Patents
Literature
339 results about "Optical correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Method for determining and correcting vision
InactiveUS20050124983A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove visual effectsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
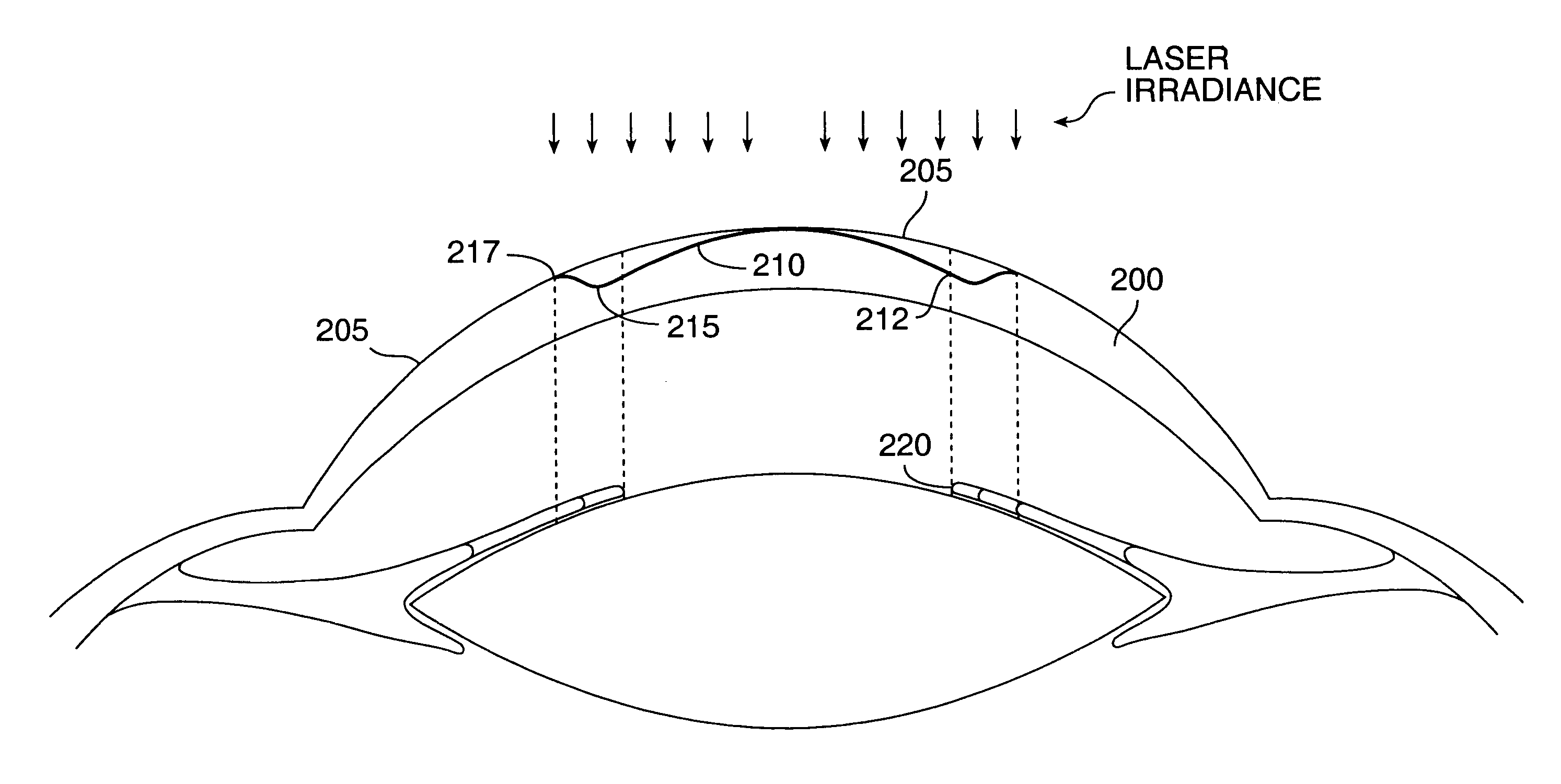
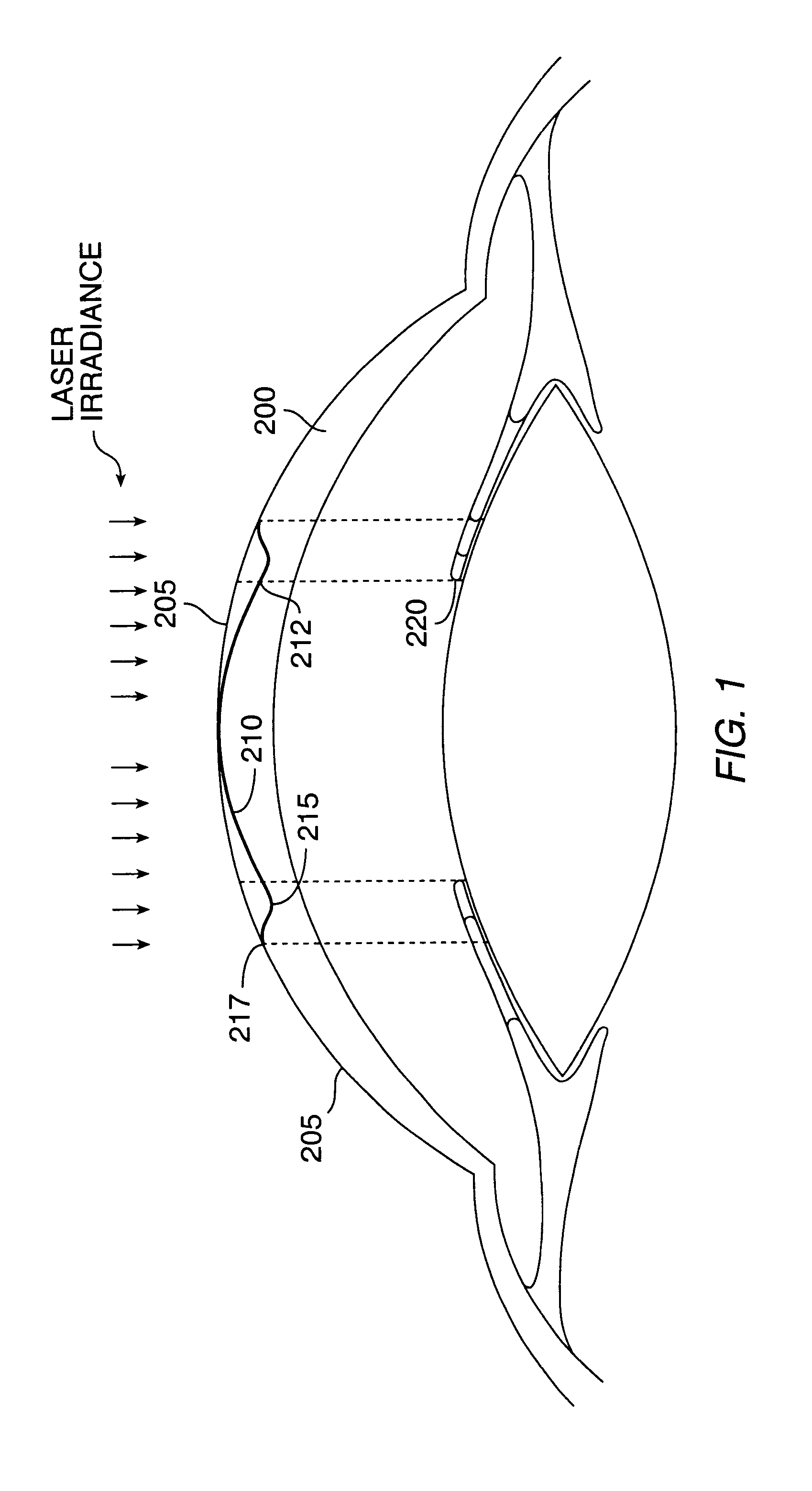
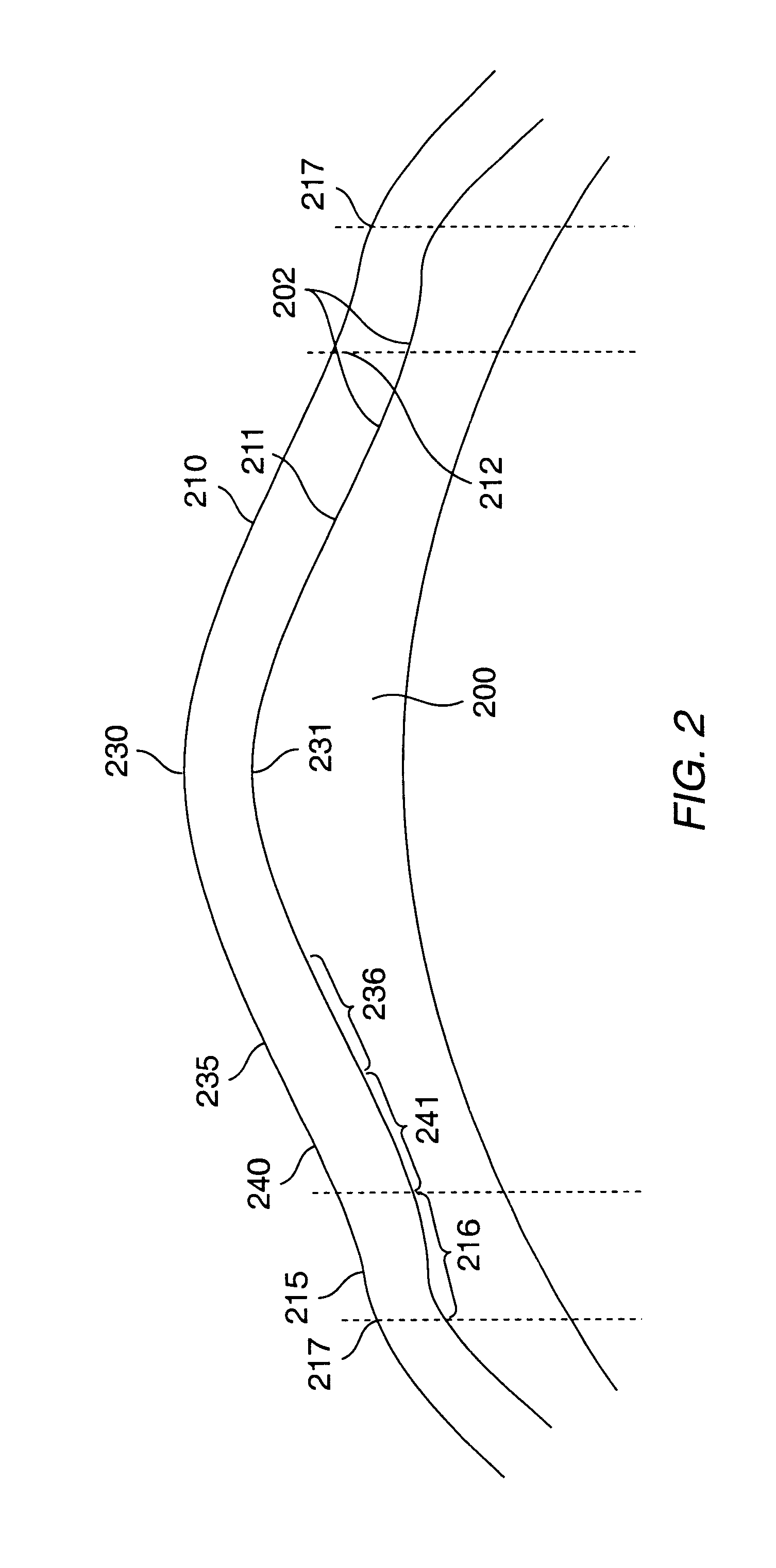
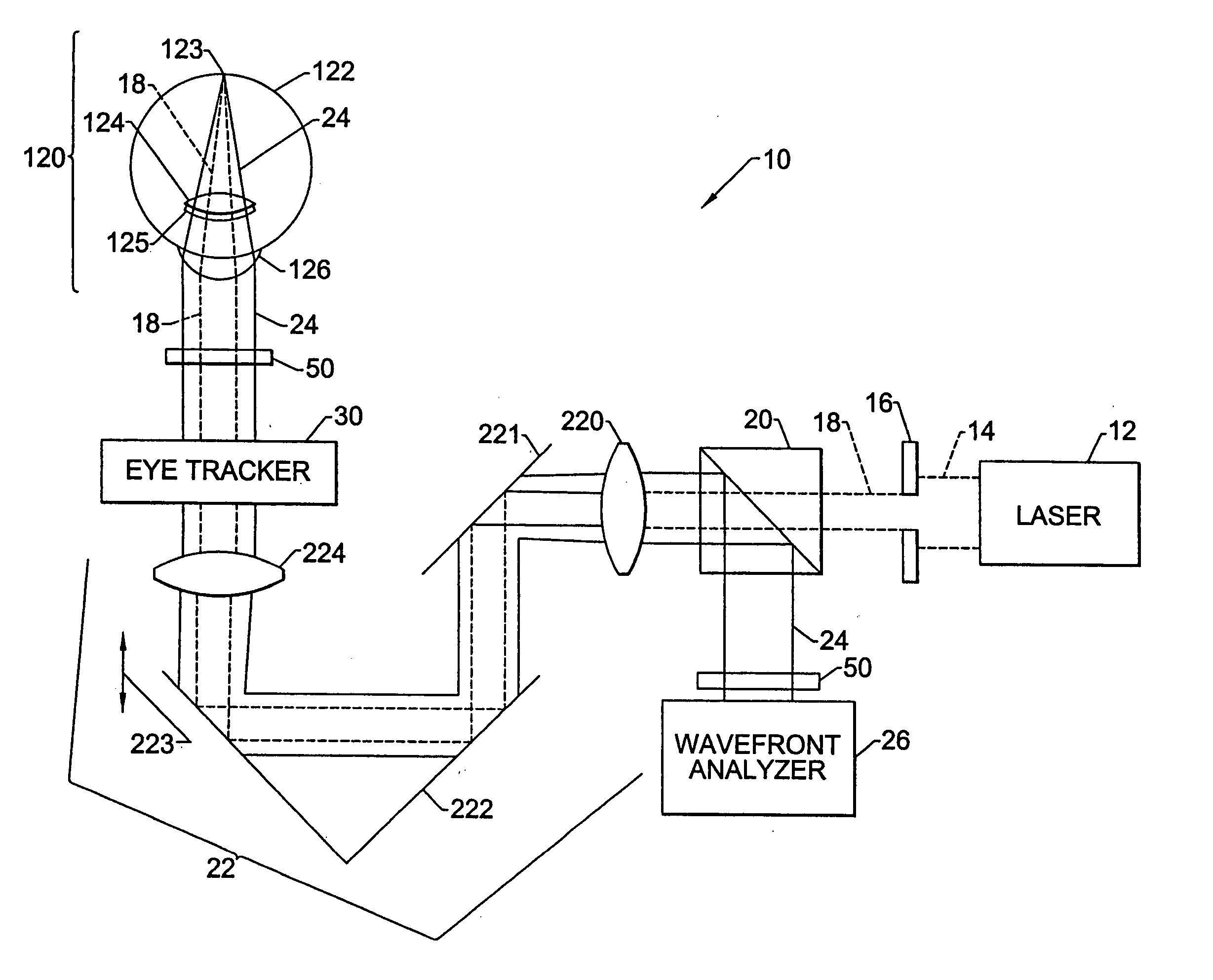
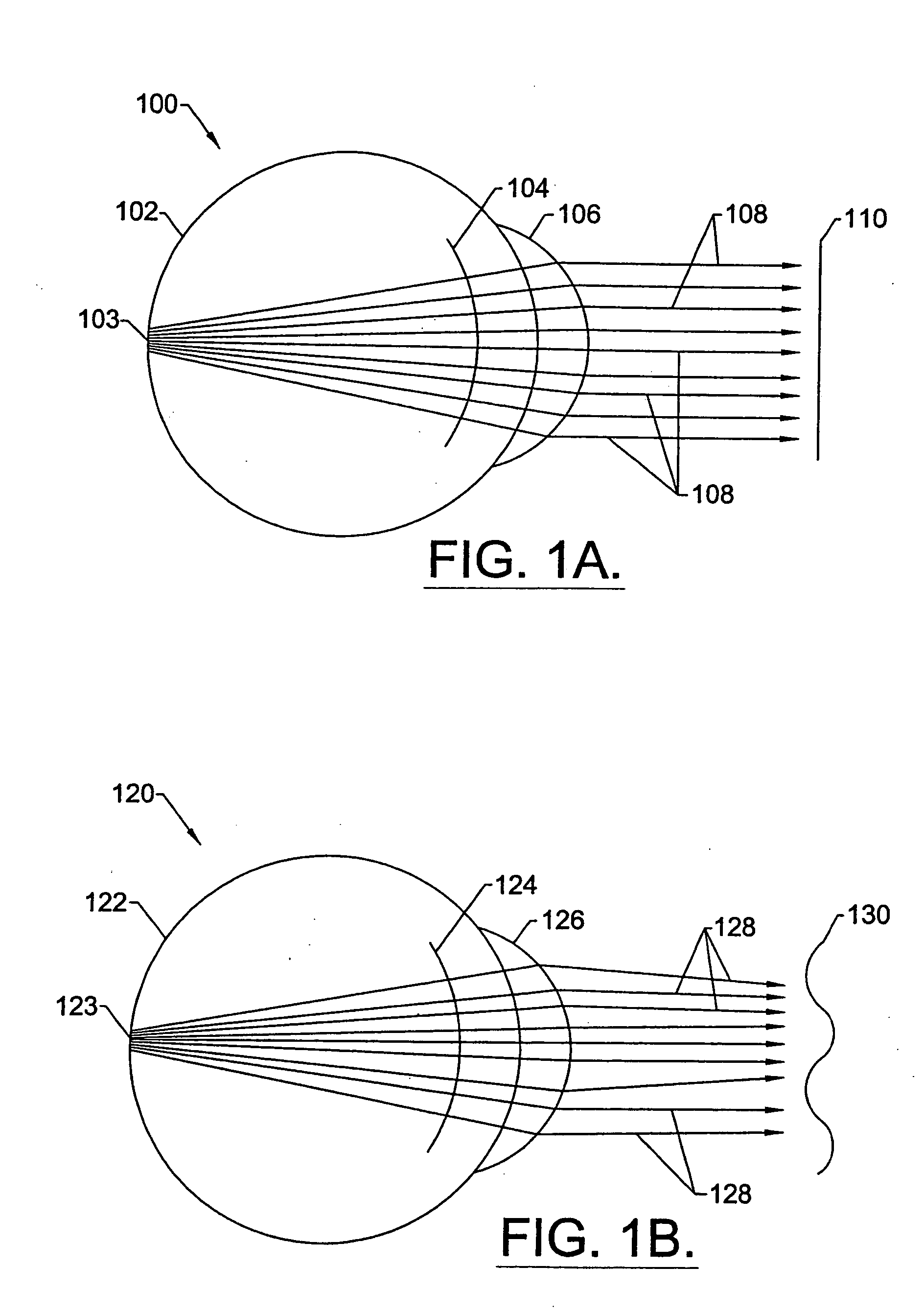
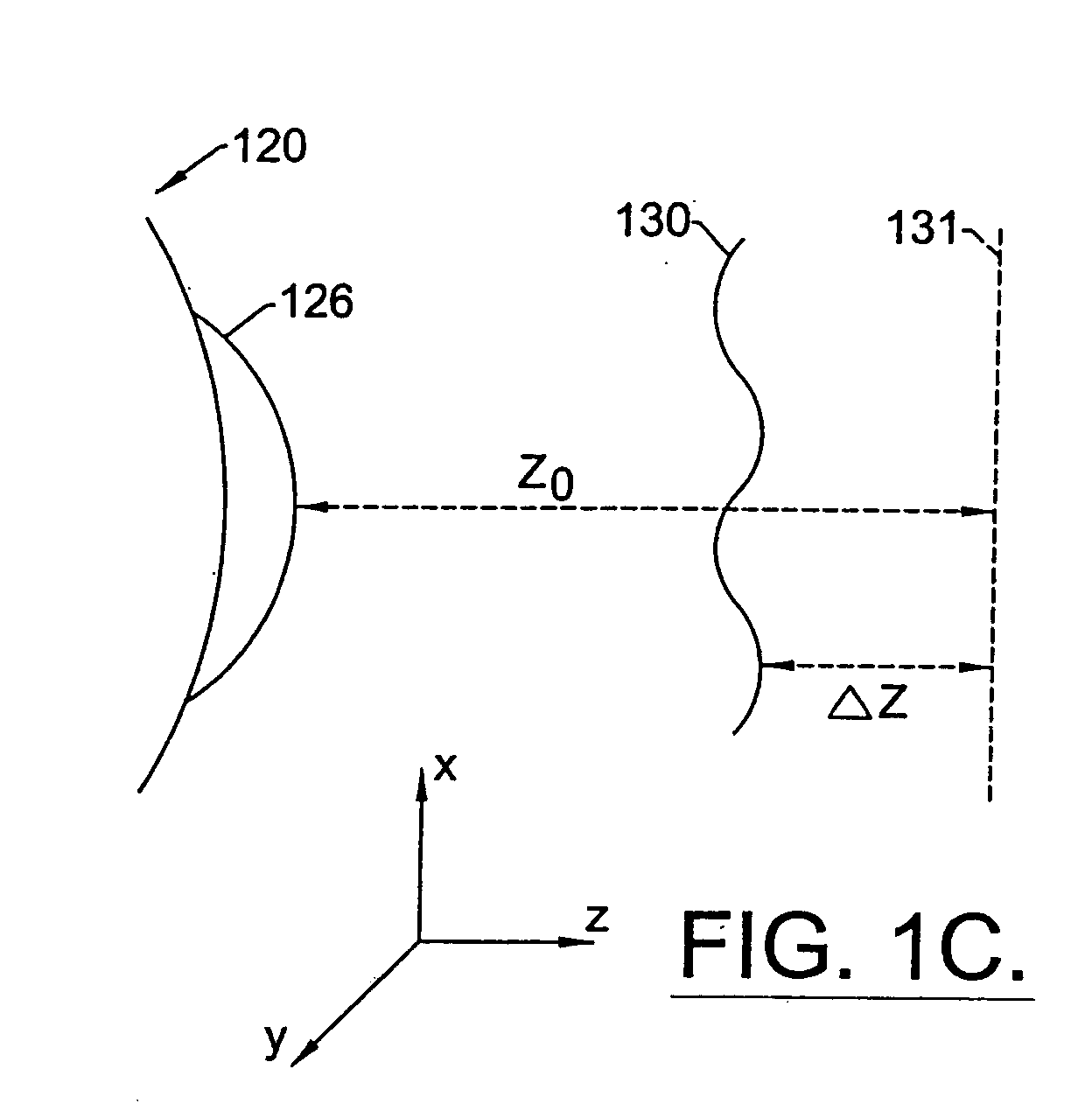
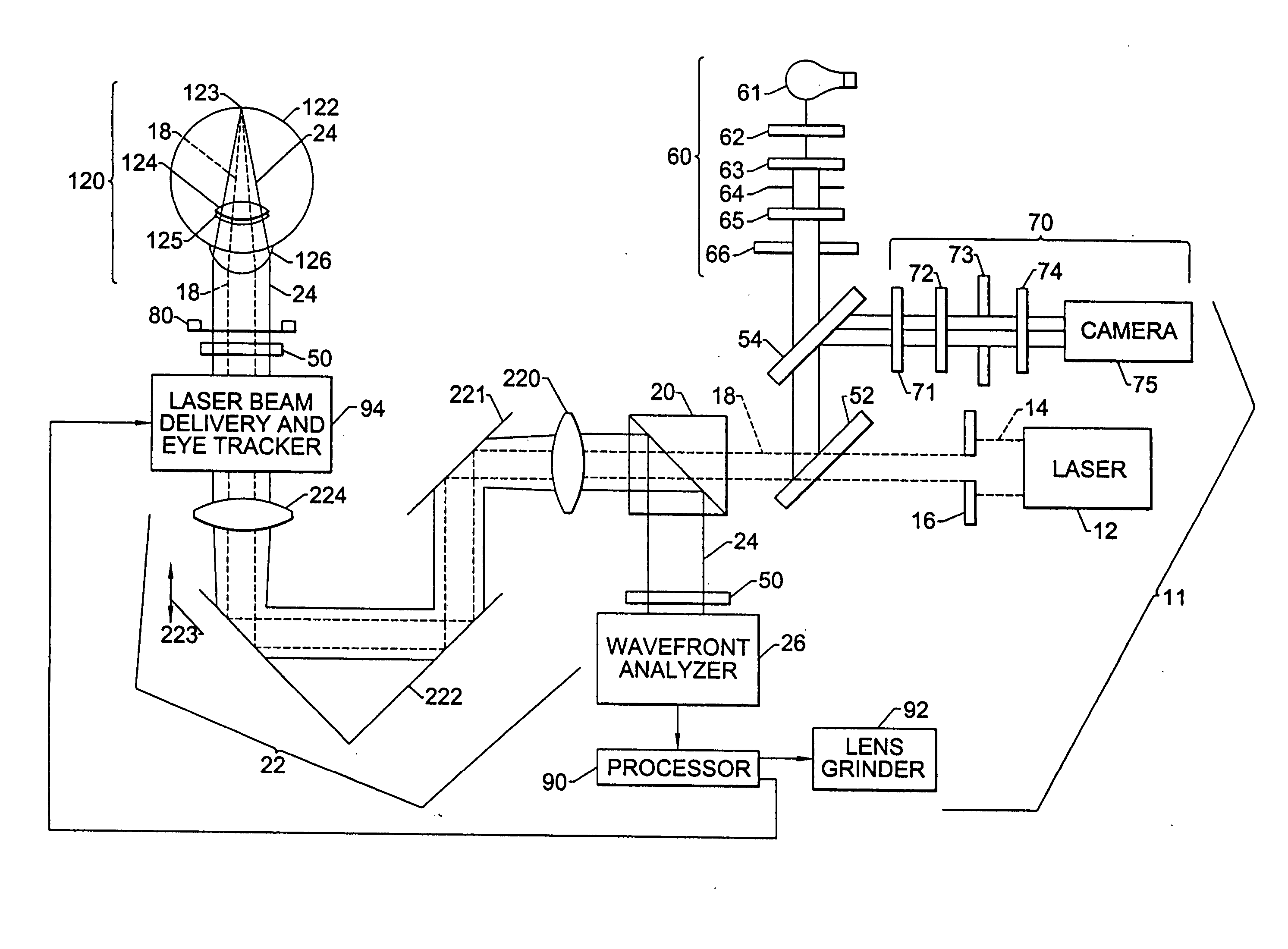
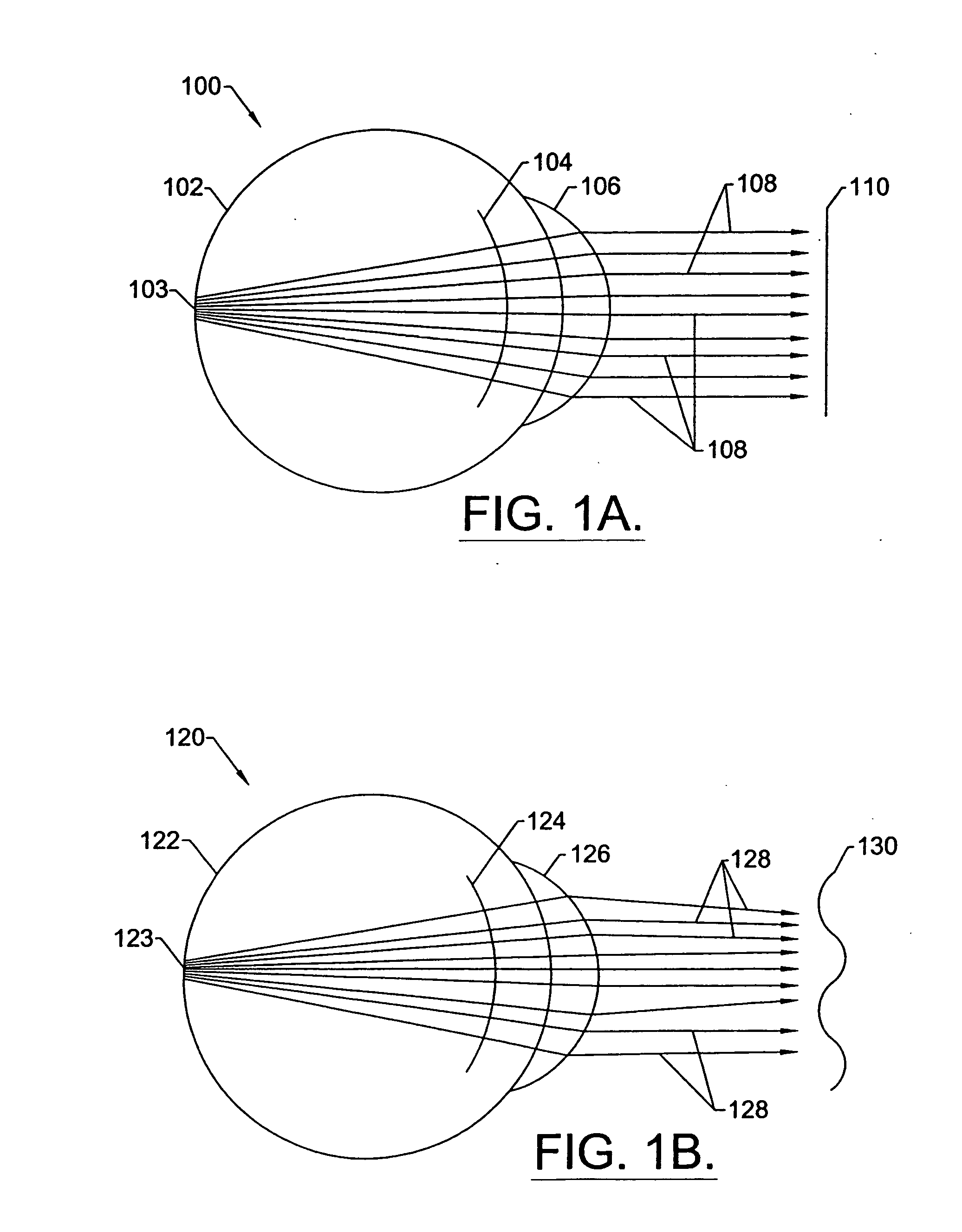
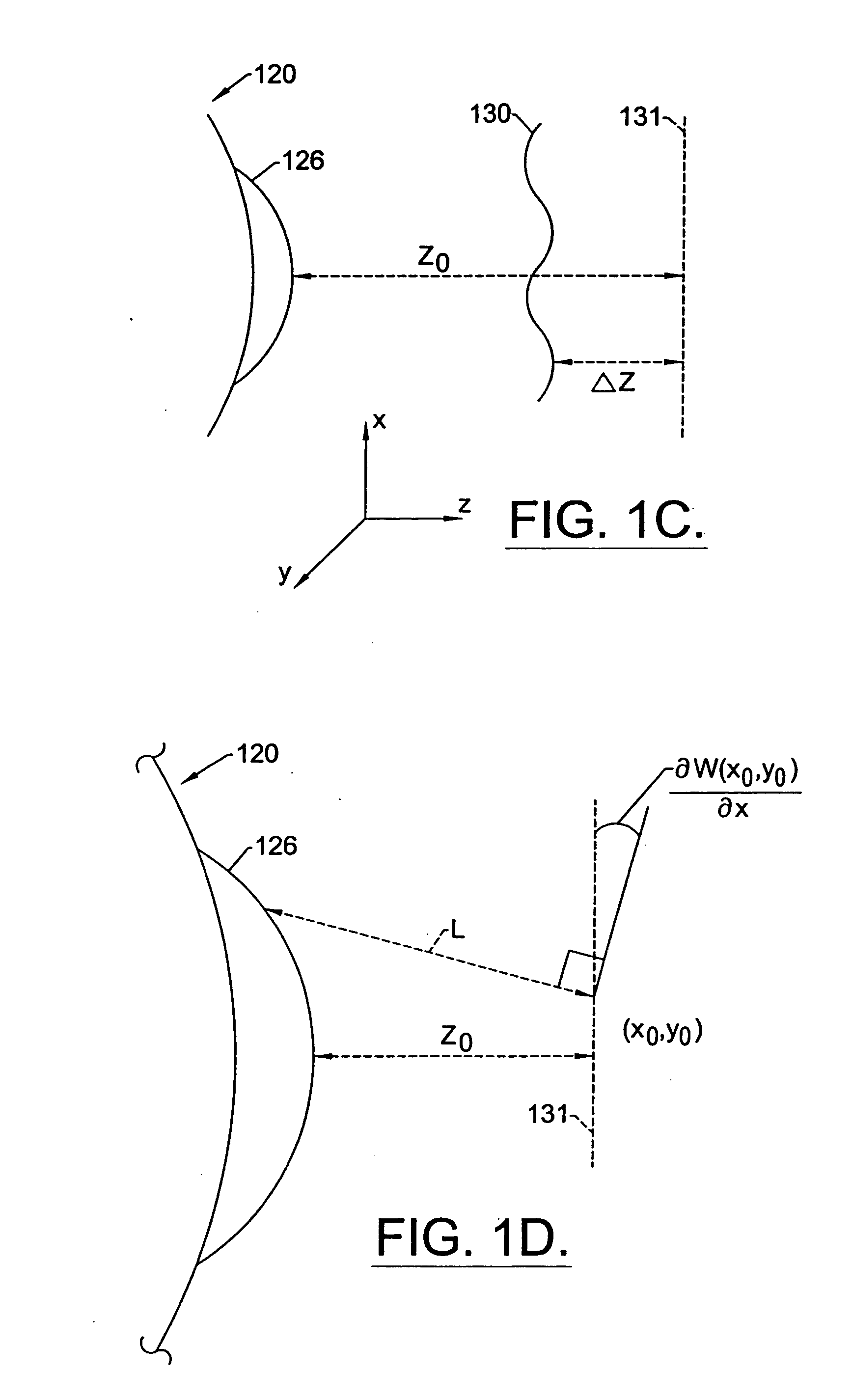
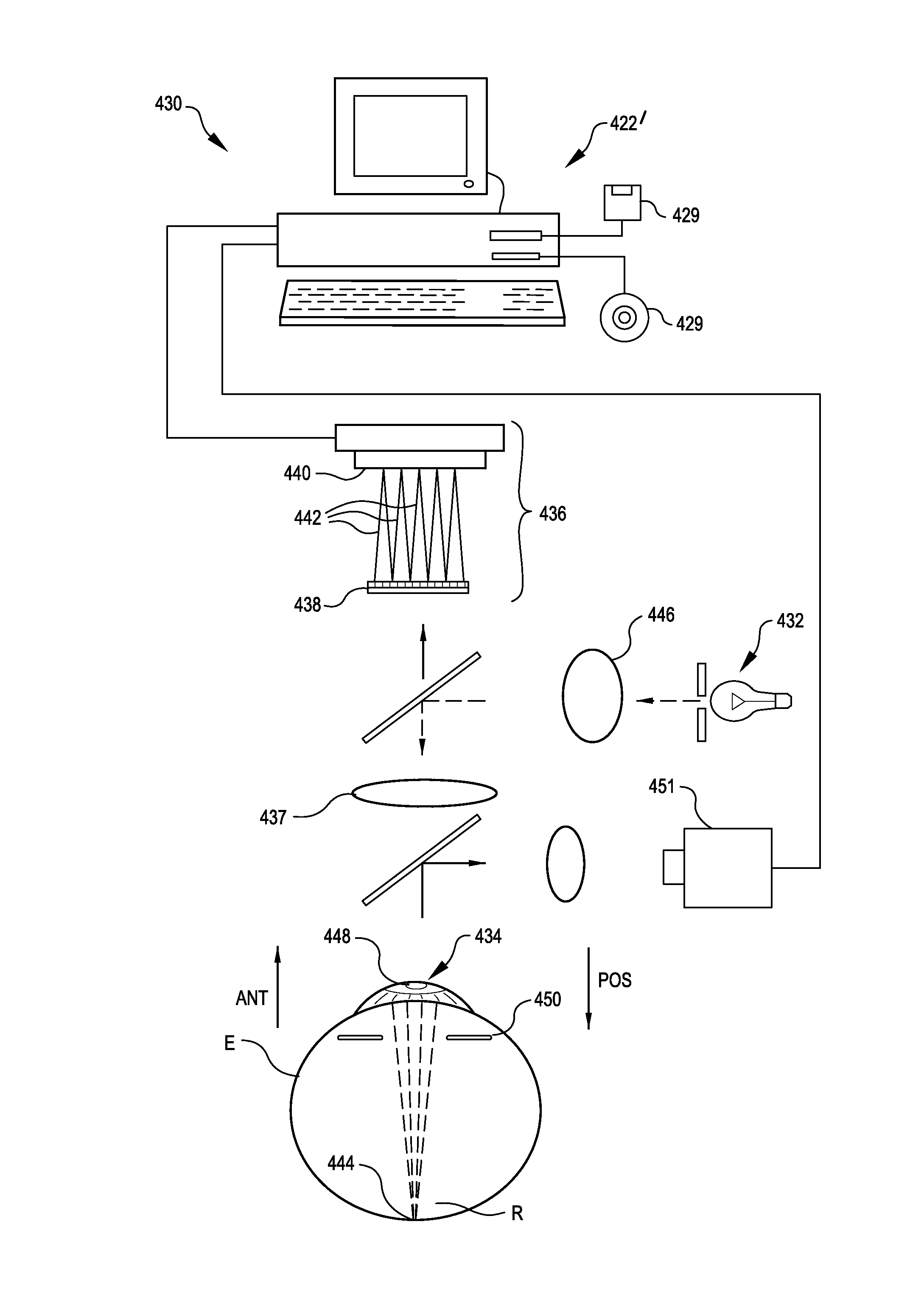
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
InactiveUS6891596B2Large numerical apertureGuaranteed true stateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistBeam diameter
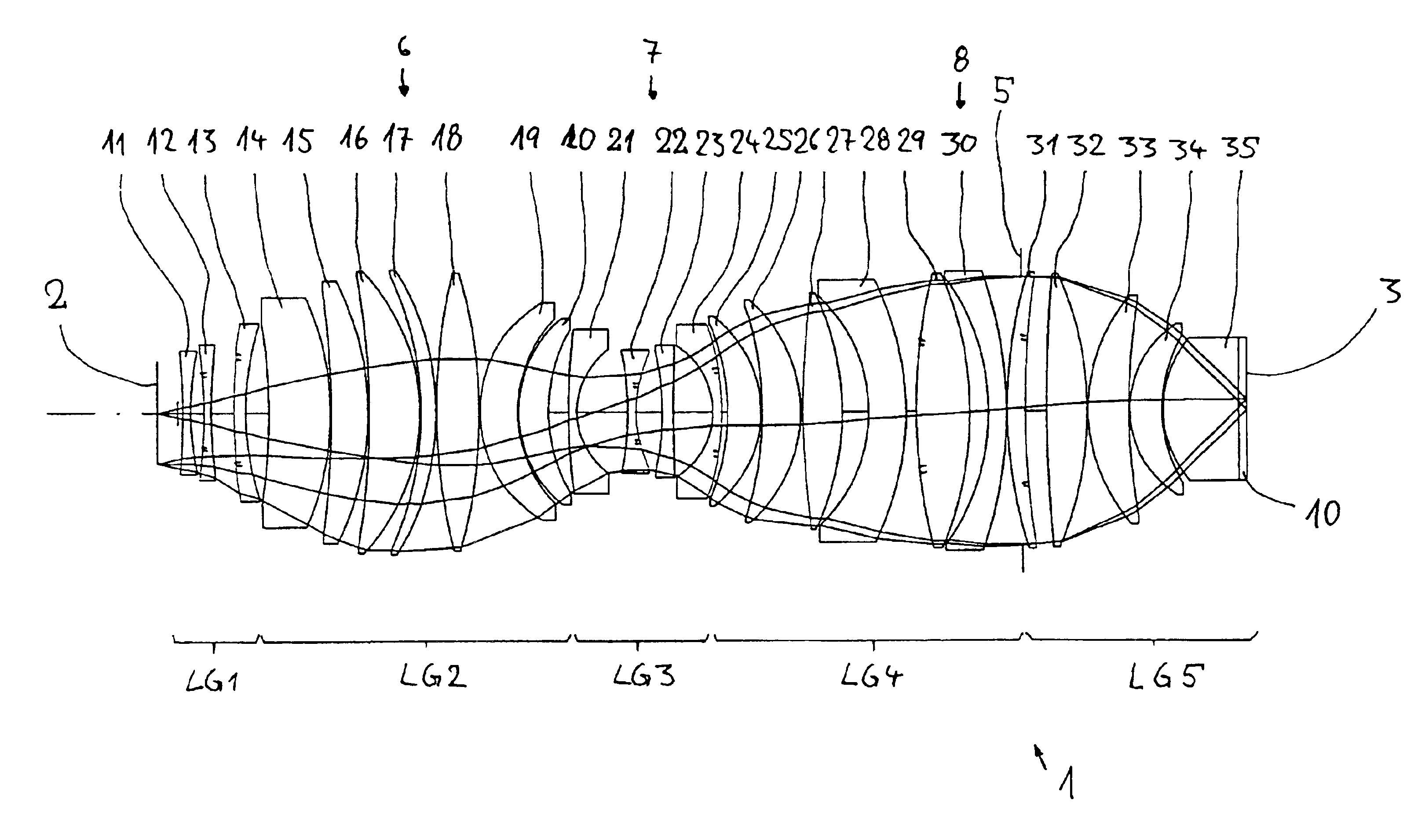
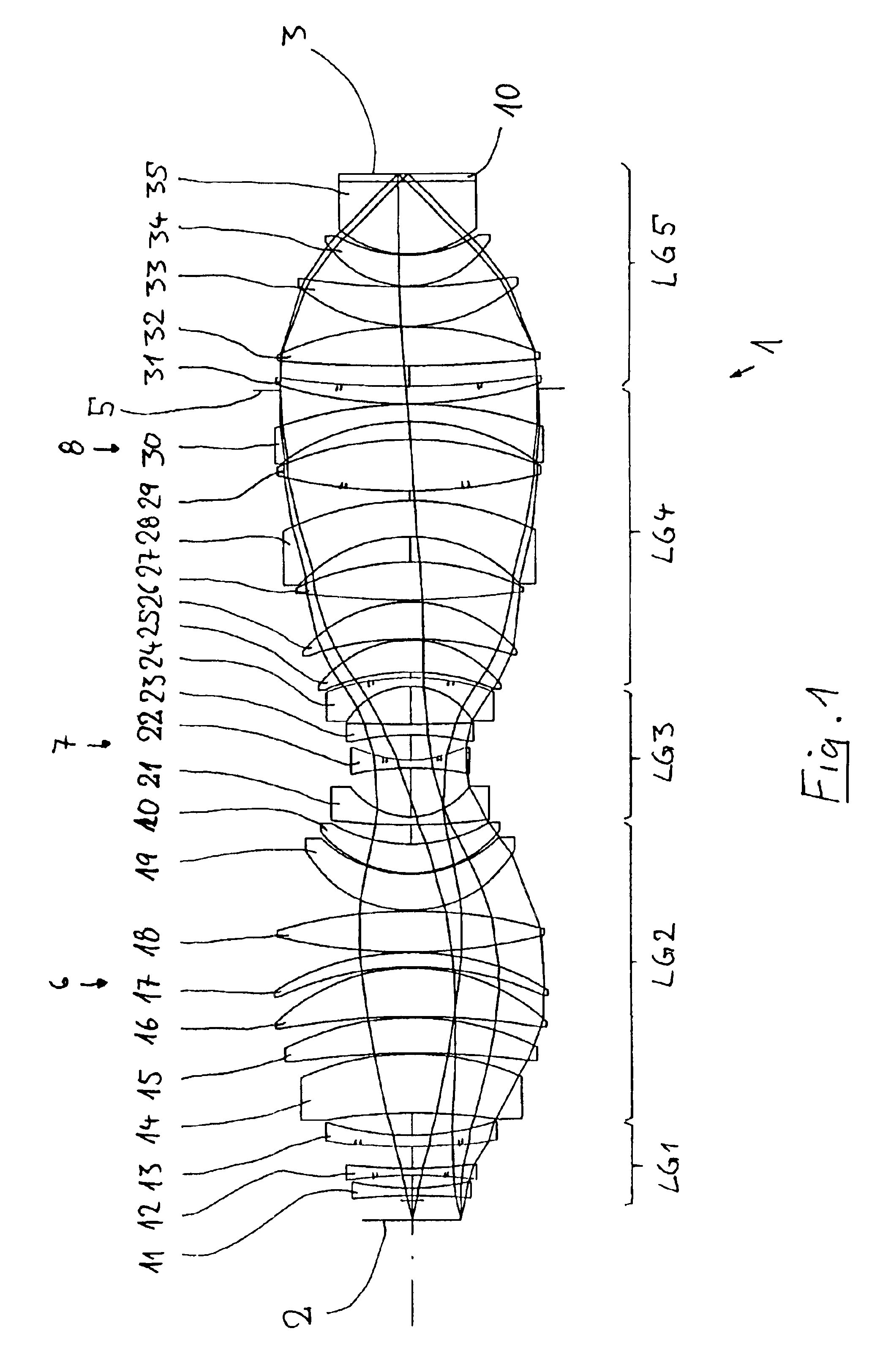
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion micro-lithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with a negative refracting power, a second lens group with a positive refracting power, a third lens group with a negative refracting power, a fourth lens group with a positive refracting power and a fifth lens group with a positive refracting power are provided. The system aperture is in the region of maximum beam diameter between the fourth and the fifth lens group. Embodiments of projection objectives according to the invention achieve a very high numerical aperture of NA>1 in conjunction with a large image field, and are distinguished by a good optical correction state and moderate overall size. Pattern widths substantially below 100 nm can be resolved when immersion fluids are used between the projection objective and substrate in the case of operating wavelengths below 200 nm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
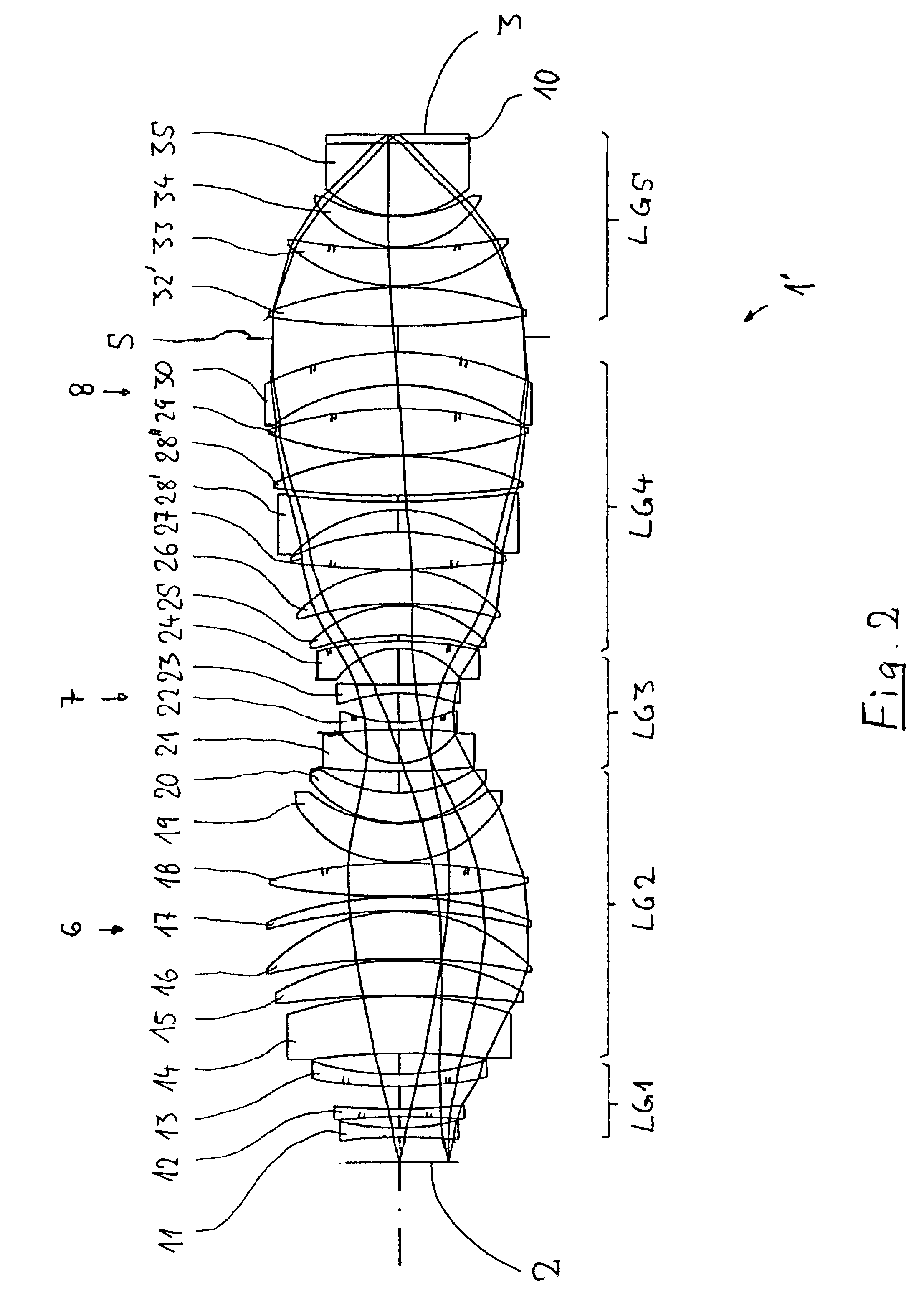
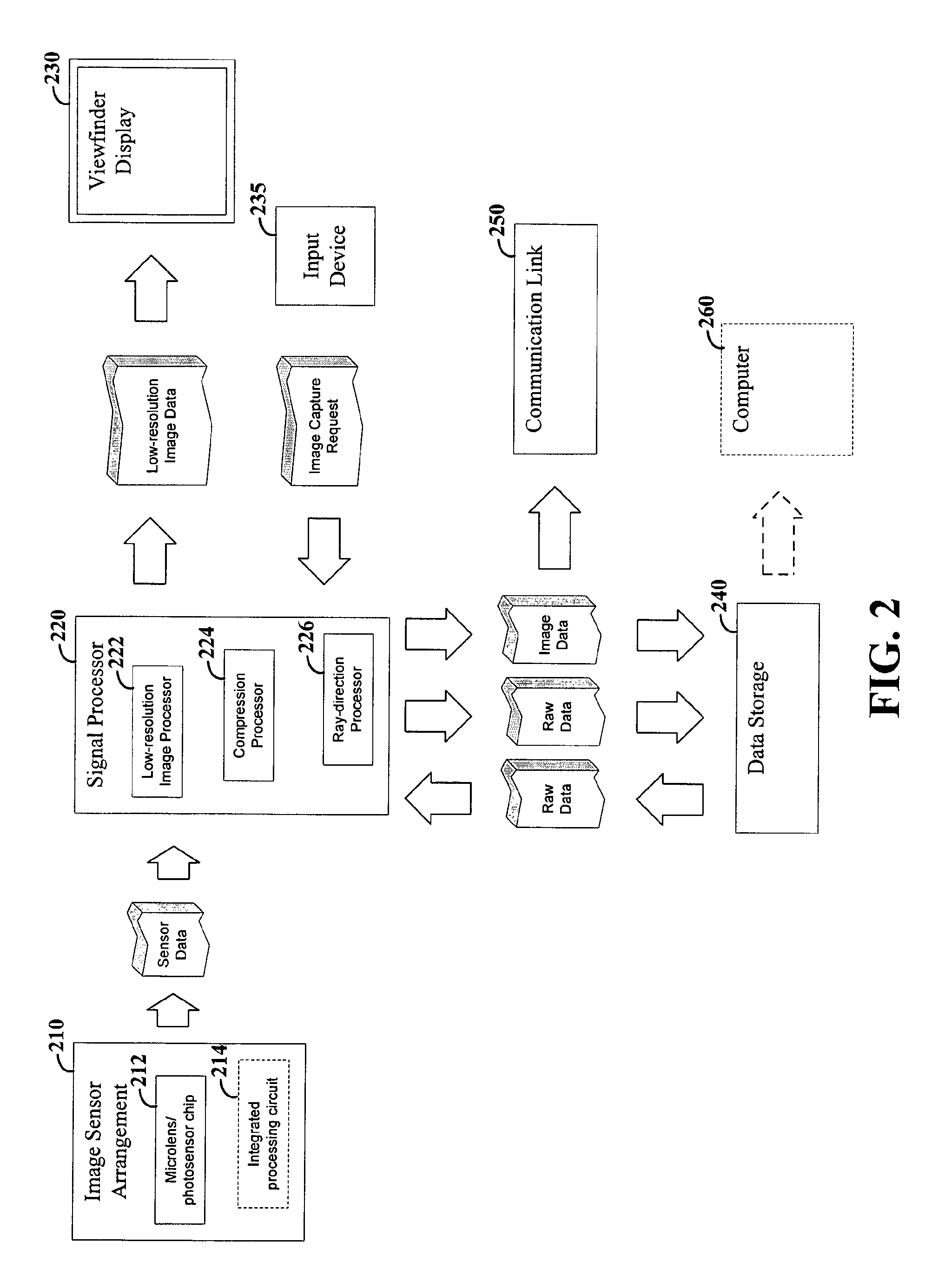
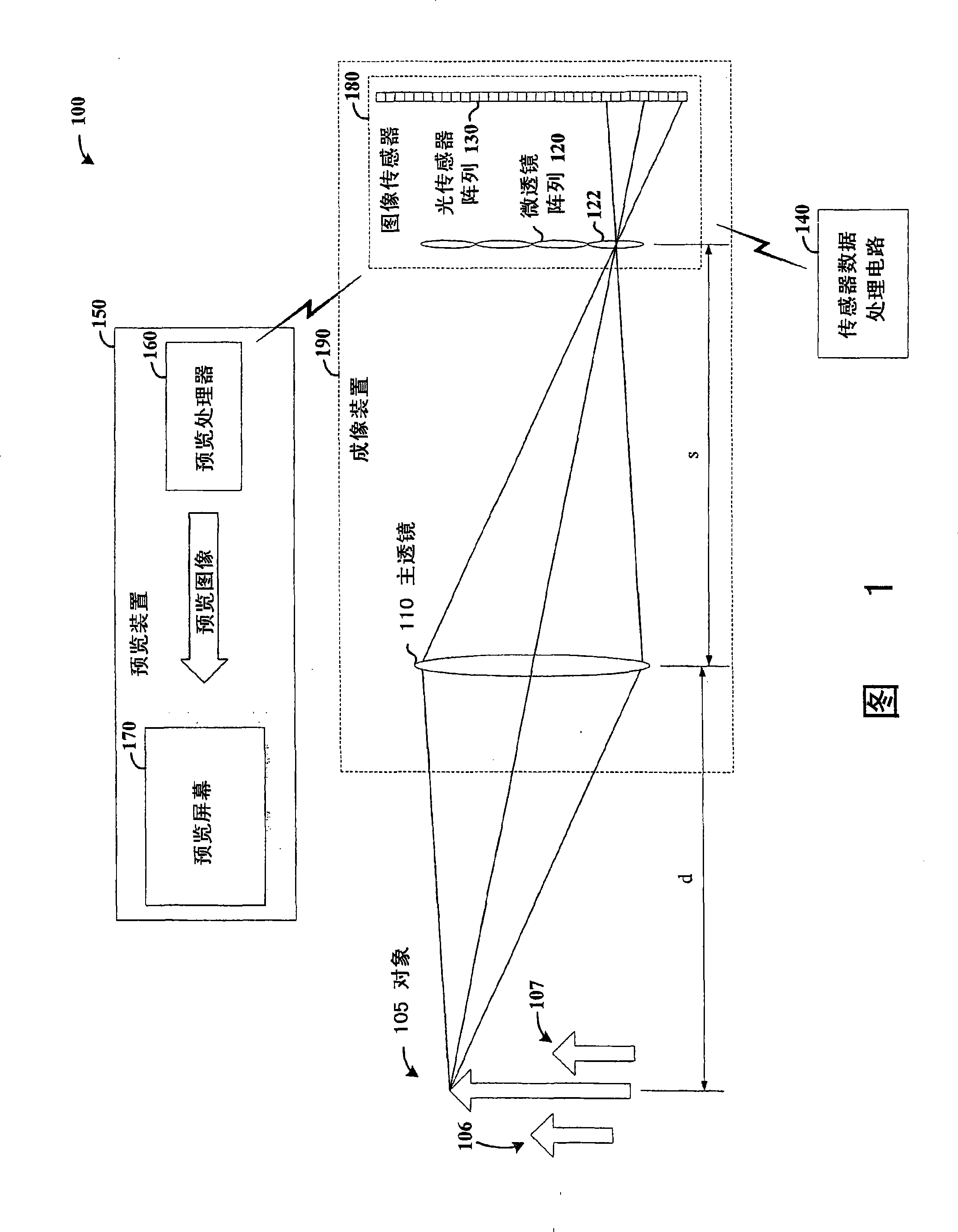
Imaging arrangements and methods therefor
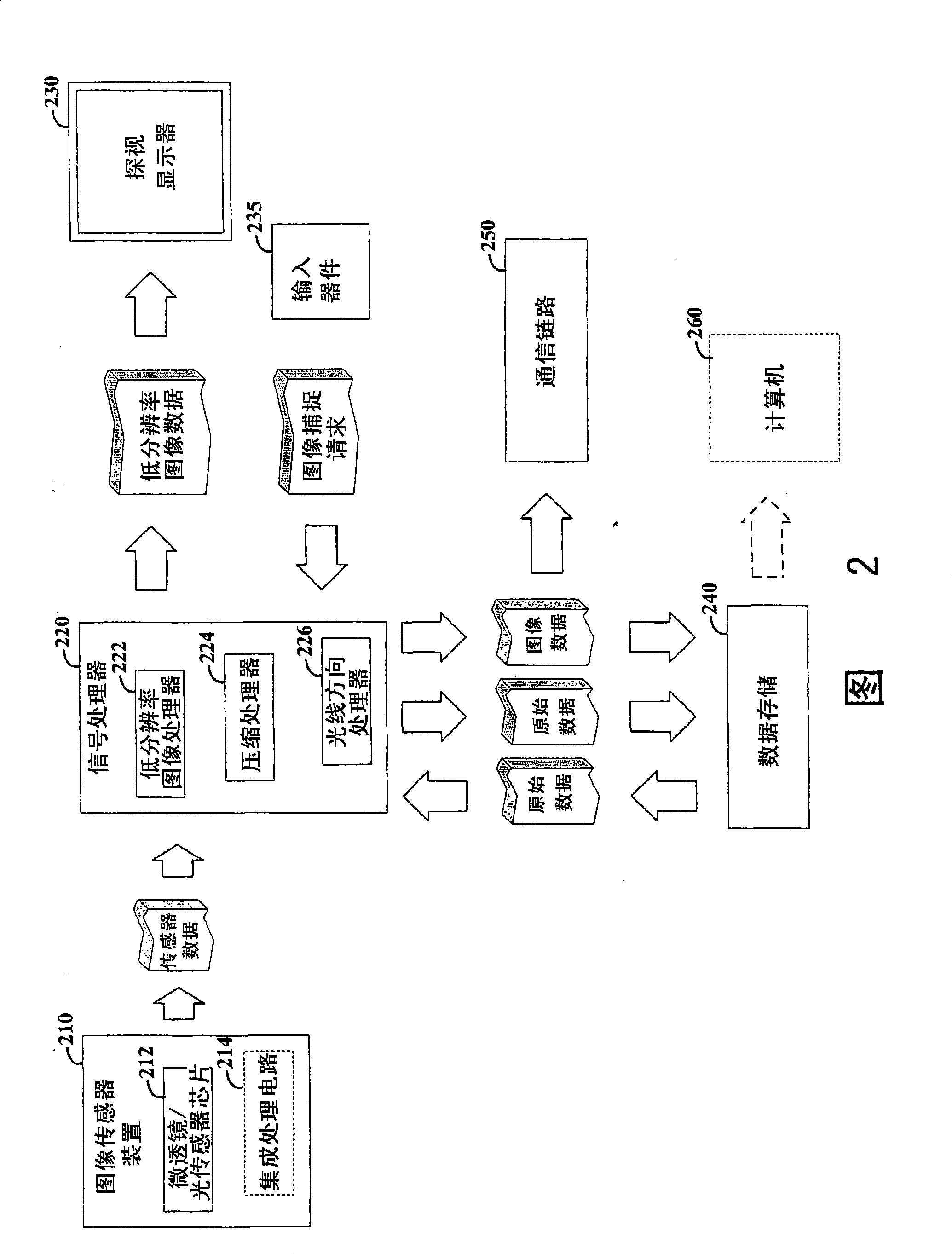
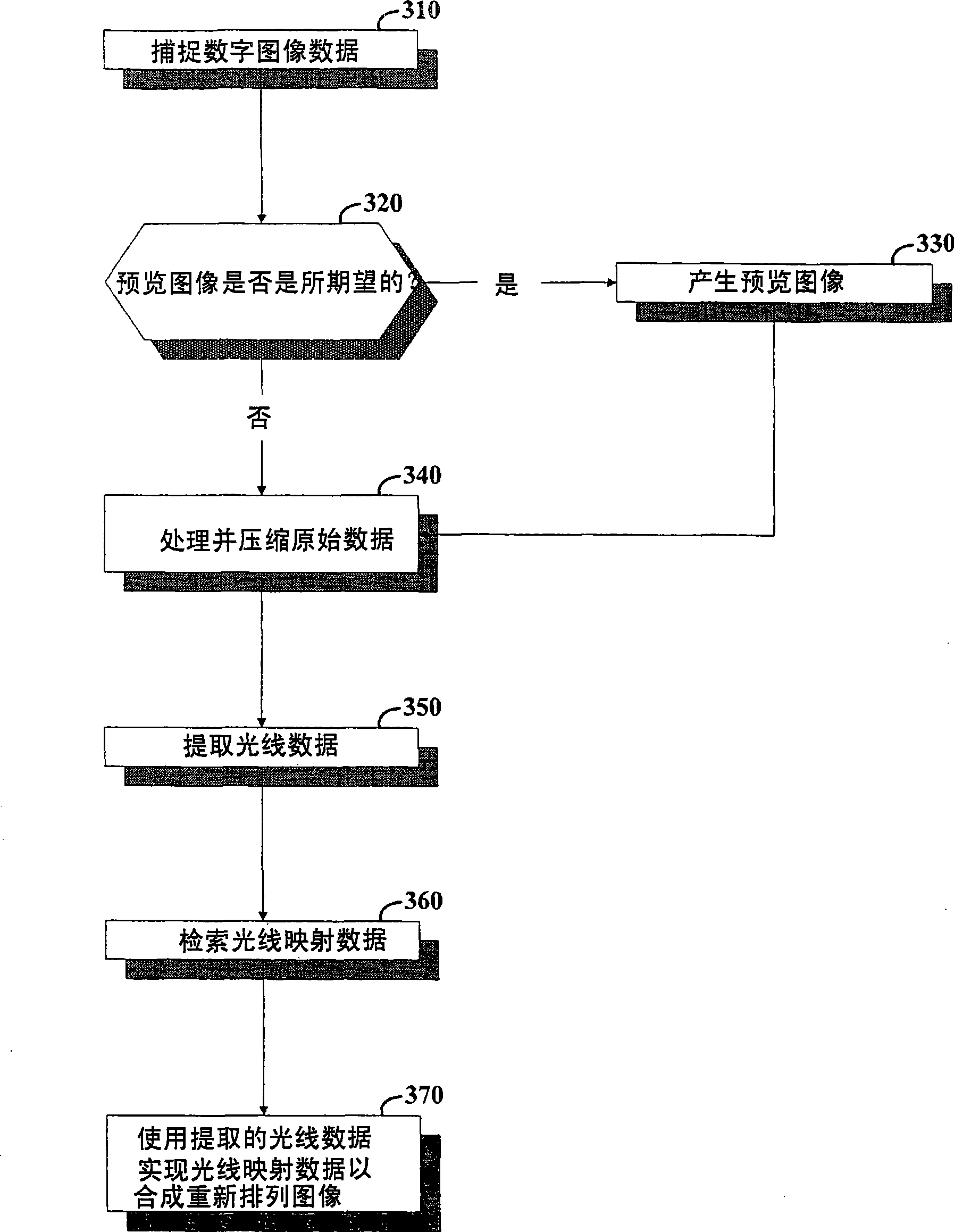
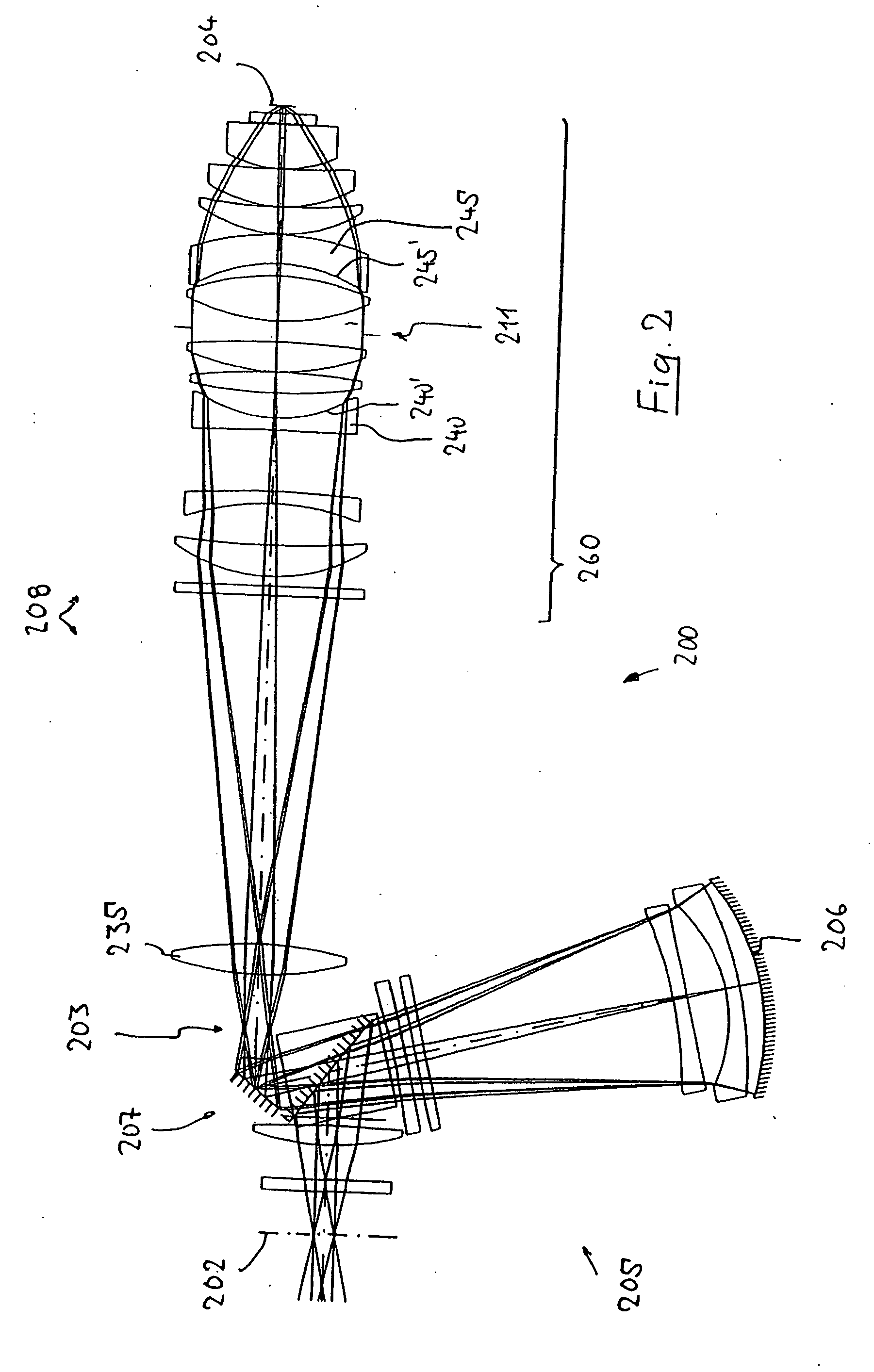
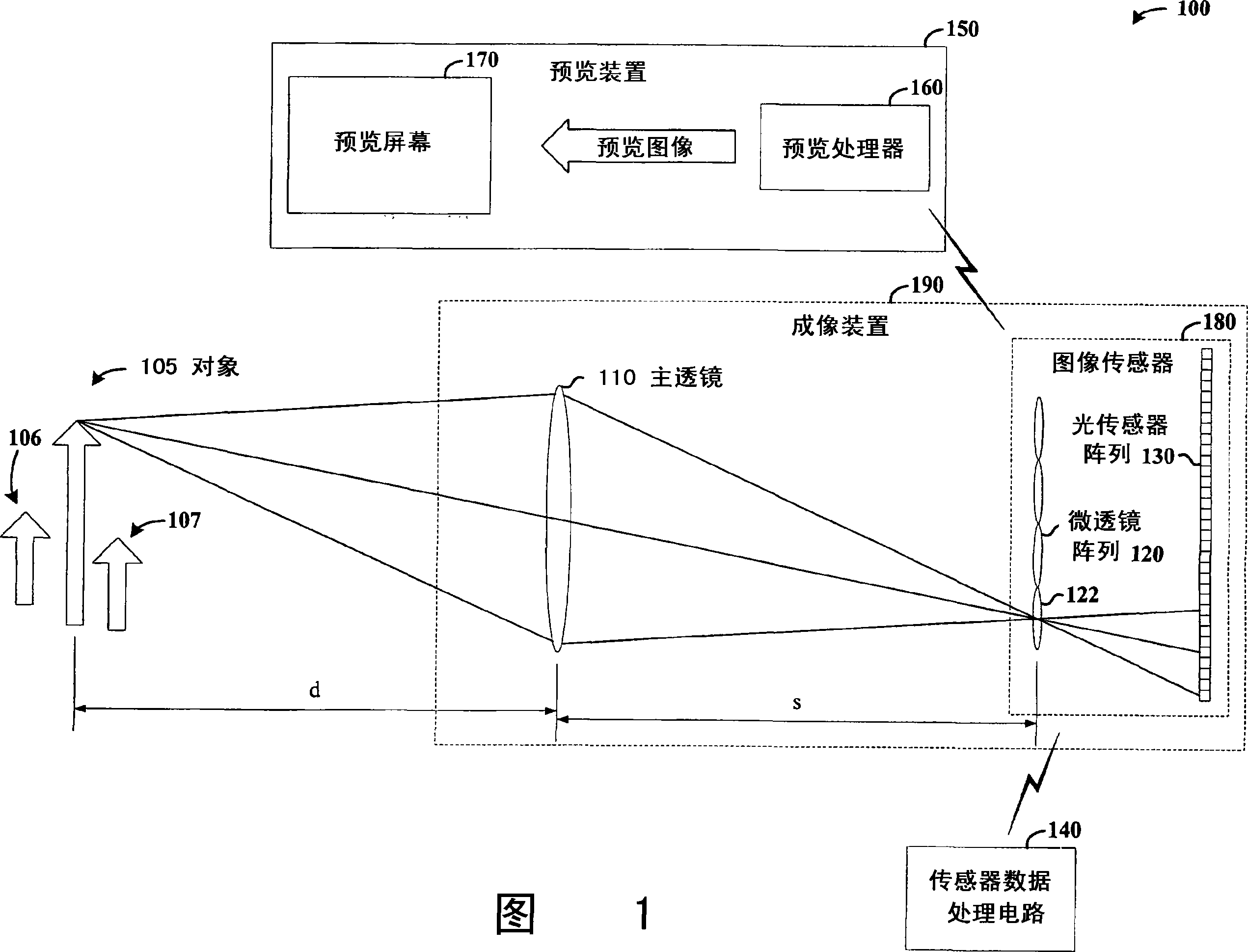
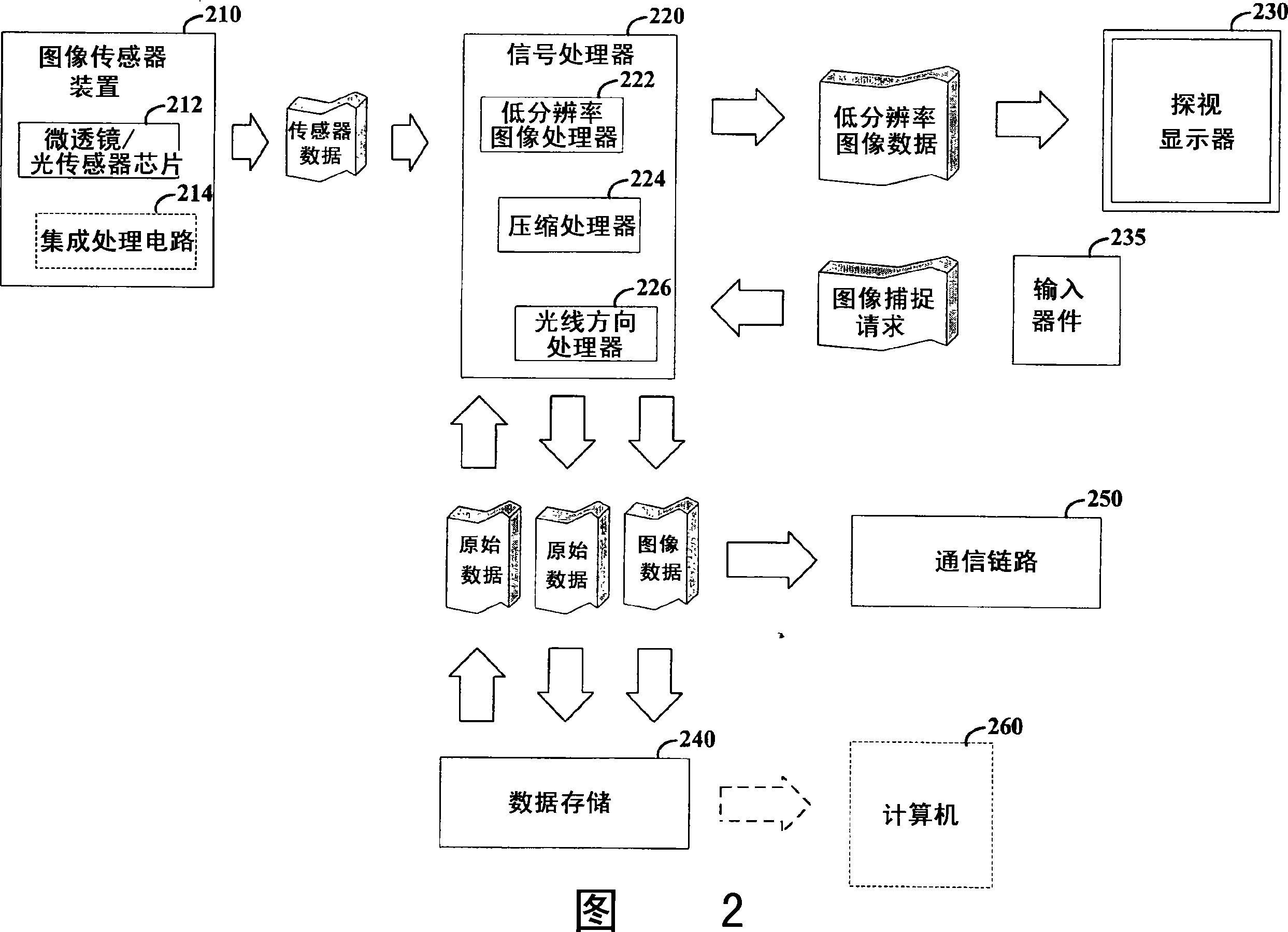
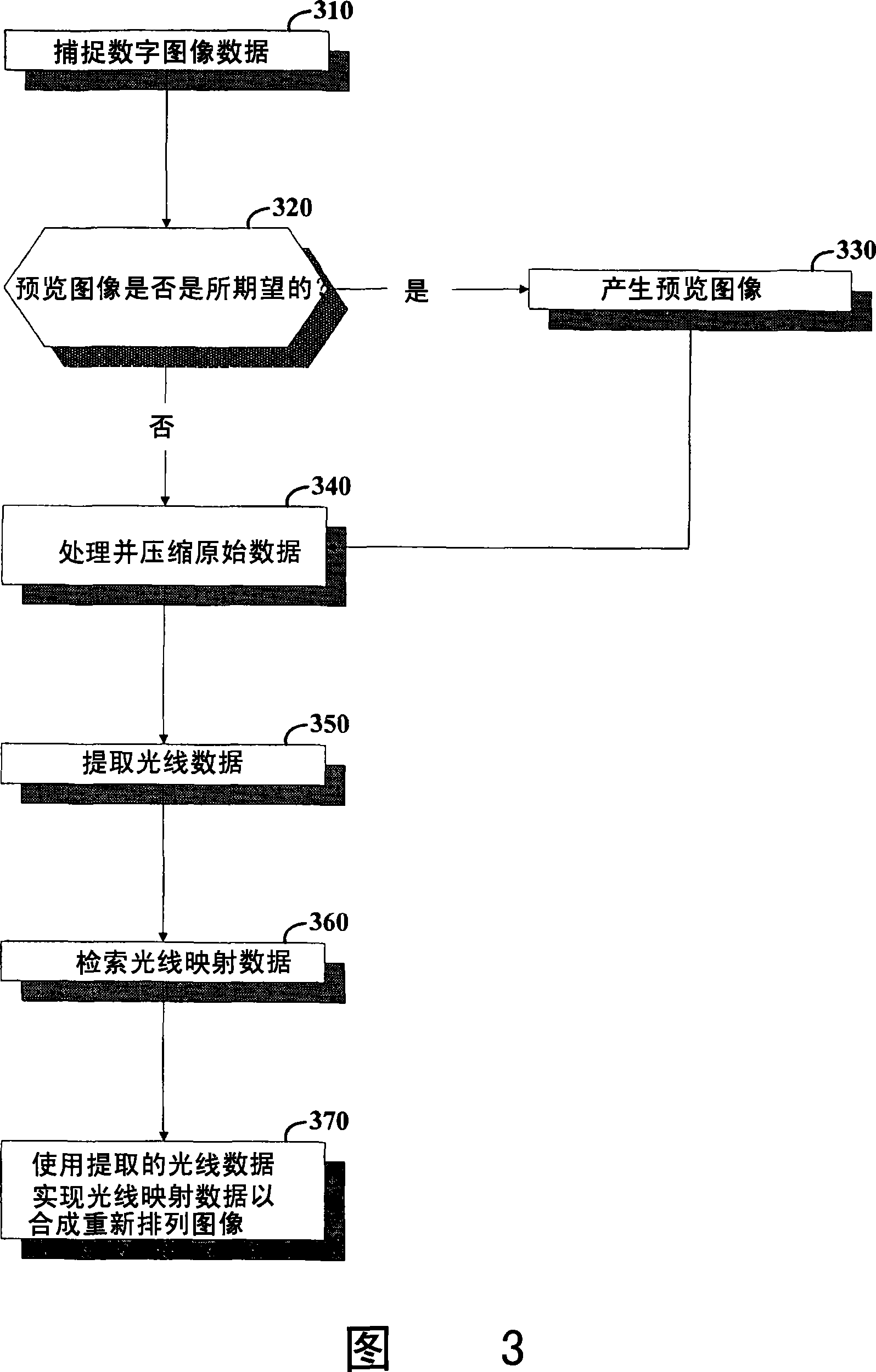
Image data is processed to facilitate focusing and / or optical correction. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, an imaging arrangement collects light data corresponding to light passing through a particular focal plane. The light data is collected using an approach that facilitates the determination of the direction from which various portions of the light incident upon a portion of the focal plane emanate from. Using this directional information in connection with value of the light as detected by photosensors, an image represented by the light is selectively focused and / or corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
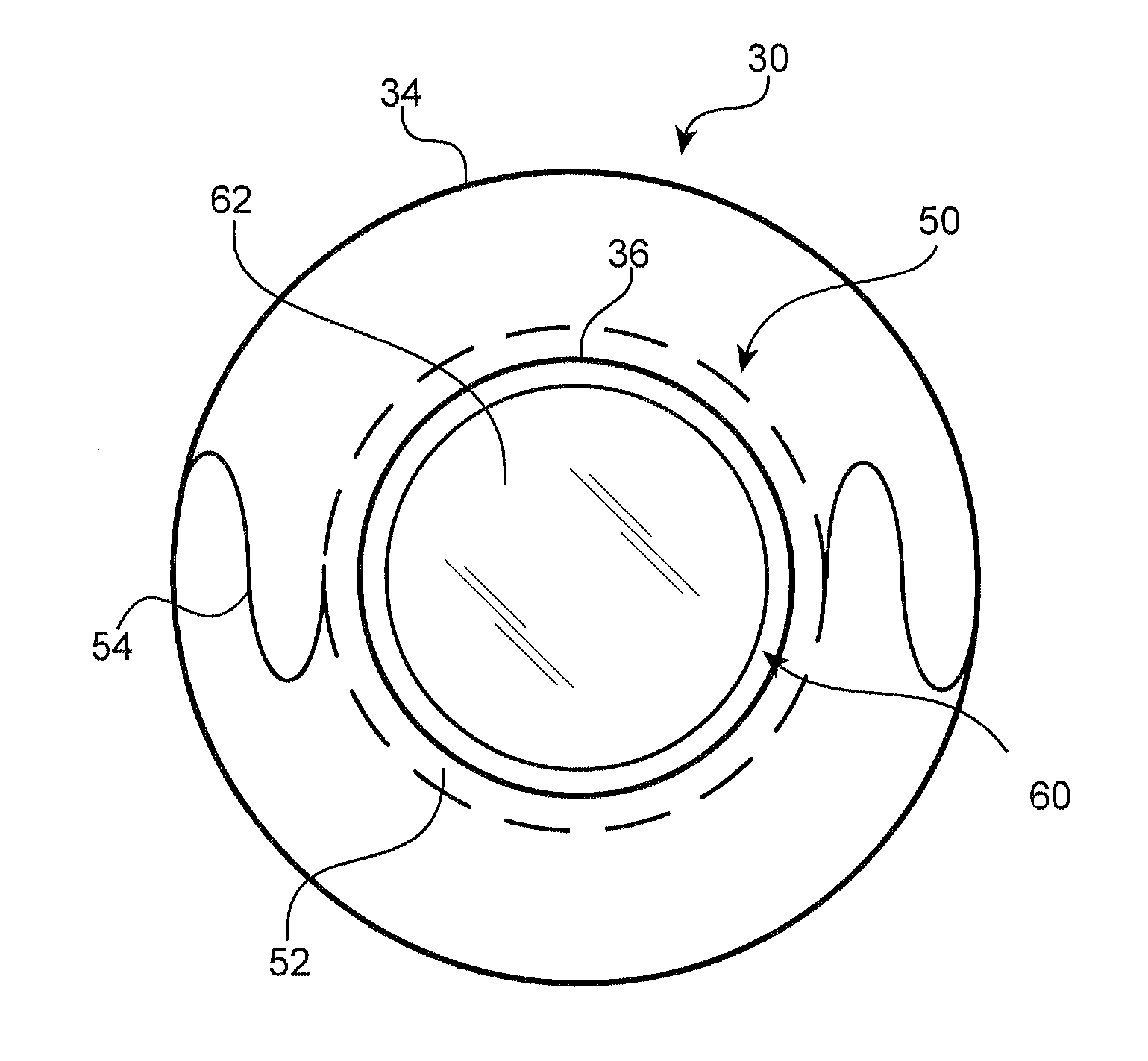
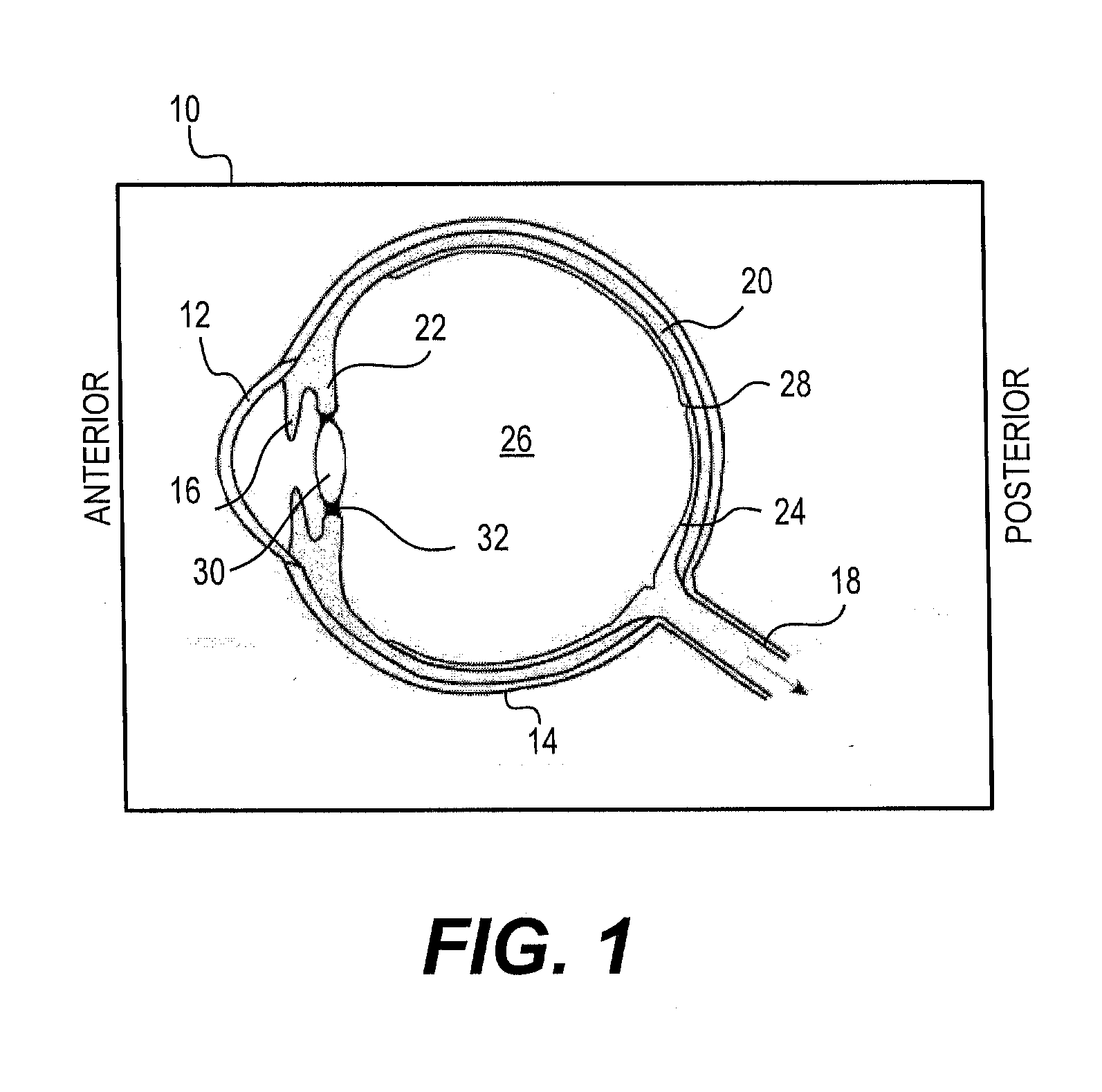
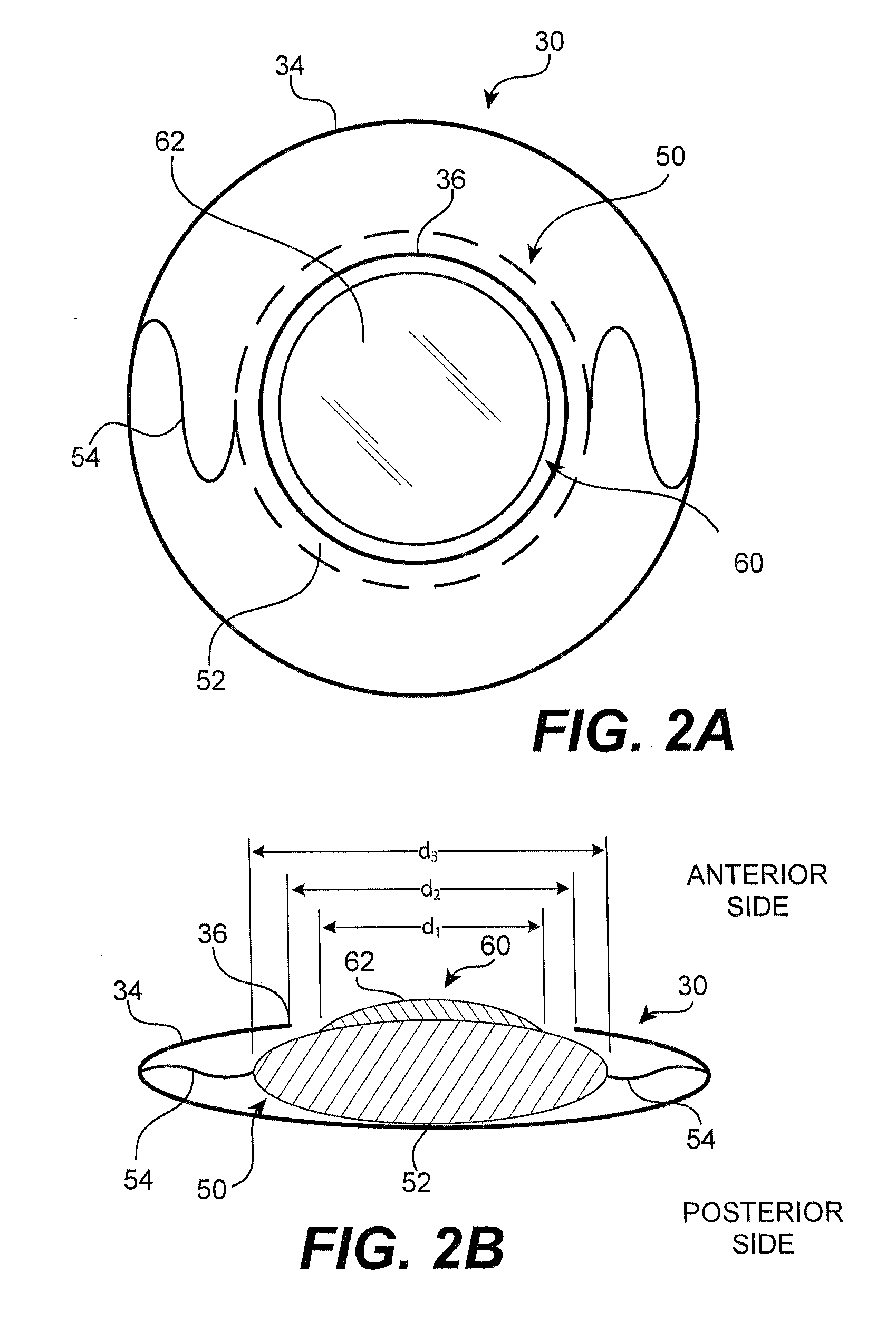
Modular intraocular lens designs and methods
ActiveUS20130190868A1Minimize for interference in lightAvoid interferenceEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical correction
A modular IOL system including intraocular primary and secondary components, which, when combined, form an intraocular optical correction device, wherein the secondary component is placed on the primary component within the perimeter of the capsulorhexis, thus avoiding the need to touch or otherwise manipulate the capsular bag. The secondary component may be manipulated, removed, and / or exchanged for a different secondary component for correction or modification of the optical result, on an intra-operative or post-operative basis, without the need to remove the primary component and without the need to manipulate the capsular bag. The primary component may have haptics extending therefrom for centration in the capsular bag, and the secondary component may exclude haptics, relying instead on attachment to the primary lens for stability. Such attachment may reside radially inside the perimeter of the capsulorhexis and radially outside the field of view to avoid interference with light transmission.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
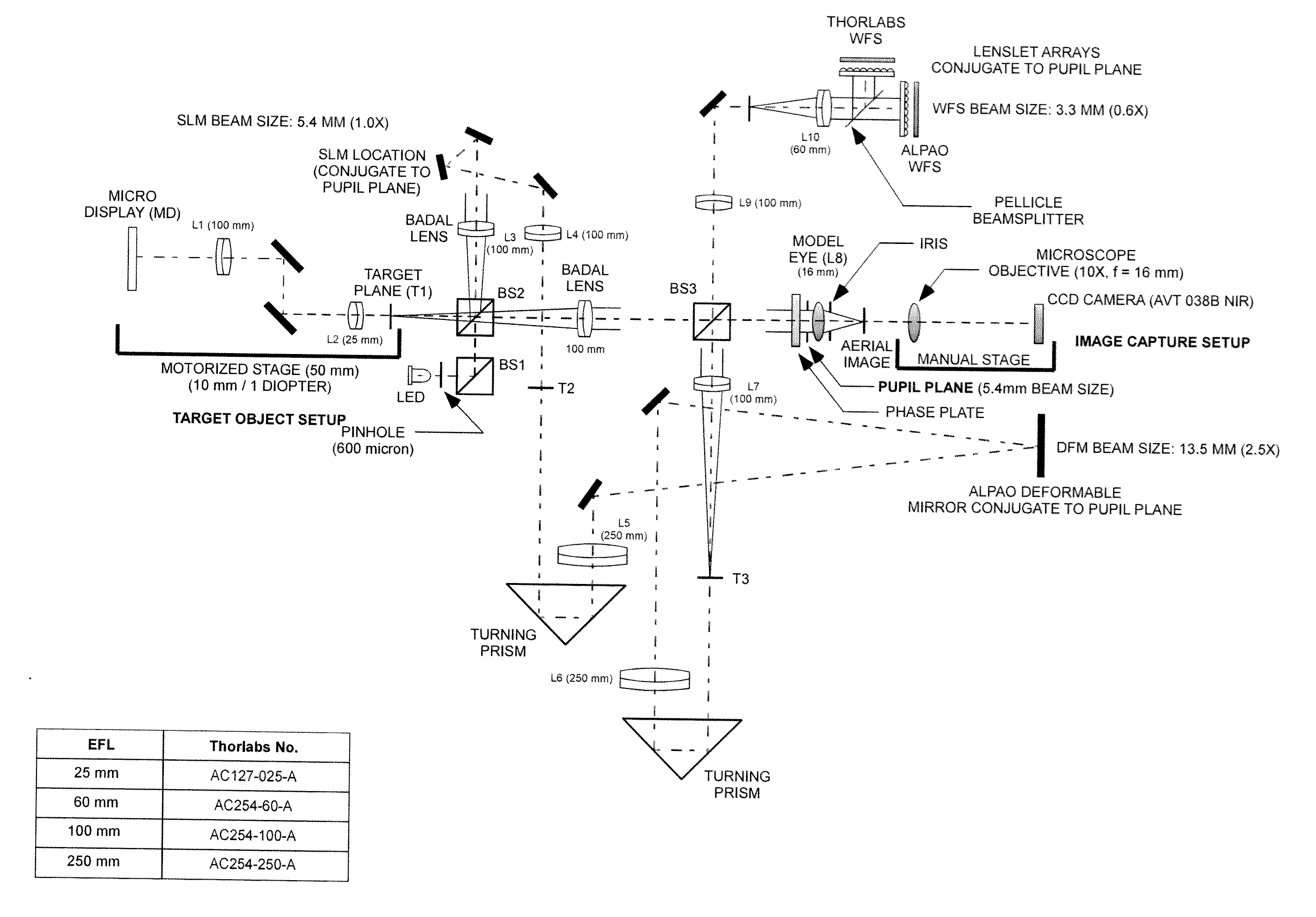
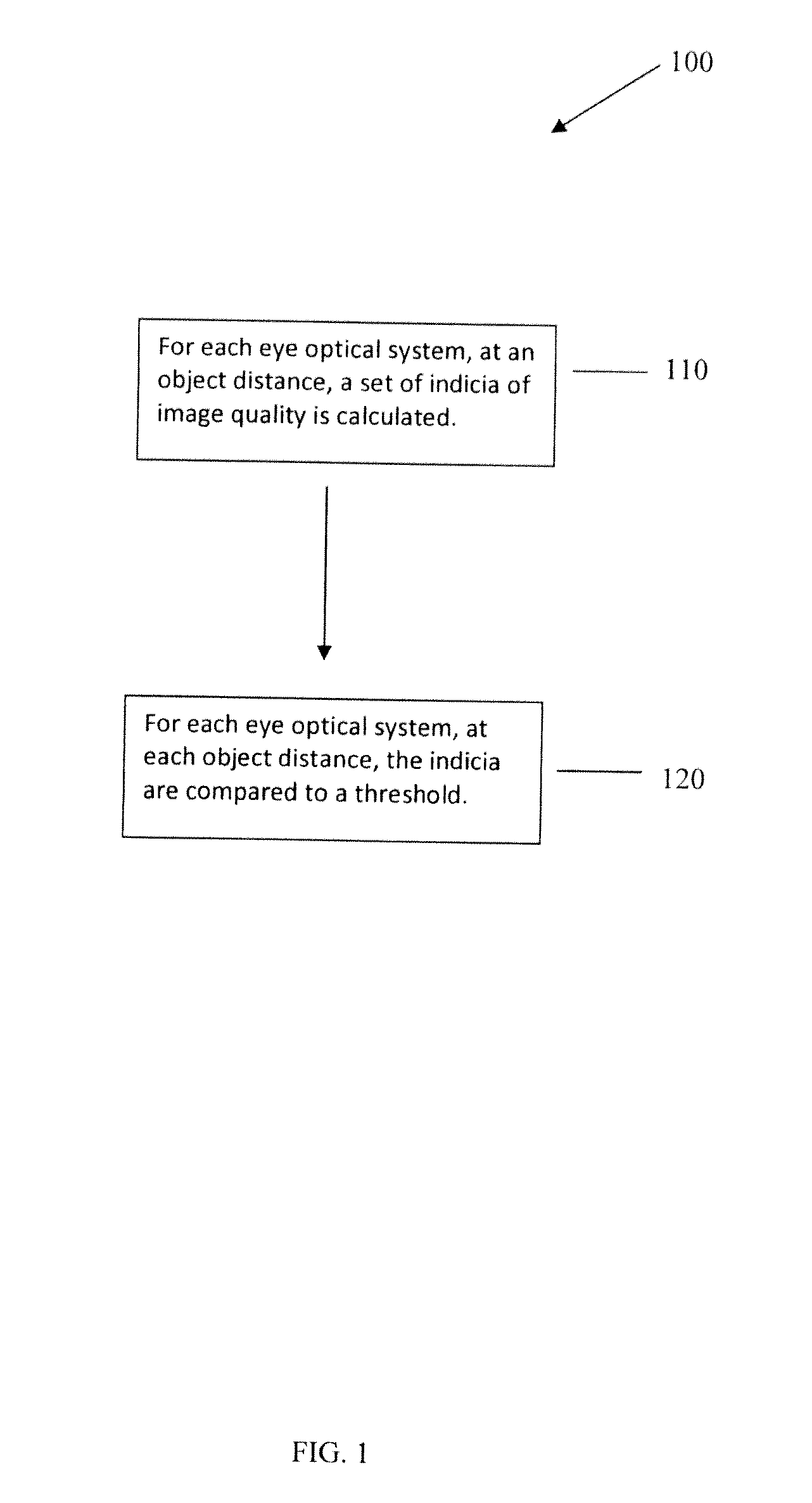
Use of an optical system simulating behavior of human eye to generate retinal images and an image quality metric to evaluate same
A method of predicting clinical performance of an ophthalmic optical correction using simulation by imaging a series of objects of different sizes by each of a plurality of eye optical systems, each of the eye optical systems including the ophthalmic optical correction, the method providing an output value representing the resolution and contrast performance of the optical design at that vergence for the eye optical systems.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
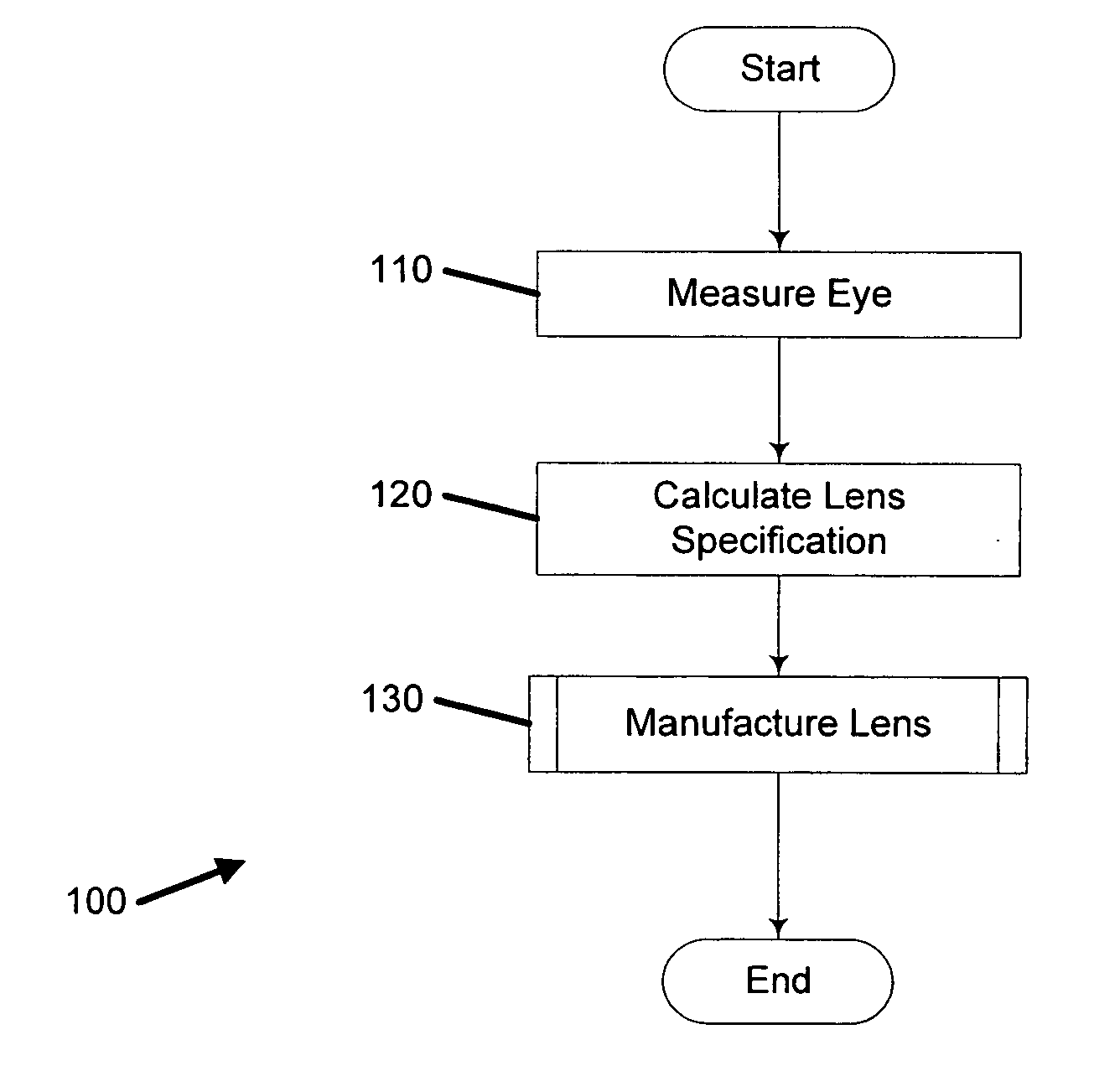
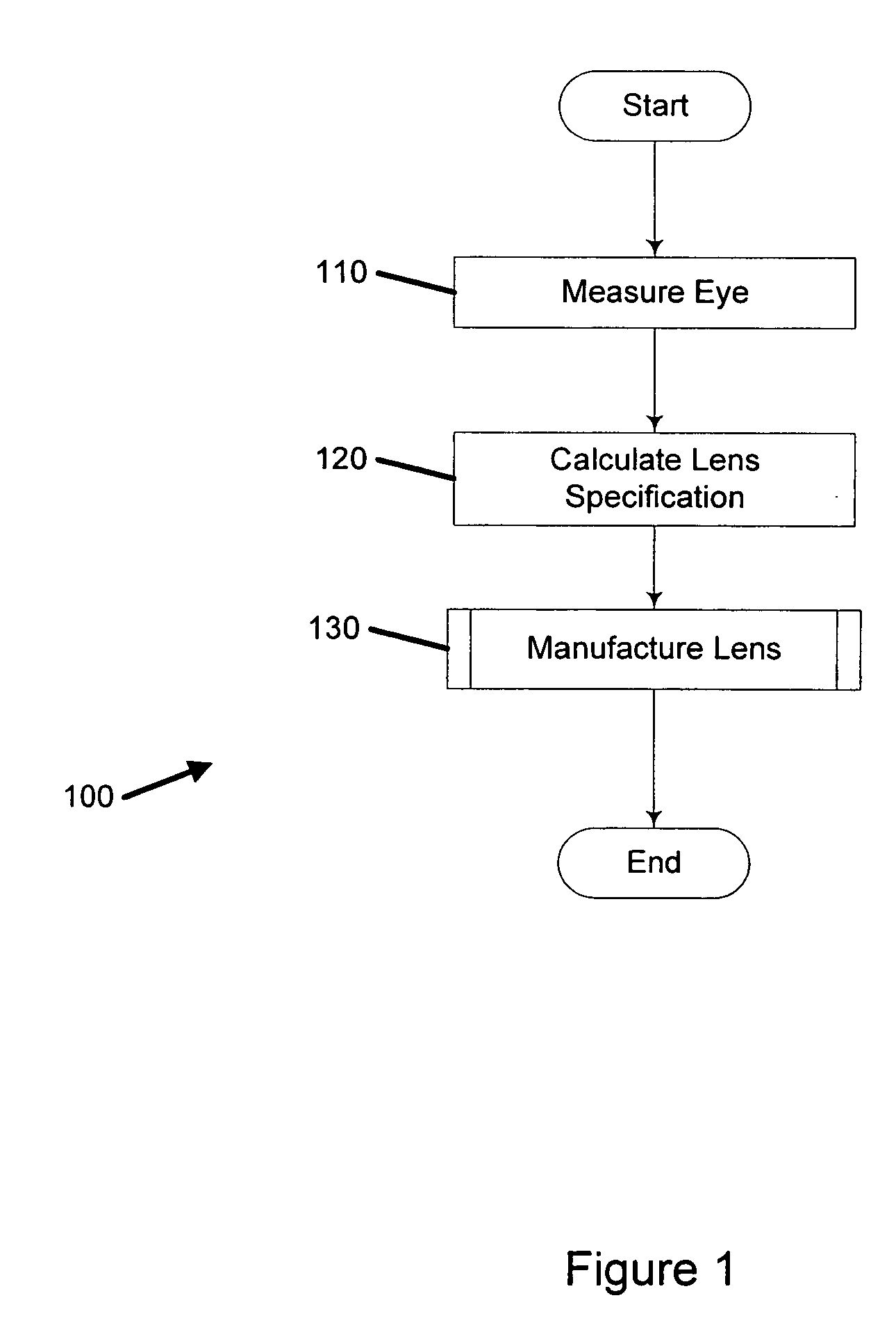
Method of manufacturing an optical lens
InactiveUS20050104240A1Convenient and economical methodHigh order aberrationSpectales/gogglesOptical surface grinding machinesCamera lensOptical correction
A method of manufacturing an optical lens that is configured to correct high order aberrations. One embodiment is a method of customizing optical correction in an optical system. The method includes measuring optical aberration data of the optical system. The method further includes calculating a lens definition based on the optical aberration data. Calculating the lens definition may include calculating a correction of at least one high order optical aberration. The method further includes fabricating a correcting lens based on the lens definition.
Owner:ENTERPRISE PARTNERS VI
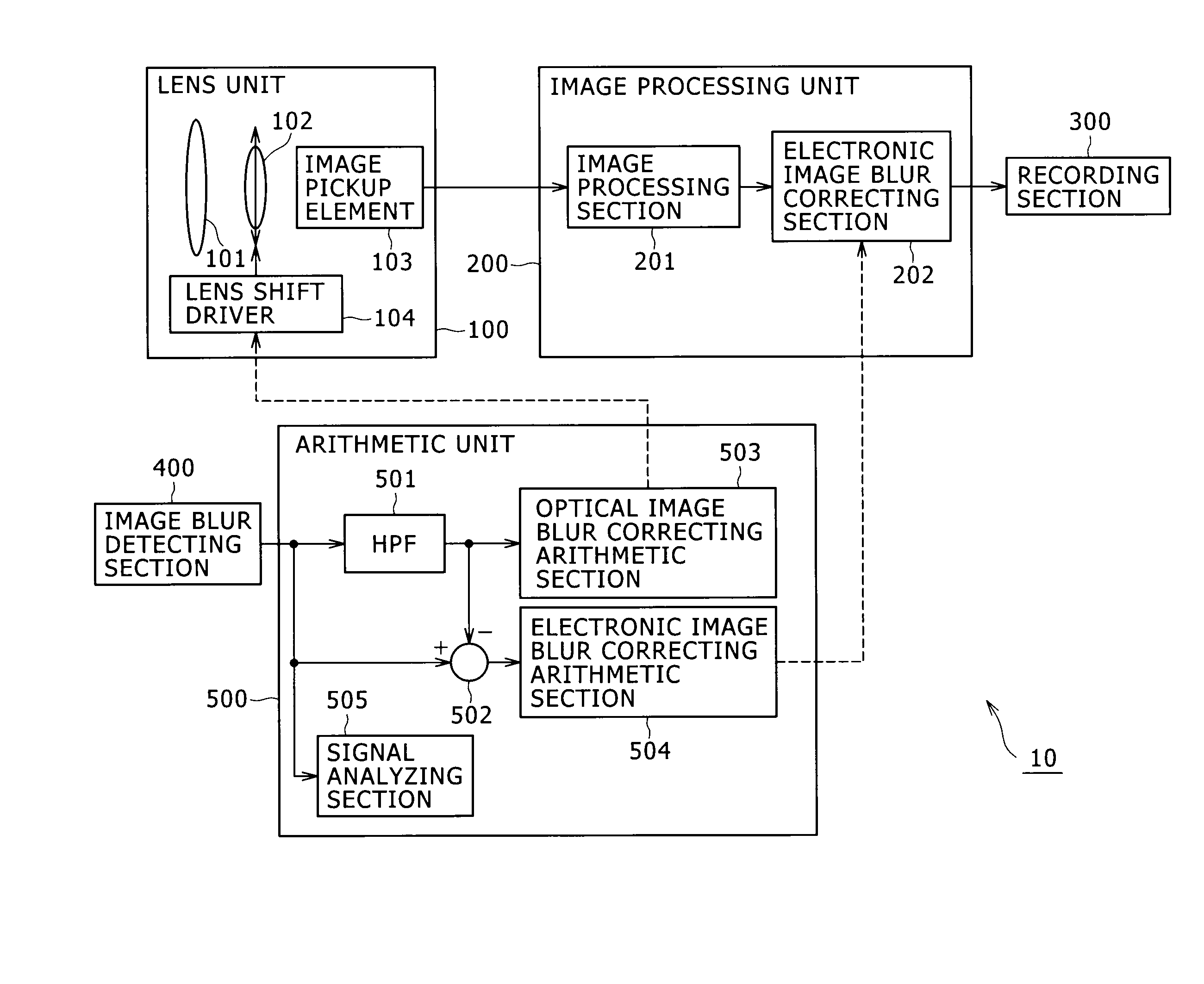
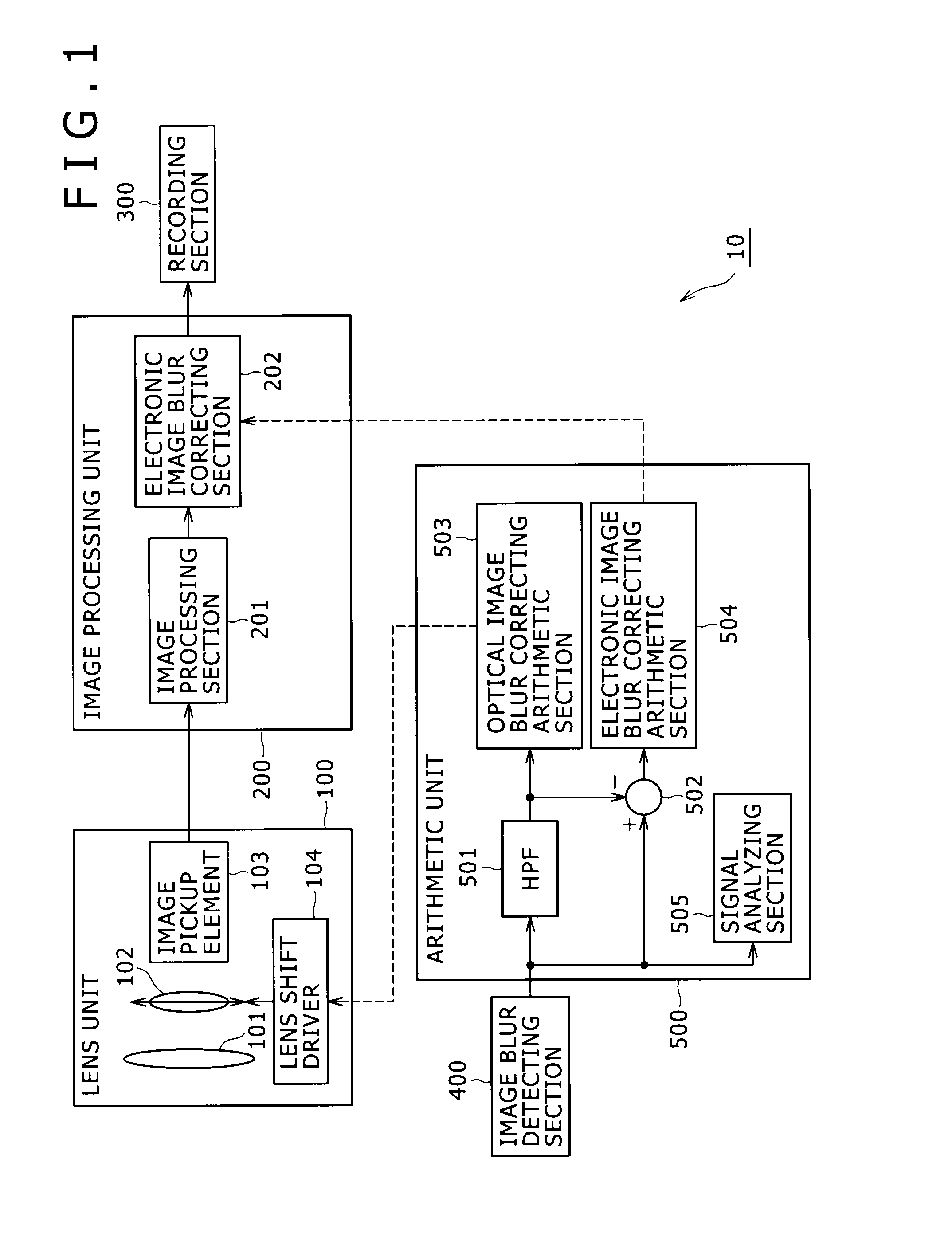
Image pickup device, image blur correcting method, and program
InactiveUS20090316010A1Sufficient correction marginEffective imagingTelevision system detailsPrintersImaging processingMotion sensing
An image pickup device includes: an image pickup optical system configured to form a subject image; an image pickup element configured to generate a picked-up image from the subject image formed by the image pickup optical system; an image blur detecting section configured to output an image blur signal using a motion detecting sensor; an arithmetic section configured to calculate an amount of image blur correction including an amount of optical correction and an amount of electronic correction on a basis of the image blur signal; an optical image blur correcting section configured to move at least one of an optical element forming a part of the image pickup optical system and the image pickup element in accordance with the amount of optical correction; and an electronic image blur correcting section configured to correct electronically an image blur of the picked-up image by image processing based on the amount of electronic correction.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for objective measurement and correction of optical systems using wavefront analysis
InactiveUS20050099600A1Simple and inexpensive designPractical applicationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
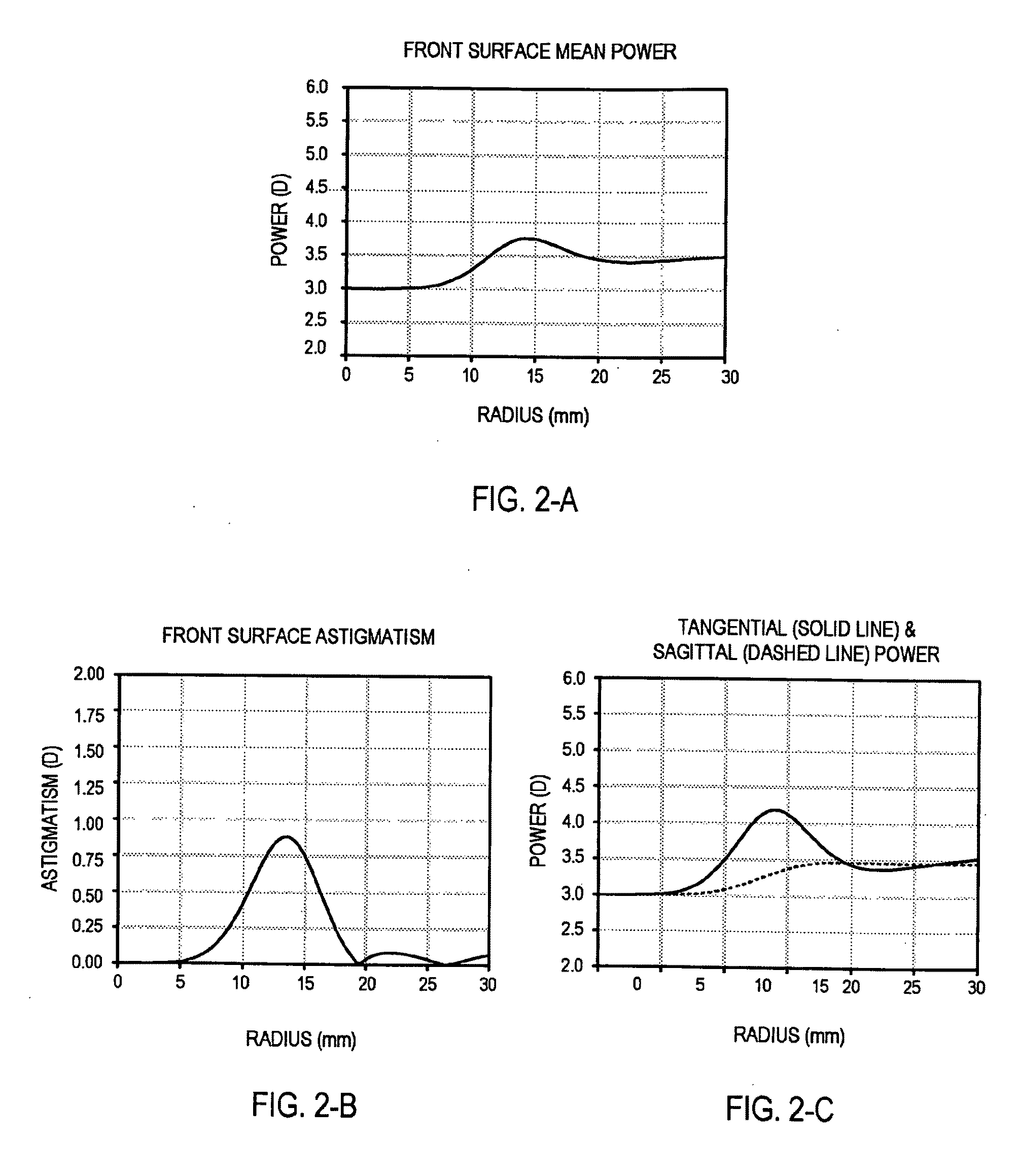
Ophthalmic lens element for myopia correction
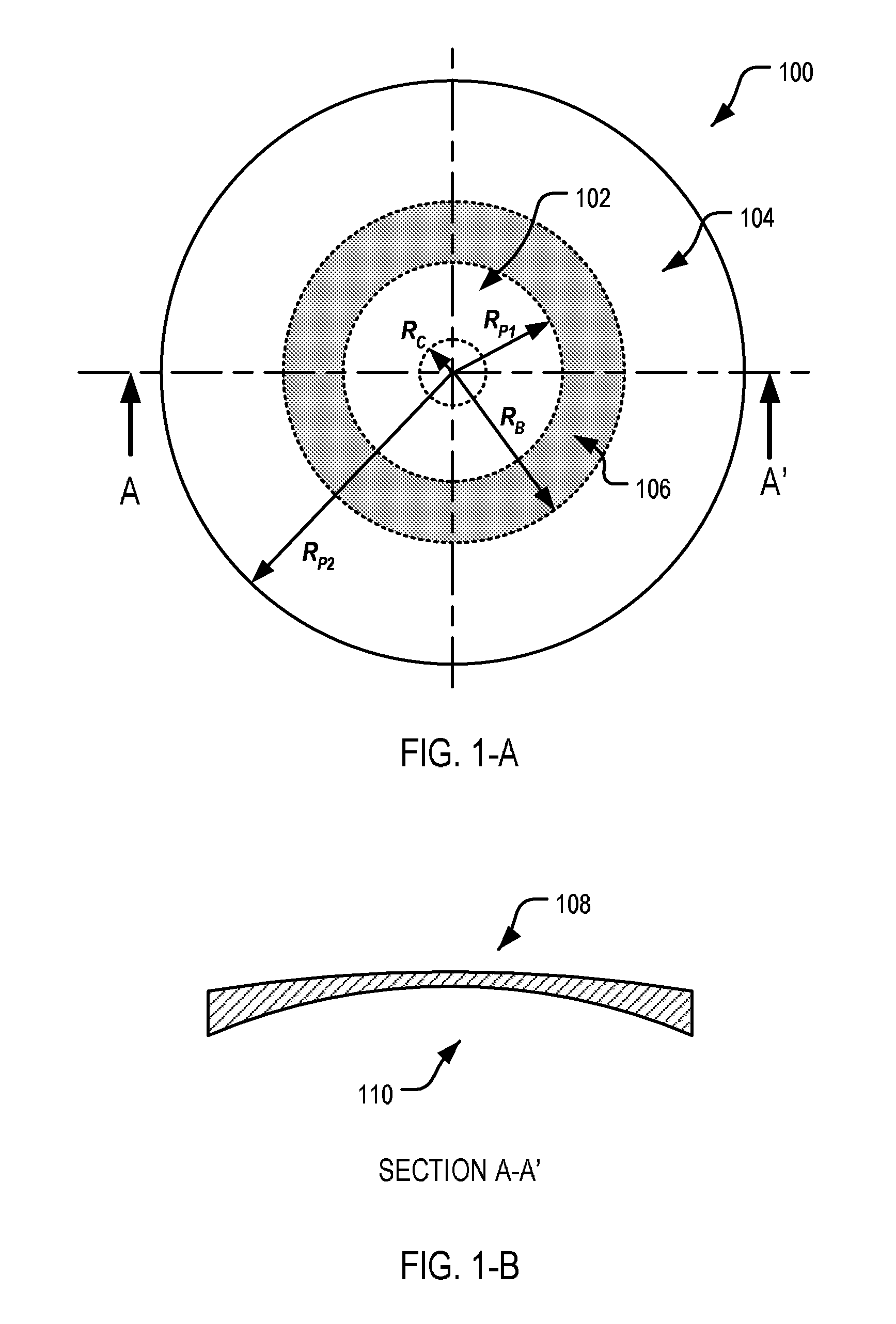
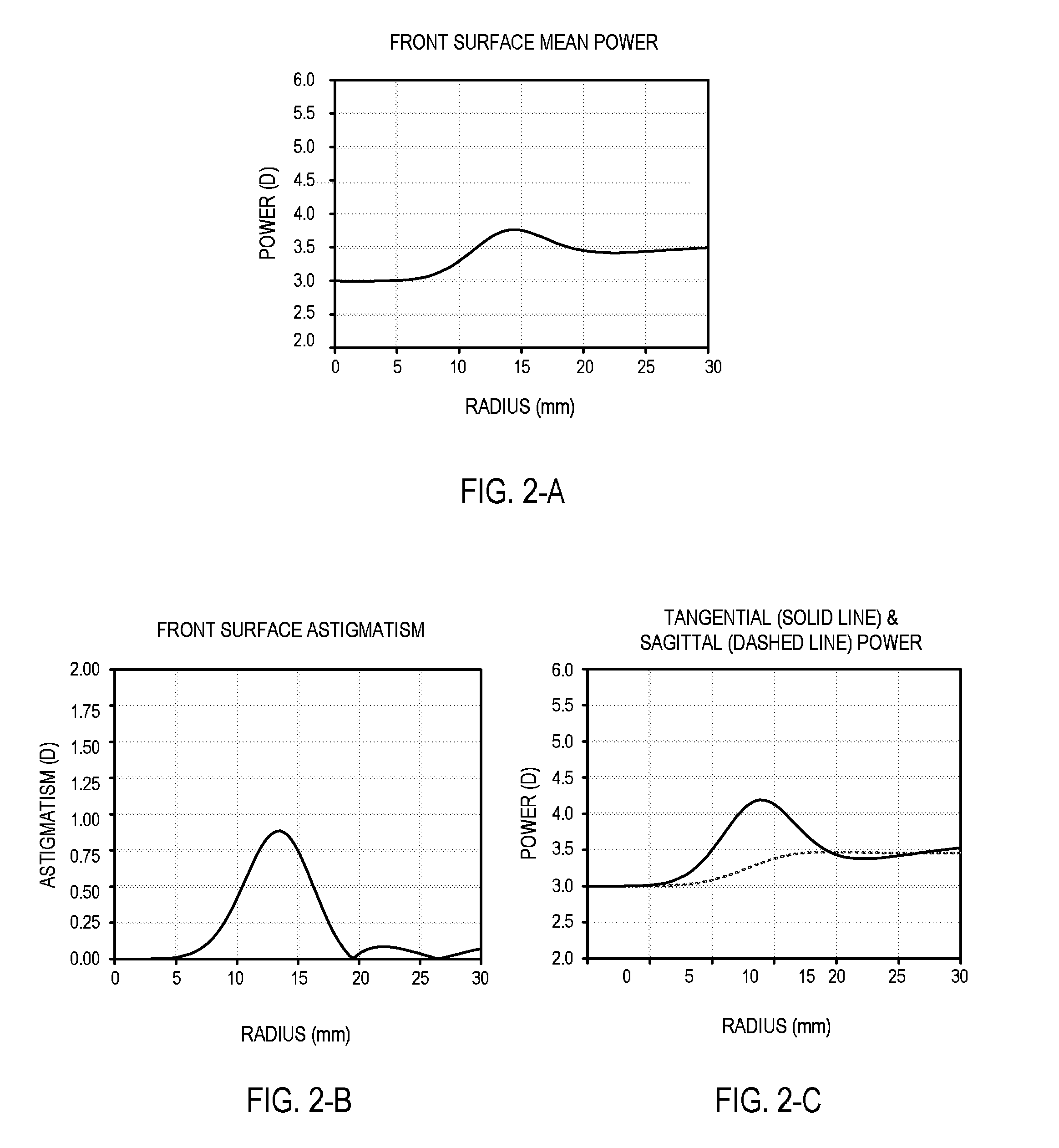
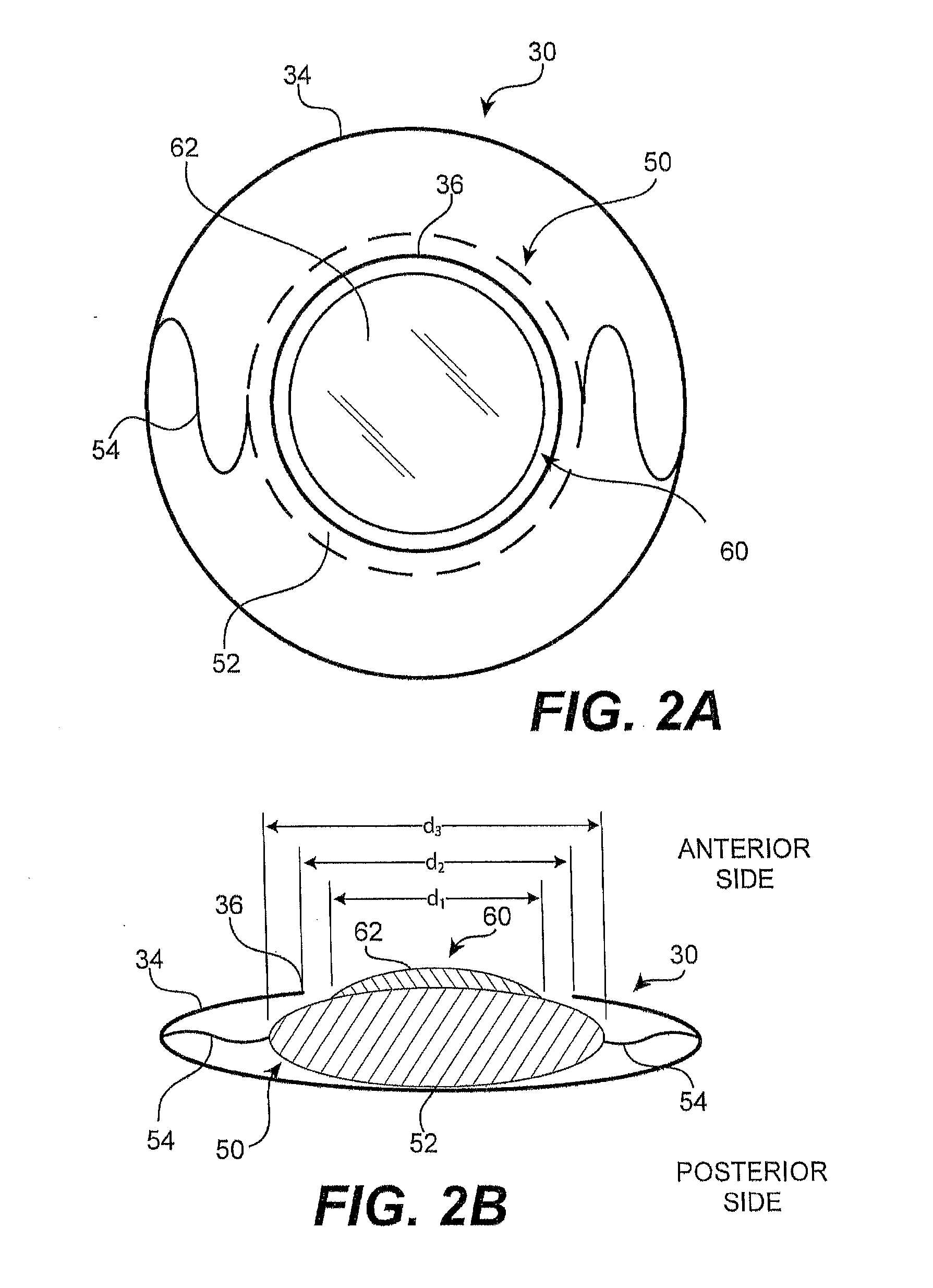
ActiveUS7862171B2Improve concentrationCorrects, orSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessOptical correction
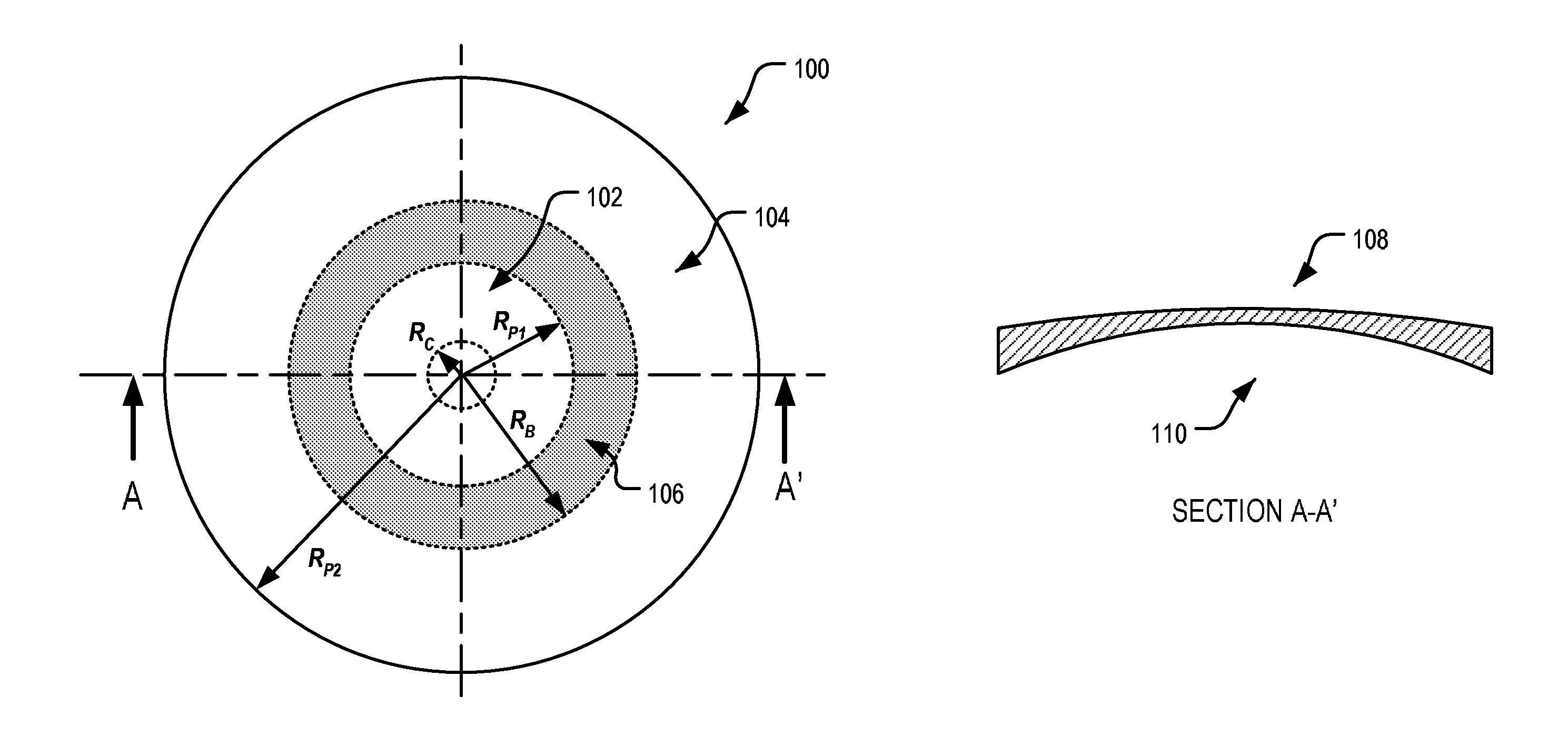
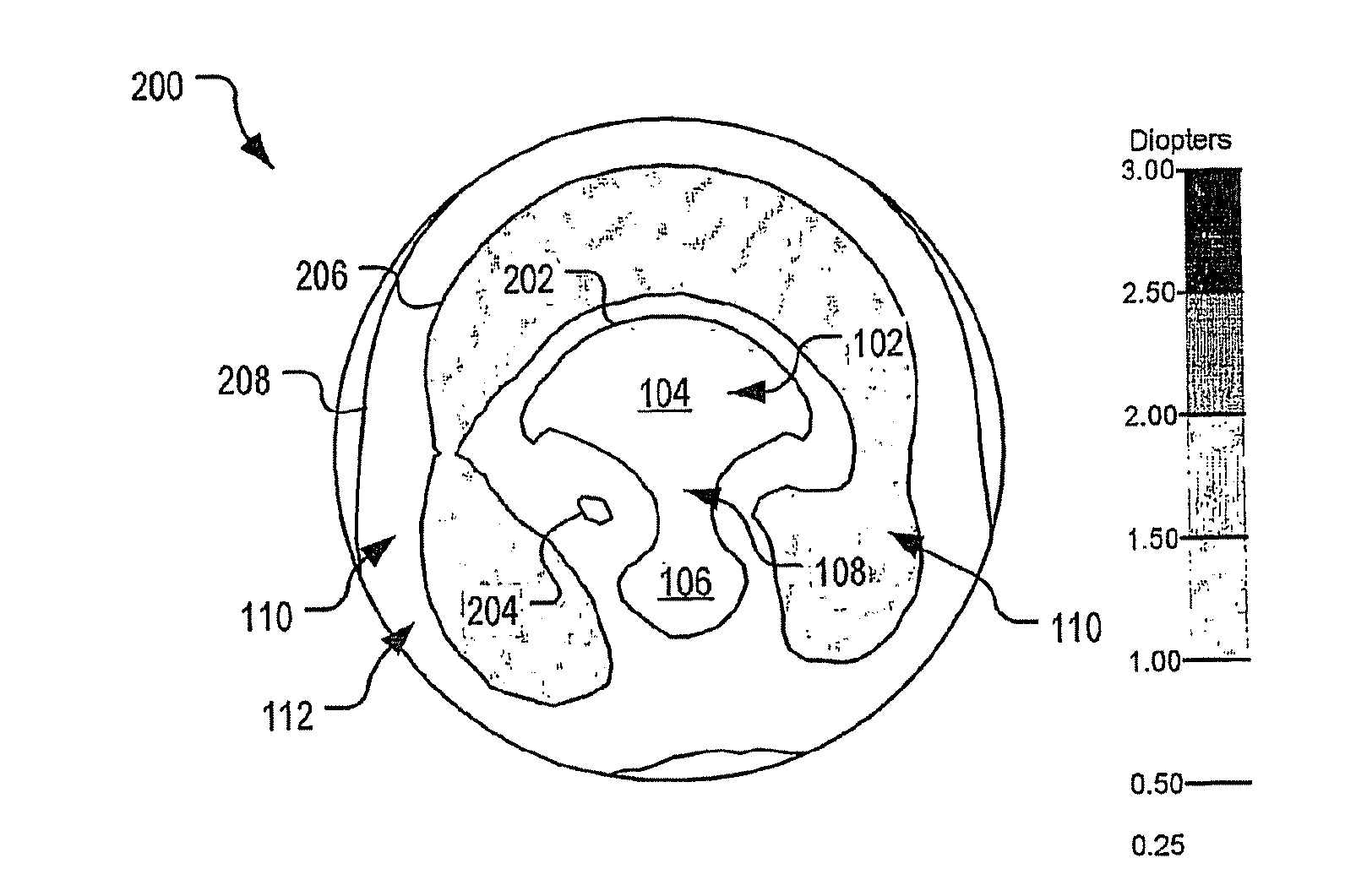
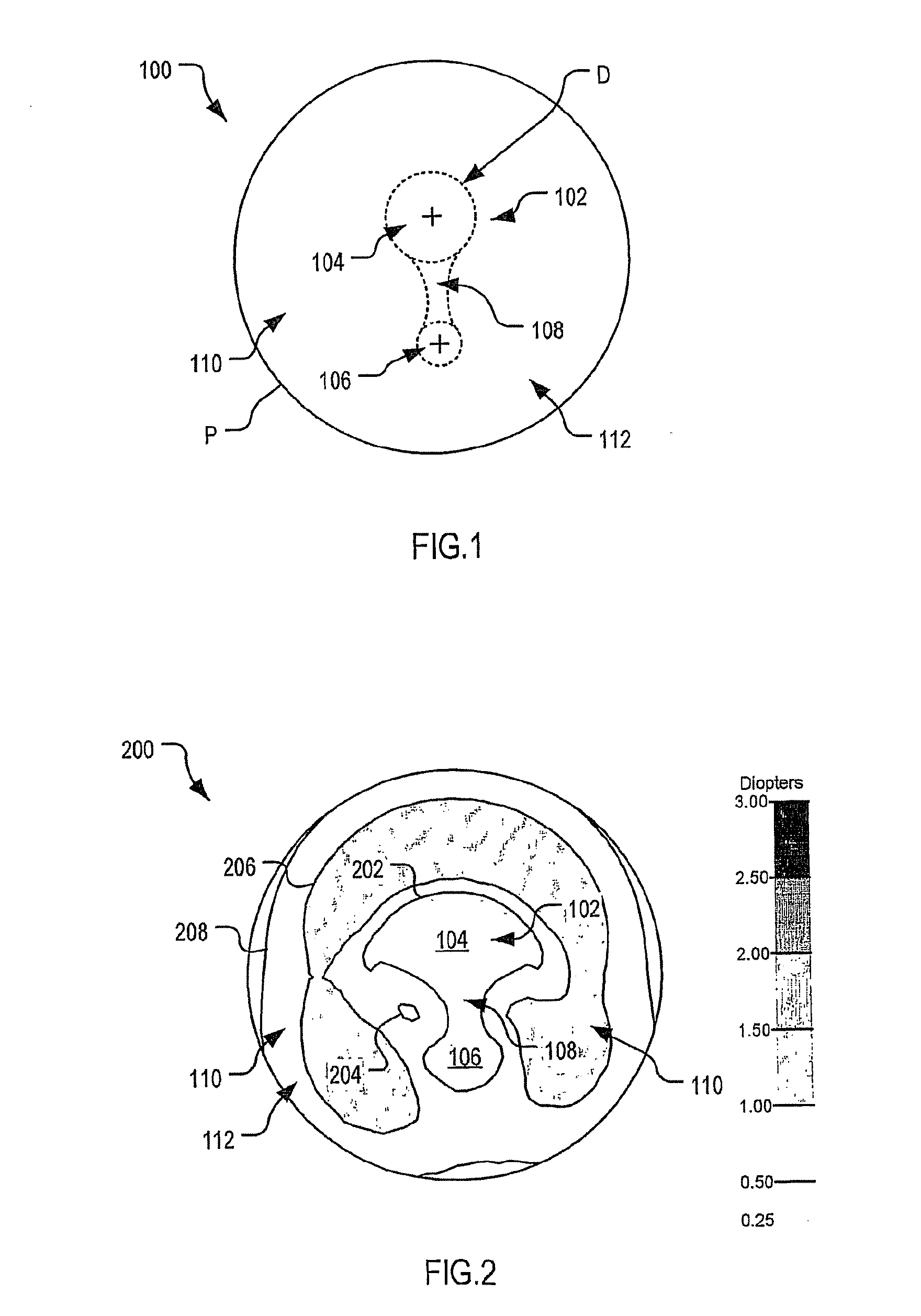
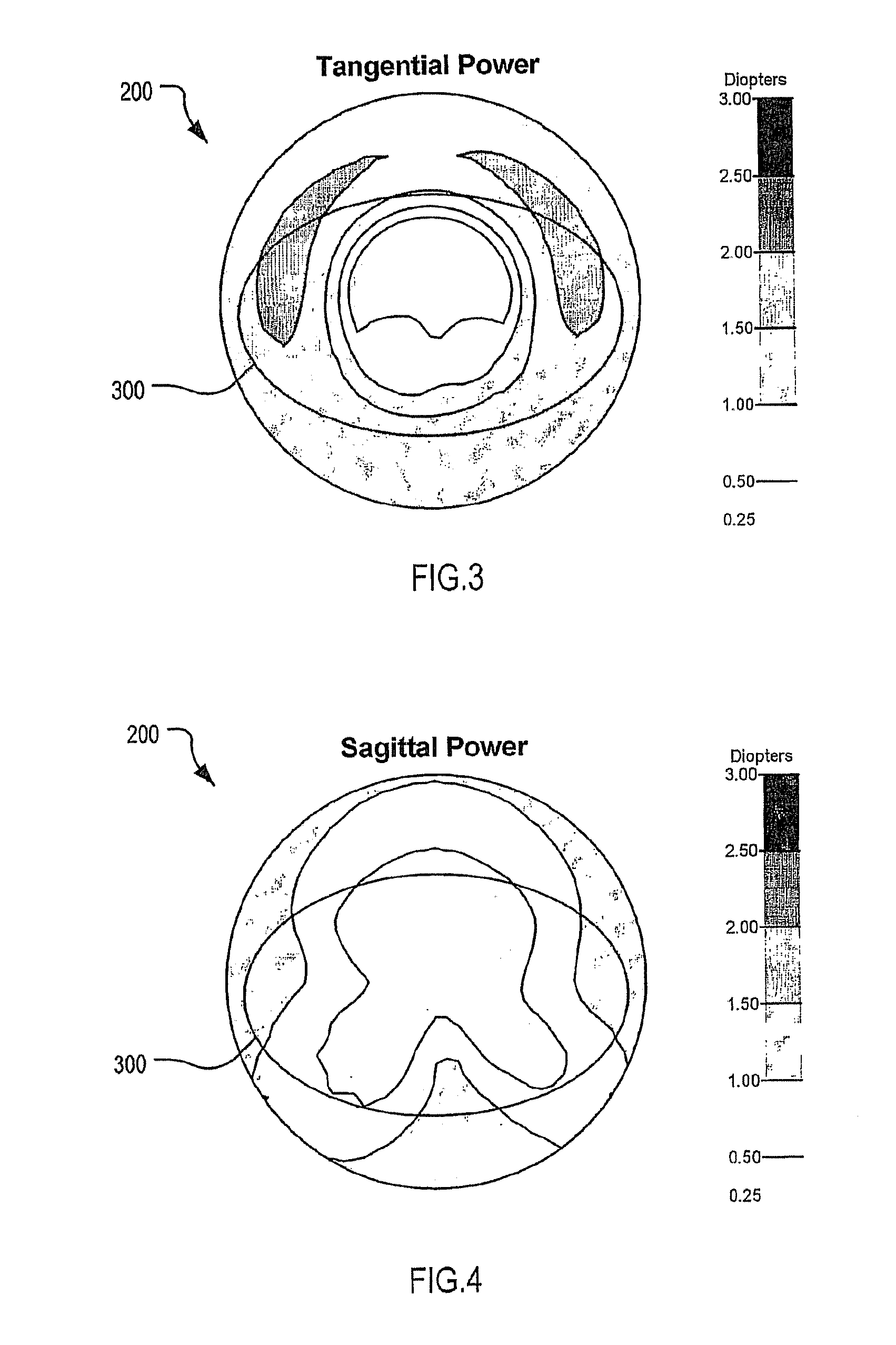
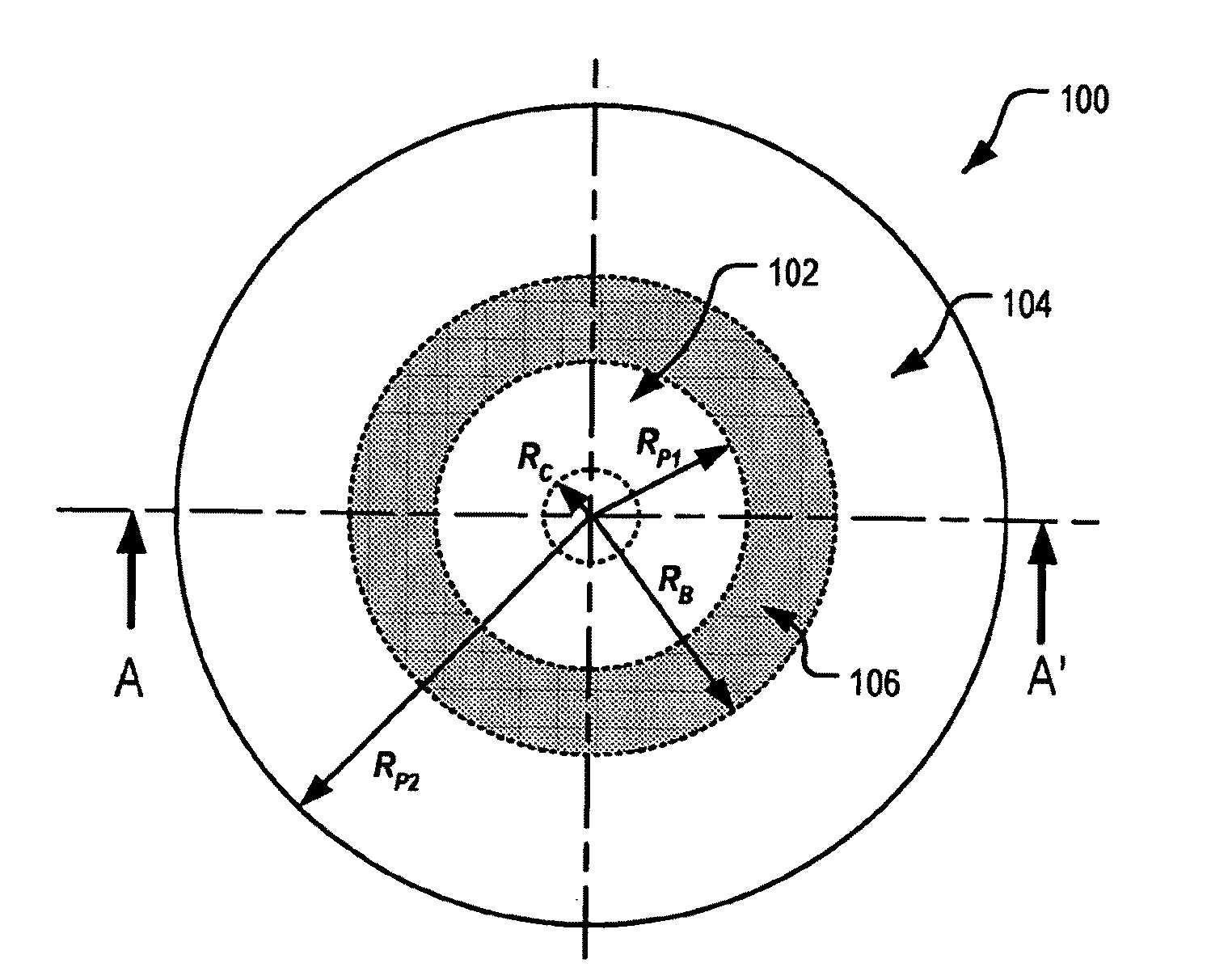
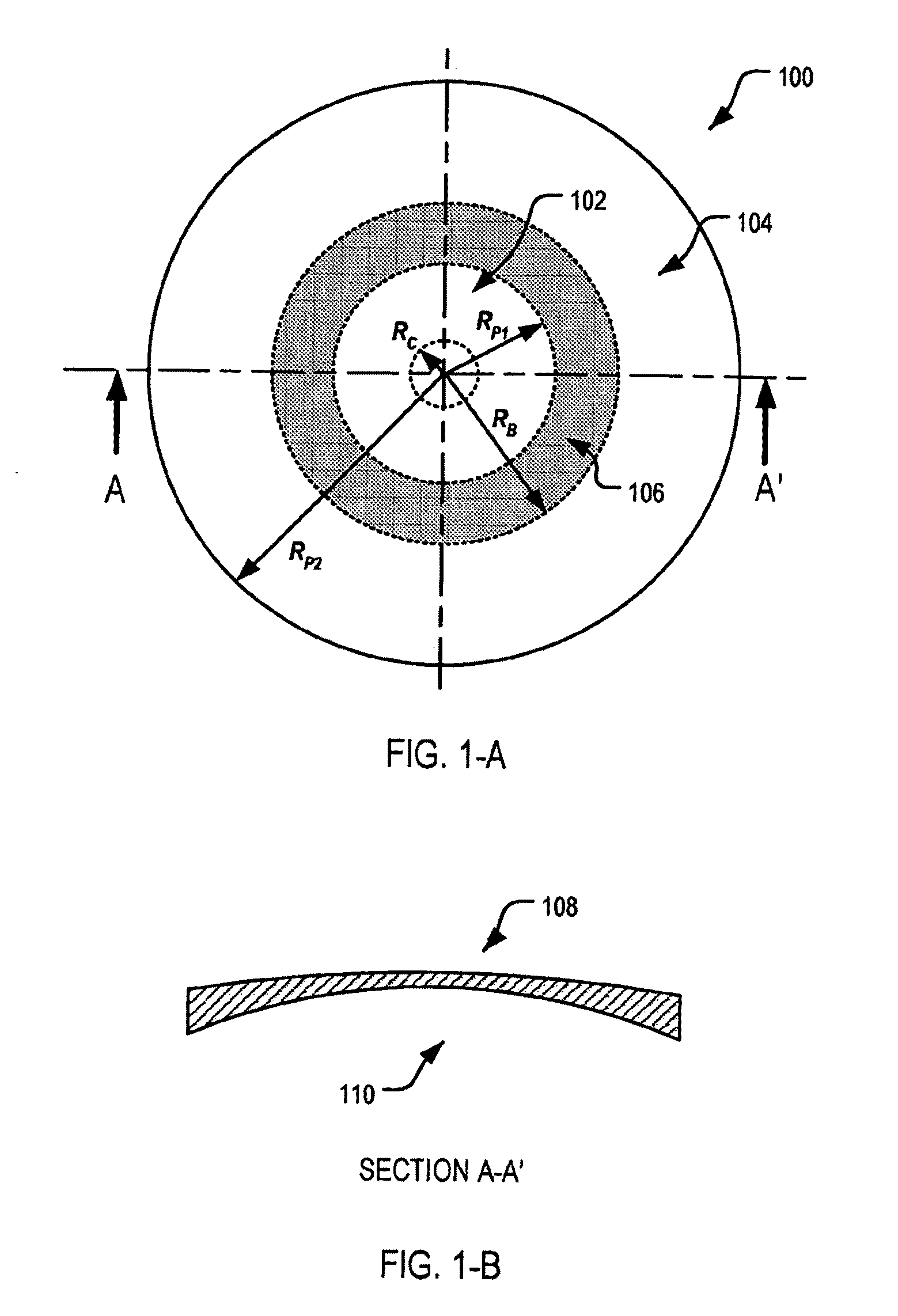
An ophthalmic lens element (100) for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is disclosed. The lens element (100) includes a central zone (102) and a peripheral zone (104). The central zone (102) provides a first optical correction for substantially correcting myopia associated with the foveal region of the wearer's eye. The peripheral zone (104) surrounds the central zone (102) and provides a second optical correction for substantially correcting myopia or hyperopia associated with a peripheral region of the retina of the wearer's eye. A system and method for dispensing or designing an ophthalmic lens element for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO +1
Modular intraocular lens designs and methods
ActiveUS20130310931A1Interference minimizationAvoid interferenceEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical correction
Owner:ALCON INC +1
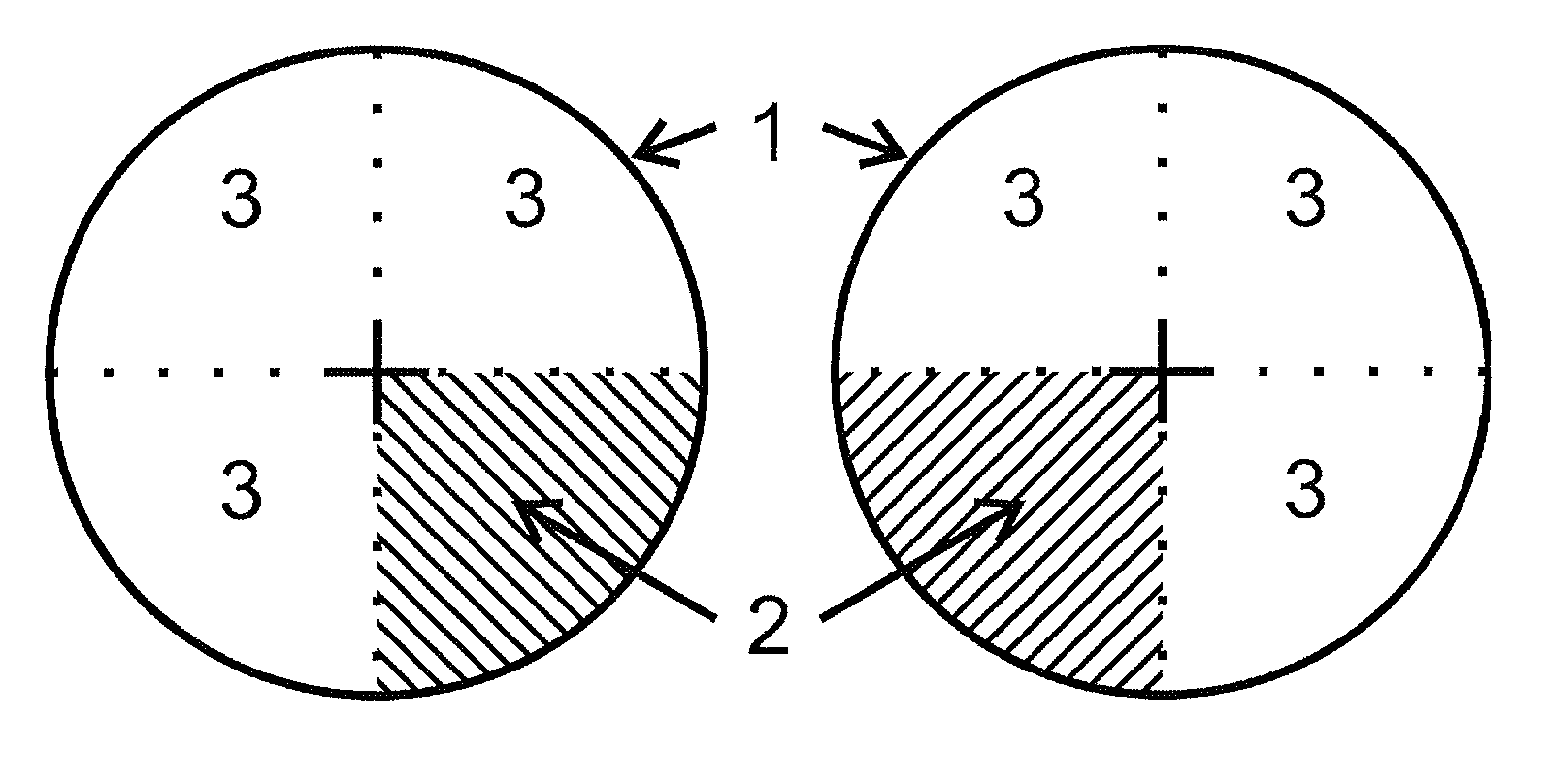
Device for asymmetrical refractive optical correction in the peripheral retina for controlling the progression of myopia
Optical device (1) for modifying the optics of the eye in its peripheral retina as prophylaxis of the progression of myopia, that it consists in a lens in which its inferior nasal quadrant (2) modifies the strength in a progressive and controlled manner from the center to the outer zone of the lens. The rest of the quadrants (3) of device (1) have a configuration of a graduated crystal or flat crystal, depending, respectively, on whether the user has some visual defect that requires optical correction or lacks said defect. The lens can be either an optical lens, a contact lens or electro-optical systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MURCIA
Optical diagnosis using measurement sequence
Devices, systems, and methods that facilitate optical analysis, particularly for the diagnosis and treatment of refractive errors of the eye. An optical diagnostic method for an eye includes obtaining a sequence of aberration measurements of the eye, identifying an outlier aberration measurement of the sequence of aberration measurements, and excluding the outlier aberration measurement from the sequence of aberration measurements to produce a qualified sequence of aberration measurements. The sequence of aberrations measurements can be obtained by using a wavefront sensor. An optical correction for the eye can be formulated in response to the qualified sequence of aberration measurements.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Ophthalmic lens element
ActiveUS7992997B2Effective retardingEffective arrestingSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentOptical correctionHigh surface
An ophthalmic lens element is disclosed. The, ophthalmic lens element includes a central region of low surface astigmatism and a peripheral region. The central region includes an upper viewing zone for providing a first power suitable for a wearer's distance vision tasks. The peripheral region has a positive power relative to the first power, and surrounds the central region. The peripheral region provides an optical correction for retarding or arresting myopia for a wearer and includes one or more regions of relatively higher surface astigmatism, a lower or near viewing zone of low surface astigmatism, and a corridor of low surface astigmatism having a surface power varying from that of the upper viewing zone to that of the lower viewing zone. The lower viewing zone is for a wearer's near vision tasks.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Ophthalmic Lens Element for Myopia Correction
ActiveUS20090257026A1Improve concentrationShorten the progressSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsFar-sightednessOptical correction
An ophthalmic lens element (100) for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is disclosed. The lens element (100) includes a central zone (102) and a peripheral zone (104). The central zone (102) provides a first optical correction for substantially correcting myopia associated with the foveal region of the wearer's eye. The peripheral zone (104) surrounds the central zone (102) and provides a second optical correction for substantially correcting myopia or hyperopia associated with a peripheral region of the retina of the wearer's eye. A system and method for dispensing or designing an ophthalmic lens element for correcting myopia in a wearer's eye is also disclosed.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO +1
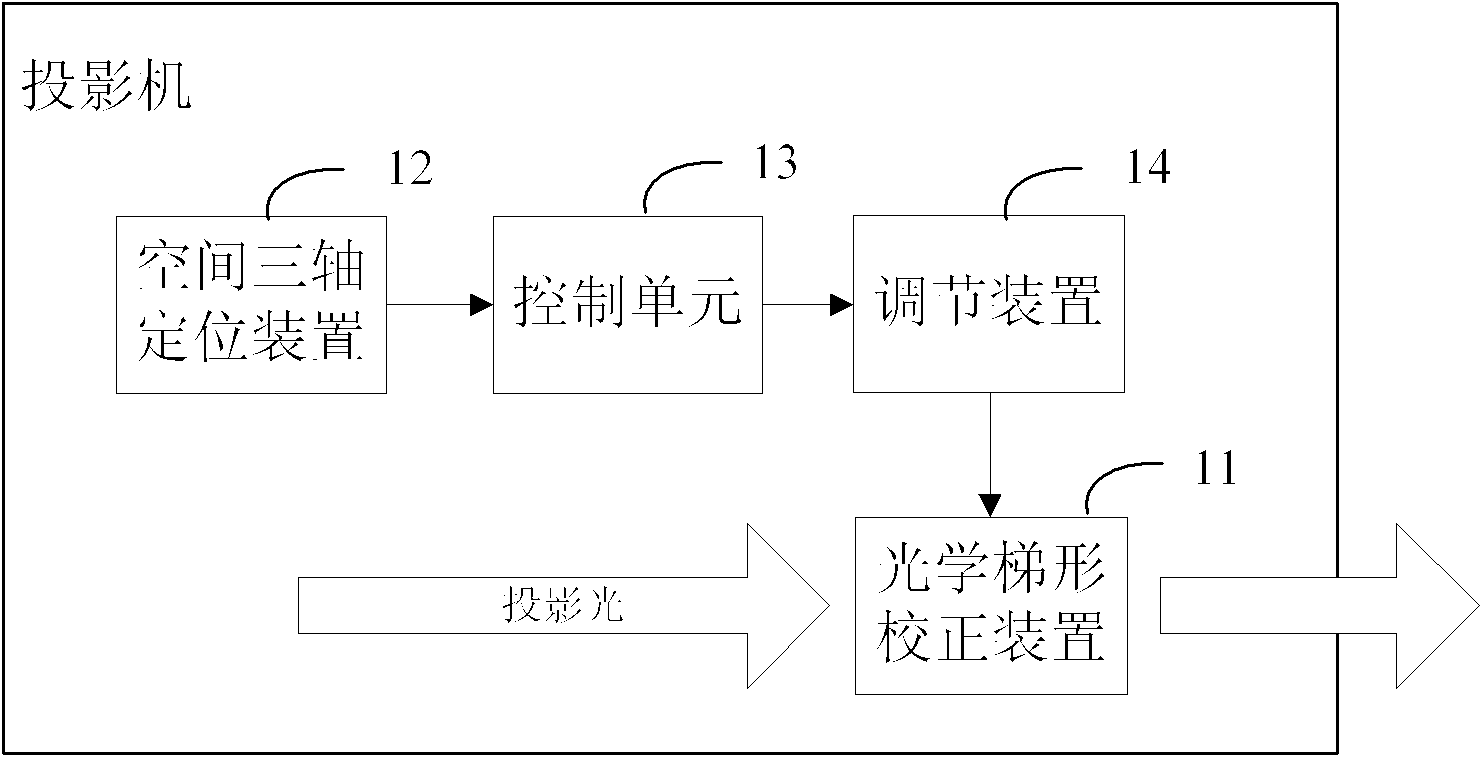
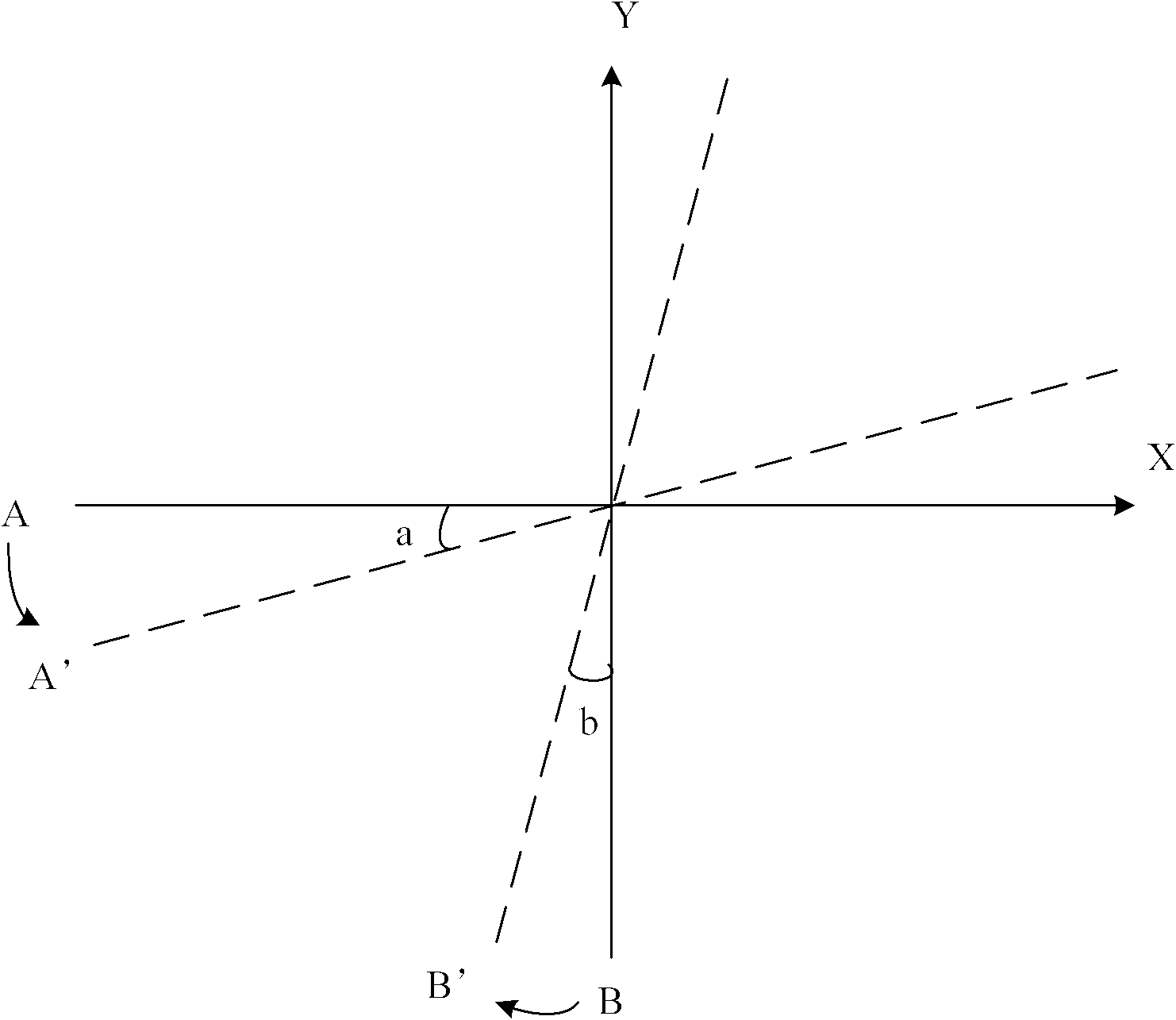
Method and system for correcting distorted projector image and projector
InactiveCN102183870ANo human intervention requiredRemove distortionProjectorsComputer graphics (images)Optical correction
The invention provides a method and a system for correcting a distorted projector image and a projector. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring position data of the projector relative to a triaxial space from a locating device of the triaxial space arranged on the projector after the projector is switched on; comparing the detected position data with reference position data and acquiring position offset of the projector; calculating an adjustment position and an adjustment angle of a trapezoid optical correction device of the projector according to the position offset; and regulating the trapezoid optical correction device according to results. By the method and the system for correcting the distorted projector image and the projector, the distorted image caused by the position offset of the projector can be automatically, conveniently and accurately corrected.
Owner:广州视声电子科技有限公司
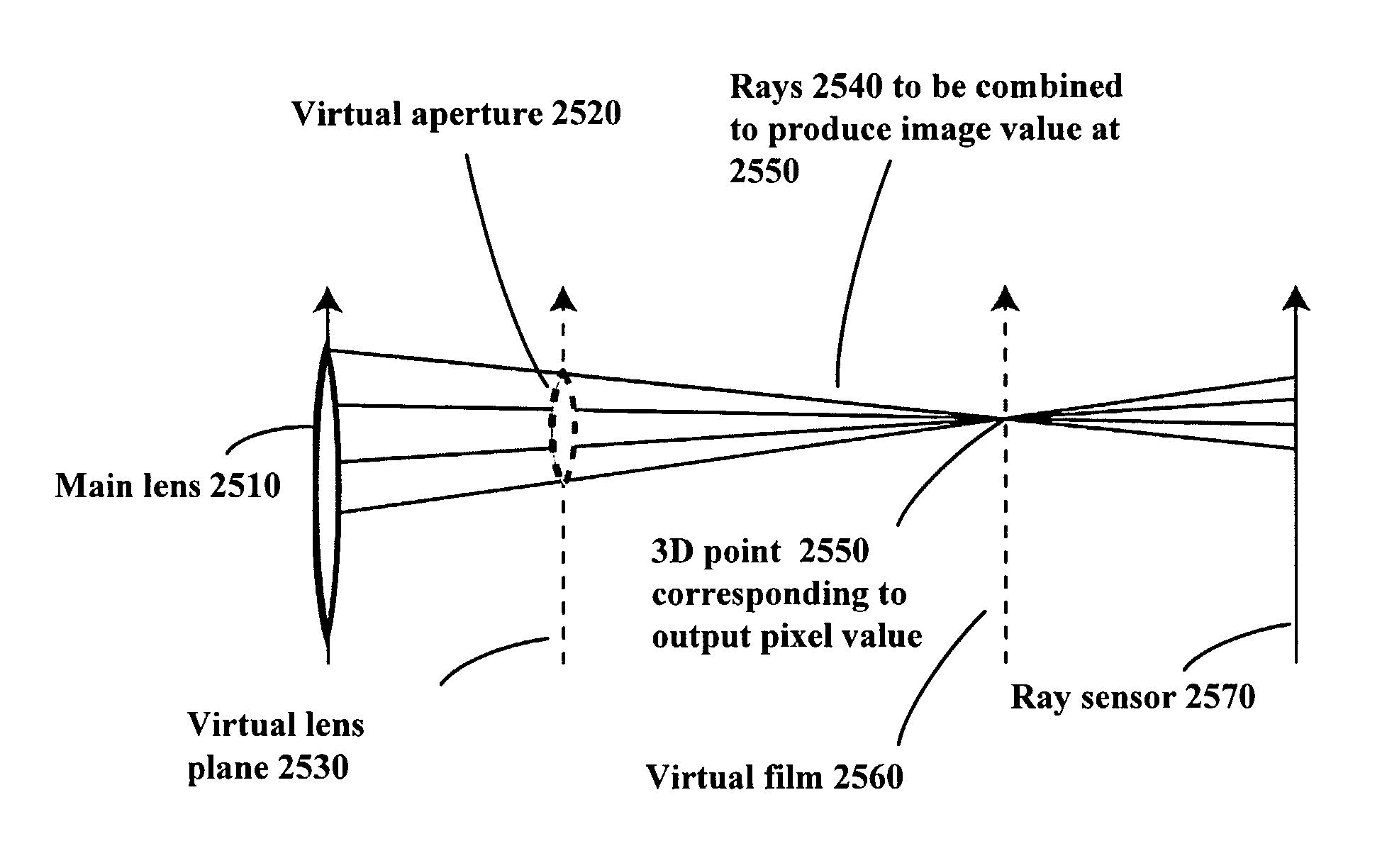
Imaging arrangements and methods therefor
Image data is processed to facilitate focusing and / or optical correction. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, an imaging arrangement collects light data corresponding to light passing through a particular focal plane. The light data is collected using an approach that facilitates the determination of the direction from which various portions of the light incident upon a portion of the focal plane emanate from. Using this directional information in connection with value of the light as detected by photosensors, an image represented by the light is selectively focused and / or corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Catadioptric projection objective
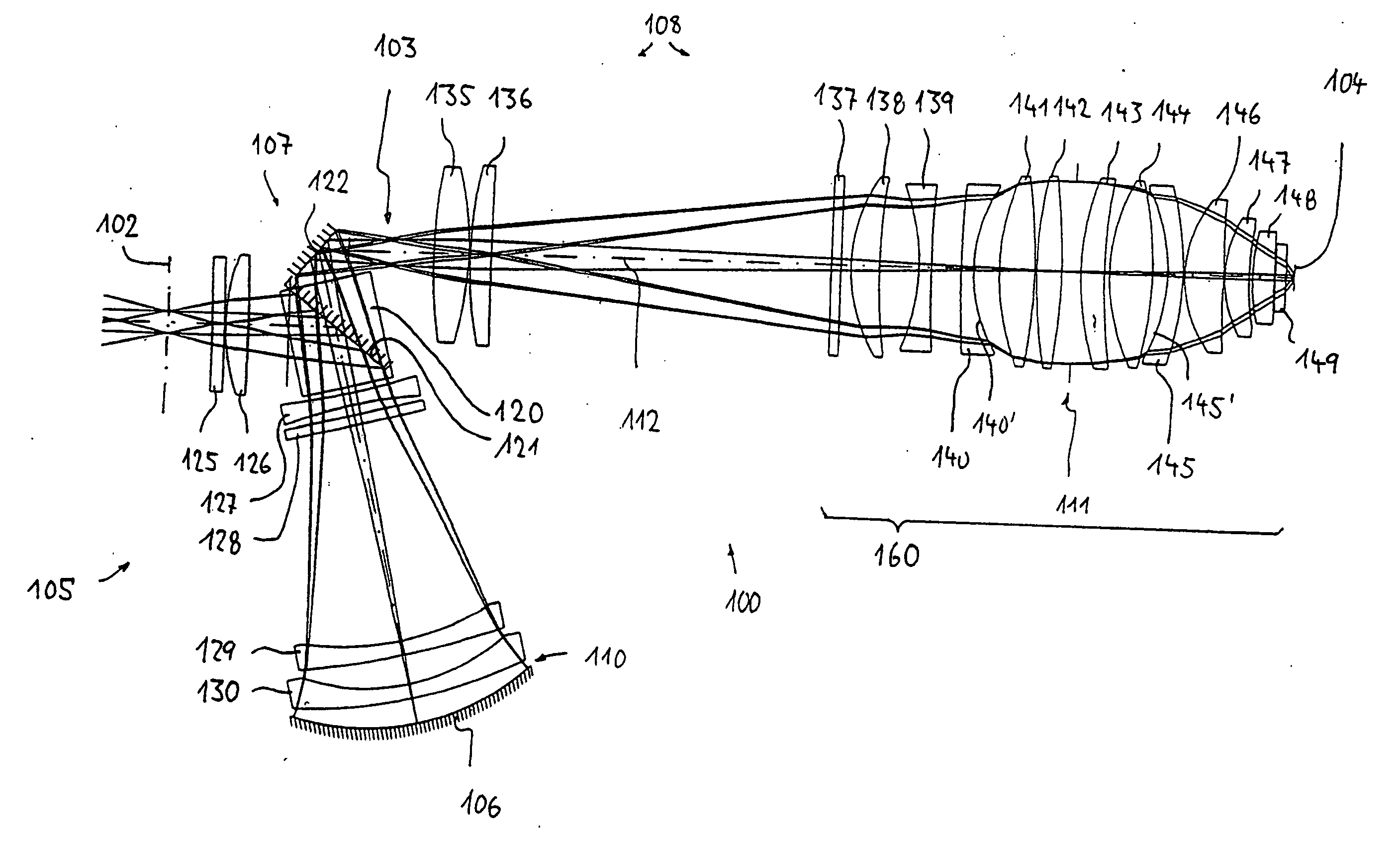
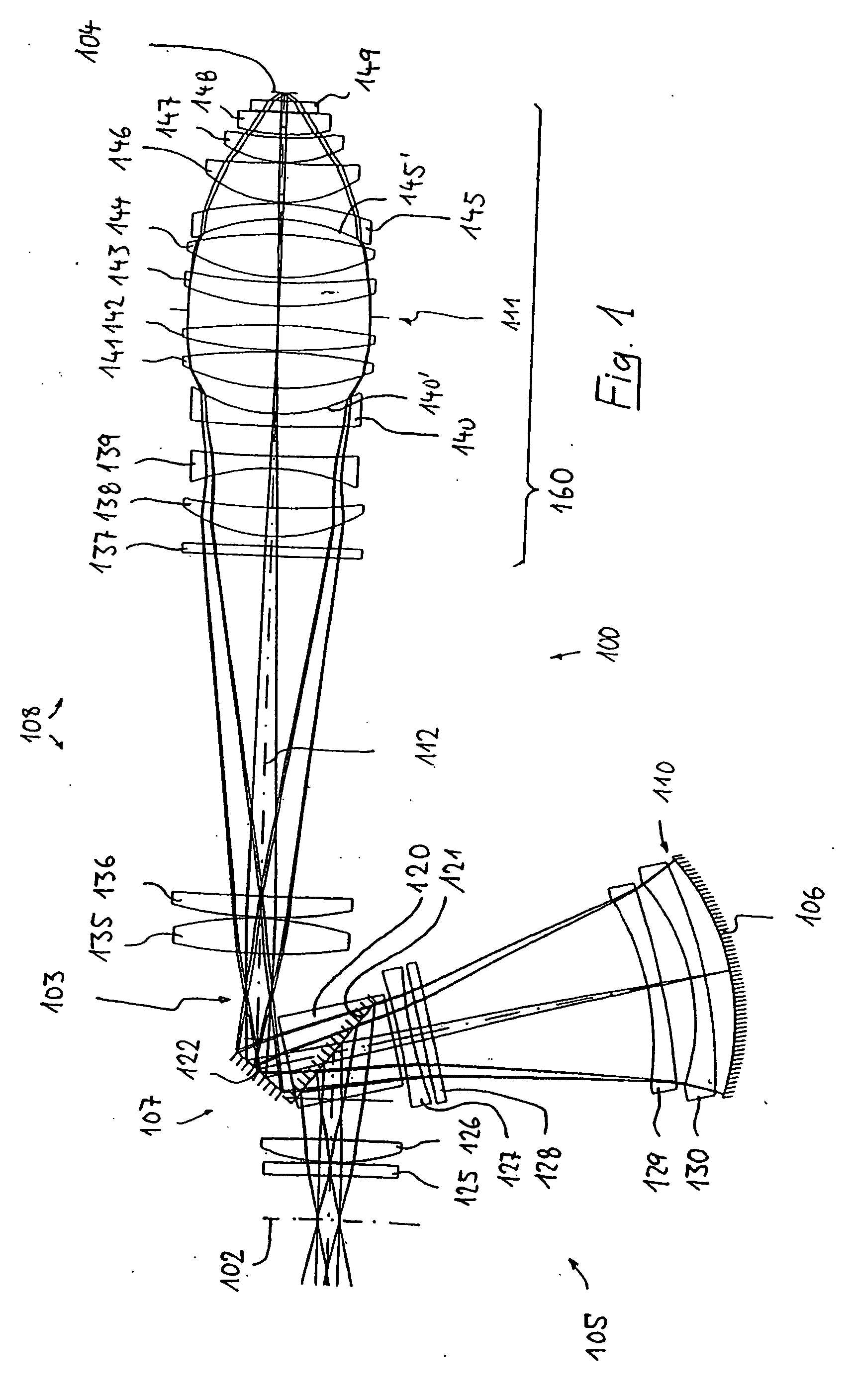
InactiveUS20060132931A1Good correction stateSave materialPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical correctionPupil
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern arranged in the object plane (102) of the projection objective into the image plane (104) of the projection objective has a catadioptric first objective part (105) having at least one concave mirror (106), and a dioptric second objective part (108) in which there is situated a pupil surface (111) near the image. At least one concave lens (140, 145) with a concave surface (140′, 145′) directed towards the pupil surface (111) is arranged in a near zone (160) of the pupil surface. There are no lenses with a strongly curved concave surface directed towards the image plane between the pupil surface and the image plane. Such projection objectives can be produced in a way which saves material in conjunction with good optical correction, and are relatively insensitive to production-induced deviations from the ideal design.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
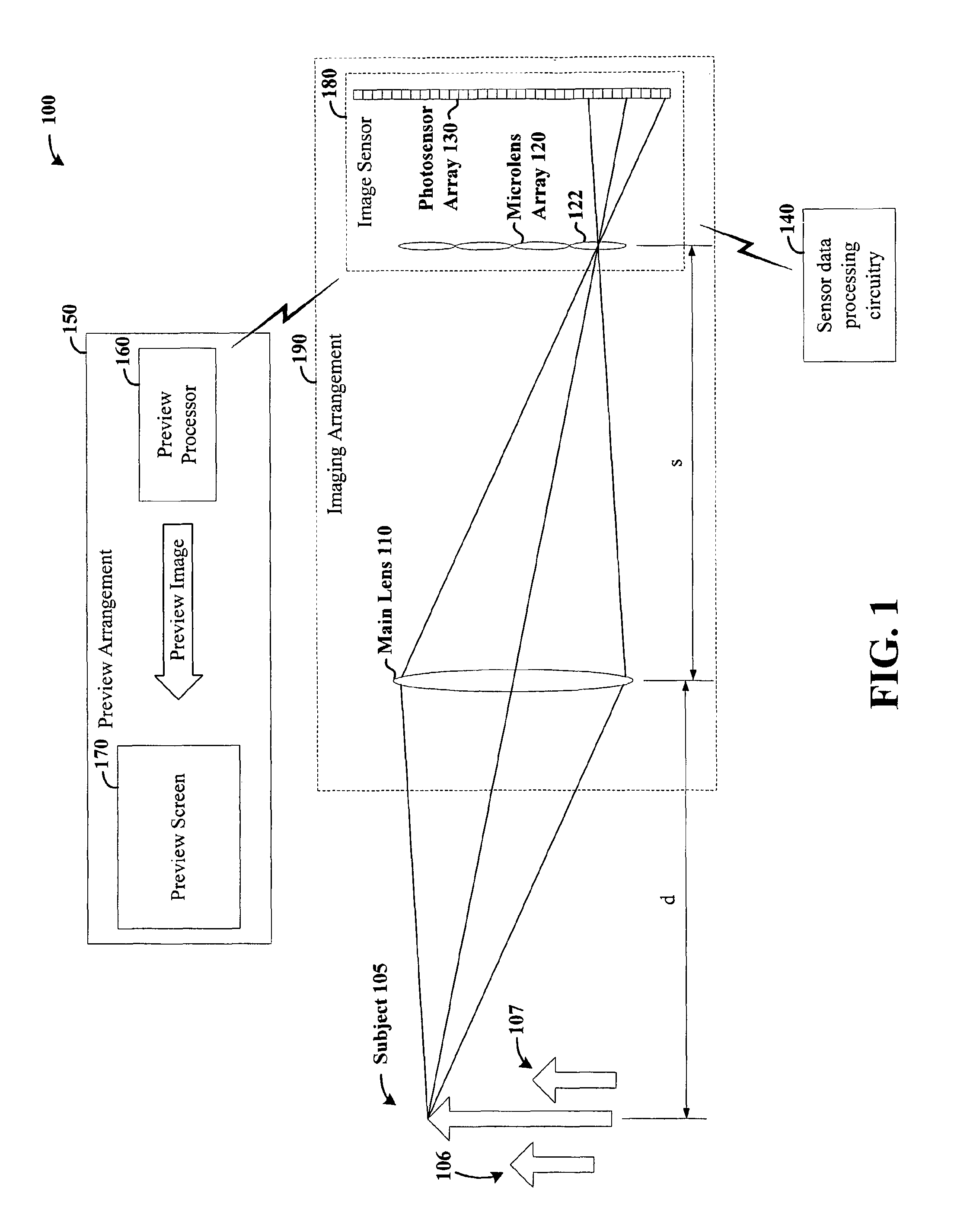
Imaging arrangements and methods therefor
Image data is processed to facilitate focusing and / or optical correction. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, an imaging arrangement collects light data corresponding to light passing through a particular focal plane. The light data is collected using an approach that facilitates the determination of the direction from which various portions of the light incident upon a portion of the focal plane emanate from. Using this directional information in connection with value of the light as detected by photosensors, an image represented by the light is selectively focused and / or corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for determining the configuration of an ophthalmic lens, ophthalmic lens produced according to said method, and method for producing said lens
ActiveUS8240850B2Add depthIncrease depth of focusSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical correctionVisual acuity
The invention relates to a method for making an ophthalmic lens intended to correct the visual acuity of a user, comprising the steps of determining the shape of a base optical corrective element, determining the profile of a phase element structure, said determination comprising the steps of defining a desired depth of focus of said ophthalmic lens; calculating the phase distribution to be created at the entrance pupil of the lens, selecting a phase distribution and performing an iterative calculation to obtain the depth of focus, finding the phase which minimizes the differences between the effective phase distribution and the desired phase distribution and of converting the phase data into geometrical data to define the profile of the phase distribution structure and juxtaposing the resulting phase element structure and the base optical corrective element.
Owner:SAV IOL
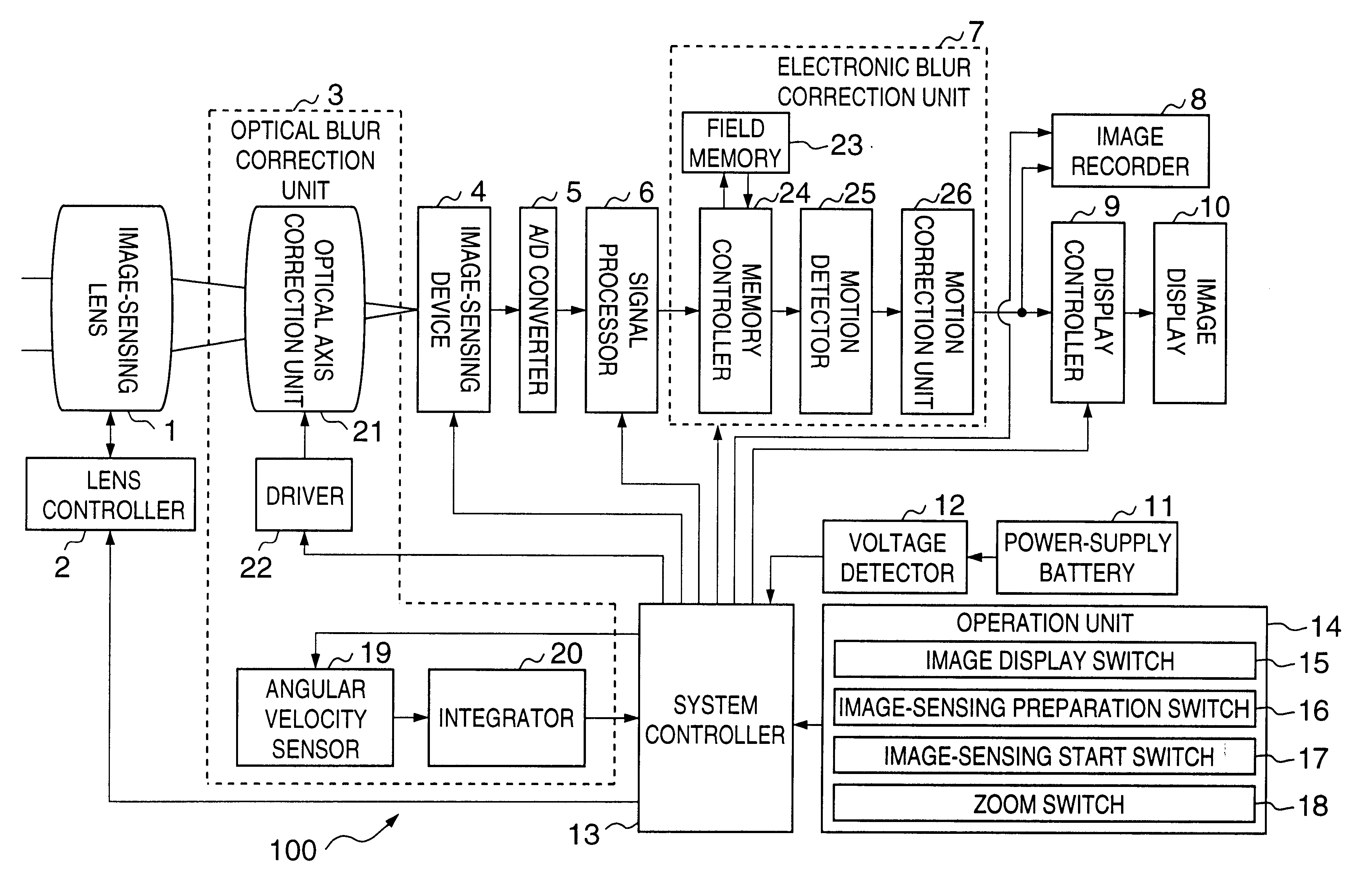
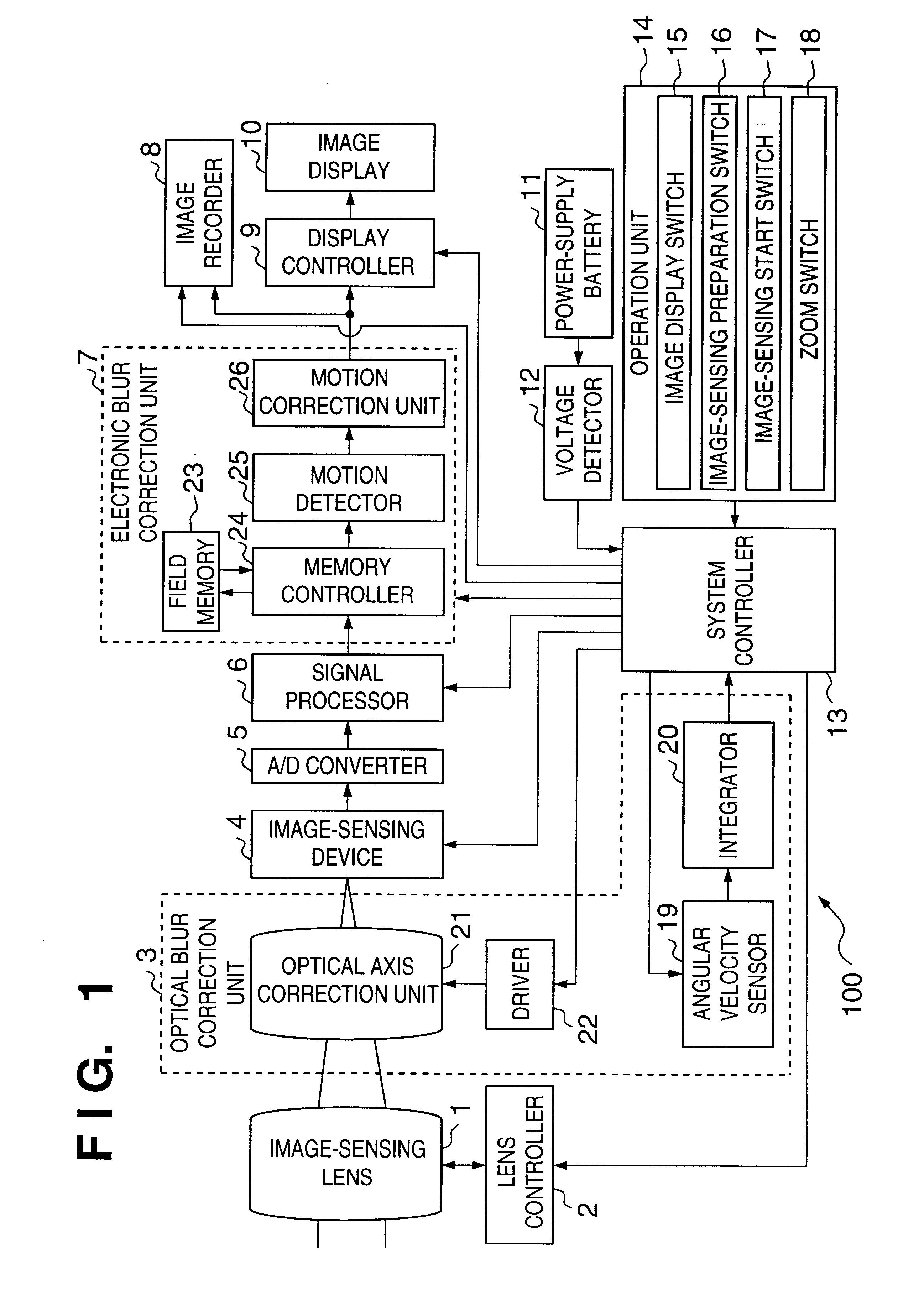
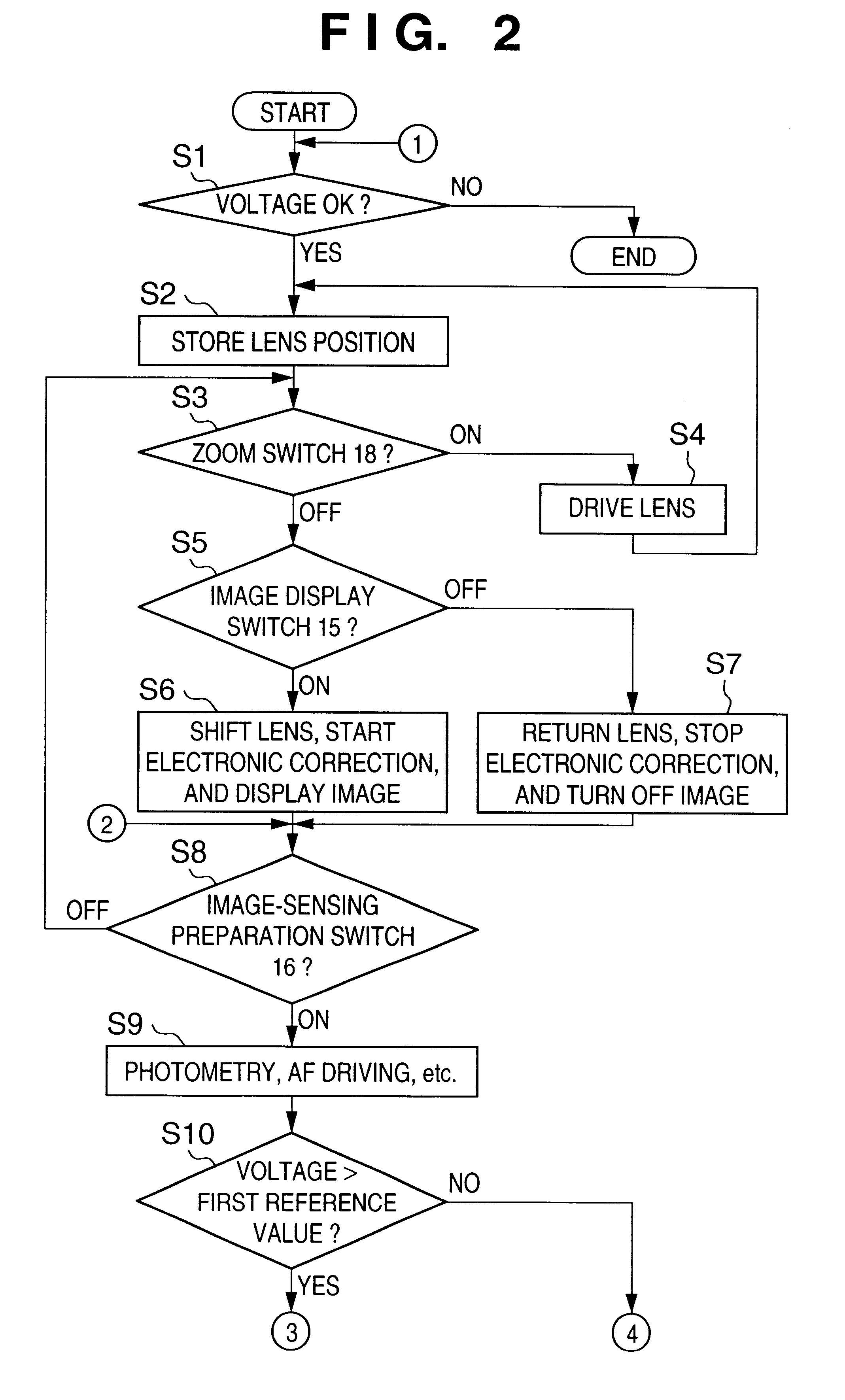
Image-sensing apparatus for selecting optical blur correction or electronic blur correction
ActiveUS6900831B2Effective correctionReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical correctionComputer science
When an object image is to be recorded, a blur of the object image is optically corrected. When an object image is to be displayed without being recorded, a blur of the object image is corrected not optically but by image signal processing.
Owner:CANON KK
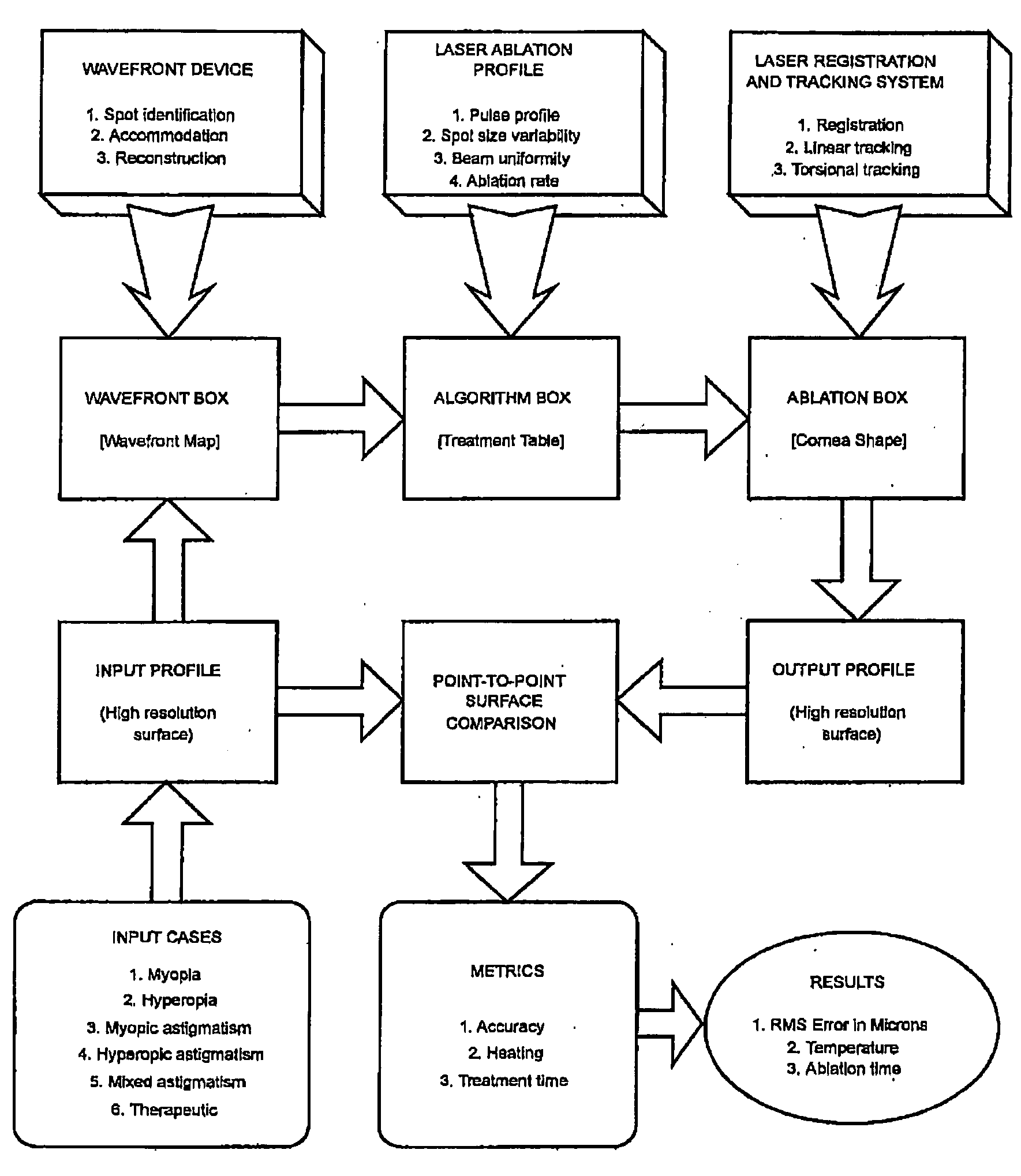
Systems and methods for correcting high order aberrations in laser refractive surgery
ActiveUS20050096640A1High order aberrationEvaluating and improving refractive surgery systemsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptical correctionOptical aberration
Optical correction methods, devices, and systems reduce optical aberrations or inhibit refractive surgery induced aberrations. Error source control and adjustment or optimization of ablation profiles or other optical data address high order aberrations. A simulation approach identifies and characterizes system factors that can contribute to, or that can be adjusted to inhibit, optical aberrations. Modeling effects of system components facilitates adjustment of the system parameters.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
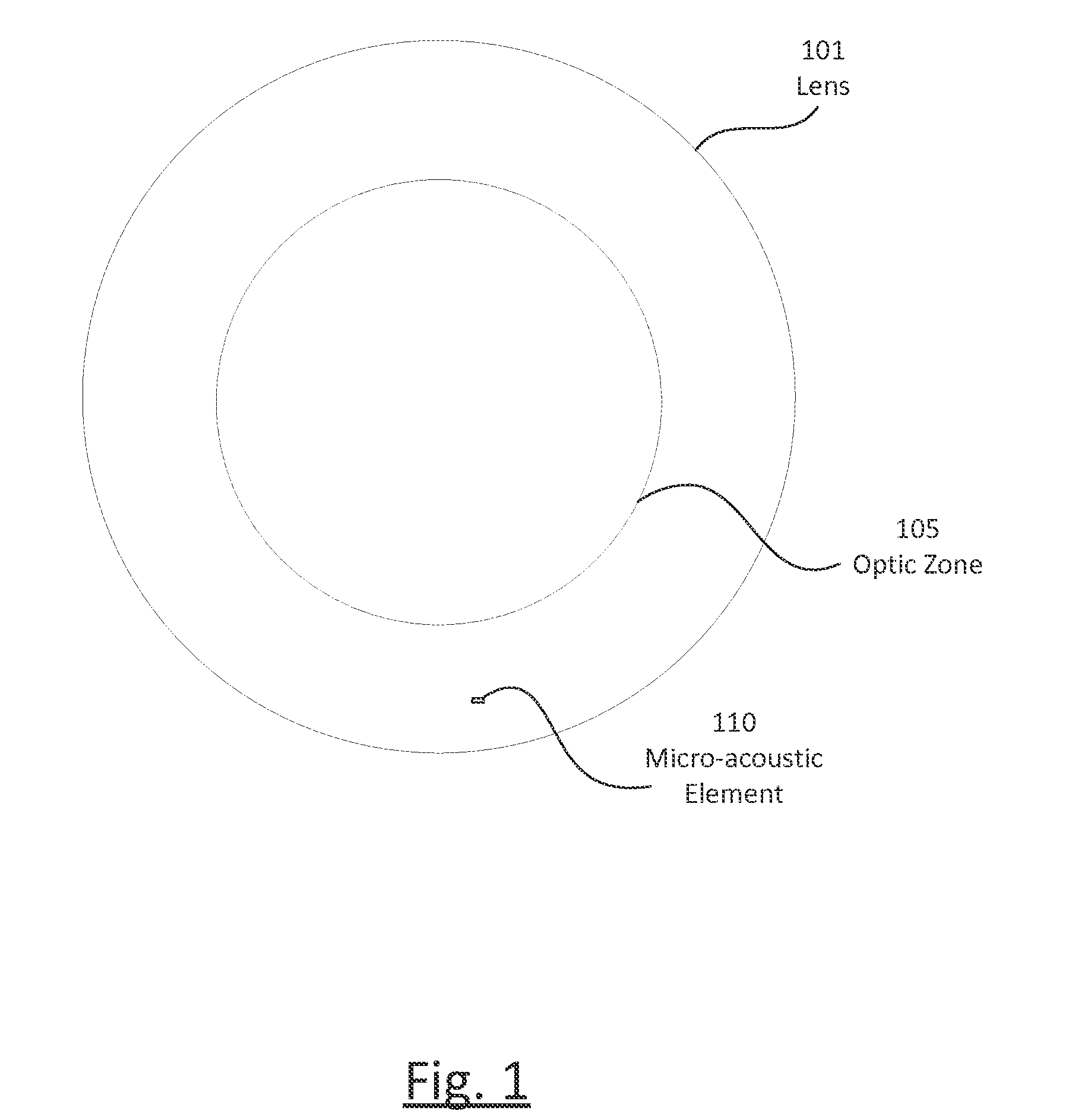
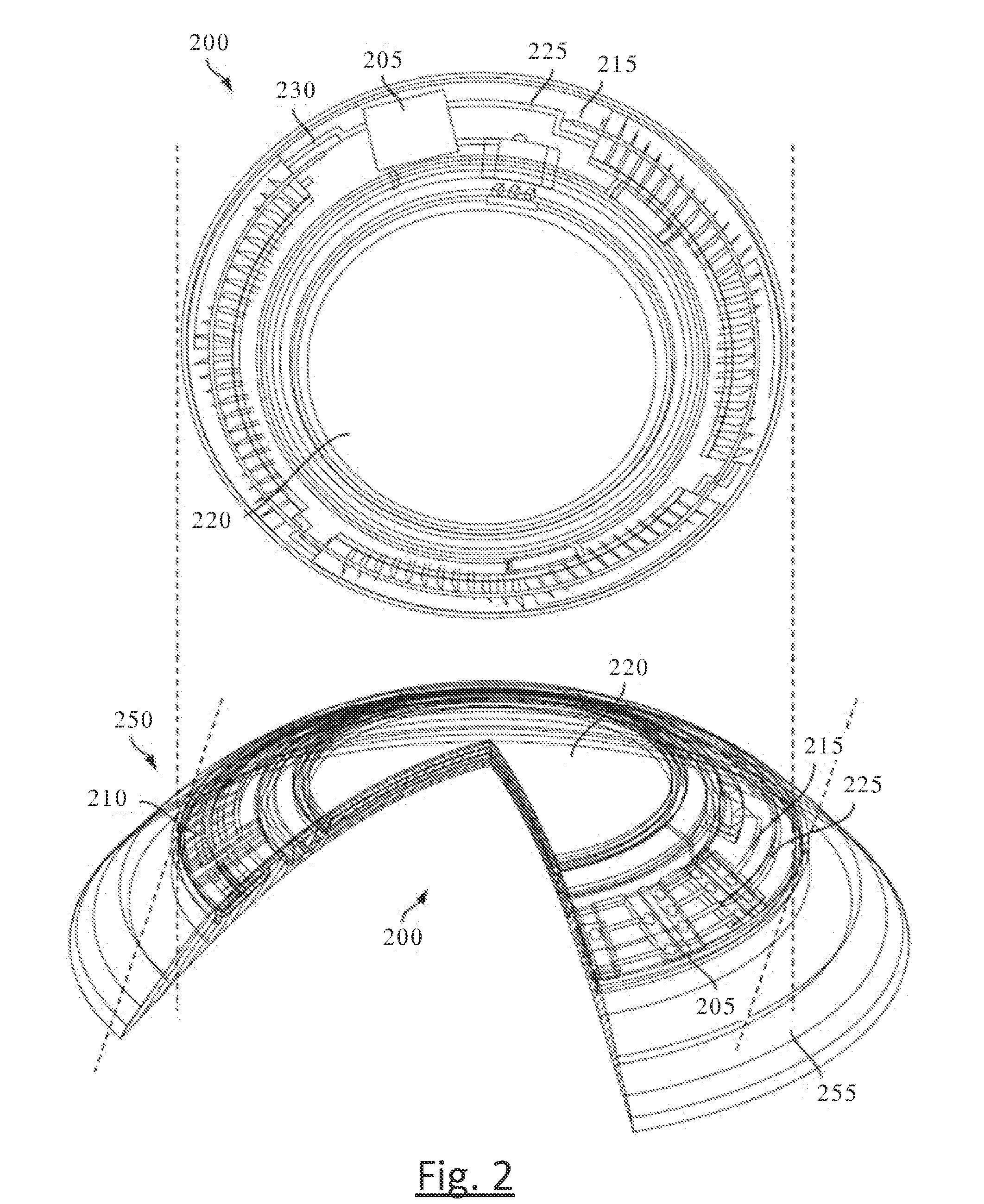
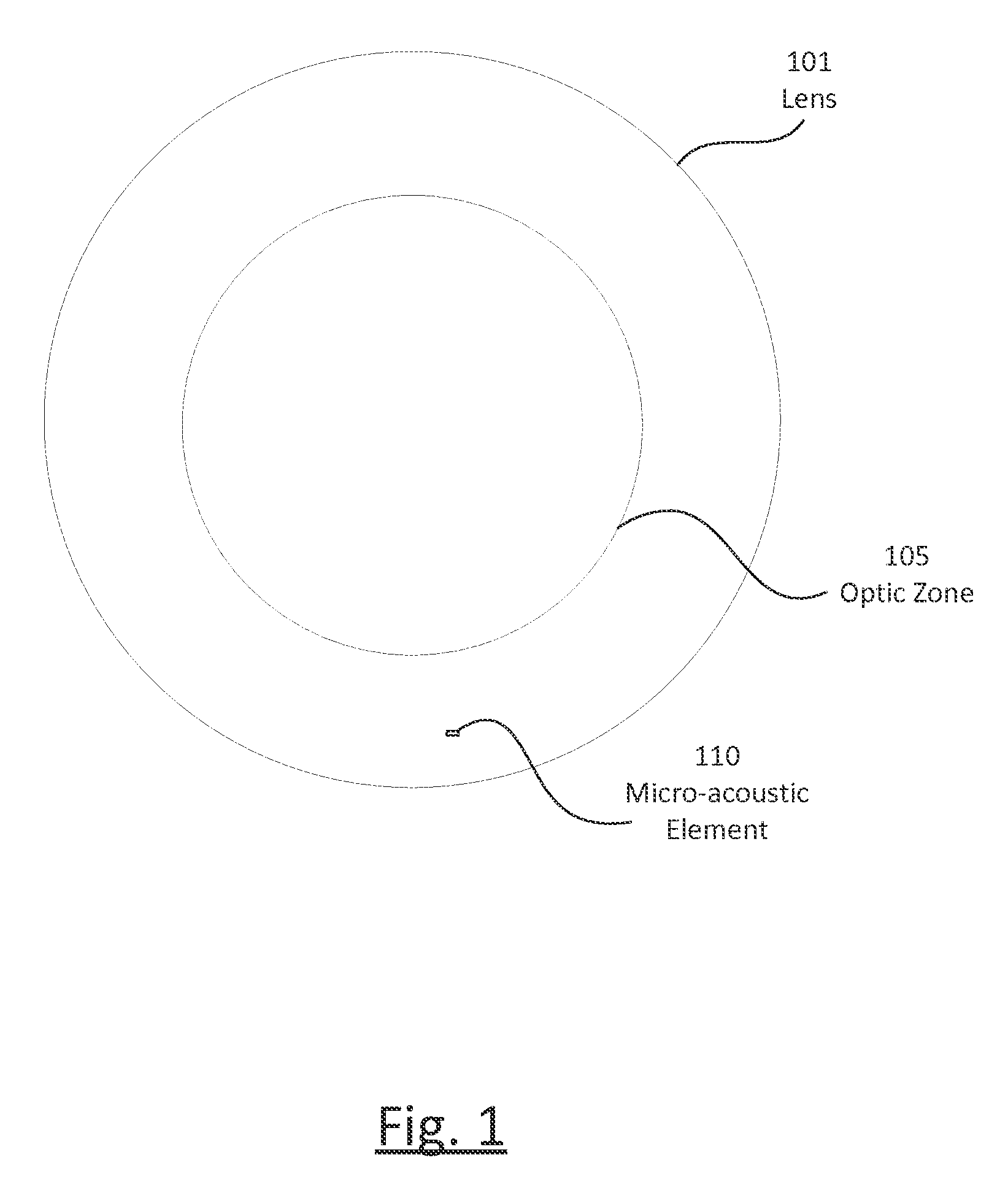
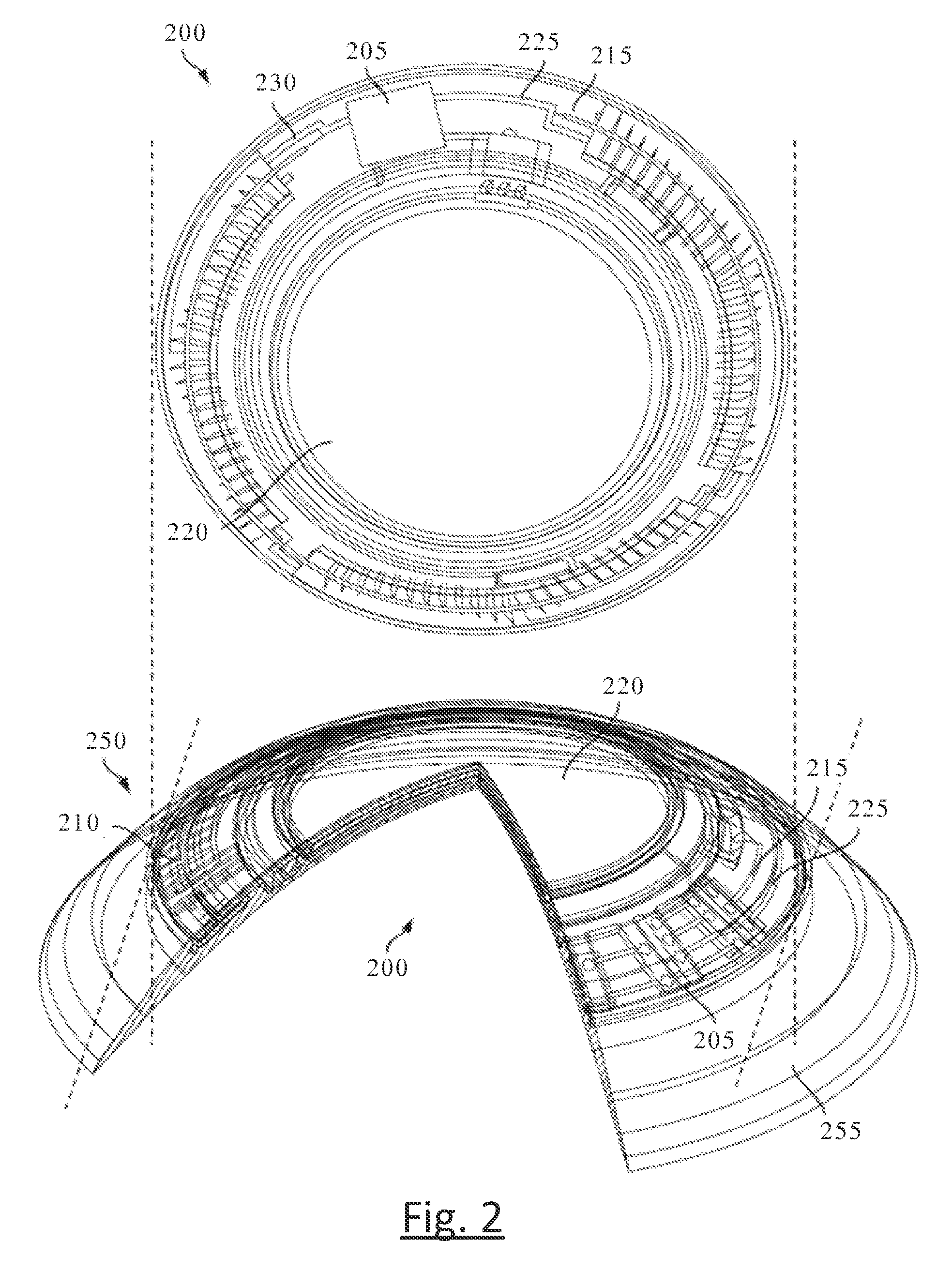
Ophthalmic lens with micro-acoustic elements
ActiveUS20150063605A1Vaccination/ovulation diagnosticsContact microphone transducersResonanceOptical correction
The present invention discloses an ophthalmic device with micro-acoustic electromechanical elements and associated methods. In some embodiments, the micro-acoustic electromechanical elements may be useful for the purpose of providing audible warnings and / or messages to a user. The audible warnings and / or messages can include, for example, messages transmitted wirelessly through a communication element of the ophthalmic device and / or generated within the ophthalmic device. In addition, in some embodiments the ophthalmic device can be an energized contact lens that is used both for optical correction and the transmission of sound through bone resonance to the inner ear of a user.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Image pickup apparatus and image shake correction method
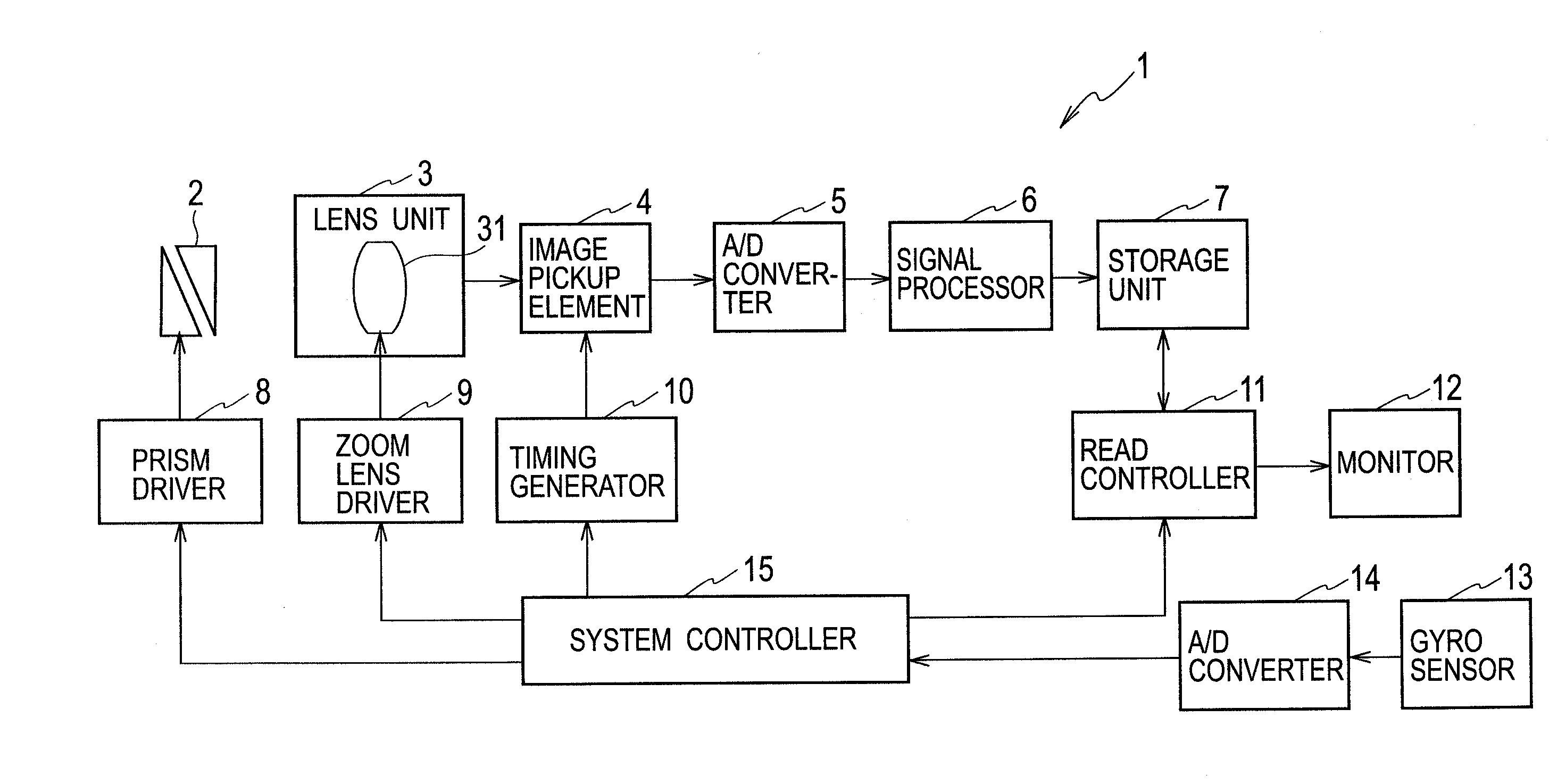
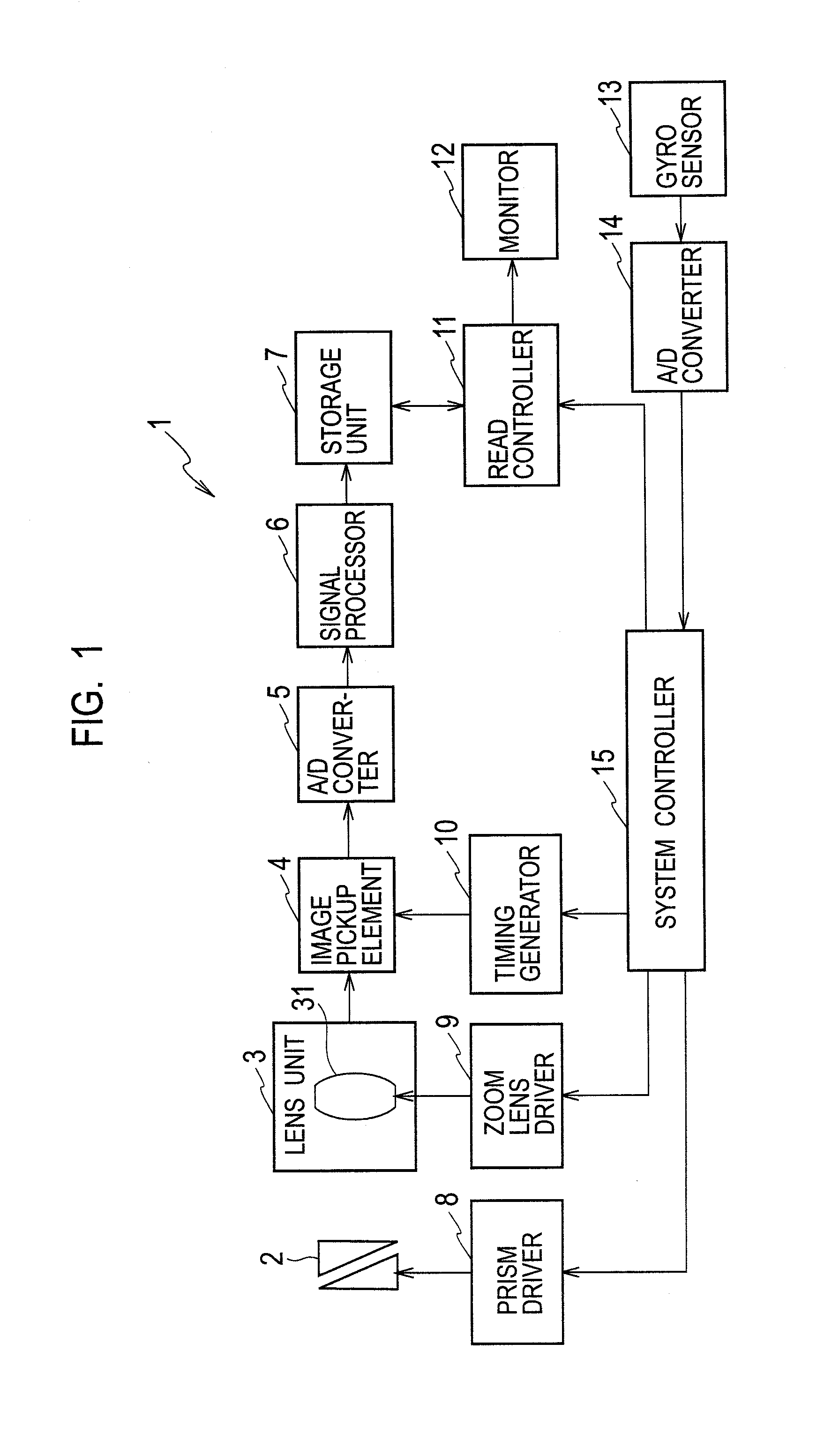
ActiveUS20120293672A1Extend correctable rangeSuppresses degradation of image qualityTelevision system detailsPrintersGyroscopeOptical correction
A system controller sets an optical correction ratio, which is a distribution ratio in which a shake angle detected by a gyro sensor is distributed to optical shake correction, in accordance with an optical zoom magnification and controls a prism driver to correct the shake angle multiplied by the optical correction ratio by the optical shake correction, and also controls a read controller to correct the rest of the angle by electronic shake correction.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Ophthalmic lens with micro-acoustic elements
ActiveUS9185486B2Vaccination/ovulation diagnosticsContact microphone transducersResonanceOptical correction
The present invention discloses an ophthalmic device with micro-acoustic electromechanical elements and associated methods. In some embodiments, the micro-acoustic electromechanical elements may be useful for the purpose of providing audible warnings and / or messages to a user. The audible warnings and / or messages can include, for example, messages transmitted wirelessly through a communication element of the ophthalmic device and / or generated within the ophthalmic device. In addition, in some embodiments the ophthalmic device can be an energized contact lens that is used both for optical correction and the transmission of sound through bone resonance to the inner ear of a user.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Systems and methods for correcting high order aberrations in laser refractive surgery
InactiveUS20130190736A1High order aberrationEvaluating and improving refractive surgery systemsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOphthalmologyOptical correction
Optical correction methods, devices, and systems reduce optical aberrations or inhibit refractive surgery induced aberrations. Error source control and adjustment or optimization of ablation profiles or other optical data address high order aberrations. A simulation approach identifies and characterizes system factors that can contribute to, or that can be adjusted to inhibit, optical aberrations. Modeling effects of system components facilitates adjustment of the system parameters.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
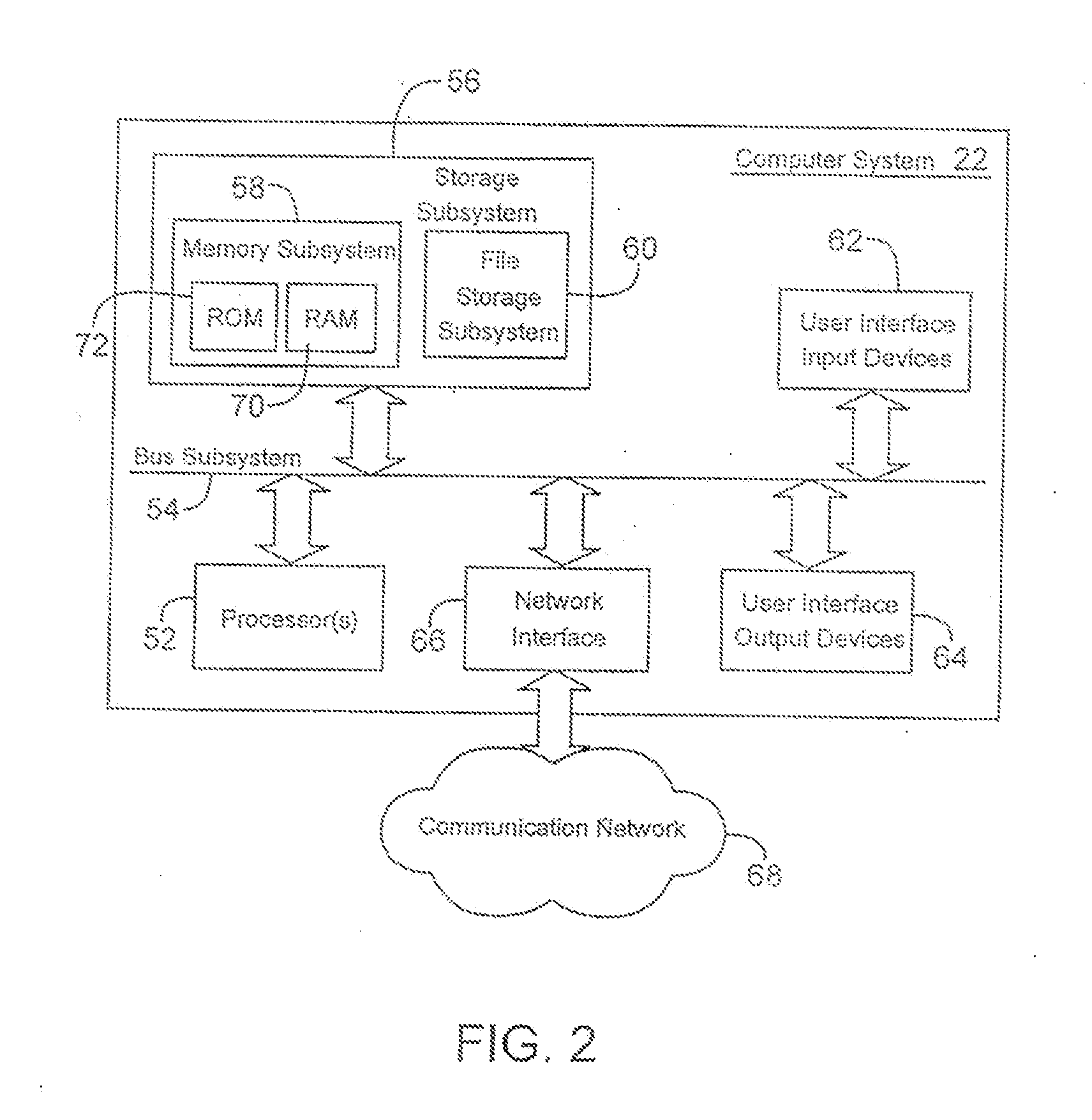
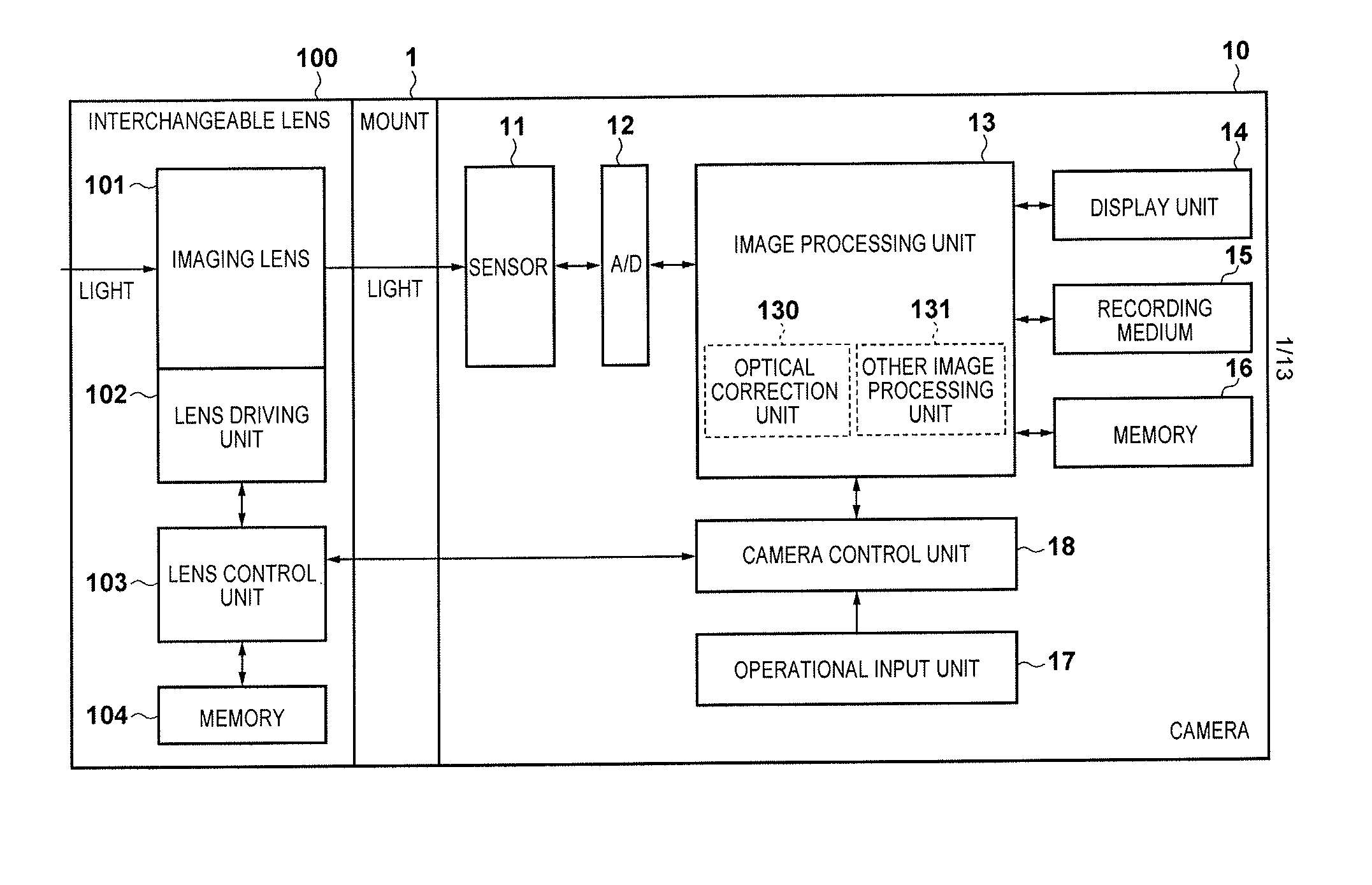
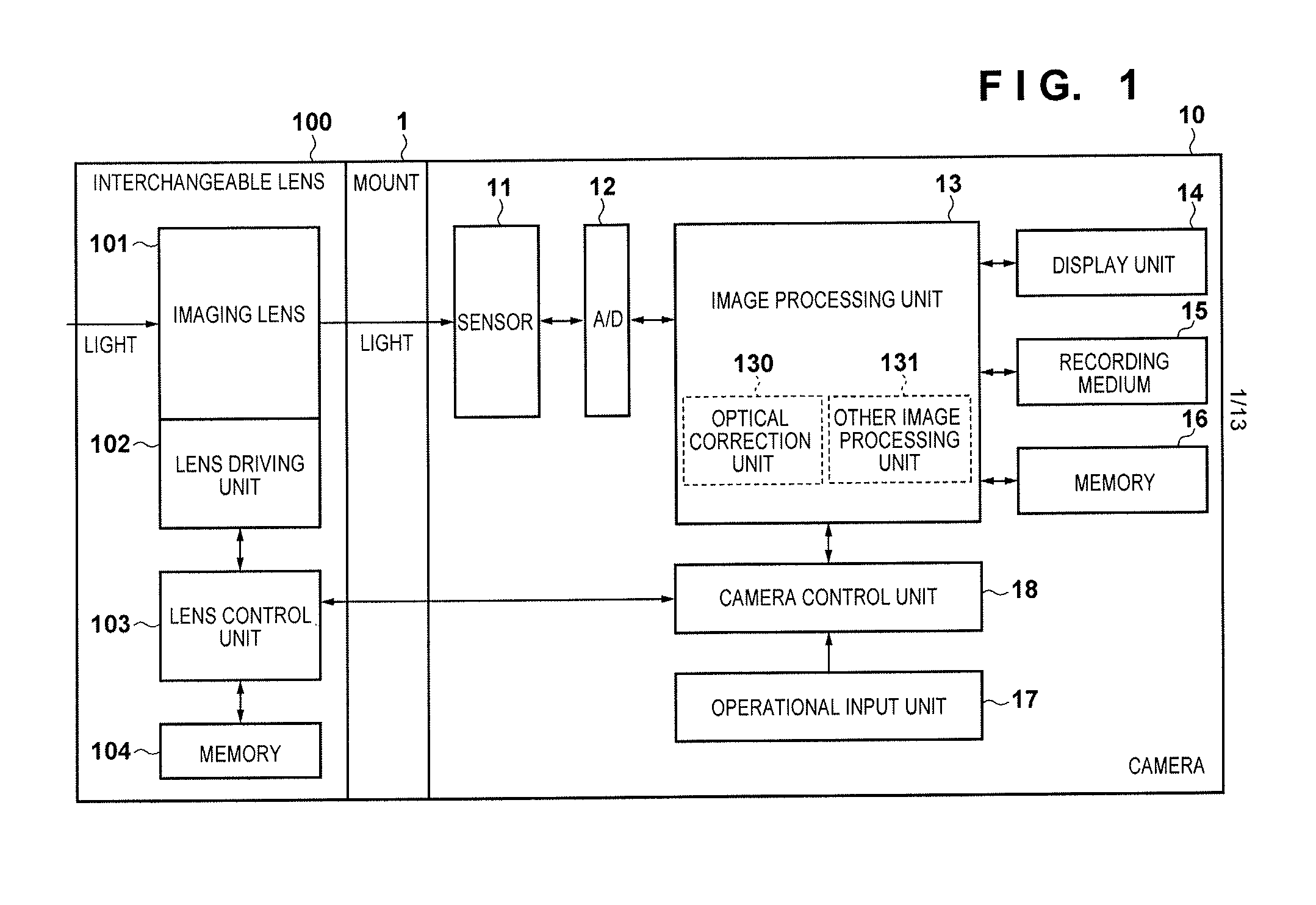
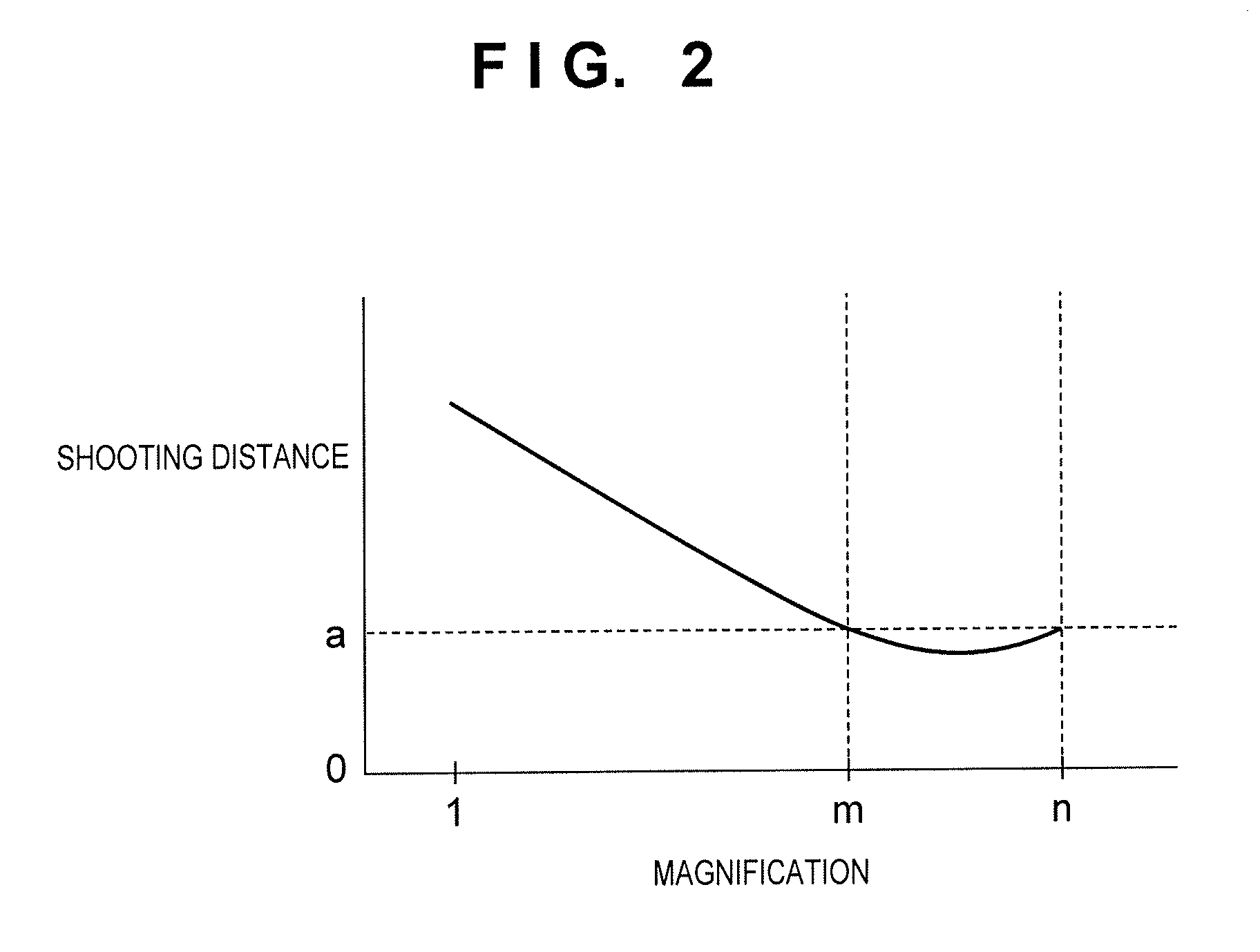
Image capture apparatus and control method thereof, and lens unit
A plurality of types of interchangeable lenses having mutually different optical parameters required for identifying the optical correction values can be attached to the image capture apparatus. First, predetermined optical parameters are obtained regardless of what type of interchangeable lens is attached. Furthermore, in the case where the type of the attached interchangeable lens is a type that requires different optical parameters than the predetermined optical parameters for identifying the optical correction value, the necessary optical parameters are obtained. The optical correction value is identified based on the type of the attached interchangeable lens using the predetermined optical parameters, other optical parameters, and so on, and optical correction is then carried out.
Owner:CANON KK
Self-adaptive optical correction method and system based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109031654ASimple structureEasy to implementNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsWavefrontBeam splitting
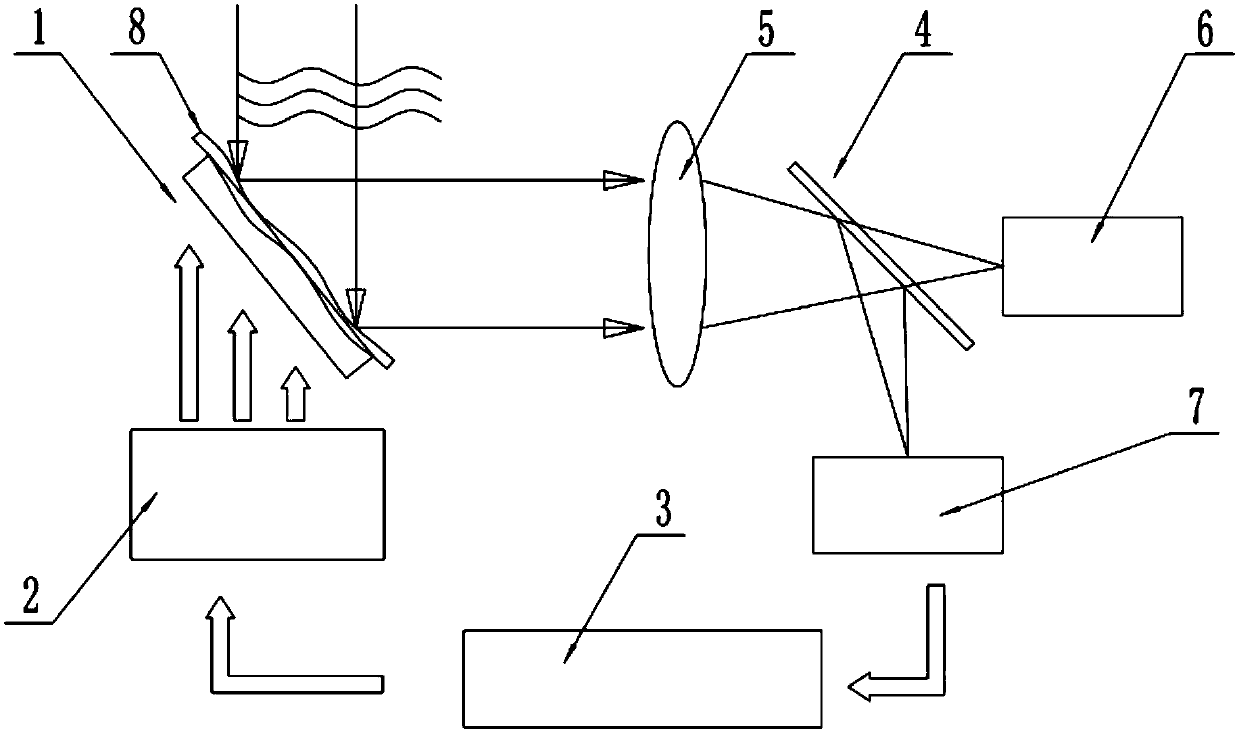
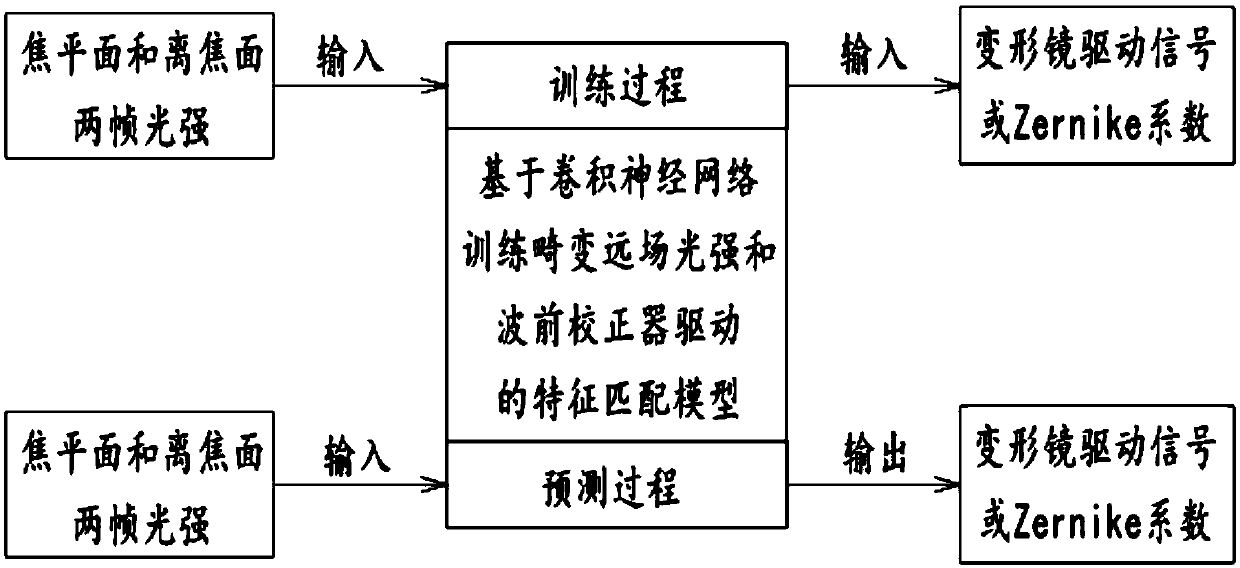
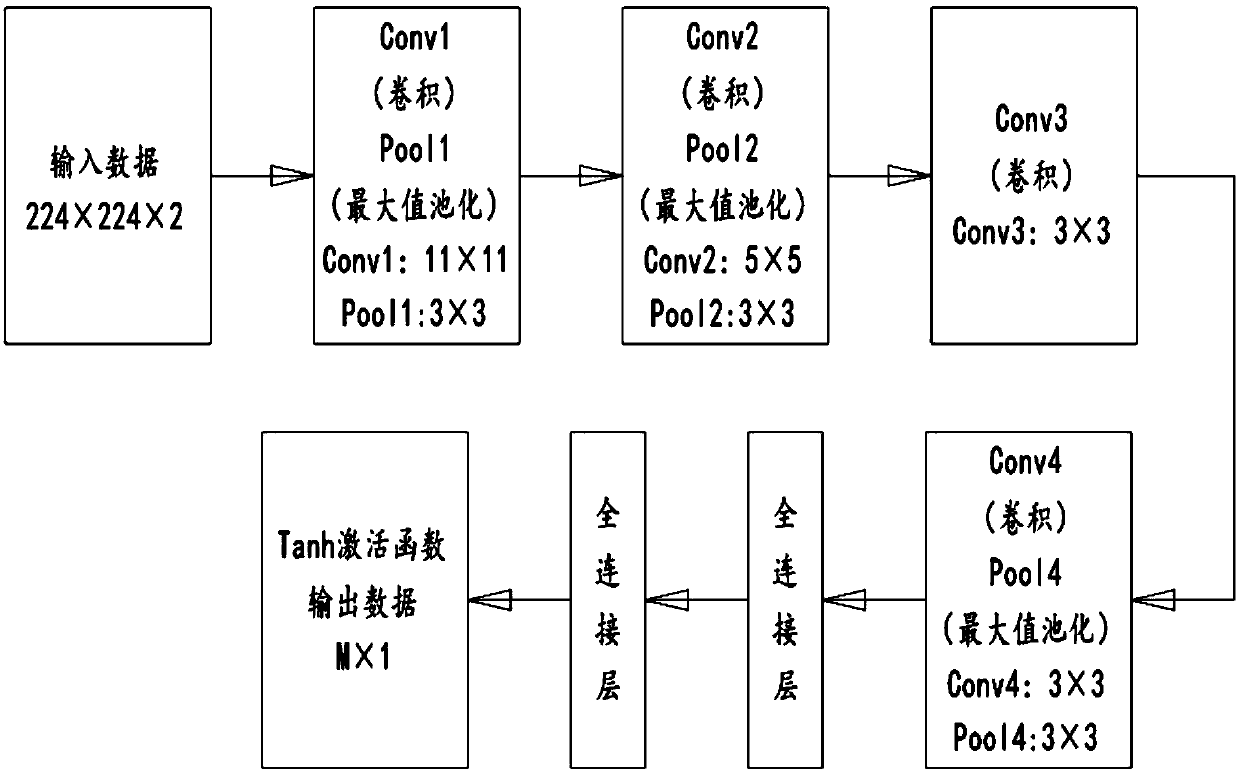
The invention discloses a self-adaptive optical correction method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps of S1, based on the convolutional neural network, training a convolutional neural network model of a distorted far-field light intensity image and a wavefront corrector driving signal; and S2, after the convolutional neural network model is built, dividing a to-be-corrected distorted wavefront into two parts after reflection by a wavefront corrector and beam splitting of a light path, and performing imaging on a focus plane CCD and an out-of-focusplane CCD. The method has the beneficial effects that the wavefront corrector driving signal is obtained directly according to the input light intensity by utilizing the convolutional neural network model; the driving signal is used for controlling the wavefront corrector to generate a deformation amount which is conjugated with the to-be-corrected wavefront so as to correct an aberration of an incident wavefront; the wavefront detection and the corresponding reconstruction calculation do not need to be carried out, and the iteration optimization does not need to be carried out; and a system is simple in structure, easy to implement, low in cost and wide in bandwidth.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Image capture apparatus and control method therefor
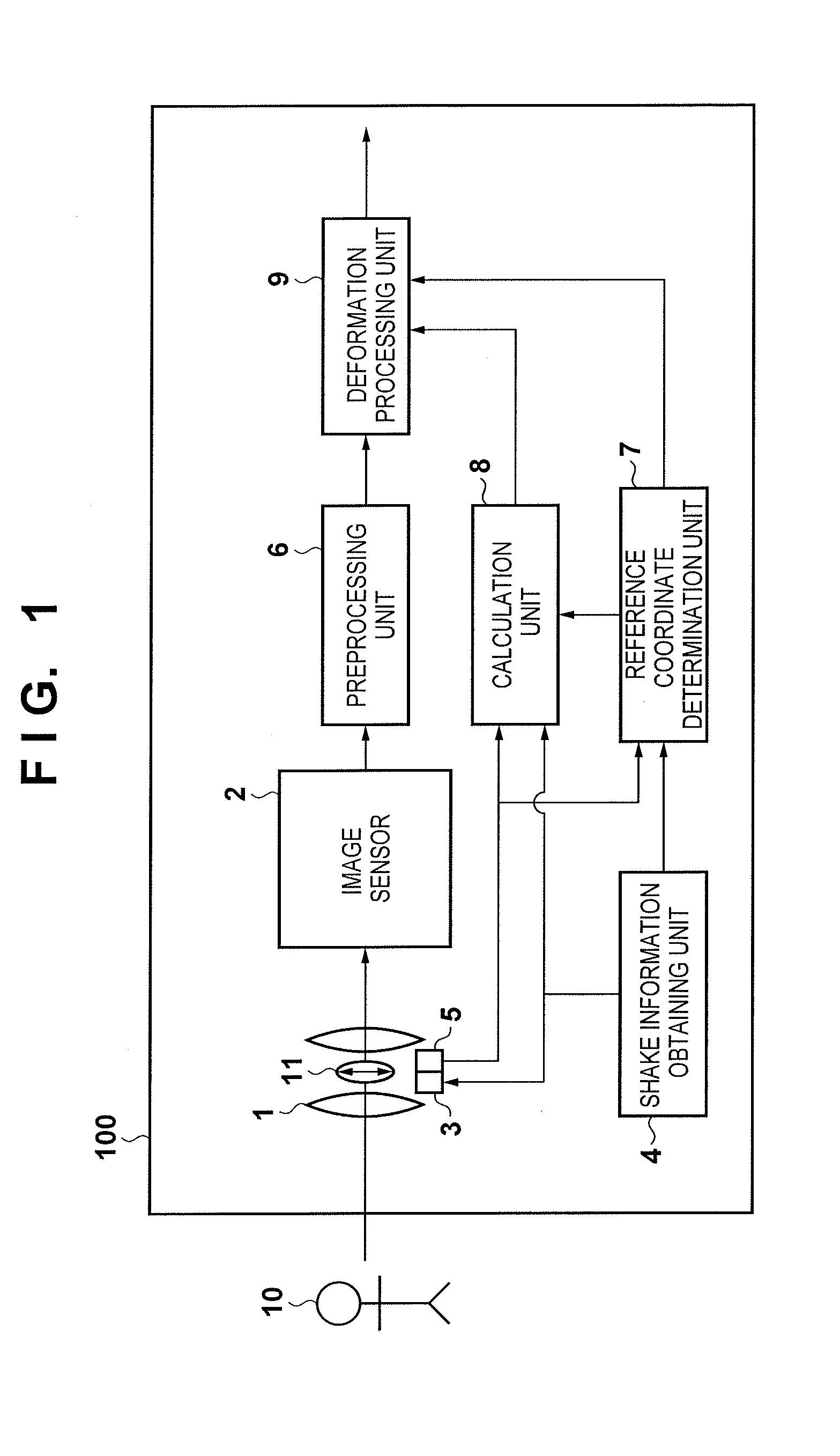
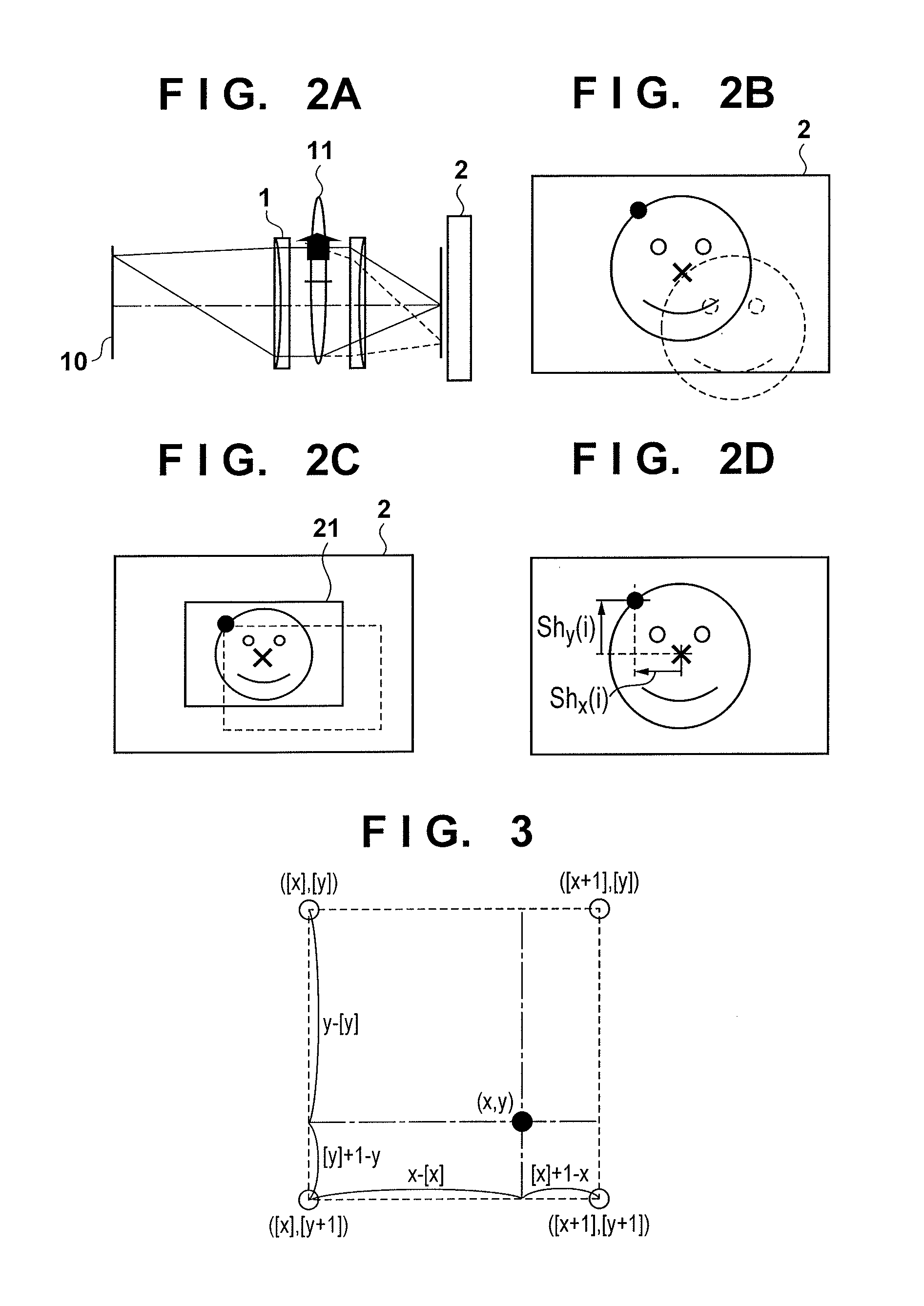
ActiveUS20150022678A1Improve accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Optical axis
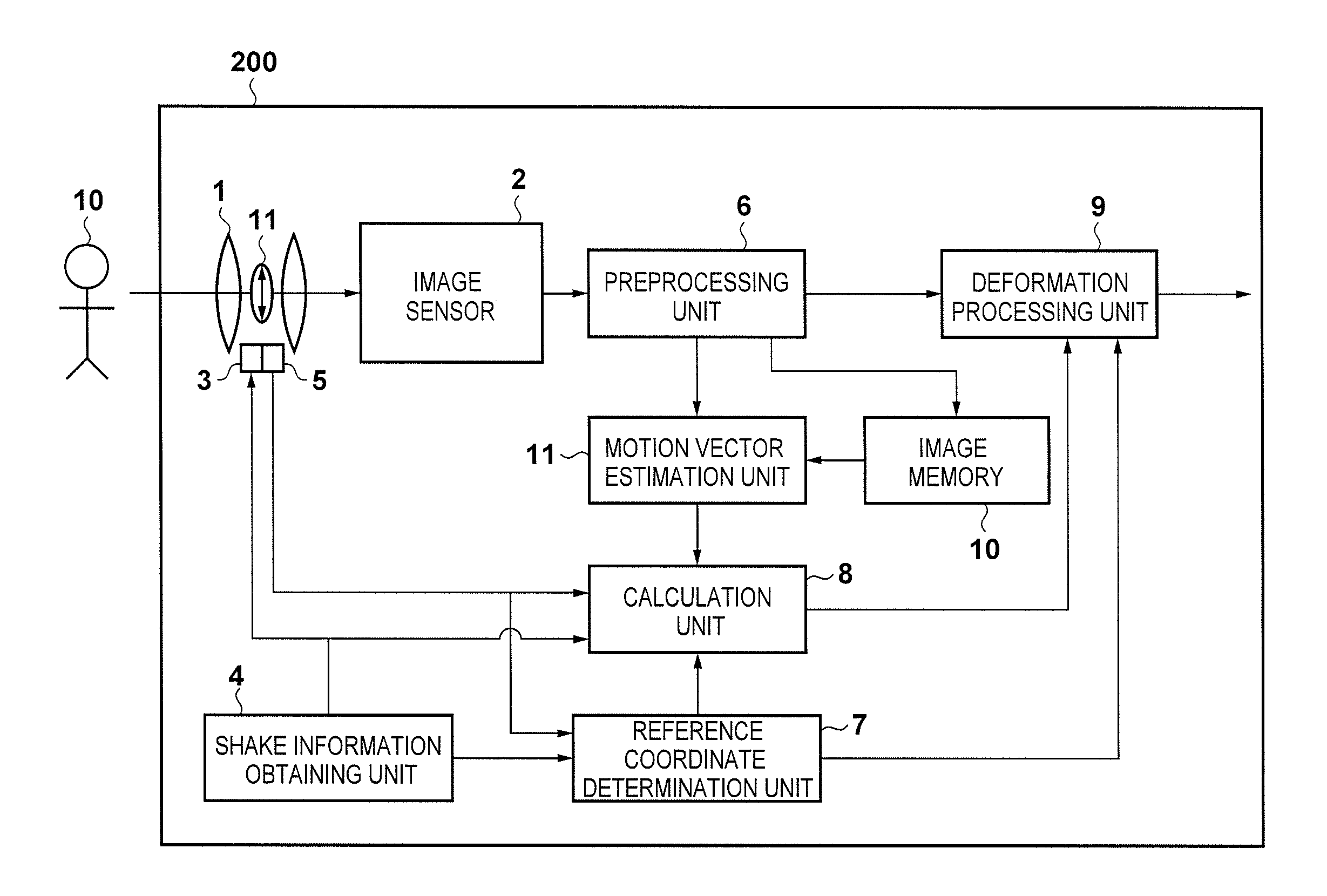
An image capture apparatus has an image sensor and an optical anti-shake mechanism that reduces a shake of a captured image by driving an optical correction element in a different direction from an optical axis of an imaging optical system in accordance with a detected shake. Reference coordinates for geometric deformation processing applied to the captured image are determined based on an amount and direction of a movement of the optical correction element. The geometric deformation processing is applied to the captured image using these reference coordinates and an amount of geometric deformation based on the detected shake. Coordinates of the captured image corresponding to an intersection of the optical axis and the image sensor before the optical correction element is moved through the driving are determined as the reference coordinates.
Owner:CANON KK
Three-dimensional laser alignment positioner for particle image velocimetry
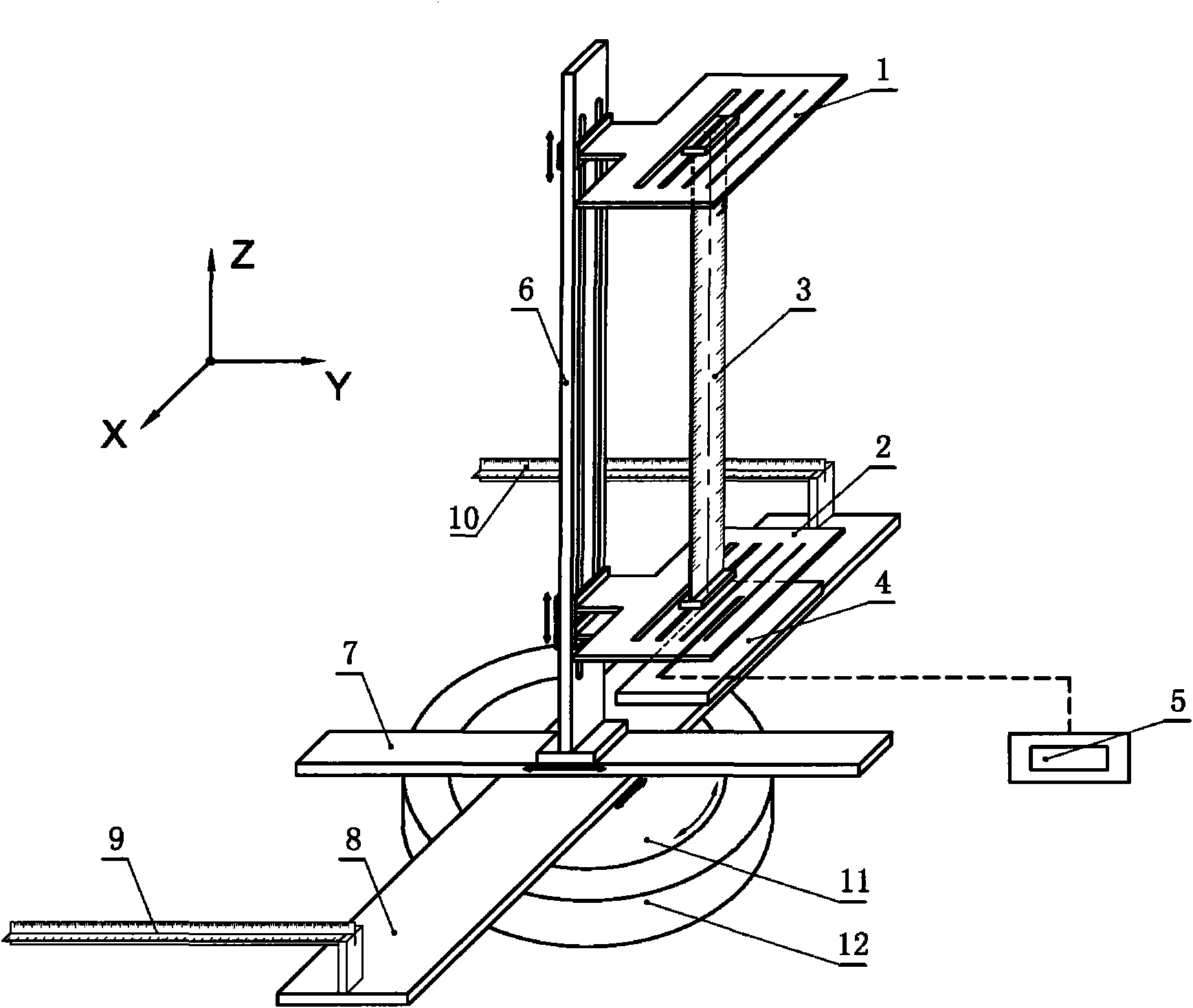
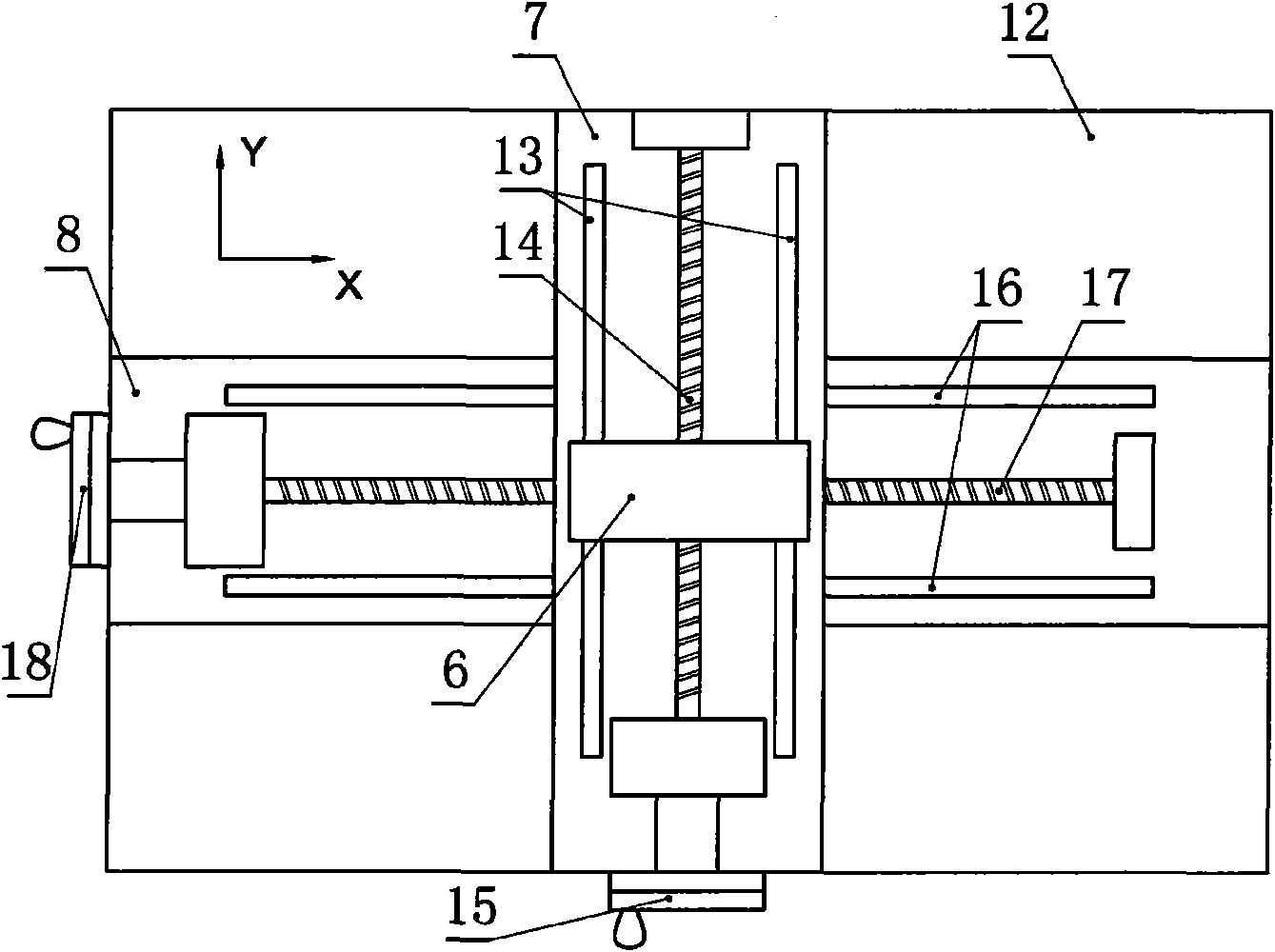
InactiveCN101900744AAvoid human errorSimplify the calibration processSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsFluid speed measurementOptical correctionVisual inspection
The invention discloses a three-dimensional laser alignment positioner for a particle image velocimetry and belongs to the technical field of fluid dynamic experiments. The positioner comprises a three-dimensional coordinate adjusting frame and a laser sheet optical correction system. The three-dimensional coordinate adjusting frame comprises a Z-direction coordinate frame, a Y-direction coordinate frame, an X-direction coordinate frame, a front positioning cross ruler, a rear positioning cross ruler, a rotating substrate and a base; and the laser sheet optical correction system comprises two upper and lower laser sheet optical correction boards with the same structure, a focusing ruler, a photoelectric detection board and a photoelectric indicator. By using the three-dimensional coordinate adjusting frame, the positioner can accurately determine the position of a testing plane, realizes the overlap of three surfaces of a flow field testing plane, a laser sheet light surface and a camera shooting surface through the laser sheet optical correction system, automatically detects the overlap ratio through a photoelectric detection device, and avoids human errors brought by the conventional visual inspection and other experimental calibration methods. Therefore, the calibration process of the particle image velocimetry is simpler and more standard and accurate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com