Patents
Literature
499 results about "Lossy compression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
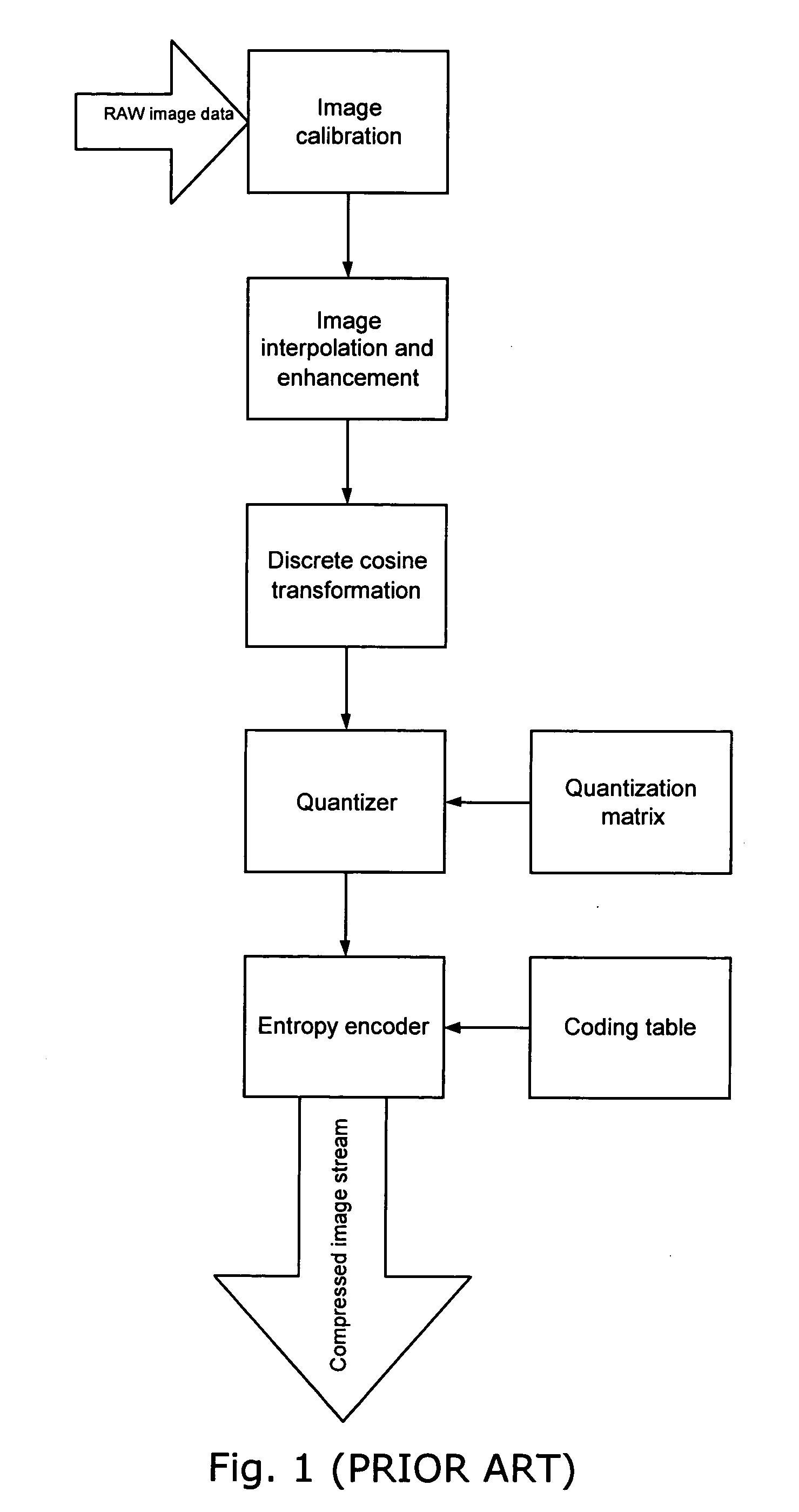
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data encoding methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size for storing, handling, and transmitting content. The different versions of the photo of the cat to the right show how higher degrees of approximation create coarser images as more details are removed. This is opposed to lossless data compression (reversible data compression) which does not degrade the data. The amount of data reduction possible using lossy compression is much higher than through lossless techniques.
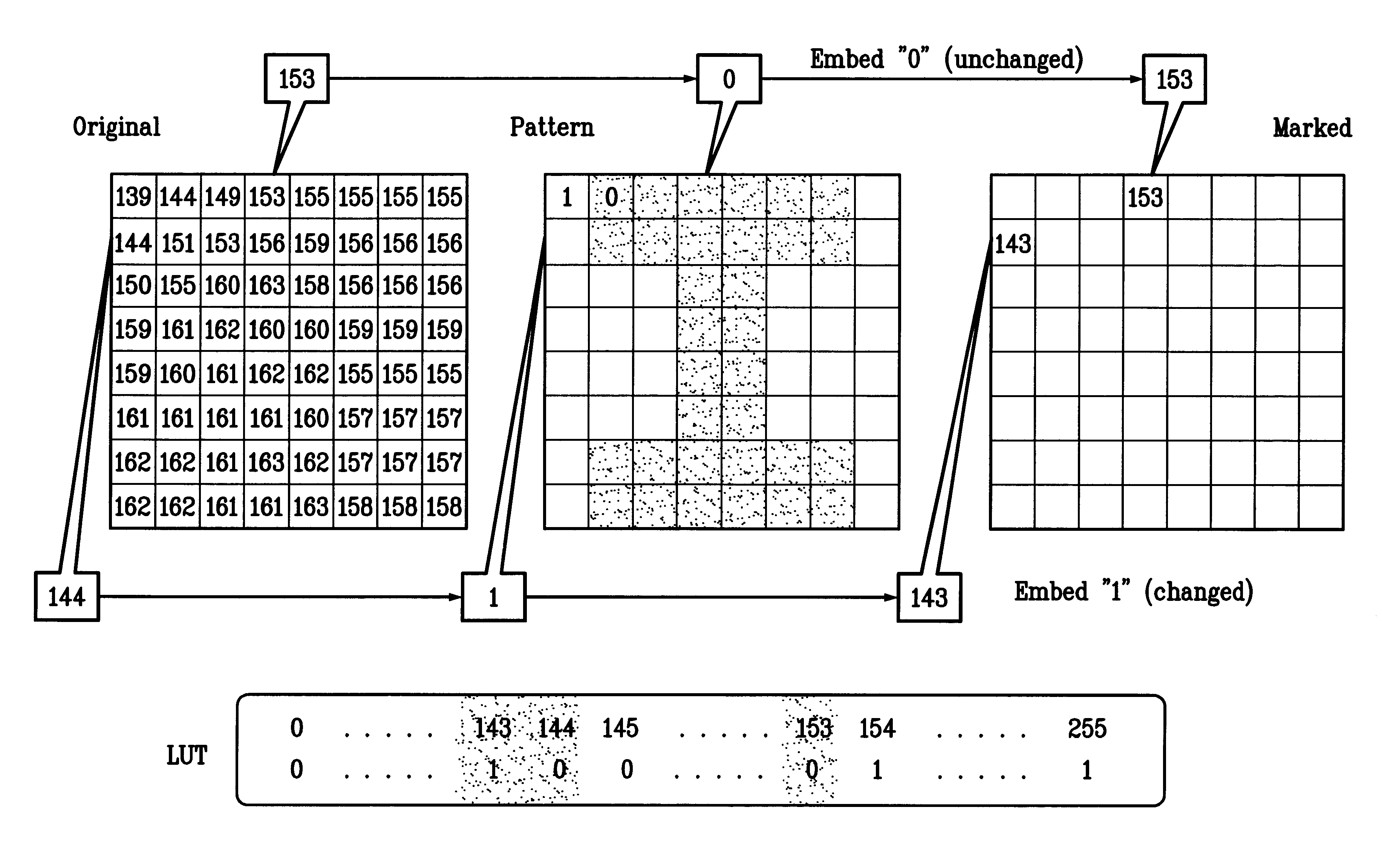
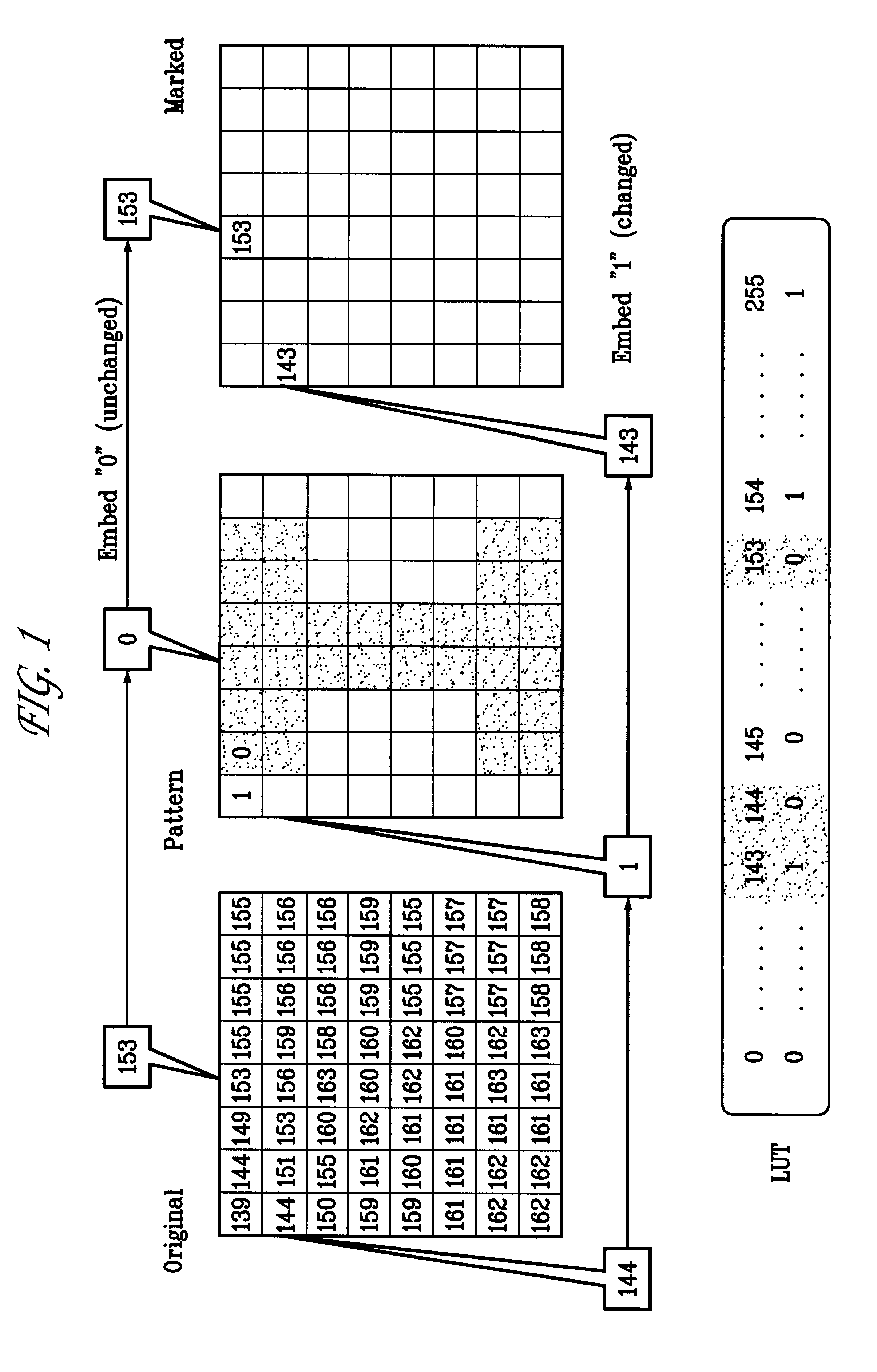
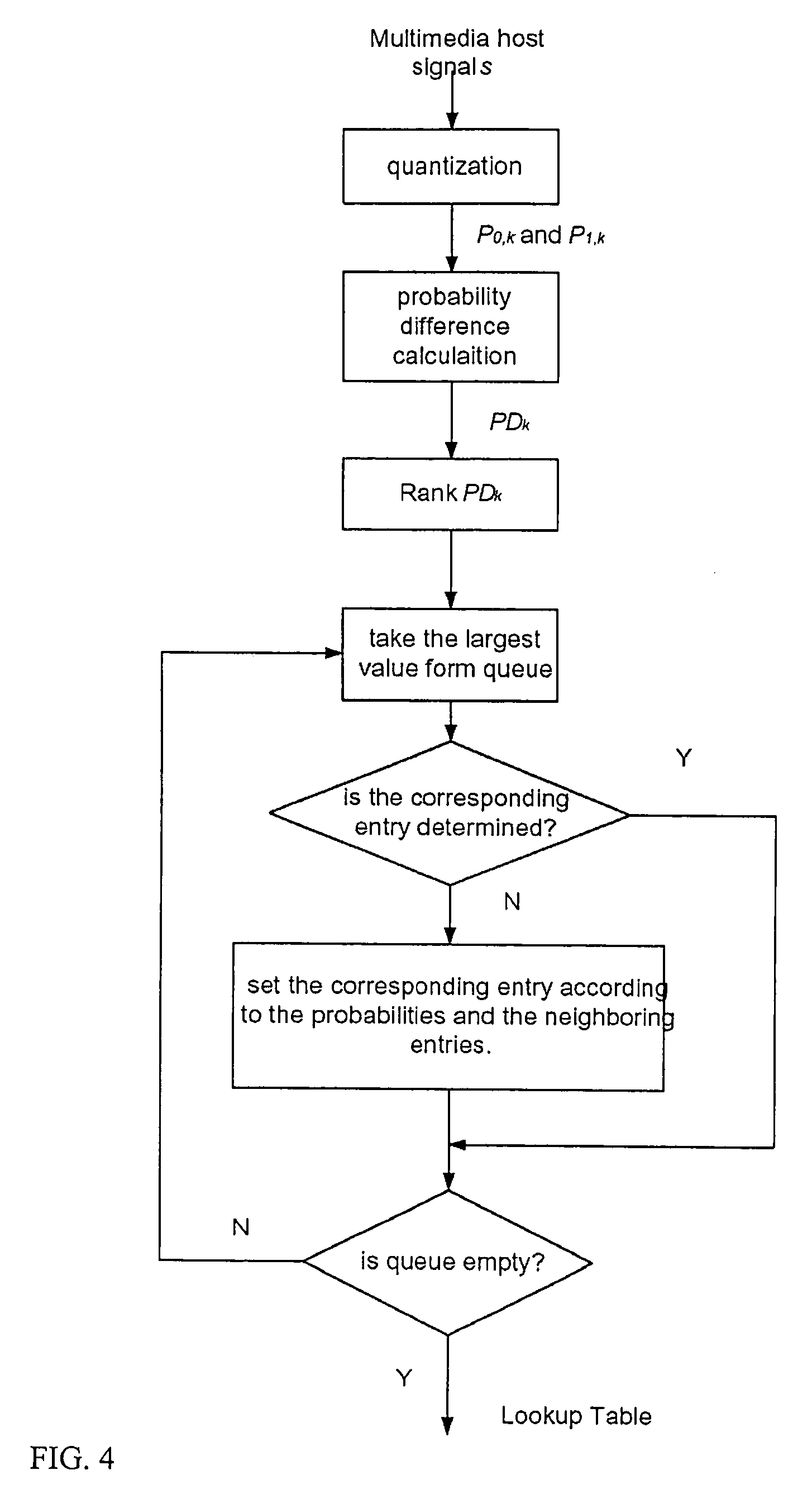
Watermarking scheme for image authentication
InactiveUS6285775B1Effective distributionQuick checkCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsWatermark methodJPEG
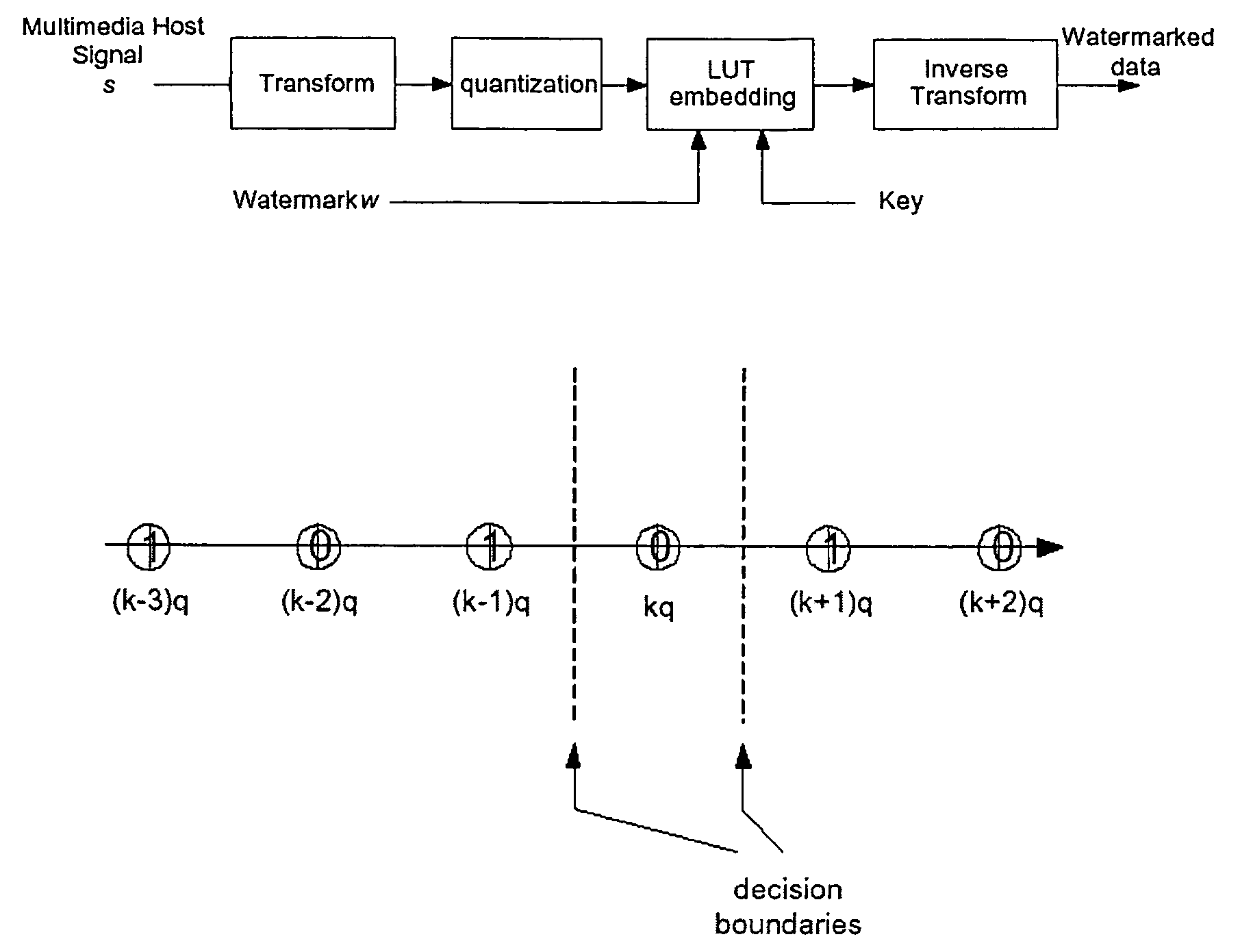
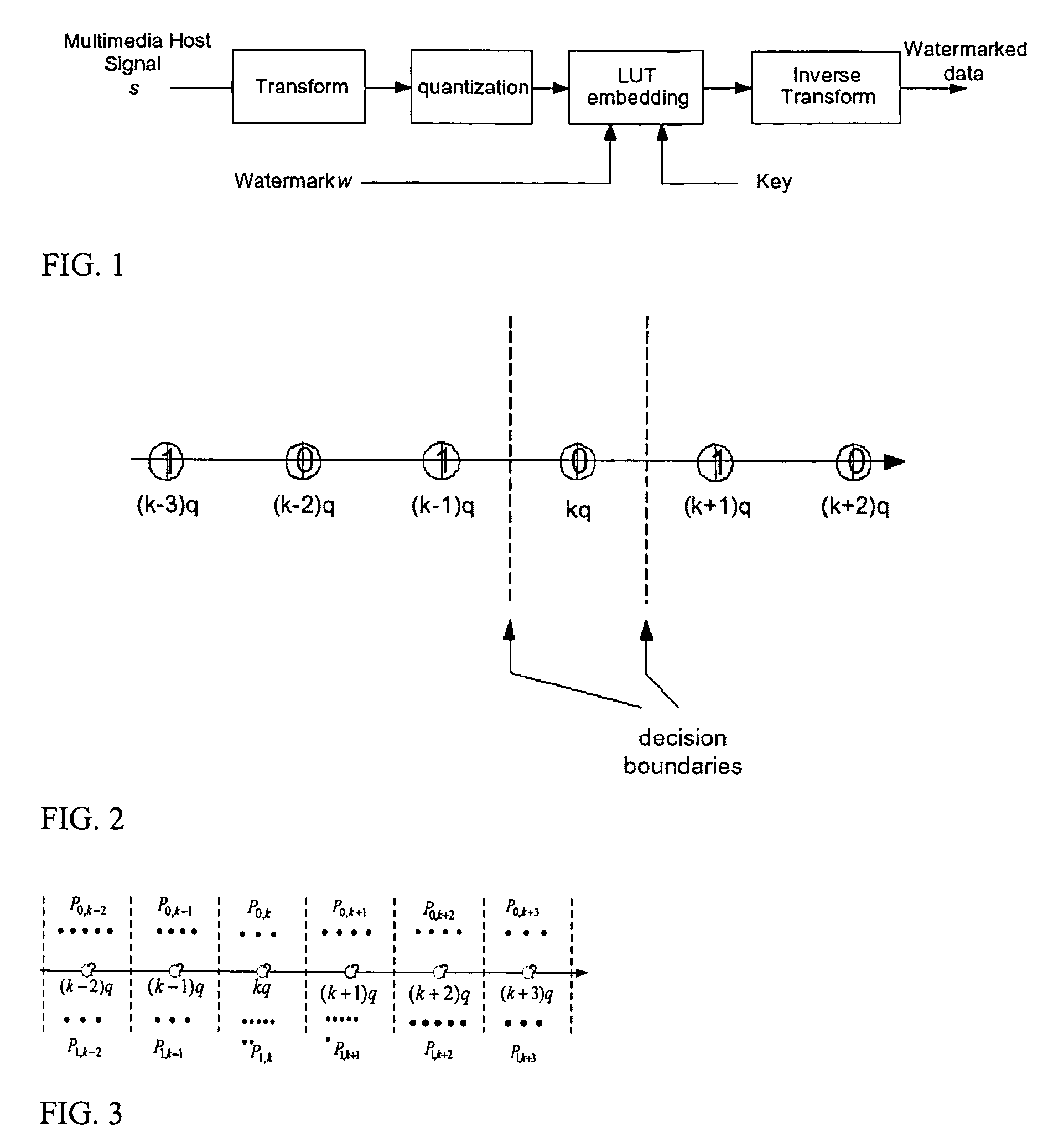
A digital watermarking process whereby an invisible watermark inserted into a host image is utilized to determine whether or not the image has been altered and, if so, where in the image such alteration occurred. The watermarking method includes the steps of providing a look-up table containing a plurality of coefficients and corresponding values; transforming the image into a plurality of blocks, wherein each block contains coefficients matching coefficients in the look-up table; and embedding the watermark in the image by performing the following substeps for at least some of the blocks: First, a coefficient is selected for insertion of a marking value representative of a corresponding portion of the watermark. Next, the value of the selected coefficient to used to identify a corresponding value in the look-up table. Finally, the identified coefficient is left unchanged if the corresponding value is the same as the marking value, and is changed if the corresponding value is different from the marking value. After the insertion of the watermark, the image may be stored in a lossy-compression form, thus permitting efficient storage and distribution. Moreover, the method may be used to produce two output signals for authentication: (1) a meaningful pattern to facilitate a quick visual check, and (2) an additional signal to detect unauthorized alteration. The method can be applied to an image compressed using JPEG or other techniques, such as Wavelet compression, and the marked image can be kept in the compressed format. Any alteration made on the marked image can be localized, making the method suitable for use in a "trustworthy" digital camera or camcorder.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PRINCETON THE
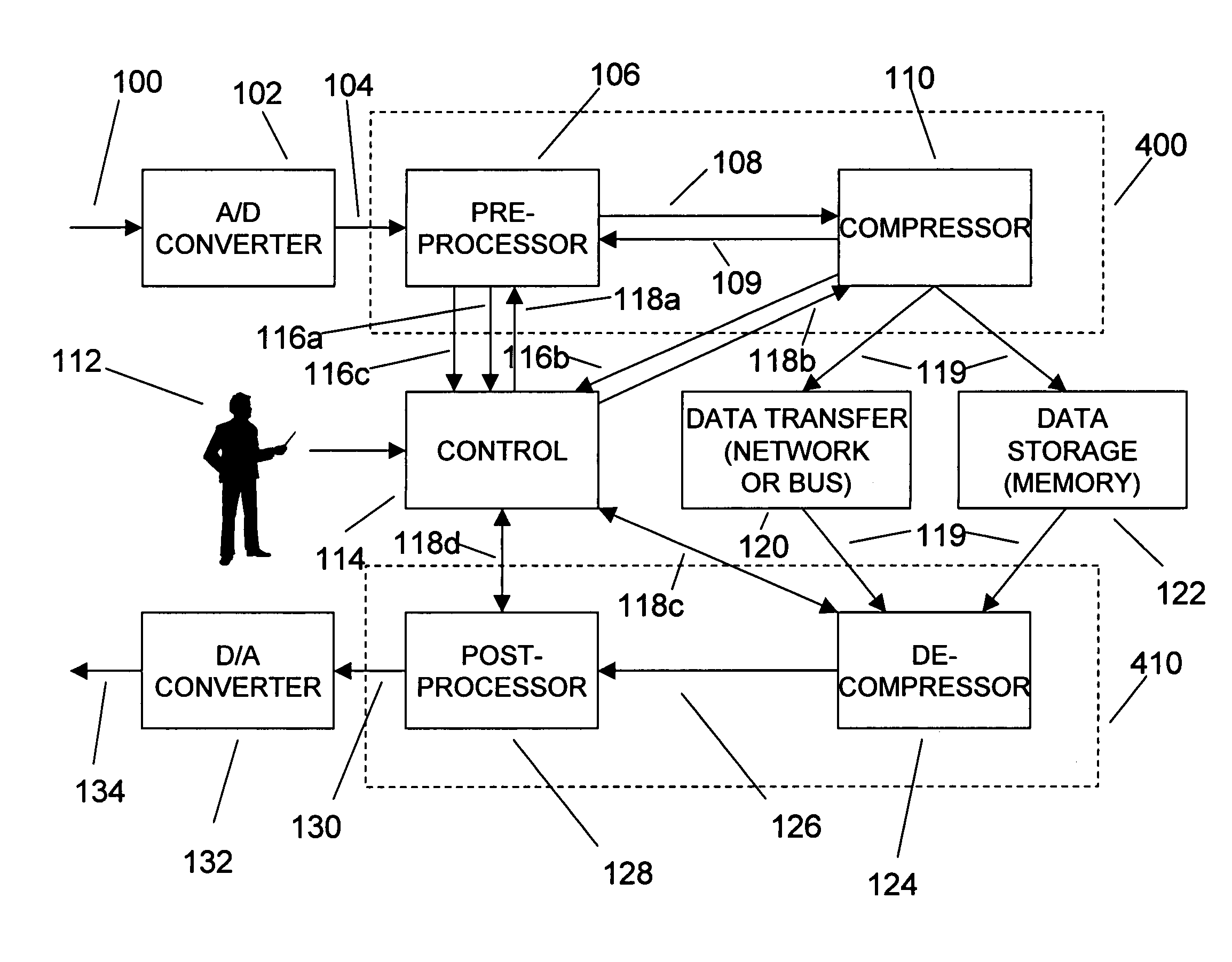
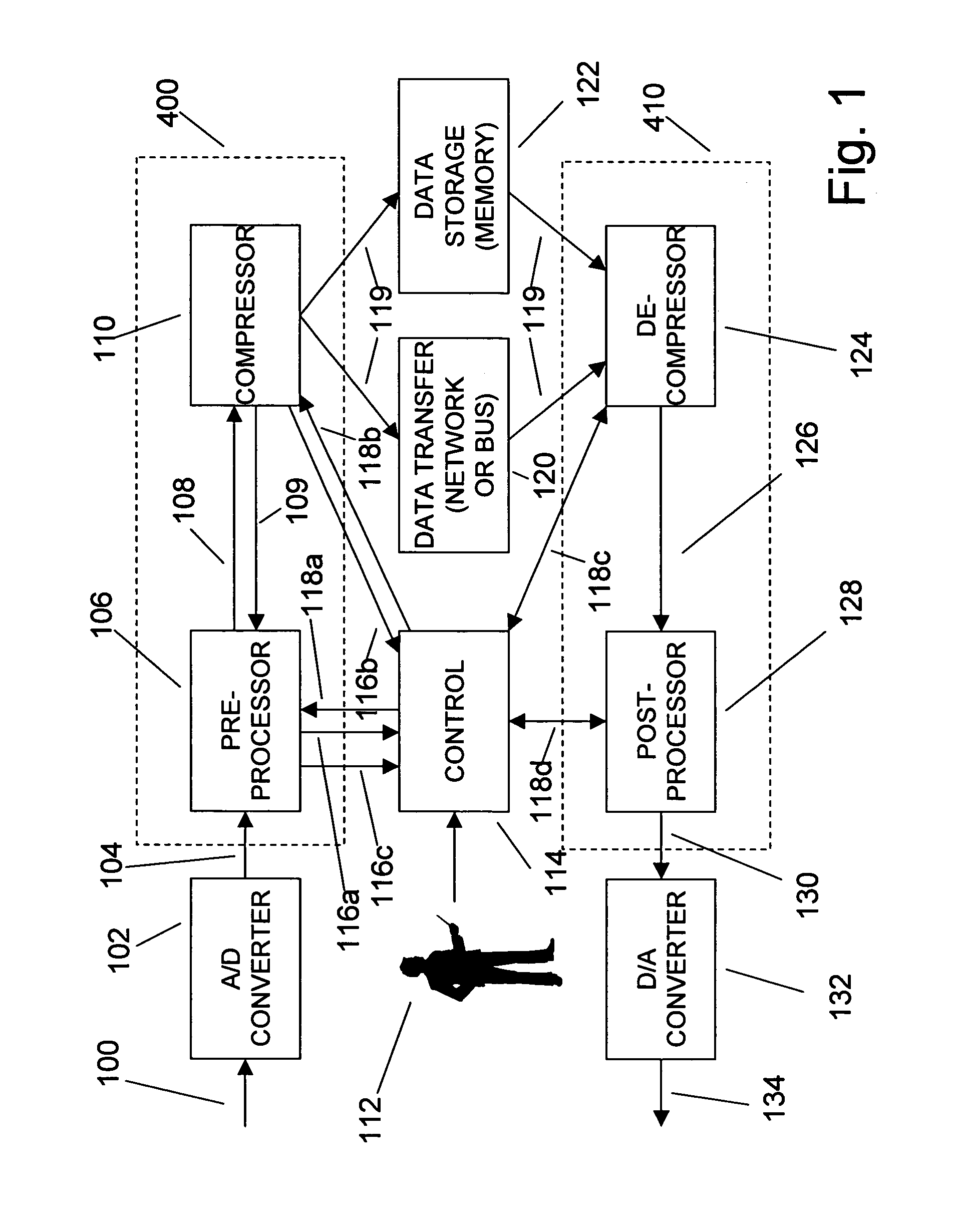
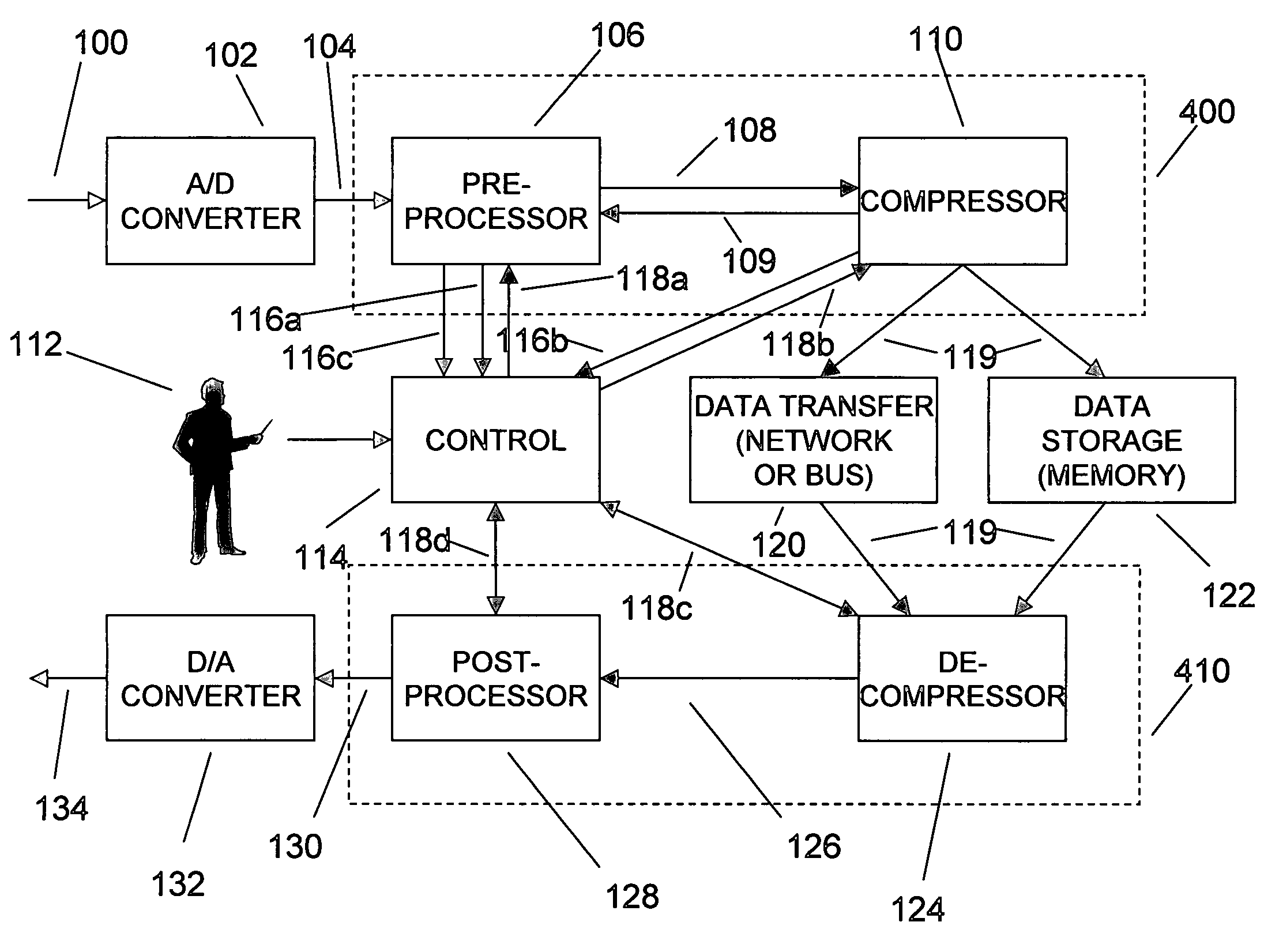
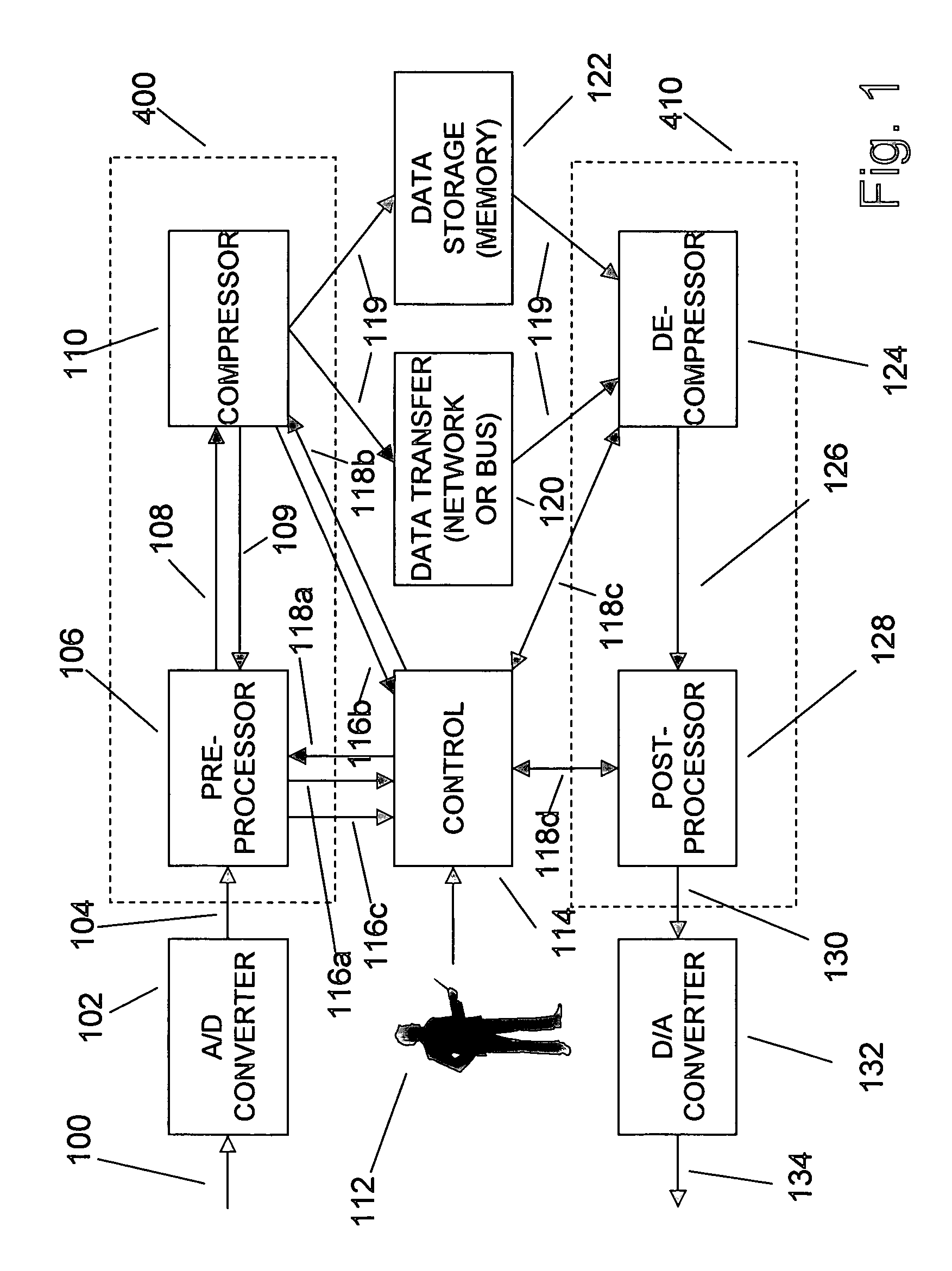
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
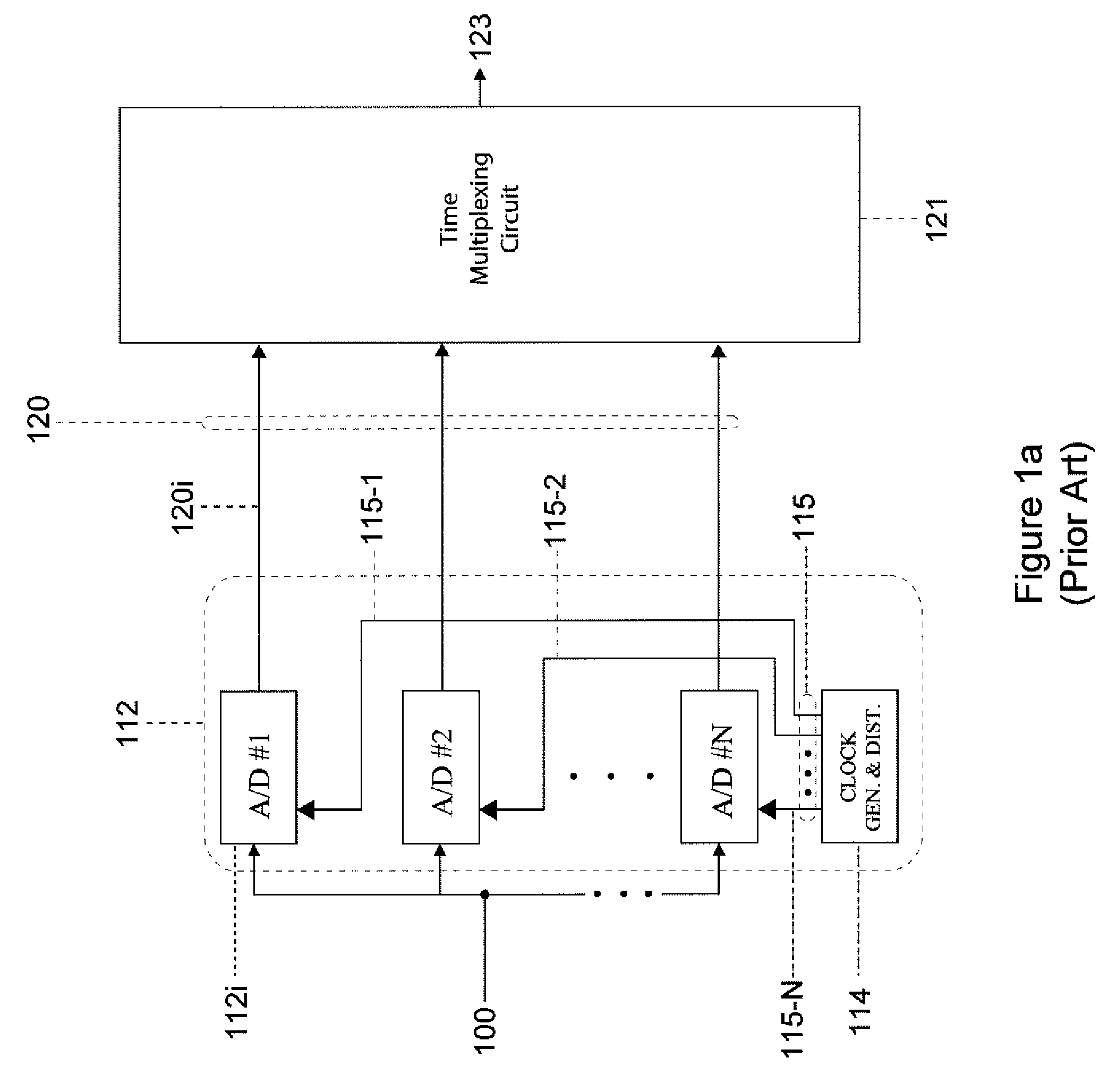
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
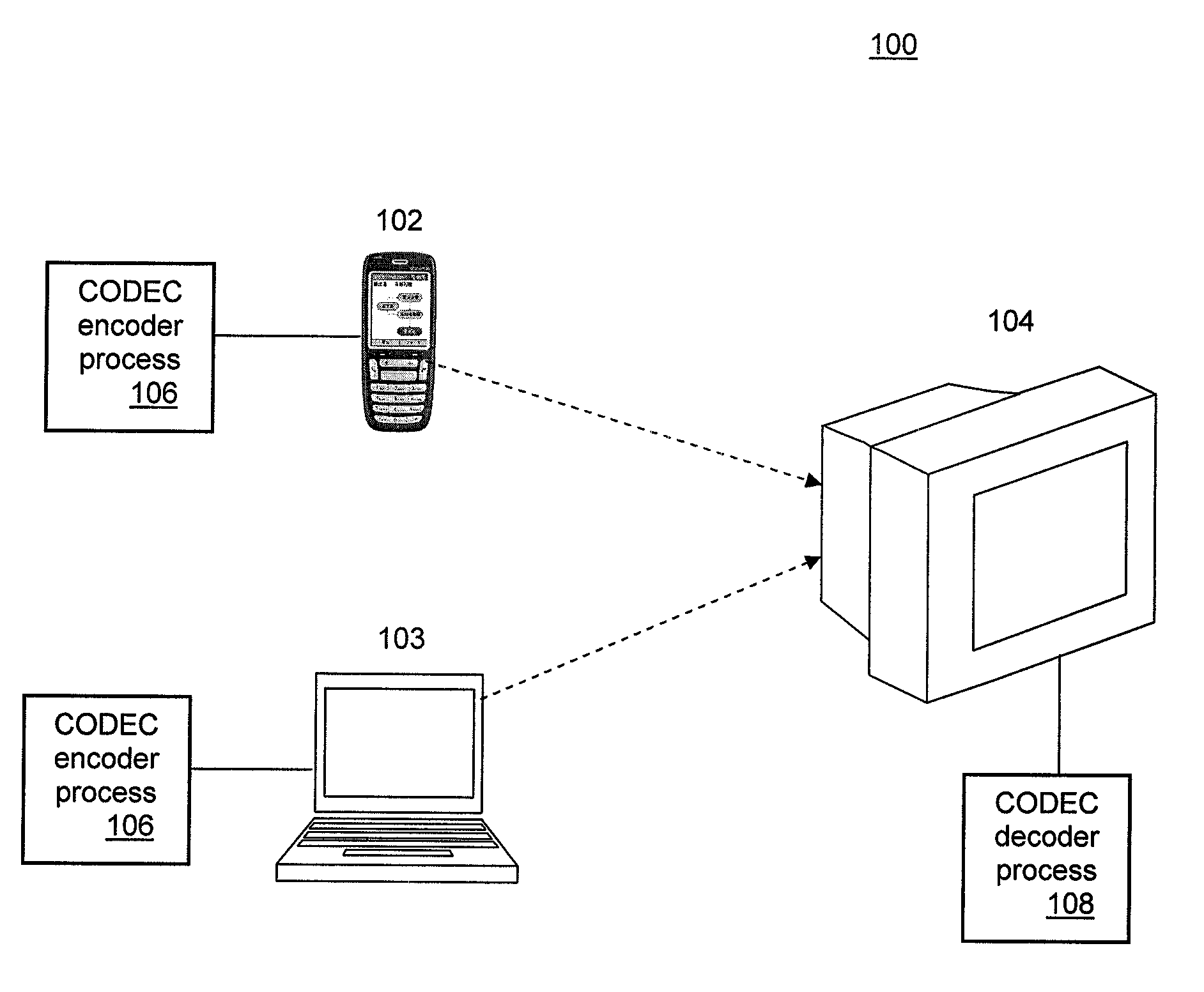
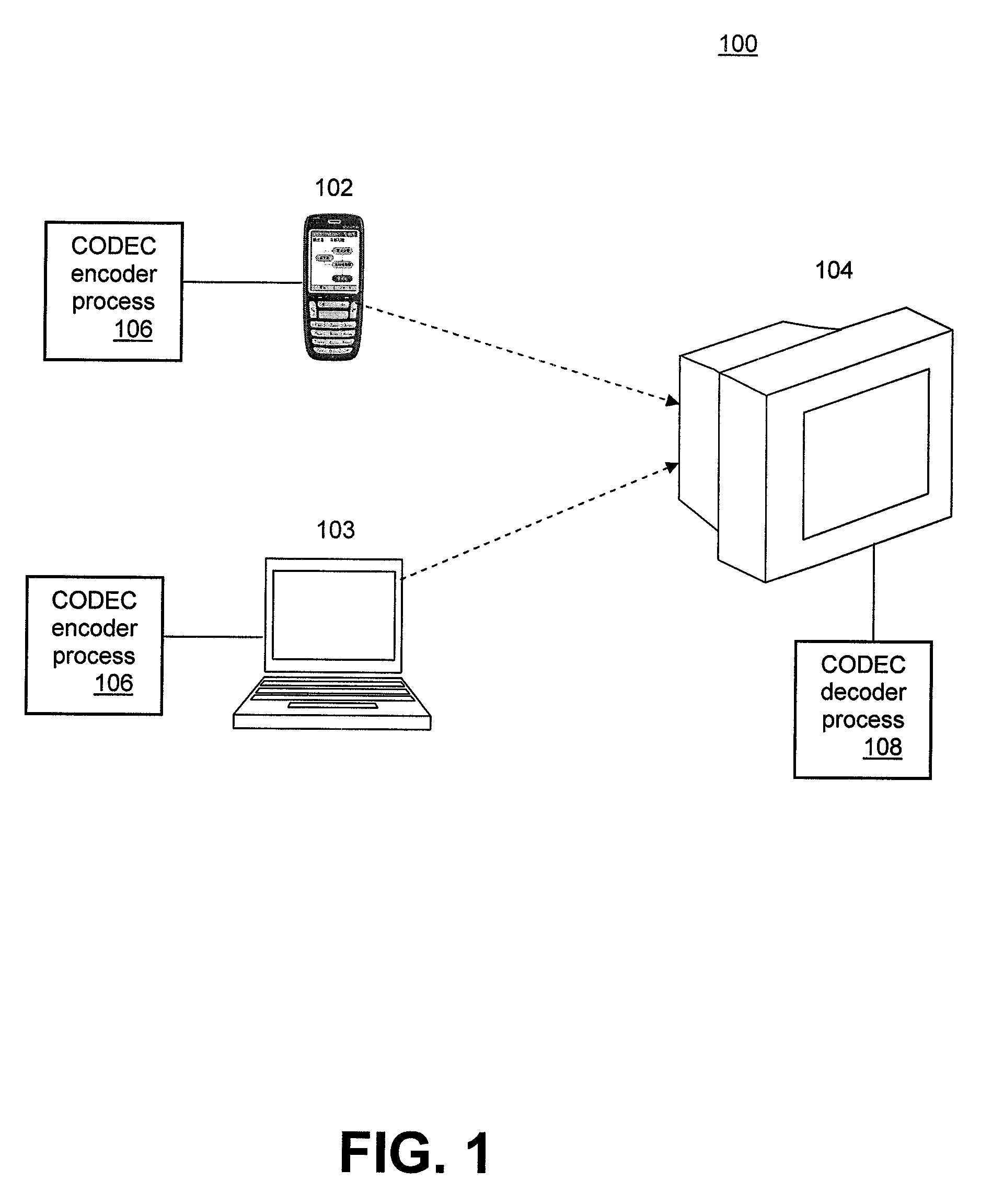
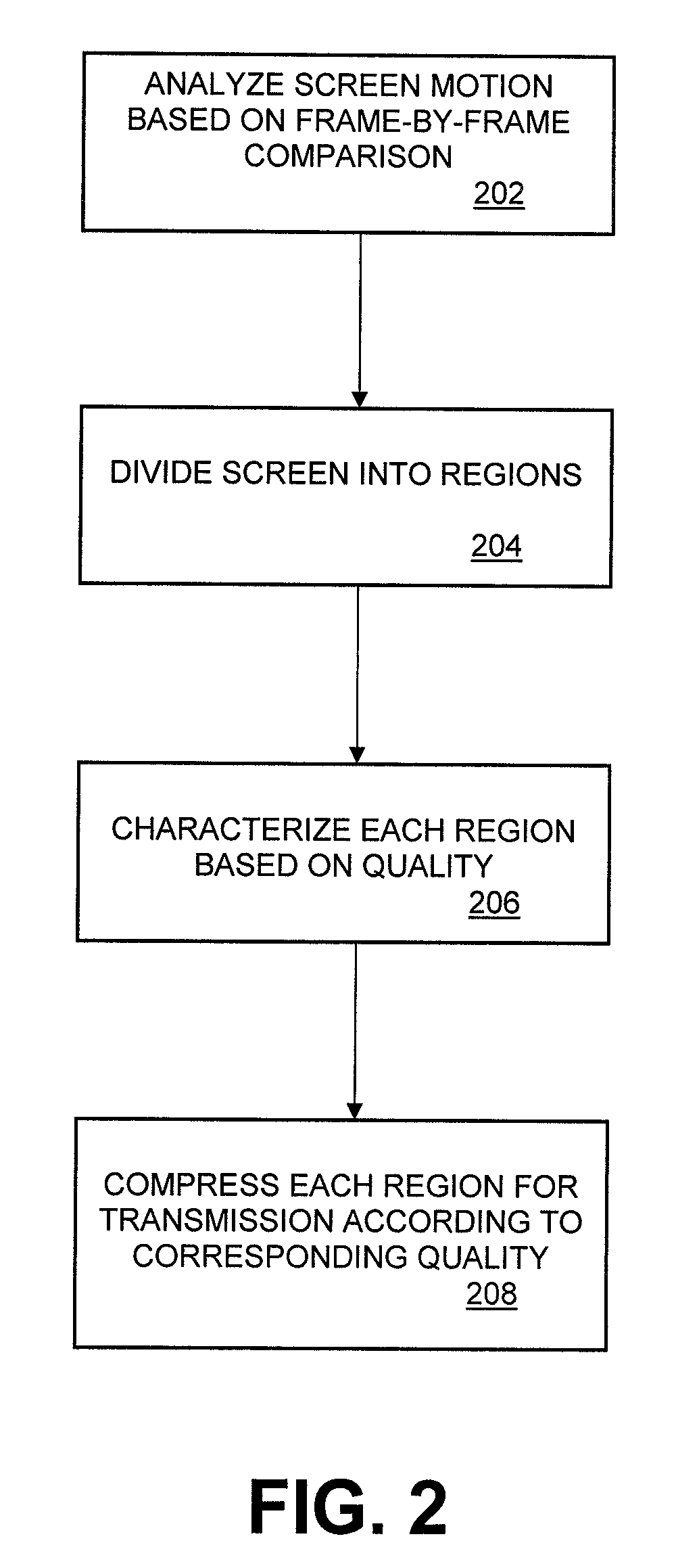
Remote Transmission and Display of Video Data Using Standard H.264-Based Video Codecs
ActiveUS20100104021A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality levelComputer graphics (images)
Embodiments include implementing a remote display system (either wired or wireless) using a standard, non-custom codec. In this system, the decoder side can be fully implemented using an existing standard from a decode / display point of view and using a single stream type. The encoder side includes a pre-processing component that analyzes screen images comprising the video data to determine an amount of difference between consecutive frames of the screen images, divides each screen image into a plurality of regions, including no change regions, high quality regions, and low quality regions. The pre-processor characterizes each region as requiring a minimum quality level, encodes the low quality regions for compression in accordance with the H.264 encoding standard; and encodes the high quality regions using the lossless compression scheme of the H.264 standard. A no change region is encoded using a version of the H.264 encoding standard that adaptively and dynamically selects between lossless and lossy compression in a manner that optimizes efficiency of the compression operation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
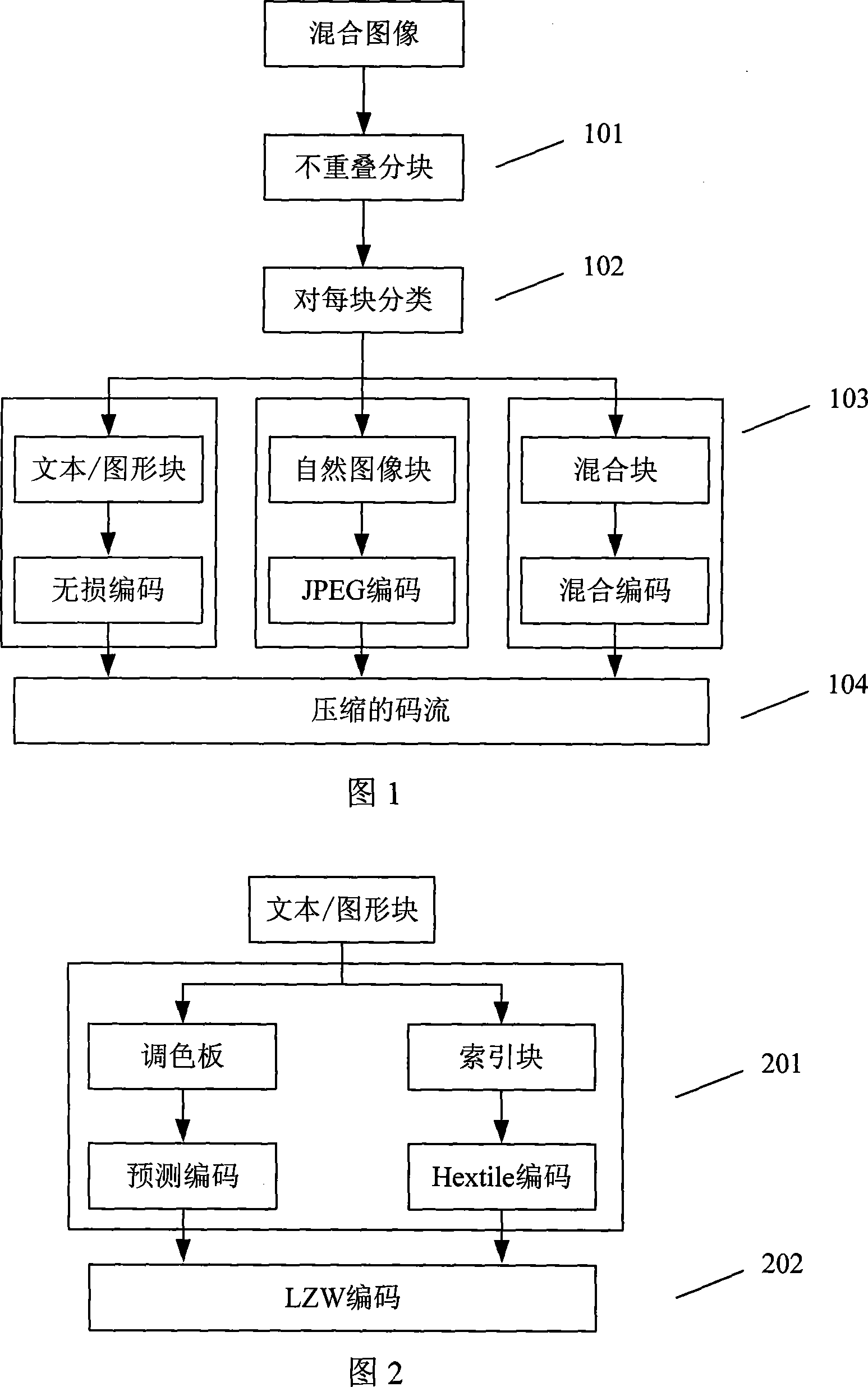
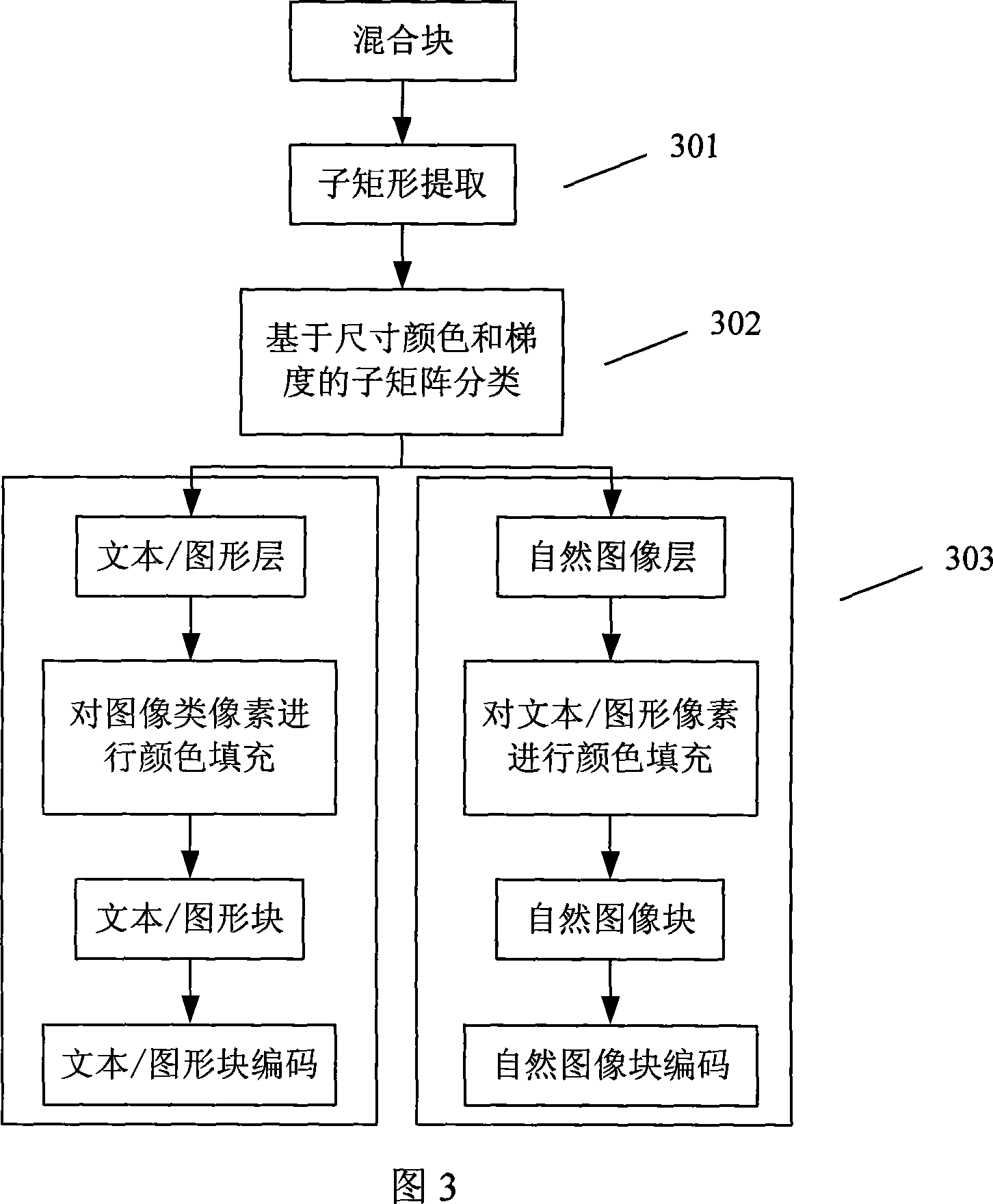
A mixed image compression method based on block classification
InactiveCN101217668AImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioAccurate segmentationImage enhancementTelevision systemsGraphicsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Enhanced data converters using compression and decompression
InactiveUS7088276B1Less bandwidthLess storageElectric signal transmission systemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital interfaceA d converter
An enhancement that reduces the digital interface rate of analog-to-digital (A / D) and digital-to-analog (D / A) converters through the use of compression and decompression is described. The present invention improves A / D converters by compressing the sampled version of the A / D converter's analog input signal in real time, thereby significantly decreasing the required bit rate of the A / D converter's digital interface. Similarly, the present invention improves D / A converters by decreasing the required bit rate of the D / A converter's digital interface. D / A converters enhanced by the present invention include a decompressor that decompresses the D / A converter's compressed digital input in real time, prior to conversion to an analog output signal. The present invention's simplicity and its ability to be implemented using multiple compression and decompression elements allow its use in A / D and D / A converters with arbitrarily high sampling rates. By selecting a desired compression ratio during lossy compression, users of the present invention can precisely control the bit rate of the A / D and D / A converter's digital interface. Users of the present invention can dynamically choose the desired balance between the quality and the bit rate of A / D and D / A converters by adjusting various compression and decompression control parameters.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
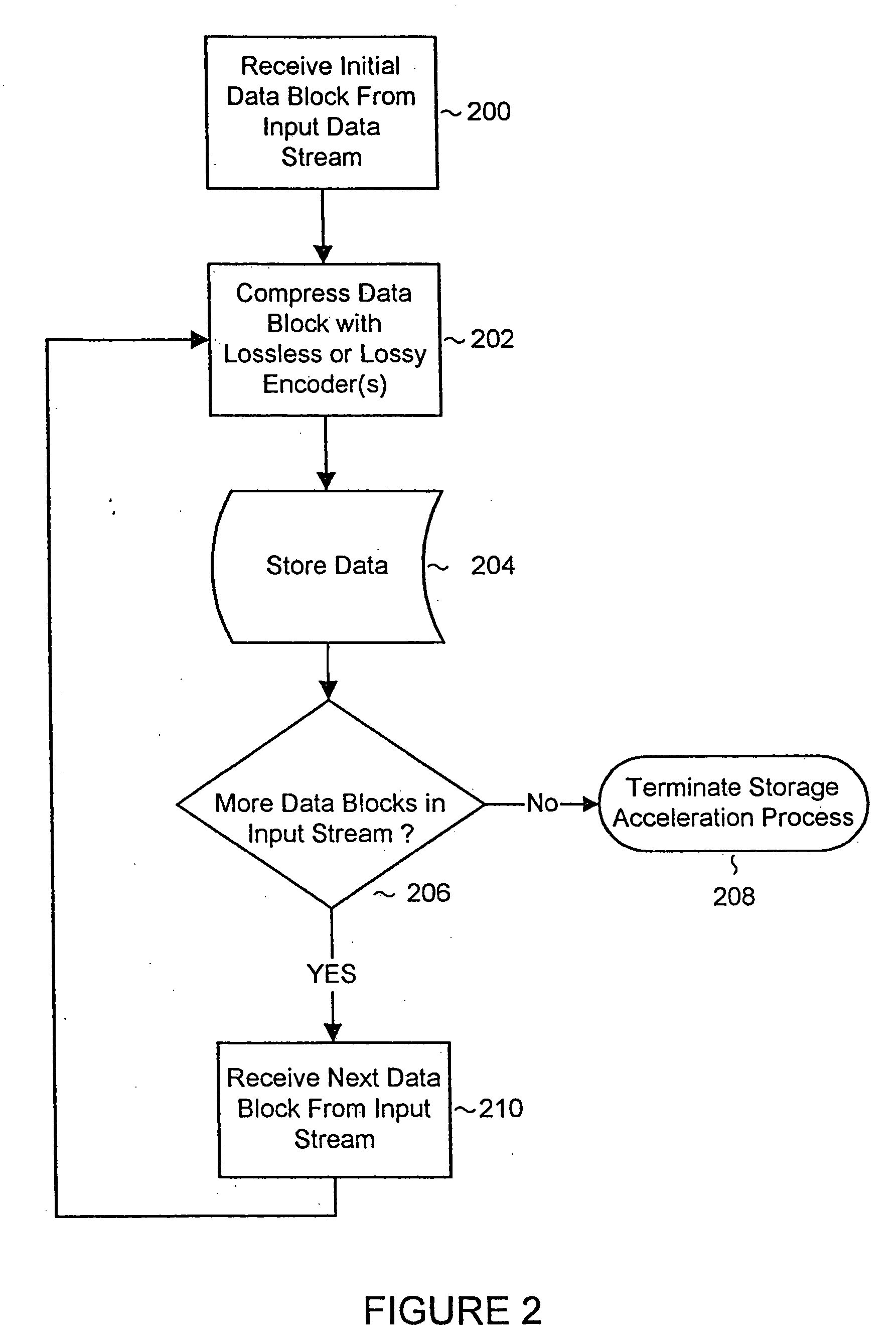
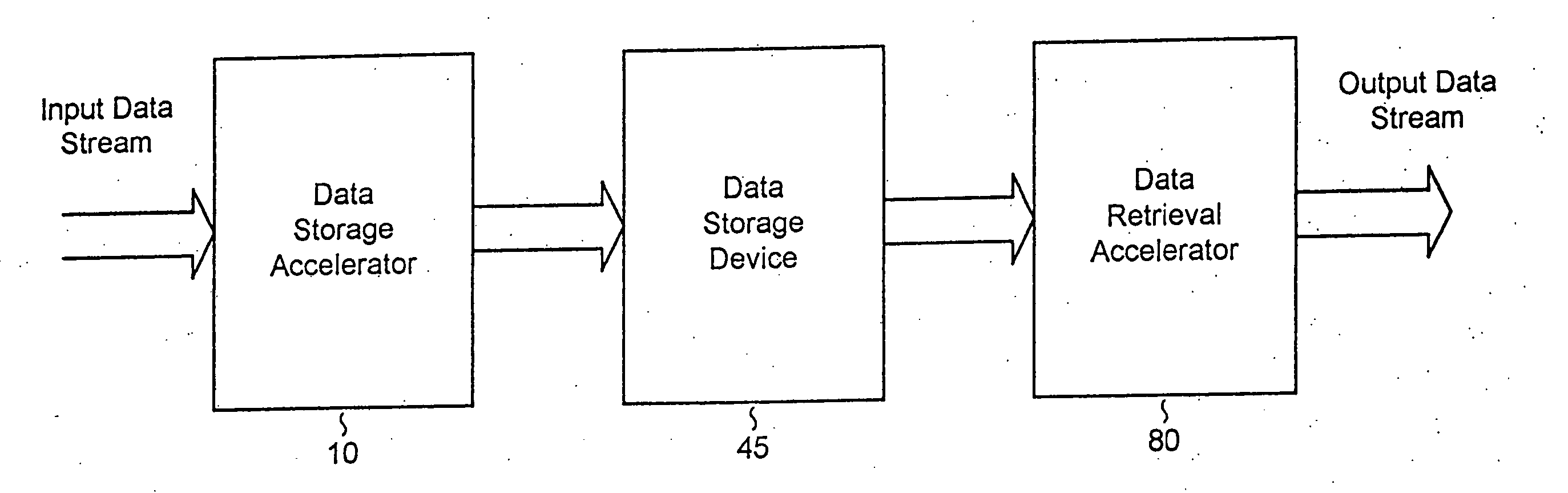
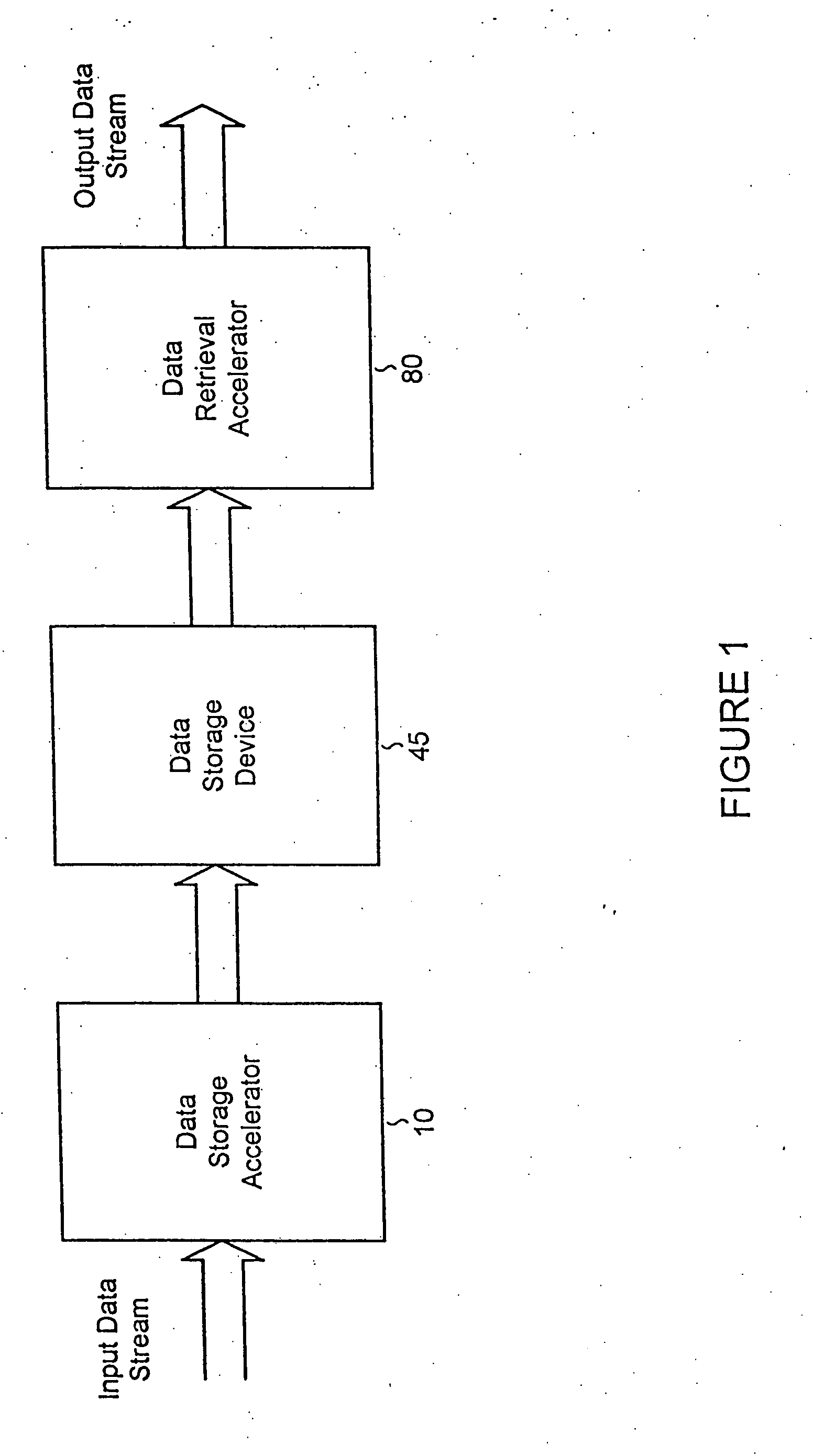
Data storewidth accelerator
InactiveUS7376772B2Improve processing speedHigh bandwidthCode conversionBootstrappingData compressionDisk controller
Data storage controllers and data storage devices employing lossless or lossy data compression and decompression to provide accelerated data storage and retrieval bandwidth. In one embodiment of the invention, a composite disk controller provides data storage and retrieval acceleration using multiple caches for data pipelining and increased throughput. In another embodiment of the invention, the disk controller with acceleration is embedded in the storage device and utilized for data storage and retrieval acceleration.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
Hybrid image data processing system and method
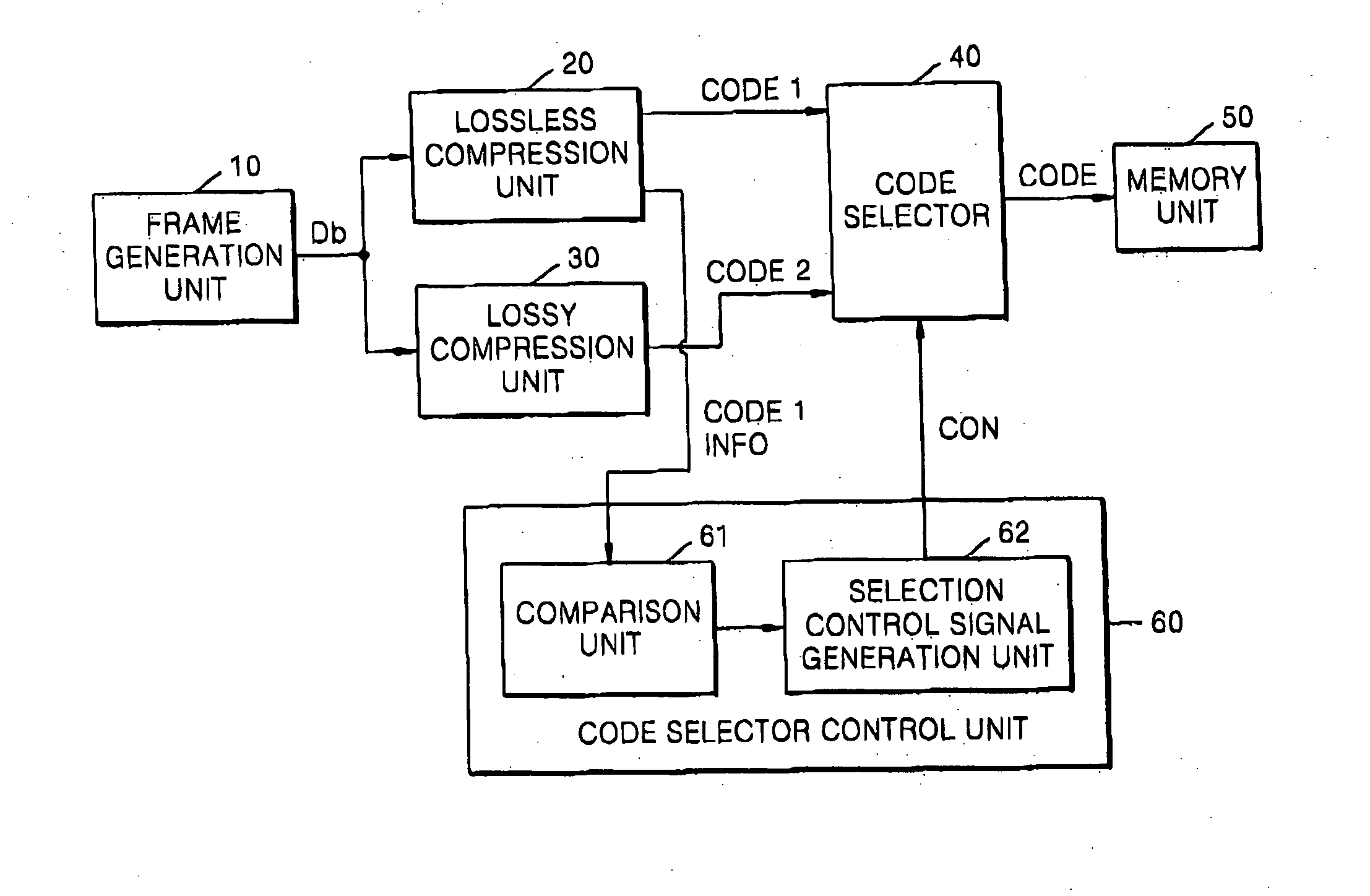
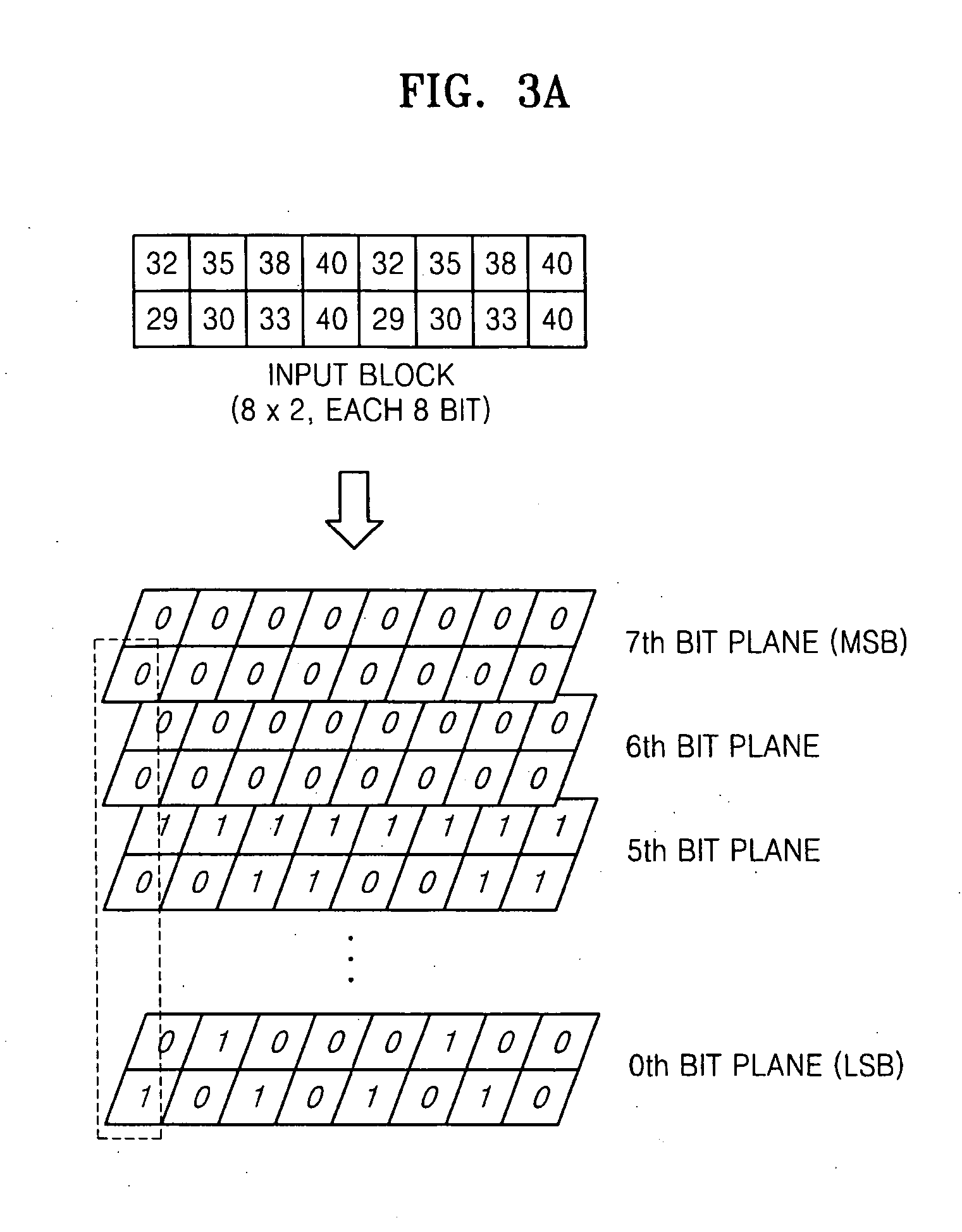
ActiveUS20070098283A1Efficient compressionCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData processing systemLossless compression
An image data compression system, for compressing a frame represented as a plurality of blocks, can include: a lossless compression unit to receive the plurality of blocks and to perform lossless compression thereon resulting in a first code; a lossy compression unit to receive the plurality of blocks and to perform lossy compression thereon resulting in a second code; and a code selection circuit to selectively output one of the first and second codes based upon a figure of merit evaluated for at least one of the first and second codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
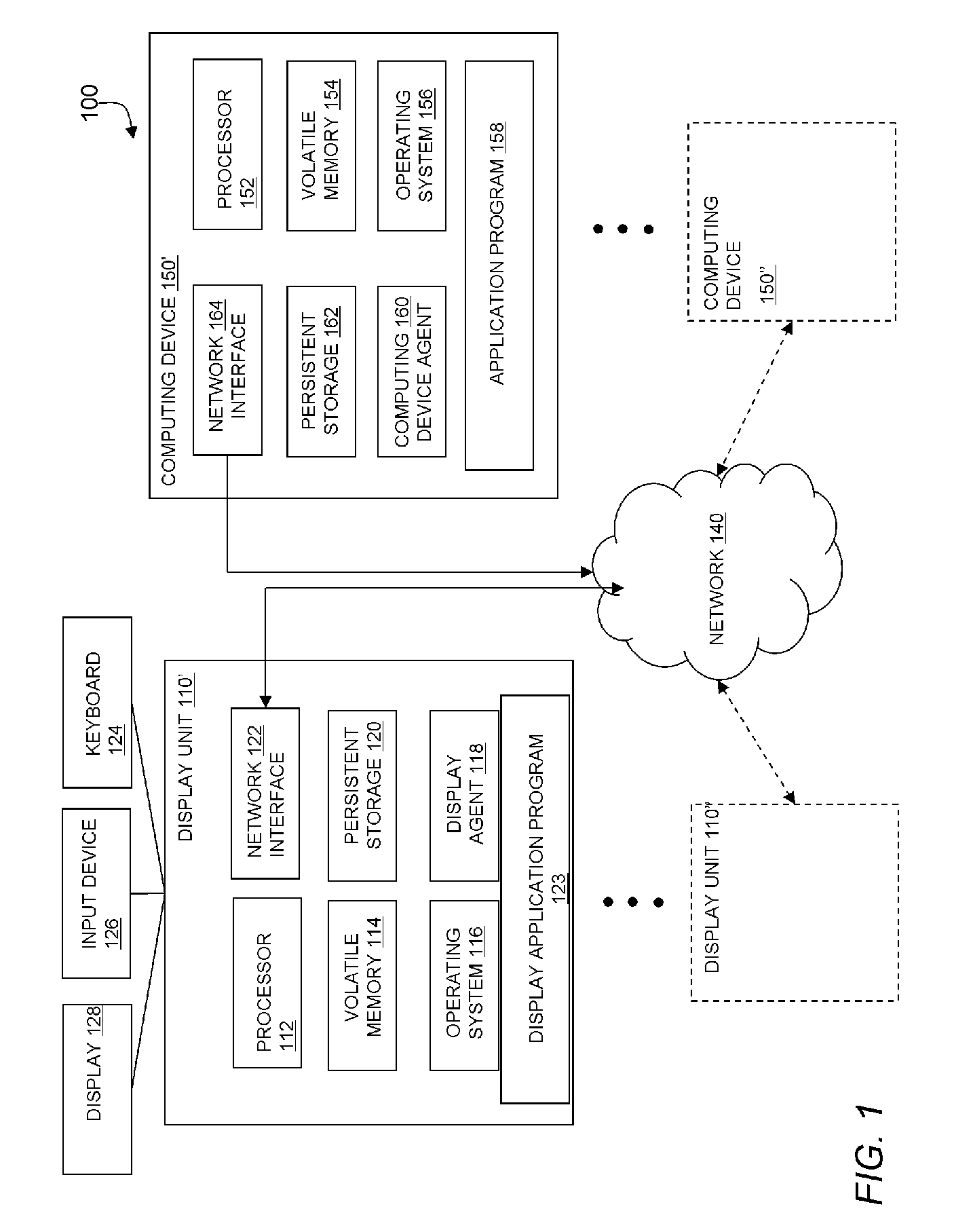
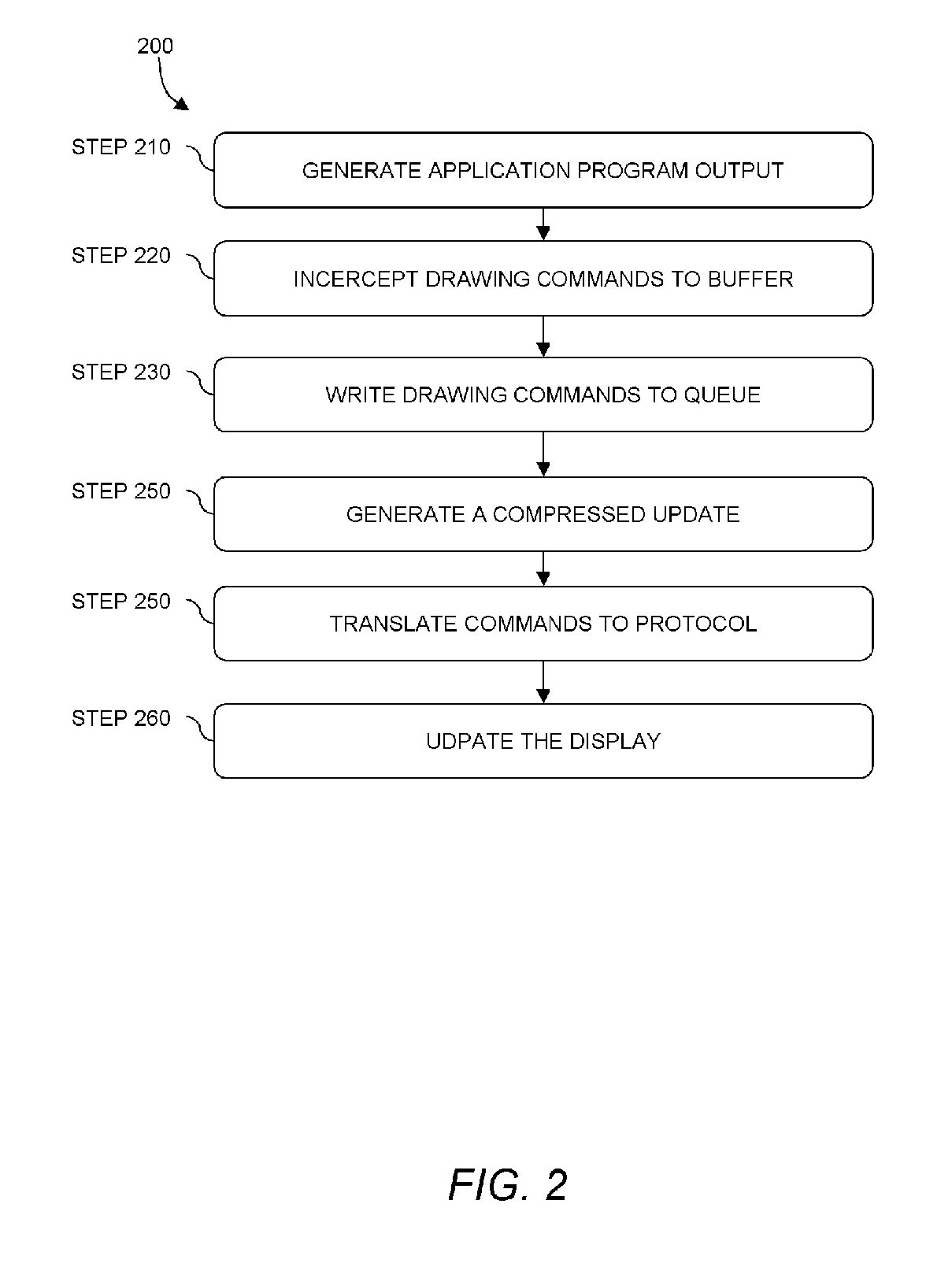
A method and apparatus for updating a graphical display in a distributed processing environment using compression
ActiveUS20060203007A1Database updatingGeometric image transformationGraphicsLossless compression algorithm
A system and method for updating a remote display unit that communicates with a computing system are described. The method includes accessing display update information from an update queue that stores drawing commands issued by an application executing on the computing system, caching the display update information, applying a lossy compression algorithm to the display update information to create a lossy display update, and transmitting the lossy update to the remote display. The method also includes applying a lossless compression algorithm to the display update information in the cache to create a lossless display update and transmitting the lossless display update a predetermined of time after transmitting the lossy update.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
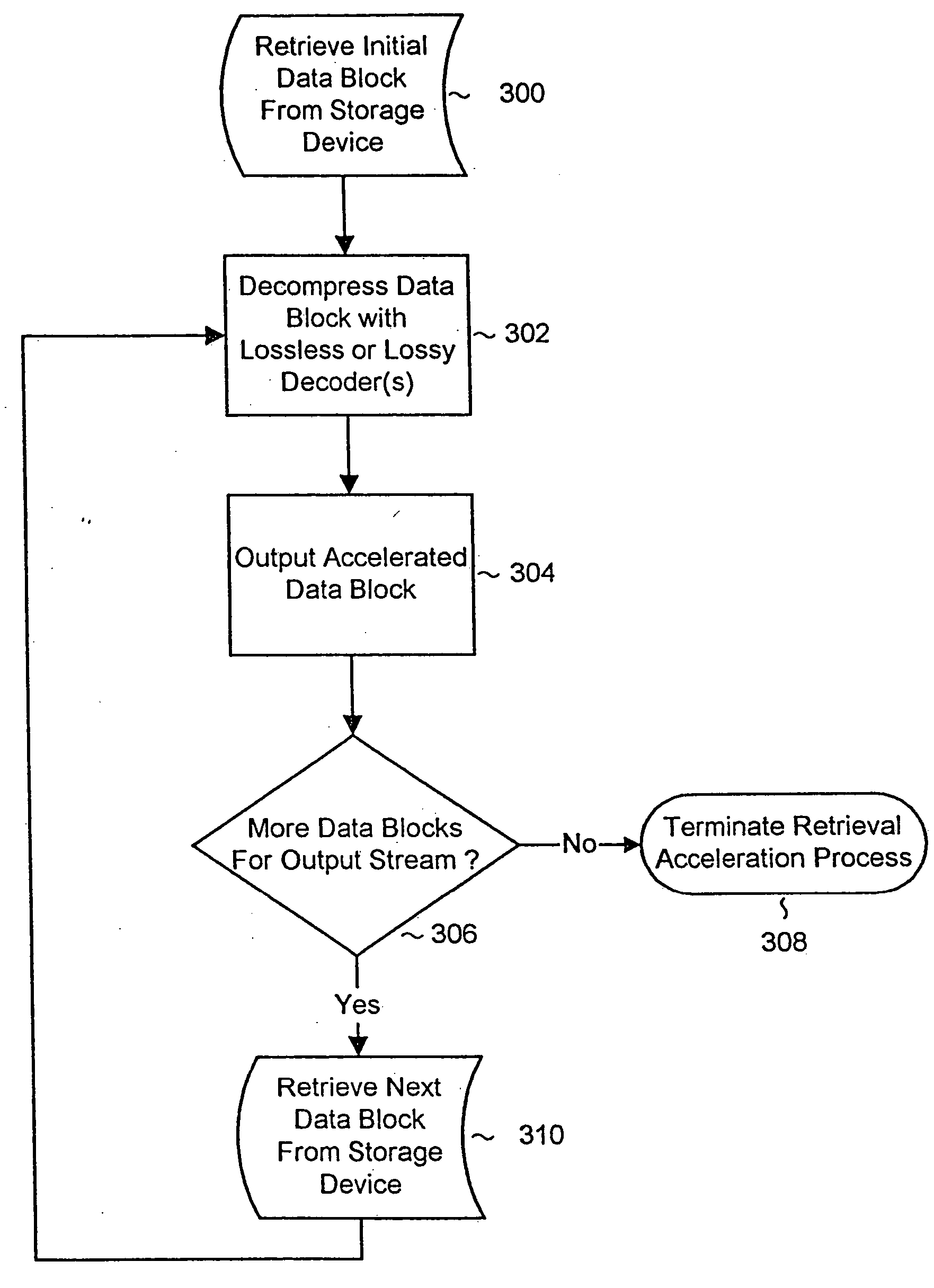
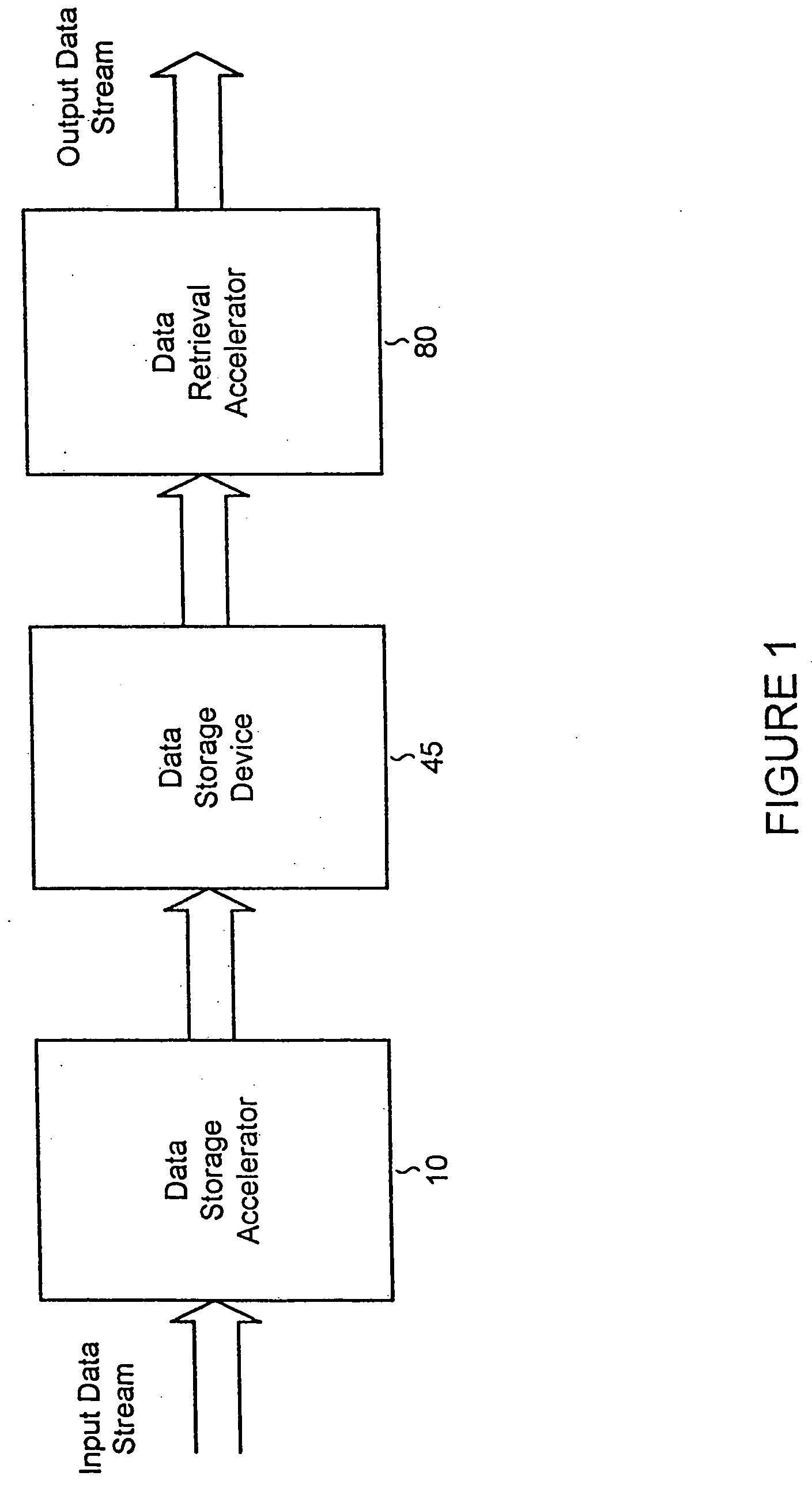
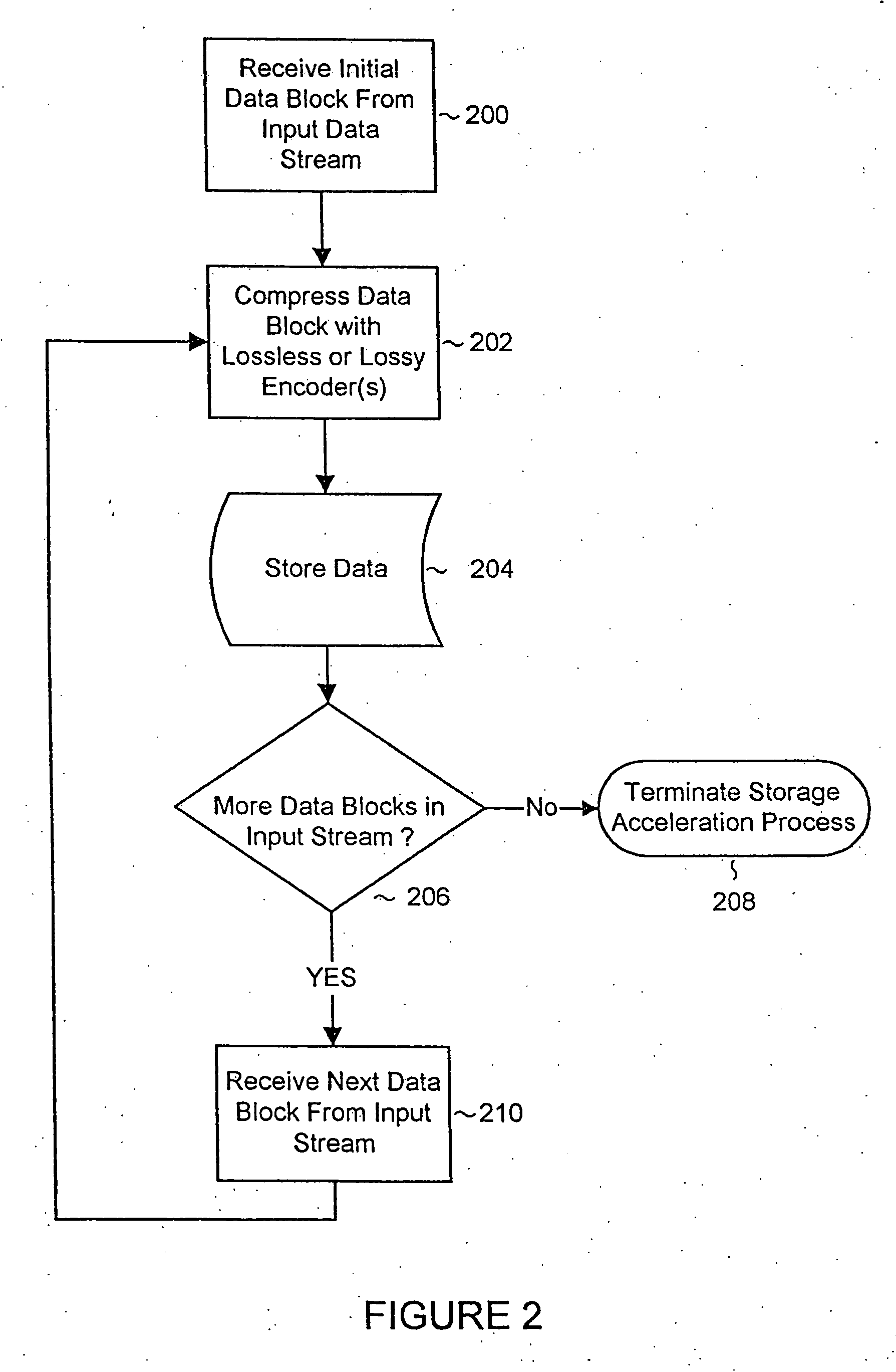
System and methods for accelerated data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS20060015650A1Shorten the timeIncrease data storageTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersData compressionData stream
Systems and methods for providing accelerated data storage and retrieval utilizing lossless and / or lossy data compression and decompression. A data storage accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data compression encoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly or lossy compress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the transmission rate of an input data stream. The compressed data is subsequently stored in a target memory or other storage device whose input data storage bandwidth is lower than the original input data stream bandwidth. Similarly, a data retrieval accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data decompression decoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly or lossy decompress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the input data stream from the target memory or storage device. The decompressed data is then output at rate data that is greater than the output rate from the target memory or data storage device. The data storage and retrieval accelerator method and system may employed: in a disk storage adapter to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from computer to disk; in conjunction with random access memory to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from random access memory; in a display controller to reduce the time required to send display data to the display controller or processor; and / or in an input / output controller to reduce the time required to store, retrieve, or transmit data.
Owner:FALLON JAMES J
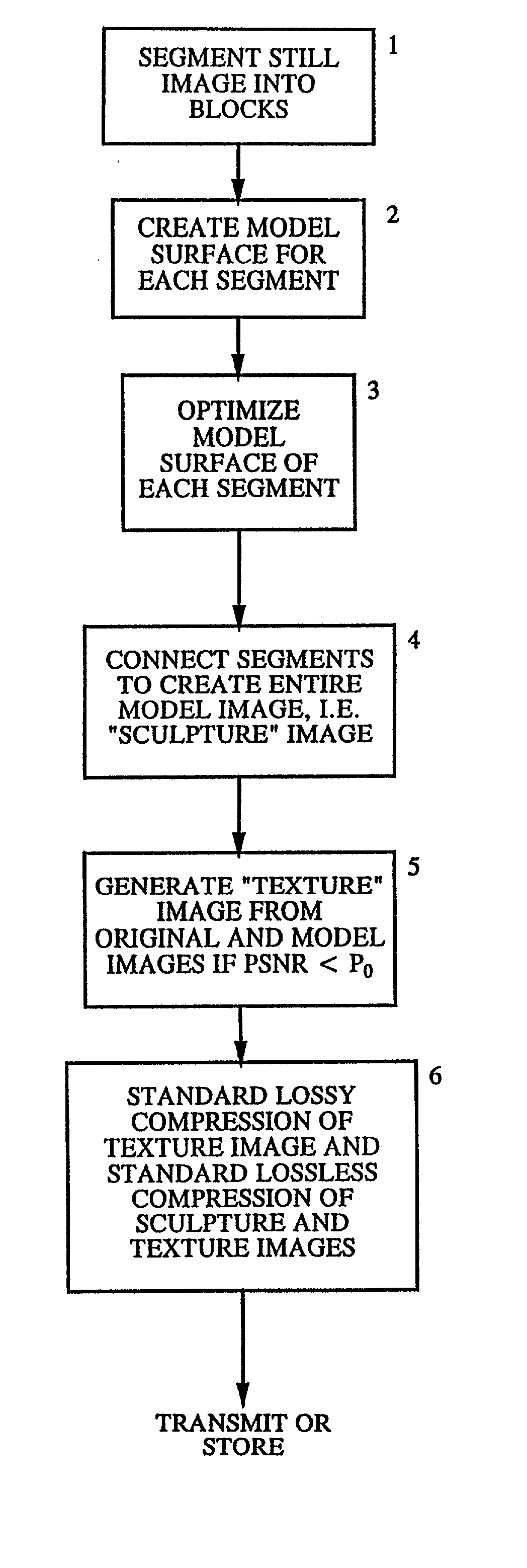
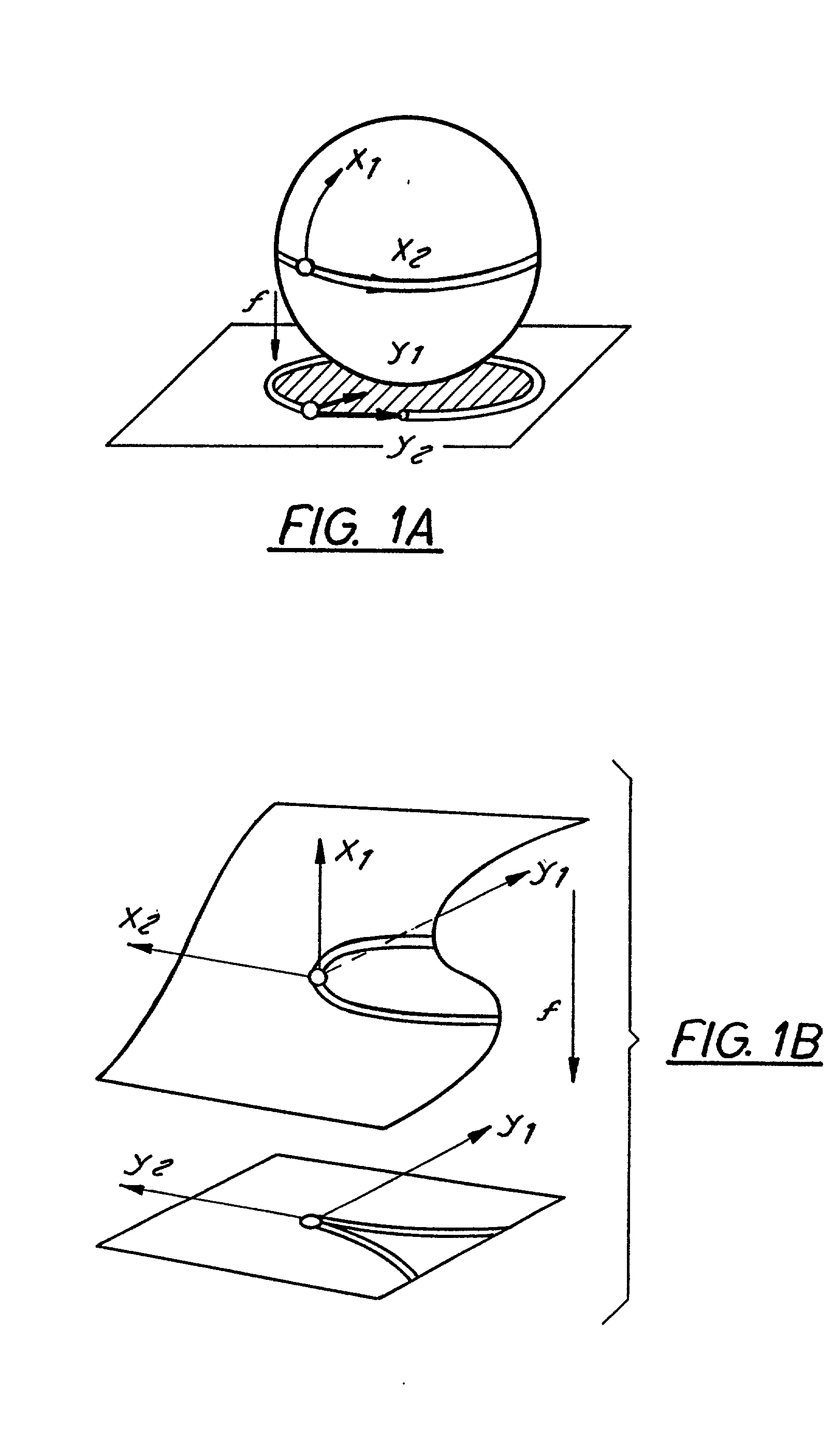
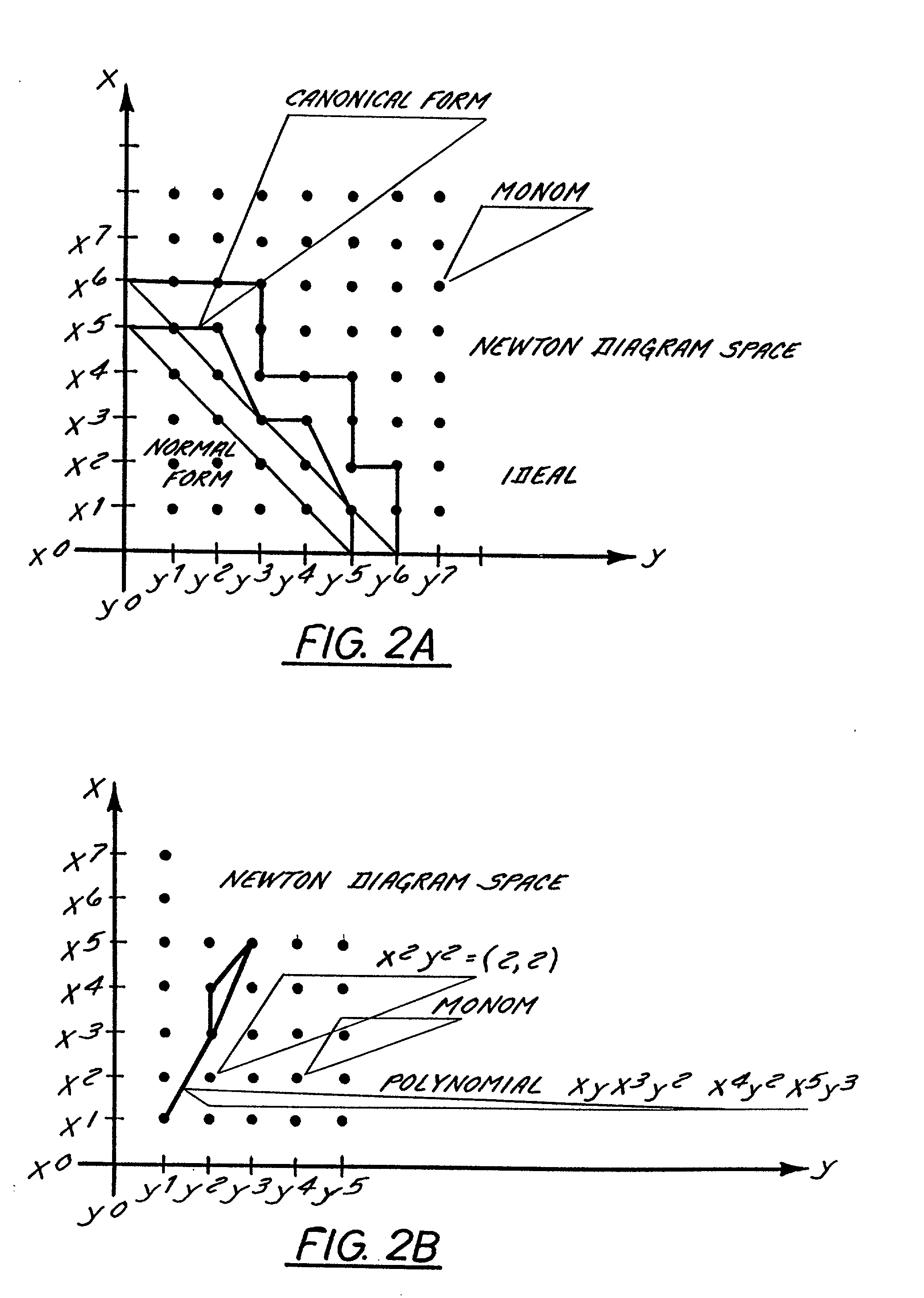
Method of isomorphic singular manifold projection still/video imagery compression
InactiveUS20020176624A1Reduction procedureReduce redundancyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingPattern recognitionImage compression
Methods and apparatuses for still image compression, video compression and automatic target recognition are disclosed. The method of still image compression uses isomorphic singular manifold projection whereby surfaces of objects having singular manifold representations are represented by best match canonical polynomials to arrive at a model representation. The model representation is compared with the original representation to arrive at a difference. If the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, the difference data are saved and compressed using standard lossy compression. The coefficients from the best match polynomial together with the difference data, if any, are then compressed using lossless compression. The method of motion estimation for enhanced video compression sends I frames on an "as-needed" basis, based on comparing the error between segments of a current frame and a predicted frame. If the error exceeds a predetermined threshold, which can be based on program content, the next frame sent will be an I frame. The method of automatic target recognition (ATR) including tracking, zooming, and image enhancement, uses isomorphic singular manifold projection to separate texture and sculpture portions of an image. Soft ATR is then used on the sculptured portion and hard ATR is used on the texture portion.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Image compression for rapid high-quality imaging
ActiveUS20050276496A1Improve performanceLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsImage compressionDigital image data
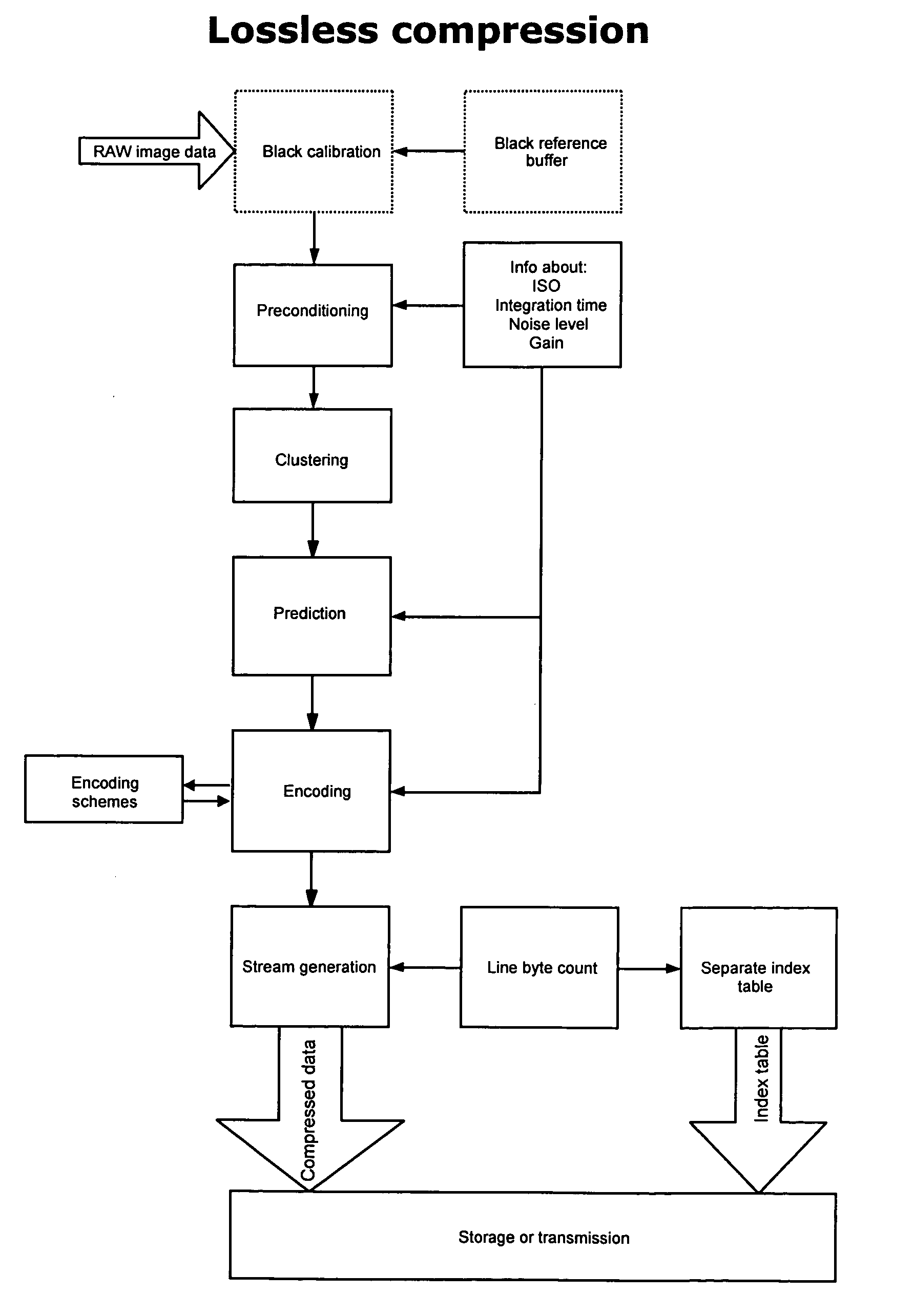
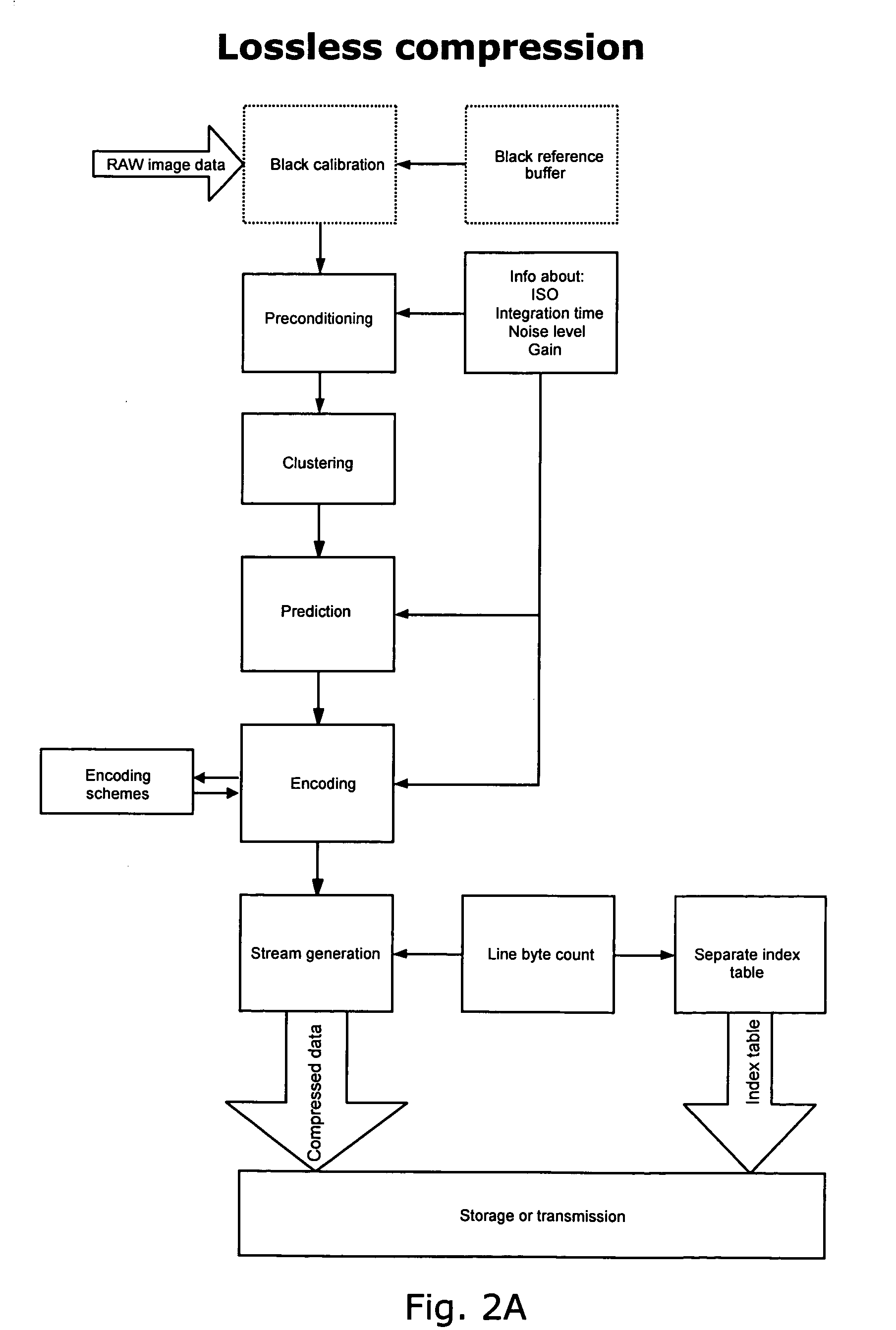
The invention relates to lossless, near-lossless, and lossy compression and decompression of digital image data. Image data can be compressed and decompressed on-the-fly with no need for external RAM resources for temporary data storage while compressing / decompressing image data. Implementing the algorithm only requires a very limited amount of silicon and yields very high performance in relation to very low power consumption. The described implementation is optimized for raw image data from a sensor with a Bayer filter pattern but can be used on data from image sensors with any color filter. The compression algorithm contains a line indexing format which enables very fast subsampling of an already compressed image and the possibility to decompress only parts of an image—this improves performance and reduces the need for temporary RAM storage greatly when zooming and in postprocessing.
Owner:PHASE ONE
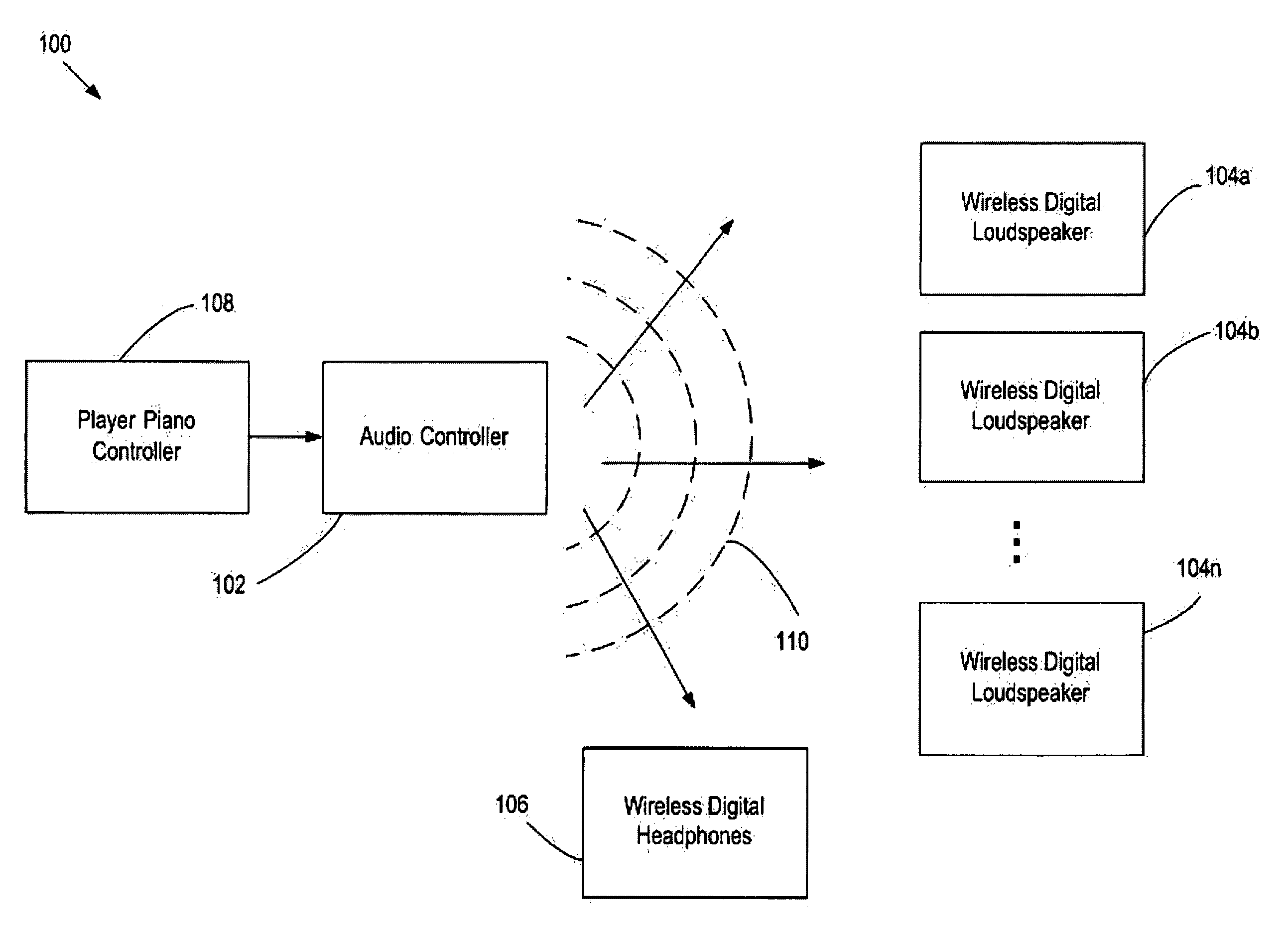
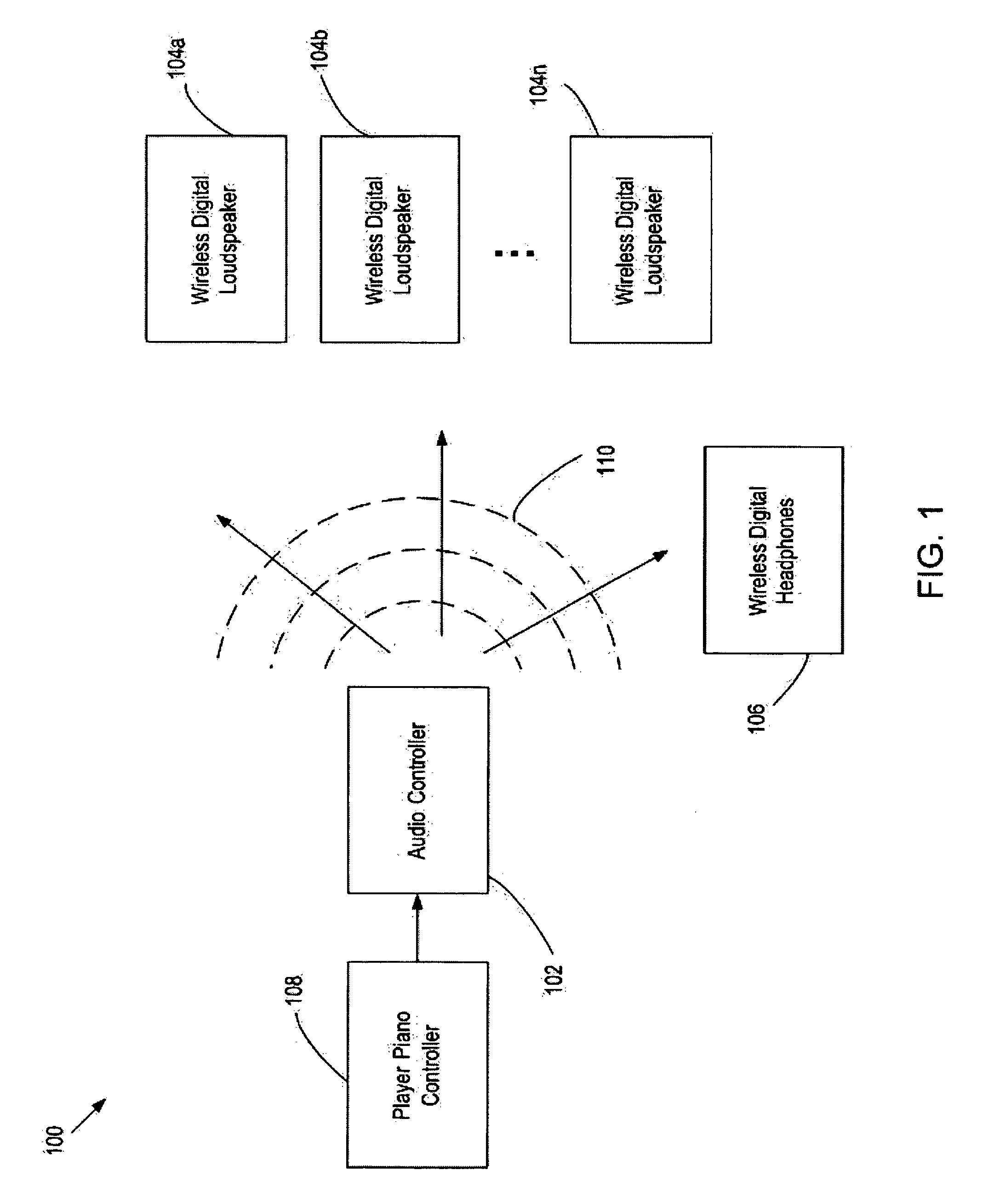
Method and apparatus for wireless digital audio playback for player piano applications
InactiveUS7742832B1Improve performanceLow costElectrophonic musical instrumentsBroadcast specific applicationsData compressionSystems design
The present invention discloses methods and systems for providing very high quality audio playback using all-digital wireless paths from a source to speaker transducers and / or headphones located anywhere within a distance allowed by the FCC. Each speaker has a separate digital amplifier dedicated to each transducer within it (e.g. woofer, tweeter). The present invention also discloses a system that provides a data link capable of sending an all-digital, full-bandwidth, signal from the original digital source material to each separate transducer in the system without using sound degrading lossy data compression. This system is designed to read, broadcast, and reproduce with accurate audio loudspeaker time-alignment (<100 uS) and low overall latency (less than 7 milliseconds) all popular audio formats in full-bandwidth and without data compression in the effort to maintain the integrity of the entire audio signal, wherein the audio signal may include an accompaniment to a player piano.
Owner:NEOSONIK
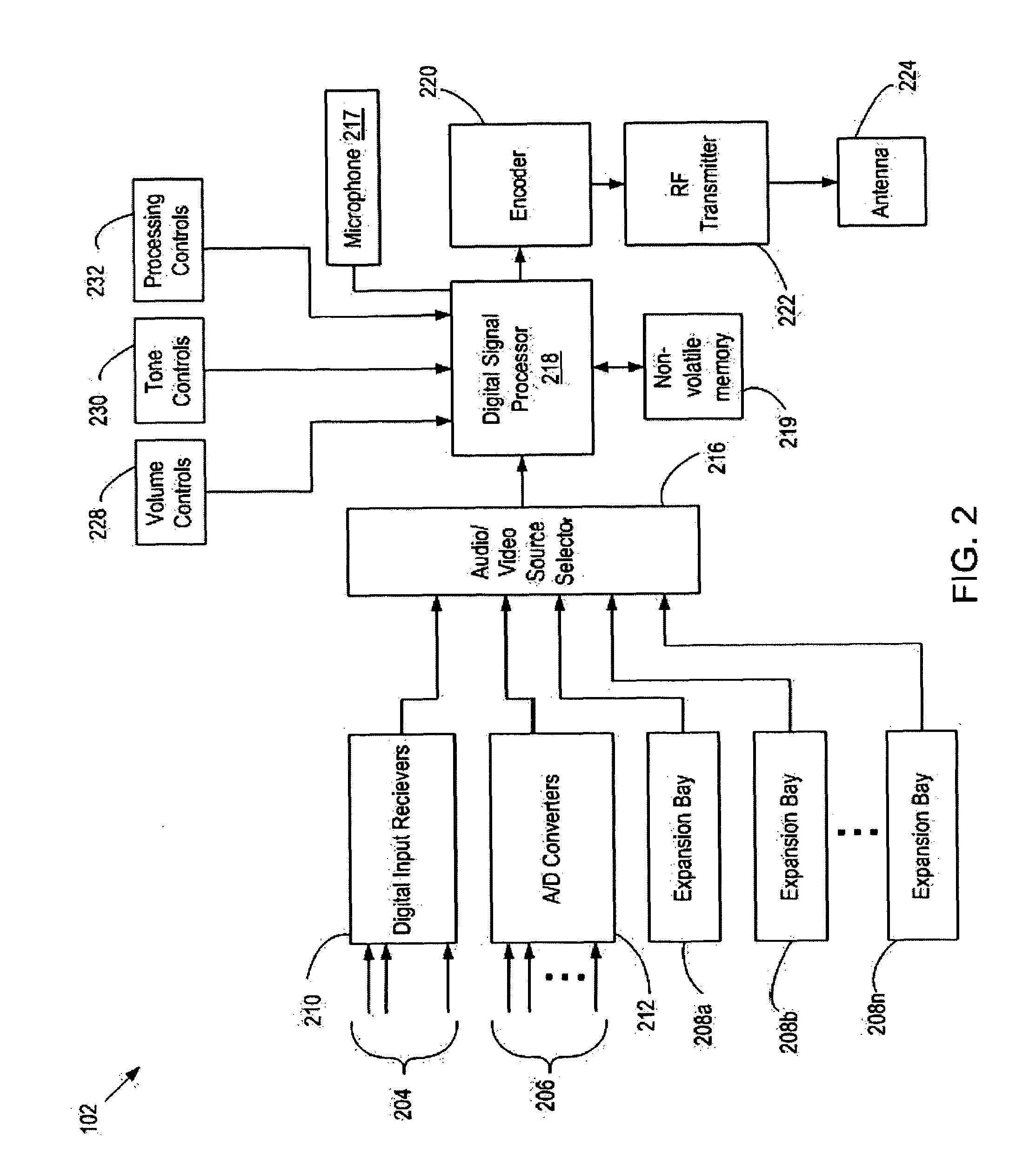
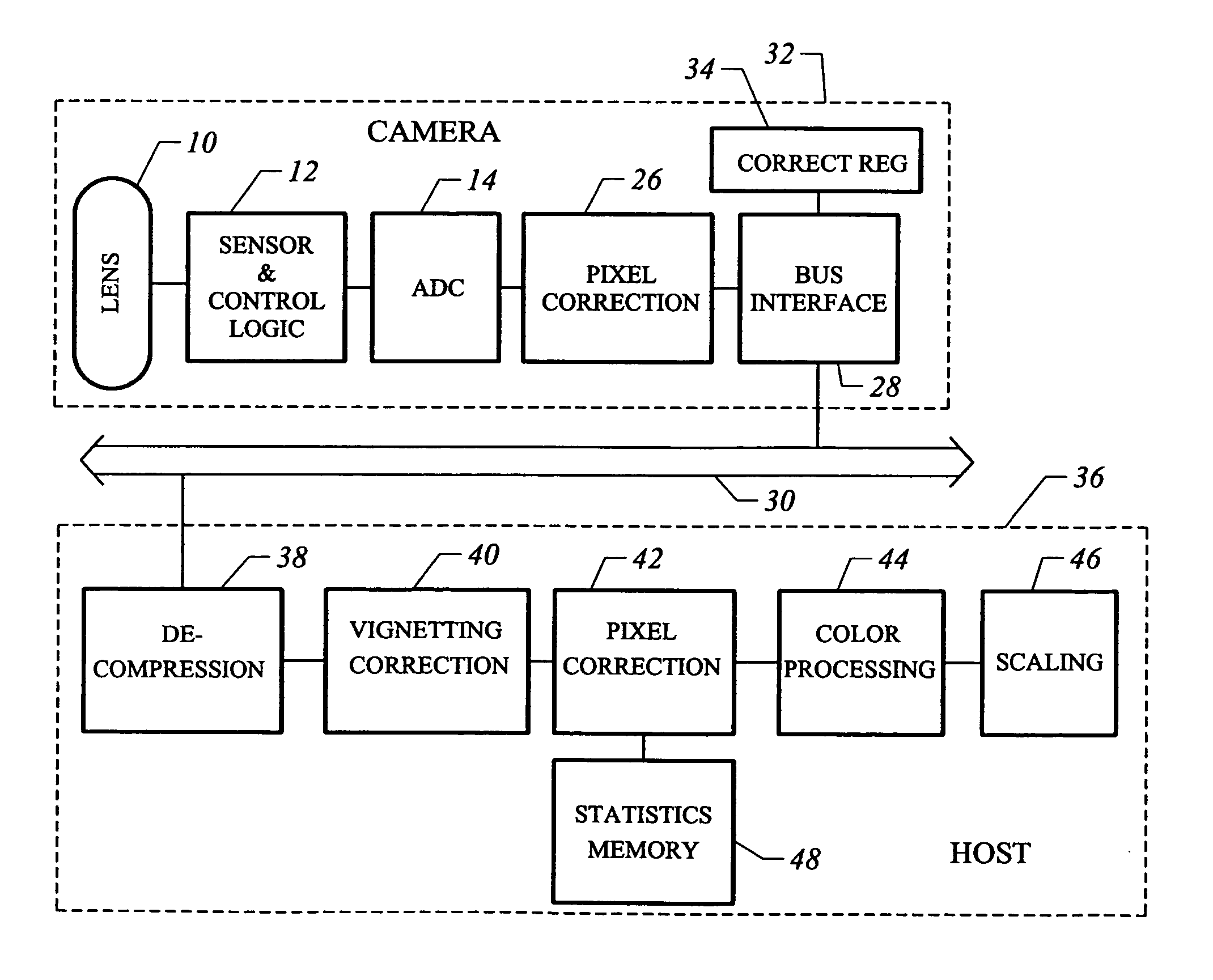
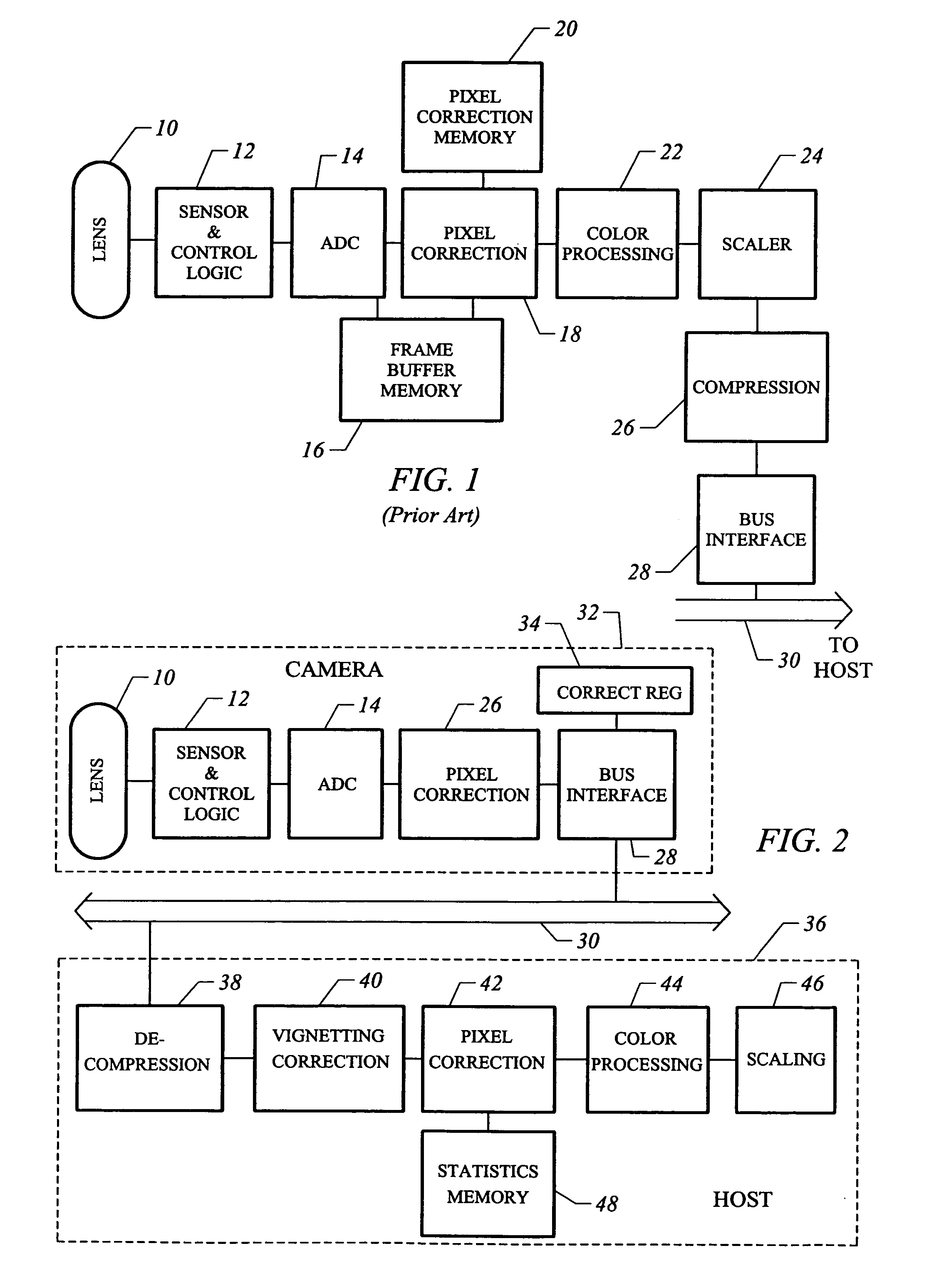
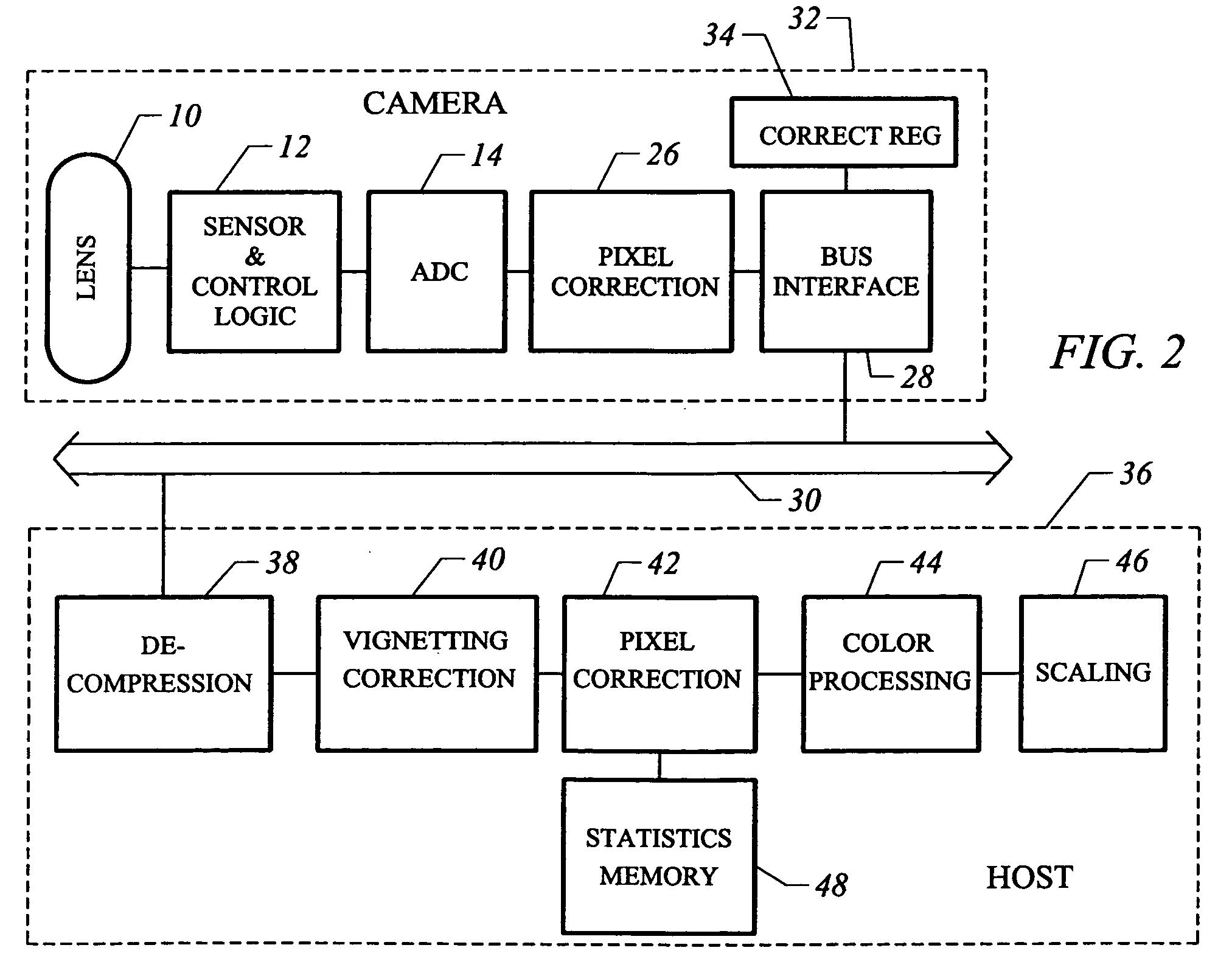
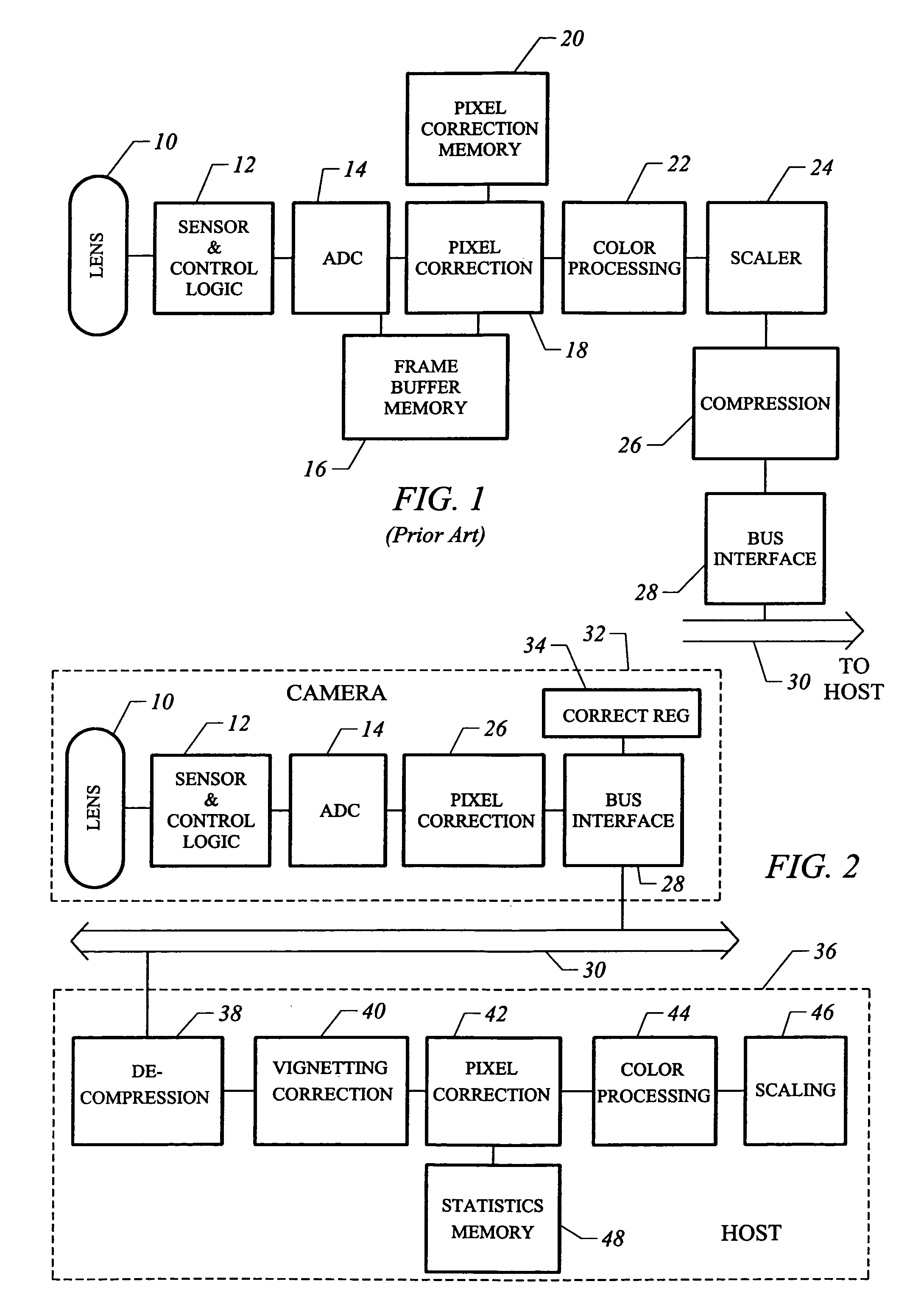
Video camera with major functions implemented in host software
InactiveUS20050162531A1Low costIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsCode conversionComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
A low cost camera by implementing the major functions in host software is provided. This is accomplished by sending raw, digitized data from the camera directly to the host. The increased volume of raw data is handled by either an improved compression / decompression scheme using lossless compression, using lossy compression or using a shared bus with higher bandwidth. By moving such functions as color processing and scaling to the host, the pixel correction can also be moved to the host. This in turn allows the elimination of the frame buffer memory from the camera. Finally, the camera can use a low cost lens by implementing vignetting, distortion, gamma or aliasing correction with a correction value stored in a register of the camera for later access by the host to perform corrections.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
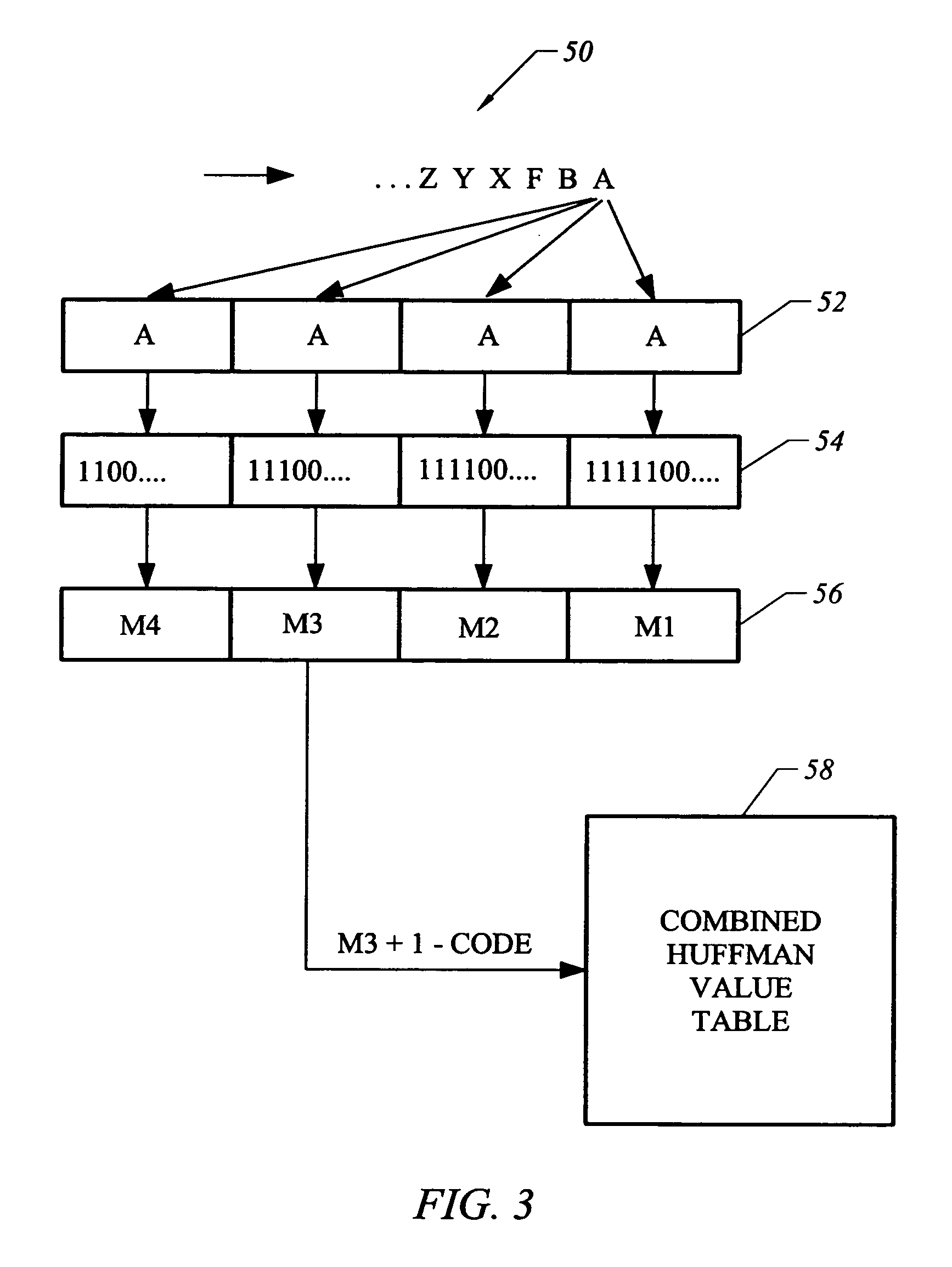
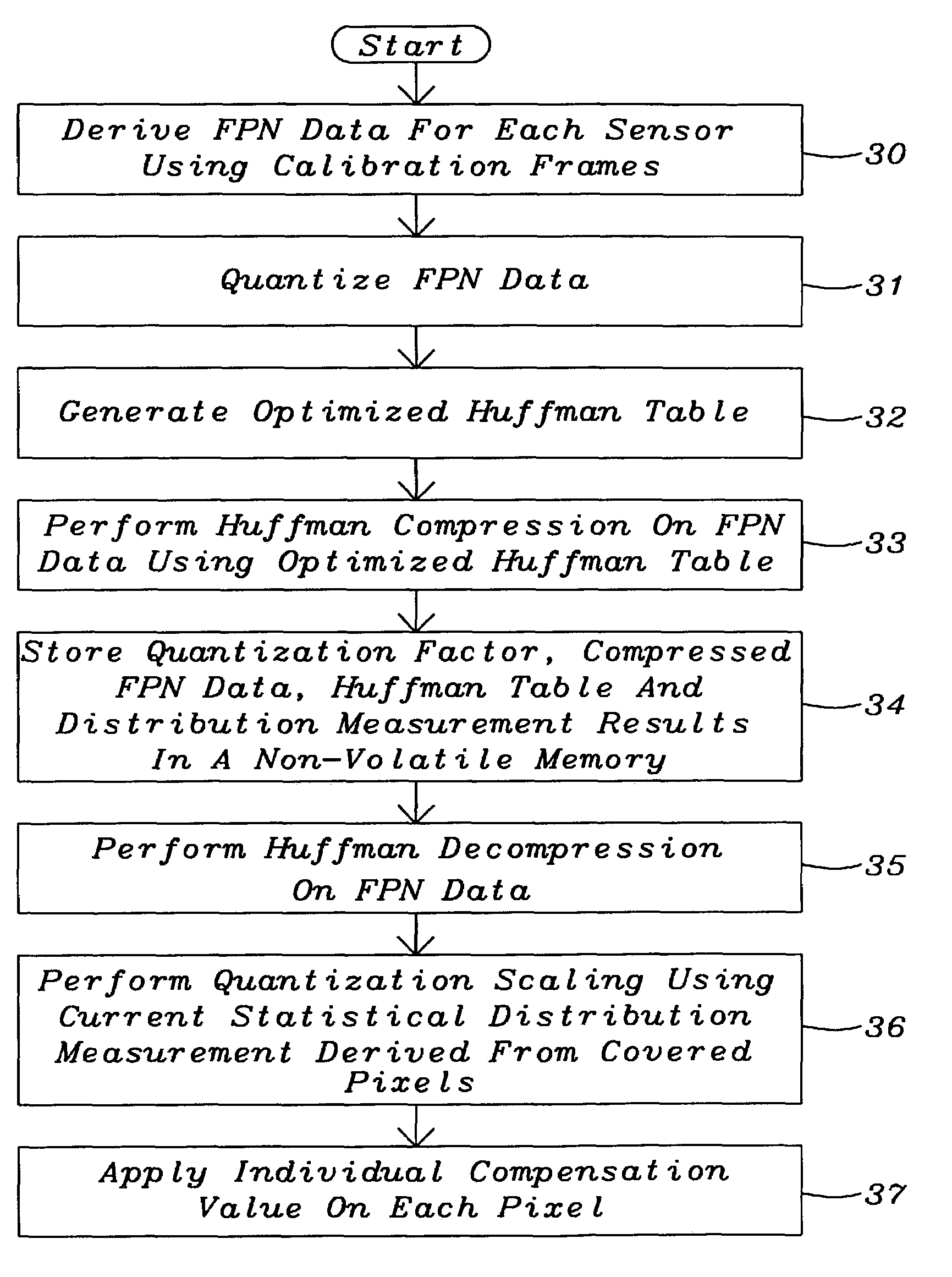
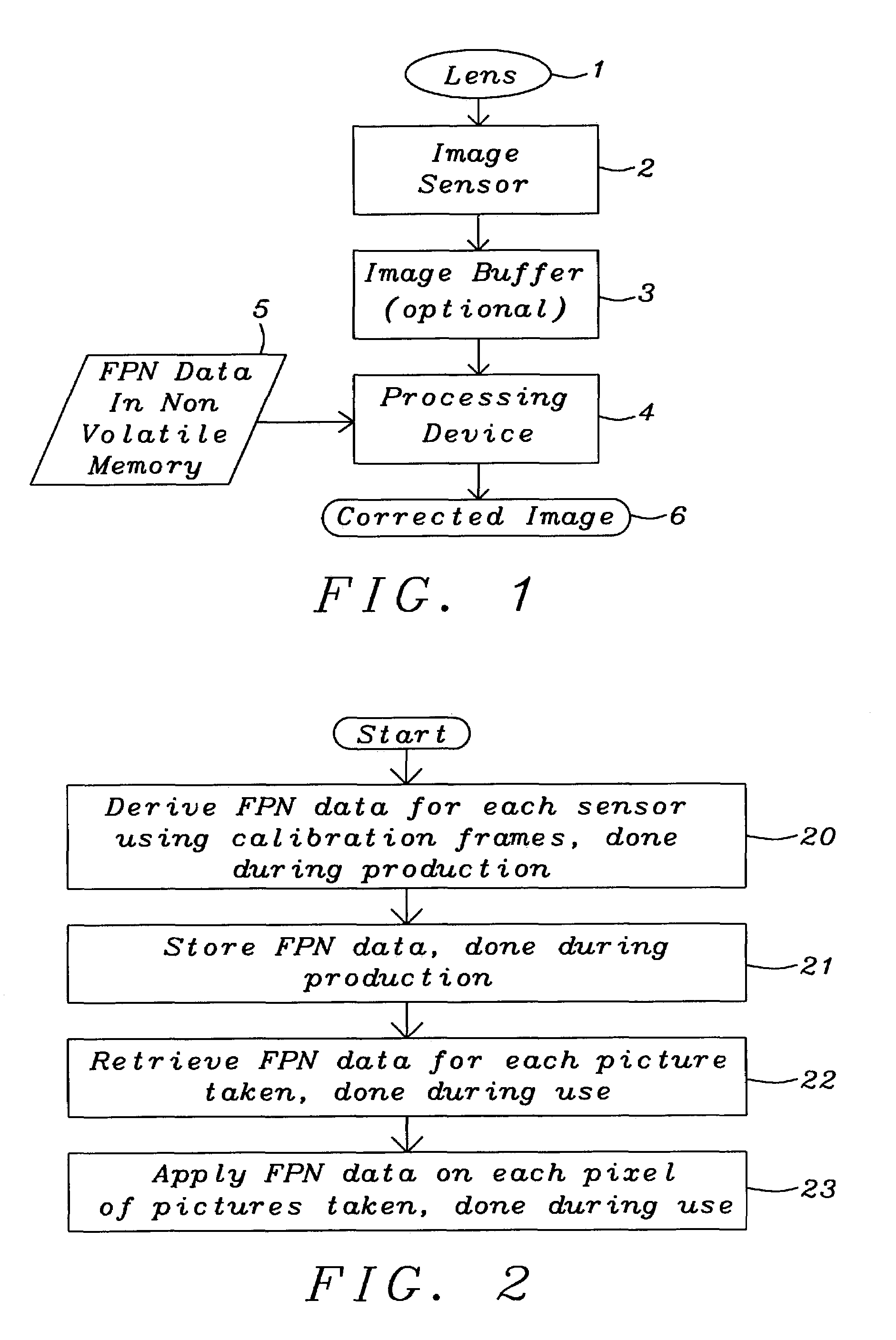
Fixed pattern noise compensation with low memory requirements
InactiveUS6995346B2Reduce memory requirementsCompensation of fixed pattern noiseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPattern recognitionComputer module
A method and a system for the compensation of Fixed Pattern Noise (FPN) in digital images have been achieved. The FPN compensation is based on processing done during the production of said images. The fixed pattern noise is here defined as the fixed pattern seen in the individual pixel offsets. The fixed pattern noise is uncorrelated noise but it has a statistical distribution that can be scaled to fit all images. The general idea is to measure the distribution for each individual camera, compress it, and save it in the module. For each image that is then taken with the module the noise pattern can be retrieved and rescaled to fit the image. Covered pixels are employed to normalize the FPN data to the current frame. In order to minimize memory requirements a compression scheme has to be used. A method combining a quantization step with a non-lossy compression is used. The black level is corrected for as part of the operation.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
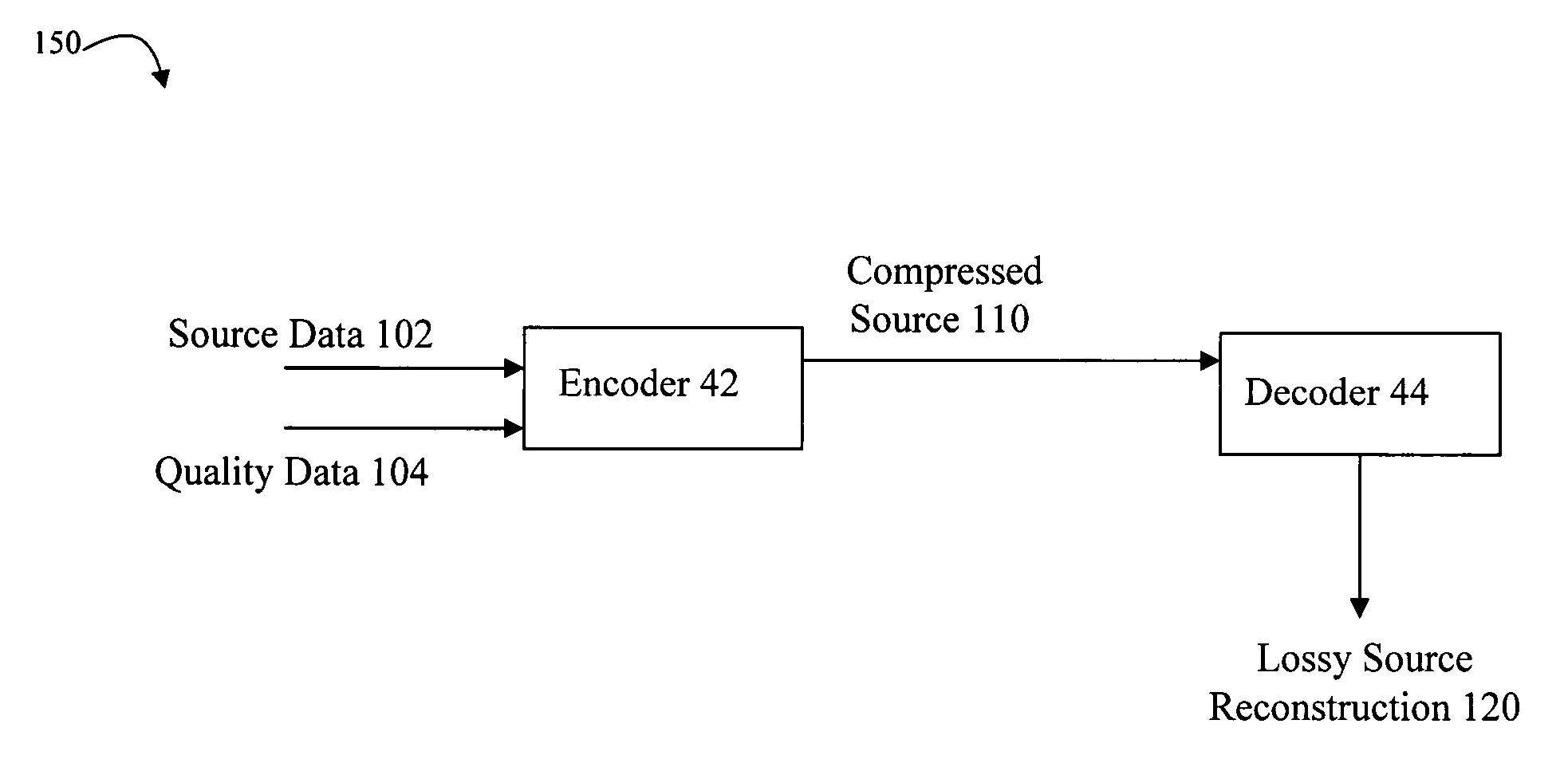
Lossy data compression exploiting distortion side information
InactiveUS7327287B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionSide information
Described are techniques for performing lossy encoding. Source data and quality data are received by an encoder. The encoder maps the source data into a compressed representation having a level of distortion in accordance with the quality information. The compressed representation may be decoded without using the quality information.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Video camera with major functions implemented in host software
InactiveUS6995794B2Low costIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
A low cost camera by implementing the major functions in host software is provided. This is accomplished by sending raw, digitized data from the camera directly to the host. The increased volume of raw data is handled by either an improved compression / decompression scheme using lossless compression, using lossy compression or using a shared bus with higher bandwidth. By moving such functions as color processing and scaling to the host, the pixel correction can also be moved to the host. This in turn allows the elimination of the frame buffer memory from the camera. Finally, the camera can use a low cost lens by implementing vignetting, distortion, gamma or aliasing correction with a correction value stored in a register of the camera for later access by the host to perform corrections.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Diagnosis oriented lossy compression of medical images
InactiveUS6937767B1Reduce memory requirementsSufficient dataPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage codingCompression methodLossy compression
A method of compressing a medical image, including:providing a medical diagnostic image, having associated therewith at least one windowing parameter;automatically selecting a desired compression quality, responsive to the at least one windowing parameter; andcompressing the image, using a lossy compression method, such that a decompressed image will have substantially the desired compression quality. Preferably, the at least one windowing parameter is provided by an imaging technician. Preferably, the compression method is a wavelet compression method.
Owner:ALGOTEC SYST
Remote desktop protocol compression system
InactiveUS7171444B2Not exactStatic indicating devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionRemote desktop
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a remote desktop communication protocol that includes spatial and temporal compression techniques. Multimedia presentation data is generated at a server from a source. A compression facility modifies the presentation data by both spatially and temporally compressing the presentation data to transmittable data. In some embodiments, a check is performed to ensure that the least amount of data is selected prior to sending the transmittable data to a remote client. The remote client receives the transmittable data and re-constructs the original multimedia presentation data. In some embodiments that use lossy compression, the reconstruction may not exactly re-construct the original multimedia presentation data. Once re-created, the remote client presents the presentation data at the remote client. The presentation data could be audio, video, or other data or a combination of them.
Owner:SHARP KK
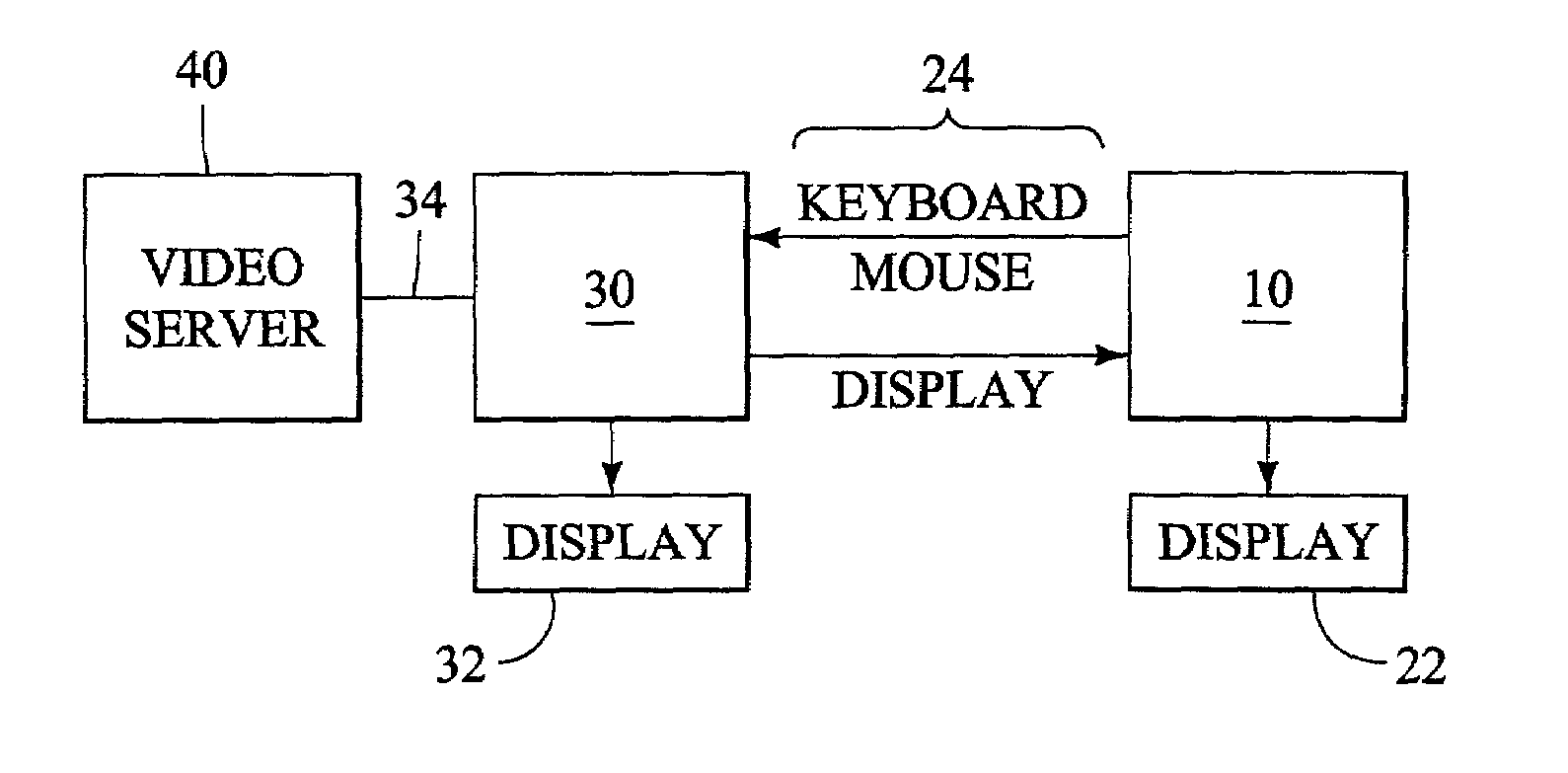
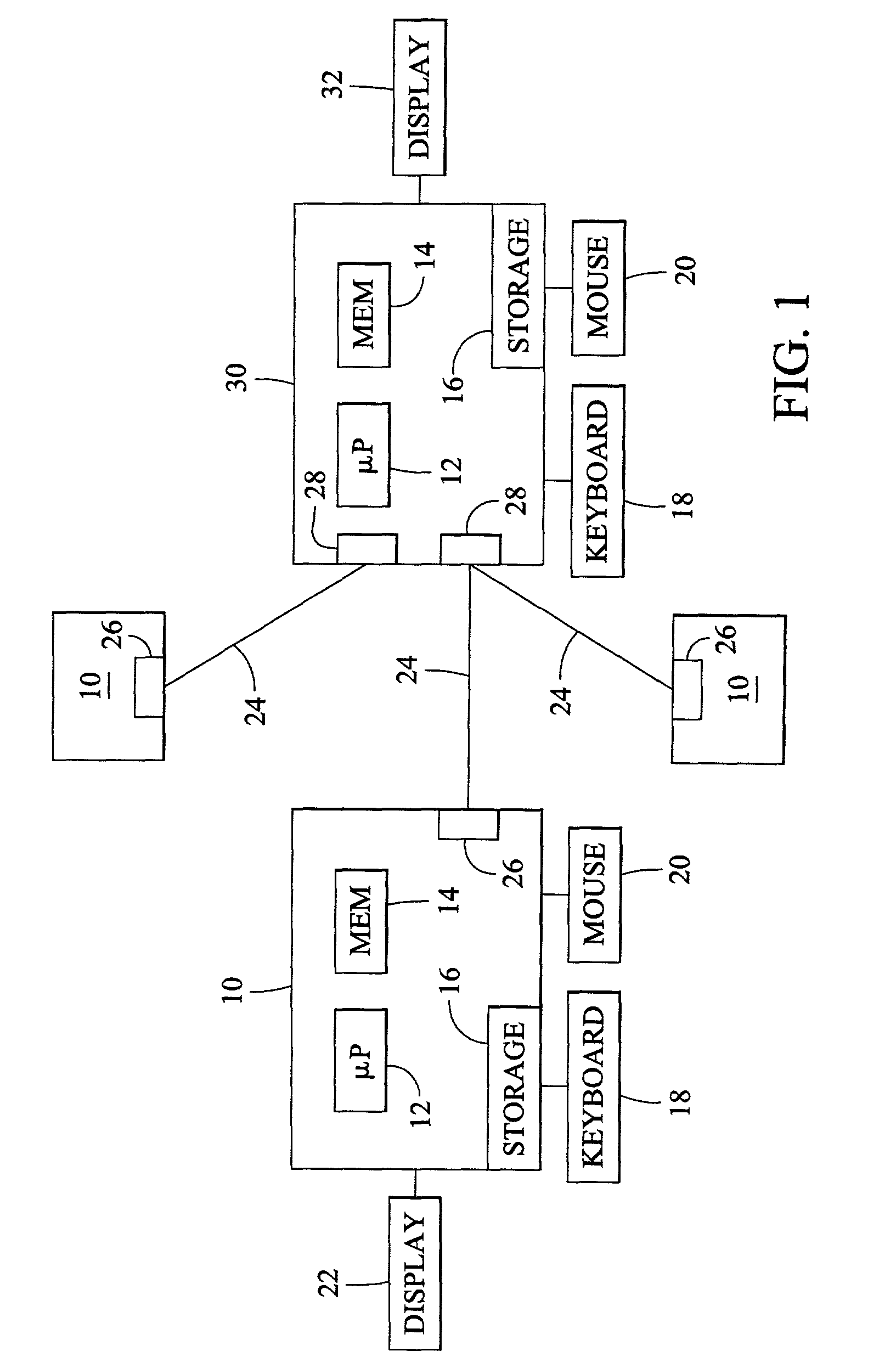
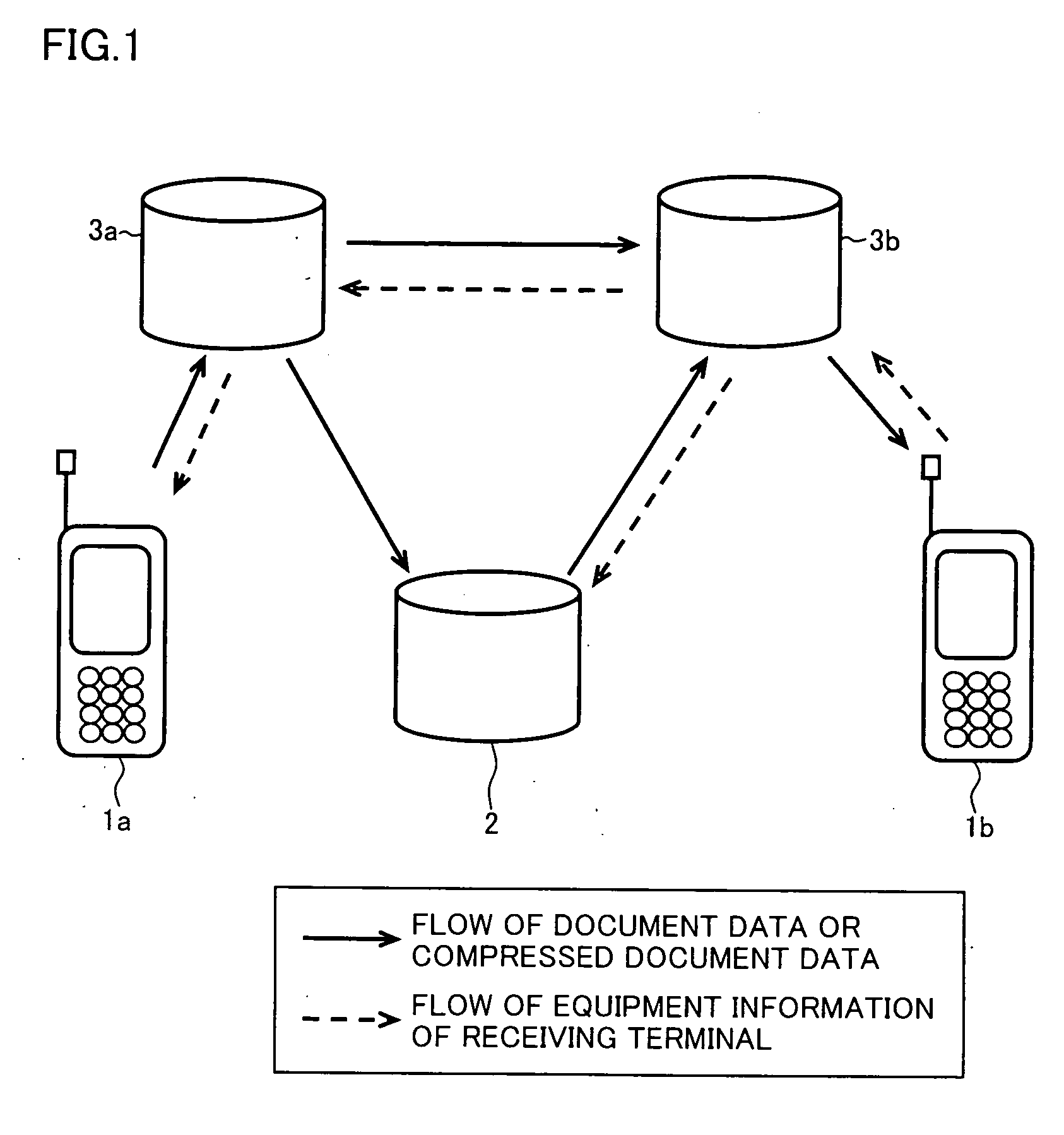
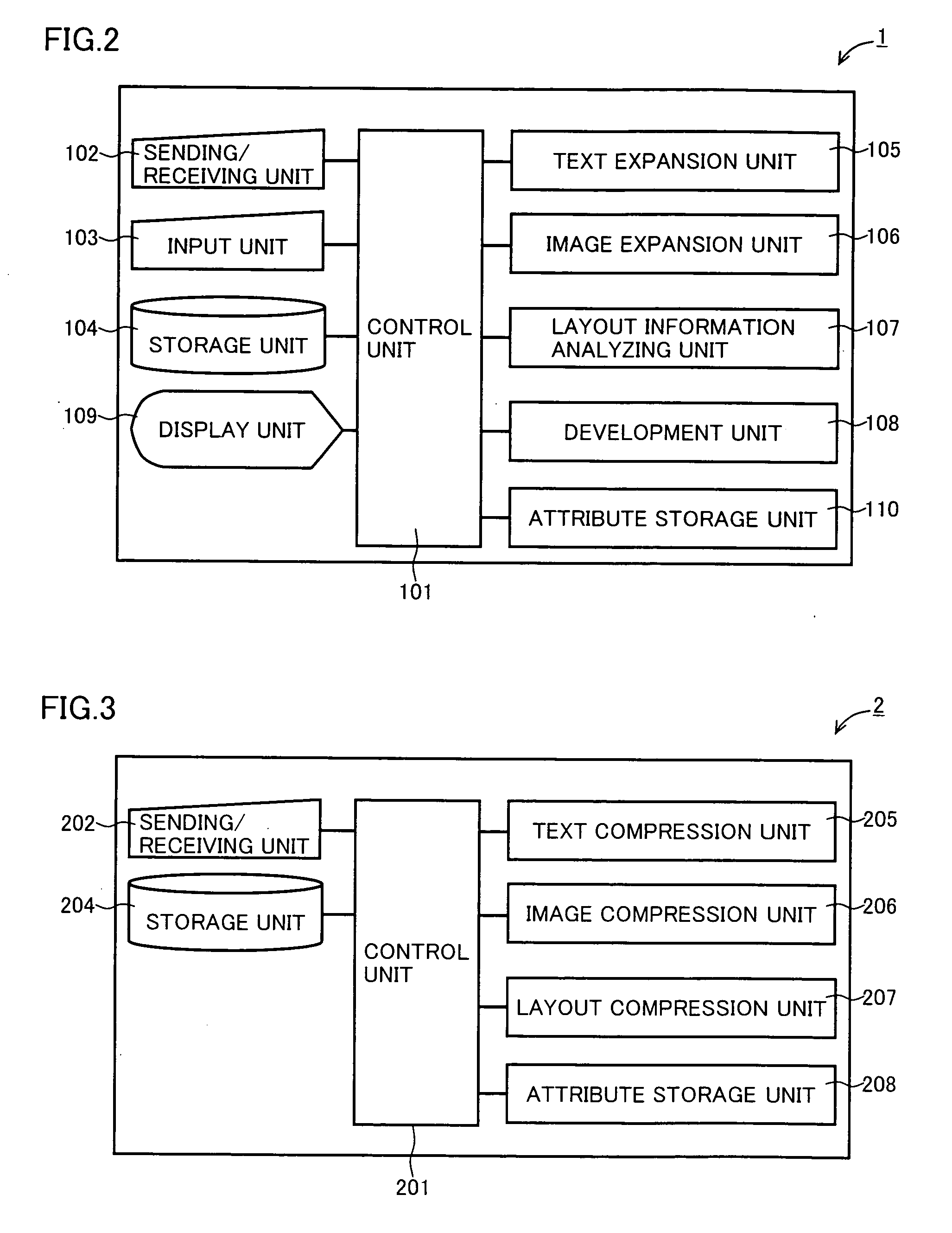
Document data output device capable of appropriately outputting document data containing a text and layout information
InactiveUS20070055931A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData displayOutput device
A document data display system uses document data composed of text and image portions and layout information and creates from it compressed document data by lossless compressing the text portion and lossless or lossy compressing the image portion in order to reduce traffic in communication. A document data display device 1 expands text or image portions from received compressed document data at a text expansion unit or an image expansion unit, and uses the analysis of the layout information by a layout information analyzing unit to arrange the text or image portions at a development unit before being displayed by a display unit.
Owner:SHARP KK
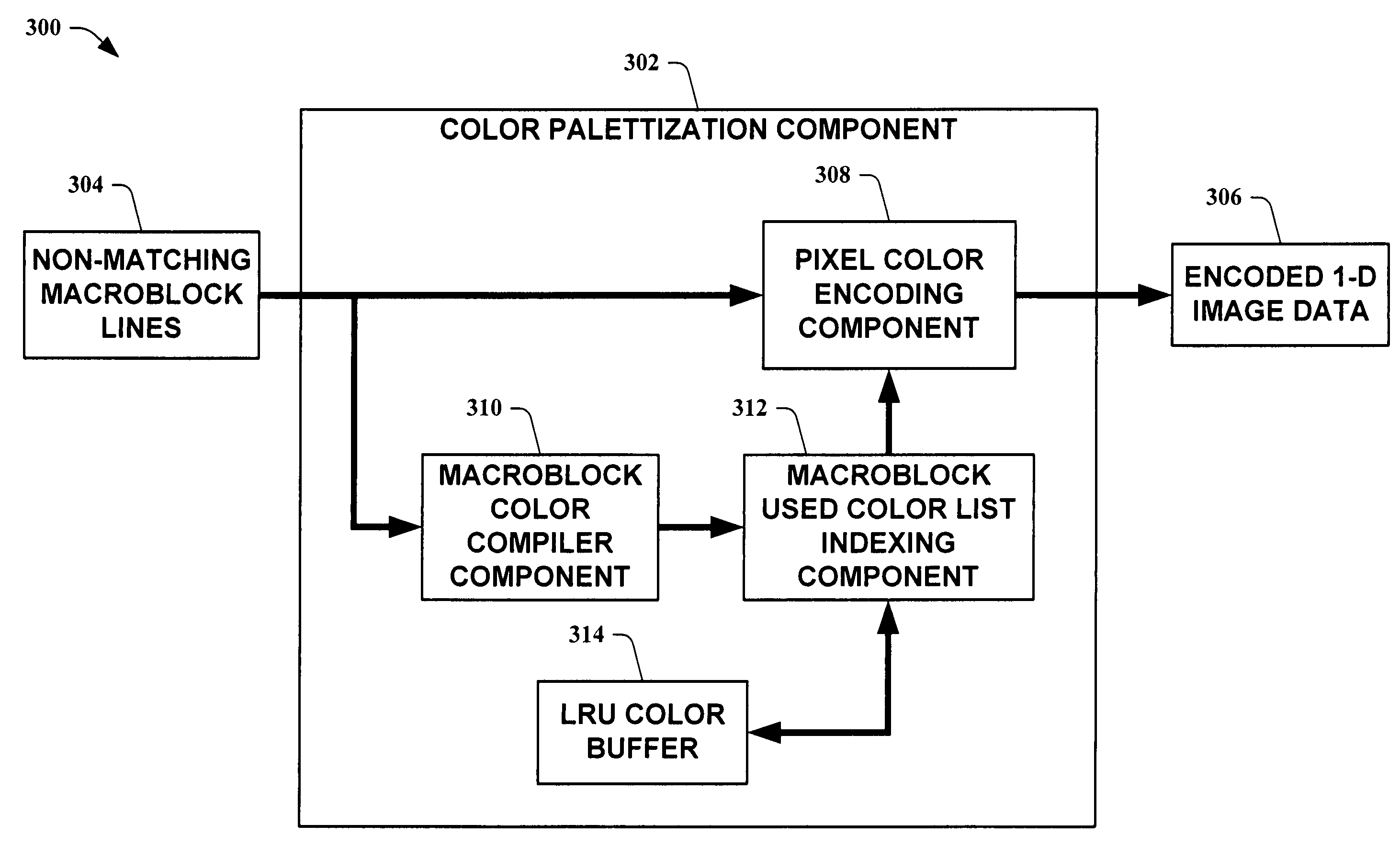
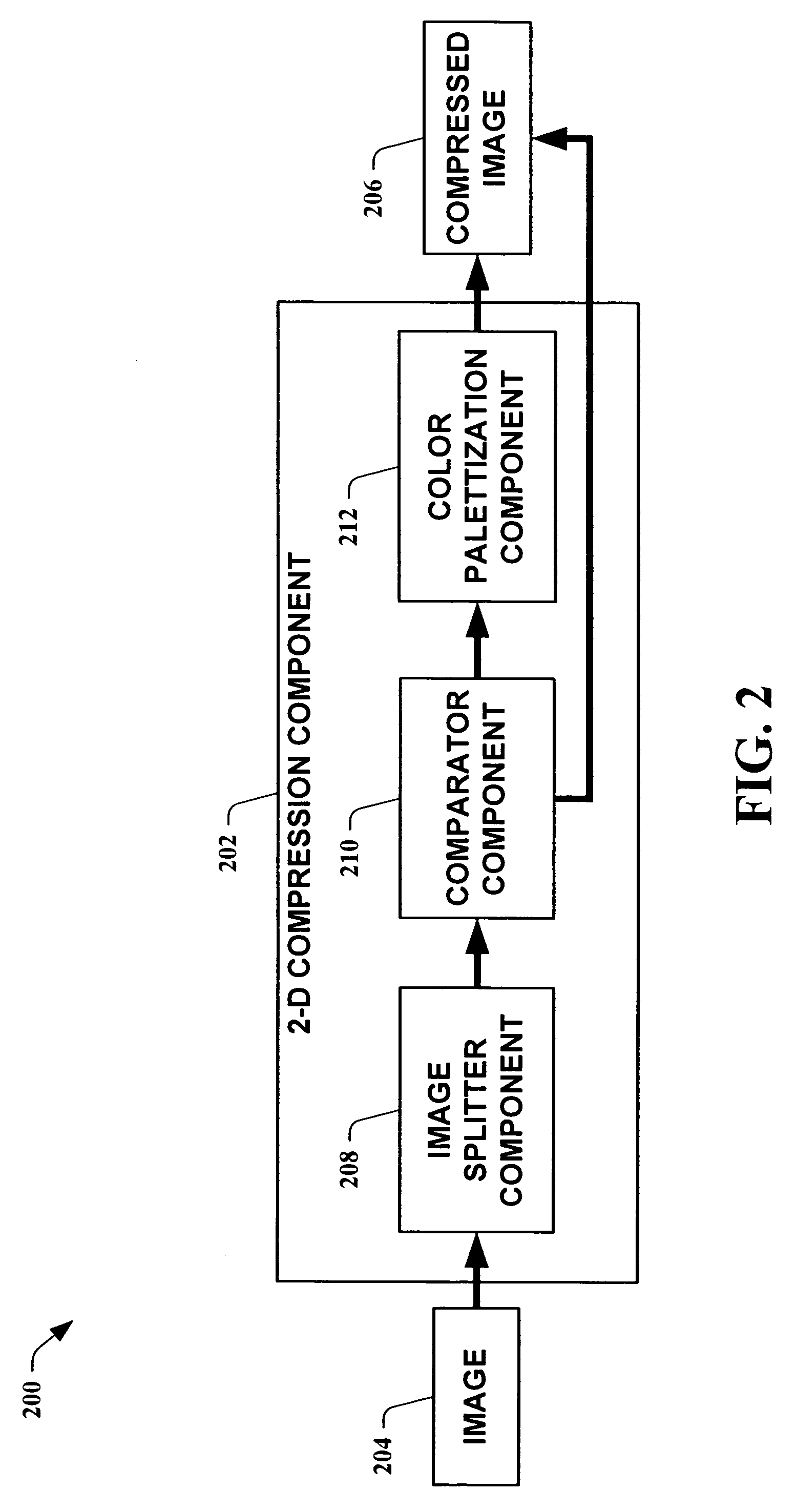
Dynamic, locally-adaptive, lossless palettization of color and grayscale images
InactiveUS7343037B1Efficient data transferImprove compression performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Data information
The present invention leverages a lossless pixel palettization scheme to locally compress portions of at least a two-dimensional image. This provides a lossless compression means with a compression ratio comparable with lossy compression means, allowing for efficient data transfers without loss of image information. By utilizing locally-adaptive palettization, two-dimensional pixel information can be exploited to increase compression performance. In one instance of the present invention, a locally-adaptive, lossless palettization scheme is utilized in conjunction with a one-dimensional compression scheme to yield a further increase in compression ratio. This allows for the exploitation of two-dimensional data information along with the further compression of information reduced to one dimension.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
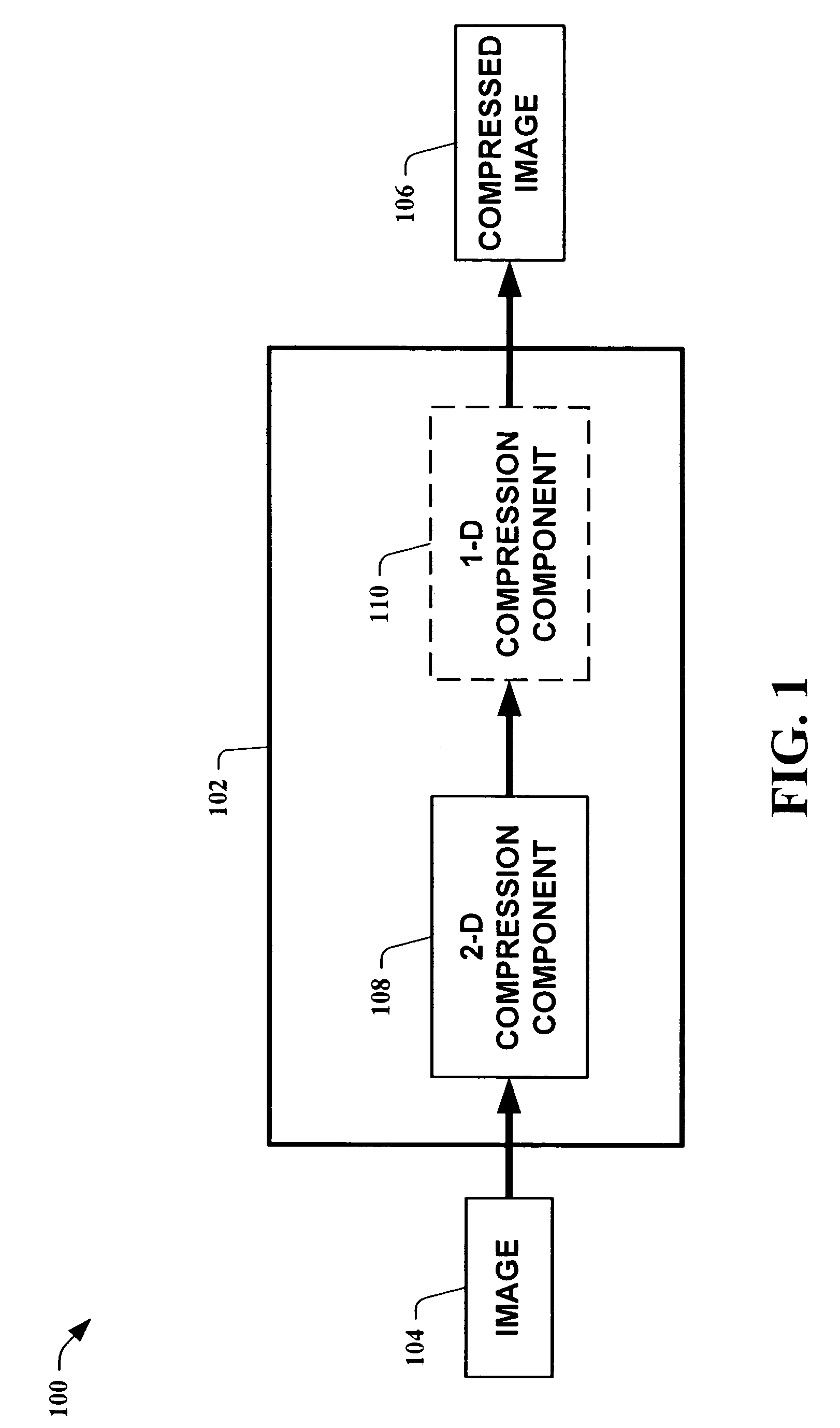
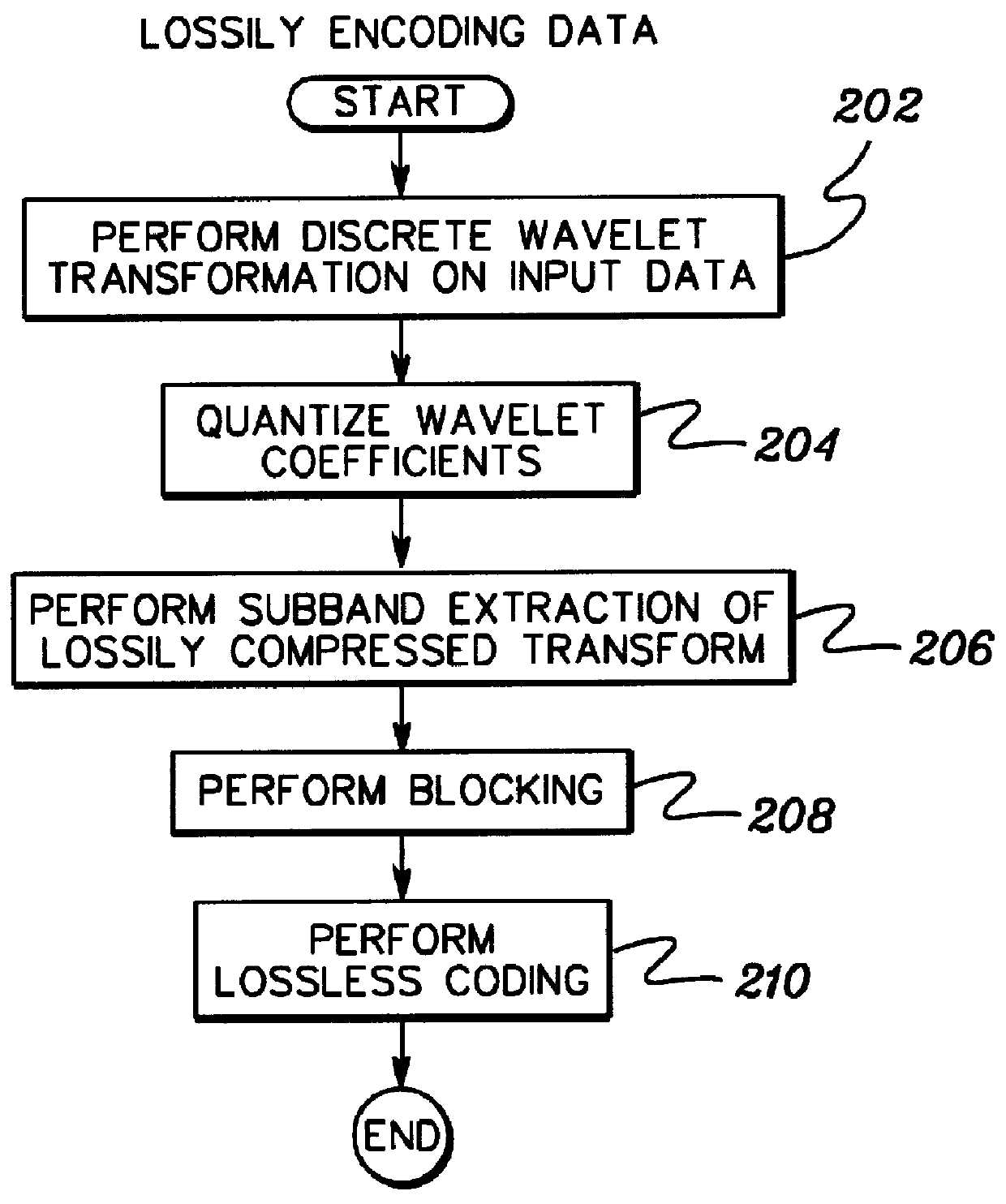
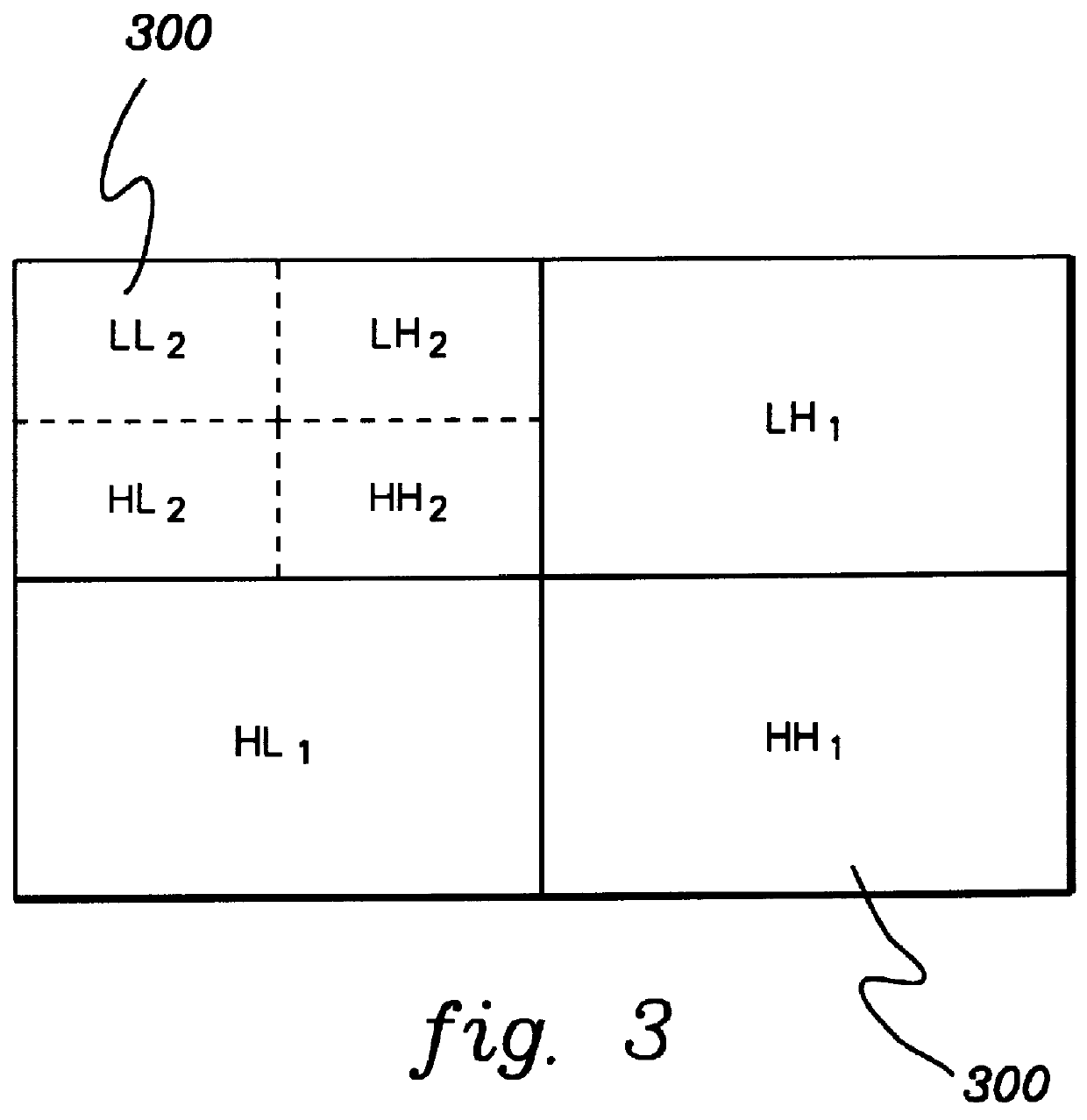
Multiresolution lossless/lossy compression and storage of data for efficient processing thereof
InactiveUS6021224AEfficient storage and retrievalEasy retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingLossless codingImage resolution
Data representing, for instance, an image is lossily encoded, and a residual of the data is losslessly encoded. The lossily encoded data and the losslessly encoded residual provide a losslessly compressed data representation of the original data. The losslessly compressed data is then organized and stored on a storage system according to one or more criteria selected for the particular losslessly encoded data to be organized. This enables the efficient retrieval and processing of the compressed data, including retrieval of portions of the compressed data.
Owner:IBM CORP
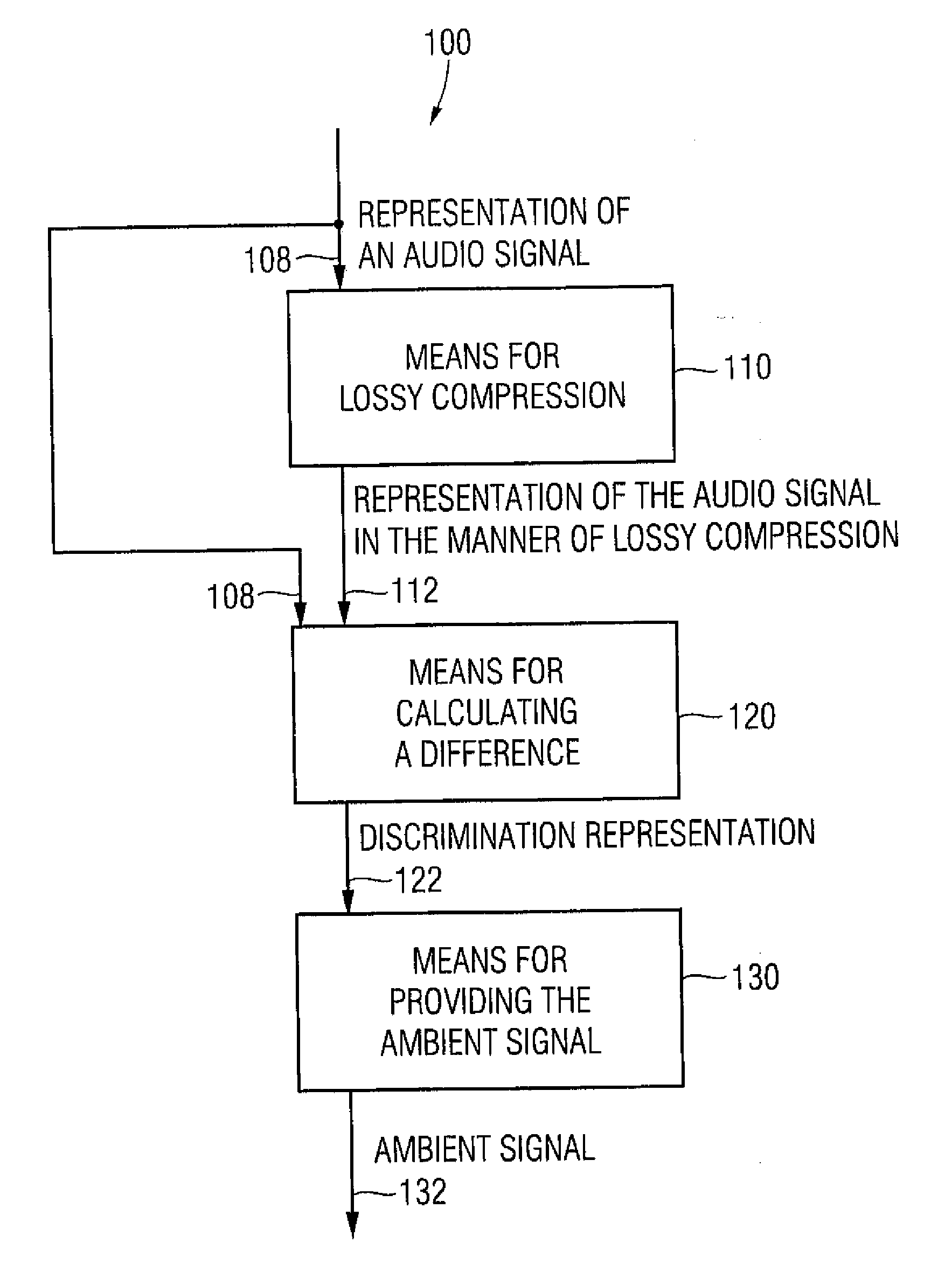
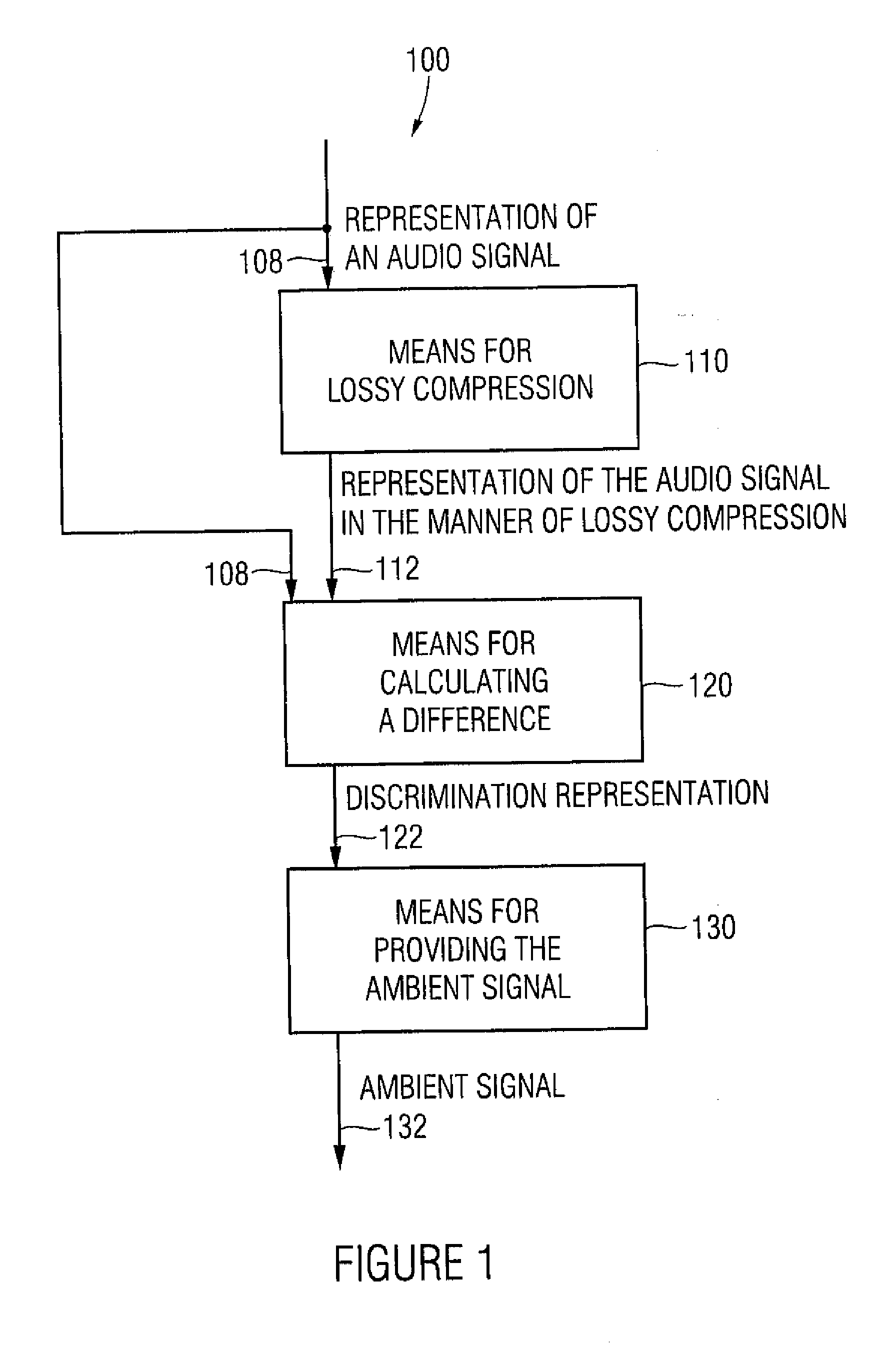
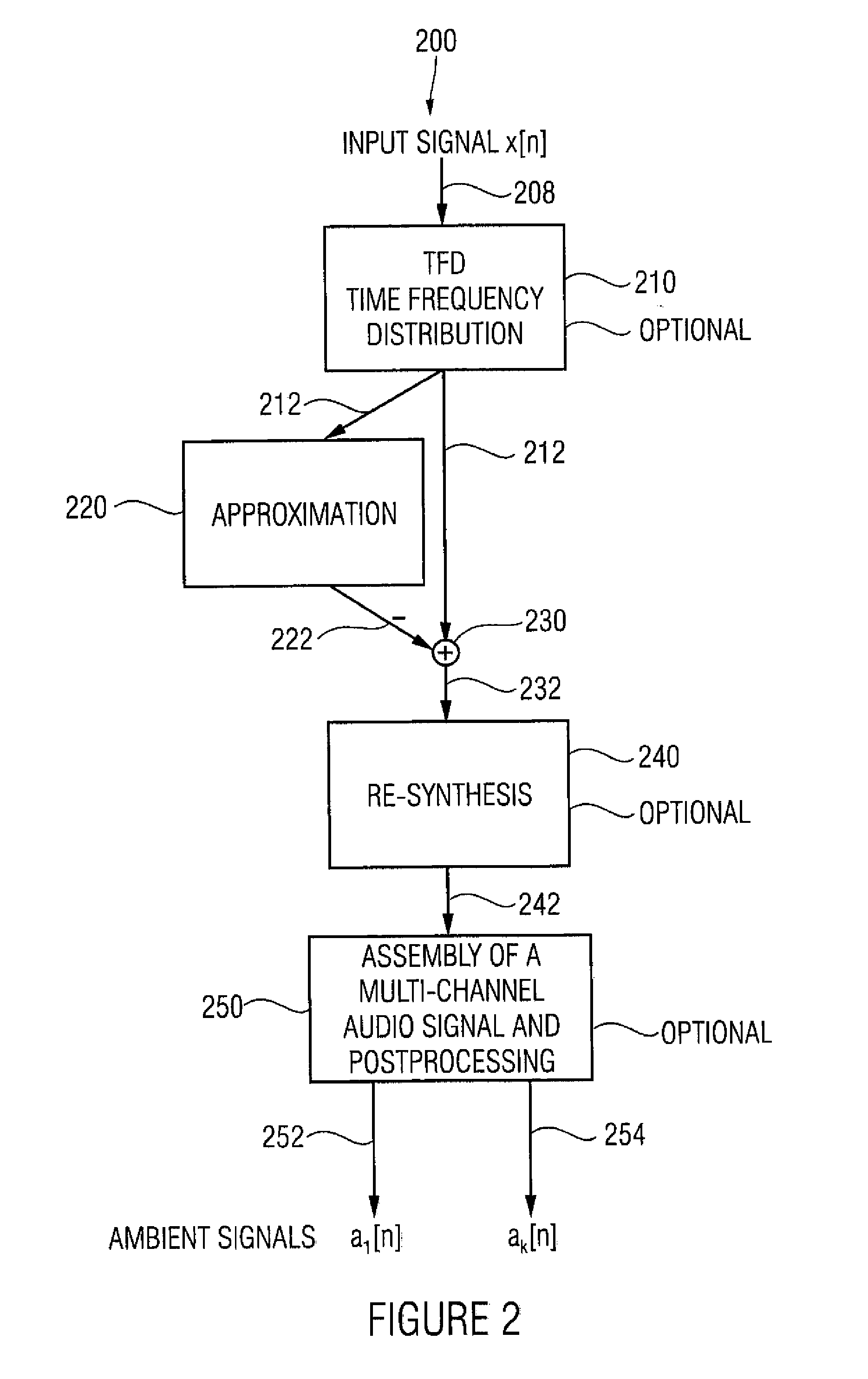
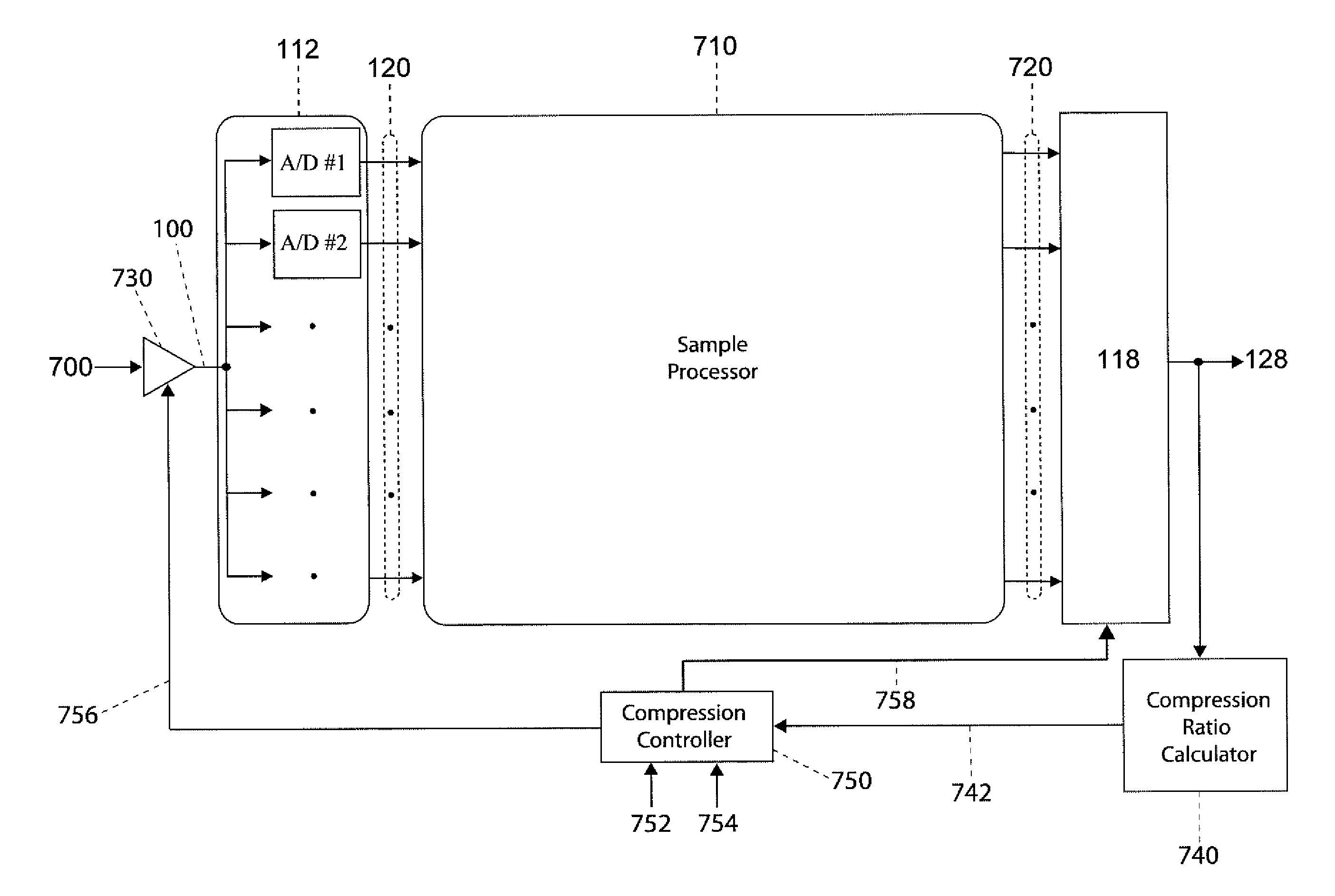
Apparatus and method for generating an ambient signal from an audio signal, apparatus and method for deriving a multi-channel audio signal from an audio signal and computer program
ActiveUS20100030563A1Simple stepsIncrease impressionGain controlSpeech analysisVocal tractLoudspeaker
An apparatus for generating an ambient signal from an audio signal includes a compressor for lossy compression of a representation of the audio signal so as to obtain a compressed representation of the audio signal describing a compressed audio signal. The apparatus for generating the ambient signal further includes a calculator for calculating a difference between the compressed representation of the audio signal and the representation of the audio signal so as to obtain a discrimination representation. The apparatus further includes a provider for providing the ambient signal using the discrimination representation. An apparatus for deriving a multi-channel audio signal from an audio signal includes an apparatus for generating an ambient signal from an audio signal, an apparatus for providing the audio signal as a front-loudspeaker signal and an apparatus for providing the ambient signal as a back-loudspeaker signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Enhanced Time-Interleaved A/D Conversion Using Compression
InactiveUS20080018502A1Increase the compression ratioDegrade signal qualityAnalogue/digital conversionBinary multiplierAnalog signal
Compression of signal samples output from a parallel, time-interleaved analog to digital converter (TIADC) for a baseband signal, includes calculating first or higher order differences of consecutive signal samples followed by lossless or lossy encoding of the difference samples to produce compressed samples. Compression of a TIADC output signal with a nonzero center frequency, includes calculating sums or differences of pairs of signal samples separated by an appropriate number of sampling intervals followed by lossless or lossy encoding. The sums or differences of the signal samples have lower magnitudes than the original samples, allowing more efficient compression. Lossy compression alternatives produce compressed data with a fixed bit rate or with a fixed quality in the decompressed samples. Alternatives for lossy compression include attenuating the analog signal before sampling by the TIADC, applying bit shifters or multipliers after sampling to reduce the magnitudes of the signal samples, and lossy encoding.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Watermark embedding and detecting methods, systems, devices and components
InactiveUS7693297B2Character and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsNormal densityAlgorithm
Method determining lookup table (“LUT”) for embedding watermark. For each quantization cell, calculating probabilities that signal point falls into cell. Selecting cell by probabilities. Setting LUT value to watermark value with largest probability, subject to run constraint. For remaining cells, repeating selecting and setting steps. Other method determining quantization ensemble by calculating probability density function for signal points where the watermark value to be embedded. Distortion and robustness functions are formulated. Given robustness or distortion is selected. Functions optimized, and ensemble of quantizers determined with parameters that comply. Other method quantizing in association with lossy compression. Strength of compression determined. Adapting strength of watermark with strength of compression by a mapping. Other method selecting points for embedding watermark. Determine threshold between large and small signal points using statistical method. Select signal points for embedding according to threshold. Also, processors, computer programs, and systems.
Owner:ZHANG XIAO PING +1
System and methods for accelerated data storage and retrieval
InactiveUS20060184696A1Increases effective data access rateHigh bandwidthTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersData compressionData stream
Systems and methods for providing accelerated data storage and retrieval utilizing lossless and / or lossy data compression and decompression. A data storage accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data compression encoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly or lossy compress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the transmission rate of an input data stream. The compressed data is subsequently stored in a target memory or other storage device whose input data storage bandwidth is lower than the original input data stream bandwidth. Similarly, a data retrieval accelerator includes one or a plurality of high speed data decompression decoders that are configured to simultaneously or sequentially losslessly or lossy decompress data at a rate equivalent to or faster than the input data stream from the target memory or storage device. The decompressed data is then output at rate data that is greater than the output rate from the target memory or data storage device. The data storage and retrieval accelerator method and system may employed: in a disk storage adapter to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from computer to disk; in conjunction with random access memory to reduce the time required to store and retrieve data from random access memory; in a display controller to reduce the time required to send display data to the display controller or processor; and / or in an input / output controller to reduce the time required to store, retrieve, or transmit data.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
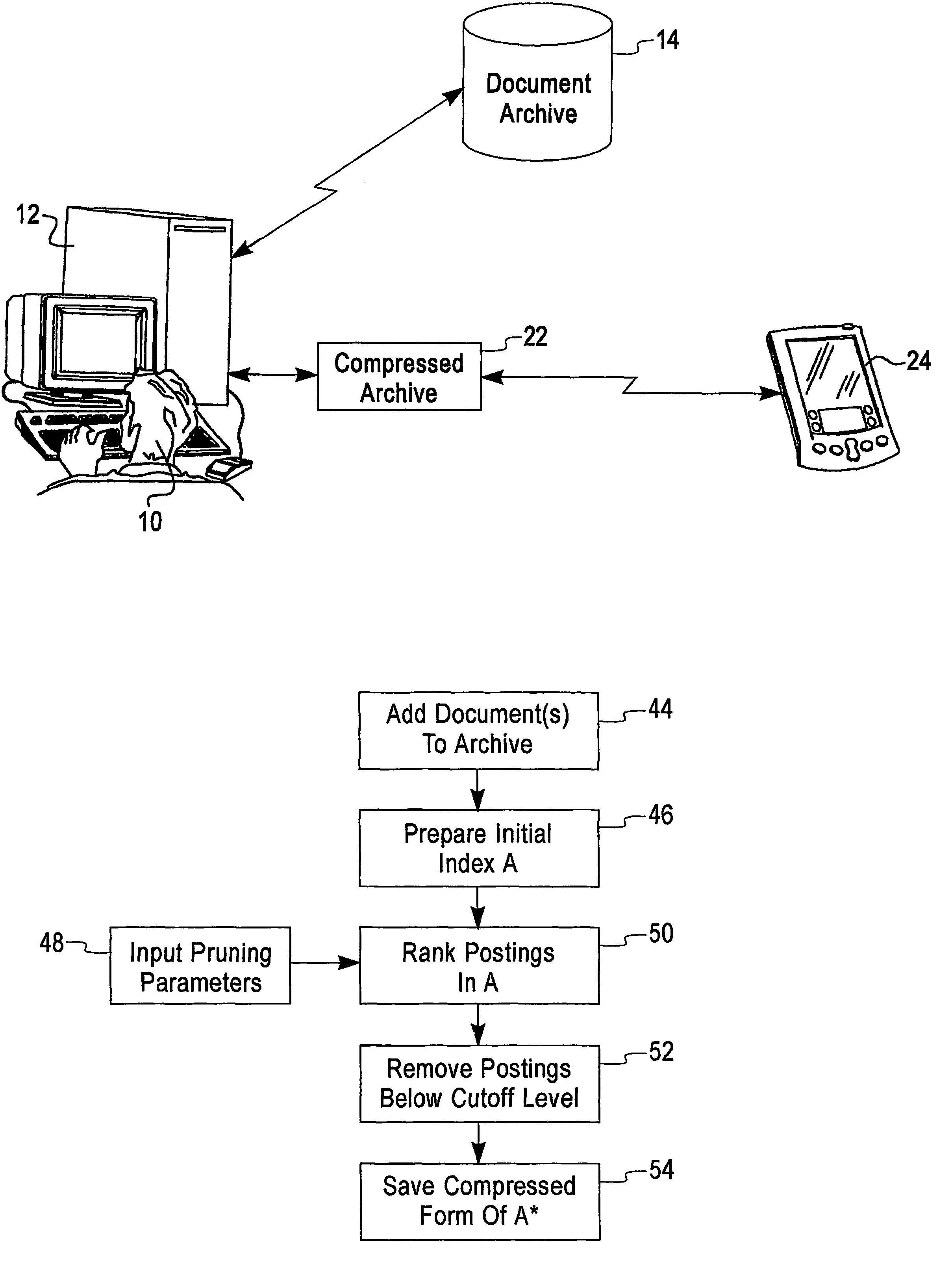
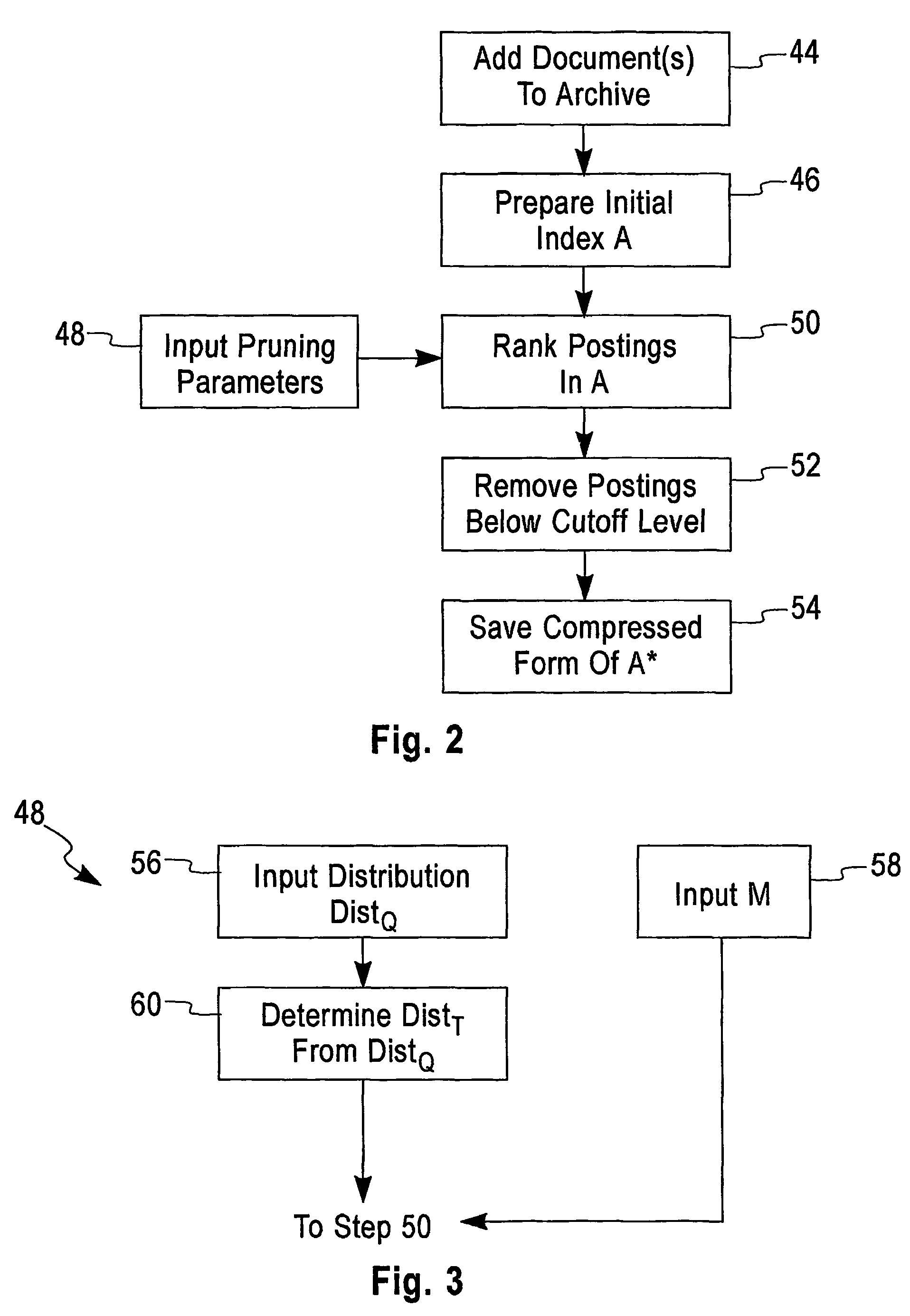
Lossy index compression
InactiveUS7356527B2Small sizeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRankingIndex compression
An apparatus and method is provided for pruning an index of a corpus of text documents by creating an inverted index of terms appearing in the documents, wherein the index includes postings of the terms in the documents, ranking the postings in the index, and pruning from the index the postings below a given level in the ranking.
Owner:IBM CORP
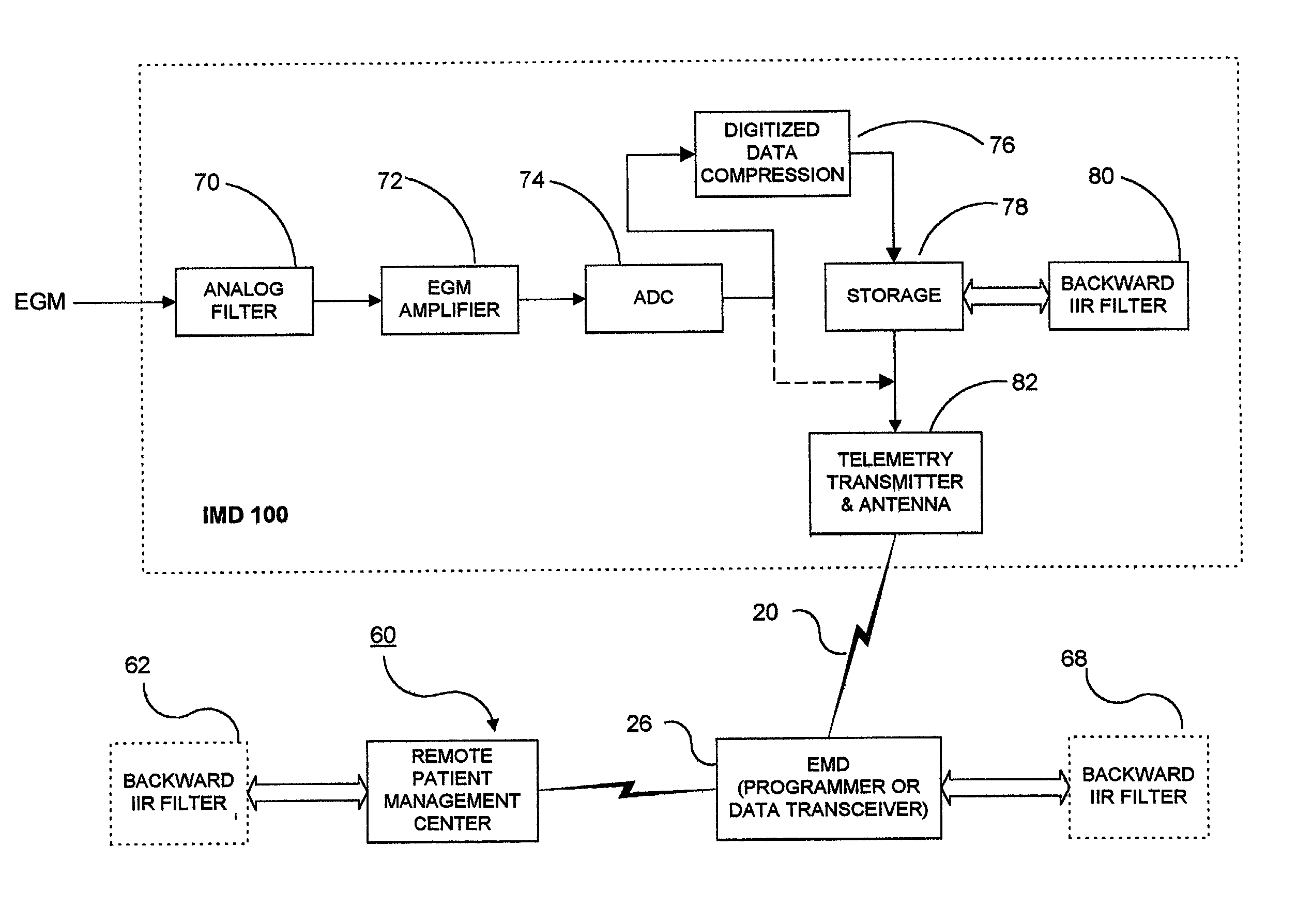
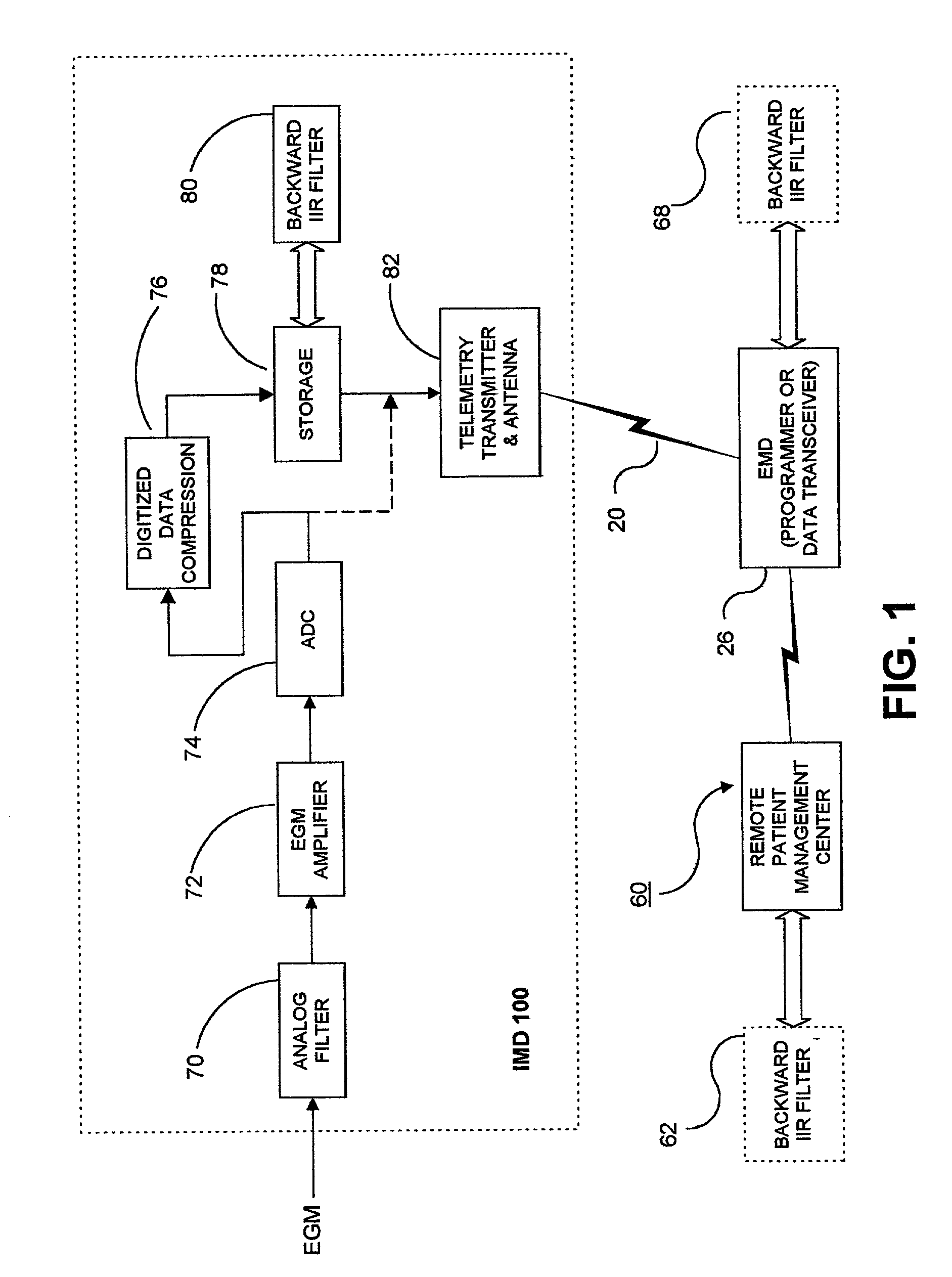
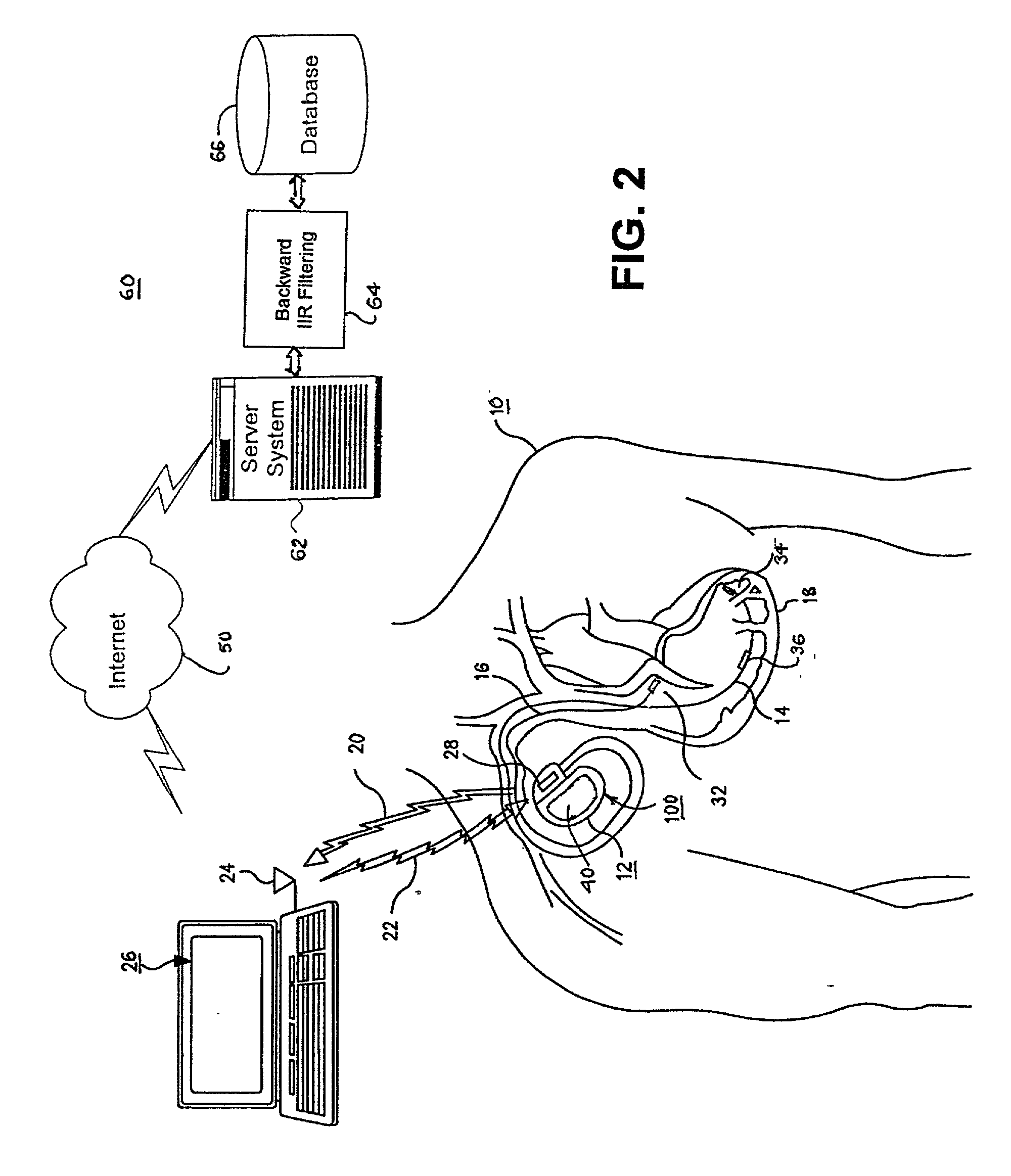
Methods and apparatus for filtering EGM signals detected by an implantable medical device
An analog physiologic signal, e.g., the cardiac EGM, sensed by an IMD is filtered with a high pass filter (HPF), the cut-off frequency of the HPF being within a predetermined frequency bandwidth, wherein a low-band portion of the predetermined frequency bandwidth is attenuated in the filtered physiologic signal. The filtered physiologic signal is digitized in real time order, and the digital data set is filtered in reverse time order employing a digital IIR filter having characteristics substantially matching the cut-off frequency and filter characteristics of the HPF. When the system is implemented within an IMD, the filtered digital data set is compressed by lossy compression algorithm, and the compressed data set is filtered in reverse time order. In certain embodiments, the filtered digital data set is uplink telemetry transmitted to an external medical device, and the uplink telemetered data set is filtered in reverse time order employing a digital backward IIR filter resident in the external medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
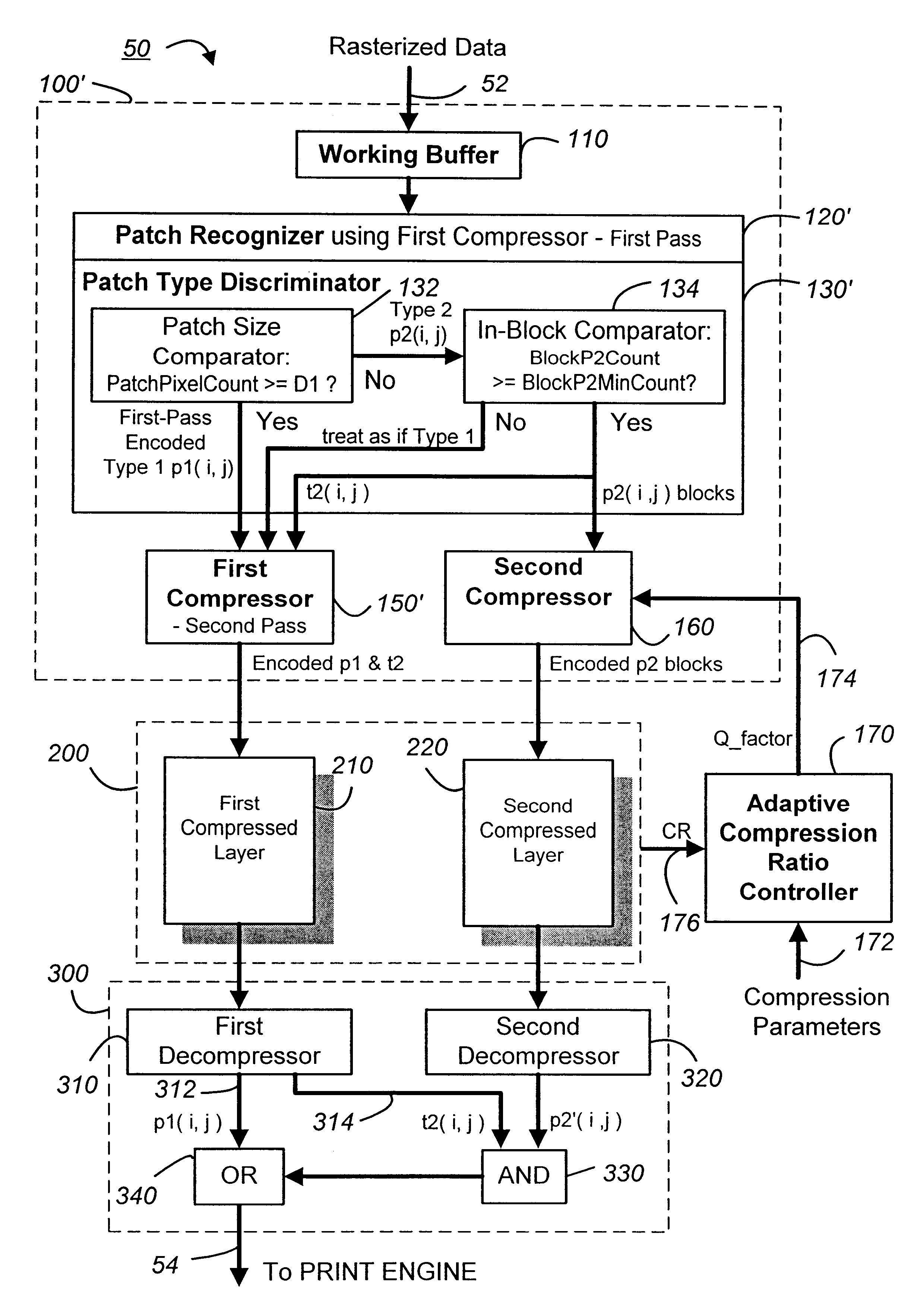
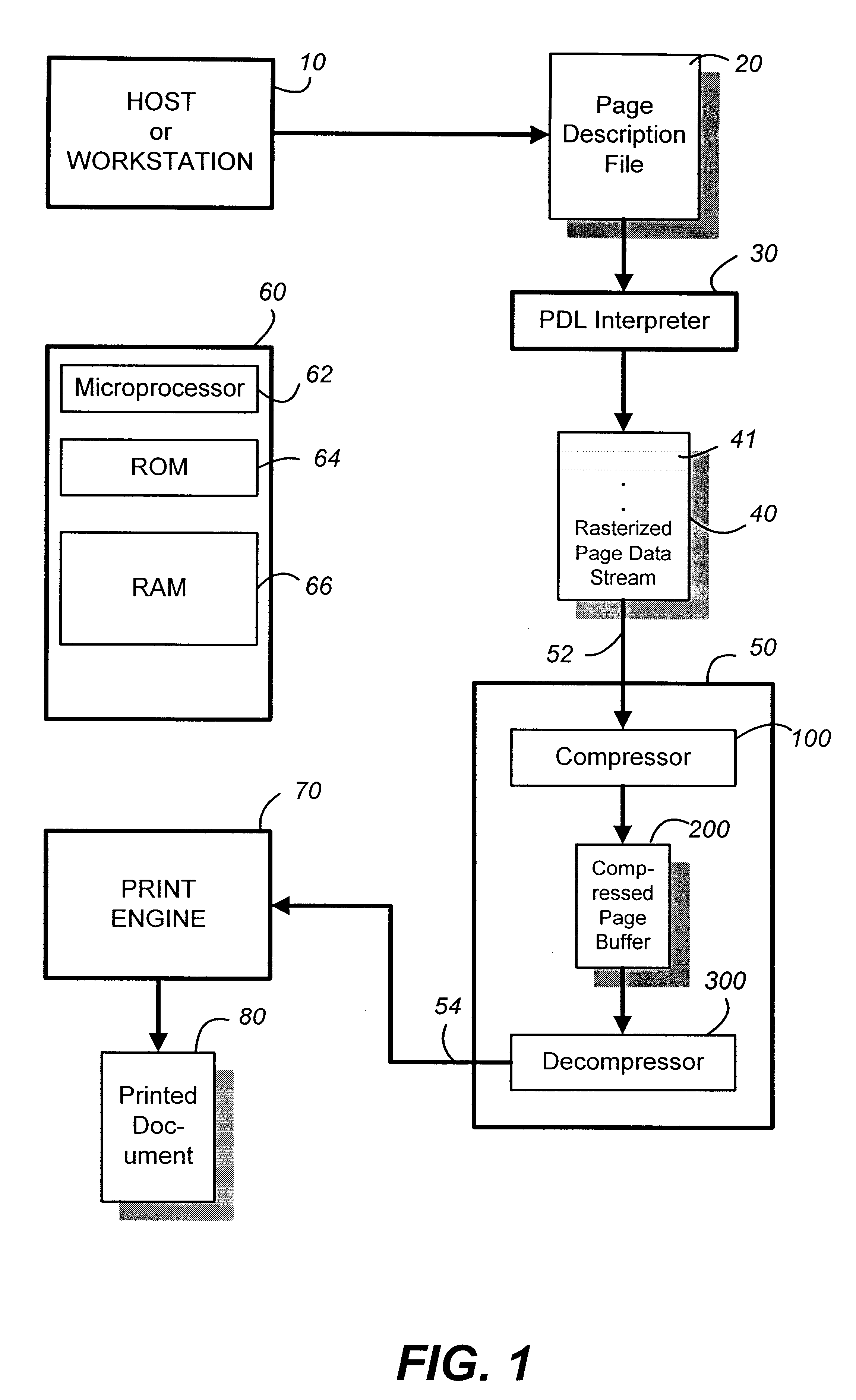
Apparatus and method for hybrid compression and decompression of raster data
InactiveUS6330363B1Reduce dataEasy to compressImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAdaptive compression
From a raster page, patches of connected pixels of the same color are identified. Patches of at least a predetermined sized, typically corresponding to text or line art objects, are subjected to a lossless compression. Patches below the predetermined size, typically corresponding to image or photo objects, are substantially subjected to a lossy compression. The patch predetermined size controls the mix of lossless and lossy compression procedures. Optimum compression is achieved by maximizing the lossless compression while attaining a targeted compression ratio. Various features include efficient recognition and encoding of patches, refined treatment of the boundaries between the lossless- and the lossy-compressed pixels, adaptive compression ratio control, and fail-safe compression provisions.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING INC
Methods and means for image and voice compression
A system for lossy compression of digital data for transmission to a remote location or to a storage medium and subsequently reconstructing the digital data includes an encoder which compares sequences of characters with an encoder database of data records to generate a compressed code. The compressed code includes pointer information relating to locations within the encoder database of data records corresponding within a given average distortion tolerance level per character to the sequences, and update information for the addition to the encoder database of new data records corresponding within the average distortion tolerance level per character to the sequences. The system also includes a decoder for receiving the compressed code, the receiver processing the compressed code to substantially reconstruct the digital data.
Owner:AMSTR INVESTMENTS 2 K G
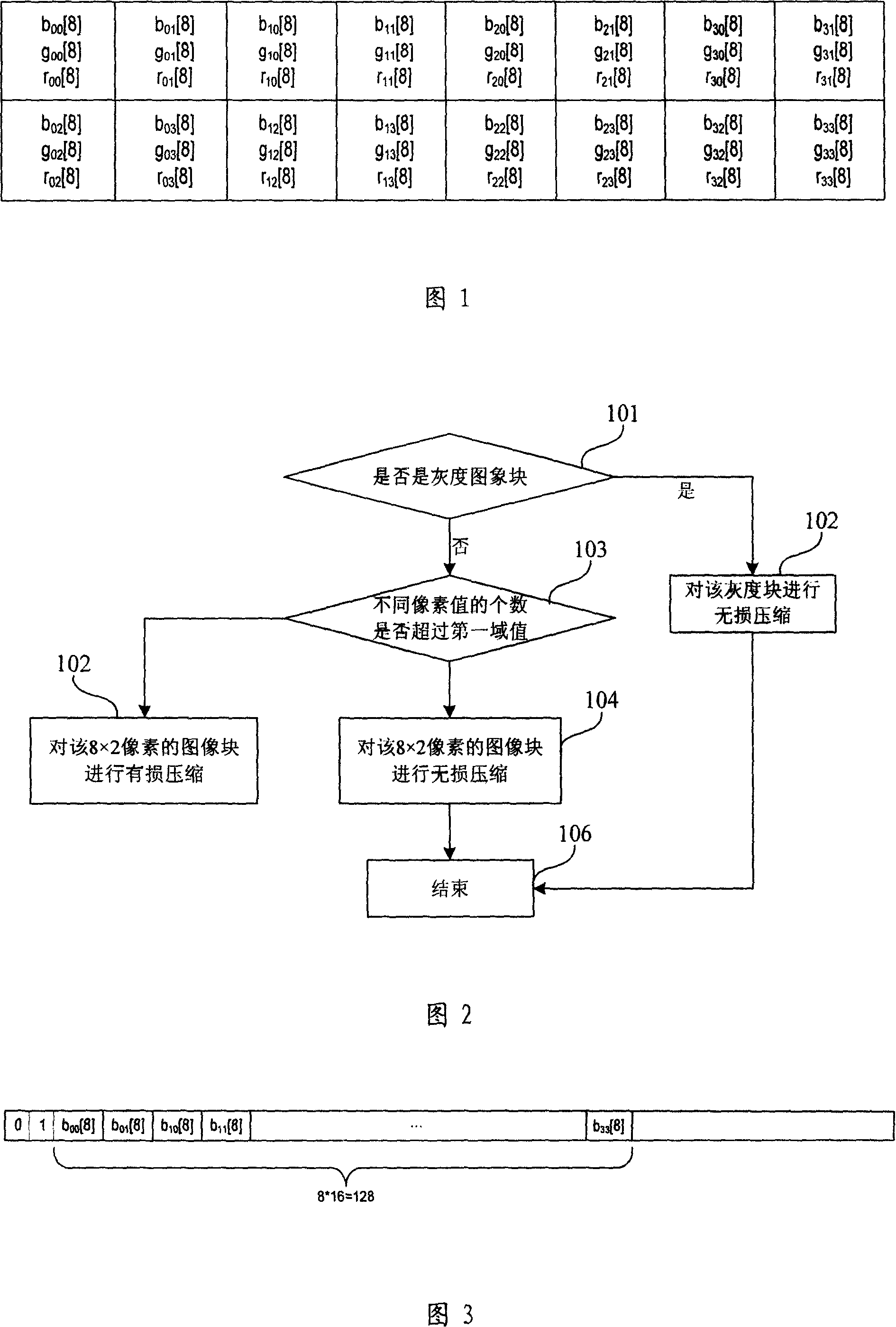
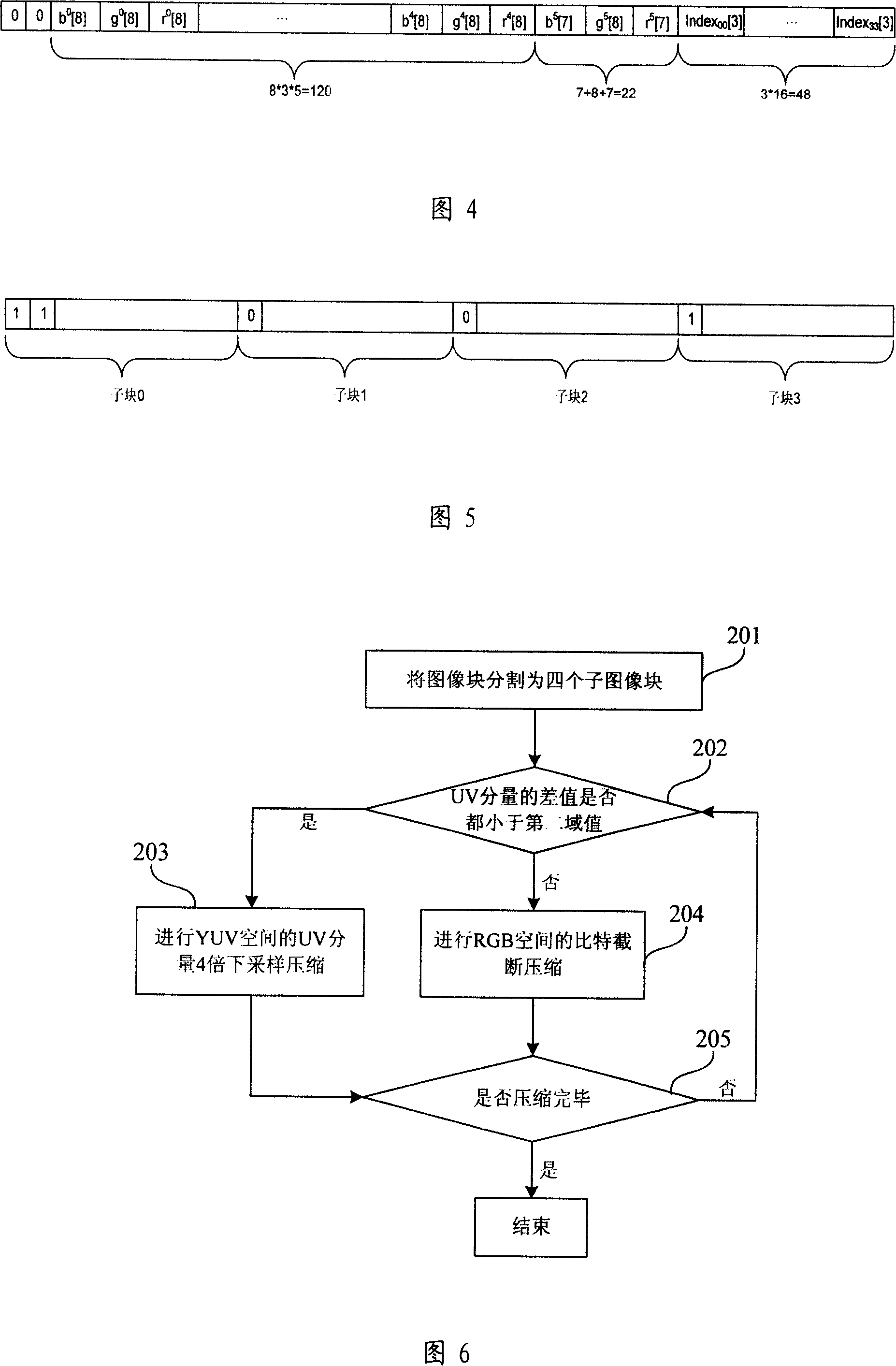
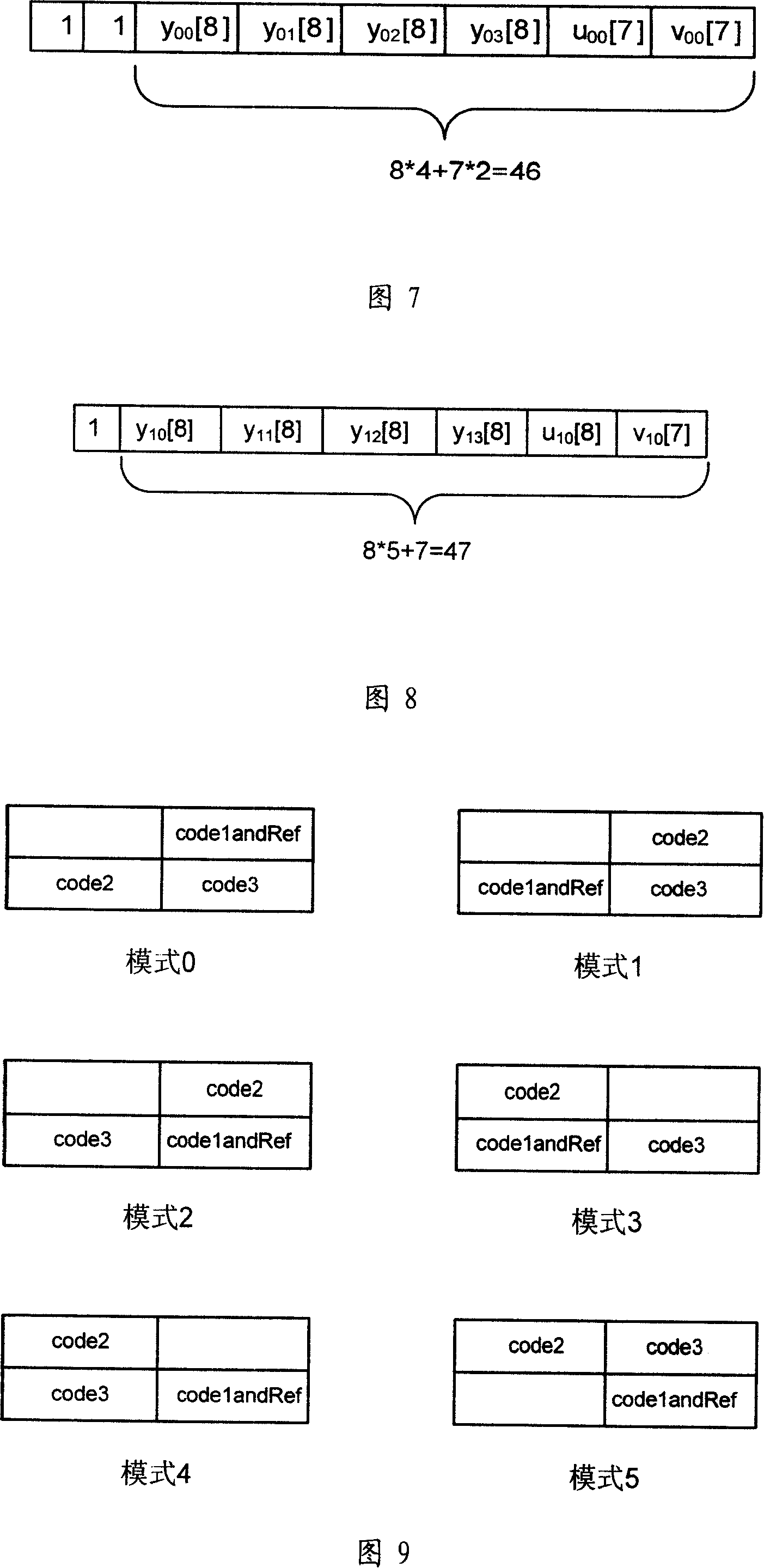
Image compression method
ActiveCN101106709AGood image compressionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage compressionLossless compression
The invention relates to an image compression method, including the following steps: step (1), conduct gray scale detection on image blocks separated from the original image data, if gray image block, then execute step (2); otherwise execute step (3); step (2), conduct lossless compression on the gray image block, and execute step (6); step (3), calculate the number of different pixel values in the image block, if the number of different pixel values in the image block doesn't exceed the first threshold value, then execute step (4), if the number of different pixel values in the image block exceeds the first threshold value, then execute step (5); step (4), conduct lossless compression on the image block, and execute step (6); step (5), conduct lossy compression on the image block, and execute step (6); step (6), end. Therefore, the image compression method in the invention can self-adapt to adopting different compression methods based on difference of image contents, and use less resource to realize high quality image compression.
Owner:逐点半导体(上海)股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com