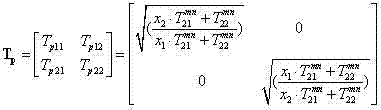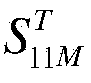Patents
Literature
415 results about "Scattering parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
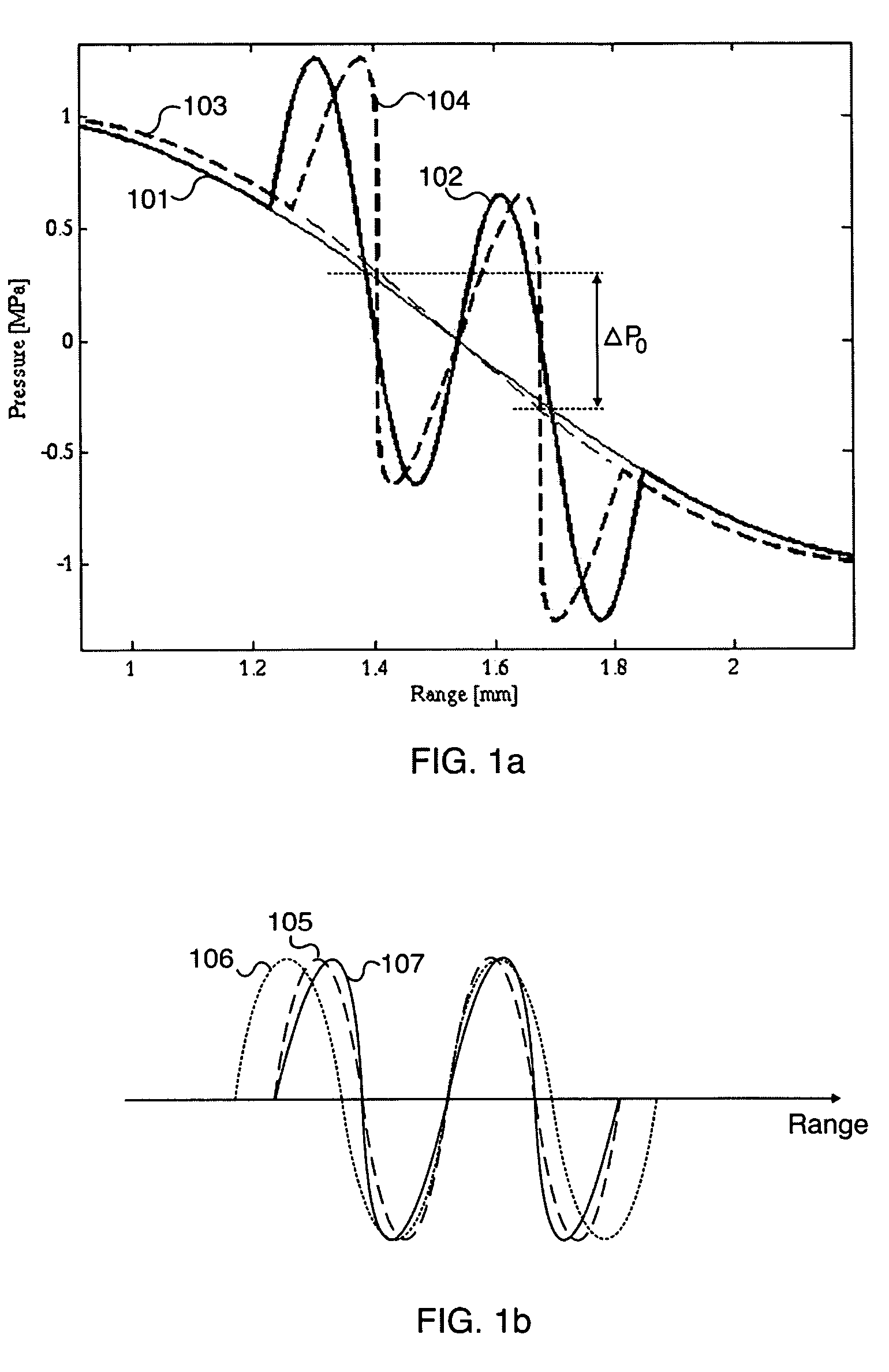
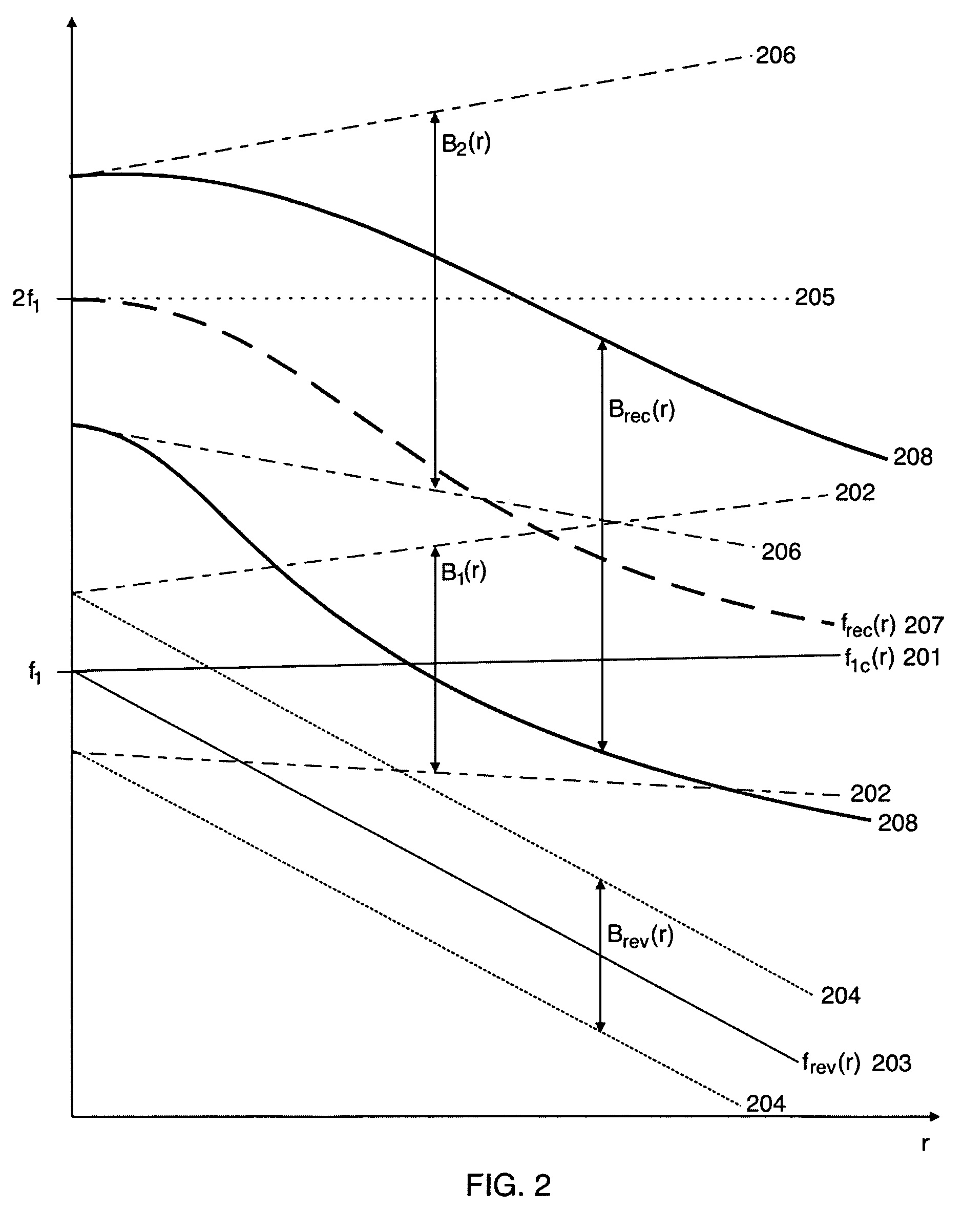
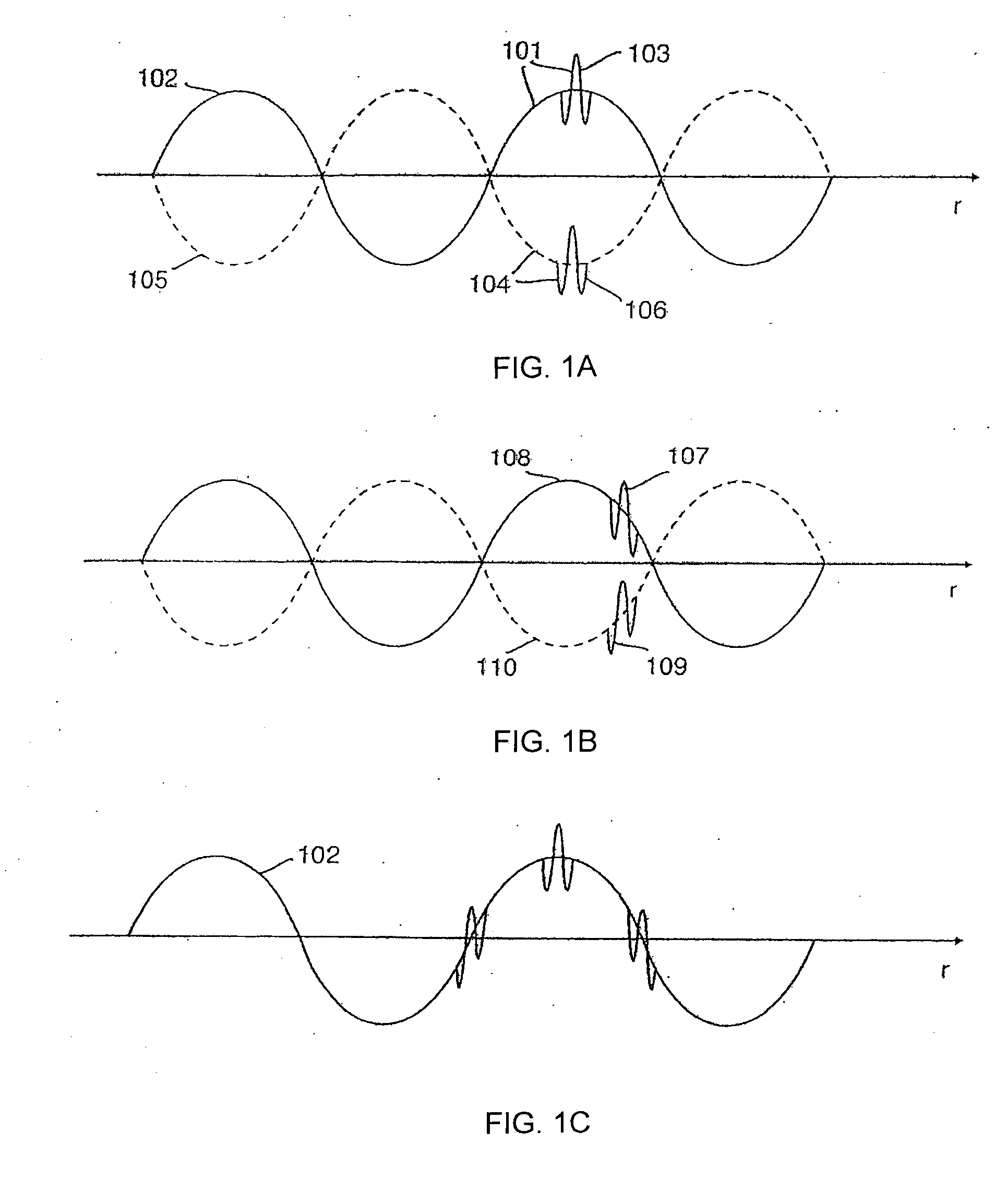
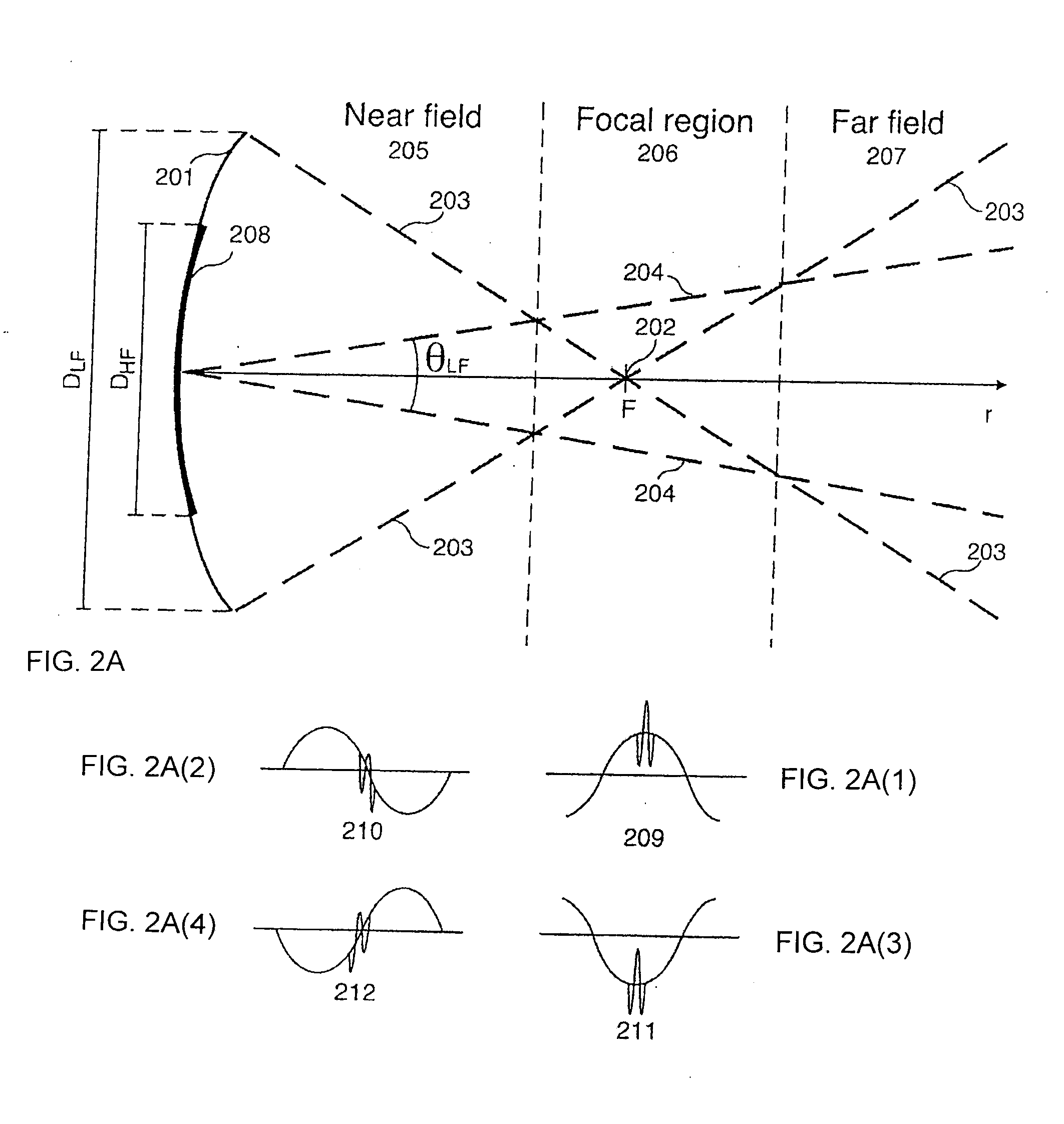
Scattering parameters or S-parameters (the elements of a scattering matrix or S-matrix) describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals.
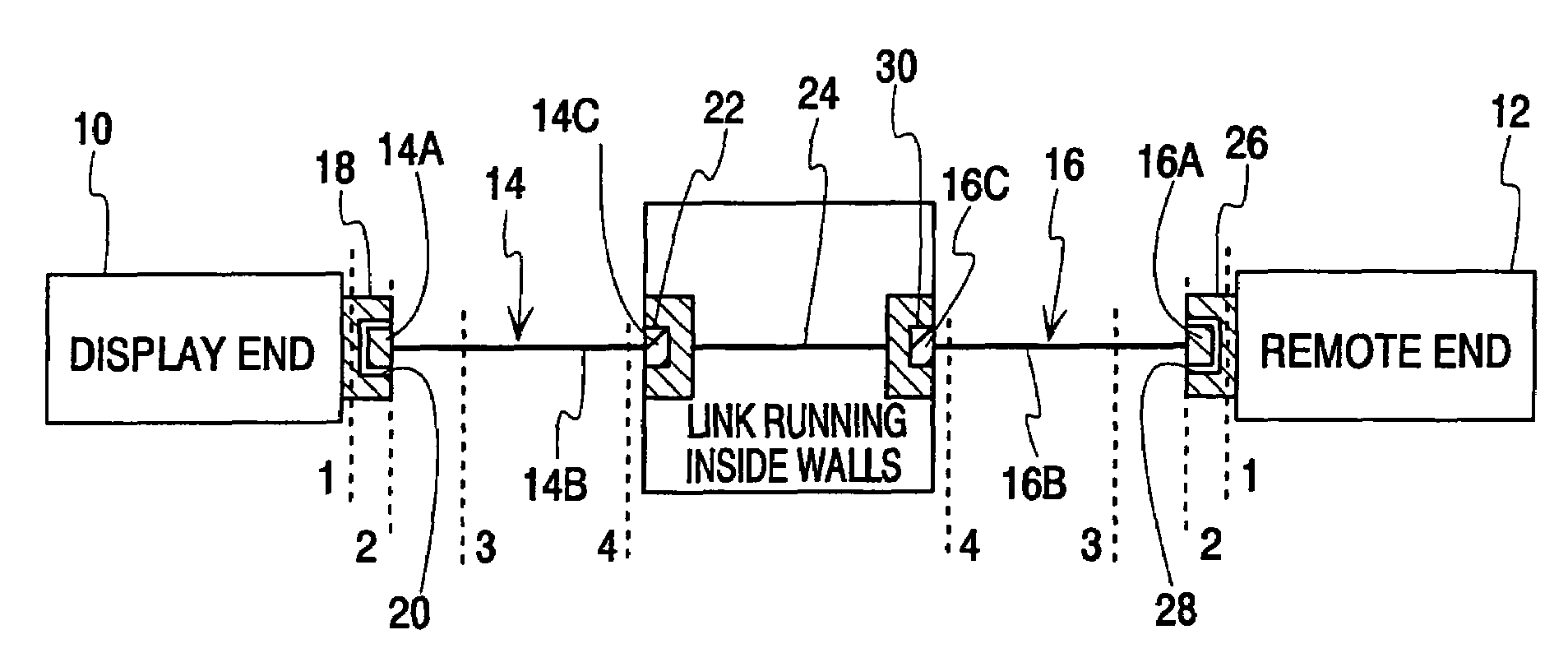
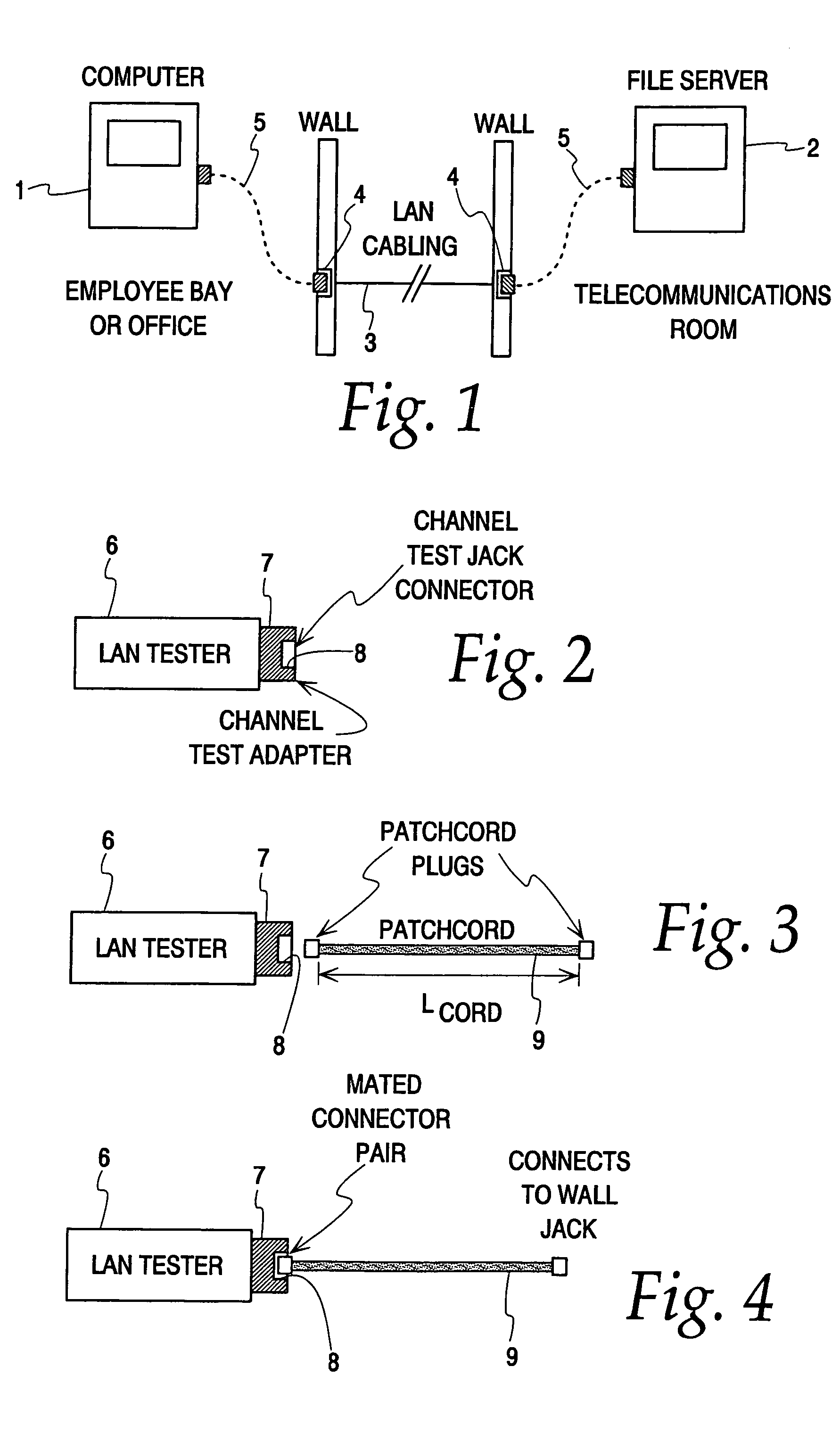
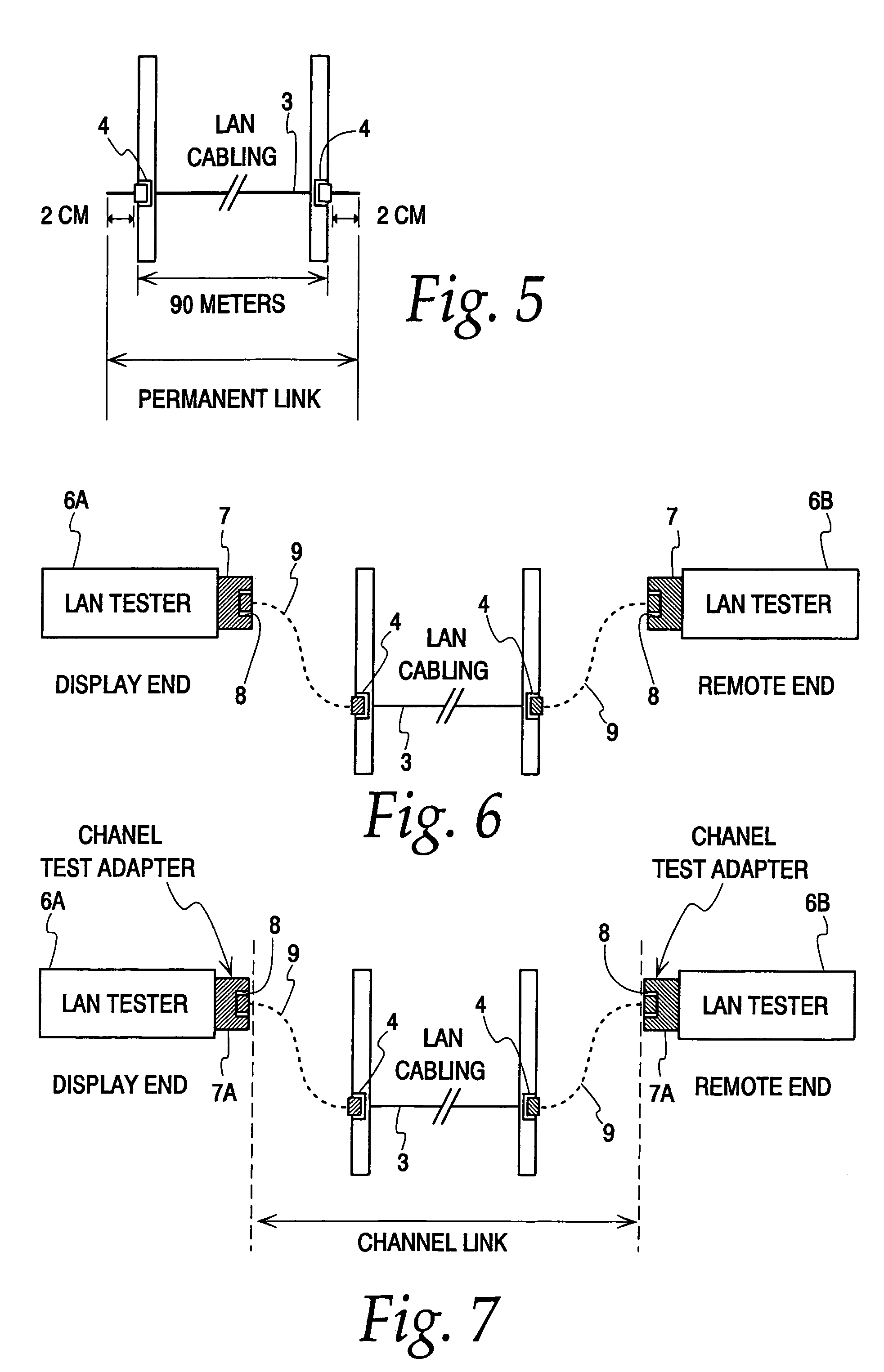
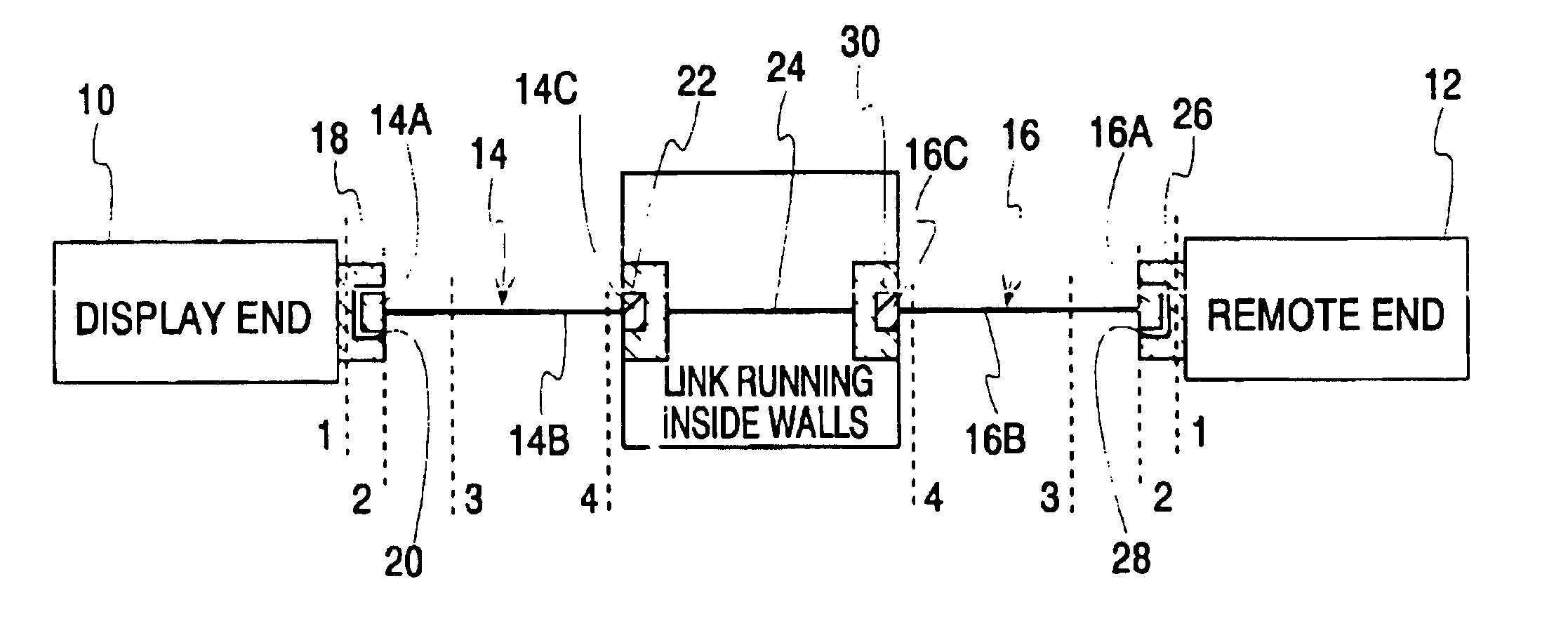
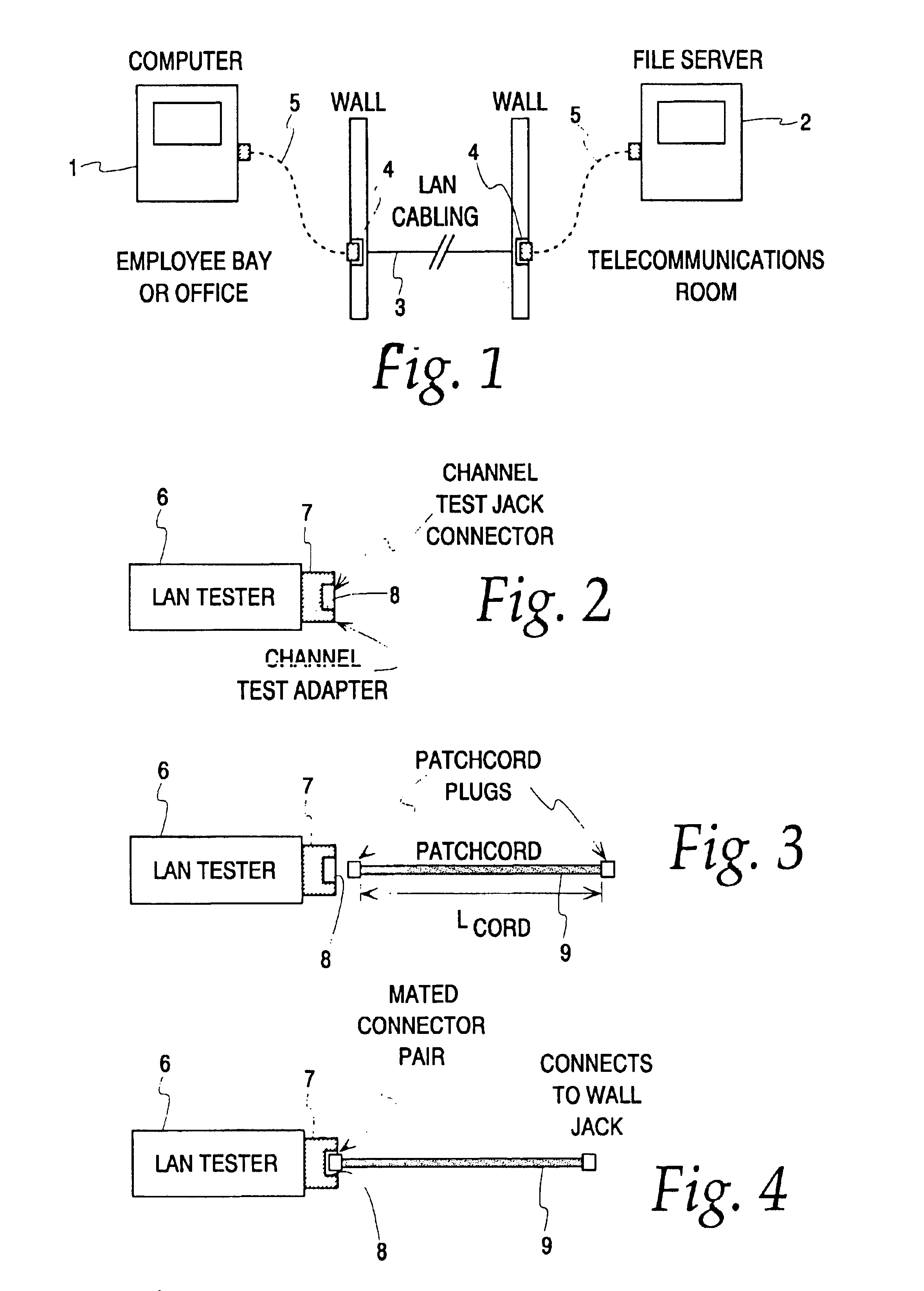
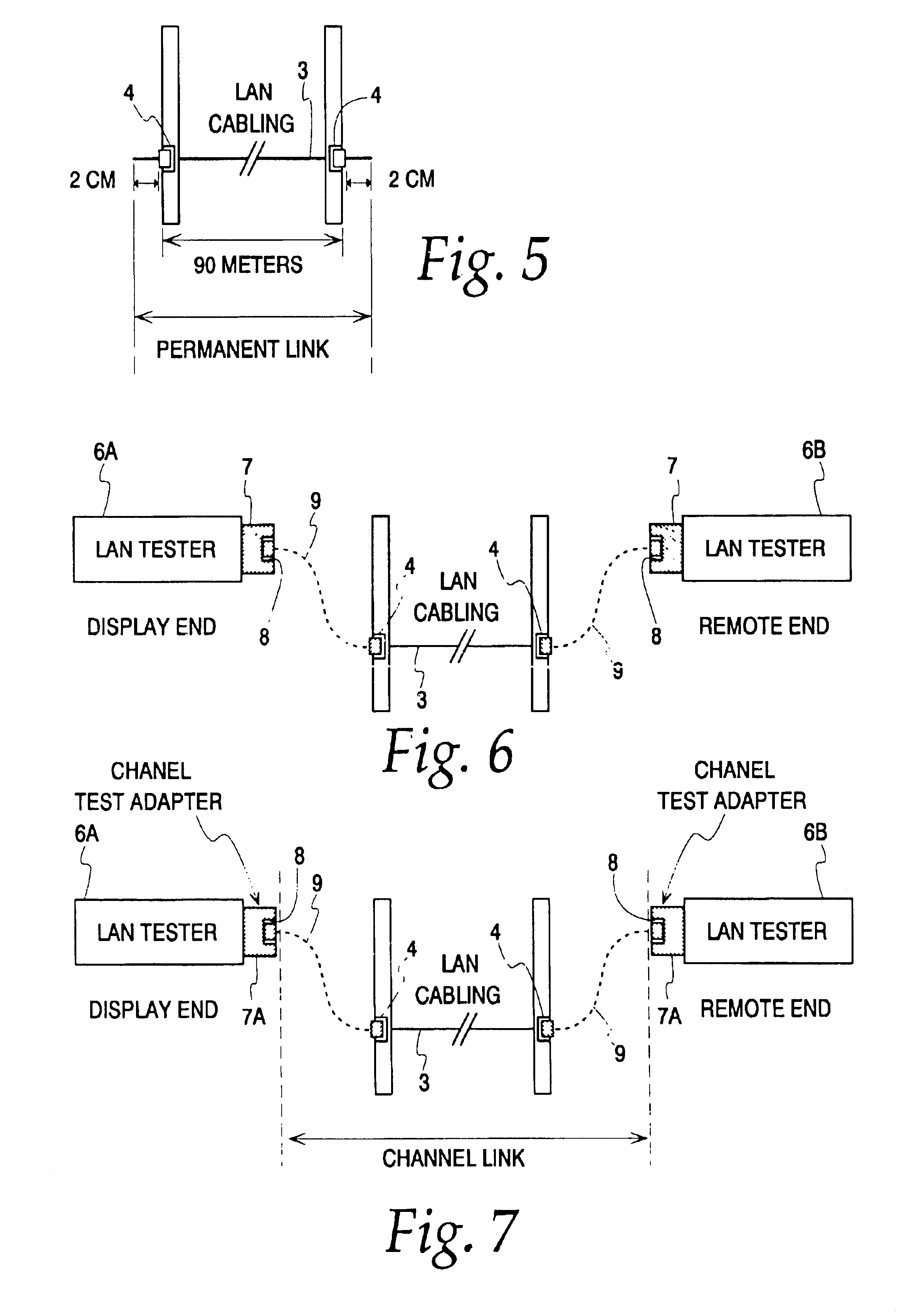
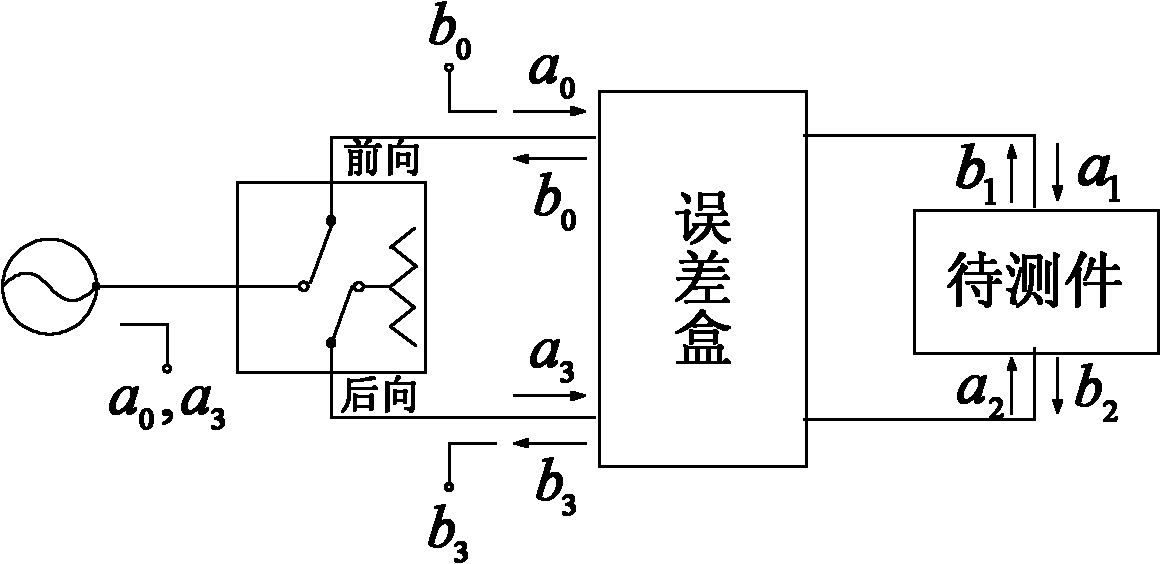
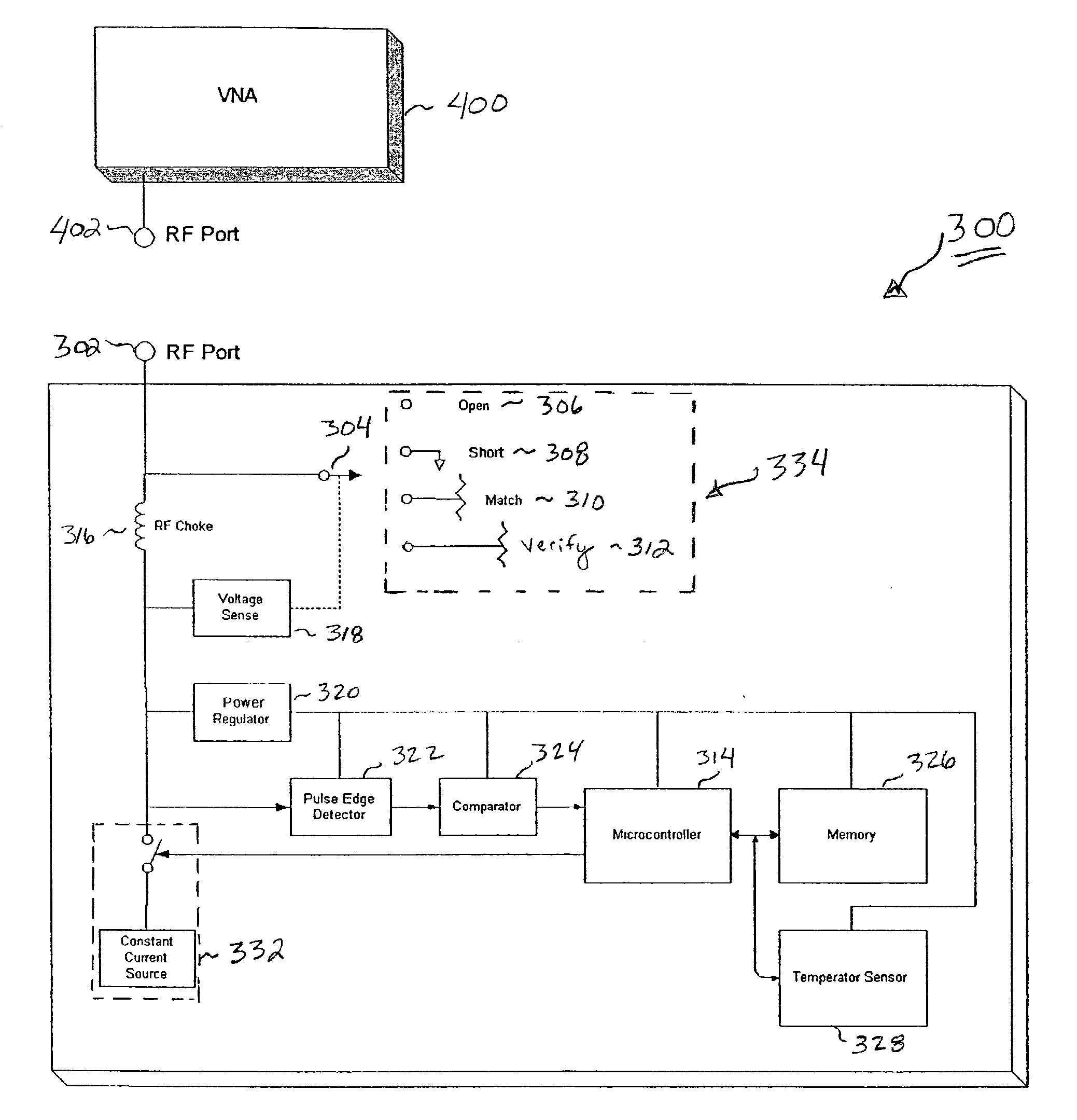
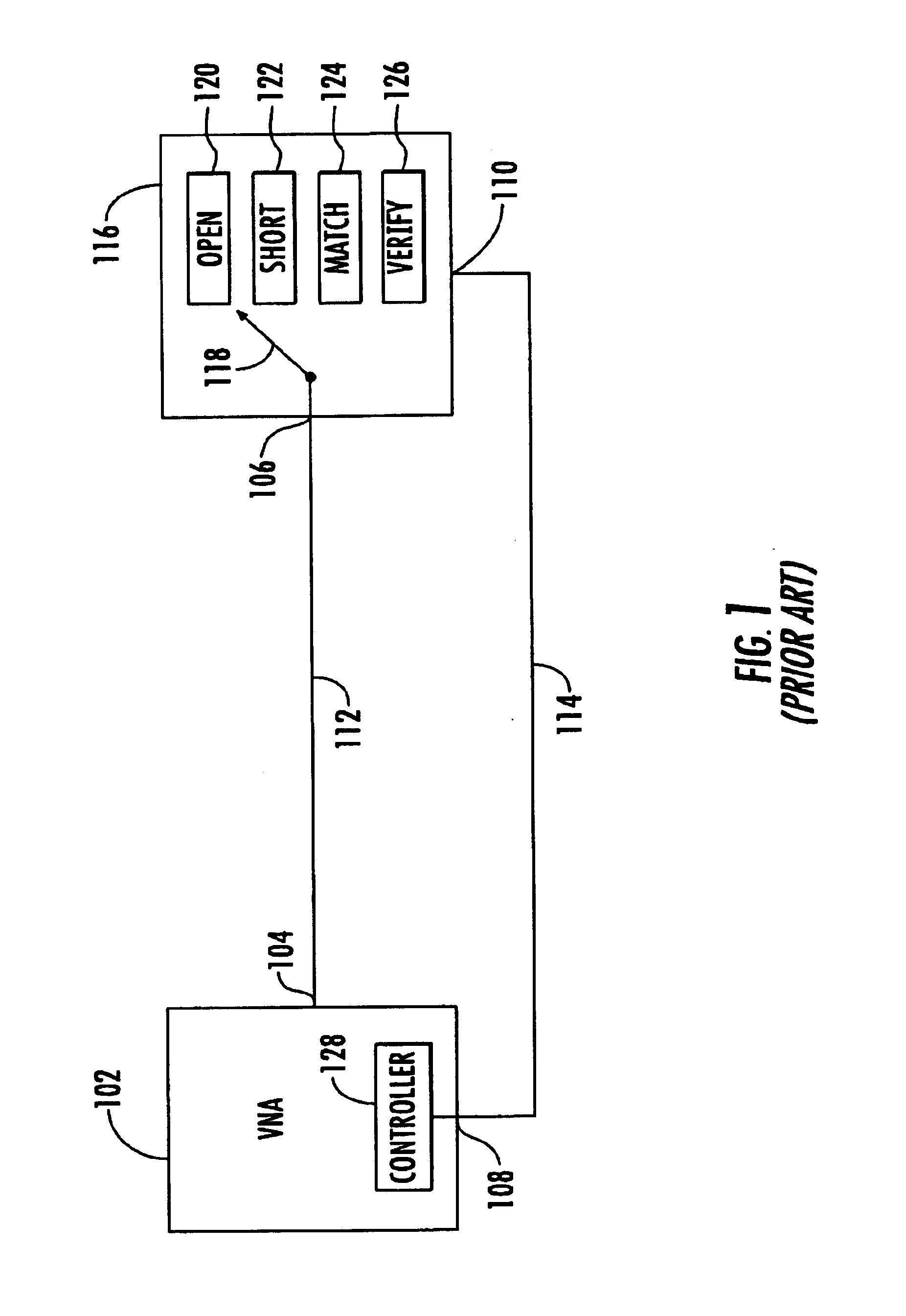
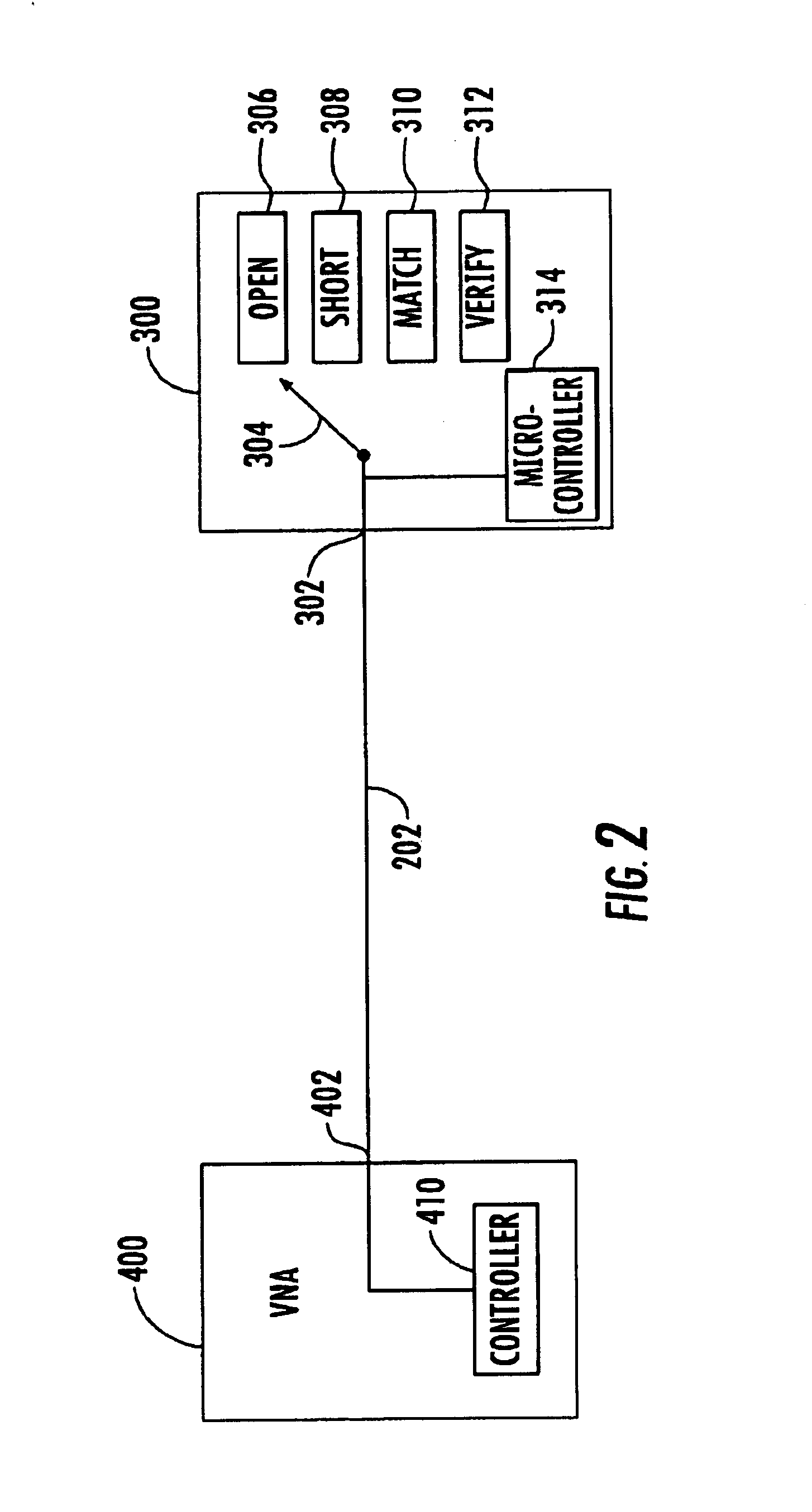
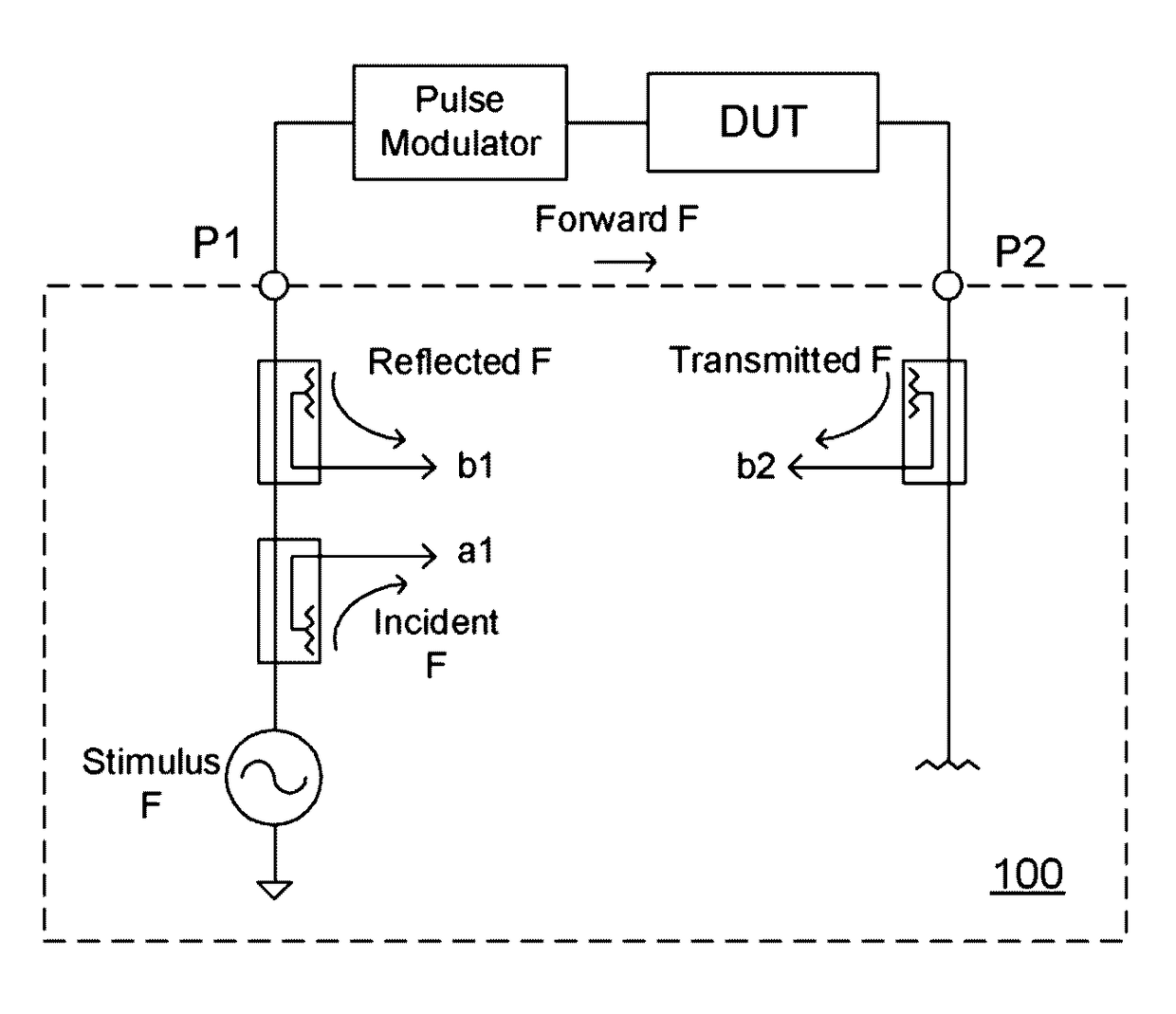
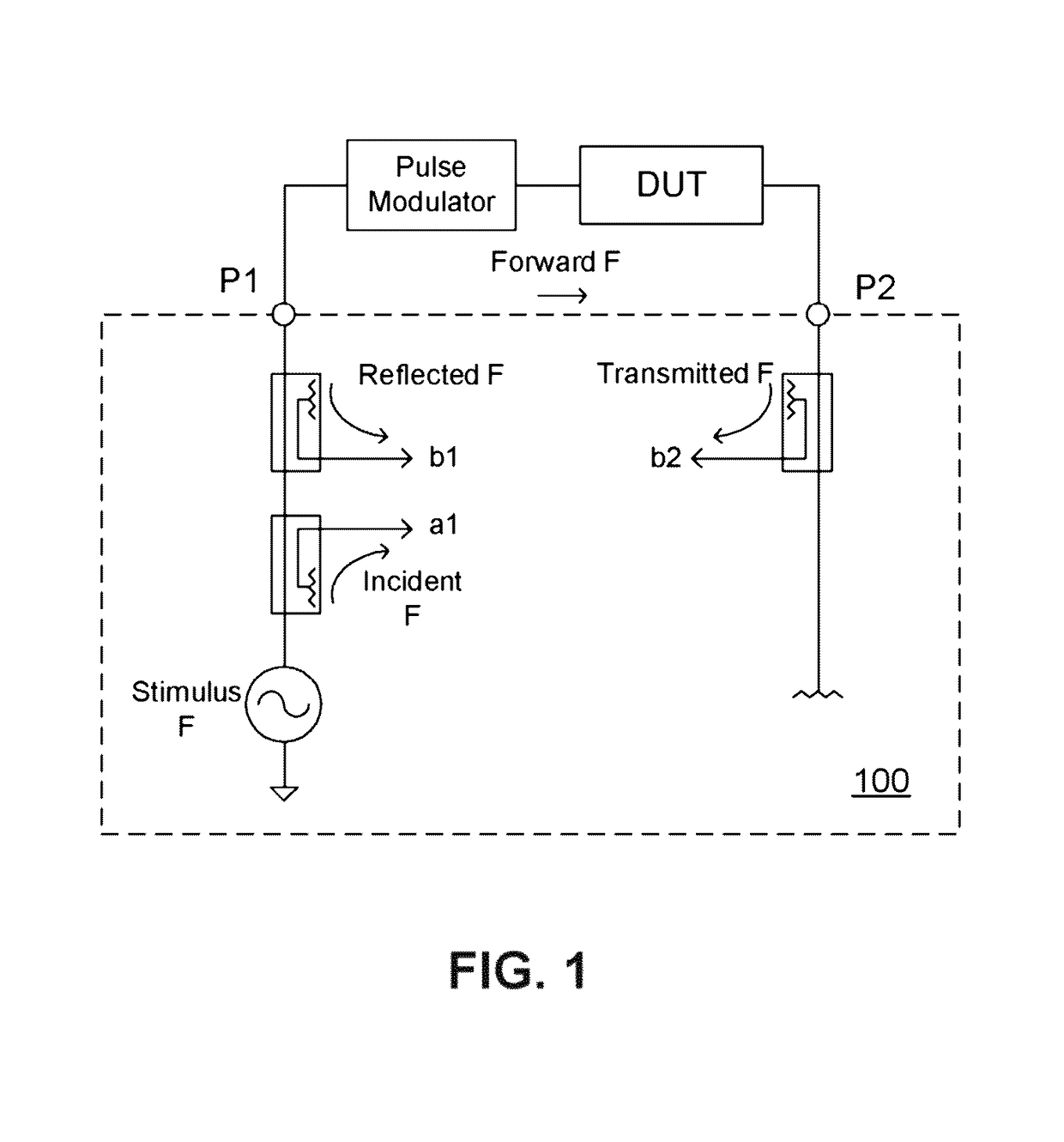
Hand-held tester and method for local area network cabling
InactiveUS7479776B2Simple processLow costError preventionTransmission systemsTester deviceDisplay device
A LAN tester has display and remote units each having a connector jack attached to an adapter board for connection to the plug of a patch cord. Both the display and remote units have circuits which are capable of measuring the phase between a drive signal voltage and the corresponding coupled or reflected signal due to the drive signal. Scattering parameters for the mated connector pairs and the patch cord itself are measured during a field calibration. A computer in one or both of the tester units stores the measured scattering parameters and uses the scattering parameters to move the reference plane to any desired location along the patch cord. Channel link or permanent link tests can be conducted using the same equipment.
Owner:IDEAL IND NETWORKS LTD
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS20060052699A1Easy to measureFrame rateOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryLinearityAcoustical imaging
Acoustic imaging provides images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object. The received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes is processed with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. The scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) domain provides a signal with suppression of reverberation noise with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
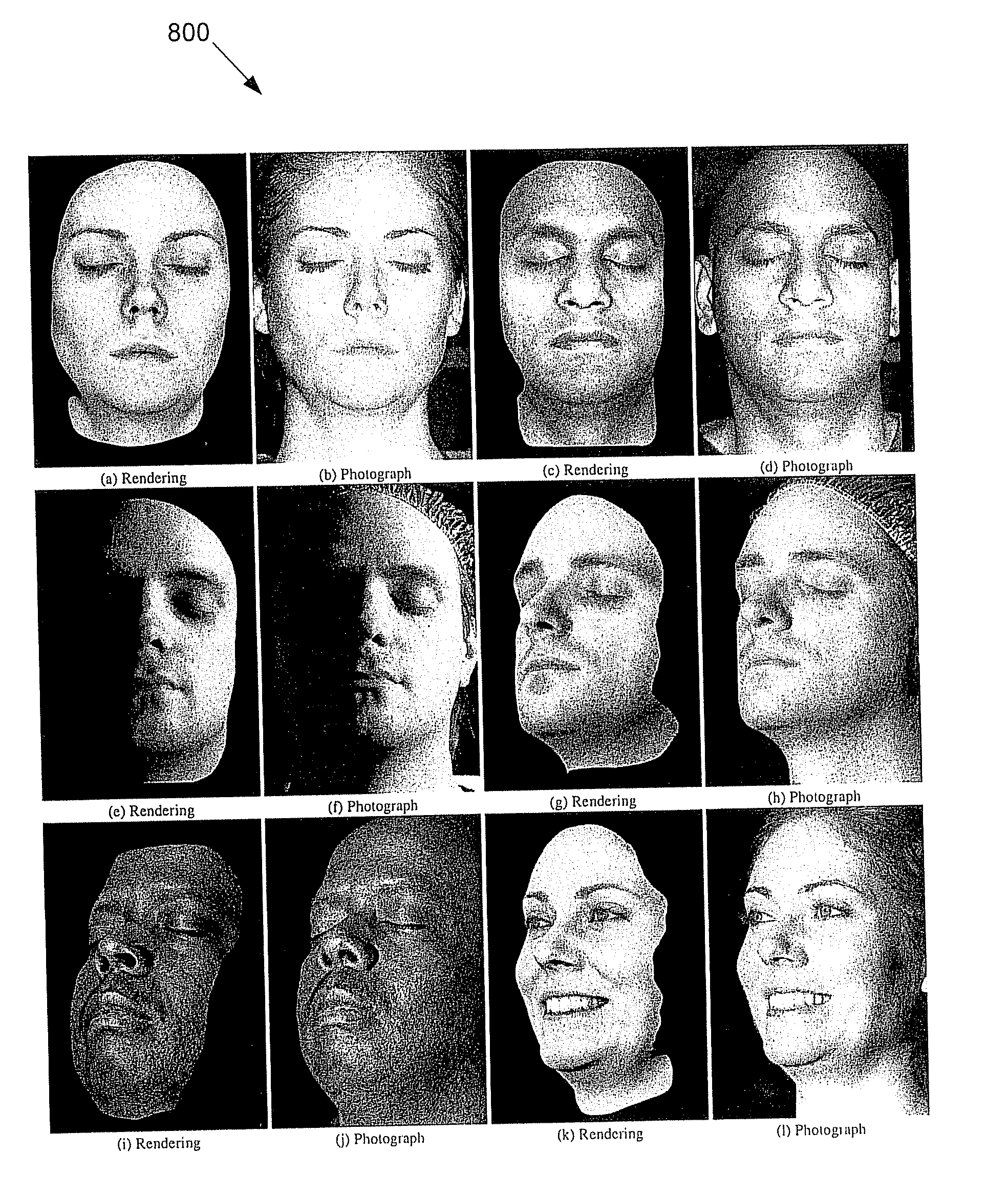
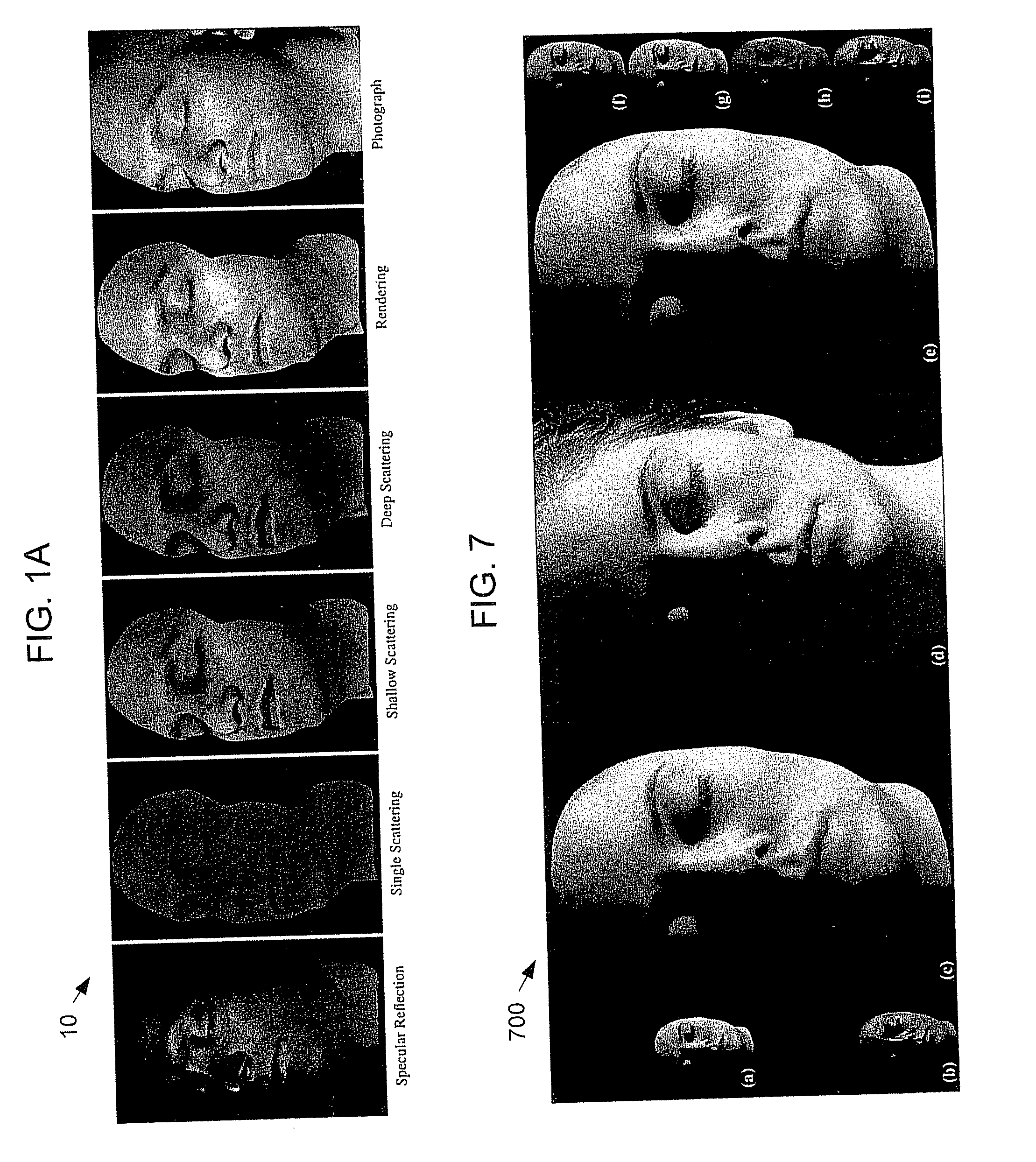
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
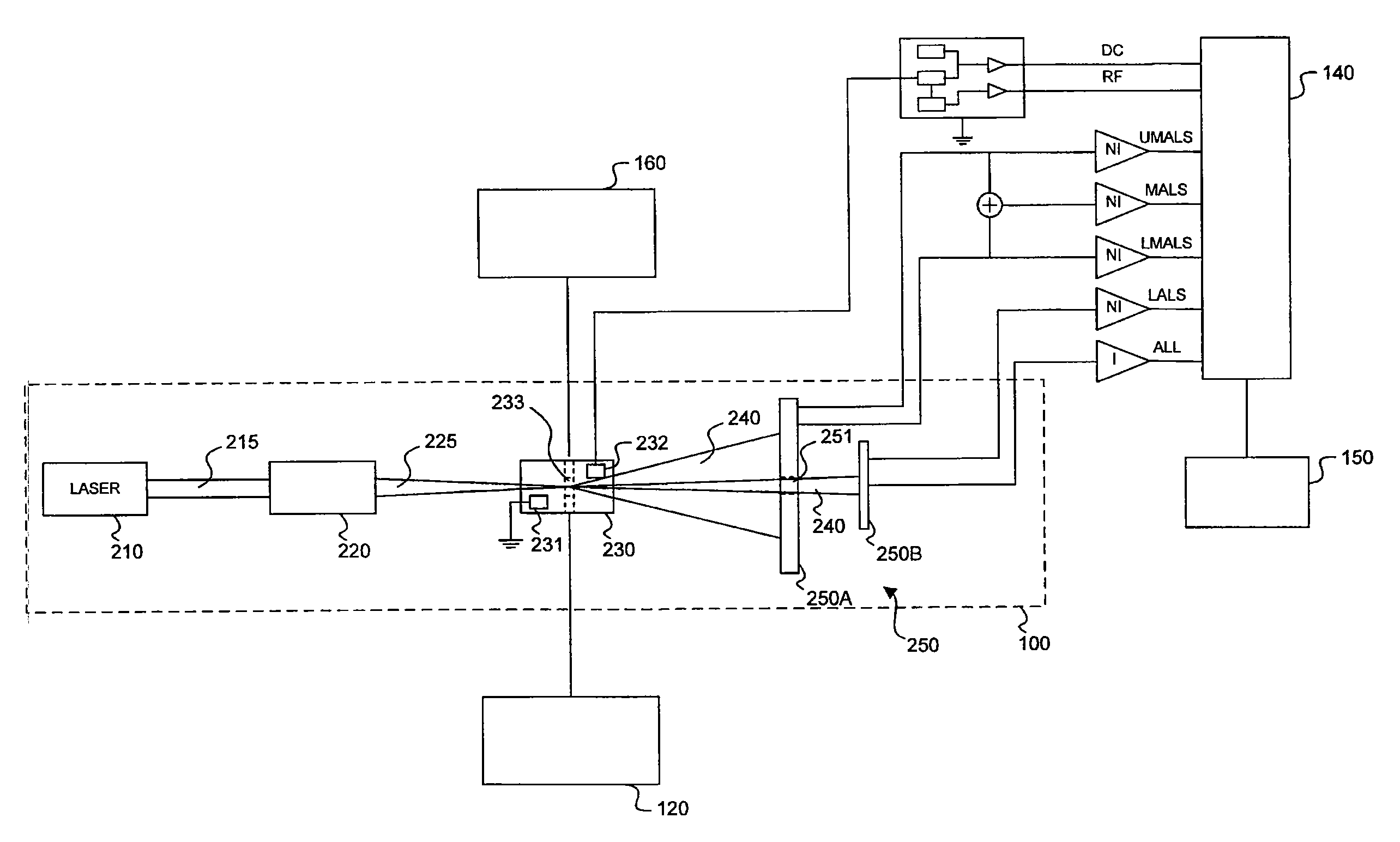
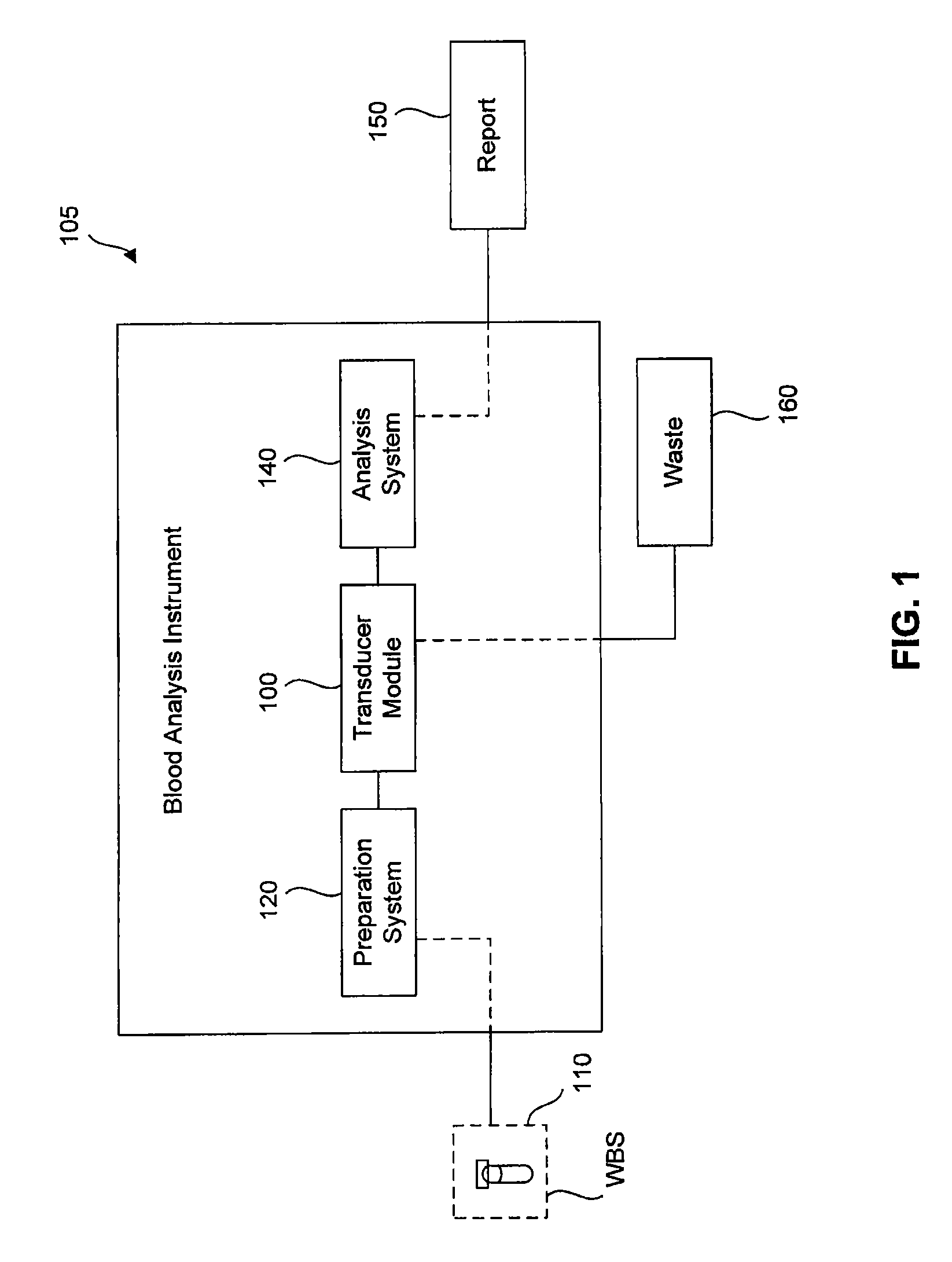
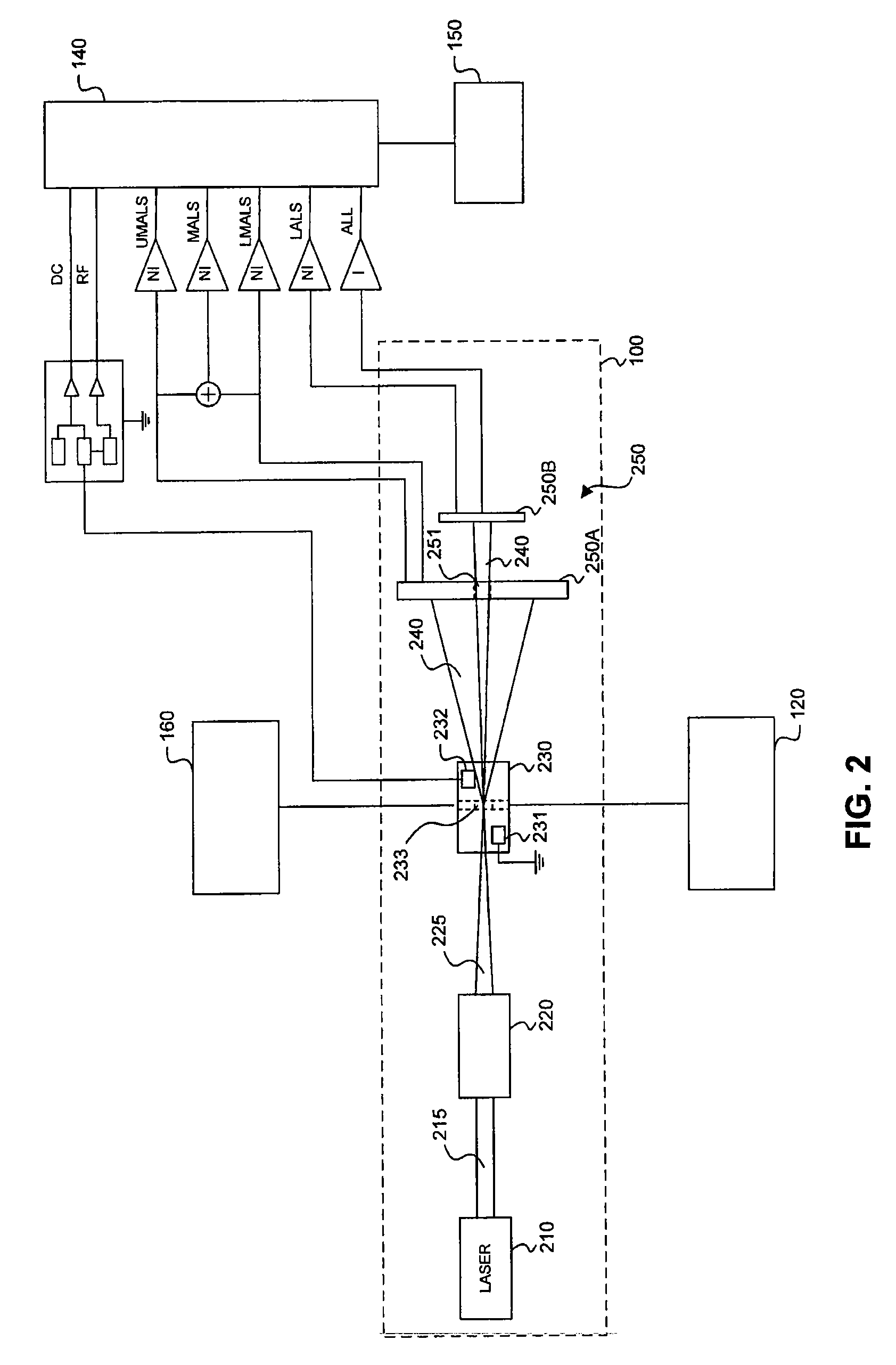
Transducer module
ActiveUS8094299B2Material analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisPresent methodTransducer
Transducer modules for use in a blood analysis instrument and methods for analyzing a blood sample. The transducer modules presented generally include a light source, a focus-alignment system, a flow cell, and a light scatter detection system. Electrodes within the flow cell allow for the measurement of the DC impedance and RF conductivity of cells passing through a cell-interrogation zone in the flow cell. Light scatter from the cells passing through the cell-interrogation zone is measured by the light scatter detection system. The light scatter detection system measures the light scatter parameters of upper median light scatter, lower median angle light scatter, low angle light scatter, and axial light loss. The presented methods for analyzing a blood sample generally include aspirating a whole blood sample into a blood analysis instrument, preparing the blood sample for analysis, passing the blood sample through a flow cell in a transducer system, and measuring axial light loss, multiple angles of light scatter, DC impedance and / or RF conductivity.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS8038616B2Easy to measureFrame rateMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionWavefront aberrationApproximation property
Methods of acoustic imaging provide images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object, and estimation methods of corrections for wave front aberrations produced by spatial variations in the acoustic propagation velocity. The methods are based on processing of the received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for the image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse is used to manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays and optionally also amplitudes, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
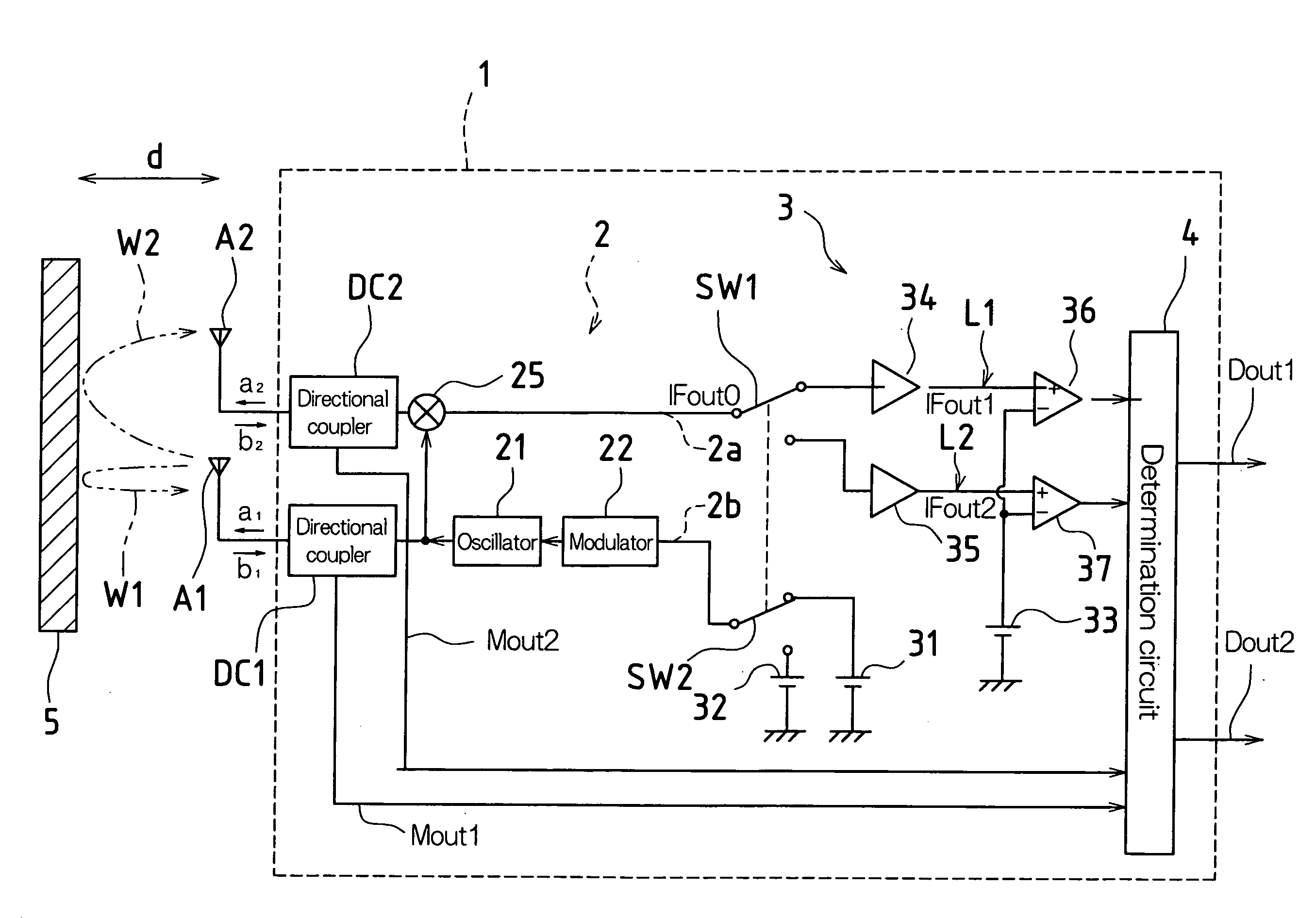
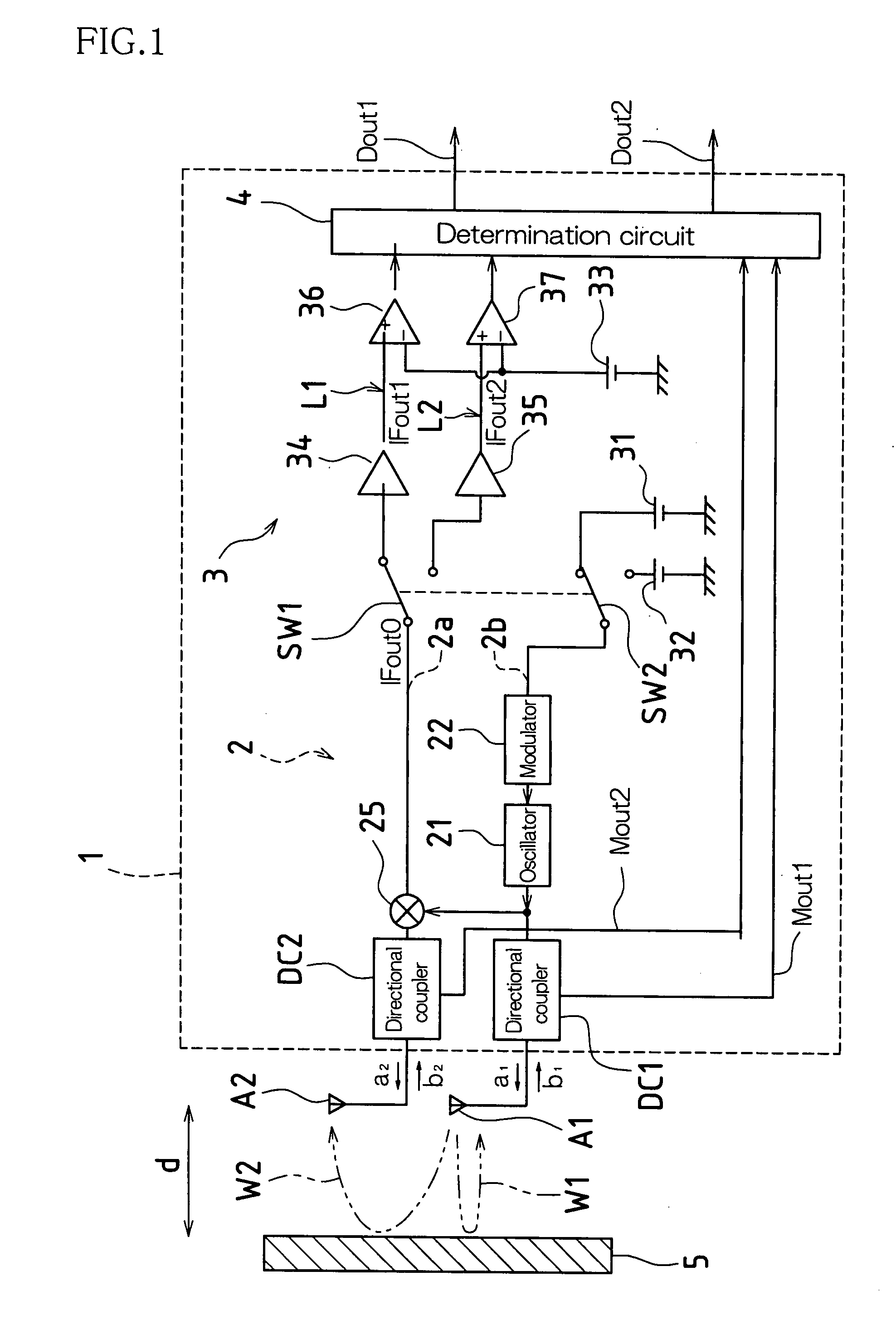
Microwave Sensor
InactiveUS20080165002A1Increase in sizeIncrease costDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionReflectance propertiesMicrowave sensor
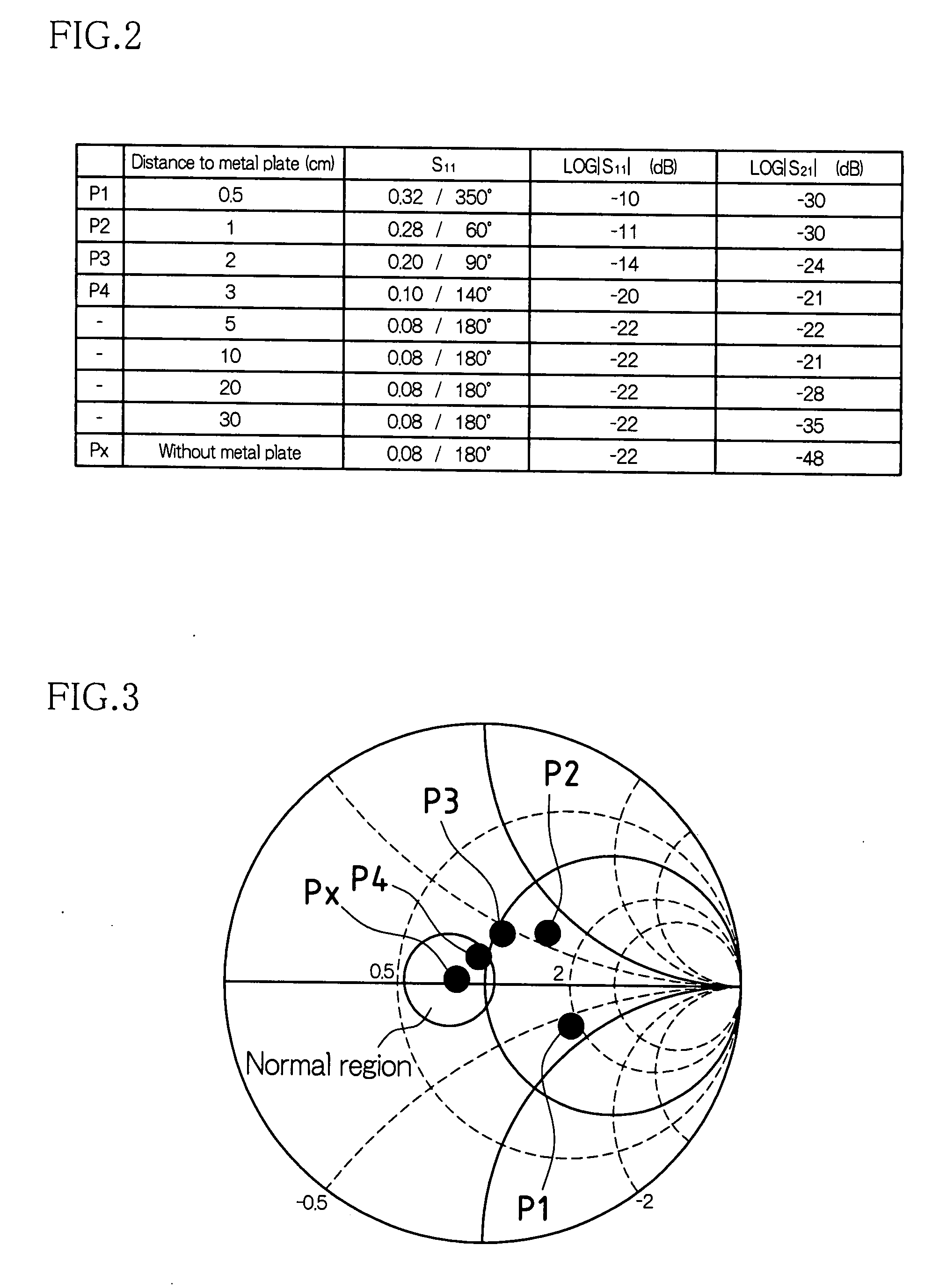
According to one embodiment, a microwave sensor includes: a first directional coupler (DC1) connected on a path of a transmission antenna unit (A1); a second directional coupler (DC2) connected on a path of a reception antenna unit (A2), and a determination unit (4) that obtains, based on monitor outputs from these, a scattering parameter S11 corresponding to a reflectance property at the transmission antenna unit (A1) and a scattering parameter S21 corresponding to a transmission property from the transmission antenna unit (A1) to the reception antenna unit (A2), and outputs an alarm signal (Dout2) when at least one of the scattering parameter S11 and the scattering parameter S21 continuously exhibits a value outside its respective pre-set range over a predetermined period of time.
Owner:OPTEX CO LTD
Using s-parameter measurements to manage SAR and transmit gain
ActiveUS20100244840A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifierEngineering
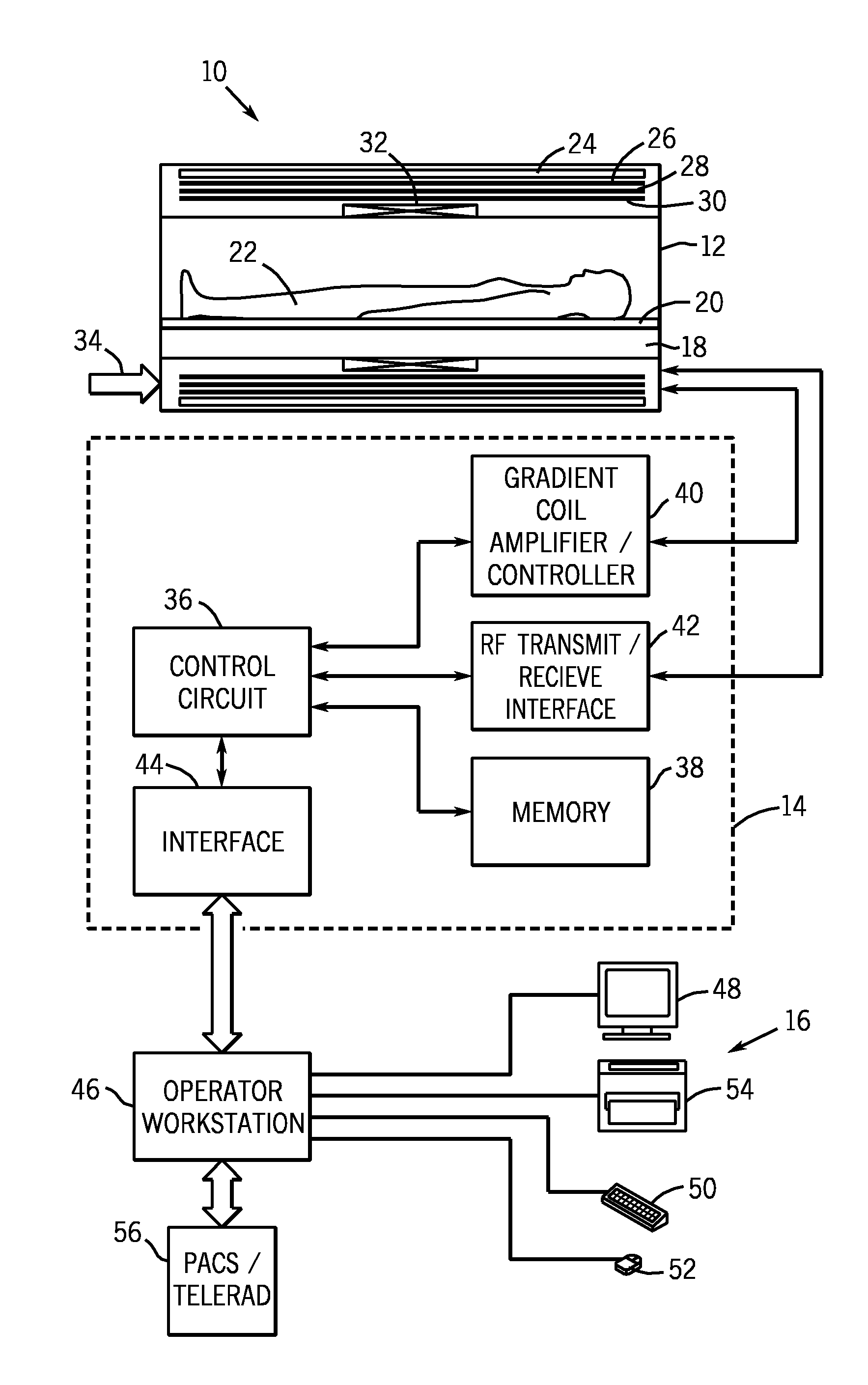
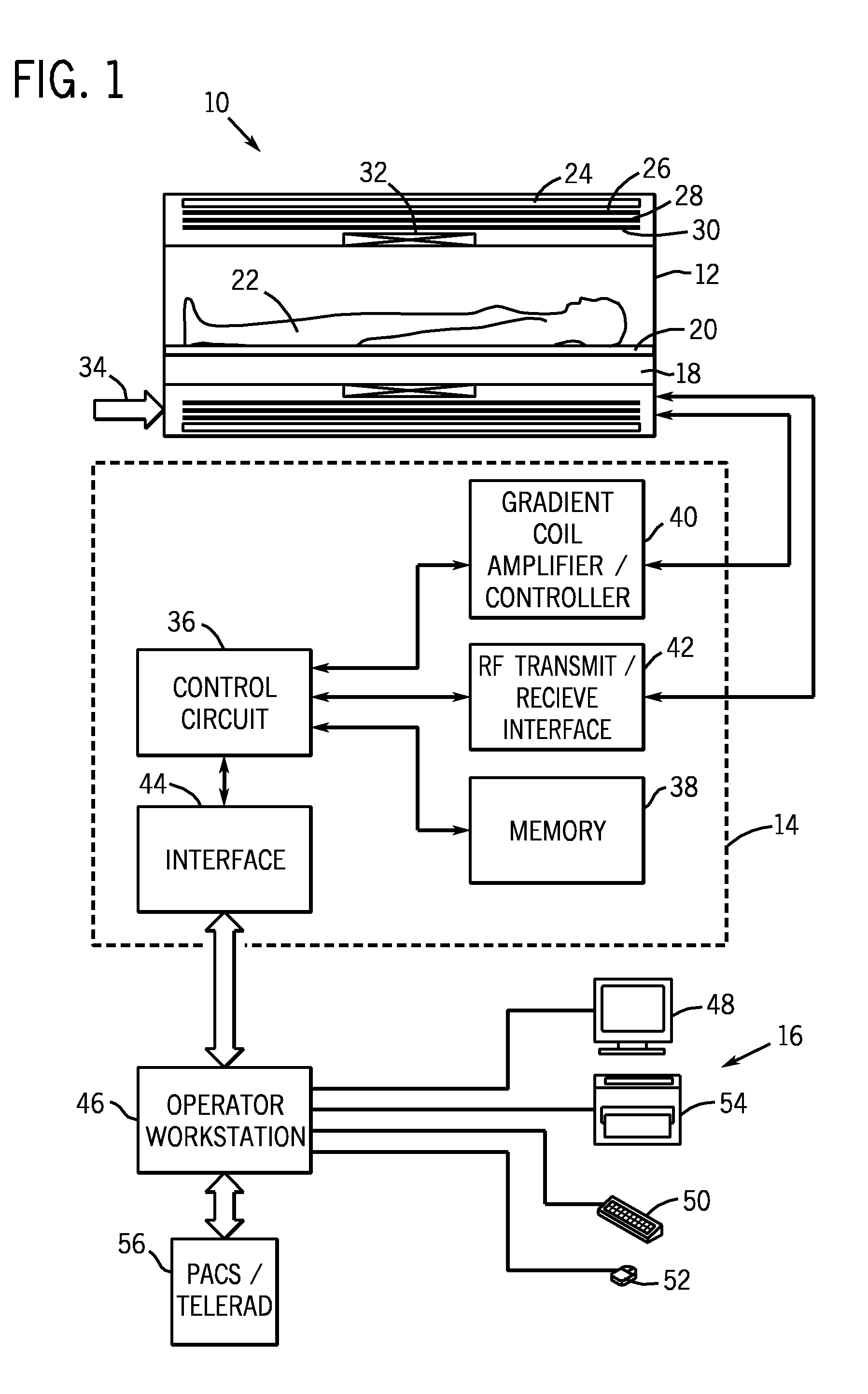
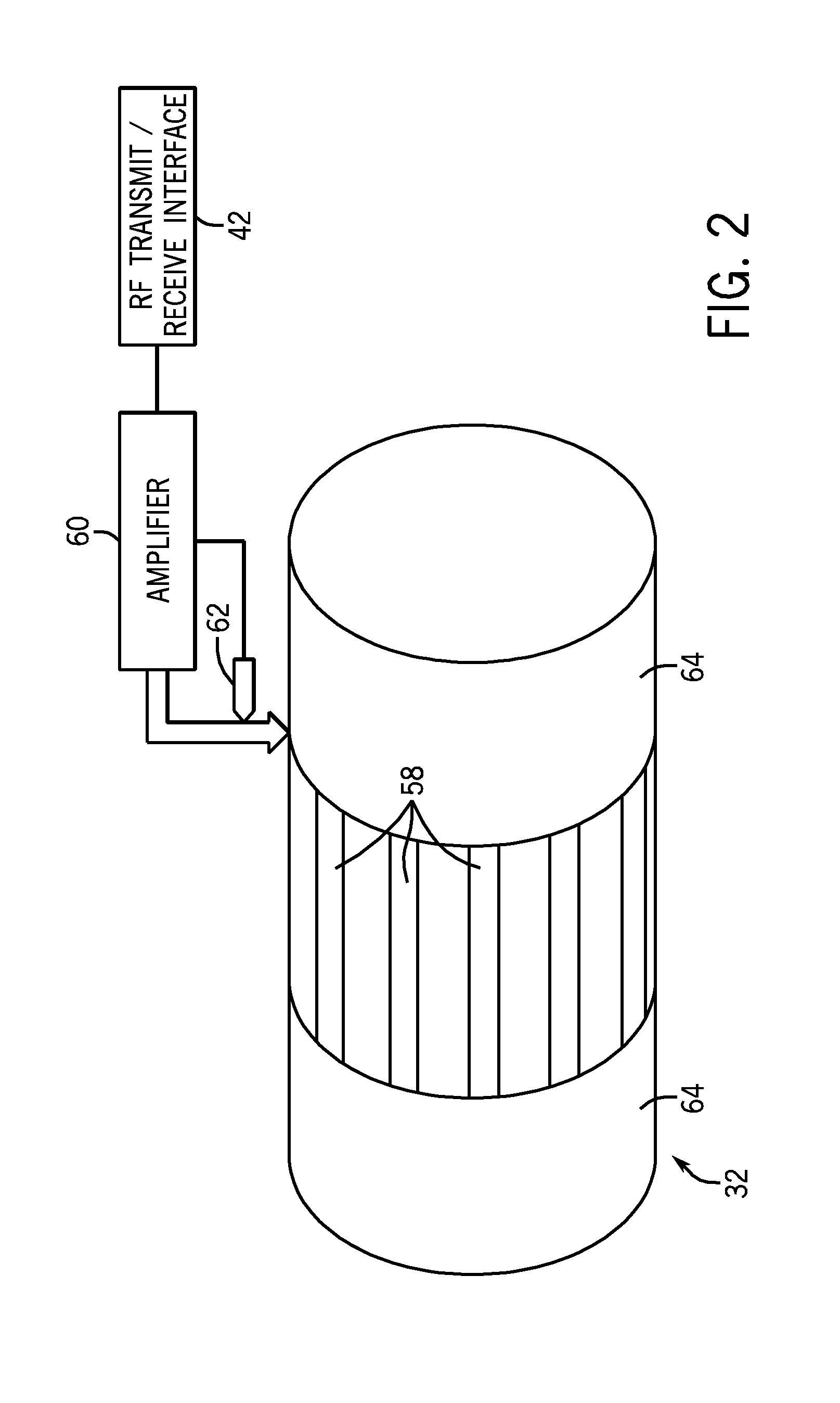
Systems and methods for controlling a magnetic resonance imaging system are provided. In one embodiment, a magnetic resonance imaging system includes a radio frequency coil with a plurality of conductive coil elements, control circuitry that determines, based at least in part on a measurement of scattering parameters, a plurality of forward voltages that will cause power deposition into an object within a predetermined specific absorption rate, and an amplifier configured to apply the determined plurality of forward voltages respectively to the plurality of coil elements. The control circuitry may determine the plurality of forward voltages based at least in part on an unloaded measurement of scattering parameters and a loaded measurement of scattering parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for calibrating a frequency domain reflectometer
InactiveUS20050234662A1Accurate estimateAccurate modelingElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringReflectometry
A calibration system is provided for calibrating frequency domain reflectometers in the field by using both the scattering parameters of the multi-port junction determined at the factory and changing the offset and gain terms used in generating a complex reflection coefficient by using internal calibrated loads so that heavy, cumbersome external calibrated transmission lines are not required. In one embodiment the internal calibrated loads include RLC circuits and in another embodiment the internal calibrated loads include attenuators. Further, retesting or recalibration does not necessitate reconnecting the cable under test, which may remain connected to the reflectometer's test port throughout the procedure.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Microwave device impedance measurement calibration method
InactiveCN103675457AOvercome Difficult Machining ProblemsReduce the numberResistance/reactance/impedenceUltra-widebandMicrowave
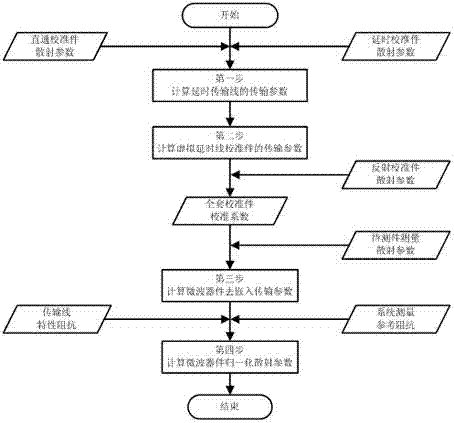
The invention introduces a microwave device impedance measurement calibration method. The method comprises the following steps: (1), calculating time-delay transmission line transmission parameters through real-time measured data of straight-through calibration member scattering parameters and time-delay calibration member scattering parameters; (2), embedding a newly added virtual transmission line in an original time-delay calibration member, and calculating the transmission parameters of a virtual time-delay calibration member; (3), according to a conventional TRL calibration method, extracting calibration coefficients of a measuring clamp, and performing matrix inversion and multiplication operation to obtain a microwave device de-embedding transmission parameters; and (4), performing impedance normalization transformation on the microwave device de-embedding transmission parameters to obtain normalized microwave device normalization scattering parameters relative to system measurement reference impedance. The method makes up the measurement errors caused by inconsistence of transmission line characteristic impedance and the system measurement reference impedance, and realizes microwave device impedance measurement with an ultra wide band and high precision. At the same time, the improved microwave device impedance measurement calibration method can substantially reduce design processing requirements of a calibration device, thereby having high versatility.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and apparatus for calibrating a frequency domain reflectometer
InactiveUS7254511B2Accurately measure the magnitude of each faultCompensation effectElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringMulti port
A calibration system is provided for calibrating frequency domain reflectometers in the field by using both the scattering parameters of the multi-port junction determined at the factory and changing the offset and gain terms used in generating a complex reflection coefficient by using internal calibrated loads so that heavy, cumbersome external calibrated transmission lines are not required. In one embodiment the internal calibrated loads include RLC circuits and in another embodiment the internal calibrated loads include attenuators. Further, retesting or recalibration does not necessitate reconnecting the cable under test, which may remain connected to the reflectometer's test port throughout the procedure.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Hand-held tester and method for local area network cabling
InactiveUS6847213B2Low costReduce LAN measurement overhead support costsCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceTester deviceDisplay device
A LAN tester has display and remote units each having a connector jack attached to an adapter board for connection to the plug of a patch cord. Both the display and remote units have circuits which are capable of measuring the phase between a drive signal voltage and the corresponding coupled or reflected signal due to the drive signal. Scattering parameters for the mated connector pairs and the patch cord itself are measured during a field calibration. A computer in one or both of the tester units stores the measured scattering parameters and uses the scattering parameters to move the reference plane to any desired location along the patch cord. Channel link or permanent link tests can be conducted using the same equipment.
Owner:IDEAL IND NETWORKS LTD
Method for calibrating two-port vector network analyzer based on ten-error model
InactiveCN102279376AReduce testing costsSimplify the calibration stepsElectrical measurementsErrors and residualsComputer science
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a two-port vector network analyzer based on a ten-error model, belonging to a method for calibrating a vector network analyzer. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting an error model according to the hardware topological structure of the vector network analyzer; preparing a 50-ohm short-open-thru (SOT) transmission line calibration piece of which the characteristic is known and the length is unknown for serving as a device under test (UDT), and evaluating the transmission characteristic of a UL (Unknown Line) according to the scattering parameter measured value of an SOT-UL standard piece and the scattering parameter measured value of an SOT standard piece; evaluating the normalized wave ratio of a DUT incident port during the measurement of an SO (Short-Open) standard piece according to the scattering parameter measured value and real value of the SOT-UL standard piece; and when an unknown DUT is connected, evaluating the real value of a DUT scattering parameter according to the measured value and real value of the standard piece scattering parameter and the DUT scattering parameter measured value. By adopting the method, the testing cost is lowered, and the calibration process is simplified greatly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
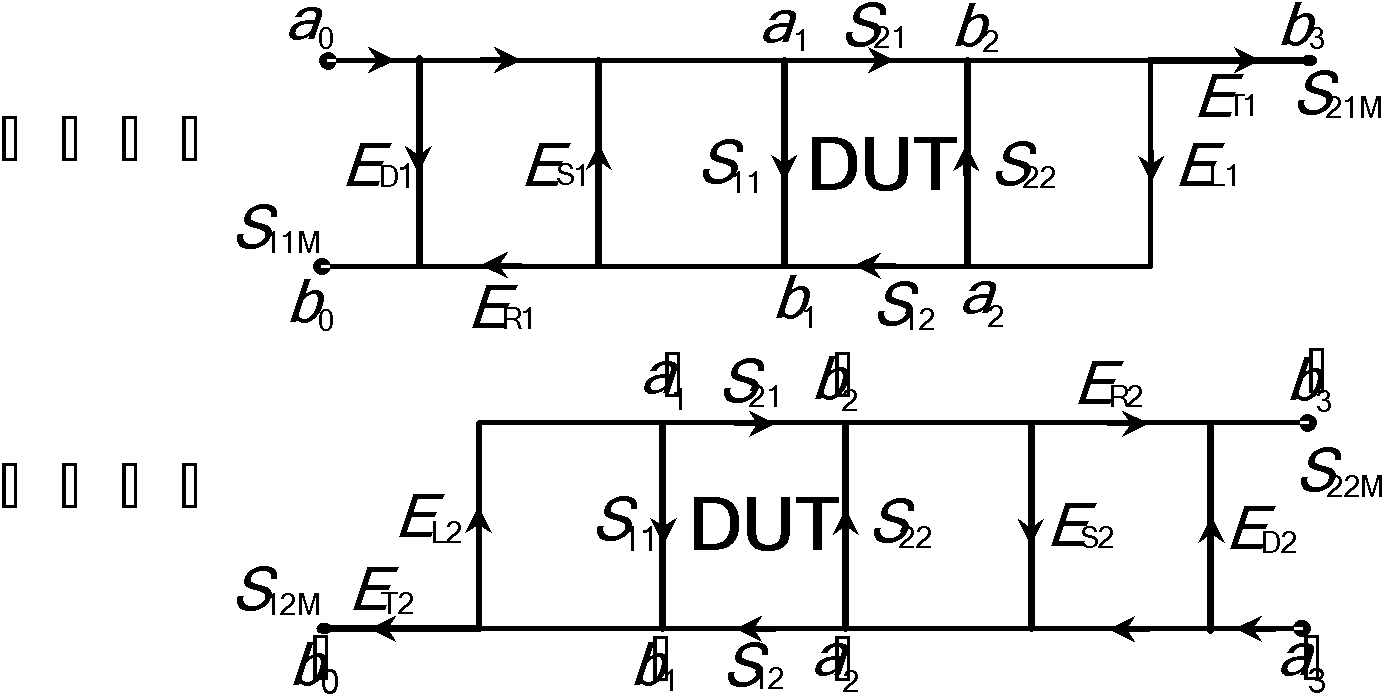
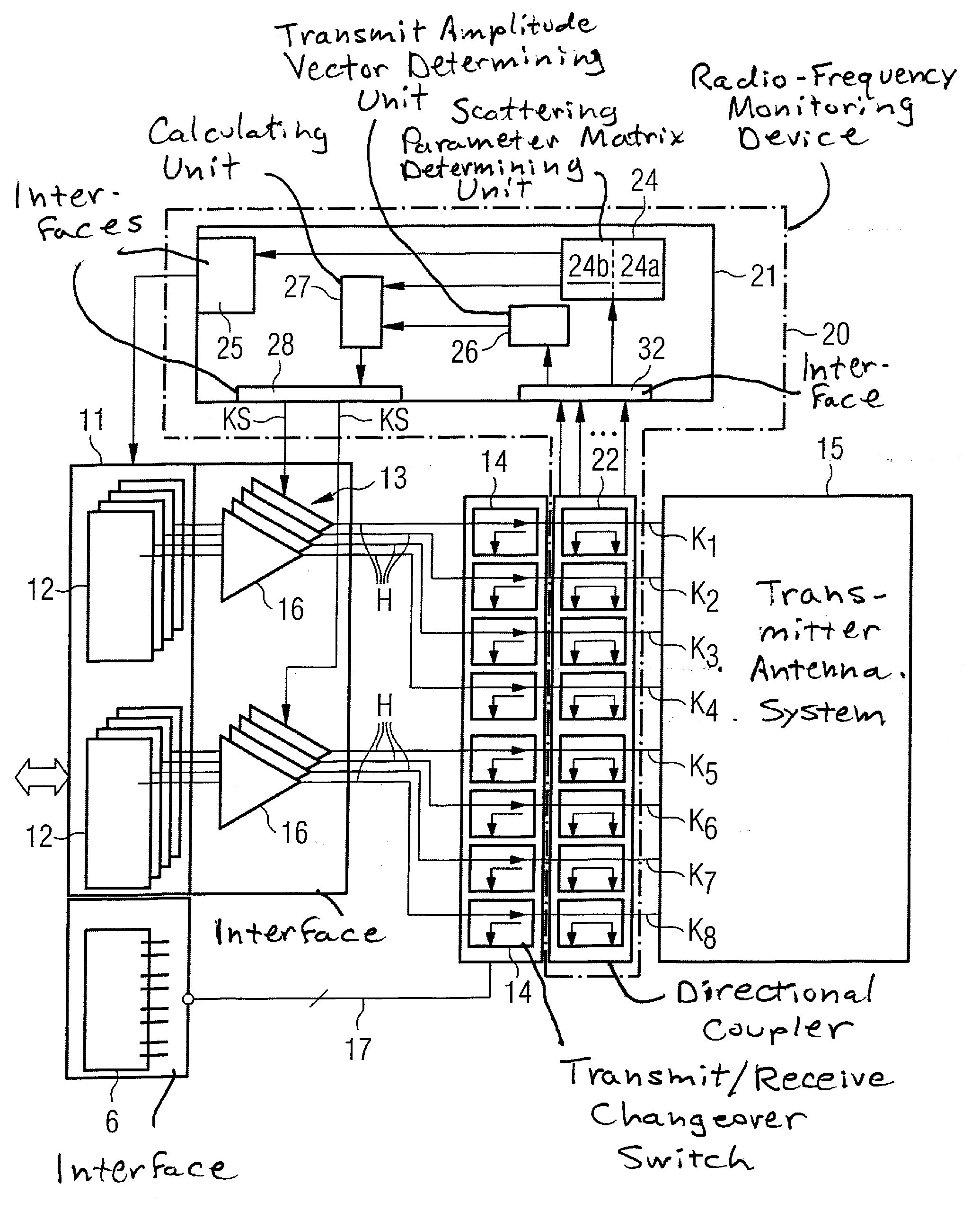
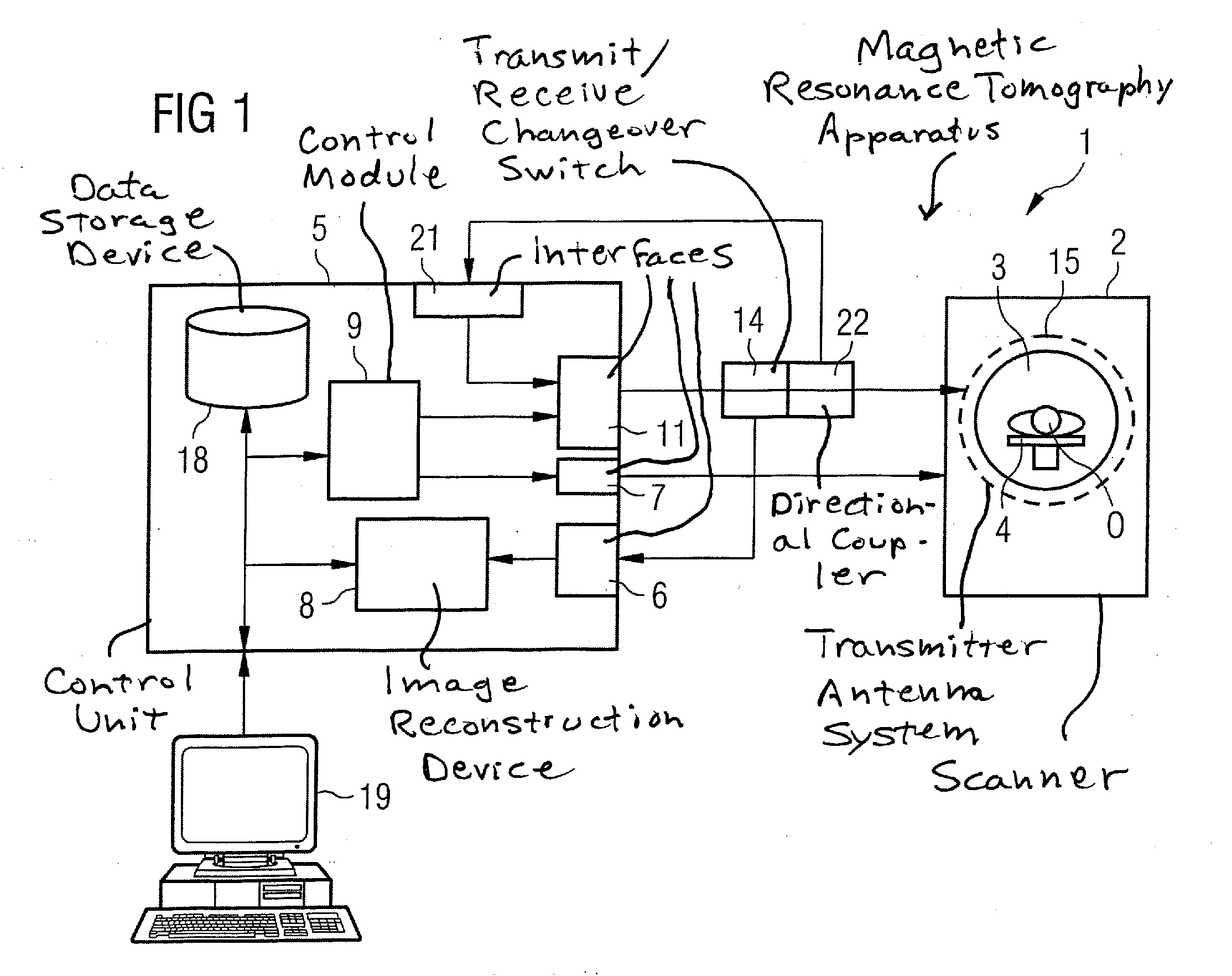
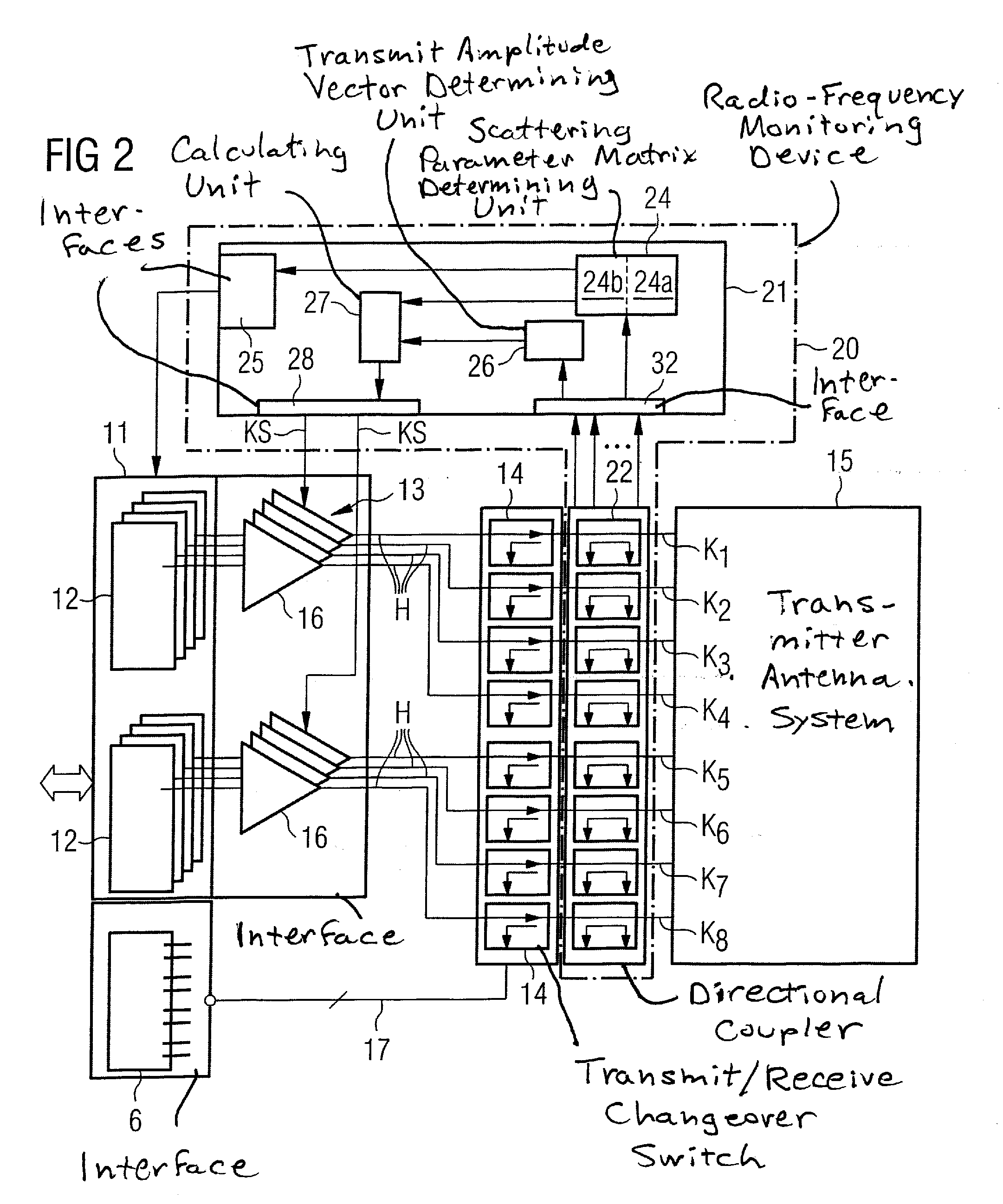
Method and device for monitoring a radio-frequency transmitter device in a magnetic resonance tomography system
ActiveUS20100167668A1Peak loading is avoidedThreshold value is exceededModulation with suppressed carrierDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementVoltage amplitude
In a method and device for monitoring a radio-frequency transmit device of a magnetic resonance tomography system, having a transmitter antenna system that has a number of transmit channels, during a magnetic resonance measurement of an examination subject, a reference scattering parameter matrix of the transmitter antenna system is determined in the unloaded state, and a subject-specific scattering parameter matrix of the transmitter antenna system is determined in a state loaded with the subject of examination. Moreover, transmitter amplitude vectors are determined in time-dependent fashion that represent the radio-frequency voltage amplitudes on the individual transmit channels. On the basis of the subject-specific scattering parameter matrix, the reference scattering parameter matrix, and the transmit amplitude vectors, radio-frequency power values absorbed at particular transmit times in the subject are determined. Based on a large number of the determined radio-frequency power values, a number of monitoring values are formed. The radio-frequency transmit device is limited in its functioning when a monitoring value reaches or exceeds a prespecified boundary monitoring value.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Electrically controlled detecting device for microwave medium coating and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN102590637AComply with monitoring standard requirementsEasy to handleResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityMicrowave
The invention relates to detection of microwave coating dielectric properties, particularly to an electrically controlled detecting device for a microwave medium coating and a detecting method thereof. The detecting device is provided with a rectangular waveguide, parallel coupled microstrip electrodes, a DC stabilized voltage supply, a vector network analyzer, a computer and a short circuit plate, wherein the front end of the rectangular waveguide is connected with a port of the vector network analyzer; the parallel coupled microstrip electrodes are arranged in the middle of the rectangular waveguide; the rear end of the rectangular waveguide is connected with the short circuit plate; an output end of the DC stabilized voltage supply is connected with the parallel coupled microstrip electrodes; and the vector network analyzer is connected with an input port of the computer. The microstrip electrodes are arranged on a to-be-tested sample, placed in the end surface of the waveguide and clamped by the short circuit plate for testing, and the microstrip electrodes are connected; voltage is applied to the microstrip electrodes, so as to observe the variation of the scattering parameters; and a known air layer and a PTFE coating are tested, the dielectric constant is calculated, and electromagnetic parameters of the known coating and the testing result are compared, so as to determine the stability, the testing error and the testing precision of the testing system.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Multiport scattering parameter test method based on four-port vector network analyzer
InactiveCN106771649AReduced Port Count RequirementsReduce testing costsResistance/reactance/impedenceComputer scienceCalibration algorithm
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Method and system for adaptive modeling and simulation of lossy transmission lines
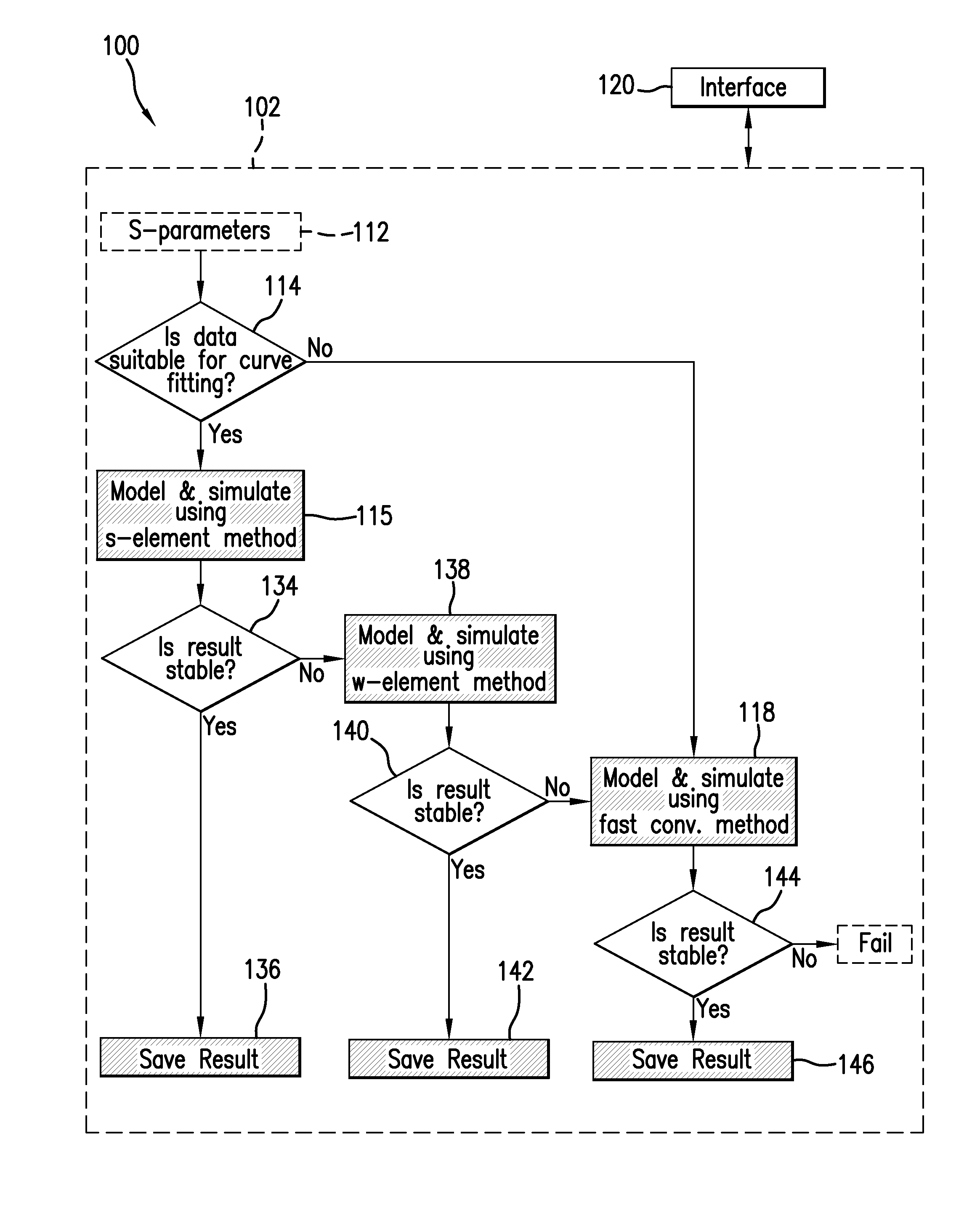
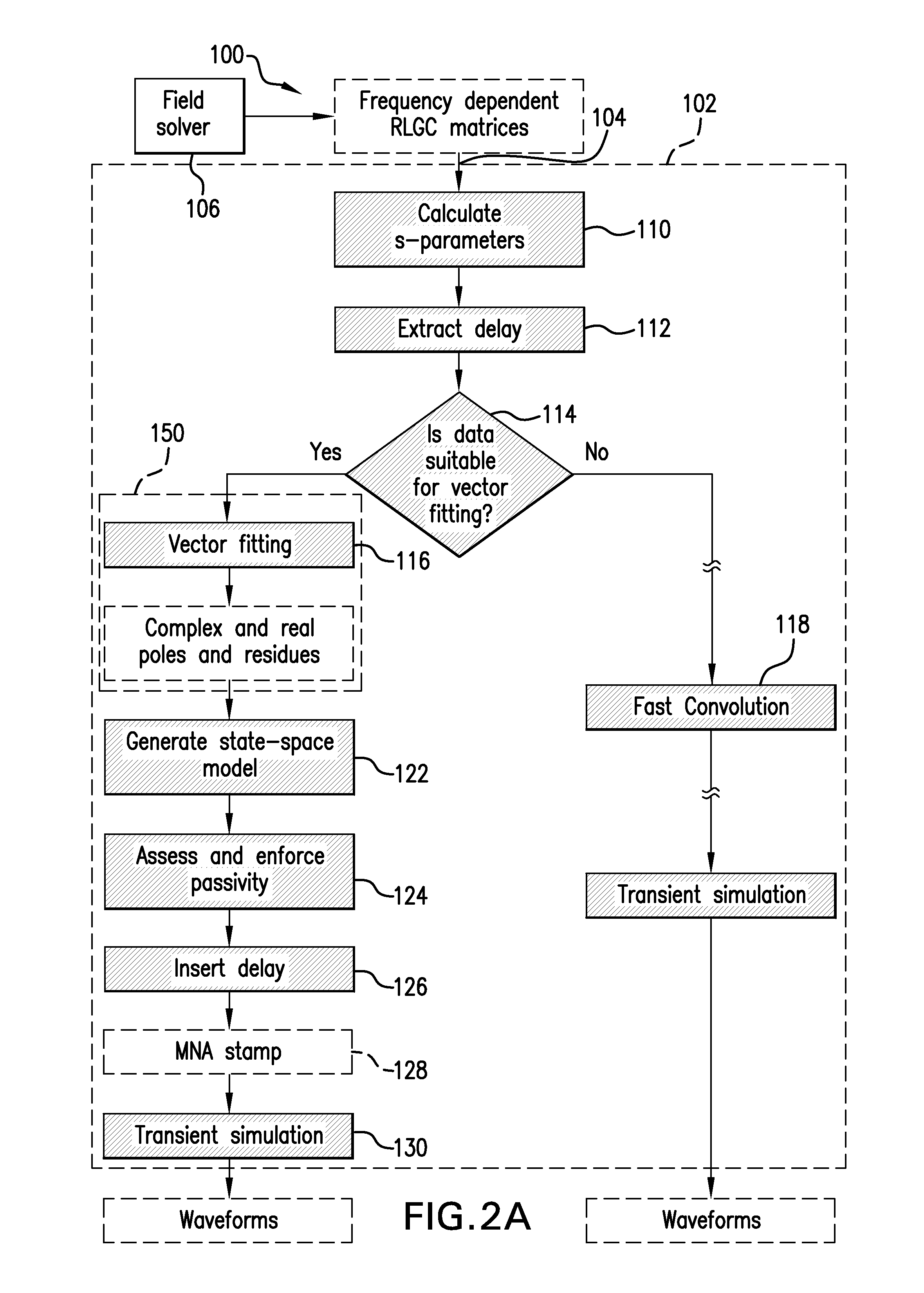
InactiveUS8386216B1Efficient and accurate results in frequency dependent environmentComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designLossy transmission linesModeling and simulation
A method and system are provided for adaptively modeling and simulating high speed response of a transmission line. A simulation unit maintains a plurality of curve approximation options for modeling the transmission line. The suitability of a predefined primary one of the curve approximation options for modeling is determined based on frequency-domain modal scattering parameters obtained according to frequency-dependent data characterizing the transmission line. One of the options is selectively executed in response to the determination, in order to generate a macromodel of the transmission line. The primary option is executed upon determination of suitability, while a secondary one of the curve approximation options is alternatively executed upon determination of non-suitability. Transient simulation is then executed upon the resulting macromodel of the transmission line.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Radio frequency current probe characteristic calibrating method based on electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application
InactiveCN101782637AMastering Measurement Conversion FactorsEasy to operateResistance/reactance/impedenceConversion coefficientsRadio frequency
The invention discloses a radio frequency current probe characteristic calibrating method based on electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application and belongs to the field of electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application and electromagnetic interference noise measurement. According to a frequency section needing to be measured, in the method, the transfer impedance of a current probe is tested in a time domain by utilizing a dual-trace oscilloscope and then tested in a frequency domain by utilizing a vector network analyzer and adopting a scattering parameter method; and finally, a measurement conversion coefficient of the current probe can be more accurately obtained. The method has simple operation and accurate test, enables a result of electromagnetic interference noisemeasured by the current probe to be more accurate, and provides a theoretical basis for conducting the electromagnetic interference noise.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Calibration method for free space material electromagnetic parameter test system
The invention provides a calibration method for a free space material electromagnetic parameter test system; the method is used for realizing the calibration of dual port network scattering parameter matrixes of the free space material test system by adopting a calibration method with a vector network analyzer and preset formulas. By adopting the scheme, the calibration of the free space material test system can be carried out effectively; by creating a separation error term transmission / reflection model, transceiver antennae are not needed to be moved by a precision clamp, only a simple calibration kit is used by combining a time domain gate technology, thus the calibration of the free space material electromagnetic parameter test system is completed, and the dependence on the high-precision test clamp is avoided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Single port single connection VNA calibration apparatus
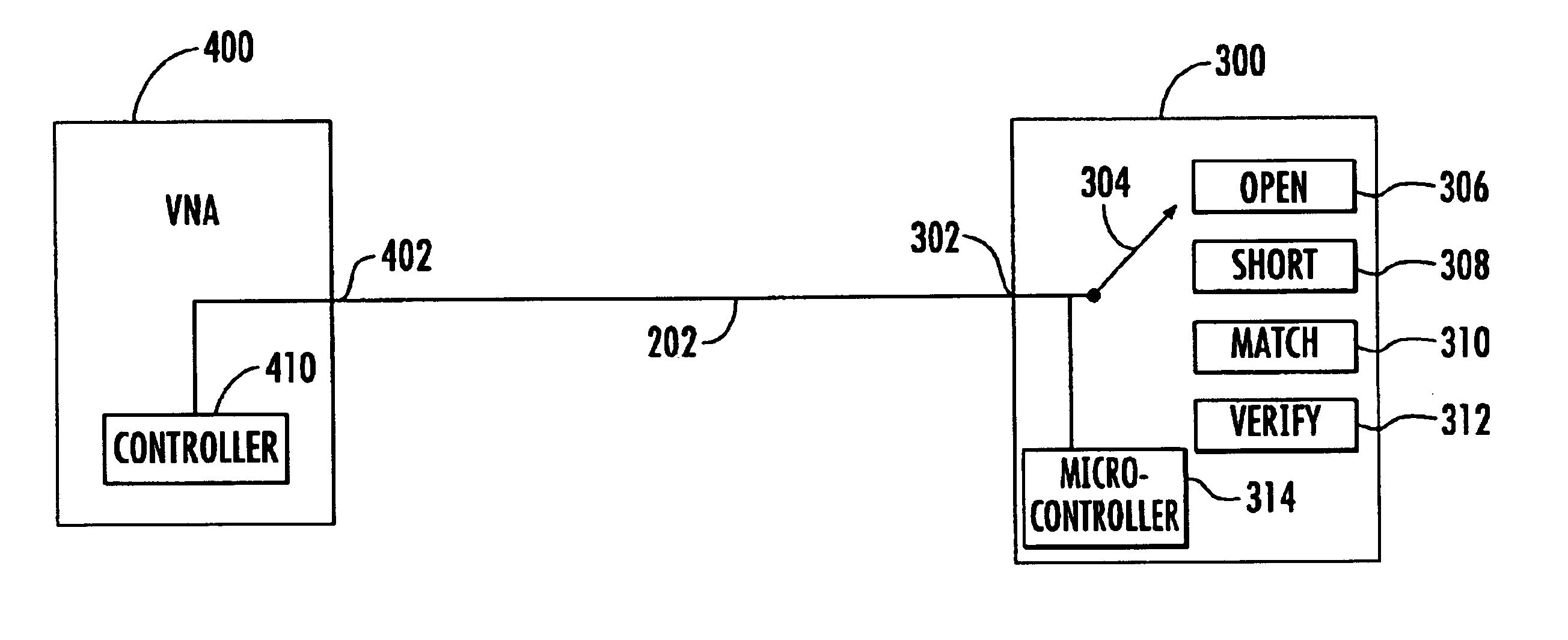
InactiveUS20040054490A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsControl signalVoltage source
A method and apparatus are used to calibration a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA). The method includes providing a calibration module with a single port, providing within the calibration module a set of reflecting components with known scattering parameters, providing control signals to the calibration module through the single port, providing the known scattering parameters to the VNA through the single port, coupling one of reflecting components to the VNA, measuring scattering parameters, and comparing the measured scattering parameters with the known scattering parameters. The apparatus includes a calibration module and a controller module. In one embodiment, the calibration module includes a set of reflecting components, a memory that stores the characterization data, and a current source which sends characterization data in the form of current pulses to the controller module. The controller module includes a voltage source that generates the control signals used by the calibration module.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Hybrid systems and methods for multi-modal acquisition of intravascular imaging data and counteracting the effects of signal absorption in blood
ActiveUS20160228097A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound attenuationHybrid system
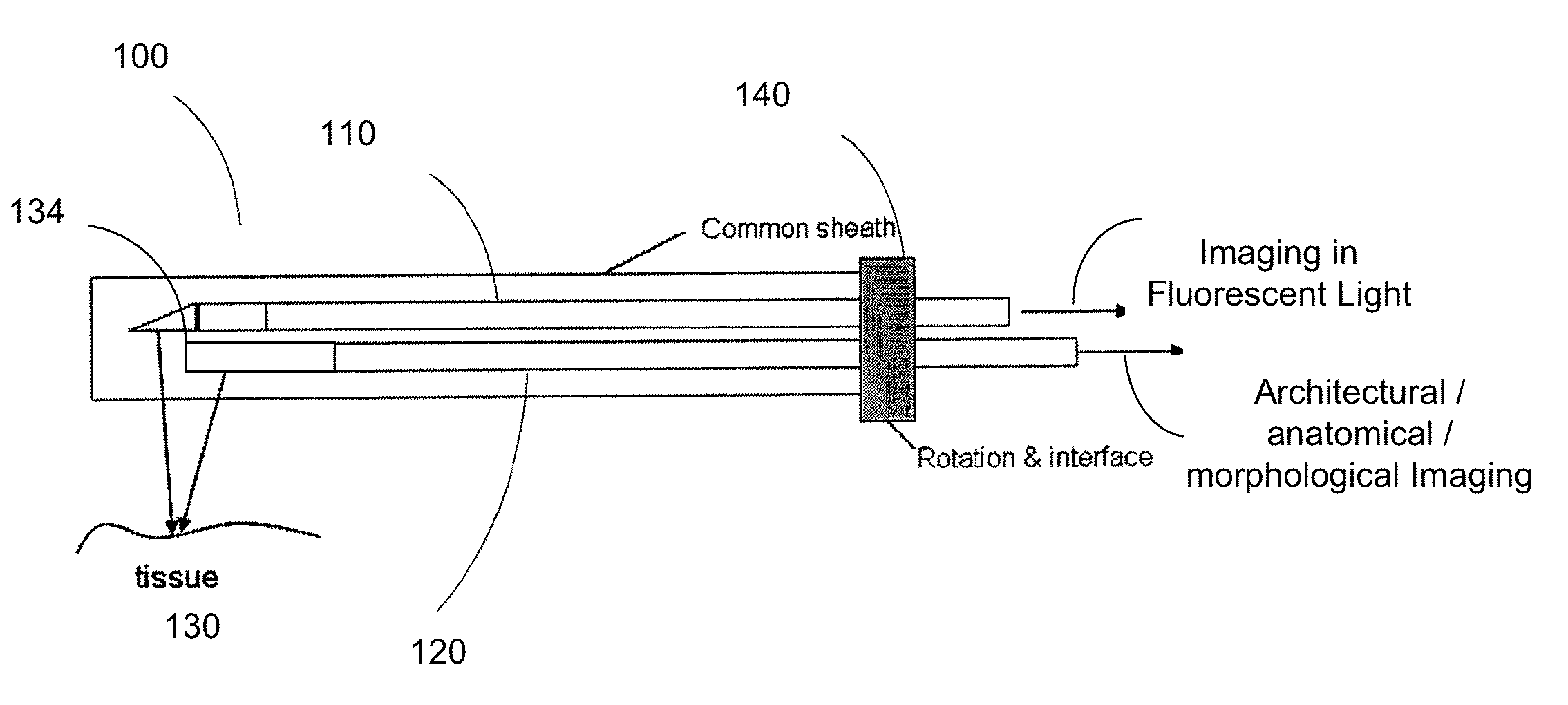
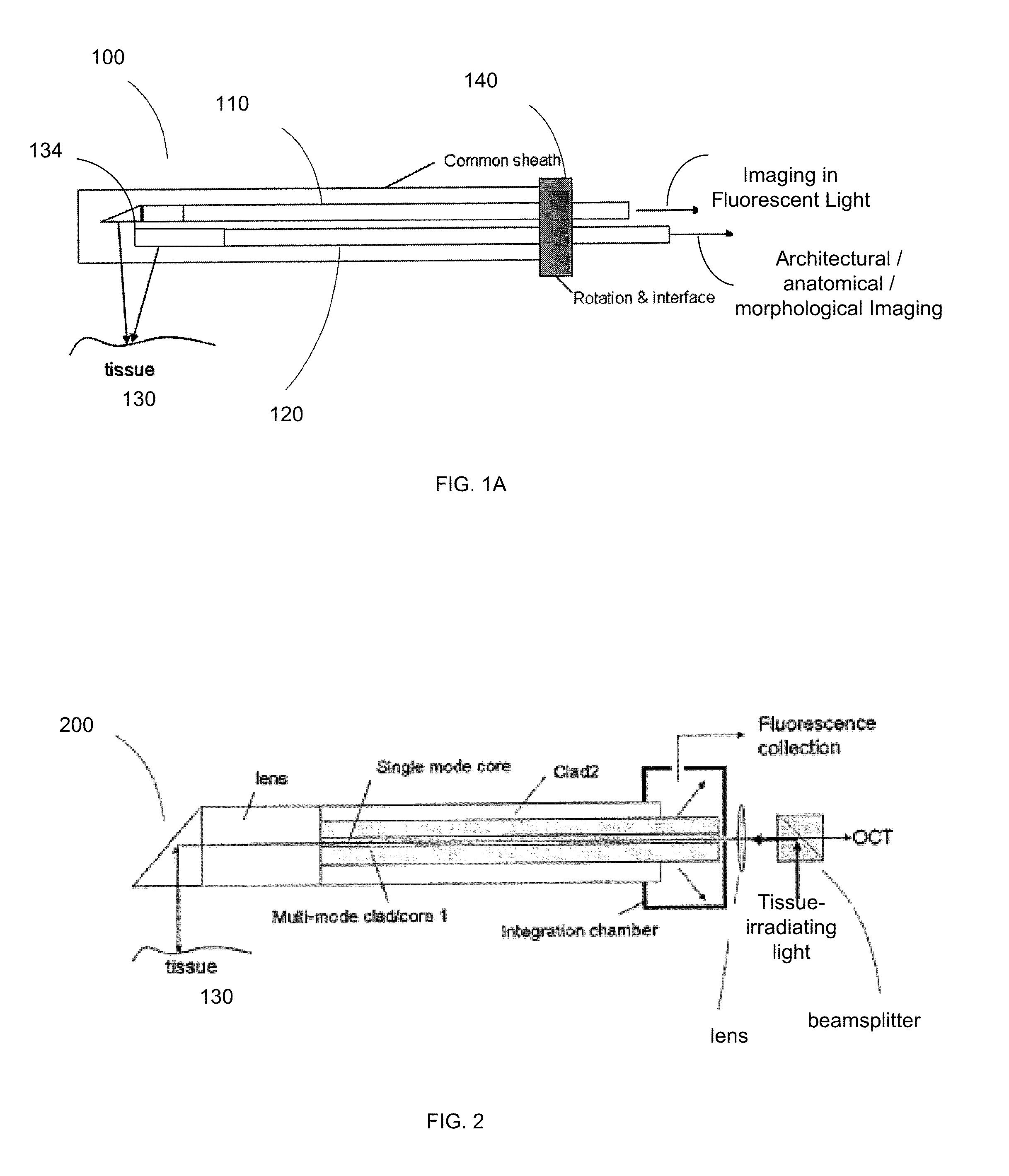
A multi-modal catheter combining at least NIRF and IVUs imaging channels used to reveal integrated biological and structural features of a lumen intravascularly imaged through flowing blood in vivo and corrected for distance-related attenuation and / or scattering parameters of in vivo blood to compensate for discovered overestimation of the degree of in-vivo-blood attenuation of NIRF signal Enhancing the sensitivity of detection of vascular injury and / or plaque deposition beyond the capability of a standalone IVUS imaging as a result of the use of such corrected catheter.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Measurement and Imaging of Scatterers with Memory of Scatterer Parameters Using at Least Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20140150556A1Solve insufficient capacityImprove performanceMultiple-port networksAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcousticsLow frequency
Measurement or imaging of elastic wave nonlinear scatterers with a memory of scattering parameters comprises selecting LF pulses having characteristics to change the scattering parameters of nonlinear scatterers. A transmit time relation is selected so that the incident HF pulse propagates sufficiently close to the LF pulse that the effect of the incident LF pulse on its scatterer parameters is observed by the HF pulse. At least two elastic wave pulse complexes comprising a high frequency (HF) pulse and a selected low frequency (LF) pulse are transmitted towards the region. Received HF signals are combined to form nonlinear HF signals representing the scatterers with memory, with suppression of received HF signals from other scatterers. At least one of the received HF signals may be corrected by time delay correction and / or speckle correction with a speckle correction filter, determined by movement of the scattering object. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
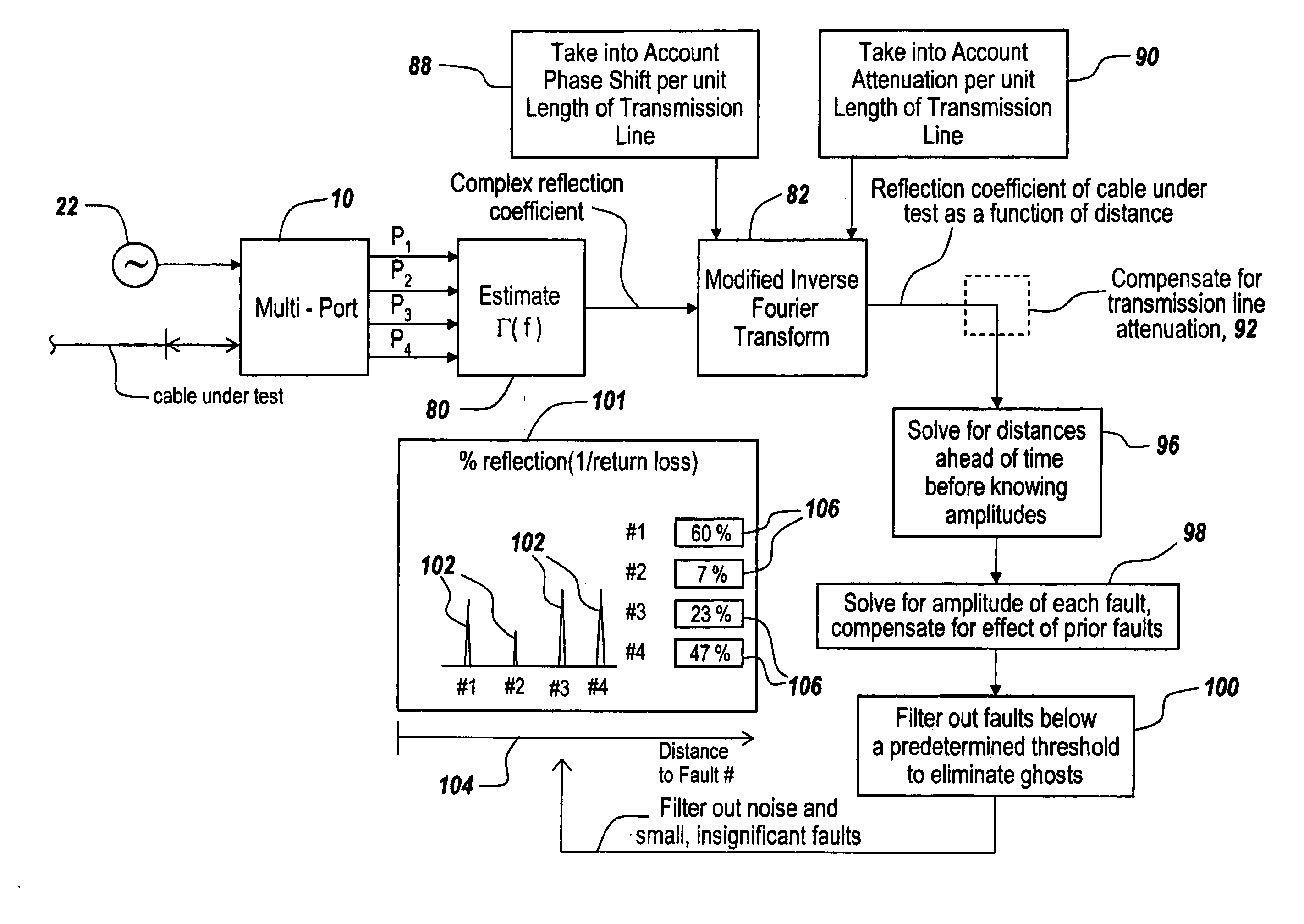
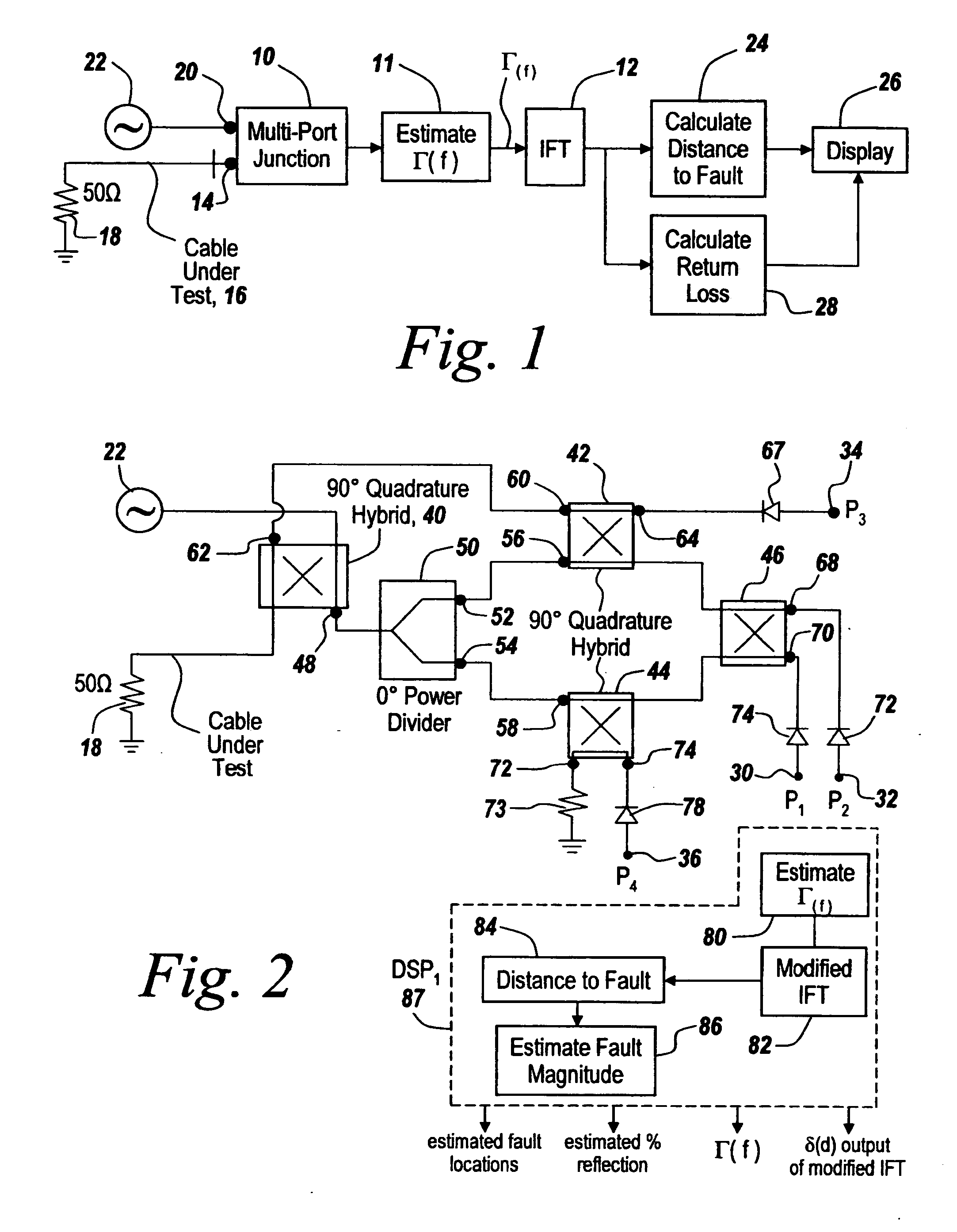
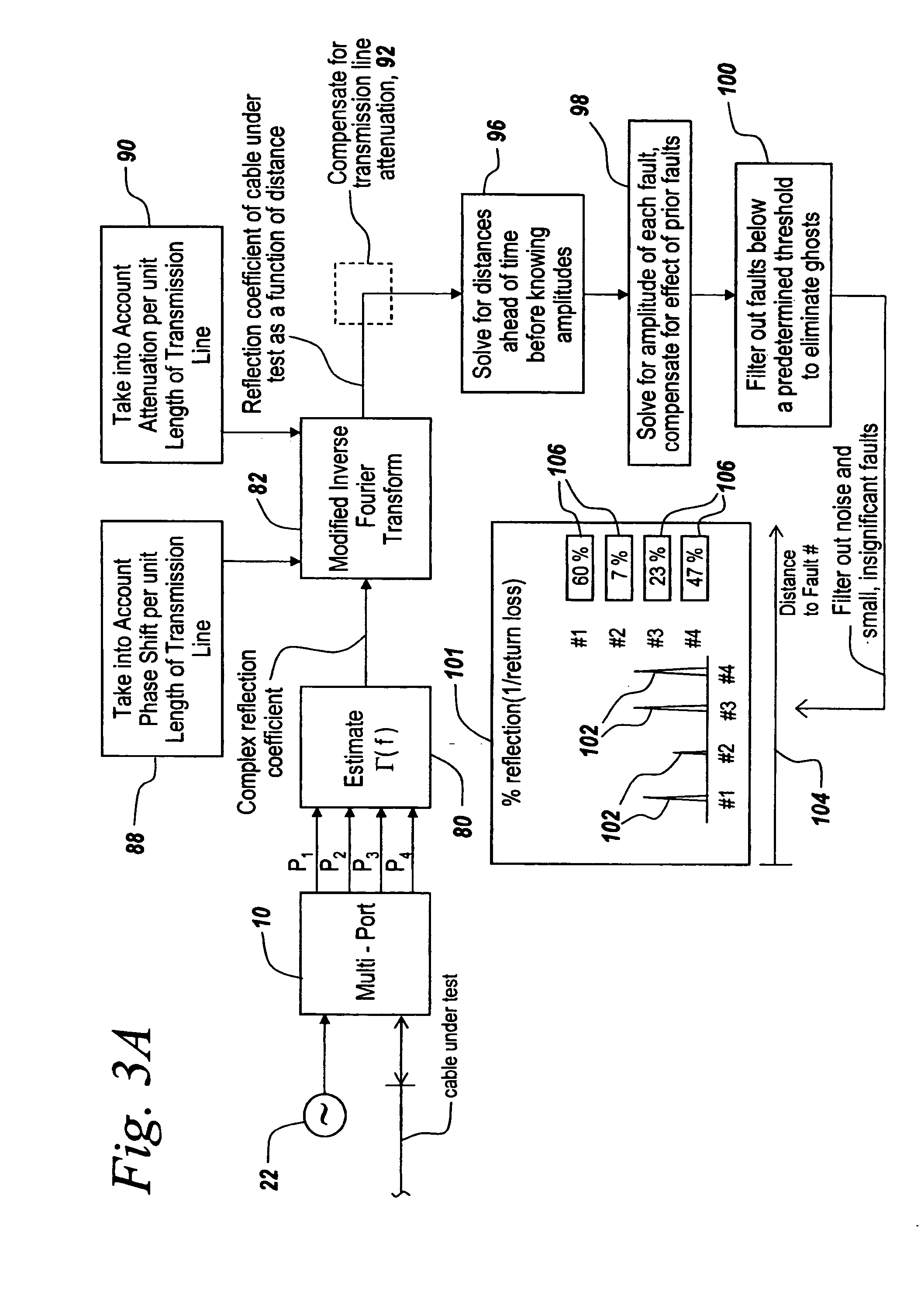
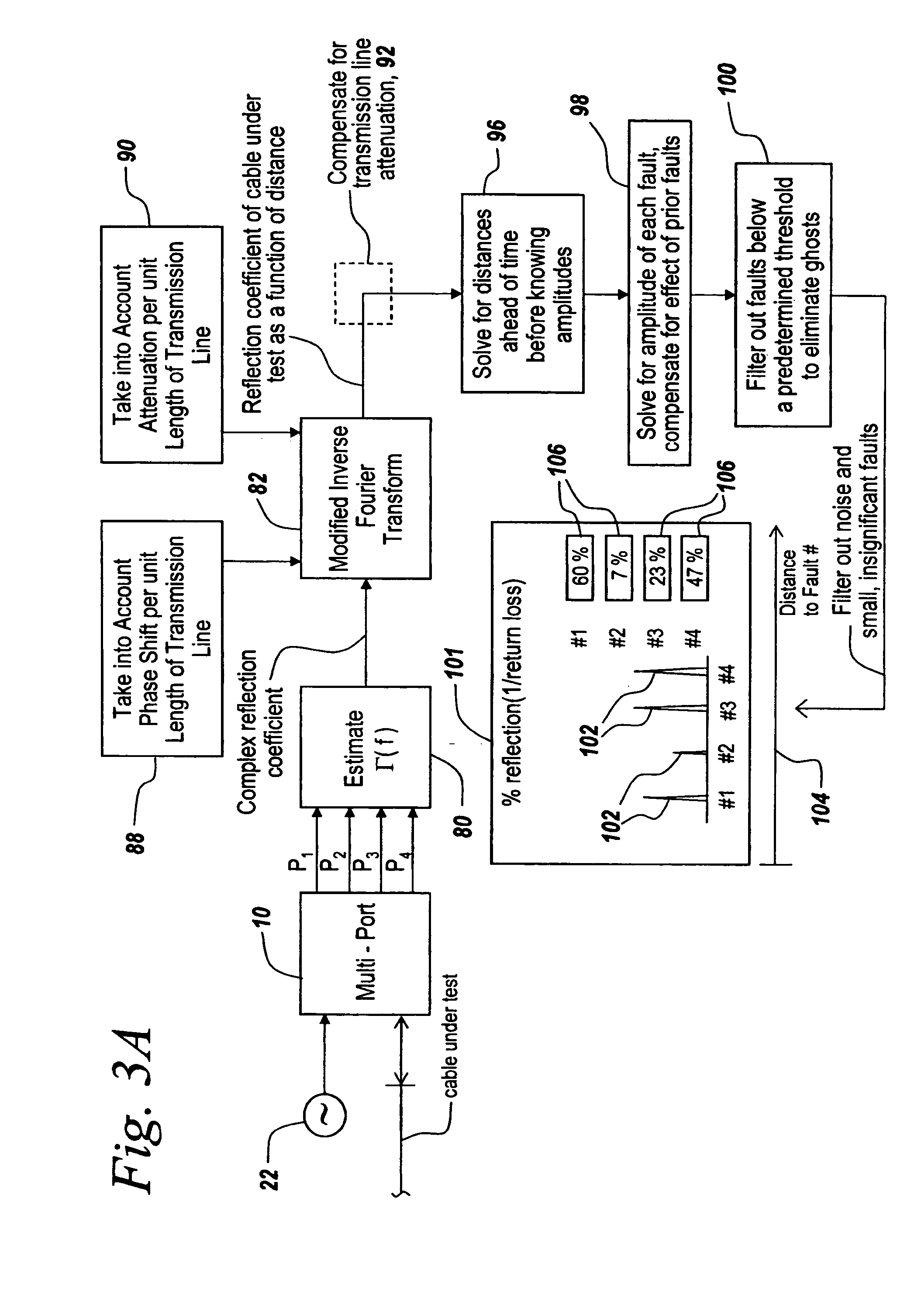
Distance-to-fault measurement system capable of measuring complex reflection coefficients
ActiveUS20100312506A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesCommunications systemMulti port
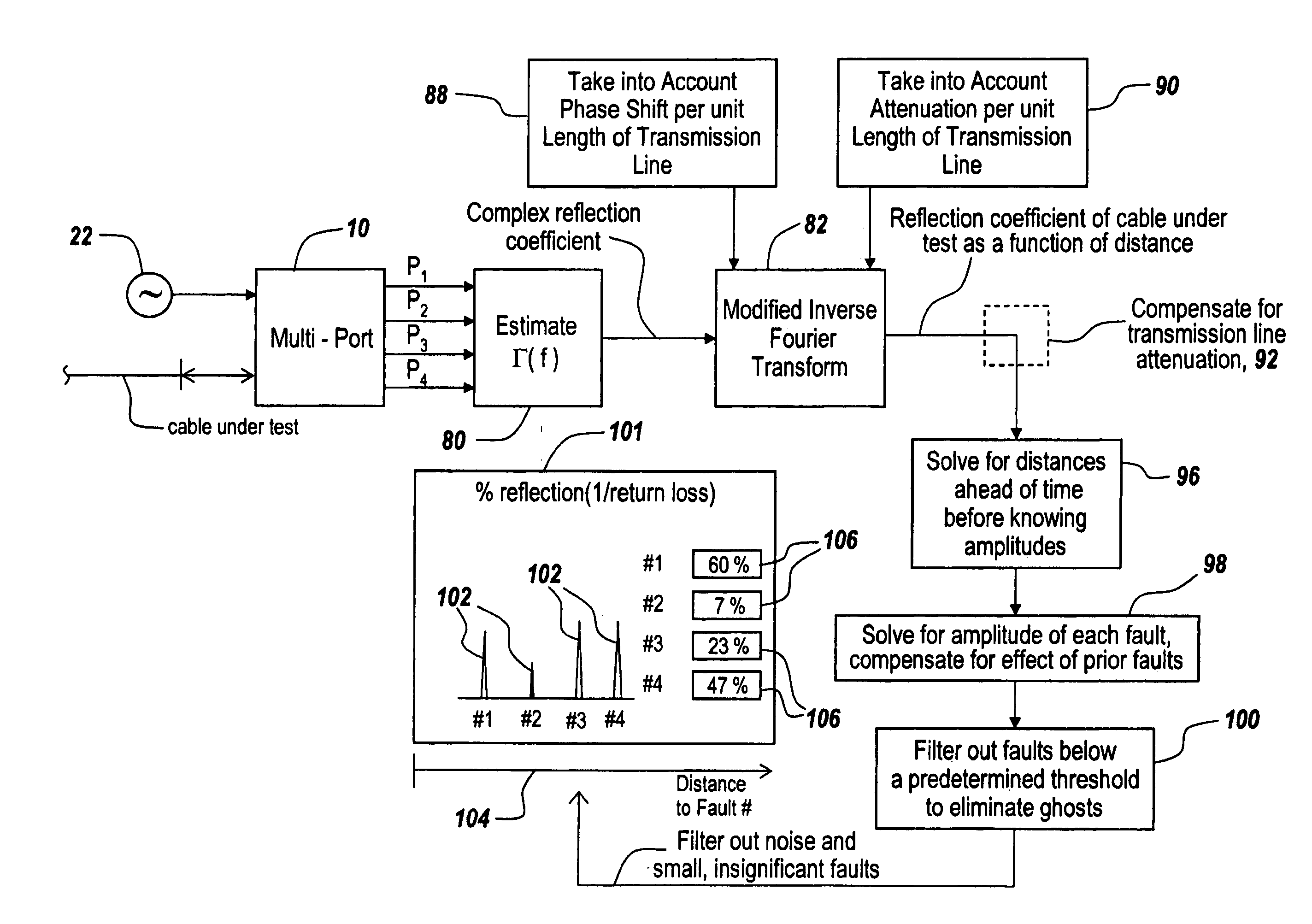
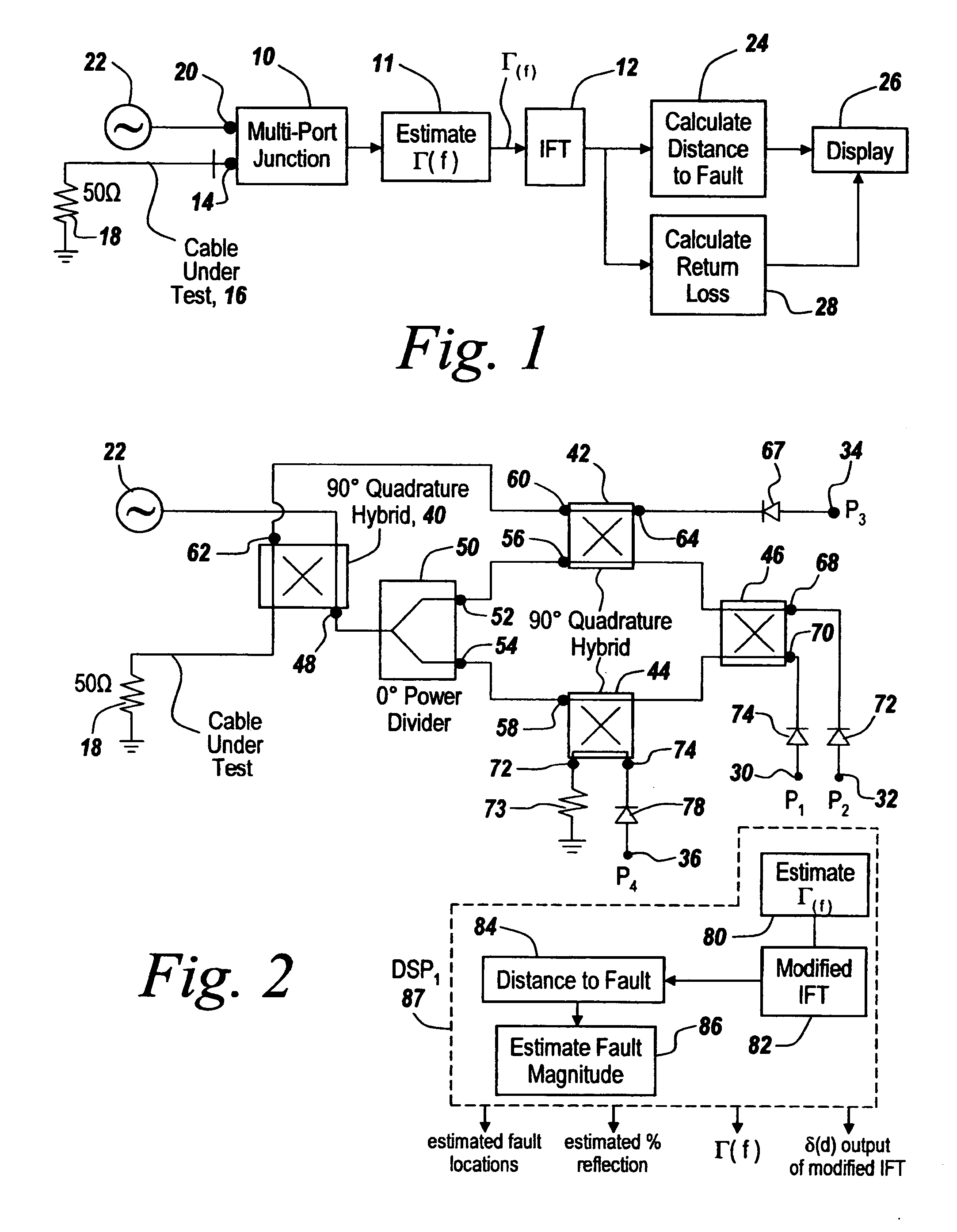
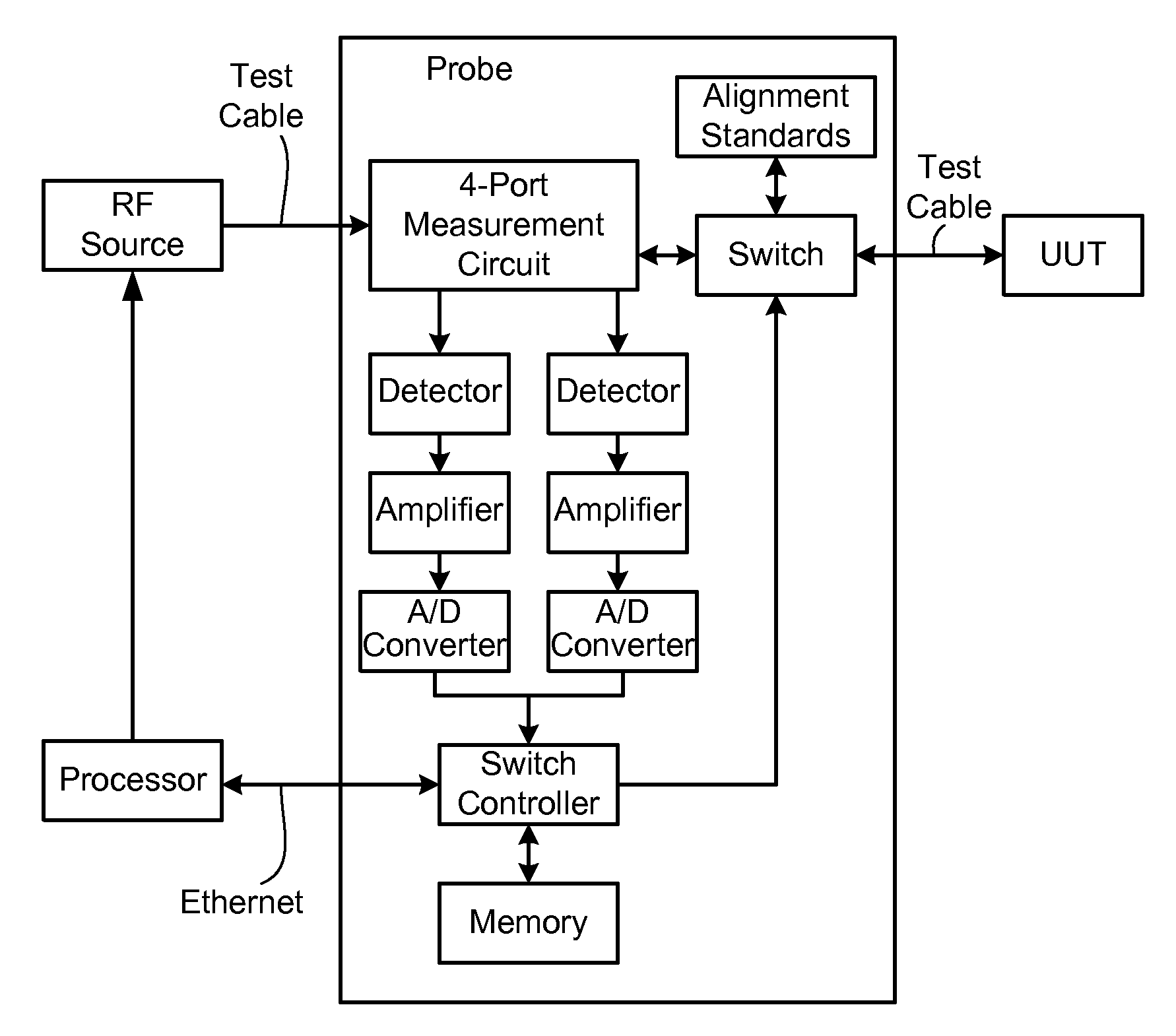
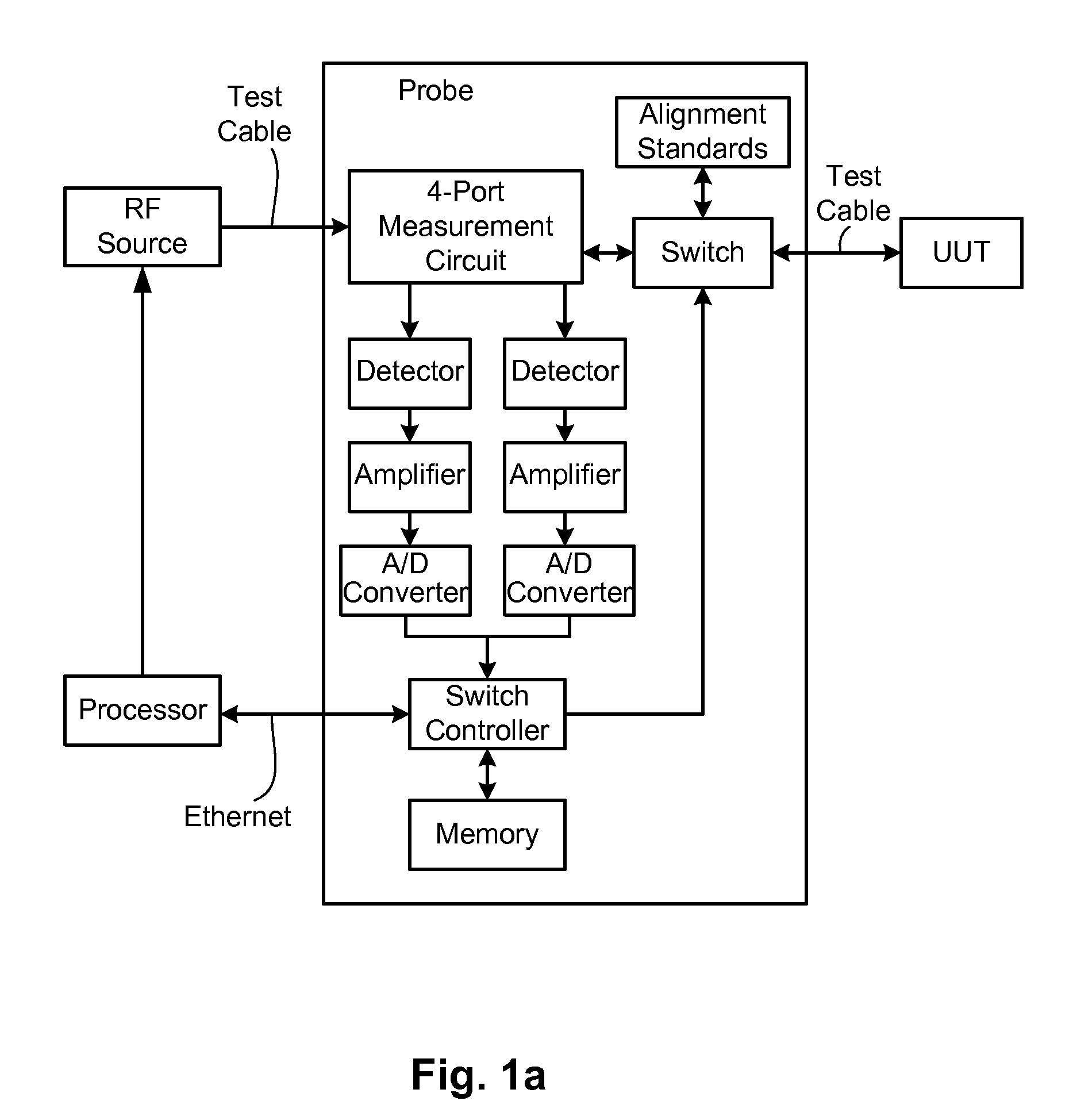
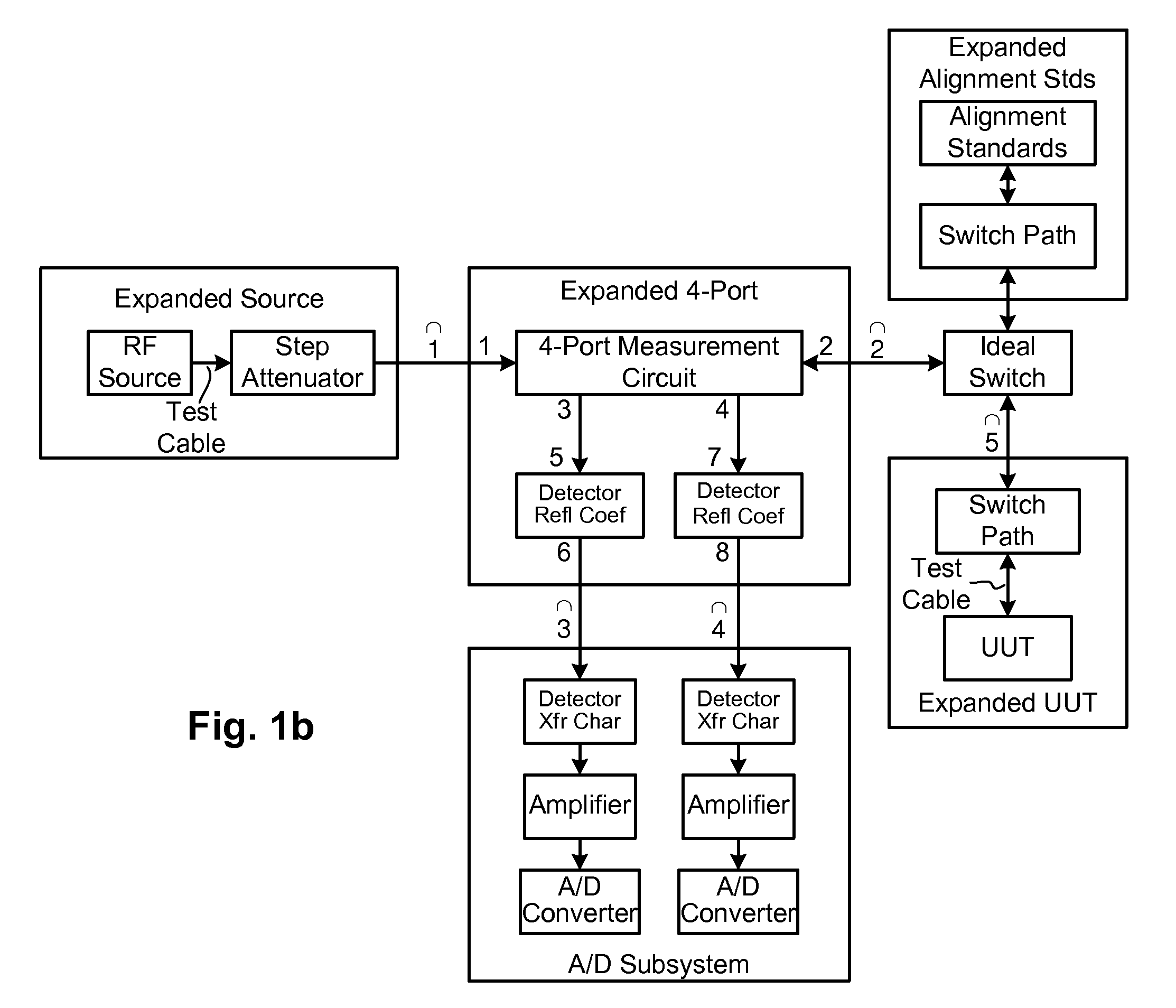
Techniques are disclosed for computing distance-to-fault (DTF) in communication systems. The techniques can be embodied, for instance, in a DTF system that provides a multi-port probing device and DTF functionality, including computing distances to faults and the fault magnitudes. In addition, the DTF system is further configured with the ability to accurately measure complex reflection coefficient of the UUT, and / or return loss of the UUT. The complex reflection coefficient and / or return loss of the UUT can be computed as a function of known scattering parameters of a multi-port measurement circuit included in the probe of the DTF system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
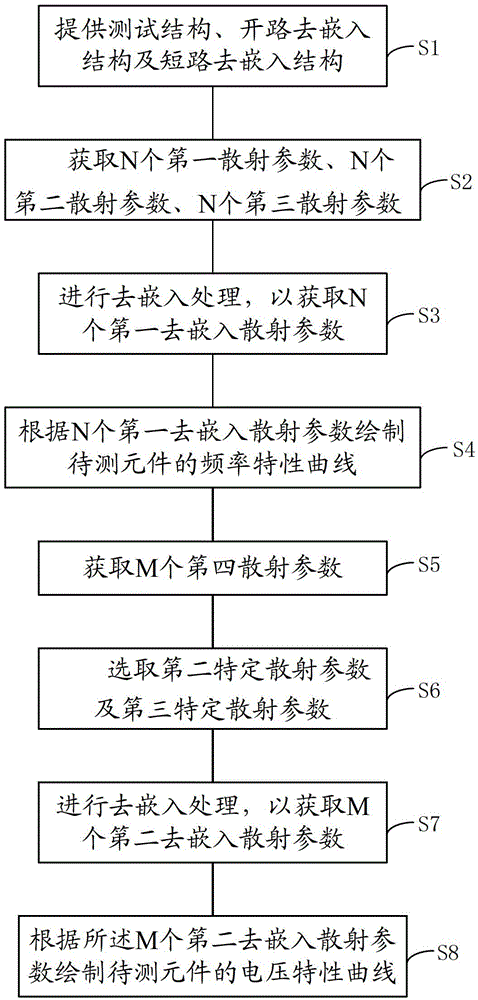
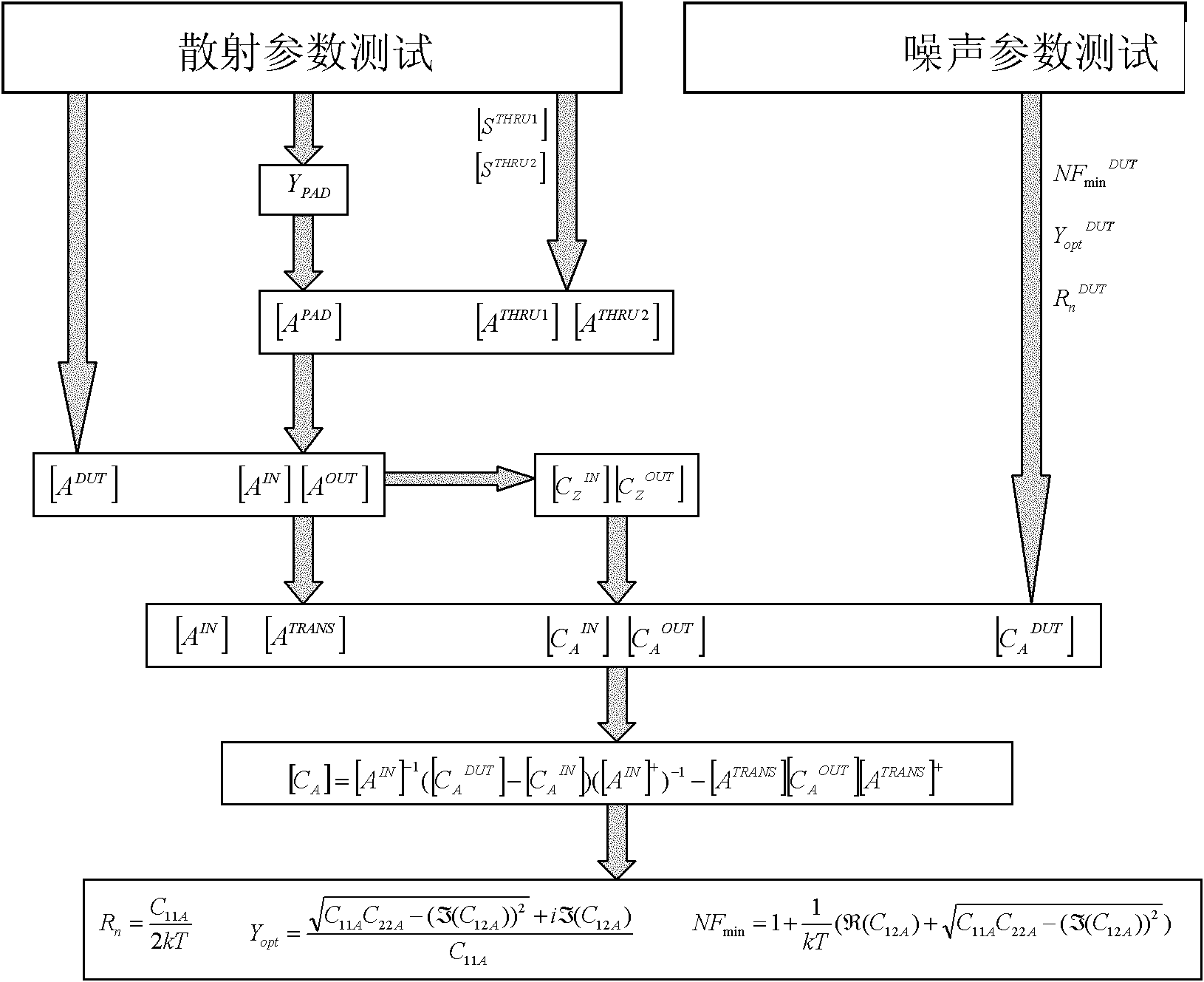
De-embedding method
The invention discloses a de-embedding method. A scattering parameter under a testing signal of a plurality of different frequencies of a vector network analysis meter surveying testing structure, an open circuit de-embedding structure and a short circuit de-embedding structure is used. A plurality of scattering parameters of the open circuit de-embedding structure and a plurality of scattering parameters of the short circuit de-embedding structure are stored at the same time. The scattering parameters under the specific frequency of the testing signal frequency of the open circuit de-embedding structure are not needed to be surveyed and the scattering parameters under the specific frequency of the testing signal frequency of the short circuit de-embedding structure are not needed to be surveyed when de-embedding scattering parameters under the specific frequency of the testing signal frequency of a to-be tested component obtained follow-up. The de-embedding method is simple and occupation of the vector network analysis meter is reduced. The specific frequency is needed to be changed many times when voltage characteristics of the to-be tested component is analyzed comprehensively, thus effect of a technical scheme is prominent.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Radio frequency noise de-embedding method
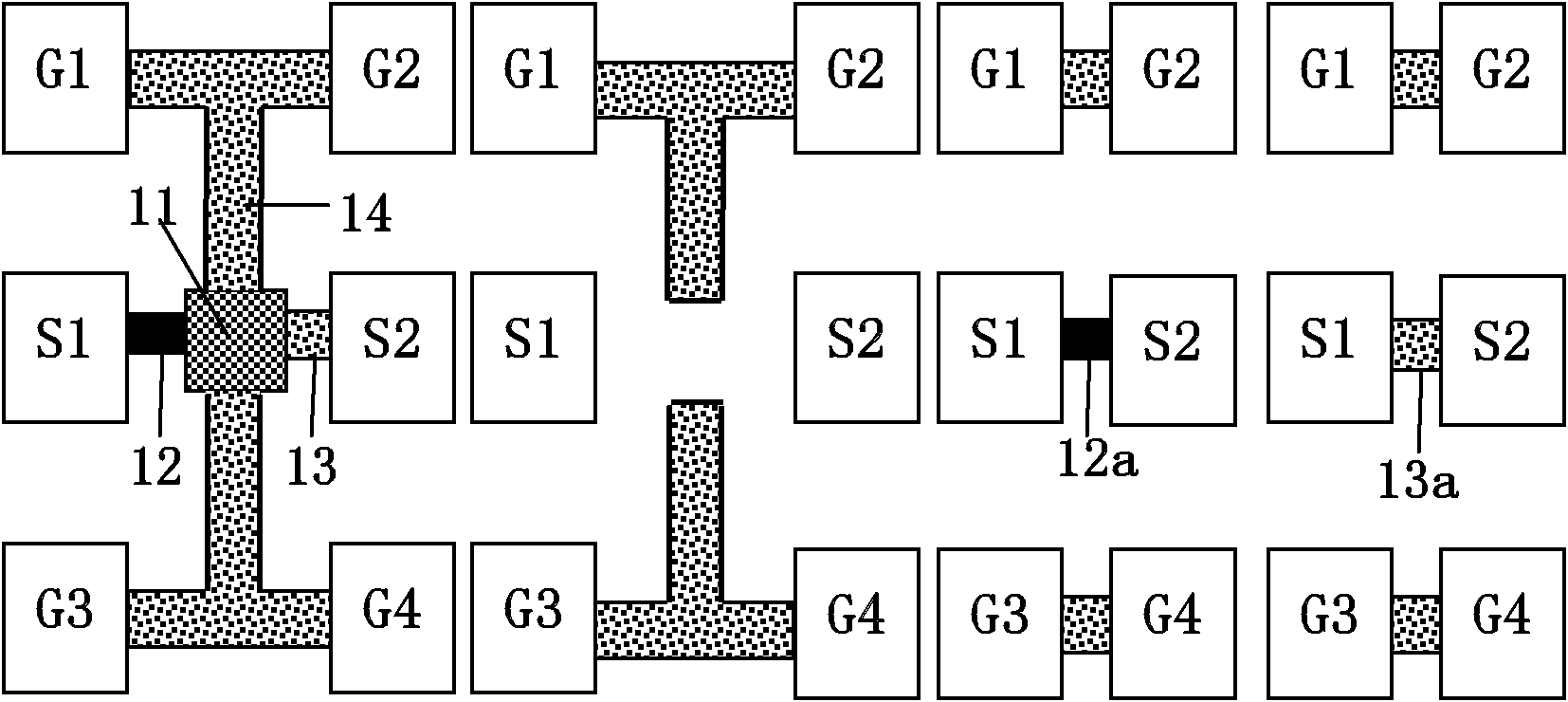
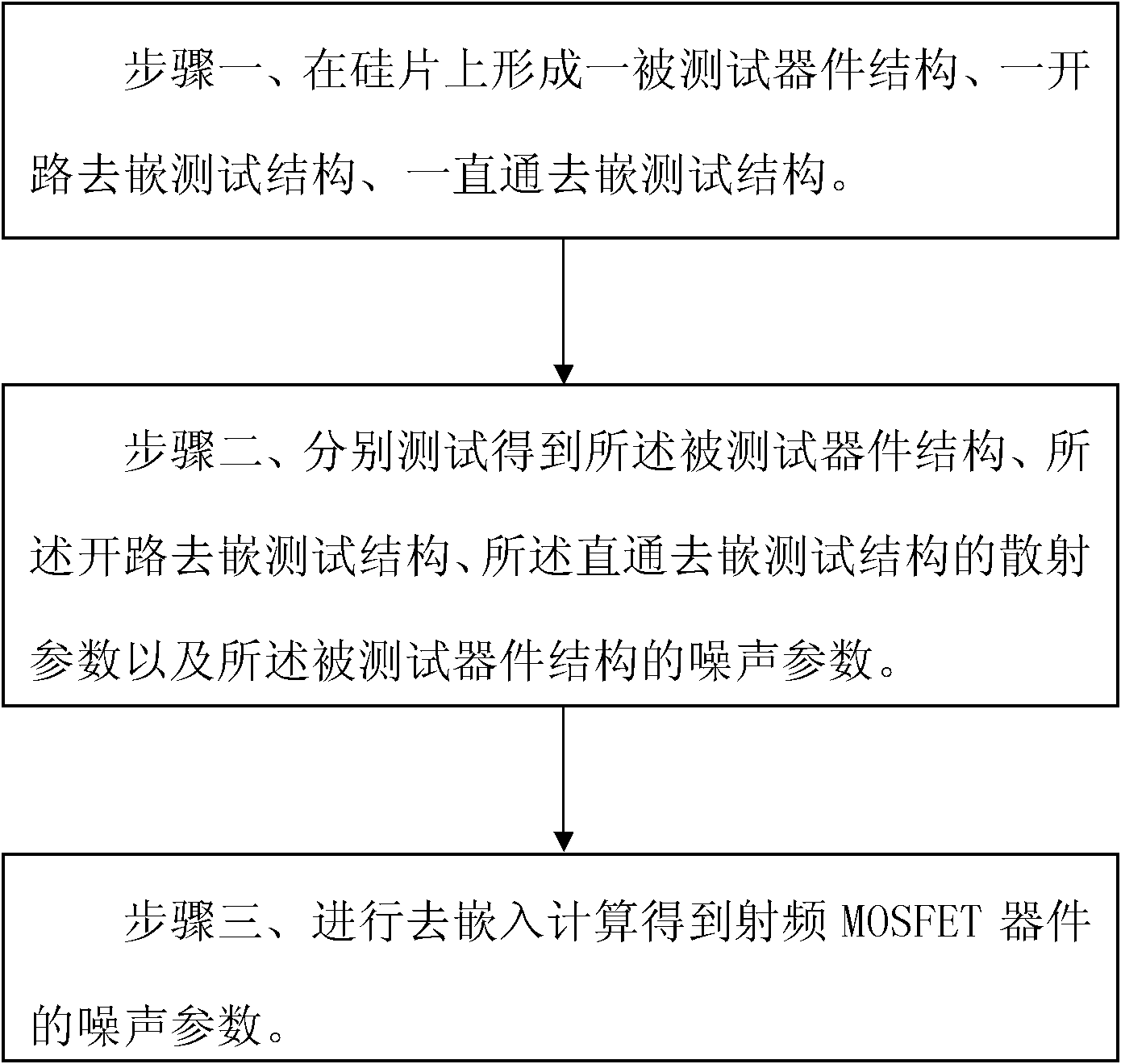
ActiveCN102466773AReduce in quantityReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTested timeCharacteristic impedance
The invention discloses a radio frequency noise de-embedding method, which comprises the following steps of: forming a device under test, an open de-embedding test structure and a thru de-embedding test structure on a silicon chip; performing tests to obtain scattering parameters of the device under test, the open de-embedding test structure and the thru de-embedding test structure and a noise parameter of the device under test; and performing de-embedding calculation by utilizing each scattering parameter and the noise parameter of the device under test to obtain a noise parameter of a radio frequency device, wherein the normalized characteristic impedance and propagation constant of a pure metal wire are calculated by utilizing the scattering parameters of inter-signal metal wires of the thru de-embedding test structure, and then an ABCD parameter of an input end metal wire or an output end metal wire of the device under test is calculated. By the method, the number of the thru de-embedding test structures on the silicon chip can be greatly decreased, the area of the silicon chip can be saved, test time can be shortened, and cost can be greatly decreased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Single port single connection VNA calibration apparatus
InactiveUS6917892B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceSpecial data processing applicationsControl signalVoltage source
A method and apparatus are used to calibration a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA). The method includes providing a calibration module with a single port, providing within the calibration module a set of reflecting components with known scattering parameters, providing control signals to the calibration module through the single port, providing the known scattering parameters to the VNA through the single port, coupling one of reflecting components to the VNA, measuring scattering parameters, and comparing the measured scattering parameters with the known scattering parameters. The apparatus includes a calibration module and a controller module. In one embodiment, the calibration module includes a set of reflecting components, a memory that stores the characterization data, and a current source which sends characterization data in the form of current pulses to the controller module. The controller module includes a voltage source that generates the control signals used by the calibration module.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Electric control radiation directional diagram reconfigurable antenna
InactiveCN102157792AInfluence of electromagnetic characteristicsHigh gainAntennasEngineeringElectric control
The invention relates to an electric control radiation directional diagram reconfigurable antenna. The reconfiguration of the directional diagram of the antenna is finished by the following steps of: (1) selecting the working frequency f of an antenna; (2) confirming an arrangement cycle of an artificial structure material unit in three directions, an antenna integral structure and a metal structure and the substrate material of a formed unit, wherein the arrangement cycle comprises geometric parameters of the substrate material and the metal structure; (3) adding a variode on an opening of the metal structure; (4) calculating the transmission spectrum S21 phase of the unit by utilizing electromagnetic simulation software, continuously changing a capacitance value of the variode, recording the corresponding phase of a scattering parameter and drawing a phase-capacitance C curve; (5) arranging an artificial material along the horizontal plane cycle, dividing the artificial structure material into N areas with equal distance, and controlling a voltage value loaded on the variode in the unused area, wherein all the areas have equal structural size and contain equal amount of units. The antenna is a controllable antenna of a broadband and can realize positive / negative 40-degree deflection or so of a main lobe of the radiation directional diagram of the antenna.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring phase fractions of oil-water two-phase flows based on ultrasonic attenuation mechanism model
ActiveCN106226392AAvoid nonlinear responseNo corrosionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound attenuationDiffusion
The invention relates to a method for measuring the phase fractions of oil-water two-phase flows based on an ultrasonic attenuation mechanism model. According to the method, one main receiving sensor and six auxiliary ultrasonic receiving sensors are adopted. The method comprises the following steps: setting a detection signal of the main receiving sensor as V2, respectively setting detection signals of the six auxiliary ultrasonic receiving sensors as V3......V8, and calculating the ultrasonic intensity attenuation of the detection signals V2, V3......V8 and a drive signal V1; calculating the sum of a total ultrasonic attenuation coefficient of an oil-water two-phase-flow fluid and the ultrasonic diffusion attenuation amount of each auxiliary ultrasonic receiving sensor; detecting transit time from a time point when the drive signal is emitted by a signal emitting sensor to a time point when the signal is received by the main receiving sensor; calculating an oil-water two-phase scattering parameter; and calculating each phase fraction of the oil-water two-phase flows. By virtue of the method, the estimation precision of the moisture content can be increased.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
New method for testing clamp effect in dual-port-removed network
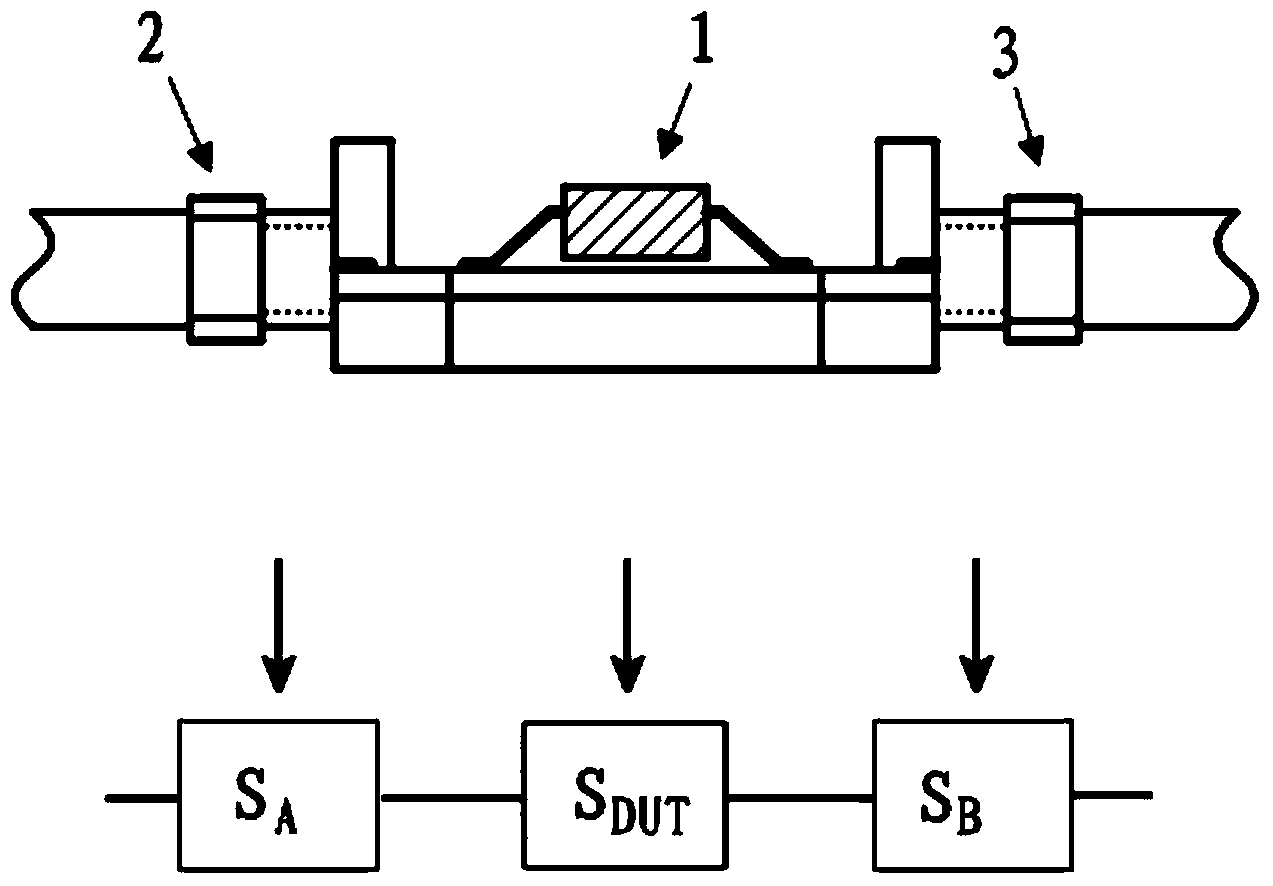
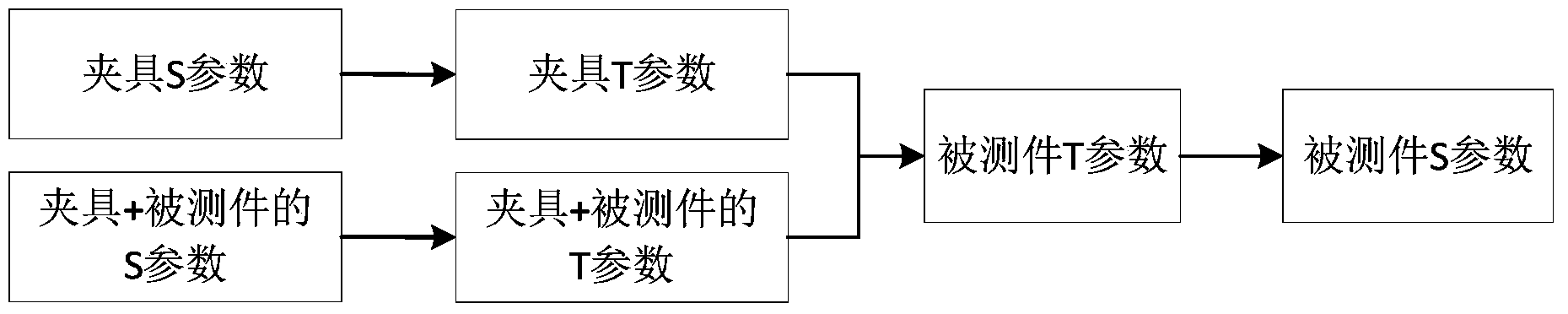
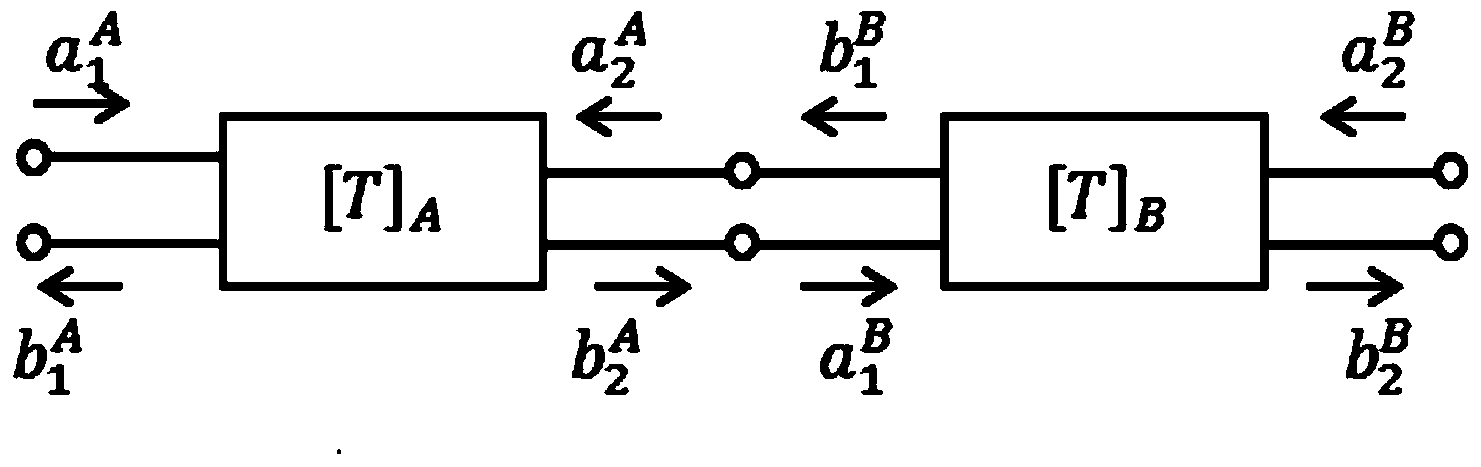
ActiveCN104297597AReal-time accessEasy accessElectrical testingModeling and simulationTime-Consuming
The invention discloses a new method for testing the clamp effect in a dual-port-removed network. According to the method, a whole clamp system is measured through a vector network analysis instrument, the chain shape scattering parameter of a tested piece is obtained by converting the S parameter into the chain shape scattering parameter and through network cascading and matrix operation, the chain shape scattering parameter is converted into the S parameter, and then the true value of the tested piece can be obtained. The measurement process of a non-standard connector device is effectively simplified, the S parameter of the de-embedded tested piece can be rapidly obtained in real time, and therefore the implementation difficulty and complex steps in a traditional method are avoided. In addition, when the method is adopted, no calibration piece of a non-standard connector needs to be manufactured, no complex and time-consuming modeling and simulation needs to be conducted, the method can be programmed to and embedded in the vector network analysis instrument, and therefore the measurement result can be rapidly displayed in real time, and large-scale production and testing are facilitated.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
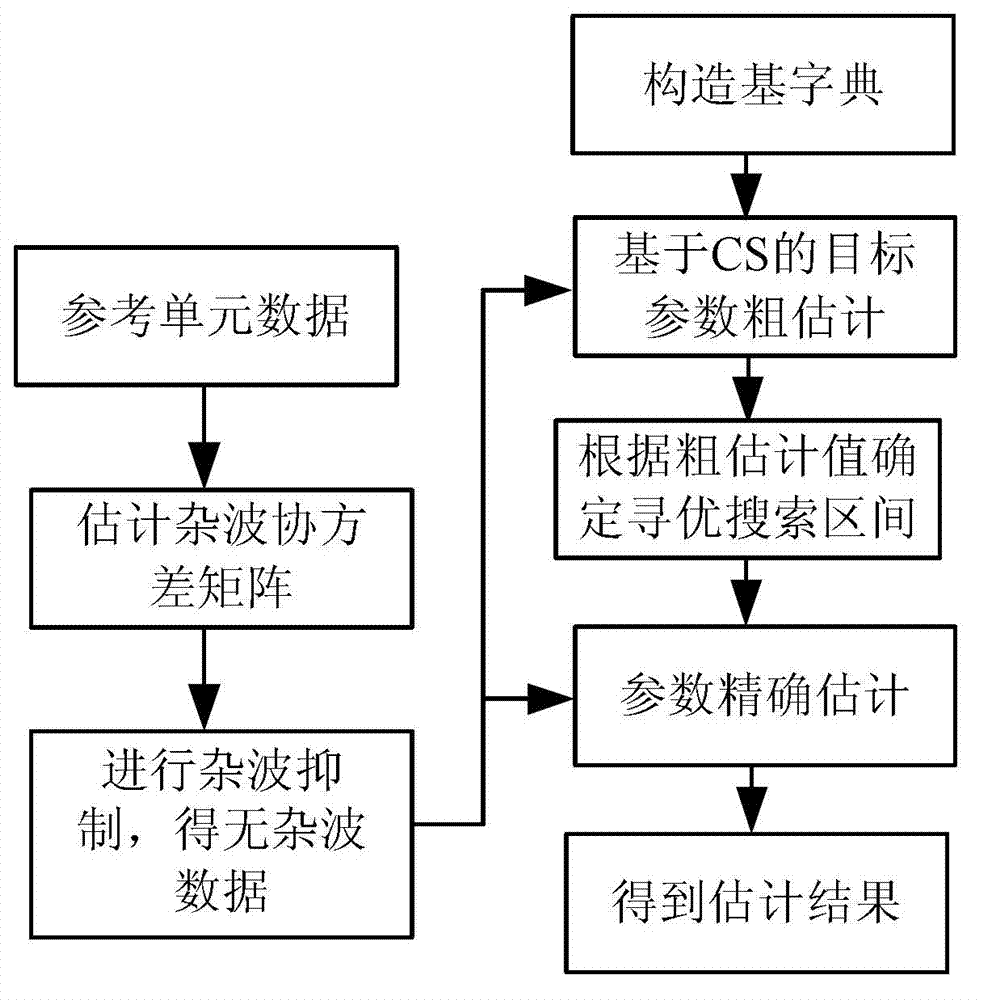
Maneuvering target parameter estimation method based on compressed sensing
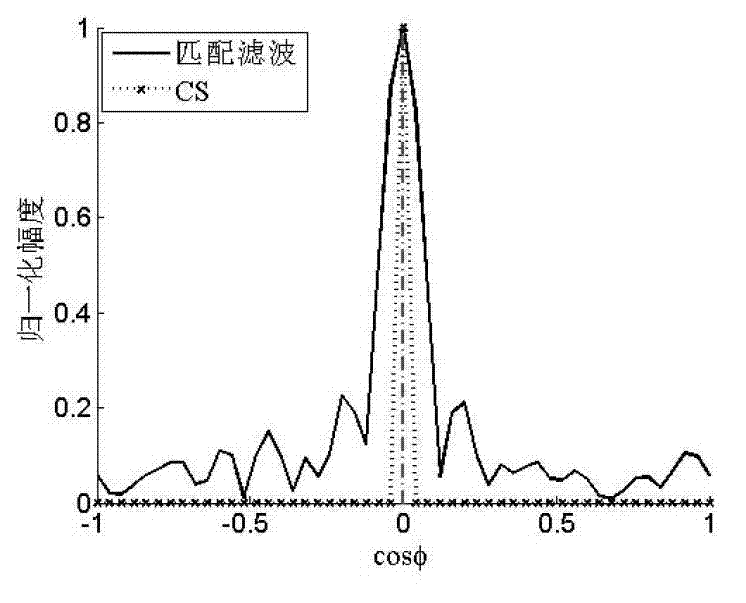
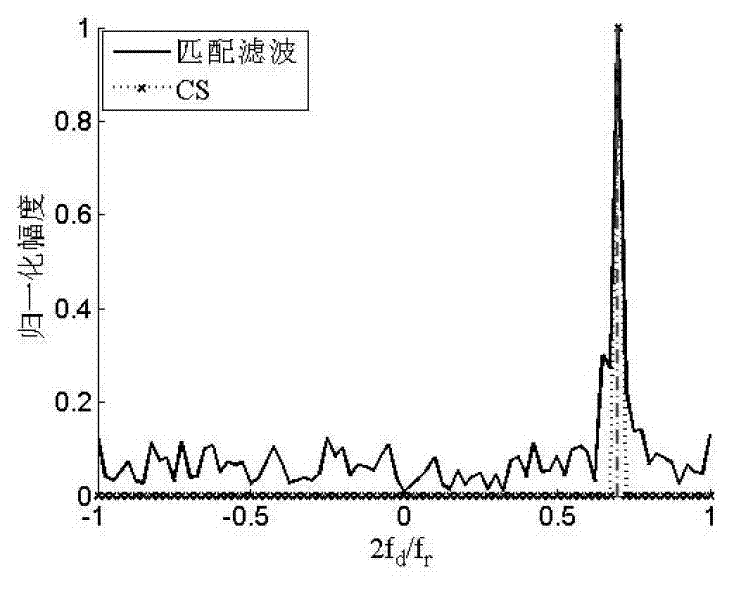
InactiveCN103091669ASolve the correlationSolve problems that are not conducive to sparse signal recoveryWave based measurement systemsSpace time frequencyScattering parameters
A maneuvering target parameter estimation method based on compressed sensing comprises the following steps: estimating a clutter covariance matrix by using data of a reference unit, restraining clutter to data of a unit under a test, scattering coming directional angle space, speed space and acceleration space of a objective, establishing objective space-time frequency three dimensional parameters according to scattered parameter space and estimating required base dictionary, obtaining objective parameter rough estimating values based on compressed sensing through sparse solution and recording the objective parameter rough estimating values as construction cost function, raking in a local range with the rough estimating values as domain to achieve objective parameter accurate estimate, and obtaining final estimating results. The maneuvering target parameter estimation method based on the compressed sensing can be used for realizing that an airborne phased array radar accurately estimates space-time frequency three dimensional parameters of an air maneuvering objective.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Systems and methods for time/frequency indexed pulse calibrations for vector network analyzers
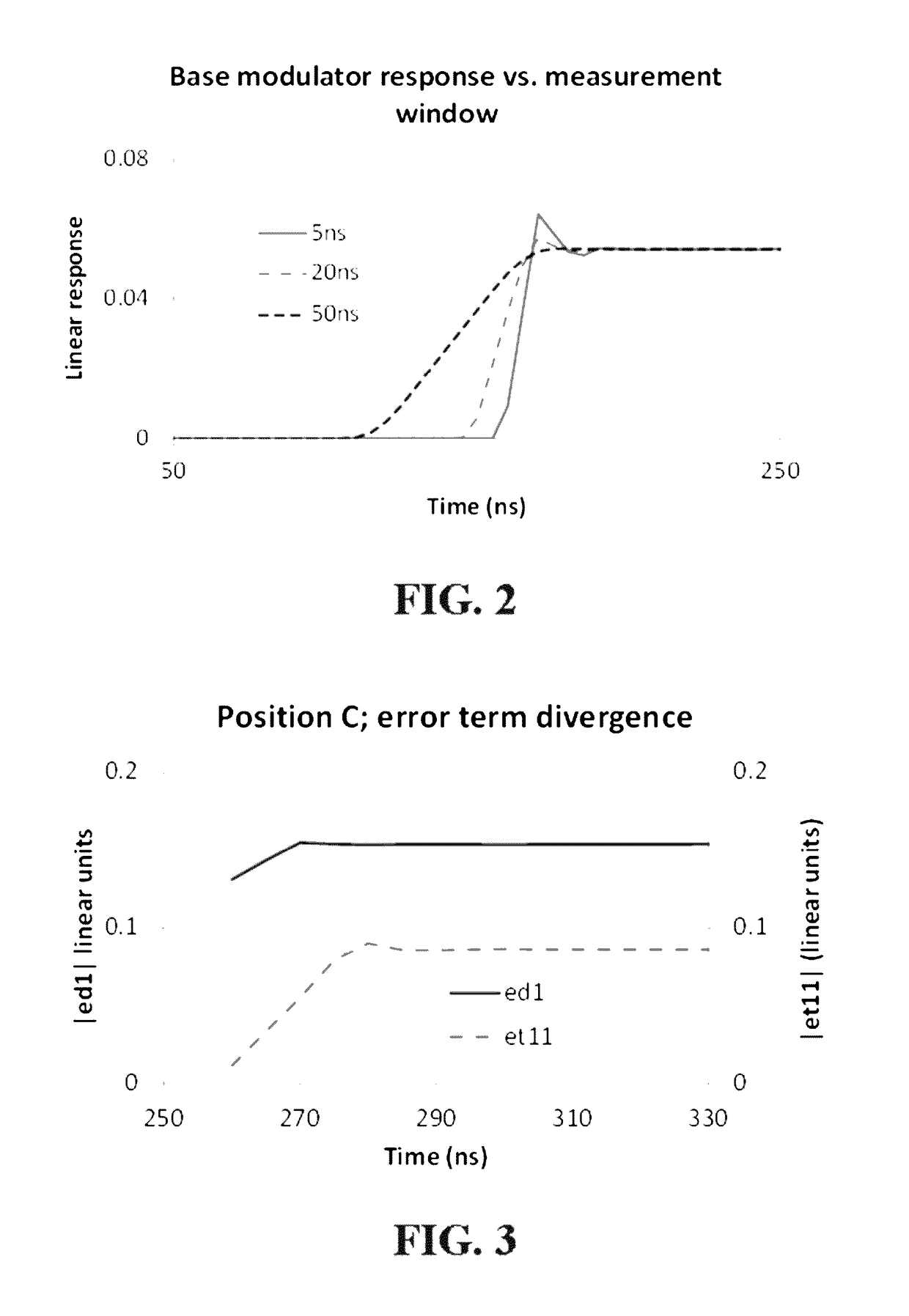
A method for measuring scattering parameters in a device under test (DUT) using a vector network analyzer (VNA), includes calibrating the VNA to generate corrections for deterministic setup defects and mapping a plurality of error terms based on a plurality of time indices, wherein each time indicia is associated with an error term. A test signal is transmitted to the DUT to obtain a measurement signal from the DUT in response to the test signal. The generated corrections to obtained measurements are time aligned based on the mapped error terms.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com