Patents
Literature
402 results about "Low work function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
External electrode fluorescent lamp with optimized operating efficiency
InactiveUS20080036354A1Improve electron emission rateReduce functionGas-filled discharge tubesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureDisplay deviceEngineering
An EEFL-type fluorescent lamp for backlighting of displays or screens, whereby the encapsulating glass and / or a (partial) coating of the interior surface of the encapsulating glass are provided which possess a low work function Wa for the electrons of <6 eV, preferably <5 eV, more preferably 0 eV<Wa<5 eV, especially preferably 0 eV<Wa<4 eV, more especially preferably 0 eV<Wa<3 eV. This allows for the operating efficiency to be optimized and the firing voltage to be lowered.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Organic devices, organic electroluminescent devices, organic solar cells, organic FET structures and production method of organic devices
ActiveUS20050098207A1TransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectronic transmissionOrganic solar cell
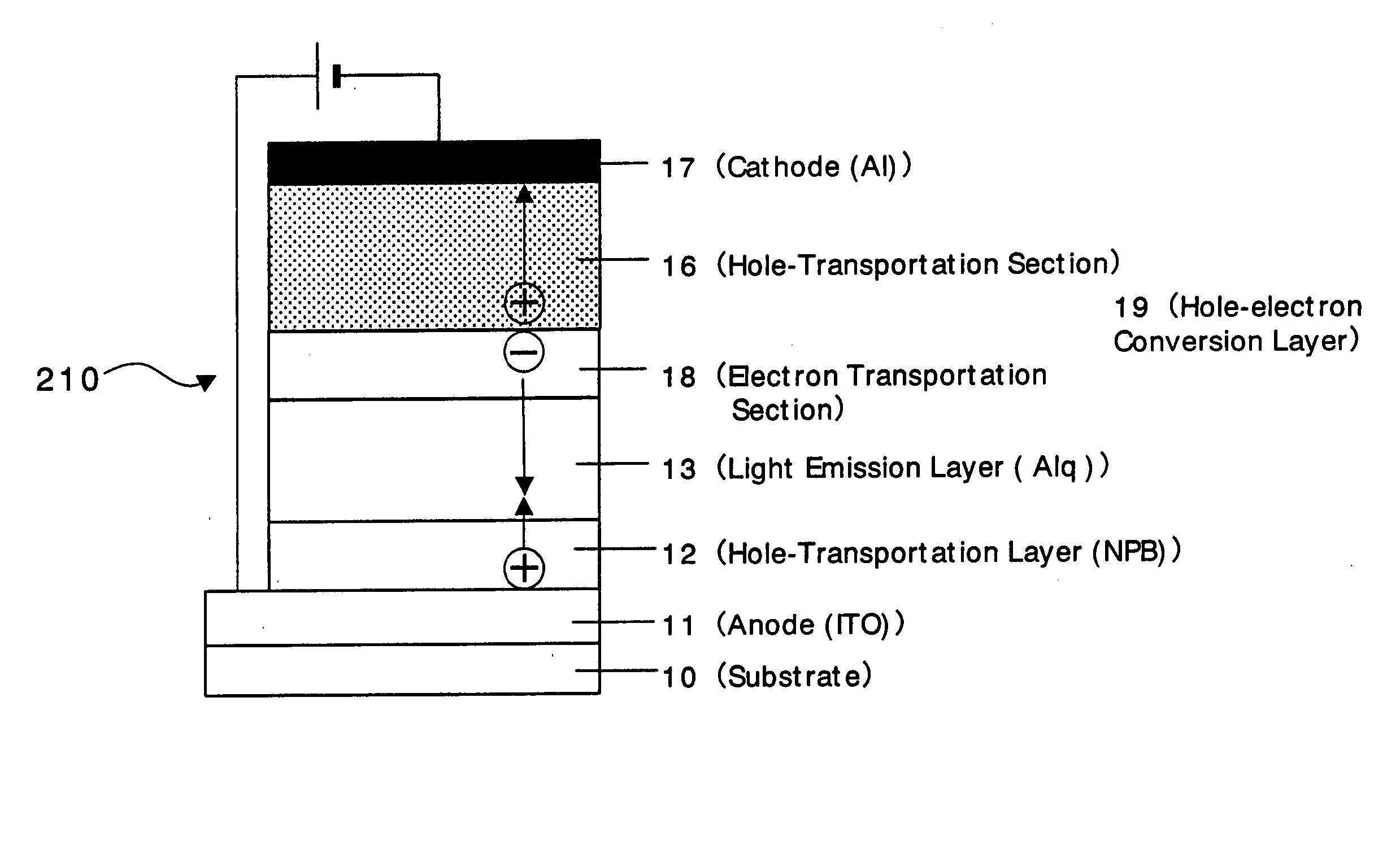
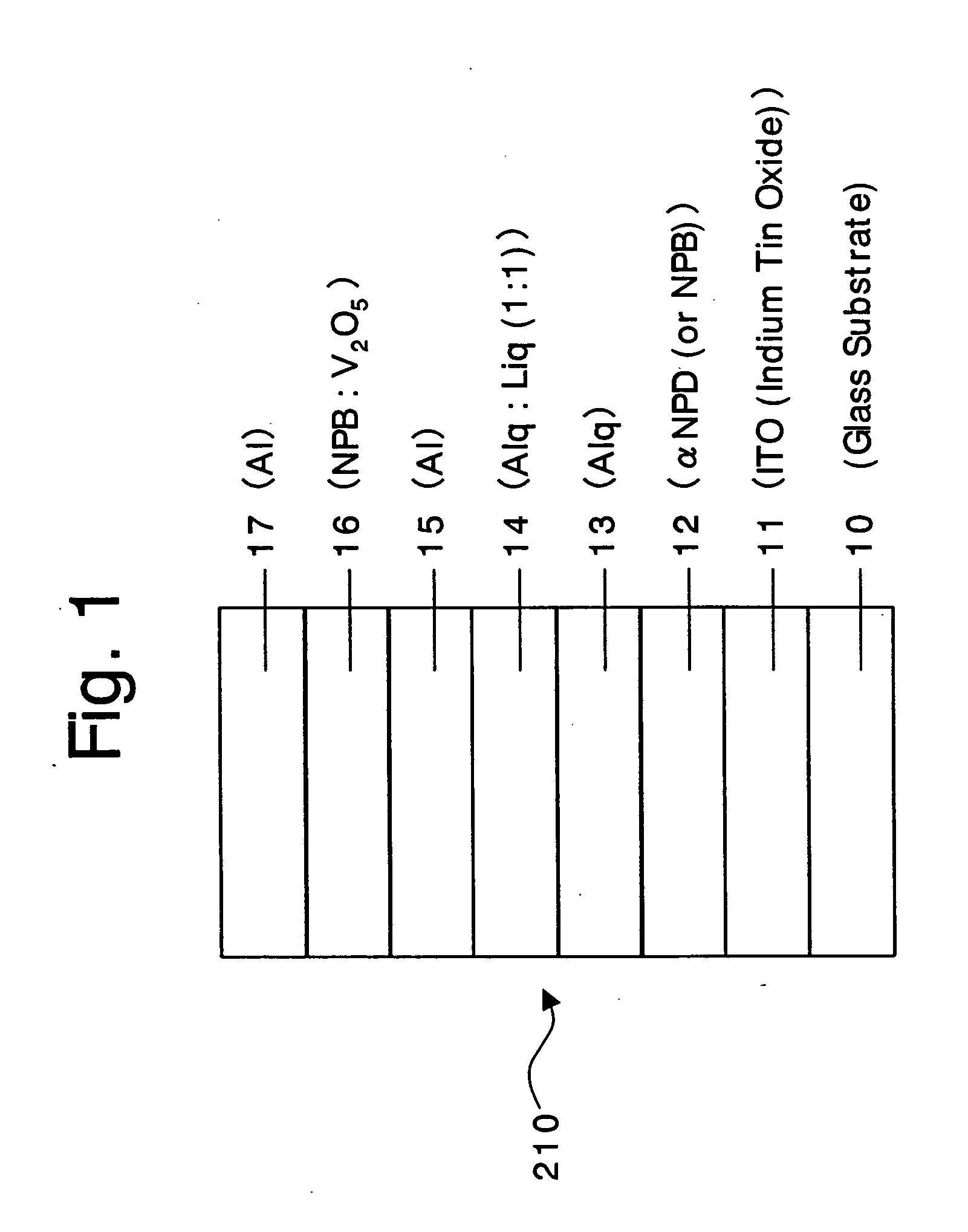
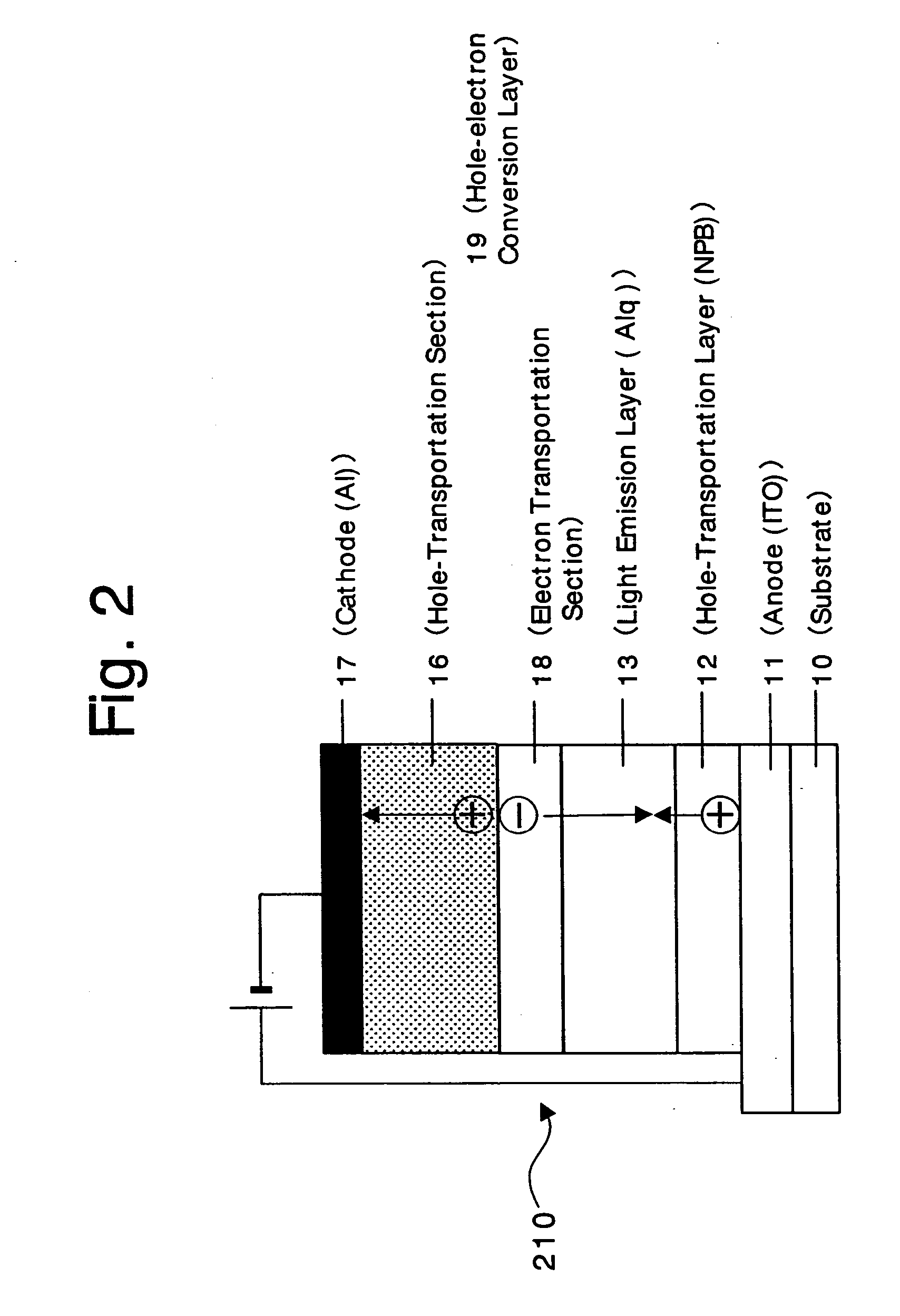
An organic device has a hole current-electron current conversion layer which comprises a laminate of an electron transportation section and a hole transportation section. The electron transportation section includes a charge transfer complex formed upon an oxidation-reduction reaction between a reduced low work function metal and an electron-accepting organic compound, the reduced metal being produced upon an in-situ thermal reduction reaction caused upon contact, through lamination or mixing by co-deposition, of an organic metal complex compound or an inorganic compound containing at least one metal ion selected from ions of low work function metals having a work function of not more than 4.0 eV, and a thermally reducible metal capable of reducing a metal ion contained in the organic metal complex compound or the inorganic compound in vacuum to the corresponding metal state, and the electron transportation section having the electron-accepting organic compound in the state of radical anions. The hole transportation section includes an organic compound having an ionization potential of less than 5.7 eV and an electron-donating property and an inorganic or organic substance capable of forming a charge transfer complex upon its oxidation-reduction reaction with the organic compound, the organic compound and the inorganic or organic substance being contacted through lamination or mixing, and the electron-donating organic compound is in the state of radical cations.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
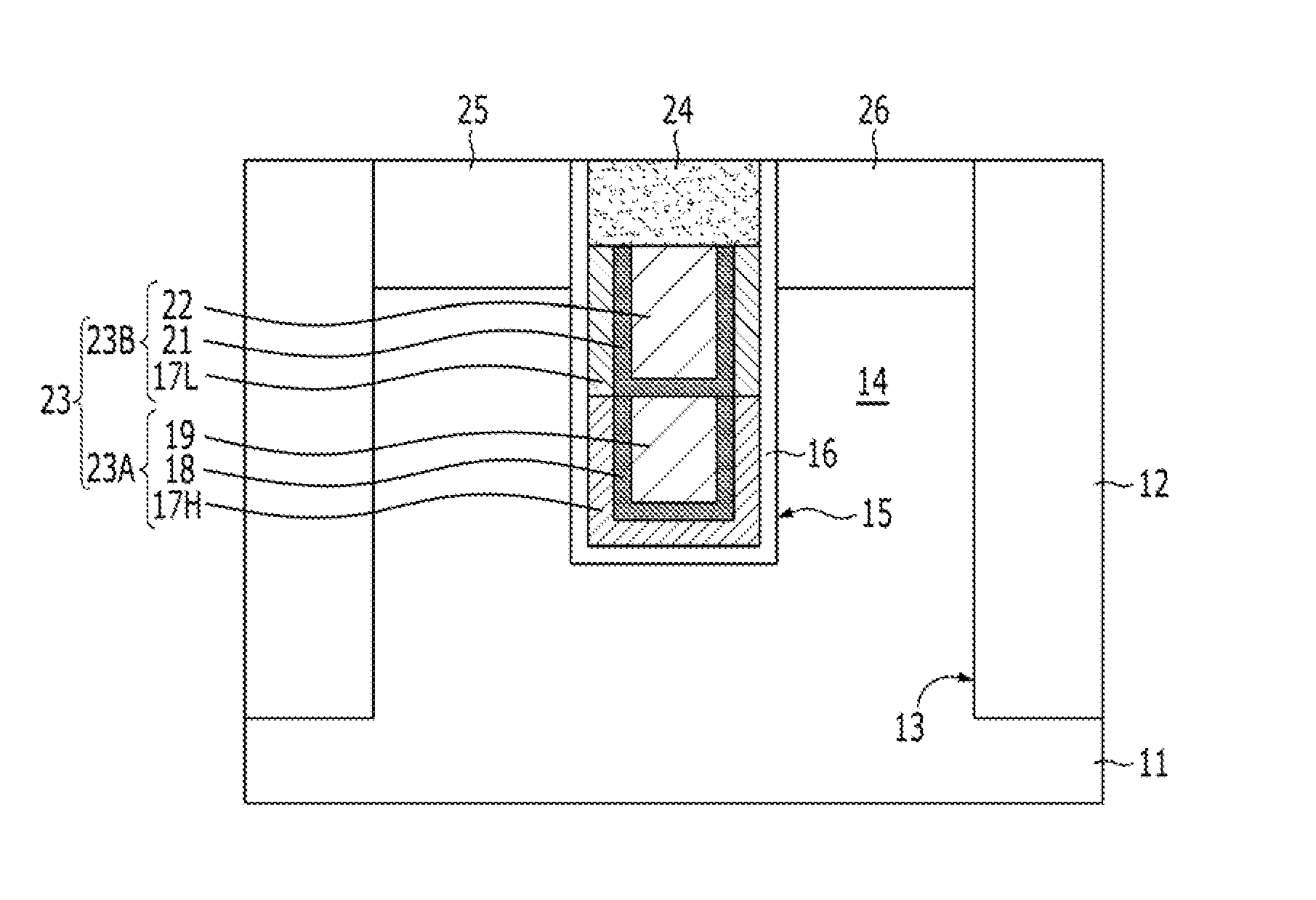
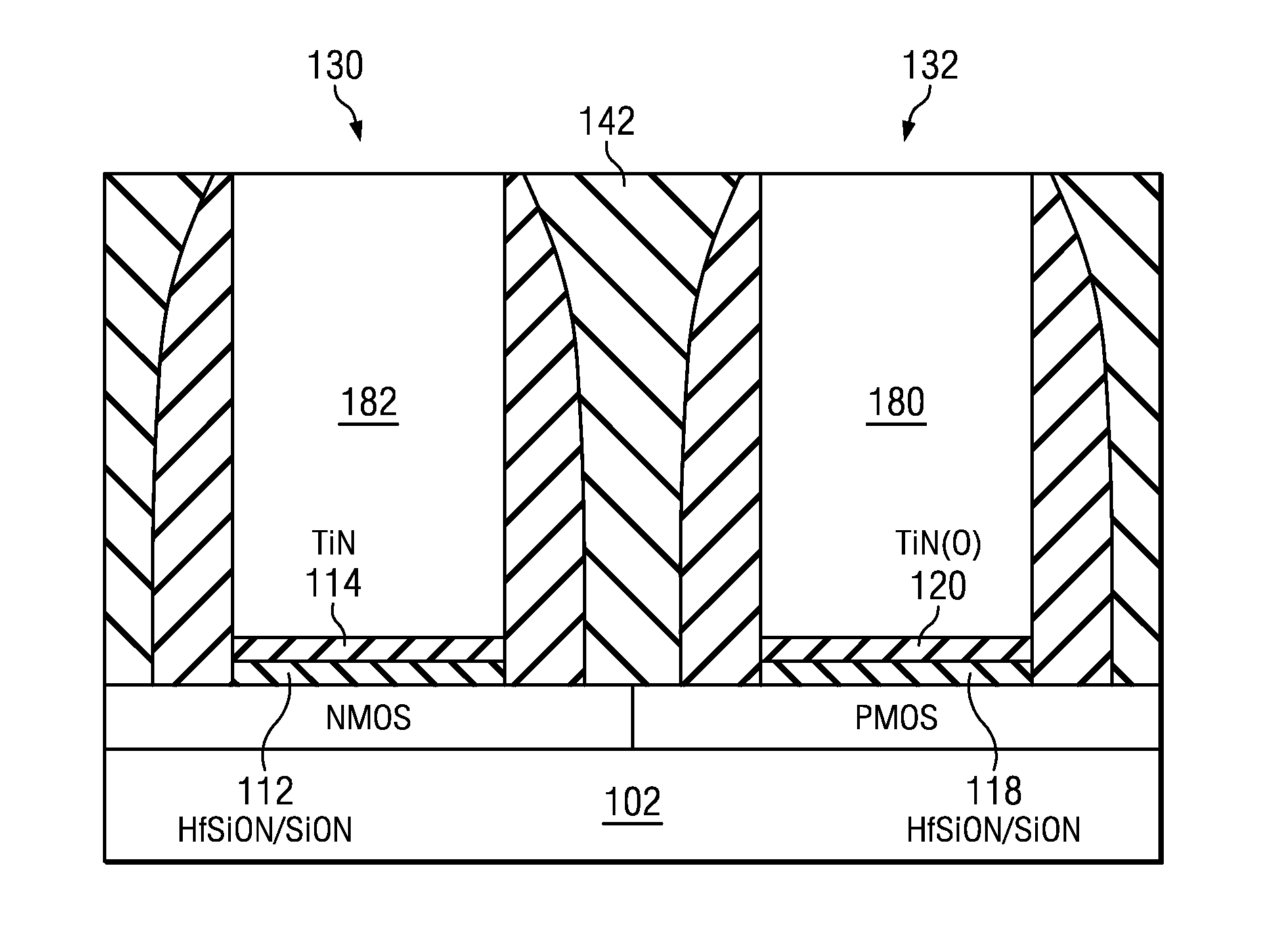
Dual work function buried gate-type transistor, method for forming the same, and electronic device including the same
ActiveUS20150349073A1Increase heightImprove rendering capabilitiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTitanium nitrideEngineering
A transistor includes: a source region and a drain region that are formed in a substrate to be spaced apart from each other; a trench formed in the substrate between the source region and the drain region; and a buried gate electrode inside the trench, wherein the buried gate electrode includes: a lower buried portion which includes a high work-function barrier layer including an aluminum-containing titanium nitride, and a first low-resistivity layer disposed over the high work-function barrier layer; and an upper buried portion which includes a low work-function barrier layer disposed over the lower buried portion and overlapping with the source region and the drain region, and a second low-resistivity layer disposed over the low work-function barrier layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of fabricating a MOSFET device with metal containing gate structures
InactiveUS6869868B2Improve device performanceLow working voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium nitrideTwo step
A method of forming a composite gate structure for a planar MOSFET device, as well as for vertical, double gate, FINFET device, has been developed. The method features a composite gate structure comprised of an overlying silicon gate structure shape, and an underlying titanium nitride gate structure shape. The titanium nitride component allows a lower work function, and thus lower device operating voltages to be realized when compared to counterpart gate structures formed with only polysilicon. A novel, two step gate structure definition procedure, featuring an anisotropic first etch procedure for definition of the polysilicon gate structure shape, followed by a wet or dry isotopic second etch procedure for definition of the titanium nitride gate structure shape, is employed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High mobility enhancement mode FET
ActiveUS8803242B2Reduce variationReduce impurityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETSemiconductor structure
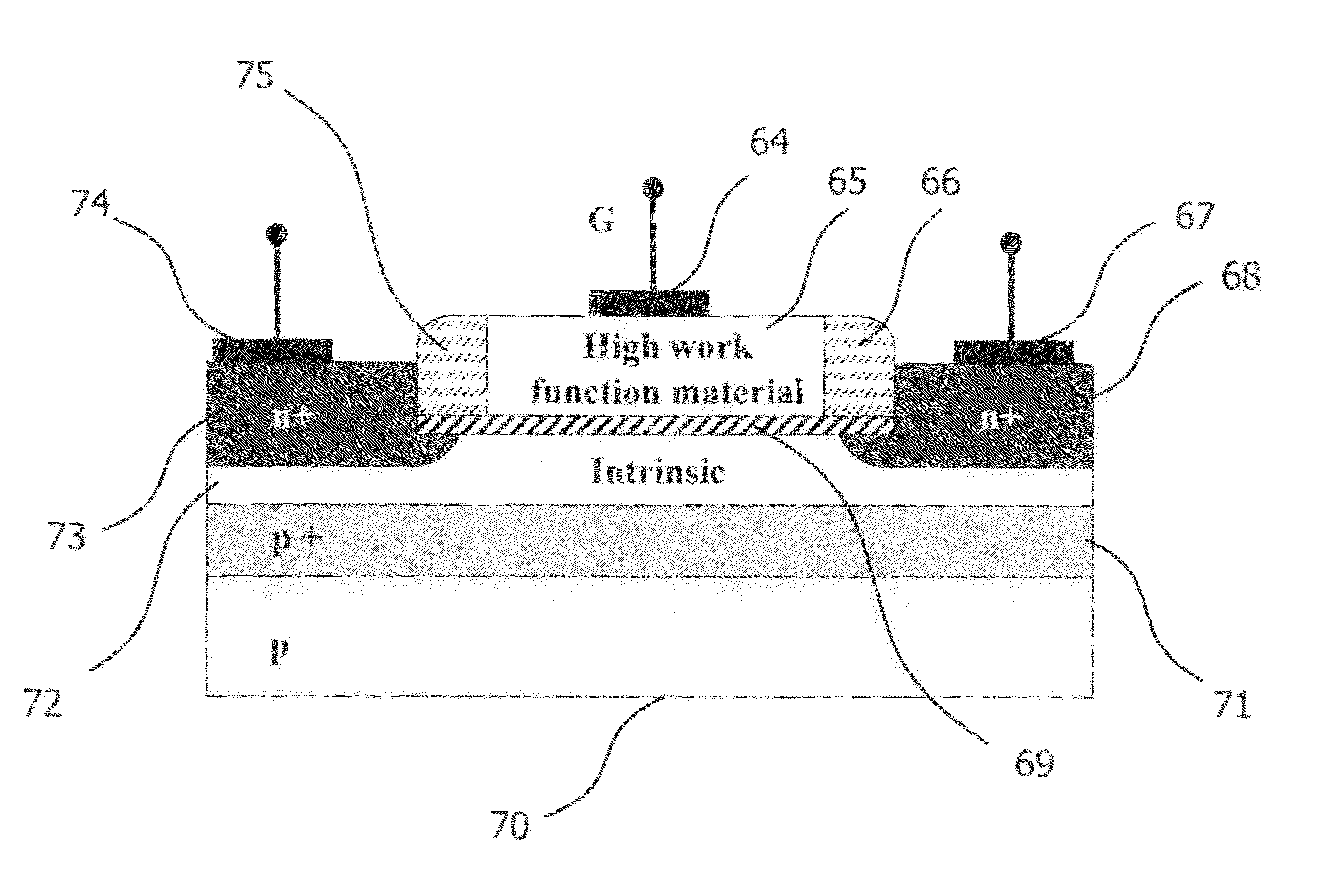
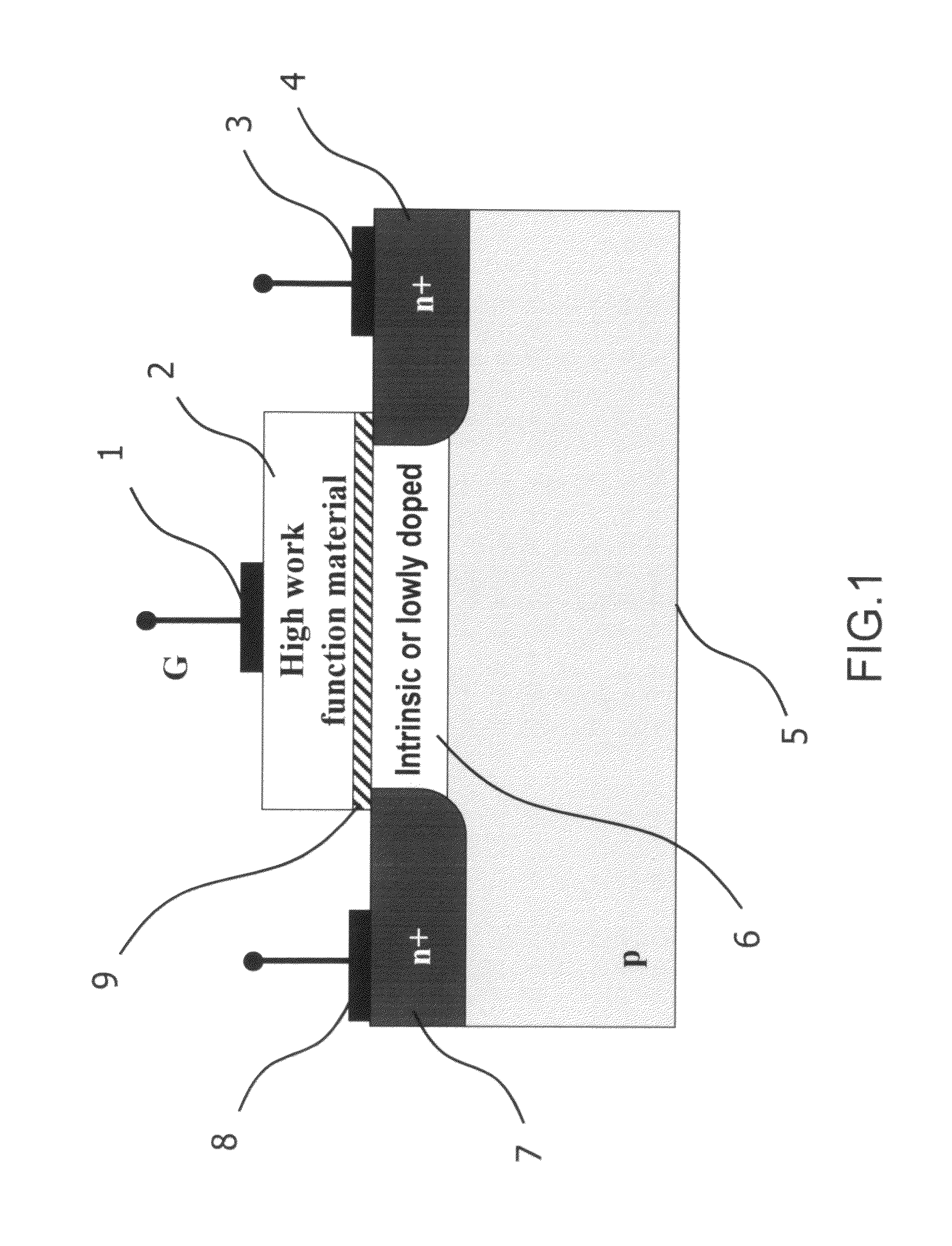
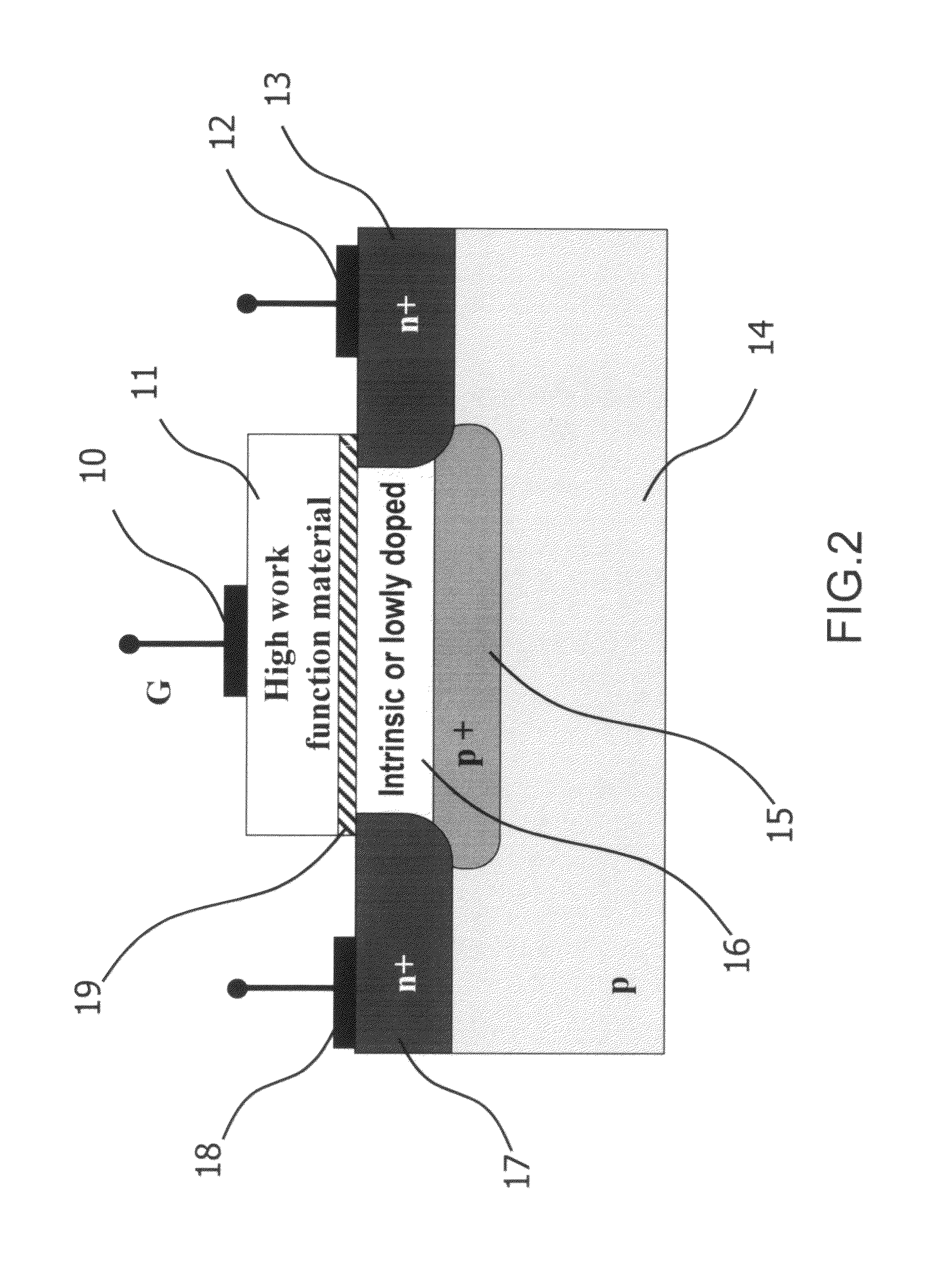
A novel semiconductor transistor is presented. The semiconductor structure has a MOSFET like structure, with the difference that the device channel is formed in an intrinsic region, so as to effectively decrease the impurity and surface scattering phenomena deriving from a high doping profile typical of conventional MOS devices. Due to the presence of the un-doped channel region, the proposed structure greatly reduces Random Doping Fluctuation (RDF) phenomena decreasing the threshold voltage variation between different devices. In order to control the threshold voltage of the device, a heavily doped poly-silicon or metallic gate is used. However, differently from standard CMOS devices, a high work-function metallic material, or a heavily p-doped poly-silicon layer, is used for a n-channel device and a low work-function metallic material, or heavily n-doped poly-silicon layer, is used for a p-channel FET.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dual work function CMOS devices utilizing carbide based electrodes
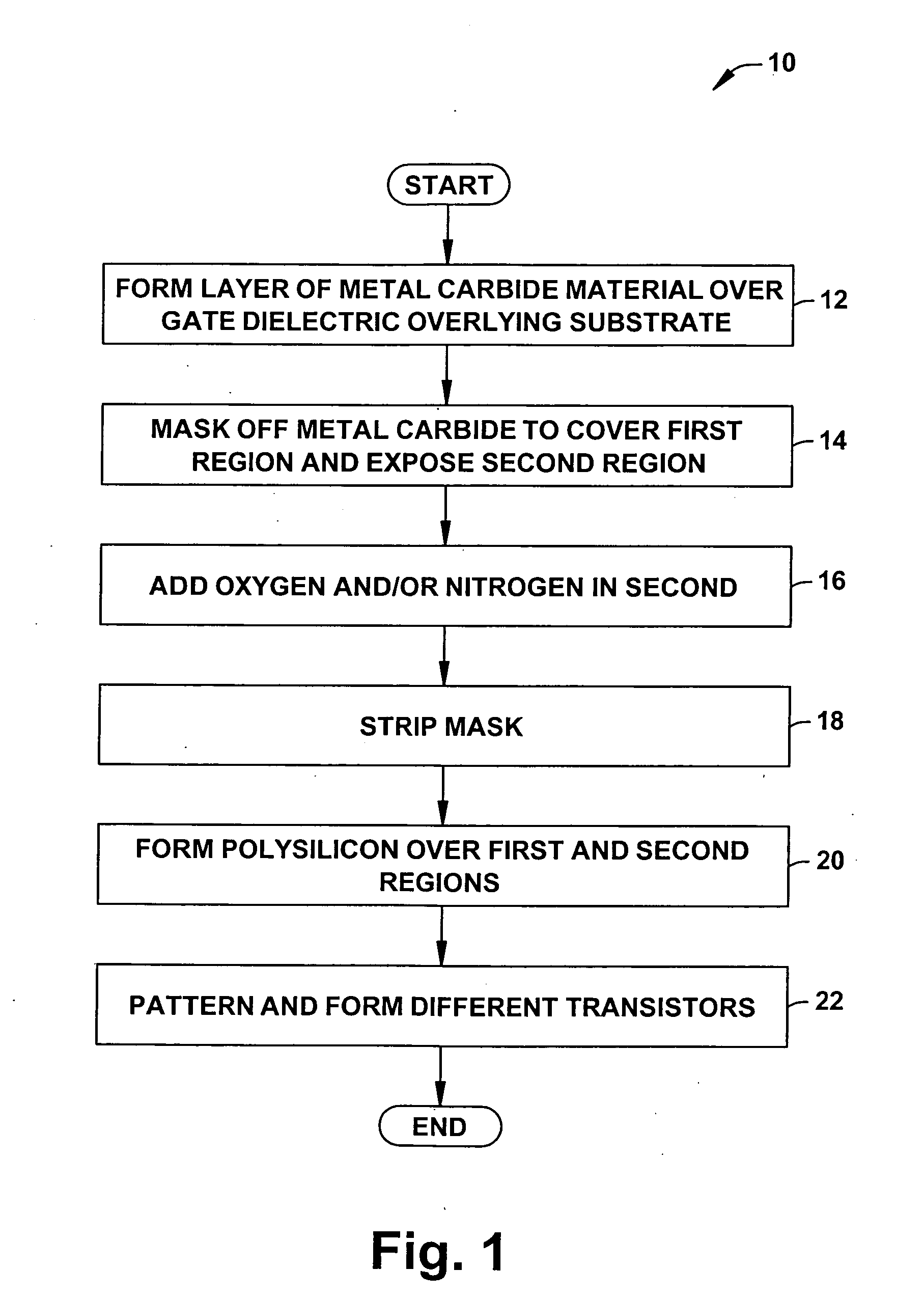
ActiveUS20070037335A1Efficiently formedHigh bulk densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSCarbide
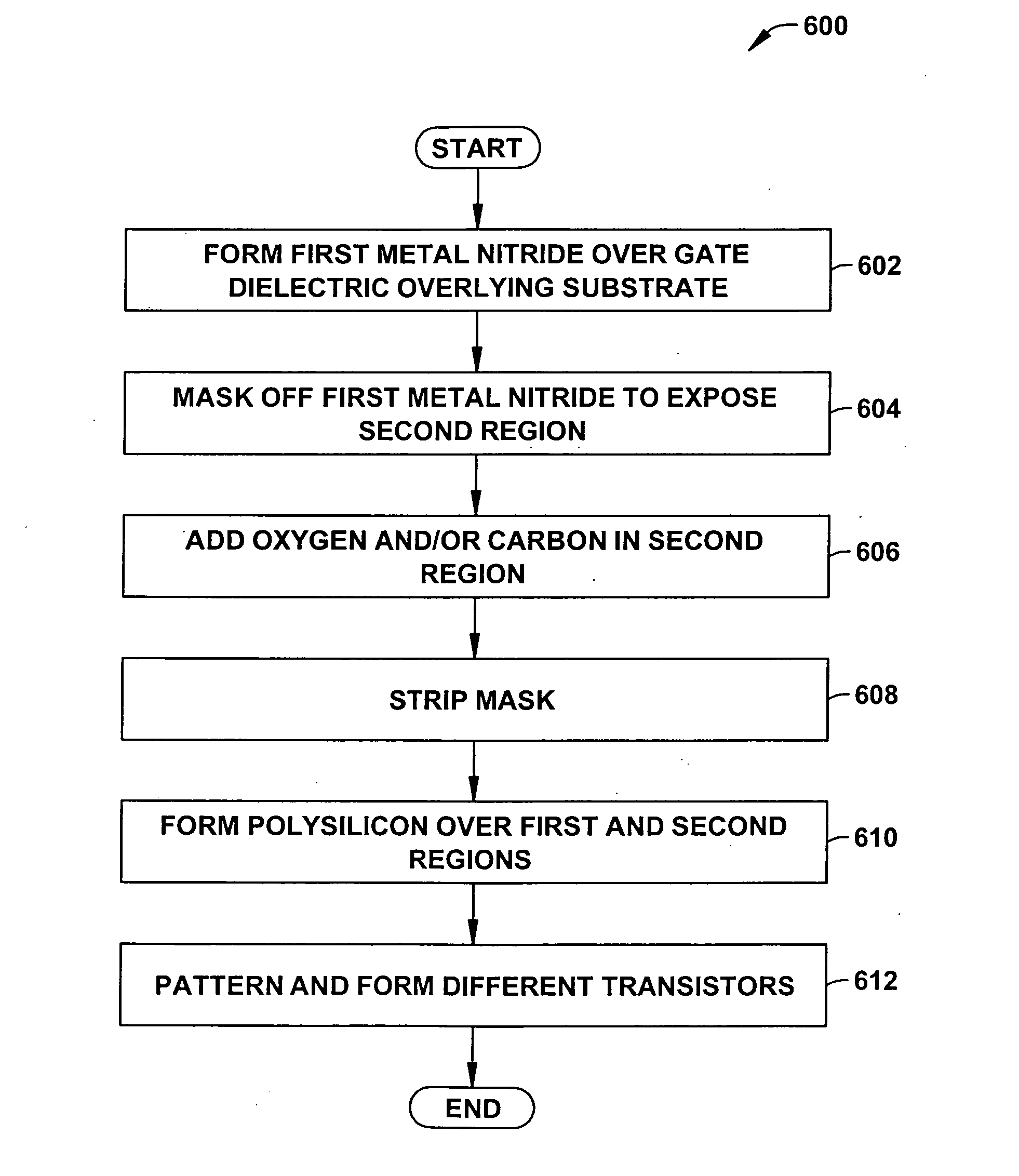
Concurrently forming different metal gate transistors having respective work functions is disclosed. In one example, a metal carbide, which has a relatively low work function, is formed over a semiconductor substrate. Oxygen and / or nitrogen are then added to the metal carbide in a second region to establish a second work function in the second region, where the metal carbide itself establishes a first work function in a first region. One or more first metal gate transistor types are then formed in the first region and one or more second metal gate transistor types are formed in the second region.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
OLED device using reduced drive voltage
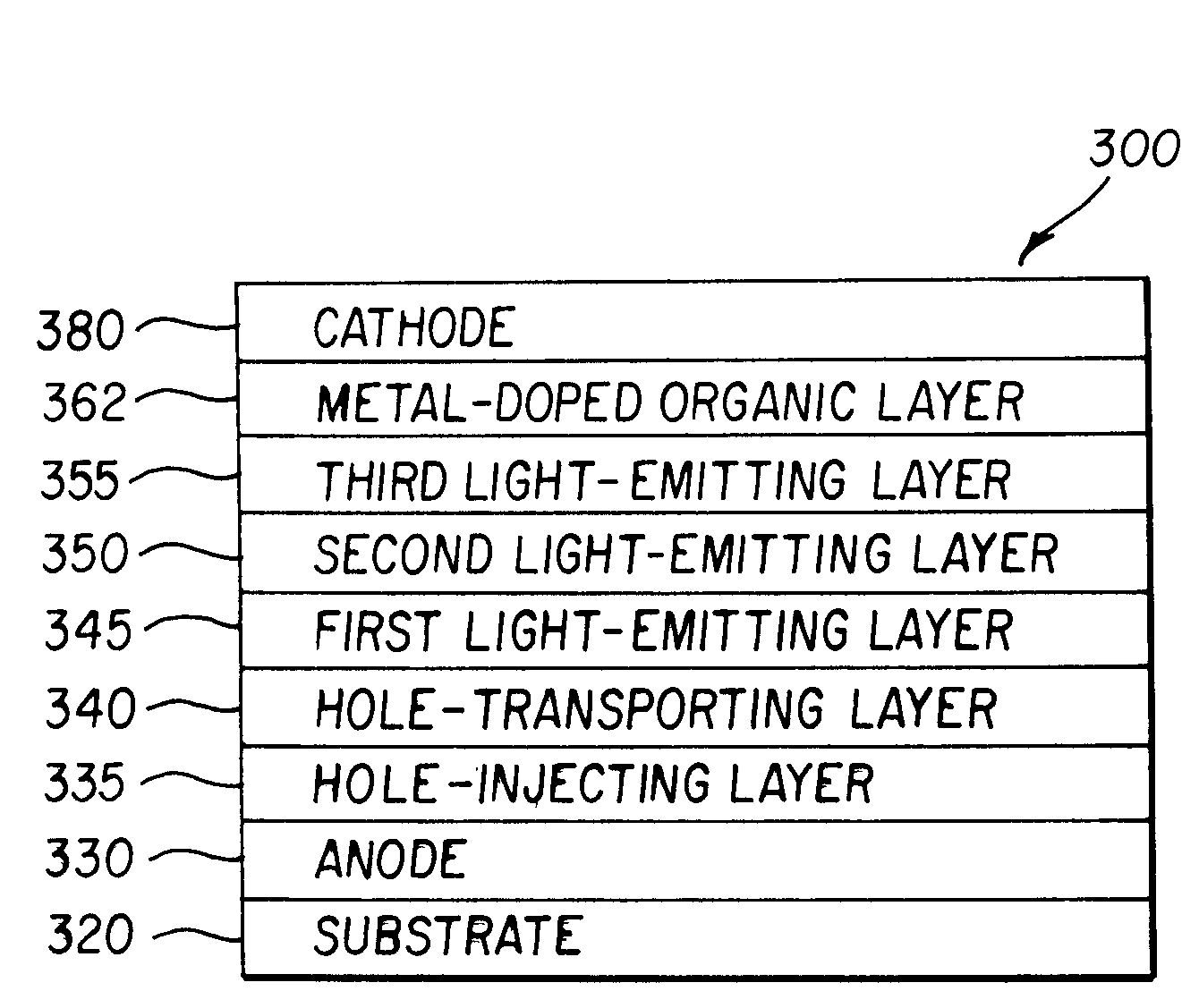
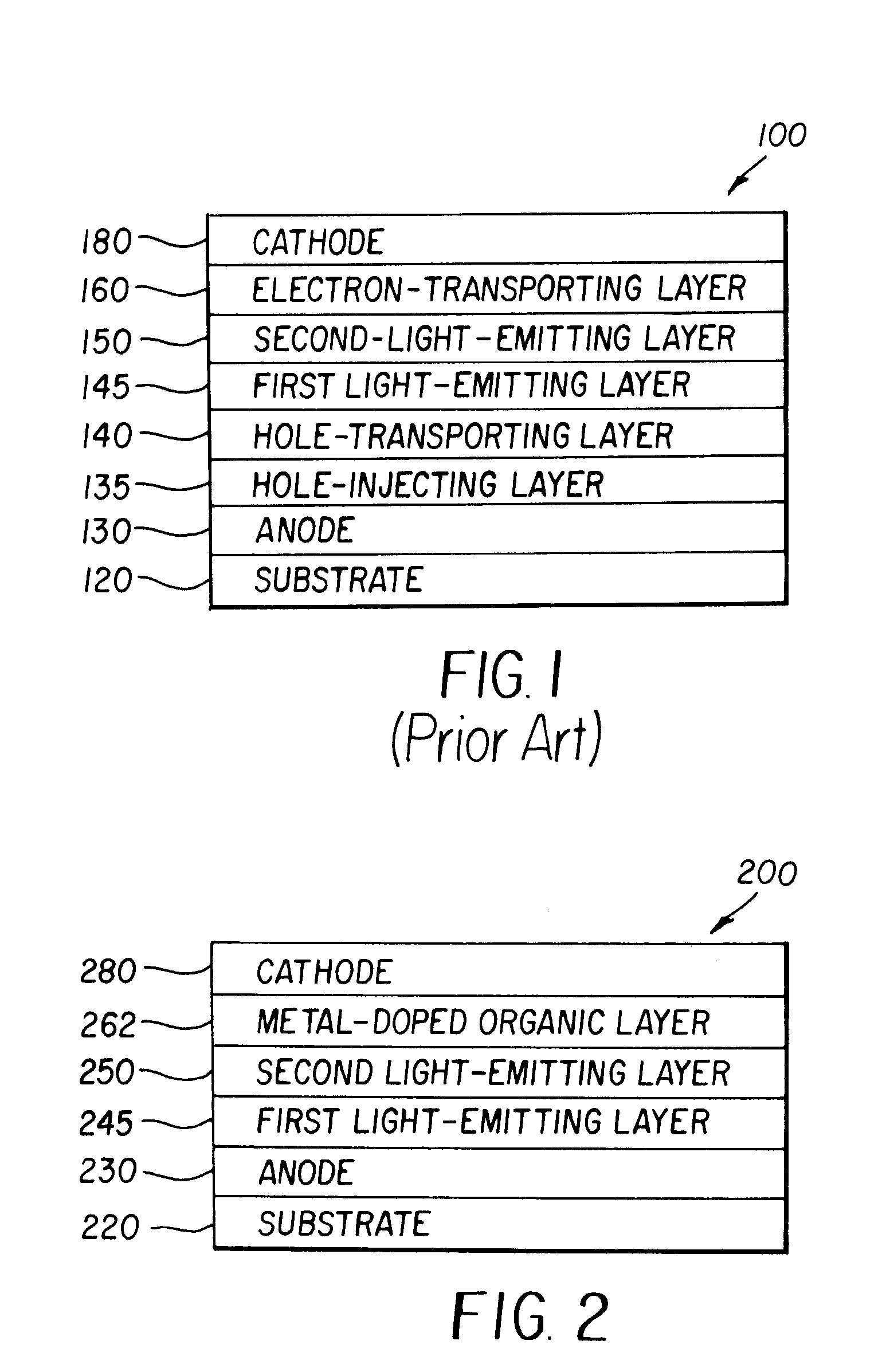
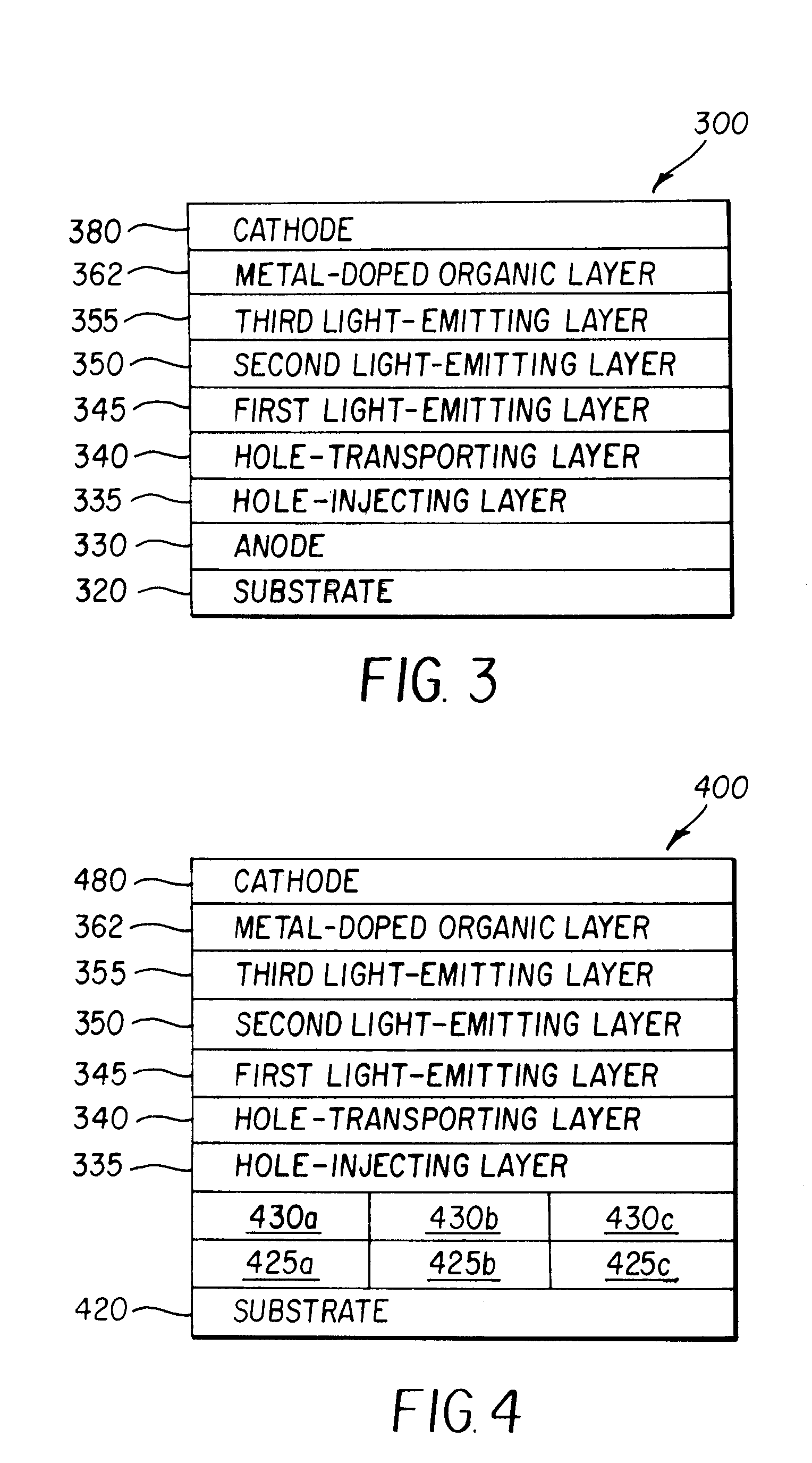
ActiveUS7192659B2High luminous efficiencyReduce the driving voltageIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerEngineering
An OLED device includes an anode, a first light-emitting layer disposed over the anode, and a second light-emitting layer disposed over the first light-emitting layer. The device also includes a metal-doped organic layer containing an organic electron-transporting material and a low work function metal disposed over the second light-emitting layer, and a cathode disposed over the metal-doped organic layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Front contact with high-function TCO for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
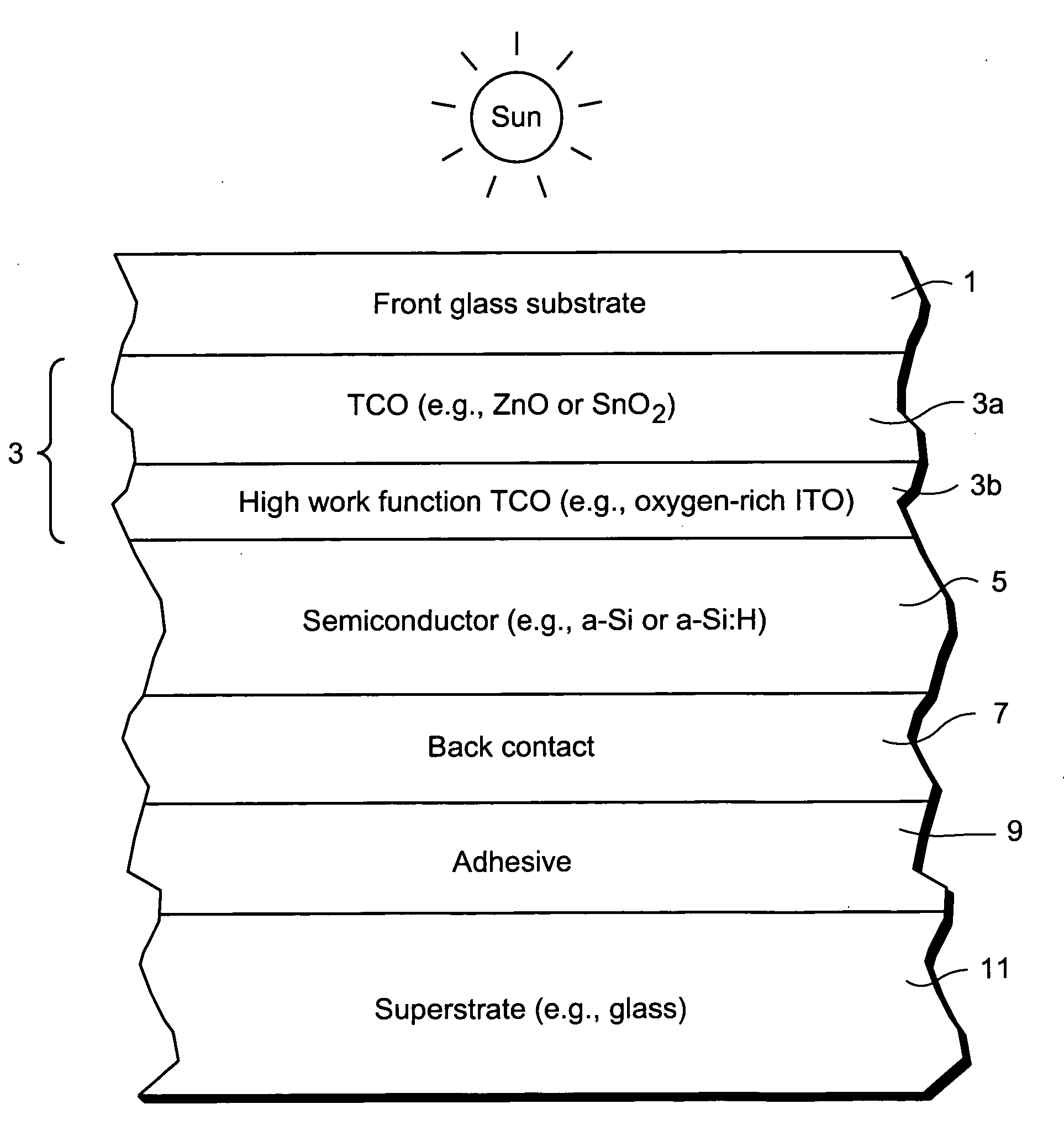
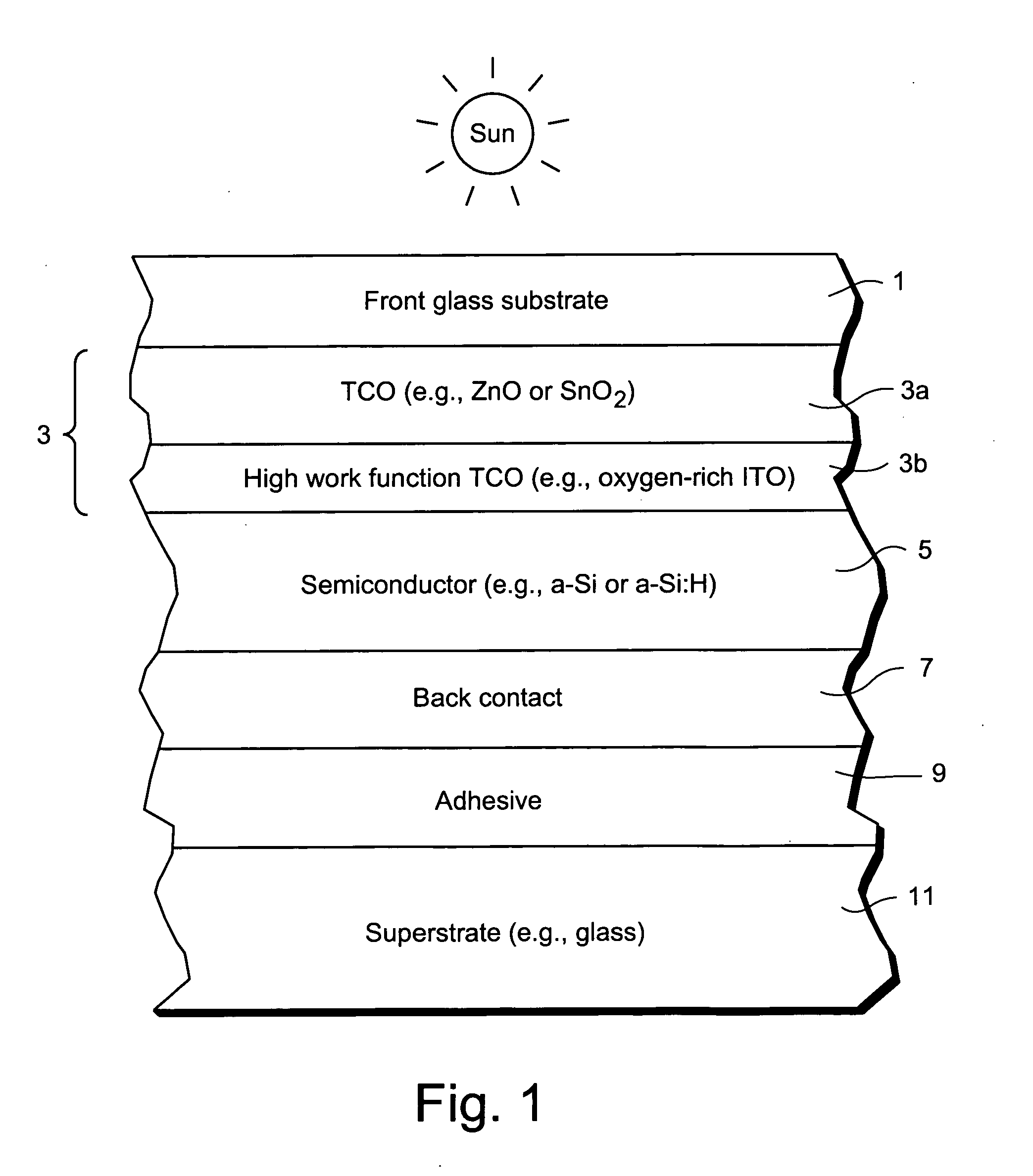
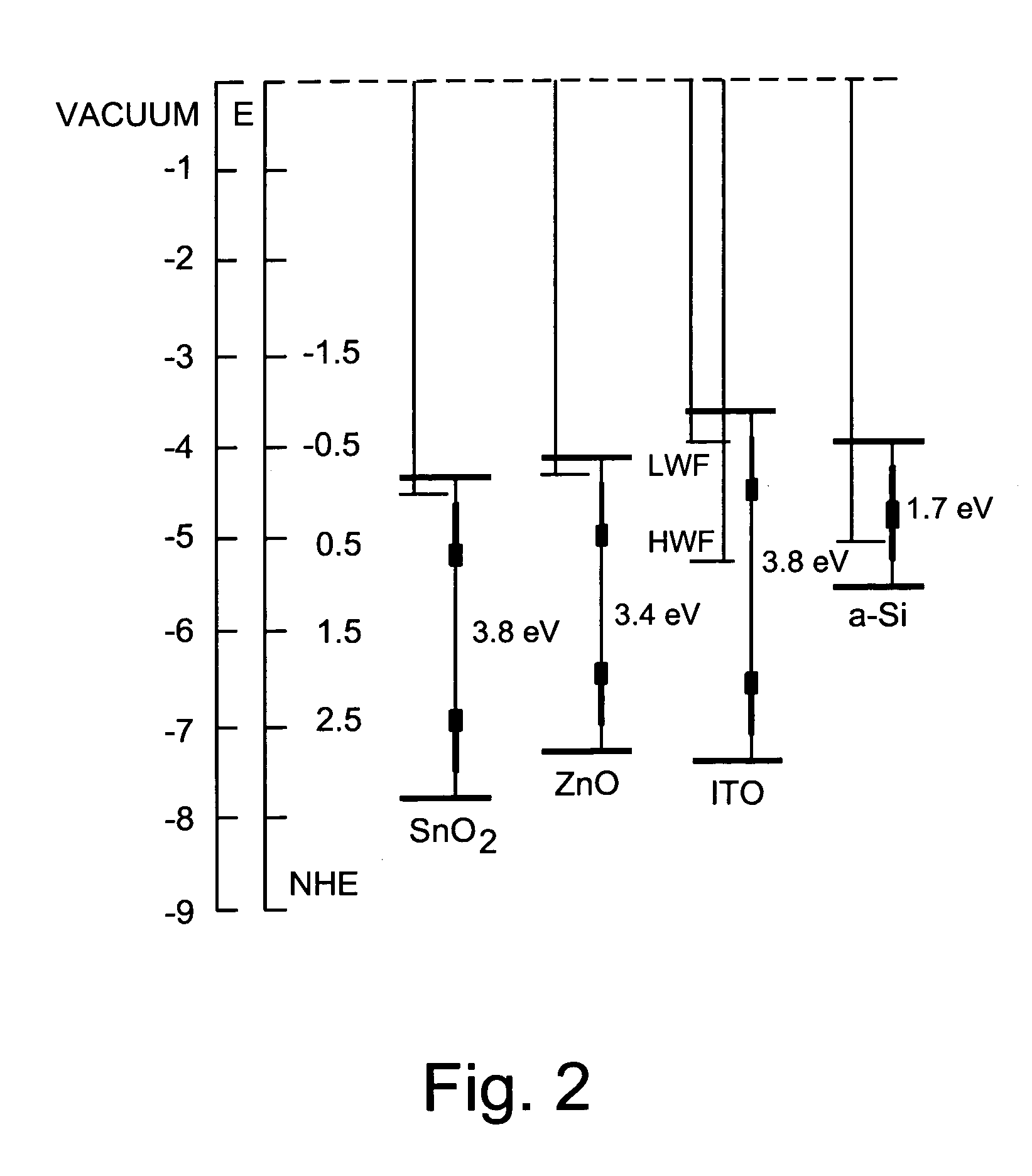
InactiveUS20080047602A1Reduce potential barrierLower work functionSemiconductor devicesIndium tin oxideZinc
This invention relates to a front contact for use in an electronic device such as a photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front contact of the photovoltaic device includes a low work-function transparent conductive oxide (TCO) of a material such as tin oxide, zinc oxide, or the like, and a thin high work-function TCO of a material such as oxygen-rich ITO (indium tin oxide) or the like. The high-work function TCO is located between the low work-function TCO and the uppermost semiconductor layer of the photovoltaic device so as to provide for substantial work-function matching between the low work-function TCO and the high work-function uppermost semiconductor layer of the device in order to reduce a potential barrier for holes extracted from the device by the front contact.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Electronic light emissive displays incorporating transparent and conductive zinc oxide thin film
InactiveUS6541908B1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceOxide cathode
The present invention provides co-doped zinc oxide to flat panel, light emissive display devices and vacuum microelectronic devices to improve their efficiency and lifetime. This material has a low growth temperature and is compatible with metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) processing technology. It is tranparent, chemically stable and has a low work function, which result in many advantages when being used as the cathode for the aforementioned devices. In one embodiment of the emissive display device, an organic light diode (OLED) display has a high work function metal anode, such as platinum (Pt), gold (Au) or nickel (Ni) and a low work function co-doped zinc oxide cathode. Because of the energy level alignment provided by these two materials, the potential energy barriers to injection of electrons from the cathode and holes from the anode into the organic emissive medium are minimized so the display device operates more efficiently.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same, and flat panel display device haviing the same
InactiveUS20090315026A1Good ohmic contactLower Schottky Barrier HeightTransistorNon-linear opticsOhmic contactEngineering
A thin film transistor, a method of manufacturing the same, and a flat panel display device having the same use an oxide semiconductor as an active layer, wherein the thin film transistor includes: an oxide semiconductor layer formed on a substrate and having a channel region, a source region, and a drain region; a gate electrode insulated from the oxide semiconductor layer by a gate insulating layer; an ohmic contact layer formed on the source region and the drain region of the oxide semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode coupled to the source region and the drain region through the ohmic contact layer, the ohmic contact layer being formed of a metal having a lower work function lower than work functions of the source electrode and the drain electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Fin field effect transistor having low leakage current and method of manufacturing the finfet
ActiveUS20100270619A1Reduce leakage currentHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate leakage currentEngineering
Provided is a fin field effect transistor (FinFET) having low leakage current and a method of manufacturing the same. The FinFET includes: a bulk silicon substrate; a fence-shaped body formed by patterning the substrate; an insulating layer formed on a surface of the substrate to a first height of the fence-shaped body; a gate insulating layer formed at side walls and an upper surface of the fence-shaped body at which the insulating layer is not formed; a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer; source / drain formed at regions of the fence-shaped body where the gate electrode is not formed. The gate electrode includes first and second gate electrodes which are in contact with each other and have different work functions. Particularly, the second gate electrode having a low work function is disposed to be close to the drain. As a result, the FinFET according to the present invention increases a threshold voltage by using a material having the high work function for the gate electrode and lowers the work function of the gate electrode overlapping with the drain, so that gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) can be reduced.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method and apparatus for vacuum diode heat pump
InactiveUS6089311AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringKinetic energy
A new use for thermionic vacuum diode technology is disclosed wherein a vacuum diode is constructed using very low work function electrodes. A negative potential bias is applied to the cathode relative to the anode, and electrons are emitted. In the process of emission the electrons carry off kinetic energy, carrying heat away from the cathode and dissipating it at an opposing anode. The resulting heat pump is more efficient than conventional cooling methods, as well as being substantially scalable over a wide range of applications. Fabrication using conventional microelectronic fabrication techniques is possible.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Long lifetime polymer light-emitting devices with improved luminous efficiency and improved radiance
InactiveUS6849869B1Improve reflectivityImprove work functionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadianceHigh reflectivity
The luminous efficiency and radiance of light emitting diodes (LEDs) fabricated from organic emissive materials can be increased by using a multilayer cathode including a low work function layer and a high work function high reflectivity layer, in combination with a high work function, high reflectivitity anode material in the device.
Owner:DUPONT DISPLAY +1
OLED device using reduced drive voltage
ActiveUS20050233166A1High luminous efficiencyReduce the driving voltageIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerEngineering
An OLED device includes an anode, a first light-emitting layer disposed over the anode, and a second light-emitting layer disposed over the first light-emitting layer. The device also includes a metal-doped organic layer containing an organic electron-transporting material and a low work function metal disposed over the second light-emitting layer, and a cathode disposed over the metal-doped organic layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Photovoltaic devices using semiconducting nanotube layers
InactiveUS20110203632A1Improve light absorptionPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSchottky barrierMetal insulator
Photovoltaic (PV) devices employing layers of semiconducting carbon nanotubes as light absorption elements are disclosed. In one aspect a layer of p-type carbon nanotubes and a layer of n-type carbon nanotubes are used to form a p-n junction PV device. In another aspect a mixed layer of p-type and n-type carbon nanotubes are used to form a bulk hetero-junction PV device. In another aspect a metal such as a low work function metal electrode is formed adjacent to a layer of semiconducting nanotubes to form a Schottky barrier PV device. In another aspect various material deposition techniques well suited to working with nanotube layers are employed to realize a practical metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) PV device. In another aspect layers of metallic nanotubes are used to provide flexible electrode elements for PV devices. In another aspect layers of metallic nanotubes are used to provide transparent electrode elements for PV devices.
Owner:NANTERO
Conjugated oligoelectrolyte electron transporting layers
InactiveUS20090230362A1Clear molecular structureGood reproducibilitySilicon organic compoundsElectrolytic capacitorsPolyelectrolyteCharge injection
An organic electronic or an optoelectronic device containing a conjugated oligoelectrolyte. In more particularized embodiments, the conjugated oligoelectrolyte is the charge injection or transport layer. The conjugated oligoelectrolyte can be positively or negatively charged, and used in conjunction in a device with either or high or low work function metal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS6316874B1Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic layerOrganic electroluminescence
The object of the invention is to provide an organic EL device which possesses the merits of both an organic material and an inorganic material, has an extended life, an improved efficiency, a low driving voltage and high luminance, and is fabricated at low cost. This object is achieved by the provision of an organic EL device comprising a substrate, a hole injecting electrode and a cathode formed on the substrate, and at least one organic layer located between these electrodes. An inorganic insulating electron injecting layer is located between the cathode and the organic layer. The inorganic insulating electron injecting layer comprises as an oxide having a low work function at least one oxide having a work function of lower than 2.5 eV, and as an oxide having a high work function at one oxide having a work function of 2.5 to 4 eV.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Low work function metal alloy
InactiveUS20060286802A1Easy to implementTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal alloyLanthanide
Low work function metals for use as gate electrode in nMOS devices are provided. The low work function metals include alloys of lanthanide(s), metal and semiconductor. In particular, an alloy of nickel-ytterbium (NiYb) is used to fully silicide (FUSI) a silicon gate. The resulting nickel-ytterbium-silicon gate electrode has a work function of about 4.22 eV.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Electrosurgical apparatus with low work function electrode
InactiveUS20120083782A1Enhances electrical discharge activityHigh activitySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicro structureAlkaline earth metal
An electrosurgical apparatus includes an active electrode with a low-work function coating to improve ablation performance. Low-work function coatings include compounds of alkali metals and alkali earth metals. Additionally, the active electrode may include various micro-structures or asperities or nano-structures or asperities. An array of carbon nanotubes may be aligned and secured on the active electrode. A return electrode comprises a high-work function coating to suppress electrical discharge activity on the return electrode.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
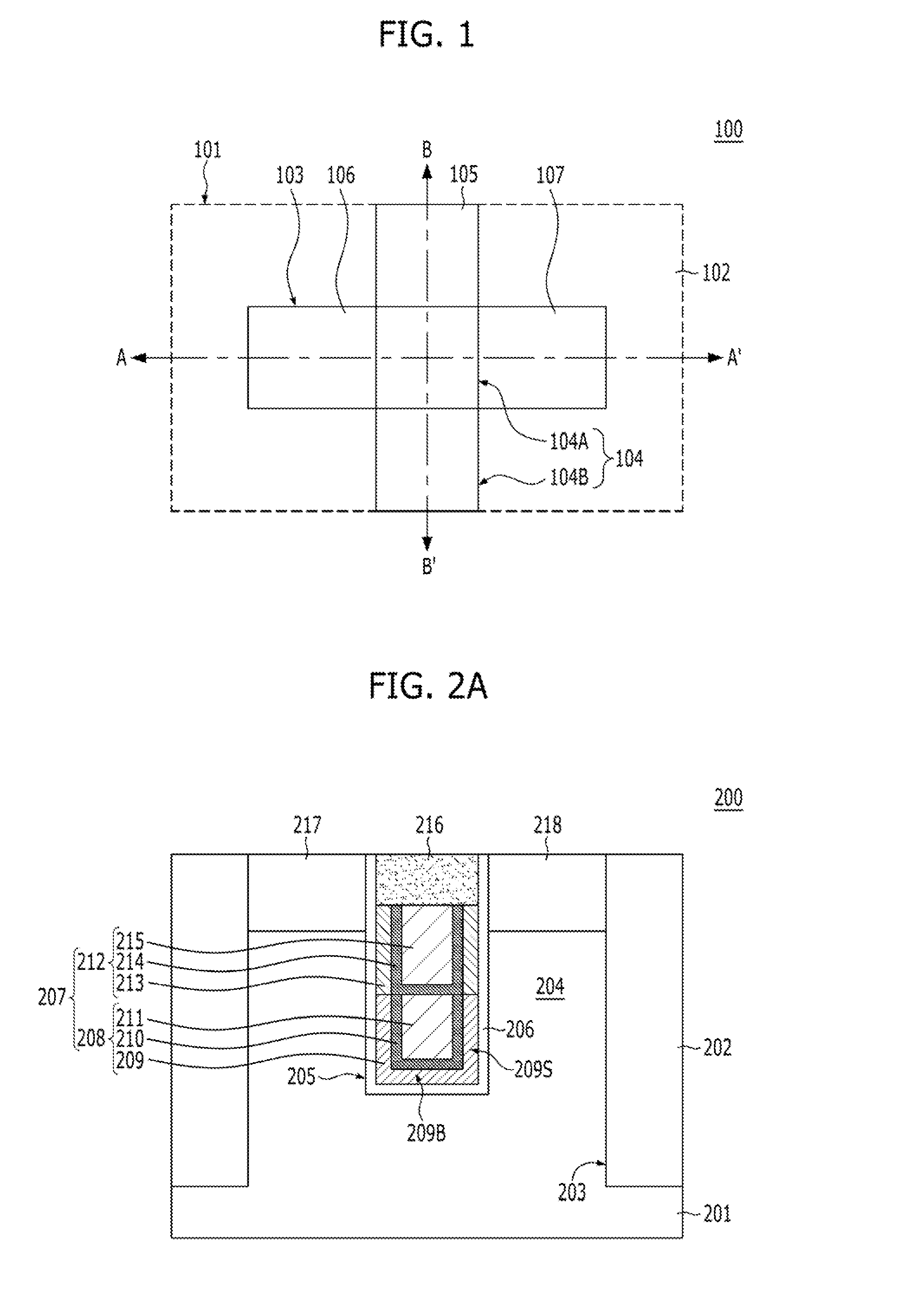
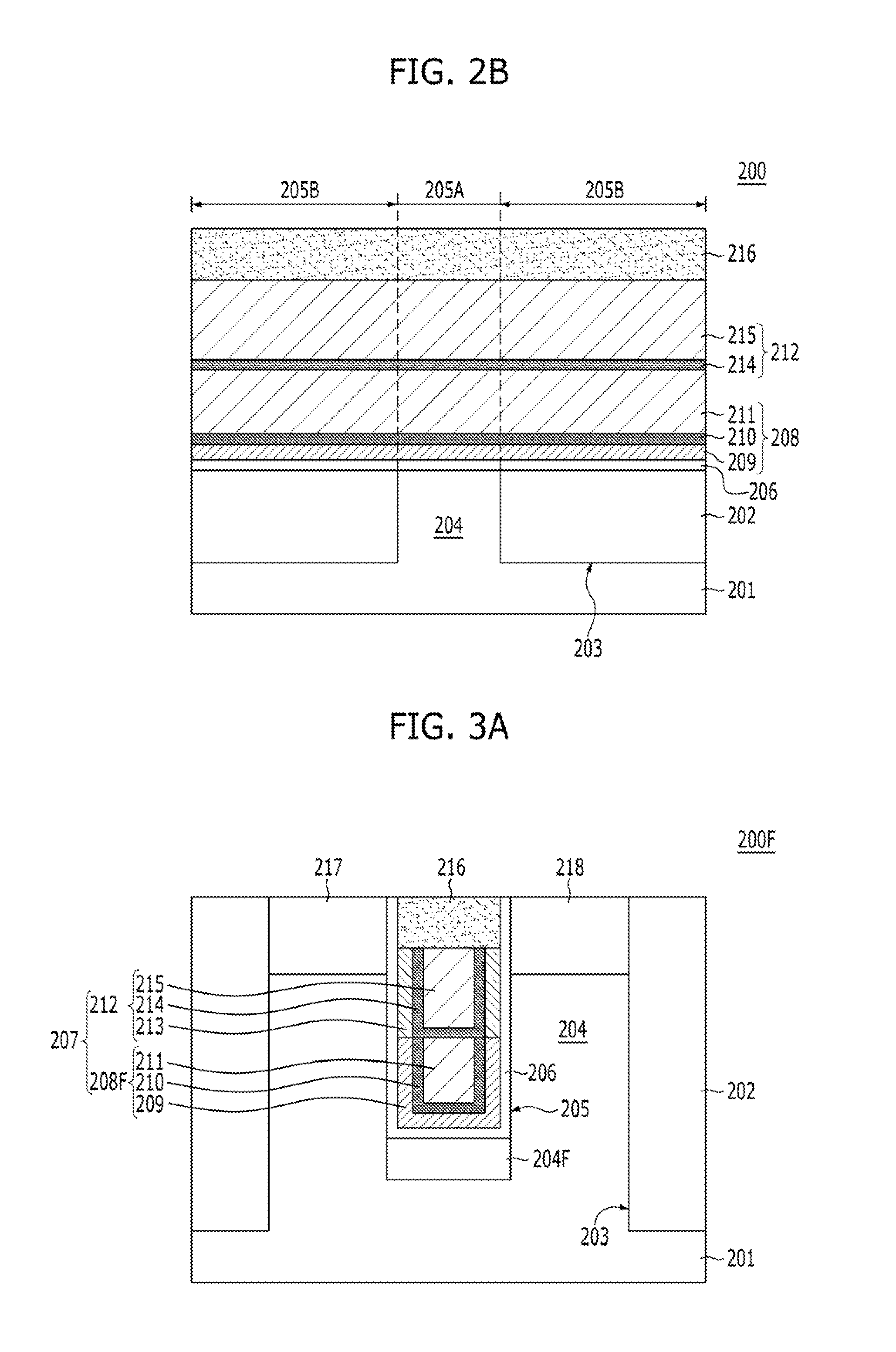
Dual work function buried gate type transistor and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20150214362A1Reducing gate-induced drain leakageImprove current drivabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLow resistance
A transistor may include a source region and a drain region separately formed in a substrate, a trench defined in the substrate between the source region and the drain region, and a buried gate electrode formed. The buried gate electrode includes a high work function liner layer having a bottom portion which is positioned over a bottom of the trench and sidewall portions which are positioned on lower sidewalls of the trench; a low work function liner layer positioned on upper sidewalls of the trench, and overlapping with the source region and the drain region; and a low resistance layer contacting the high work function liner layer and the low work function liner layer, and partially filling the trench.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Organic optoelectronic device
InactiveUS20060231844A1Long life-timeGood lookingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic light emitting deviceElectrical connection
An organic optoelectronic device includes a substrate having an upper surface and a lower surface, at least one organic diode situated on the upper surface of the substrate, the organic diode including, an anode including a material of high work function situated over the upper surface of the substrate, an organic optoelectronic material at least partially overlaying the anode, a cathode including a material of low work function at least partially overlaying the organic optoelectronic material, the cathode being transparent or semi-transparent, wherein the substrate includes at least one connecting via extending through the substrate from the lower surface to the upper surface, the connecting via being suitable for providing an electrical connection between at least one of the anode and / or the cathode of the organic diode and an external circuit. The invention has application in organic light emitting devices and organic photovoltaic devices.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
Two-terminal switching devices and their methods of fabrication
InactiveUS20080105870A1High work functionMaximizes forward currentTransistorSolid-state devicesActive matrixLiquid crystal
Two-terminal switching devices characterized by high on / off current ratios and by high breakdown voltage are provided. These devices can be employed as switches in the driving circuits of active matrix displays, e.g., in electrophoretic, rotataing element and liquid crystal displays. The switching devices include two electrodes, and a layer of a broad band semiconducting material residing between the electrodes. According to one example, the cathode comprises a metal having a low work function, the anode comprises an organic material having a p+ or p++ type of conductivity, and the broad band semiconductor comprises a metal oxide. The work function difference between the cathode and the anode material is preferably at least about 0.6 eV. The on / off current ratios of at least 10,000 over a voltage range of about 15 V can be achieved. The devices can be formed, if desired, on flexible polymeric substrates having low melting points.
Owner:FANTASY SHINE LTD +1
Organic/high molecular light emitting diode
ActiveCN1555103AFacilitates electron injectionImprove quantum efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyHole injection layer
An organic high polymer light emitting diode is composed of a cathode, a light emitting layer, a hole injection layer, an anode and a substrate laminate orderly characterizing that an electronic injection layer is set between the cathode and the light emitting layer applying a conjugate polymer of polarity units containing a polar group or an ionic group, the said cathode applies high work function metals with the work functions larger than or equal to 3.6 electron-V. This invention can get the same quantum efficiency as the low work function injection electrodes get or even higher than that.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Structure And Method For Dual Work Function Metal Gate CMOS With Selective Capping
ActiveUS20120018810A1Apparent advantageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSEngineering
A CMOS device having an NMOS transistor with a metal gate electrode comprising a mid-gap metal with a low work function / high oxygen affinity cap and a PMOS transistor with a metal gate electrode comprising a mid gap metal with a high work function / low oxygen affinity cap and method of forming.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Group III nitride field emitters
Field emitter as a source of electrons and method for making are provided. The emitter is formed by growth of a nitride compound of a group III element or alloys of group III elements on a substrate having a lattice mismatch with the thin film. The lattice mismatch causes columnar growth in the film. The micro columns have tips, thus forming an array of crystalline microtips of the low work function nitride material. The nitride compound is doped during growth. Gallium nitride grown on (111) silicon and doped with silicon produces a surface having low threshold electric field for emission and high current per unit area.
Owner:HOUSTON UNIV OF
Fin field effect transistor having low leakage current and method of manufacturing the FinFET
ActiveUS7906814B2Reduce leakage currentHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesLow leakageField-effect transistor
Provided is a fin field effect transistor (FinFET) having low leakage current and a method of manufacturing the same. The FinFET includes: a bulk silicon substrate; a fence-shaped body formed by patterning the substrate; an insulating layer formed on a surface of the substrate to a first height of the fence-shaped body; a gate insulating layer formed at side walls and an upper surface of the fence-shaped body at which the insulating layer is not formed; a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer; source / drain formed at regions of the fence-shaped body where the gate electrode is not formed. The gate electrode includes first and second gate electrodes which are in contact with each other and have different work functions. Particularly, the second gate electrode having a low work function is disposed to be close to the drain. As a result, the FinFET according to the present invention increases a threshold voltage by using a material having the high work function for the gate electrode and lowers the work function of the gate electrode overlapping with the drain, so that gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) can be reduced.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
High efficiency electroluminescent devices and methods for producing the same
InactiveUS8574937B2High-efficiency and bright displaySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityPoly(ethylene glycol) dimethyl ether
Aspects of the disclosure include electroluminescent devices and methods for making the same. The devices include a substrate, a hole-injection electrode layer, an electroluminescent layer, and an electron-injection electrode layer, such as a layer that includes an air-stable, low work function material, which layer is capable of achieving efficient electron injection with reduced current leakage. In certain embodiments, the devices may contain an efficient electron injection layer that includes a composition comprising a polymer, e.g., a polymer that contains polar components (such as a polar functional group), and a metal diketonate. In certain embodiments, the devices may contain an electron injection layer that includes polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether and barium or calcium acetylacetonate. Methods of manufacturing such devices, for instance, employing a solution processing step for the deposition of an electron injection layer, as well as the use of the produced device(s) in electroluminescent displays is also provided herein.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Tellurium zincium vestalium thin-film solar cell
ActiveCN101276854AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove stabilityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesTransformation efficiencyTe element
The invention discloses a CdZnTe thin film solar energy cell comprising: a glass substrate where a transparent conductive oxide front electrode layer, a n type CdS window layer, a p type Cd<1-x>ZnxTe absorption layer, a p type ZnTe:Cu back contact electrode layer are deposited. The advantages of the invention lie in: the p type Cd<1-x>ZnxTe absorption layer is an absorption layer gradually changes with gap that expand the responding wave section of the solar energy cell by gradual changes with gap. When combined with the p type ZnTe:Cu back contact electrode layer, the p type Cd<1-x>ZnxTe absorption layer has a lower work function characteristic, which effectively solves the ohm contact problem to improve photoelectric transformation efficiency and stability of the cell.
Owner:上海太阳能电池研究与发展中心
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same, and flat panel display device having the same
InactiveCN101609843AReduce contact resistanceImproved current-voltage characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesOhmic contactEngineering
A thin film transistor, a method of manufacturing the same, and a flat panel display device having the thin film transistor, wherein the thin film transistor includes: an oxide semiconductor layer formed on a substrate and having a channel region, a source region, and a drain region; a gate electrode insulated from the oxide semiconductor layer by a gate insulating layer; an ohmic contact layer formed on the source region and the drain region of the oxide semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode coupled to the source region and the drain region through the ohmic contact layer, the ohmic contact layer being formed of a metal having a lower work function lower than work functions of the source electrode and the drain electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
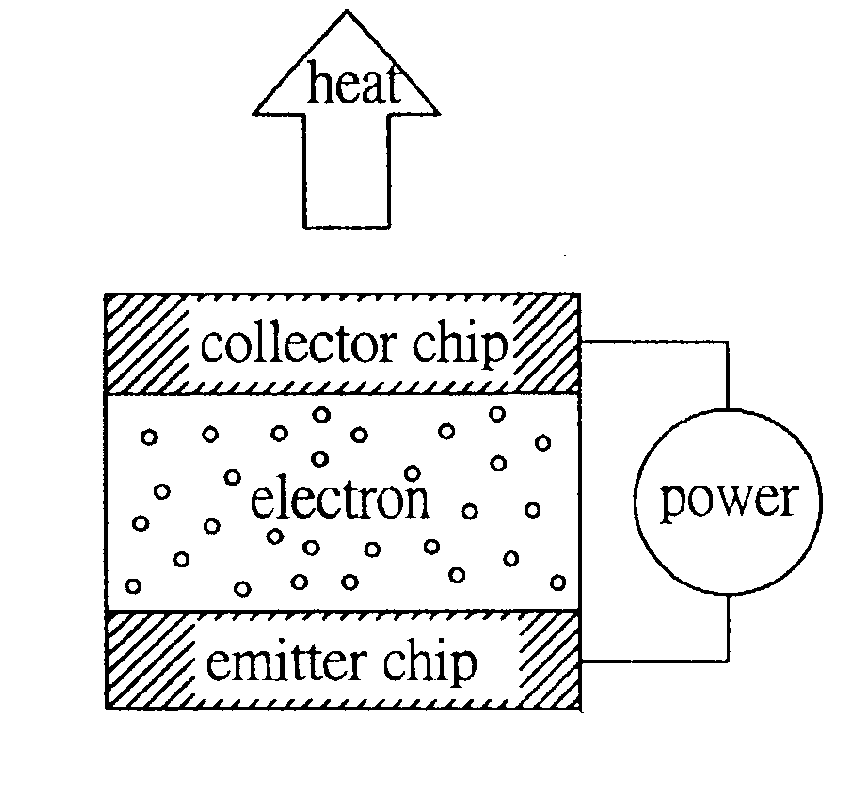
Micro cooling and power supply structure
ActiveUS6914329B1Easy to produceEvenly arrangedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEnergy efficient heating/coolingEngineeringCantilever
A micro cooling and power supply structure is proposed, which includes an emitter end chip having an emitting surface, a collector end chip having a collecting surface that corresponds to the emitting surface and is separated from the emitting surface, and a plurality of micro cantilever beam components formed on the emitting surface. Each micro cantilever beam component has a projecting part as an electron emitter. A distance between the projecting part and the collecting surface is sensed by a sensor component and maintained by an actuating component at an optimal value to produce an electron tunneling effect, so as to lessen the requirement for a planar chip surface and the low work function material. With the capacity of the micro cantilever beam components to position the tunneling distance, the frequency of electron tunneling to the collecting surface is increased, and excellent cooling and power supply efficiency are achieved.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com