Patents
Literature
369 results about "Optical tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical tomography is a form of computed tomography that creates a digital volumetric model of an object by reconstructing images made from light transmitted and scattered through an object. Optical tomography is used mostly in medical imaging research. Optical tomography in industry is used as a sensor of thickness and internal structure of semiconductors.
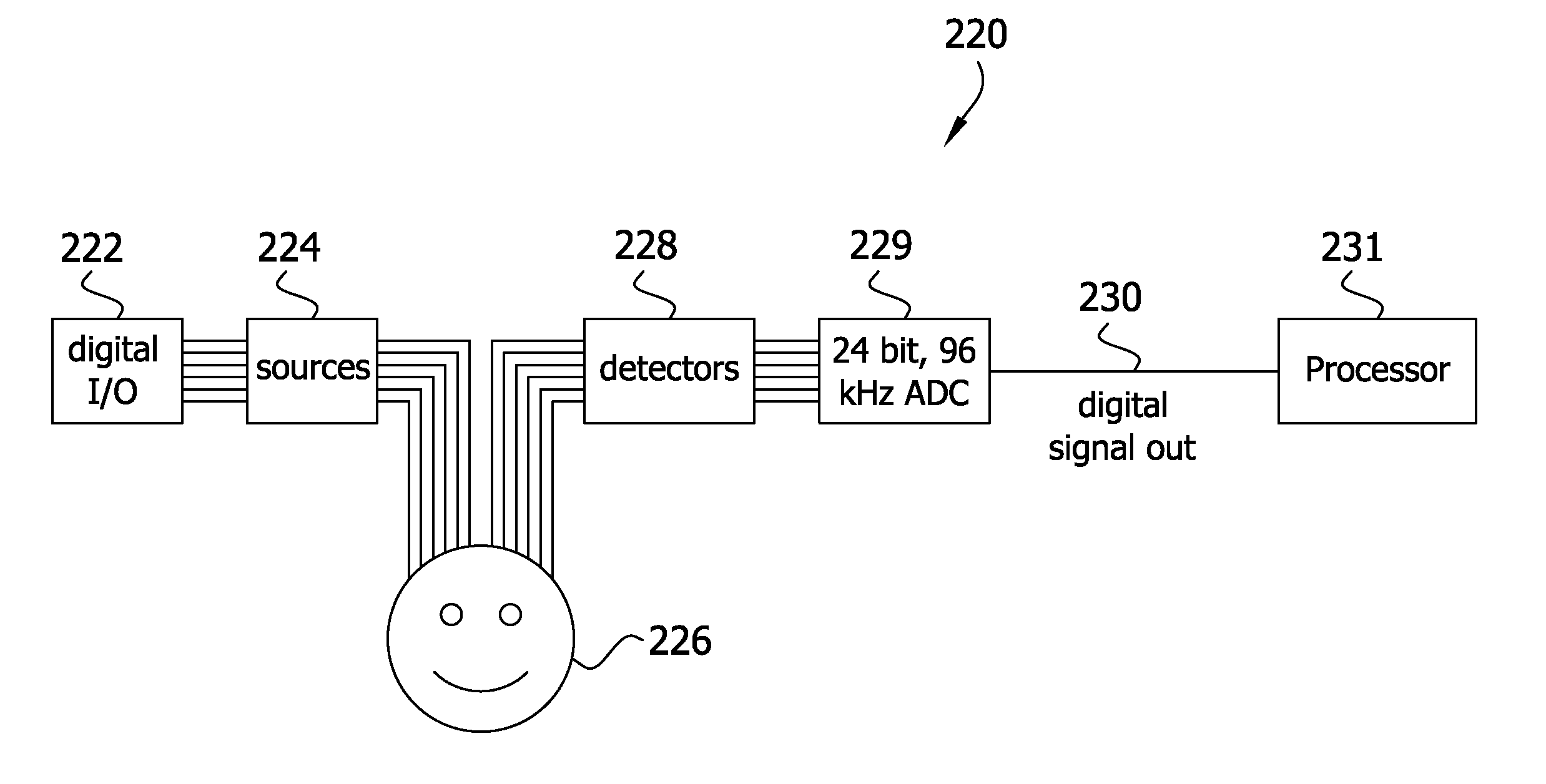
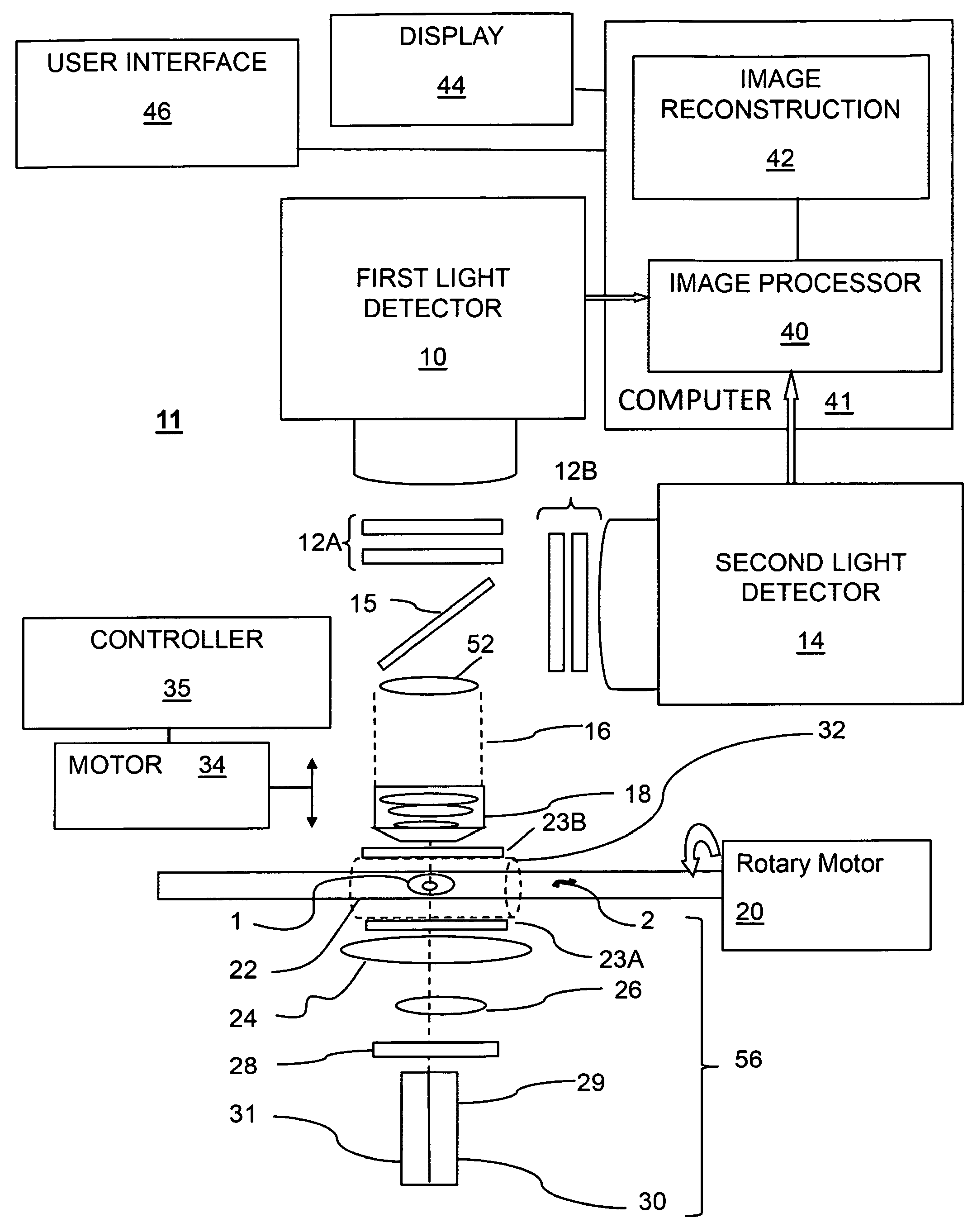
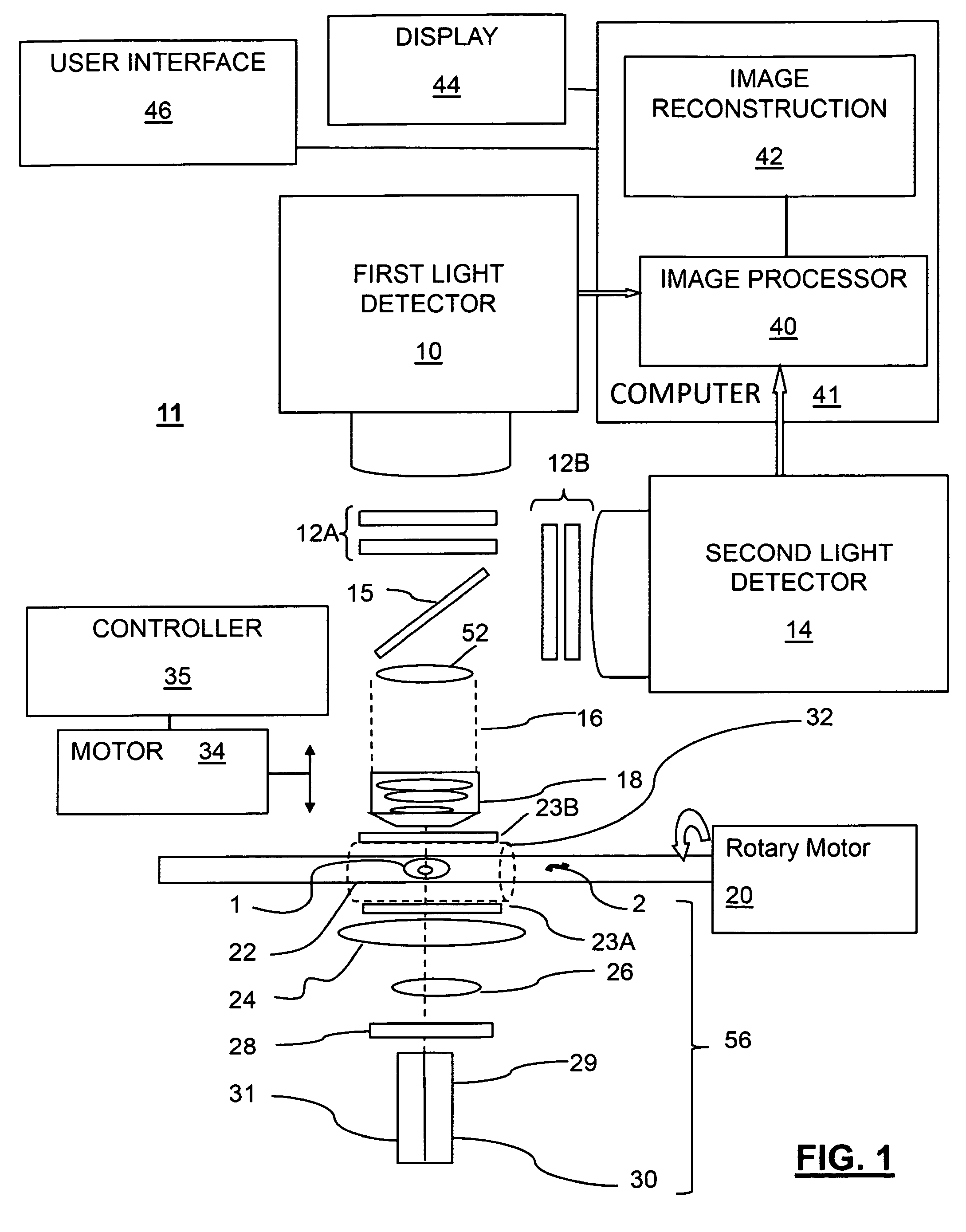
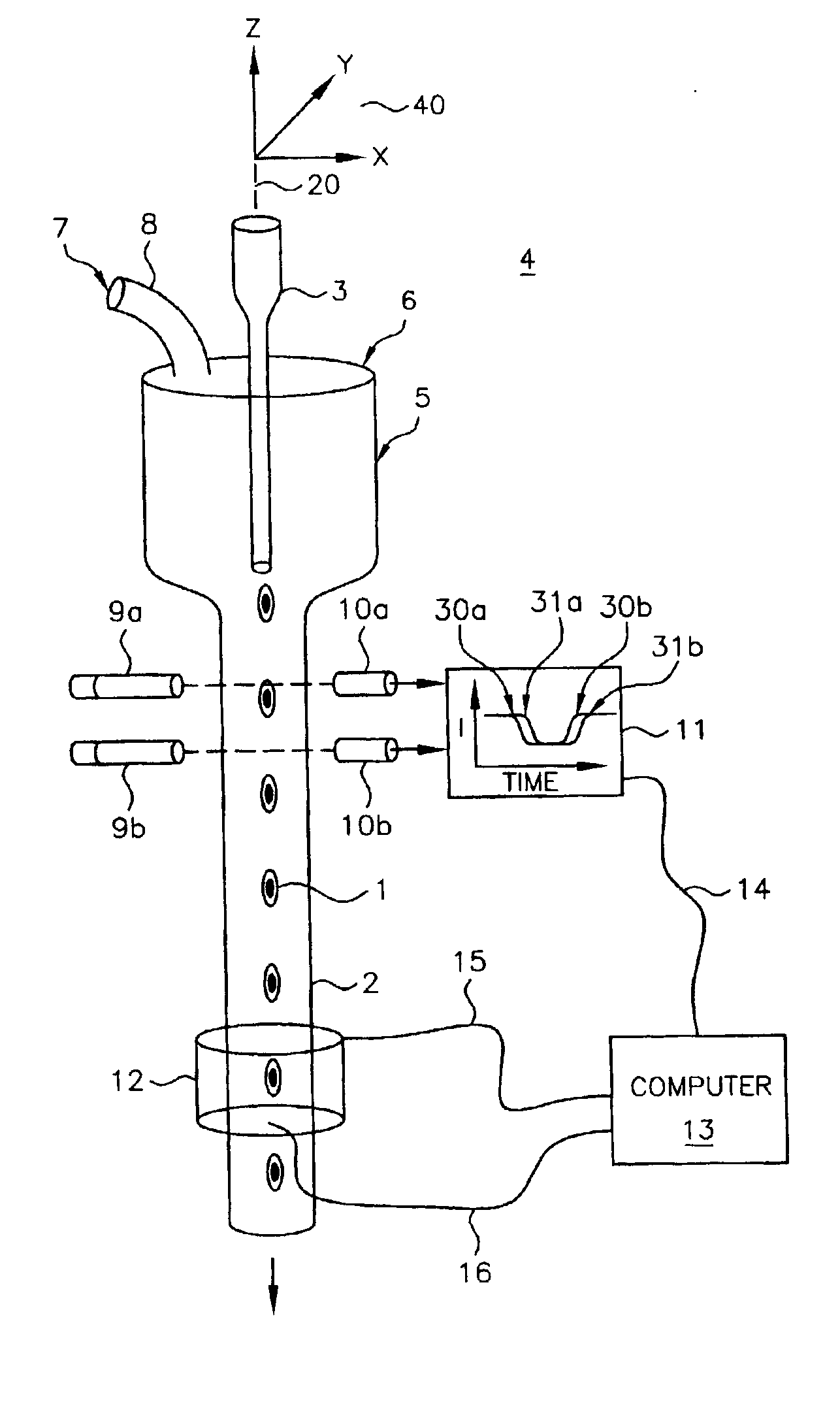
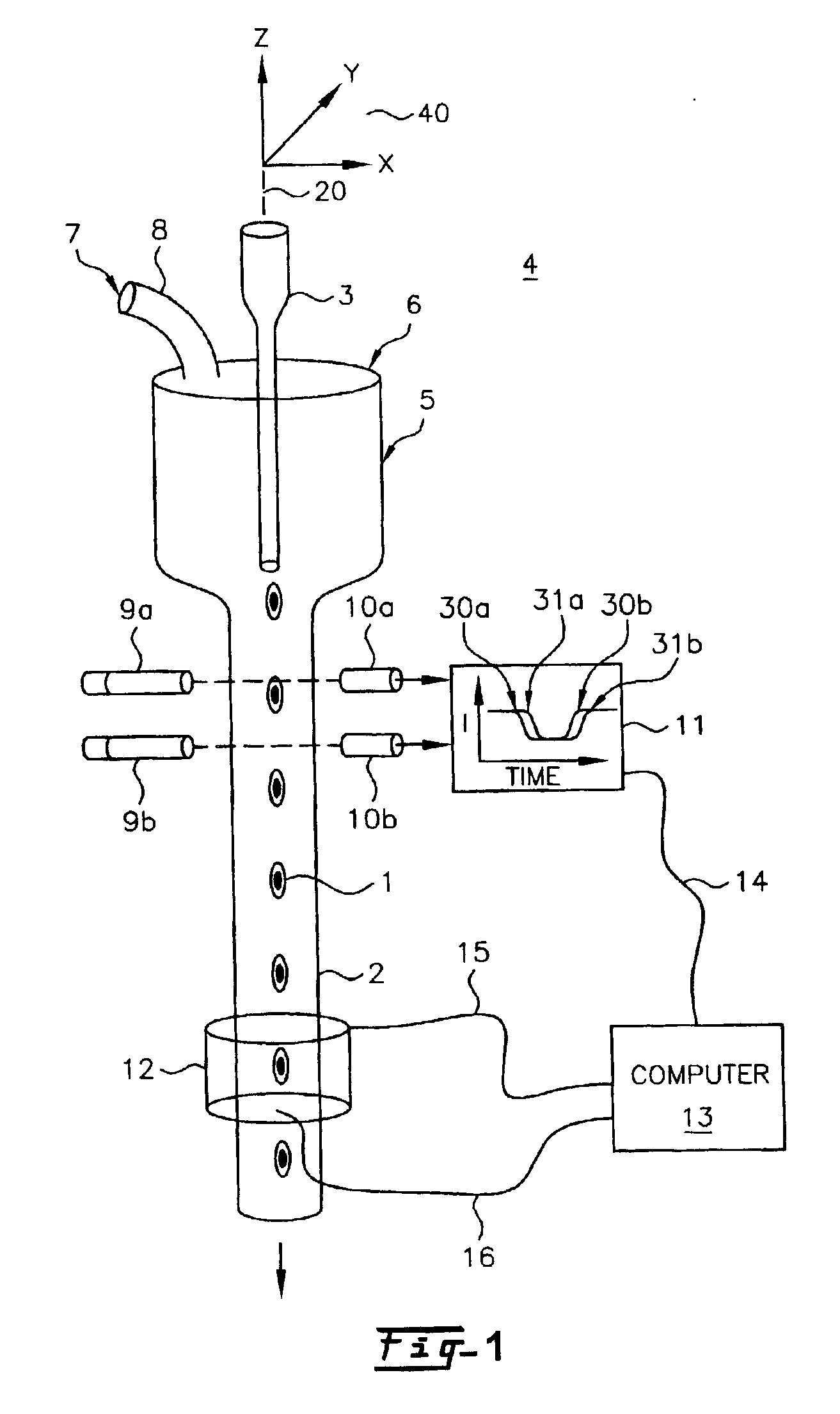
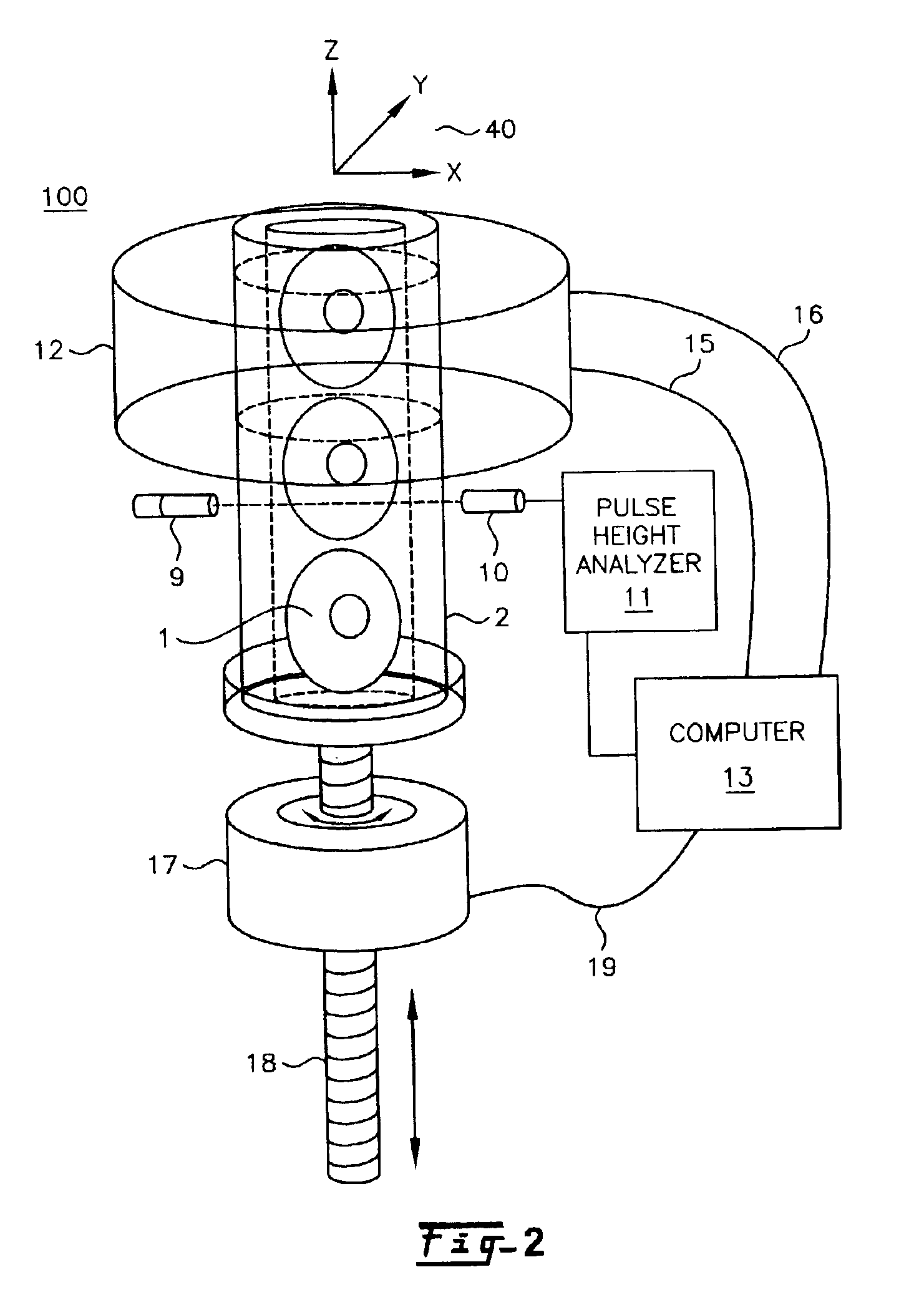
High performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography and associated method of use
ActiveUS7983740B2High bandwidthImprove performanceDiagnostics using tomographySensorsOptical tomographyImaging quality
A high performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography is disclosed. A dense grid utilizing sources, e.g., light emitting diodes (“LEDs”), that achieve high performance at high speed with a high dynamic range and low inter-channel crosstalk are complemented by a system of discrete, isolated receivers, e.g., avalanche photodiodes (“APDs”). The source channels have dedicated reconfigurable encoding control signals, and the detector channels have reconfigurable decoding, allowing maximum flexibility and optimal mixtures of frequency and time encoding and decoding. Each detector channel is analyzed by dedicated, isolated, high-bandwidth receiver circuitry so that no channel gain switching is necessary. The resulting improvements to DOT system performance, e.g., increased dynamic range and decreased crosstalk, enable higher density imaging arrays and provide significantly enhanced DOT image quality. A processor can be utilized to provide sophisticated three dimensional modeling as well as noise reduction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
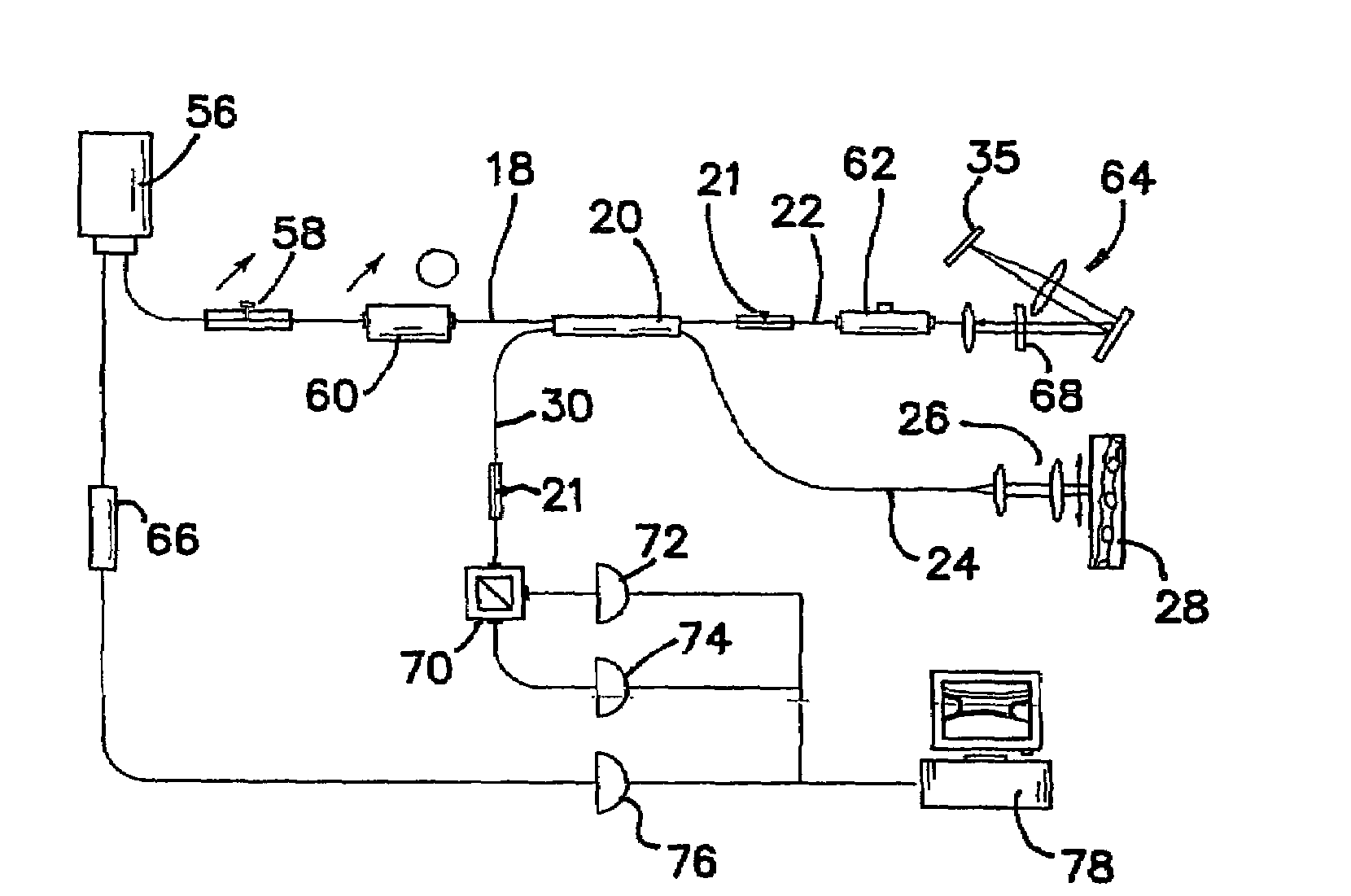
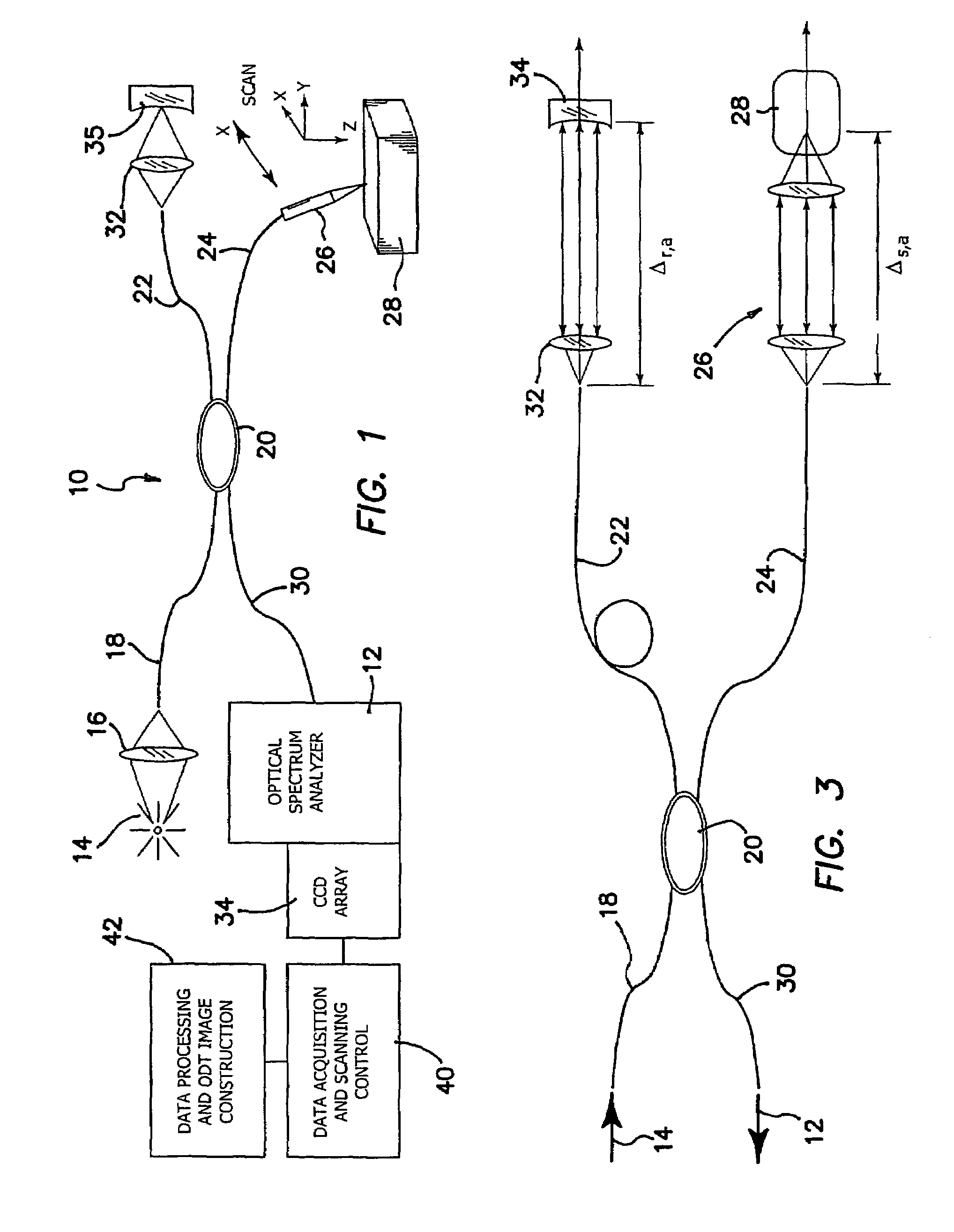
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
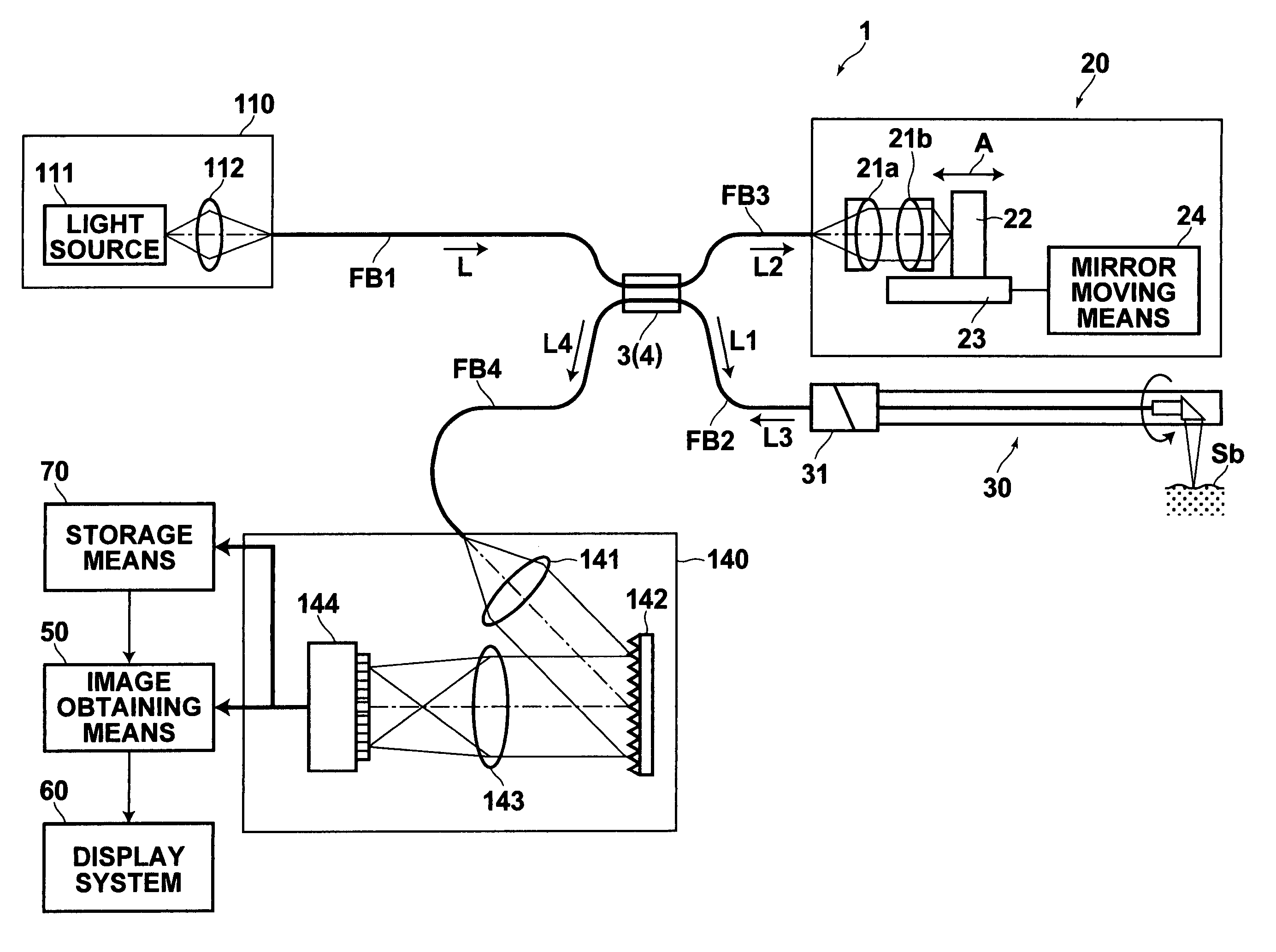
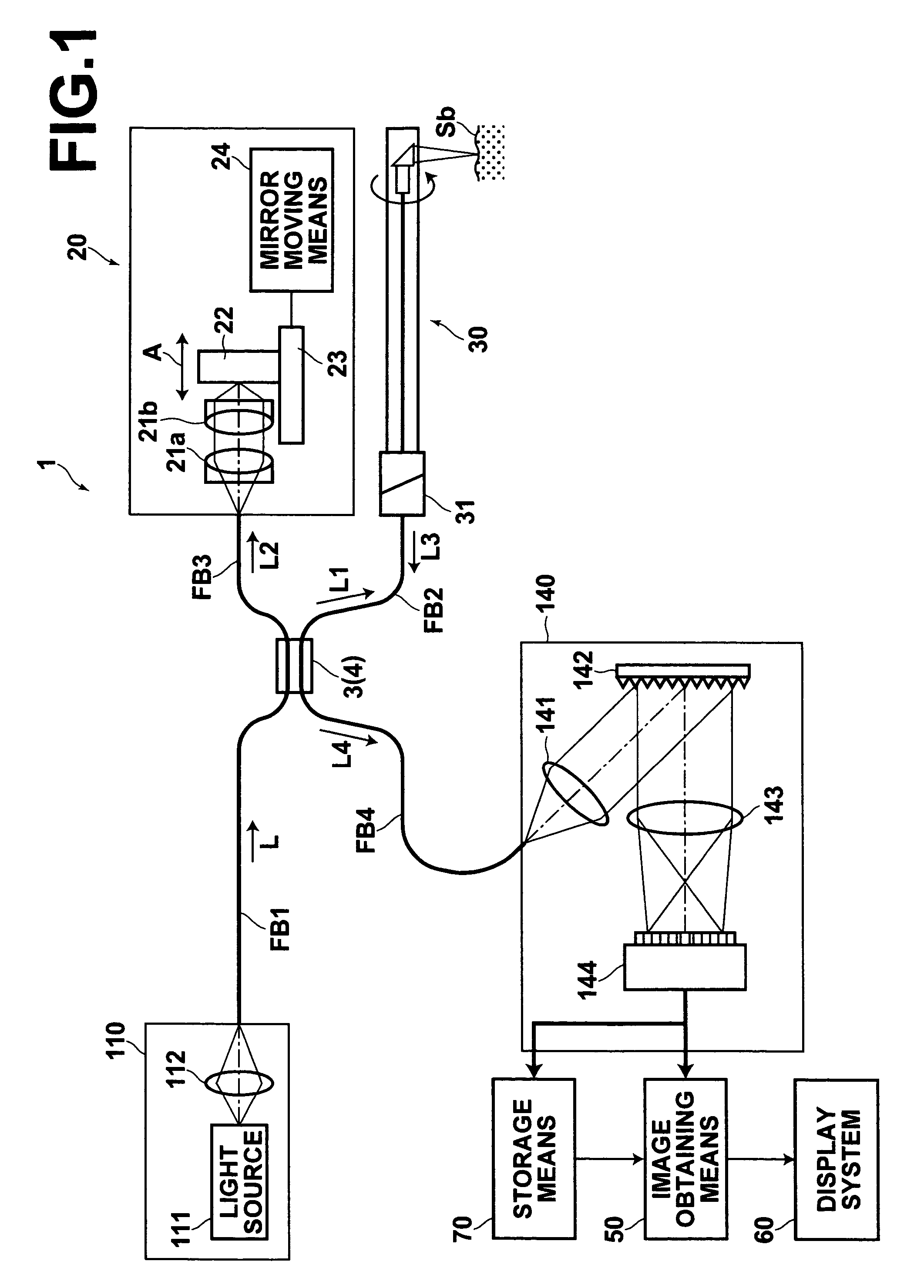
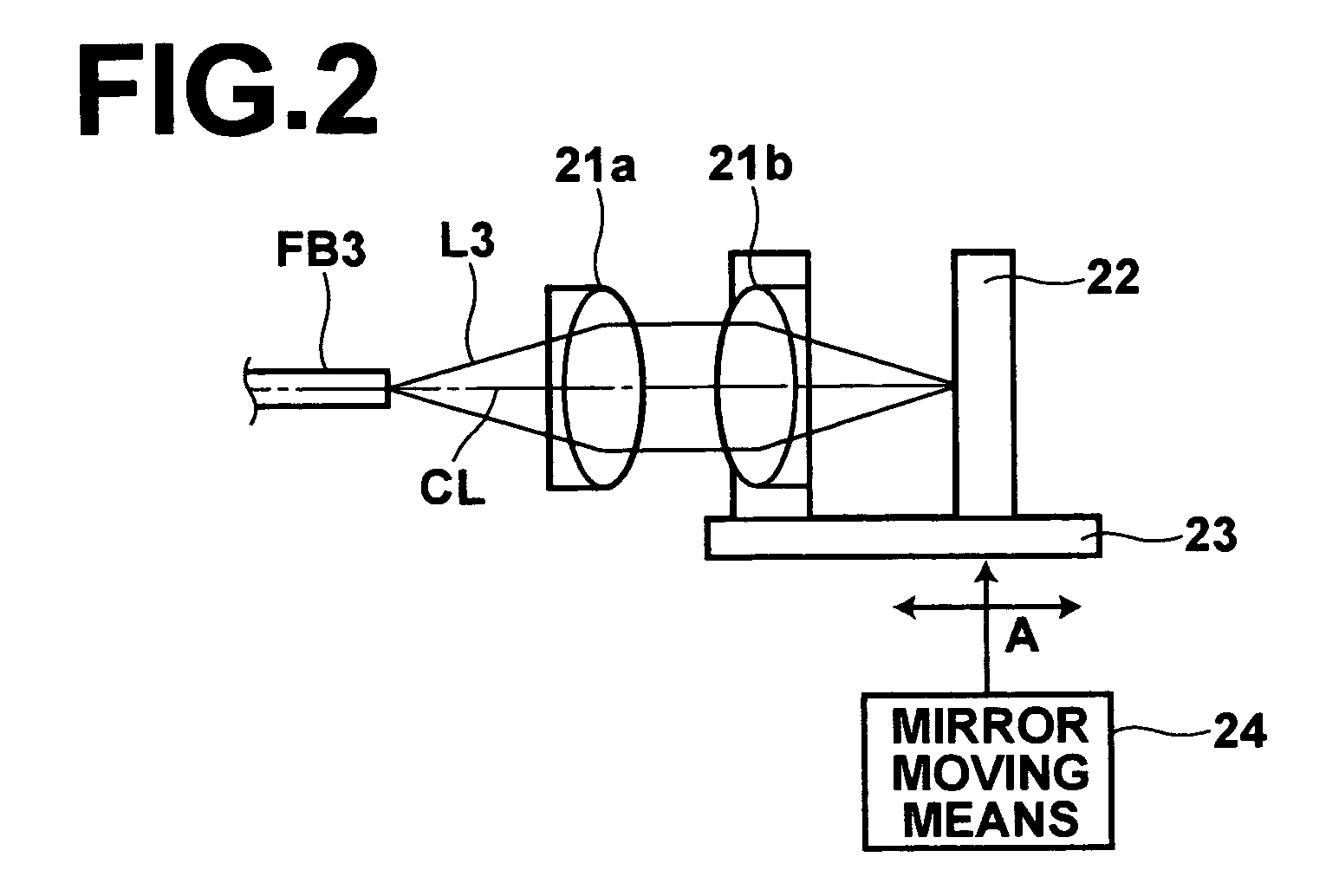
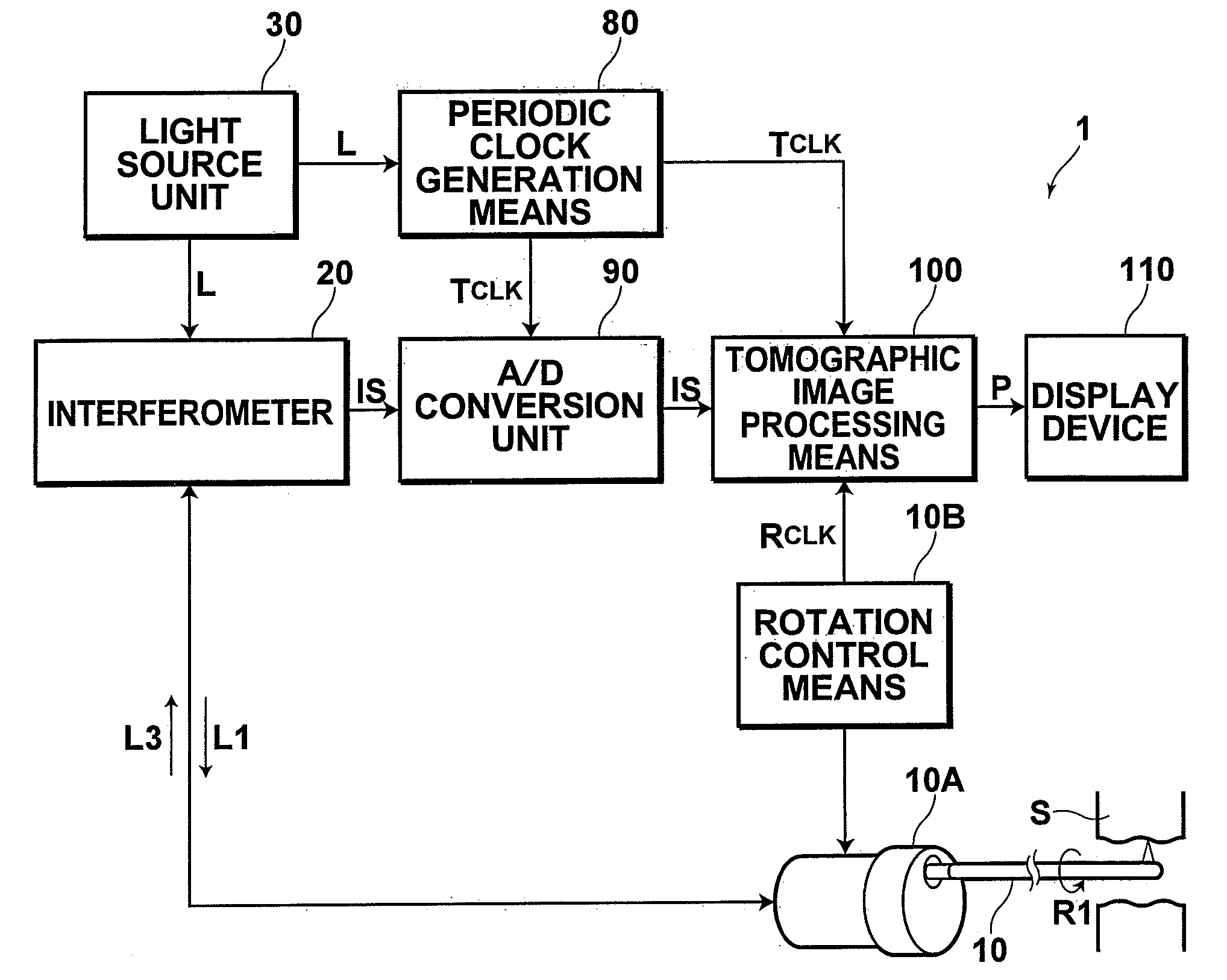
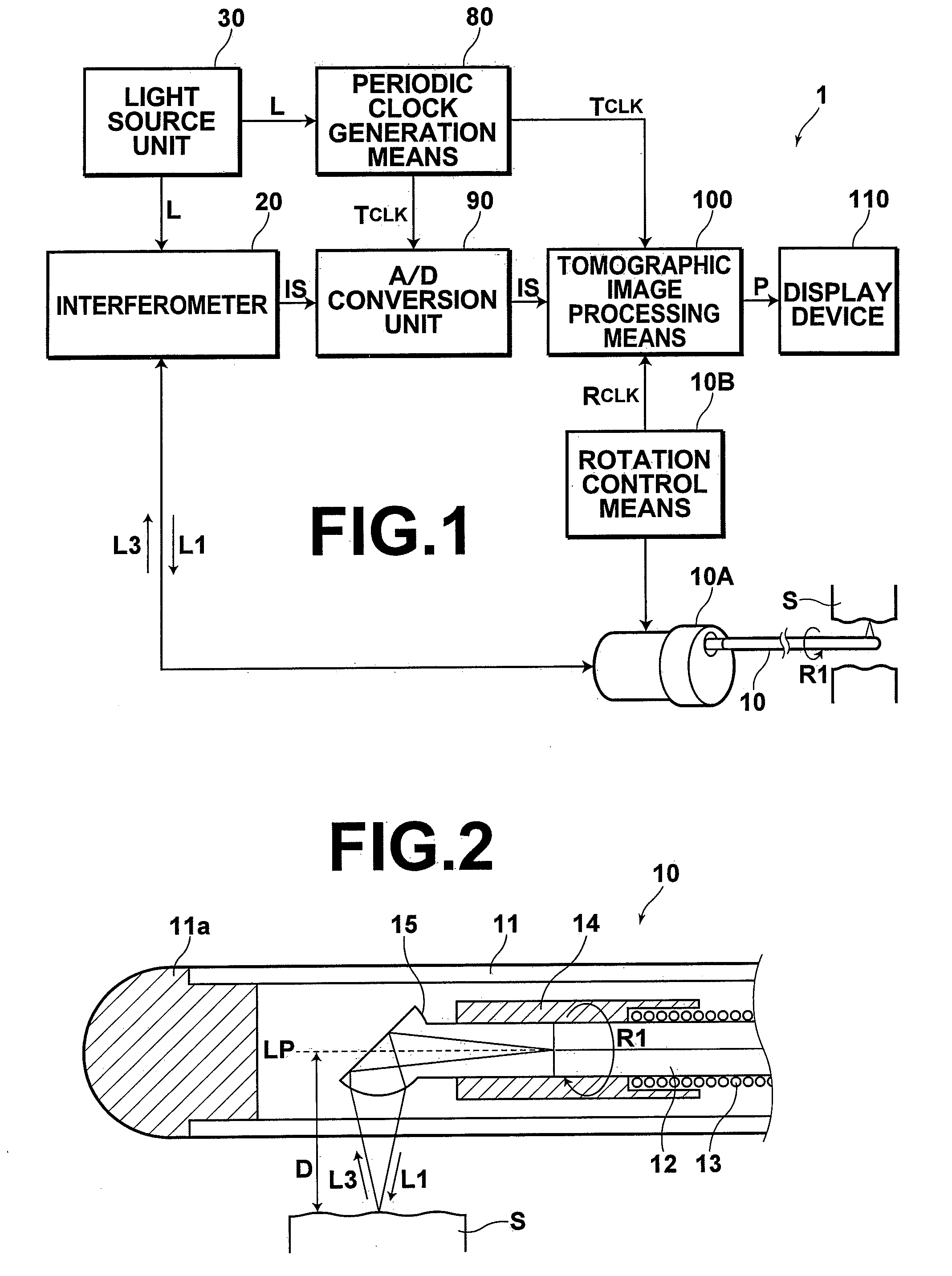
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
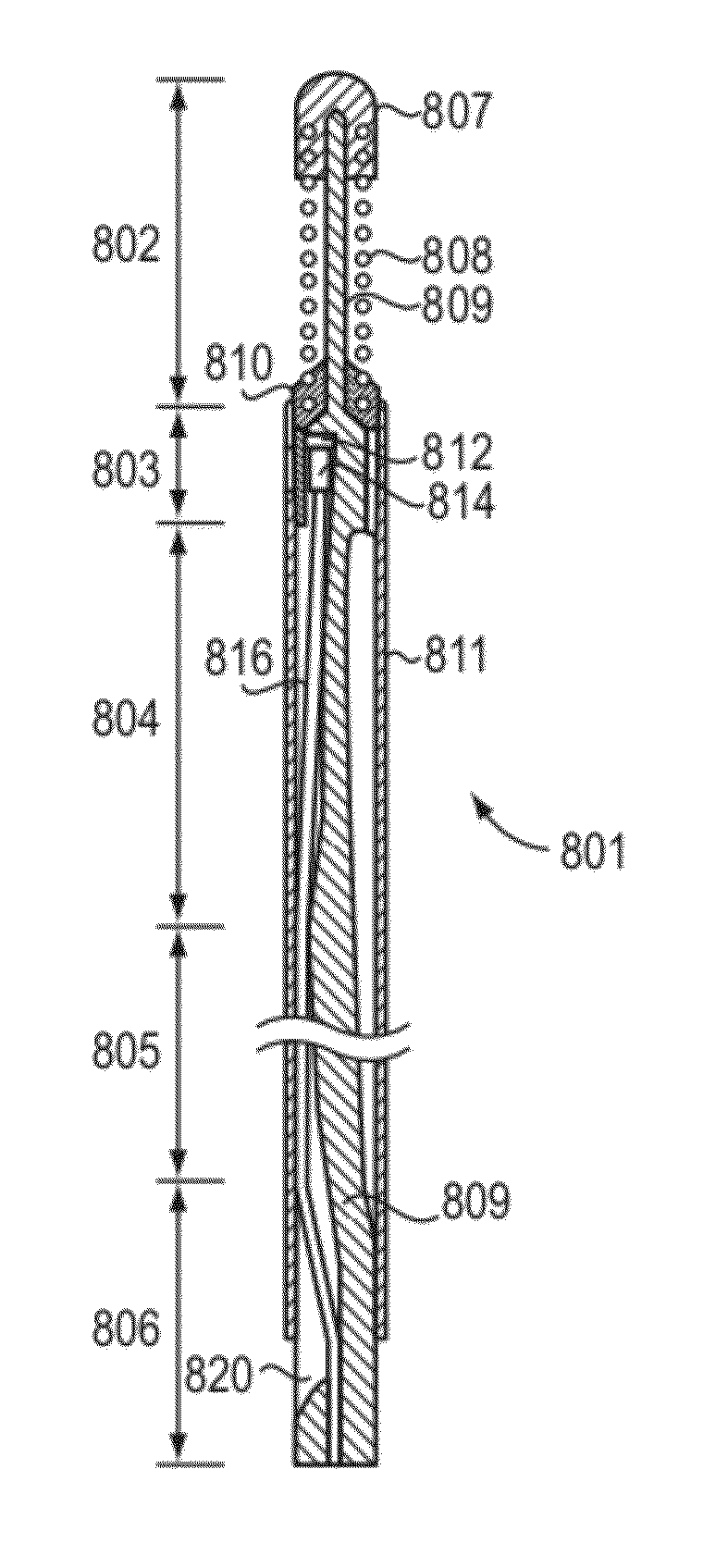
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
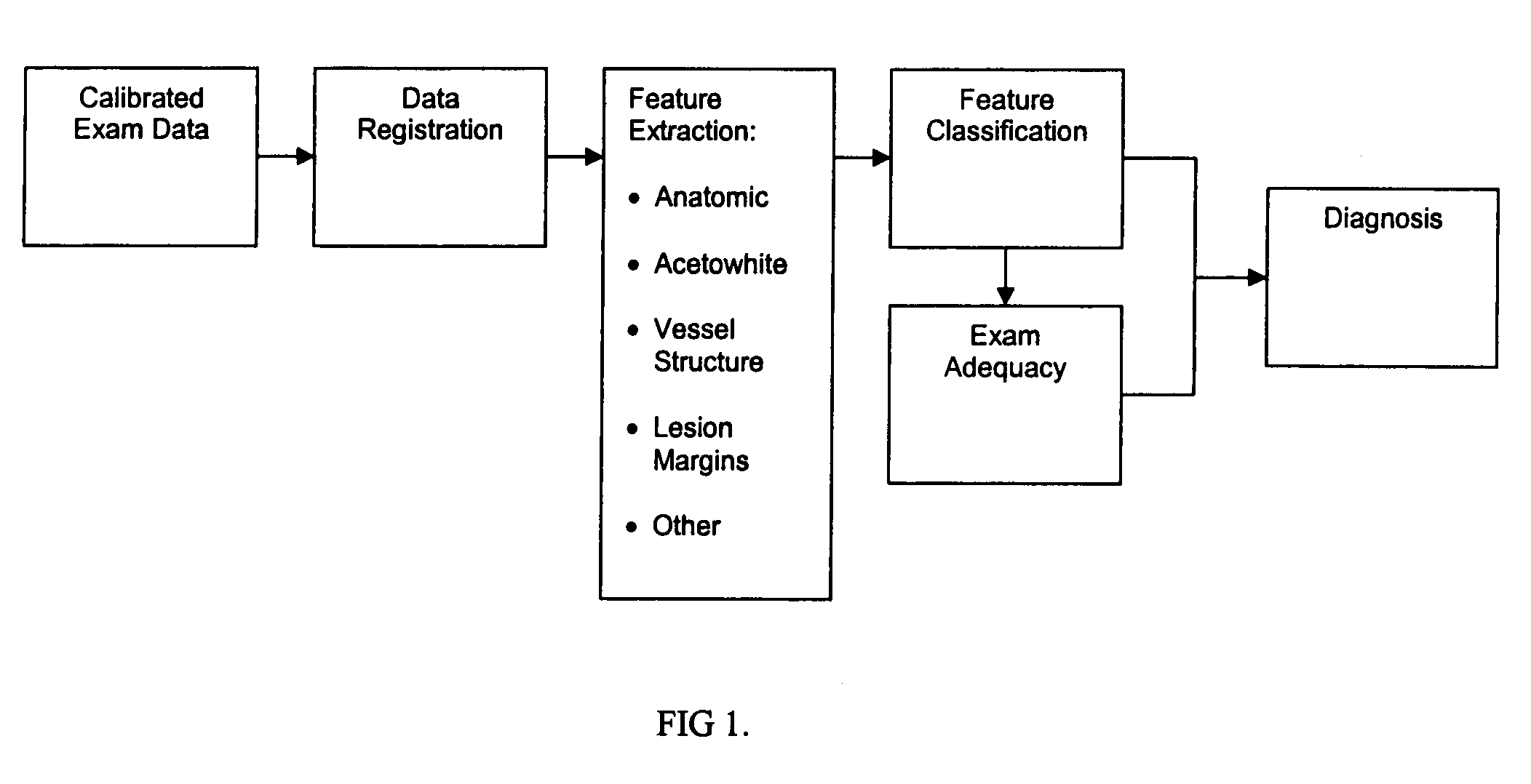
Uterine cervical cancer computer-aided-diagnosis (CAD)
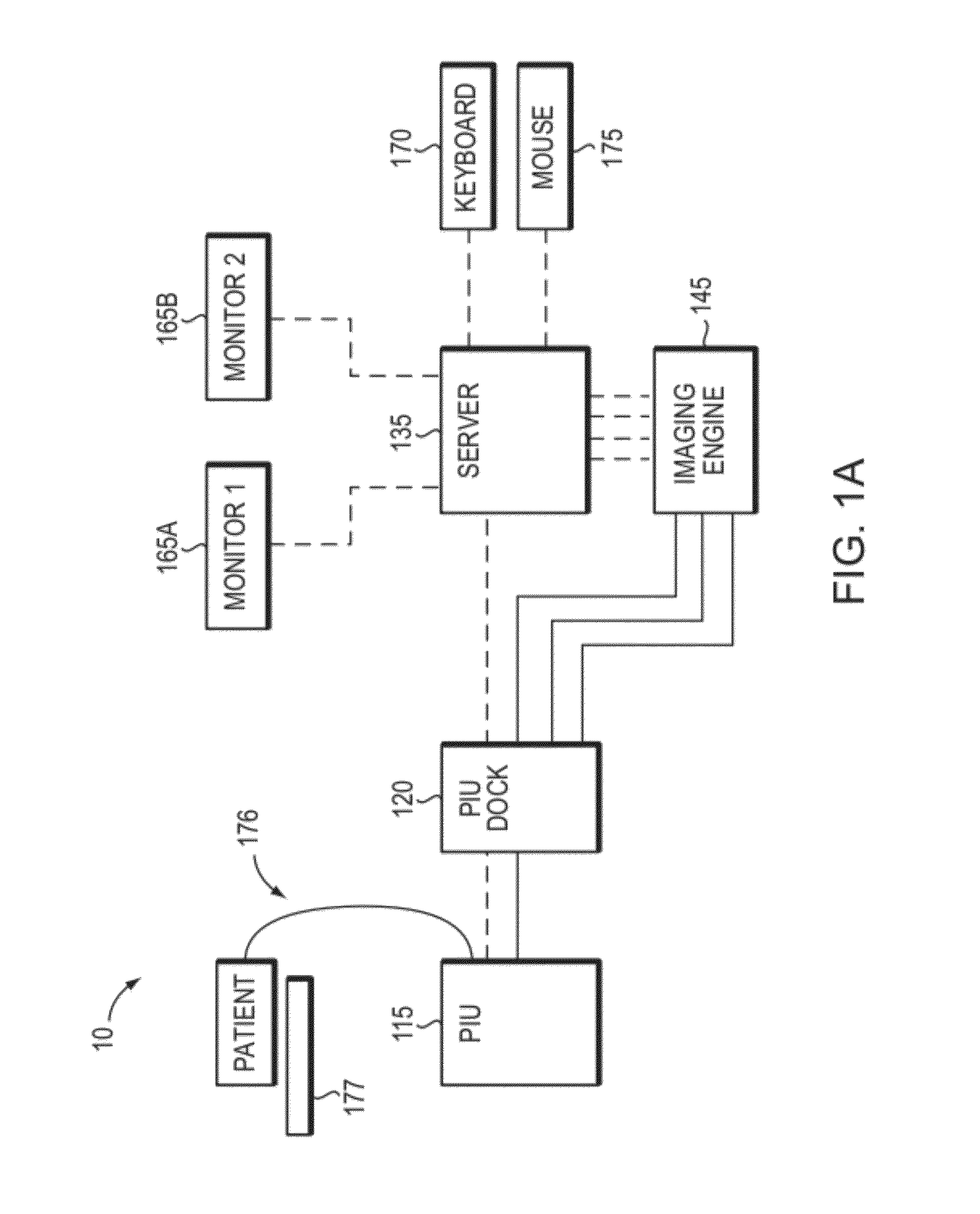
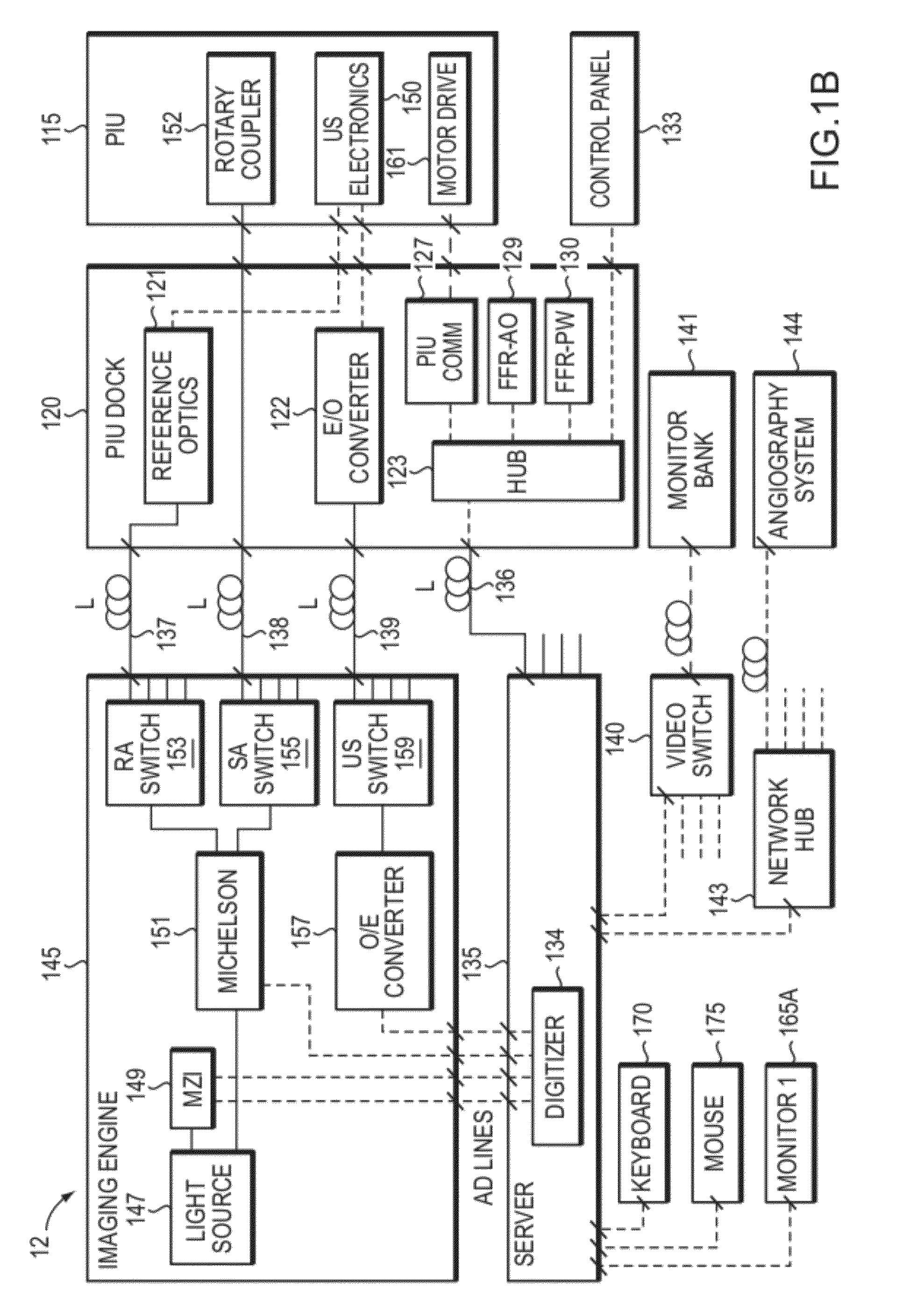
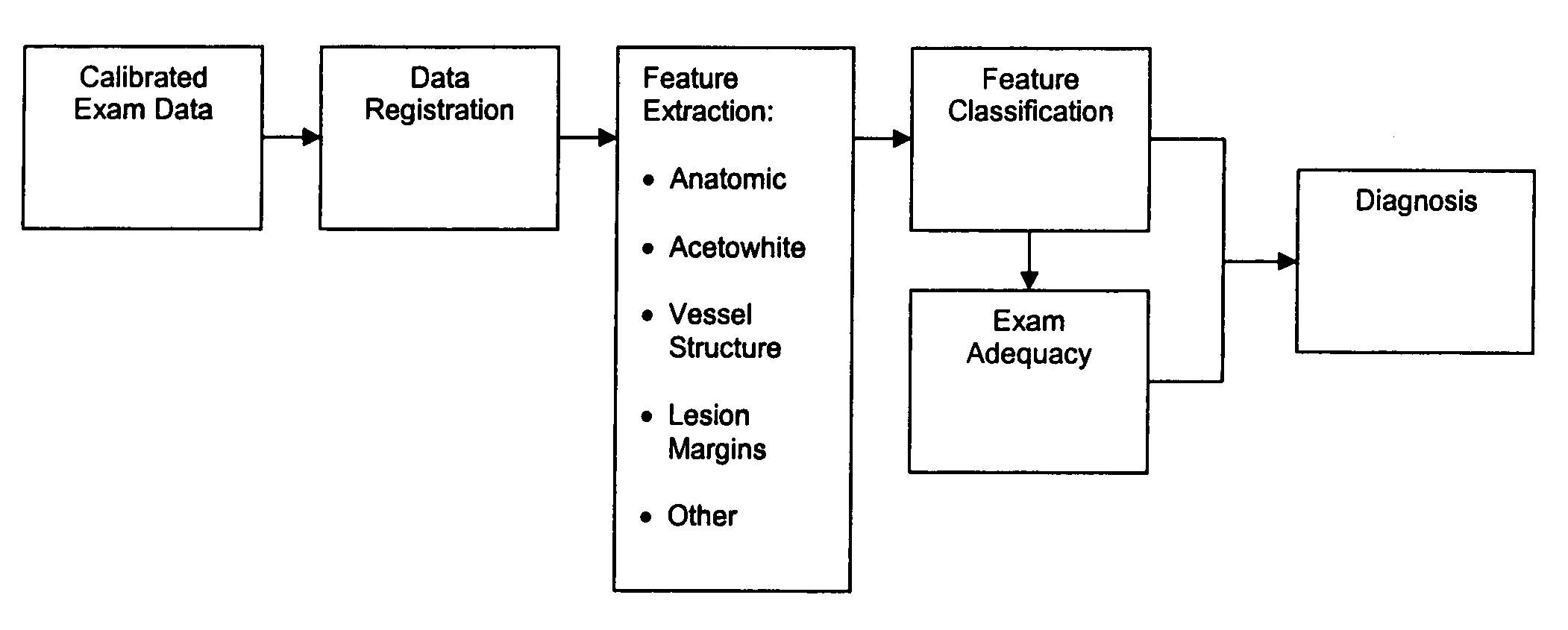
Uterine cervical cancer Computer-Aided-Diagnosis (CAD) according to this invention consists of a core processing system that automatically analyses data acquired from the uterine cervix and provides tissue and patient diagnosis, as well as adequacy of the examination. The data can include, but is not limited to, color still images or video, reflectance and fluorescence multi-spectral or hyper-spectral imagery, coherent optical tomography imagery, and impedance measurements, taken with and without the use of contrast agents like 3-5% acetic acid, Lugol's iodine, or 5-aminolevulinic acid. The core processing system is based on an open, modular, and feature-based architecture, designed for multi-data, multi-sensor, and multi-feature fusion. The core processing system can be embedded in different CAD system realizations. For example: A CAD system for cervical cancer screening could in a very simple version consist of a hand-held device that only acquires one digital RGB image of the uterine cervix after application of 3-5% acetic acid and provides automatically a patient diagnosis. A CAD system used as a colposcopy adjunct could provide all functions that are related to colposcopy and that can be provided by a computer, from automation of the clinical workflow to automated patient diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
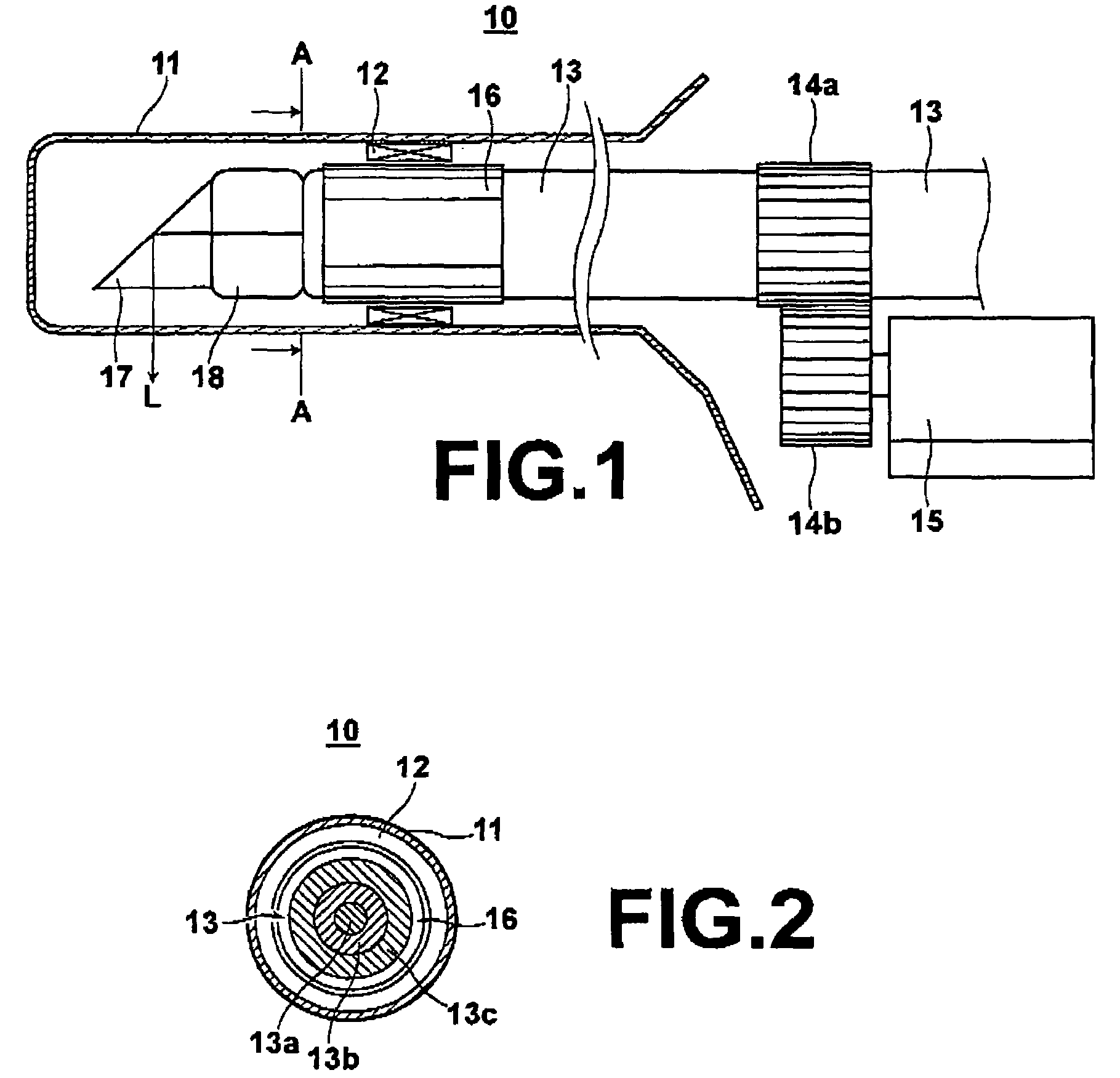
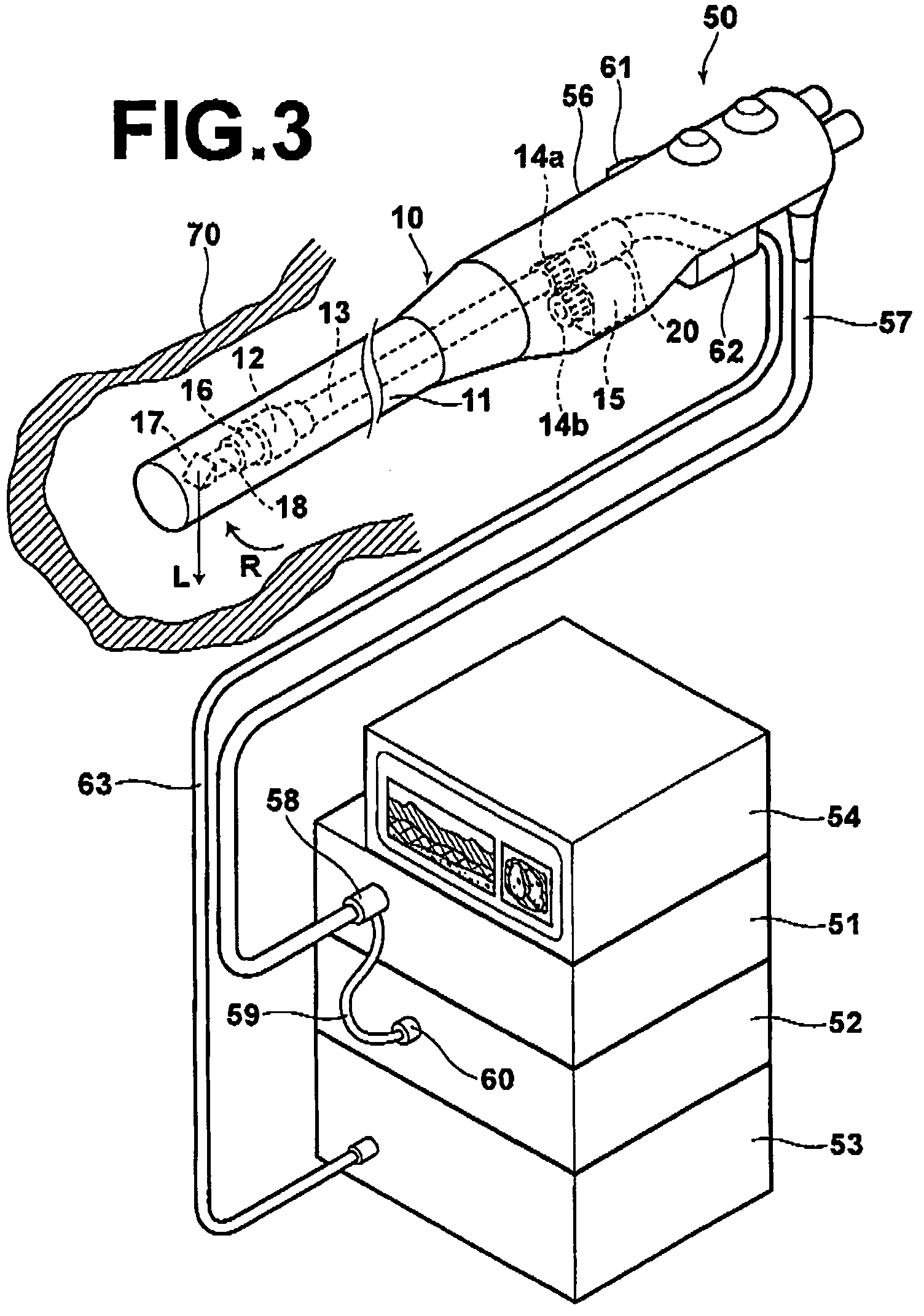
Oct optical probe and optical tomography imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090198125A1Inexpensive and safeImprove accuracySurgeryEndoscopesOptical reflectionInterior space
An OCT optical probe to be inserted into a subject includes: a cylindrical sheath to be inserted into a subject; an optical fiber disposed in the internal space of the sheath; a rotatably-supporting portion fixed to the optical fiber in the vicinity of a distal end of the optical fiber; a distal optical system to deflect light emitted from the distal end of the optical fiber toward the subject; a holding portion to hold the distal optical system such that the optical system is rotatably supported by the rotatably-supporting portion; and a flexible shaft covering the optical fiber in the internal space, wherein the holding portion is fixed to a distal end of the flexible shaft. Using the OCT optical probe of the invention, the problem of degradation of measurement accuracy due to optical insertion loss and optical reflection loss at a rotary joint can be eliminated inexpensively and safely.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
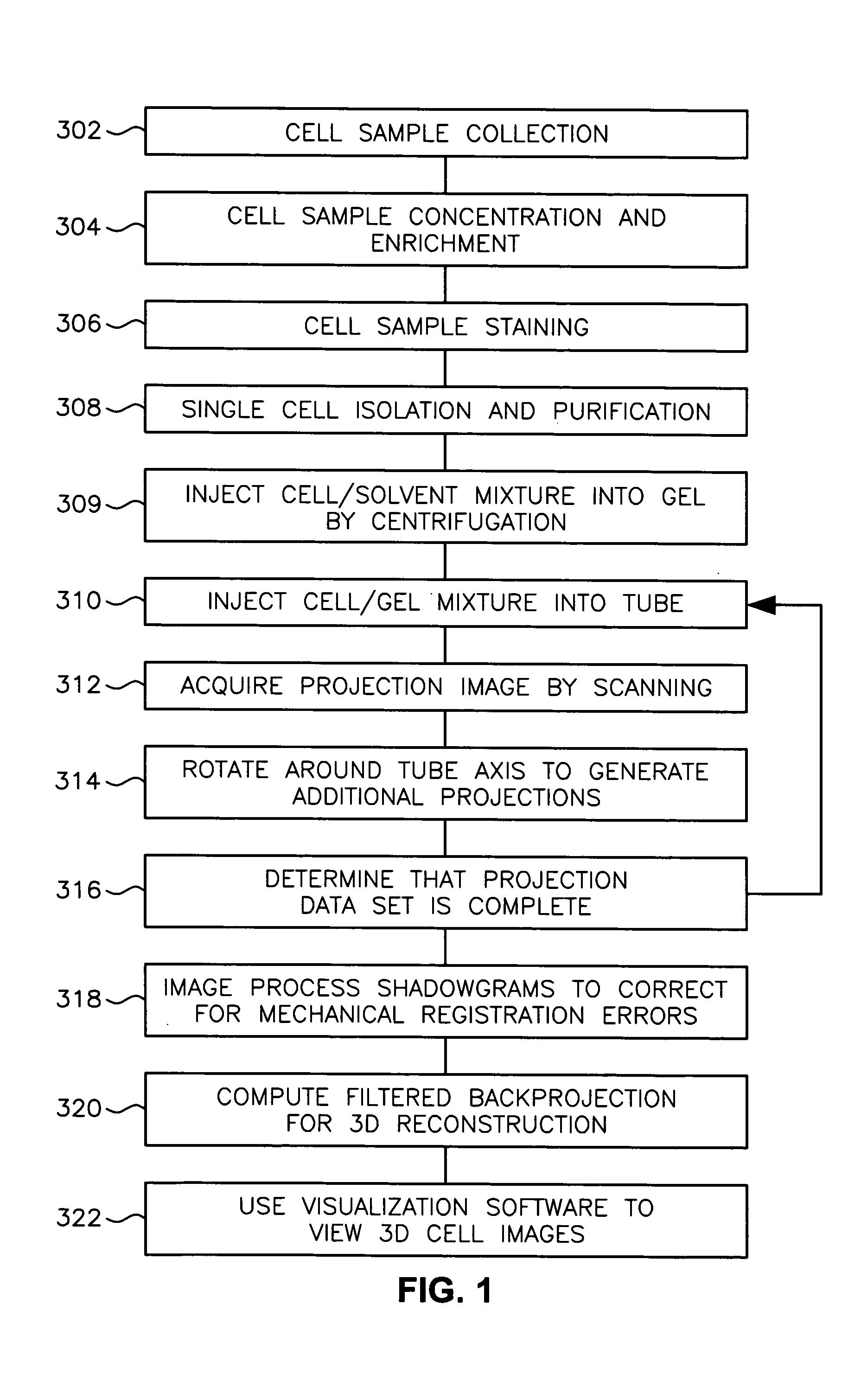
System and method for processing specimens and images for optical tomography
ActiveUS20050085721A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological cellOptical tomography
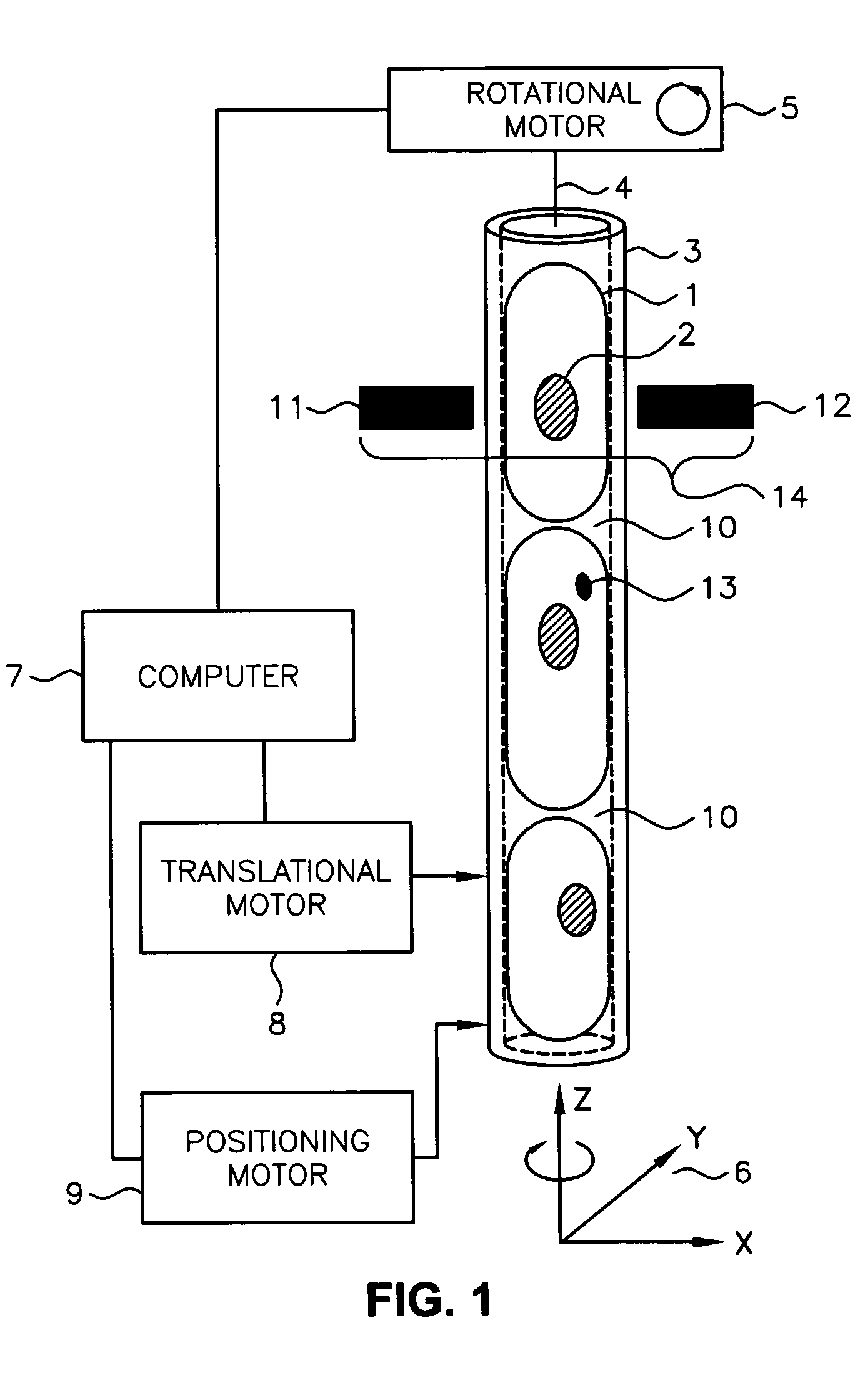
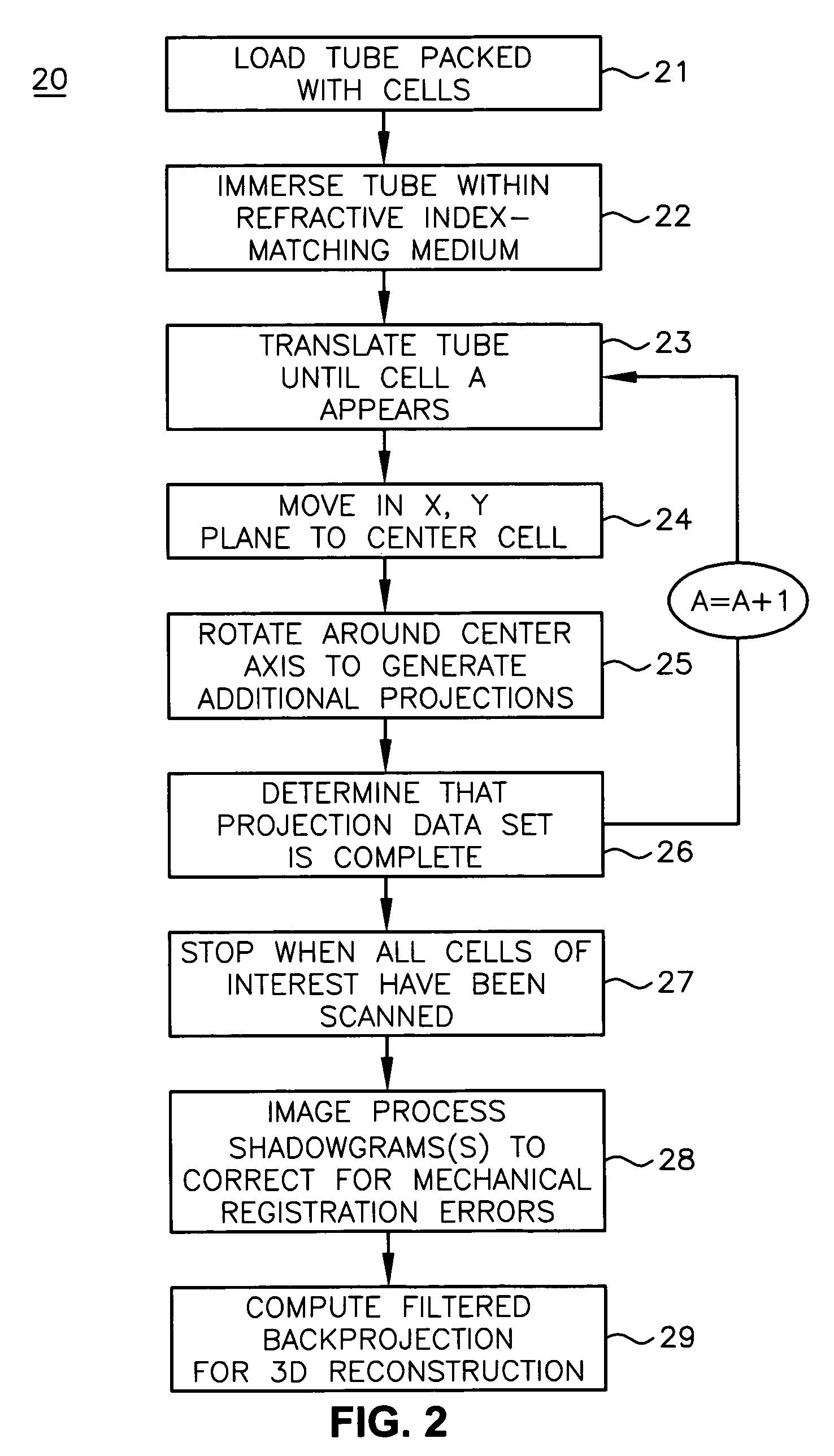
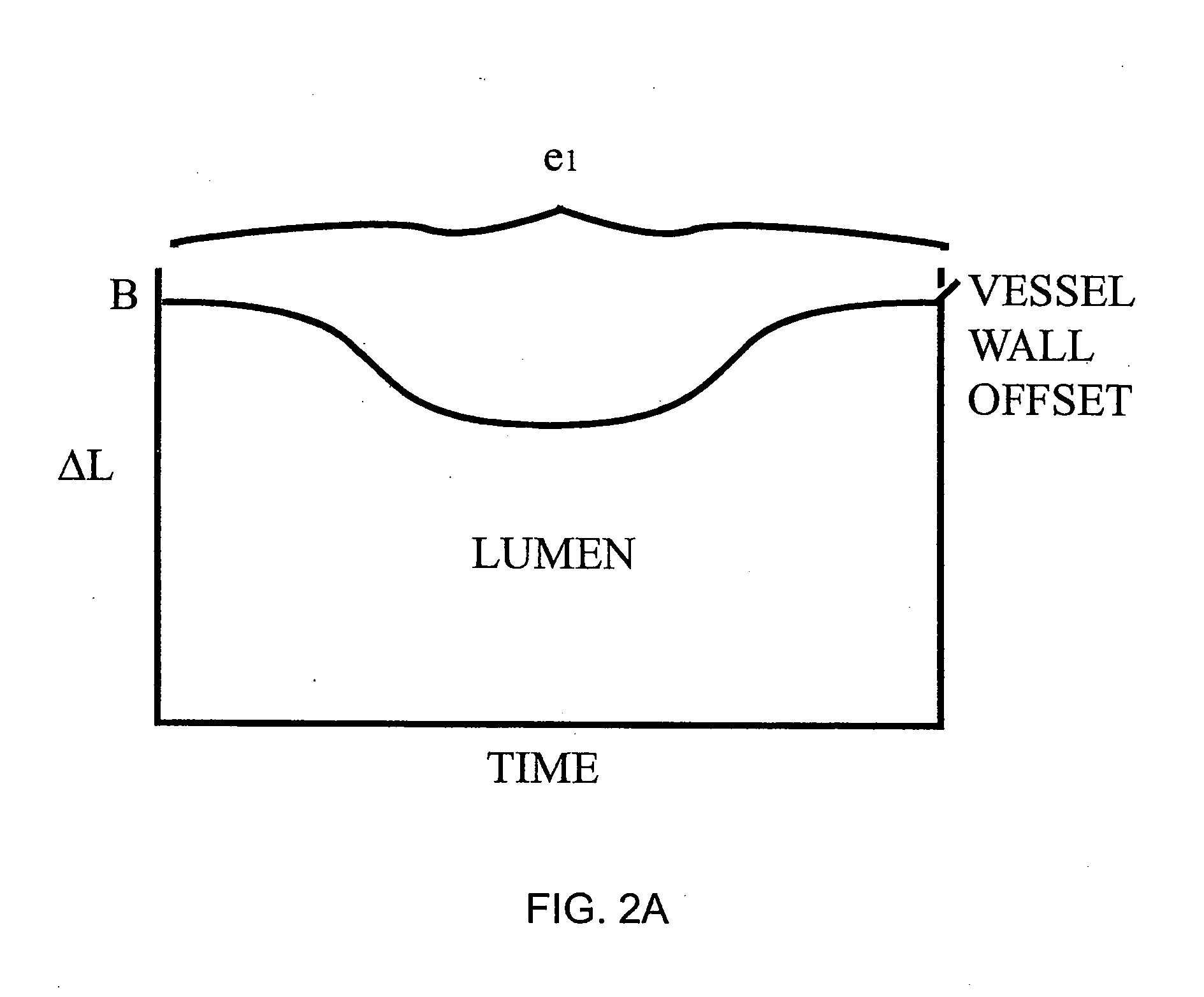
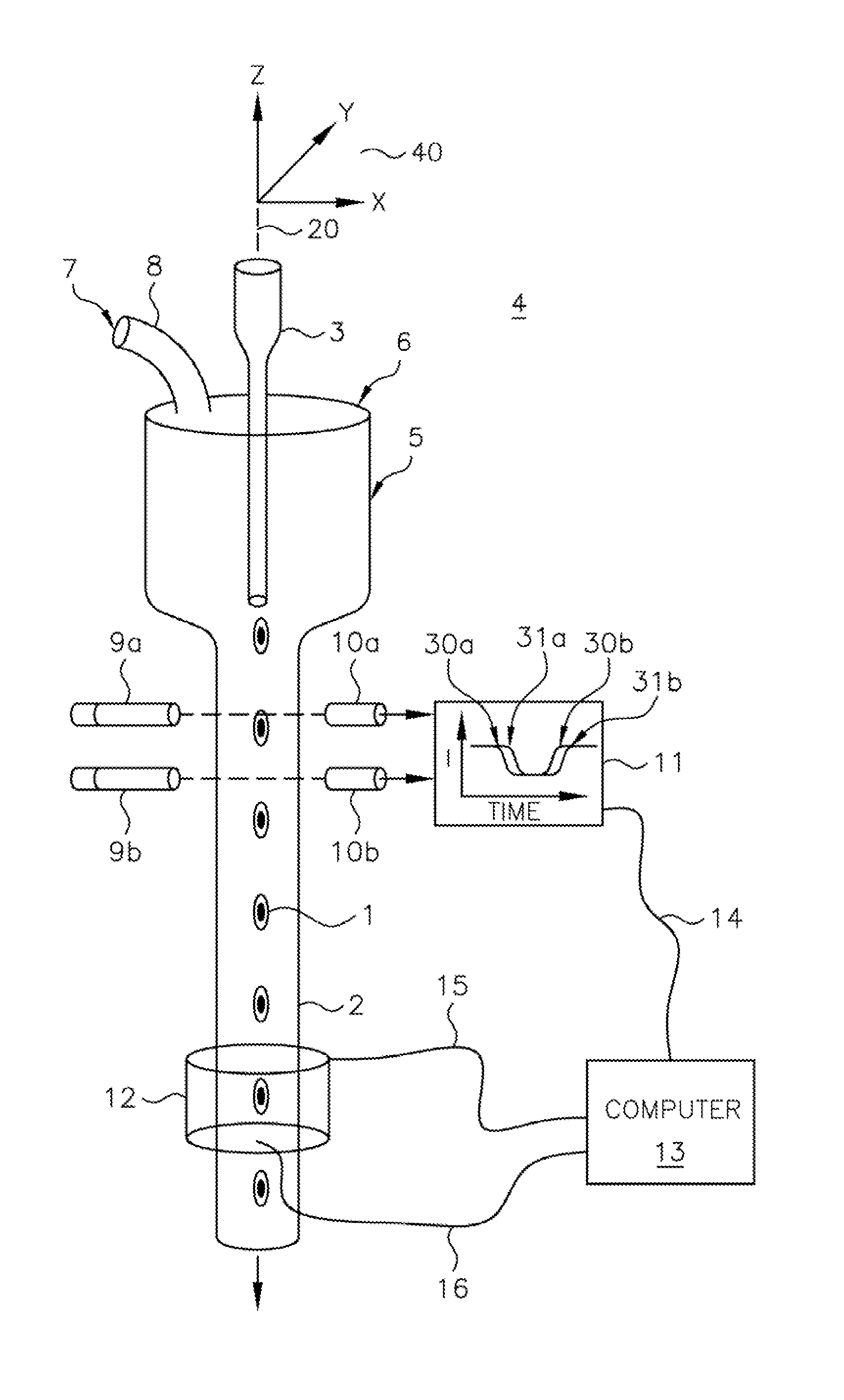
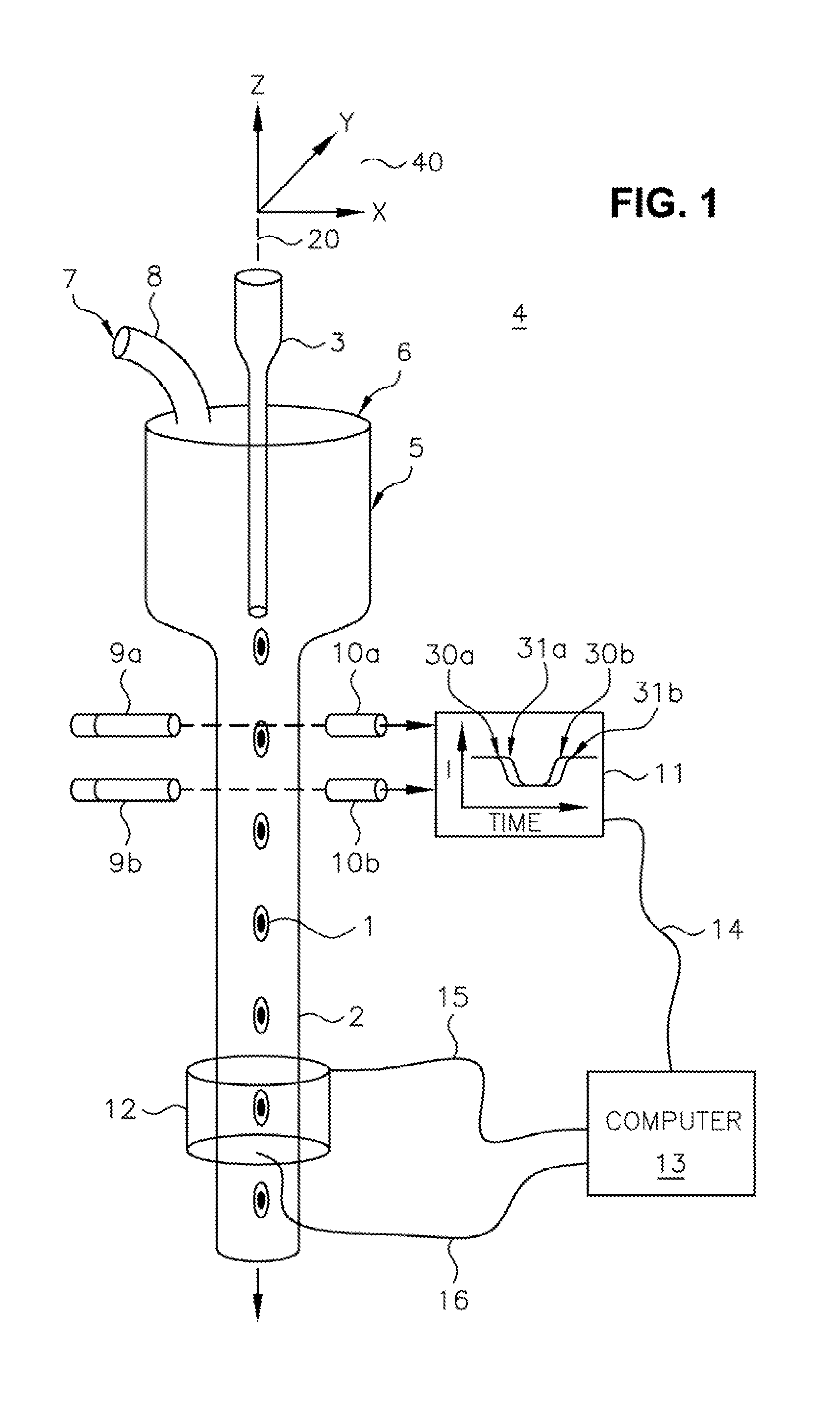
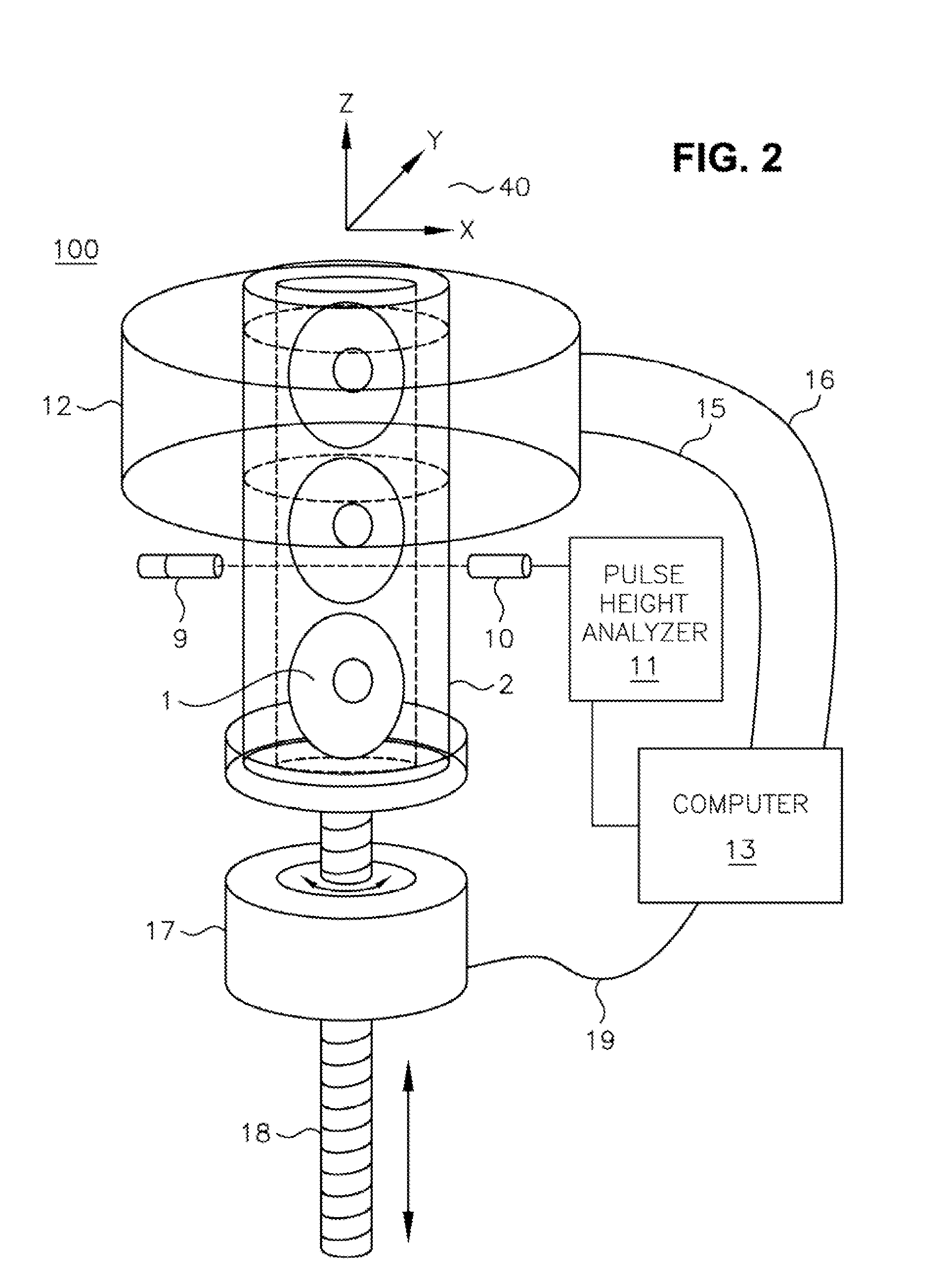
A scanning method for scanning samples of biological cells using optical tomography includes preparing, acquiring, reconstructing and viewing three-dimensional images of cell samples. Concentration and enrichment of the cell sample follows. The cell sample is stained. Cells are isolated from the cell sample and purified. A cell / solvent mixture is injected into a gel by centrifugation. A cell / gel mixture is injected into a capillary tube until a cell appears centered in a field of view using a step flow method. An optical imaging system, such as a fixed or variable motion optical tomography system acquires a projection image. The sample is rotated about a tube axis to generate additional projections. Once image acquisition is completed, the acquired shawdowgrams or image projections are corrected for errors. A computer or other equivalent processor is used to compute filtered backprojection information for 3D reconstruction.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
System and method for quantifying the dynamic response of a target system
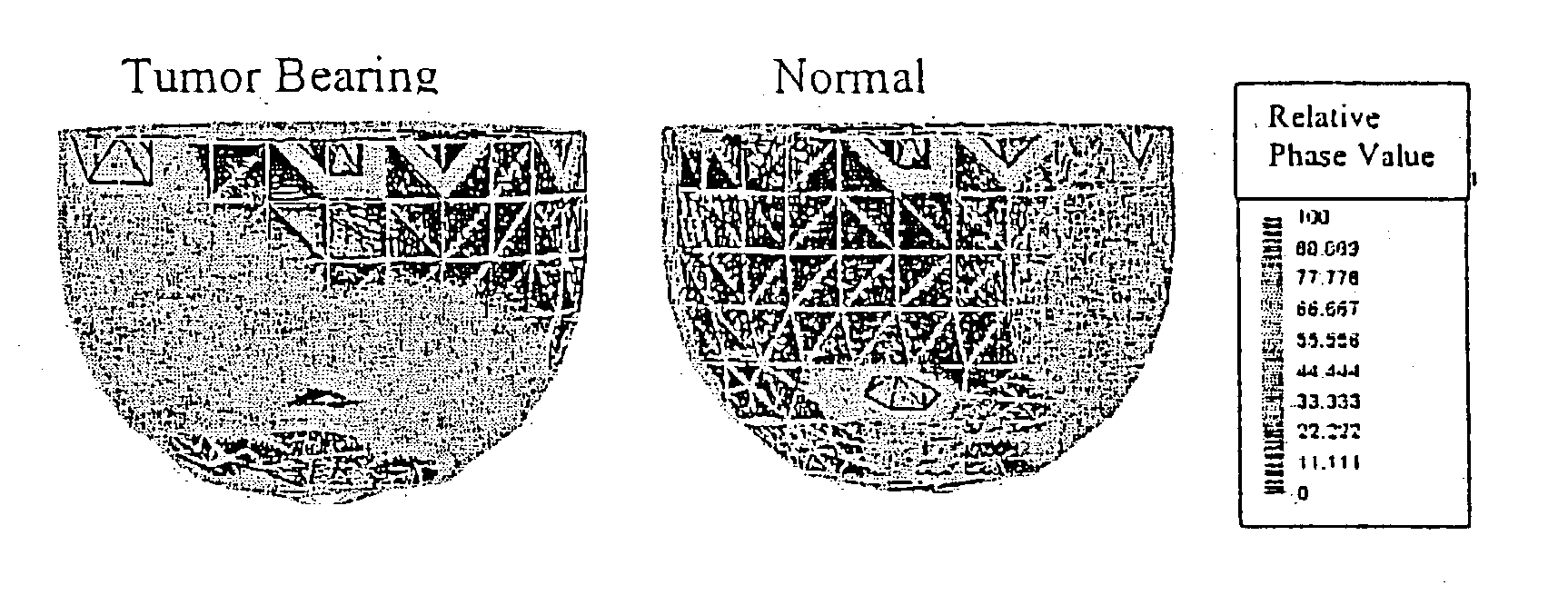
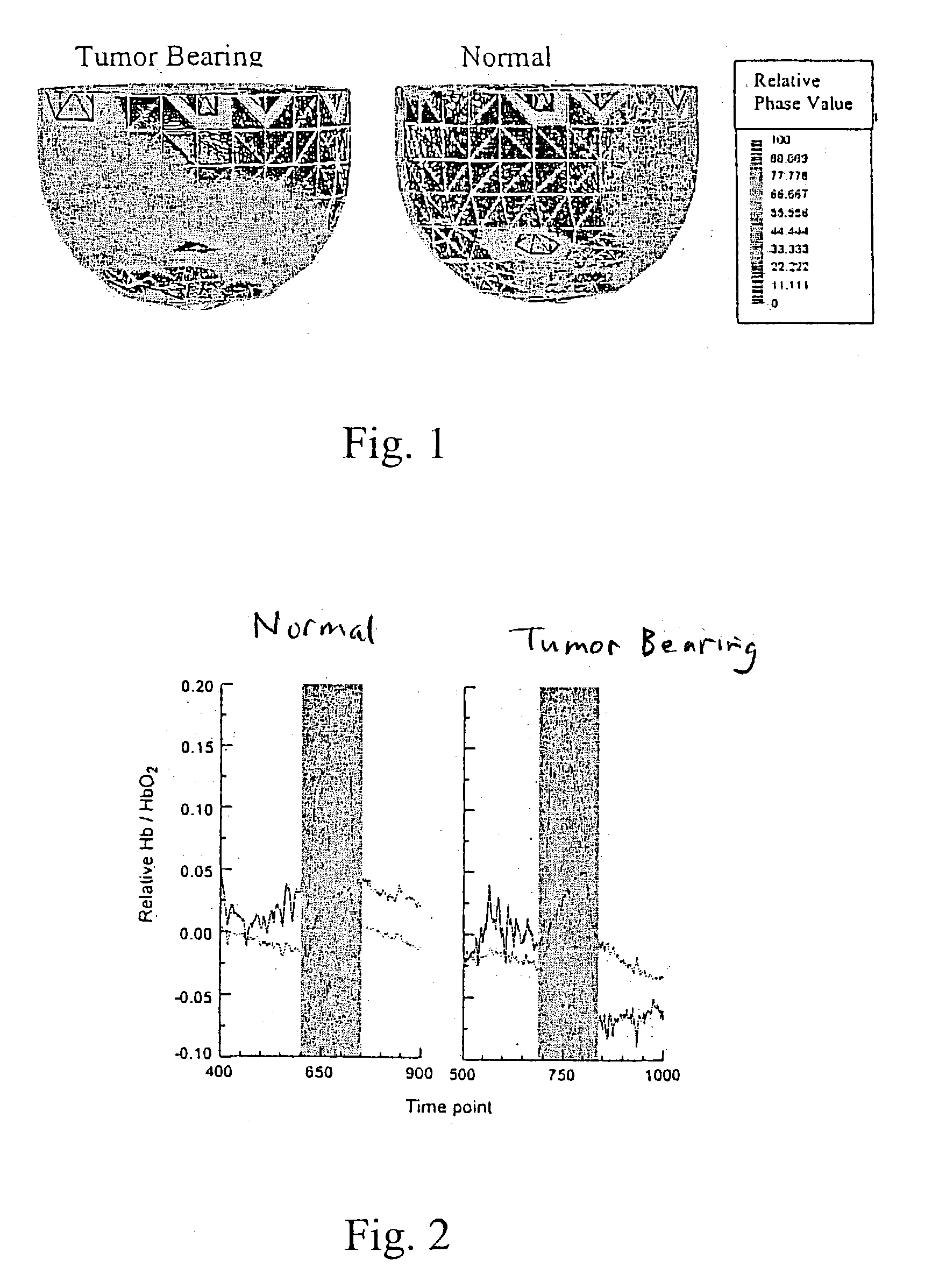
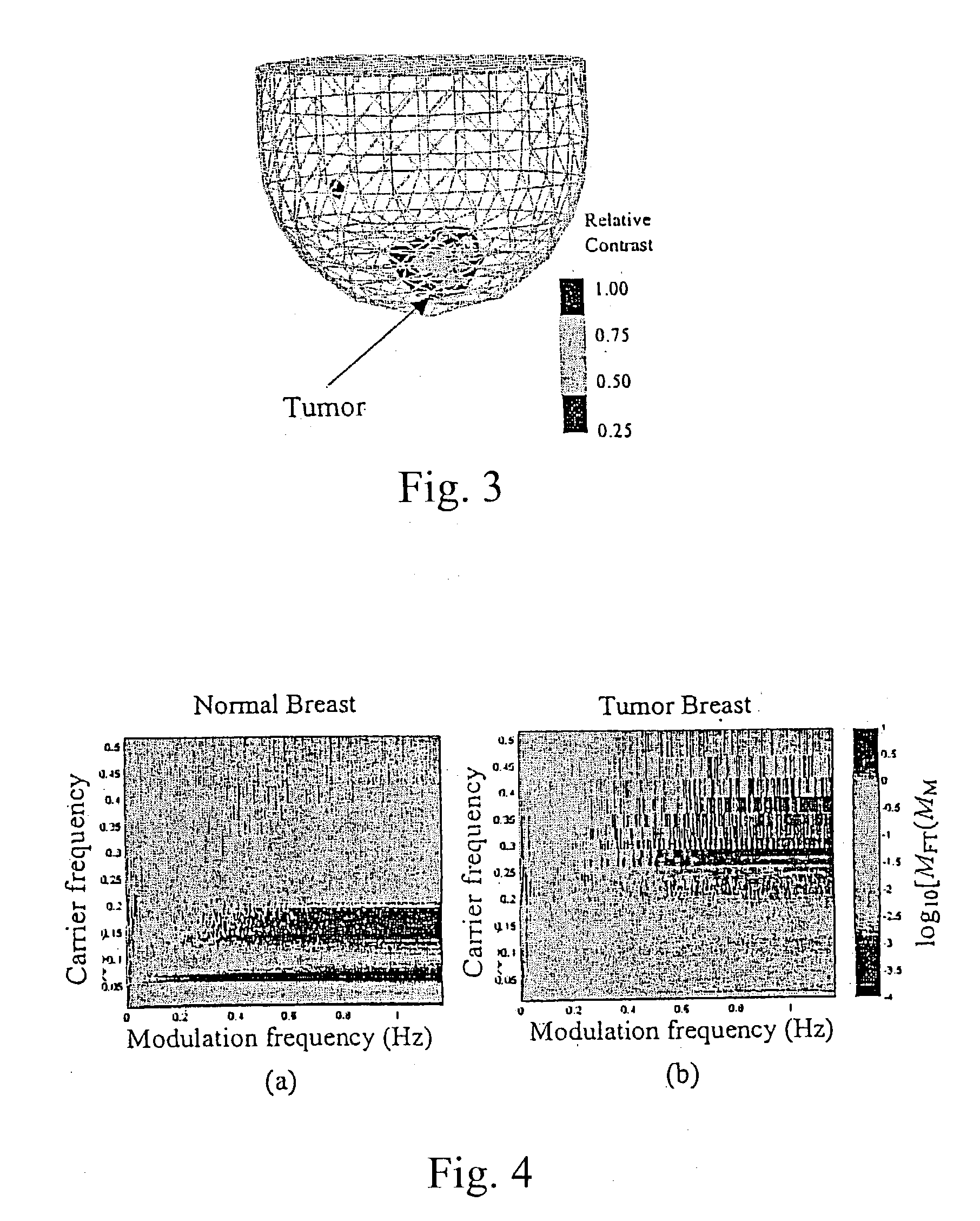
A time series of optical tomography data is obtained for a target tissue site in a human (or animal), using an optical wavelength, such as near infrared, at which hemoglobin is absorptive, to observe properties of the vasculature of the human. The data may be compared to baseline data of a corresponding tissue site, e.g., from a healthy human, or from another, corresponding tissue site of the human. For example, a suspected cancerous breast of a human may be compared to a known healthy breast to detect differences in the vasculature. Measures may be made of flow, oxygen supply / demand imbalance, and evidence of altered regulation of the peripheral effector mechanism. The function of the target tissue site may be analyzed, along with the coordinated interaction between multiple sites of the target system. A provocation may be administered to identify surrogate markers of an underlying state or process.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
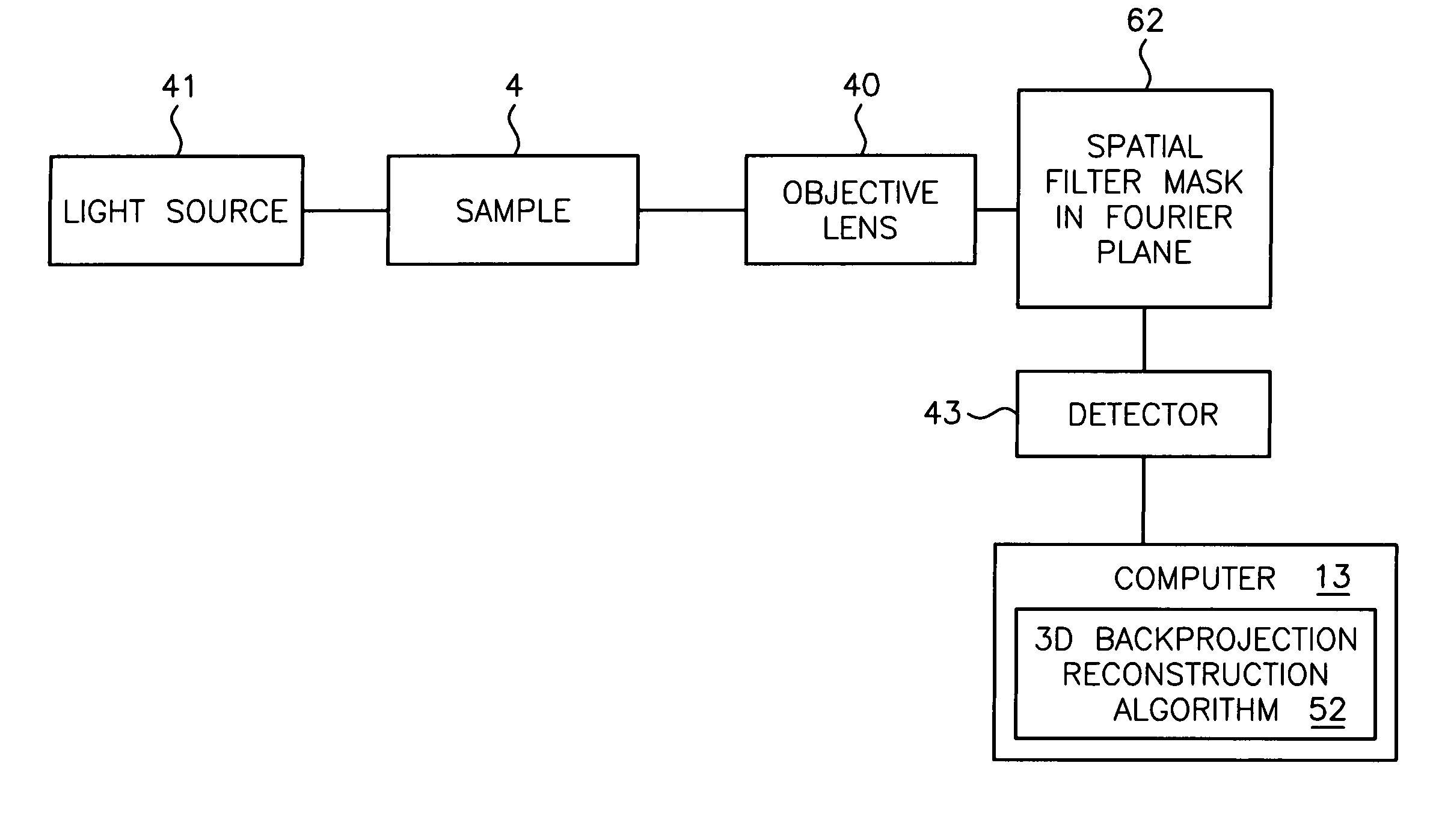
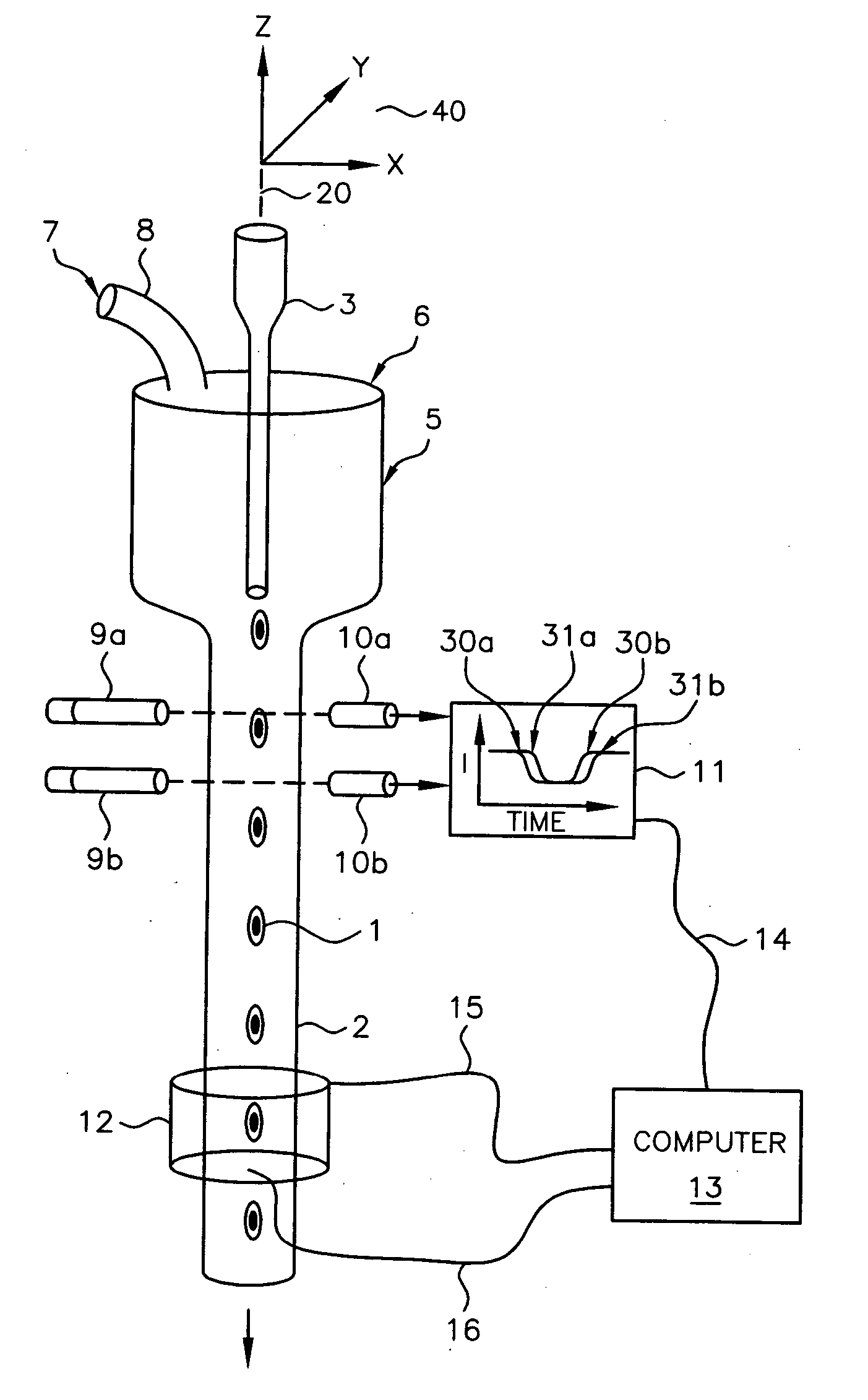
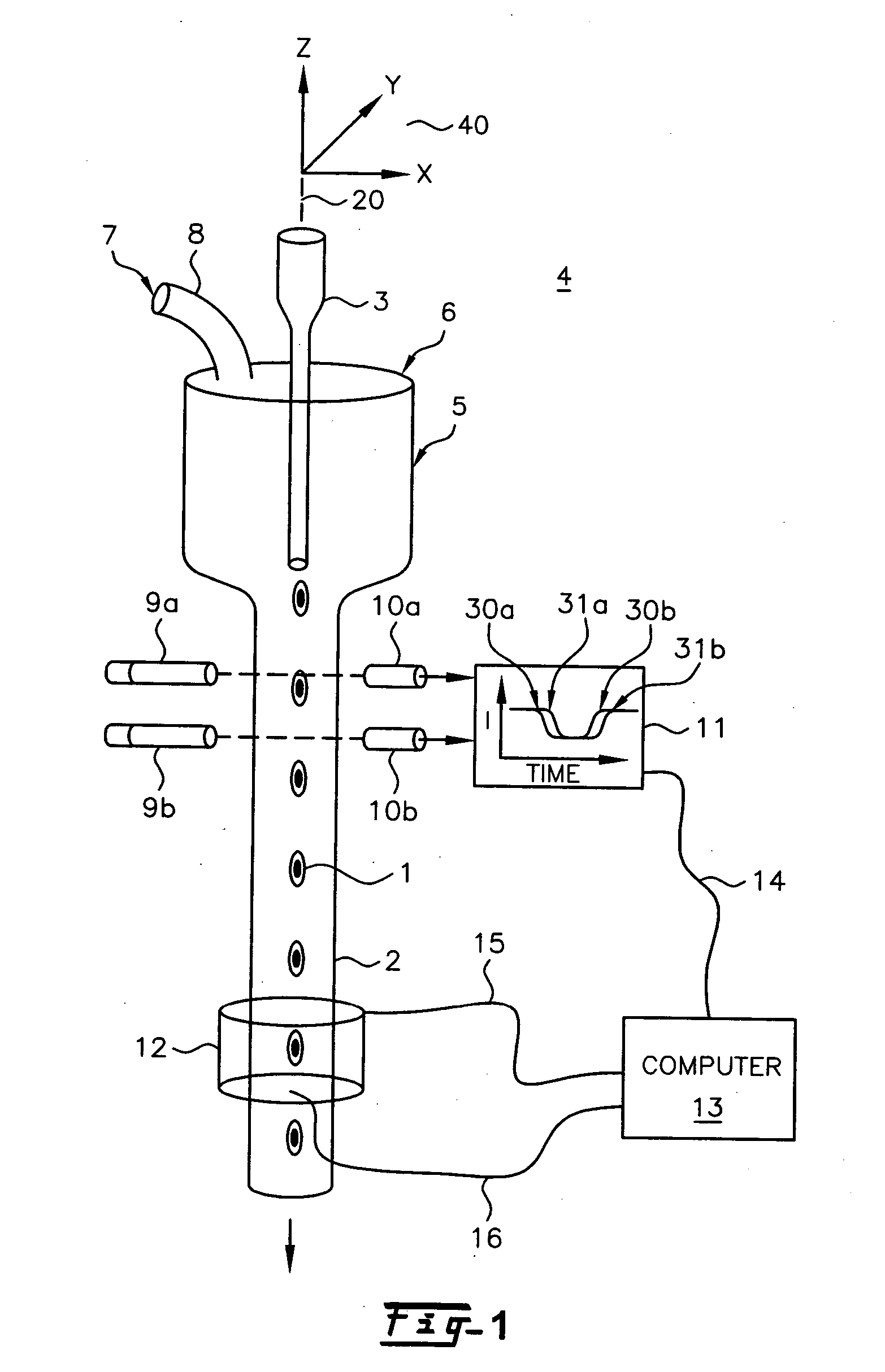
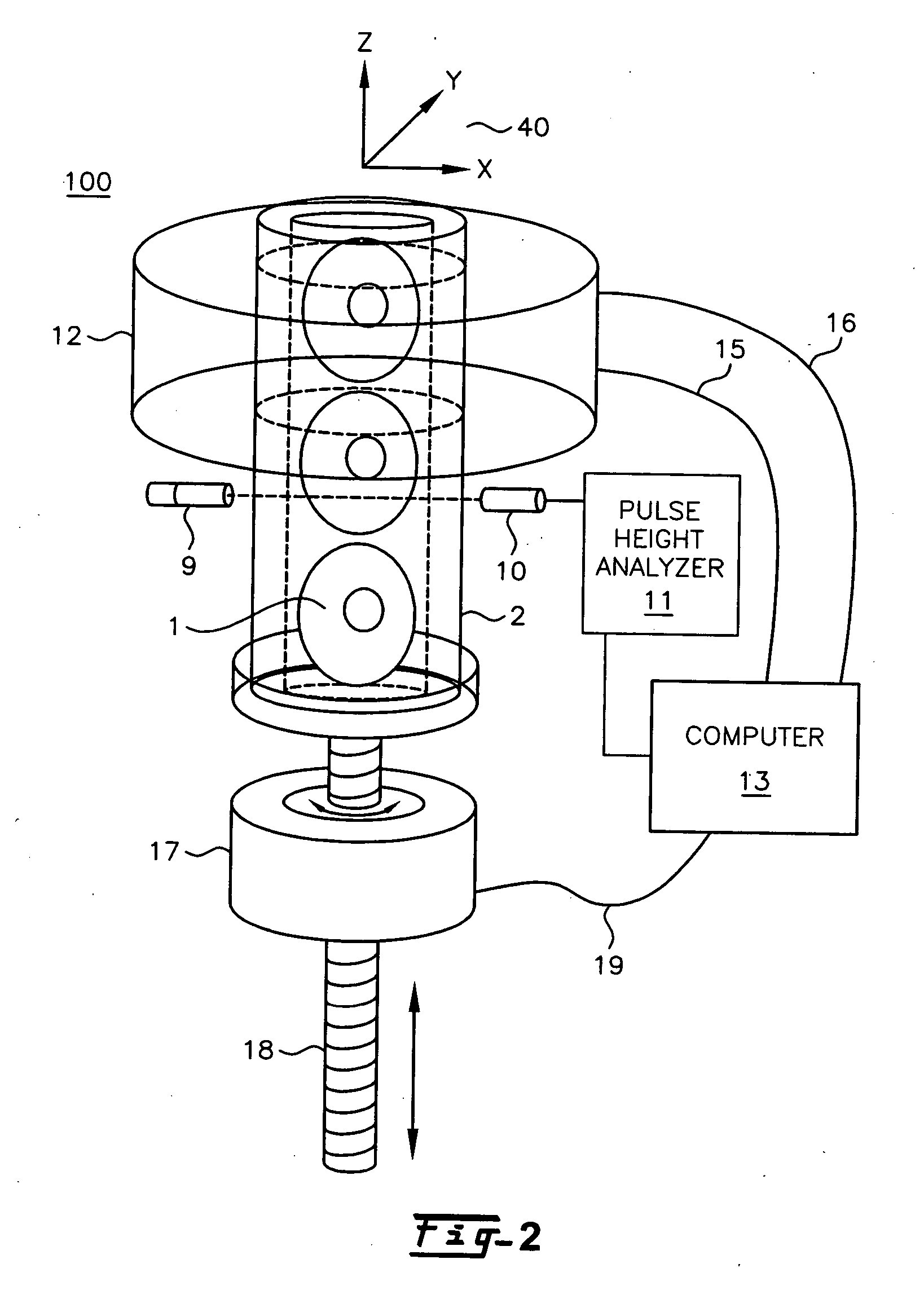
Method and apparatus for pseudo-projection formation for optical tomography
ActiveUS7738945B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiple perspectiveOptical tomography
A system for optical imaging of a thick specimen that permits rapid acquisition of data necessary for tomographic reconstruction of the three-dimensional (3D) image. One method involves the scanning of the focal plane of an imaging system and integrating the range of focal planes onto a detector. The focal plane of an optical imaging system is scanned along the axis perpendicular to said plane through the thickness of a specimen during a single detector exposure. Secondly, methods for reducing light scatter when using illumination point sources are presented. Both approaches yield shadowgrams. This process is repeated from multiple perspectives, either in series using a single illumination / detection subsystem, or in parallel using several illumination / detection subsystems. A set of pseudo-projections is generated, which are input to a three dimensional tomographic image reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
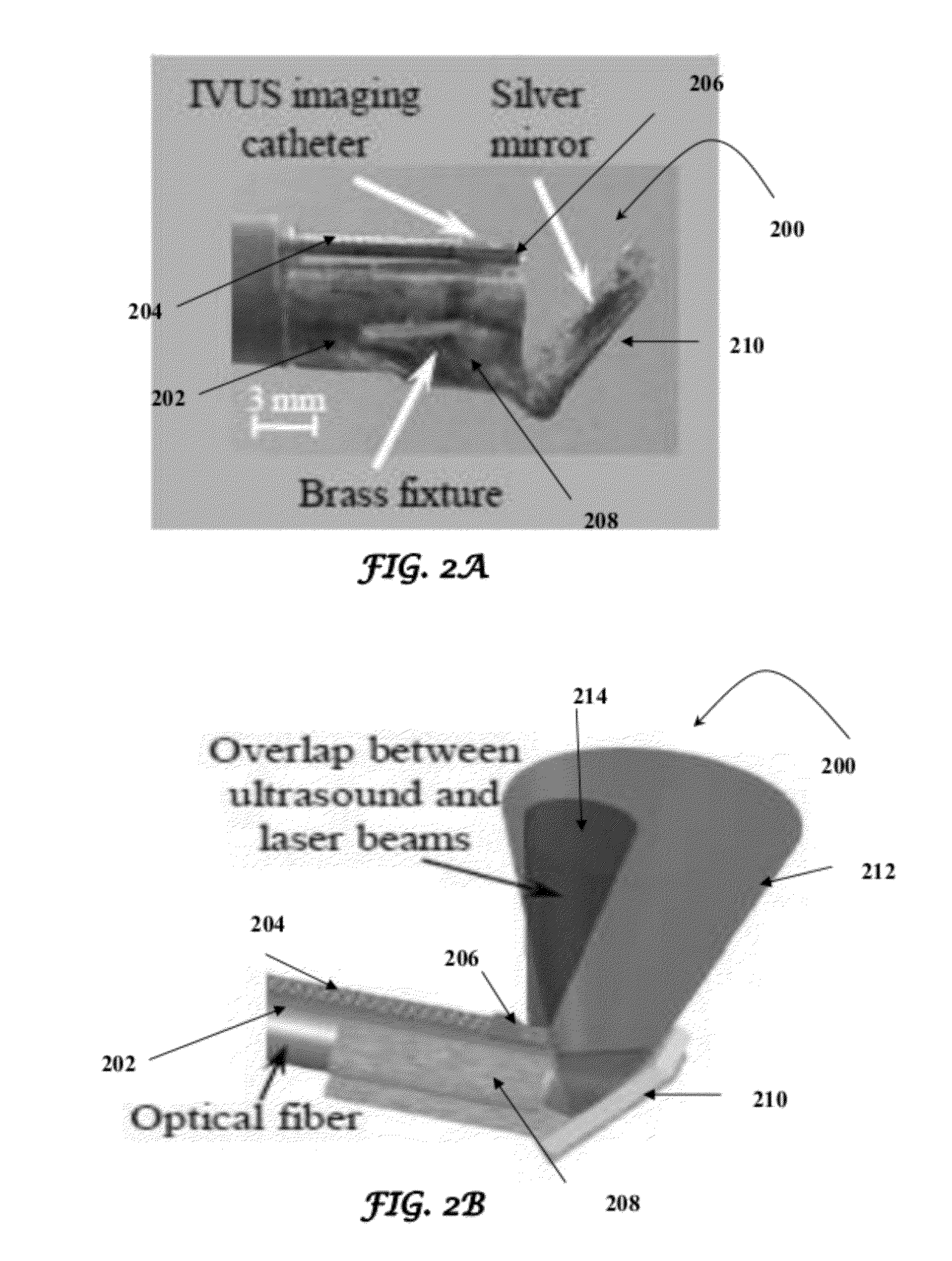
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS20120271170A1Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorElastography
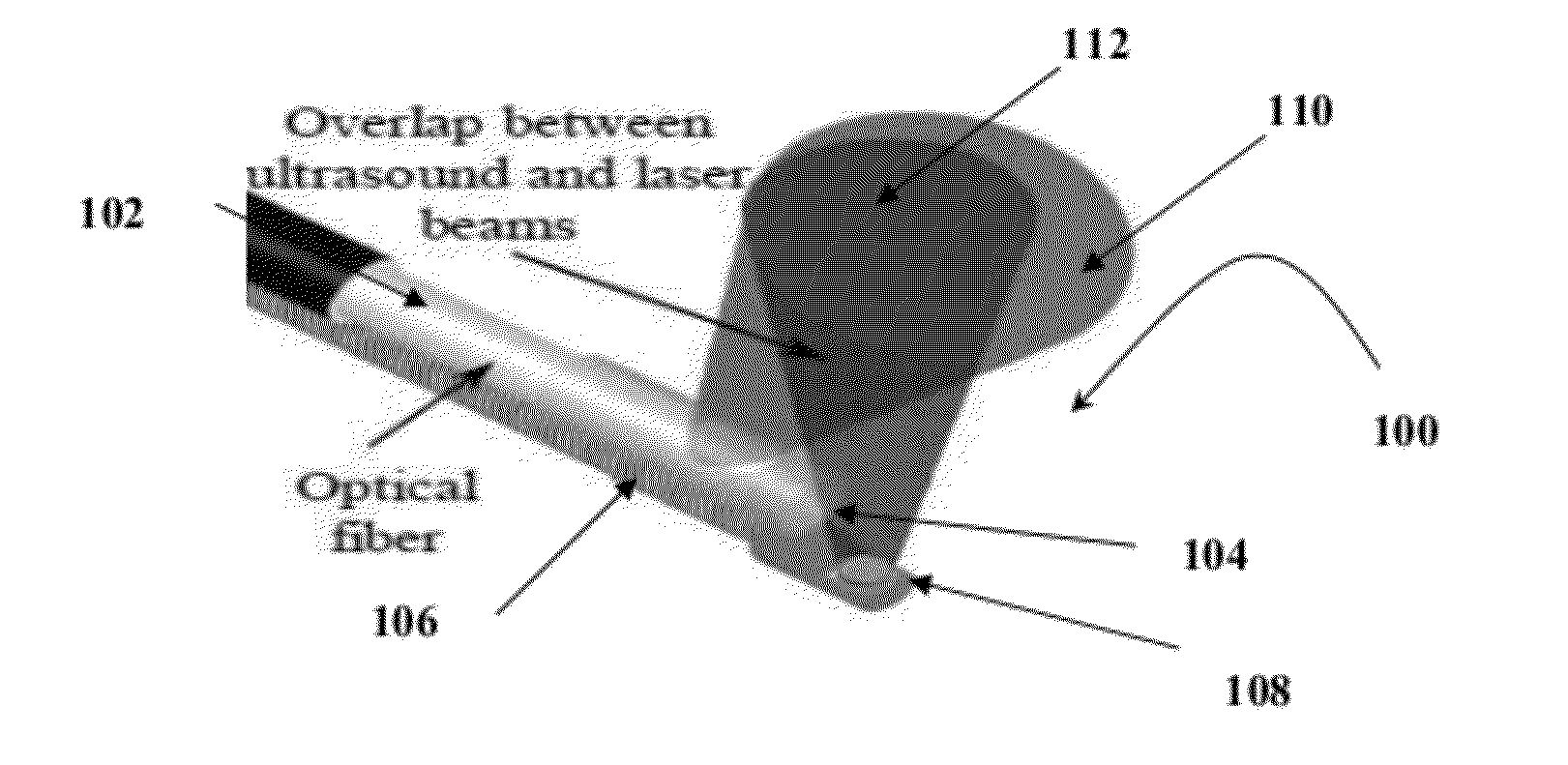
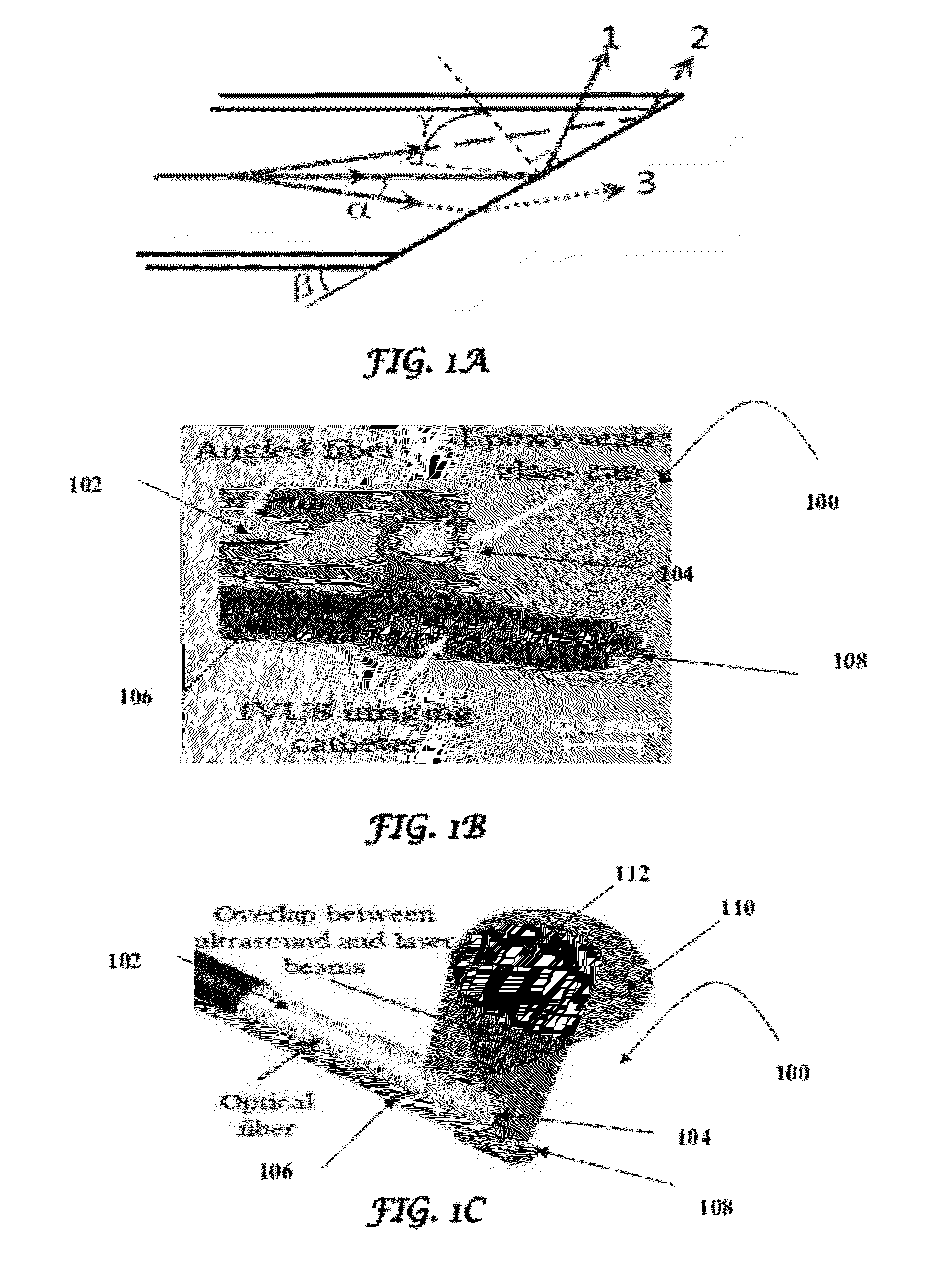
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
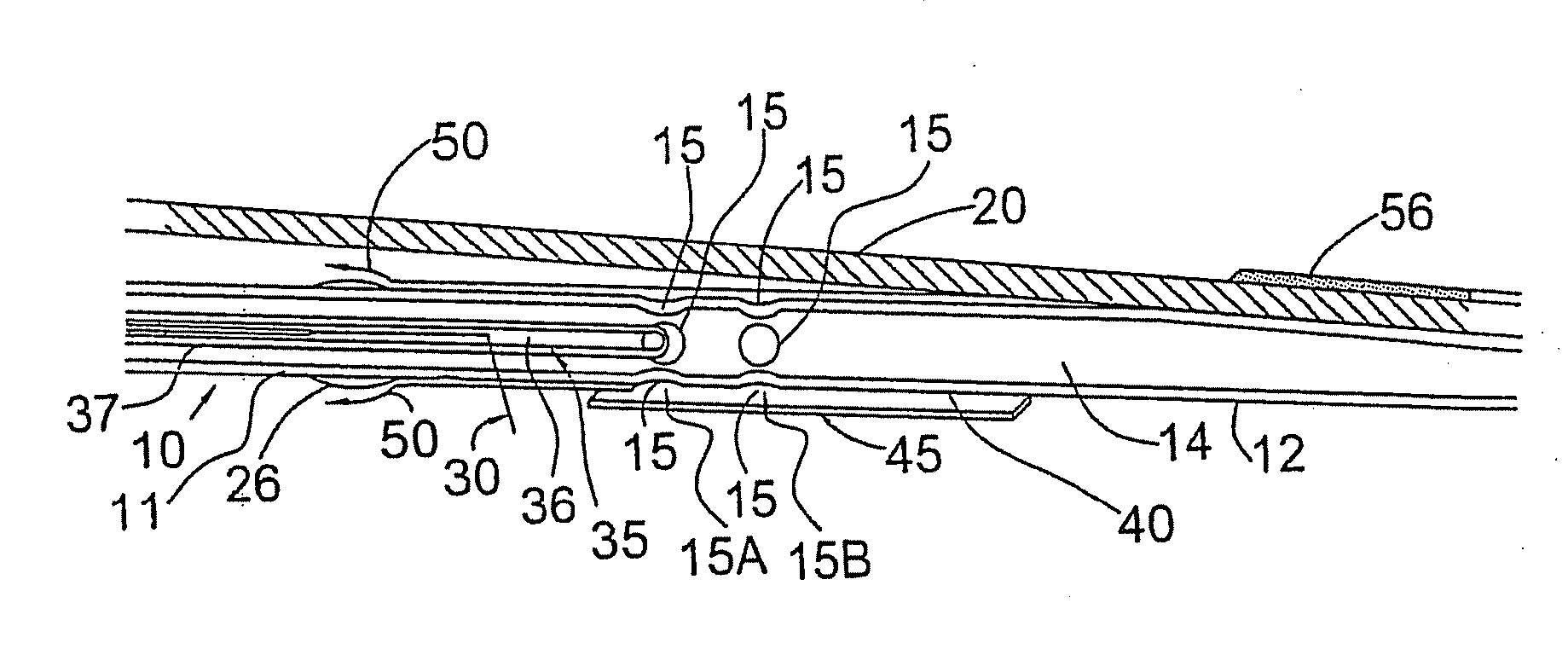
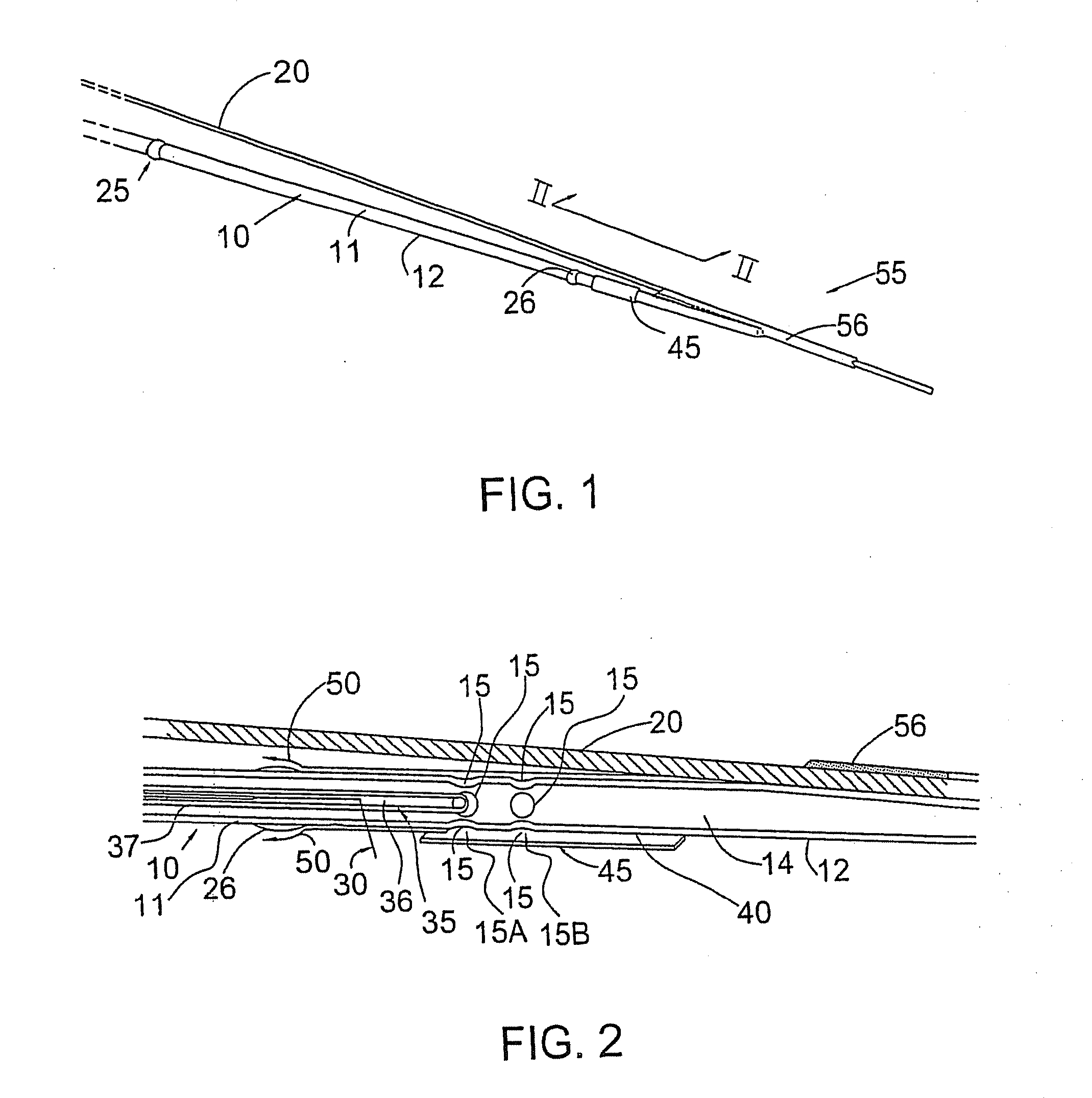
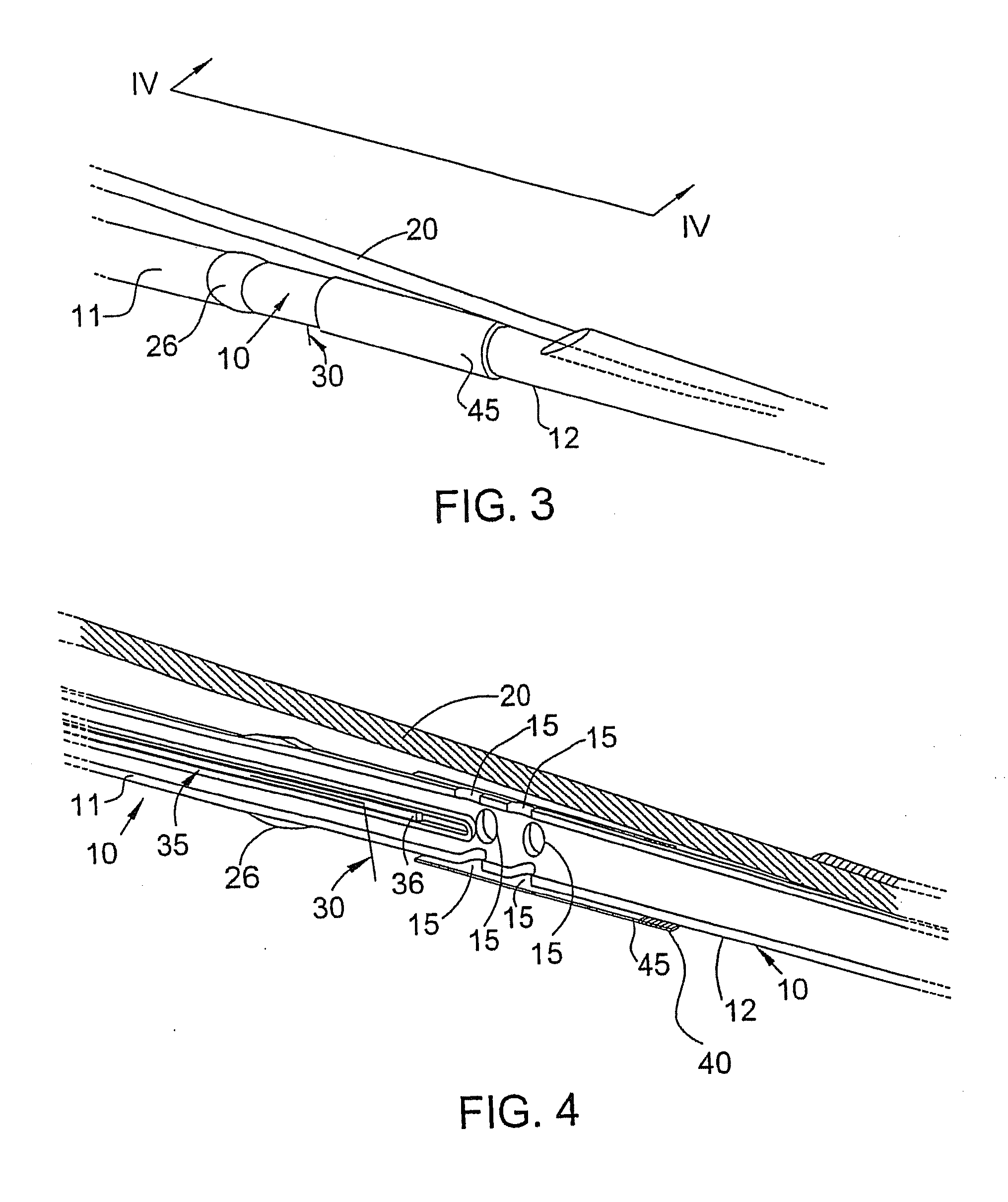
Flush catheter with flow directing sheath
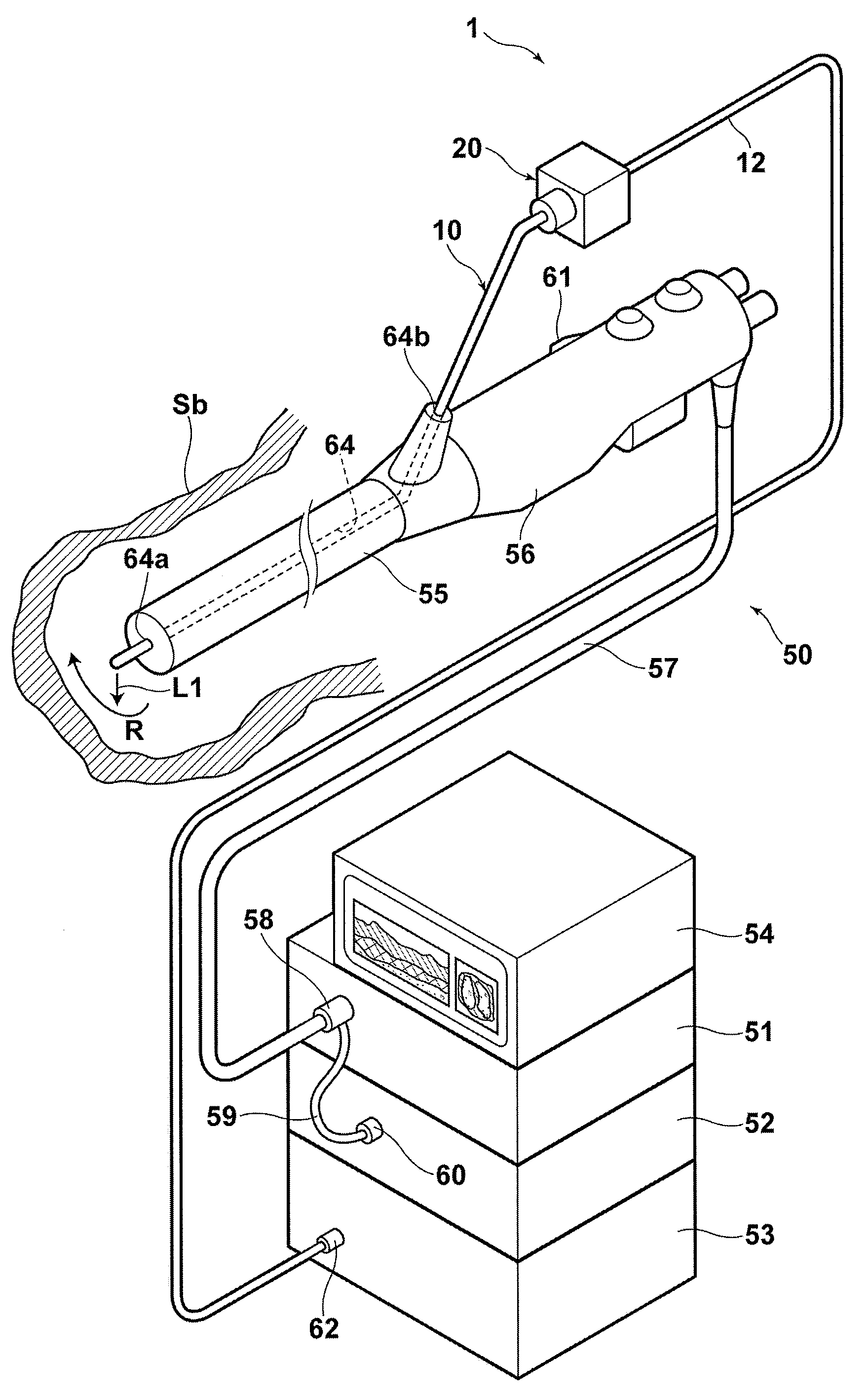
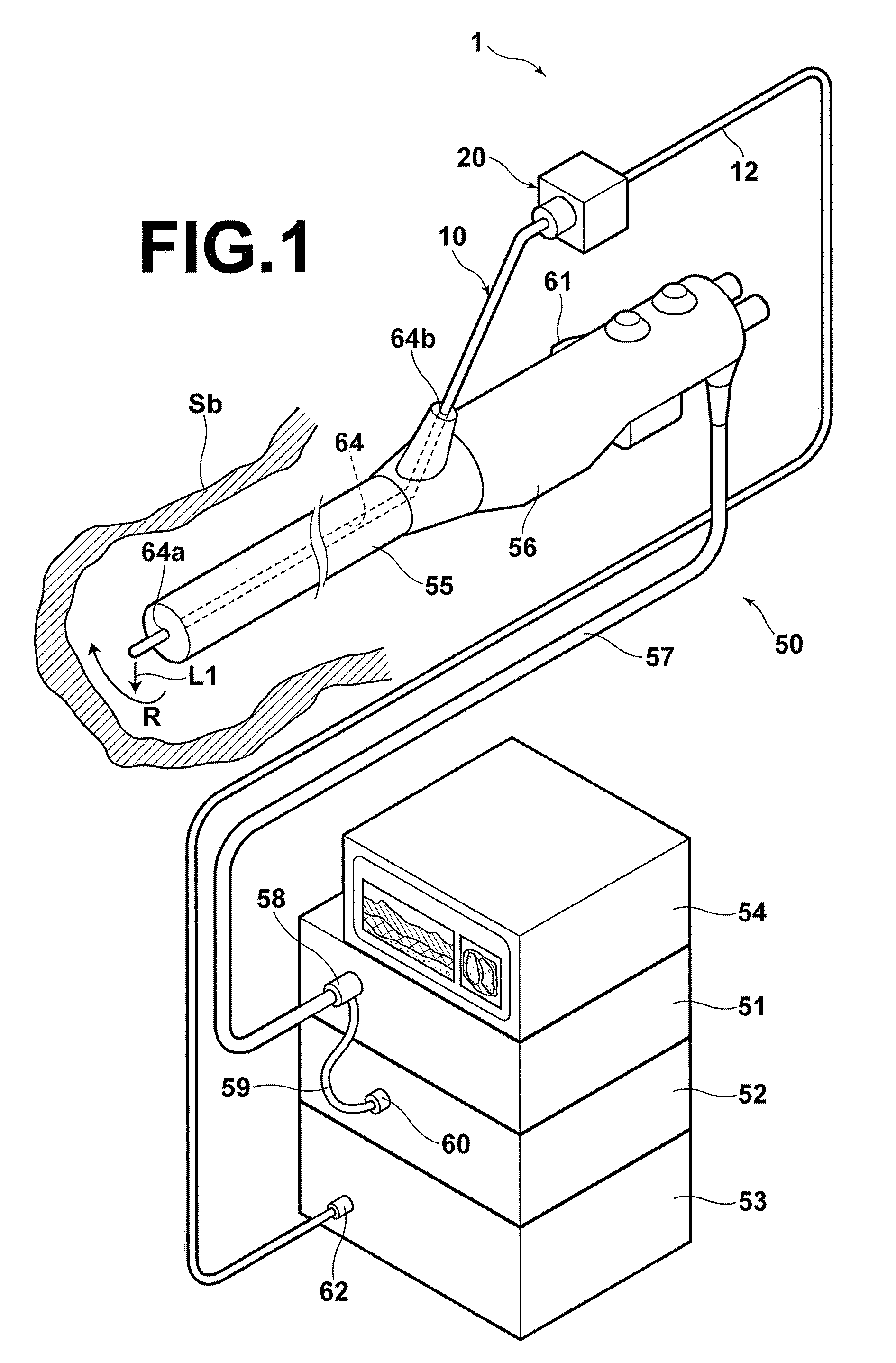
In certain embodiments, the invention provides a method of flushing a lumen of interest having a first diameter and a lumen wall. The method can include the steps of selecting a flush solution such that the flush solution lowers a fluid removal rate of a plurality of terminating lumens, the terminating lumens branching from and in fluid communication with the lumen of interest, at least one of the terminating lumens having a second diameter, the second diameter smaller than the first diameter; flushing the lumen with the flush solution; and collecting optical tomography scan data relative to a portion of the lumen wall.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
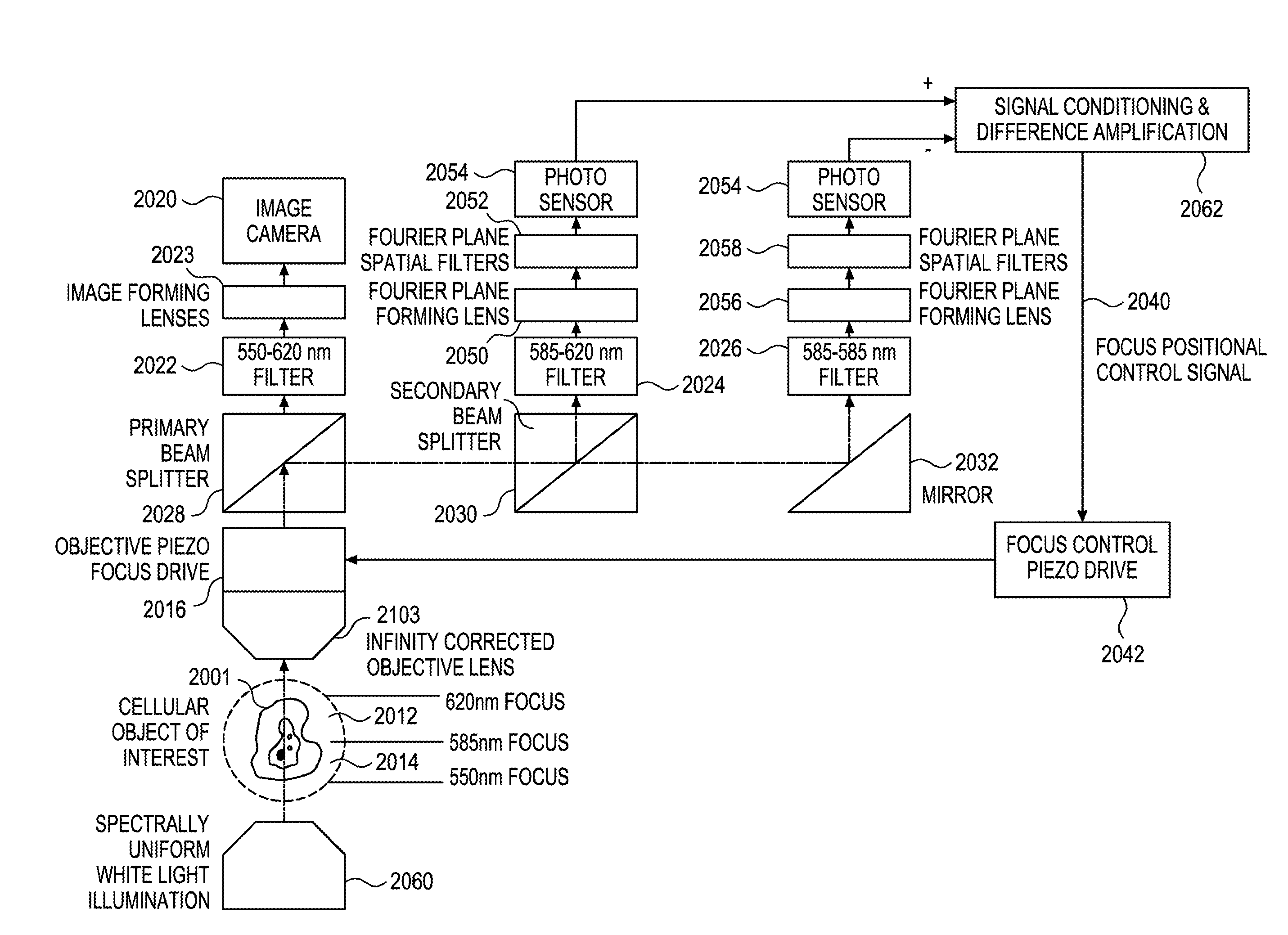
Depth of Field Extension for Optical Tomography
ActiveUS20090103792A1Photometry using wholly visual meansMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical projection tomographyOptical tomography
An optical projection tomography system is illuminated with a light source. An object-containing tube, a portion of which is located within the region illuminated by the light source, contains an object of interest that has a feature of interest. A detector is located to receive emerging radiation from the object of interest. A lens, including optical field extension elements, is located in the optical path between the object region and the detector, such that light rays from multiple object planes in the object-containing tube simultaneously focus on the detector. The object-containing tube moves relatively to the detector and the lens operate to provide multiple views of the object region for producing an image of the feature of interest at each view.
Owner:VISIONGATE
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
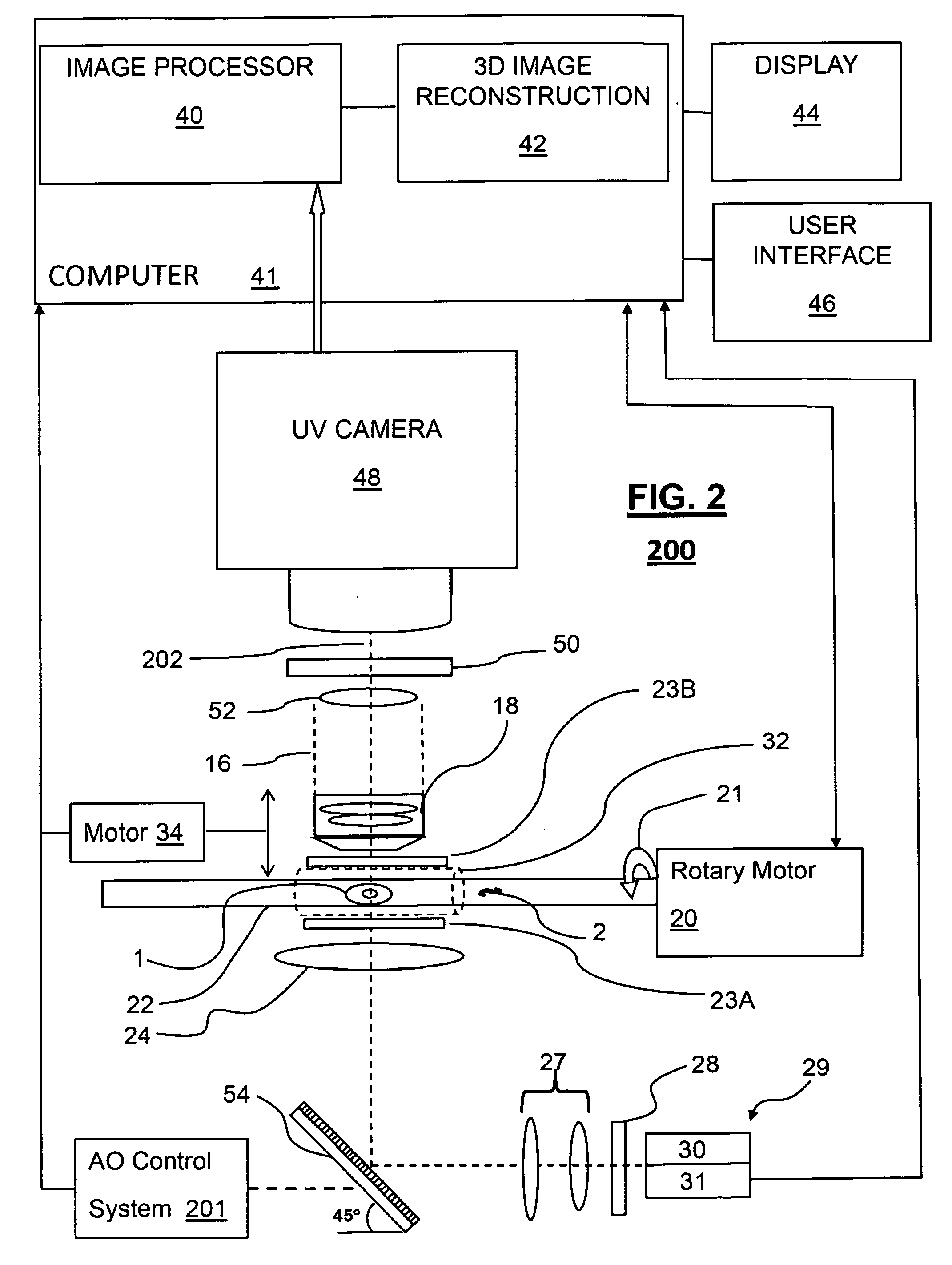
3D imaging of live cells with ultraviolet radiation
InactiveUS20090208072A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical tomographyFluence
A method for 3D imaging of cells in an optical tomography system includes moving a biological object relatively to a microscope objective to present varying angles of view. The biological object is illuminated with radiation having a spectral bandwidth limited to wavelengths between 150 nm and 390 nm. Radiation transmitted through the biological object and the microscope objective is sensed with a camera from a plurality of differing view angles. A plurality of pseudoprojections of the biological object from the sensed radiation is formed and the plurality of pseudoprojections is reconstructed to form a 3D image of the cell.
Owner:VISIONGATE
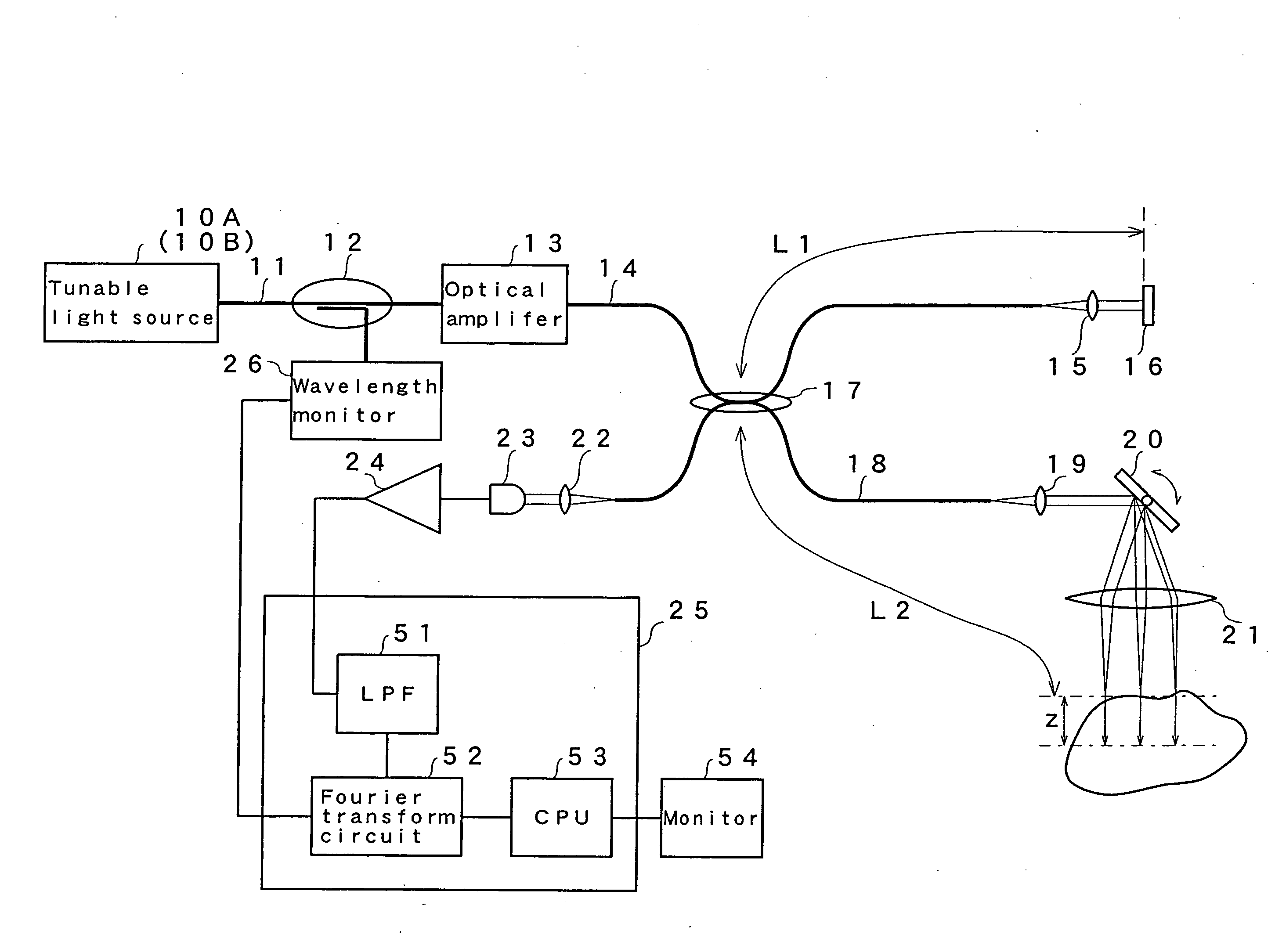
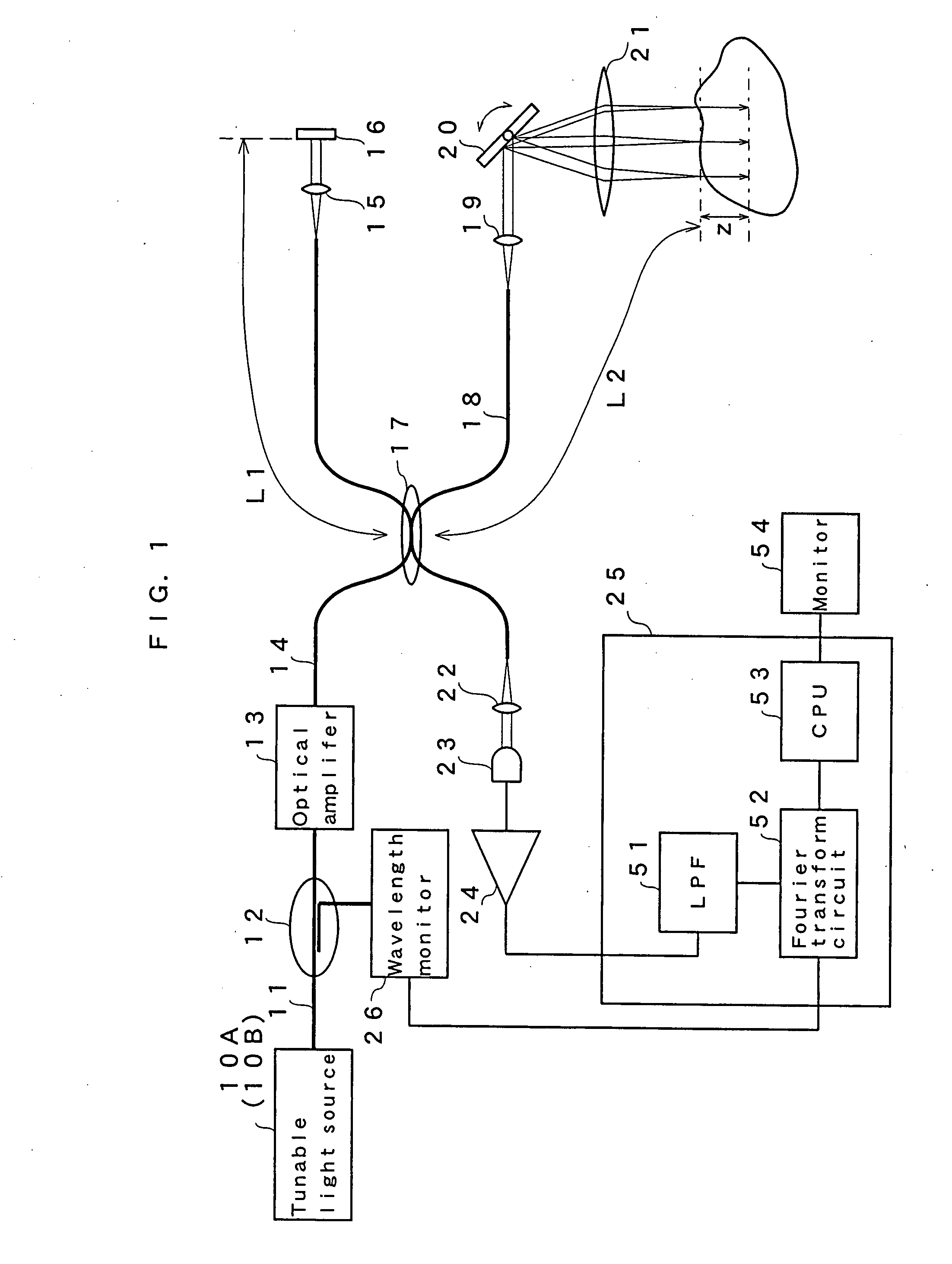
Optical tomography method and optical tomography system
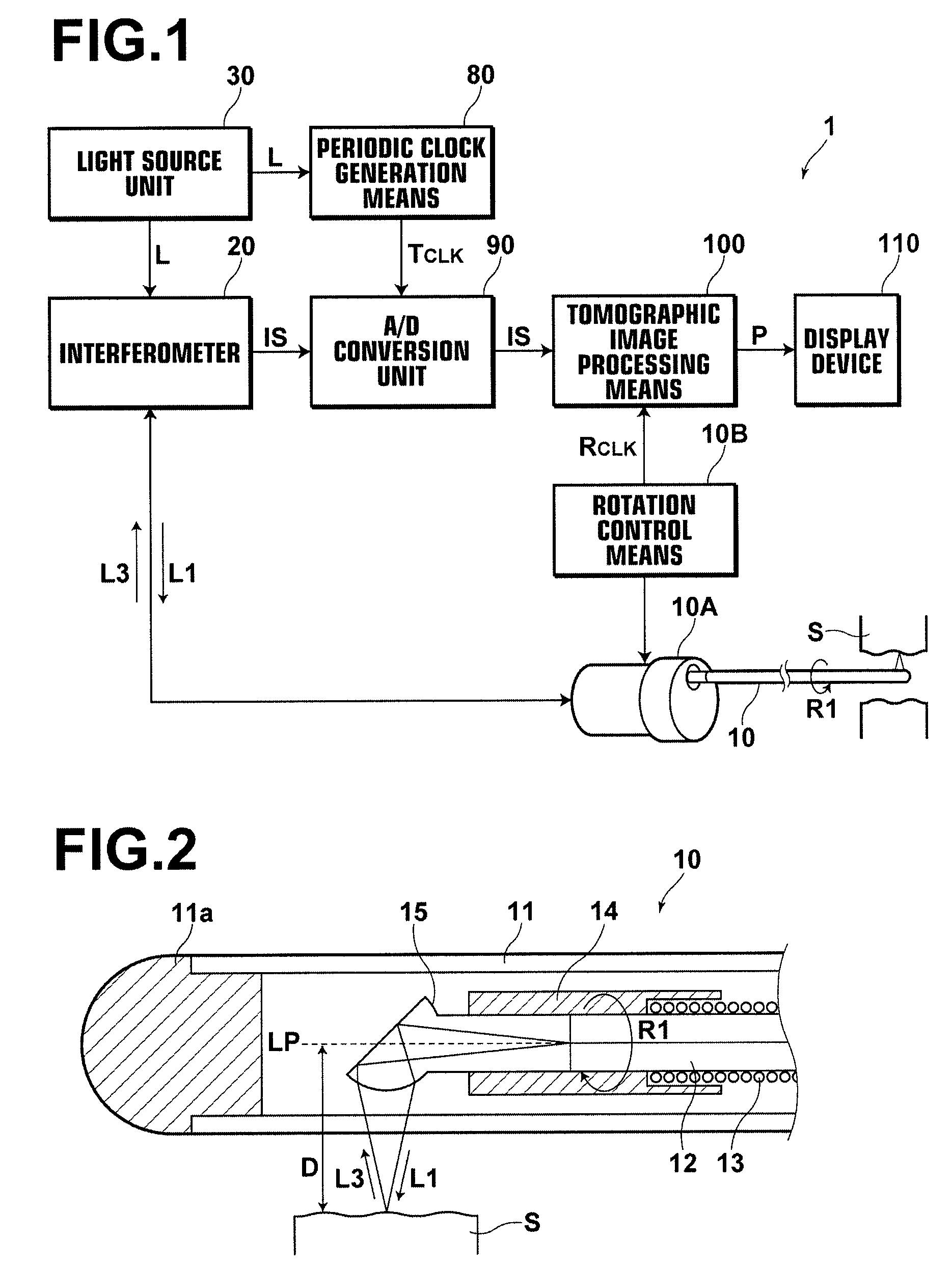
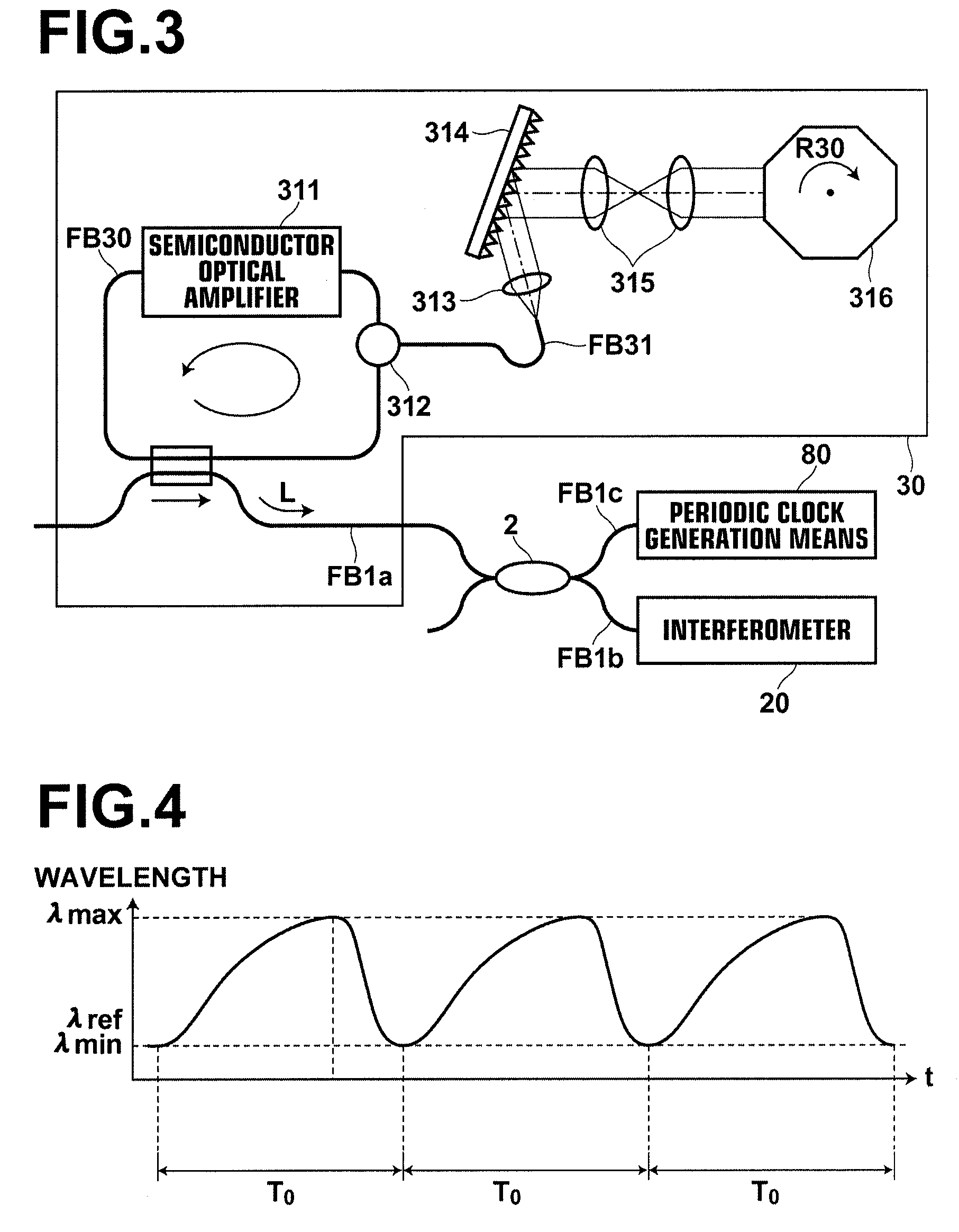
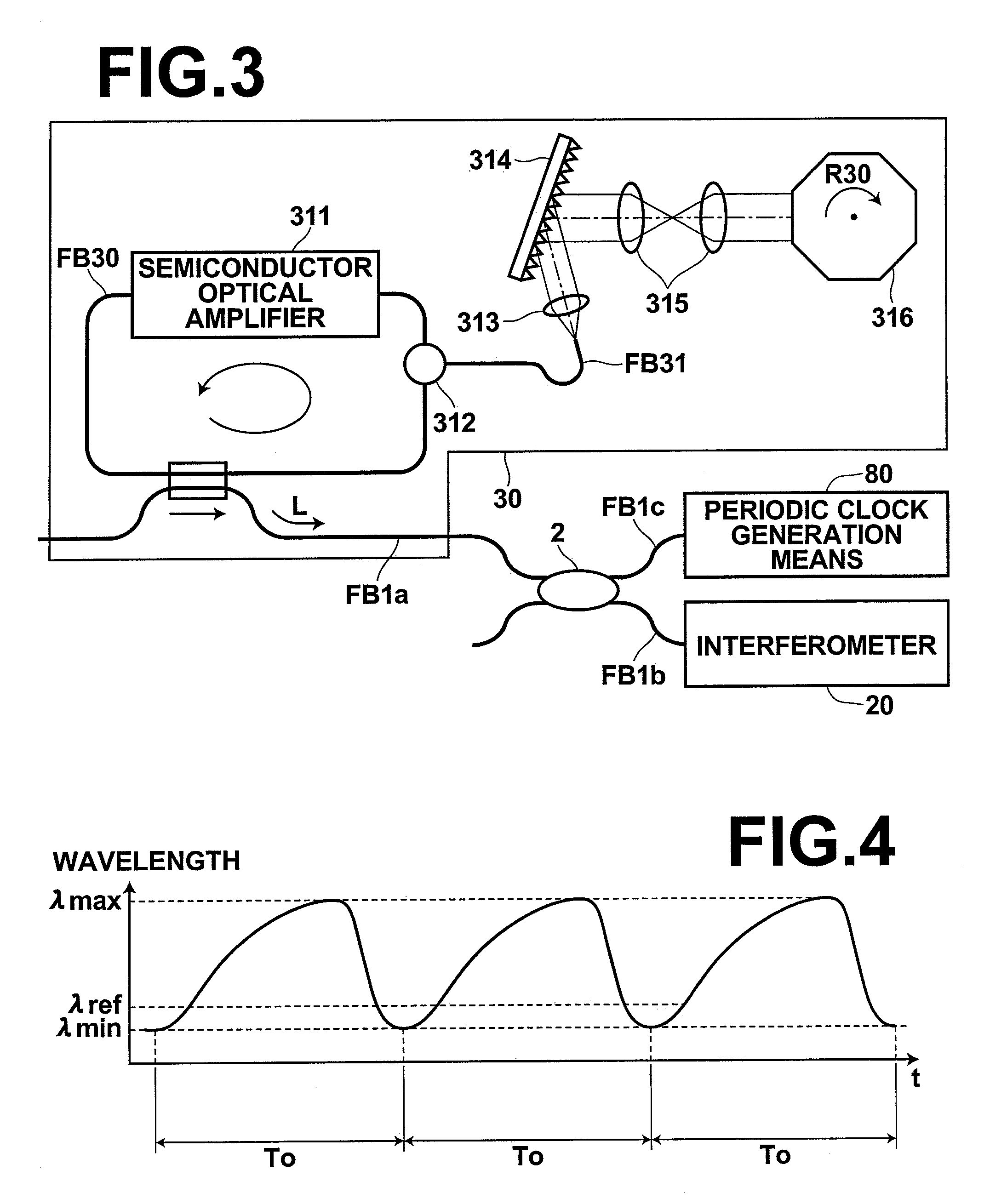
ActiveUS7542145B2Accurate imagingAccurate tomographic image can be stably obtainRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical tomographyTomographic image
Light emitted from a light source is divided into measuring light and reference light. The reflected light from the object and the reference light are superposed. Interference light of the reflected light and reference light which have been superposed is detected. Intensities of the reflected light in a plurality of positions in the direction of depth of the object are detected on the basis of the frequency and the intensity, and a tomographic image of the object is obtained on the basis of the intensity of the reflected light in each position in the direction of depth. A compensating signal is obtained by removing the spectral components of the measuring light from an interference signal obtained by detection of the interference light, and the compensating signal is provided for detection of the intensities of the reflected light after a Gaussian transform.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of wounds using spatially structured illumination
InactiveUS20100210931A1High sensitivityReduce sensitivityDiagnostics using lightSensorsDiseaseQualitative property
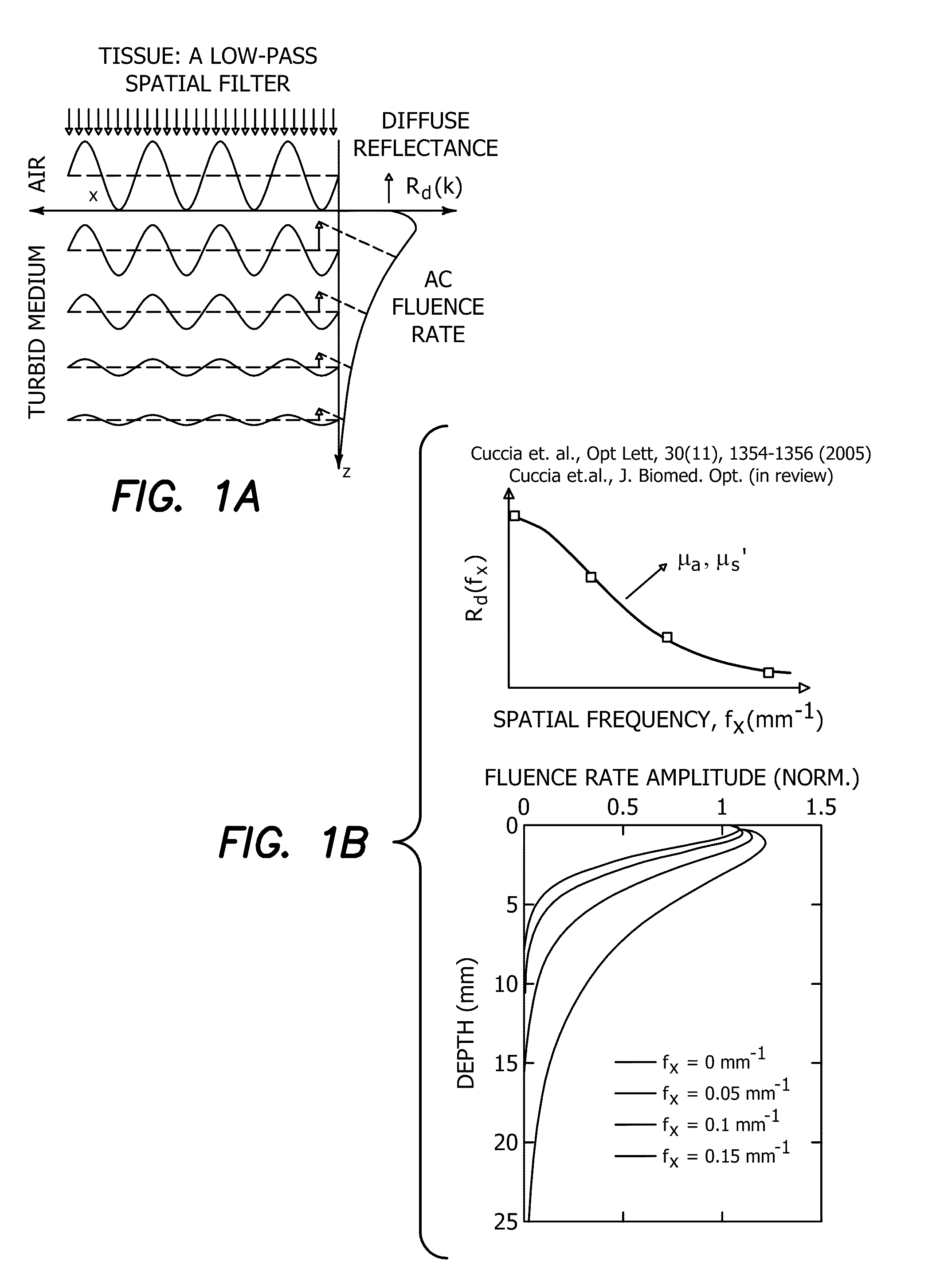
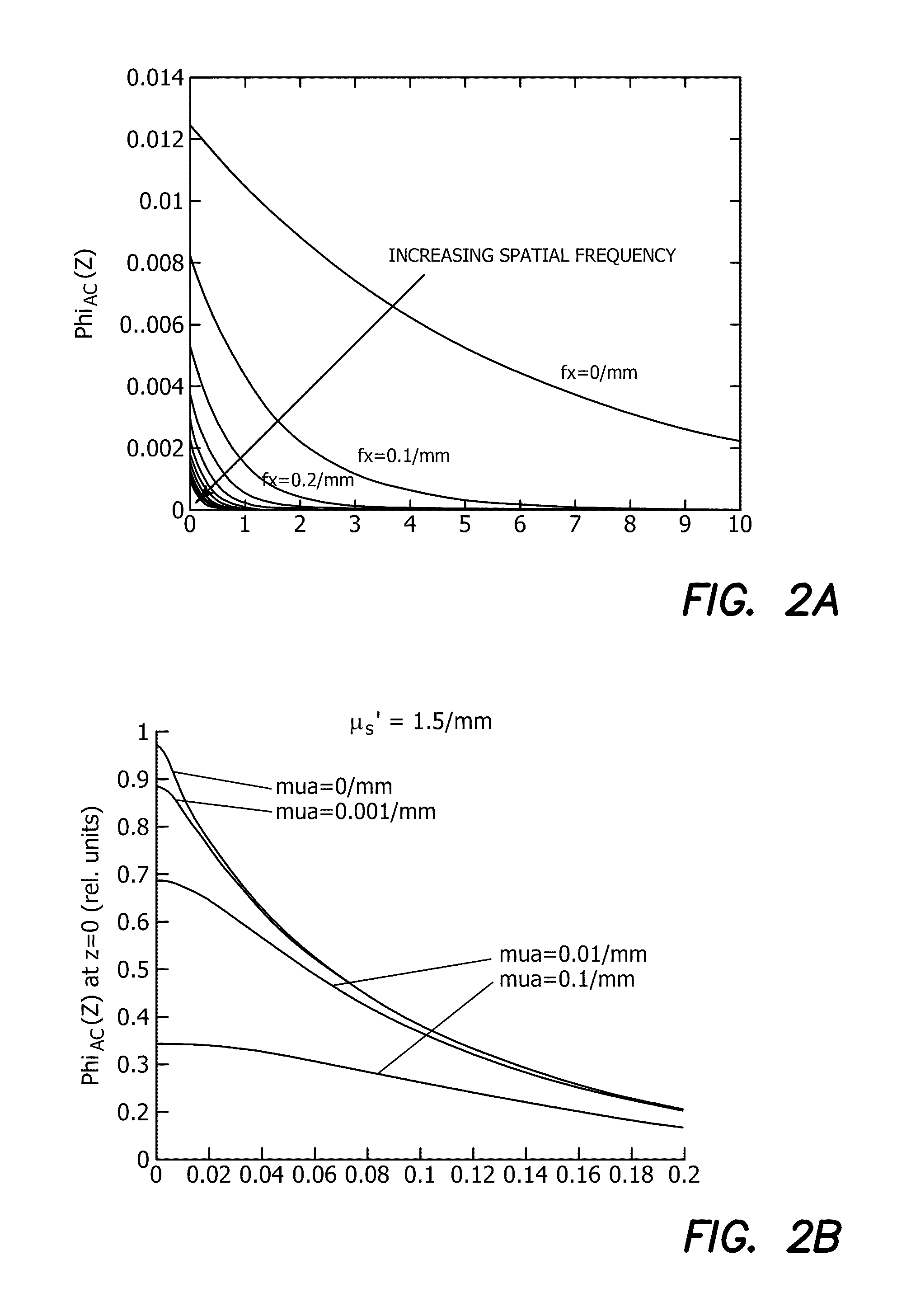
A method of noncontact imaging for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of wounds includes the step of performing structured illumination of surface and subsurface tissue by both diffuse optical tomography and rapid, wide-field quantitative mapping of tissue optical properties within a single measurement platform. Structured illumination of a skin flap is performed to monitor a burn wound, a diabetic ulcer, a decubitis ulcer, a peripheral vascular disease, a skin graft, and / or tissue response to photomodulation. Quantitative imaging of optical properties is performed of superficial (0-5 mm depth) tissues in vivo. The step of quantitative imaging of optical properties of superficial (0-5 mm depth) tissues in vivo comprises pixel-by-pixel demodulating and diffusion-model fitting or model-based analysis of spatial frequency data to extract the local absorption and reduced scattering optical coefficients.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
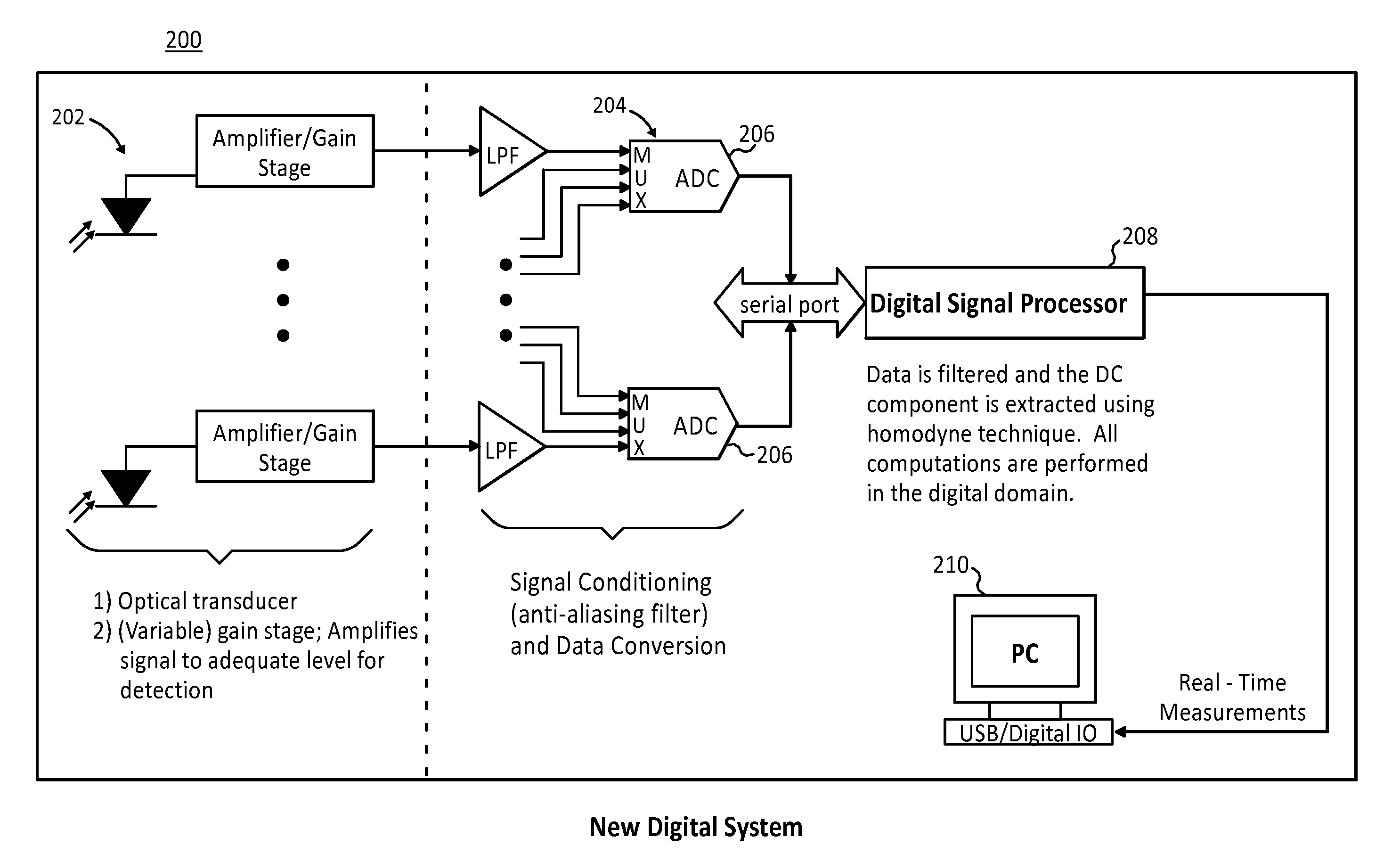
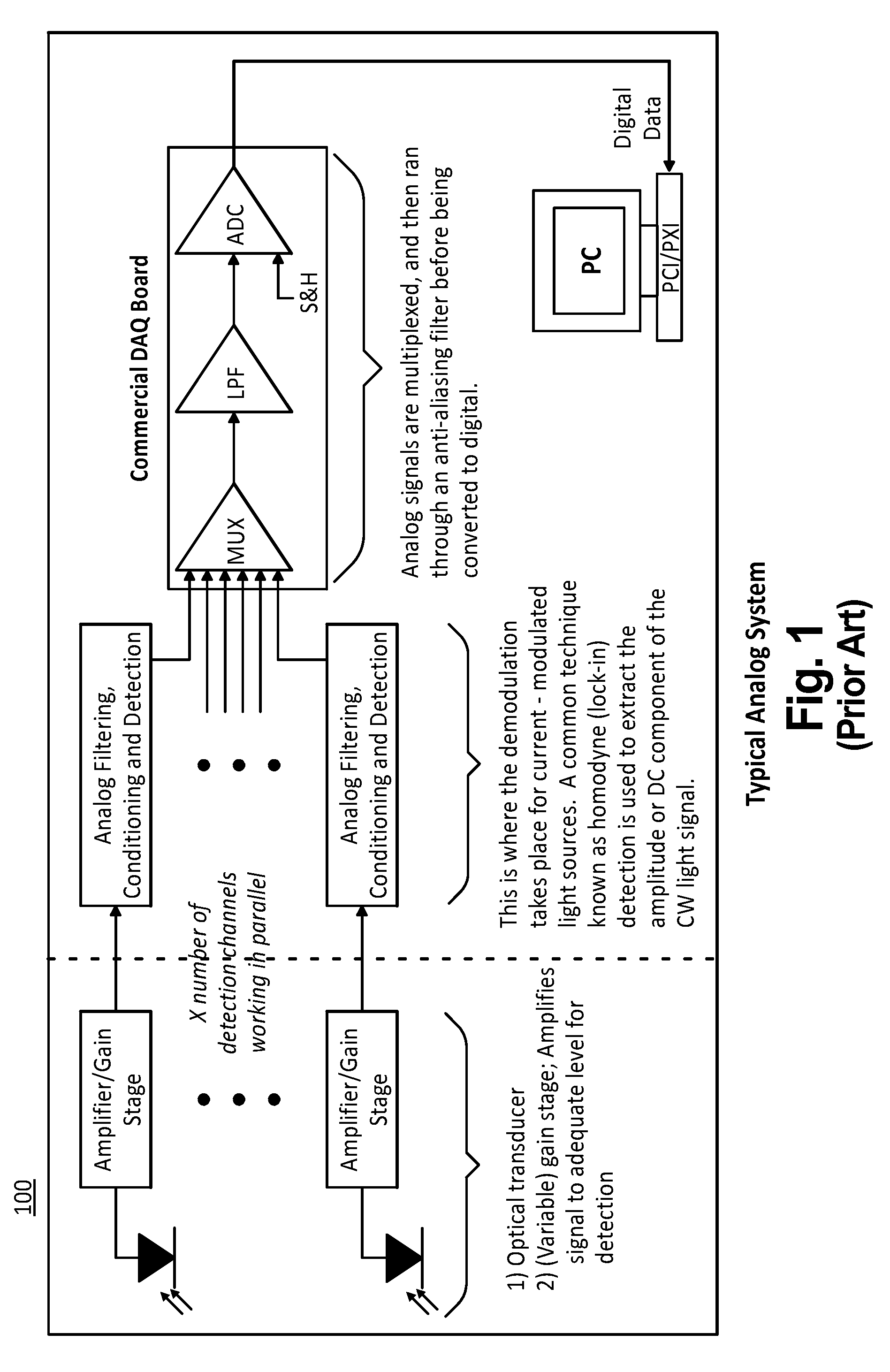
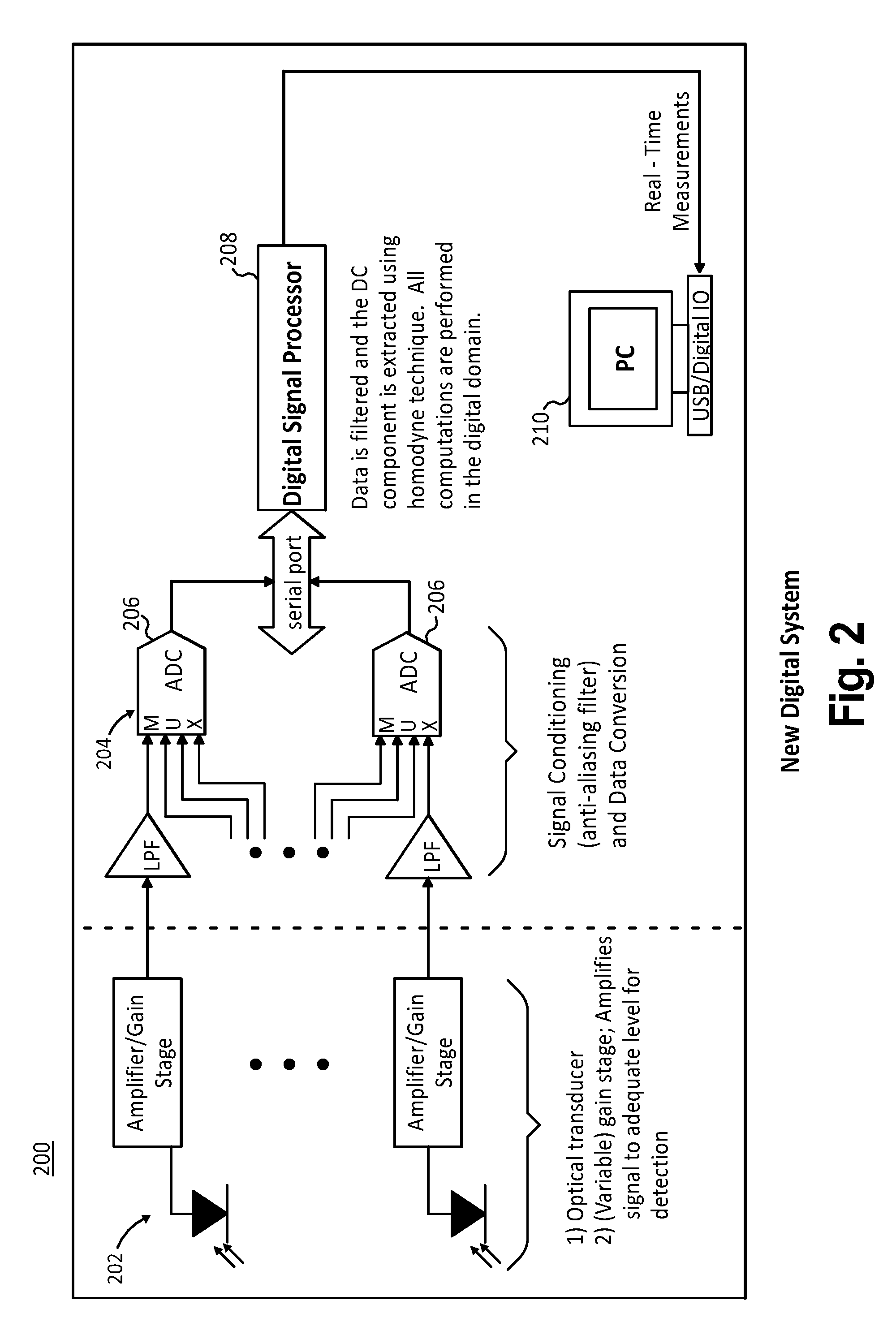
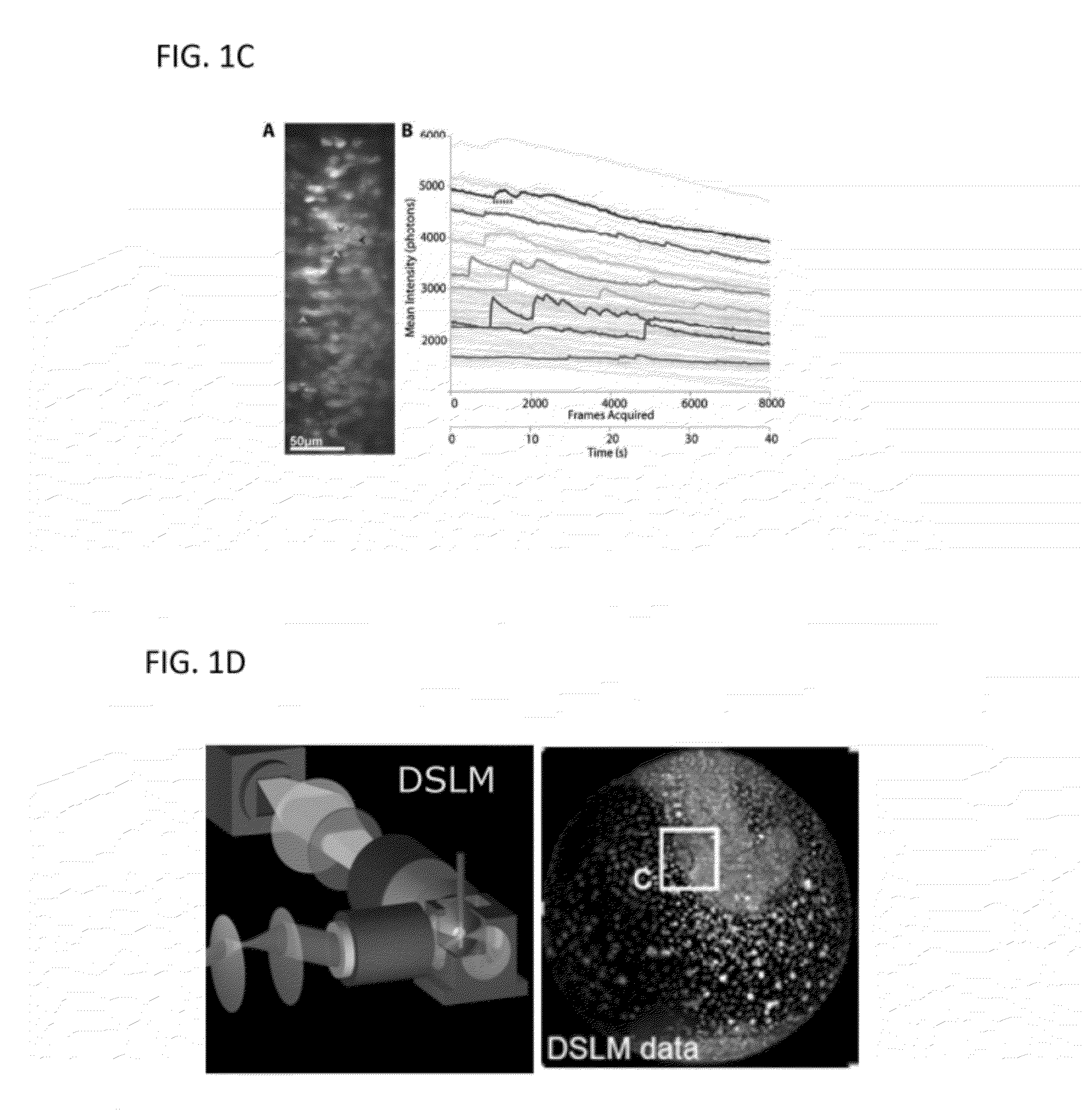
Digital signal processor-based detection system, method, and apparatus for optical tomography
ActiveUS7463362B2Easy accessScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansDigital signal processingAverage filter
The present invention provides systems, methods and apparatuses that perform digital detection for use in optical tomography. Methods and systems are provided in which digital lock-in detection is performed using an algorithm that employs a phase-independent quadrature technique. Methods and systems are provided in which a unique manipulation of an ordinary averaging filter optimized for sources discrimination and the consequent sampling constraints is presented as a novel filtering scheme for the lock-in detection. Systems and apparatuses are provided which include a digital signal processor which performs digital lock-in detection and an integrated complex programmable logic device for timing control. Apparatuses are provided which include an instrument having an integrated digital signal processor for performing digital processing and detection for use in optical tomography.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
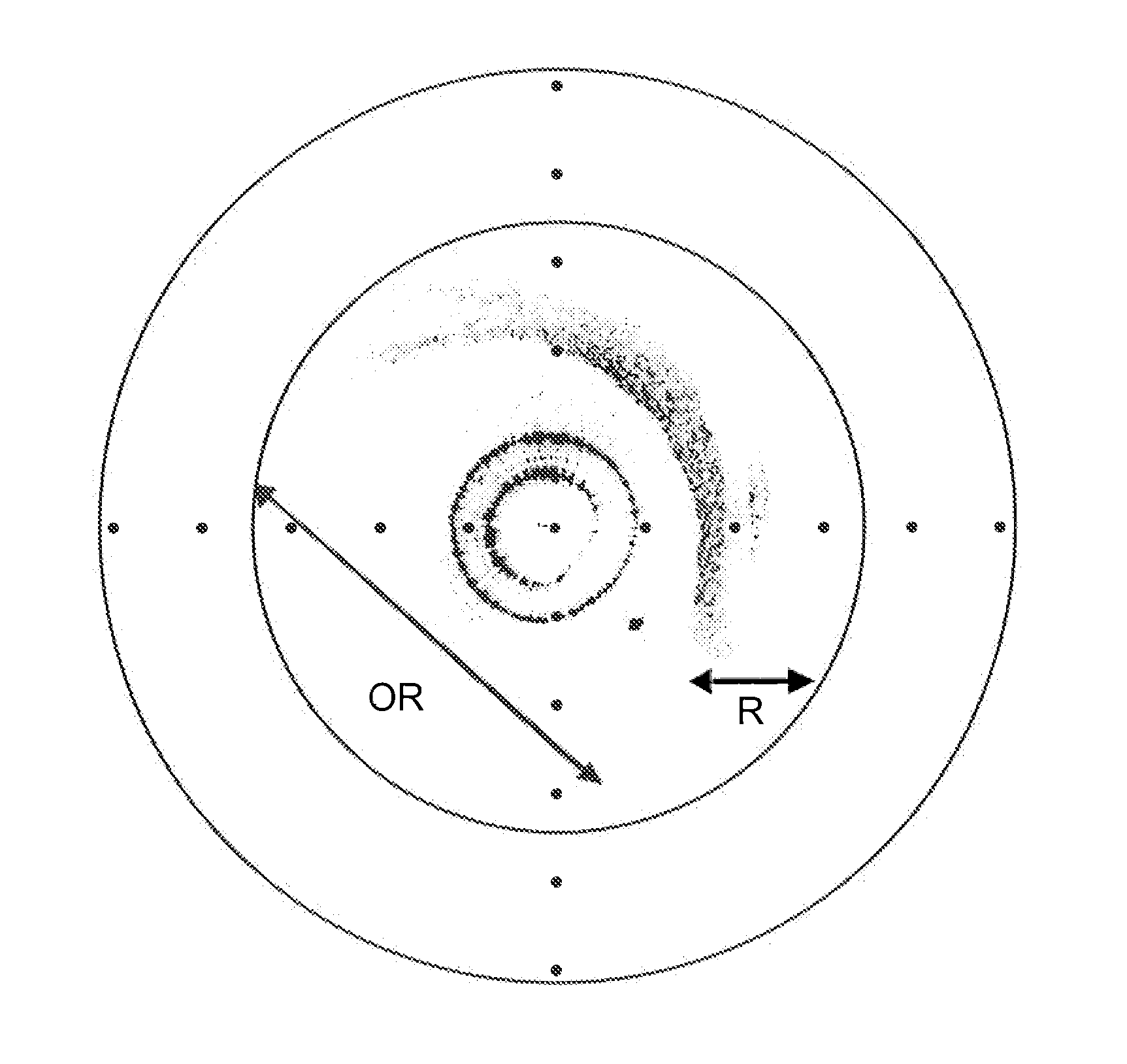
Optical tomography of small objects using parallel ray illumination and post-specimen optical magnification
A shadowgram optical tomography system for imaging an object of interest. The shadowgram optical tomography system includes a parallel ray light source for illuminating the object of interest with a plurality of parallel radiation beams, an object containing tube, where the object of interest is held within the object containing tube such that it is illuminated by the plurality of parallel radiation beams to produce emerging radiation from the object containing tube, a detector array located to receive the emerging radiation, and a system and mehtod for tracking an image of the object of interest.
Owner:VISIONGATE
Optical tomography of small objects using parallel ray illumination and post-specimen optical magnification
InactiveUS6944322B2Easy to controlUniform intensity distributionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOptical tomographyMagnifying glass
A parallel-beam optical tomography system for imaging an object of interest includes a parallel ray beam radiation source that illuminates the object of interest with a plurality of parallel radiation beams. After passing through the object of interest the pattern of transmitted or emitted radiation intensities is magnified by a post specimen optical element or elements. An object containing tube is located within an outer tube, wherein the object of interest is held within or flows through the object containing tube. A motor may be coupled to rotate and / or translate the object containing tube to present differing views of the object of interest. One or more detector arrays are located to receive the emerging radiation from the post specimen magnifying optic. Two- or three-dimensional images may be reconstructed from the magnified parallel projection data.
Owner:VISIONGATE
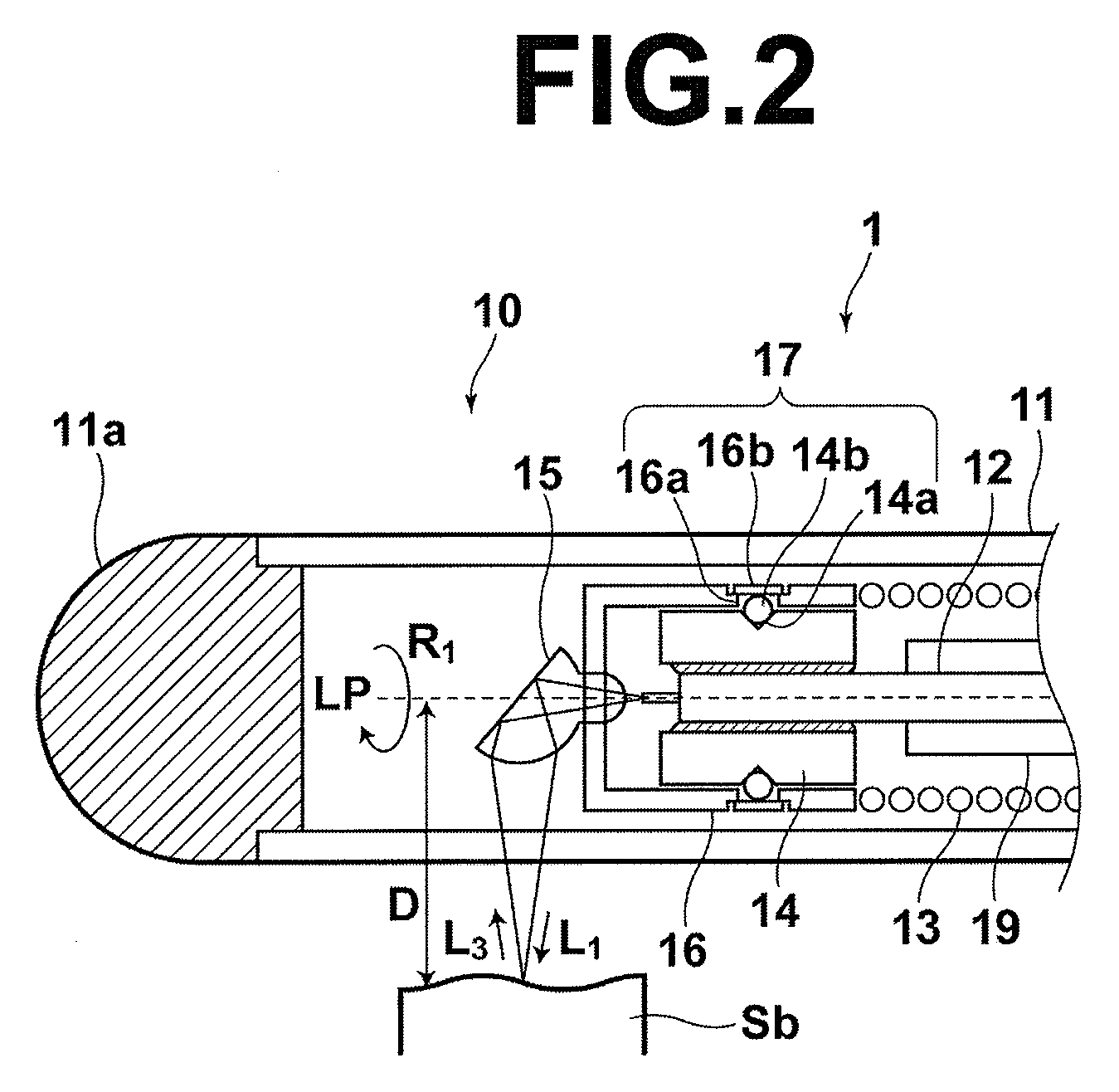
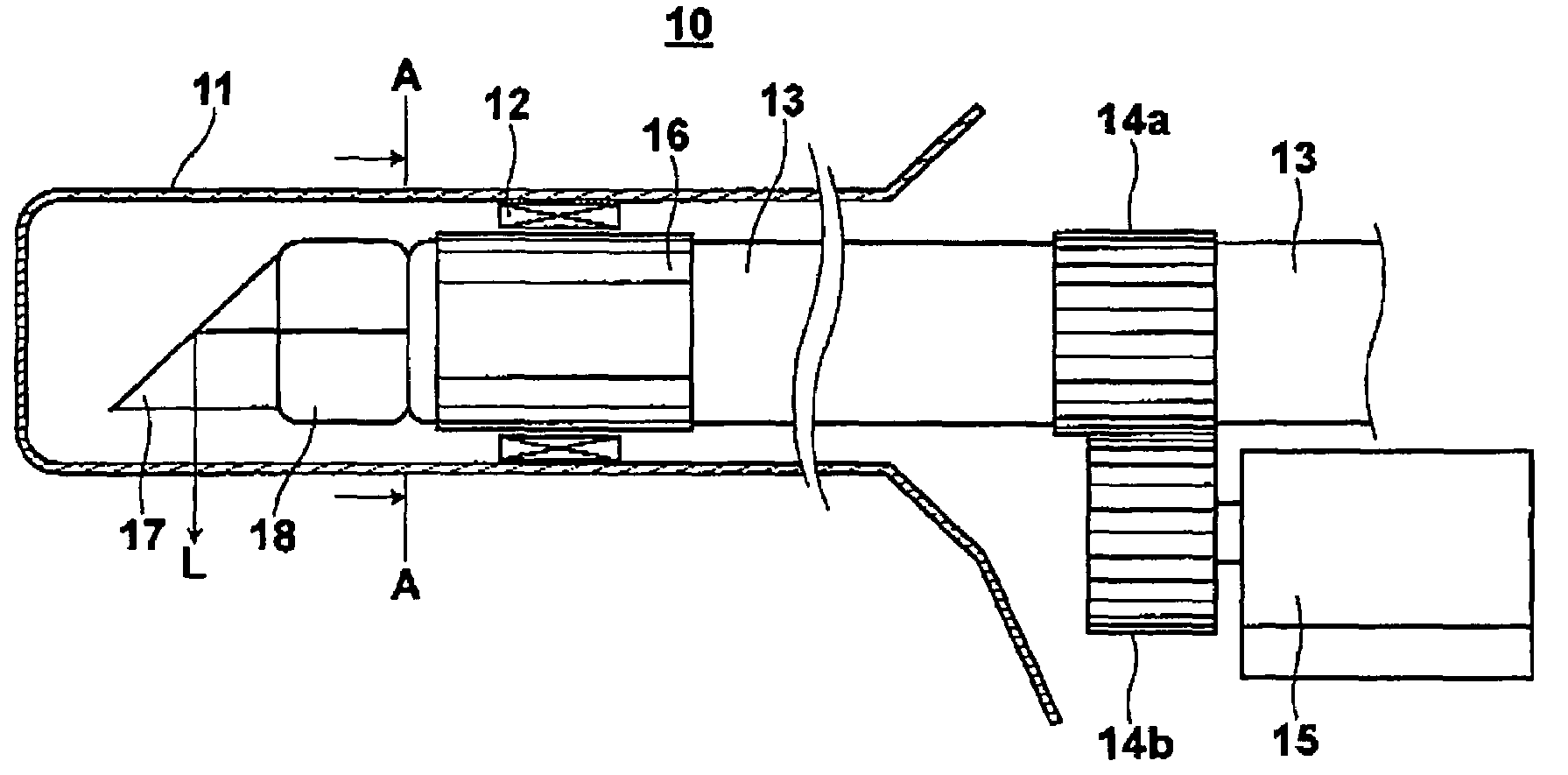
Optical probe and optical tomography system
InactiveUS7539362B2Easy to thinLow costDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resistanceOptical tomography
An optical probe includes a tubular outer envelope and a optical fiber which extends in the longitudinal direction of the outer envelope inside the outer envelope. By fixing a light deflecting element to the optical fiber and rotating the optical fiber by a driver, the light deflecting element is rotated. A protective member which has a higher resistance to wear than the outer peripheral surface of the optical fiber is fixed to a part of the outer peripheral surface of the optical fiber in a position near the front end of the optical fiber and is borne for rotation by a bearing portion on the probe outer envelope.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
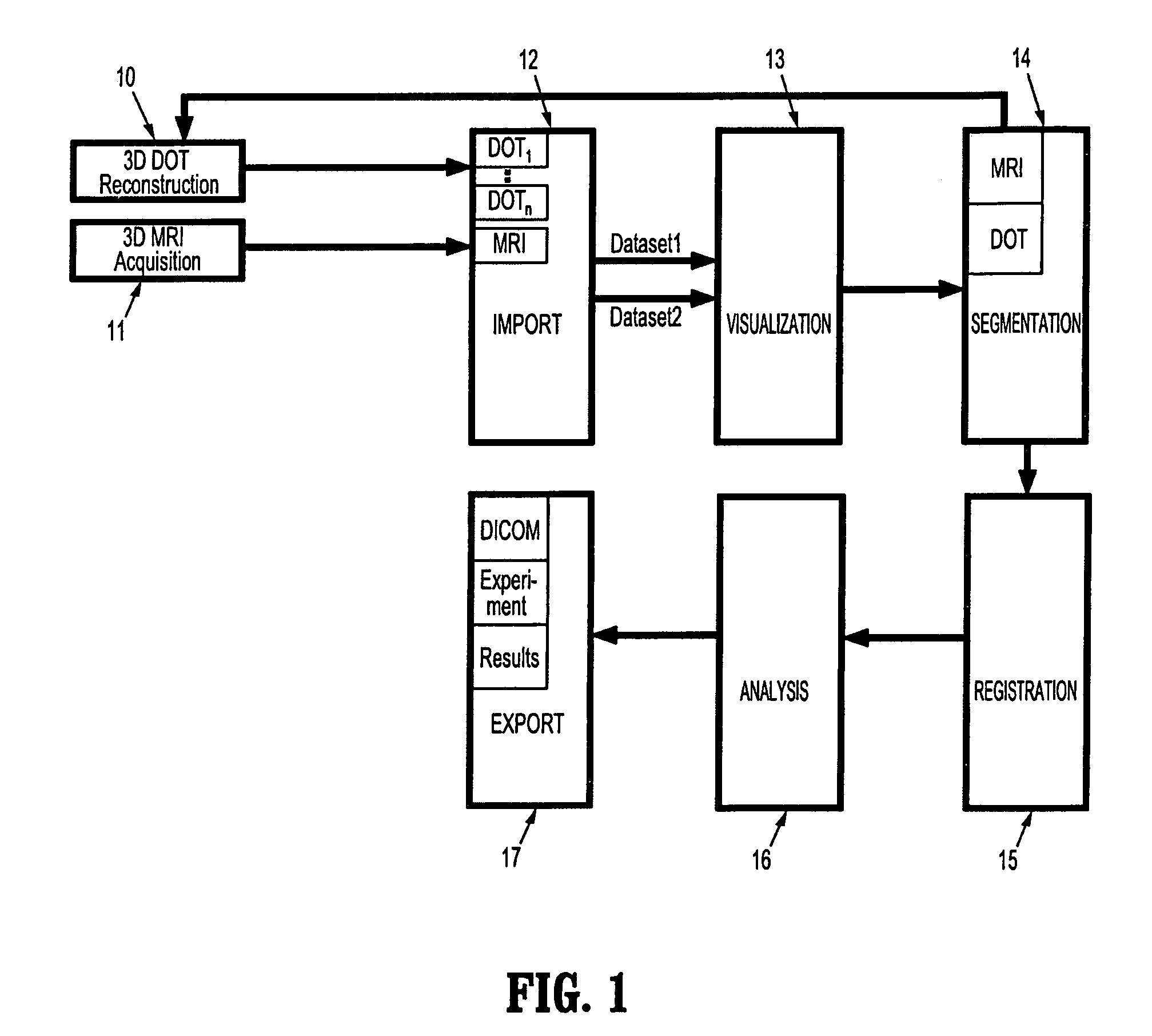
System and method for coregistration and analysis of non-concurrent diffuse optical and magnetic resonance breast images
InactiveUS20080292164A1Facilitate tissue analysisData augmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPhysiological valuesVoxel
A method for joint analysis of non-concurrent magnetic resonance (MR) and diffuse optical tomography (DOT) images of the breast includes providing a digitized MR breast image volume comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a 3-dimensional (3D) grid of voxels, providing a digitized DOT breast dataset comprising a plurality of physiological values corresponding to a finite set of points, segmenting the breast MR image volume to separate tumorous tissue from non-tumorous tissue, registering a DOT breast dataset and the MR image volume and fusing said registered DOT and MR datasets, wherein said fused dataset is adapted for analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
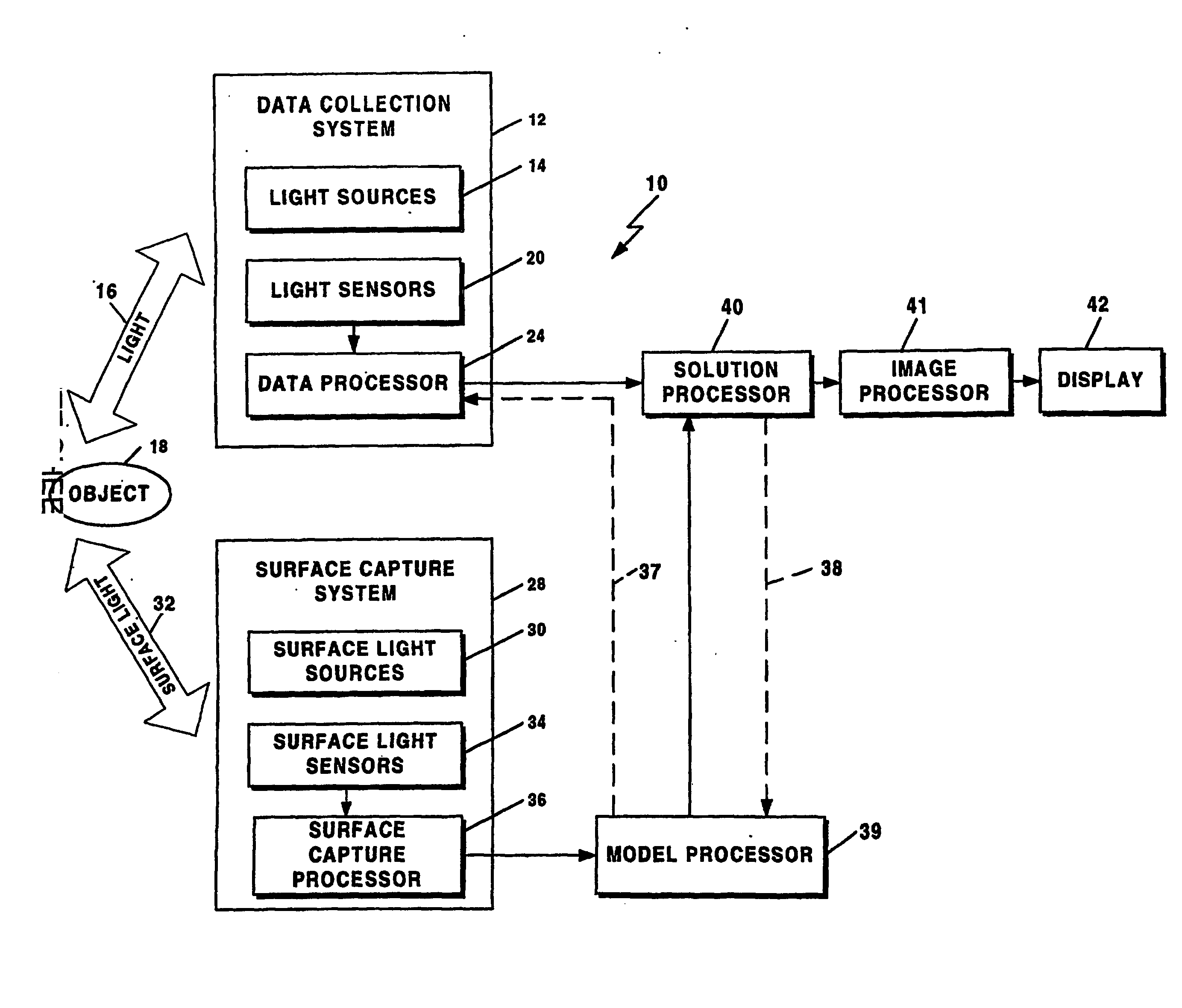
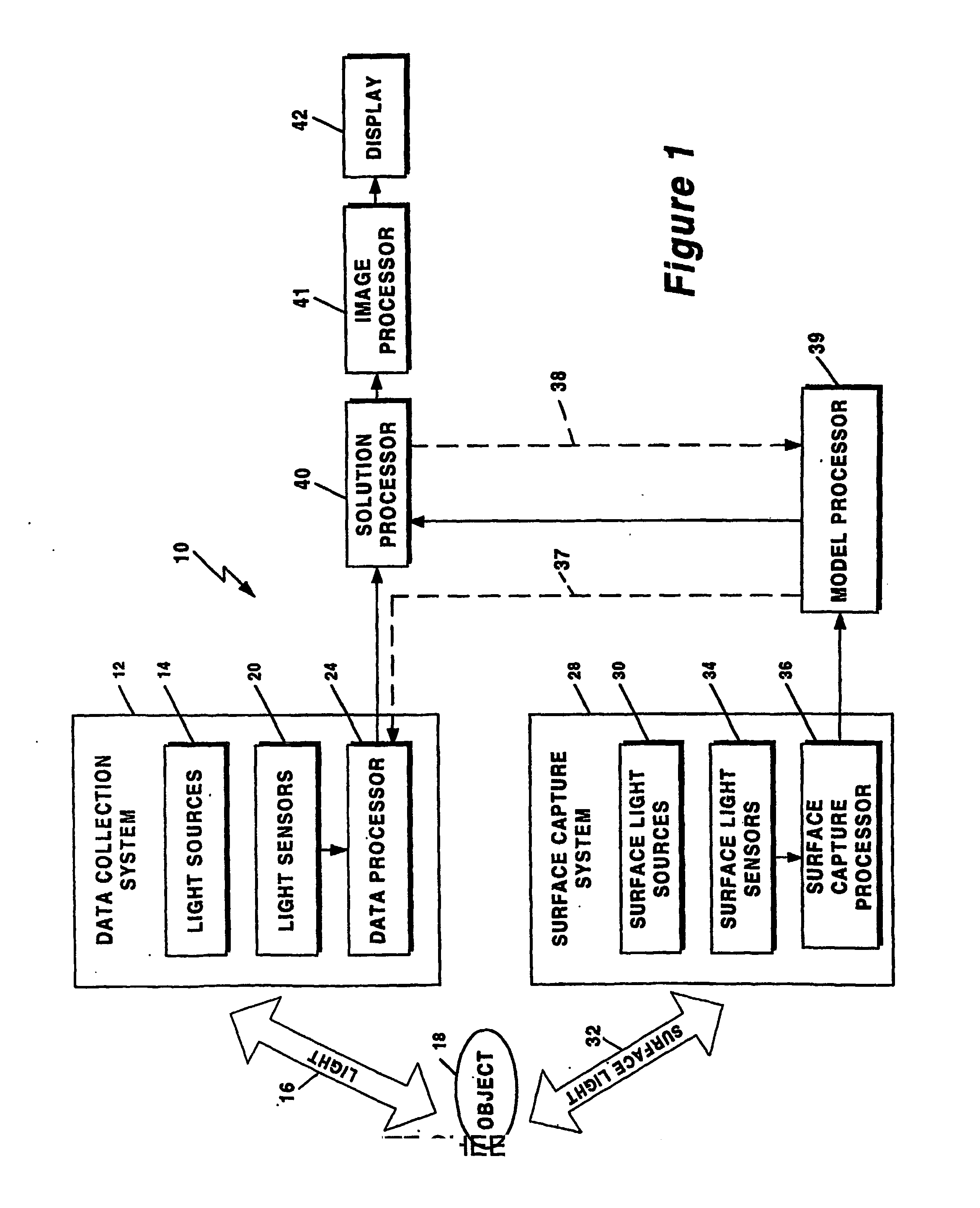
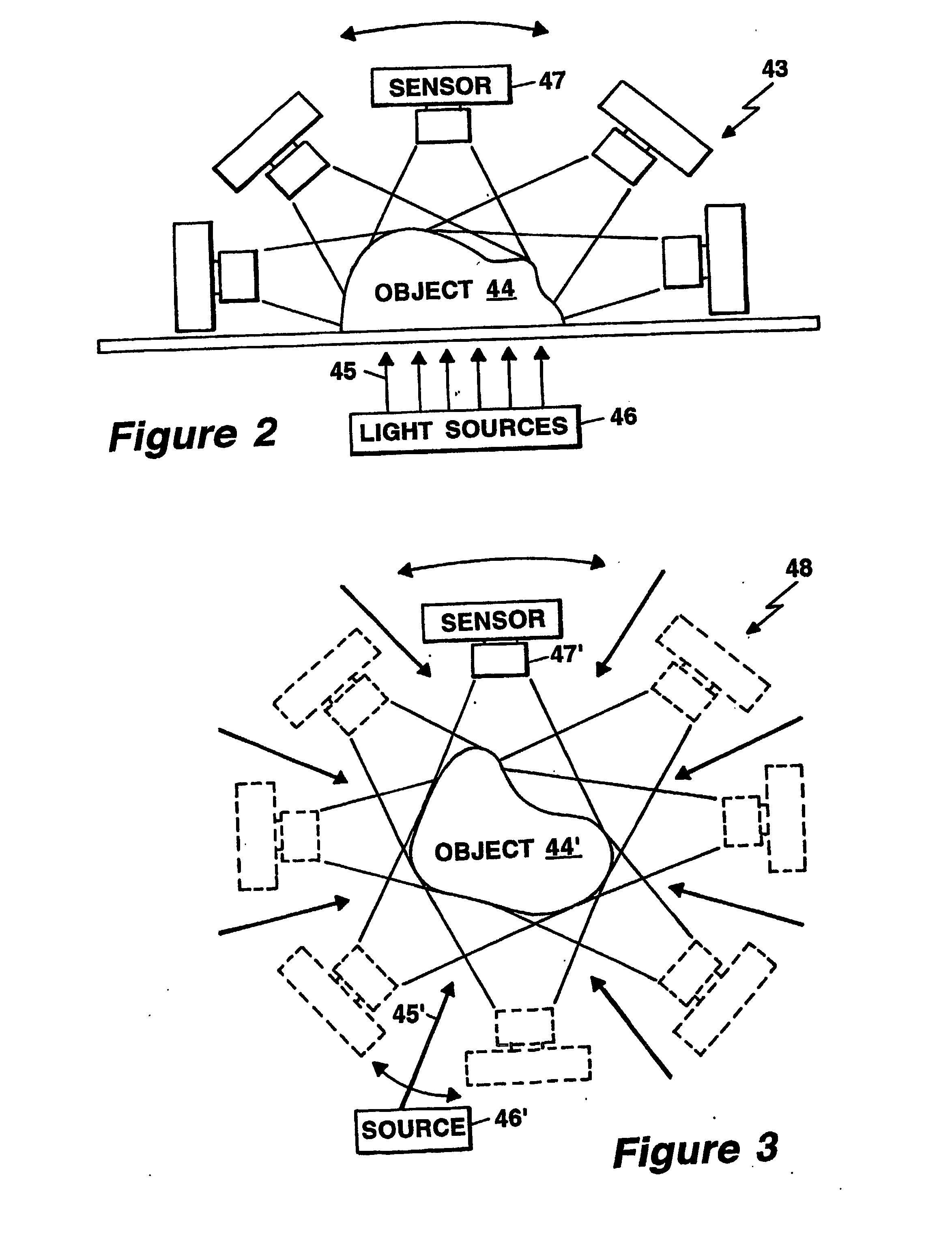
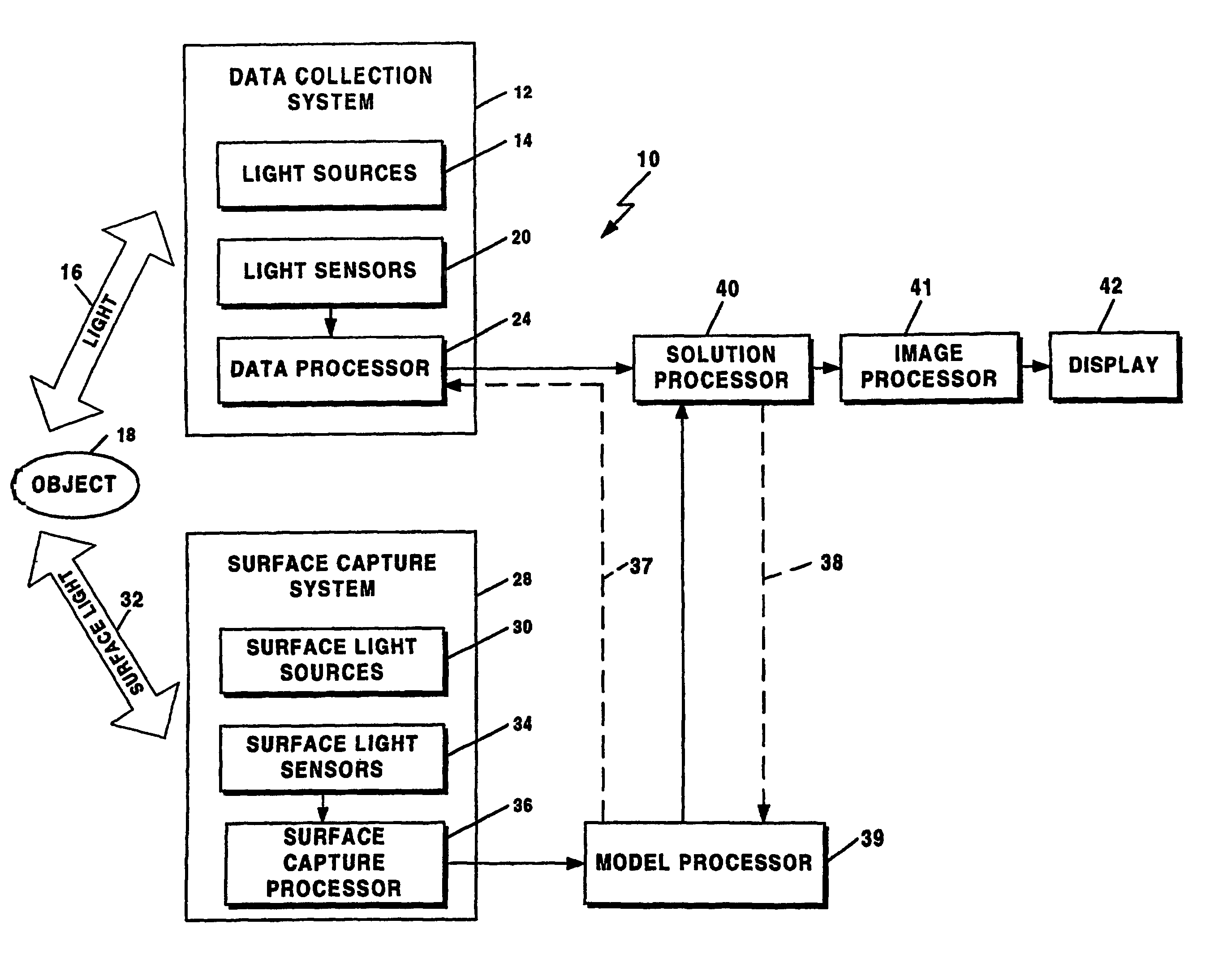
Method and system for free space optical tomography of diffuse media
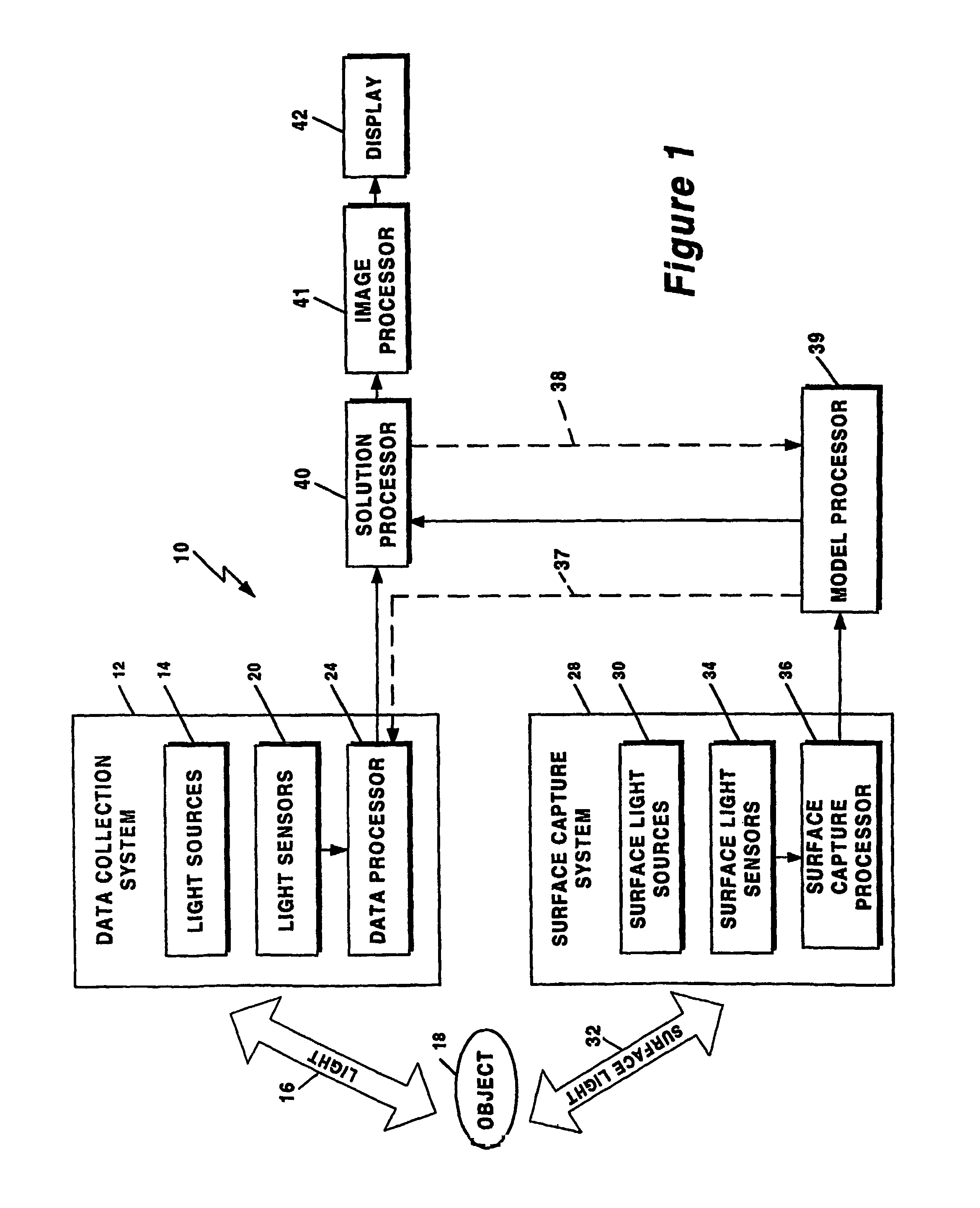
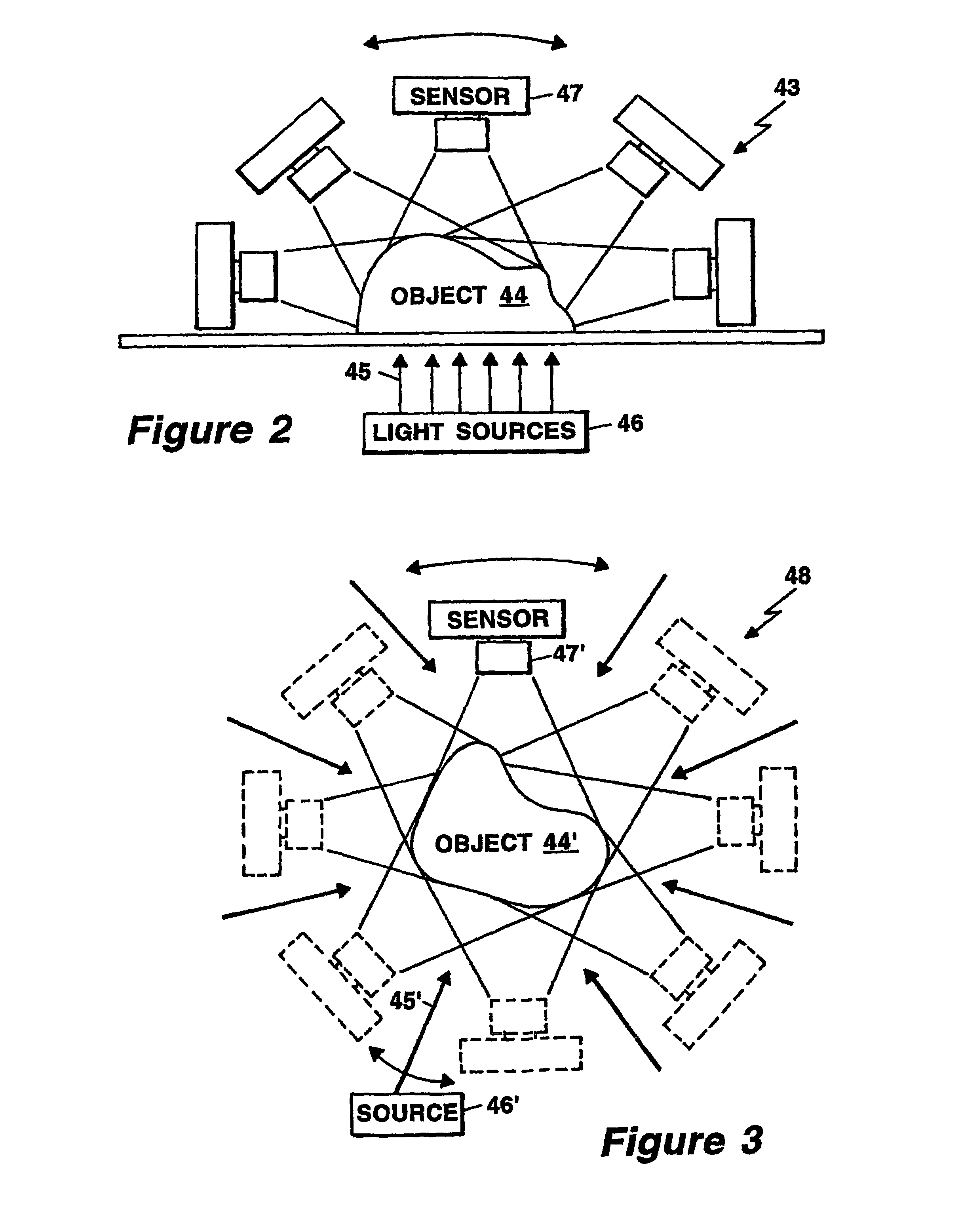
A method and a system for free space optical tomography provides one or more light source and one or more light sensors spaced, which in one embodiment are spaced apart from and object to be imaged. A surface capture system coupled to a variety of optical models provides the method and system with the ability to render accurate tomographic images though the light has propagated both through a diffuse medium and, in on embodiment, also through free space to the one or more light sensors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and system for producing tomographic image by optical tomography with processing of interference light signals
ActiveUS7944568B2High motion-image response characteristicLow cost processingInterferometersUsing optical meansOptical tomographyLength wave
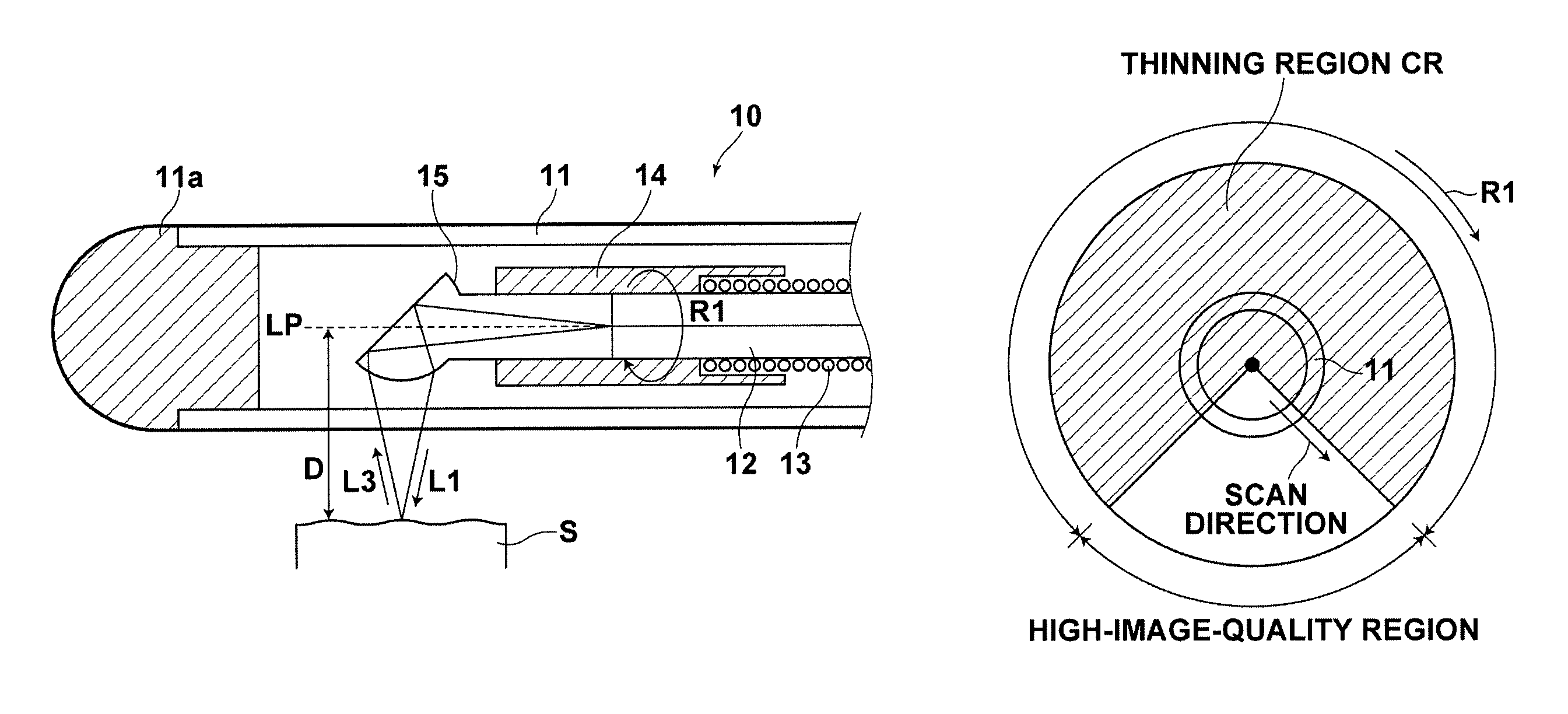
When reflection light, reflected from a measurement target that has been irradiated with measurement light in such a manner to scan the measurement target, and reference light are combined in each wavelength sweep, interference light is detected as interference signals. When a thinning region in which the interference signals obtained by detecting the interference light in each wavelength sweep are thinned so that the interference signals that are used to produce the tomographic image remain is set, thinning is performed on the plurality of interference signals in the thinning region. Light intensity information about the measurement target in the thinning region is obtained, based on the interference signals for the respective wavelength sweeps, the interference signals remaining after thinning. The tomographic image in the thinning region is produced based on the obtained light intensity information.
Owner:KK TOPCON
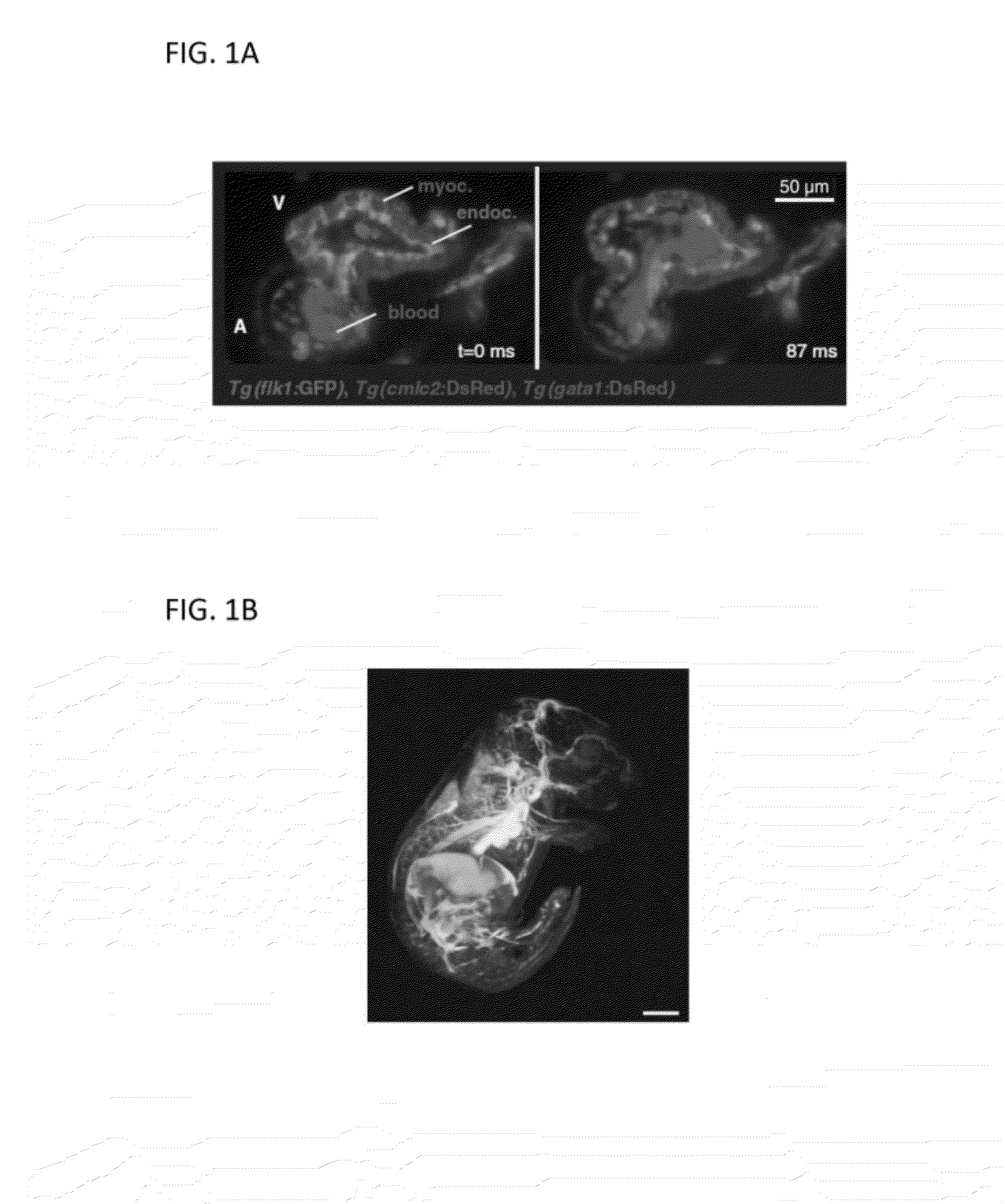
Simultaneous orthogonal light sheet microscopy and computed optical tomography
An apparatus for and method of performing orthogonal light sheet microscopy (OLM) and computer optical tomography (COT) simultaneously in a single device are provided. The dual-mode imaging microscope allows for the use of both OLM and COT in a single instrument. This dual-mode device will allow researchers to have access to both types of microscopy, allowing access to the widest possible selection of samples, and improved imaging results. In addition, the device will reduce the high costs and space requirements associated with owning two different imagers (OLM and COT).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
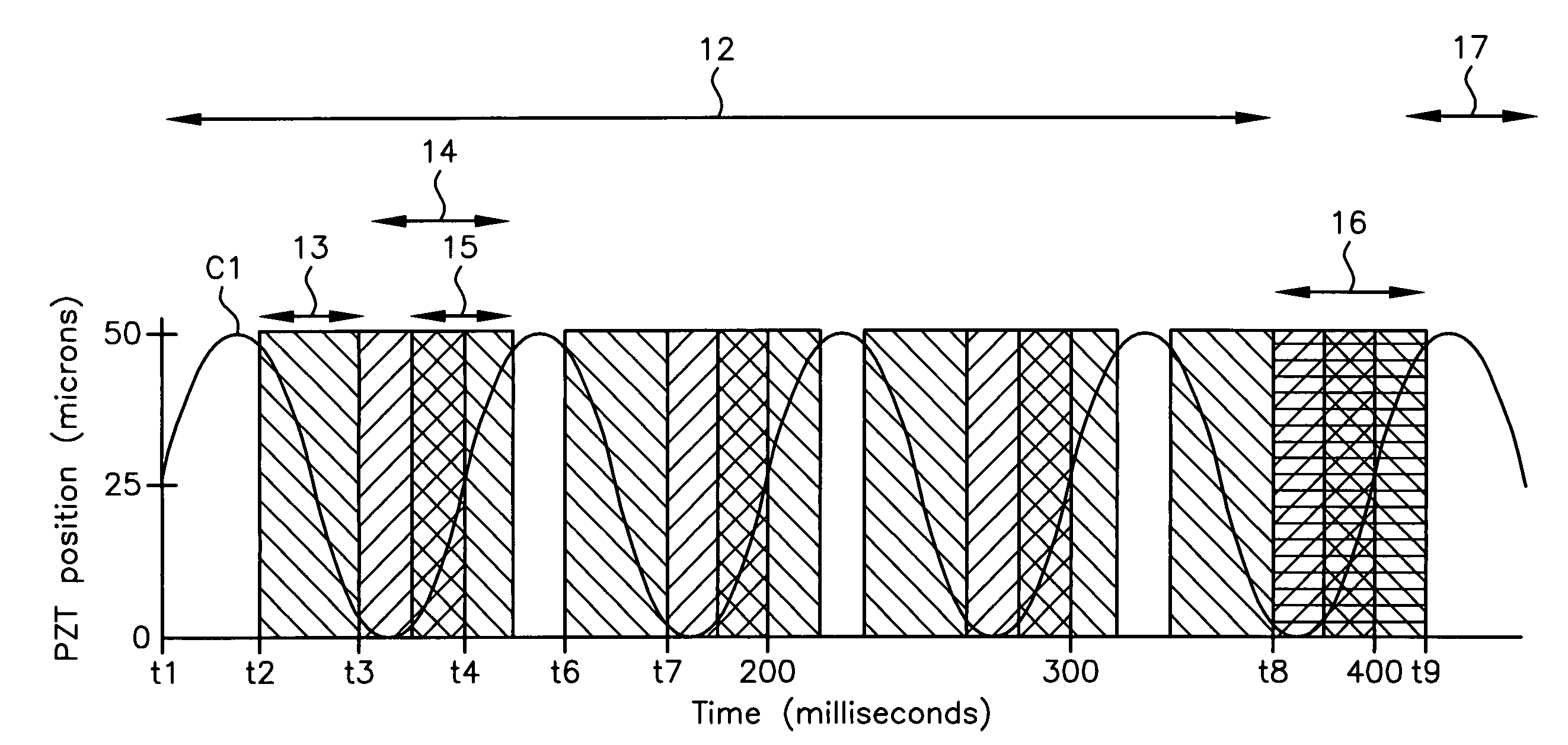
Method and Apparatus for Improving Image Clarity and Sensitivity in Optical Tomography Using Dynamic Feedback to Control Focal Properties and Coherence Gating
InactiveUS20110201924A1Accurately determineMoved much faster and more accuratelyInterferometersScattering properties measurementsOptical tomographyFeedback control
Methods for optical imaging, particularly with optical coherence tomography, using a low coherence light beam reflected from a sample surface and compared to a reference light beam, wherein real time dynamic optical feedback is used to detect the surface position of a tissue sample with respect to a reference point and the necessary delay scan range. The delay is provided by a tilting / rotating mirror actuated by a voltage adjustable galvanometer. An imaging probe apparatus for implementing the method is provided. The probe initially scans along one line until it finds the tissue surface, identifiable as a sharp transition from no signal to a stronger signal. The next time the probe scans the next line it adjusts the waveform depending on the previous scan. An algorithm is disclosed for determining the optimal scan range.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
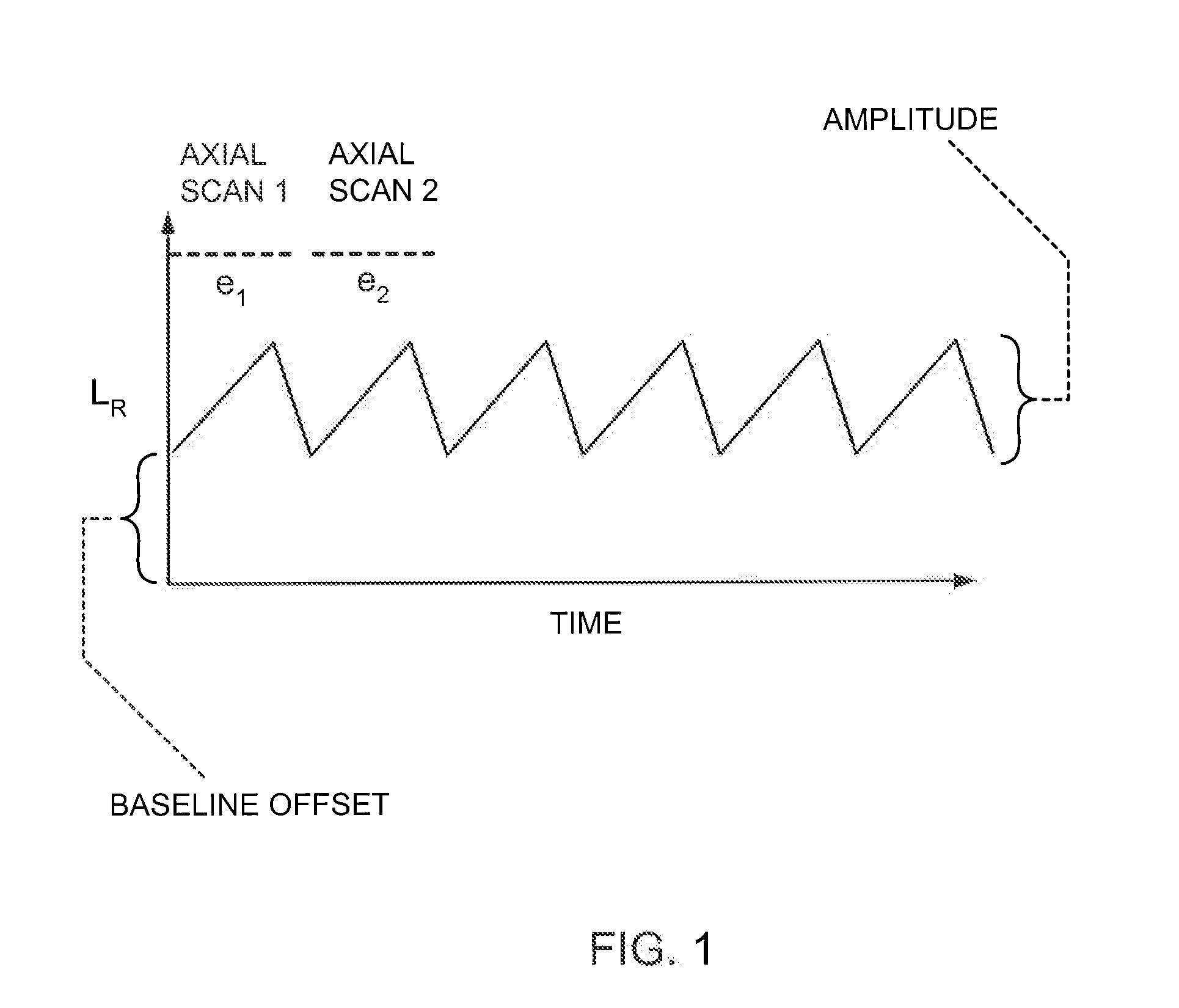
Focal Plane Tracking for Optical Microtomography
ActiveUS20100322494A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical tomographyDetector array
An optical tomography system for imaging an object of interest including a light source for illuminating the object of interest with a plurality of radiation beams. The object of interest is held within an object containing tube such that it is illuminated by the plurality of radiation beams to produce emerging radiation from the object containing tube, a detector array is located to receive the emerging radiation and produce imaging data used by a mechanism for tracking the object of interest.
Owner:VISIONGATE +1
System for producing tomographic image by optical tomography
ActiveUS20090174886A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioInterferometersUsing optical meansOptical tomographyLength wave
Owner:KK TOPCON
Method and system for free space optical tomography of diffuse media
A method and a system for free space optical tomography provides one or more light source and one or more light sensors spaced, which in one embodiment are spaced apart from and object to be imaged. A surface capture system coupled to a variety of optical models provides the method and system with the ability to render accurate tomographic images though the light has propagated both through a diffuse medium and, in on embodiment, also through free space to the one or more light sensors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Optical coherent tomography
ActiveUS20080159468A1Increase speedContinuous changeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFast Fourier transformOptical tomography
A surface emission laser light source is used as a tunable laser light source. Since the surface emission laser light source can realize a broad frequency scanning range at a high speed and in the single mode, a coherent length is longer than that of a multi mode light source. For this reason, when a tomography image is calculated by executing the Fourier transform for an output obtained from an interference optical device, measuring depth can be deepened.
Owner:SANTEC
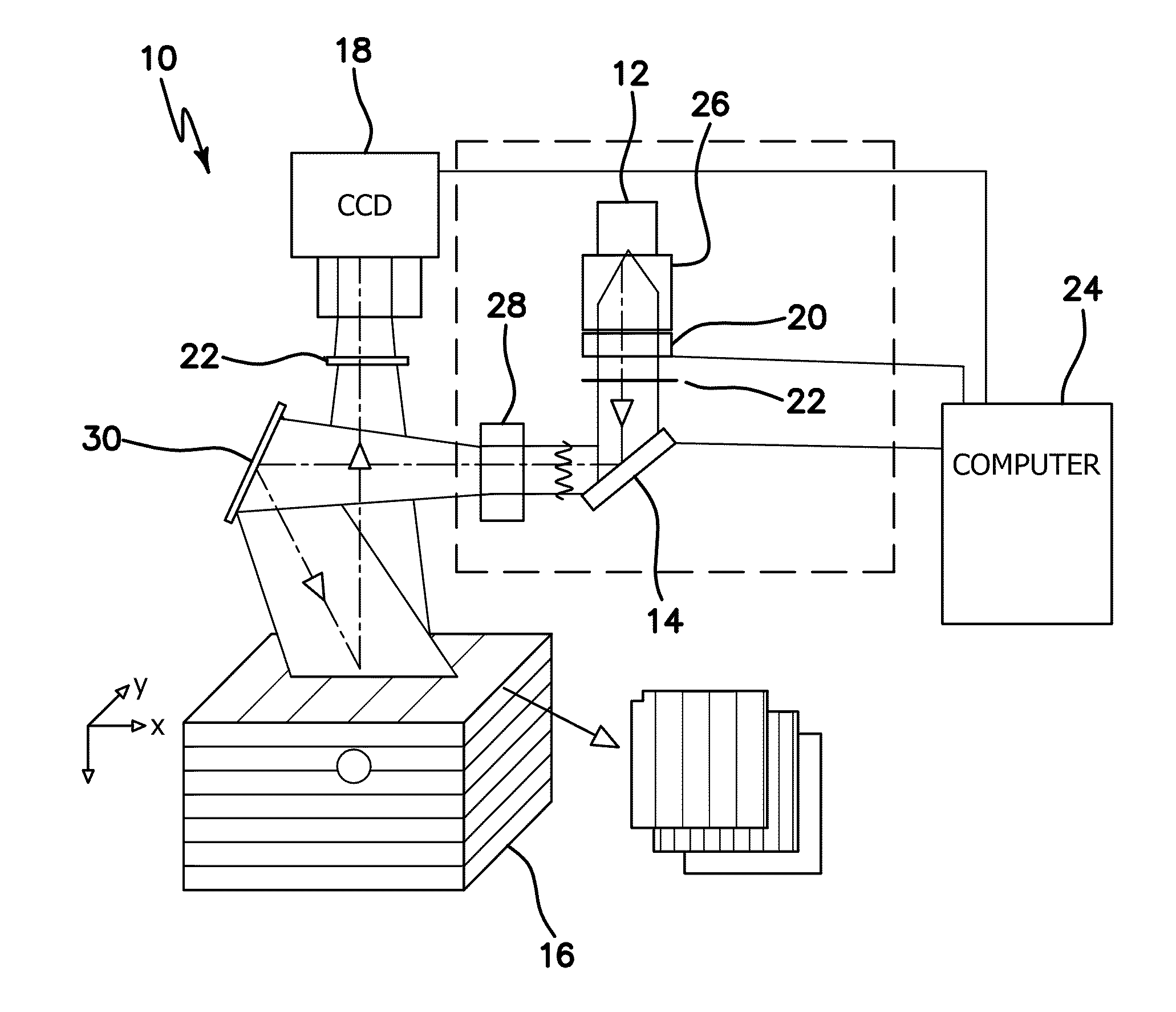
Measurement apparatus
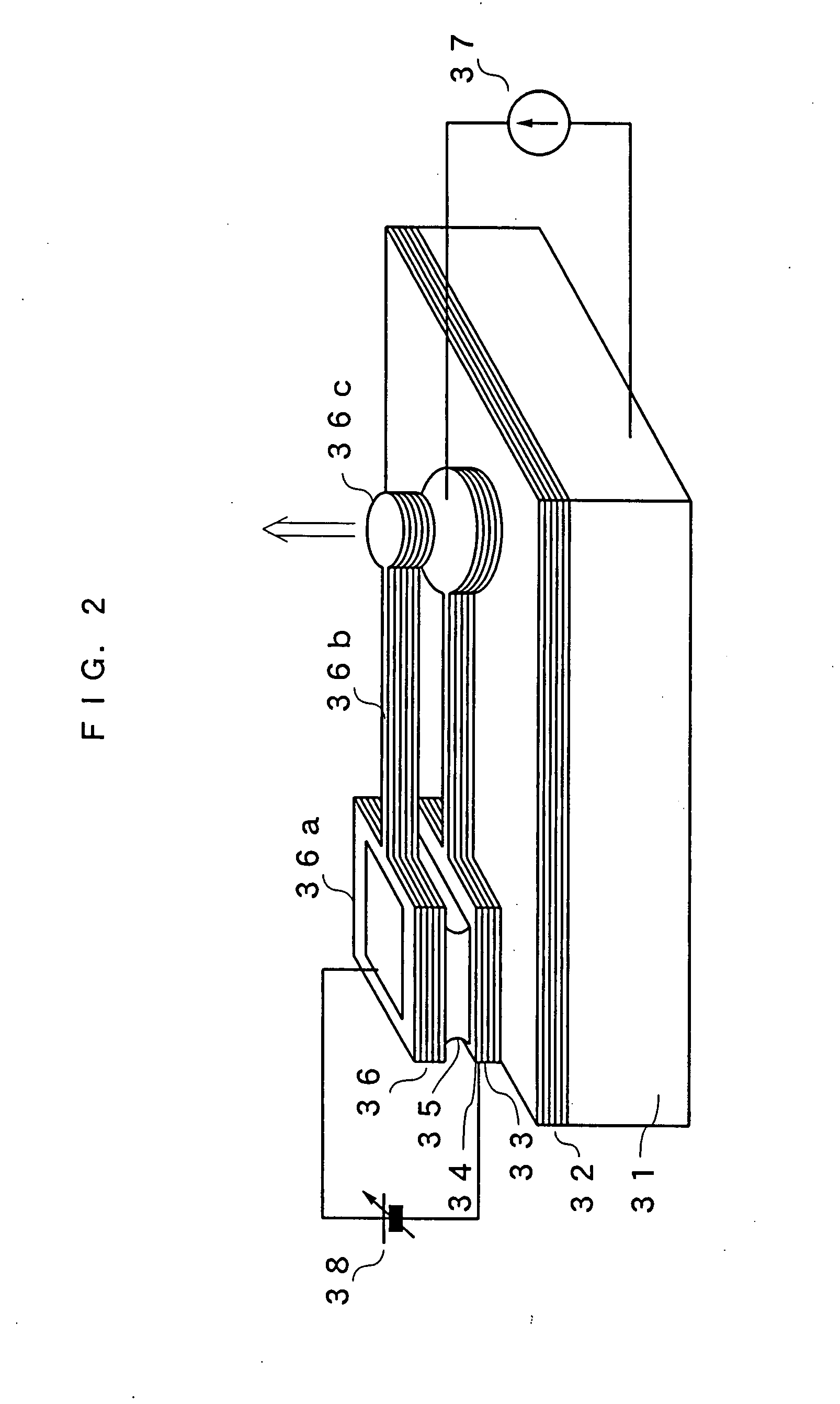
A measurement apparatus is configured to measure a spectroscopic characteristic of a measurement site in a specimen by applying acousto-optical tomography. The measurement apparatus includes a measurement unit configured to measure a light intensity of each of measurement areas that are set differently from the measurement site on a light propagation path from the measurement site to a detection position of a light detector and a signal processing device configured to sequentially modify the spectroscopic characteristics of the measurement areas and the measurement site on the light propagation path from the detection position of the light detector to the measurement site by using a light intensity that is measured by the measurement unit in the measurement area that is closer to a surface layer of the specimen than the measurement site.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com