Patents
Literature
1321 results about "Propagation delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Propagation delay is the length of time taken for the quantity of interest to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics.
Accident avoidance system
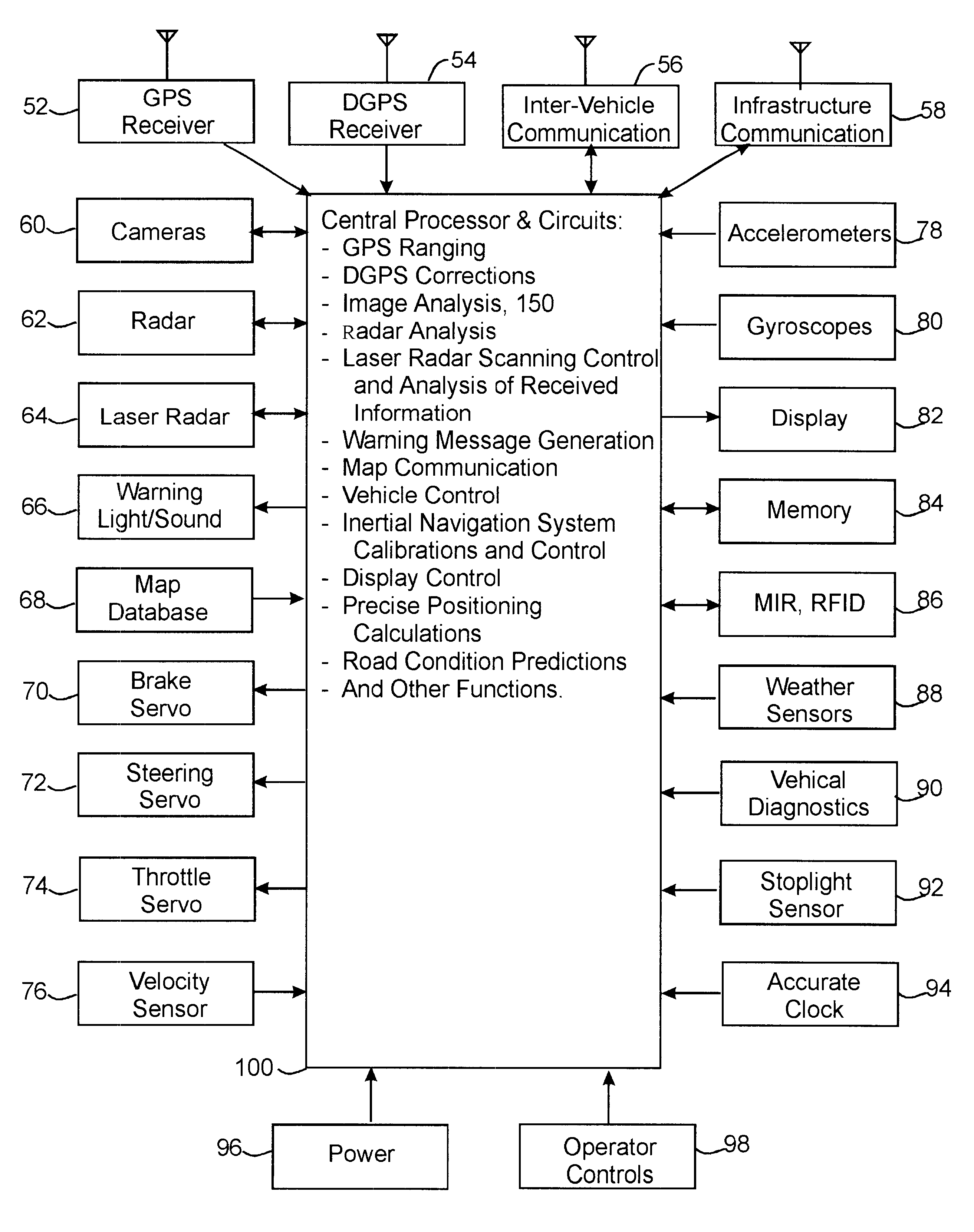
System and method for preventing vehicle accidents in which GPS ranging signals relating to a host vehicle's position on a roadway on a surface of the earth are received on a first communication link from a network of satellites and DGPS auxiliary range correction signals for correcting propagation delay errors in the GPS ranging signals are received on a second communication link from a station or satellite. The host vehicle's position on a roadway on a surface of the earth is determined from the GPS, DGPS, and accurate map database signals with centimeter accuracy and communicated to other vehicles. The host vehicle receives position information from other vehicles and determines whether any other vehicle from which position information is received represents a collision threat to the host vehicle based on the position of the other vehicle relative to the roadway and the host vehicle. If so, a warning or vehicle control signal response to control the host vehicle's motion is generated to prevent a collision with the other vehicle.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
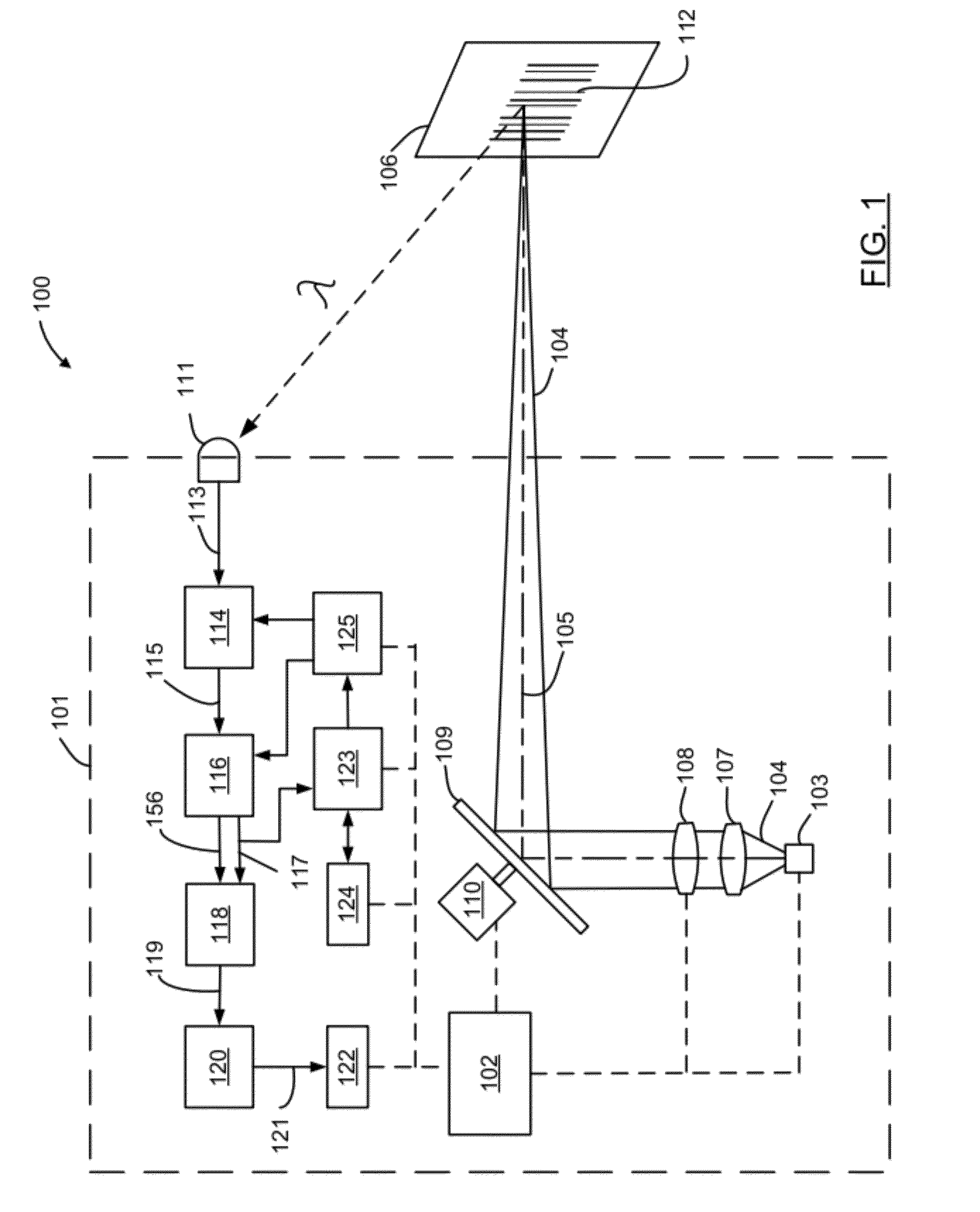
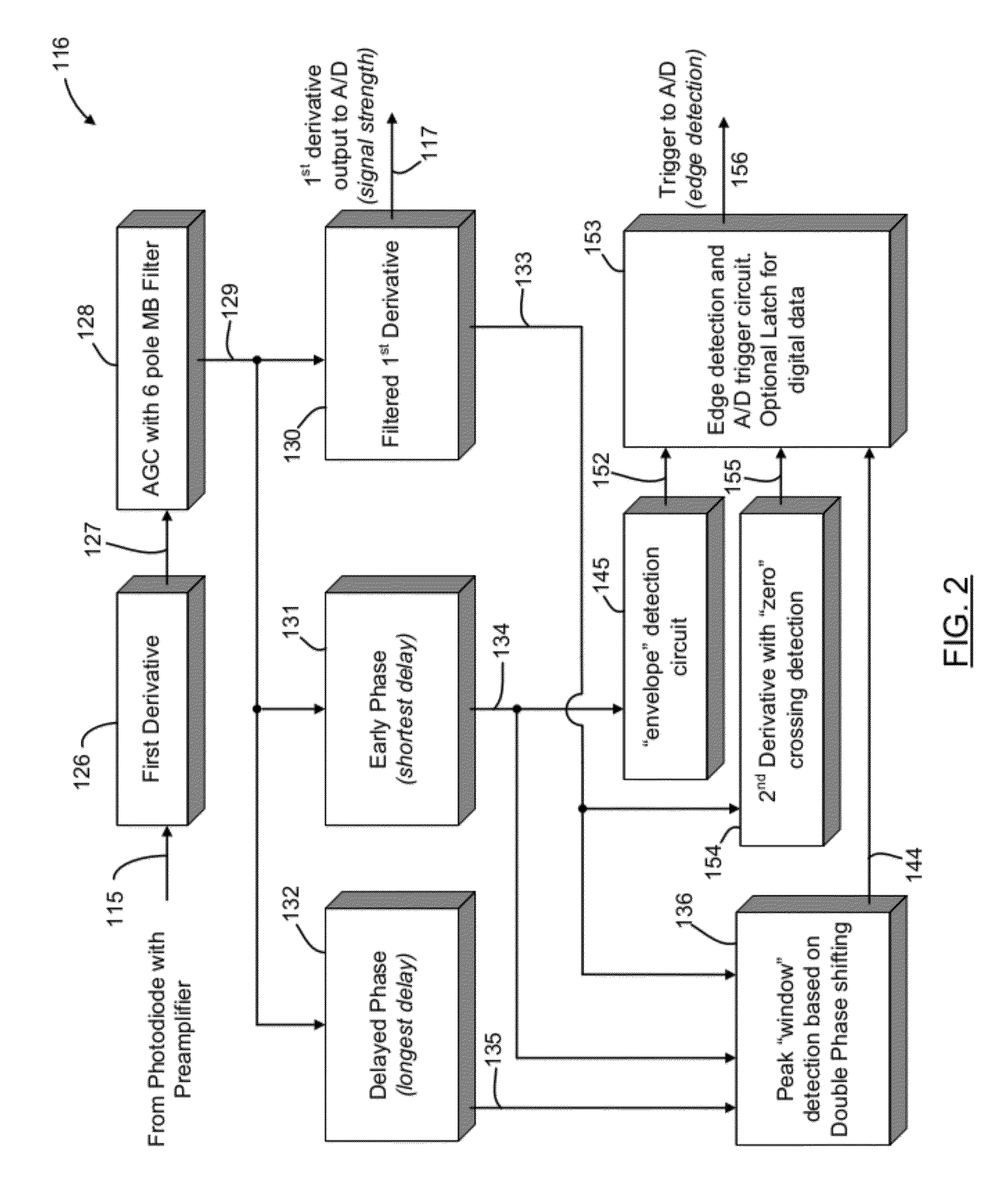
Barcode reader with edge detection enhancement
ActiveUS8950678B2Character and pattern recognitionElectric pulse generatorPropagation delayTelecommunications
An optical reader for decoding an encoded symbol character of a symbology includes a scan data signal processor having as an input a scan data signal encoding information representative of the encoded symbol character. The scan data signal processor includes a first time delay stage adapted to provide a primary phase waveform from the scan data signal, a second time delay stage adapted to provide an early phase waveform from the scan data signal, and a third time delay stage adapted to provide a delayed phase waveform from the scan data signal. The early phase waveform has a propagation delay less than the primary phase waveform, and the delayed phase waveform has a propagation delay greater than the primary phase waveform. The scan data signal processor further includes a peak window detection stage for generating a peak window timeframe when an amplitude of the primary phase waveform is greater than, less than, or equal to both an amplitude of the early phase waveform and the delayed phase waveform. The optical reader further includes a digitizer circuit adapted to accept, within the peak window timeframe, the scan data signal processor output.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS +1
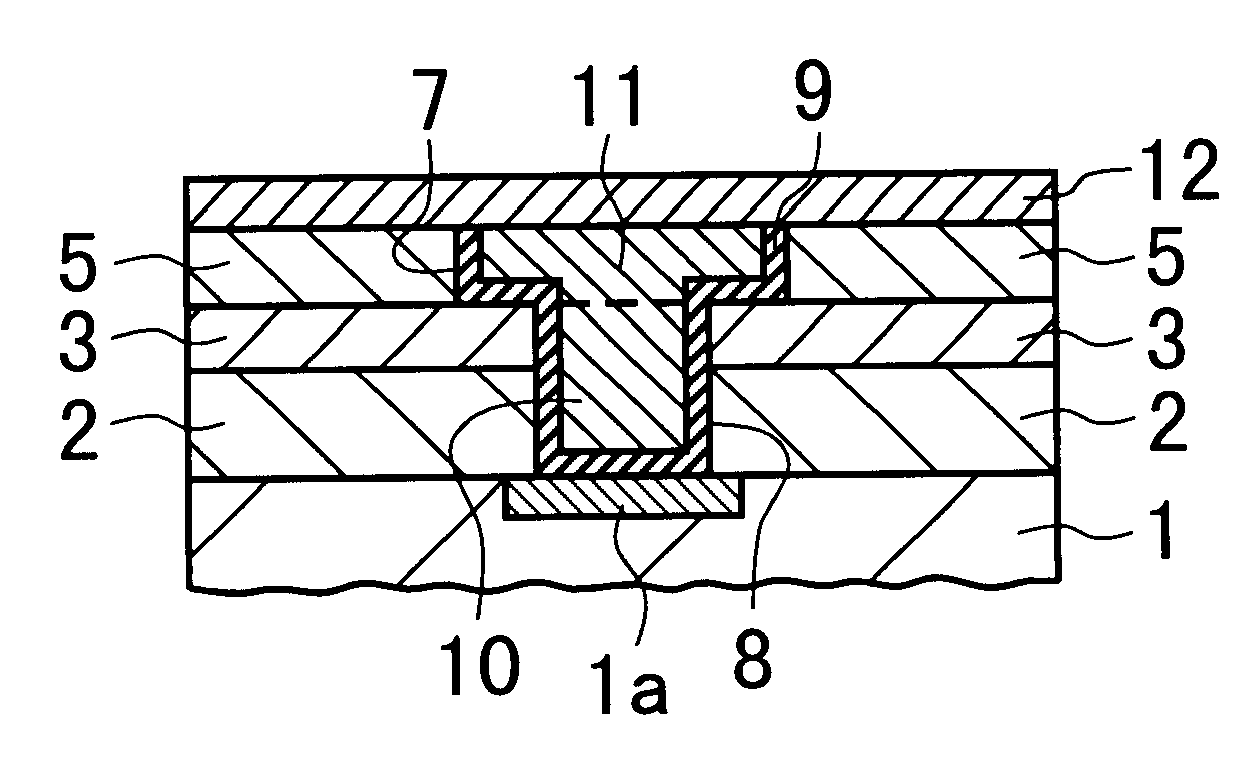
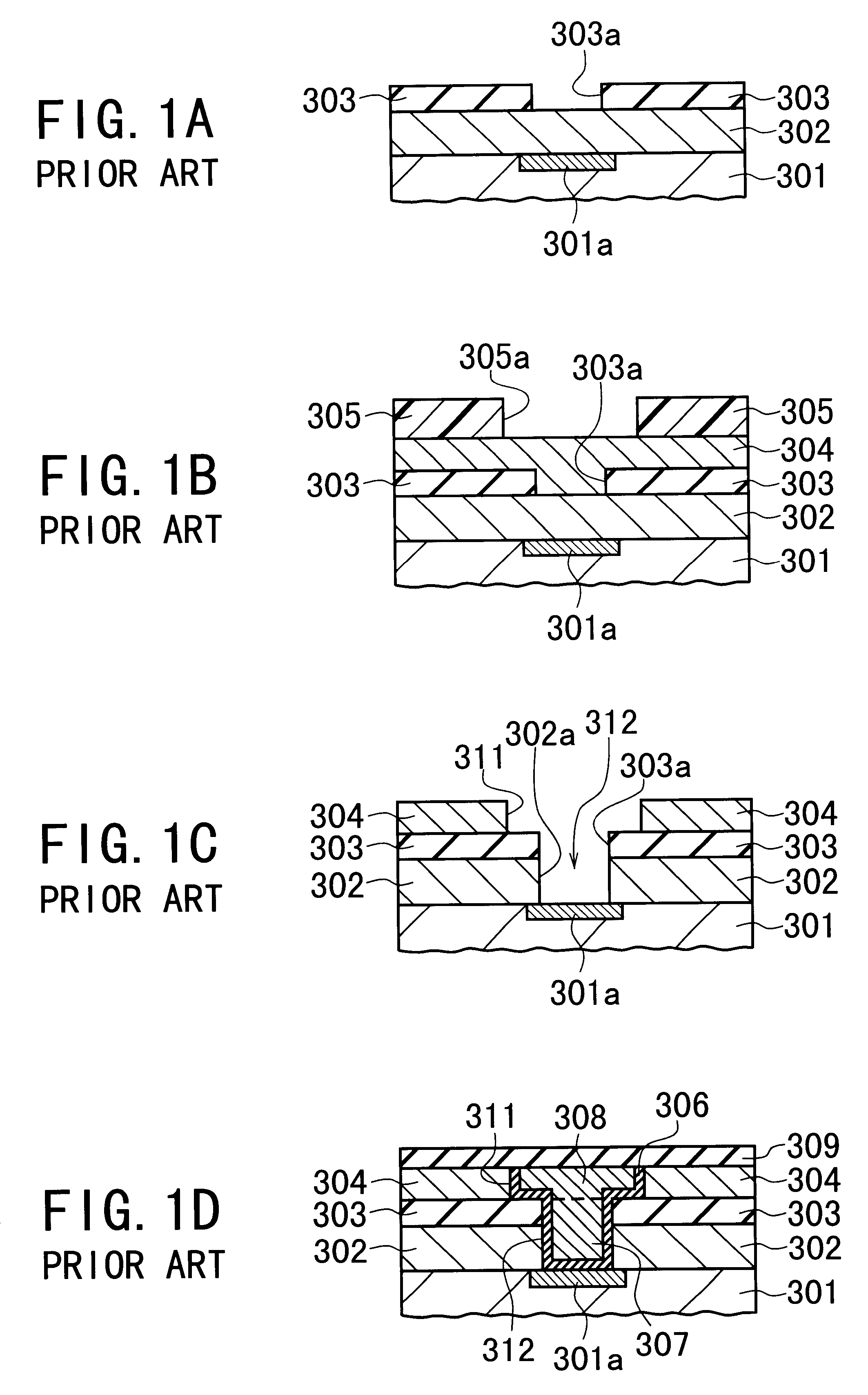
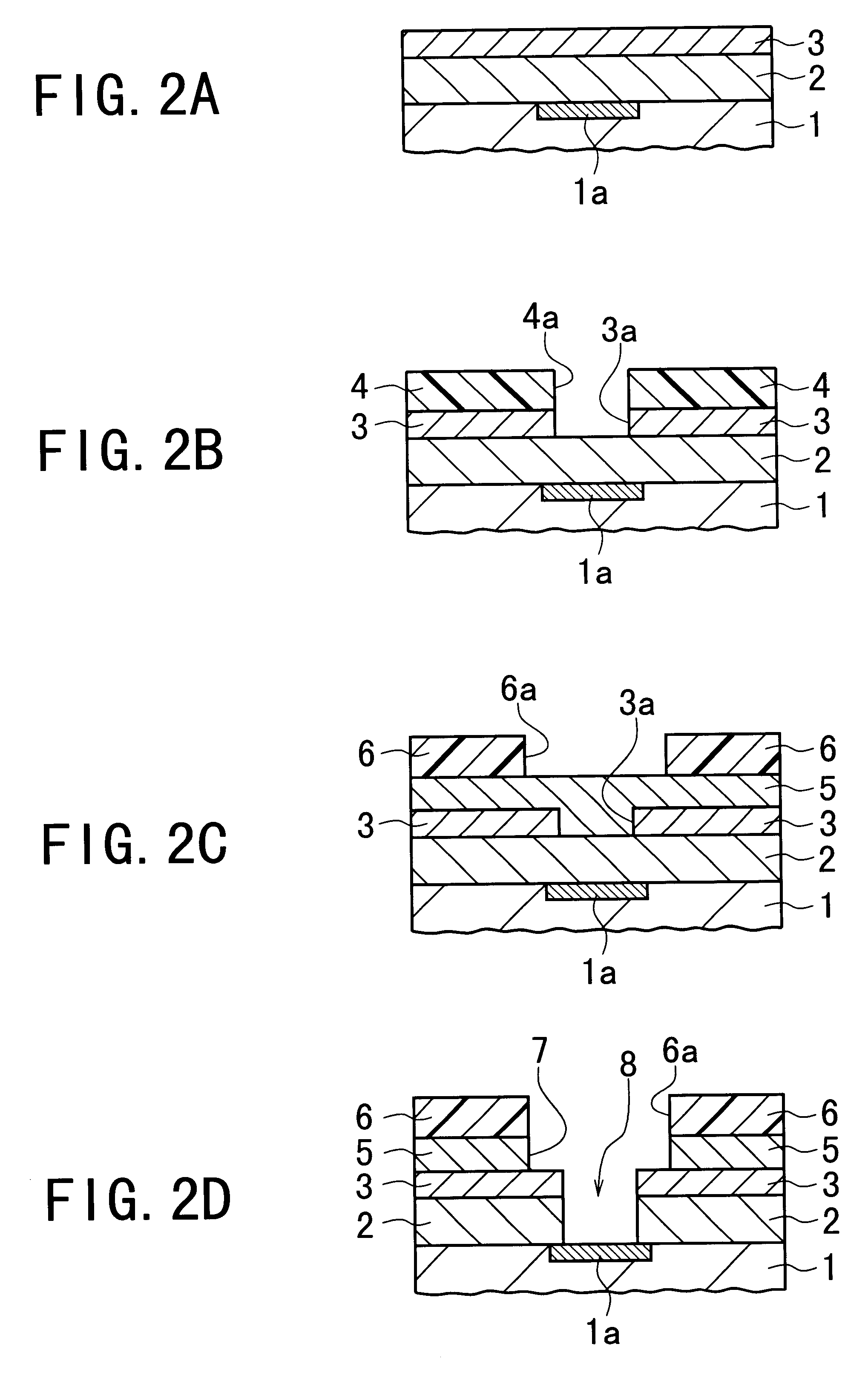
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS6245665B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPropagation delayElectronic component
A semiconductor device equipped with the dual damascene structure that is provided, which suppresses the propagation delay of signals effectively without using any complicated processes. The device is comprised of (i) a semiconductor substrate having a lower wiring layer and electronic elements; (ii) a first interlayer dielectric layer formed on the substrate; (iii) a second interlayer dielectric layer formed on the first interlayer dielectric layer, the second interlayer dielectric layer being made of carbon-containing SiO2; (iv) a third interlayer dielectric layer formed on the second interlayer dielectric layer; (v) a fourth interlayer dielectric layer formed on the third interlayer dielectric layer, the fourth interlayer dielectric layer being made of carbon-containing SiO2; (vi) the first and second interlayer dielectric layers having a via hole penetrating therethrough; (vii) the third interlayer dielectric layer having a recess overlapping with the via hole, the recess being formed to communicate with the via hole; (viii) a metal plug formed in the via hole to be contacted with the lower wiring layer or the electronic elements in the substrate; (ix) a metal wiring layer formed in the recess; and (x) a fourth interlayer dielectric layer formed on the third interlayer dielectric layer to cover the metal wiring layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
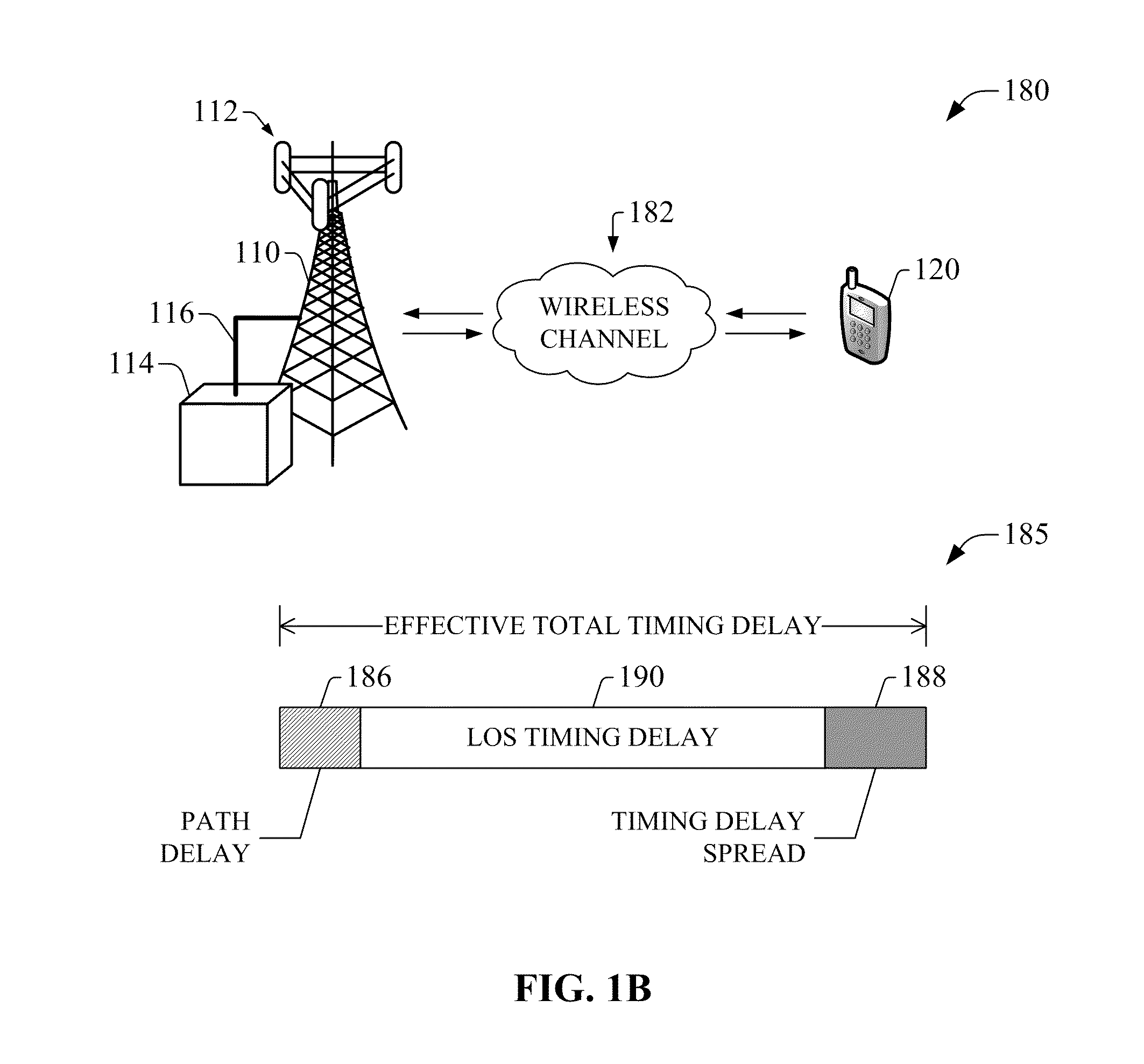
Compensation of propagation delays of wireless signals
ActiveUS20100190509A1Weakening rangeImprove accuracySynchronisation arrangementLocation information based servicePropagation delayRadio networks
System(s) and method(s) for compensation of propagation delay offsets of wireless signals. Compensation is accomplished through determination of an effective wireless signal propagation delay that accounts for signal path delay and propagation delay over the air. Such determination is based at least in part on statistical analysis of accurate location estimates of reference positions throughout a coverage sector or cell, and location estimates of the reference positions generated through time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of wireless signals. Determination of propagation or signal path delay offset also is attained iteratively based at least in part on reference location estimates and TOF location estimates. High-accuracy location estimates such as those obtained through global navigation satellite systems are employed as reference location estimates. Position of probes or wireless beacons, deployed throughout a sector or cell, also are employed as reference locations. Compensation of propagation delay offset improves accuracy of conventional TOF location estimates and radio network performance.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
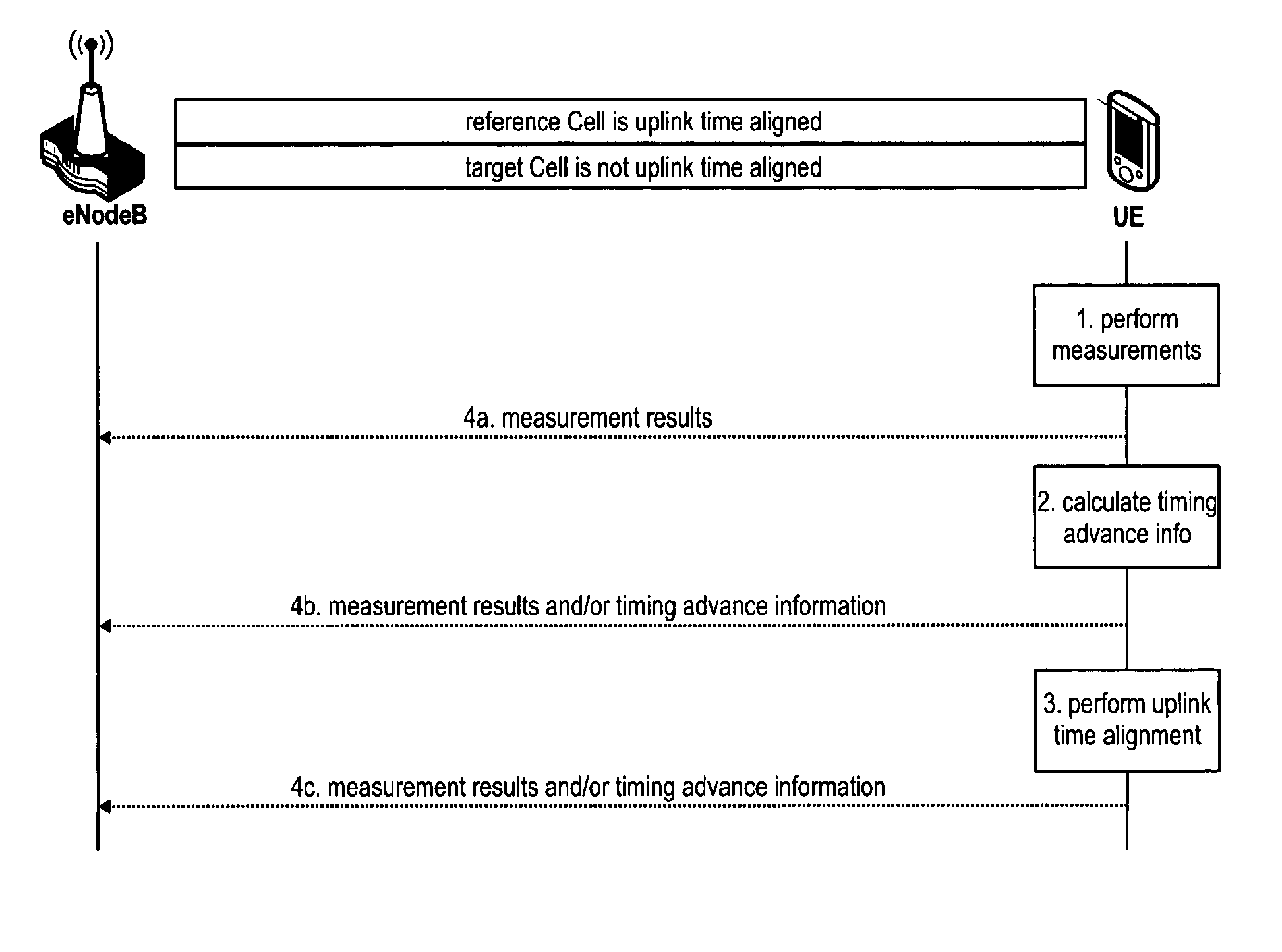
Propagation delay difference reporting for multiple component carriers
The invention relates to methods for reporting on downlink timings by a mobile terminal in a mobile communication system. In order to allow for an aggregation access point to obtain information on propagation delay differences of downlink transmissions on aggregated serving cells, the invention suggests the mobile terminal to report timing information based on reception time difference information for a the target / reference cell. The mobile terminal performs measurements relating to transmission and / or reception time differences on the target / reference cell, and reports same to the eNodeB. The eNodeB compares the measurement result to a predefined maximum propagation delay time difference. Alternatively, the mobile terminal performs the measurements, compares same to the predefined maximum propagation delay time difference and then report the comparison result to the eNodeB.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
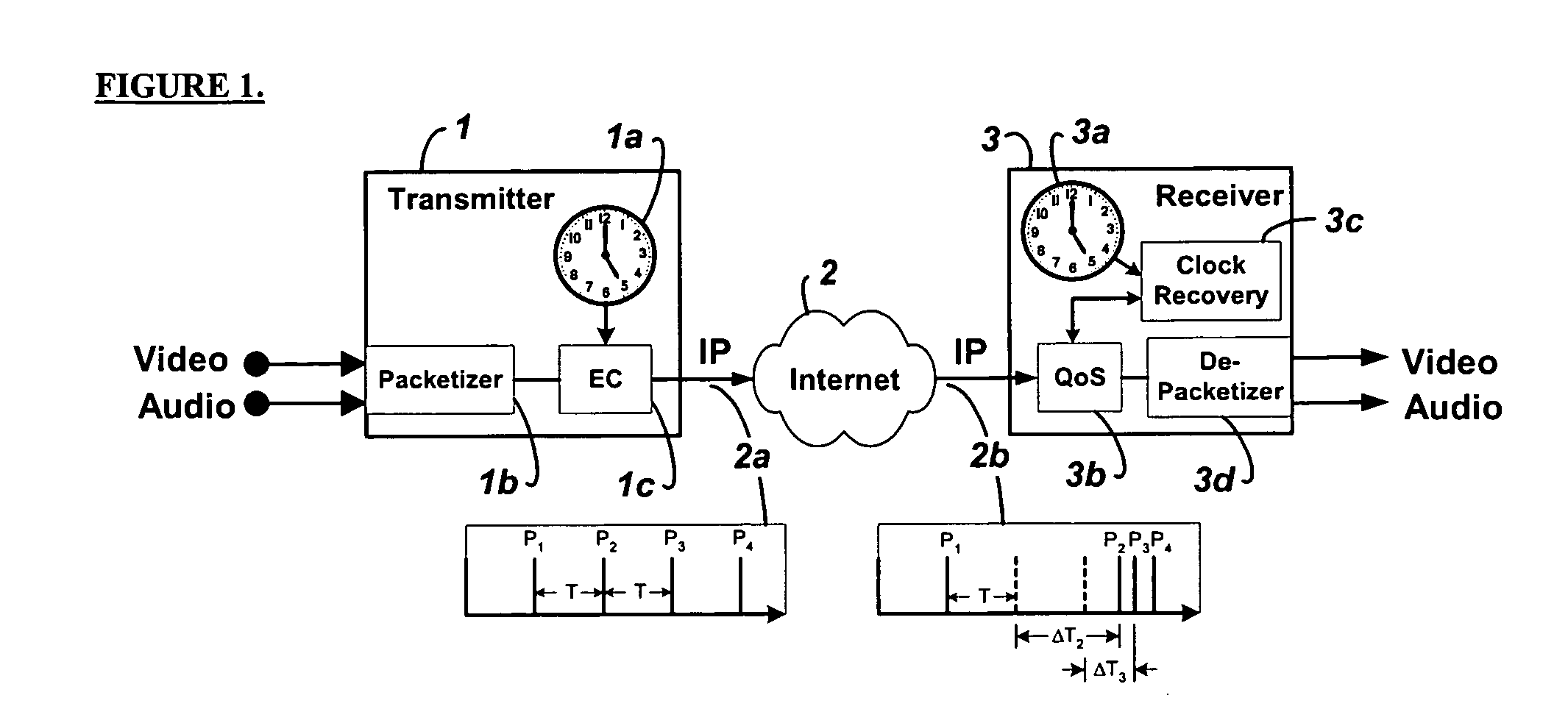
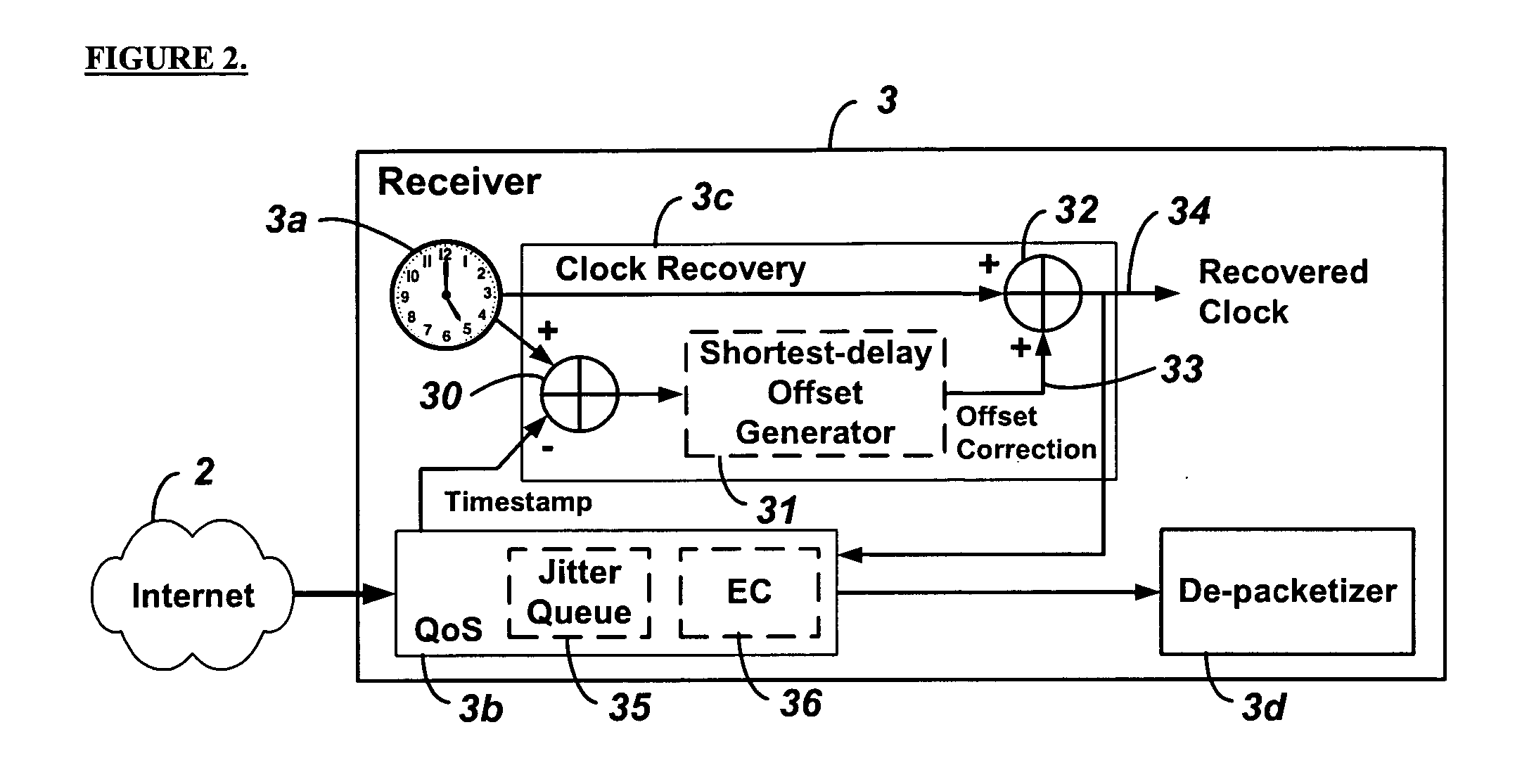
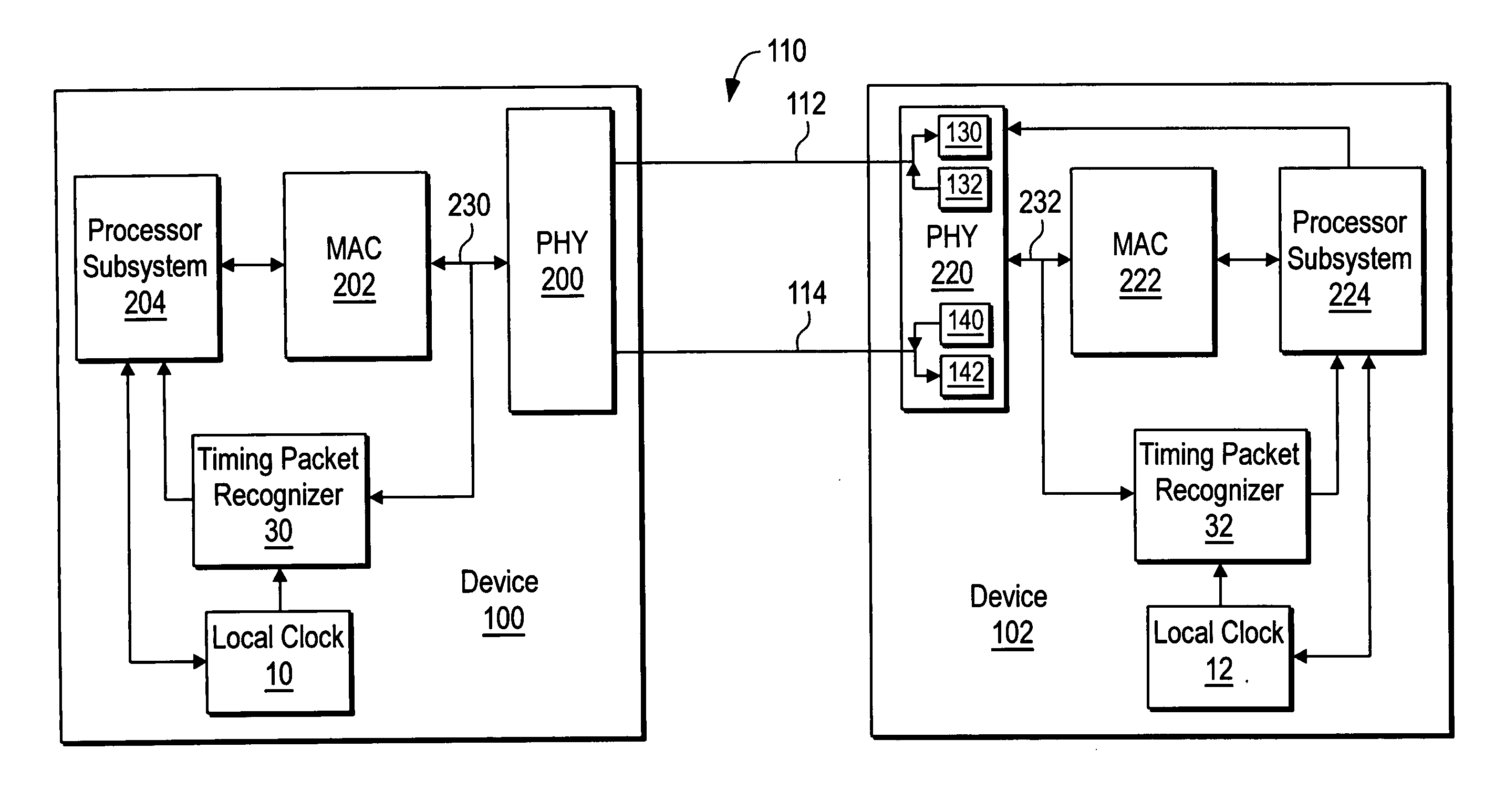
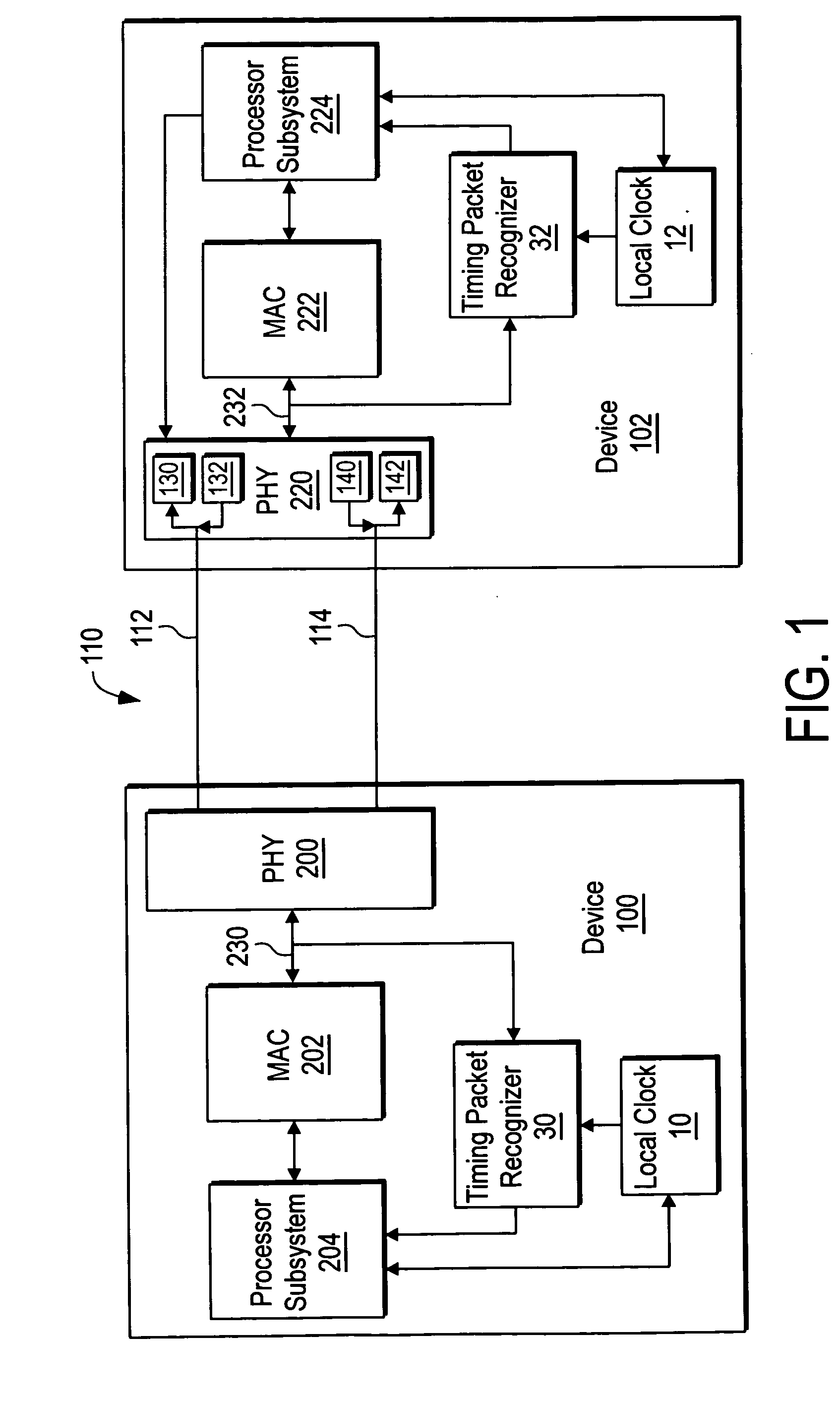
System and method for clock synchronization over packet-switched networks
ActiveUS20060013263A1Easy to replaceImprove abilitiesTime-division multiplexTransmissionQuality of serviceThe Internet
Embodiments of the invention enable the synchronization of clocks across packet switched networks, such as the Internet, sufficient to drive a jitter buffer and other quality-of-service related buffering. Packet time stamps referenced to a local clock create a phase offset signal. A shortest-delay offset generator uses a moving-window filter to select the samples of the phase offset signal having the shortest network propagation delay within the window. This shortest network propagation delay filter minimizes the effect of network jitter under the assumption that queuing delays account for most of the network jitter. The addition of this filtered phase offset signal to a free-running local clock creates a time reference that is synchronized to the remote clock at the source thus allowing for the transport of audio, video, and other time-sensitive real-time signals with minimal latency.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
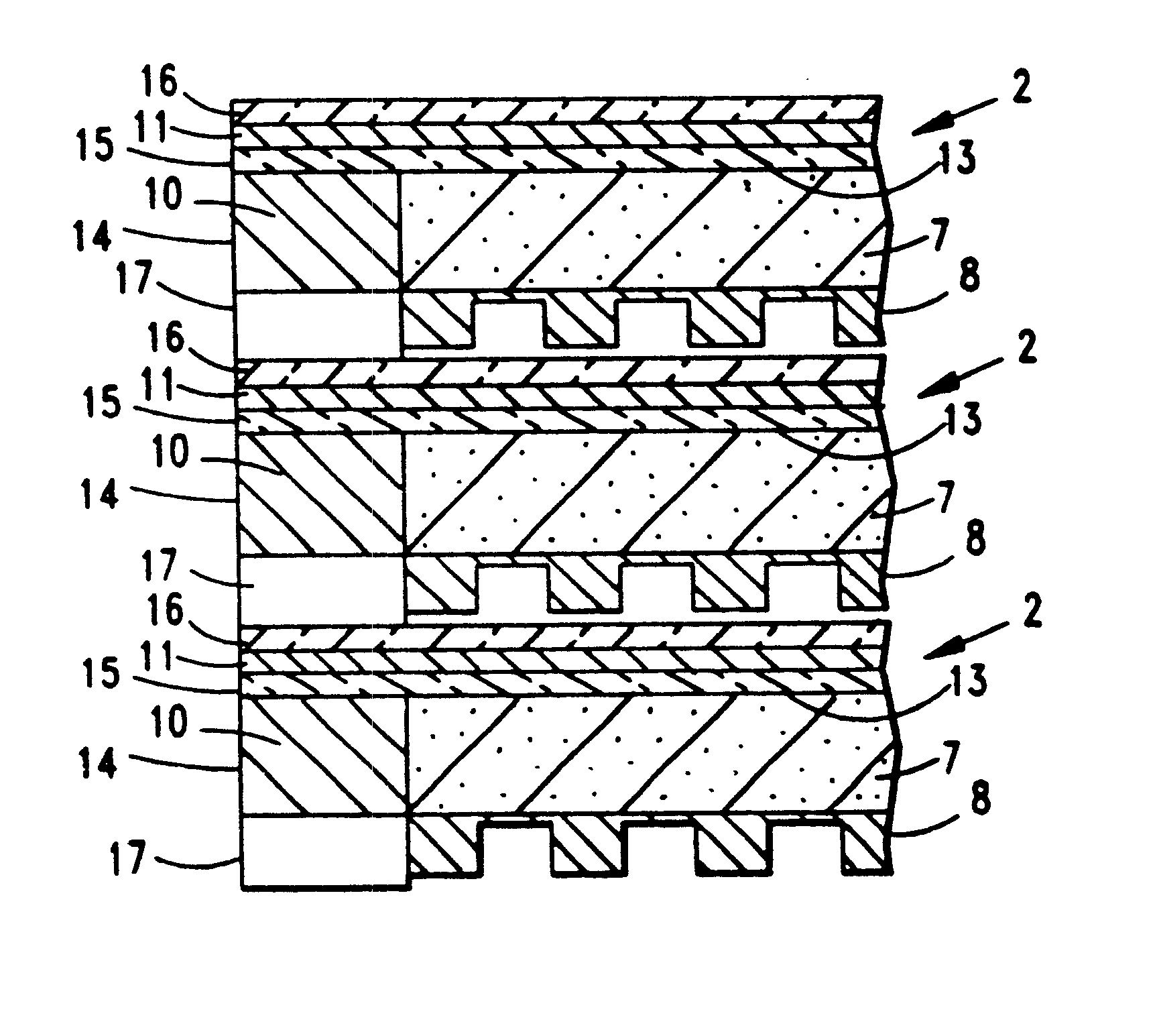
Three-dimensional packaging technology for multi-layered integrated circuits
InactiveUS6355976B1Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPropagation delayEngineering
Disclosed is method and apparatus for packaging multilayered integrated circuit (IC) chips, on which logic circuits and / or memory arrays are disposed and interconnected in a novel way permitting the addressing (i.e. selection) of the logic circuits and / or arrays on these IC chip layers using a minimum number of connections and with the shortest propagation delays.
Owner:REVEO
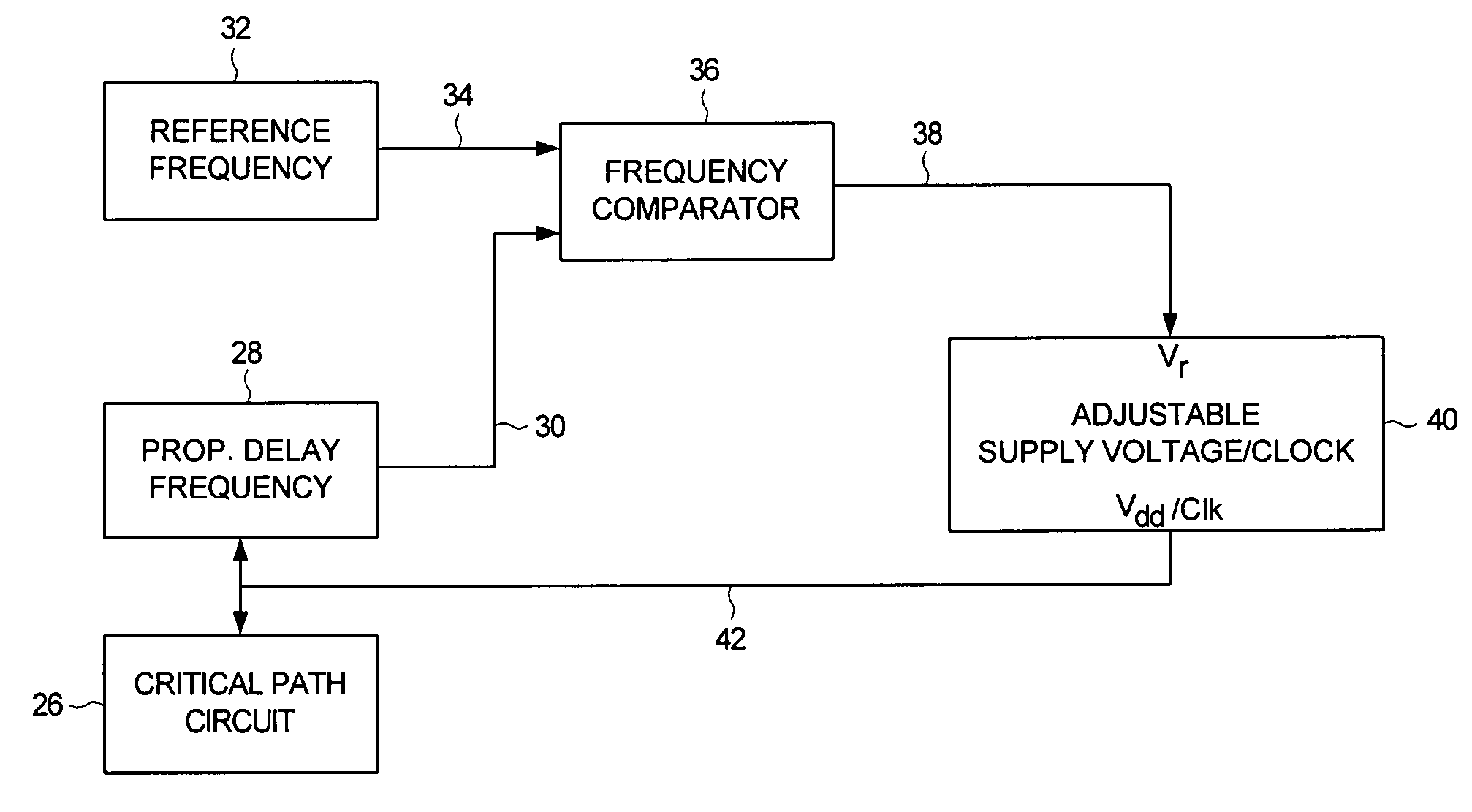
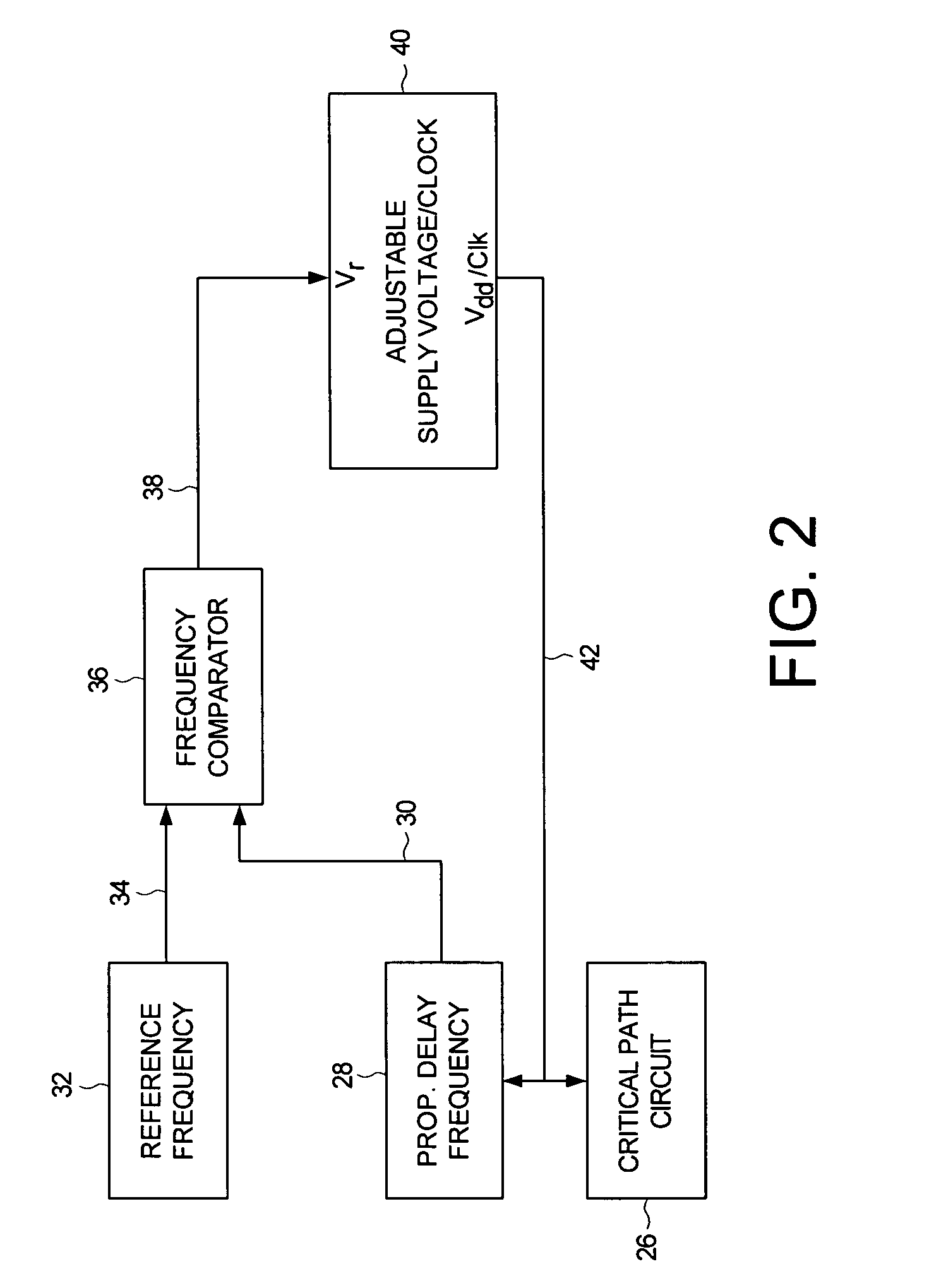
Adjusting power consumption of digital circuitry by generating frequency error representing error in propagation delay
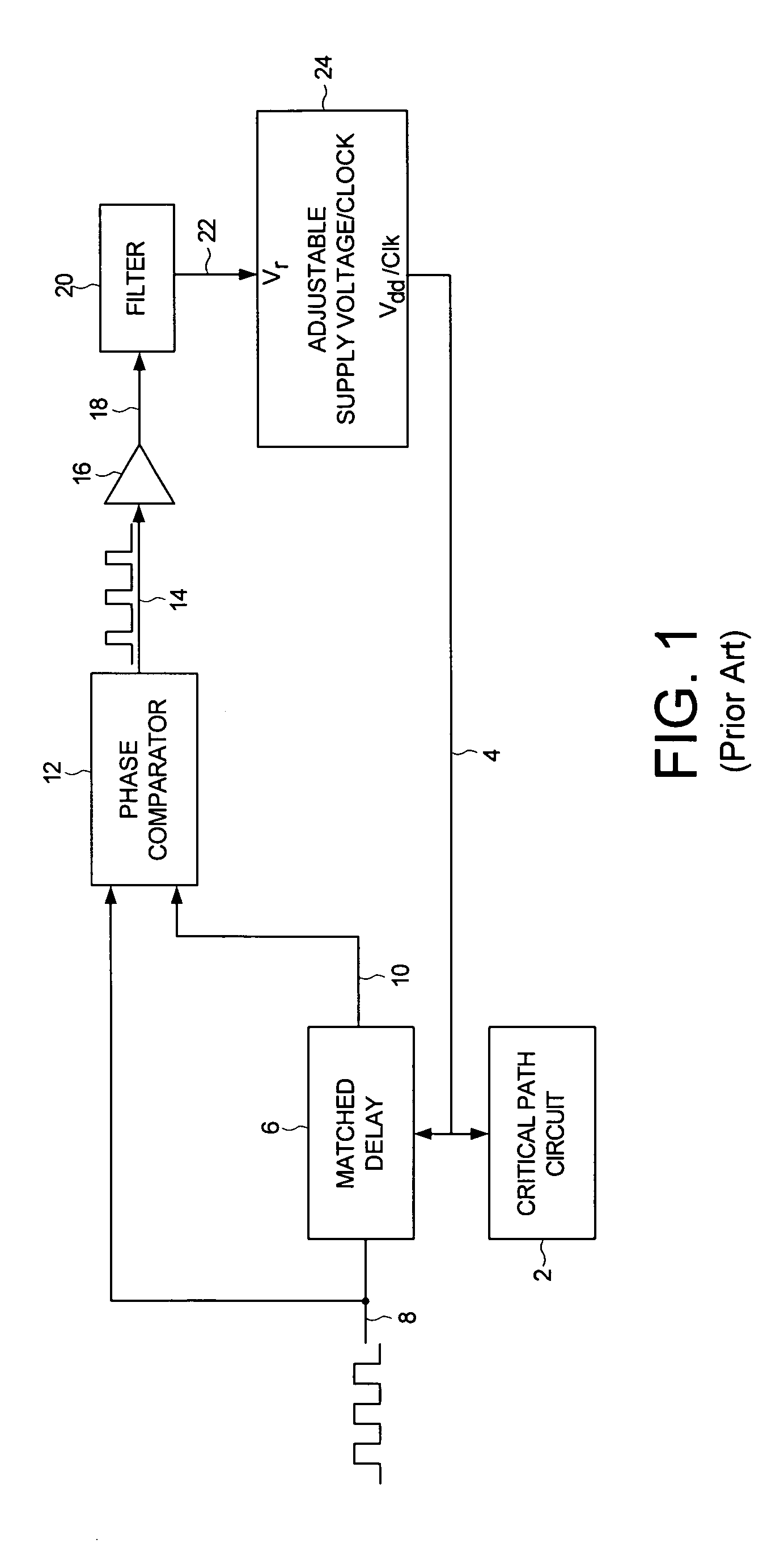
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting at least one of a supply voltage and a clocking frequency applied to digital circuitry of a computing device, wherein the digital circuitry comprises a critical path circuit. A propagation delay frequency representing a propagation delay of the critical path circuit is generated, and a frequency error signal is generated representing a difference between a reference frequency and the propagation delay frequency. At least one of the supply voltage and the clocking frequency is adjusted in response to the frequency error signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for estimation of mobile station velocity in a cellular system based on geographical data
ActiveUS20110287778A1Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork traffic/resource managementPropagation delayCommunications system
A system and method for estimating velocity of a mobile station in a wireless communication system using time-frequency signal processing and a geographical database. The geographical database is used for prediction of ray trajectory and ray power to provide an estimate of propagation delay associated with database points.
Owner:CYBERBIT
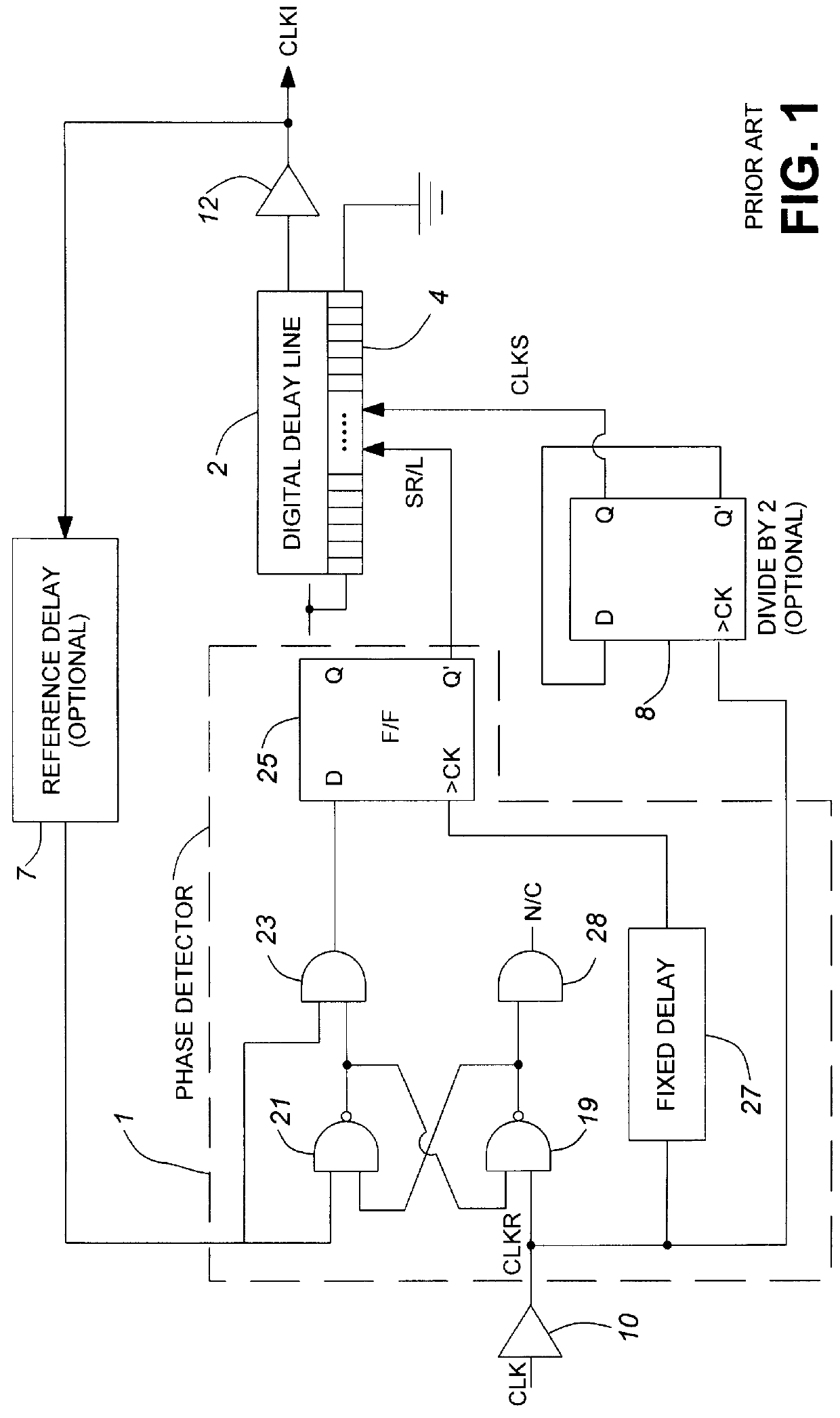
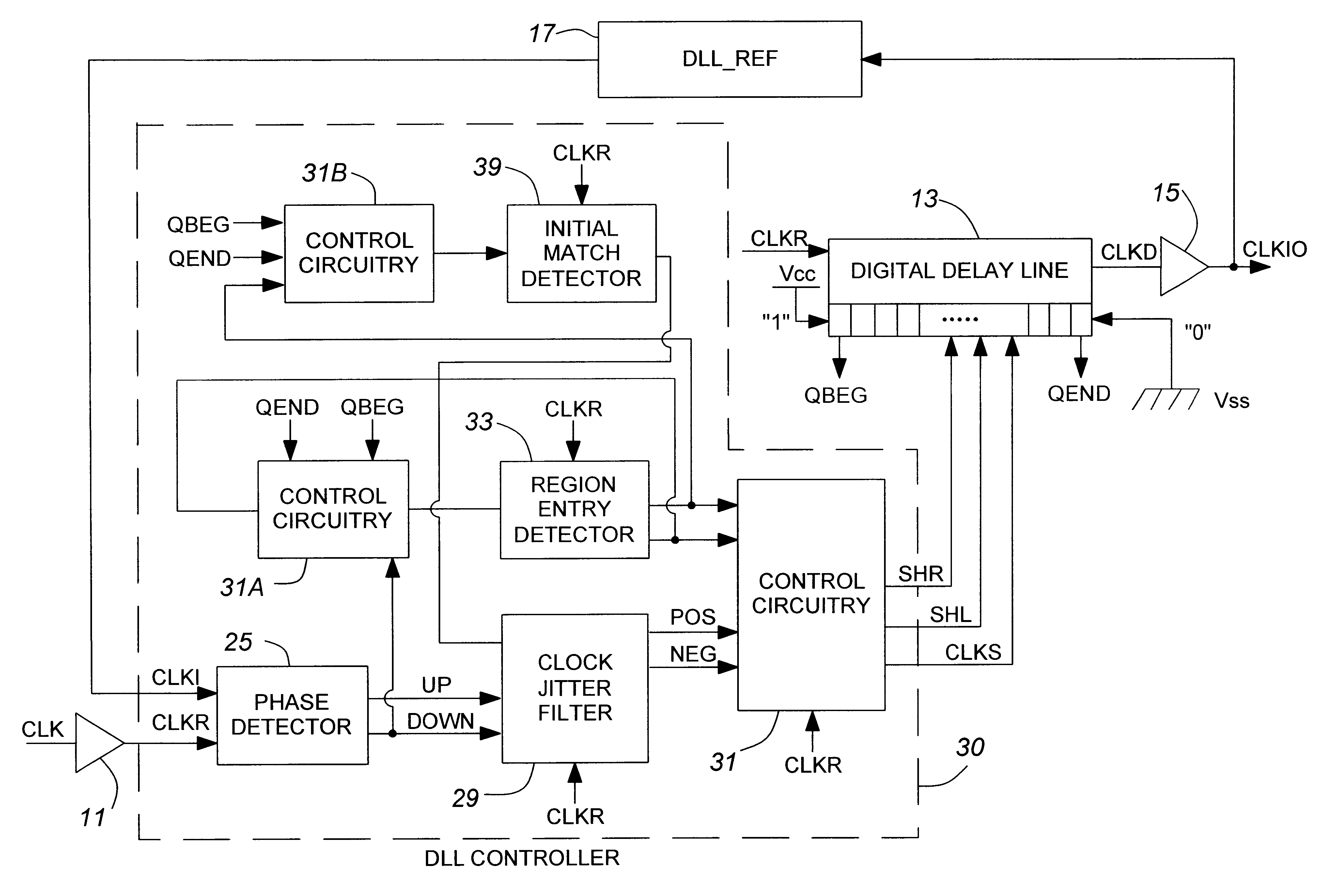
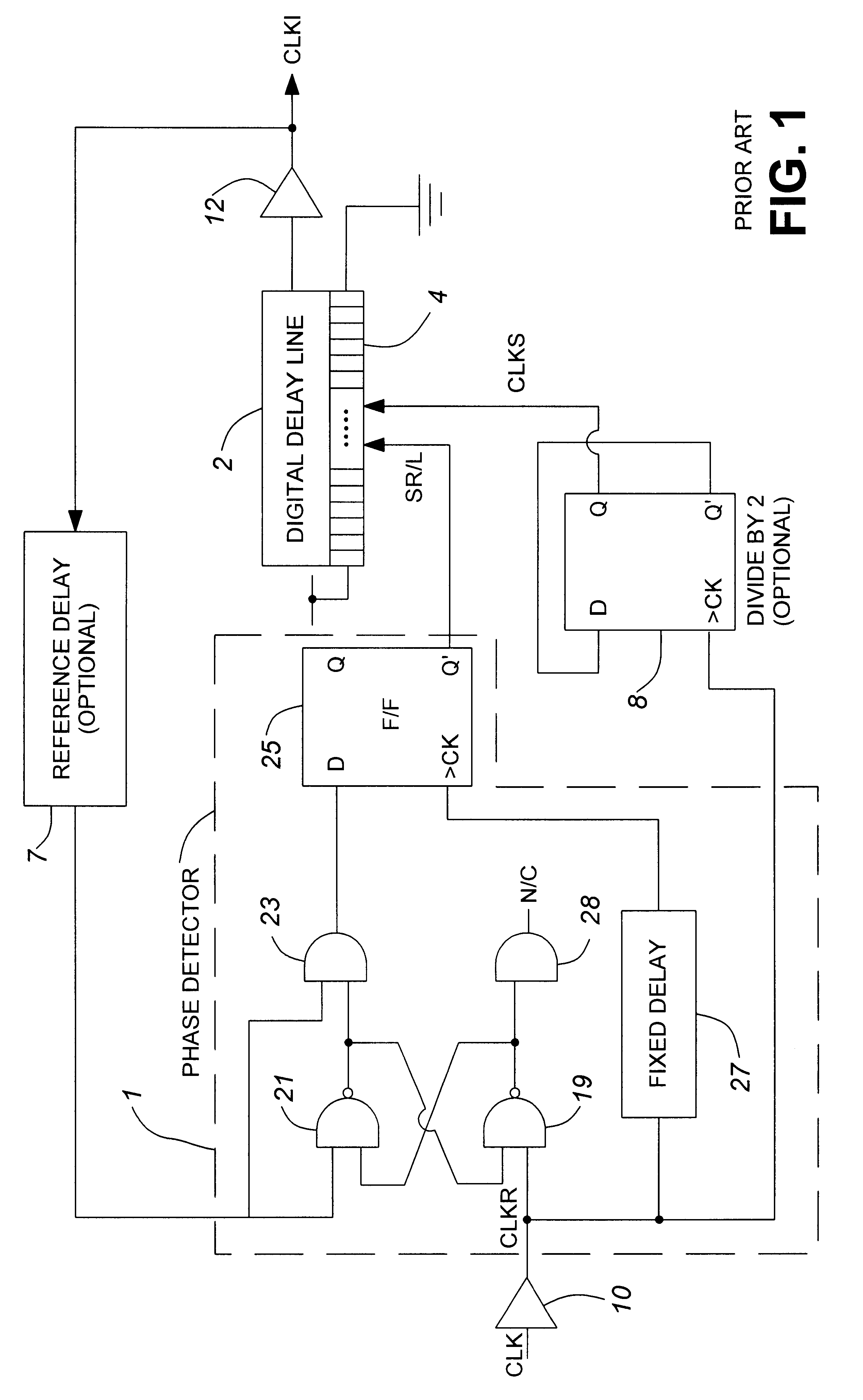
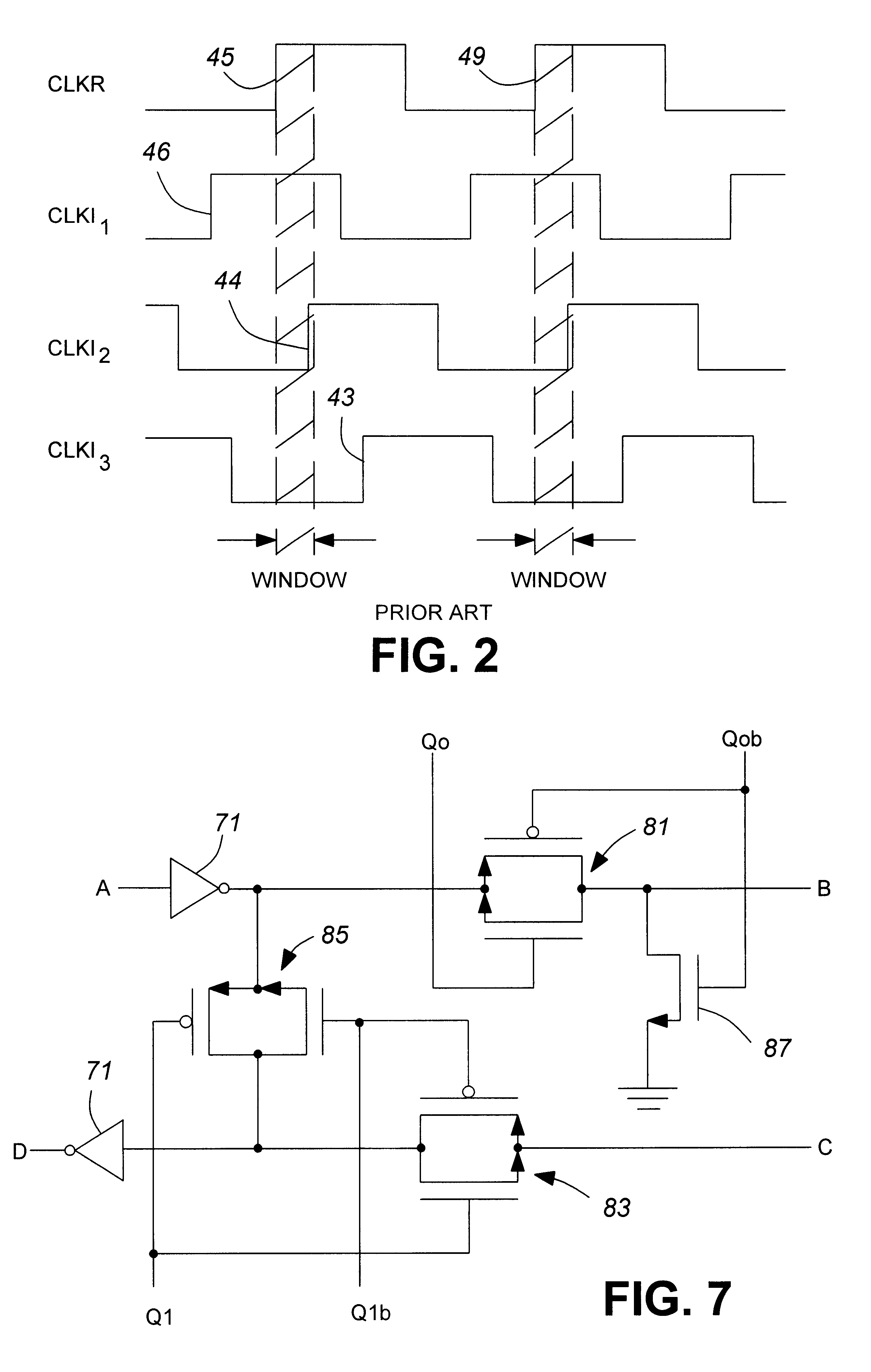
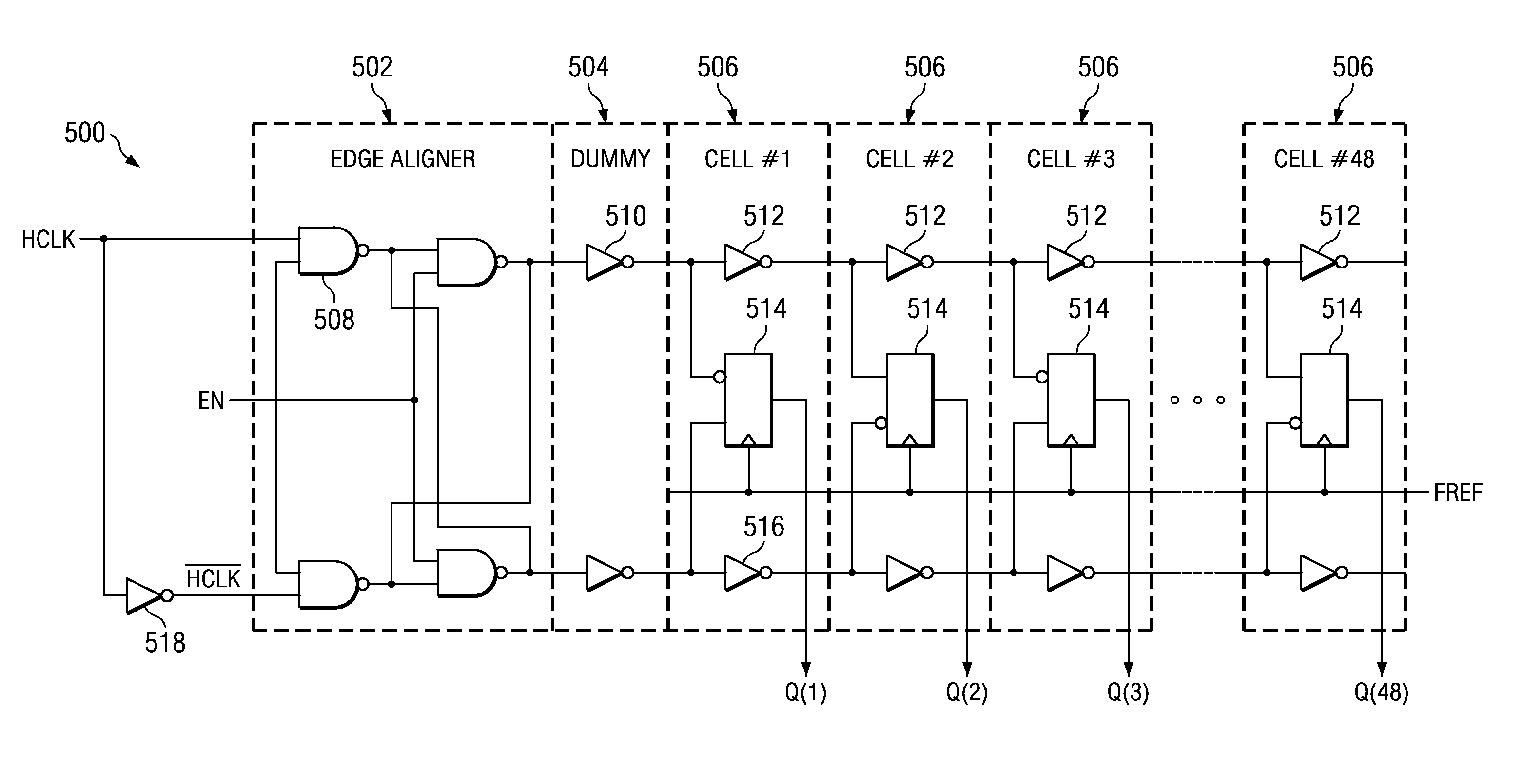
Digital delay locked loop
An improved edge-triggered fully digital delay locked loop (DLL), which maintains reliable synchronization from startup and in spite of system clock jitter is described. An internal clock signal is synchronized with a reference clock signal by propagating the reference clock signal through a variable digital delay path. A wide phase detection region surrounds a selected rising edge of the internal clock signal. The DLL loop is open as long as the internal clock signal and a target edge of the reference clock signal are not simultaneously within the phase detection region. To achieve a DLL locked condition, the variable delay is increased from a minimum setting until the edge of the phase detection region is shifted in time just past the target edge of the reference clock. Once the DLL loop has been closed, a clock jitter filter is enabled to reject reference clock jitter effects on the DLL locked condition. A digital phase detector controls the delay line propagation delay to establish synchronization between the internal clock and the reference clock. Unused delay elements within the variable delay path are deactivated to save power.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Distance measurement using half-duplex RF techniques
A system, apparatus, and method for determining the distance between two objects using an indirect propagation delay measurement is disclosed. A frequency hopping scheme (such as the Bluetooth.TM. technology) is used to measure the relative phase offset of the received signal between the various frequencies. For a given distance between the objects, the phase offset vs. frequency curve is a straight line with the slope dependent upon the measured distance. After the phase of the received signals is detected, the data is plotted on a curve and the slope is calculated. A wireless slave device remains phase locked with another device in a half-duplex communication mode by employing a low-drift phase locked loop employing a voltage controlled crystal oscillator. The phase locked loop further employs a mechanism that provides immunity from transitory phase slip at a time when the loop is opened.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
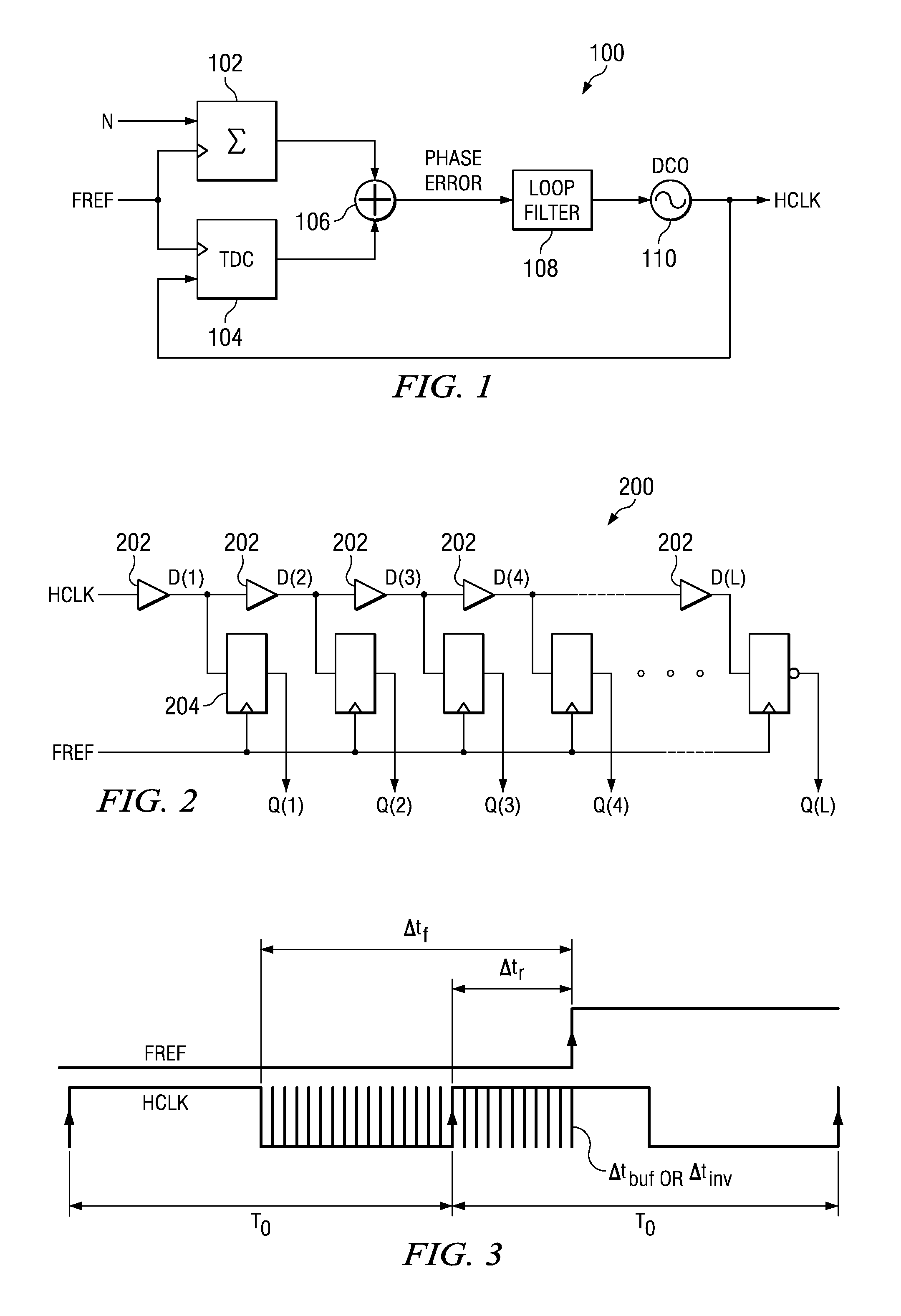
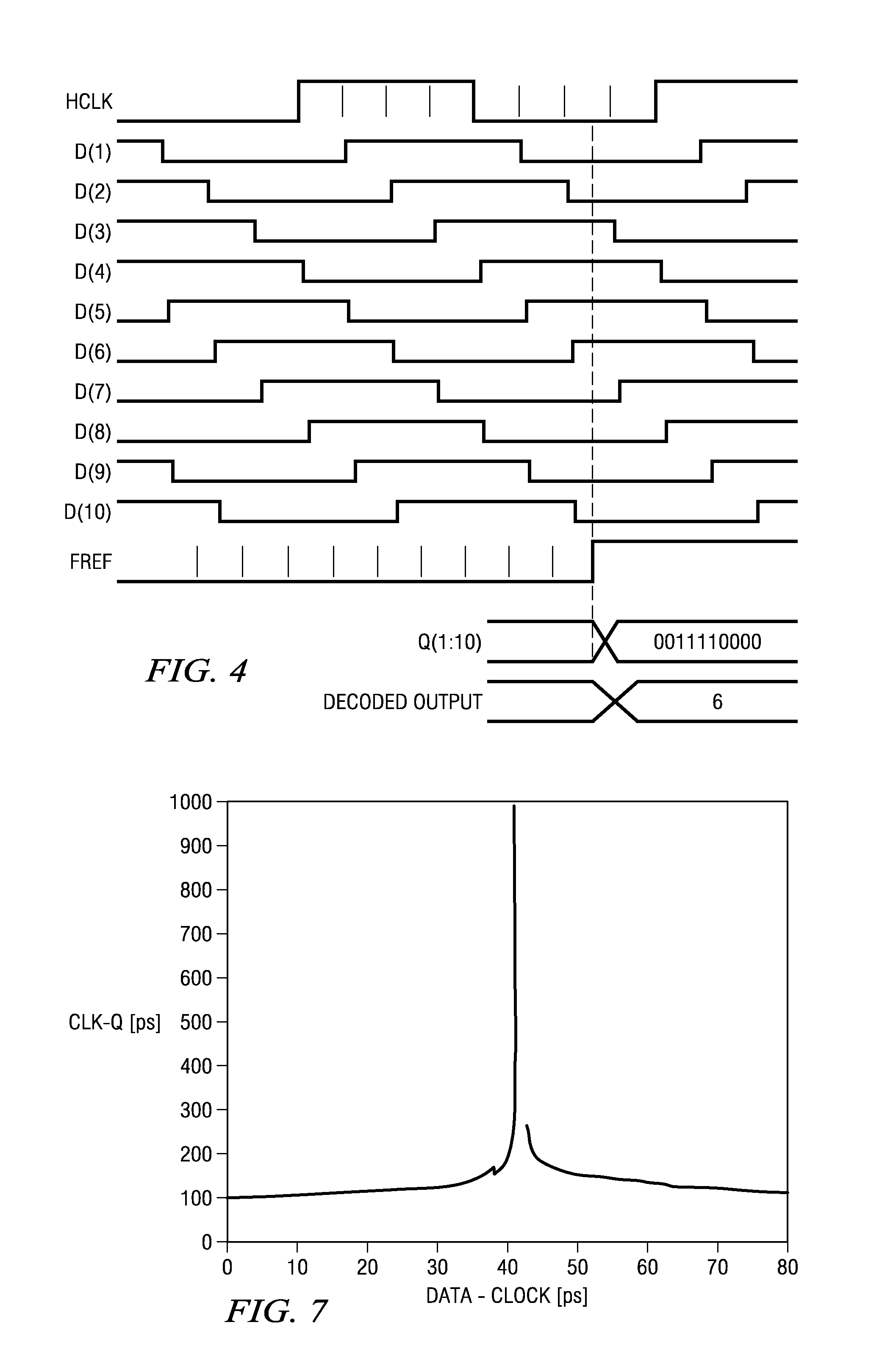
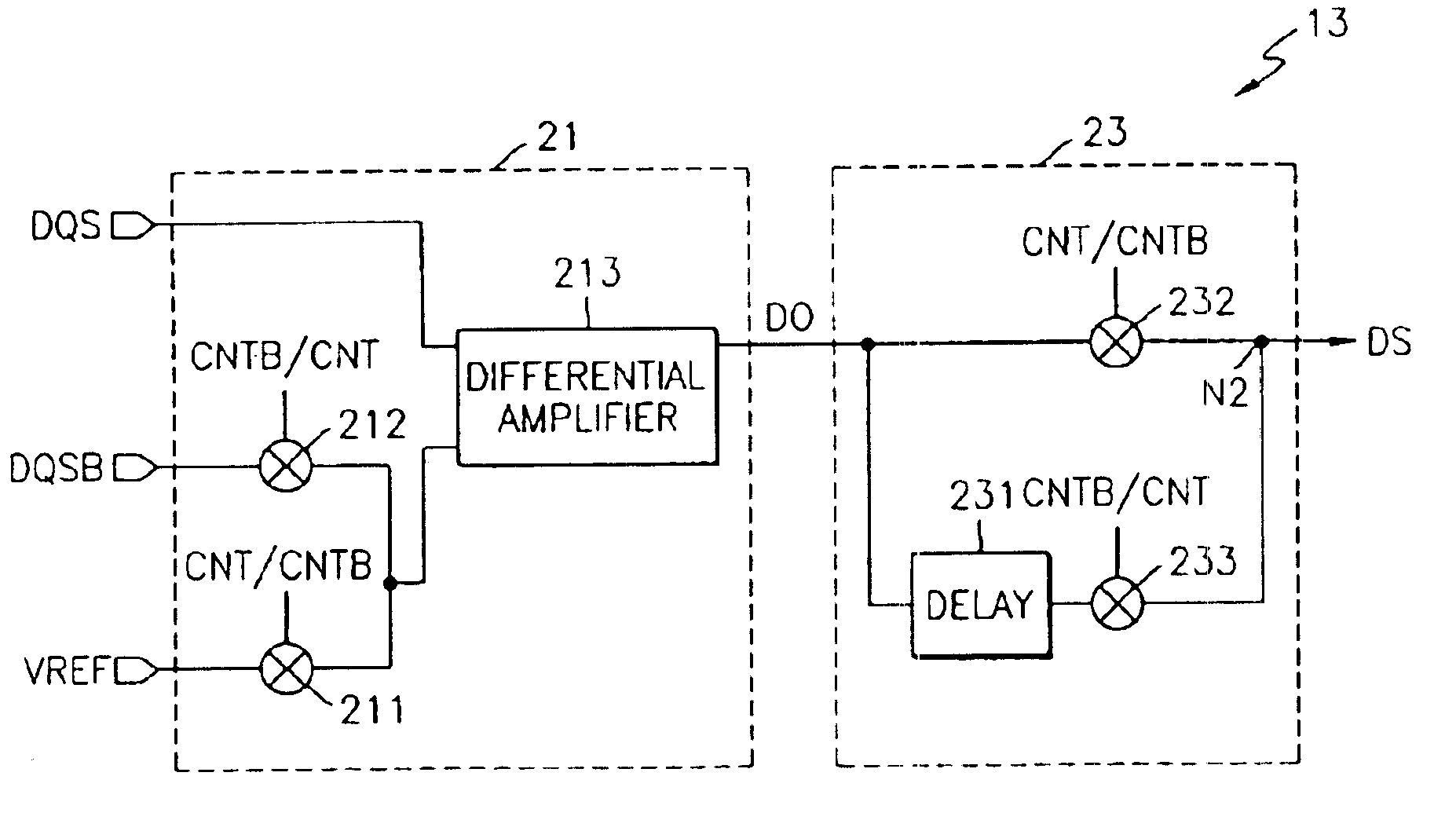
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS20060103566A1Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlEngineeringDigital converter
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital delay locked loop
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
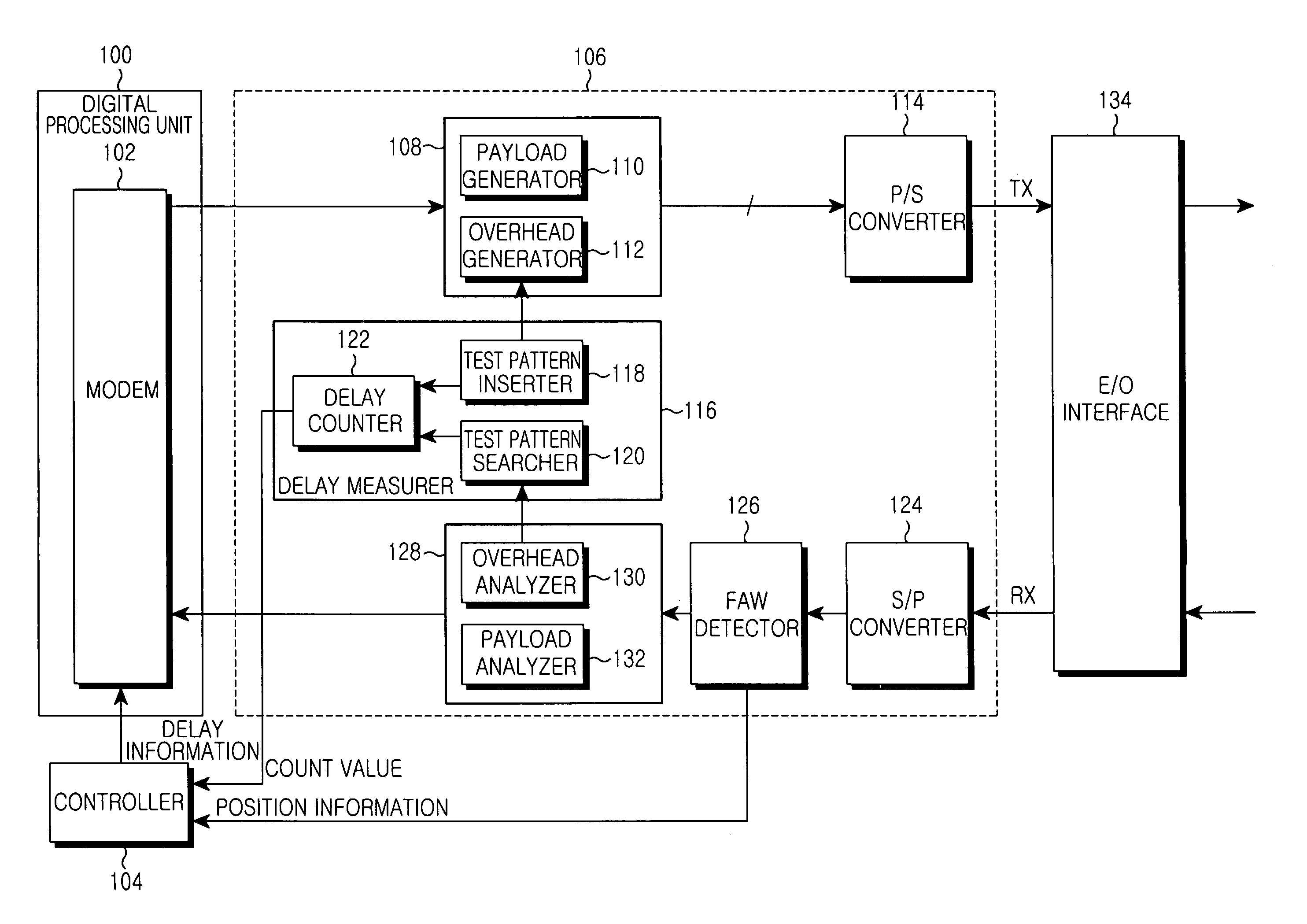
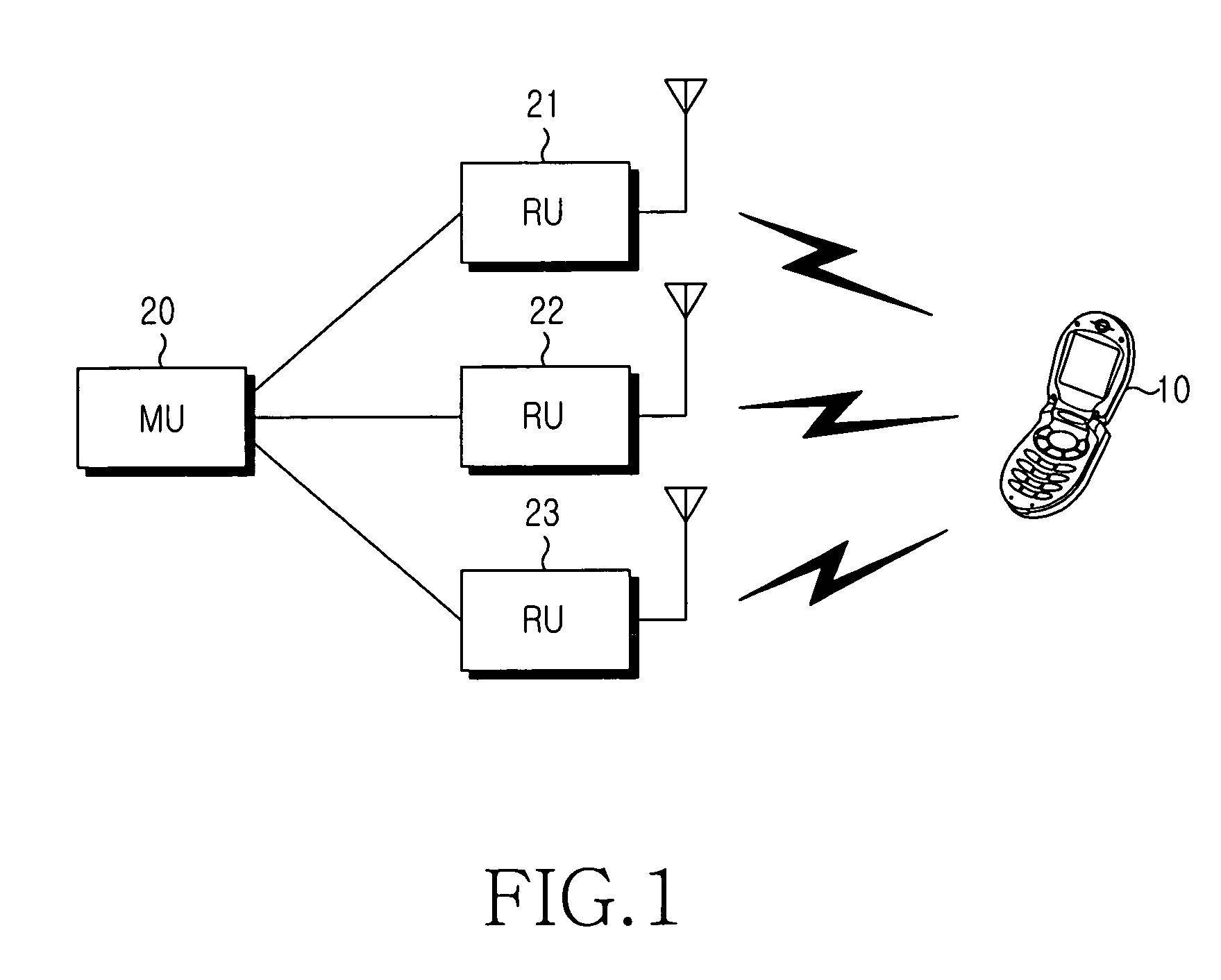
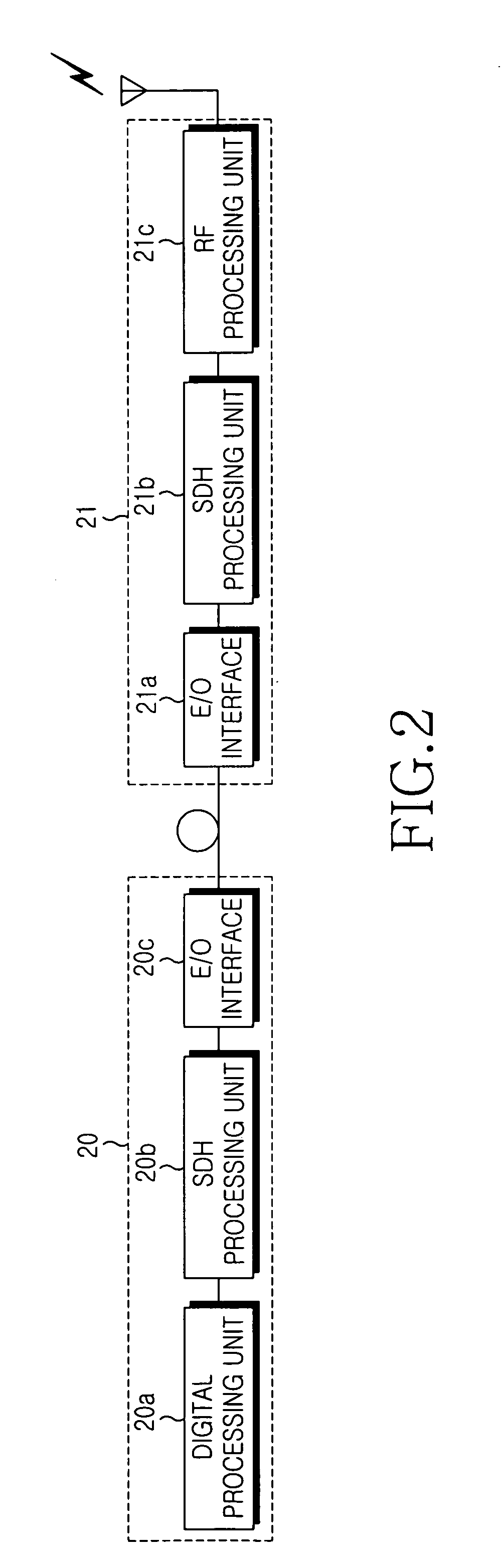
Apparatus and method for measuring and compensating delay between main base station and remote base station interconnected by an optical cable
InactiveUS7359408B2Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPropagation delayModem device
An apparatus and method for measuring and compensating for delay between a main base station and a remote base station interconnected by an optical cable. The main base station inserts a test pattern into an overhead part of an SDH frame to transmit the SDH frame to the remote base station, receives the SDH frame looped back by the remote base station to detect the test pattern, and measures propagation delay according to the test pattern. At least one frame alignment word (FAW) is detected at a predetermined position in the received SDH frame, and a delay error is calculated according to FAW detection information. The measured propagation delay with the delay error is compensated and produces propagation delay caused by the optical cable. A modulator / demodulator (MODEM) compensates for delay of a baseband signal to be transmitted to the remote base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
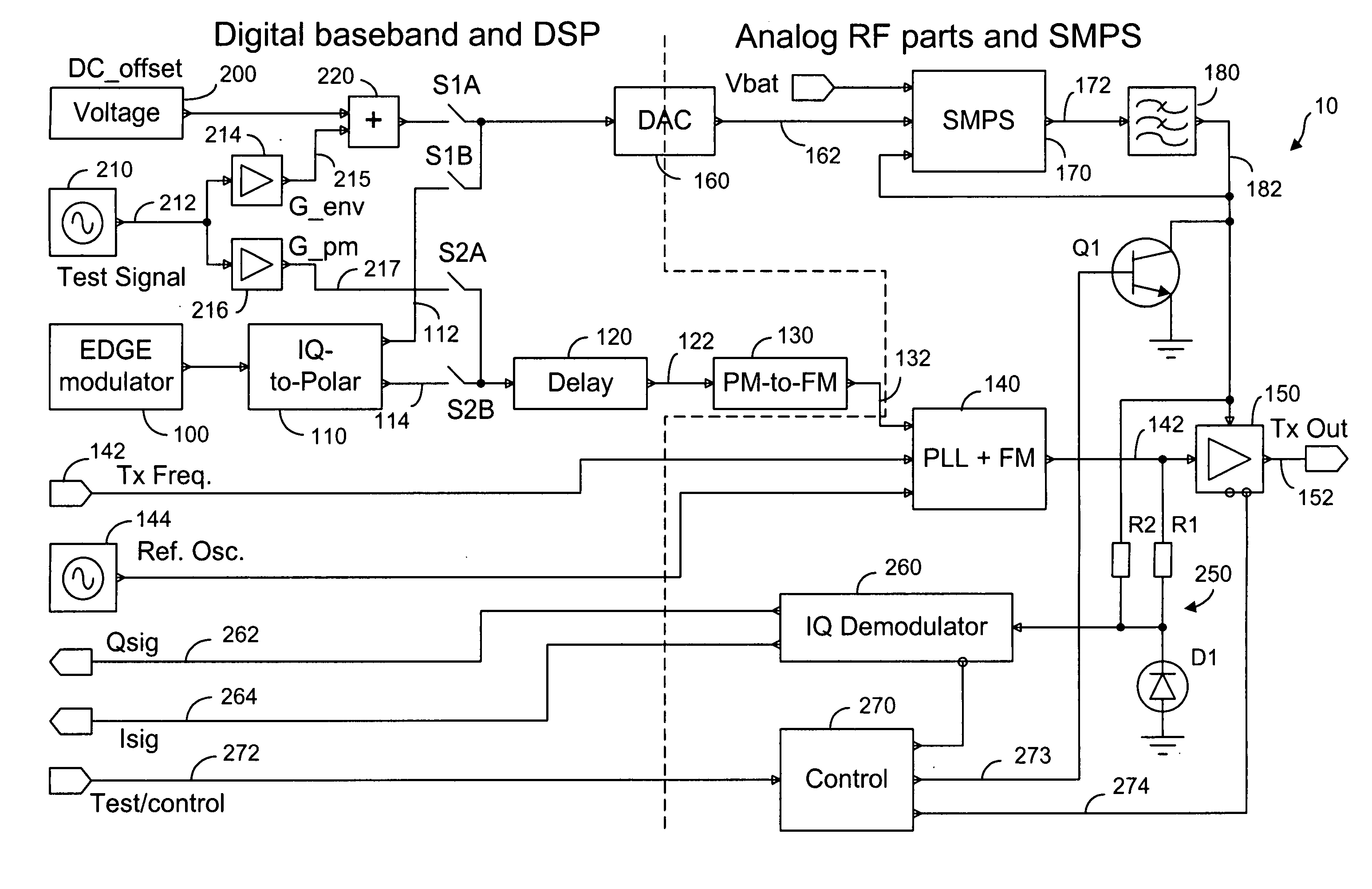
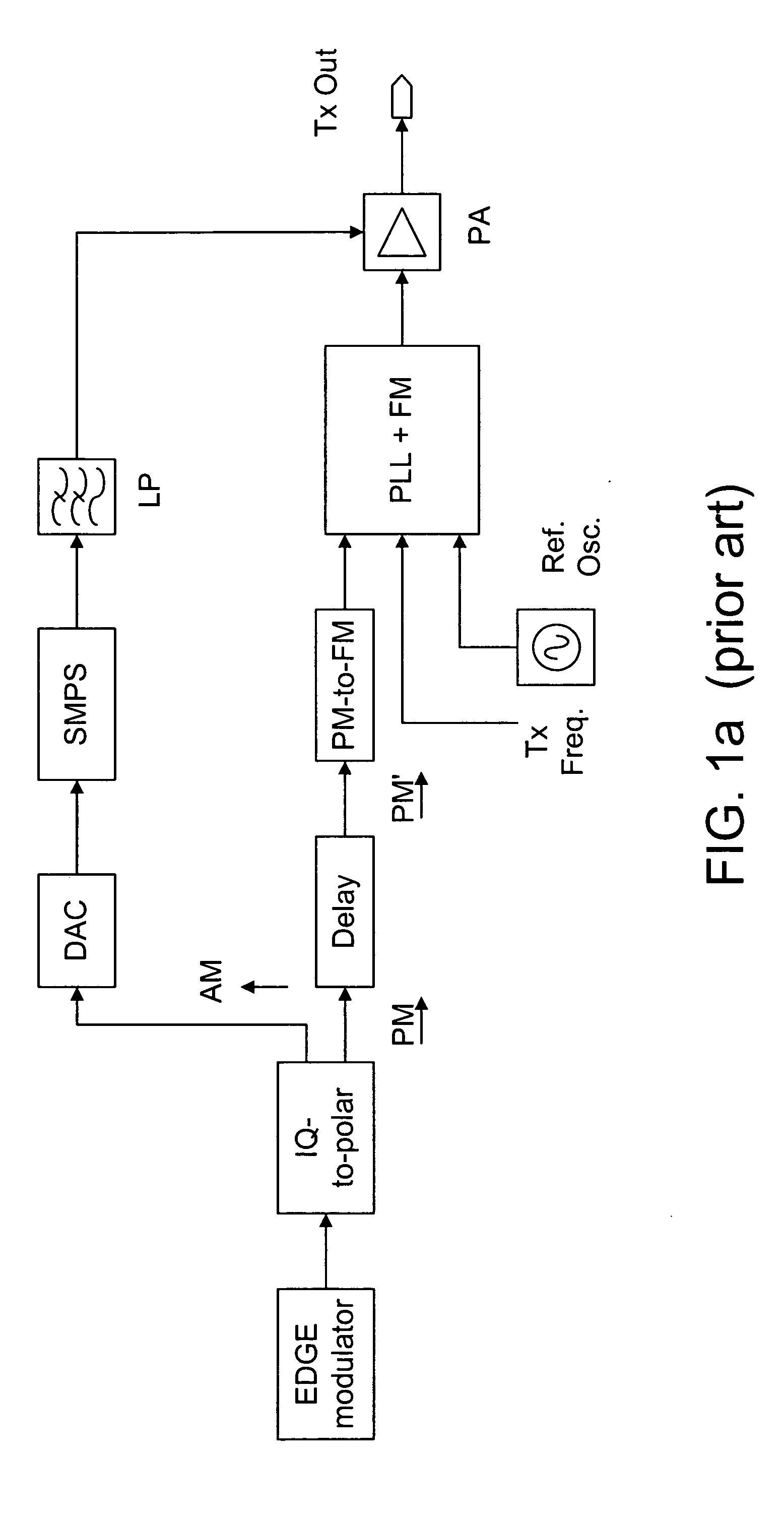
Method and system for transmitter envelope delay calibration
ActiveUS20070183532A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersPropagation delayTransceiver
A test signal comprising a periodic waveform, such as a triangular waveform and sawtooth waveform, is used for propagation delay matching in a transceiver front-end. The test signal is separately fed to the envelope path and the RF path. At the power amplifier stage, a phase modulator is used to obtain the envelope signal and the phase modulated RF signal for demodulation by an IQ demodulator. At the output end of the IQ demodulator, the I-signal is measured while the delay block is adjusted in order to vary the propagation delay. When the propagation delay matching is correct, the peak-to-peak value of the I-signal is a minimum. Preferably, during calibration using the test signal, the transmitter RF power amplifier is disabled so that no spurious signals will be sent. The transmitter can be an EDGE polar transmitter, a non-EDGE transmitter or a EER polar transmitter.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS7205924B2Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsDigital converterCmos process
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
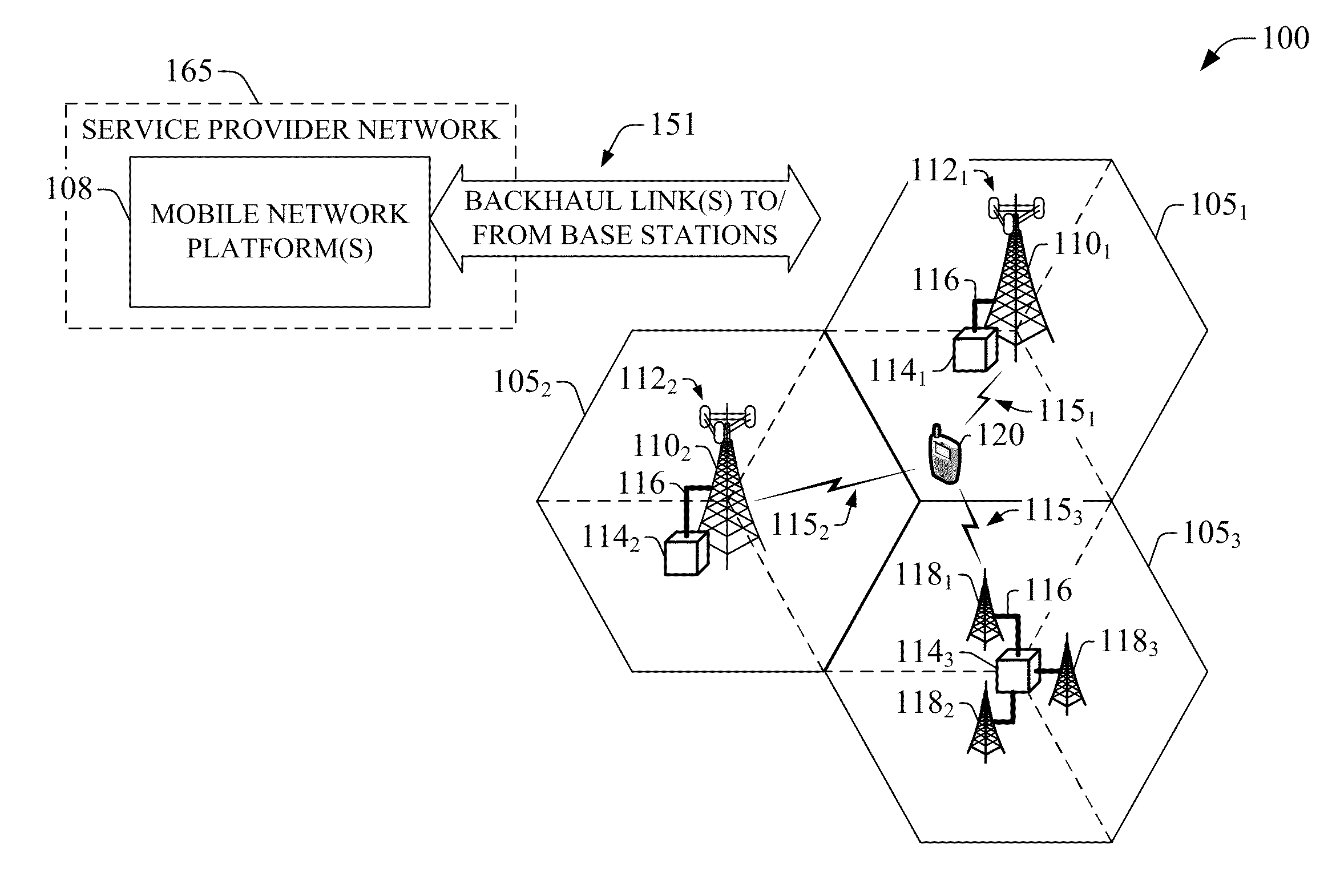
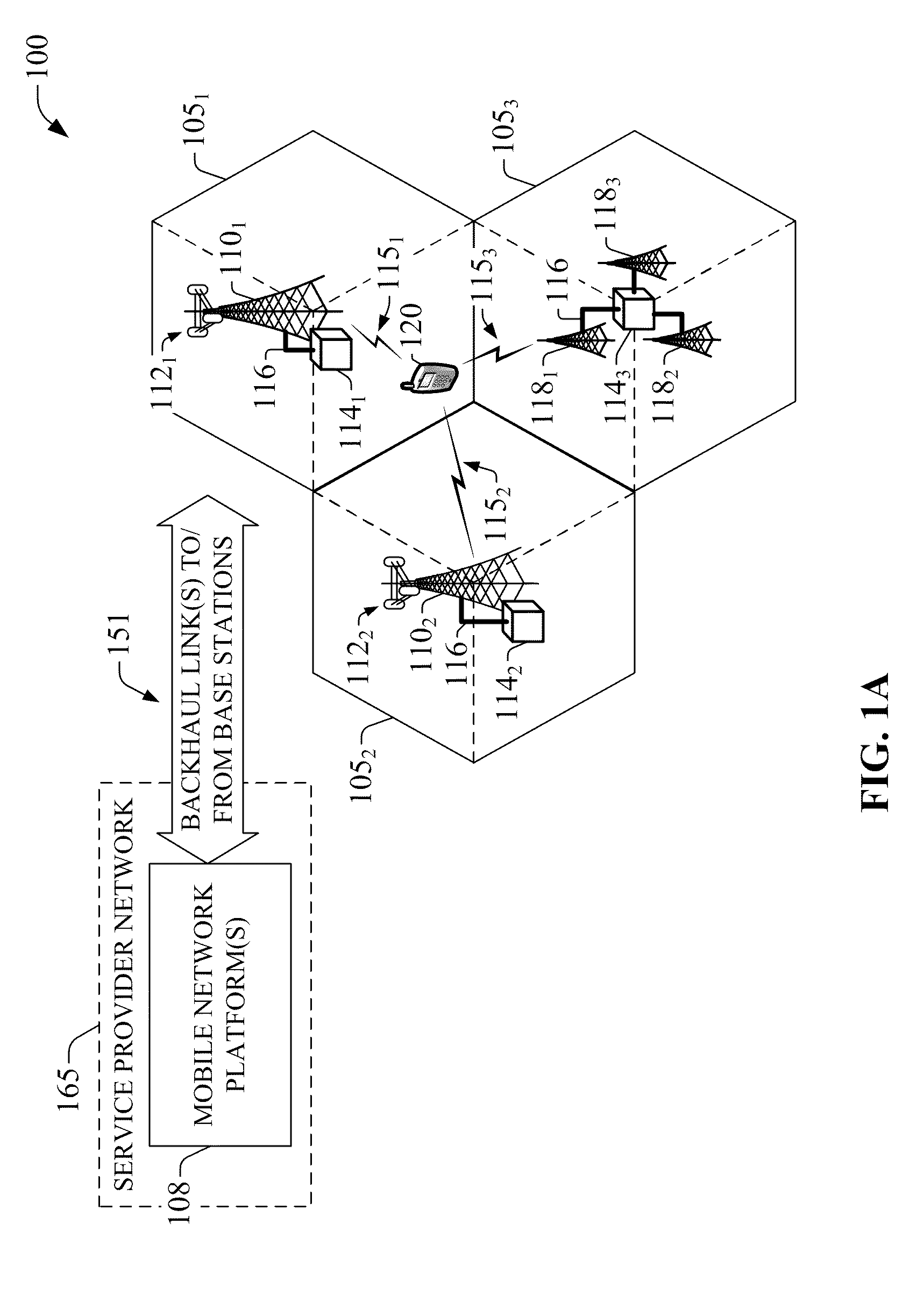
Position determination in a wireless communication system with detection and compensation for repeaters
InactiveUS20020115448A1Direction finders using radio wavesFrequency-division multiplex detailsPropagation delayCommunications system
Techniques to detect whether or not a remote terminal is under the coverage of a repeater within a wireless communication network, which may be based on (1) a list of base stations expected to be received while under the repeater's coverage, (2) the characterized environment of the repeater, and / or (3) the propagation delays for a transmission received at the remote terminal. Additional ambiguity resulting from being under a repeater's coverage may also be accounted for and / or compensated by (1) discarding time measurements from repeated base stations, (2) adjusting the processing for position estimation to account for the additional ambiguity due to the repeater, (3) computing a series of position estimates based on multiple transmissions received from the same originating base station and selecting the best estimate, and / or (4) computing a series of position estimates based on multiple transmissions from multiple originating base stations and selecting the best estimate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
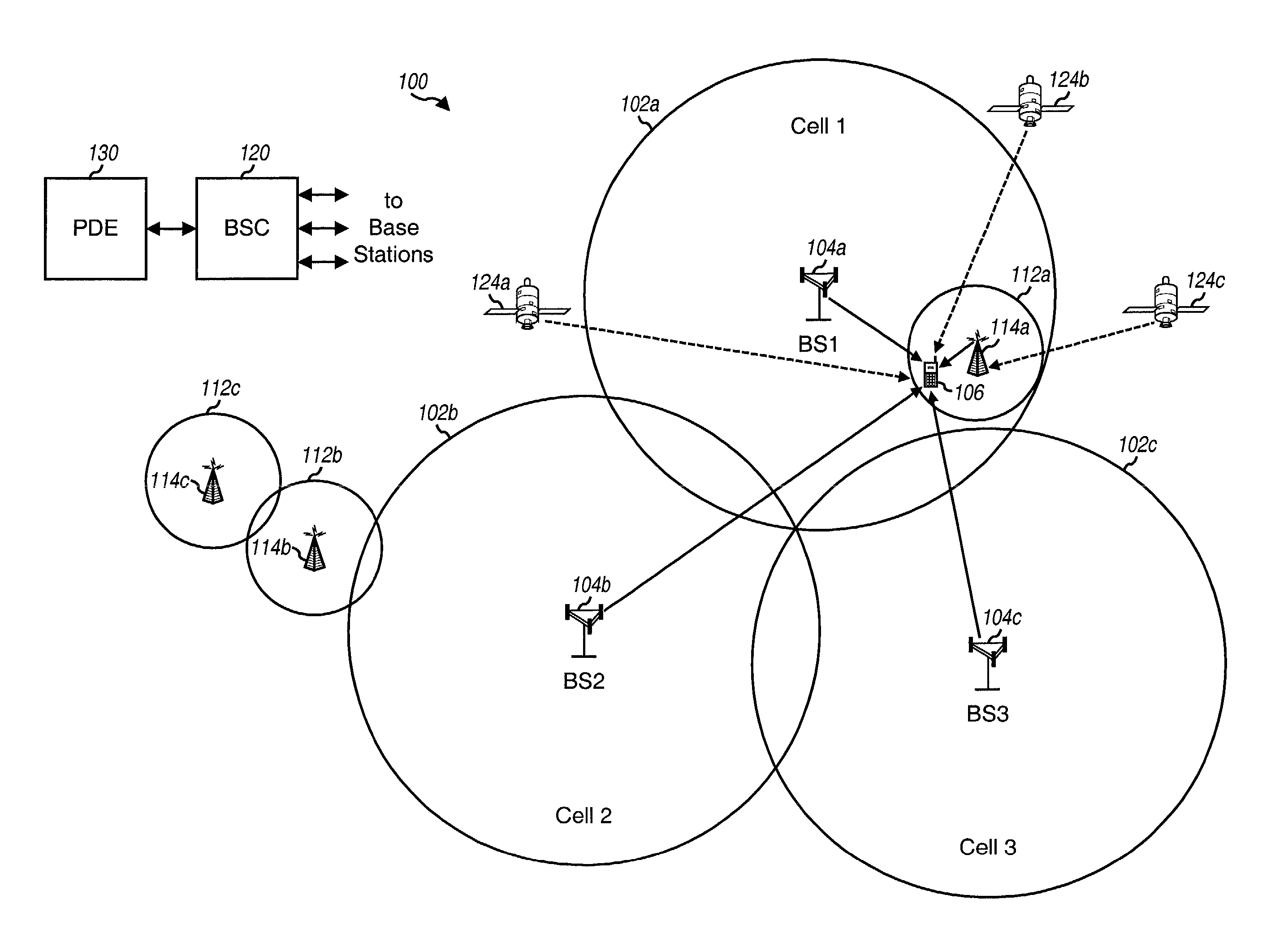
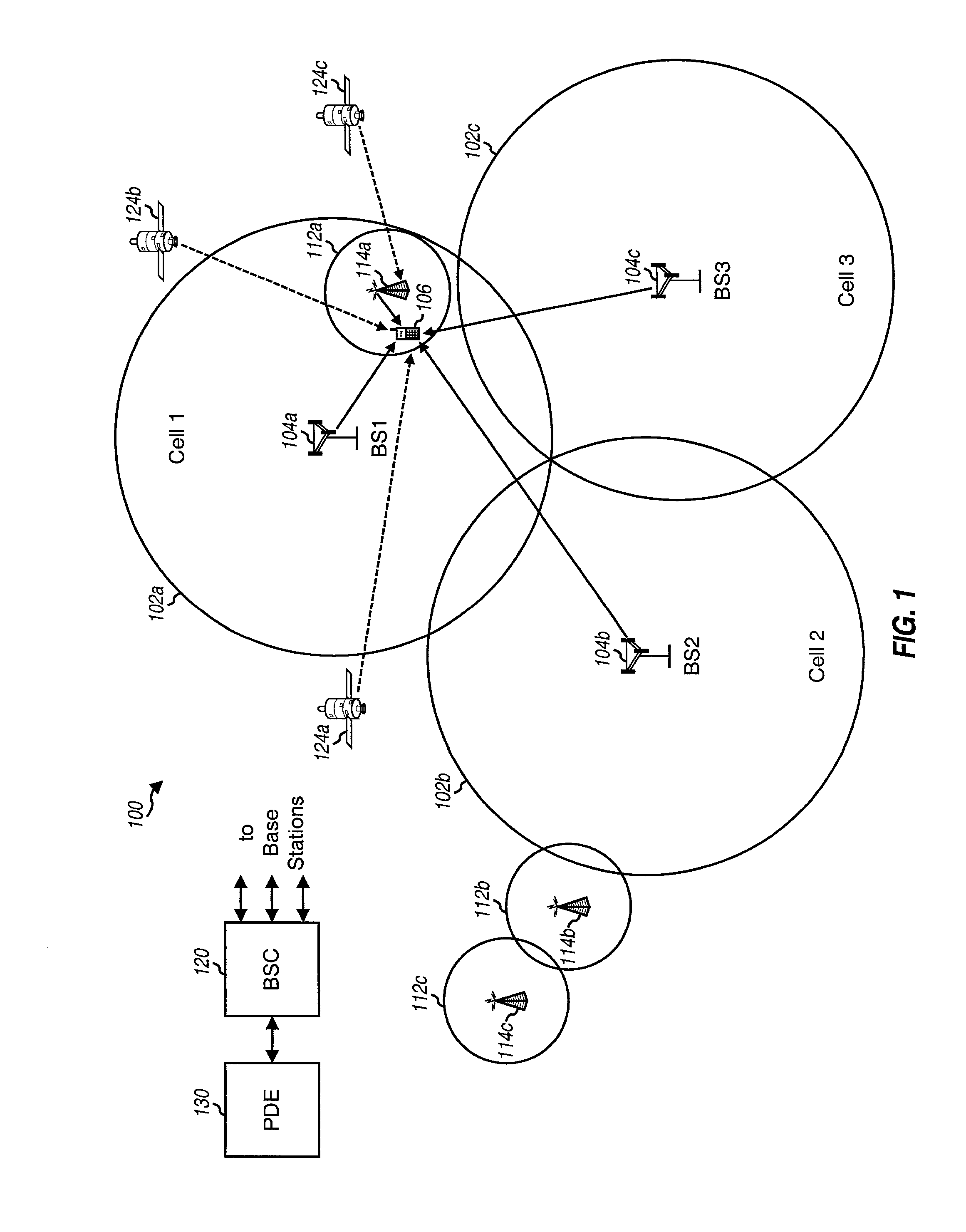
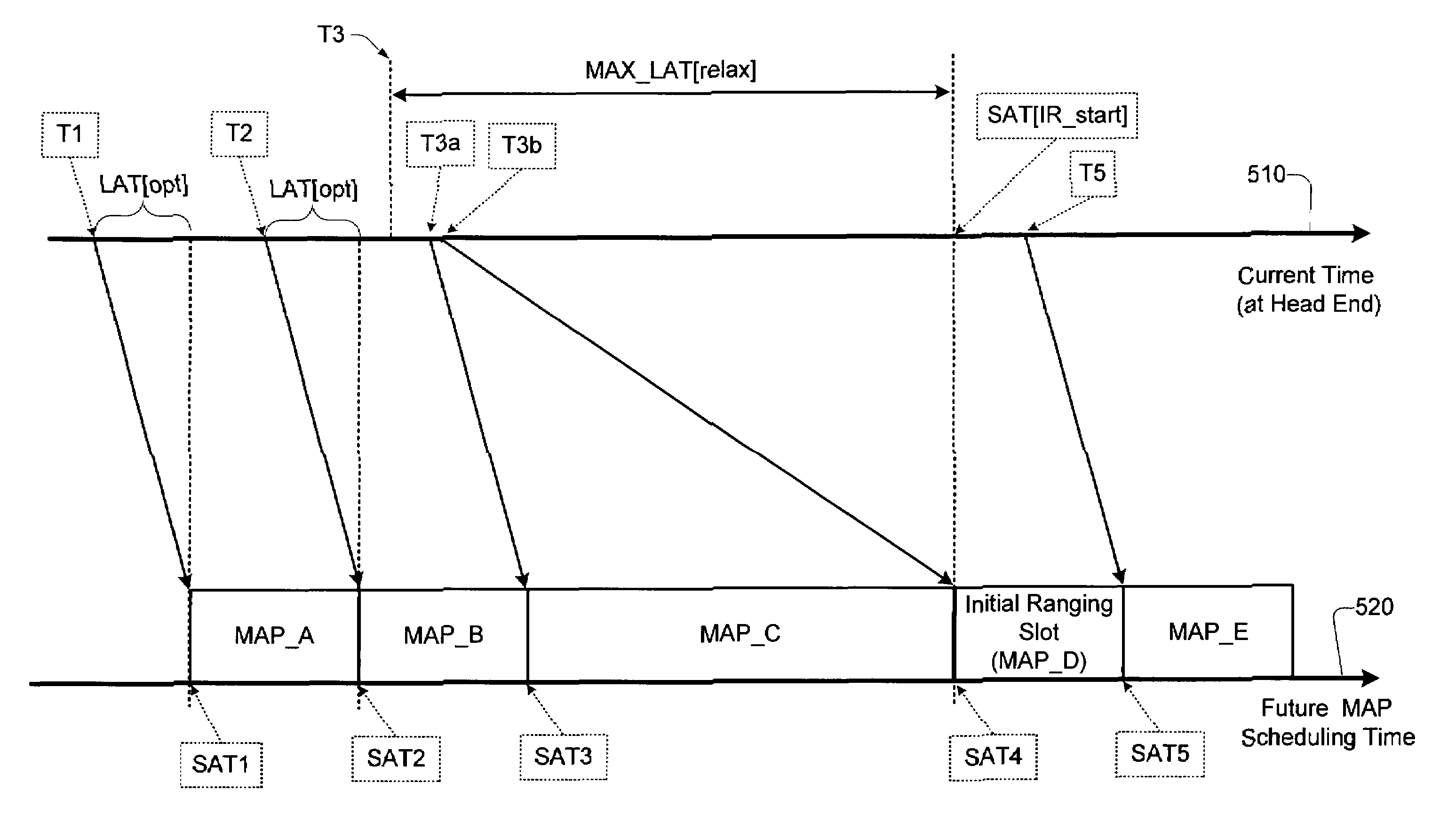
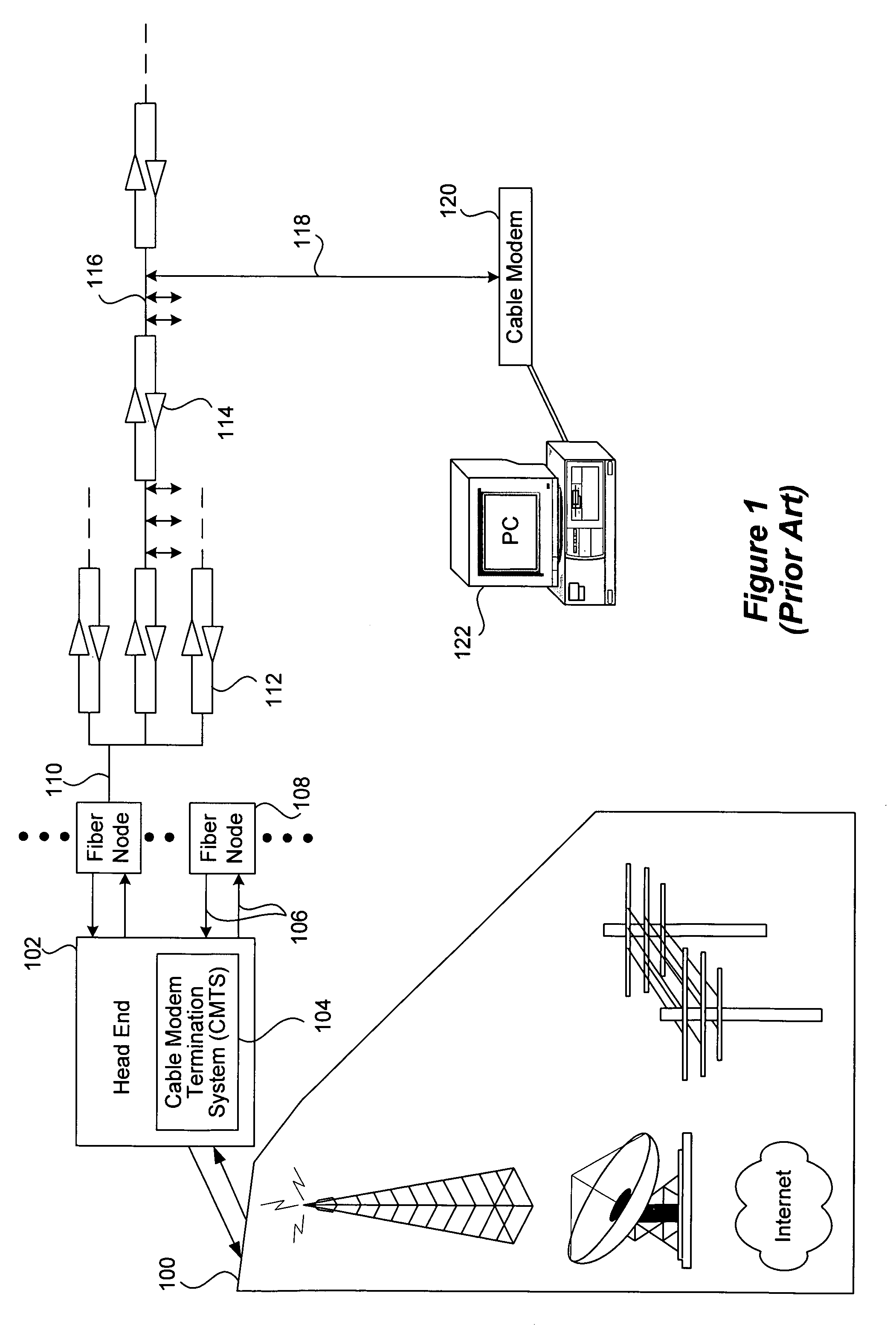
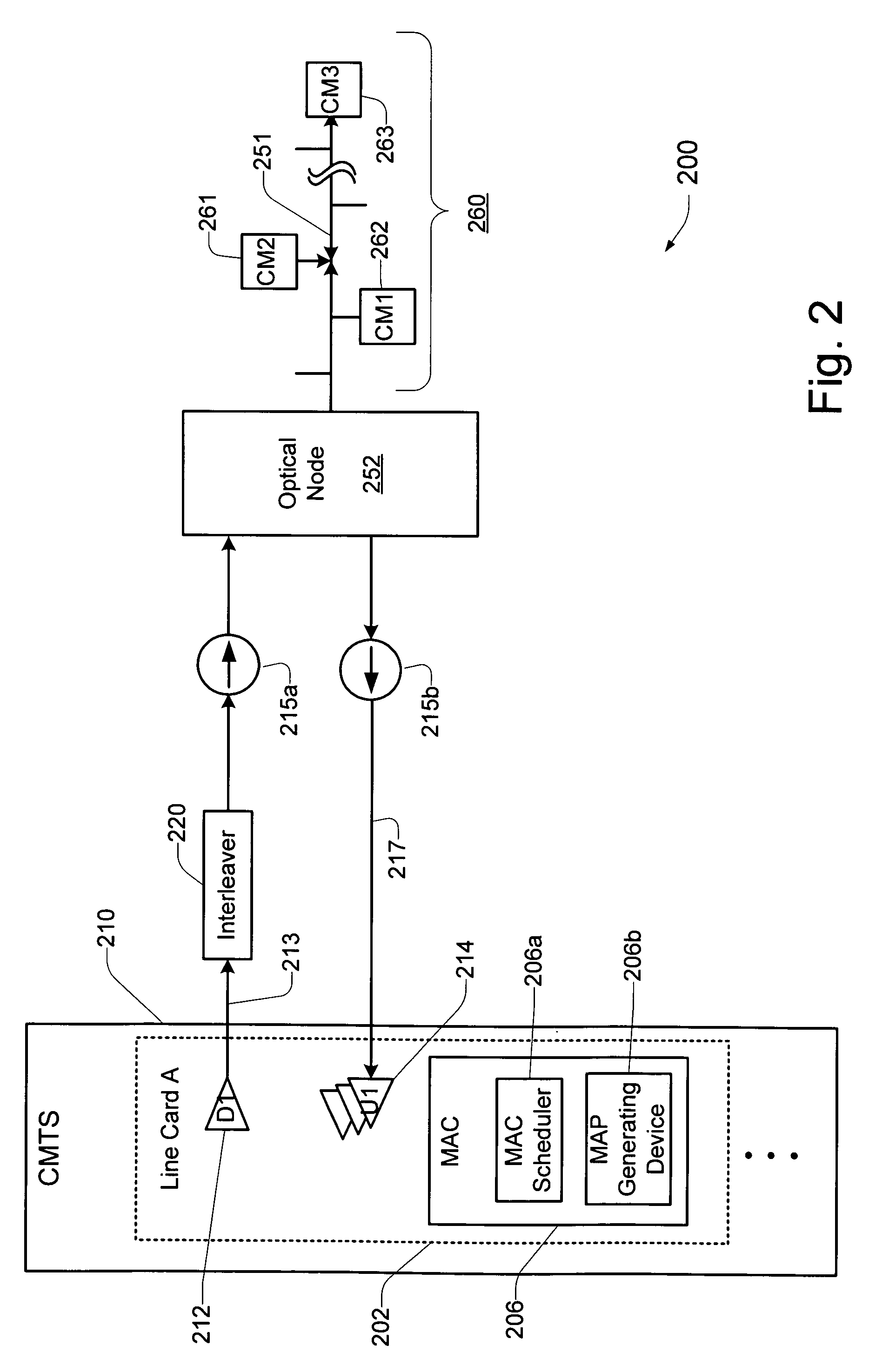
Technique for dynamically adjusting lookahead time for channel map messages to achieve optimal packet performance over an access network
InactiveUS6956865B1Improve performanceBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexAccess networkPropagation delay
A technique is described for improving packet performance in an access network. The access network comprises a Head End and a plurality of nodes. The access network further includes at least one shared-access upstream channel used by the first plurality of nodes to communicate with the Head End. Propagation delay data associated with at least a portion of the plurality of nodes using the at least one upstream channel is obtained. The propagation delay data is then used to dynamically adjust the lookahead time value associated with the generating of MAP messages for the at least one upstream channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Corrrecting time synchronization inaccuracy caused by asymmetric delay on a communication link
ActiveUS20070147562A1Time-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementPropagation delayTelecommunications link
Techniques for correcting time synchronization inaccuracy caused by asymmetric delays on a communication link. Time synchronization according to the present techniques includes determining an asymmetry in a propagation delay on a communication link used by a first device and a second device to exchange timing information and incorporating the asymmetry into a determination of a clock offset between the first and second devices.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Data transmitting apparatus data receiving apparatus and data transmission control apparatus
InactiveUS6128316ATelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionPropagation delayComputer hardware
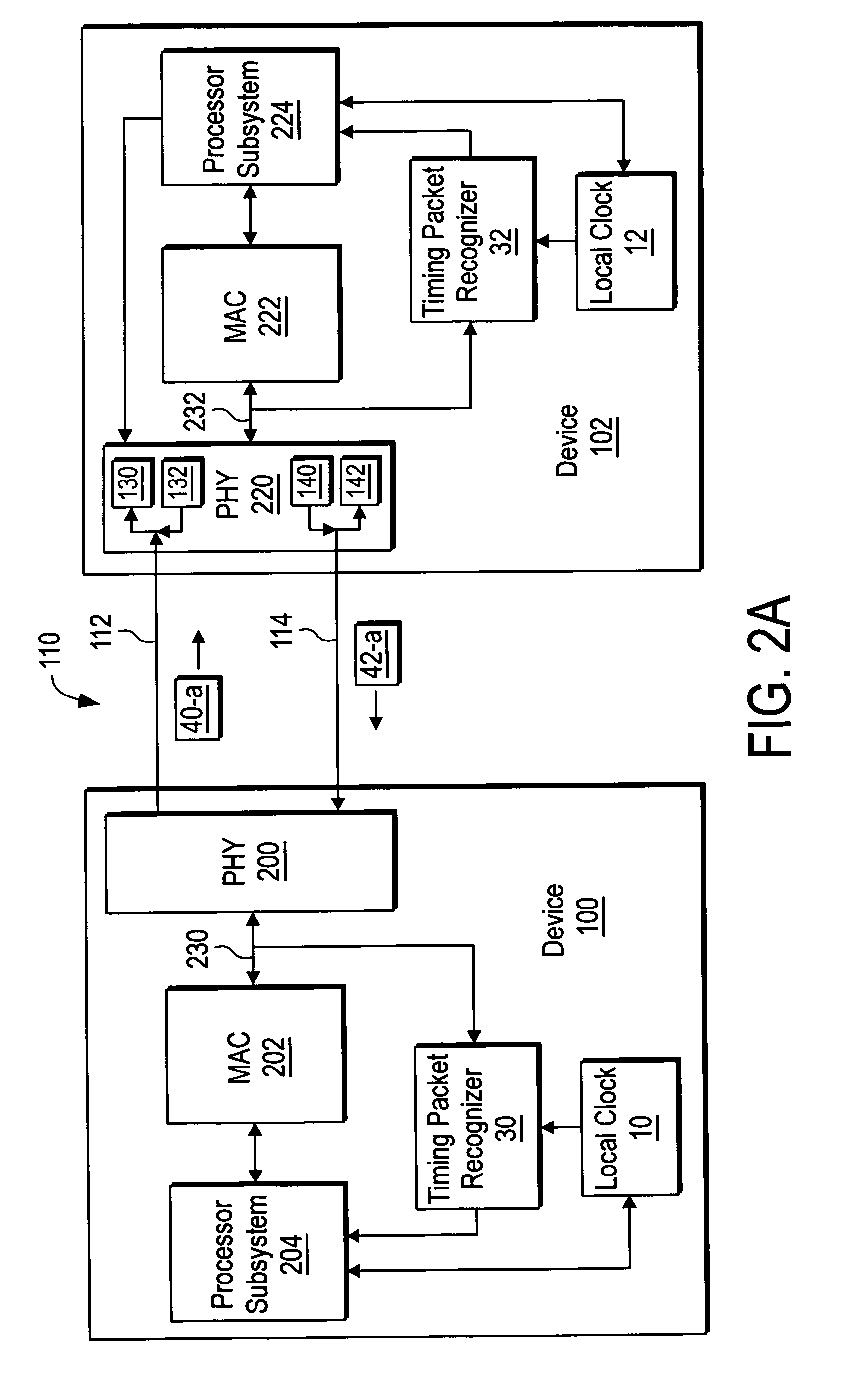
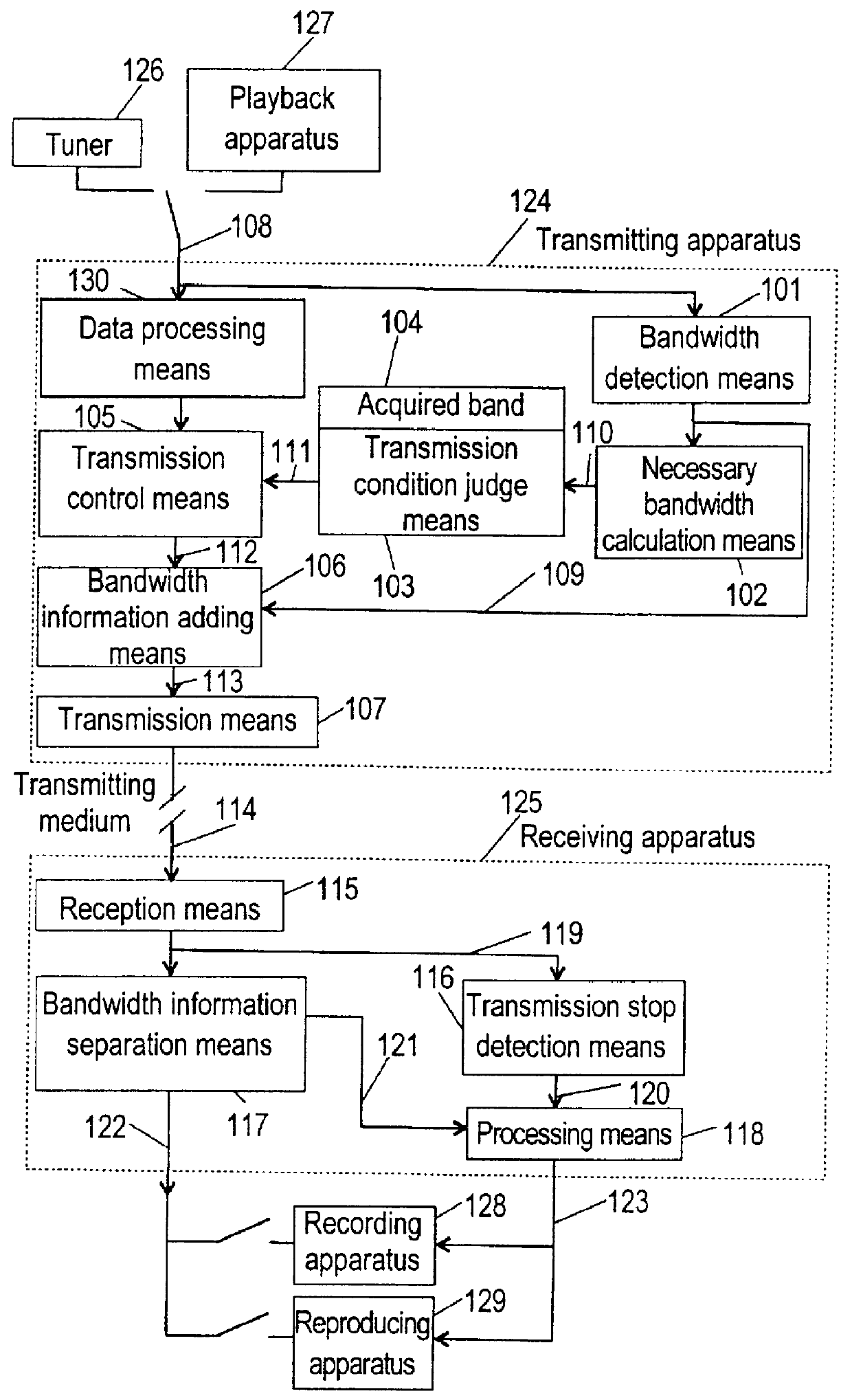
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01123 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 34477 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 31, 1996It is objected to simplify a procedure concerning bandwidth acquisition. Bandwidth acquiring means 809 of a second transmitting apparatus 814 acquires a bandwidth which was used by a first transmitting apparatus 806 by using a propagation delay identifier 804 read from first transmitting apparatus 806 and a maximum transmission data size 805 after stopping transmission of first transmitting apparatus 806. Each apparatus is composed so that transmission is started using this bandwidth and because returning and re-acquisition are not accompanied when the transmission is switched, necessary procedure can be simplified. Further, it is possible to effectively use the bandwidth by using a propagation delay identifier.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
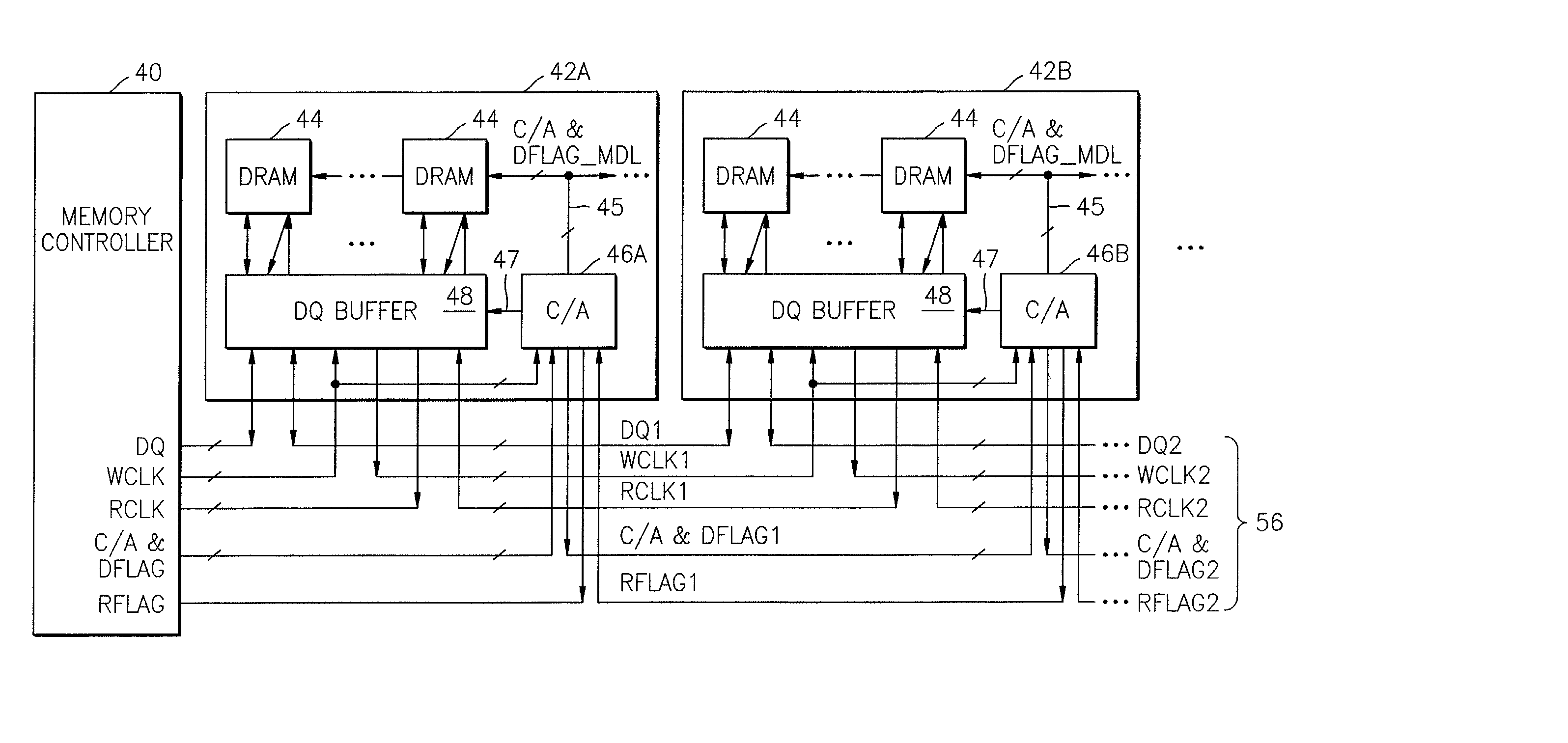
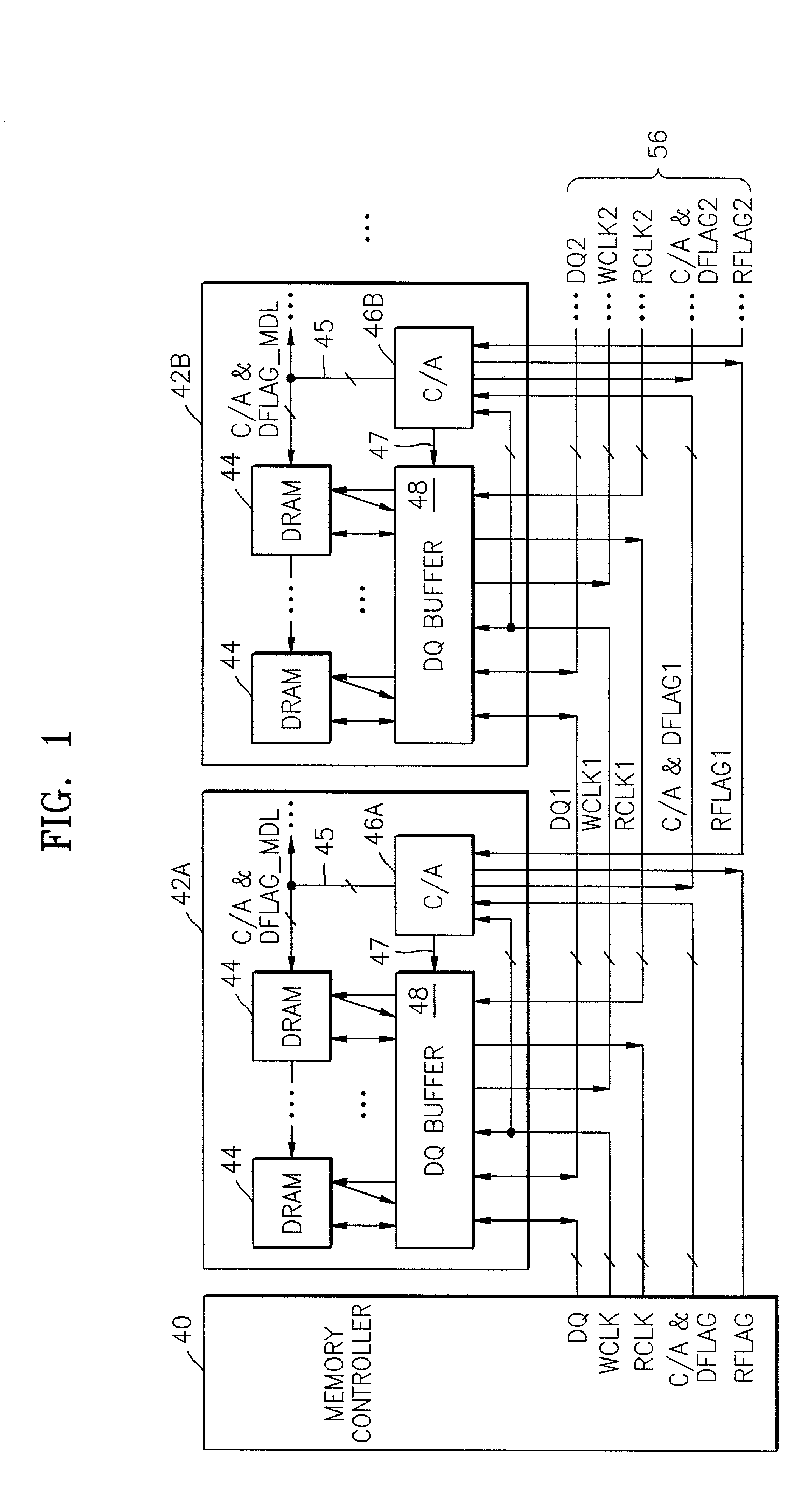
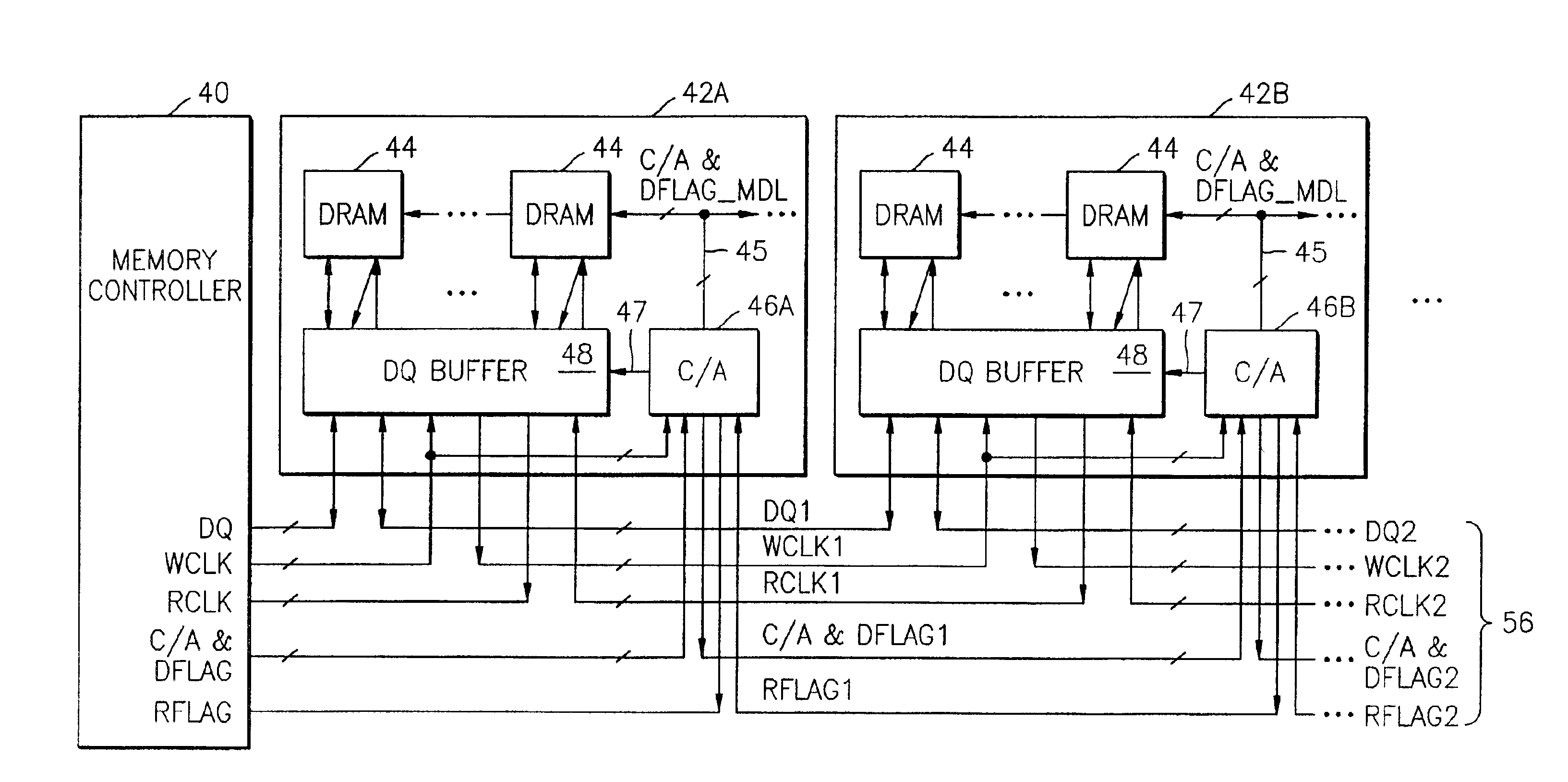
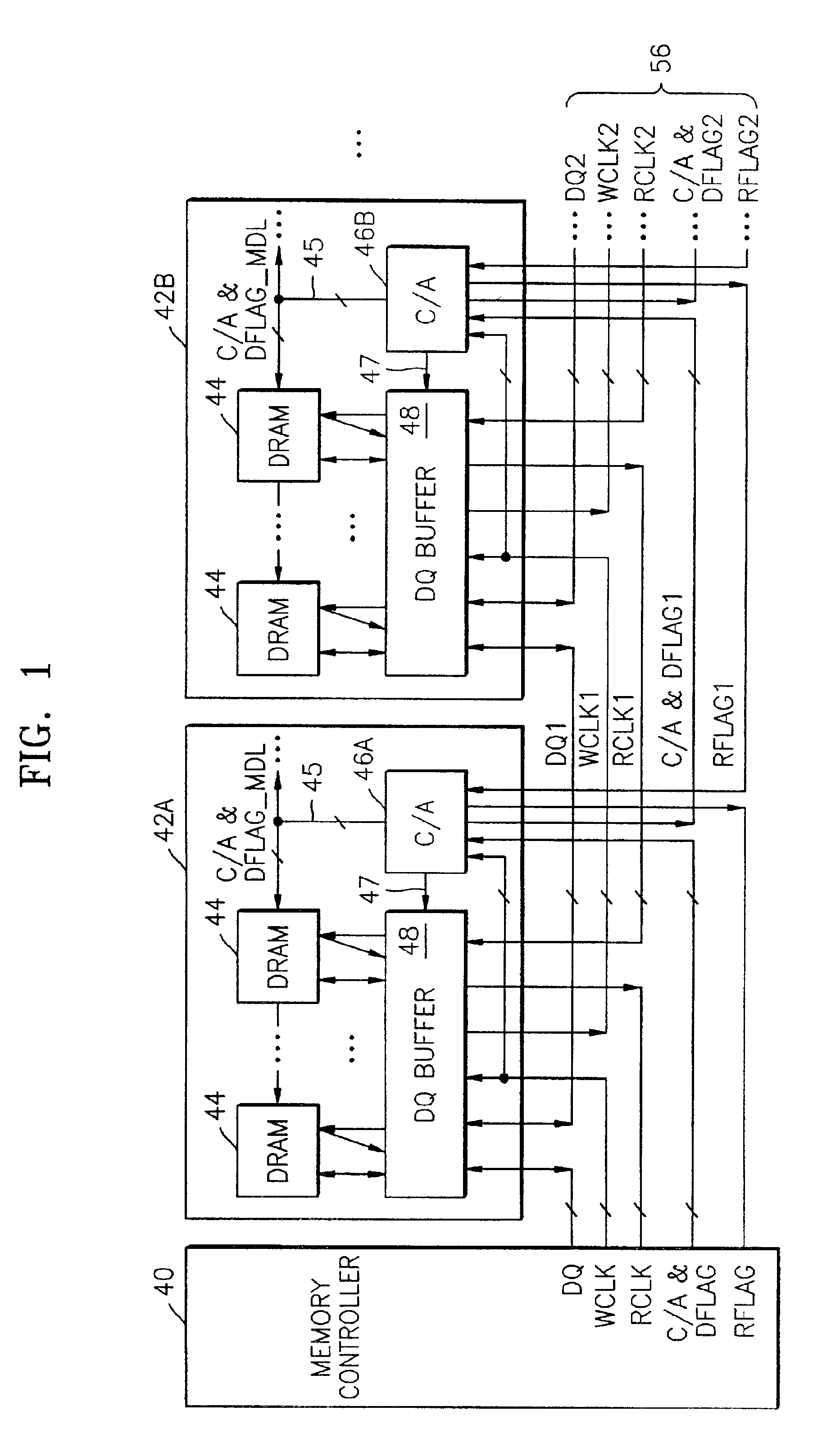
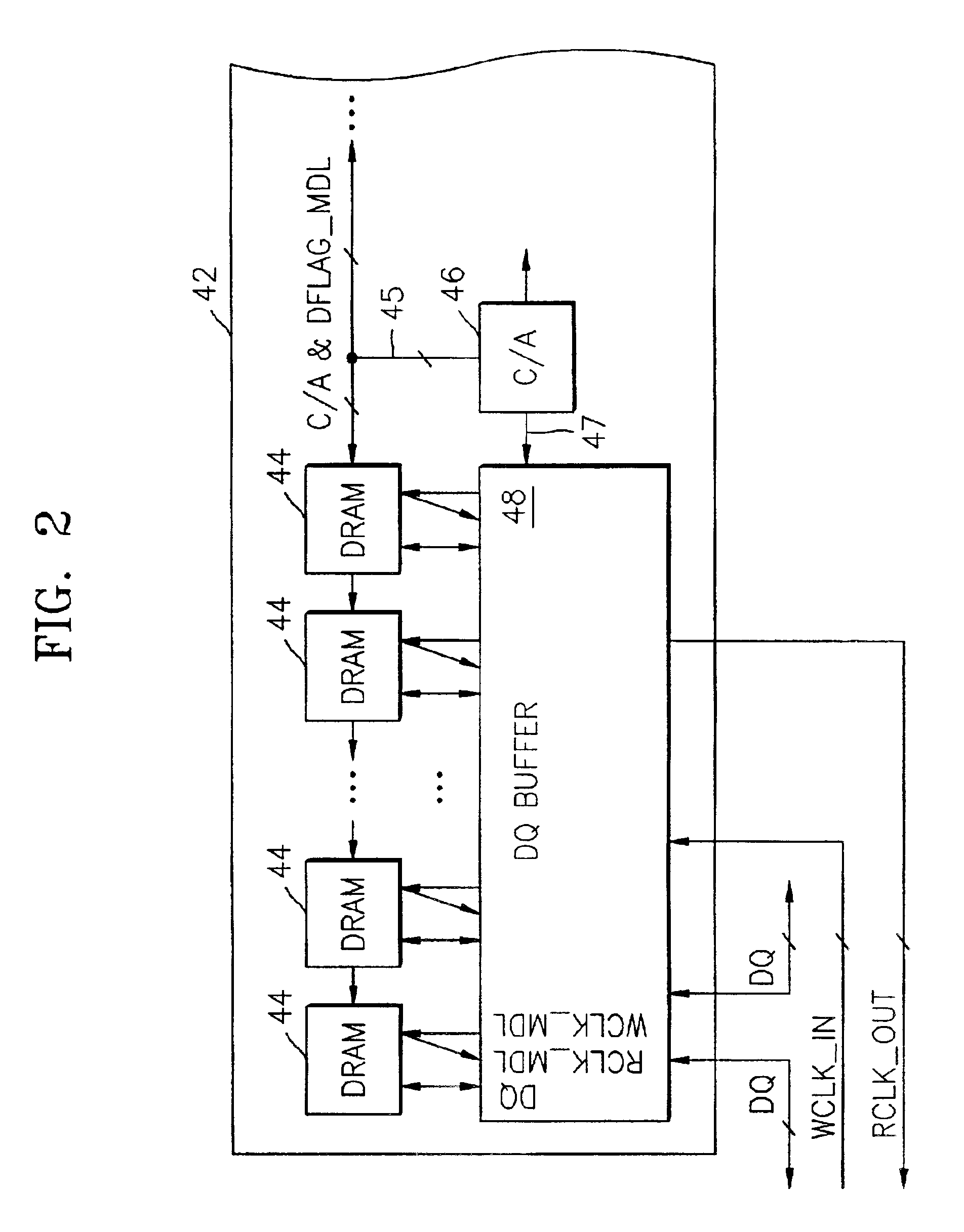
Memory system having point-to-point bus configuration
A clocking system and method in a point-to-point bus configuration overcomes the limitations of conventional approaches. In one embodiment, the present invention ensures the same phase relationship for the write clock in the write direction for all data transfers between modules, and similarly the same phase relationship for the read clock in the read direction for all data transfers between modules, regardless of module location. In another embodiment, on a given module, all transfers of data between a data buffer and a memory device in both read and write directions are clocked by a read clock signal and a write clock signal that have the same phase relationship and have the same propagation delay as the data bus between the buffer and the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
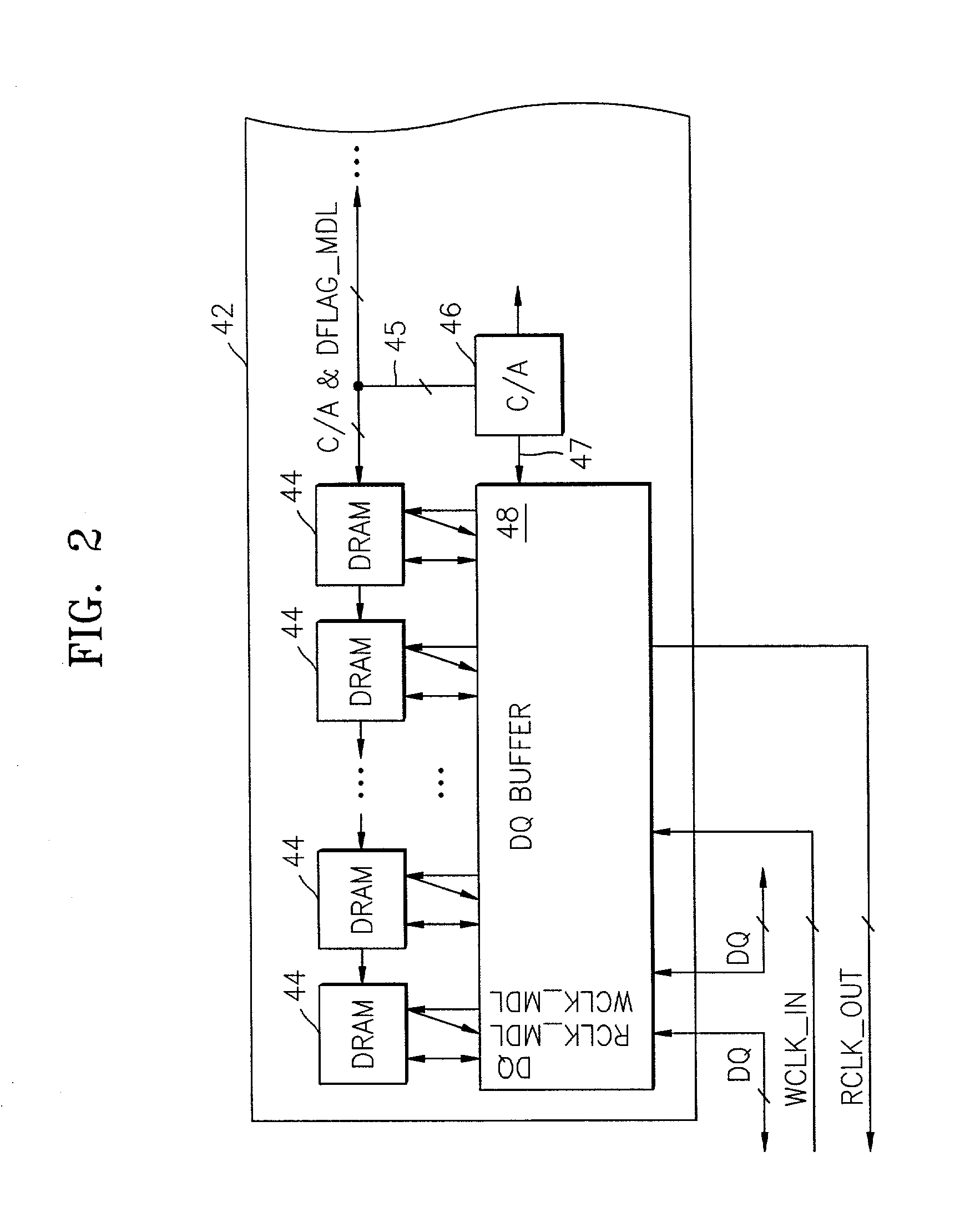
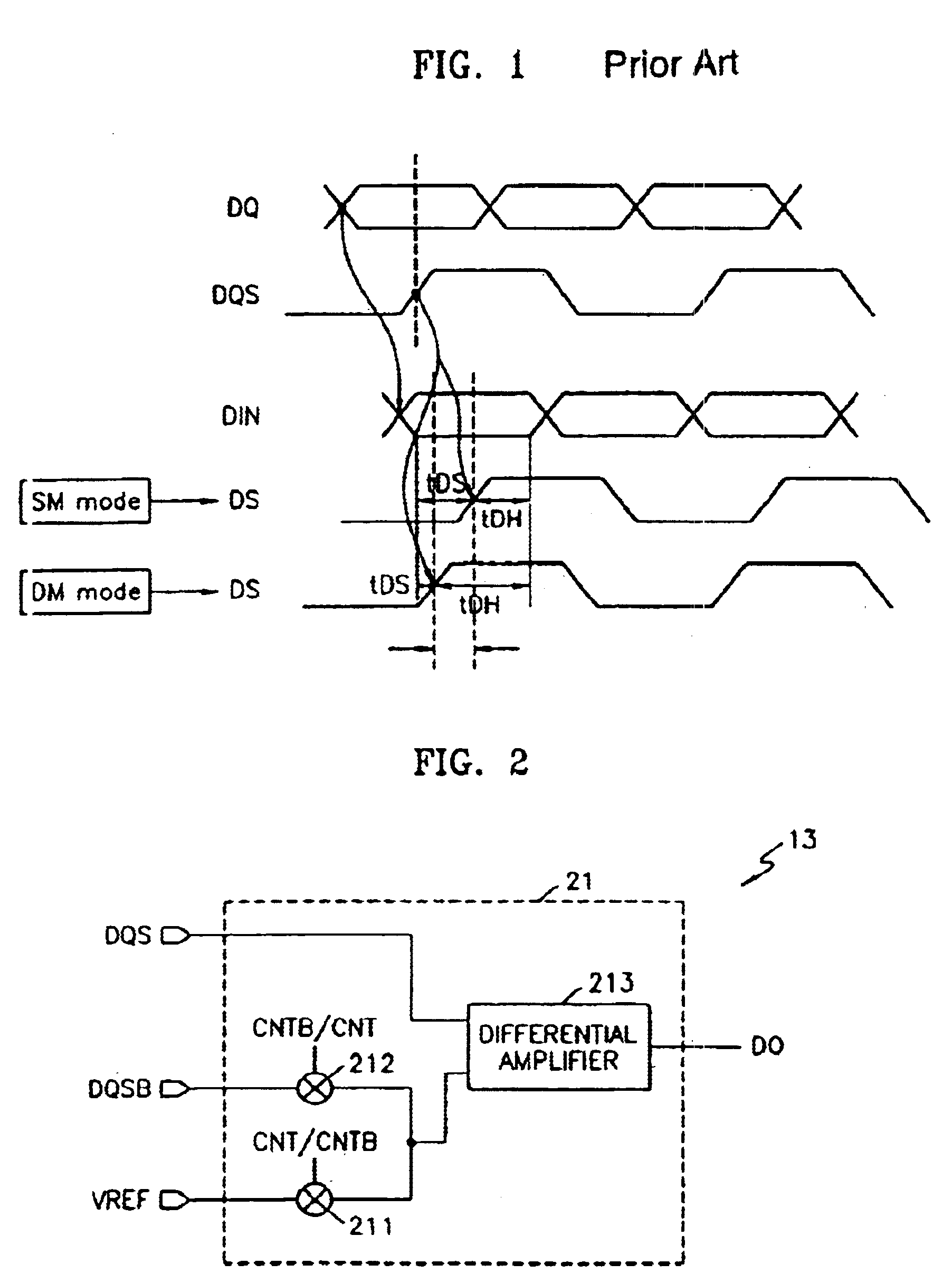
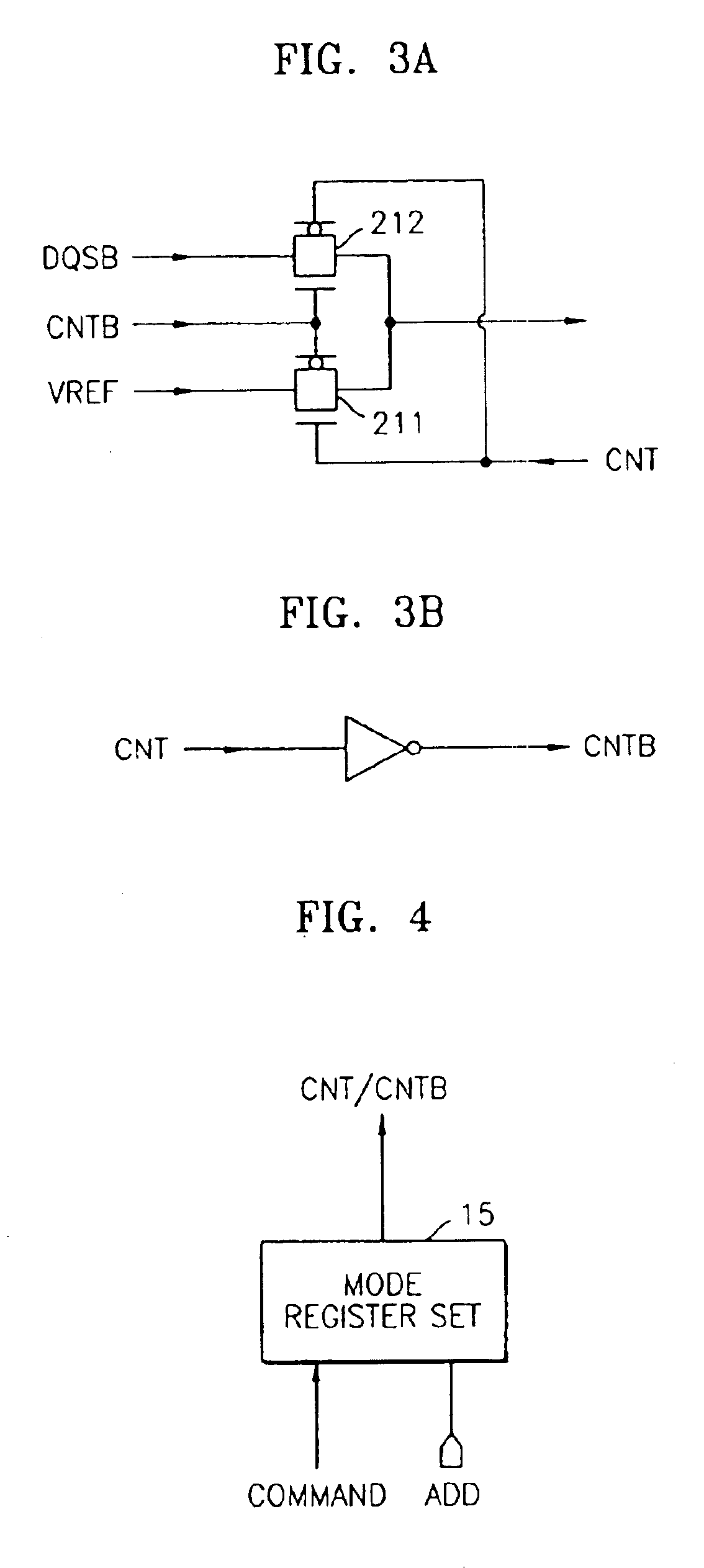
Multimode data buffer and method for controlling propagation delay time
A data buffer, such as a data strobe input buffer or a data input buffer, which may operate in multiple modes, such as a single mode (SM) and a dual mode (DM) and where the mode is selected by providing a signal, such as an external signal such as an address signal or an external command signal. A data buffer which can be used for a SM / DM dual-use and can improve a data setup / hold margin. A semiconductor memory device including one or more of the data buffers described above. A method for controlling propagation delay times which can improve a data setup / hold margin in a SM / DM dual-use data buffer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Accurate distance measurement using RF techniques
InactiveUS6859761B2Accurate distance measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPropagation delayRelative phase
A system, apparatus, and method for determining the distance between two objects using an indirect propagation delay measurement is disclosed. A frequency hopping scheme (such as the Bluetooth™ technology) is used to measure the relative phase offset of the received signal between the various frequencies. For a given distance between the objects, the phase offset vs. frequency curve is a straight line with the slope dependent upon the measured distance. After the phase of the received signals is detected, the data is plotted on a curve and the slope is calculated.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS20060052699A1Easy to measureFrame rateOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryLinearityAcoustical imaging
Acoustic imaging provides images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object. The received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes is processed with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. The scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) domain provides a signal with suppression of reverberation noise with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Memory system having point-to-point bus configuration
A clocking system and method in a point-to-point bus configuration overcomes the limitations of conventional approaches. In one embodiment, the present invention ensures the same phase relationship for the write clock in the write direction for all data transfers between modules, and similarly the same phase relationship for the read clock in the read direction for all data transfers between modules, regardless of module location. In another embodiment, on a given module, all transfers of data between a data buffer and a memory device in both read and write directions are clocked by a read clock signal and a write clock signal that have the same phase relationship and have the same propagation delay as the data bus between the buffer and the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Location Estimation of a Mobile Device in a UMTS Network
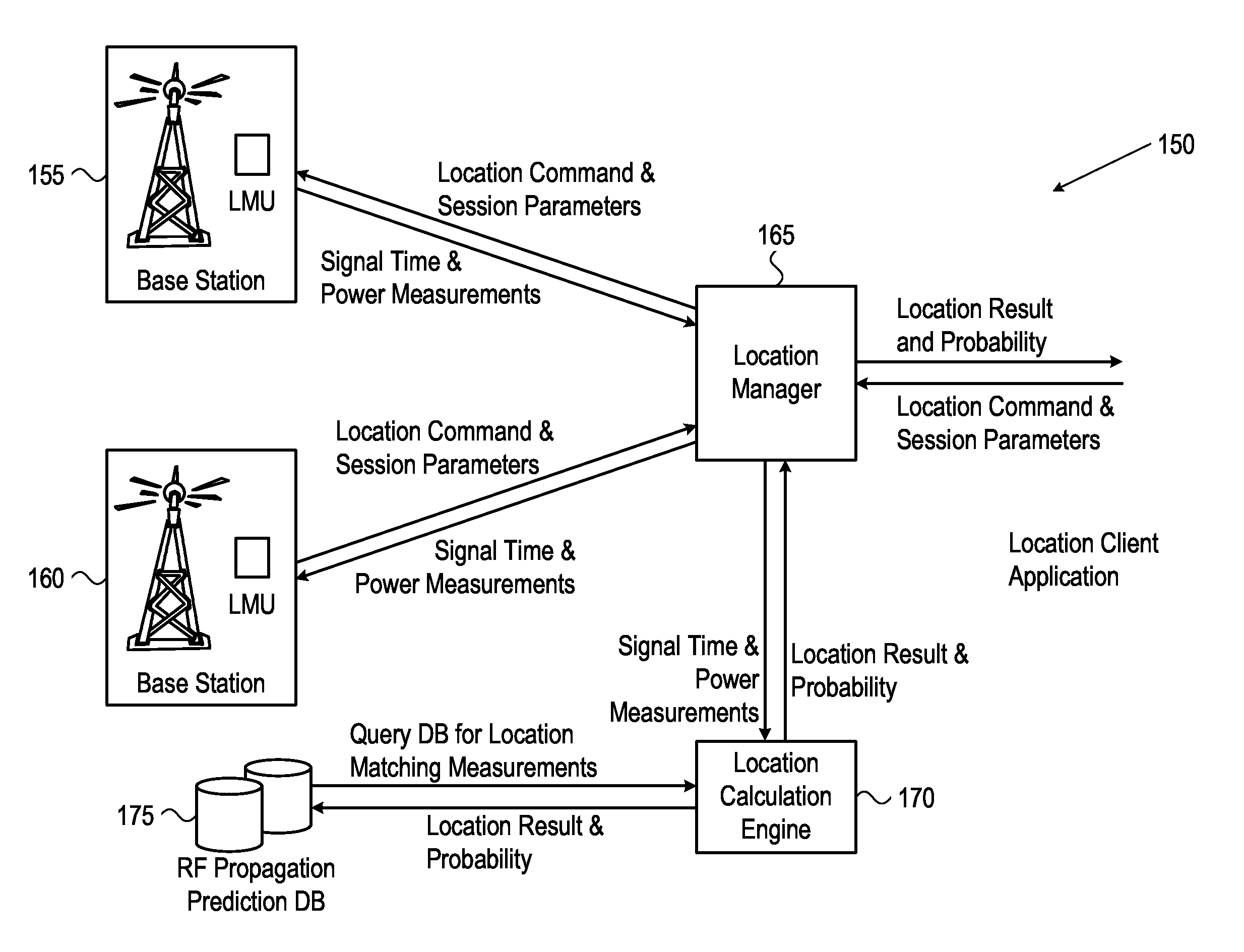
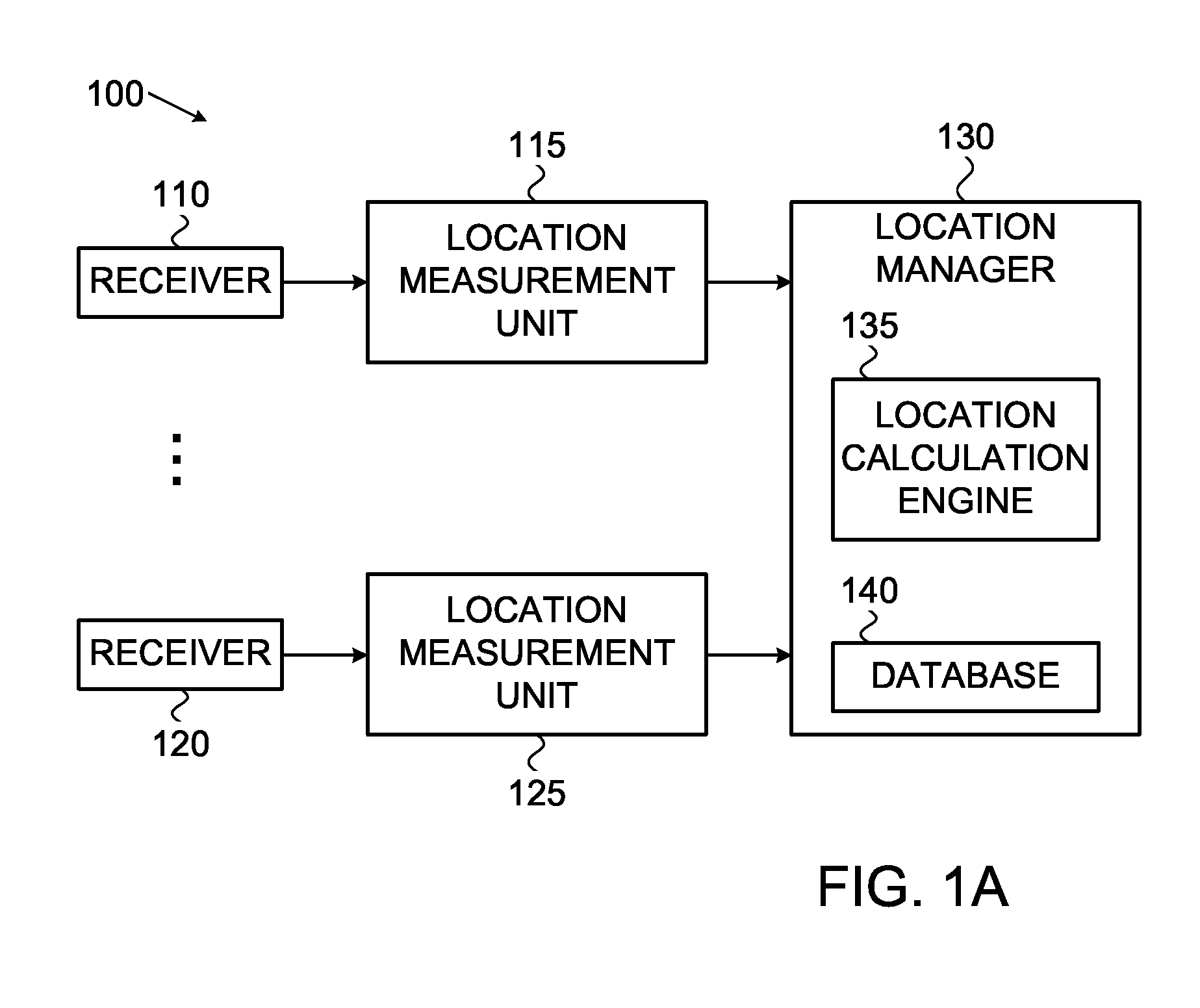
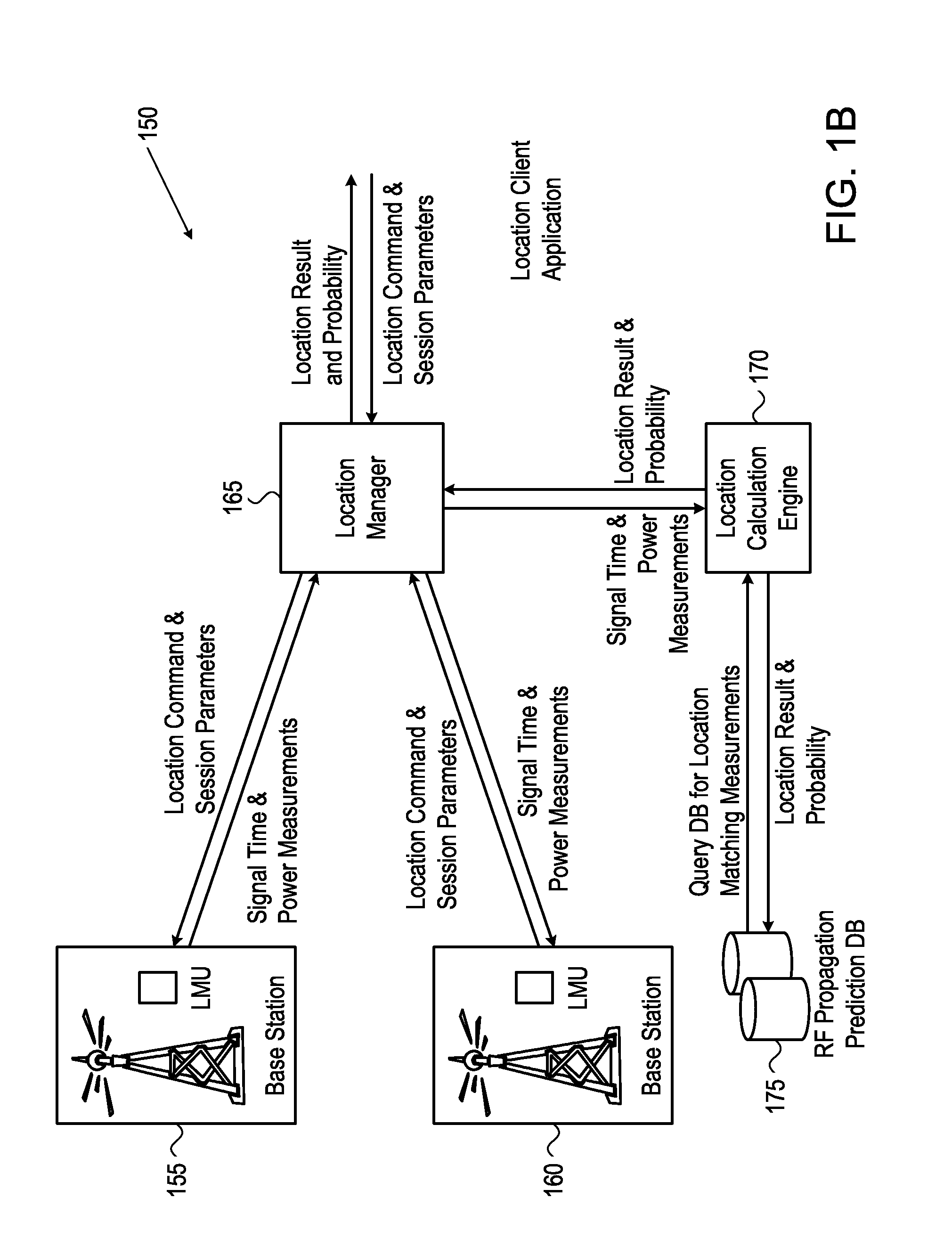
ActiveUS20120052883A1Radio wave finder detailsSpecial service for subscribersPropagation delayCrowd sourcing
The present disclosure provides devices, systems, and methods to utilize relative timing offset information reported by one or more mobile devices. When coupled with AGPS information reported by one or more mobile devices, the offset information is be used to calibrate calculations and subsequently to locate all 3G mobiles with GPS-like accuracy, whether or not a GPS receiver is available on said mobile device being located. A determination of a propagation delay between one or more cell sites and a mobile device is reported to a network and used to calibrate unknown information such as a timing offset, to improve the accuracy of a detected location. The relative timing offset can be applied to determine a location for all other mobile devices within the area served by the known base station. The present disclosure utilizes this method in conjunction with information crowd-sourced from a plurality of mobile devices.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Timing advance configuration for multiple uplink component carriers
ActiveUS9402255B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexPropagation delayUplink transmission
The invention relates methods for time aligning uplink transmissions by a mobile terminal in a mobile communication system, and to methods for performing a handover of a mobile terminal to a target aggregation access point. The invention is also providing apparatus and system for performing these methods, and computer readable media the instructions of which cause the apparatus and system to perform the methods described herein. In order to allow for aligning the timing of uplink transmissions on uplink component carriers, where different propagation delays are imposed on the transmissions on the uplink component carriers, the inventions suggests to time align the uplink component carriers based on a reference time alignment of a reference cell and a reception time difference or propagation delay difference between the downlink transmissions in the reference cell and the other radio cells, the uplink component carriers of which need to be time aligned.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
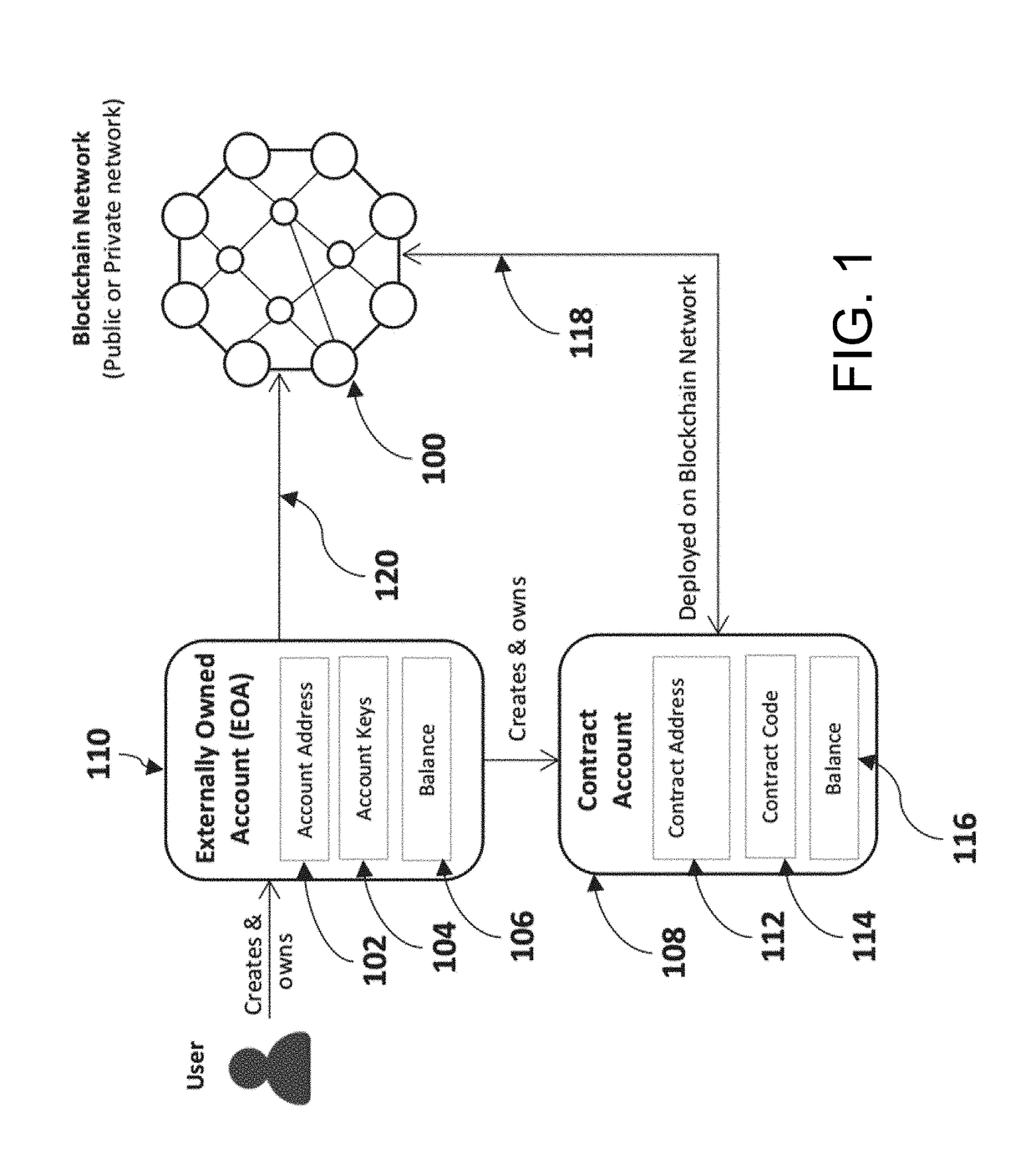
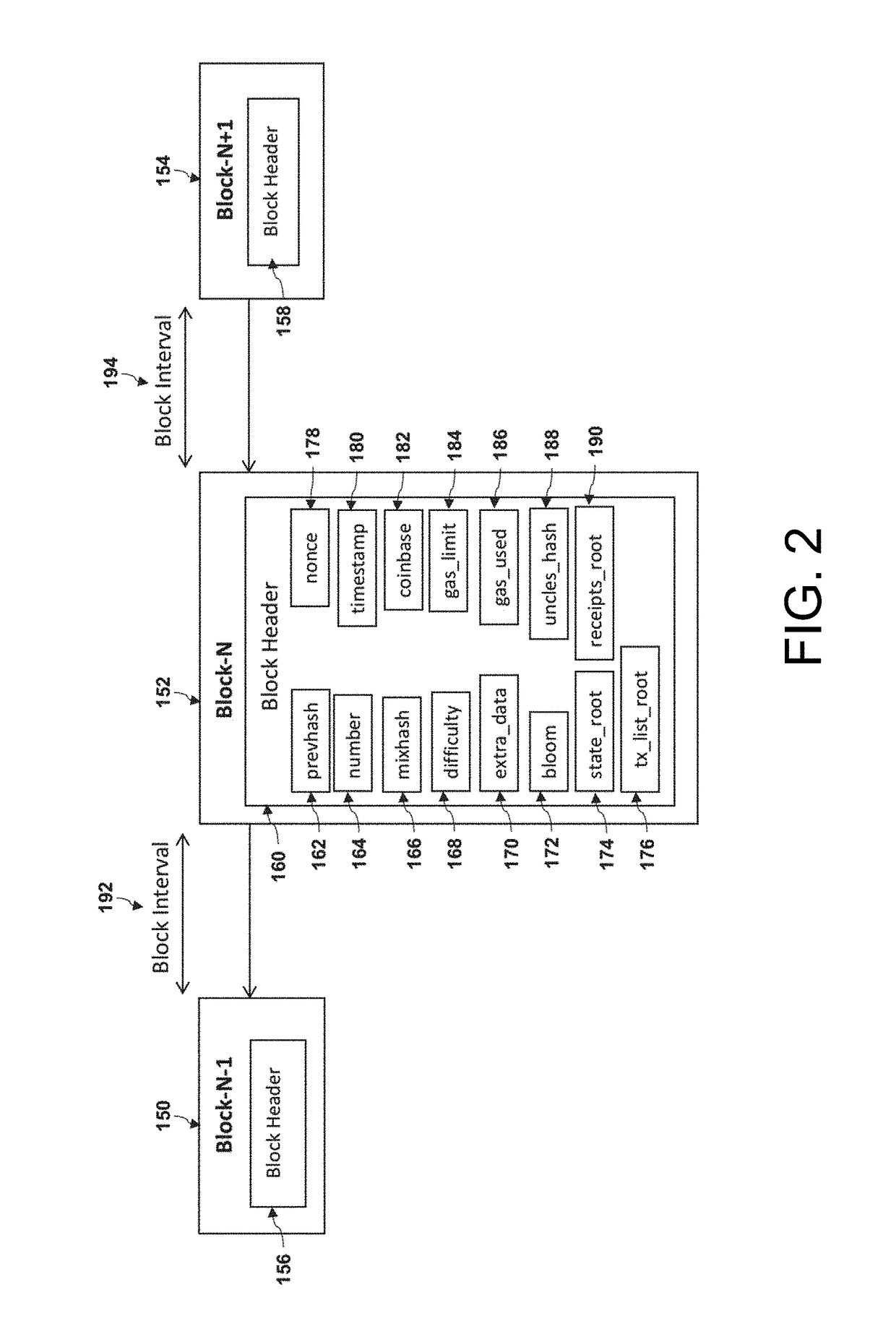
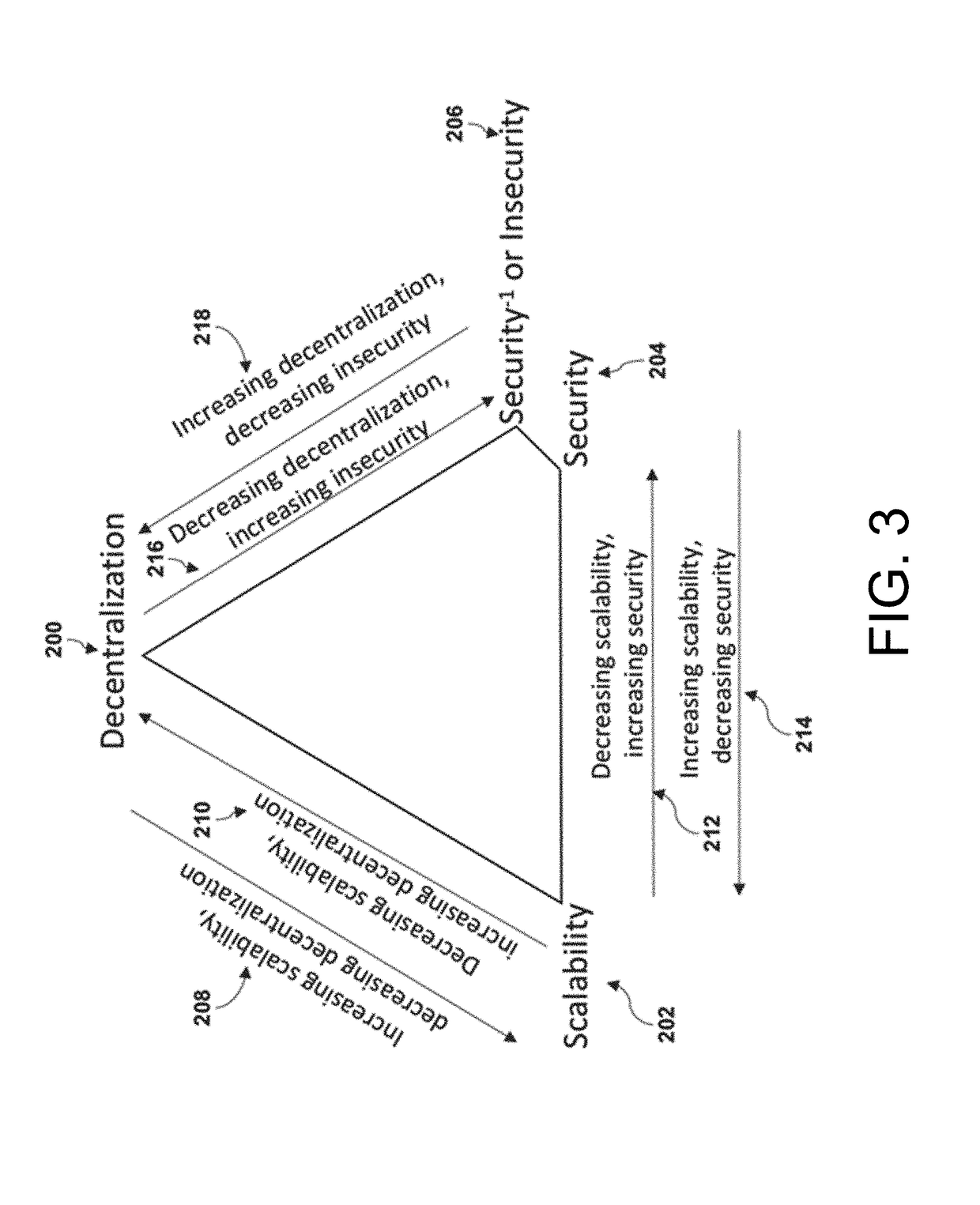
Method and System for Tuning Blockchain Scalability, Decentralization, and Security for Fast and Low-Cost Payment and Transaction Processing
ActiveUS20190018887A1Privacy protectionScalability issueSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPropagation delayPayment
A method of processing and validating transactions on a multi-chain network including receiving first and second pluralities of transactions, recording the first and second pluralities of transactions to first and second blocks on a first blockchain in a multi-chain network, publishing the first and second plurality of transactions to a first managed topic associated with the multi-chain network on a first messaging server, defining a first published transactions, and transmitting the first published transactions to a first subscriber, defining a first transmitted transaction. Receipt of the first transmitted transaction initiates generation of a first merged block comprising the first published transactions and recording of the first merged block to a second blockchain on the multi-chain network. The first blockchain has a parameter difference from the second blockchain selected from the group consisting of block generation time, transaction throughput, transaction latency, stale block rate, block propagation delay and consensus algorithm used.
Owner:MADISETTI VIJAY K
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20060034142A1Reading data is accurateIncrease speedRead-only memoriesDigital storagePropagation delayHemt circuits
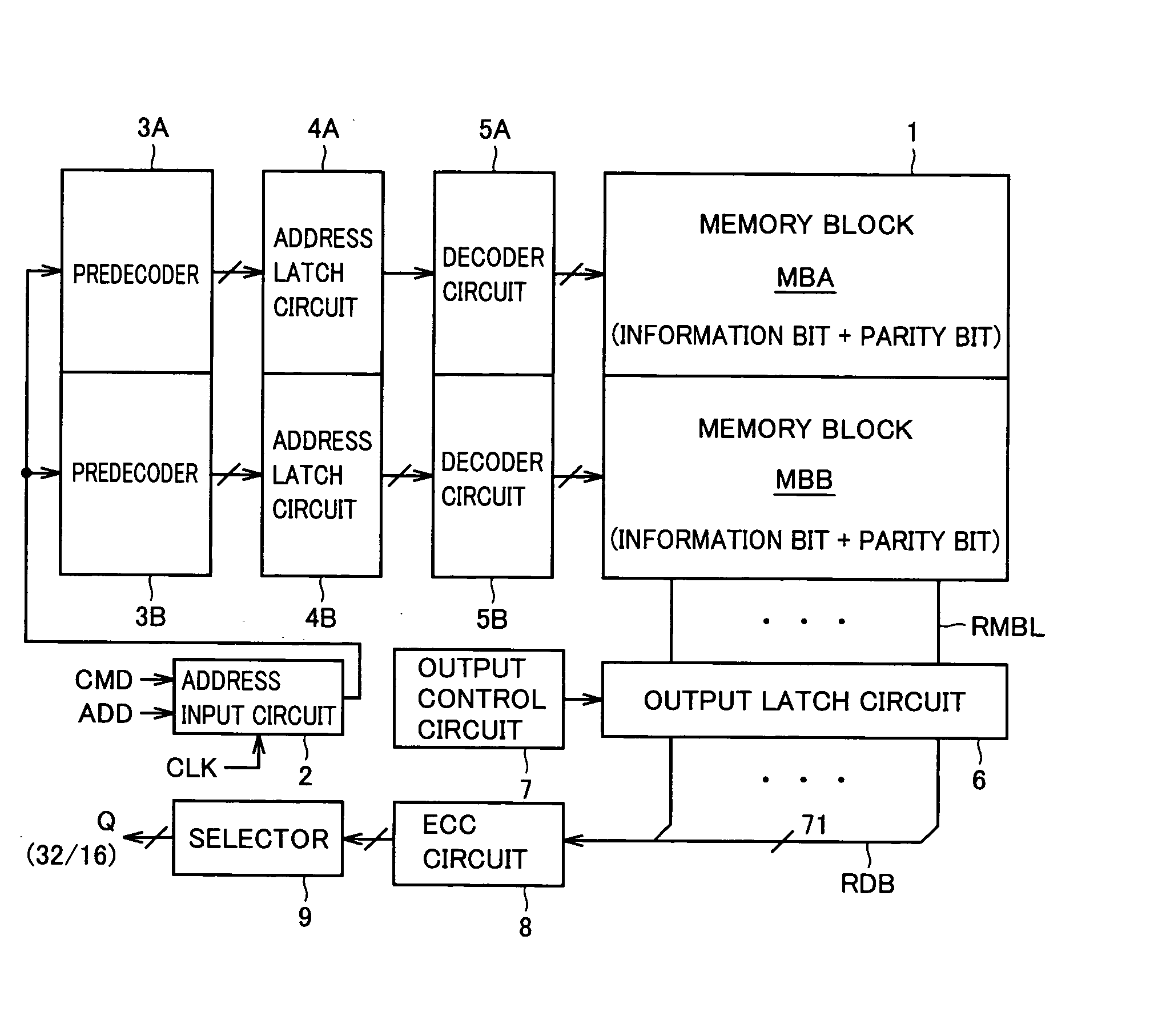
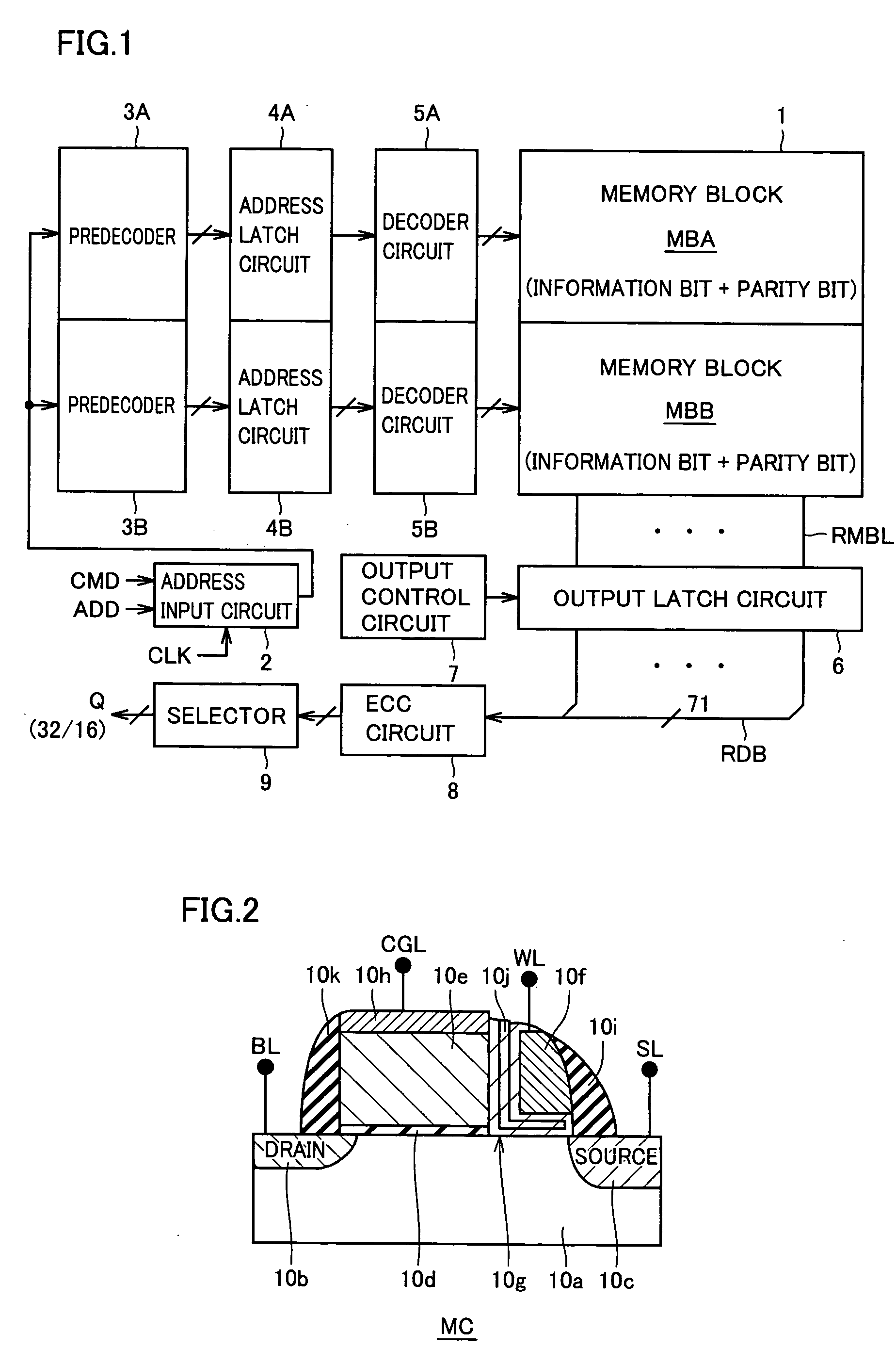
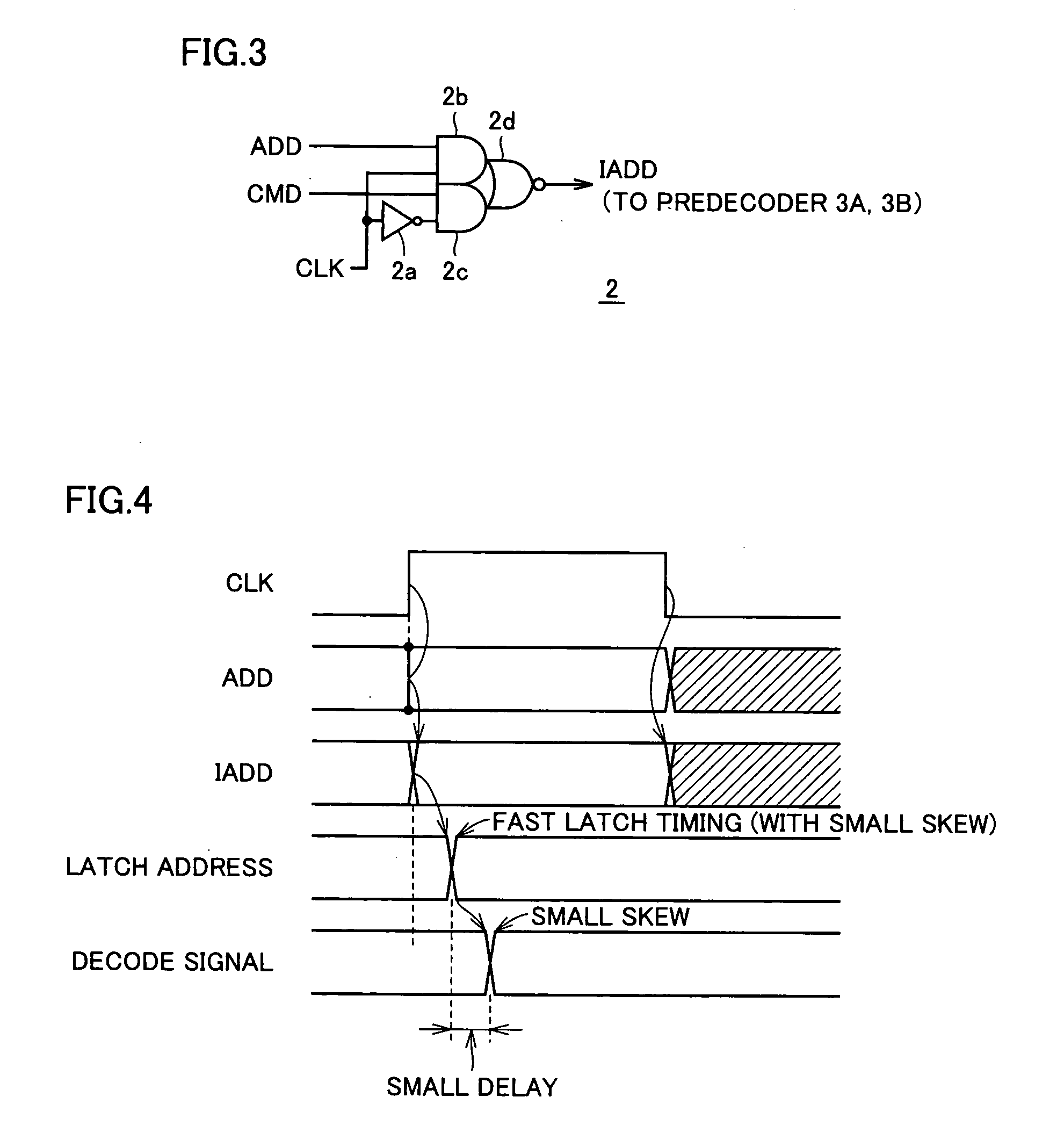
For each memory block, a predecoder for predecoding an applied address signal, an address latch circuit for latching the output signal of the predecoder, and a decode circuit for decoding an output signal of the address latch circuit and performing a memory cell selecting operation in a corresponding memory block are provided. Propagation delay of latch predecode signals can be made smaller and the margin for the internal read timing can be enlarged. In addition, the internal state of the decoder and memory cell selection circuitry are rest to an initial state when a memory cell is selected and the internal data output circuitry is reset to an initial state in accordance with a state of internal data reading. Thus, a non-volatile semiconductor memory device that can decrease address skew and realize an operation with sufficient margin is provided.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
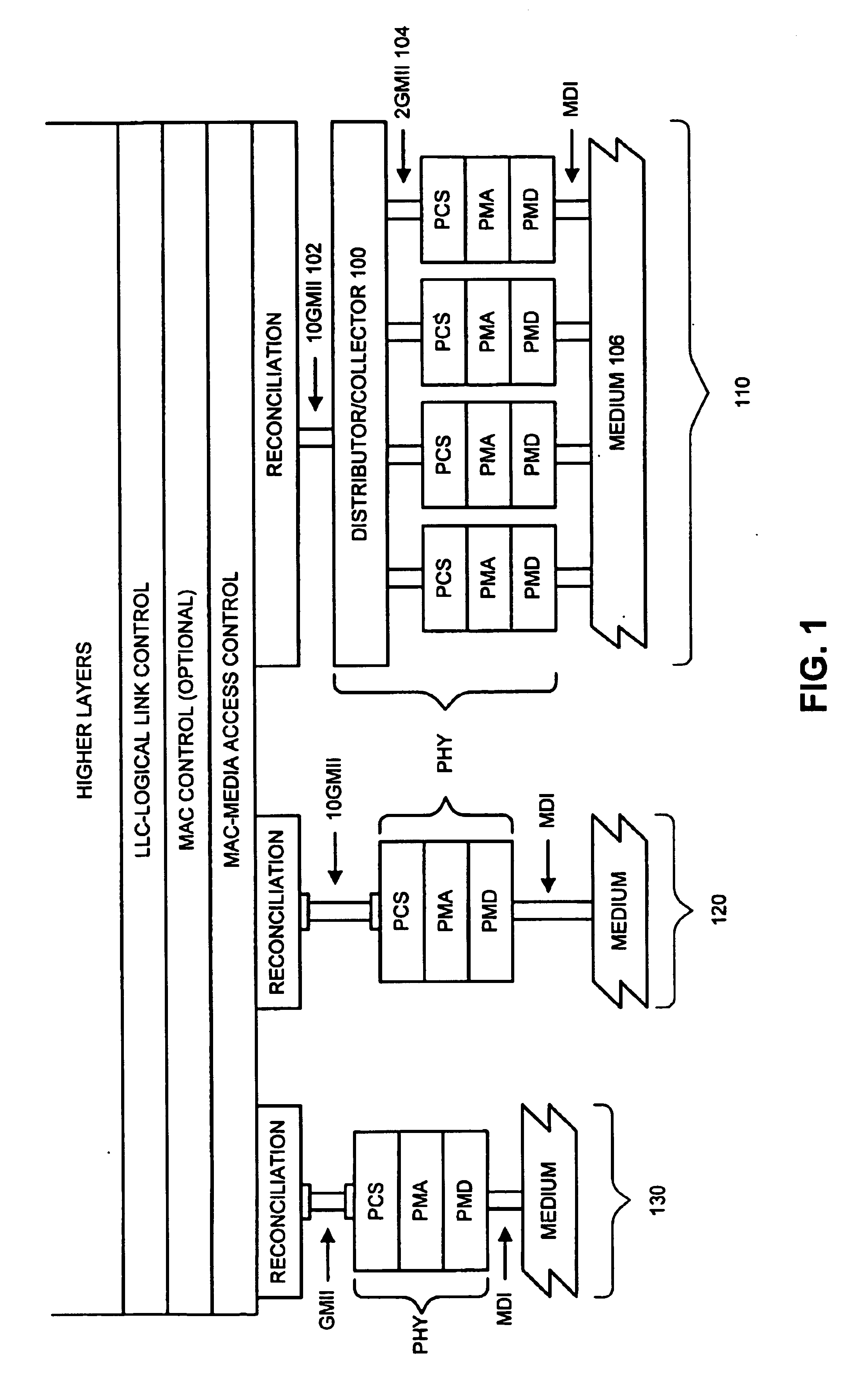
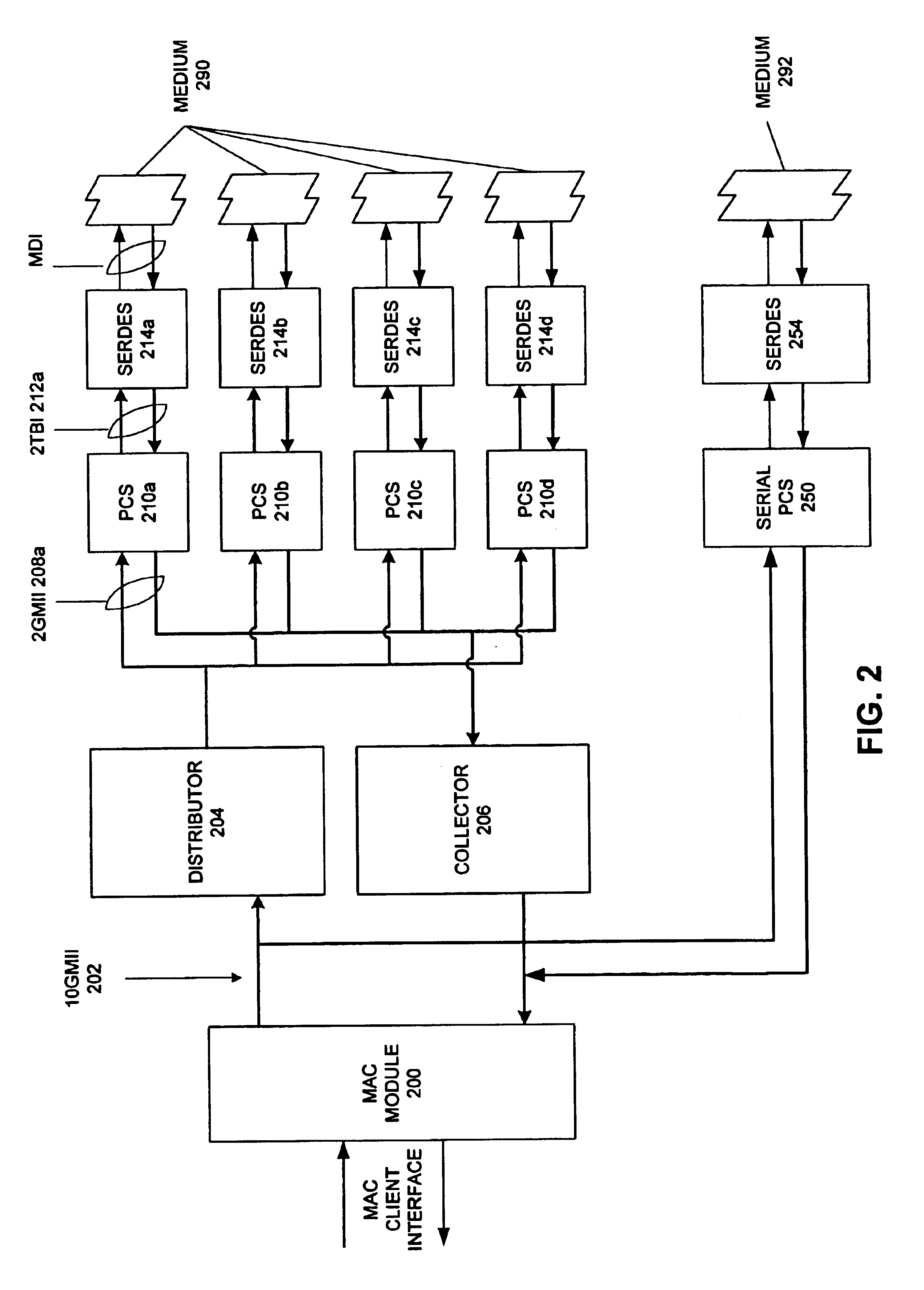
Method and apparatus for a multi-gigabit ethernet architecture
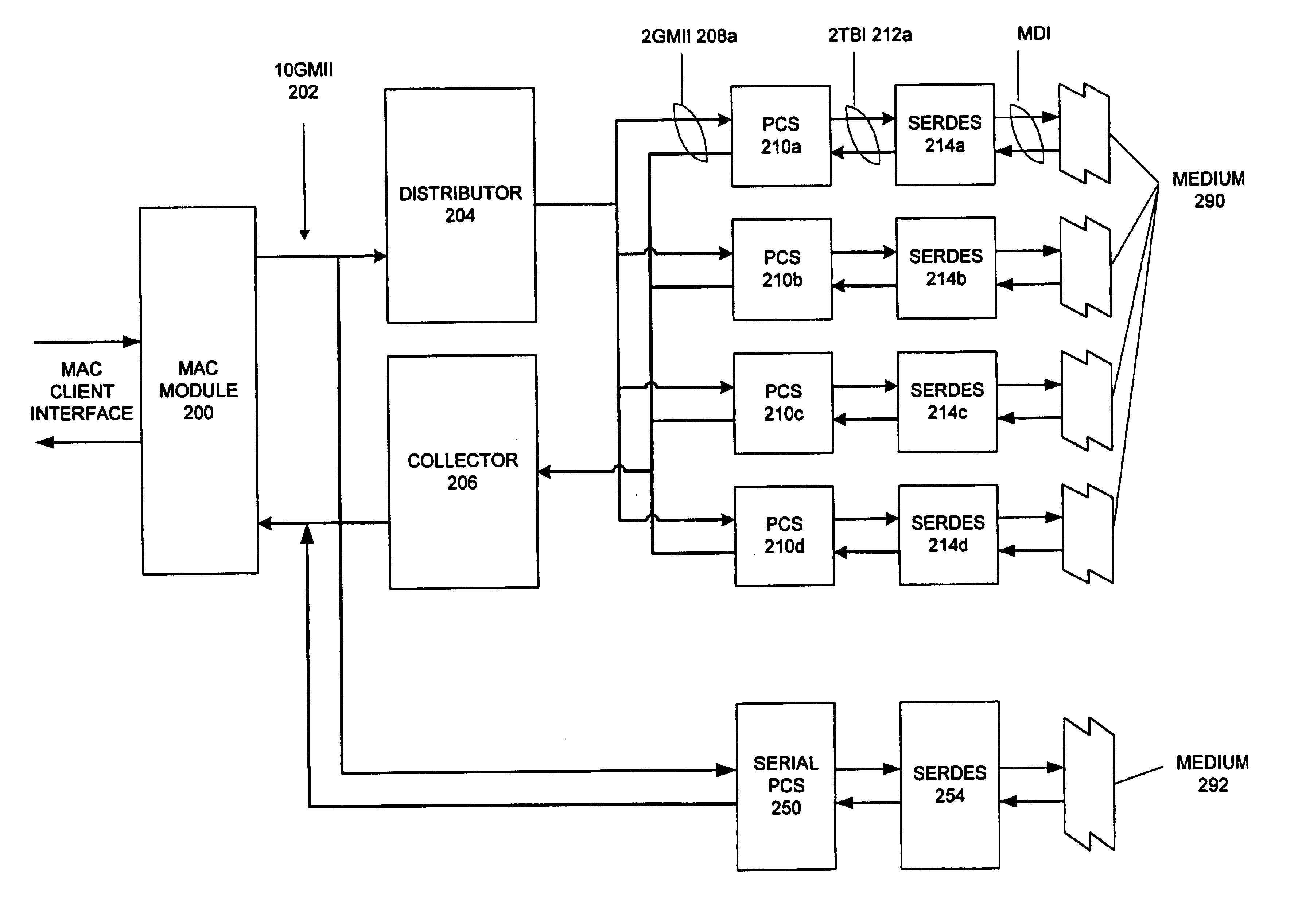
InactiveUS6873630B1Communication speed be lowerTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsMultiplexingPropagation delay
An Ethernet architecture is provided for connecting a computer system or other network entity to a dedicated Ethernet network medium. The network interface enables the transmission and receipt of data by striping individual Ethernet frames across a plurality of logical channels and may thus operate at substantially the sum of the individual channel rates. Each channel may be conveyed by a separate conductor (e.g., in a bundle) or the channels may be carried simultaneously on a shared medium (e.g., an electrical or optical conductor that employs a form of multiplexing). On a sending station, a distributor within the sender's network interface receives Ethernet frames (e.g., from a MAC) and distributes frame bytes in a round-robin fashion on the plurality of channels. Each “mini-frame” is separately framed and encoded for transmission across its channel. On a receiving station, the receiver's network interface includes a collector for collecting the multiple mini-frames (e.g., after decoding) and reconstructing the frame's byte stream (e.g., for transfer to the receiver's MAC). The first and last bytes of each frame and mini-frame are marked for ease of recognition. Multiple unique idle symbols may be employed for transmission during inter-packet gaps to facilitate the collector's synchronization of the multiple channels and / or enhance error detection. A maximum channel skew is specified, and each received channel may be buffered with an elasticity that is proportional to the maximum skew so that significant propagation delay may be encountered between channels without disrupting communications.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com