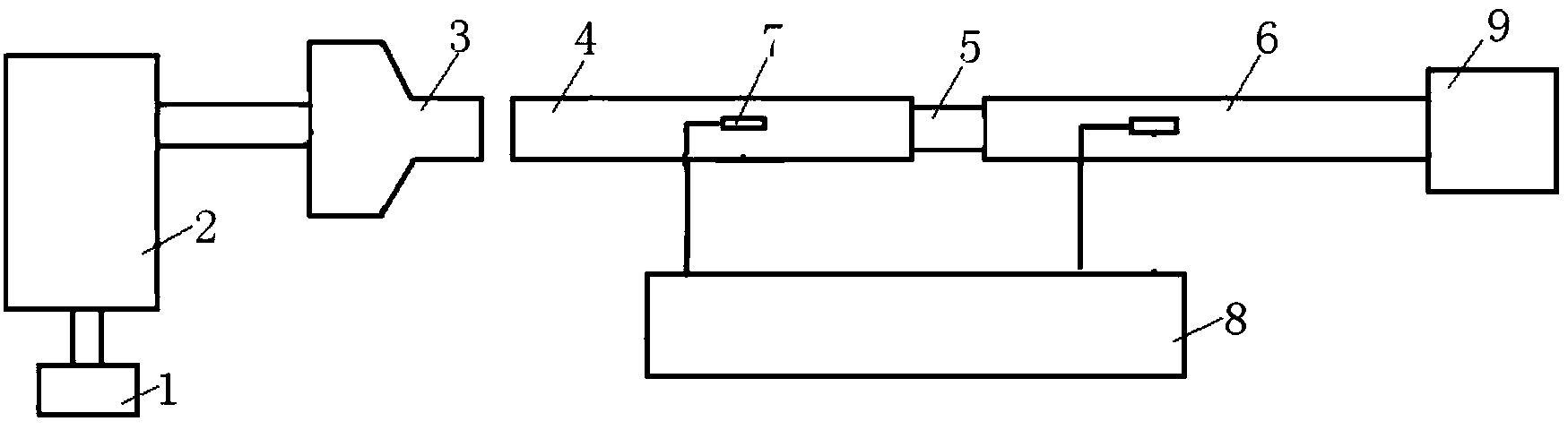
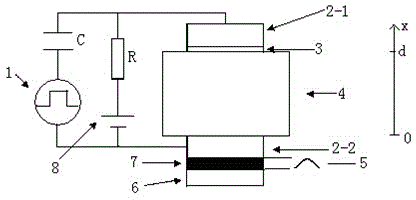
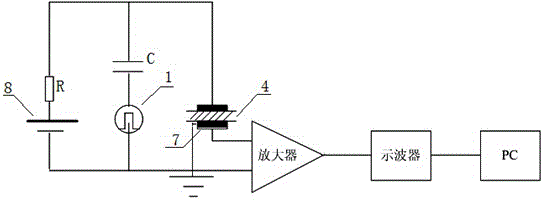
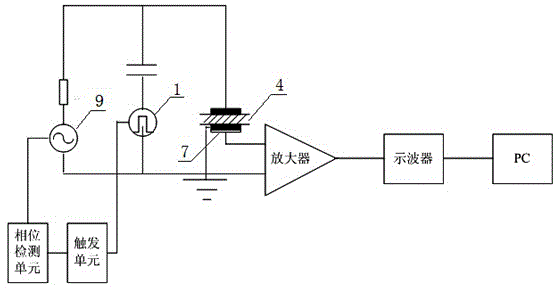
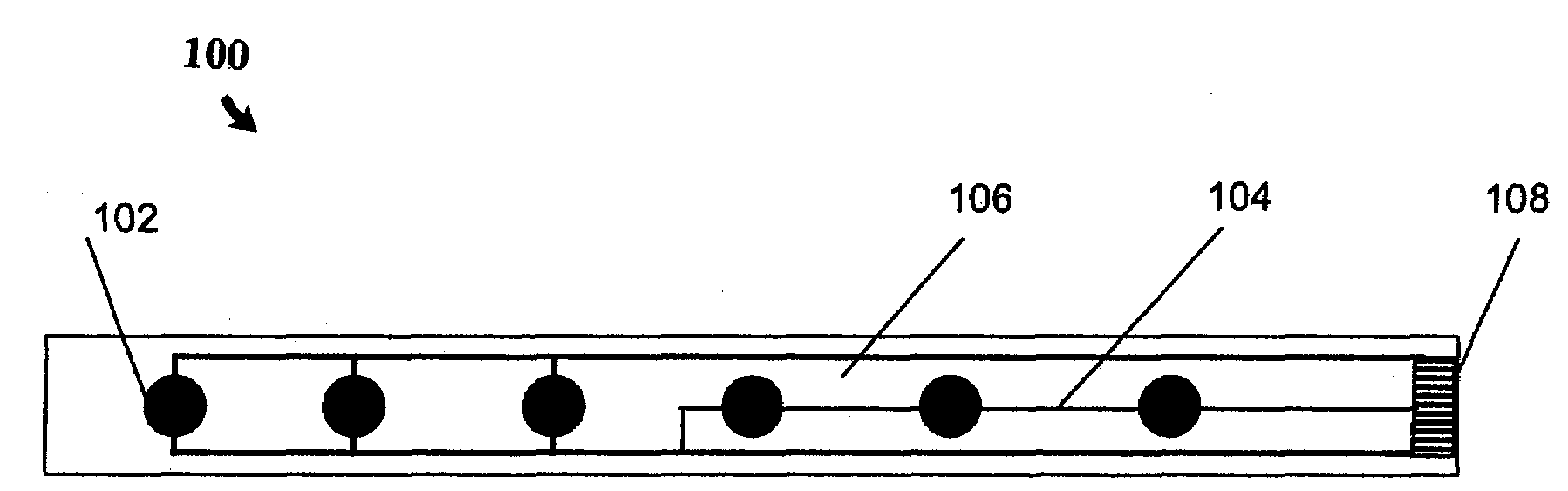
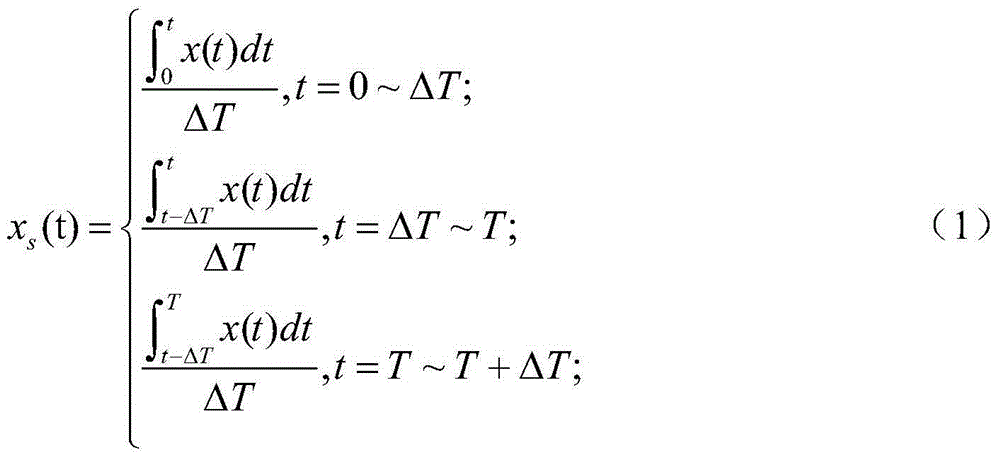Patents
Literature
889 results about "Stress wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
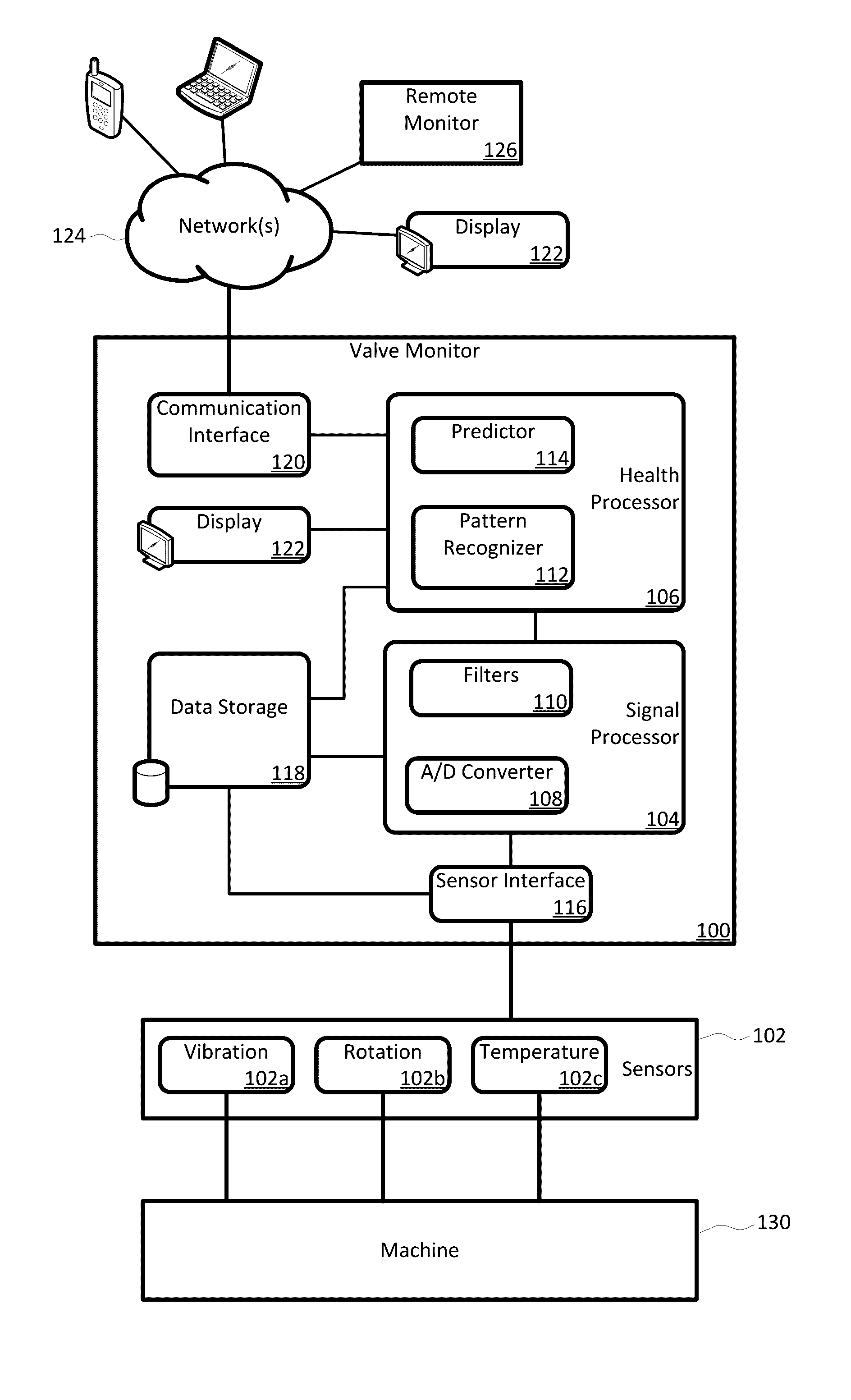
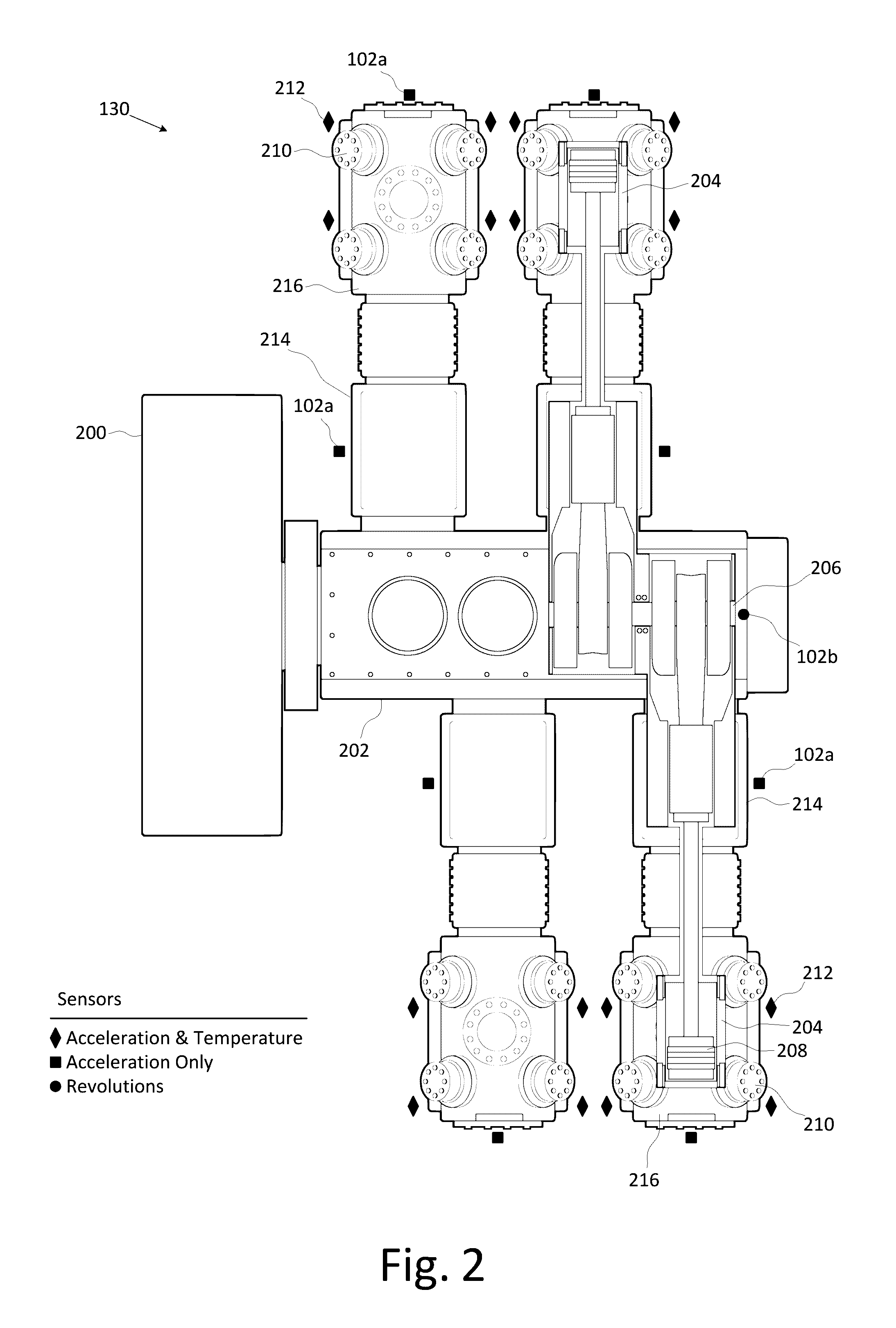
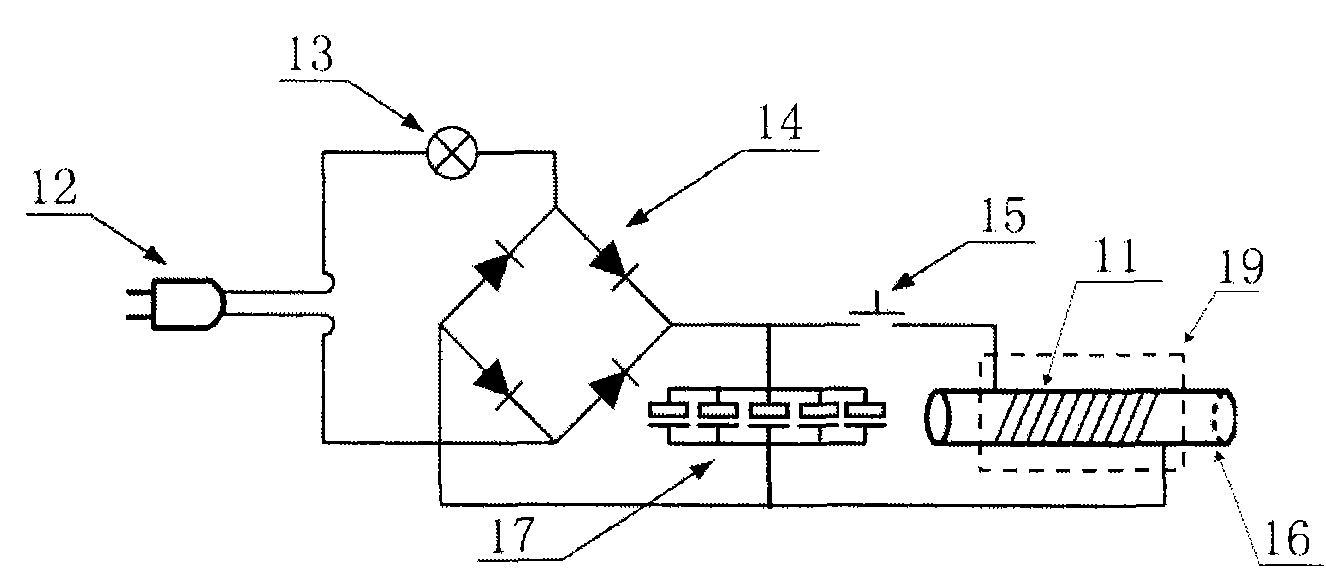
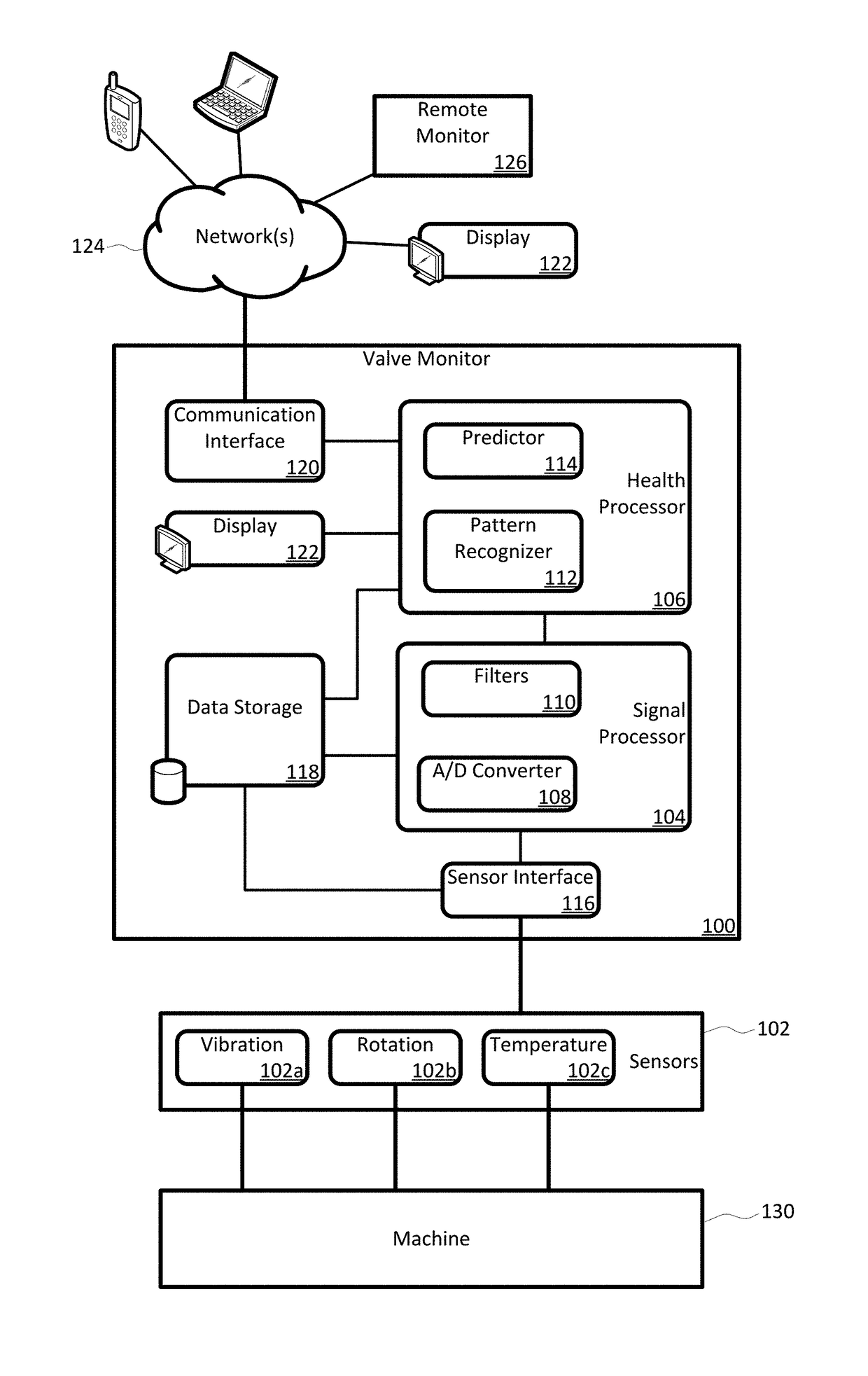
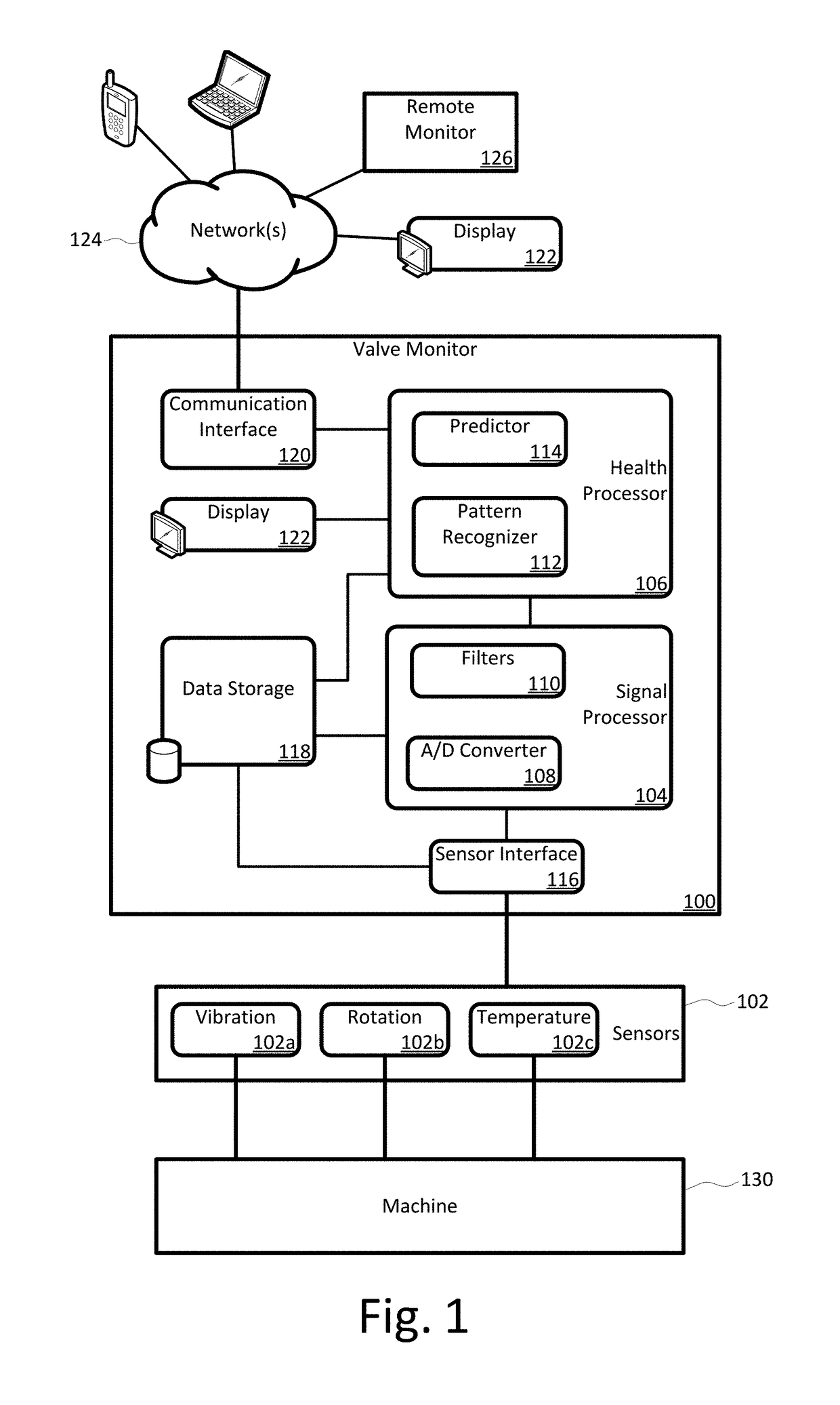
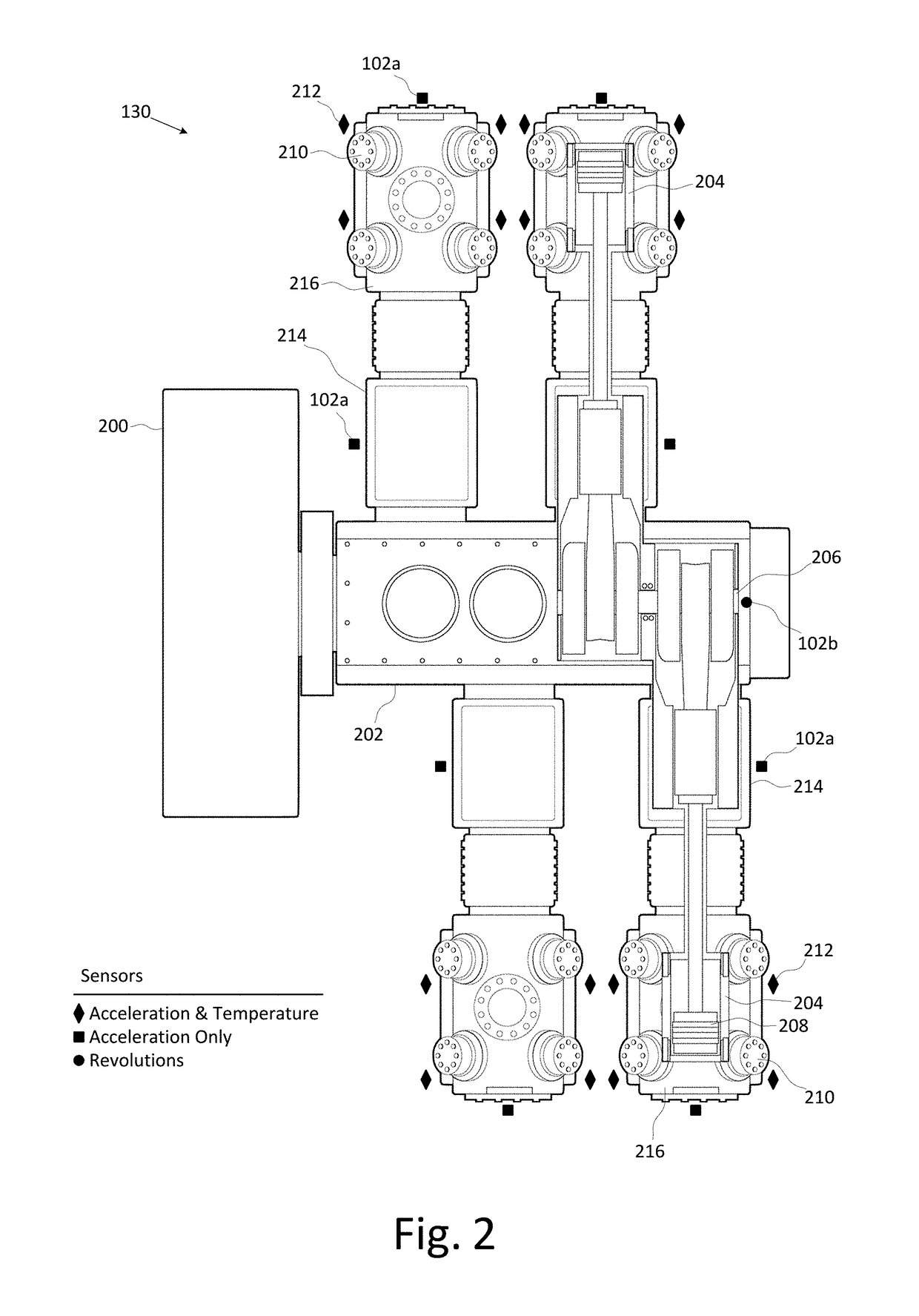
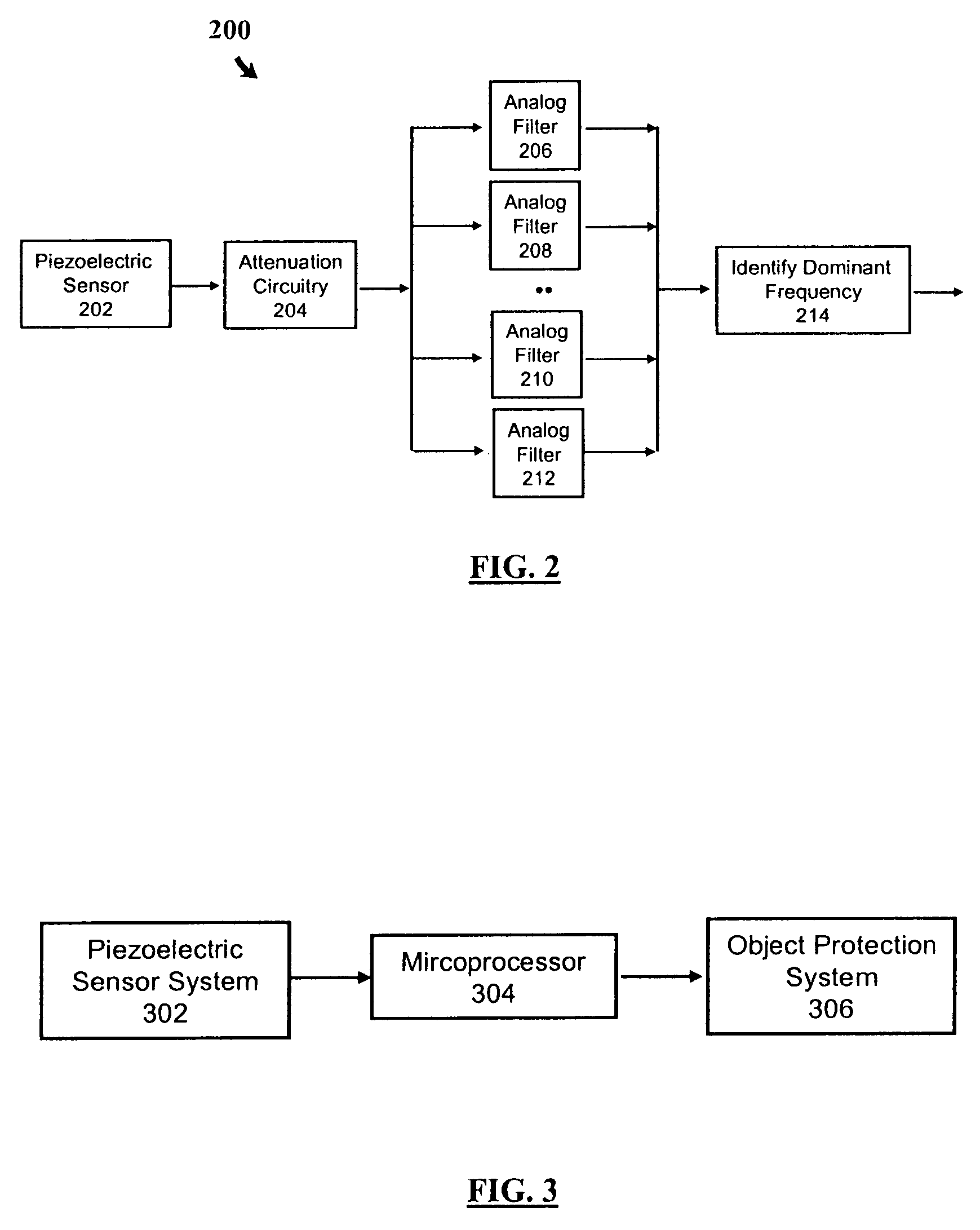
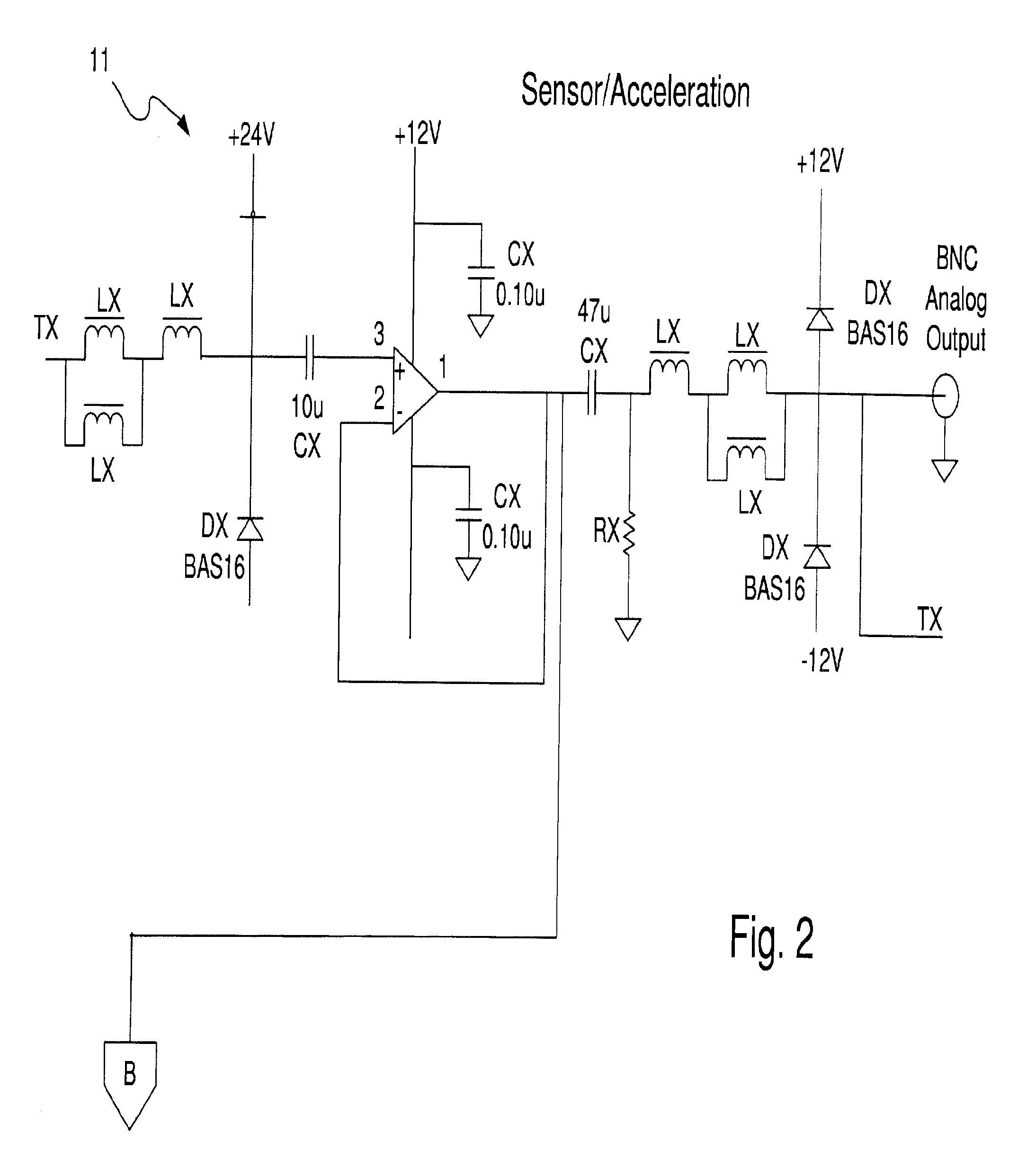
Compressor Valve Health Monitor
ActiveUS20170030349A1Improve analysisImprove notificationsExternal parameterPositive displacement pump componentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A rotating machine valve health monitor. Aspects of the valve monitor include instrumenting each valve of a reciprocating compressor, or other rotating machine, with a sensor capable of detecting at least vibration and instrumenting the crank shaft with a sensor capable of detecting at least rotation. A controller directly monitors the operation and condition of each valve to precisely identify any individual valve exhibiting leakage issues rather than only identifying the region of the leakage. The valve monitor uses a relatively high frequency stress wave analysis technique to provide a good signal-to-noise ratio to identify impact events indicative of leakage. The valve monitor uses circular waveforms of vibration data for individual valves to identify leakage by pattern recognition or visual identification. The valve monitor provides ongoing data collection to give warning of predicted valve failure and scheduling of preventative maintenance for failing valves.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL SYST
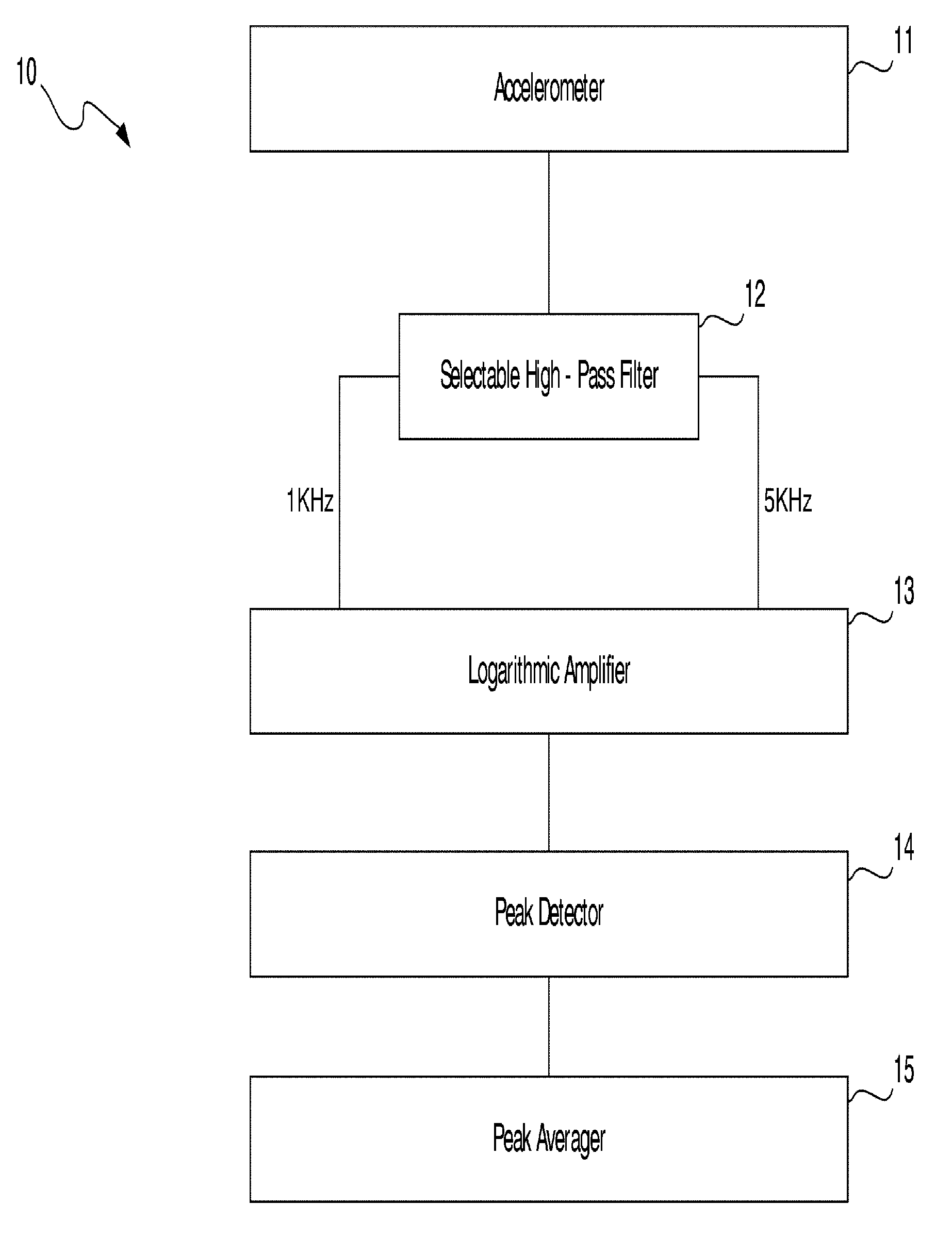
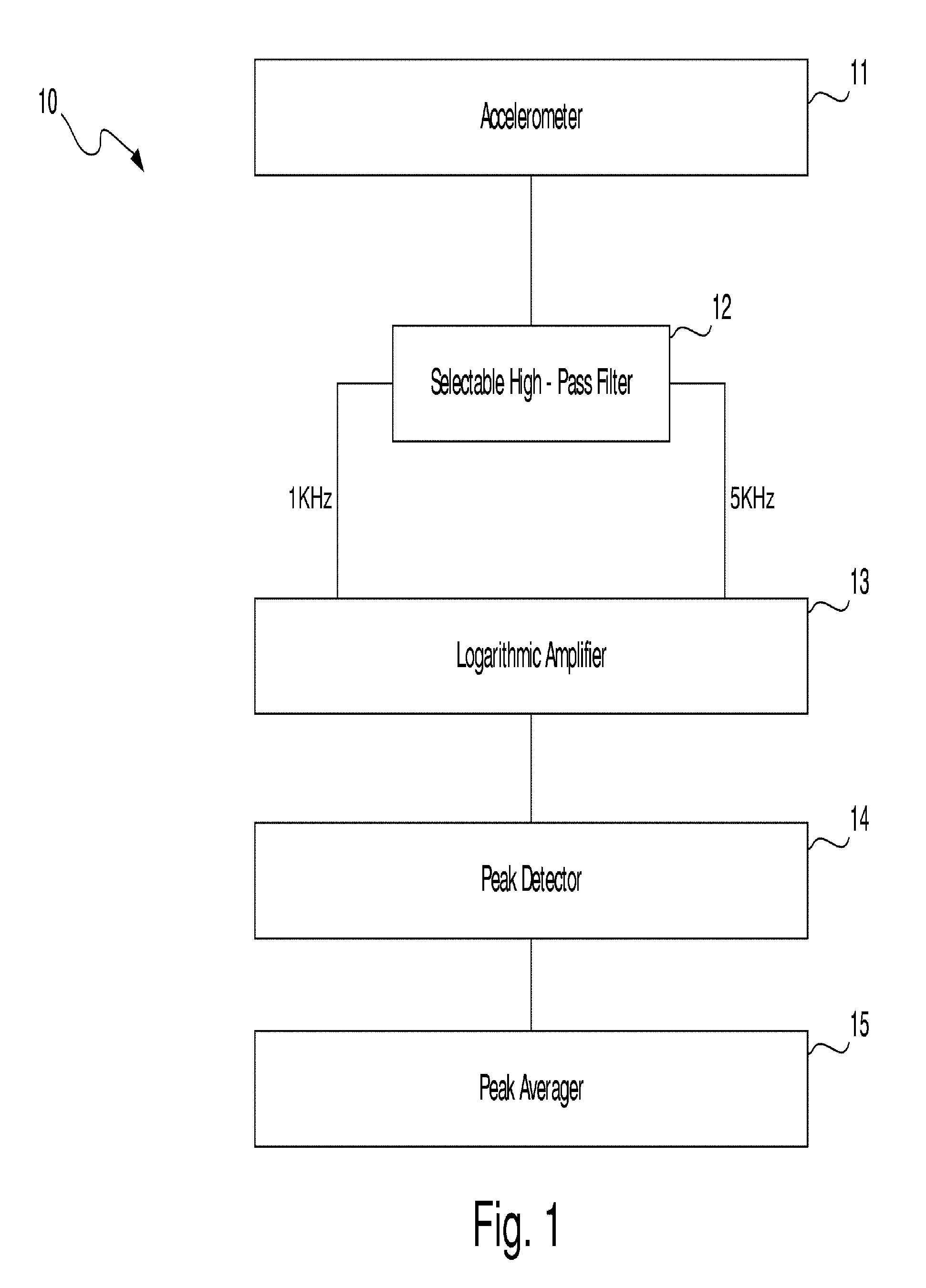
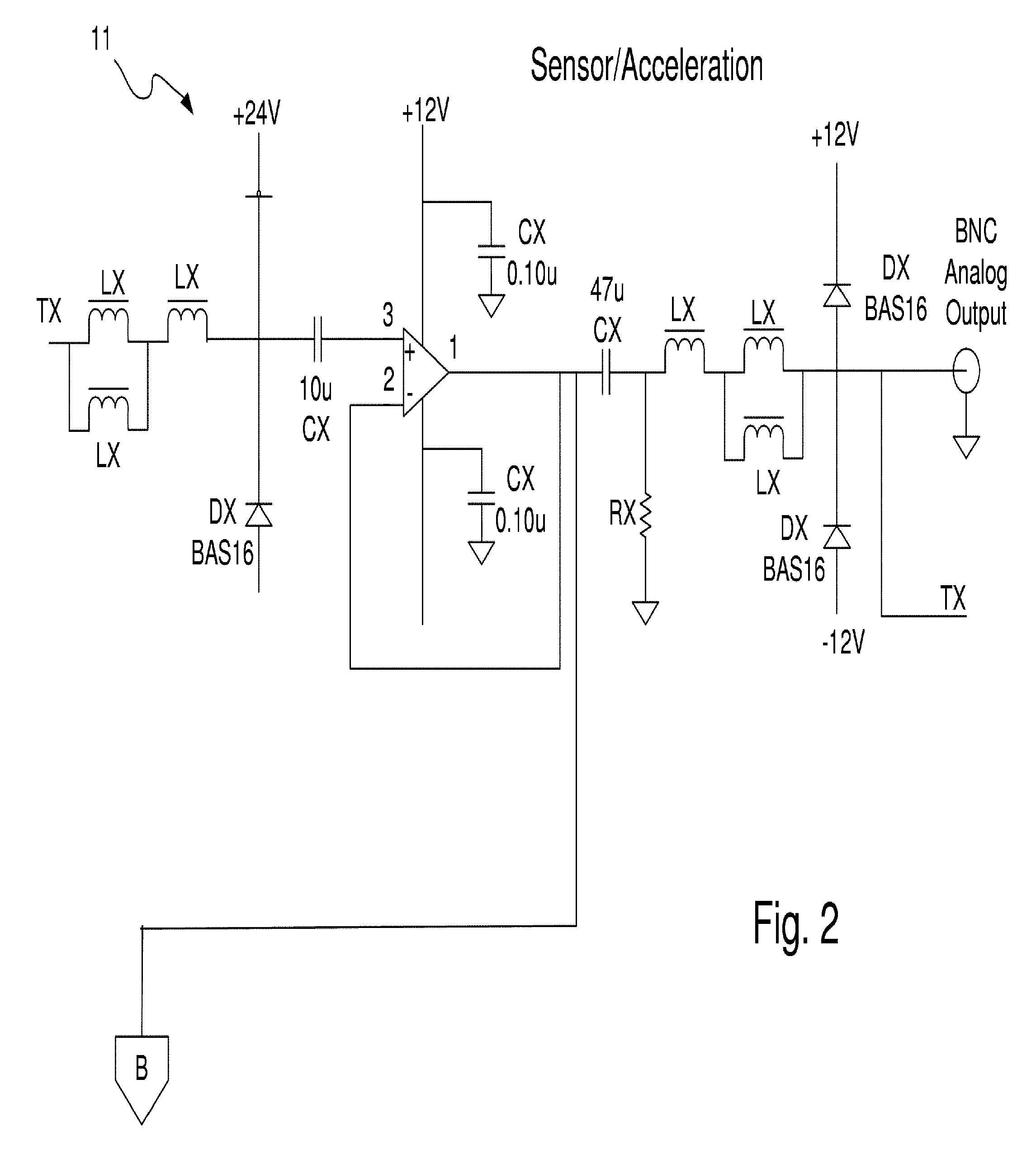
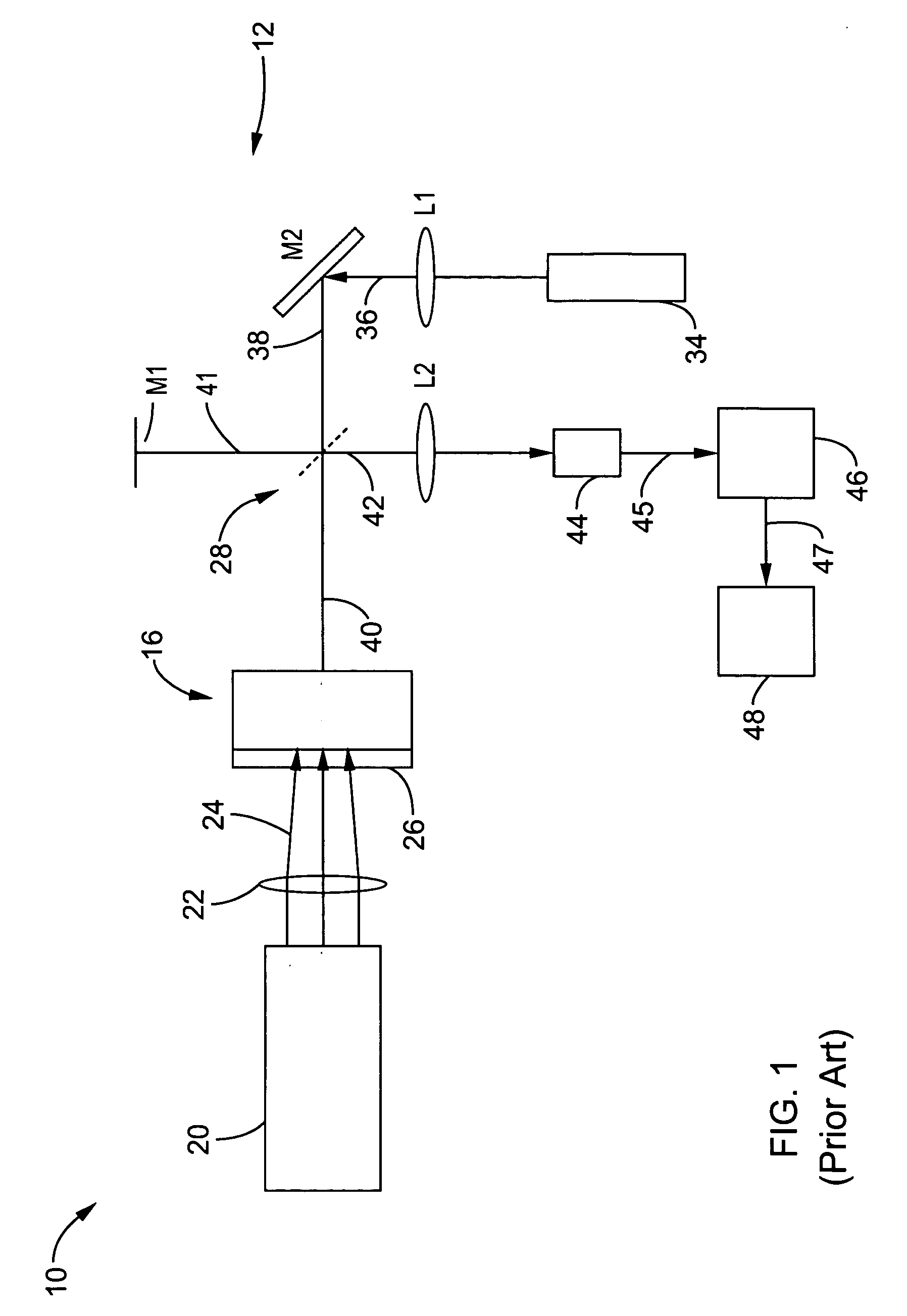
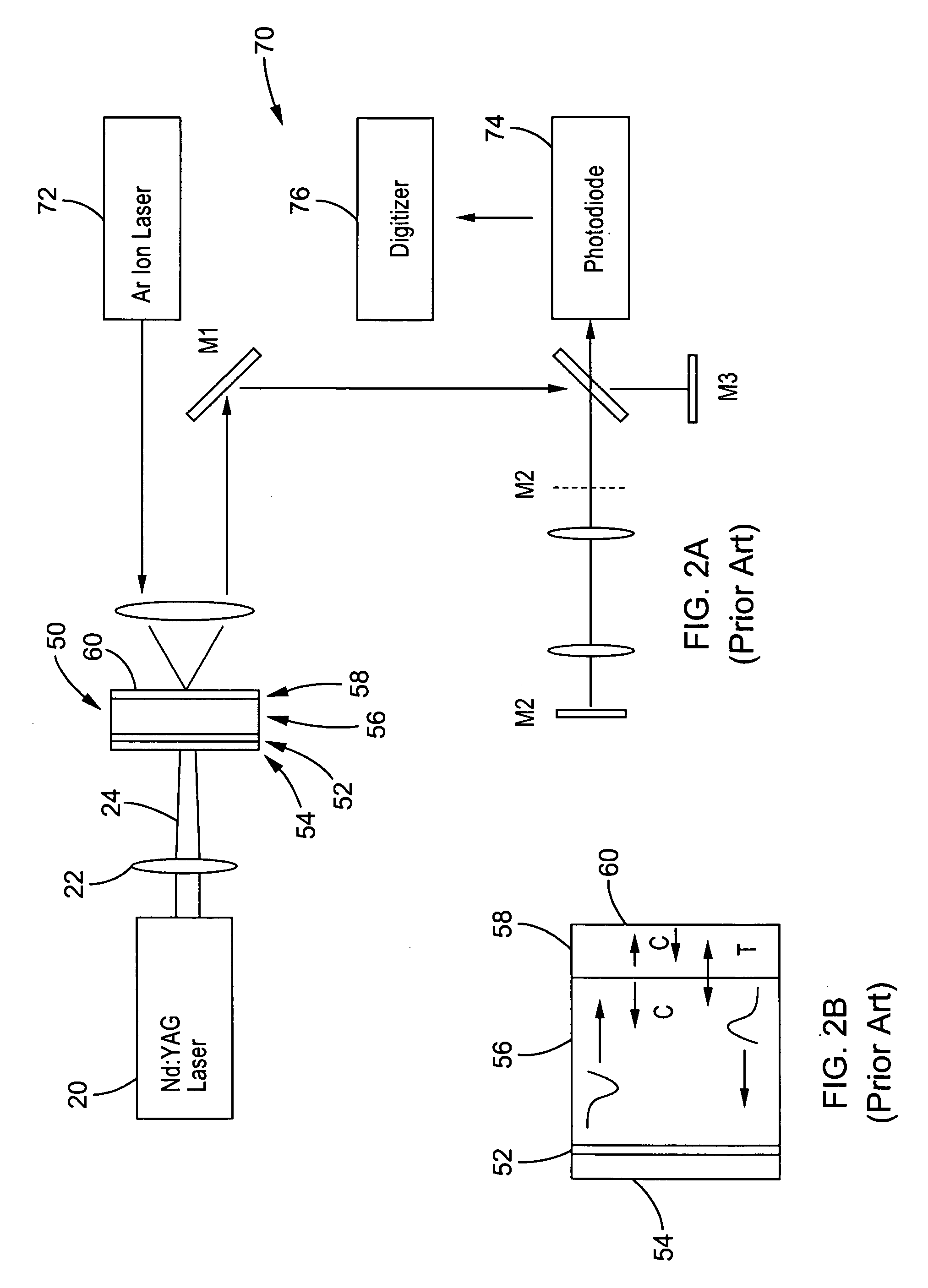
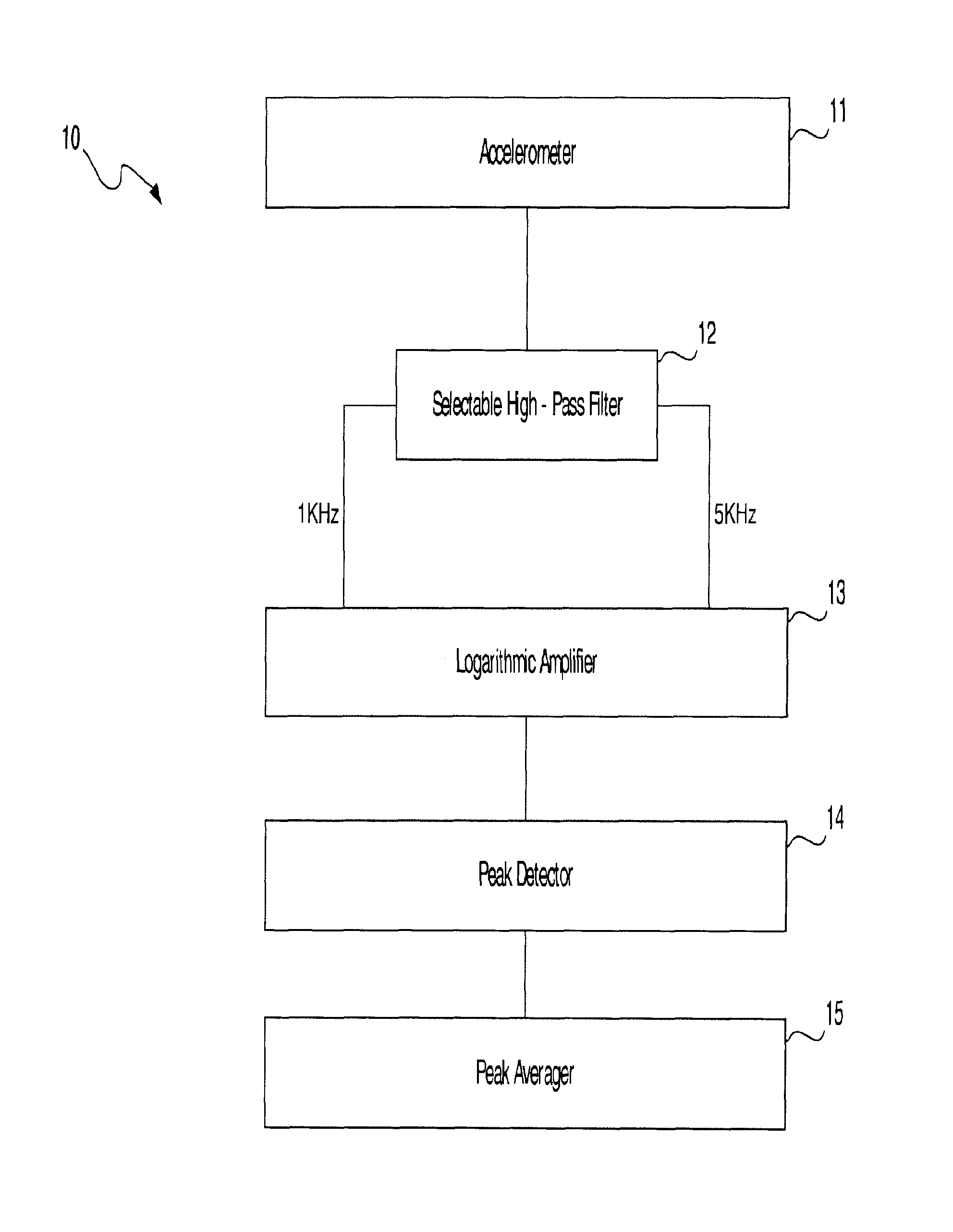
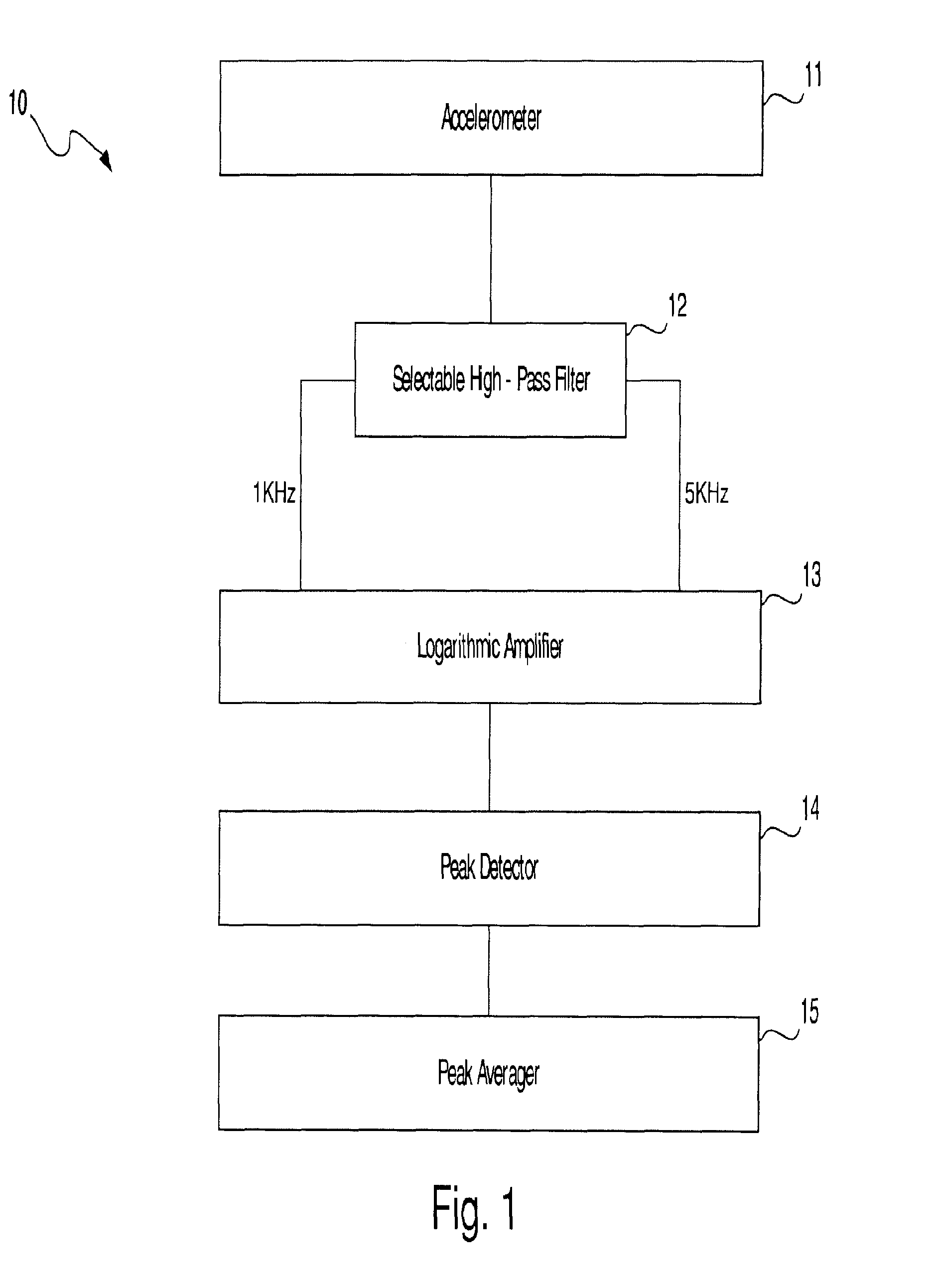
Method and apparatus for vibration sensing and analysis
InactiveUS20050011266A1Readily apparentVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingPeak valueAcoustics
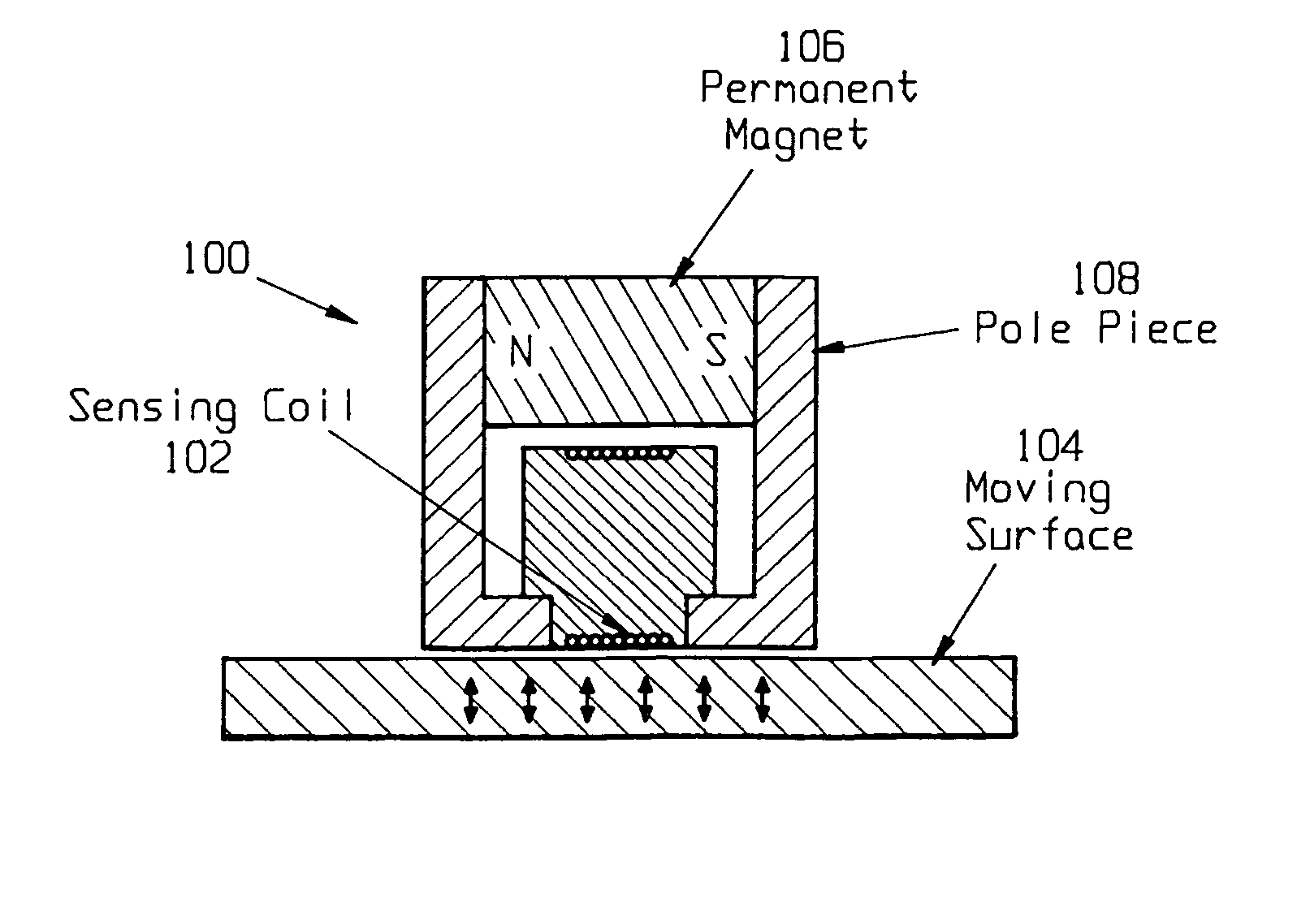
A method and apparatus for sensing and measuring stress waves. The method comprises the steps of: a.) sensing motion, where the motion comprises a stress wave component and a vibration component; b.) separating the stress wave component from the vibration component with a high pass filter to create a signal proportional to the stress wave; c.) amplifying the signal to create an amplified signal; d.) processing the amplified signal with a sample and hold peak detector over a predetermined interval of time to determine peaks of the amplified signal over said predetermined period of time; e.) creating an output signal proportional to the determined peaks of the amplified signal; and, f.) repeating steps d.) and e.). The invention also includes an apparatus for implementing the method of the invention.
Owner:PCB PIEZOTRONICS IMI SENSORS +1
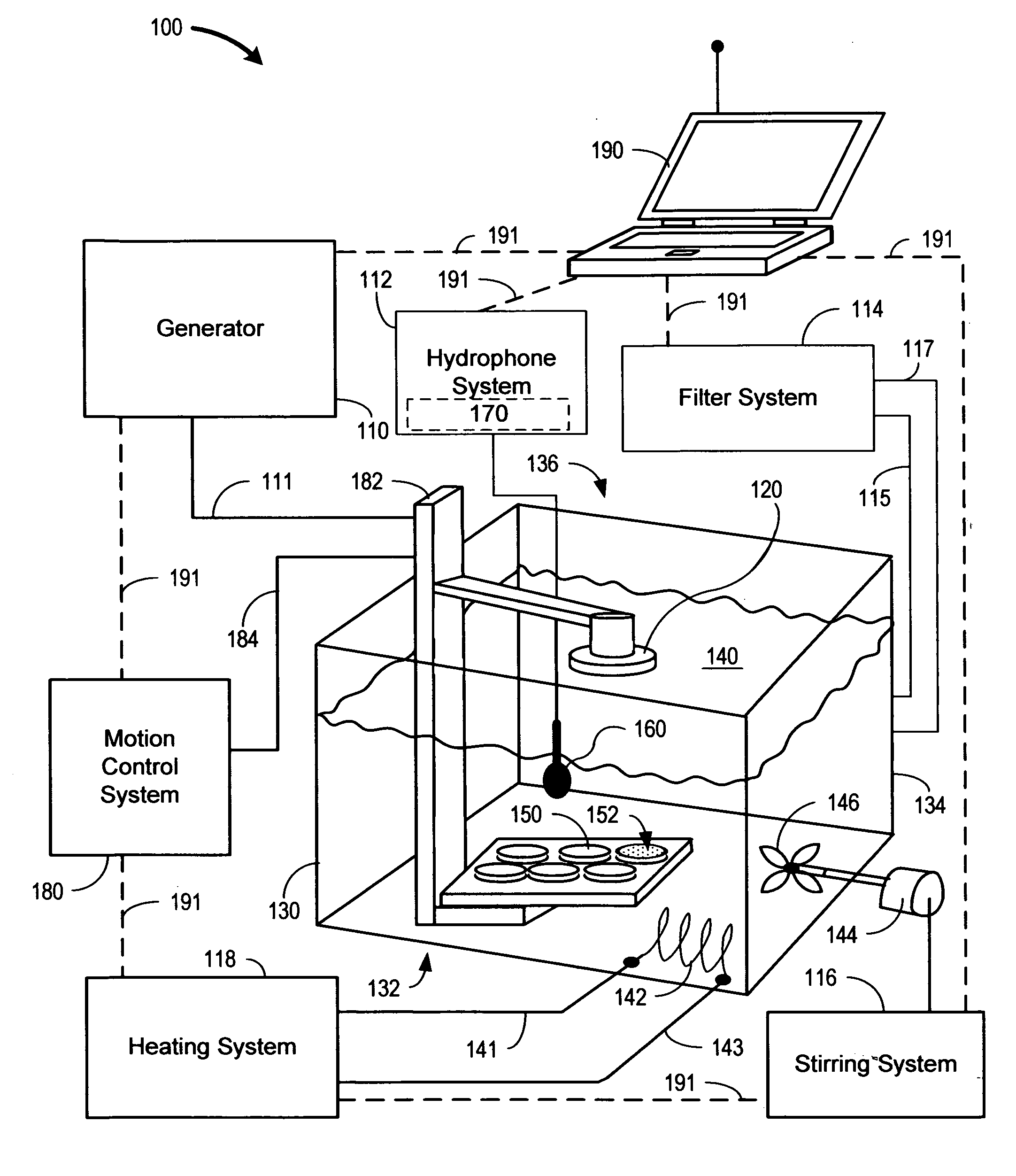
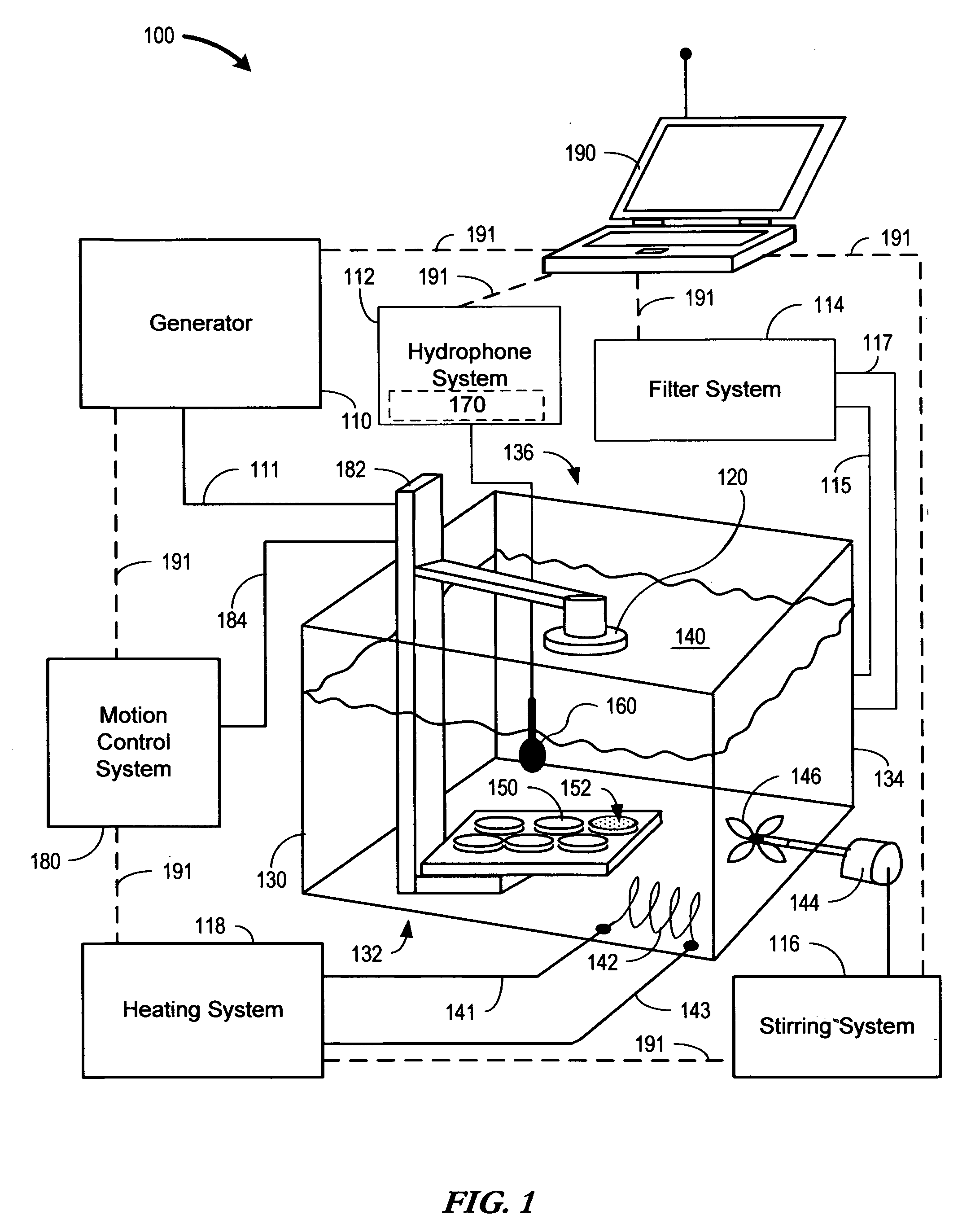
Sonoporation systems and methods
InactiveUS20100009424A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrophone
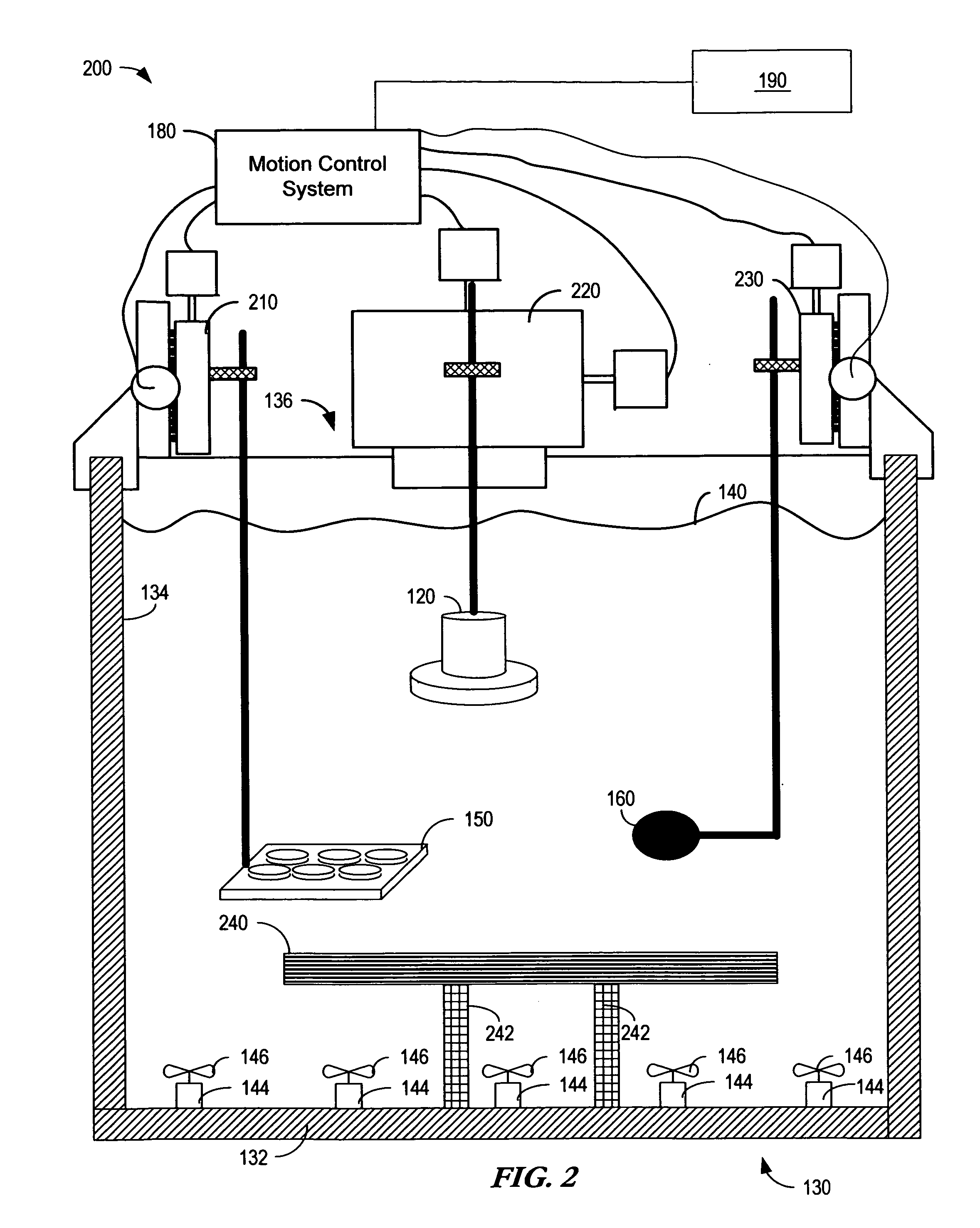
The present invention is directed to devices and methods that apply ultrasonic energy for the purpose of inducing transfection and cell transformation. A sonoporation system in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes an ultrasonic electrical energy generator connected to an ultrasonic transducer producing stress waves. The ultrasonic transducer is connected to a fluid containment tank configured to accept at least a portion of the ultrasonic transducer whereby the ultrasonic stress waves may be delivered into the fluid medium. A cell holder is configured to hold one or more cells desirable for transfection. A hydrophone may be electrically connected to an acoustic stress wave intensity detection circuit. A motion control system having an arm configured to receive one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone is configured to provide motion of one or both of the cell holder and the hydrophone within the fluid medium.
Owner:ARTISON
Light Emitting Diode having vertical topology and method of making the same
ActiveUS20070295952A1Efficient implementationEnsure structural stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress waveSemiconductor
An LED having vertical topology and a method of making the same is capable of improving a luminous efficiency and reliability, and is also capable of achieving mass productivity. The method includes forming a semiconductor layer on a substrate; forming a first electrode on the semiconductor layer; forming a supporting layer on the first electrode; generating an acoustic stress wave at the interface between the substrate and semiconductor layer, thereby separating the substrate from the semiconductor layer; and forming a second electrode on the semiconductor layer exposed by the separation of the substrate.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD +1
Laser system and method for non-destructive bond detection and evaluation
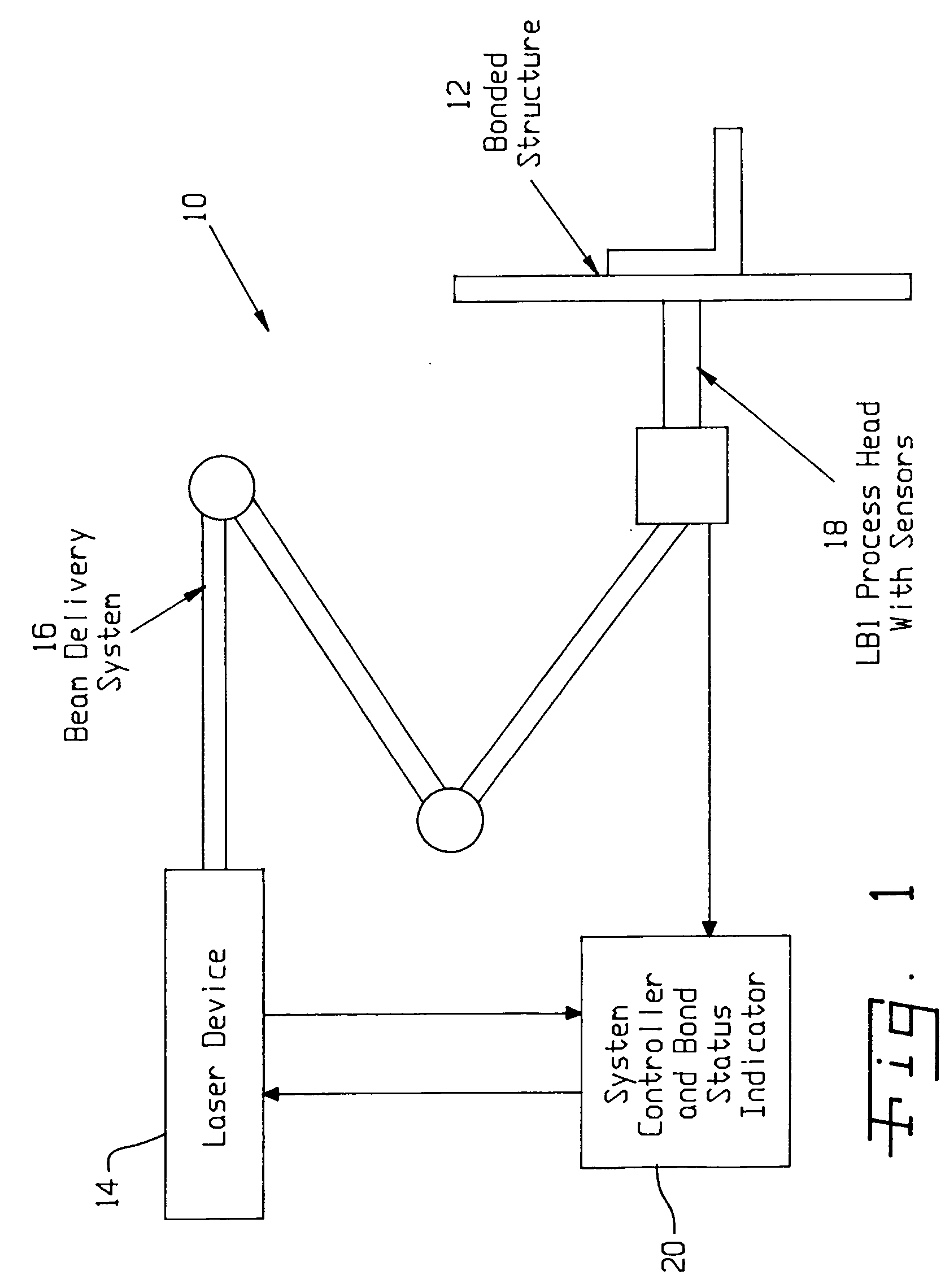
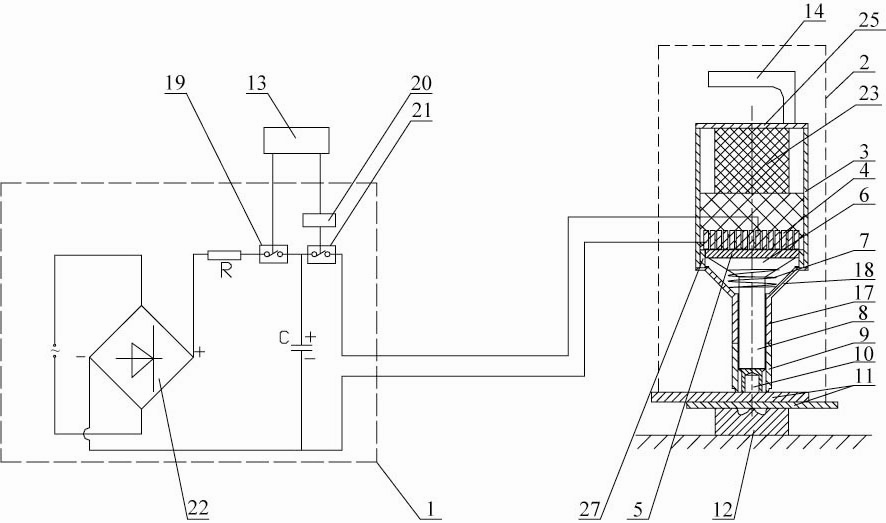
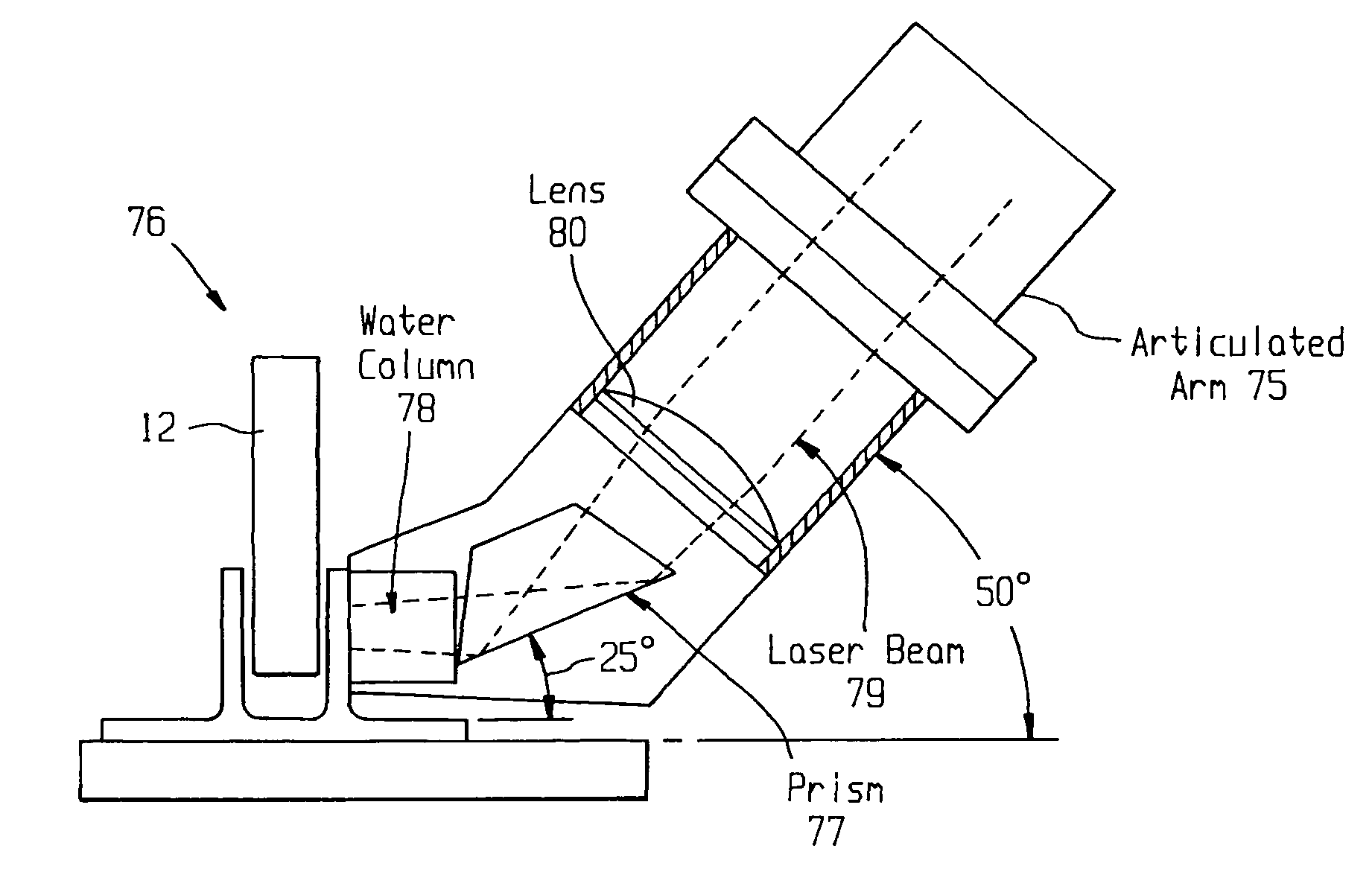
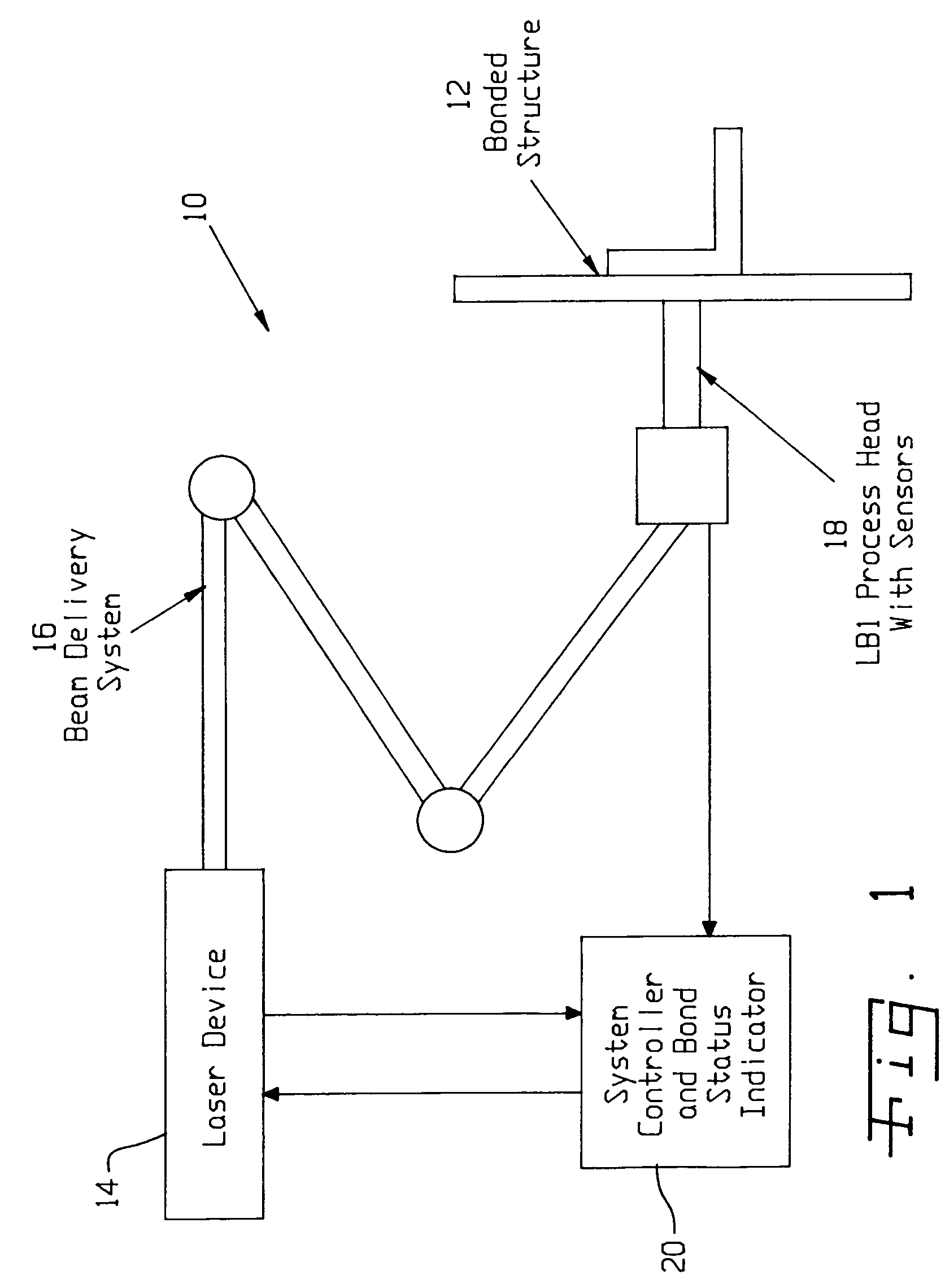
ActiveUS20050120803A1Easy to collectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesNon destructiveLight beam
A system for evaluating the integrity of a bonded joint in an article includes a laser configured in a laser shock processing arrangement to perform a laser shock processing treatment on the article. A beam delivery system employs an articulated arm assembly to communicate the radiant energy emitted by the laser to a process head proximate the article. The laser shock processing treatment causes the formation of shockwaves that propagate through the article, inducing internal stress wave activity that characteristically interacts with the bonded joint. A sensor detects a stress wave signature emanating from the article, which is indicative of the integrity of the bond. A detector such as a non-contact electromagnetic acoustic transducer provides a measure of the stress wave signature in the form of surface motion measurements.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
System and method for performing impact loading on micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property
InactiveCN102135480ASolve the study of dynamic mechanical properties at high strain ratesLaunch fastStrength propertiesFerroelectric thin filmsStress–strain curve
The invention relates to a system and a method for performing impact loading on a micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property. The method comprises the following steps of: instantly accelerating a bullet by using an electromagnetic pulse launch technology and launching the bullet at high speed; transmitting a stretching stress wave generated by collision of the bullet to the micro test piece by using a separated Hopkinson bar technology so as to generate the impact loading on the micro test piece; recording strain data of an input bar and an output bar, and acquiring an enlarged surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece; analyzing and obtaining a stress strain curve of the micro test piece subjected to the impact loading having different strain rates; and analyzing the surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece and obtaining a distribution of a bidimensional displacement field and a strain field during dynamic impact loading of the micro test piece. By the system and the method, the problem of research on the dynamic mechanical property of a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and membrane materials such as piezoelectric thin films, ferroelectric thin films and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Smart repair patch and associated method
ActiveUS7398698B2Structure moreLow costAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNuclear monitoringNon destructiveData acquisition
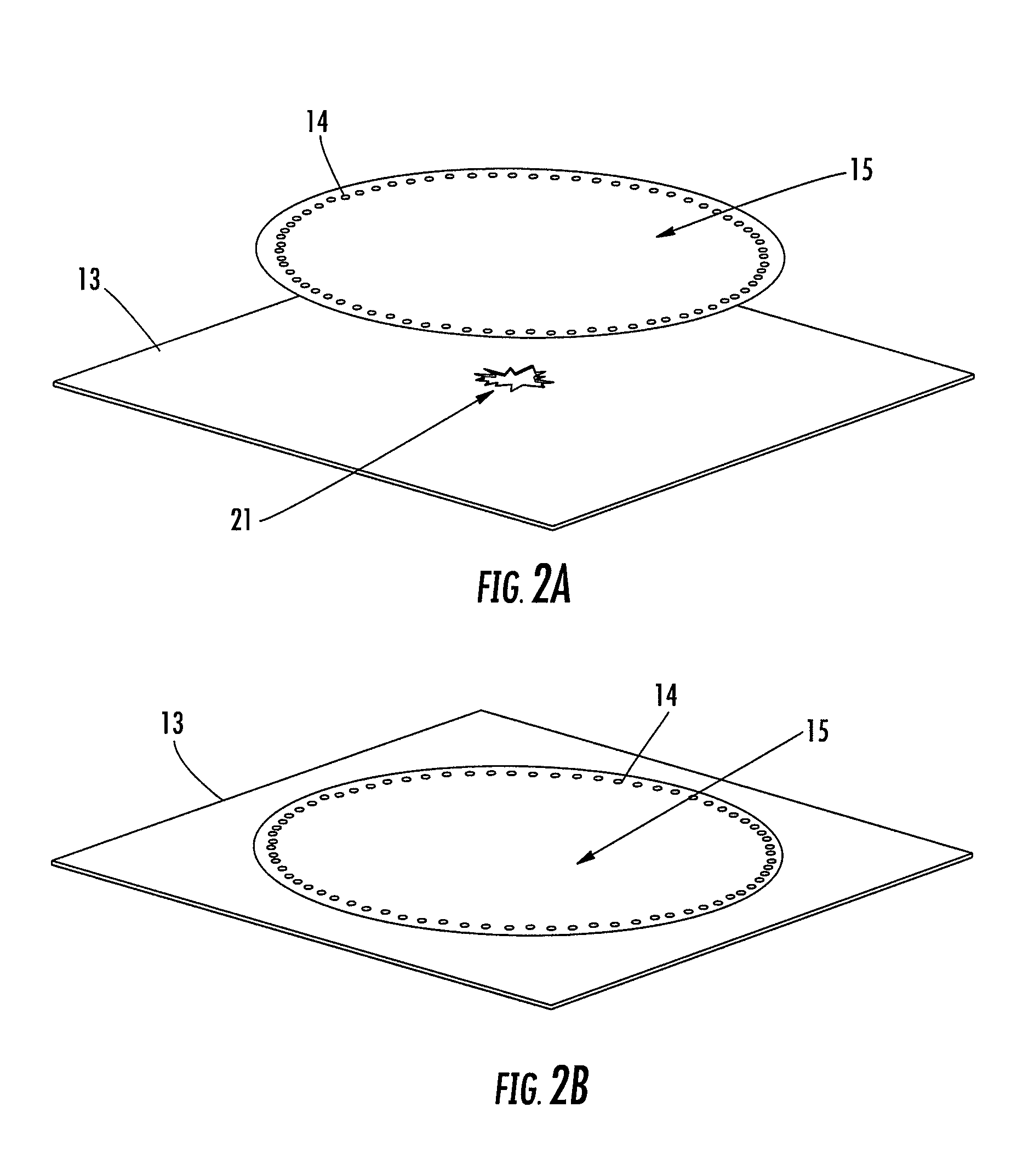
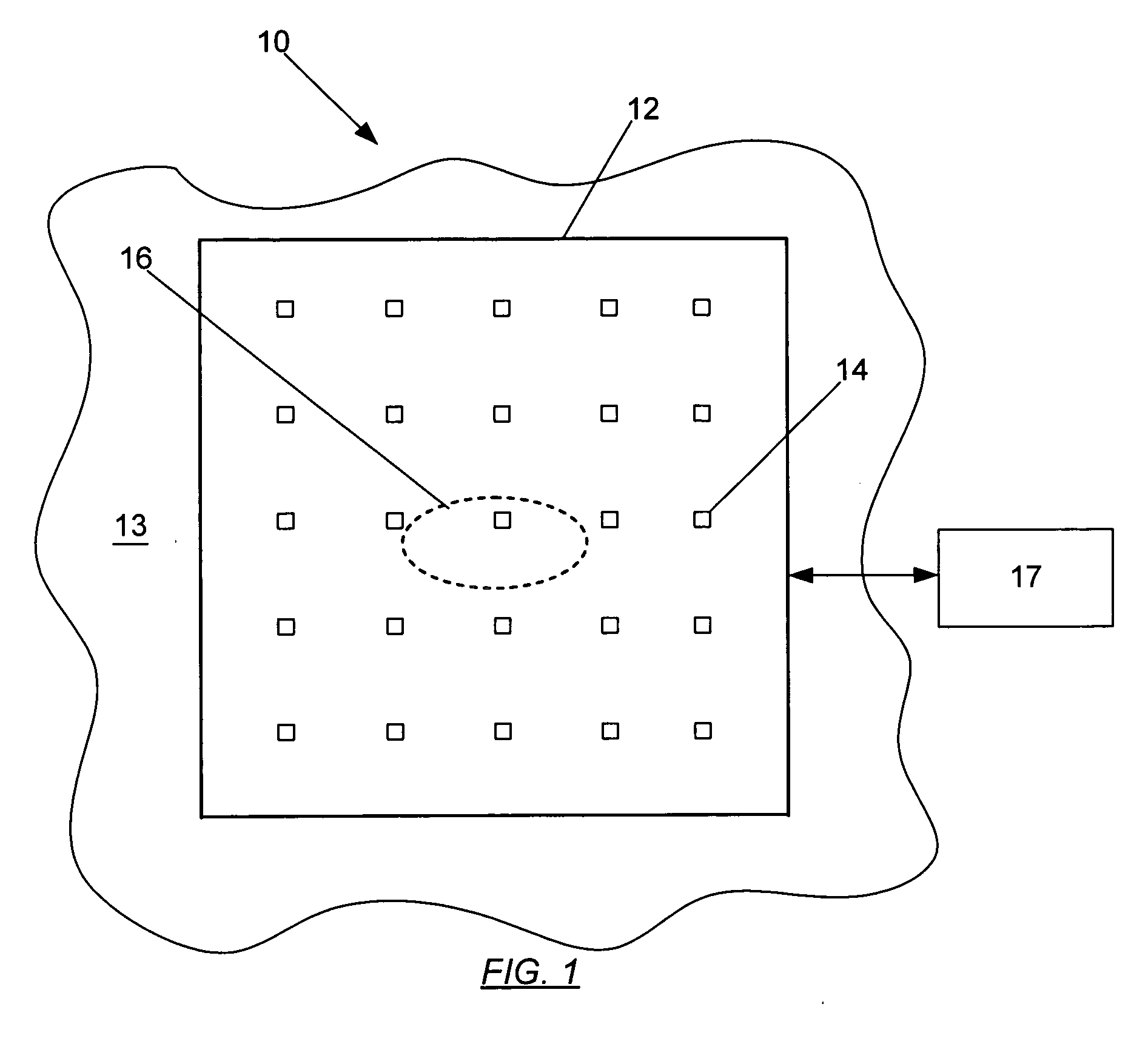
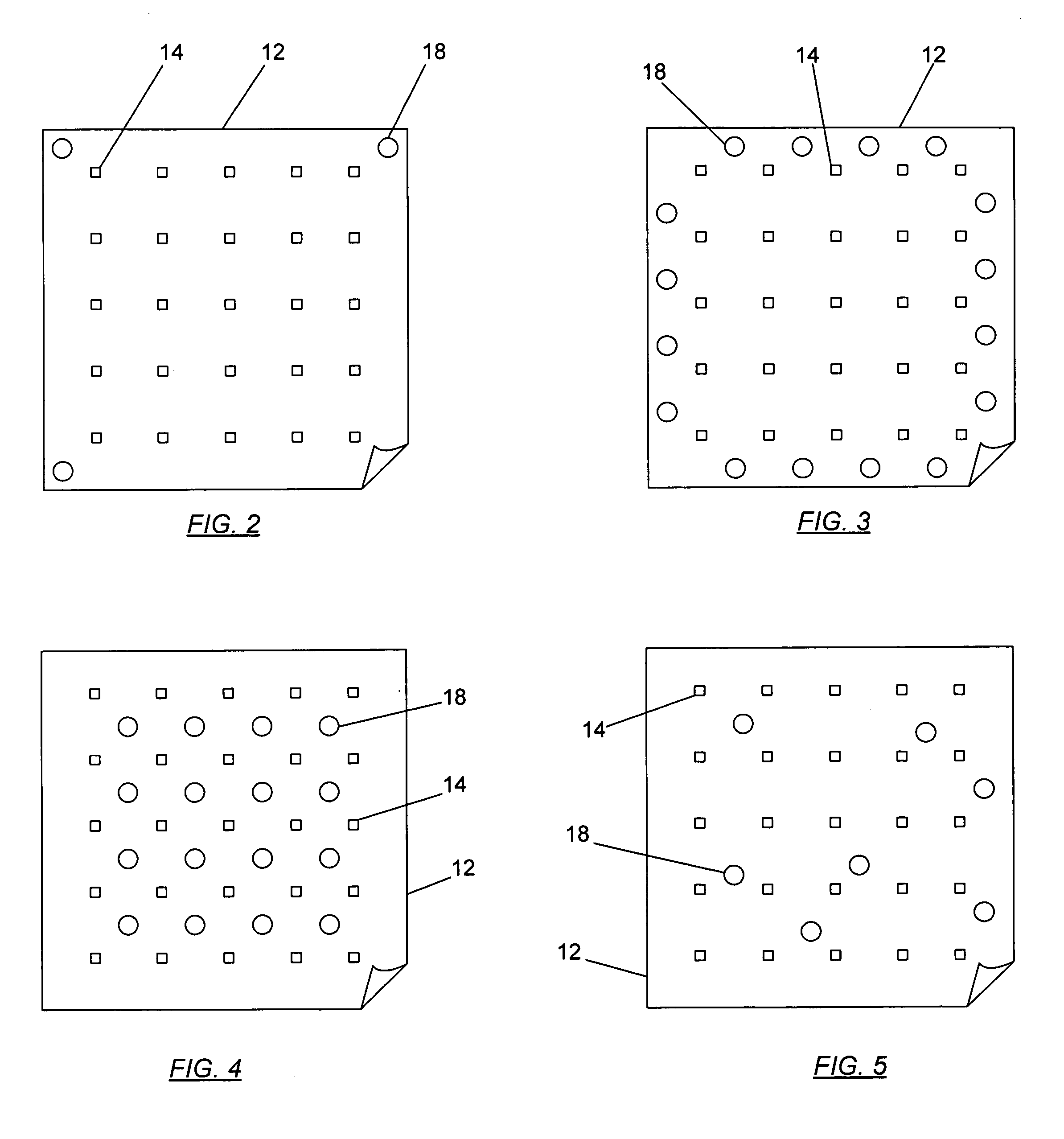
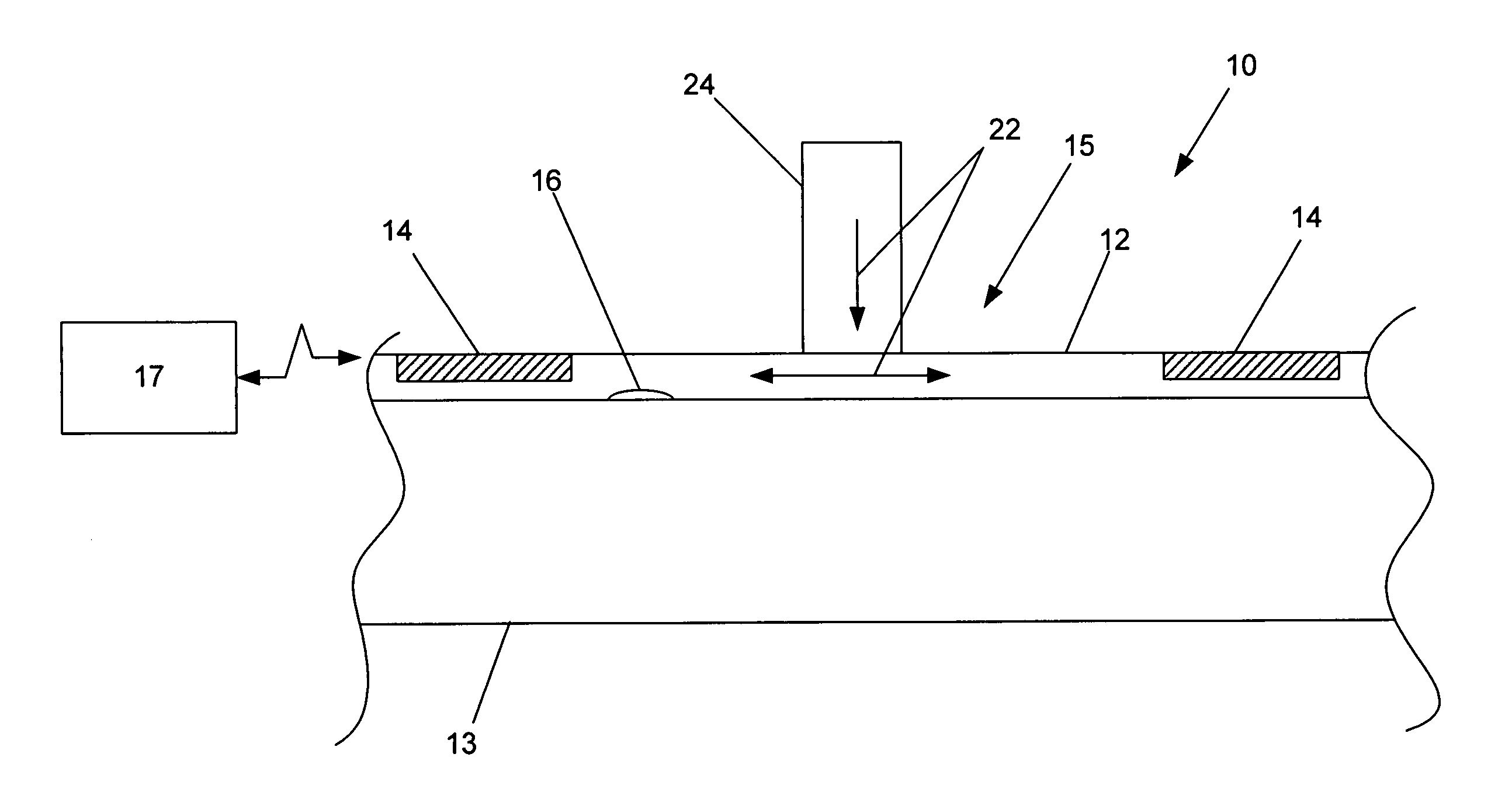
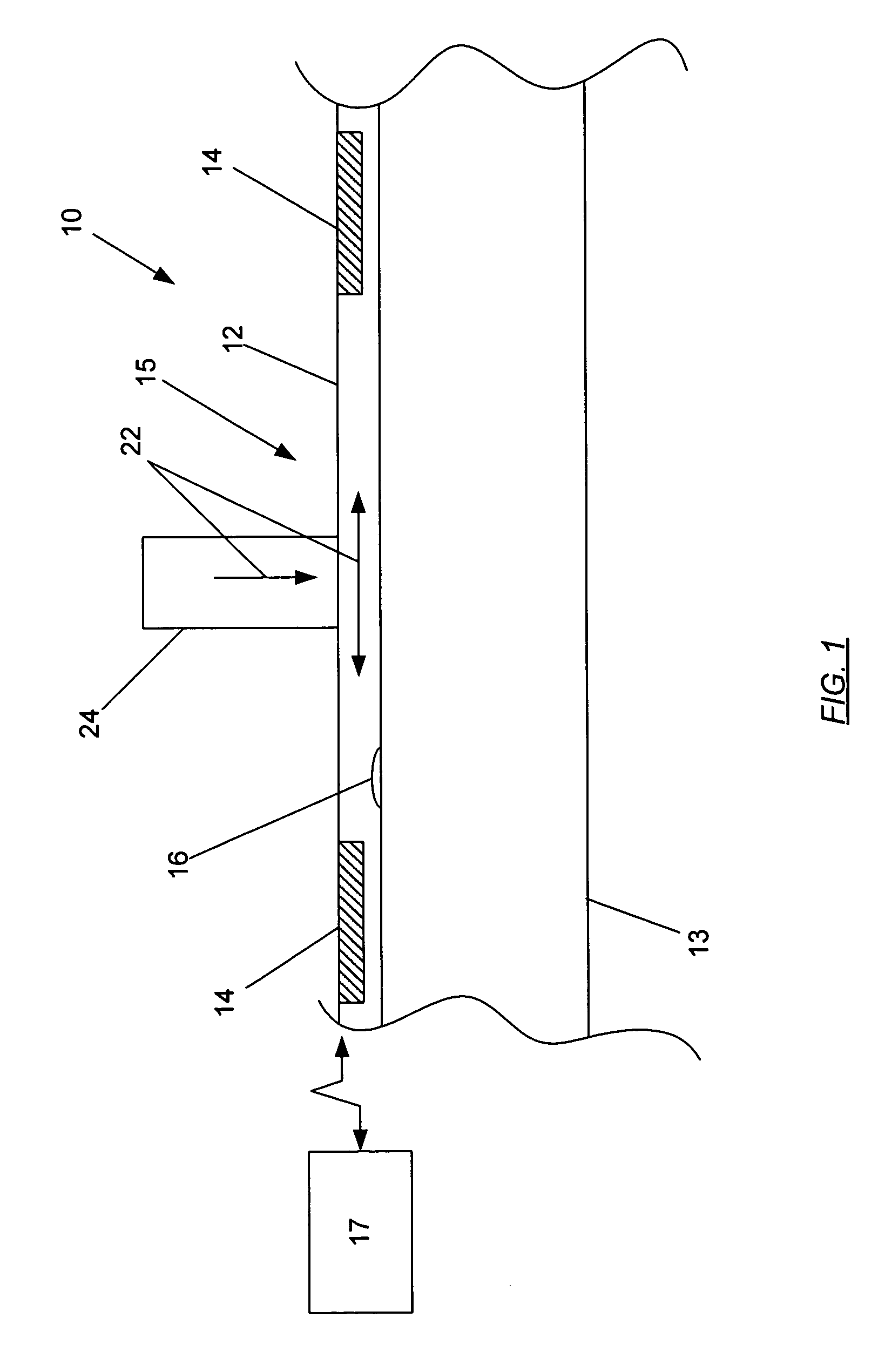
A system and method for identifying defects in a repair patch applied to a structure are provided. The system includes a sheet of material configured to be attached to the structure, and a mechanism operable to generate stress waves within and along the sheet of material. The system also includes a plurality of non-destructive sensors carried by the sheet of material. Each sensor is capable of detecting the stress waves. The system further includes a data acquisition system capable of communicating with the sensors such that the data acquisition system is also capable of generating information indicative of at least a portion of the sheet of material based on the data detected by the sensors.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Stretching and compression stress wave generator based on electromagnetic force and experimental method
ActiveCN103994922AEasy to controlGood repeatabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAudio power amplifierExperimental methods
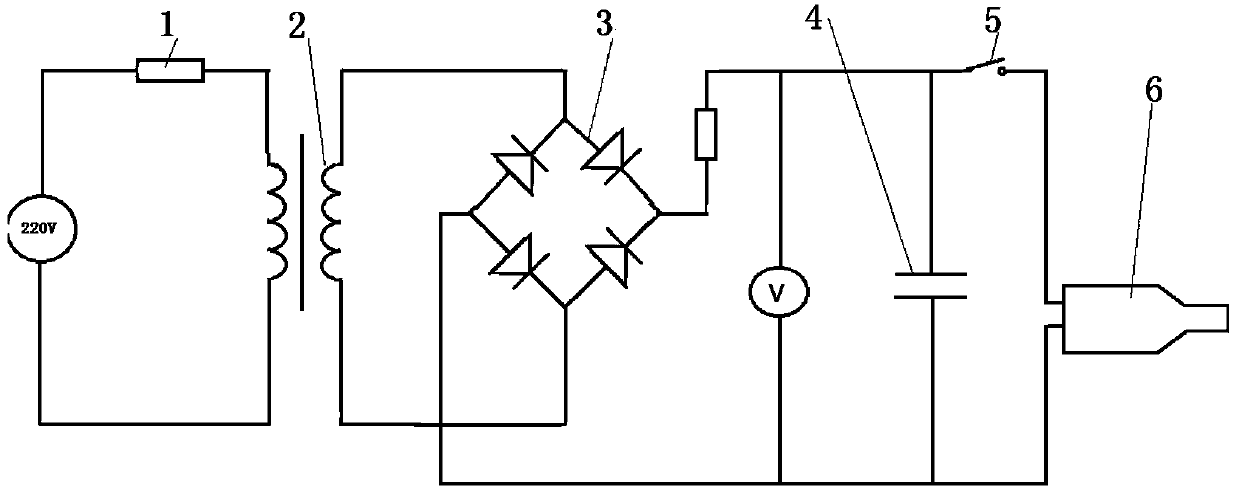
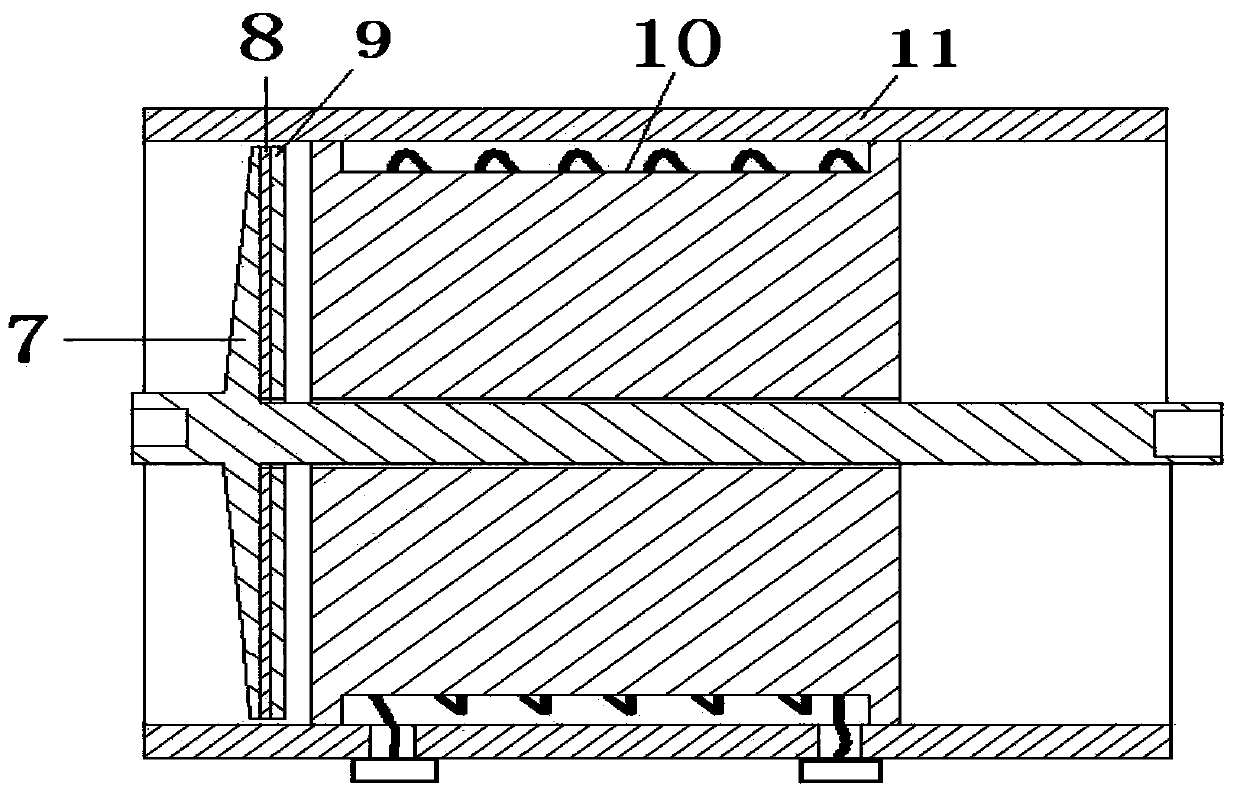
The invention provides a stretching and compression stress wave generator based on electromagnetic force and an experimental method. The stress wave generator is such structured that a capacitor charger is connected with a loading gun. A main coil, an insulating layer and a secondary coil all sleeve the locating shaft of a tapered amplifier. A power supply system is employed to provide the main coil of the loading gun with instant strong current, so strong eletromagnetic repulsion is generated between the main coil and the secondary coil; and the eletromagnetic repulsion is converted into stress waves which are amplified by the tapered amplifier and then output to a Hopkinson bar. The stretching and compression stress wave generator has a simple structure and strong controllability, can realize a strain rate and a strain scope which cannot be reached by a traditional disconnect-type Hopkinson bar, allows Hopkinson bar experimental techniques to be standardized, realizes integration of experimental apparatuses of a pull bar and a pressure bar and reduces complexity and occupied space of equipment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
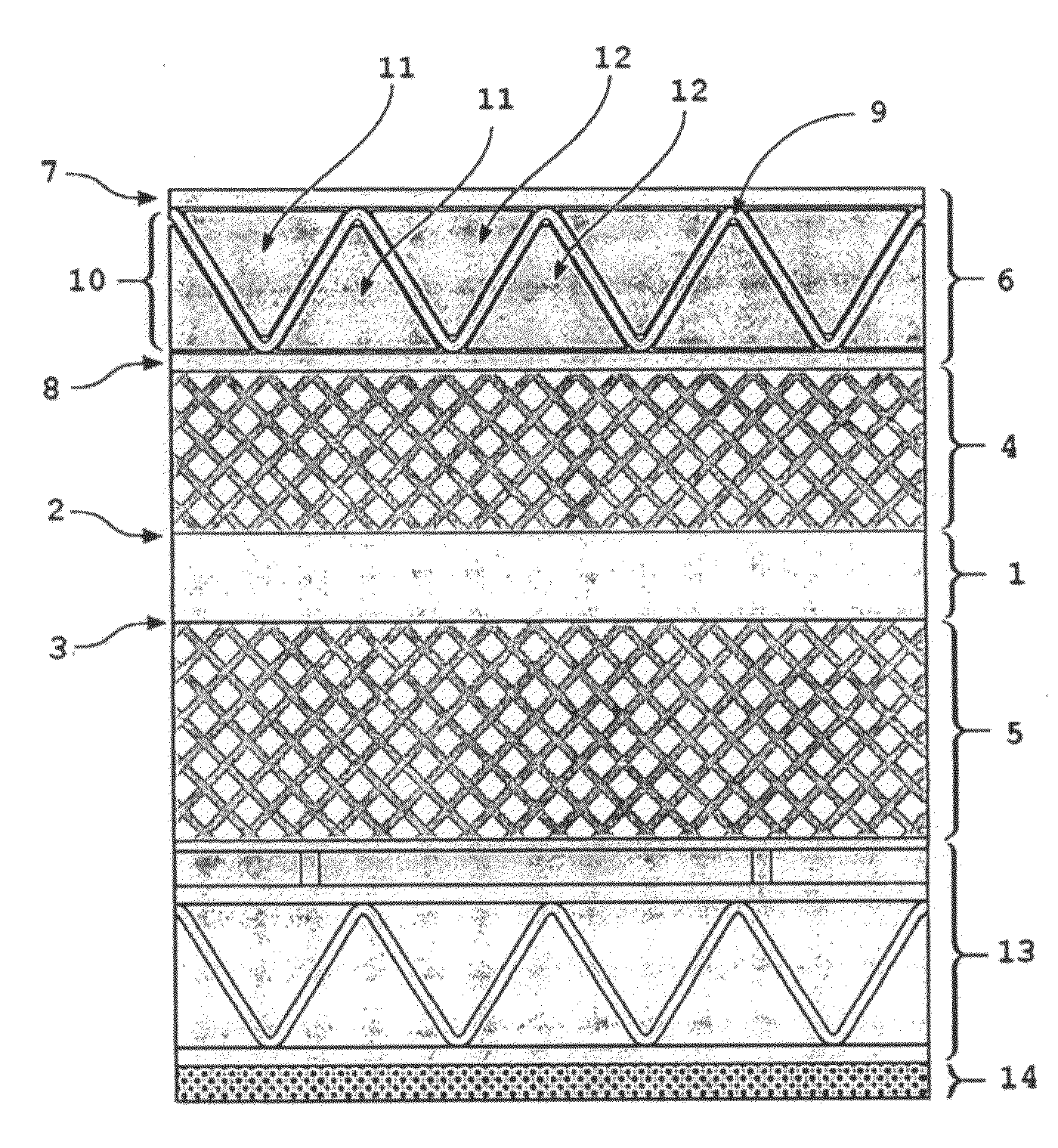
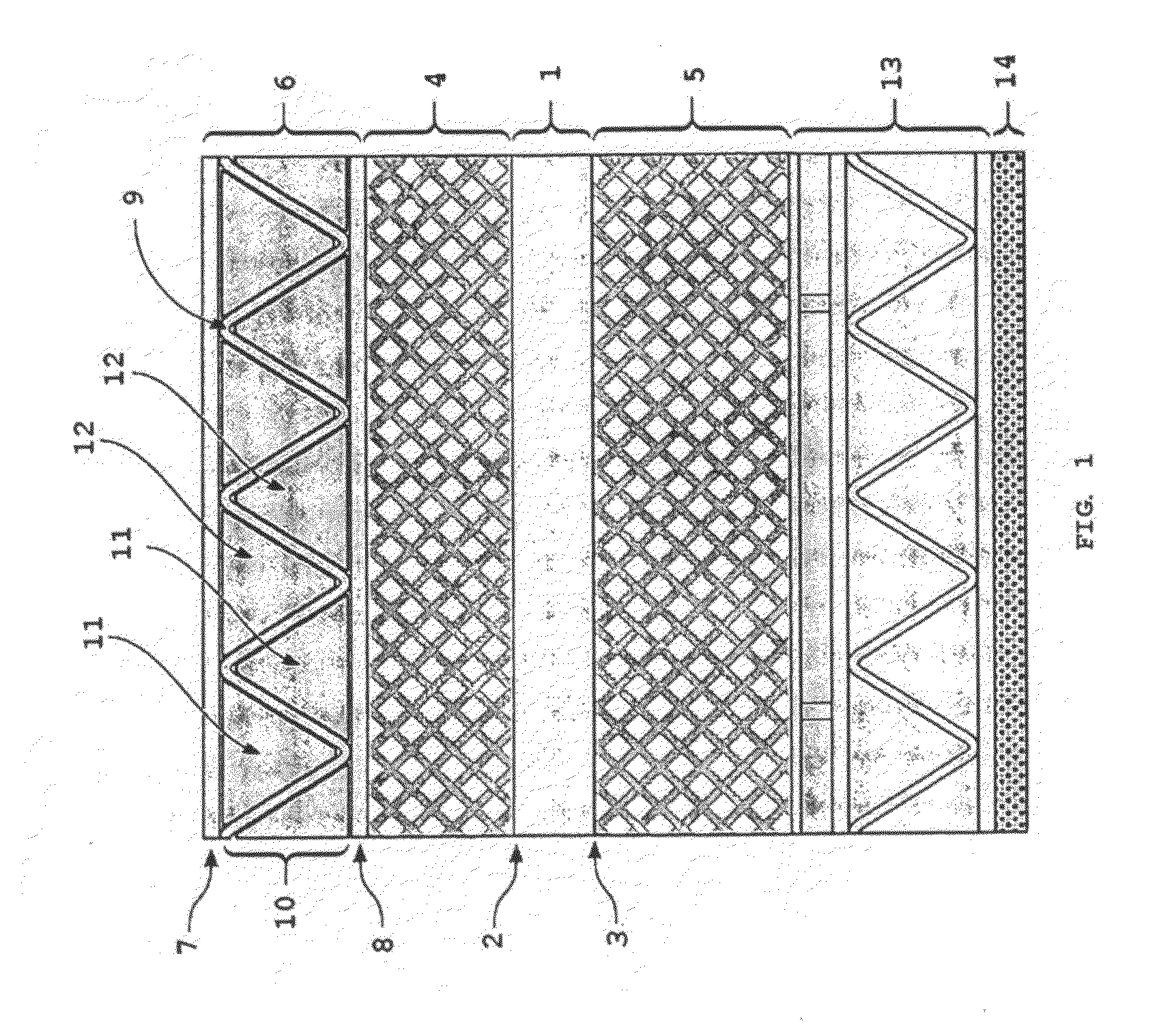
Synergistically-Layered Armor Systems and Methods for Producing Layers Thereof
The armor system according to the present invention also exploits synergistic multi-layering to provide different properties as a function of depth within a sandwich panel. Various embodiments of the invention include a combination of composite sandwich topology concepts with hard, strong materials to provide structures that (i) efficiently support static and fatigue loads, (ii) mitigate the blast pressure transmitted to a system that they protect, (iii) provides very effective resistance to projectile penetration, and (iv) minimizes shock (stress wave) propagation within the multi-layered armor sandwich structure. By using small pieces of highly constrained ceramic, the concept has significant multi-hit potential.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Non-destructive inspection system and associated method
ActiveUS20070017297A1Low costStructure moreAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElasticity measurementNon destructiveProximate
An assembly, system, and method for identifying defects in a structure are provided. The assembly includes a structure of a metallic or composite material, and a flexible sheet of material positioned adjacent to the structure. The assembly also includes a plurality of non-destructive sensors secured to the flexible sheet, and a mechanism operable to impact the flexible sheet or proximate to the flexible sheet to generate stress waves within and along a surface of the structure. The system further provides a data acquisition system capable of communicating with the sensors such that the data acquisition system generates feedback indicative of at least a portion of the structure based on data from the stress waves acquired by the sensors.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Smart repair patch and associated method
ActiveUS20070100582A1Low costStructure moreAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDigital computer detailsNon destructiveData acquisition
A system and method for identifying defects in a repair patch applied to a structure are provided. The system includes a sheet of material configured to be attached to the structure, and a mechanism operable to generate stress waves within and along the sheet of material. The system also includes a plurality of non-destructive sensors carried by the sheet of material. Each sensor is capable of detecting the stress waves. The system further includes a data acquisition system capable of communicating with the sensors such that the data acquisition system is also capable of generating information indicative of at least a portion of the sheet of material based on the data detected by the sensors.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Experimental device of split hopkinson pressure bar based on electromagnetic force load
ActiveCN103913382AGood repeatabilityEasy to operateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesElectromagnetic shieldingEngineering
The invention discloses an experimental device of a split hopkinson pressure bar based on electromagnetic force load. The experimental device comprises an electromagnetic riveting device and a split hopkinson pressure bar experiment device, wherein the electromagnetic riveting device is arranged at one end of an incident bar of the split hopkinson pressure bar experiment device; the end face of an electromagnetic riveting gun on the electromagnetic riveting device is in full contact with the end face of the end of the incident bar, so that the electromagnetic riveting device can generate stress pulse which is directly input into the incident bar and generated pulse signals can be accurately controlled. By adopting the experimental device, the split hopkinson pressure bar is not greatly improved; the electromagnetic riveting device is only used for replacing an air gun in a conventional split hopkinson pressure bar system; accurate control of stress wave is achieved in an electromagnetic way; meanwhile, the width of the stress wave generated by the electromagnetic load is not limited by the length of an impacting bar, so that the width of the stress wave generated by the experimental device is large enough at a high strain rate, thereby achieving the normalization of experimental technologies of the split hopkinson pressure bar.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
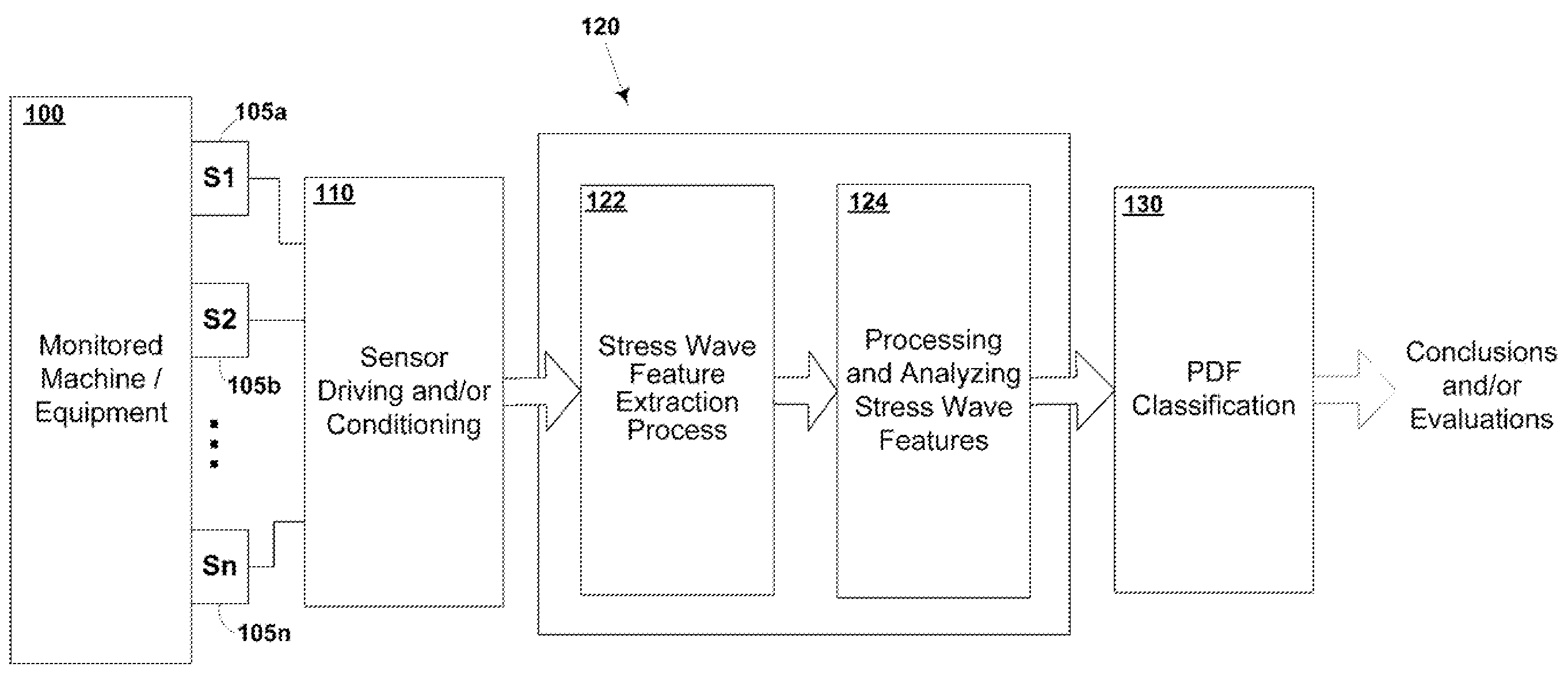
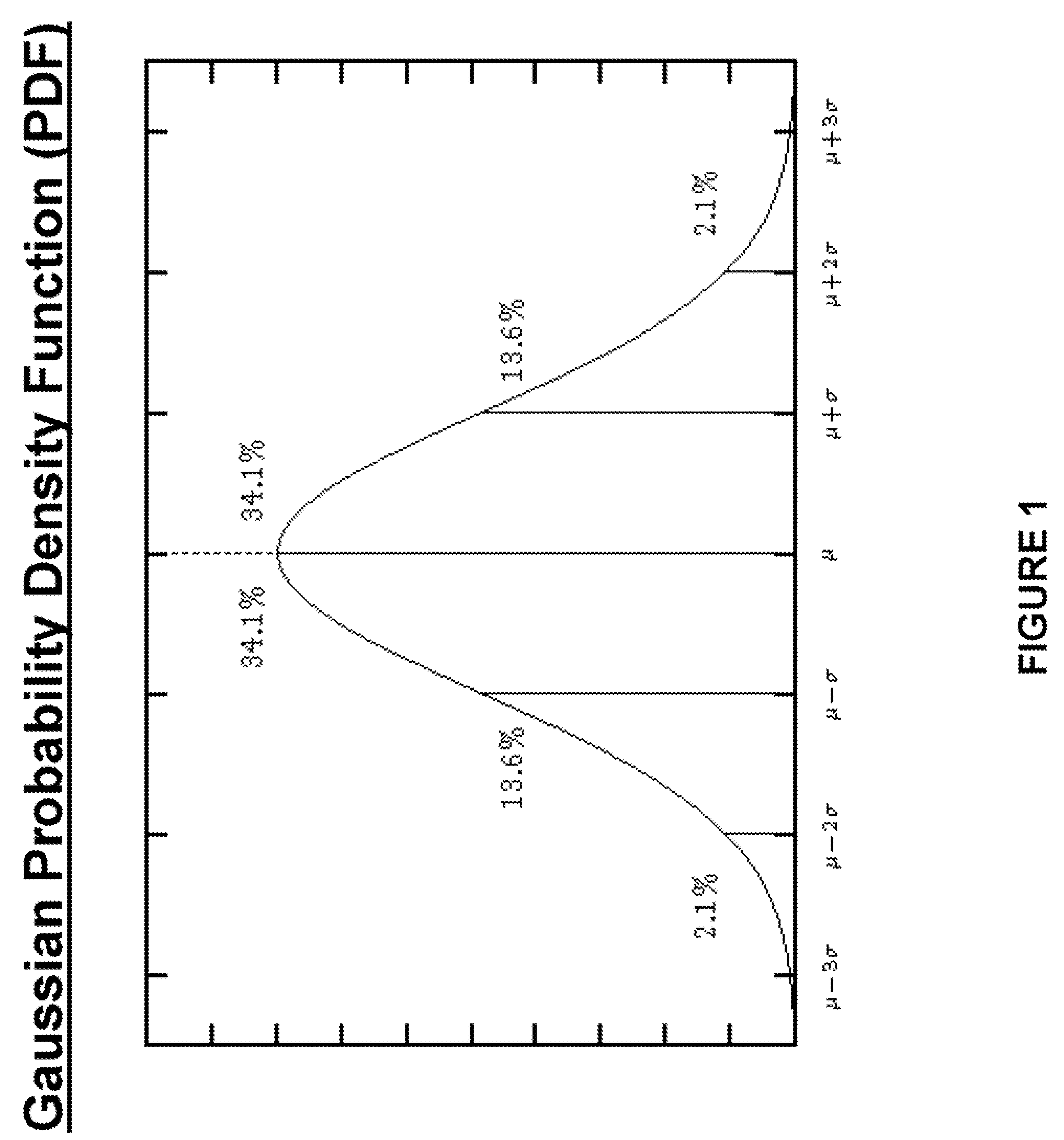
Probabilistic stress wave analysis system and method
A statistical process, and system for implementing the process, is described for the analysis of stress waves generated in operating machinery or equipment. This technique is called Probabilistic Stress Wave Analysis. The process is applied to a population of individual “feature” values extracted from a digitized time waveform (such as a 2 second Stress Wave Pulse Train, or a 2 month history of Stress Wave Energy). Certain numeric descriptors of the statistical distributions of computed features are then employed as inputs to decision making routines (such as neural networks or simple threshold testing) to accurately classify the condition represented by the original time waveform data, and thereby determine a status of the operating machine / equipment.
Owner:CURTISS WRIGHT FLOW CONTROL CORP
Compressor valve health monitor
ActiveUS9759213B2Improve analysisImprove notificationsExternal parameterPositive displacement pump componentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A rotating machine valve health monitor. Aspects of the valve monitor include instrumenting each valve of a reciprocating compressor, or other rotating machine, with a sensor capable of detecting at least vibration and instrumenting the crank shaft with a sensor capable of detecting at least rotation. A controller directly monitors the operation and condition of each valve to precisely identify any individual valve exhibiting leakage issues rather than only identifying the region of the leakage. The valve monitor uses a relatively high frequency stress wave analysis technique to provide a good signal-to-noise ratio to identify impact events indicative of leakage. The valve monitor uses circular waveforms of vibration data for individual valves to identify leakage by pattern recognition or visual identification. The valve monitor provides ongoing data collection to give warning of predicted valve failure and scheduling of preventative maintenance for failing valves.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL SYST
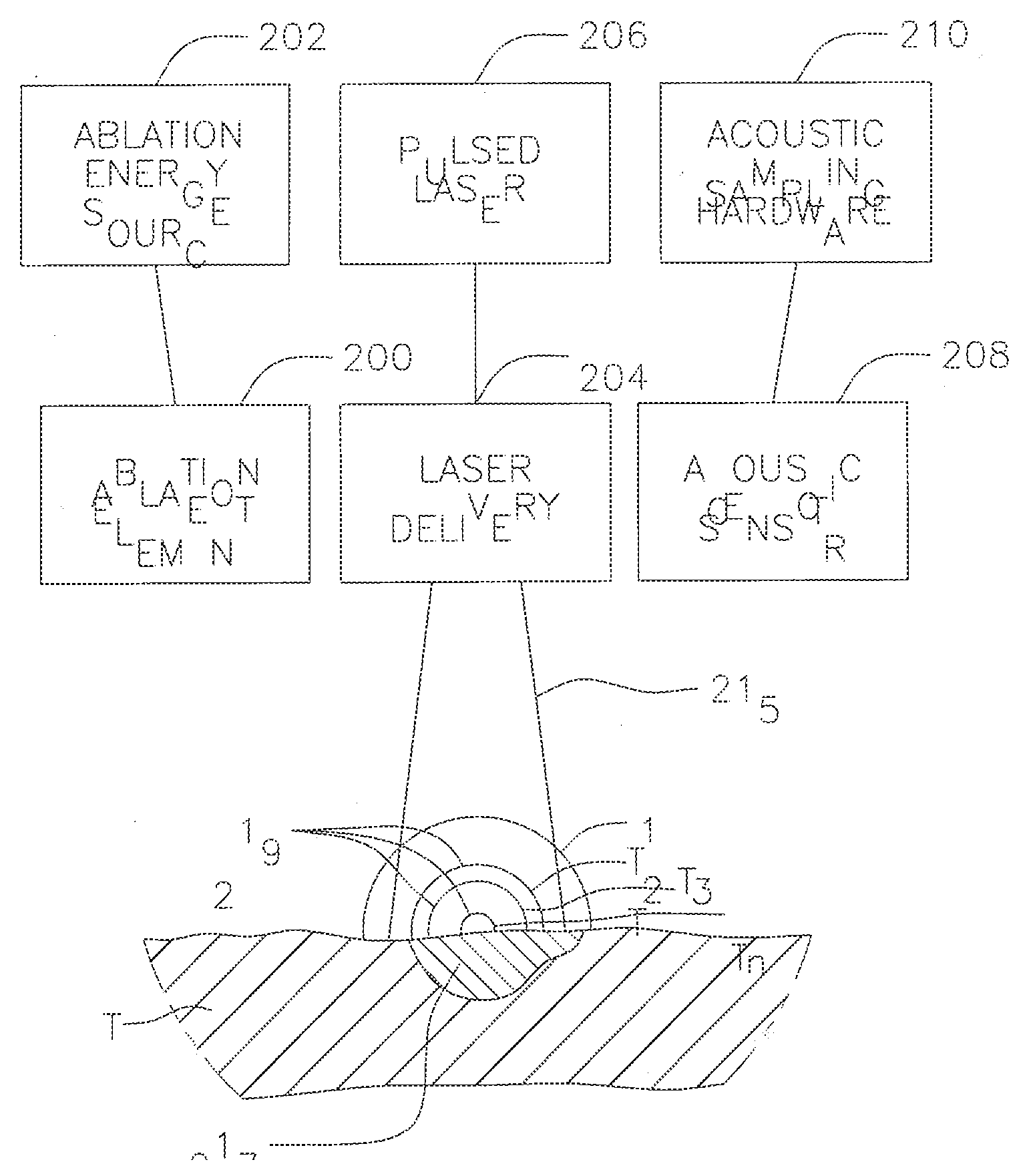
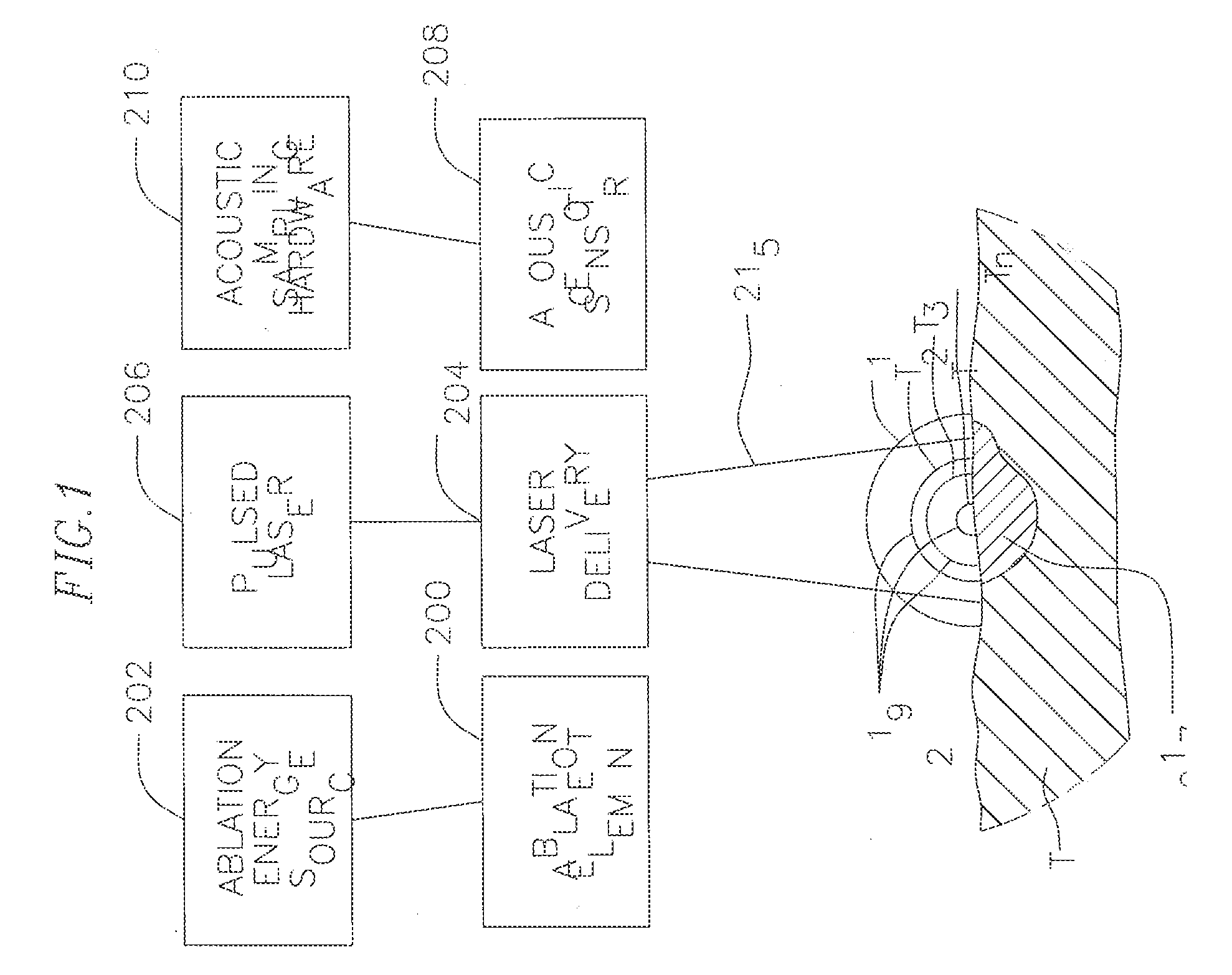
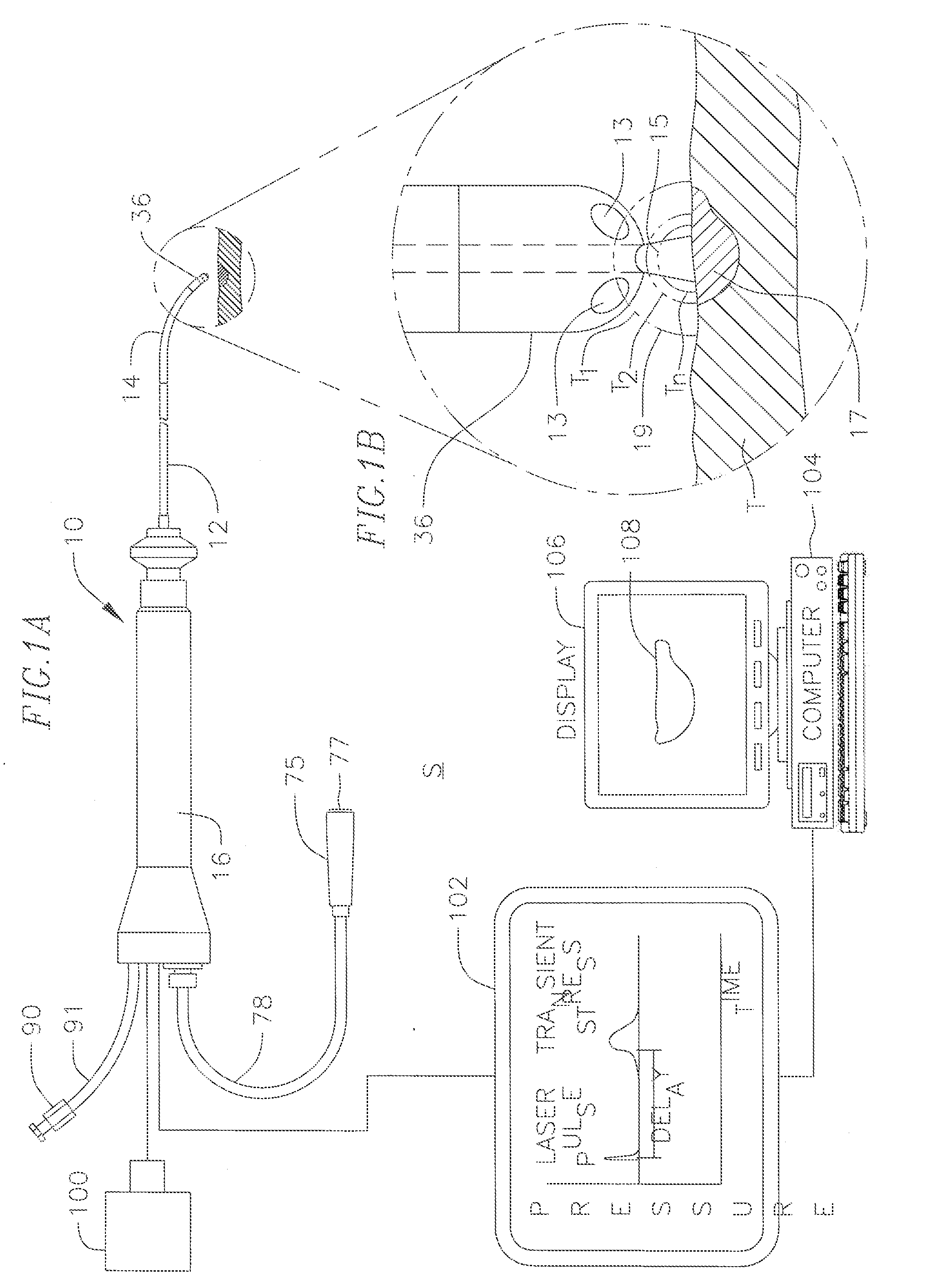
Real-time optoacoustic monitoring with electophysiologic catheters
InactiveUS20080154257A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionCatheterSurgical instrument detailsRf ablationLesion progression
A system and method for opto-acoustic tissue and lesion assessment in real time on one or more of the following tissue characteristics: tissue thickness, lesion progression, lesion width, steam pop, and char formation, system includes an ablation element, laser delivery means, and an acoustic sensor. The invention involves irradiating tissue undergoing ablation treatment to create acoustic waves that have a temporal profile which can be recorded and analyzed by acoustic sampling hardware for reconstructing a cross-sectional aspect of the irradiated tissue. The ablation element (e.g., RF ablation), laser delivery means and acoustic sensor are configured to interact with a tissue surface from a common orientation; that is, these components are each generally facing the tissue surface such that the direction of irradiation and the direction of acoustic detection are generally opposite to each other, where the stress waves induced by the laser-induced heating of the tissue below the surface are reflected back to the tissue surface.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Electromagnetic induction type Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar loading device and experimental method
ActiveCN105571961AStable incomingEasy to controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementCapacitanceExperimental methods
The invention discloses an electromagnetic induction type Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar loading device and an experimental method. An anode output line of a capacitance charger is connected with an anode line of a loading gun while a cathode output line of the capacitance charger is connected with a cathode line of the loading gun, and consequently both compressive stress waves and tensile stress waves can be generated, and application to loading of Hopkinson torsion and pressure bars is realized. Loading systems of the Hopkinson torsion and pressure bars can be arranged on the same device, the strain rate and the strain range which are beyond the reach of traditional split Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar experiments are realized to further realize technical standardization of the Hopkinson torsion and pressure bar experiments, integration of torsion and pressure bar experiment devices is realized, and accordingly equipment complexity and space occupancy are reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
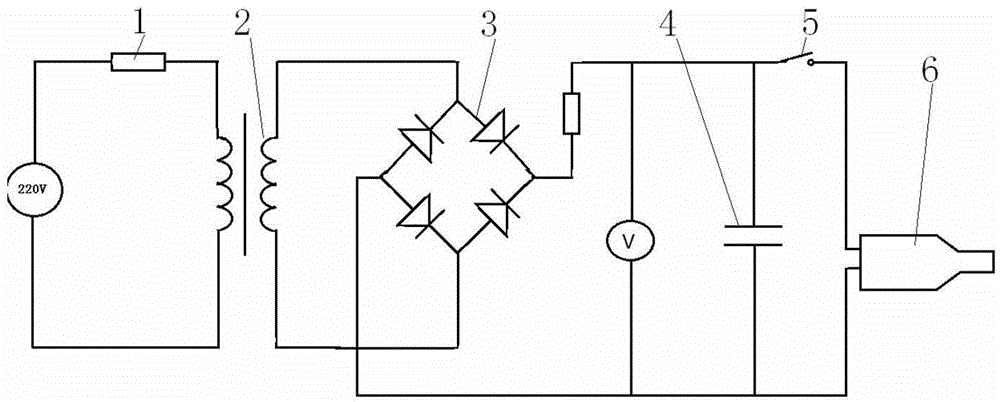
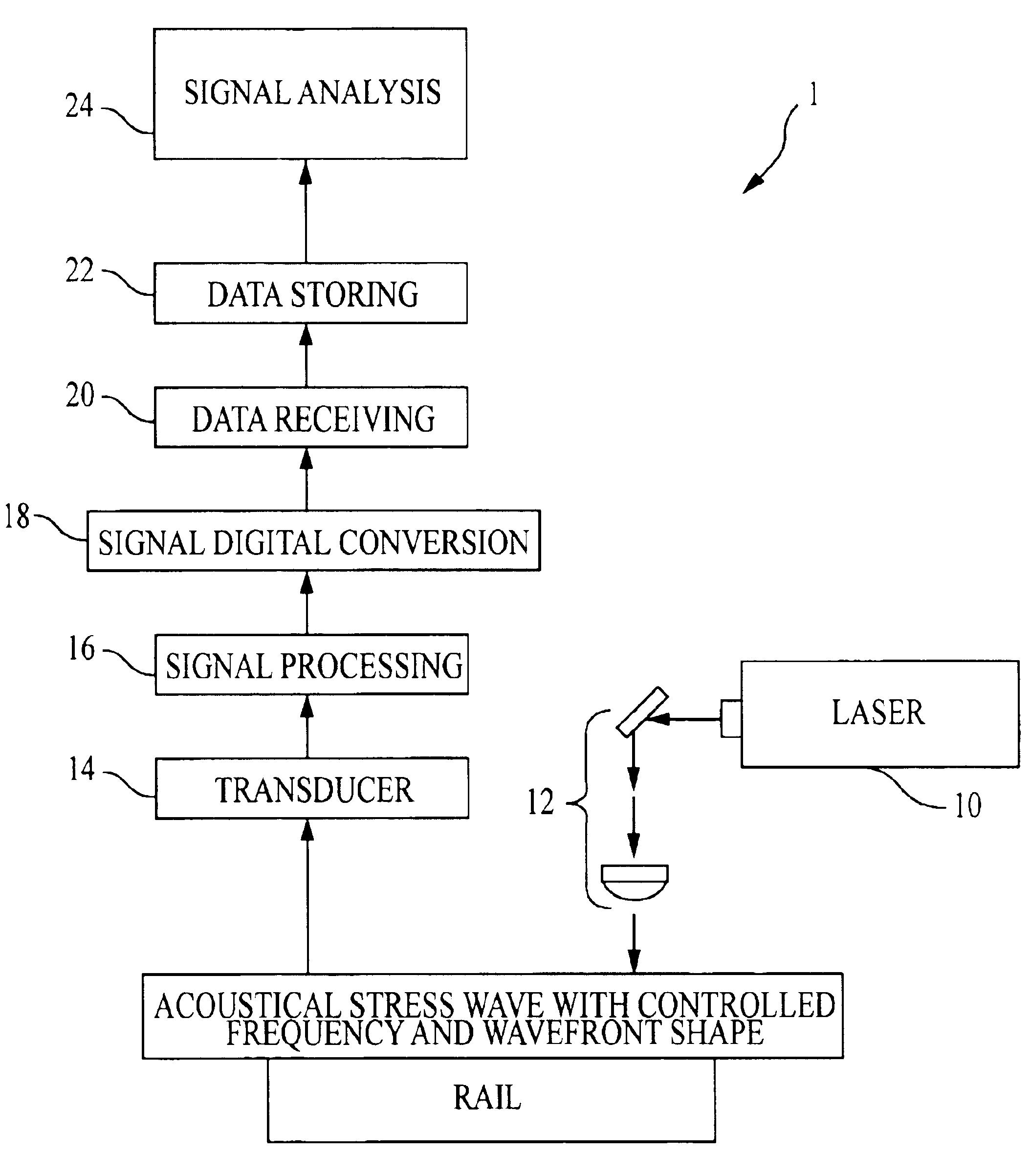
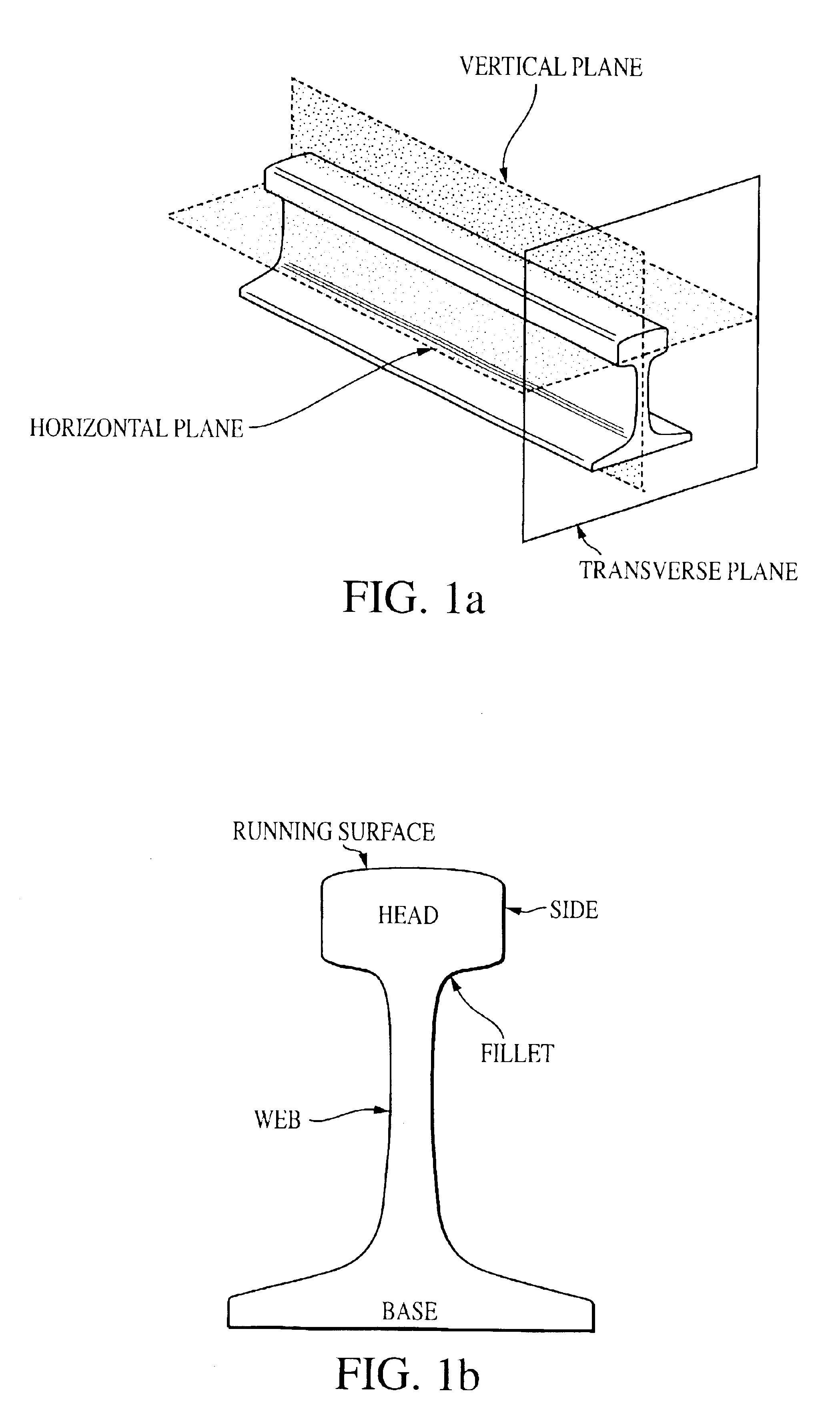
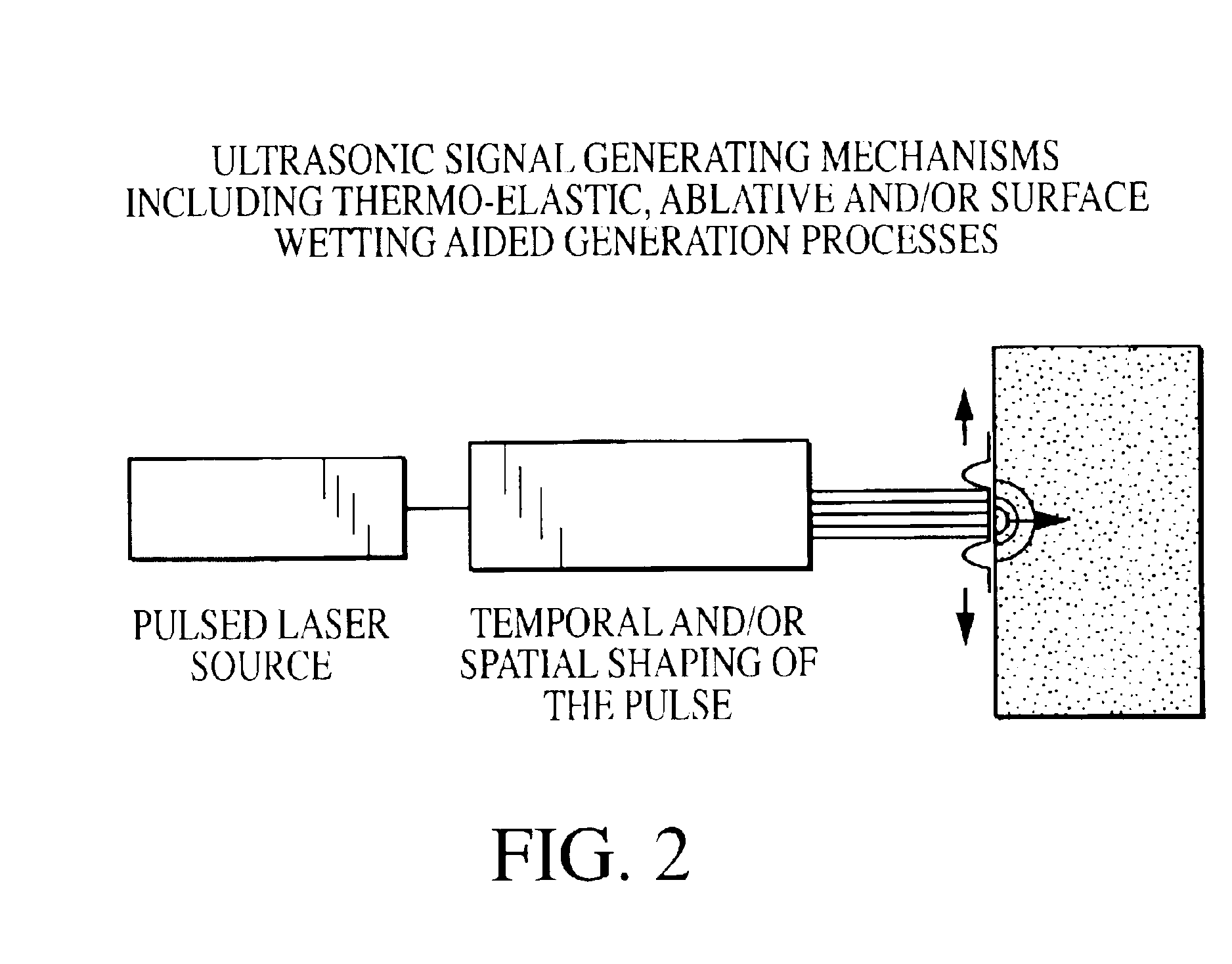
Laser-air, hybrid, ultrasonic testing of railroad tracks
InactiveUS6945114B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRailroad industryWavefront
Formed Laser Sources (FLS) using pulsed laser light for generation of ultrasonic stress waves are combined with air-coupled detection of ultrasound to provide for the hybrid non-contact, dynamic and remote ultrasonic testing of structural materials, especially railroad tracks. Using this hybrid technique, multimode and controlled frequency and wavefront surface acoustic waves, plate waves, guided waves, and bulk waves are generated to propagate on and within the rail tracks. The non-contact, remote nature of this methodology enables high-speed, fill access inspections of rail tracks. The flexibility and remote nature of this methodology makes possible the detection of critical cracks that are not easy, or impossible to detect, with current inspection techniques available to the railroad industry.
Owner:MATERIALS & SENSORS TECH
Gas explosion simulation test system and method
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electromagnetic-force-based Hopkinson tie/pressure bar stress wave generator and experimental method
ActiveCN103926138AEasy to controlGood repeatabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesExperimental methodsAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses an electromagnetic-force-based Hopkinson tie / pressure bar stress wave generation device and an electromagnetic-force-based Hopkinson tie / pressure bar stress wave generation method. The stress wave generation device consists of a loading gun and a power supply system, wherein the power supply system is used for providing instantaneous high current for a primary coil of the loading gun, so as to generate high electromagnetic repulsive force between the primary coil and each secondary coil. A capacitor is short in discharge time and high in discharge current, so that instantaneous high repulsive force can be generated between the primary coil and each secondary coil to generate high stress pulses, and the stress pulses are output to Hopkinson bars after being amplified by a tapered amplifier. According to the device and the method, an electromagnetic riveter is structurally improved to be applied to the loading of the separable Hopkinson pressure bars and tie bars, so that loading systems of the Hopkinson pressure bars and tie bars can be simultaneously implemented on a same device; the device and the method have the characteristics of simplicity in operation and high controllability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Double-air path bidirectional automatic assembling device for high-temperature Hopkinson pressure bar experiment
InactiveCN1888851AGuaranteed synchronicityReduce temperature unevennessStrength propertiesEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
Two-way double steam paths self-motion assembled equipment for high temperature Hopkinson pressure-bar experiment belongs to material high temperature dynamic mechanics capability research field. Each gas driving rack set on incidence perch and transmission perch and push them towards specimen in assembling to form two-way assemble in order to keep specimen in the availability heating range. Push the driving gas path of rack and separate setting of air cannon startup gas path and set gas chief valve control the switch of driving gas path and air cannon startup gas path. It makes the driving rack and air cannon startup linkage without influence. Set small gas storage tin as driving gas source and control its air pressure to control the driving speed of the driving rack. It can keep the assembled stability of the equipment and enhance assembled success probability. It assures the synchronism of assembled equipment when the stress wave arrives to specimen to avoid the temperature of specimen rapidly drop for leaving heat fountain.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Device and method for self-piercing riveting of half-hole rivet loaded by pulse magnet field force
InactiveCN101817056ARealize stamping self-riveting rivetingIncreasing the thicknessPulse loadLow voltage
The invention discloses a device and a method for the self-piercing riveting of a half-hole rivet loaded by a pulse magnet field force, which relate to the device and the method for the self-piercing riveting of the half-hole rivet and aim to solve the problem that a conventional punching self-riveting process has the problems of complex riveting process, bad riveting quality and low efficiency in the pre-punching of a riveting component. A punch head is arranged below a stress wave modulator; a female die is arranged under an electromagnetic riveting gun; a control box controls the on / off of an electromagnetic riveting charging switch of a low-voltage electromagnetic riveting device and is connected with the signal input end of a high-voltage pulse generator of the low-voltage electromagnetic riveting device; and the signal output end of the high-voltage pulse generator is used for controlling the on / off of a high-frequency thyristor discharging switch of the low-voltage electromagnetic riveting device. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, a capacitor bank is charged; secondly, a discharging loop is switched on and the capacitor bank is discharged to apply the action of an axially downward pulse load to a driven piece; and finally, the stress wave modulator is amplified and acts on the half-hole self-punching rivet through the punch head to realize self-punching riveting. The device and the method are used for the self-punching riveting of a connected piece.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Laser system and method for non-destructive bond detection and evaluation
ActiveUS7770454B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesTransducerLight beam
A system for evaluating the integrity of a bonded joint in an article includes a laser configured in a laser shock processing arrangement to perform a laser shock processing treatment on the article. A beam delivery system employs an articulated arm assembly to communicate the radiant energy emitted by the laser to a process head proximate the article. The laser shock processing treatment causes the formation of shockwaves that propagate through the article, inducing internal stress wave activity that characteristically interacts with the bonded joint. A sensor detects a stress wave signature emanating from the article, which is indicative of the integrity of the bond. A detector such as a non-contact electromagnetic acoustic transducer provides a measure of the stress wave signature in the form of surface motion measurements.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
System and method for measuring high voltage cable space charges based on electroacoustic pulse method
InactiveCN103605008ARealize space charge distribution measurementReliable data baseElectrostatic field measurementsCapacitanceHigh voltage capacitors
The invention relates to a system and a method for measuring high voltage cable space charges based on an electroacoustic pulse method. A high voltage pulse source and a high voltage capacitor are connected in series and are then connected with measuring electrodes at two ends of a tested piece, a high voltage power source is further connected with the measuring electrodes at two ends of the tested piece through a current limit resistor, a piezoelectric sensor closely clings to the lower measuring electrode, the piezoelectric sensor acquires a stress wave signal and sends the processed signal to a computer to form the measuring system, the high voltage power source can be a direct current high voltage power source and further can be an alternating current high voltage power source, the alternating current high voltage power source is connected with a phase detection unit, and a phase detection circuit outputs a synchronous control signal to a pulse generation unit of the high voltage pulse source. The high voltage power source forms space charges in an insulation layer of an electric power cable through electrodes, disturbance of the charges in the insulation layer of the electric power cable is realized through the high voltage pulse source to form dynamic stress waves, the measuring system acquires a signal of a pressure sensor, and a distribution state of the space charges of the electric power cable is analyzed. Through the system and the method, measurement on the distribution state of the space charges in the insulation layer of the electric power cable under the alternating current state is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
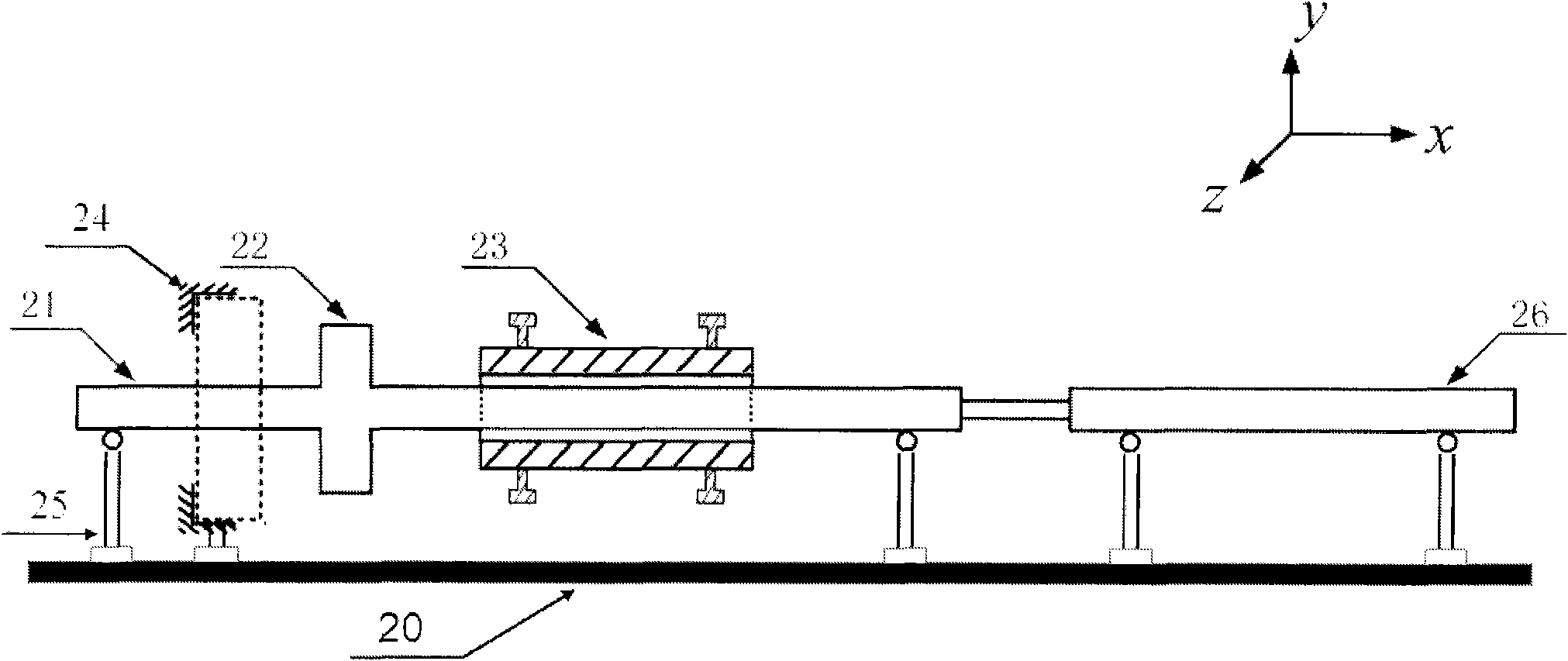
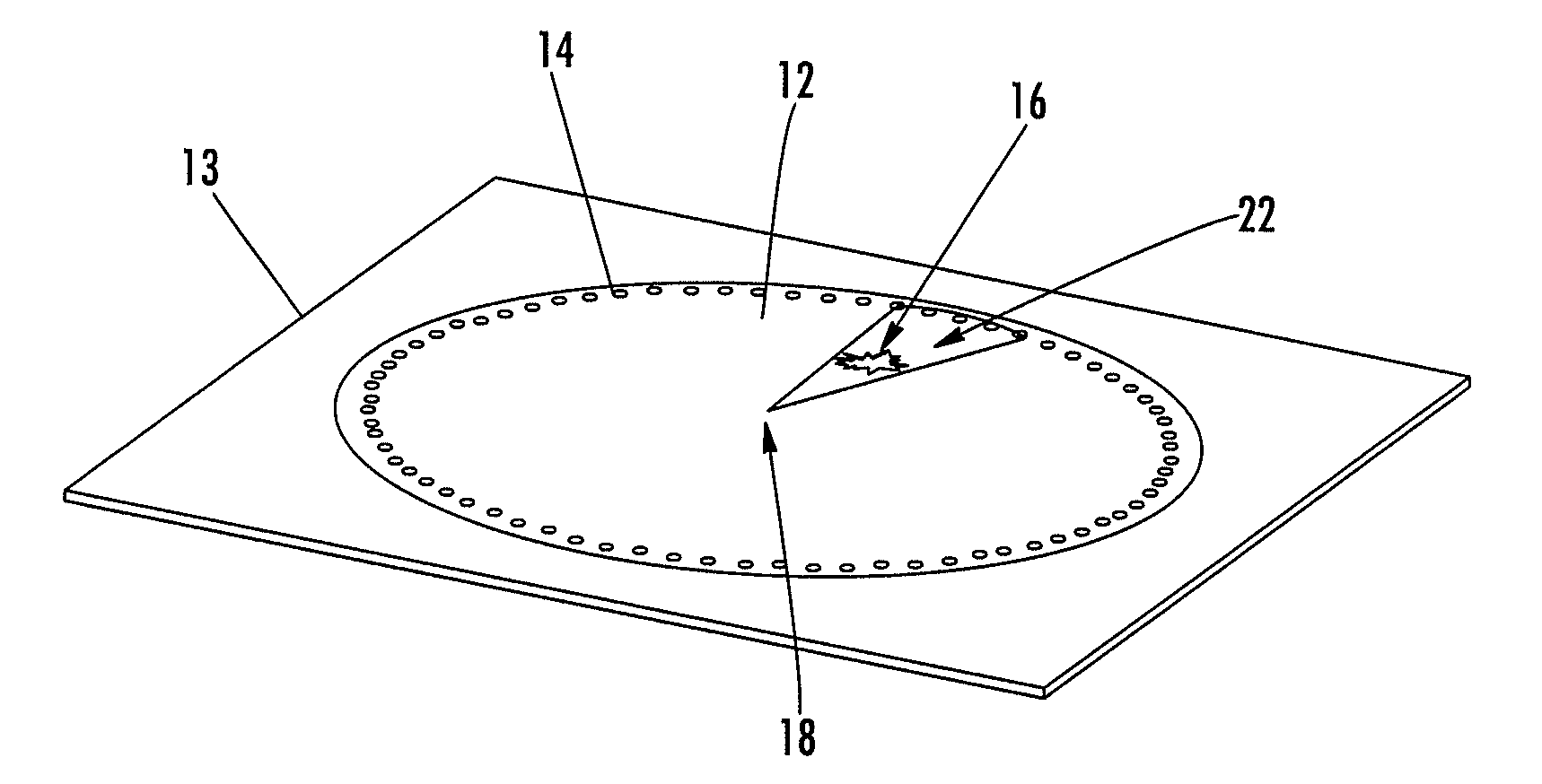
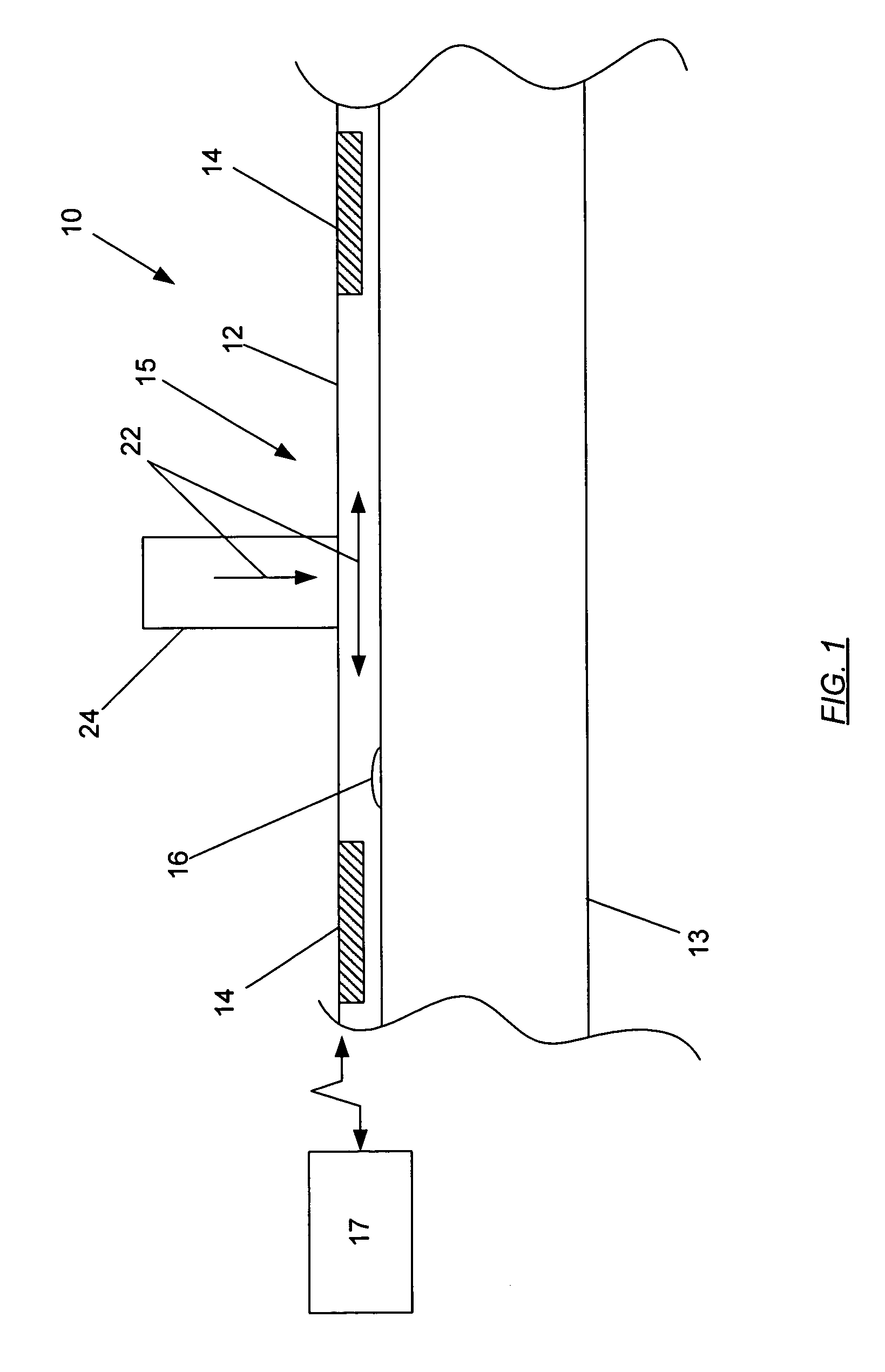
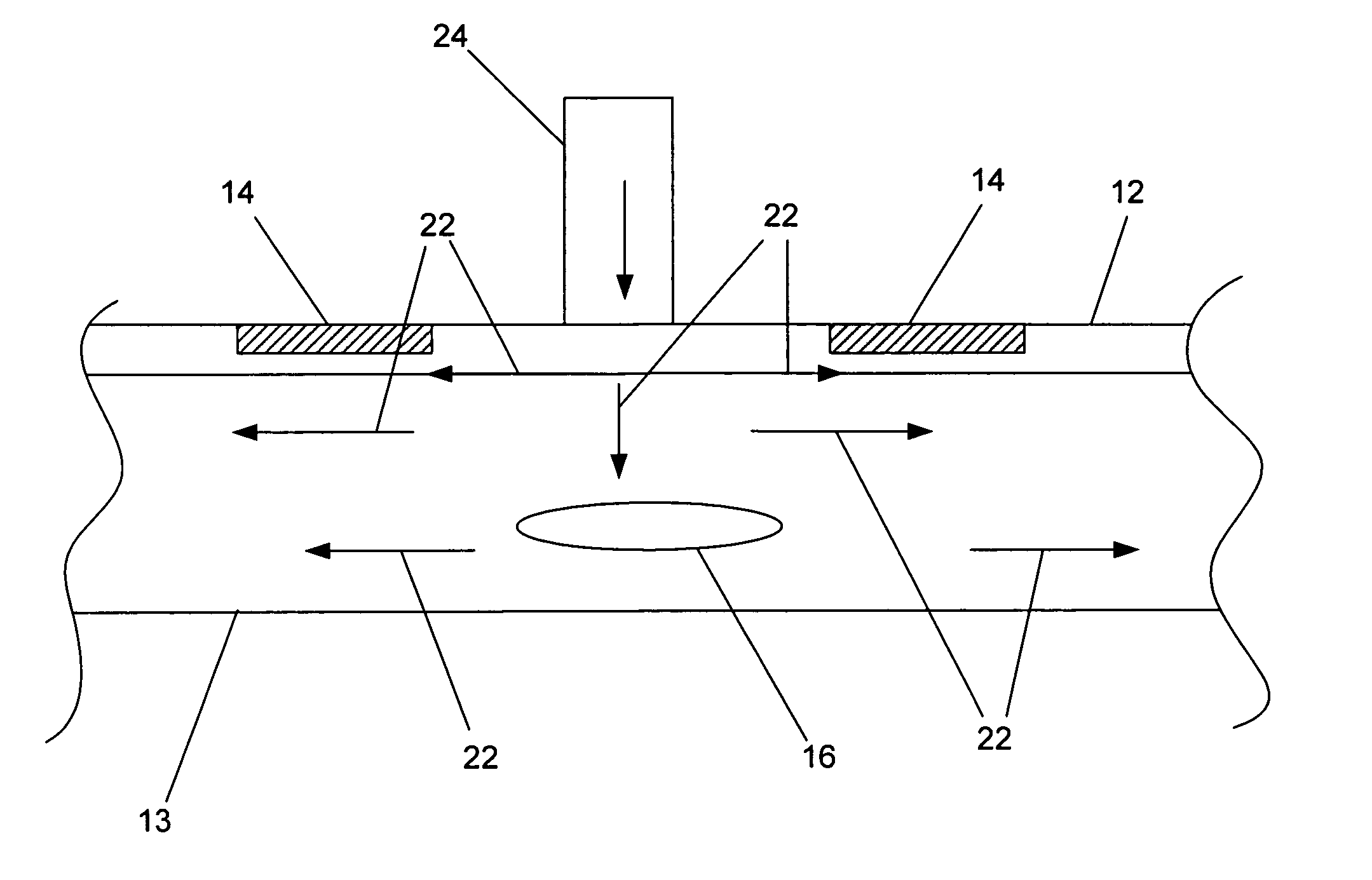
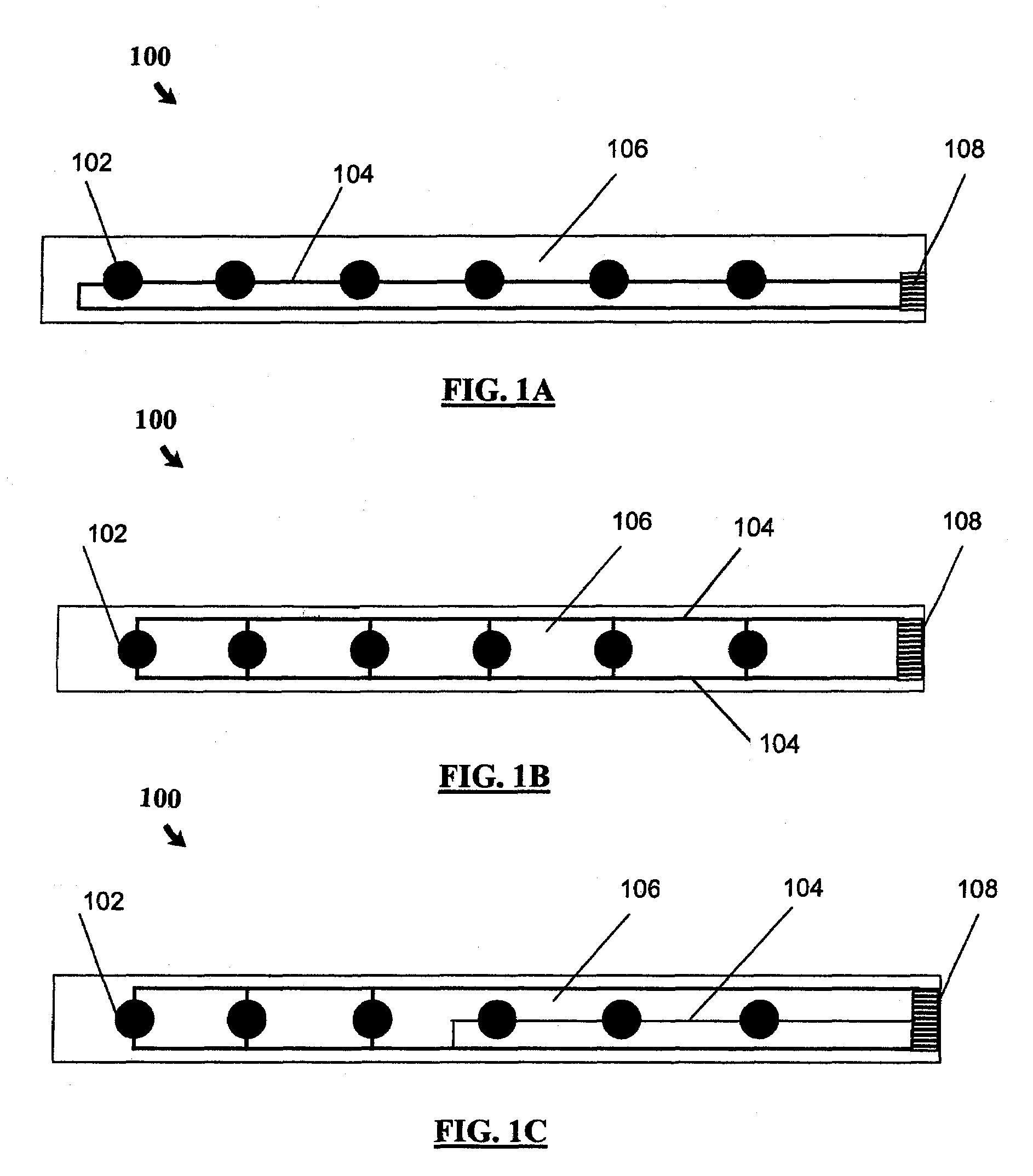
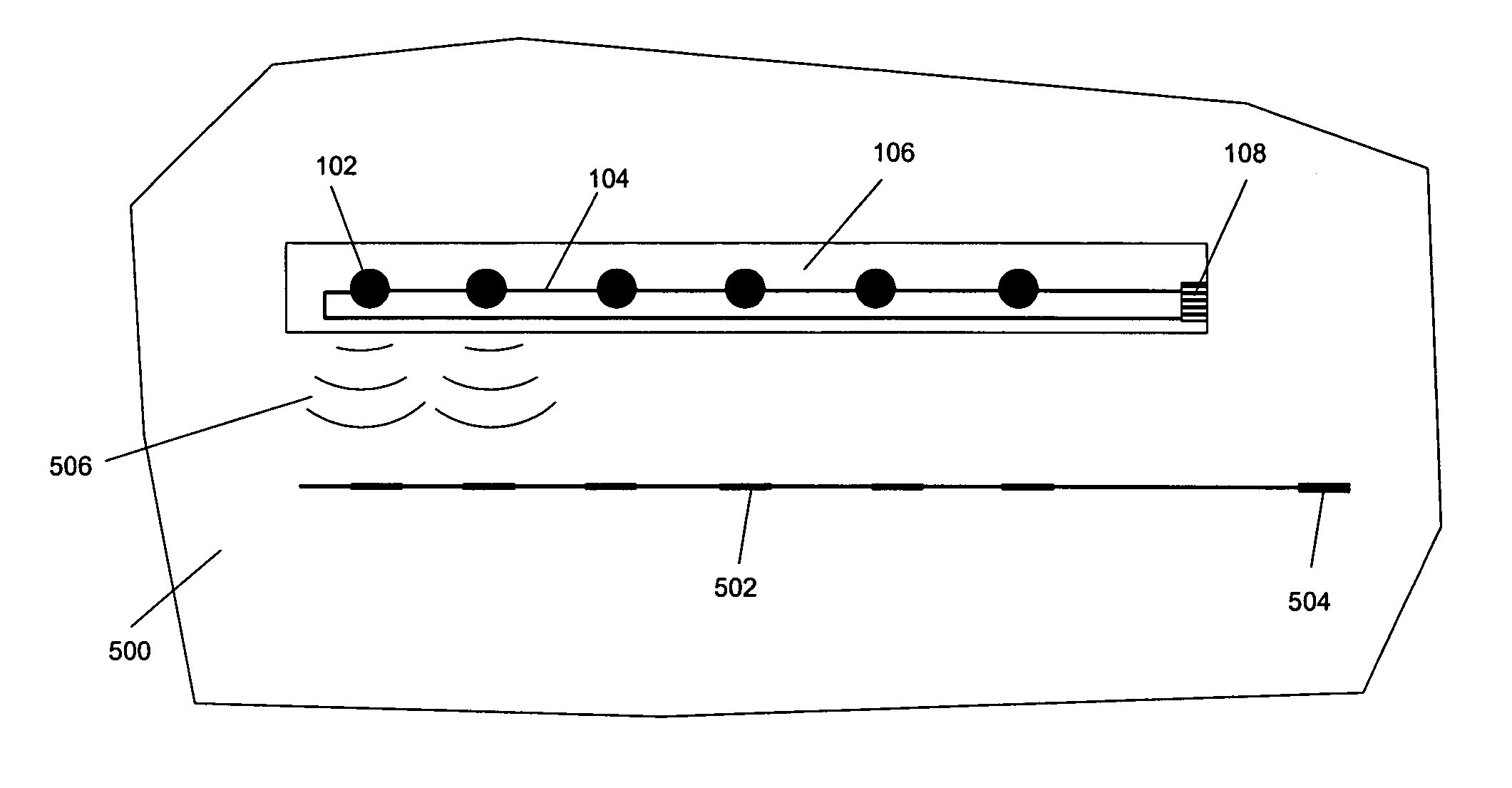
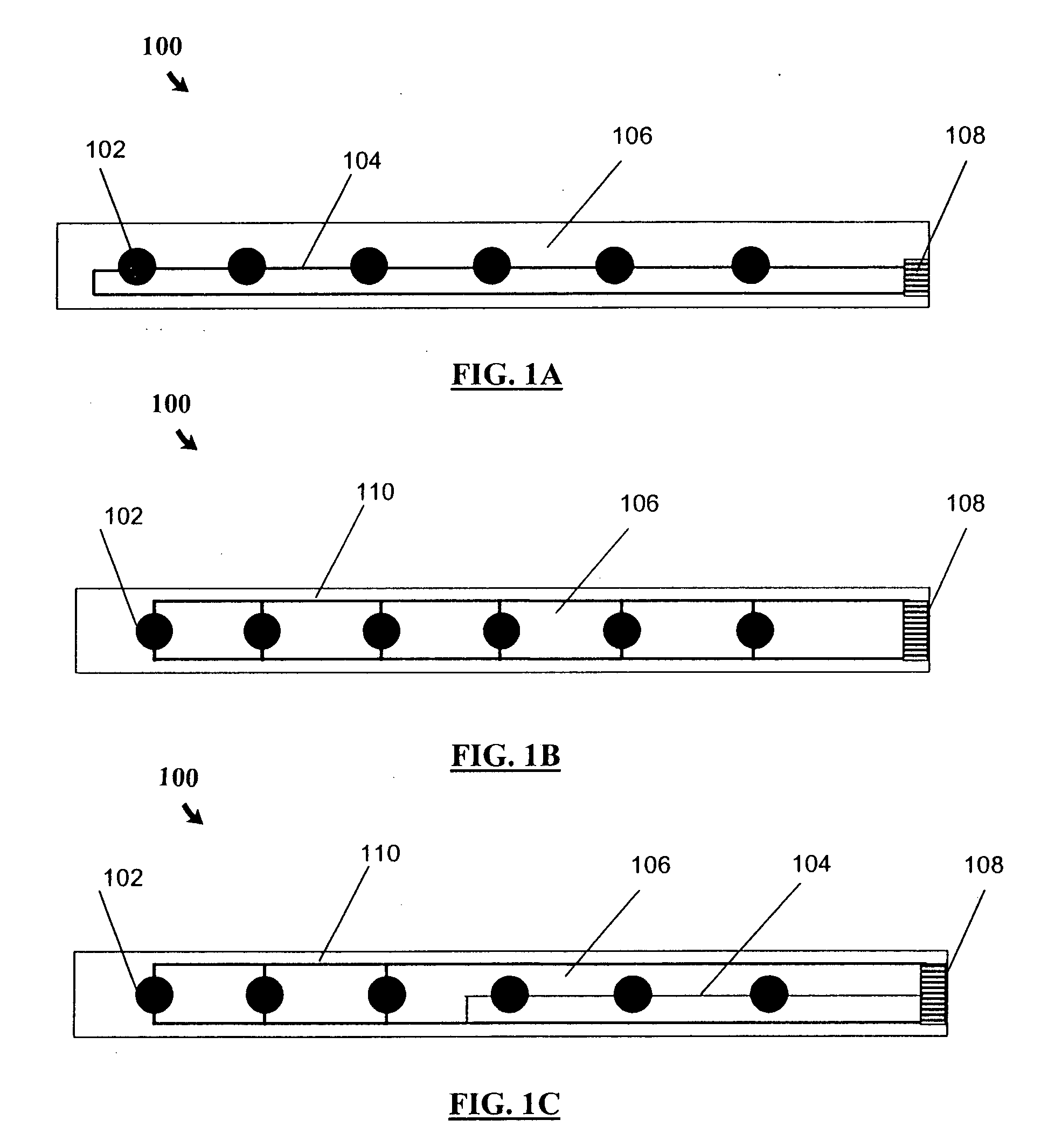
Single-wire sensor/actuator network for structure health monitoring
ActiveUS7387033B2Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricityStructural health monitoring
A sensor / actuator network configured with a number of electrically-interconnected elements. More specifically, the sensors / actuators are each placed in electrical communication with the same transmission line. Various embodiments of such networks employ sensors / actuators connected in electrical series and in electrical parallel. Networks having these configurations, when placed upon a structure, are capable of detecting and / or transmitting stress waves within the structure so as to detect the presence of an impact, or actively query the structure. Advantageously, as these networks employ a single transmission line, they utilize fewer wires than current sensor / actuator networks, thus making them easier to install and maintain. They can also be configured as flexible layers, allowing for further ease of installation and maintenance.
Owner:ACELLENT TECH
Bidirectional static and dynamic loading roof key block caving test device and method
InactiveCN108827578AAccurate and controllable two-way dynamic disturbance conditionsShock testingModel sampleInstability
The invention discloses a bidirectional static and dynamic loading roof key block caving test device and method, and the device comprises an overall frame, a lateral pressure loading system, a vertical pressure loading system, a lateral pendulum bob impact disturbance system, a vertical drop-hammer impact disturbance system, an incident wave monitoring system and a response measurement system. Thetesting method comprises the steps: a first work condition: carrying out the bidirectional static and dynamic loading disturbance testing of a tunnel overall model sample to explore the initial stress state of the surrounding rocks of a tunnel and the initial stress condition of a key block rock, and observing an overall phenomena of the propagation law of cracks, a forming process of a key blockand the instability of the key block in the disturbance process; a second work condition: carrying out the bidirectional static and dynamic loading disturbance instability testing of a key block model sample, taking the result under the first work condition as the basis, abstracting the key block and the surrounding rocks at two sides to more precisely explore the law that a stress wave causes the propagation of cracks, a critical condition that the key block slides in an instable manner, and an action mechanism that the disturbance effect causes the instability.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for detecting quality of large-diameter tubular pile at low strain
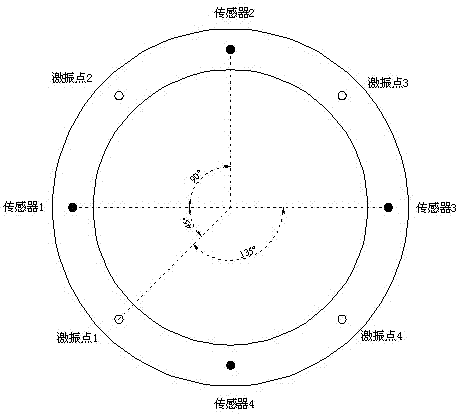
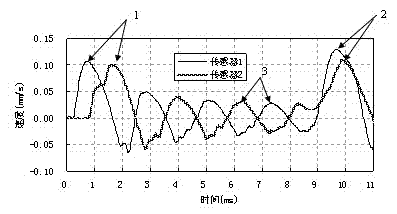
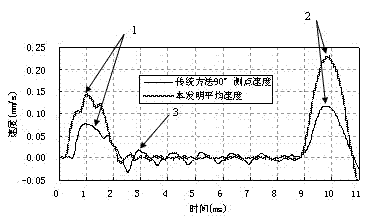
ActiveCN102877490AEliminate the effects of 3D effectsEliminate high-frequency interference wave problemsFoundation testingControl theoryInterference wave
The invention discloses a method for detecting the quality of a large-diameter tubular pile at a low strain. A plurality of acceleration sensors are arranged on the top of the tubular pile; a central angle corresponding to two adjacent acceleration sensors is 90 DEG; central angles between exciting points and all the acceleration sensors are 45 DEG or 135 DEG; acceleration responses are obtained through the measurement of the acceleration sensors, and speed responses are obtained through acceleration response integrals; an average value is obtained by superposing the speed responses obtained through the measurement at all measuring points to obtain an average speed response curve; and the integrity of a pile body is determined according to the obtained average speed response curve. By the method, a plurality of sensors are use for multipoint measurement, so that the propagation law of stress waves along the circumferential direction of a pile wall can be obtained, and the influence of a three-dimensional effect is eliminated; and due to the adoption of the average speed response curve, the problem of high-frequency interference waves can be completely solved, and the excitation of the points which form an angle of 45 DEG or 135 DEG with the acceleration sensors is better than the conventional excitation of the points which form an angle of 90 DEG with the sensors. The method for detecting the quality of the large-diameter tubular pile is easy to operate, convenient to implement, low in measurement cost, high in measurement accuracy and high in efficiency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Measurement system and measurement method for stress waves of Hopkinson bars by using flexoelectric effect
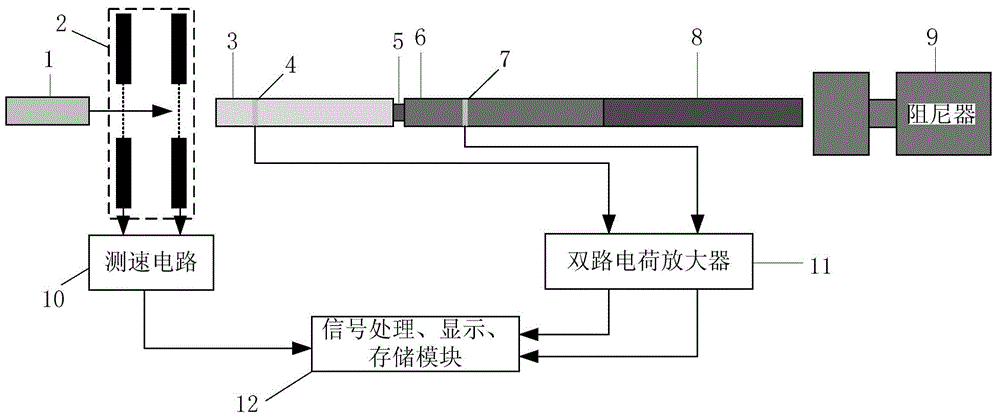
ActiveCN104406846AHigh stress waveform measurement accuracyImprove accuracyApparatus for force/torque/work measurementStrength propertiesAudio power amplifierSnubber
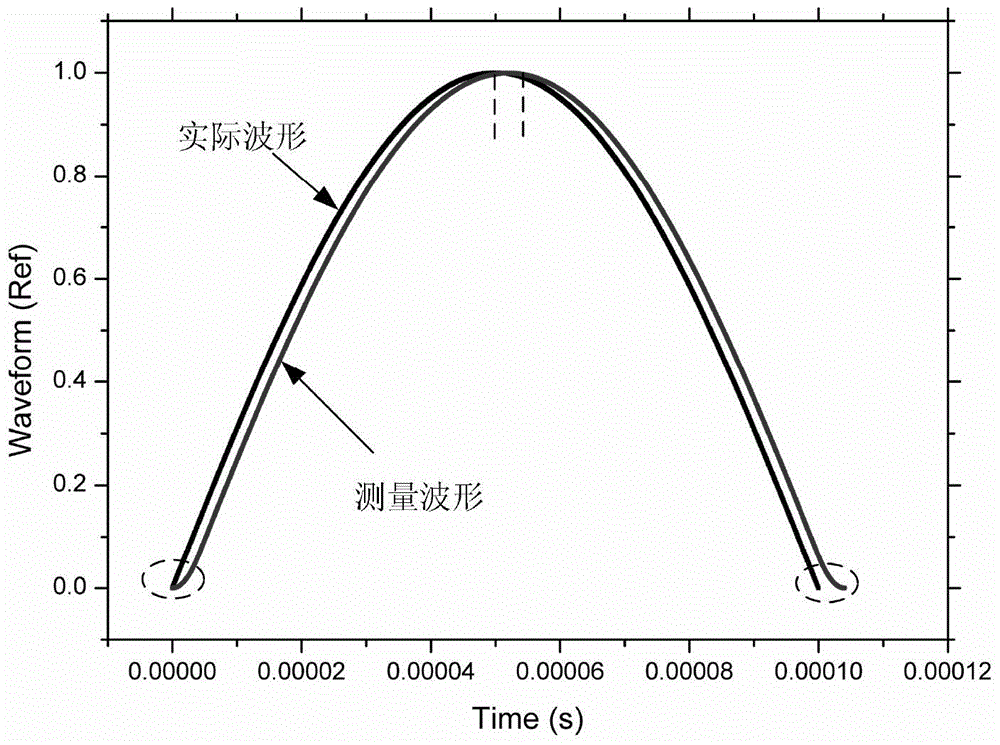
The invention relates to a measurement system and measurement method for stress waves of Hopkinson bars by using a flexoelectric effect. The system comprises a bullet, a laser velocimeter, an input bar, an output bar, an absorbing bar, a damper, a first strain gradient sensor, a second strain gradient sensor, a speed measuring circuit and a two-way charge amplifier, wherein the first strain gradient sensor and the second strain gradient sensor are respectively attached to the input bar and the output bar, the speed measuring circuit is optically connected with the laser velocimeter, and the two-way charge amplifier is electrically connected with the first strain gradient sensor and the second strain gradient sensor; the speed measuring circuit and the output end of the two-way charge amplifier are electrically connected with signal processing, displaying and storing modules. During stress wave measurement, a test piece is fixed between the input bar and the output bar, the absorbing bar and the damper are sequentially arranged behind the output bar, and the bullet and the input bar are respectively arranged on the same horizontal plane on the two ends of the laser velocimeter. As the passive strain gradient sensors based on a flexoelectric principle are arranged, the measurement system can measure the first-order derivative of a real waveform, can directly carry out integral computation for the waveform, and can obtain the more real waveform of the stress waves, and the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
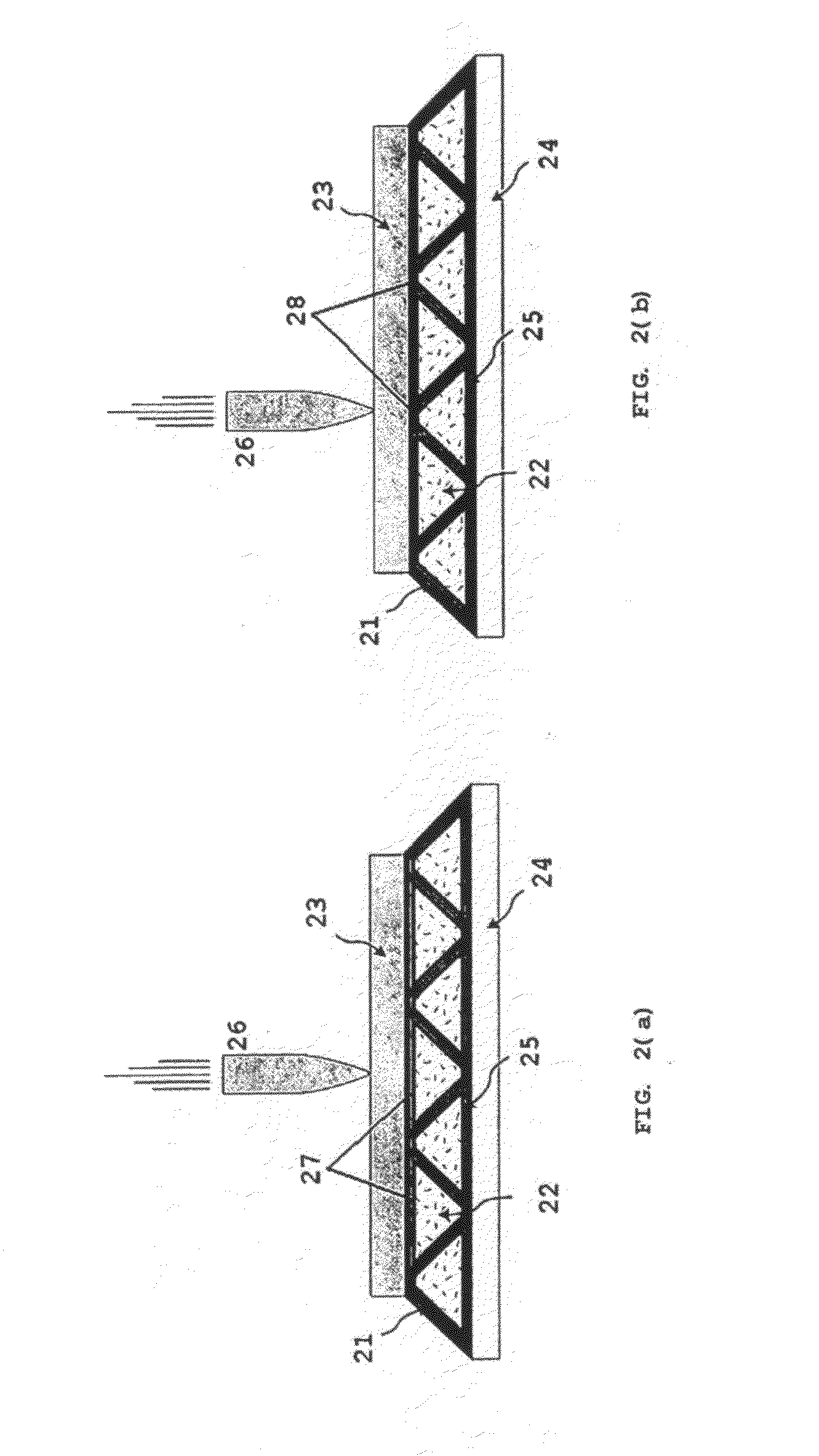
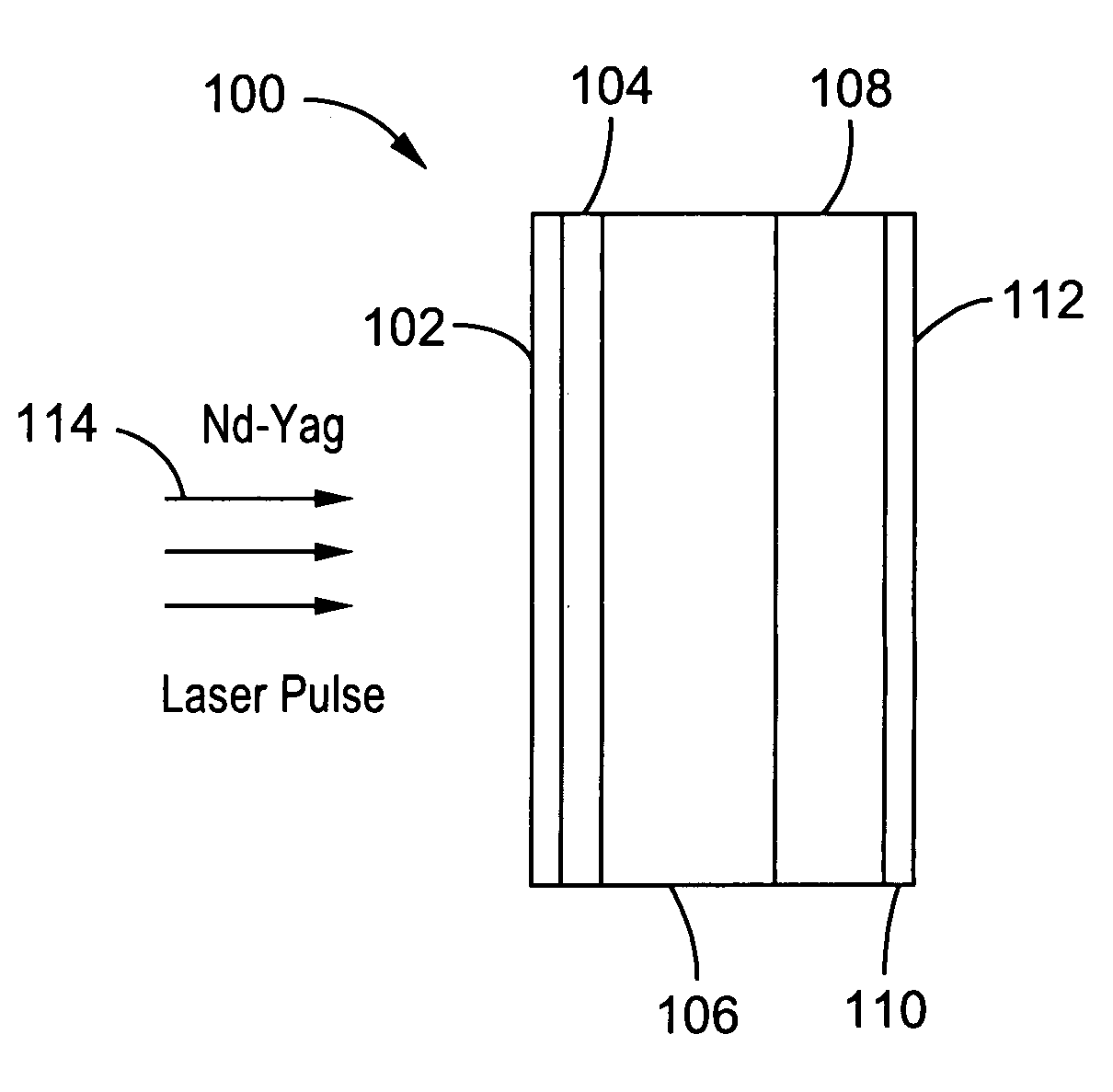
Glass-modified stress waves for separation of ultra thin films and nanoelectronics device fabrication
ActiveUS20070039395A1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A device for generating a tensile force between a substrate and a coating, wherein the substrate has a thickness defined by a first side and a second side in a first axis, and the coating is applied to the first side of the substrate such that the coating and substrate are axially spaced along the first axis in intimate facing contact with each other to form a coating / substrate interface. The apparatus has a glass element disposed on the second side of the substrate and axially spaced along the first axis. The glass element is configured to propagate a stress wave to the coating / substrate interface to generate a tensile force between the substrate and the coating.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for vibration sensing and analysis
A method and apparatus for sensing and measuring stress waves. The method comprises the steps of: a.) sensing motion, where the motion comprises a stress wave component and a vibration component; b.) separating the stress wave component from the vibration component with a high pass filter to create a signal proportional to the stress wave; c.) amplifying the signal to create an amplified signal; d.) processing the amplified signal with a sample and hold peak detector over a predetermined interval of time to determine peaks of the amplified signal over said predetermined period of time; e.) creating an output signal proportional to the determined peaks of the amplified signal; and, f.) repeating steps d.) and e.). The invention also includes an apparatus for implementing the method of the invention.
Owner:PCB PIEZOTRONICS IMI SENSORS +1
Single-wire sensor/actuator network for structural health monitoring
ActiveUS20060283266A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectricityLine sensor
A sensor / actuator network configured with a number of electrically-interconnected elements. More specifically, the sensors / actuators are each placed in electrical communication with the same transmission line. Various embodiments of such networks employ sensors / actuators connected in electrical series and in electrical parallel. Networks having these configurations, when placed upon a structure, are capable of detecting and / or transmitting stress waves within the structure so as to detect the presence of an impact, or actively query the structure. Advantageously, as these networks employ a single transmission line, they utilize fewer wires than current sensor / actuator networks, thus making them easier to install and maintain. They can also be configured as flexible layers, allowing for further ease of installation and maintenance.
Owner:ACELLENT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com