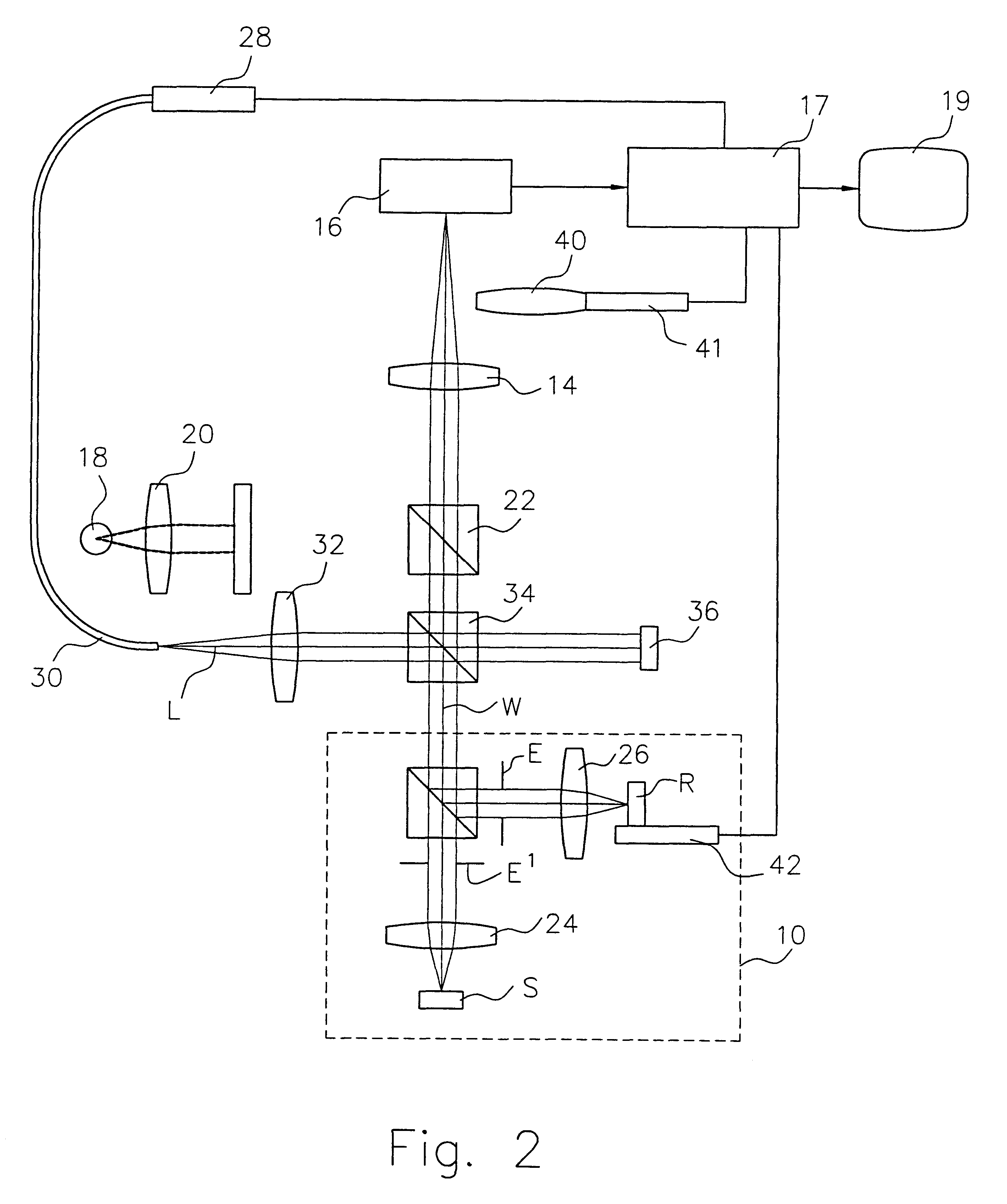
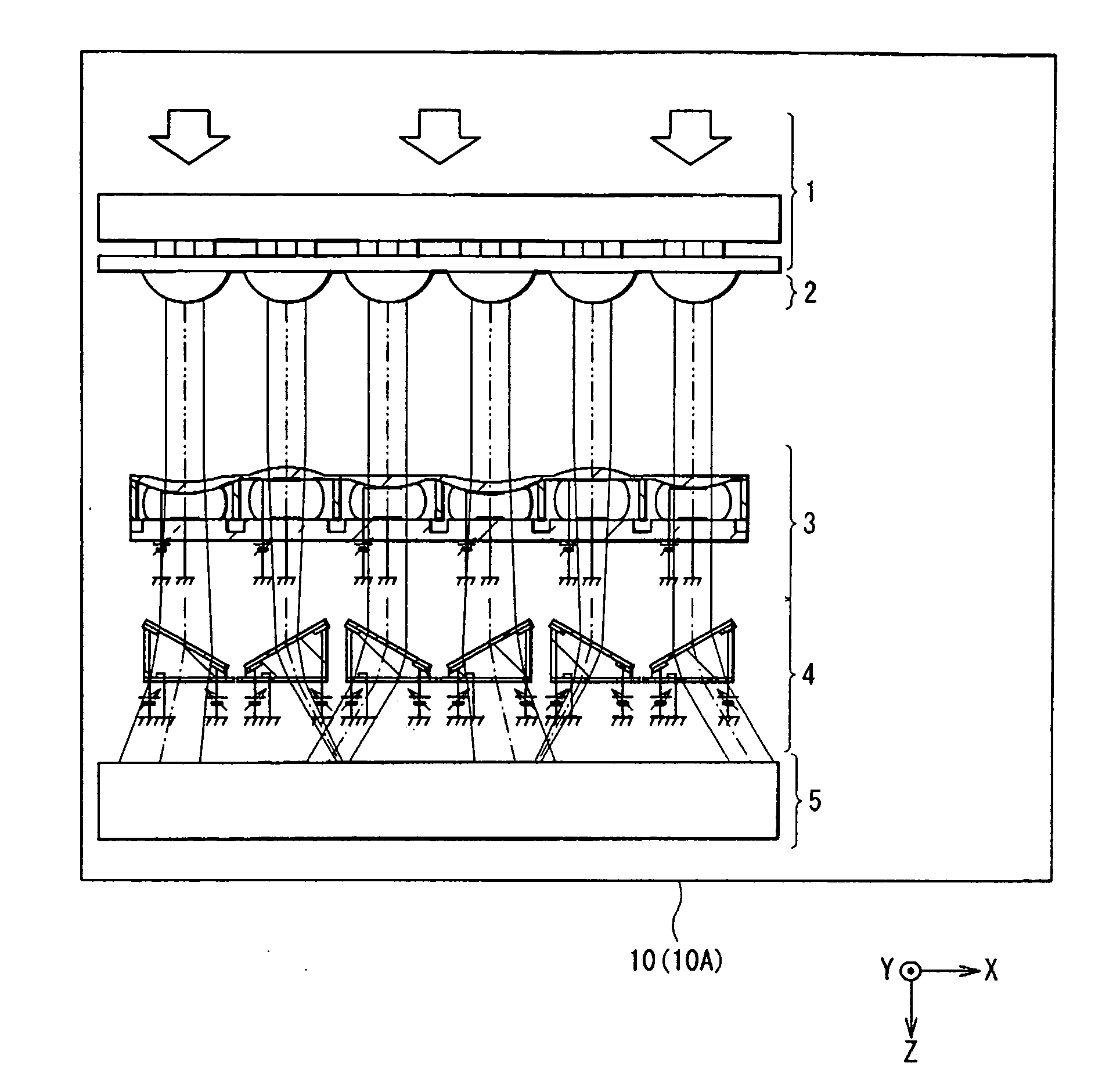
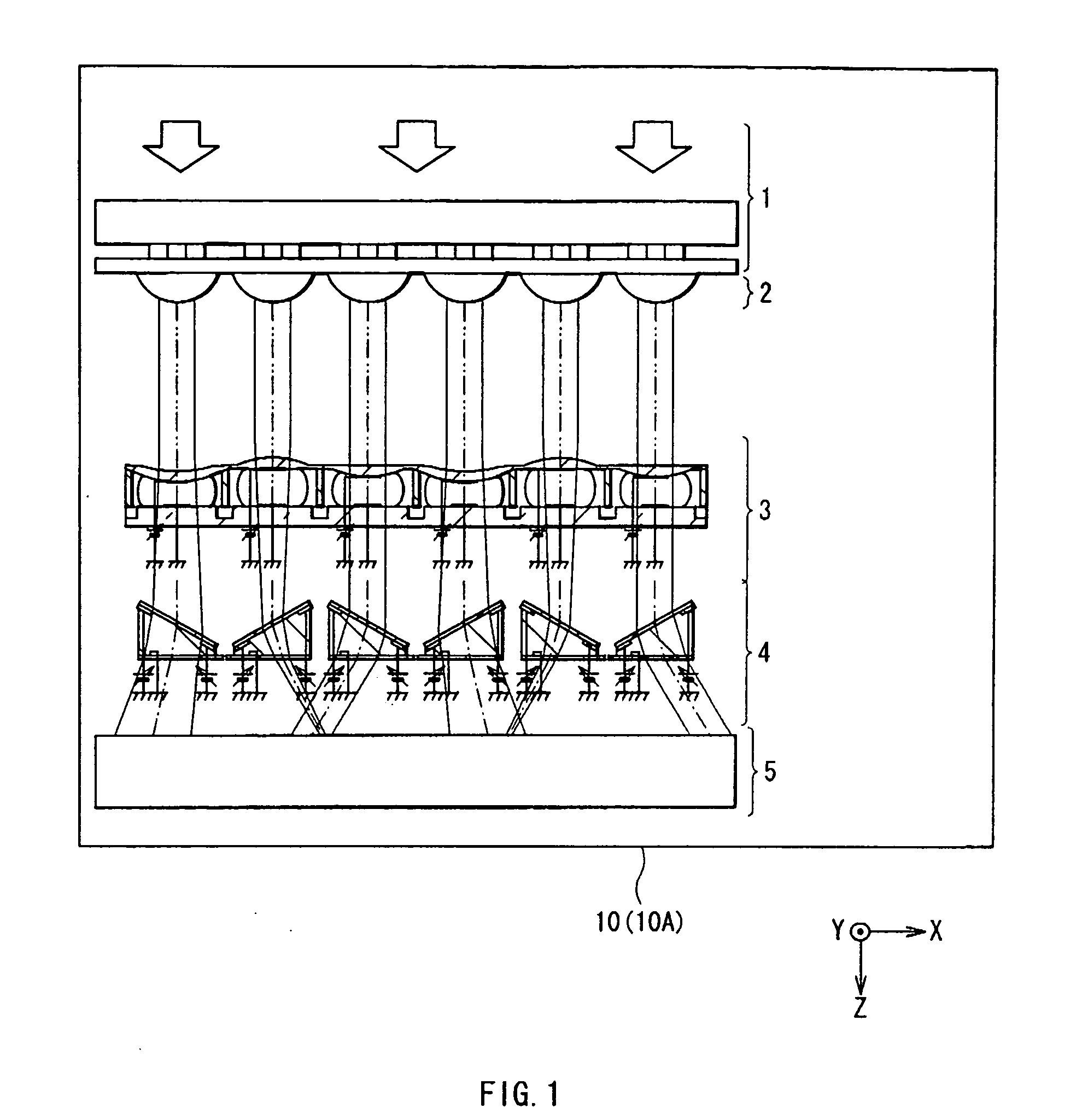
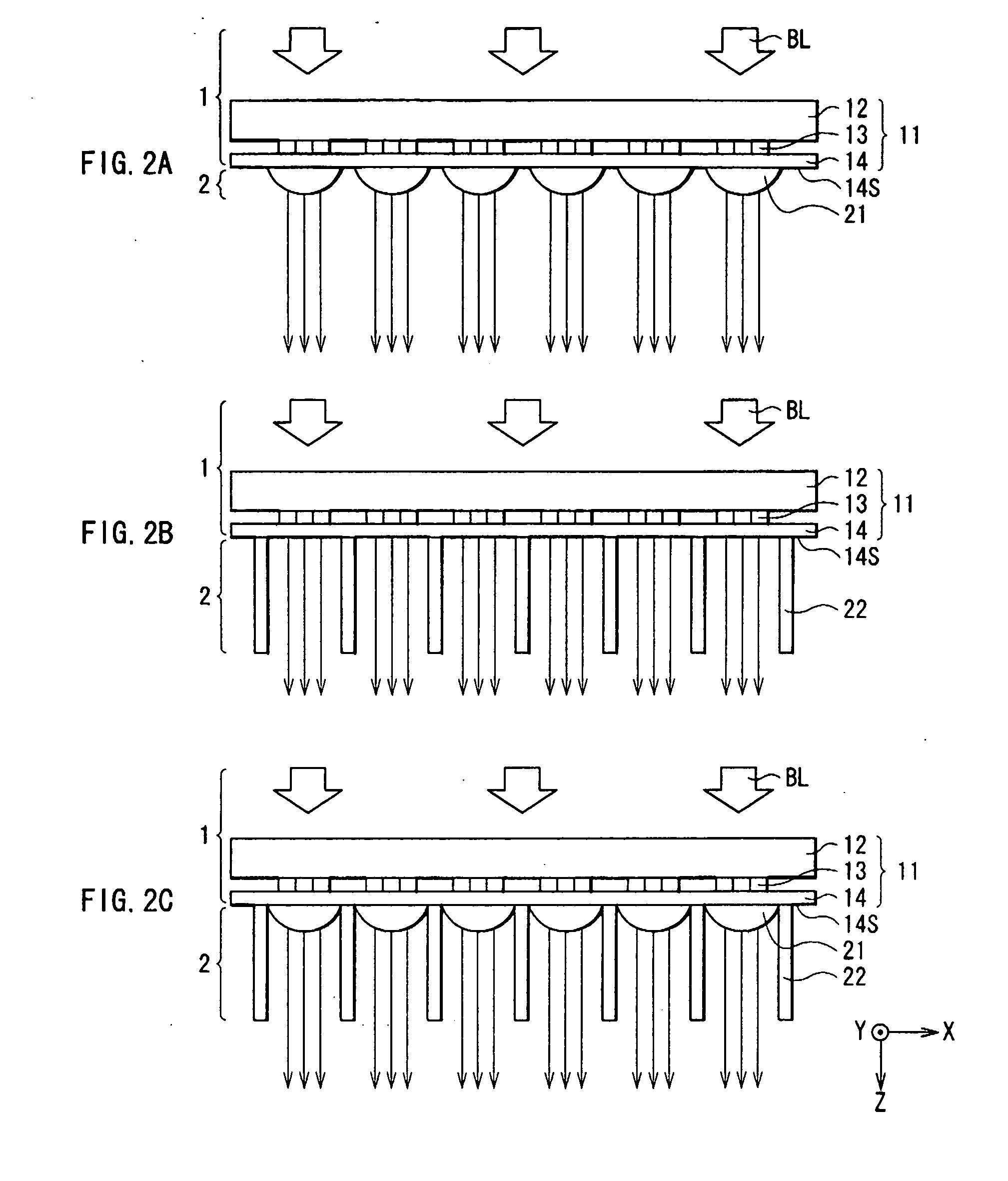
Patents
Literature
2076 results about "Wavefront" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a wavefront of a time-varying field is the set (locus) of all points where the wave has the same phase of the sinusoid. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, at each point, vary sinusoidally in time with a single temporal frequency (otherwise the phase is not well defined).
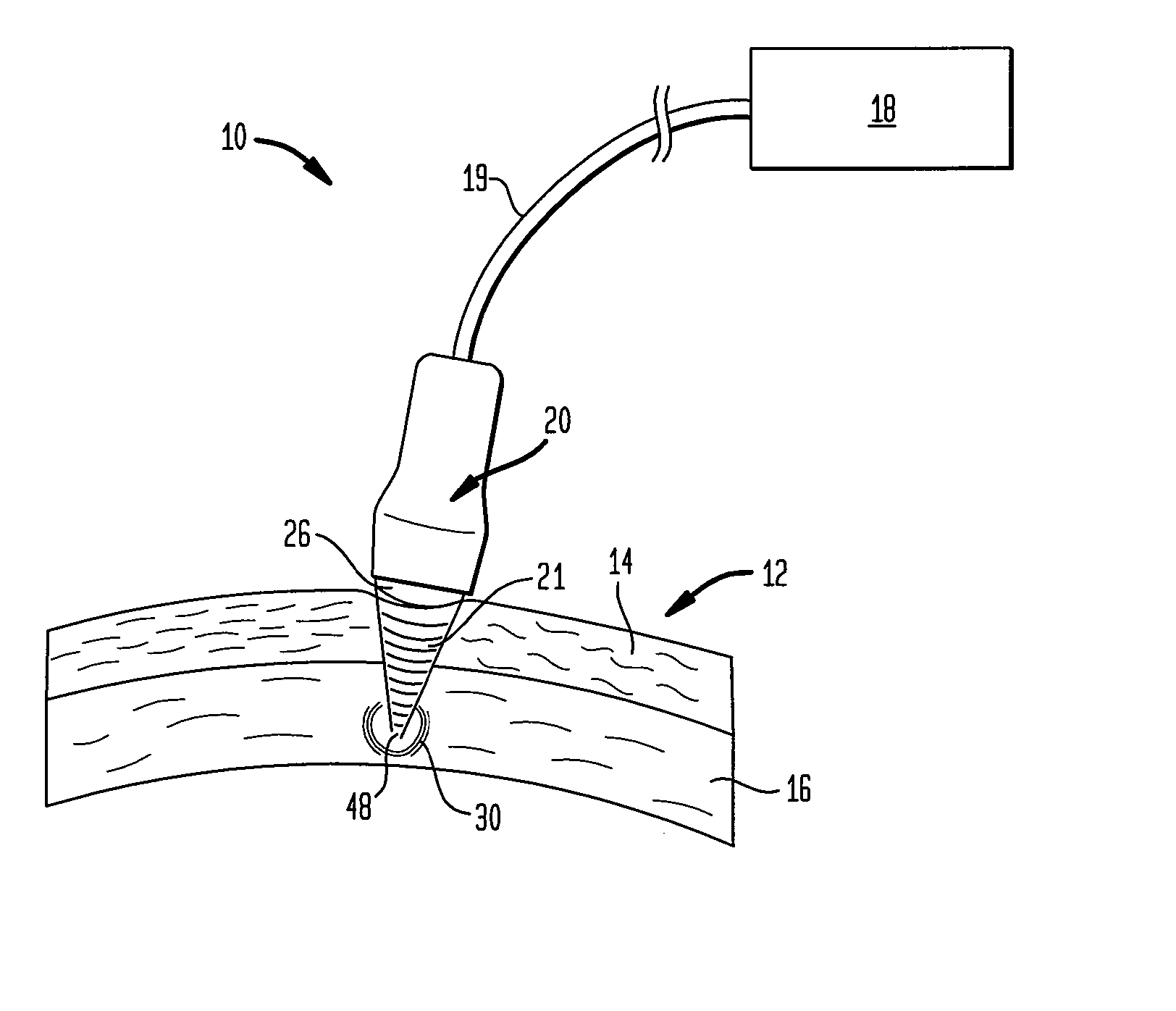
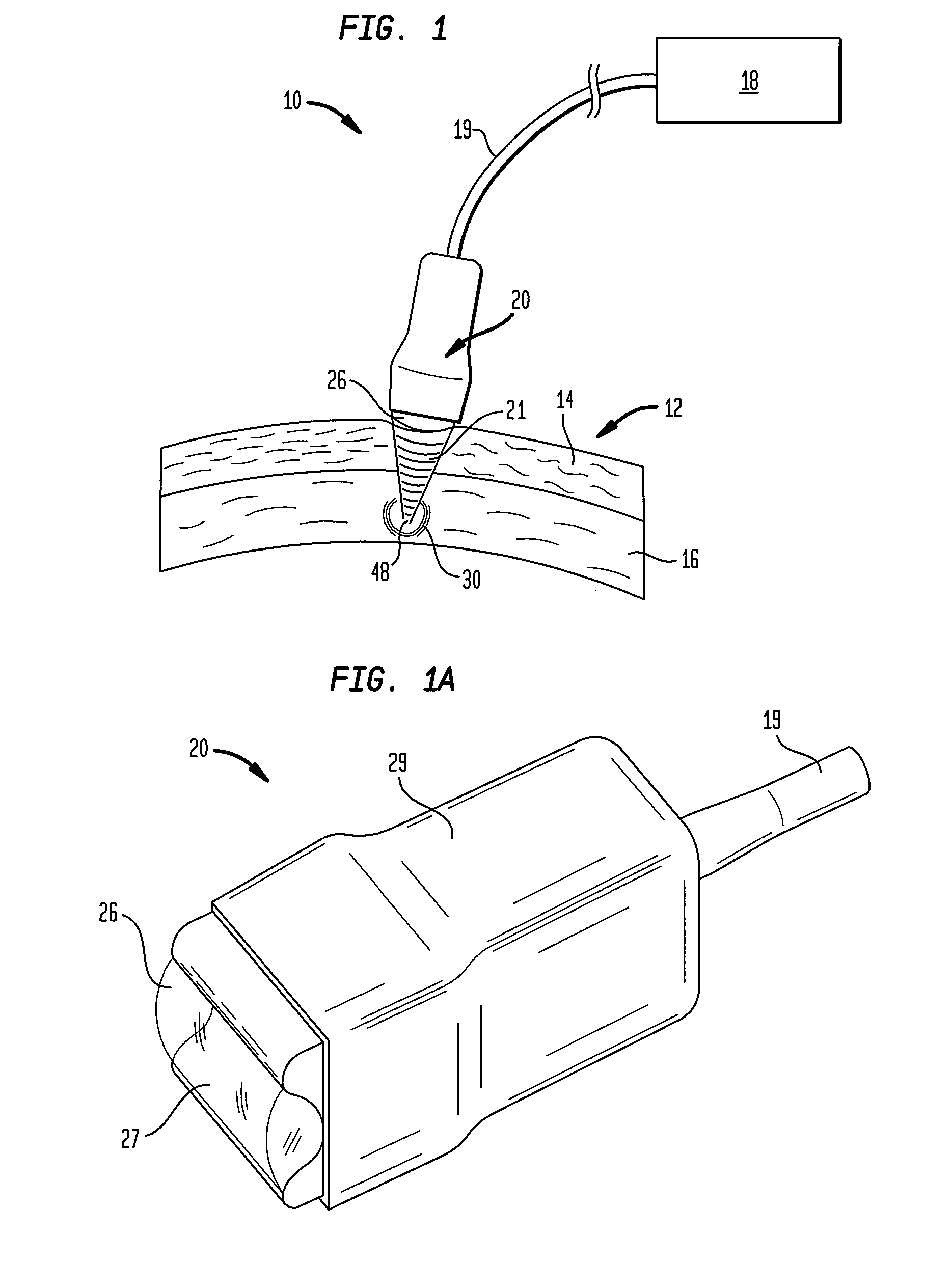
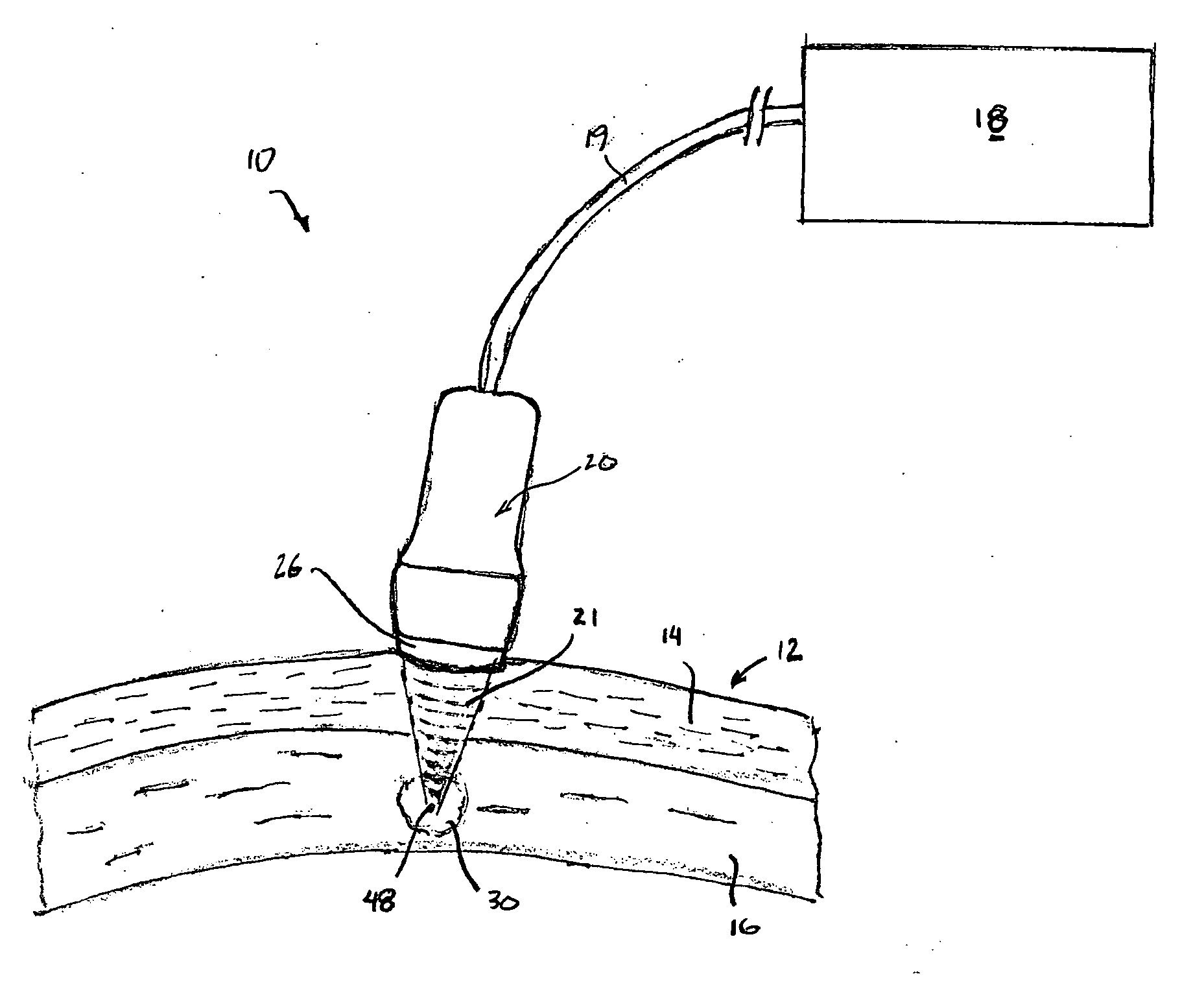
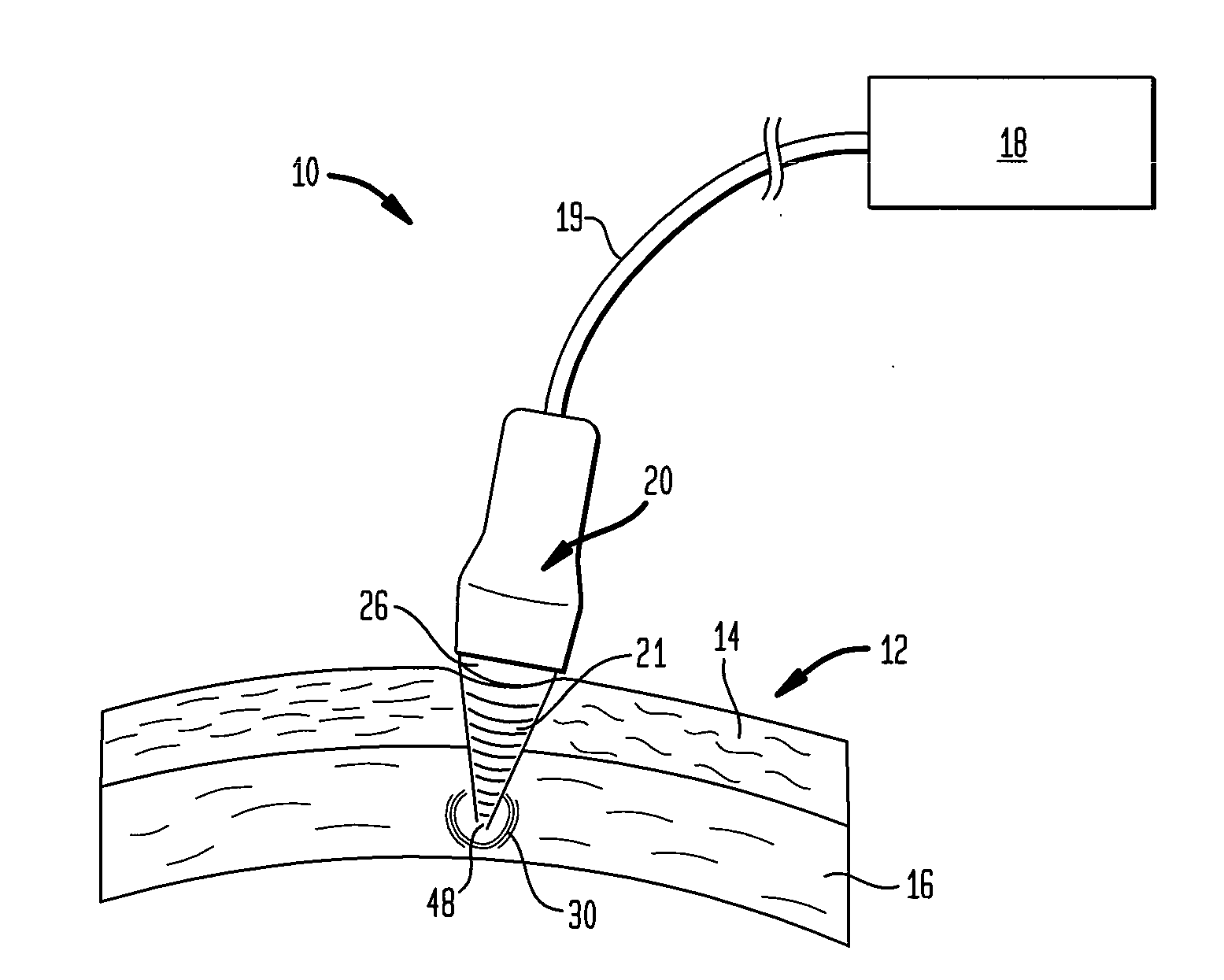
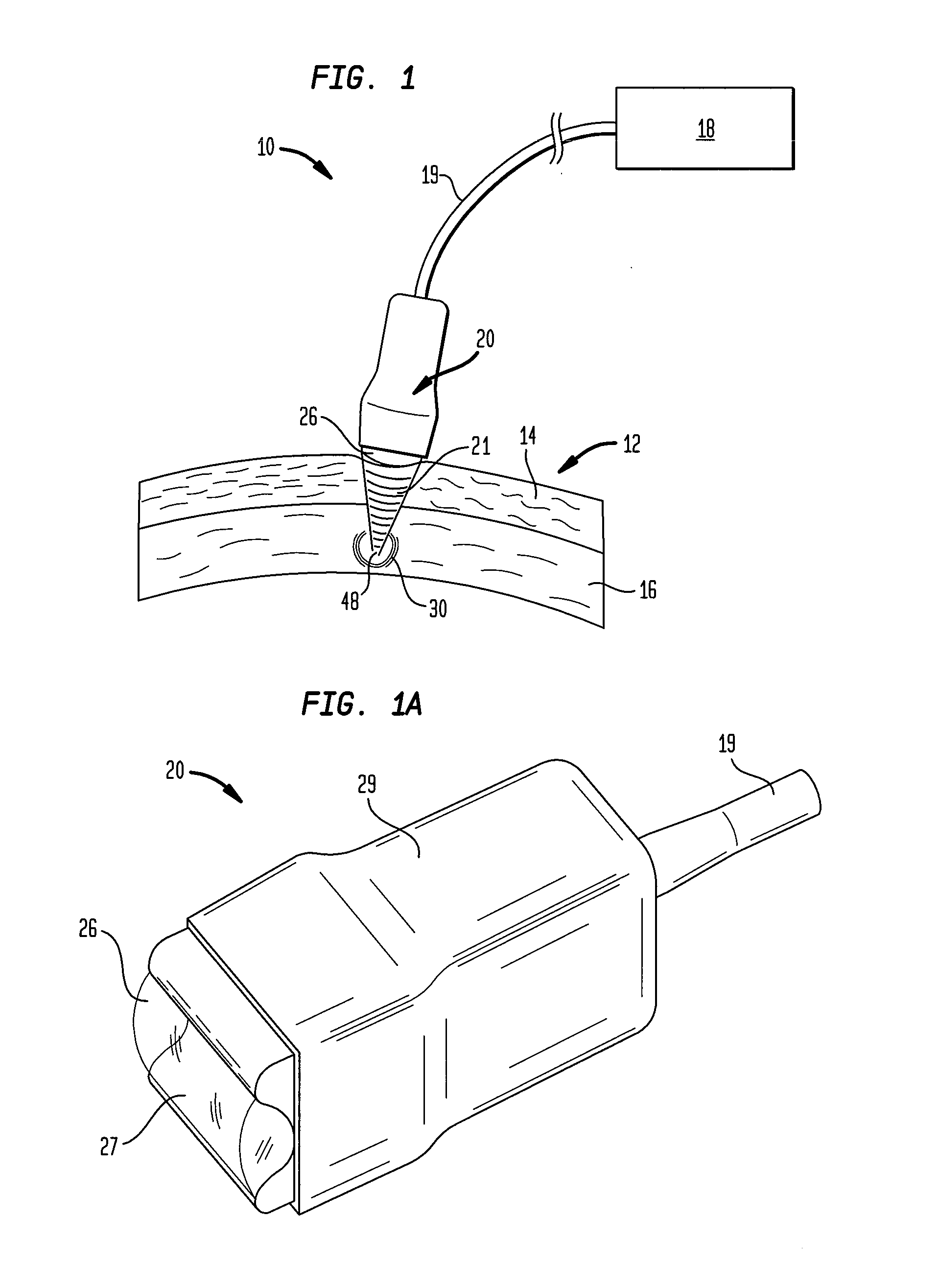
Multi-focal treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20080027328A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocal treatmentWavefront
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for applying acoustic energy to the skin. Acoustic waveguides with elements of varying thickness or shape are disclosed which deliver energy to more than one depth below a surface of the skin substantially simultaneously. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
Treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20060184071A1Lower capability requirementsCompensation DistortionUltrasound therapySurgeryFocus ultrasoundWavefront
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for applying acoustic energy to the skin whereby the wavefront can be controlled to confine the focused energy to a desired subsurface region. Acoustic waveguides are disclosed which compensate for distortions that otherwise occur when a focused acoustic beam crosses a boundary, such as the transition from a treatment device to a target region of skin. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
Method for determining and correcting vision
InactiveUS20050124983A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove visual effectsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
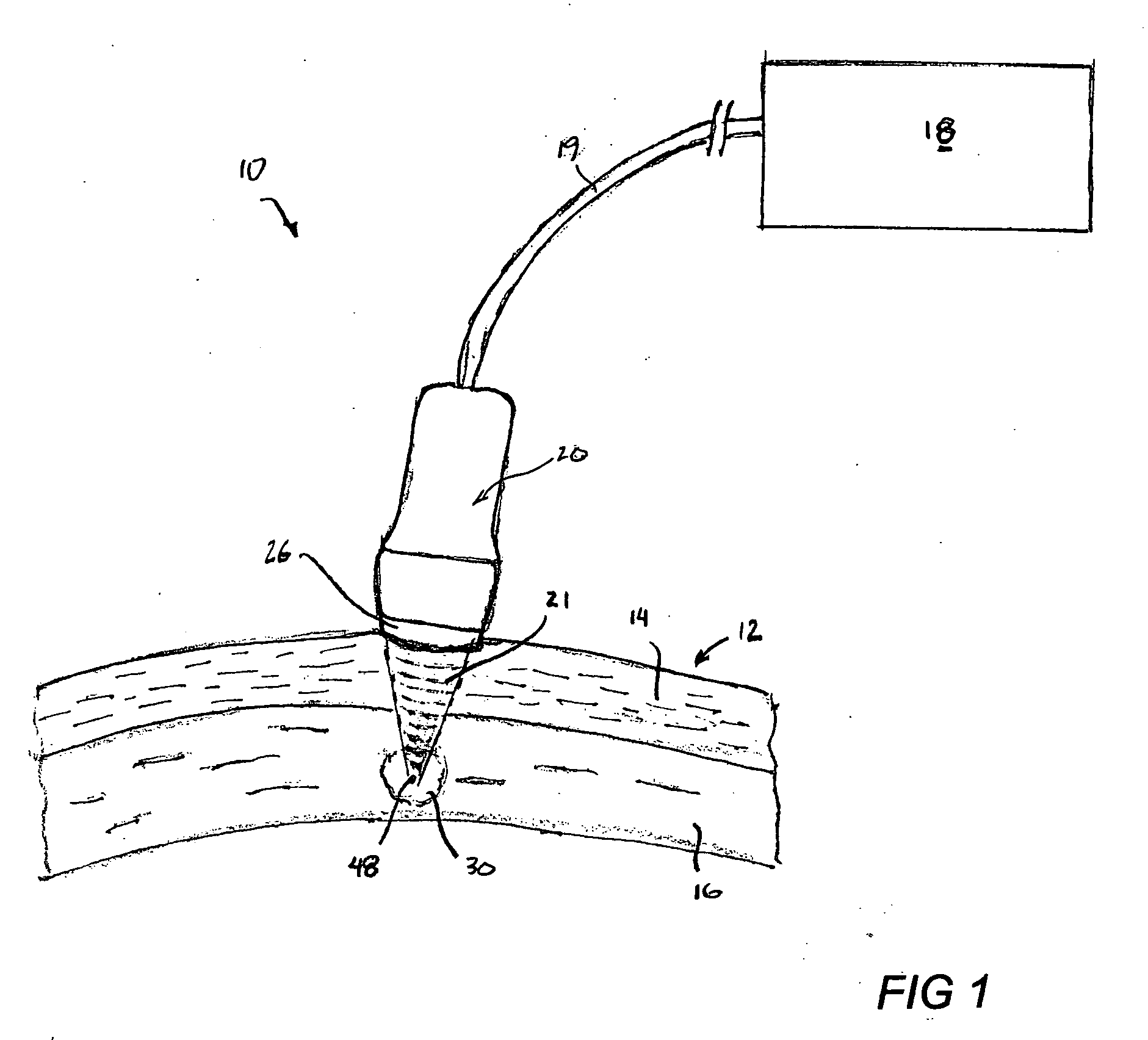
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
Method of computing a hologram
ActiveUS20060139711A1Reduce calculationQuality improvementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsWavefrontComputer science
A method of computing a hologram by determining the wavefronts at the approximate observer eye position that would be generated by a real version of an object to be reconstructed. In normal computer generated holograms, one determines the wavefronts needed to reconstruct an object; this is not done directly in the present invention. Instead, one determines the wavefronts at an observer window that would be generated by a real object located at the same position of the reconstructed object. One can then back-transforms these wavefronts to the hologram to determine how the hologram needs to be encoded to generate these wavefronts. A suitably encoded hologram can then generate a reconstruction of the three-dimensional scene that can be observed by placing one's eyes at the plane of the observer window and looking through the observer window.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
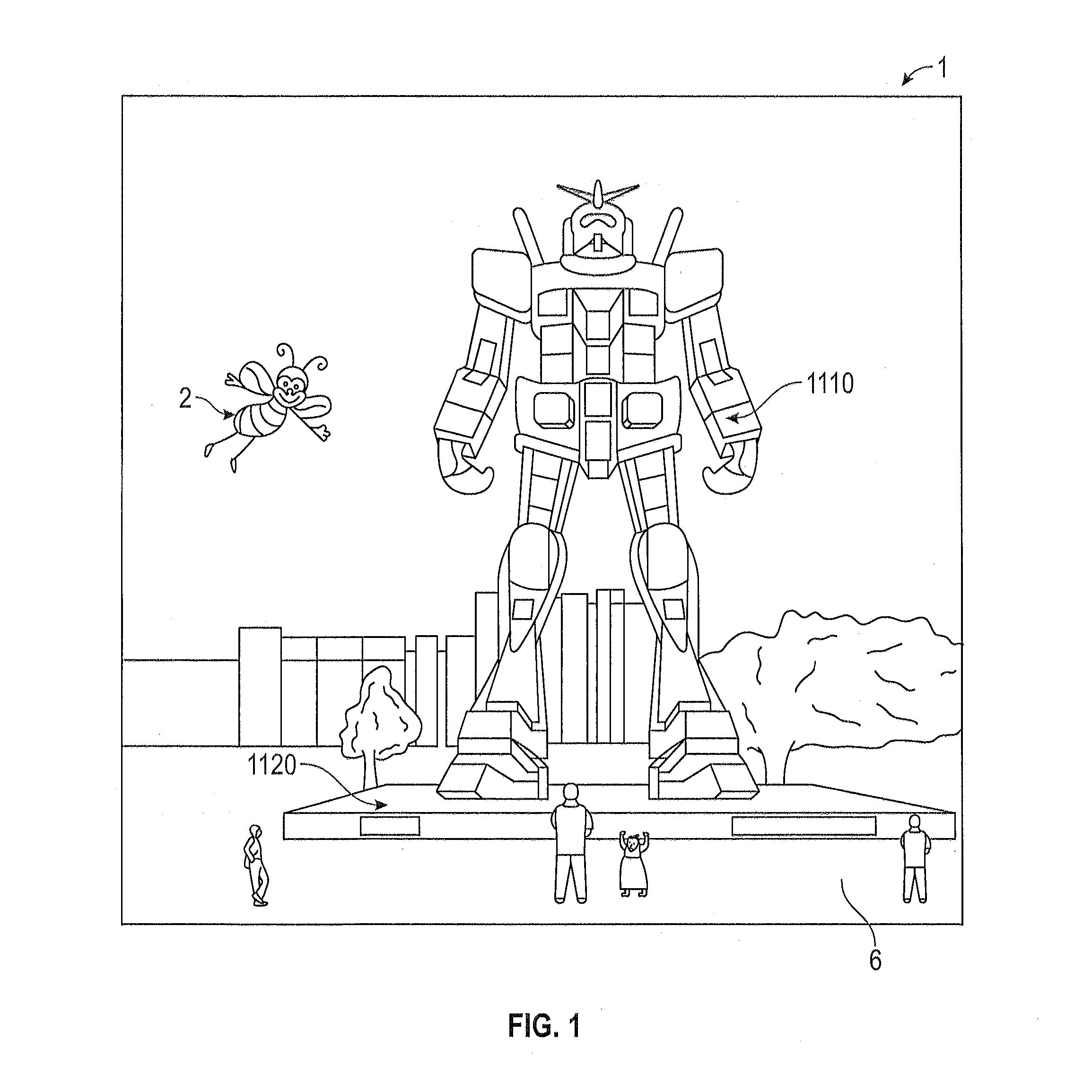
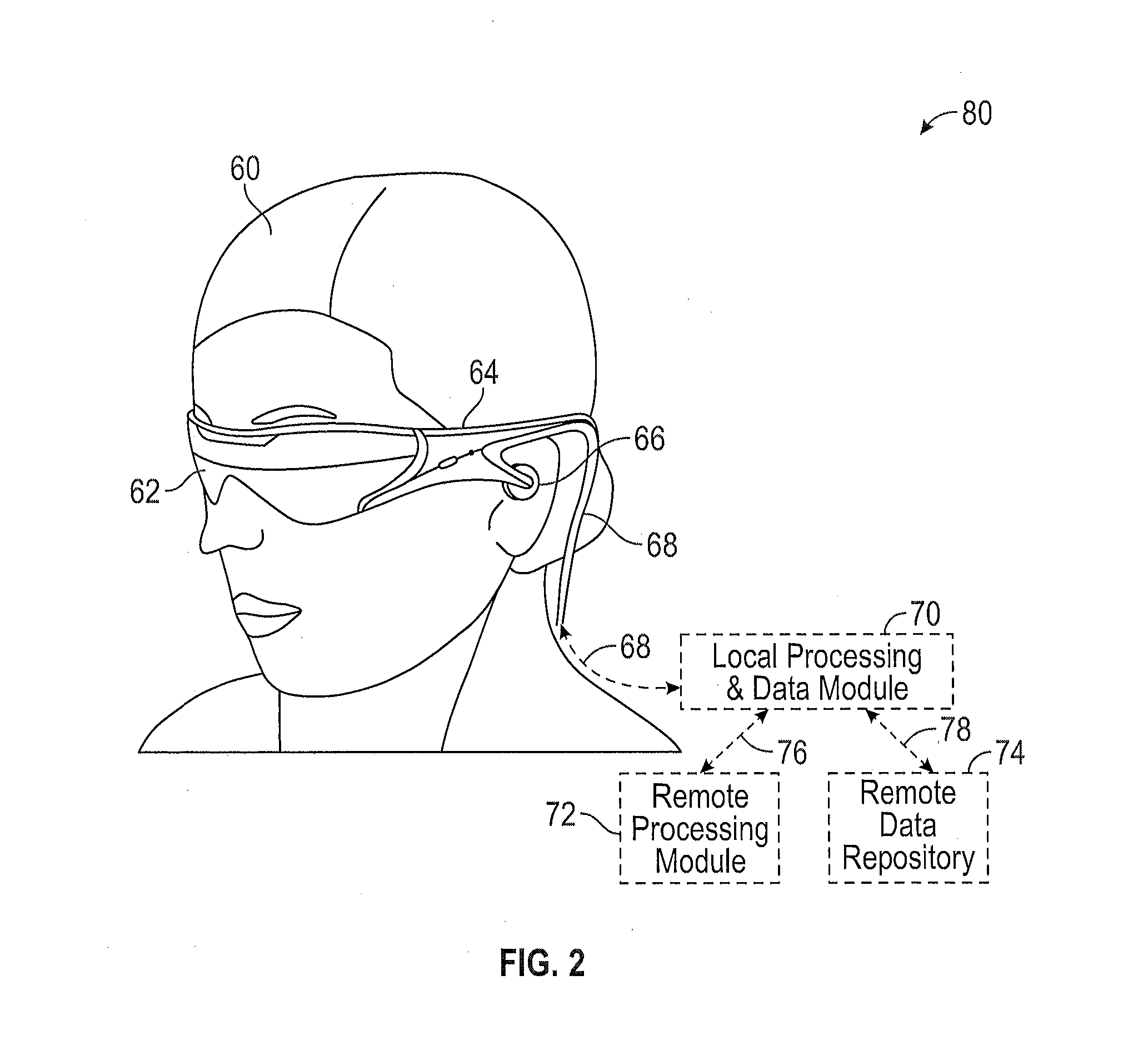
Augmented reality display system for evaluation and modification of neurological conditions, including visual processing and perception conditions
ActiveUS20170365101A1Increase alertnessImprove plasticityMedical automated diagnosisMental therapiesWavefrontPattern perception
In some embodiments, a display system comprising a head-mountable, augmented reality display is configured to perform a neurological analysis and to provide a perception aid based on an environmental trigger associated with the neurological condition. Performing the neurological analysis may include determining a reaction to a stimulus by receiving data from the one or more inwardly-directed sensors; and identifying a neurological condition associated with the reaction. In some embodiments, the perception aid may include a reminder, an alert, or virtual content that changes a property, e.g. a color, of a real object. The augmented reality display may be configured to display virtual content by outputting light with variable wavefront divergence, and to provide an accommodation-vergence mismatch of less than 0.5 diopters, including less than 0.25 diopters.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods
ActiveUS20170010488A1High diffraction efficiencyReduce sensitivityPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsWavefrontBeam steering
Methods of manufacturing a liquid crystal device including depositing a layer of liquid crystal material on a substrate and imprinting a pattern on the layer of liquid crystal material using an imprint template are disclosed. The liquid crystal material can be jet deposited. The imprint template can include surface relief features, Pancharatnam-Berry Phase Effect (PBPE) structures or diffractive structures. The liquid crystal device manufactured by the methods described herein can be used to manipulate light, such as for beam steering, wavefront shaping, separating wavelengths and / or polarizations, and combining different wavelengths and / or polarizations.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
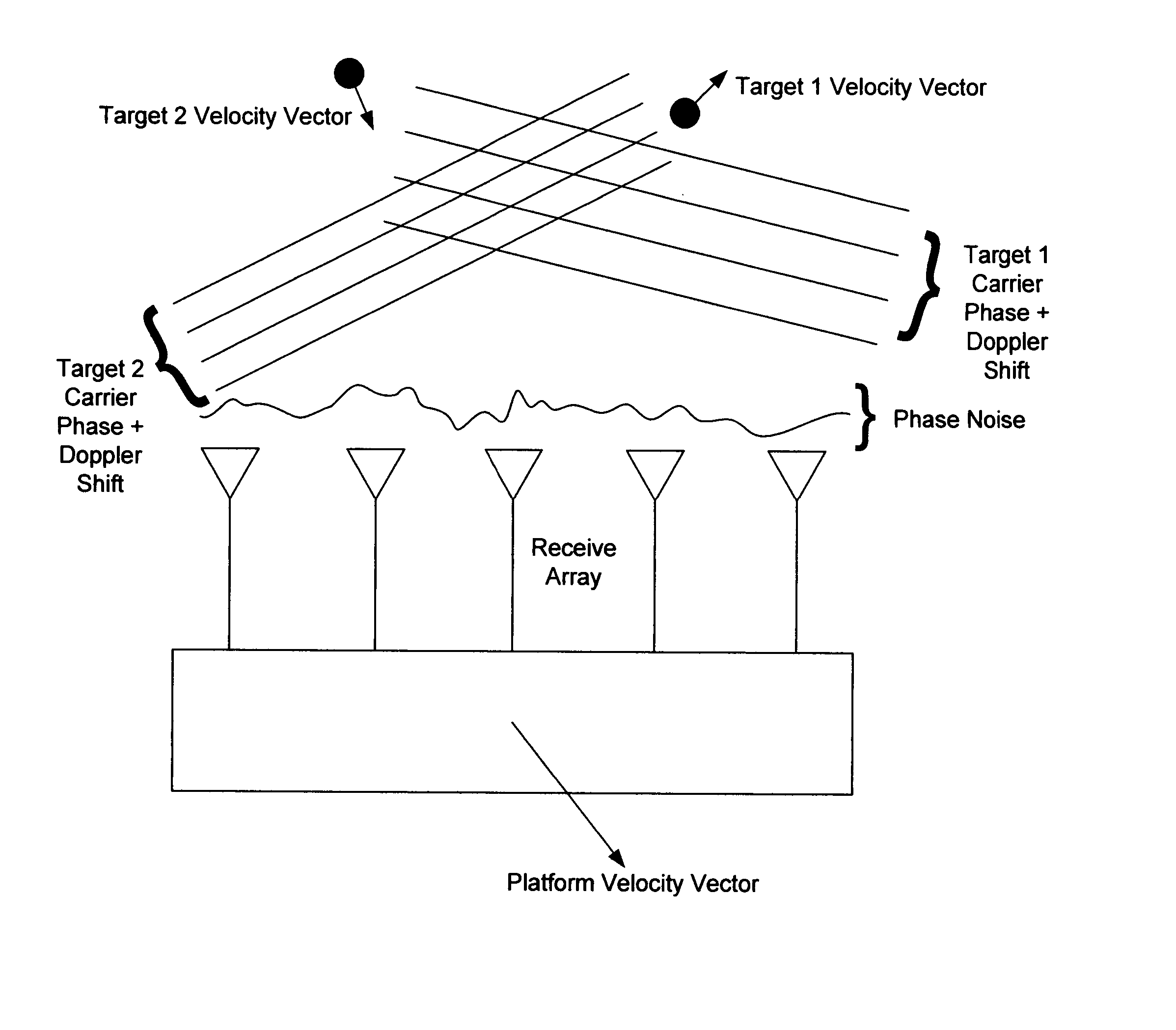
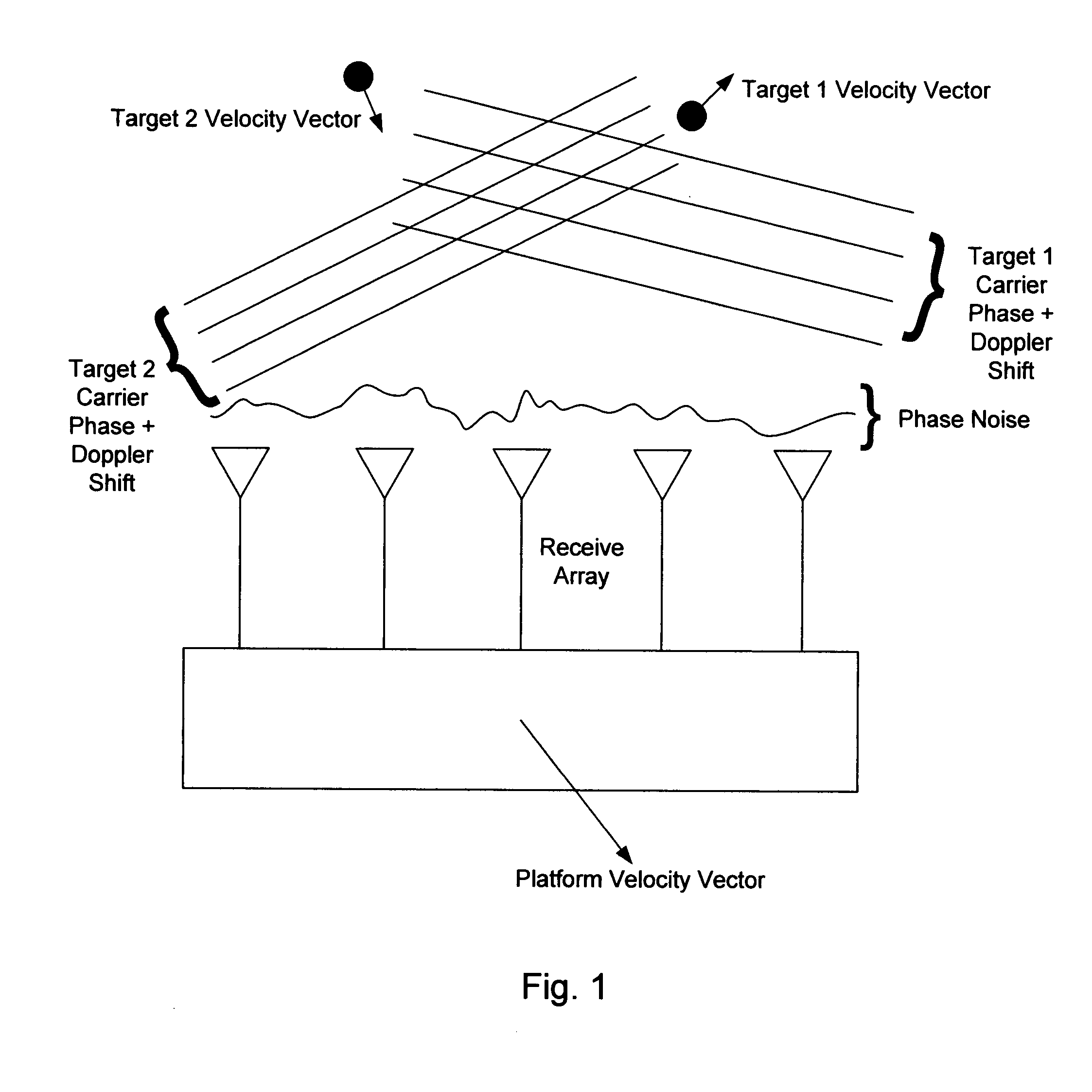
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS20070285315A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint or the number of array elements. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
Phased arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS20050195103A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsSonarWavefront
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
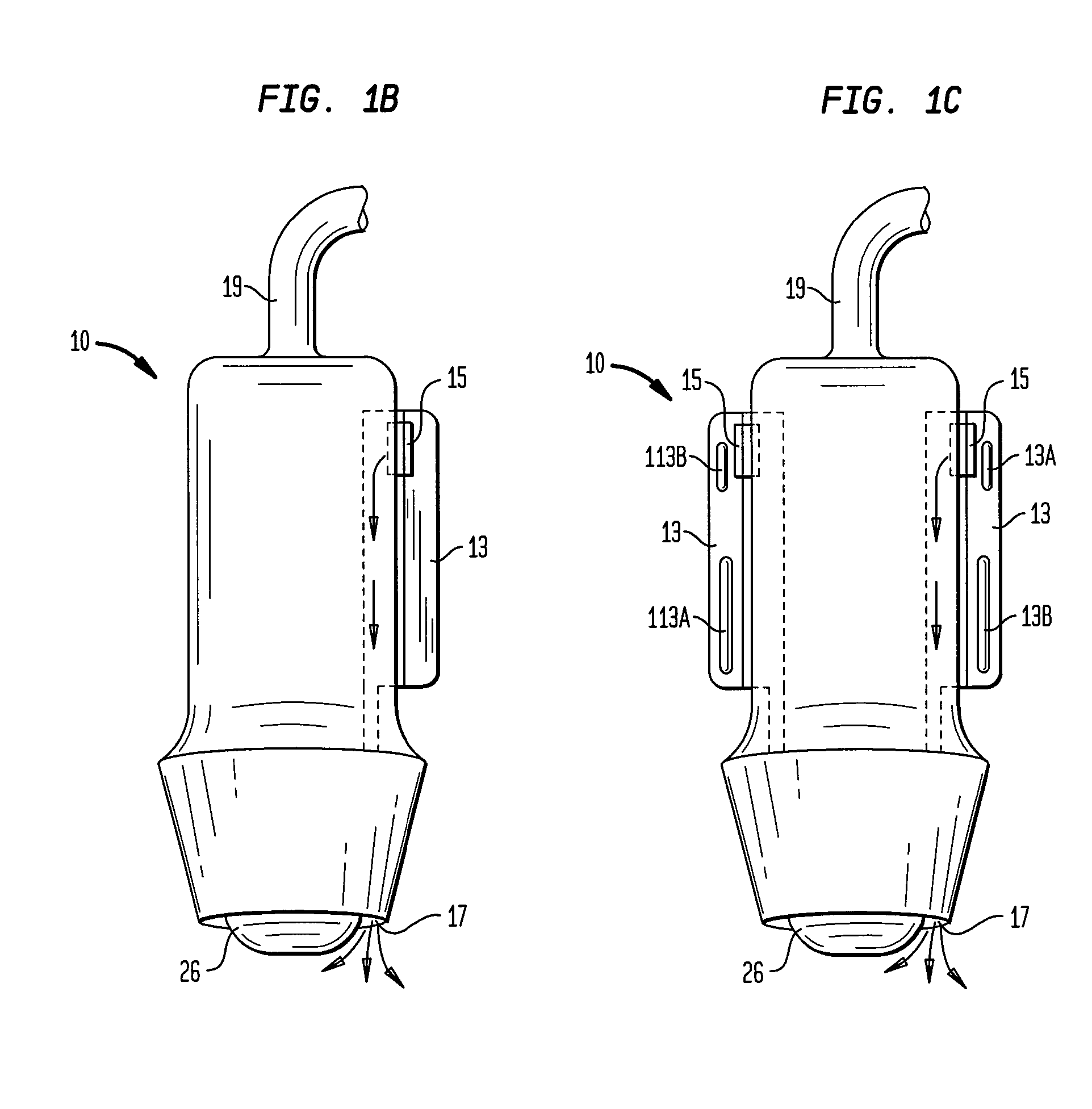
Gel dispensers for treatment of skin with acoustic energy
InactiveUS20080146970A1Lower capability requirementsCompensation DistortionUltrasound therapySurgeryWavefrontAcoustic energy
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for dispensing fluid in an apparatus for applying acoustic energy to the skin. Acoustic waveguides are disclosed which compensate for distortions that otherwise occur when a focused acoustic beam crosses a boundary, such as the transition from a treatment device to a target region of skin. The invention is especially useful with devices that focus ultrasound energy by condensing a propagating wavefront. The invention compensates for the mismatch in acoustic properties of the device's waveguide and the biological tissue that typically cause portions of the collapsing wavefront to lag behind other portions and, thereby, limit the focusing capabilities of acoustic treatment devices.
Owner:JULIA THERAPEUTICS
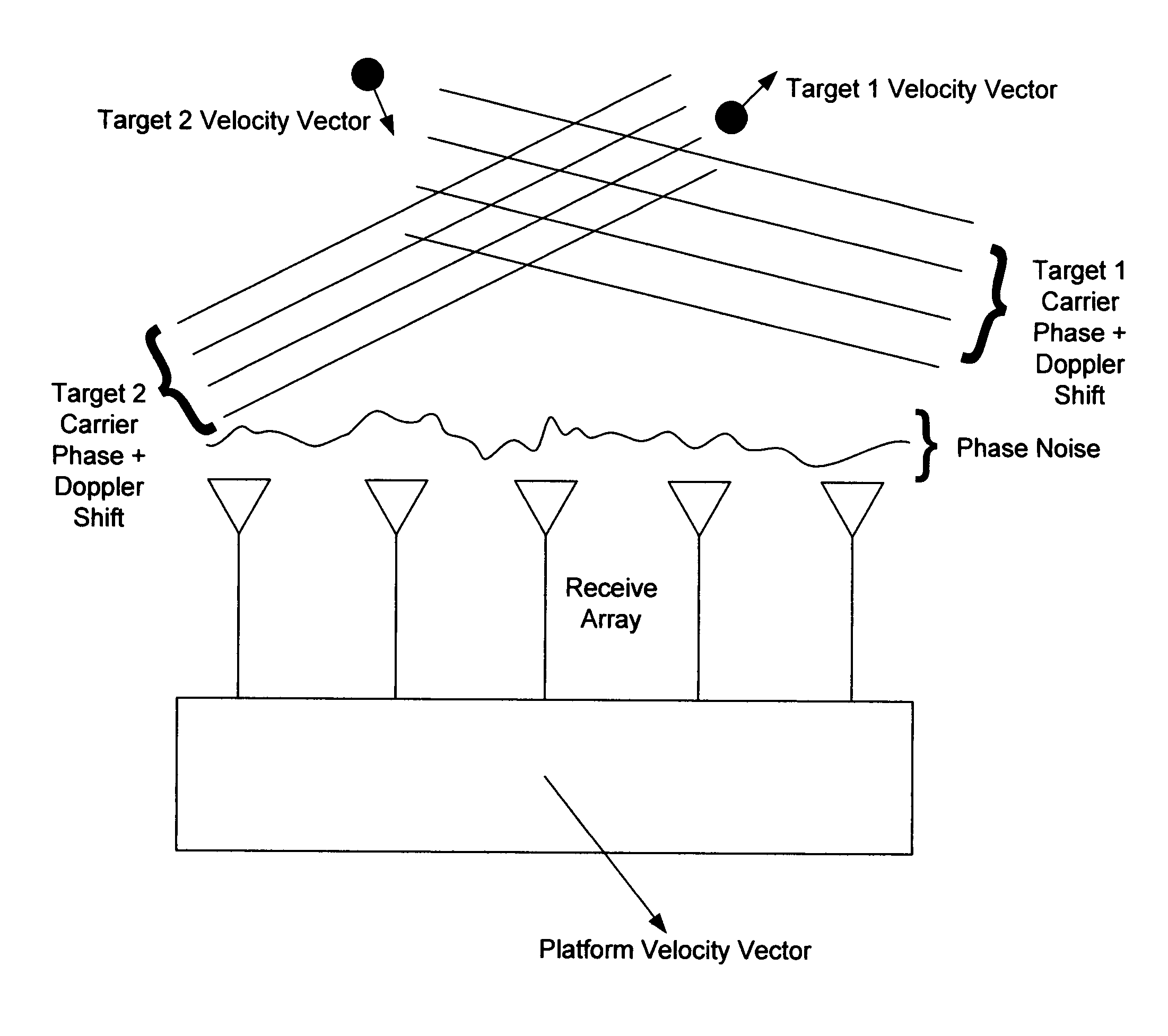
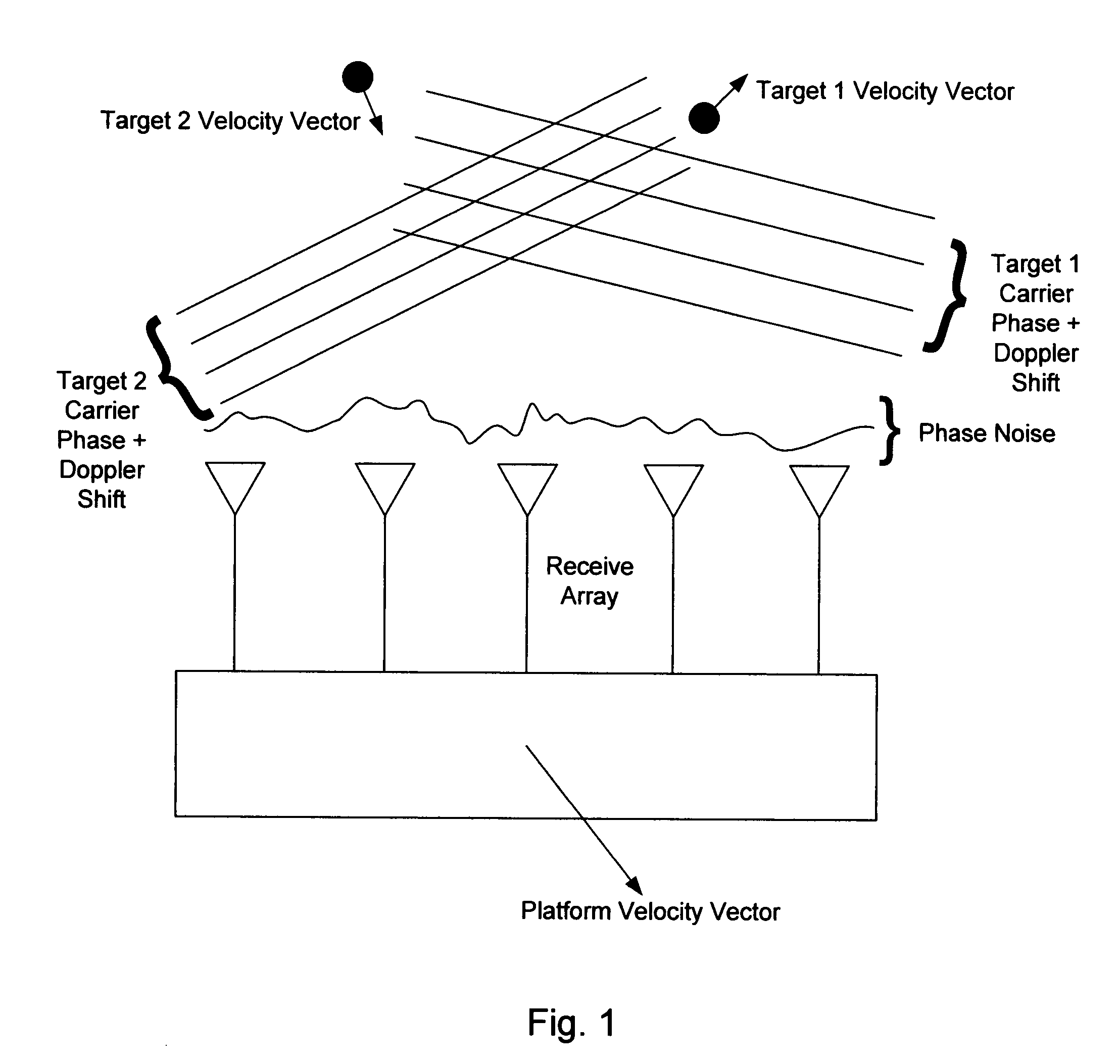
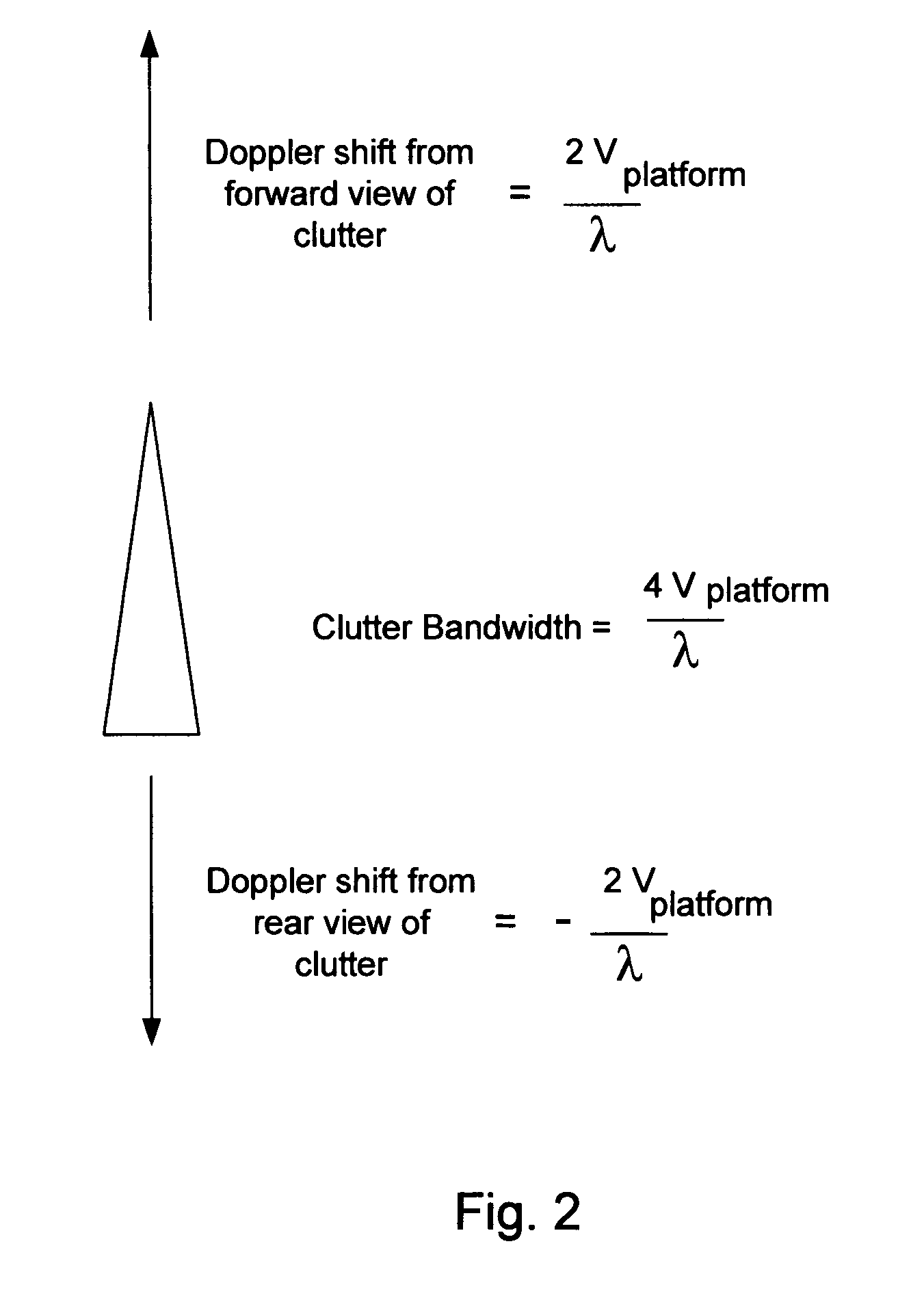
Wavefront detection and disambiguation of acknowledgments
One or more flow control modules, implemented on various types of network topologies, provide a number of functionalities for controlling the flow of IP packets (such as TCP / IP packets) over a network connection. The flow control modules may be implemented within a sender and / or receiver or may be deployed into a network as a separate device without requiring significant additional resources.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Embedded interferometer for reference-mirror calibration of interferometric microscope
InactiveUS6545761B1Implemented easily and economicallyAccurately determineInterferometersUsing optical meansClosed loopOptoelectronics
A laser interferometer is embedded into an interference microscope to precisely determine the in-focus position of the microscope objective's reference mirror. A collimated laser beam is introduced into the microscope system and split into two beams directed toward a calibration reference surface and the interference objective. The light reflected from the calibration reference surface is returned to the camera. The light into the interference objective is focused onto the reference mirror and returned to the camera. For the purpose of calibration, the two beams are combined at the camera to produce interference fringes. When the reference mirror is in focus, the returned beam is collimated; if the mirror is on either side of focus, the beam is either converging or diverging. Accordingly, the interferogram produced at the camera reflects the in-focus or out-of-focus condition of the reference mirror. The curvature of the wavefront returned from the reference mirror is determined electronically by analyzing the interference fringes produced with the beam returned from the calibration reference surface. By minimizing the curvature of the reference-mirror wavefront as the mirror is translated along the optical path, the reference mirror can be focused with an accuracy greater than possible by visual observation. Furthermore, by automating the focusing system with a precise translation mechanism driven by closed-loop control, operator-to-operator variations are completely eliminated.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Three-dimensional display
In the three-dimensional display, a two-dimensional display section generates a two-dimensional display image based on an image signal, and a lens array converts the wavefront of the display image light from the two-dimensional display section into a wavefront having a curvature which allows the display image light to focus upon a focal point where an optical path length from an observation point to the focal point is equal to an optical path length from the observation point to a virtual object point, so a viewer can obtain information about an appropriate focal length in addition to information about binocular parallax and a convergence angle. Therefore, consistency between the information about binocular parallax and a convergence angle and the information about an appropriate focal length can be ensured, and a desired stereoscopic image can be perceived without physiological discomfort.
Owner:SONY CORP
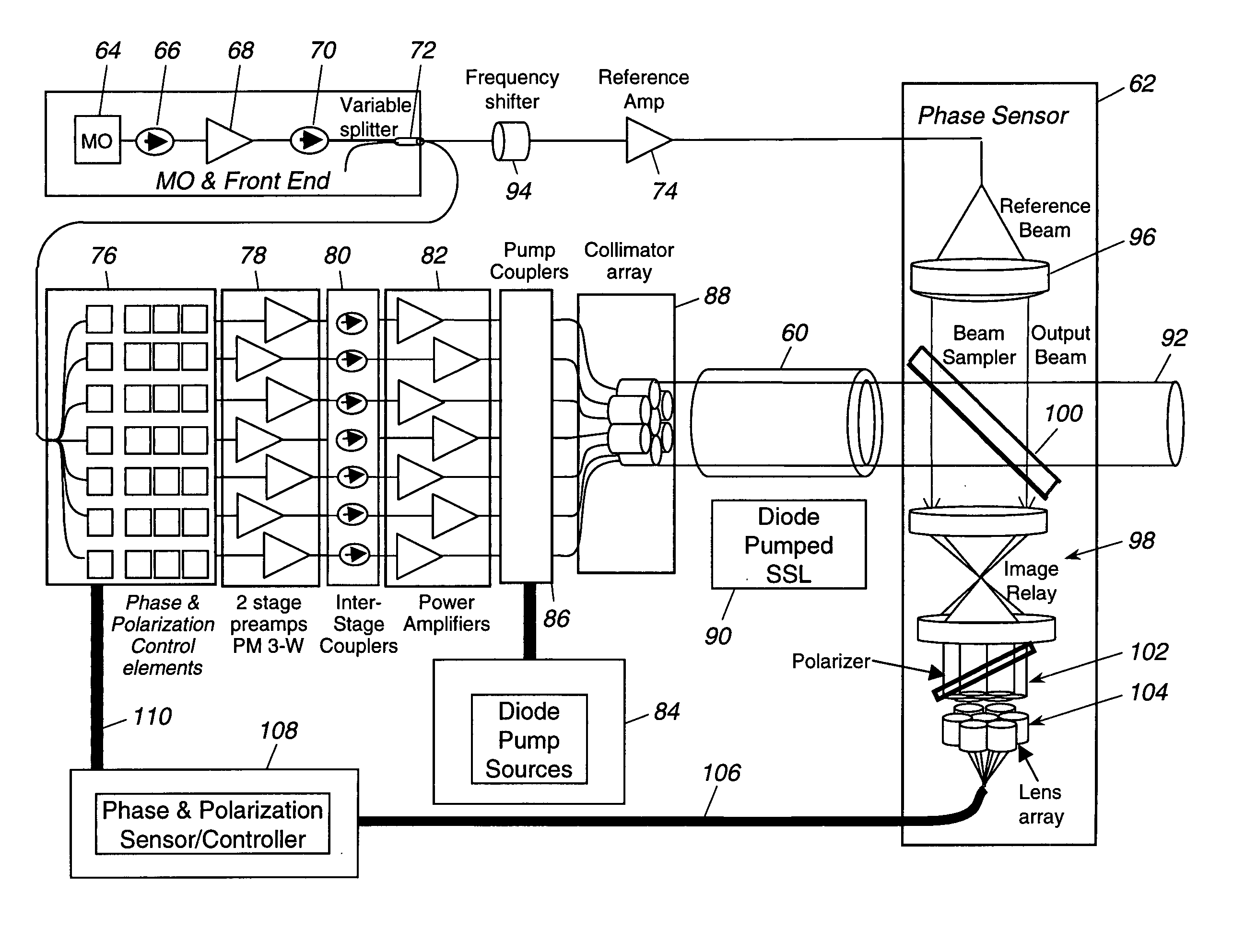
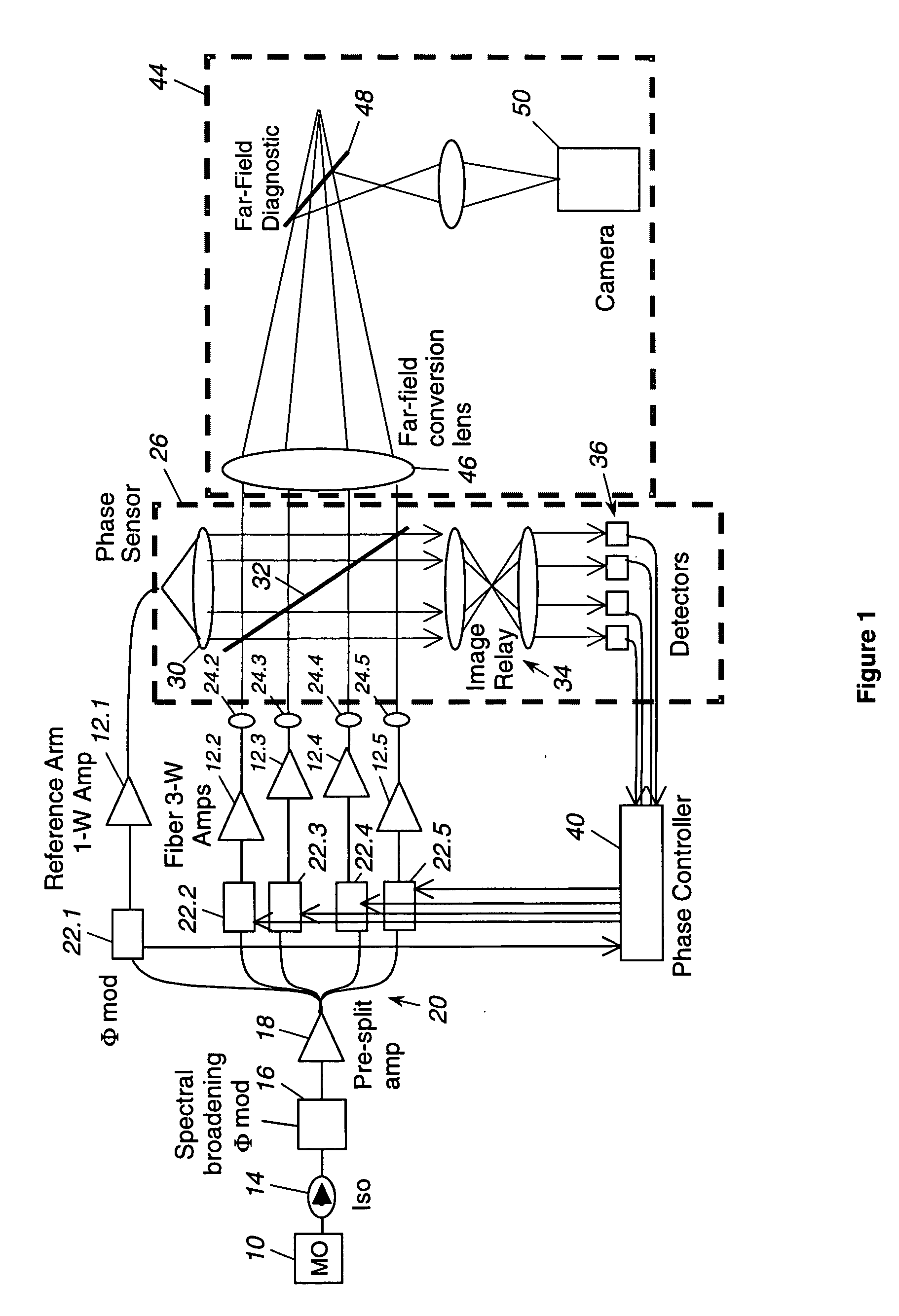
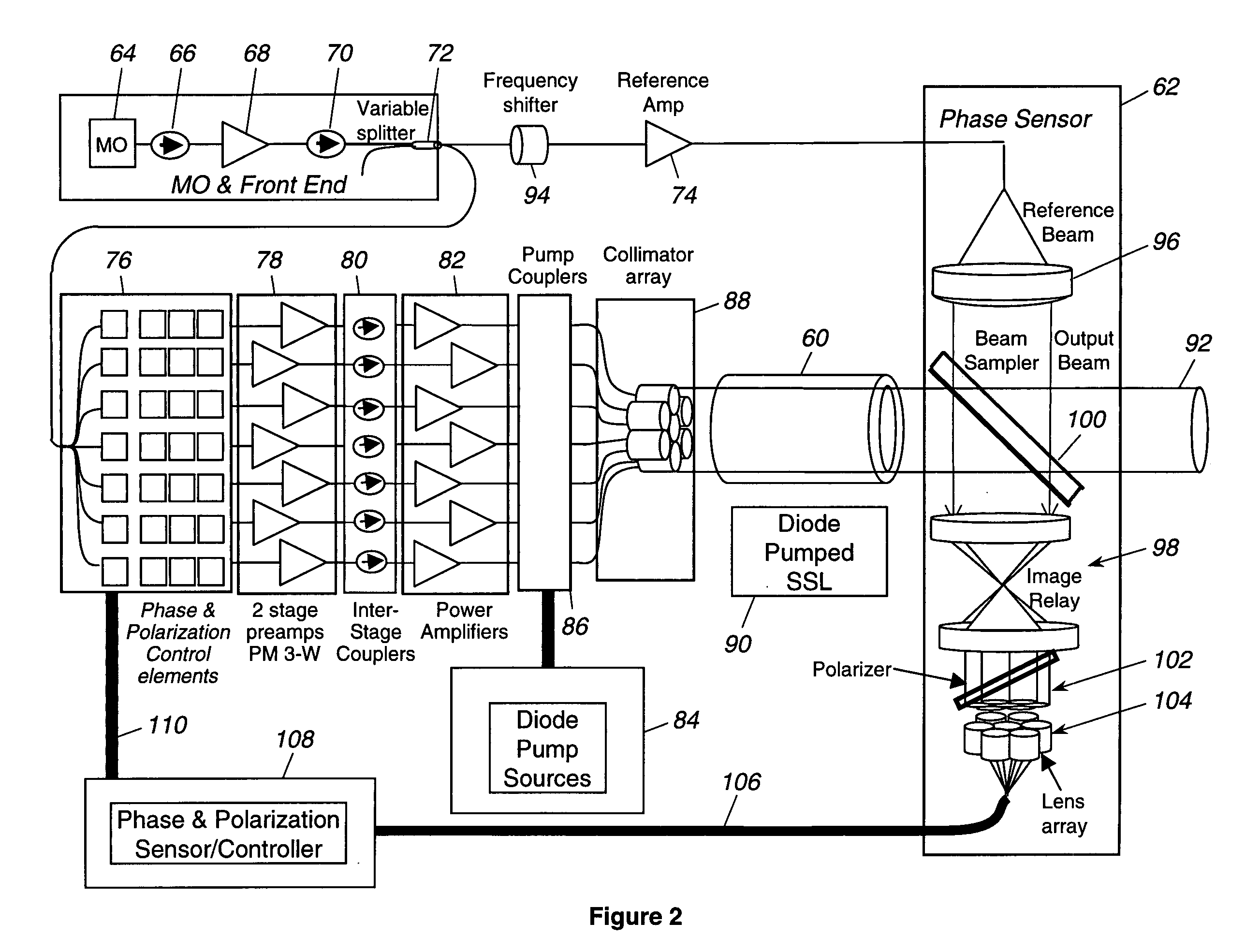
Laser source comprising amplifier and adaptive wavefront/polarization driver
ActiveUS20050201429A1Compensation DistortionOptical measurementsLaser using scattering effectsWavefrontAudio power amplifier
A hybrid laser source including a solid state laser driven by an array of fiber laser amplifiers, the inputs of which are controllable in phase and polarization, to compensate for distortions that arise in the solid state laser, or to achieve desired output beam properties relating to direction or focus. The output beam is sampled and compared with a reference beam to obtain phase and polarization difference signals across the output beam cross section, at spatial positions corresponding with the positions of the fiber laser amplifiers providing input to the solid state laser. Therefore, phase and polarization properties of the output beam may be independently controlled by predistortion of these properties in the fiber laser amplifier inputs.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
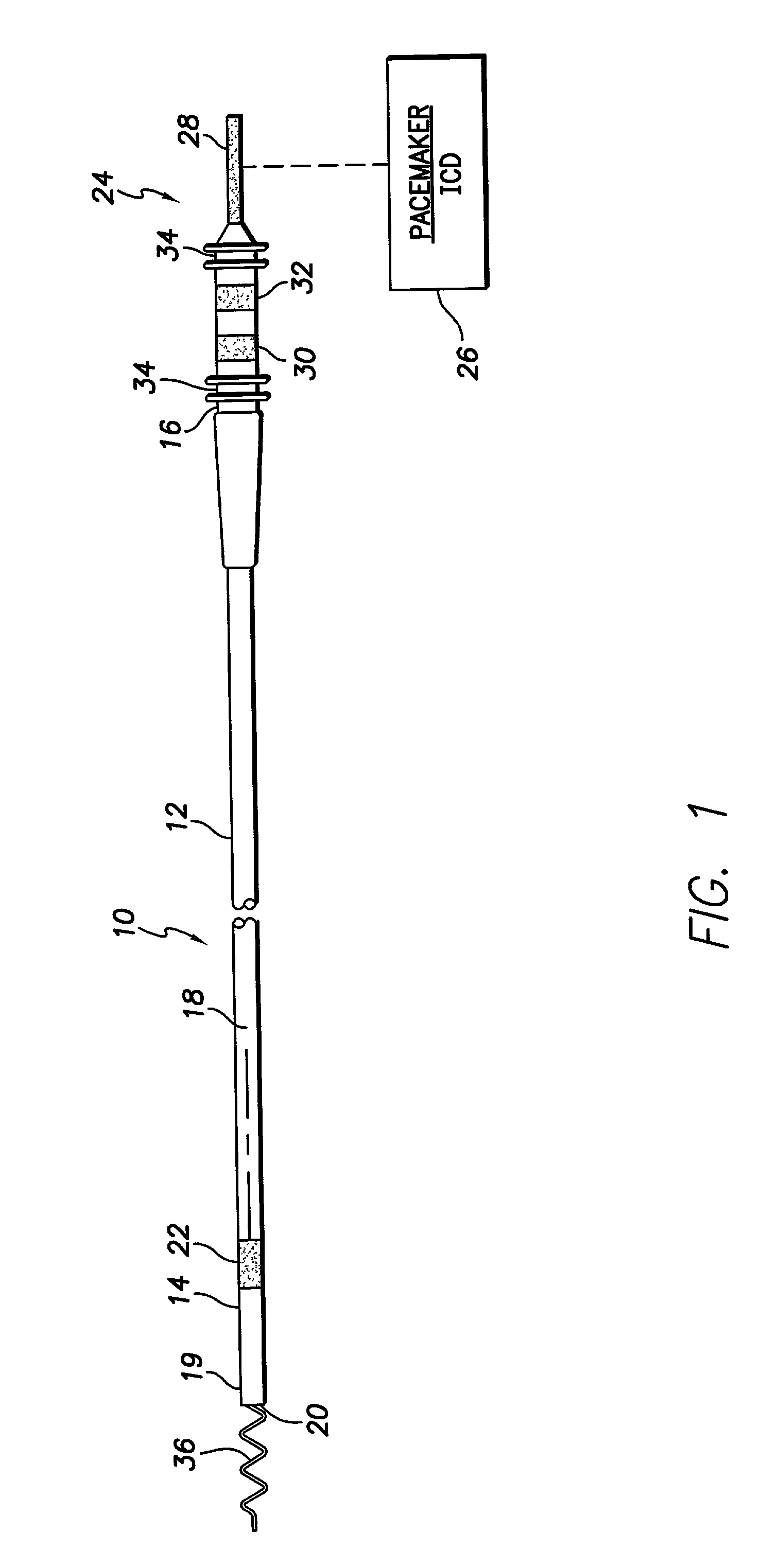
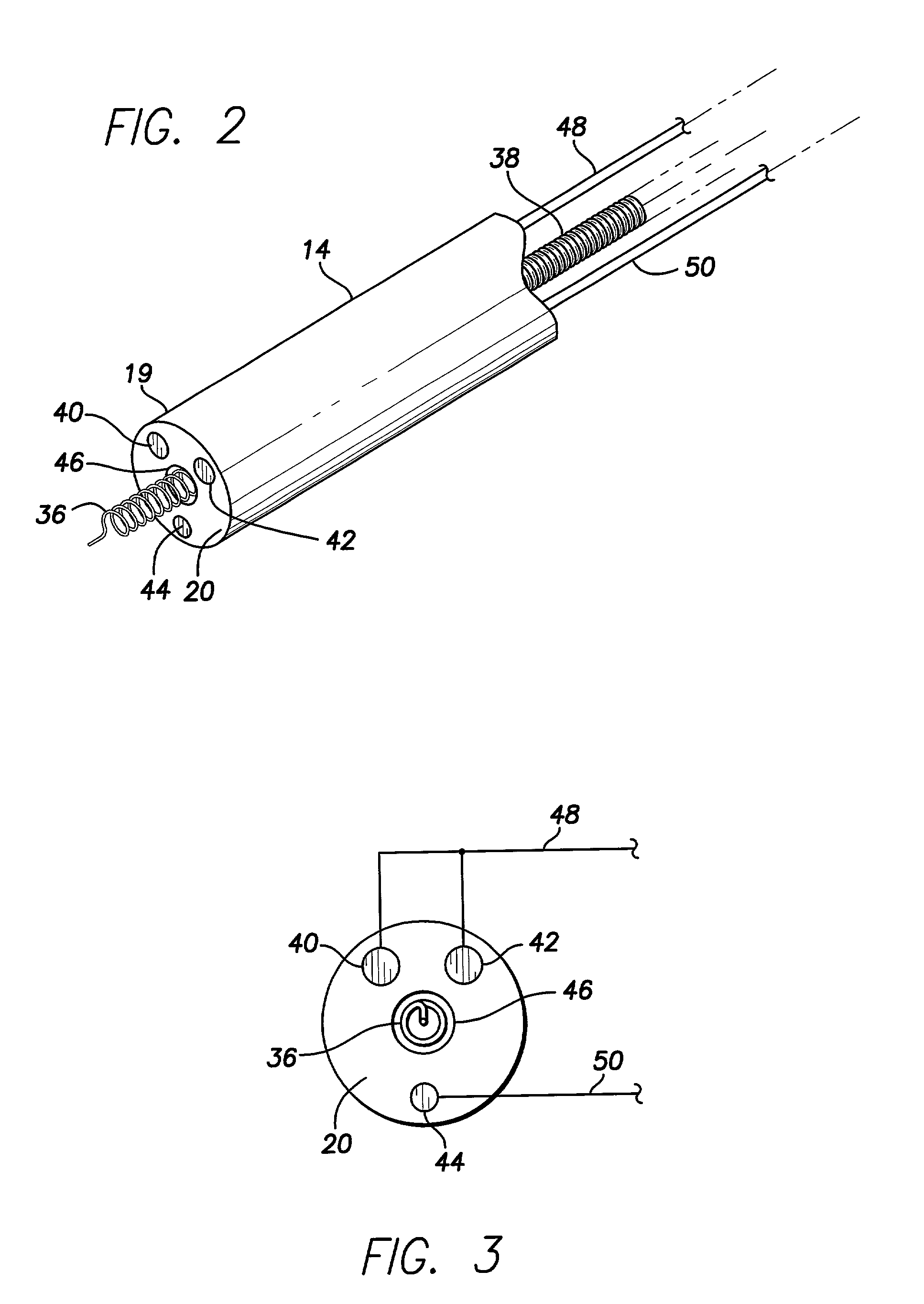
Lead with distal tip surface electrodes connected in parallel
InactiveUS7027852B2High pacing impedanceAdvantageous anode-to-cathode surface area ratioTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringLow noiseWavefront
An body implantable stimulation lead is provided including tip electrode patterns and configurations producing low noise, clean sensed signals devoid of far field components, such sensed signals being generated irrespective of the direction of the incident depolarization wavefront. The invention also provides high pacing impedances and advantageous anode-to-cathode surface area ratios. Further, implantable leads utilizing the features of the present invention are particularly suitable for left side stimulation therapies.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
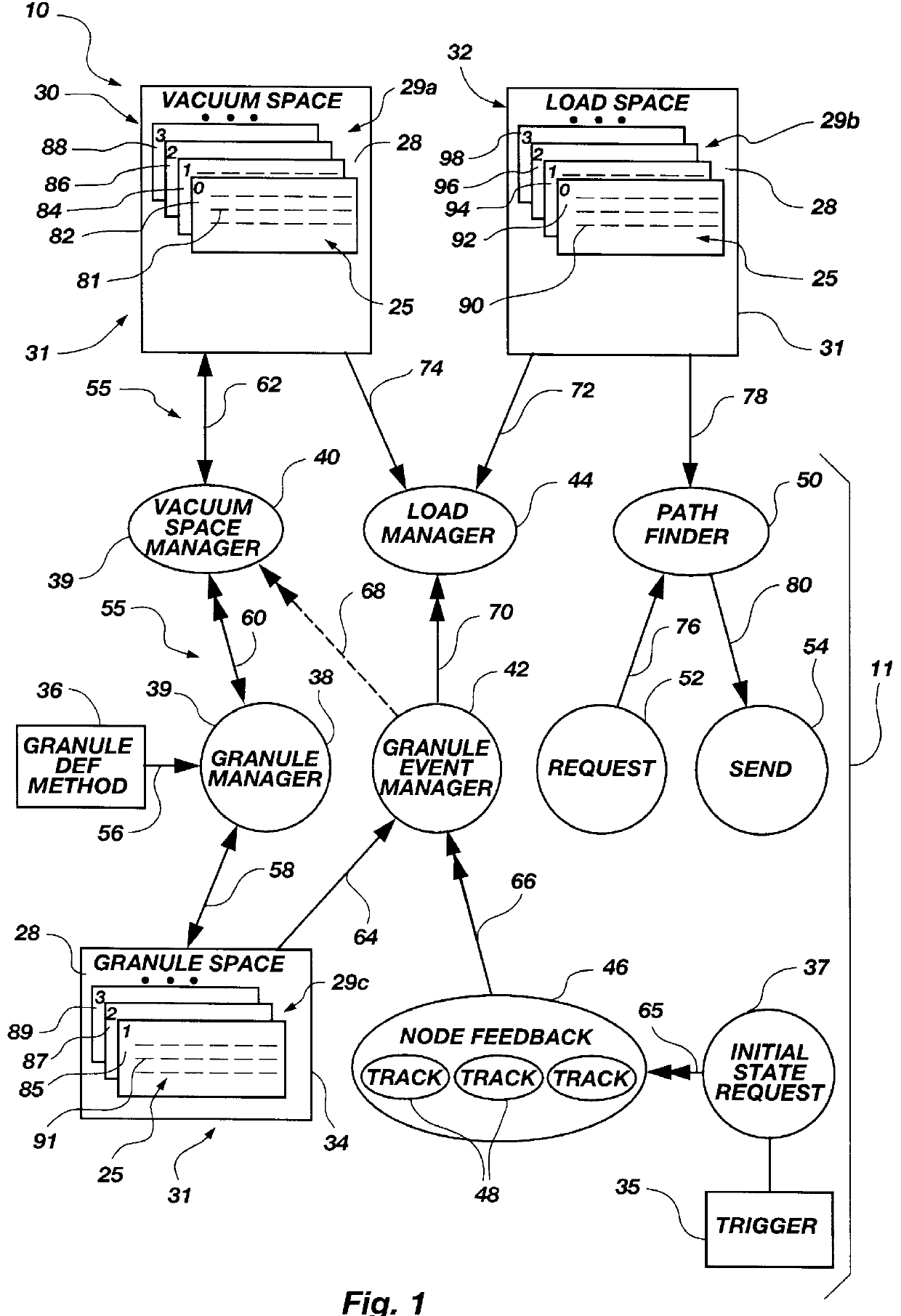
Extrinsically influenced near-optimal path apparatus and method
InactiveUS6067572ARapidly and automatically determineRapidly and automatically designateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavefrontOperational system
A method and apparatus for dynamically providing a path through a network of nodes or granules may use a limited, advanced look at potential steps along a plurality of available paths. Given an initial position, at an initial node or granule within a network, and some destination node or granule in the network, all nodes or granules may be represented in a connected graph. An apparatus and method may evaluate current potential paths, or edges between nodes still considered to lie in potential paths, according to some cost or distance function associated therewith. In evaluating potential paths or edges, the apparatus and method may consider extrinsic data which influences the cost or distance function for a path or edge. Each next edge may lie ahead across the advancing "partial" wavefront, toward a new candidate node being considered for the path. With each advancement of the wavefront, one or more potential paths, previously considered, may be dropped from consideration. Thus, a "partial" wavefront, limited in size (number of nodes and connecting edges) continues to evaluate some number of the best paths "so far." The method deletes worst paths, backs out of cul-de-sacs, and penalizes turning around. The method and apparatus may be implemented to manage a computer network, a computer internetwork, parallel processors, parallel processes in a multi-processing operating system, a smart scissor for a drawing application, and other systems of nodes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for augmented reality
Methods and systems for triggering presentation of virtual content based on sensor information. The display system may be an augmented reality display system configured to provide virtual content on a plurality of depth planes using different wavefront divergences. The system may monitor information detected via the sensors, and based on the monitored information, trigger access to virtual content identified in the sensor information. Virtual content can be obtained, and presented as augmented reality content via the display system. The system may monitor information detected via the sensors to identify a QR code, or a presence of a wireless beacon. The QR code or wireless beacon can trigger the display system to obtain virtual content for presentation.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
InactiveUS7714782B2Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
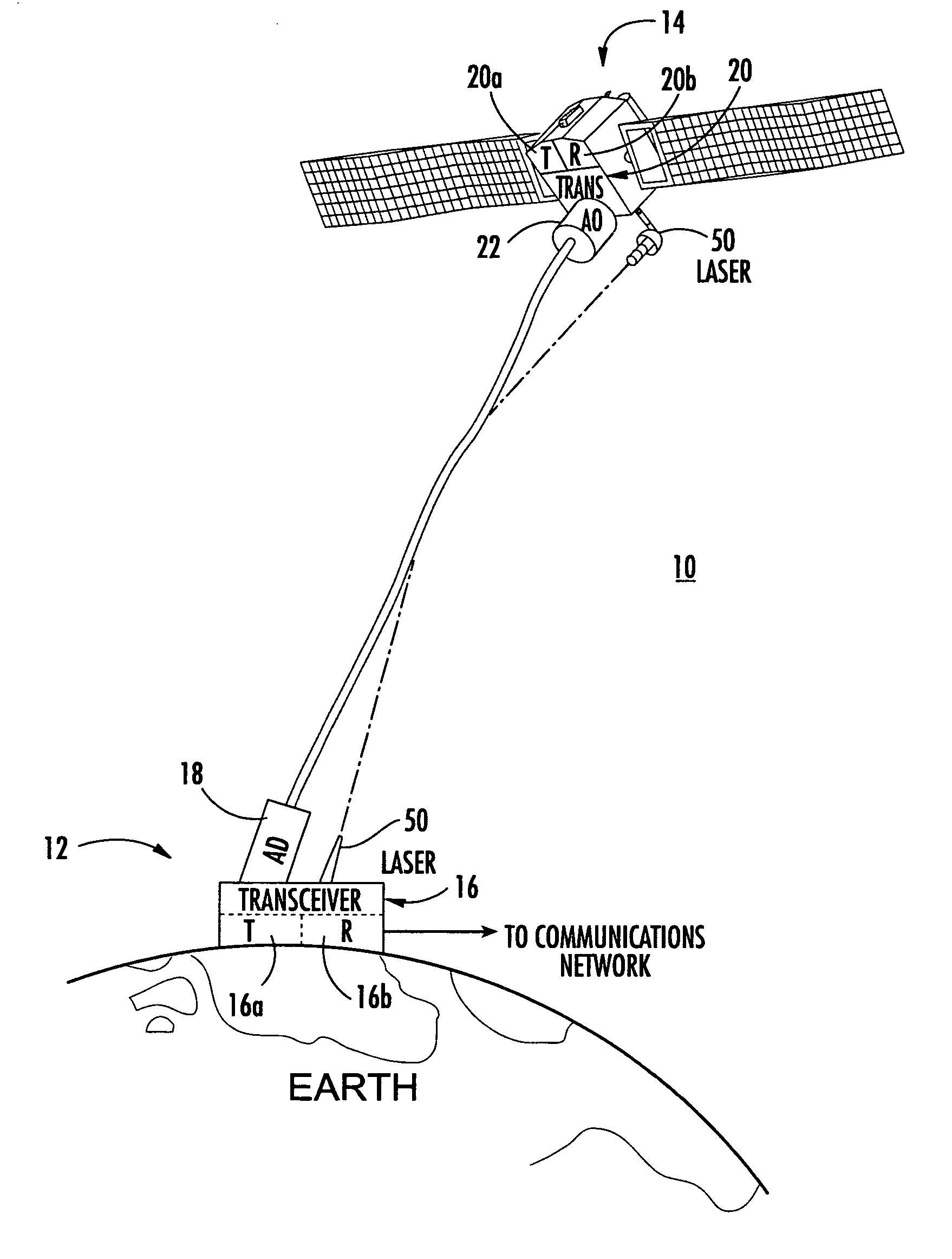
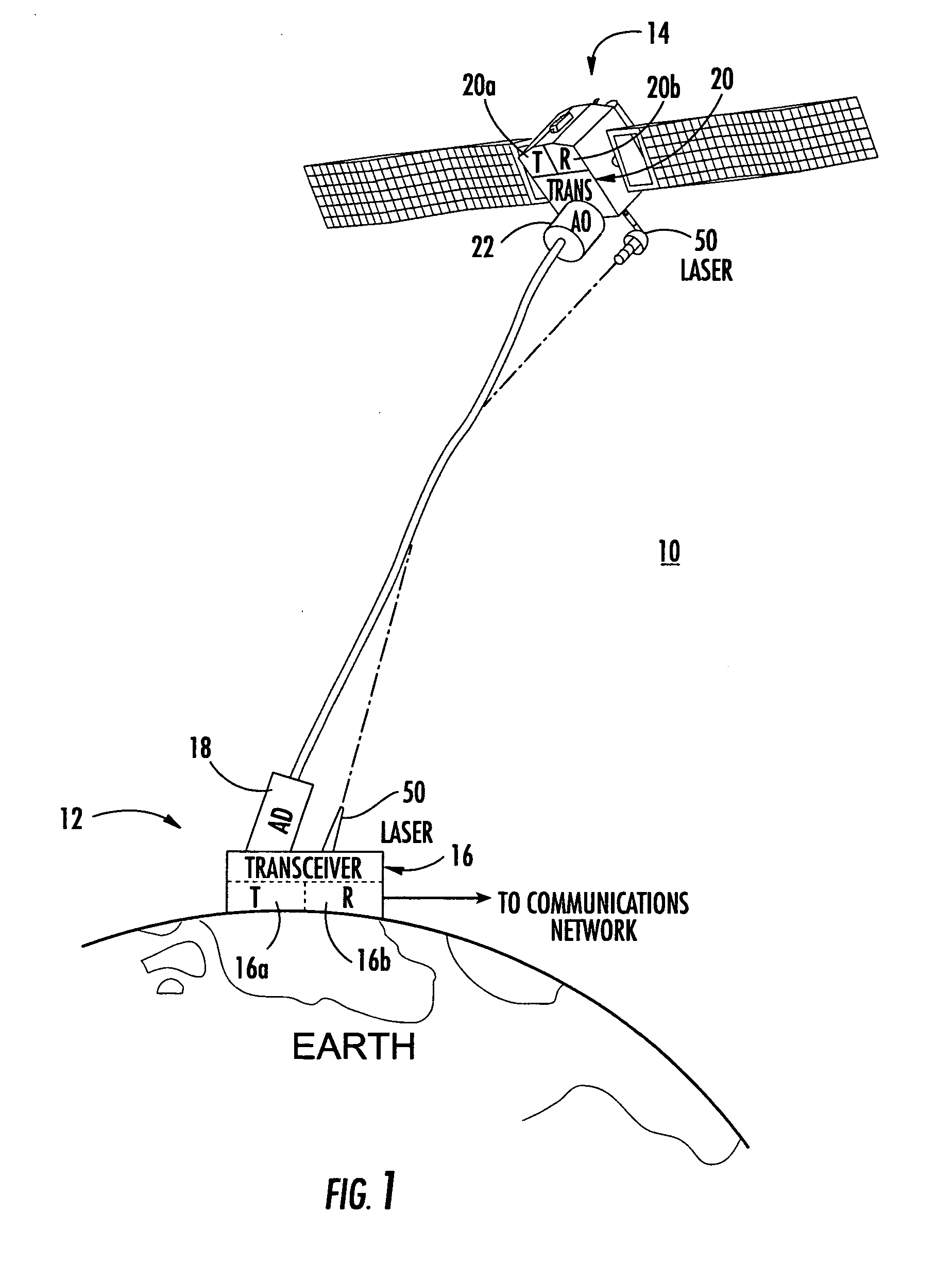
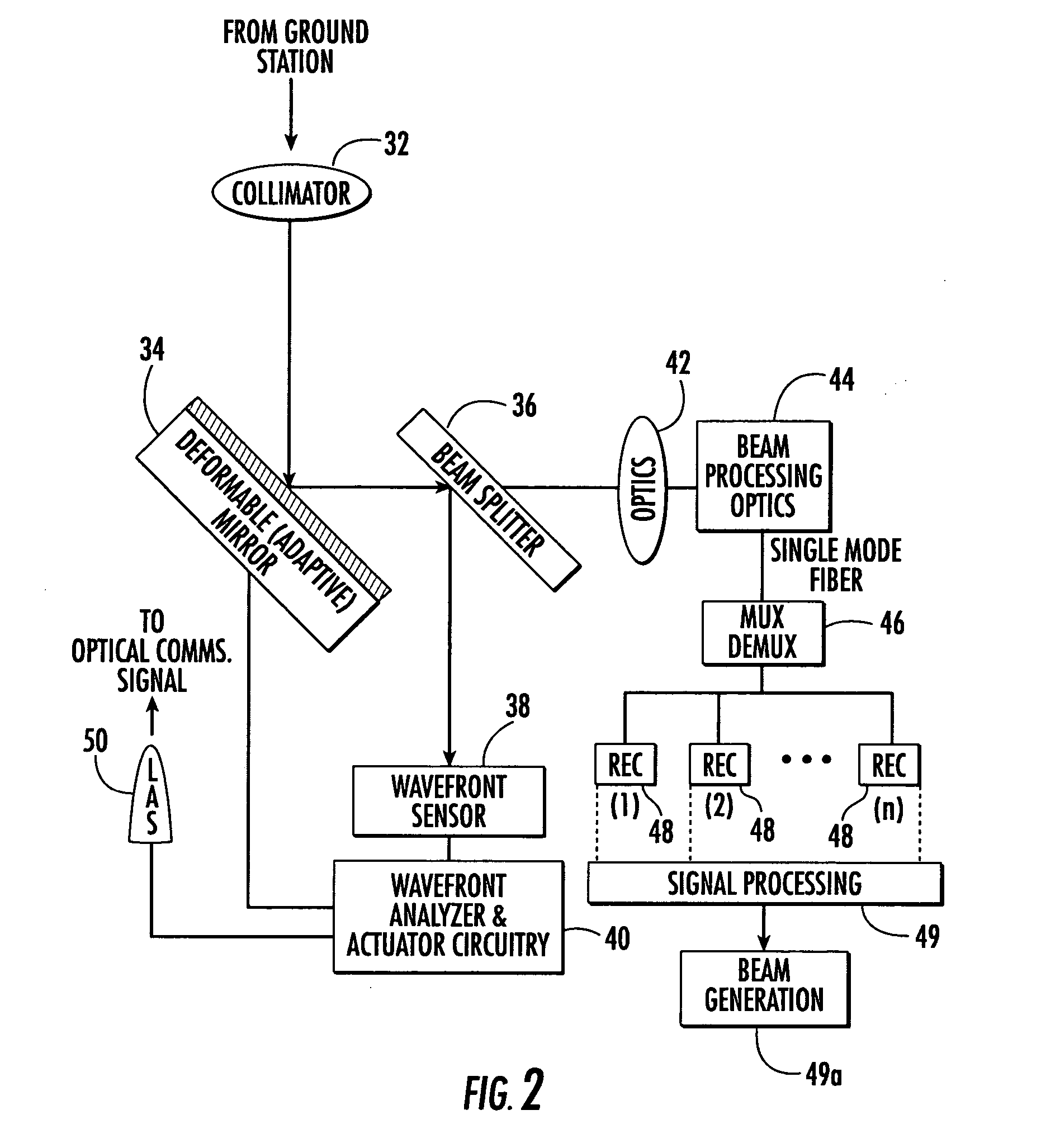
System and method of free-space optical satellite communications
InactiveUS20050100339A1Reduce and eliminate distortionIncrease volumeSatellite communication transmissionWavefrontTransceiver
A system and method of free-space optical satellite communications includes a ground station and transceiver for transmitting and receiving an optical communications signal. Adaptive optics at the ground station are operative with the transceiver for determining the shape of any distortions in the wavefront of the optical communications signal and compensating at the ground station for the distortions. A satellite includes a transceiver for transmitting and receiving the optical communications signal and includes adaptive optics for determining the shape of any distortions in the waveform of the optical communications signal and compensating at the satellite for the distortions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Pixelated phase-mask interferometer
ActiveUS20050046865A1Avoiding chromatic dispersionAvoid complexityInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase differenceDetector array
A phase-difference sensor measures the spatially resolved difference in phase between orthogonally polarized reference and test wavefronts. The sensor is constructed as a pixelated phase-mask aligned to and imaged on a pixelated detector array. Each adjacent pixel of the phase-mask measures a predetermined relative phase shift between the orthogonally polarized reference and test beams. Thus, multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be synthesized at the same time by combining pixels with identical phase-shifts. The multiple phase-shifted interferograms can be combined to calculate standard parameters such as modulation index or average phase step. Any configuration of interferometer that produces orthogonally polarized reference and object beams may be combined with the phase-difference sensor of the invention to provide, single-shot, simultaneous phase-shifting measurements.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Three-dimensional simultaneous multiple-surface method and free-form illumination-optics designed therefrom
InactiveUS20050086032A1Need be addressComputation using non-denominational number representationCondensersWavefrontFree form
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
Augmented reality systems and methods for user health analysis
ActiveUS20170323485A1Input/output for user-computer interactionMechanical apparatusData criteriaWavefront
Augmented reality systems and methods for user health analysis. Methods for user health analysis may include collecting data for an initial prediction model and continuing to collect additional data based on one or more data criteria. The methods may further include updating the initial prediction model based on the additional data to produce a revised prediction model or causing an intervention to occur based on the additional data. The data may be collected by a display system including one or more sensors configured to collect user-specific data and a display device configured to present virtual content to a user. The display device may be configured to output light with variable wavefront divergence.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
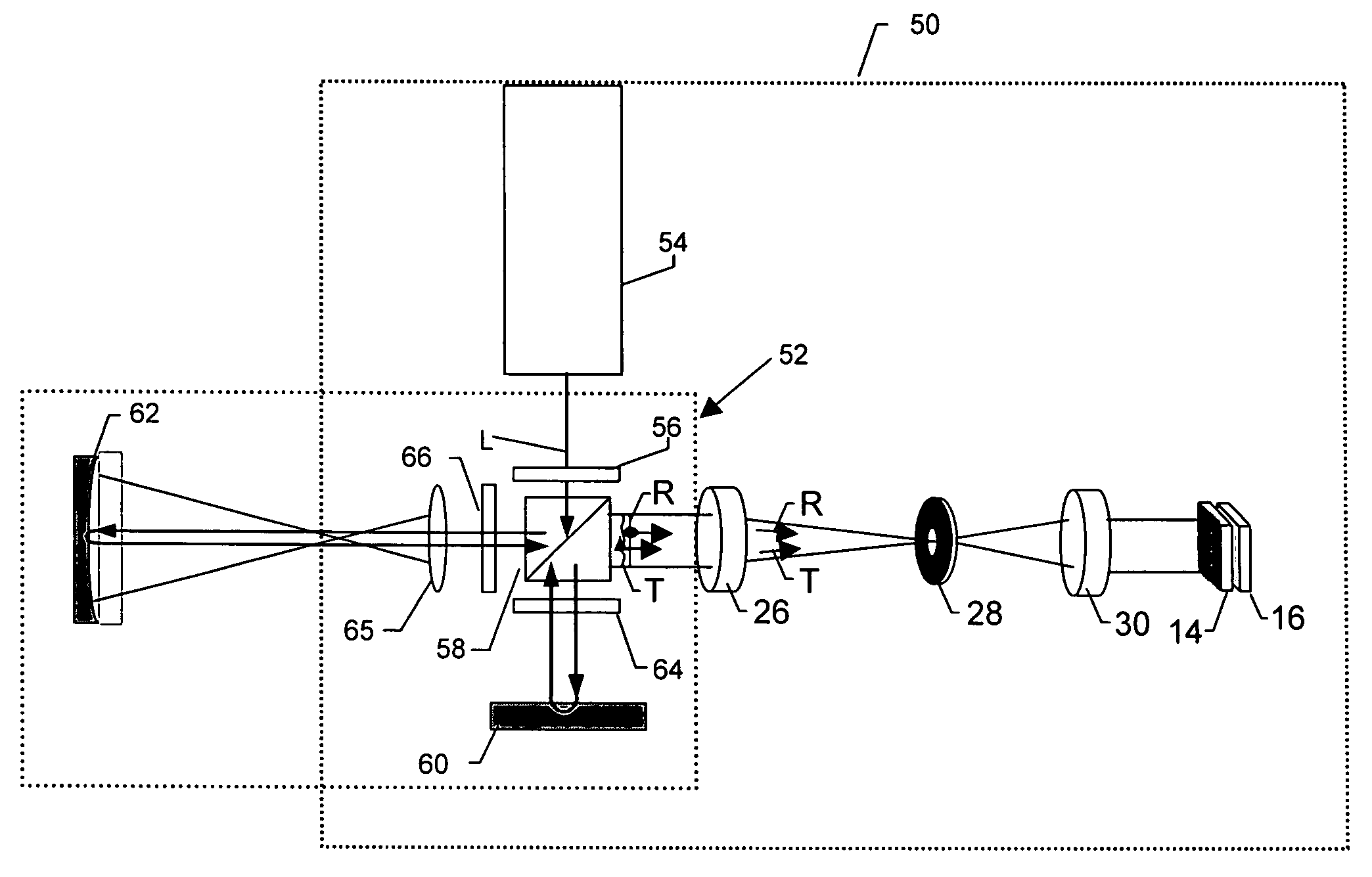
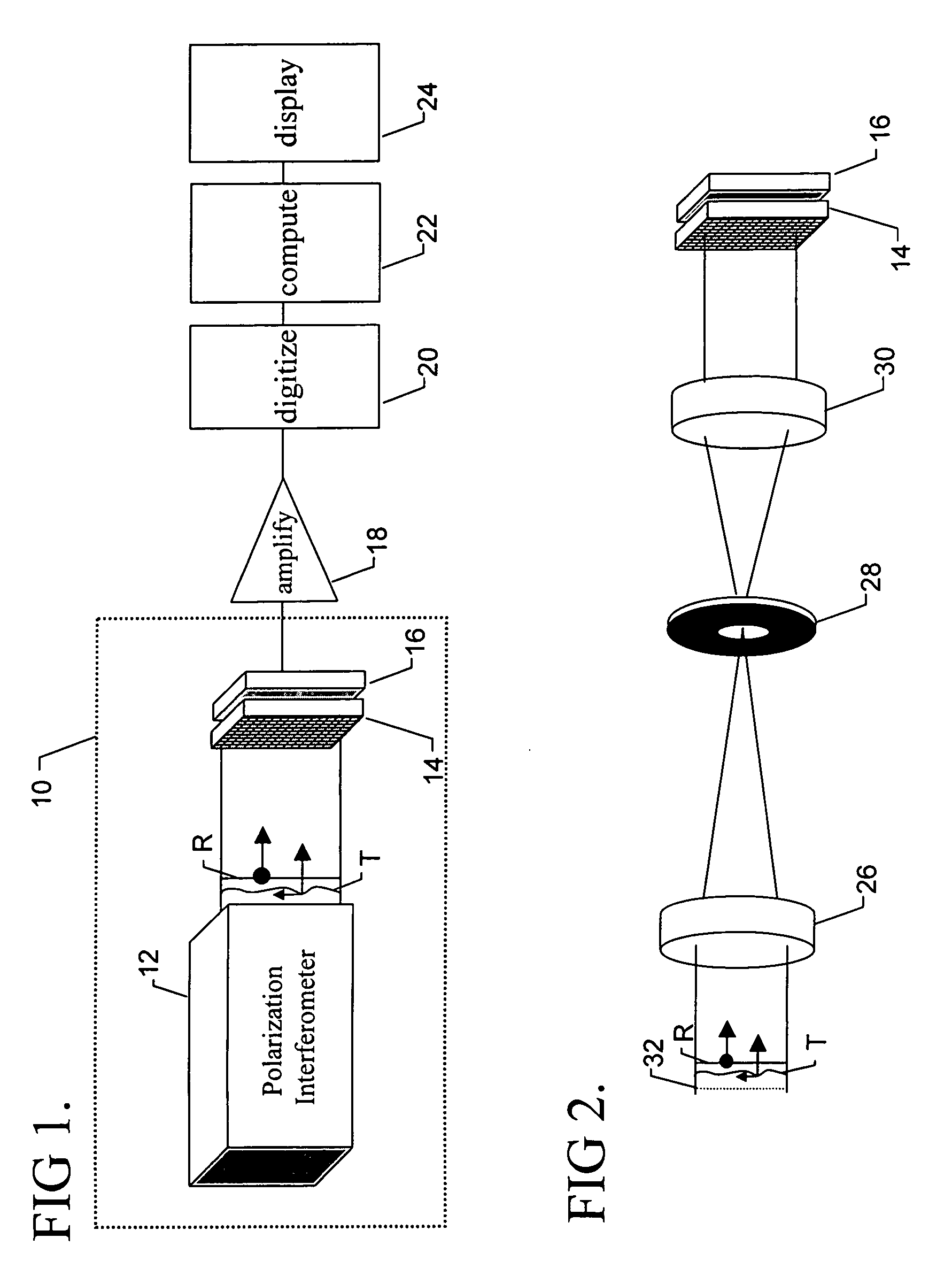
Apparatus and method for determining subjective responses using objective characterization of vision based on wavefront sensing
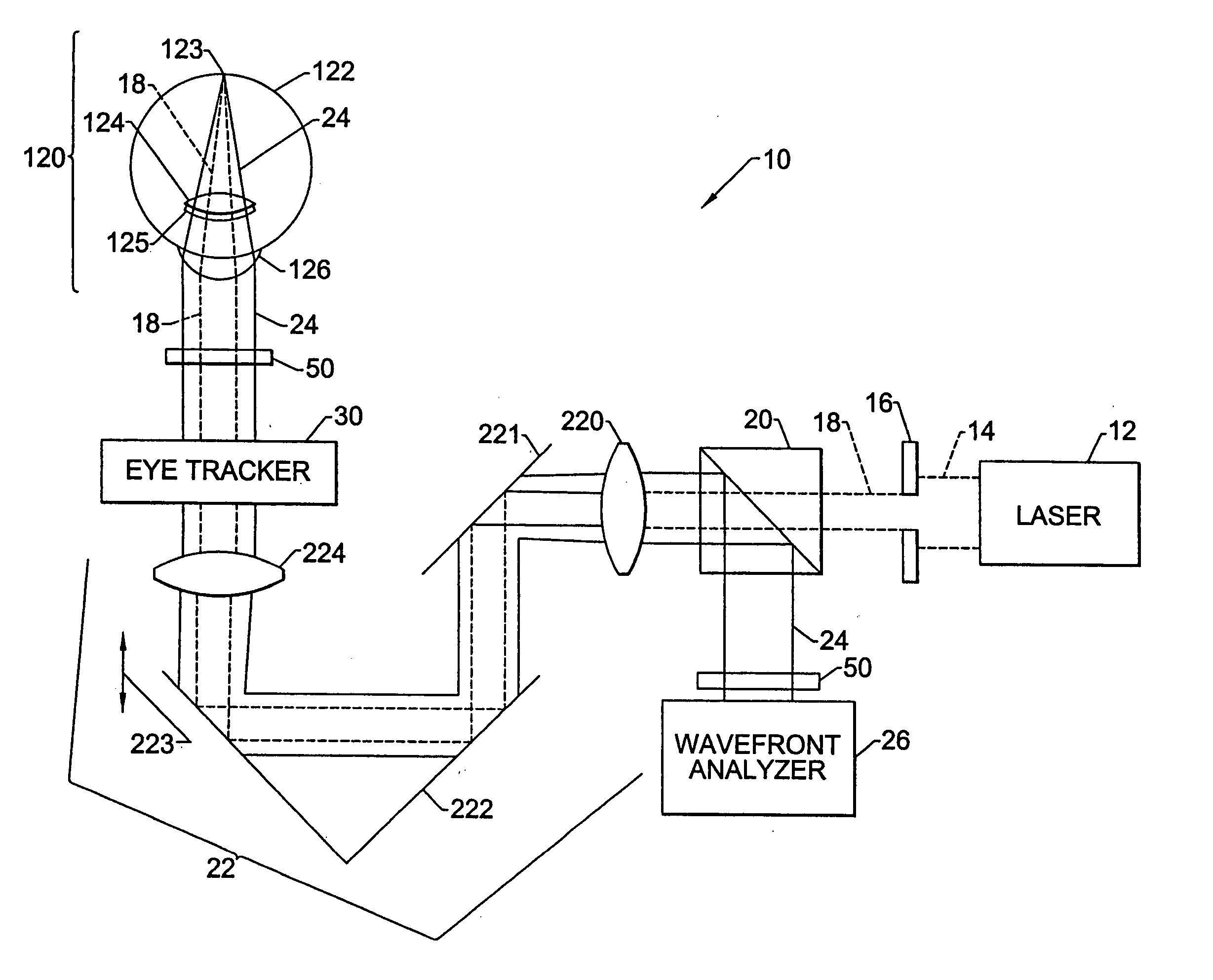
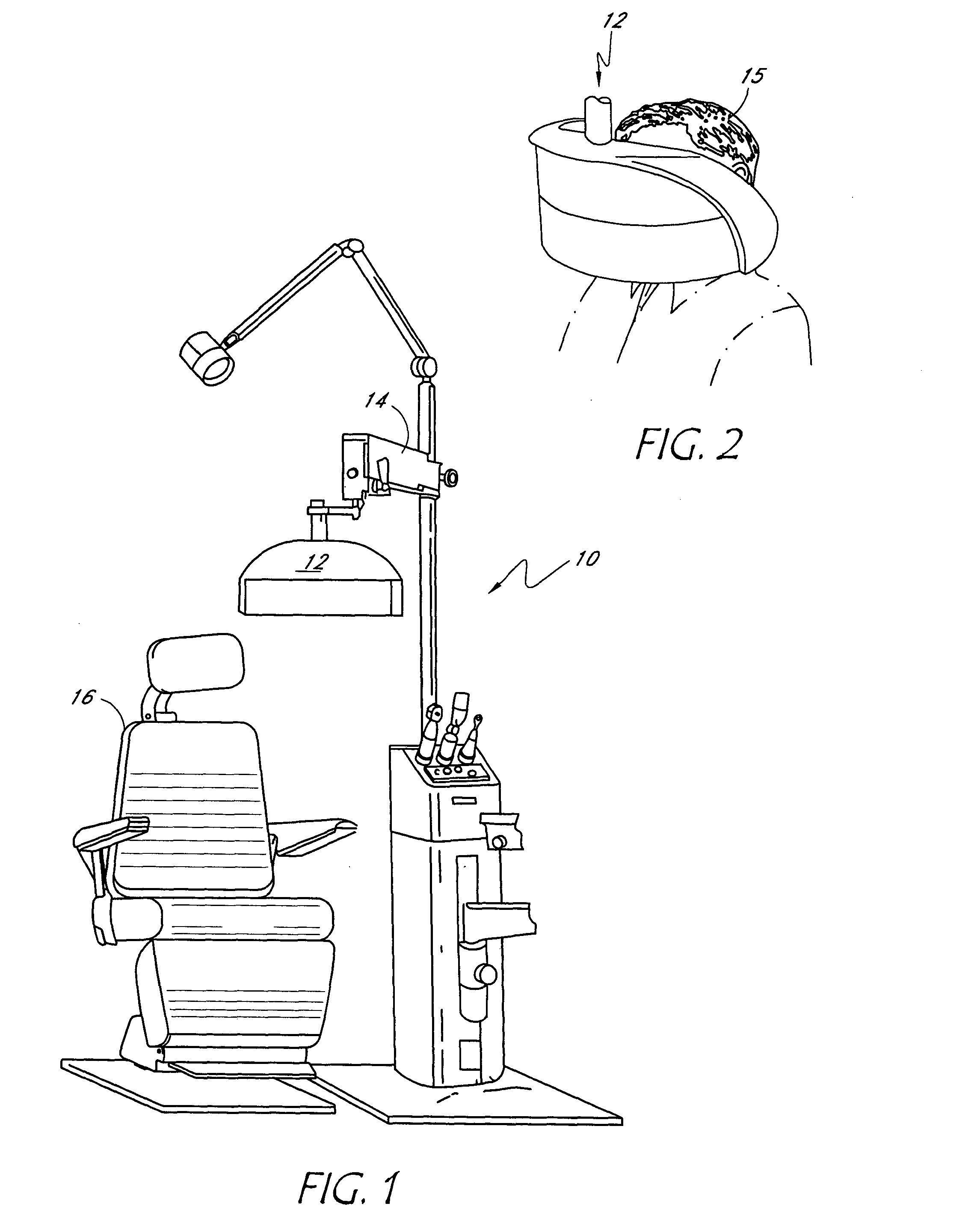
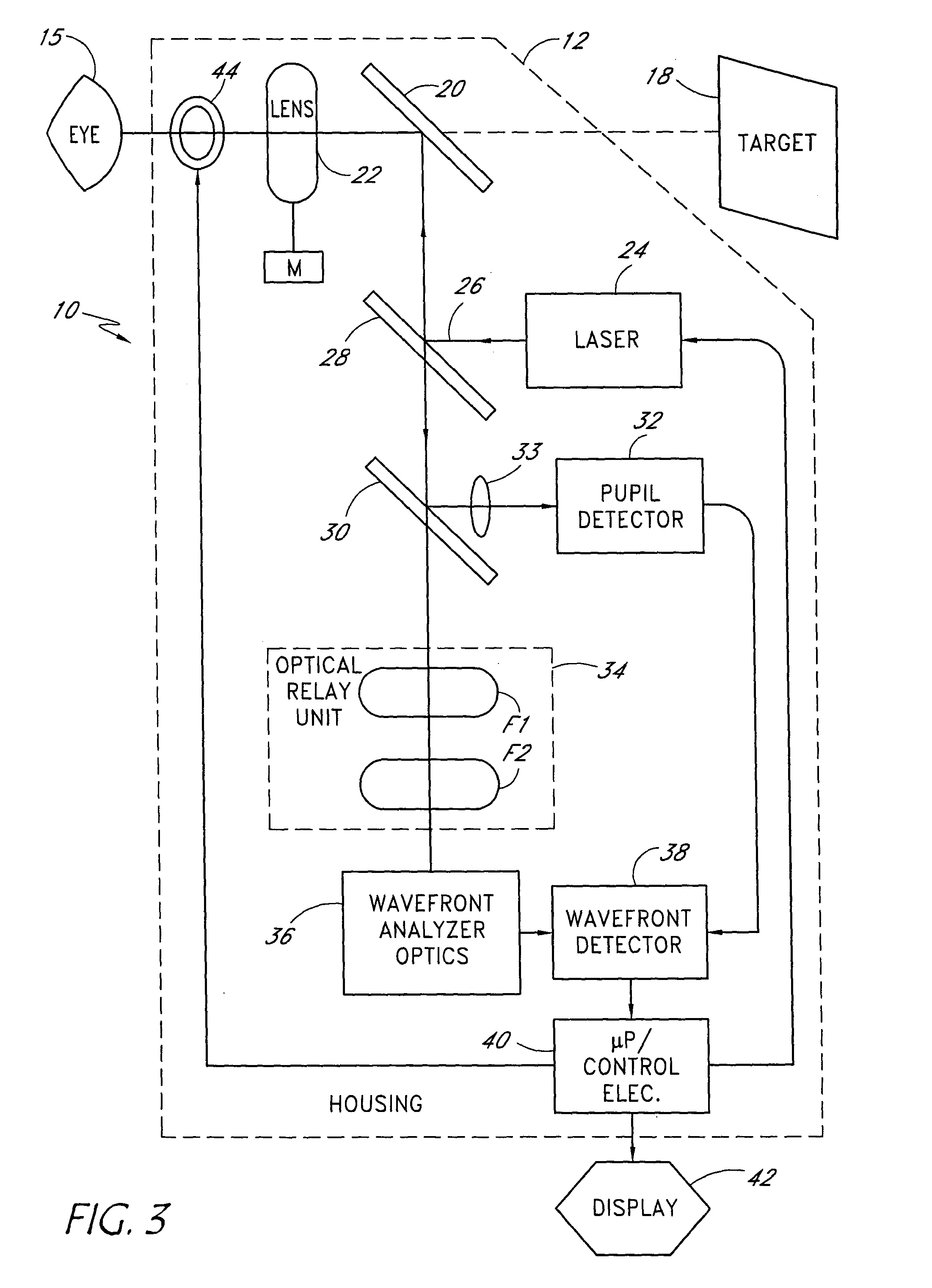
An apparatus for determining the refraction of a patient's eye includes a wavefront measurement device that determines aberrations in a return beam from the patient's eye viewing a target through a corrective test lens in the apparatus. The wavefront measurement device preferably outputs an display representative of the quality of vision afforded the patient through the test lens. The display may be, e.g., a representation of a Snellen chart convolved with the optical characteristics of the patient's vision, an overall quality of vision scale, or the optical contrast function, all of which are based on the wavefront measurements of the patient's eye. The examiner may use the display information to conduct a refraction examination or other vision tests without the subjective response from the patient.
Owner:ENTERPRISE PARTNERS VI
Optical systems
InactiveUS20100165429A1Easy to implementActive addressable light modulatorOptical elementsProjection opticsHead-up display
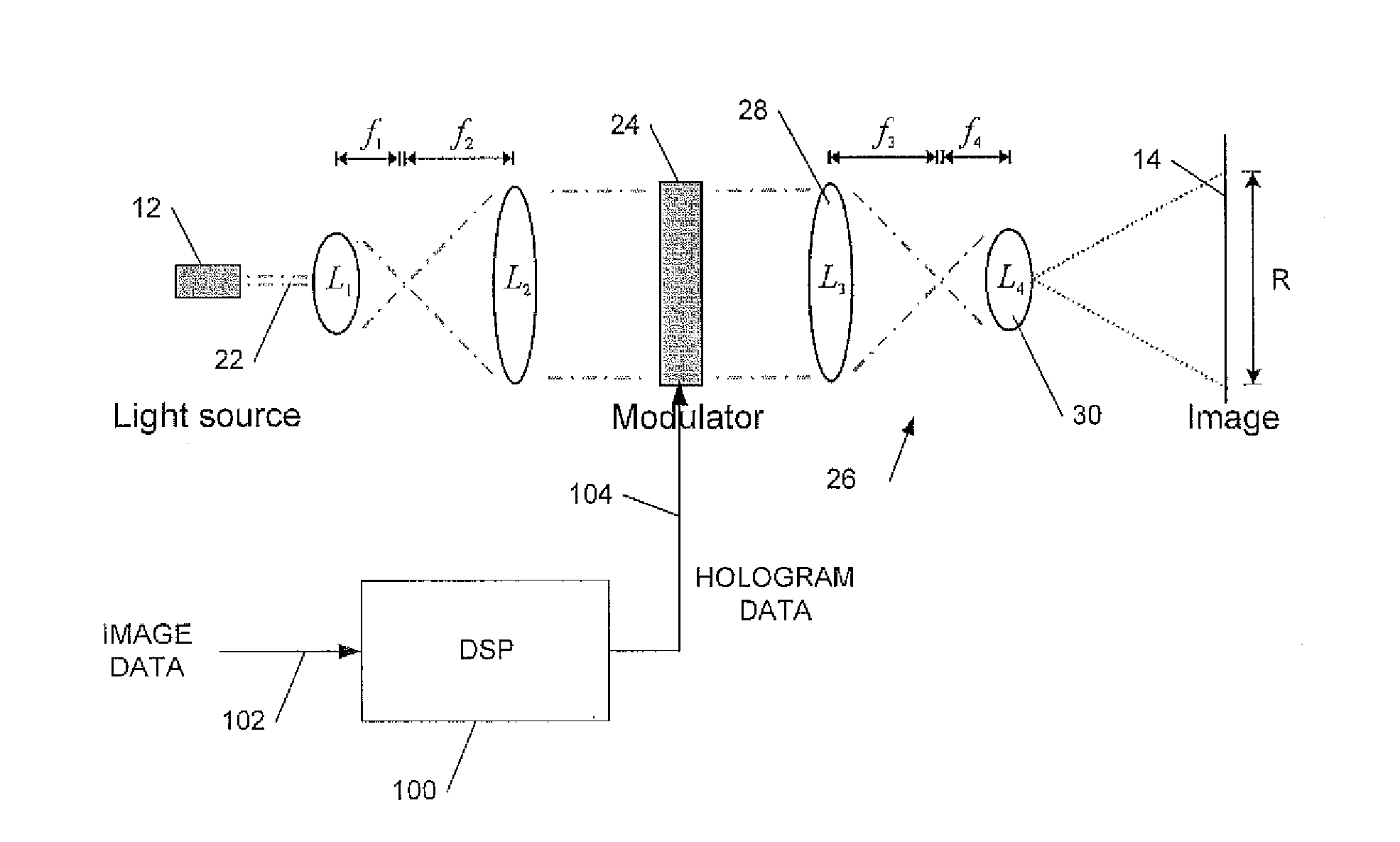
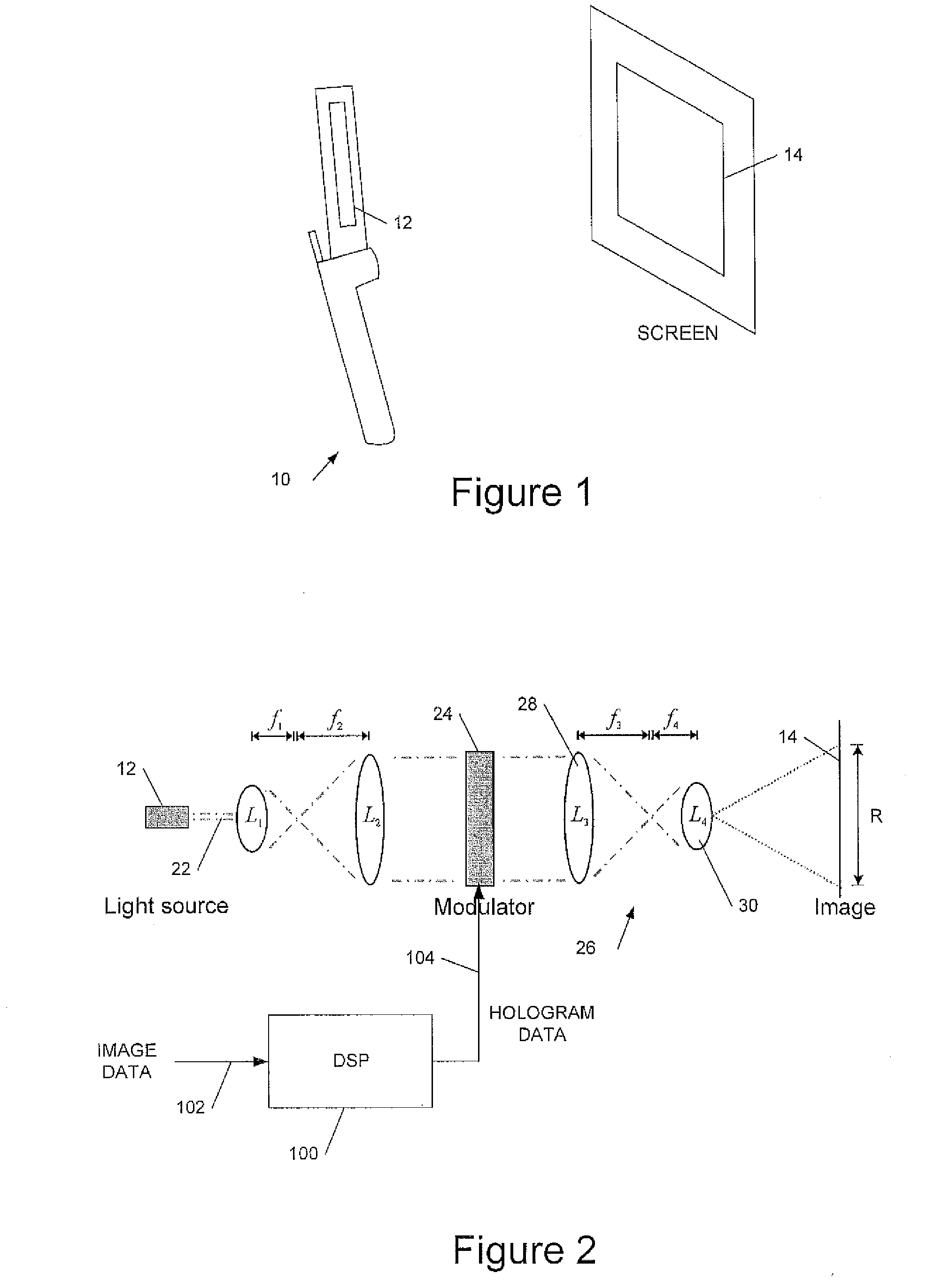
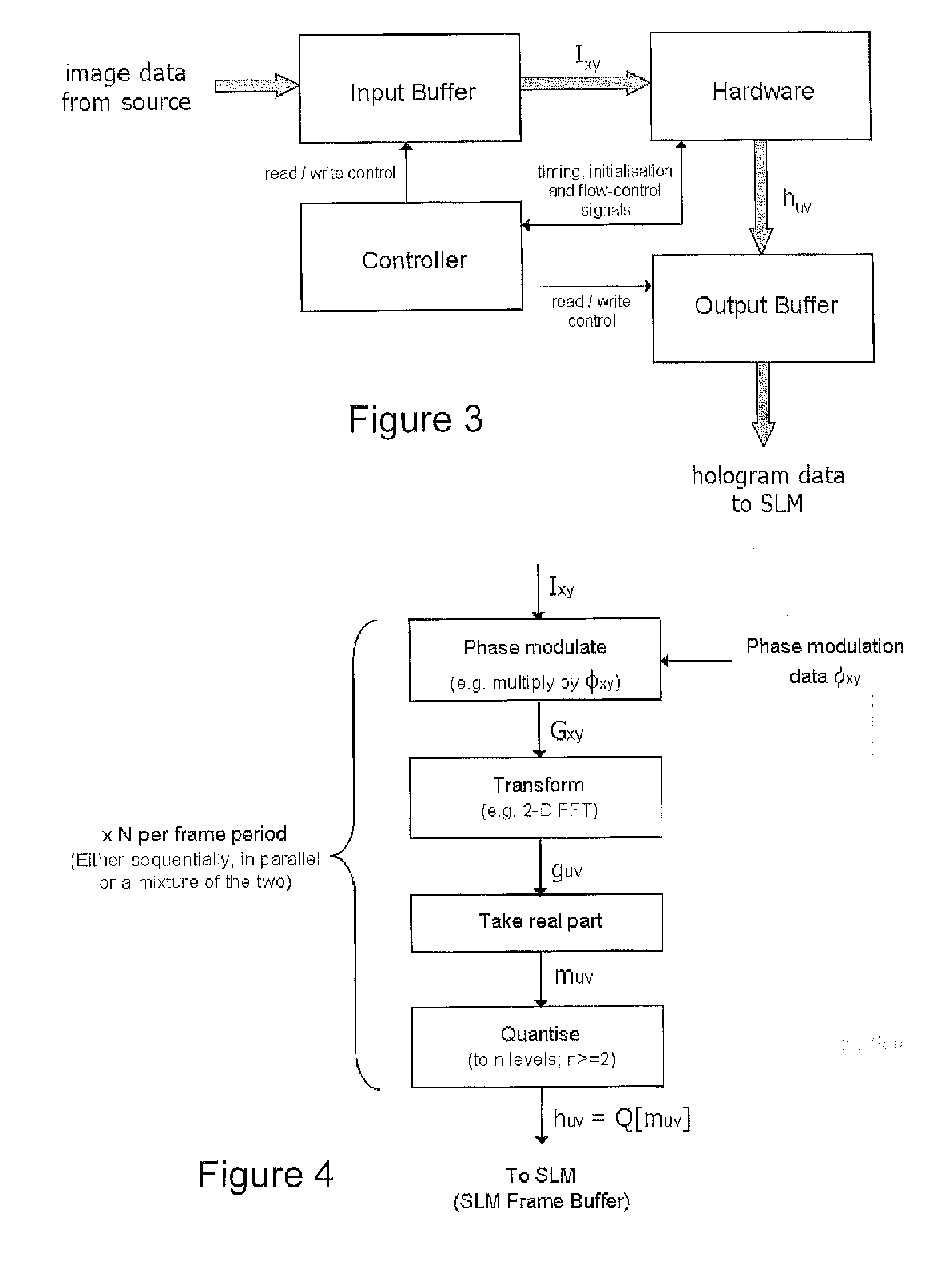
A holographic head up display (HUD) for a vehicle to display an image holographically on a curved display surface such as a windshield is disclosed. The HUD can include a spatial light modulator (SLM) to display a hologram, an illumination system to illuminate said displayed hologram, projection optics to project light from said hologram onto said display surface to form said image, and a processor configured to process said image data to generate hologram data for display on the SLM to form said image. The HUD can further include a non-volatile data memory coupled to said processor to store wavefront correction data for said display surface, and the processor can be configured to apply a wavefront correction responsive to said stored wavefront correction data when generating the hologram data to correct the image for aberration due to a shape of said display surface.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Method and apparatus for reducing or eliminating the progression of myopia
ActiveUS7401922B2Reducing and eliminating progressionReduce and eliminate progressionSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsWavefrontLens plate
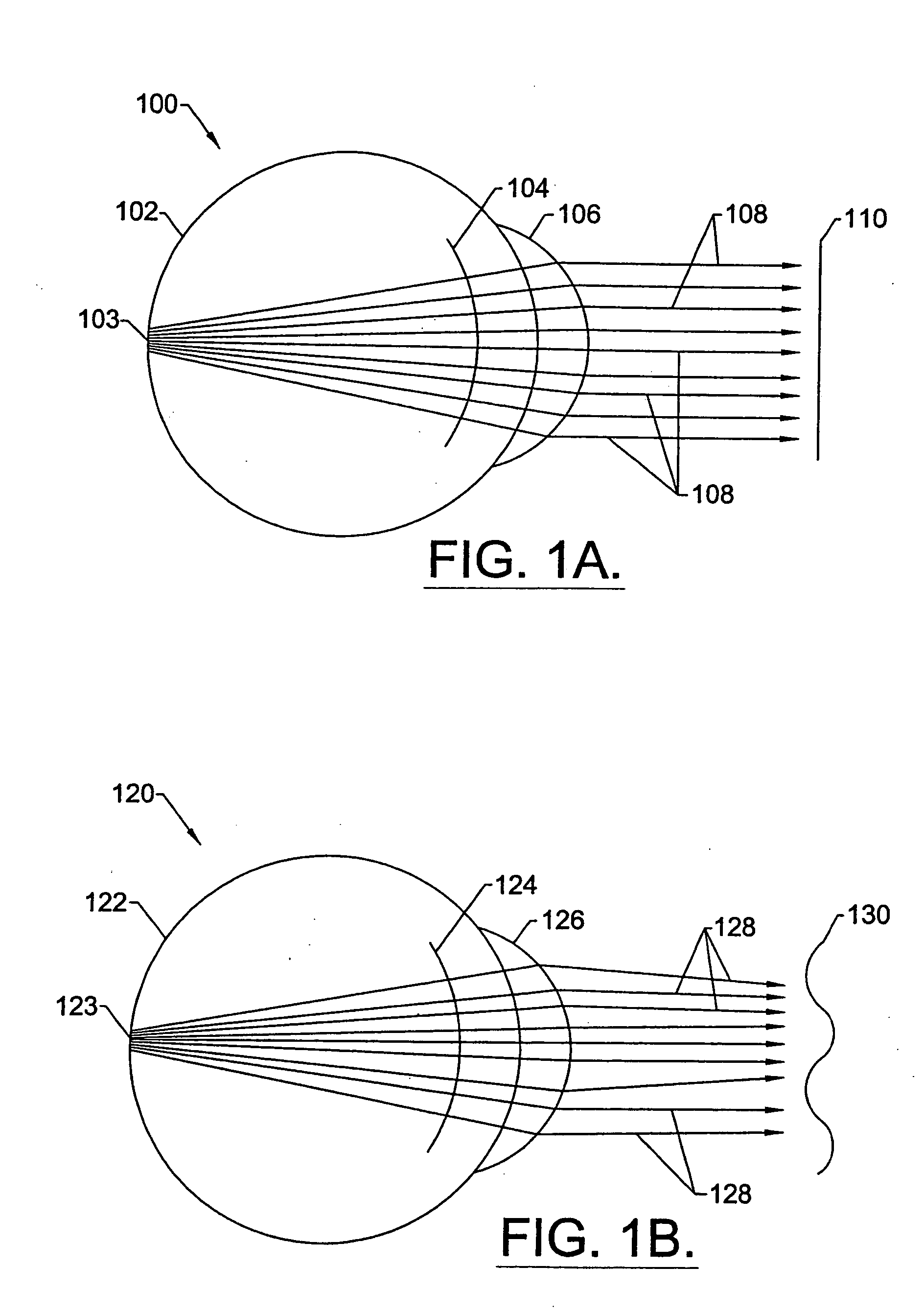
Apparatus and methods are provided for reducing or eliminating the progression of myopia, including a lens having an intentionally created aberration pattern for reducing or eliminating the progression of myopia. The aberration pattern may comprise a positive spherical aberration that produces a wavefront error in which the paracentral wavefront is disposed in front of the retina, thereby producing a signal that counters axial length growth of the eye and preventing the progression of myopia.
Owner:SYNERGEYES
Three-dimensional simultaneous multiple-surface method and free-form illumination-optics designed therefrom
InactiveUS7460985B2Computation using non-denominational number representationCondensersWavefrontFree form
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
Custom contact lens molding system and methods
Apparatus and methods for manufacturing custom contact lenses and molds is provided wherein a reconfigurable mold has a cavity including deformable surface that is deformed by an array of actuators to define a specified surface contour that will result in a desired wavefront. The specified surface contour may be imparted to moldable material deposited in the cavity, and the array of actuators may be repositioned to optimize the vision correction provided by the custom contact lens. Methods of using the reconfigurable mold to manufacture custom contact lens molds also are provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Lens-eye model and method for predicting in-vivo lens performance
InactiveUS6626535B2Easily impartedRate of evaporationSpectales/gogglesPhase-affecting property measurementsModel systemEngineering
An eye model system for remotely predicting the in-vivo performance of a vision altering optic includes a representative cornea, a dispersion medium, and a retinal surface. The corneal surfaces provide anatomical shape, optical power, and higher order aberration content. The dispersion medium mimics chromatic dispersion in an actual eye. The retinal surface is moveable to provide selected defocus. A humidity and temperature enclosure may be provided. Model eye elements can be tilted or decentered to simulate actual conditions. An associated method for remotely measuring the performance of a vision altering optic to predict its performance in-vivo includes making topography, wavefront, interferometry, PSF, MTF, or other optical and / or physical measurements of the model eye system with and without the optic in combination.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Waveguide laser illuminator incorporating a despeckler
There is provided an illumination device having: a laser; a waveguide including at least first and second transparent lamina; a first grating device for coupling light from the laser into a TIR path in the waveguide; a second grating device for coupling light from the TIR path out of the waveguide; and a third grating device for applying a variation of at least one of beam deflection, phase retardation or polarization rotation across the wavefronts of the TIR light. The first second and third grating devices are each sandwiched by transparent lamina.
Owner:DIGILENS
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Method and apparatus for plural document detection
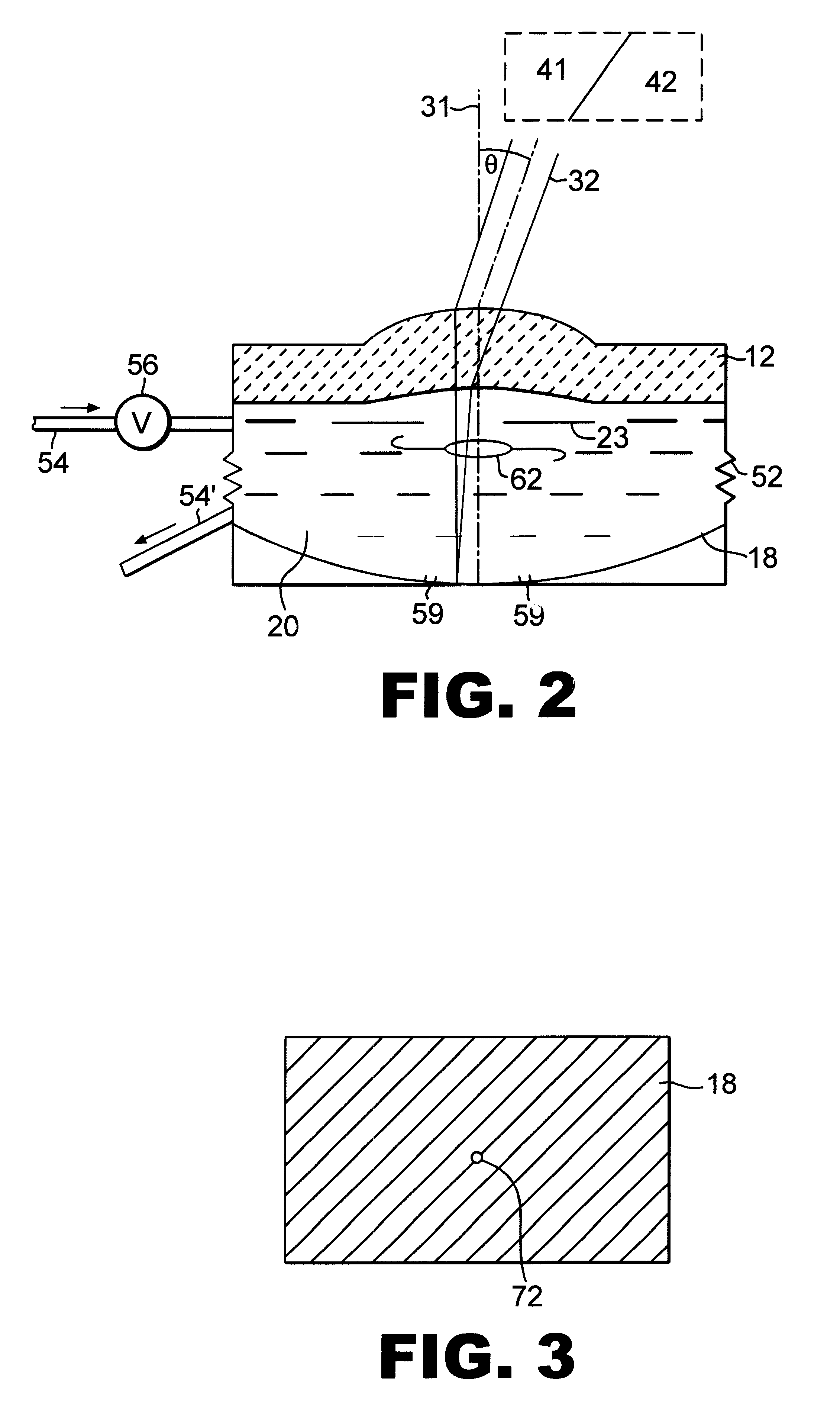
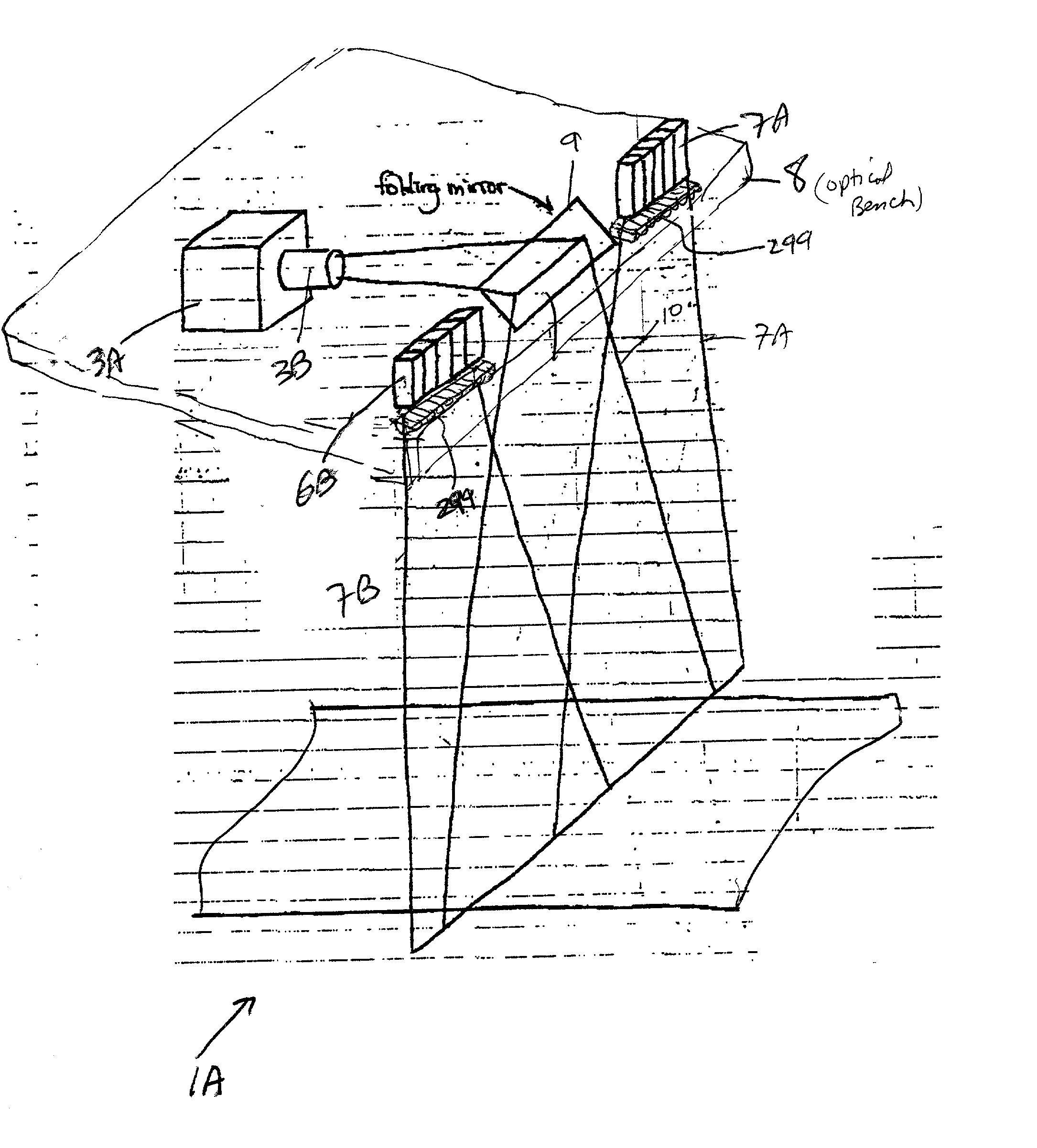
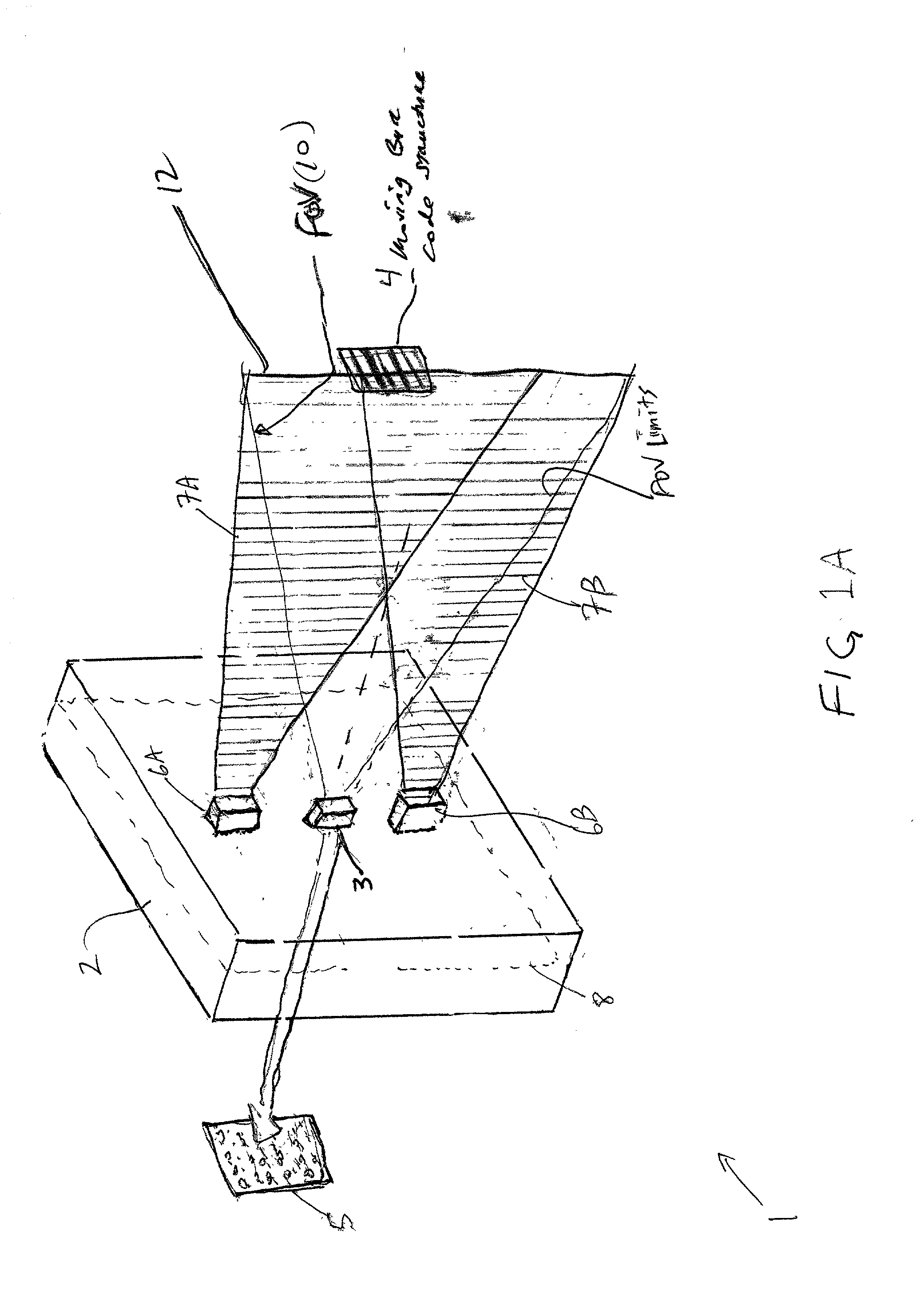
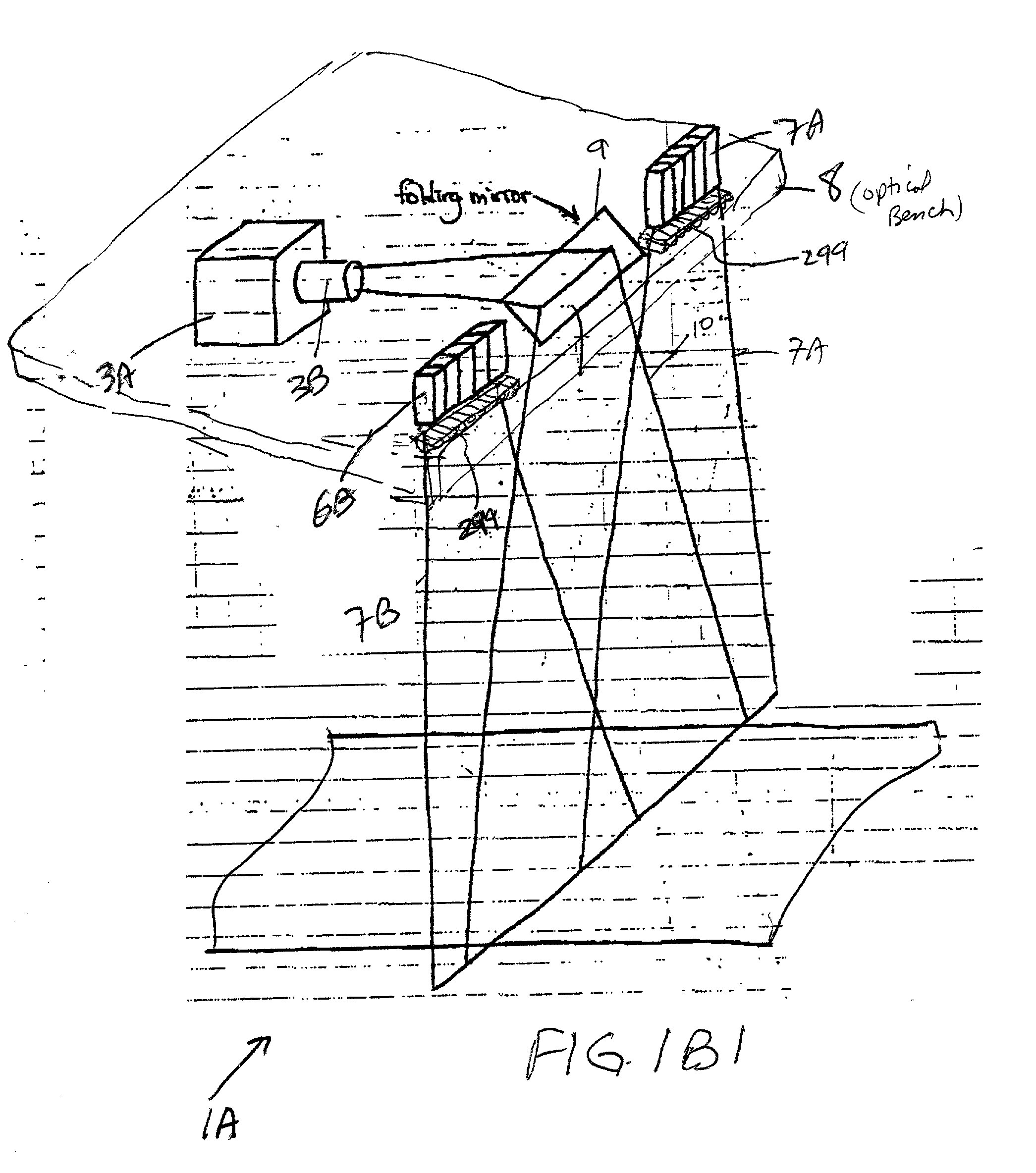
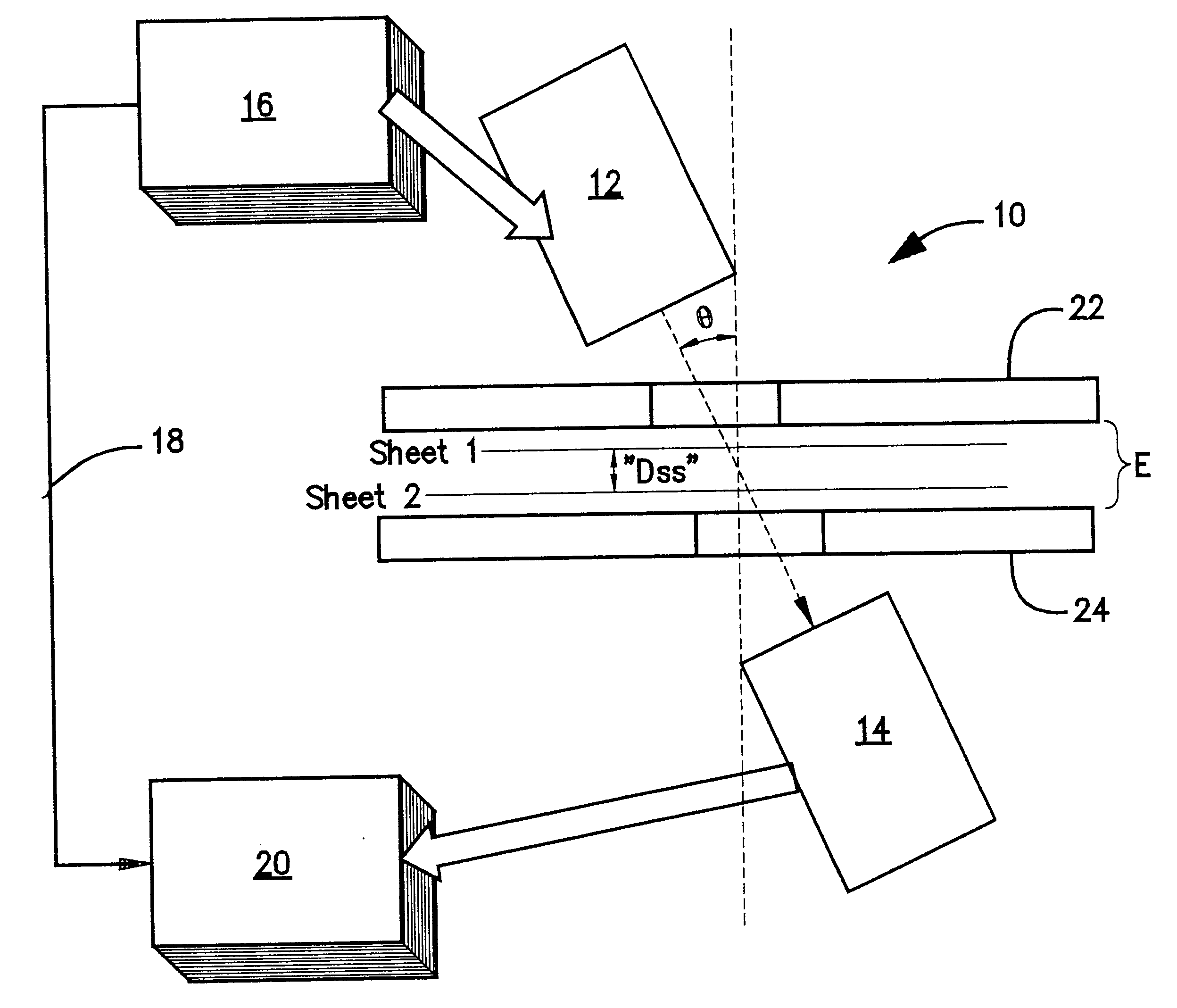
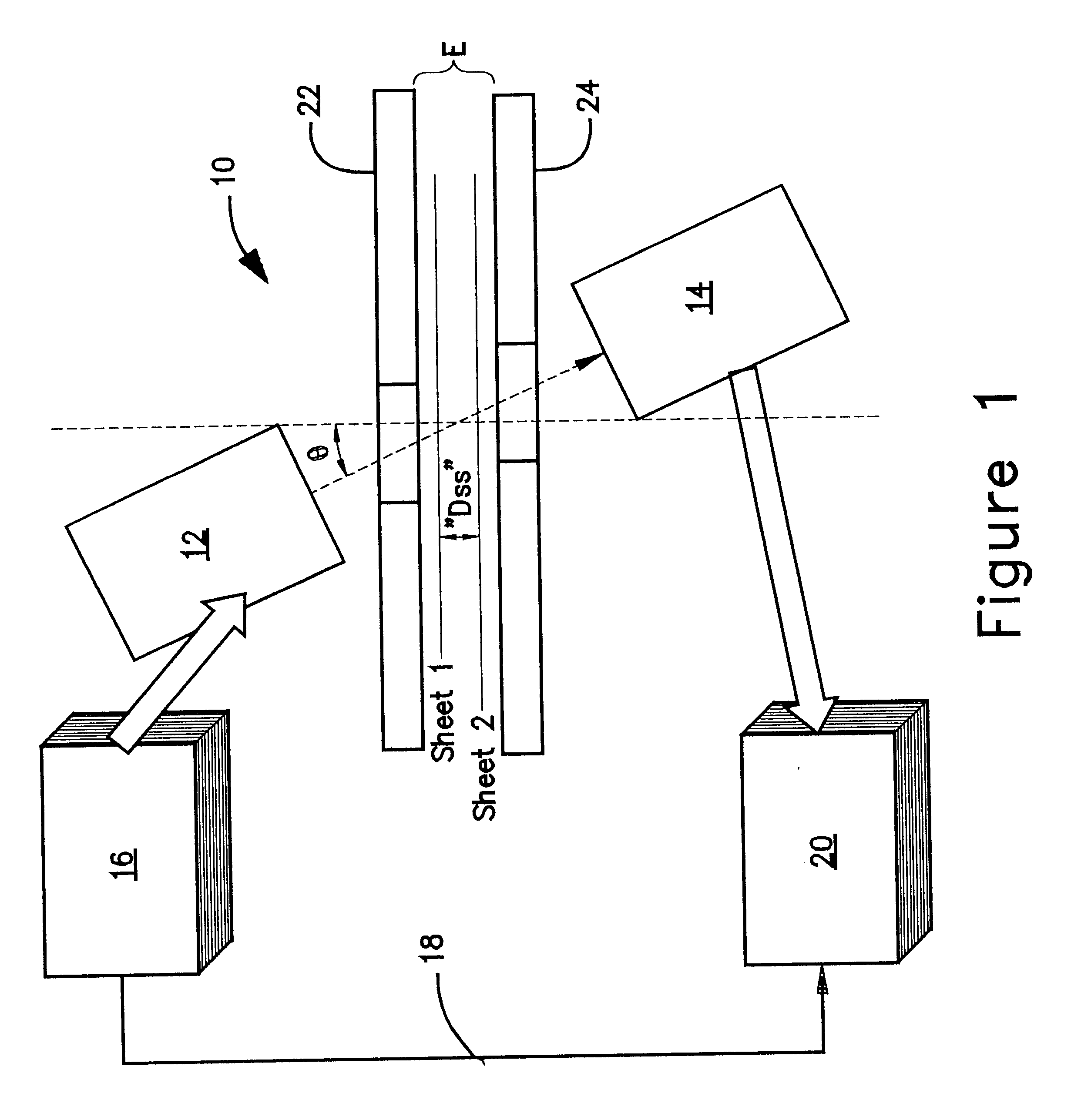
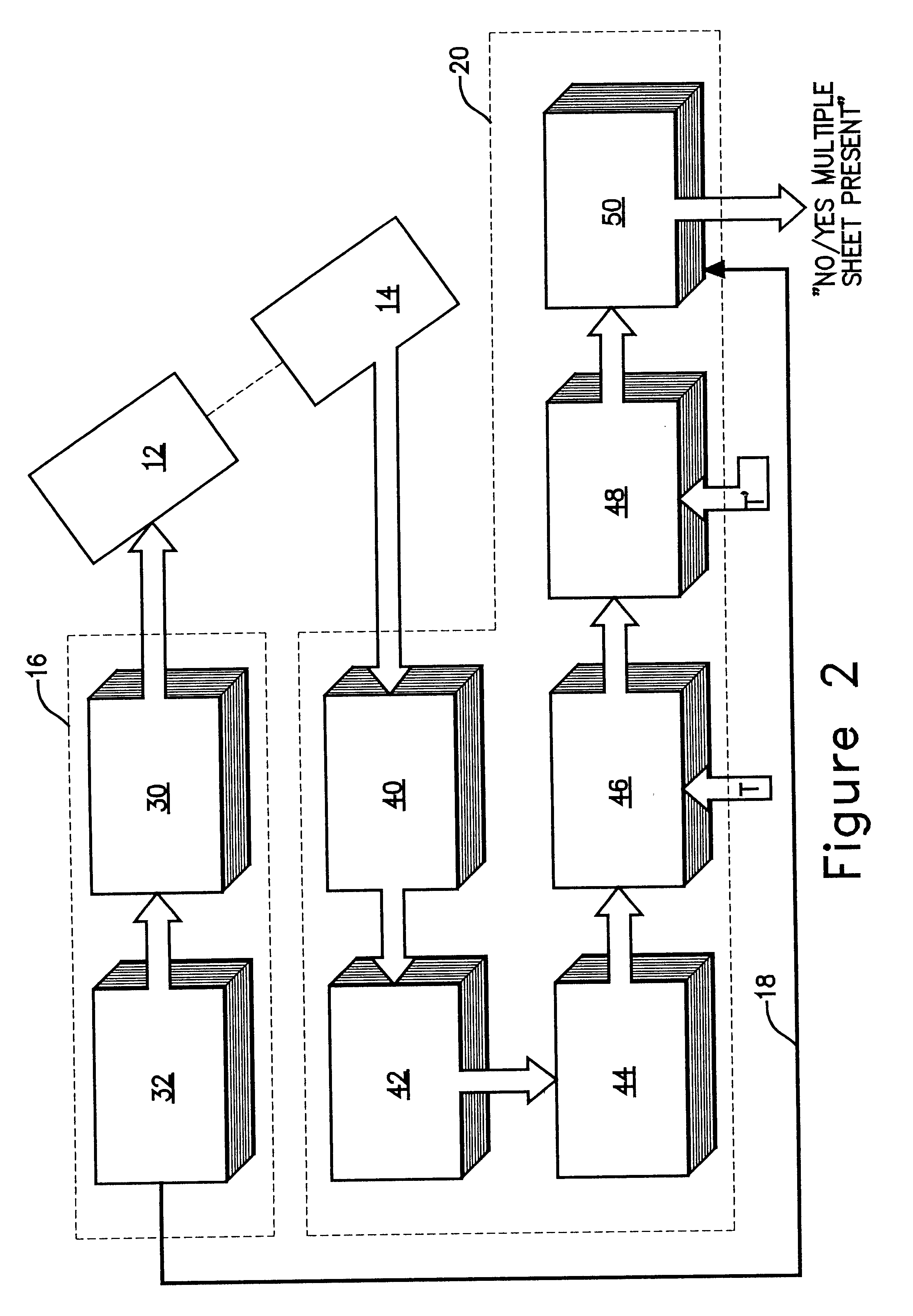
The presence of overlapped sheets on a paper transport is detected by employing such sheets as an acoustic interference filter. A beam of ultrasonic energy of appropriate frequency, angularly oriented to the planar transport path, will be attenuated to a much greater extent than the attenuation calculated based on the attenuation of a single sheet, as a result of destructive combining of wavefronts reflected from the facing surfaces of the overlapped sheets.
Owner:PATRIARCH PARTNERS AGENCY SERVICES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com