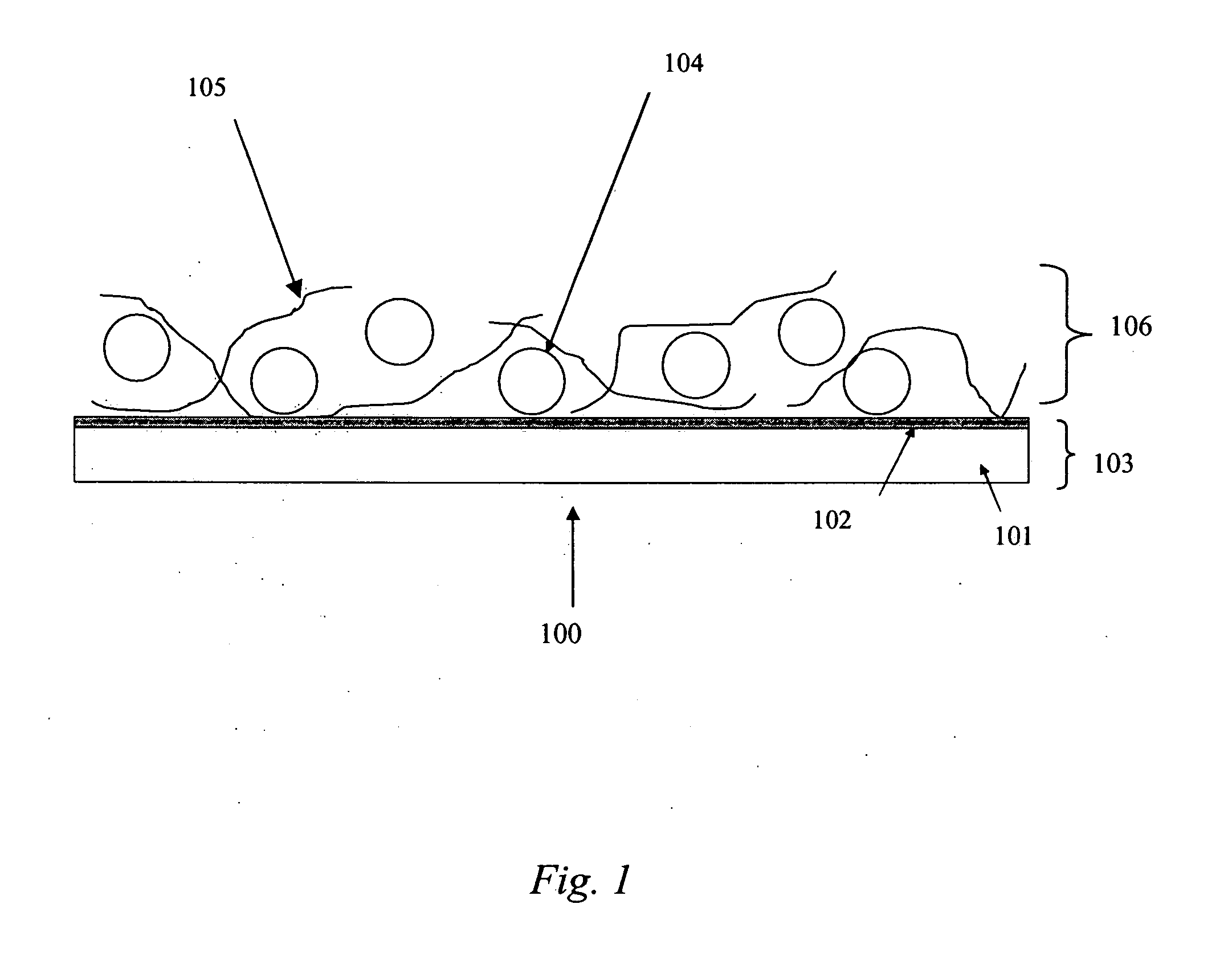
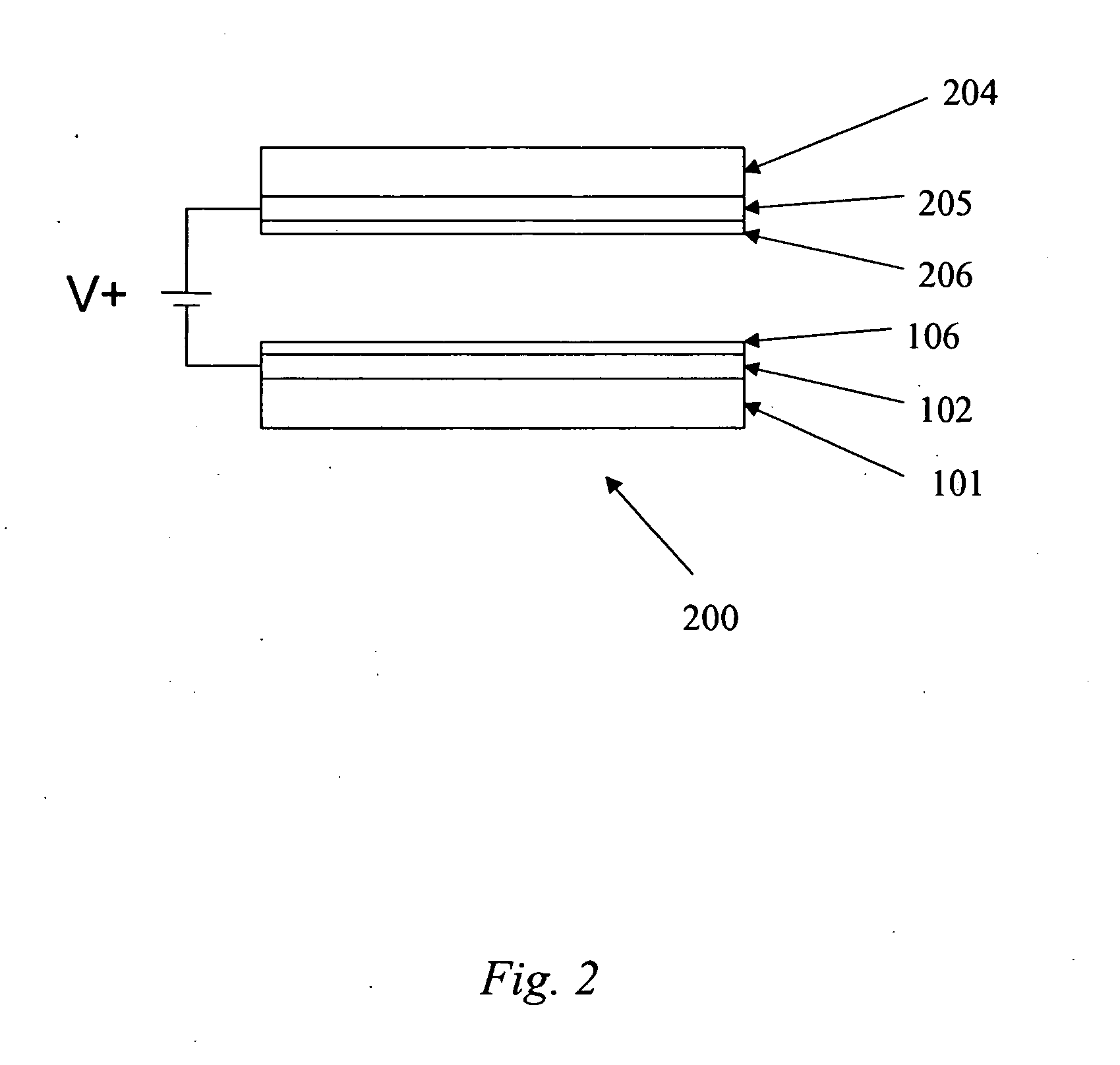
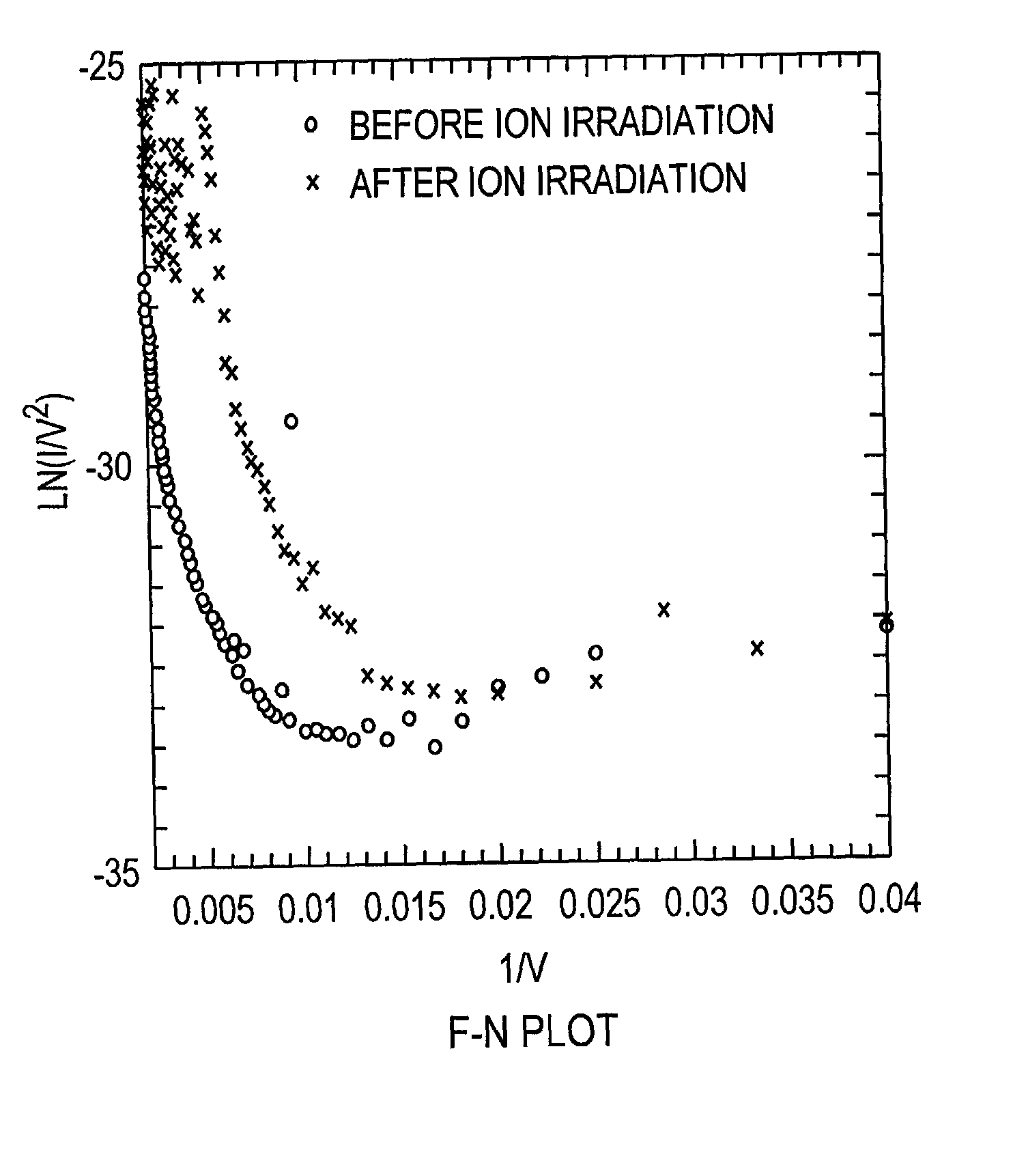
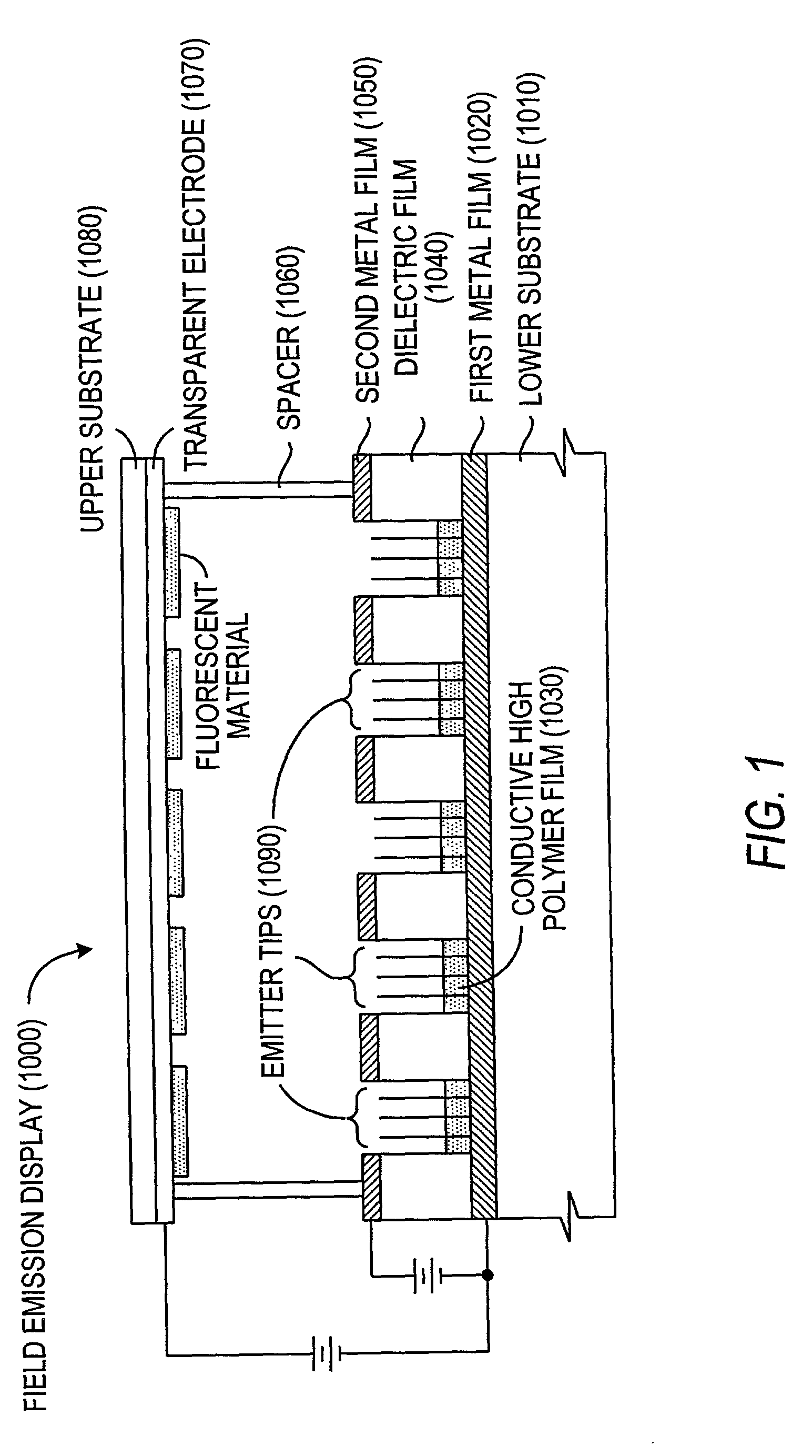
Patents
Literature
932 results about "Field emission display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
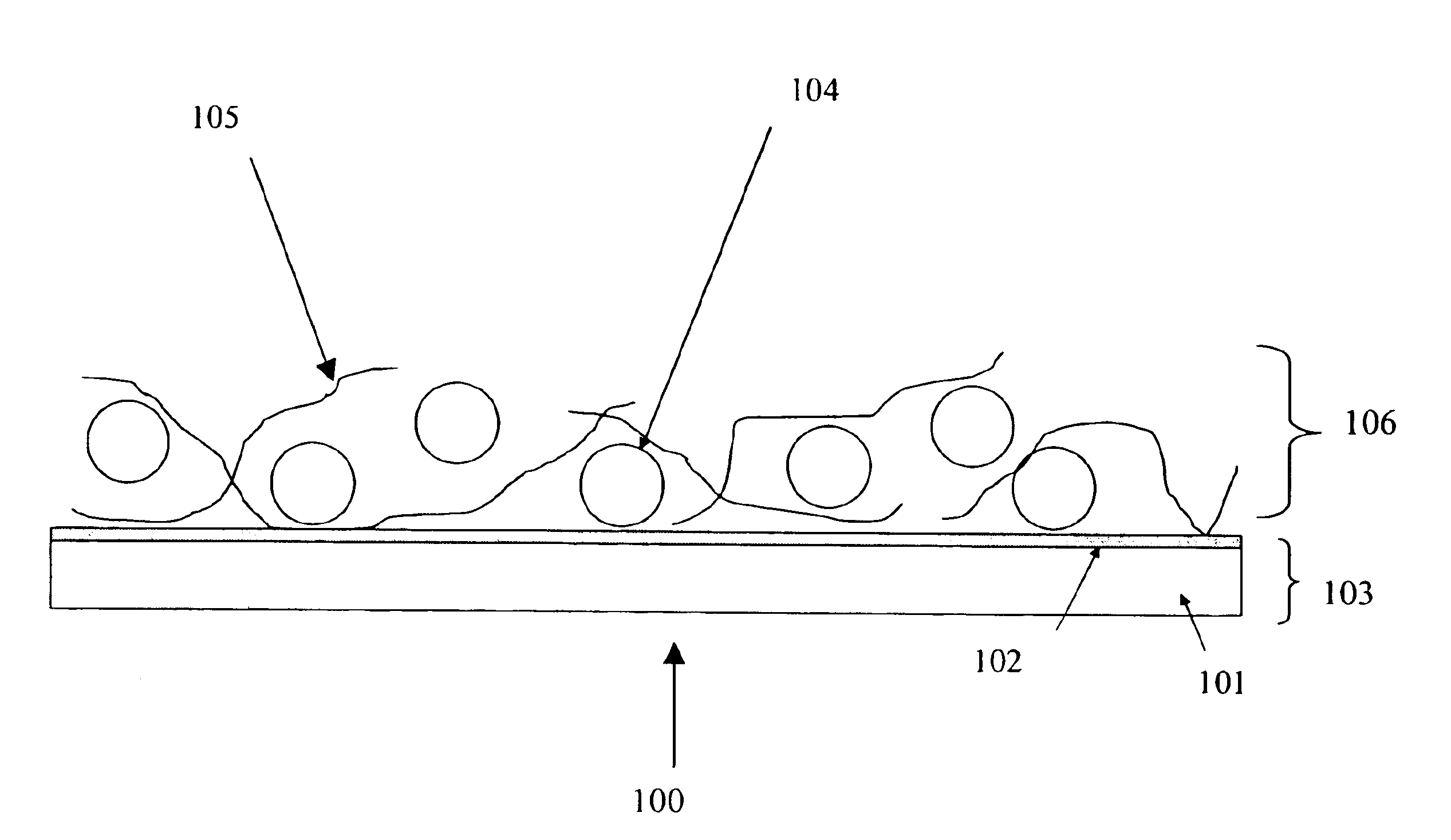
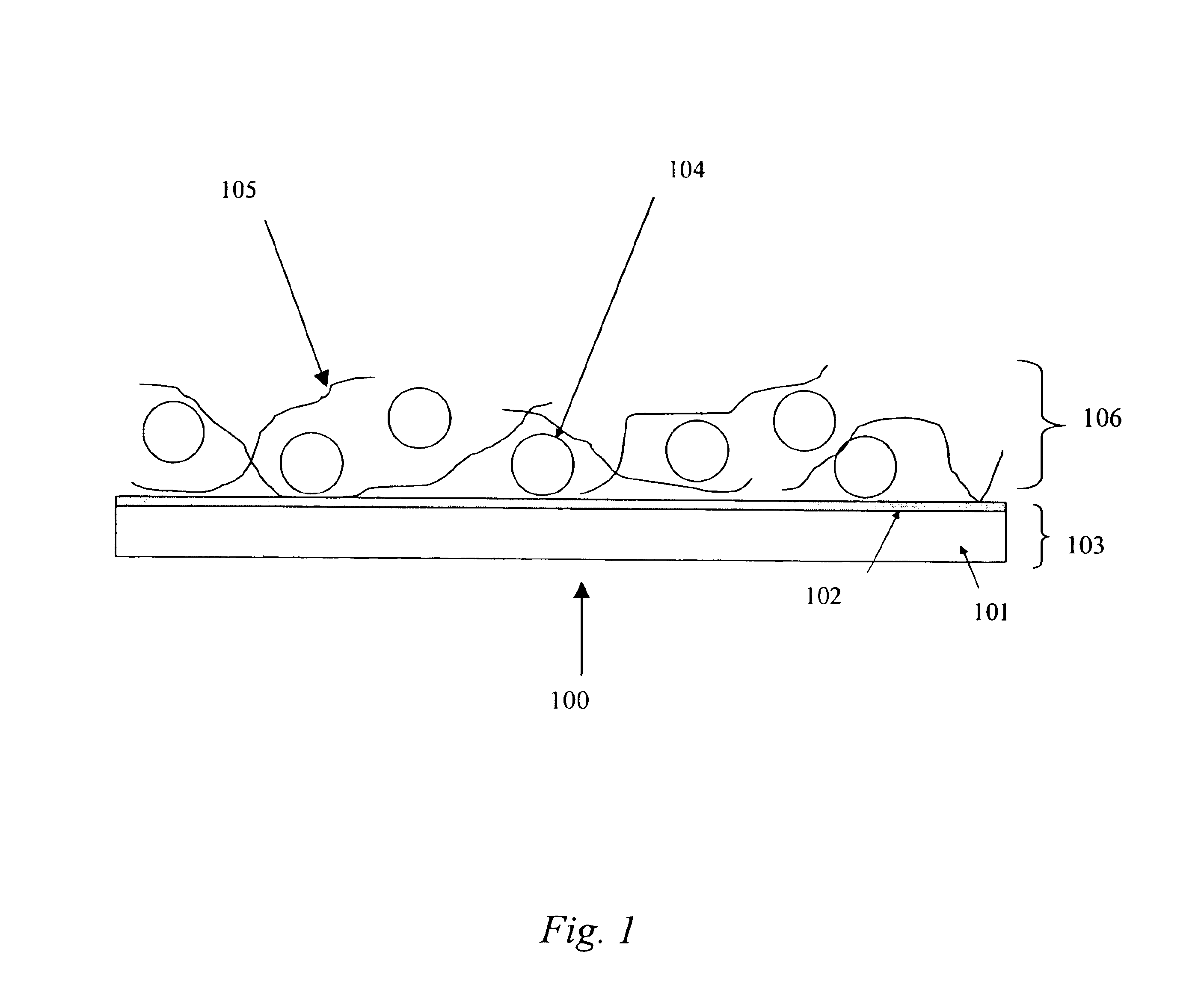
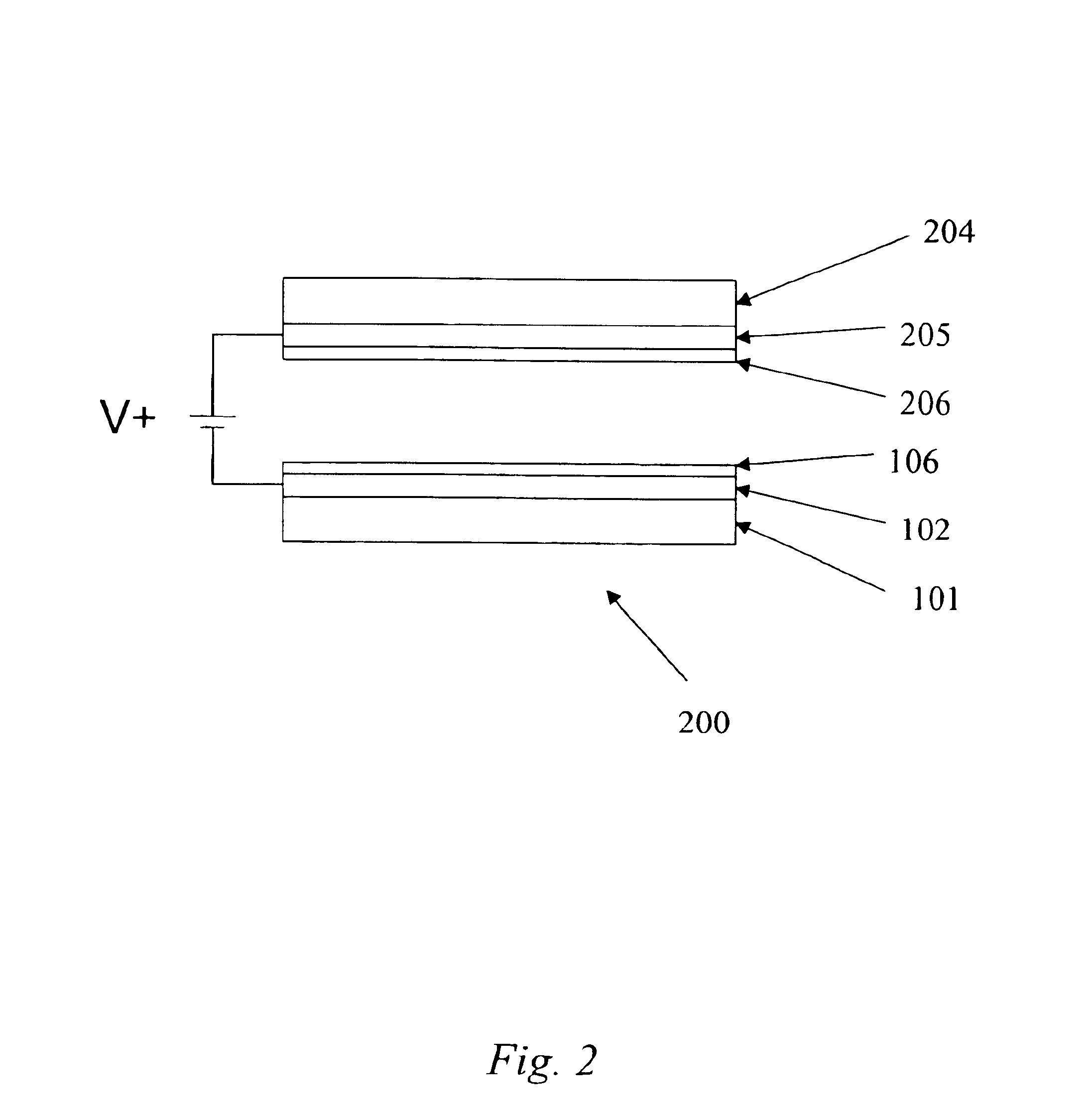
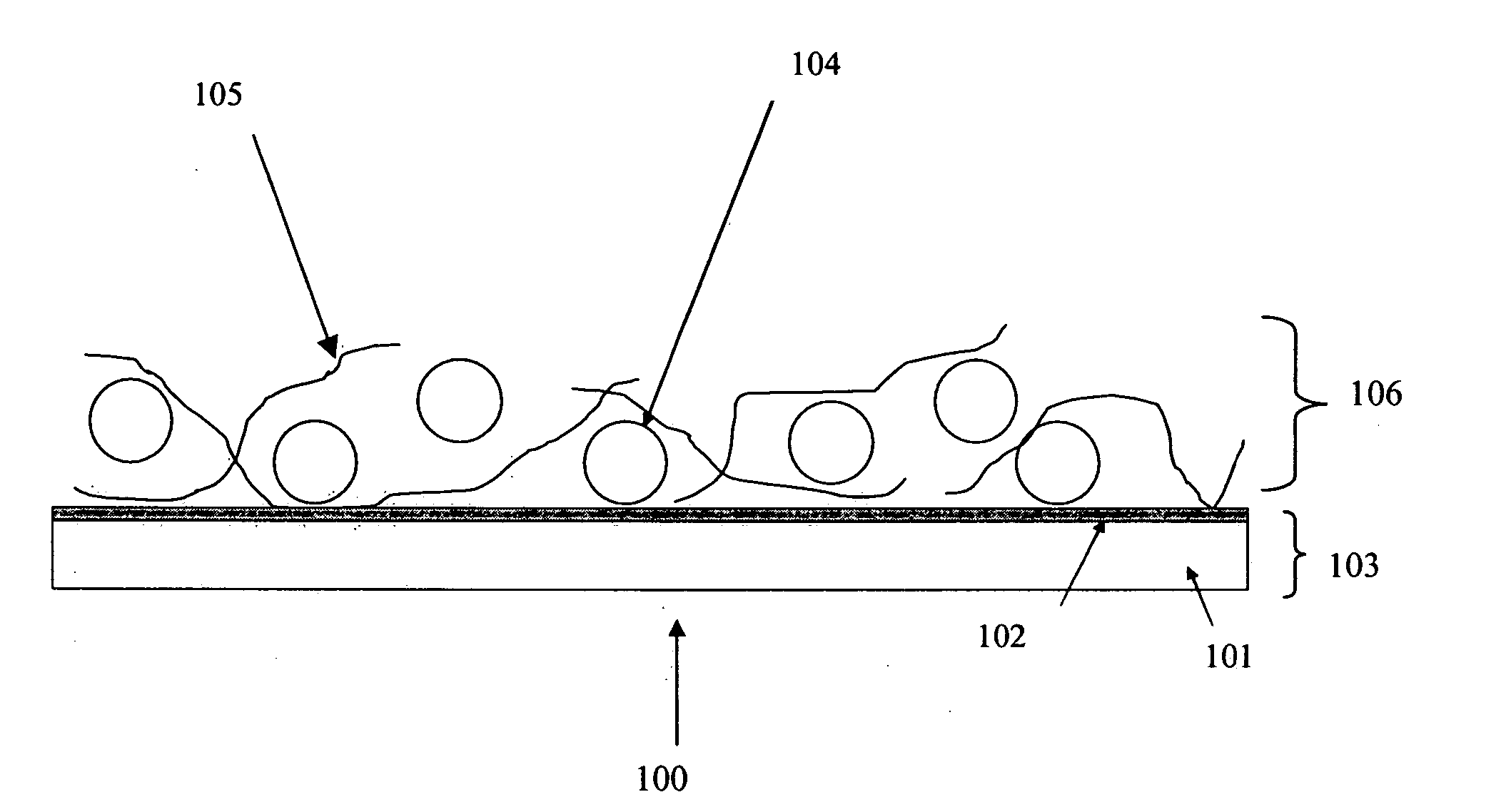
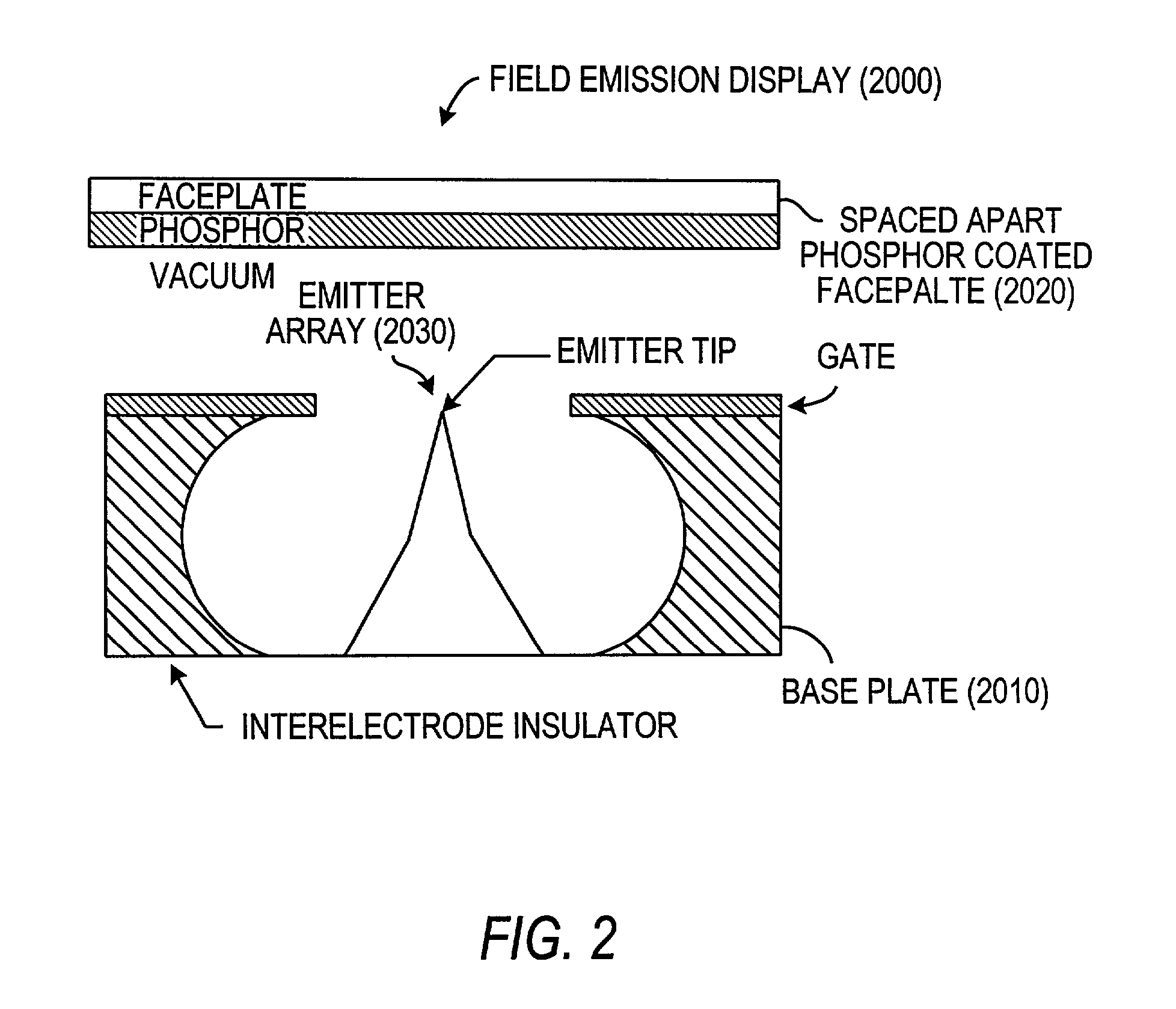
A field-emission display (FED) is a flat panel display technology that uses large-area field electron emission sources to provide electrons that strike colored phosphor to produce a color image. In a general sense, an FED consists of a matrix of cathode ray tubes, each tube producing a single sub-pixel, grouped in threes to form red-green-blue (RGB) pixels. FEDs combine the advantages of CRTs, namely their high contrast levels and very fast response times, with the packaging advantages of LCD and other flat-panel technologies. They also offer the possibility of requiring less power, about half that of an LCD system.
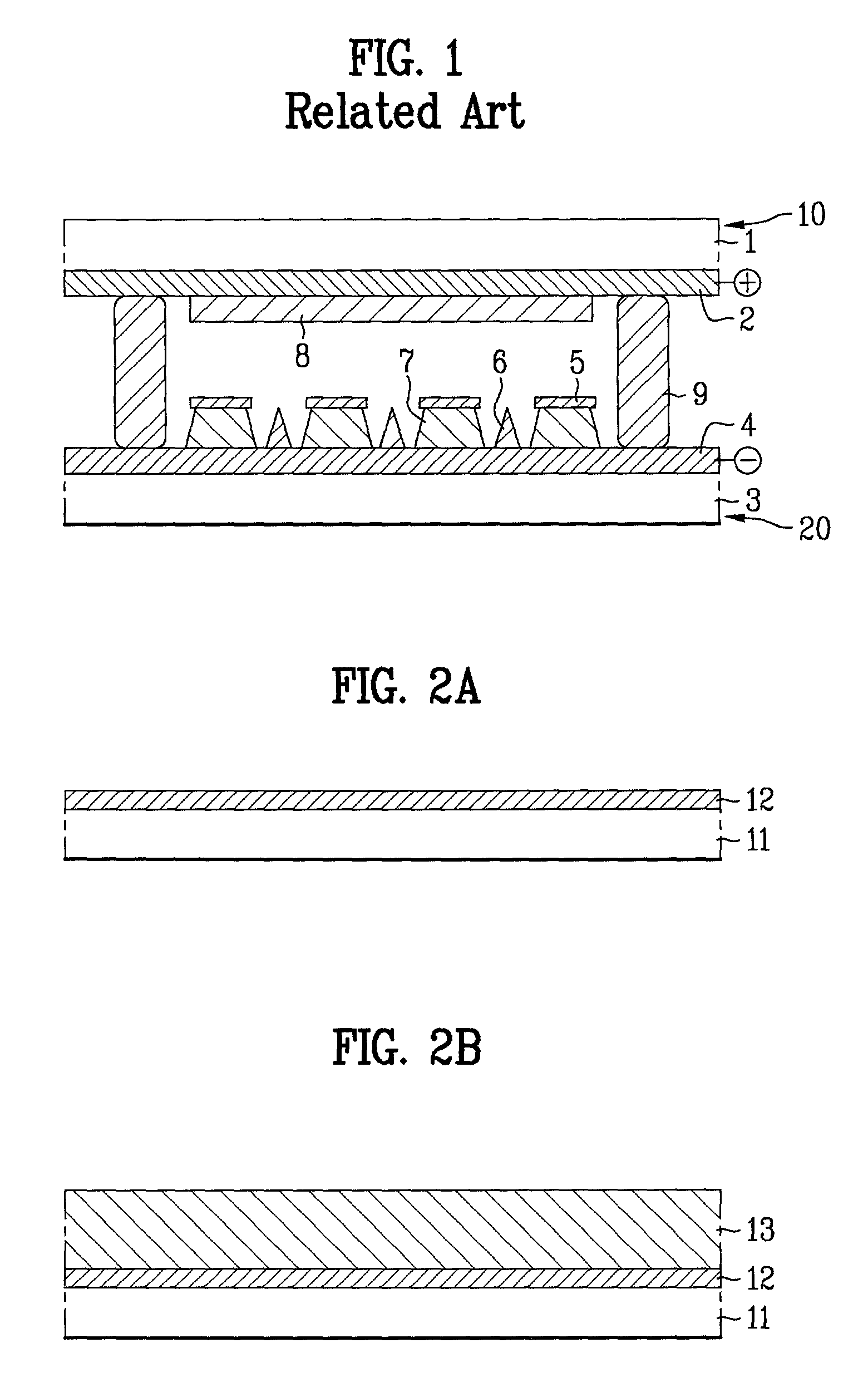
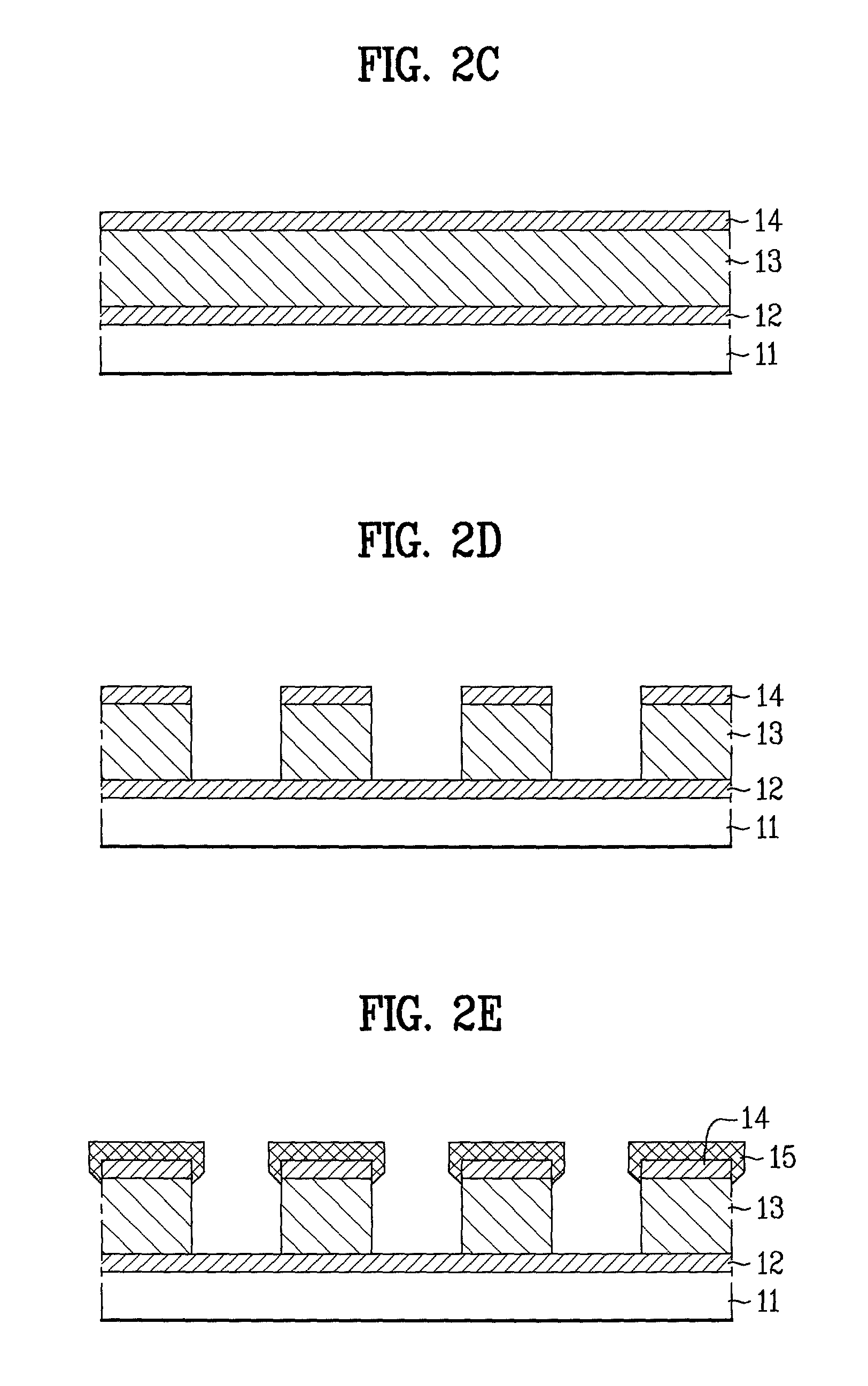
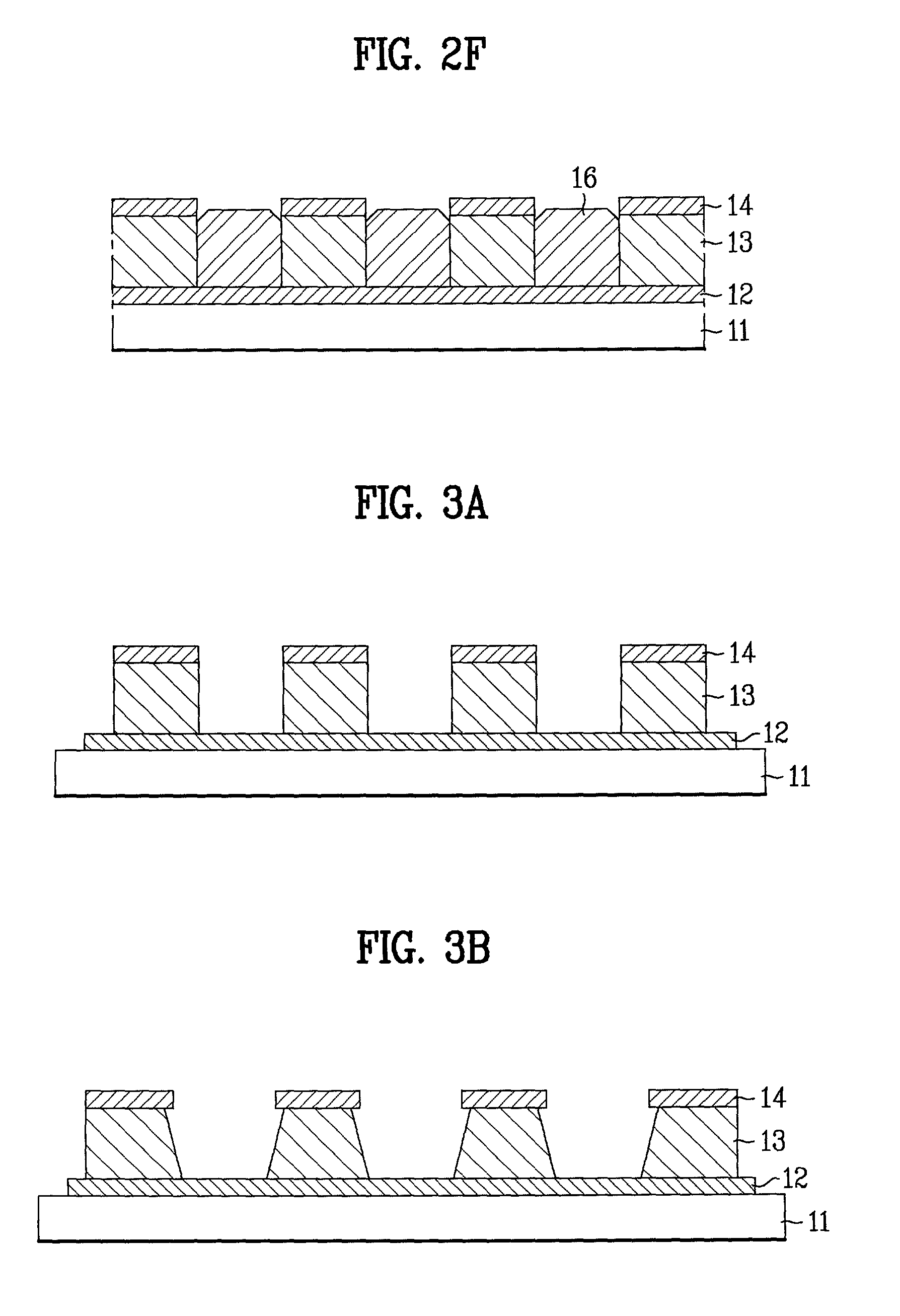
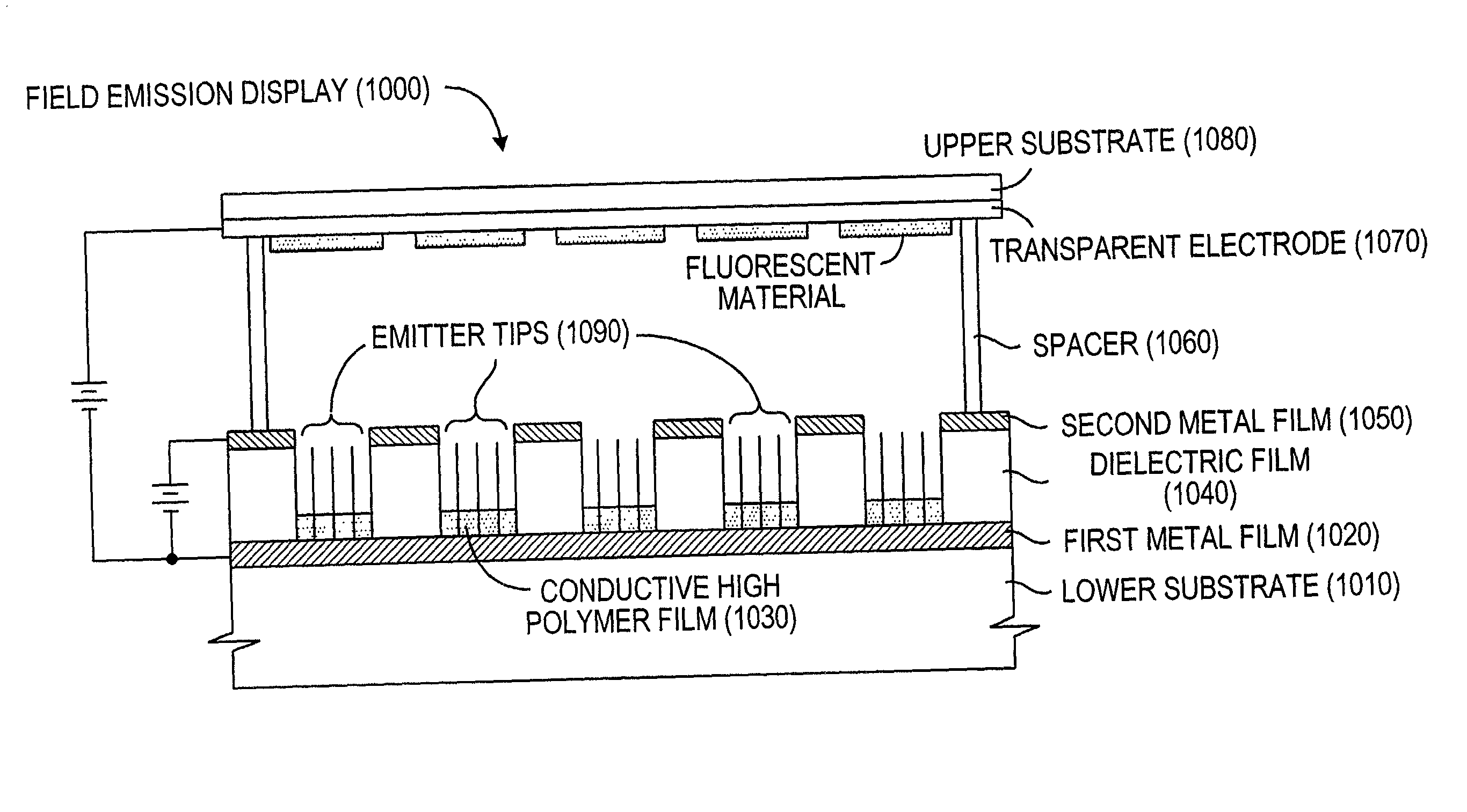
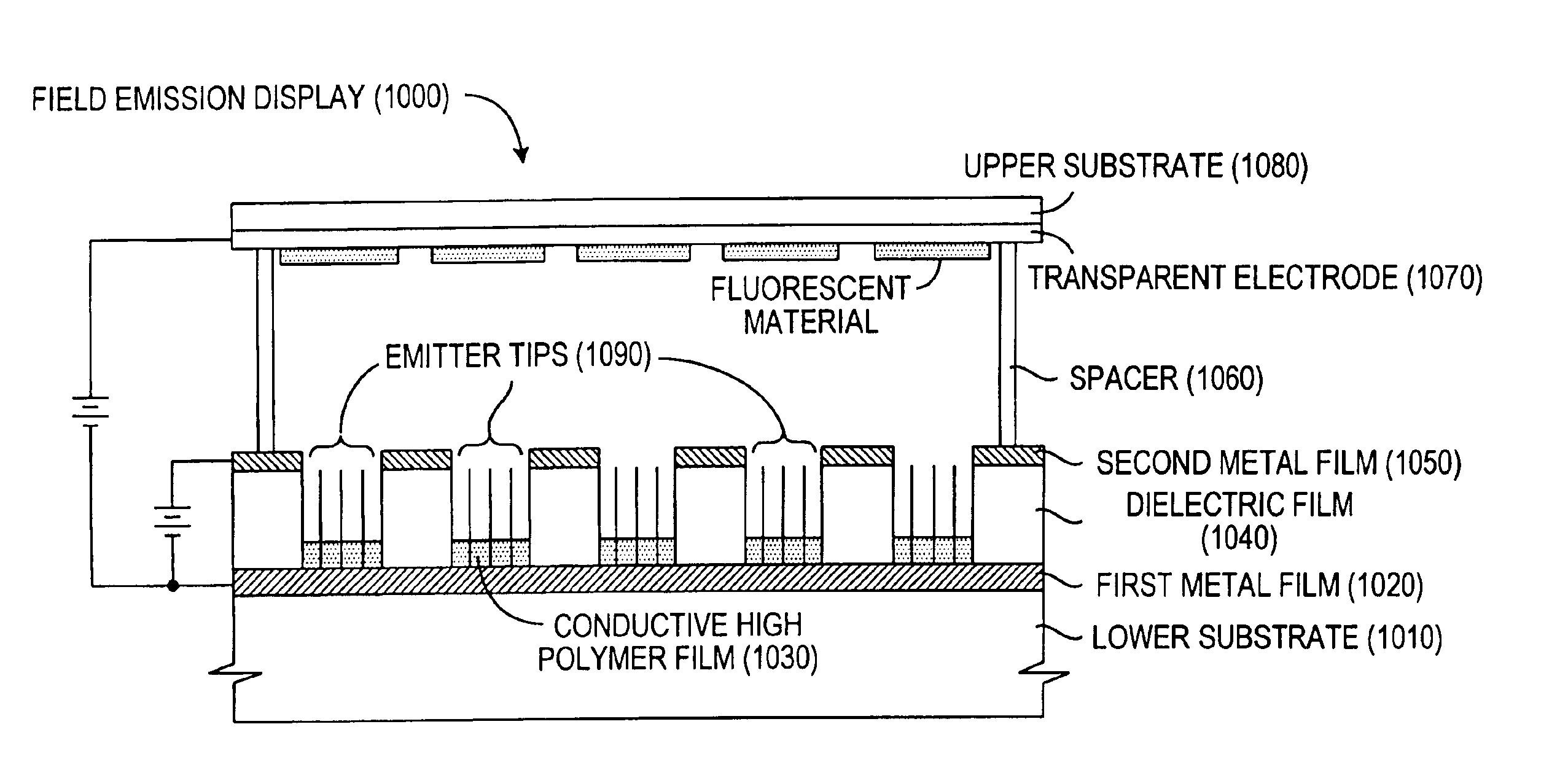
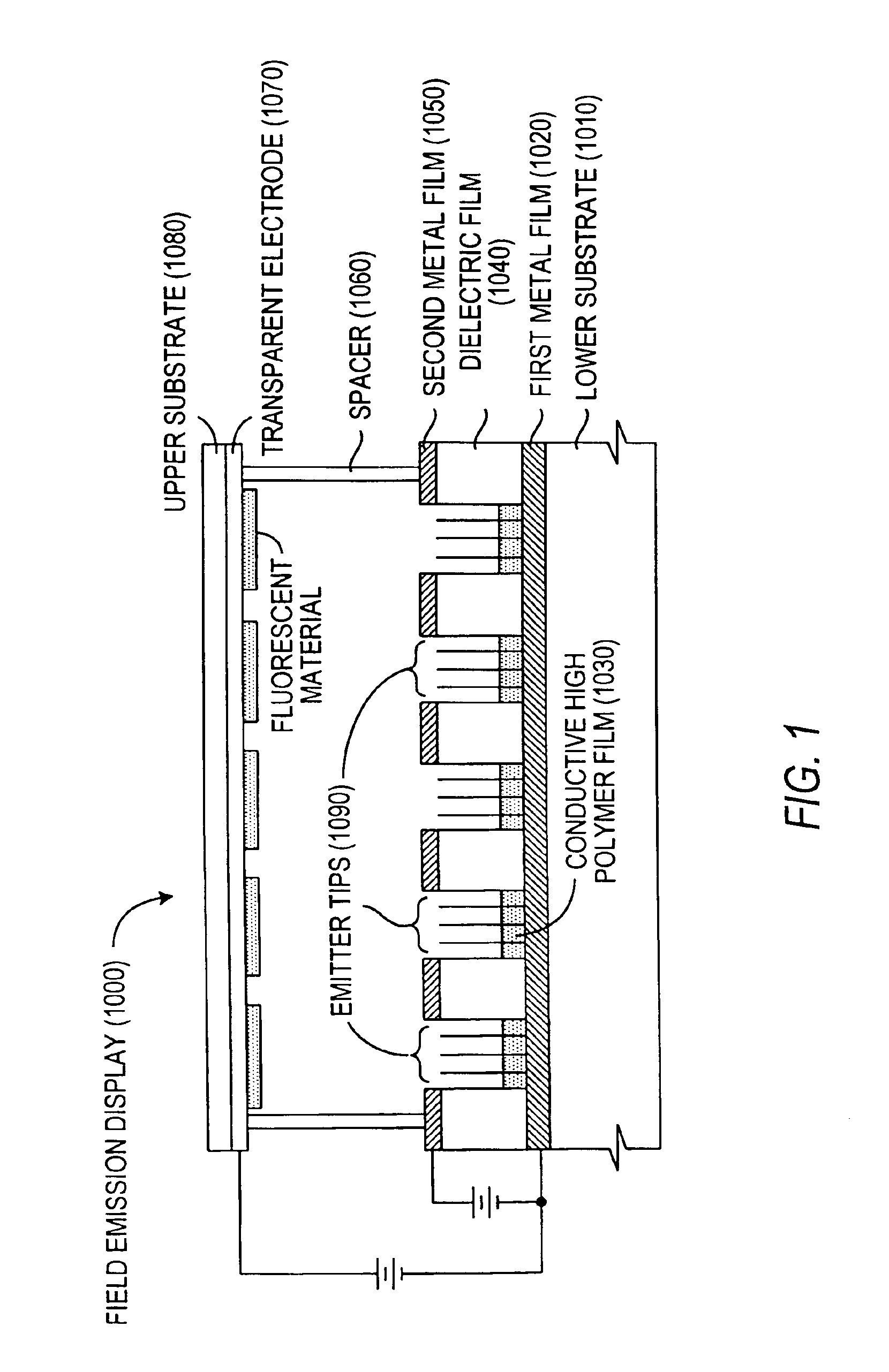
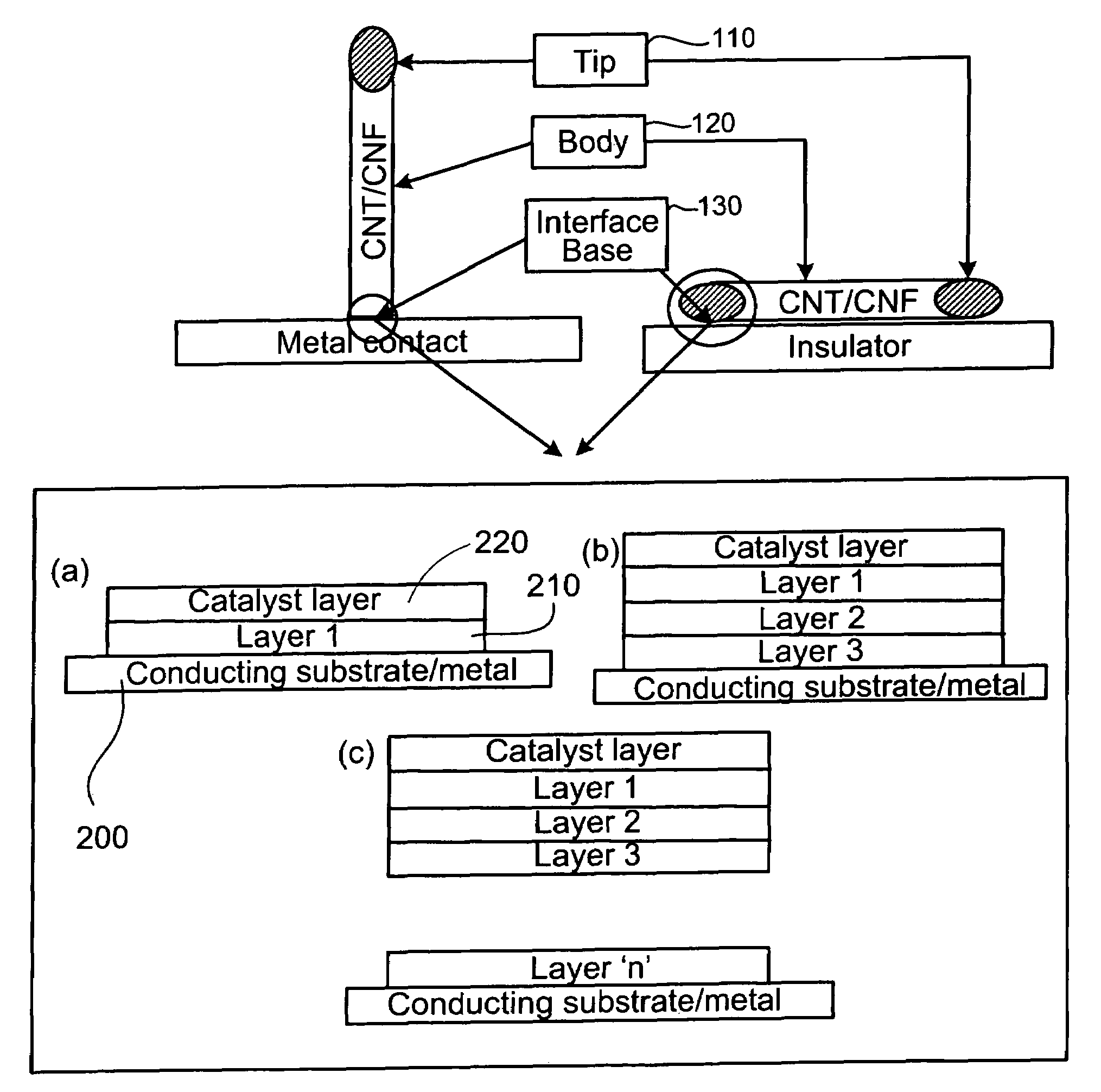
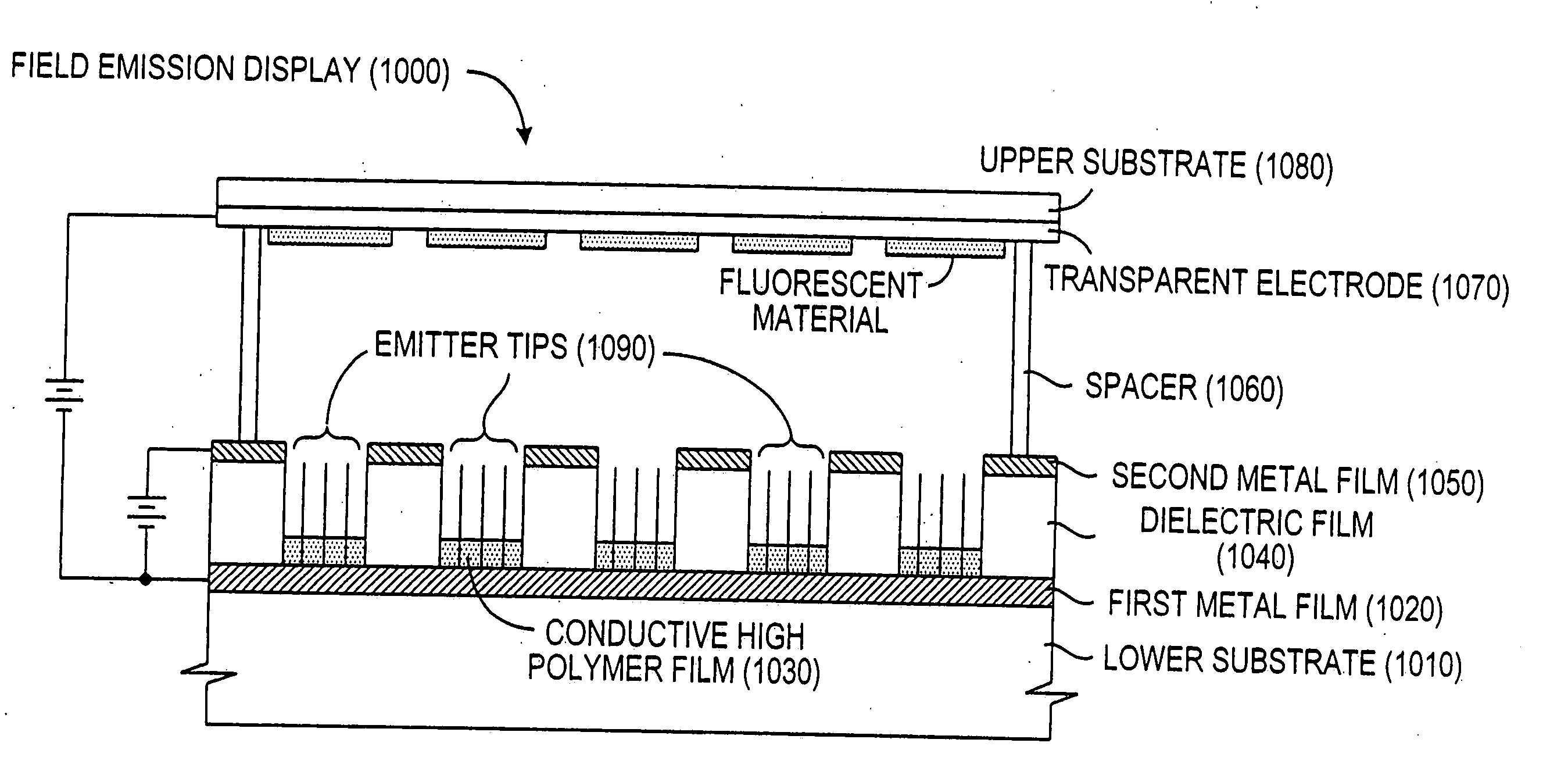
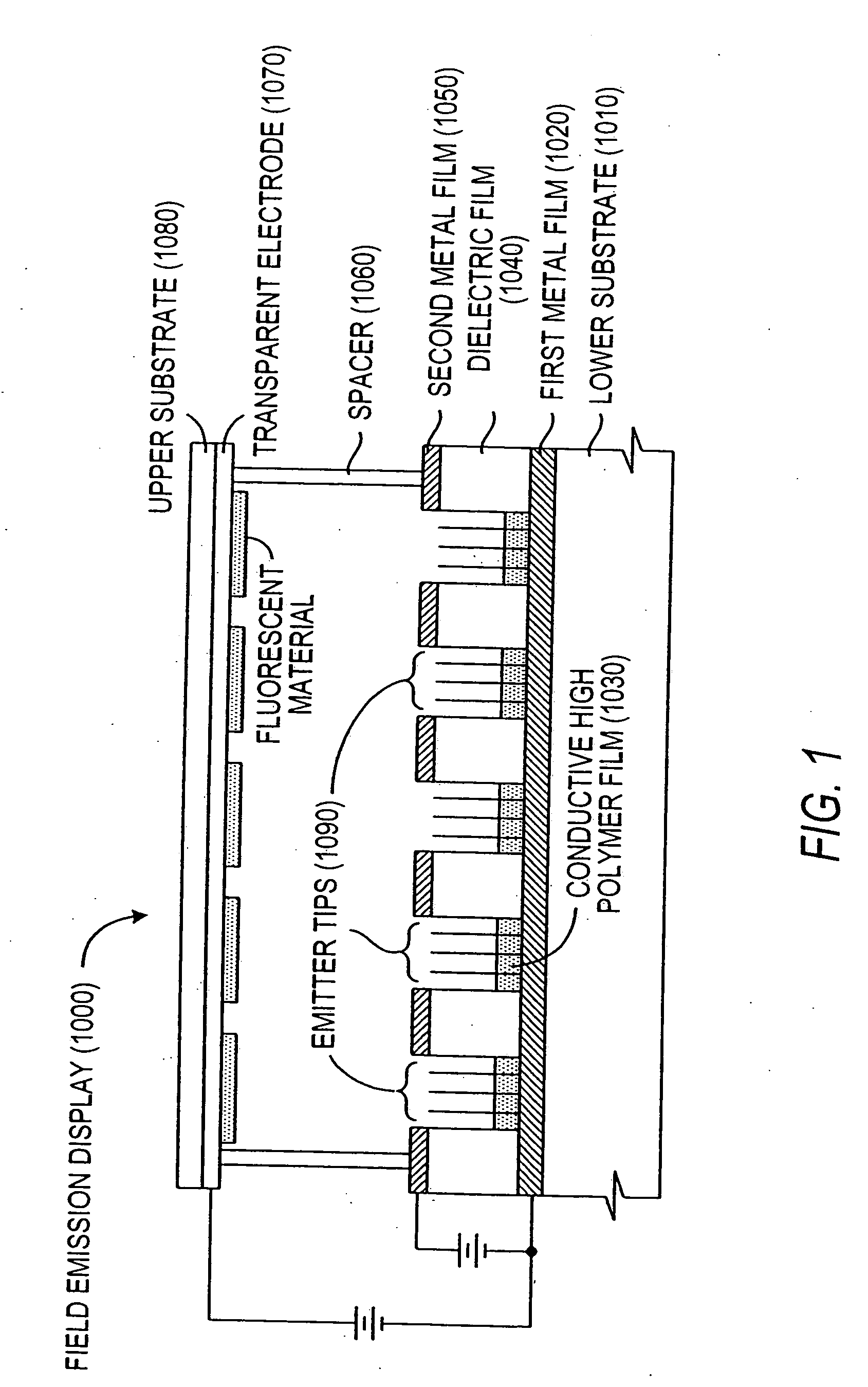
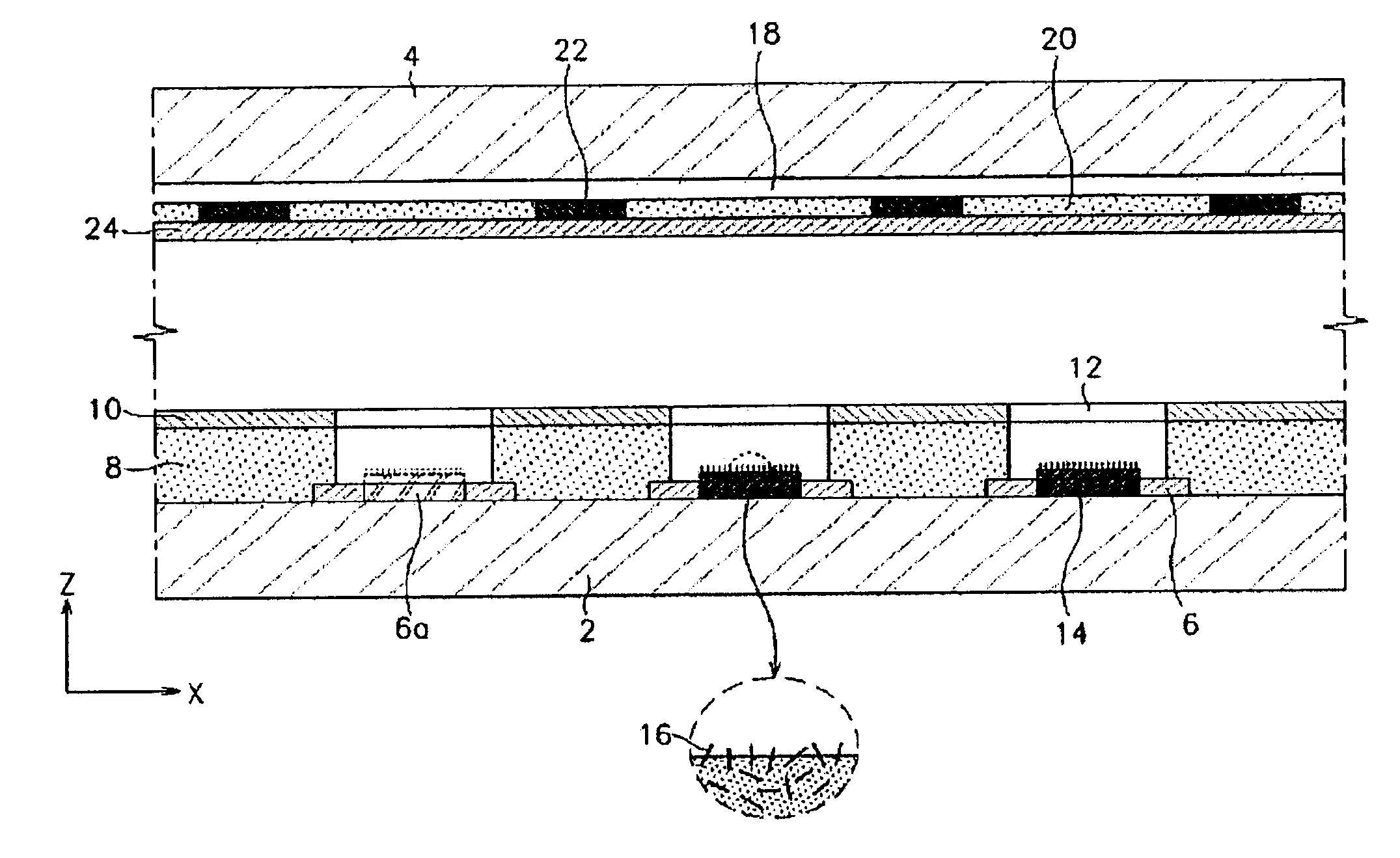
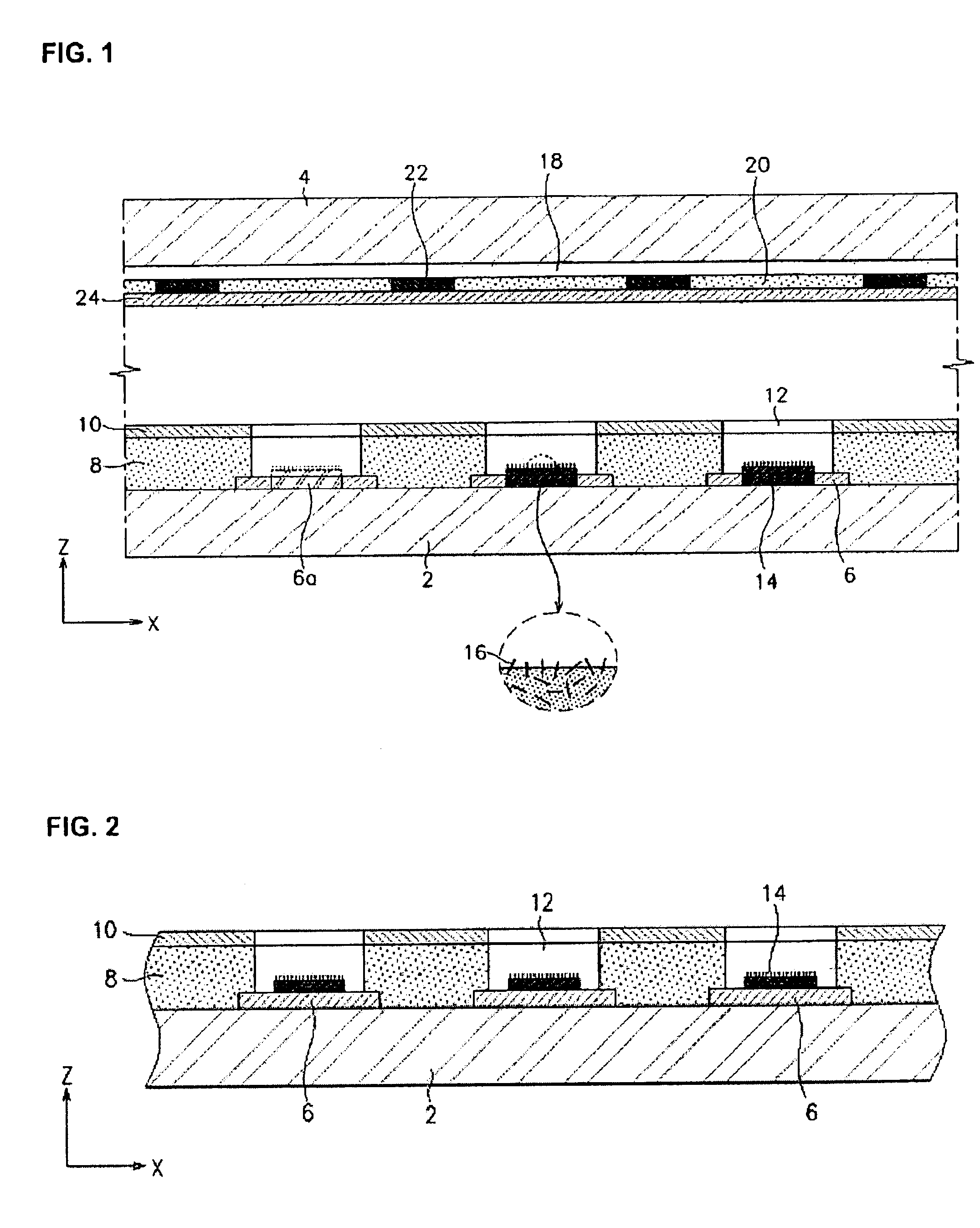
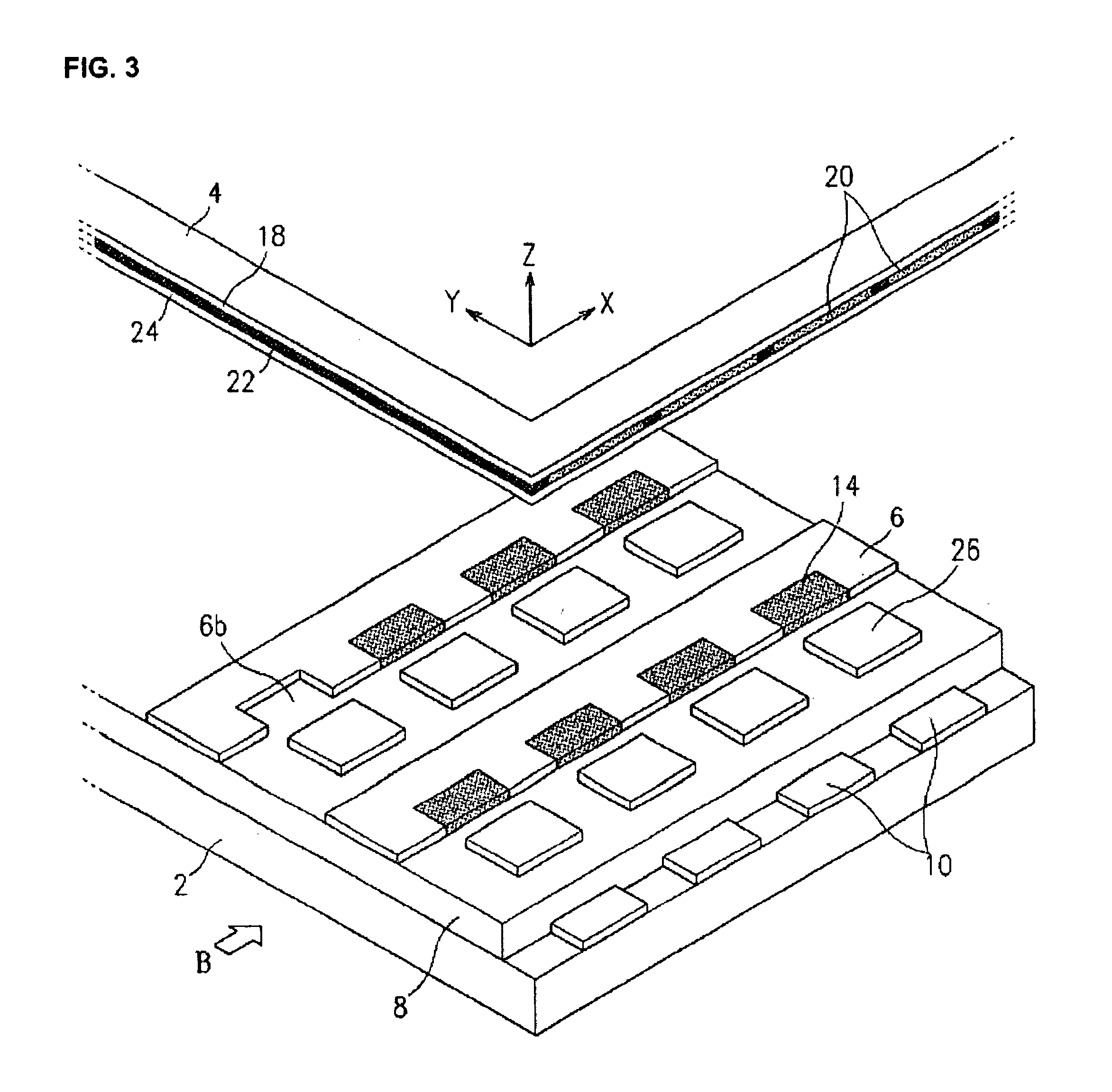
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20010004979A1Stable driving voltageUniform characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLow voltageCarbon nanotube
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same, the field emission display including a cathode array having a cathode electrode formed on a substrate, insulating layers and carbon nanotube films for use as emitter electrodes formed alternately on the cathode electrode, and a gate electrode formed on the insulating layer, thereby permitting fabrication of a large sized cathode plate at a low cost because the film is formed by screen printing and exposure, which can reduce the cumbersome steps in fabrication of the related art Spindt emitter tip, and both a low voltage and a high voltage FEDs because the carbon nanotube film used as the emitter has a low work function, with an easy and stable electron emission capability.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030090190A1Accelerate emissionsReduce voltageNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Field emission display and methods of forming a field emission display
A field emission device and method of forming a field emission device are provided in accordance with the present invention. The field emission device is comprised of a substrate (12) having a deformation temperature that is less than about six hundred and fifty degrees Celsius and a nano-supported catalyst (22) formed on the substrate (12) that has active catalytic particles that are less than about five hundred nanometers. The field emission device is also comprised of a nanotube (24) that is catalytically formed in situ on the nano-supported catalyst (22), which has a diameter that is less than about twenty nanometers.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Molybdenum sputtering targets
InactiveUS20060042728A1High purityImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDevice materialThin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display
Molybdenum, sputtering targets and sintering characterized as having no or minimal texture banding or through thickness gradient. The molybdenum sputtering targets having a fine, uniform grain size as well as uniform texture, are high purity and can be micro-alloyed to improved performance. The sputtering targets can be round discs, square, rectangular or tubular and can be sputtered to form thin films on substrates. By using a segment-forming method, the size of the sputtering target can be up to 6 m×5.5 m. The thin films can be used in electronic components such as Thin Film Transistor—Liquid Crystal Displays, Plasma Display Panels, Organic Light Emitting Diodes, Inorganic Light Emitting Diode Displays, Field Emission Displays, solar cells, sensors, semiconductor devices, and gate device for CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) with tunable work functions.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
InactiveUS20040070326A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6911767B2Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
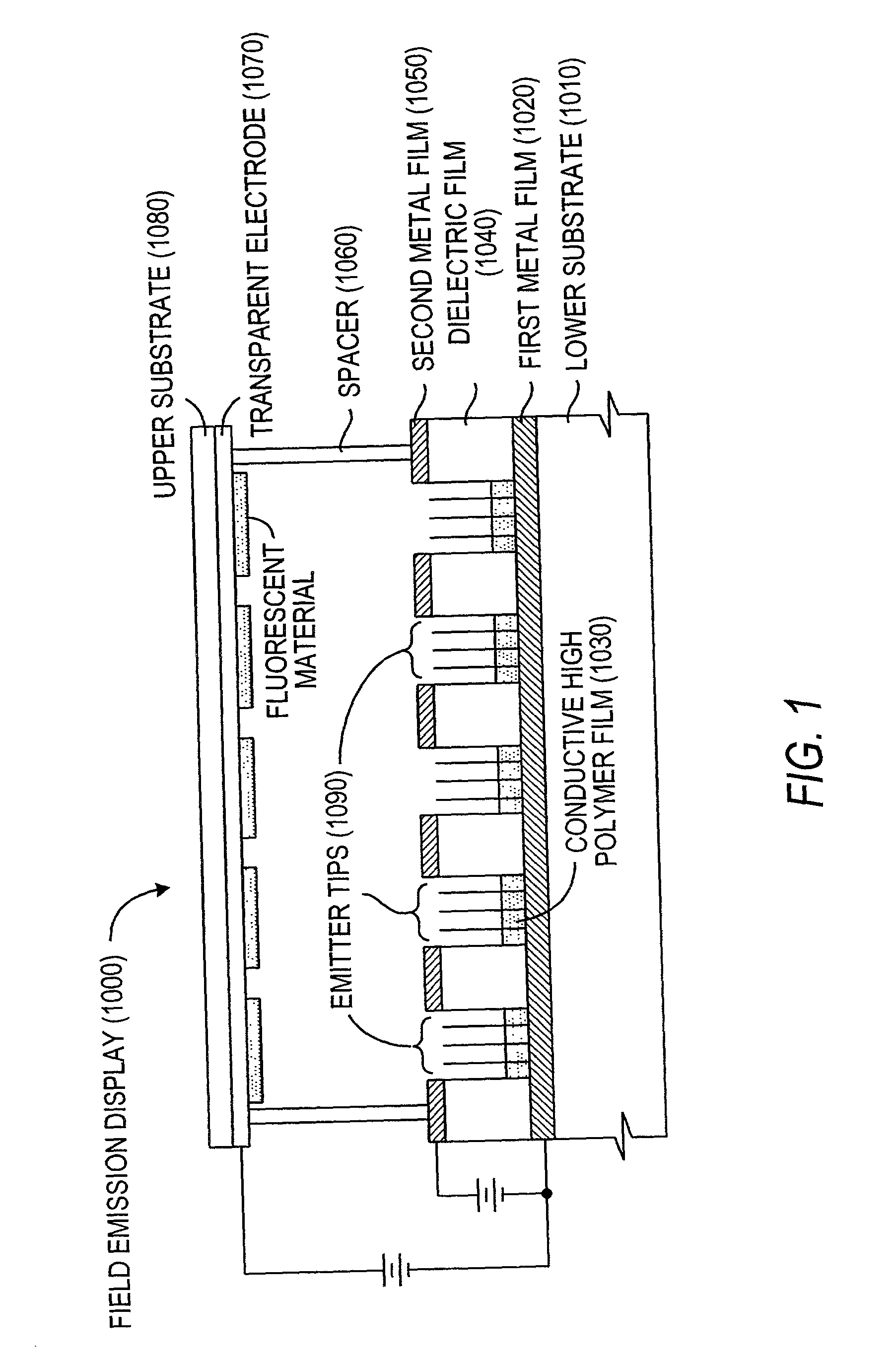
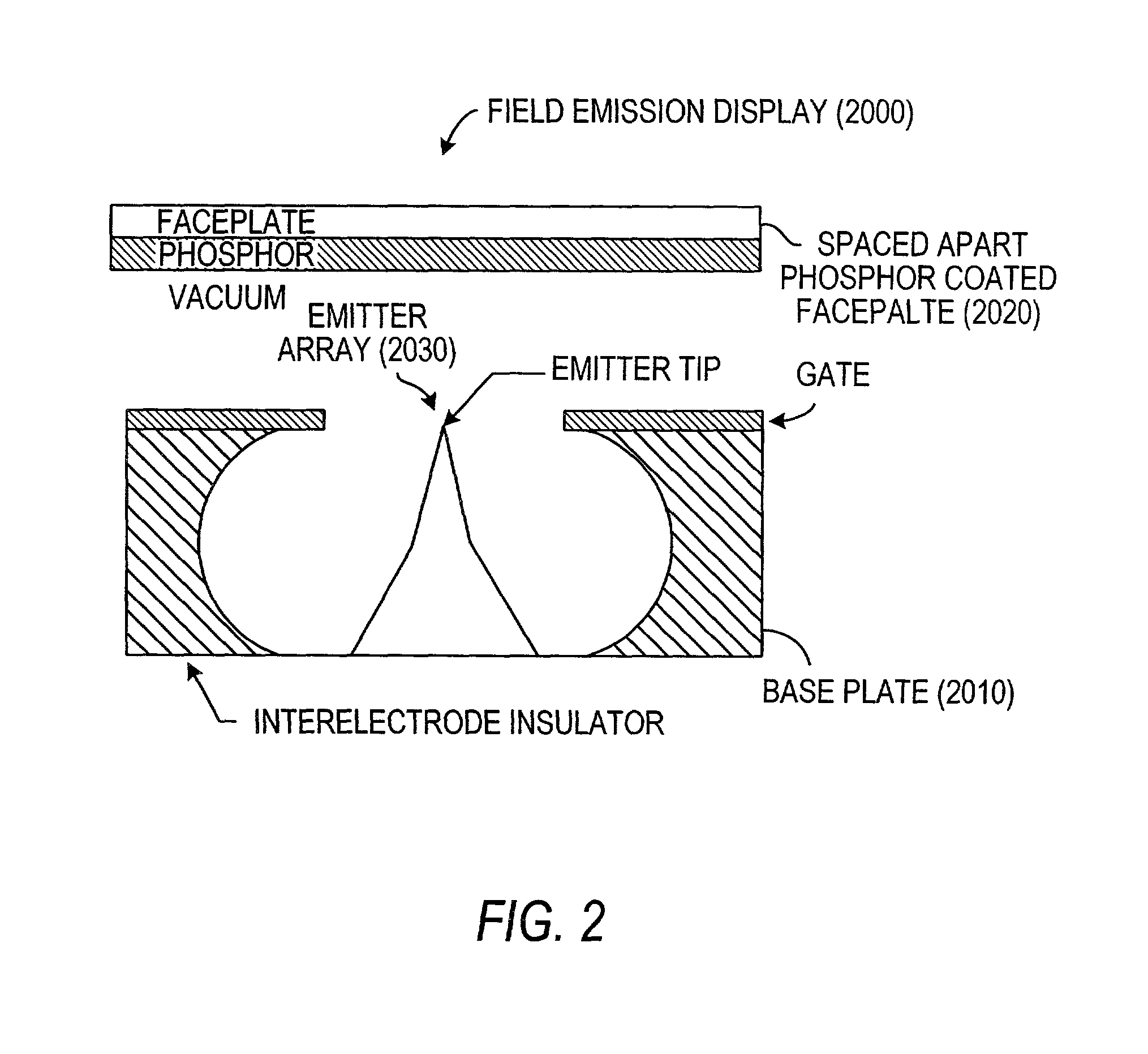
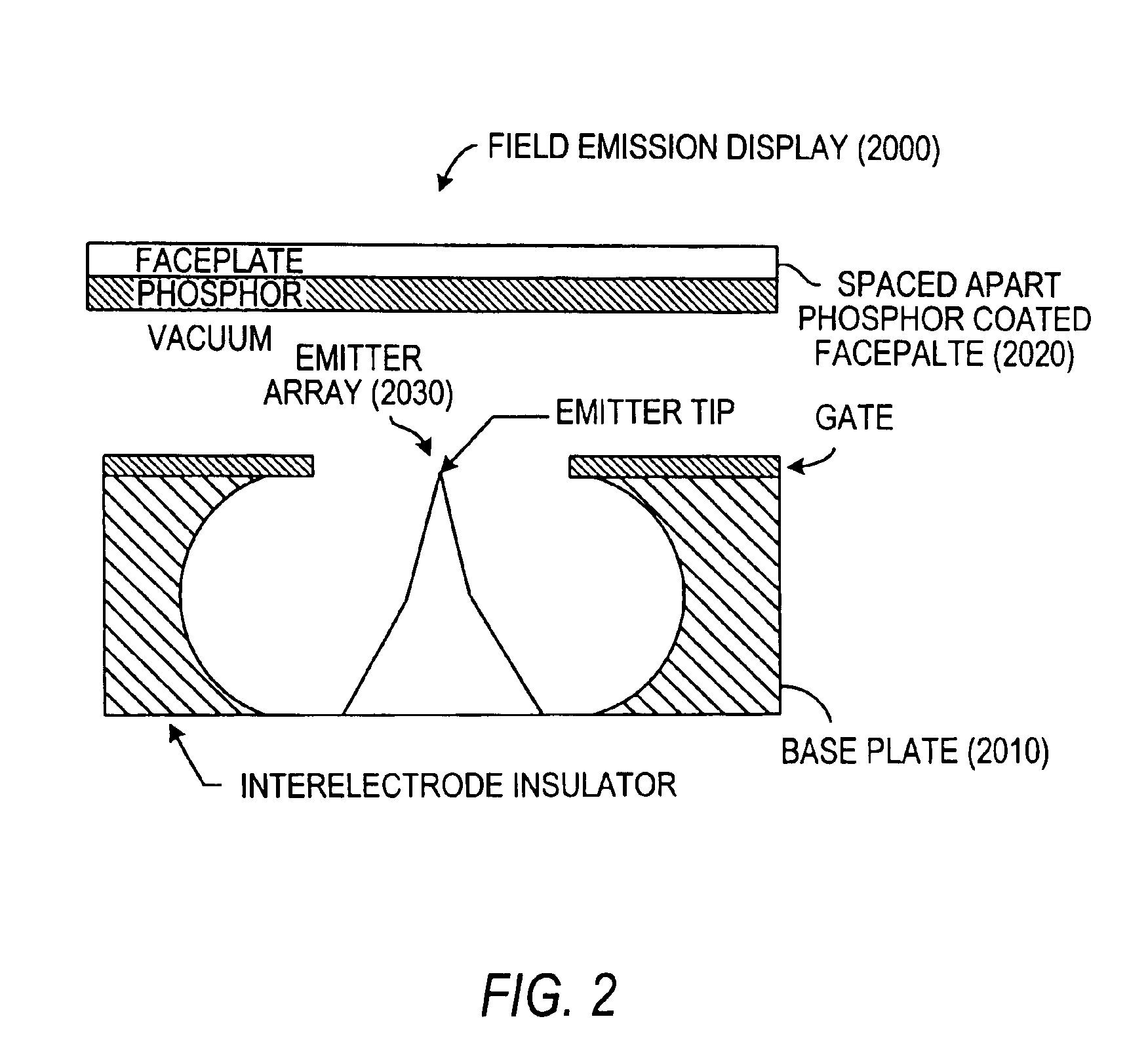
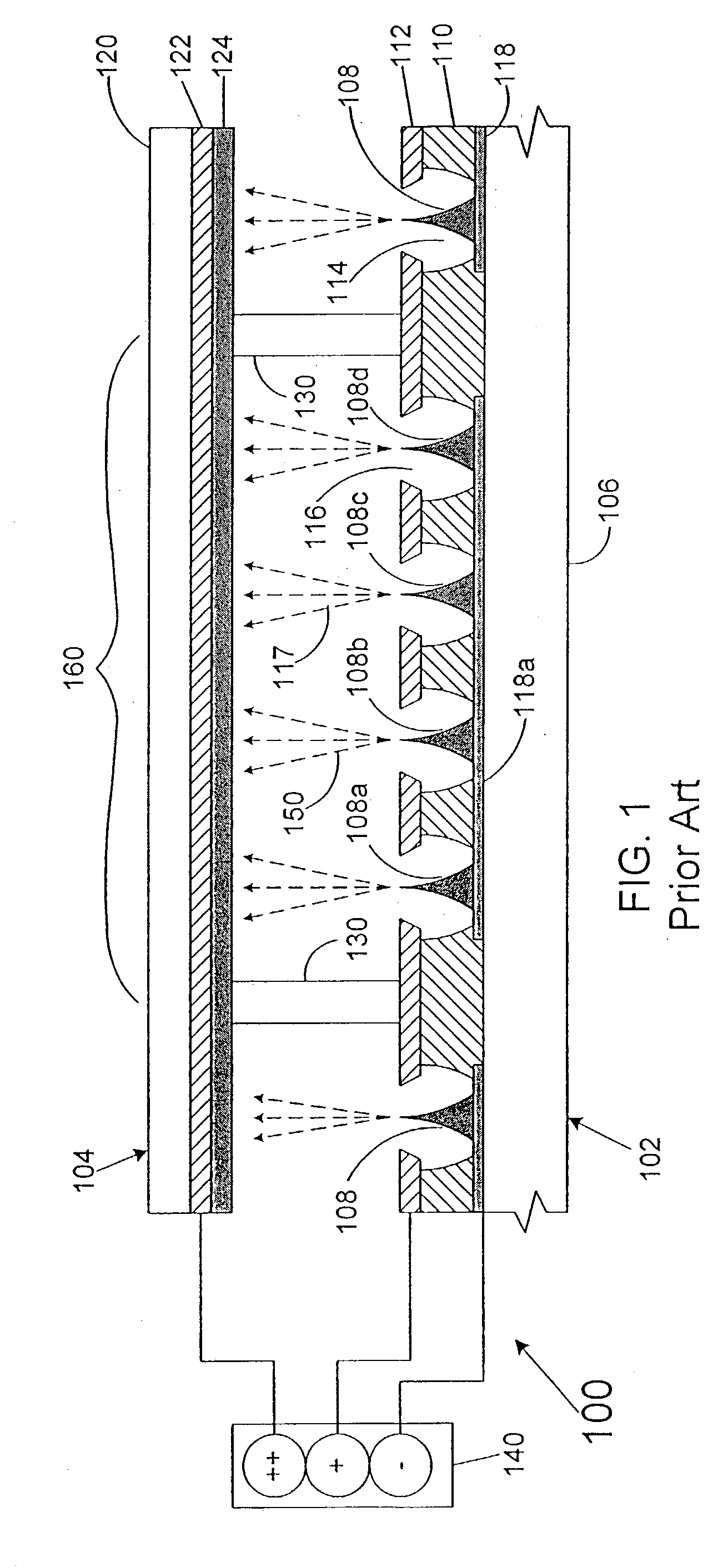
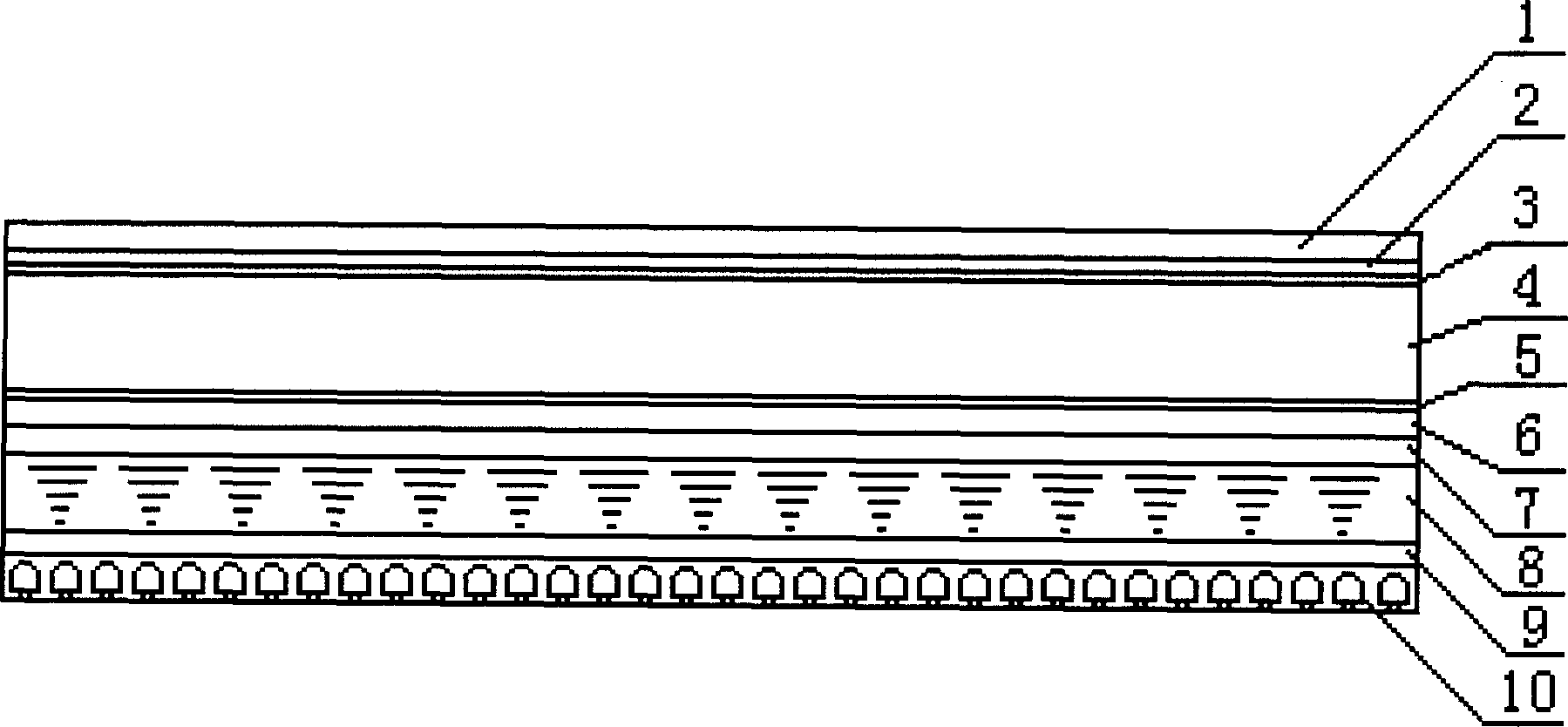
Field emission display
InactiveUS6172456B1Reduce in quantityIncrease in costGas filling substance selectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensField emission displayDisplay device
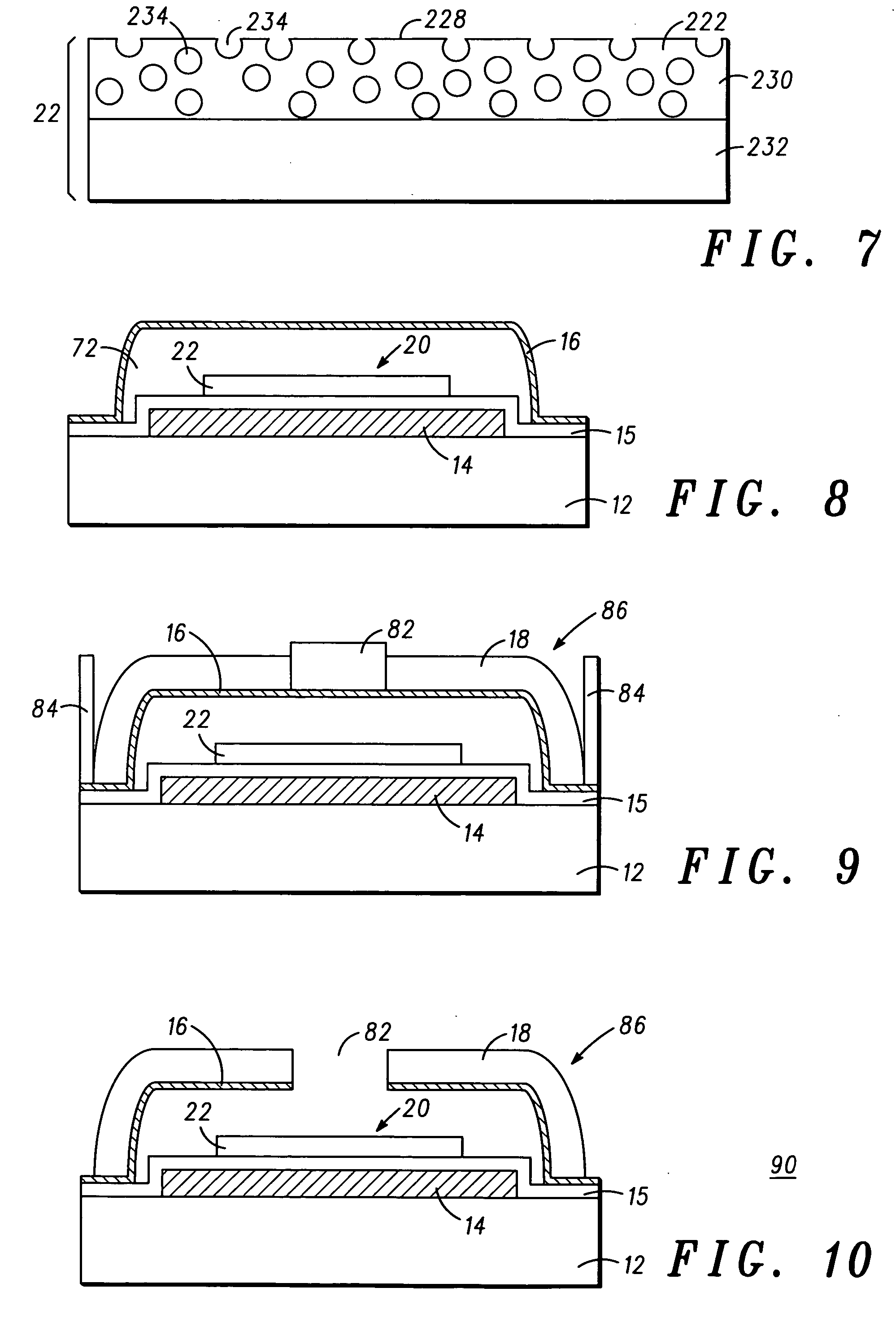
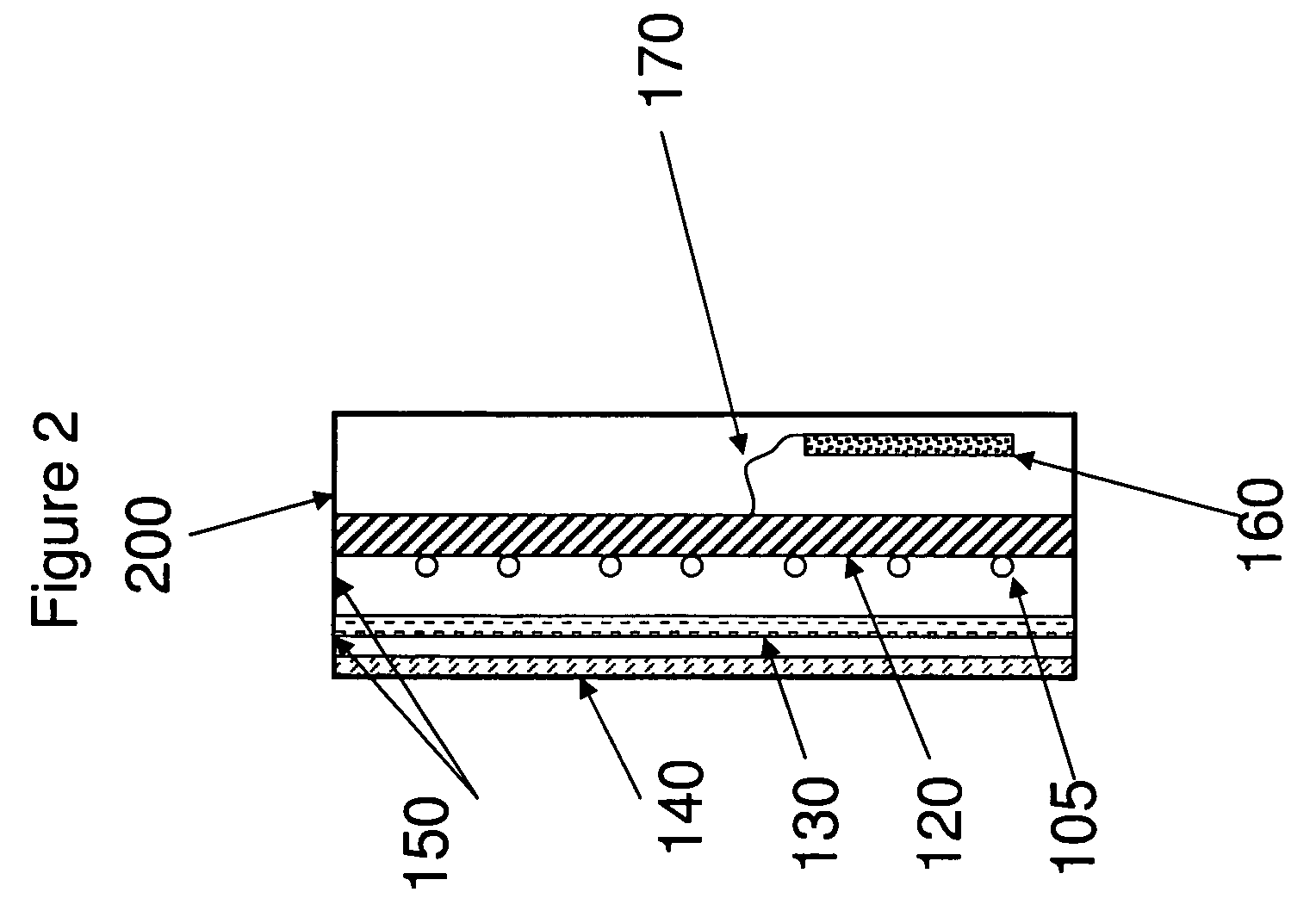
A flat-panel field emission display comprises a luminescent faceplate, a rigid backplate, and an interposed or sandwiched emitter or cathode plate. A positioning spacer or connector ridge is formed on the rear surface of the faceplate to space the cathode plate a fixed distance behind the faceplate. A peripheral seal is formed between the faceplate and the backplate. The faceplate, backplate, and peripheral seal define an evacuated internal space which contains the cathode plate. The backplate is spaced behind the cathode plate to create a rearward vacuum space in which a getter is located.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
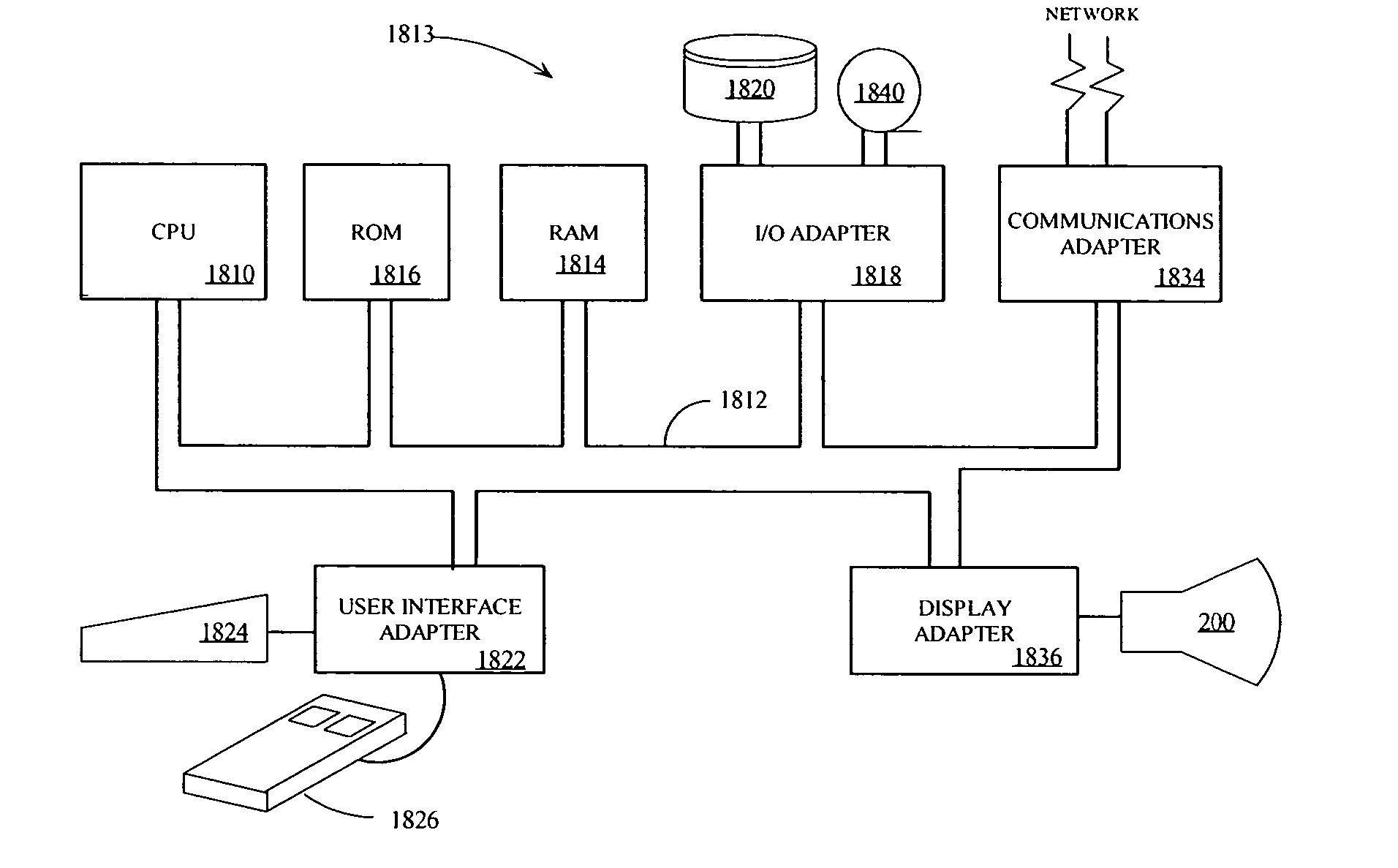
Image display device incorporating driver circuits on active substrate and other methods to reduce interconnects
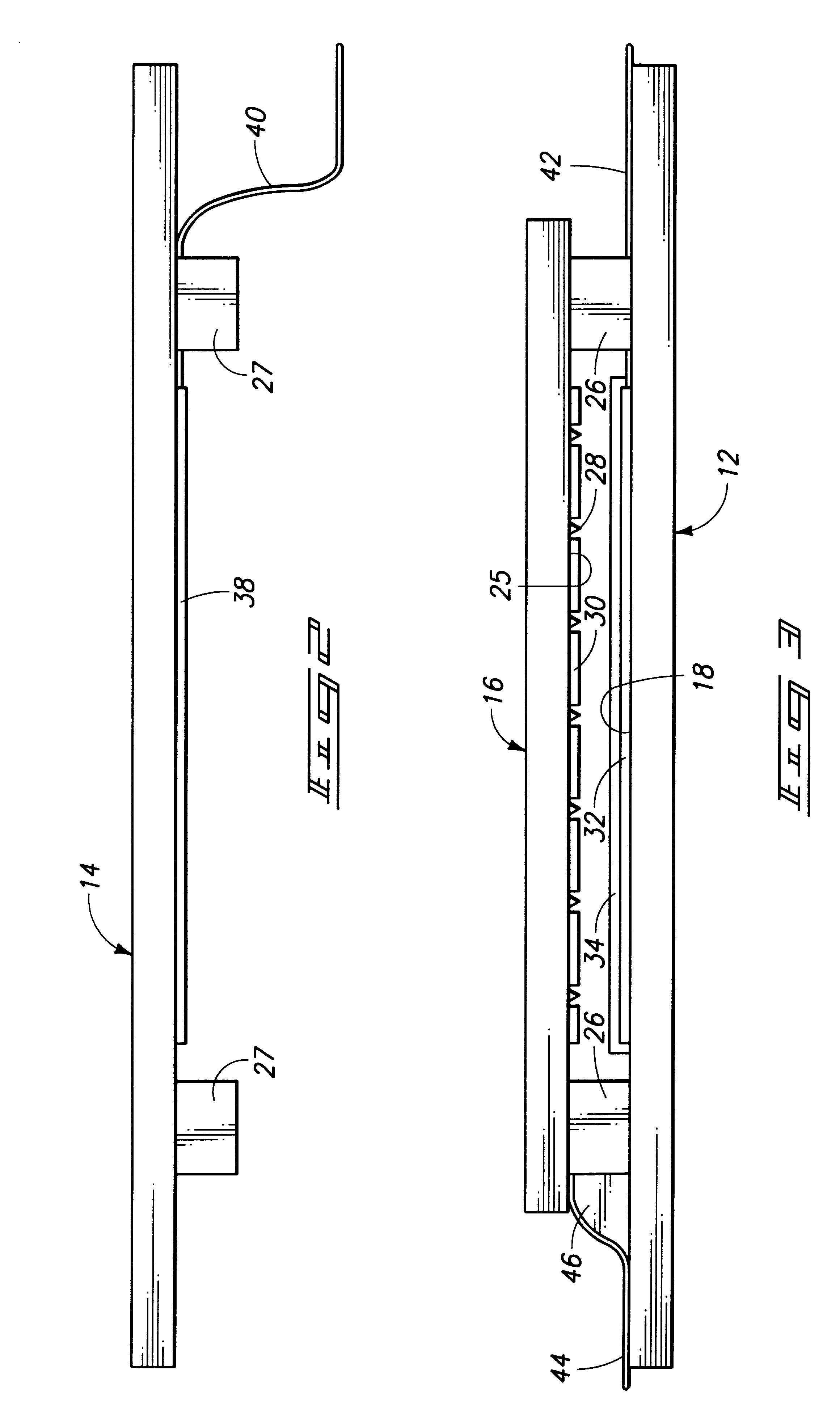
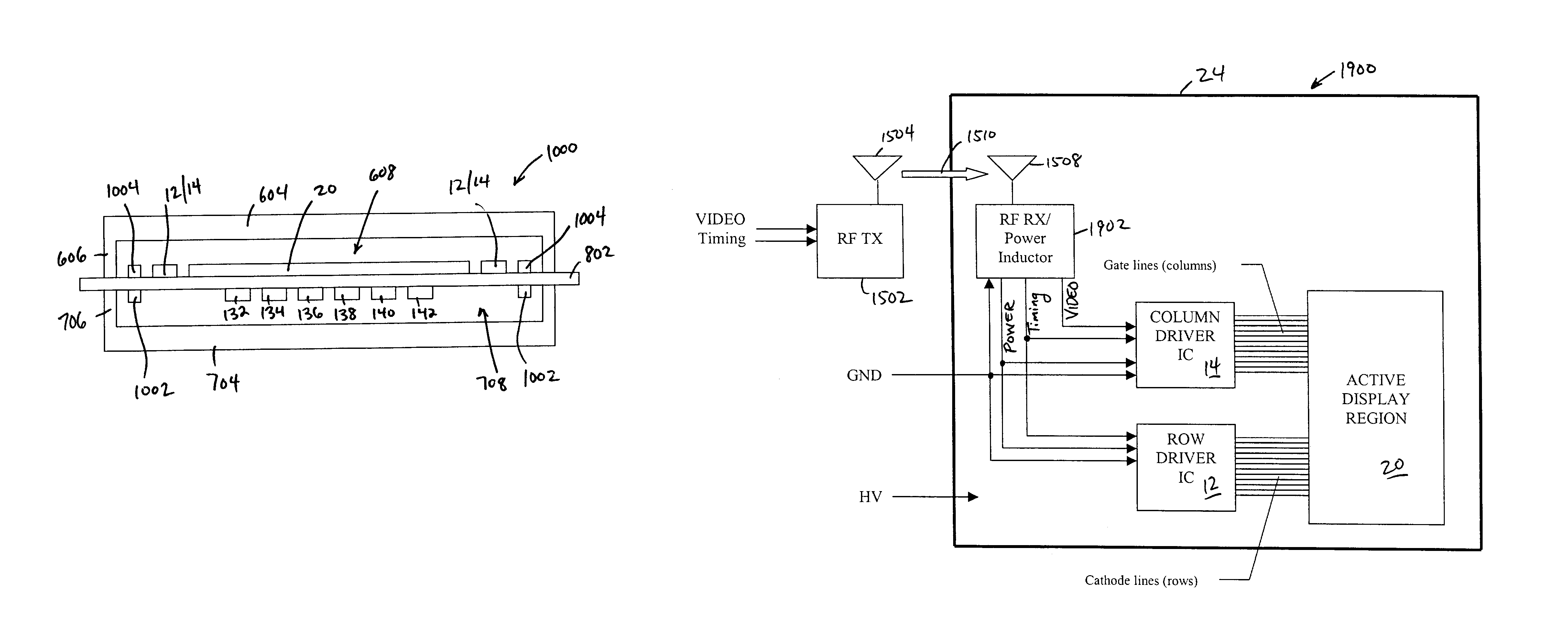
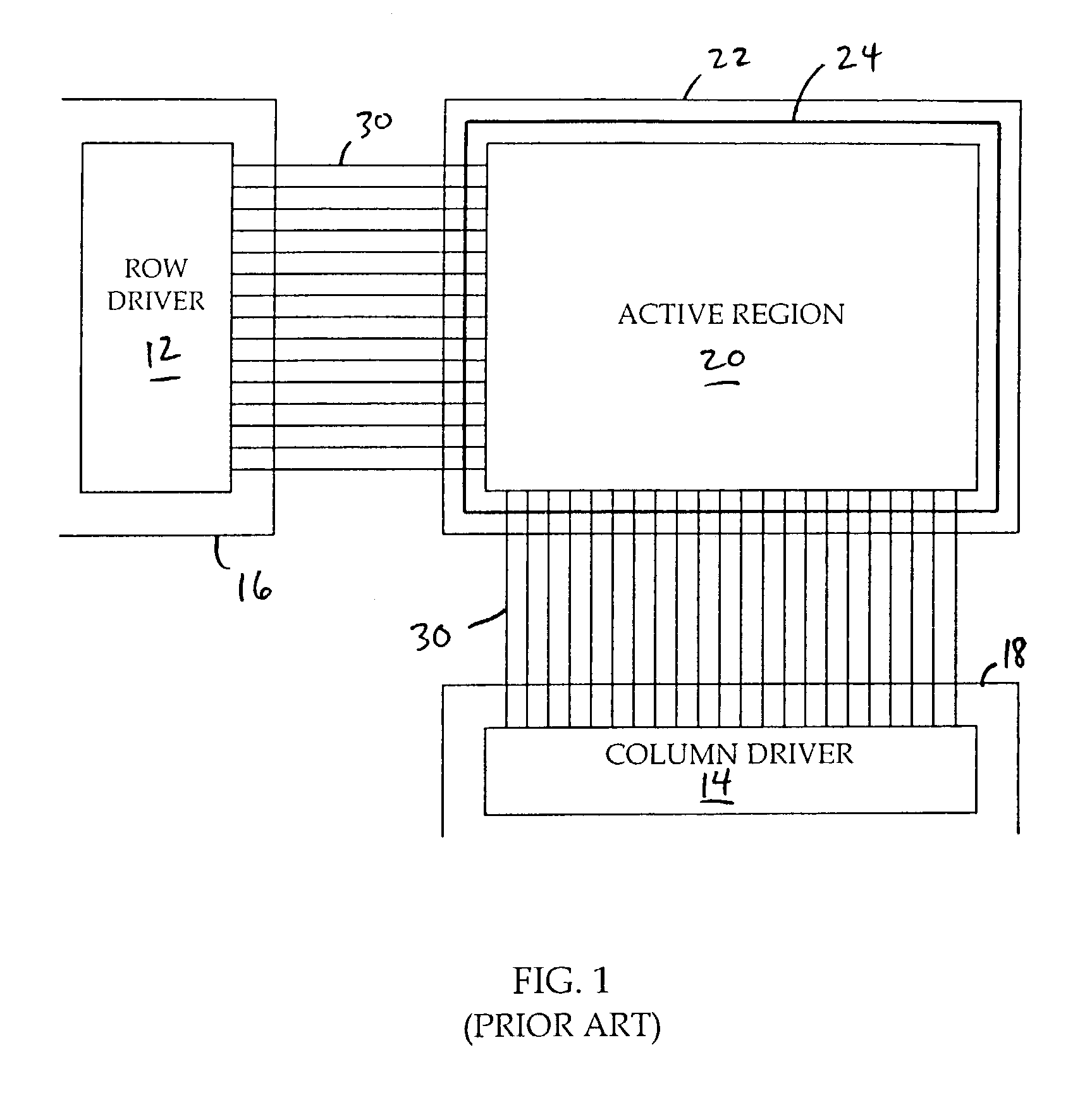
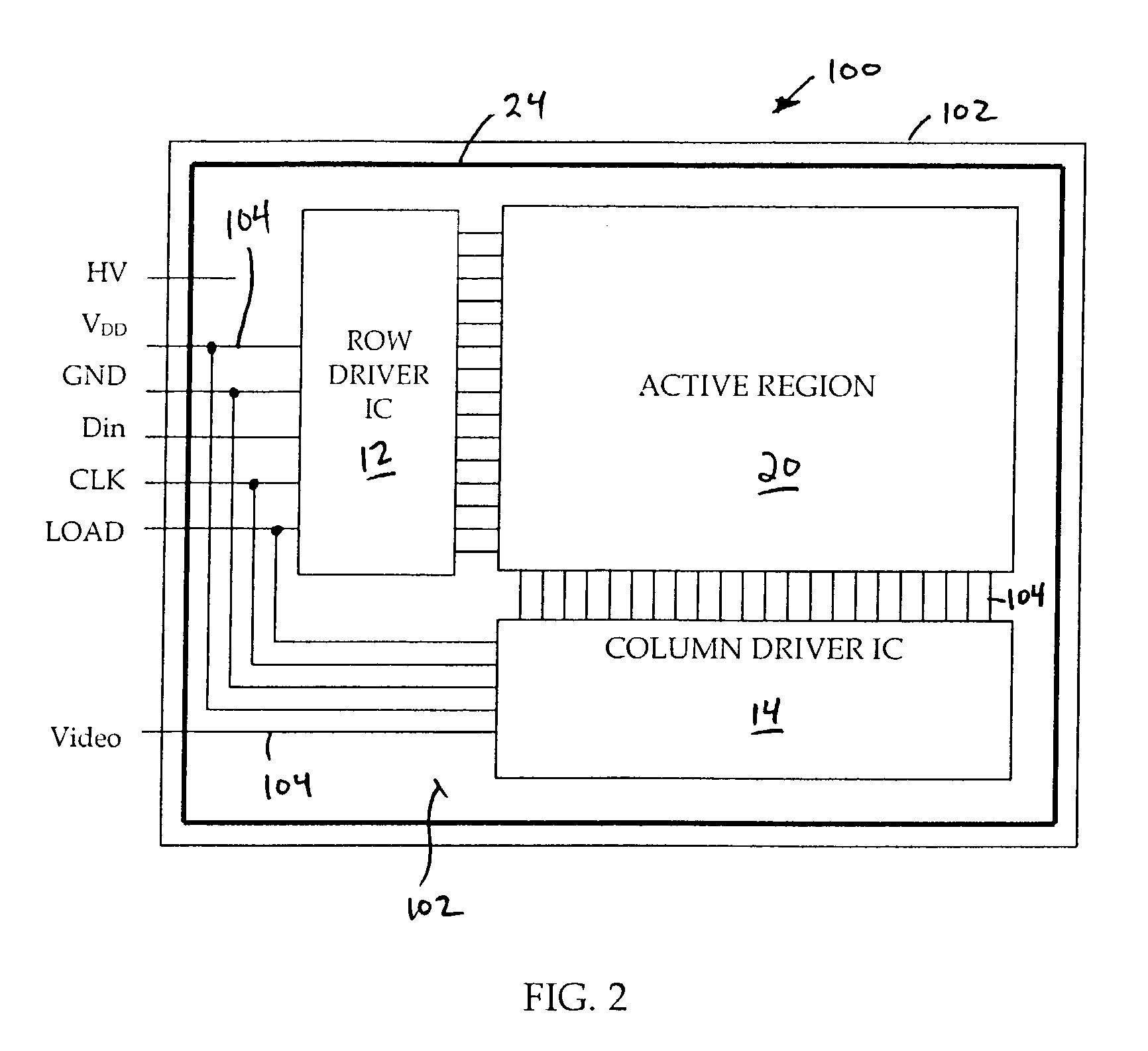
InactiveUS7071629B2Reduce in quantityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDriver circuitLiquid-crystal display
Flat panel displays, such as field emission displays (FEDs), plasma displays, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), and electroluminescent displays (ELs), are provided incorporating driver circuitry on the same substrate as the active display region of the display device and further reducing through-vacuum and substrate-to-substrate interconnects. In one implementation, an image display device comprises a substrate; an active display region formed on the substrate and including addressable rows and columns defining pixels; and one or more driver ICs on the substrate, respective outputs of each driver IC coupled to respective ones of the addressable rows and columns, the driver ICs adapted to drive the active display region to display an image. The device also comprises a wireless receiver coupled to the driver ICs, the wireless receiver adapted to wirelessly receive a wireless signal including an input video signal for display and couple the input video signal to the driver ICs.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
InactiveUS6798127B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp incadescent bodiesField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Enhanced field emission from carbon nanotubes mixed with particles
ActiveUS20050001528A1Optimizing electron field emission performanceEmission reductionDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsField emission deviceCarbon nanotube
The present invention is directed toward cathodes and cathode materials comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and particles. The present invention is also directed toward field emission devices comprising a cathode of the present invention, as well as methods for making these cathodes. In some embodiments, the cathode of the present invention is used in a field emission display. The invention also comprises a method of depositing a layer of CNTs and particles onto a substrate to form a cathode of the present invention, as well as a method of controlling the density of CNTs used in this mixed layer in an effort to optimize the field emission properties of the resulting layer for field emission display applications.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030044519A1Easy to disassembleReduce voltageCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Display device with an array of display drivers recessed onto a substrate
InactiveUS6998644B1Gas-filled discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDeterministic methodField emission display
Apparatuses and methods for forming displays are claimed. One embodiment of the invention relates to dispensing display drivers over a substrate. The display drivers, for example, may be a plurality of emitters and gates in order to form a display such as a field emission display (FED). Alternatively, the display drivers may be rods for a plasma display. Another embodiment of the invention relates to forming an electronic device along a length of substrate using template transfer or FSA to deposit display drivers into recessed regions or holes of a substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using FSA and a deterministic method such as “pick and place” to place display drivers onto a substrate. Another embodiment of the invention relates to using donor transfer of display drivers to a substrate.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
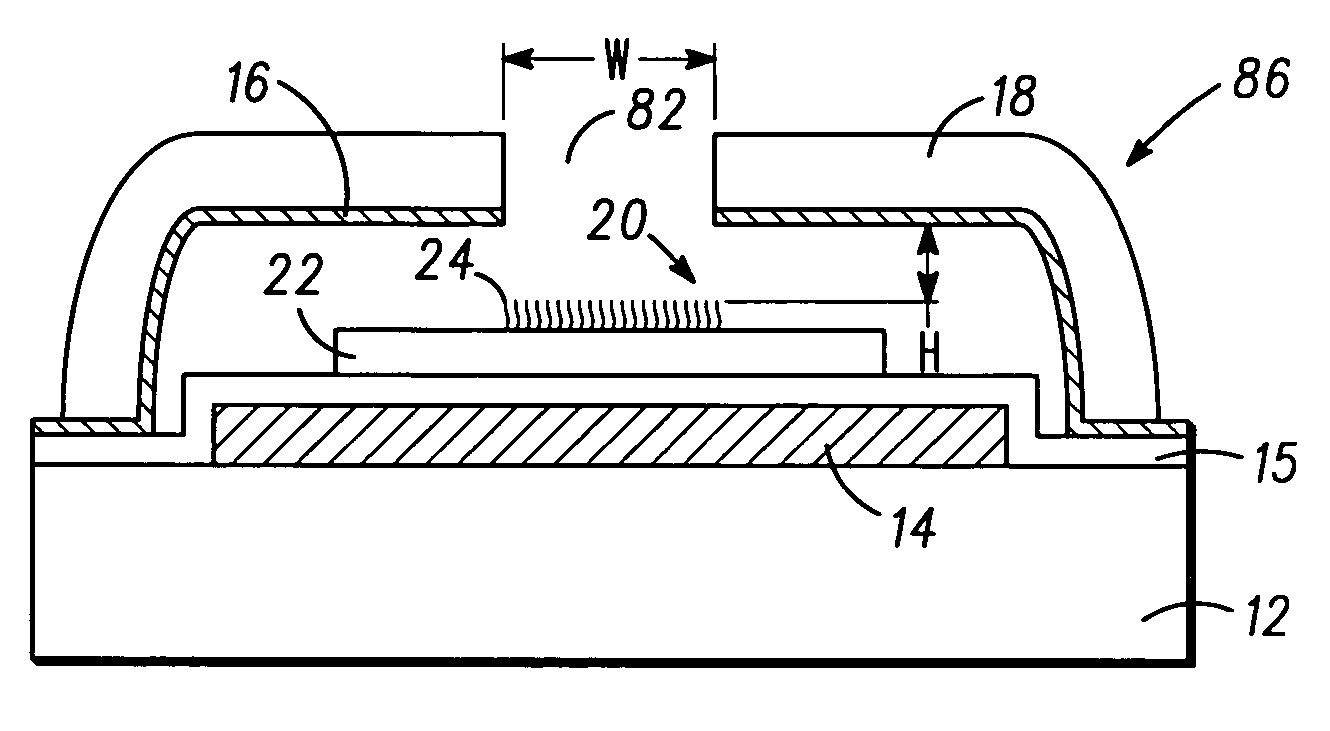
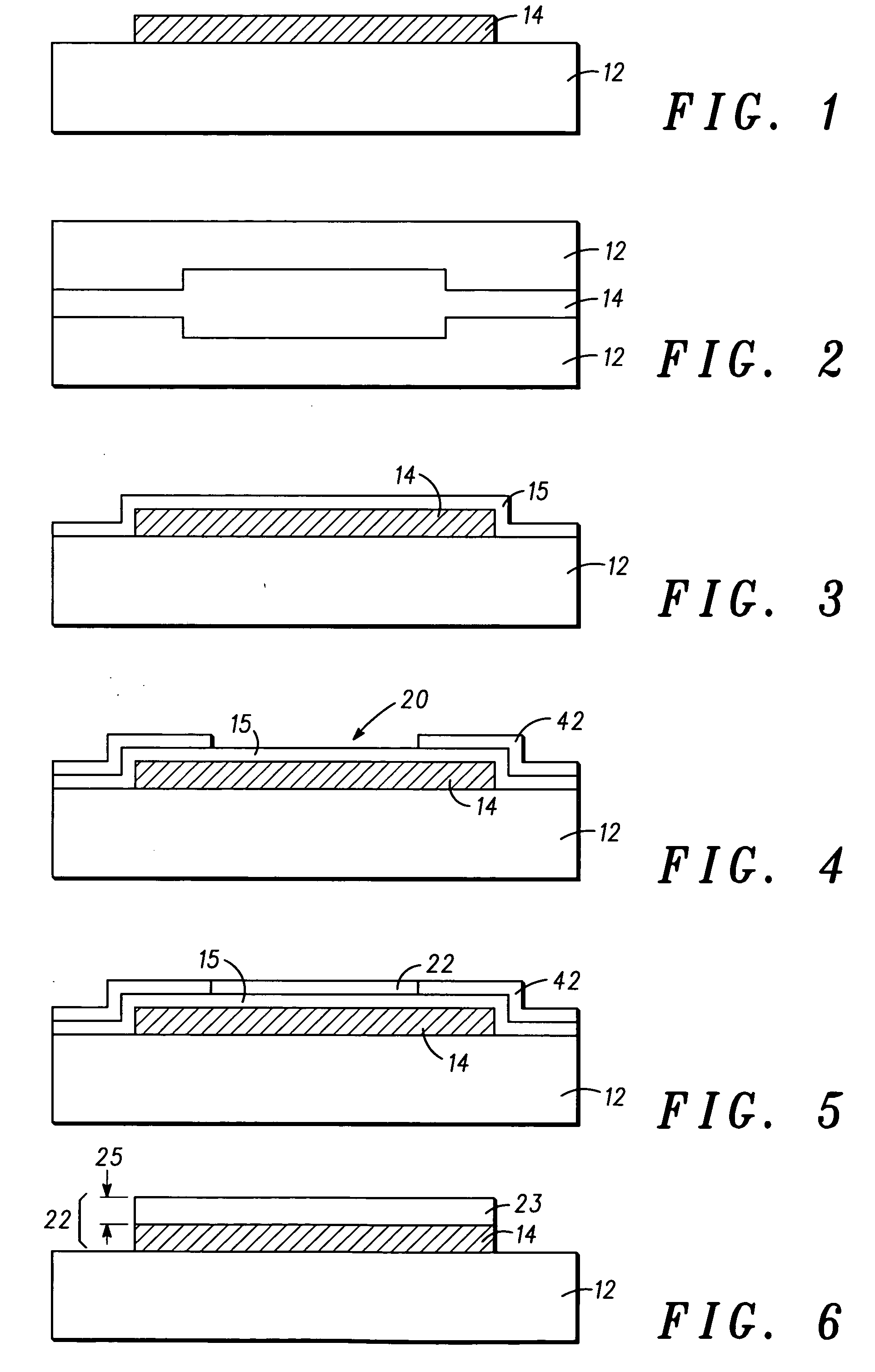
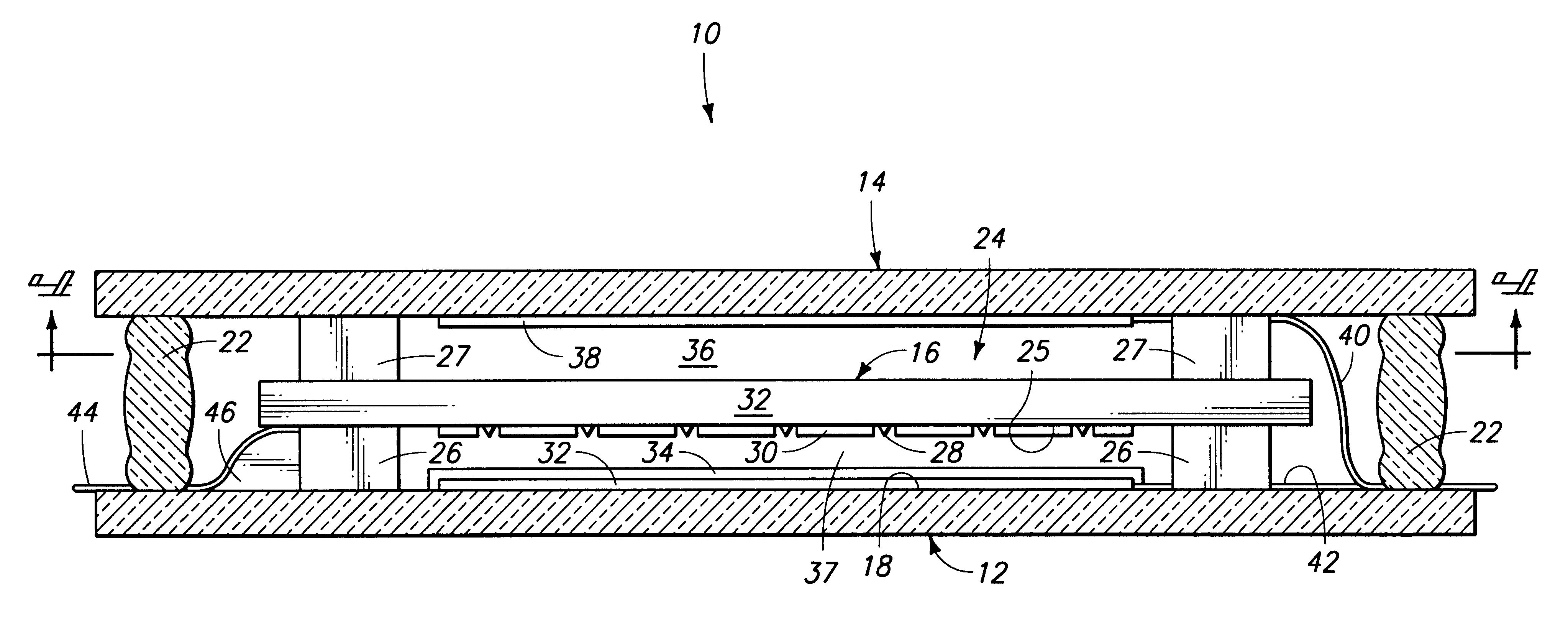
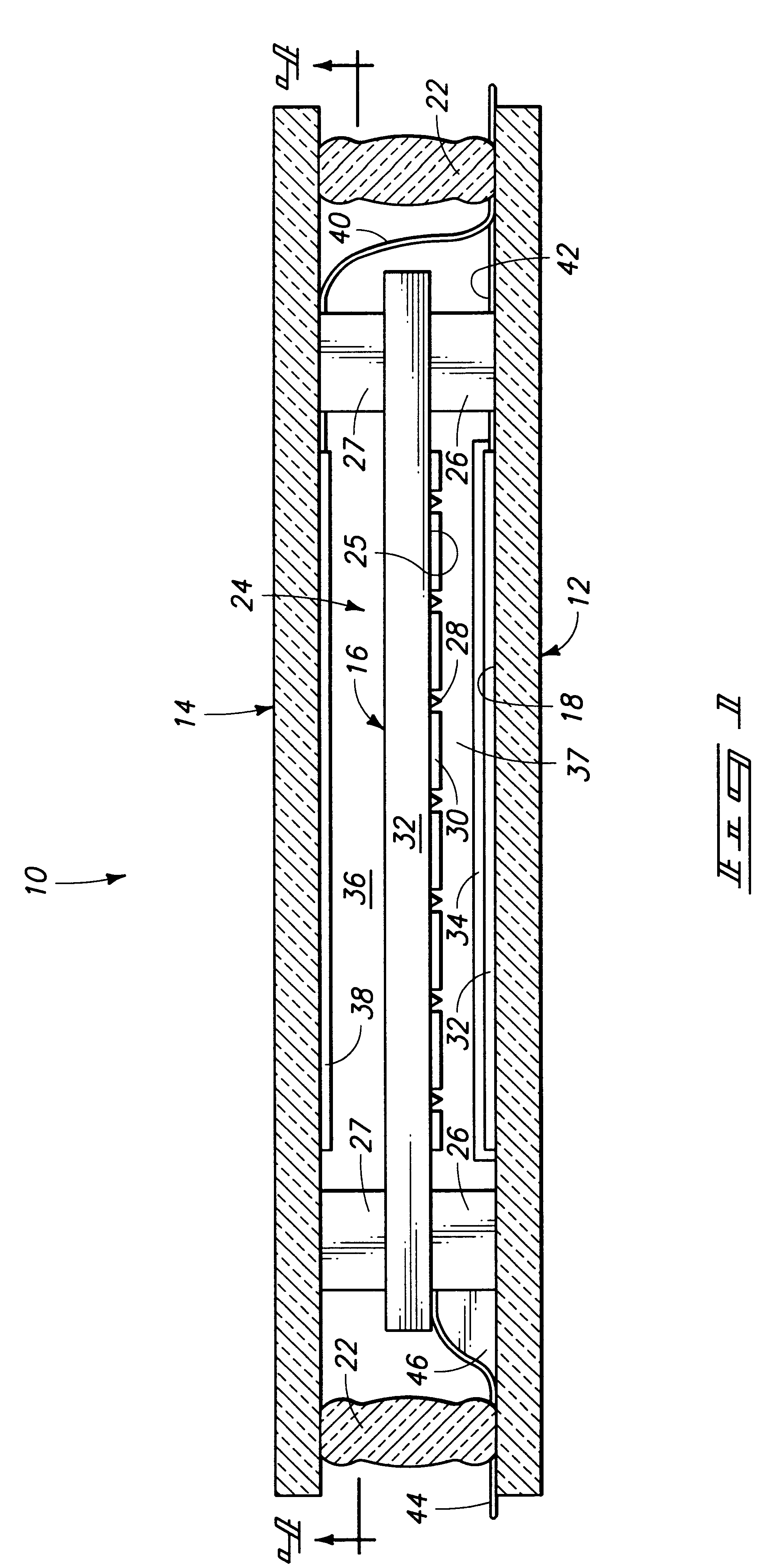
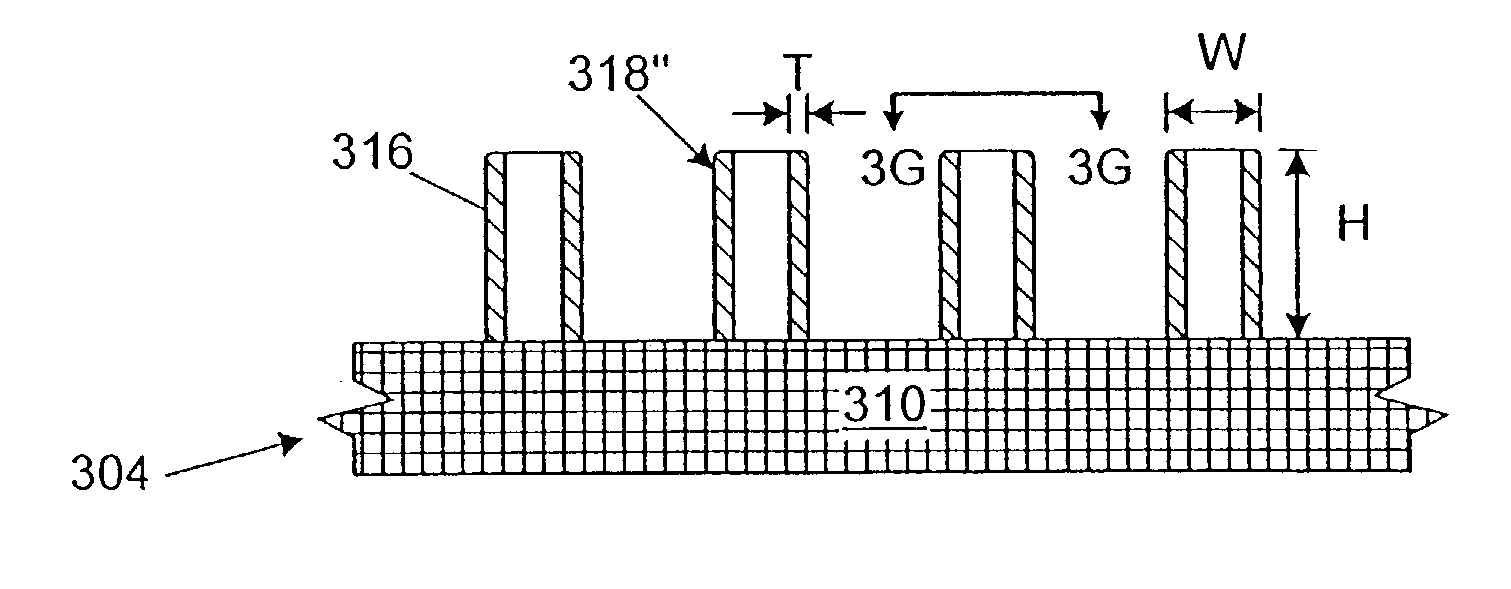
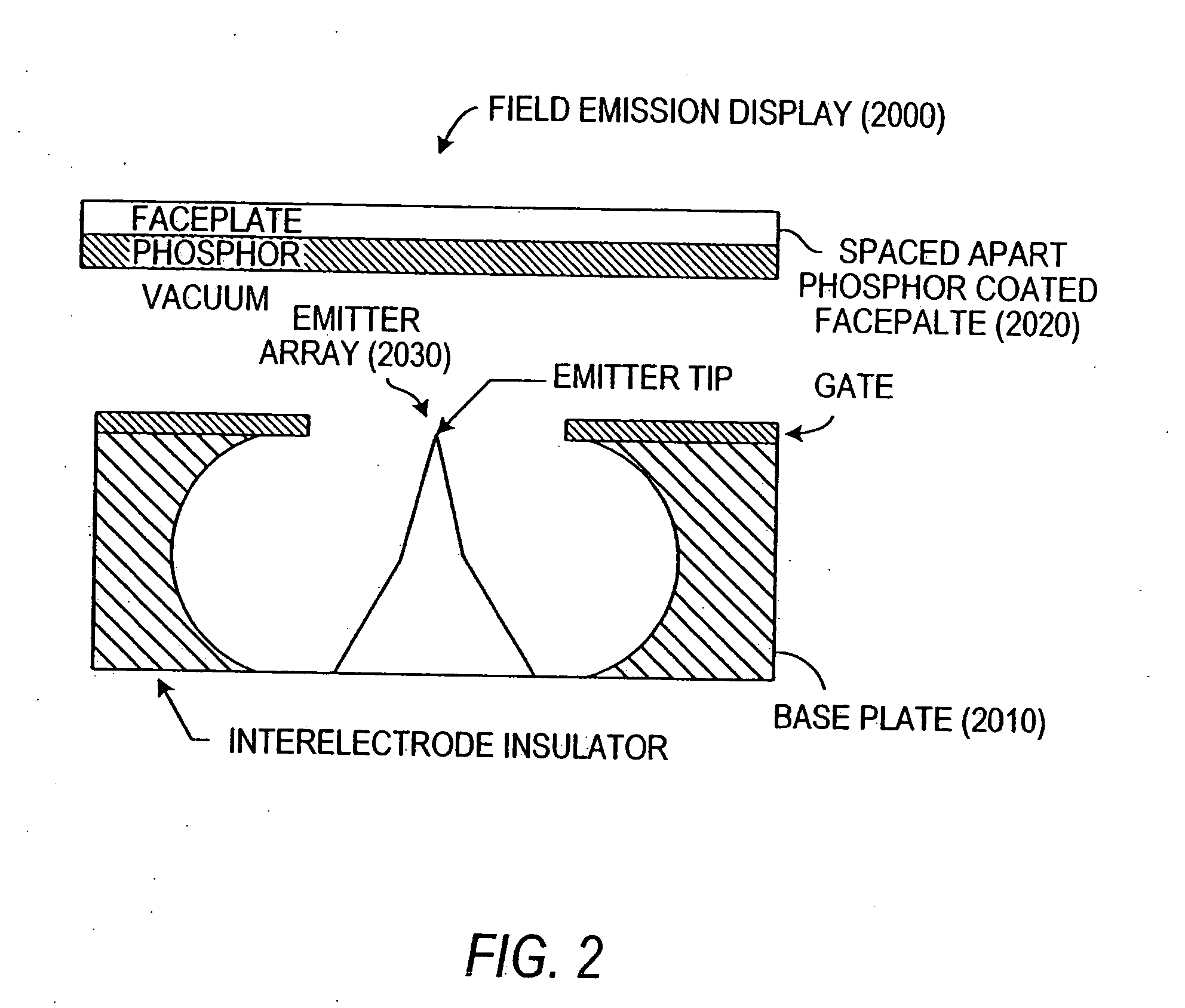
Spacers for field emission displays
InactiveUS20030085650A1Precise positioningQuality improvementCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersElectrode and associated part arrangementsField emission displayDisplay device
The disclosed method for forming a field emission display includes forming a cathode and an anode, forming a plurality of photoresist posts over the cathode, and coating the posts with a coating material. The coating material forms sidewalls around the posts. The photoresist posts may then be removed from within the sidewalls. The anode may then be fitted onto the sidewalls so that the sidewalls function as spacers in the field emission display.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Silicon Nitride Powder for Siliconnitride Phosphor, CaAlSiN3 Phosphor Using Same, Sr2Si5N8 Phosphor Using Same, (Sr, Ca)AlSiN3 Phosphor Using Same, La3Si6N11Phosphor Using Same, and Methods for Producing the Phosphors
Provided are: a silicon nitride powder for siliconitride phosphors with higher luminance, which can be used for a fluorescent display tube (VFD), a field emission display (FED), a plasma display panel (PDP), a cathode ray tube (CRT), a light emitting diode (LED), and the like; a CaAlSiN3 phosphor, an Sr2Si5N8 phosphor, an (Sr, Ca)AlSiN3 phosphor and an La3Si6N11 phosphor, each using the silicon nitride powder; and methods for producing the phosphors. The present invention relates to a silicon nitride powder for siliconitride phosphors, which is characterized by being a crystalline silicon nitride powder that is used as a starting material for producing a siliconitride phosphor that includes silicon element and nitrogen element but does not contain oxygen element as a constitutent element, and which is characterized by having an oxygen content of 0.2% by weight to 0.9% by weight; a CaAlSiN3 phosphor, an Sr2Si5N8 phosphor, an (Sr, Ca)AlSiN3 phosphor and an La3Si6N11 phosphor, each using the silicon nitride powder; and methods for producing the phosphors.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
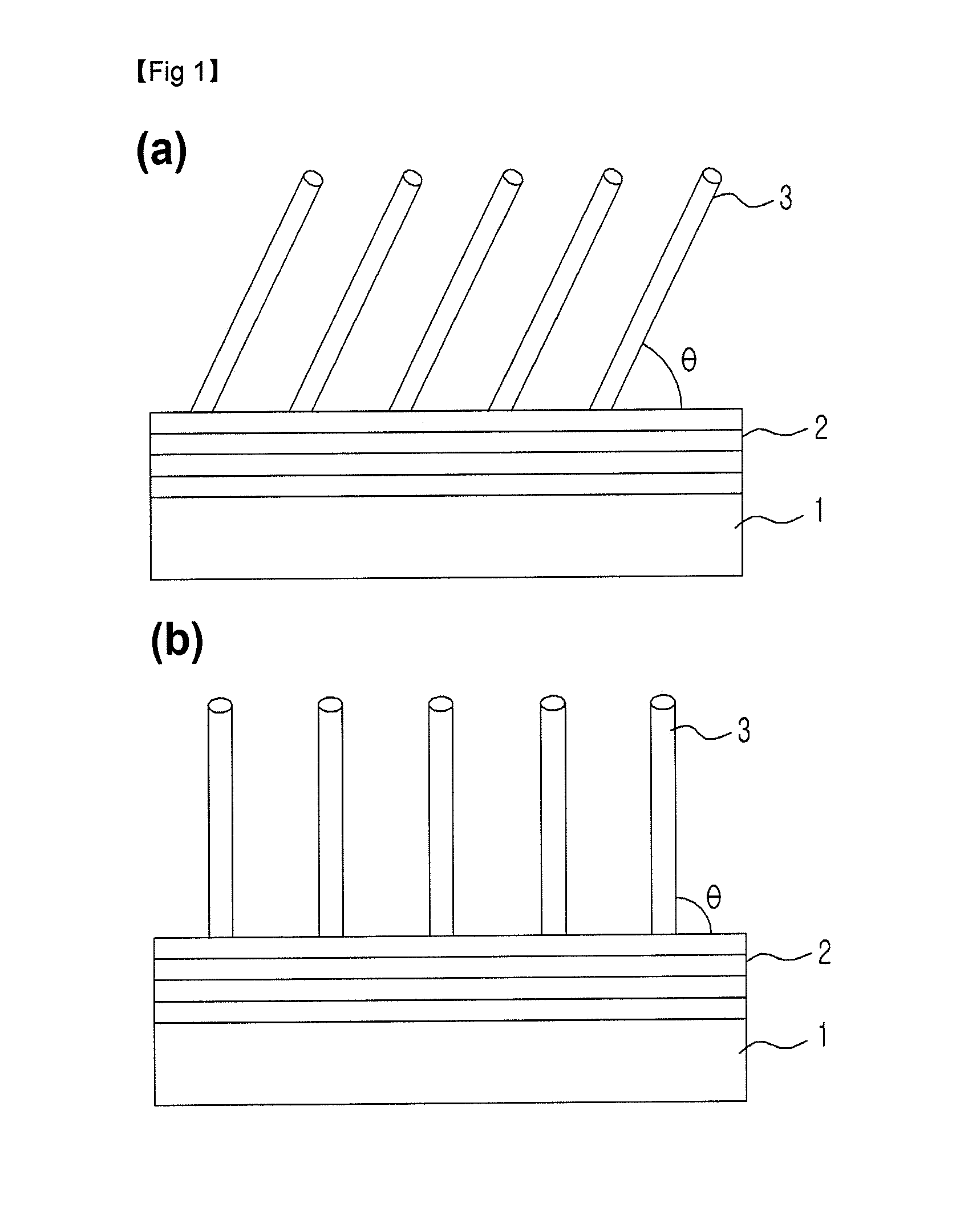
Controlled growth of a nanostructure on a substrate
ActiveUS7687876B2Optimization mechanismMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismField emission displayDisplay device
The present invention provides for nanostructures grown on a conducting substrate, and a method of making the same. The nanostructures grown according to the claimed method are suitable for manufacturing electronic devices such as an electron beam writer, and a field emission display.
Owner:SMOLTEK AB
Carbonaceous Nanocomposite Having Novel Structure And Fabrication Method Thereof
ActiveUS20120192931A1Improve adhesionHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsHigh current densityElectrical resistance and conductance
Disclosed is a carbonaceous nanocomposite including: a substrate; a graphene sheet formed on a top surface of the substrate in parallel with the substrate; and a carbonaceous nanomaterial provided on another surface of the graphene sheet, the nanomaterial having an aspect ratio of 2 to 75,000 to make a predetermined angle with the graphene sheet. The carbonaceous nanocomposite according to the present disclosure has excellent adhesivity to the substrate and can be attached to the substrate without undergoing a pasting process. Since a two-directional current flow is generated, the electrical resistance of the graphene and carbon nanotube is considerably reduced. In addition, the graphene allows the carbon nanotube to have a high current density and a high specific surface area, thereby accelerating a redox reaction. The excellent heat-radiating property of the graphene sheet allows fast transfer of heat generated in the carbon nanotube to outside, thereby avoiding degradation of the carbon nanotube. Thus, when employed as an electrode for a battery or a field emission display, a higher current density and an extended lifespan can be achieved when compared with the existing art.
Owner:INJE UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Advertising displays
ActiveUS20090241388A1Non-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLuminescent polymersField emission display
Exemplary embodiments comprise static and dynamic advertising displays where the backlight is provided by any one of the following: LED's, organic light emitting diodes (OLED), field emitting display (FED), light emitting polymer (LEP), and organic electro-luminescence (OEL). The backlights for both the static and dynamic advertising displays may be constructed of multiple tiles of lights, such that a single tile may be replaced without having to replace the entire backlight assembly. The display may be mounted on a vertical surface, and components may be repaired or replaced without having to remove the entire display from its mounted position.
Owner:MFG RESOURCES INT INC
Nanotube-based electron emission device and systems using the same
InactiveUS6512235B1Minimizes angular divergence of beamLess sensitiveThermometer detailsNanostructure manufactureElectron sourceLithographic artist
A device that produces an electron beam with high optical quality for processing a sample, is presented. The optical quality is manifested by very high brightness and low energy spread. The device includes an electron source device comprising an electrode in the form of a shaped first layer, preferably in the form of a conducting crater carrying at least one nanotube, and an extracting electrode, which is formed with at least one aperture and is insulated from the firs layer. The source can be used in any column that requires such properties. The column according to the invention may be a full size or a miniature electron microscope, a lithography tool, a tool used for direct writing of wafers or a field emission display.
Owner:EL MUL TECH
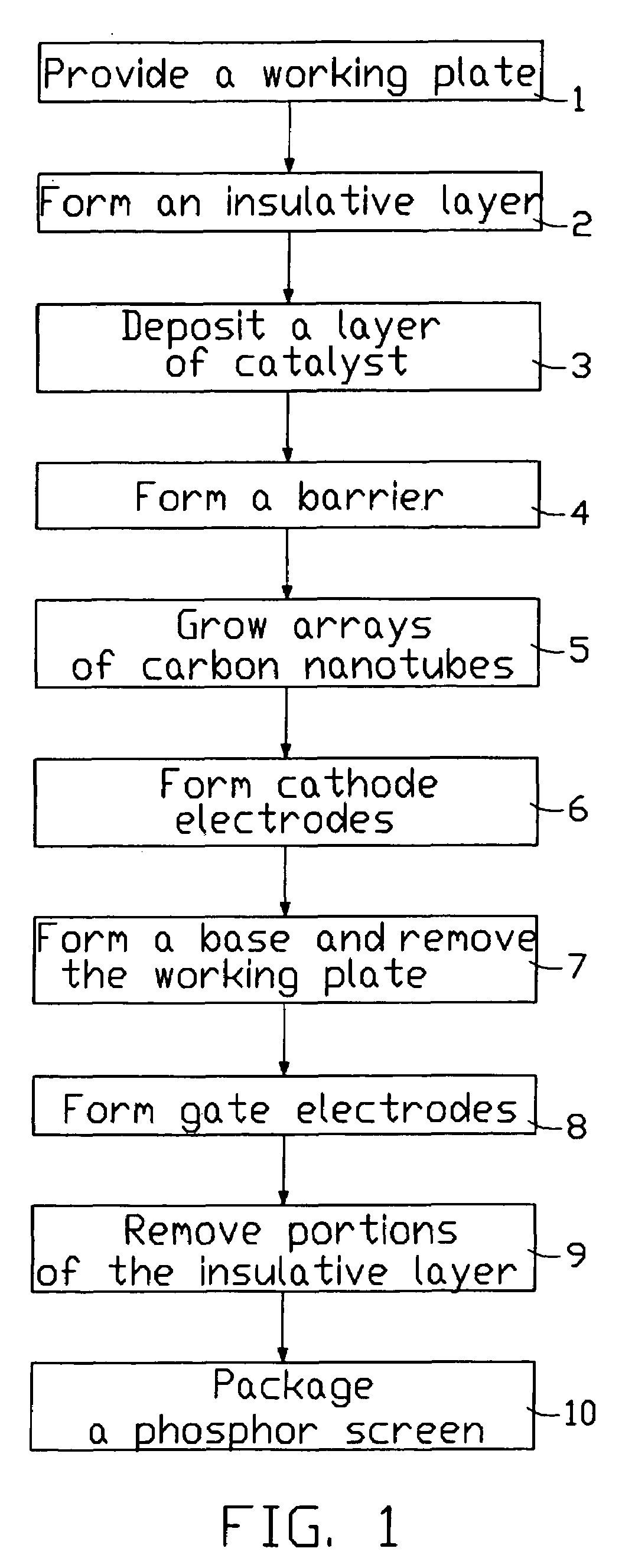
Method for making a carbon nanotube-based field emission display
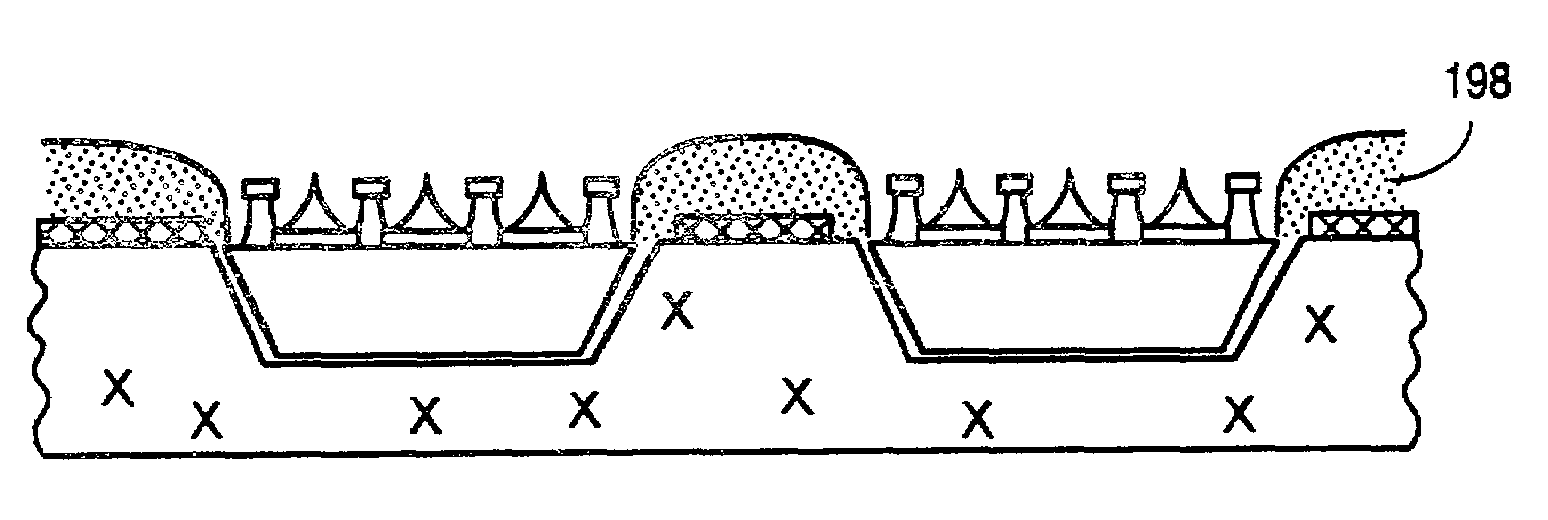
A method for making a field emission display includes: (1) providing a detachable substrate having a plane surface; (2) forming gate electrodes in a predetermined pattern on the plane surface of the detachable substrate; (3) forming an intermediate layer on the gate electrodes; (4) forming a catalyst layer on the intermediate layer; (5) forming a spacer in a manner corresponding to a predetermined pattern on the layer of catalyst material; (6) forming carbon nanotube arrays extending from the layer of catalyst material; (7) forming cathode electrodes on first ends of the carbon nanotube arrays; and (8) removing the detachable substrate, and removing portions of the intermediate layer corresponding to positions of the carbon nanotube arrays so as to expose opposite second ends of the carbon nanotube arrays that face toward the gate electrodes.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Advertising displays
ActiveUS8016452B2Non-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLuminescent polymersField emission display
Exemplary embodiments comprise static and dynamic advertising displays where the backlight is provided by any one of the following: LED's, organic light emitting diodes (OLED), field emitting display (FED), light emitting polymer (LEP), and organic electro-luminescence (OEL). The backlights for both the static and dynamic advertising displays may be constructed of multiple tiles of lights, such that a single tile may be replaced without having to replace the entire backlight assembly. The display may be mounted on a vertical surface, and components may be repaired or replaced without having to remove the entire display from its mounted position.
Owner:MFG RESOURCES INT INC
Molybdenum Tubular Sputtering Targets with Uniform Grain Size and Texture
ActiveUS20080193798A1High purityImprove performanceCellsVacuum evaporation coatingDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
Molybdenum sputtering targets and sintering characterized as having no or minimal texture banding or through thickness gradient. The molybdenum sputtering targets having a fine, uniform grain size as well as uniform texture, are high purity and can be micro-alloyed to improved performance. The sputtering targets can be round discs, square, rectangular or tubular and can be sputtered to form thin films on substrates. By using a segment-forming method, the size of the sputtering target can be up to 6 m×5.5 m. The thin films can be used in electronic components such as Thin Film Transistor—Liquid Crystal Displays, Plasma Display Panels, Organic Light Emitting Diodes, Inorganic Light Emitting Diode Displays, Field Emitting Displays, solar cells, sensors, semiconductor devices, and gate device for CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) with tunable work functions.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
Method for manufacturing cathode assembly of field emission display
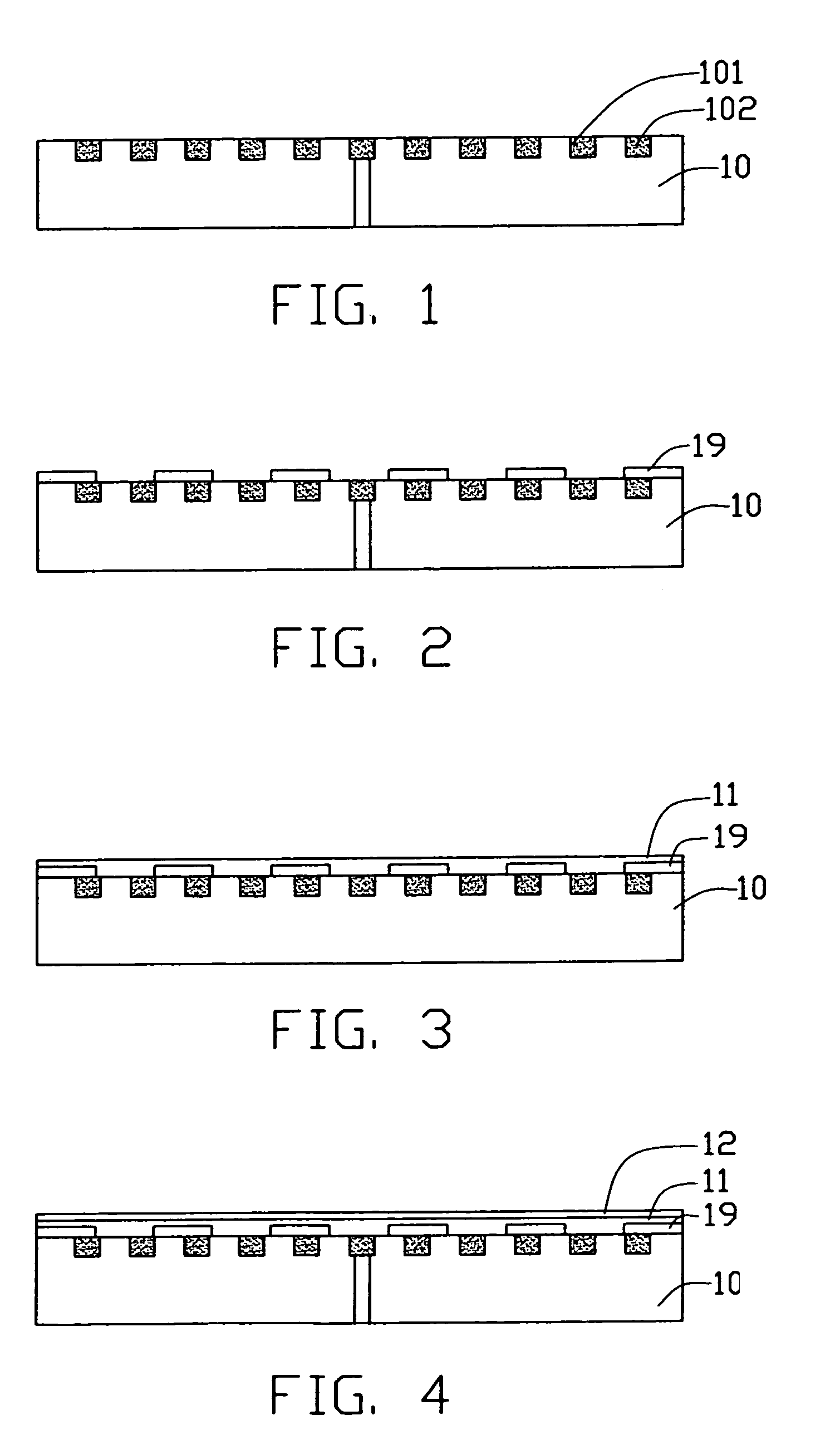
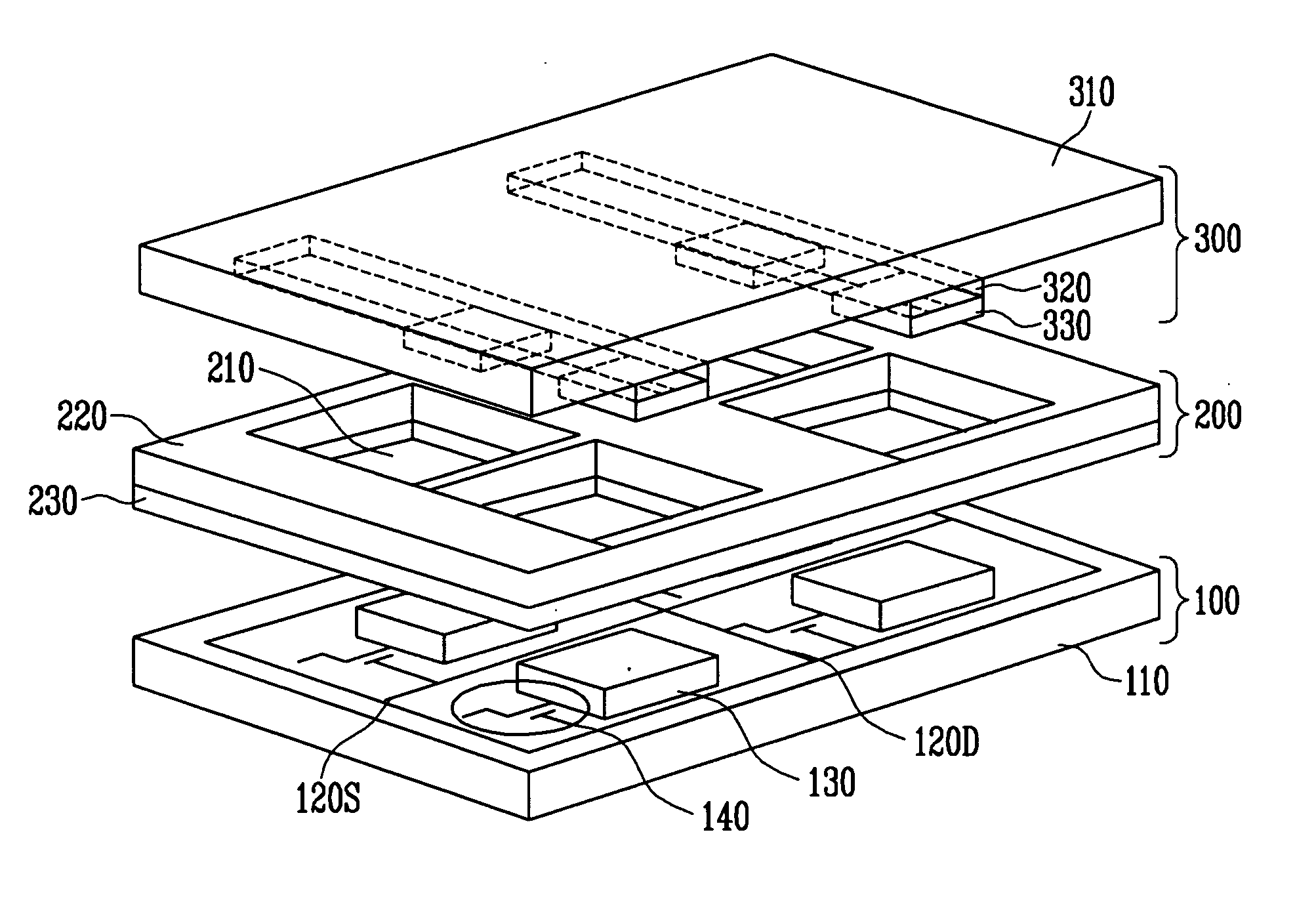
ActiveUS7785907B2Avoid contactProbability of shortingCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersNanoinformaticsField emission displayDisplay device
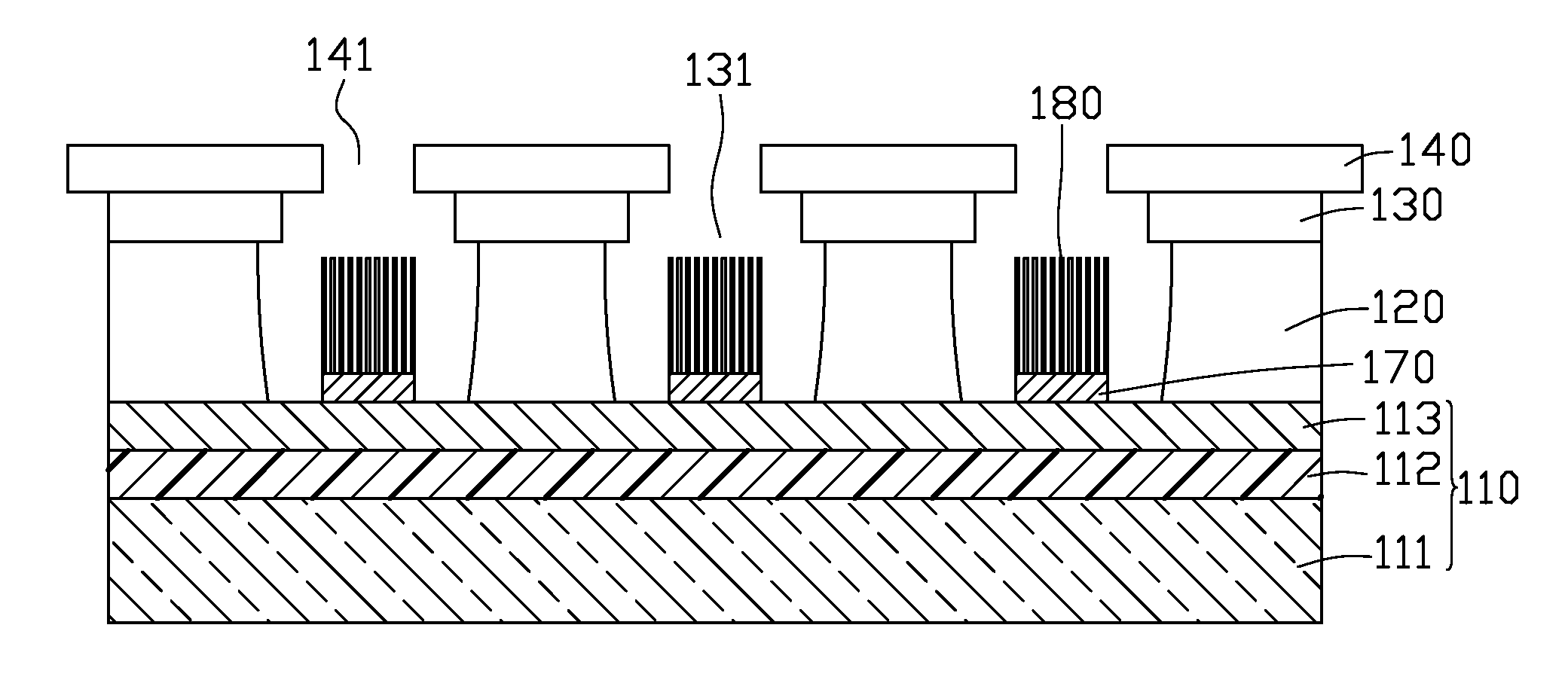
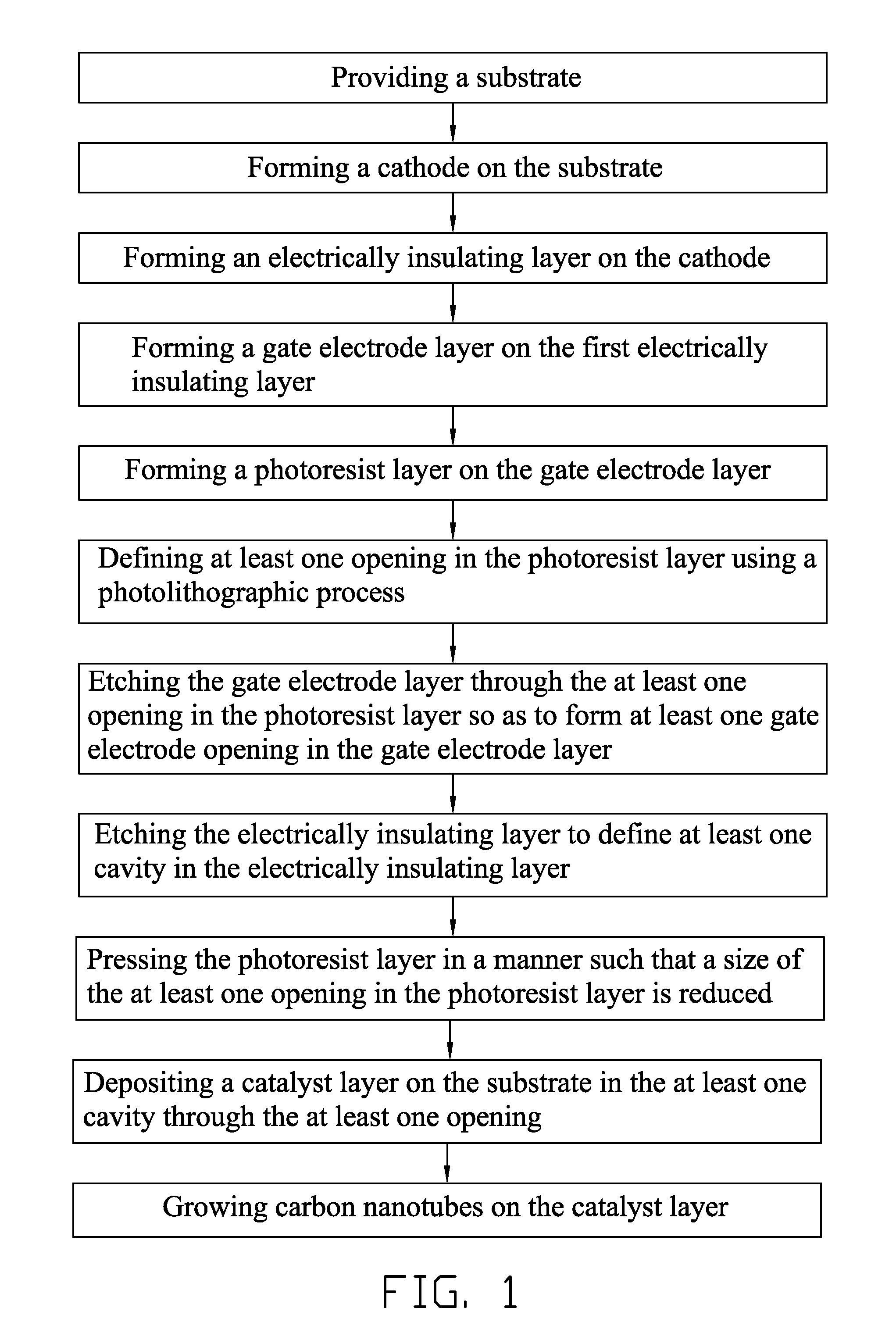
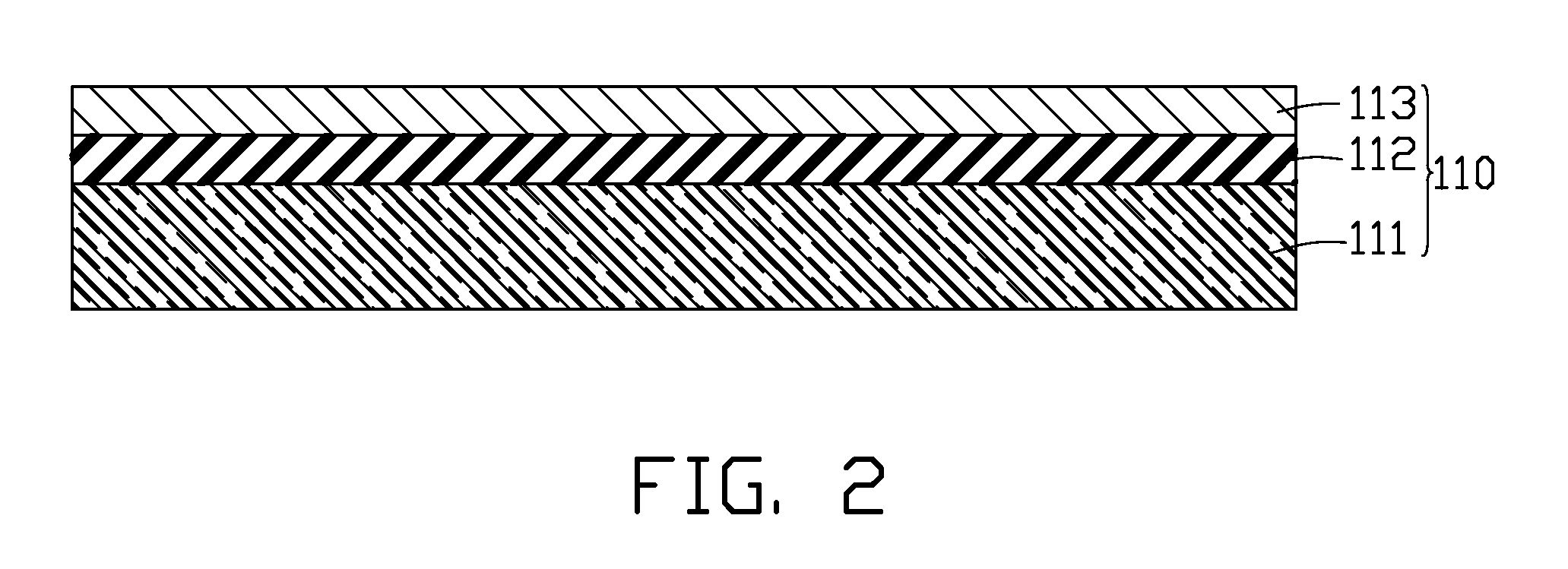
A method for manufacturing a cathode assembly of a field emission display, includes the steps of: providing a substrate (110) with a cathode (113) formed thereon; forming an electrically insulating layer (120), a gate electrode layer (130) and a photoresist layer (140) on a cathode in series; defining at least one opening (141) in the photoresist layer using a photolithographic process; etching the gate electrode layer through the at least one opening so as to form at least one gate electrode opening (131) in the gate electrode layer; etching the electrically insulating layer to define at least one cavity (121) in the electrically insulating layer; pressing the photoresist layer in a manner such that a size of the at least one opening is reduced; depositing a catalyst layer (170) in the at least one cavity through the at least one opening; and growing carbon nanotubes (180) on the catalyst layer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
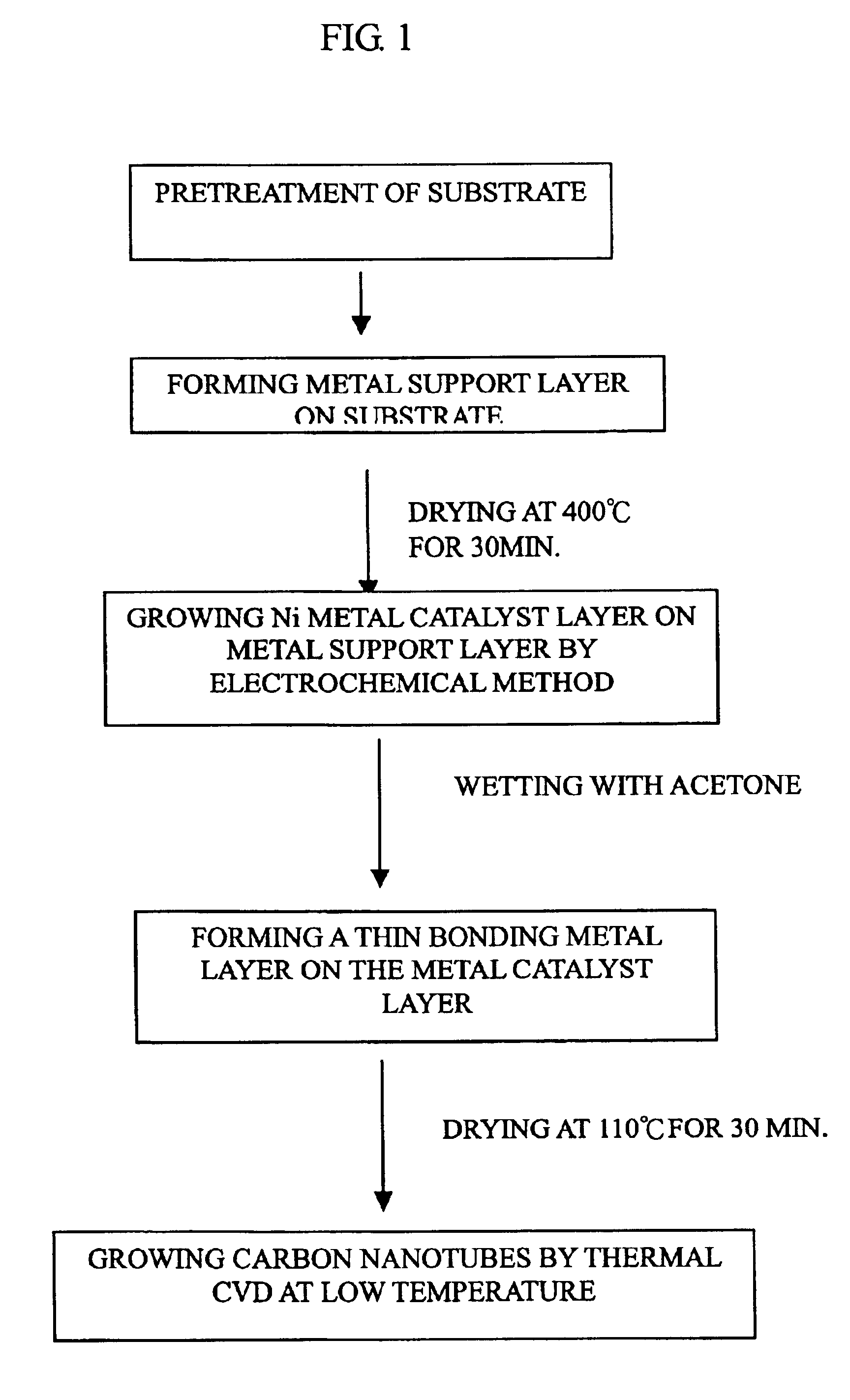
Process of direct growth of carbon nanotubes on a substrate at low temperature
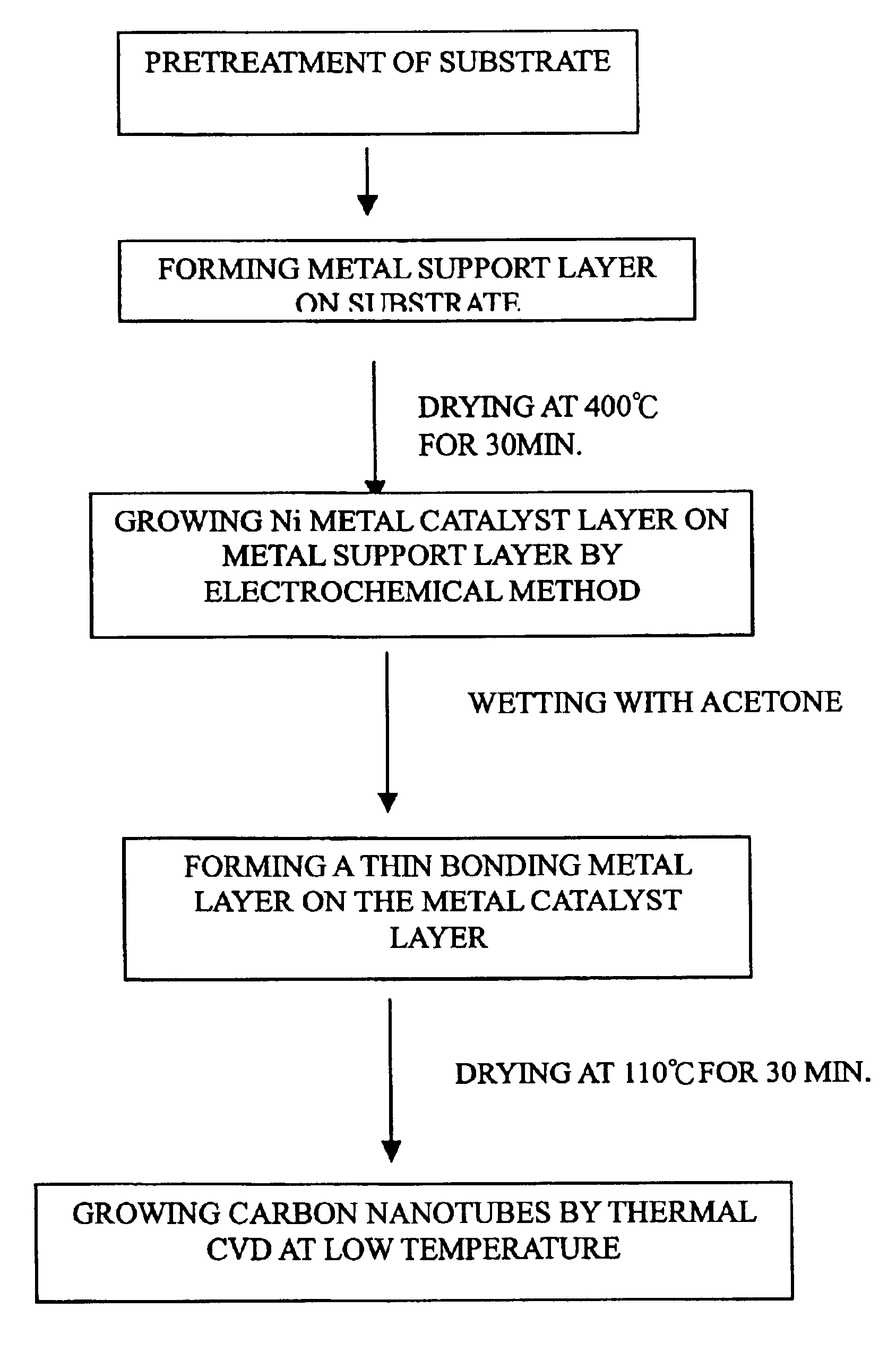
InactiveUS6855376B2Easy to prepareEasy to adjustMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureDisplay deviceAlloy
Carbon nanotubes are directly grown on a substrate surface having three metal layers thereon by a thermal chemical vapor deposition at low-temperature, which can be used as an electron emission source for field emission displays. The three layers include a layer of an active metal catalyst sandwiched between a thick metal support layer formed on the substrate and a bonding metal layer. The active metal catalyst is iron, cobalt, nickel or an alloy thereof; the metal support and the bonding metal independently are Au, Ag, Cu, Pd, Pt or an alloy thereof; and they can be formed by sputtering, chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, screen printing or electroplating.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IP LTD
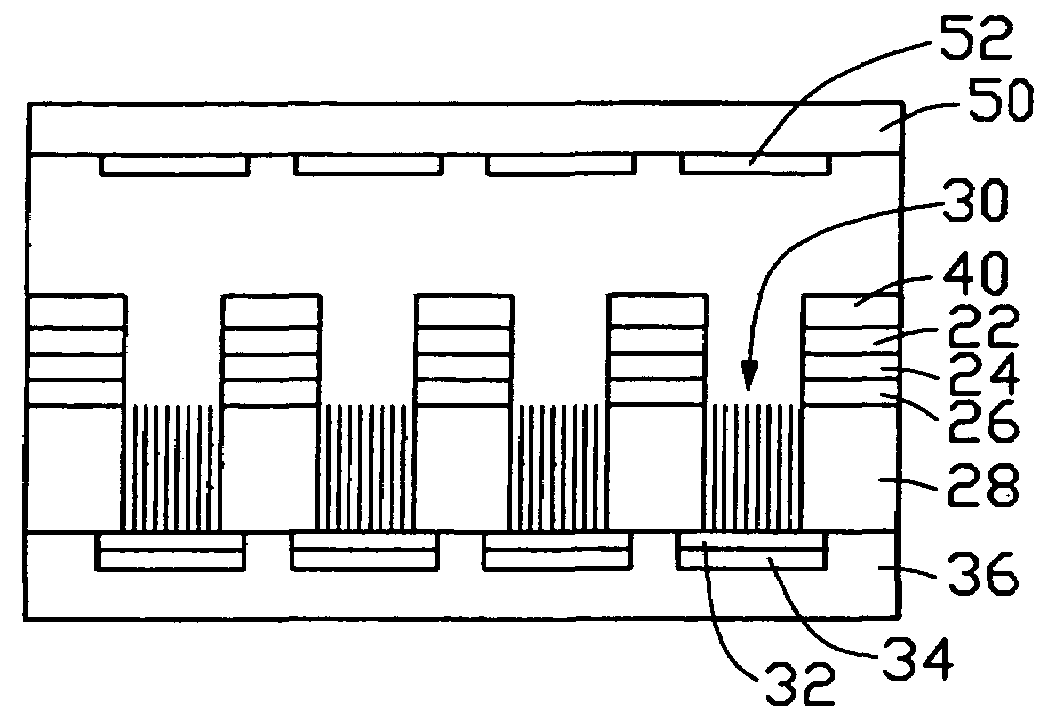
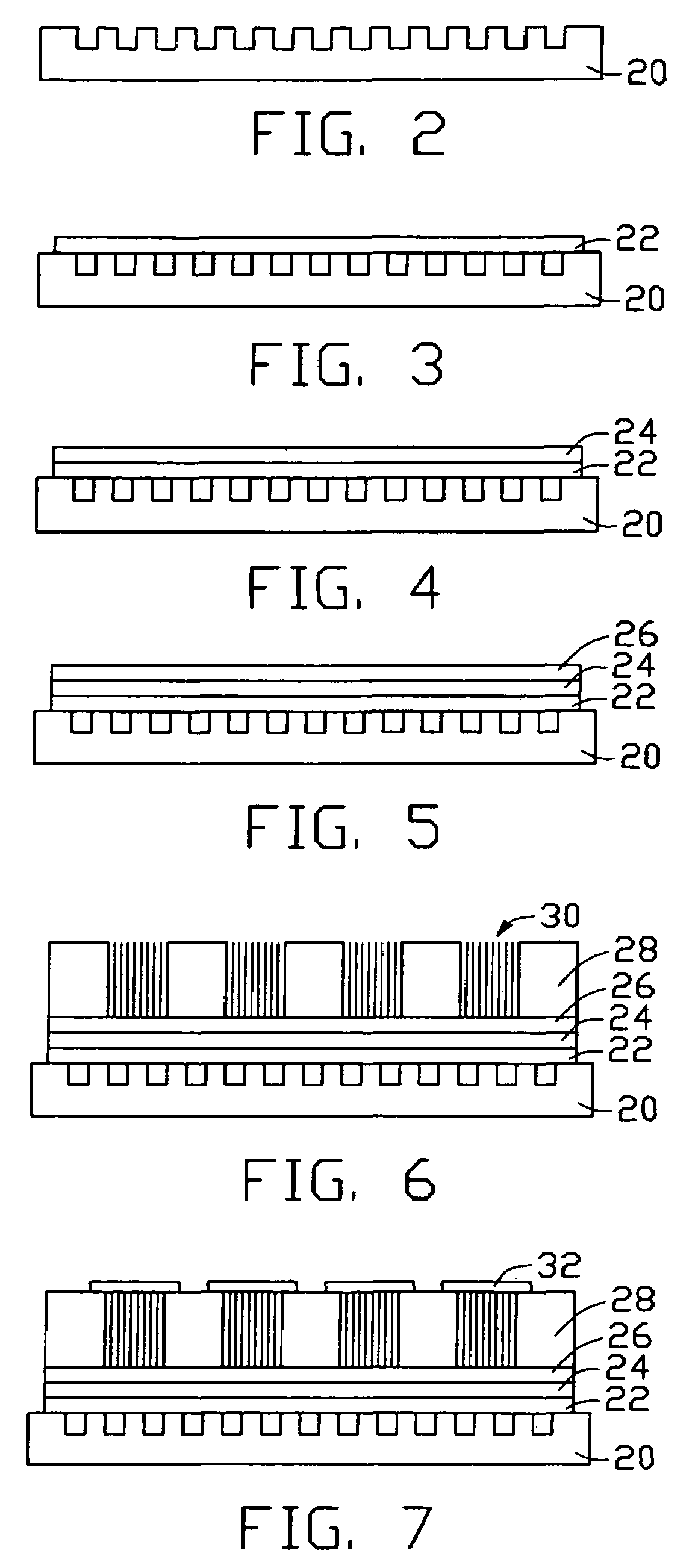
Method for making a carbon nanotube-based field emission display
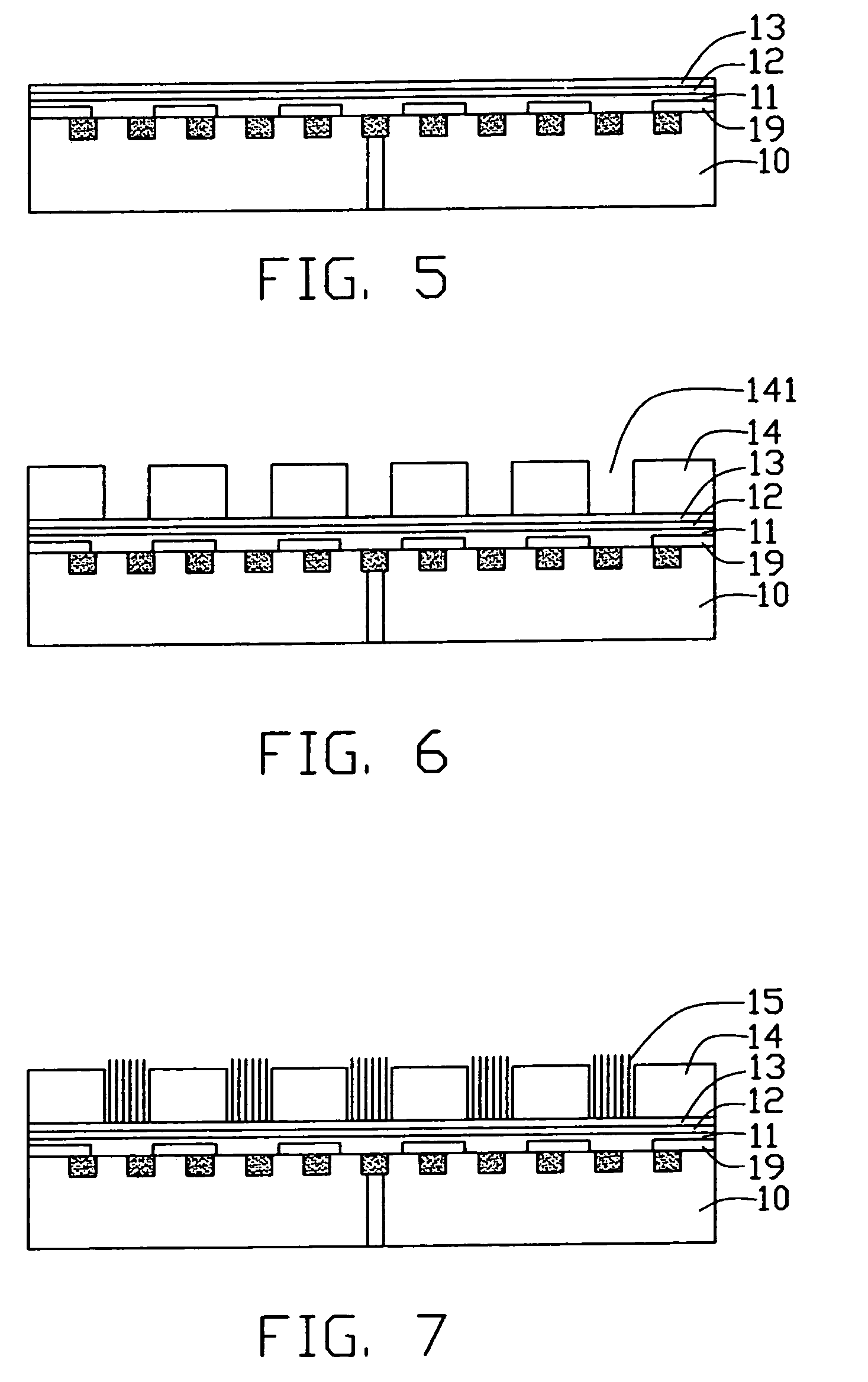
A method for making a carbon nanotube-based field emission display device includes the following steps: providing an insulative layer (22) having a first surface; depositing a layer of catalyst (26) on the first surface of the insulative layer; forming a spacer (28) having a number of openings therein such that patterned areas of the layer of catalyst are exposed in the openings; forming arrays of carbon nanotubes (30) extending from the layer of catalyst in the openings; forming a cathode electrode (34) on a top of each of the arrays of carbon nanotubes; forming gate electrodes (40) on a second, opposite surface of the insulative layer offset from the patterned areas; removing portions of the insulative layer corresponding to the arrays of carbon nanotubes so as to expose the arrays of carbon nanotubes; and attaching an anode electrode (50) having a phosphor screen (52) to the above obtained structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Field emission display device in separated structure
InactiveCN1805105AImprove display qualityReduce difficultyImage/pattern display tubesNon-linear opticsLiquid crystal light valvePhotocathode
The invention relates to a separated field emission display device, which comprises a glass basic plate and the three primary colors fluorescent powder and aluminum film mounted on the glass basic plate. Wherein, there is a sealed vacuum chamber between the glass basic plate and the ITO glass basic plate; the aluminum film and the ITO glass basic plate are individually connected to the anode and cathode of direct current and high voltage; the ITO glass basic plate is plated with a photo-electric cathode array; the liquid crystal light valve is mainly formed by a upper ITO glass basic plate with directional layer, a liquid crystal layer and a lower ITO glass basic plate with directional layer, while the lower end of said liquid crystal light valve has a negative light source of light-emitting diode. The invention uses the electric beam to impact the fluorescent powder, the liquid crystal light valve and the negative light source, therefore, it has the energy saving, portable and better display properties of CRT and plane display, and compared to the surface conductive electric emitting display, it can avoid the preparation of nanometer slit to reduce the difficulty of technique and process.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050275331A1Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Electron emission source composition for field emission display device and field emission display device fabricated using same
Disclosed is an electron emission source composition for a field emission display device including 1 to 20% by weight of carbon nano tubes; glass frit; an organic binder resin comprising ethyl cellulose and acrylate resin and / or acryl resin; and an organic solvent, wherein the glass frit is present in an amount of 1 to 500 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the carbon nano tubes.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
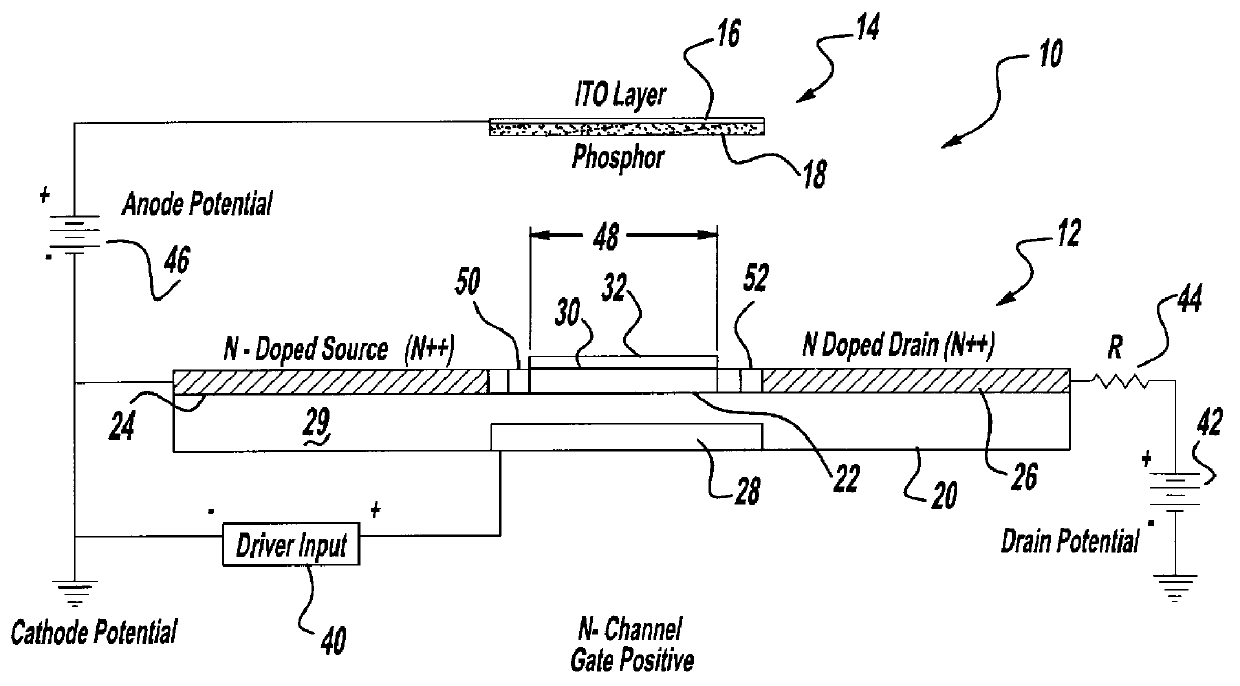
Flat surface emitter for use in field emission display devices
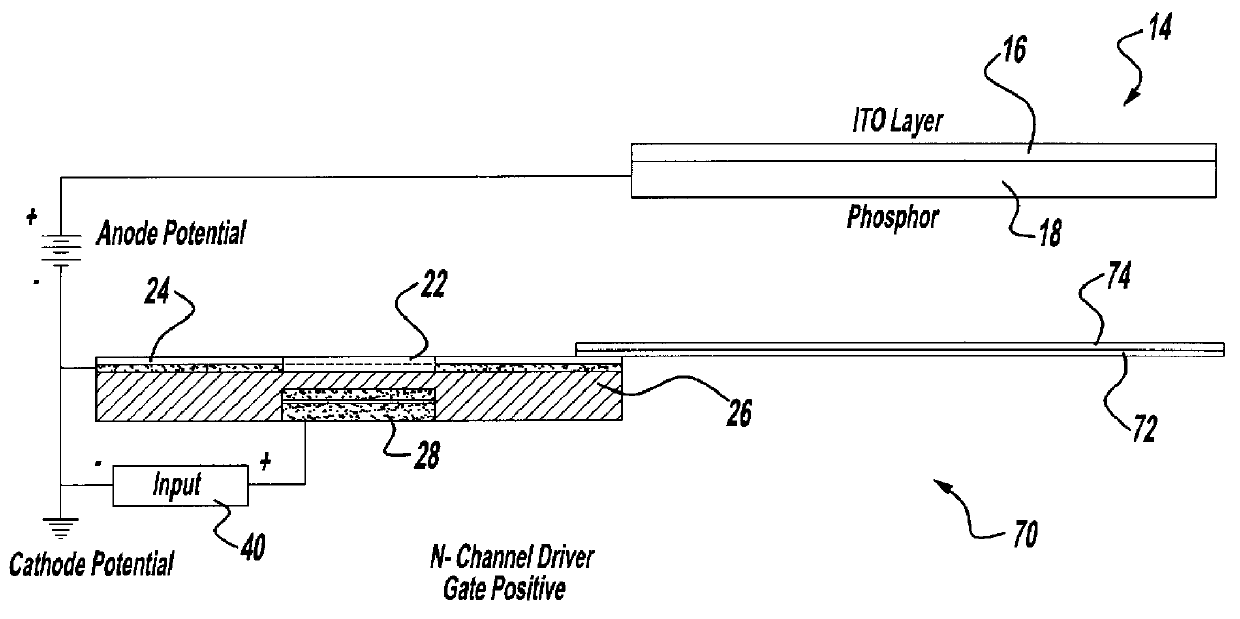
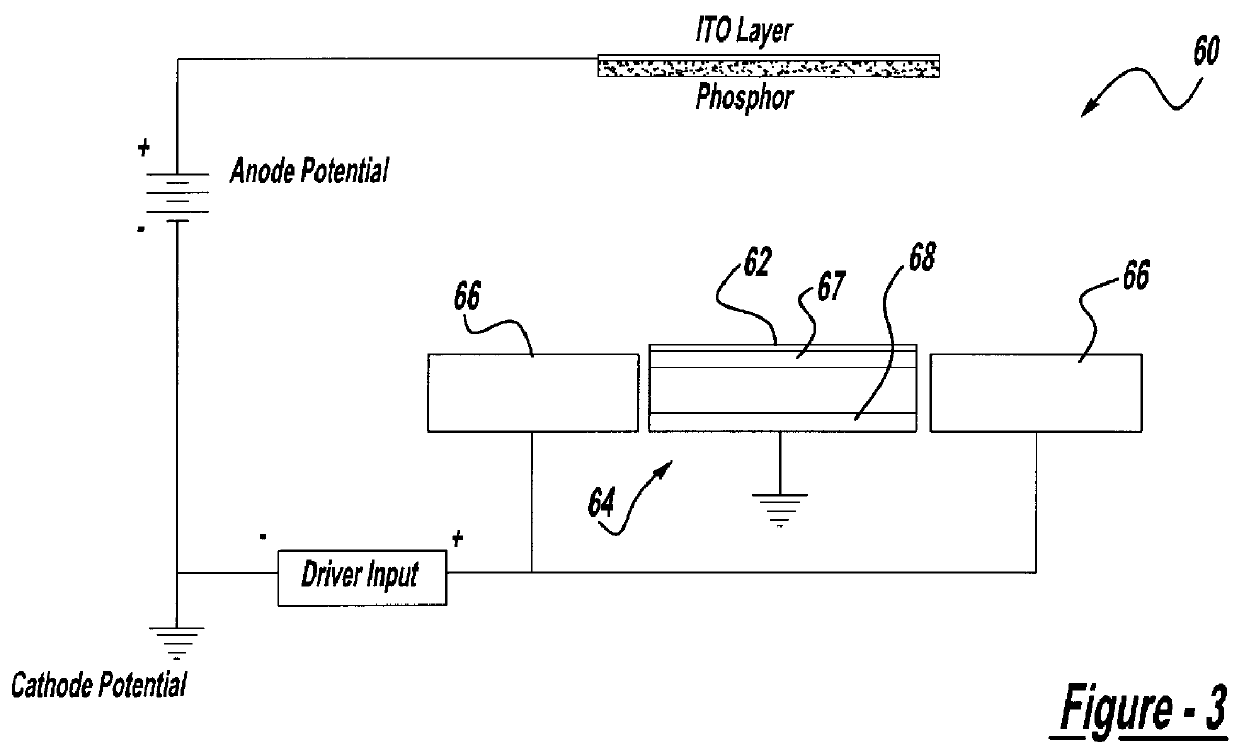
InactiveUS6011356AImprove efficiencyExcellent optical propertiesElectric discharge tubesStatic indicating devicesSecondary electronsVoltage source
For use in cathodoluminescent field emission display devices, a cathode emitter can comprise an inverted field effect transistor having a diamond film or other low effective work function material deposited onto the channel layer of the transistor, such that the diamond film provides a source of primary electron emissions. A variable voltage source is applied to the gate of the transistor creating an electric field that controls the conductivity of the channel layer, thereby activating or deactivating electron emissions from this cathode emitter structure. In addition, electron blocking junctions can be incorporated into the emitter structure to inhibit current flow through the device during a deactivated state. In a variation, the transistor of the cathode emitter has the diamond film being deposited onto an electrically conductive pad that is electrically connected to, and extending outwardly from, the transistor. Alternatively, a sideways laterally gated transistor structure can be used with the emitter surface being applied to the transistor's drain. A near mono-molecular oxide film of high secondary electron emission material can also be included on the emitter surface for enhanced electron emissions.
Owner:ST CLAIR INTPROP CONSULTANTS
Field emission display having carbon nanotube emitter and method of manufacturing the same
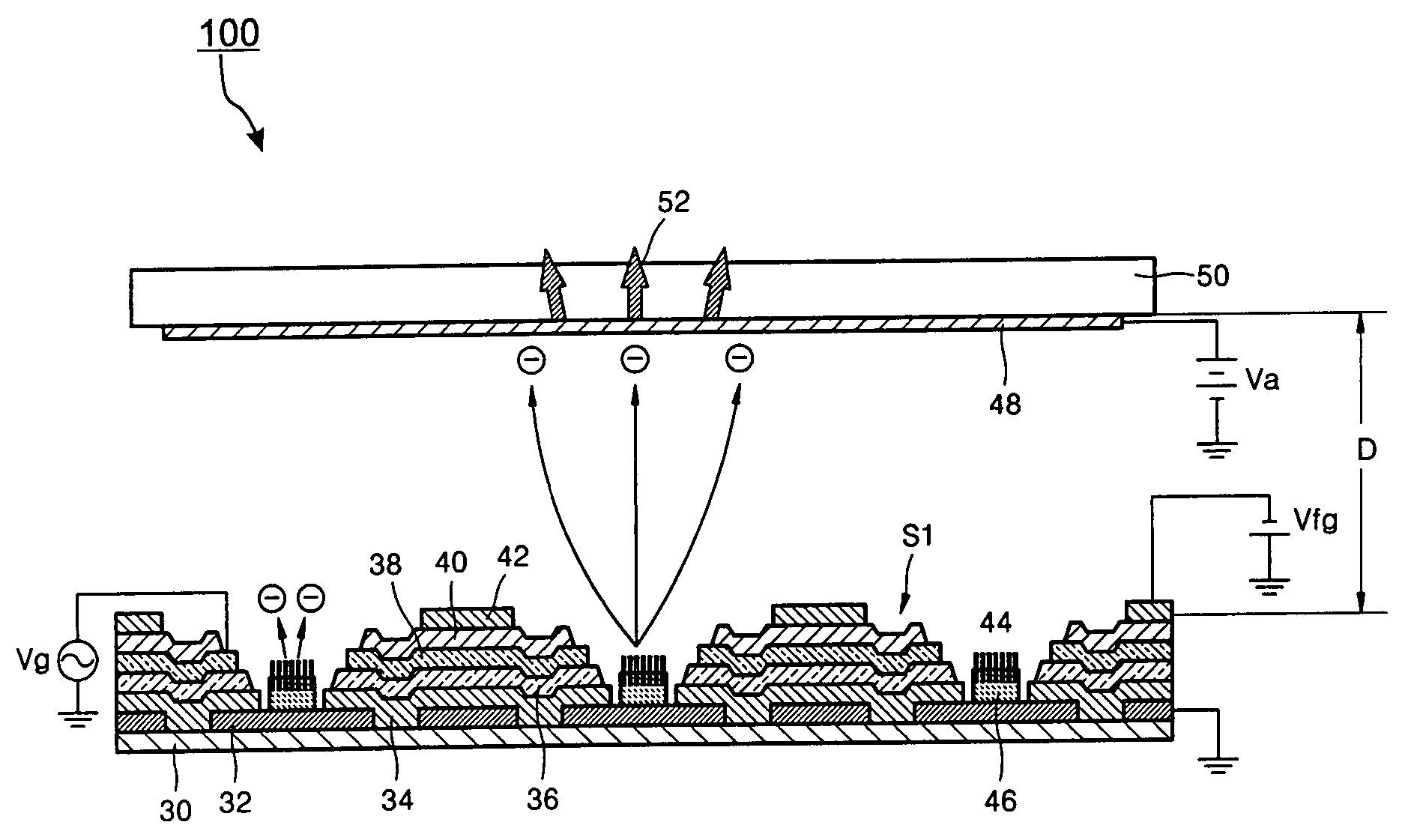
InactiveUS20050035701A1Good step coverageReduce leakage currentNanoinformaticsElectrode and associated part arrangementsSilanesCarbon nanotube
Provided is a field emission display (FED) with a carbon nanotube emitter and a method of manufacturing the same. A gate stack that surrounds the CNT emitter has a mask layer that covers an emitter electrode adjacent to the CNT emitter, and a gate insulating film, a gate electrode, a focus gate insulating film (SiOx, X<2), and a focus gate electrode formed on the mask layer. The focus gate insulating film has a thickness 2 μm or more, and preferably 3˜15 μm and is preferably made using PECVD. A flow rate of silane and nitric acid for forming the focus gate insulating film and / or the gate insulating film are maintained at 50˜700 sccm and 700˜4,500 sccm, respectively. By doing so and by making the oxide thick, the oxide is less apt to crack and thus less apt to generate a leakage current.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Field emission display
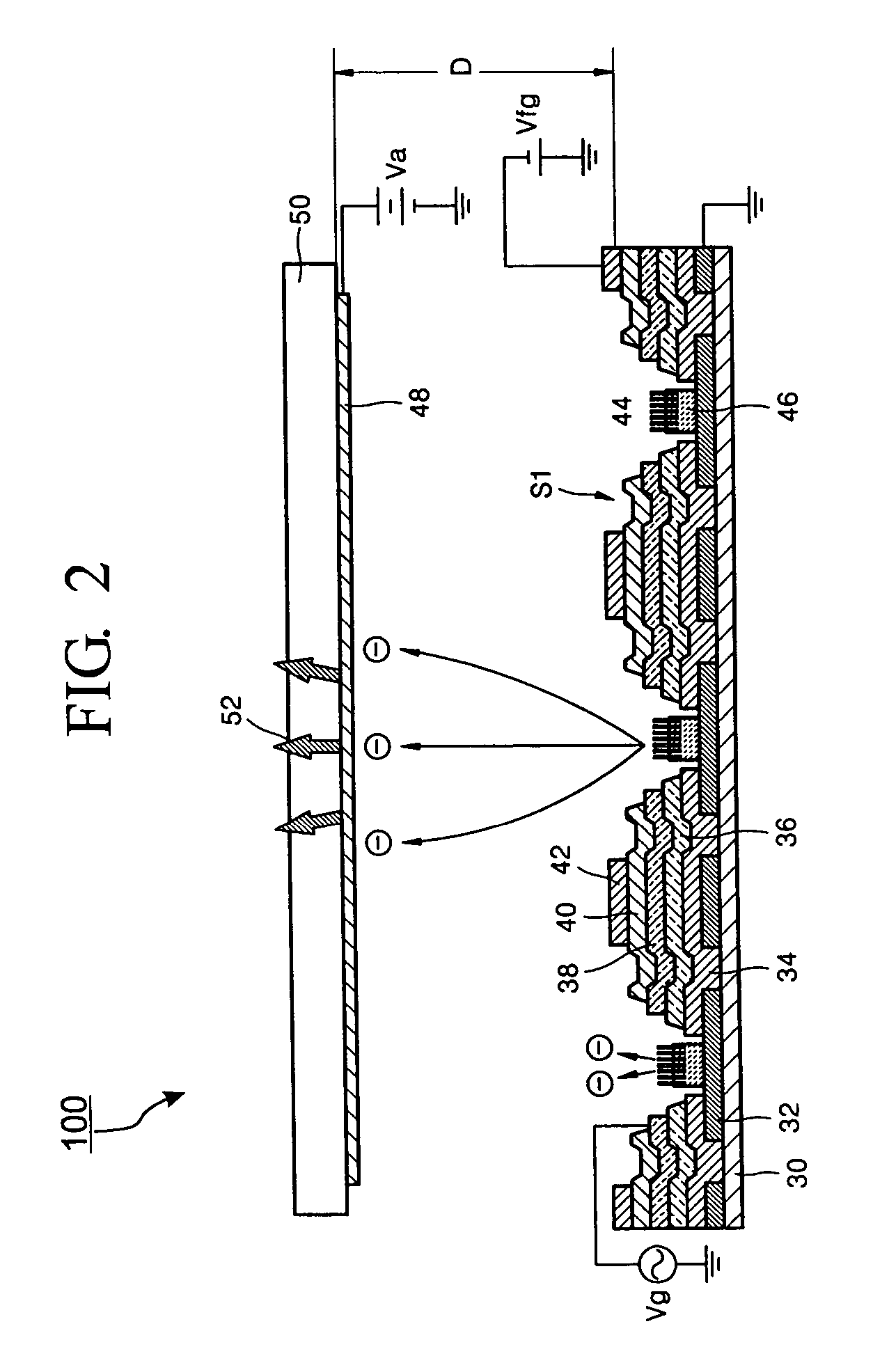
ActiveUS20050248256A1High voltageIncrease brightnessControl electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorField emission display
Provided is a field emission display, which includes: a cathode portion including row signal lines and column signal lines in a stripe form allowing matrix addressing to be carried out on a substrate, and pixels defined by the row signal lines and the column signal lines, each pixel having a field emitter and a control device which controls the field emitter with two terminals connected to at least the row signal line and the column signal line and one terminal connected to the field emitter; an anode portion having an anode electrode, and a phosphor connected to the anode electrode; and a gate portion having a metal mesh with a plurality of penetrating holes, and a dielectric layer formed on at least one region of the metal mesh, wherein the gate portion is disposed between the cathode portion and the anode portion to allow the surface where the dielectric layer is formed to be faced to the cathode portion and to allow electrons emitted from the field emitter to collide with the phosphor via the penetrating holes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com