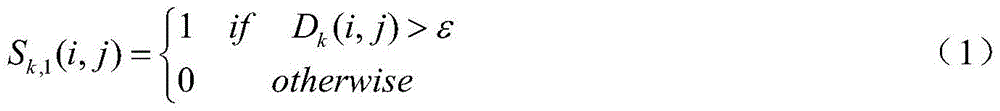Patents
Literature
170 results about "Field shaping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
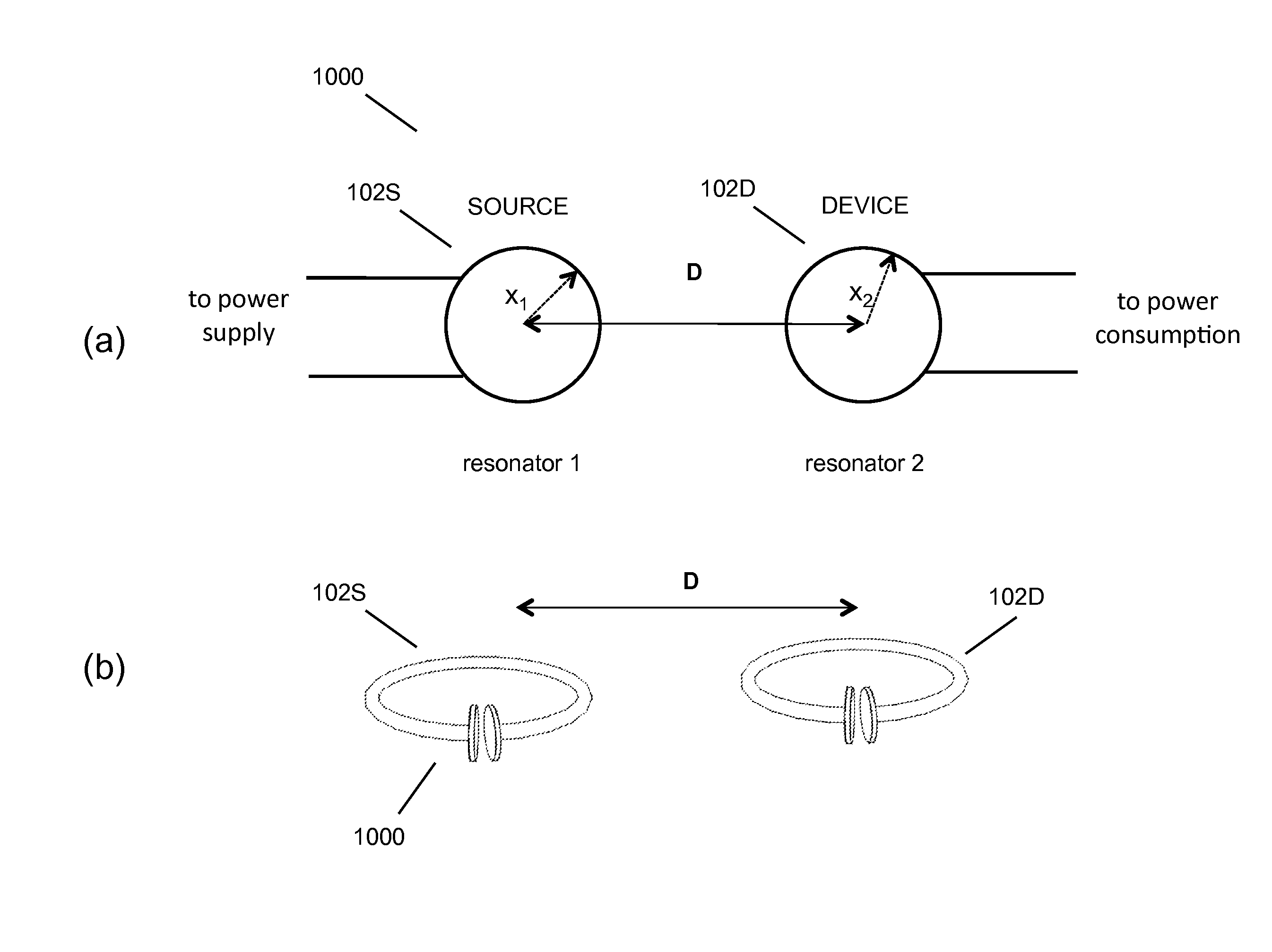
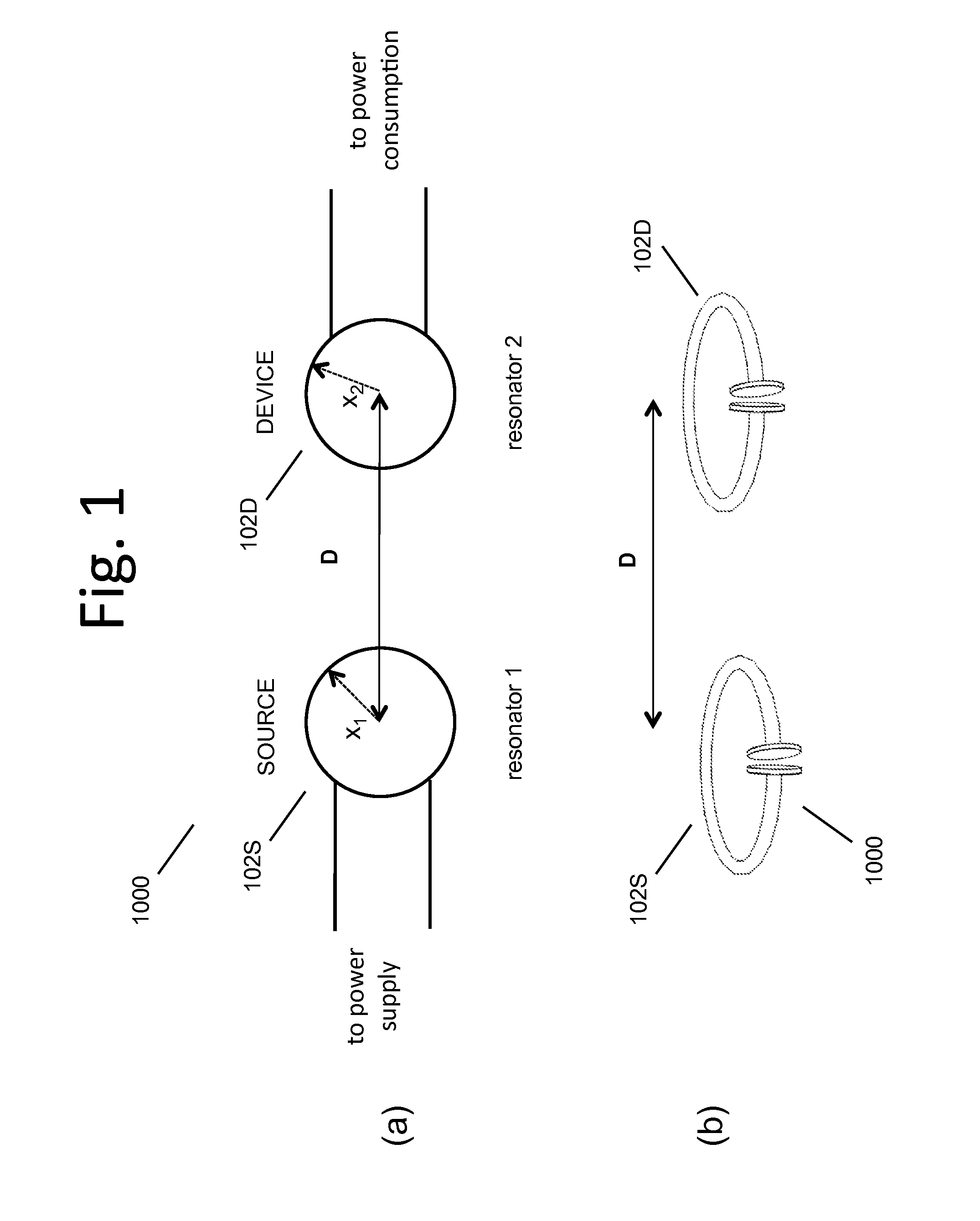
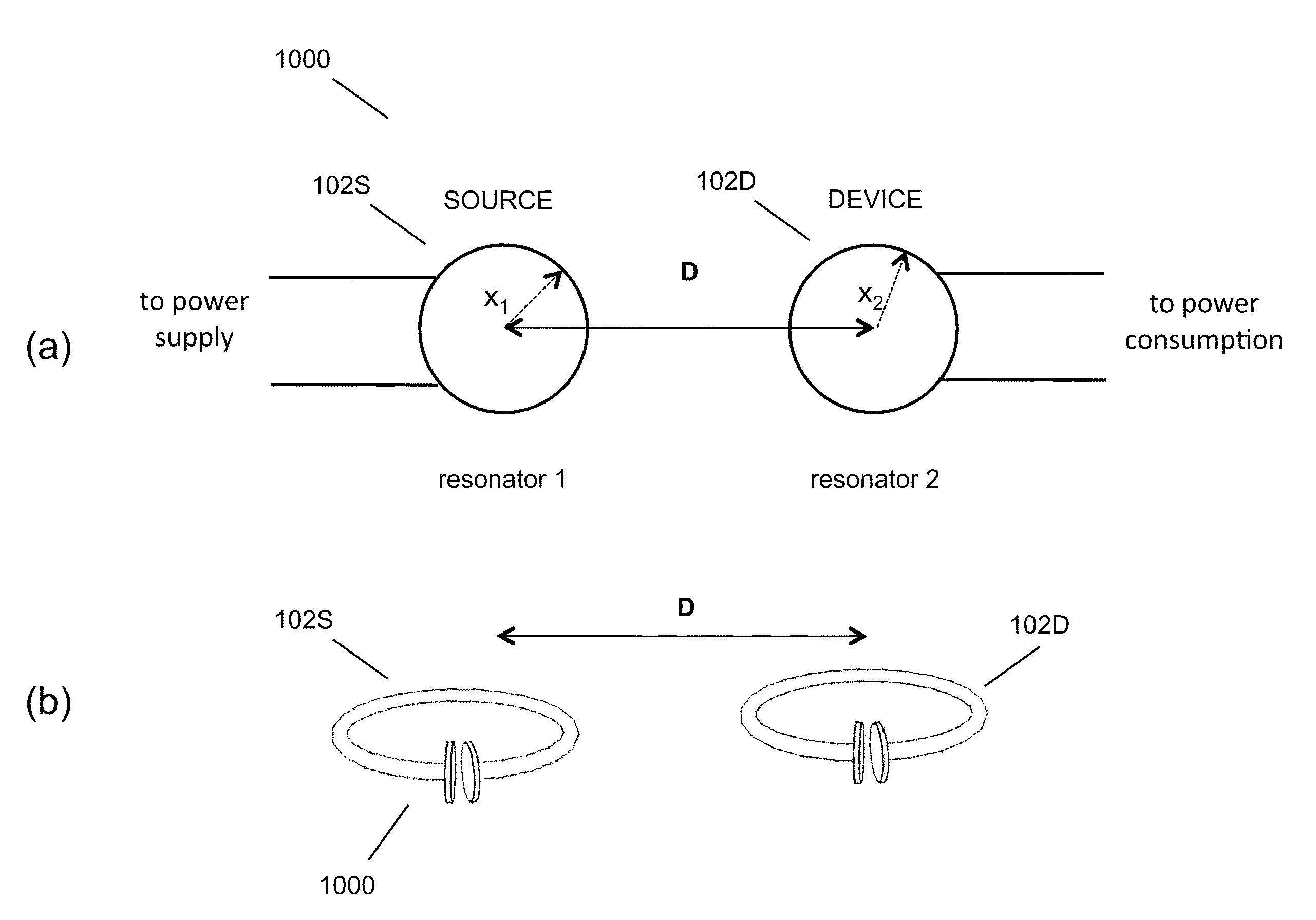
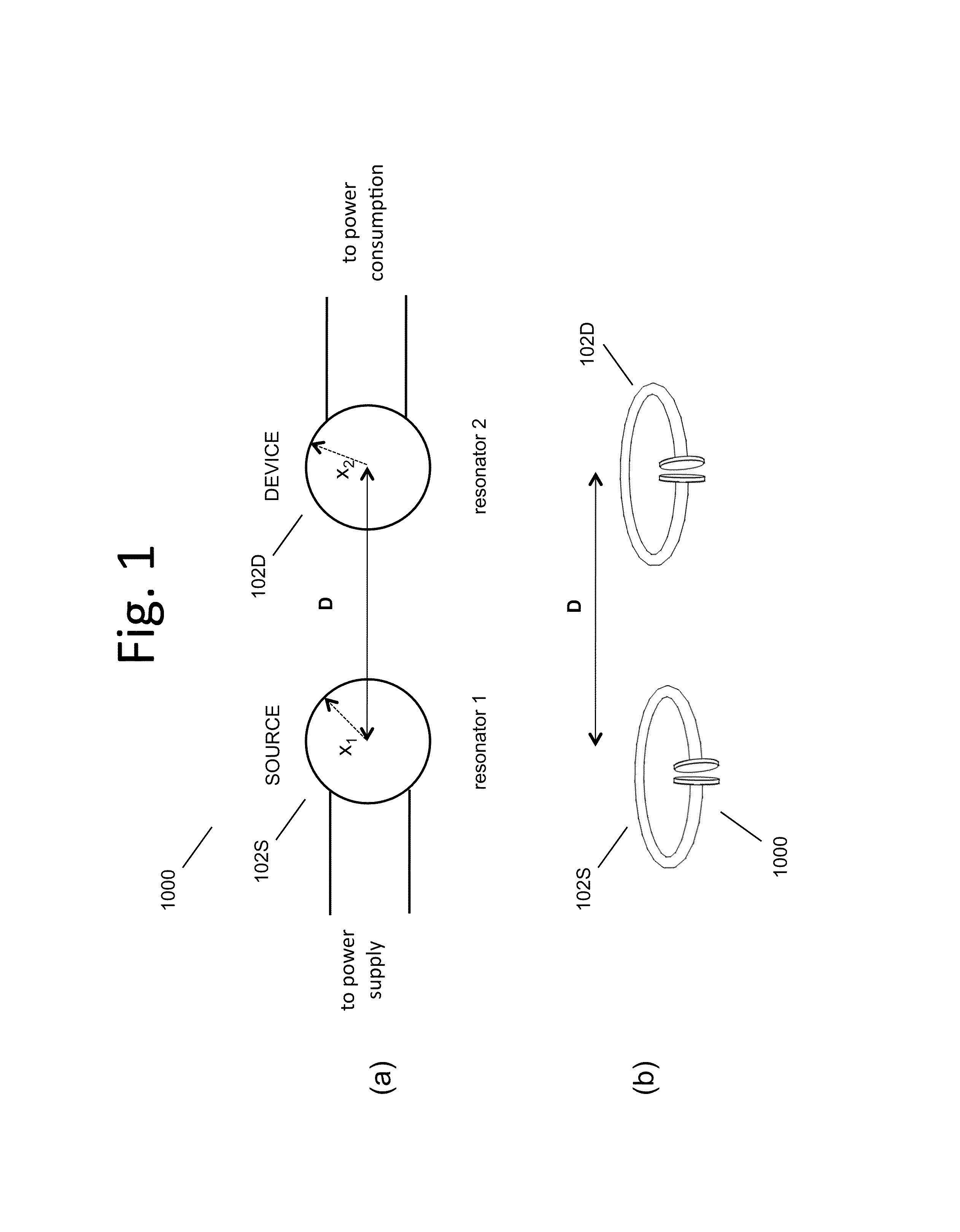
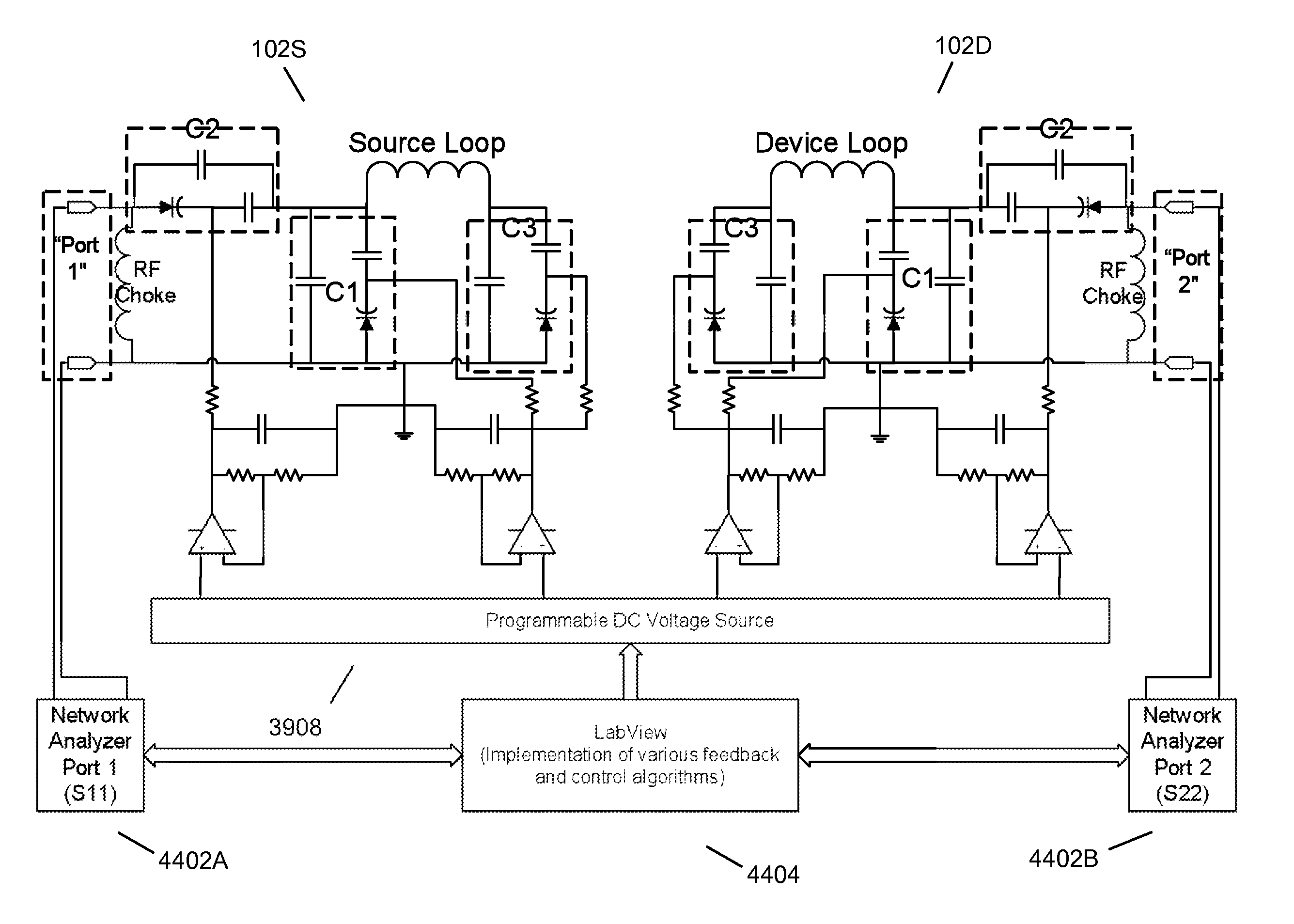
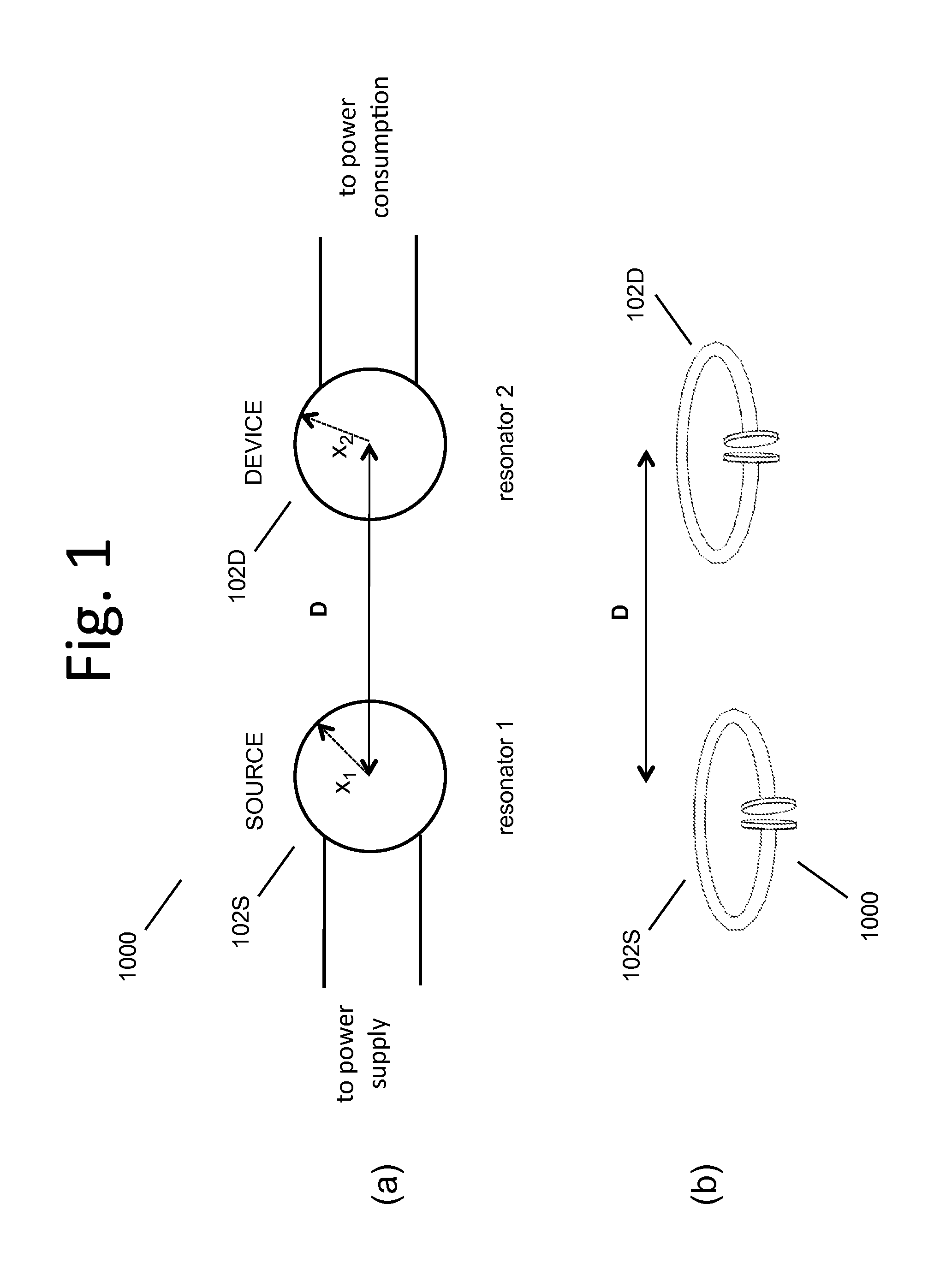
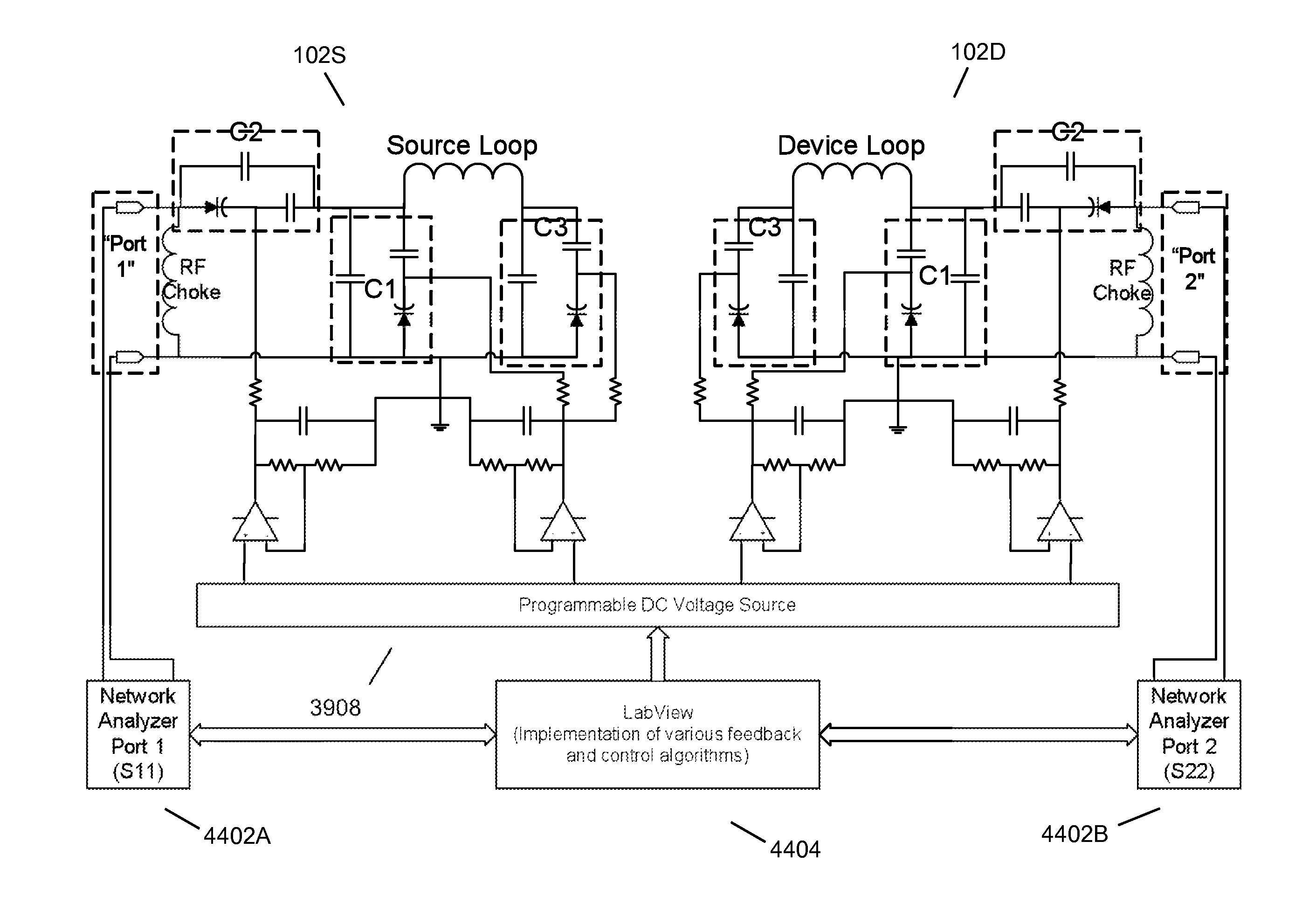
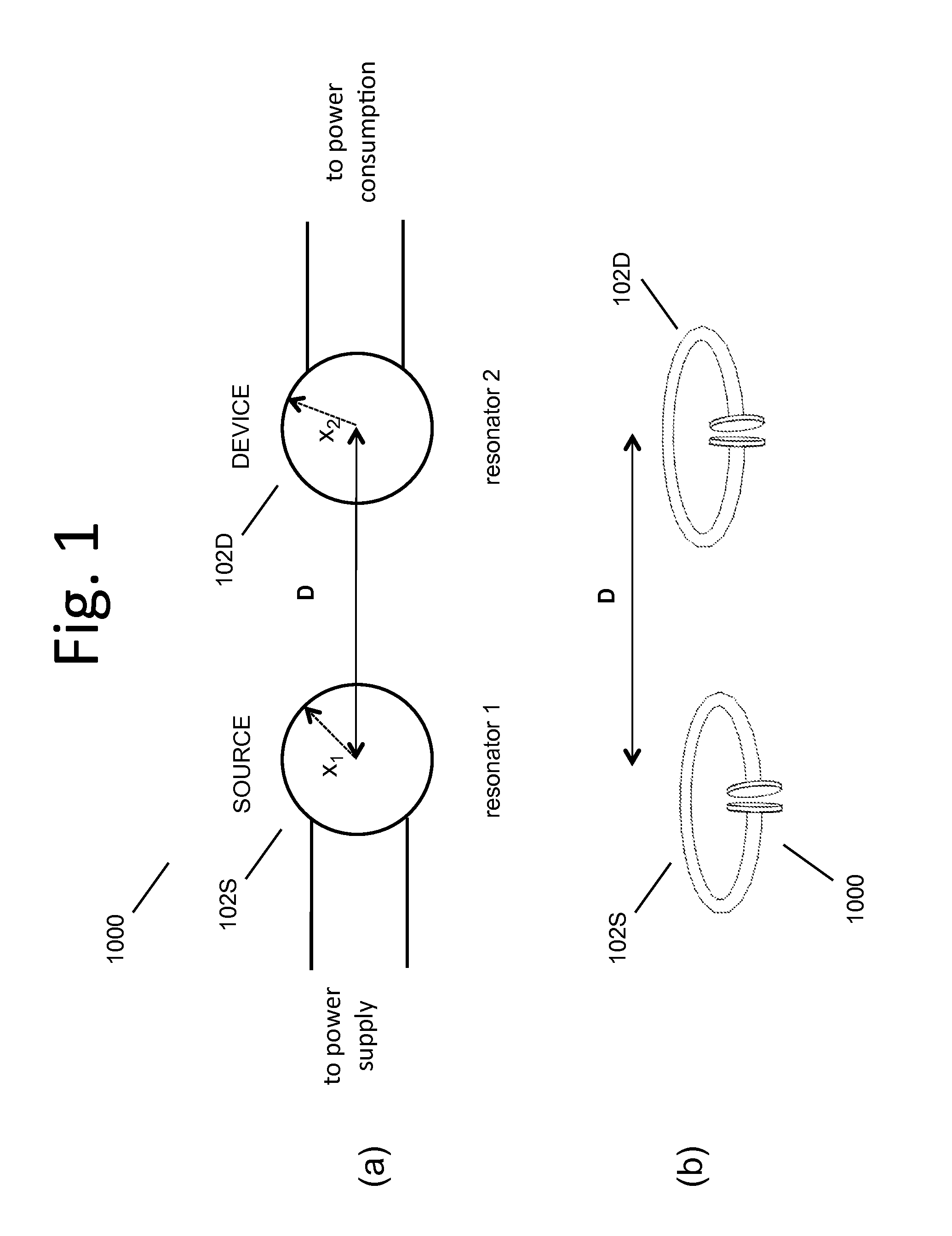
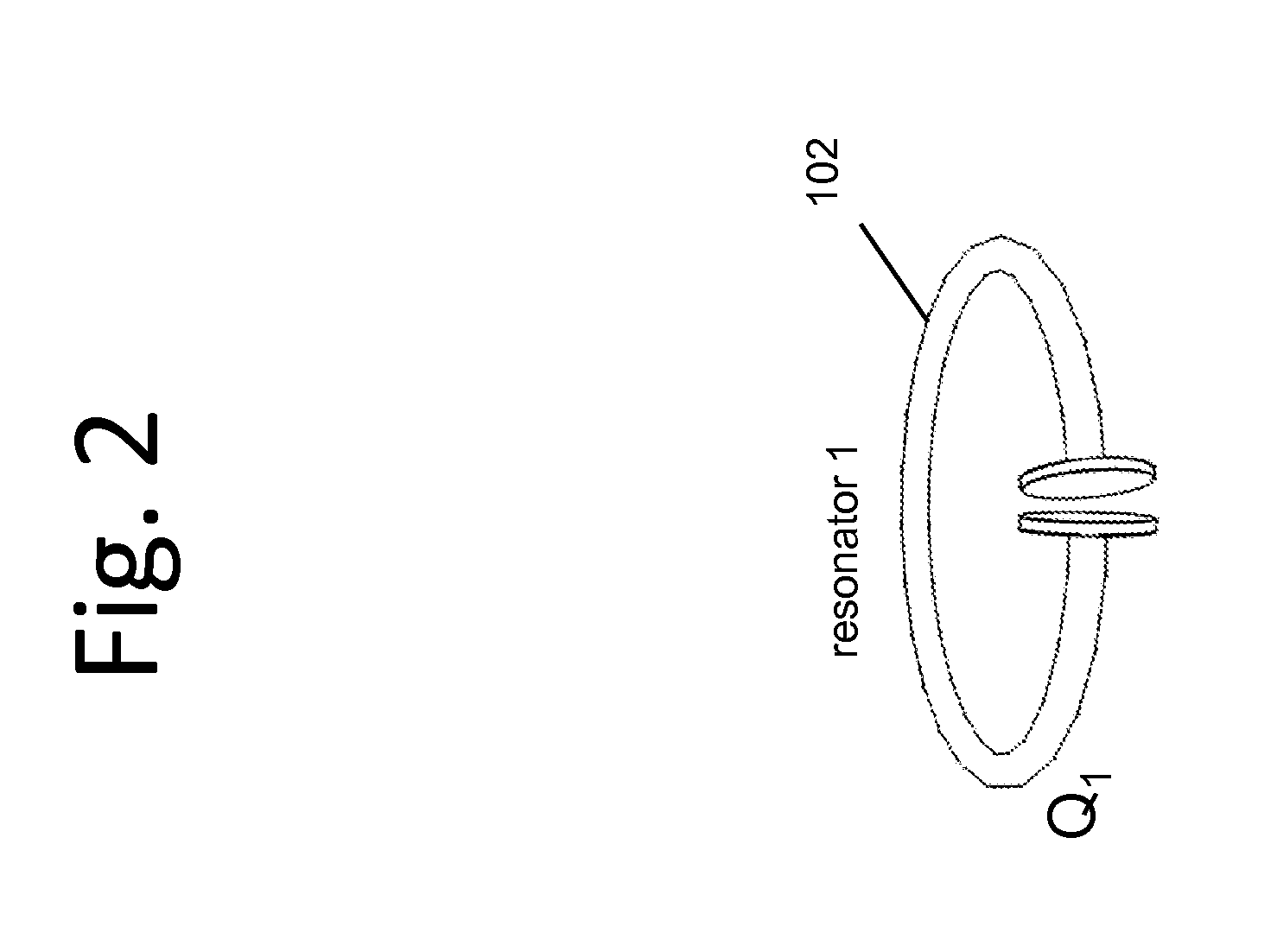
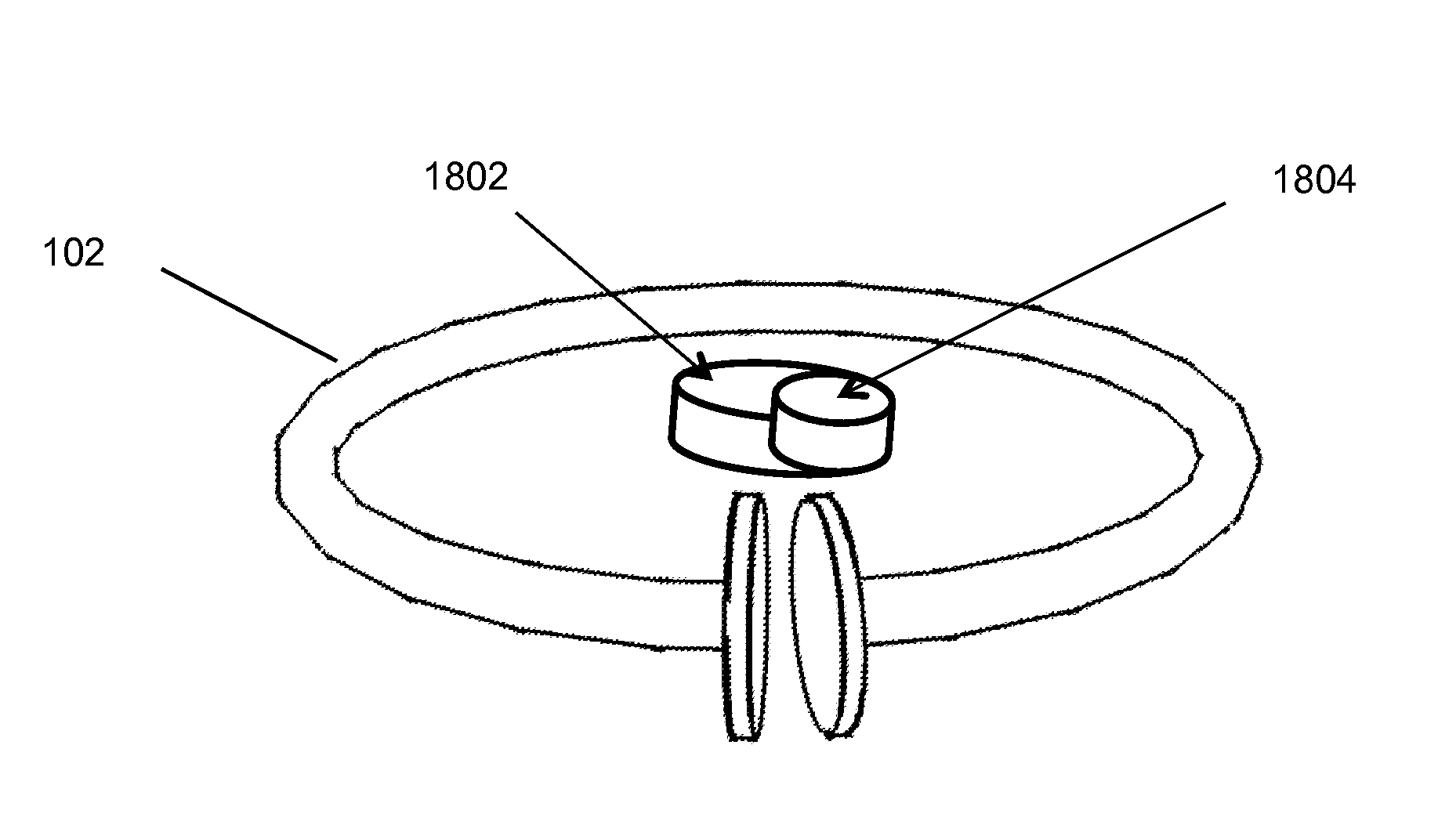
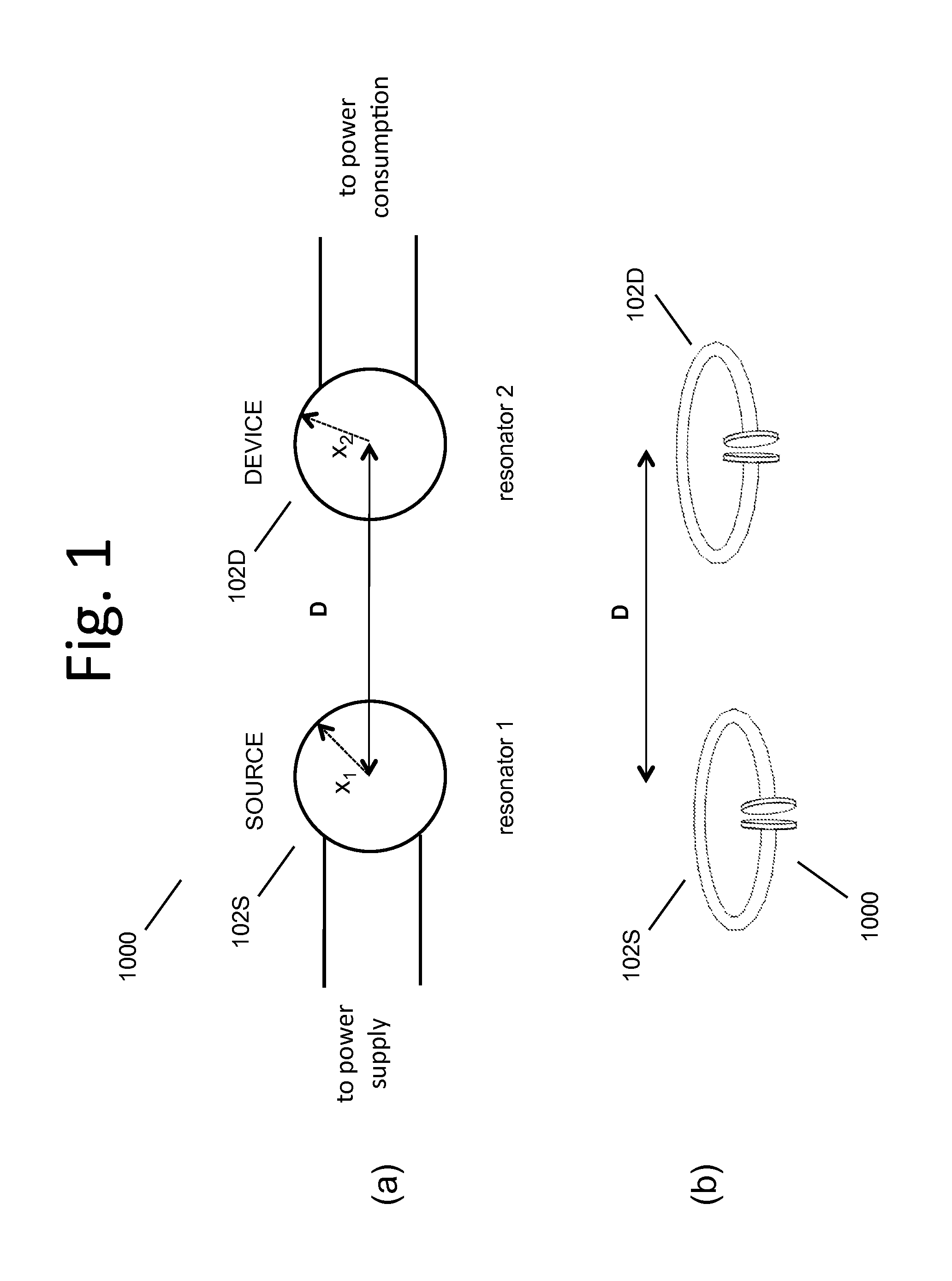
Wireless energy transfer using field shaping to reduce loss
ActiveUS20110043047A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a source resonator optionally coupled to an energy source and a second resonator located a distance from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the source resonator and the second resonator and where the field of at least one of the source resonator and the second resonator is shaped to avoid a loss-inducing object.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
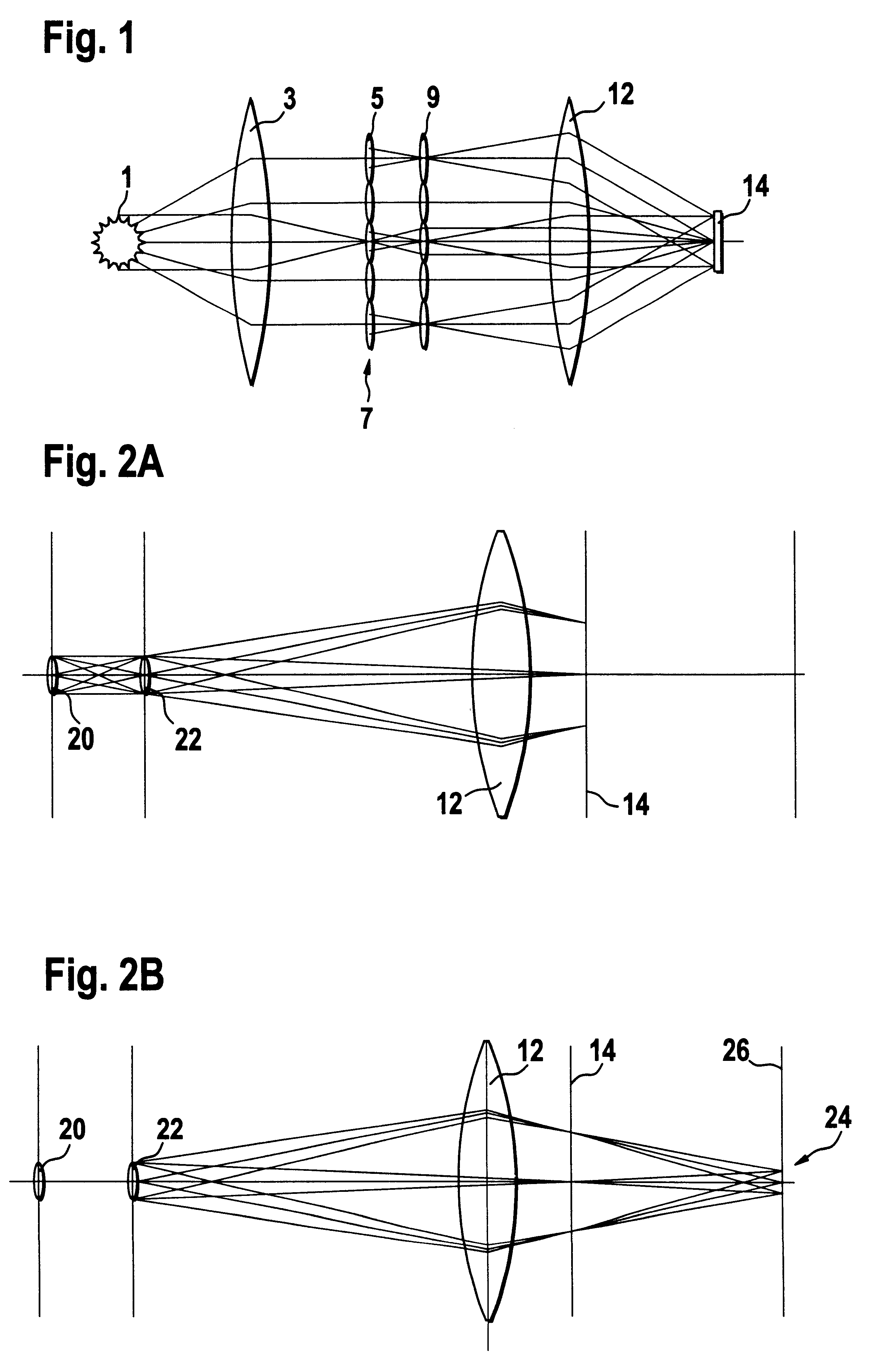
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
Wireless energy transfer using field shaping to reduce loss
ActiveUS8304935B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksCircuit monitoring/indicationEnergy transferCondensed matter physics
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a source resonator optionally coupled to an energy source and a second resonator located a distance from the source resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the source resonator and the second resonator and where the field of at least one of the source resonator and the second resonator is shaped to avoid a loss-inducing object.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer over distance using field shaping to improve the coupling factor
ActiveUS8471410B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferCoupling
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a first resonator optionally coupled to an energy source and a second resonator located a variable distance from the source resonator and not connected by any wires to the first resonator, where the first resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the first resonator and the second resonator, and where the field of at least one of the first resonator and the second resonator is shaped to increase the coupling factor among the resonators.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer across variable distances using field shaping with magnetic materials to improve the coupling factor
ActiveUS20120153738A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferCoupling
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a first resonator coupled to an energy source generating a field having magnetic material, and a second resonator located a variable distance from the source resonator having magnetic material and not connected by any wire or shared magnetic material to the first resonator, where the source resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the source resonator and the second resonator, and where the field of at least one of the source resonator and the second resonator is shaped using magnetic materials to increase the coupling factor among the resonators.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Wireless energy transfer over distance using field shaping to improve the coupling factor
ActiveUS20120153737A1Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferCoupling
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a method and system comprising a first resonator optionally coupled to an energy source and a second resonator located a variable distance from the source resonator and not connected by any wires to the first resonator, where the first resonator and the second resonator are coupled to provide near-field wireless energy transfer among the first resonator and the second resonator, and where the field of at least one of the first resonator and the second resonator is shaped to increase the coupling factor among the resonators.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
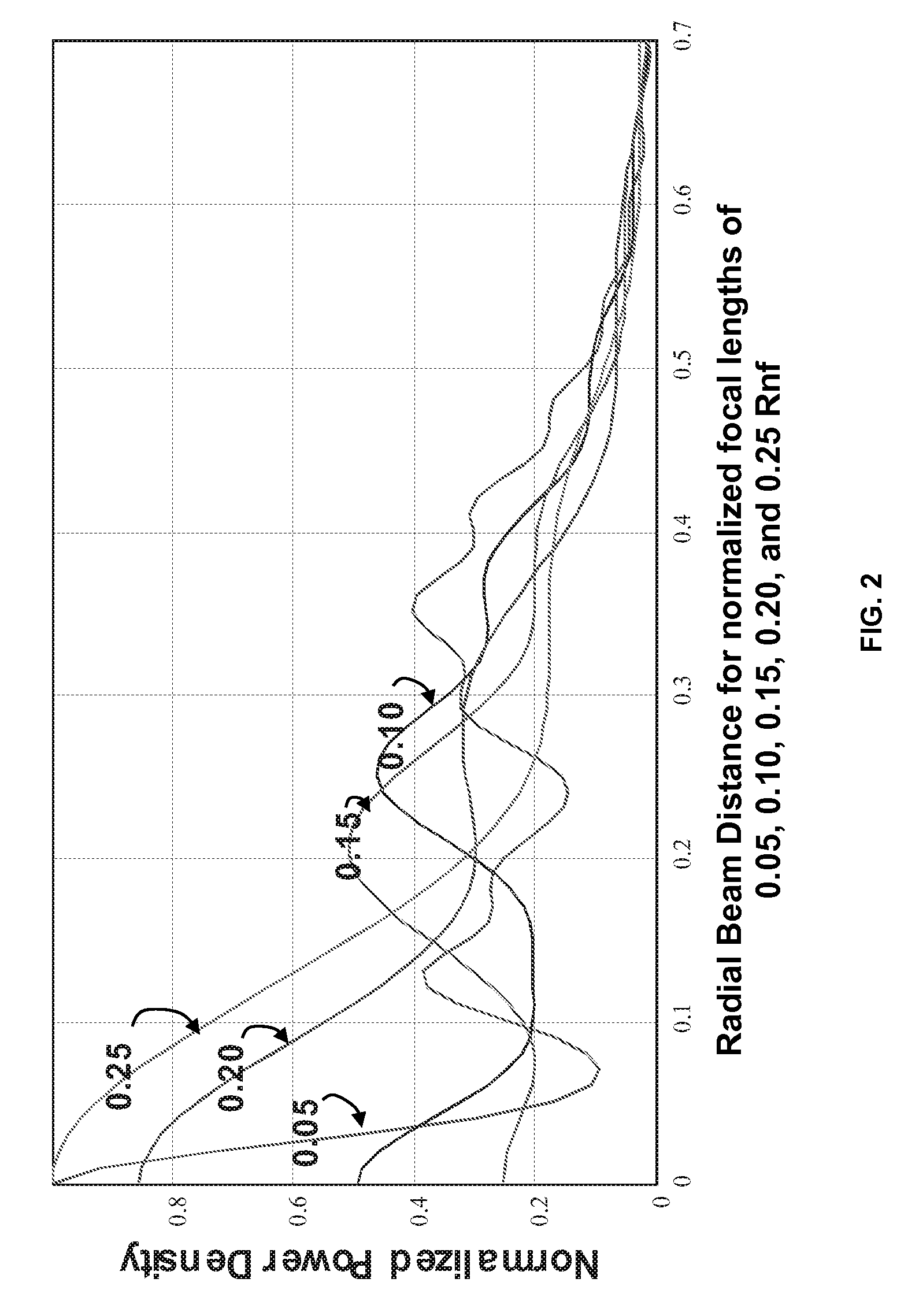
Optimization of near field antenna characteristics by aperture modulation
The approximate radius of curvature of the spherical phase front at the aperture of a transmitting microwave antenna is controlled by an inner section of the aperture attached to the outer section of the aperture by a small number of programmable transducers, thereby controlling the near field shape and power distribution of the transmitted beam.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
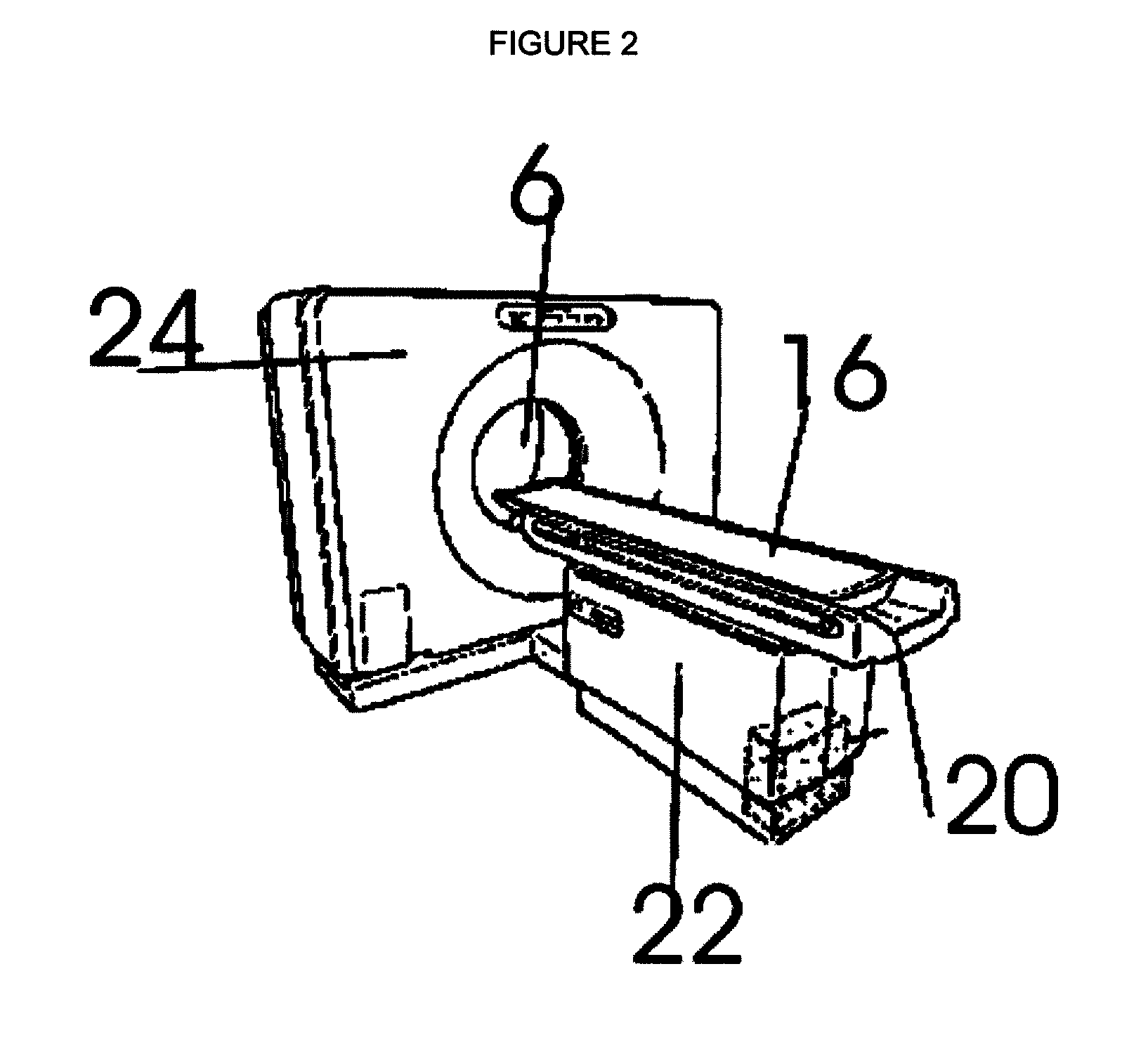
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
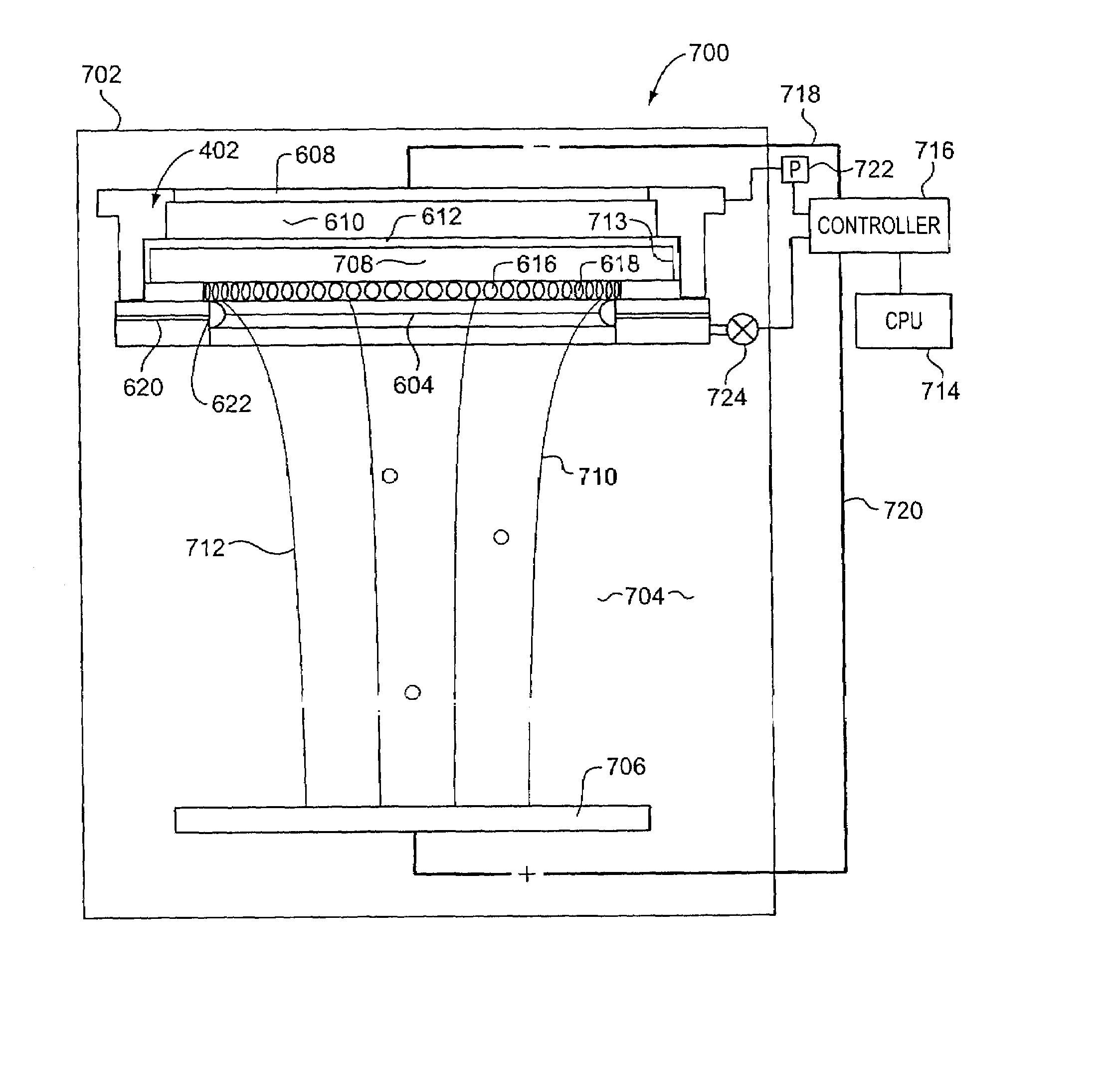
Dynamically variable field shaping element
InactiveUS7070686B2Uniform current distributionUniform currentAnodisationMachining electric circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrochemical response
In an electrochemical reactor used for electrochemical treatment of a substrate, for example, for electroplating or electropolishing the substrate, one or more of the surface area of a field-shaping shield, the shield's distance between the anode and cathode, and the shield's angular orientation is varied during electrochemical treatment to screen the applied field and to compensate for potential drop along the radius of a wafer. The shield establishes an inverse potential drop in the electrolytic fluid to overcome the resistance of a thin film of conductive metal on the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Multiple medical accelerators and a kV-CT incorporated radiation therapy device and semi-automated custom reshapeable blocks for all field synchronous image guided 3-D-conformal-intensity modulated radiation therapy
S-band, C-band or X-band microwave powered linear accelerators capable of delivering therapeutic photon and electron beams are mounted to a gantry with extensions to hold multiple accelerators and are combined with a kV CT for 3-D conformal—IMRT and IGRT to treat a patient by SSD or SAD methods and in a full circle. The invention's tertiary collimator system consists of semi-automated reusable custom field shaping with tungsten powder or melted Cerrobend blocks. The beam's intensity modulation is by means of simultaneous but independently operating multiple accelerators. This system's multiple accelerators enable to avoid interrupted subfractionated radiation therapy to each treatment fields. Hence its effective dose rate at the tumor site is high. The improved radiobiology reduces the total radiation dose to treat a tumor, reducing the incidence of developing second primary tumors is also minimized.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Wireless energy transfer across variable distances using field shaping with magnetic materials to improve the coupling factor
ActiveUS8669676B2Efficient deliveryEfficient energy transferMultiple-port networksBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy transferCoupling
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
Single session interactive ultra-short duration super-high biological dose rate radiation therapy and radiosurgery
A medical accelerator system consisting of coplanar and non-coplanar beams, on line magnetic resonance anatomic and functional imaging and cone beam computed tomographic imaging for single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy and radiosurgery is provided. This system enables single session simulation, field-shaping block making, treatment planning, dose calculations and treatment of tumors. The radiation exposure time to the tumor and the normal tissue is reduced to a few seconds to less than a minute. In filed intensity modulated radiation is rendered by combined divergent and pencil beam, multiple smaller fields within a larger field, selectively varying beam's energy, dose rate and beam weight. Since all the treatment fields are treated simultaneously the dose rate at the tumor site is the sum of each of the converging beam's dose rate at depth. This super-high biological dose rate impairs the lethal and sublethal damage repair.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
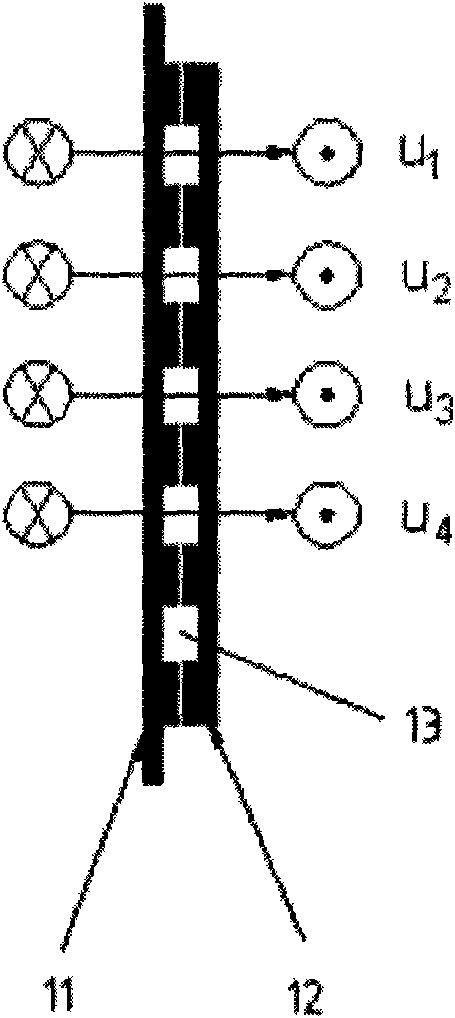
Photonic mixer and use thereof
ActiveUS20110255071A1High resolutionSmall sizeOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesDopantPhotonics
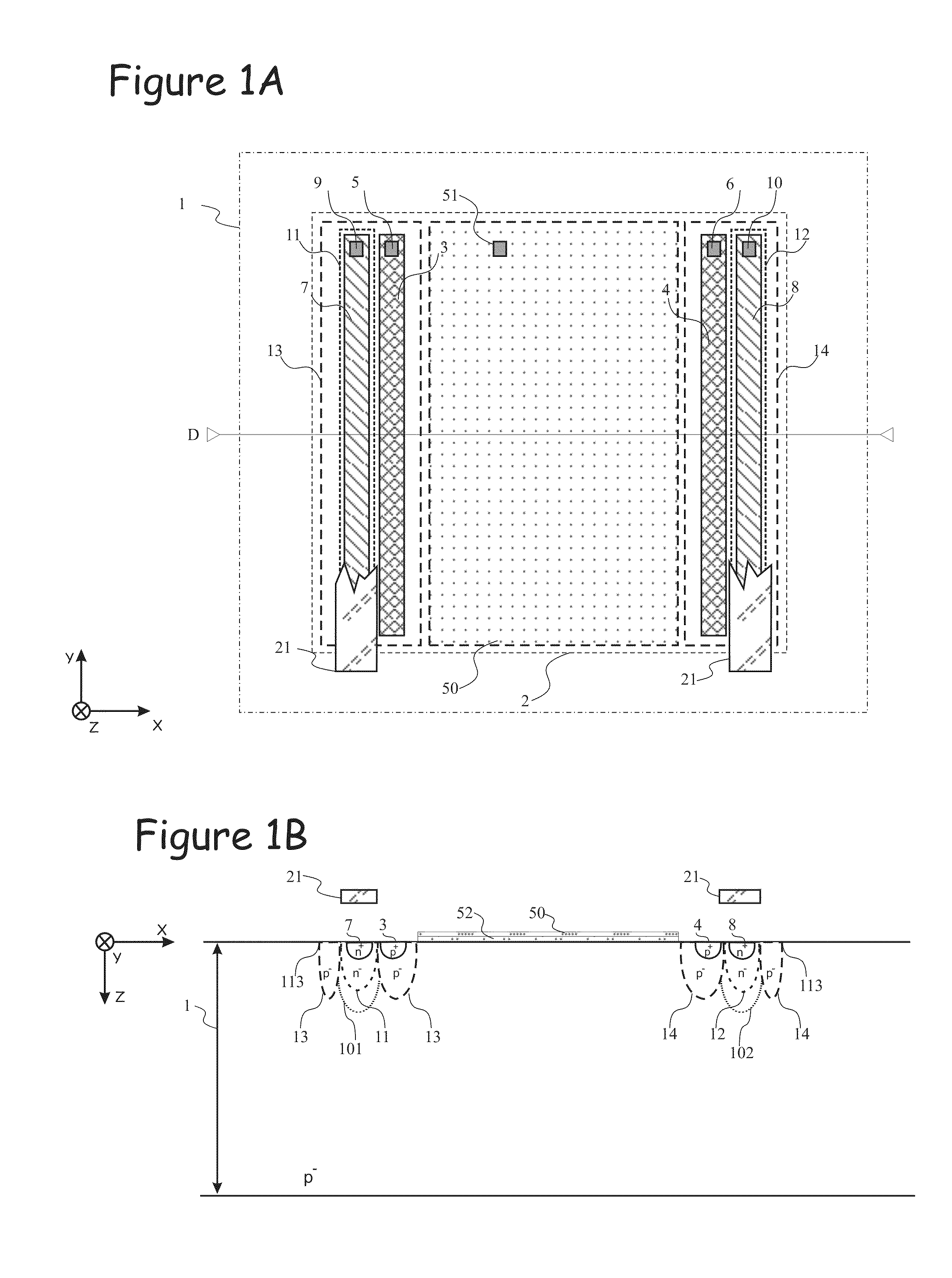
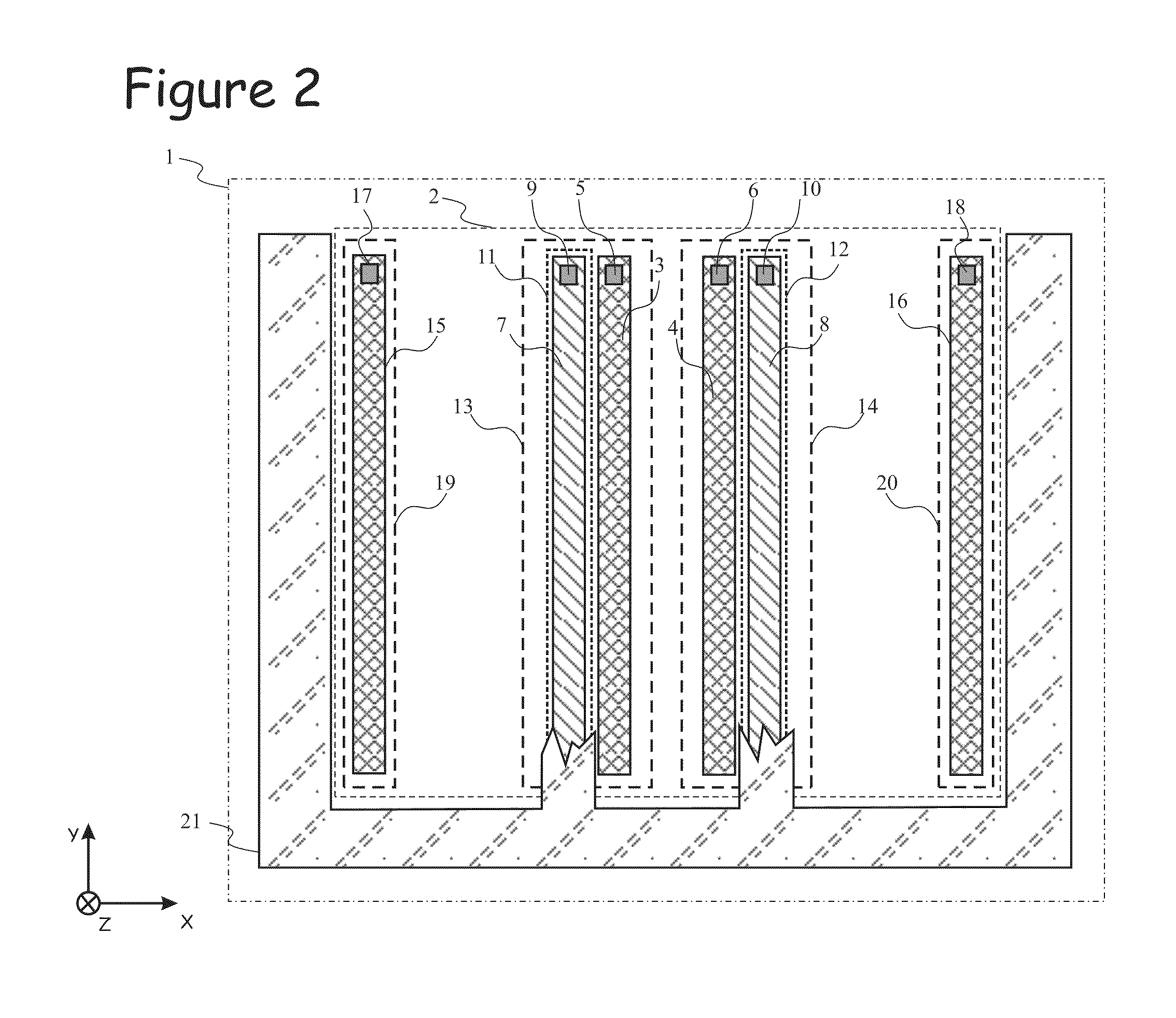
The photonic mixer comprises a couple of an injecting contact region (3,4) for injecting the majority carrier current into the semiconductor substrate (1) and a detector region (7,8) for collecting the photocurrent. The injecting contact region (3,4) is doped with a dopant of the first conductivity type (p+) at a higher dopant concentration than the semiconductor substrate (1). The detector region (7,8) is doped with a dopant of a second conductivity type (n+) opposite the first conductivity type and has a junction (11,12) with the semiconductor substrate (1), a zone of the semiconductor substrate (1) around said junction (11,12) being a depleted substrate zone (101, 102). The couple further comprises a field shaping zone (13, 14) of the first conductivity type (p−) defining a lateral edge of the couple and having a dopant concentration higher than the dopant concentration of the semiconductor substrate (1), for example between the dopant concentrations of the semiconductor substrate (1) and the injecting contact region (3,4), which field shaping zone (13, 14) is designed to limit said depleted substrate zone (101, 102) laterally.
Owner:SOFTKINETIC SENSORS +1
Method for calculation radiation doses from acquired image data
InactiveUS20080091388A1Fast rebuildMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputation using non-denominational number representationDeterministic methodComputer science
Various embodiments of the present invention provide processes for applying deterministic radiation transport solution methods for calculating doses and predicting scatter in radiotherapy and imaging applications. One method embodiment of the present invention is a process for using deterministic methods to calculate dose distributions resulting from radiotherapy treatments, diagnostic imaging, or industrial sterilization, and for calculating image scatter for the purposes of image reconstruction. In one embodiment of the present invention, a method provides a means for transport of external radiation sources through field-shaping devices. In another embodiment of the present invention, a method includes a process for calculating the dose response at selected points and volumes prior to radiotherapy treatment planning.
Owner:FAILLA GREGORY A +3
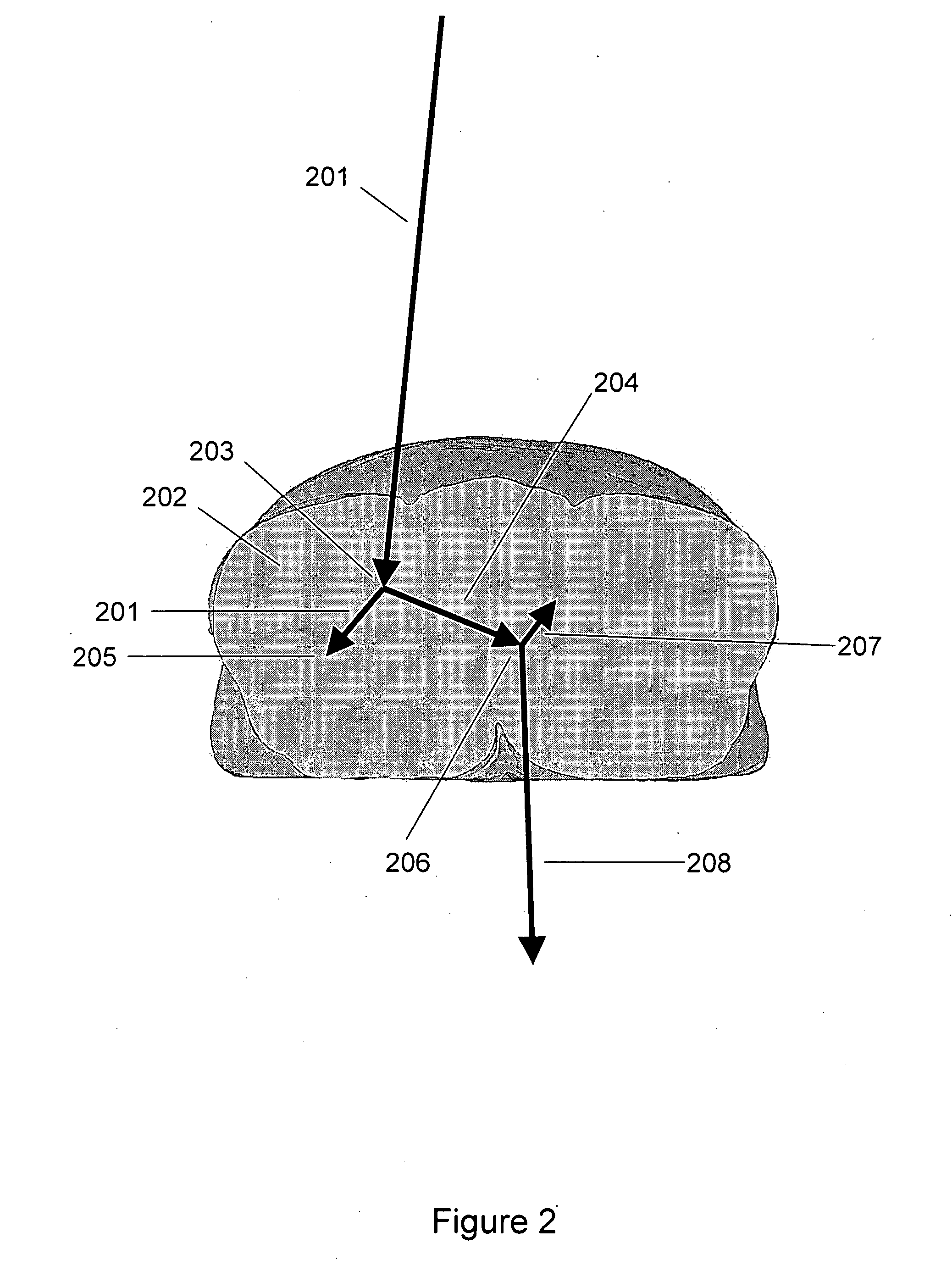
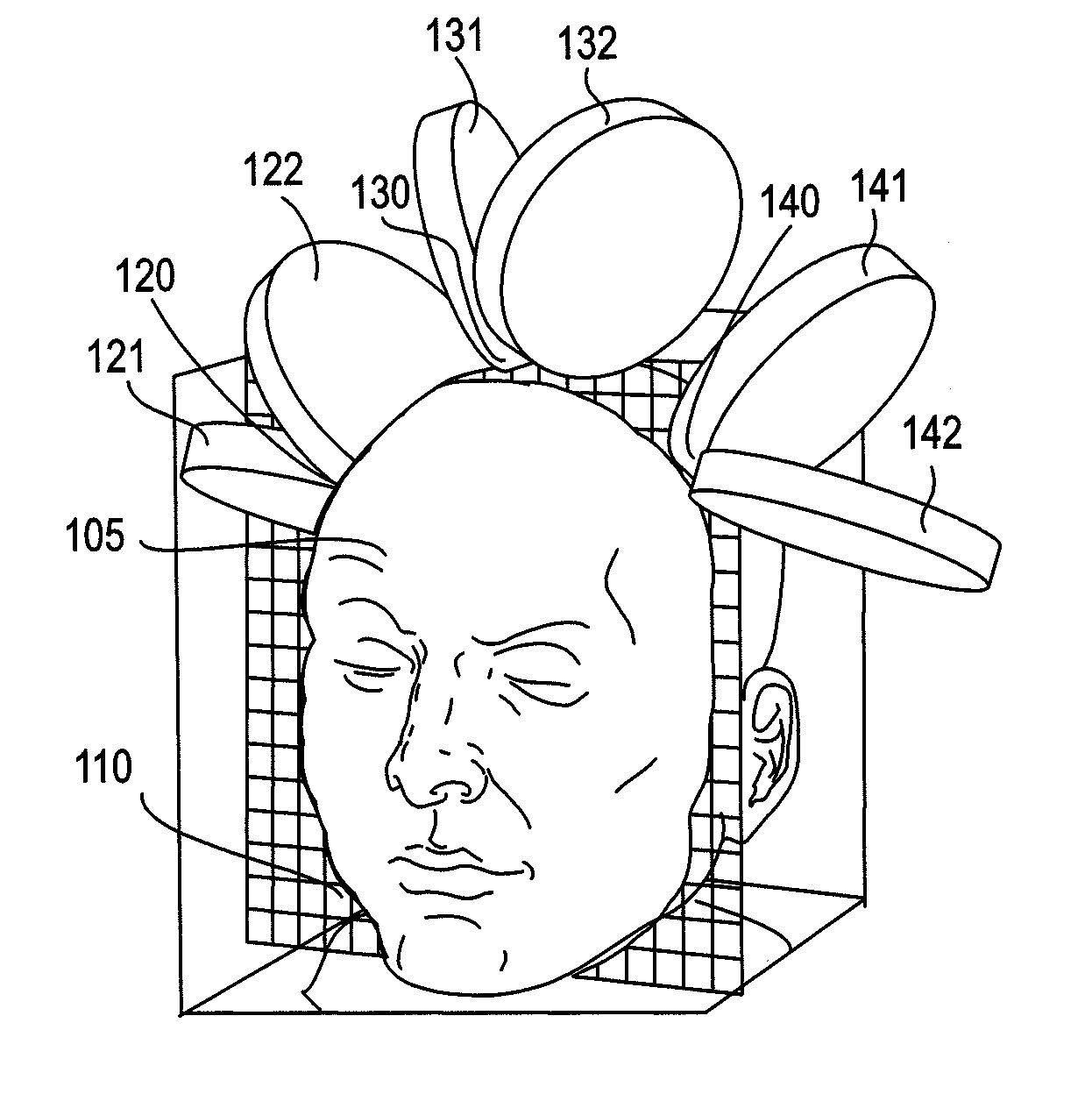
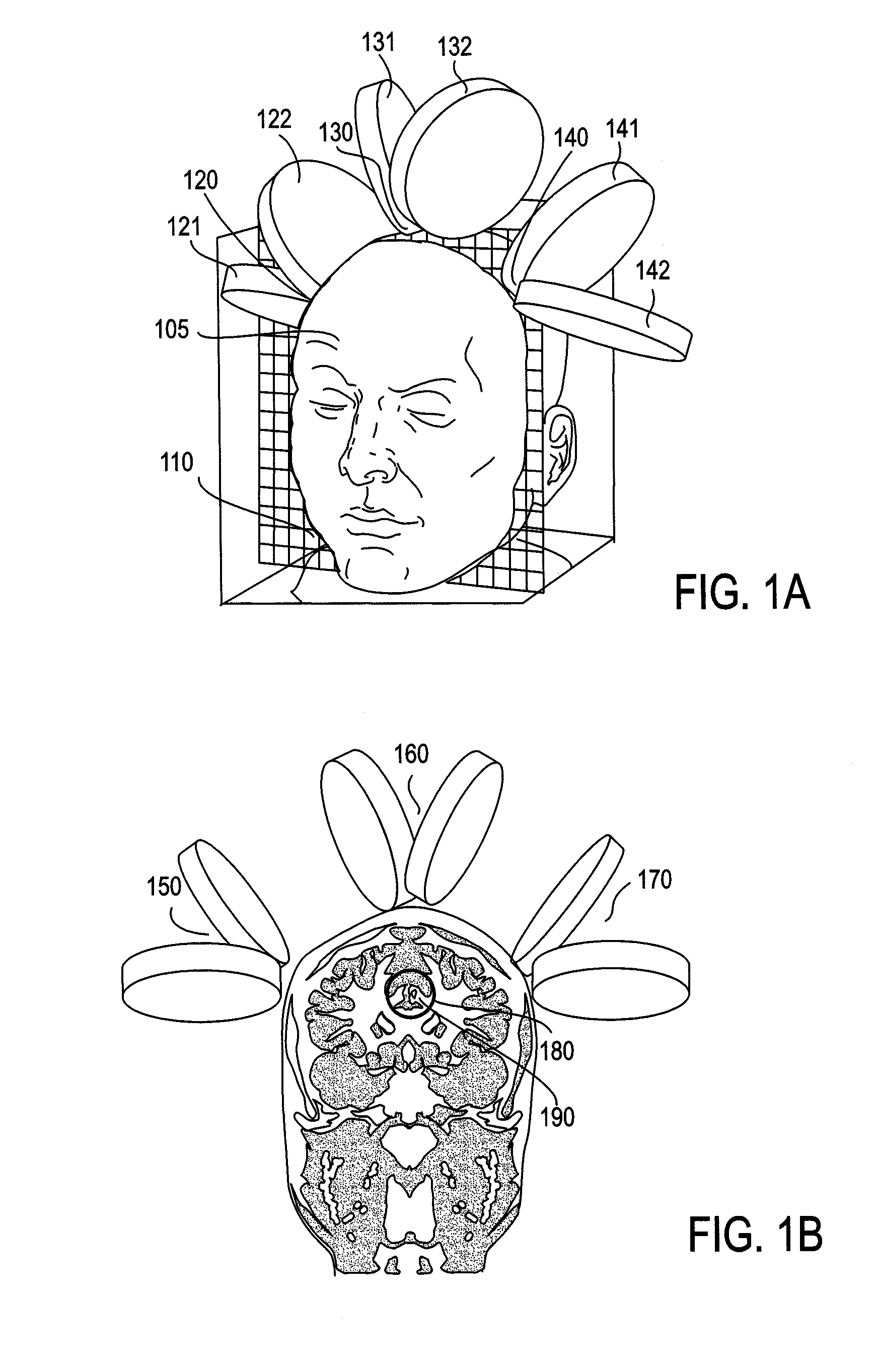
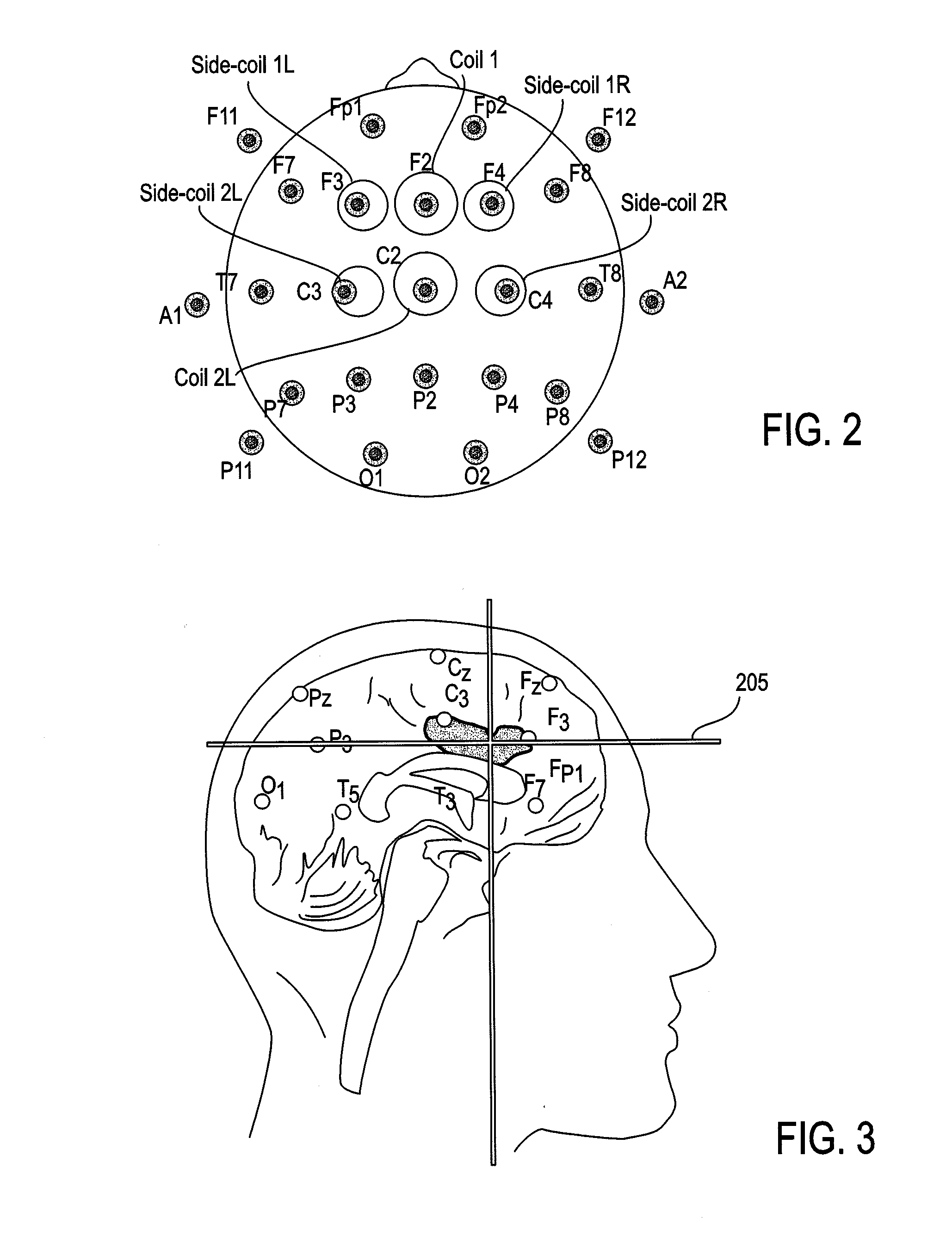
Transcranial magnetic stimulation field shaping
ActiveUS20100286470A1Improve concentrationReduce and prevent painElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectrical polarityEngineering
Described herein are Transcranial Magnetic Simulation (TMS) systems and methods of using them for emitting focused, or shaped, magnetic fields for TMS. In particular, described herein are arrays of TMS electromagnets comprising at least one primary (e.g., central) TMS electromagnet and a plurality of secondary (e.g., lateral or surrounding) TMS electromagnets. The secondary TMS electromagnets are arranged around the primary TMS electromagnet(s), and are typically configured to be synchronously fired with the primary TMS electromagnets. Secondary TMS electromagnets may be fired at a fraction of the power used to energize the primary TMS electromagnet to shape the resulting magnetic field. The secondary TMS electromagnets may be stimulated at opposite polarity to the primary TMS electromagnet(s). Focusing in this manner may prevent or reduce stimulation of adjacent non-target brain regions.
Owner:BRAINSWAY
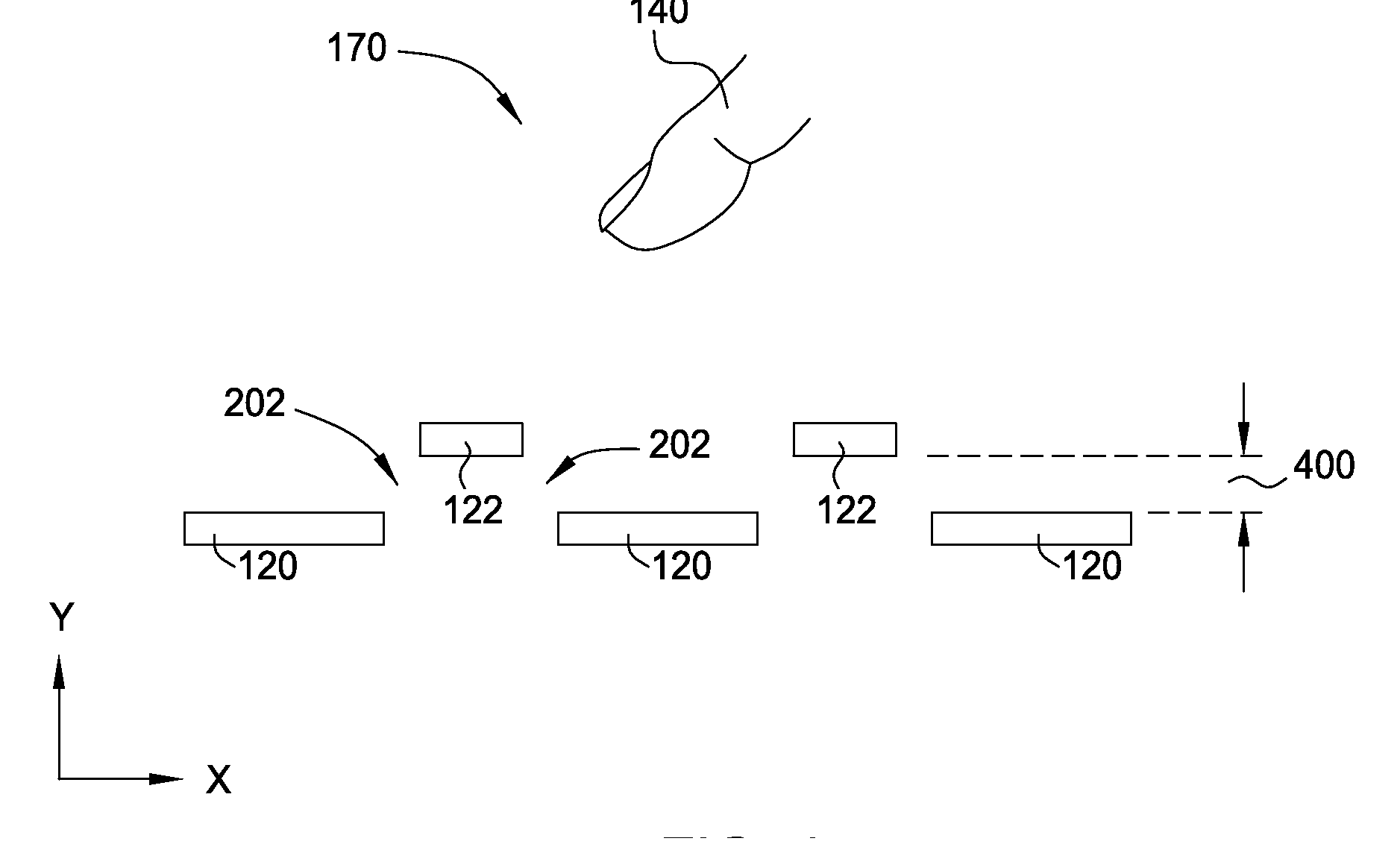
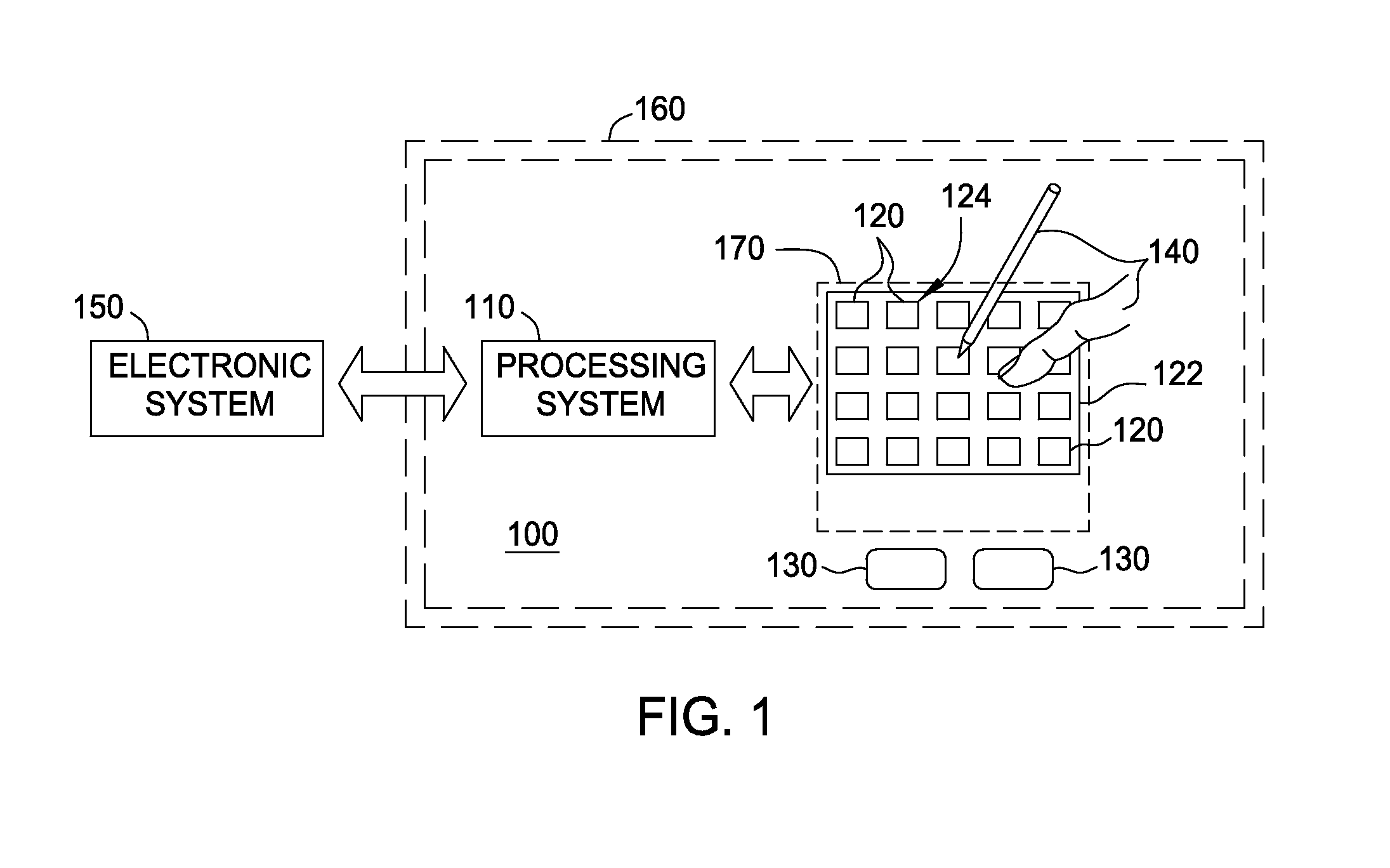
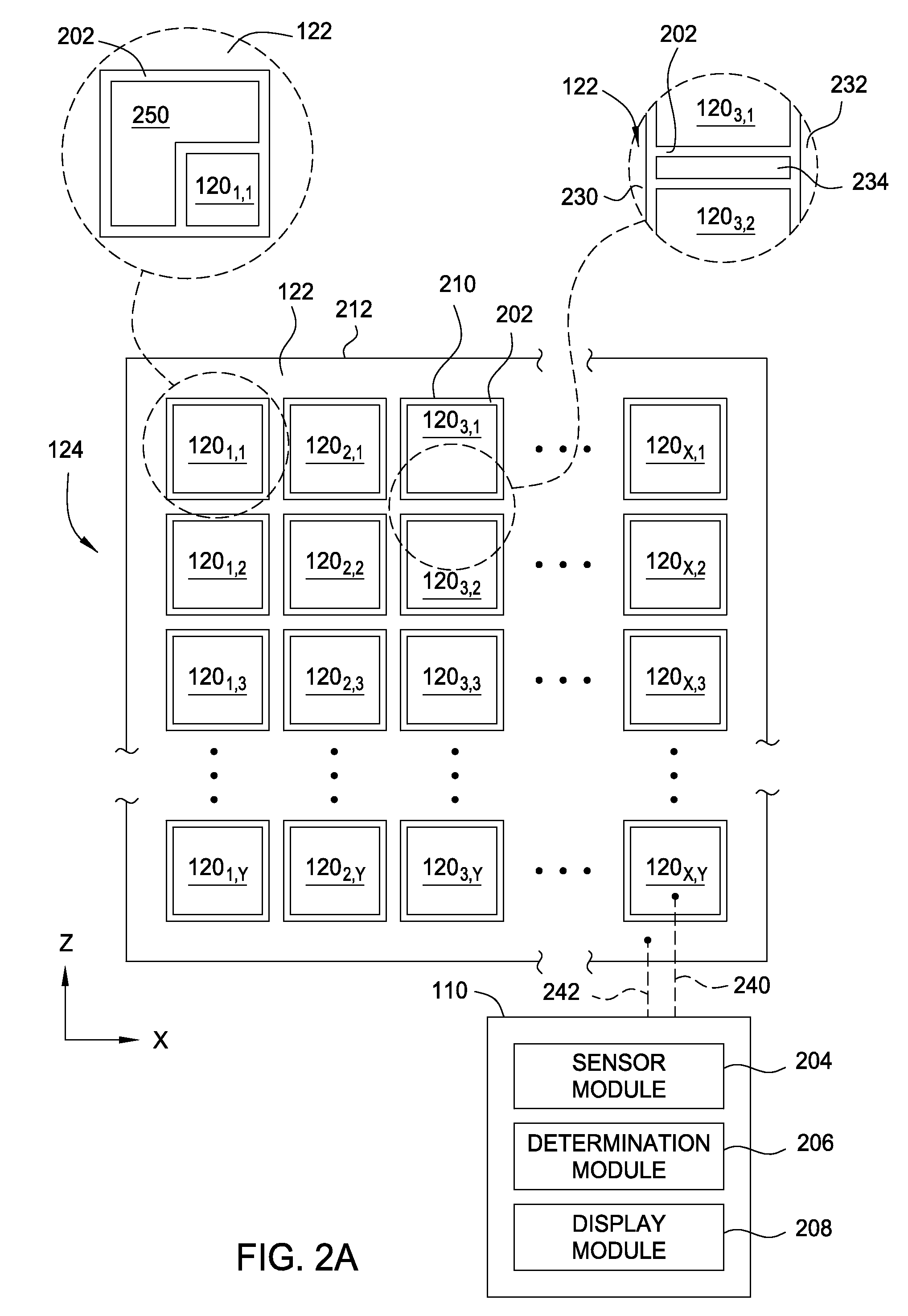
Matrix sensor for image touch sensing
ActiveUS20150091587A1Capacitance measurementsInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesDisplay device
Embodiments described herein include a display device having a capacitive sensing device, a processing system and a method for detecting presence of an input object using a capacitive sensing device. In one embodiment, the display device includes a plurality of sensor electrodes, a field shaping electrode, and a processing system. Each sensor electrode includes at least one common electrode. Dimensions of each sensor electrode correspond to dimension of pixel elements of the display device. The field shaping electrode is disposed between two of the plurality of sensor electrodes. Dimensions of the field shaping electrode correspond to the dimension of pixel elements of the display device. The field shaping electrode is laterally spaced apart from the two sensor electrodes a distance corresponding to dimensions of the pixel elements. The processing system is coupled to the sensor electrodes and the field shaping electrode. The processing system is configured to, in a first processing mode, drive a transmitter signal onto a first sensor electrode of the sensor electrodes and receiving a resulting signal with the first sensor electrode of the sensor electrodes comprising effects corresponding to the transmitter signal.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
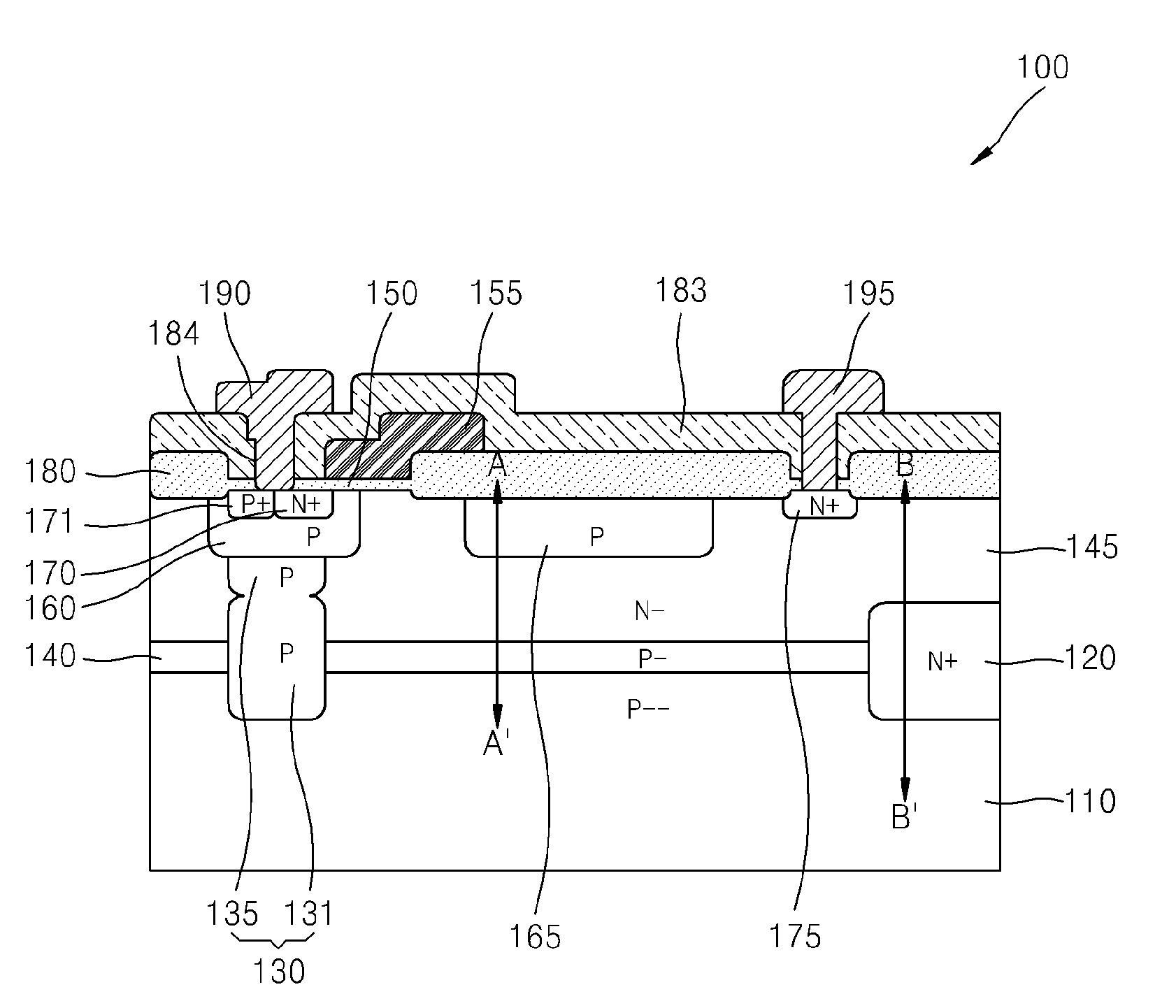
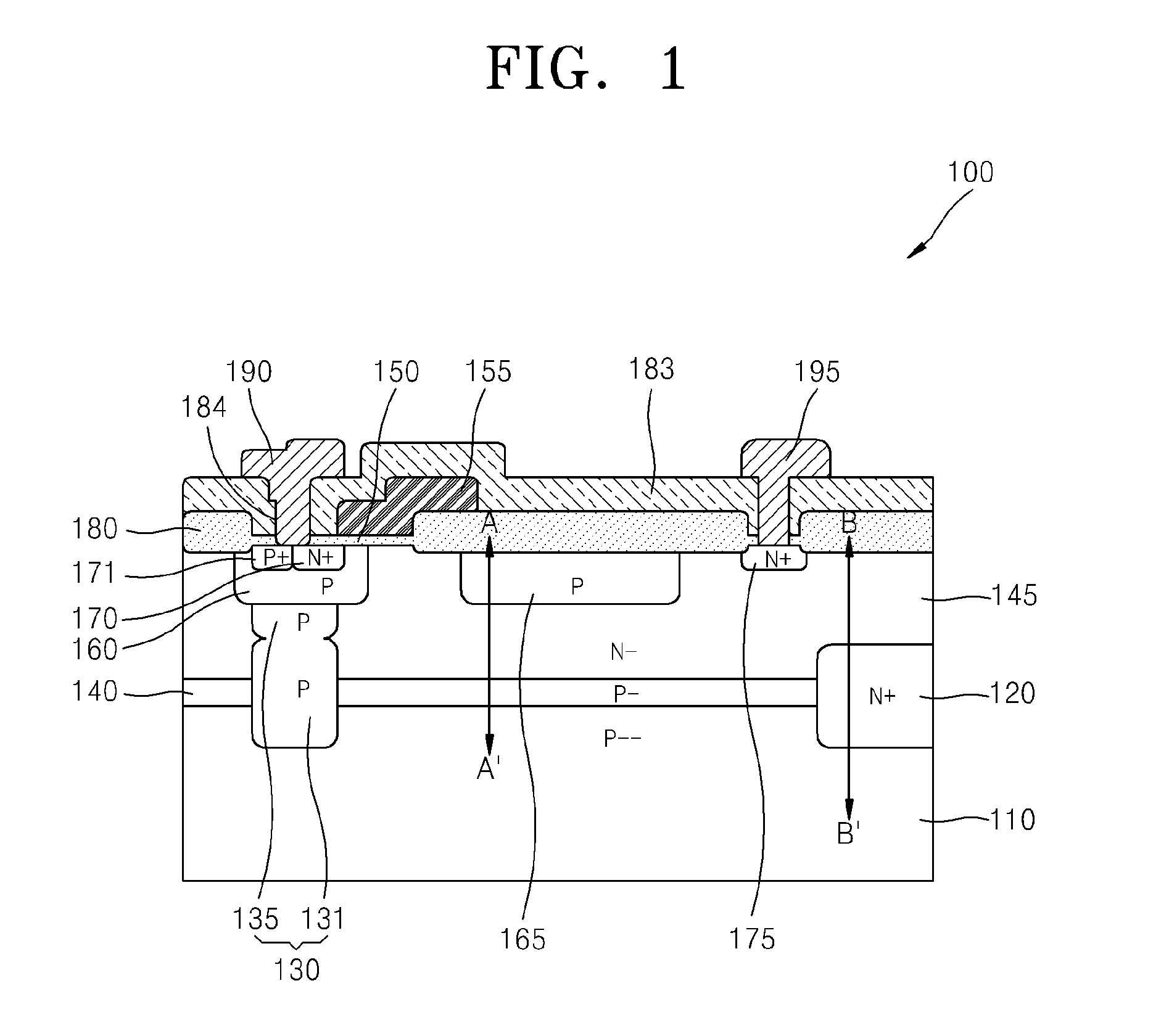
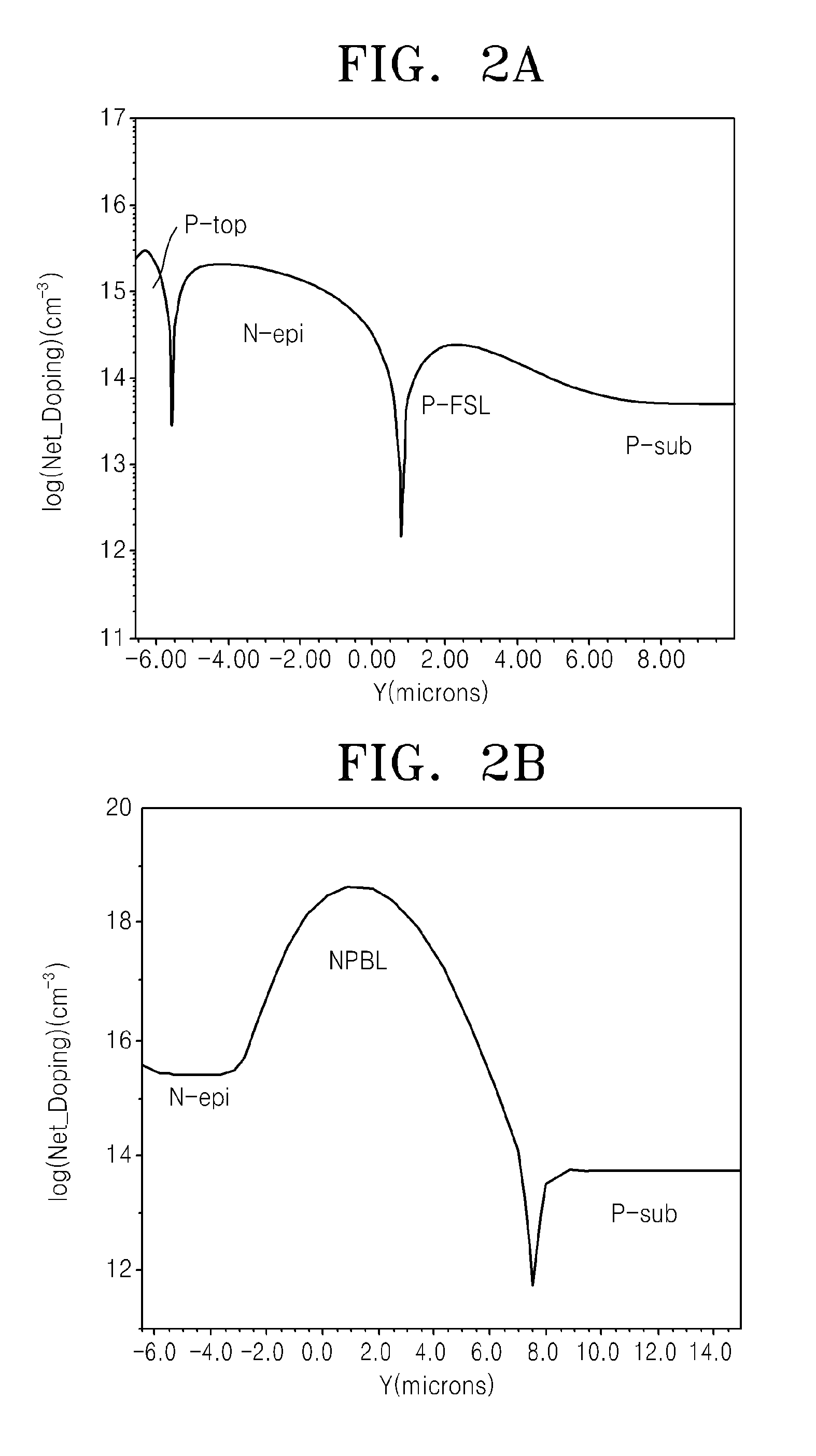
High voltage semiconductor device including field shaping layer and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100001343A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureBody region
Provided are a high voltage semiconductor device in which a field shaping layer is formed on the entire surface of a semiconductor substrate and a method of fabricating the same. Specifically, the high voltage semiconductor device includes a first conductivity-type semiconductor substrate. A second conductivity-type semiconductor layer is disposed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate, and a first conductivity-type body region is formed in semiconductor layer. A second conductivity-type source region is formed in the body region. A drain region is formed in the semiconductor layer and is separated from the body region. The field shaping layer is formed on the entire surface of the semiconductor layer facing the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
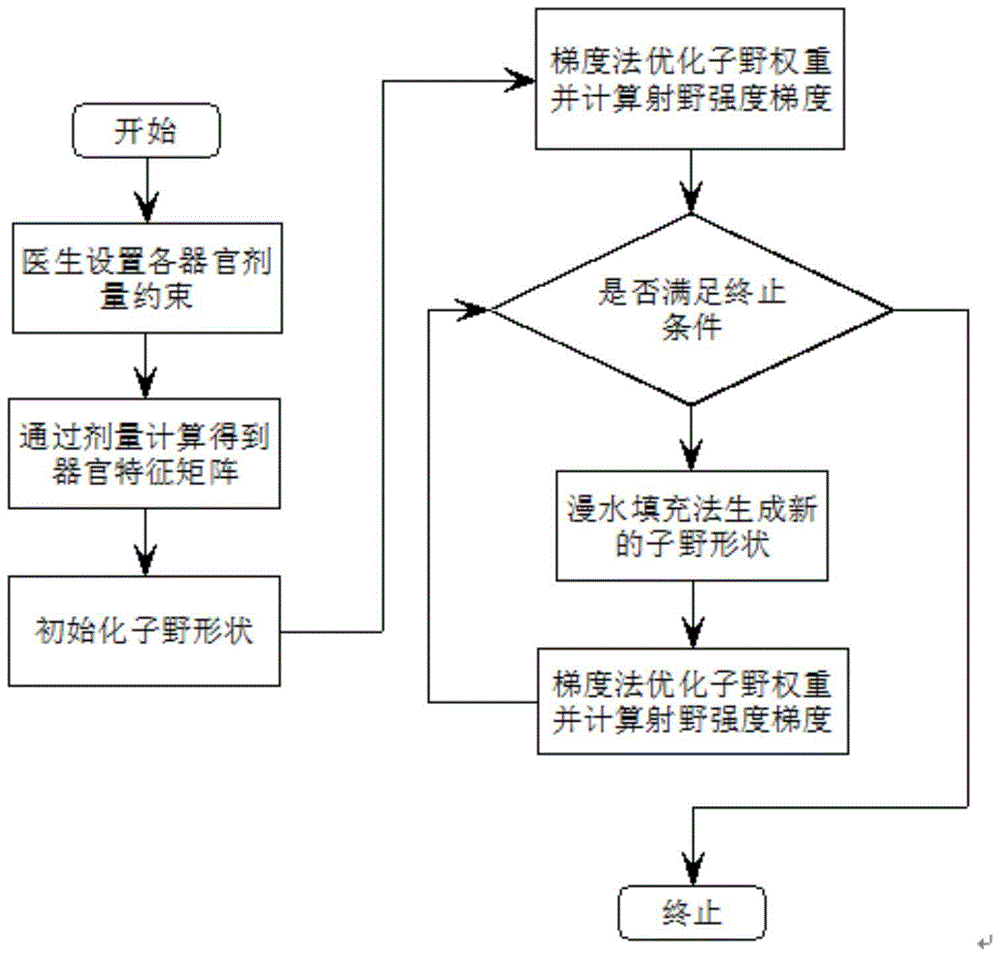
Intensity-modulated sub-field optimization method based on gradient method and floodfill algorithm
InactiveCN105709341AMeet the requirementsSolving the intensity modulated subfield optimization problemX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAlgorithmRadiation field
The invention provides an intensity-modulated sub-field optimization method based on the gradient method and the floodfill algorithm. The method comprises steps of firstly establishing an optimization model according to conditions of information of targets and endangered organs, beam parameters and dosage (size) constraints and initializing an initial sub-field of each radiation field; secondly, by adopting the gradient method, optimizing sub-field weight and obtaining an intensity gradient on a radiation field; thirdly, based on the intensity gradient, by using the floodfill algorithm, calculating a new sub-field shape of the corresponding radiation field; and at last, returning to the step 2 until existing the optimization. According to the invention, solving speed is quick; optimization effects are favorable; the algorithm is stable; and robustness is high.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hall effect thruster with anode having magnetic field barrier
InactiveUS6982520B1Improve efficiencyReduces anode sheath voltageElectric arc lampsDirect voltage acceleratorsMagnetic fluxCondensed matter physics
An efficiency enhancing anode-magnetic structure of a Hall effect thruster produces a radially directed magnetic field between inner and outer poles at the exit portion of a gas distribution channel. The field-shaping structure includes magnetic material extending alongside the channel with an associated secondary flux-generating component to create an axially directed magnetic field in the area between the anode of the thruster and the exit portion of the gas distribution channel.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
Field emission display with electron trajectory field shaping
InactiveUS20060119248A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsField emission deviceField emission display
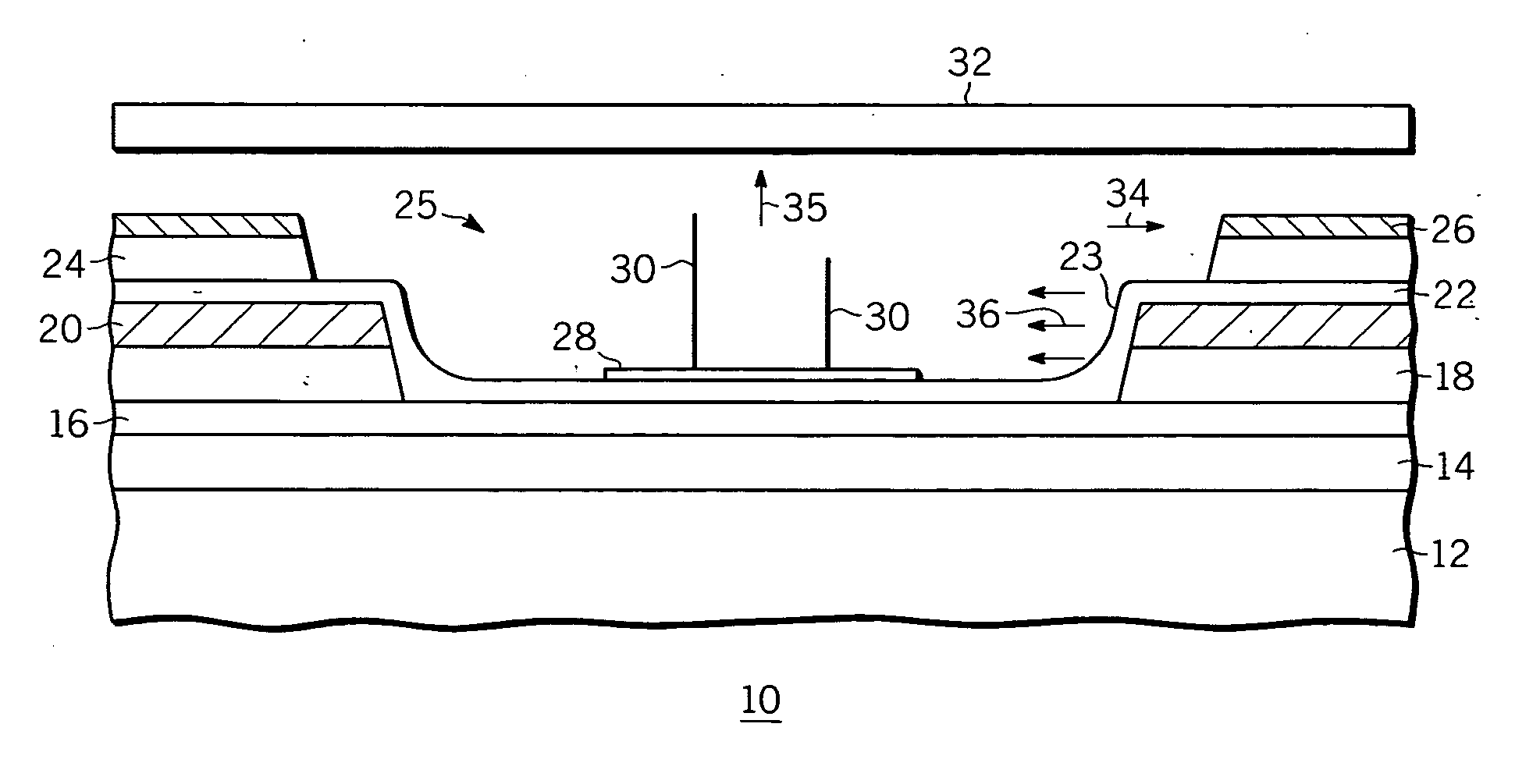
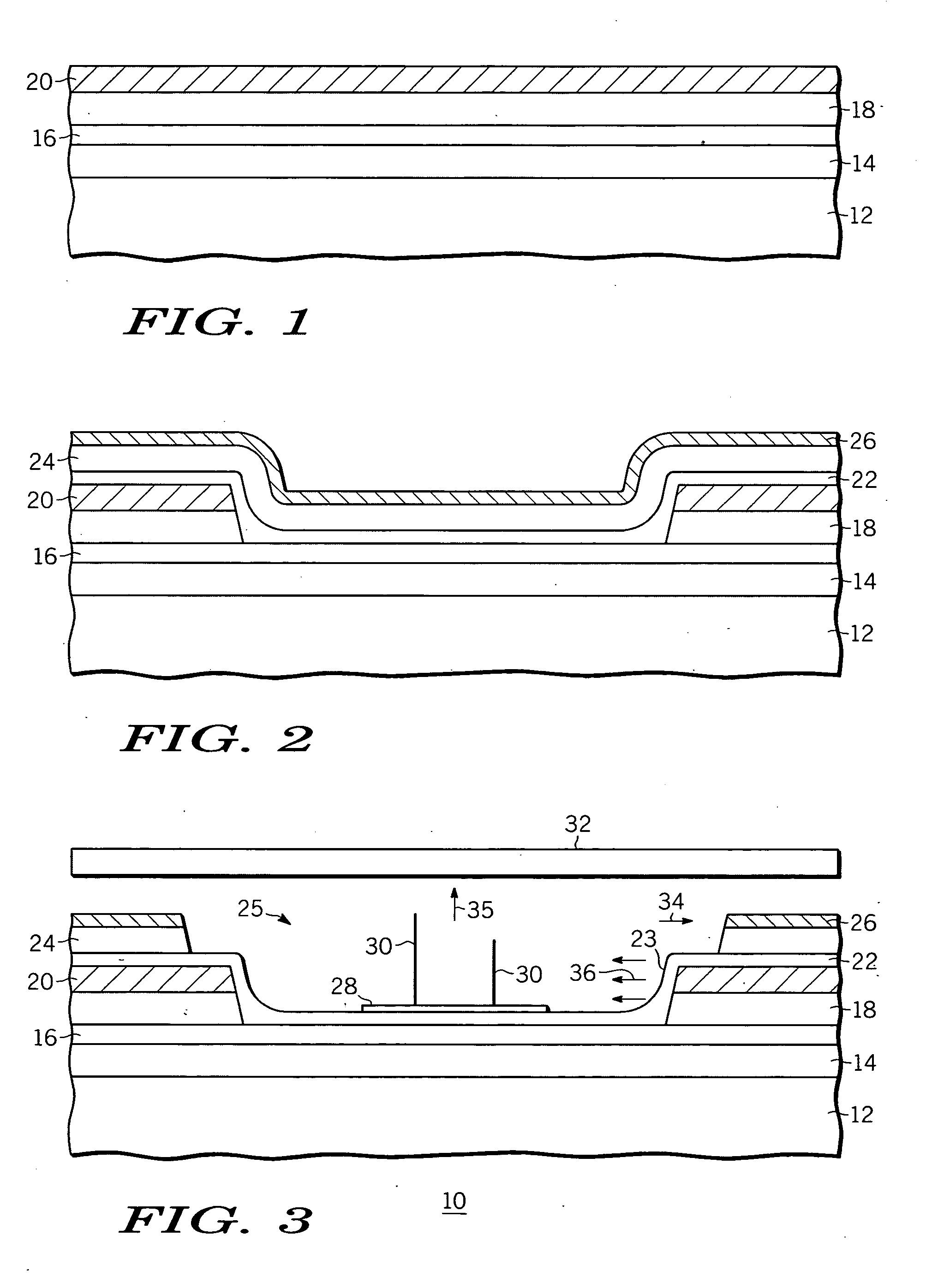
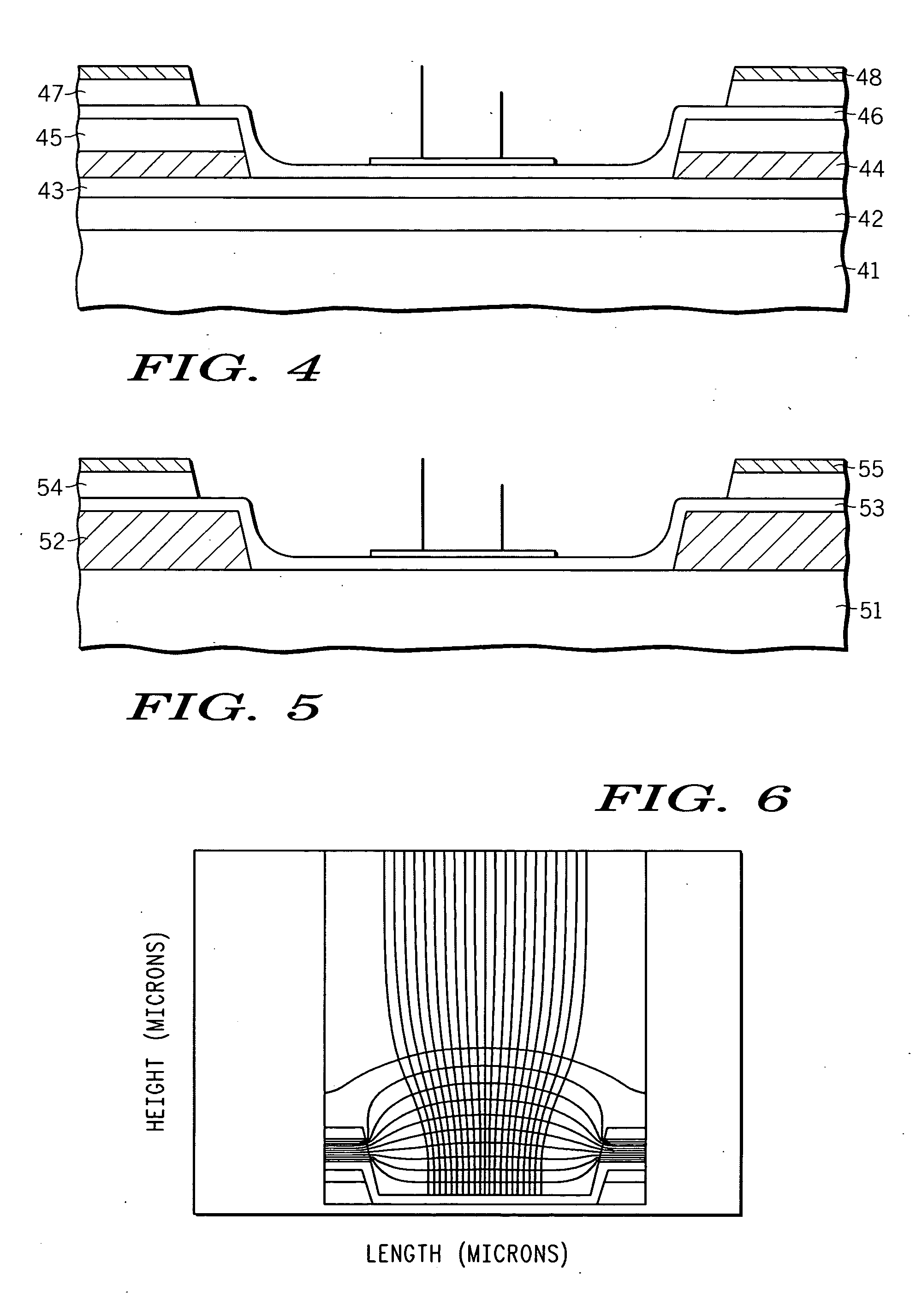
An apparatus is provided for focusing electrons being emitted from a field emission device. The apparatus comprises a substrate (12,41,51) having first and second portions, and a cathode metal layer (20,44,52) formed over the substrate (12,41,51) in the first portion to partially define a sidewall (23) for a trench (25) in the second portion. A ballast layer (22,46,53) is formed over the substrate (12,41,51) in the second portion, the cathode metal layer (20,44,52), and the sidewall (23). A first dielectric layer (24,47,54) is formed over the ballast layer (22,46,53) in the first portion. A gate extraction metal layer (26,48,55) is formed over the first dielectric layer. At least one emitter (30) comprising a high aspect ratio conductive material is formed above the substrate and in the trench (25) having a sidewall (23) defined by the first dielectric layer (24,47,54) and the cathode metal layer (20,44,52). The ballast layer (22,46,53) extends along the sidewall and conductively contacts the cathode metal layer and the at least one emitter. An anode (32) is positioned to receive electrons from the at least one emitter (30). The ballast layer (22,46,53) provides a force that counteracts the sidewise pull of the gate extraction metal layer (26,48,55).
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
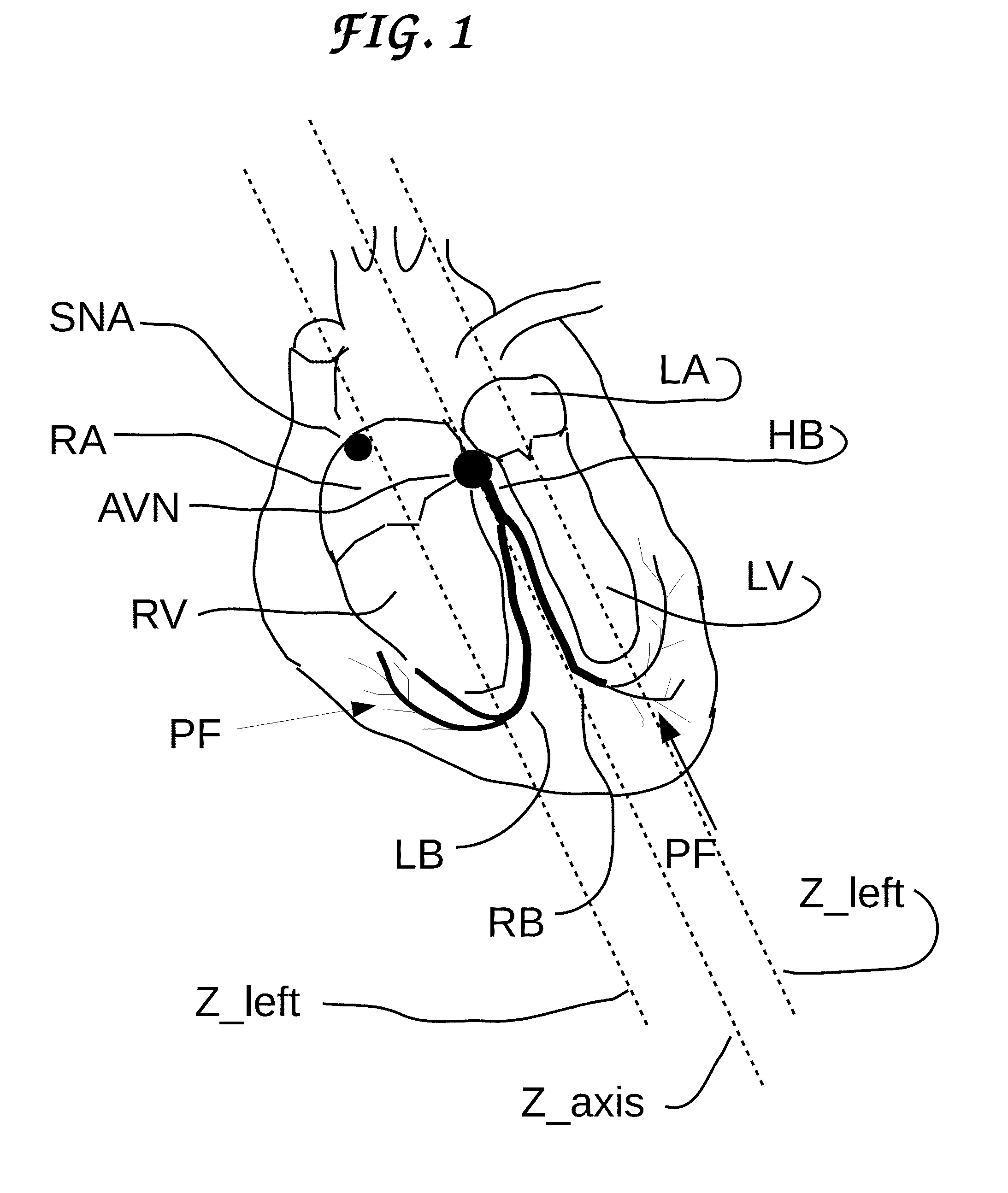
Cell electric stimulator with separate electrodes for electrical field shaping and for stimulation
An electric stimulator for heart, brain, organs and general cells with a possibly random shape and position of electrodes which enhances its performance for breaking the symmetry. Two types of electrodes are introduced: type-1, or active electrodes are similar to prior art, while type-2, or passive electrodes have not been used in this context. Passive electrodes are electrically insulated, being unable to inject current in the surrounding medium, but they are capable of shaping the electric field, which has consequence on the path of the stimulating currents injected by type-1 electrodes. The invention also discloses a supercapacitor-type passive electrode of type-2, which maximizes the stored charge on the electrode—therefore increasing the electric field magnitude created by it.
Owner:LEE CHONG IL +1
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) fluid mover with field shaping feature at leading edge of collector electrodes
InactiveUS8508908B2Minimizing ion migrationSpeed up the flowWave amplification devicesDigital data processing detailsLeading edgeElectricity
Small form-factor ion flow fluid movers that provide electrostatically operative surfaces in a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode, but upstream of a collector electrode or electrodes, can shape operative electric fields and influence ion flows in ways that accentuate downstream flow while minimizing upstream ion migration. In some cases, dielectric surfaces (or even electrically isolated conductive surfaces) along a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode can be configured to collect and retain an initial population of generated ions and thereafter electrostatically repel further ions. Depending on the configuration of such dielectric or electrically isolated conductive surfaces, these repelling electrostatic forces may dissuade ion migration or flow from sensitive but closely proximate components and / or may shape fields to enhance ion flows in a desired downstream direction.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Hall effect thruster with anode having magnetic field barrier
InactiveUS20060076872A1Improve efficiencyIncrease depositionElectric arc lampsMachines/enginesCondensed matter physicsField shaping
An efficiency enhancing anode-magnetic structure of a Hall effect thruster produces a radially directed magnetic field between inner and outer poles at the exit portion of a gas distribution channel. The field-shaping structure includes magnetic material extending alongside the channel with an associated secondary flux-generating component to create an axially directed magnetic field in the area between the anode of the thruster and the exit portion of the gas distribution channel.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
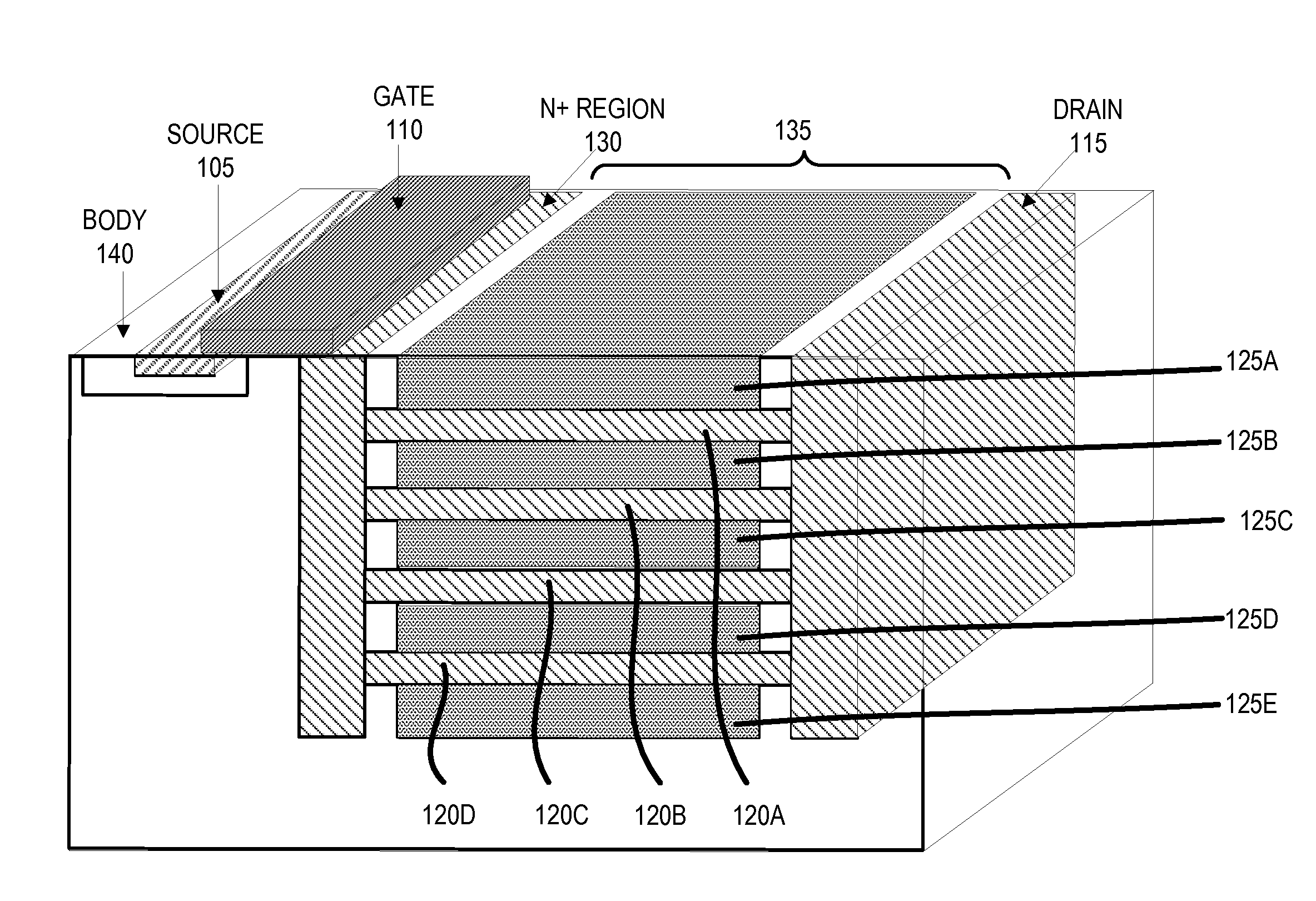
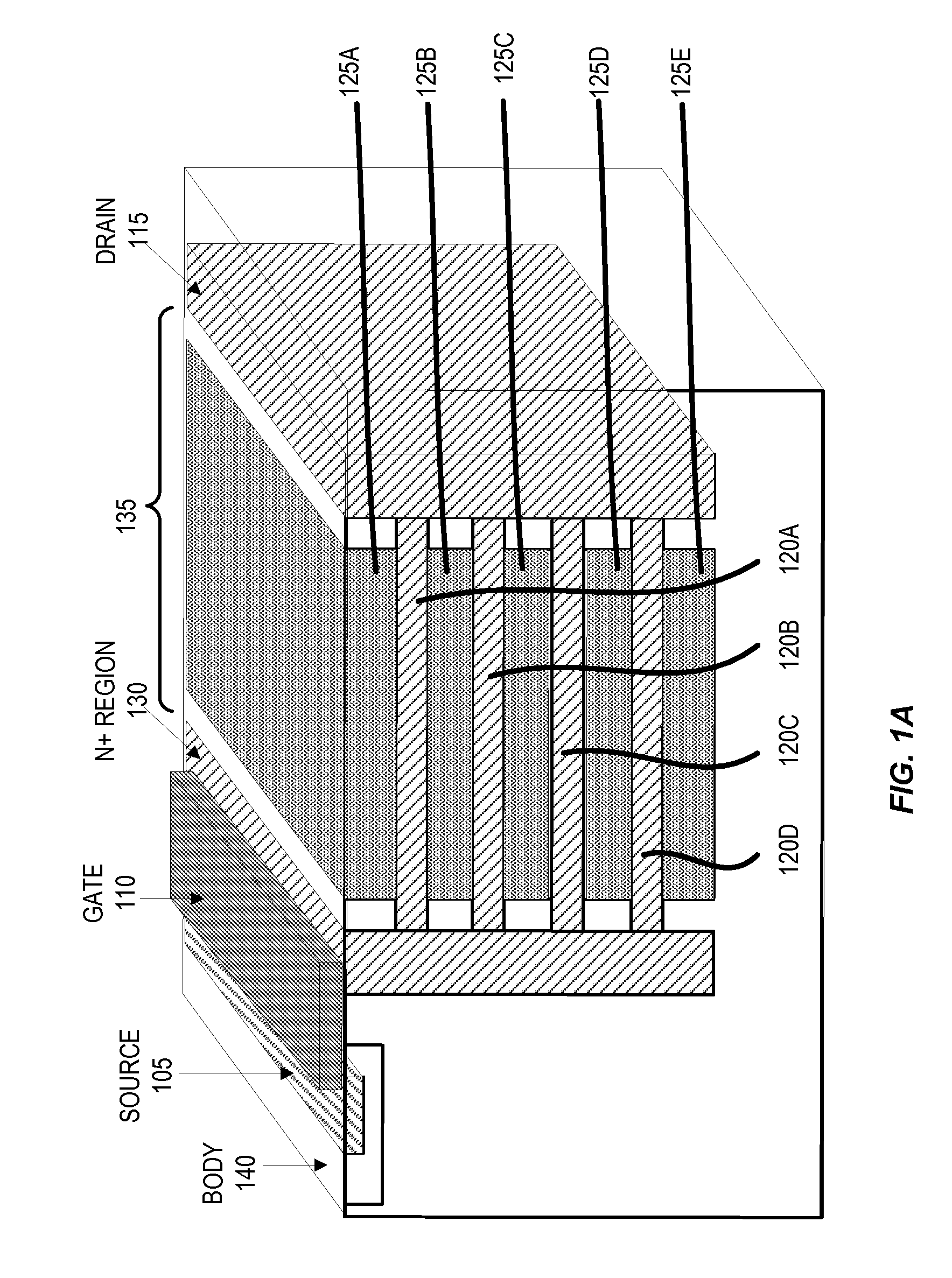
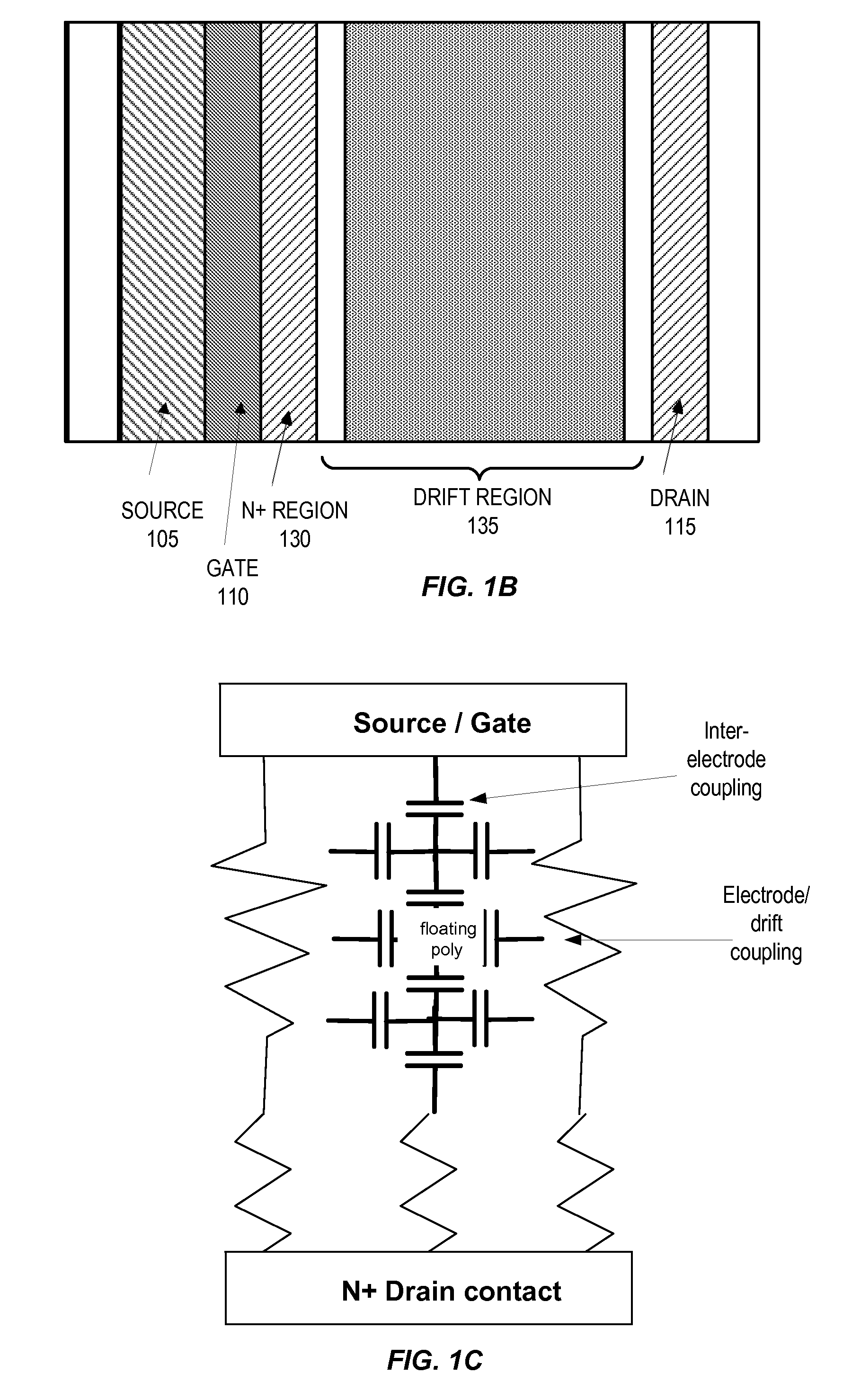
Multi-level Lateral Floating Coupled Capacitor Transistor Structures
ActiveUS20100123171A1Lower on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceFloating charge
A semiconductor device includes a source region, a drain region, a gate region, and a drift region. The drift region further includes an active drift region and inactive floating charge control (FCC) regions. The active drift region conducts current between the source region and the drain region when voltage is applied to the gate region. The inactive FCC regions, which field-shape the active drift region to improve breakdown voltage, are vertically stacked in the drift region and are separated by the active drift region. Vertically stacking the inactive FCC regions reduce on-resistance while maintaining higher breakdown voltages.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
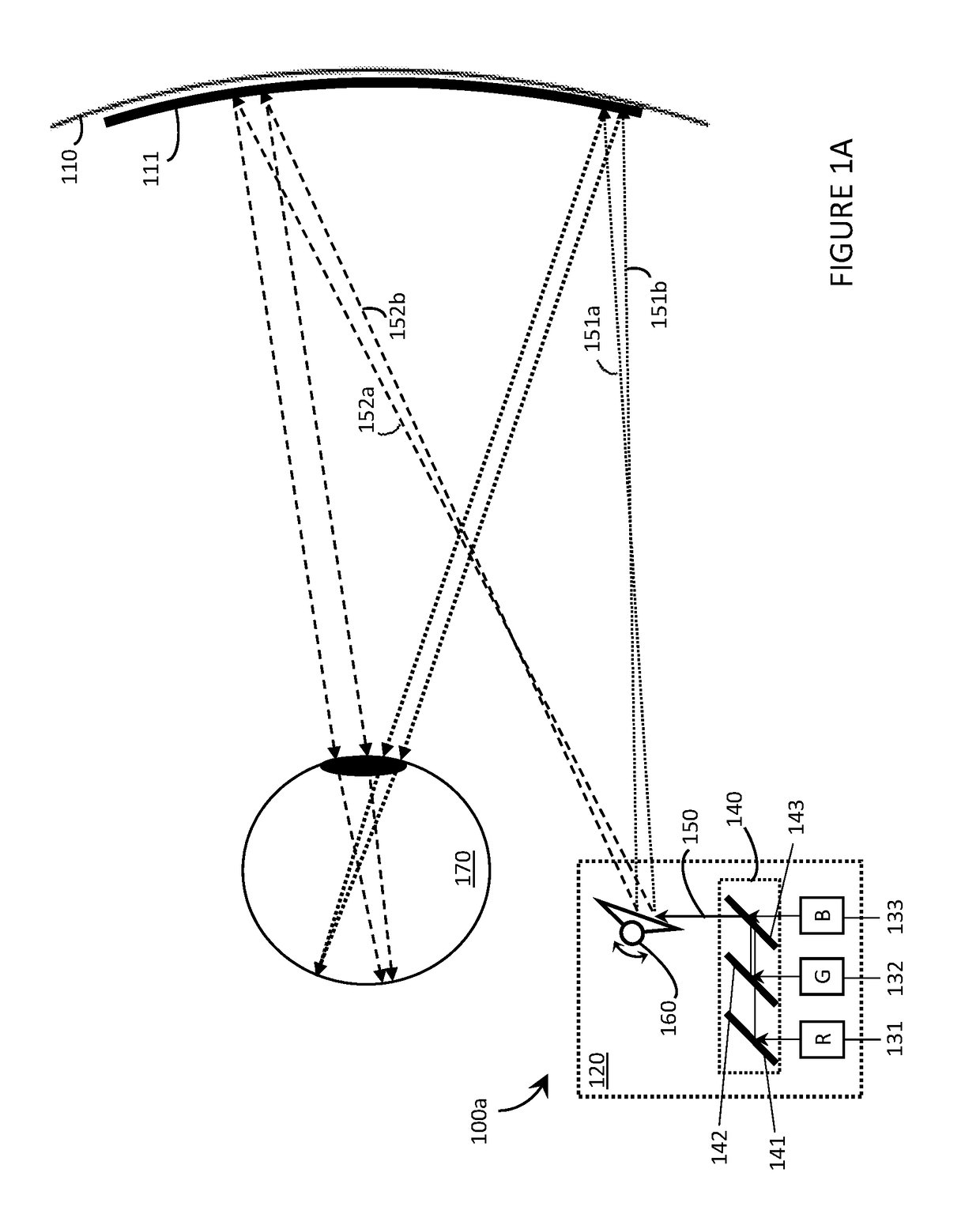
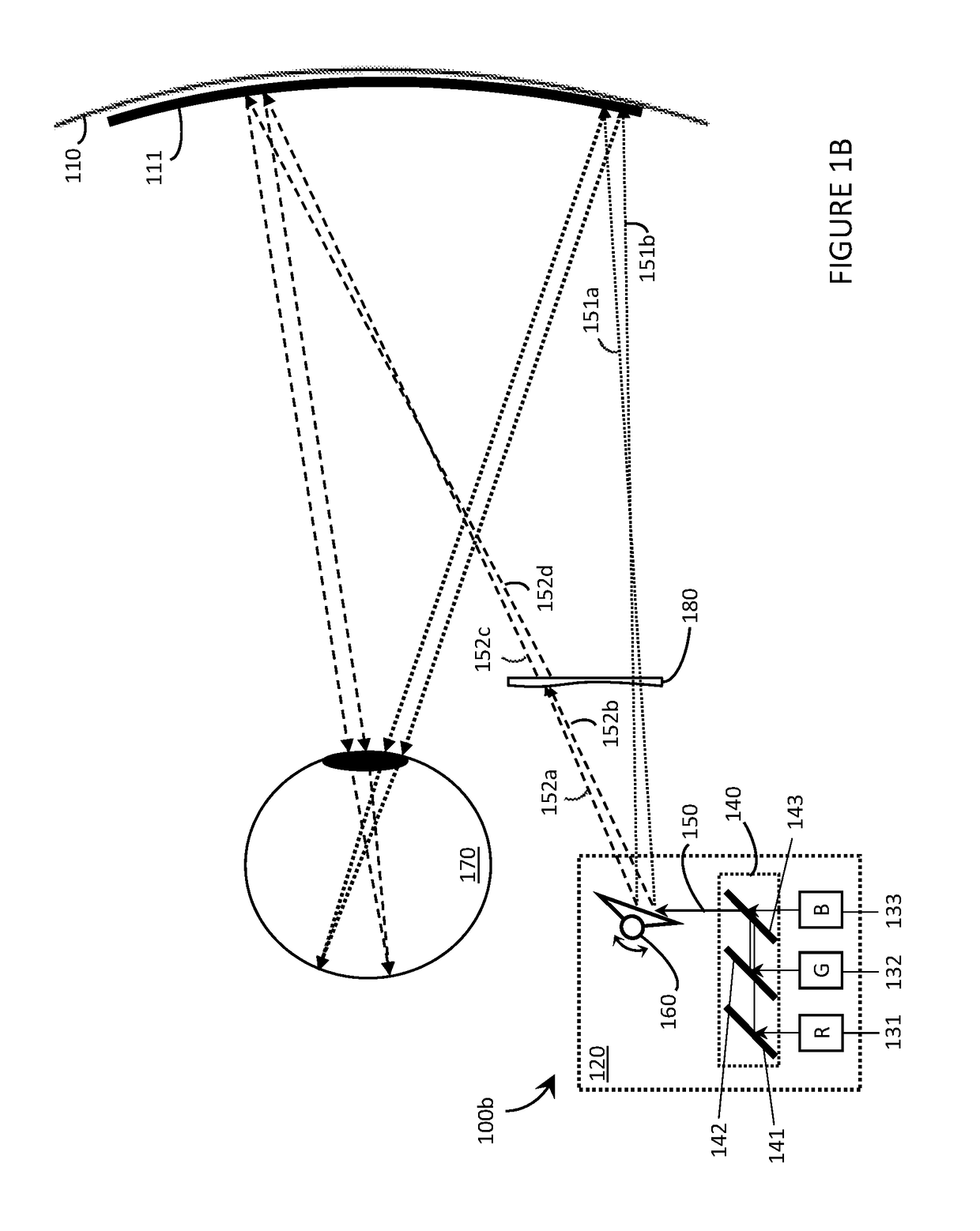
Systems, devices, and methods for field shaping in wearable heads-up display
Systems, devices, and methods for field shaping in wearable heads-up displays (WHUD) with laser projectors are described. A WHUD includes a support structure carrying a laser projector, a field shaper optic, and a transparent combiner to combine the projected laser light and environmental light. The laser projector generates a laser light having a field. The laser light is scanned through the field shaper optic and over the transparent combiner. The field shaper optic heterogeneously varies the focal length of the laser light depending on the laser light properties to alter the field of the laser light to approximately match a shape of the transparent combiner. The transparent combiner redirects the laser light to a field of view of a user to create a focused image at an eye of the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Large focus domain forming method for phase control array focusing supersonics
InactiveCN1820804AStable temperatureLong-term stable directional conformal heatingUltrasound therapyMechanical vibrations separationSonificationHeat sensitive
The present invention relates to supersonic focusing phase control array method to form large focus domain. Heat field shape is set based on the size and shape of the target tissue, and the supersonic focusing phase control array transducer has its element exciting signal phases and amplitudes regulated to generate various modes of multiple focus supersonic field distribution, so as to form required focus domain shape and size, provide supersonic energy for heating the target tissue and form intracorporeal local stereo heating region up to 30 mm. For even larger target tissue, the divisional synthesis mode is adopted. The formed multiple focus supersonic field may be exchanged or rotated to ensure homogeneous heat distribution. The present invention makes it possible to realize shaped directional heating of deep body target tissue, and this provides the technological foundation for the treating technology of directional opening of heat sensitive liposome and the heat synergistic effect of carried heat sensitive medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
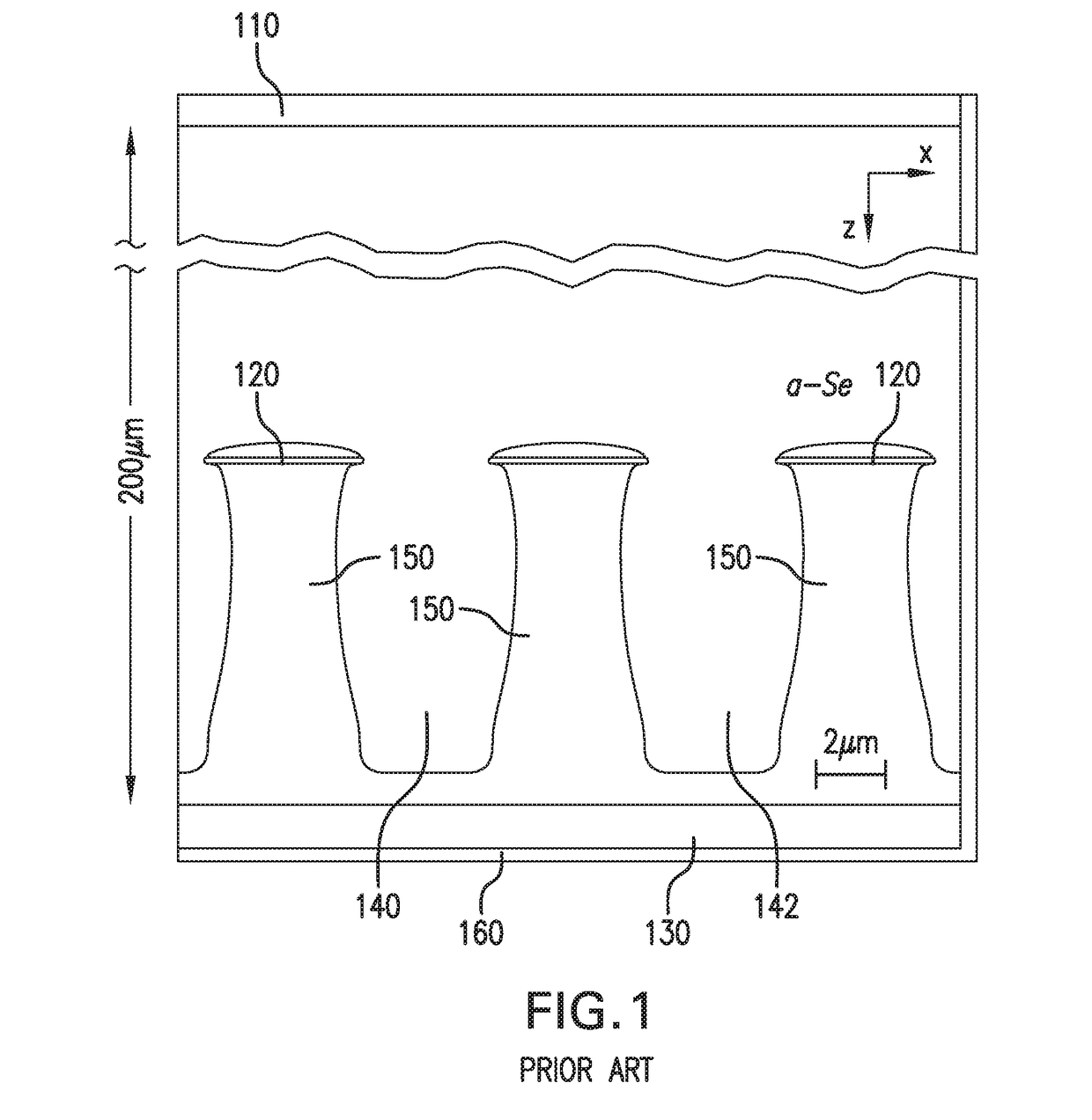
Multi-well selenium device and method for fabrication thereof
Provided is a field shaping multi-well detector and method of fabrication thereof. The detector is configured by depositing a pixel electrode on a substrate, depositing a first dielectric layer, depositing a first conductive grid electrode layer on the first dielectric layer, depositing a second dielectric layer on the first conductive grid electrode layer, depositing a second conductive grid electrode layer on the second dielectric layer, depositing a third dielectric layer on the second conductive grid electrode layer, depositing an etch mask on the third dielectric layer. Two pillars are formed by etching the third dielectric layer, the second conductive grid electrode layer, the second dielectric layer, the first conductive grid electrode layer, and the first dielectric layer. A well between the two pillars is formed by etching to the pixel electrode, without etching the pixel electrode, and the well is filled with a-Se.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Phase grating displacement sensor
InactiveCN101571376AUp to measurement resolutionHigh precisionUsing optical meansPhase gratingImage resolution
The invention relates to the field of precision instruments, in particular to a phase grating displacement sensor, which achieves displacement detection function by projecting Moire fringes formed by a scale grating and an indication grating to a field-shaped photoelectric receiving element, outputting four-phase signals with phase difference of 90 degrees and forming an ideal Lissajous circle. In order to improve performance, a high-power fine electronic division encrypting circuit also can be added to carry out high-power fine division for the four-phase signals so as to achieve the measurement resolution needed by a system; and a measuring bar can be provided with a measuring bar motion system applying the air damping principle to improve the stability and reliability. The applied displacement measuring system has the advantages of simple structure, convenient adjustment, strong capability of receiving signals, stability and high precision, and can correct error in real time.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIANGXING ELECTRONICS TECH
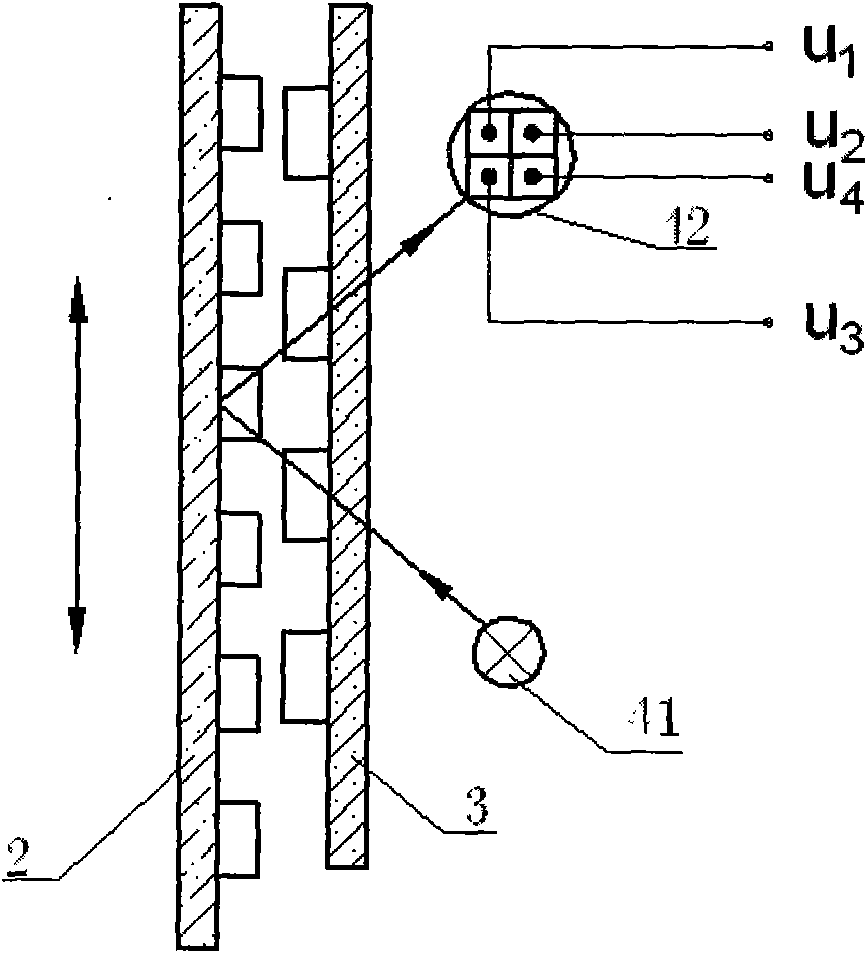
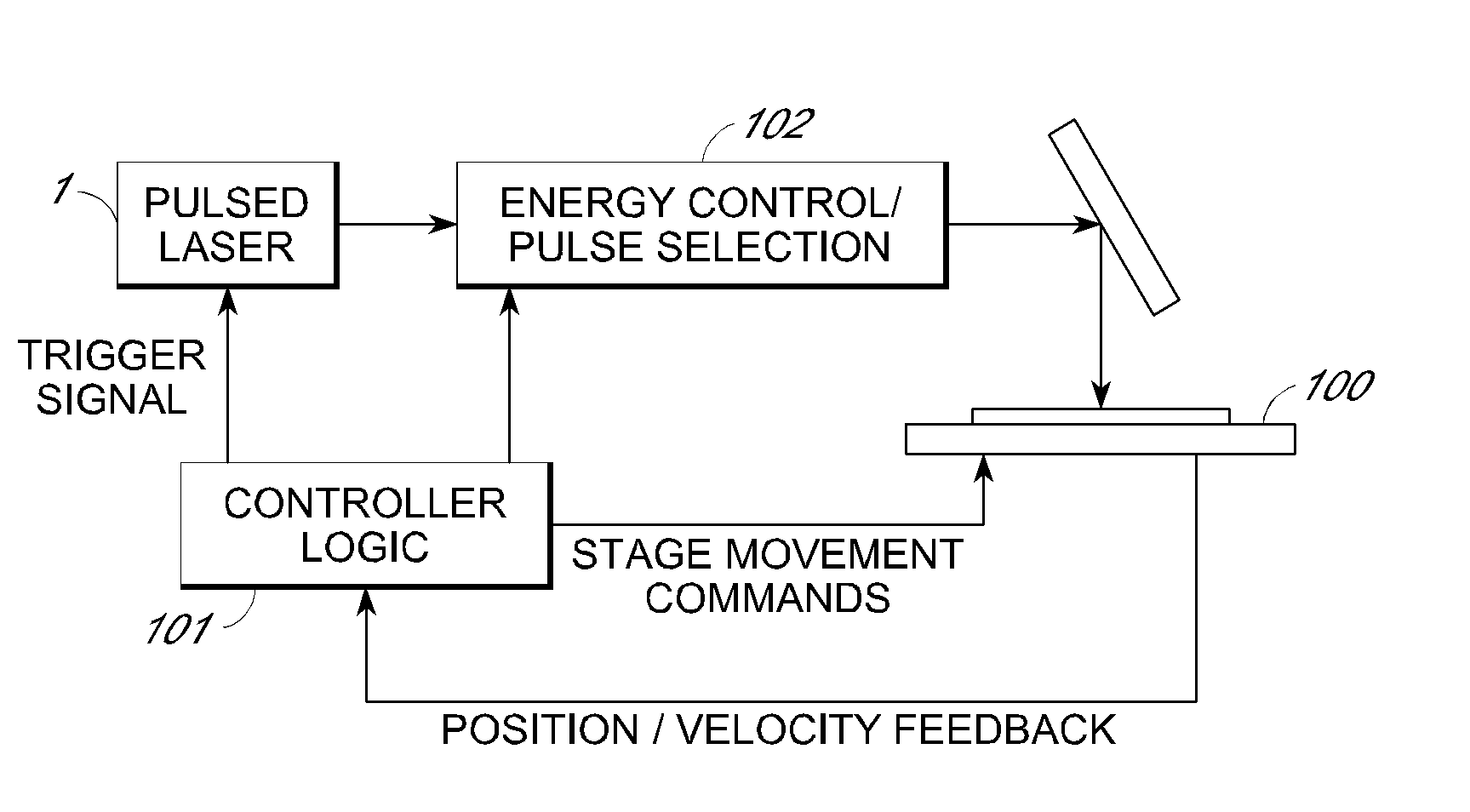
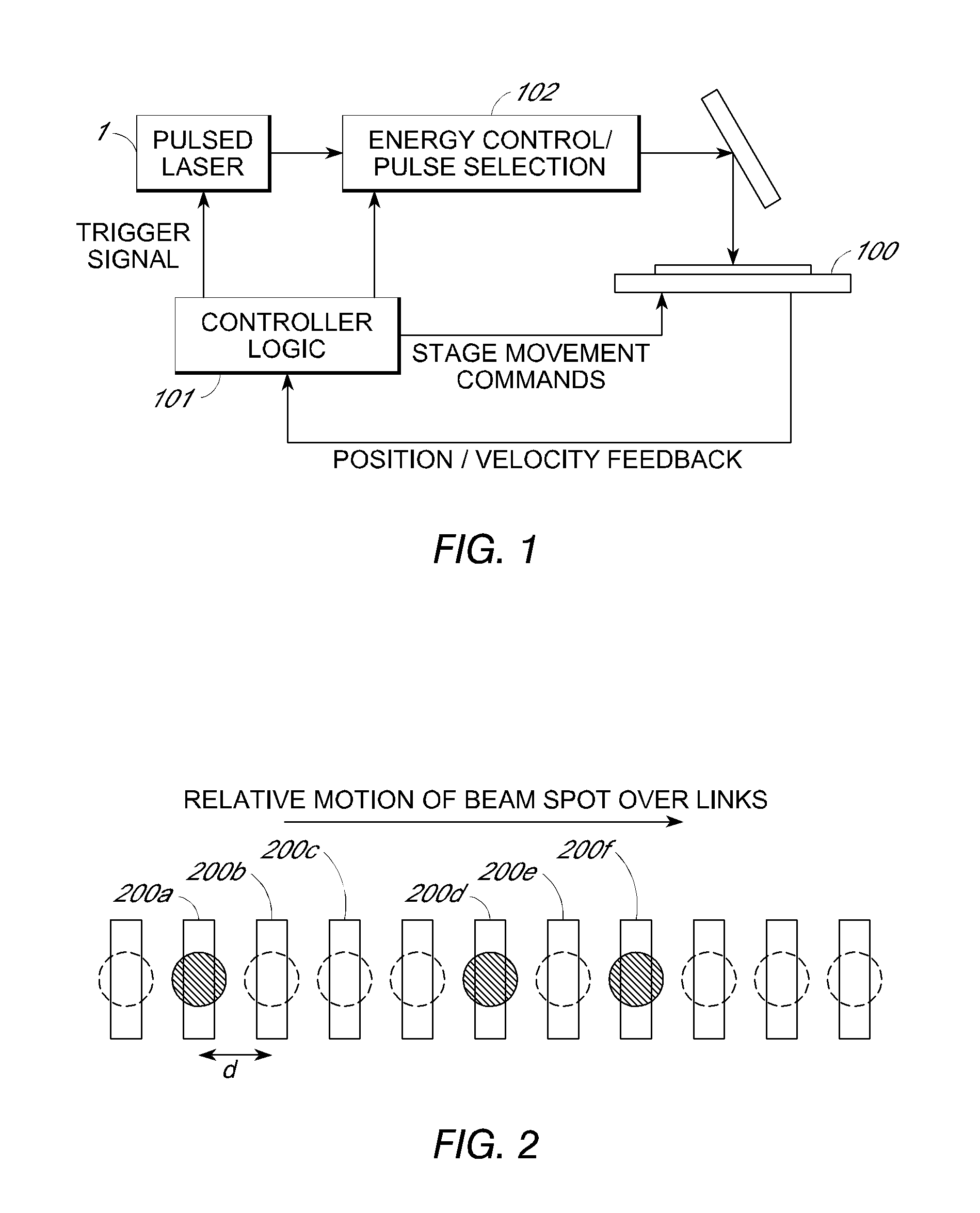
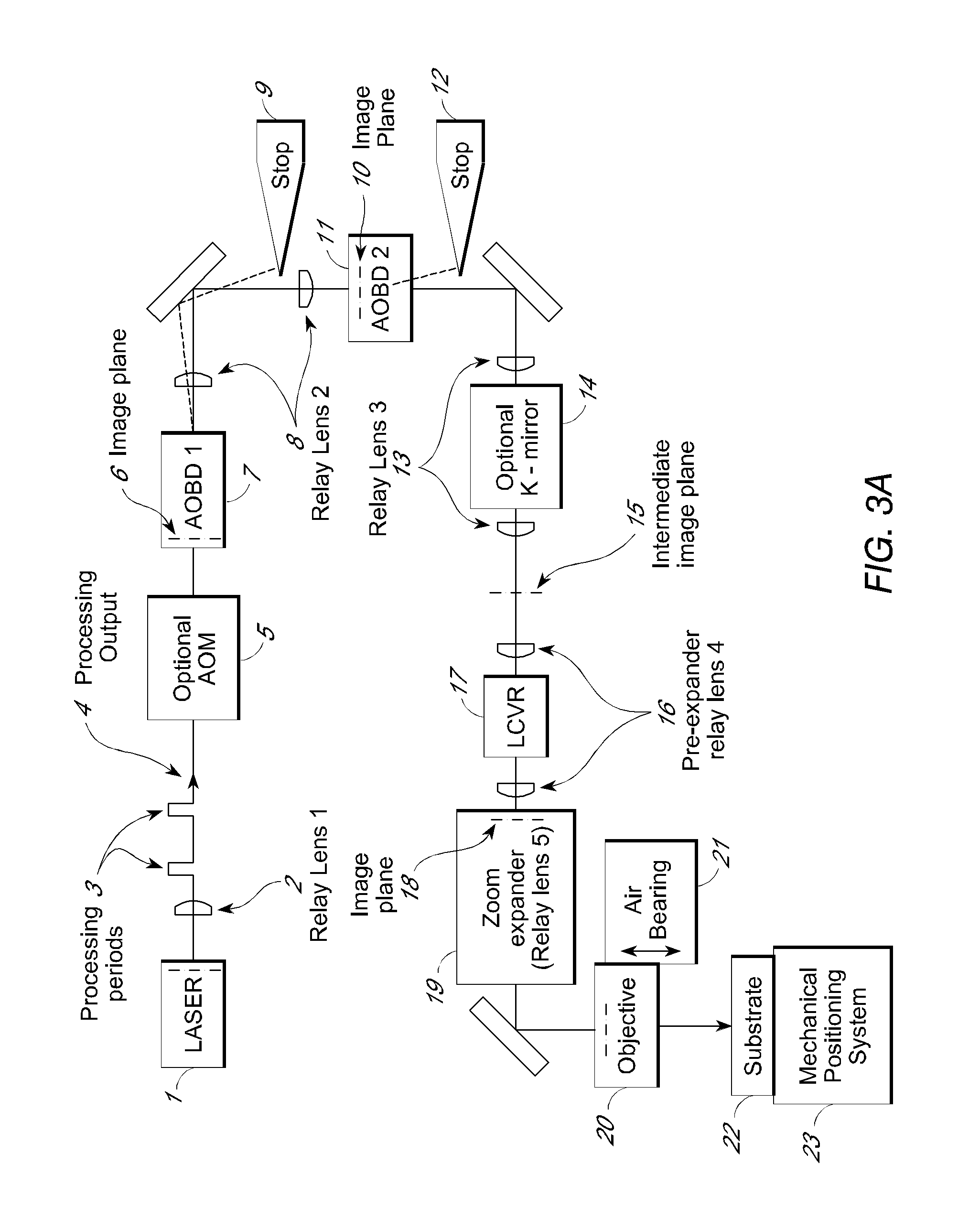
Predictive link processing
InactiveUS20120241427A1Avoid interactionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLaser processingOptoelectronics
A method of processing material of device elements by laser interaction is disclosed. According to one aspect, the method includes generating a pulsed laser processing output along a laser beam axis, the output including a plurality of laser pulses triggered sequentially at times determined by a pulse repetition rate. A trajectory relative to locations of device elements to be processed is generated. A position of one or more designated device elements relative to an intercept point position on the trajectory at one or more laser pulse times is determined, and a laser beam is deflected based on the predicted position within a predetermined deflection range. According to some aspects, the predetermined deflection range may correspond to a compass rose or cruciform field shape. As a result, a deflection accuracy for laser processing may be improved.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Optimization method and optimization system for adaptive radiotherapy
ActiveCN104866928ASimple change relationshipQuality improvementForecastingRadiation therapyAnatomical structuresAlgorithm
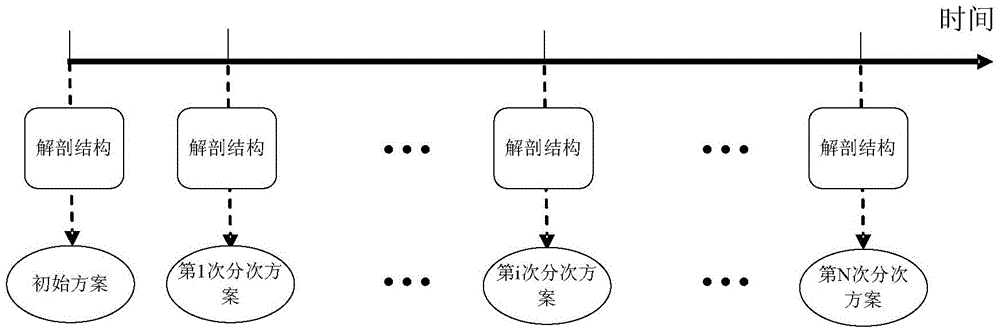
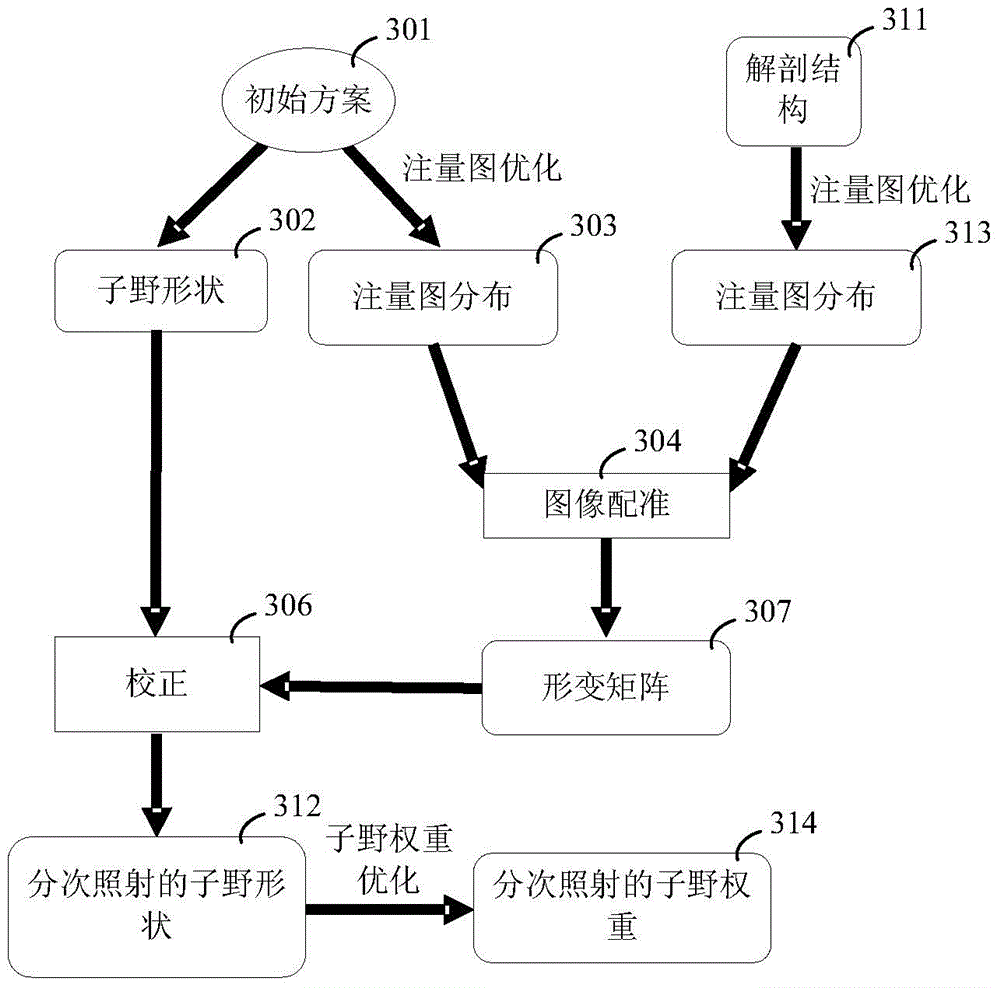
The invention provides an optimization method and an optimization system for adaptive radiotherapy. The method comprises the following steps that: an initial anatomical structure of a patient is determined; an initial scheme applicable to initial irradiation is determined on the basis of the initial anatomical structure; fluence map optimization is carried out according to the initial anatomical structure to obtain fluence map distribution; before each time of multi-time irradiation, a current anatomical structure of the patient is determined, and the fluence map optimization is carried out according to the current anatomical structure to obtain the fluence map distribution of the current time irradiation; the fluence map distribution of the current time irradiation and the fluence map distribution of the reference irradiation are registered to obtain a deformation matrix, wherein the reference irradiation is any one irradiation before the current time irradiation; the deformation matrix is used for correcting the sub field shape of the reference irradiation to obtain the sub field shape of the current time irradiation; and a sub field weight optimization algorithm is adopted for determining the sub field weight of the current time irradiation. The optimization method and the optimization system can more precisely and fast determine the sub field shape in the multi-time radiotherapy scheme.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com