Patents
Literature
1887 results about "Optical path length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
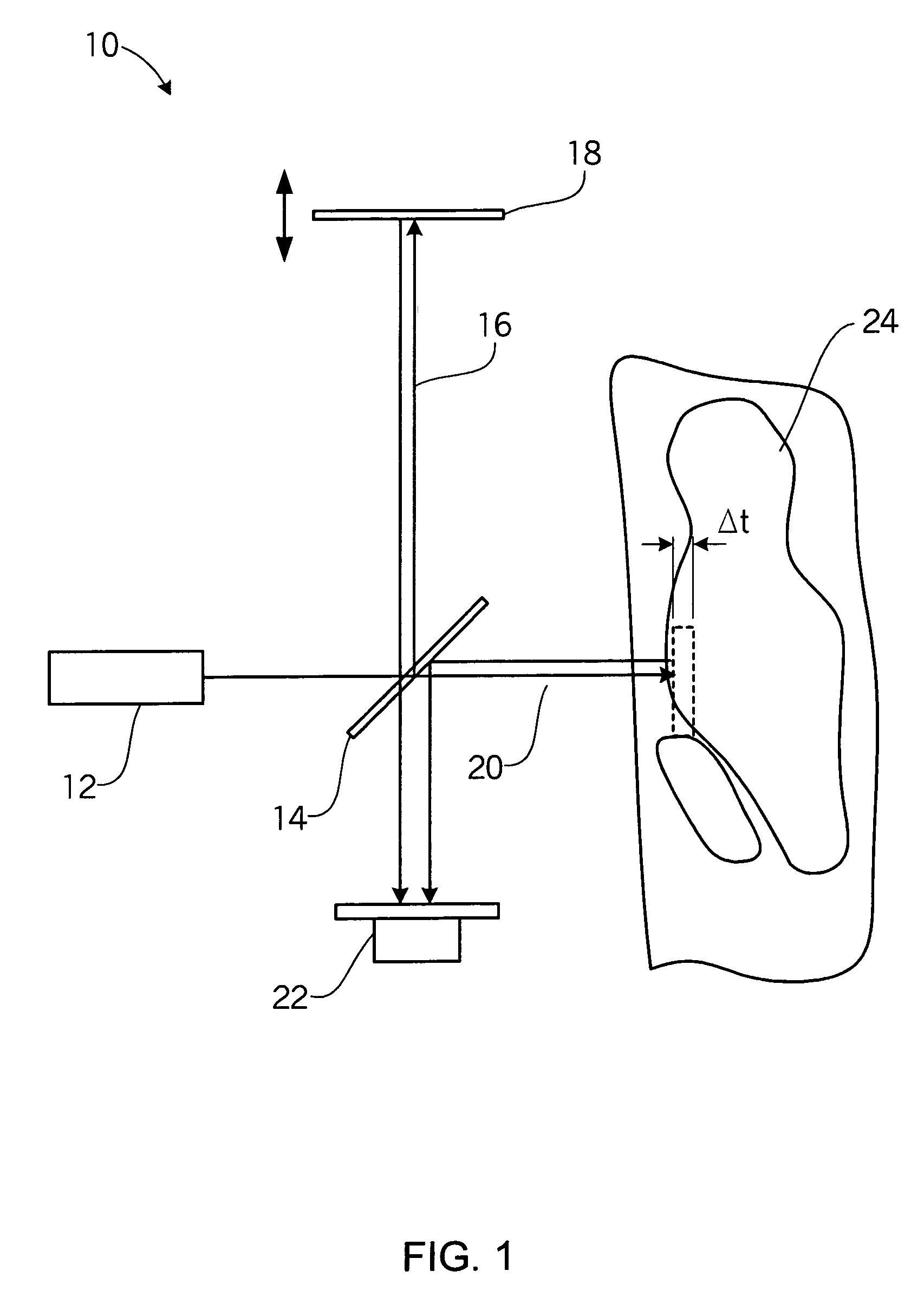
In optics, optical path length (OPL) or optical distance is the product of the geometric length of the path followed by light through a given system, and the index of refraction of the medium through which it propagates. In many textbooks, it is symbolically written as Λ. A difference in optical path length between two paths is often called the optical path difference (OPD). OPL and OPD are important because they determine the phase of the light and governs interference and diffraction of light as it propagates.
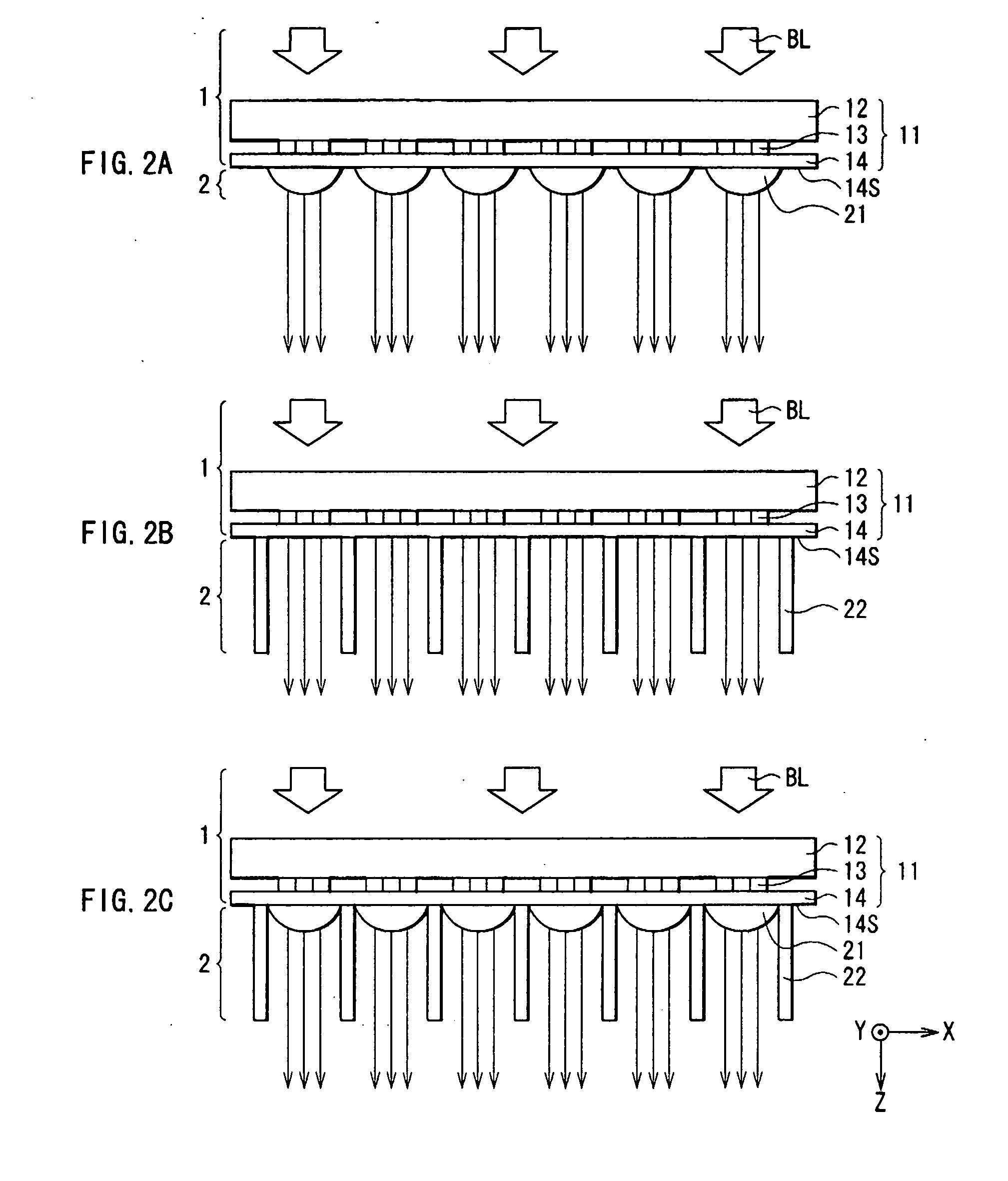
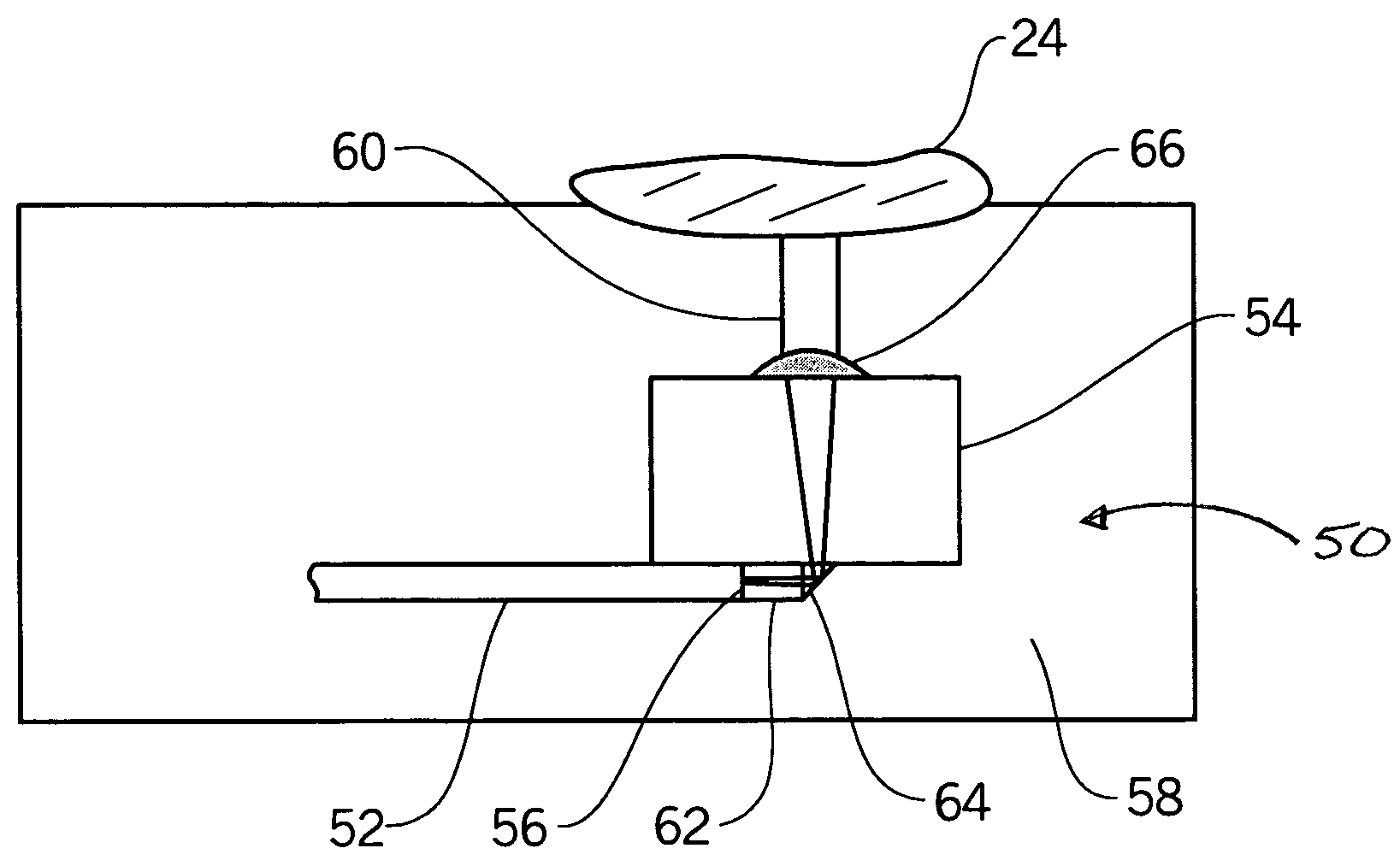
Fiber optic position and shape sensing device and method relating thereto
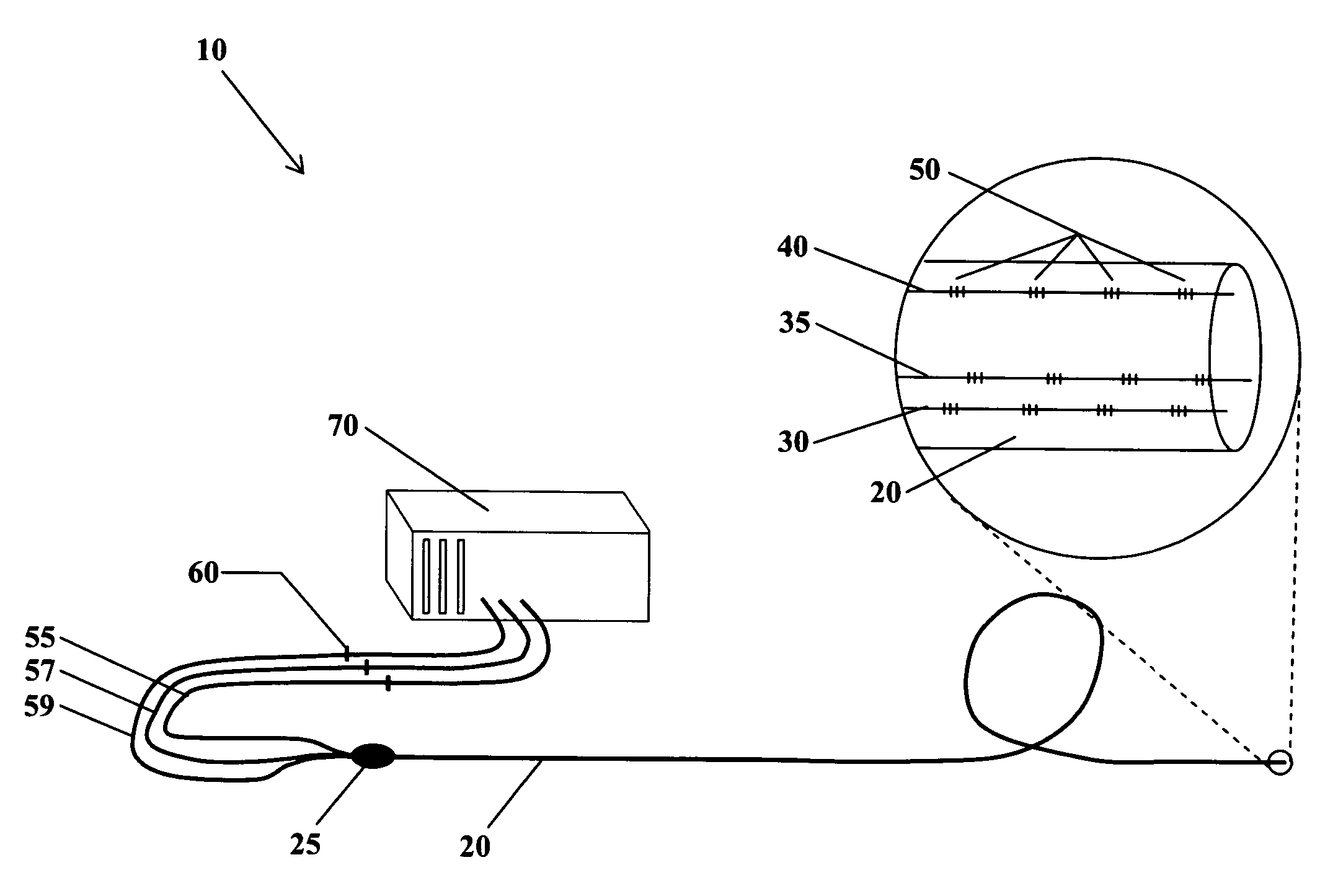
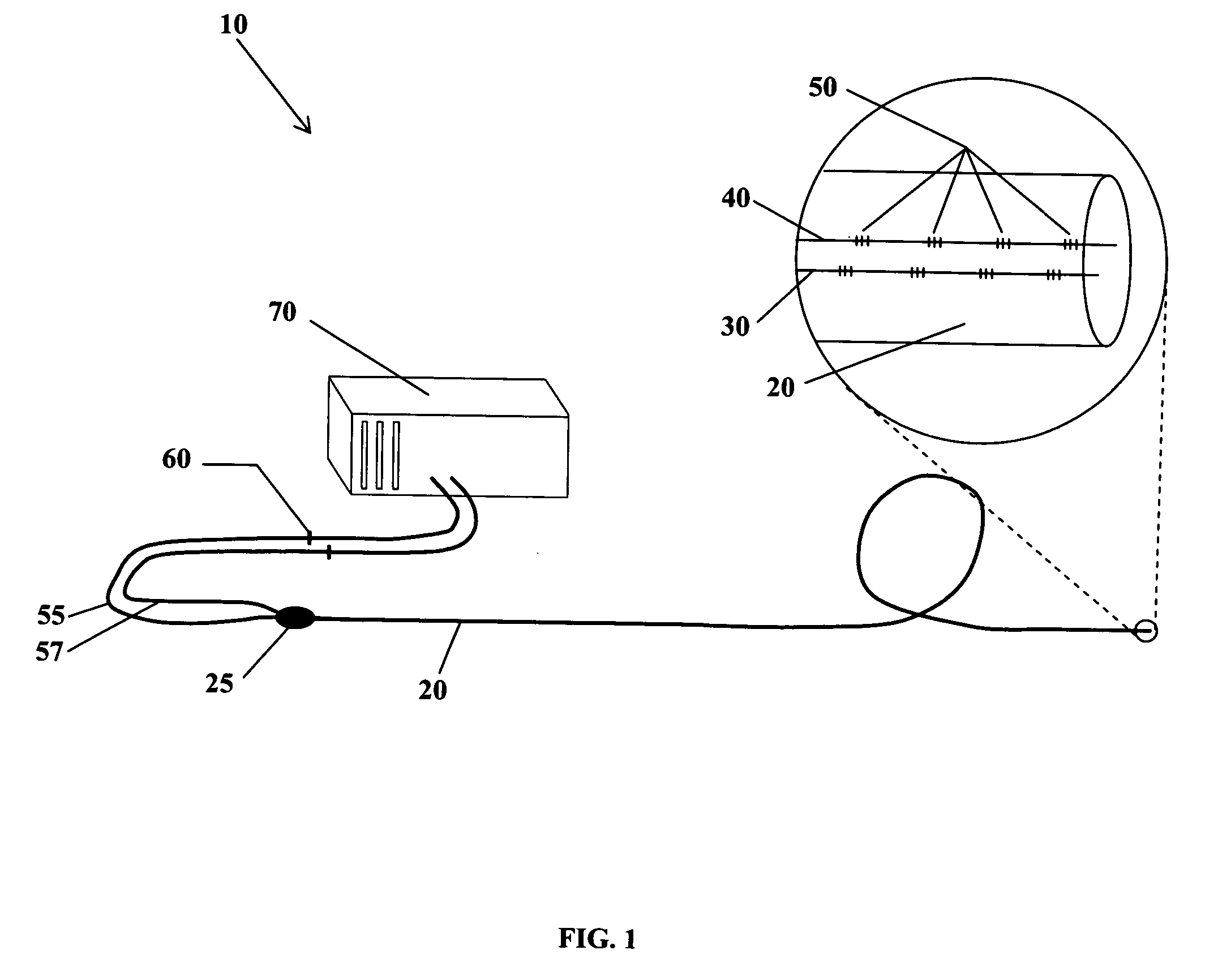
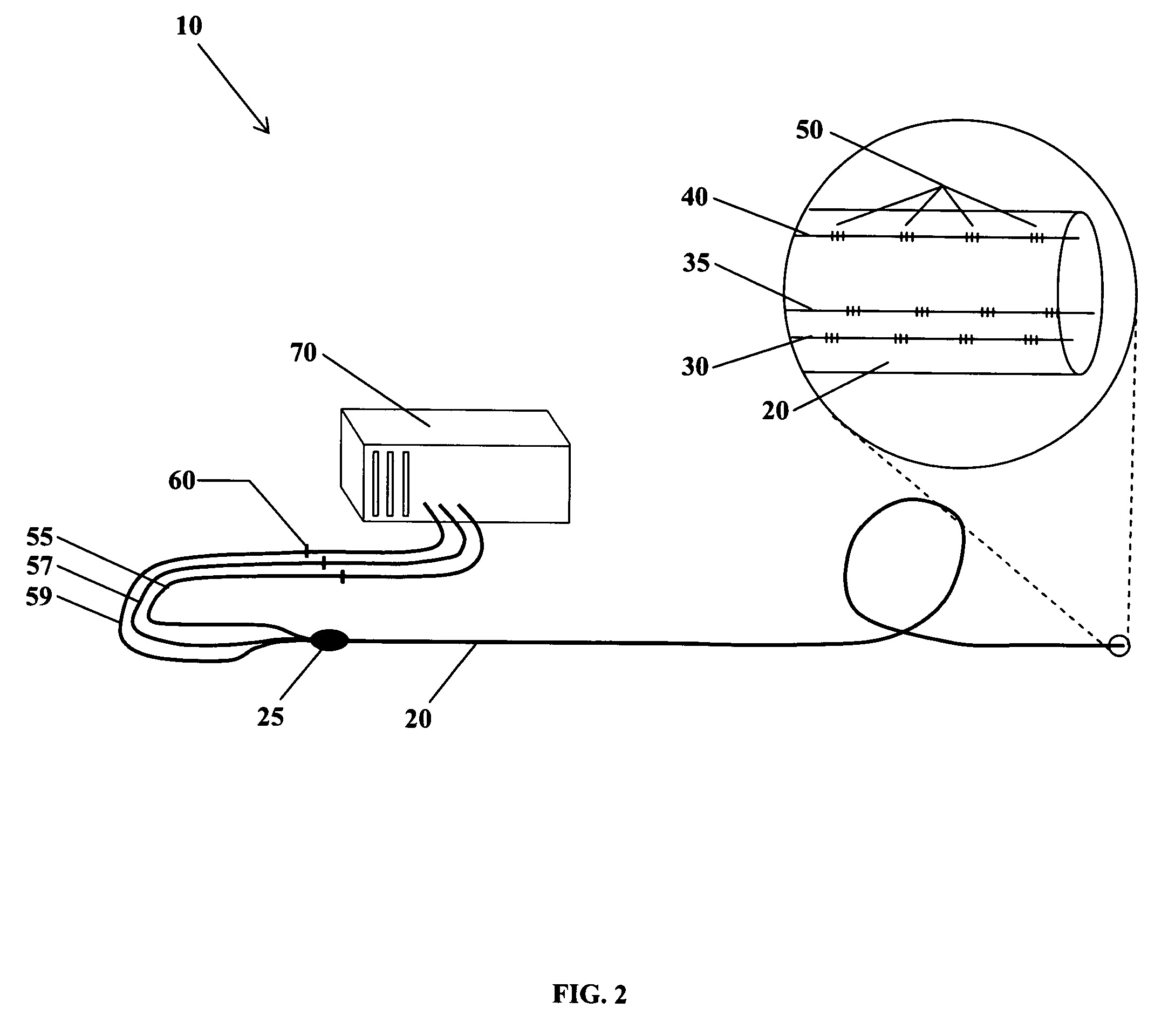
The present invention is directed toward a fiber optic position and shape sensing device and the method of use. The device comprises an optical fiber means. The optical fiber means comprises either at least two single core optical fibers or a multicore optical fiber having at least two fiber cores. In either case, the fiber cores are spaced apart such that mode coupling between the fiber cores is minimized. An array of fiber Bragg gratings are disposed within each fiber core. A broadband reference reflector is positioned in an operable relationship to each fiber Bragg grating wherein an optical path length is established for each reflector / grating relationship. A frequency domain reflectometer is positioned in an operable relationship to the optical fiber means. In use, the device is affixed to an object. Strain on the optical fiber is measured and the strain measurements correlated to local bend measurements. Local bend measurements are integrated to determine position or shape of the object.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
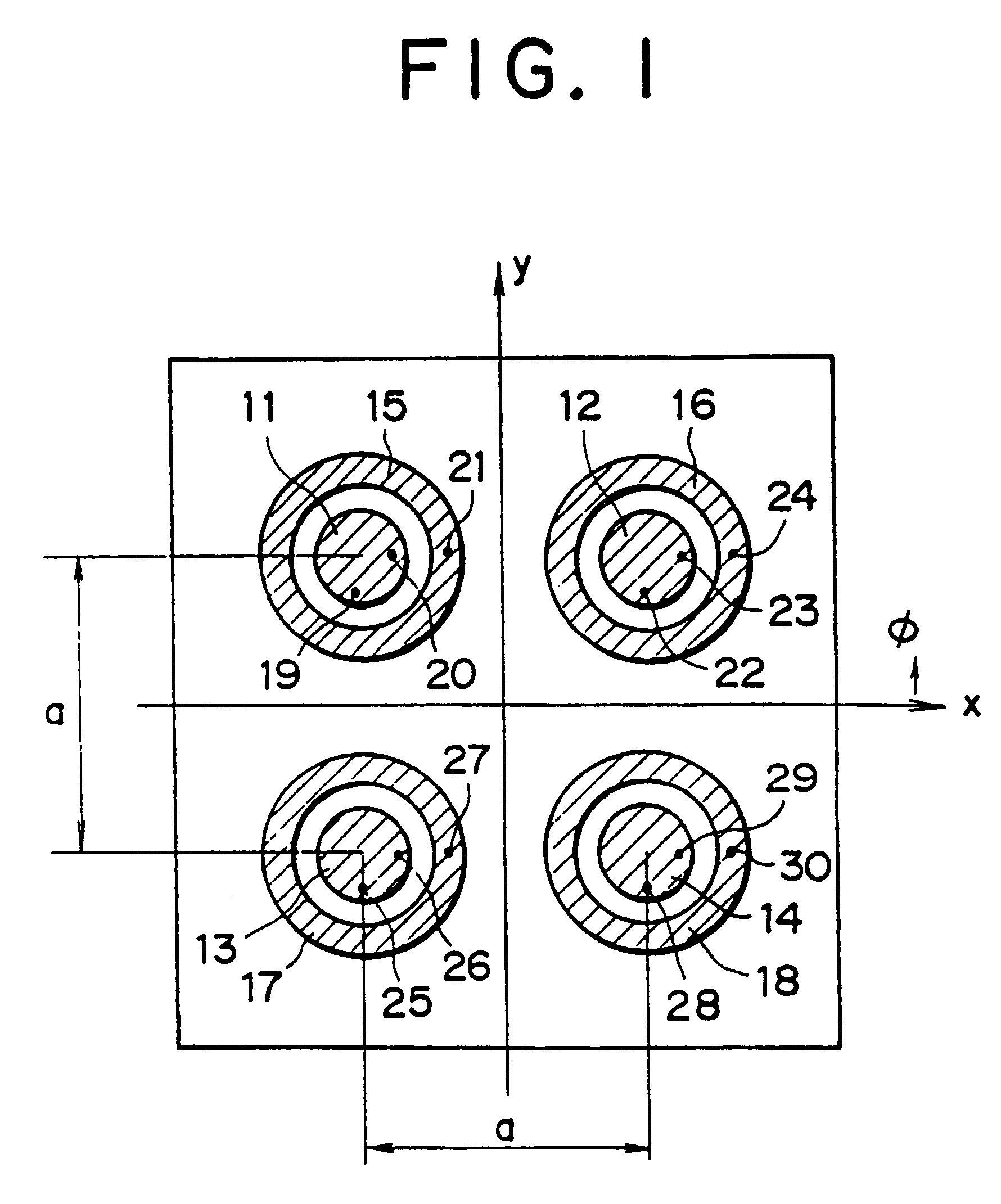
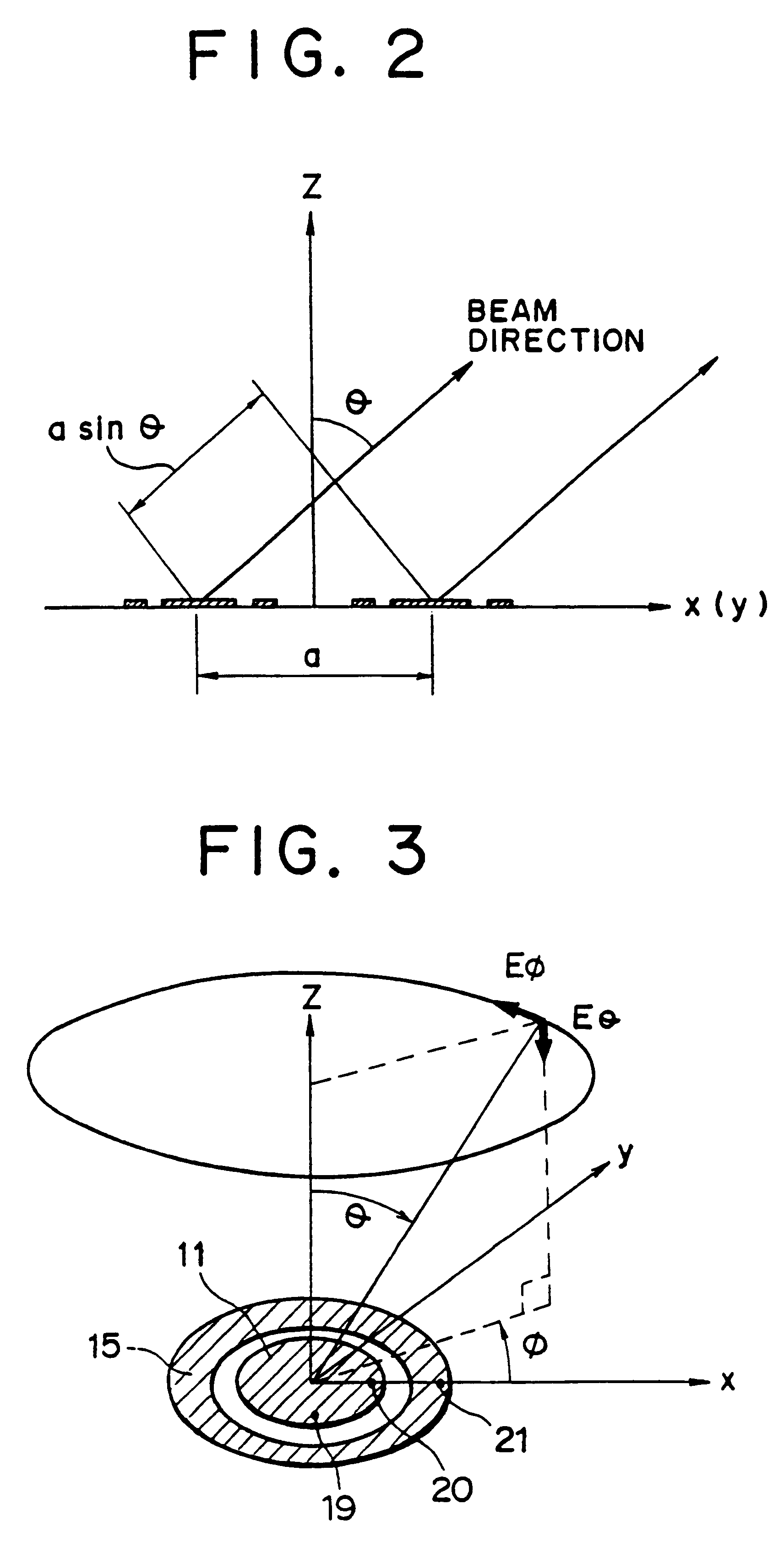
Beam scanning antennas with plurality of antenna elements for scanning beam direction
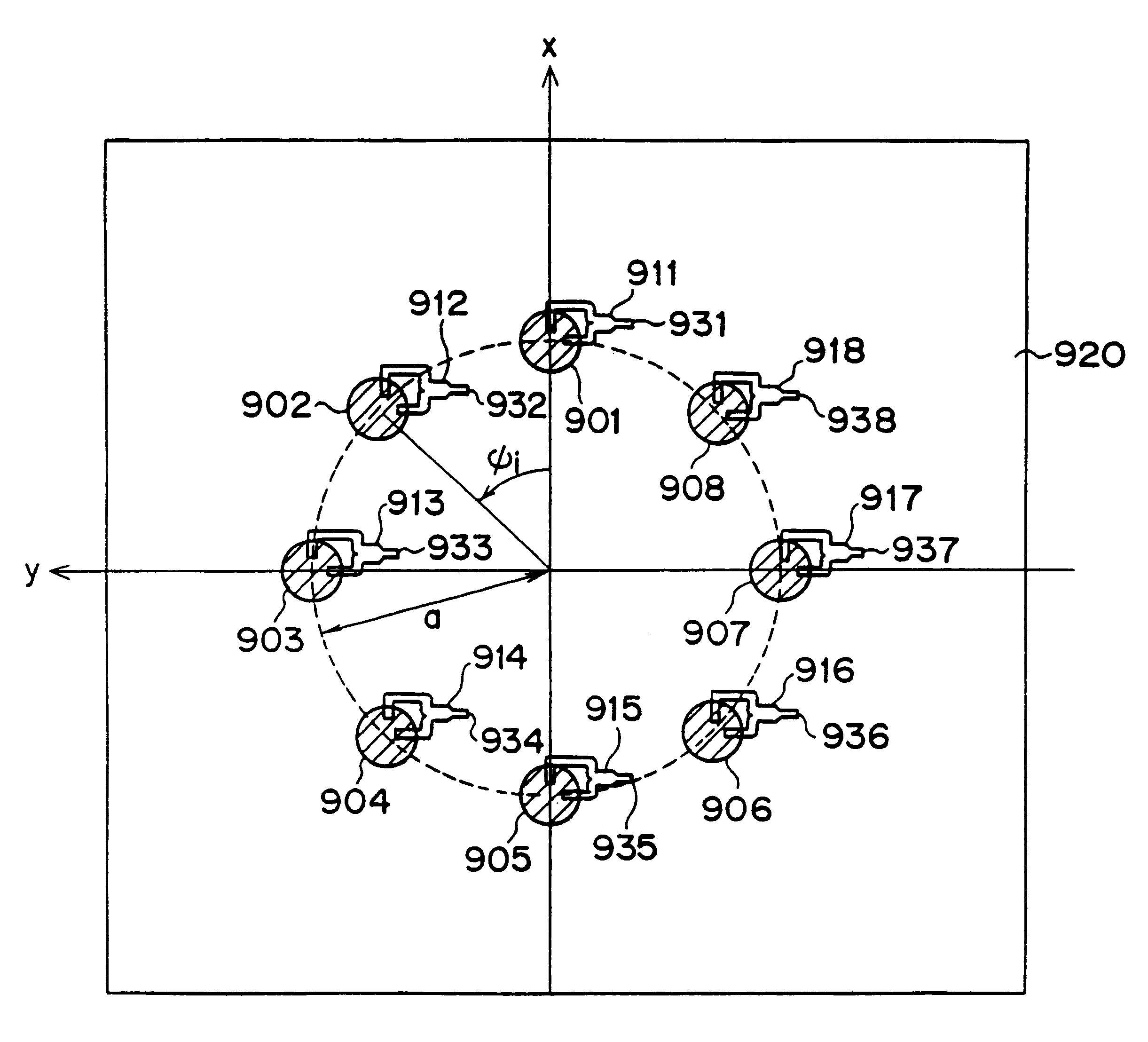
An array antenna is formed of a plurality of antenna elements, each of which scans a beam in the direction of an angle theta to a boresight of the antenna and electrically varies the direction of a rotation angle phi of the beam. The antenna elements are disposed so that the optical path difference of radio waves transmitted or received by two adjacent antenna elements in the directions of a plurality of direction angles phi on the plane tilted for an angle theta to the boresight of the antenna is nearly a multiple of the wave length of the radio waves.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
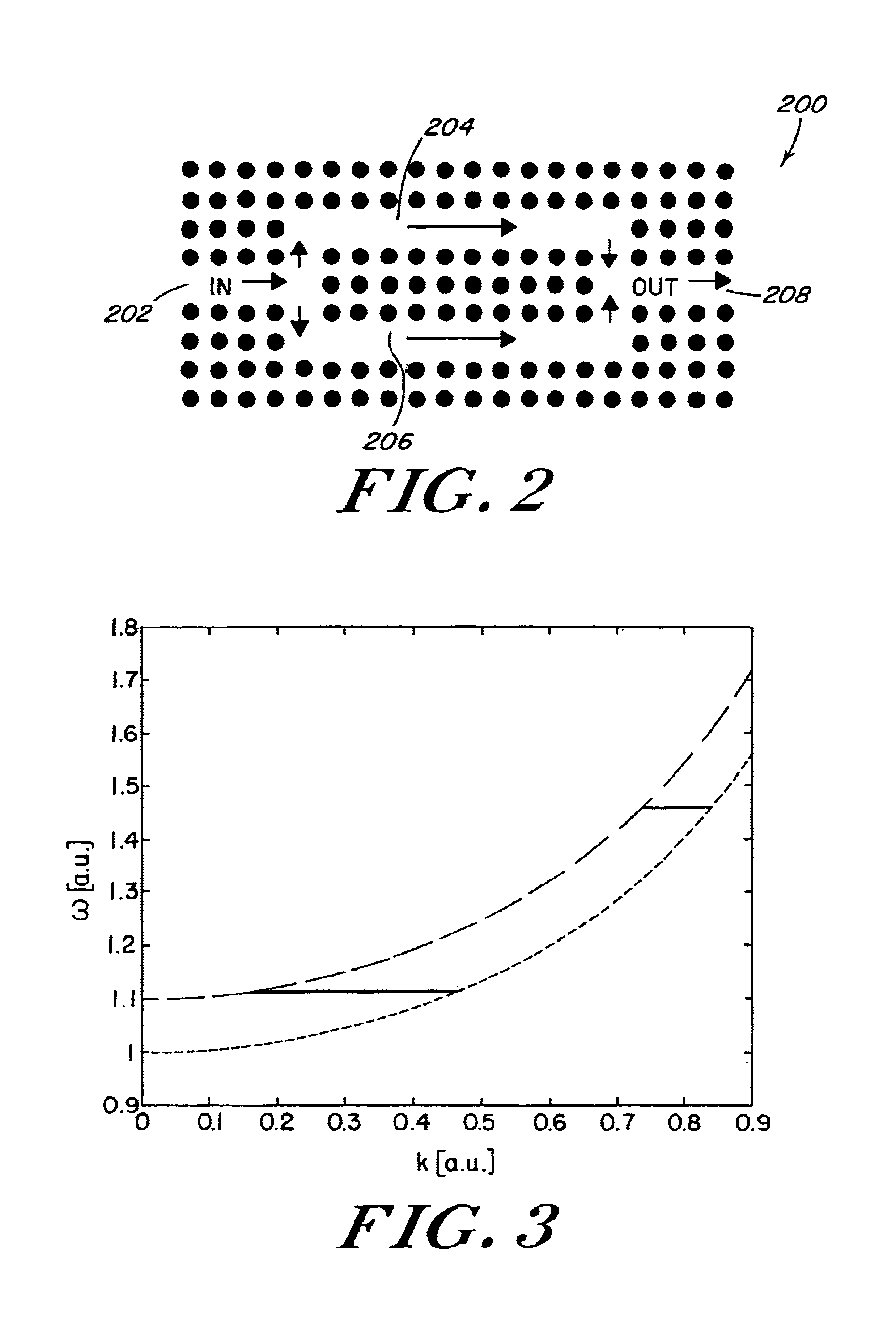
Mach-Zehnder interferometer using photonic band gap crystals
InactiveUS6917431B2Small sizeLarge operating bandwidthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic crystalMach–Zehnder interferometer
A photonic crystal optical switch having a periodic dielectric structure including at least one input waveguide. First and second waveguide arms branch from the input waveguide in which the relative optical path lengths of electromagnetic radiation within the arms are controlled by stimuli. At least one output waveguide that combines the electromagnetic radiation propagating within the first and second waveguide arms.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
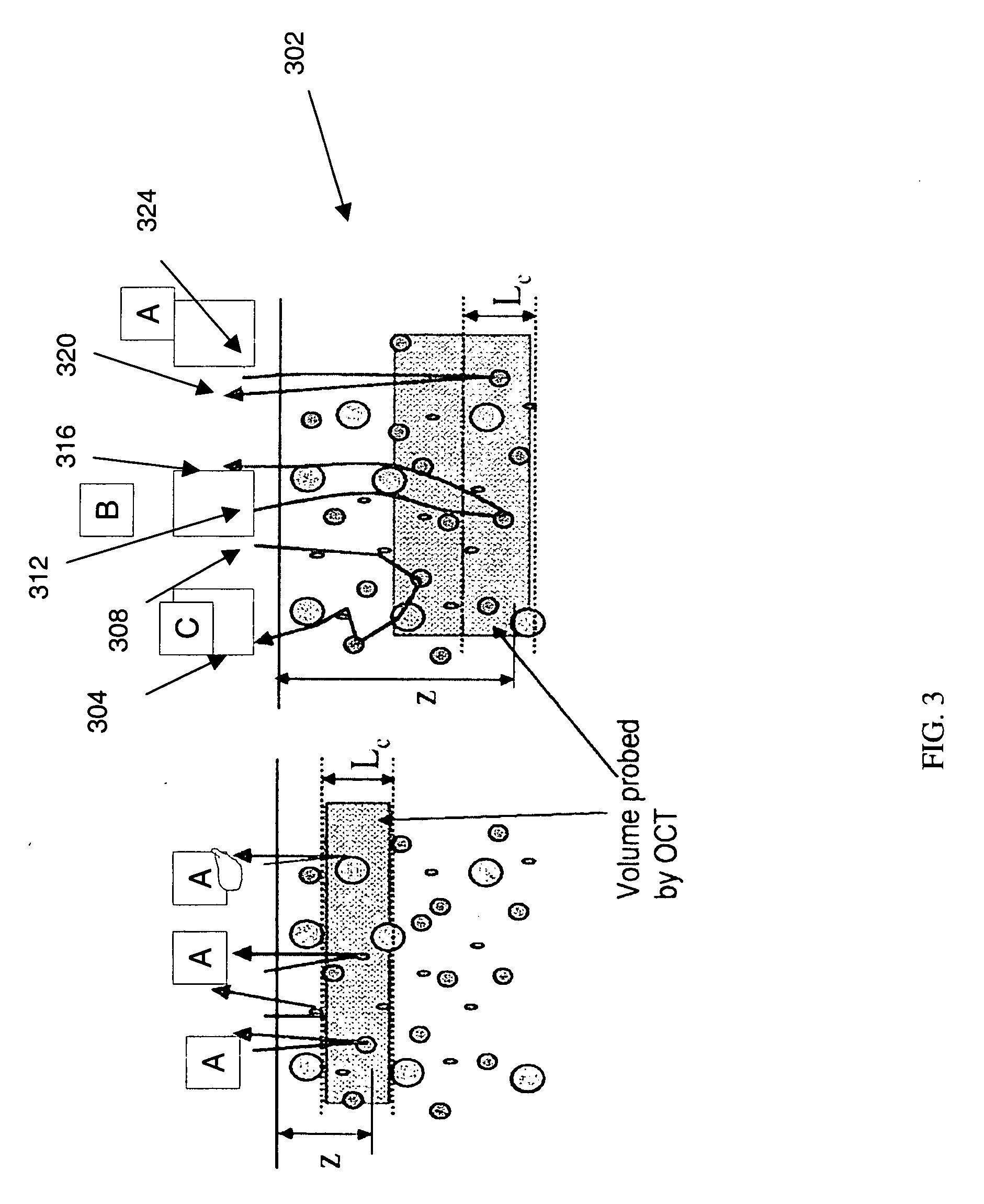
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
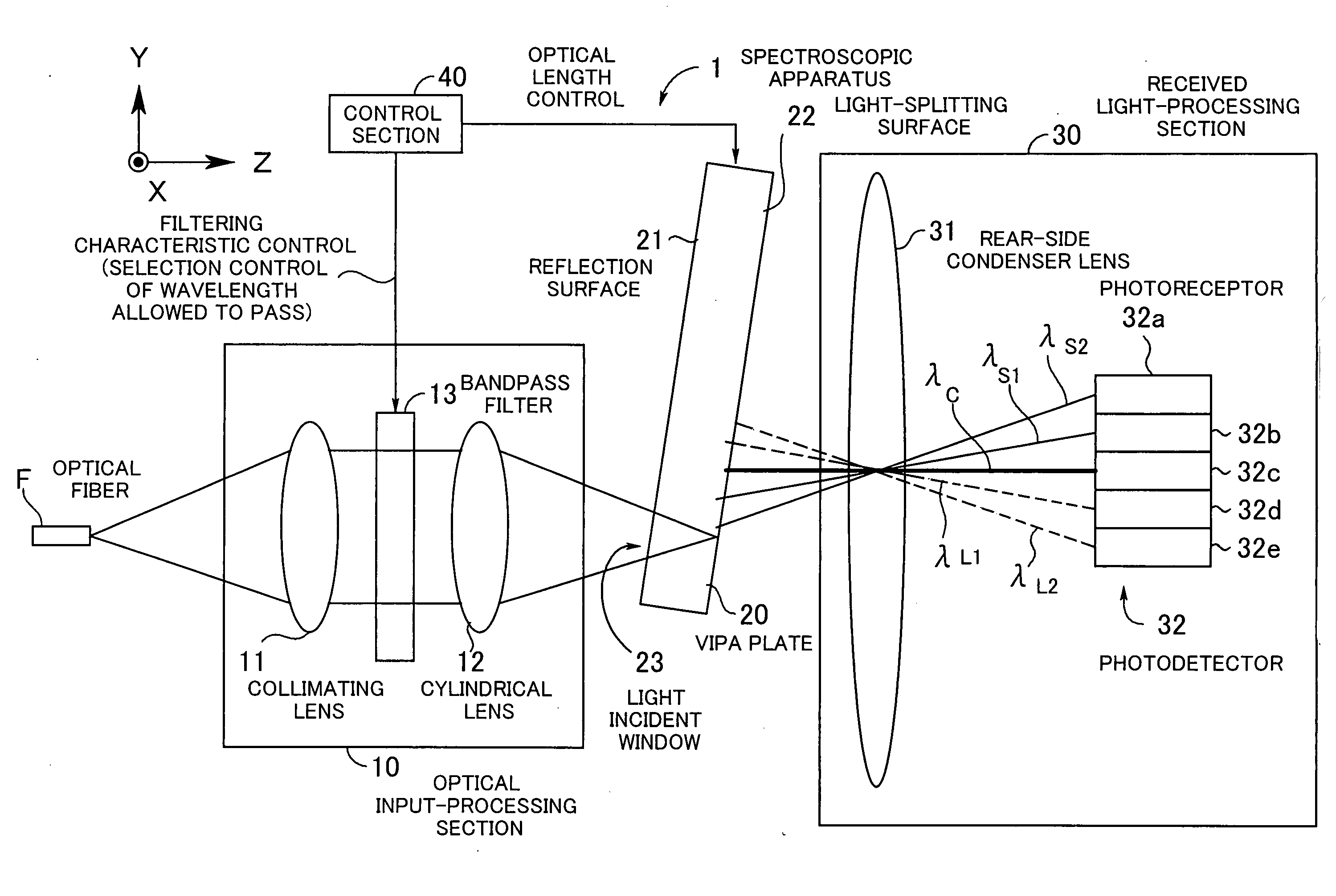
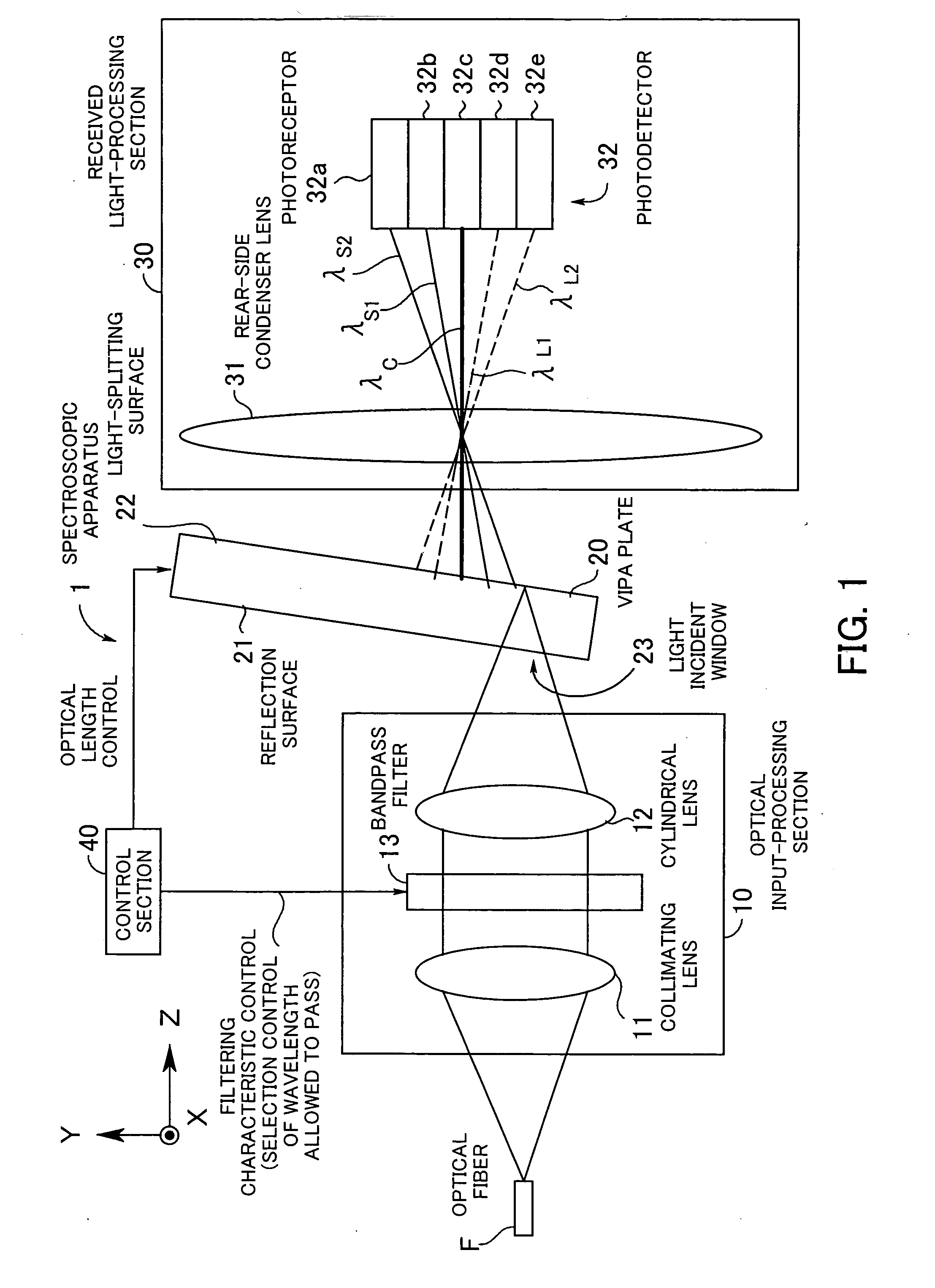
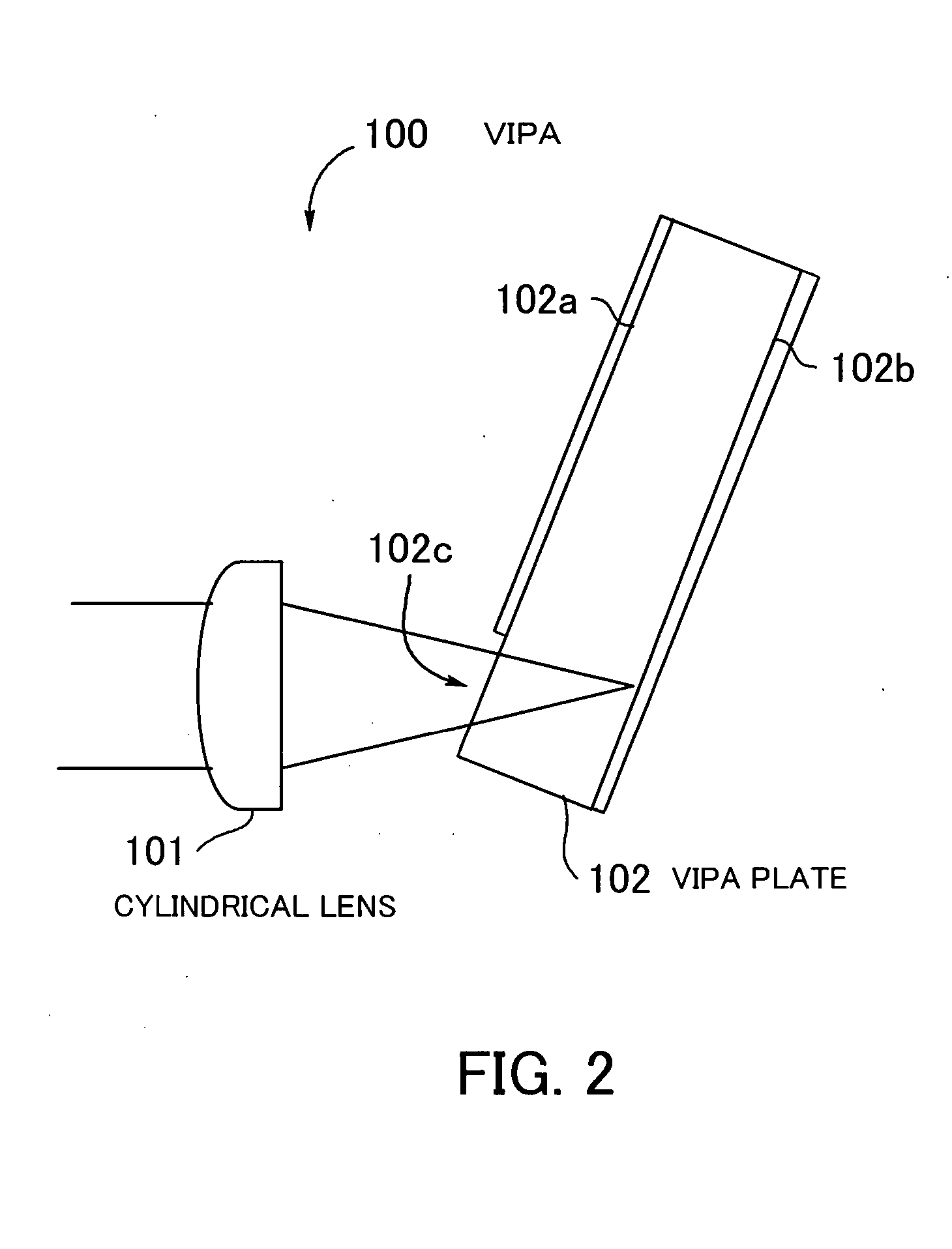
Spectroscopic apparatus
InactiveUS20050046837A1Small sizeLarge angular dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for determining and correcting vision
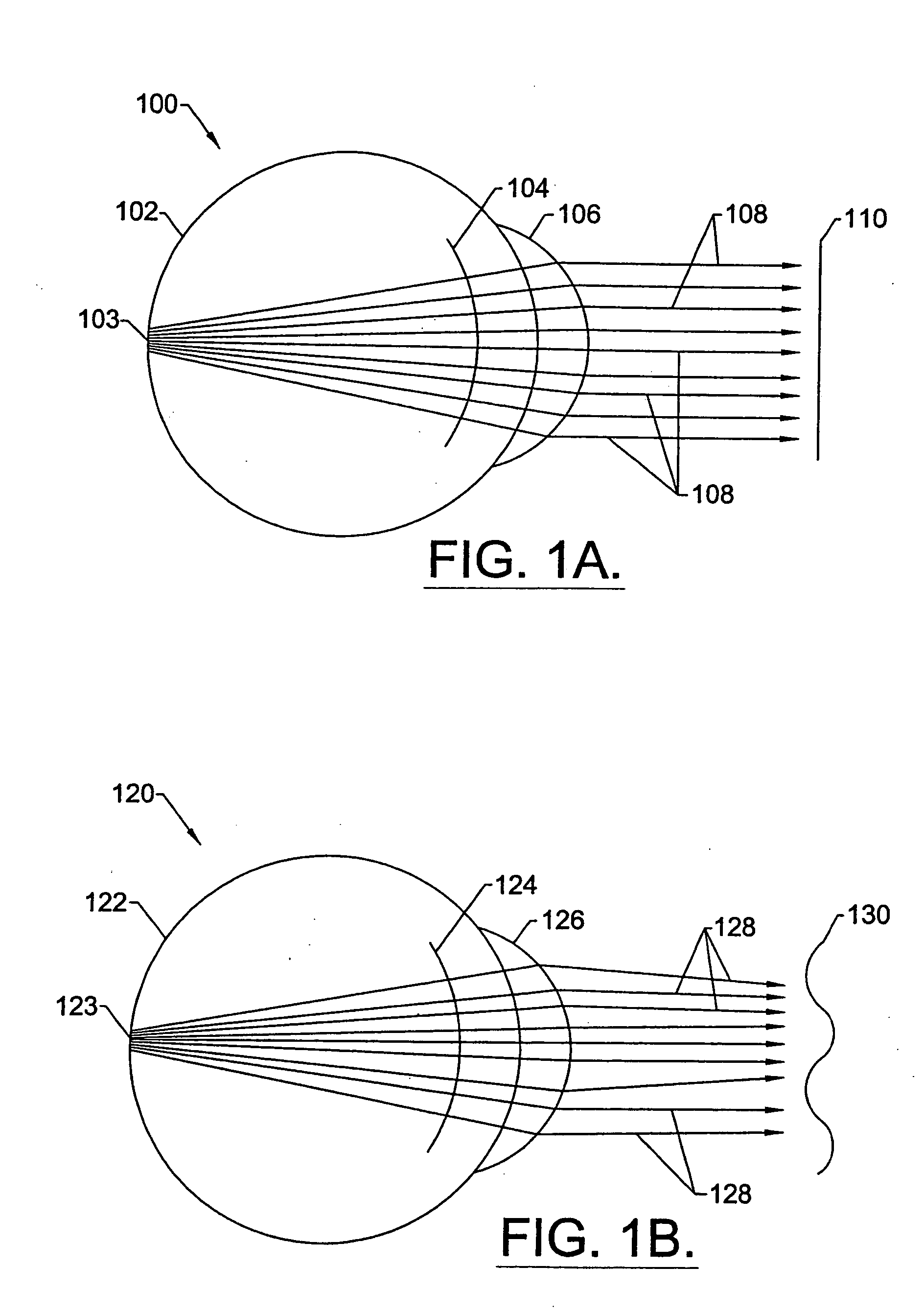
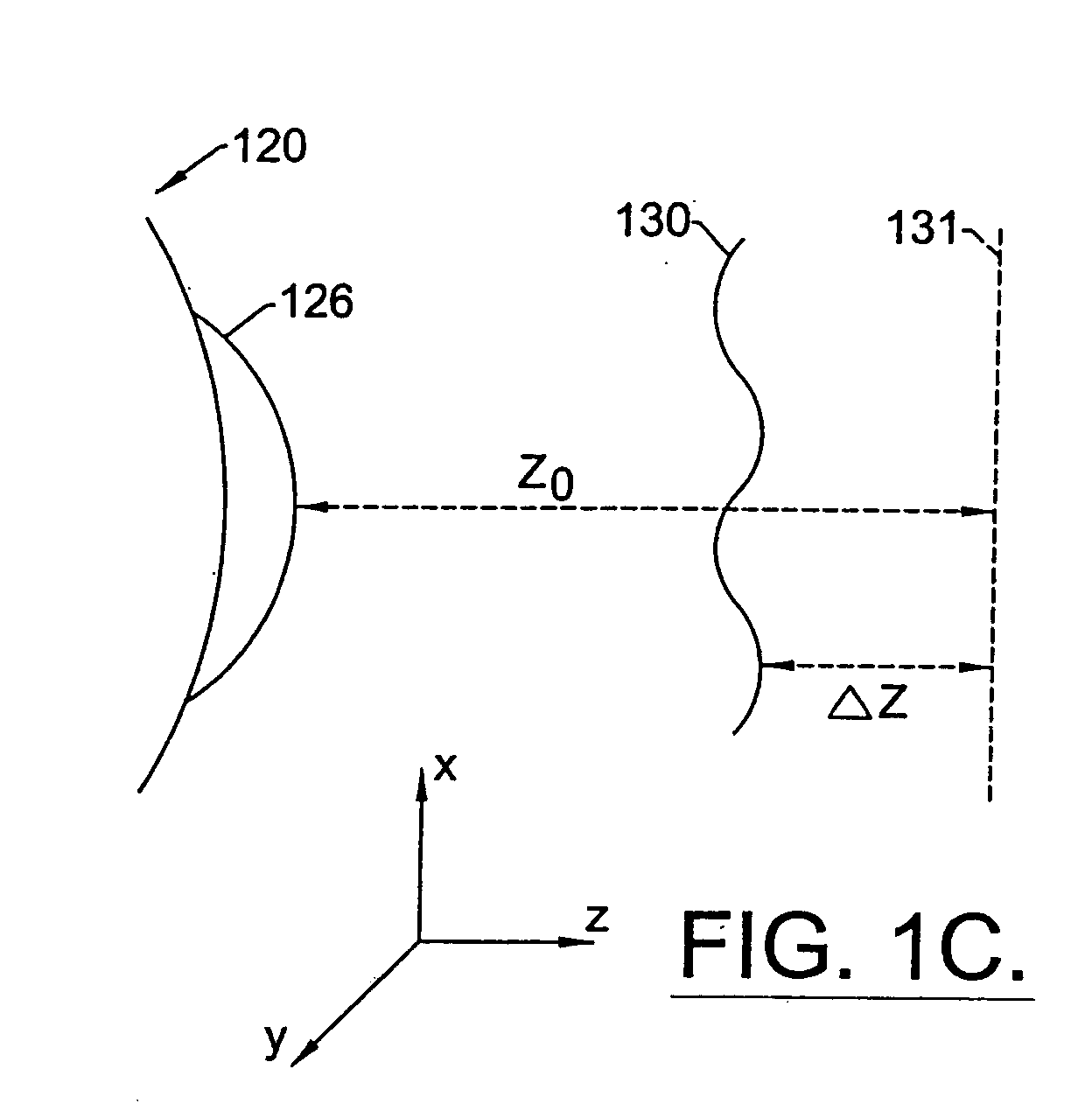
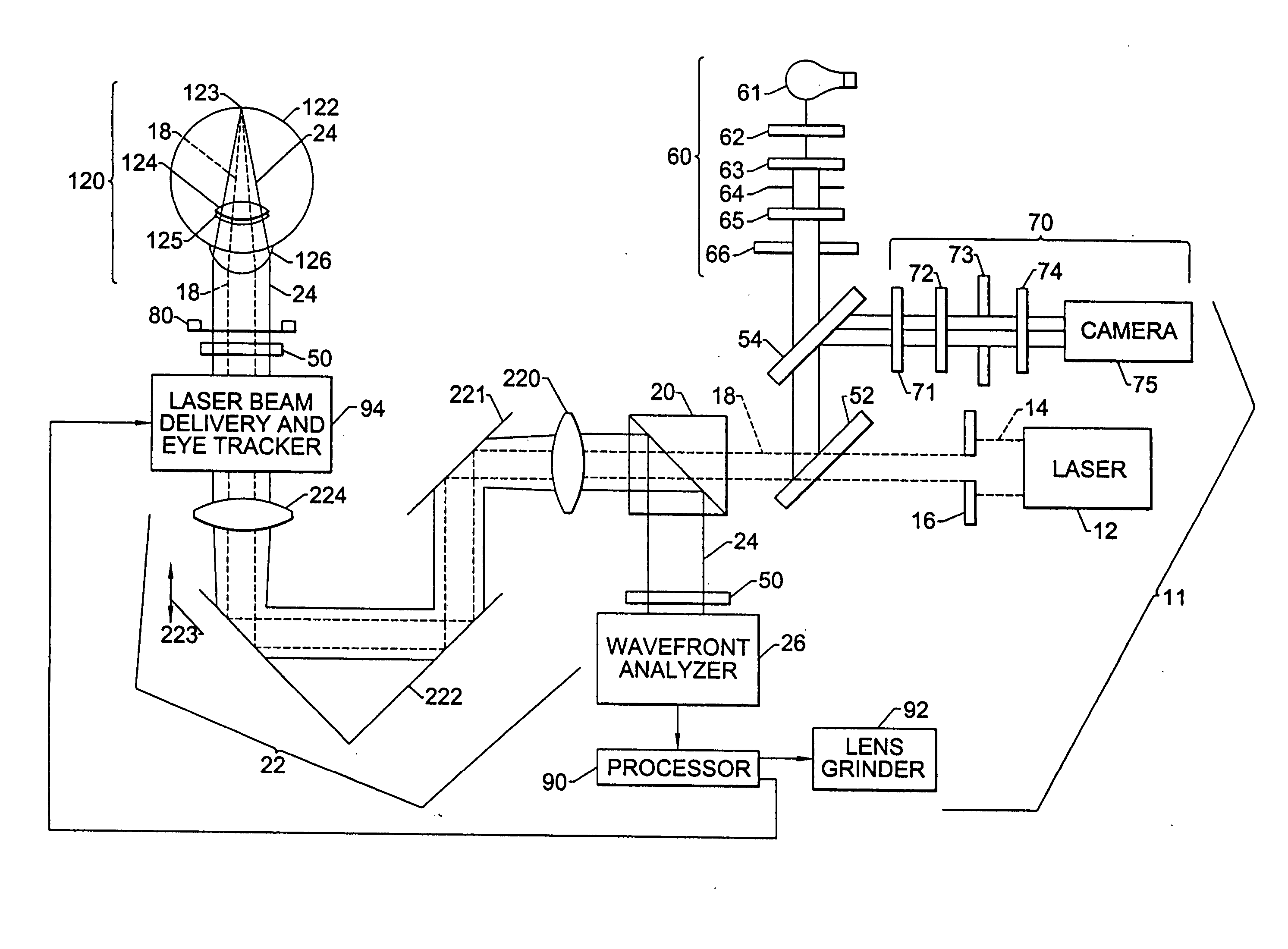
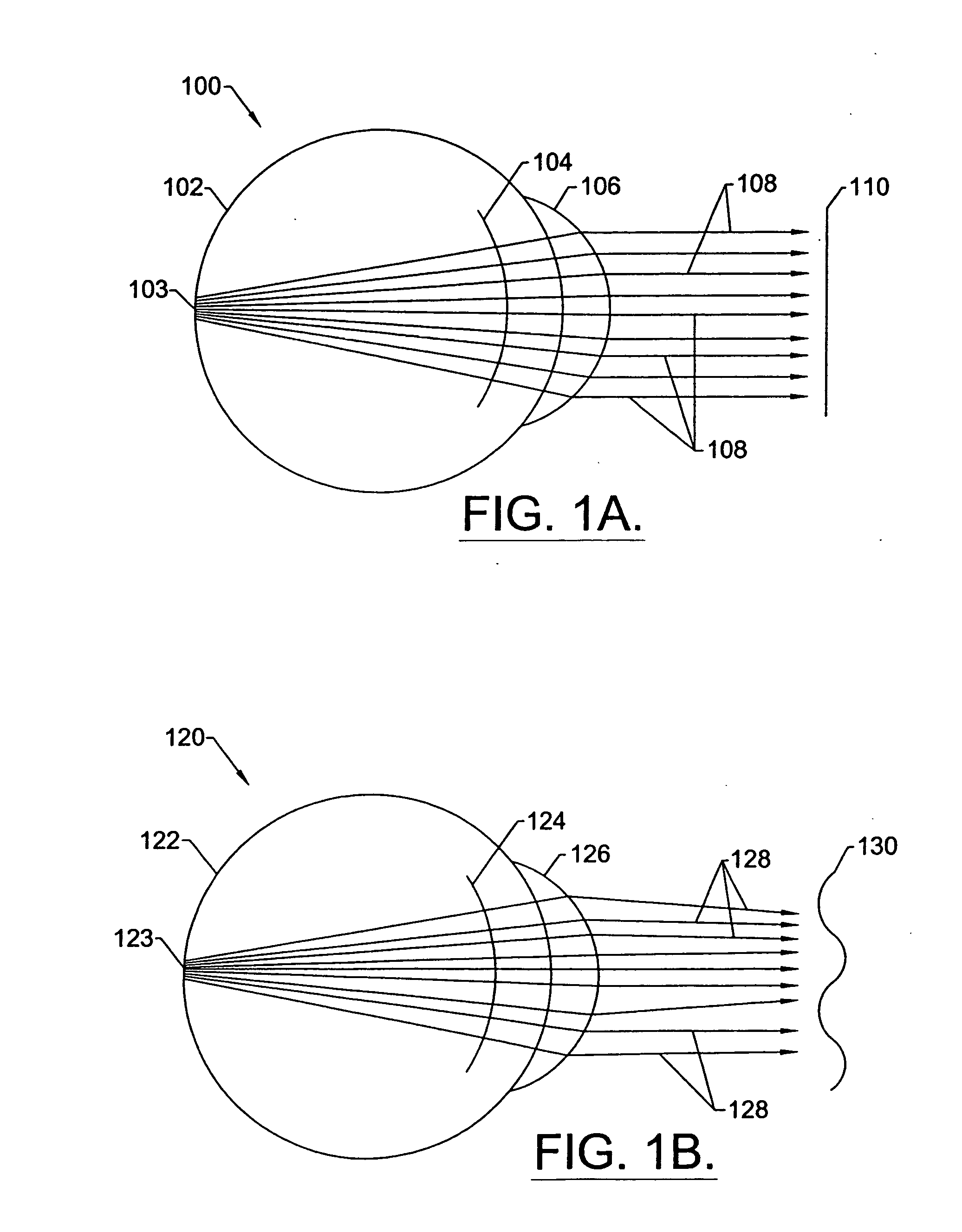
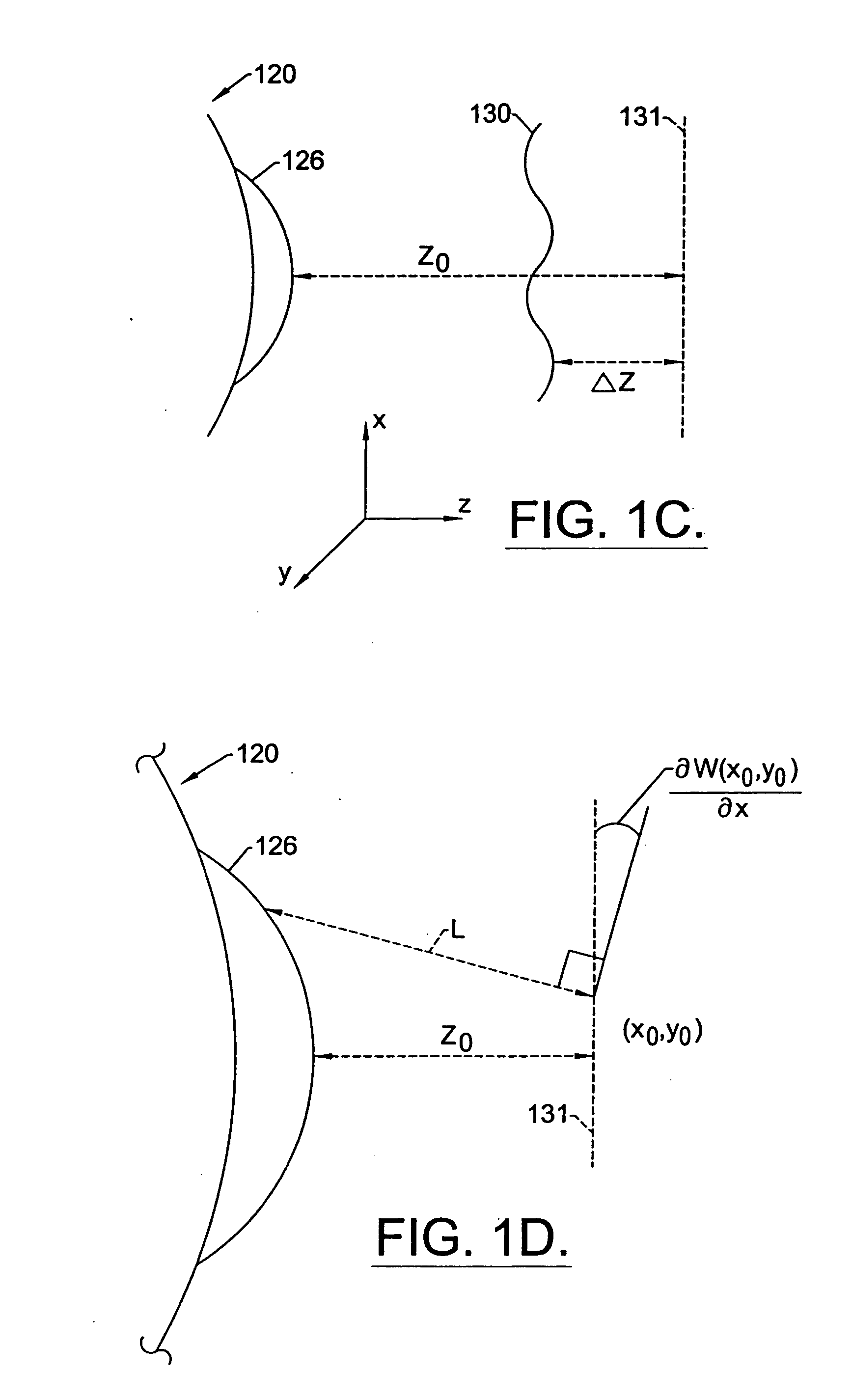
InactiveUS20050124983A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove visual effectsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
Interferometric sensor for characterizing materials
ActiveUS20050190372A1Fast and inexpensiveRobust designScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberInterferometric sensor
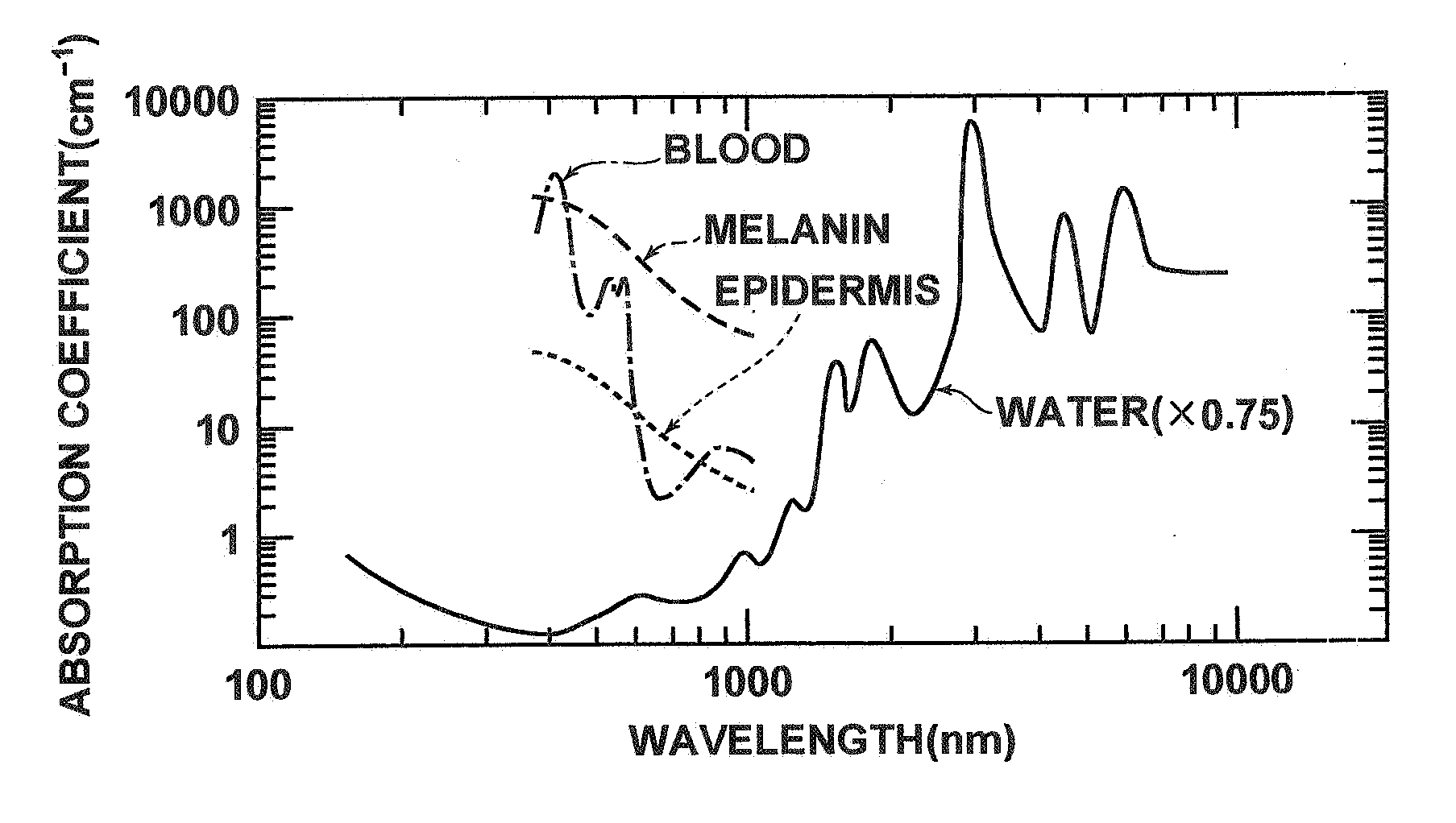
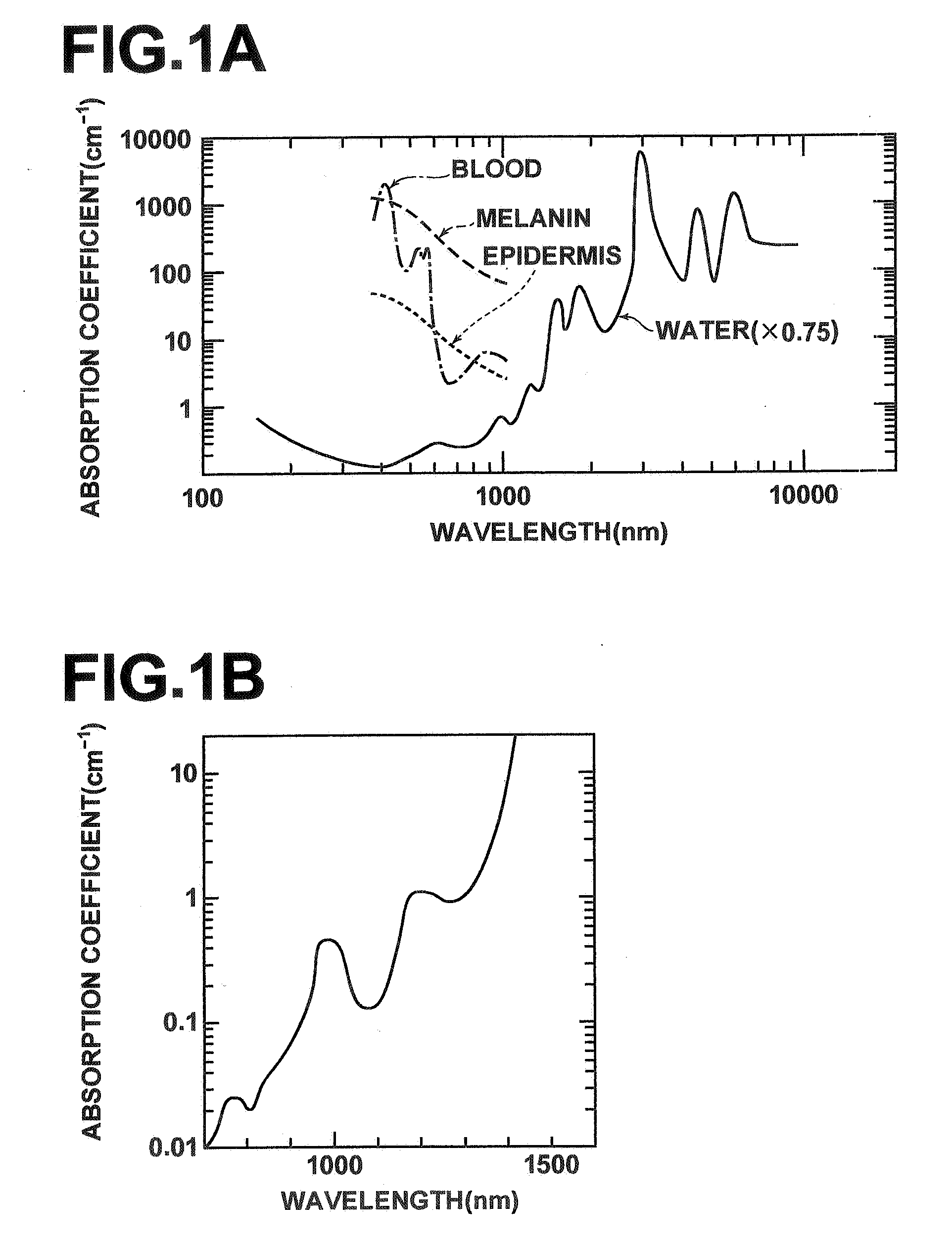
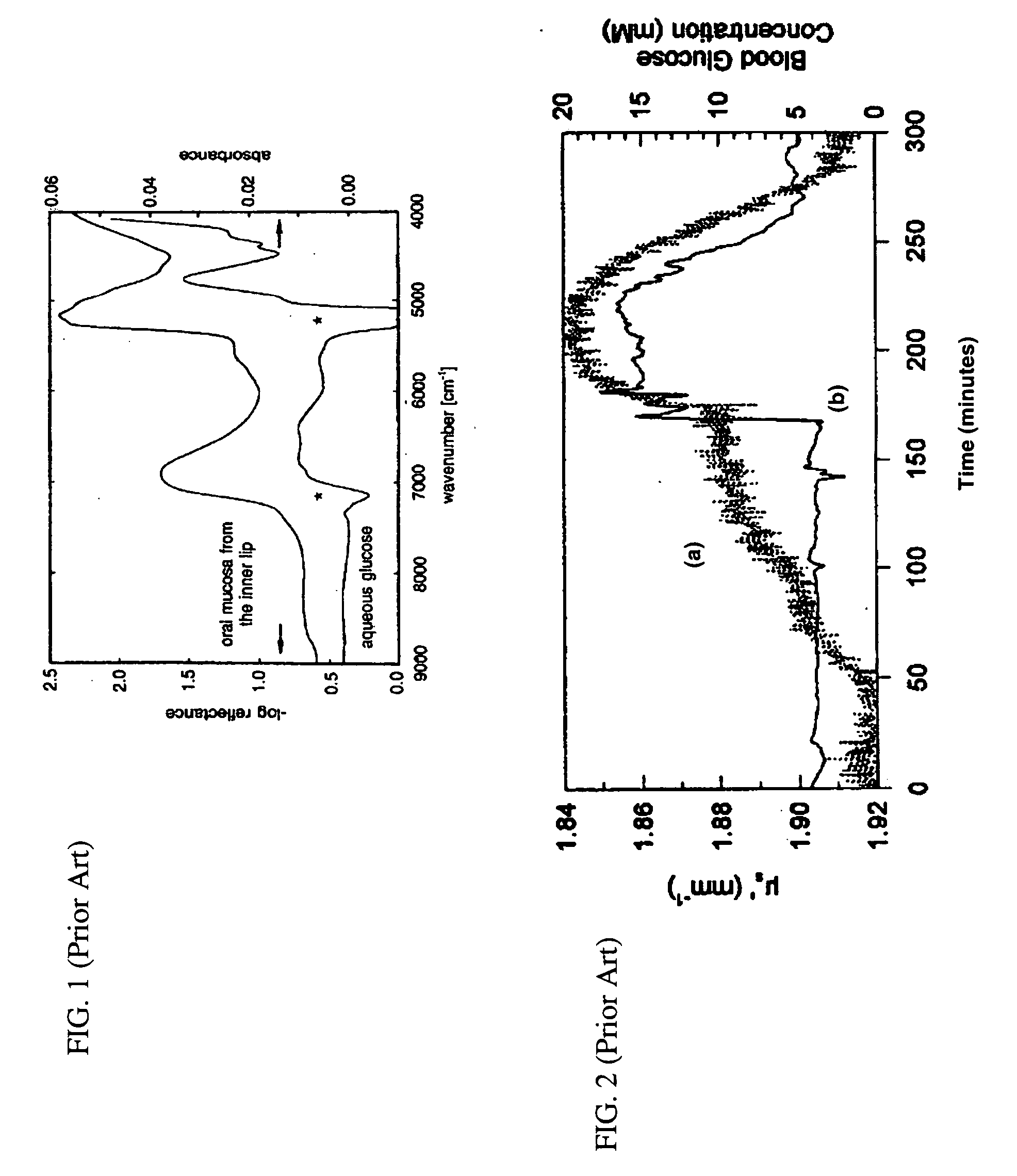
An integrated optical sensor, using low coherence interferometry, is capable of determining analyte concentration in a material sample based on absorption, scattering and polarization. The sensor includes one or more light collectors, with each collector having a separation distance from the region where the sample is illuminated by the source. The light backscattered from the sample is combined with reference arm light at the same optical path length for each light collector. The intensity of interference may be correlated with the concentration of an analyte in the material, for example the glucose concentration in a turbid medium like skin. The sensor operation can be based on fiber optics technology, integrated optics, or a combination of these. The operation is such that the spectrally resolved scattering and absorption coefficients can be measured simultaneously. In addition, the operation of the sensor can be synchronized with other sensors, for example temperature, pressure, or heartrate.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
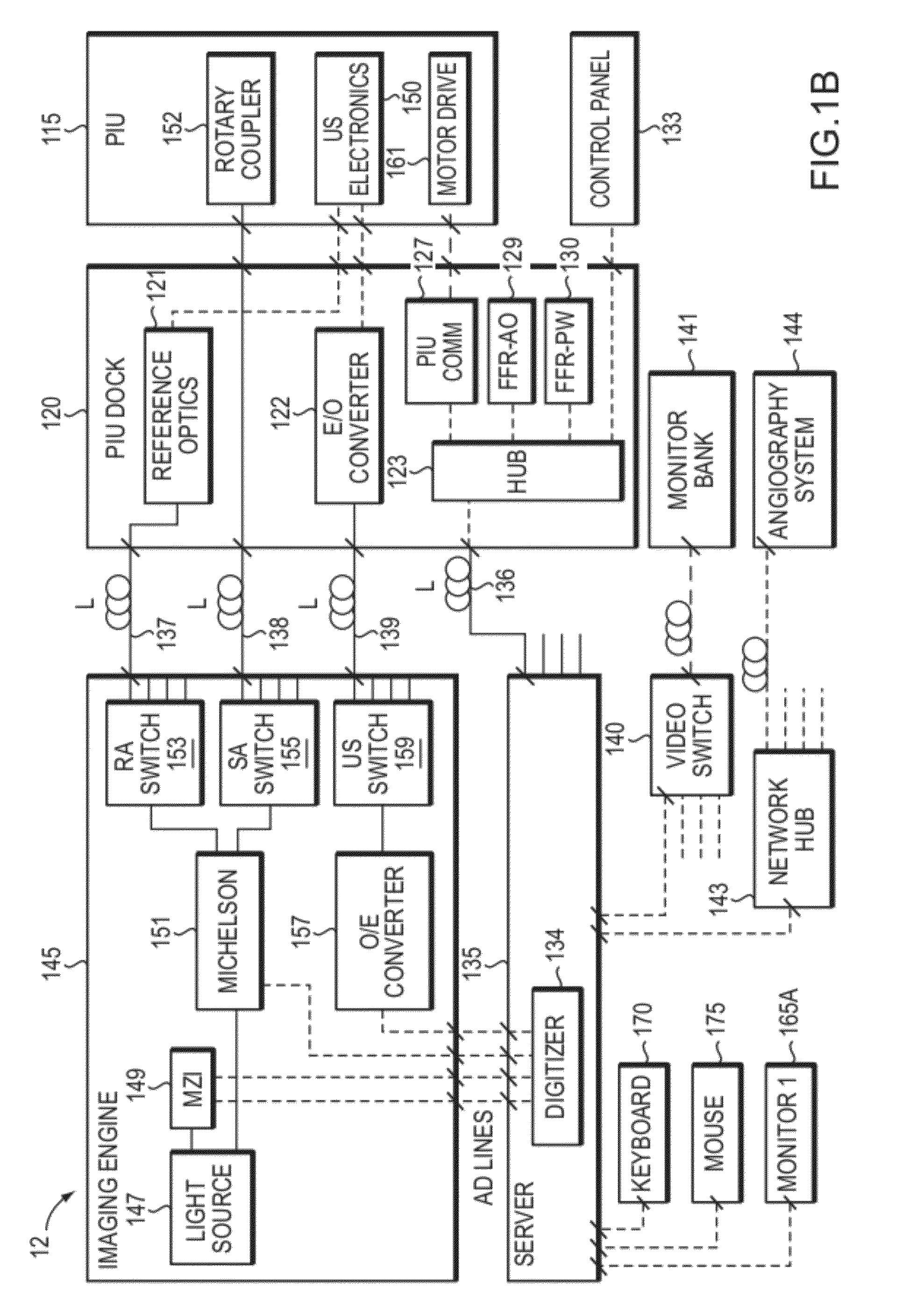
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
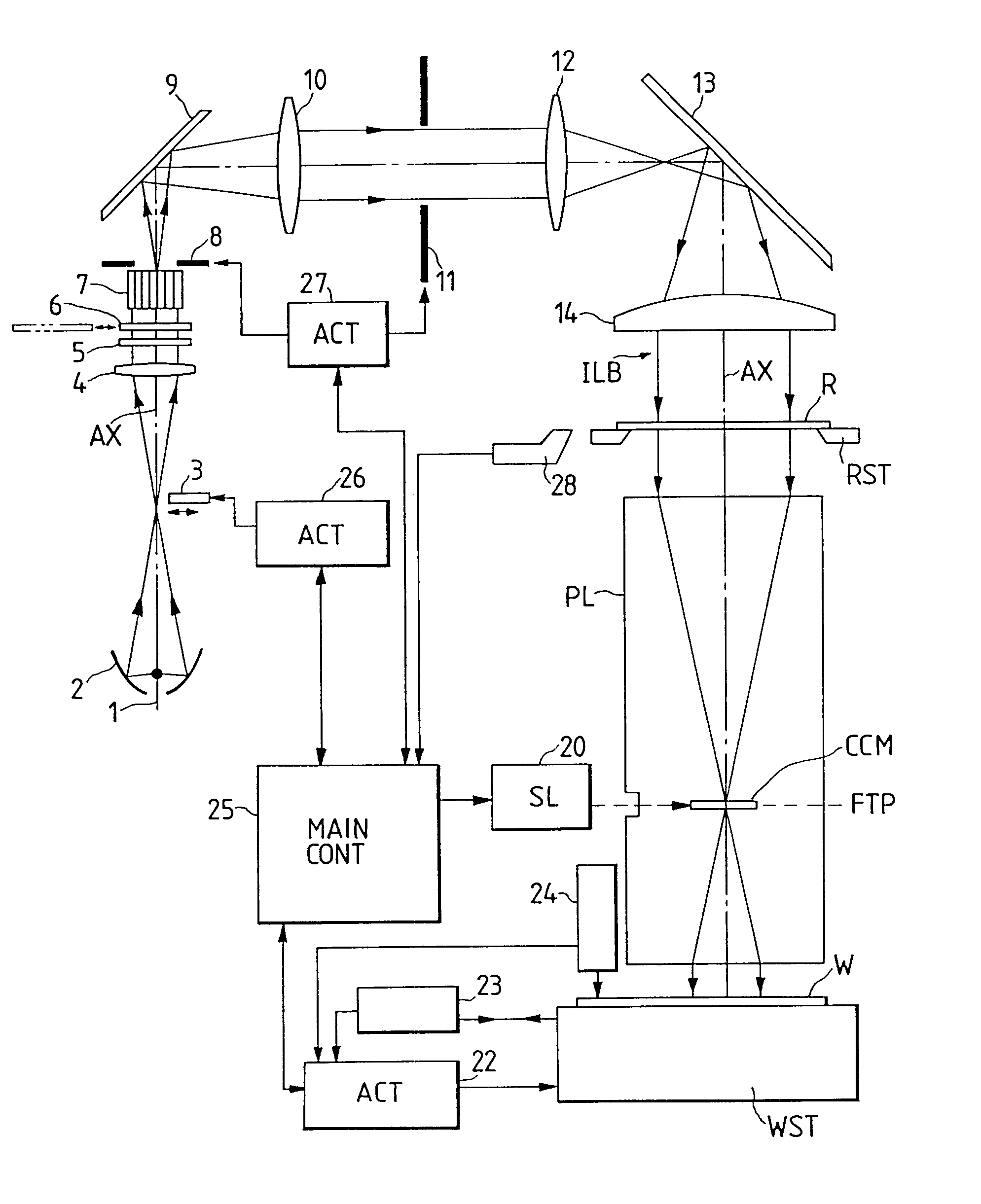
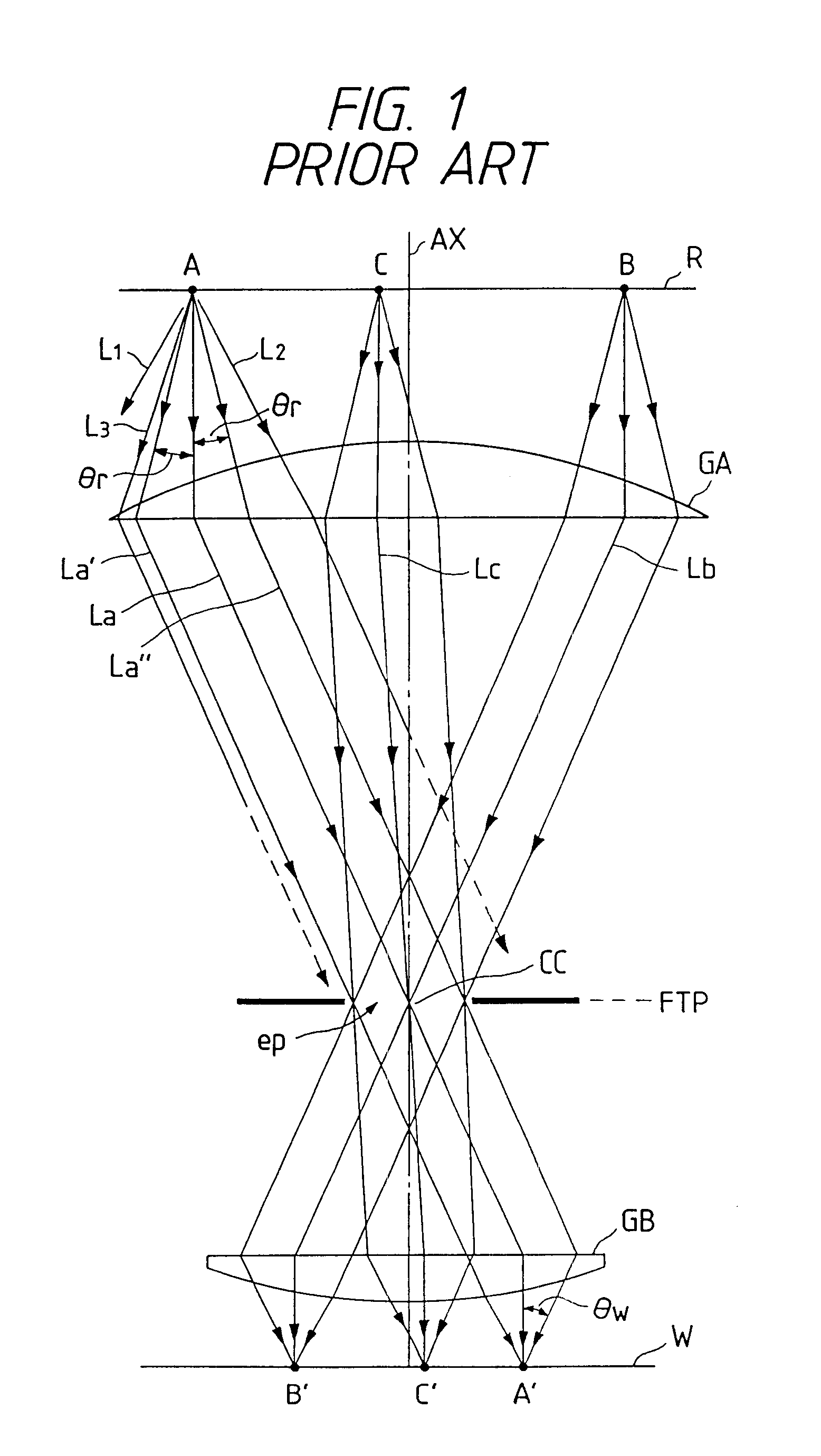
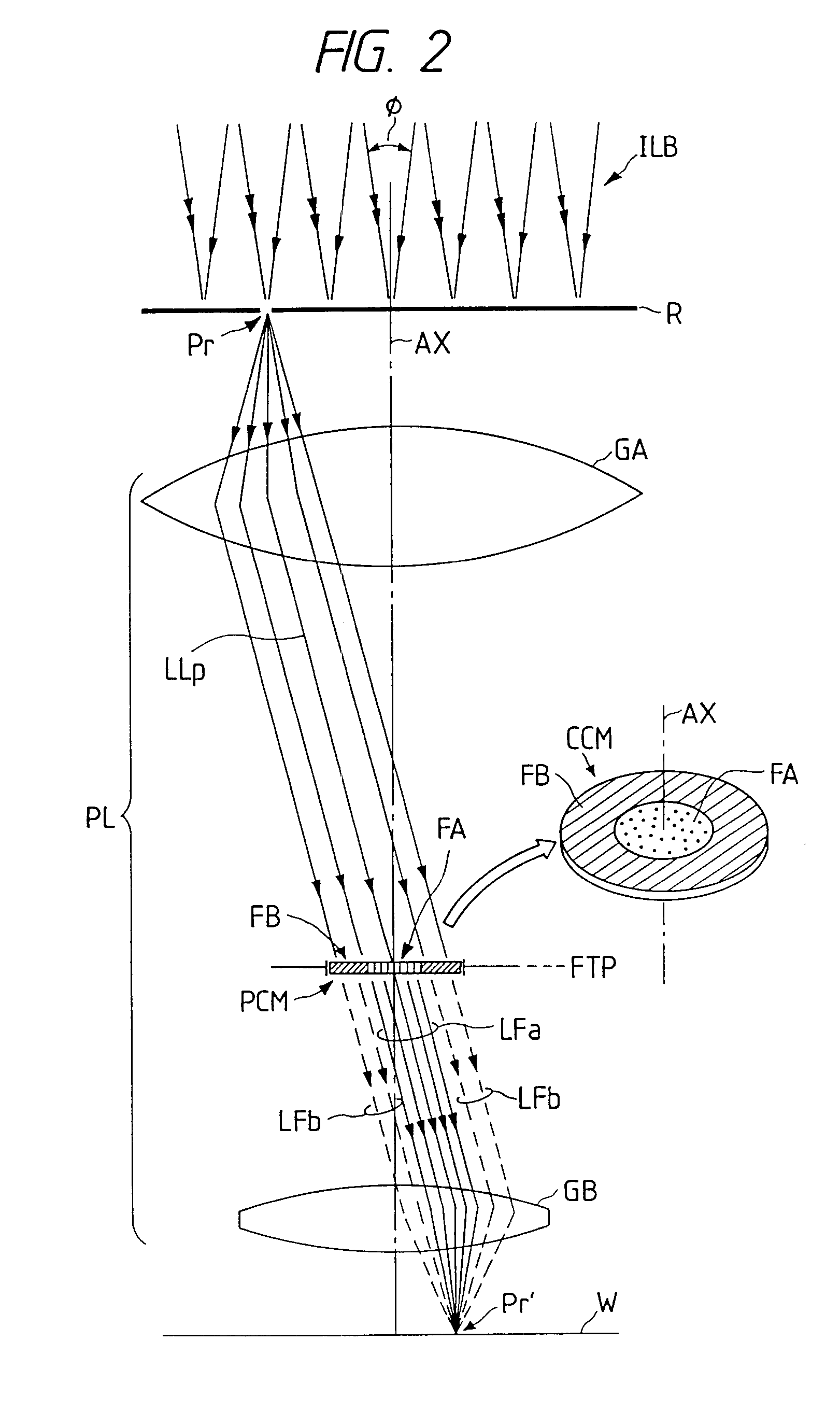
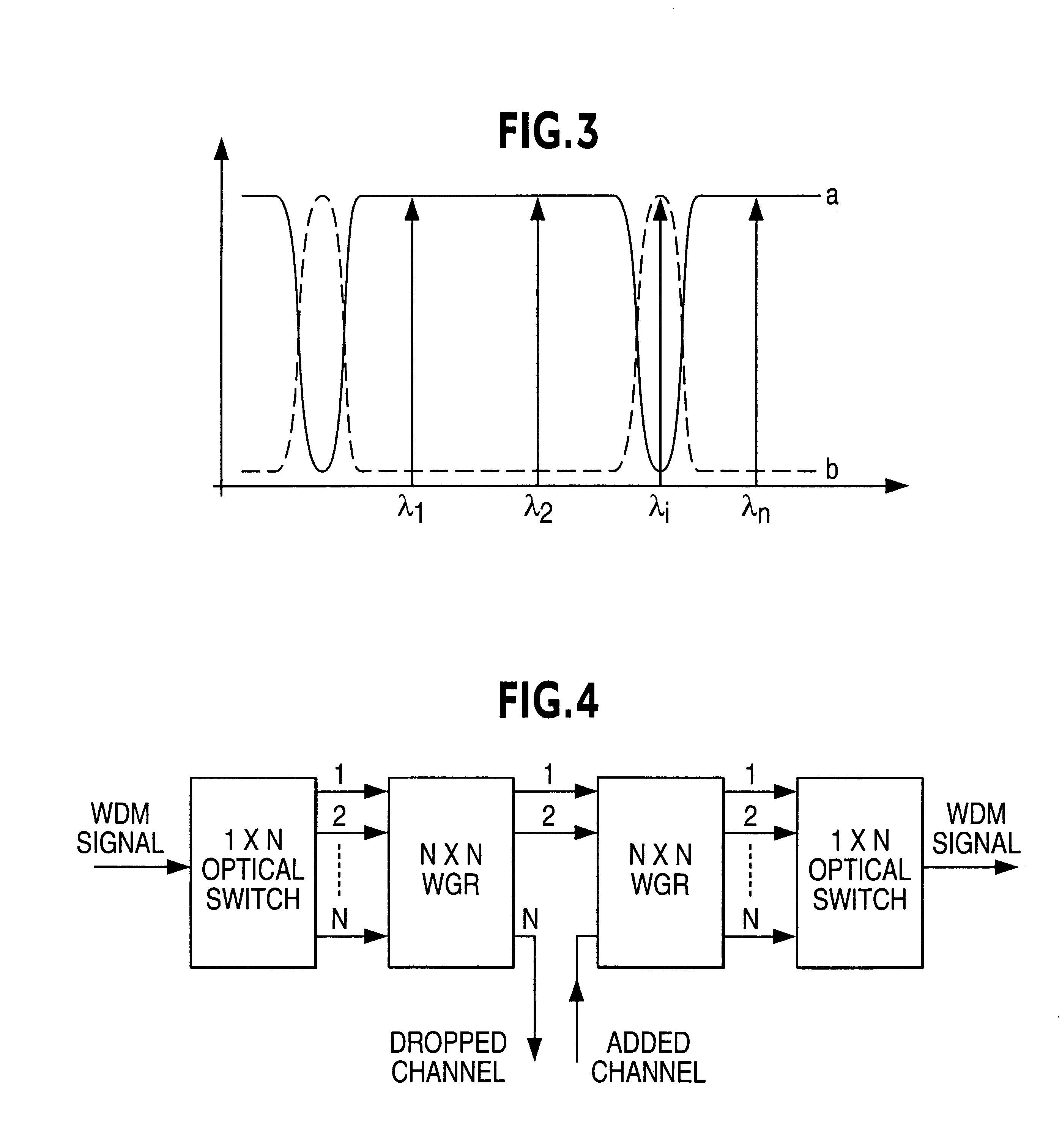
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6404482B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Devices and arrangements for performing coherence range imaging using a common path interferometer
ActiveUS7995210B2InterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Three-dimensional display
In the three-dimensional display, a two-dimensional display section generates a two-dimensional display image based on an image signal, and a lens array converts the wavefront of the display image light from the two-dimensional display section into a wavefront having a curvature which allows the display image light to focus upon a focal point where an optical path length from an observation point to the focal point is equal to an optical path length from the observation point to a virtual object point, so a viewer can obtain information about an appropriate focal length in addition to information about binocular parallax and a convergence angle. Therefore, consistency between the information about binocular parallax and a convergence angle and the information about an appropriate focal length can be ensured, and a desired stereoscopic image can be perceived without physiological discomfort.
Owner:SONY CORP
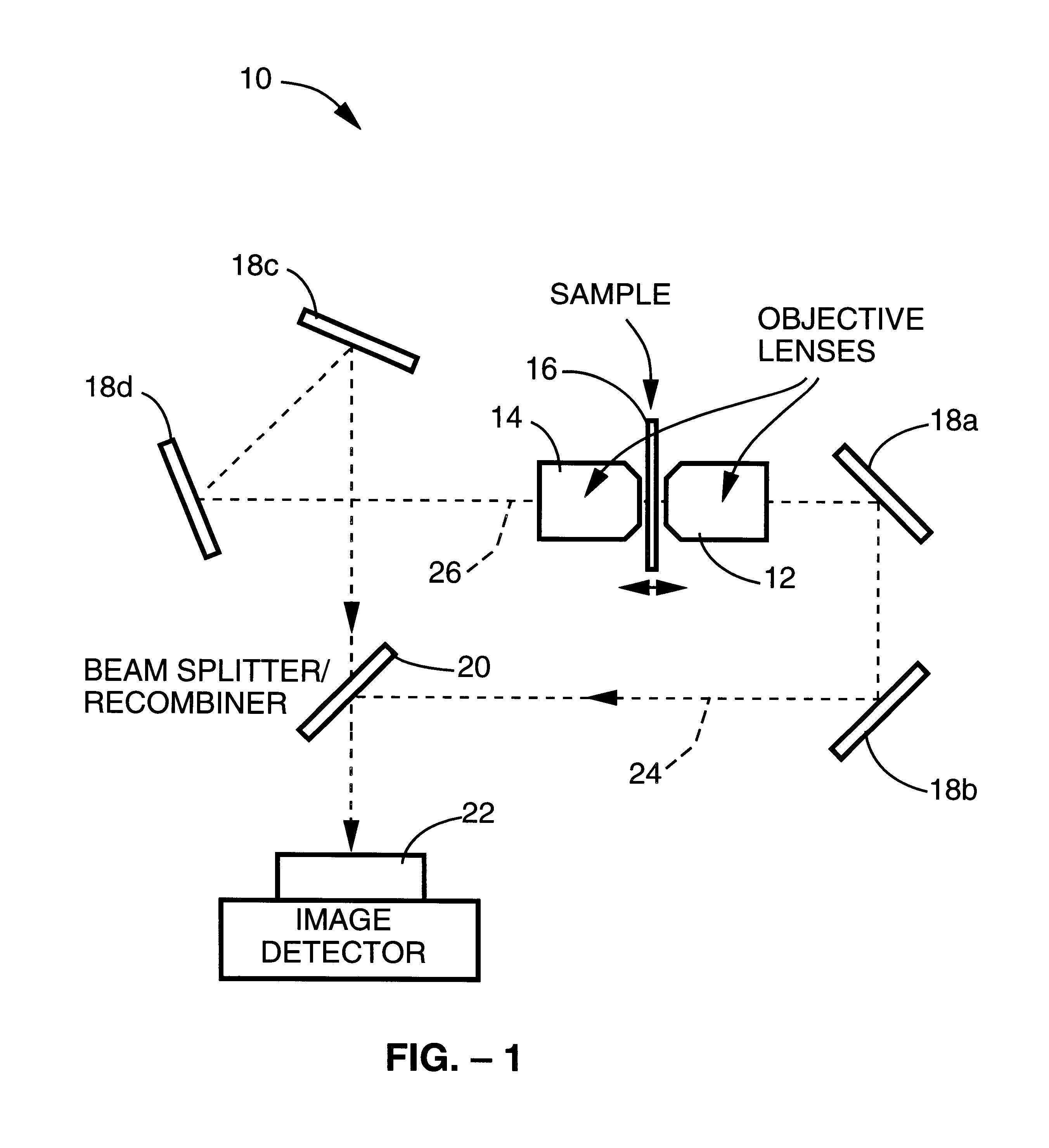
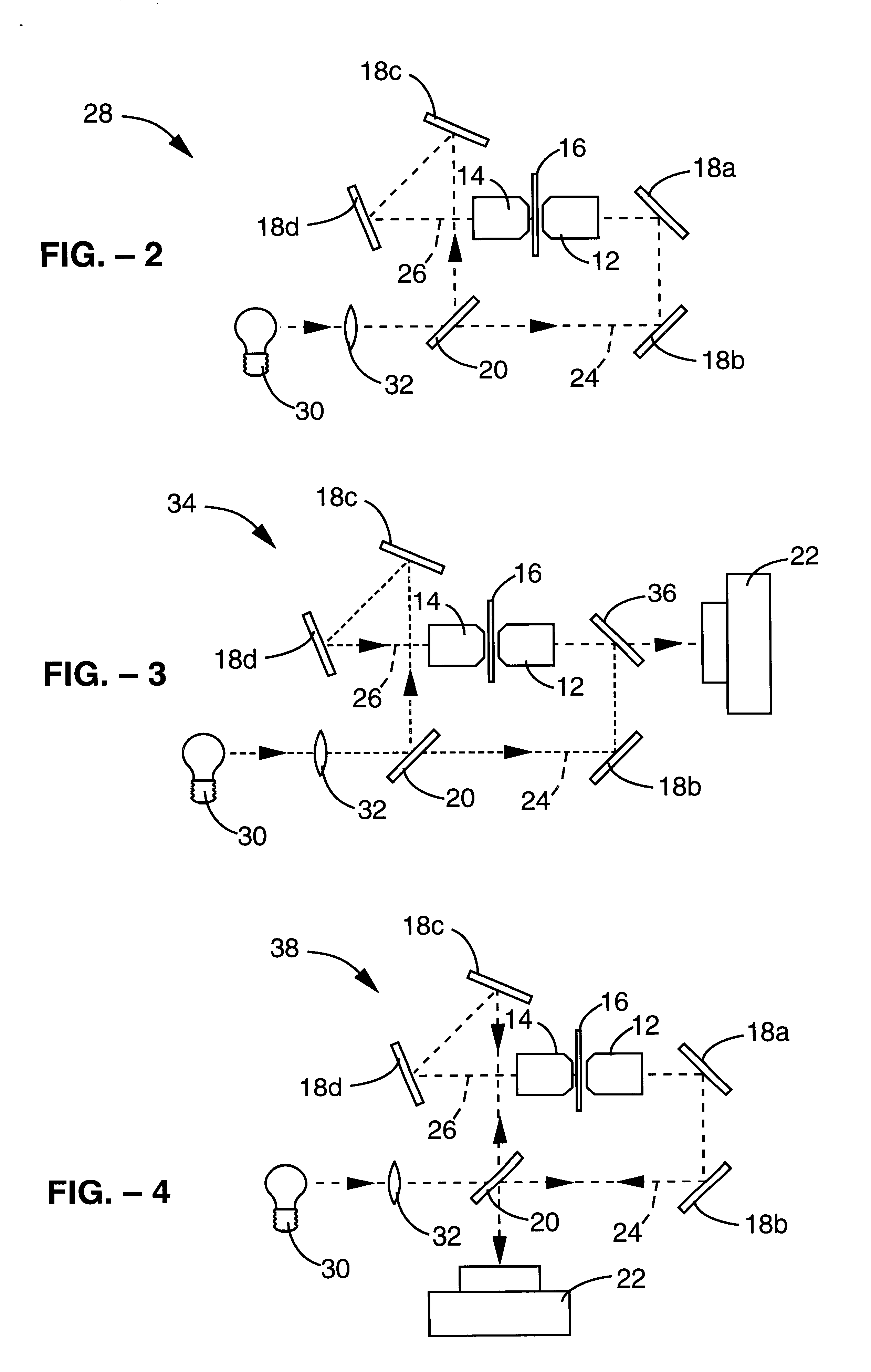
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional microscopy with enhanced resolution
InactiveUSRE38307E1Add depthImprove resolutionMicroscopesColor/spectral properties measurementsOphthalmologyImage resolution
A method and apparatus for three dimensional optical microscopy is disclosed which employs dual opposing objective lenses about a sample and extended incoherent illumination to provide enhanced depth or Z.Iadd.-.Iaddend.direction resolution. In a first embodiment, observed light from both objective lenses are brought into coincidence on an image detector and caused to interfere thereon by optical path length adjustment. In a second embodiment, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is detected to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere with a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. Observed light from one objective lens is then recorded. In a third embodiment, which combines the first two embodiments, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is directed to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere within a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. The observed light from both lenses is caused to interfere on the image detector by the same optical path length adjustment. .Iadd.In a fourth embodiment of the invention, further spatial structure is introduced into the illumination light. Computational processing is used to enhance lateral or XY resolution as well as depth or Z resolution..Iaddend.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tunable laser having liquid crystal waveguide
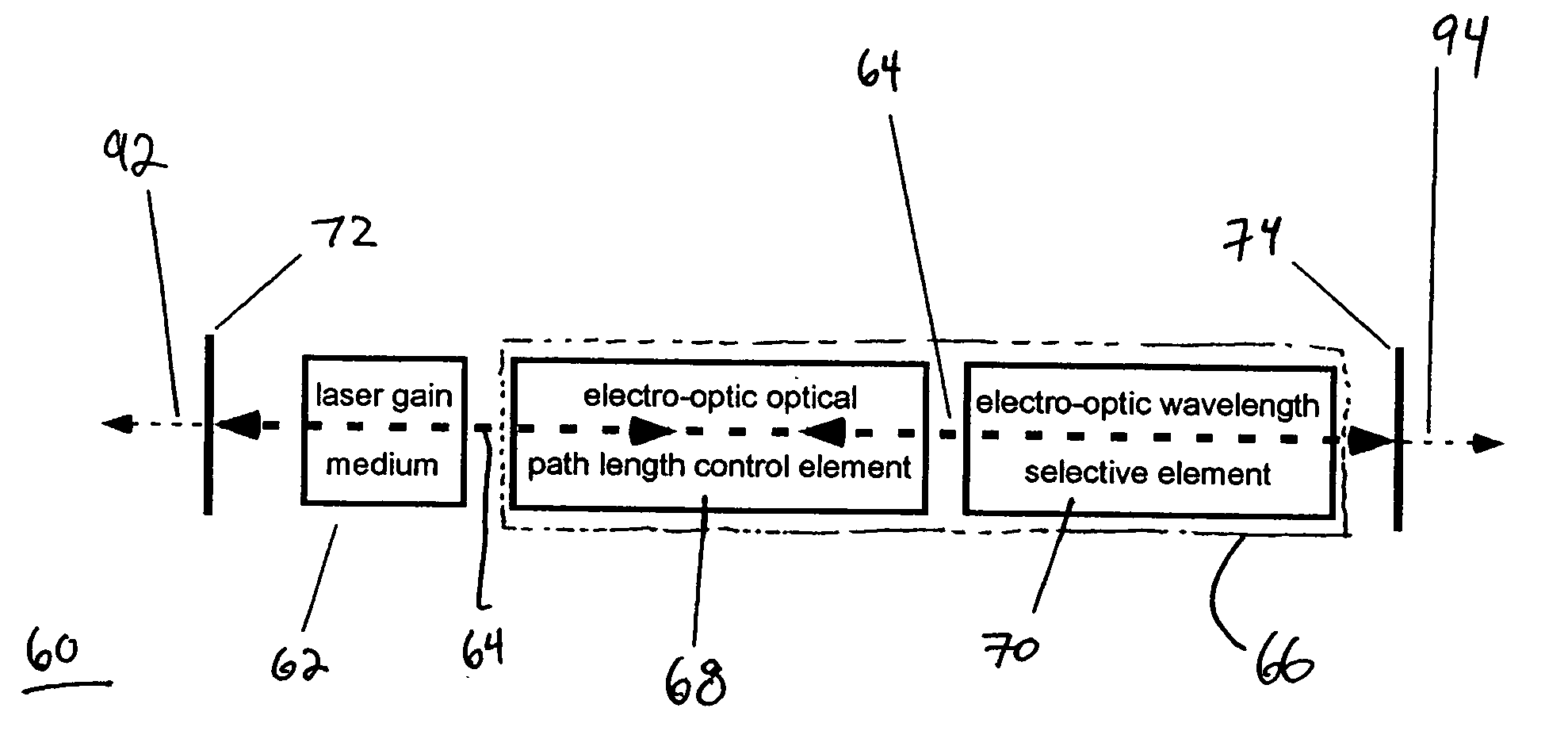
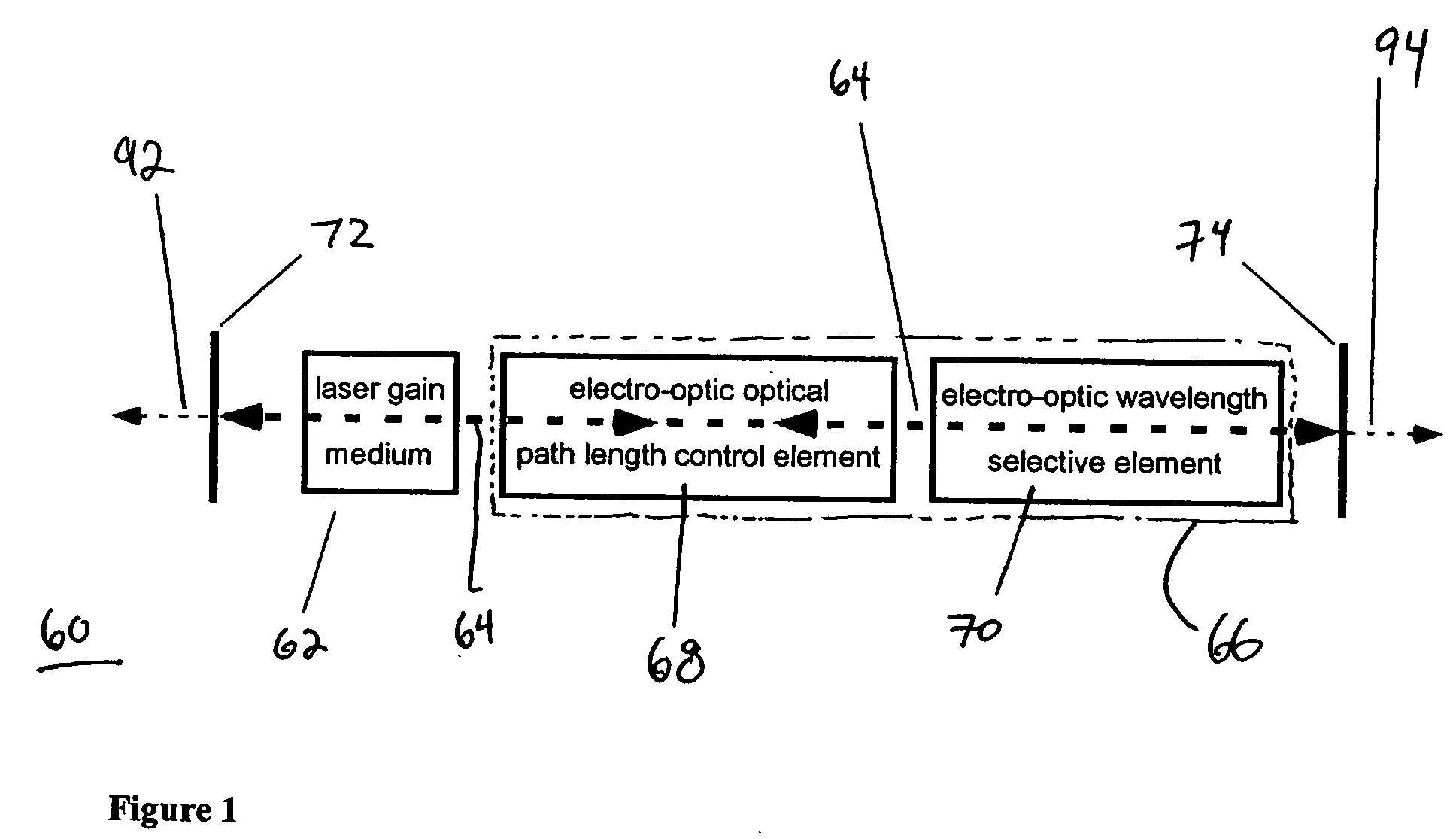
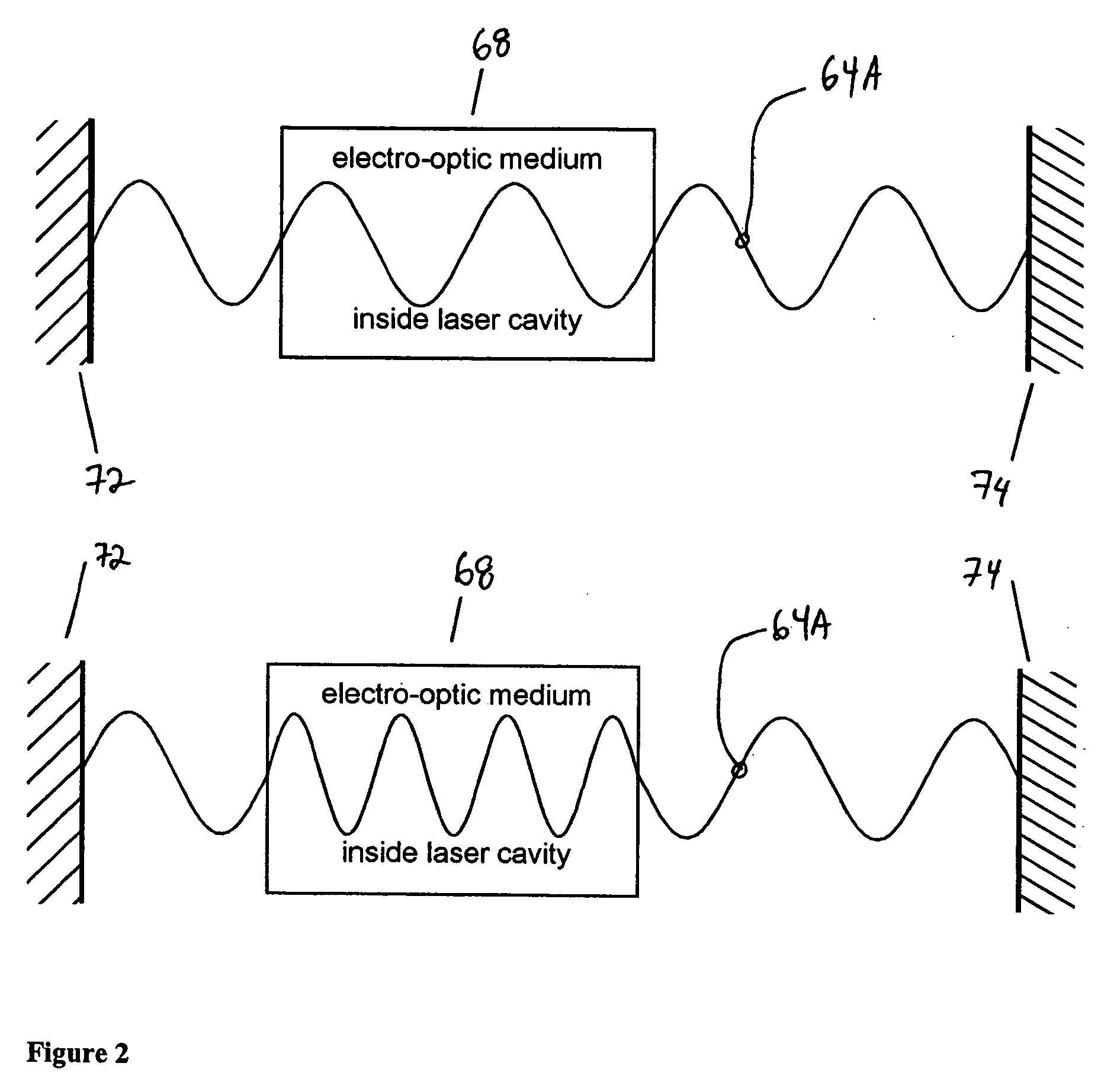
A tunable laser for providing a laser beam with a selectable wavelength. In one example, the tunable laser includes a gain medium for generating the laser beam; a waveguide for processing the laser beam, the waveguide having liquid crystal material or other electro-optic material disposed therein; an optical path length control element disposed within said waveguide for controlling an effective optical path length of the laser cavity; and a wavelength selective element for controlling the wavelength of the laser beam. The tunable laser may be designed without any moving mechanical parts if desired.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Devices and arrangements for performing coherence range imaging using a common path interferometer
ActiveUS20060109478A1Path length mismatchDispersion mismatchInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Devices, arrangements and apparatus adapted to propagate at least one electro-magnetic radiation are provided. In particular, a probe housing, a sample arm section and a reference arm section can be included. For example, the sample arm section can be at least partially situated within the probe housing, and configured to propagate a first portion of the electro-magnetic radiation that is intended to be forwarded to a sample. The reference arm section can be at least partially situated within the probe housing, and configured to propagate a second portion of the electro-magnetic radiation that is intended to be forwarded to a reference. In addition or as an alternative, an interferometer may be situated within the probe housing. The first and second portions may travel along substantially the same paths, and the electro-magnetic radiation can be generated by a narrowband light source that has a tunable center wavelength. Further, the first and second portions may be at least partially transmitted via at least one optical fiber. A splitting arrangement may be provided which splits the electro-magnetic radiation into the first and second portions, and positioned closer to the sample than to the source of the electro-magnetic radiation, and the first and second portions may be adapted to propagate in different directions. An apparatus may be provided that is configured to control an optical path length of the second portion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
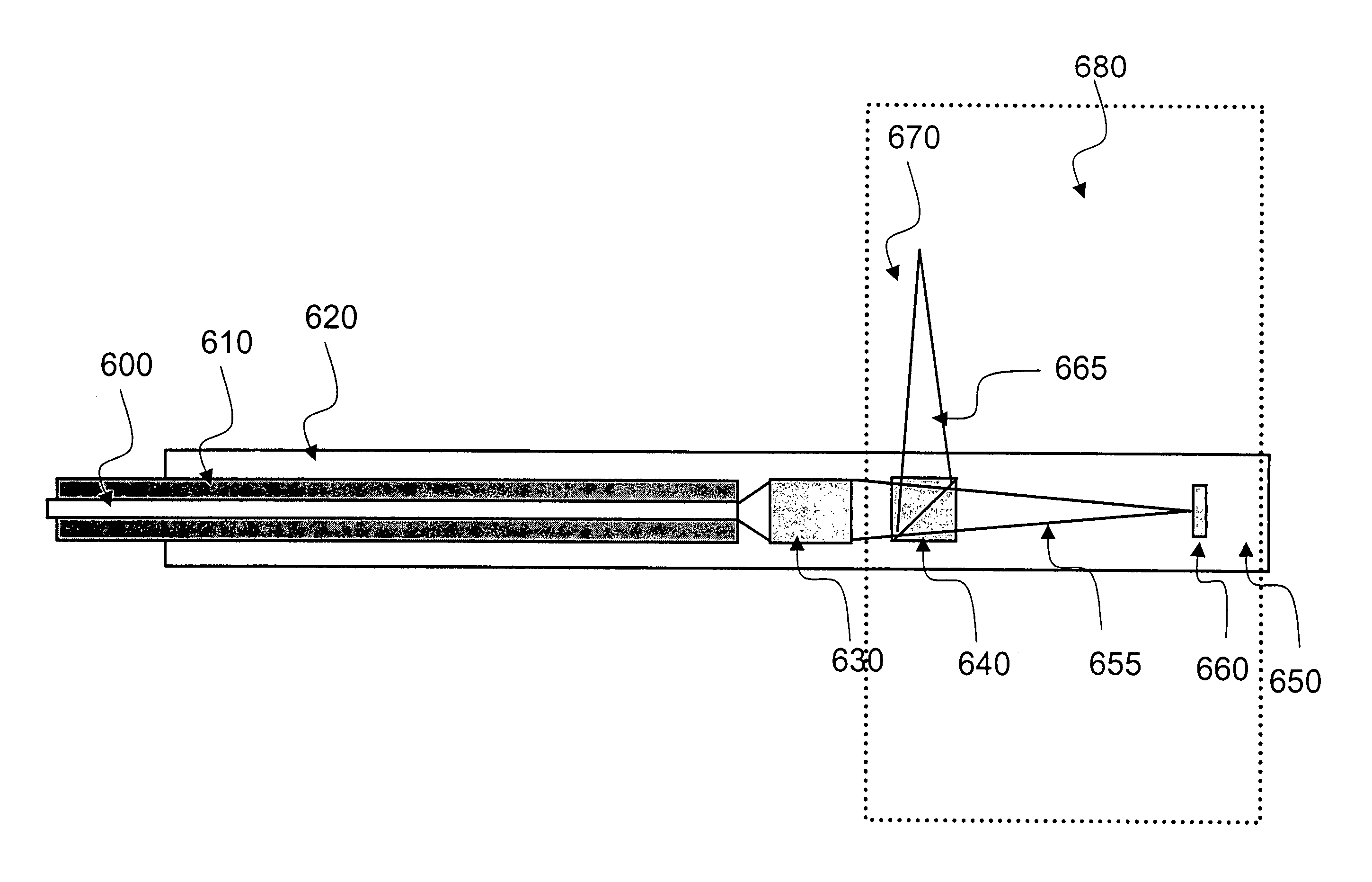
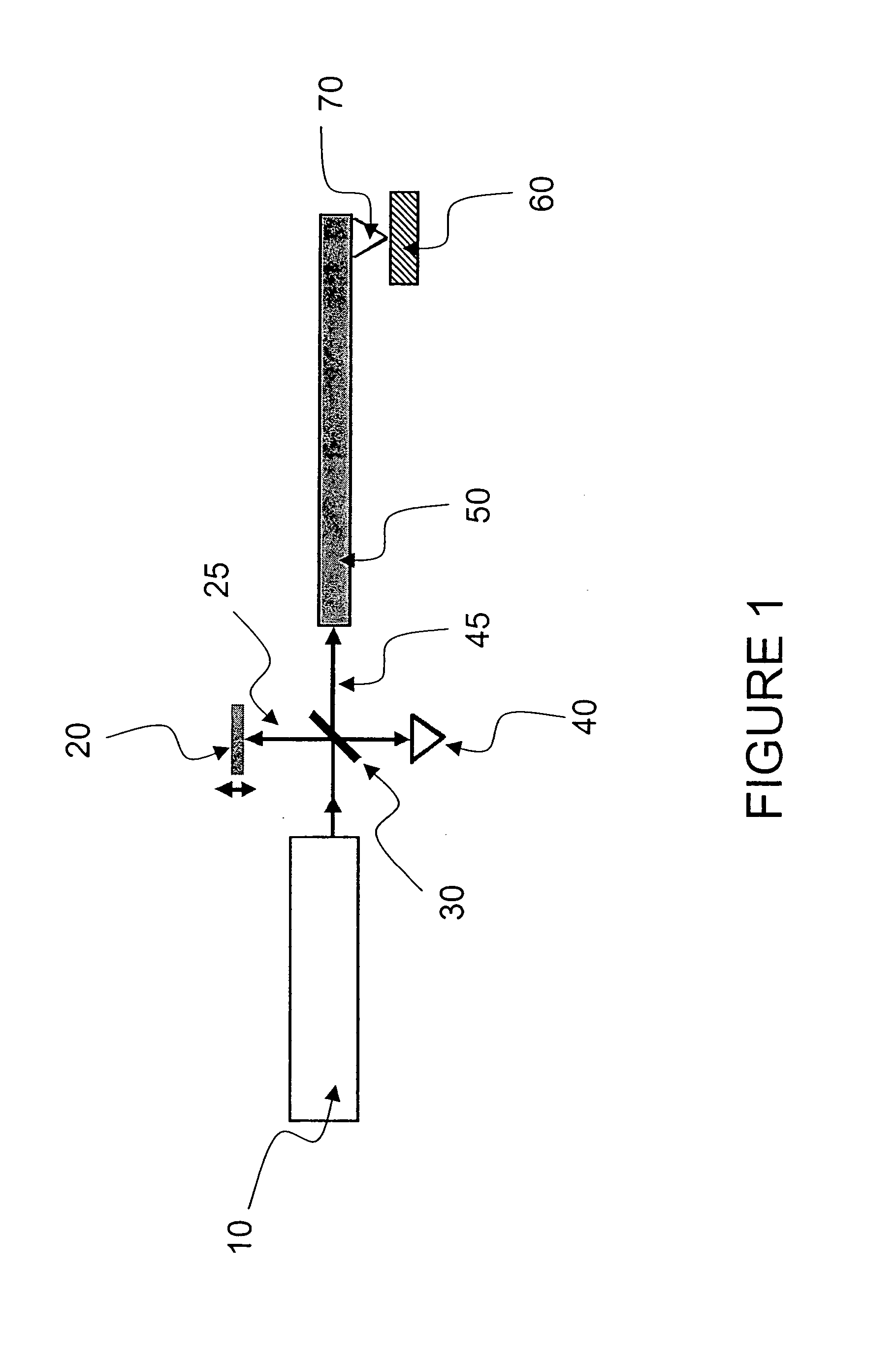
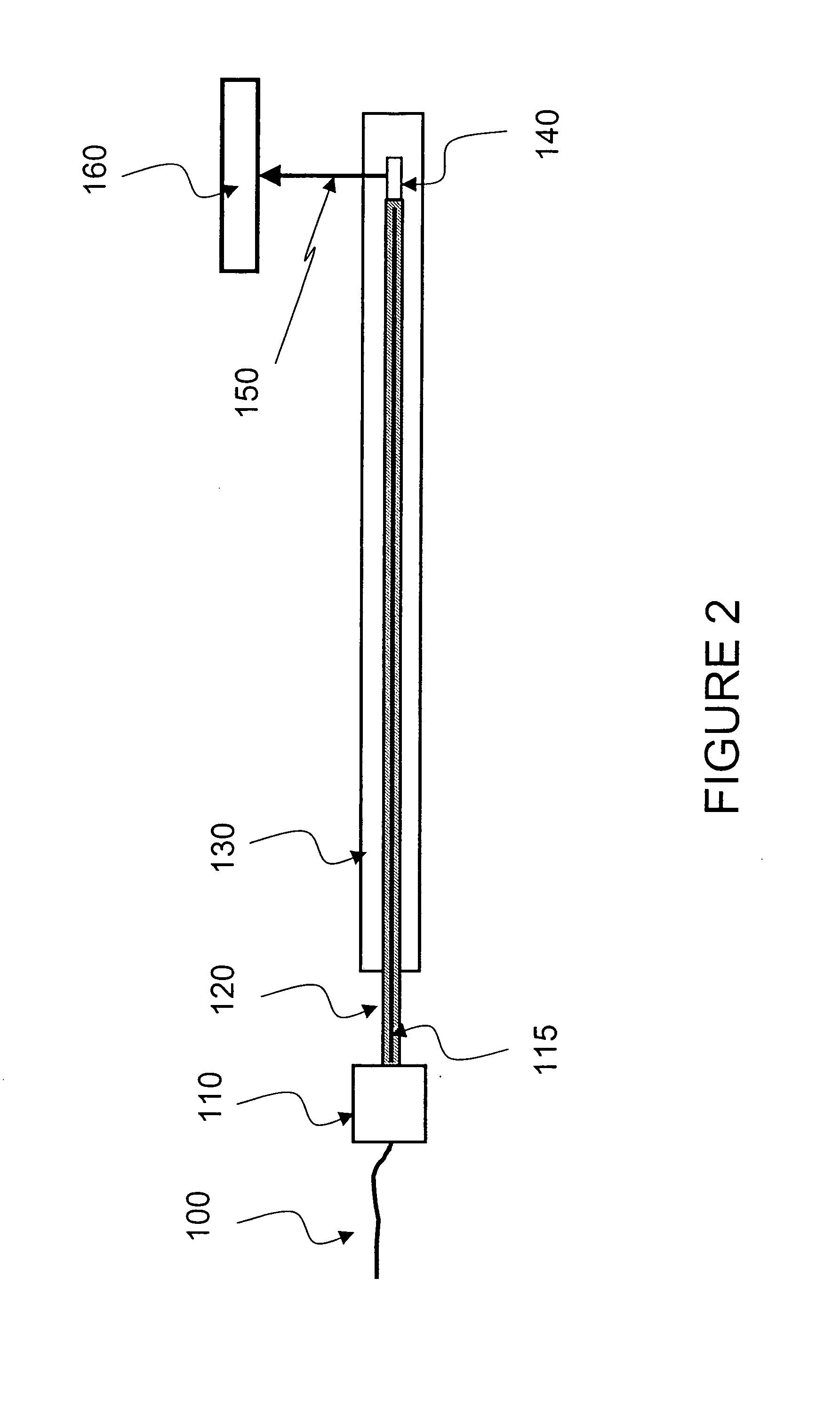
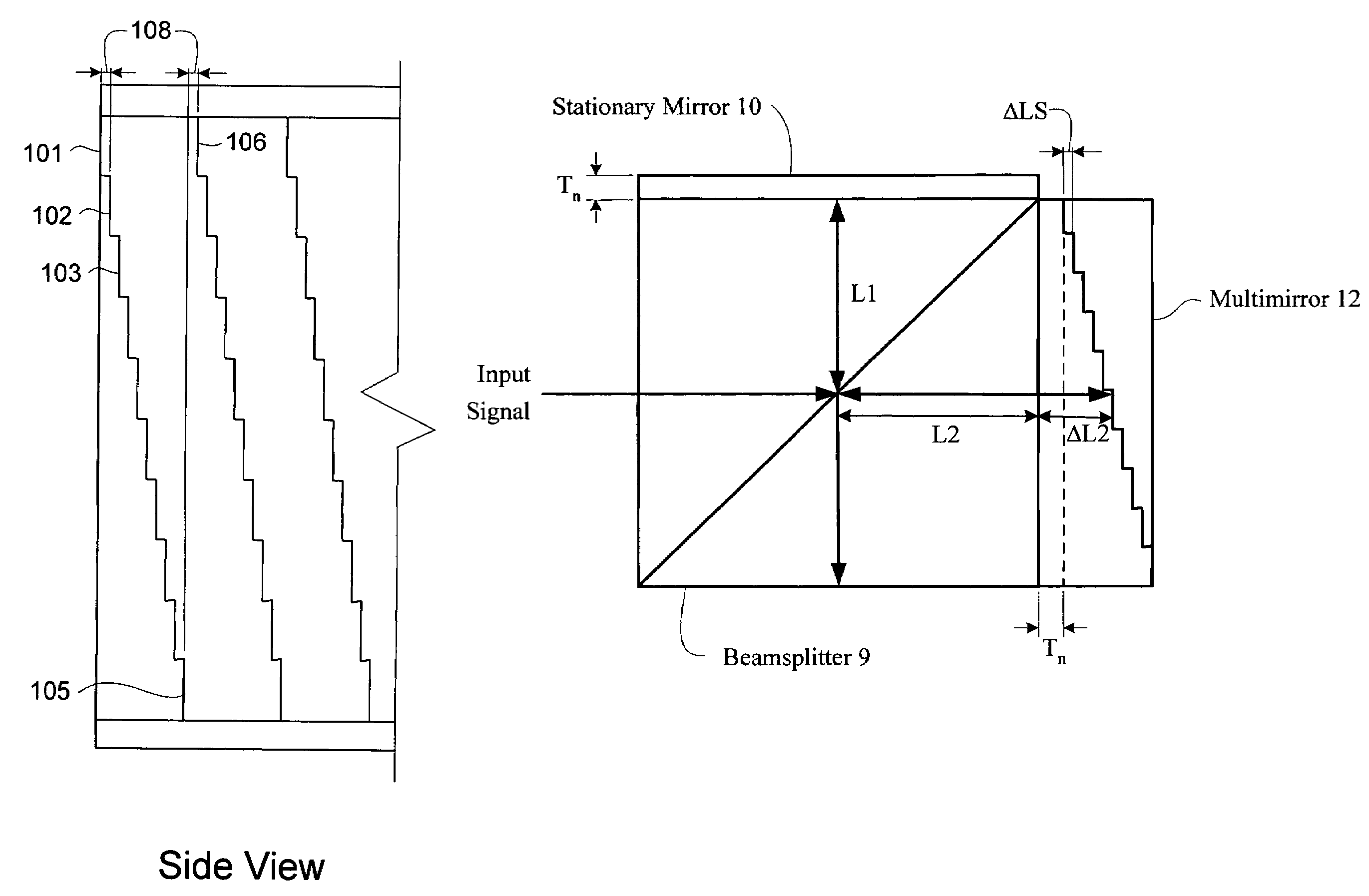
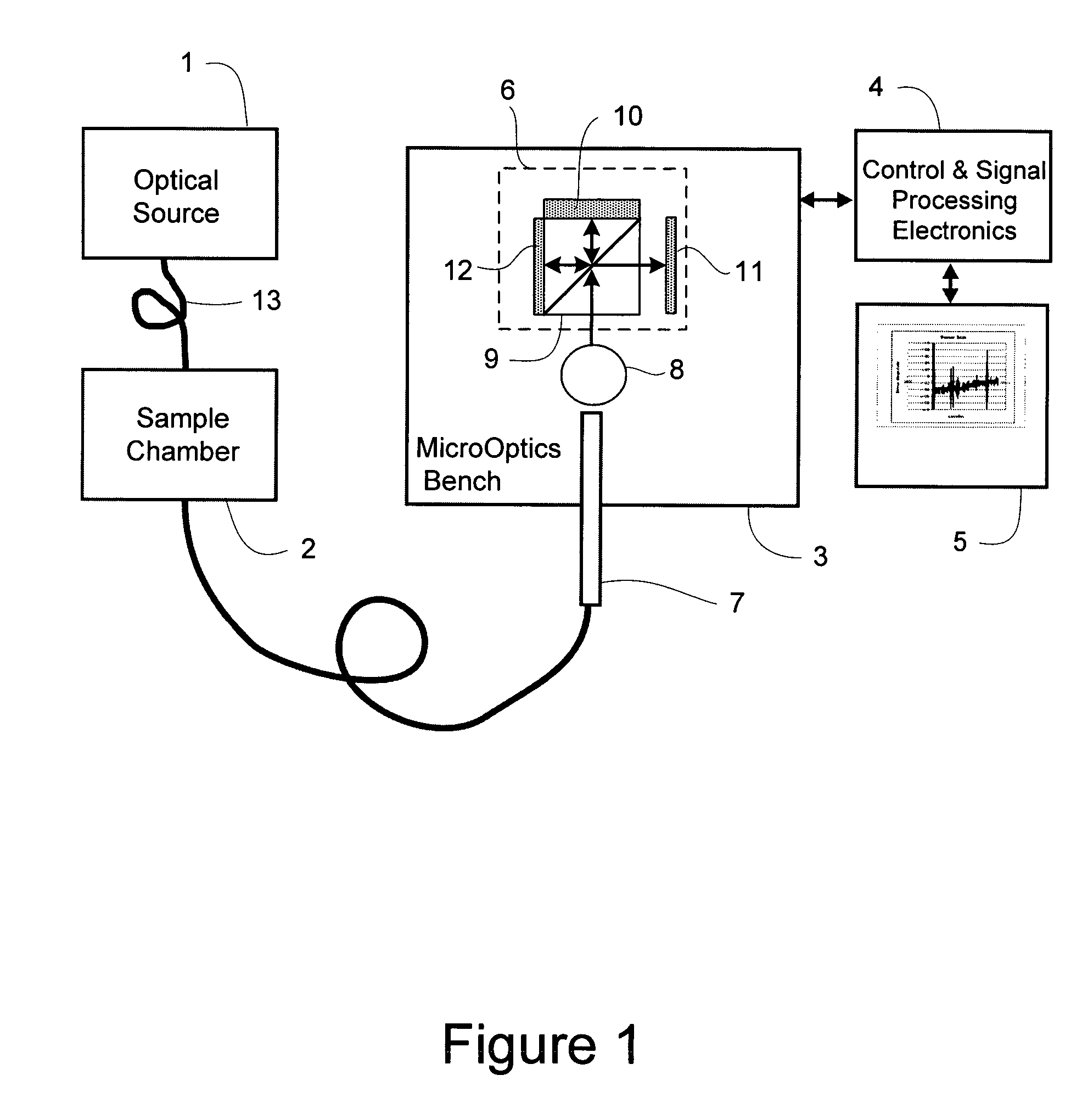
Miniature fourier transform spectrophotometer
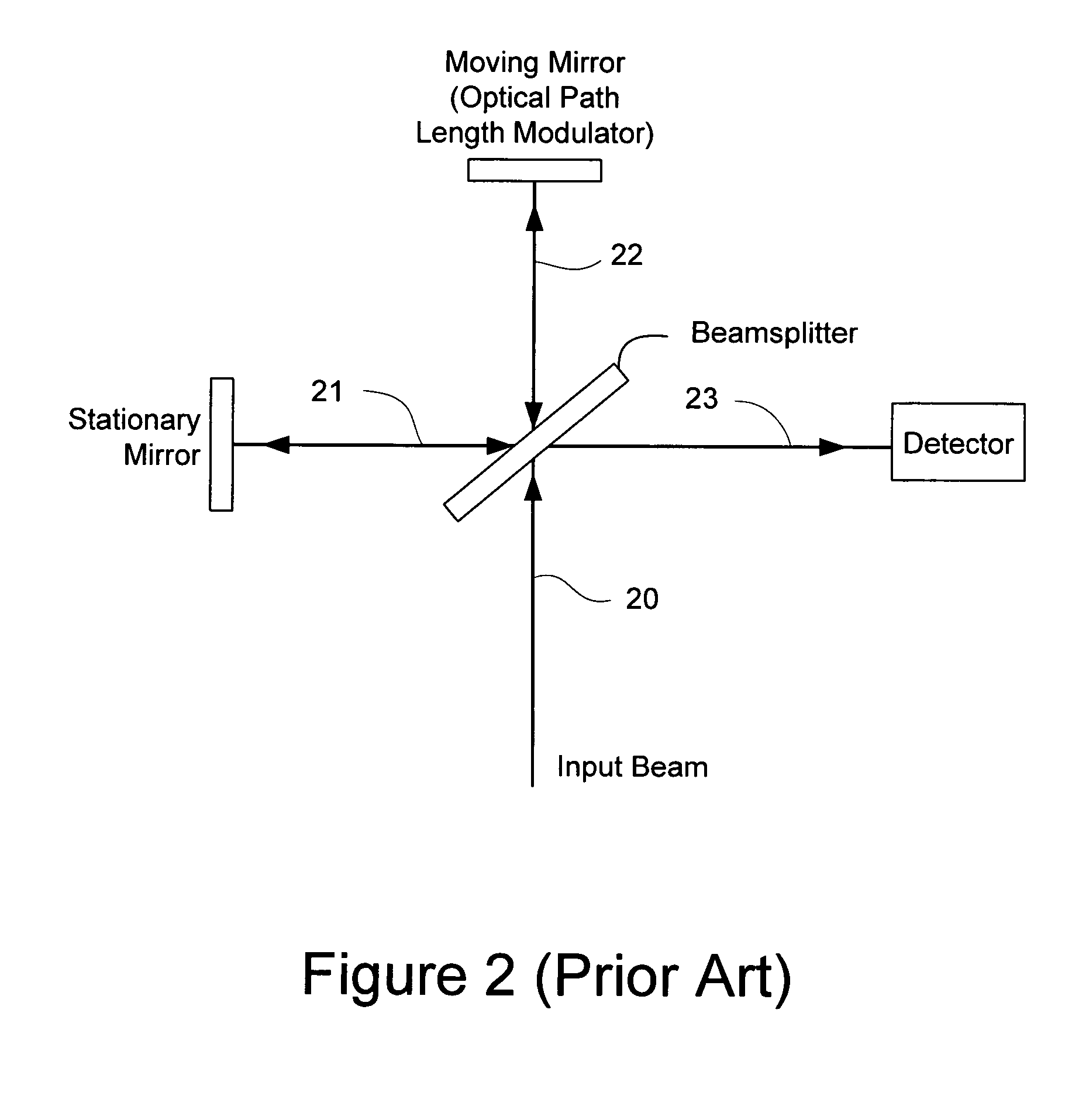
ActiveUS7359058B2Decreased wavelengthRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMichelson interferometerOptical path length
The Miniature Fourier Transform Spectrophotometer provides the capability, in a miniaturized device, of determining the light absorption / transmission spectra of a collected sample of gas or liquid though Fourier Transform spectroscopy techniques. The device takes an optical input from an optical fiber, manipulates that light through miniature optical components, and launches it into a miniaturized Michelson interferometer with a scanning mirror that acquires the interferogram of the optical input. The interferogram can be processed to retrieve the spectrum of the input light. A novel multi-stepped micro-mirror operates as the optical path length modulator in the miniaturized interferometer. A unique monolithic beamsplitter / mirror combination provides for accurate alignment of the components and greatly simplifies product integration. The device is designed to cover various optical spectra of interest. During operation, the precision and accuracy of the microfabricated components in the device allow operation and resolution even at extremely low wavelengths. In addition, the miniaturized nature of the device allows it to be used in new and extremely space-constrained applications.
Owner:MORGAN RES CORP
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6310679B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
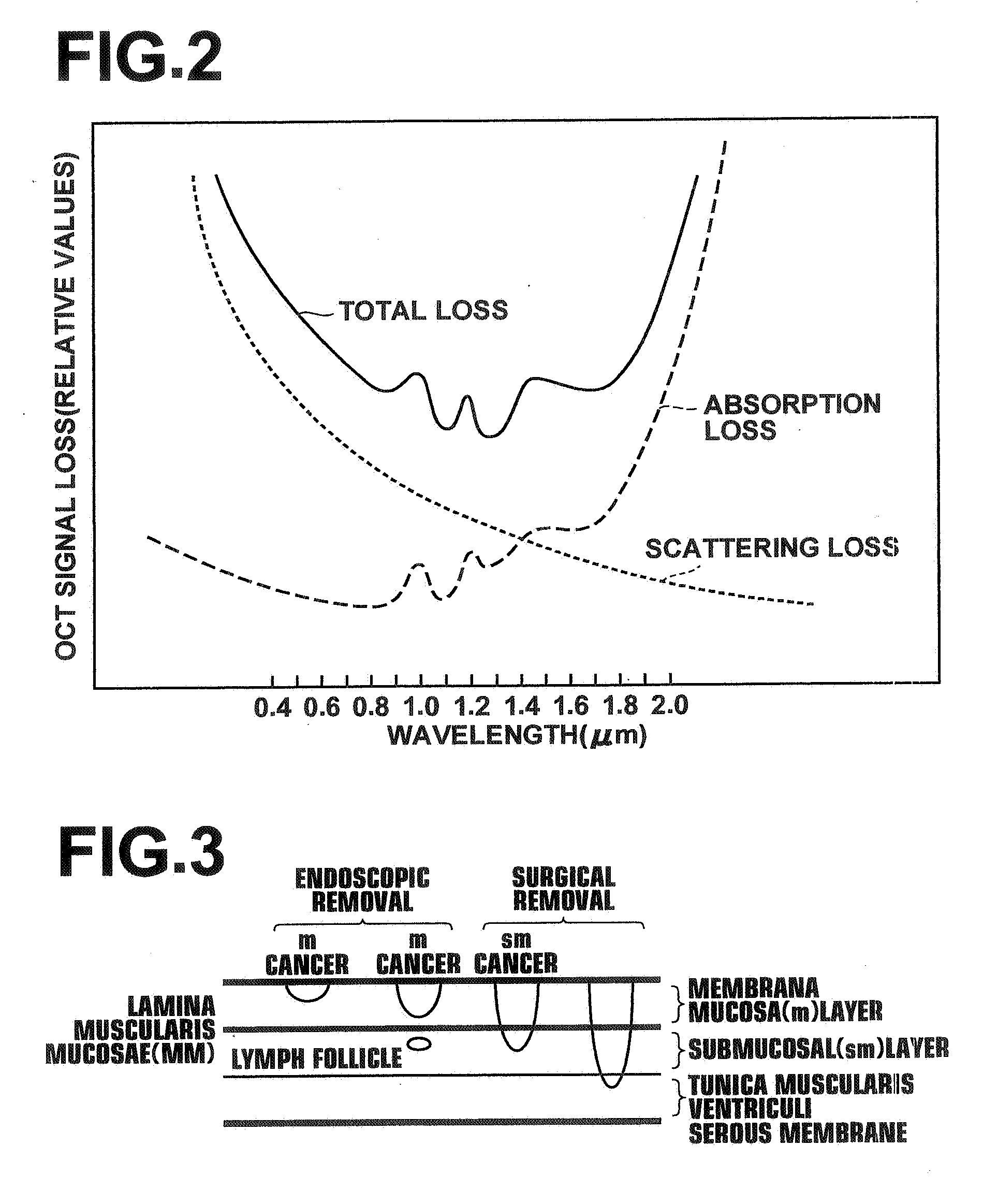
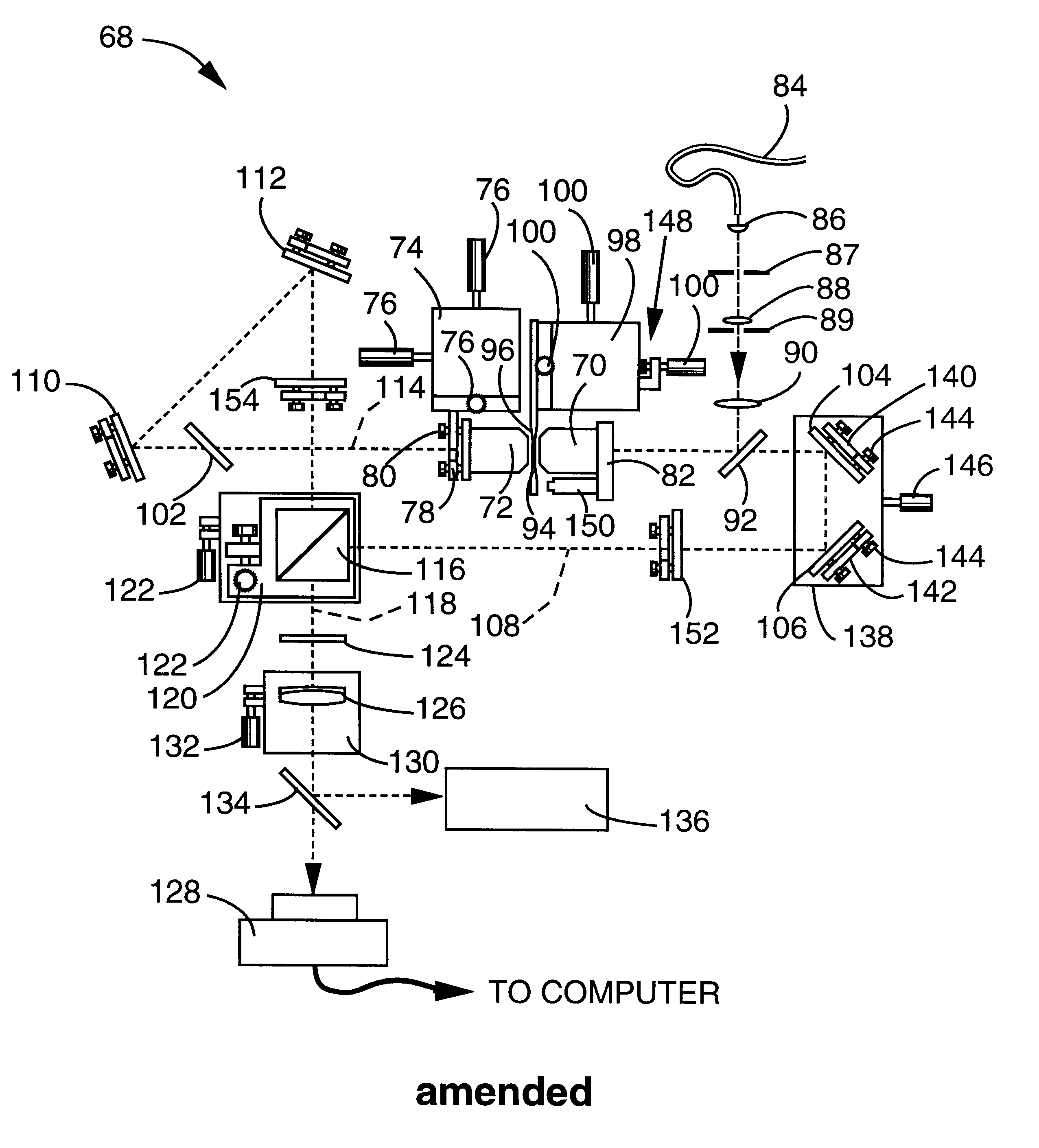
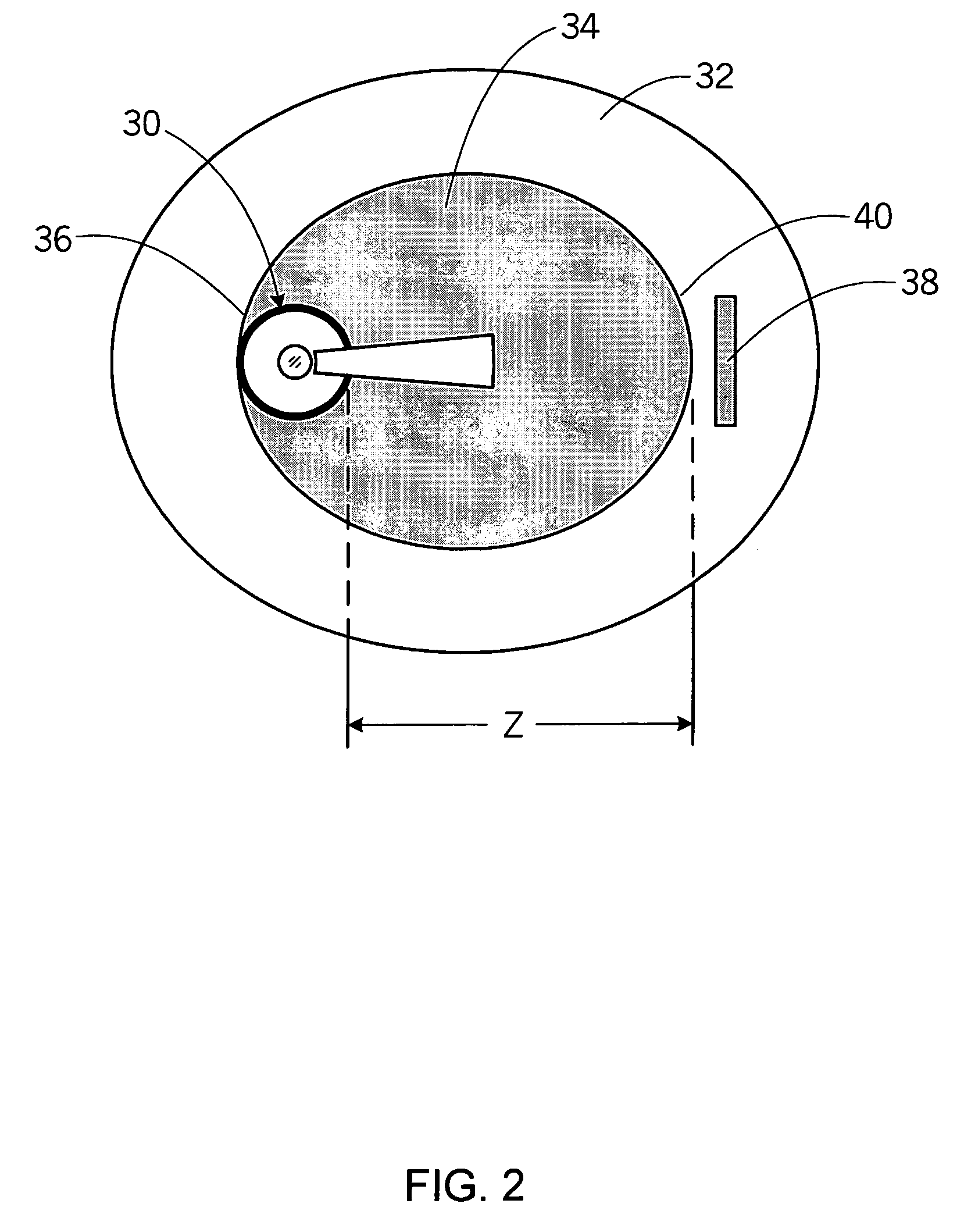
Device for tissue characterization
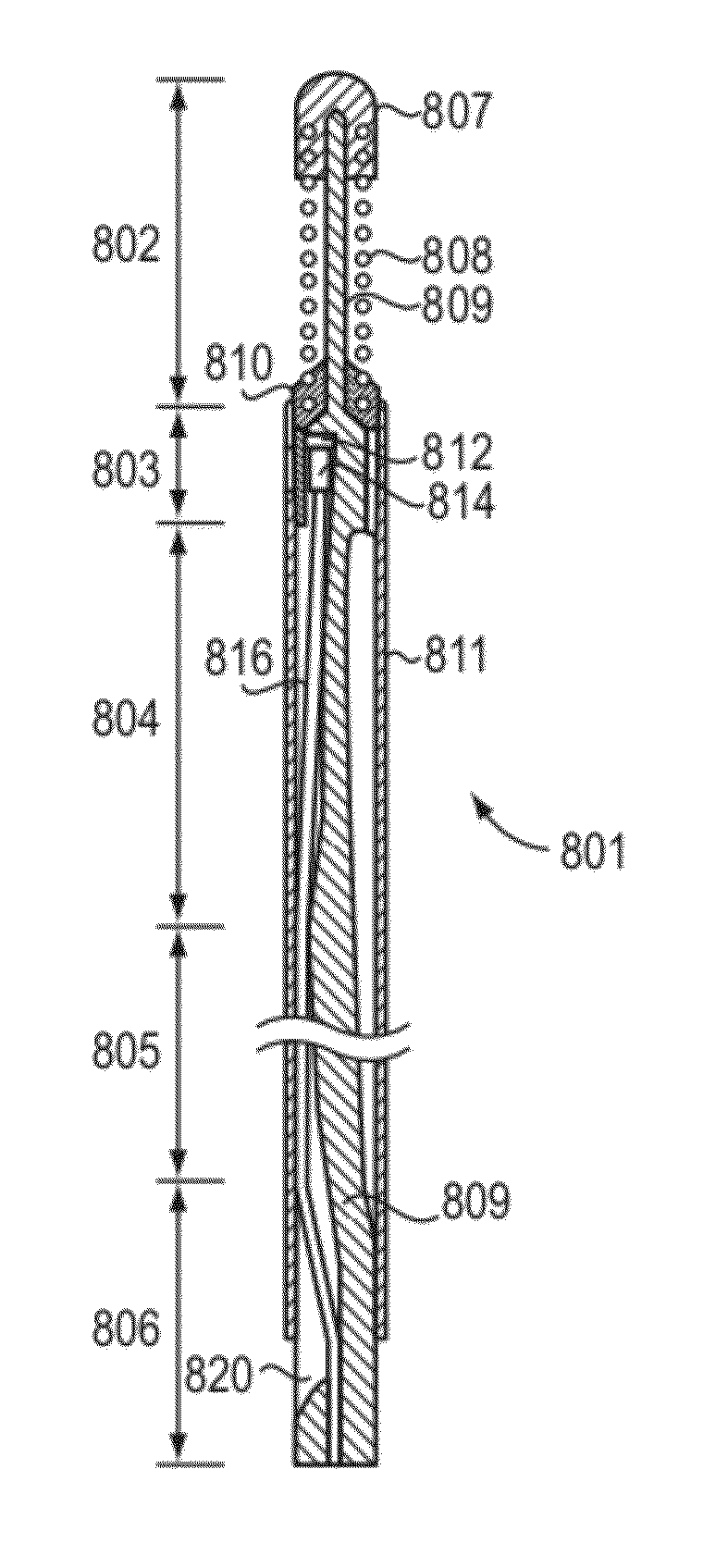
InactiveUS7242832B2Keep the flowMaintain normal flowPhase-affecting property measurementsSurgeryDistal portionTissue characterization
Owner:MEDEIKON
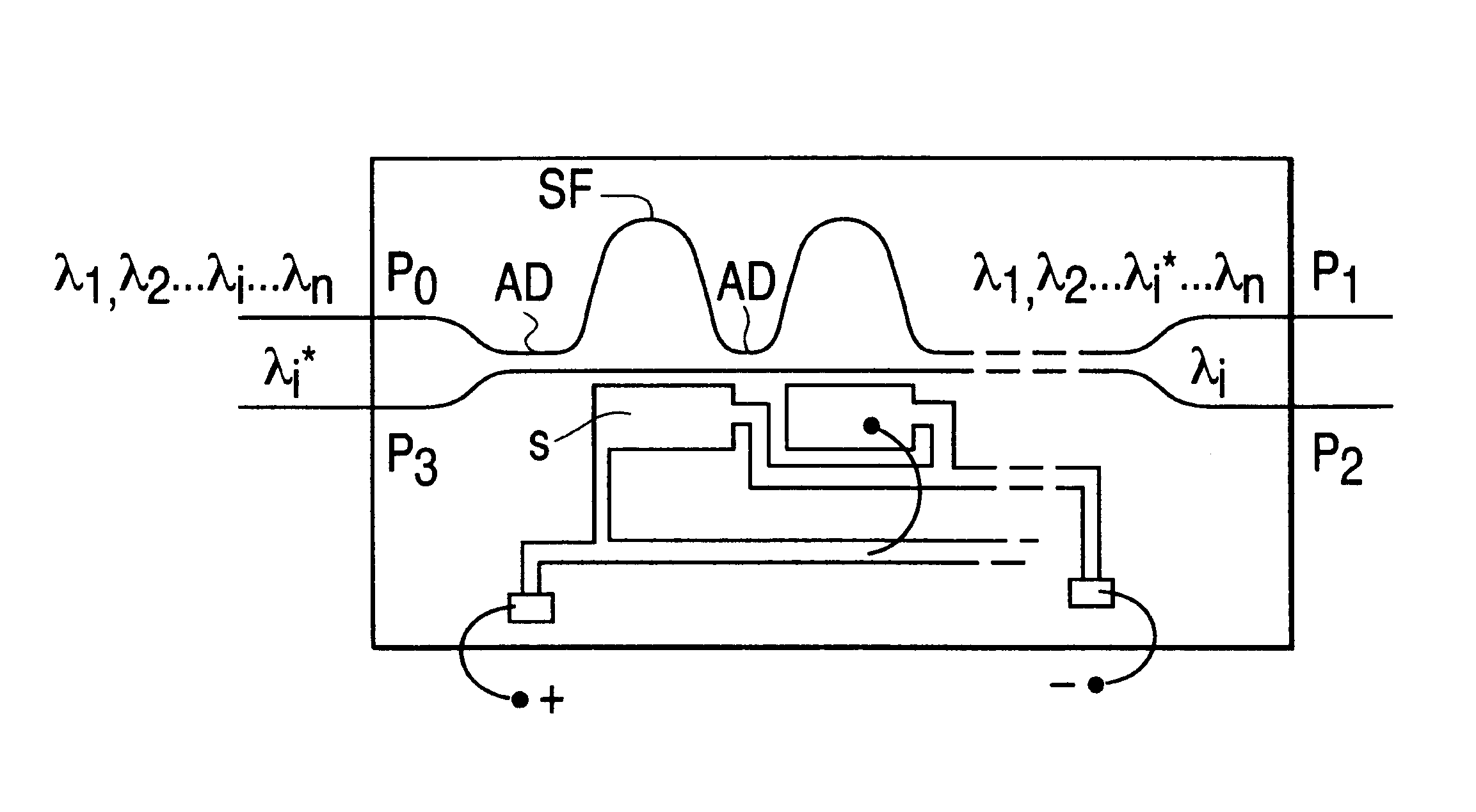
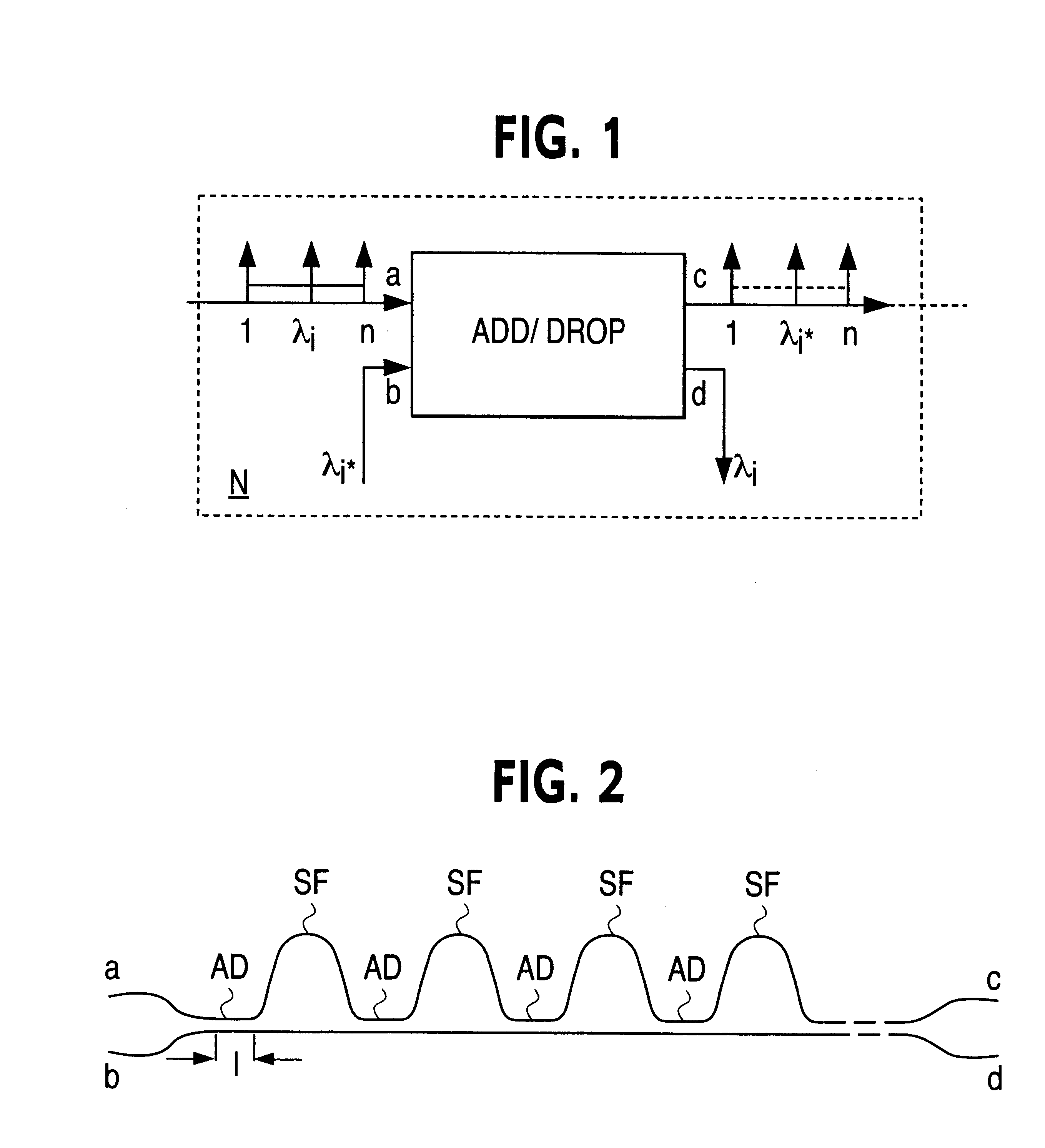
Tunable add/drop optical device
InactiveUS6285810B1Reduce complexityLow costCoupling light guidesTransmission monitoringRefractive indexCarrier signal
Tunable add / drop optical device for injecting or extracting (add / drop) at least a selected optical channel or carrier wavelength in or from a set of multiplexed channels or carriers of different wavelengths comprising a plurality of directional couplers (AD1 . . . AD6) and a plurality of phase-shift stages (SF1 . . . SF5) alternately connected in cascade, wherein each phase-shift stage defines a certain optical path length difference (DELTAL1 . . . DELTAL5) between two distinct optical paths of the stage. The tuning is performed modifying the refraction index of one path of said phase shift stages by means of Joule effect heating strips (L1 . . . L5) or by means of metallic field plates adapted to receive a signal suitable to modify the electric field intensity. The first two phase-shift stages of said plurality of phase-shift stages have differences of length of optical paths different from each other and in a preestablished ratio while the remaining phase-shift stages have differences of length of optical paths identical. It is thus possible to provide a device having an exceptionally flat cross response characteristic, substantially free of ripple due to an inevitable truncation of the Fourier expansion series.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
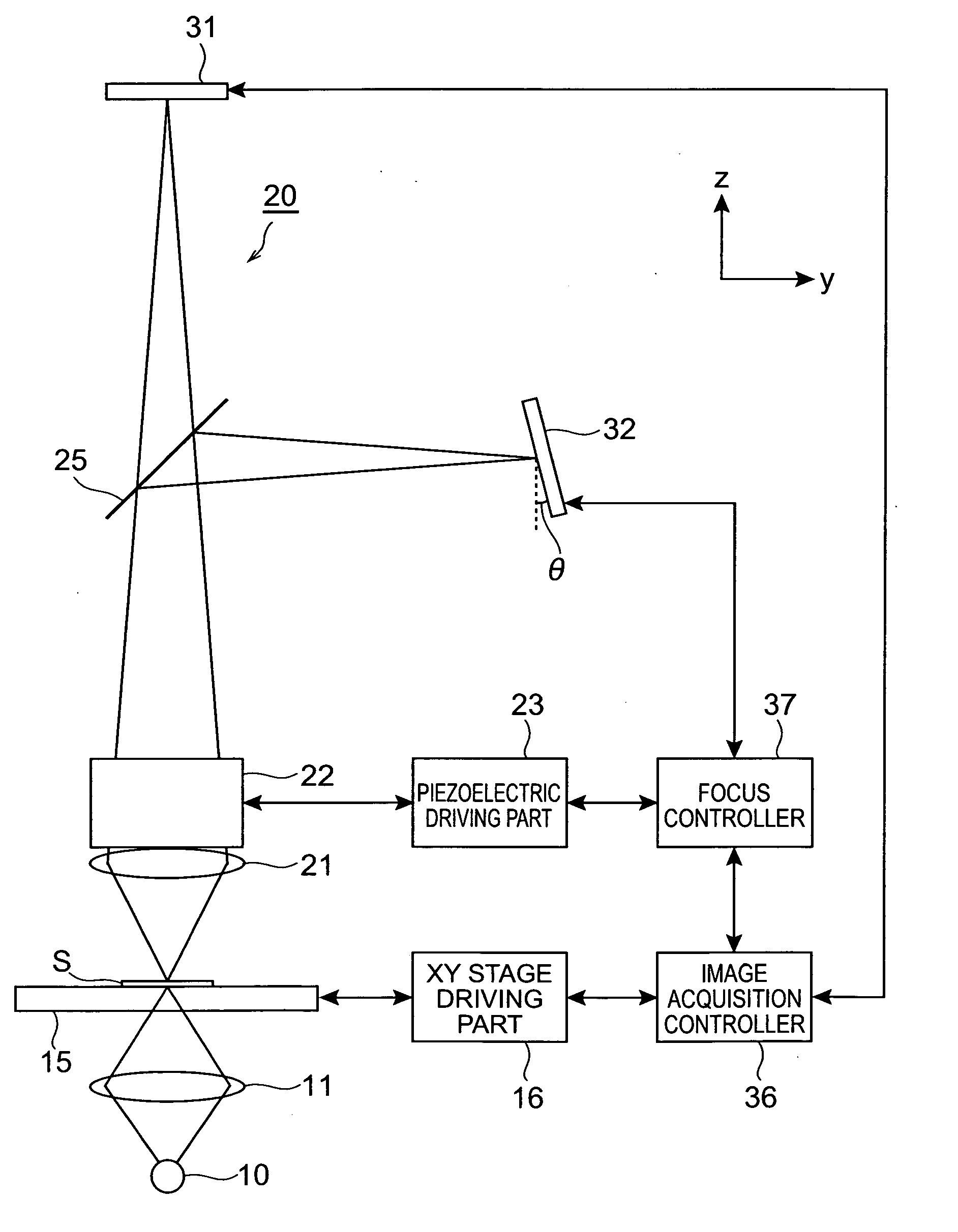
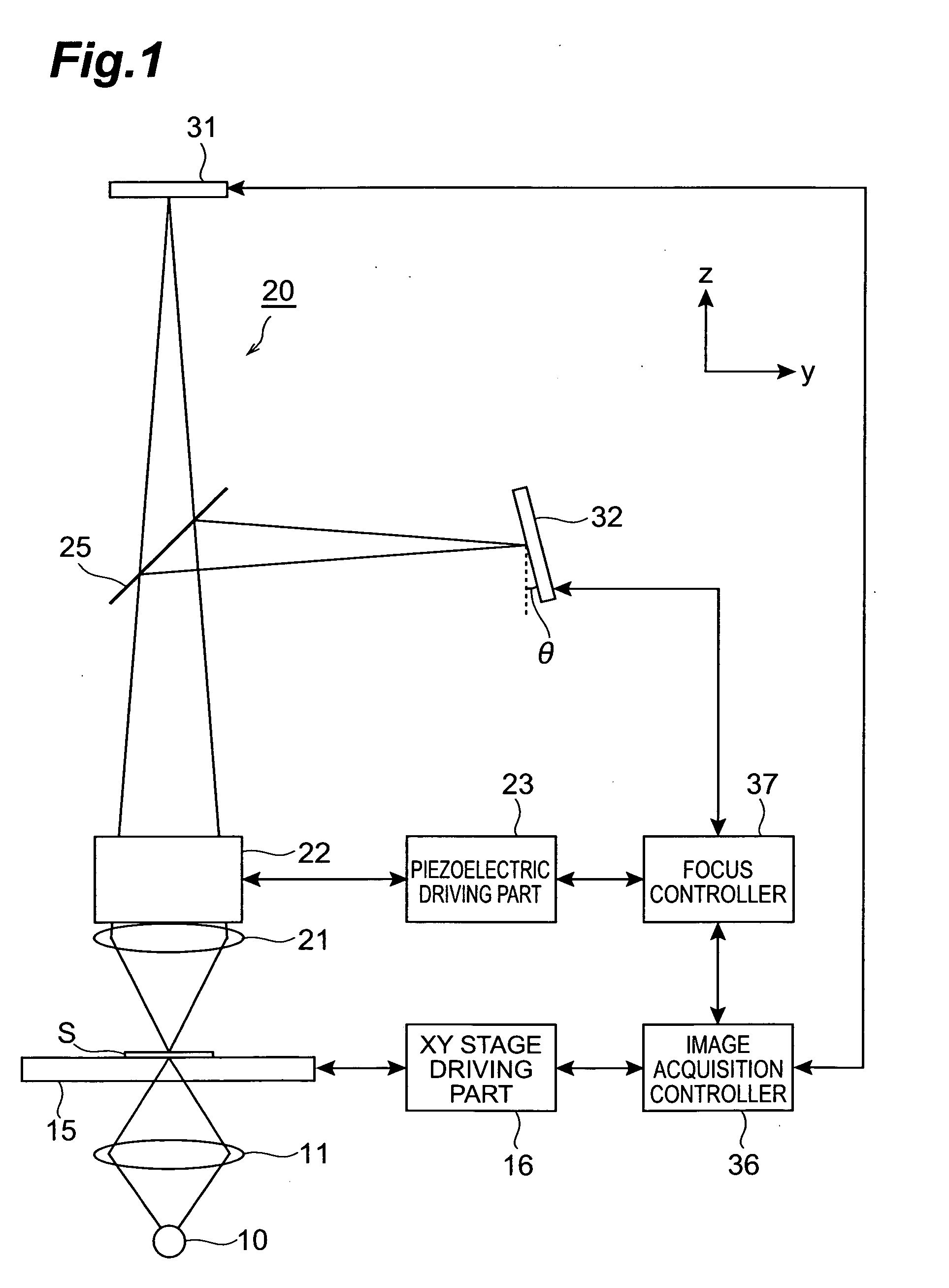
Microscope system
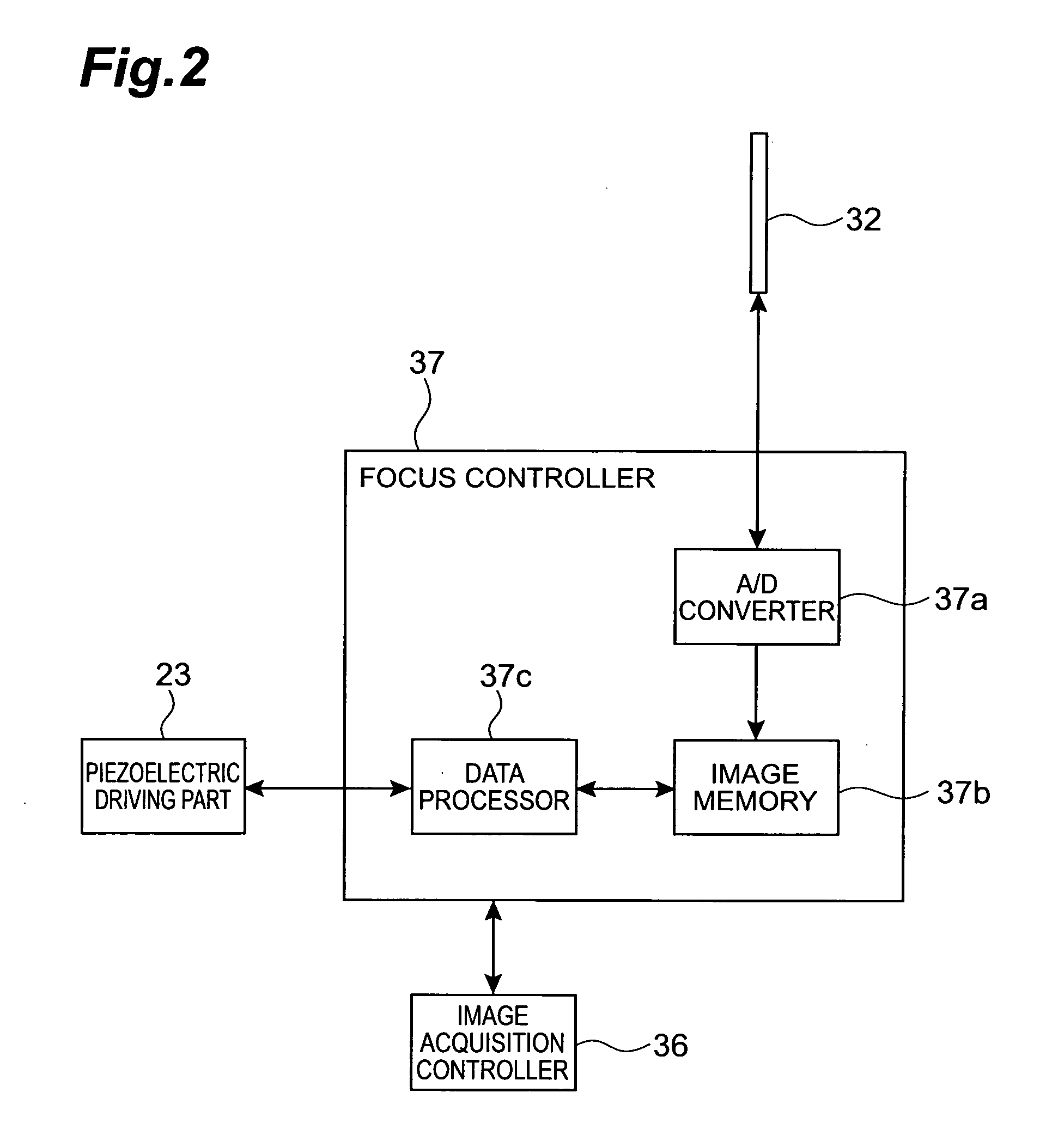
ActiveUS20050258335A1Suitable performanceControl precisionMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
A microscope system comprises a light guiding optical system 20 containing an objective lens 21 and a beam splitter 25 for splitting an optical image of a sample S to a first optical path and a second optical path, a photodetector 31 disposed on the first optical path used to acquire an image of the sample S, and a CCD camera 32 disposed on the second optical path for acquiring a two-dimensional image for focus control. The camera 32 is disposed being inclined at an angle of θ with respect to the optical path so that the optical path length in the light guiding optical system 20 varies along the z-axis direction. The image acquired by the camera 32 is analyzed by a focus controller 37, and the focal point for image pickup with respect to the sample S is controlled on the basis of the analysis result. Accordingly, there can be implemented a microscope system in which image acquisition of the sample and focus control for image pickup can be simultaneously performed.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Apparatus and method for interferometric measurement of a sample
ActiveUS7982881B2Quick measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLight beamWavelength
A device for the interferometric measurement of a sample, in particular the eye, including an interferometer arrangement with a first measurement beam path, through which a measurement beam falls onto the sample, and a first reference beam path, through which a reference beam runs, which is applied to the measuring beam for interference. The interferometer arrangement includes a second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path. The optical path lengths of the second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path are different from one of the first beam paths. The wave length difference is selected according to a distance of two measuring areas which are arranged at a distance in the depth direction of the sample.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Match filters for a real time fingerprint sensor and verification system
InactiveUS6111671AAcquiring/reconising fingerprints/palmprintsOptical elementsPhase correlationSpatial light modulator
A real time fingerprint verification system includes a recording device and a verification device each having a fingerprint scanner for generating a flat, dimensionally undistorted, high contrast, fingerprint image, and an intensity sensitive, spatial light modulator (SLM) for receiving and transforming the flat fingerprint image into a planar, coherent light image. In the recording device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint from the SLM is Fourier transformed, and input into a microscope objective lens system which expands the Fourier transformed beam image sufficiently to allow mechanical blocking of its central portion or order, whereupon it is directed to interact as an object beam with a reference beam from the particular coherent light source to record a holographic matched filter. In the verification device, the planar coherent light image beam of the fingerprint is Fourier transformed and input into a microscope objective lens system to allow similar mechanical blocking of its central portion or order whereupon it is directed to interrogates a previously recorded holographic matched filter of a fingerprint image as an object beam for determining a match or not between the respective recorded and interrogating images. The spatial light modulator (SLM) in both the respective recording and verification devices enables phase correlation (optical path length determination) of one device to another device. X-Y alignment and rotational orinentation of the respective real time image and holographic matched filter image is accomplished by jittering (orbiting and angularly oscillating) either the interrogating object beam, real time, relative to the matched filter or visa versa.
Owner:ADVANCED PRECISION TECH
Systems, methods and computer-accessible medium which provide microscopic images of at least one anatomical structure at a particular resolution
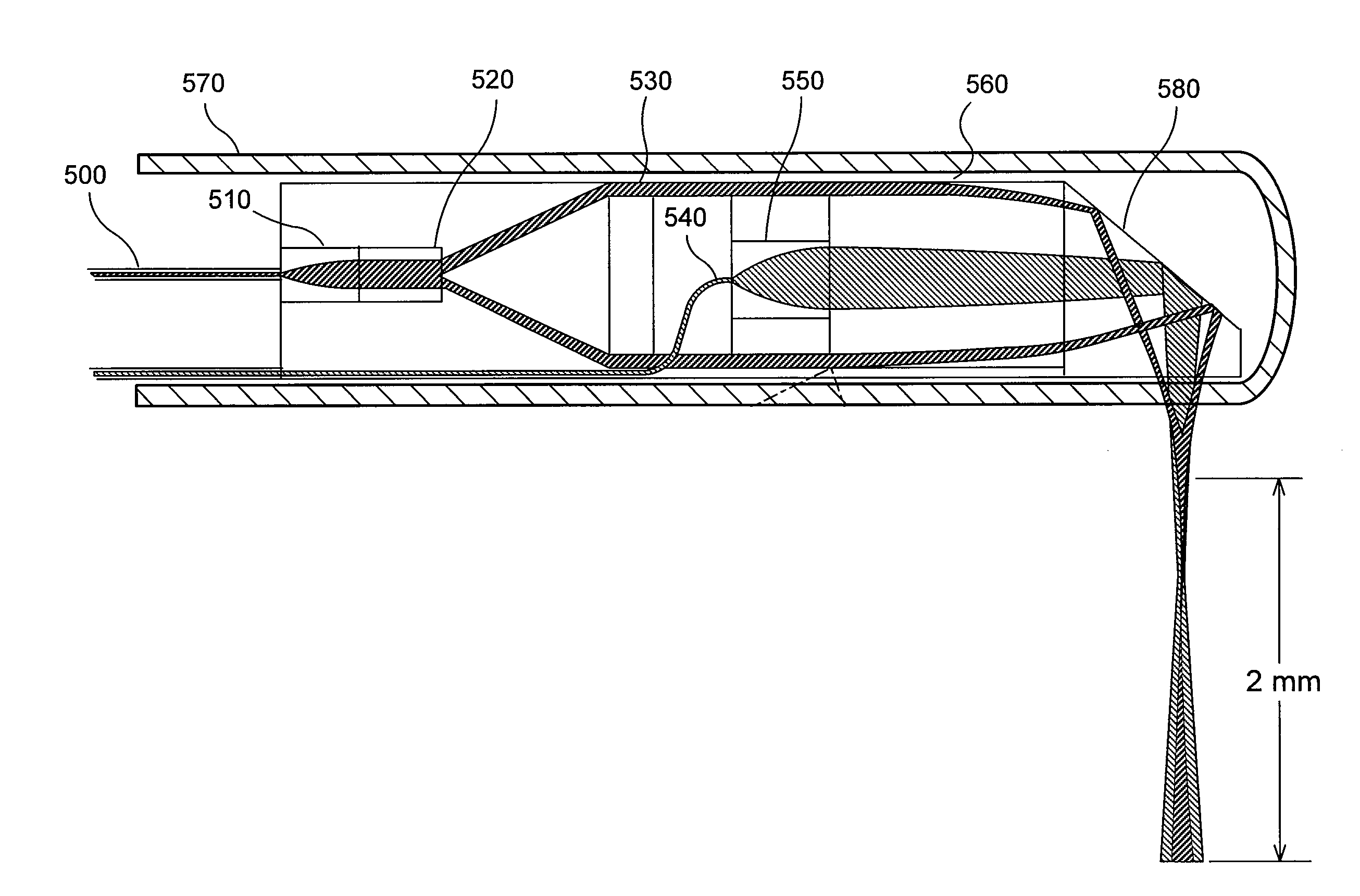
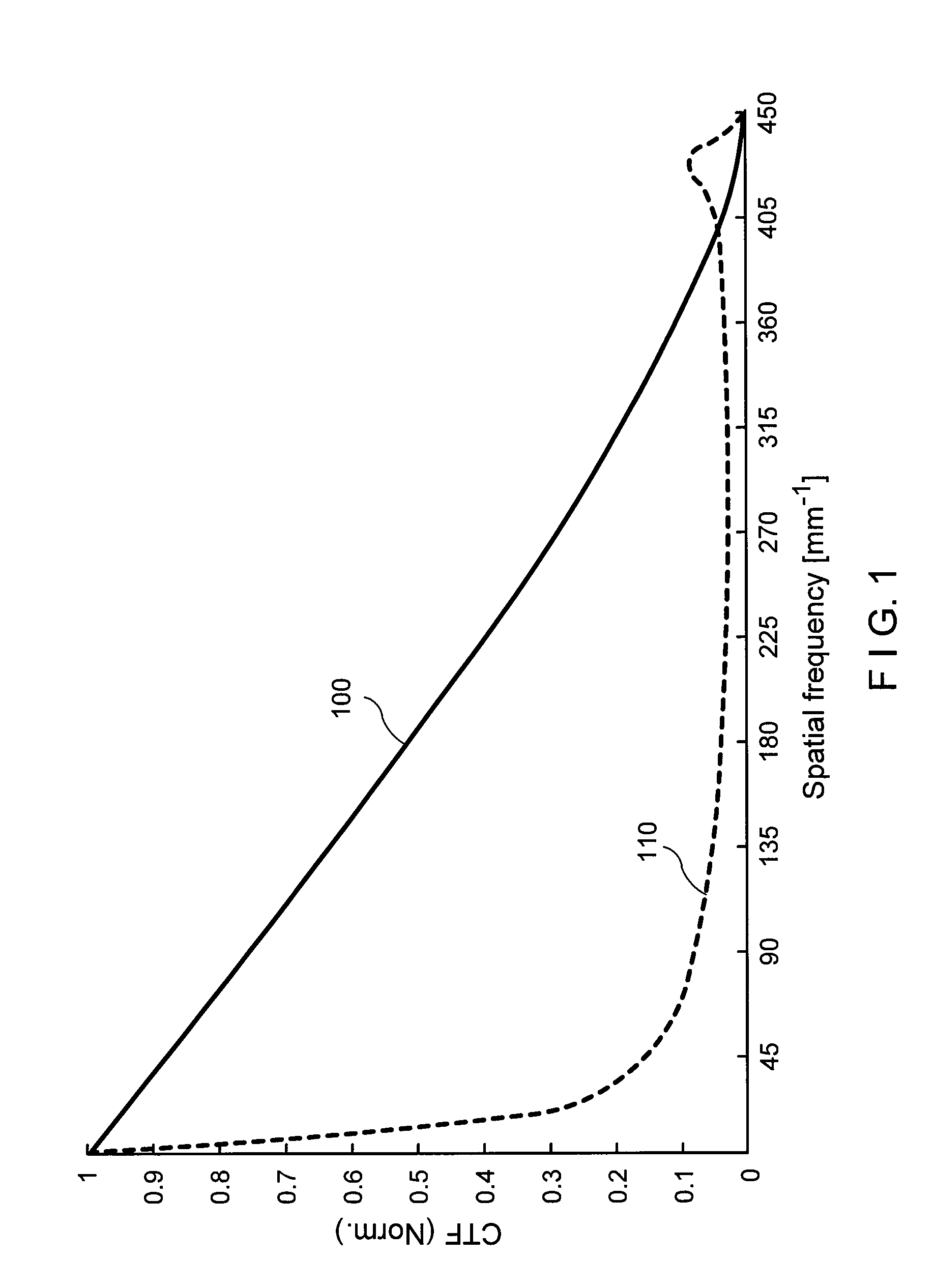
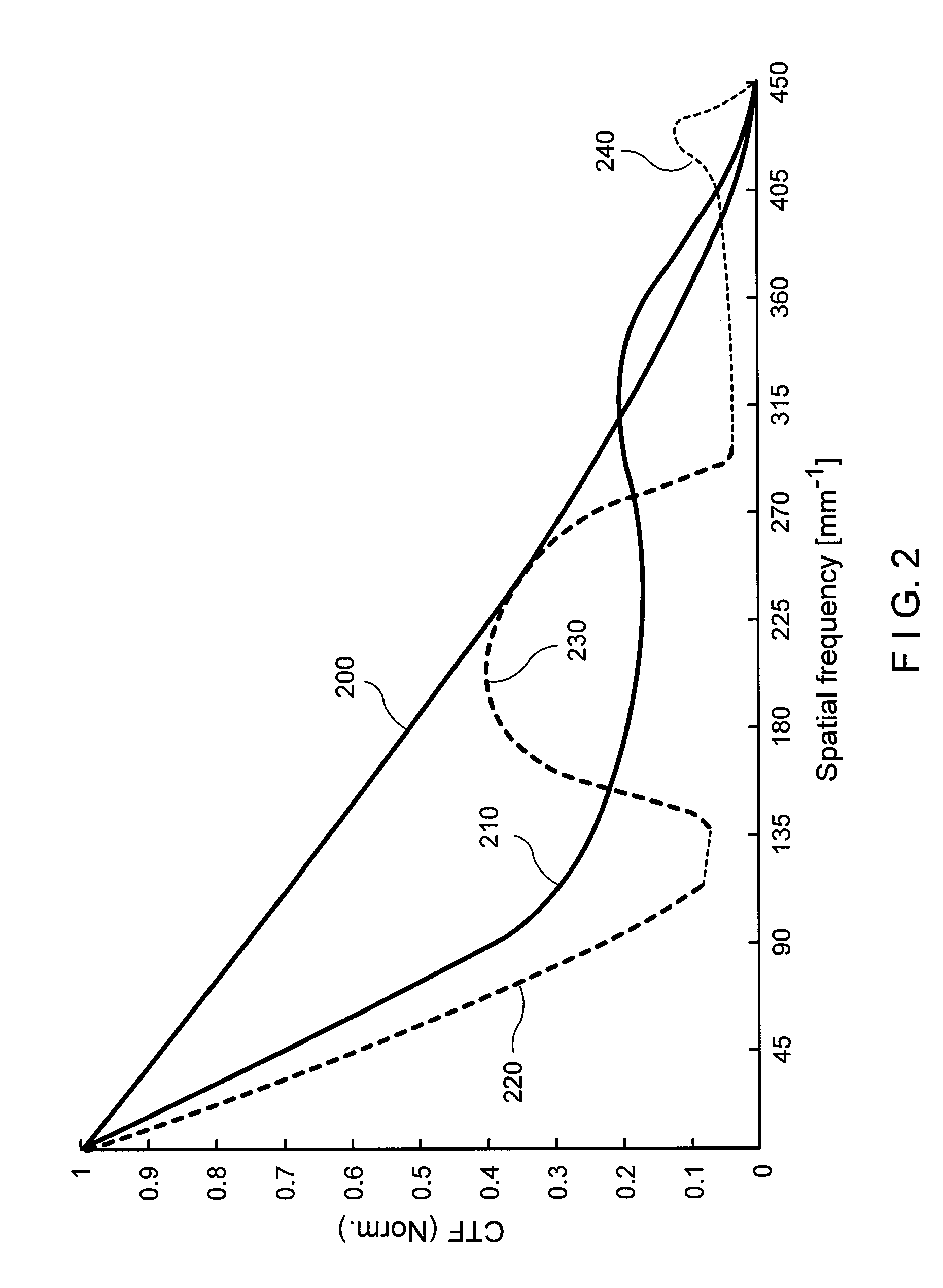
ActiveUS20110218403A1Facilitate the μOCT CTFFacilitate a depth-of-field extensionSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMicroscopic image
Exemplary embodiments of probes, apparatus, systems and methods can be provided which provide at least one electro-magnetic radiation to at least one sample. For example, a plurality of axicon lenses can be provided which are configured to provide the electro-magnetic radiation(s) having at least partially annulus shape. In addition or alternatively, at least one optical arrangement can be provided which is configured to forward at least one radiation to the sample therethrough having at least partially circularly-symmetric pattern. For example, at least one first portion of the radiation transmitted through a circular section of the pattern can have an optical path-length that is different from an optical path-length of at least one second portion of the radiation transmitted through at least one other section of the pattern.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
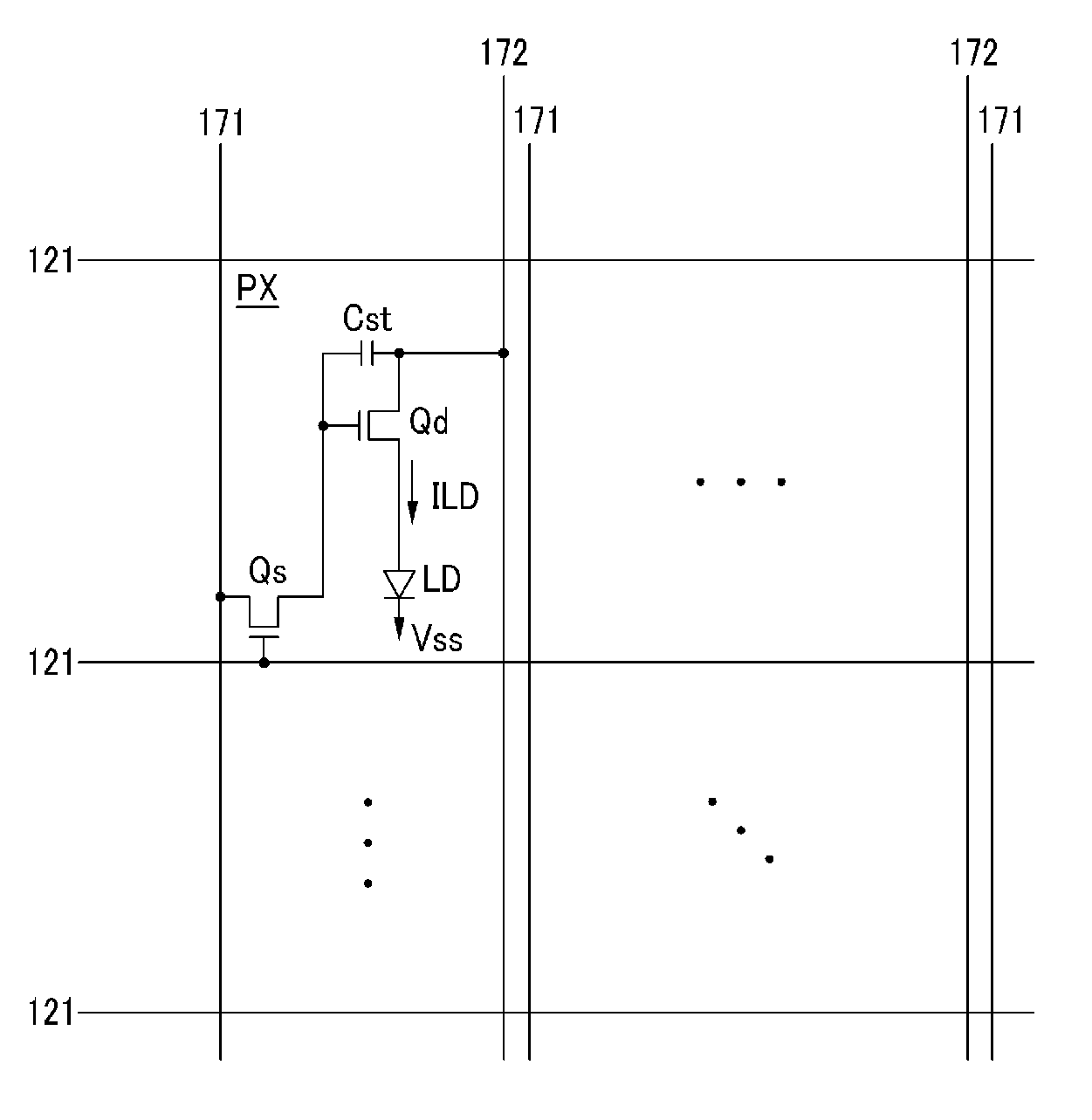
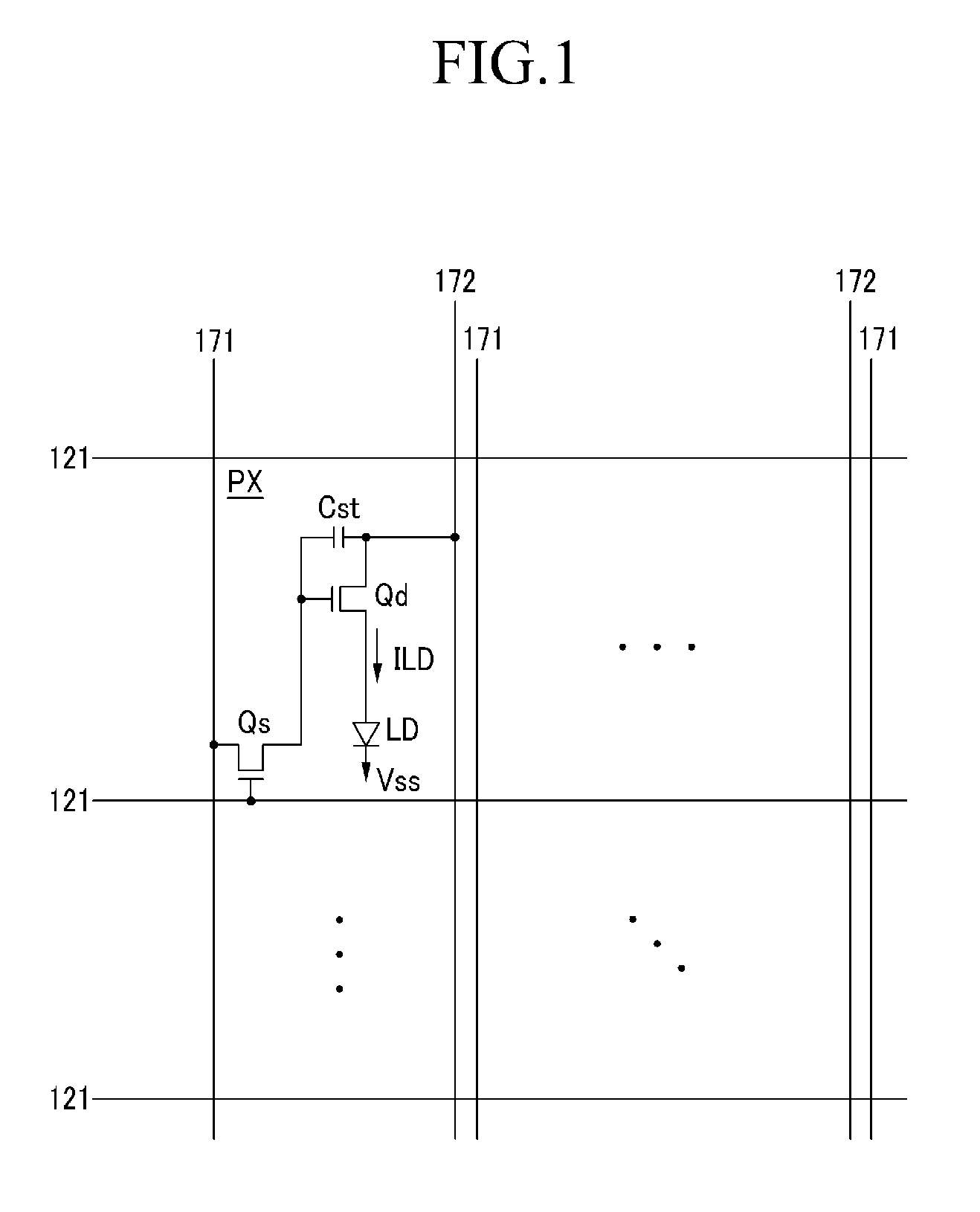
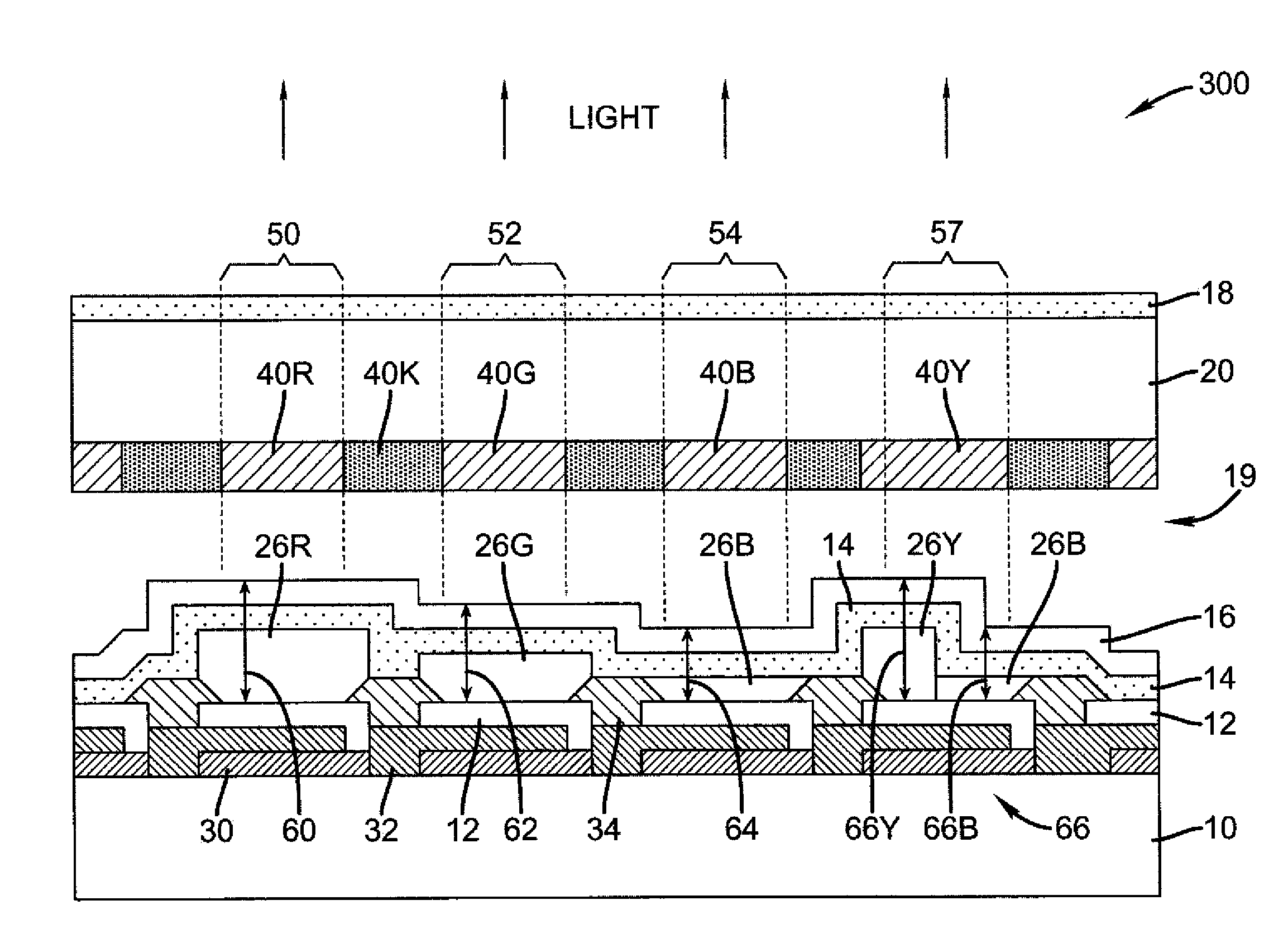
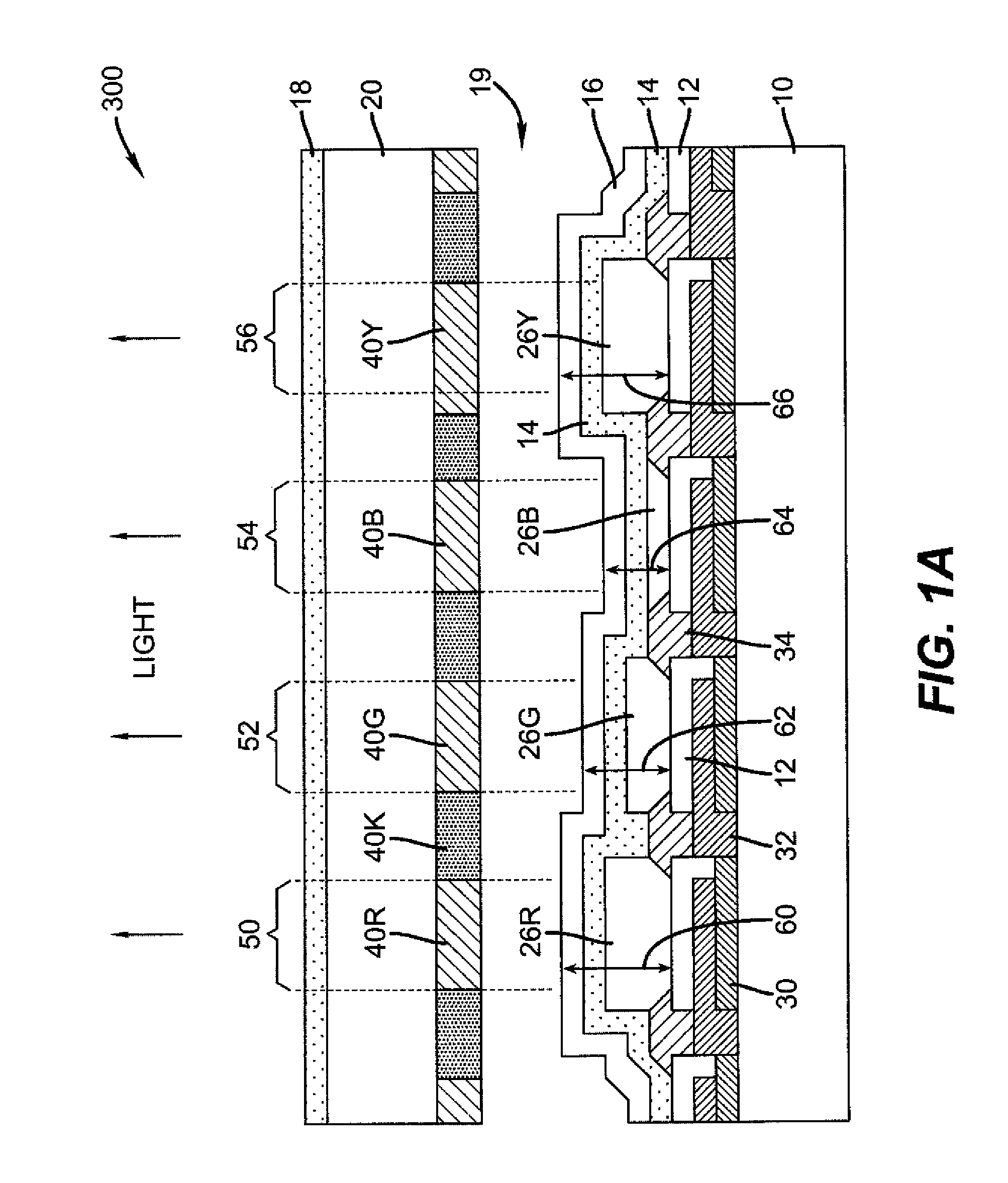
Organic light emitting diode display and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090115706A1Improve color reproducibilityImprove luminanceStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesPath lengthOrganic light emitting device
An organic light emitting device including a first pixel, a second pixel and a third pixel displaying different colors from each other according to the present invention, the organic light emitting device includes a reflecting electrode and a translucent member forming a micro-cavity along with the reflecting electrode, wherein a optical path length is an interval between the reflecting electrode and the translucent member, and wherein the light path lengths of at least two pixels among the first pixel, the second pixel and the third pixel are the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
LED device having improved light output
ActiveUS20090102352A1Improve light outputReduces any angular color changeDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesOptical cavityRefractive index
A light-emitting optical cavity light-emitting diode device, comprising:a) a substrate;b) a reflective electrode formed over the substrate;c) an unpatterned light-emitting layer formed over the reflective electrode;d) a transparent electrode formed over the unpatterned light-emitting layer;e) one or more different optical spacers, defining at least two different optical path lengths, are formed in different locations over the substrate, between the reflective electrode and the transparent electrode; andf) a low-index layer formed over the transparent electrode.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Phase subtraction cell counting method
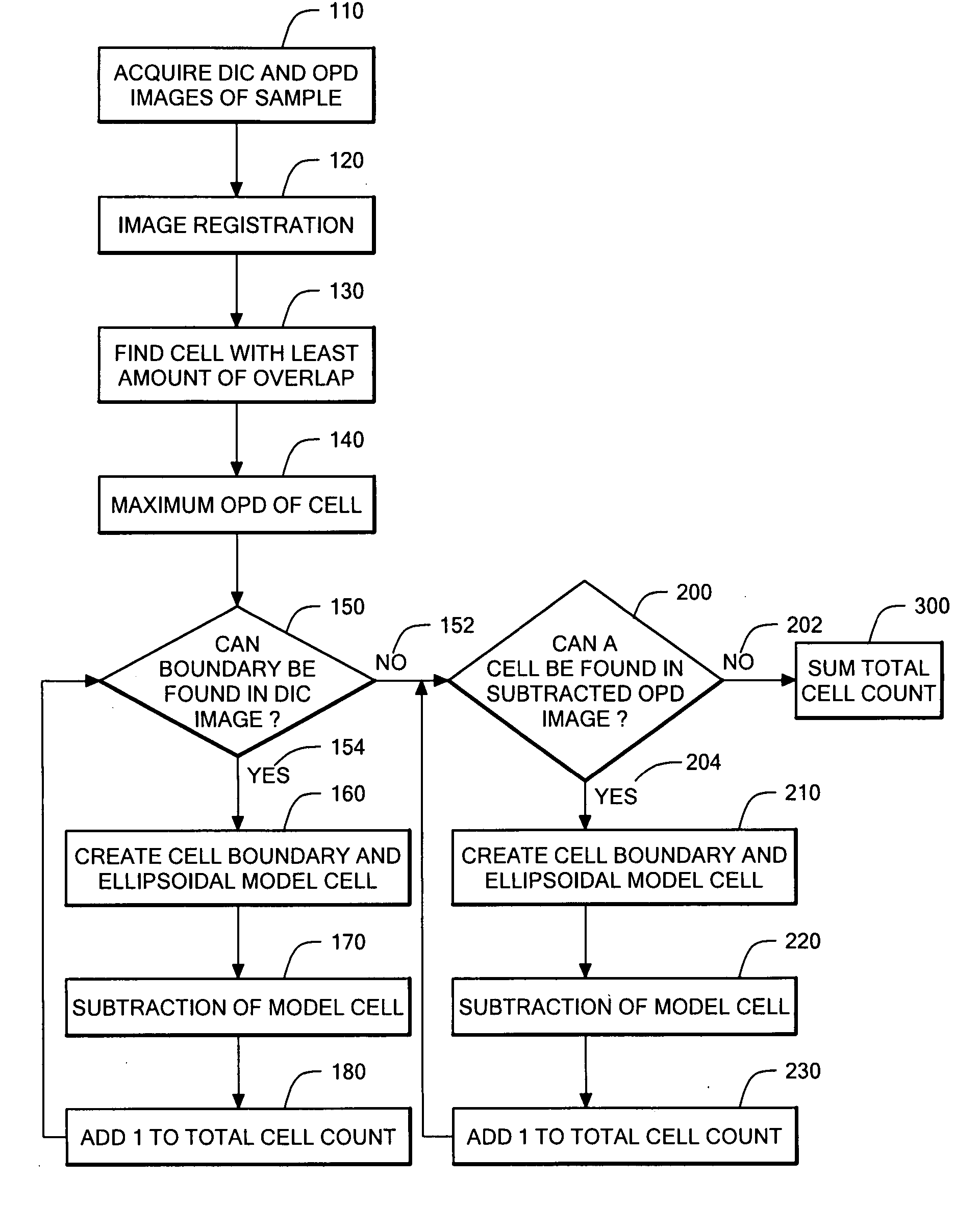
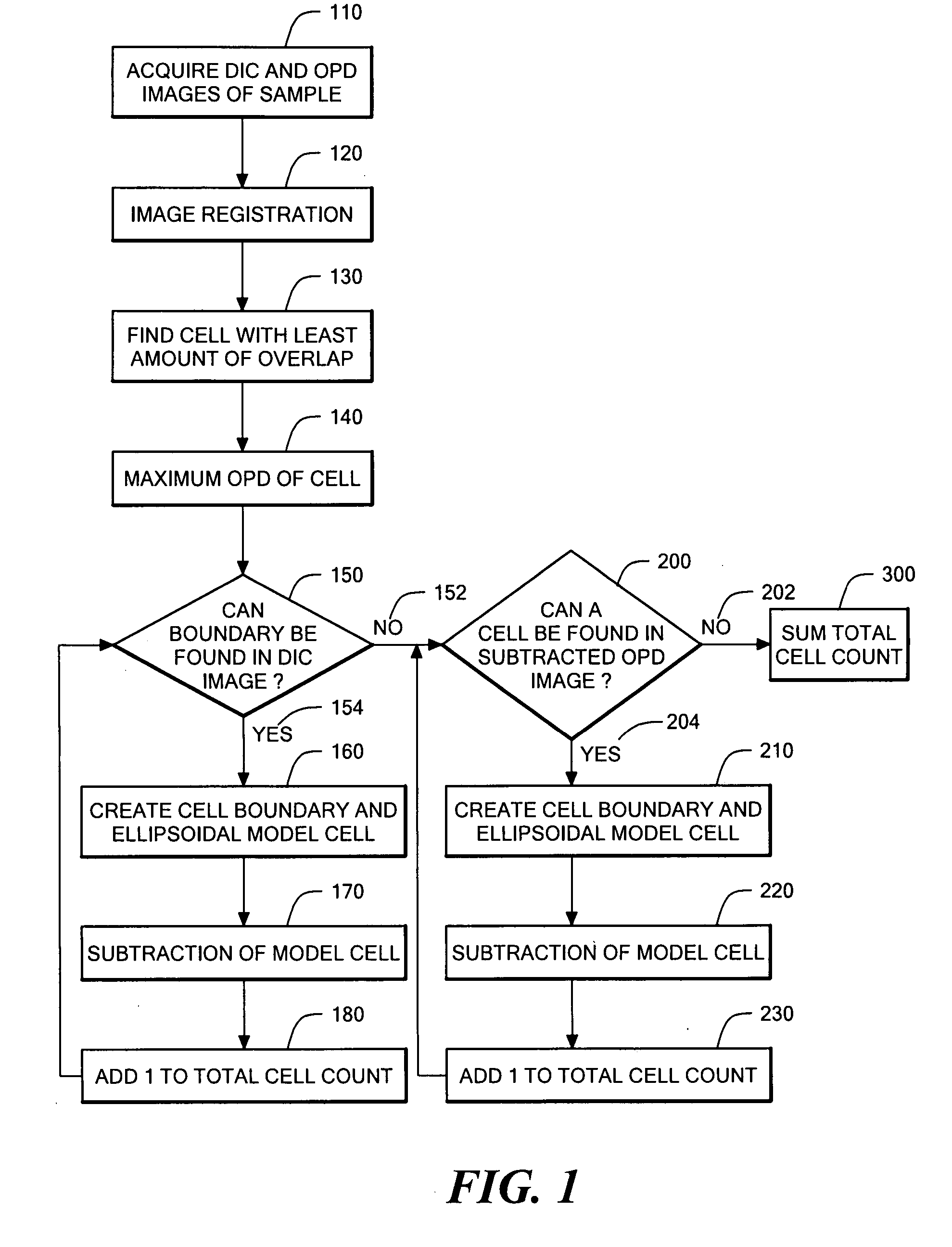
InactiveUS20080032325A1Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDevelopmental stage
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
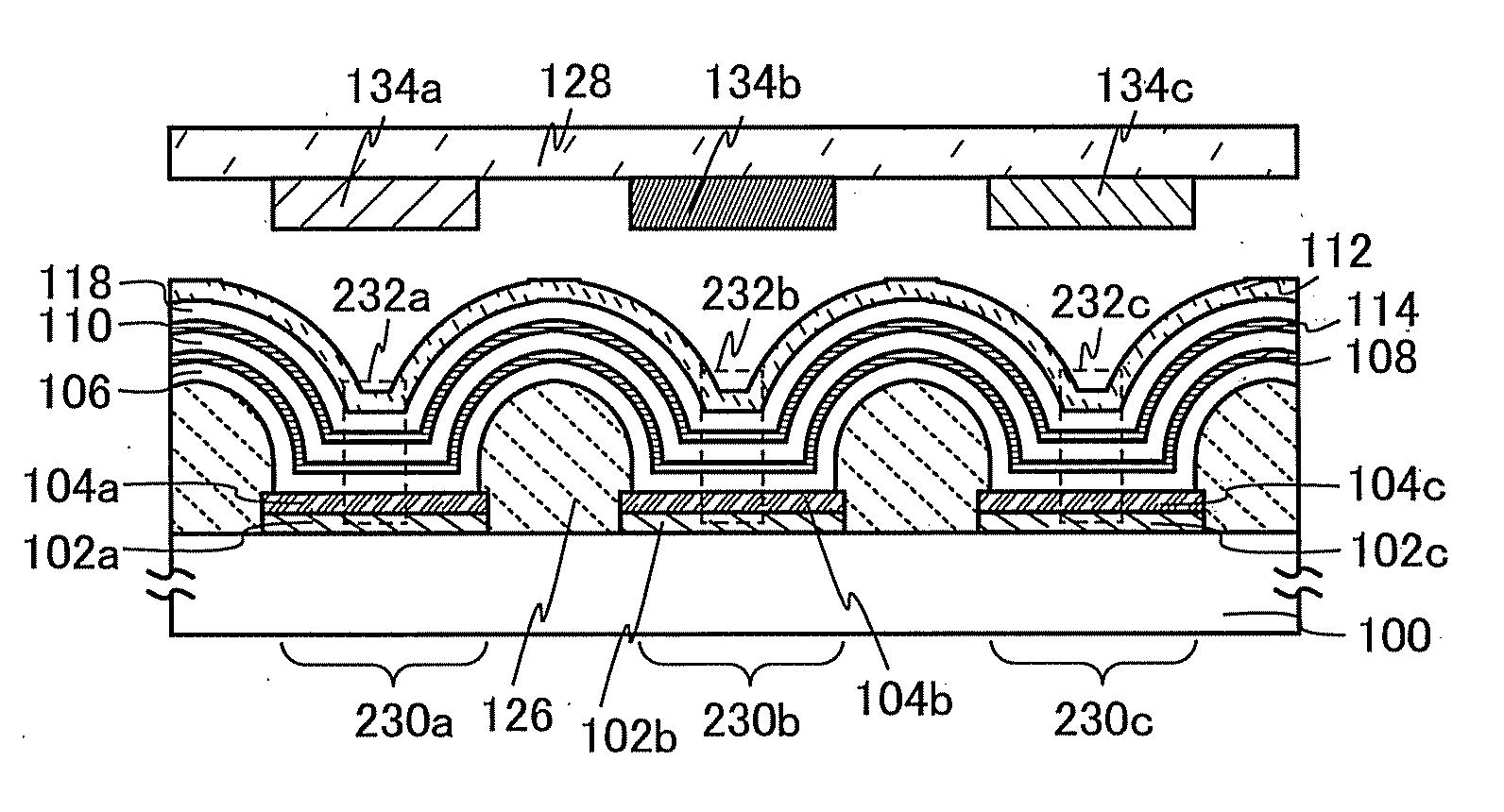
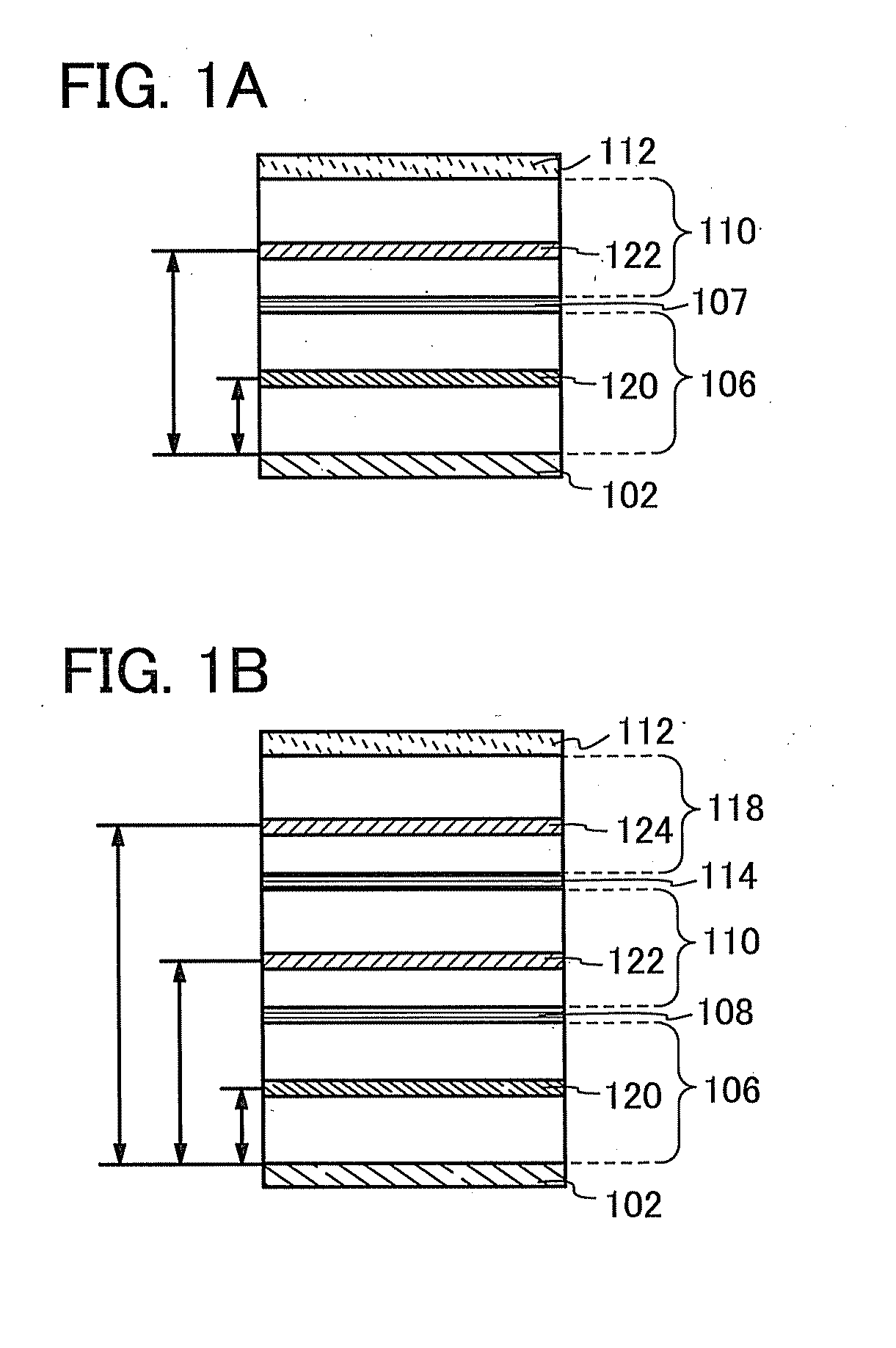
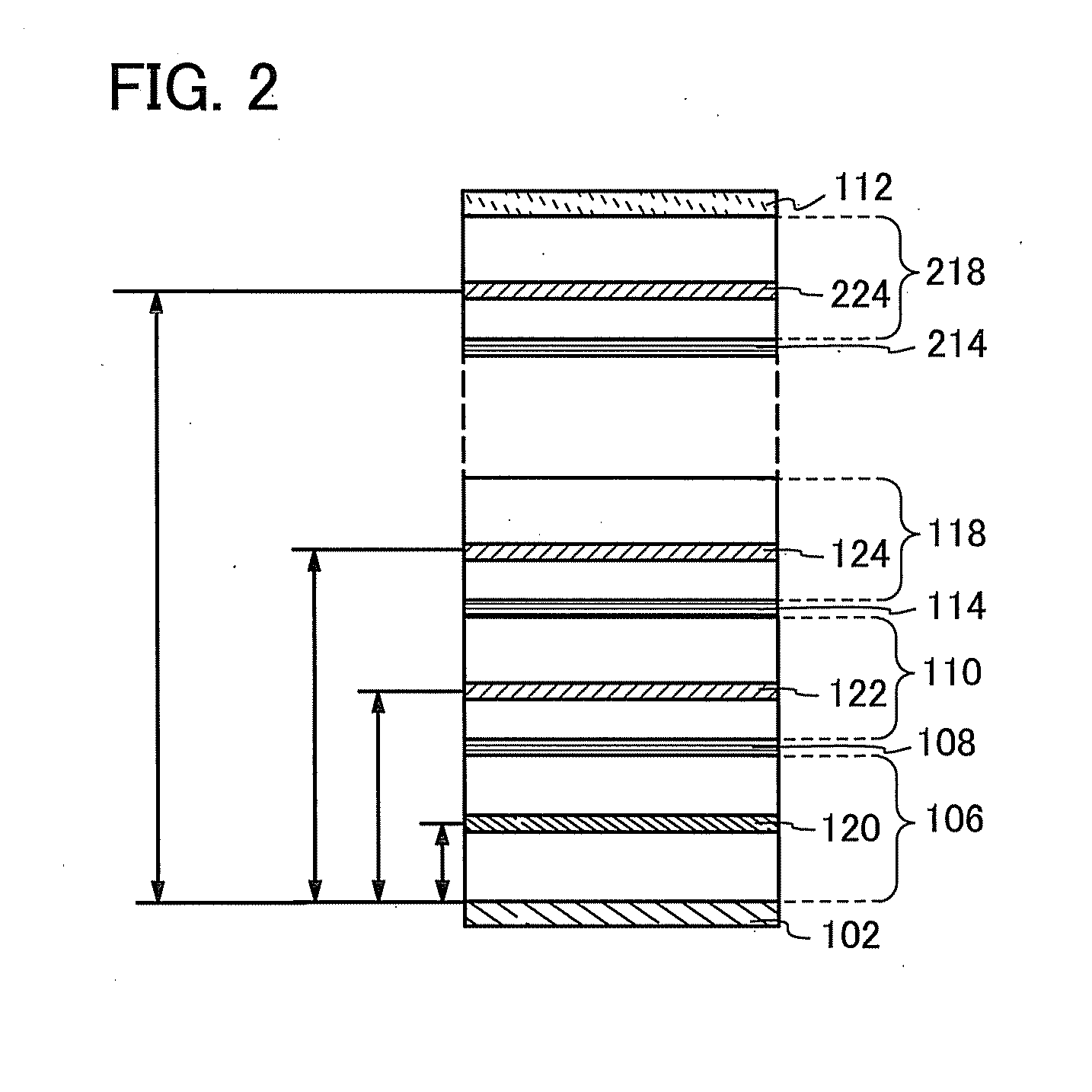
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, and Display Device
ActiveUS20120205685A1Improve productivityHigh color puritySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProduction rateDisplay device
A light-emitting element with which a reduction in power consumption and an improvement in productivity of a display device can be achieved is provided. A technique of manufacturing a display device with high productivity is provided. The light-emitting element includes an electrode having a reflective property, and a first light-emitting layer, a charge generation layer, a second light-emitting layer, and an electrode having a light-transmitting property stacked in this order over the electrode having a reflective property. The optical path length between the electrode having a reflective property and the first light-emitting layer is one-quarter of the peak wavelength of the emission spectrum of the first light-emitting layer. The optical path length between the electrode having a reflective property and the second light-emitting layer is three-quarters of the peak wavelength of the emission spectrum of the second light-emitting layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
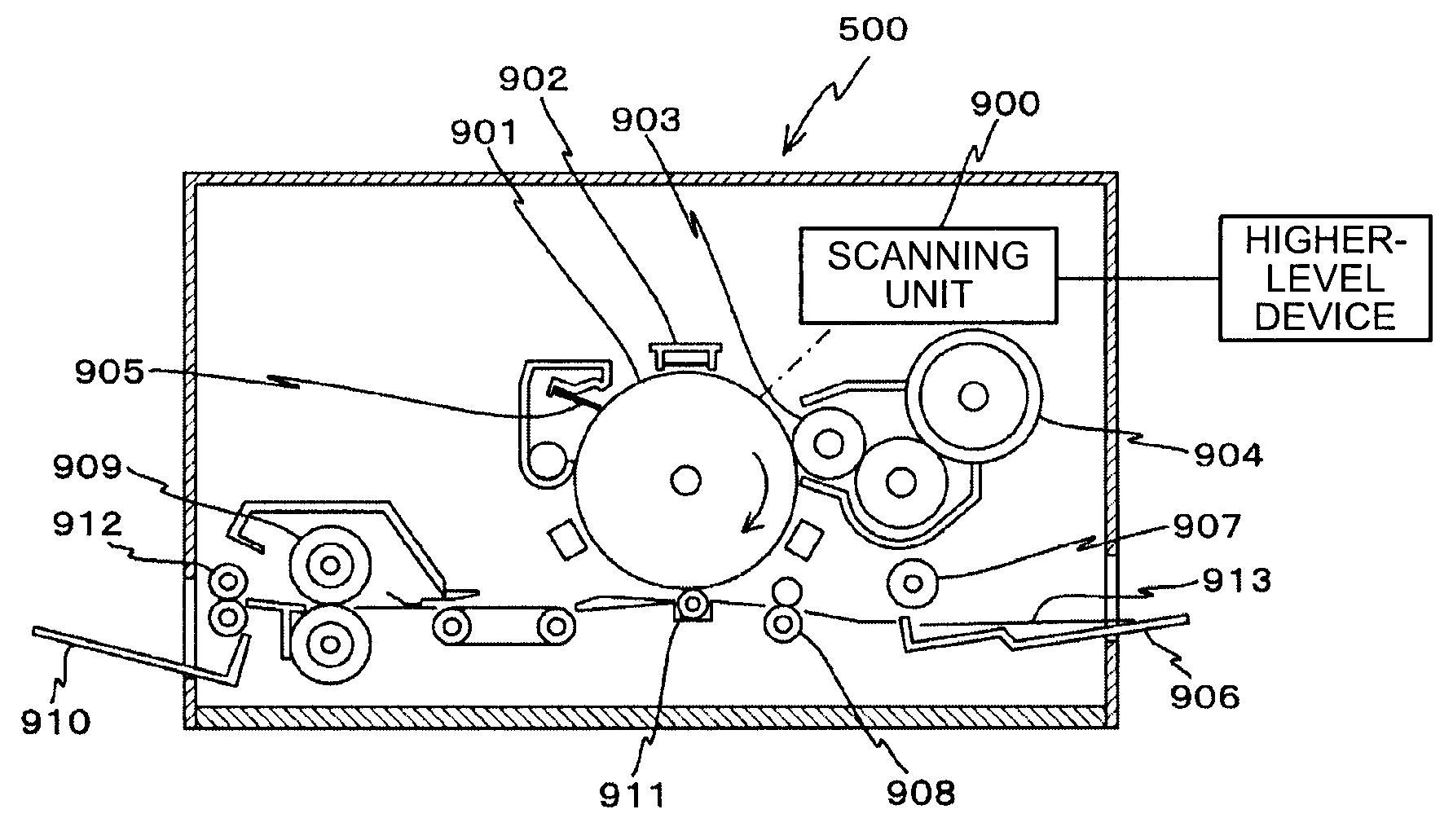
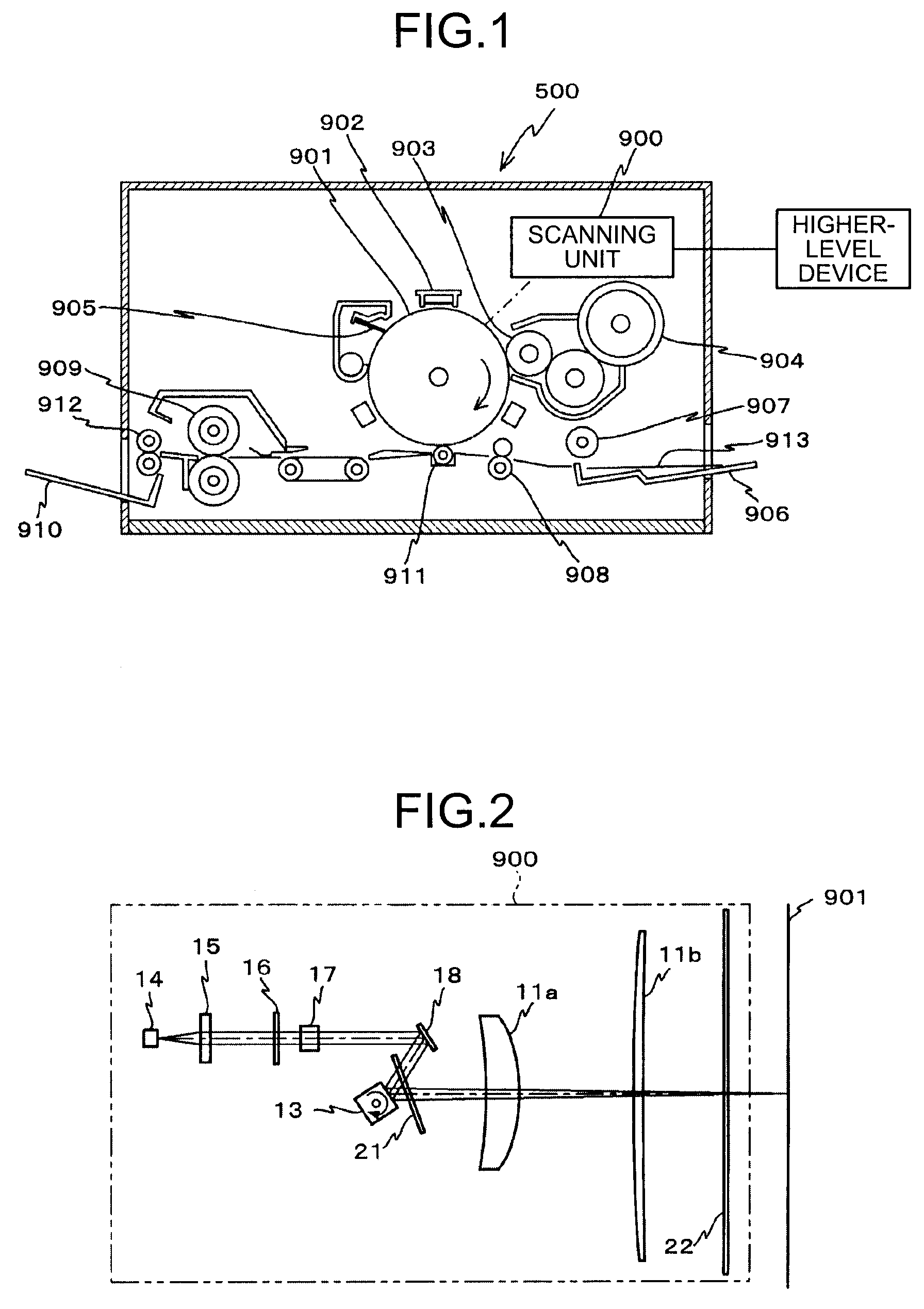
Scanning unit and image forming apparatus
A scanning unit in an image forming apparatus includes a light source, a coupling lens, an aperture, an image forming lens, and a polygon mirror. The light source includes a plurality of surface-emitting lasers. The coupling lens, the aperture, and the image forming lens are arranged on the optical path of light beams emitted by the light source. The polygon mirror deflects light beams of an image formed by the coupling lens towards a photosensitive drum for scanning. The focal length of the image forming lens in a sub-scanning direction is set to be equal to or smaller than an optical path length between the image forming lens and the aperture.
Owner:RICOH KK
Laser light source, method of laser oscillation, and method of laser processing
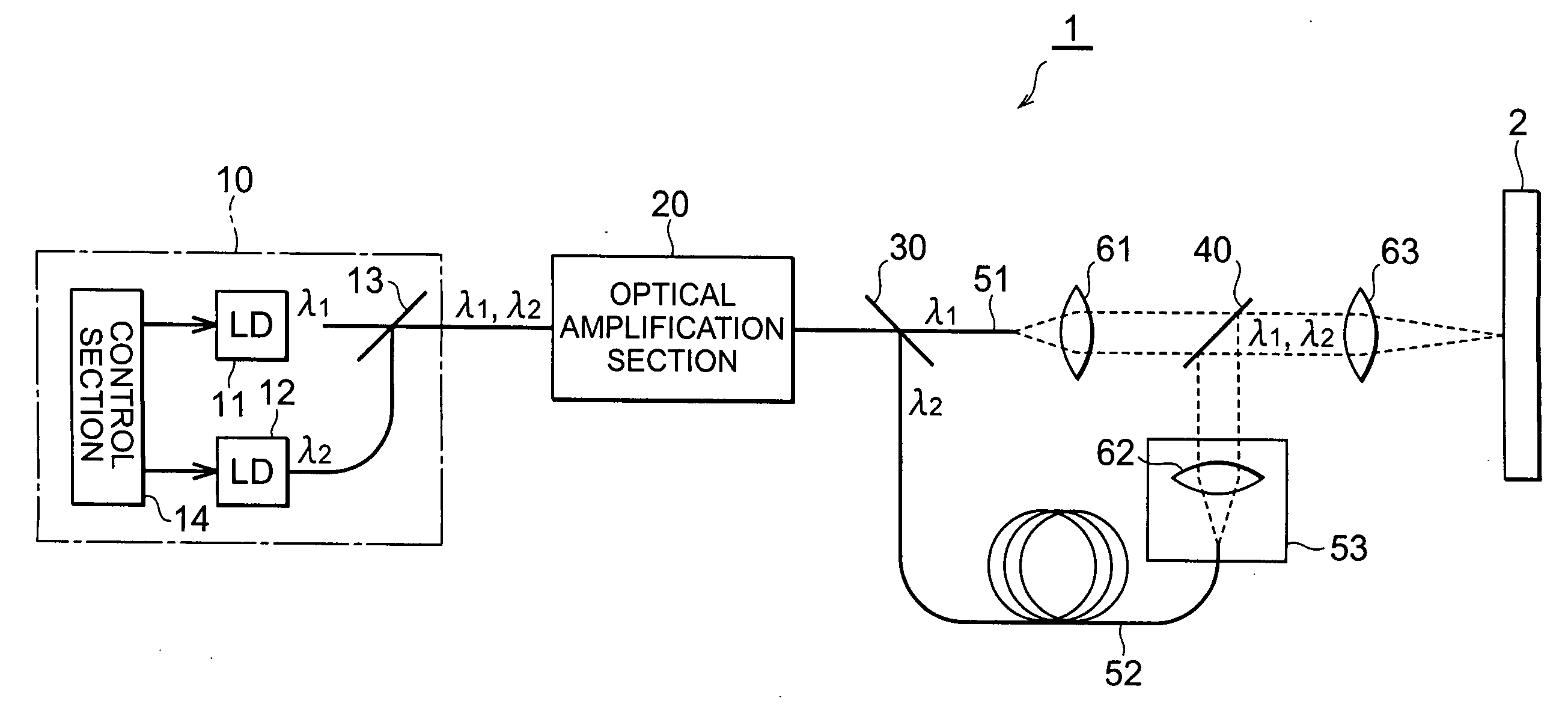
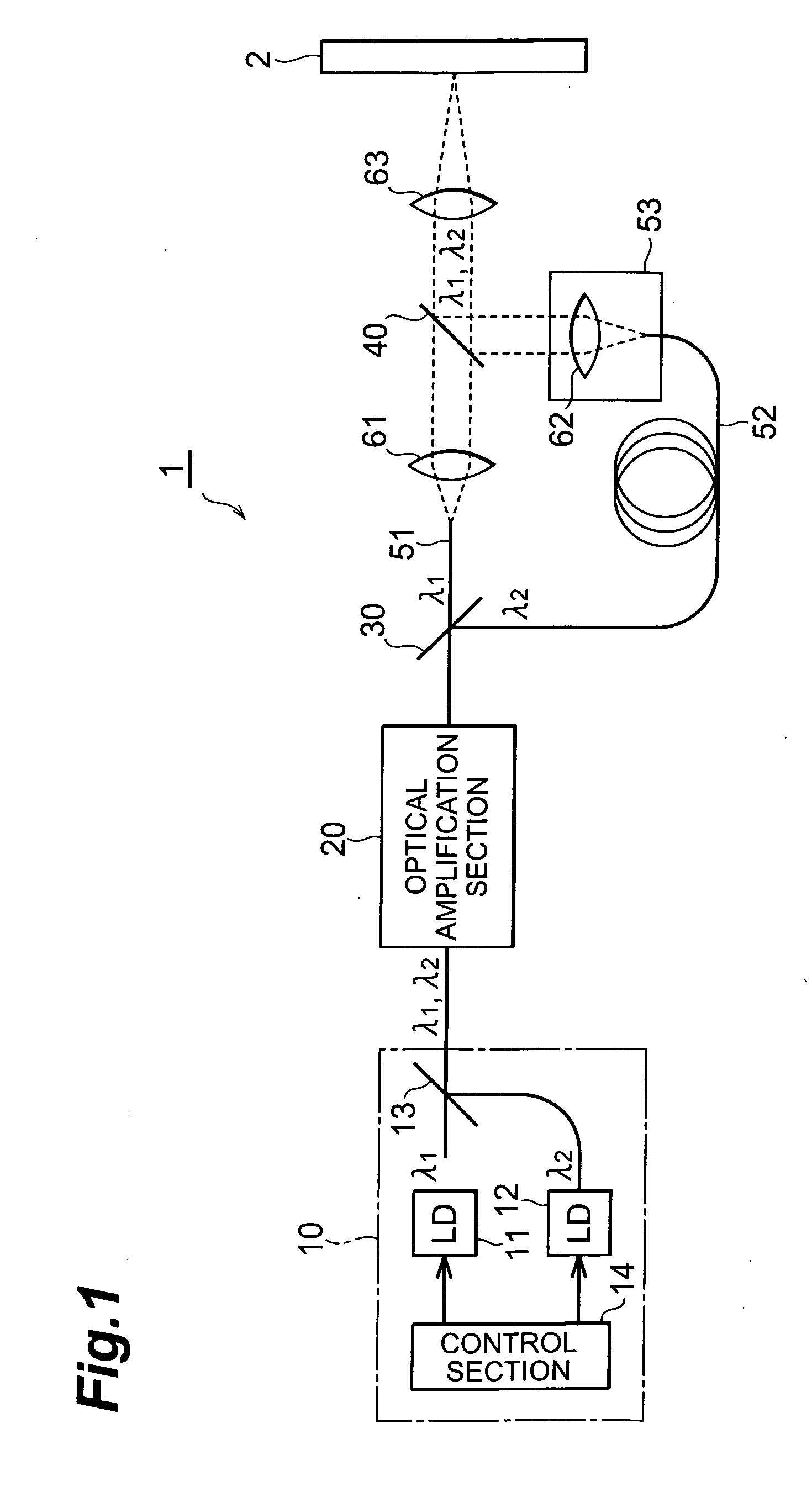
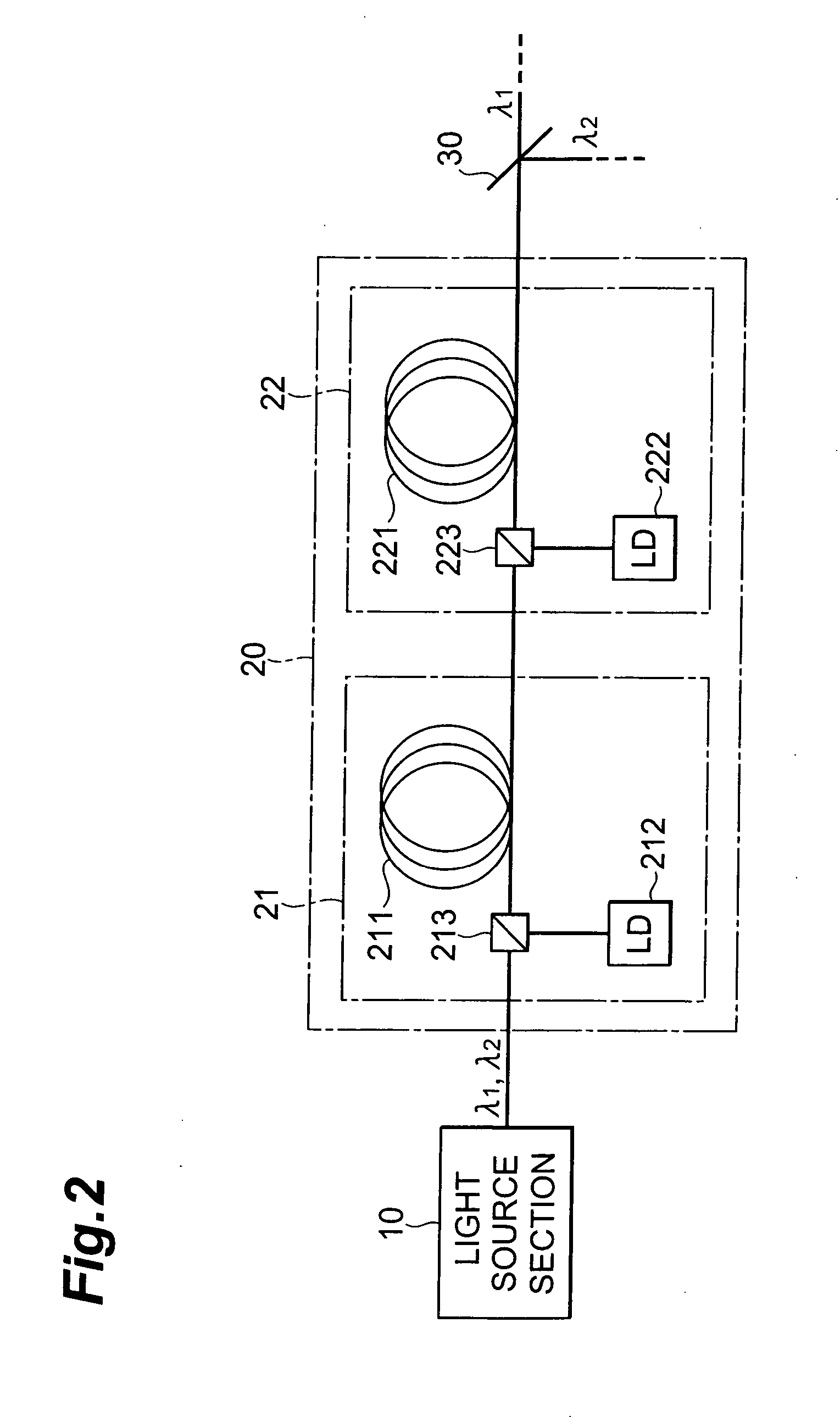
InactiveUS20060257150A1Precise processingGuaranteed uptimeLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingLaser processing
A laser light source includes a light source section for outputting pulse laser light λ1, λ2 with a mutually identical repetition frequency, an optical amplification section for amplifying and outputting the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 output from the above light source section by means of a common optical amplification medium, an optical demultiplexing section for mutually demultiplexing pulse laser light λ1, λ2, an optical multiplexing section for multiplexing and outputting the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 demultiplexed in the above optical demultiplexing section, and an optical path length difference setting section for adjusting an optical path length difference between the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 in between the optical demultiplexing section and the optical multiplexing section.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Apparatus for detecting focusing status of taking lens
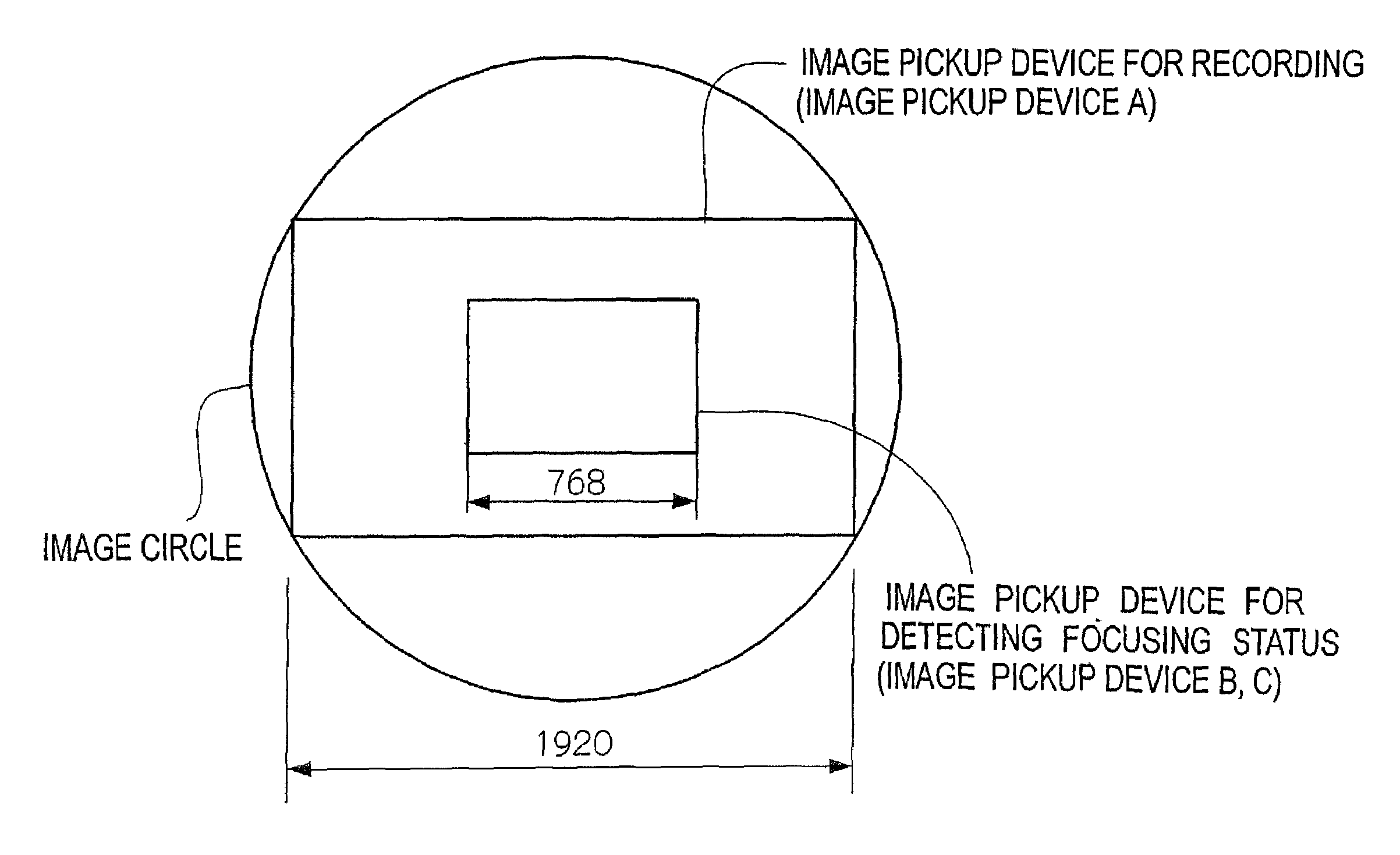
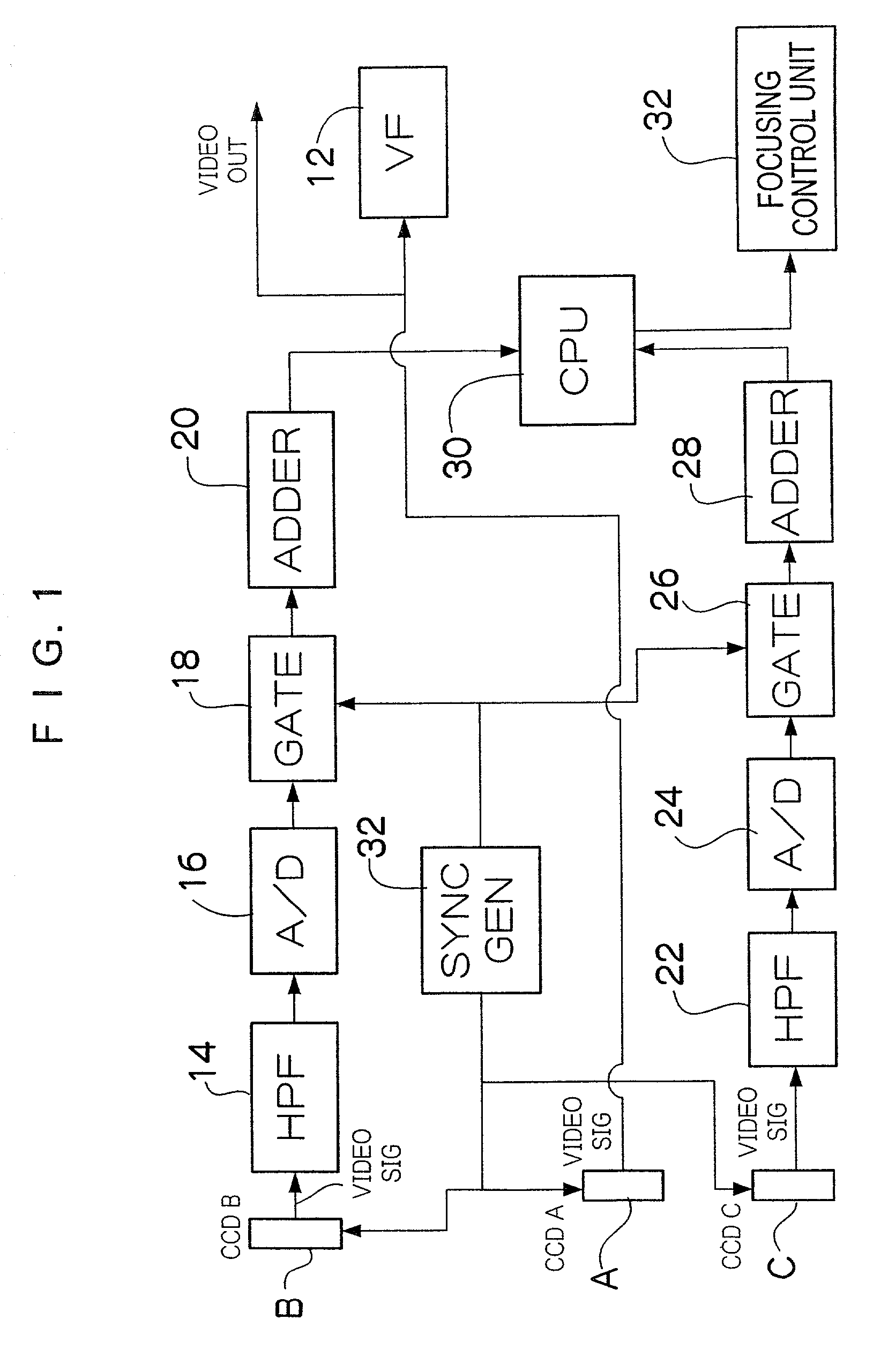
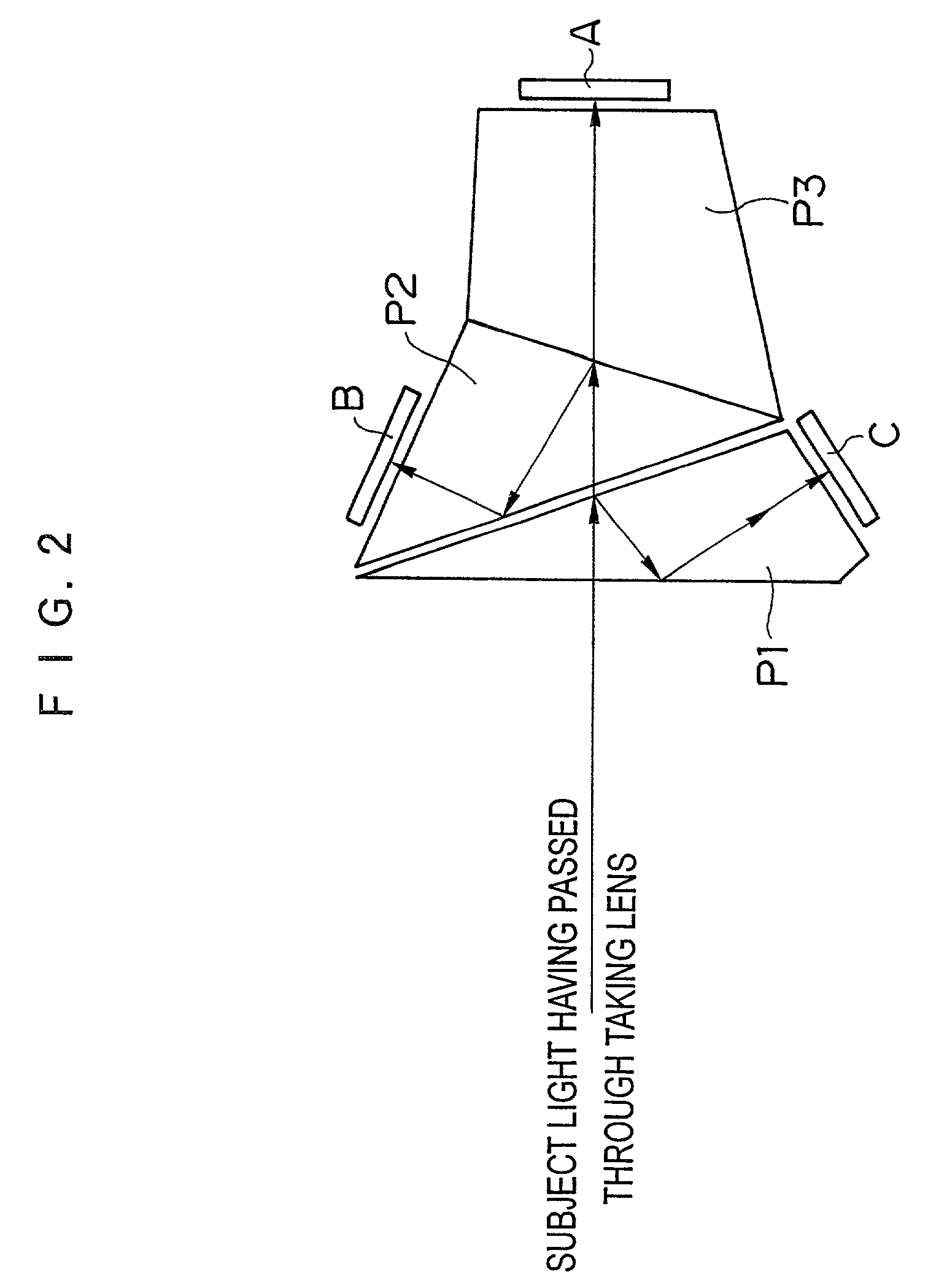
ActiveUS7030927B2Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical path length
The number of pixels of image pickup devices for detecting a focusing status is smaller than the number of pixels of an image pickup device for image-output, or an image pickup size of the image pickup devices for detecting the focusing status is smaller than the image pickup size of the image pickup device for image-output, so that the apparatus for detecting the focusing status that is inexpensive, consumes reduced power, and includes a circuit reduced in size is provided. Two image pickup devices for detecting the focusing status with different optical path lengths are provided with respect to an image pickup device for obtaining an image to be outputted, and subject light intended to be incident on the image pickup device is split to be incident on the image pickup devices for detecting the focusing status. Then, focusing evaluation values are obtained based on video signals from the image pickup devices for detecting the focusing status, and the focusing status is determined to be front focus, rear focus, or in focus based on the magnitudes of the focusing evaluation values. As the image pickup devices for detecting the focusing status, CCDs having less number of pixels and smaller image pickup size than the image pickup device for image-output is used.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
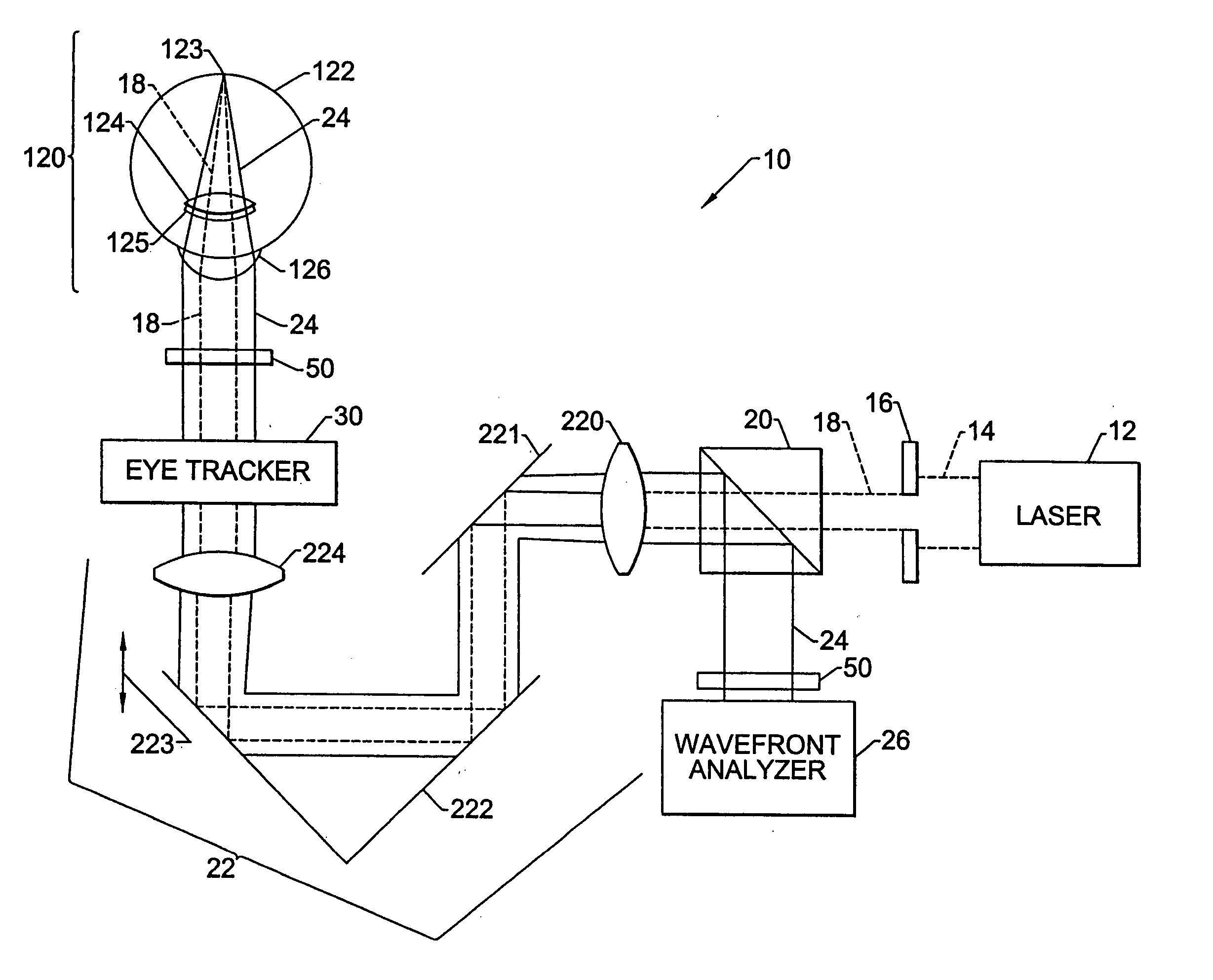
Apparatus and method for objective measurement and correction of optical systems using wavefront analysis
InactiveUS20050099600A1Simple and inexpensive designPractical applicationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com