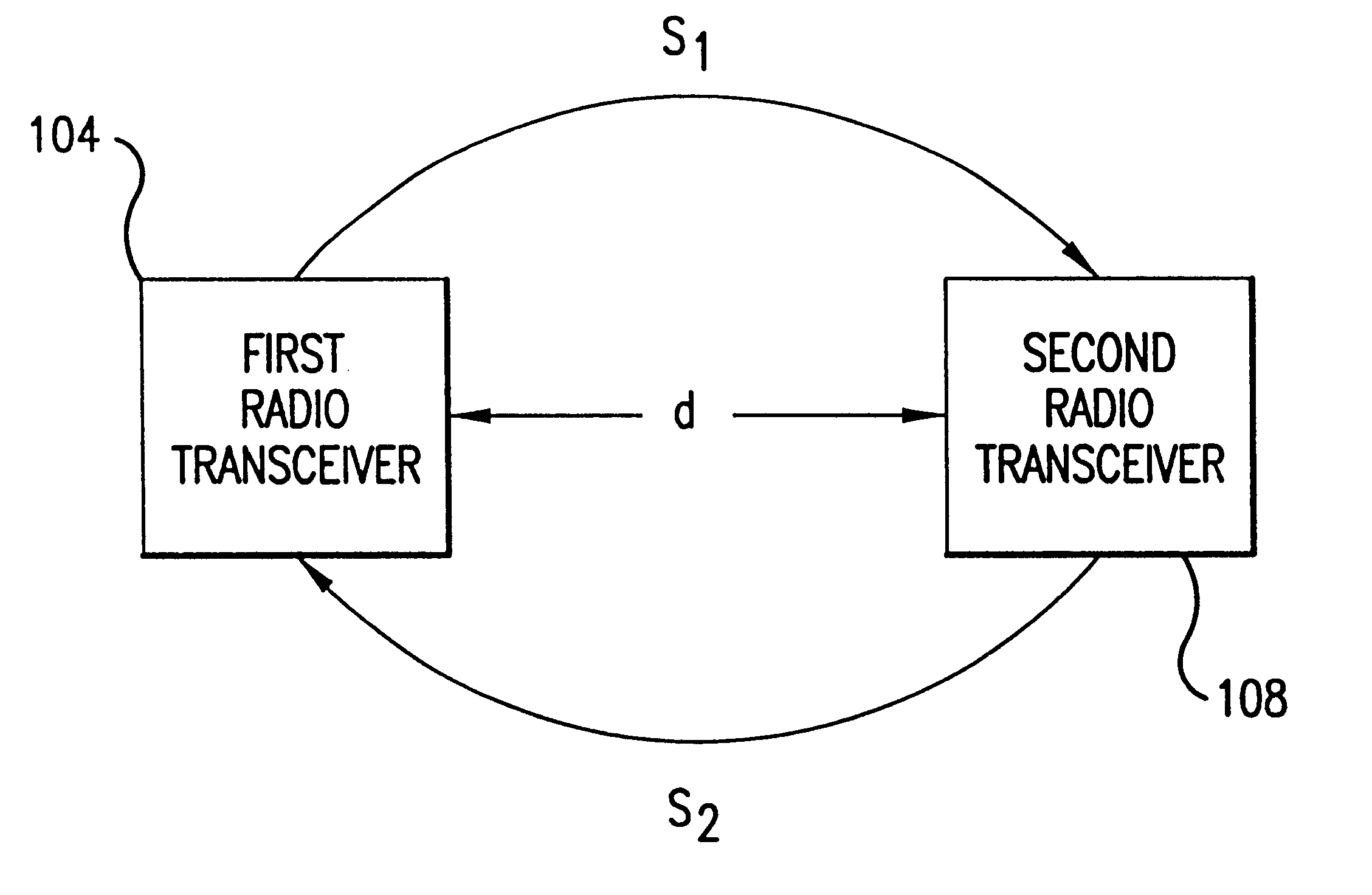
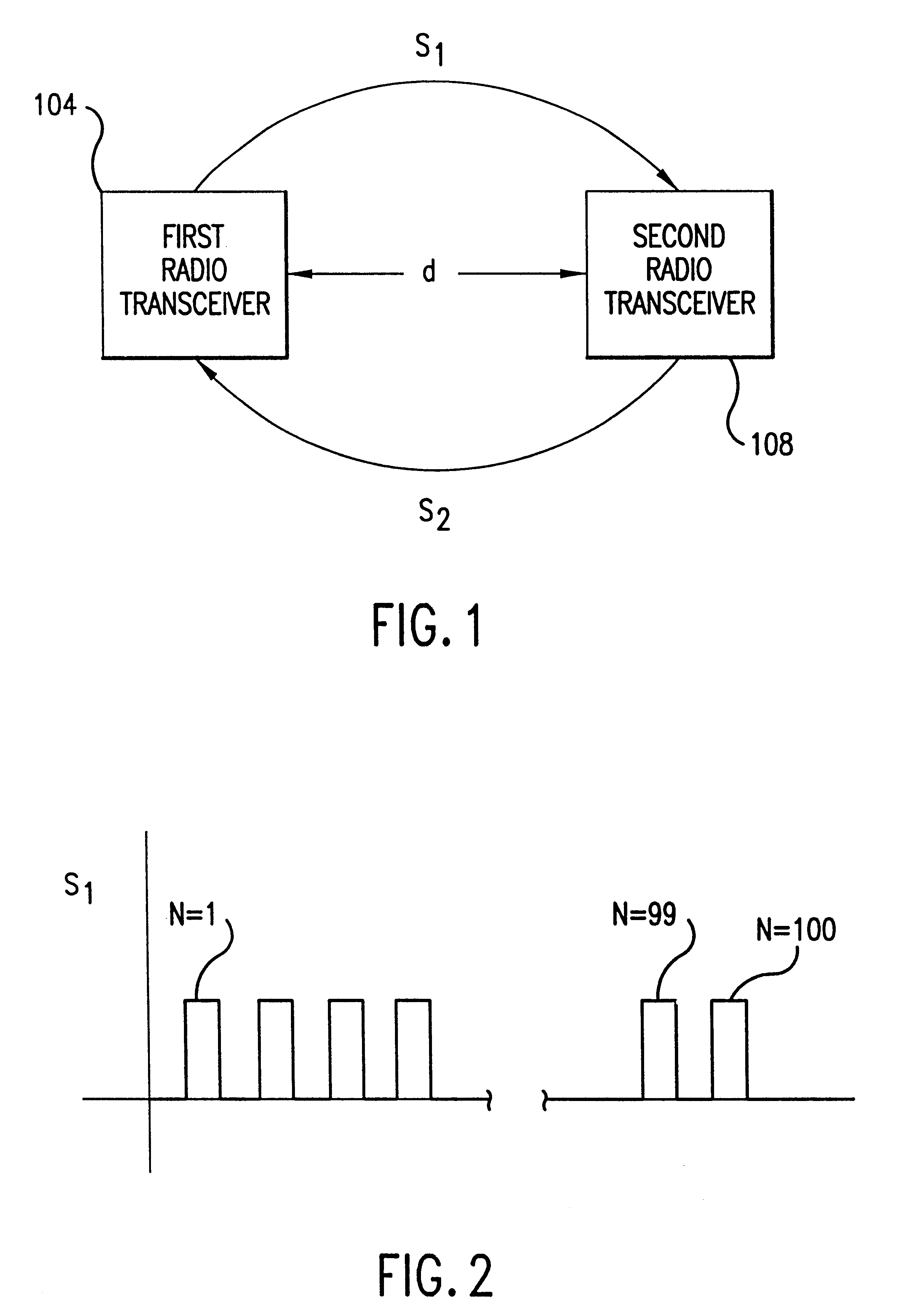
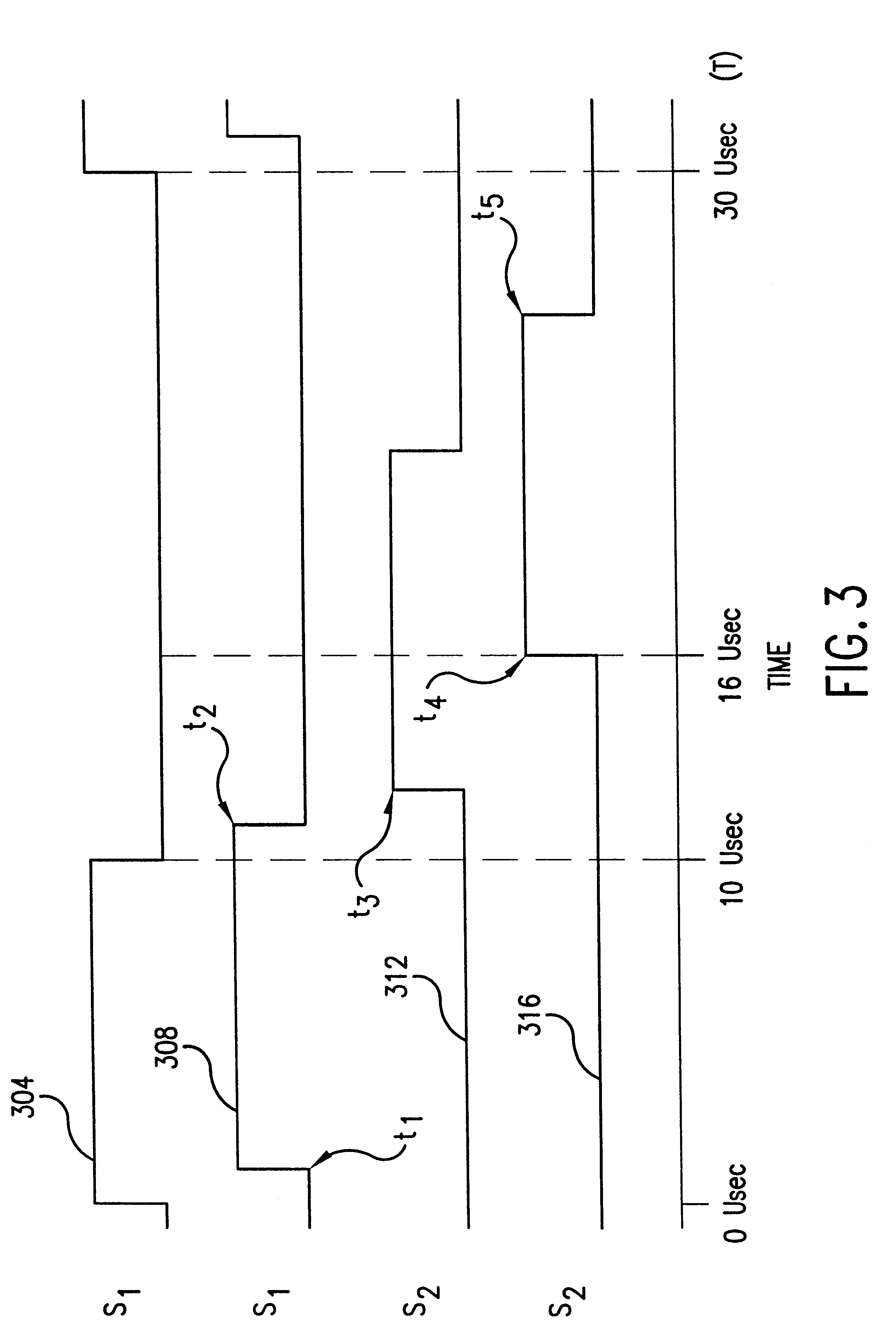
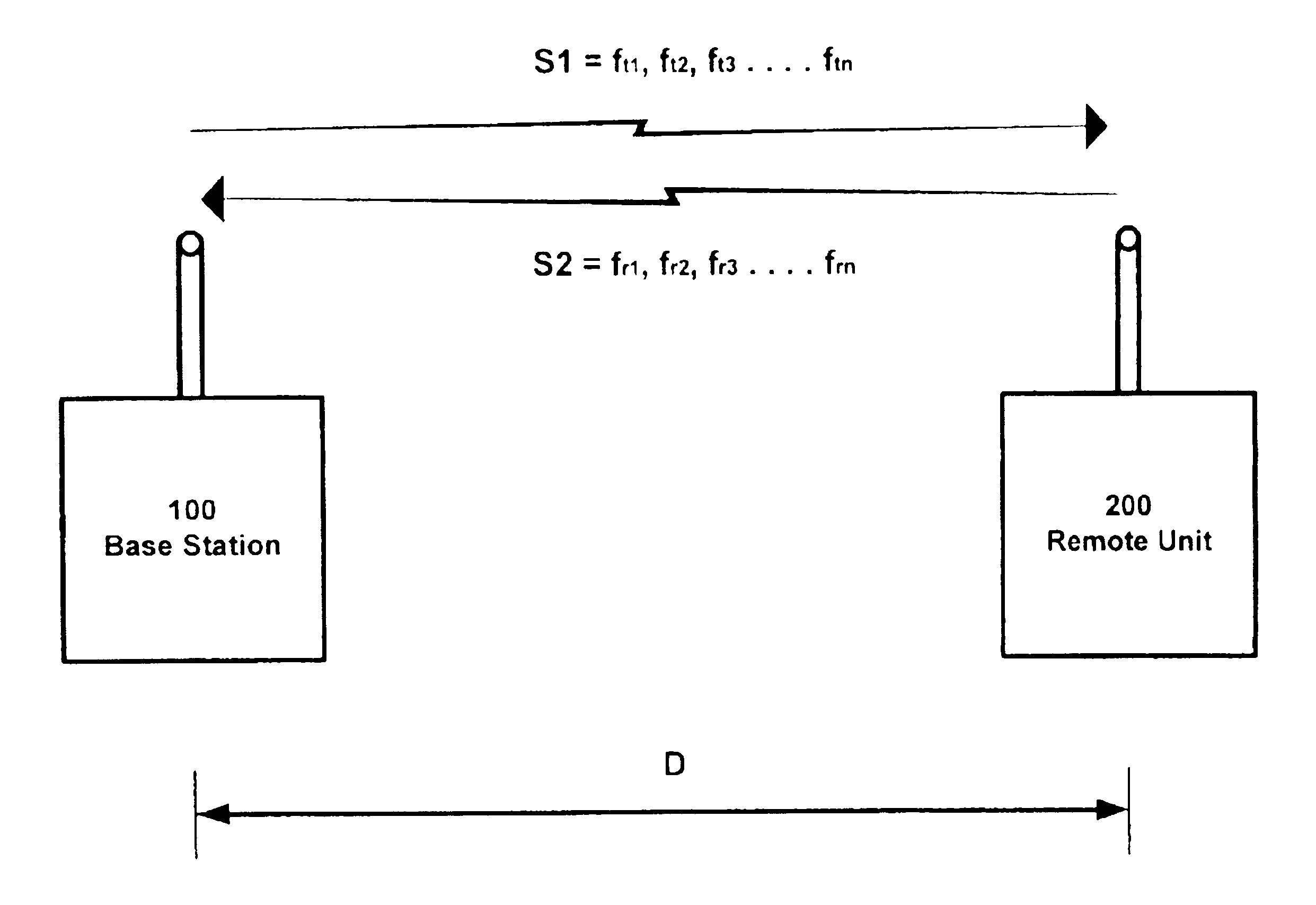
System and method for distance measurement by inphase and quadrature signals in a radio system
InactiveUS6295019B1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverTime delays
A system and a method for distance measurement utilizes a radio system. The distance is measured by determining the time it takes a pulse train to travel from a first radio transceiver to a second radio transceiver and then from the second radio transceiver back to the first radio transceiver. The actual measurement is a two step process. In the first step, the distance is measured in coarse resolution, and in the second step, the distance is measured in fine resolution. A first pulse train is transmitted using a transmit time base from the first radio transceiver. The first pulse train is received at a second radio transceiver. The second radio transceiver synchronizes its time base with the first pulse train before transmitting a second pulse train back to the first radio transceiver, which then synchronizes a receive time base with the second pulse train. The time delay between the transmit time base and the receive time base can then be determined. The time delay indicates the total time of flight of the first and second pulse trains. The time delay comprises coarse and fine distance attributes. The coarse distance between the first and second radio transceivers is determined. The coarse distance represents the distance between the first and second radio transceivers in coarse resolution. An in phase (I) signal and a quadrature (Q) signal are produced from the time delay to determine the fine distance attribute. The fine distance indicates the distance between the first and second transceivers in fine resolution. The distance between the first and second radio transceivers is then determined from the coarse distance and the fine distance attributes.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
Distance measurement using half-duplex RF techniques
A system, apparatus, and method for determining the distance between two objects using an indirect propagation delay measurement is disclosed. A frequency hopping scheme (such as the Bluetooth.TM. technology) is used to measure the relative phase offset of the received signal between the various frequencies. For a given distance between the objects, the phase offset vs. frequency curve is a straight line with the slope dependent upon the measured distance. After the phase of the received signals is detected, the data is plotted on a curve and the slope is calculated. A wireless slave device remains phase locked with another device in a half-duplex communication mode by employing a low-drift phase locked loop employing a voltage controlled crystal oscillator. The phase locked loop further employs a mechanism that provides immunity from transitory phase slip at a time when the loop is opened.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
Land software tool
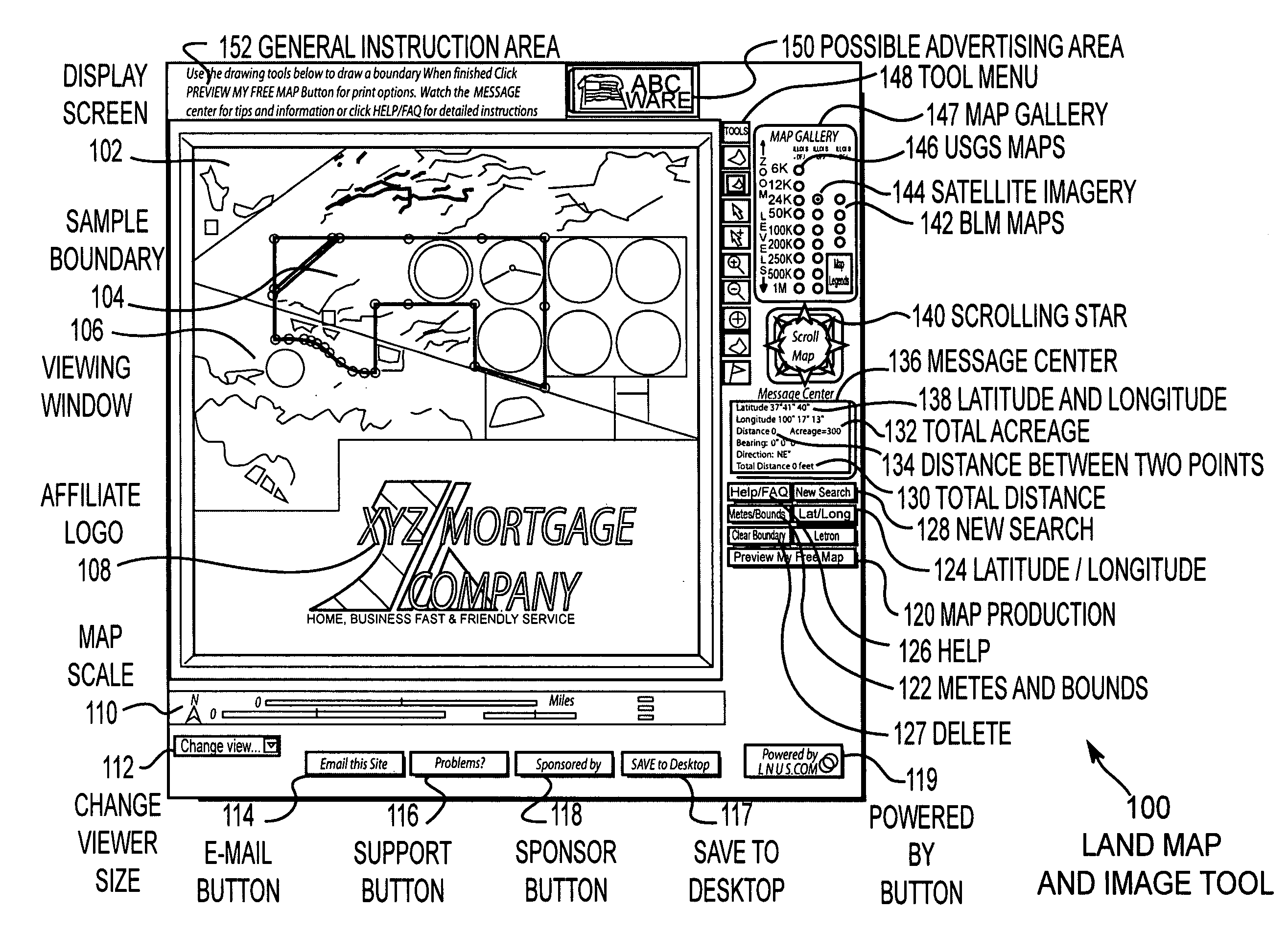
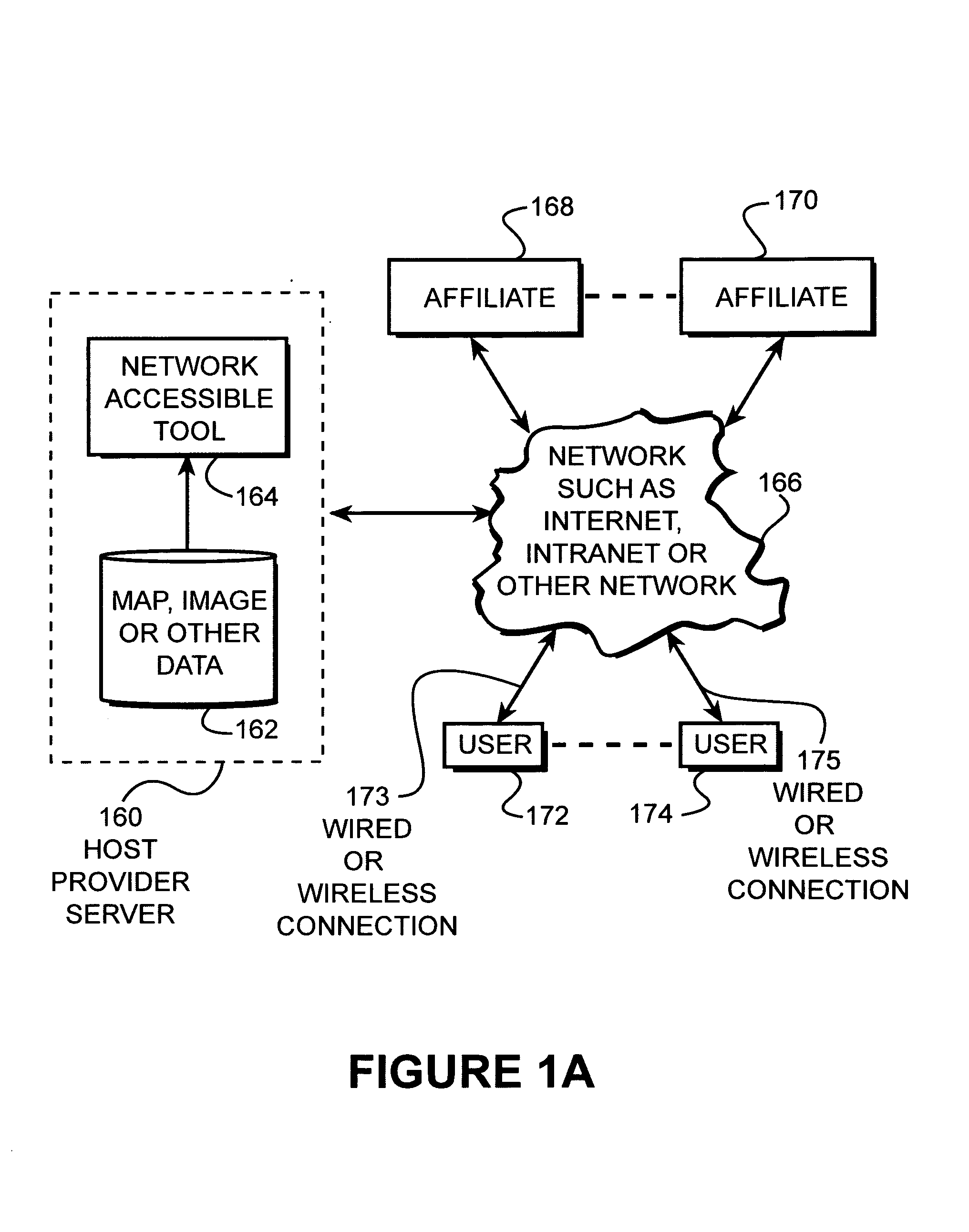
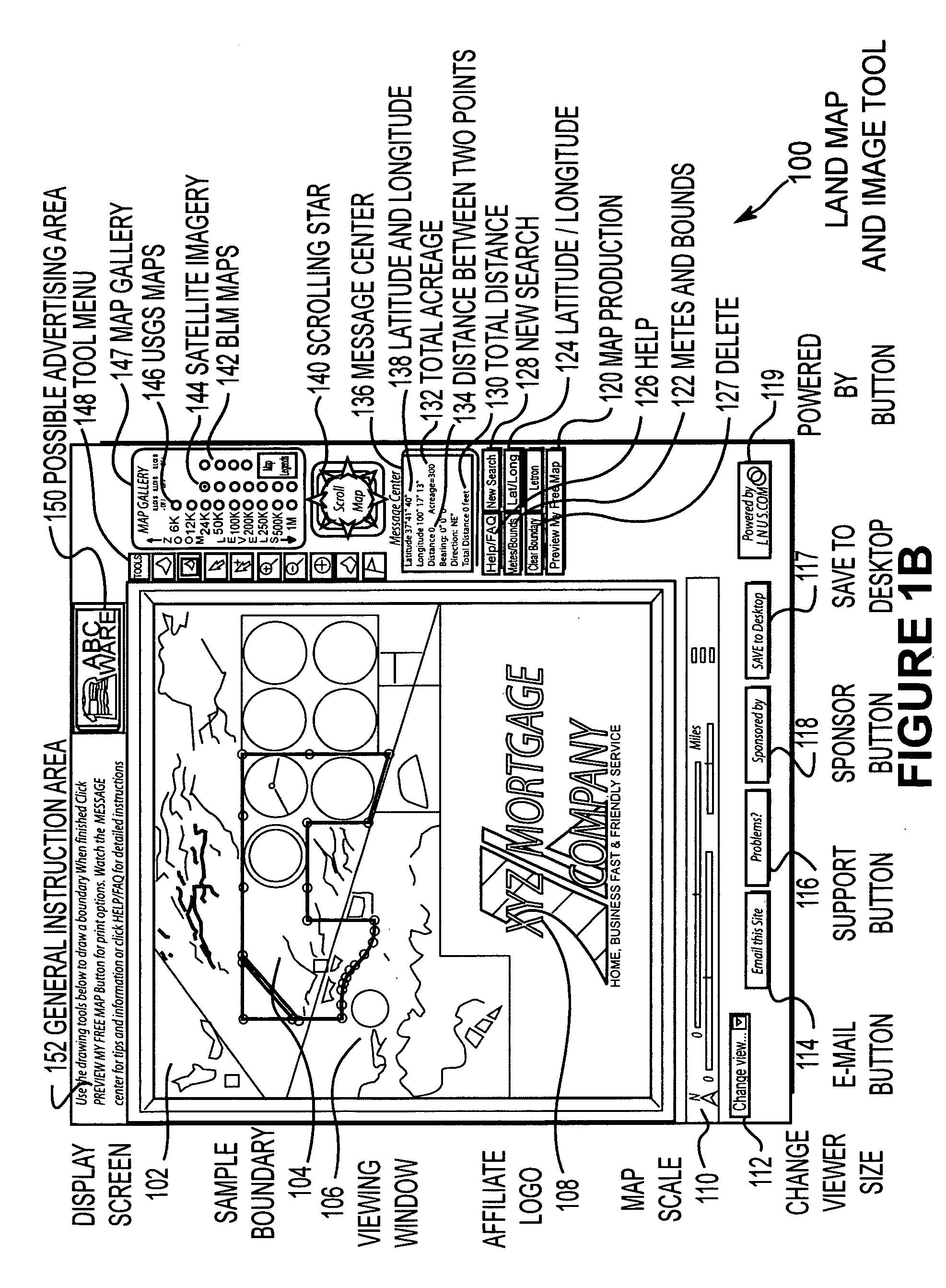
InactiveUS7054741B2Simple and easy fashionComprehensive functionsInstruments for road network navigationFinanceUser inputInternet users
Disclosed is a network accessible tool that is capable of providing map and satellite image data, as well as other photographic image data to locate, identify, measure, view, and communicate information about land over the Internet-to-Internet users. The network accessible tool includes a location tool that allows the user to locate areas on a map using geographic names, township, range and section descriptions, county names, latitude and longitude coordinates or zip codes. Network accessible tool also includes a metes and bounds tool that draws boundaries on the map and image data in response to metes and bounds descriptions that have been entered by the Internet user. The network accessible tool also includes a lat / long drawing tool that draws boundaries on the map and image data based upon latitude and longitude coordinate pairs that have been entered by the Internet user. A cursor drawing tool allows the Internet user to draw and edit boundaries on the map and image data by simply clicking the cursor on the corner points of the boundary. An acreage calculation tool is also provided that calculates the acreage of an enclosed boundary. A distance measurement tool is also provided. The cursor information tool provides information relating to the name and creation date of the map and image data in accordance with the location of the cursor on the screen. The information can be communicated by printing, downloading, or e-mailing.
Owner:LANDNET CORP
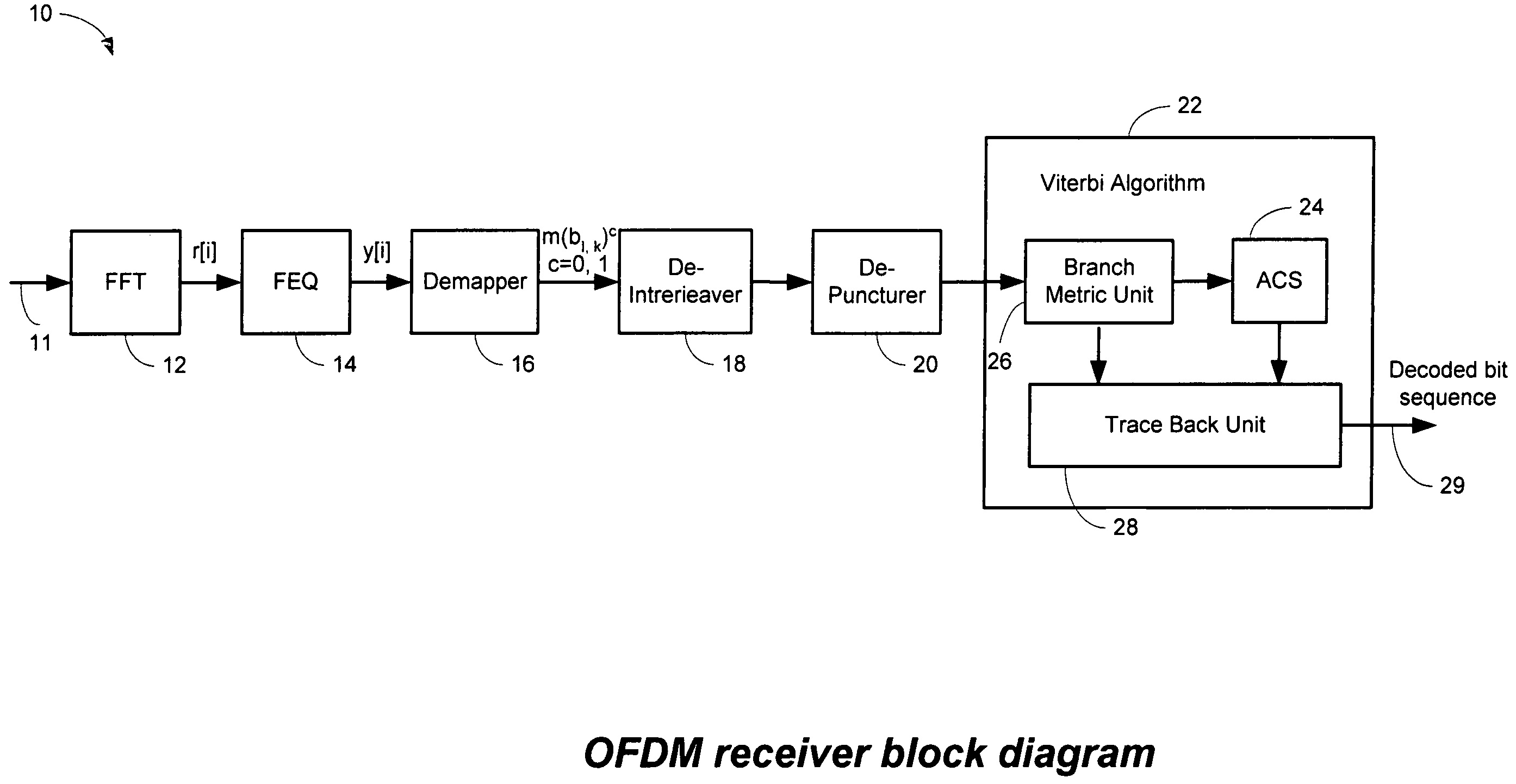
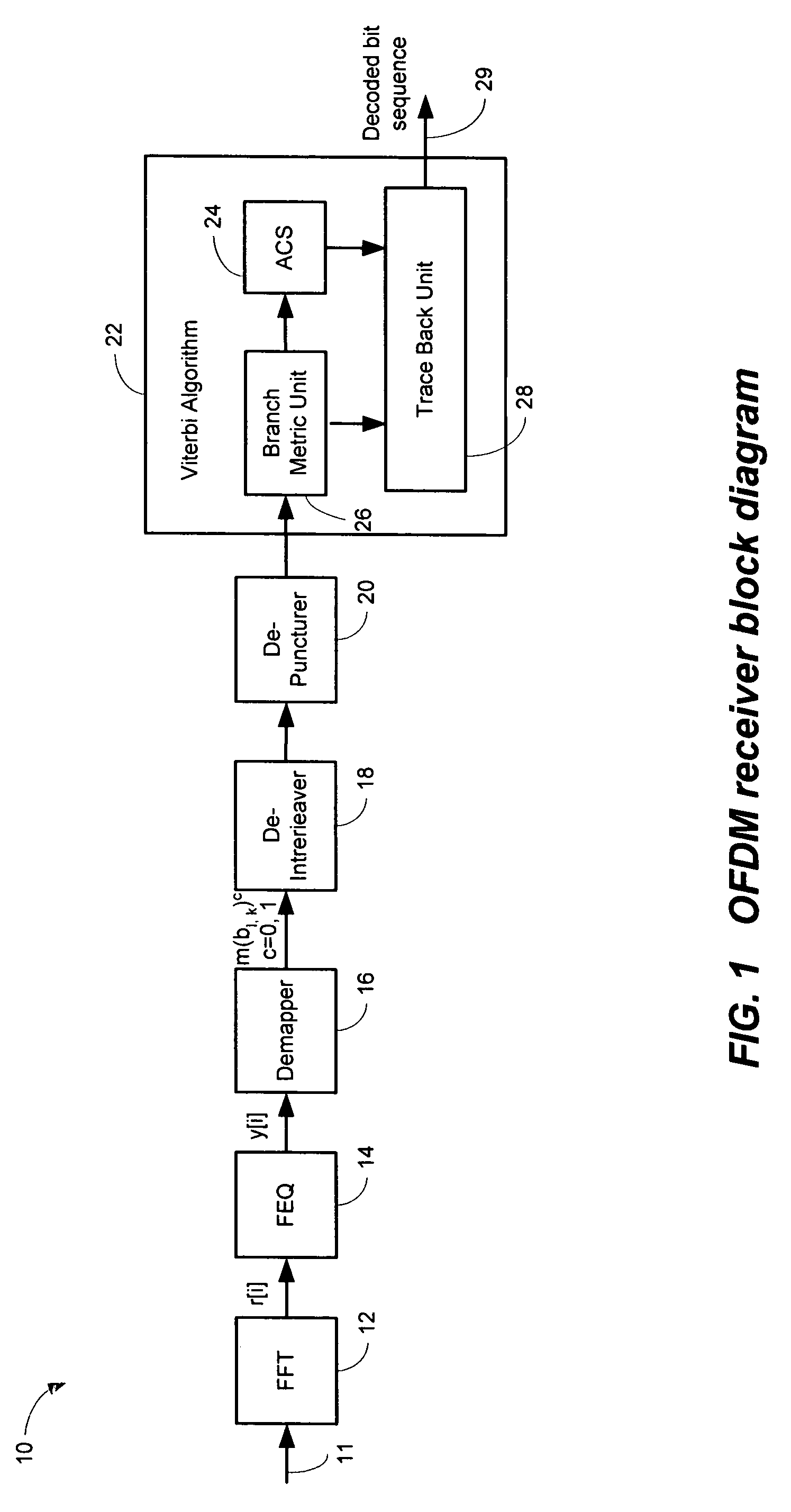
Efficient soft decision demapper to minimize viterbi decoder complexity
InactiveUS7313750B1Improve performanceSmall sizeData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderComputer science
A receiver system that receives signals and has a demapper device that is responsive to an equalizer output and generates a demapper output including one or more bit metrics. The receiver system also generates equalizer output, and the demapper uses distance measure to calculate bit metrics. The receiver system uses demapper output to generate a processed output. The receiver system further includes a convolutional decoder which is responsive to the processed output, and subsequently generates a decoded bit sequence, as well as uses the processed output to generate one or more path metrics. The convolutional decoder uses bit metrics and path metrics to the decode processed output, to generate a decoded bit sequence. The receiver system uses the distance measure to reduce the size of the bit metrics and the size of the path metrics to improve the performance of said convolutional decoder.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
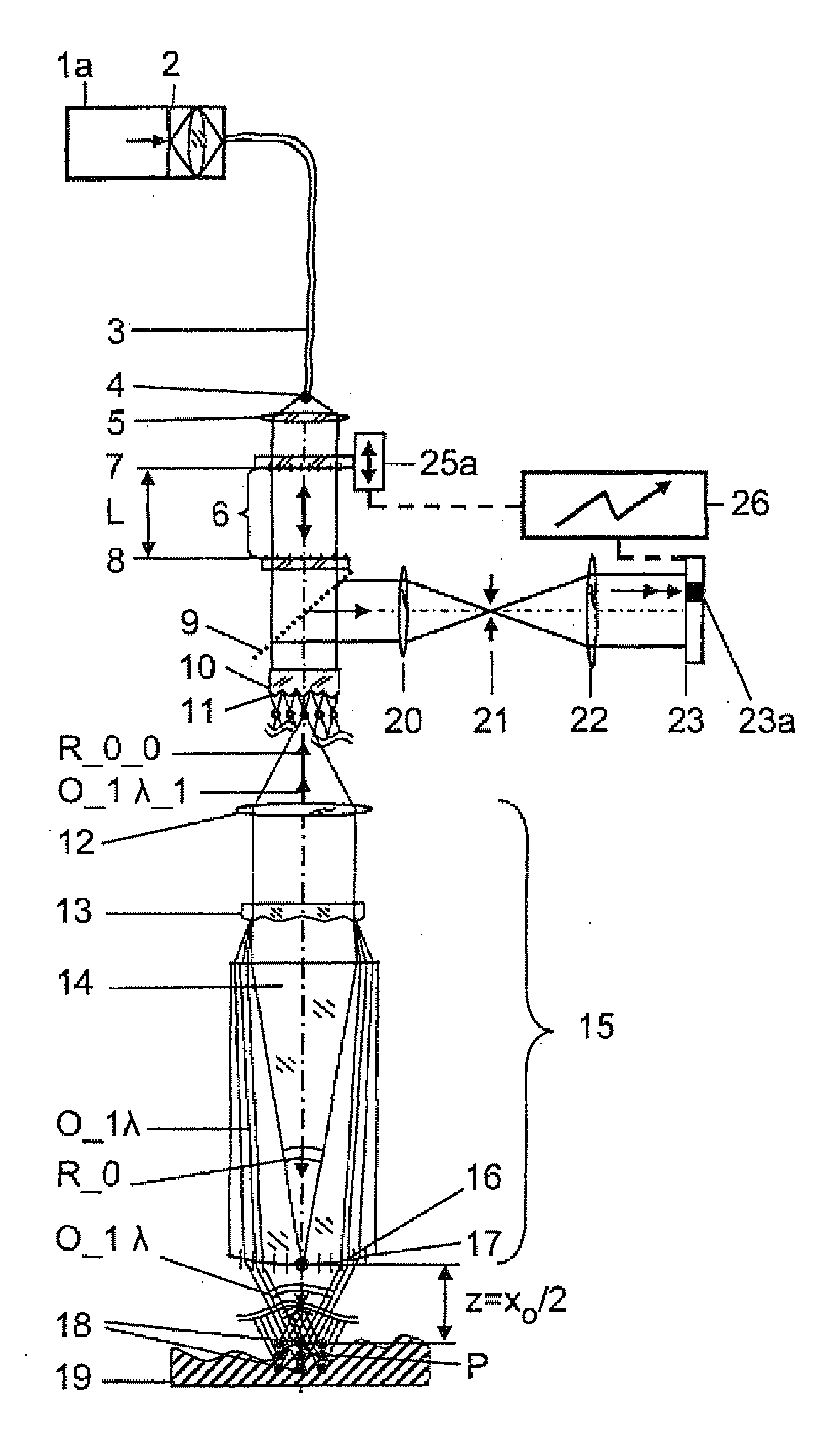
Method and apparatus for interferometry
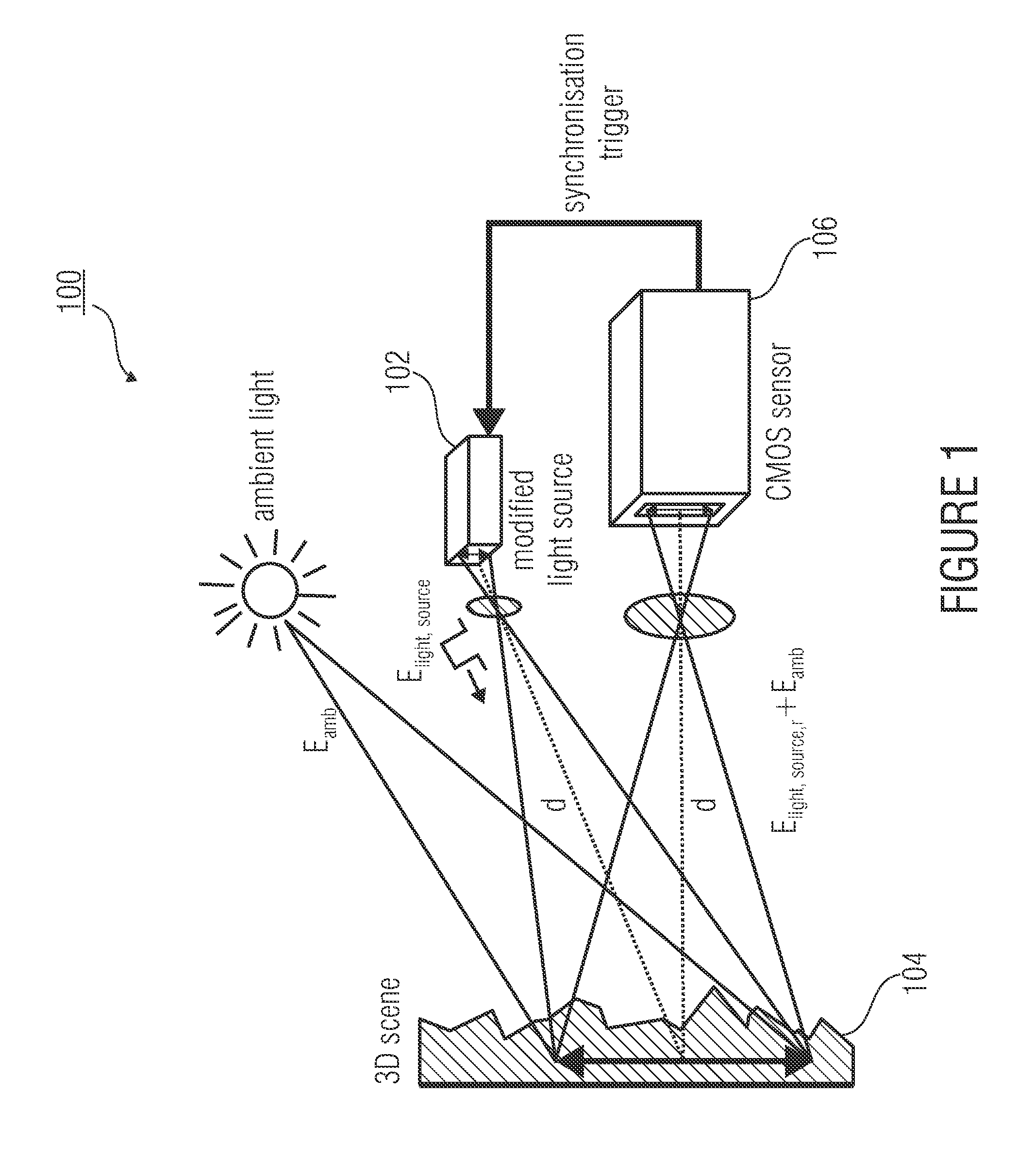
InactiveUS20110235045A1High measurementImprove scanning accuracyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryHelical computed tomographyEngineering
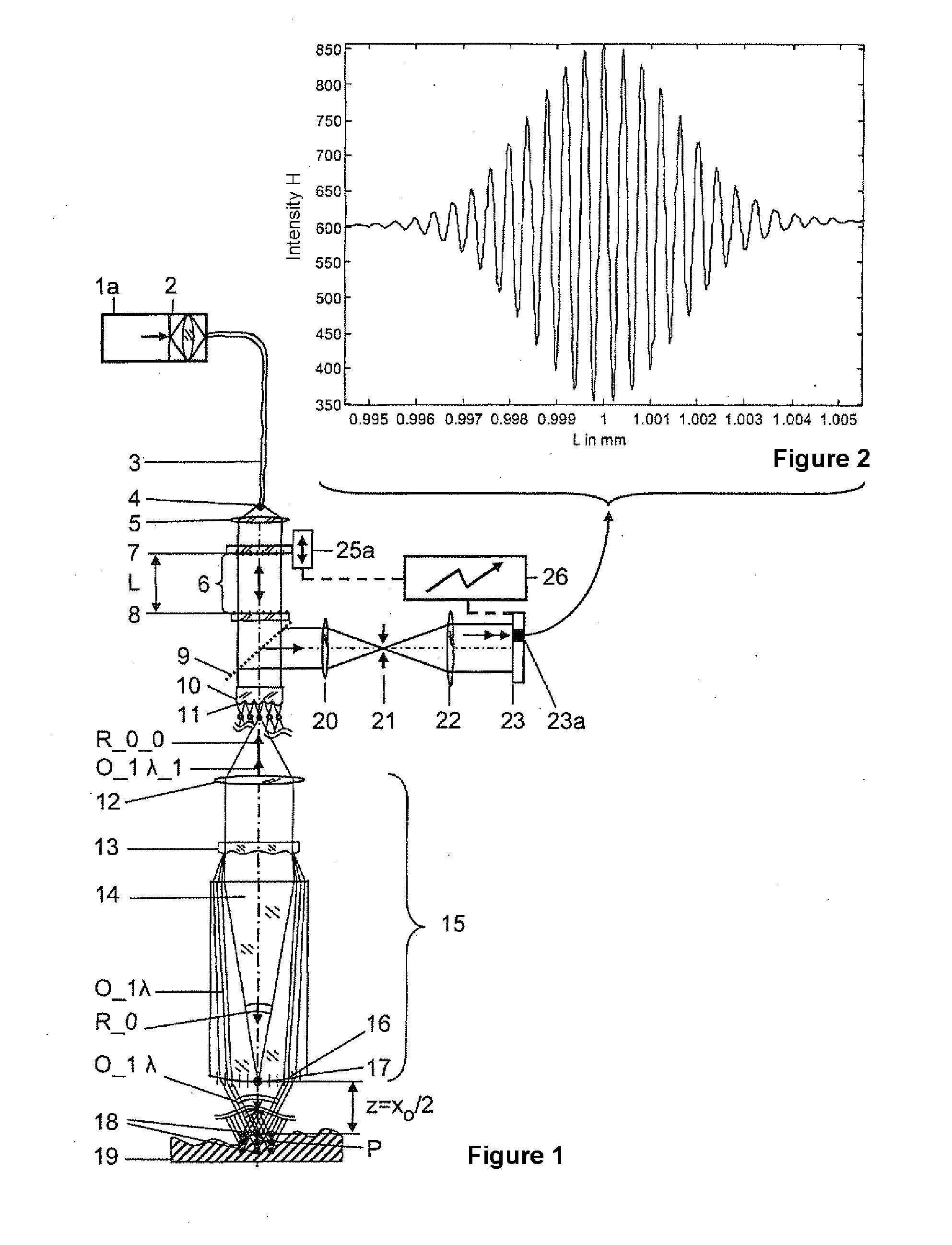
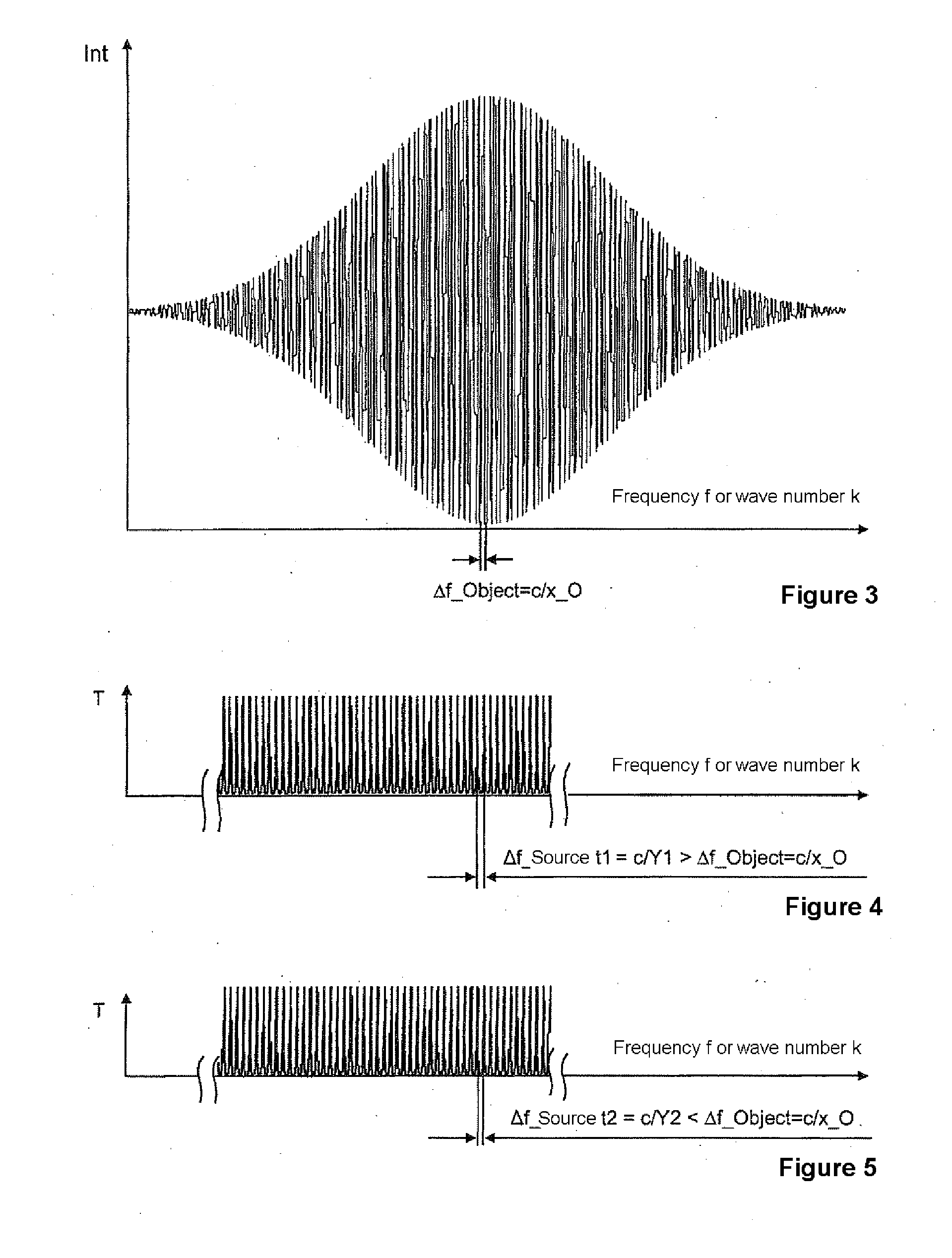
A method and an arrangement are provided for scalable confocal interferometry for distance measurement, for 3-D detection of an object, for OC tomography with an object imaging interferometer and at least one light source. The interferometer has an optical path difference not equal to zero at each optically detected object element. Thus, the maxima of a sinusoidal frequency wavelet, associated with each detected object element, each have a frequency difference Δf_Objekt. At least one spectrally integrally detecting, rastered detector is arranged to record the object. The light source preferably has a frequency comb, and the frequency comb differences Δf_Quelle are changed in a predefined manner over time in a scan during measuring. In the process, the frequency differences Δf_Quelle are made equal to the frequency difference Δf_Objekt or equal to an integer multiple of the frequency differences Δf_Objekt at least once for each object element.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
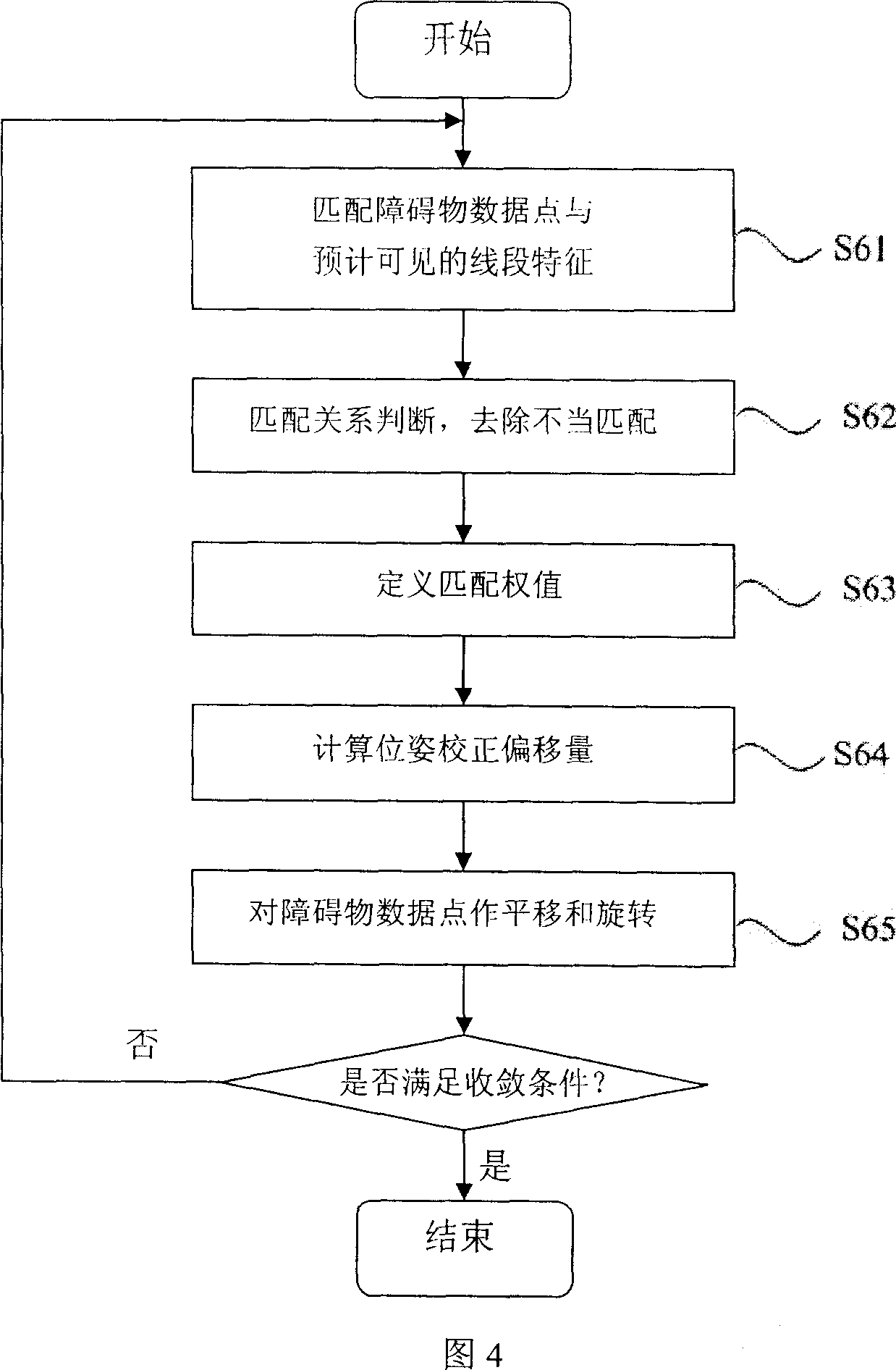
Method for moving robot simultanously positioning and map structuring at unknown environment
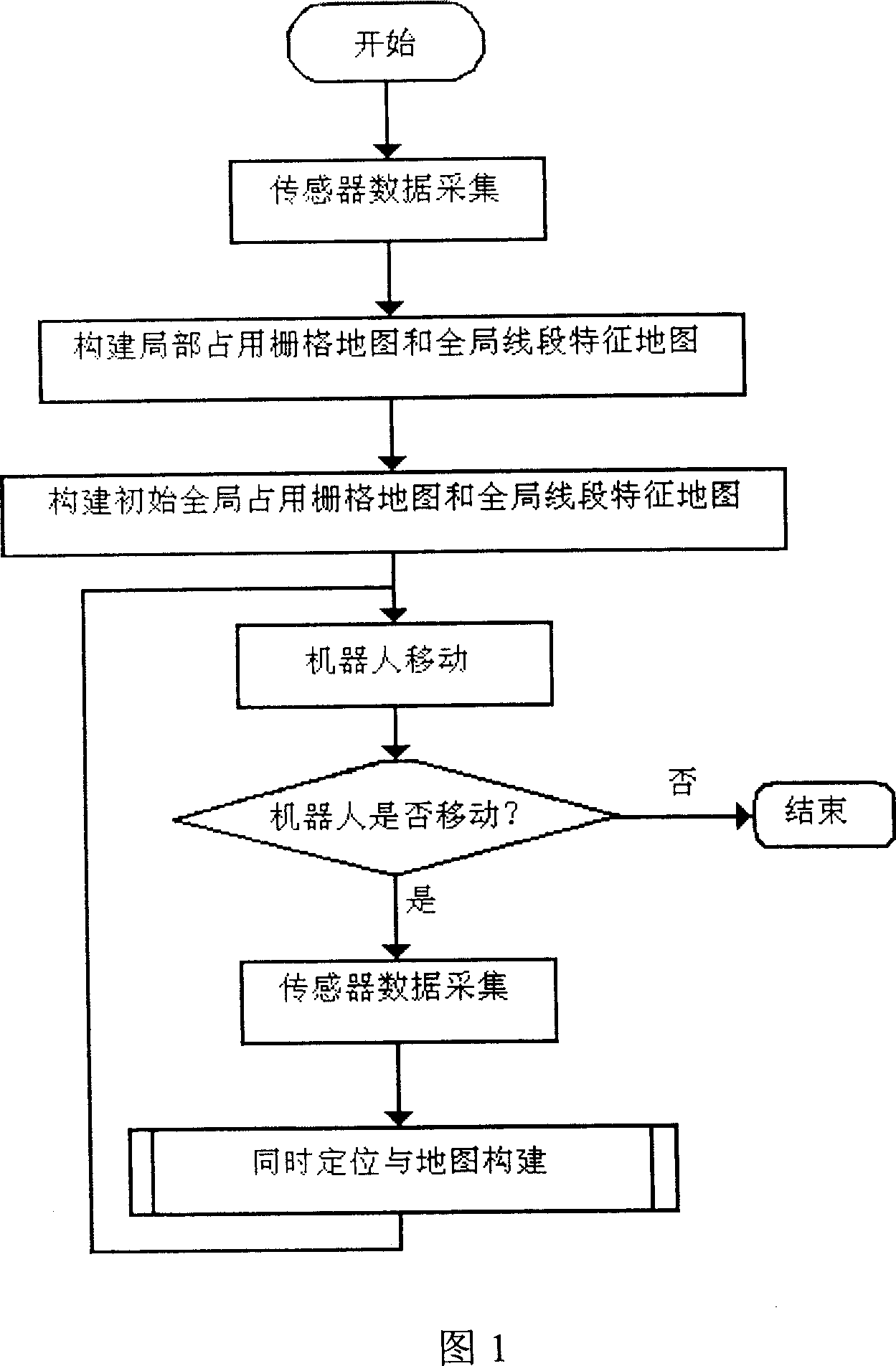
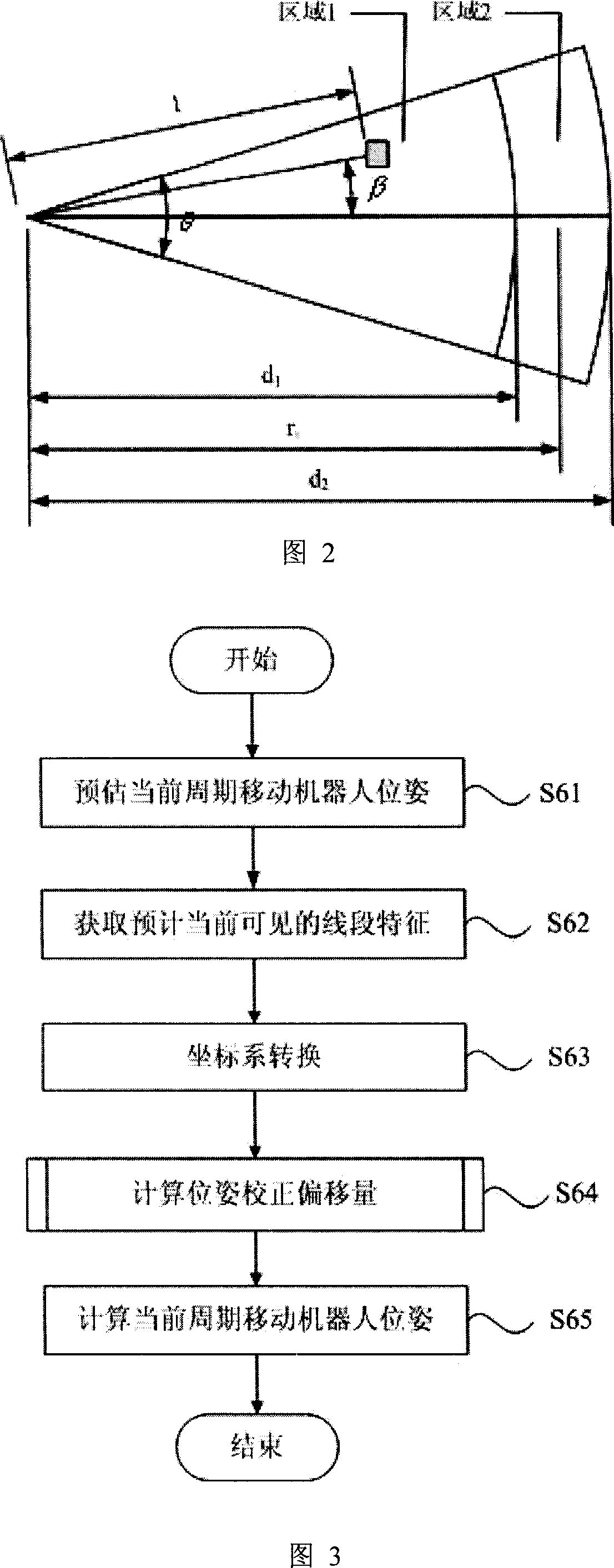
InactiveCN101000507AResolve uncertaintyUncertainties in addressing map building are interconnectedImage analysisPosition/course control in two dimensionsTransducerComputer science
A method for simultaneously carrying out positioning and map-making by mobile robot at unknown environment includes setting-up current local occupation lattice map and local section map according to data obtained by distance-measurement transducer on mobile robot, estimating current period pose of mobile robot based on certain data and some set-up map, setting-up obtained local section map and local occupation lattice map according to pose estimation of current period mobile robot and updating global occupation lattice map and global section map.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
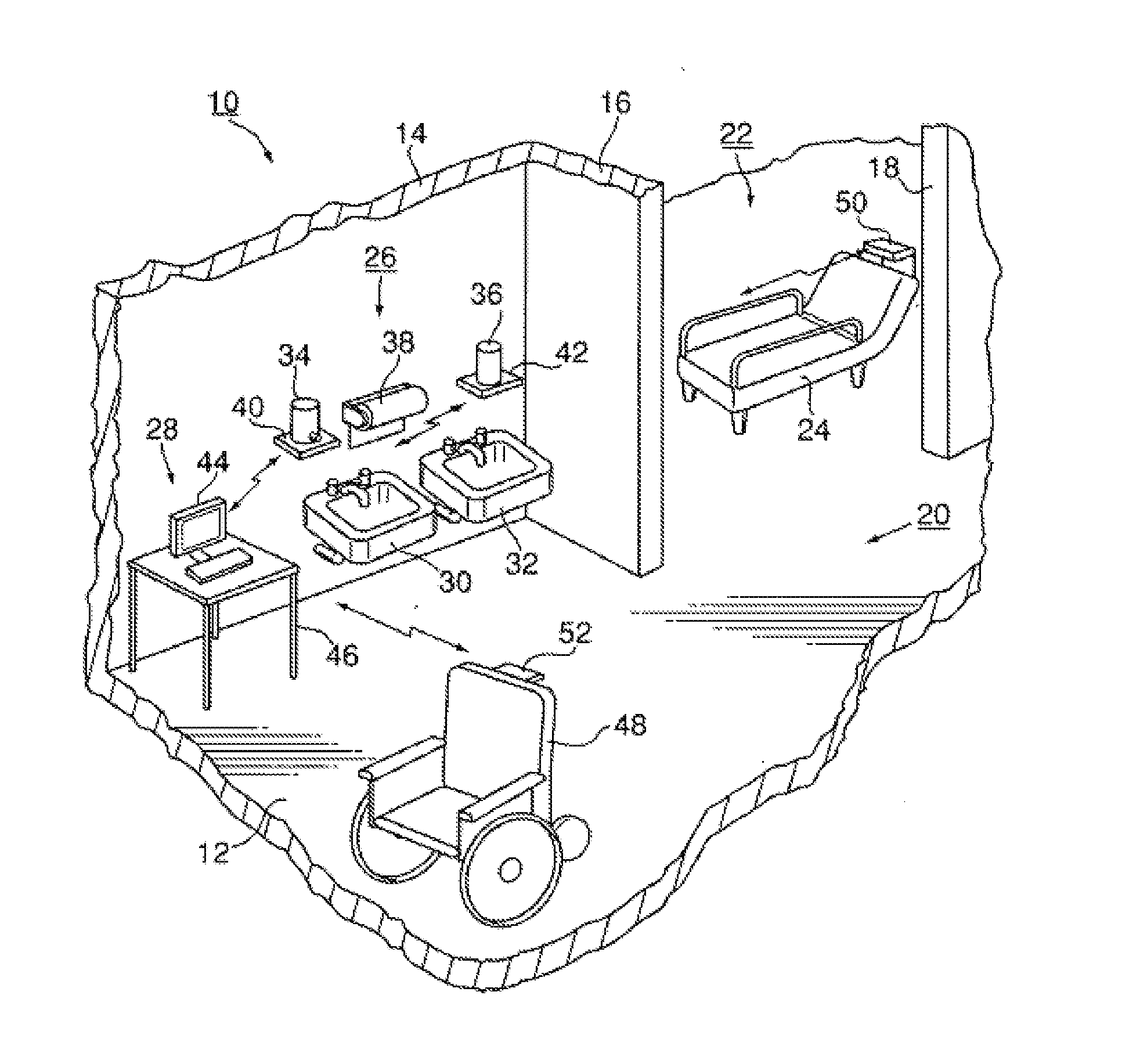
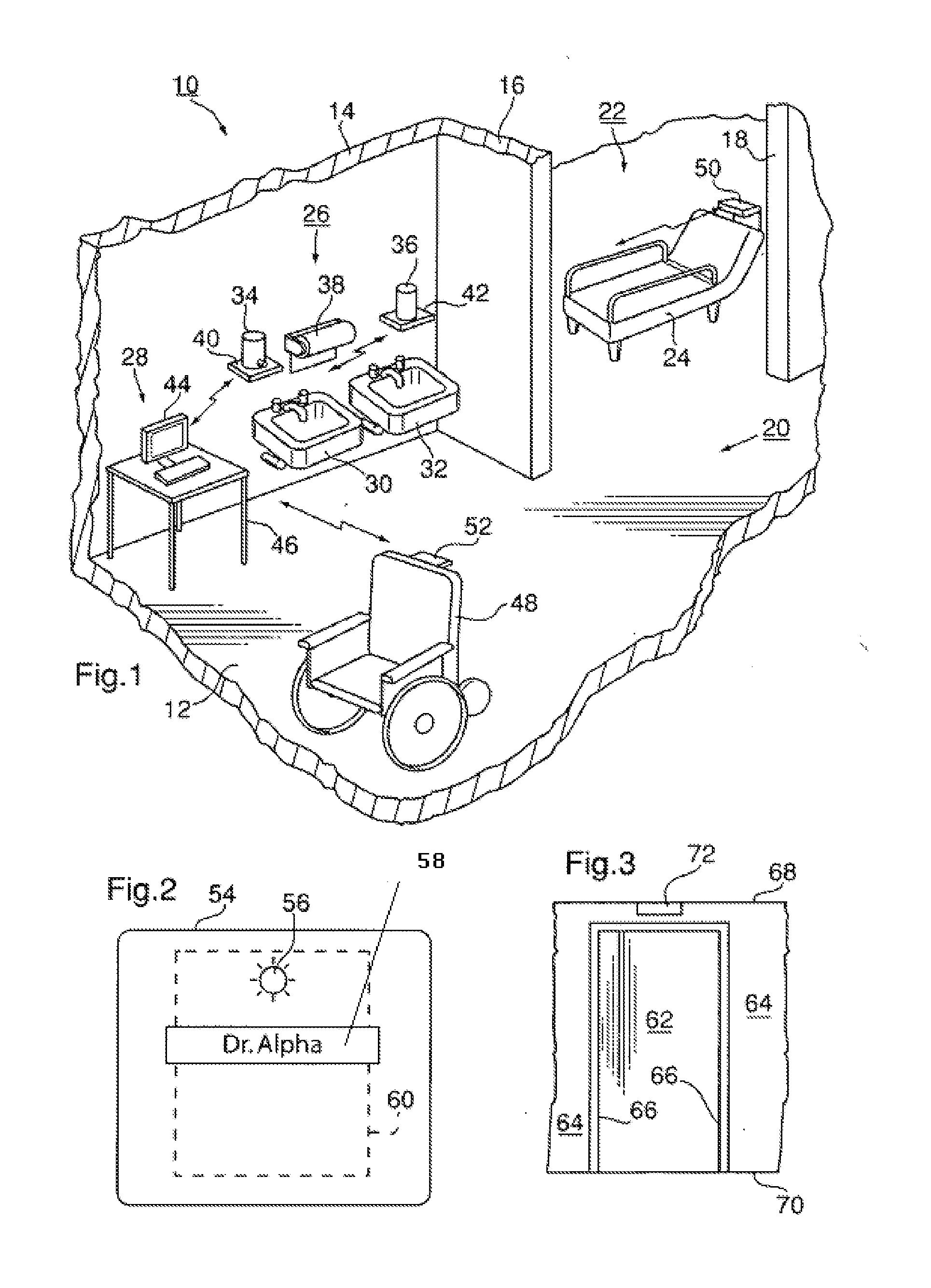
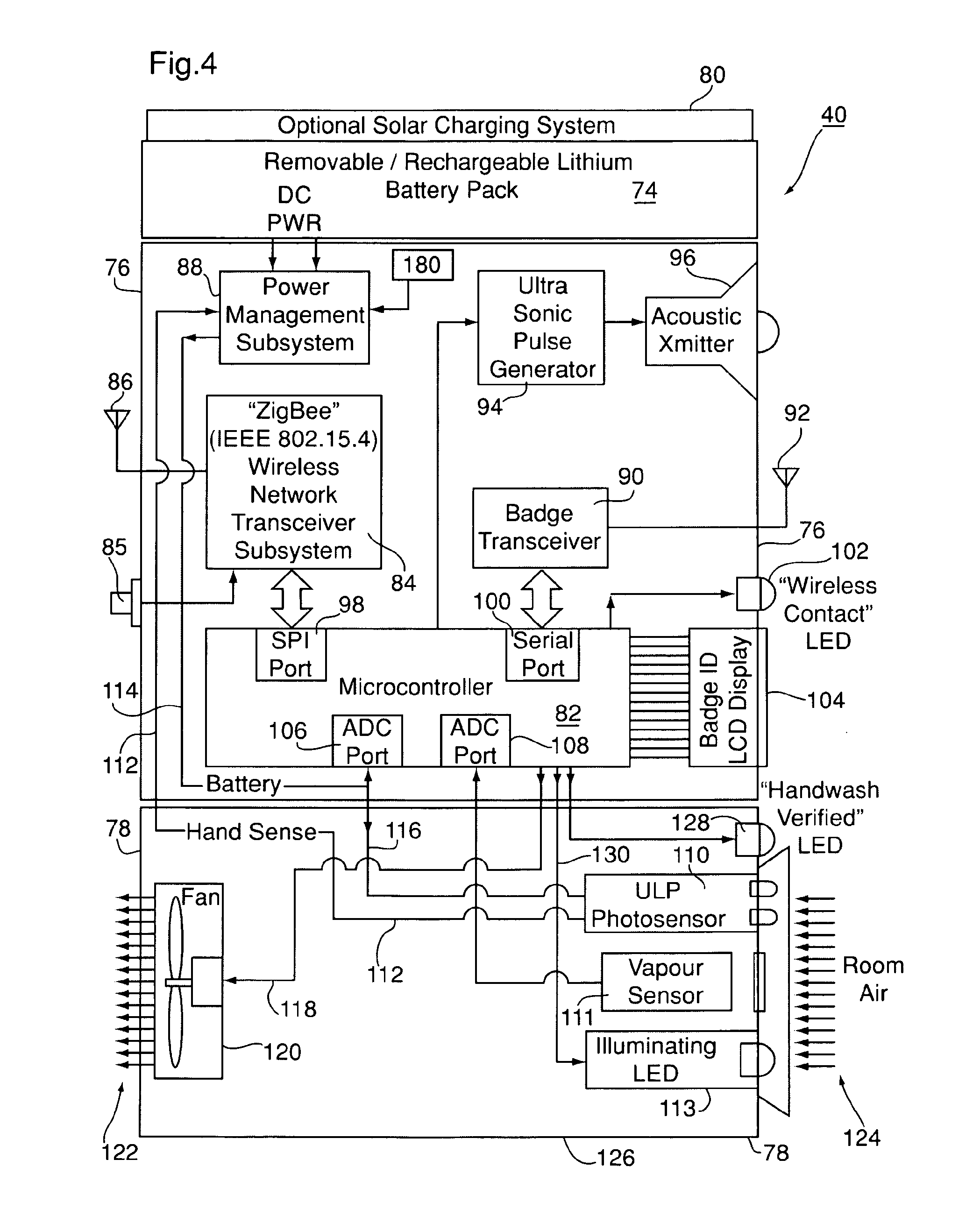
Personnel location and monitoring system and method for enclosed facilities
InactiveUS20110227740A1Limit power usageMeet growth requirementsRegistering/indicating time of eventsPosition fixationMotion detectorMonitoring system
A wireless time-of-flight distance measurement device a motion detector is used at each of a plurality of stations in a wireless network in an enclosed facility to accurately locate a badge-wearing person near the station. The location, badge number and time of detection are transmitted through the network and stored in a computer memory. In a healthcare facility, hand washing detectors are located at some of the stations and caused to energize a hand wash status indicator light on the badge when the wearer has washed his or her hands. The light remains “on” for only a certain length of time, but will be extinguished sooner by a monitor device near each patient when the healthcare worker leaves the vicinity of the patient. These events also are transmitted and stored so that a timed record of each worker's hand washing and visits to patients is created.
Owner:XHALE
Measurement system for determining six degrees of freedom of an object
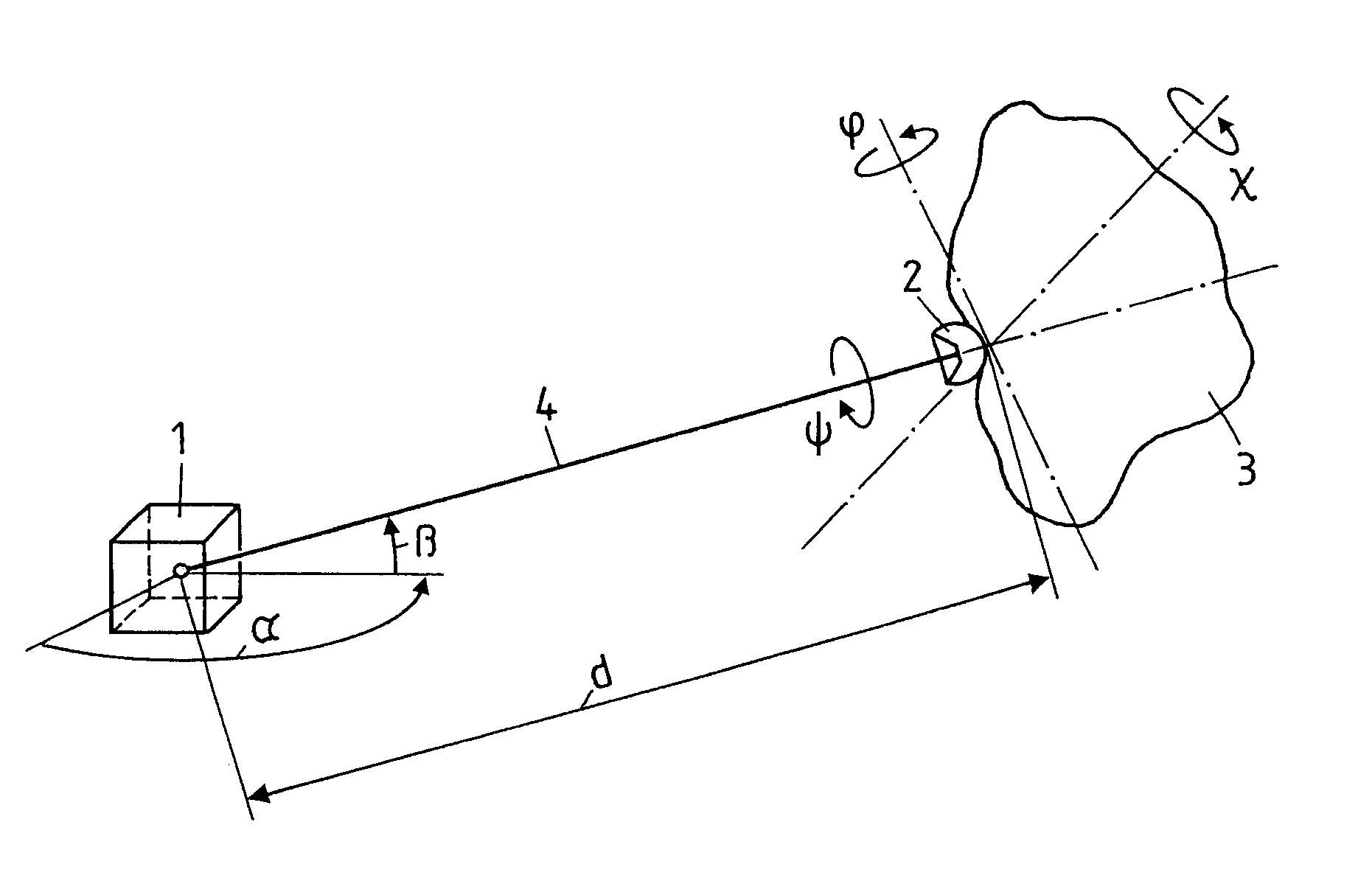
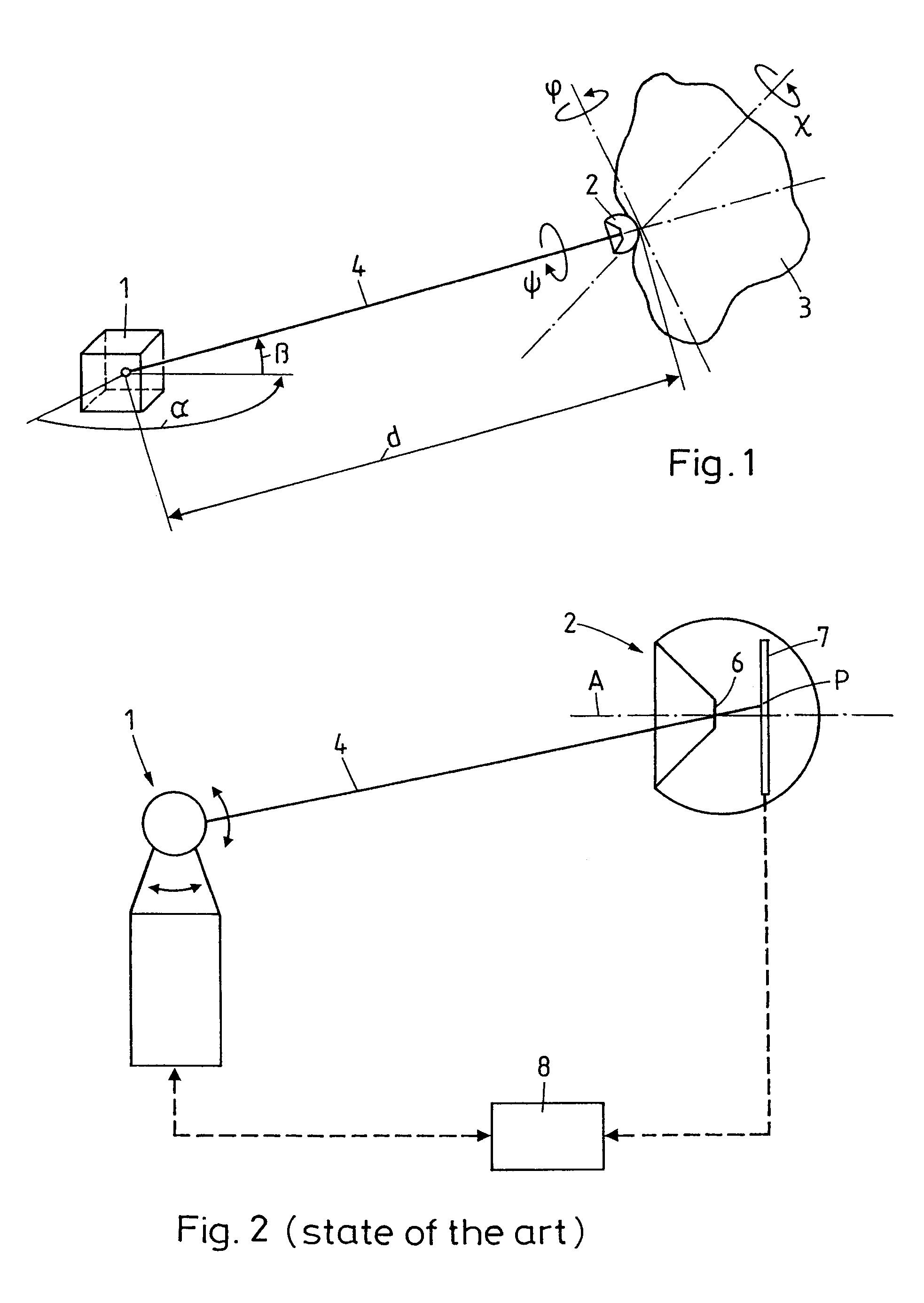
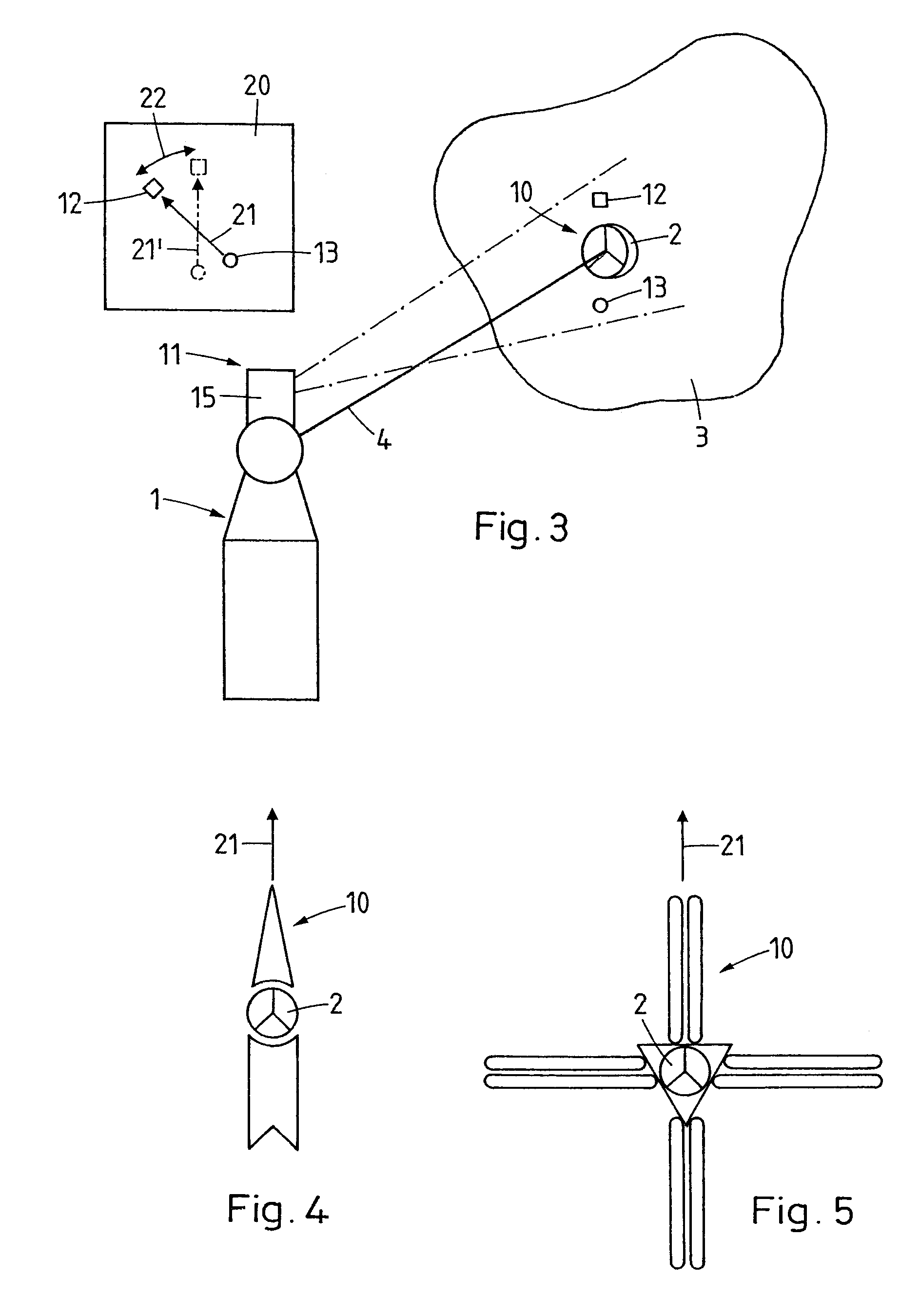
A measurement system for determining six degrees of freedom (α, β, d, φ, χ, ψ) of a reflector (2) or of an object (3) on which the reflector is arranged, comprises an angle- and distance measurement apparatus (1), e.g. a laser tracker, operating with a laser beam as a measurement beam (4). The reflector (2) is designed for a parallel reflection of the measurement beam (4) and has an apical opening or surface (6), in a manner such that a part of the measurement beam (4) directed onto the reflector (2), passes through the apical opening or surface (6), and is incident on a light-sensitive surface (7) arranged behind the reflector apex. Five degrees of freedom (α, β, d, φ, χ) of the reflector (2) or the object (3) are computed from measurement data produced by the angle- and distance measurement apparatus (1) and by the light-sensitive surface (7).
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks
InactiveUS20090011713A1Distance can be measured is lengthenEnhanced distance estimateSatellite radio beaconingTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsSignal strength
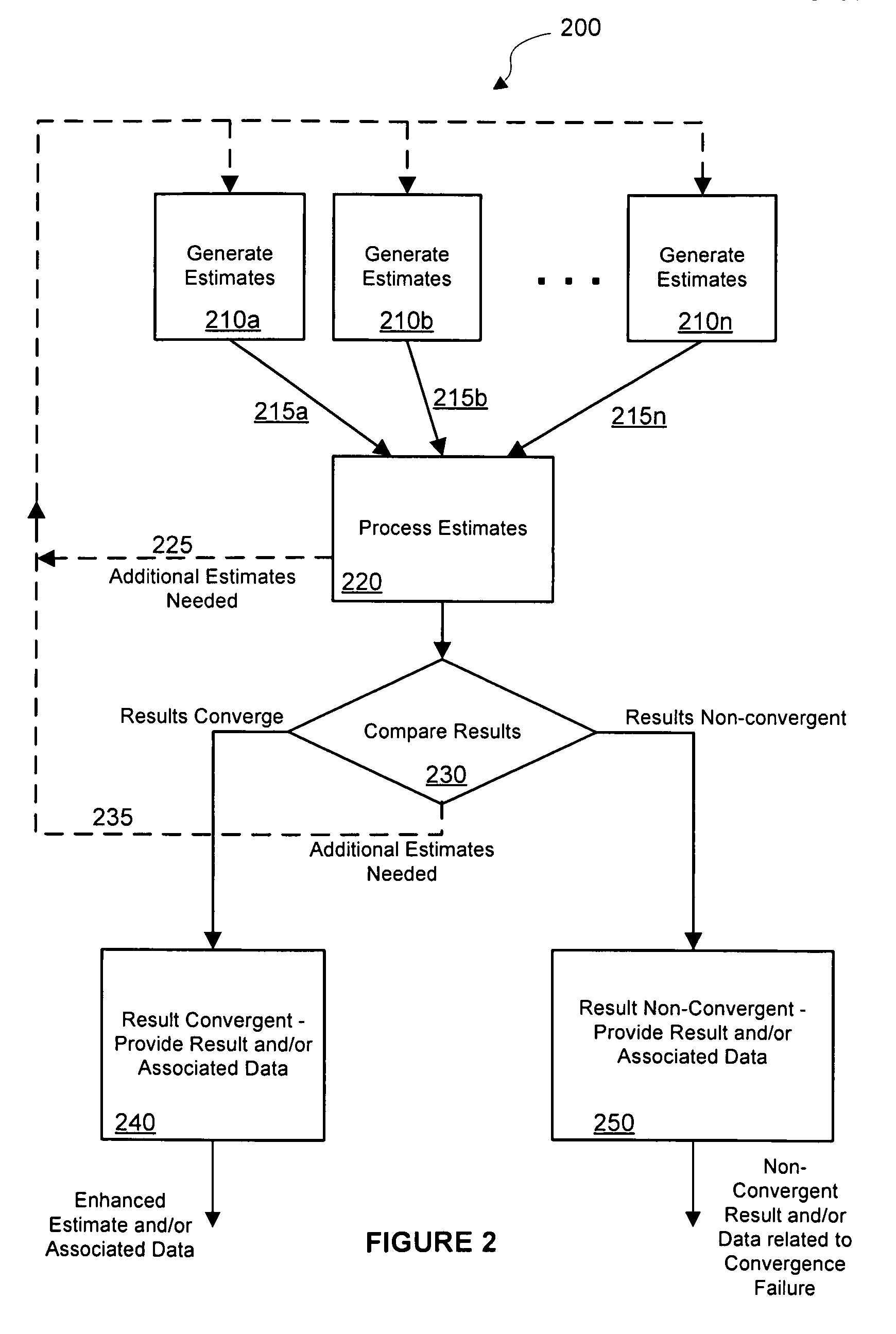
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks are disclosed. A method for measuring distance between nodes or devices in a wireless network comprises estimating a distance between network devices based on a first distance measurement method, estimating the distance based on a second distance measurement method, and processing the first and second distance estimates to determine convergence and to generate an enhanced distance measurement. Additional distance estimates may be combined to further improve accuracy. Convergence information may be provided indicating whether two or more distance estimates converge. In some implementations, the first distance estimate may be generated by a transmission time estimation method, the second distance estimate may be generated by a received signal strength distance estimate, the two estimates may be combined by averaging to generate an enhanced distance estimate, and the difference between the estimates may be compared to a threshold to determine whether the estimates have sufficiently converged to within a desired convergence range.
Owner:PROXIMETRY
Three dimensional display device and method of controlling parallax barrier
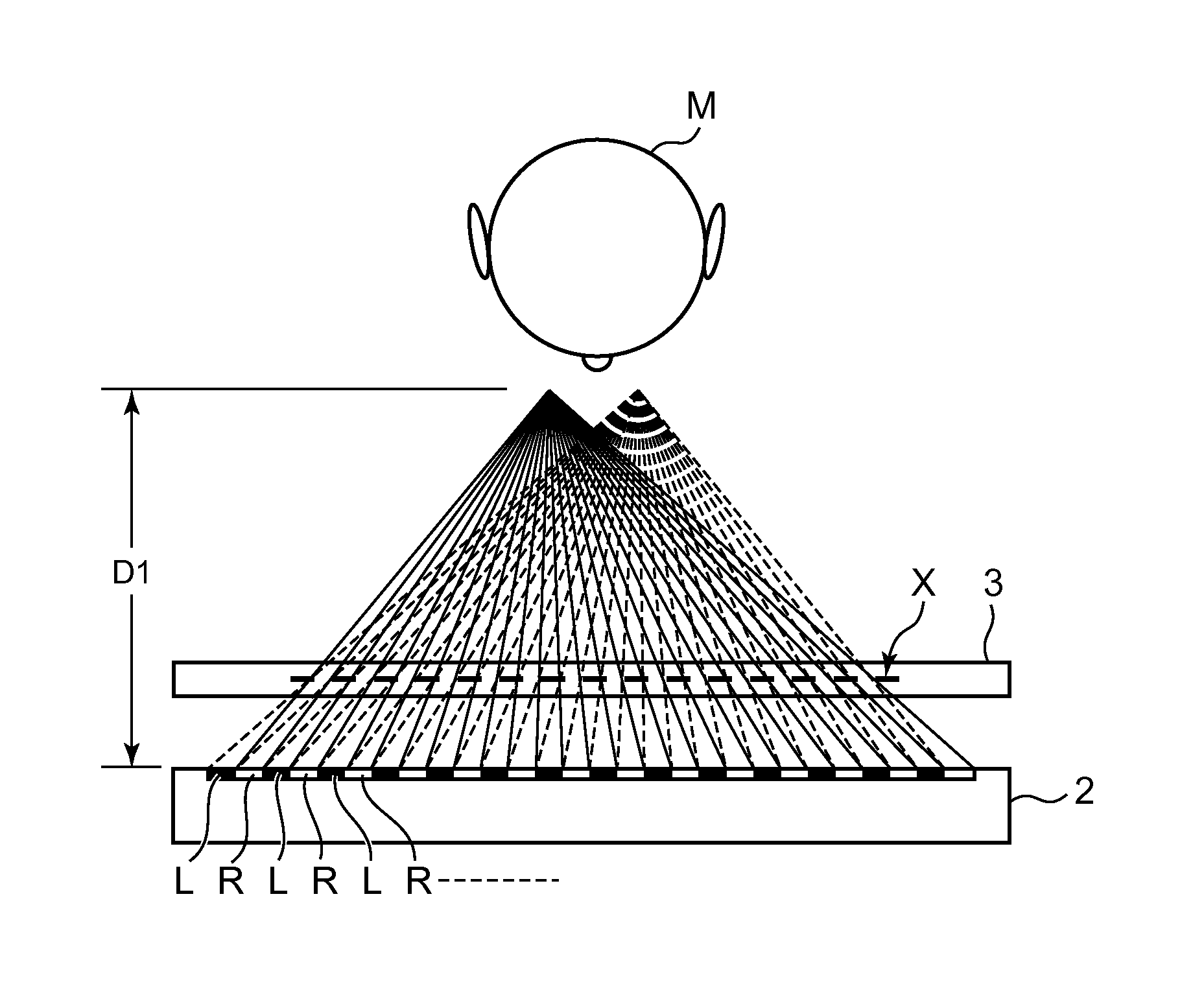
ActiveUS8817369B2Improve visibilityIncrease rangeSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsComputer scienceParallax barrier
A three-dimensional display device includes a display unit that displays a left eye image and a right eye image by dividing the images thereof into a plurality of vertically elongated stripes of images and by alternately arranging the divided left eye image and the divided right eye image in a horizontal direction, a barrier formation unit that forms a parallax barrier in front of the display unit, the parallax barrier including a pattern of a plurality of slits to selectively transmit the left eye image and the right eye image towards spatially different points, respectively, that correspond to a left eye and a right eye of the viewer, and a distance measurement unit that measures a distance between the display unit and a viewer viewing the display unit, wherein the barrier formation unit changes the pattern of the slits in the parallax barrier in accordance with the distance measured by the distance measurement unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Optically-based location system and method for determining a location at a structure
InactiveUS6865347B2Beacon systems using electromagnetic wavesPosition fixationDelayed timePositioning system
An optically based location system and method of determining a location at a structure include a lighting infrastructure having lights at a structure. Each light is configured to illuminate and to transmit a respective relative or absolute terrestrial position through modulation of emitted light. An optical receiver is configured to detect the lights, to demodulate the position of detected lights, and to determine from the detection a position of the receiver. The receiver can have a conventional optical detector for determining a two-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light, or can have a three-dimensional spot collimating lens and charged couple device optical detector for determining a three-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light. The receiver and lights can be synchronized for converting a delay time into a distance measurement to calculate a distance between a light and the receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
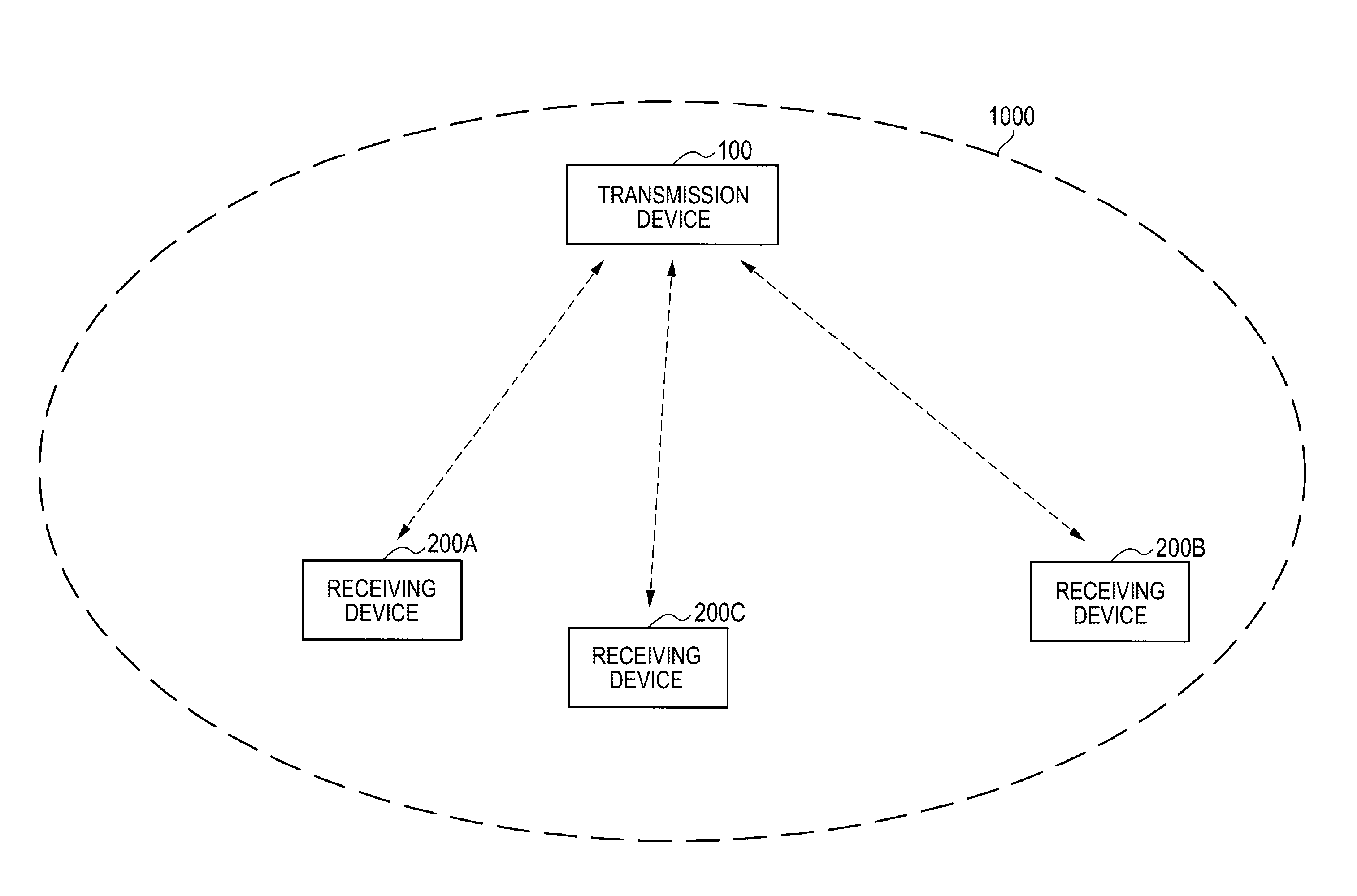
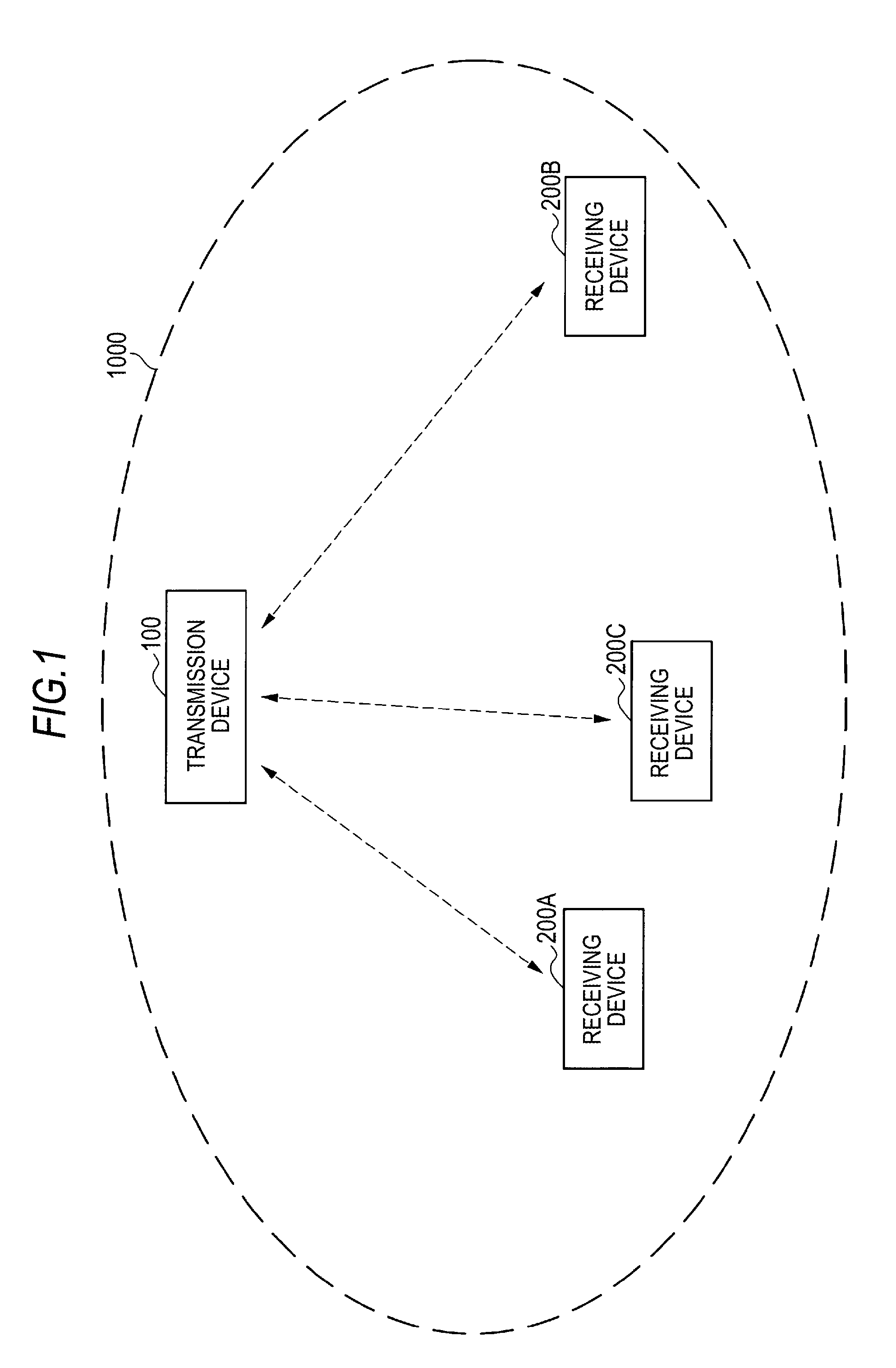
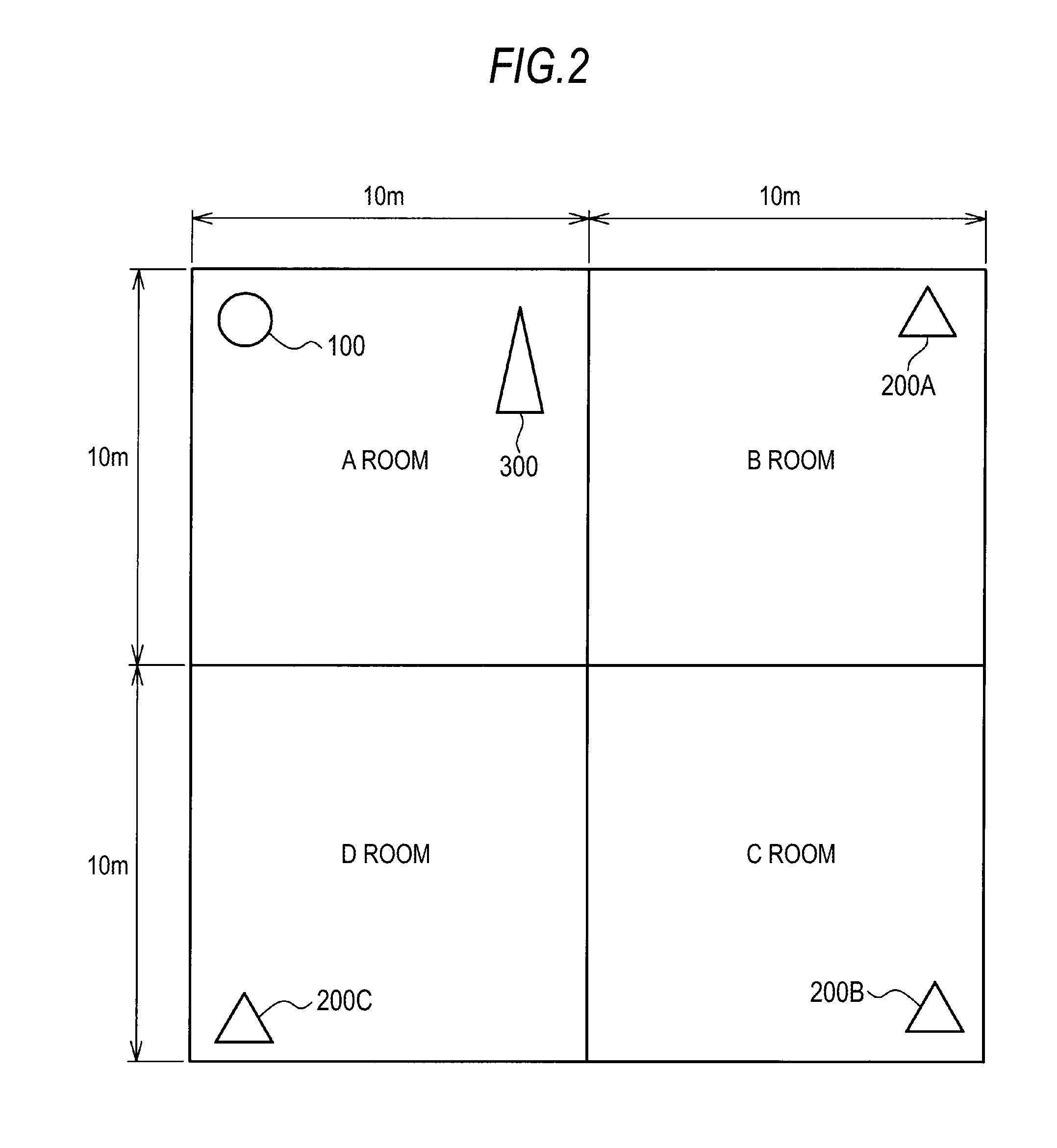
Transmission device and transmission method
ActiveUS8520870B2Uncomfortable feelingIncrease probabilityNear-field transmissionReceivers monitoringTime informationData set
A transmission device includes: a communication unit performing communication with one or more receiving devices; a distance measurement unit measuring direct distances to the receiving devices; a transmission data setting unit setting transmission data including content data including audio and time information indicating the time when reproduction of content data is started for the receiving devices whose distances are measured based on the measured distances; and a transmission processing unit transmitting transmission data set by the transmission data setting unit to corresponding receiving devices of transmission targets all at once. The transmission data setting unit sets time when the device itself starts reproduction of the content data as a reference time, and sets the time information for synchronizing audio indicated by the content data reproduced in the device itself with audio indicated by the content data reproduced in the receiving devices for each receiving device using the set reference time.
Owner:SONY CORP
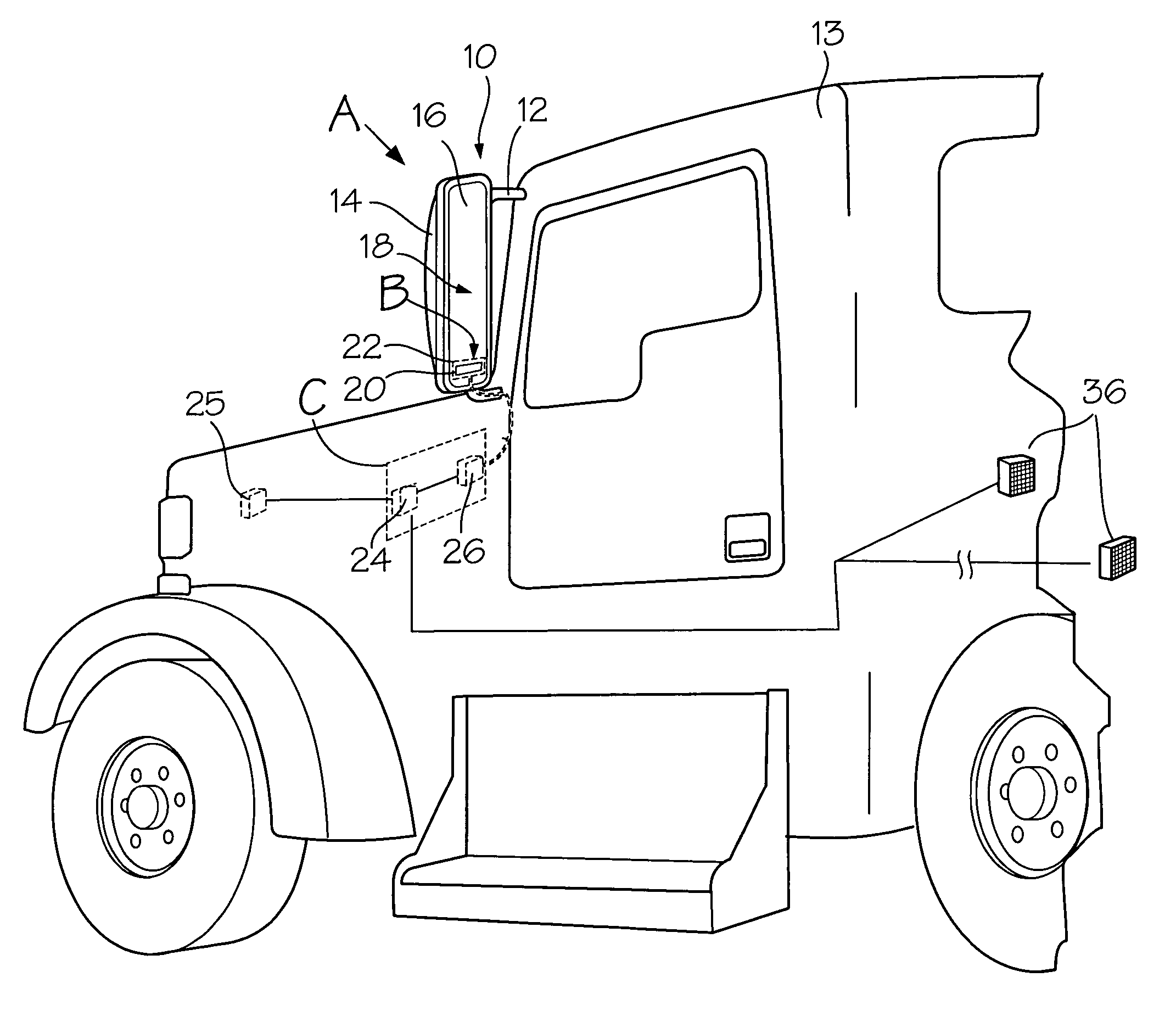
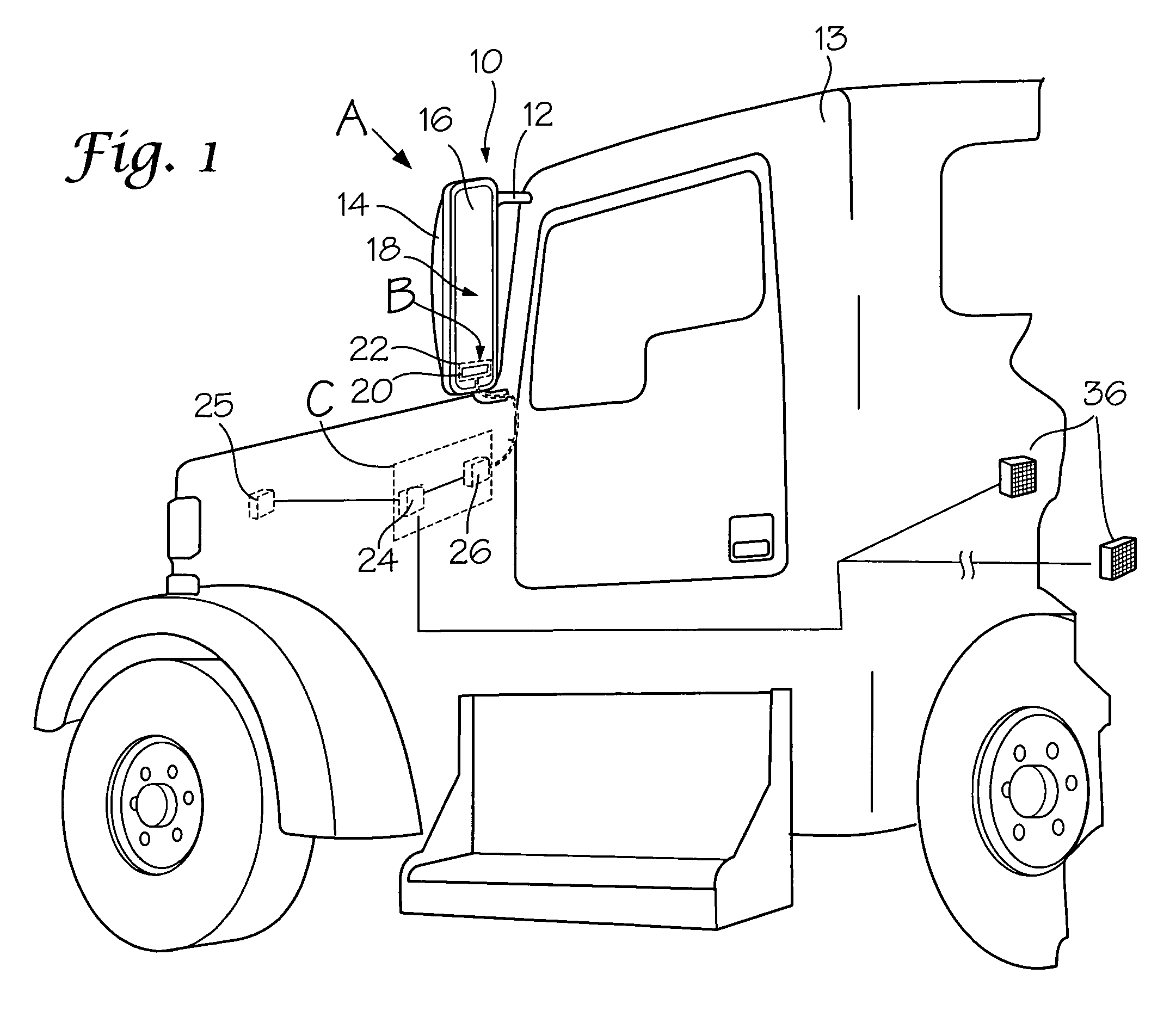
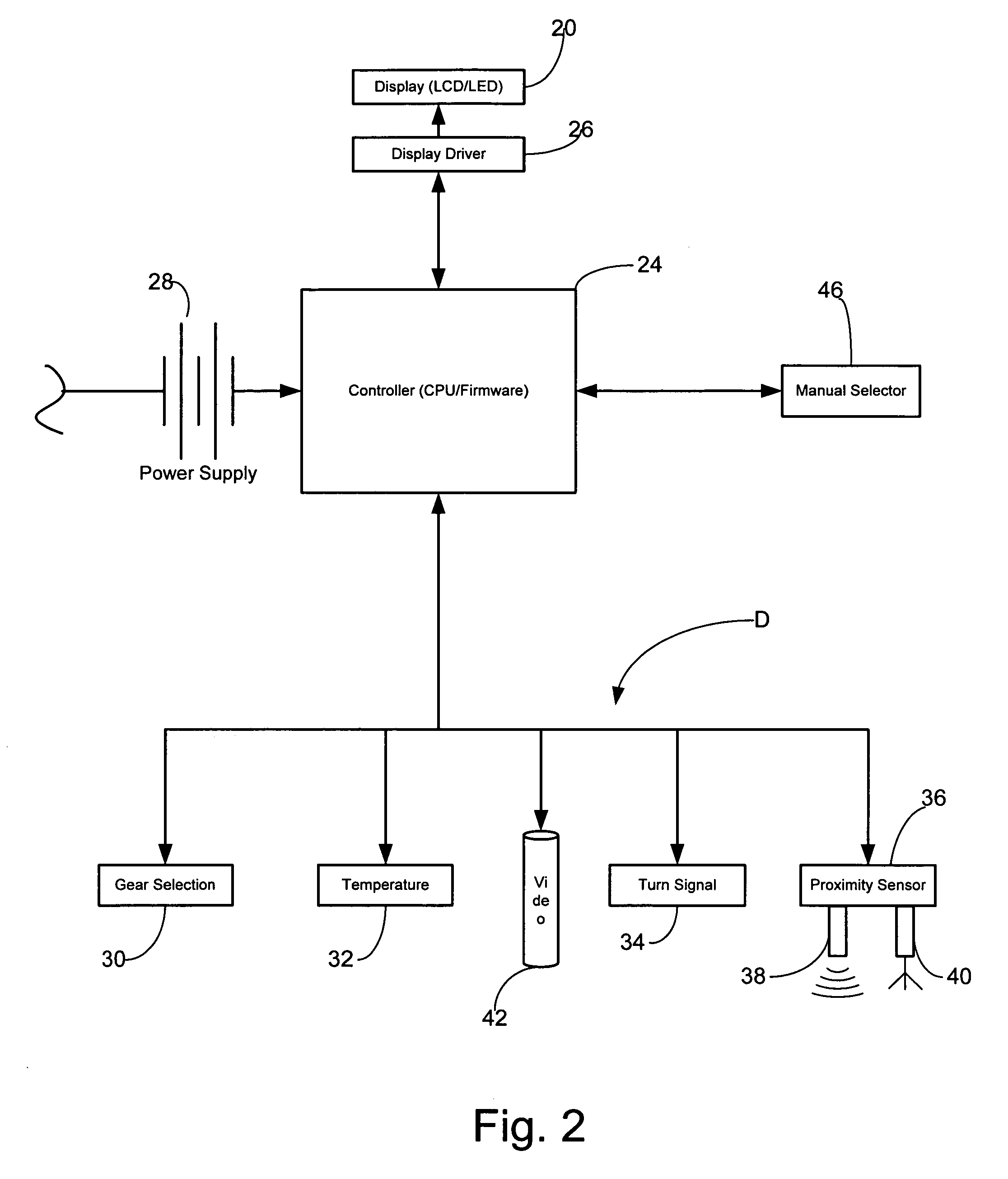
Multifunction exterior display for a vehicle mirror
InactiveUS7496439B2Digital data processing detailsPower-operated mechanismProximity sensorEmbedded system
A display unit carried in an exterior rearview mirror assembly having a generic display matrix displaying numbers, text and indicia interchangeably. A vehicle status sensor in communication with the display unit for providing vehicle status information for display, and a proximity sensor in communication with the display unit for providing object avoidance information for display in the form of a distance measurement between the vehicle and an object in the vehicle's path. A controller carried in the vehicle interior operatively associated with the display unit for selectively displaying object avoidance information or vehicle status information based on whether the vehicle is placed in a reverse gear. A display driver in communication with the controller causes the display unit to display the vehicle status information when the vehicle is not in a reverse gear, and to display the object avoidance information when the vehicle is place in a reverse gear.
Owner:LANG MEKRA NORTH AMERICA LLC
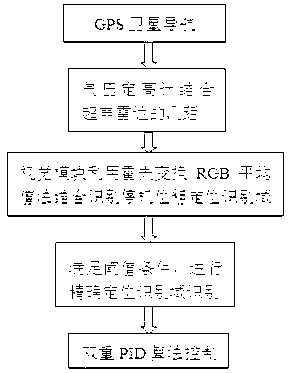
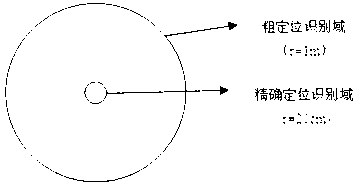
Image-processing-based unmanned plane accurate position landing method
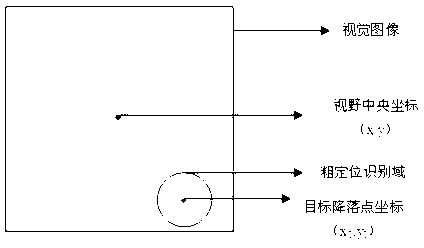
InactiveCN103226356AHigh degree of intelligent controlAddressed bugs with missed landingsPosition/course control in three dimensionsVisual perceptionAND gate
The invention discloses an image-processing-based unmanned plane accurate position landing method, which comprises the following steps: (1) a GPS (global position system) satellite navigation system enables an unmanned plane to be located above a ground parking apron; (2) an air pressure height measurement gauge and a distance measurement module of an ultrasound radar are combined to control the ground clearance for the unmanned plane to land; (3) a vision module identifies a coarse positioning identification domain in real time, and combines Hough Transform and RGB mean value method and gate position identification to process a coordinate of a targeted landing point; (4) when landing of the unmanned plane meets the threshold condition of the coarse positioning identification domain, the algorithm in the step (3) is utilized to perform accurate positioning treatment on the accurate positioning identification domain; and (5) the unmanned plane is controlled for accurate landing by taking the treated deviation value as the input quantity and adopting the double PID algorithm. According to the invention, the defect that insufficient GPS accuracy of the unmanned plane causes a fault landing is overcome, the intelligence for the unmanned plane control is improved, and the cost for using an accurate sensor is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Intensity compensation for interchangeable chromatic point sensor components
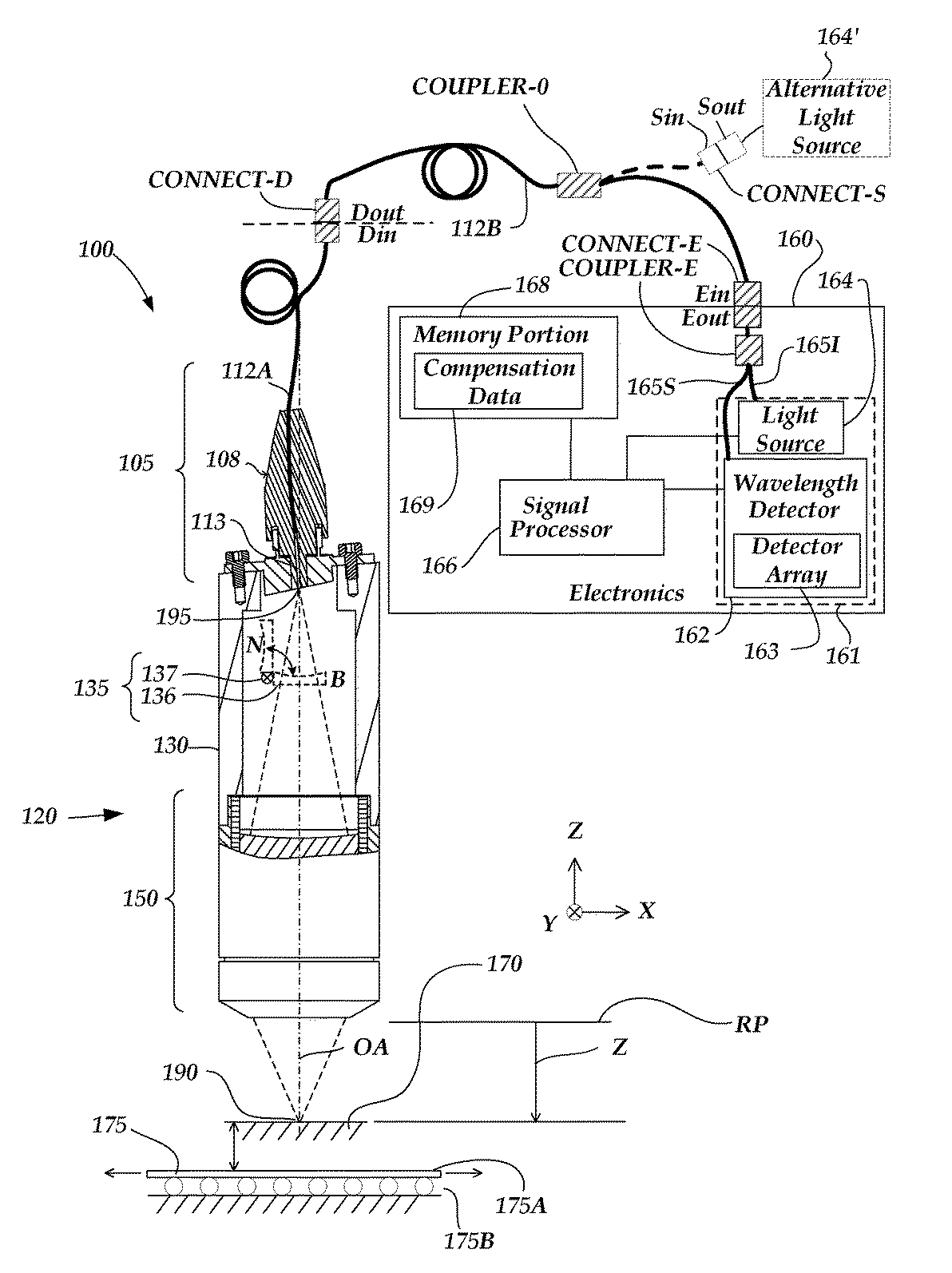
ActiveUS7876456B2Economy calibrationPracticality economyUsing optical meansMicroscopesPeak valueLength wave
Methods for providing compensation for non-uniform response of a light source and wavelength detector subsystem of a chromatic point sensor (CPS) are provided. Light from the light source is input into an optical path that bypasses the measurement path through a CPS optical pen and provides the bypass light to the wavelength detector to provide a raw intensity profile distributed over the pixels of detector. The resulting set of raw intensity profile signals are analyzed to determine a set of error compensation factors for wavelength-dependent intensity variations that occur in the raw intensity profile signals. Later, the error compensation factors may be applied to reduce distortions and asymmetries that may otherwise occur in the shape of the signals in the peak region of CPS distance measurement profile signal data. The disclosed methods may provide enhanced accuracy, robustness, field-testing, and interchangeability for CPS components, in various embodiments.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
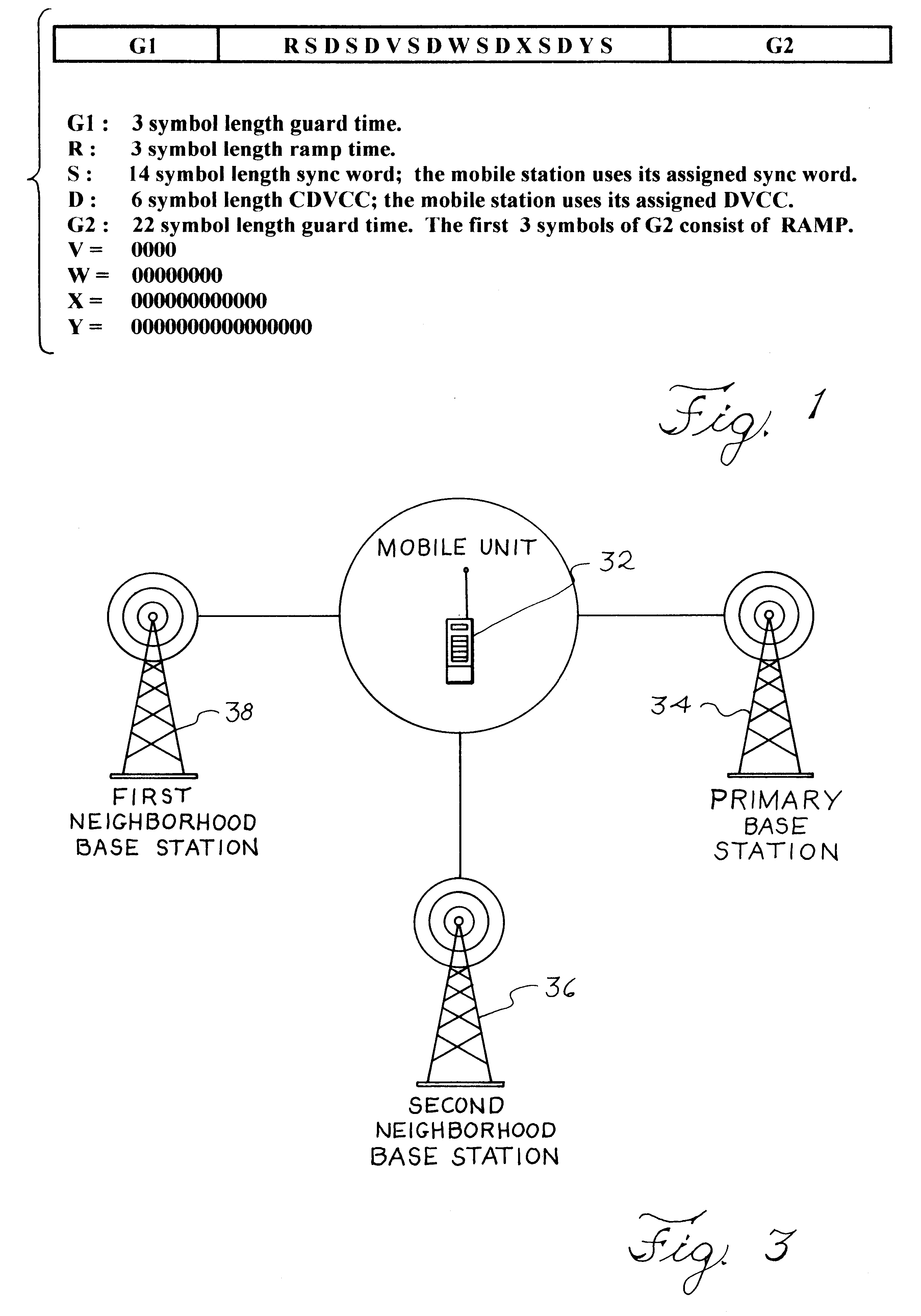
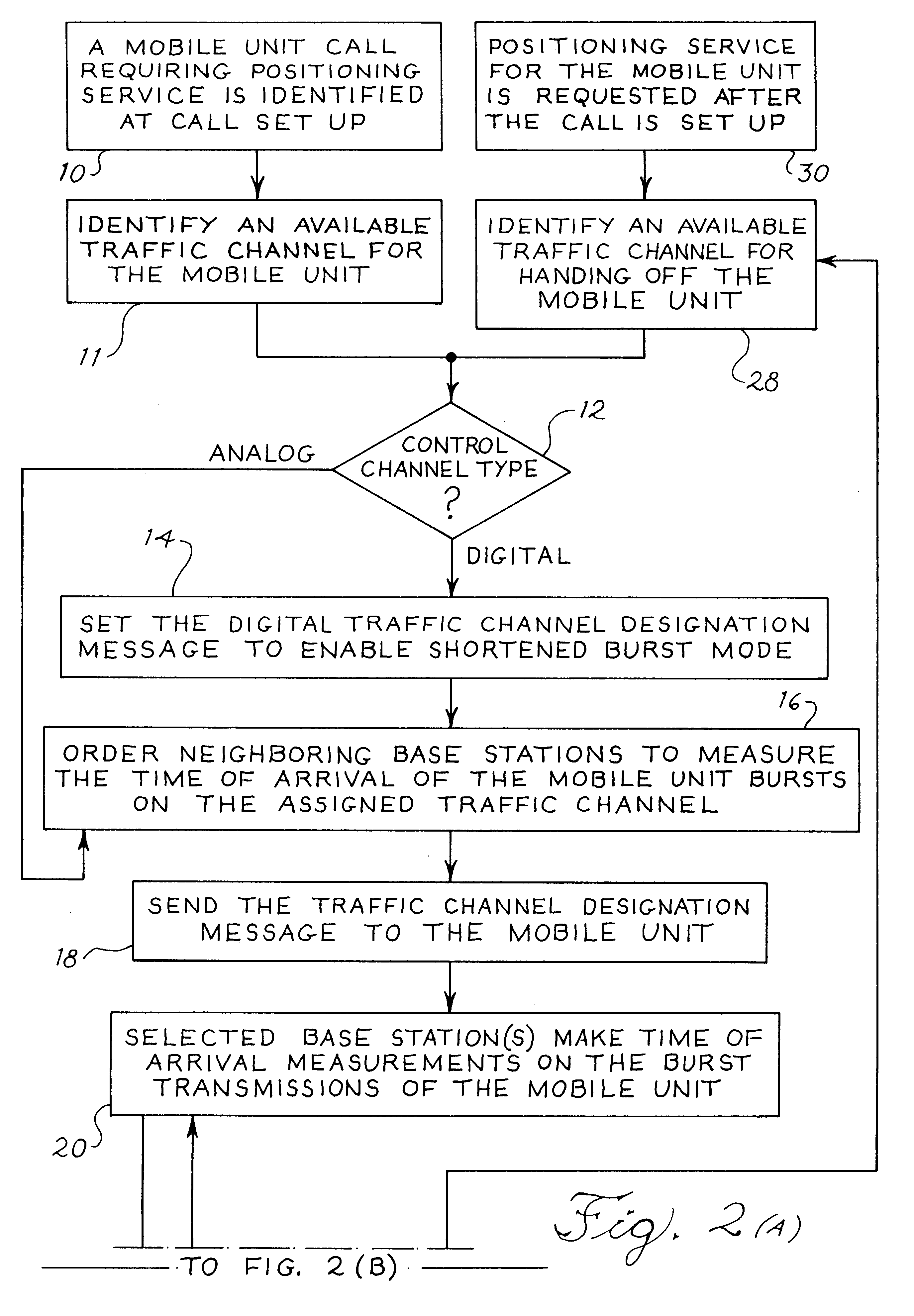
Mobile positioning method for a portable communications device using shortened repetitive bursts
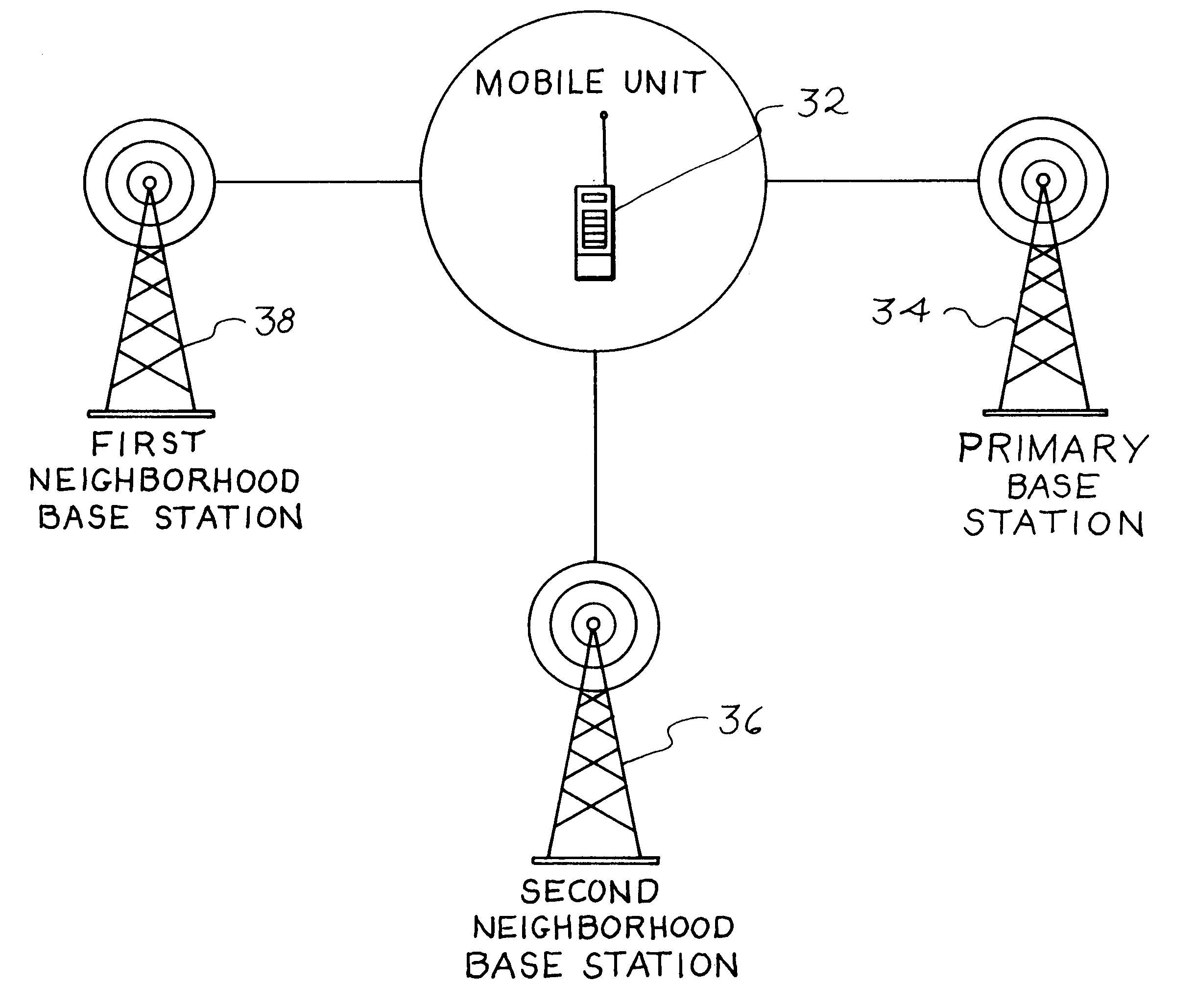
InactiveUS6243588B1Accurate locationAccurately determineError preventionDirection finders using radio wavesBurst transmissionPrimary station
Standard mobile cellular telephones use shortened burst signal transmissions to synchronize the transmission of a call over a cellular telephone network. These shortened bursts as well as other traffic channel bursts can be used to locate the position of the cell phone. In operation, a primary base station sends a traffic channel designation message to a selected mobile phone which then initiates selected traffic channel burst transmissions, such as shortened bursts, over an interval of five seconds or less. The primary station and at least two other neighboring base stations receive these burst transmissions and determine their respective distances from the cell phone based upon the time of arrival of the bursts or some other suitable distance related measurement. A command center determines the location of the cell phone by triangulating the distance measurements of the base stations.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Voice activated distance measuring device
InactiveUS20060270450A1Physical therapies and activitiesGymnastic exercisingComputer hardwareLoudspeaker
Owner:GARRATT REGINALD G +2
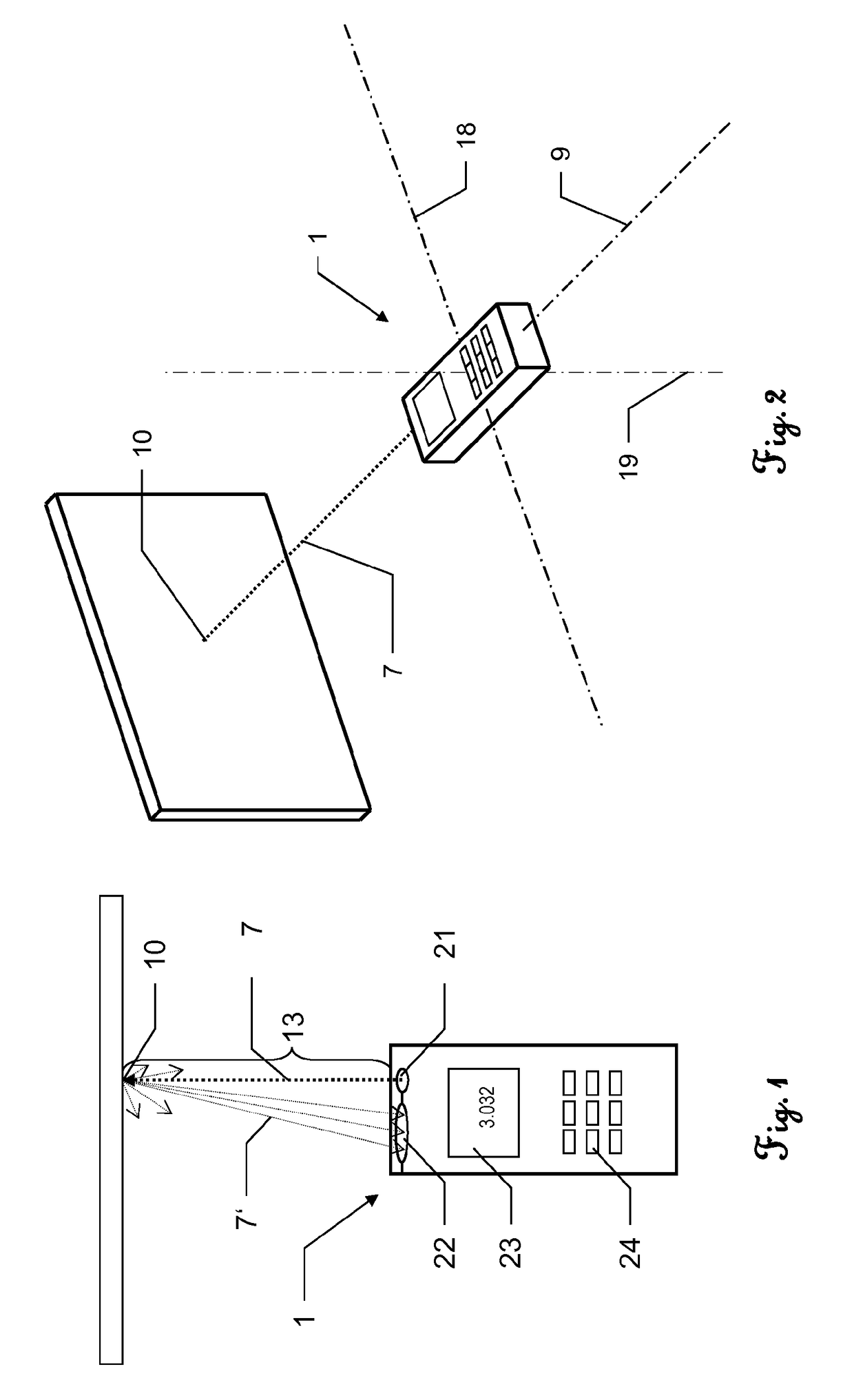
Chopper-stabilized absolute distance meter
An absolute distance measurement device is provided, including reference and measurement laser signal paths, comprising a laser source providing a laser signal and a chopper assembly, comprising a rotatable surface defining at least one aperture provided through a portion of the rotatable surface; wherein the laser signal is directed to different points on the rotatable surface of the chopper assembly such that as the rotatable surface is rotated, the aperture selectively permits transmission and selectively prevents transmission of each of said at least two laser signal paths.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
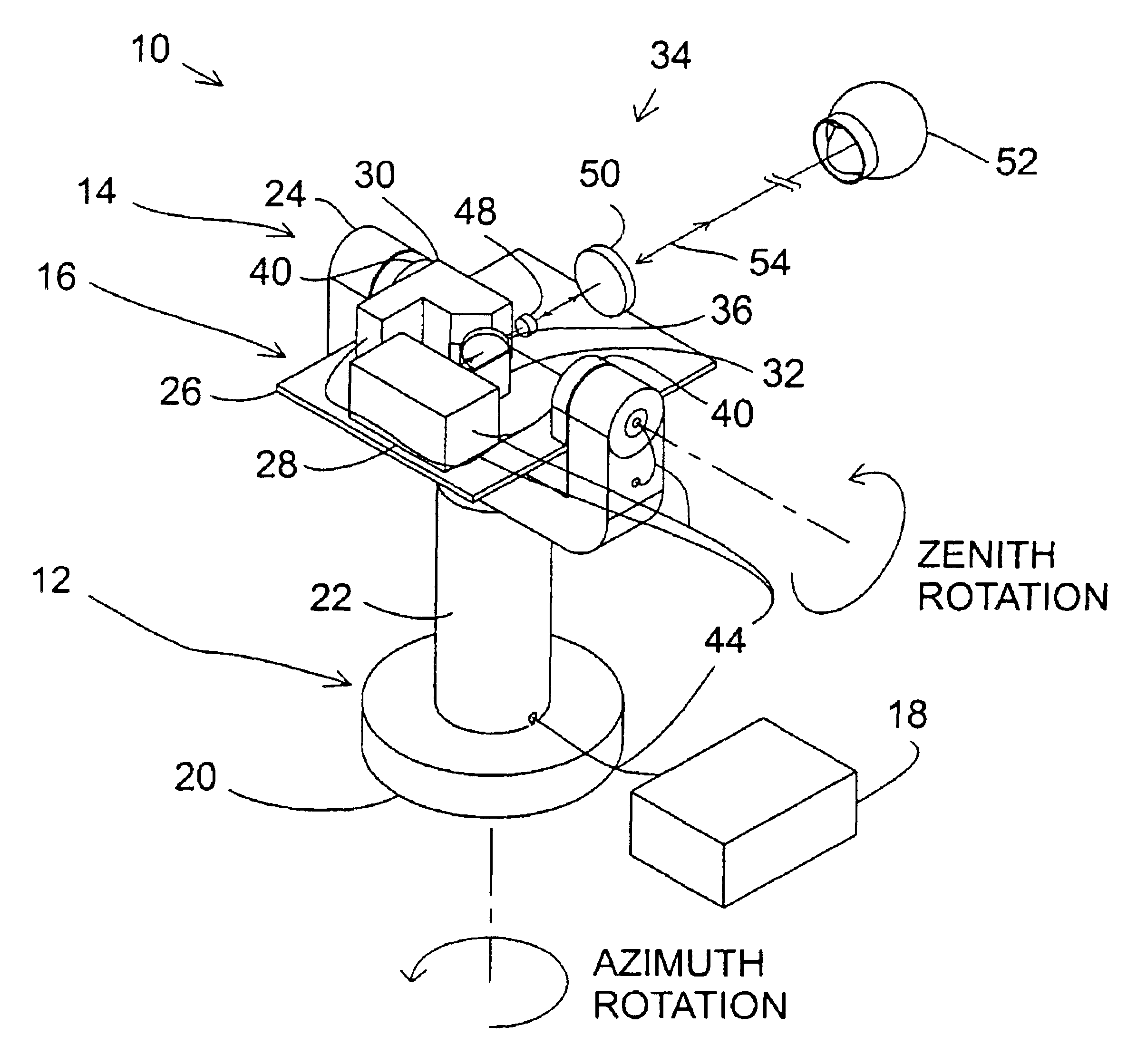
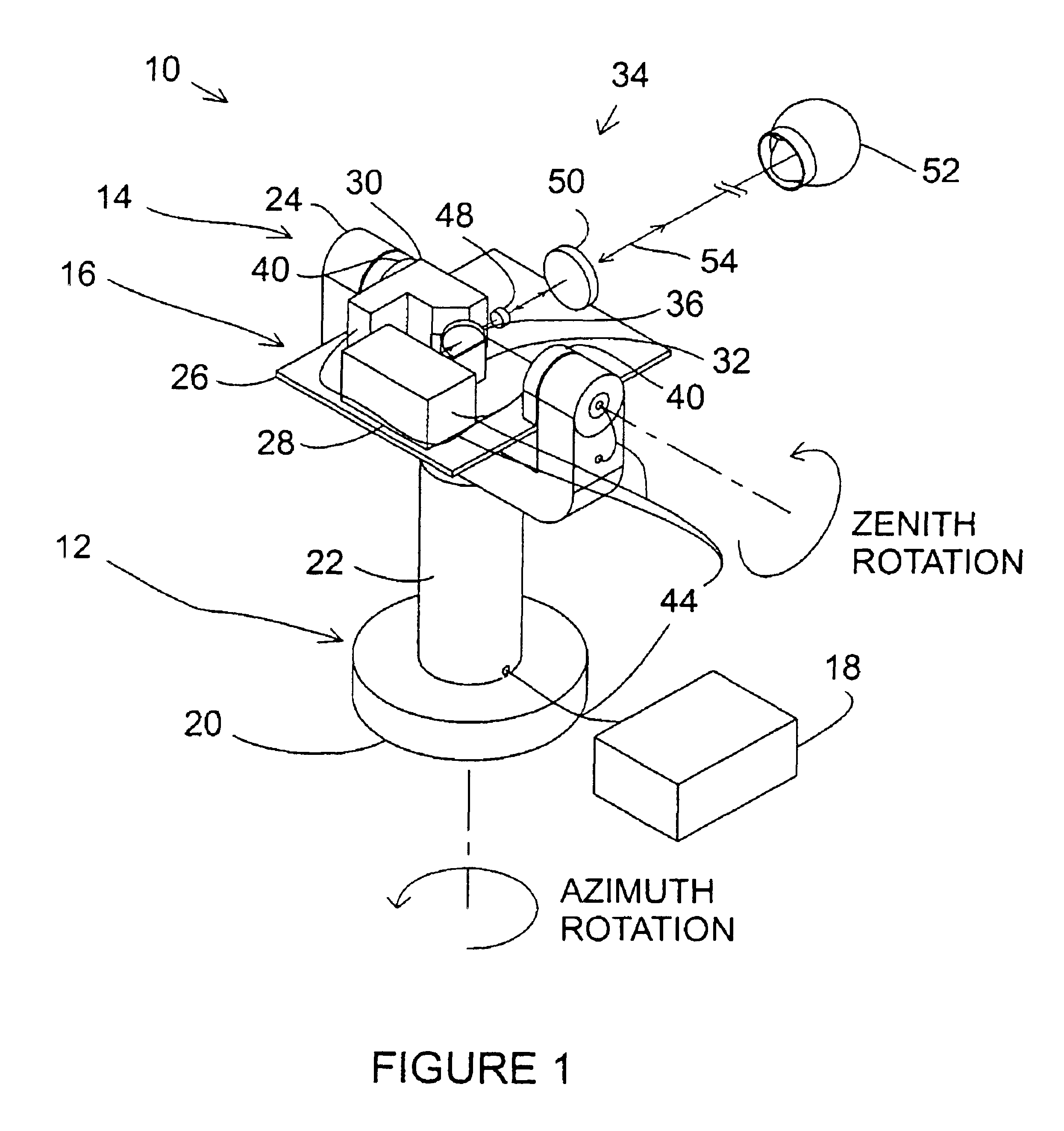
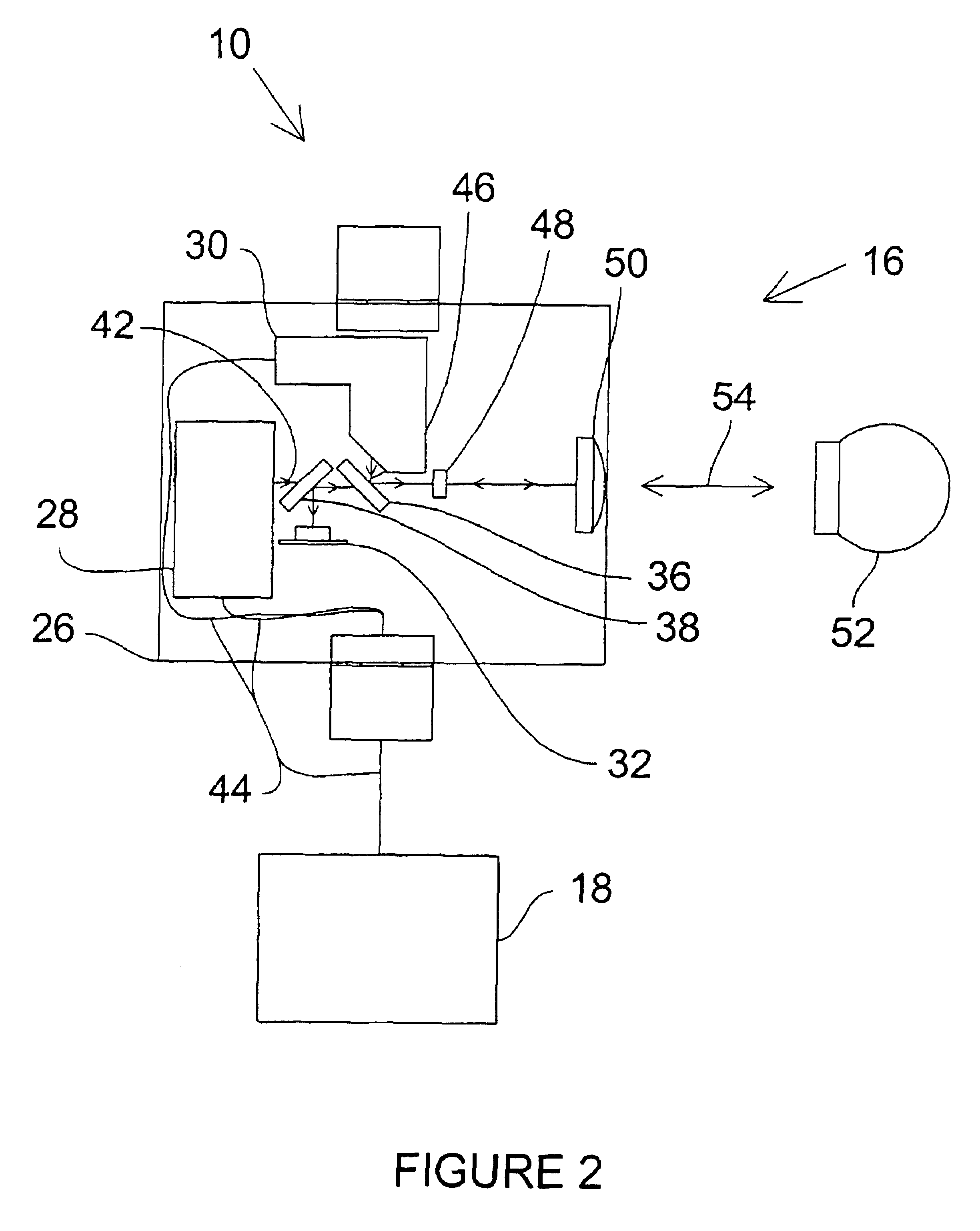
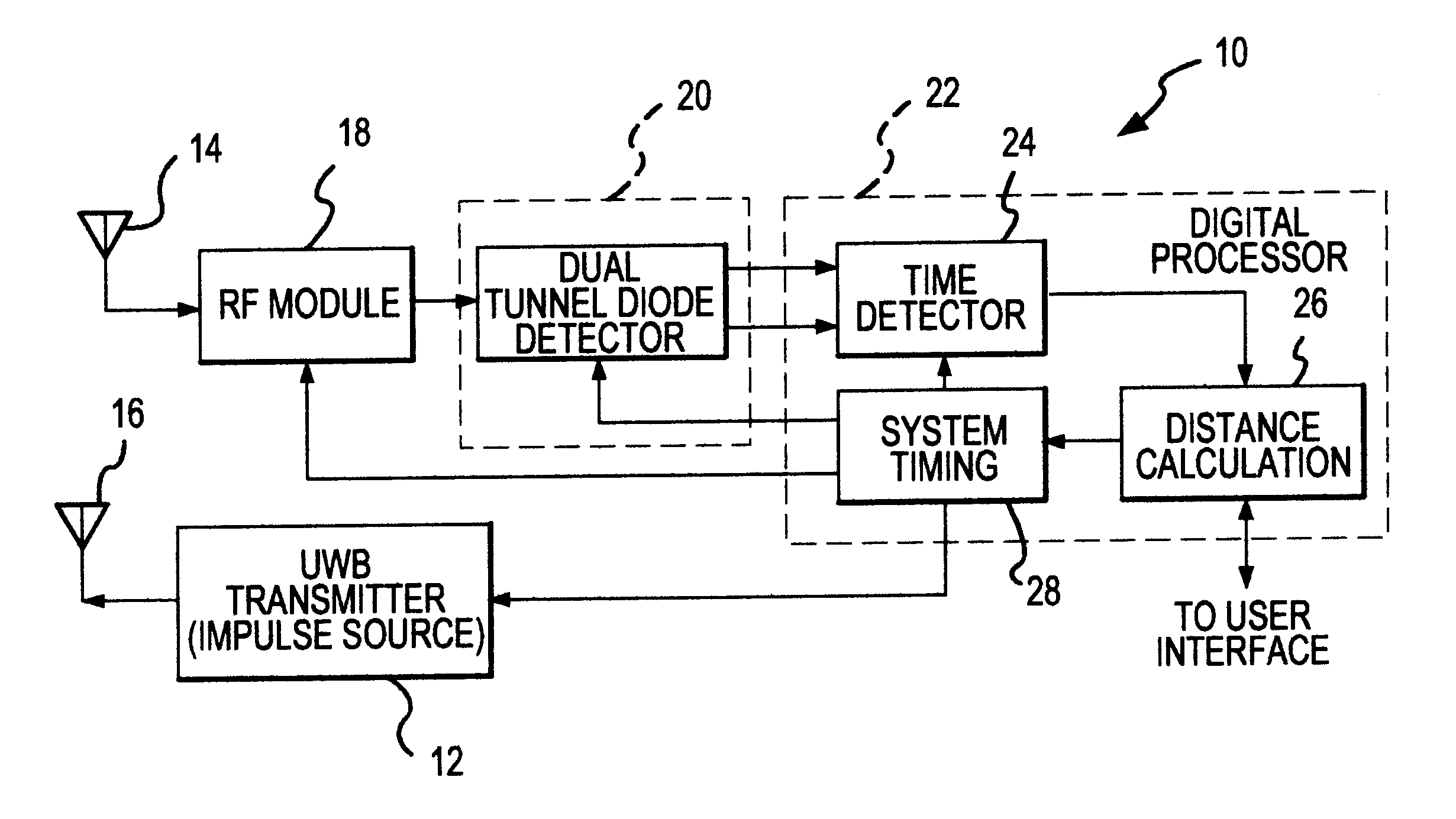
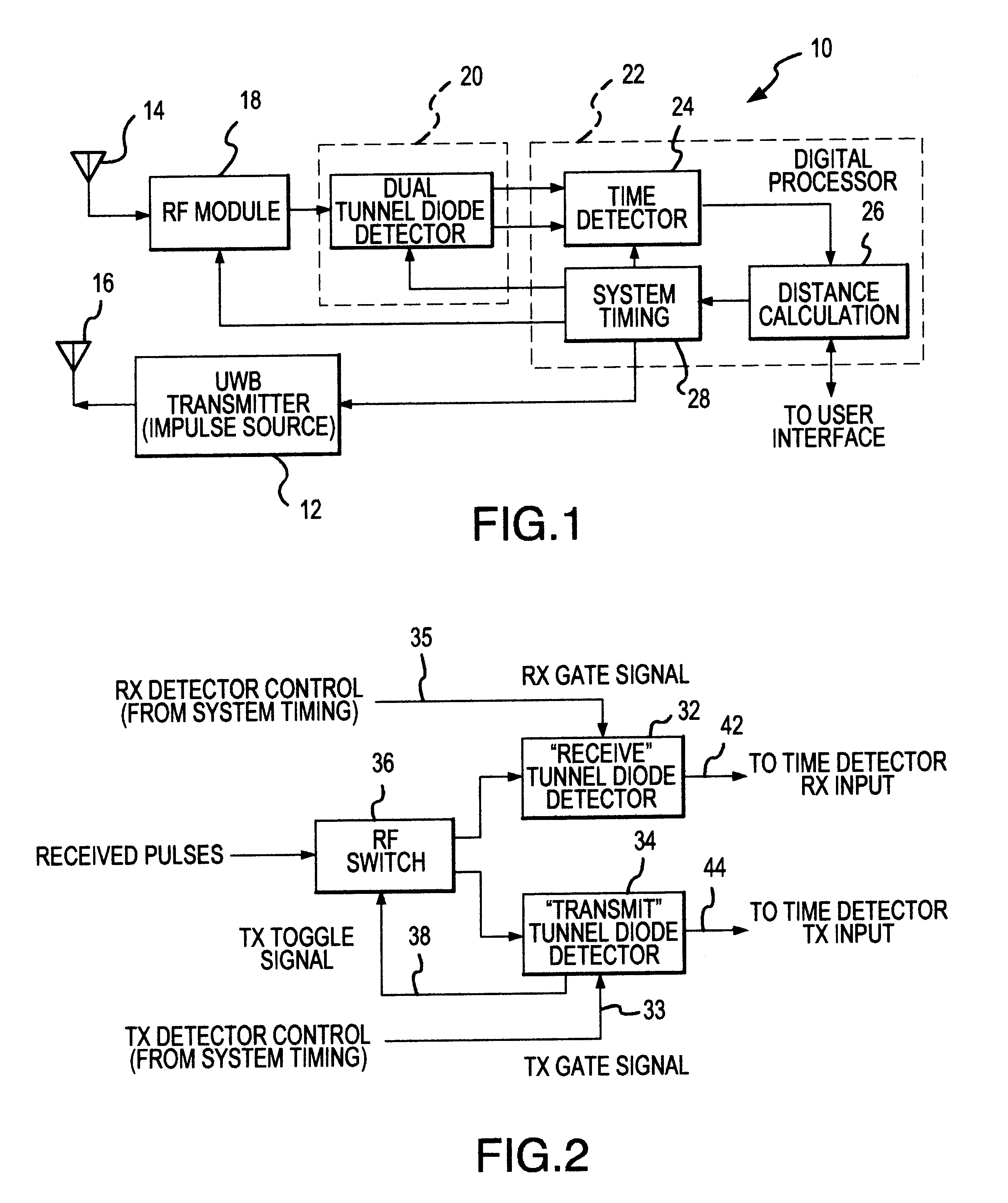
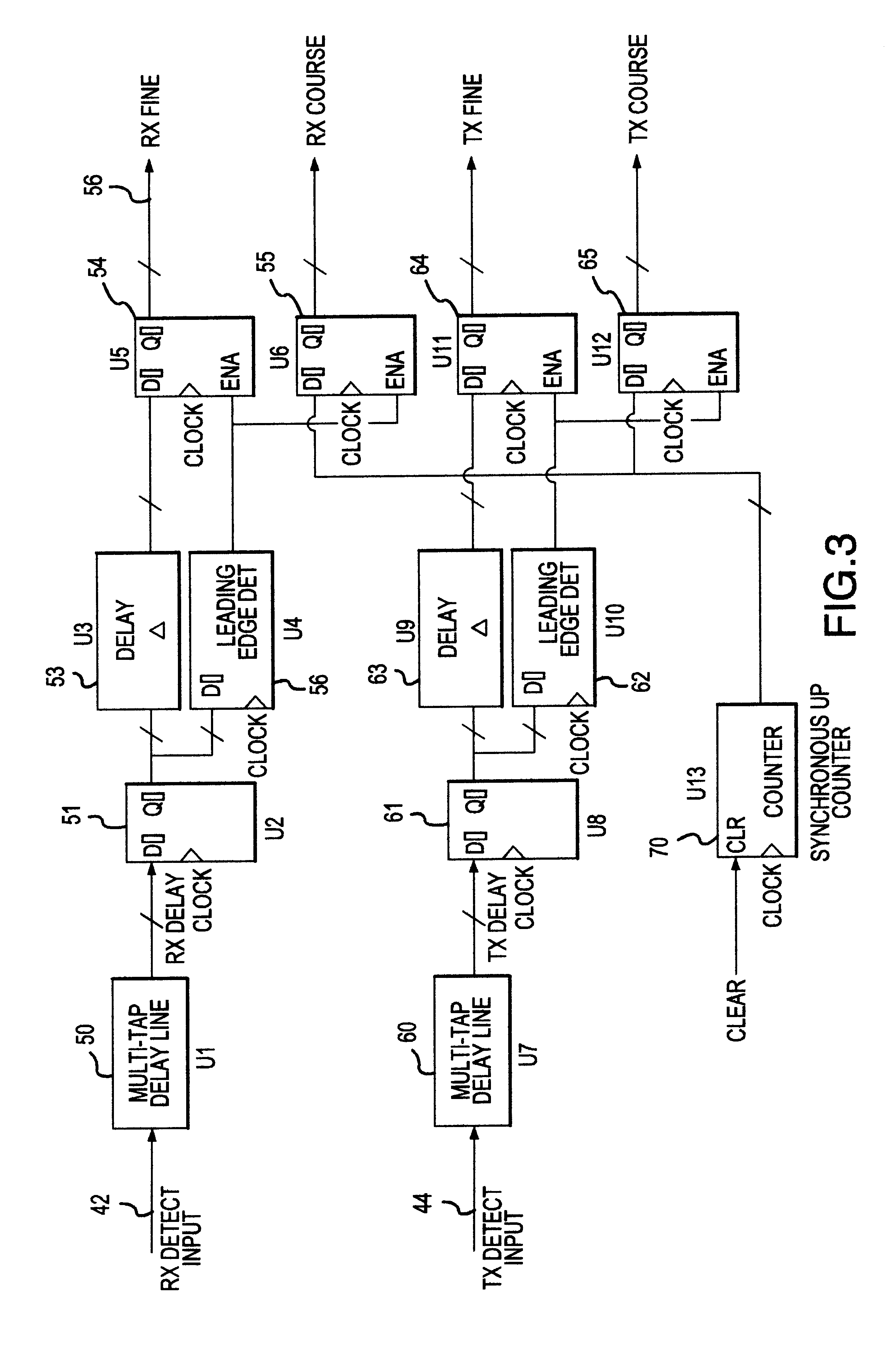
UWB dual tunnel diode detector for object detection, measurement, or avoidance
InactiveUS6239741B1Baseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTunnel diode
A highly sensitive, high-speed dual tunnel diode detector is described for use in Ultra Wideband (UWB) object detection systems, such as a radar. The extended capability of the detector to both extremely short (sub-foot) and long distance (tens of thousands of feet) ranges is unique and permits the application of low power UWB radar to a wide variety of applications including high resolution radar altimetry at altitudes exceeding 10,000 feet and for autonomous on-deck landing operations (e.g., one-foot altitudes), the detection of extremely low radar cross section (RCS) targets for such applications as suspended wire detection for helicopters and other manned and unmanned craft, etc. High noise and interference immunity of the detector permits co-location of a UWB radar sensor with other active systems. The invention has immediate and significant application to all areas, both military and commercial, of precision distance measurement, intrusion detection, targeting, etc. over a wide range of distances.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
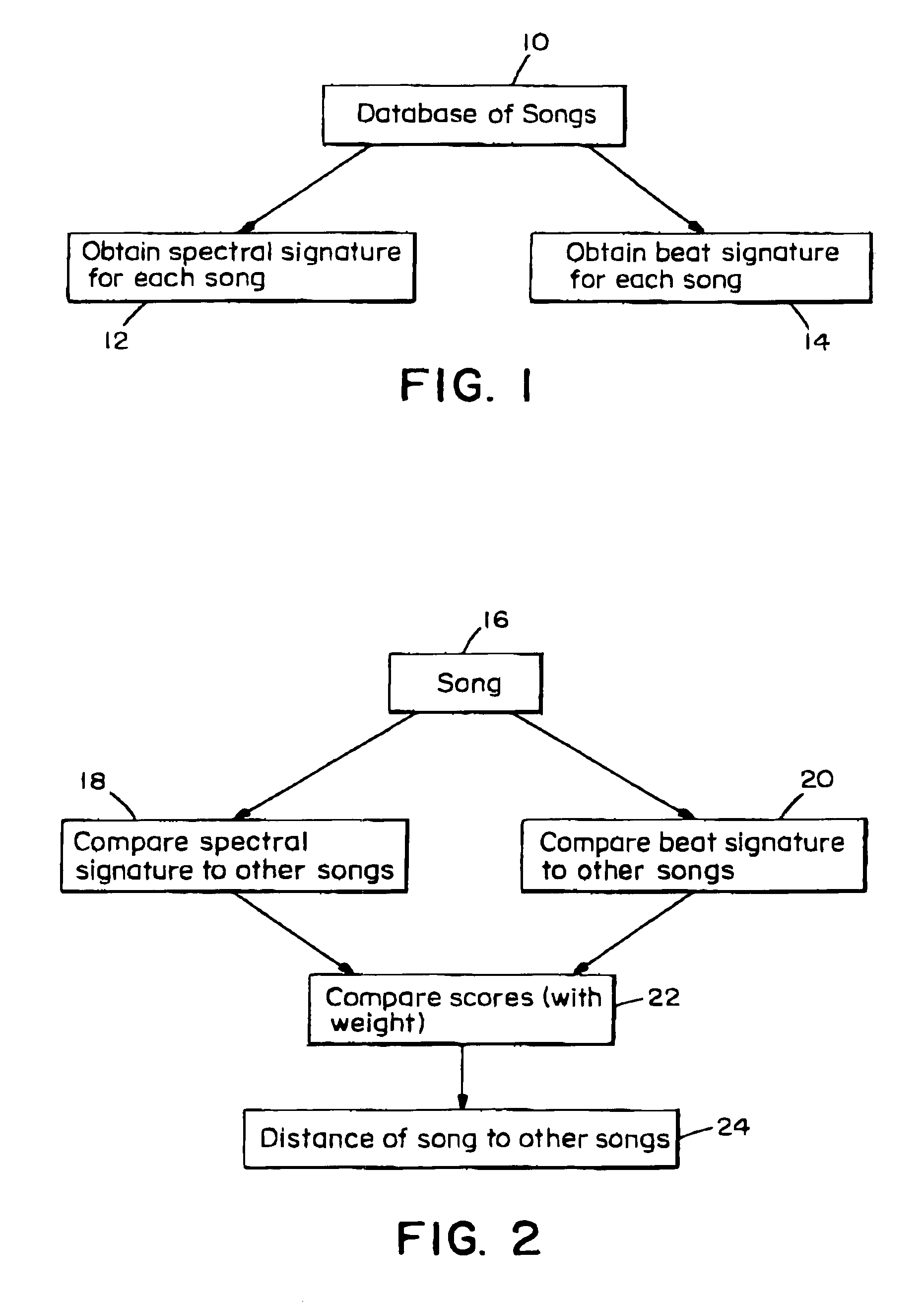
Music similarity function based on signal analysis
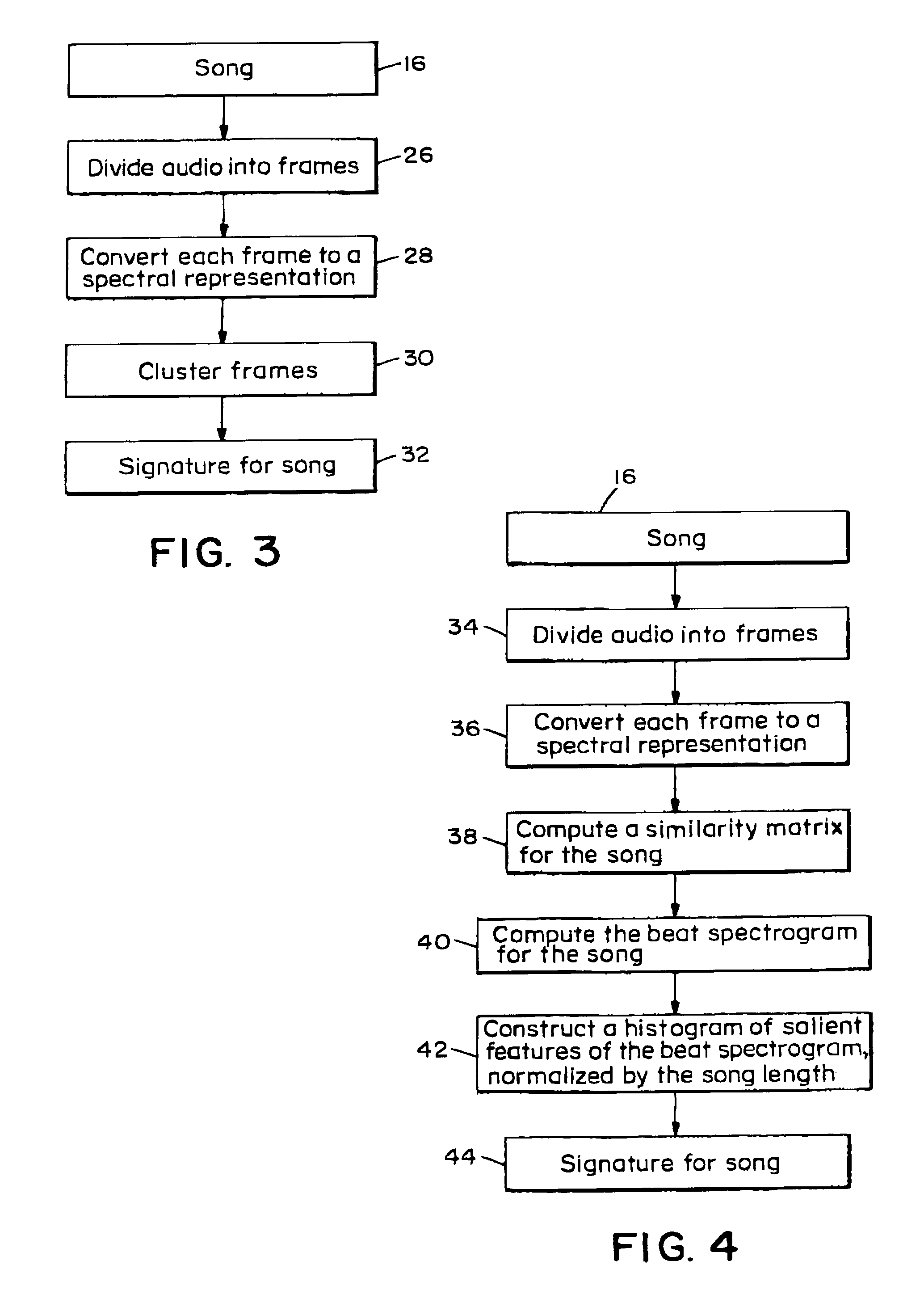
InactiveUS7031980B2Television system detailsData processing applicationsComputer methodsDistance measurement
The present invention computer method and apparatus determines music similarity by generating a K-means (instead of Gaussian) cluster signature and a beat signature for each piece of music. The beat of the music is included in the subsequent distance measurement.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Concept for optical distance measurement
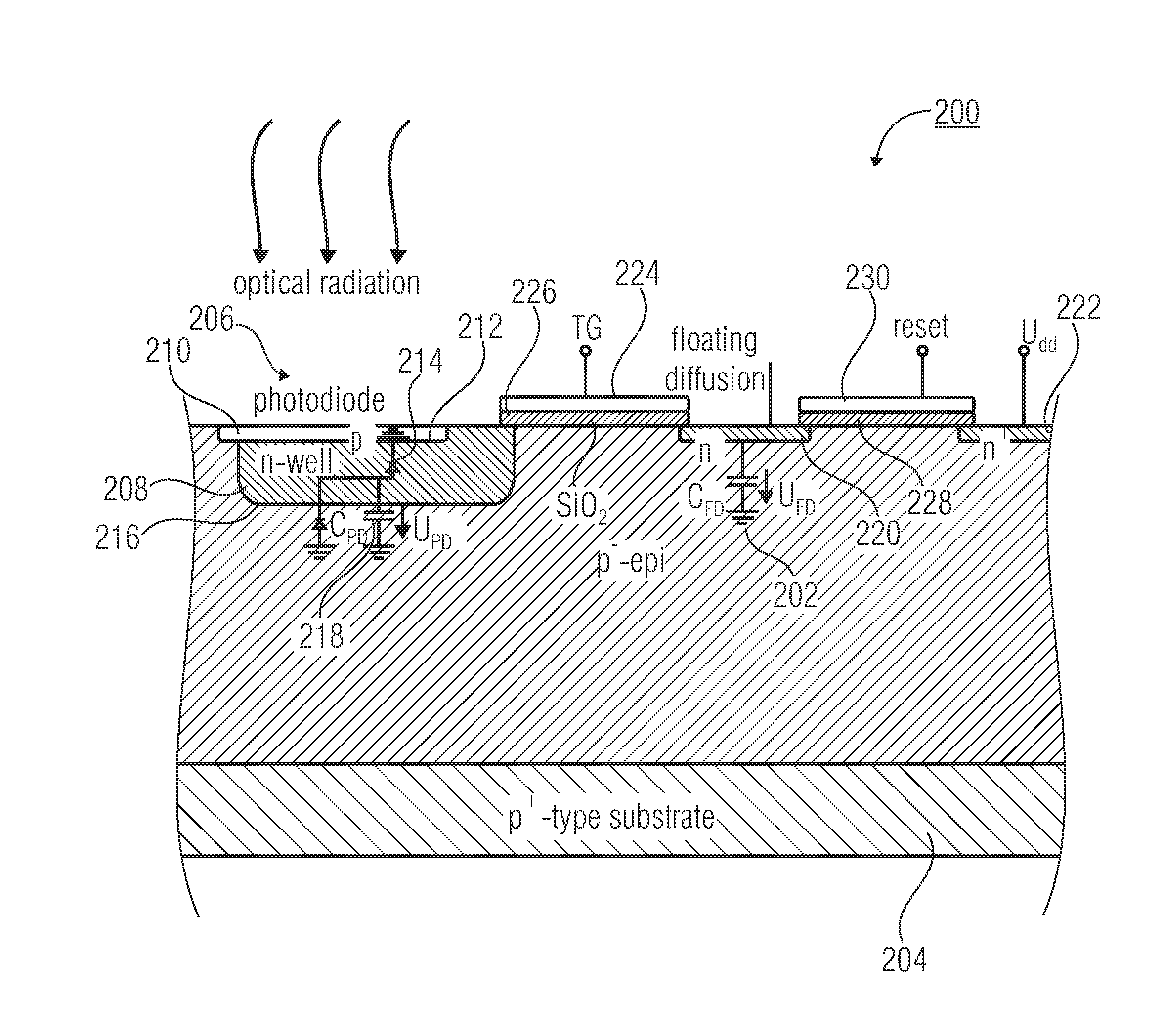
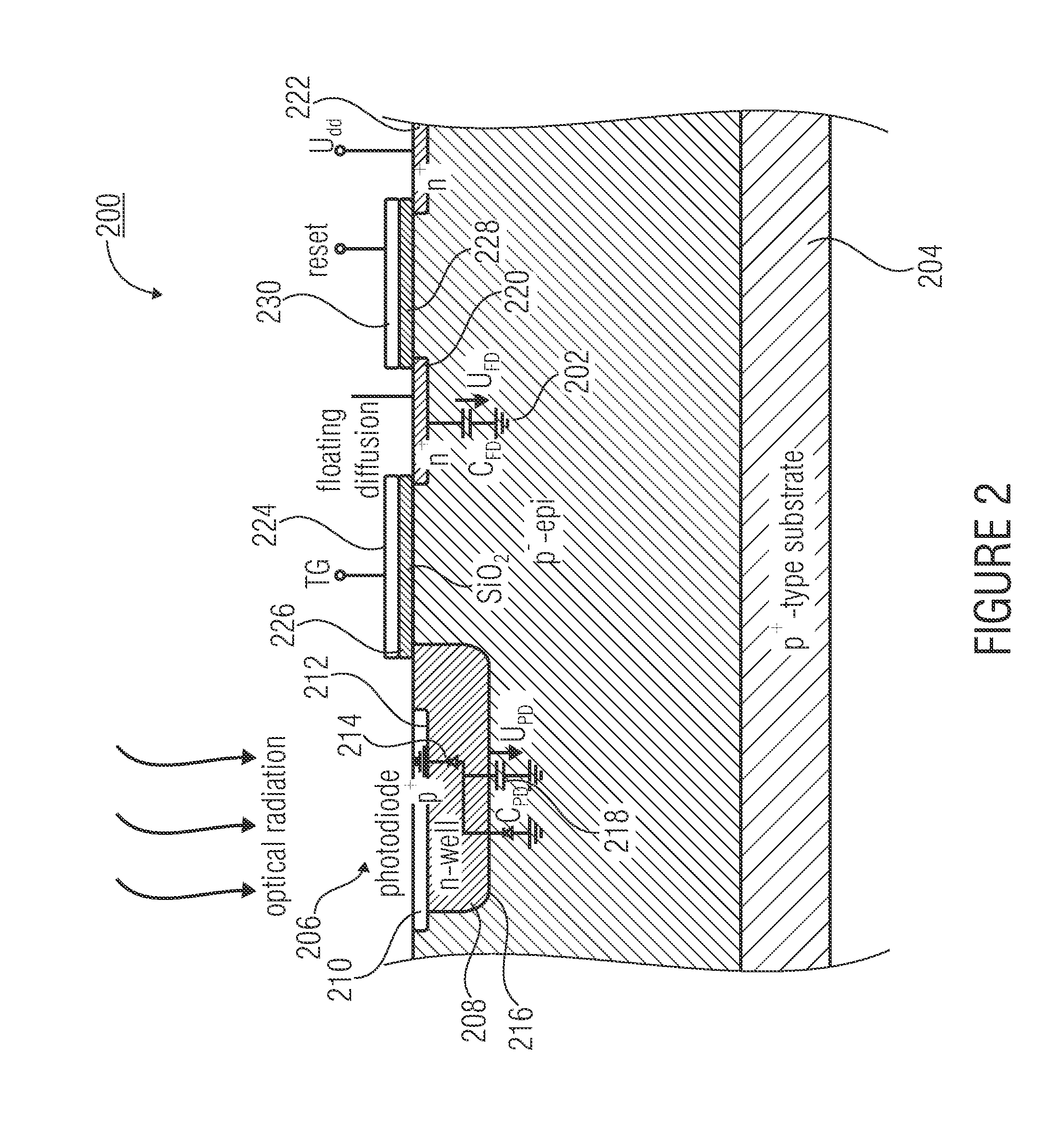
ActiveUS20110037969A1Halving laser energyDoubling measuring speedOptical rangefindersDiodeCharge-carrier densityCharge carrier
The present invention relates to a concept for optical distance measurement, wherein a radiation pulse is emitted in the direction of an object of measurement. At least two different transfer gates which couple a photoactive region to at least two different evaluating capacities are driven during different drive intervals so that charge carriers generated during the drive intervals by a radiation pulse reflected from the object of measurement and / or by ambient radiation can be transported from the photoactive region to the evaluating capacities each coupled to the at least two transfer gates. Another transfer gate is driven during a time outside the drive intervals of the at least two transfer gates to connect the photoactive region to a reference potential terminal acting as a charge carrier sink during the time outside the drive intervals of the at least two transfer gates.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Method and apparatus for supporting an element to be supported, in particular the body of a patient, making it possible to support said element at a predetermined float line
InactiveUS6009580AHigh pressureStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesControlled releaseMeasurement device
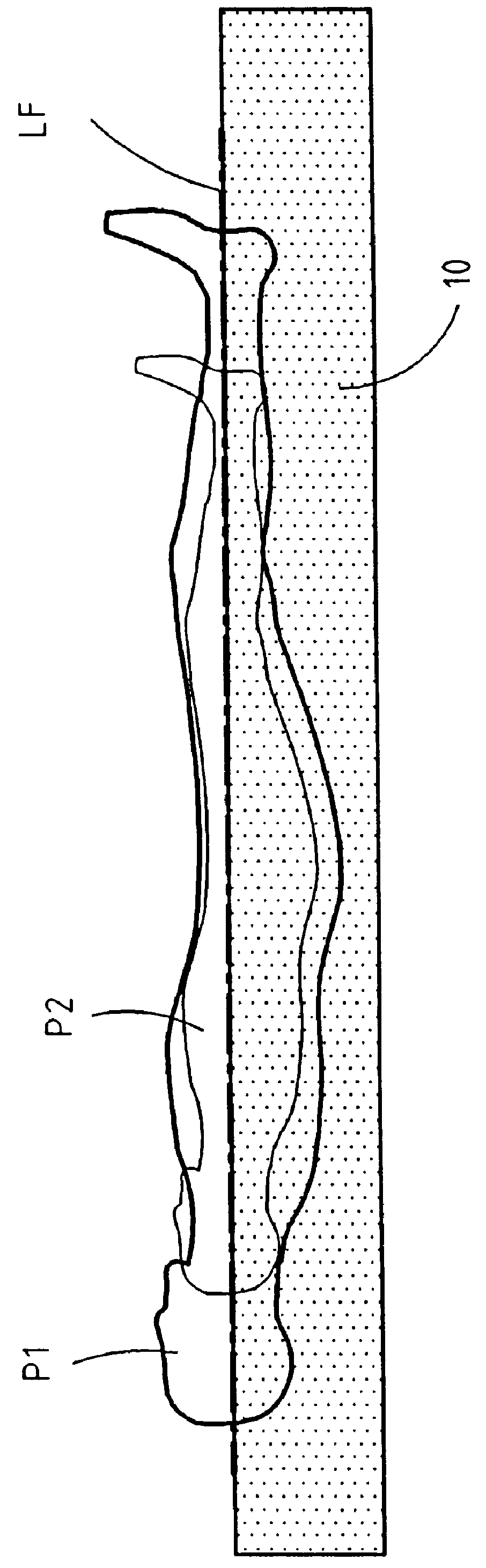
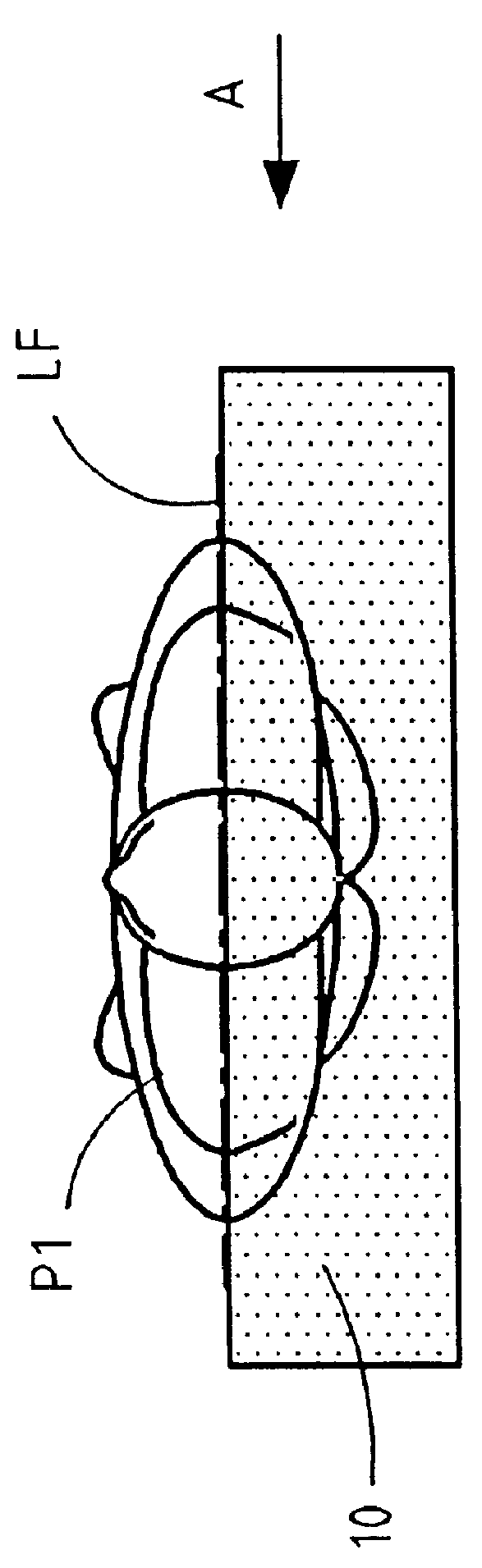
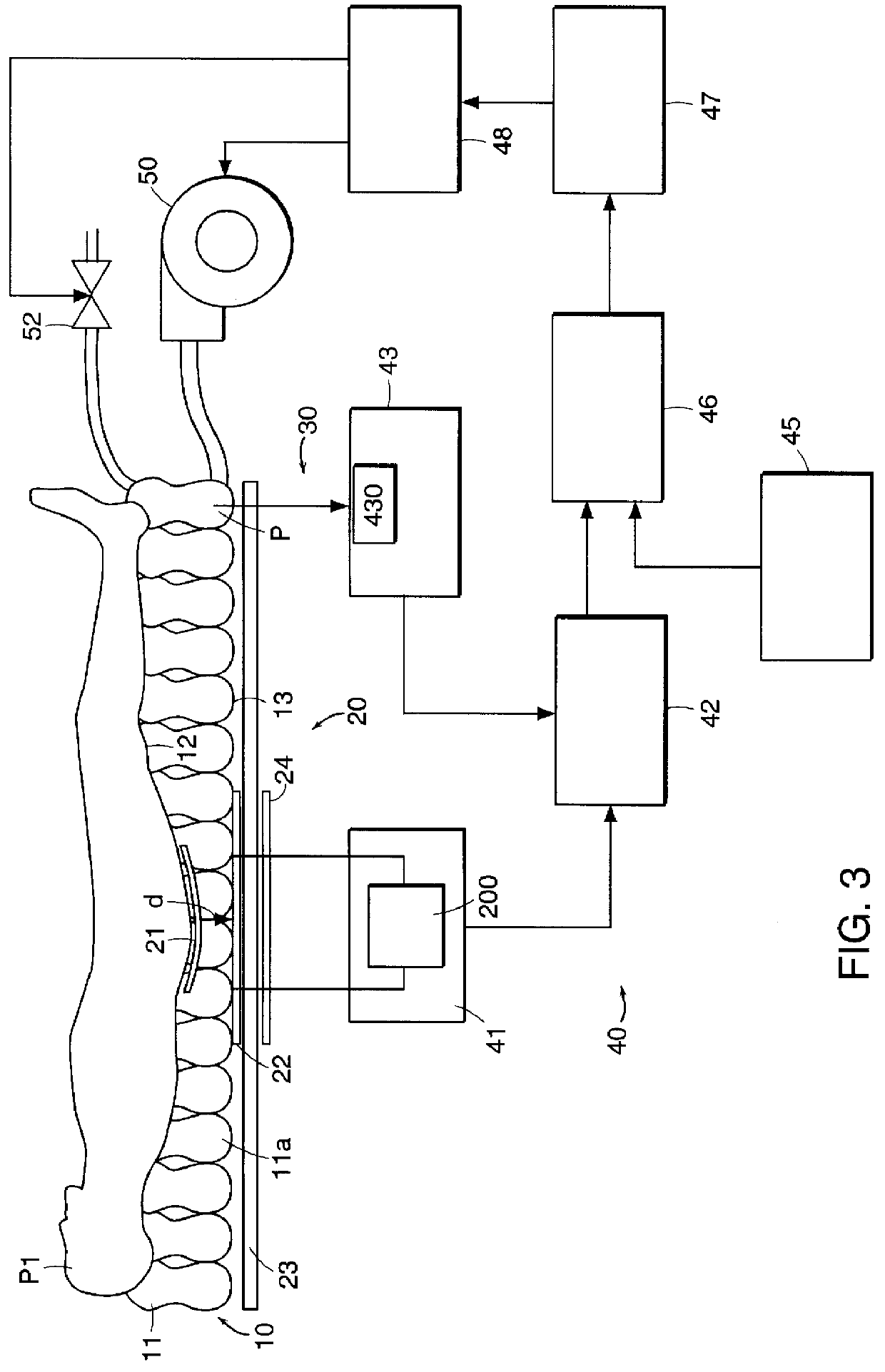
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for supporting a body element. The apparatus includes at least one support device with at least one closed or controlled-release chamber, a filling device and an emptying means device for filling said chamber with a filling fluid and emptying the fluid from the chamber, and a distance-measurement device for measuring the distance between a top face and a bottom face of the chamber. The apparatus further includes a reaction-measurement device for measuring the reaction of the support device relative to the morphological data of the body element to be supported, and a control system including a combination device for combining the measurement of the penetration distance d provided by the distance-measurement device and the measurement of the reaction provided by the reaction-measurement device. This combination is advantageously constituted by summing the two obtained measurements. The invention makes it possible to support the element to be supported substantially in a position of equilibrium corresponding substantially to a predetermined float line.
Owner:HILL ROM INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com