Patents
Literature
5767 results about "Oscilloscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
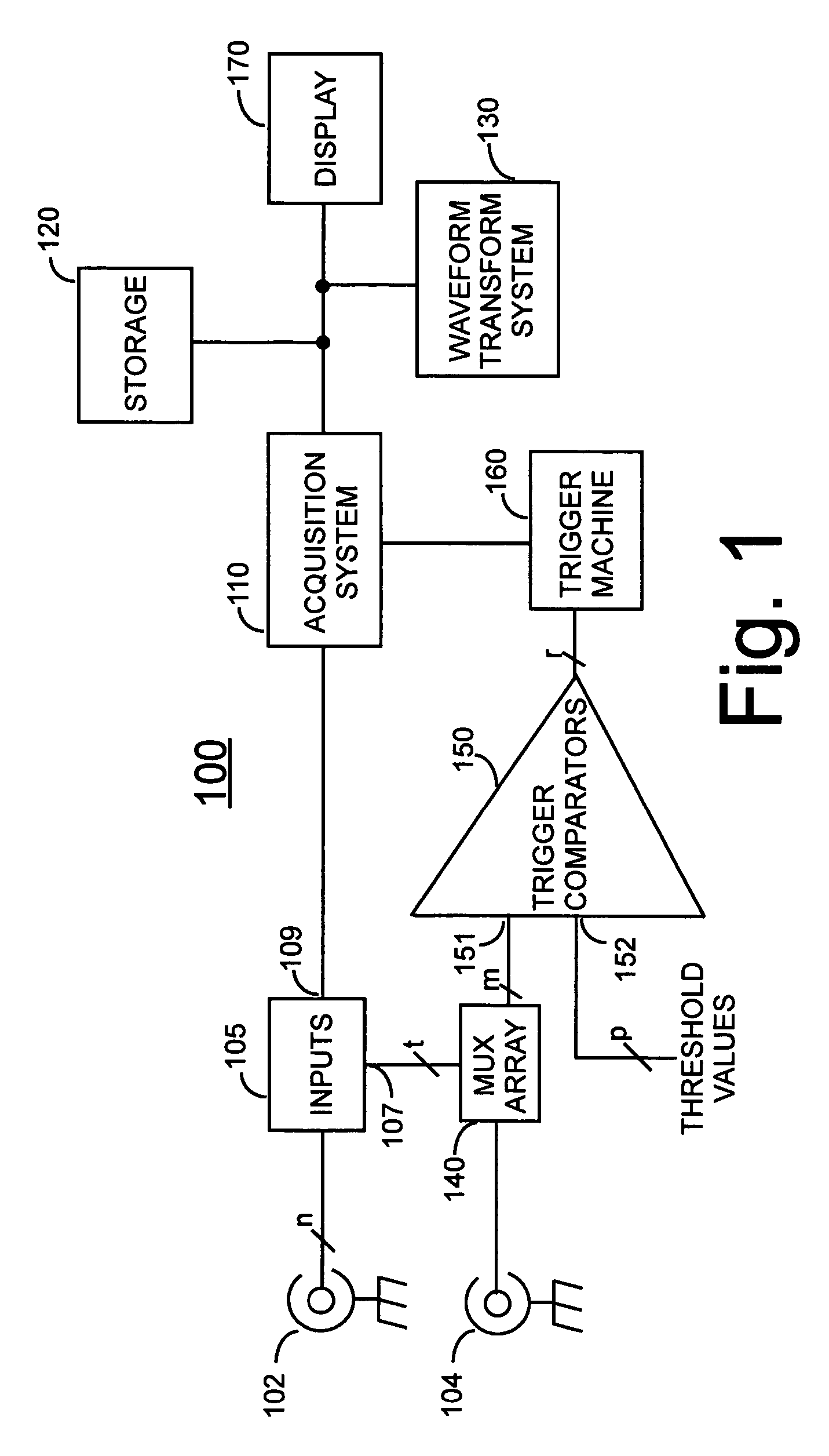
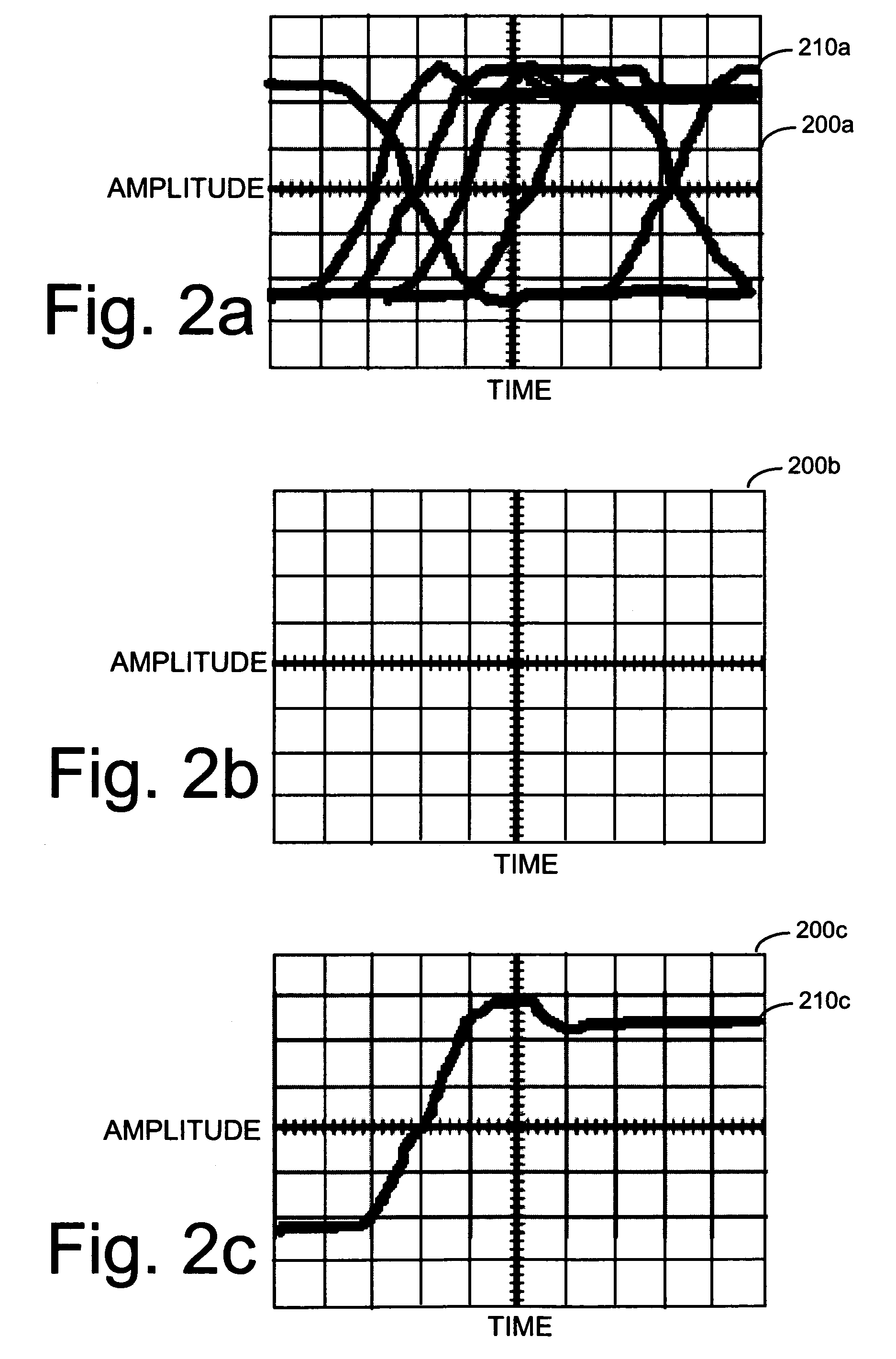
An oscilloscope, previously called an oscillograph, and informally known as a scope or o-scope, CRO (for cathode-ray oscilloscope), or DSO (for the more modern digital storage oscilloscope), is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. Other signals (such as sound or vibration) can be converted to voltages and displayed.
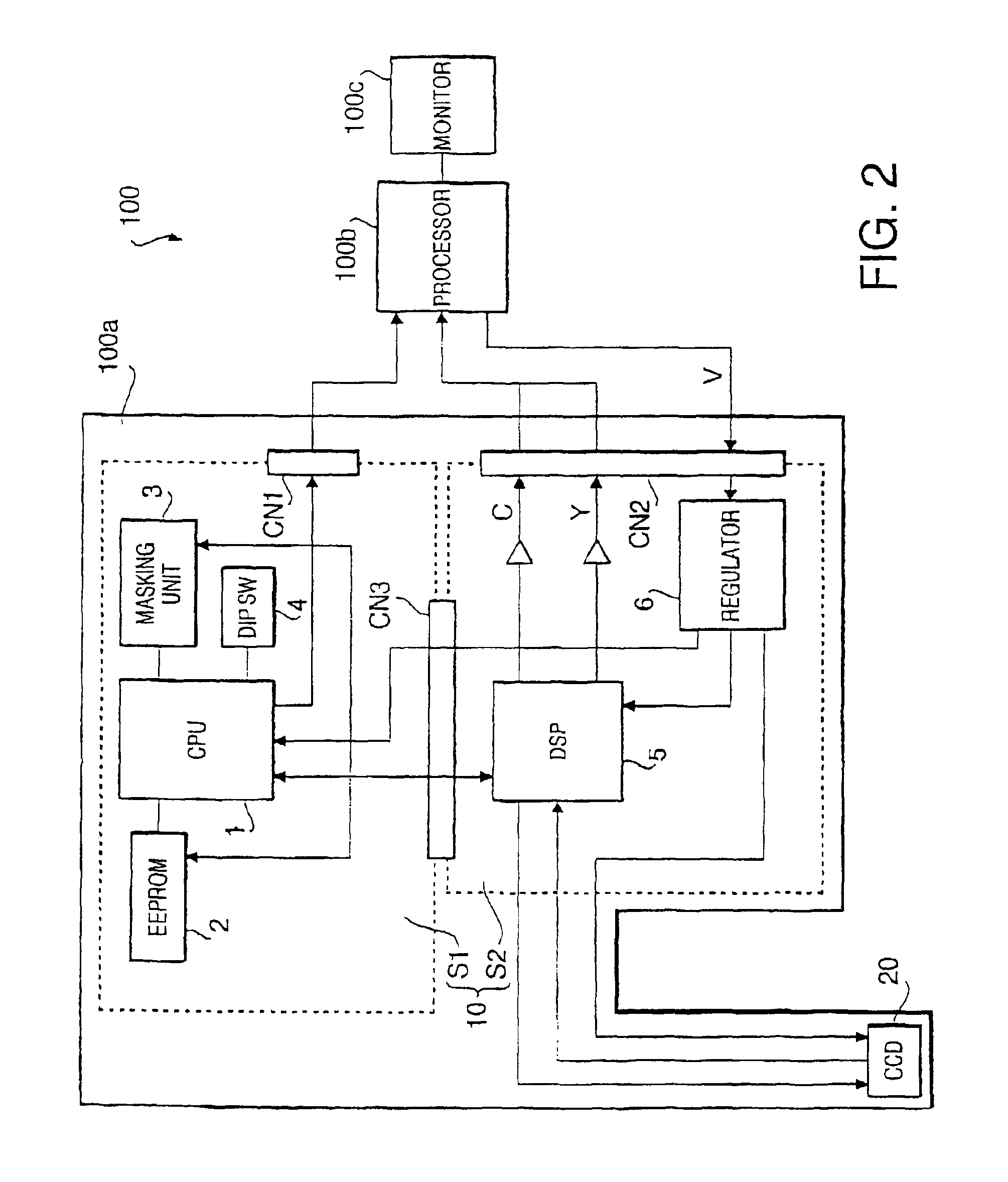
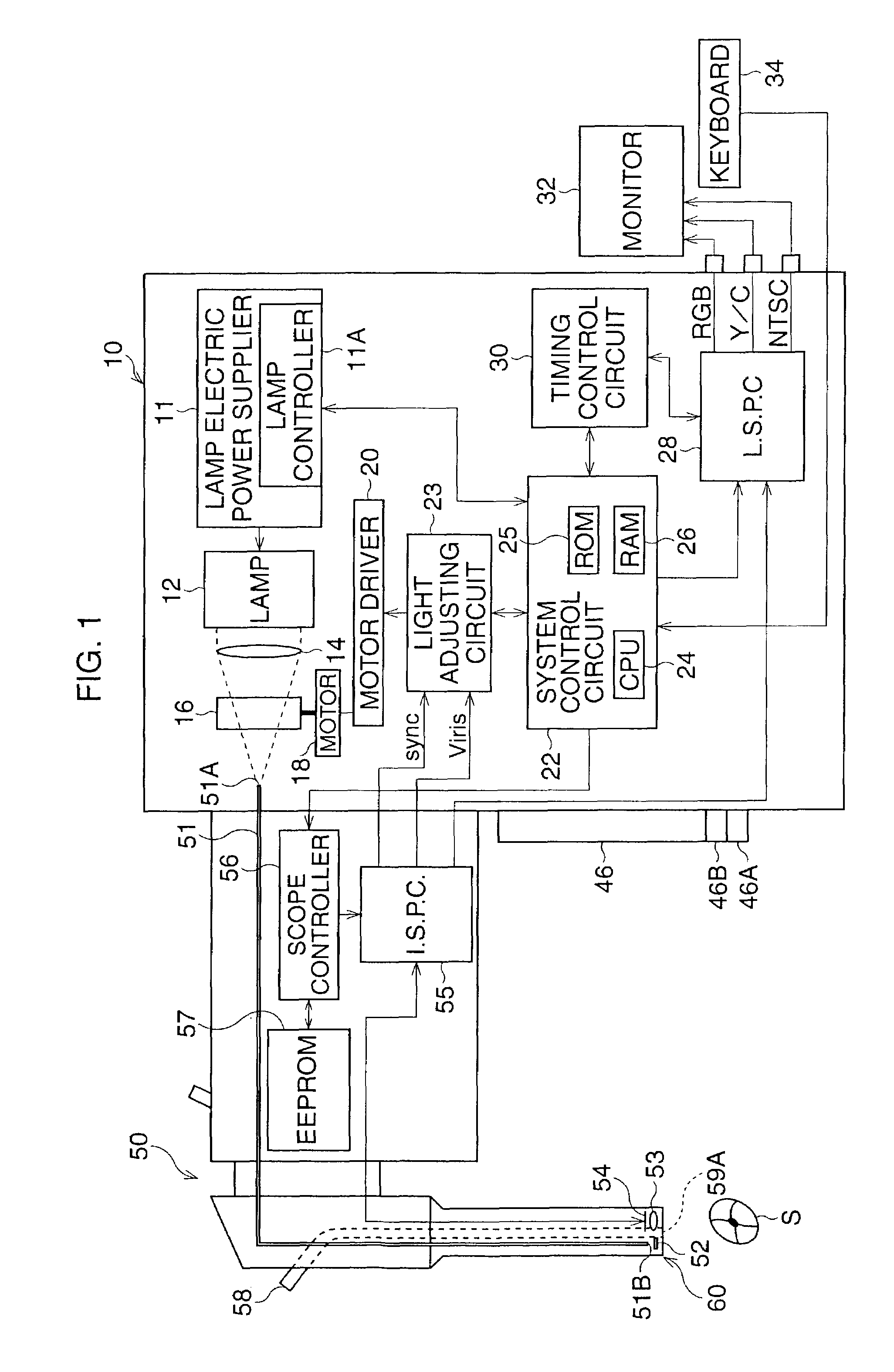
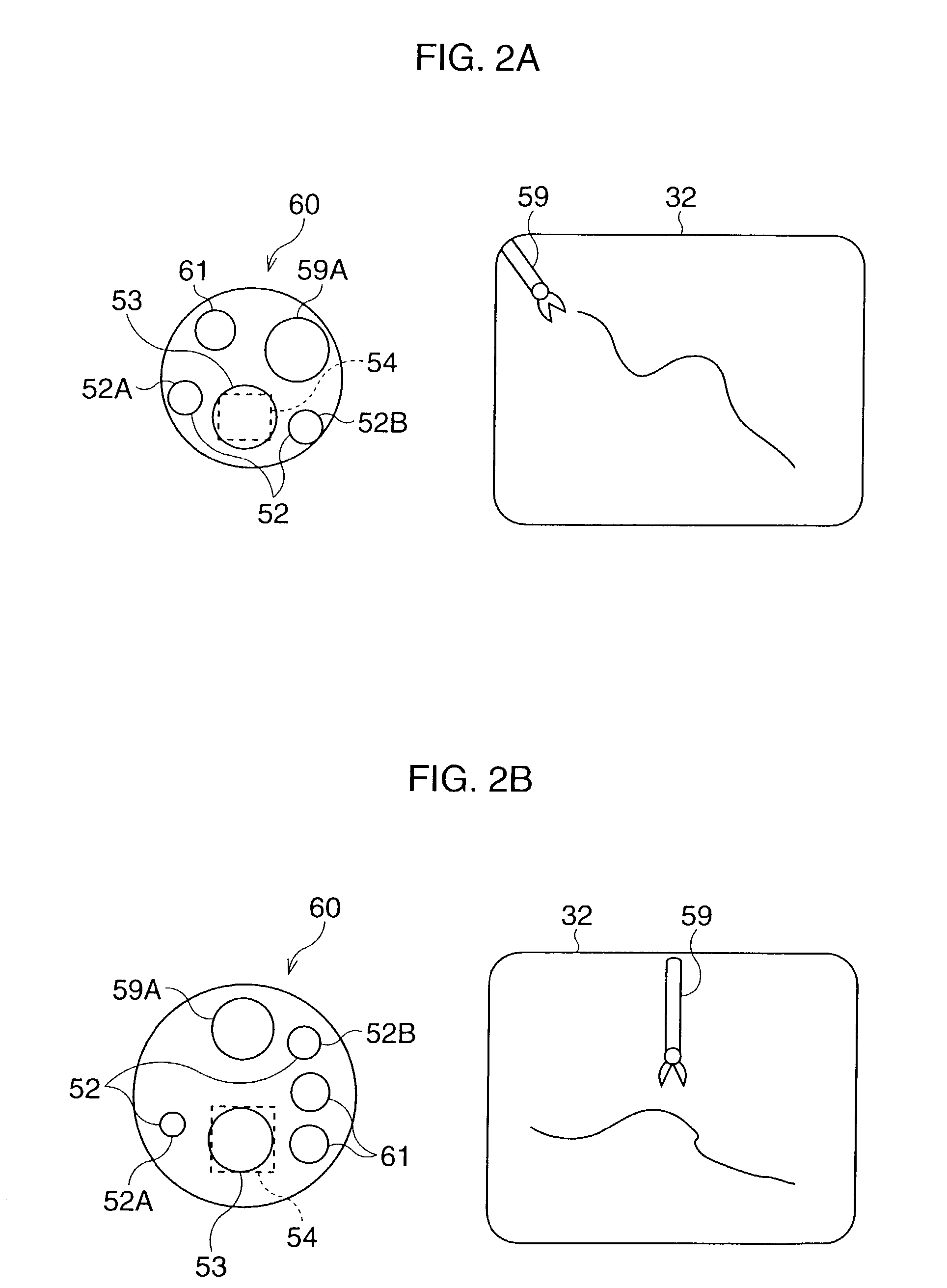
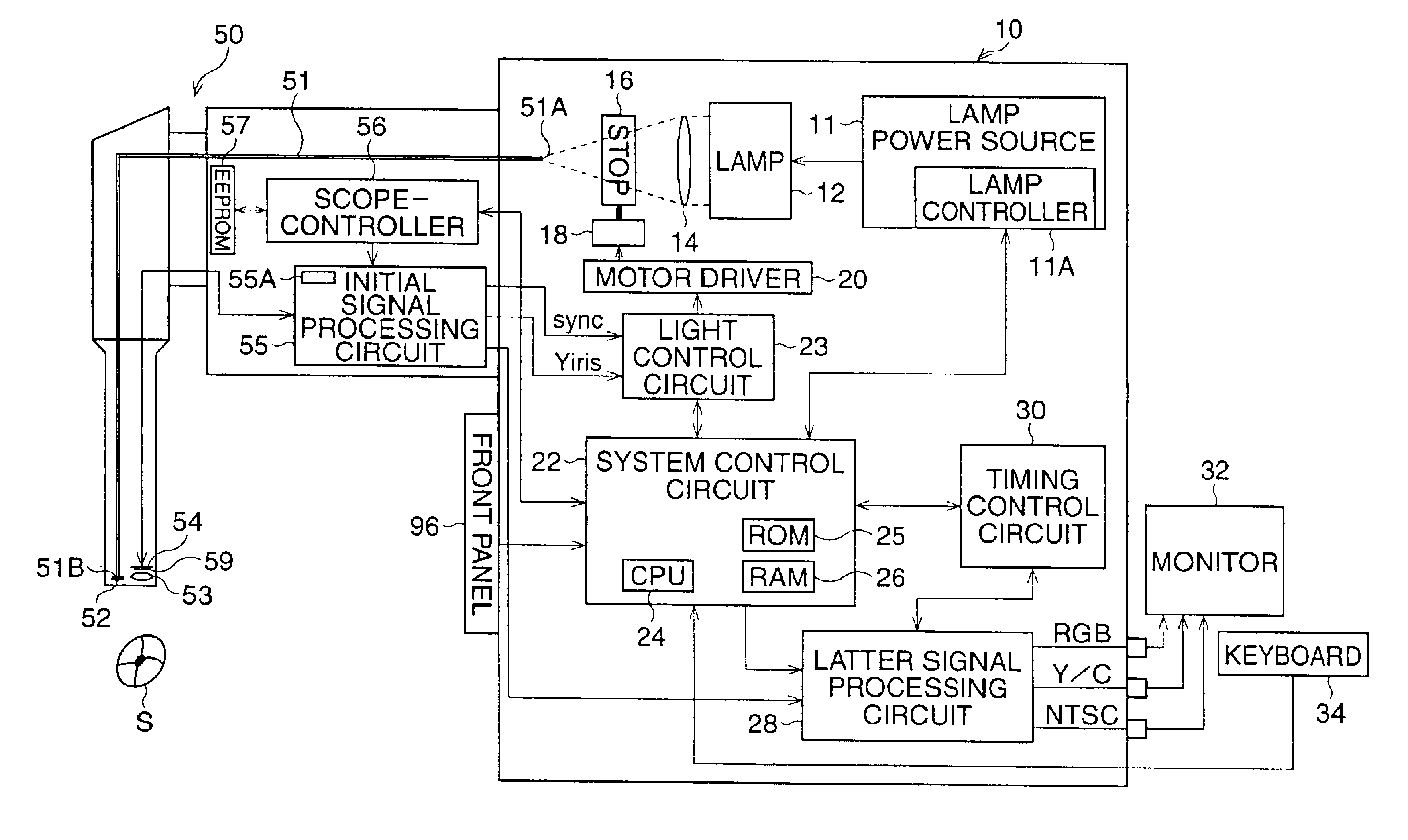
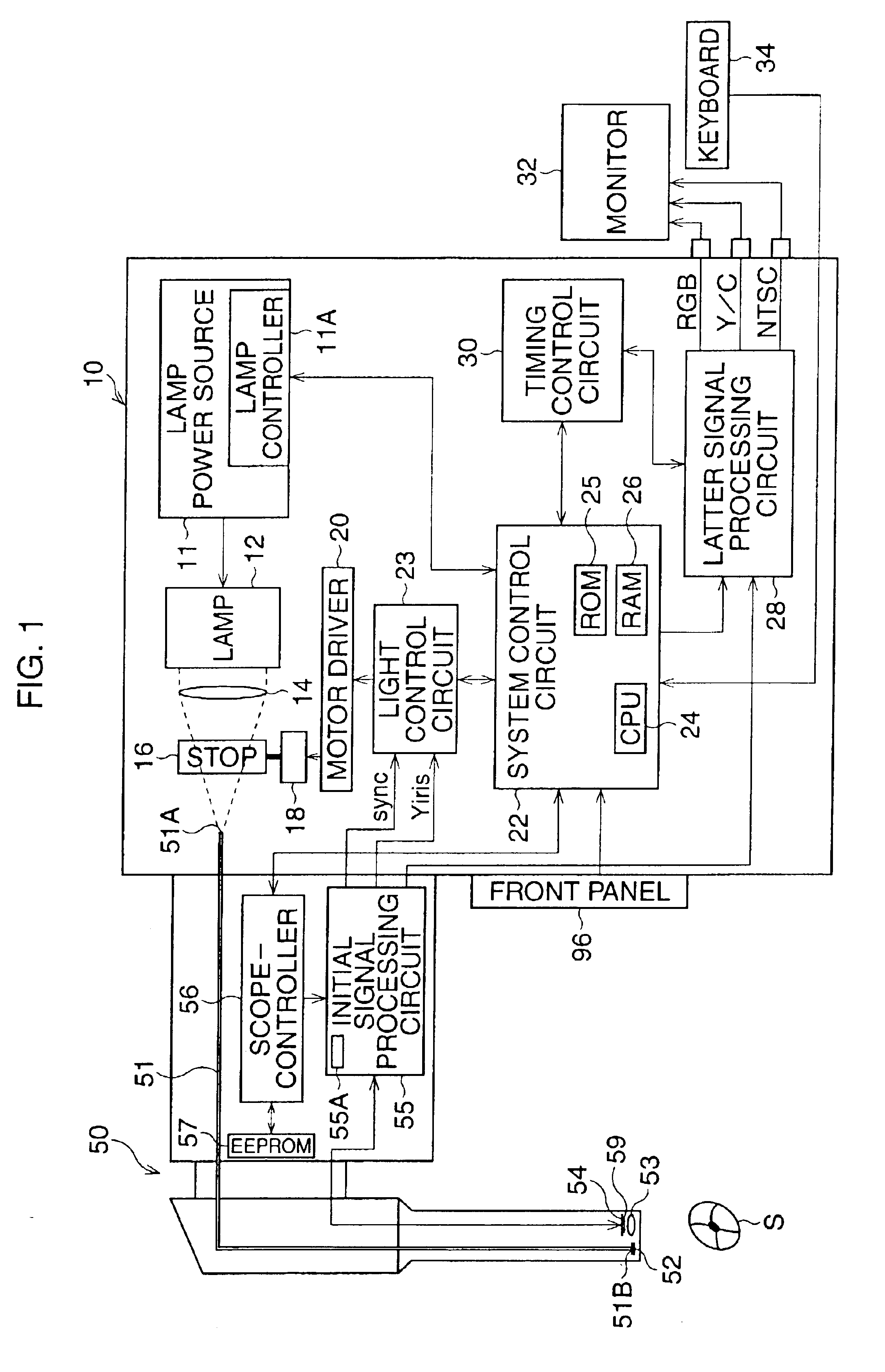
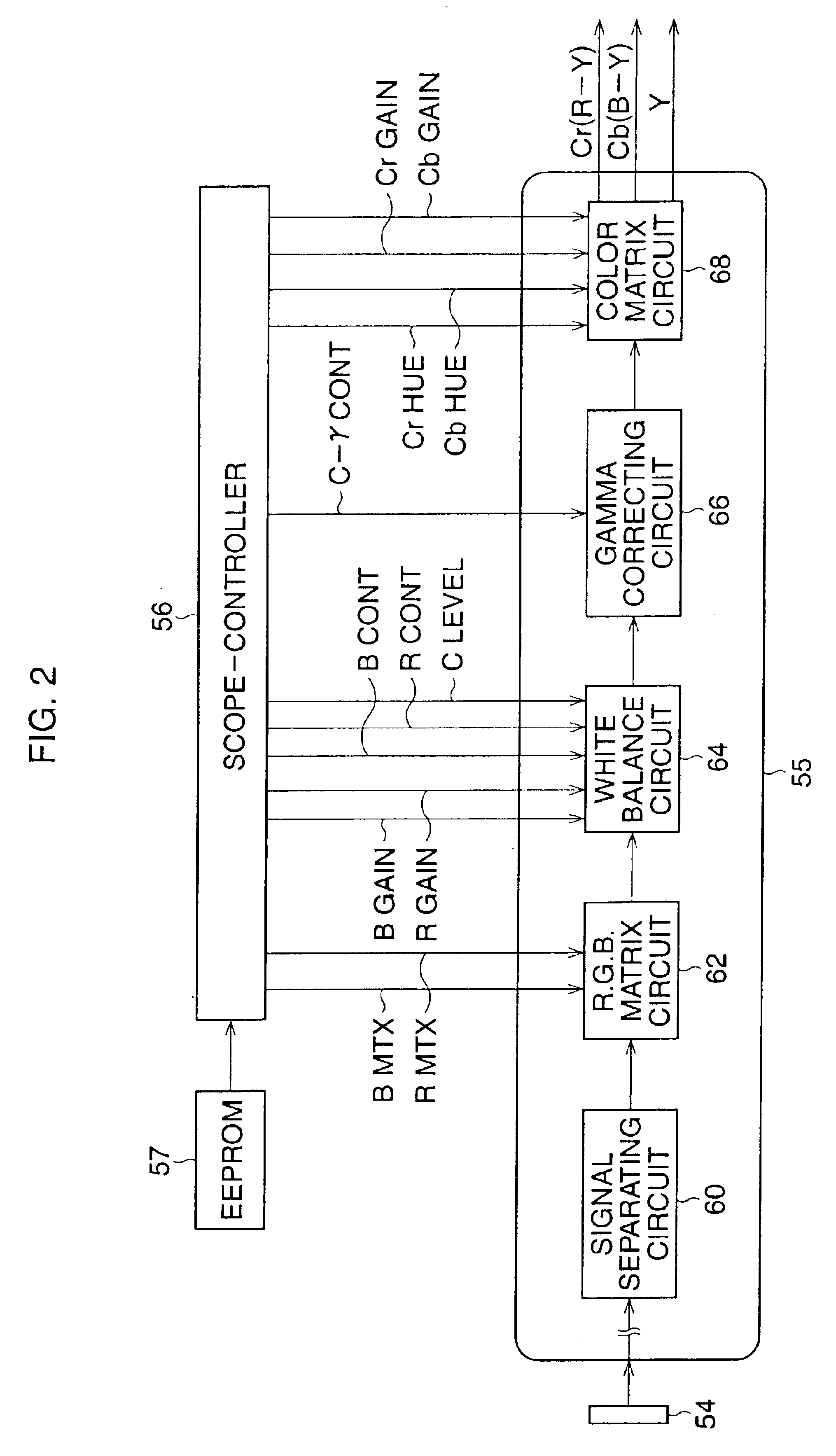
Endoscope system
InactiveUS20090290016A1Easy to updateEndoscopesColor television detailsImaging processingParallel computing
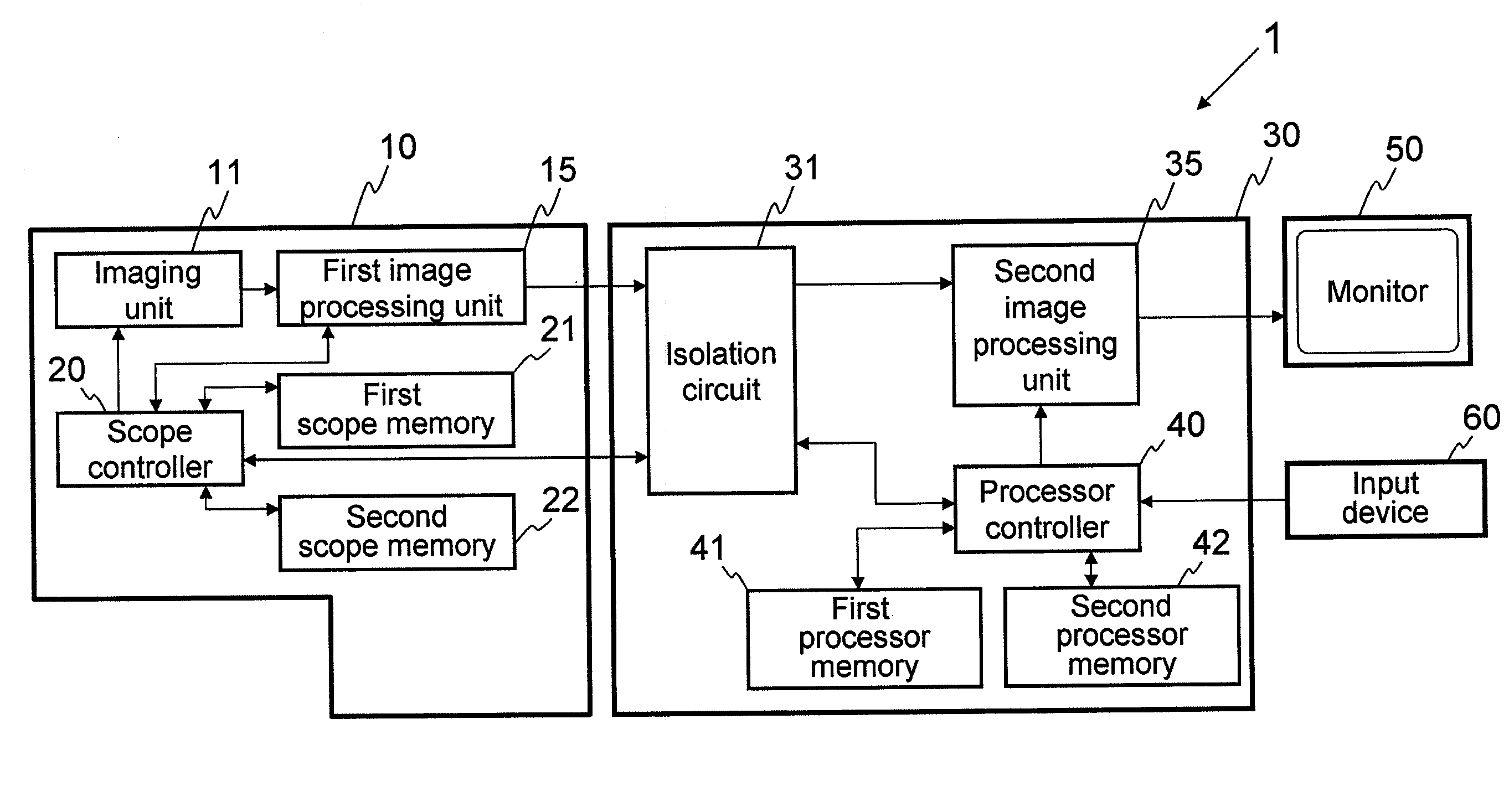
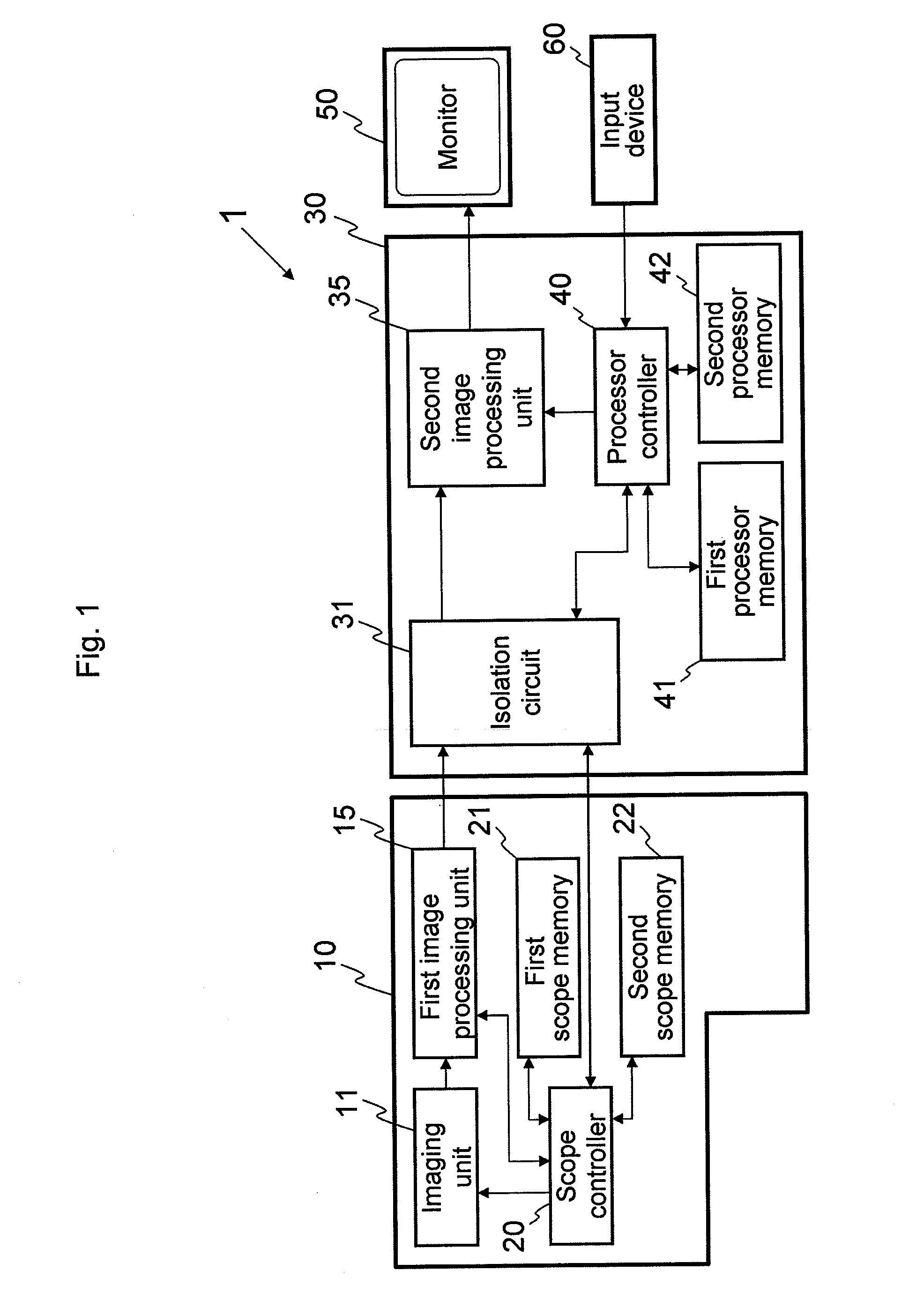
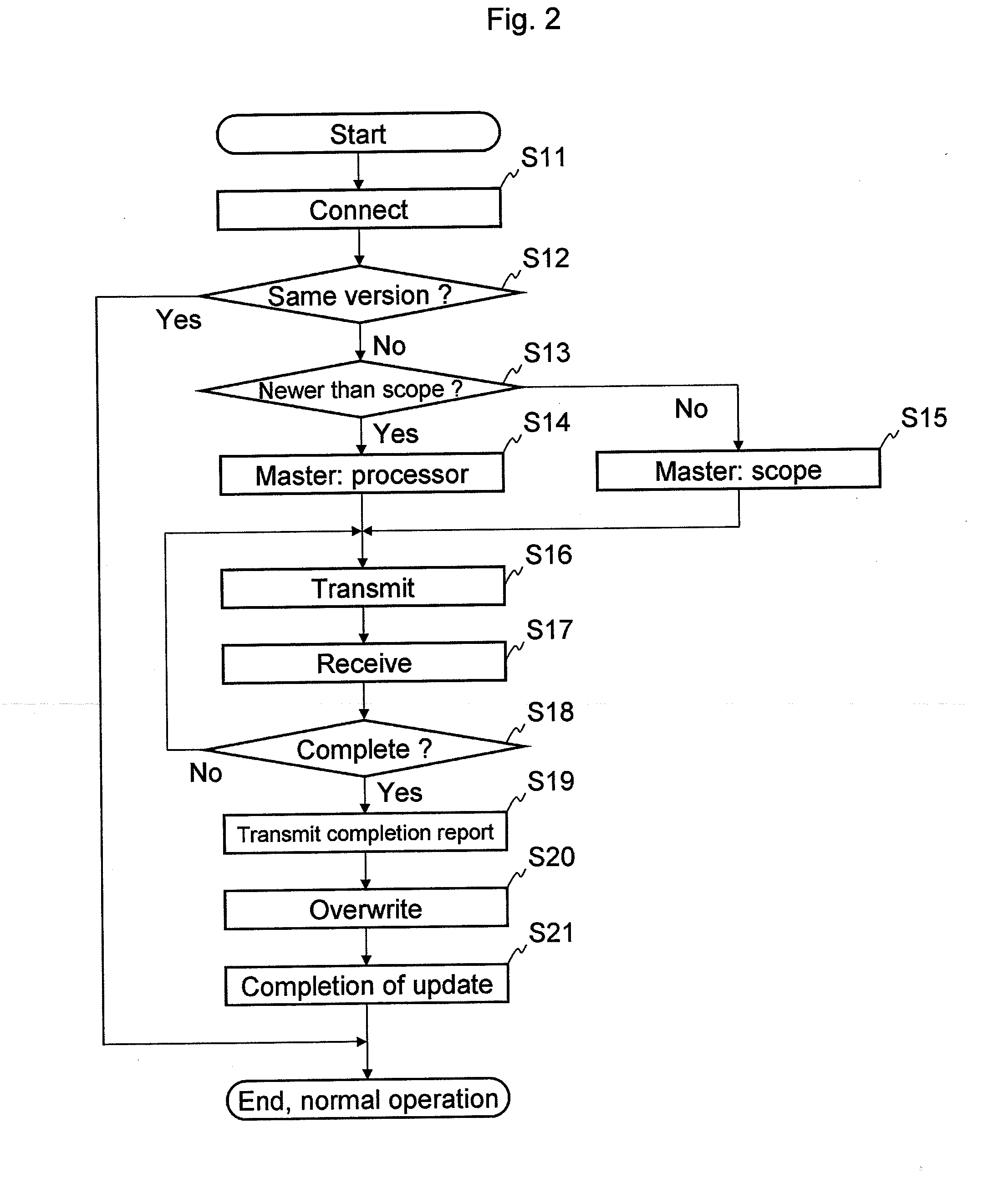
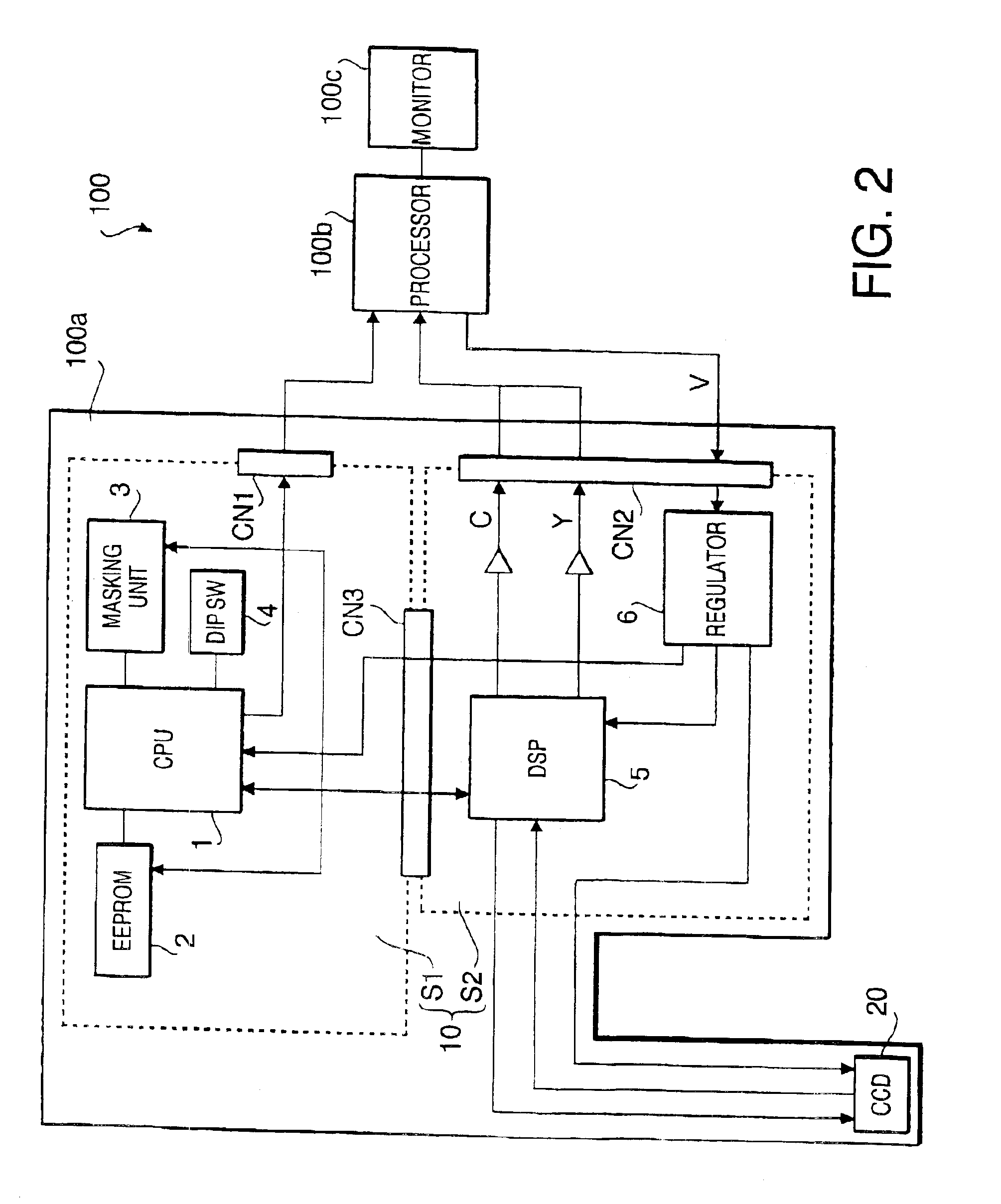
An endoscope system comprises a scope and a processor. The scope has an imaging sensor, a first image-processing unit that performs primary image processing, a first memory, and a second memory. The first and second memories are non-volatile. The processor has a second image-processing unit that performs secondary image processing, and a processor memory that is non-volatile. The first memory stores an system data that includes parameters for the primary and secondary image processing. The processor memory stores the system data. The second memory is used for storing the system data stored in the processor memory when it is determined that the system data stored in the first memory is older than the system data stored in the processor memory. The system data stored in the second memory is overwritten onto the first scope memory after the system data is stored in the second memory.
Owner:HOYA CORP
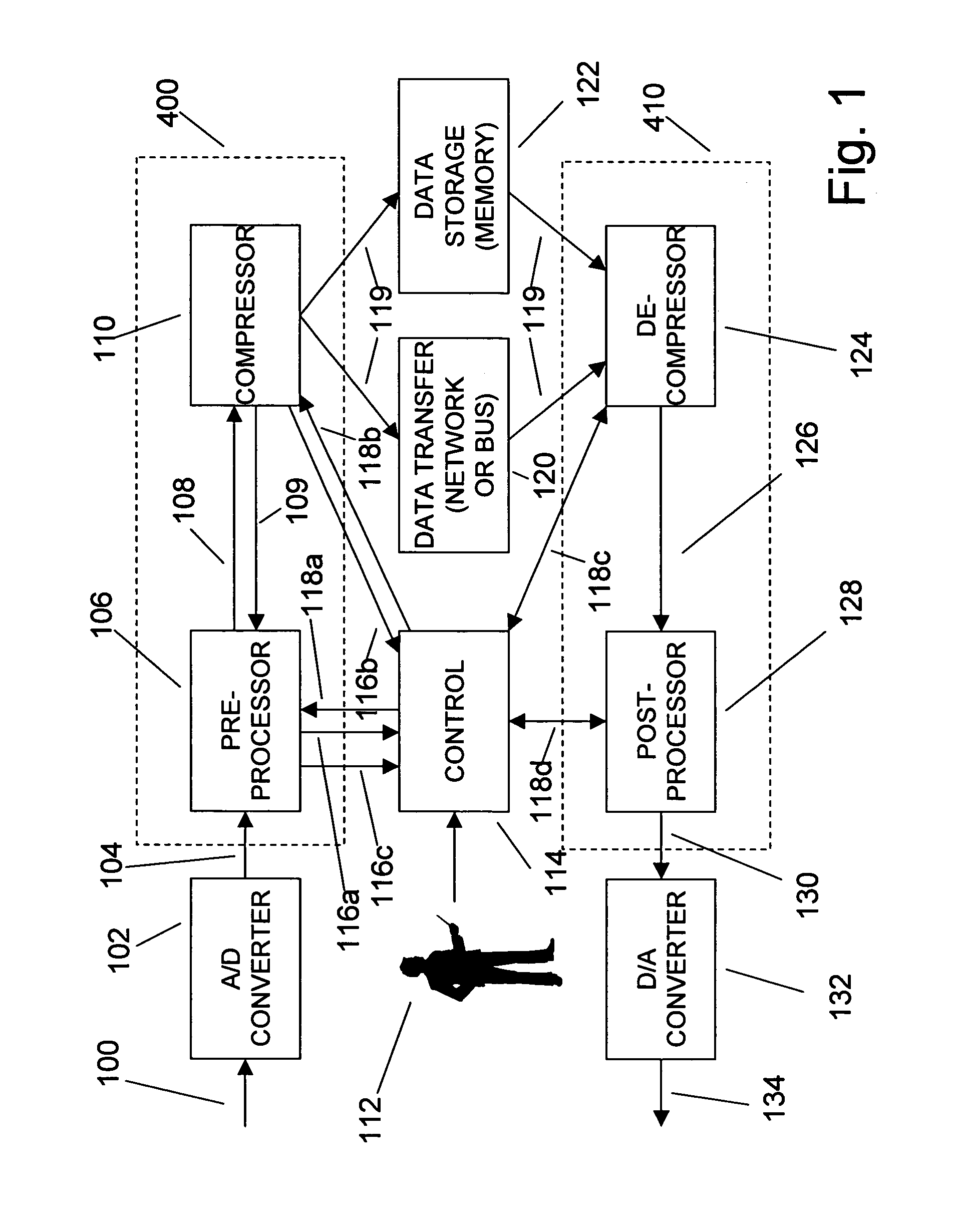
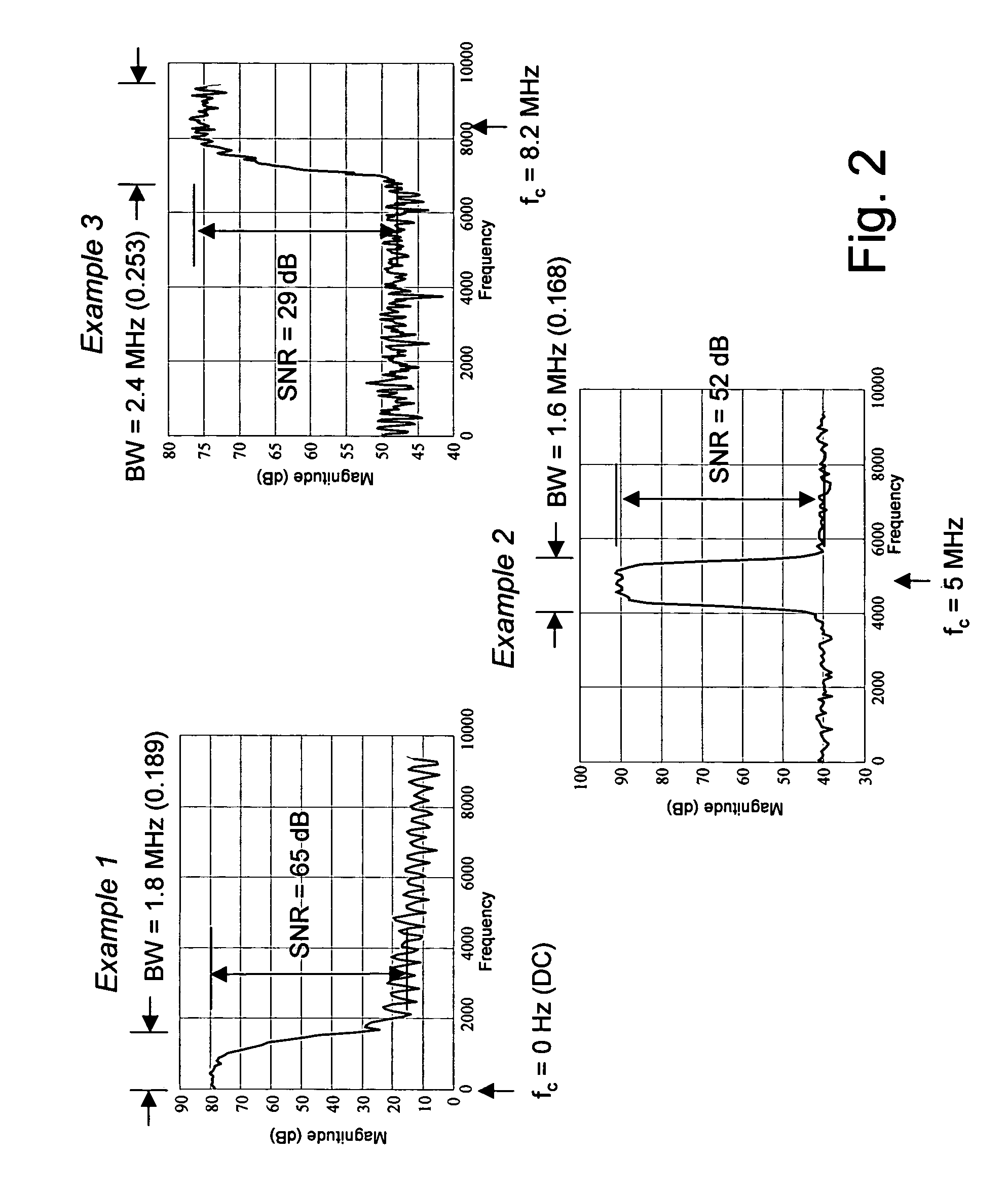
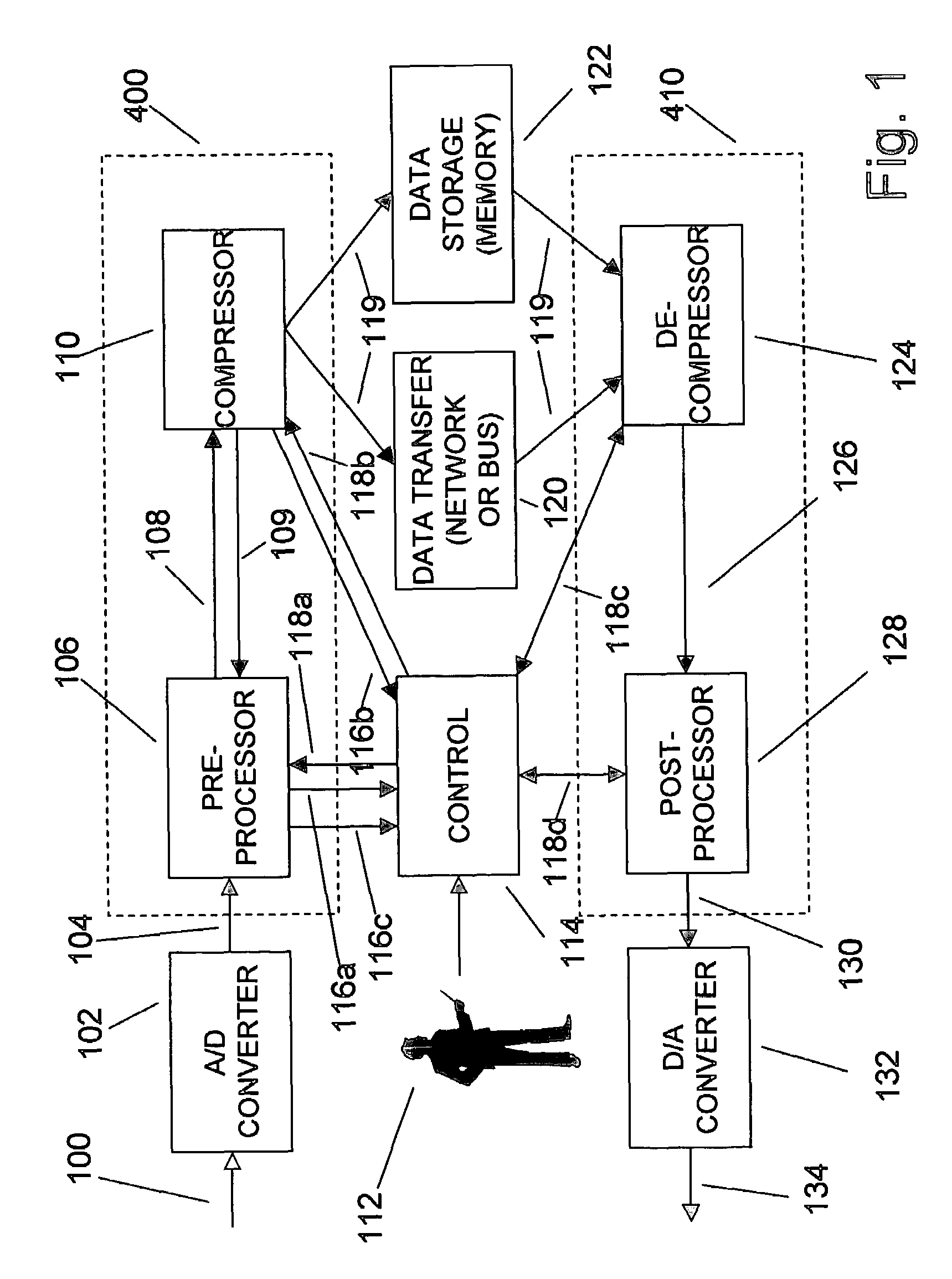
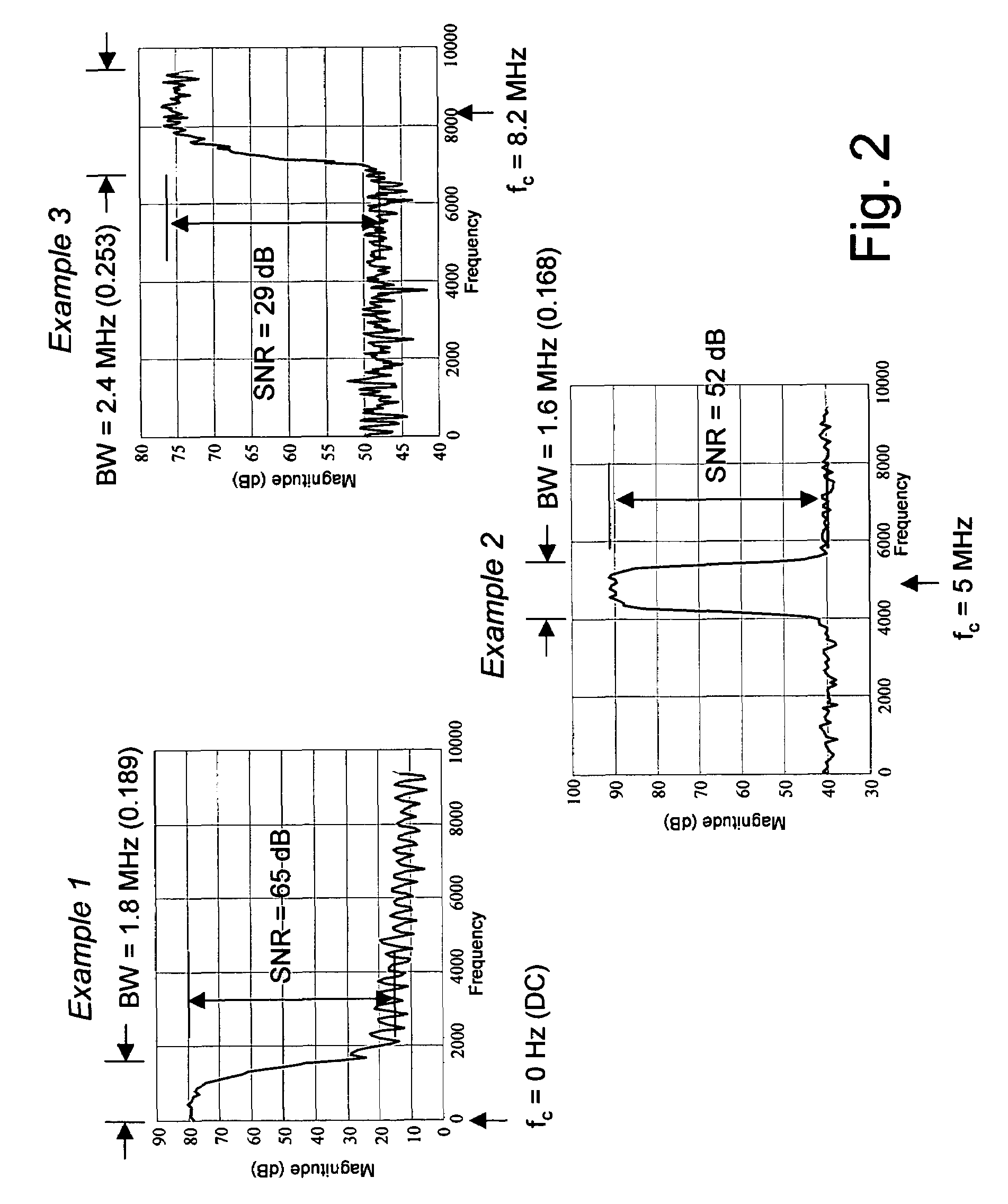
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
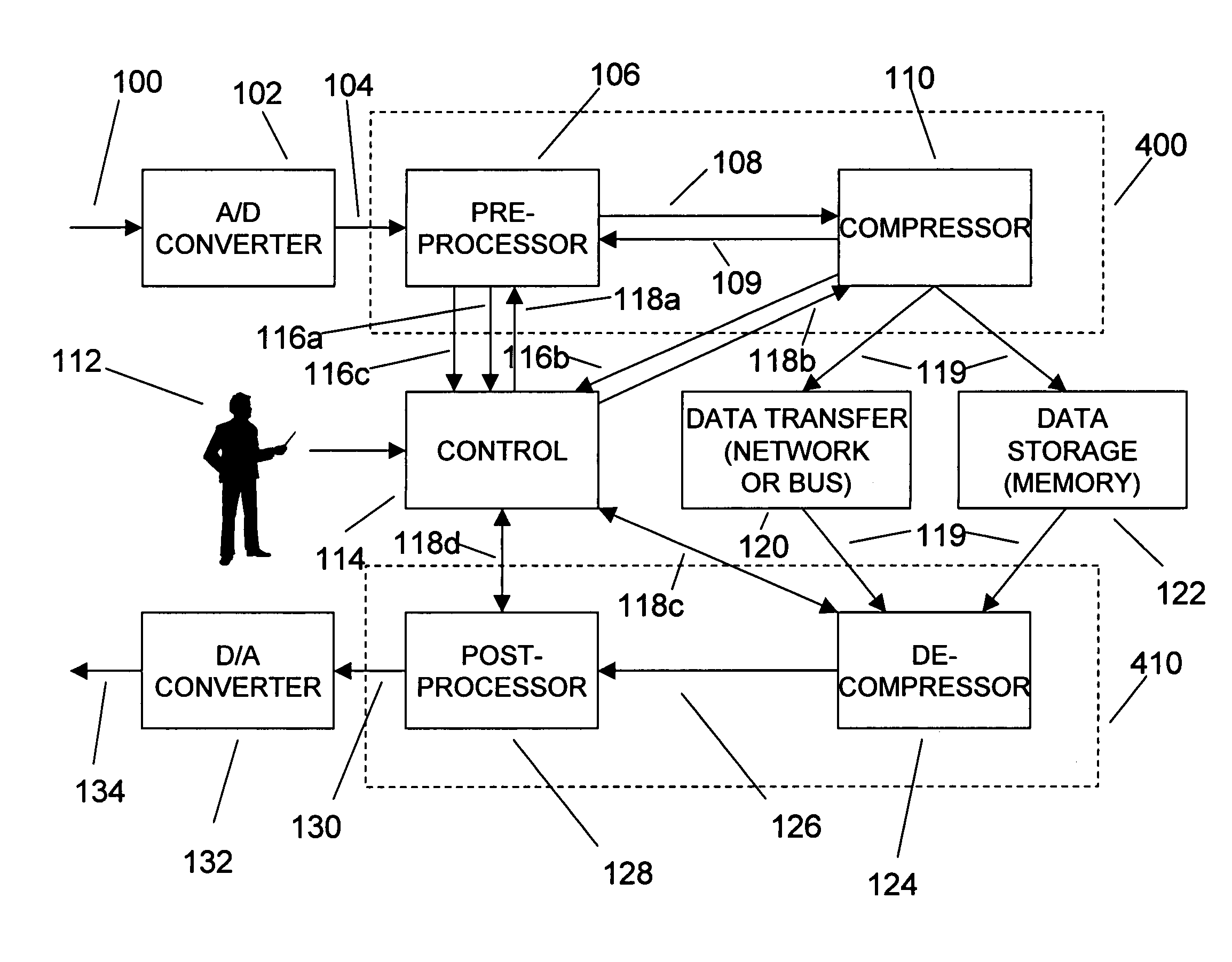
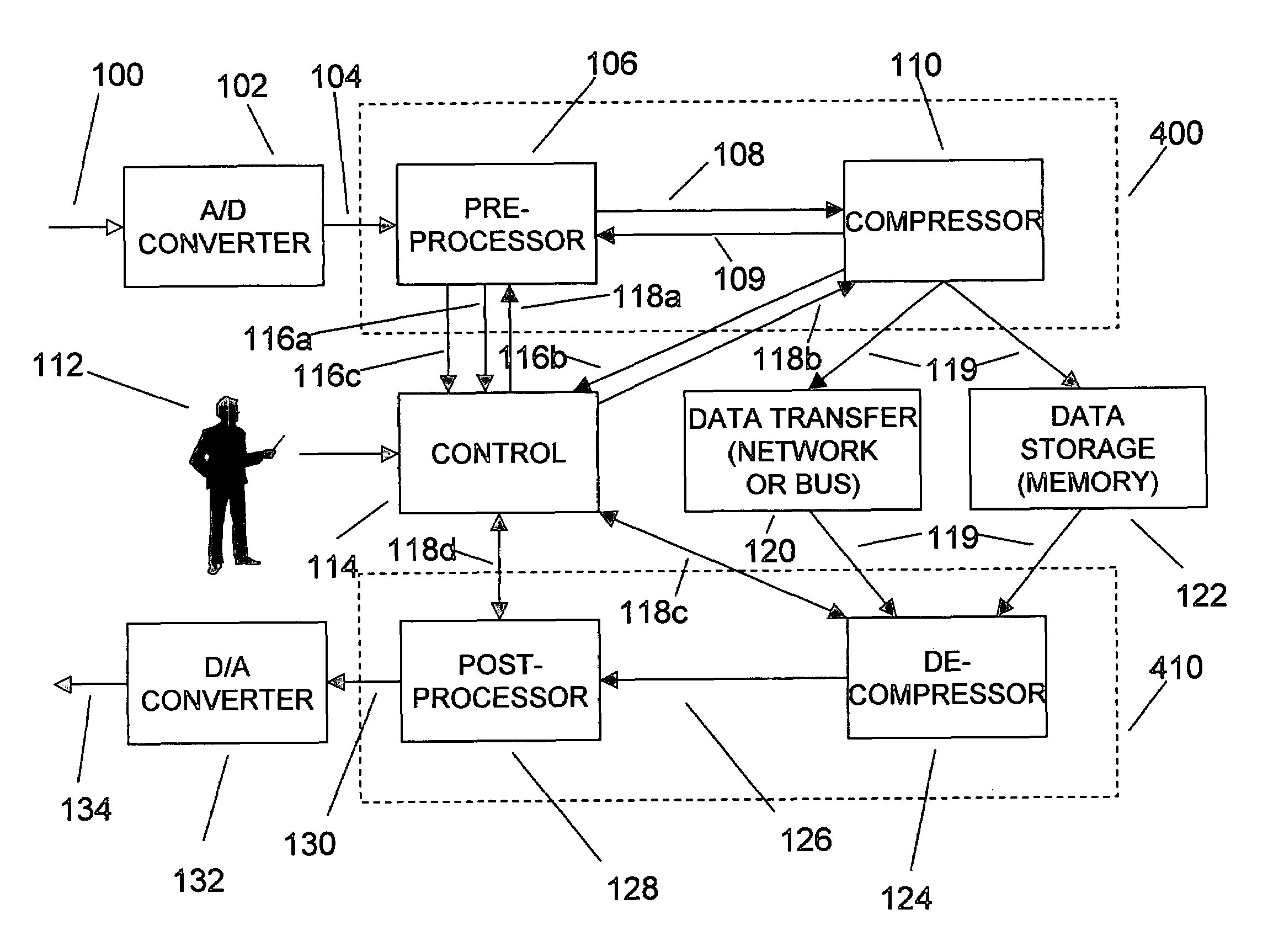
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Scope adjustment method and apparatus
InactiveUS6886287B1Facilitate windage adjustmentEasy to correctSighting devicesPlumb lines for surveyingField of viewEmbedded system
A rifle scope system allows adjustment of the scope while a shooter maintains the shooting posture and the scope sight picture. The scope system comprises an adjustment system comprising an electromechanical mechanism that responds to a signal from a remote controller manipulated by the shooter without having to significantly disturb the shooting posture. The adjustment system allows the shooter to adjust the scope's point of aim to coincide with a bullet's point of impact at a target. Such adjustment can be performed either by the shooter. Alternatively, such adjustment could be performed by a processor configured to adjust the point of aim based on a ballistic parameter associated with the bullet or the shooting environment. The adjustment system allows such processor-determined adjustments to be effected in a quick manner.
Owner:BELL JOHN CURTIS +1
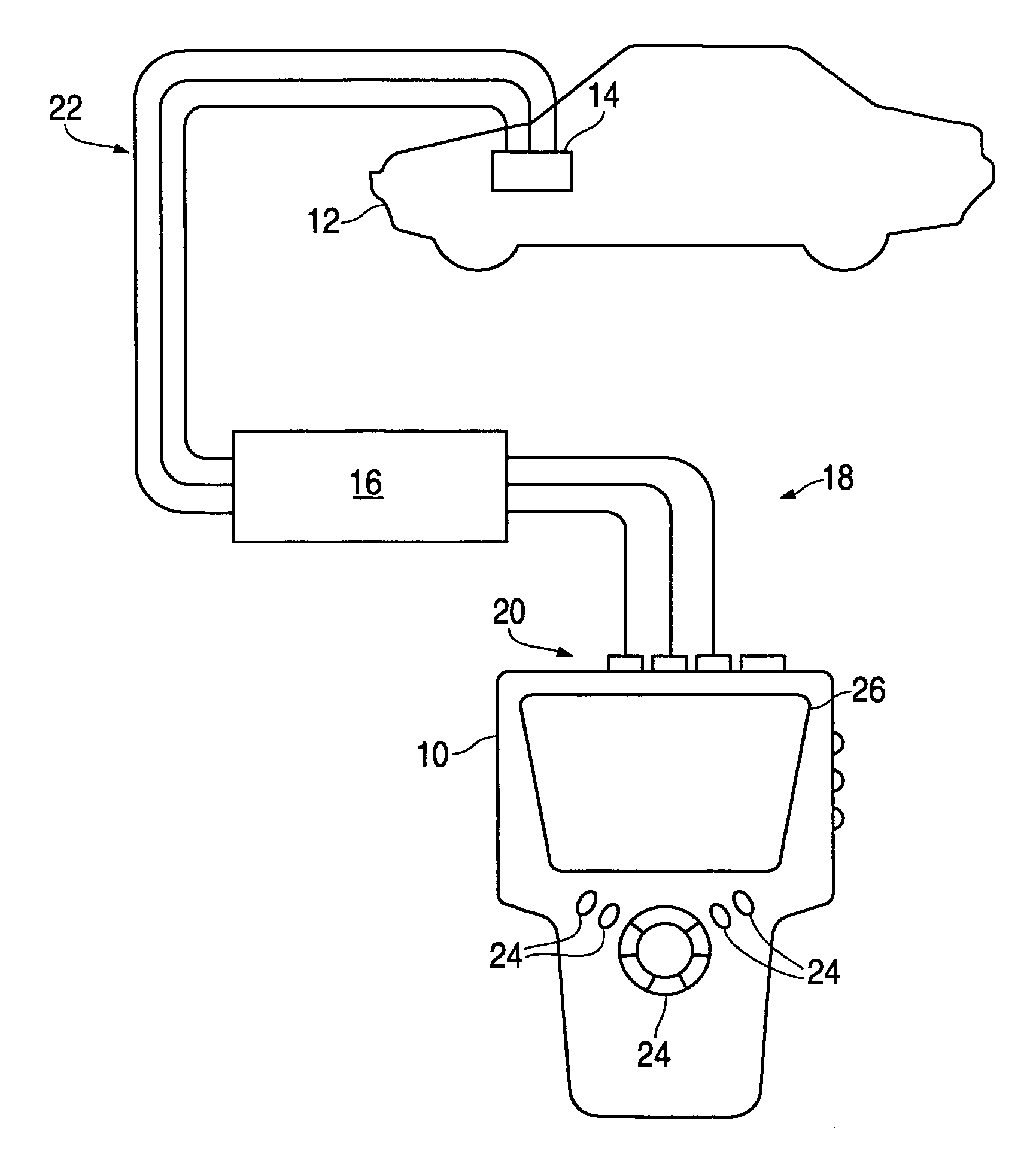
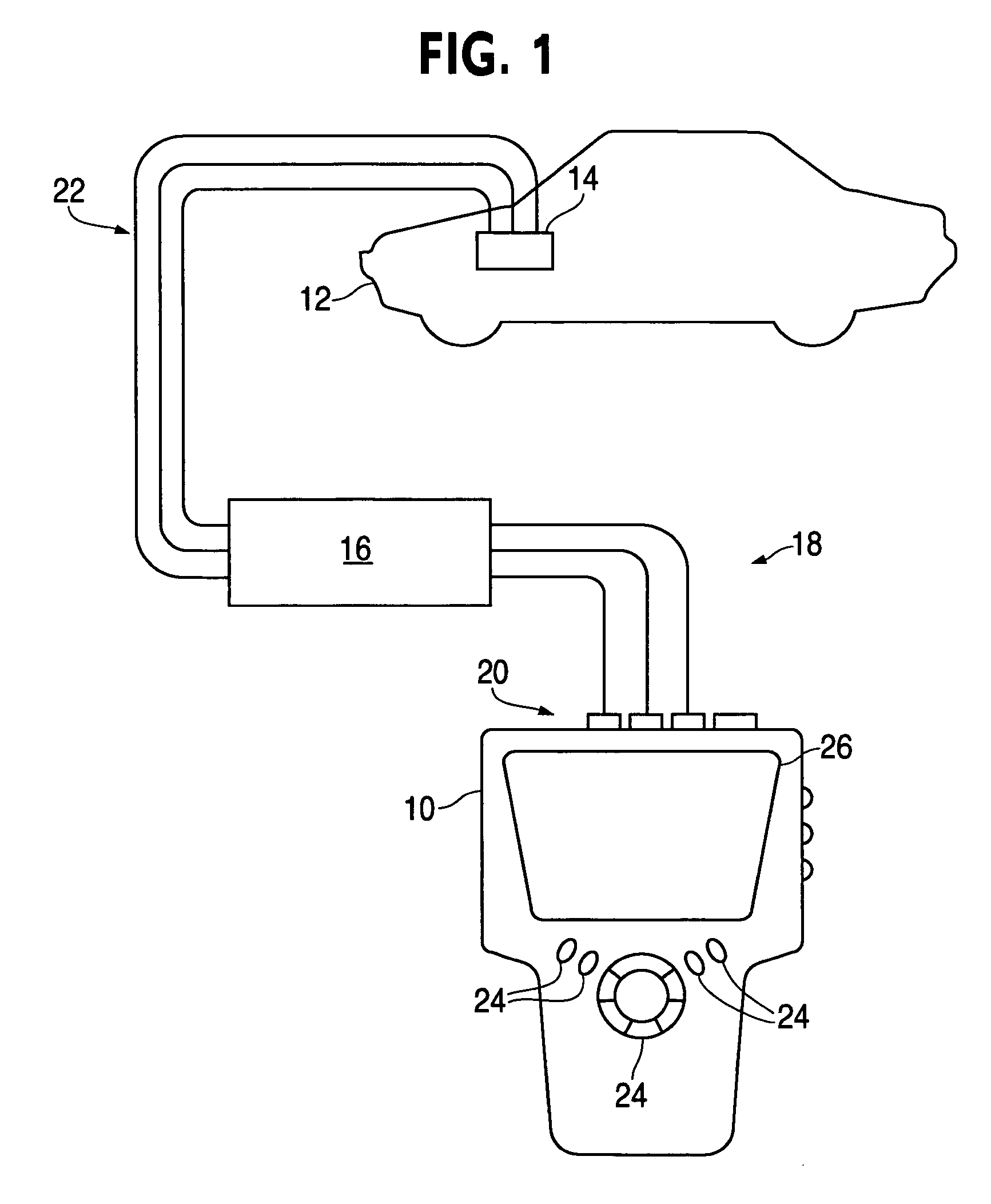
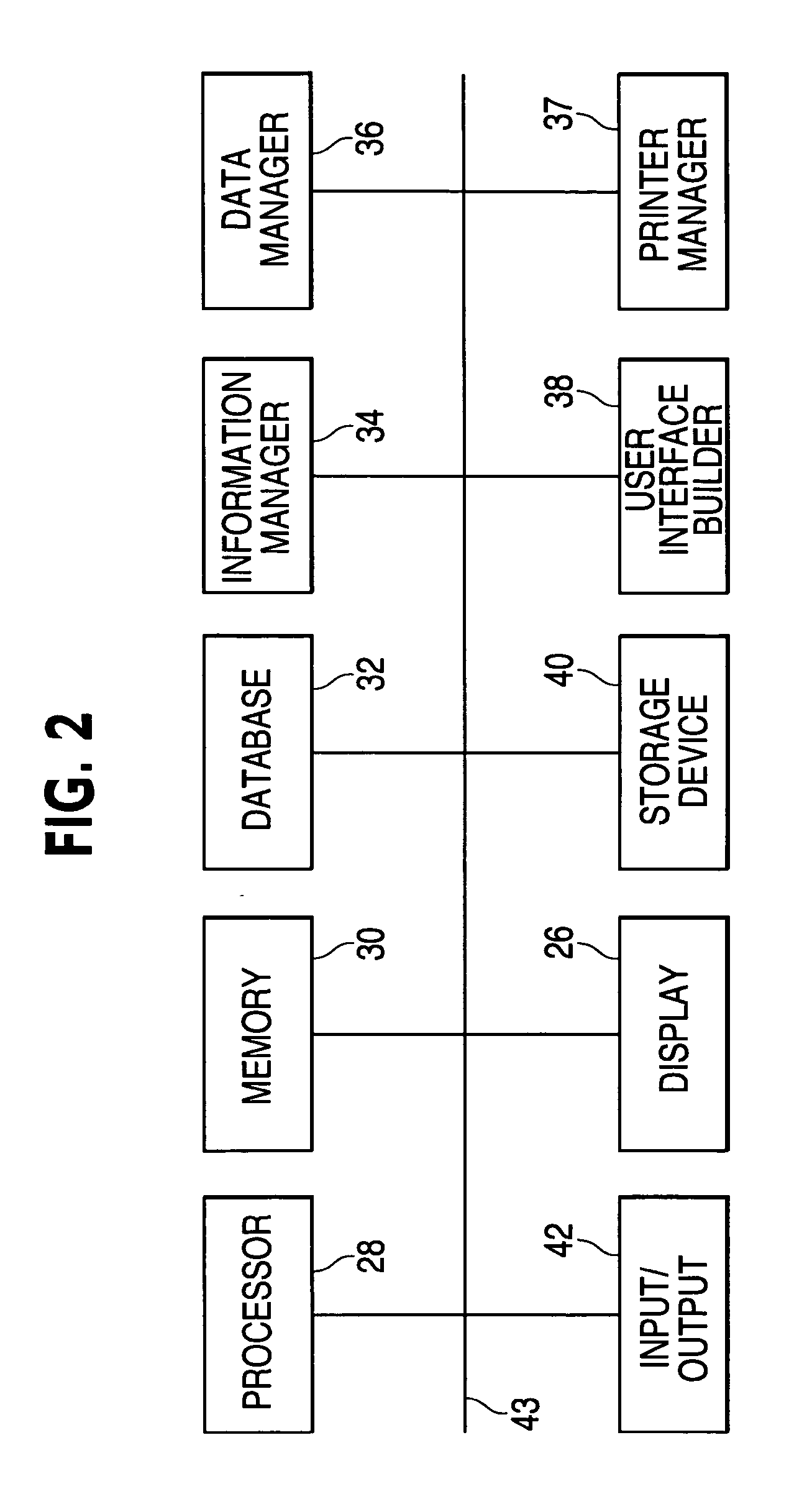
Technical information management apparatus and method for vehicle diagnostic tools
InactiveUS20070100520A1Facilitates user selectionVehicle testingDigital data information retrievalData displayUser interface
A technical information management device includes an information manager, a data manager, a user interface builder, and a vehicle technical information database. The information manager accesses the database in order to provide a segment of the vehicle technical information to the user interface builder. The data manager receives conditioned input data from a vehicle diagnostic tool and sends it to the user interface builder. The user interface builder includes a graphics generator and a display screen formatter. The graphics generator converts the vehicle diagnostic data into graphical coordinate data and the display screen formatter formats the graphical coordinate data for real time display in a digital multimeter mode or in a scope mode. The user interface builder further can display a dual-display screen wherein half of the screen is a vehicle diagnostic data display and the other half of the screen displays vehicle technical information.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
Video game apparatus, image processing method and program
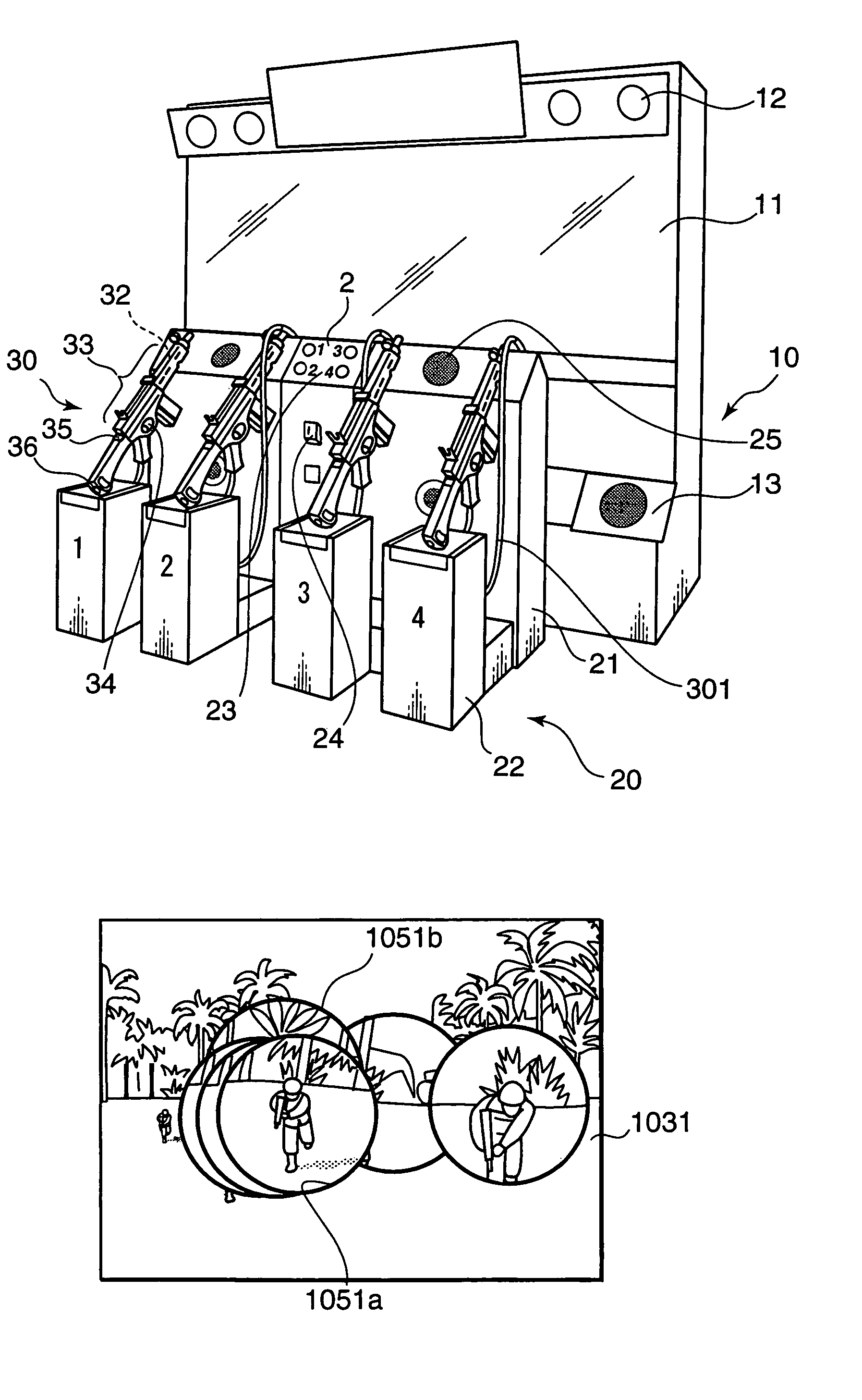
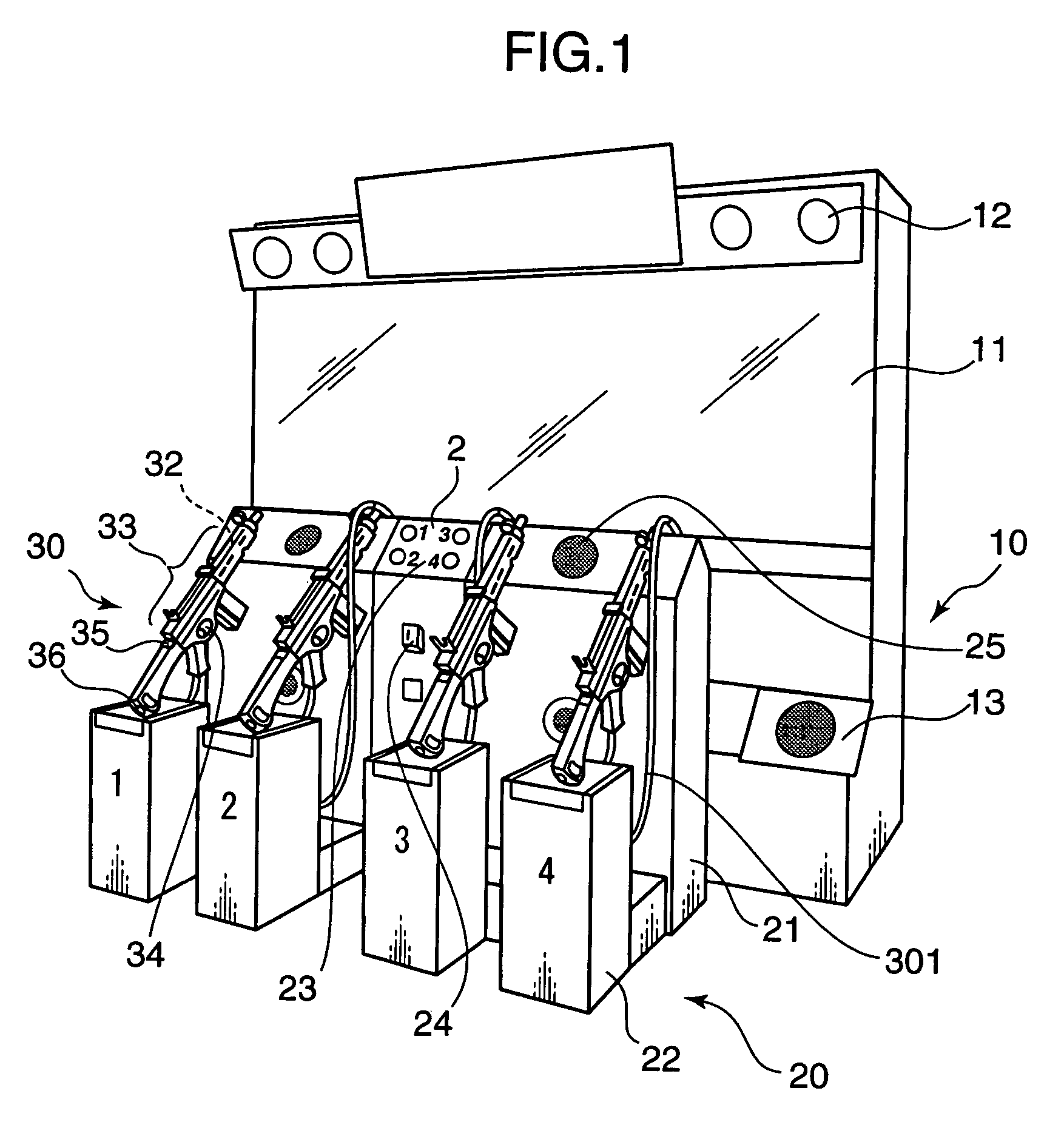
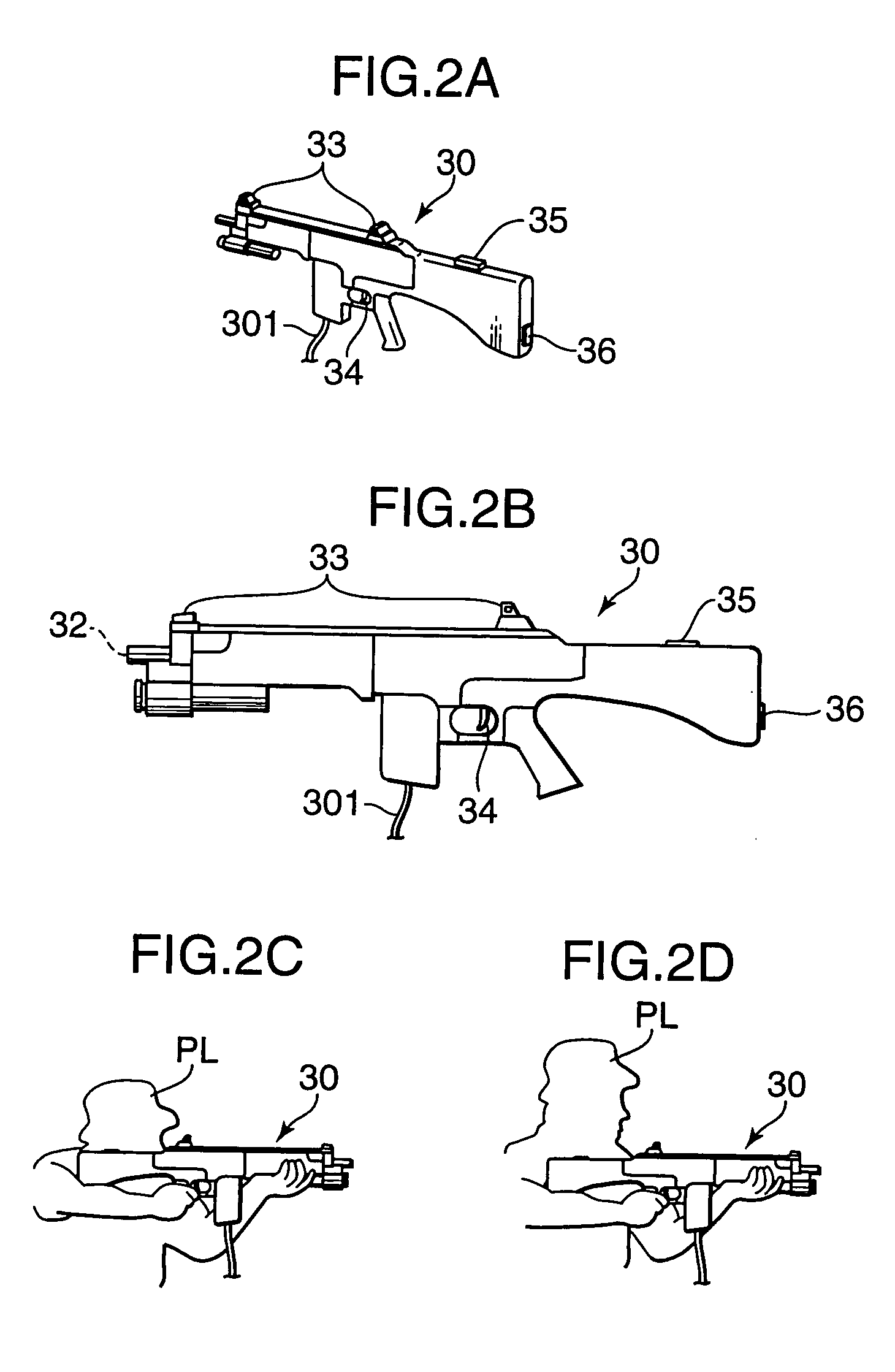
ActiveUS7140962B2Easy to operateIncrease pressureVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingLight spot
It is an object of the present invention to increase the game operability, and to increase the feeling of pressure and feeling of actual presence on the scene, by making it possible to display partial enlarged images of the scope displays or each of a plurality of players in a manner that allows mutual influence on the screen on which the game images are displayed. The apparatus of the present invention is a video game apparatus in which the game is caused to proceed by shooting with four imitation guns 30 from the front surface of a display part 11 on which game images are displayed; in this apparatus, respective enlarged images are created and displayed from an infrared camera 40 that can detect in a discriminating manner respective light spots on the screen from the laser light emitters 32 of the respective imitation guns 30, and positional data of the images displayed in regions that include the light spots corresponding to partial regions that include the respective light spots on the screen of the display part 11.
Owner:KONAMI DIGITAL ENTERTAINMENT CO LTD
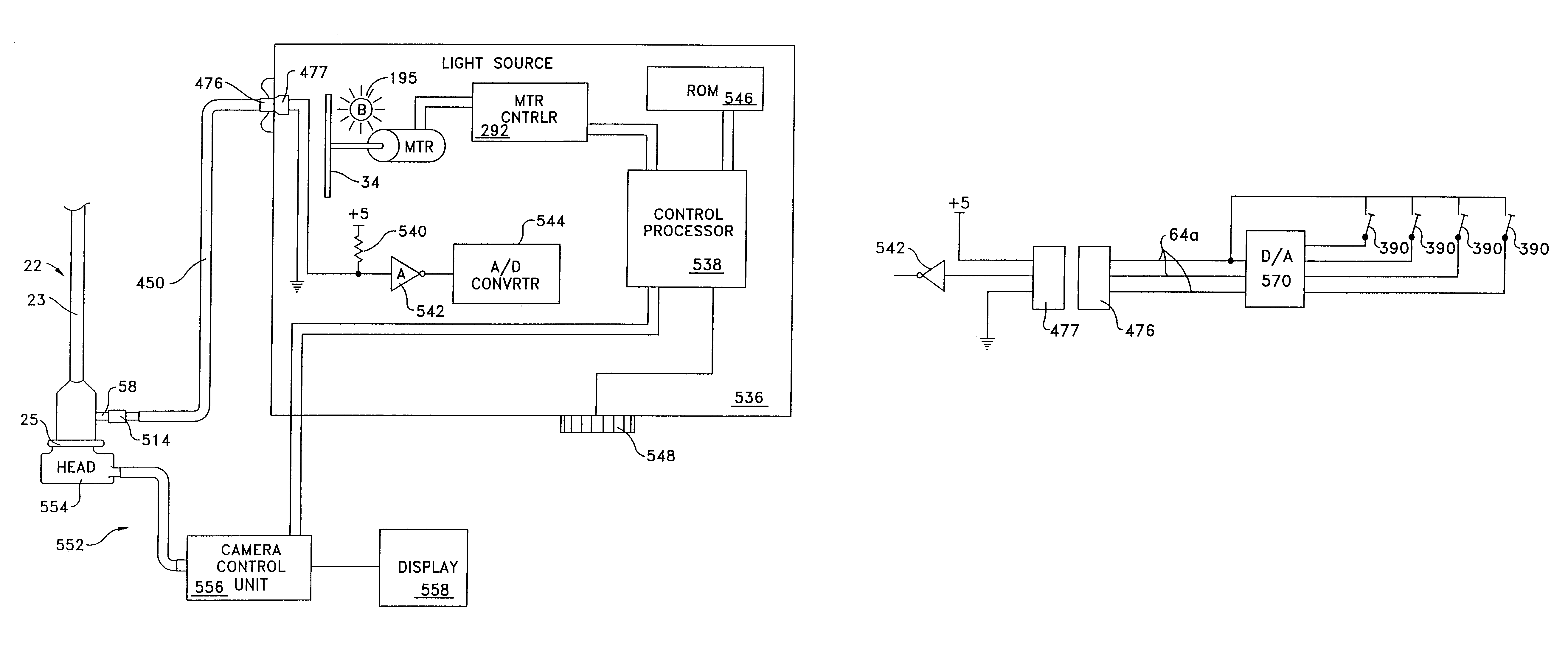
Endoscope assembly useful with a scope-sensing light cable
An endoscope assembly consisting of an endoscope 622, a light source, 626 and a camera 552 with display 558. The endoscope contains a memory 670 with data that describes the endoscope and its operating characteristics. When the light source is connected to the endoscope with a fiber optic cable 628, the data in the memory are read into a control processor 538a internal to the light source. The control processor, based on the endoscope data configures the light source so that it emits an appropriate amount of light for that endoscope. The light source also sends a control unit 556 of the camera data indicating the type of endoscope to which the camera is attached. Based on this endoscope type data, the control unit processes the image signals generated by the camera head in an appropriate form for the attached endoscope so as to produce appropriate signals for presenting an image on the display.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Electric energy quality and electrical power system malfunction detection wave recording device and method
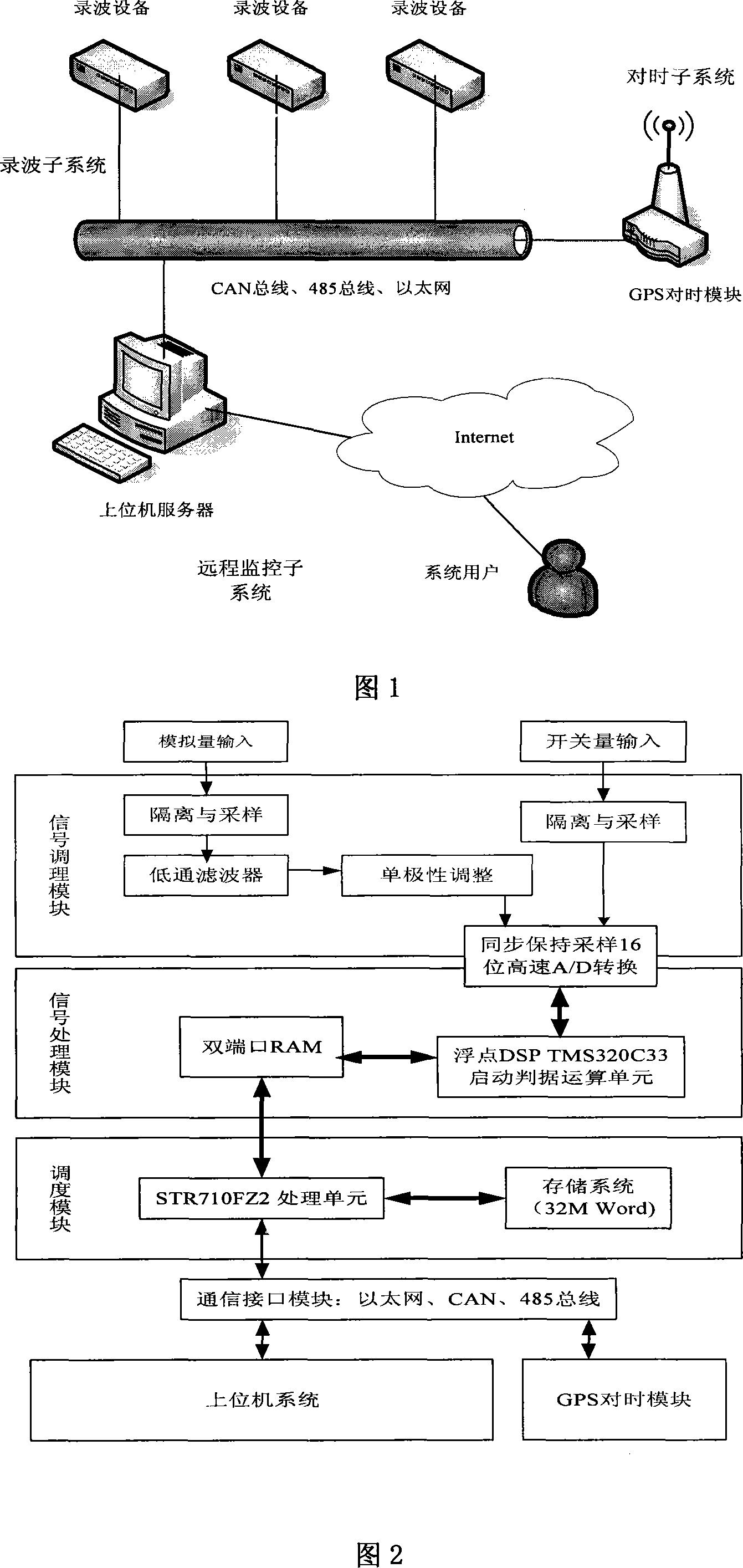
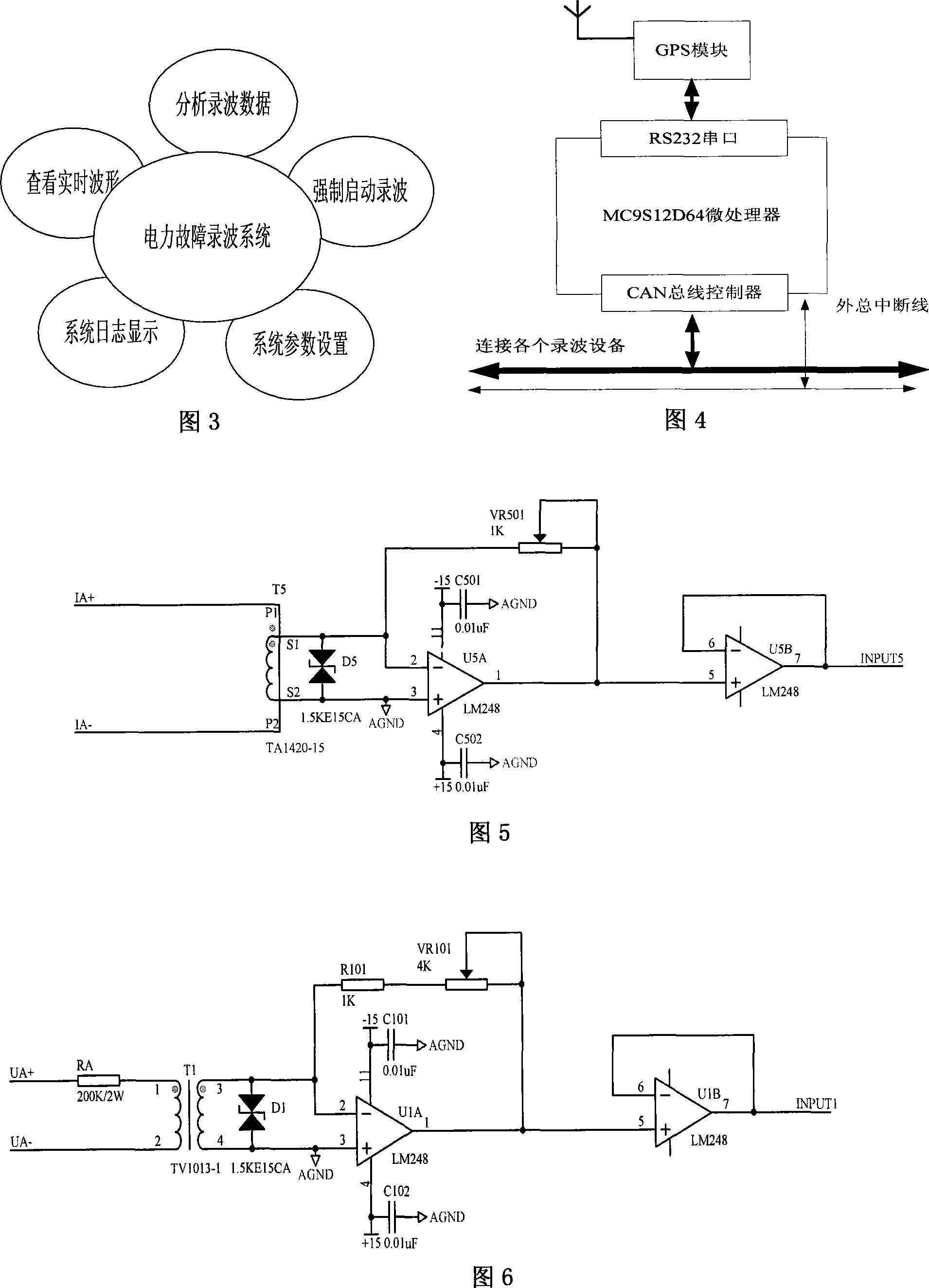
InactiveCN101097653AElectric signal transmission systemsFault locationElectric power systemThe Internet
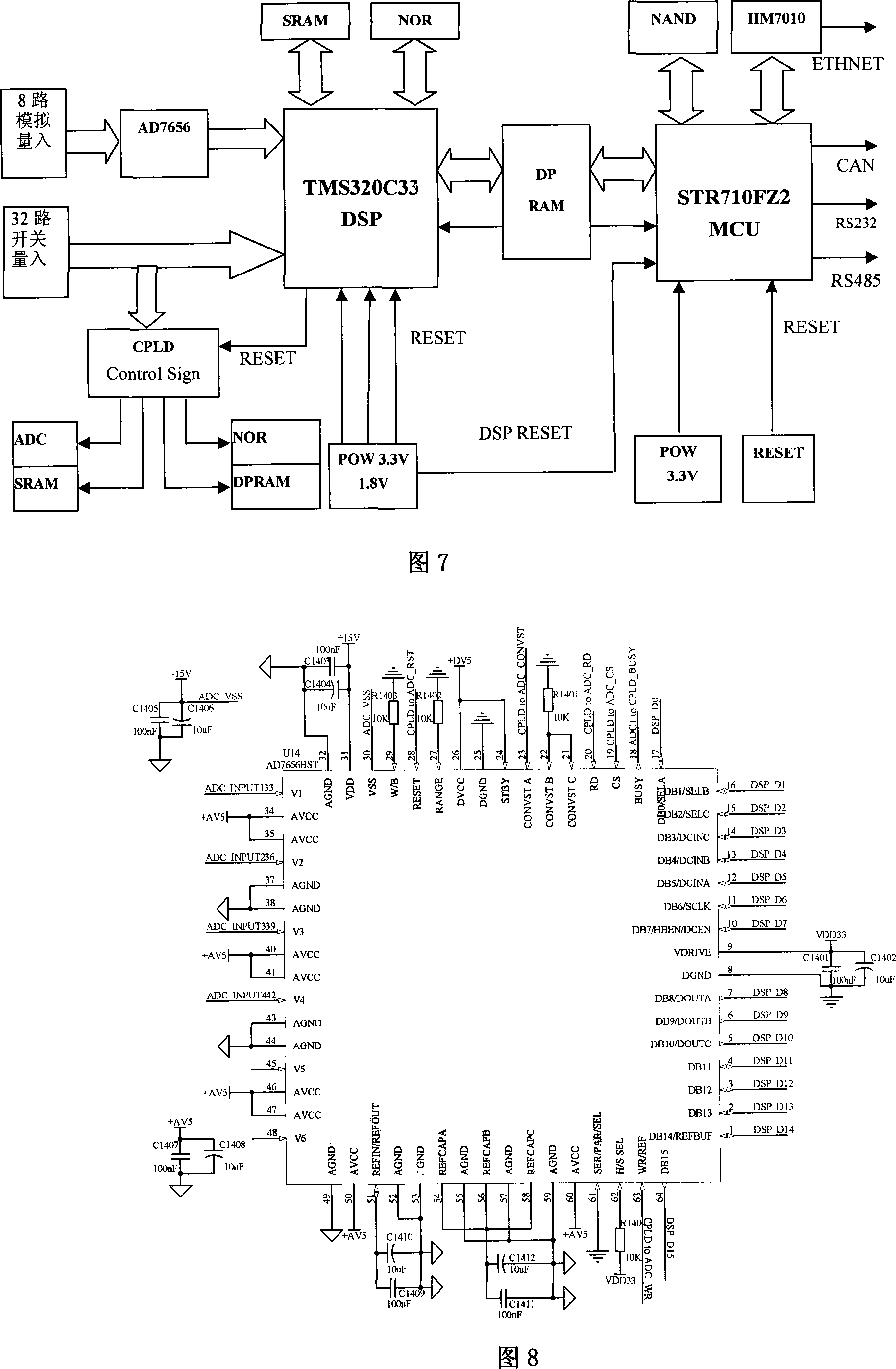
A kind of fault detection oscilloscope device and method for the quality of power and the electrical system are disclosed, which belongs to the field of detection technique of electric system, and it includes three subsystems: detection oscilloscope subsystem, remote-control monitor subsystem, and time setting subsystem; the oscilloscope subsystem can do multi-point diagnosis for electric system, and detects and records the quality parameters of power; the remote-control monitor subsystem consists of precedence sever and Internet client, and it can realize the double action that transmitting fault information and monitoring the daily running of protective and safe device; the time setting subsystem provides the system time and insures the time synchronization with system; the realizing method includes dynamic parameter measurement, fault time division; starting criterion, fault oscilloscope, uploading record, and remote-control command procession. The invention realizes the digitalization, network, intelligent, and integration of detection oscilloscope device, and it can improve the quality of power, ensure the equipment running safely and steadily.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
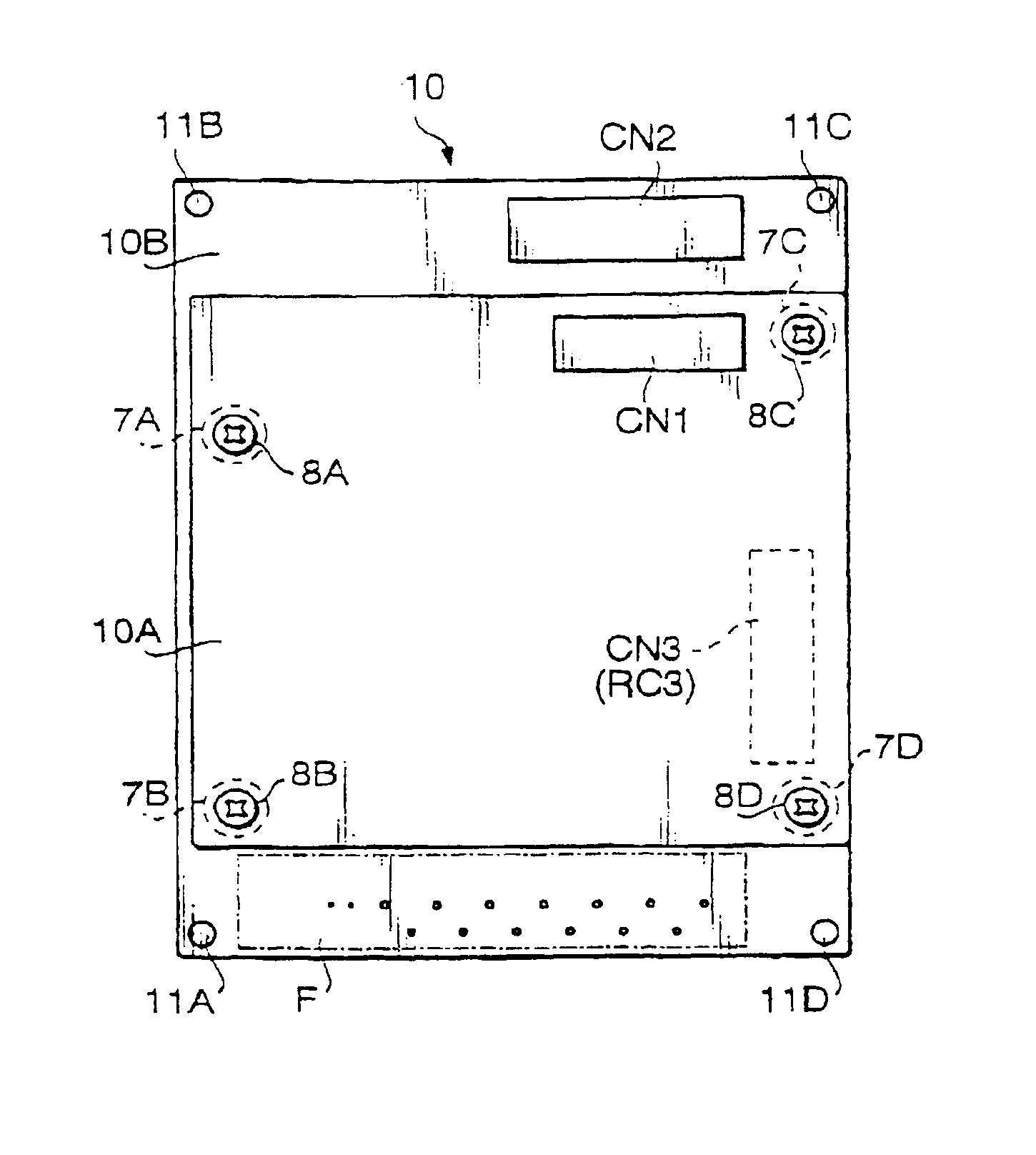
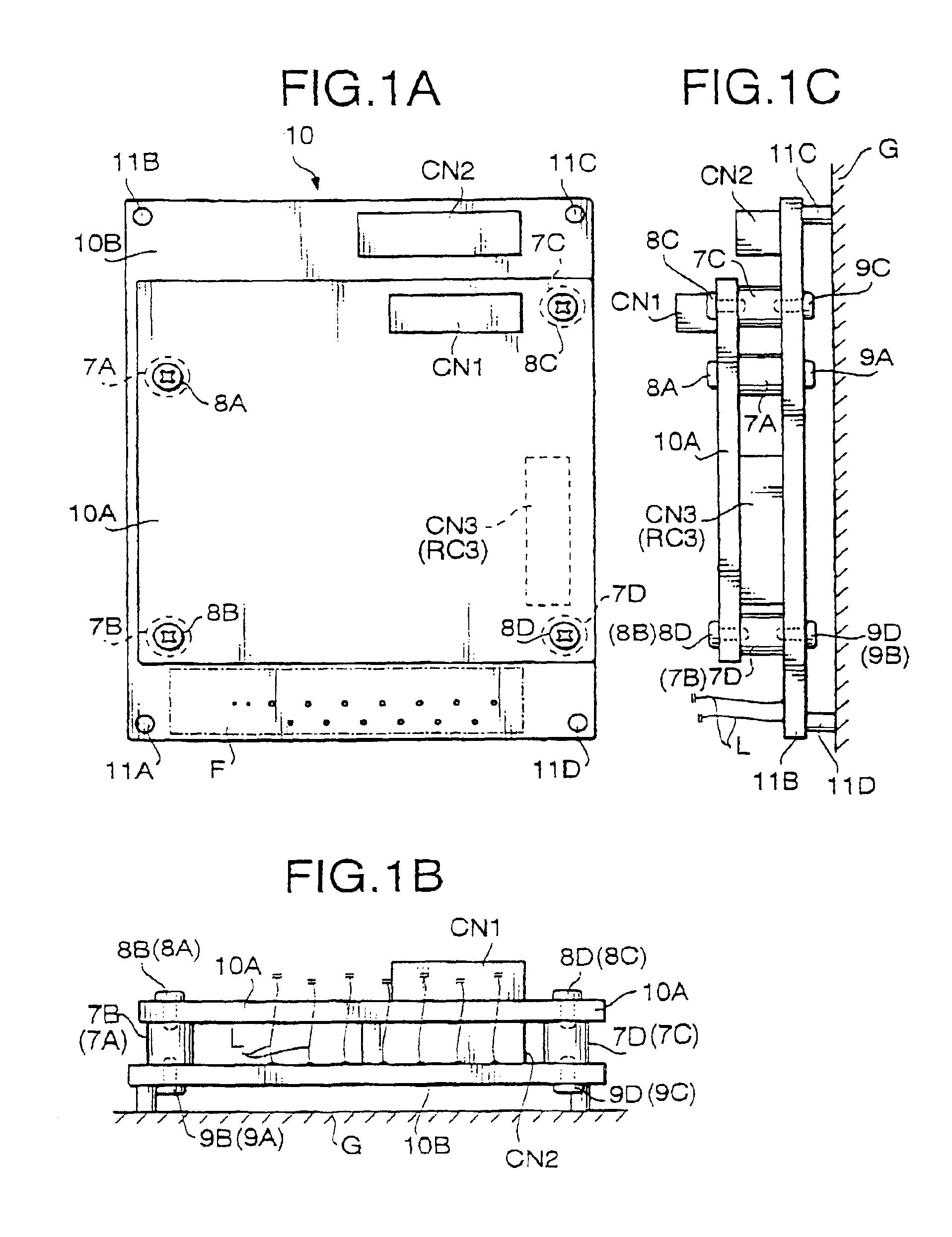
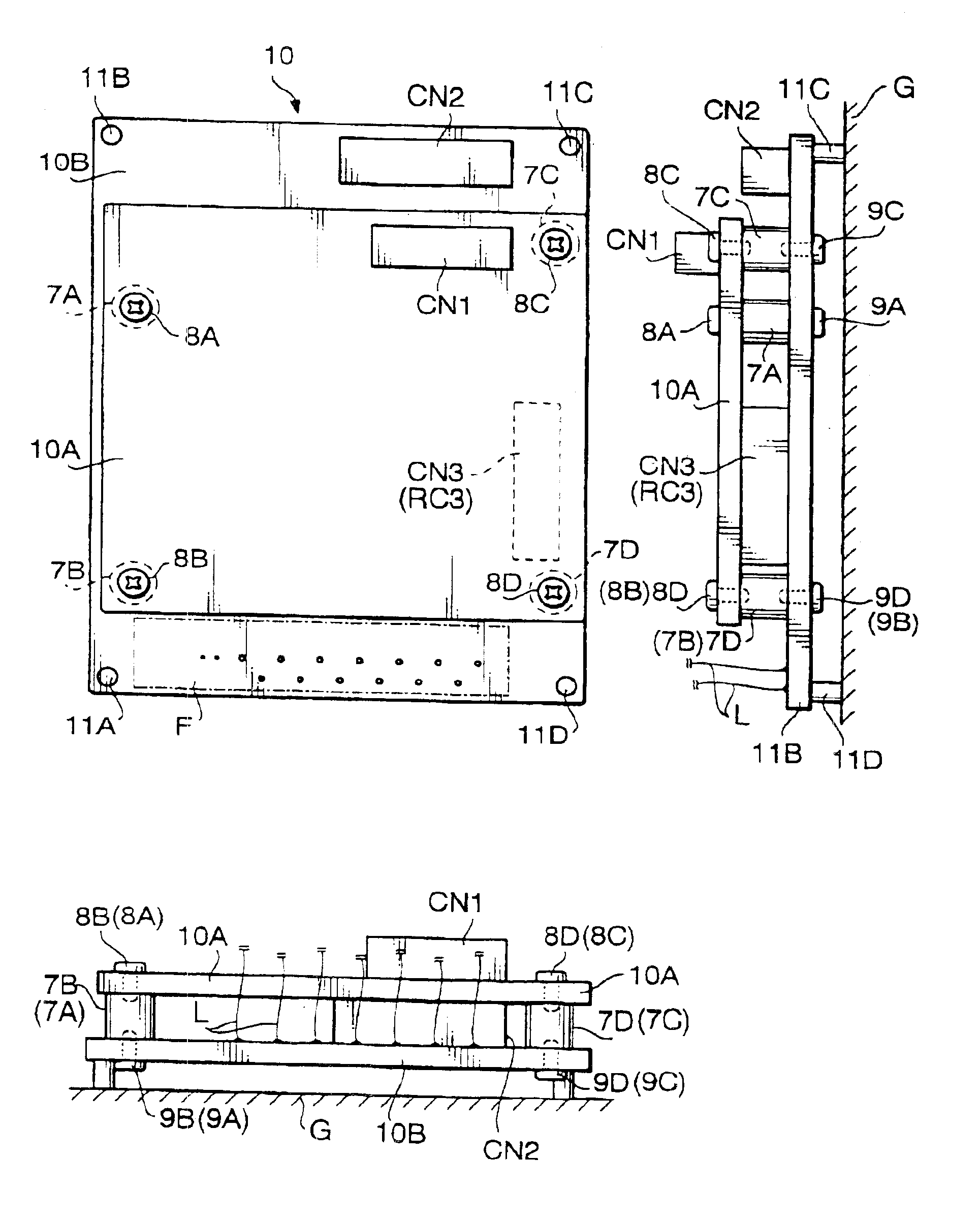
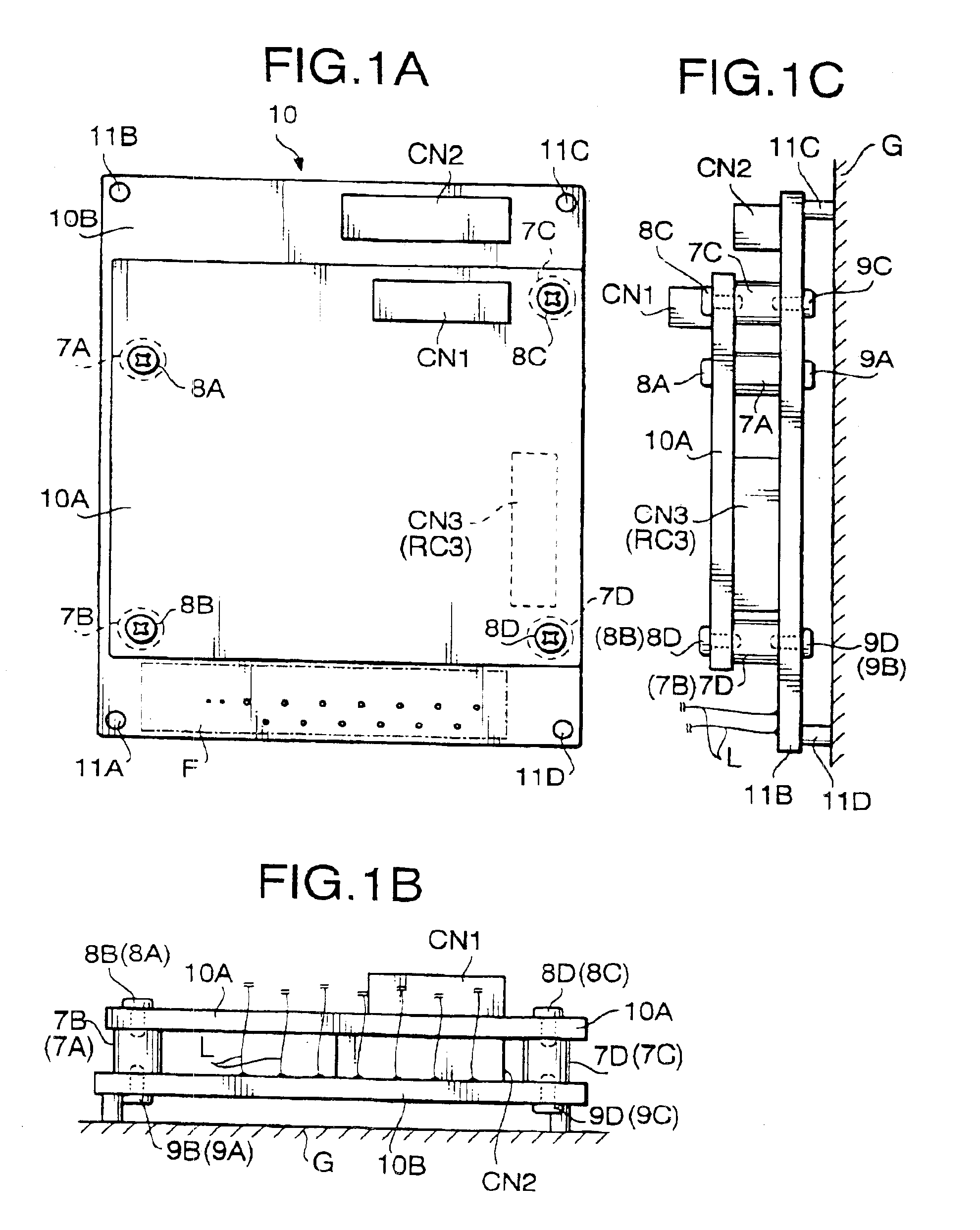
PCB structure for scope unit of electronic endoscope
InactiveUS6944031B2Simple structureElectrical connectionTelevision system detailsSurgeryBoard structurePrinted circuit board
A printed circuit board structure for a scope unit of an electronic endoscope system, which is provided with a first printed circuit board formed with a first circuit section, and a second printed circuit board formed with a second circuit section. The first printed circuit board is piled on the second printed circuit board. The second printed circuit board having an area covered with the first printed circuit board and at least one area which is not covered with the first circuit board. The at least one area is used for electrically connecting the second circuit section with an electrical unit other than the second circuit section.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
PCB structure for scope unit of electronic endoscope
InactiveUS6898086B2Simple structureElectrical connectionTelevision system detailsEndoscopesEngineeringBoard structure
A printed circuit board structure for a scope unit of an electronic endoscope system, which is provided with a first printed circuit board formed with a first circuit section, and a second printed circuit board formed with a second circuit section. The first printed circuit board is piled on the second printed circuit board. The second printed circuit board having an area covered with the first printed circuit board and at least one area which is not covered with the first circuit board. The at least one area is used for electrically connecting the second circuit section with an electrical unit other than the second circuit section.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
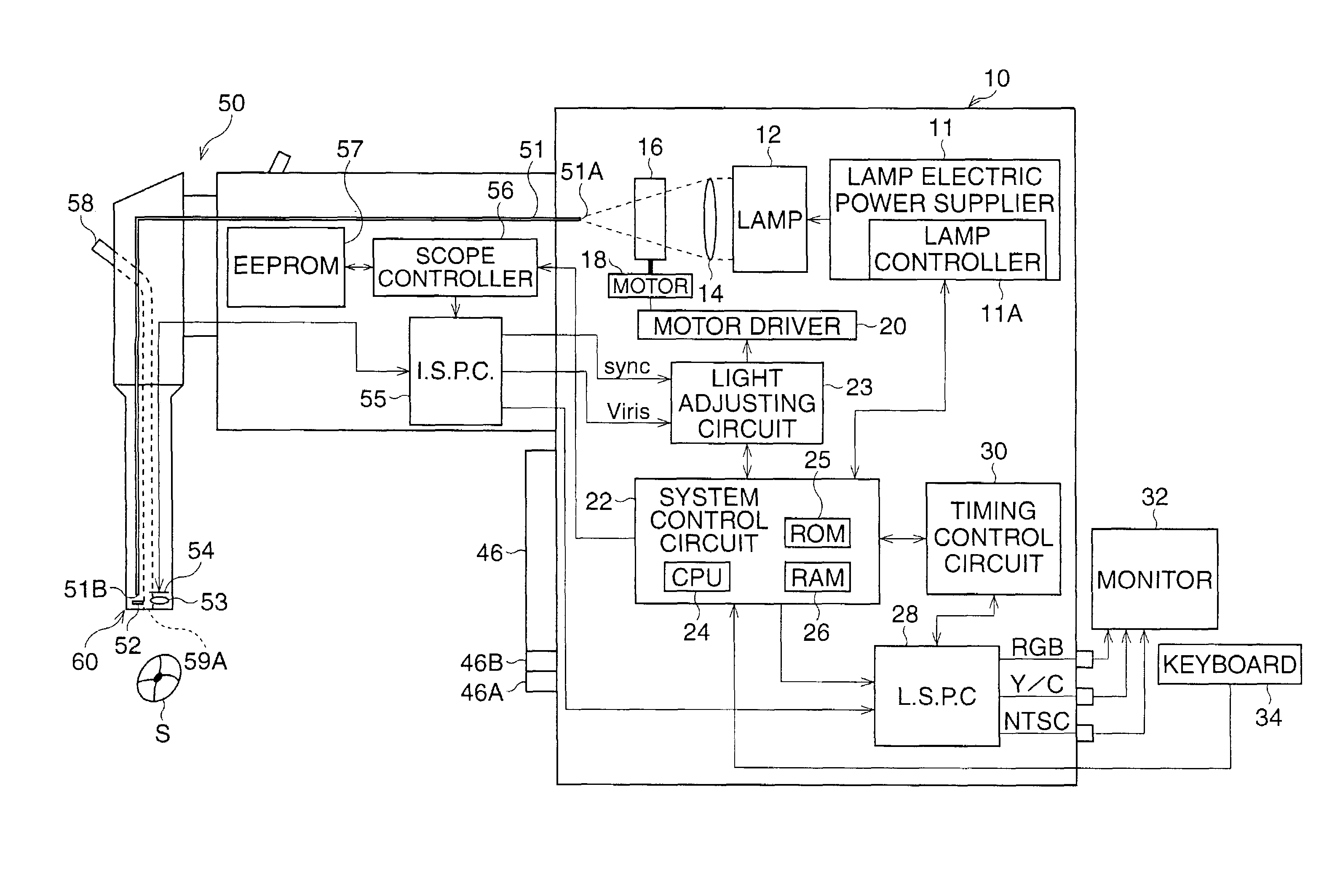
Electronic endoscope with light-amount adjustment apparatus
An electronic endoscope has a video-scope with an image sensor and a video-processor. The video-scope has an objective lens and an illuminating lens in a tip portion. Further, the electronic endoscope has a luminance calculator and a light-amount adjuster. The luminance calculator divides the total area of a subject image into a plurality of division areas, defines weighted areas from the plurality of division areas in accordance with the tip characteristics of the video-scope, and calculates a total luminance value of the subject image by putting priority on predetermined weighted areas relative to the other areas. The light-amount adjuster adjusts the quantity of light illuminating the subject in accordance with the total luminance value.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Electronic endoscope with color adjustment function
InactiveUS6943822B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageVideo processing
An electronic endoscope includes a video-scope with an image sensor and a video-processor, to which the video-scope is detachably connected. The electronic endoscope has a light source that emits illuminating light for illuminating a subject, a color adjuster that performs a color adjustment process for color image signals read from the image sensor, which include a plurality of color signal components corresponding to a plurality of color elements, and a light source detector that detects the type of the light source. The color adjuster performs the color adjustment process in accordance with the type of the light source such that color in displayed subject image is properly reproduced.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Multi modality brain mapping system (MBMS) using artificial intelligence and pattern recognition
ActiveUS20160035093A1Easy to trainUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionBrain mapping
A Multimodality Brain Mapping System (MBMS), comprising one or more scopes (e.g., microscopes or endoscopes) coupled to one or more processors, wherein the one or more processors obtain training data from one or more first images and / or first data, wherein one or more abnormal regions and one or more normal regions are identified; receive a second image captured by one or more of the scopes at a later time than the one or more first images and / or first data and / or captured using a different imaging technique; and generate, using machine learning trained using the training data, one or more viewable indicators identifying one or abnormalities in the second image, wherein the one or more viewable indicators are generated in real time as the second image is formed. One or more of the scopes display the one or more viewable indicators on the second image.
Owner:INT BRAIN MAPPING & INTRA OPERATIVE SURGICAL PLANNING FOUND +1
Stereoscopic endoscope system and TV imaging system for endoscope
An armor (111a) of a scope unit (131) and a diaphragm (123) are arranged to be mutually freely turnable. The shape of an outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the shape of the inside of a scope joint (130a) of a TV camera unit (130) substantially agree with each other, and the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the inside of the scope joint (130a) engage with each other. In a state in which the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the inside of the scope joint (130a) are engaged with each other, a ring screw (133) is meshed with a thread (130b) so that the scope unit (131) and TV camera unit (130) will unitedly be joined with each other. At this time, since the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) is engaged with the scope joint (130a), the diaphragm and TV camera unit can be turned relative to an objective optical system (119) and relay optical system (121) with the optical axis of the relay optical system (121) as an axis of turning. Moreover, a liquid-crystal shutter 124 in the TV camera unit (130) has two interceptive areas (124a, 124b) which can be switched temporally alternately. The interceptive areas (124a, 124b) intercept one of two light beams passing through either of aperture stops (123a, 123b).
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
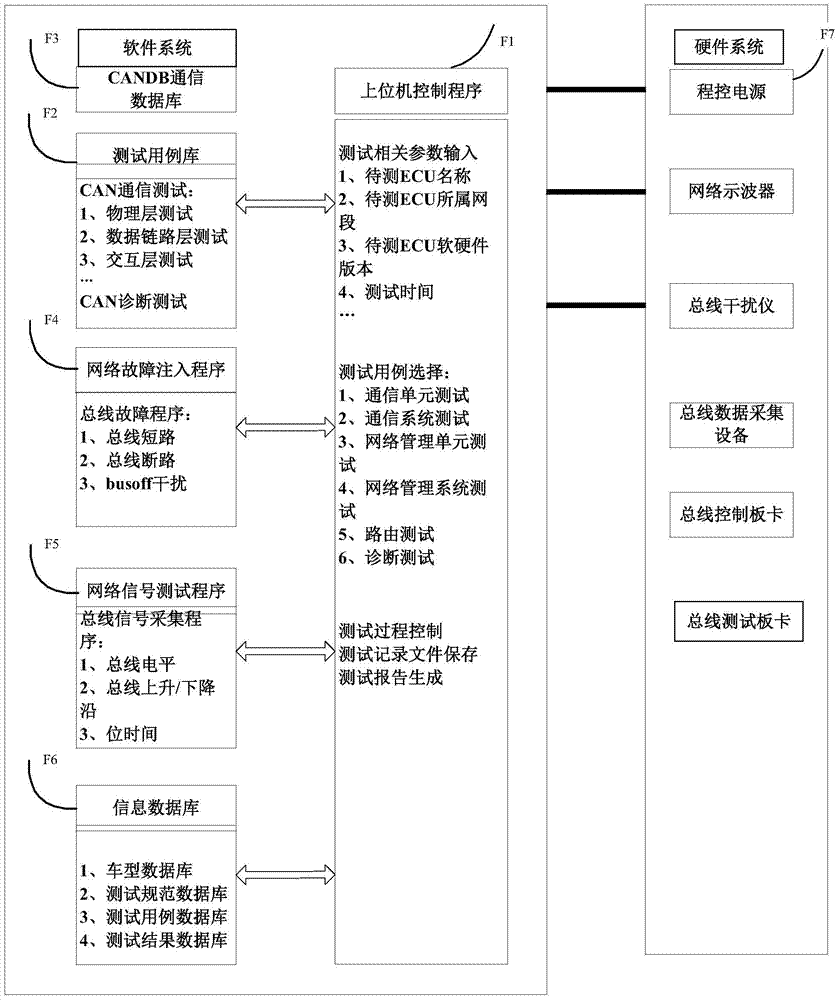
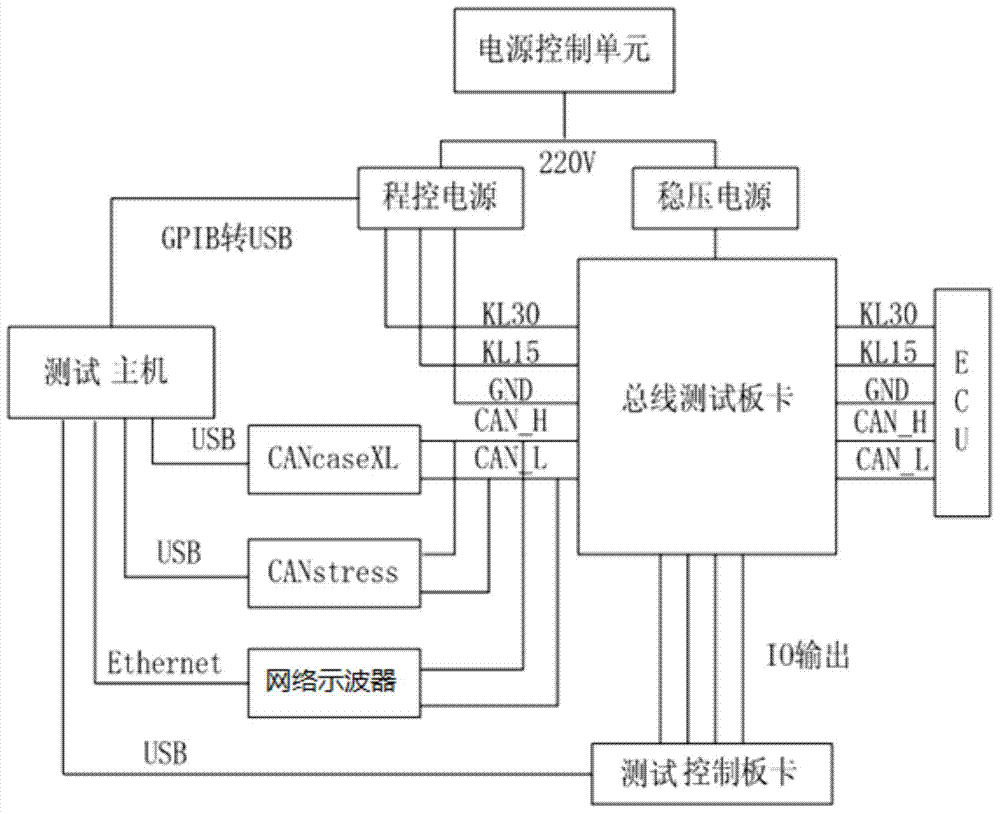
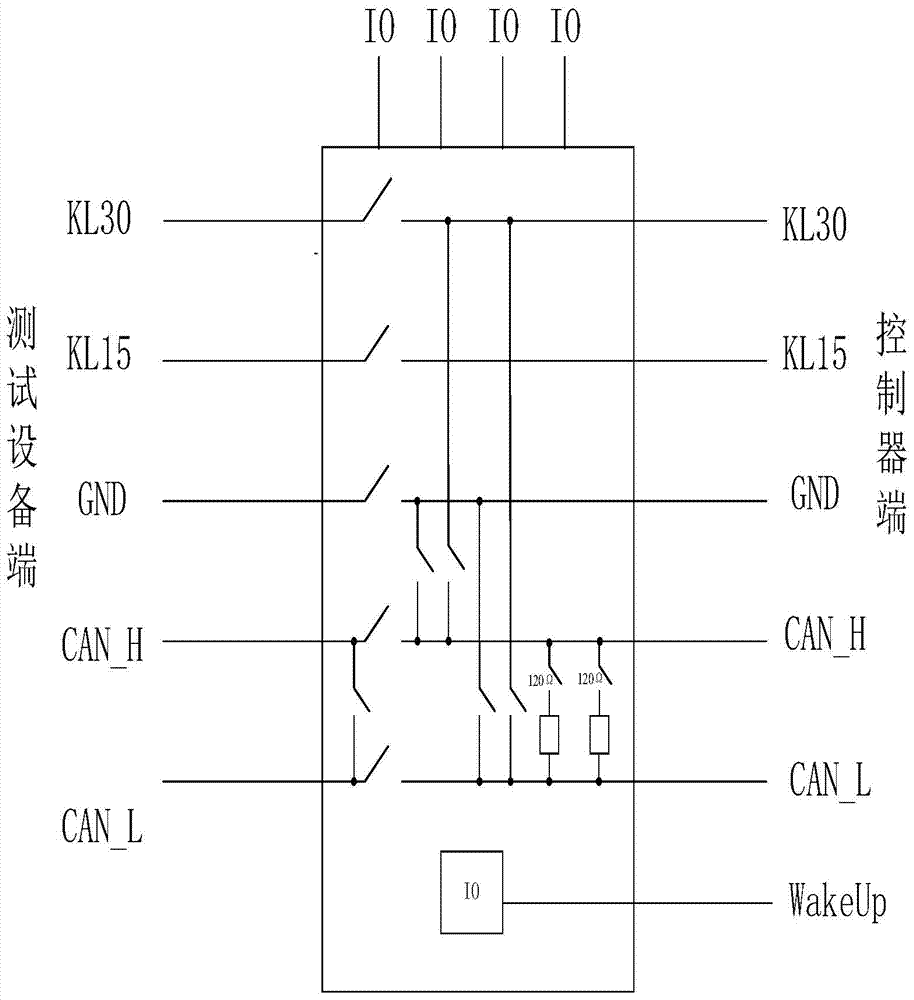
Automatic vehicle-mounted electronic control unit CAN bus communication testing device and system
InactiveCN104298224AReduce duplication of effortAffect accuracyElectric testing/monitoringData acquisitionTest fixture
The invention relates to an automatic vehicle-mounted electronic control unit CAN bus communication testing device. A testing host of the device controls a programmable power supply to output different amplitudes of voltages according to working requirements of an ECU; physical layer testing signals of a CAN bus are output to a network oscilloscope to be displayed, and physical layer testing data are transmitted to the testing host through the network oscilloscope; ECU testing data are transmitted to the testing host through a bus data acquisition device; the testing host records, analyzes and evaluates the testing data of the ECU and the CAN bus to generate a test report. A bus interferometer is used for interfering with bus waveforms of the tested ECU in real time. The testing host controls on-off states of relays of a bus testing board card through a testing control card board to execute the bus fault injection operation. By means of the automatic vehicle-mounted electronic control unit CAN bus communication testing device, various defects of a manual test are overcome, unnecessary repeated labor of a vehicle-mounted network engineer is reduced, and the testing result is accurate.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Wireless video stylet with display mounted to laryngoscope blade and method for using the same
InactiveUS20090192350A1Avoiding and minimizingAvoid and minimize traumaBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesWireless videoDisplay device
A scope adapted for insertion and manipulation in a difficult pathway is disclosed. The scope comprises at least one module for manipulating the scope. The scope may further comprise an illumination source, an image sensor, a power source, and a viewing member for viewing images of a cavity or other anatomical member of a patient. In one embodiment the scope is intended to facilitate insertion of an intubating device, which comprises an elongated semi-rigid stylet including first and second ends and at least one inner lumen connected to a module. Additionally, a flexible tip is provided for manipulating one end of the scope and allowing greater flexibility when maneuvering a difficult pathway. A method for navigating a difficult pathway and for using the apparatus described herein is also disclosed.
Owner:MEJIA MAURICIO
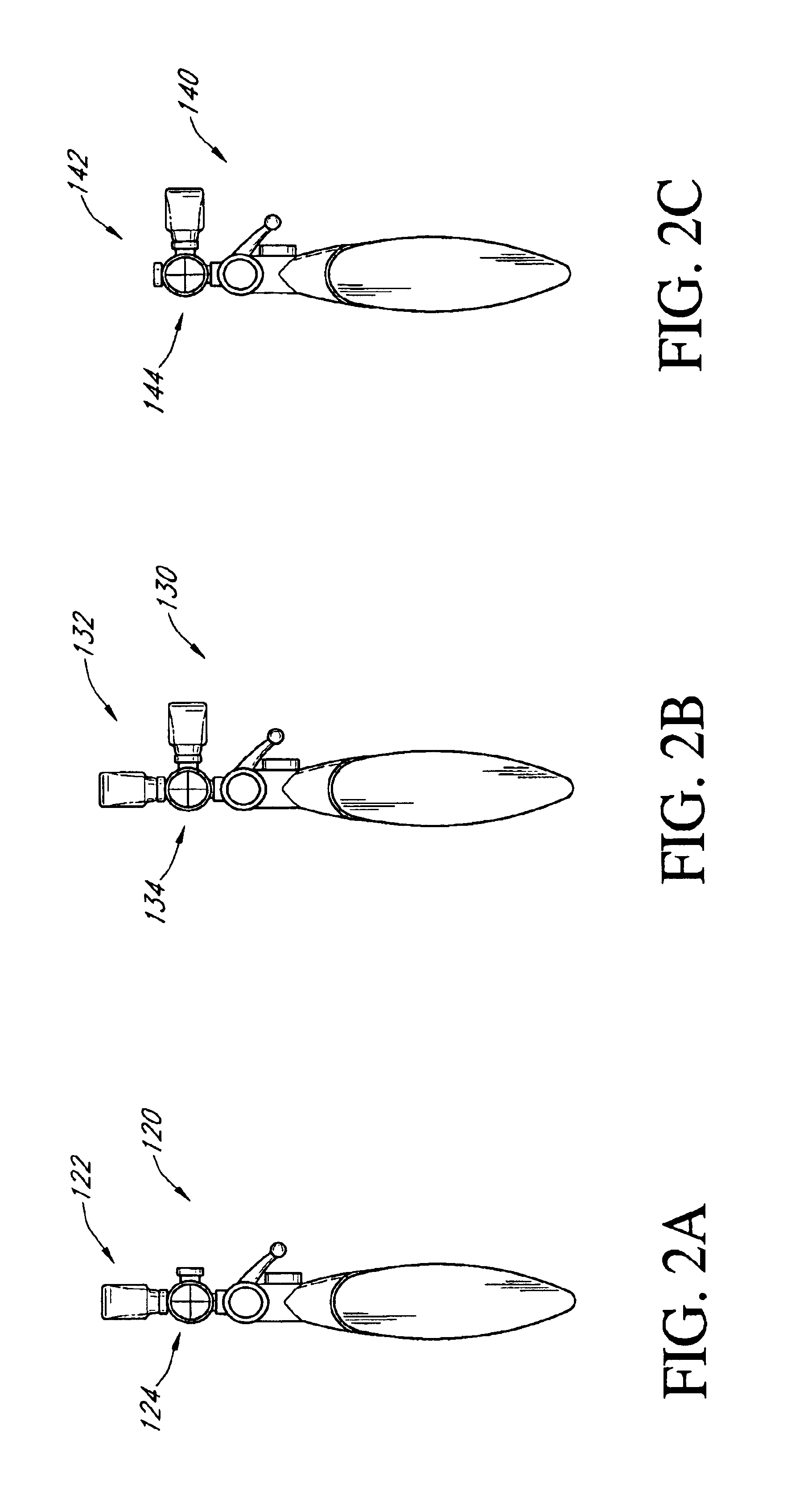
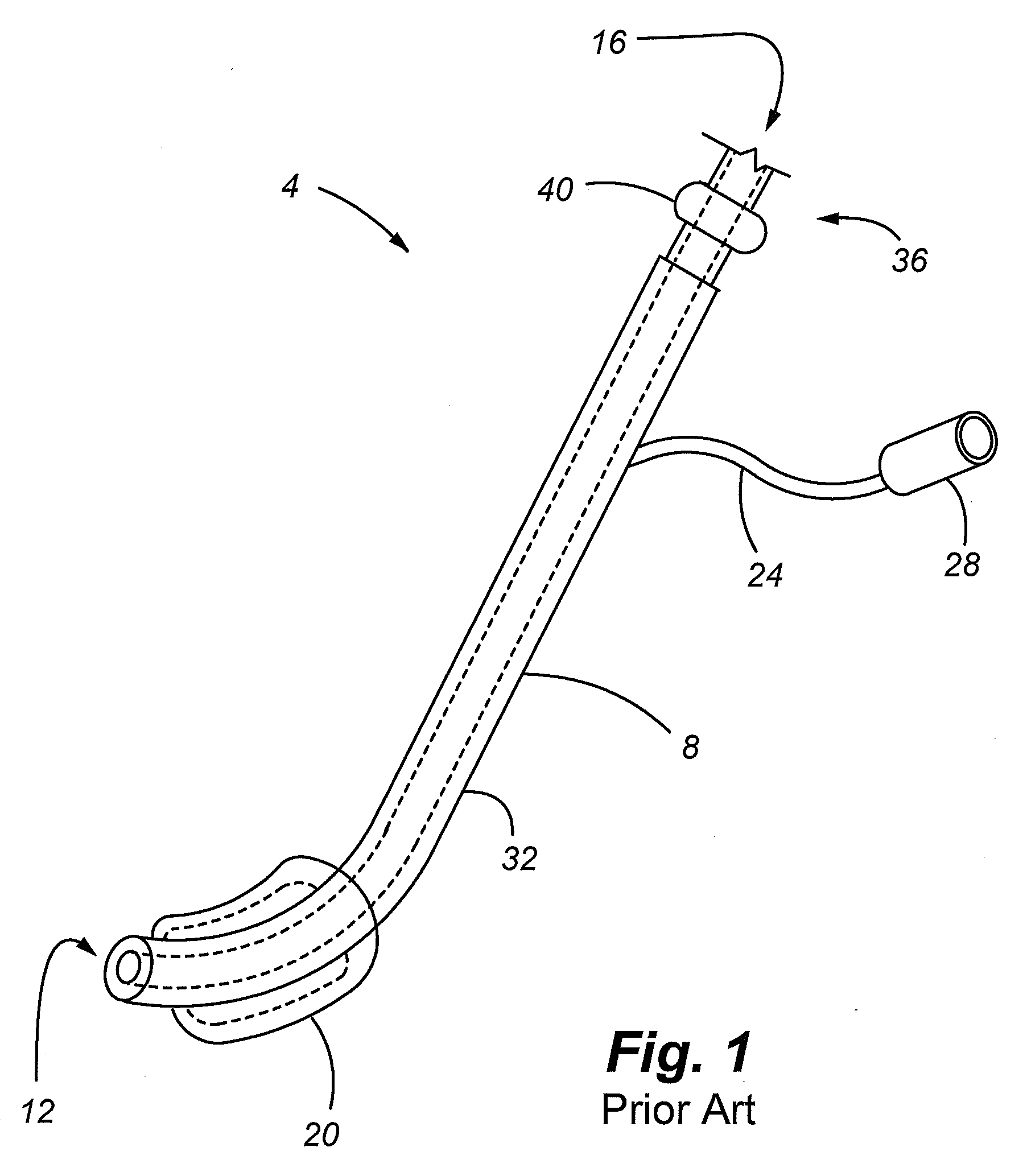
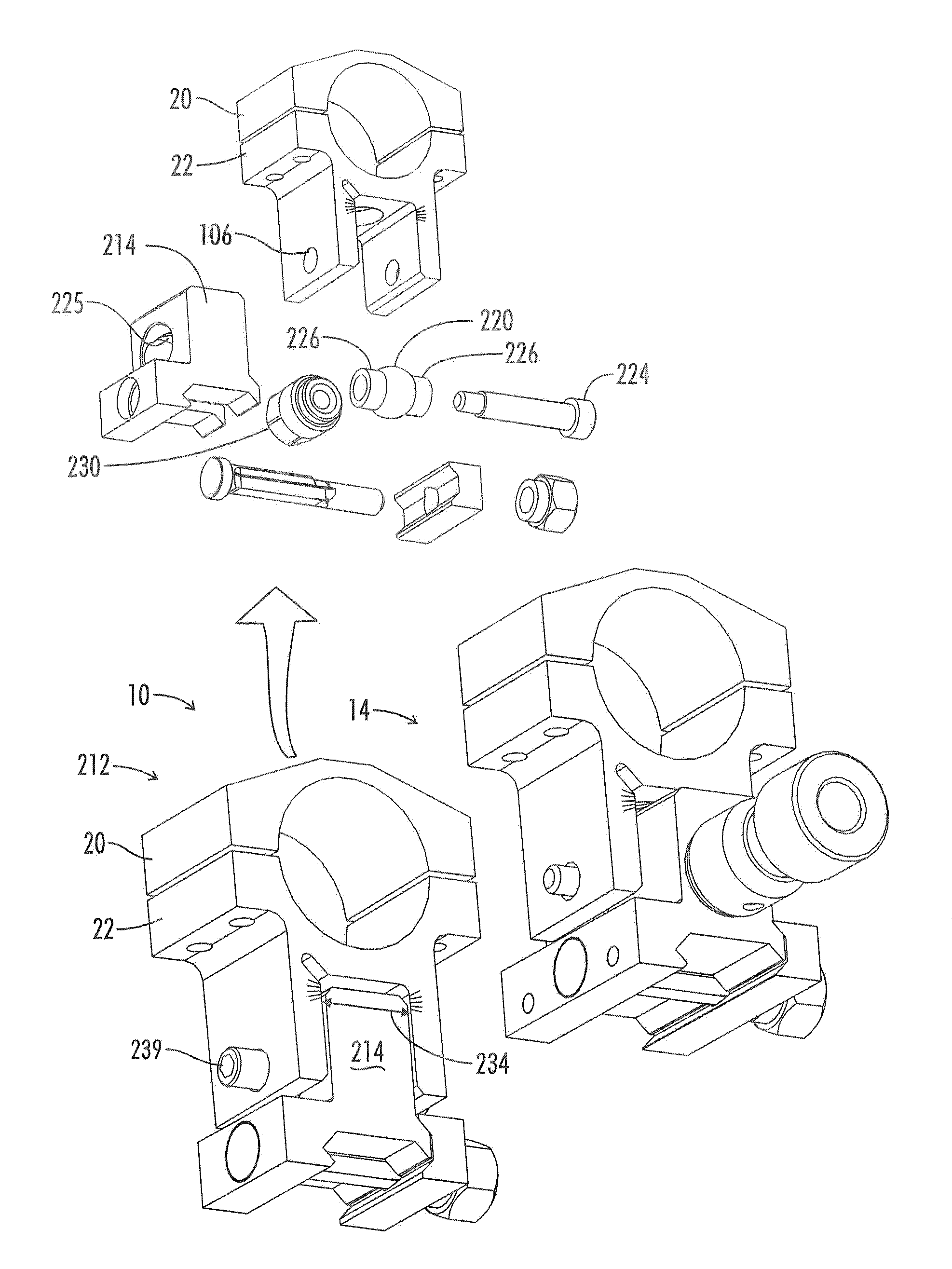
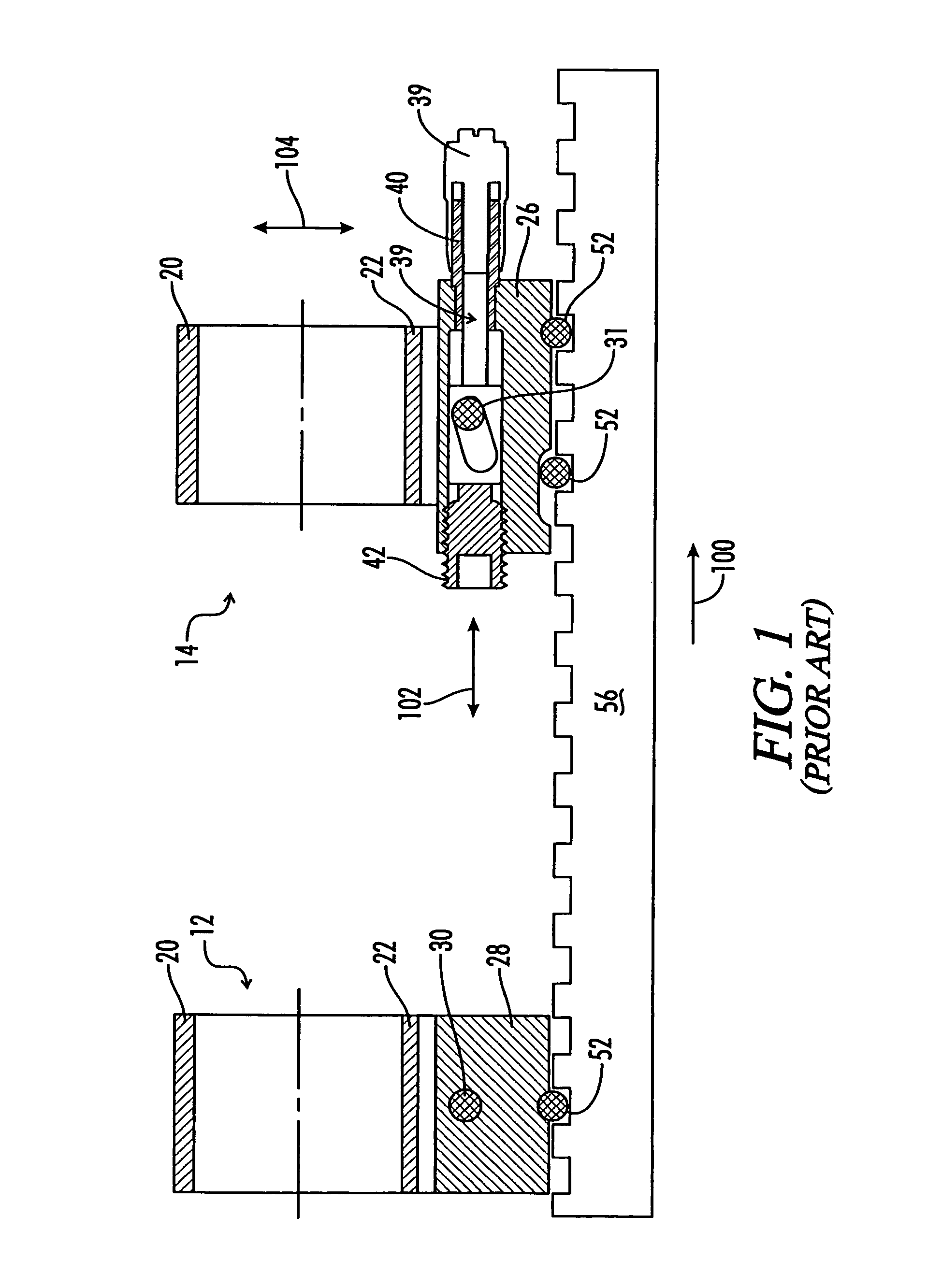
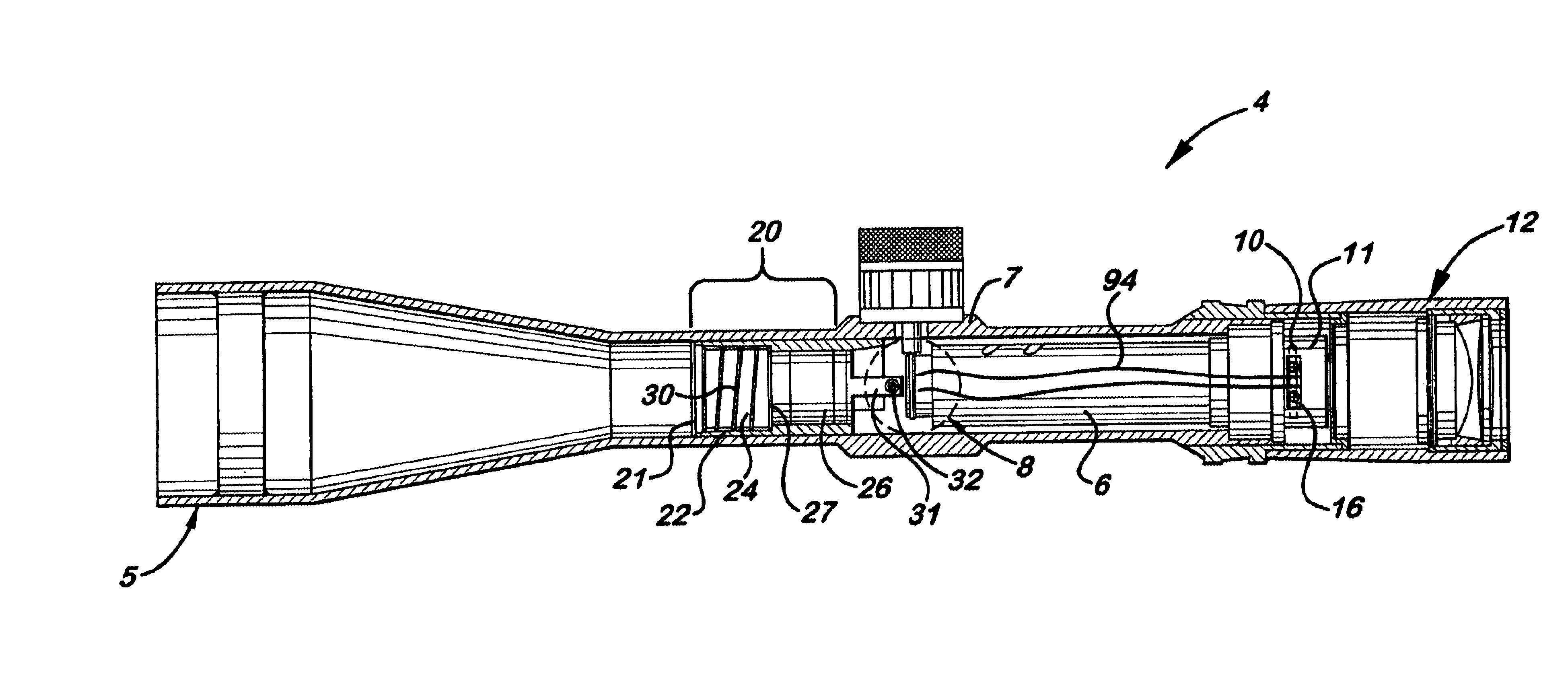
Adjustable scope mounting system
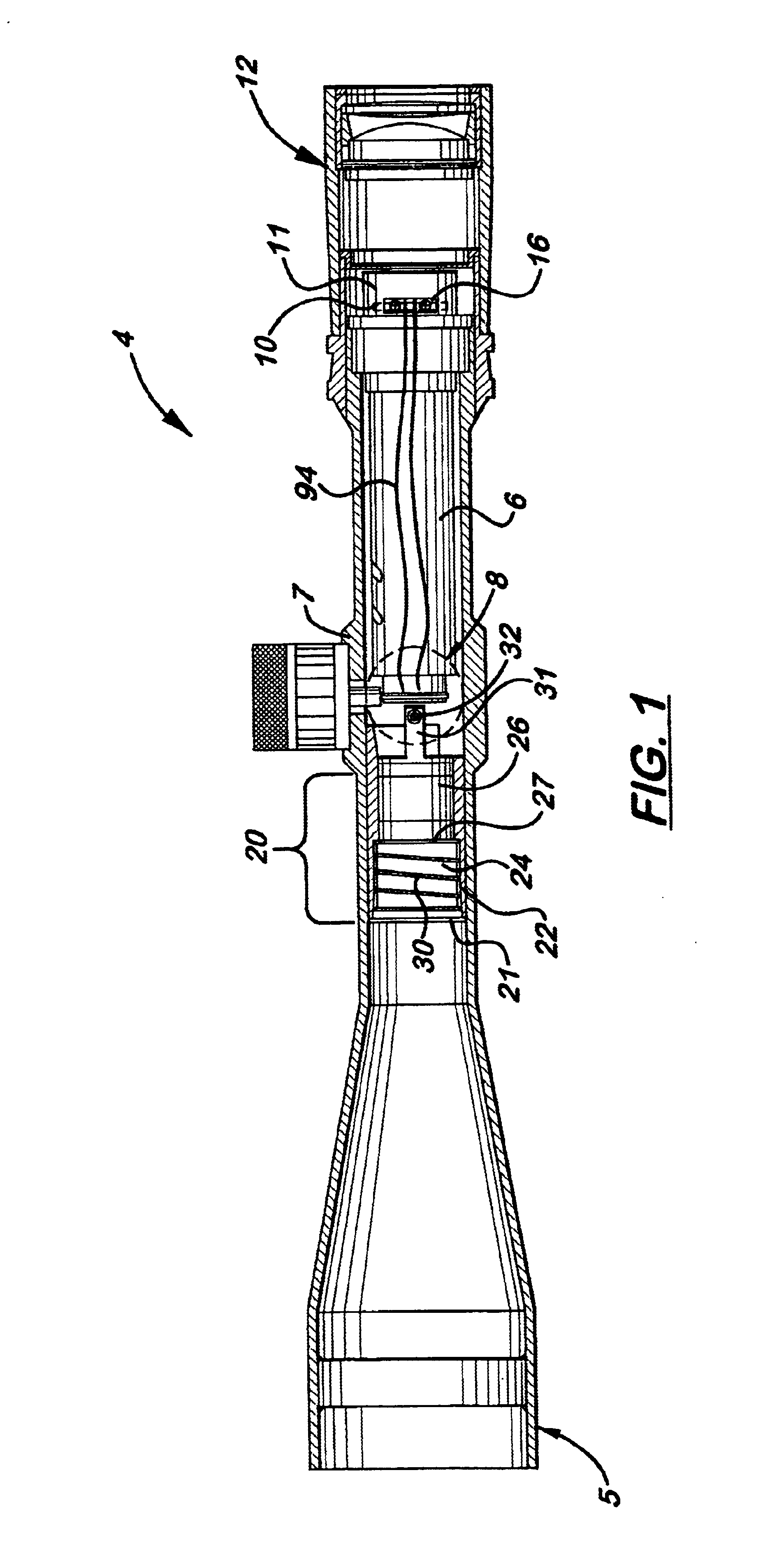
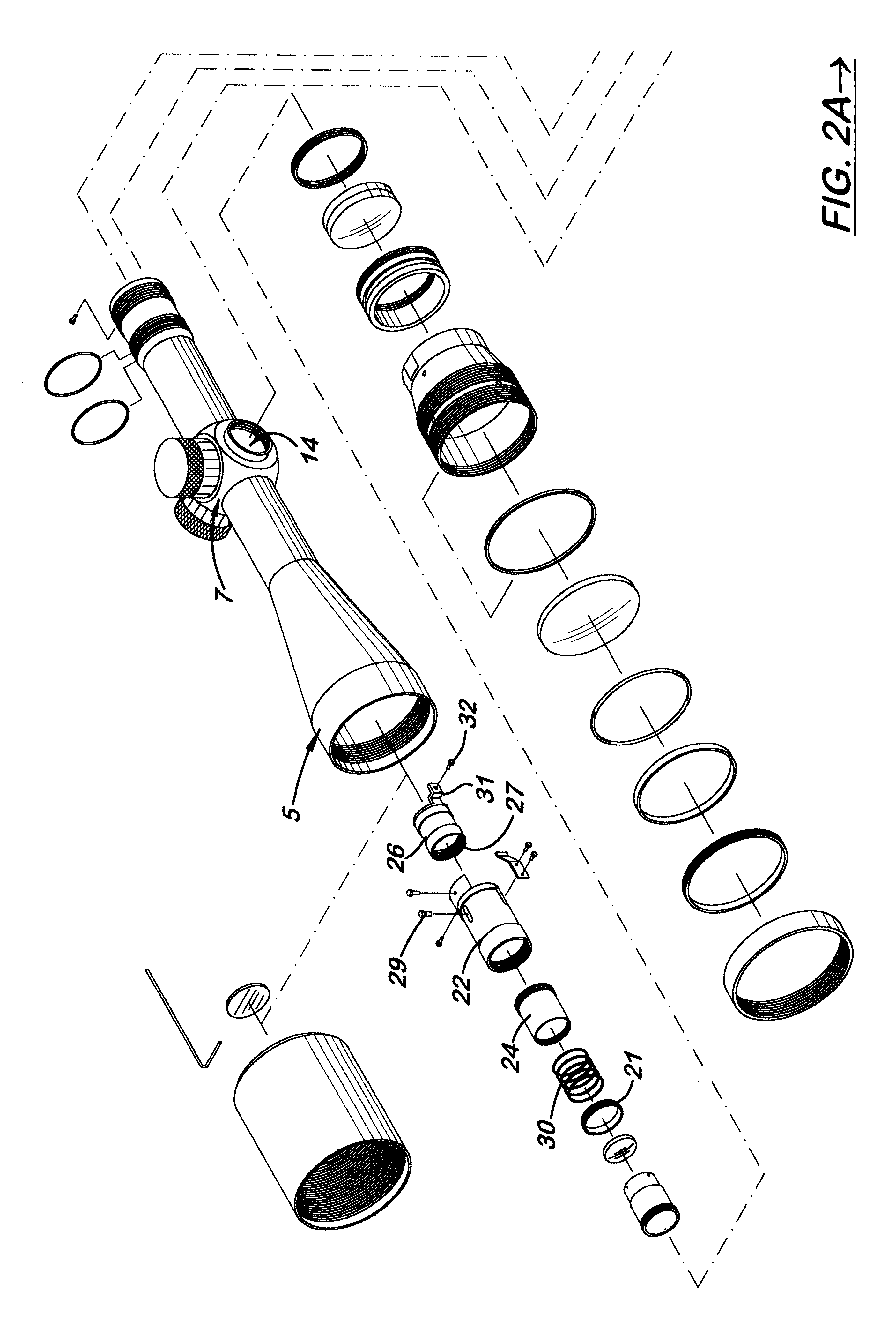
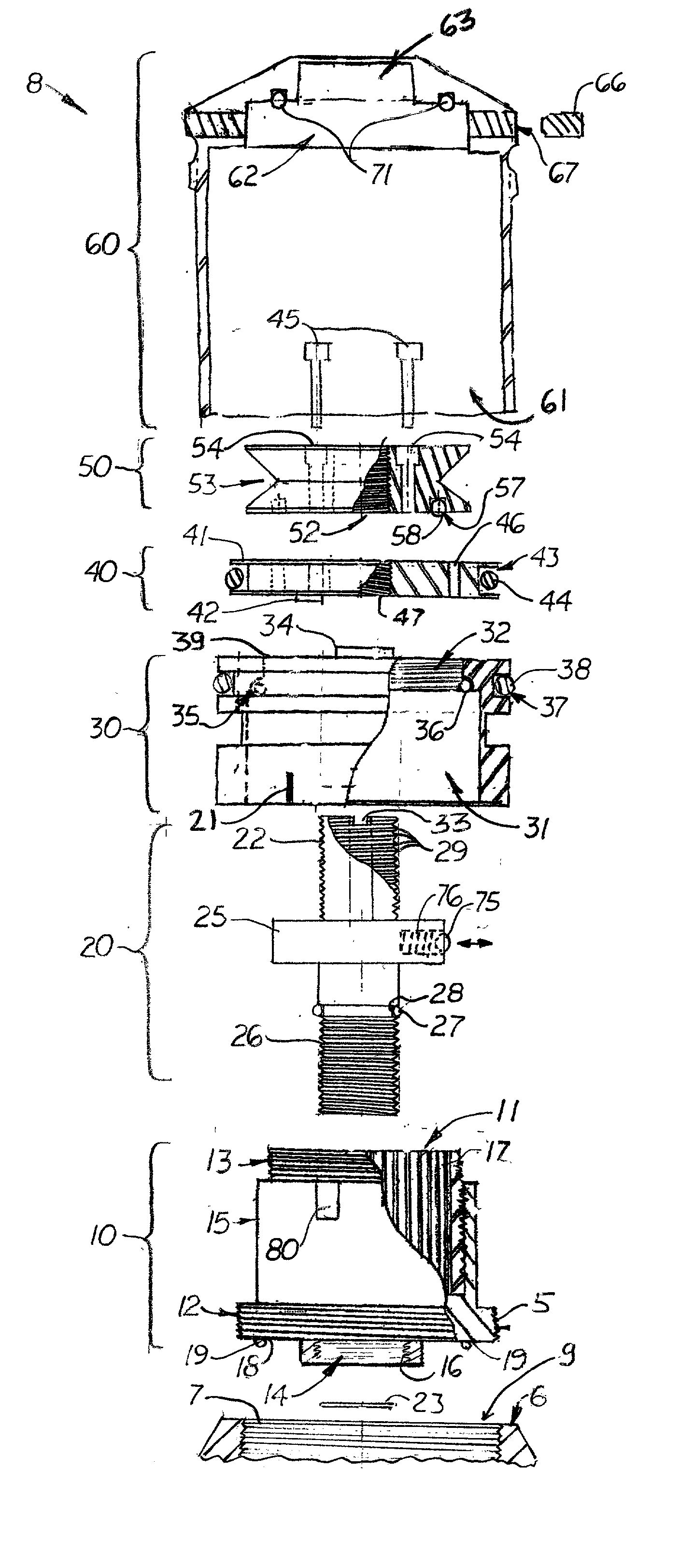
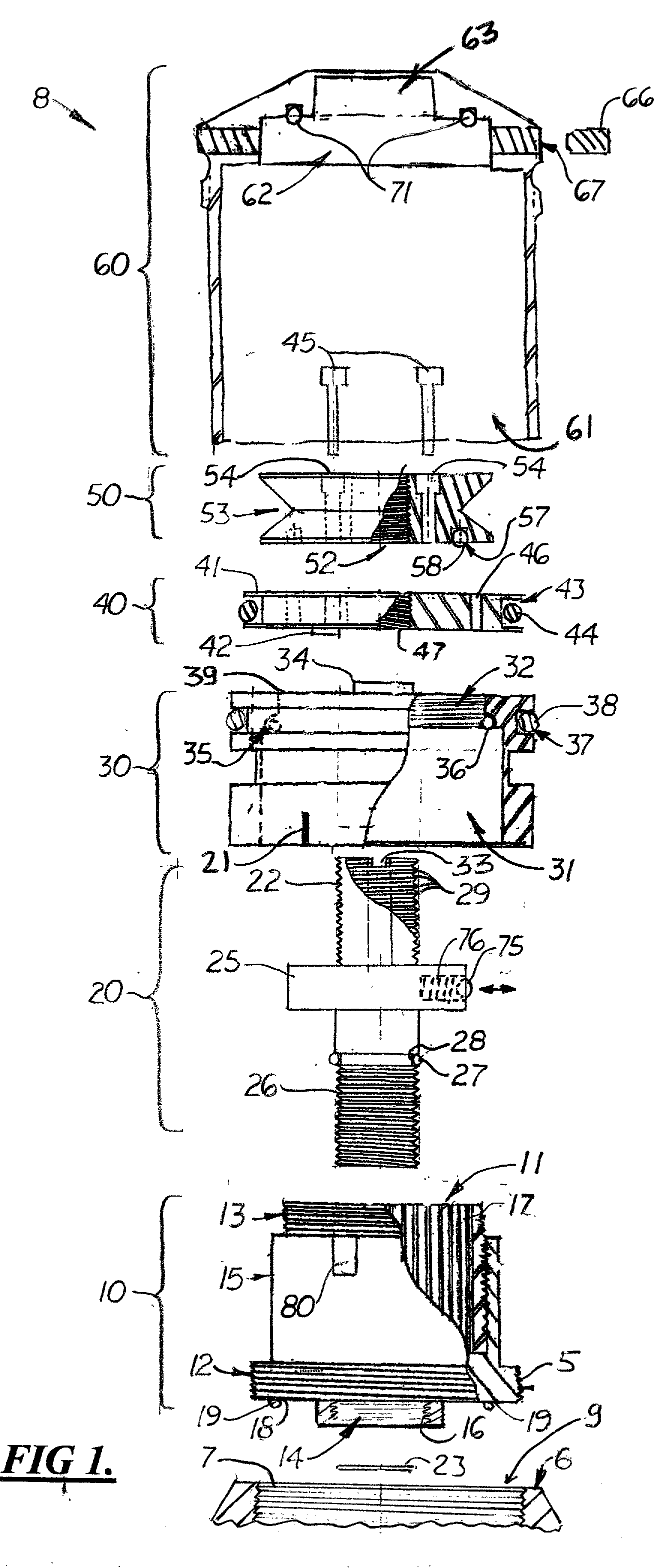
An adjustable mounting system for a telescopic scope includes an adjustable elevation mount formed from a scope ring and an adjustable sub-base. A clevis portion of the scope ring holds an elevation pin that is received by a vertical slot in the adjustable sub-base. An internally longitudinal bore is disposed though the adjustable sub-base and an externally threaded barrel disposed in an opening of the longitudinal bore. A cylindrical elevation cam having an angled slot is disposed in the longitudinal bore and includes a positioning rod that extends through a bore disposed through the barrel. The angled slot receives the elevation pin as it extends through the vertical slot of the adjustable sub-base. The angled slot may be smooth or stepped. A bi-directional cam capture means is mechanically coupled to the elevation cam and provides for longitudinal displacement of the elevation cam through the cam bore. Detent mechanisms are incorporated in the cam capture means to provide audible or felt indication of elevation position. In various embodiments the cam capture means may be: a rack and pinion device operated by dial handle; a plunger attached to the positioning rod and extending through the rear of the sub-base, a lever attached to the positioning rod and extending through a notched slot in the side of the sub-base, a position dial including a dial thimble affixed to the positioning rod and threadably engaged with a barrel disposed on the sub-base. Other embodiments include a windage gib adjustably positioned in a bore of a lower portion of the sub-base and adapted to laterally offset the sub-base from the firearm rail.
Owner:IVEY STEPHEN
Sulfur hexafluoride discharge decomposed gas component analysis system and its usage method
InactiveCN101059485AImprove sealingGuaranteed validityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationTransformerSulfur hexafluoride
A sulfur hexafluoride discharge decomposition gas component analysis system is composed of a pressure adjuster console 1, an insulation transformer 2, a non-blooming test transformer 3, a non-local-discharge protective resistance 4, a capacitor bleeder 5, a sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, a non-inductive check resistance 7, a match resistance 8, an oscillometer 9, and a gas spectrometer 10. And the method comprises that (1), using a vacuum pump 18 to vacuum the sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, (2), using an inlet needle valve 17 to feed SF6 gas into the sulfur hexafluoride discharge decompose device 6, (3), measuring maximum external test voltage and initial PD voltage, (4), generating PD under different electrodes, (5), collecting gas, (6), analyzing gas components, (7), collecting PD pulse signal wave shape, diagnosing accident and recognizing mode. The invention has wide application in research, teach, academy and industry, used in theory analysis and research of PD online state check of GIS device.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
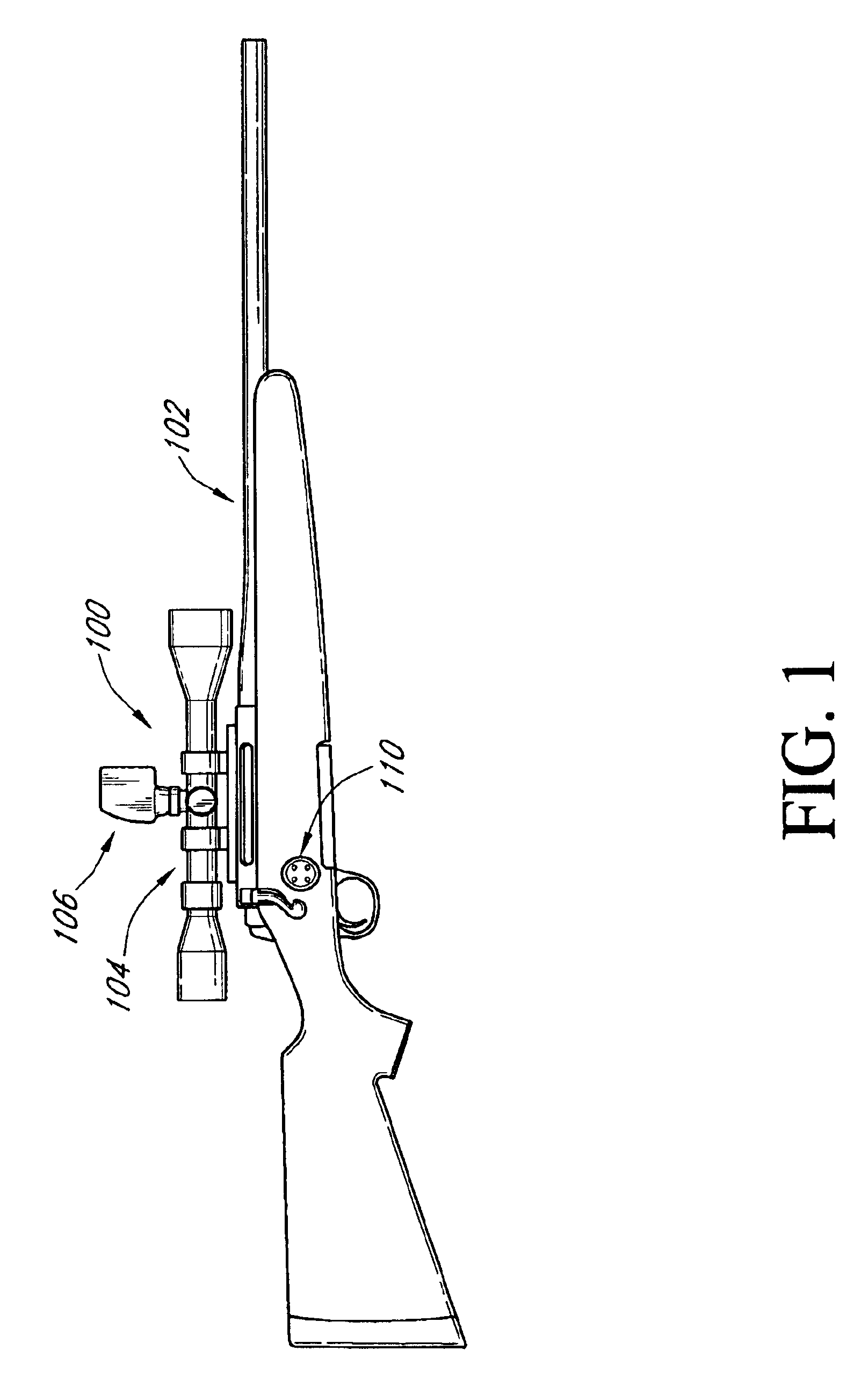
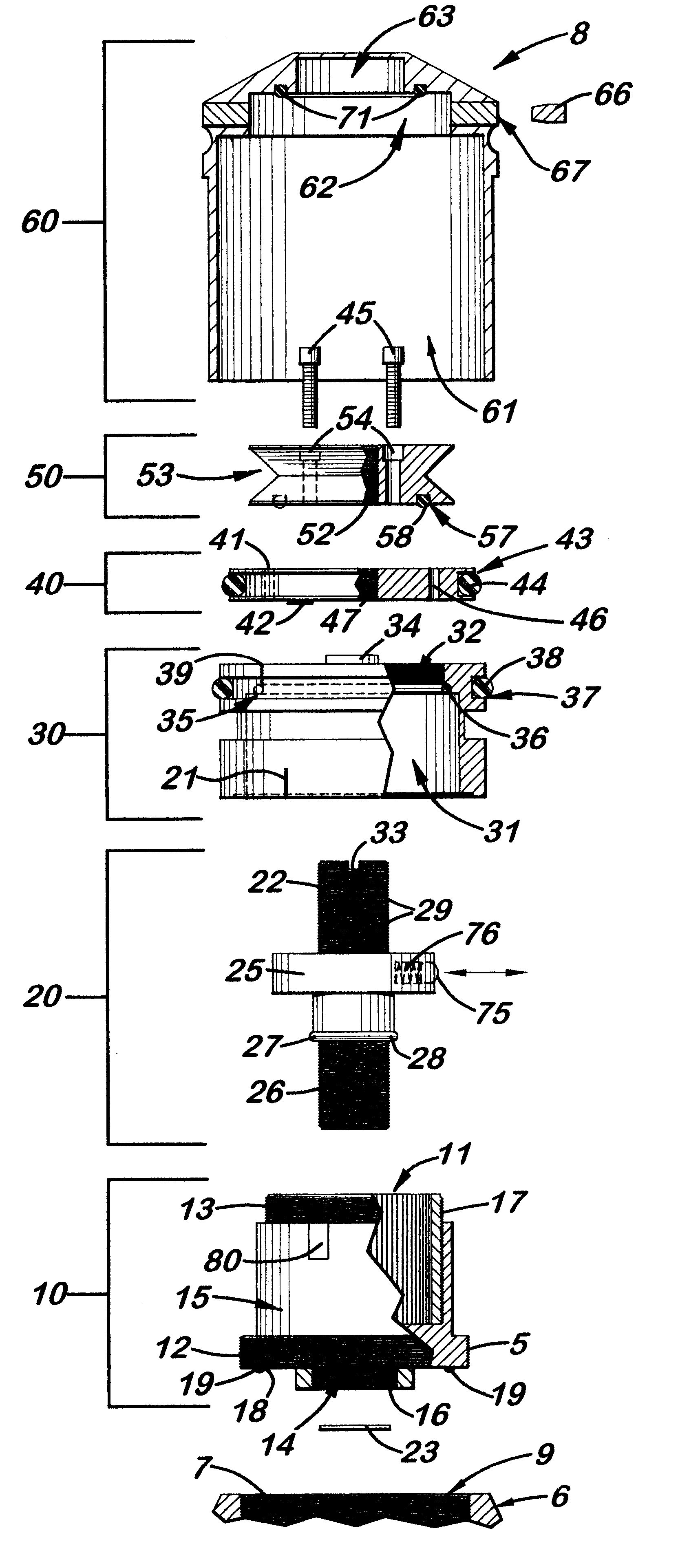
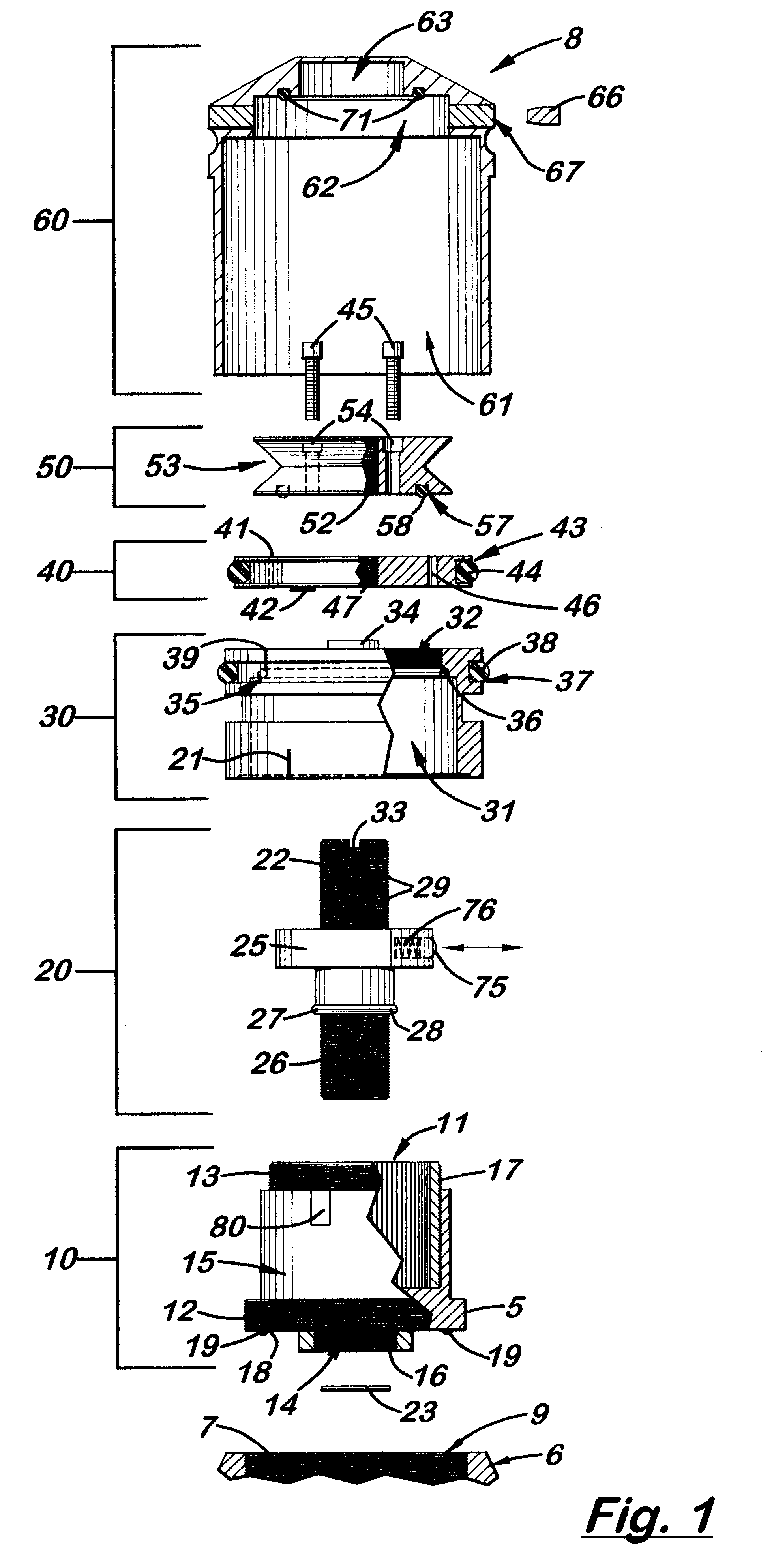
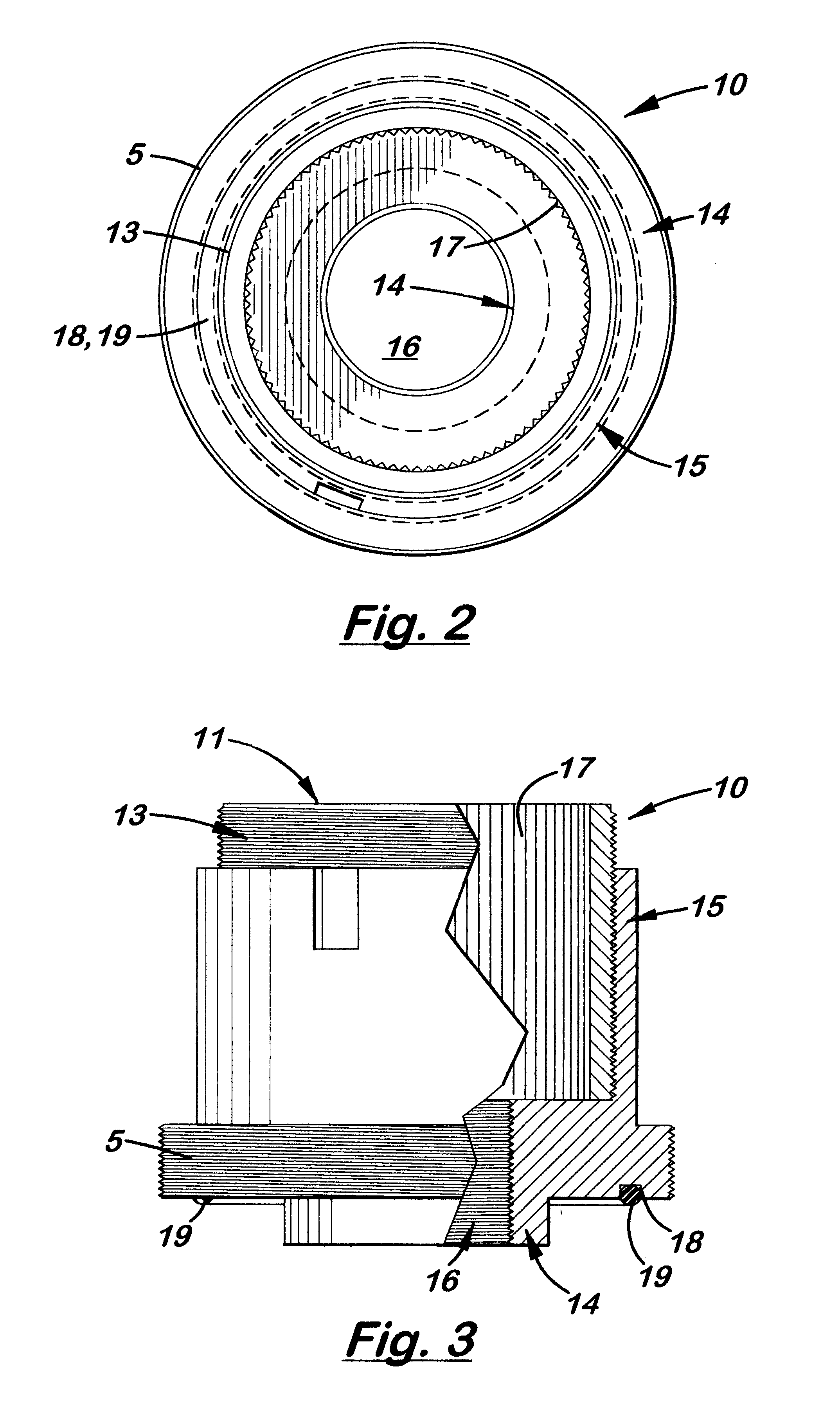
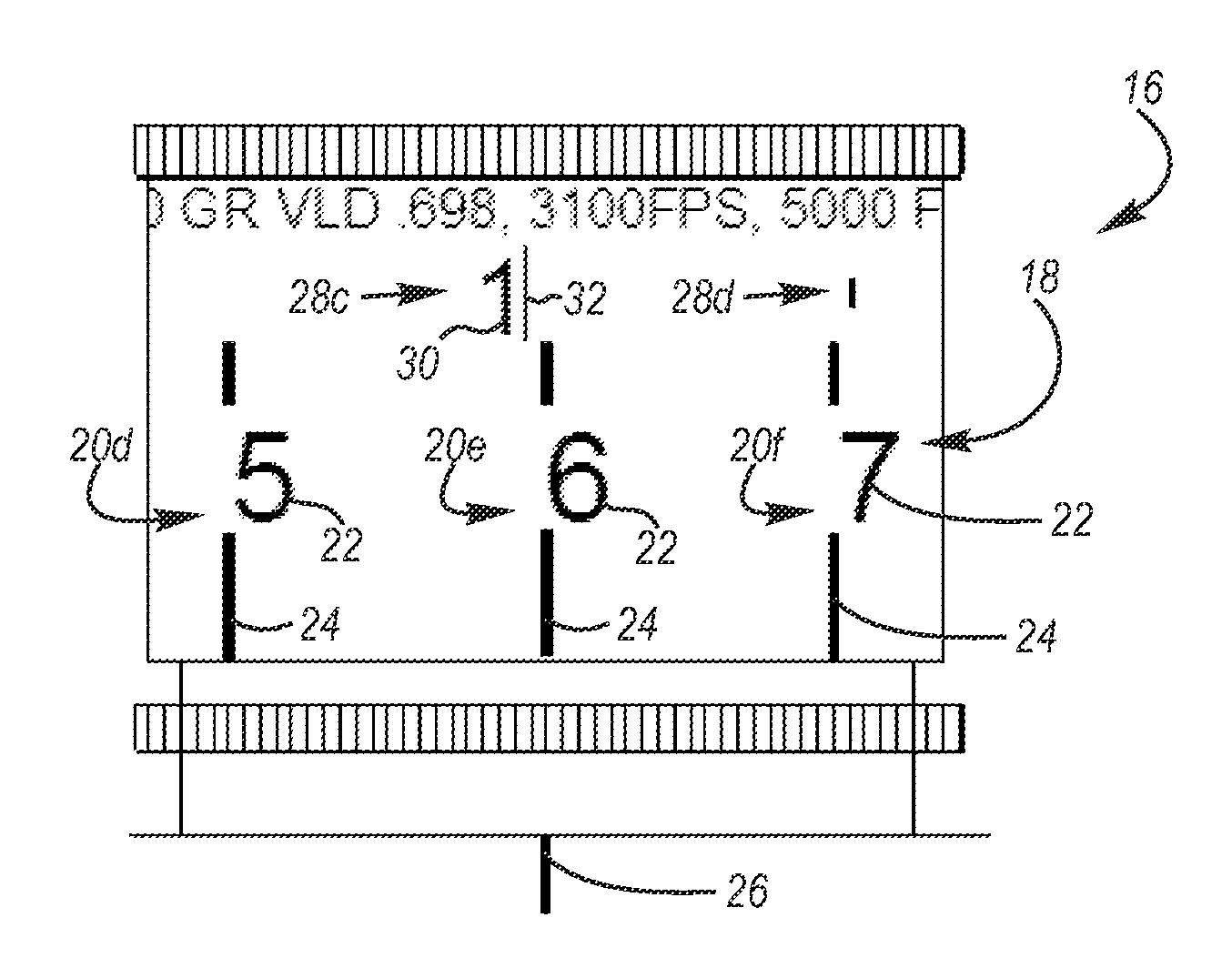
Zero stop adjustable rifle scope
A "zero stop" rifle scope adjustment mechanism that allows a user to establish the "zero point" at any point in the scope range, and still maintain ¼ minute clicks and with unlimited rotations of the adjustment knob. The mechanism includes a T-shaped adjustment bolt that is vertically aligned inside an adjustment body fixed in position on the turret of the rifle scope. The adjustment body includes a small threaded central bore to which the adjustment bolt is attached. The adjustment body also includes an upward cavity with splines formed on the inside surface. When assembled, the threaded upper section of the adjacent bolt extends above the top surface of the adjustment body. Disposed longitudinally and locked in position over the threaded upper section of the adjustment bolt and around the adjustment body is an index dial. Attached to the threaded upper section that extends above the index dial is a stop ring and a lock ring that are selectively locked together on the upper section of the adjustment bolt. A tab element is formed on the top surface of the index dial body which is engaged by a complimentary-shaped tongue member of the stop ring which locks the index dial body and stop plate together to prevent further downward rotation of the stop plate over the body. An outer cap is then longitudinally aligned and inserted over the stop ring, lock ring, index dial, and the adjustment body. The outer cap includes locking screw which when tightened, is forced against the lock ring to lock the outer cap thereto.
Owner:LIGHTFORCE USA
Combined illuminated reticle and focus knob
A combined focus and reticle illumination system for a riflescope which uses a single, dual functioning turn knob mounted on the scope turret for focusing and activating and deactivating the illuminated reticle. During use, the turn knob is rotated to adjust the relative position of a sliding focusing cell assembly located inside the scope body in front of the erector tube. The reticle, attached to the proximal end of the erector tube, includes a side mounted LED. The turn knob has a push-pull movement and a battery located therein that disconnects and connects, respectively, the electric circuit. The sliding focusing cell includes a rigid outer housing that is resistant to bending and a rear sliding lens cell that is biased in a rearward direction to be self-centering during recoil. Wires extend from the turn knob to the LED along the scope sidewalls and are designed to preclude twisting.
Owner:LIGHTFORCE USA
Zero stop adjustable rifle scope
A "zero stop" rifle scope adjustment mechanism that allows a user to establish the "zero point" at any point in the scope range, and still maintain ¼ minute clicks and with unlimited rotations of the adjustment knob. The mechanism includes a T-shaped adjustment bolt that is vertically aligned inside an adjustment body fixed in position on the turret of the rifle scope. The adjustment body includes a small threaded central bore to which the adjustment bolt is attached. The adjustment body also includes an upward cavity with splines formed on the inside surface. When assembled, the threaded upper section of the adjacent bolt extends above the top surface of the adjustment body. Disposed longitudinally and locked in position over the threaded upper section of the adjustment bolt and around the adjustment body is an index dial. Attached to the threaded upper section that extends above the index dial is a stop ring and a lock ring that are selectively locked together on the upper section of the adjustment bolt. A tab element is formed on the top surface of the index dial body which is engaged by a complimentary-shaped tongue member of the stop ring which locks the index dial body and stop plate together to prevent further downward rotation of the stop plate over the body. An outer cap is then longitudinally aligned and inserted over the stop ring, lock ring, index dial, and the adjustment body. The outer cap includes locking screw which when tightened, is forced against the lock ring to lock the outer cap thereto.
Owner:LIGHTFORCE USA
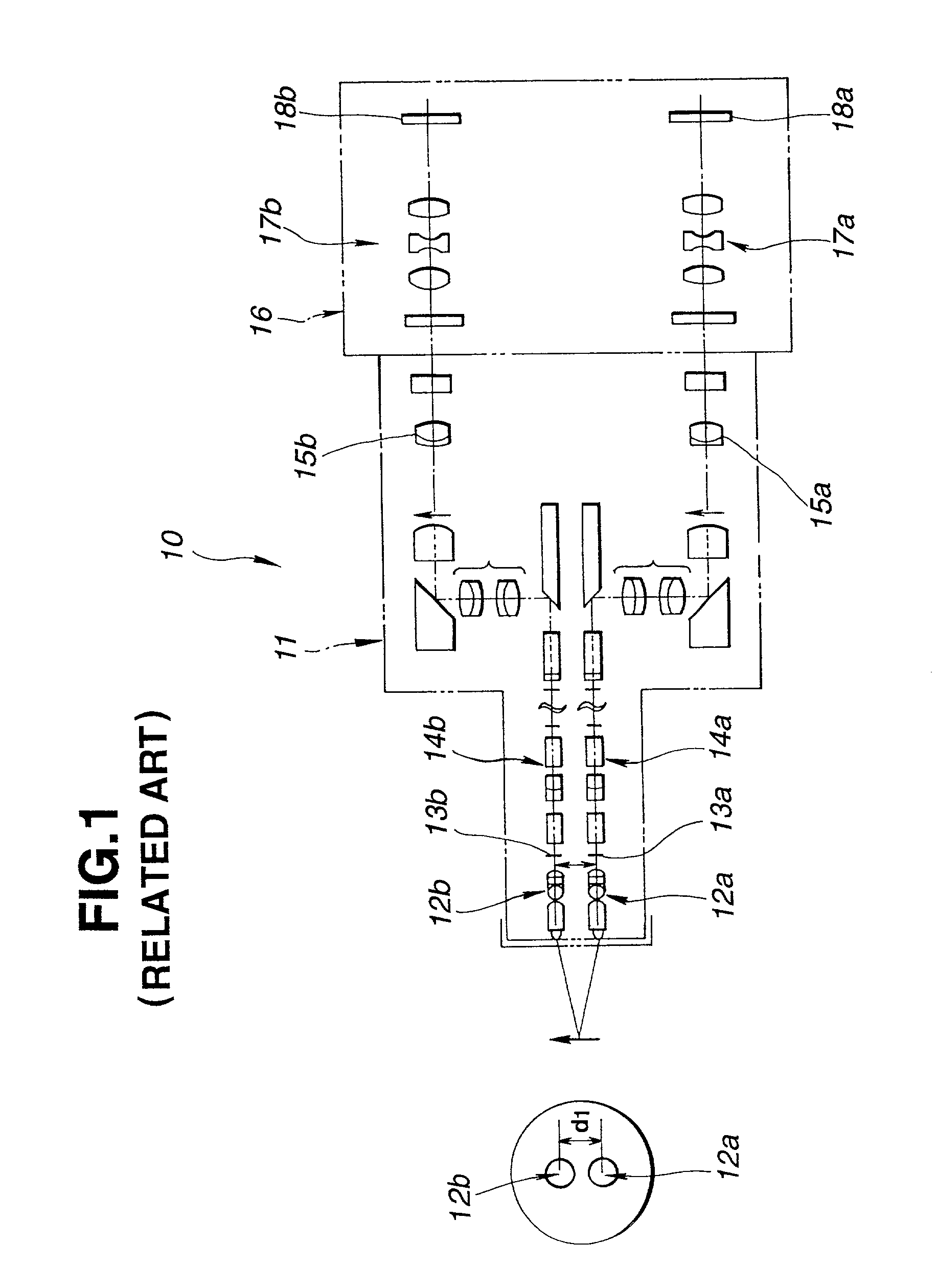
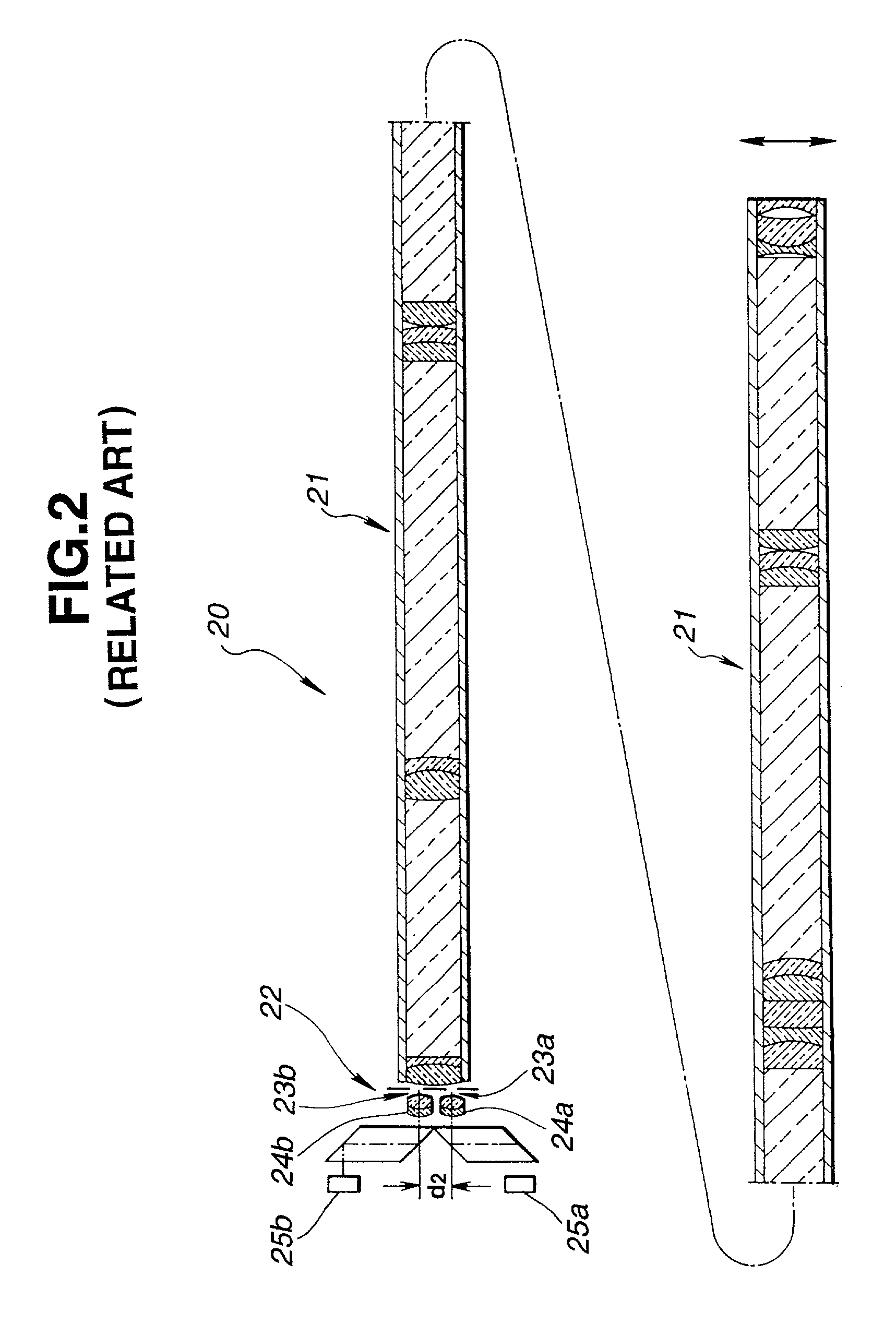
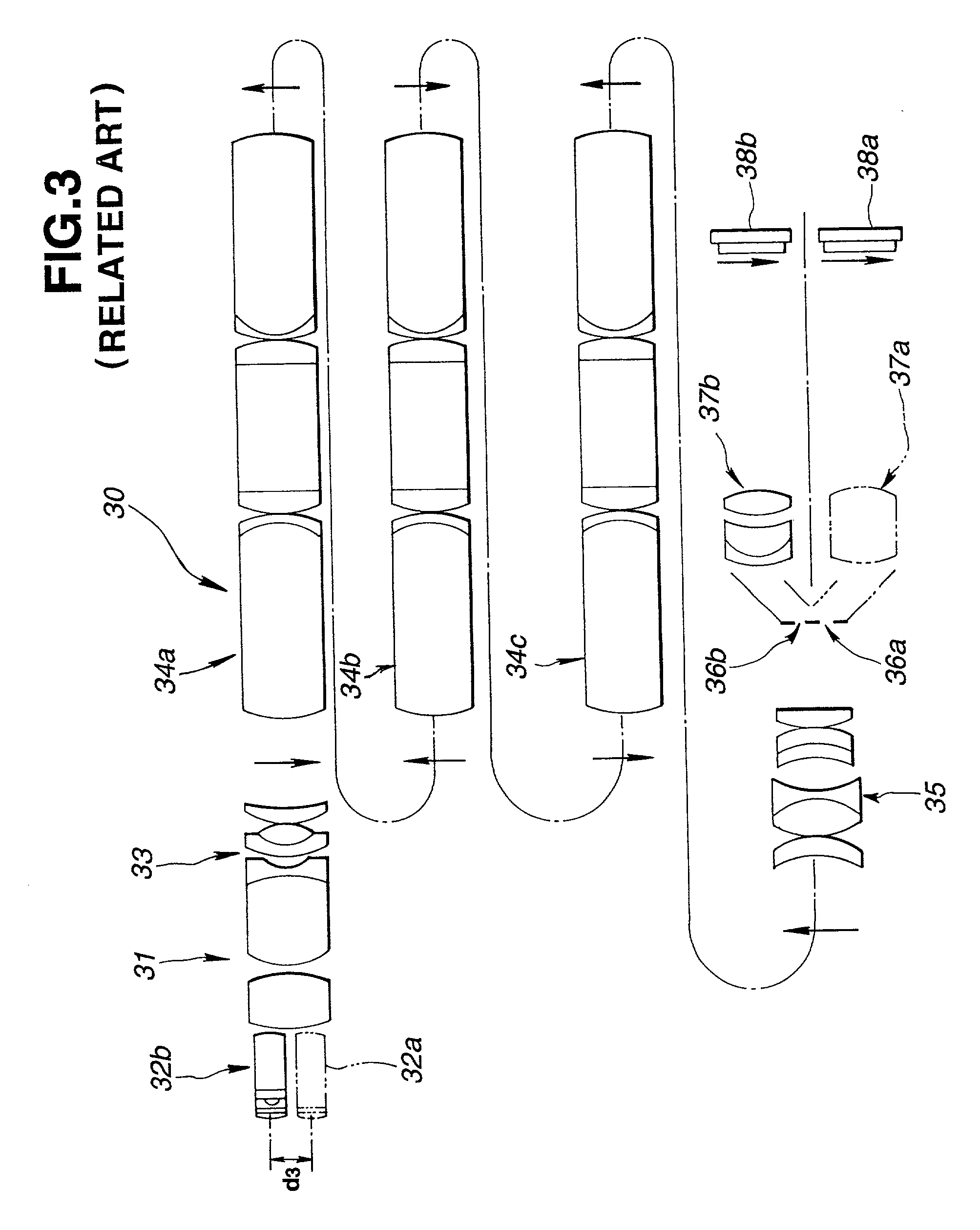
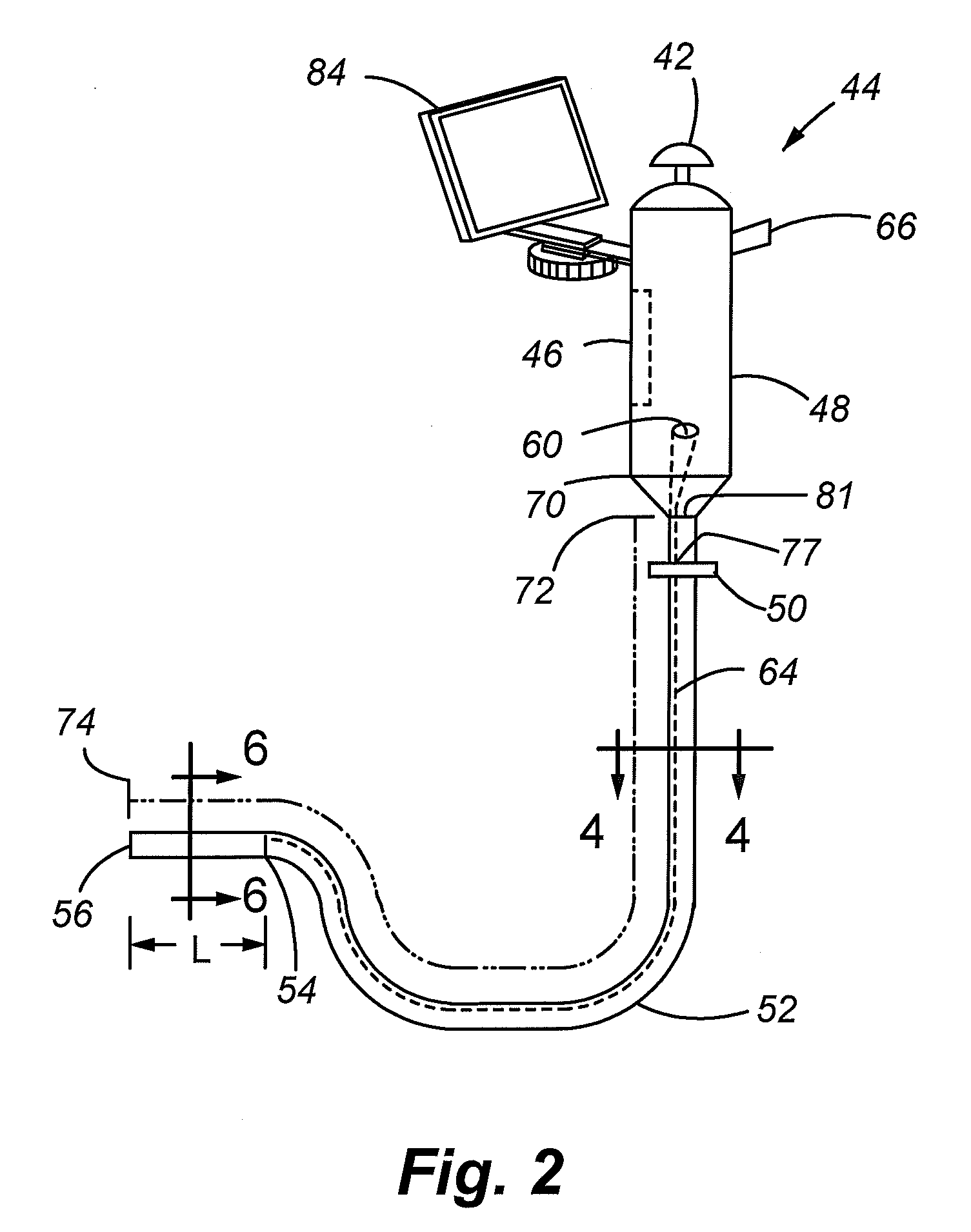
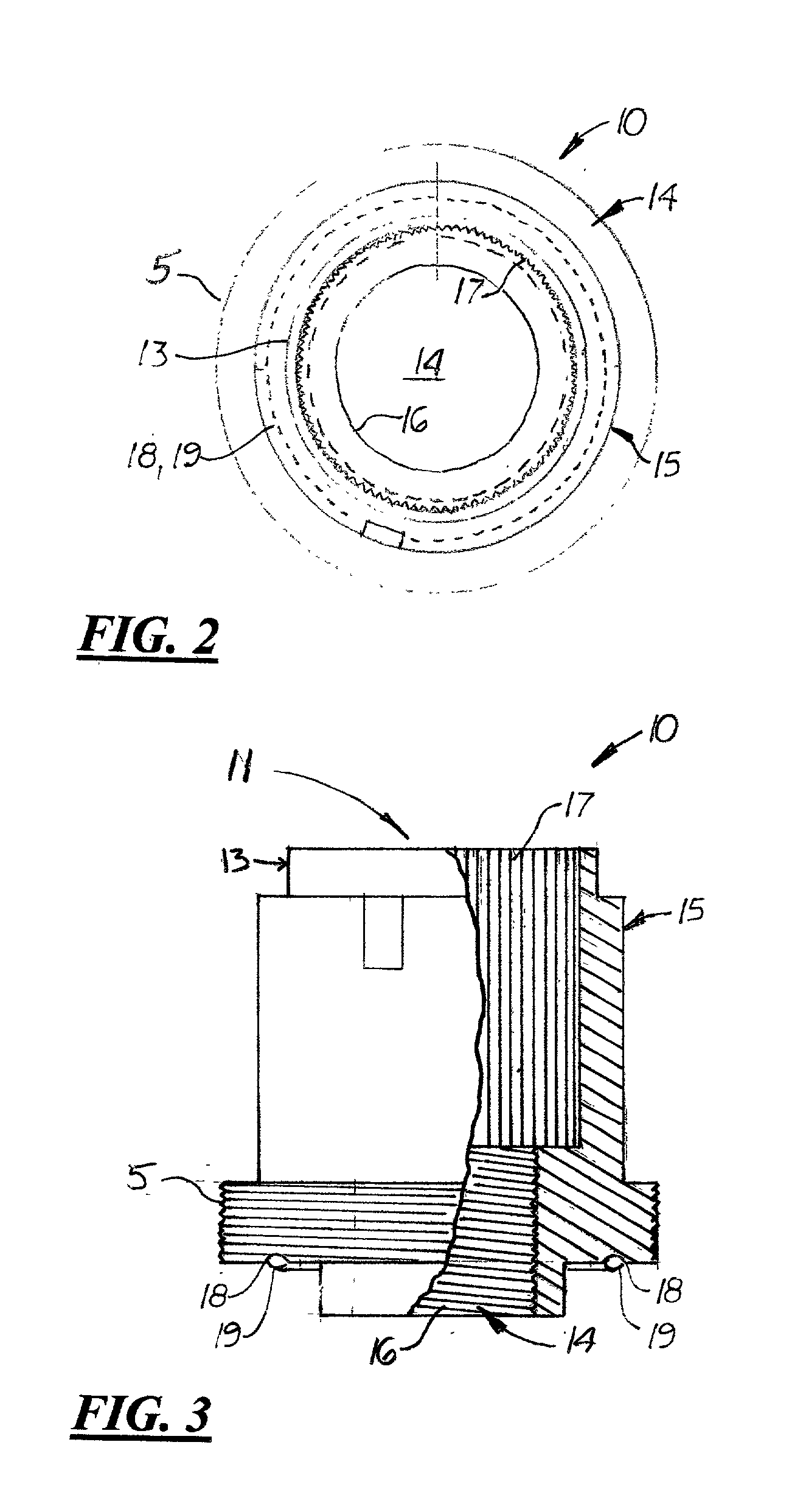
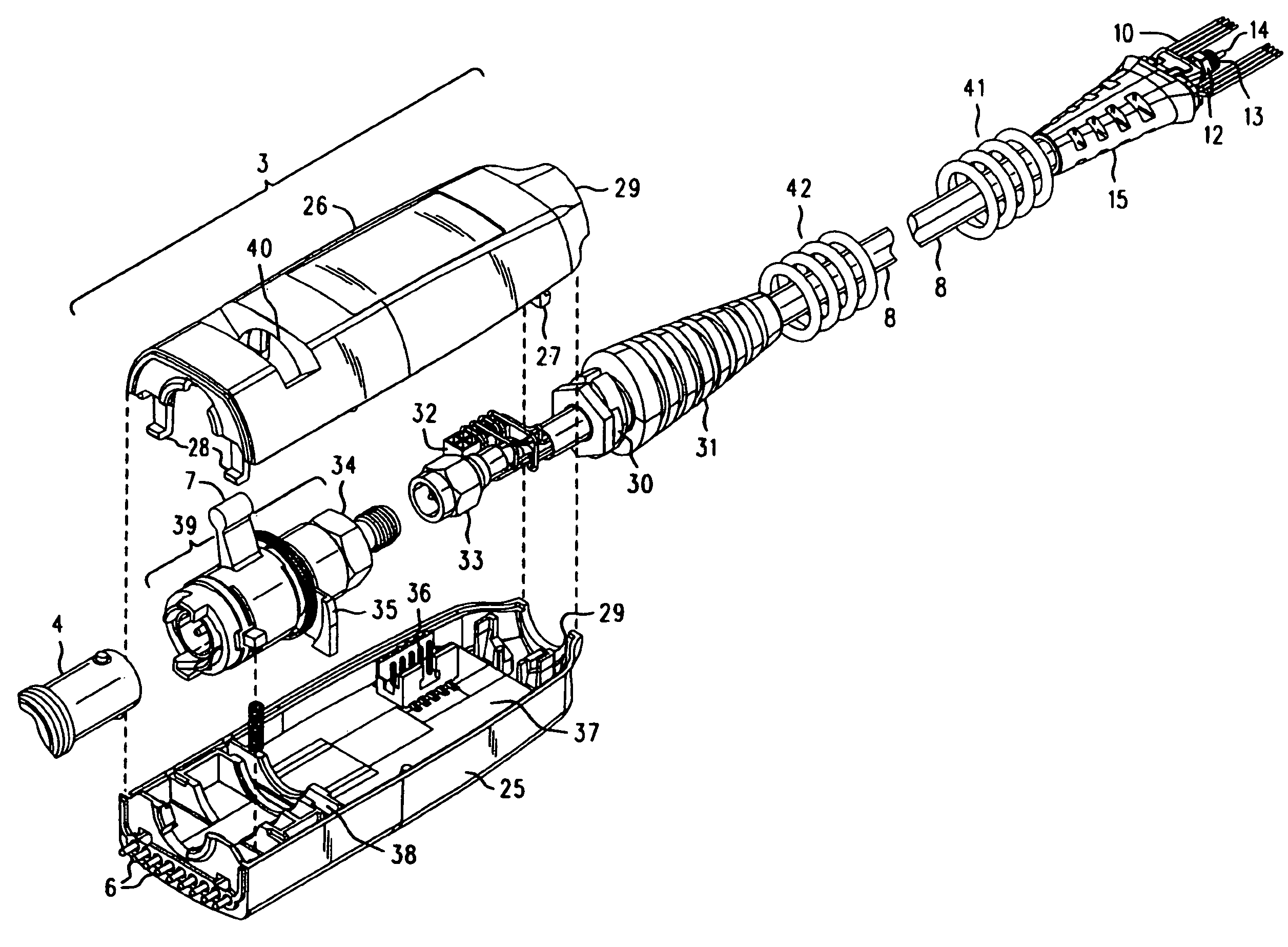
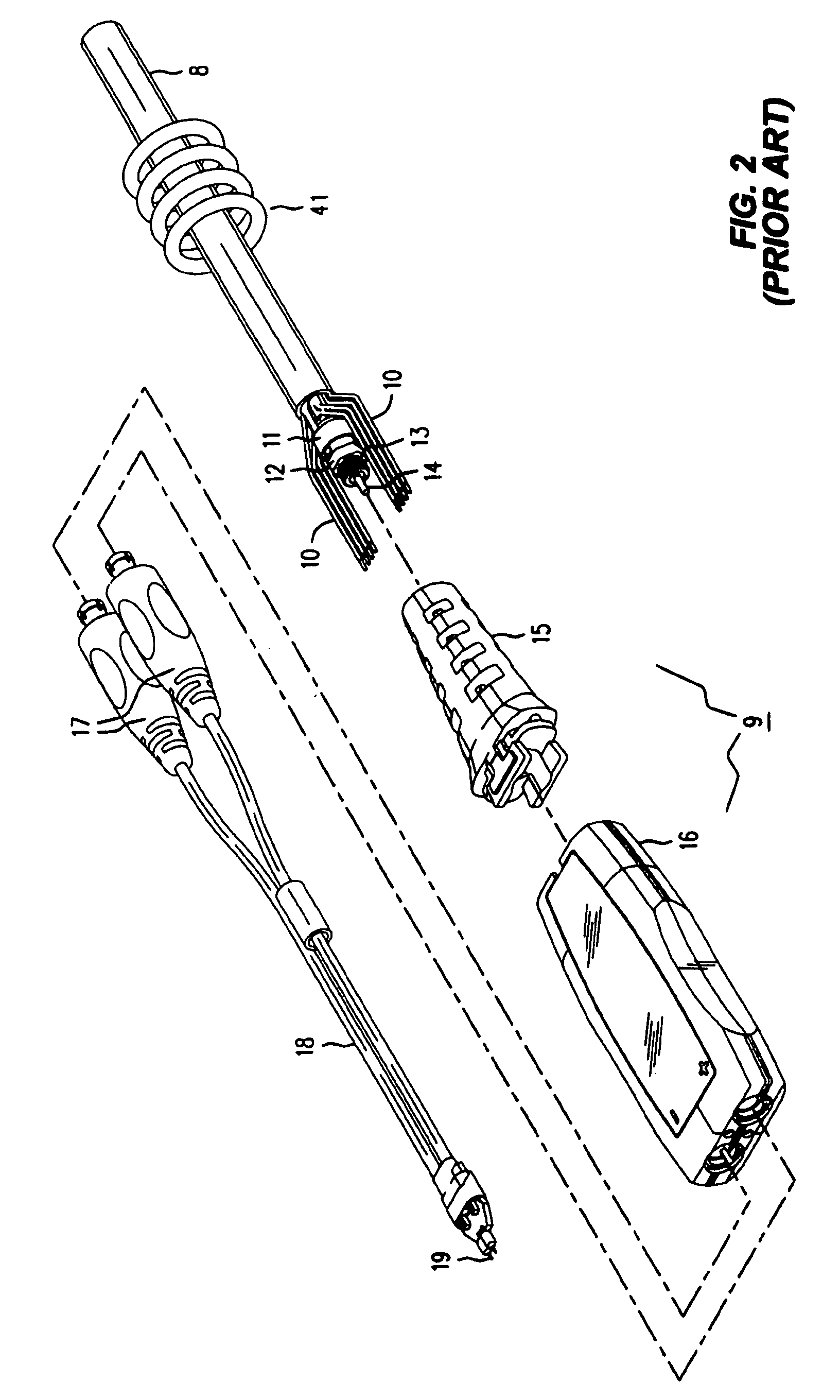
High bandwidth oscilloscope probe with replaceable cable
InactiveUS6933713B2Electrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsHigh bandwidthElectrical conductor
A probe pod housing is connected by a cable to an active probe. The probe pod housing carries a male push-on precision BNC connector that is also a cross-series adapter. The center conductor of the cable receives a male connector that then mates with the non-BNC end of the cross-series adapter. Auxiliary conductors that may also be carried by the cable are connected to male pins (soldered to a circuit board carried within the probe pod) with a push-on female in-line connector. The active probe itself uses a soldered-to-the-shield threaded nut technique. The nut threads into a metallic body that contains the impedance converter and that is enclosed by the body of the active probe. The cable is replaced by first unsoldering the center conductor (and also any auxiliary conductors). Then the nut (which is still soldered to the shield) is unscrewed from the metallic body, and the cable is free from the probe. At the probe pod end the cable mounted male connector is simply unscrewed from the cross-series adapter, and any auxiliary conductors disconnected by removing the female wire-mounted in-line connector.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
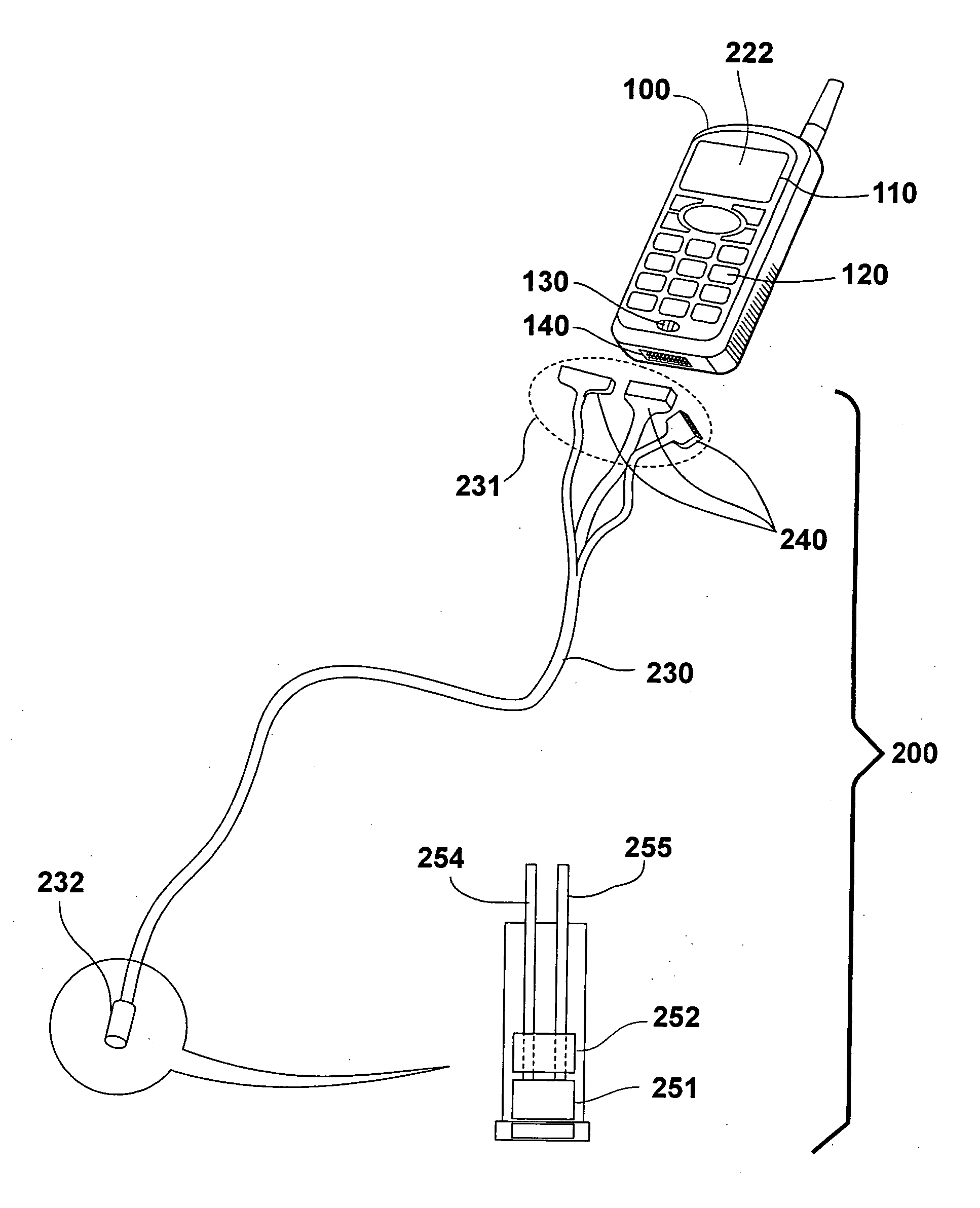
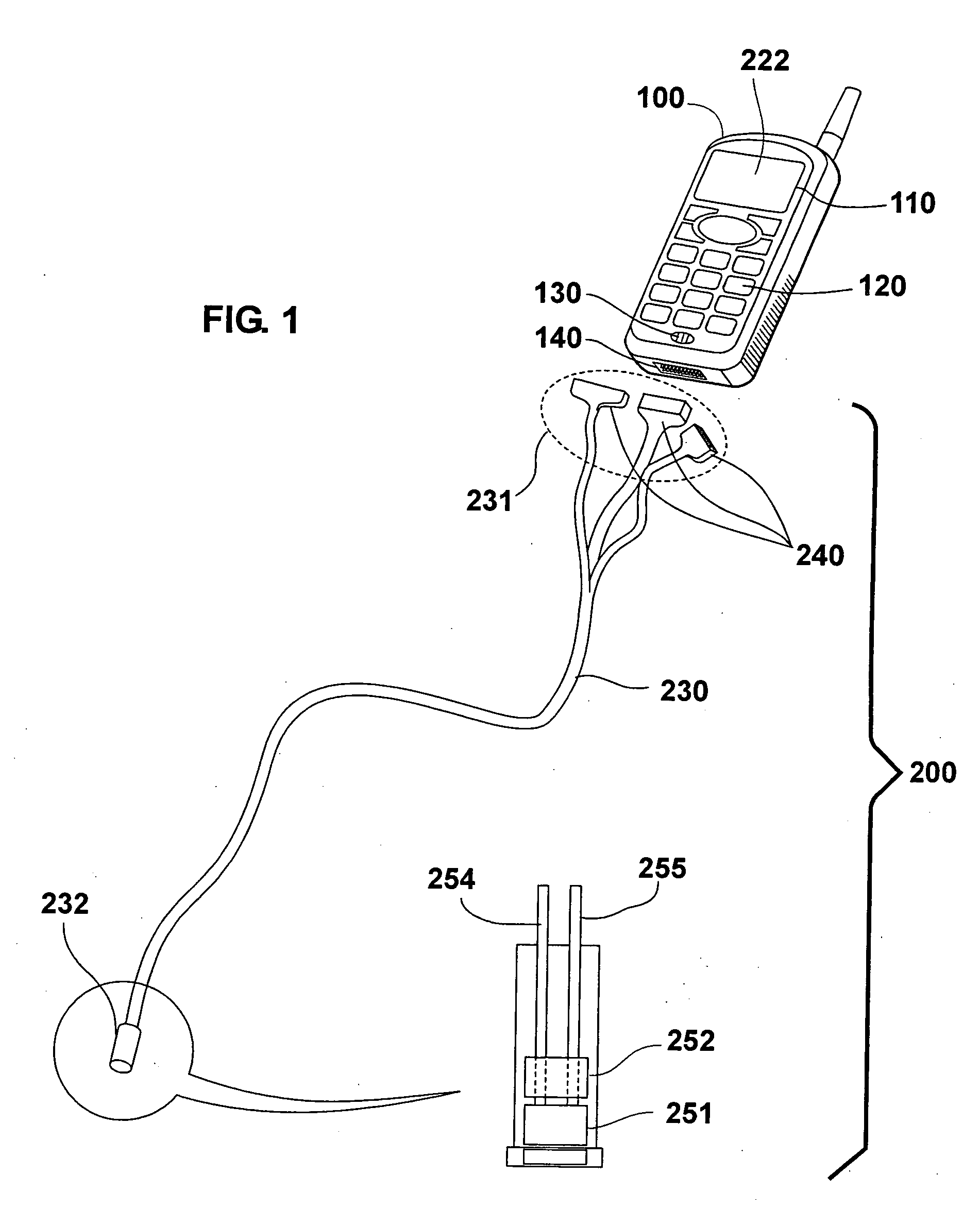
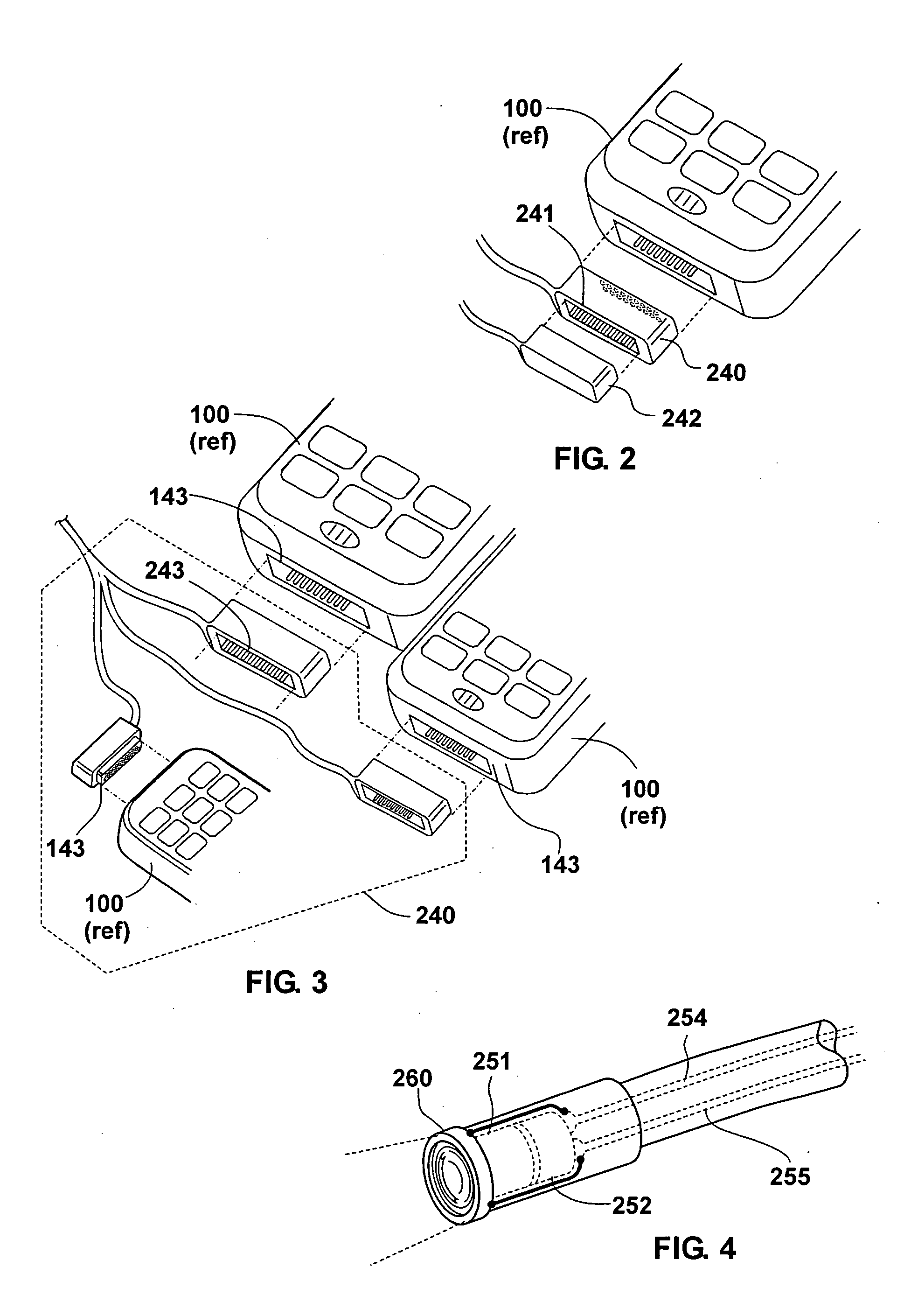
Cellular telephone with remote video scope and motion detector
A cellular telephonic video scope and motion detector with the video scope and motion detector remotely and removably connected to the input / output port of the cellular telephone. A further embodiment allows control of the direction of the distal end of the video scope. A further embodiment allows attachment of the motion detector to the video scope. A further embodiment allows control of the video scope and motion detector via the cellular telephone keypad and cellular telephone transmission.
Owner:HAVIV YEHUDA
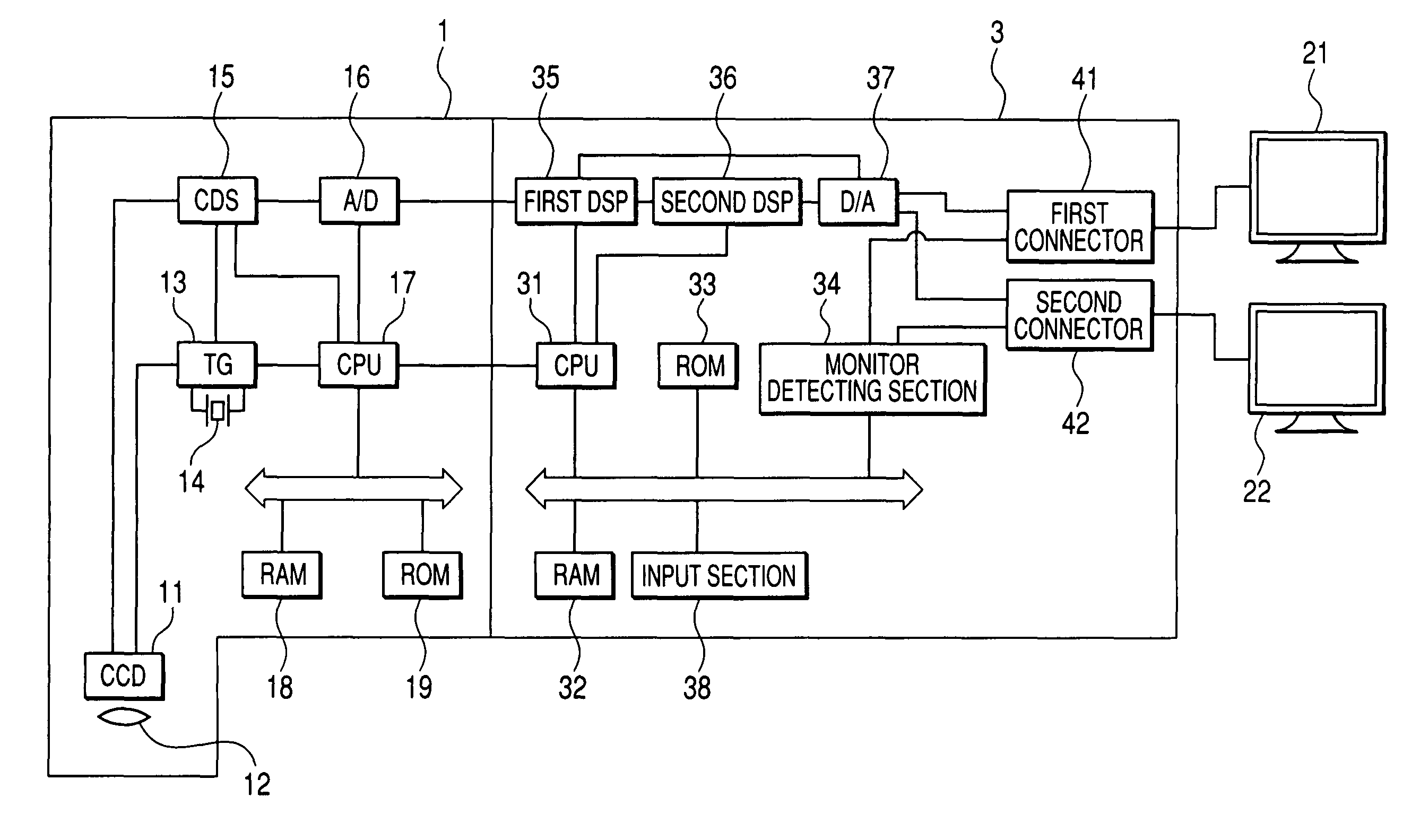
Endoscope visual imaging and processing apparatus
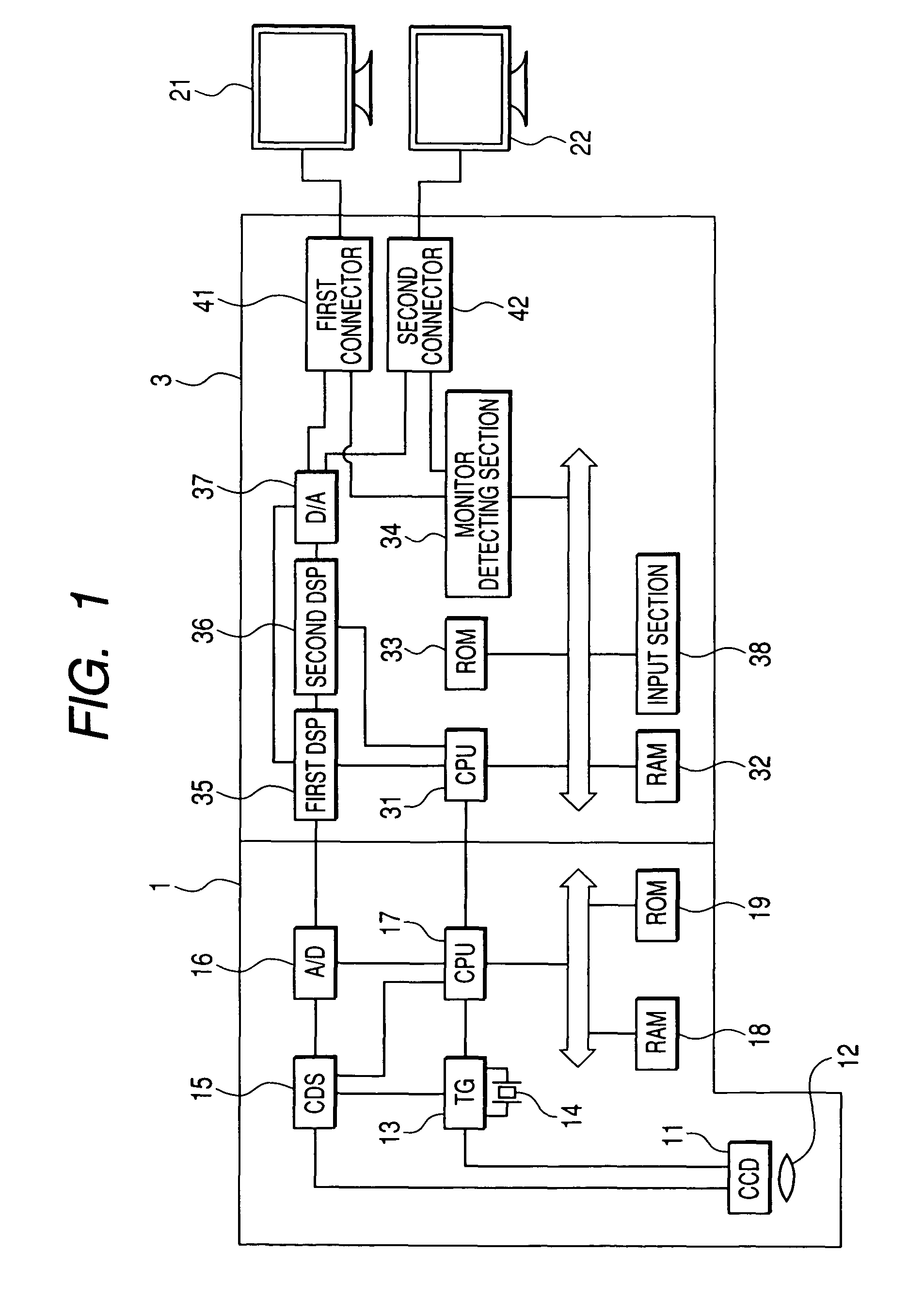
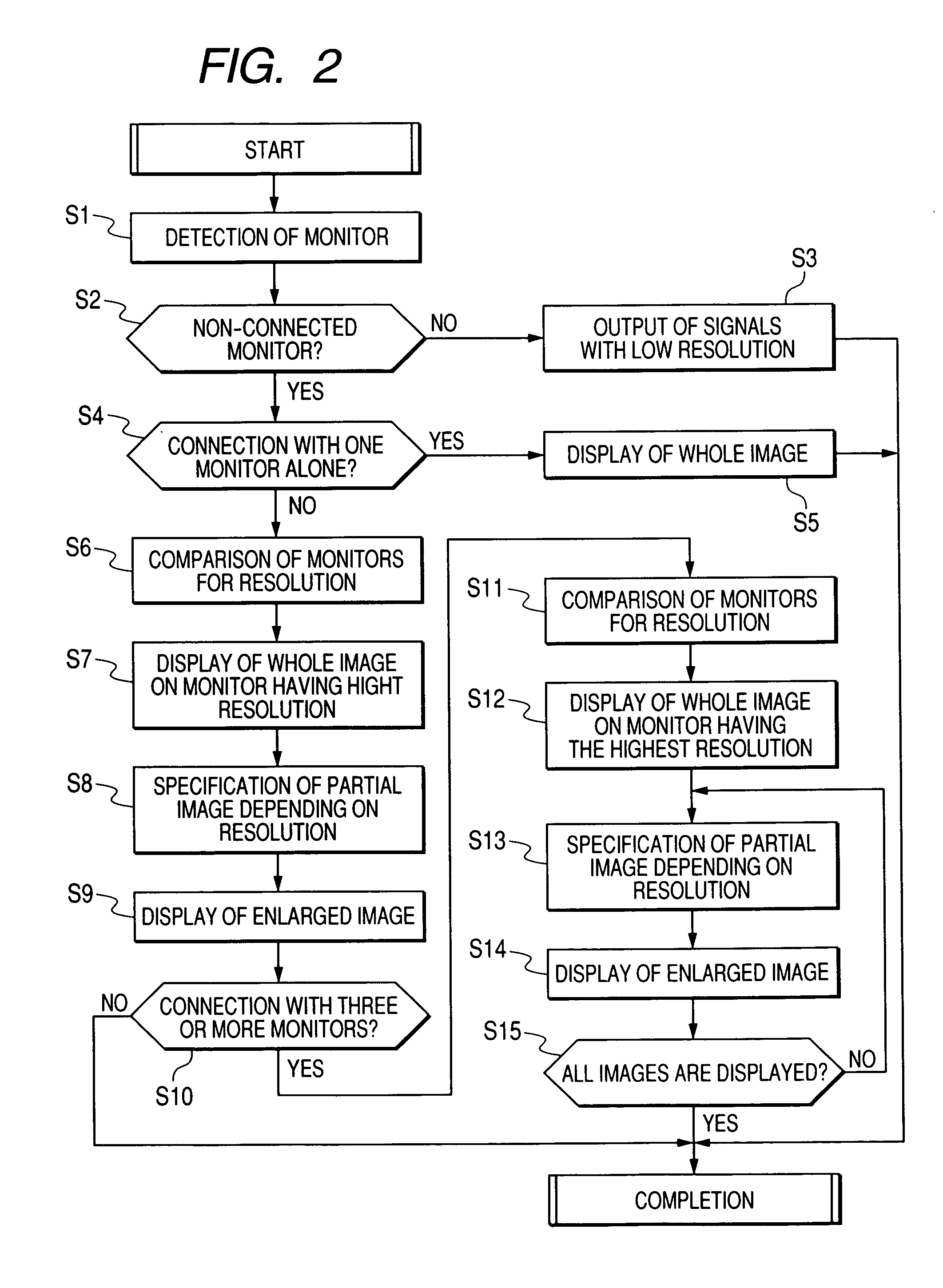
An endoscope apparatus comprises: a scope comprising a solid imaging device; a processor unit which forms an observation image from signals emitted from the solid imaging device, the processor being connected to the scope; and a plurality of monitors each of which is connected to the processor unit, wherein a whole image of the observation image is displayed on at least one of said plurality of monitors, and a partial image of the observation image is enlarged and displayed on the other one(s) of said plurality of monitors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Self-cleaning wireless video stylet with display mounted to laryngoscope blade and method for using the same
InactiveUS20100094090A1Avoiding and minimizing patient traumaAvoid and minimize traumaBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesWireless videoDisplay device
A scope adapted for insertion and manipulation in a difficult pathway is disclosed. The scope comprises at least one module for manipulating the scope. The scope may further comprise an illumination source, an image sensor, a power source, and a viewing member for viewing images of a cavity or other anatomical member of a patient. In one embodiment the scope is intended to facilitate insertion of an intubating device, which comprises an elongated semi-rigid stylet including first and second ends and at least one inner lumen connected to a module. Additionally, a flexible tip is provided for manipulating one end of the scope and allowing greater flexibility when maneuvering a difficult pathway. In another embodiment, fluids are provided through an interior portion of the scope, allowed to at least partially contact the lens located at the distal end of the scope, and subsequently cleanse or defog the lens for improving vision via the scope. A method for navigating a difficult pathway and for using the apparatus described herein is also disclosed.
Owner:MEJIA MAURICIO
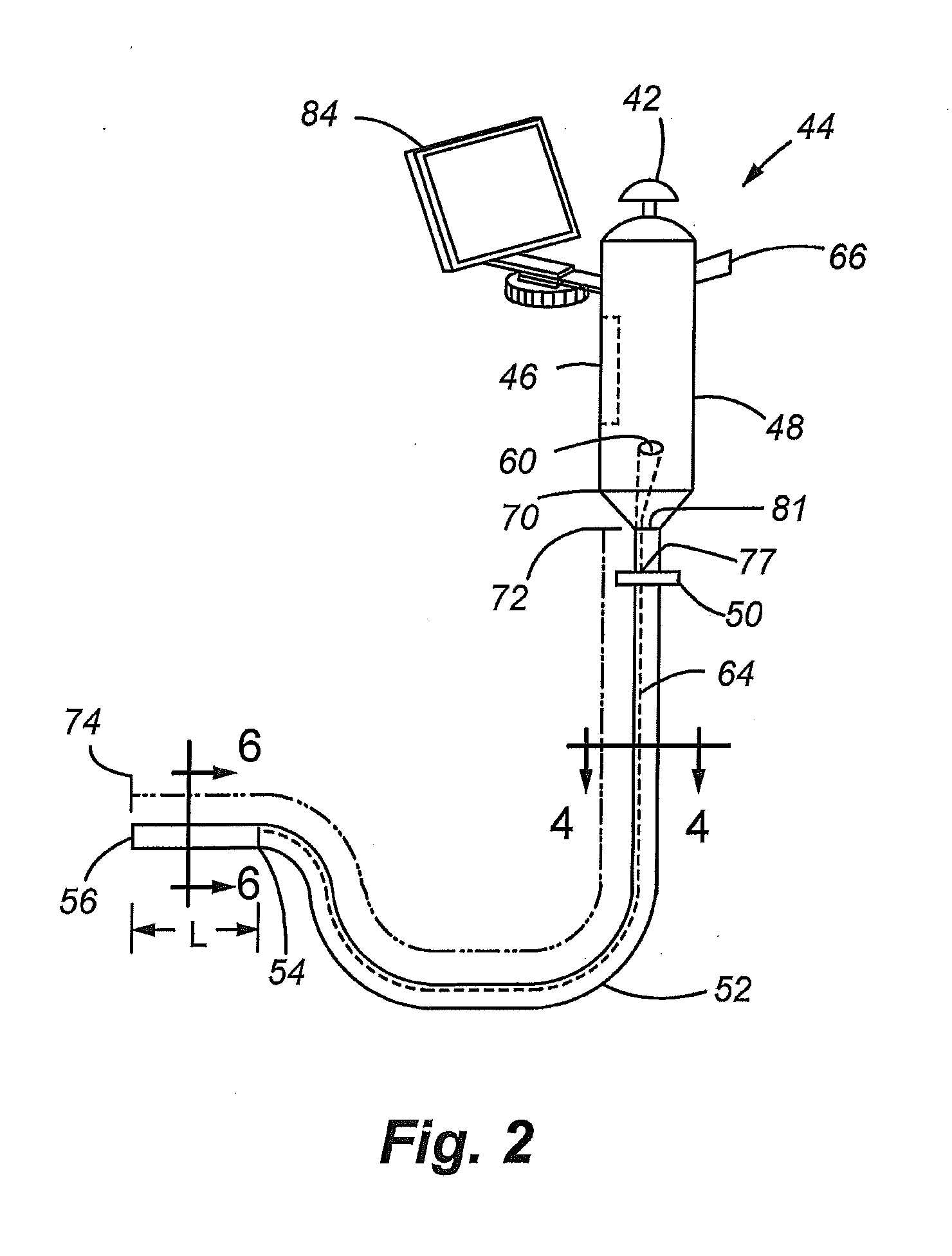
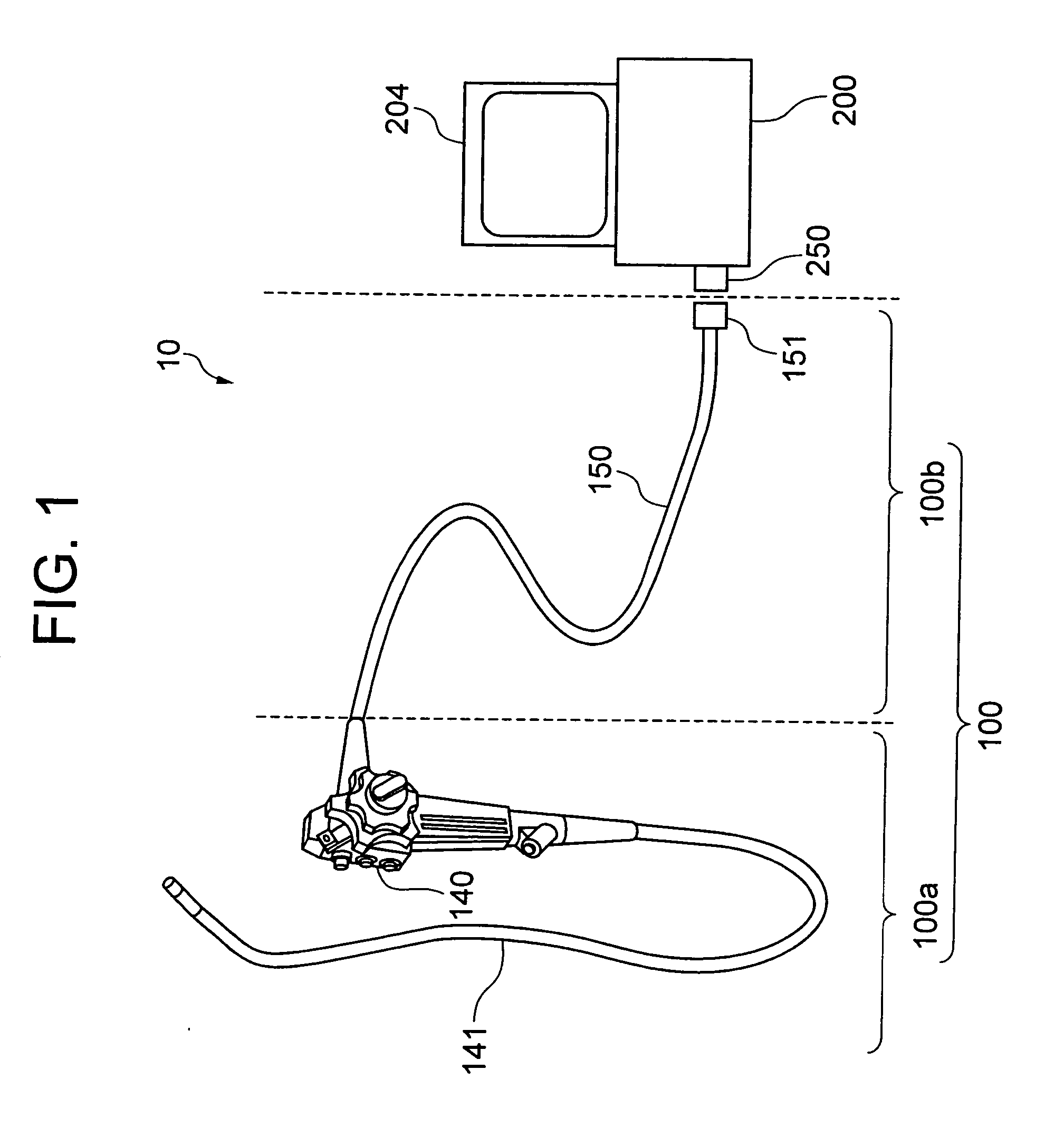
Electronic endoscope system
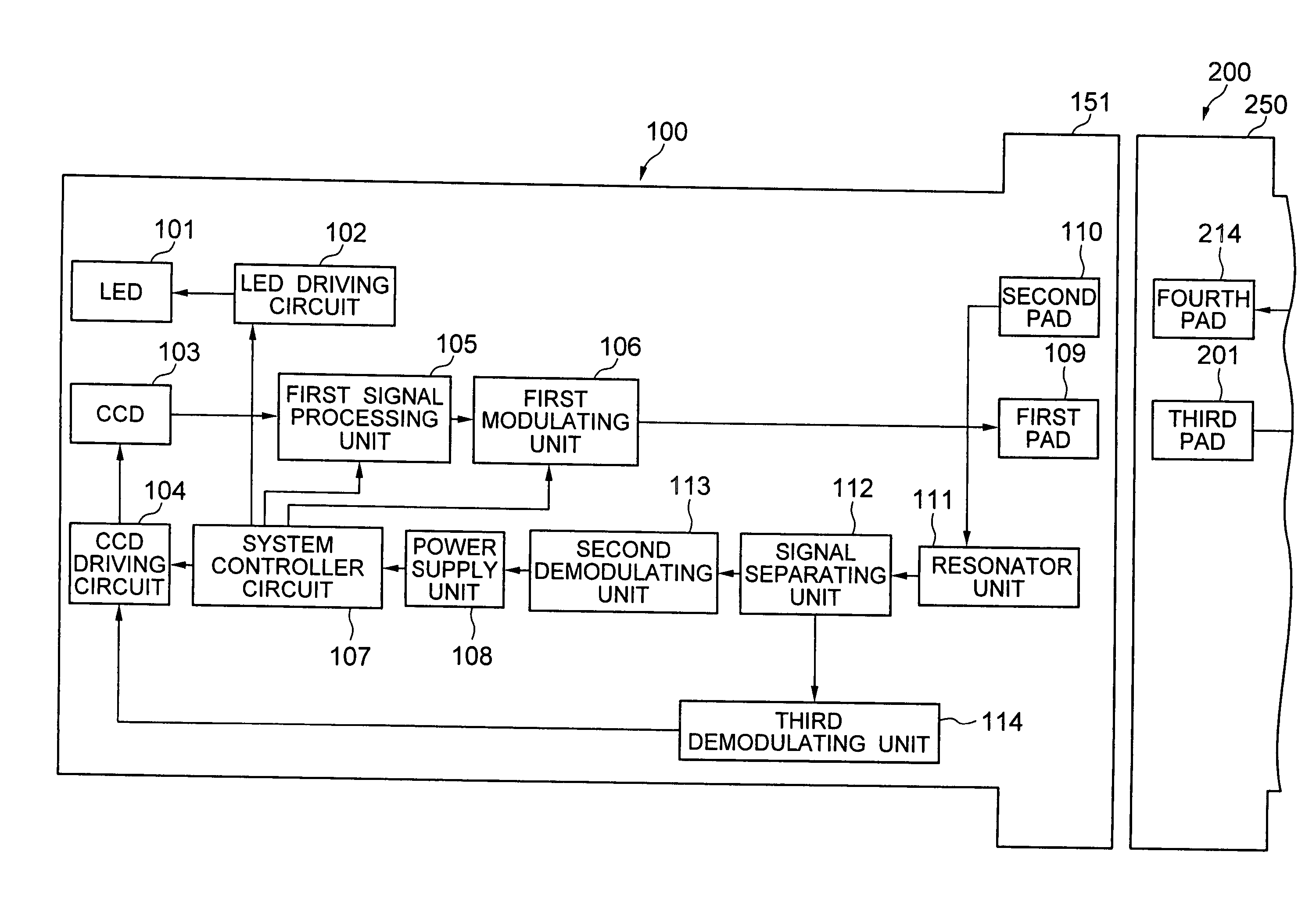
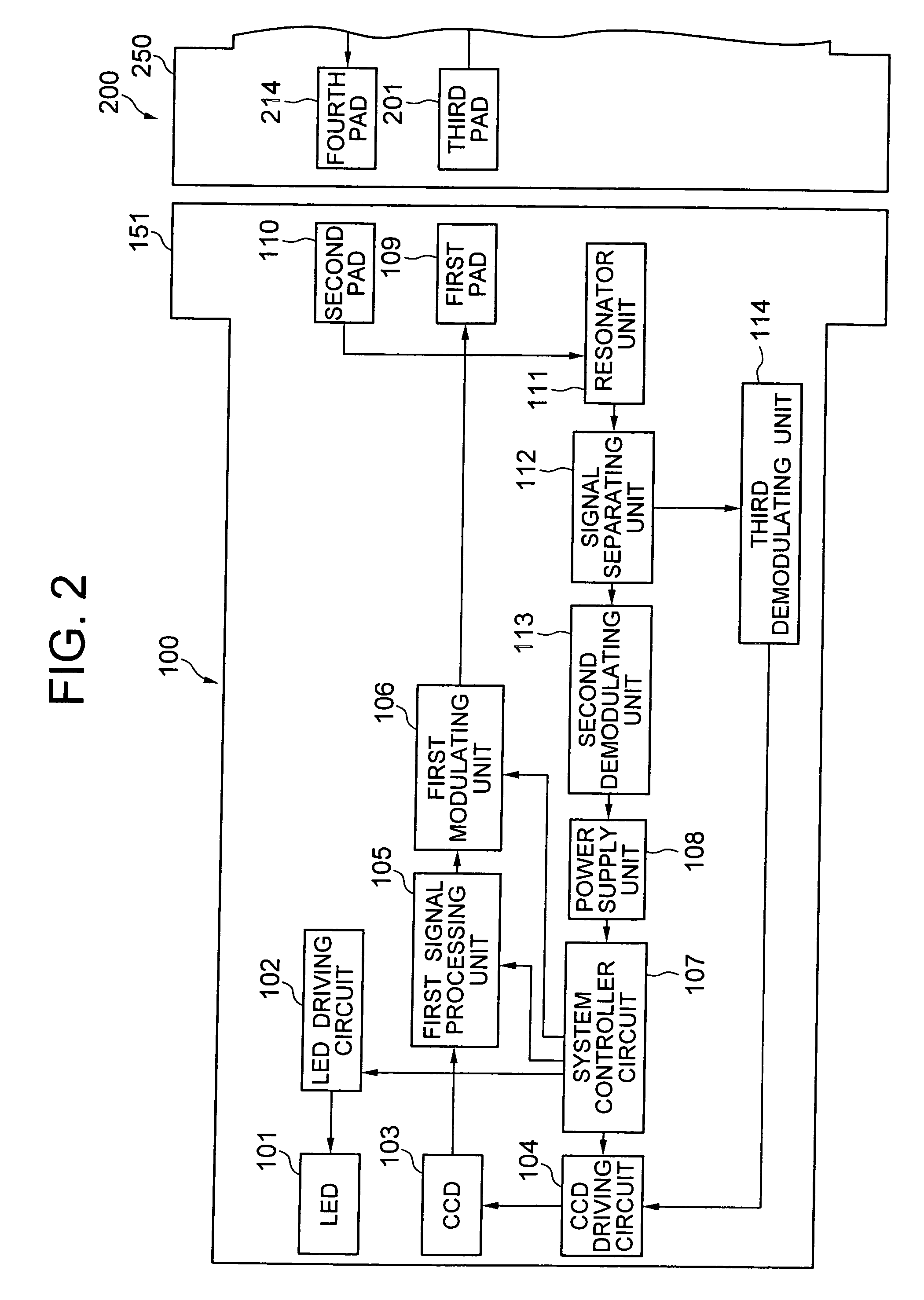
An electronic endoscope system includes a scope section, an in vitro apparatus which is installed outside a body, and a connecting cord section which connects the scope section and the in vitro apparatus. Each of the in vitro apparatus and the connecting cord section includes pads which are structured to be air tight and water tight, and connecting sections for bringing close upon facing each of the pads. Furthermore, for performing a communication of a signal between a pair of pads facing each other, the electronic endoscope system includes a first modulating unit which applies a voltage on one of the pads upon modulating the signal, and a demodulating unit which demodulates the signal from a change in an electric potential of the other pad.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
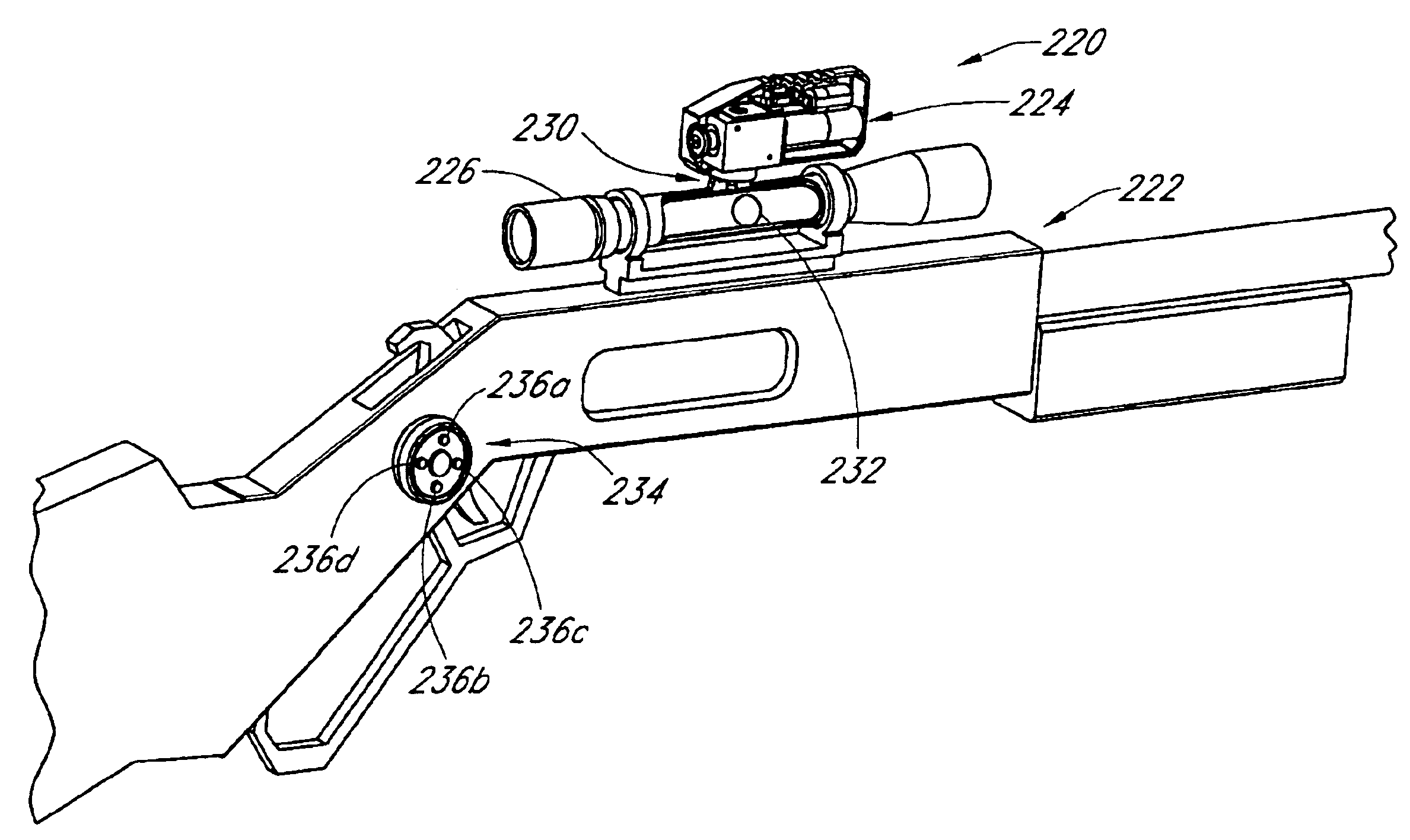
Ballistics systems and methods
ActiveUS8001714B2Quick selectionQuick identificationWave based measurement systemsComputer controlComputer moduleEngineering
A scope may include an adjustment dial, which may be moved among a plurality of positions to configure the scope to compensate for projectile drops. The adjustment dial may be labeled with dial-calibration data, which may include one or more distance indicators and / or one or more windage hold-off indicators. The scope may be attached to a gun and the dial-calibration data may be at least partially generated using ballistics performance data based on shots fired by the gun. The dial-calibration data may be at least partially generated using shooting conditions. An electronic device may include a derived distance calculation module, which may be configured to use a distance to a target and actual shooting conditions to calculate a derived distance. The derived distance may be used in connection with an adjustment dial labeled with dial-calibration data at least partially generated using shooting conditions different from the actual shooting conditions.
Owner:HUSKEMAW OPTICS
Enhanced test and measurement instruments using compression and decompression
InactiveUS7071852B1Less bandwidthLess storageDigital variable displayElectric signal transmission systemsMeasuring instrumentParallel compression
An enhancement that improves the performance of test and measurement equipment such as digital oscilloscopes and arbitrary waveform generators through the use of compression and decompression is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or cannot effectively be compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention improves digital oscilloscopes by compressing the sampled version of an analog waveform under observation in real time, allowing a significantly longer duration of the waveform to be stored in the oscilloscope's capture memory, when compared with the duration of the same signal's uncompressed waveform stored in the same memory. Similarly, the present invention improves arbitrary waveform generators by storing a compressed version of a desired arbitrary waveform, instead of the uncompressed version of the arbitrary waveform, in the signal generator's waveform memory. During signal generation, the compressed waveform is decompressed in real time. The uncompressed waveform drives a D / A converter that generates the desired analog waveform. The present invention's simplicity, and its ability to be implemented using parallel compression and decompression elements, allows its use at the high sampling rates of test and measurement instruments. Using the present invention, storage elements in test and measurement equipment can hold significantly longer waveforms in a fixed amount of memory. Users of the present invention can also determine the proper balance between the fidelity and the duration of the decompressed waveform by adjusting various compression and decompression control parameters.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
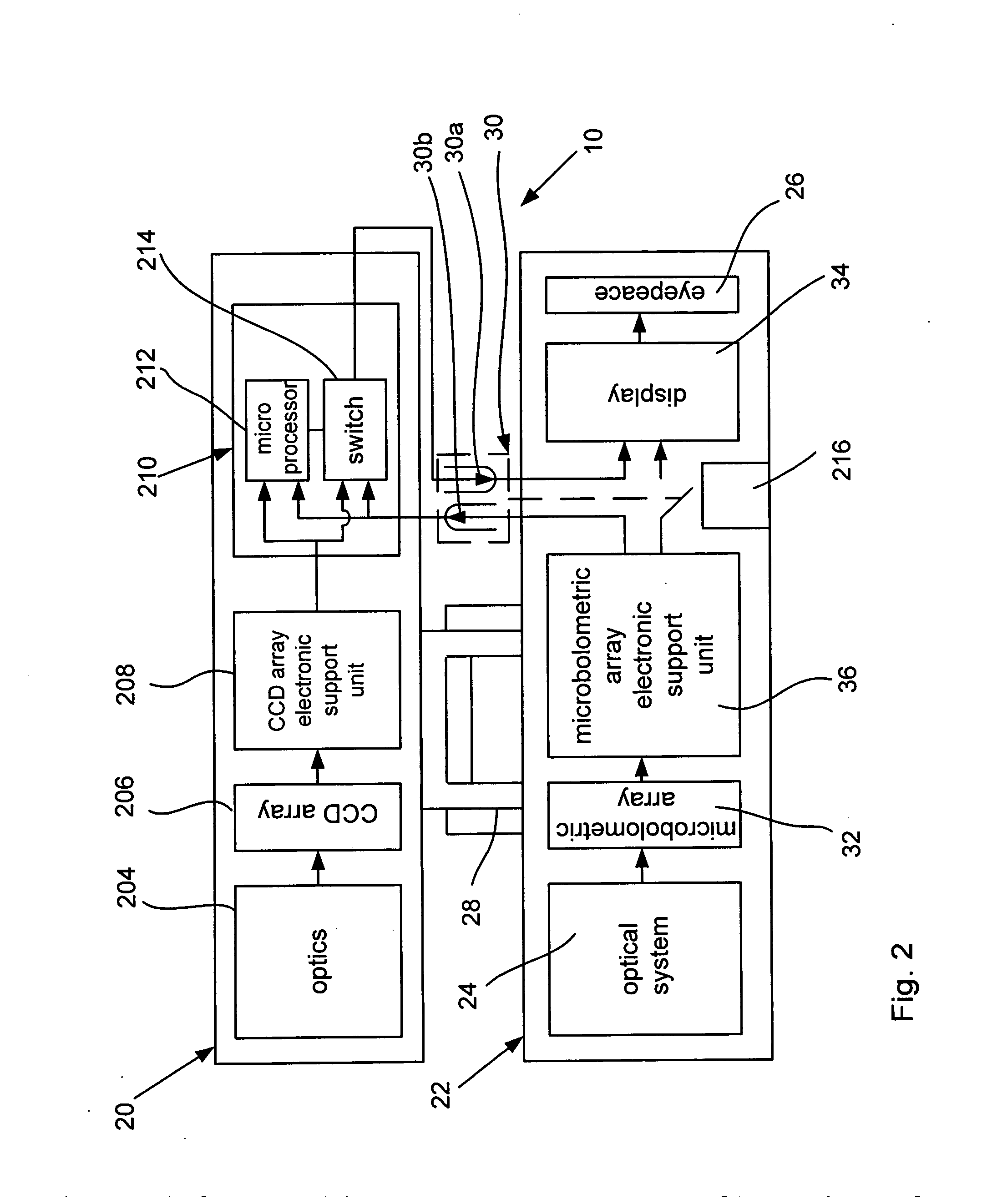
Optical system with automatic switching between operation in daylight and thermovision modes
InactiveUS20120007987A1Easy to storeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDaylightComputer science
An optical sight system that comprises a combination of a thermal scope with a CCD visual-range attachment connectable to the thermal scope with a quick-release connector. The system is equipped with a device that automatically activates the CCD visual-range attachment when the latter is connected to the thermal scope and with a comparator that compares the video signal of the CCD attachment with the video signal of the thermal scope for sending the brightest video signal to the thermal scope display.
Owner:AMERICAN TECH NETWORK
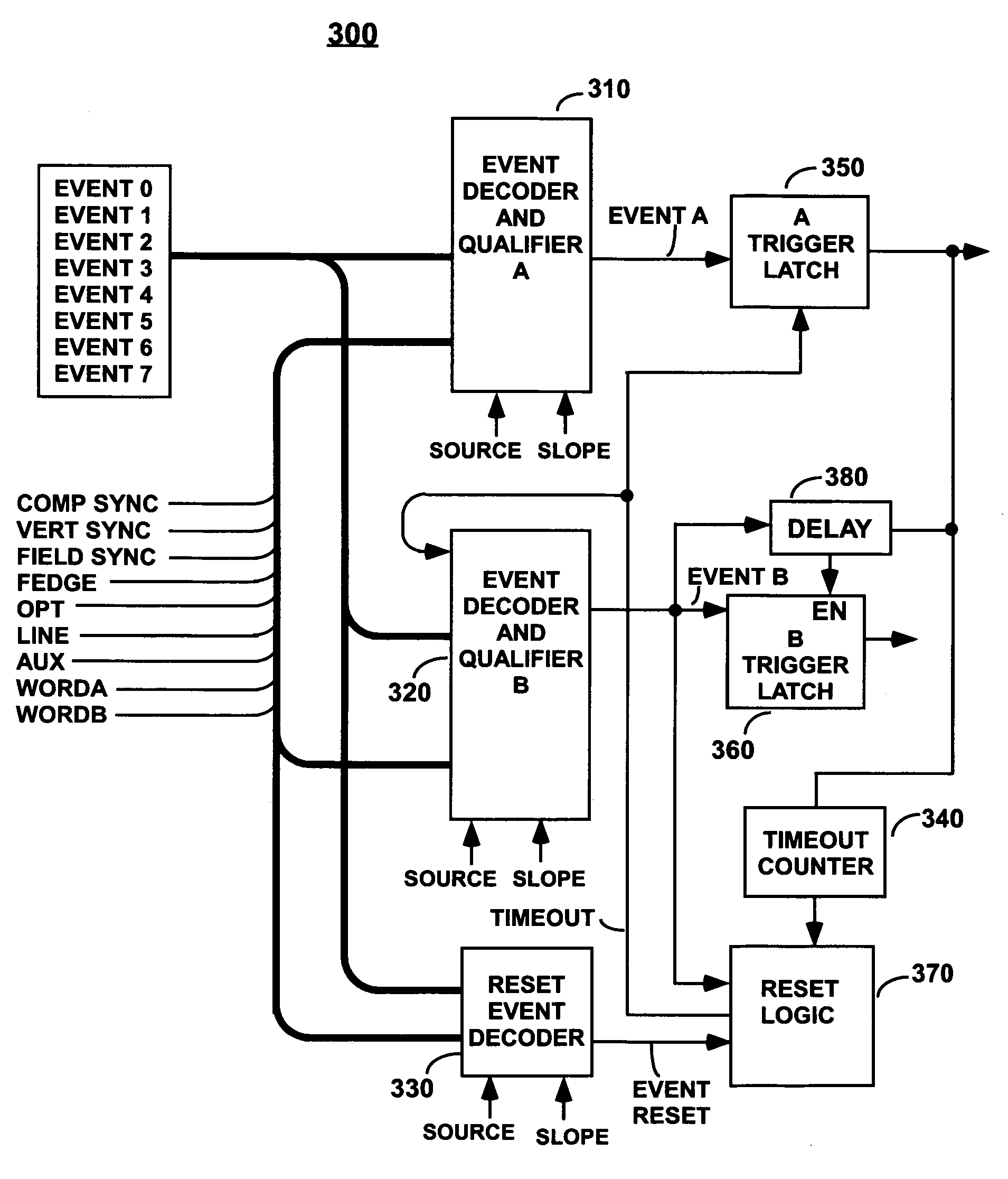
Oscilloscope having advanced triggering capability
ActiveUS7191079B2Digital variable displayNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTimerTime signal
An advanced trigger circuit includes two trigger decoders, each triggering on one of respective pluralities of continuous-time trigger events. In one embodiment, a programmable timer begins timing in response to an output signal of the first trigger decoder and generates an end-of-time signal at the expiration of its time period. A reset circuit resets the first trigger decoder if the second selected continuous-time trigger event failed to occur before the end-of-time signal was generated. In another embodiment, a reset decoder generates a reset signal in response to an occurrence of a selected continuous-time trigger event. The reset circuit is responsive to the reset signal for resetting the first trigger decoder if the second selected continuous-time trigger event failed to occur before the reset signal was generated. In other embodiments, the advanced trigger circuit triggers on a serial lane skew violation or on a beacon width violation.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
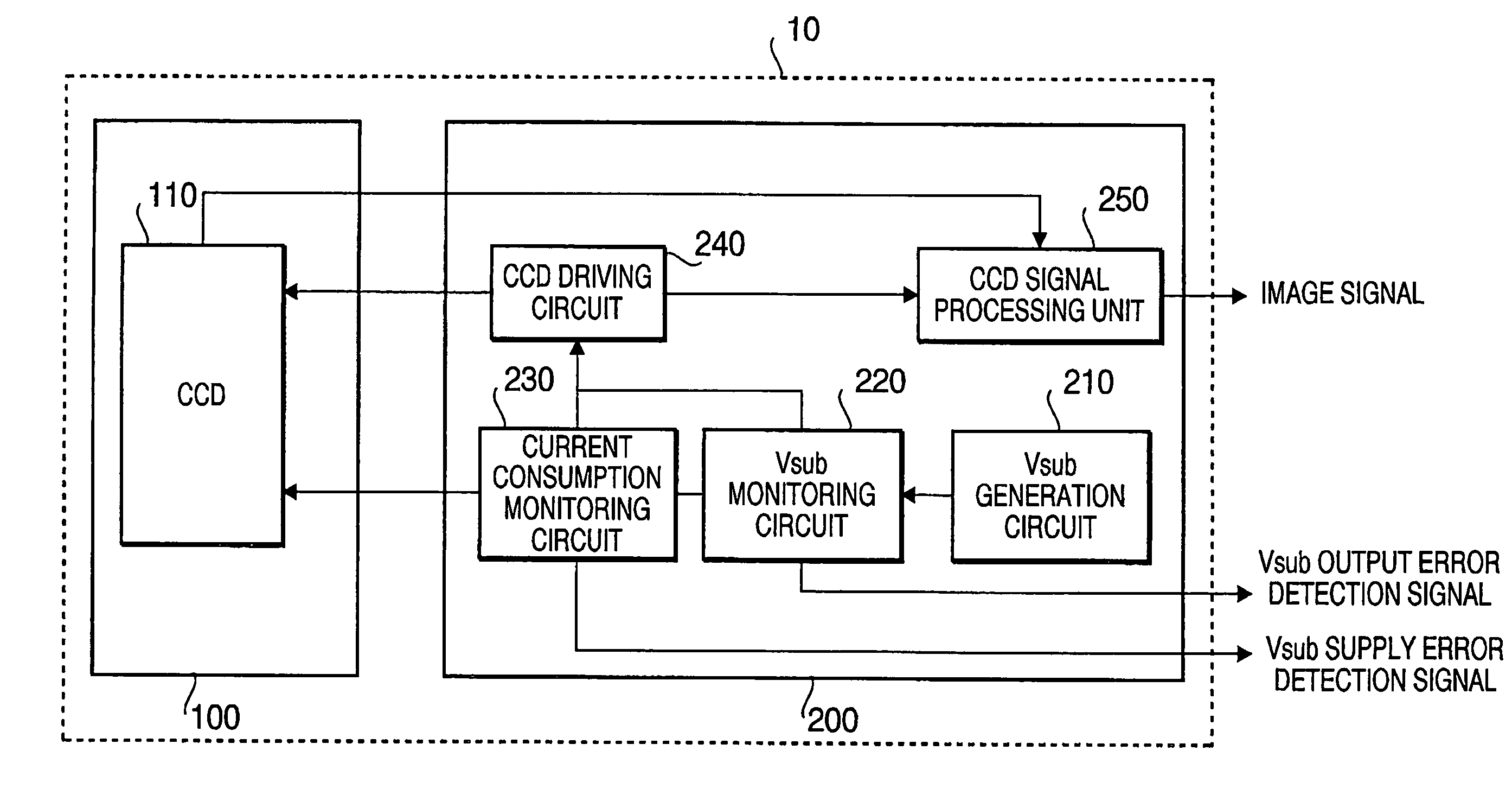
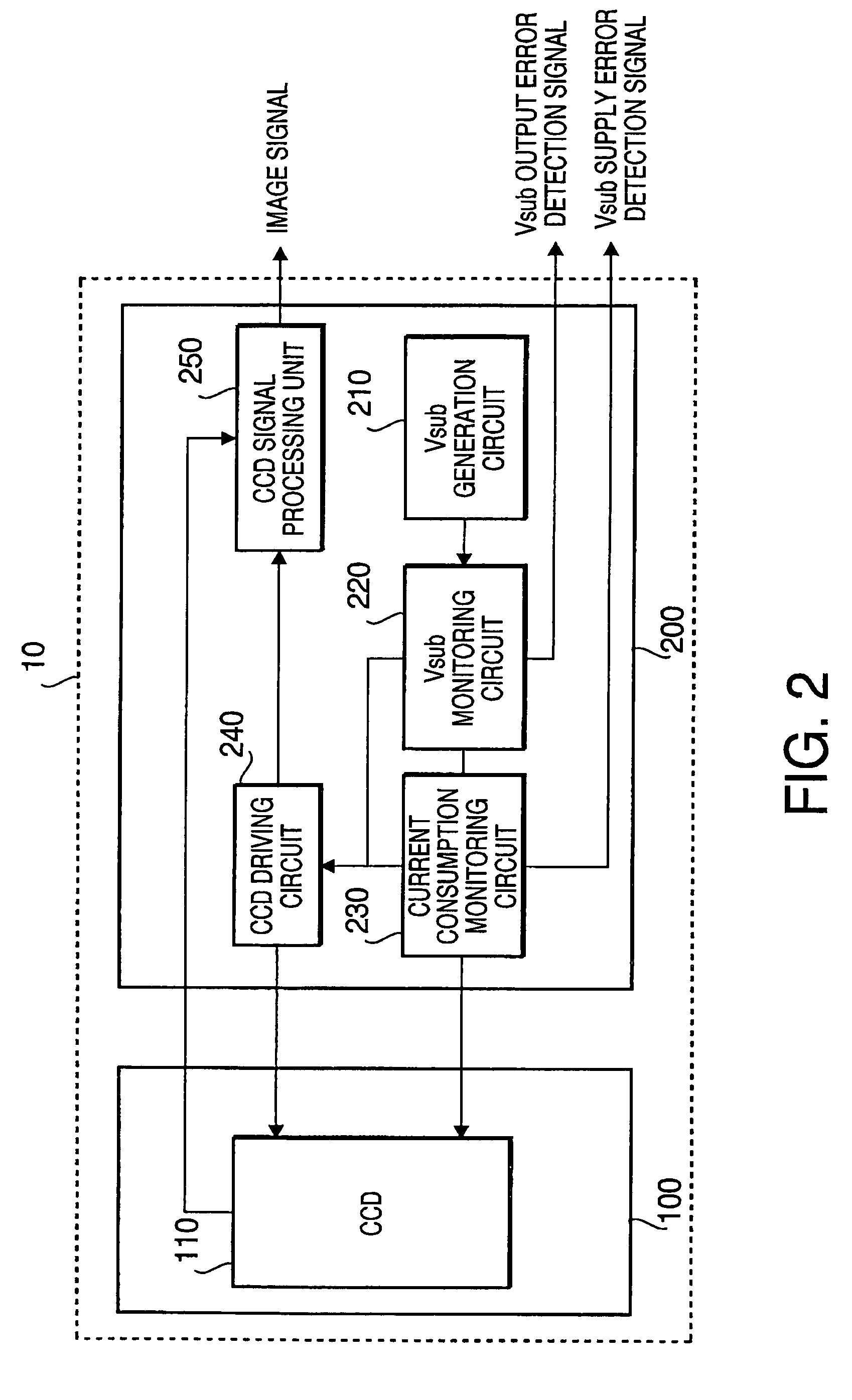
CCD breakage prevention system
InactiveUS7593051B2Avoid breakingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl systemCurrent consumption
An electronic endoscope is provided with a CCD control system which can prevent CCD breakage caused by a latchup, etc. by detecting a Vsub output error and a Vsub supply error without placing any device near the CCD. The endoscope system has a scope including a CCD placed at the scope's distal end, a driving section that supplies a drive signal to a CCD and drives the CCD and a bias voltage generation that generates a substrate bias voltage, a processor, a voltage monitoring section that monitors the voltage value of the substrate bias voltage, a current consumption monitoring section that monitors the current consumption corresponding to the substrate bias voltage, a drive stopping section that stops supplying the drive signal to the CCD when the voltage monitoring section or the current consumption section determines an error occurs.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com