Patents
Literature
3291 results about "High-pass filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
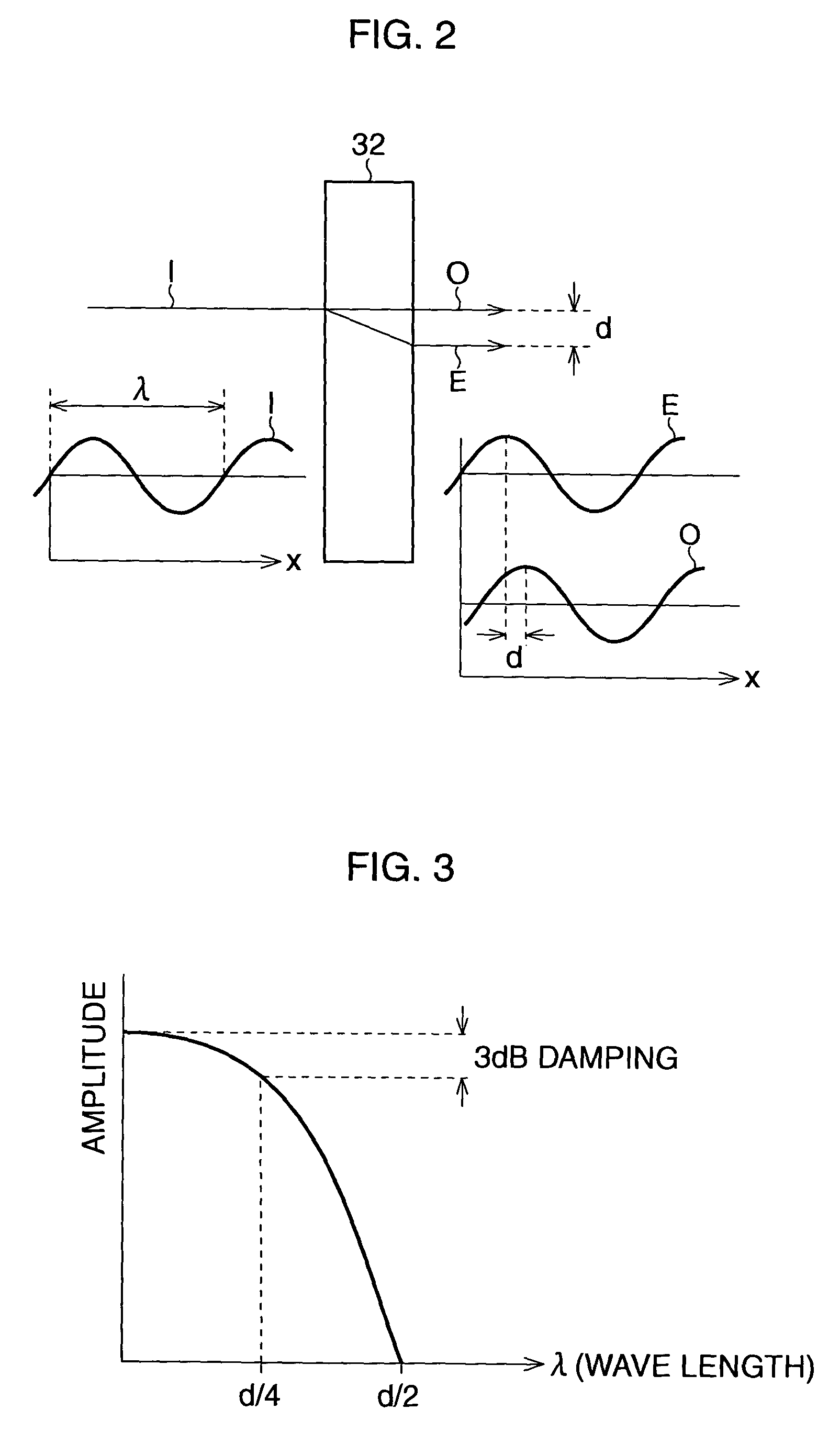
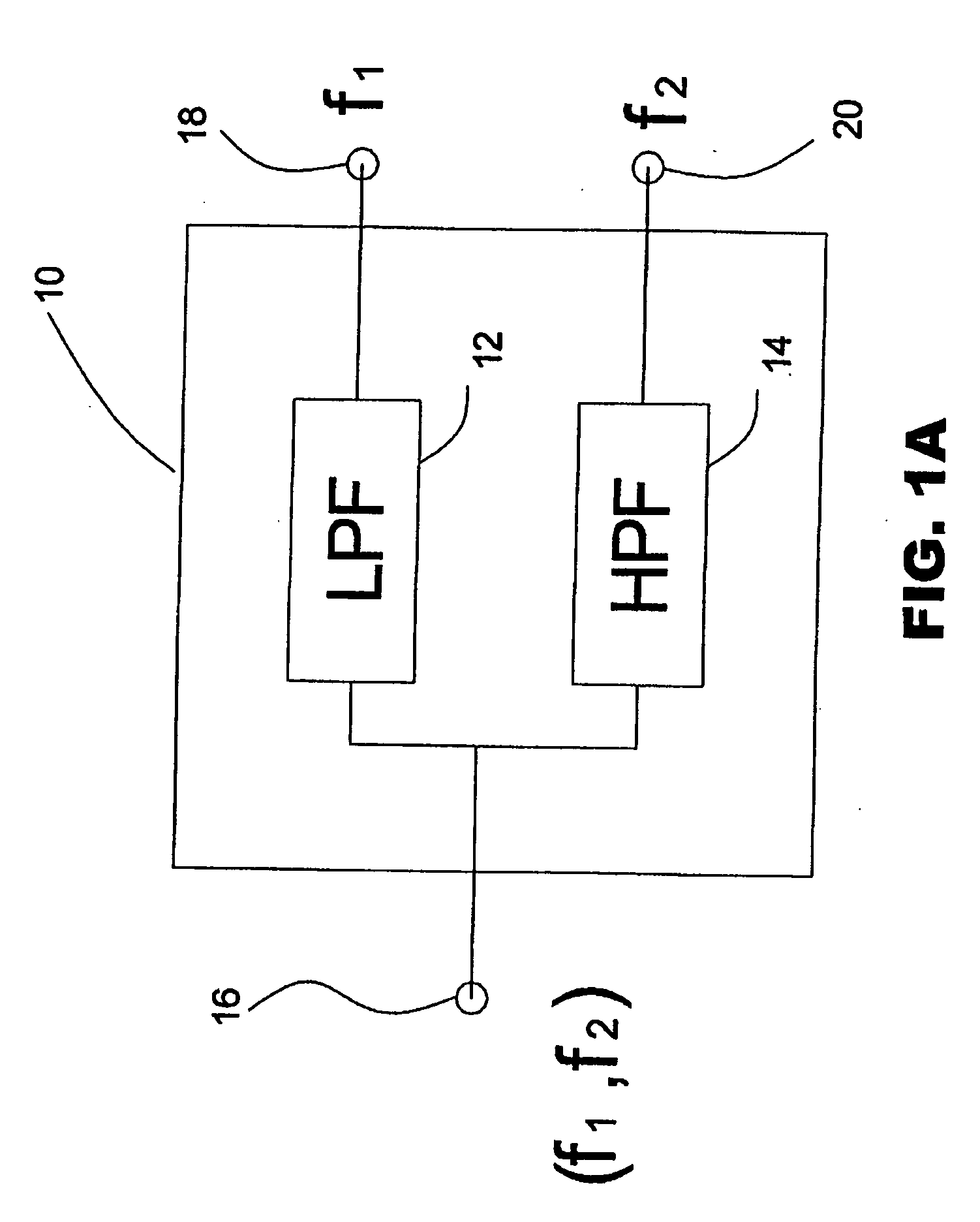
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter that passes signals with a frequency higher than a certain cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. The amount of attenuation for each frequency depends on the filter design. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system. It is sometimes called a low-cut filter or bass-cut filter. High-pass filters have many uses, such as blocking DC from circuitry sensitive to non-zero average voltages or radio frequency devices. They can also be used in conjunction with a low-pass filter to produce a bandpass filter.
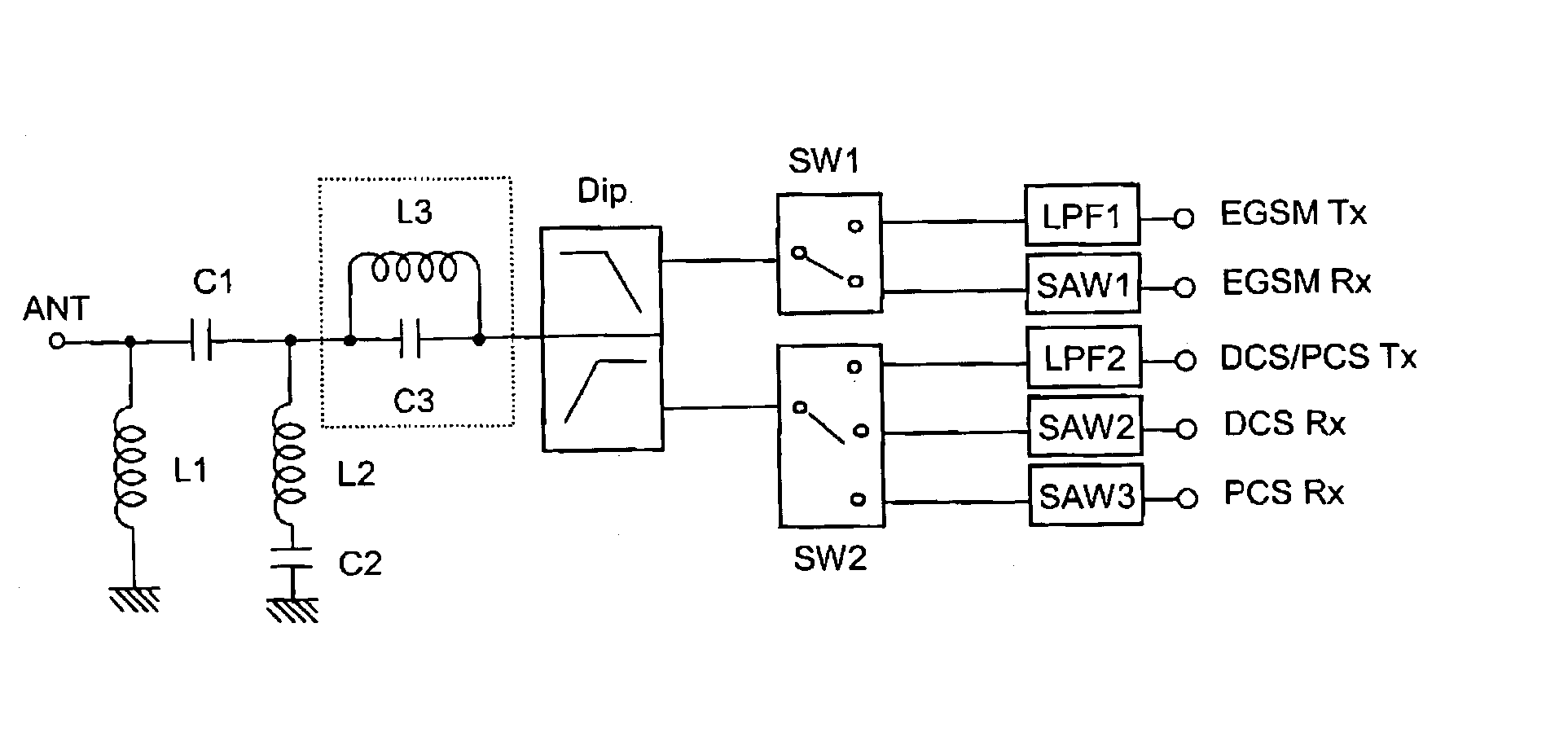
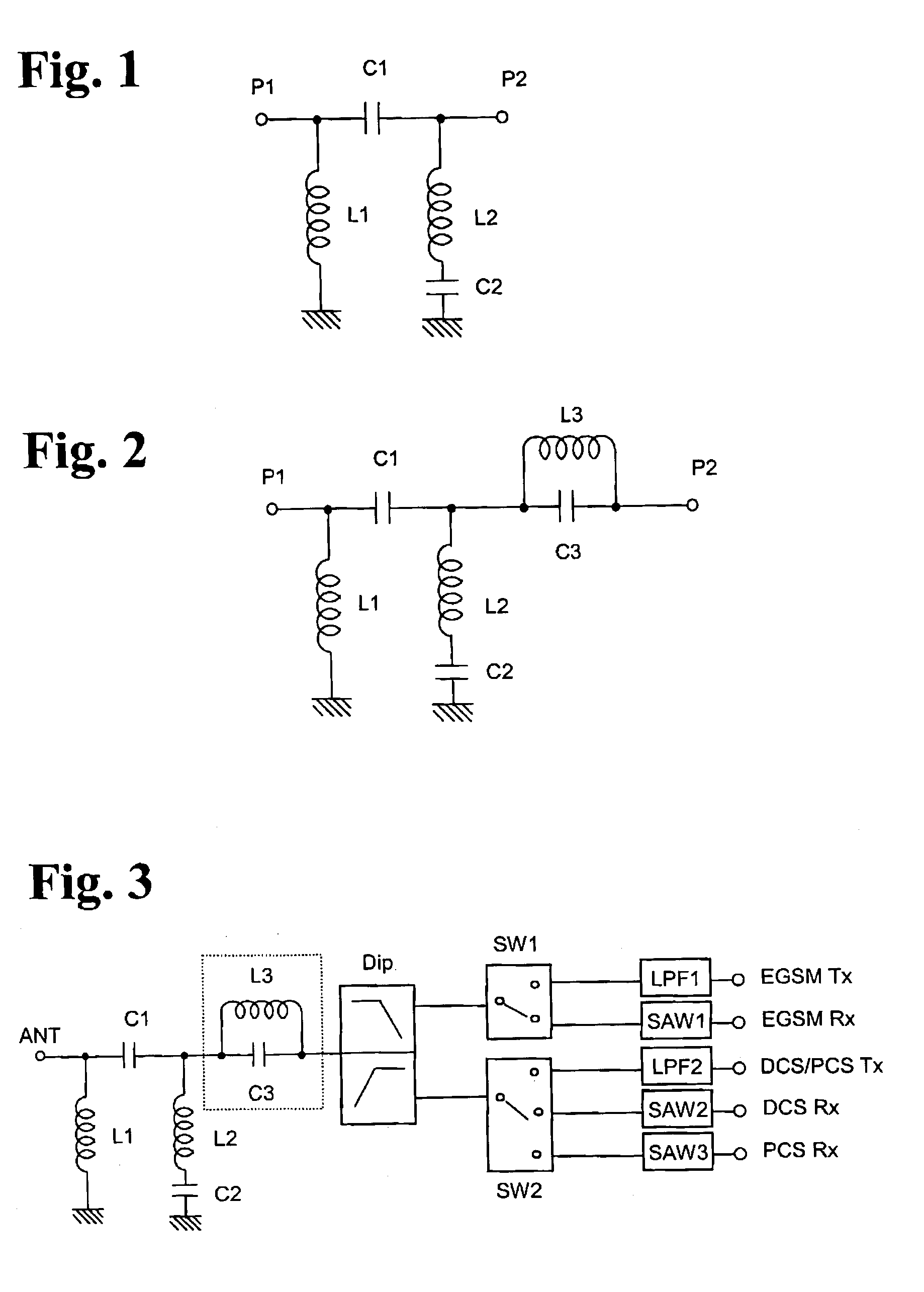
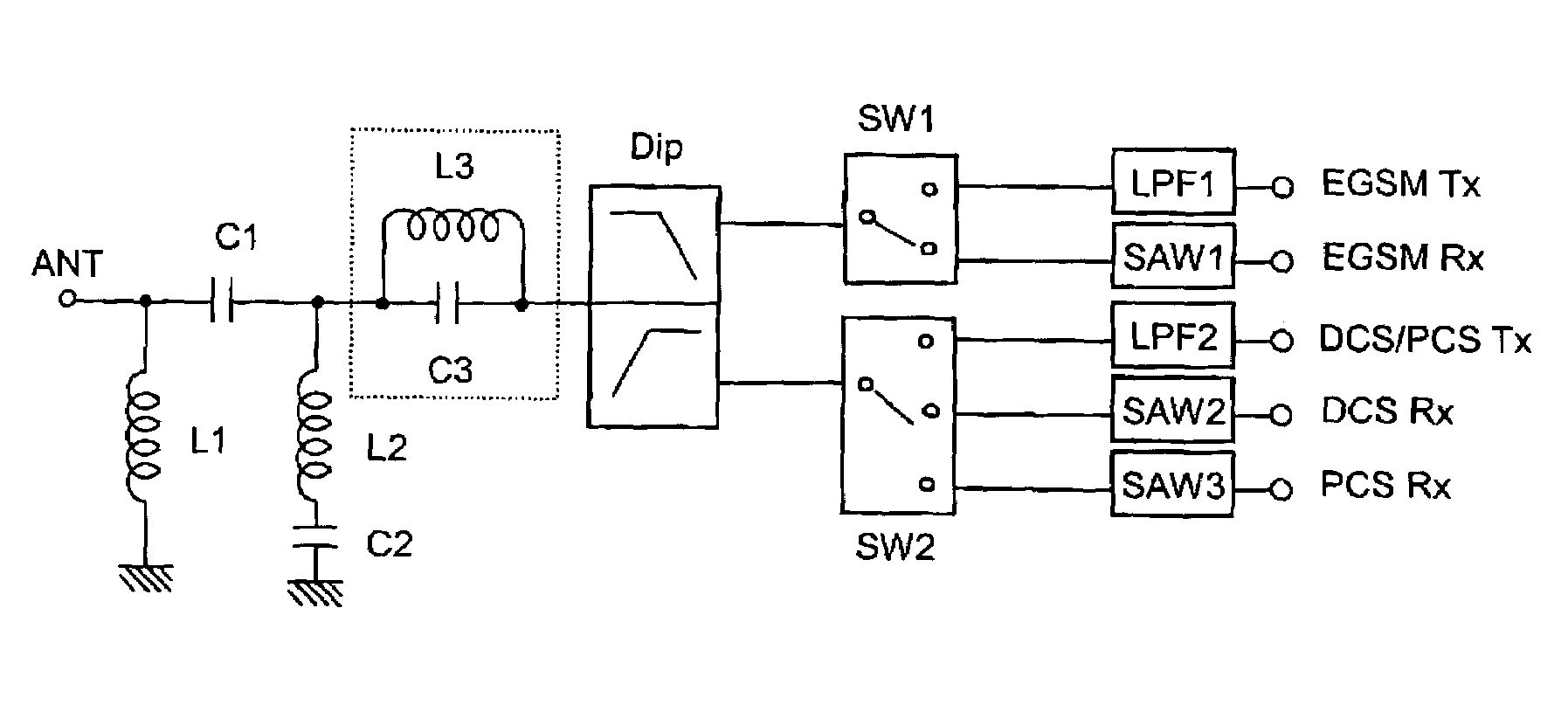
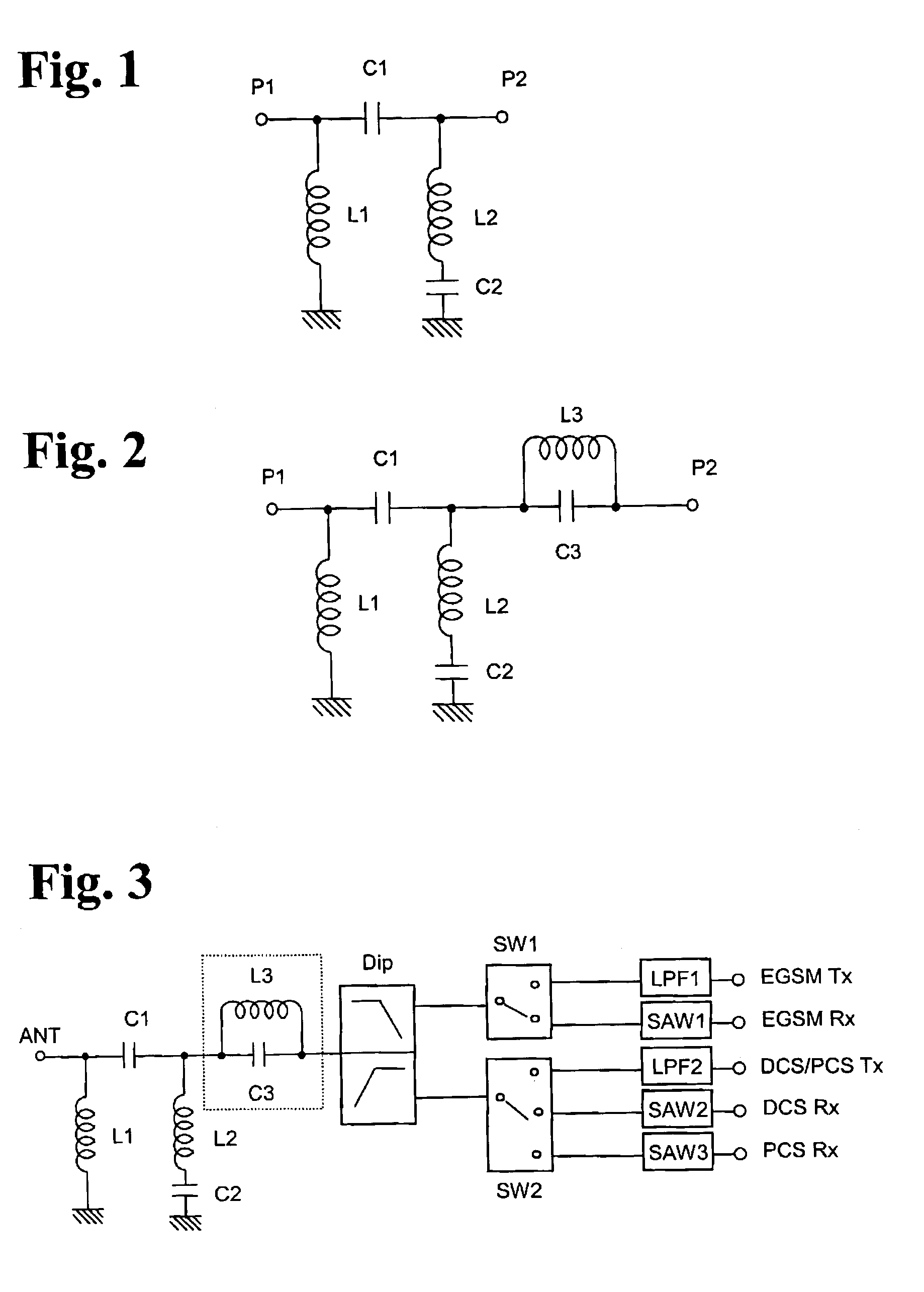
Bypass filter, multi-band antenna switch circuit, and layered module composite part and communication device using them
InactiveUS20040266378A1Add partsImprove matchMultiple-port networksRadio transmissionMulti bandEngineering
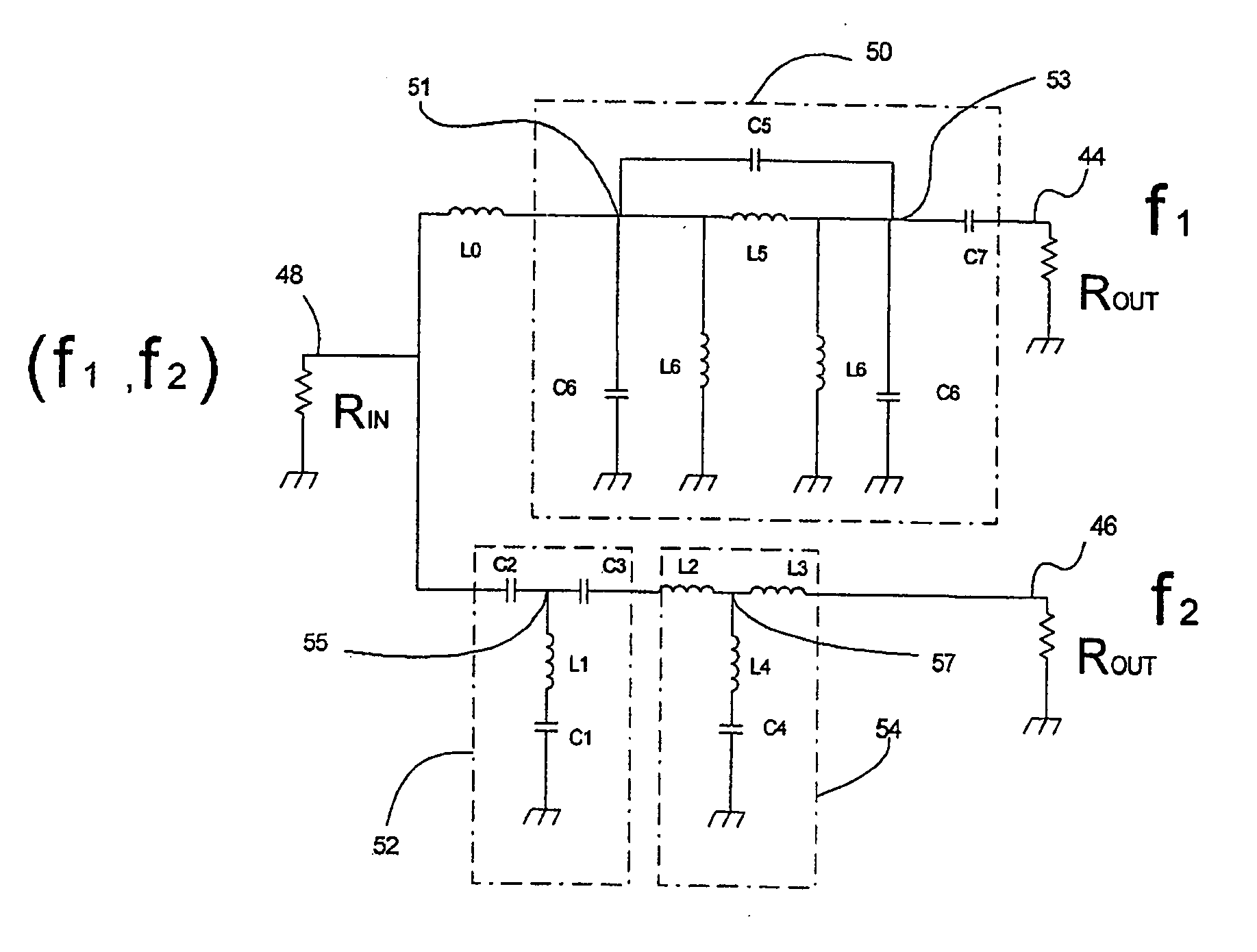
A multi-band antenna switch circuit including a diplexer connected to an antenna terminal for demultiplexing signals of different passing bands, a first and a second switch circuit for switching a high frequency signal and a low frequency signal demultiplexed by the diplexer to a plurality of transmission / reception terminals, a first and a second low pass filter connected to a transmission path between the diplexer and the transmission terminal or between the first and the second switch circuit and the transmission terminal, and a notch filter provided between the diplexer and the first switch circuit or between the diplexer and the second switch circuit. The multi-band antenna switch circuit includes a high pass filter having an input terminal and an output terminal and provided at least between die diplexer and the antenna terminal and including a first inductor connected between the input terminal and the ground, a first capacitor connected between the input terminal and the output terminal, a second inductor connected to the output terminal, and a second capacitor connected between the second inductor and the ground.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Bypass filter, multi-band antenna switch circuit, and layered module composite part and communication device using them
A multi-band antenna switch circuit including a diplexer connected to an antenna terminal for demultiplexing signals of different passing bands, a first and a second switch circuit for switching a high frequency signal and a low frequency signal demultiplexed by the diplexer to a plurality of transmission / reception terminals, a first and a second low pass filter connected to a transmission path between the diplexer and the transmission terminal or between the first and the second switch circuit and the transmission terminal, and a notch filter provided between the diplexer and the first switch circuit or between the diplexer and the second switch circuit. The multi-band antenna switch circuit includes a high pass filter having an input terminal and an output terminal and provided at least between die diplexer and the antenna terminal and including a first inductor connected between the input terminal and the ground, a first capacitor connected between the input terminal and the output terminal, a second inductor connected to the output terminal, and a second capacitor connected between the second inductor and the ground.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
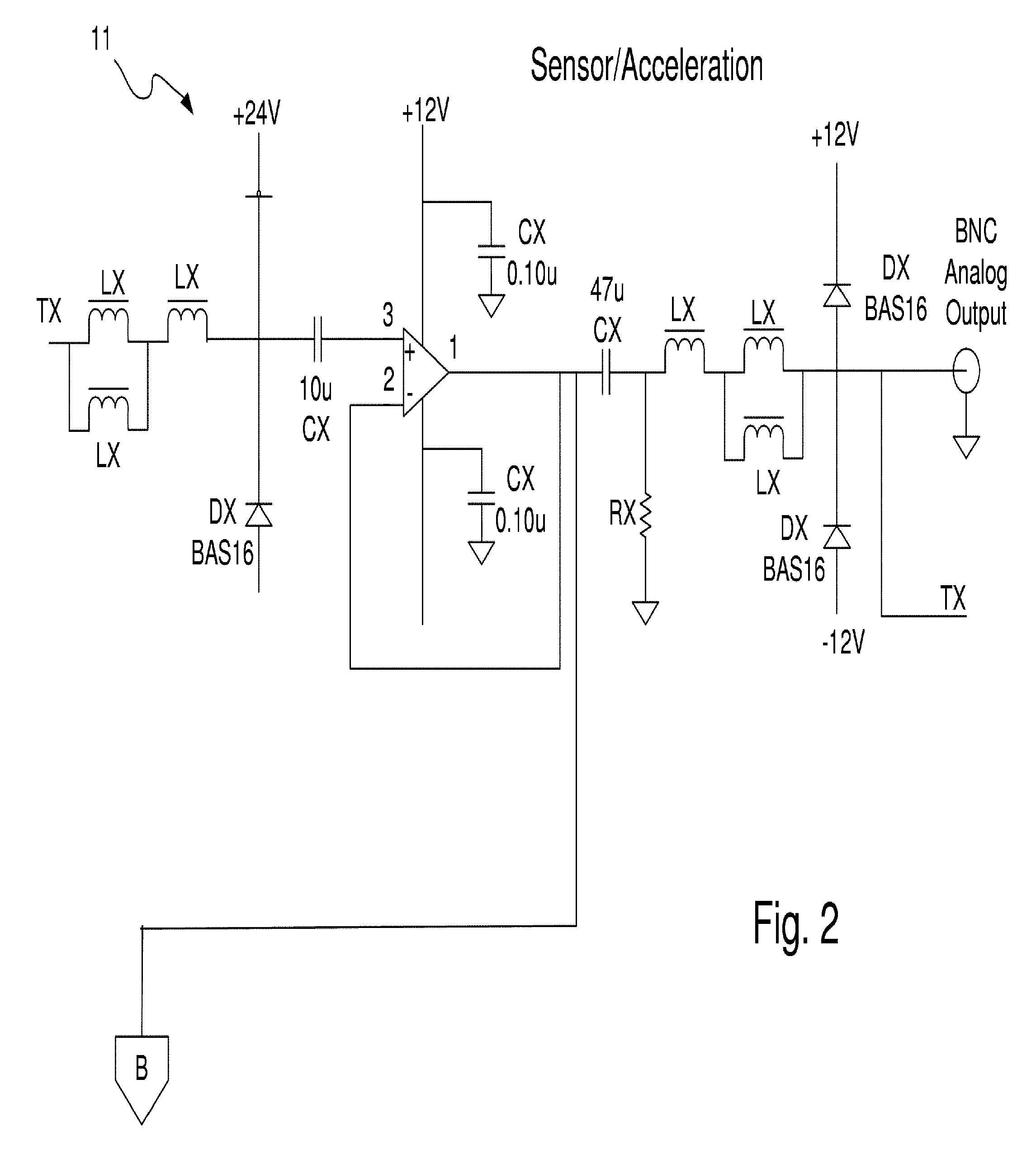
Method and apparatus for vibration sensing and analysis
InactiveUS20050011266A1Readily apparentVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingPeak valueAcoustics
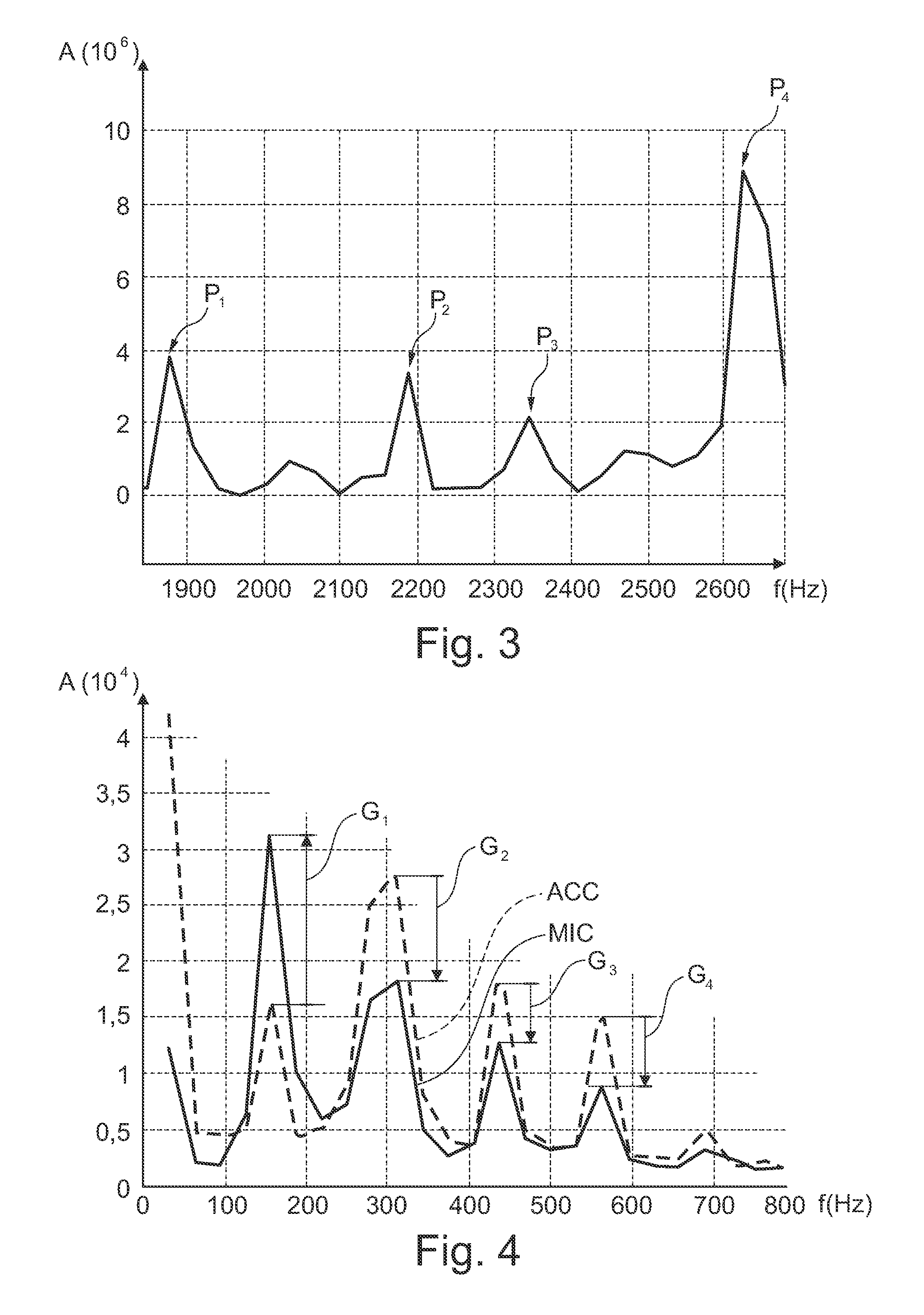
A method and apparatus for sensing and measuring stress waves. The method comprises the steps of: a.) sensing motion, where the motion comprises a stress wave component and a vibration component; b.) separating the stress wave component from the vibration component with a high pass filter to create a signal proportional to the stress wave; c.) amplifying the signal to create an amplified signal; d.) processing the amplified signal with a sample and hold peak detector over a predetermined interval of time to determine peaks of the amplified signal over said predetermined period of time; e.) creating an output signal proportional to the determined peaks of the amplified signal; and, f.) repeating steps d.) and e.). The invention also includes an apparatus for implementing the method of the invention.
Owner:PCB PIEZOTRONICS IMI SENSORS +1
Low frequency noise reduction circuit architecture for communications applications
ActiveUS20080069373A1Economical yet effective high-pass filterAchieve adaptiveFrequency response correctionTransmission noise suppressionCapacitanceLow noise
A noise reduction circuit for reducing the effects of low frequency noise such as wind noise in communications applications is described. In one embodiment, the noise reduction circuit features a high pass filter formed by exploiting the existing off-chip AC coupling capacitances in making the connection to the source of audio signals. The filter may be adaptive to environmental low frequency noise level through programming the shunt resistances. A low-noise wide dynamic range programmable gain amplifier is also described. Adaptive equalization of the audio signal is also described through the utilization of programmable front-end resistors and a back-end audio equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Implementing a hybrid wireless and coaxial cable network
InactiveUS20050034159A1Miniaturized installationIncrease data rateBroadband local area networksClosed circuit television systemsCoaxial cableVideo processing
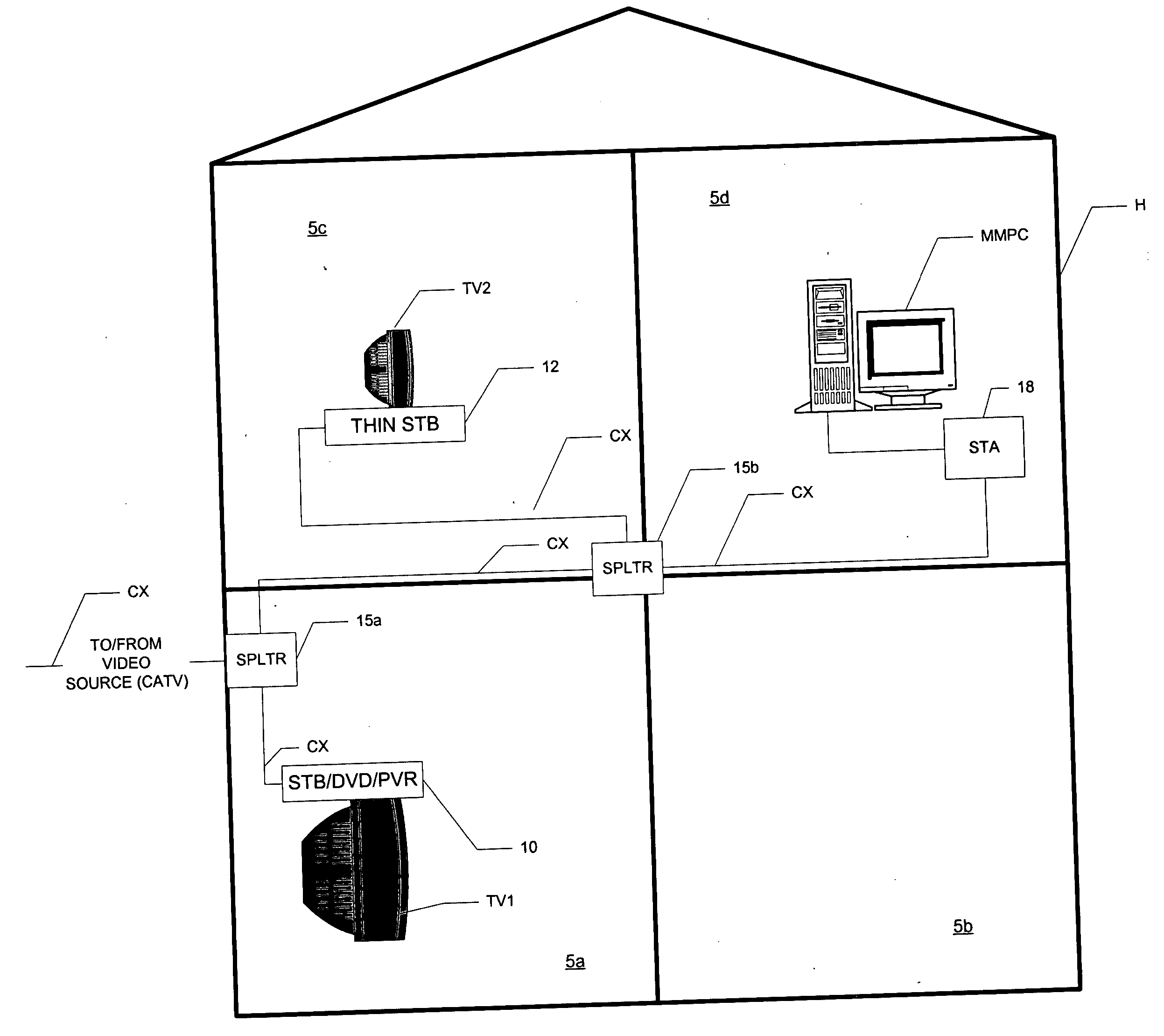
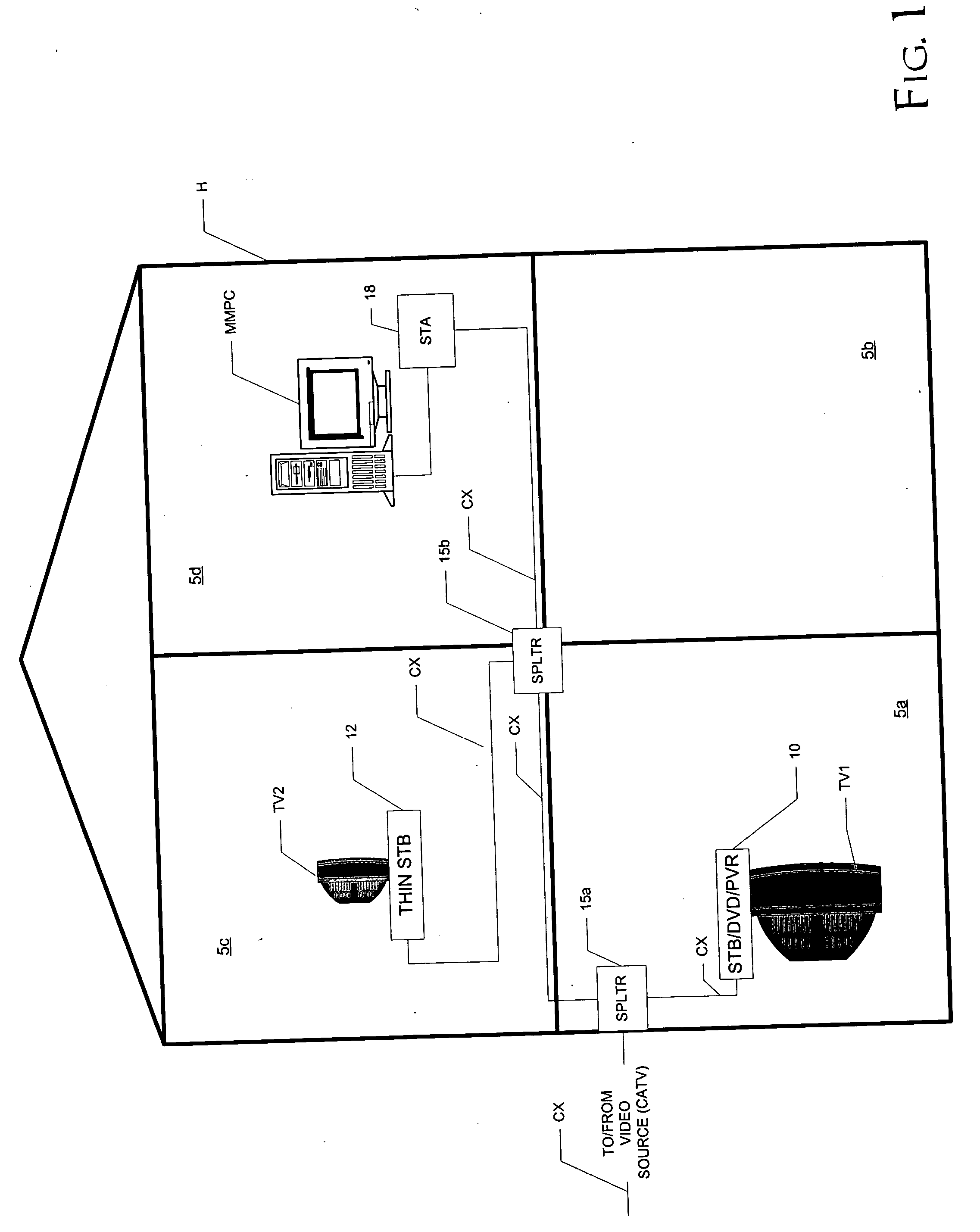
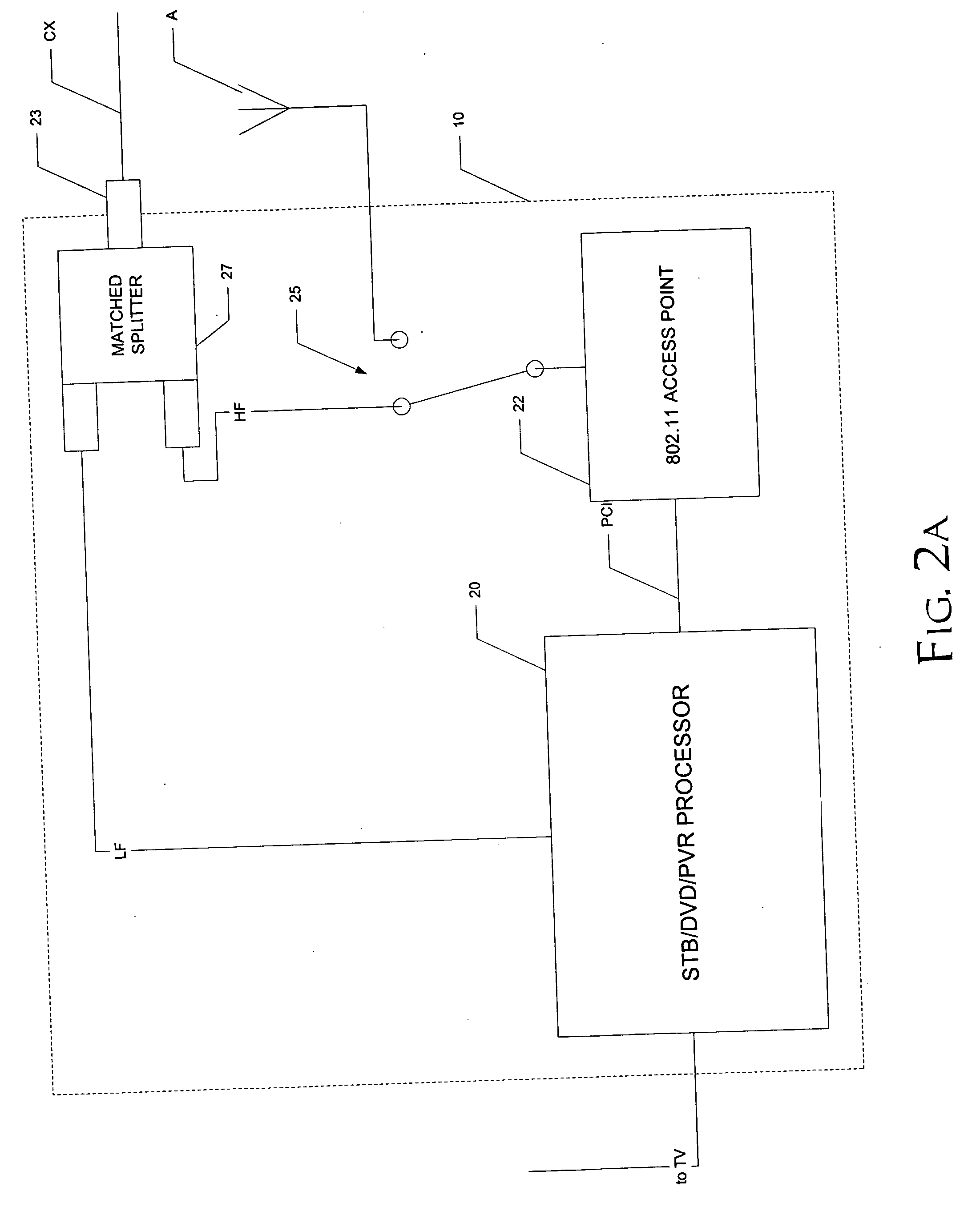
A home video network, and a home video and data network, utilizing wireless protocol communications over coaxial cable (CX) are disclosed. In the home video network, a main network station (10) includes video processing functionality, such as one or more of a DVD player, personal video recorder (PVR), and a set-top box (STB) for cable or satellite television reception. The main network station (10) also includes a matched splitter (27) that receives coaxial cable (CX) inputs, and provides low-pass filtered and high-pass filtered output. The low-pass filtered output (LF) corresponding to video signals is provided to the video processing functionality (20) and the high-pass filtered output (HF) corresponding to wireless protocol communications is provided to a wireless access point function (22). Other network stations and combinations of functions are also disclosed, including those that utilize a function switch (25) to switch between network communications over coaxial cable (CX) and communications over an antenna (A), in either a single BSS mode or a double BSS mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Vibration compensation method for single-rotor compressor and controller
ActiveCN103967794AReduce vibrationImprove noiseRotary/oscillating piston pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsVibration compensationHigh-pass filter
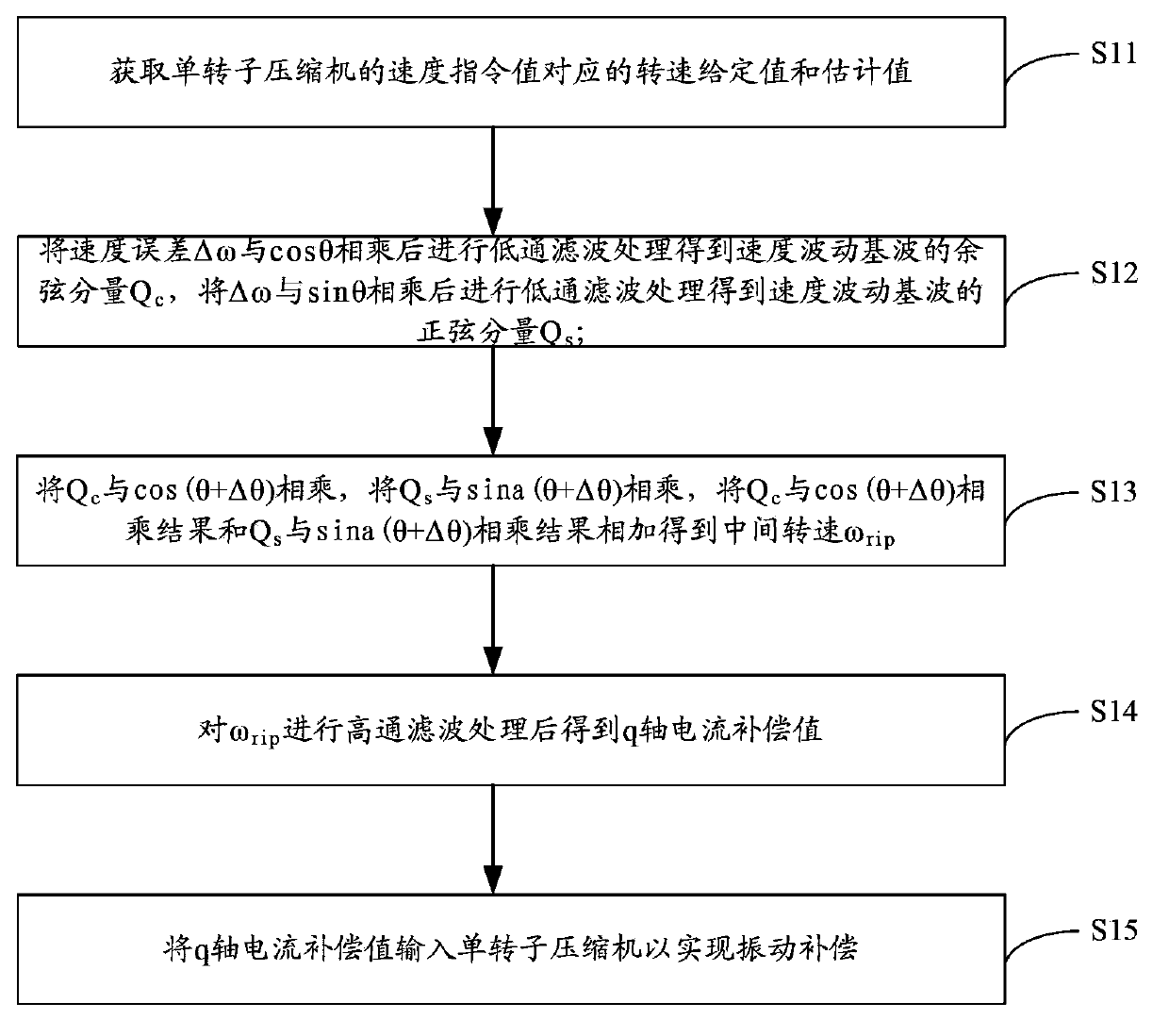
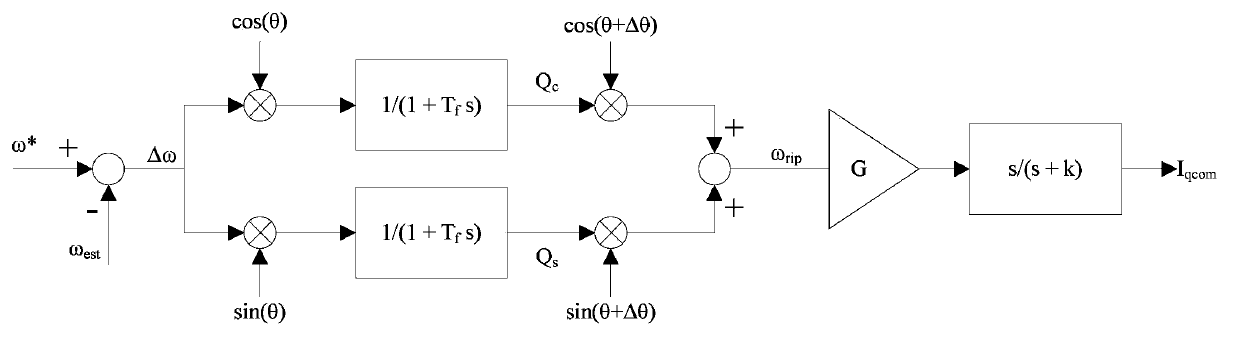
The invention is applicable to the technical field of household electrical appliances and provides a vibration compensation method for a single-rotor compressor and a controller. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a rotating speed set value omega* and a rotating speed estimated value omega e corresponding to a speed command value; multiplying a speed error delta omega by cos theta, carrying out low pass filtering so as to obtain the cosine component Qc of a speed fluctuation fundamental wave, multiplying delta omega by sin theta and carrying out low pass filtering so as to obtain the sine component Qs of the speed fluctuation fundamental wave; multiplying Qc by cos (theta+delta theta), multiplying Qs by sin (theta+delta theta) and adding the result of multiplication of Qc by cos (theta+delta theta) and the result of multiplication of Qs by sin (theta+delta theta) together so as to obtain an intermediate rotating speed omega rip; subjecting omega rip to high pass filtering so as to obtain a q-shaft current compensation value; and inputting the q-shaft current compensation value into the single-rotor compressor to realize vibration compensation. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the advantages of reduction in vibration of the single-rotor compressor and easy realization are obtained.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD
TV and data cable system ingress noise blocker
InactiveUS6094211APrevents loss of picture qualityLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal qualityModem device
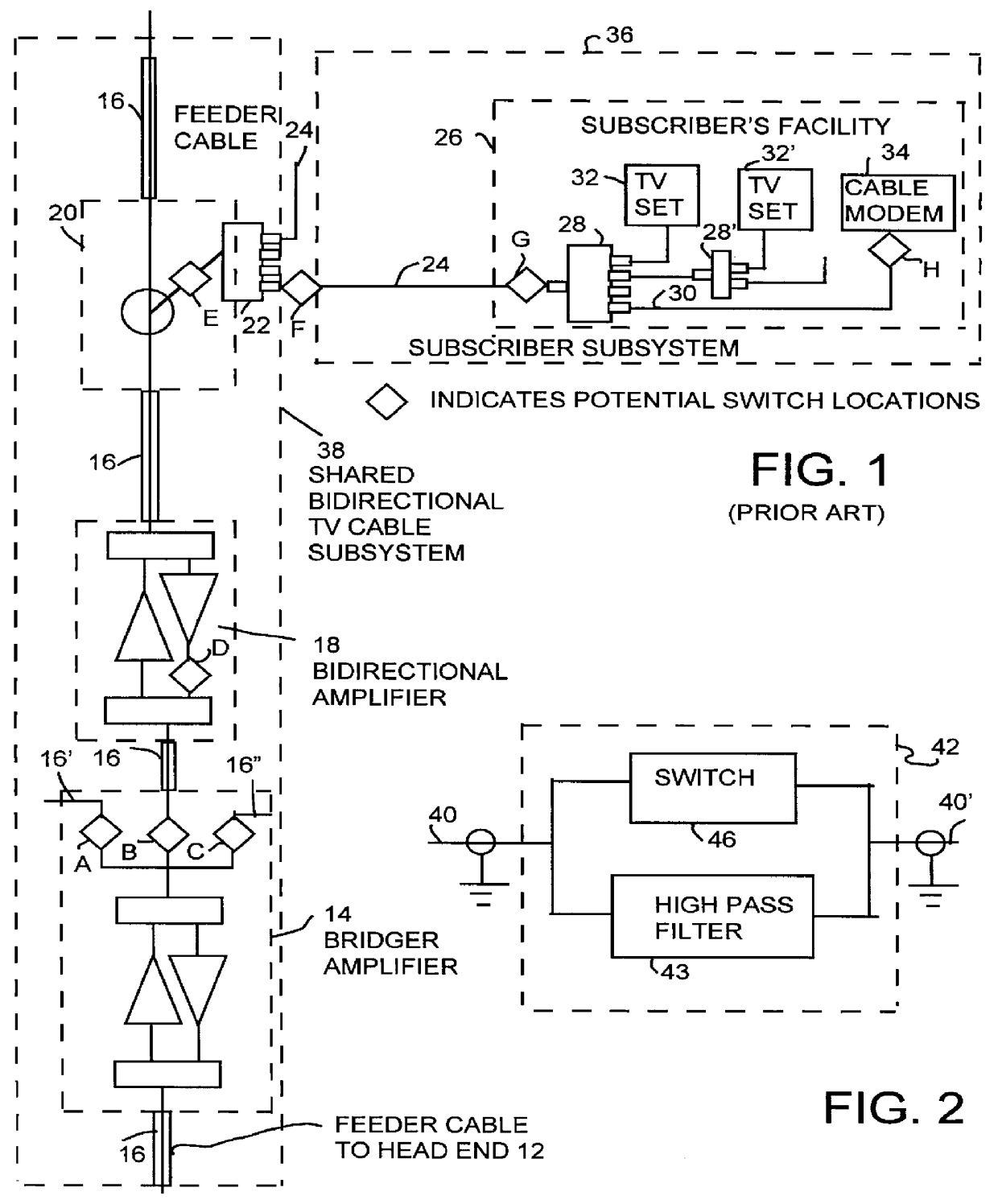
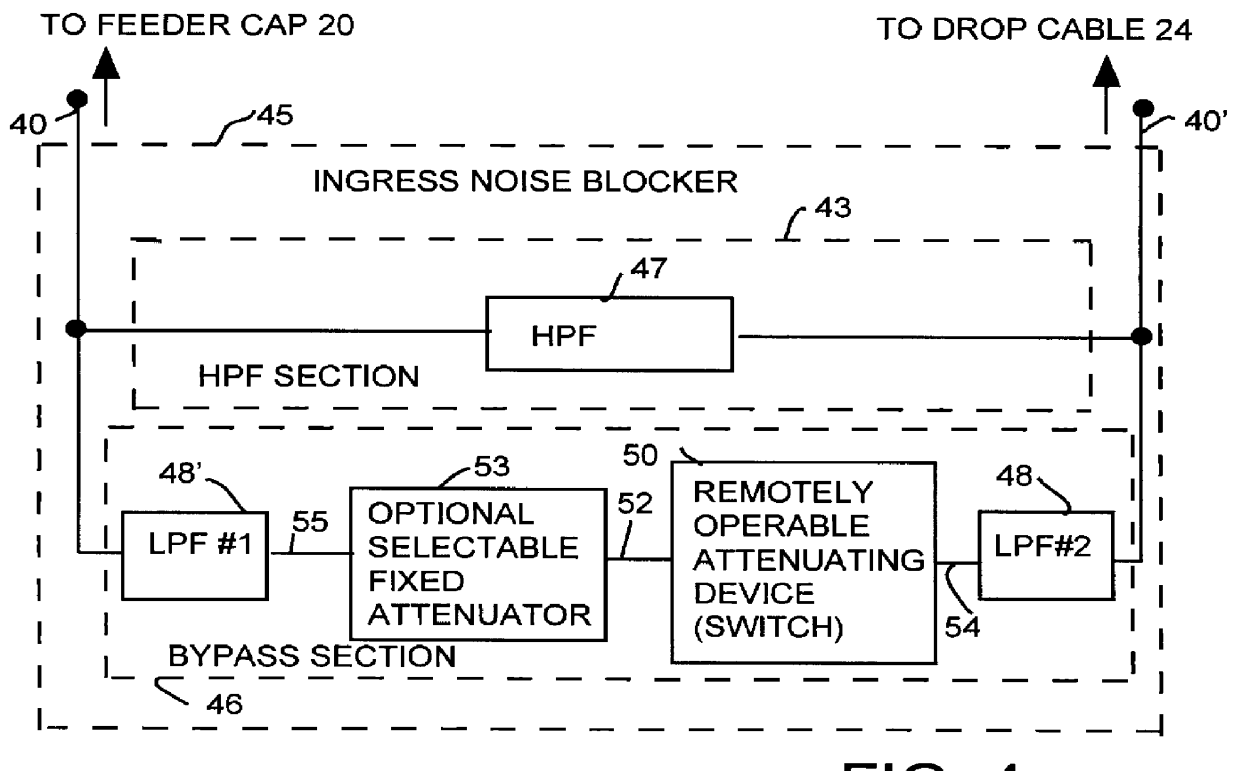
This invention permits the upstream transmission of short packets of information in a cable TV system, and blocking upstream noise at all other times, and does so without interfering with image quality of normal TV viewing. A remotely operable ingress noise blocking filter is placed at the terminating junction between a subscriber's coaxial drop cable and a corresponding feeder tap in a cable TV system. The ingress noise blocking filter contains a high pass filter to pass the normal TV band. This high pass filter is bypassed by a section containing low pass filters and a switch operated when receiving a control signal from a cable modem during those short durations the cable modem is authorized to transmit an upstream signal. Low pass filters isolate the switching elements so that switching transients cannot occur in the downstream TV band. The level of the amplitude of the downstream signal is unaffected whether the switching elements are open or closed. Further, the switching arrangement provides a relatively constant impedance, both when the switching element is on and off to provide a high return loss and avoid signal reflections and maintain signal quality. In a diagnostic mode, the location of each noise source is determined by correlating the energy measured at each a set of frequencies across the band at the headend during those periods when the cable modem is allowed to transmit versus the energy received during those periods when the same cable modem is not authorized to transmit.
Owner:ARRIS INT
High frequency and low frequency audio signal encoding and decoding system
InactiveUS6772114B1Low computing performanceCode conversionTransmissionFrequency spectrumTransmitter
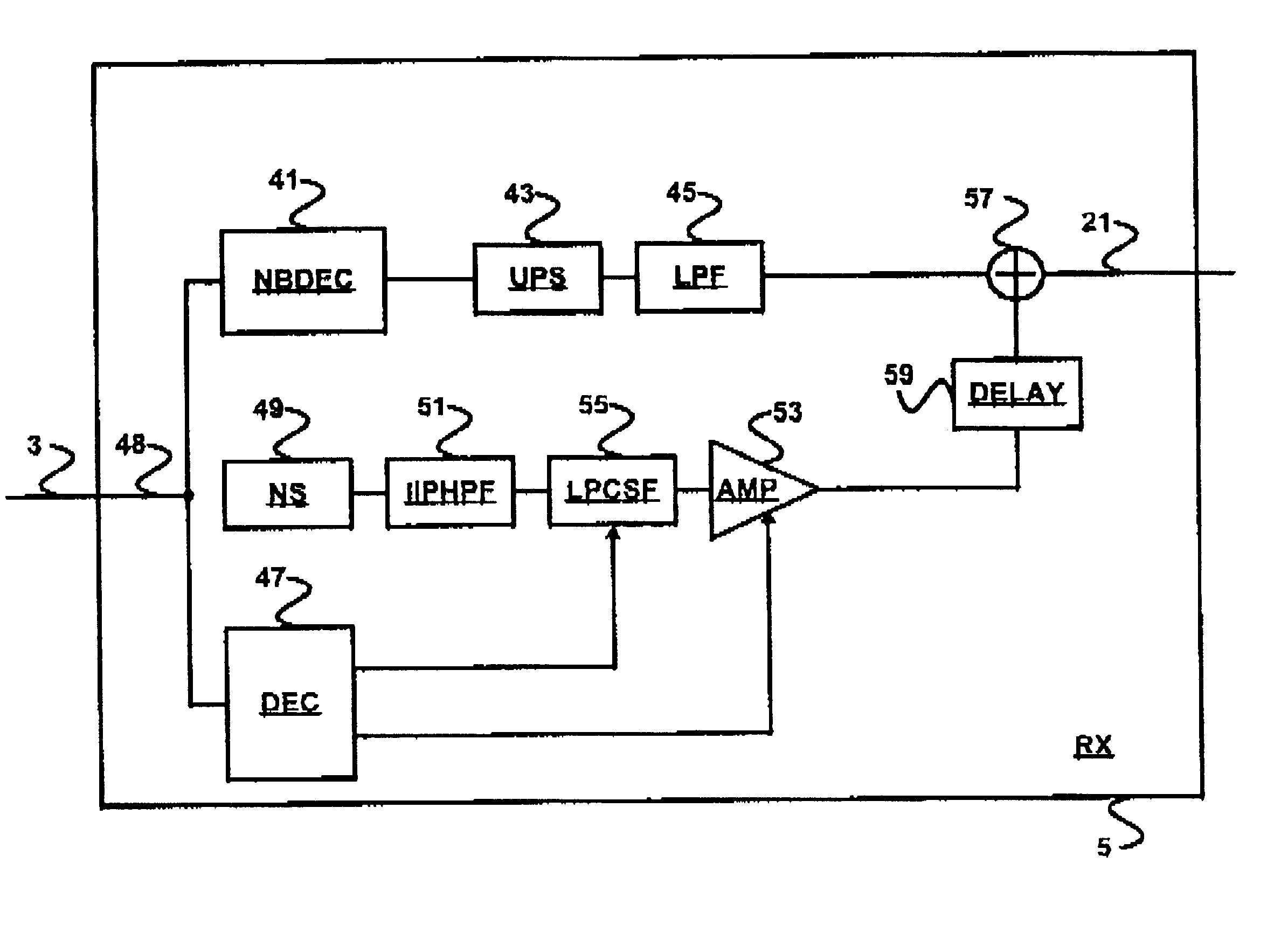
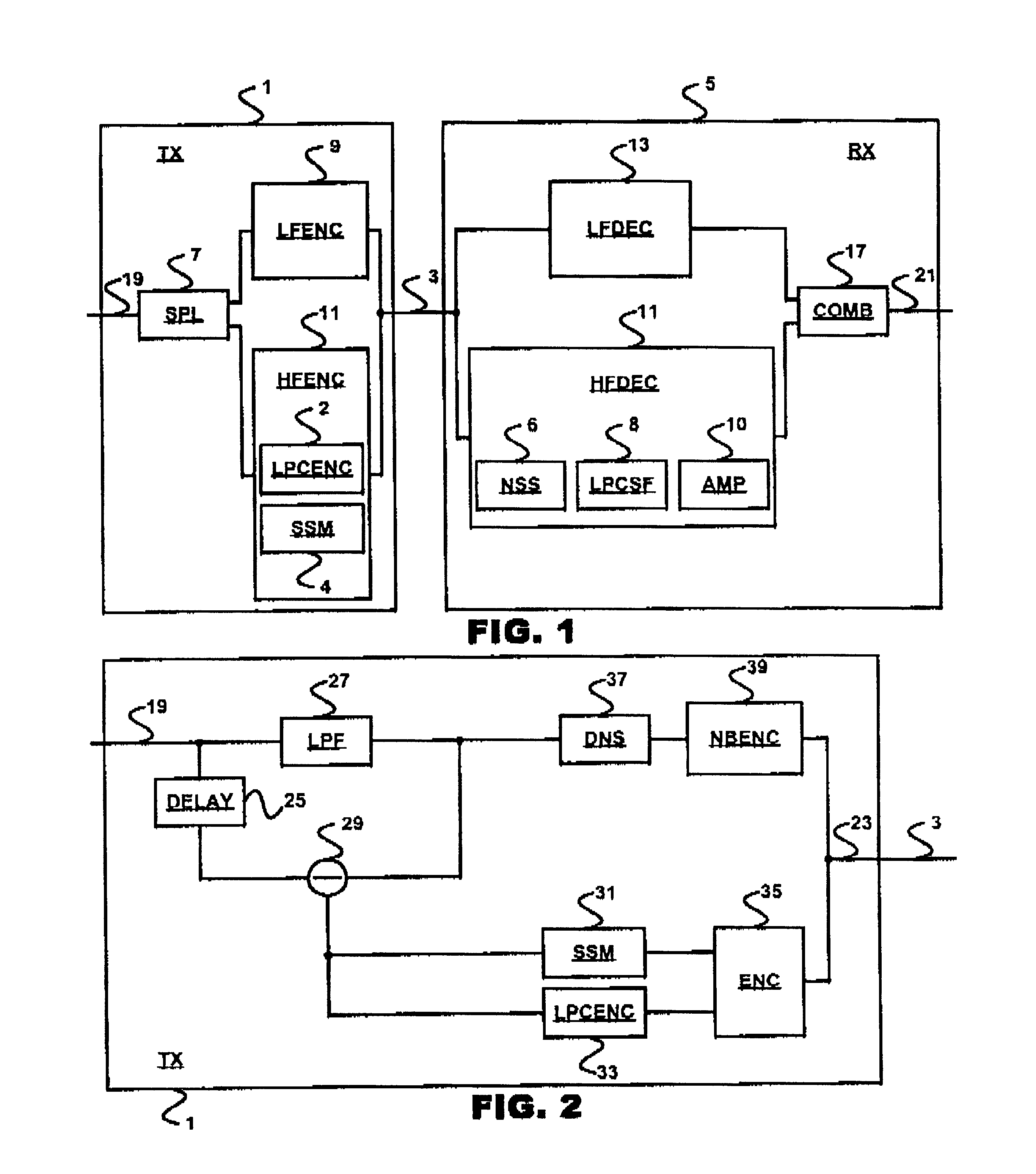
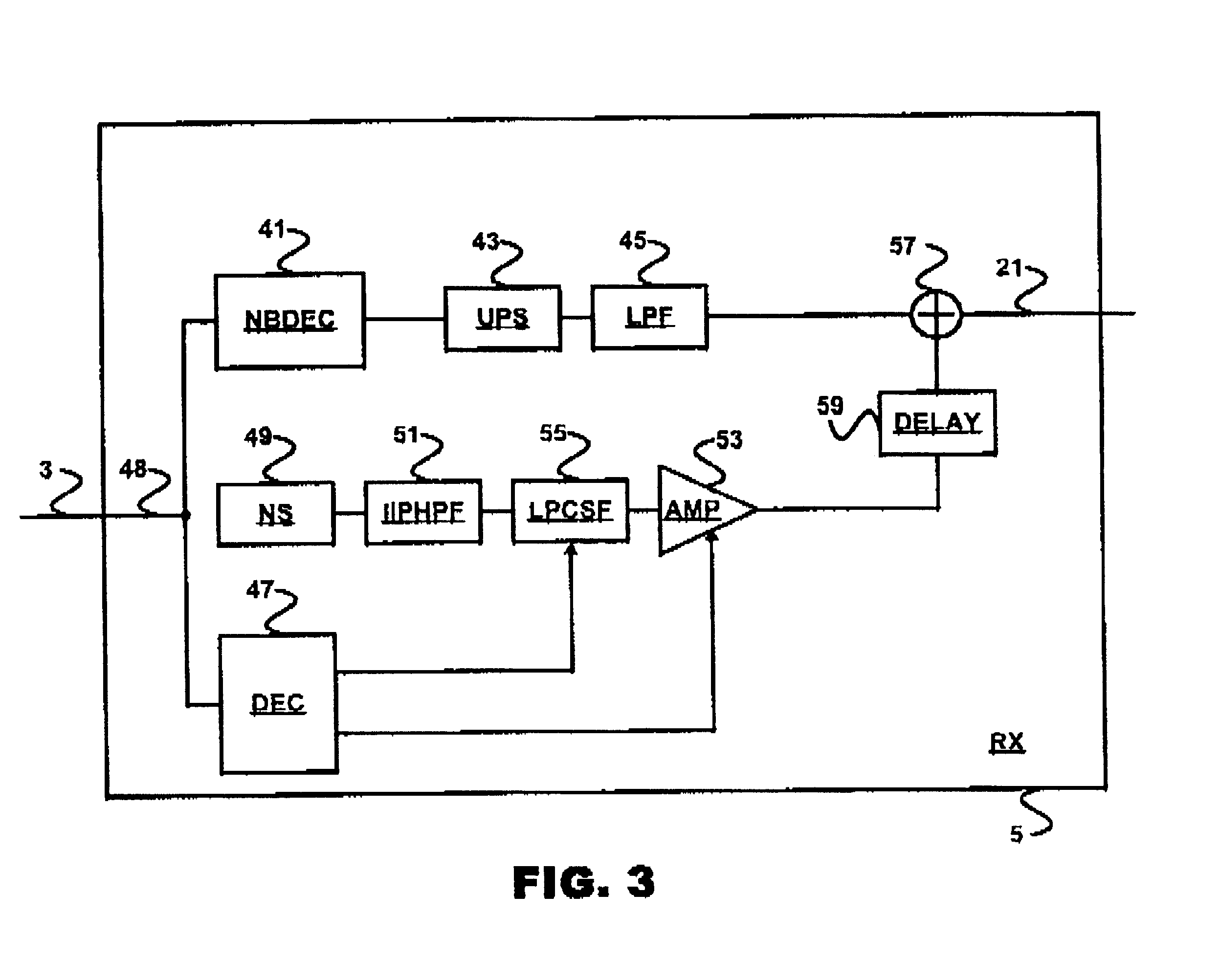
In an audio transmission system, an input signal is split up into two spectral portions in a transmitter. These spectral portions are coded by their own respective coder. The low-frequency signal portion is coded by a regular narrow-band coder and the high frequency portion is coded using a coder that outputs LPC codes and signal amplitude codes. In the receiver, the low frequency signal portion is reconstructed by a narrow-band decoder and the high frequency portion is reconstructed by applying a high pass filter to a white noise signal and applying an LPC filter that is controlled by the LPC codes to this filtered white noise signal and adjusting the signal amplitude with an amplifier that is controlled using the amplitude codes of the transmitter. The reconstructed low frequency signal and the reconstructed high frequency signal are then combined to yield a reconstructed output signal containing both frequency ranges.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Connector
InactiveUS6979226B2Improve responseJitters are reducedCoupling for high frequencyTwo-part coupling devicesDifferential signalingDigital signal
The present invention relates to a connector which includes a plug unit and a receptacle. The plug unit includes a housing board and a transmission path board. The housing board has a housing board body and first connection terminals and second connection terminals. The transmission path board has a transmission path board body, plural differential signal patterns which are connected to the first connection terminals and the second connection terminals of the housing board, and high pass filters which are connected to each of the differential signal patterns. The receptacle has a receptacle body and pin contacts. According to the present invention, a low-frequency component of a digital signal is attenuated. Thus, since an attenuation factor of the high-frequency component and an attenuation factor of the low-frequency component of the digital signal can be set substantially the same, the digital signal can be transmitted surely.
Owner:JST MFG CO LTD
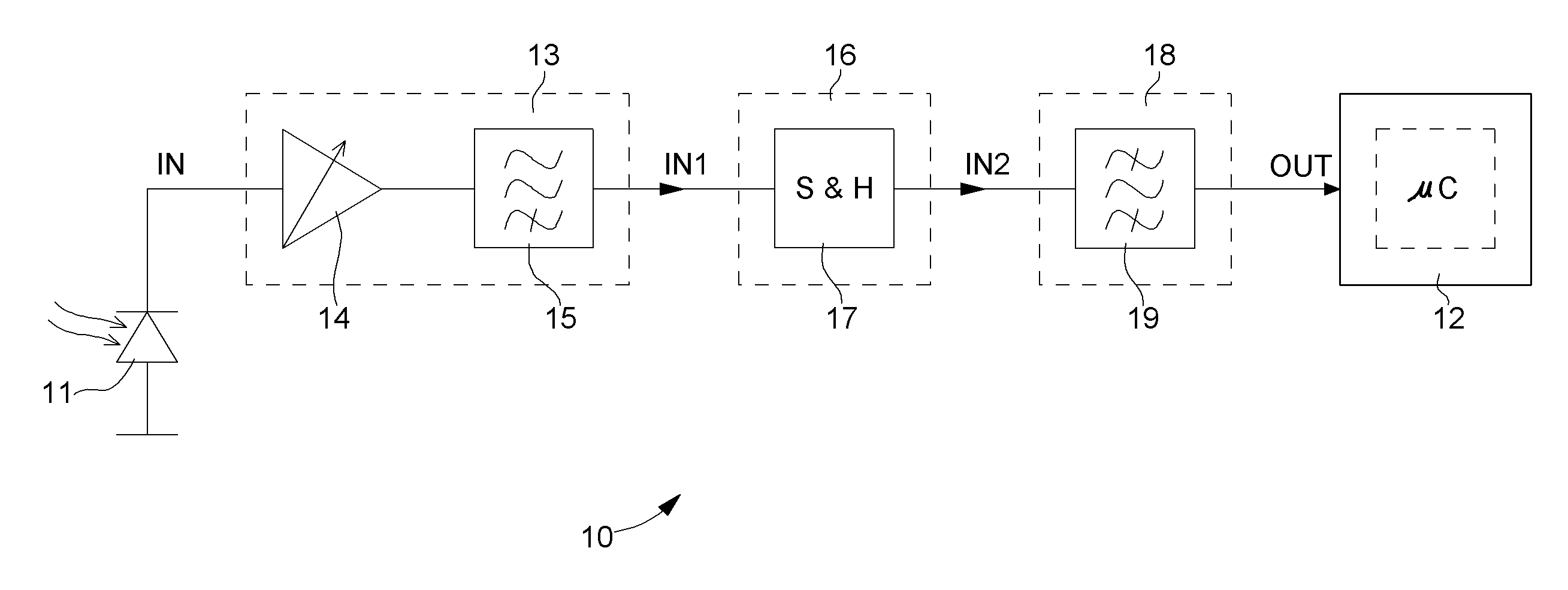
Signal conditioning circuit between an optical device and a processing unit
ActiveUS20070213020A1CatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal conditioning circuitsBandpass filtering
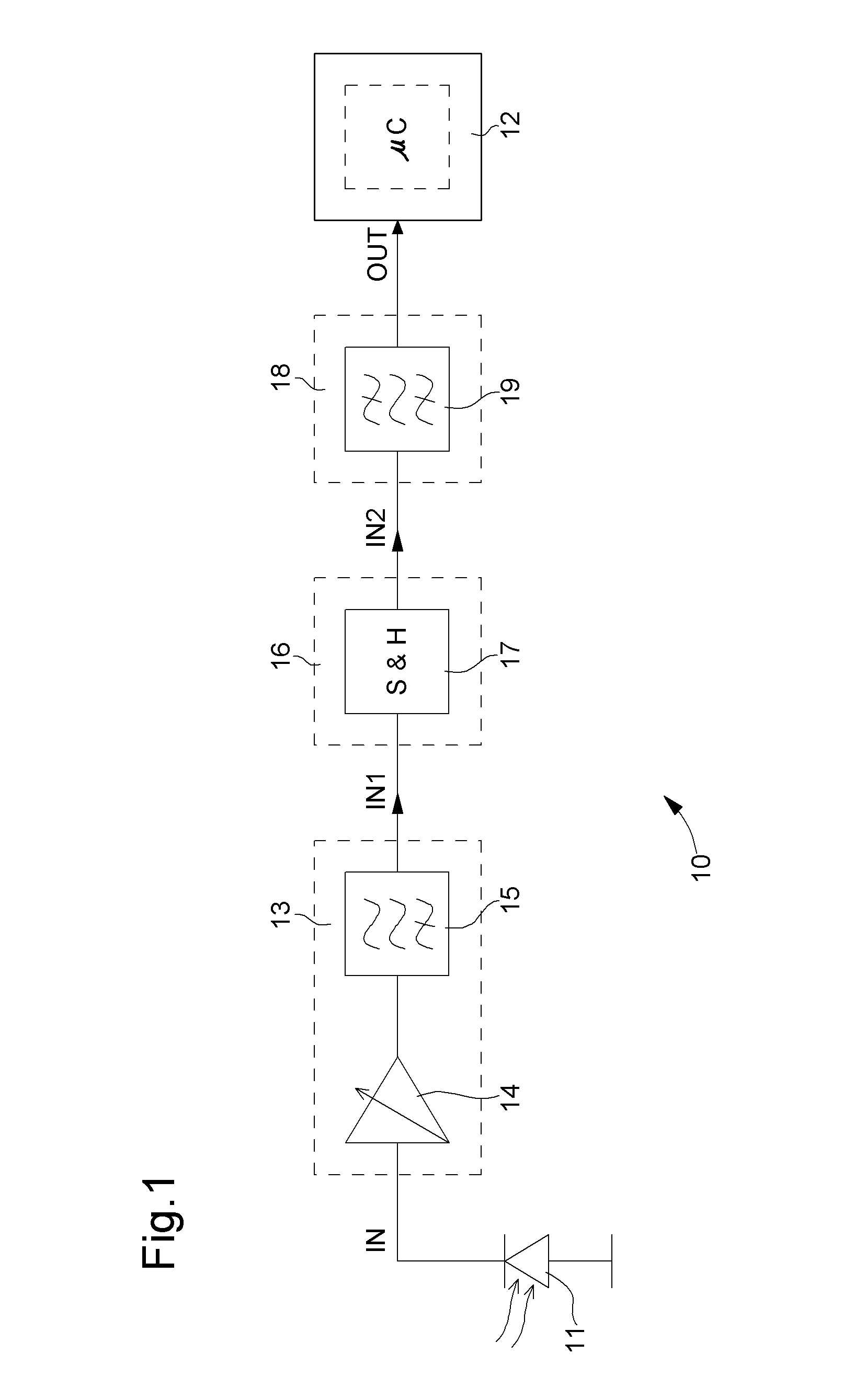
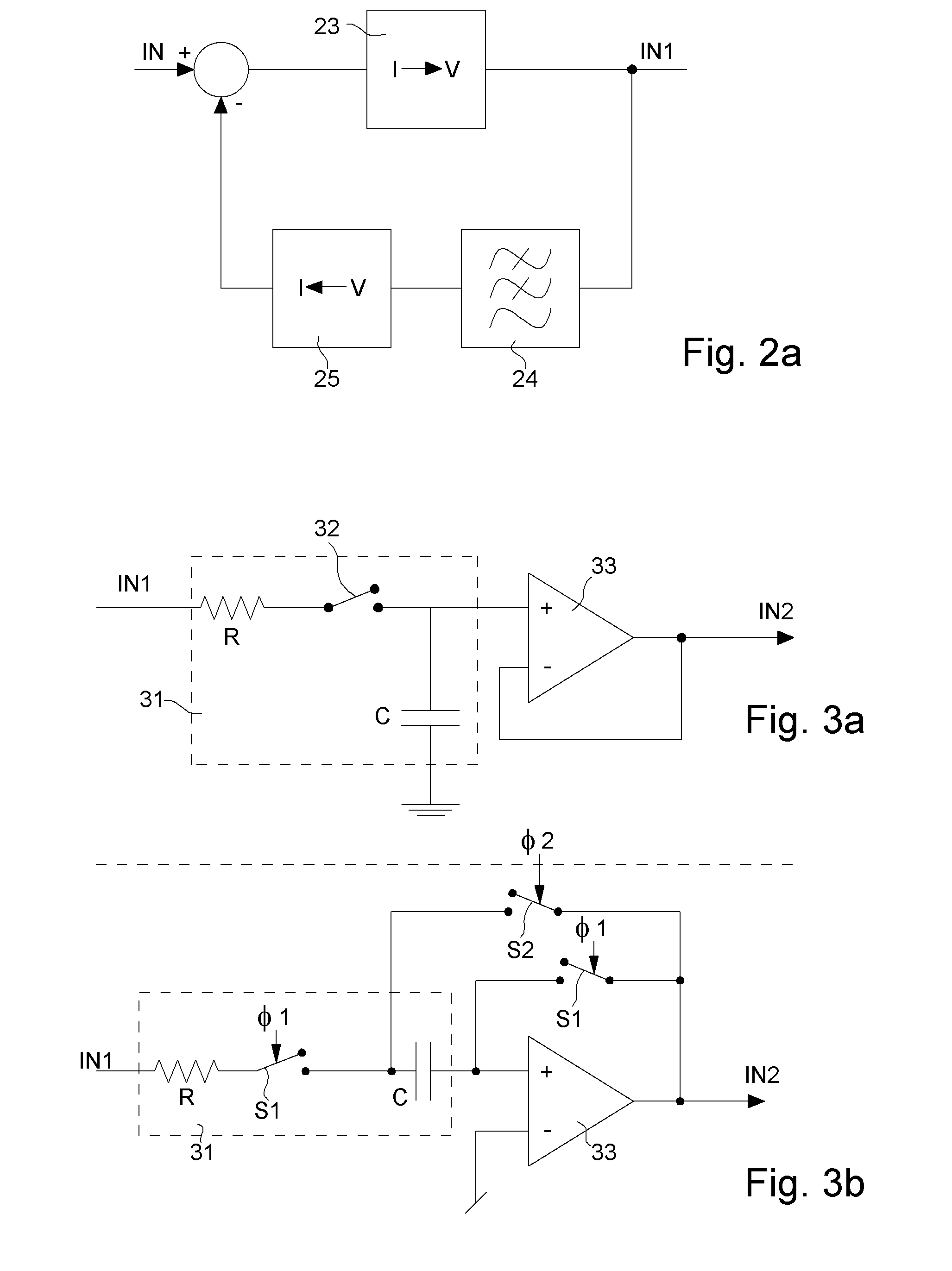
The invention concerns a conditioning circuit (10) for an external signal (IN) representative of a physiological quantity, arranged between an optical sensor (11) and a processing unit (12), the received external signal (IN) being broken down into a useful component and an ambient component, characterized in that the conditioning circuit includes a first stage (13) including a transimpedance amplifier with an incorporated high pass filter (15) using a feedback loop to subtract the ambient signal component from the received external signal, and to deliver at output an amplified useful signal (IN1), a second stage (16) including a blocker sampler circuit (17) for demodulating the amplified useful signal and delivering at output a demodulated useful signal (IN2), and a third stage (18) including a bandpass filter (19) for filtering the demodulated useful signal in the frequency band of the physiological quantity to be detected and for transmitting a conditioned signal (OUT) to the processing unit.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
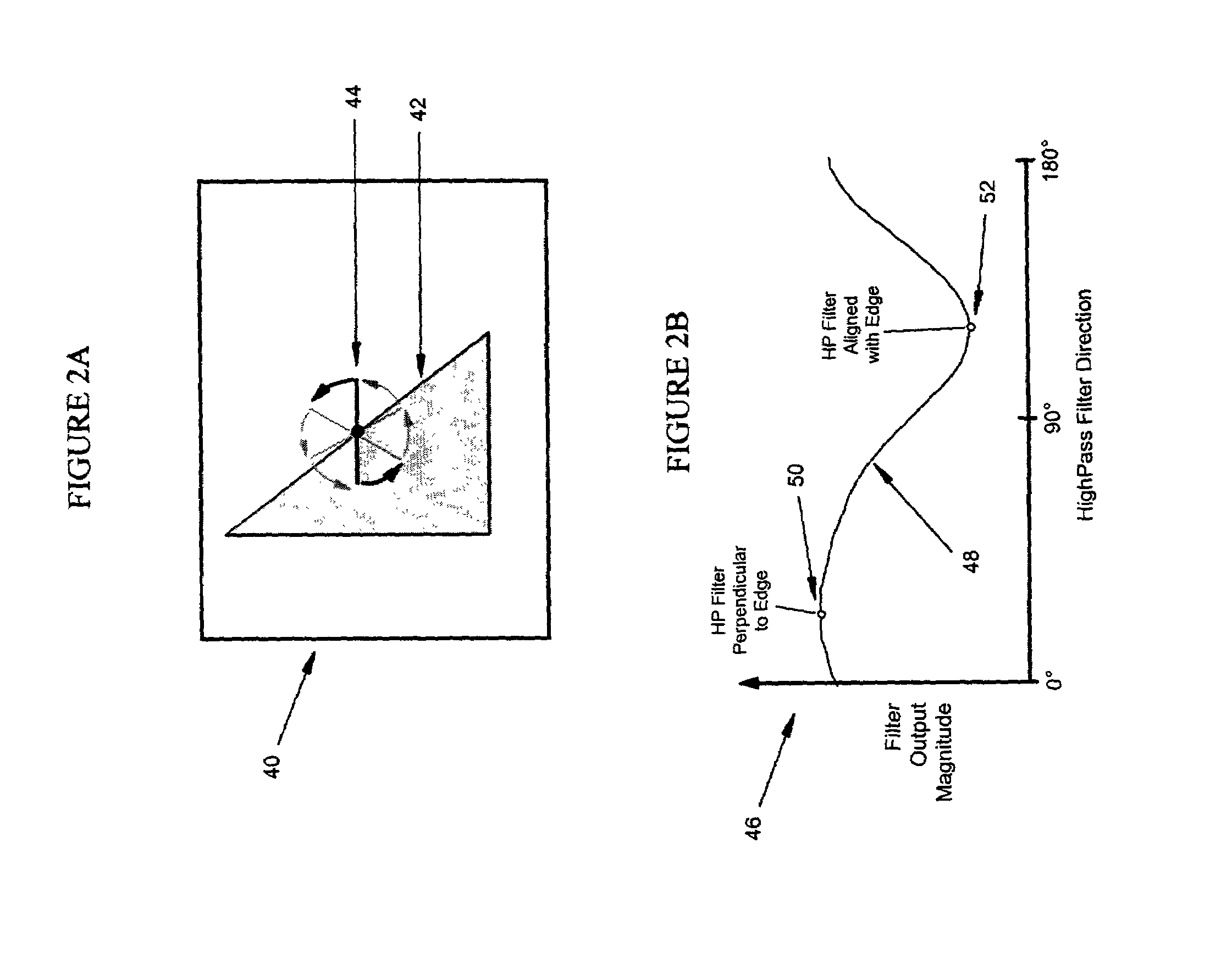
Deinterlacing of video sources via image feature edge detection
ActiveUS7023487B1Reduce artifactsPreserves maximum amount of vertical detailImage enhancementTelevision system detailsInterlaced videoProgressive scan
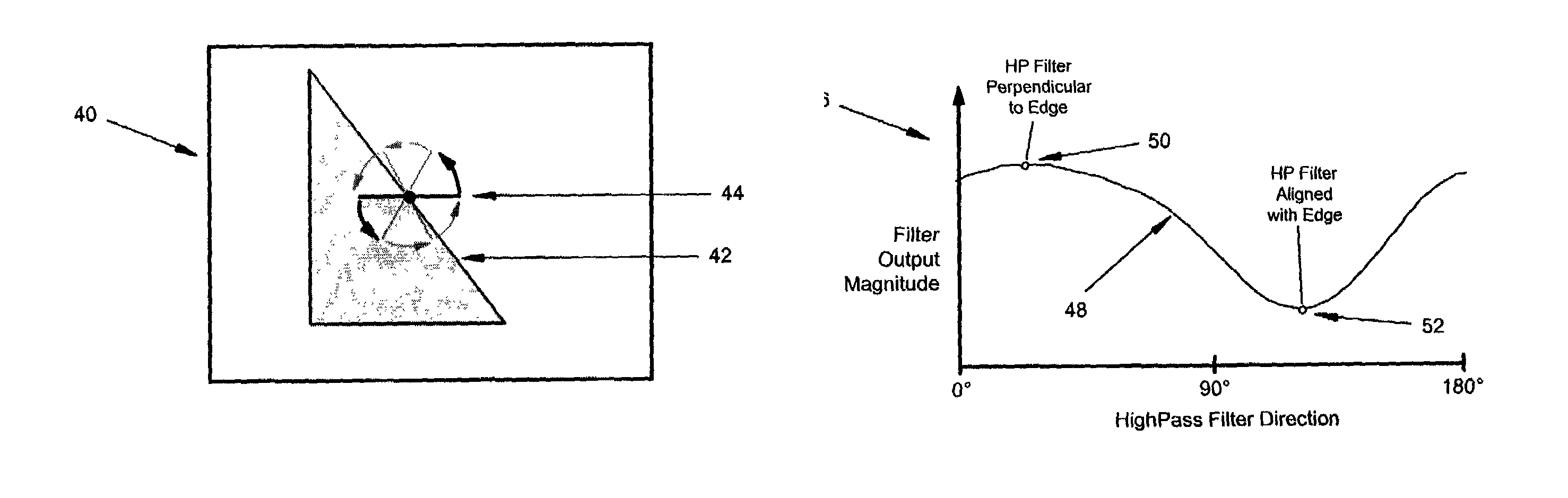
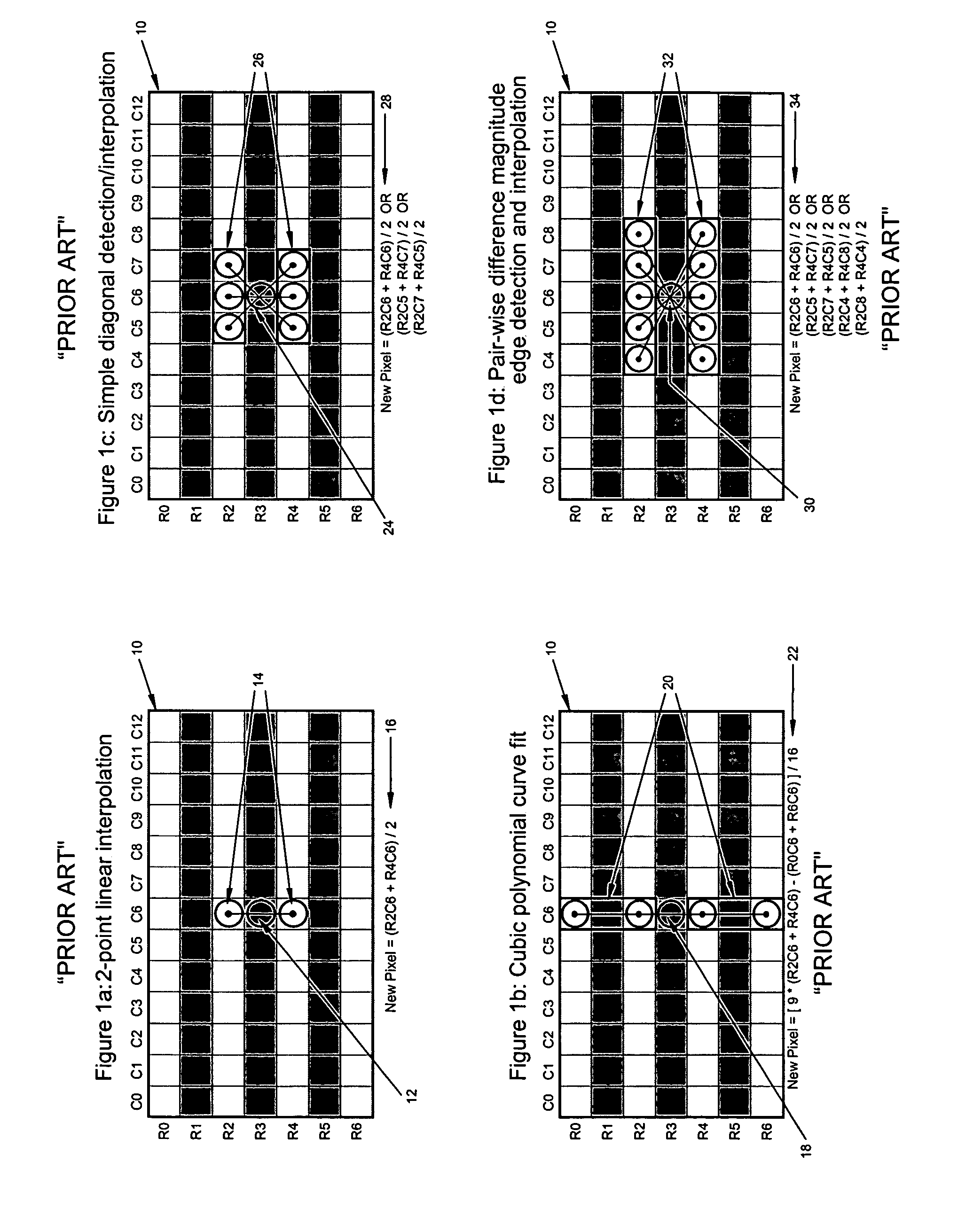
An interlaced to progressive scan video converter which identifies object edges and directions, and calculates new pixel values based on the edge information. Source image data from a single video field is analyzed to detect object edges and the orientation of those edges. A 2-dimensional array of image elements surrounding each pixel location in the field is high-pass filtered along a number of different rotational vectors, and a null or minimum in the set of filtered data indicates a candidate object edge as well as the direction of that edge. A 2-dimensional array of edge candidates surrounding each pixel location is characterized to invalidate false edges by determining the number of similar and dissimilar edge orientations in the array, and then disqualifying locations which have too many dissimilar or too few similar surrounding edge candidates. The surviving edge candidates are then passed through multiple low-pass and smoothing filters to remove edge detection irregularities and spurious detections, yielding a final edge detection value for each source image pixel location. For pixel locations with a valid edge detection, new pixel data for the progressive output image is calculated by interpolating from source image pixels which are located along the detected edge orientation.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
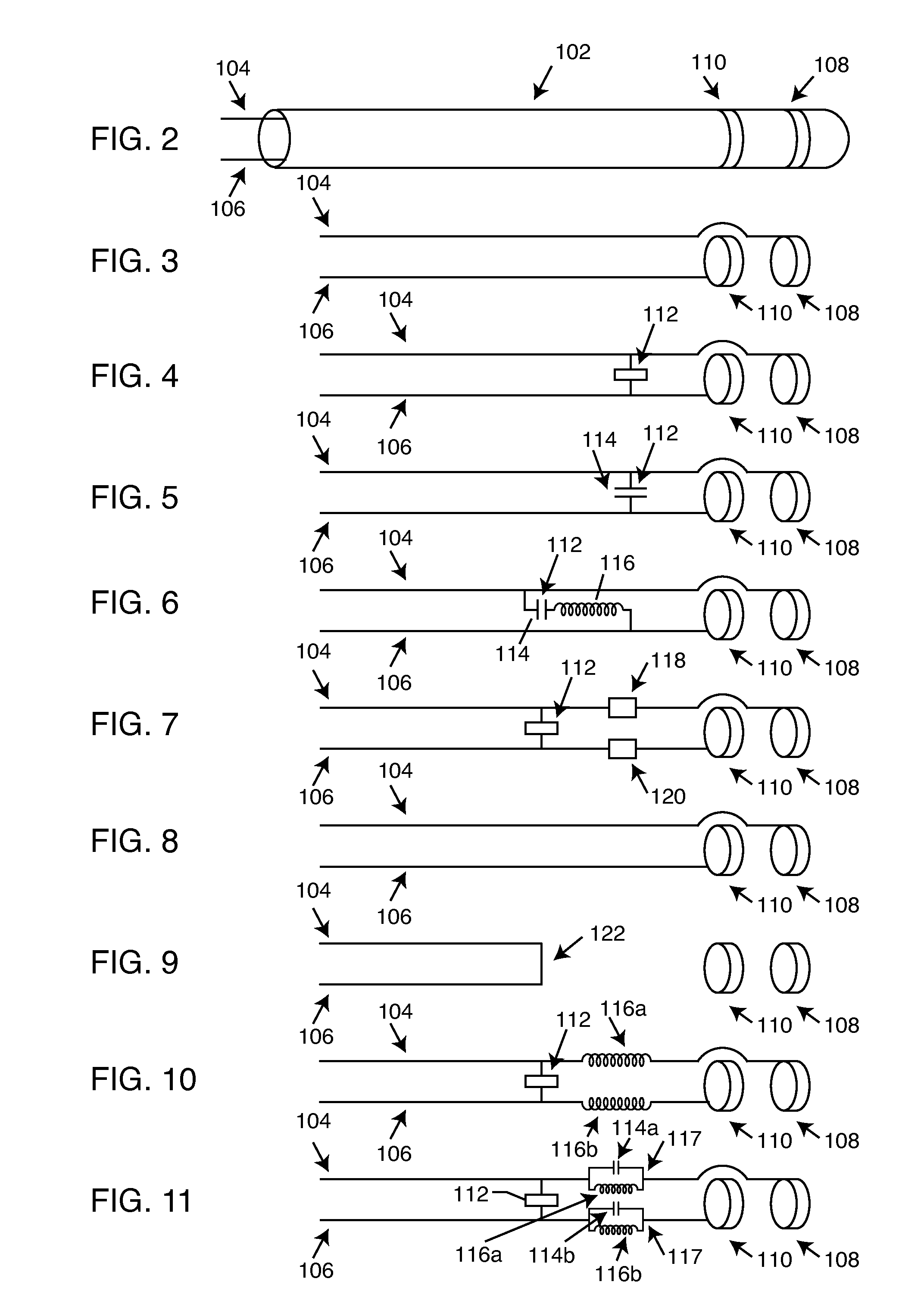
Low-pass filter for a PLL, phase-locked loop and semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7030688B2Reduce circuit sizeReduce circuit areaPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLoop filterBand-pass filter
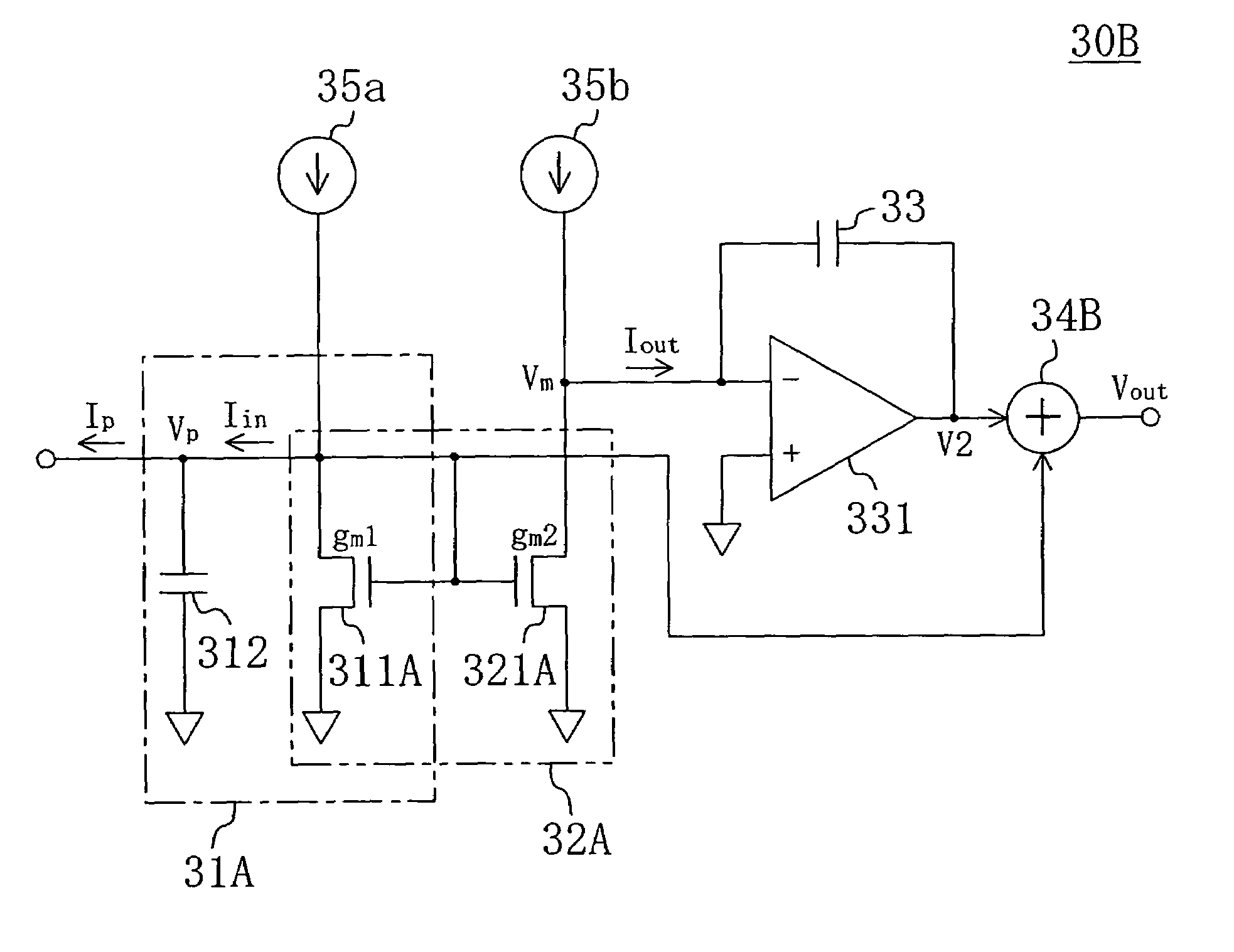
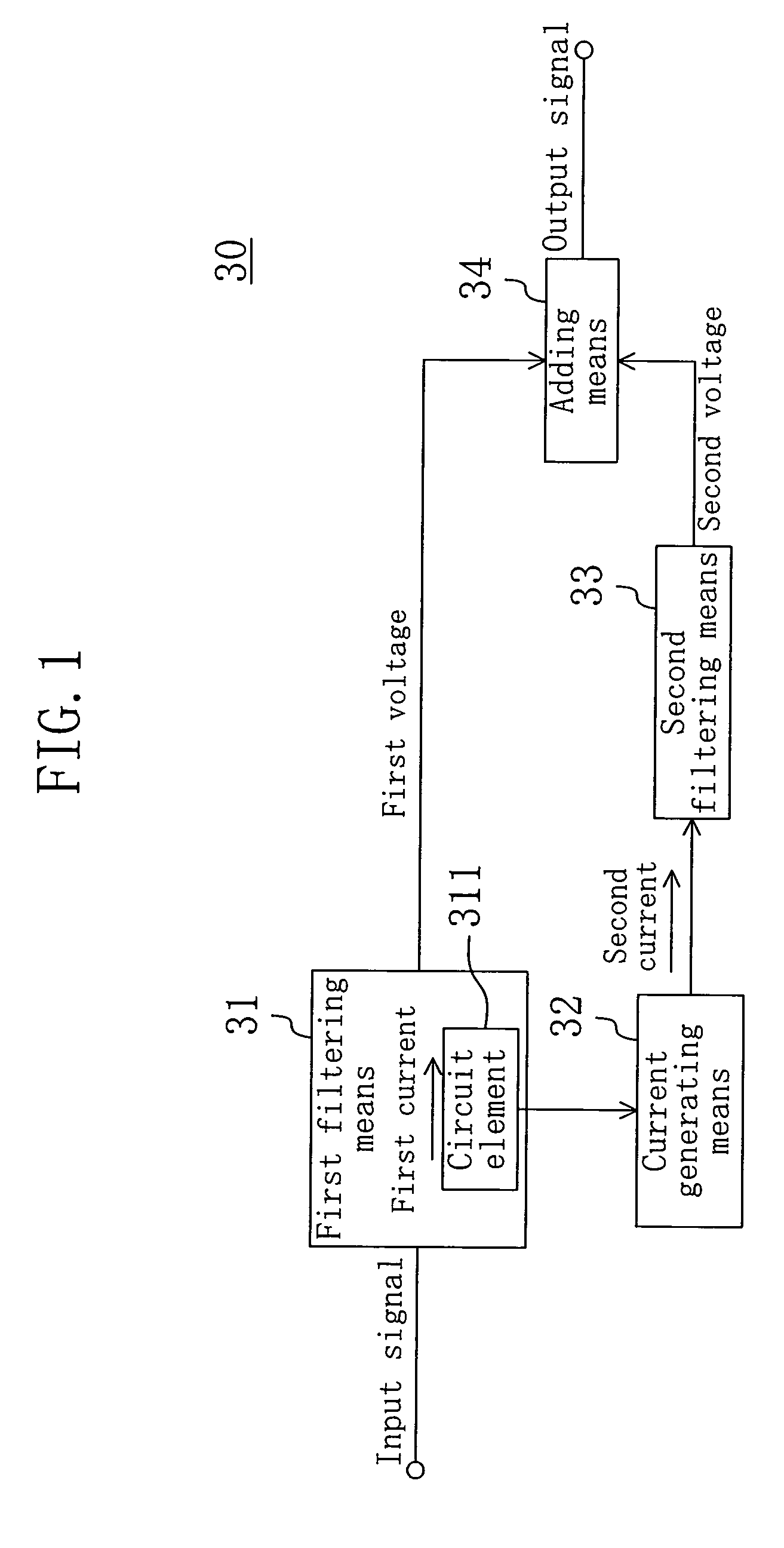
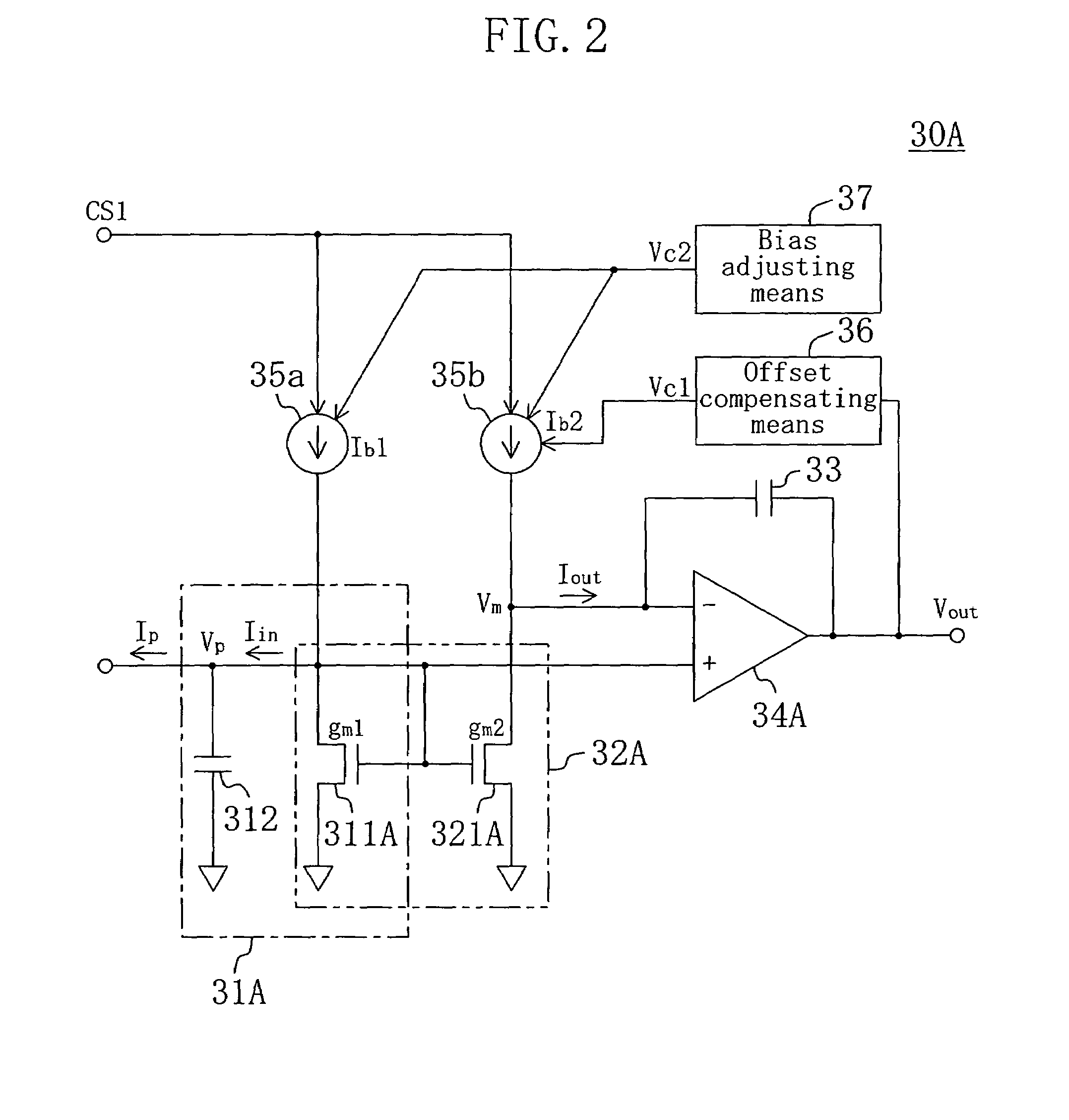
The invention provides a low-pass filter suitably used as a loop filter for a PLL or a DLL that has a filtering characteristic equivalent to that of a conventional one and can be realized in a smaller circuit area. The low-pass filter includes first filtering means (31) for accepting, as an input, an input signal to the low-pass filter and outputting a first voltage; a circuit element (311) included in the first filtering means (31) for allowing a first current to flow in accordance with the first voltage; current generating means (32) for generating a second current at a given rate to the first current; second filtering means (33) for accepting, as an input, the second current and outputting a second voltage; and adding means (34) for adding the first voltage and the second voltage and outputting an output signal of the low-pass filter, in which the second current is set to be smaller than the first current.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
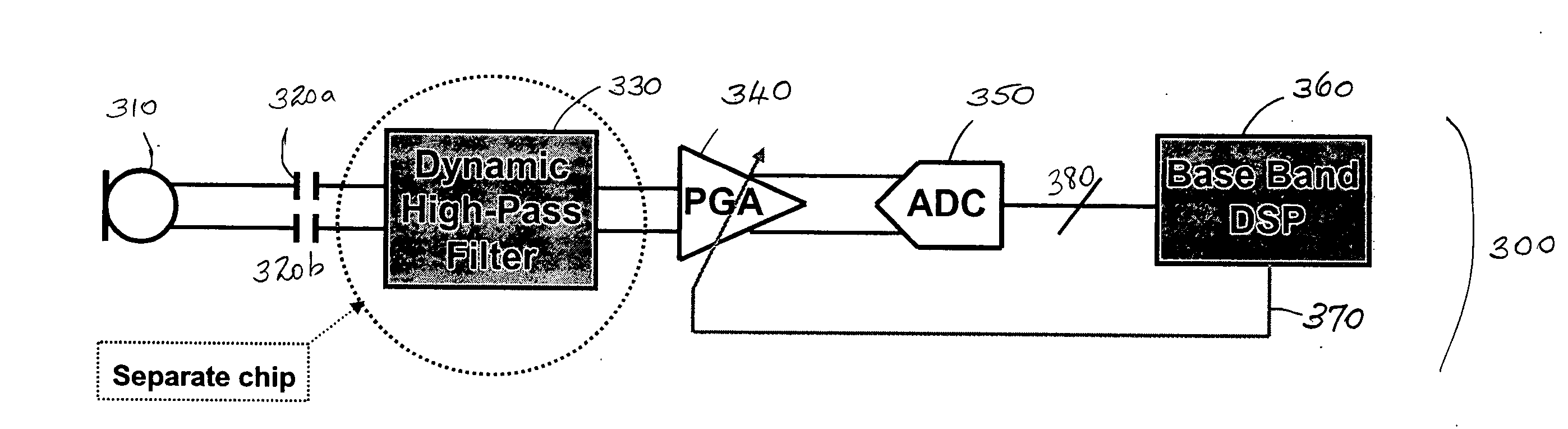
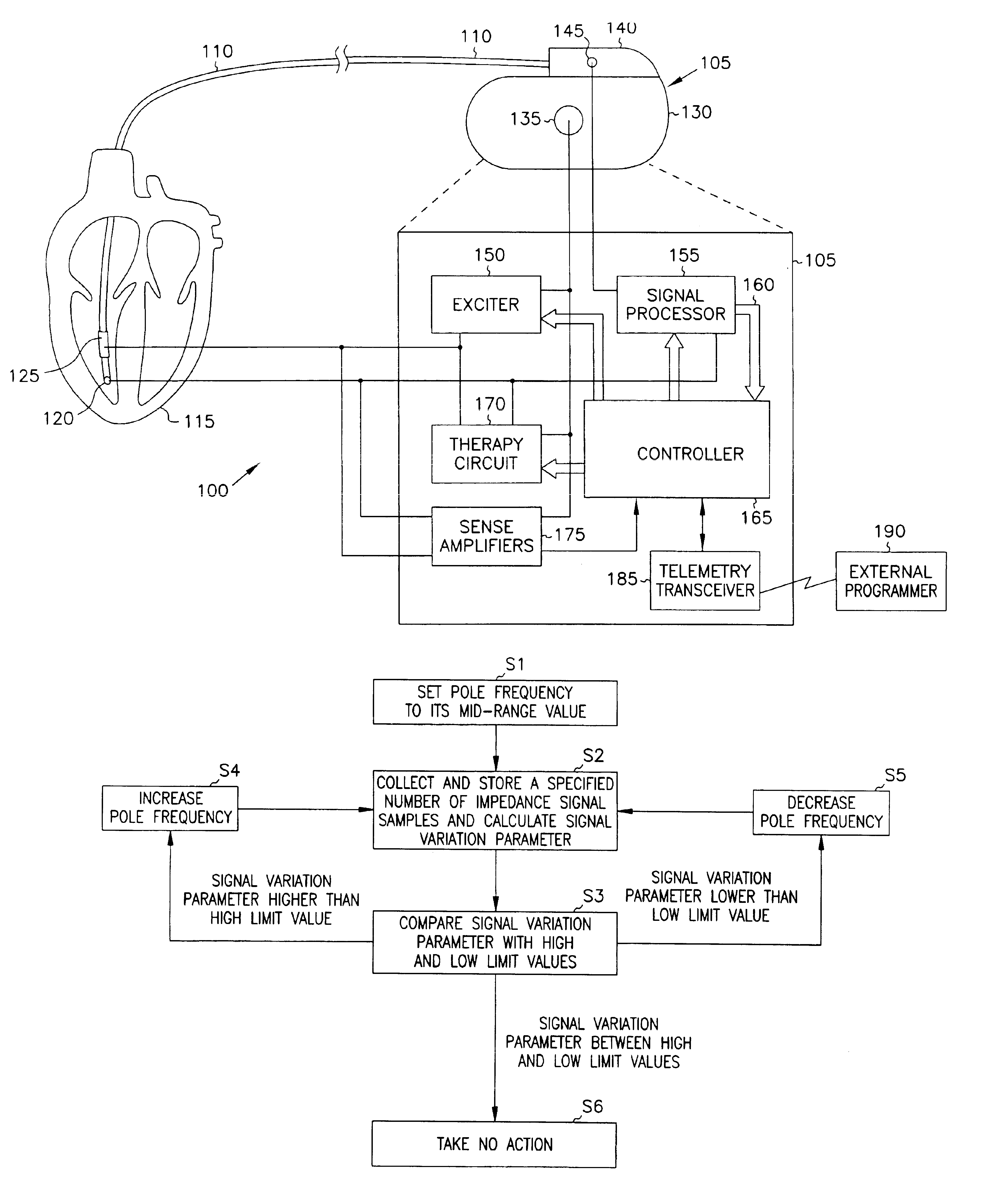
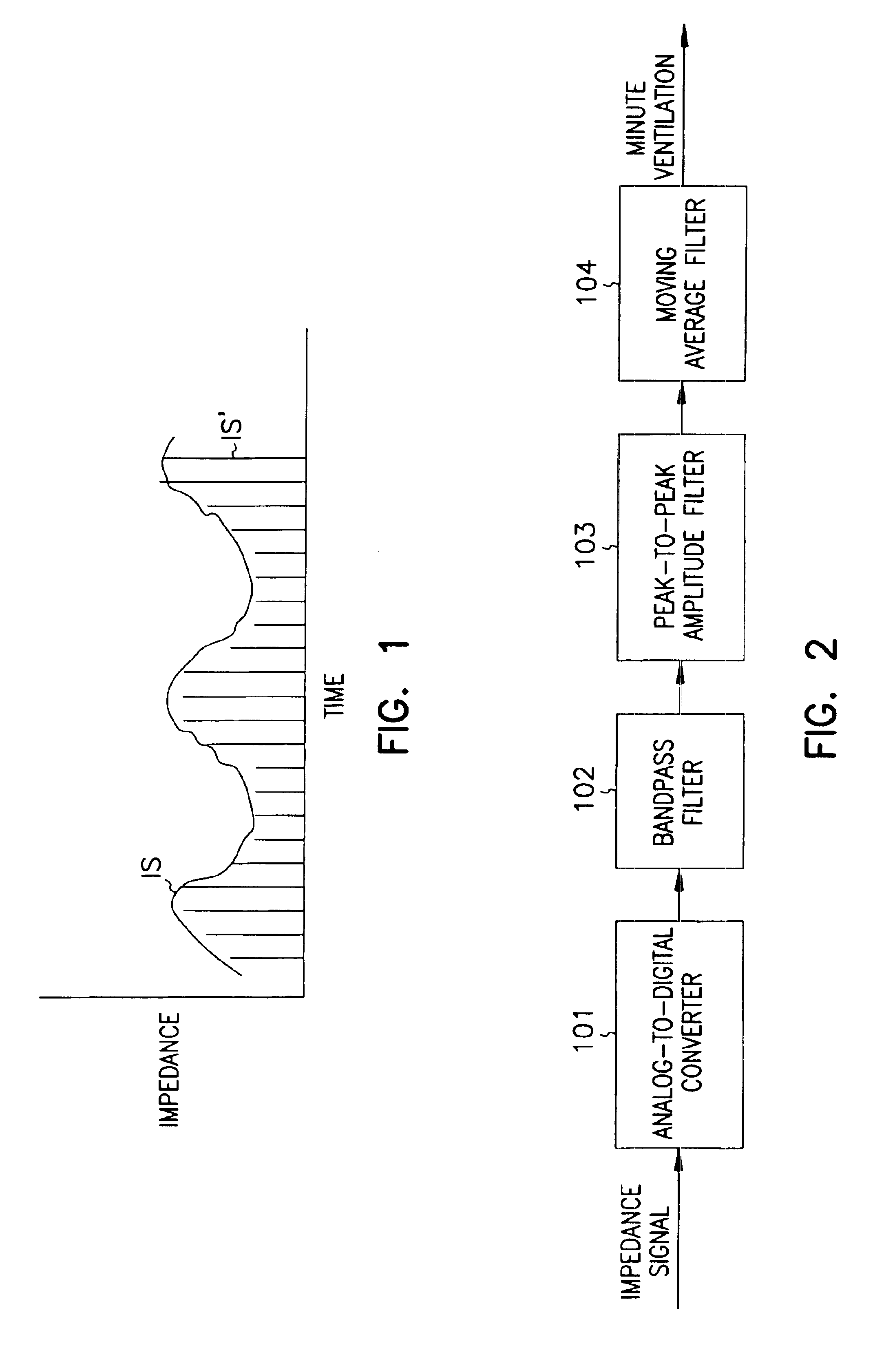
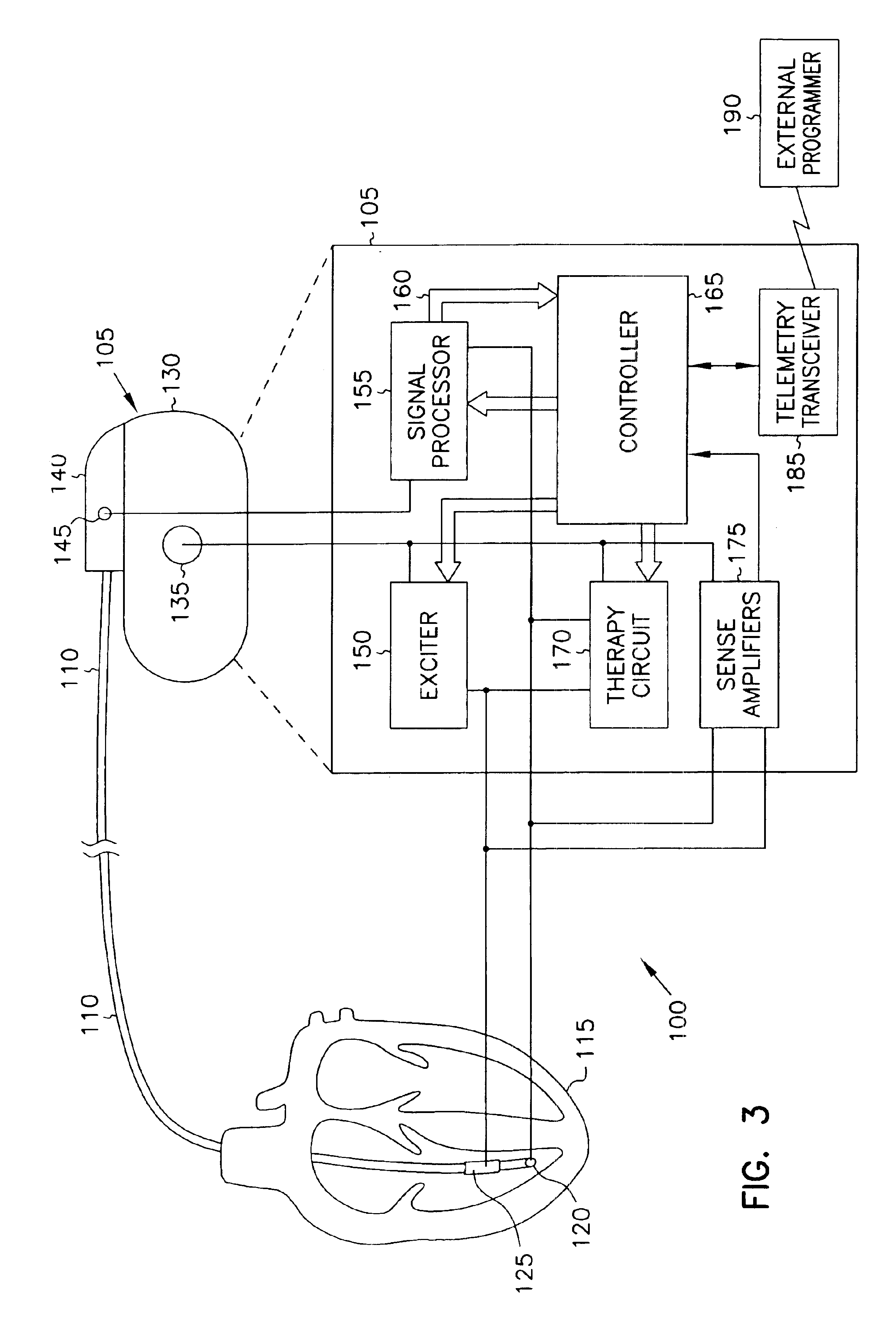
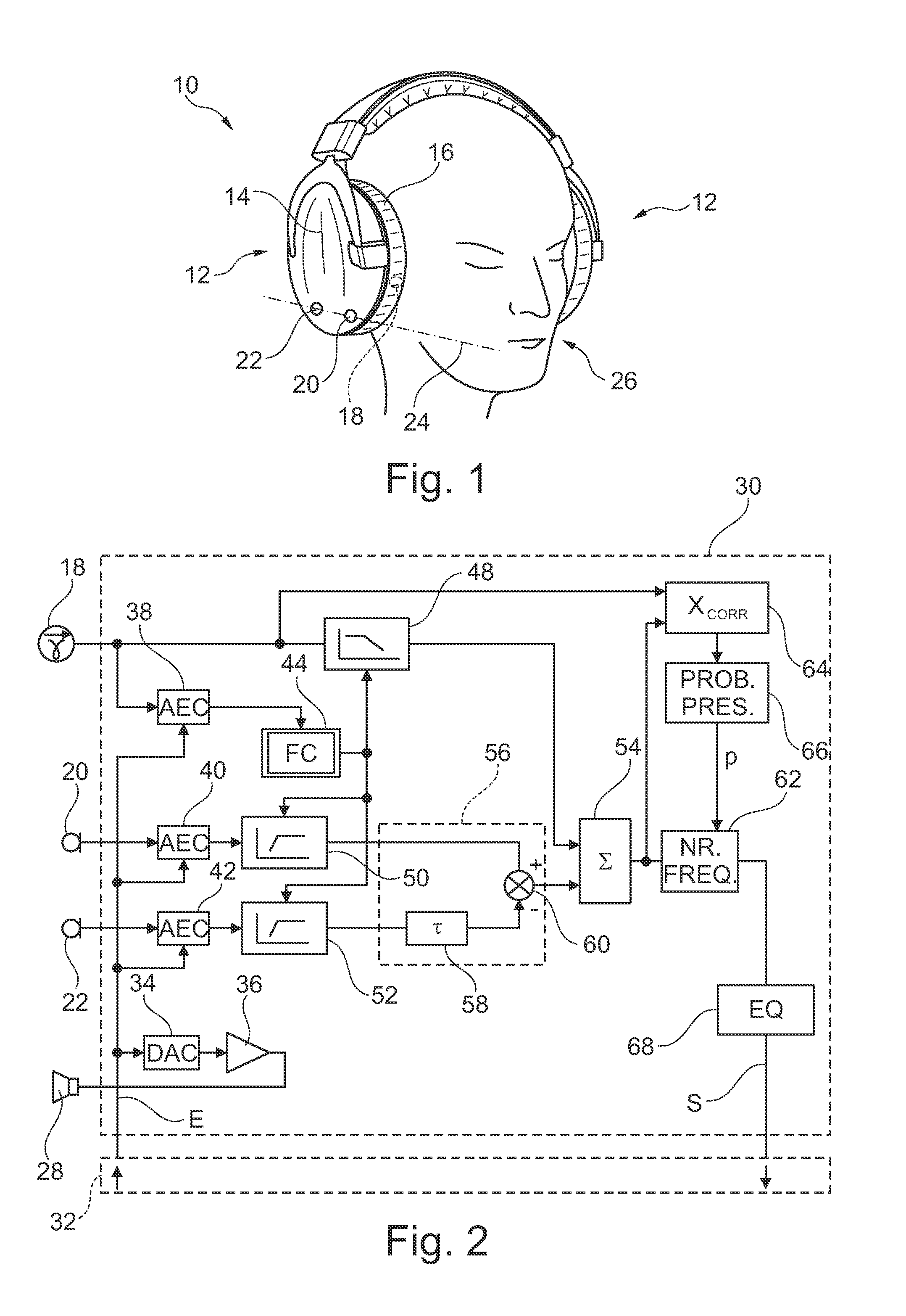
Minute ventilation sensor with automatic high pass filter adjustment
A minute ventilation sensing device in which transthoracic impedance is measured to generate an impedance signal from which a ventilation signal is derived, where the ventilation signal is proportional to minute ventilation. An adaptive high pass filter is used to filter the impedance signal into a ventilation band. The pole frequency of the high pass filter is adjusted in accordance with changes in a calculated signal variation parameter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
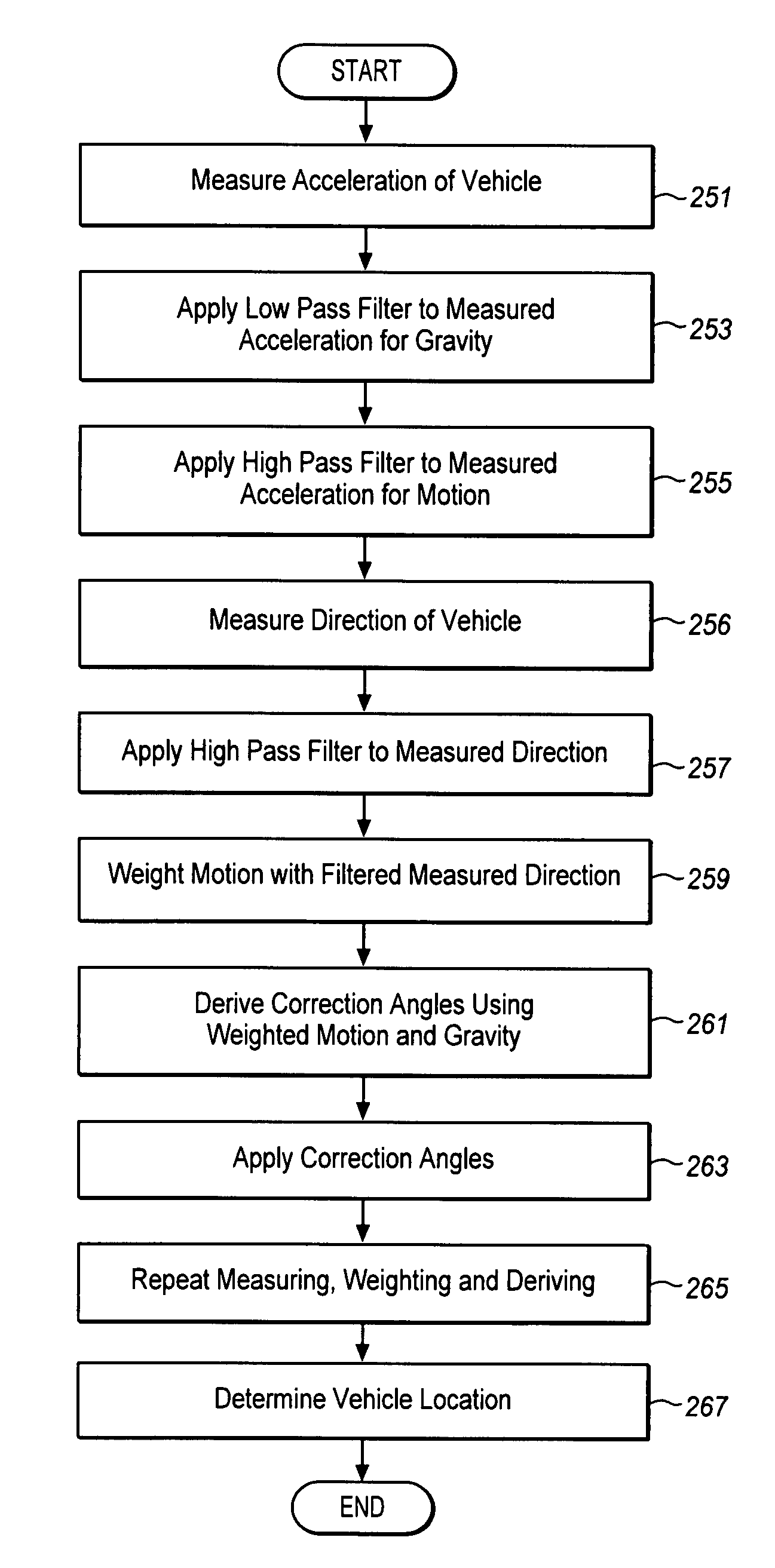
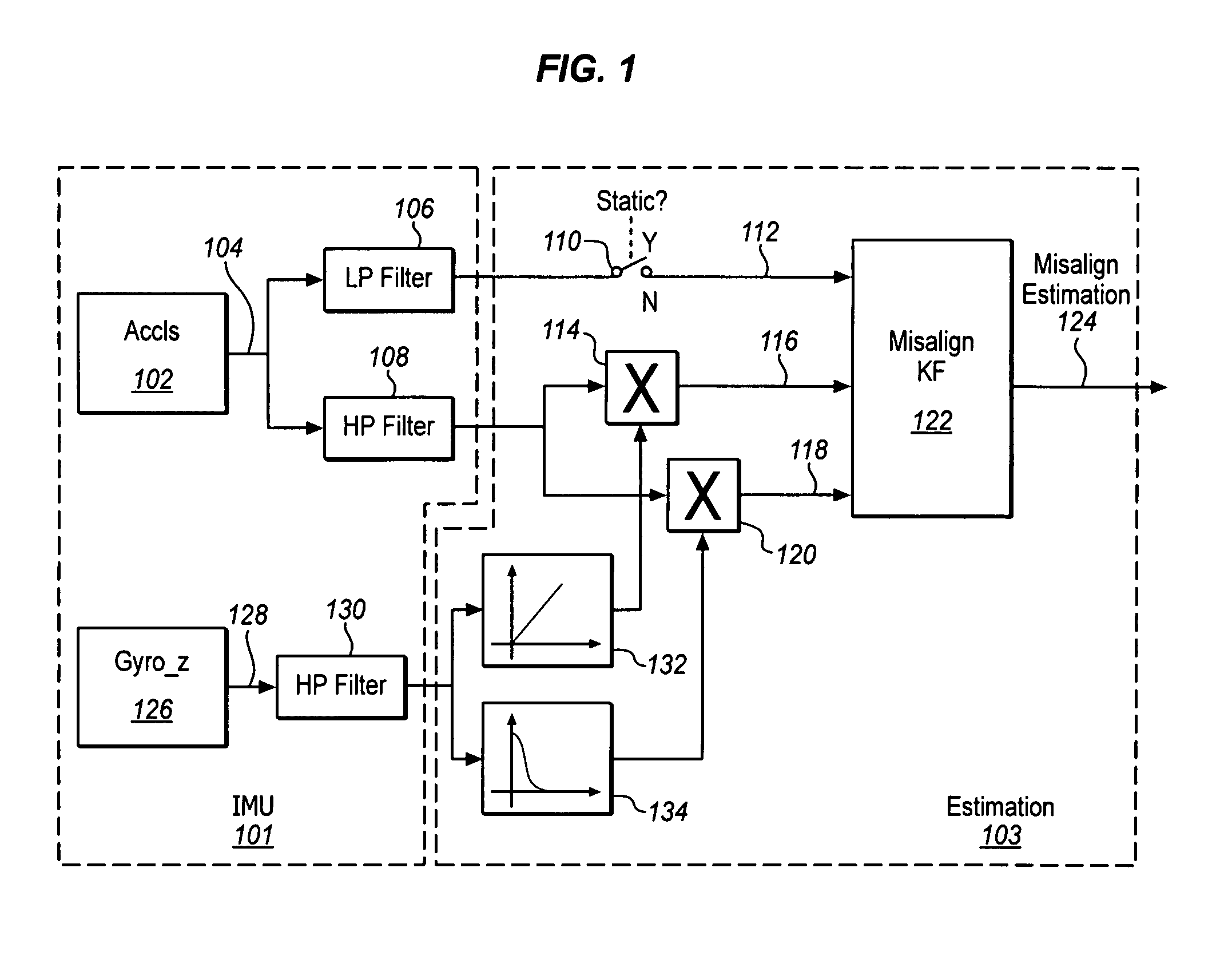
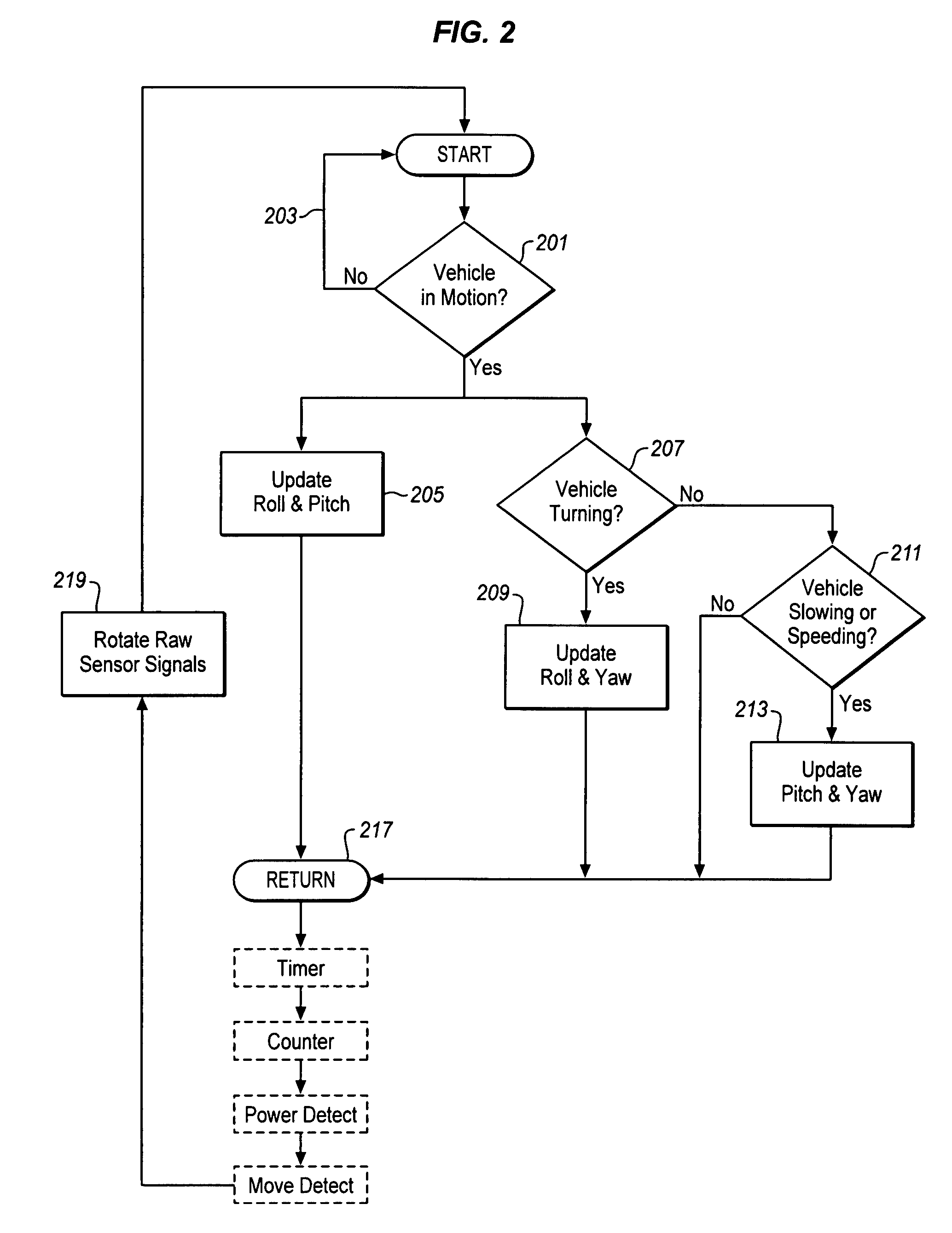
Compensation for mounting misalignment of a navigation device
ActiveUS20090254279A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringMarine navigation
Compensating for the misalignment of a navigation device with respect to a vehicle is described. In one example, the compensation is made by applying a high pass filter to a measured acceleration of the vehicle to produce a motion acceleration signal, weighting the motion acceleration signal with a measured steering rate of the vehicle, and deriving misalignment parameters for the navigation device with respect to the vehicle using the weighted motion acceleration signal.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
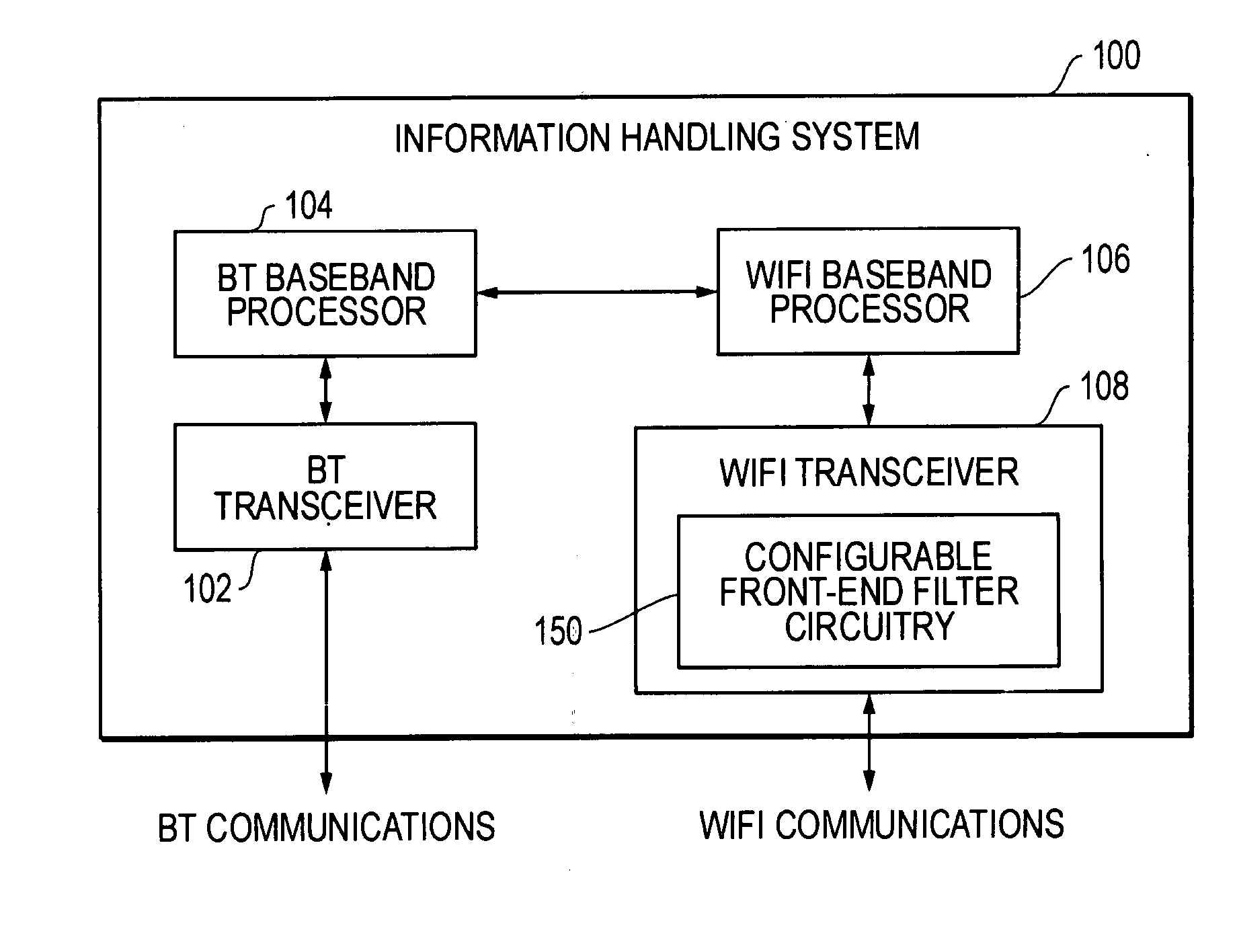
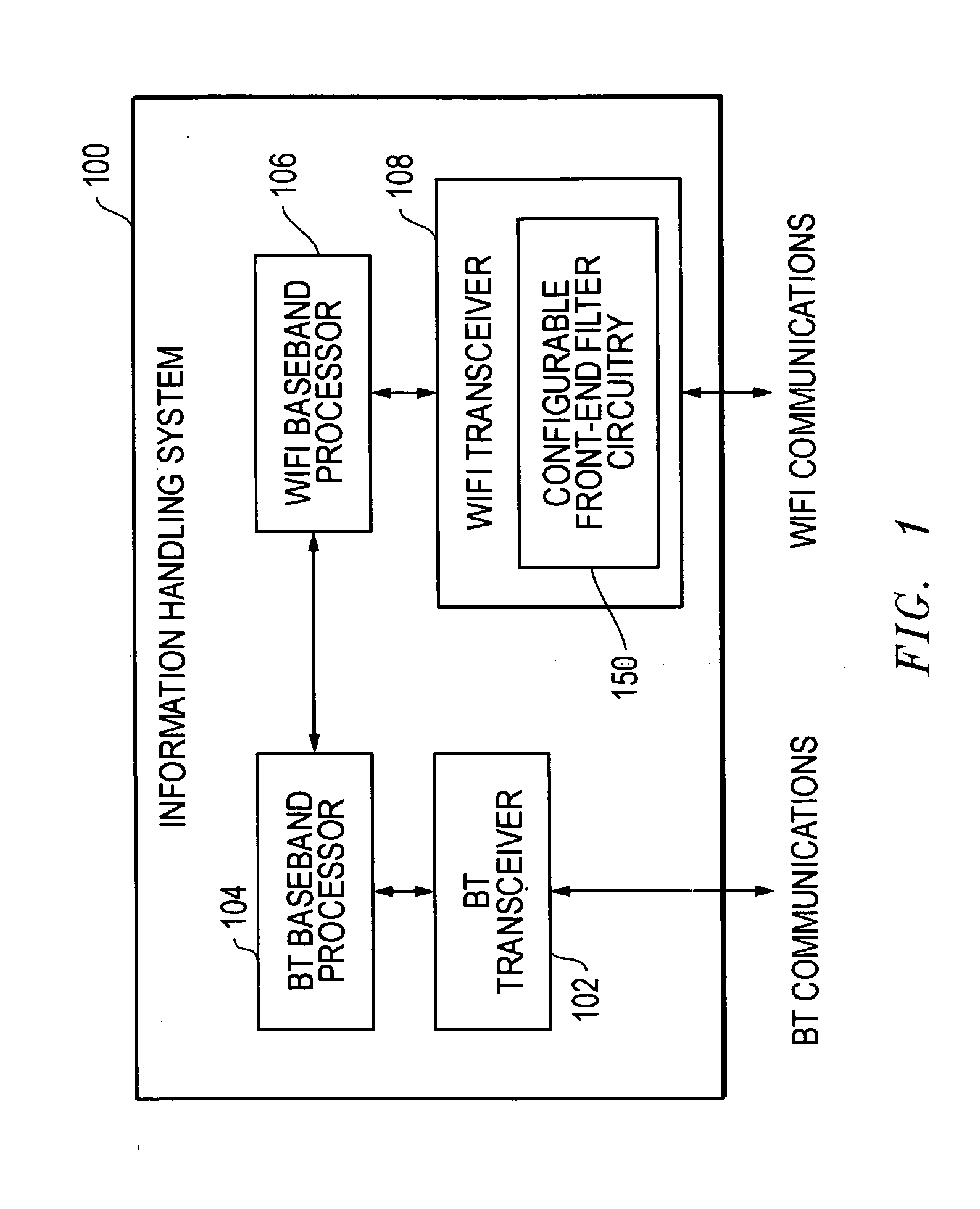
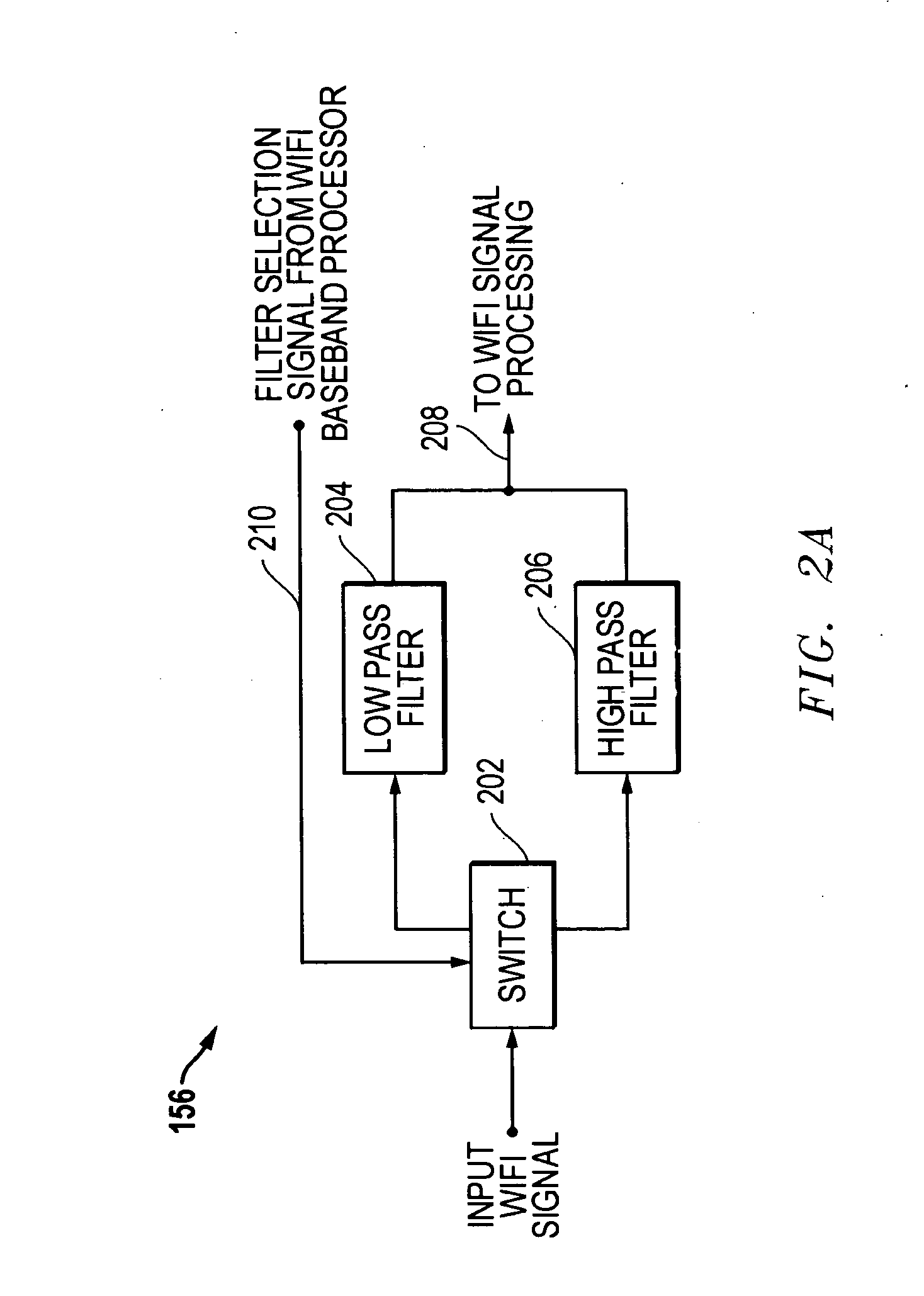
System and method for reducing signal interference between bluetooth and WLAN communications
ActiveUS20080045152A1Reduce signal interferenceFilter out Bluetooth communicationsNetwork topologiesTransmission noise suppressionHigh-pass filterEngineering
Methods and systems are disclosed for reducing signal interference between Bluetooth (BT) and WLAN (e.g. WiFi) communications in an information handling system. The WLAN receiver has configurable front-end filter circuitry. Based upon information concerning the BT frequency region for current BT communications, the WLAN receiver can adjust or set its configurable front-end filter circuitry to filter out the BT communications. As the BT communications hop from frequency to frequency, the WLAN receiver can continue to adjust its configurable front-end filter circuitry accordingly. Example implementations for the configurable front-end filter circuitry include bandpass filters and selectable low pass and high pass filters. These filters are selected and / or tuned such that BT frequency regions are filtered from the WLAN input signal before further WLAN signal processing is conducted, thereby improving the performance of simultaneous BT and WLAN communications.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
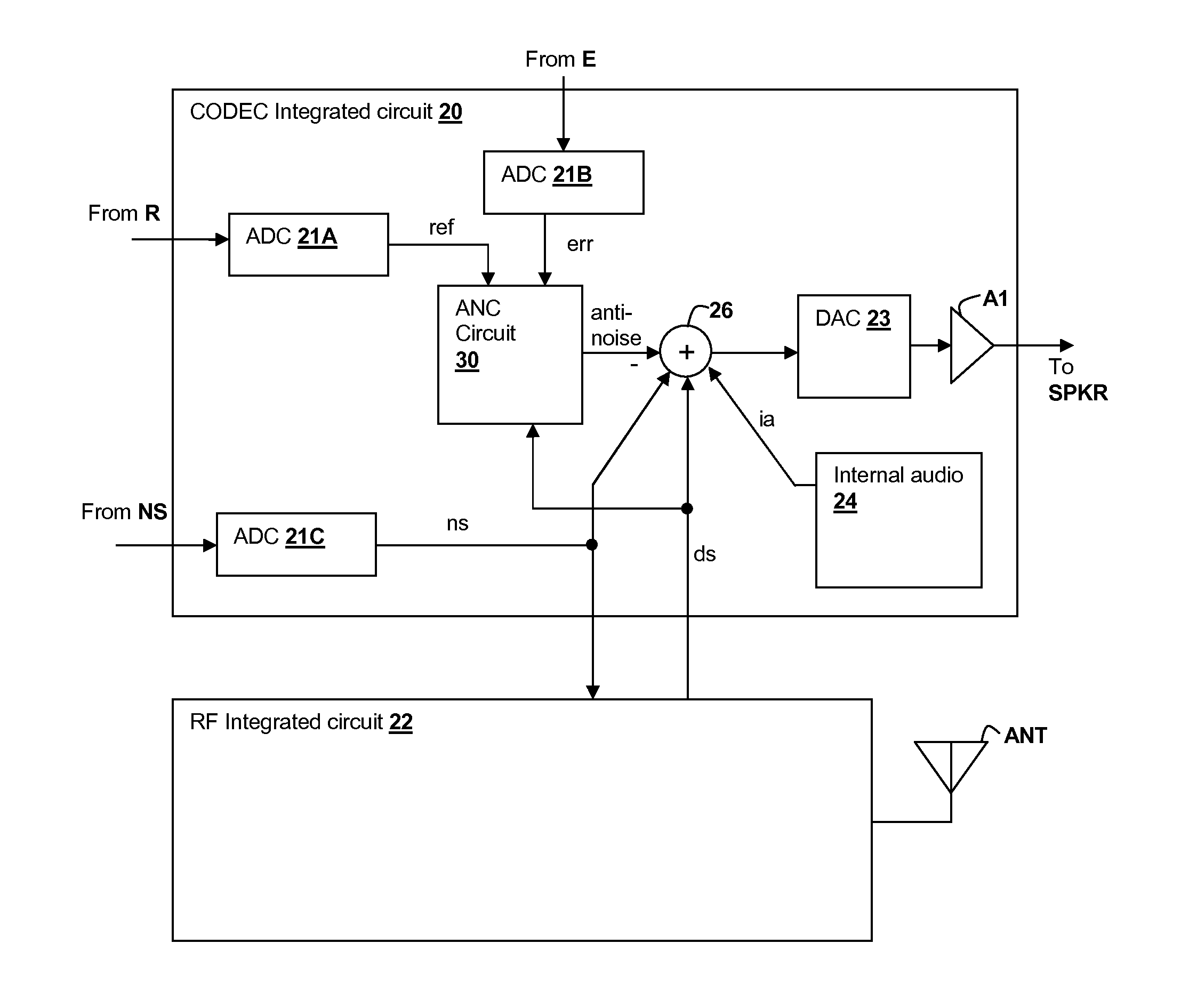
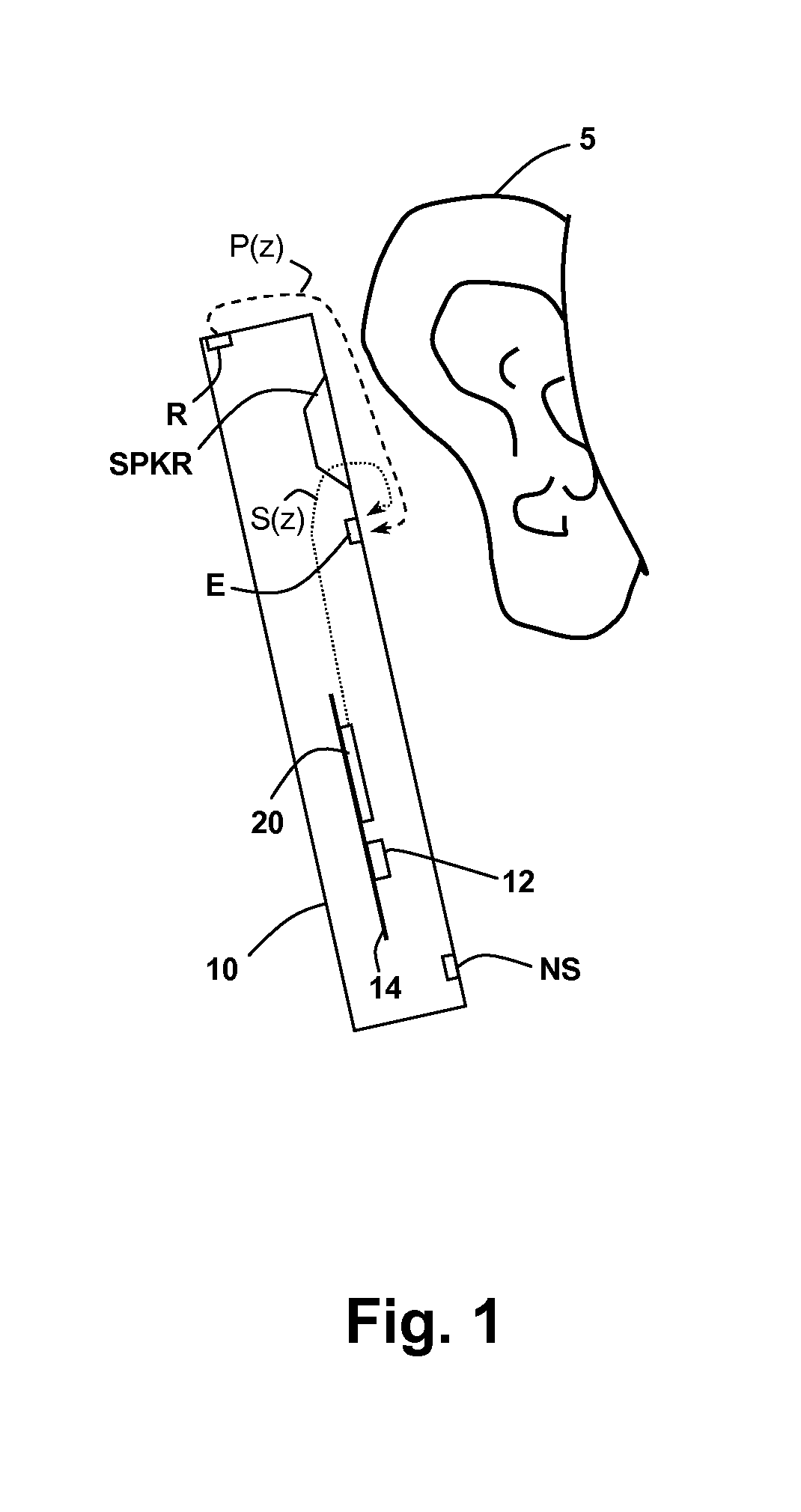
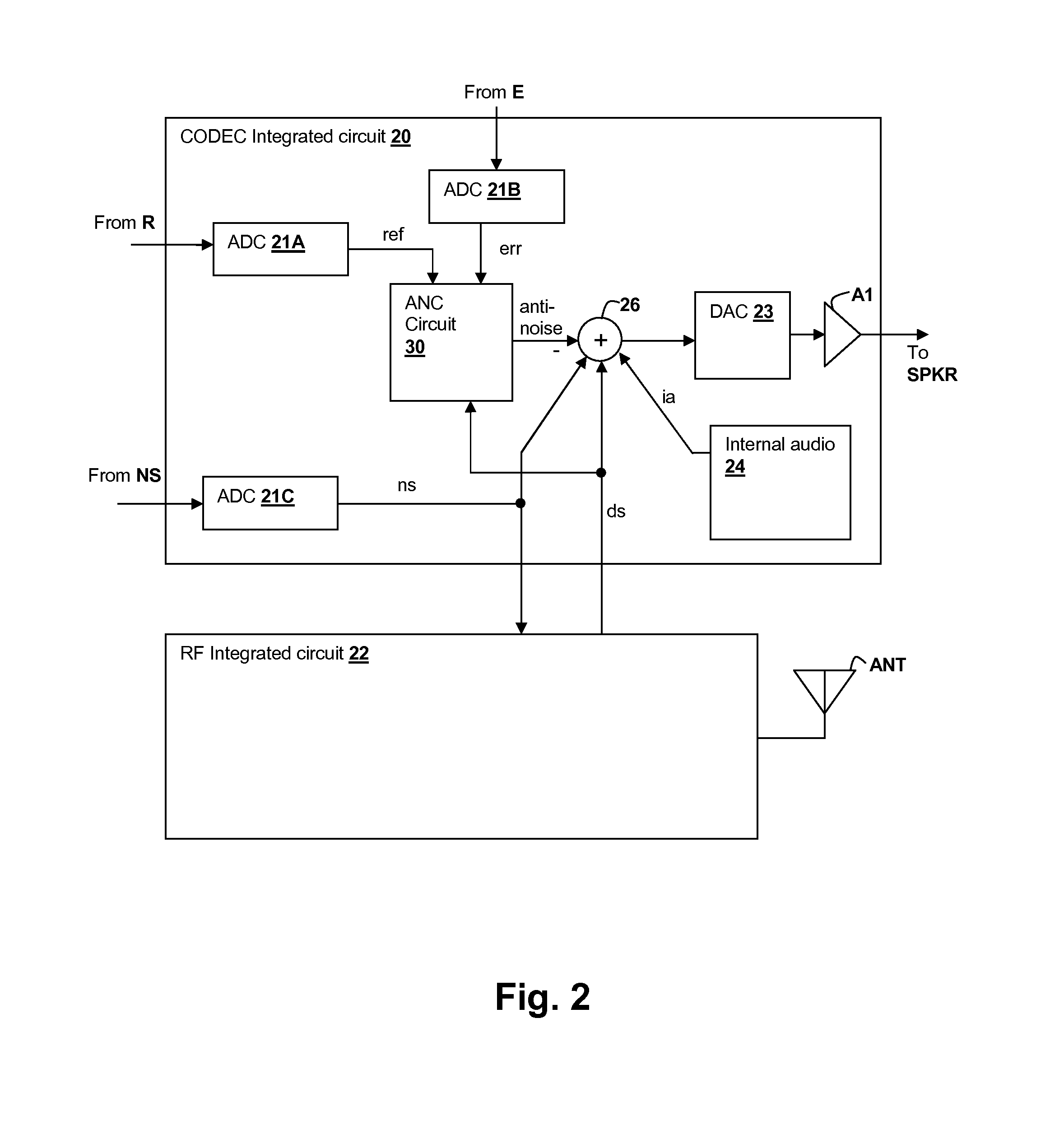
Adaptive noise canceling architecture for a personal audio device
ActiveUS20120308025A1Reduce widthEffective noise cancellationEar treatmentMicrophones signal combinationAdaptive filterTransducer
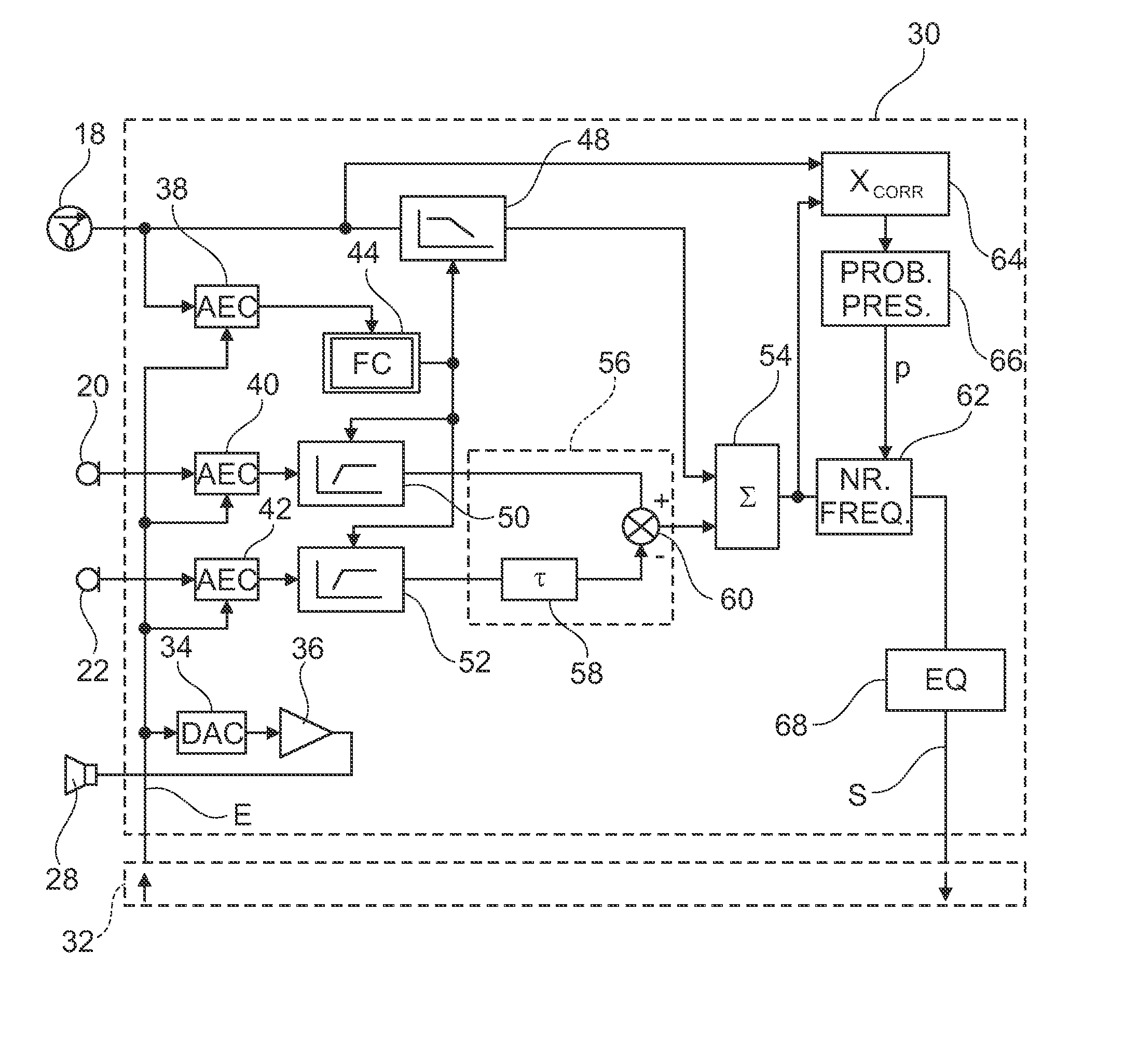
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, includes an adaptive noise canceling (ANC) circuit that adaptively generates an anti-noise signal from a reference microphone signal that measures the ambient audio and an error microphone signal that measures the output of an output transducer plus any ambient audio at that location and injects the anti-noise signal at the transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. A processing circuit uses the reference and error microphone to generate the anti-noise signal, which can be generated by an adaptive filter operating at a multiple of the ANC coefficient update rate. Downlink audio can be combined with the high data rate anti-noise signal by interpolation. High-pass filters in the control paths reduce DC offset in the ANC circuits, and ANC coefficient adaptation can be halted when downlink audio is not detected.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
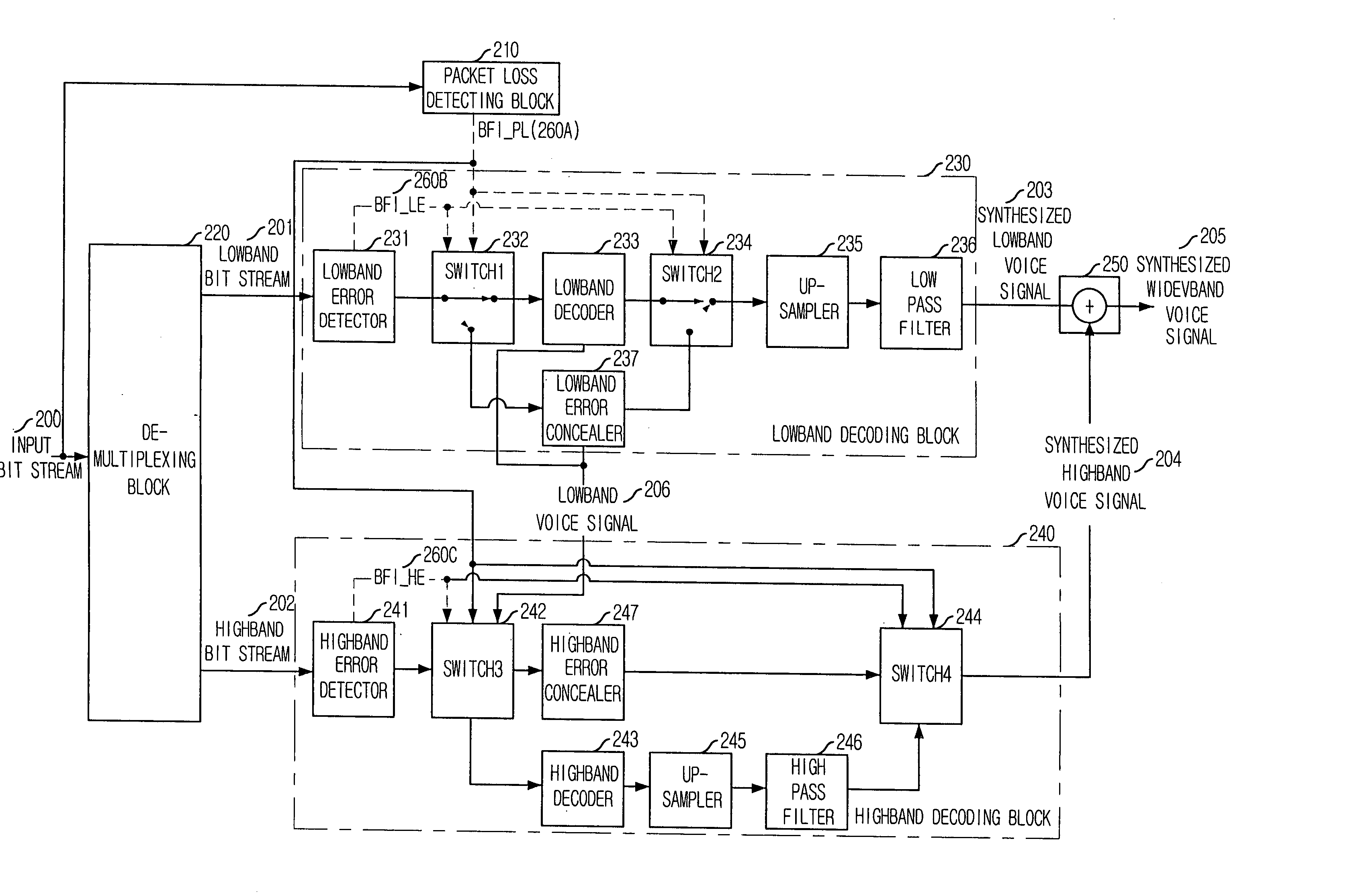
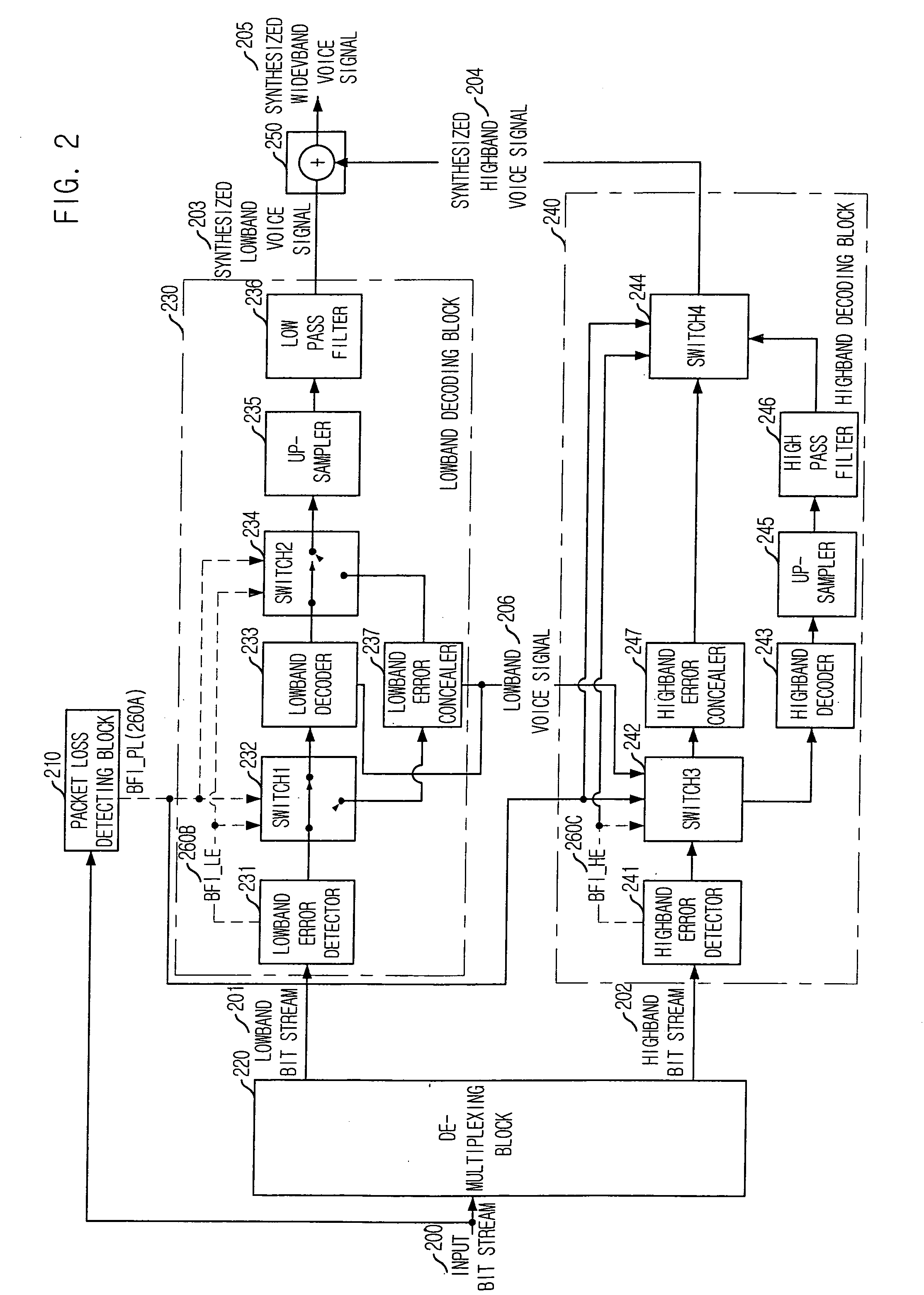
Apparatus and method for concealing highband error in spilt-band wideband voice codec and decoding system using the same
InactiveUS20050143985A1Quality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsBroadbandExcitation signal
An apparatus for concealing a highband error in a spilt-band wideband voice codec in accordance with the present invention is disclosed. The apparatus includes: a lowband LPC coefficient extracting unit for extracting a lowband linear predictive coding (LPC) coefficient from a lowband voice signal passed by a lowband decoding unit; a highband excitation signal generating unit for generating a highband excitation signal based on the lowband voice signal and the lowband LPC coefficient; a highband LPC coefficient generating unit for generating a highband LPC coefficient based on the lowband LPC coefficient; a highband voice synthesizing unit for synthesizing a highband voice signal based on the highband excitation signal and the highband LPC coefficient; and a high pass filtering unit for removing a lowband component of the synthesized highband voice signal by the highband voice synthesis unit and generating the synthesized highband voice signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
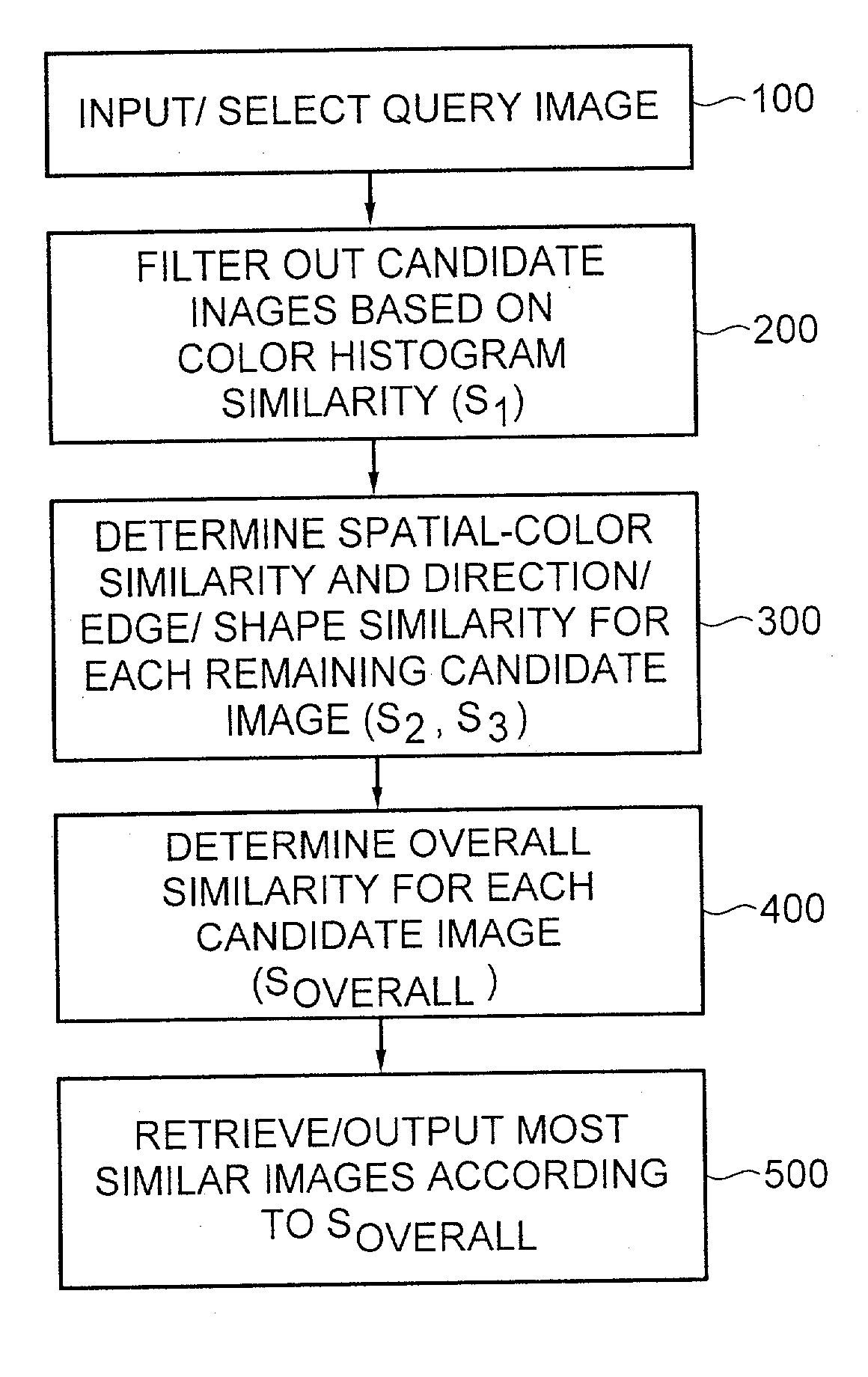
Method for automatic retrieval of similar patterns in image databases
InactiveUS20030179213A1Fast and accurate imageCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDecompositionDatabase index
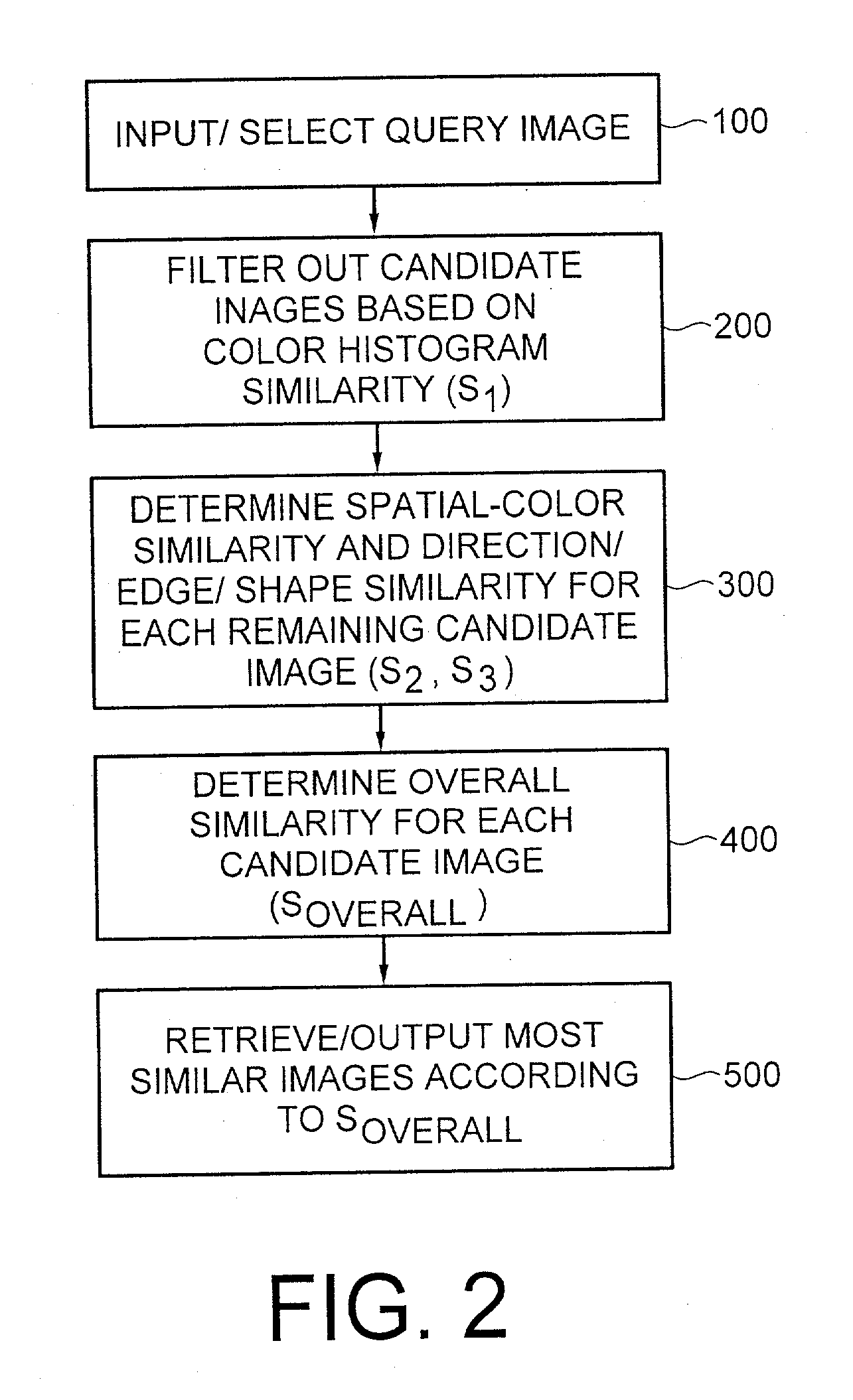
An image retrieval system and method that combines histogram-based features with Wavelet Frame decomposition features, as well as two-pass progressive retrieval process. The proposed invention is robust against illumination changes as well as geometric distortions. During the first round of retrieval, moment features of image histograms in the Karhunen-Loeve color space are derived and used to filter out most of the dissimilar images. During the second round of retrieval, multi-resolution WF decomposition is recursively applied to the remaining images. A set of coefficients of low-pass filtered subimages at the coarsest level, after being mean-subtracted and normalized, are utilized as features containing spatial-color information. Modulus and direction coefficients are calculated from the high-pass filtered X-Y directional subimages at each level, and central moments are derived from the direction histogram of the most significant direction coefficients to obtain TRSI direction / edge / shape features. Since the proposed invention is fast and robustness against illumination and geometric distortions, the invention is quite appealing for real-time image / video database indexing and retrieval applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
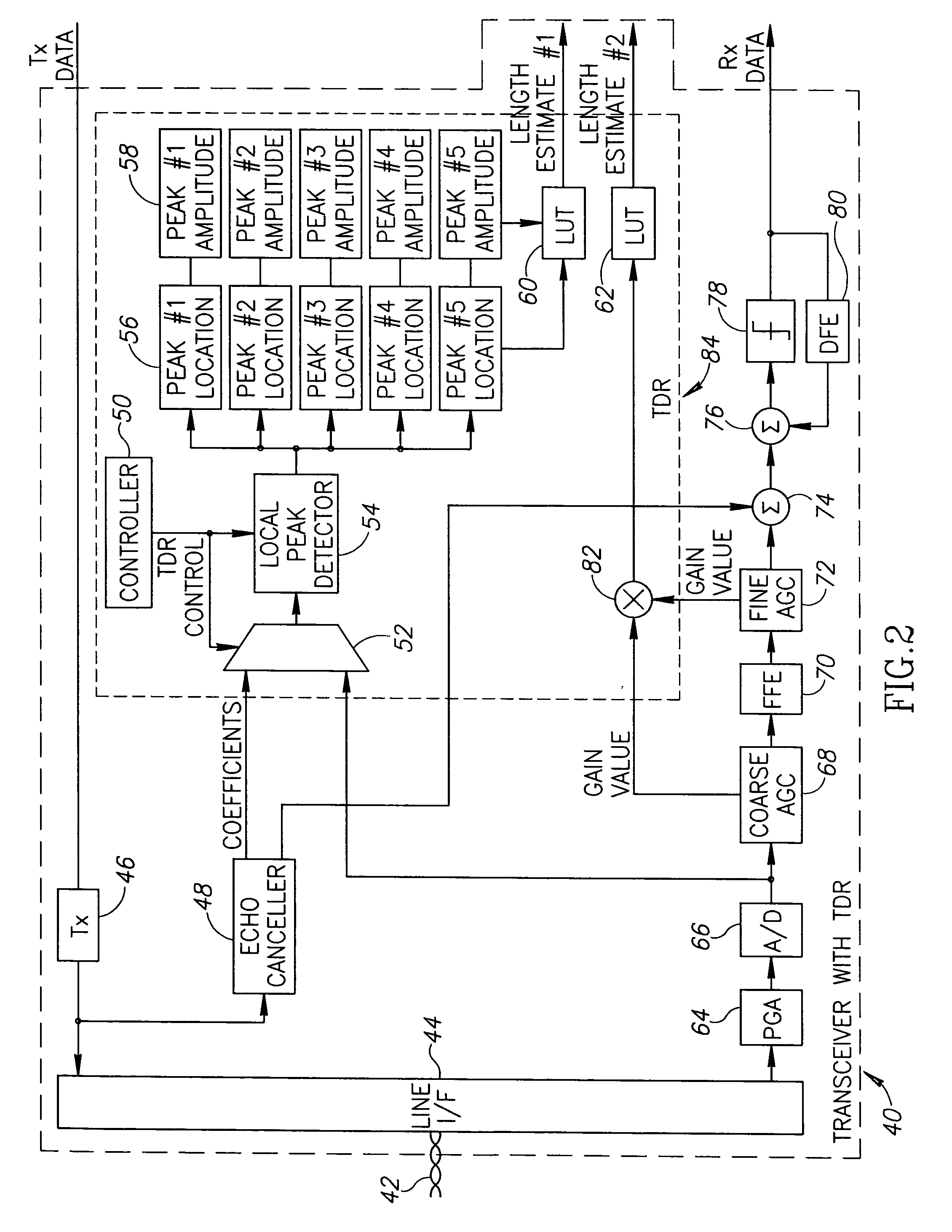
Apparatus for and method of cable diagnostics utilizing time domain reflectometry
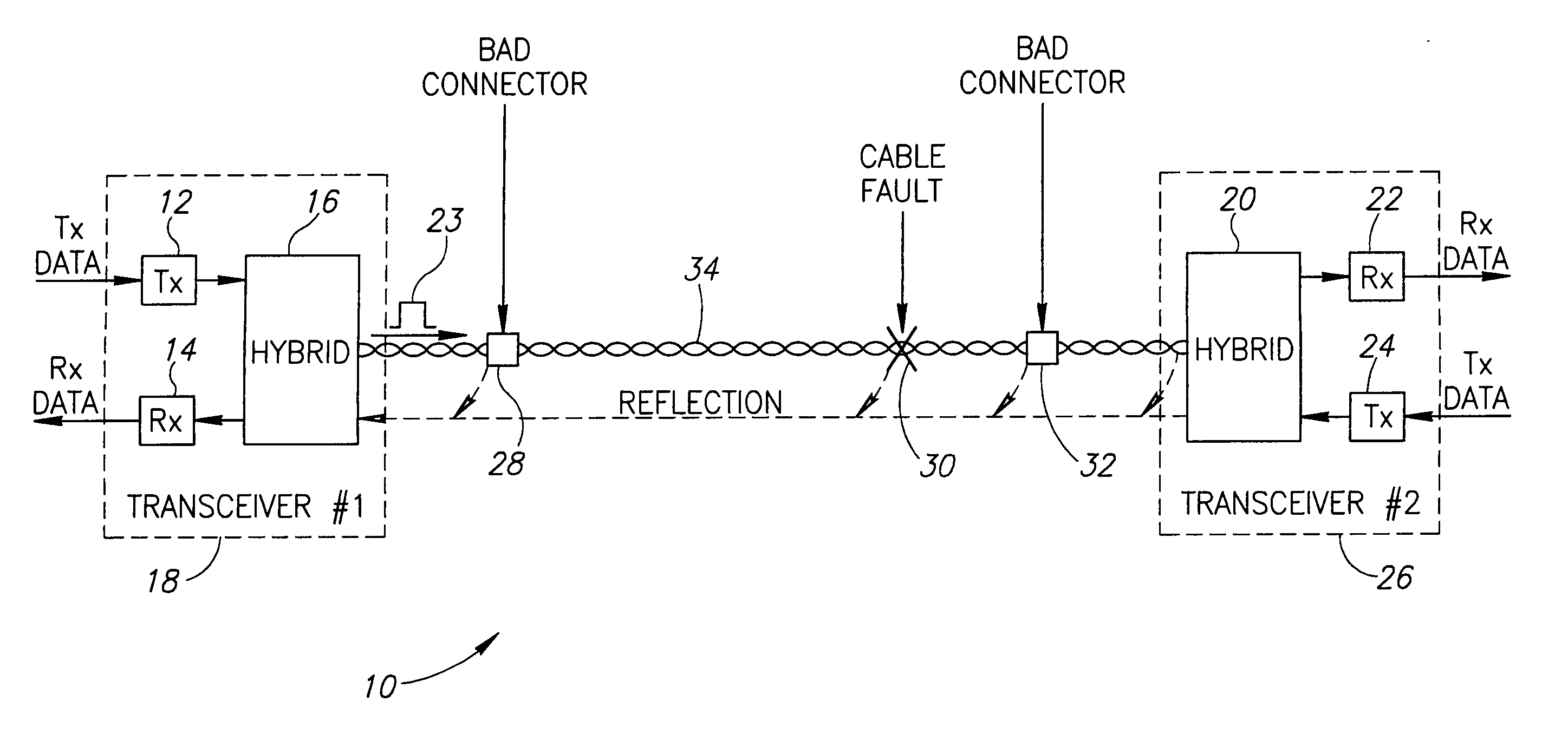
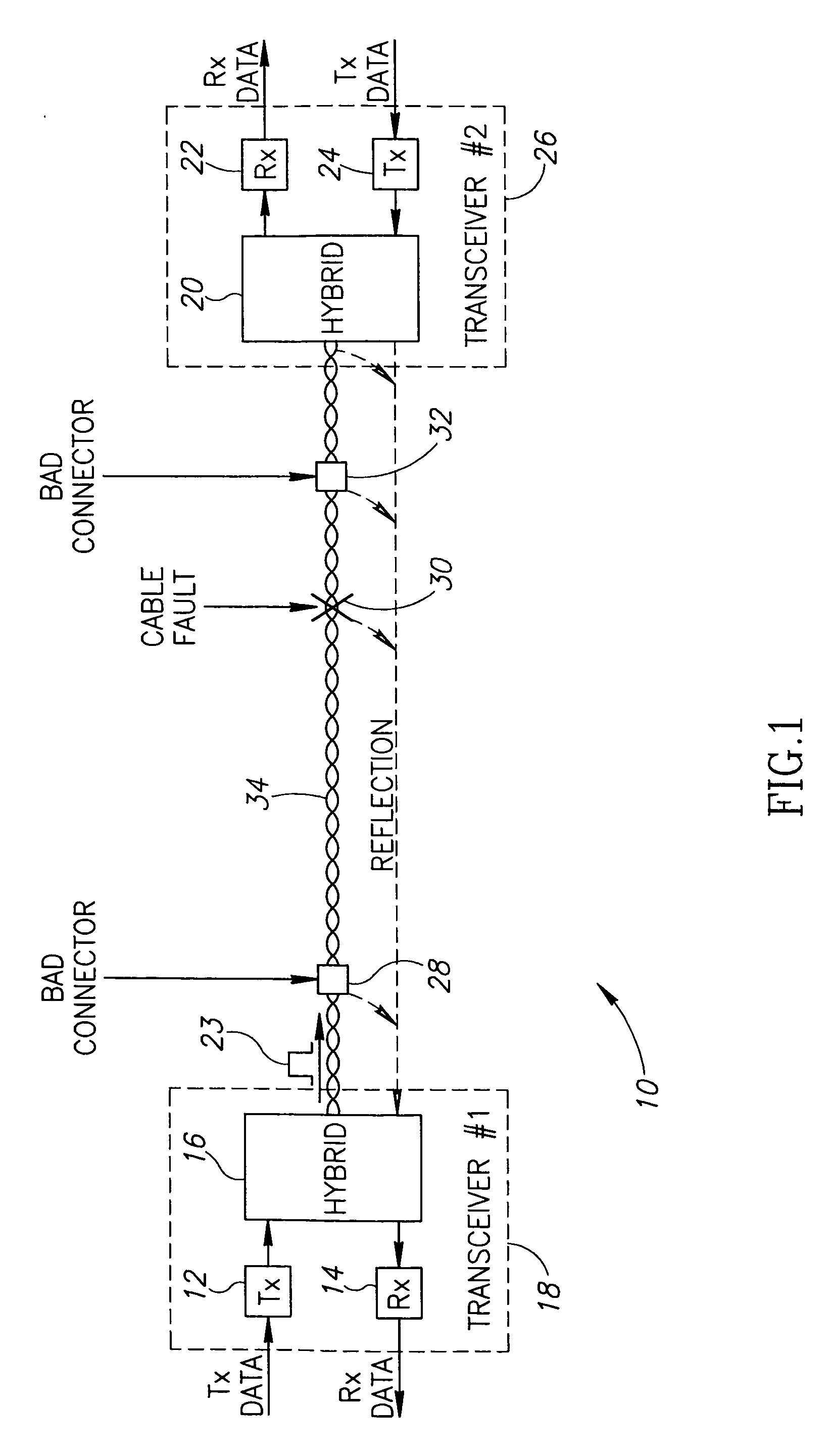
ActiveUS20060181283A1Improve accuracyMinimal modificationResistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsTime domainCoaxial cable
A novel mechanism for performing high accuracy cable diagnostics. The mechanism utilizes time domain reflectometry (TDR) to detect and identify cable faults, perform estimations of cable length, identify cable topology, identify load and irregular impedance on metallic paired cable, such as twisted pair and coaxial cables. The TDR mechanism transmits pulses whose shapes are programmable and analyzes the signal reflections. The shapes of the pulses transmitted can be optimized in accordance with the channel characteristics. Further, the TDR mechanism is adapted to operative in the presence of high pass filters in the channel.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
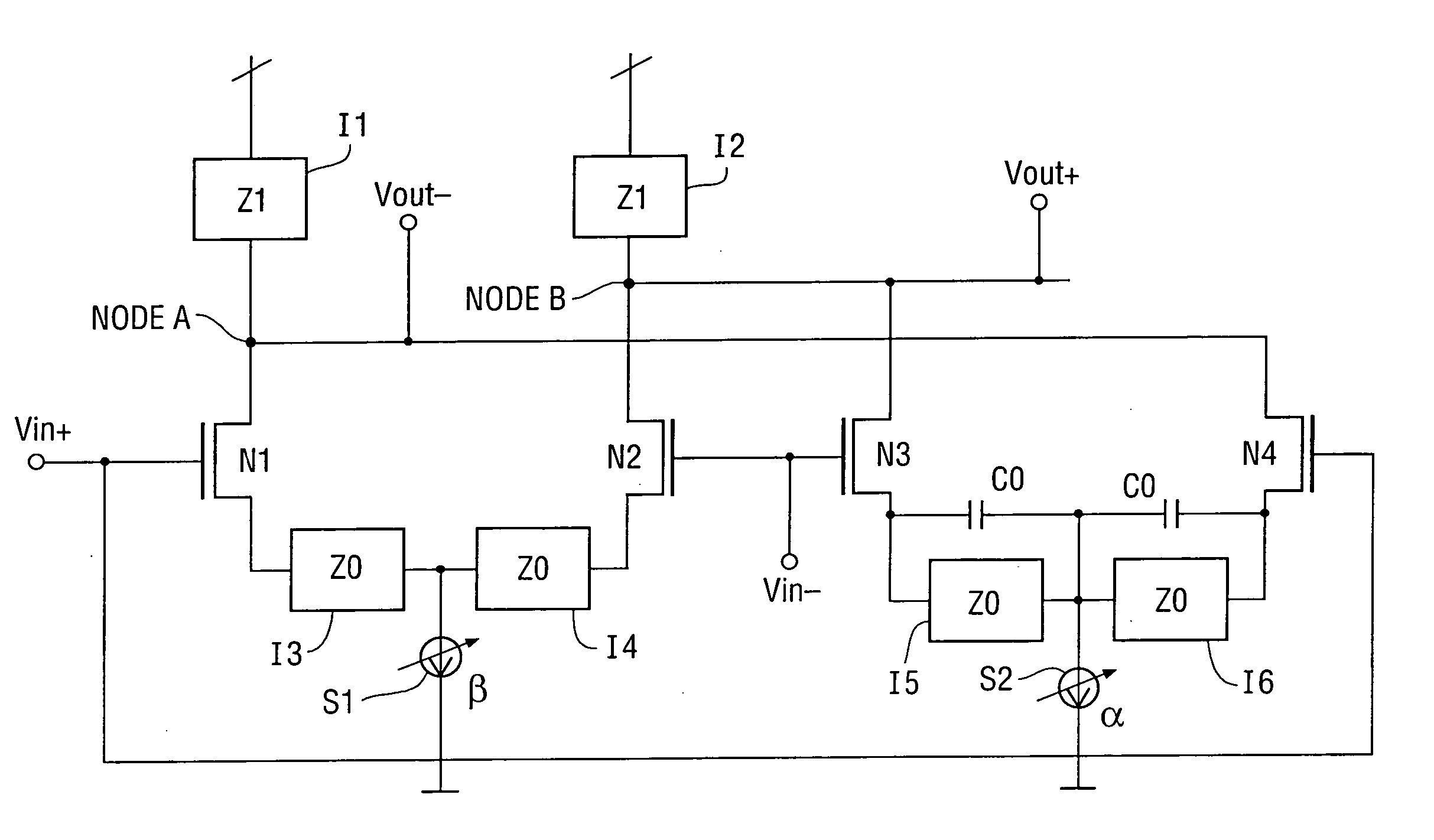
Equalizer with controllably weighted parallel high pass and low pass filters and receiver including such an equalizer
ActiveUS20070201546A1Multiple-port networksMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCMOSHigh-pass filter
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Impedance circuit, and filter circuit, amplifier circuit, semiconductor integrated circuit, electronic component, and wireless communications device using the same
InactiveUS20050093645A1Small sizeMultiple-port networksCoupling devicesEngineeringCommunication device
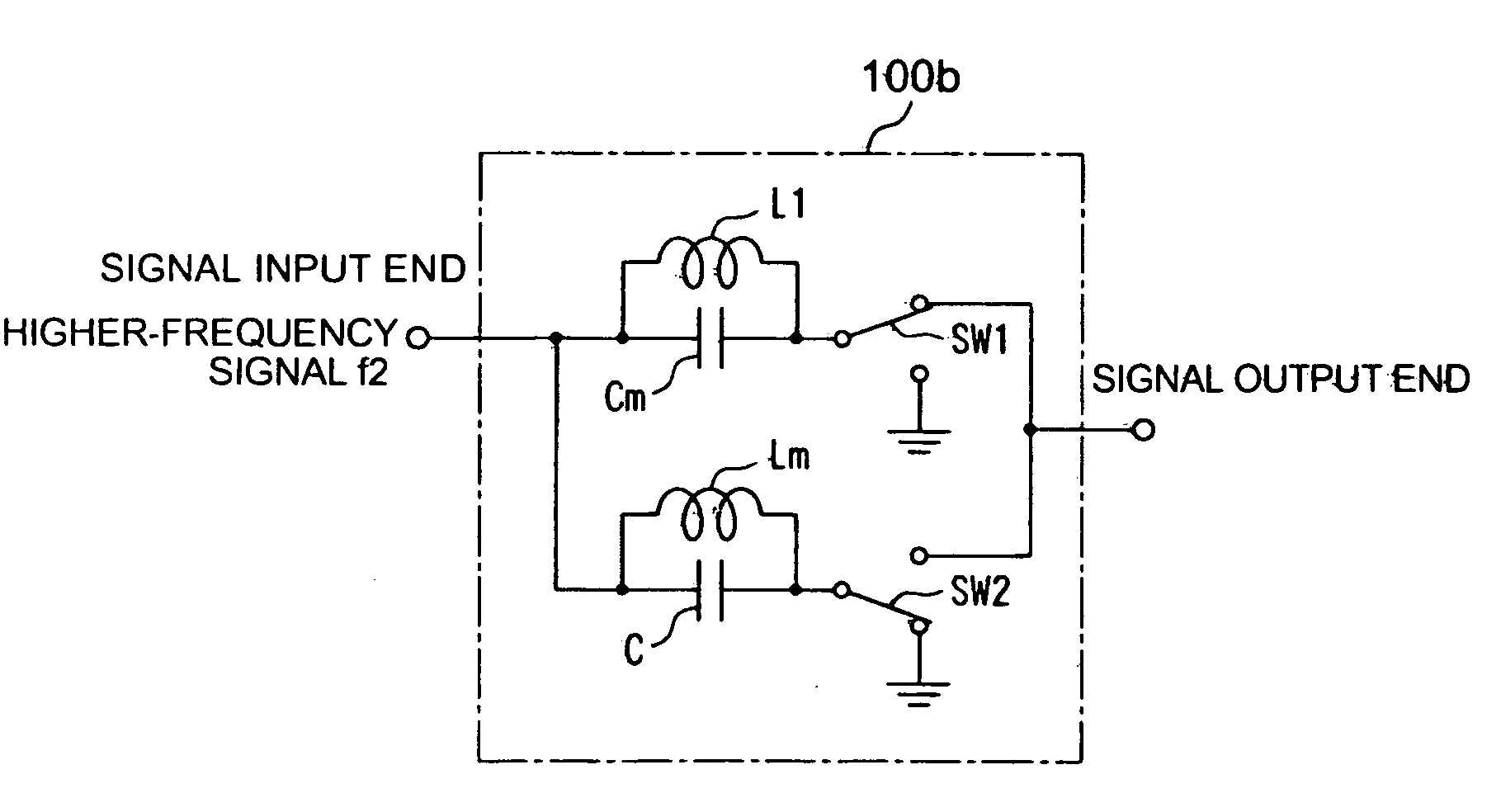
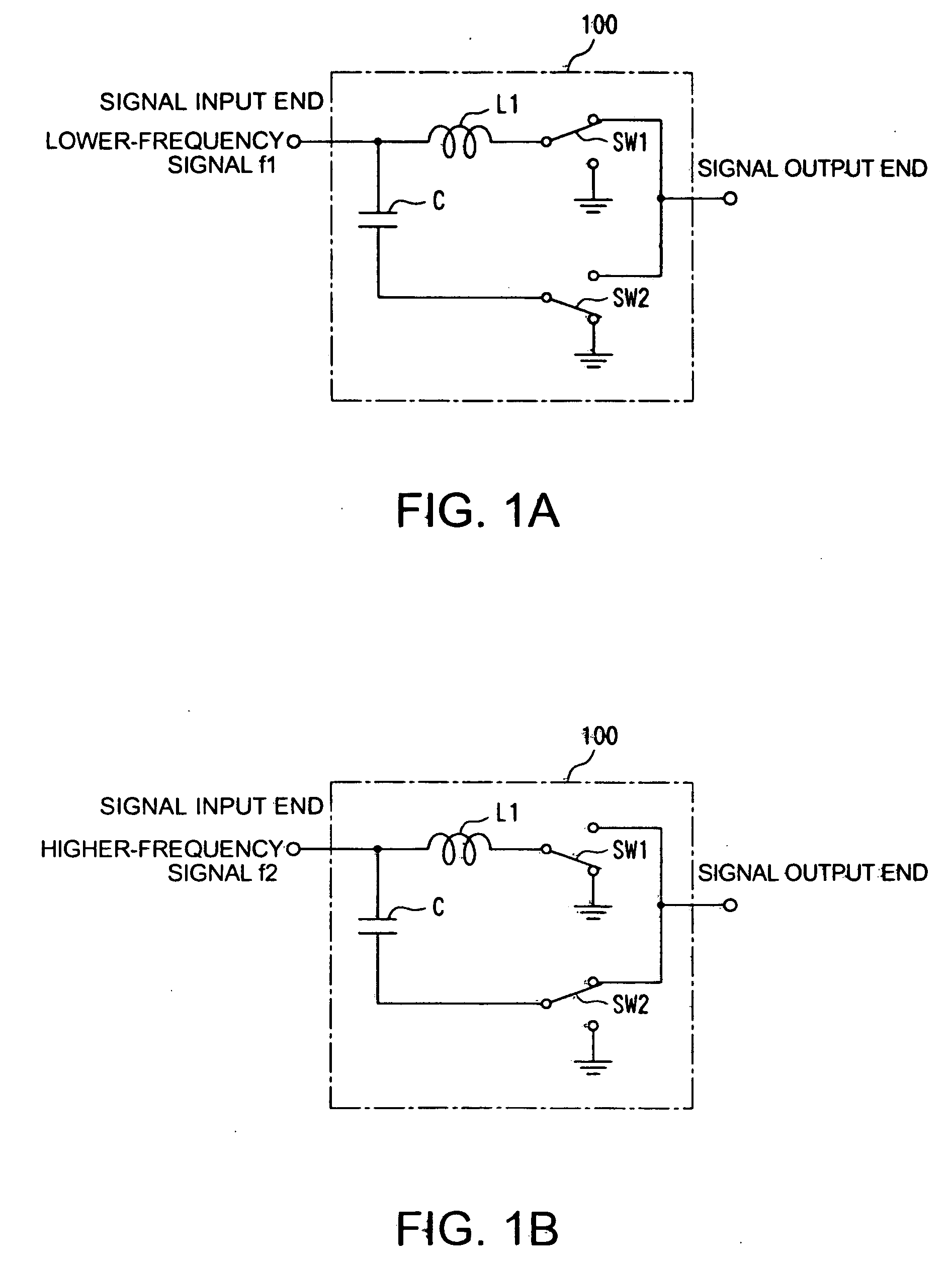
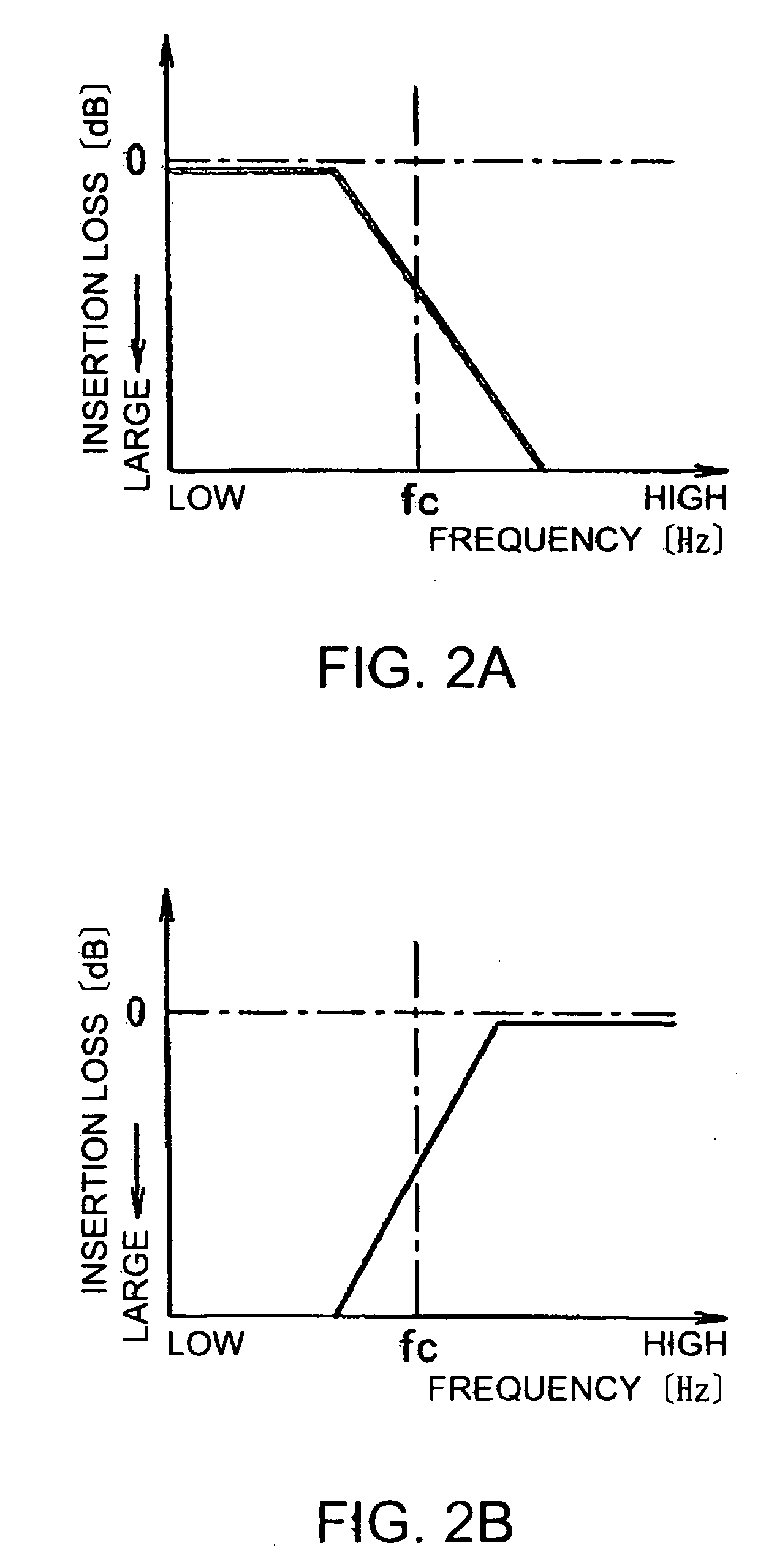
A filter circuit is provided wherein one end of an inductor is connected to one end of a capacitor to form a signal input end. The other end of the inductor is connected to a first switch circuit, and the other end of the capacitor is connected to a second switch circuit. When a lower-frequency signal in a 2.4 GHz band is to be inputted, a low-pass filter circuit is formed by connecting the other end of the inductor to a signal output end and the other end of the capacitor to ground, and when a higher-frequency signal in a 5 GHz band is to be inputted, a high-pass filter circuit is formed by connecting the other end of the inductor to ground and the other end of the capacitor to the signal output end, by manipulating the first and second switch circuits.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
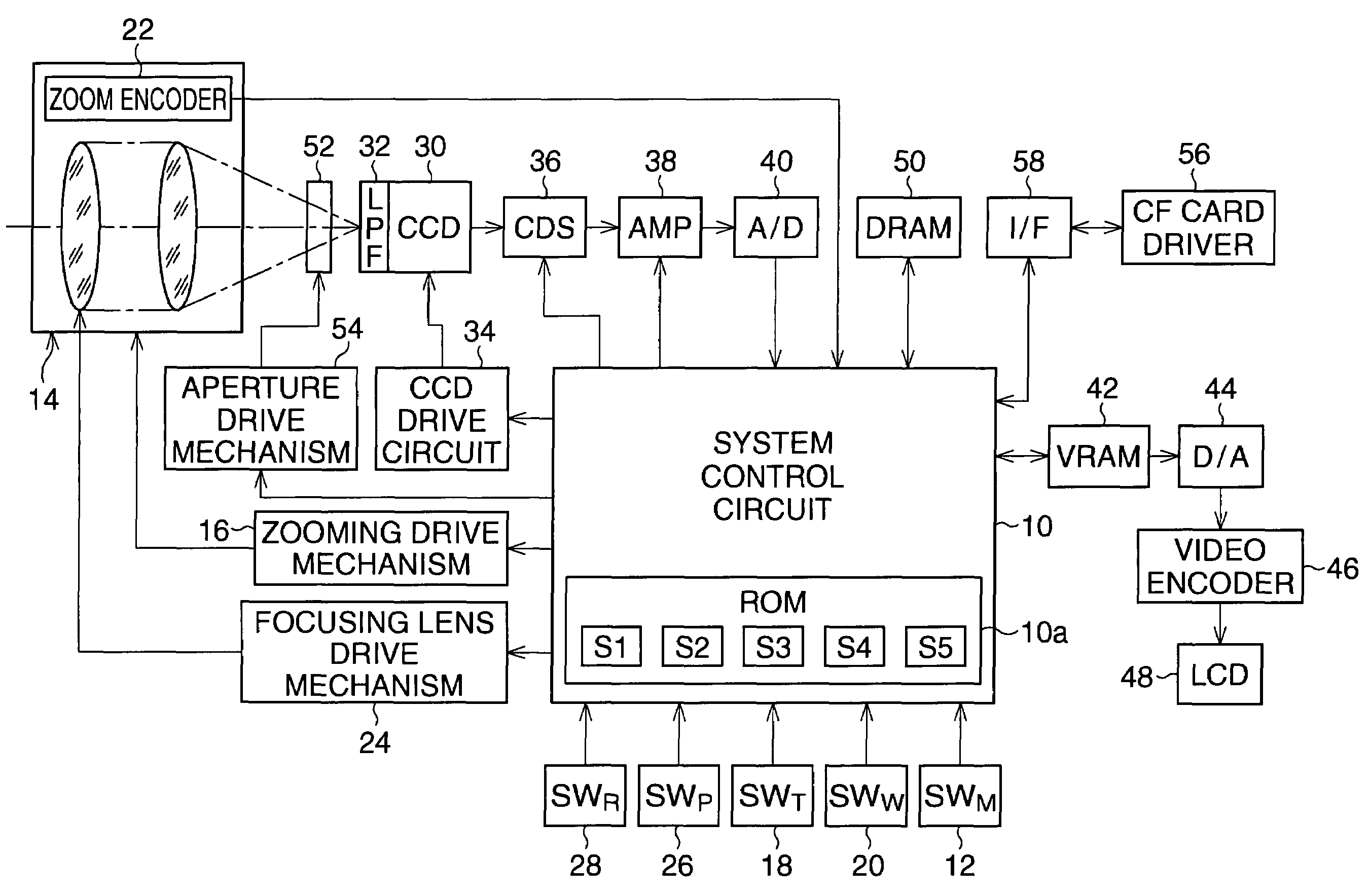
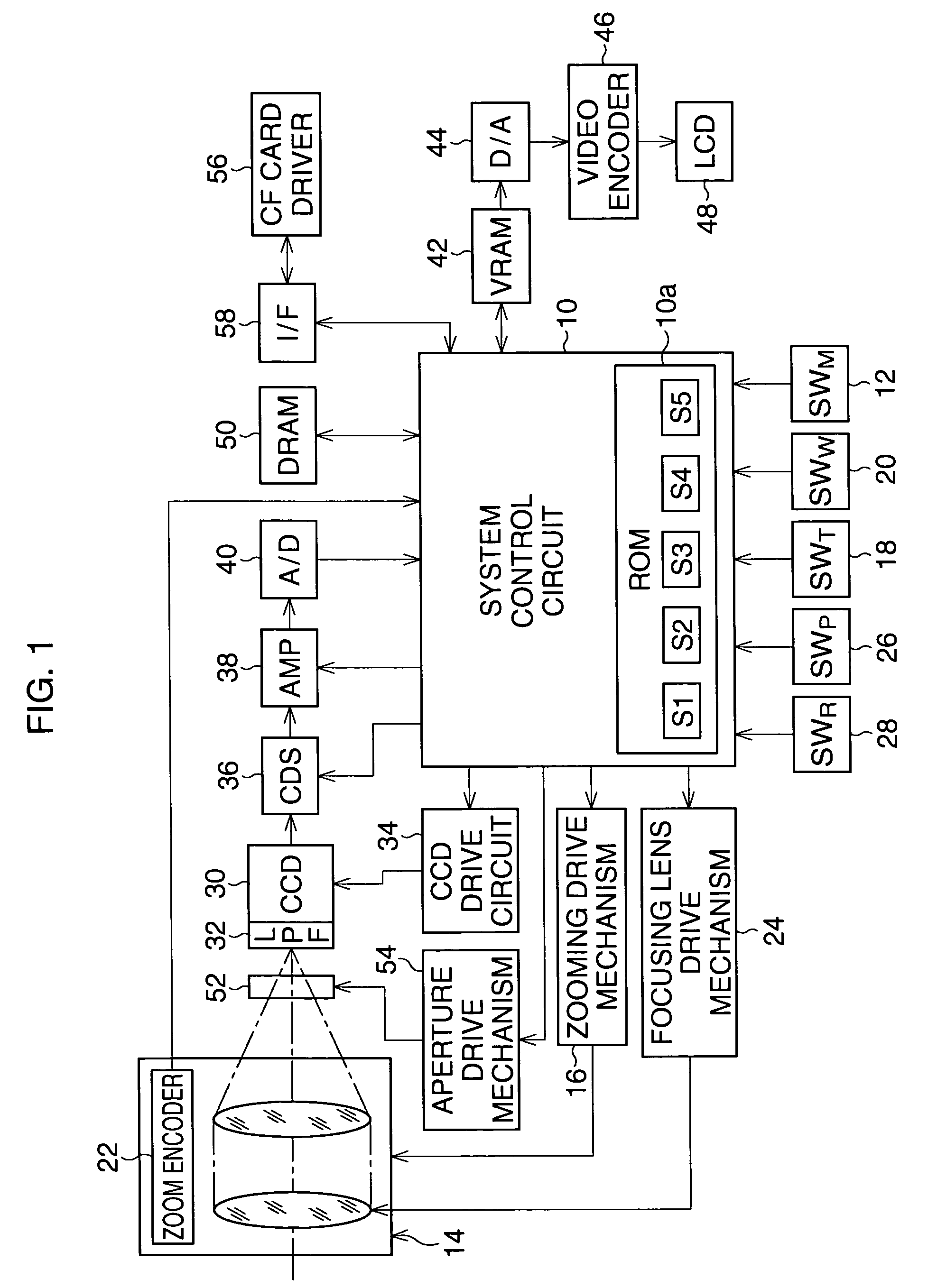
Digital camera
InactiveUS7221394B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsBand-pass filterTime control
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Connector
InactiveUS20050032430A1Improve responseIncrease costCoupling for high frequencyTwo-part coupling devicesDigital signalLow frequency
The present invention relates to a connector which includes a plug unit and a receptacle. The plug unit includes a housing board and a transmission path board. The housing board has a housing board body and first connection terminals and second connection terminals. The transmission path board has a transmission path board body, plural differential signal patterns which are connected to the first connection terminals and the second connection terminals of the housing board, and high pass filters which are connected to each of the differential signal patterns. The receptacle has a receptacle body and pin contacts. According to the present invention, a low-frequency component of a digital signal is attenuated. Thus, since an attenuation factor of the high-frequency component and an attenuation factor of the low-frequency component of the digital signal can be set substantially the same, the digital signal can be transmitted surely.
Owner:JST MFG CO LTD
High-frequency circuit and high-frequency device
ActiveUS20070190954A1Excellent electrical propertiesAvoid interferenceMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityBandpass filteringCapacitance
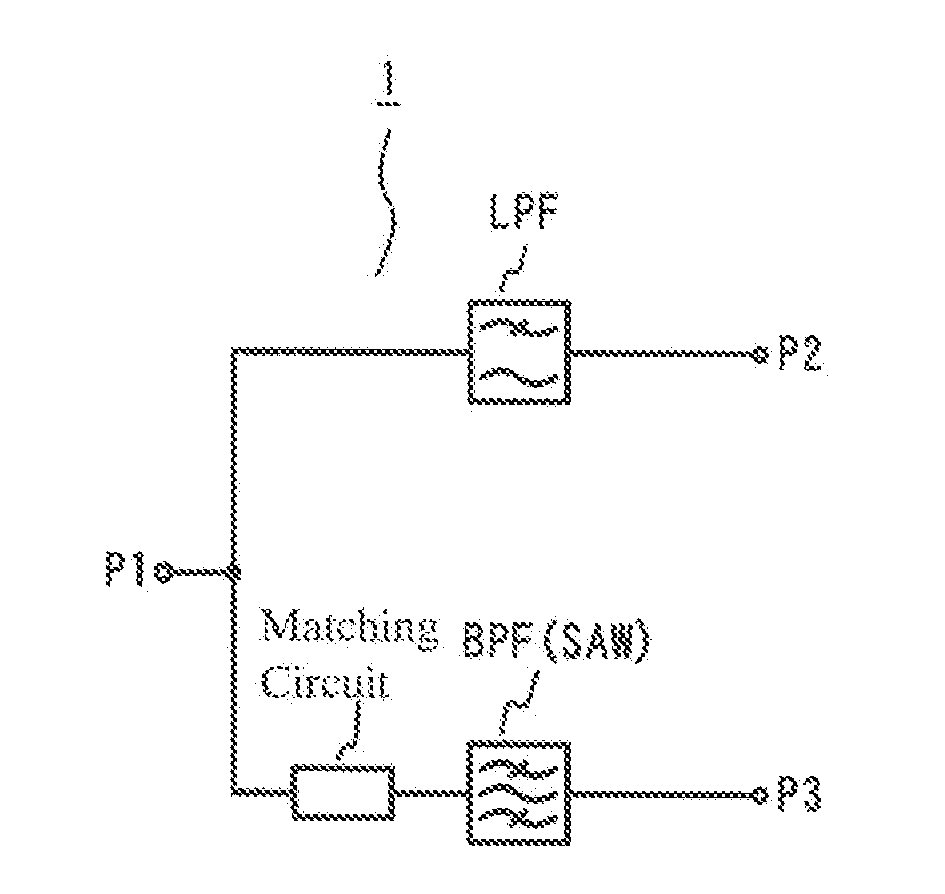
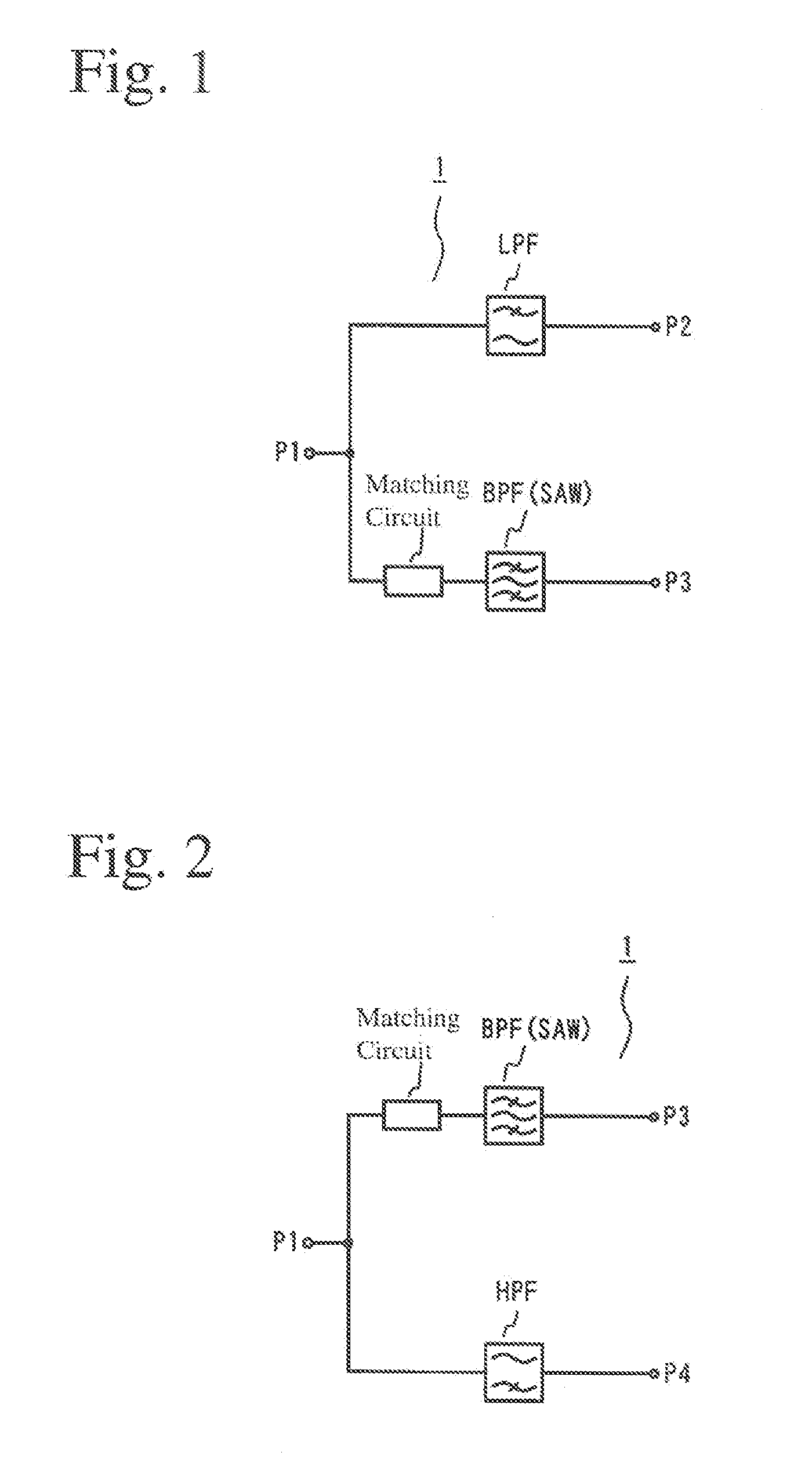
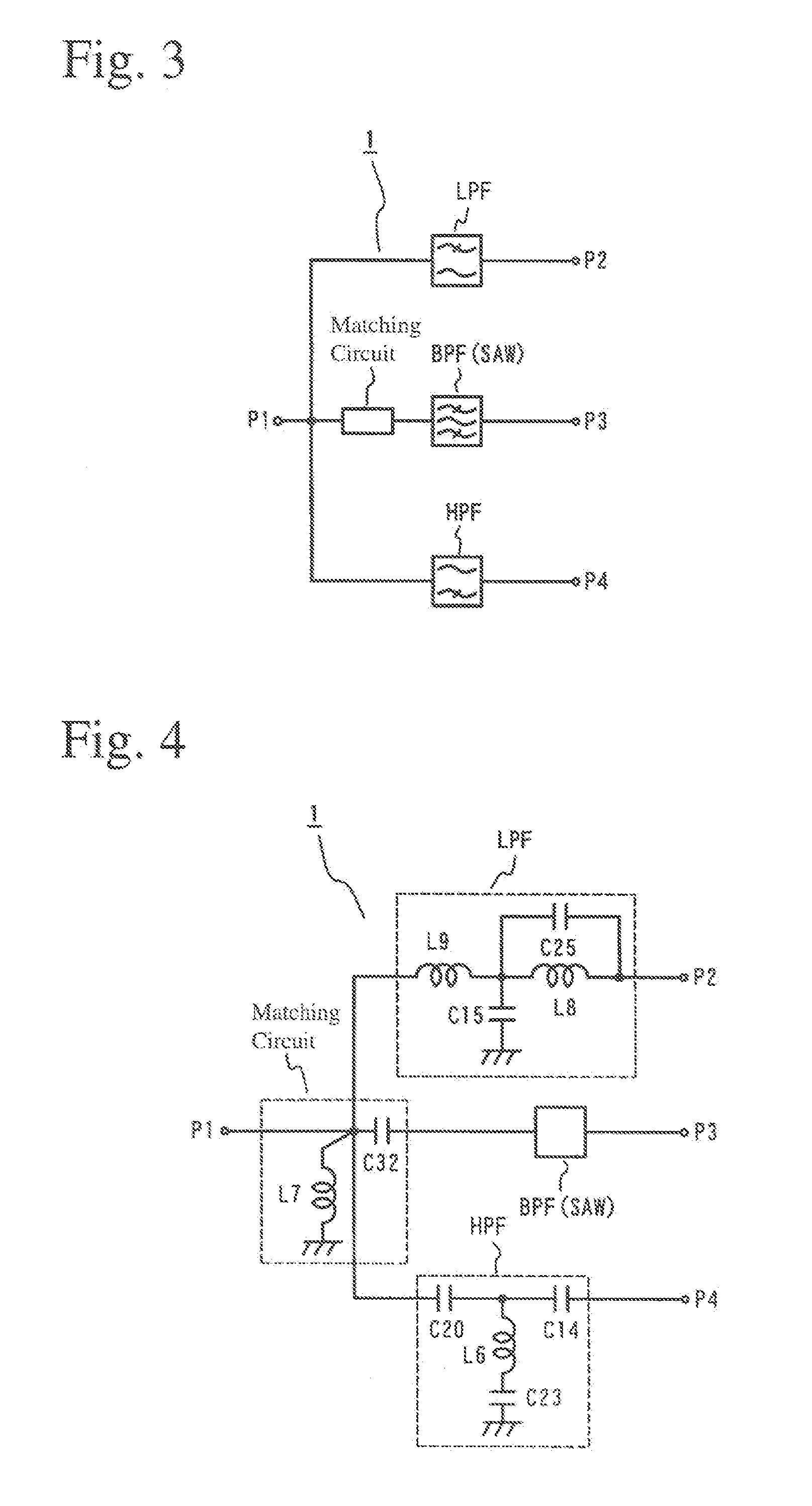
A high-frequency circuit for branching high-frequency signals for pluralities of communications systems of different frequencies, which comprises a lowpass filter circuit disposed between first and second ports and / or a highpass filter circuit disposed between the first port and a fourth port; and a matching circuit and a bandpass filter circuit disposed between the first port and a third port; the lowpass filter circuit, the highpass filter circuit and the matching circuit comprising capacitance elements and inductance elements; the bandpass filter circuit being a SAW filter; and the passband f1 of the lowpass filter circuit, the passband f2 of the bandpass filter circuit, and the passband f3 of the highpass filter circuit meeting the condition of f1<f2<f3.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multiplexers employing bandpass-filter architectures
ActiveUS20060145782A1Multiple-port networksTransmission path multiple useBandpass filteringMobile Telephone Service
A multiplexer, such as a diplexer, is delineated. The multiplexer may be employed in a communications system that may communicate in multiple frequency bands within a predefined range of frequencies, e.g., 2400 MHz-4900 MHz. The communications system may operate in a network, such as a wireless local area network, without significant interference from signals used by a cellular / mobile telephone system. The multiplexer may include multiple channels with bandpass filters that may be formed with lumped inductors and lumped capacitors. In at least one of the channels, the bandpass filter may be formed by combining at least one lowpass filter with at least one highpass filter.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Combined microphone and earphone audio headset having means for denoising a near speech signal, in particular for a " hands-free" telephony system
InactiveUS20120278070A1Reduce noiseEasy to useBone conduction transducer hearing devicesSpeech analysisEngineeringHands free
The headset comprises: a physiological sensor suitable for being coupled to the cheek or the temple of the wearer of the headset and for picking up non-acoustic voice vibration transmitted by internal bone conduction; lowpass filter means for filtering the signal as picked up; a set of microphones picking up acoustic voice vibration transmitted by air from the mouth of the wearer of the headset; highpass filter means and noise-reduction means for acting on the signals picked up by the microphones; and mixer means for combining the filtered signals to output a signal representative of the speech uttered by the wearer of the headset. The signal of the physiological sensor is also used by means for calculating the cutoff frequency of the lowpass and highpass filters and by means for calculating the probability that speech is absent.
Owner:PARROT
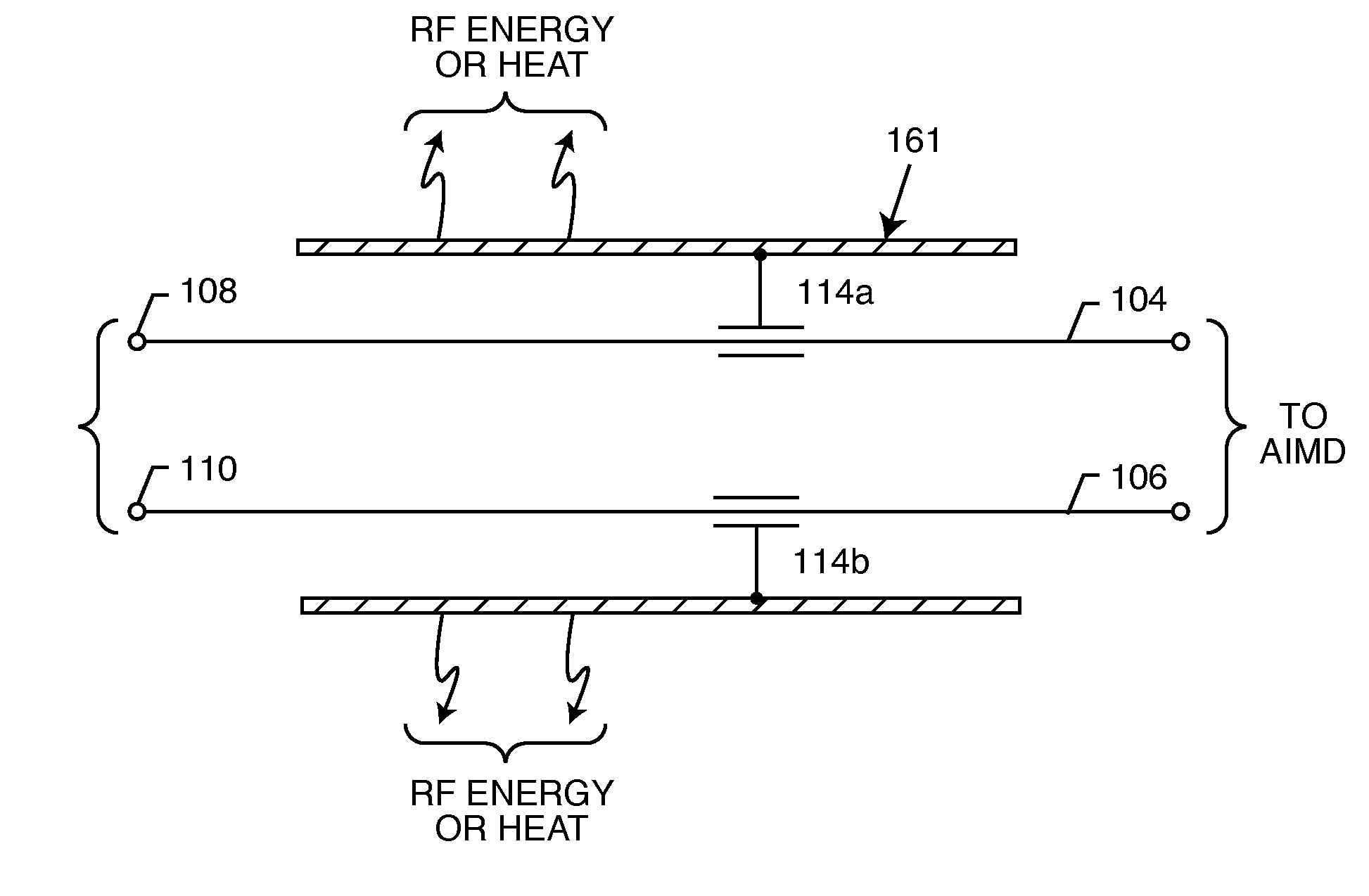
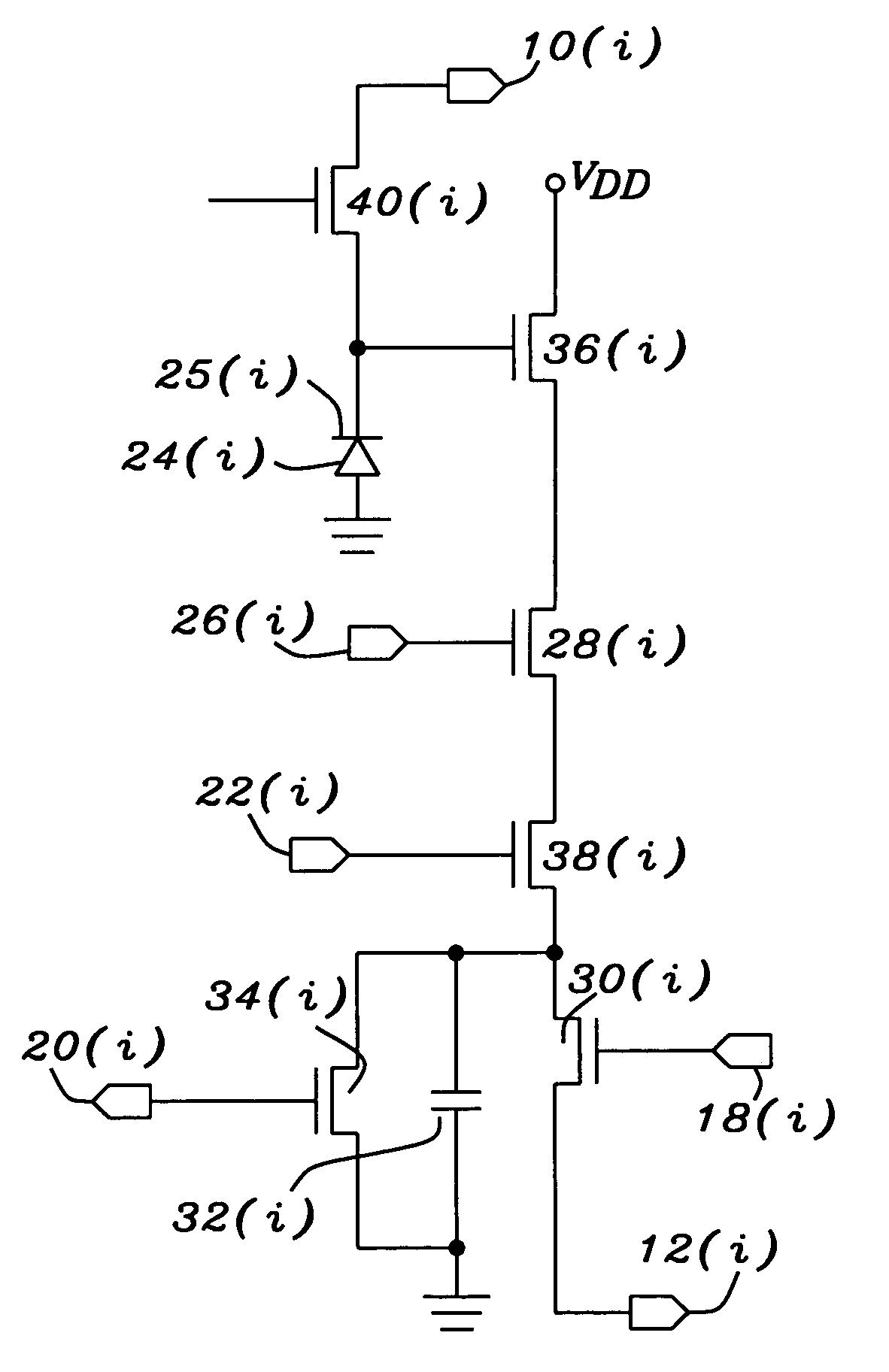
Switched diverter circuits for minimizing heating of an implanted lead and/or providing EMI protection in a high power electromagnetic field environment
InactiveUS20100191236A1Avoid passingMultiple-port networksElectrocardiographyNonlinear circuit elementsEnergy transfer
An energy management system that facilitates the transfer of high frequency energy induced on an implanted lead or a leadwire includes an energy dissipating surface associated with the implanted lead or the leadwire, a diversion or diverter circuit associated with the energy dissipating surface, and at least one non-linear circuit element switch for diverting energy in the implanted lead or the leadwire through the diversion circuit to the energy dissipating surface. In alternate configurations, the switch may be disposed between the implanted lead or the leadwire and the diversion circuit, or disposed so that it electrically opens the implanted lead or the leadwire when diverting energy through the diversion circuit to the energy dissipating surface. The non-linear circuit element switch is typically a PIN diode. The diversion circuit may be either a high pass filter or a low pass filter.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
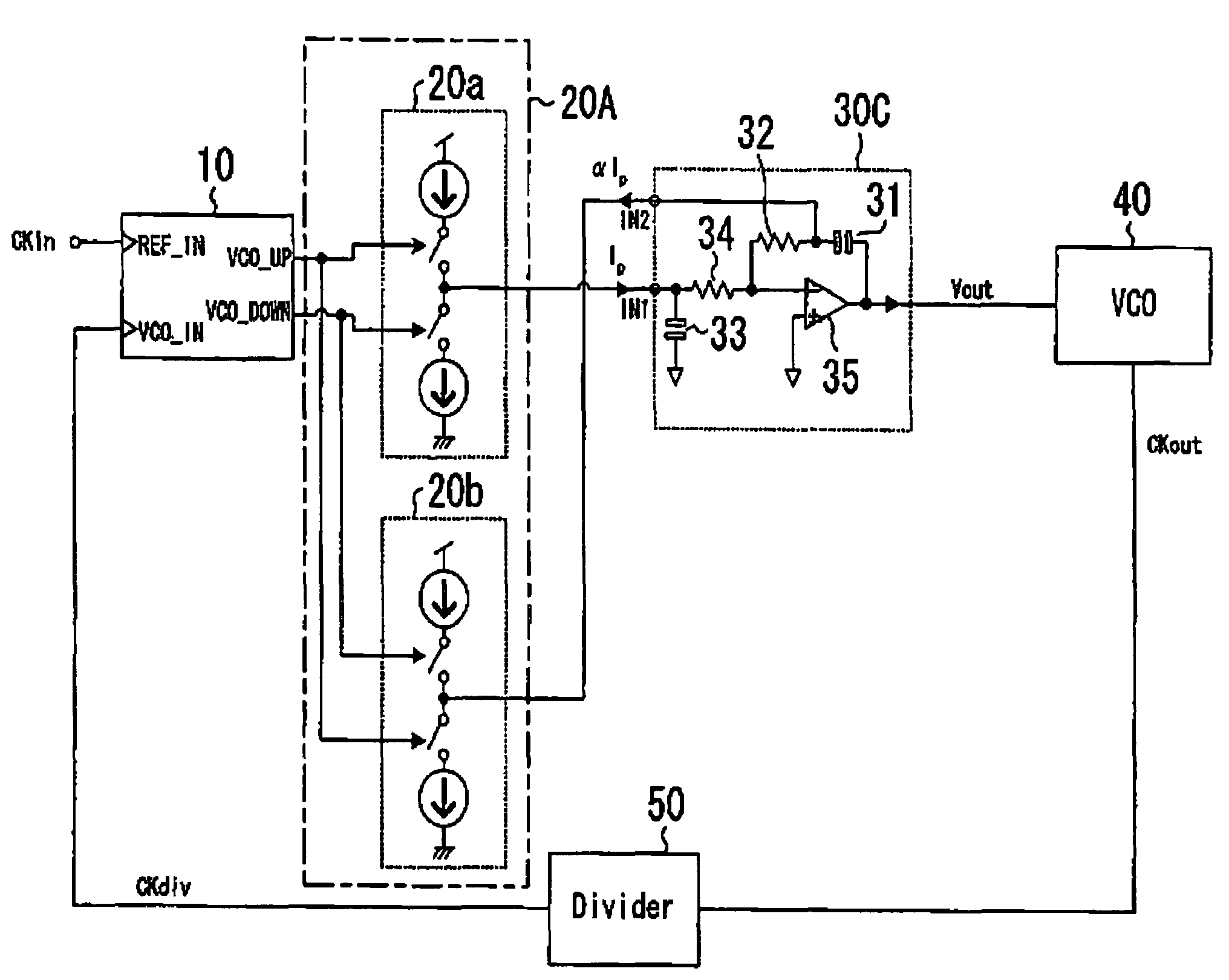
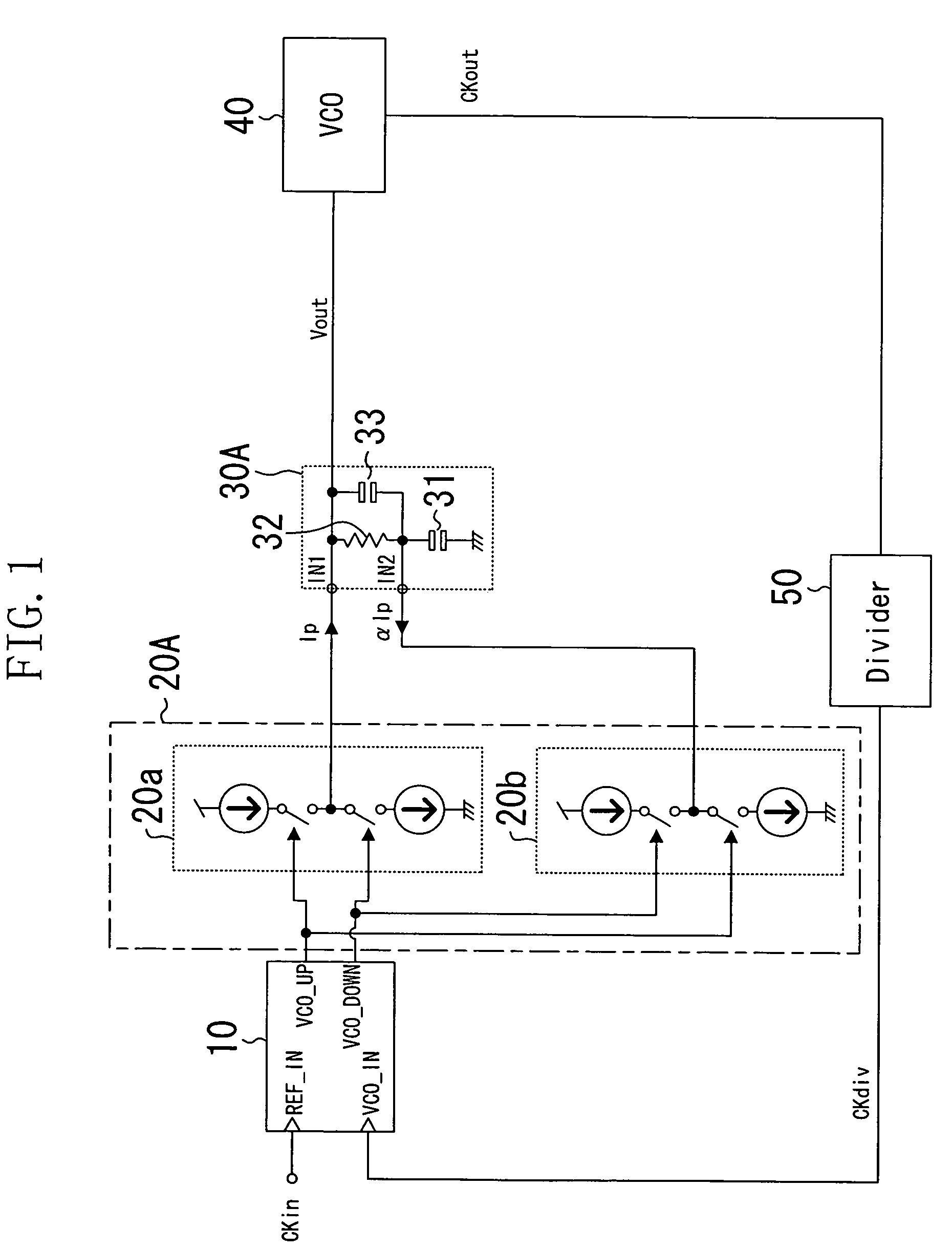
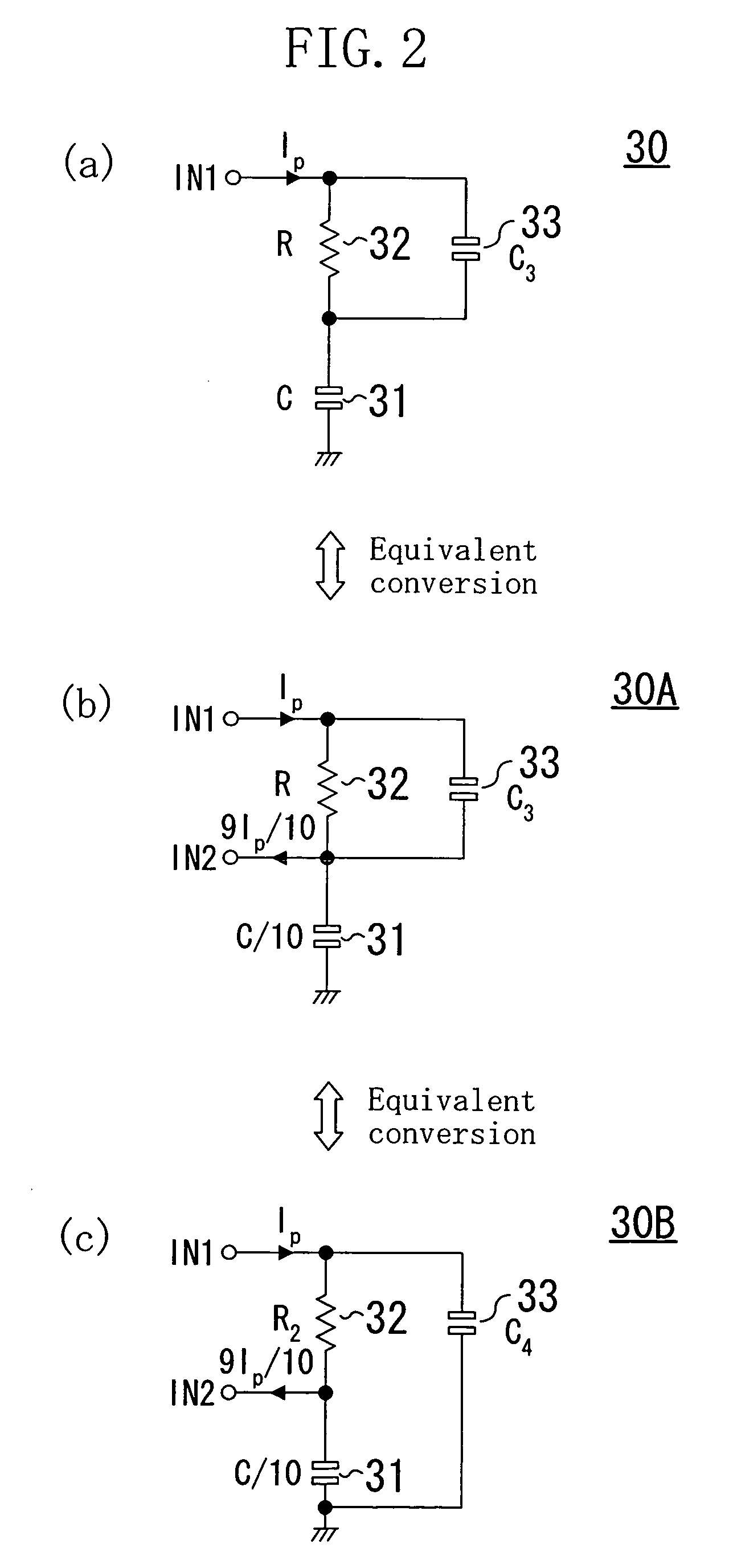
Low-pass filter, feedback system, and semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7078948B2Reduce circuit areaSmall sizeFluid heatersMultiple-port networksCircuit complexityCapacitance
In a low-pass filter which is preferably used as a loop filter in a PLL or DLL, filter characteristics which are the same as those of a conventional low-pass filter are realized without causing collateral problems, such as an increase in the circuit area, the circuit complexity, or the resistance value, which may be caused due to size reduction of a capacitive element in the conventional low-pass filter. Thus, in a loop filter including a capacitive element and a resistive element which are connected in series, the first input terminal is provided at the side including the resistive element, and the second input terminal is provided at a connection point of the capacitive element and the resistive element. The first input terminal is supplied with the first electric current. On the other hand, the second electric current, which is a part of the first electric current supplied to the first input terminal, is extracted from the second input terminal, so that the electric current flowing into the capacitive element is smaller than the electric current flowing through the resistive element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
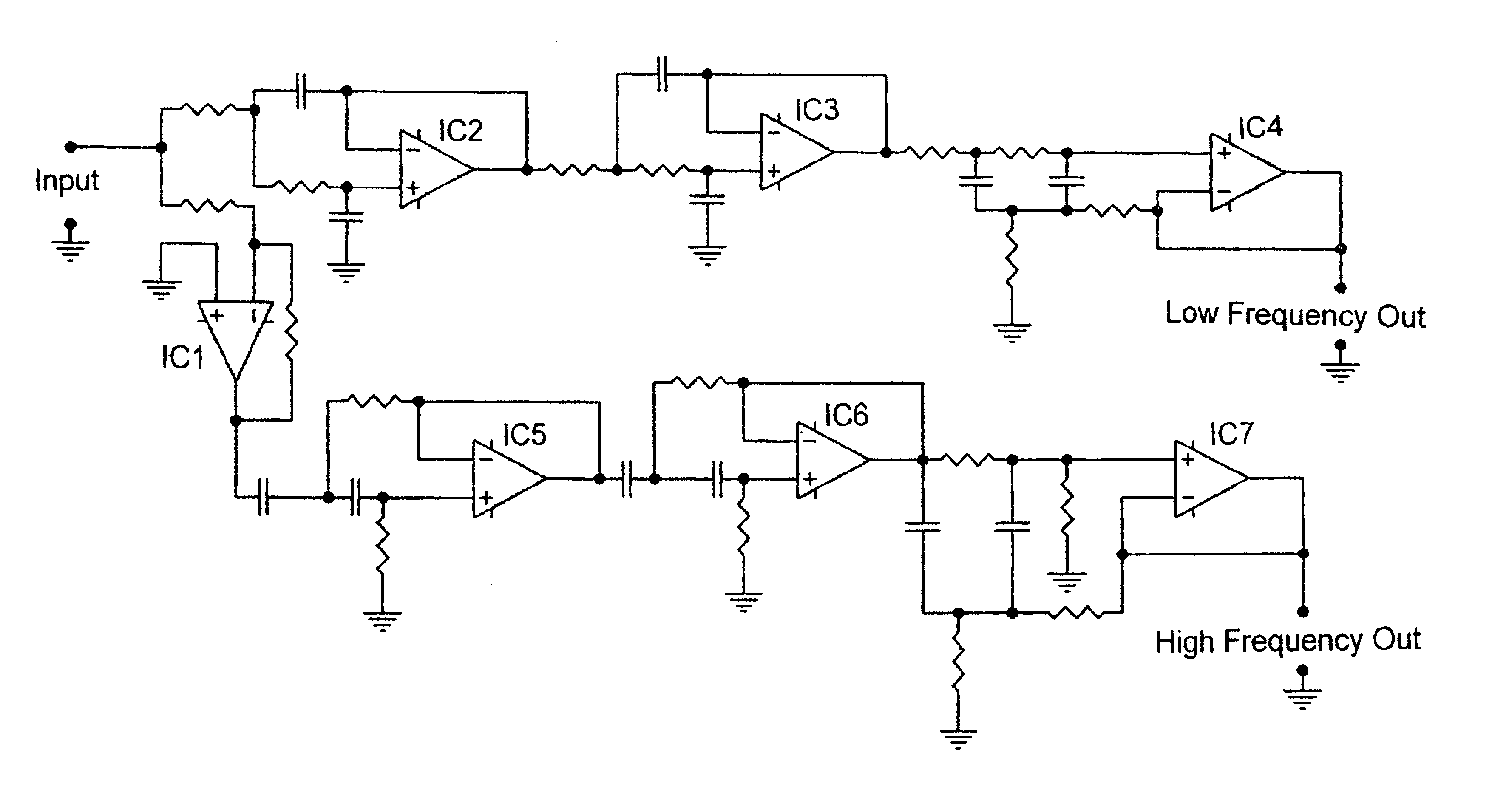
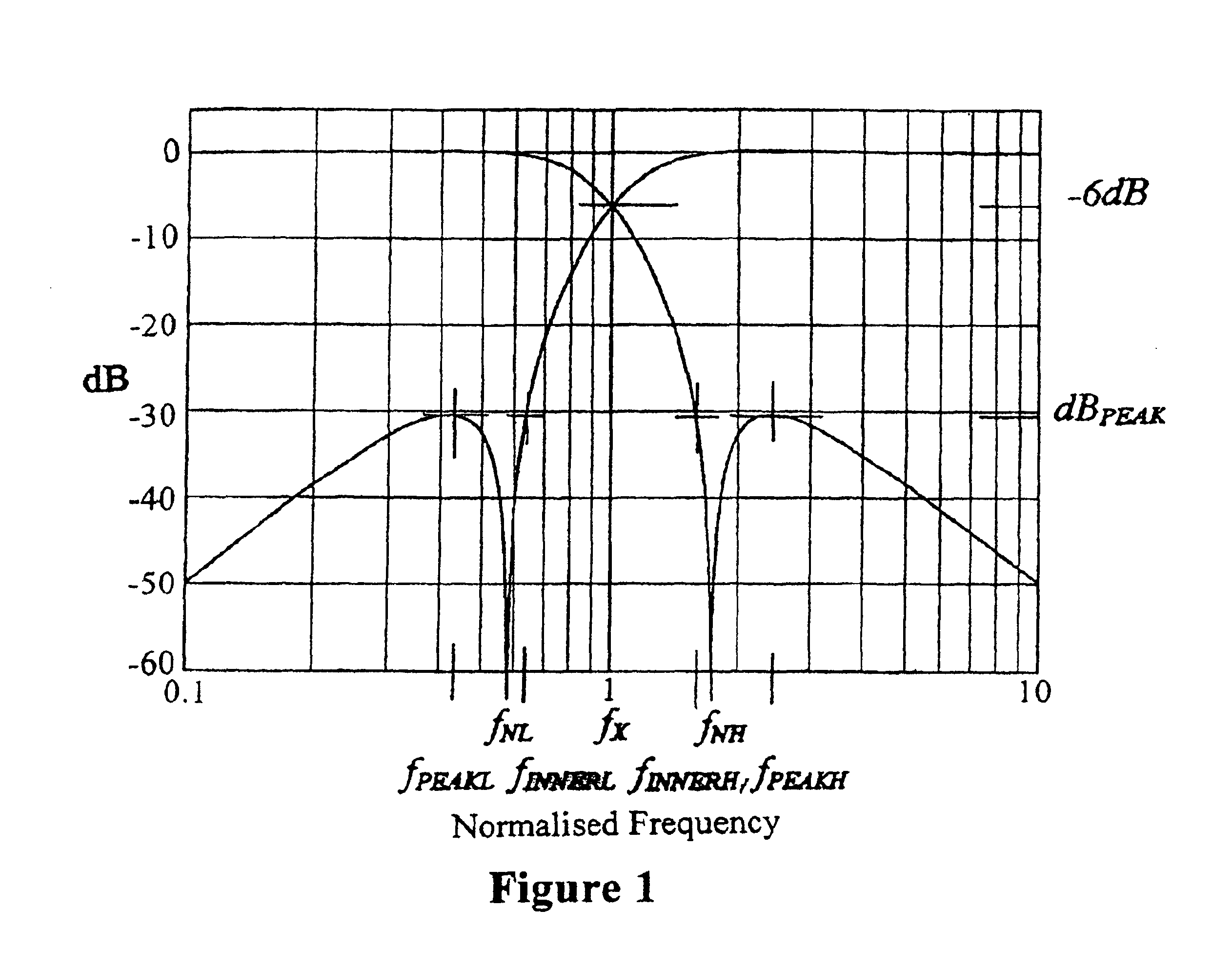
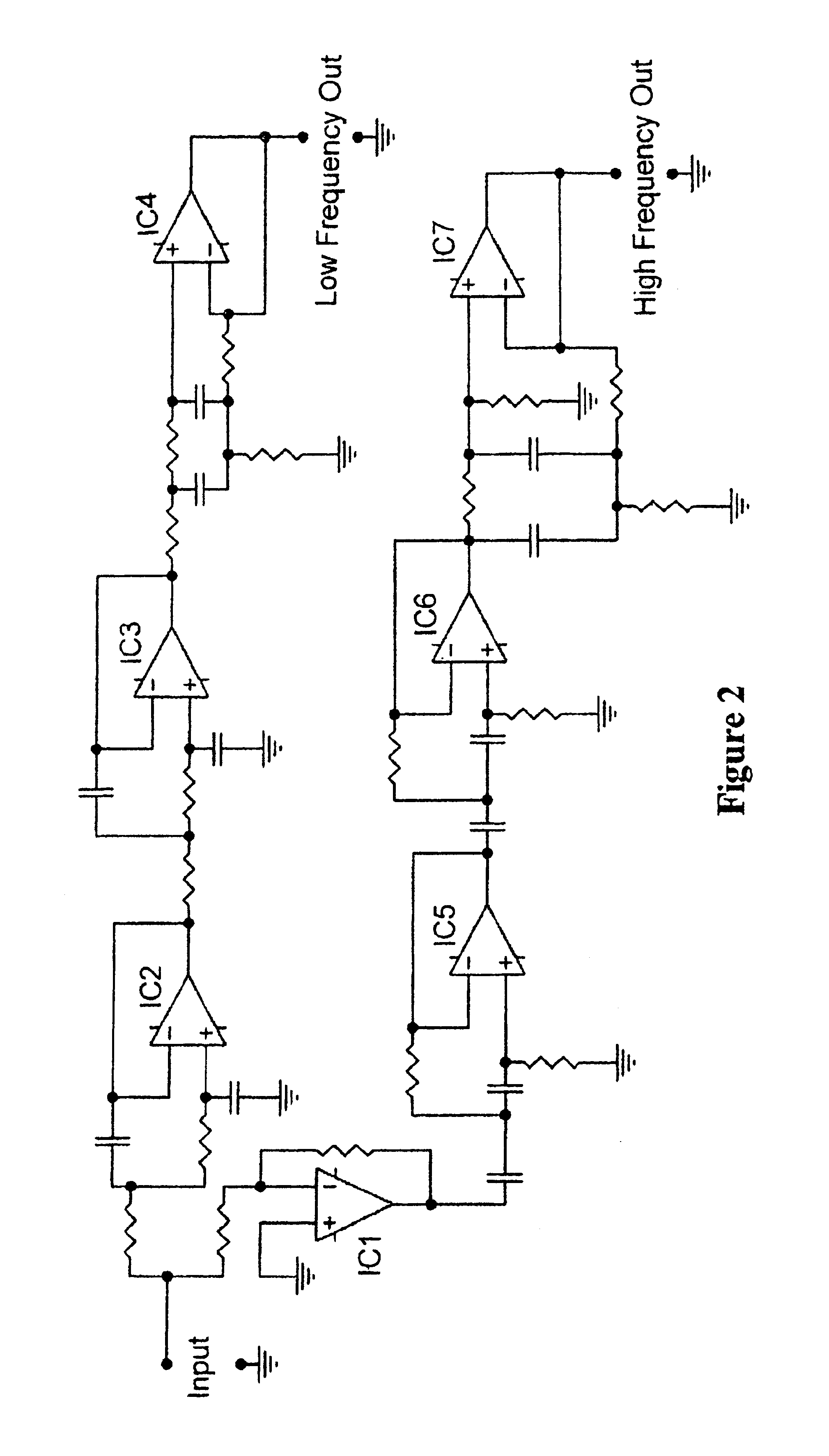
Crossover filter system and method
InactiveUS6854005B2Increased and steep roll offImproved amplitude responseElectric/magnetic computingLoudspeaker signals distributionFilter systemEngineering
A filter system including a low pass filter having a response which rolls off towards a crossover frequency and a high pass filter having a complementary response which rolls off towards the crossover frequency. The responses are arranged such that the combined response of the filters is substantially constant in amplitude at least in the region of the crossover frequency. The response of the low pass filter is defined by a low pass complex transfer function having a first numerator and a first denominator. The response of the high pass filter is defined by a high pass complex transfer function having a second numerator and a second denominator. The desired response is obtained when the second denominator is substantially the same as the first denominator and the sum of the first and second numerators has substantially the same squared modulus as the first or second denominator.
Owner:IMMERSION TECH PROPERTY
CMOS APS readout scheme that combines reset drain current and the source follower output
InactiveUS7317484B2Reduce low frequency noiseReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingEngineering
A circuit and method for reducing noise in video imagers which takes advantage of the fact that the same image information is present in the drain current in a reset transistor used to reset a photodiode in a pixel as is present in the readout current. The noise is reduced by passing the multiplexed output voltage from the source follower output transistor in an APS imager system through a high pass filter to reduce the low frequency noise from the source follower. The drain current in the reset transistor used to reset the APS is passed through a low pass filter. The low pass filter output and the high pass filter output are then combined. Since the drain current in the reset transistor contains the same image information as the voltage output of the source follower output transistor the image information can be obtained by combining the output of the low pass filter and the output of the high pass filter. Since the low frequency noise components of the source follower output transistor have been suppressed combined outputs of the low pass filter and high pass filter will provide the image information with greatly suppressed low frequency noise.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com